Patents
Literature
1282 results about "Contact plane" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
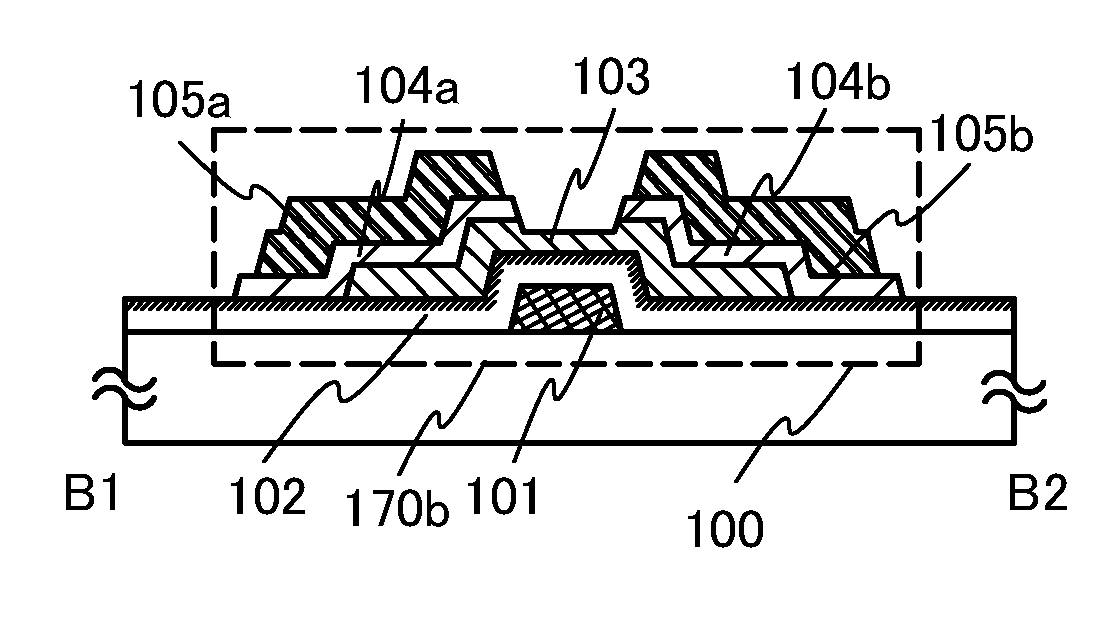
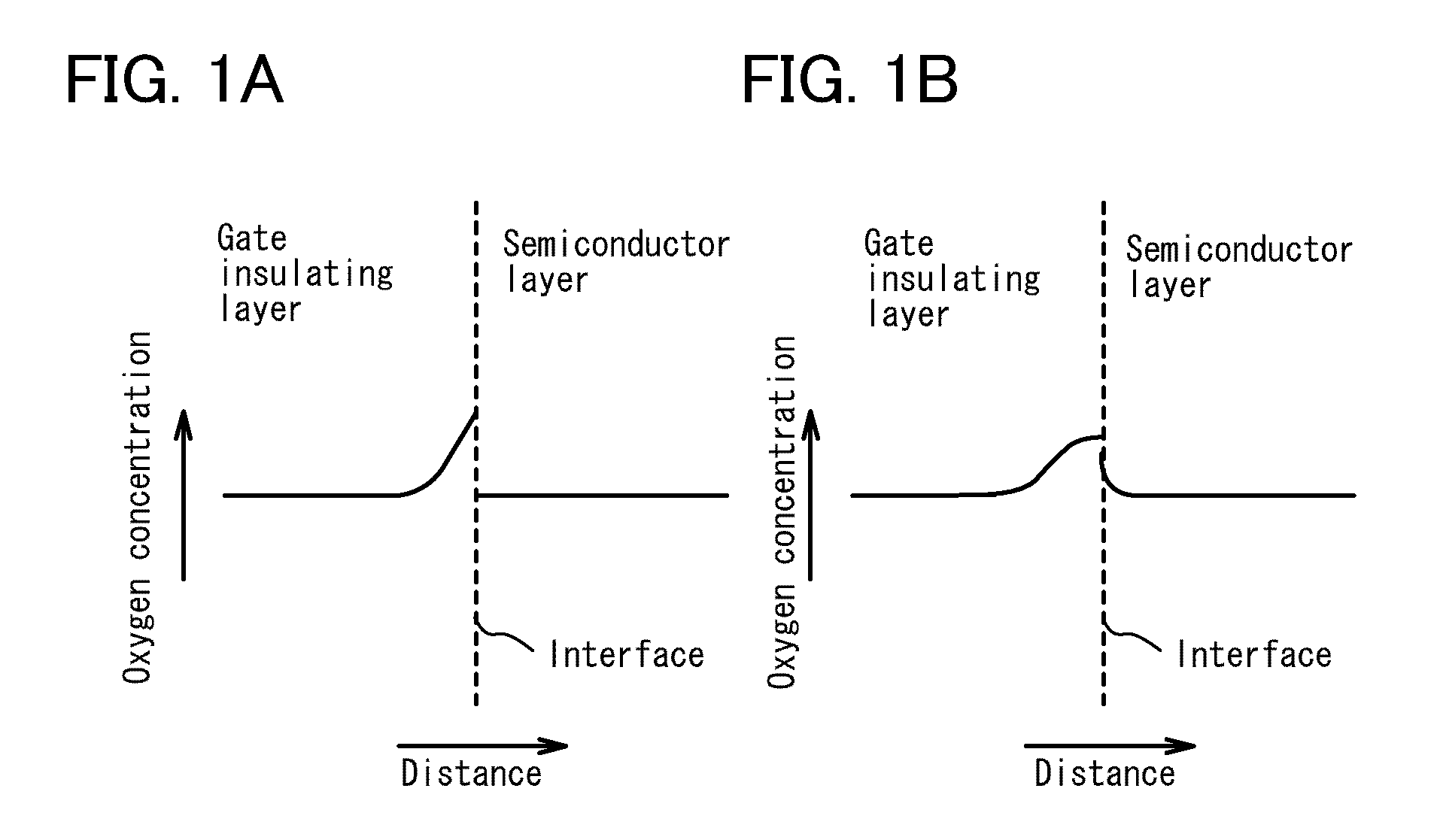
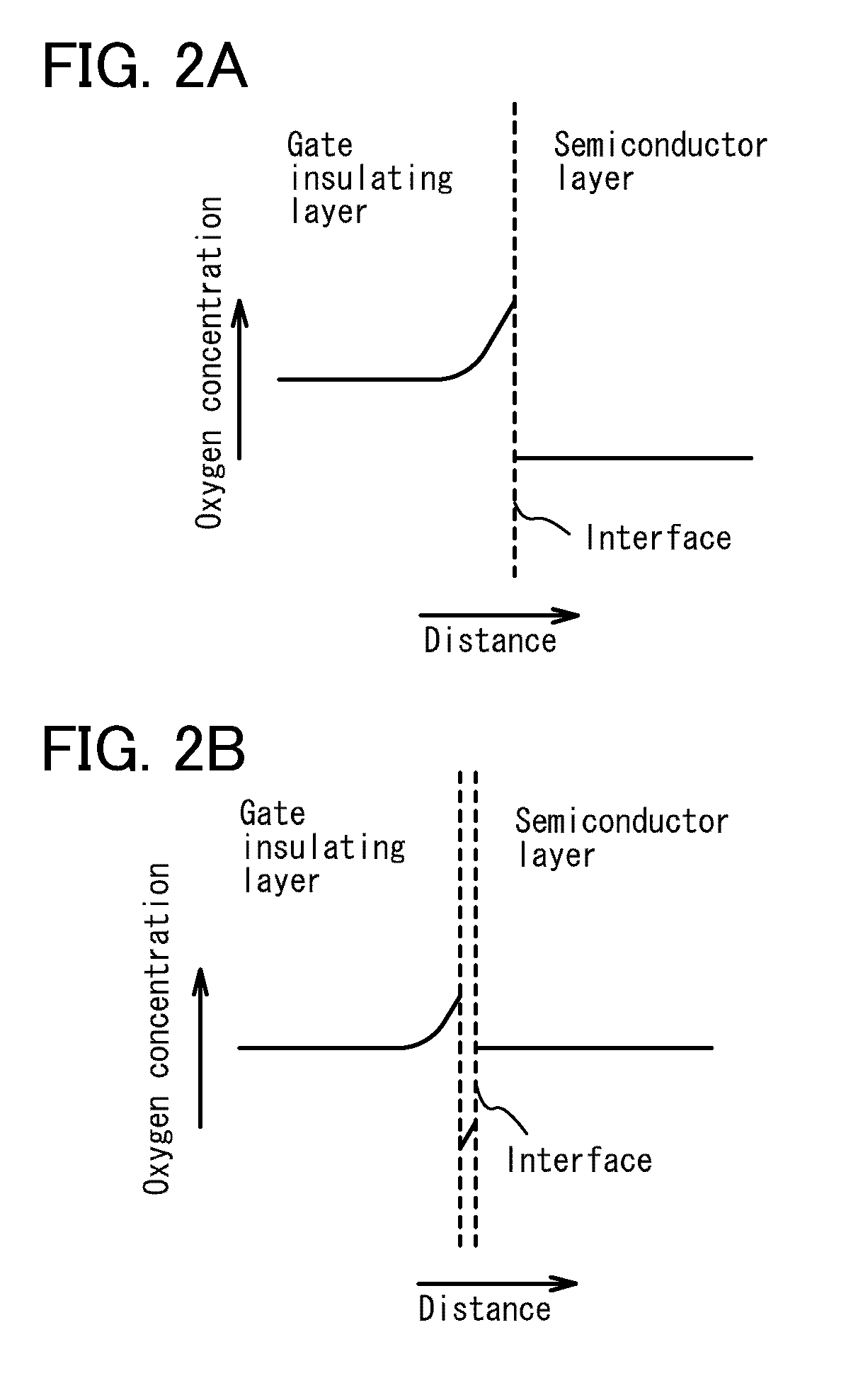
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20100051949A1Small currentHigh on-off ratioTransistorStatic indicating devicesMetallic materialsOxygen deficient
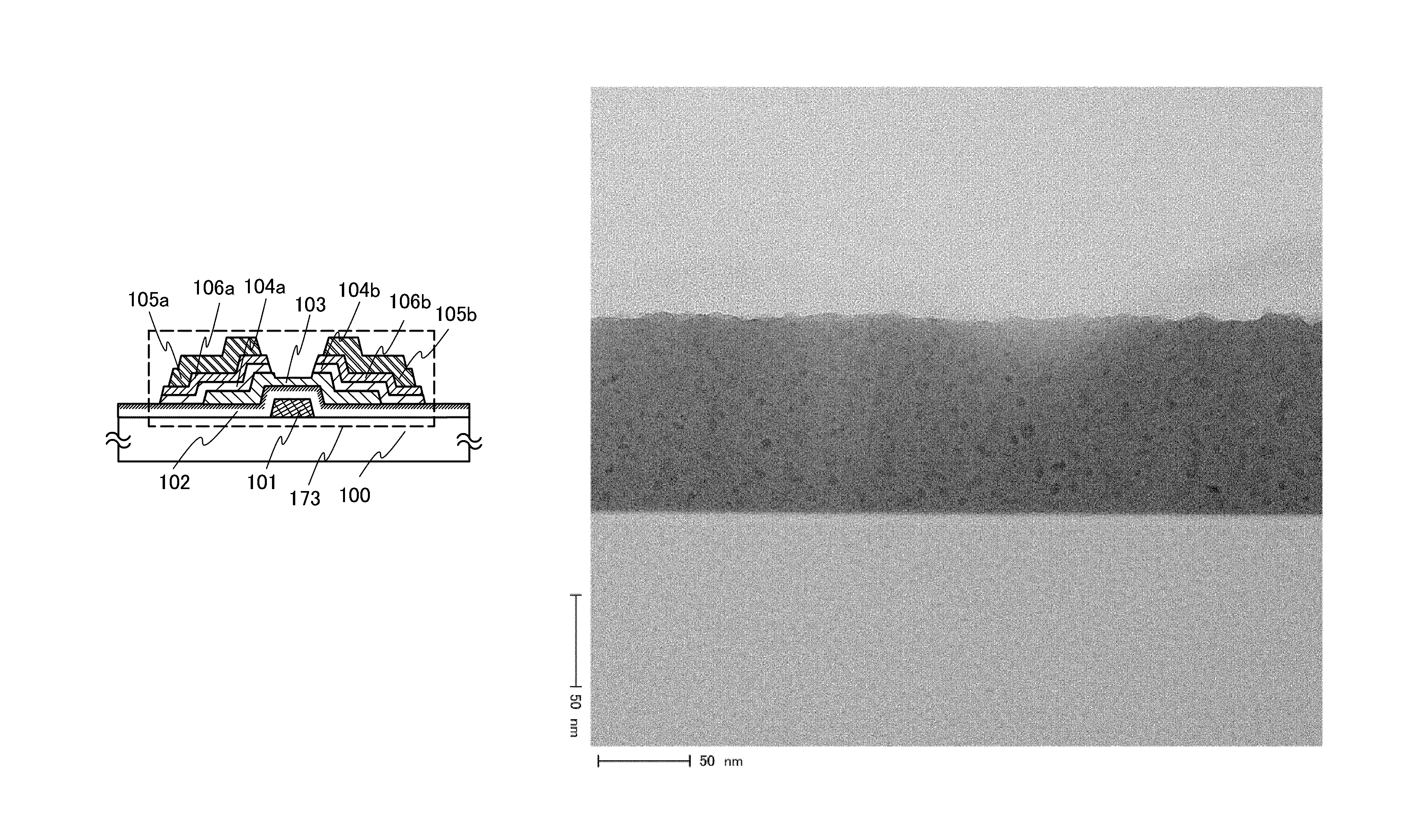
A thin film transistor structure in which a source electrode and a drain electrode formed from a metal material are in direct contact with an oxide semiconductor film may lead to high contact resistance. One cause of high contact resistance is that a Schottky junction is formed at a contact plane between the source and drain electrodes and the oxide semiconductor film. An oxygen-deficient oxide semiconductor layer which includes crystal grains with a size of 1 nm to 10 nm and has a higher carrier concentration than the oxide semiconductor film serving as a channel formation region is provided between the oxide semiconductor film and the source and drain electrodes.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
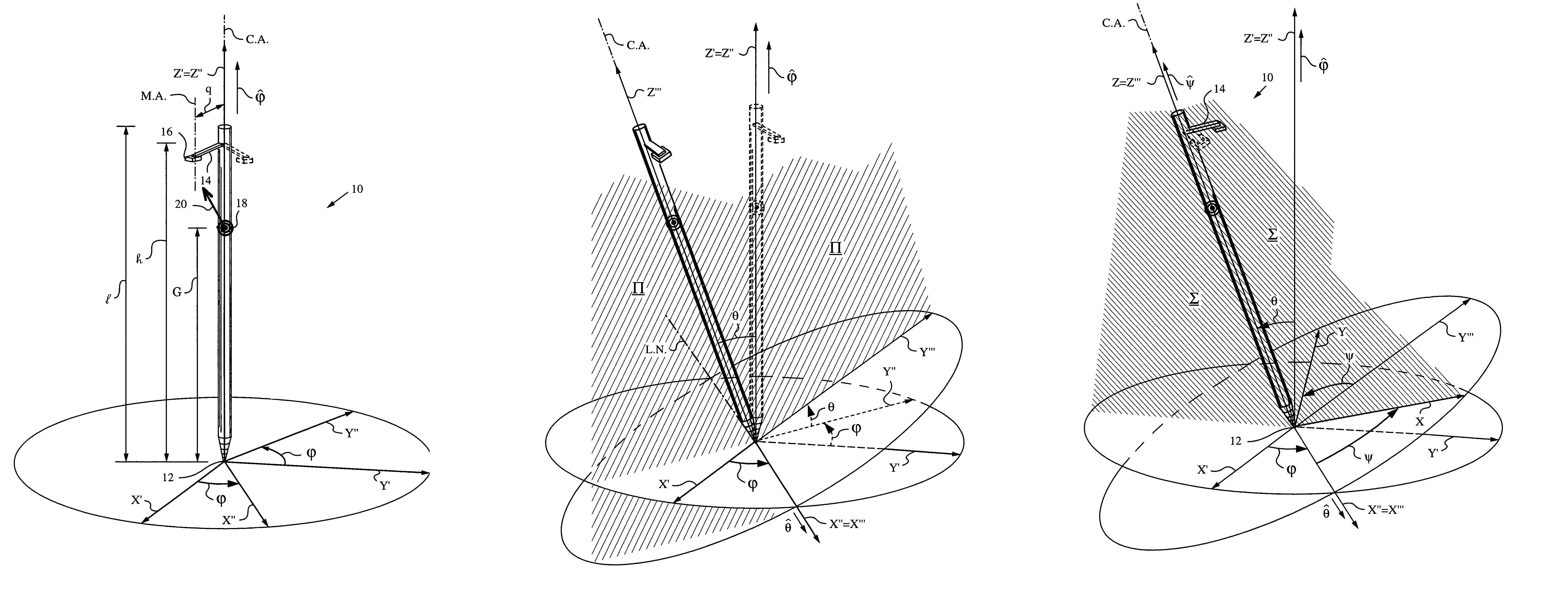
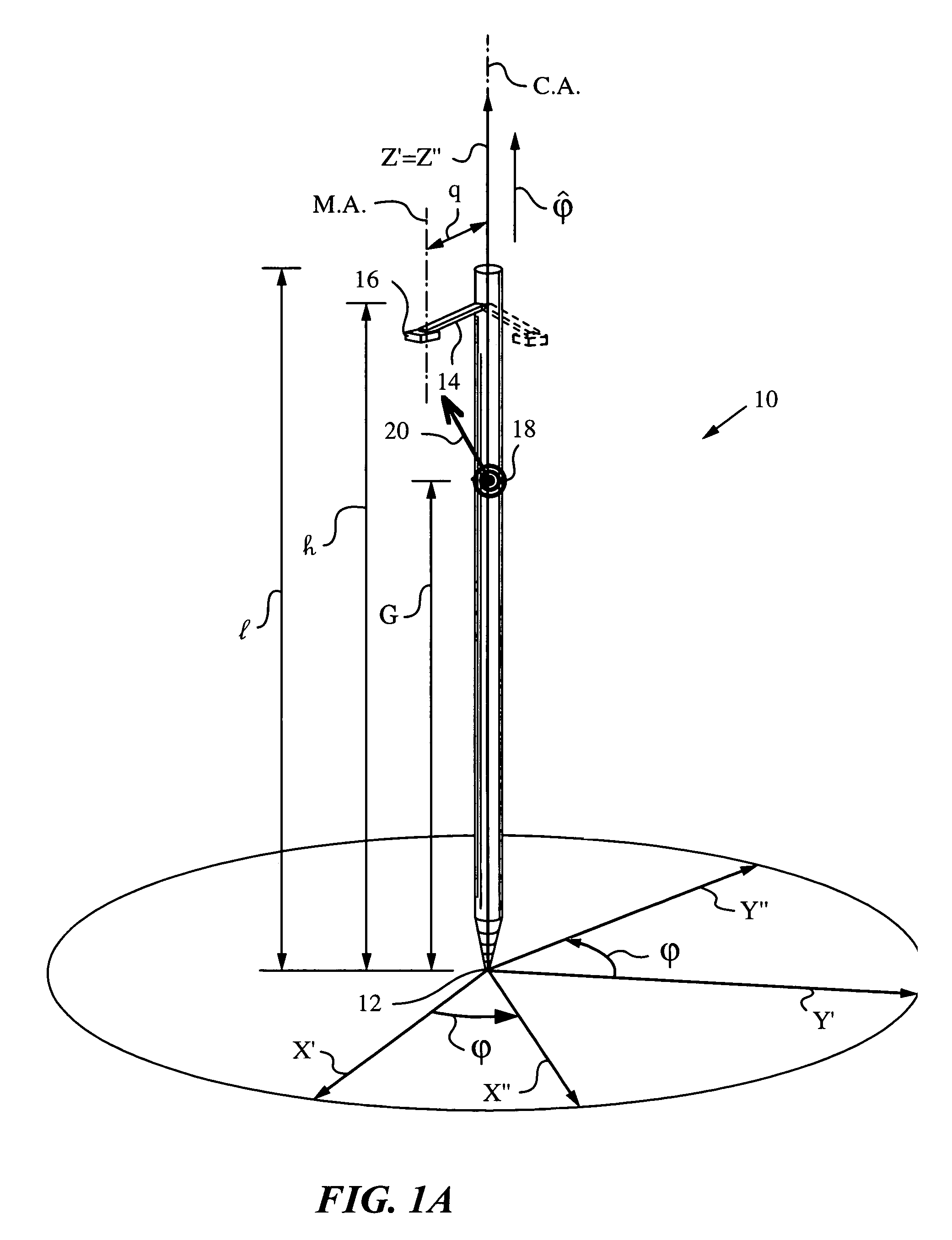
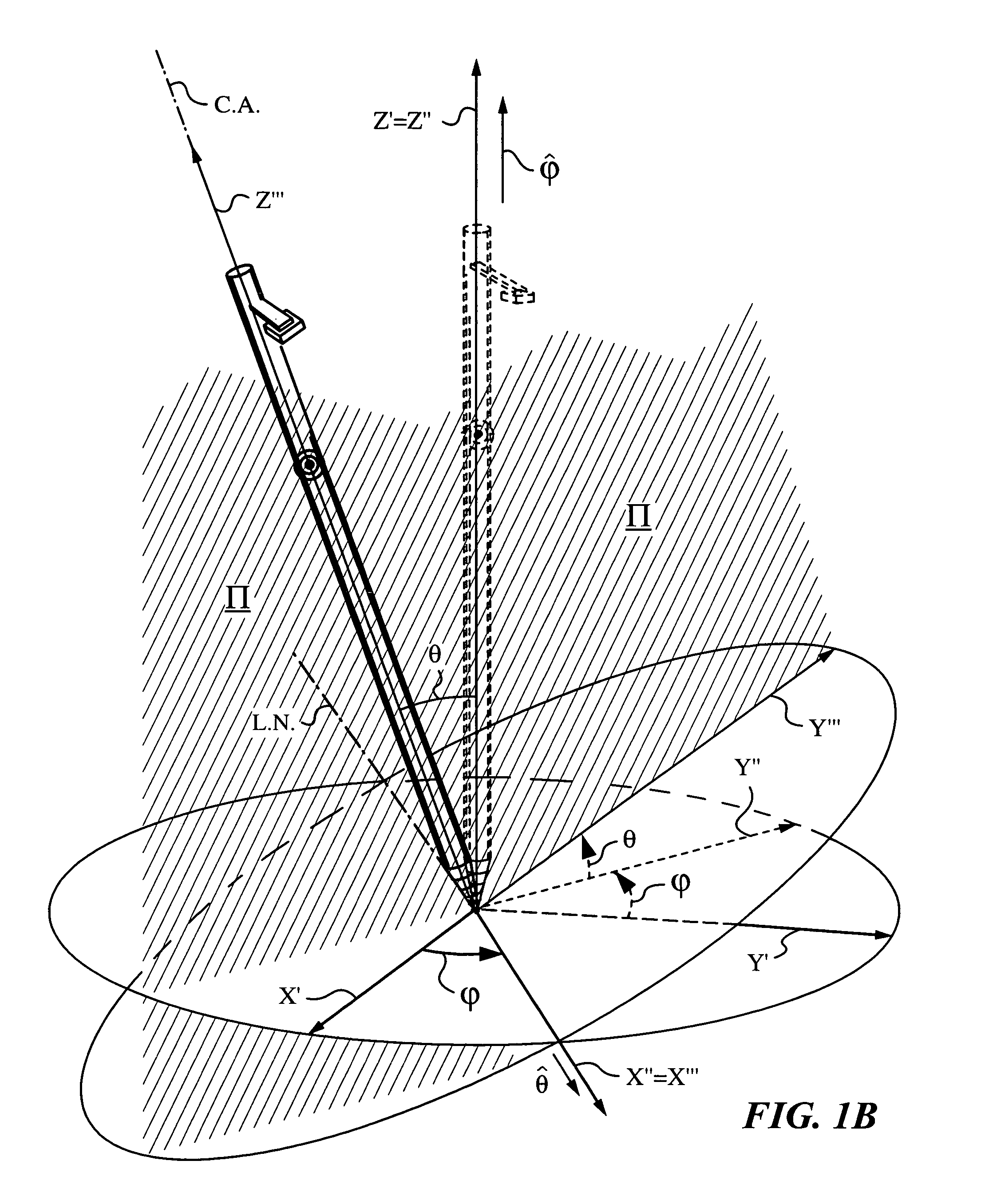
Apparatus and method for determining an inclination of an elongate object contacting a plane surface
An apparatus and method for determining an inclination angle θ between an axis of an elongate object such as a cane, a pointer or a jotting implement such as a pen, pencil, stylus or the like and a normal to a plane surface at times when a tip of the elongate object is contacting that plane surface. The apparatus has an emitter mounted on the object for illuminating the plane surface with a probe radiation at an angle σ with respect to the axis of the object. The apparatus also has a detector mounted on the elongate object for detecting a radiation characteristic of a scattered portion of the probe radiation returning from the plane surface and a computing unit for deriving the inclination angle θ from the radiation characteristic. A scanning arrangement, such as a uniaxial or biaxial scanner, or a light guiding optic can be used for varying angle σ, and the probe radiation can be emitted in the form of a scan beam. Preferably, the emitter and detector of the scattered portion of the probe radiation are integrated and the scattered portion of the probe radiation whose characteristic is being measured is the back-scattered portion. The radiation characteristic detected by the detector can be the intensity, polarization, time-of-flight or any combination thereof.
Owner:ELECTRONICS SCRIPTING PRODS
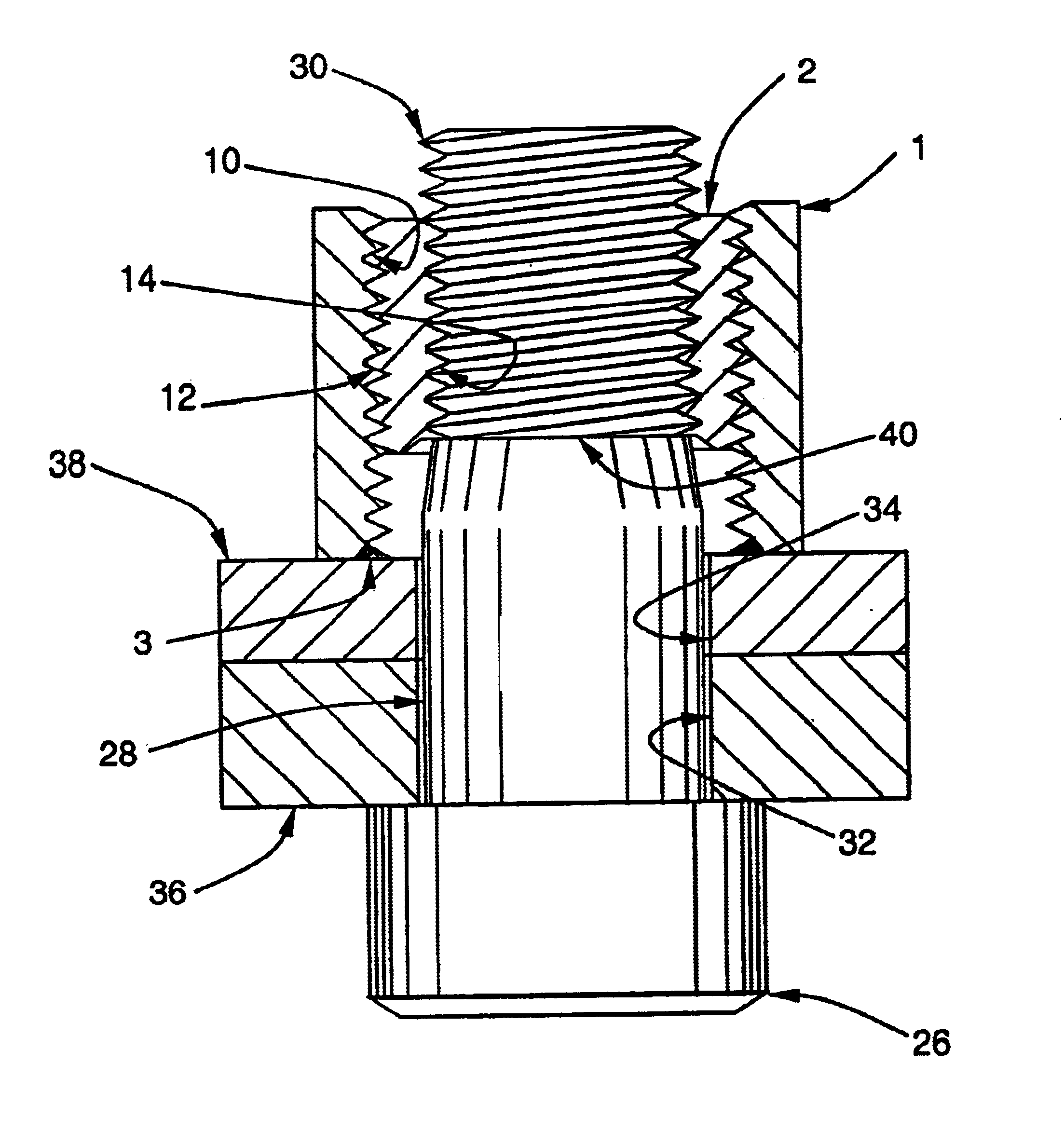
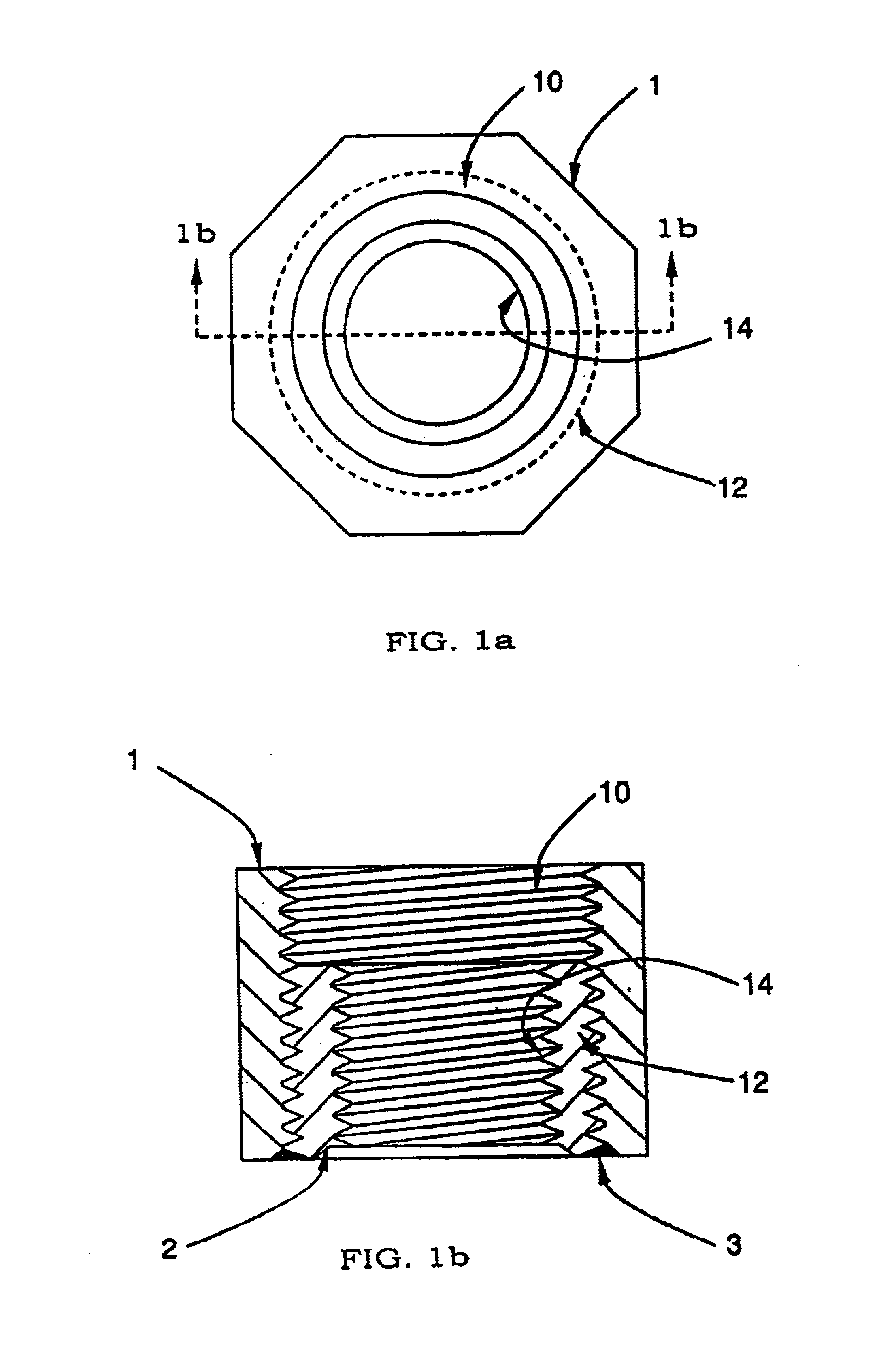
Telescopic nut
A nut assembly is disclosed that will ensure that the shank of a bolt that features a measurable grip length will pass through the contact plane of adjoining members. The nut assembly also allows the desired compressive force in the adjoining members to be attained by using a telescopic feature of the nut to allocate additional thread action for the bolt, enabling the bolt to be drawn into the nut further than what would be allowed by a standard nut. The adaptability of the nut assembly can eliminate the need for washers or shims to adjust the shank penetration of the bolt. The nut assembly is useful for application in which the specified thread length and the grip length of the bolt is incompatable with the abutment thickness of the adjoining members.
Owner:HARING JOSEPH E
Semiconductor device comprising an oxide semiconductor layer
ActiveUS9082857B2Easy to makeGuaranteed high speed operationTransistorStatic indicating devicesMetallic materialsOxygen deficient
A thin film transistor structure in which a source electrode and a drain electrode formed from a metal material are in direct contact with an oxide semiconductor film may lead to high contact resistance. One cause of high contact resistance is that a Schottky junction is formed at a contact plane between the source and drain electrodes and the oxide semiconductor film. An oxygen-deficient oxide semiconductor layer which includes crystal grains with a size of 1 nm to 10 nm and has a higher carrier concentration than the oxide semiconductor film serving as a channel formation region is provided between the oxide semiconductor film and the source and drain electrodes.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
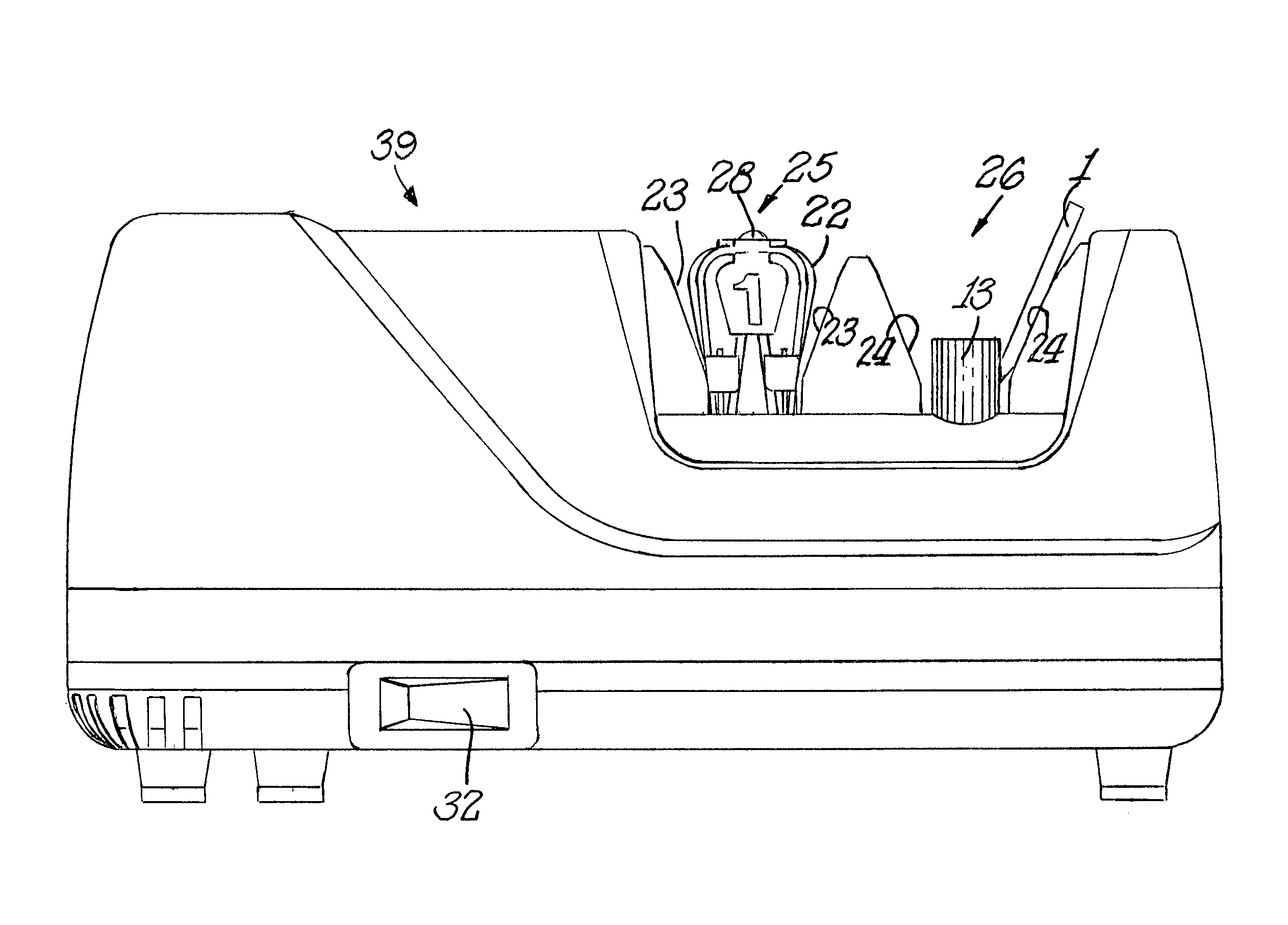
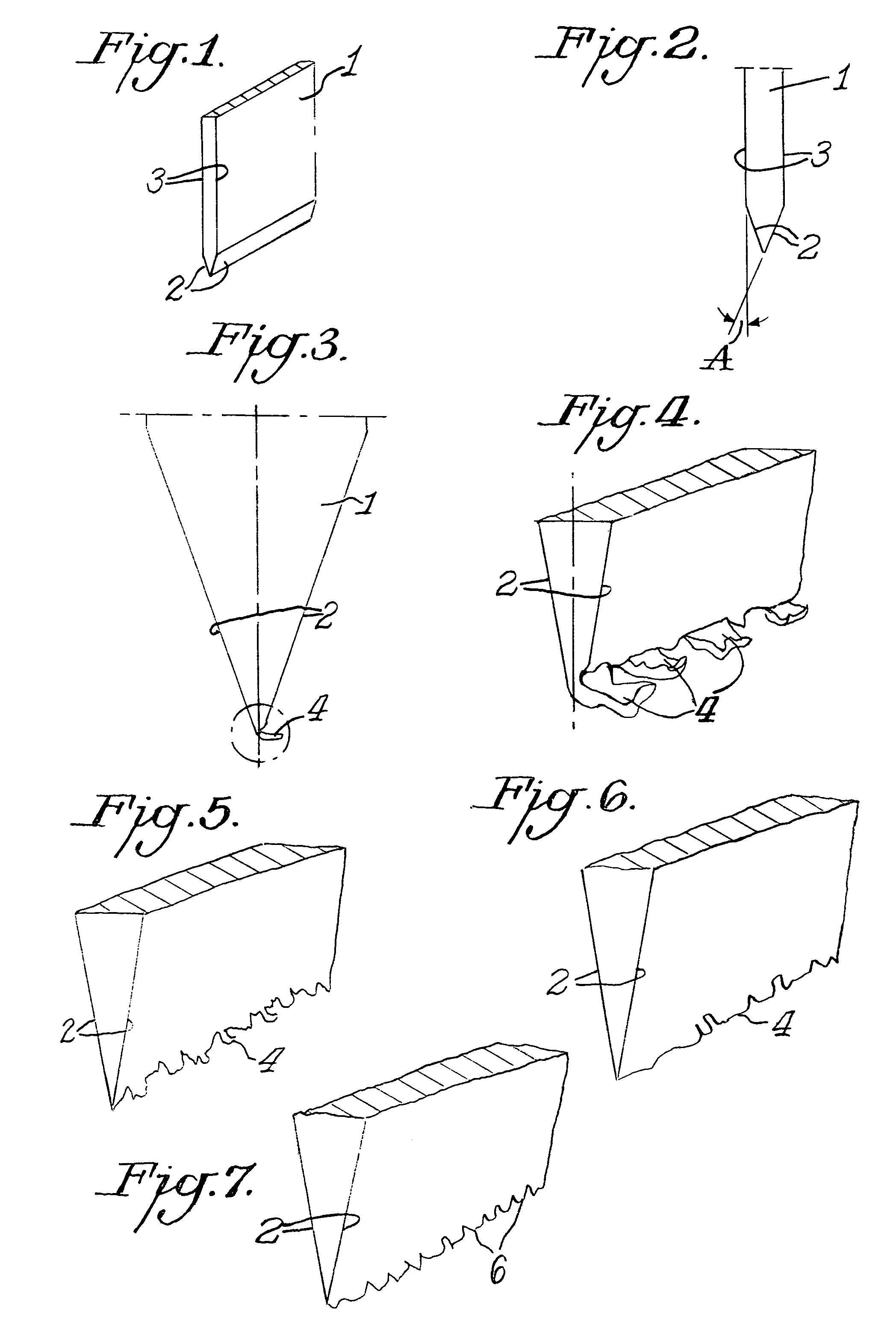
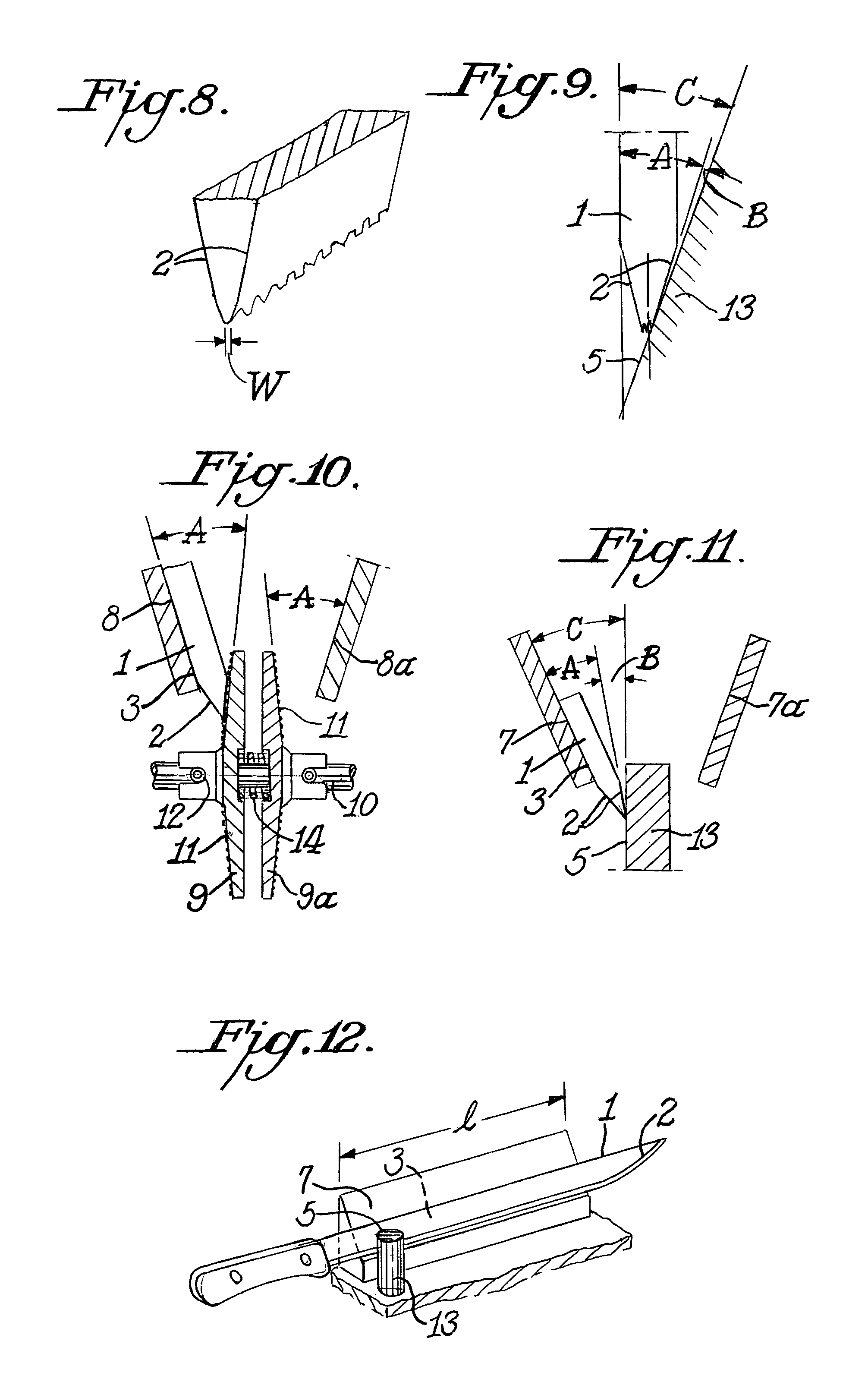
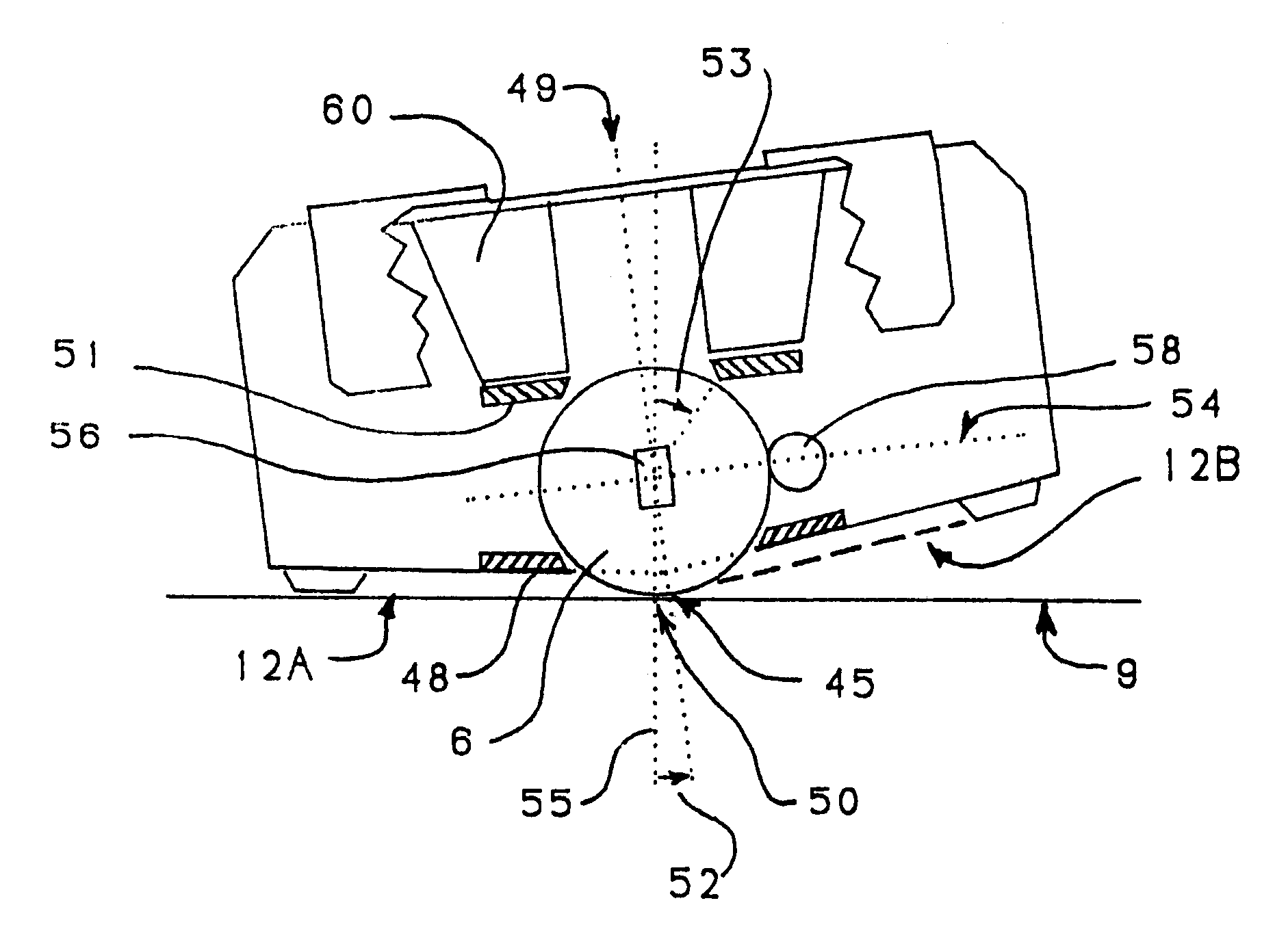
Precision means for sharpening and creation of microblades along cutting edges
A knife-edge conditioning apparatus comprises at least one precision angled knife guide with one face of the knife blade maintained in sustained sliding or rolling contact and which guides the elongated edge of the blade into sustained contact with the hardened surface of an object and positions the plane of the adjacent edge facet at a precise predetermined angle relative to the contact plane of the hardened surface made of a material of equal or greater hardness than the metal of the knife blade without any tendency to abrade as the blade face is moved along the guide with its elongated edge in sustained contact with the hardened surface.
Owner:EDGECRAFT
Multiple signaling mouse with faceted surfaces
InactiveUS6369797B1Easy to controlReduce returnsMechanical apparatusCathode-ray tube indicatorsUser interfaceFacet
A conventional monoplane mouse is constructed to move on a flat surface upon a single plane within which a contained sphere may rotate tangential with the single plane contacting the flat surface. Signal for XY cursor movement are derived from two or more counting sensors positioned at an equator of the rotatable sphere parallel with the single plane. The mouse invention defines two or more facets in the underside housing. The facet mouse can be tilted to one of the exclusive facets and moved on a flat surface to generate XY signals. The facet plane selected by tilt is identified by triggered pressure sensitive switches at each facet plane. The switches also function as undercarriage feet to define the virtual plane of contact to the flat surface. The facet planes in two and four facet embodiments are oriented with the orthogonally placed sphere counting sensors so that the interest of any two opposing facets is parallel with the plane of rotation of one of the counting wheels. A single sphere and counter apparatus can serve all facets, being placed at the intersect of all facets. To aid the hand in applying continuous downward pressure to the mouse onto a preferred facet, a hinged and elevatable palm hood is attached to the top of the mouse. The mouse enables a new user interface beyond the tradition ones of: 1.clicking keys by a finger and 2.whole arm movement of a mouse on an XY surface. By a tilting wrist motion, the user may instantly and continuously toggle 2,4, or more selection assigned to the facets provided.
Owner:MAYNARD JR STUART TYRUS
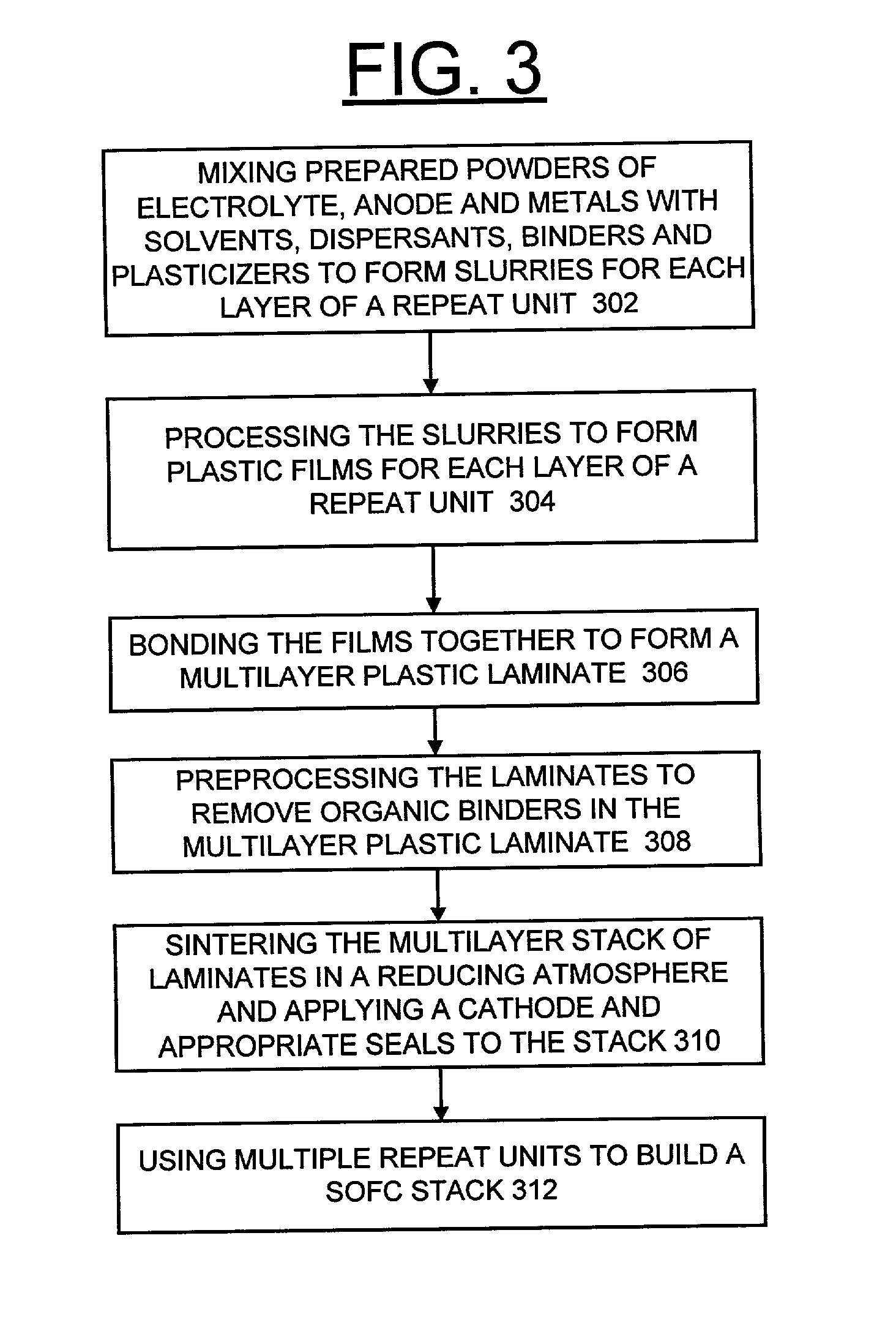
Solid oxide fuel cell with enhanced mechanical and electrical properties
InactiveUS20030232230A1Improve mechanical propertiesGood electrical propertiesFuel cells groupingCeramic shaping apparatusMechanical propertyContact resistance
A solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) repeat unit includes an oxide electrolyte, an anode, a metallic fuel flow field, a metallic interconnect, and a metallic air flow field. The multilayer laminate is made by casting tapes of the different functional layers, laminating the tapes together and sintering the laminate in a reducing atmosphere. Solid oxide fuel cell stacks are made by applying a cathode layer, bonding the unit into a gas manifold plate, and then stacking the cells together. This process leads to superior mechanical properties in the SOFC due to the toughness of the supporting metallic layers. It also reduces contact resistances in stacking the cells since there is only one physical contact plane for each repeat unit.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
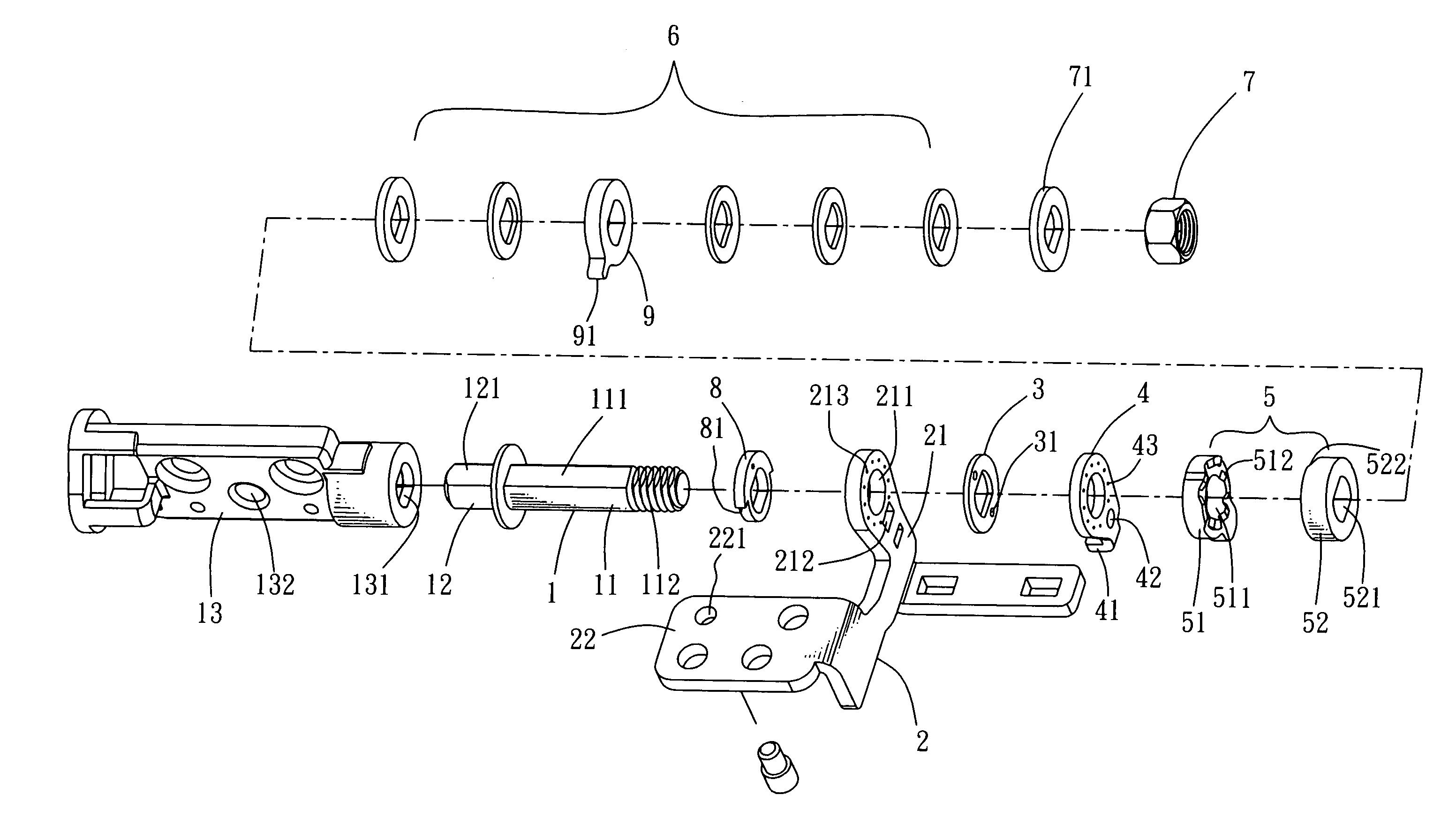
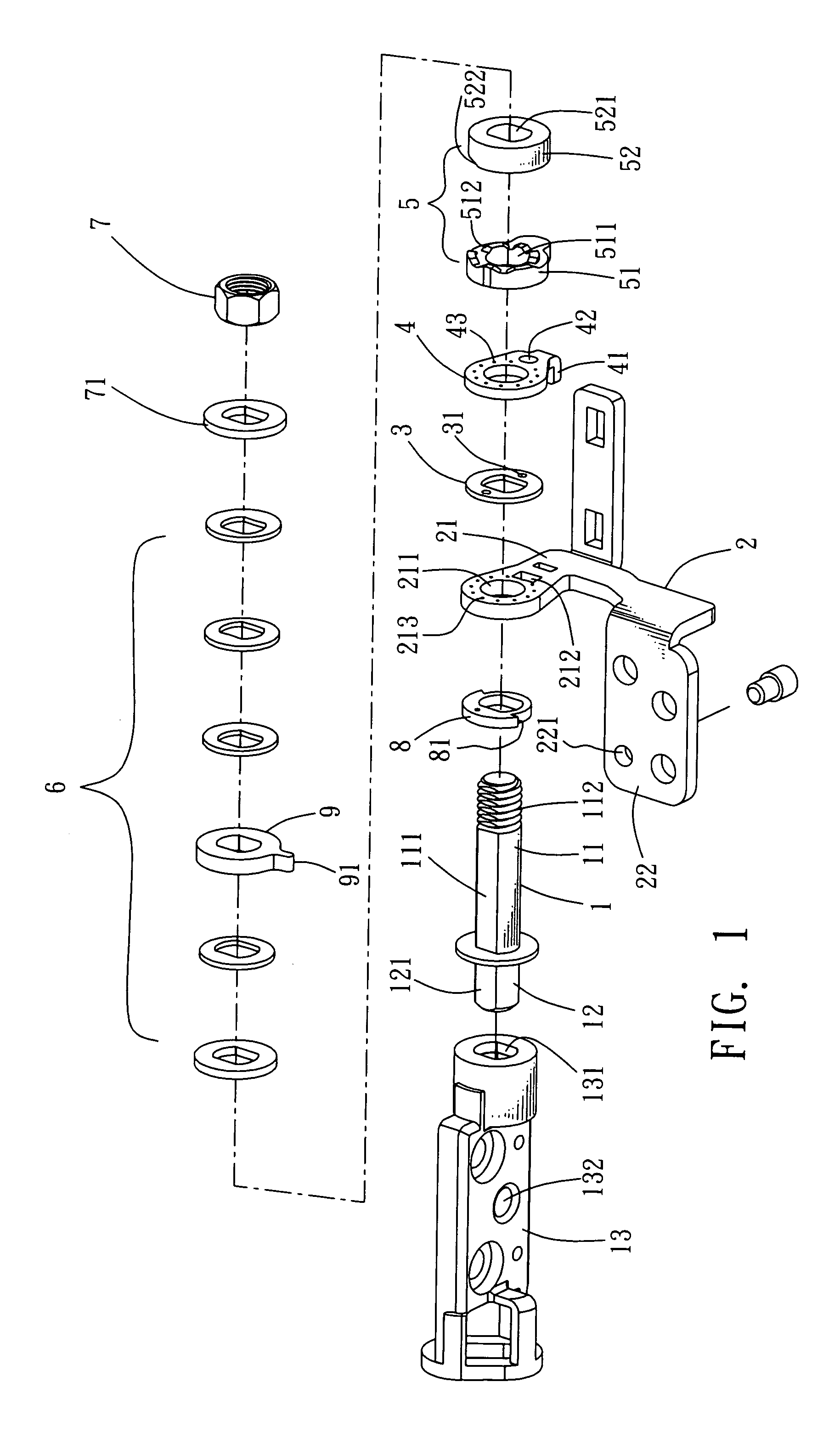
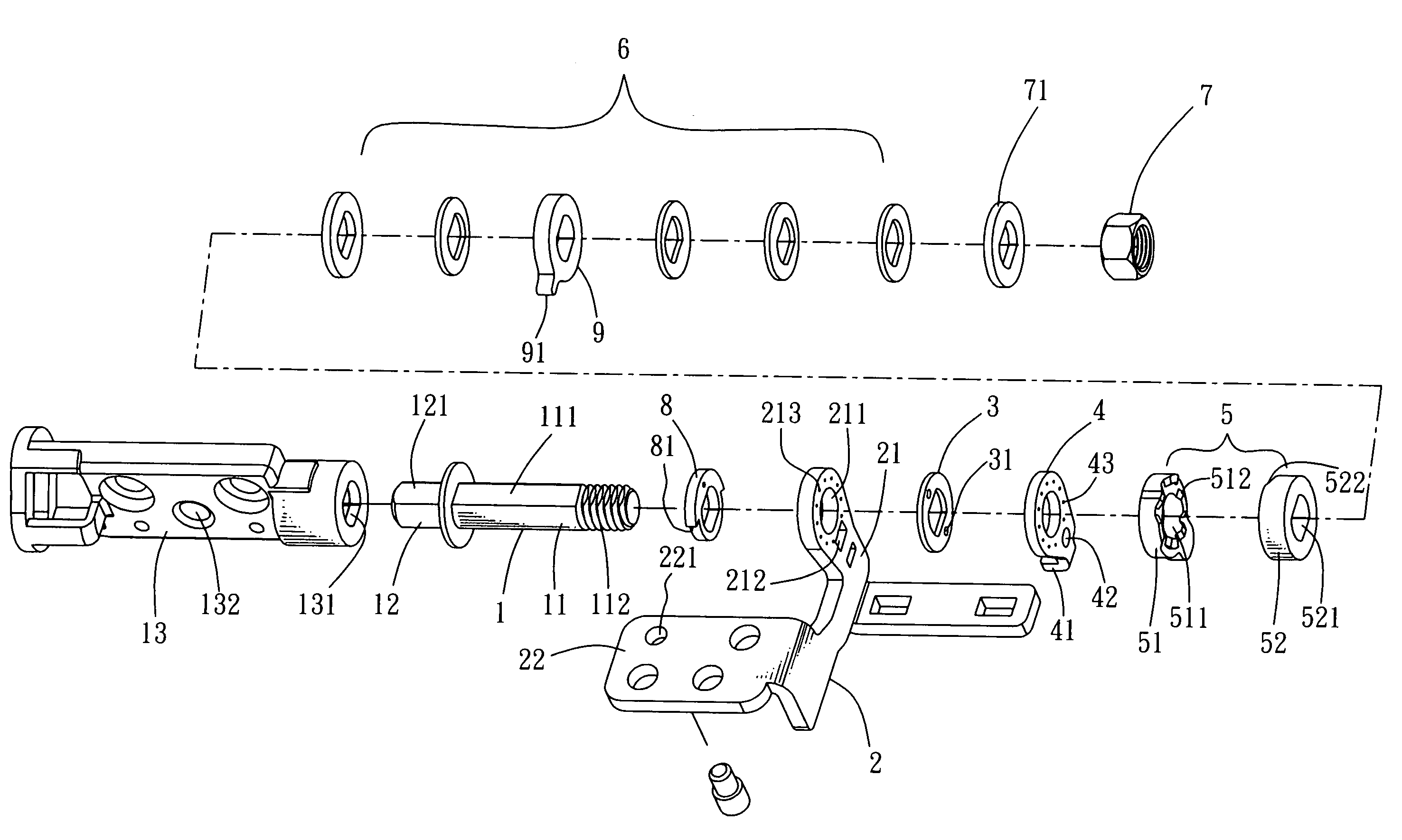
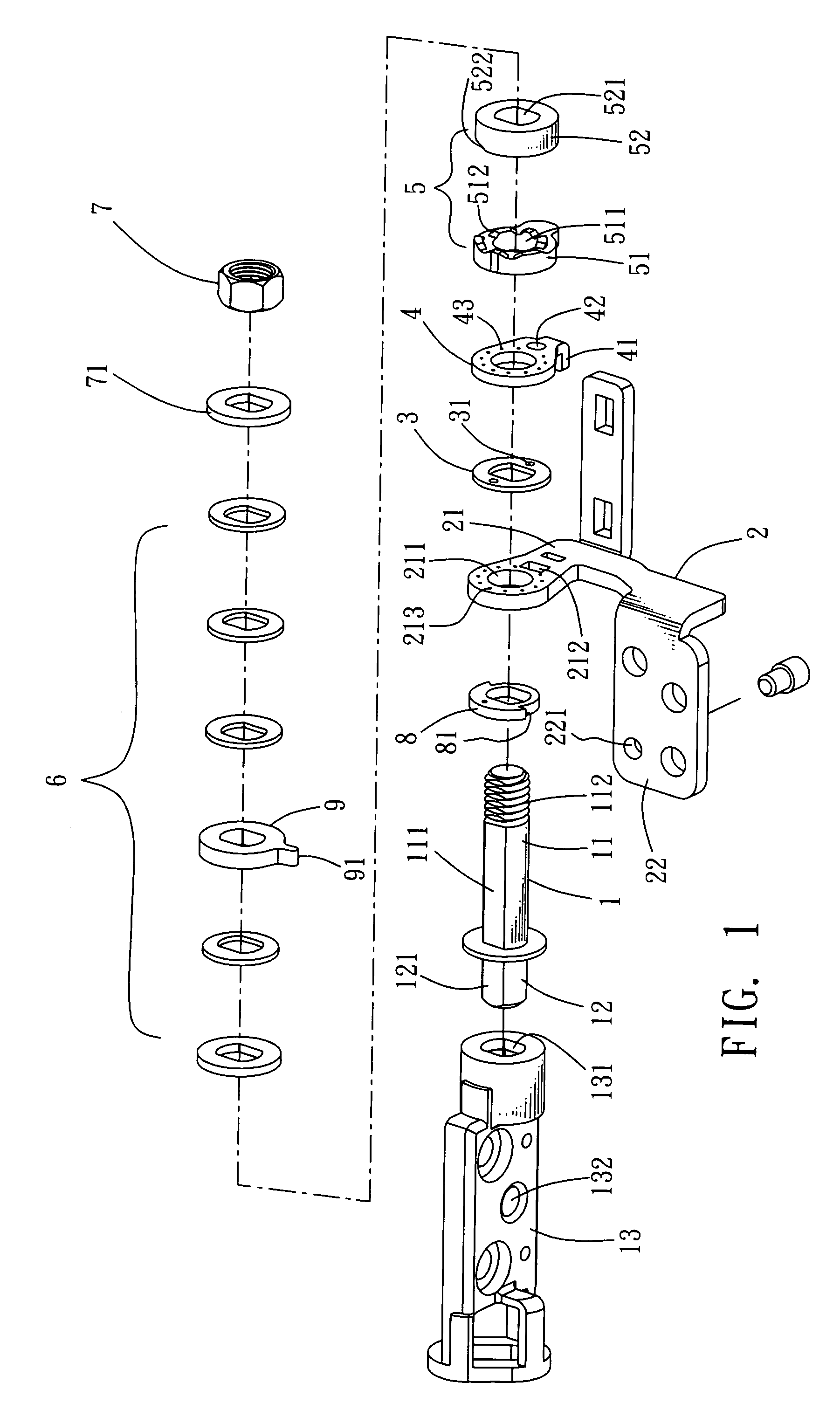
Rotating shaft structure with automatic locking mechanism
ActiveUS20070169312A1Limit angle movementWing accessoriesSubstation equipmentCircular discAxial pressure
The present invention discloses a rotating shaft structure with automatic locking mechanism, characterized in which a shaft extending axially from an axial member passes through, in sequence, the core hole of the upright frame plane of the main frame, a friction disc, a disc-like connecting part connected with the frame plane, a cam member comprising a fastening part and a sliding part, at least an elastic body, and a connecting segment on the free end of the shaft connected with a end enclosure so as to form axial pressure to constrain the elements described above. The shaft and the main frame are provided with a linking portion and a connecting portion, respectively. The outer and inner edges of the adjoining planes between the fastening part and the sliding part are provided with at least a wedge block and at least a wedge slot alternately so as to connect the fastening part and the sliding part together. Consequently, when the axial member rotates, the inclined plane of the wedge slot of the sliding part moves upward along the inclined plane of the wedge block and thus axially presses the elastic body so as to prompt the contact plane of the sliding part to rotate along the wedge blocks of the fastening part. When the axial member rotates reversely, the wedge slots of the sliding part move to the wedge blocks of the fastening part and, under the extending action of the elastic body, the wedge slots are engaged into the wedge blocks so as to form an automatic locking of butting joint.
Owner:HO CHI JUNG +2
Planar blind-mate connectors
InactiveUS6409550B1Reduce contact wearEliminate crosstalkTwo pole connectionsAntenna connectorsInterconnectionEngineering
A planar connector is constructed to permit large numbers of two part connectors to be ganged for concurrent interconnection with virtually no cross talk between adjacent connectors and minimal damage due to misalignment of the large number in the array that are concurrently connected. Cross talk is minimized by having contact of the connector elements occur in shielded regions or below the plane of contact of the opposing contact members while the engaging members are planar mating interfaces at the point of engagement, thus materially reducing wear relative to a pin and socket type contact. This feature allows these planar blind-mate connectors to operate over one hundred thousand mating cycles. Contact with antennas and printed circuits is provided, and floating inner and outer contacts provide a superior long life rotary joint providing excellent r.f. performance. The connector body is held in a support and remains stationary in said support in the presence of movement of the planar contacts.
Owner:AEROFLEX WEINSCHEL
Pallet-dolly
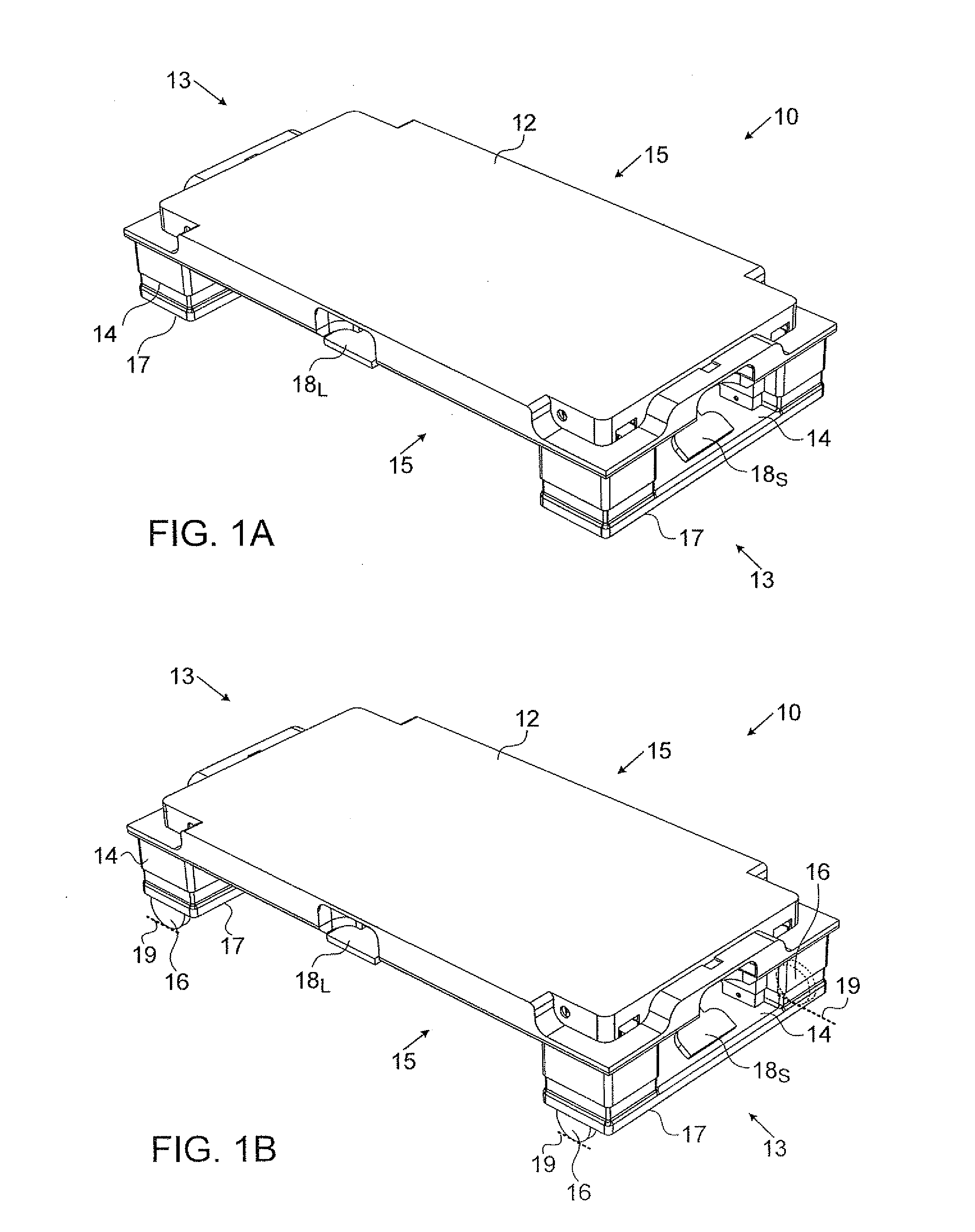
InactiveUS20130119623A1Carriage/perambulator with multiple axesHand carts with one axisGround contactEngineering
A pallet-dolly device convertible between a pallet and a dolly has a generally rectangular deck to which a set of dolly wheels are attached at a fixed height below the deck. A set of movable pallet skids are moved by a skid displacement mechanism between a skid lowered position in which a ground contacting surface of the skid is lowered below a contact plane of the wheels to provide a pallet state of the pallet-dolly device, and a skid raised position in which the skid ground contacting surface is raised above the wheel contact plane to provide a dolly state of the pallet-dolly device. At least two pedals, accessible from two adjacent sides of the deck, are deployed to be operated by a user to activate the skid displacement mechanism.
Owner:TOSCA ISRAEL REUSABLE SOLUTIONS LTD
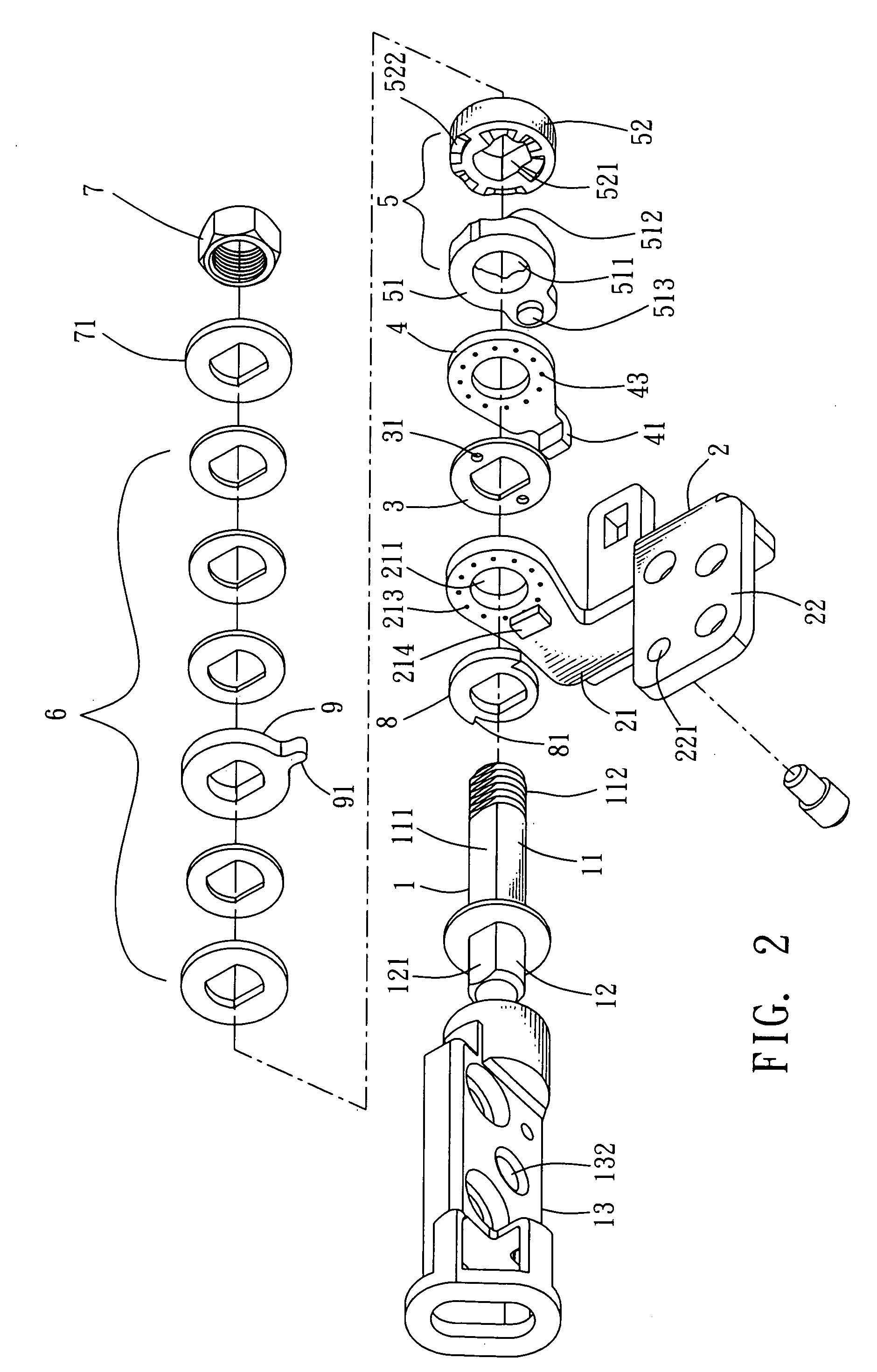
Rotating shaft structure with automatic locking mechanism
The present invention discloses a rotating shaft structure with automatic locking mechanism, characterized in which a shaft extending axially from an axial member passes through, in sequence, the core hole of the upright frame plane of the main frame, a friction disc, a disc-like connecting part connected with the frame plane, a cam member comprising a fastening part and a sliding part, at least an elastic body, and a connecting segment on the free end of the shaft connected with a end enclosure so as to form axial pressure to constrain the elements described above. The shaft and the main frame are provided with a linking portion and a connecting portion, respectively. The outer and inner edges of the adjoining planes between the fastening part and the sliding part are provided with at least a wedge block and at least a wedge slot alternately so as to connect the fastening part and the sliding part together. Consequently, when the axial member rotates, the inclined plane of the wedge slot of the sliding part moves upward along the inclined plane of the wedge block and thus axially presses the elastic body so as to prompt the contact plane of the sliding part to rotate along the wedge blocks of the fastening part. When the axial member rotates reversely, the wedge slots of the sliding part move to the wedge blocks of the fastening part and, under the extending action of the elastic body, the wedge slots are engaged into the wedge blocks so as to form an automatic locking of butting joint.
Owner:HO CHI JUNG +2
Power connector having a contact configured to transmit electrical power to separate components
ActiveUS8057266B1Electric discharge tubesCoupling contact membersElectricityElectric power transmission
Power connector including a connector housing having a mating side configured to engage an electrical connector. The connector housing also has a mounting side configured to interface with a circuit board. The connector housing includes a housing cavity that opens to the mating side. The power connector also includes a power contact that is held within the housing cavity. The power contact includes a body panel that extends along a contact plane and has board terminals and a contact terminal that extend from the body panel. The board terminals extend away from the body panel in a mounting direction to engage the circuit board. The contact terminal extends in a different direction that is one of parallel to the circuit board or away from the circuit board. The power contact is configured to transmit electrical power through the board terminals and through the contact terminal.
Owner:TYCO ELECTRONICS LOGISTICS AG (CH)
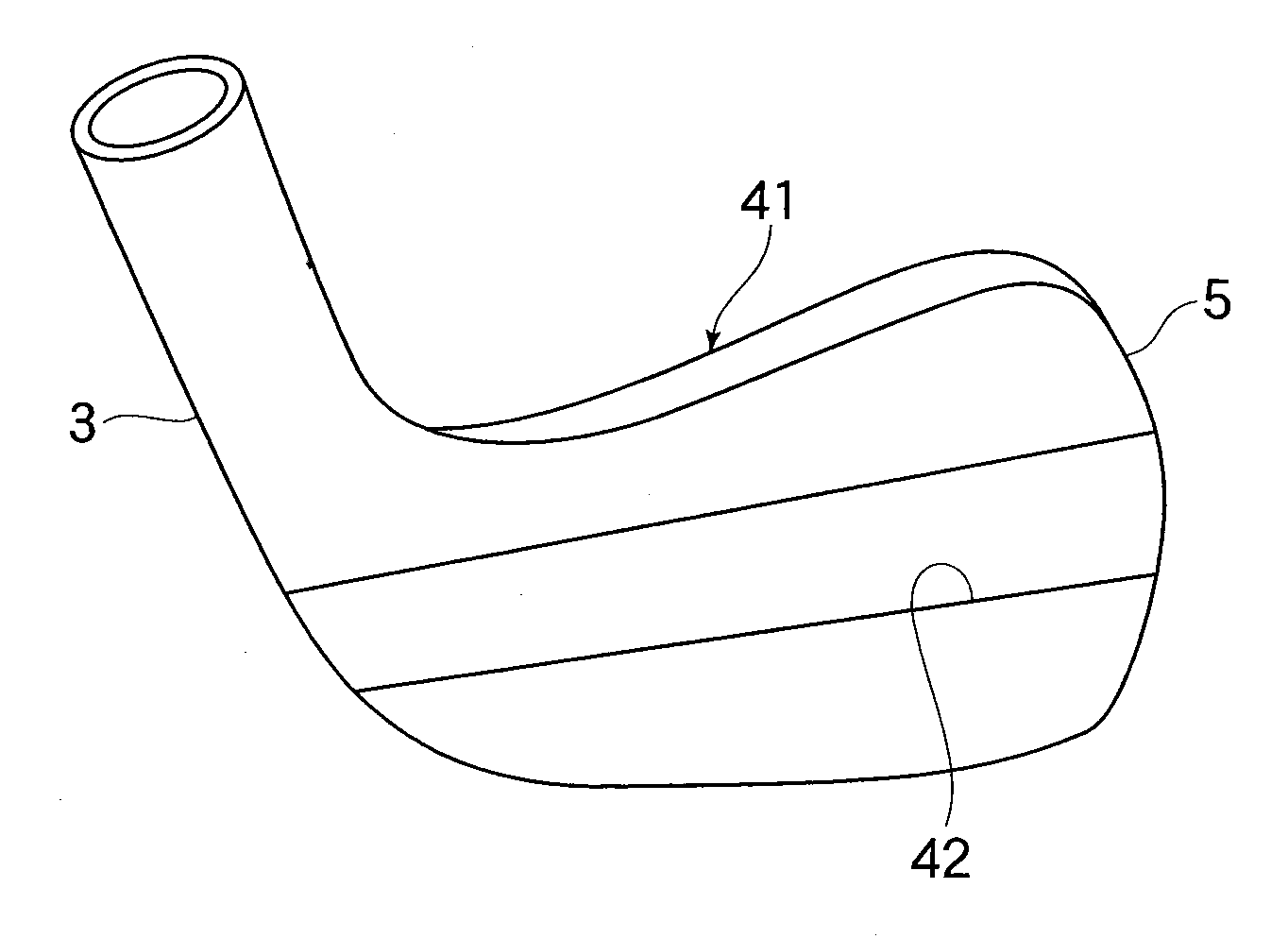
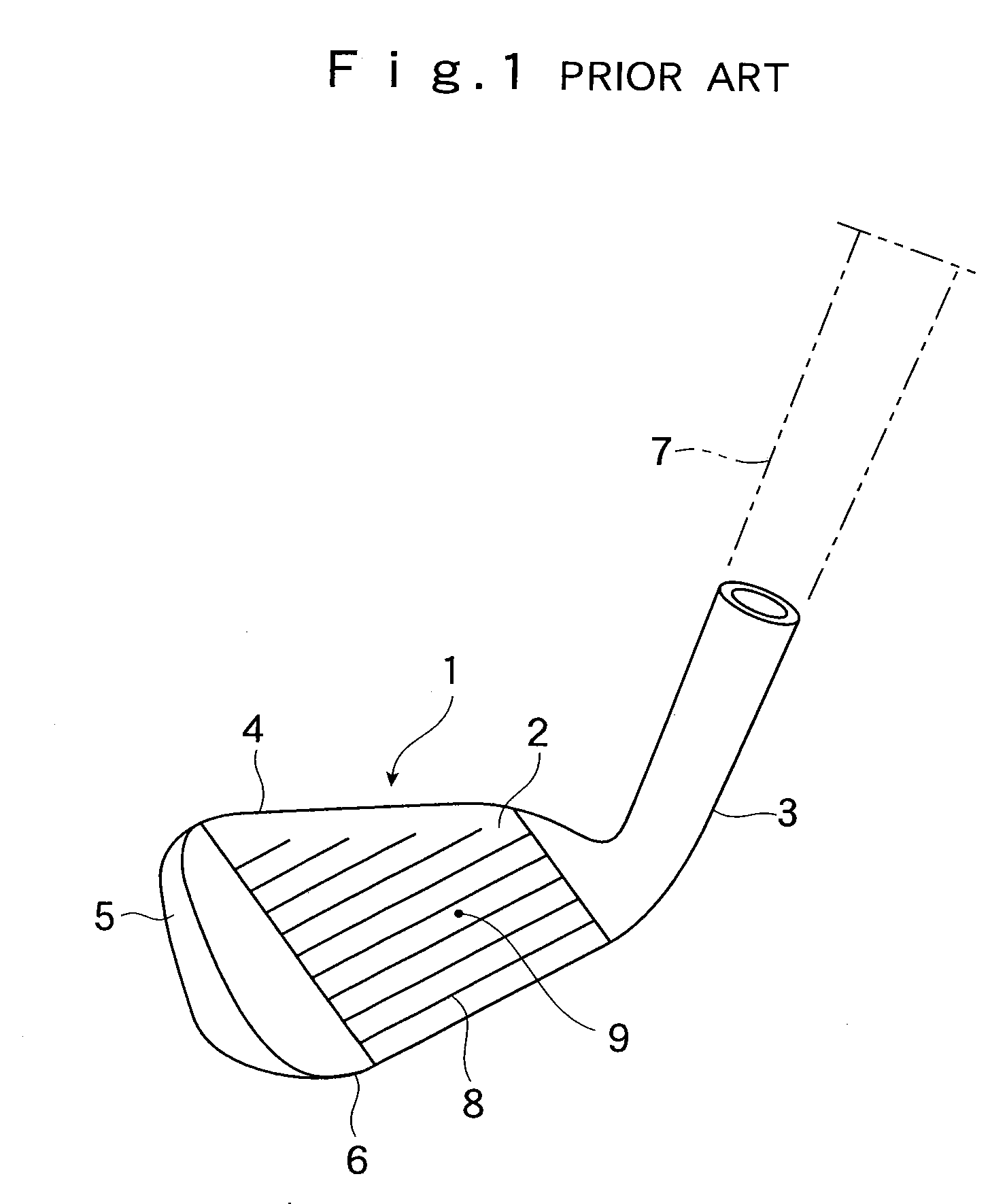
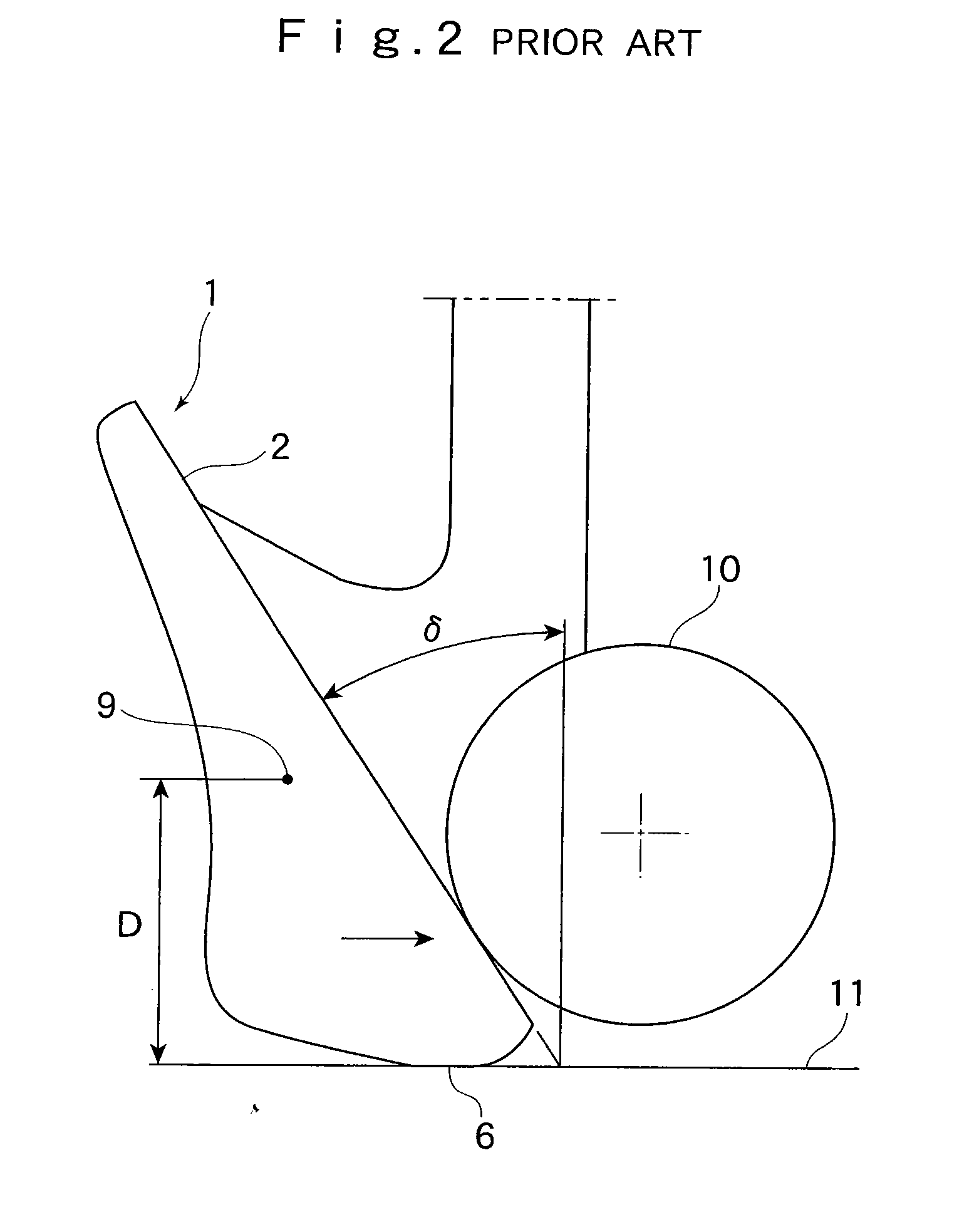
Iron golf club
InactiveUS20090023513A1Reduce decreaseIncrease flexibilityGolf clubsRacket sportsGround contactGear wheel
An iron golf club for enhancing the gear effect and accelerating backspin of a ball. The head, which comprises a face part having a ball-hitting surface, a sole part having a ground-contact plane in the bottom portion of the head, a top part, and a hosel part, is configured such that the rigidity on the ground-contact plane side of the bottom portion is lowered by either providing the portion with a cavity or changing its material. Further, the vertical moment of inertia of the head is reduced by disposing a weight in the location of the center of gravity of the head. When the length of the hosel part is 50 mm or longer, the value of the moment of inertia becomes less than 800 g·cm2, and when the length of the hosel part is less than 50 mm, the value of the moment of inertia becomes 750 g·cm2 or less. These configurations realize a golf club that enhances the gear effect and accelerates spin of a ball.
Owner:ENDO MFG COMPANY
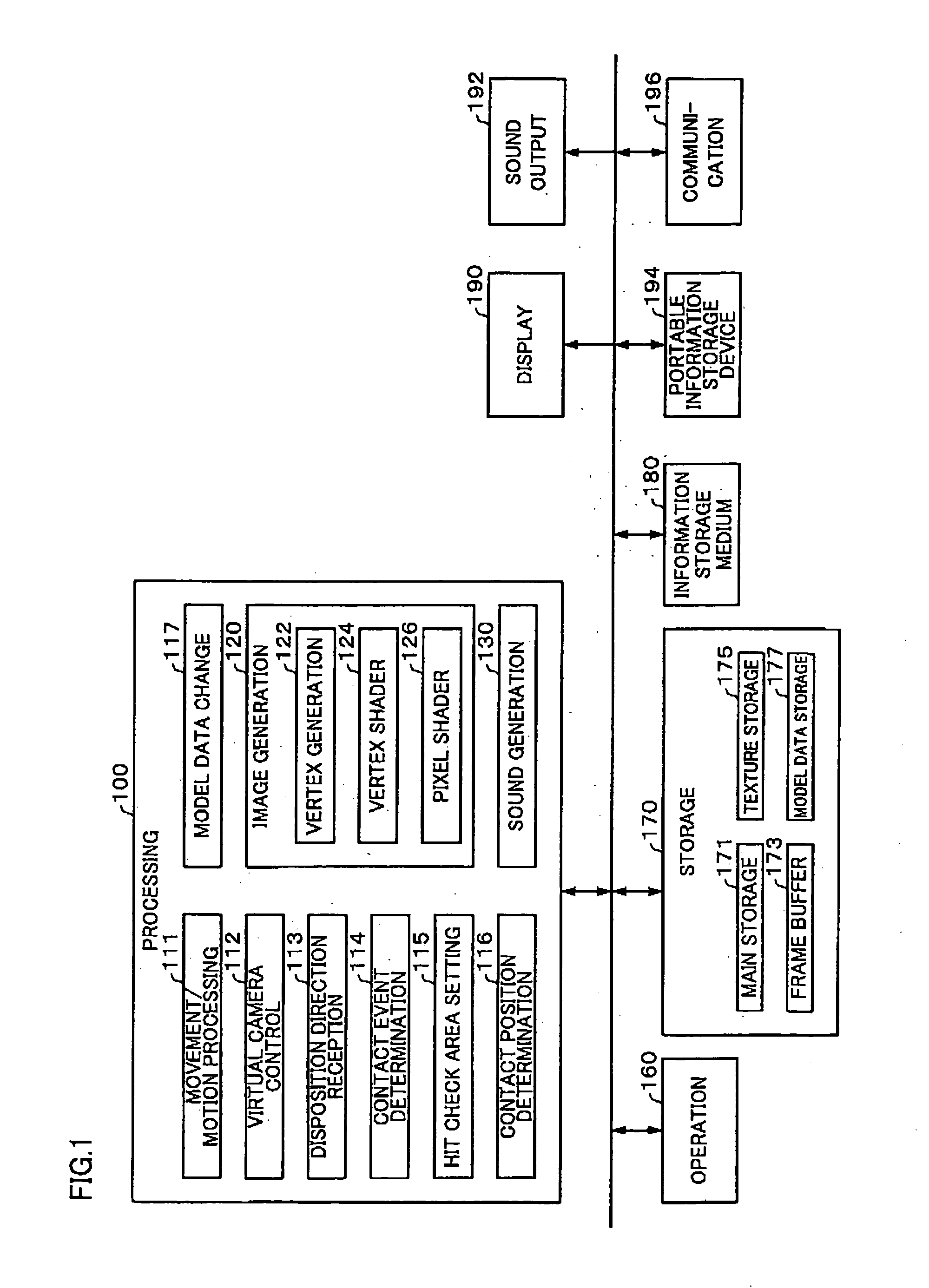
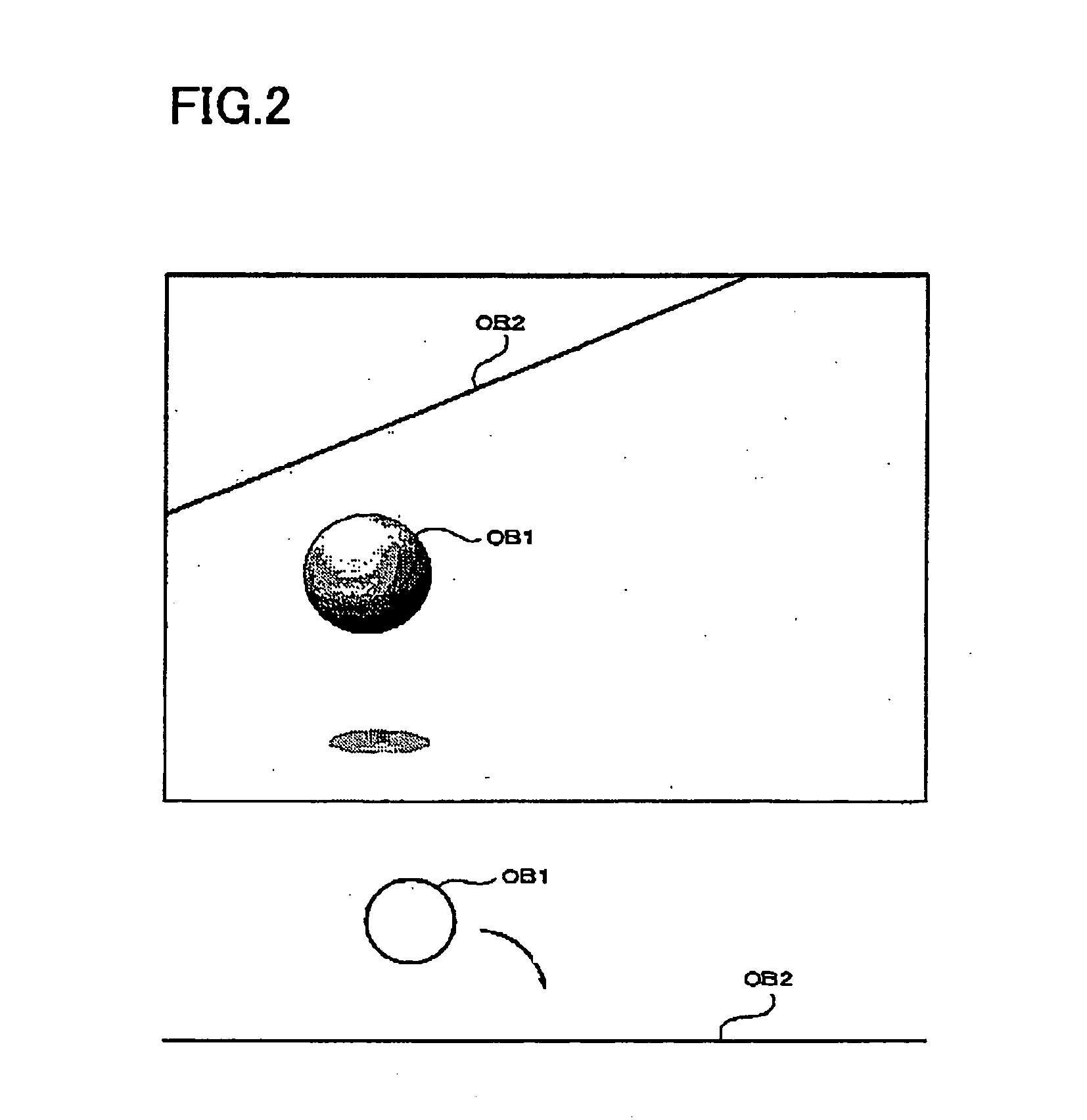
Program, information storage medium, image generation system, and image generation method
An image generation system generates an image of an object space viewed from a given viewpoint. When a contact event in which a first model object comes in contact with a second model object in the object space has occurred, height information of grid points corresponding to a contact plane of the first model object is fetched by referring to height map data in which height information of a surface of the first model object with respect to a given reference plane set for the fist model object is set in a grid pattern, and vertices of a contact plane of the second model object arm moved based on the fetched height information of the grid points.
Owner:BANDAI NAMCO ENTERTAINMENT INC
Cable structure with improved grounding termination in the connector
InactiveUS6857899B2Improve signal integrityReduce the possibilityTwo-part coupling devicesCoupling protective earth/shielding arrangementsElectrical conductorContact position
A cable structure for signal transmission comprises a connector housing and a plurality of housing contacts positioned within a defined contact plane in the connector housing. The housing contacts are configured for engaging external contacts of a device when the cable structure is coupled to a device. At least one signal conductor terminates in the connector housing, and is electrically coupled to one of the housing contacts generally in said contact plane. At least one ground conductor terminates in the connector housing, in a second plane spaced from the contact plane. A shorting bar has a first portion positioned generally in said contact plane and electrically coupled to a housing contact. A second portion of the shorting bar is positioned generally in said second plane and is electrically coupled to the ground conductor. The shorting bar maintains the signal conductor and ground conductor termination within separate spaced planes to improve the signal integrity of the cable structure while keeping the housing contacts in a common plane.
Owner:CARLISLE INTERCONNECT TECH
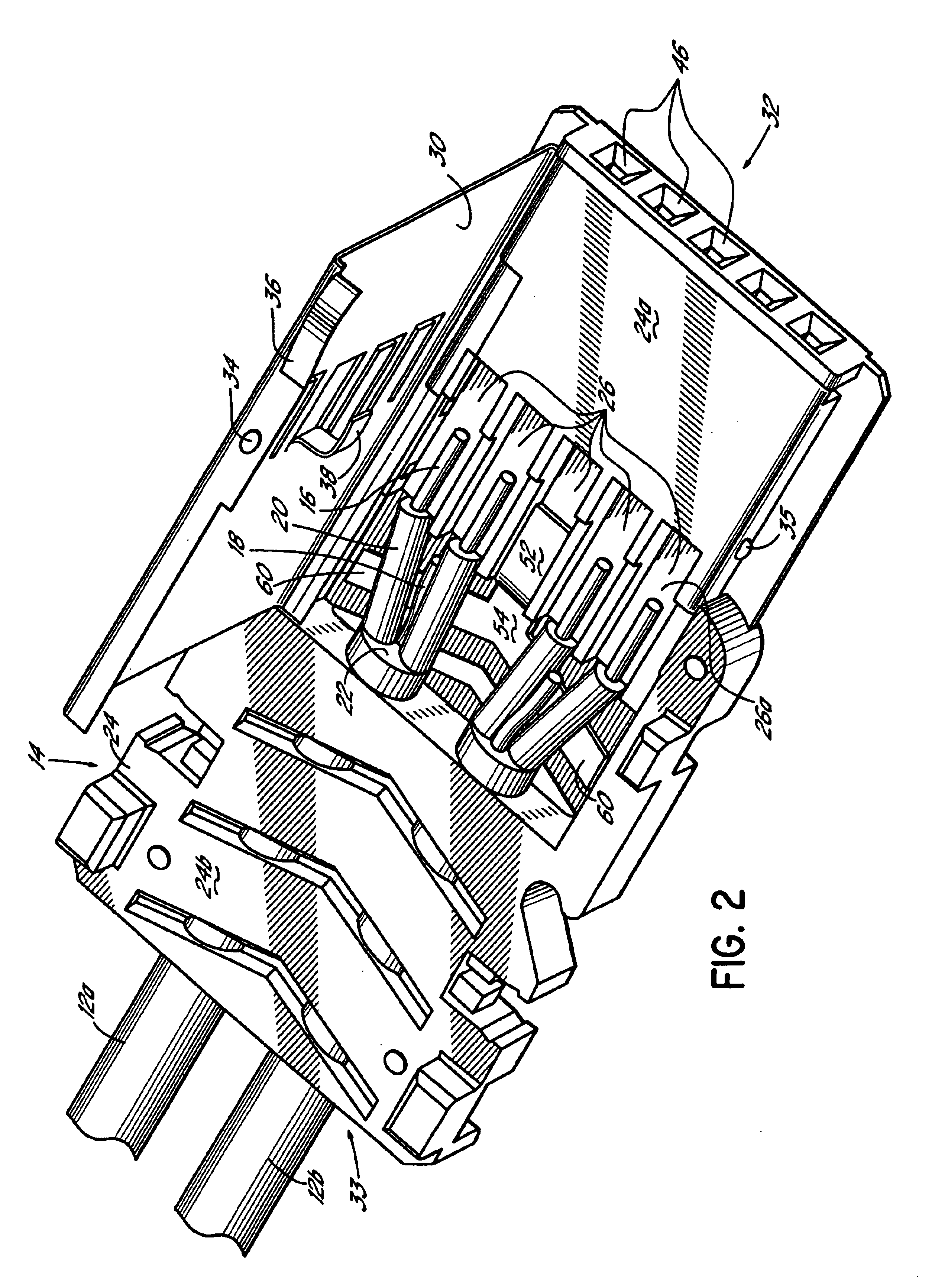
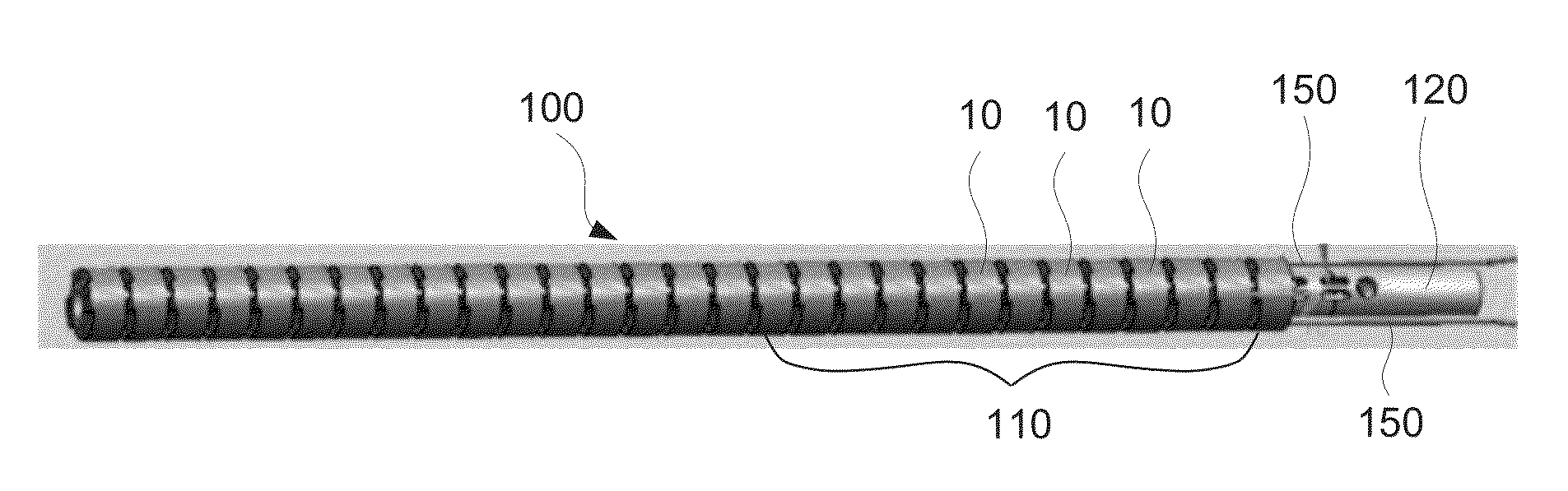
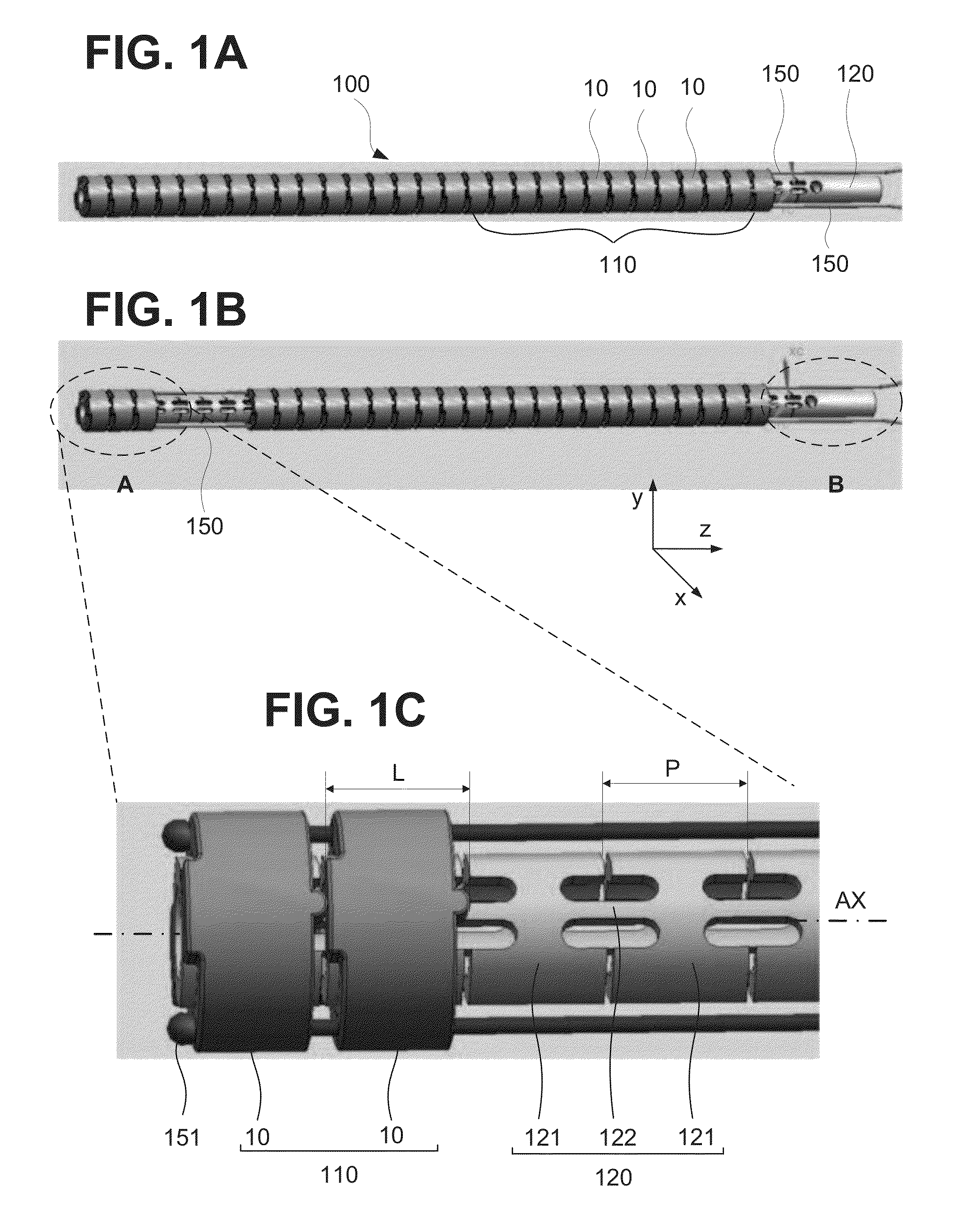
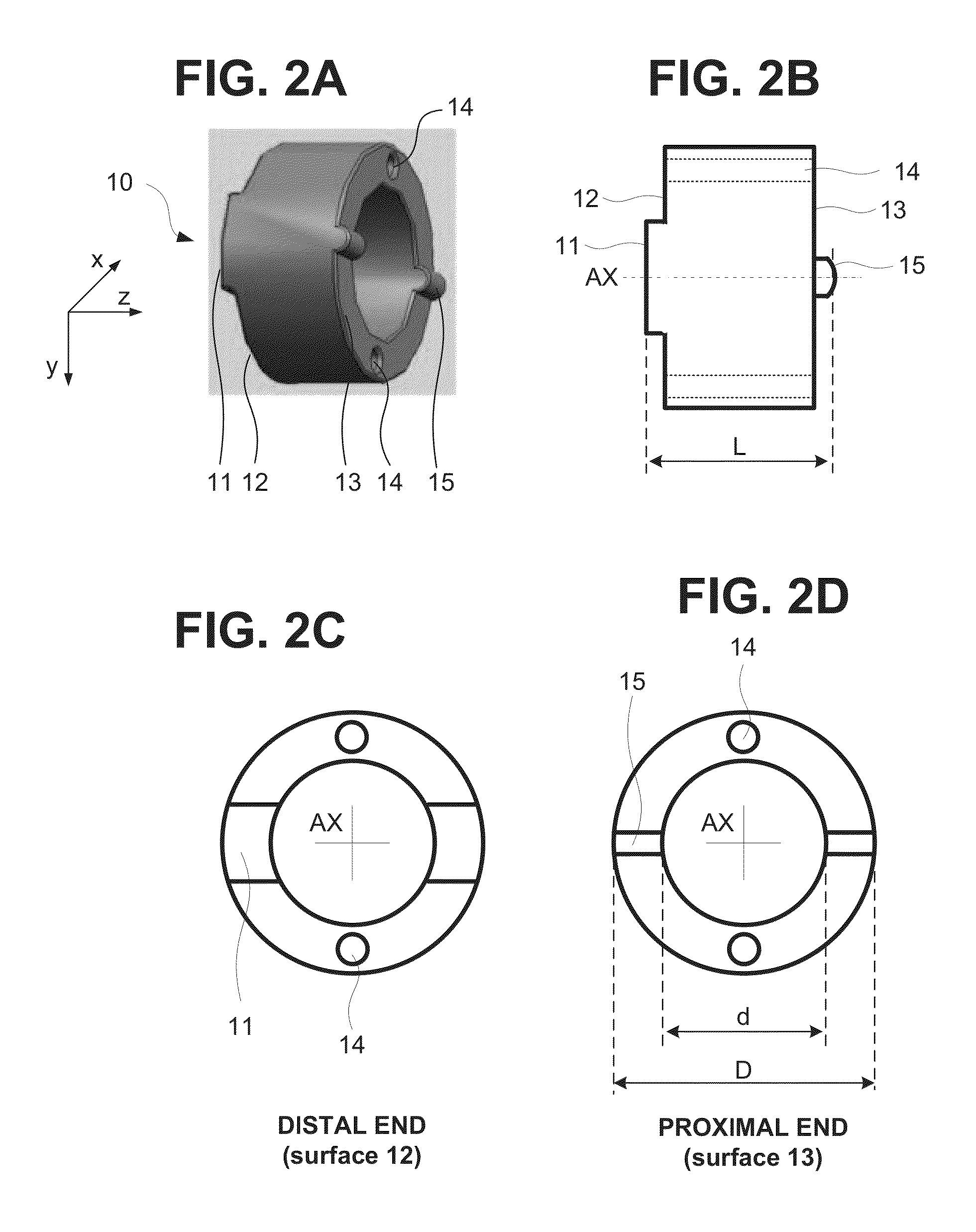
Mechanical structure of articulated sheath
A sheath apparatus includes, a plurality of node rings configured to be tilted with respect to each other, each node ring defining a substantially cylindrical wall and having at least one hole passing through said cylindrical wall, the plurality of node rings being arranged next to each other along a linear axis such that consecutive node rings contact each other at a contact plane; a manipulating wire going through the holes in said stacked node rings; and a position restoring component configured to restore said stacked node rings from a tilted position to an original position, wherein said position restoring component is located inside or outside of the stacked node rings.
Owner:CANON USA +1
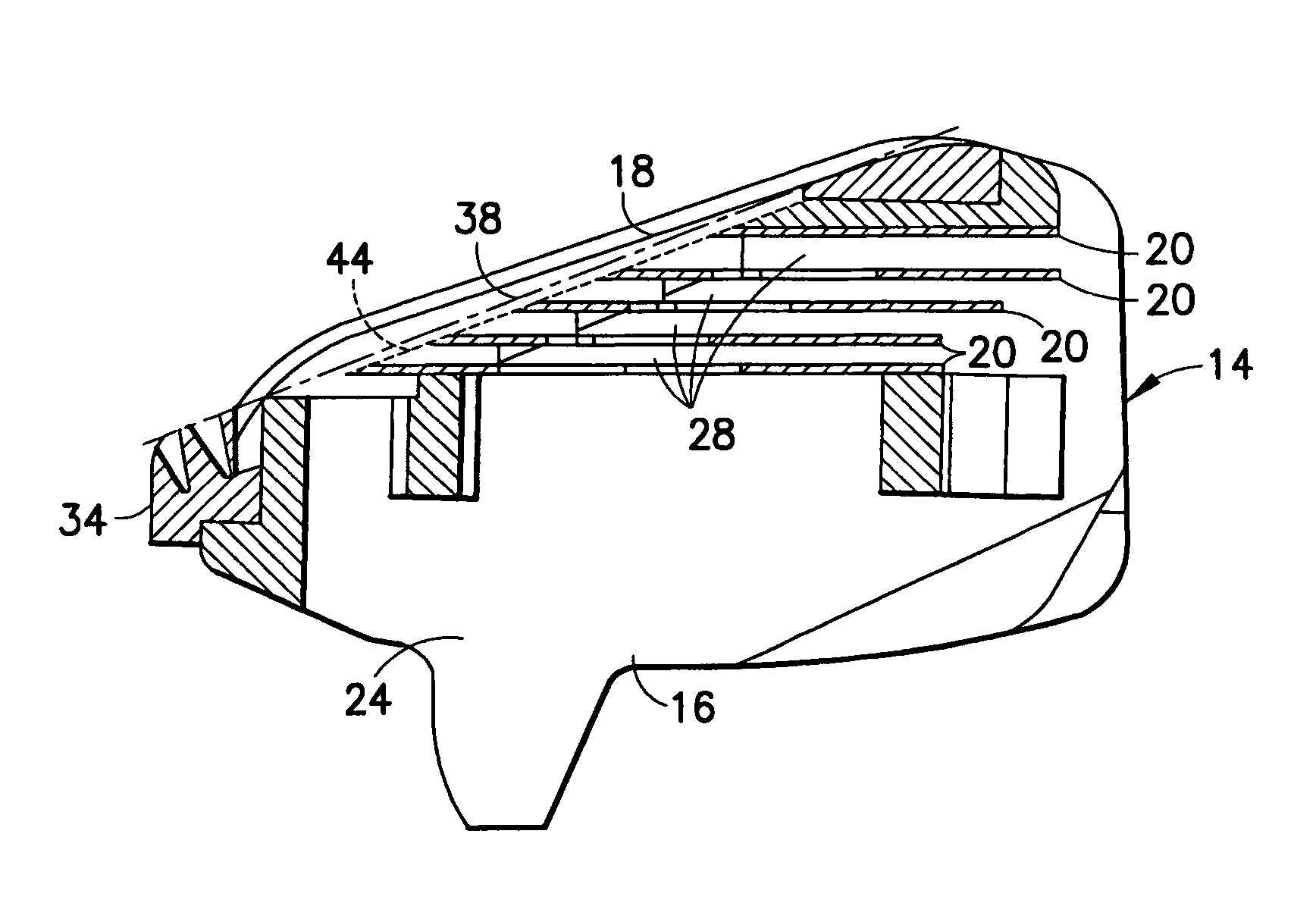
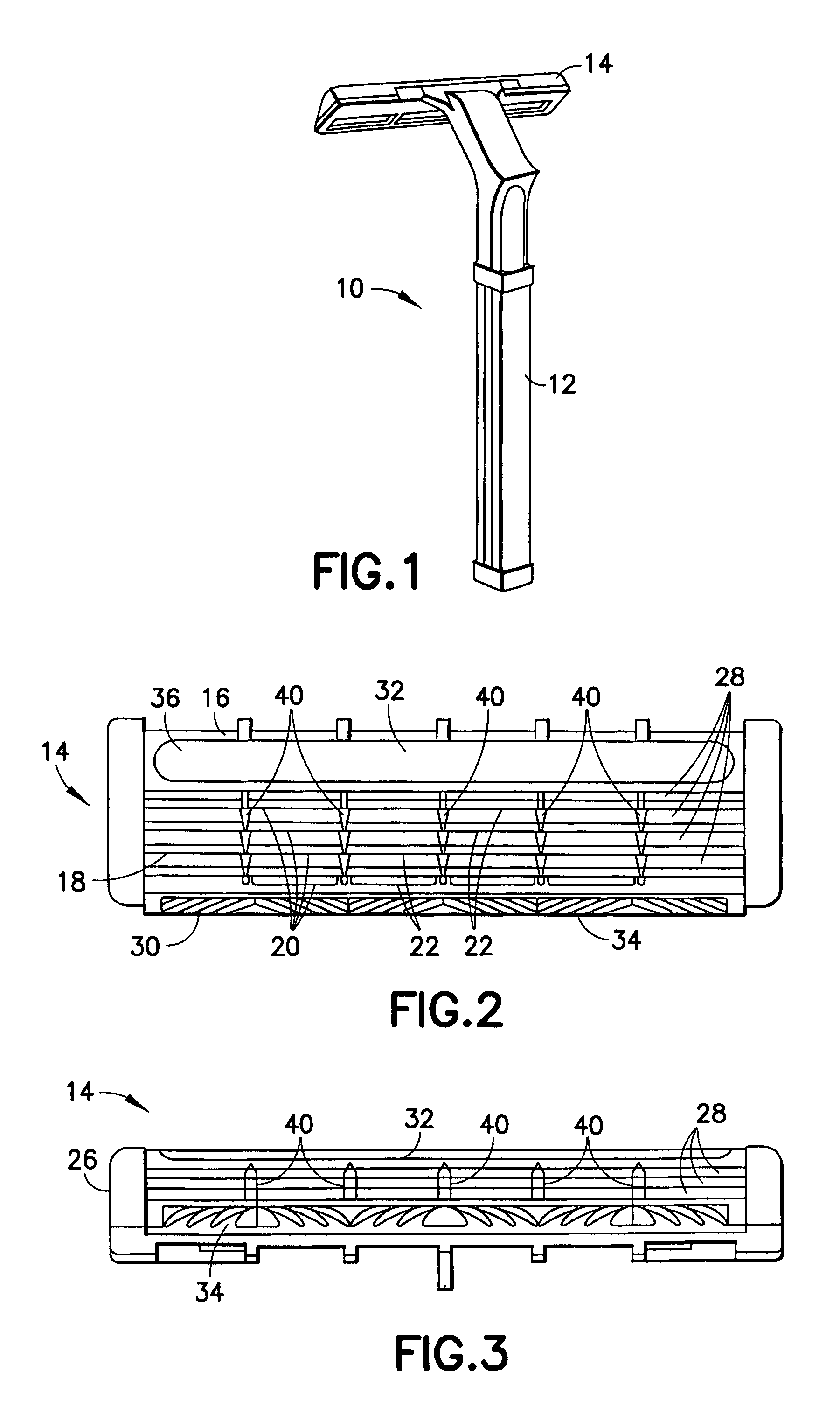
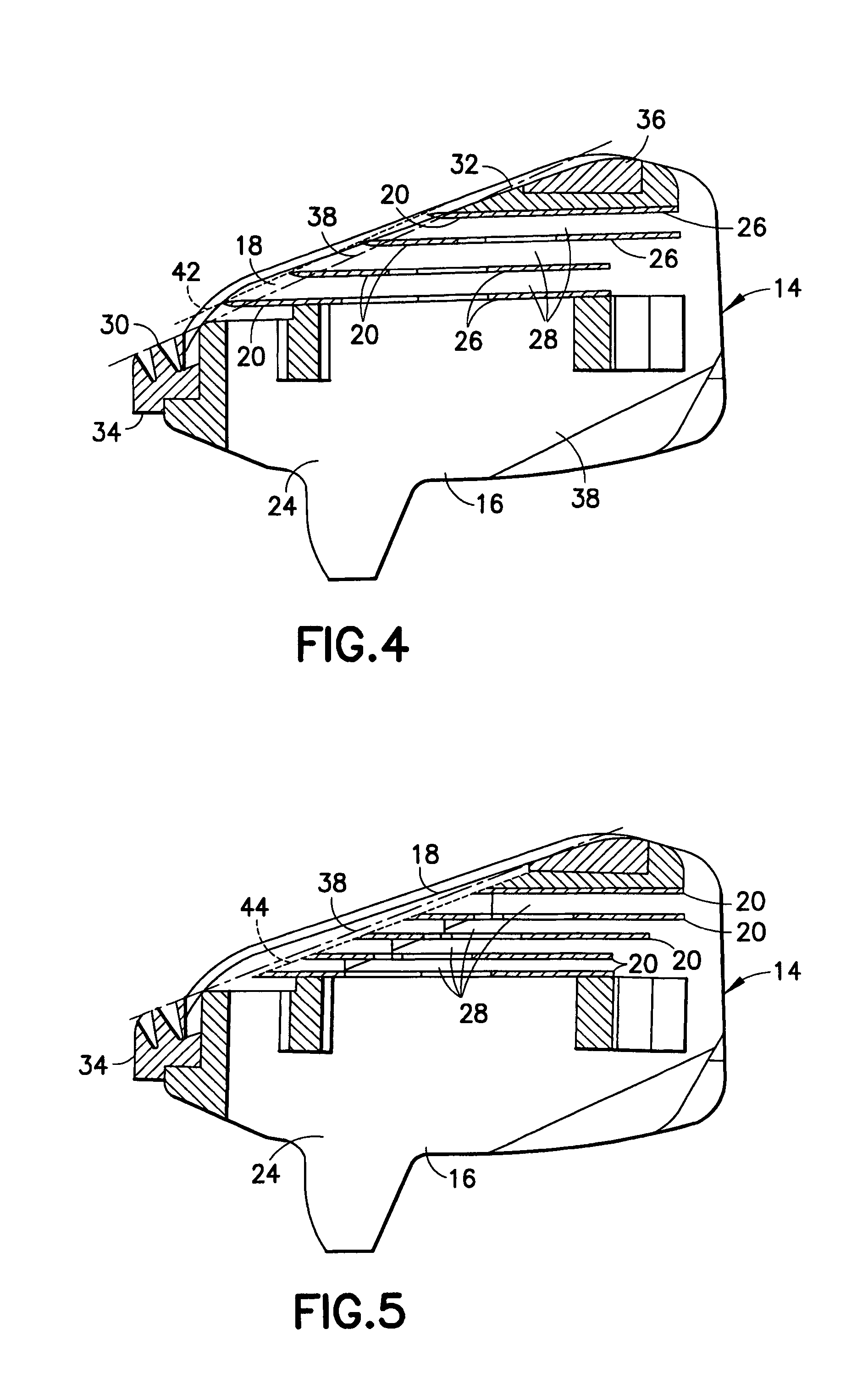
Razor cartridge
In a razor cartridge, a frame has an opening defined in part by a leading surface and a trailing surface. Positioned within the opening are a plurality of cutting edges, each cutting edge defined by a blade. In a shaving operation, a hirsute surface contacts in turn the leading surface, cutting edges, and the trailing surface. A contact plane is defined between the leading surface and the trailing surface that provides a reference for determining whether a cutting edge has a neutral, positive, or negative exposure. All of the cutting edges within the razor cartridge have an exposure relative to the contact plane that is one of all positive or all negative.
Owner:EDGEWELL PERSONAL CARE BRANDS LLC
Pluggable connector with differential pairs
InactiveUS7736159B1Reduce thicknessTwo-part coupling devicesCoupling protective earth/shielding arrangementsMating connectionEngineering
A pluggable connector that includes a housing having an inner surface that defines a housing cavity. The housing cavity extends along a central axis to an opening of the housing cavity. The opening is sized and shaped to mate with a mating connector moving along the central axis. The connector also includes a plug insert that is positioned within the housing cavity. The plug insert extends along the central axis and forms contact cavities therein that extend parallel to the central axis. The plug insert has an outer surface that is separated from the inner surface of the housing by a spacing. The connector also includes differential pairs. Each differential pair has two mating contacts that extend parallel to each other along a contact plane of the differential pair and within corresponding contact cavities. The contact planes of at least two adjacent differential pairs are perpendicular to one another.
Owner:TE CONNECTIVITY CORP
Personal workspace assembly
ActiveUS9622570B1Minimizing possibility of damageMinimize damageWallsBook-restsRange of motionAcute angle
A tablet assembly for use in a space partially defined by a wall structure having a substantially planar wall surface, the assembly comprising a first coupler supported by the wall structure, a tablet support arm assembly having a support arm length dimension between proximal and distal ends, the proximal end mounted to the first coupler adjacent the planar wall surface for rotation about a first vertical axis through a first range of motion between first and second first-axis limit positions, the arm assembly extending from the planar wall surface to form acute angles with the planar wall surface in each of the first and second first-axis limit positions and a tablet member forming top and bottom surfaces and having a side edge, the tablet member supported at the distal end of the arm for rotation about a second vertical axis through a second range of motion between first and second second-axis limit positions, wherein the limit positions limit the tablet member to positions in which the side edge of the tablet member is constrained from contacting the planar wall surface.
Owner:STEELCASE INC
Apparatus for providing an integrated printed circuit board registration coupon
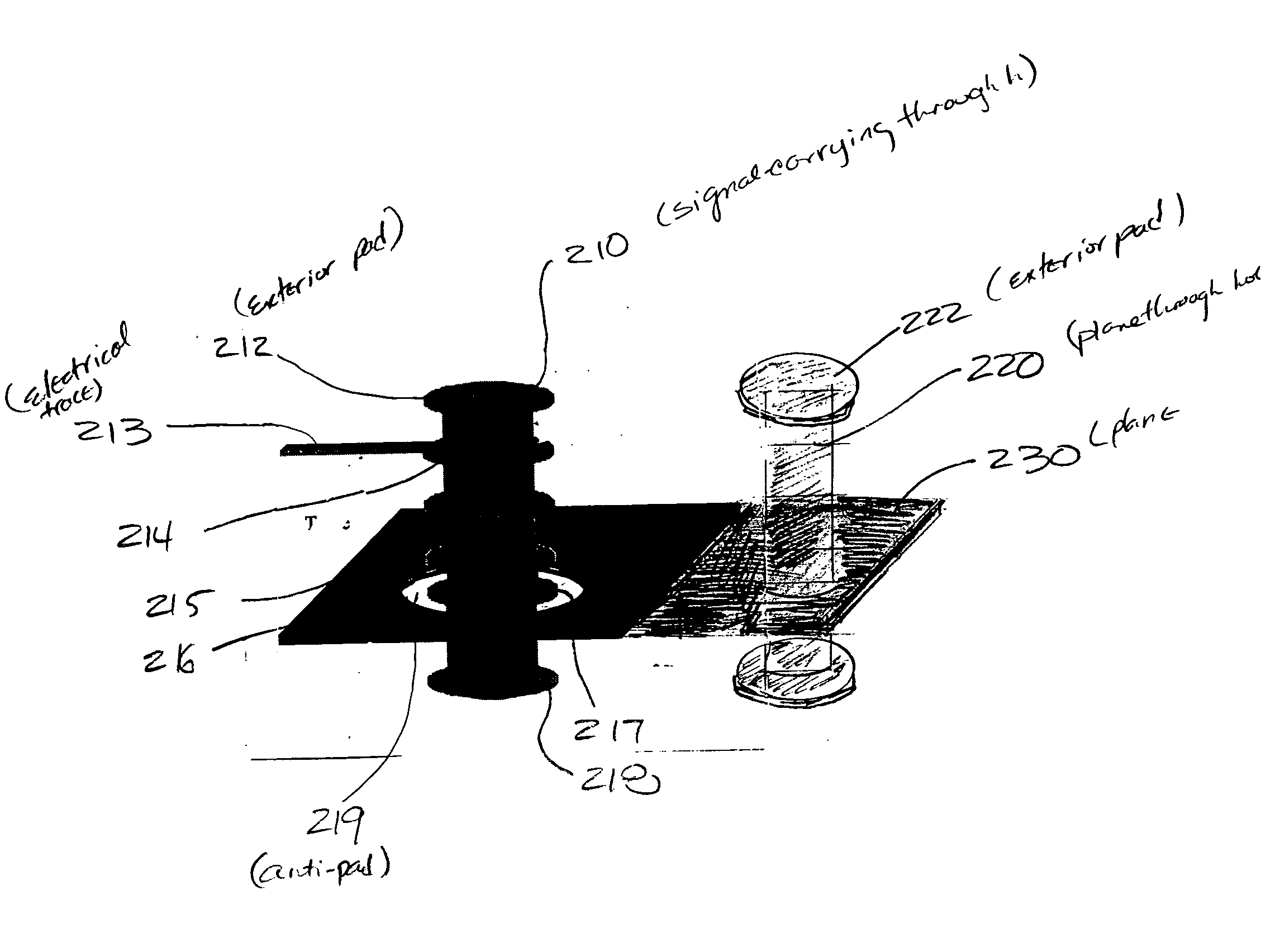
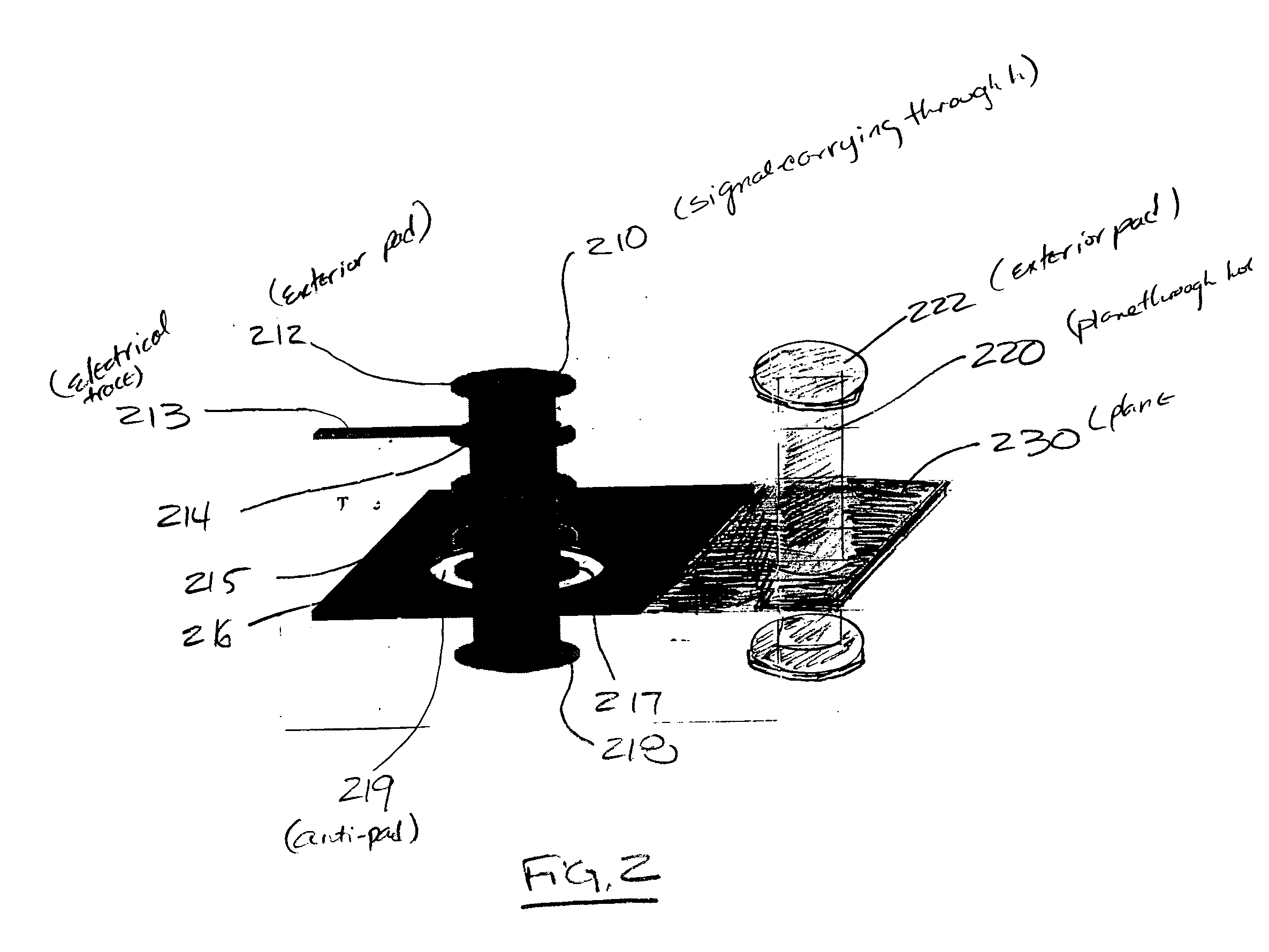
InactiveUS7583513B2Printed circuit aspectsInspection/indentification of circuitsPrinted circuit boardElectrical current
A device includes a plane metallization layer, and a plane plated through hole attached to the plane metallization layer and terminating at the at a major exterior surface with a plurality of component mounting pads. The plated through hole is attached to the plane metallization layer. The plane plated through hole is electrically isolated from the plurality of component mounting pads at the exterior surface. A method for testing the device includes contacting the signal carrying through hole, and contacting the plane through hole, and checking for current flow between the signal carrying through hole and the plane through hole. If current flows between the signal carrying through hole and the plane through hole the device fails. If no current flows between the signal carrying through hole and the plane through hole the device passes.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Passive robot joint with adjustable rigidity elasticity
InactiveCN101973037AImprove exercise energy efficiencyRealize dynamic high-speed movementJointsThighRadial motion
The invention discloses a passive robot joint with adjustable rigidity elasticity, comprising a spring reel and a joint rigidity elasticity adjustment device arranged inside the spring reel, wherein the spring reel is connected with thigh support seats; an extended end of the joint rigidity elasticity adjustment device is connected with crus support seats by crus support plates; the joint rigidity elasticity adjustment device comprises a non-contact plane volute spring of which the inner end is connected with a spring scroll and the outer end is connected with the spring reel; the middle of the spring scroll is hollow and is internally provided with a rigidity adjustment motor; one end of the spring scroll is connected with the rigidity adjustment motor; and the middle of the non-contact plane volute spring pitch is supported by a bracing piece which is connected with a rigidity adjustment reducer by a transmission gear. The bracing piece and the transmission gear perform radial motion, thus improving motion energy efficiency of the robot, realizing dynamically high-speed motion, and having good performance, compact structure and reliable operation.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Method and apparatus for providing an integrated printed circuit board registration coupon
InactiveUS20050063166A1Printed circuit aspectsInspection/indentification of circuitsPrinted circuit boardElectrical current
A device includes a plane metallization layer, and a plane plated through hole attached to the plane metallization layer and terminating at the at a major exterior surface with a plurality of component mounting pads. The plated through hole is attached to the plane metallization layer. The plane plated through hole is electrically isolated from the plurality of component mounting pads at the exterior surface. A method for testing the device includes contacting the signal carrying through hole, and contacting the plane through hole, and checking for current flow between the signal carrying through hole and the plane through hole. If current flows between the signal carrying through hole and the plane through hole the device fails. If no current flows between the signal carrying through hole and the plane through hole the device passes.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Optical transceiver with inner fiber set within tray securing thermal path from electronic device to housing
InactiveUS20120237171A1Reduce thermal resistanceFunction increaseCoupling light guidesFiberTransceiver
An optical transceiver with inner fibers to couple optical parts installed therein is disclosed. The optical transceiver of an embodiment includes a tray for arranging the inner fibers. The tray, which may be made of metal plate, includes a primary plane in contact with the electronic parts, the contact plane in contact with the housing, and the turn connecting the planes. The tray has a U-shaped cross section with a space surrounded by both planes, the turn, and the housing, where the inner fibers are secured in the space.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Connector assembly
ActiveUS20120184140A1Coupling protective earth/shielding arrangementsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A connector assembly includes contact modules each having a dielectric frame and contacts held by the dielectric frame. The contacts are arranged along a contact plane within the frame. The dielectric frame includes frame members connected by connecting segments. The frame has windows between the frame members located between adjacent contacts. Holders support corresponding contact modules. The holders are electrically grounded. The holders each have a support wall and tabs that extend outward from the support wall. The contact modules are coupled to the holders such that the tabs are received in the windows to provide shielding within the contact modules. The holders are coupled together such that the contact modules are stacked together with the tabs of at least some of the holders that extend into the contact module held by the adjacent holder and across the contact plane defined by the contact module of the adjacent holder.
Owner:TYCO ELECTRONICS LOGISTICS AG (CH)
Devices for use with computers
InactiveUS20150193023A1Slight backwards tiltComfortable rotationCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingCommunications systemComputer science
A computer mouse for use with a computer, including: a base with a lower surface configured for sliding across a work surface and having at least one portion forming part of a base contact plane; an upper body extending from the base; a contact sensor; an optical movement sensor system capable of detecting mouse movement relative to the work surface, a communication system, for communicating computer-readable movement and / or position data signals from the device to a computer, wherein the mouse is configured to operate in a first mode when orientated in a first orientation, and a second mode when orientated in a second orientation when the base contact plane is inclined with respect to the first orientation, and wherein the optical movement sensor system is configured to capture an image of the work surface in both the first and second modes to determine device movement in both modes.
Owner:SWIFTPOINT LTD
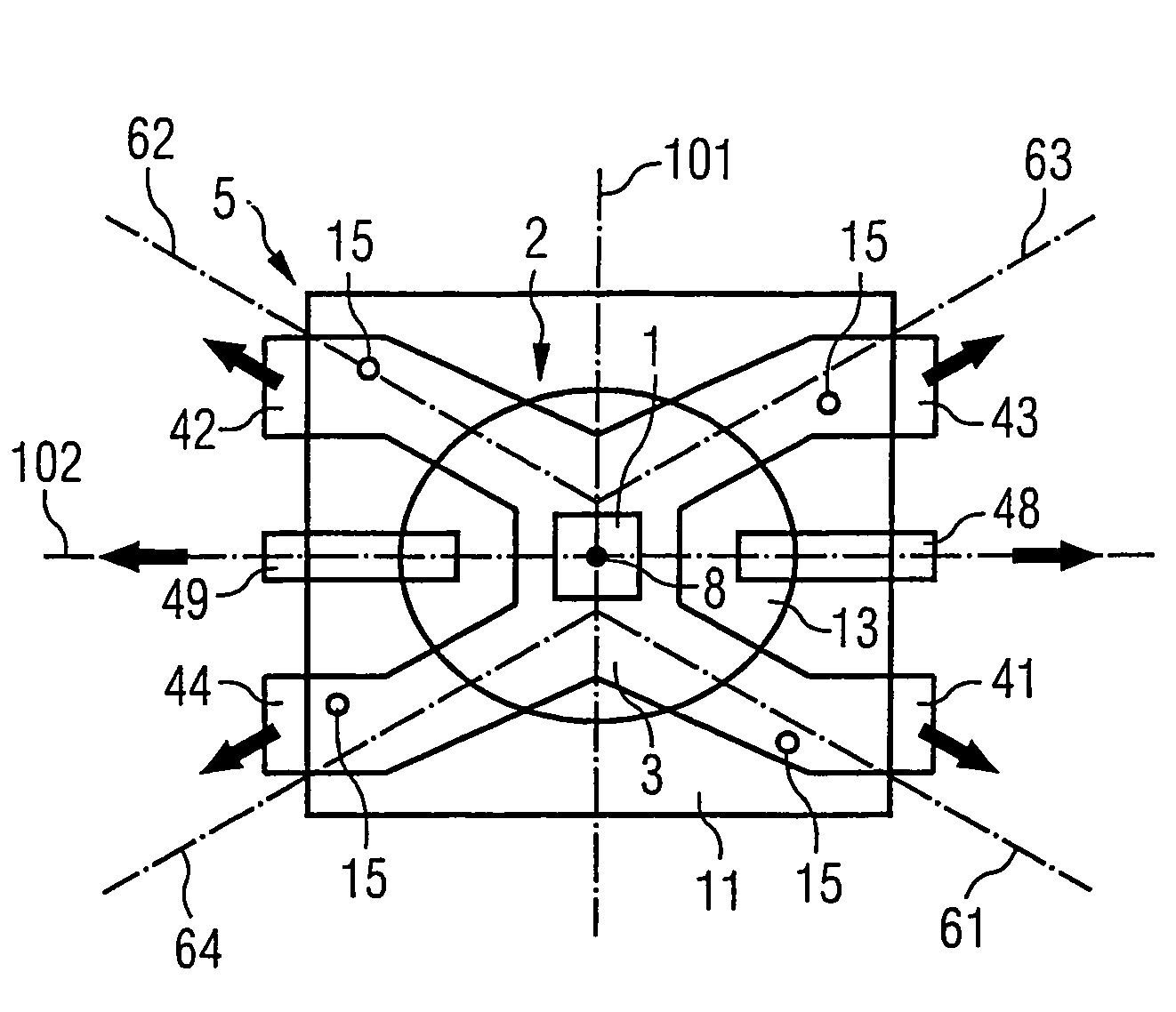
Optoelectronic component
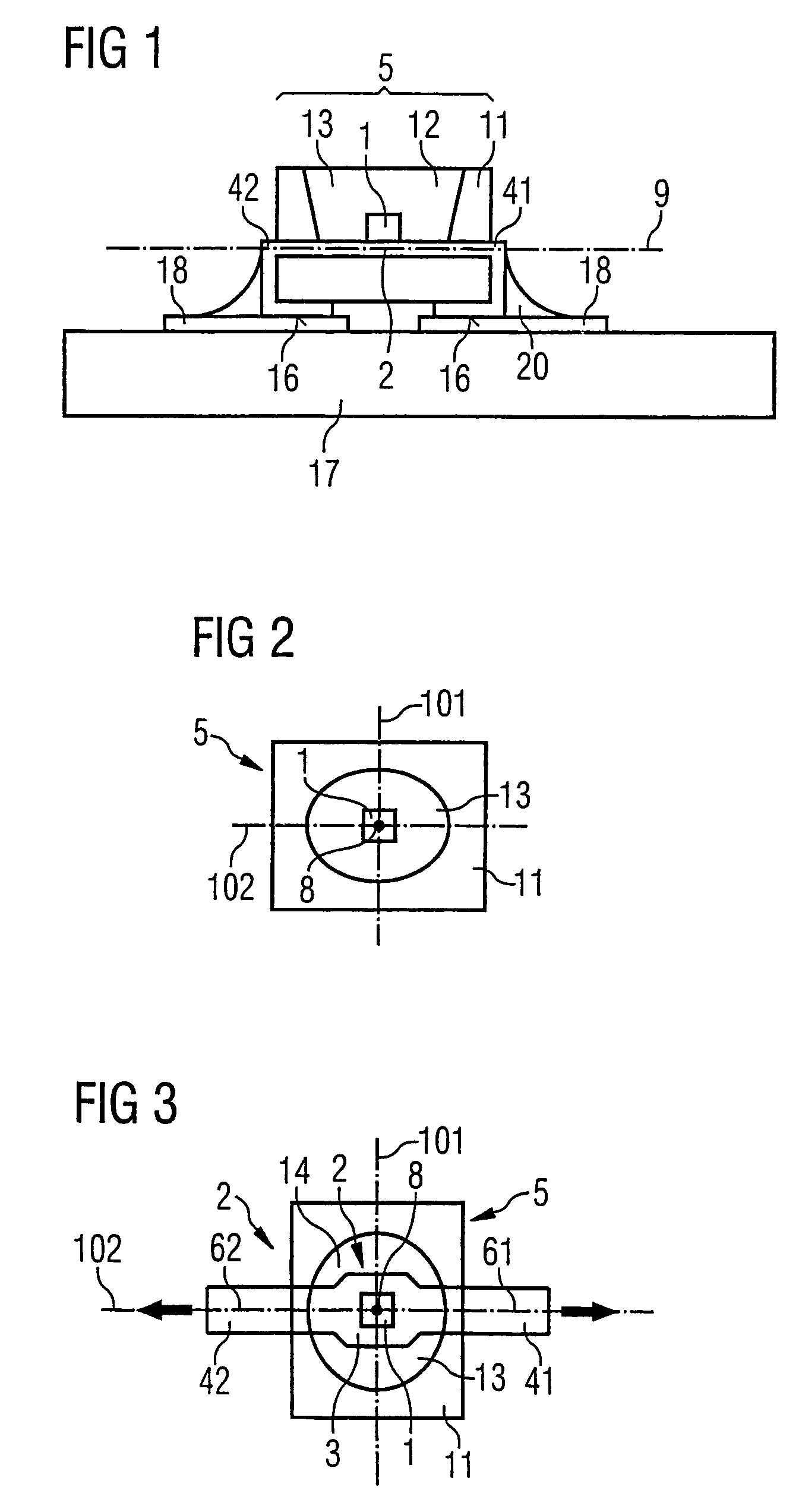
ActiveUS7271425B2Increased risk of failureImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesOpto electronicChip carrier
The invention relates to an optoelectronic component containing an optoelectronic chip (1) and containing a chip carrier (2) that has a central region (3) on which the chip is fixed and that comprises terminals (41, 42, 43, 44) extending outwardly from the central region of the chip carrier (2) to the outside, wherein the chip and portions of the chip carrier are enveloped by a body (5) and wherein the projection of the body and that of each of the longitudinal axes of the terminals onto the contact plane between the chip and the chip carrier are substantially point-symmetrical with respect to the central point of the chip. The invention further relates to an arrangement comprising said component. The advantage of the symmetrical configuration of the component is that the risk of thermomechanically induced failures of the component is reduced.
Owner:OSRAM OLED
Device for detecting residual stress close to surfaces of metal materials
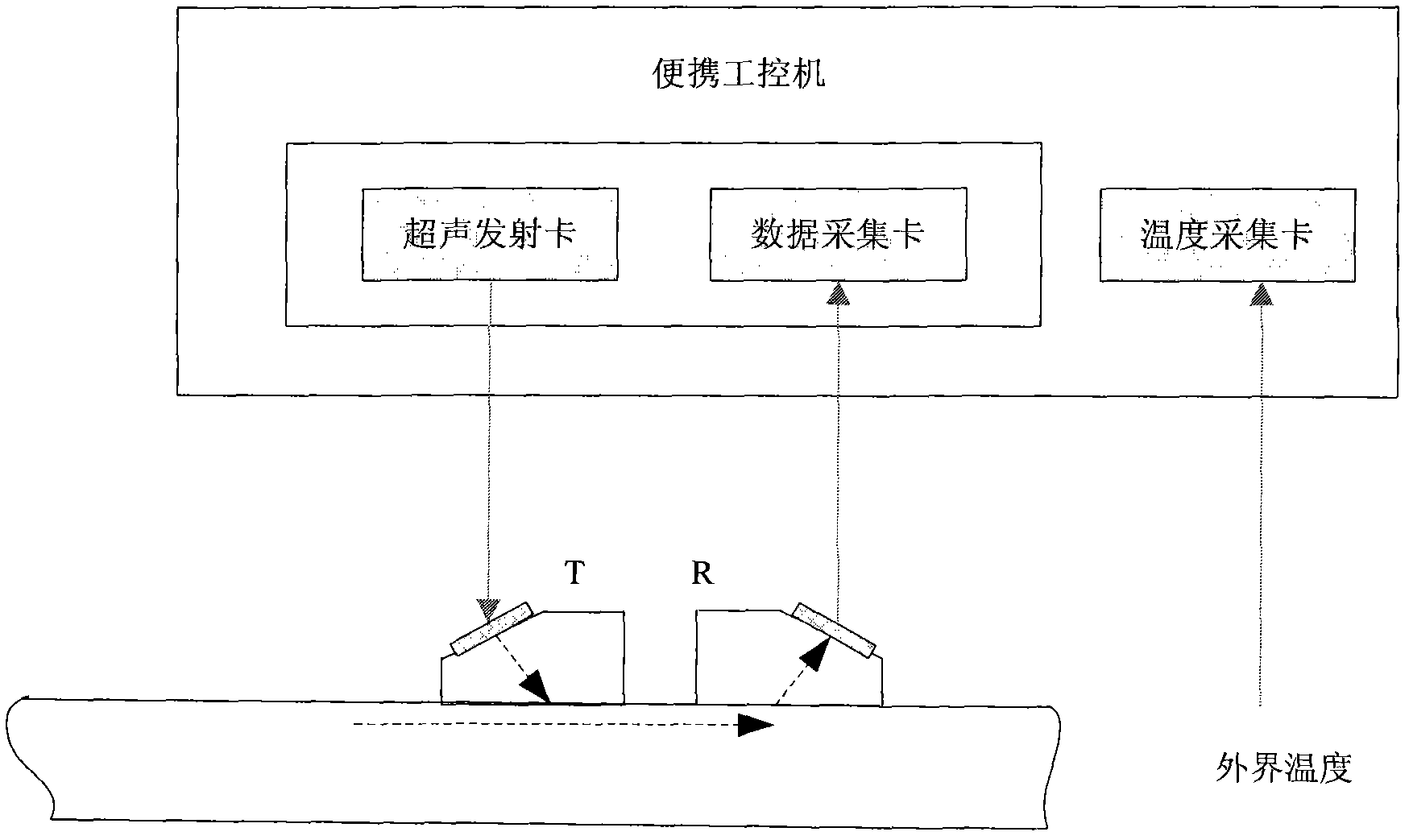
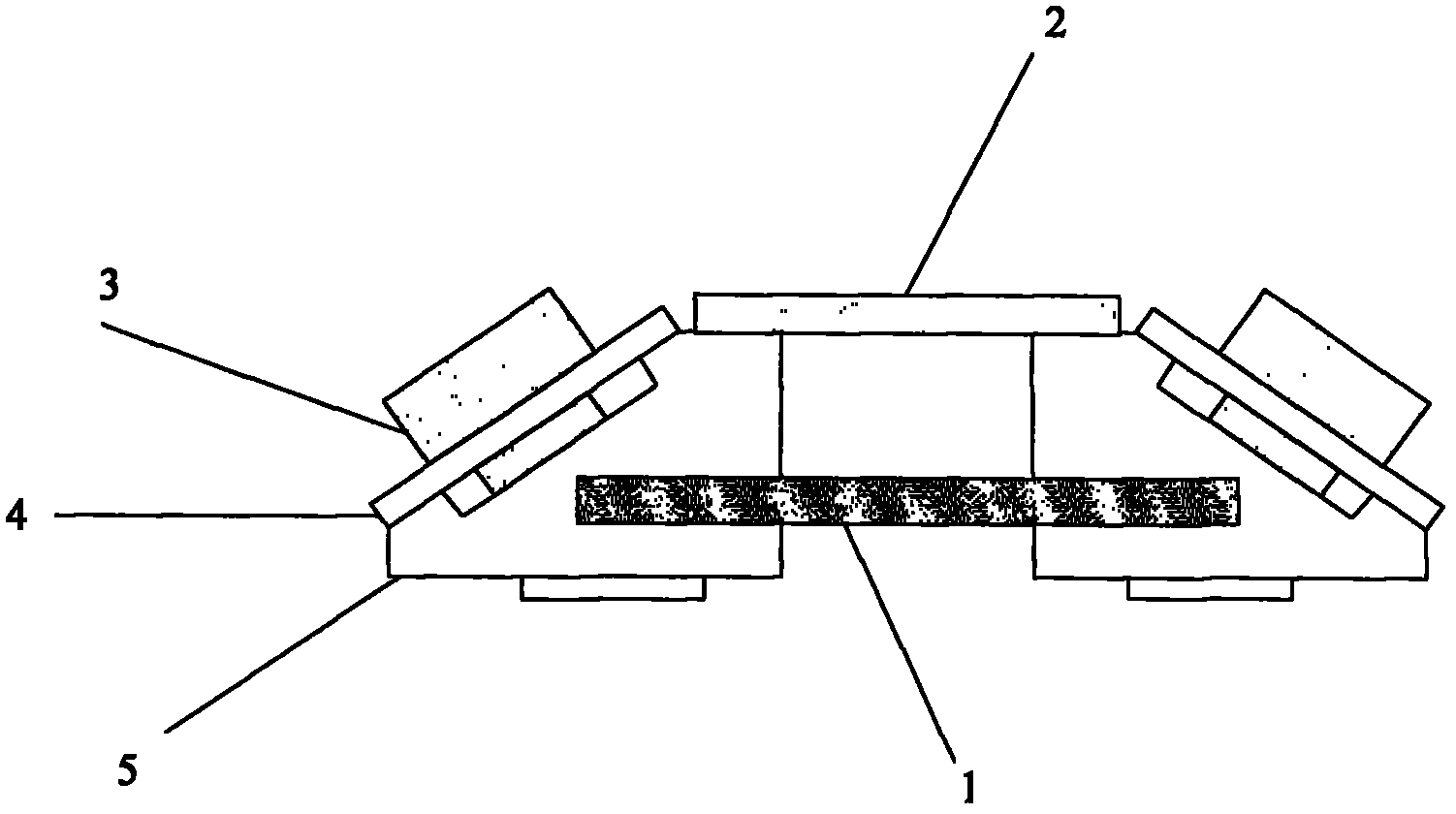
InactiveCN103017953AEasy to implementMade simpleForce measurementLongitudinal waveMetallic materials
The invention relates to a device for detecting residual stress close to surfaces of metal materials. The device stimulates a critical-refraction longitudinal wave and calculates a stress value according to an acoustic elasticity theory. According to the invention, by reducing contact area between a wedge and a part to be measured, the affect of plate surface distortion to a measurement result can be effectively eliminated; the affect caused by temperature difference can be eliminated by temperature compensation; and therefore, the system is adaptable to tests in more terrible field environments. The system is higher in integration degree, small and exquisite in appearance and convenient to carry.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Track comprised or internal and external links
InactiveUS7661774B2Avoid stress concentrationFlexible cuttingGearingTilling equipmentsEngineeringSprocket
In a track with a rotatable bushing which is brought into engagement with a sprocket of a track-type vehicle, it is intended that strength is enhanced rationally by link functionality sharing and by combination of such assigned functional tasks for achieving further improvements in rotatable bushing function. To this end, a first bolt insertion hole provided in a track shoe mount surface of an external link and a second bolt insertion hole provided in a track shoe mount surface of an internal link are arranged on the same straight line, and a straight line connecting the first bolt insertion hole and the second bolt insertion hole is situated at a position more interior than a contact plane of the external link and internal link.
Owner:KOMATSU LTD
Lithography system, method of clamping and wafer table
ActiveUS20090027649A1Reduce negative impactPhotomechanical apparatusPhotographic printingWaferingEngineering
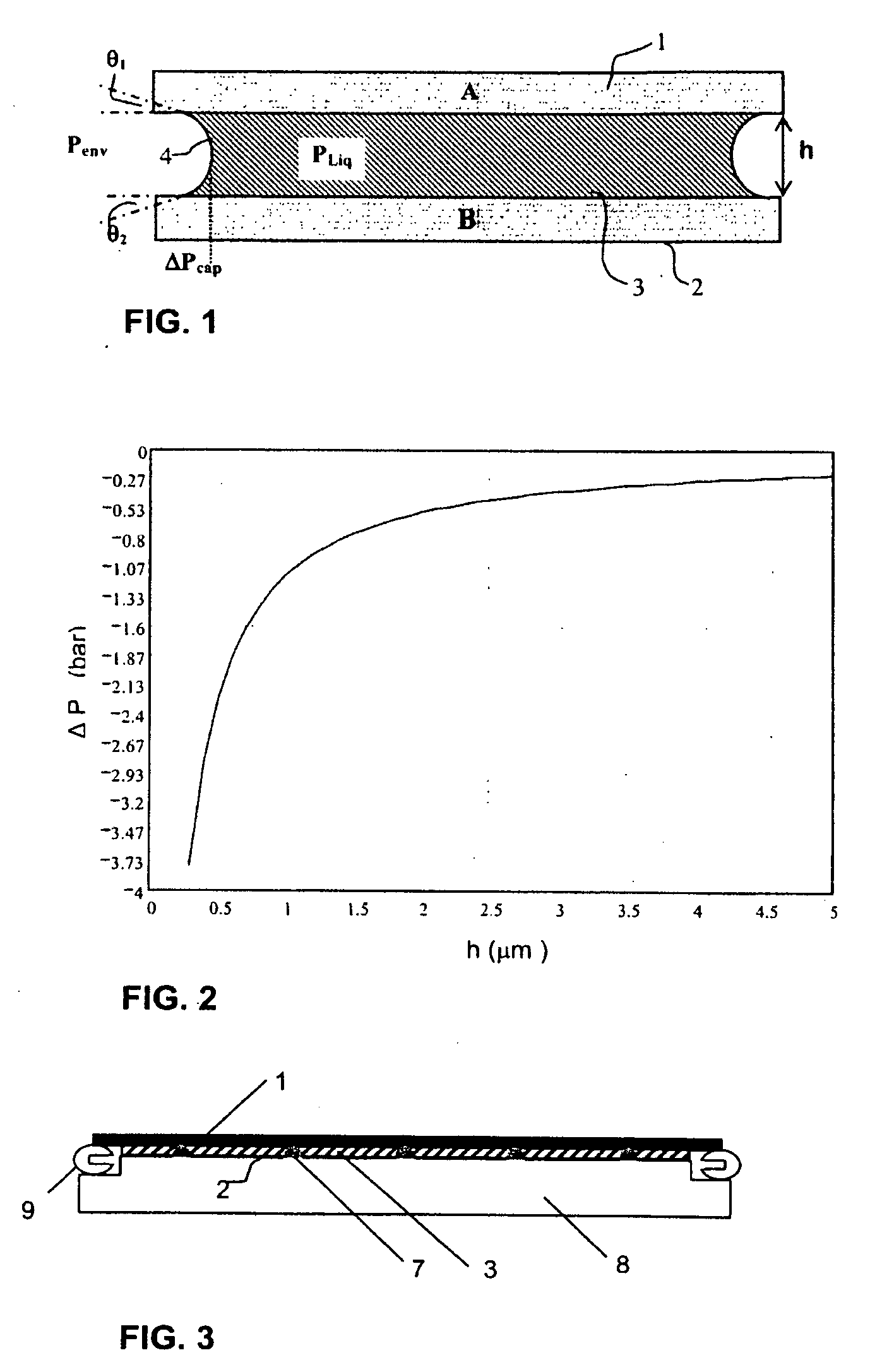
The invention relates to a lithography system, for example for projecting an image or an image pattern on to a target (1) such as a wafer, said target being included in said system by means of a target table (2), clamping means being present for clamping said target on said table. Said clamping means comprises a layer of stationary liquid (3), included at such thickness between target and target table that, provided the material of the liquid (C) and of the respective contacting faces (A, B) of the target (1) and target table (2), a pressure drop (PCap) arises.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Light deflector, optical scanner, and image forming apparatus
InactiveUS20070146856A1Stable maintenanceGood dispositional accuracyPictoral communicationOptical elementsOptical scannersLight beam
A light deflector is disclosed that includes a movable mirror serving as a deflector supported by a rotary shaft and configured to deflect a light beam emitted from a light source and scan an area to be scanned; a rotation part configured to cause the movable mirror to vibrate in a reciprocating manner by periodically applying a rotational torque to the movable mirror; a driving circuit configured to control the rotation part; a circuit board having the driving circuit provided thereon, the circuit board being configured to support the movable mirror as a unit; a contact plane contacting the circuit board in a plane perpendicular to the rotary shaft of the movable mirror; and a positioning part configured to determine the position of the rotary shaft in the contact plane.
Owner:RICOH KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com