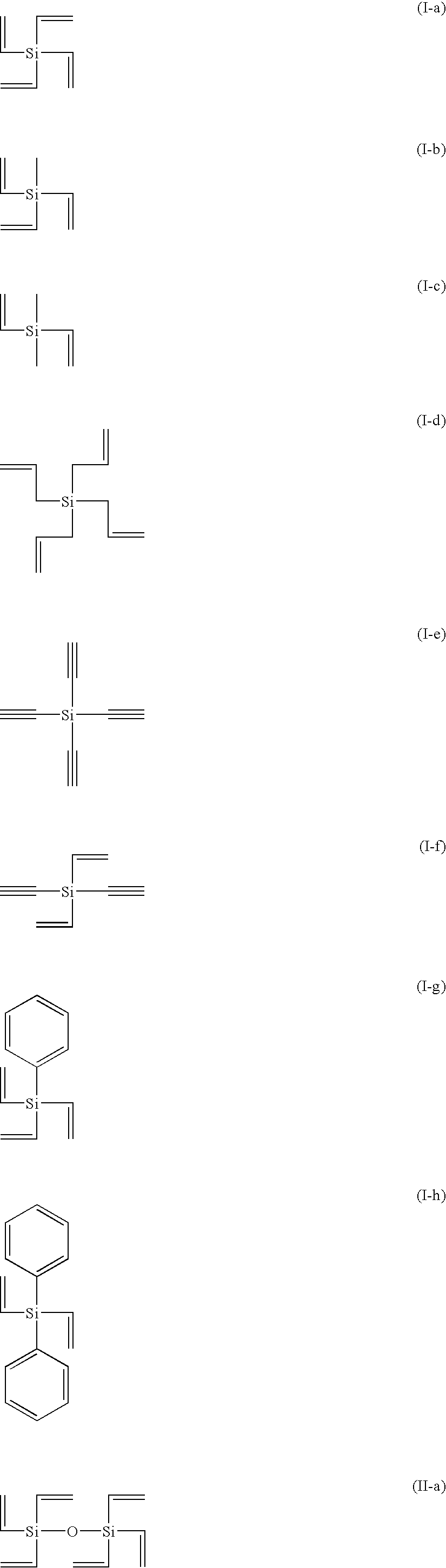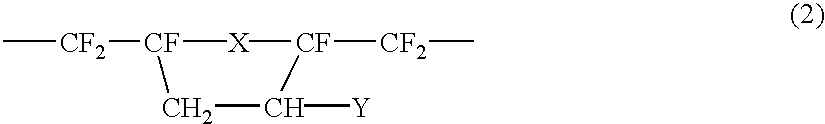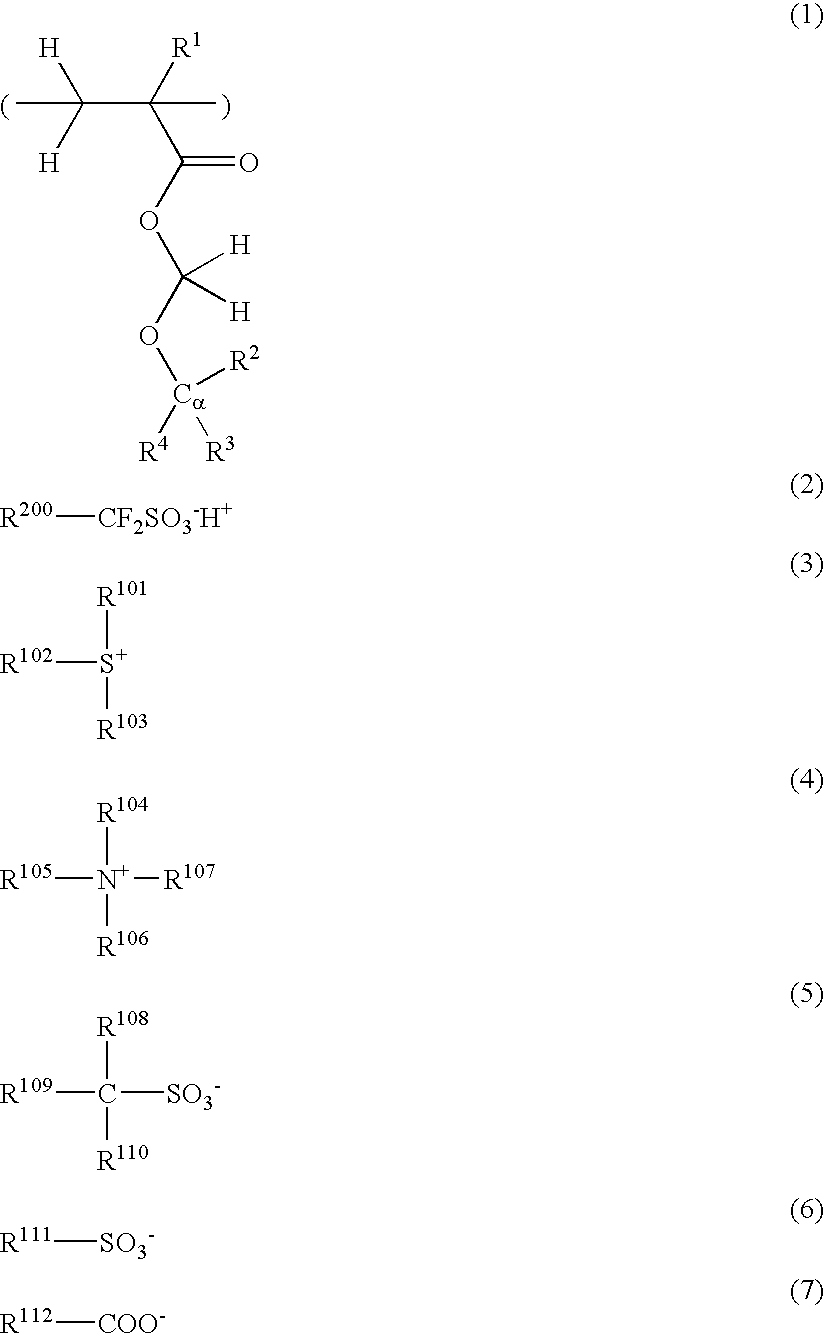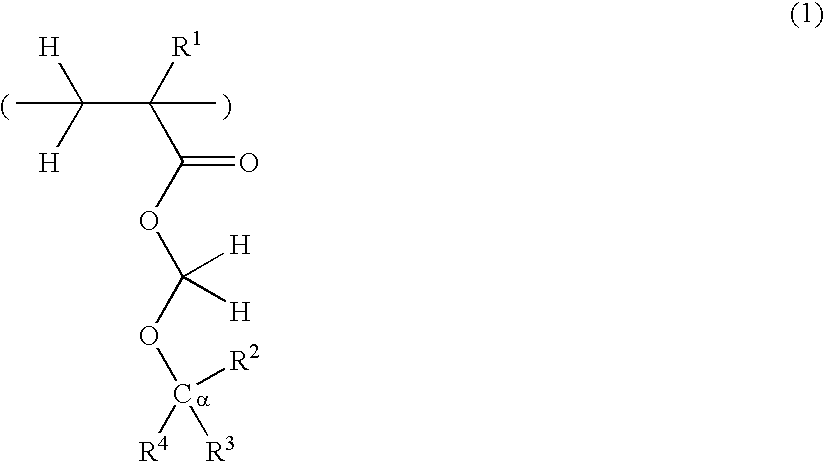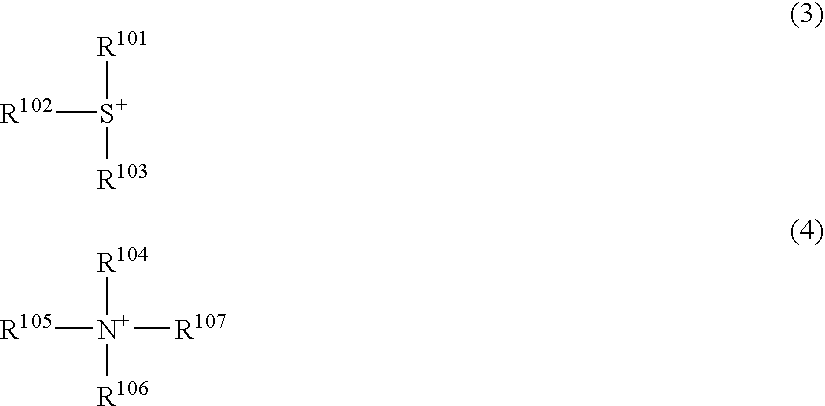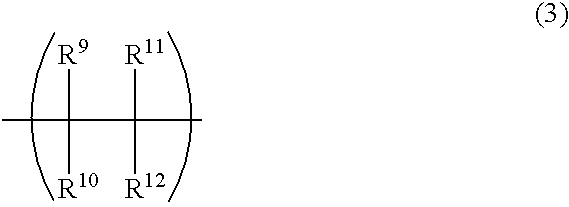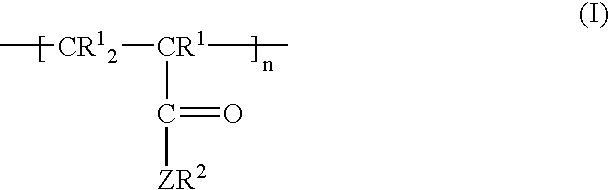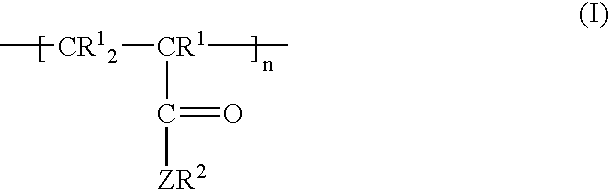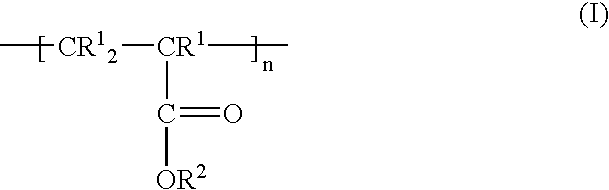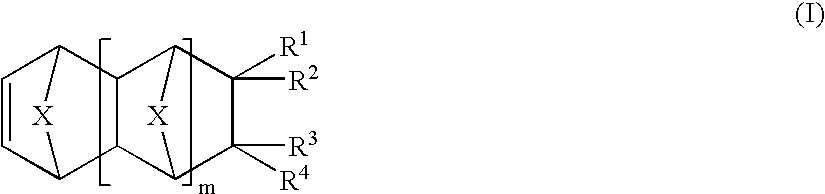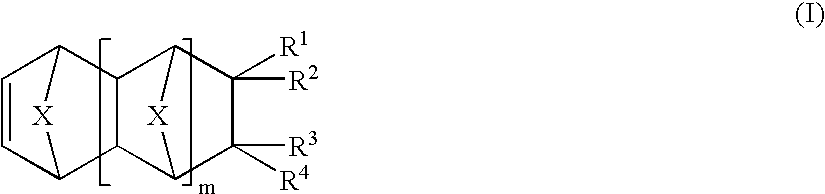Patents
Literature
6894 results about "Repeat unit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A repeat unit or repeating unit is a part of a polymer whose repetition would produce the complete polymer chain (except for the end-groups) by linking the repeat units together successively along the chain, like the beads of a necklace.
Surface topographies for non-toxic bioadhesion control
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Composition, film and formation process thereof
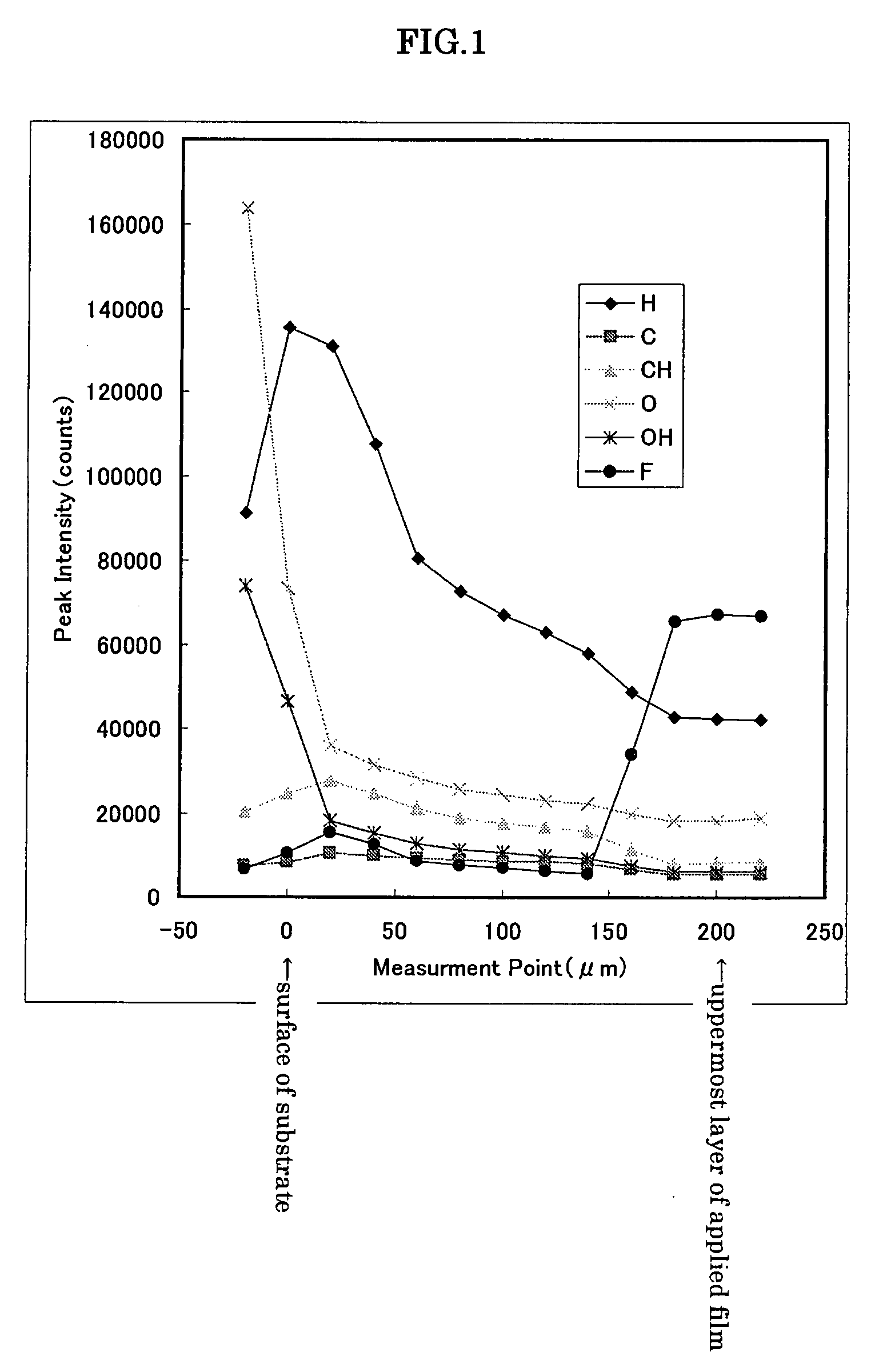
InactiveUS20080081121A1Adequately uniform thicknessImprove barrier propertiesPretreated surfacesCoatingsRepeat unitChemistry
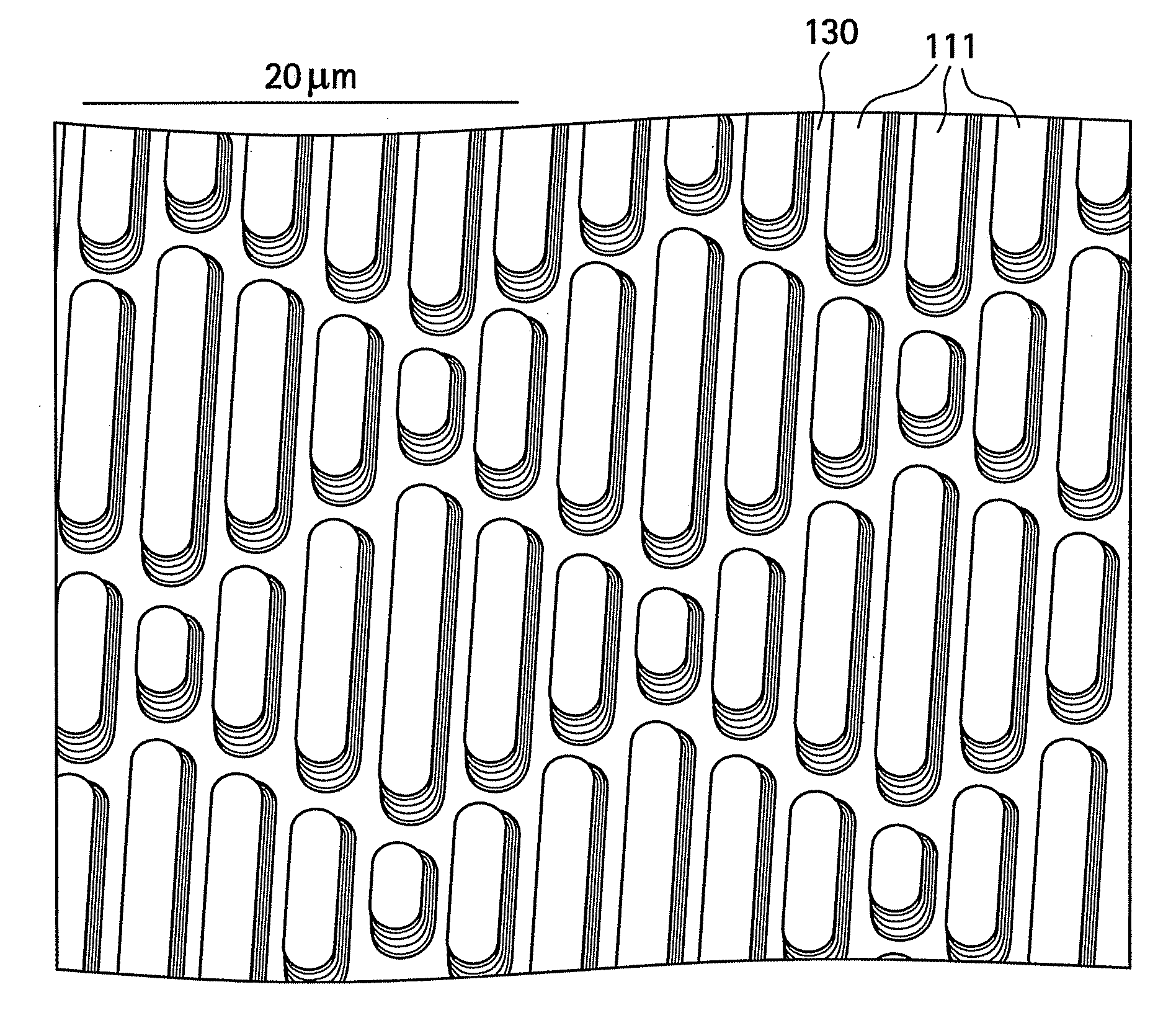
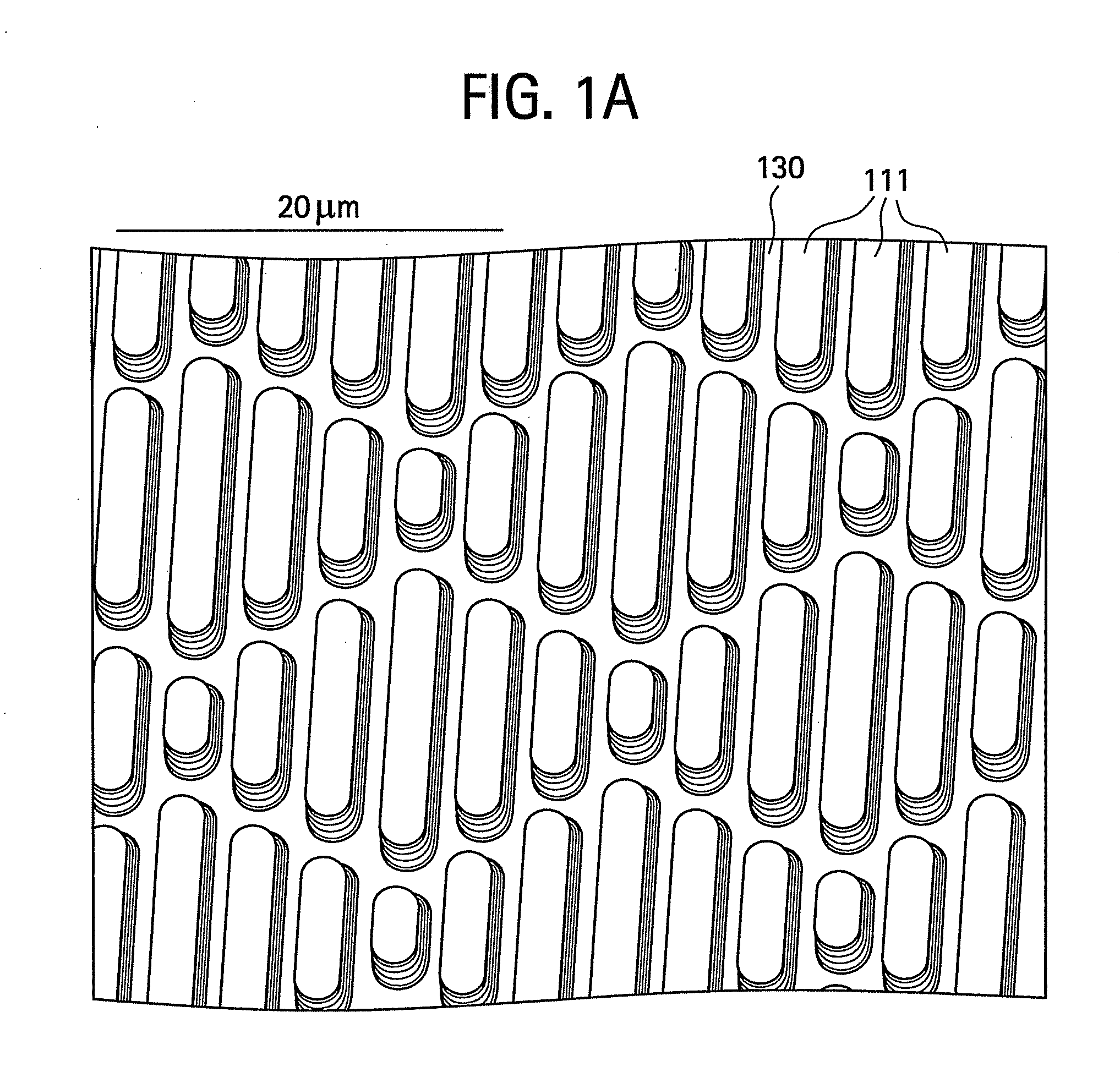
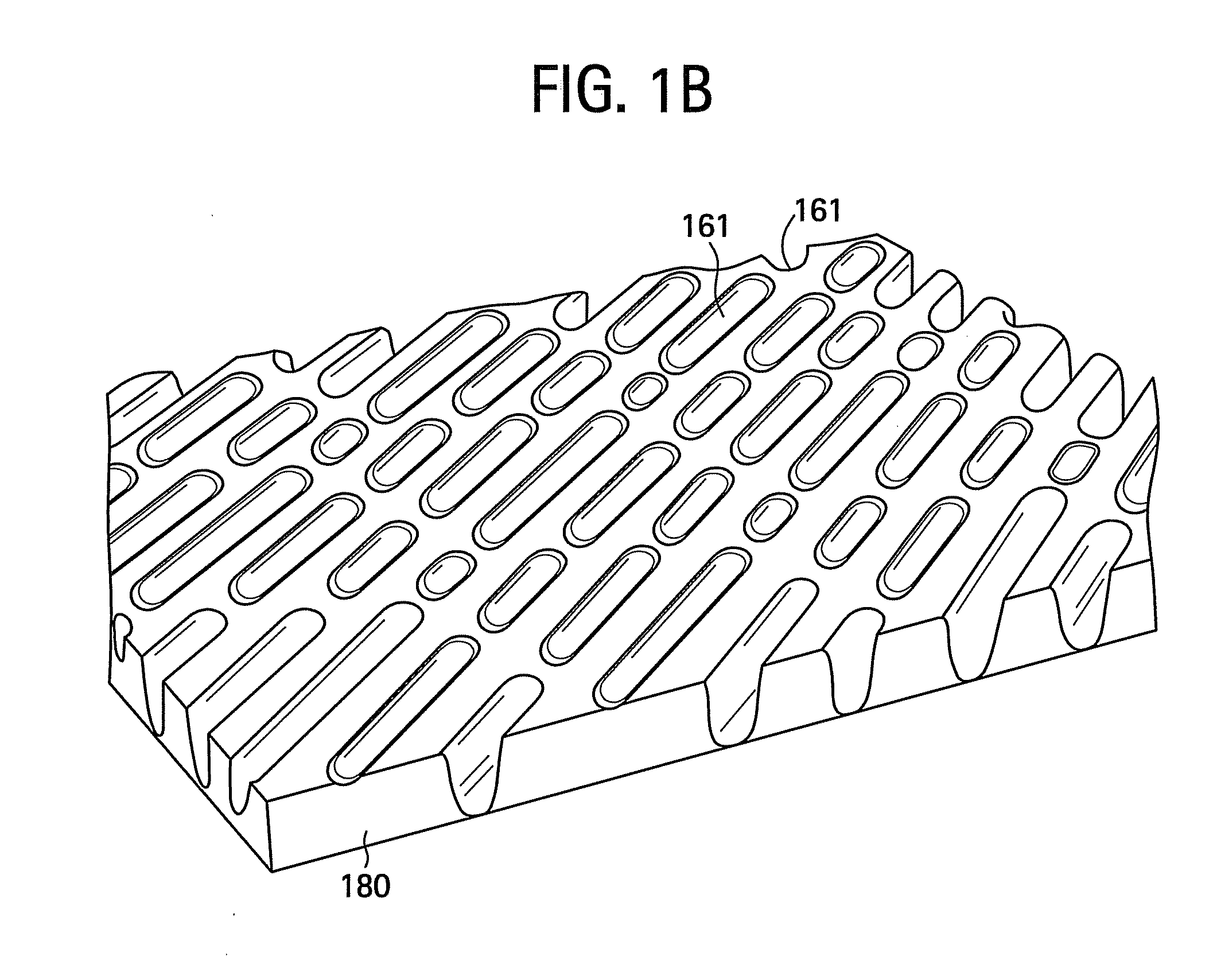
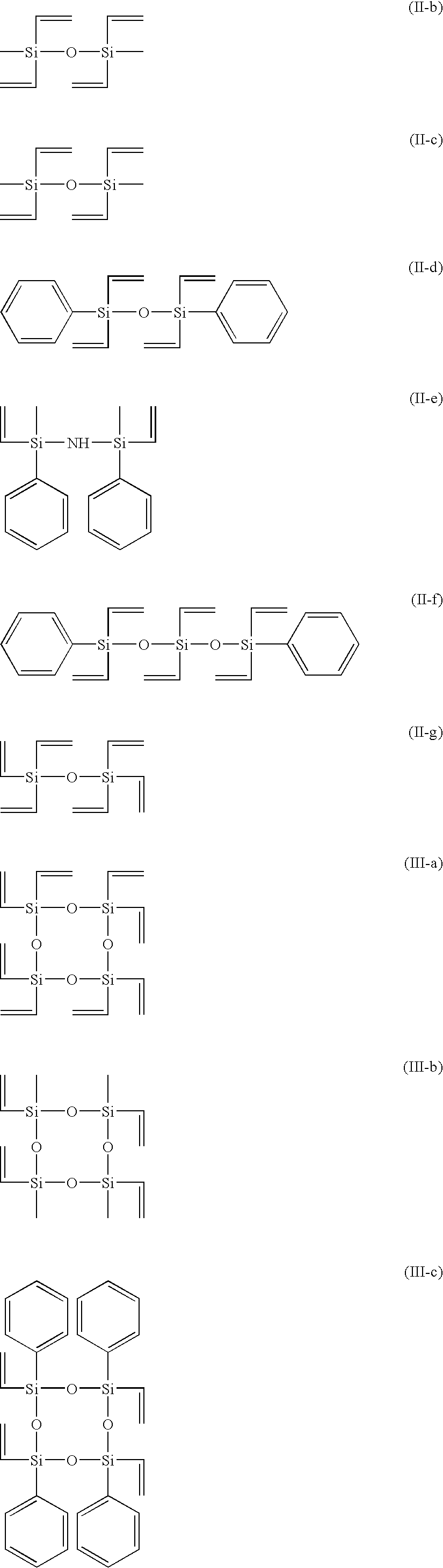
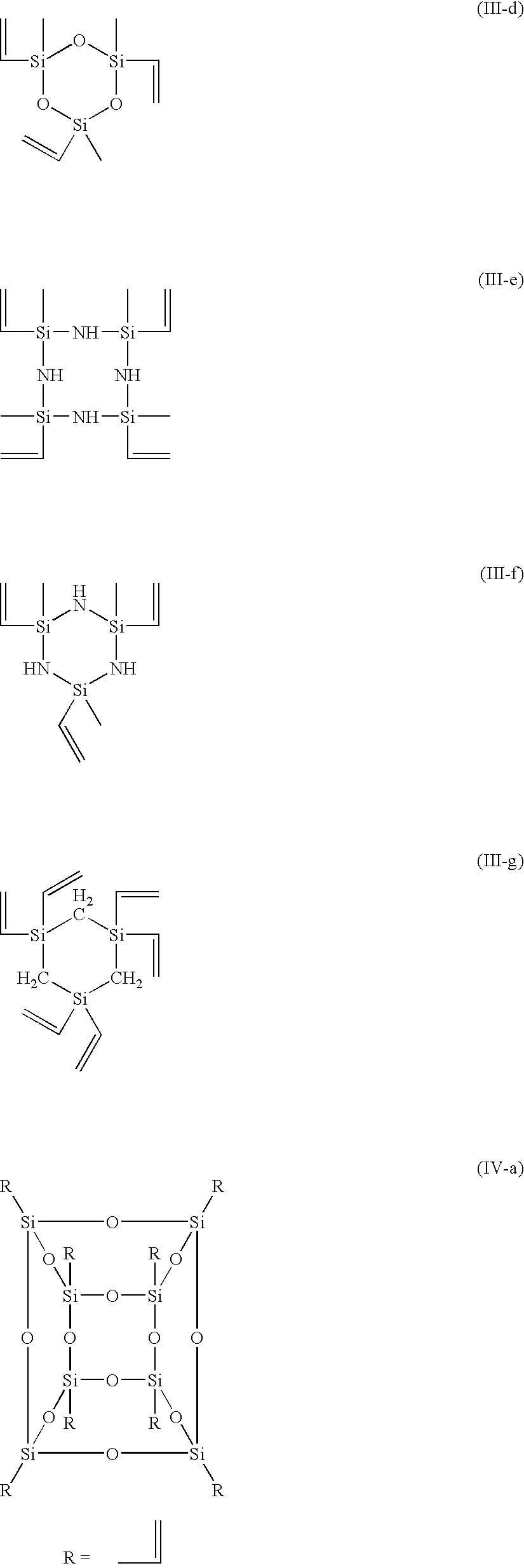
A composition includes at least one kind polymer, each of which includes a repeating unit(s) derived from at least one compound selected from the group consisting of compounds represented by the following formulas (I) to (IV): R4Si (I) R3Si—(X—SiR2)m—X—Si—R3 (II) *—(X—SiR2)n—* (III) m.RSi(O0.5)3 (IV) wherein the symbols in the formulas are defined in the specification.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Photoresist polymer and photoresist composition containing the same
InactiveUS7361447B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotosensitive material auxillary/base layersResistPolymer science
Photoresist polymers and photoresist compositions containing the same. Photoresist patterns of less than 50 nm are achieved with EUV (Extreme Ultraviolet) as an exposure light source with photoresist compositions comprising (i) a photoresist polymer comprising a polymerization repeating unit of Formula 2 or (ii) a photoresist polymer comprising a polymerization repeating unit of Formula 3 with polyvinylphenol. As a result, excellent etching resistance can be secured although the photoresist patterns have a very small thickness.wherein R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, R8, R9, R10, R11, R12, a, b, c, d, e, f and g are as defined in the specification.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Photoresist polymer and photoresist composition containing the same
InactiveUS7279256B2Enhance the imageImprove the immunityPhotosensitive materialsRadiation applicationsResistEnergy variation
Photoresist polymers and photoresist compositions are disclosed. A photoresist polymer comprising a polymerization repeating unit represented by Formula I is less sensitive to change in the amount of energy due to its higher active energy than that of a conventional photoresist polymer. As a result, a phenomenon where the portion of the pattern for the storage electrode contact region that receives relatively large amount of light becomes too thin is avoided when the device isolation film pattern is formed, and wherein pattern collapse caused by a high aspect ratio due to high etching resistance is prevented or avoided.whereinR1–R10, a, b, c and d are as defined in the description.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Positive resist composition and pattern-forming method
ActiveUS20080248425A1Suppress generationPhotosensitive materialsRadiation applicationsPolymer scienceActinic Rays
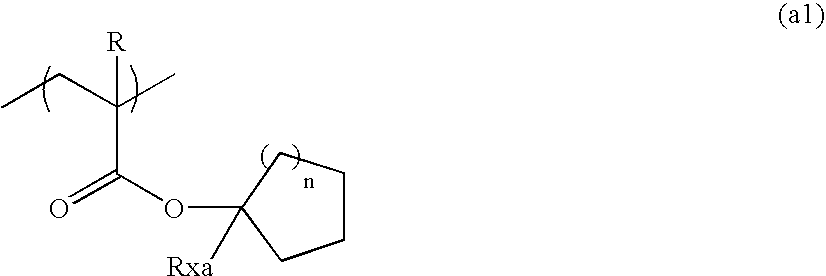
A positive resist composition comprises: (A) a resin that has a repeating unit represented by general formula (a1) and increases its solubility in an alkali developer by action of an acid; (B) a compound which generates an acid upon irradiation with an actinic ray or a radiation; and (C) a resin that has at least one of a fluorine atom and a silicon atom and has a group selected from the group consisting of (x), (y) and (z); and (D) a solvent:(x) an alkali-soluble group;(y) a group capable that decomposes by action of an alkali developer to undergo an increase in a solubility of the resin (C) in an alkali developer; and(z) a group that decomposes by action of an acid,wherein R represents a hydrogen atom or a methyl group, Rxa represents an alkyl group or a cycloalkyl group, and n represents an integer of 1 to 8.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Polymers for photoresist and photoresist compositions using the same
InactiveUS6987155B2Improve the immunityExcellent etching resistance and adhesiveness and photosensitivityElectric discharge tubesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusResistX-ray
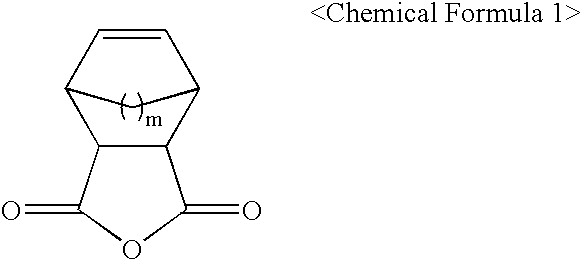
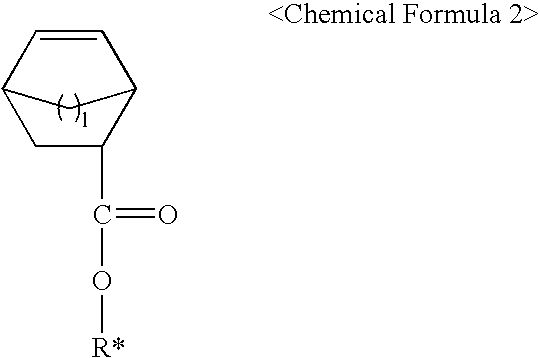
The present invention relates to photoresist monomers, polymers formed therefrom and photoresist compositions suitable for photolithography processes employing a DUV light source, such as KrF (249 nm) and ArF(193 nm); EUV; VUV; E-beam; ion-beam; and X-ray. Photoresist monomers of the present invention are represented by the following Chemical Formula 1: wherein, m is 1 or 2.Polymers of the present invention comprise repeating units derived from the comonomer of Chemical Formula 1, preferably together with monomers of the following Chemical Formula 2: wherein,R* is an acid-labile group, andl is 1 or 2.
Owner:HYUNDAI ELECTRONICS IND CO LTD
Phosphorescent compound, a phosphorescent composition and an organic light-emitting device
InactiveUS20030091862A1Extended service lifeLong stabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic light emitting deviceOrganic chemistry
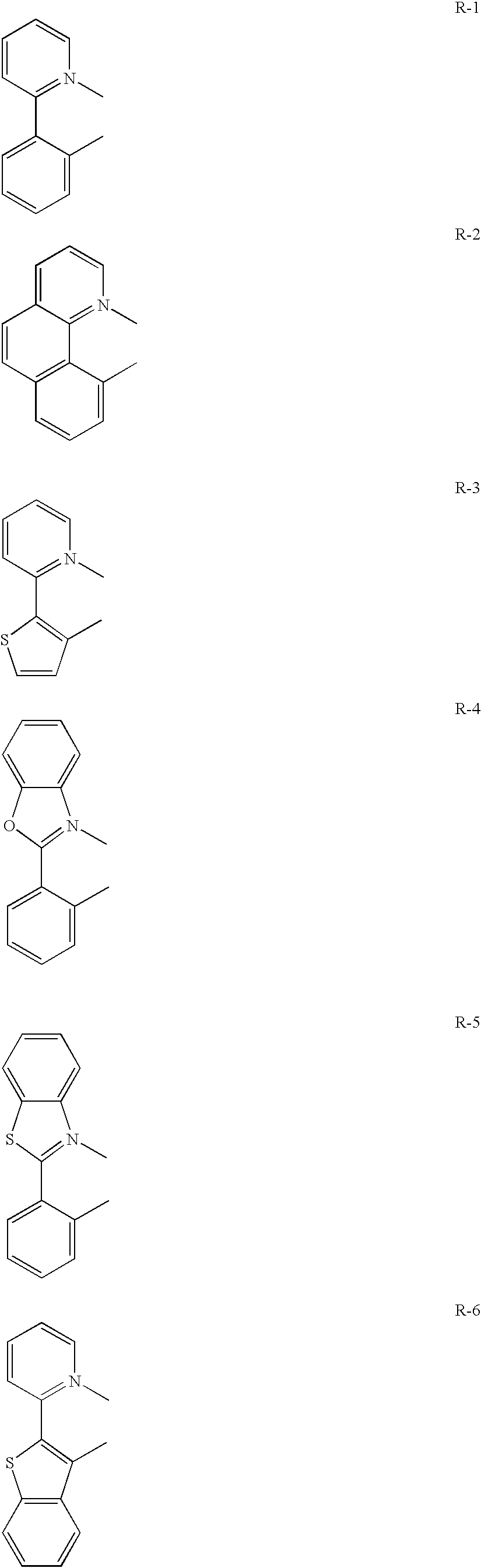
An organic polymeric phosphorescent compound that is stable and emits very highly efficient phosphorescence, used as a material of an organic light-emitting device is provided. Also, an organic light-emitting device employing the organic polymeric phosphorescent compound's provided. The phosphorescent compound according to the present invention is a neutral organic polymeric phosphorescent compound emitting phosphorescence and used in an organic light-emitting device, characterized in that a phosphorescent unit being a repeat unit for emitting phosphorescence and a carrier transporting unit being a repeat unit for transporting a carrier are included.
Owner:NIPPON HOSO KYOKAI +1
Electrophoretic media and processes for the production thereof
InactiveUS7230750B2Improve stabilityEasy to adaptMaterial nanotechnologyStatic indicating devicesElectrophoresisEthylene Homopolymers
A first electrophoretic medium comprises an electrically charged particle suspended in a suspending fluid, the particle having a polymeric shell having repeating units derived from at least one monomer the homopolymer of which is incompatible with the suspending fluid. A second, similar electrophoretic medium comprises a suspending fluid, and first and second types of electrically charged particle suspended in the suspending fluid, the two types of particle having differing optical characteristics but both having polymeric shells. The polymeric shells are arranged such that homoaggregation of the two types of particles is thermodynamically favored over heteroaggregation.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Color display devices and methods with enhanced attributes
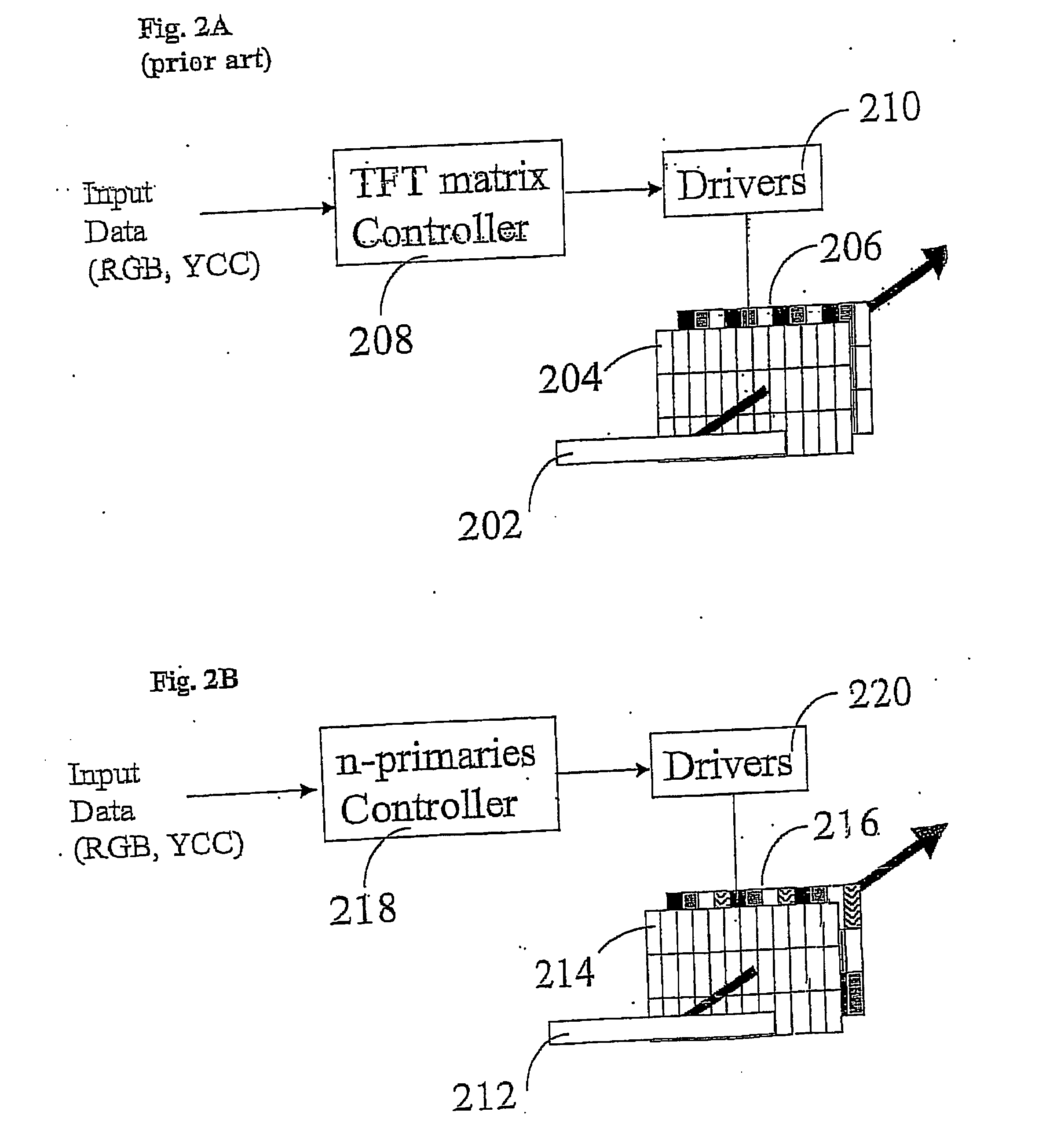
ActiveUS20050122294A1Reduce the impactWider spanColor signal processing circuitsCathode-ray tube indicatorsDisplay devicePrimary color
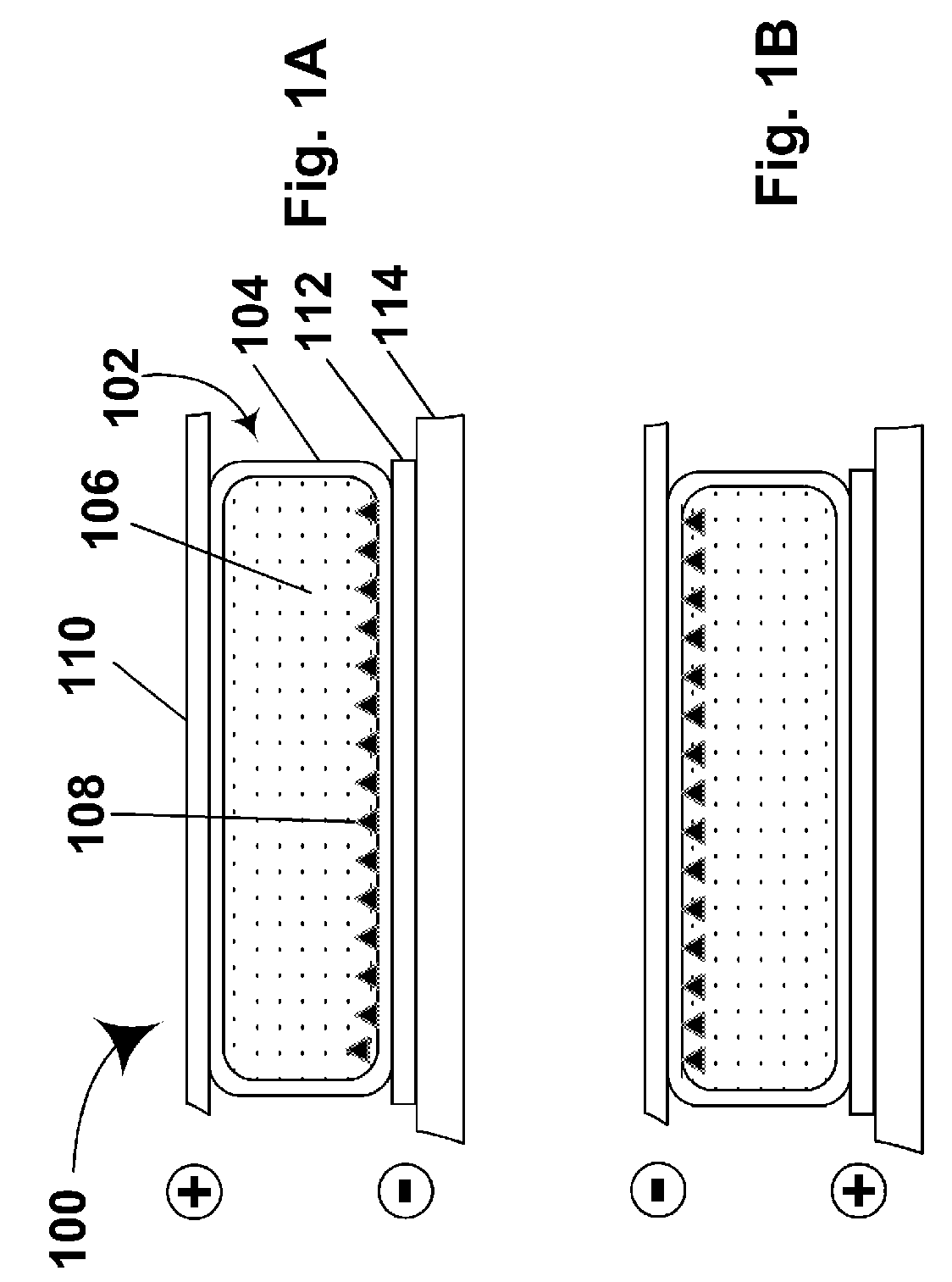
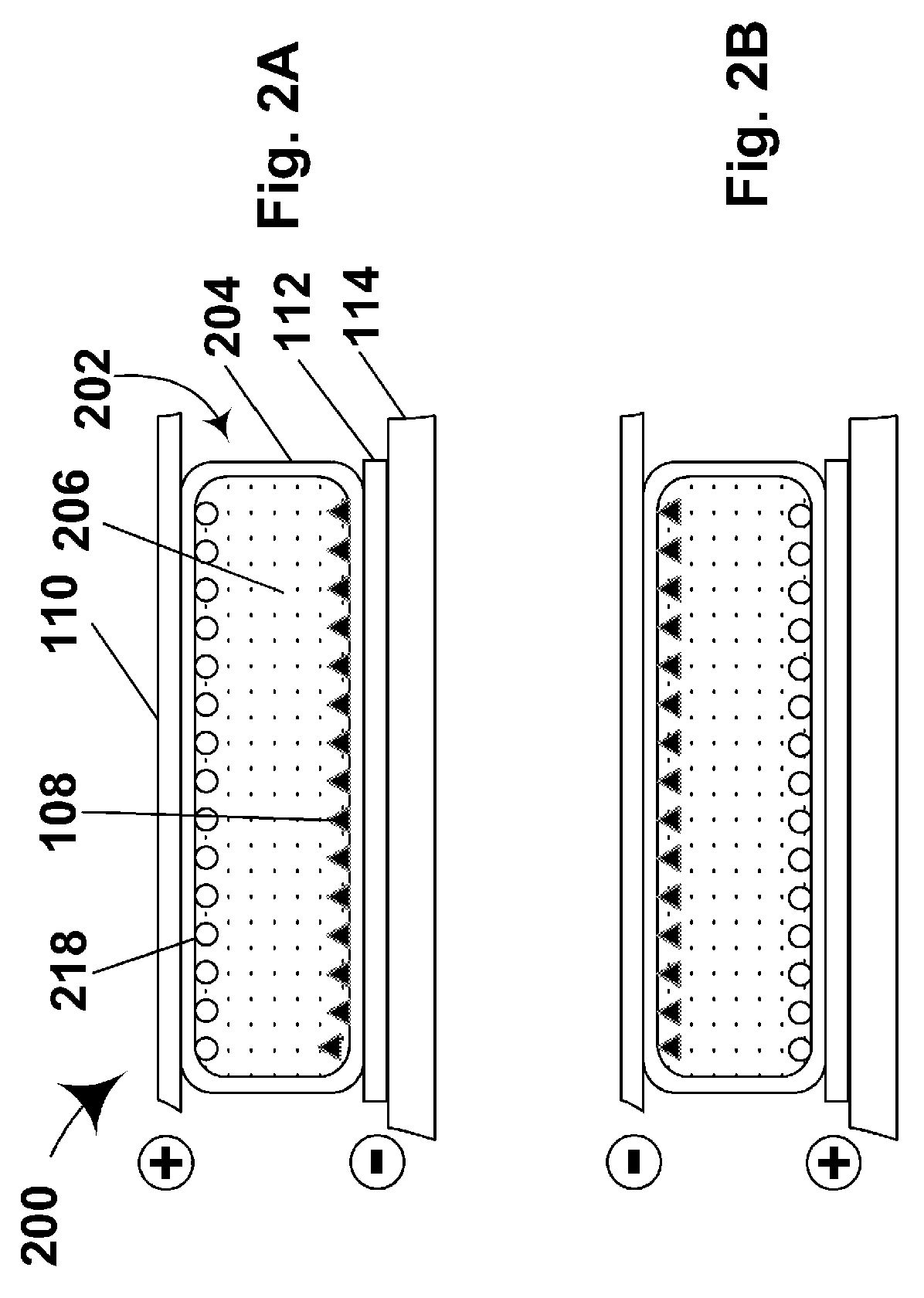
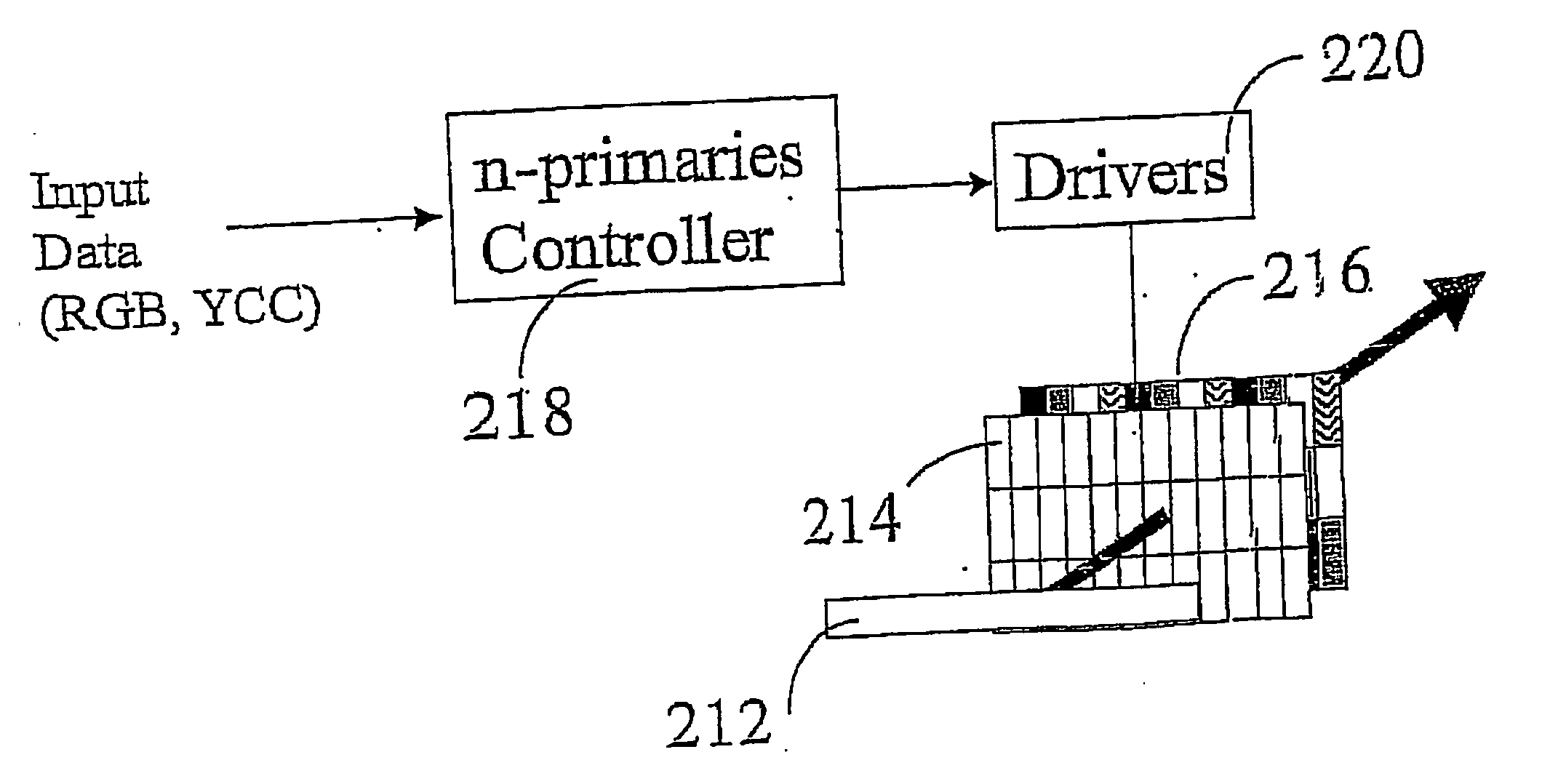
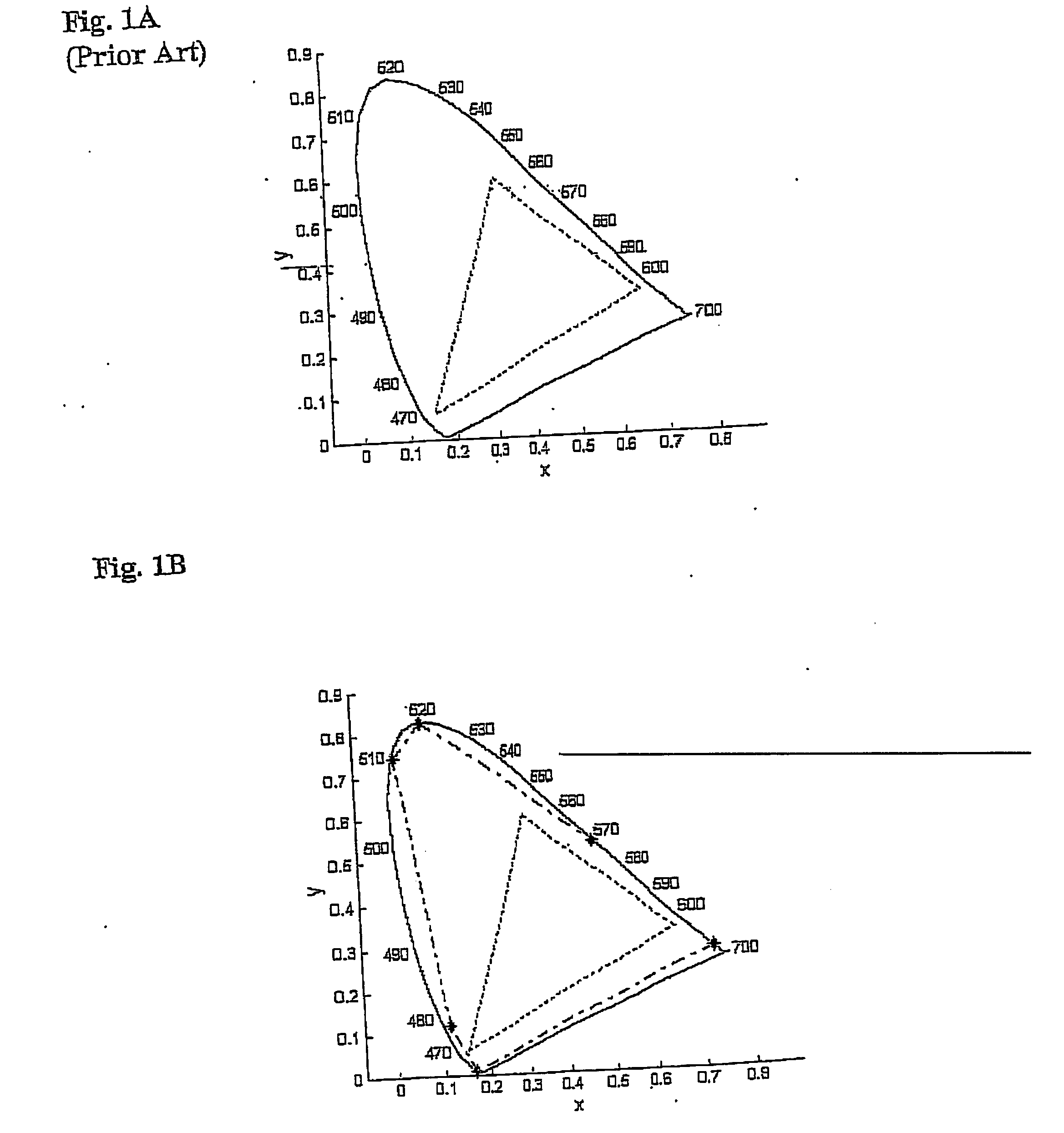
A color display device for displaying an n-primary color image wherein n is greater than three, the device including an array of sub-pixel (801) configured to have at least one repeating unit having one sub-pixel representing each of the n primary colors, wherein repeating unit (906) is configured to optimize at least one of the n-primary color image.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Resist composition
The following resist composition which is excellent particularly in transparency to light beams and dry etching properties and gives a resist pattern excellent in sensitivity, resolution, evenness, heat resistance, etc., as a chemical amplification type resist, is presented. A resist composition which comprises a fluoropolymer (A) having repeating units represented by a structure formed by the cyclopolymerization of one molecule of a fluorinated diene and one molecule of a monoene, in which the monoene unit in each repeating unit has a blocked acid group capable of regenerating the acid group by the action of an acid, an acid-generating compound (B) which generates an acid upon irradiation with light, and an organic solvent (C).
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Resist composition and patterning process
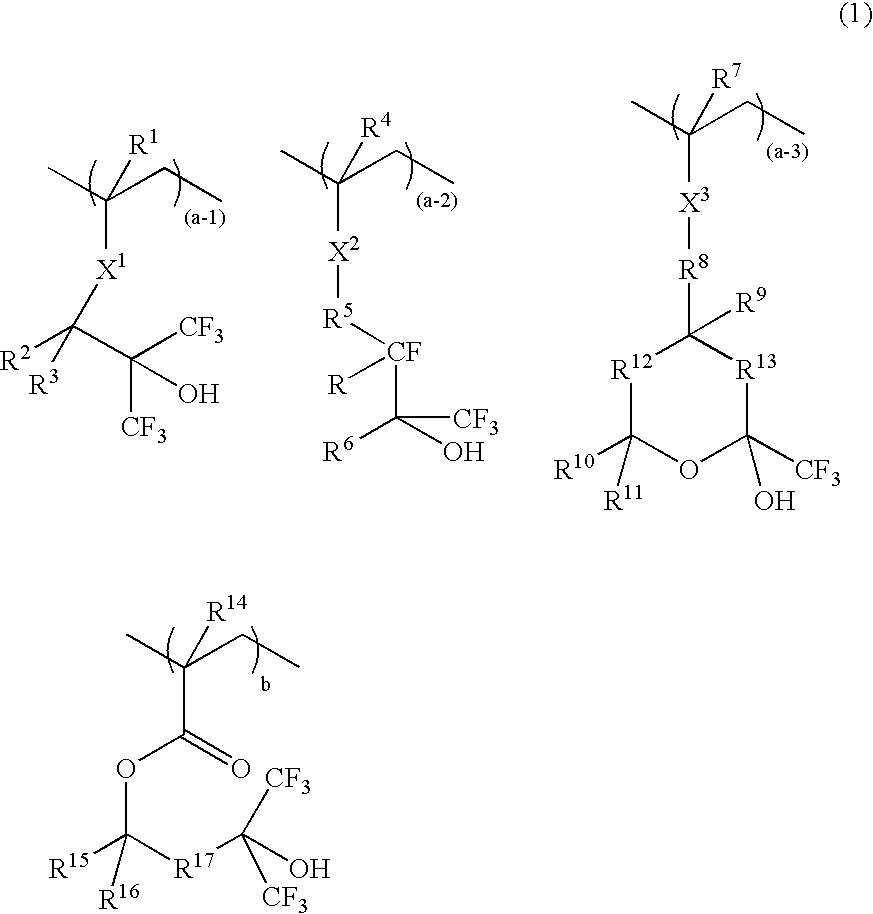
ActiveUS20080090172A1Improve barrier propertiesLow costElectric discharge tubesRadiation applicationsResistPolymer chemistry
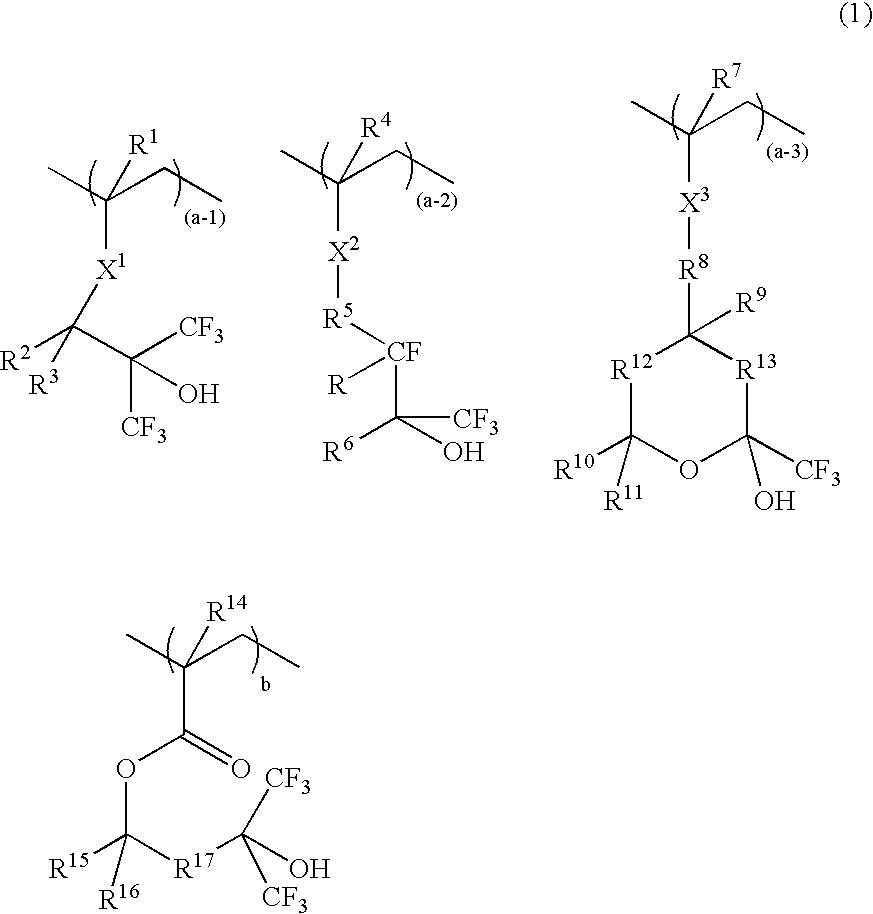
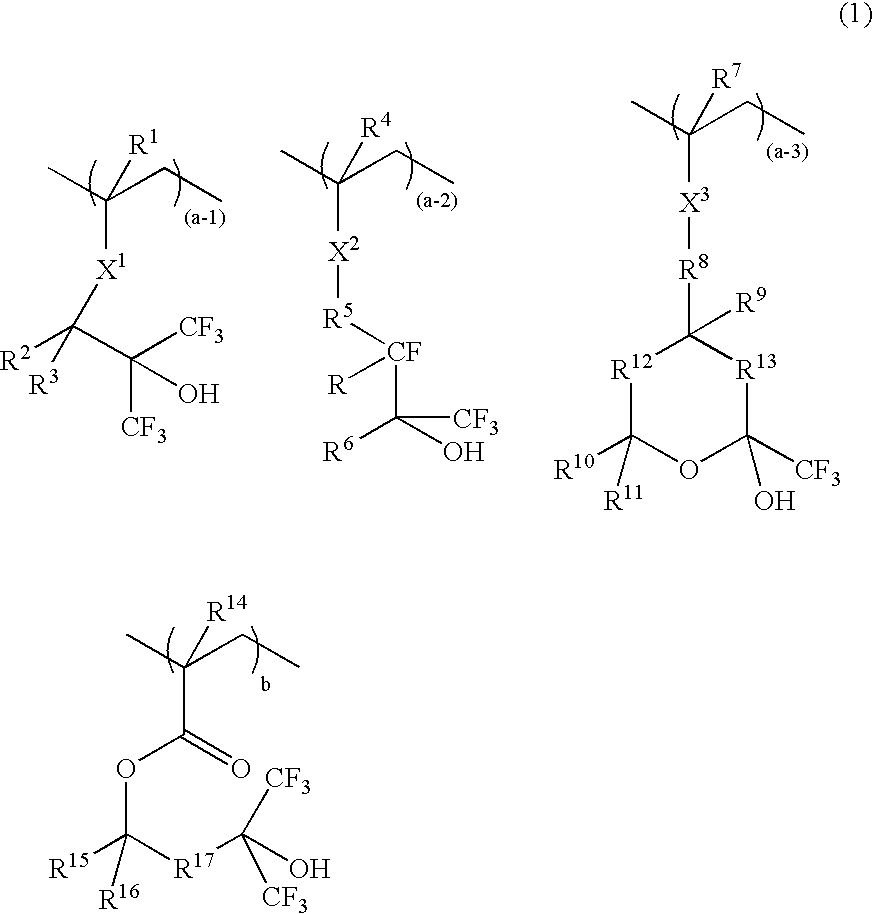
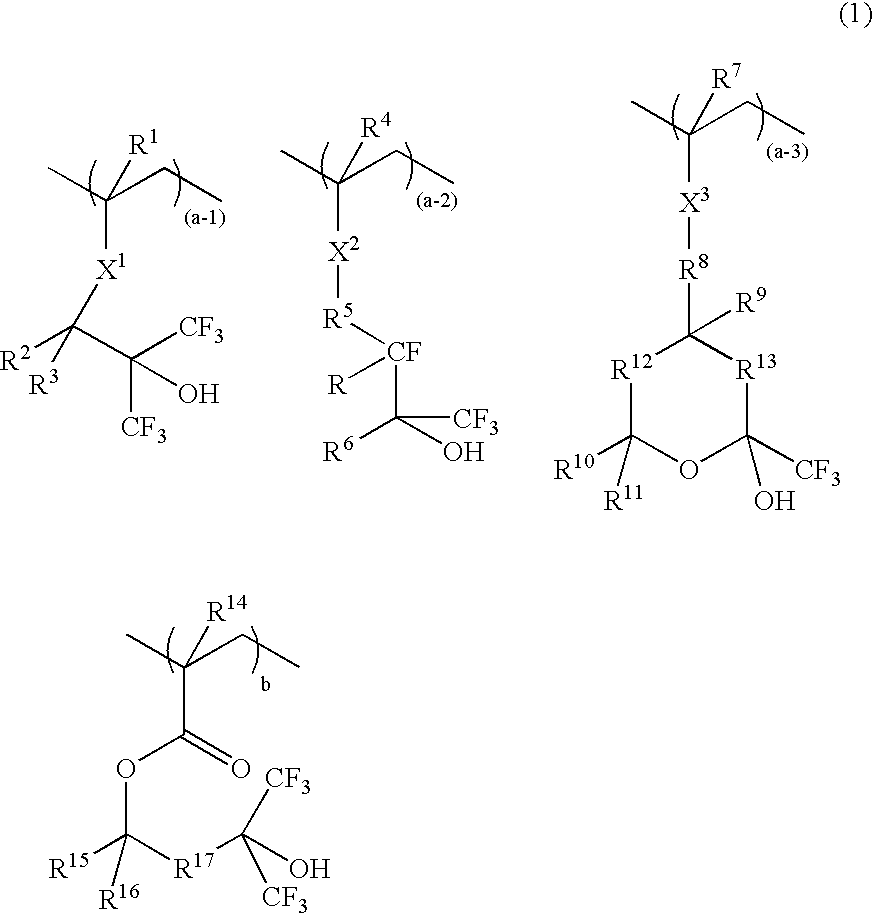
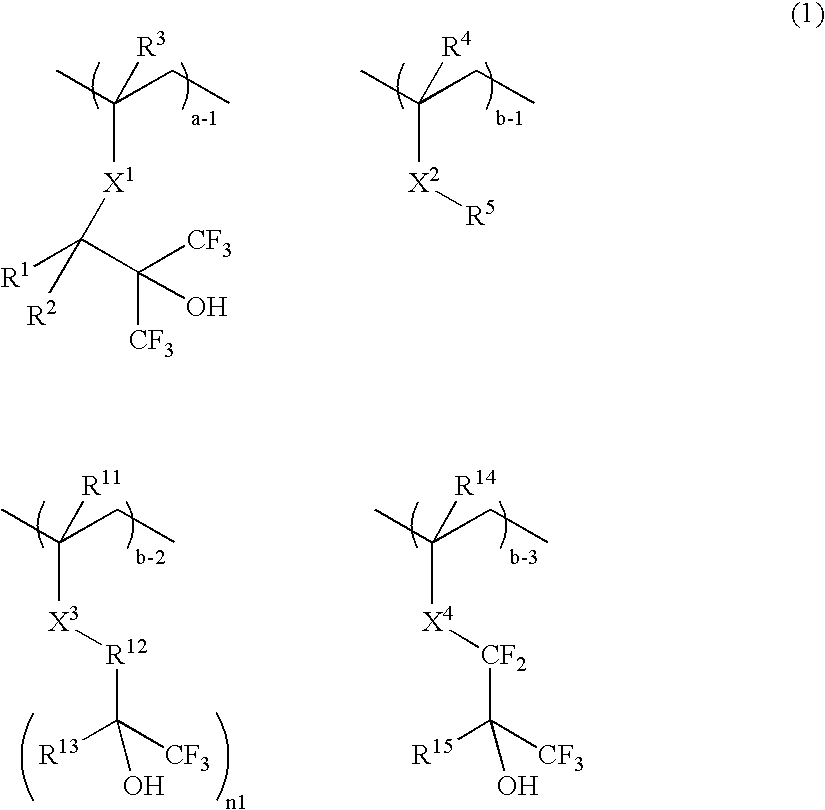
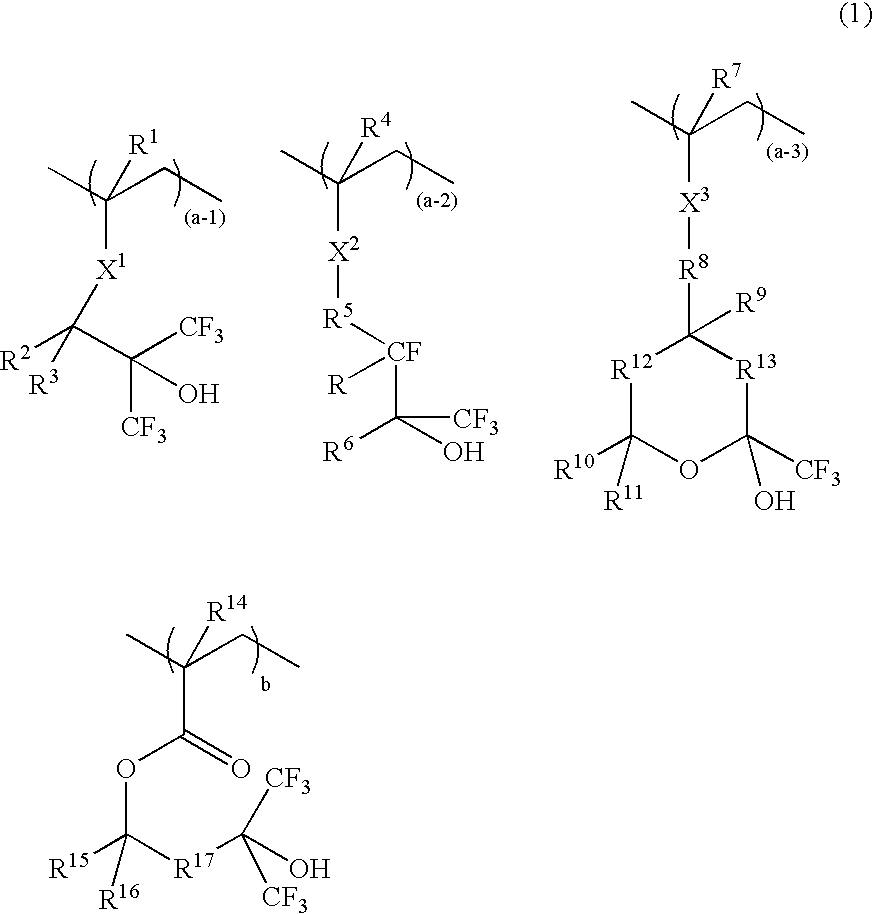
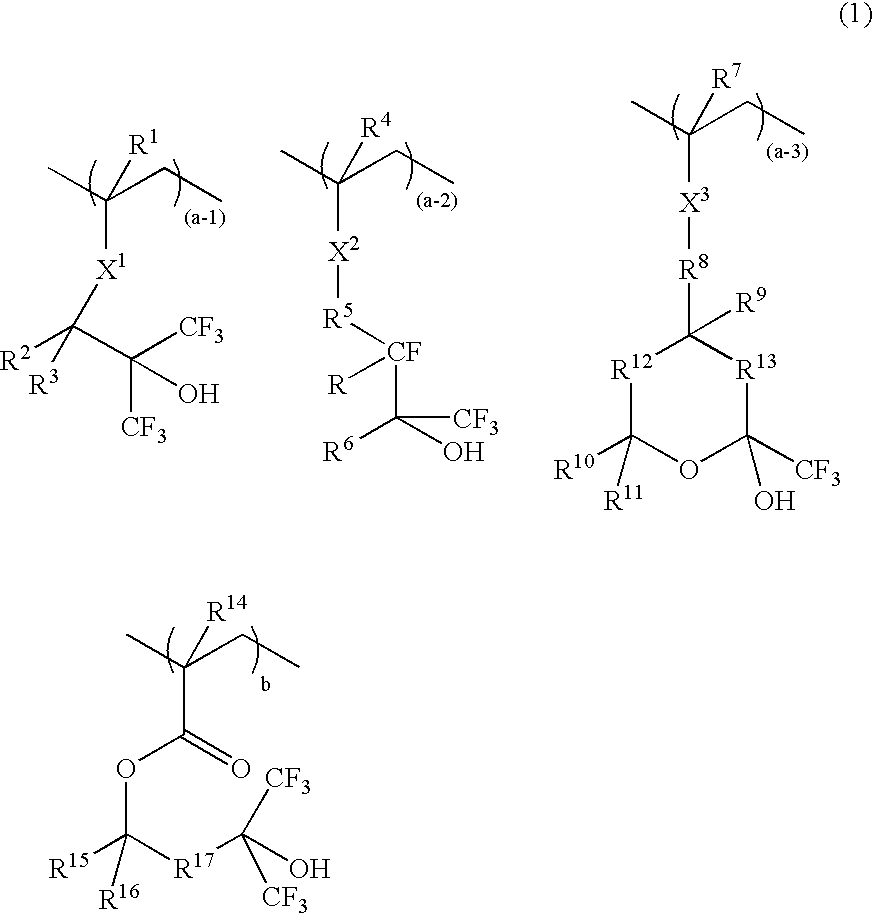
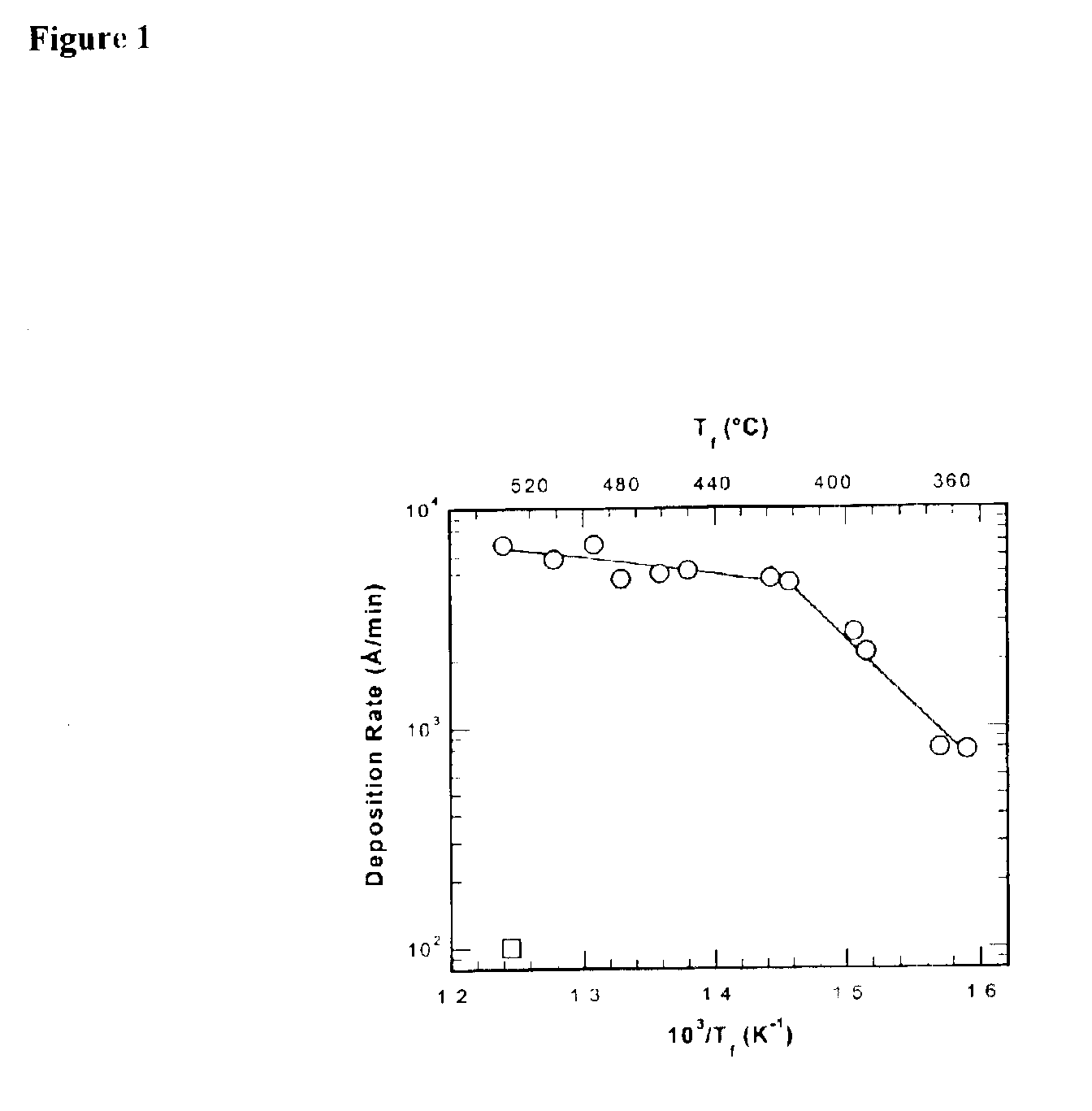
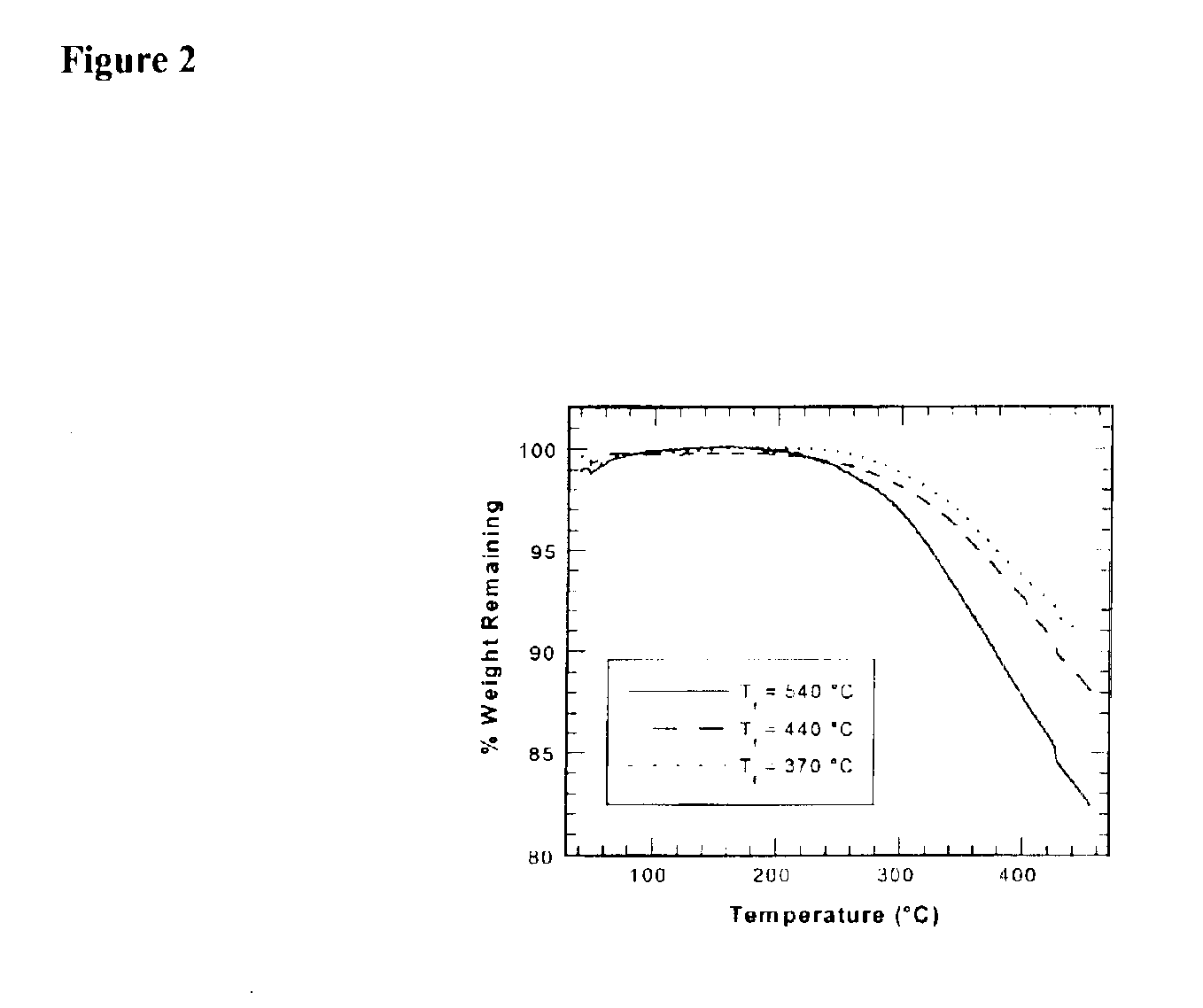
A resist composition comprises a polymer comprising recurring units having formula (1) wherein R1, R4, R7, and R14 are H or methyl, R2, R3, R15, and R16 are H, alkyl or fluoroalkyl, R is F or H, R5 is alkylene, R6 is fluorinated alkyl, R8 is a single bond or alkylene, R10 and R11 are H, F, methyl or trifluoromethyl, R12 and R13 are a single bond, —O— or —CR18R19—, R9, R18, and R19 are H, F, methyl or trifluoromethyl, R17 is alkylene, X1, X2 and X3 are —C(═O)—O—, —O—, or —C(═O)—R20—C(═O)—O— wherein R20 is alkylene, 0≦(a-1)<1, 0≦(a-2)<1, 0≦(a-3)<1, 0<(a-1)+(a-2)+(a-3)<1, 0<b<1, and 0<(a-1)+(a-2)+(a-3)+b≦1.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Positive resist composition and patterning process
ActiveUS20080153030A1Good storage stabilityHigh resolutionOrganic chemistryPhotosensitive materialsHigh energyPhotoacid generator
There is disclosed a resist composition that remarkably improves the resolution of photolithography using a high energy beam such as ArF excimer laser light as a light source, and exhibits excellent resistance to surface roughness and side lobe under use of a halftone phase shift mask; and a patterning process using the resist composition. The positive resist composition at least comprises (A) a resin component comprising a repeating unit represented by the following general formula (1); (B) a photoacid generator generating sulfonic acid represented by the following general formula (2) upon exposure to a high energy beam; and (C) an onium salt where a cation is sulfonium represented by the following general formula (3), or ammonium represented by the following general formula (4); and an anion is represented by any one of the following general formulae (5) to (7).
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Electrophoretic media and processes for the production thereof
InactiveUS20050168799A1Improve stabilityEasy to adaptMaterial nanotechnologyMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrophoresisEthylene Homopolymers
A first electrophoretic medium comprises an electrically charged particle suspended in a suspending fluid, the particle having a polymeric shell having repeating units derived from at least one monomer the homopolymer of which is incompatible with the suspending fluid. A second, similar electrophoretic medium comprises a suspending fluid, and first and second types of electrically charged particle suspended in the suspending fluid, the two types of particle having differing optical characteristics but both having polymeric shells. The polymeric shells are arranged such that homoaggregation of the two types of particles is thermodynamically favored over heteroaggregation.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Thermoplastic dicyclopentadiene-base open-ring polymers, hydrogenated derivatives thereof, and processes for the preparation of both
InactiveUS6511756B1Improve efficiencyGood moldabilityPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsSynthetic resin layered productsThermoplasticDouble bond
A thermoplastic dicyclopentadiene ring-opening polymer obtained by ring-opening polymerization of a monomer component containing a dicyclopentadiene monomer, characterized in that polycyclic rings which are repeating units of the polymer are bonded in cis-position relative to the carbon-carbon double bond of the main chain of the polymer in 50 mol % or more of the repeating units based on the total repeating units and the content of a low-molecular weight component of 2,000 or less in molecular weight is 10% by weight or less based on the total polymer components, and a hydrogenation product obtained by hydrogenating the carbon-carbon unsaturated bond of the thermoplastic dicyclopentadiene ring-opening polymer.
Owner:ZEON CORP
Cross-linkable polyionic coatings for medical devices
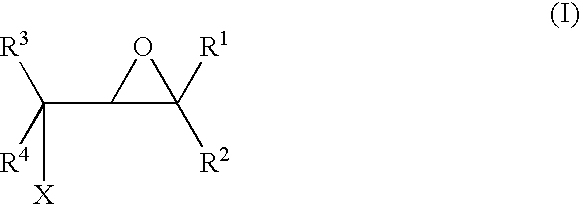
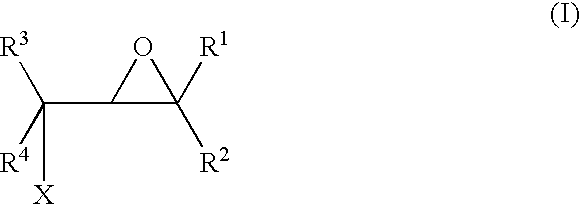
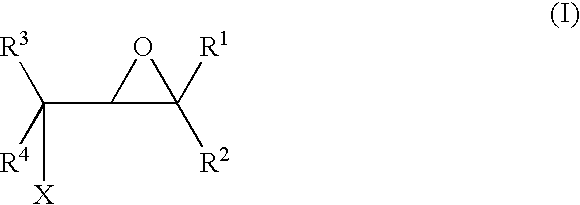
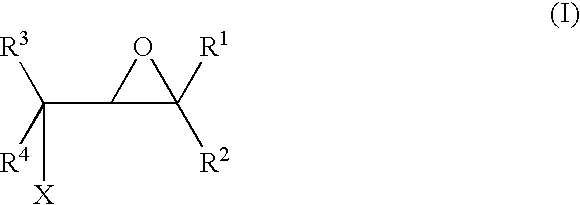
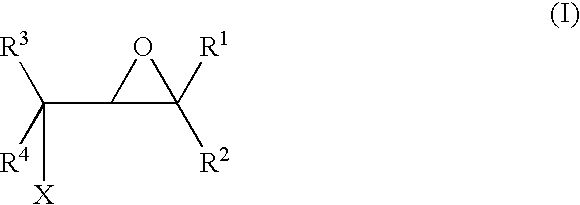
A method for making an article comprising a core material and a coating thereon, the method comprising the steps of:(a) providing the core material;(b) applying one or more layers of a crosslinkable polycationic material, wherein the polycationic material is a reaction product of:(i) an epoxide of formula (I)wherein X equals bromo, chloro, iodo, or cyano, and R1, R2, R3, R4, independently of one another, are selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, linear or branched C1-C6-alkyl, and linear or branched C1-C6-alkyl which is substituted with halogen, and(ii) a polymer having repeating units comprising one or more secondary or tertiary amine group(s);(c) applying one or more layers of a polyanionic material; and(d) cross-linking the layers of polyelectrolytes formed by steps (b) and (c).The articles obtainable by the method of the invention have desirable characteristics regarding adherence to the core material, durability, hydrophilicity, and wettability and are thus useful for the manufacture of medical articles such as ophthalmic devices.
Owner:ALCON INC
Birefringent reflectors using isotropic materials and form birefringence
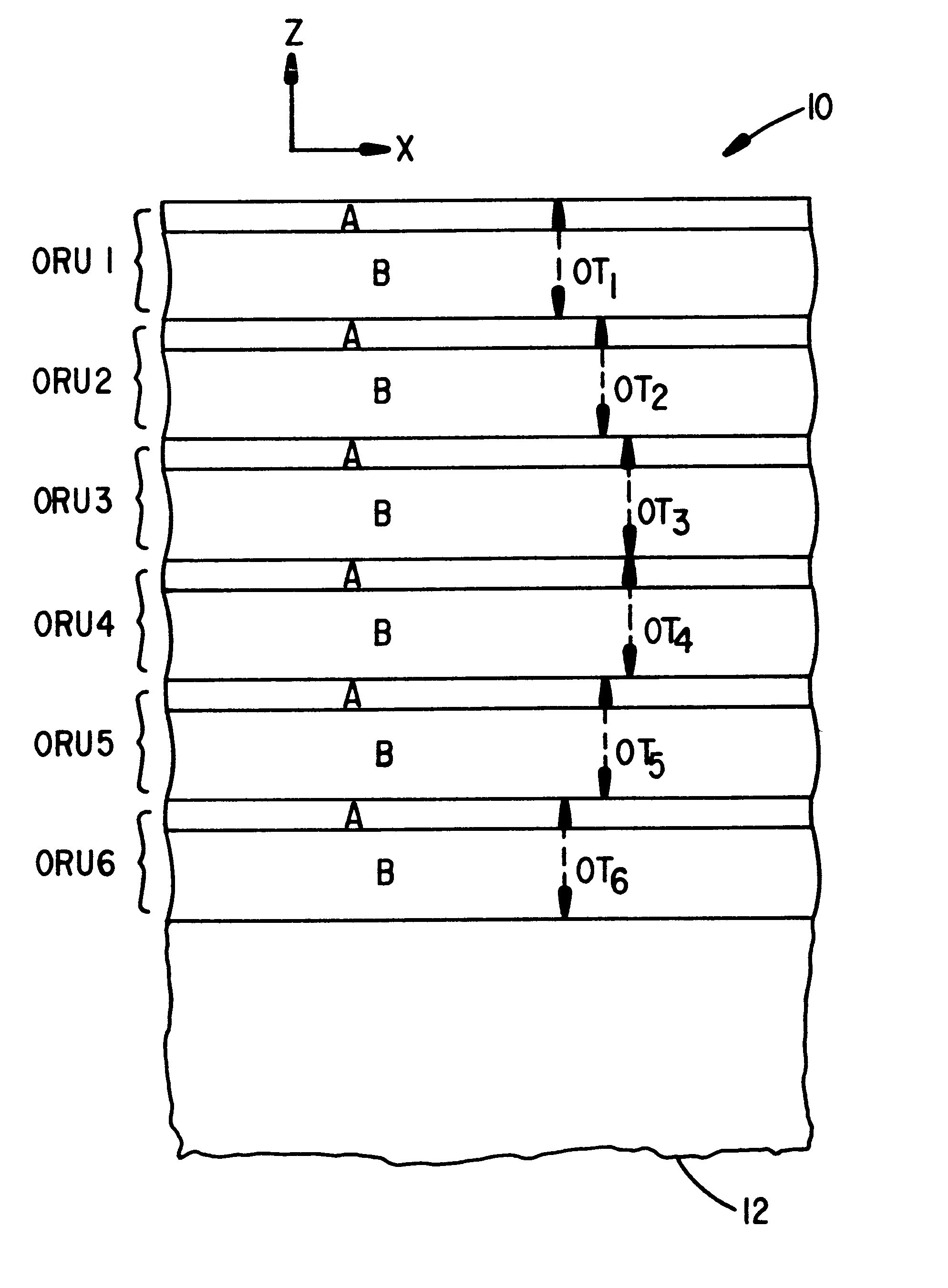
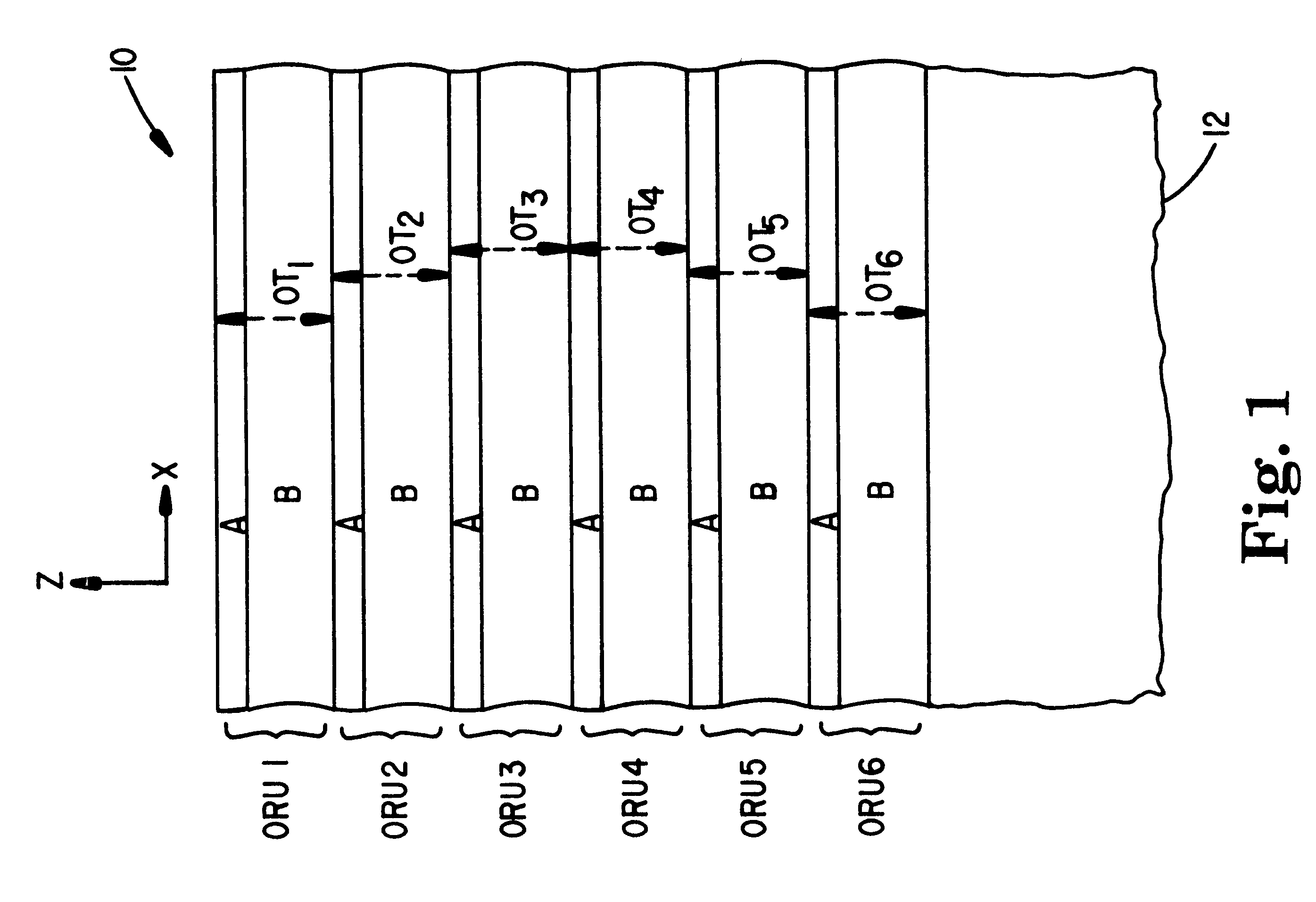
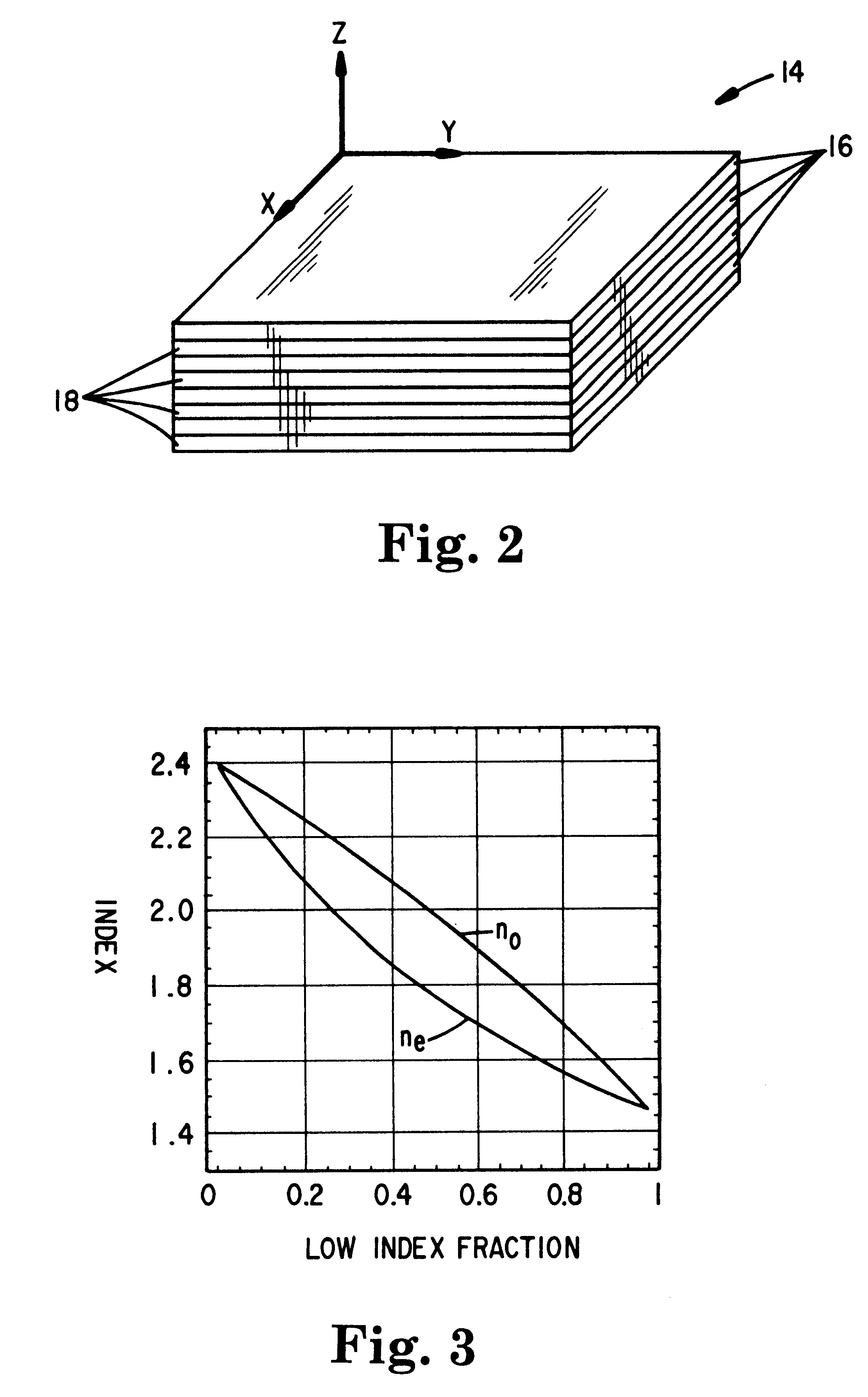
Multilayer thin film reflectors, such as mirrors and reflective polarizers, are described in which form birefringent optical layers are incorporated into a plurality of optical repeat units in the film. The form birefringent layers exhibit birefringence as a result of microscopic structures that have a dimension that is small compared to the wavelength of light but large compared to molecular distances. The optical layers within the optical repeat units have out-of-plane indices of refraction that are tailored to produce desired effects as a function of incidence angle for p-polarized light. The multilayer reflectors can be made by conventional vacuum deposition techniques using known inorganic optical materials, but can also be made entirely with polymeric materials by co-extrusion or other processes.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Method of fracturing subterranean formations utilizing emulsions comprising acrylamide copolymers
InactiveUS7482310B1Predictable and convenient and efficient preparationSufficient amountOther chemical processesMixing methodsPolymer scienceFracturing fluid
A method of treating a subterranean formation penetrated by a well bore including:(a) preparing a fracturing fluid containing a mixture resulting from:(I) providing a water-in-oil emulsion composition that includes:(i) 5% to 99% by weight of a water-in-oil emulsion polymer comprising a polymer or copolymer containing repeat units from an acrylamide monomer;(ii) 0.5% to 90% by weight of a carrier solvent; and(iii) 0 to 90% by weight of a fluidizing agent; and adding(iv) 0.1% to 10% by weight of one or more inorganic microparticles, where the total of all components is 100% by weight; and(II) adding the water-in-oil emulsion composition to water; and(b) contacting the subterranean formation with the fracturing fluid.
Owner:KROFF CHEM +1
Electrophoretic media and processes for the production thereof
InactiveUS20100148385A1Improve stabilityEasy to adaptElectrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementElectrophoresisEthylene Homopolymers
A first electrophoretic medium comprises an electrically charged particle suspended in a suspending fluid, the particle having a polymeric shell having repeating units derived from at least one monomer the homopolymer of which is incompatible with the suspending fluid. A second, similar electrophoretic medium comprises a suspending fluid, and first and second types of electrically charged particle suspended in the suspending fluid, the two types of particle having differing optical characteristics but both having polymeric shells. The polymeric shells are arranged such that homoaggregation of the two types of particles is thermodynamically favored over heteroaggregation.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Active materials for photoelectric devices and devices that use the materials
A conjugated polymer has a repeated unit having the structure of formula (I)wherein A1, A2, R1 and R2 are independently selected from the group consisting of a proton, an alkyl group comprising up to 18 carbon atoms, an alkoxy group comprising up to 18 carbon atoms, cyano, nitro, aryls and substituted aryls, and wherein Ar is selected from the group consisting of ethenylene, ethynylene, monocyclic arylene, bicyclic arylene, polycyclic arylene, monocyclic heteroarylene, bicyclic heteroarylene, polycyclic heteroarylene, and one to five such groups one of fused or linked.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Compositions comprising rigid-rod polymers and carbon nanotubes and process for making the same
InactiveUS6900264B2High modulusHigh stiffnessMaterial nanotechnologySpecial tyresFiberLiquid crystalline
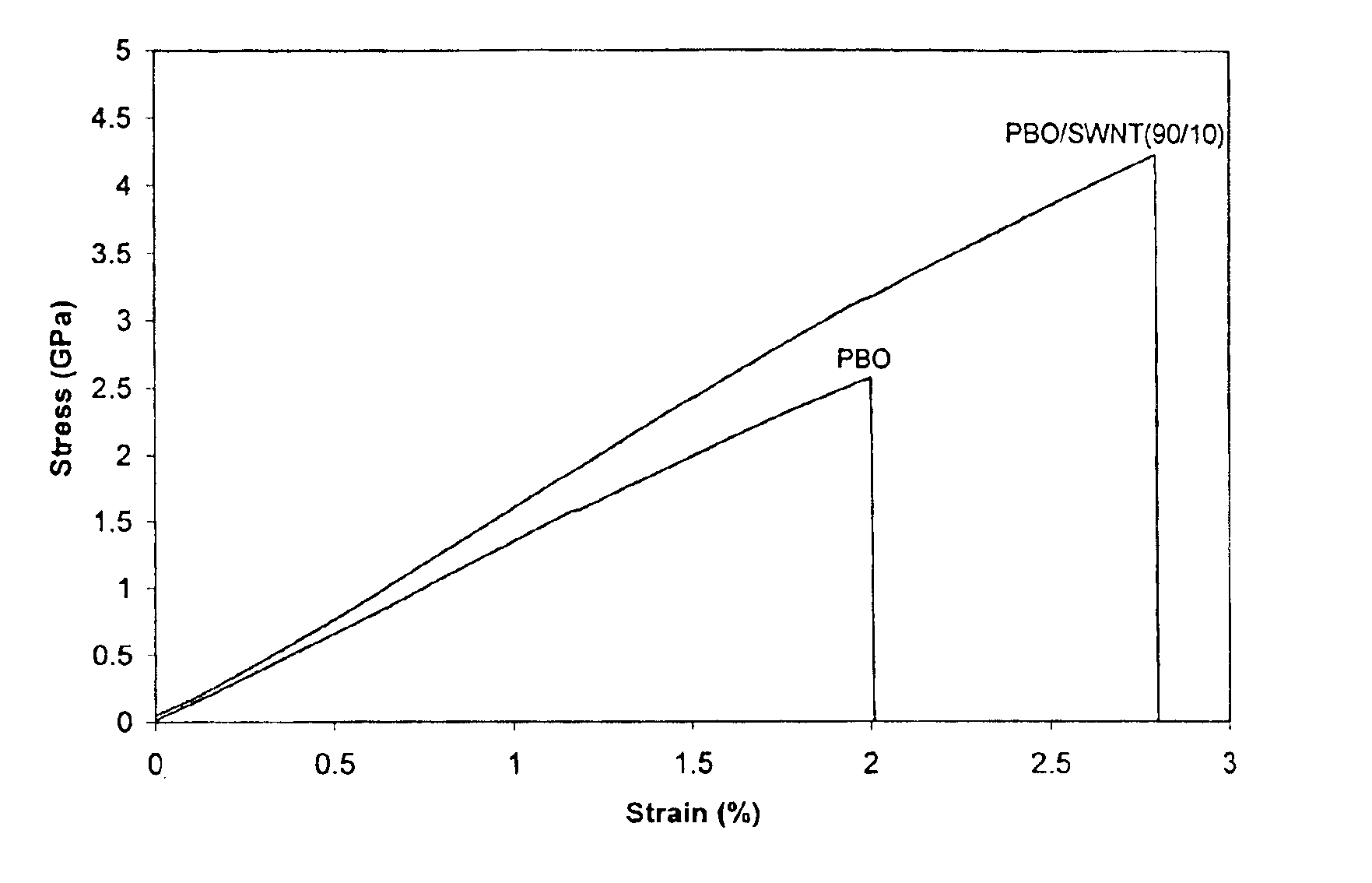
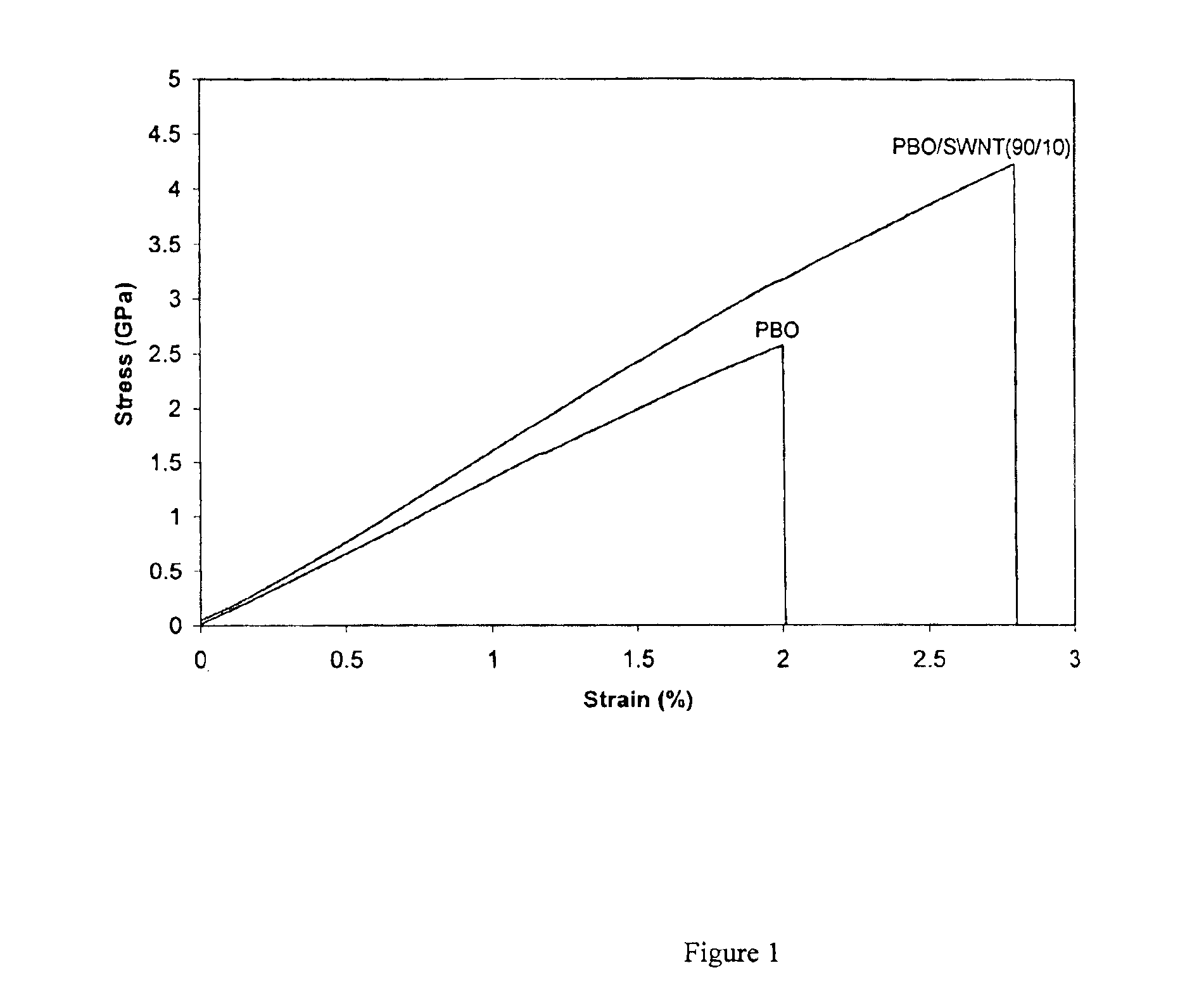
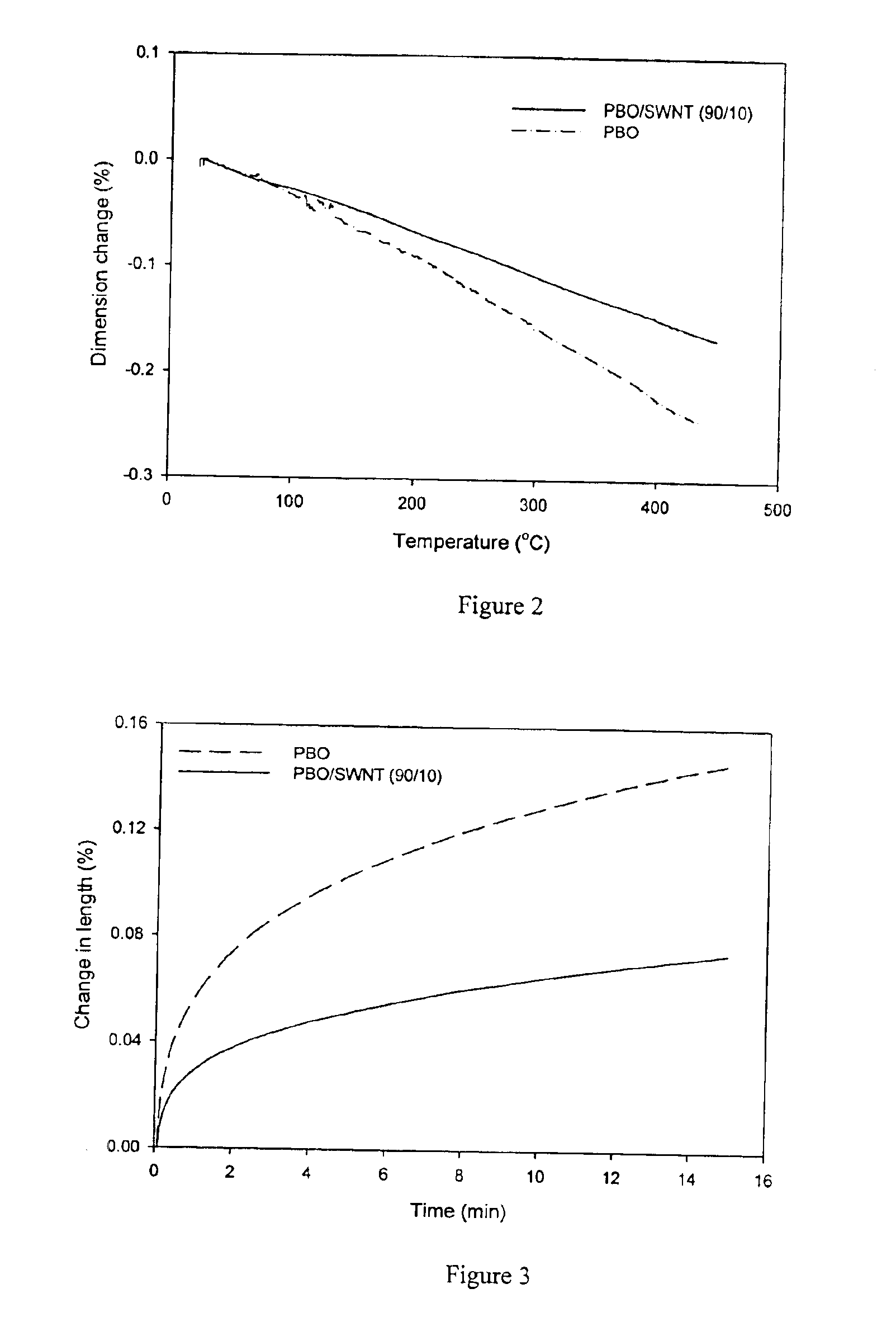
The present invention relates to compositions comprising rigid-rod polymers and carbon nanotubes. The compositions comprise dispersed carbon nanotubes aligned with rigid-rod polymers. The alignment of the nanotubes and polymers can be liquid crystalline. The rigid-rod polymers of this invention include, but are not limited to, polymers and copolymers comprising benzobisazole, pyridobisimidazole and benzamidazobenzo-phenanthroline repeat units. Dispersion of carbon nanotubes is achieved by in-situ polymerization in the presence of the carbon nanotubes, which may be either single-wall or multi-wall or a combination of both. The polymer compositions comprising carbon nanotubes may be spun into fibers or formed into films. The strength of the resulting fibers of the present invention is significantly greater than that of fibers without carbon nanotubes.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Resist composition and patterning process using the same
ActiveUS20070231738A1Low costReduce defectsPhotosensitive materialsRadiation applicationsRepeat unitContact angle
There is disclosed a resist composition comprising, at least, a polymer including repeating units represented by the following general formula (1). There can-be provided a resist composition that has a good barrier property against water, prevents resist components from leaching to water, has high receding contact angle against water, does not require a protective film, has an excellent process applicability, suitable for the liquid immersion lithography and makes it possible to form micropatterns with high precision.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Cross-linkable polyionic coatings for medical devices
A method for making an article comprising a core material and a coating thereon, the method comprising the steps of:(a) providing the core material;(b) applying one or more layers of a crosslinkable polycationic material, wherein the polycationic material is a reaction product of:(i) an epoxide of formula (I)wherein X equals bromo, chloro, iodo, or cyano, and R1, R2, R3, R4, independently of one another, are selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, linear or branched C1-C6-alkyl, and linear or branched C1-C6-alkyl which is substituted with halogen, and(ii) a polymer having repeating units comprising one or more secondary or tertiary amine group(s);(c) applying one or more layers of a polyanionic material; and(d) cross-linking the layers of polyelectrolytes formed by steps (b) and (c).The articles obtainable by the method of the invention have desirable characteristics regarding adherence to the core material, durability, hydrophilicity, and wettability and are thus useful for the manufacture of medical articles such as ophthalmic devices.
Owner:ALCON INC
Triazine ring-containing polymer and film-forming composition comprising same
ActiveUS20120049308A1Improve heat resistanceLow volume shrinkageOrganic detergent compounding agentsOrganic chemistryPolymer scienceVolumetric shrinkage
A polymer containing a triazine ring-containing repeating unit structure represented by, for example, formula (23) or (24), which alone can achieve high heat resistance, high transparency, high refraction index, high solubility and low volume shrinkage, without adding a metal oxide.
Owner:NISSAN CHEM IND LTD
Polymer Compound And Polymer Light-Emitting Device Using The Same
ActiveUS20080138651A1High luminous intensityHigh fluorescence intensityConductive layers on insulating-supportsOrganic chemistryCompound (substance)Polystyrene
High-molecular compounds comprising repeating units represented by the general formula (1) or (2) and having number-average molecular weights of 103 to 108 in terms of polystyrene: (1) [wherein Ar1 and Ar2 are each independently a trivalent aromatic hydrocarbon group or a trivalent heterocyclic group; and X1 and X2 are each independently O, S, C(═O), S(═O), SO2, C(R1)(R2), Si(R3)(R4), N(R5), B(R6), P(R7), or P(═O)(R8), with the provisos that X1 and X2 must not be the same and that X1 and Ar2 are bonded respectively to the adjacent carbon atoms constituting the aromatic ring of Ar1, and X2 and Ar1 are bonded respectively to the adjacent carbon atoms constituting the aromatic ring of Ar2] (2) [wherein Ar3 and Ar4 are each independently a trivalent aromatic hydrocarbon group or a trivalent heterocyclic group; and X3 and X4 are each independently N, B, P, C(R9), or Si(R10), with the provisos that X3 and X4 must not be the same and that X3 and Ar4 are bonded respectively to the adjacent carbon atoms constituting the aromatic ring of Ar3, and X4 and Ar3 are bonded respectively to the adjacent carbon atoms constituting the aromatic ring of Ar4].
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Composition for use in golf balls and sports equipment
The present invention relates to a novel blend composition suitable for use in sports equipment in general and in particular for use in golf ball manufacture. The composition is the reaction product of; A) a polymer of ethylene and / or one or more alpha olefins, and an acid, ester, or anhydride (“Component (A)”); and B) a compound comprising both an amine and a carboxylic acid in the same molecule which may be present in either a neutral or ionic or zwitterionic form (“Component (B)”); and C) a basic metal ion salt, capable of neutralizing the acid groups of Component (A) and / or Component (B). The metal ions including Li+, Na+, K+, Zn+, Co2+, Ca2+, Ni2+, Cu2+, Pb2+, and Mg2+, with Li+, Na+, Zn2+, Ca2+, and Mg2+ being preferred, and their salts include those of, for example, formic acid, acetic acid, nitric acid, sulfuric acid, carbonic acid, bicarbonic acid, as well as the metal oxides, hydroxides, and alkoxides (“Component (C)”). The present invention is also embodied in a blend composition including the reaction product of one or more ionomers and Component (B) which is a compound having a general formula (R2N)m—R′—(X(O)nORy)m, where R is either hydrogen, one or more C1-C20 aliphatic systems, one or more cycloaliphatic systems, one or more aromatic systems, or a combination of these. Also R′ is a bridging group comprising one or more unsubstituted C1-C20 straight chain or branched aliphatic or alicyclic groups, or one or more substituted straight chain or branched aliphatic or alicyclic groups, or one or more aromatic groups, one or more oligomers each containing up to 12 repeating units, and when X is C or S or P, m is 1-3. Also when X=C, n=1 and y=1, and when X=S, n=2 and y=1, and when X=P, n=2 and y=2. The present invention also resides in a golf ball including a core, an outer cover layer; and from 0 to 5 intermediate layers, wherein one or more of said core, outer cover, and / or intermediate layers, if present, includes the aforementioned blend compositions. Finally, the present invention is also embodied in sports equipment items comprising the aforementioned blend compositions.
Owner:TAYLOR MADE GOLF
Olefin block copolymers, processes for producing the same and uses thereof
Olefin block copolymers (A-1) are disclosed represented by the formula (I) PO1-g1-B1 . . . (I) wherein PO1 is a segment comprised of repeating units derived from an olefin having 2 to 20 carbon atoms, g1 is an ester, ether, amide, imide, urethane, urea, silylether or carbonyl linkage, and B1 is a segment containing an unsaturated hydrocarbon or a hetero atom. The olefin block copolymers are suitable for uses in adhesives, various molded articles such as construction and civil engineering materials, automobile interior and exterior materials, gasoline tanks, electric and electronic parts, medical care and sanitation materials, materials of miscellaneous goods, resin materials having environmental degradation properties, films and sheets, modifiers and dispersions.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Photosensitive compositions based on polycyclic polymers for low stress, high temperature films
InactiveUS20060020068A1Increase variabilityFilm/foil adhesivesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAddition polymerNorbornene
Vinyl addition polymer compositions, methods for forming such compositions, methods for using such compositions to form microelectronic and optoelectronic devices are provided. The vinyl addition polymer encompassed by such compositions has a polymer backbone having two or more distinct types of repeat units derived from norbornene-type monomers independently selected from monomers of Formula I: wherein each of X, m, R1, R2, R3, and R4 is as defined herein and wherein a first type of repeat unit is derived from a glycidyl ether substituted norbornene monomer and a second type of repeat unit is derived from an aralkyl substituted norbornene monomer.
Owner:PROMERUS LLC
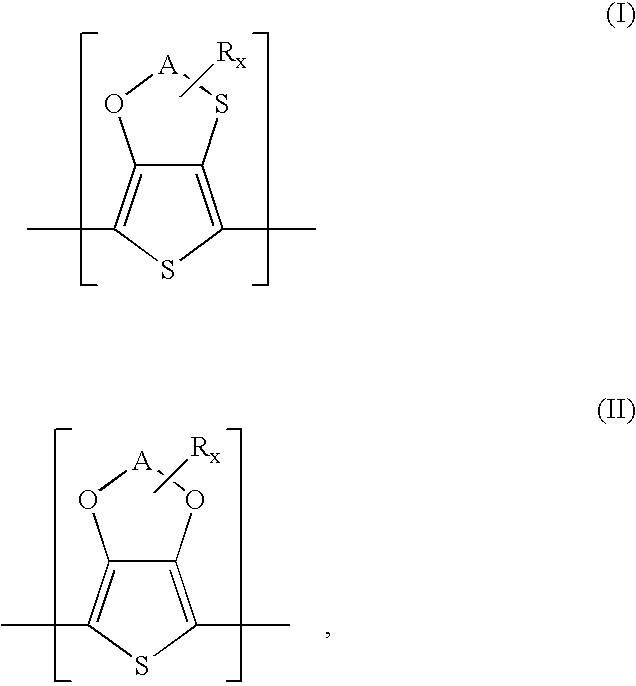
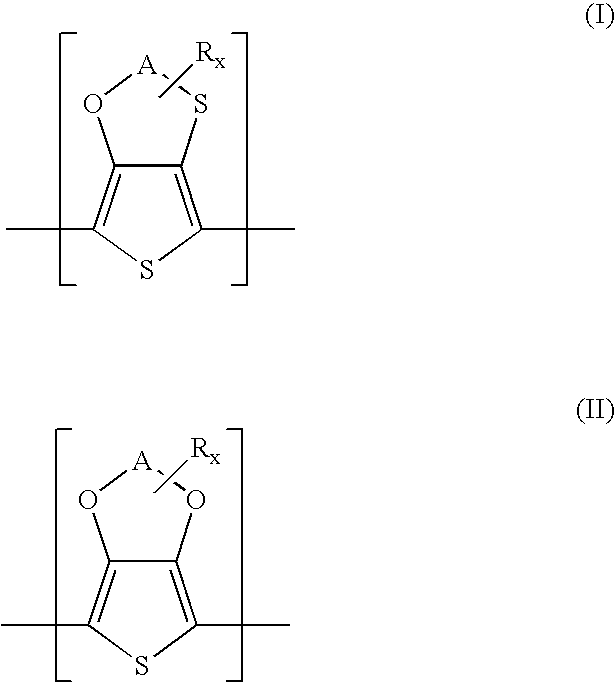
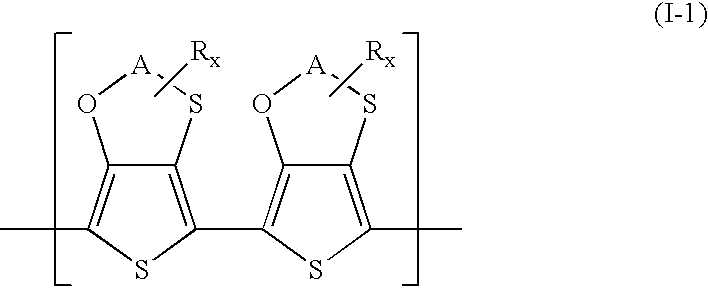
Polythiophenes having alkyleneoxythia thiophene units in electrolyte capacitors
InactiveUS7341801B2Reduce conductivityConductivity adjustableHybrid capacitor electrolytesHybrid capacitor electrodesPolymer scienceElectrolysis
Electrolyte capacitors containing certain polythiophenes are described. More particularly, the polythiophenes have backbones containing repeating units of the following general formula (I) and / or repeating units of the following general formula (II),wherein A is, for example, a C1-C5-alkylene radical, R is, for example, a C1-C18-alkyl radical, and x is an integer from 0 to 8. Also described are dispersions comprising such polythiophenes, and the use of such polythiophenes or dispersions thereof for producing conductive layers.
Owner:HERAEUS PRECIOUS METALS GMBH & CO KG
Resist composition and patterning process
A resist composition comprises a polymer comprising recurring units having formula (1) wherein R1, R4, R7, and R14 are H or methyl, R2, R3, R15, and R16 are H, alkyl or fluoroalkyl, R is F or H, R5 is alkylene, R6 is fluorinated alkyl, R8 is a single bond or alkylene, R10 and R11 are H, F, methyl or trifluoromethyl, R12 and R13 are a single bond, —O— or —CR18R19—, R9, R18, and R19 are H, F, methyl or trifluoromethyl, R17 is alkylene, X1, X2 and X3 are —C(═O)—O—, —O—, or —C(═O)—R20—C(═O)—O— wherein R20 is alkylene, 0≦(a-1)<1, 0≦(a-2)<1, 0≦(a-3)<1, 0<(a-1)+(a-2)+(a-3)<1, 0<b<1, and 0<(a-1)+(a-2)+(a-3)+b≦1.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM CO LTD
Fluorocarbon-organosilicon copolymers and coatings prepared by hot-filament chemical vapor deposition
InactiveUS6887578B2Synthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsGas phaseX-ray
Hot-filament chemical vapor deposition has been used to deposit copolymer thin films consisting of fluorocarbon and siloxane groups. The presence of covalent bonds between the fluorocarbon and organosilicon moieties in the thin film has been confirmed by Infrared, X-ray Photoelectron (XPS) and solid-state 29Si, 19F, and 13C Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. The film structure consists of chains with linear and cyclic siloxane groups and CF2 groups as repeat units.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com