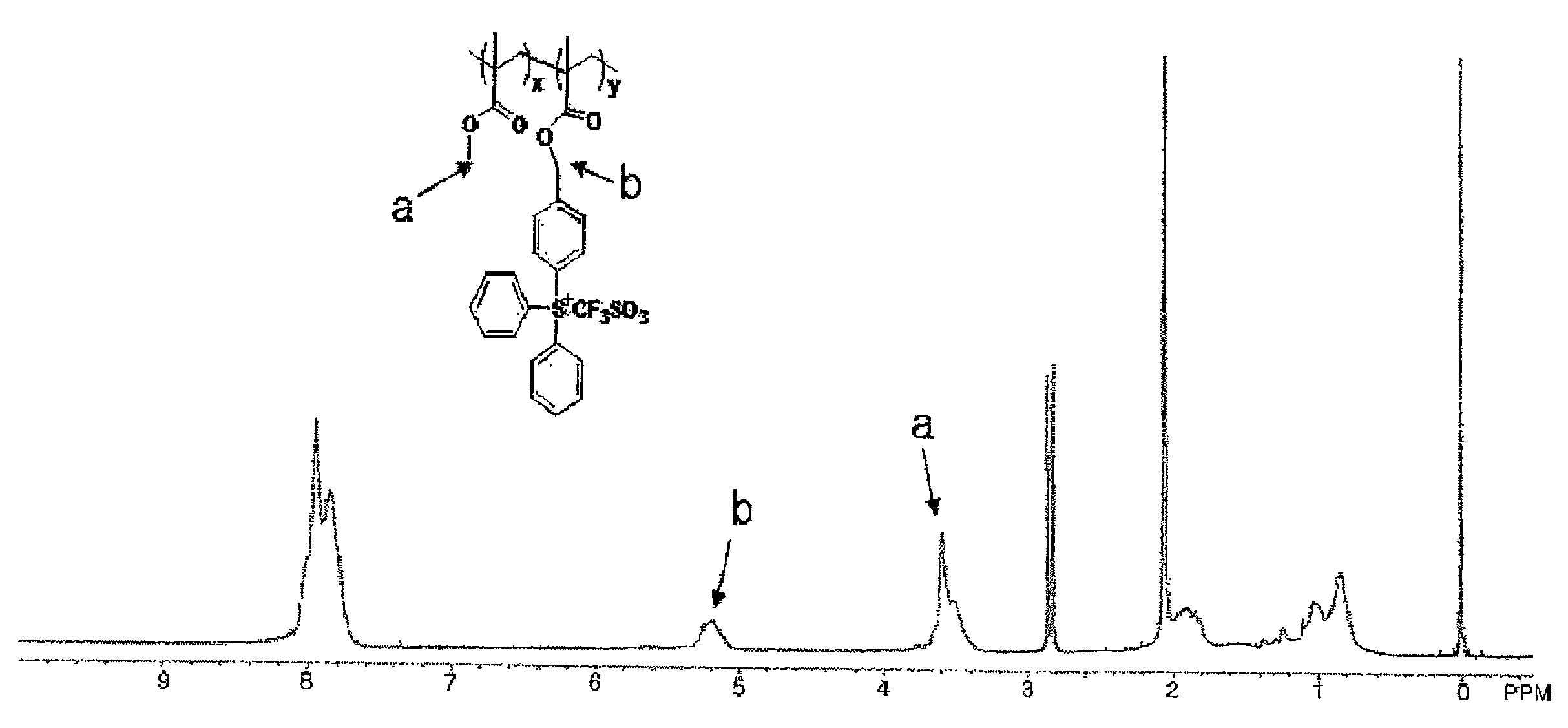
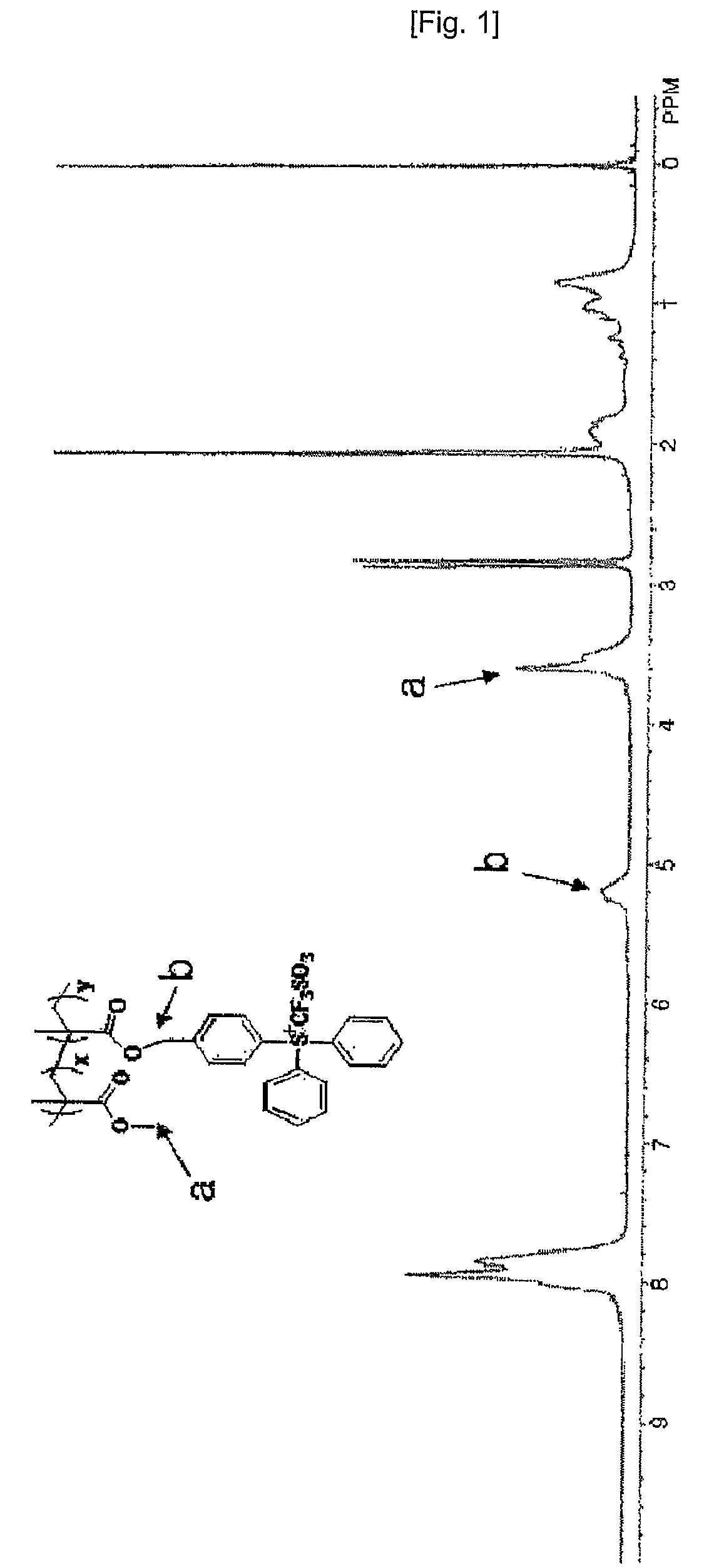
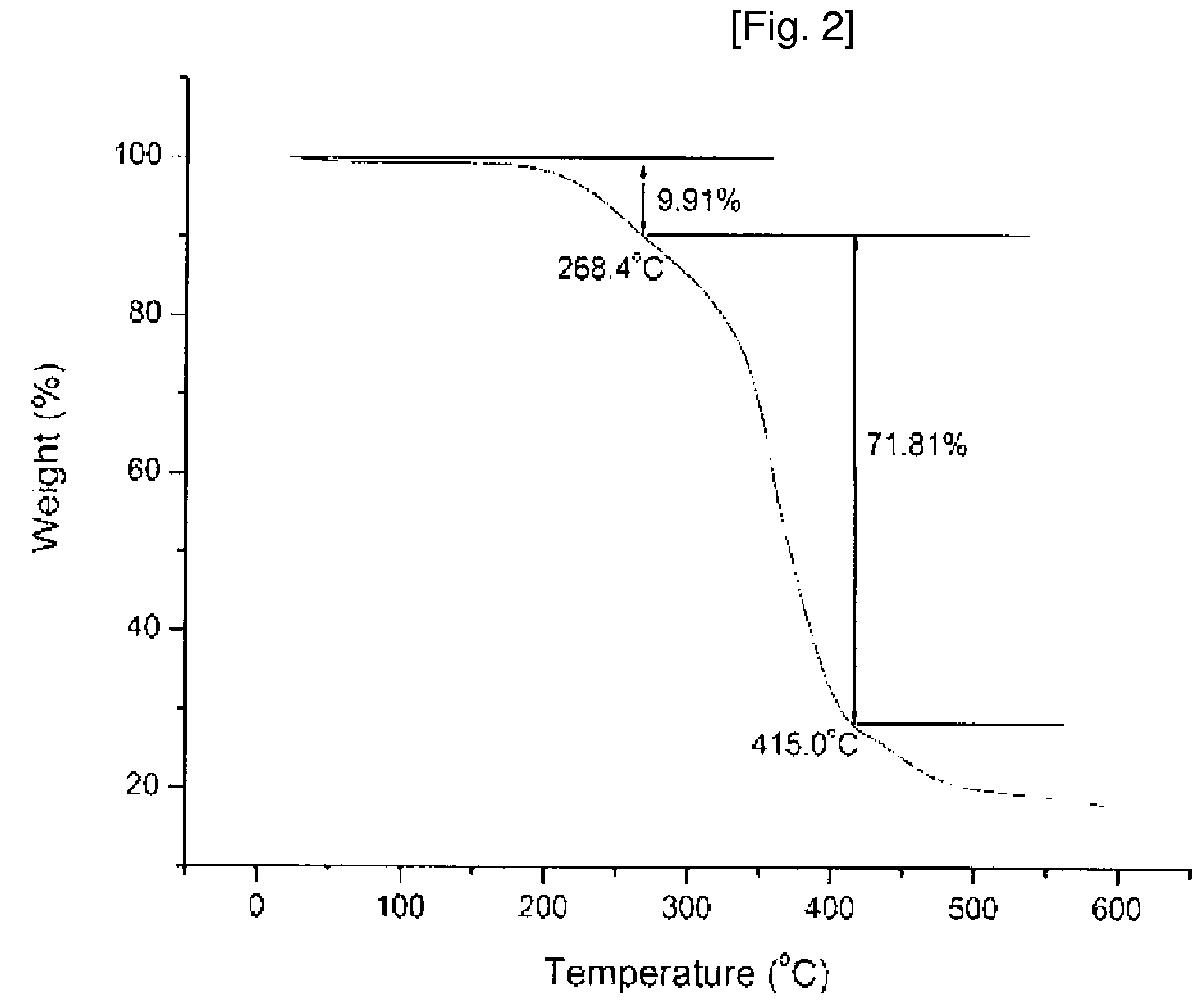
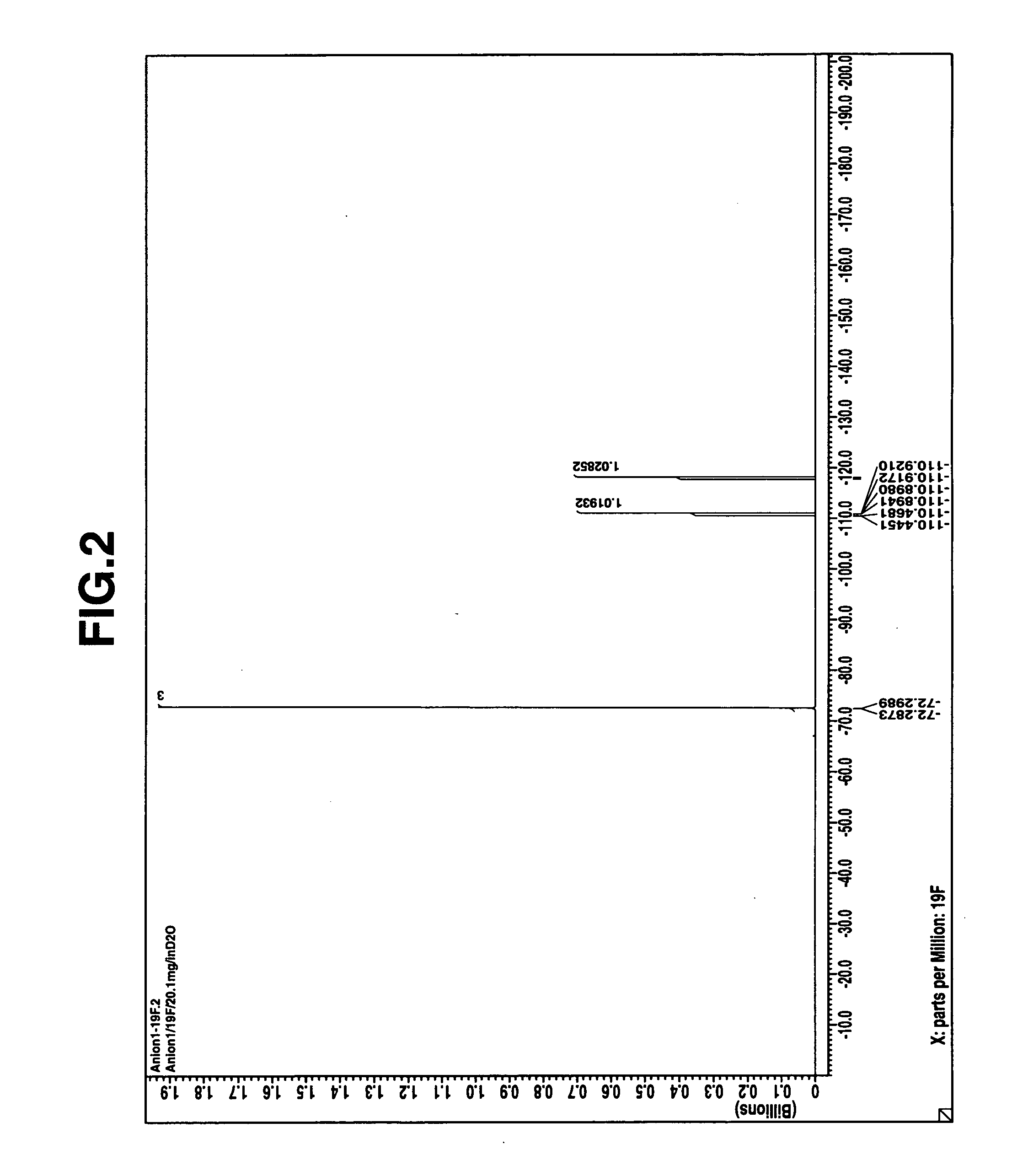
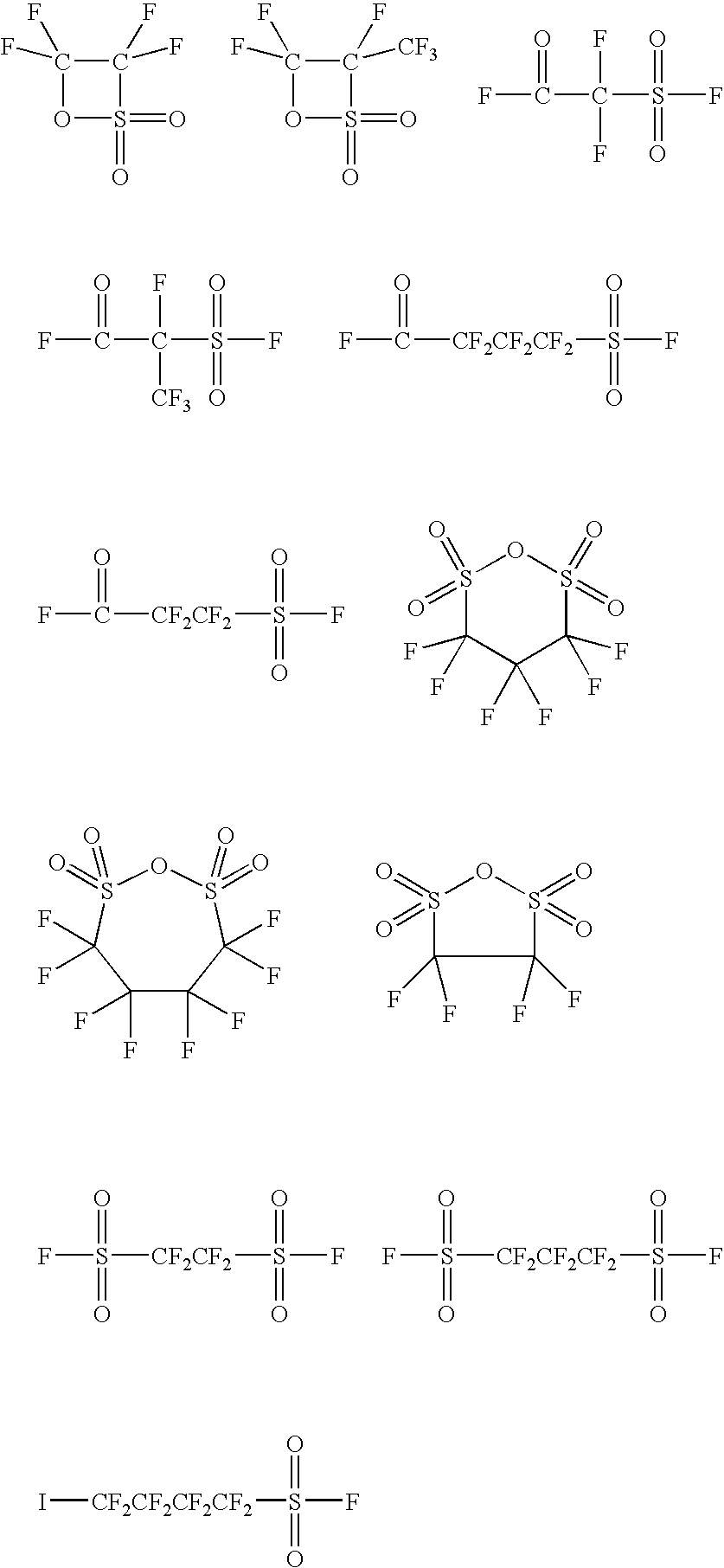
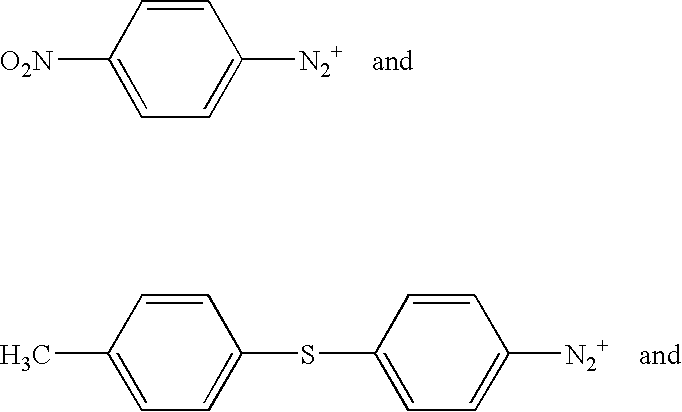
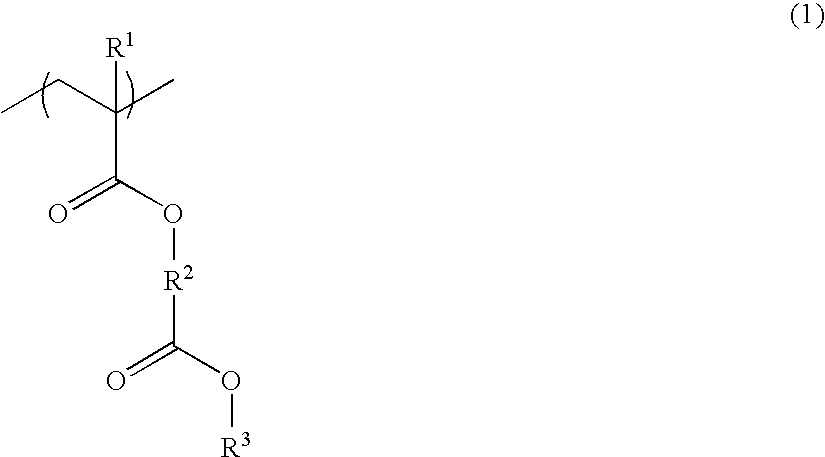
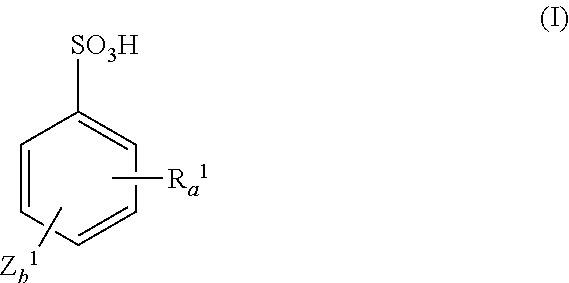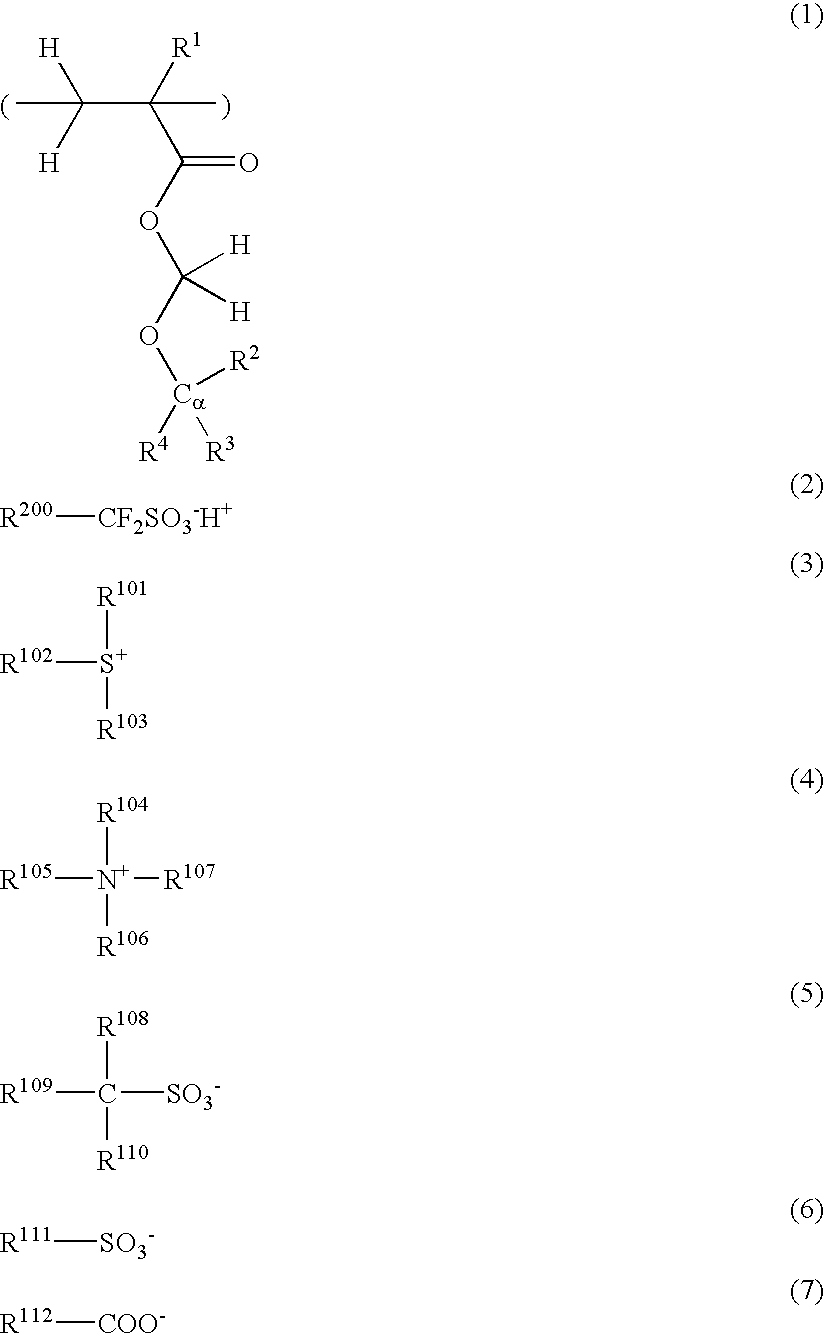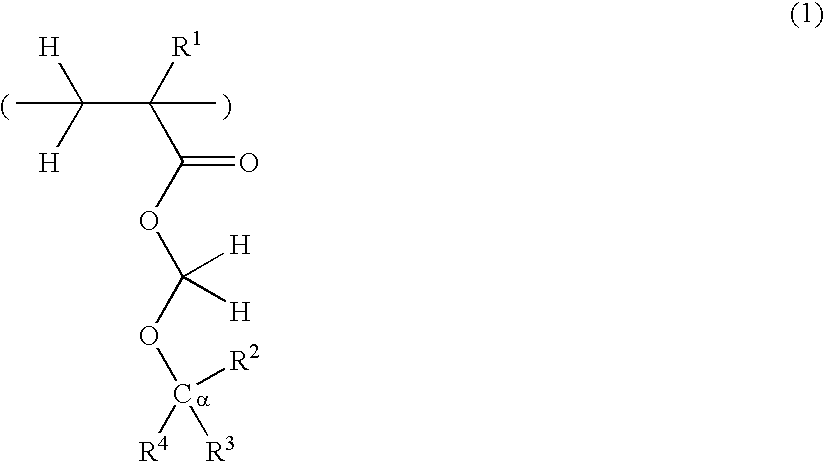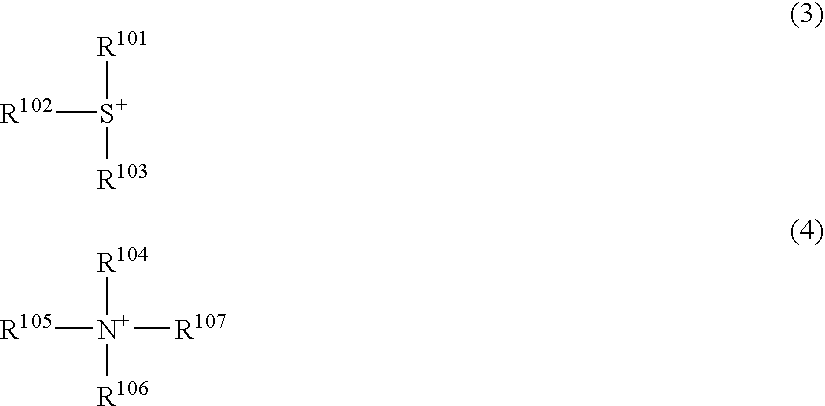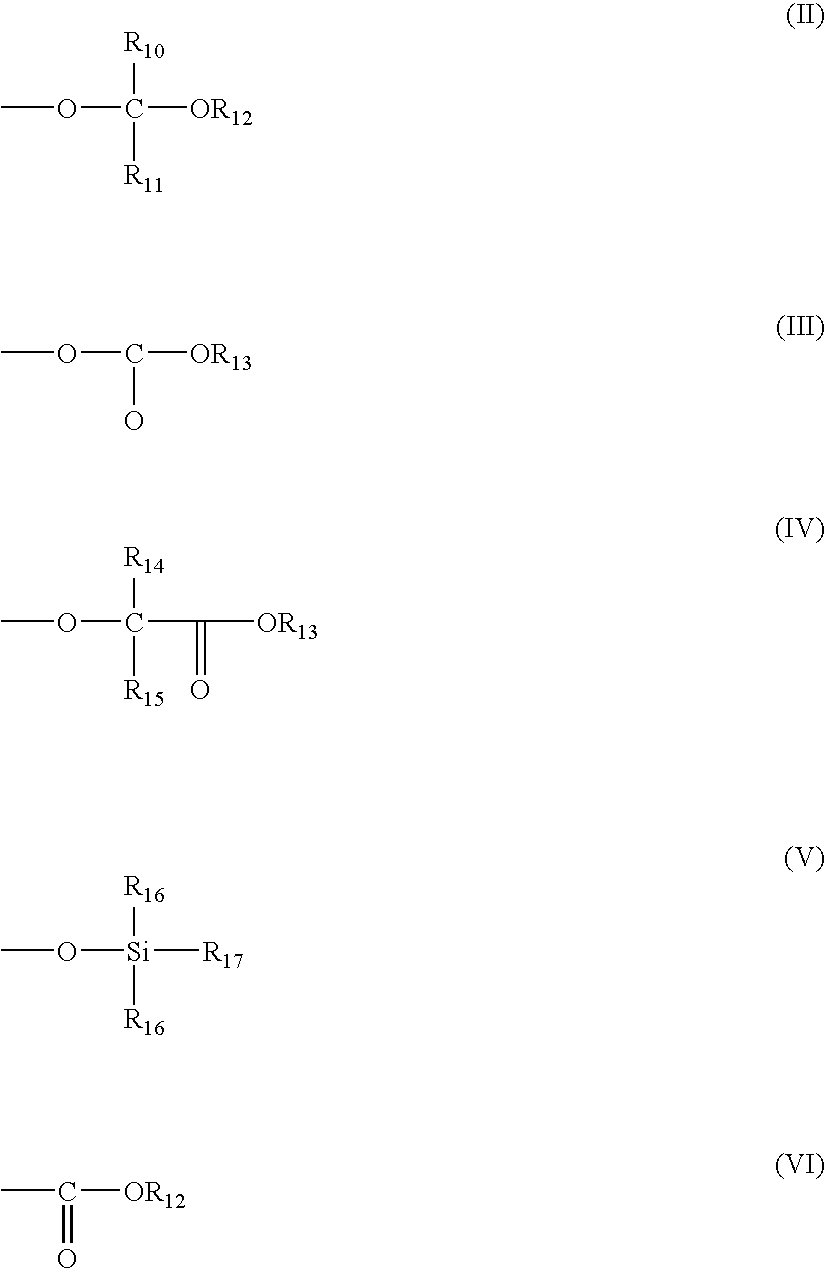Patents
Literature
1182 results about "Photoacid generator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
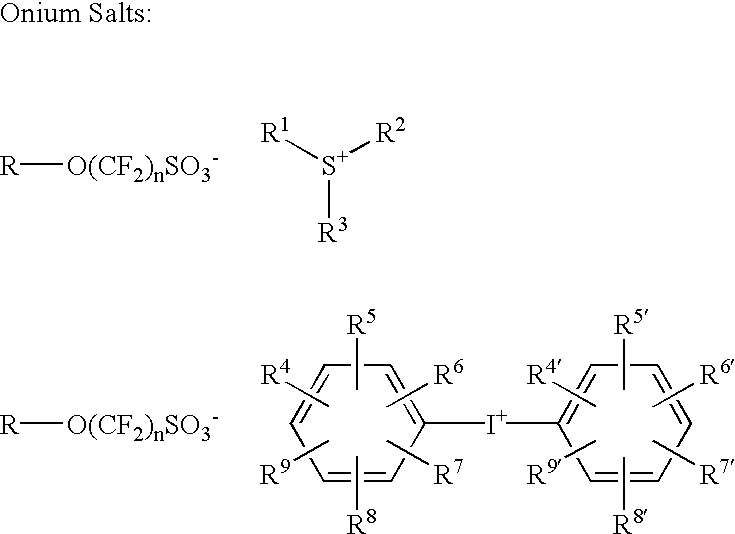
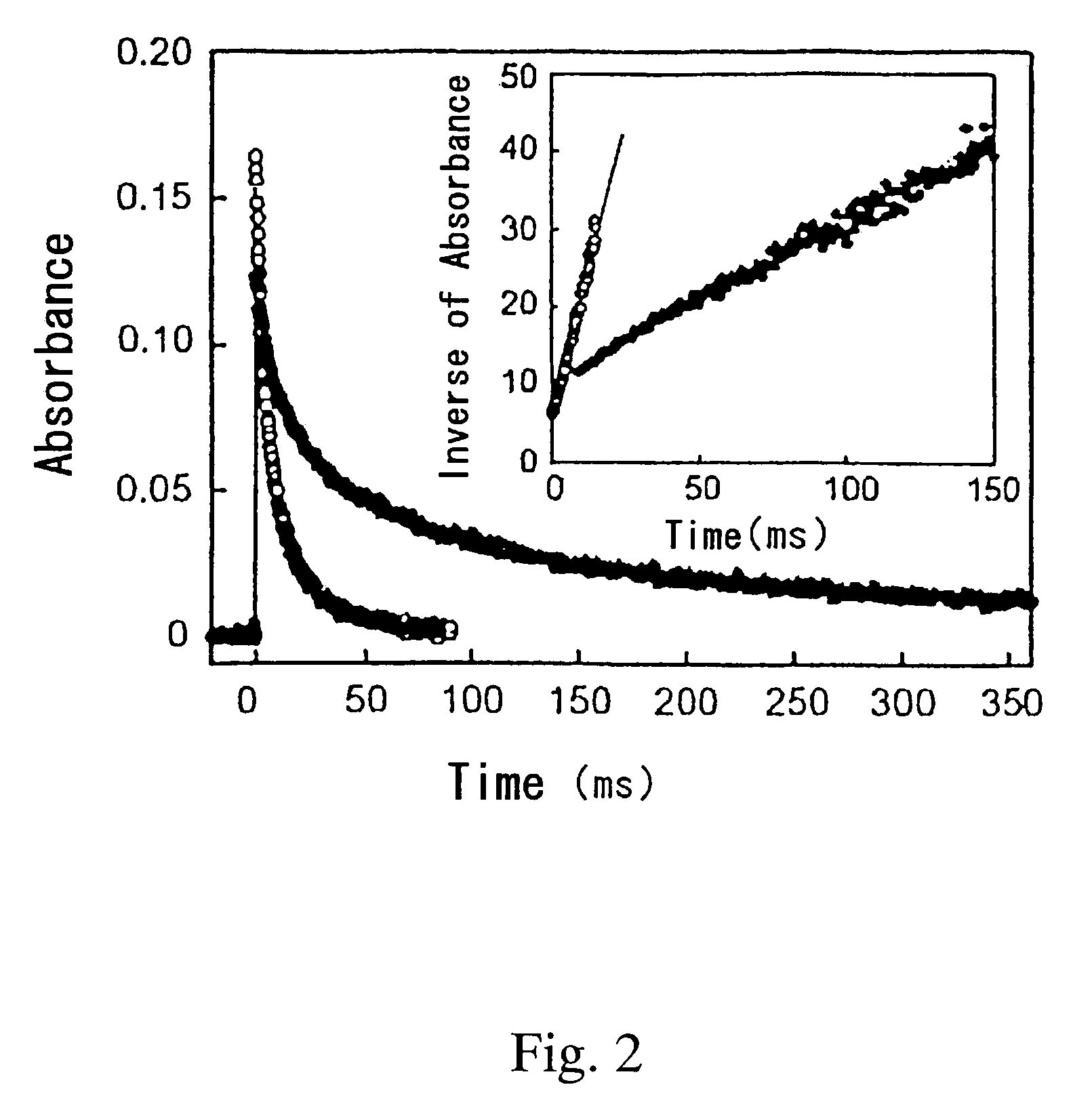
The photoacid generators are salts of onium cations which have high sensitivity to these actinic radiations, but where the decomposition products of these PAGs are reduced relative to conventional PAGs having, for example, diphenyliodonium cations and triphenylsulfonium cations, under similar conditions of photoresist composition, exposure,...
Acid generator, sulfonic acid, sulfonic acid derivatives and radiation-sensitive resin composition
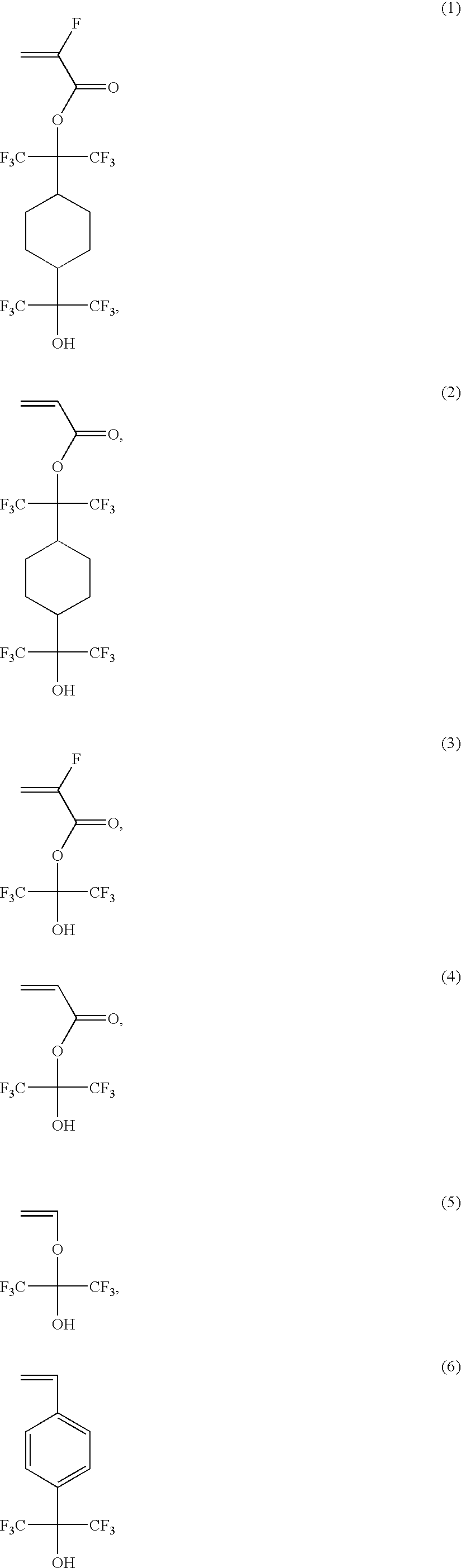
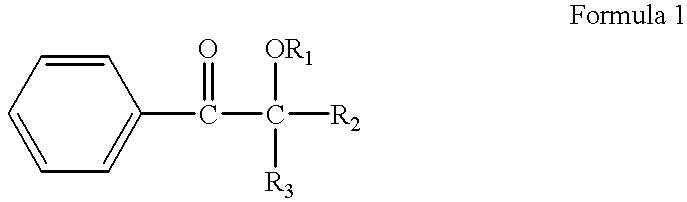
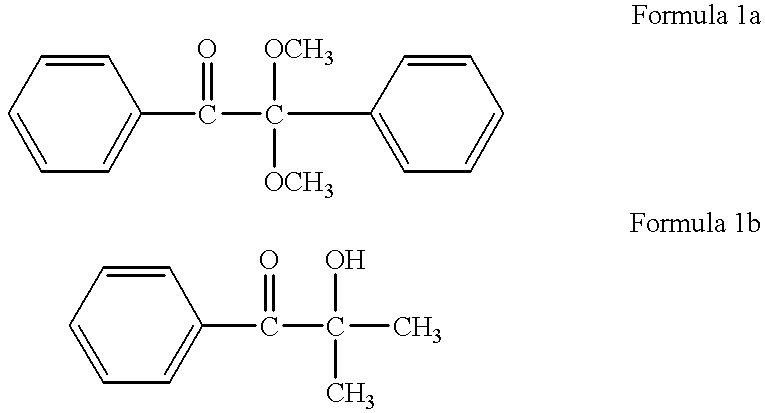
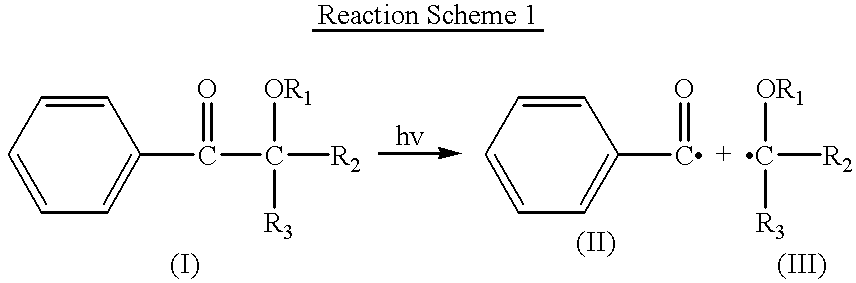
A novel photoacid generator containing a structure of the following formula (I), wherein R is a monovalent organic group with a fluorine content of 50 wt % or less, a nitro group, a cyano group, or a hydrogen atom, and Z1 and Z2 are individually a fluorine atom or a linear or branched perfluoroalkyl group having 1-10 carbon atoms, is provided. When used in a chemically amplified radiation-sensitive resin composition, the photoacid generator exhibits high transparency, comparatively high combustibility, and no bioaccumulation, and produces an acid exhibiting high acidity, high boiling point, moderately short diffusion length in the resist coating, and low dependency to mask pattern density.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON
Photoresist pattern trimming methods
ActiveUS20140186772A1Increased process windowSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotosensitive material processingResistPolymer science
Provided are methods of trimming a photoresist pattern. The methods comprise: (a) providing a semiconductor substrate; (b) forming a photoresist pattern on the substrate, wherein the photoresist pattern is formed from a chemically amplified photoresist composition comprising: a matrix polymer comprising an acid labile group; a photoacid generator; and a solvent; (c) coating a photoresist trimming composition on the substrate over the photoresist pattern, wherein the trimming composition comprises: a matrix polymer, an aromatic acid that is free of fluorine; and a solvent; (d) heating the coated substrate, thereby causing a change in polarity of the photoresist matrix polymer in a surface region of the photoresist pattern; and (e) contacting the photoresist pattern with a rinsing agent to remove the surface region of the photoresist pattern, thereby forming a trimmed photoresist pattern. The methods find particular applicability in the manufacture of semiconductor devices.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS LLC
Photoacid generators for use in photoresist compositions
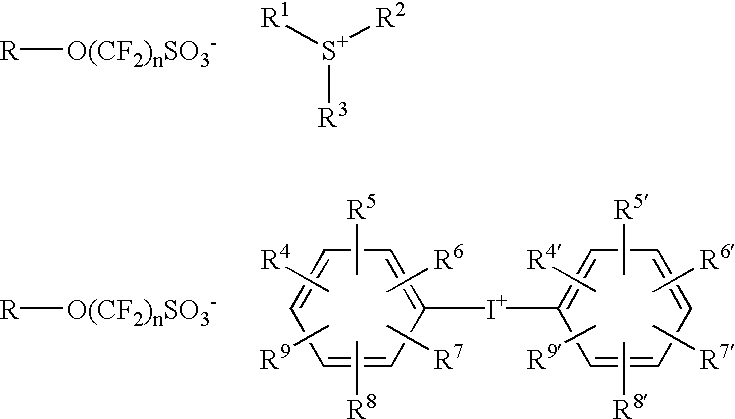
A photoacid compound having the following general structure:<paragraph lvl="0"><in-line-formula>R-O(CF2)nSO3X< / in-line-formula>wherein n is an integer between about 1 to 4; R is selected from the group consisting of: substituted or unsubstituted C1-C12 linear or branched alkyl or alkenyl, substituted or unsubstituted araalkyl, substituted or unsubstituted aryl, substituted or unsubstituted bicycloalkyl, substituted or unsubstituted tricycloalkyl, hydrogen, alkyl sulfonic acid, substituted or unsubstituted perfluoroalkyl, the general structure F((CF2)pO)m(CF2)q- wherein p is between about 1 to 4, m is between about 0 to 3 and q is between about 1 to 4, and substituted or unsubstituted partially fluorinated alkyl, halofluoroalkyl, perfluoroalkylsulfonic, or glycidyl; and X is selected from the group consisting of: organic cations and covalently bonded organic radicals.
Owner:FUJIFILM ELECTRONICS MATERIALS US
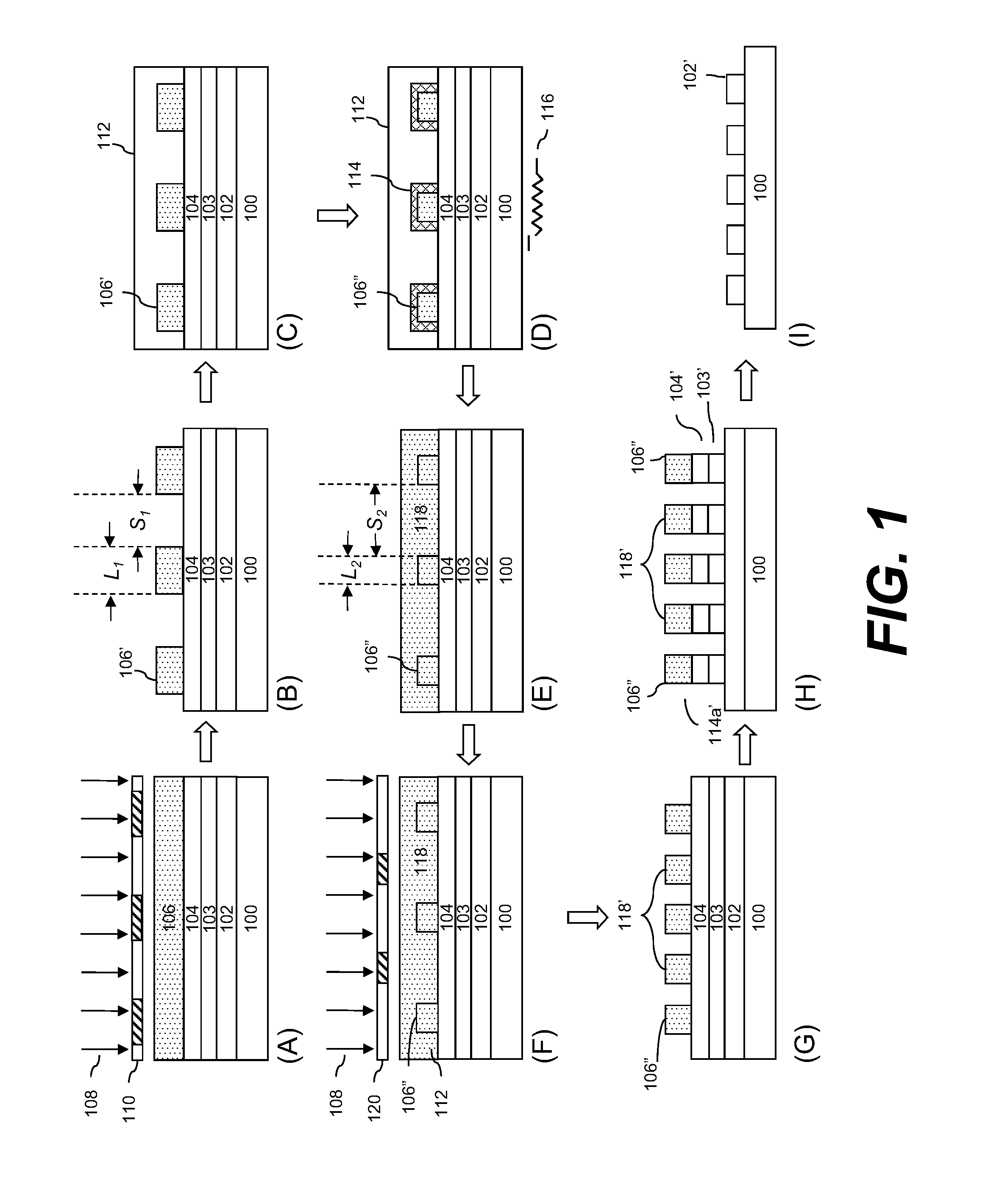
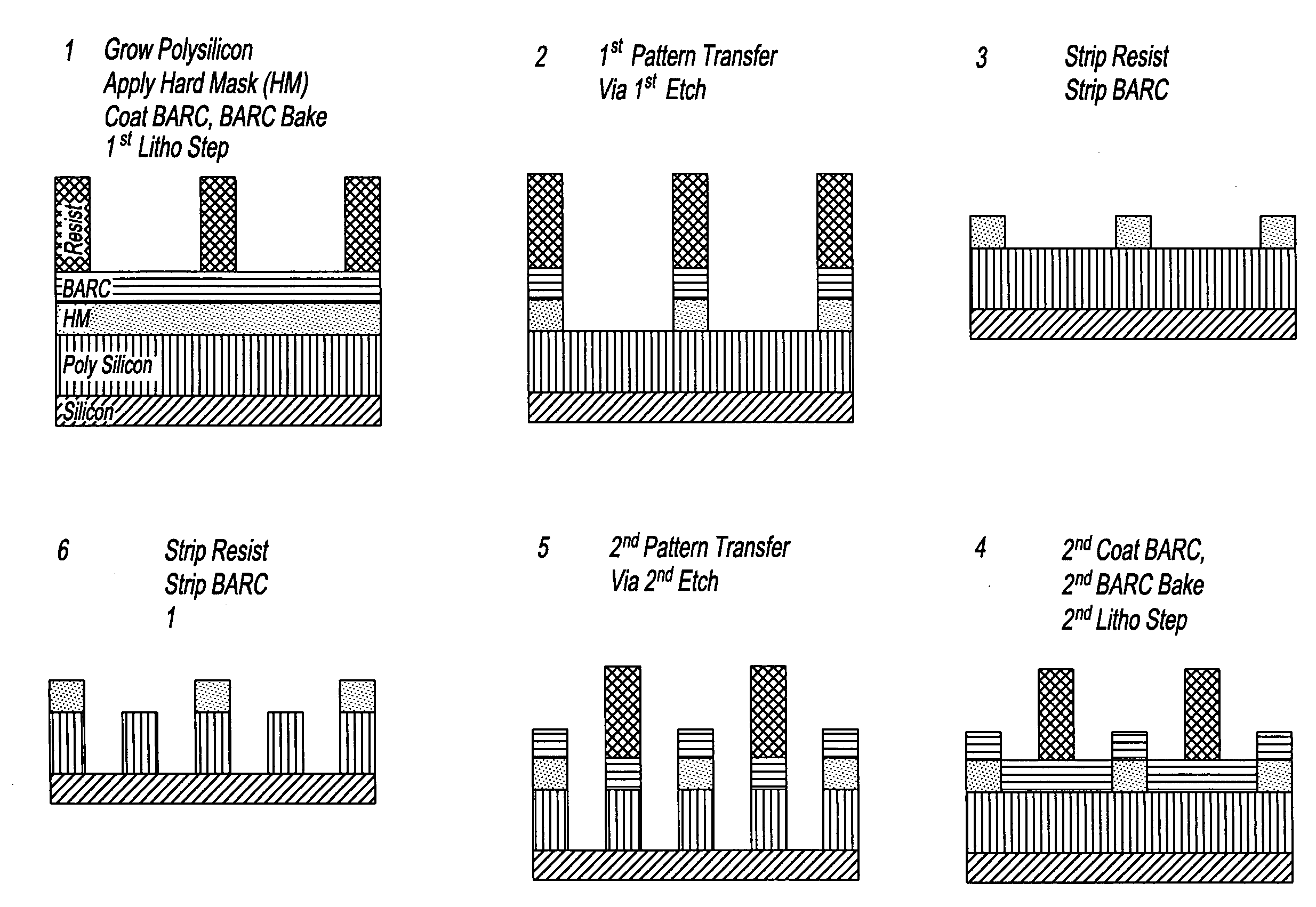
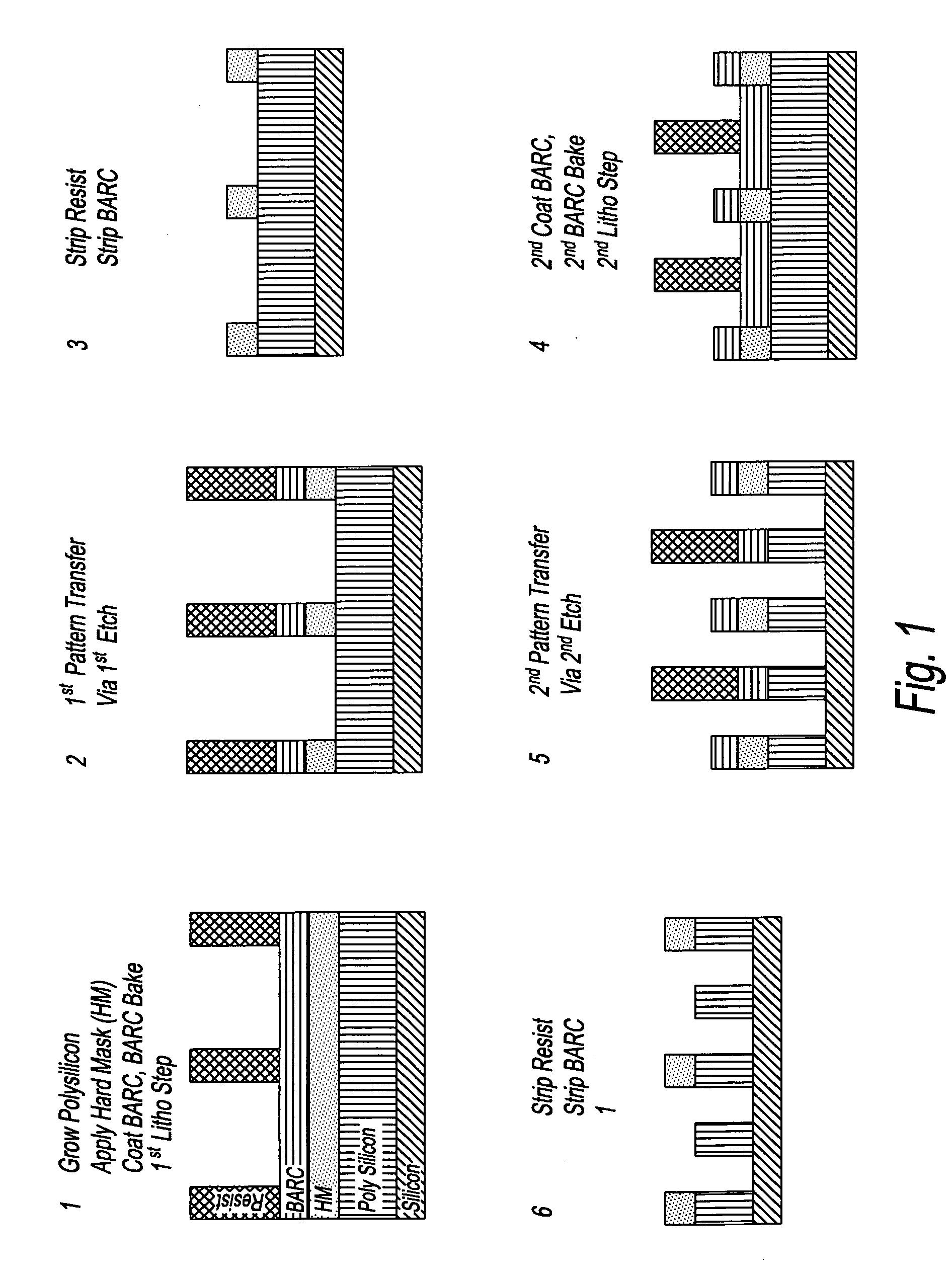
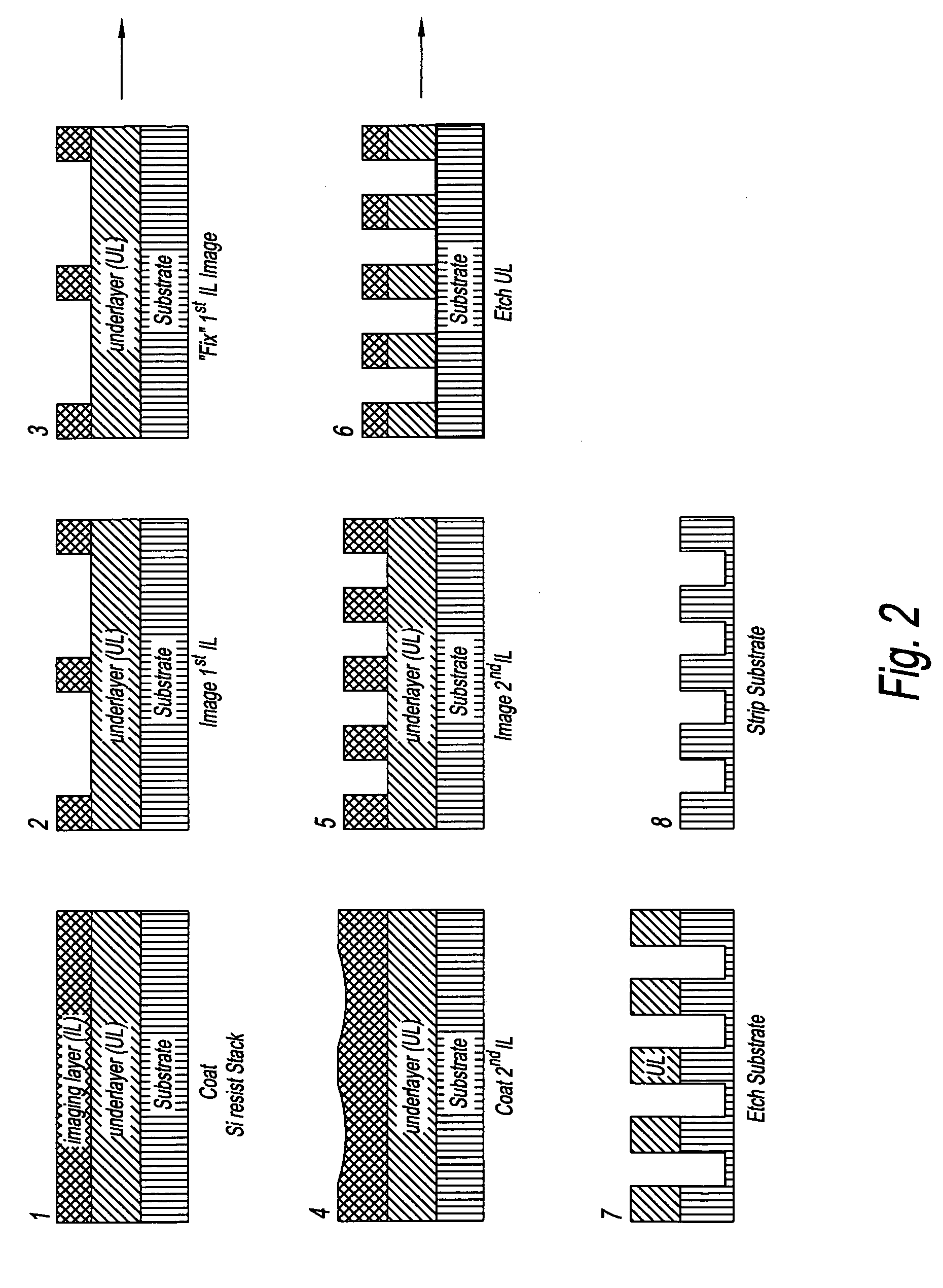
Device manufacturing process utilizing a double patterning process
InactiveUS20080199814A1Photomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSolubilityAnti-reflective coating
Manufacturing semiconductor device by steps of:a) providing substrate with antireflective coating or underlayer,b) applying first photosensitive composition over substrate,c) exposing first composition to radiation to produce first pattern,d) developing exposed first composition to produce an imaged bilayer stack,e) rinsing the stack,f) applying fixer to the stack,g) applying optional bake,h) rinsing the stack,i) applying second optional bake,j) applying second photosensitive composition onto the stack to produce multilayer stack,k) exposing second composition to produce second pattern offset from first pattern,l) developing exposed second composition to produce multilayer stack, andm) rinsing multilayer stack;the photosensitive compositions have photoacid generator and substantially aqueous base insoluble polymer whose solubility increases upon treatment with acid and further comprises an anchor group, and the fixer is a polyfunctional compound reactive with anchor group, but does not contain silicon and the substrate stays within a lithographic cell from at least first coating step until at least after final exposure.
Owner:FUJIFILM ELECTRONICS MATERIALS US
Positive resist composition and patterning process
ActiveUS20080153030A1Good storage stabilityHigh resolutionOrganic chemistryPhotosensitive materialsHigh energyPhotoacid generator
There is disclosed a resist composition that remarkably improves the resolution of photolithography using a high energy beam such as ArF excimer laser light as a light source, and exhibits excellent resistance to surface roughness and side lobe under use of a halftone phase shift mask; and a patterning process using the resist composition. The positive resist composition at least comprises (A) a resin component comprising a repeating unit represented by the following general formula (1); (B) a photoacid generator generating sulfonic acid represented by the following general formula (2) upon exposure to a high energy beam; and (C) an onium salt where a cation is sulfonium represented by the following general formula (3), or ammonium represented by the following general formula (4); and an anion is represented by any one of the following general formulae (5) to (7).
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Positive-working photoimageable bottom antireflective coating
The present invention relates to a novel absorbing, photoimageable and aqueous developable positive-working antireflective coating composition comprising a photoacid generator and a polymer comprising at least one unit with an acid labile group and at least one unit with an absorbing chromophore. The invention further relates to a process for using such a composition. The present invention also relates to a novel absorbing, photoimageable and aqueous alkali developable positive-working antireflective coating composition comprising a polymer comprising at least one unit with an acid labile group, a dye and a photoacid generator. The invention further relates to a process for using such a composition. The invention also relates to a novel process for forming a positive image with a positive photoresist and a novel photoimageable and aqueous developable positive-working antireflective coating composition, where the antireflective coating comprises a polymer comprising an acid labile group. The invention further relates to such a composition. The invention also relates to a process for imaging a photoimageable antireflective coating composition.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
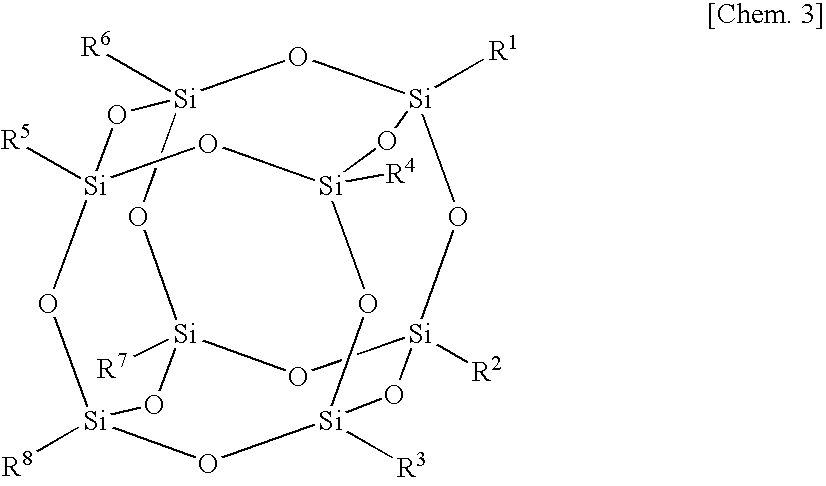
Polysiloxane composition
ActiveUS20100063221A1High transparencyImprove heat resistanceCoatingsOptical elementsSilyleneHeat resistance
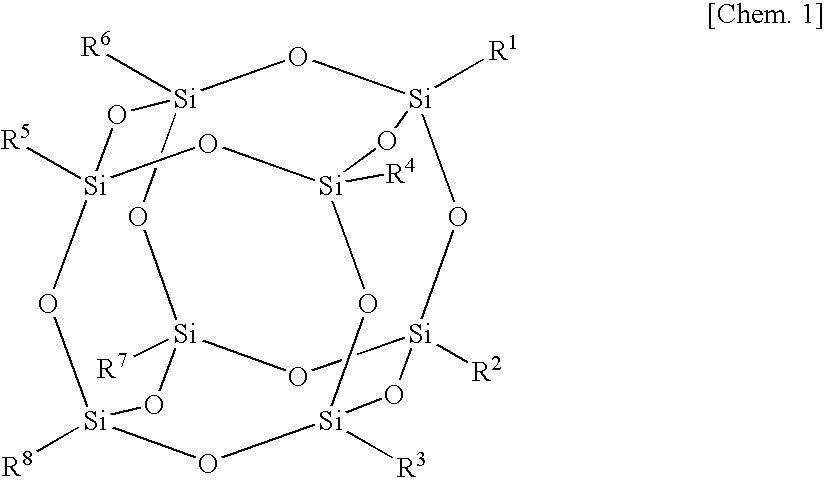
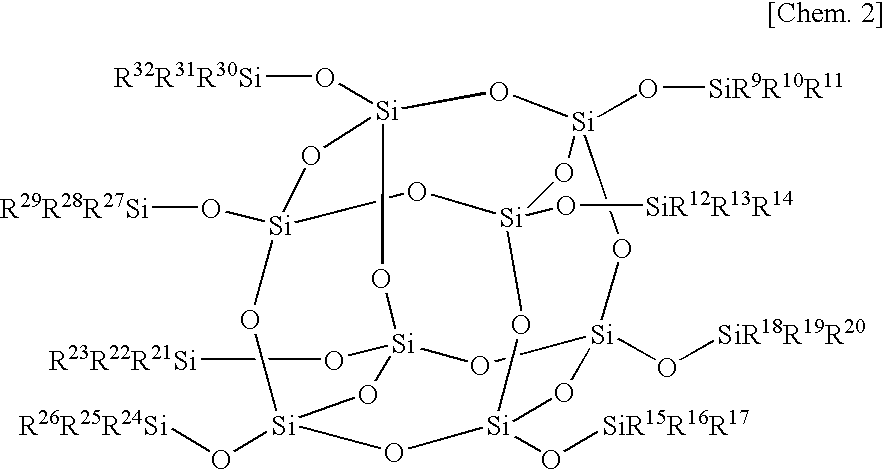
A polysiloxane composition having high transparency, while being excellent in heat resistance and light resistance is provided.A polysiloxane composition is composed of (A) a polysiloxane which is a polysiloxane compound having a polyhedral skeleton having 6 to 24 silicon atoms in its molecule and which has at least one group containing a hydrolyzable silyl group bonded to a Si atom constituting the polyhedral skeleton, and (B) a photoacid generator. The hydrolyzable silyl group is preferably an alkoxysilyl group.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Photoacid generator compounds and compositions
InactiveUS7824839B2Appropriate mobilityHomogeneous distribution of in resistOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationResistMicrofabrication
The invention provides various ionic and non-ionic photoacid generator compounds. Photoresist compositions that include the novel ionic and non-ionic photoacid generator compounds are also provided. The invention further provides methods of making and using the photoacid generator compounds and photoresist compositions disclosed herein. The compounds and compositions are useful as photoactive components in chemically amplified resist compositions for various microfabrication applications.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Monomer substituted photoacid generator of fluoroalkylsulfon and a polymer thereof
InactiveUS7534844B2Reduce solubilityImprove solubilityOrganic chemistryPhotomechanical apparatusSolubilityMethacrylate
The present invention relates to a novel compound with a fluoroalkylsulfonium photoacid generating group and novel copolymers having superior solubility in organic solvents, which is prepared from radical polymerization of the novel compound with methacrylate monomers.
Owner:IUCF HYU (IND UNIV COOP FOUND HANYANG UNIV)
Self-topcoating resist for photolithography
Resist compositions that can be used in immersion lithography without the use of an additional topcoat are disclosed. The resist compositions comprise a photoresist polymer, at least one photoacid generator, a solvent; and a self-topcoating resist additive. A method of forming a patterned material layer on a substrate using the resist composition is also disclosed.
Owner:IBM CORP
Photoacid generator
InactiveUS7550246B2Improve solubilitySensitive highPhotosensitive materialsGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsIridiumPhotoacid
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Positive-working photoimageable bottom antireflective coating
The present invention relates to a positive bottom photoimageable antireflective coating composition which is capable of being developed in an aqueous alkaline developer, wherein the antireflective coating composition comprises a polymer comprising at least one recurring unit with a chromophore group and one recurring unit with a hydroxyl and / or a carboxyl group, a vinyl ether terminated crosslinking agent, and optionally, a photoacid generator and / or an acid and / or a thermal acid generator. The invention further relates to a process for using such a composition.
Owner:AZ ELECTRONICS MATERIALS USA CORP
Photoresist composition containing photo radical generator with photoacid generator
InactiveUS6692891B2Reduce and prevent formationOrganic chemistryPhotosensitive materialsResistHigh concentration
The present invention relates to a photoresist composition containing a photo radical generator, more specifically, to a photoresist composition which comprises (a) photoresist resin, (b) a photoacid generator, (c) an organic solvent and (d) a photo radical generator. The present photoresist composition reduces or prevents a sloping pattern formation due to a higher concentration of acid in the upper portion of the photoresist relative to the lower portion of the photoresist.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Novel photoacid generator, resist composition, and patterning process
ActiveUS20090274978A1Addressing Insufficient ControlInhibits the formation of defectsPhotosensitive materialsPhoto-taking processesResistHigh energy
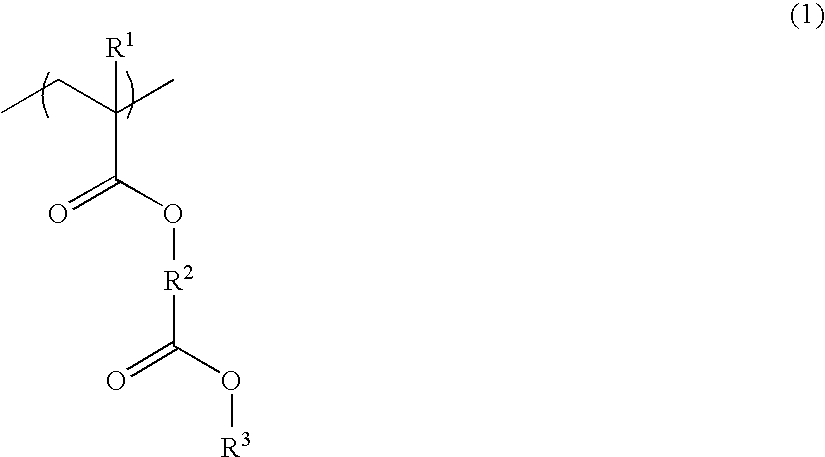
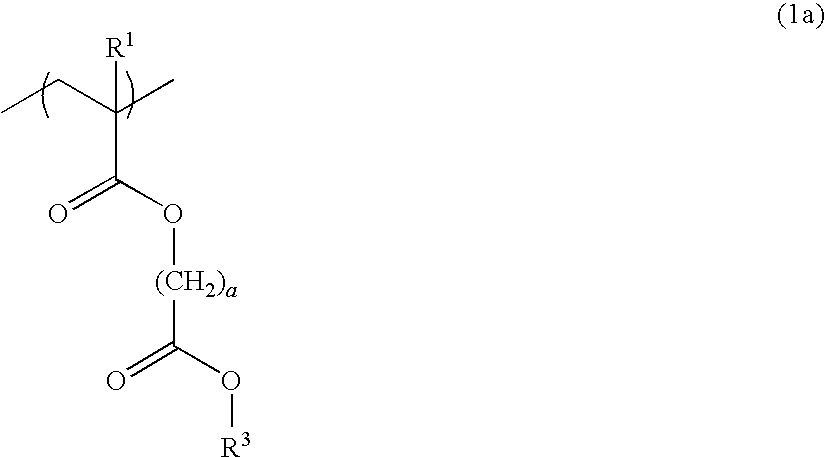
Photoacid generators generate sulfonic acids of formula (1a) or (1b) upon exposure to high-energy radiation.R1—COOCH2CF2SO3−H+ (1a)R1—O—COOCH2CF2SO3−H+ (1b)R1 is a monovalent C20-C50 hydrocarbon group of steroid structure which may contain a heteroatom. The bulky steroid structure ensures adequate control of acid diffusion. The photoacid generators are compatible with resins and suited for use in chemically amplified resist compositions.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Novel sulfonate salts and derivatives, photoacid generators, resist compositions, and patterning process
ActiveUS20060228648A1Wide spectrum of molecular designReduce molecular weightOrganic chemistryPhotosensitive materialsResistSulfonate
Sulfonate salts have the formula: CF3—CH(OCOR)—CF2SO3−M+ wherein R is C1-C20 alkyl or C6-C14 aryl, and M+ is a lithium, sodium, potassium, ammonium or tetramethylammonium ion. Onium salts, oximesulfonates and sulfonyloxyimides and other compounds derived from these sulfonate salts are effective photoacid generators in chemically amplified resist compositions.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Negative resist composition and patterning process
InactiveUS20060166133A1Increase contrastExcellent etch resistancePhotomechanical apparatusPhotosensitive material auxillary/base layersPolymer scienceHalogen
A negative resist composition is provided comprising a polymer comprising recurring units having formula (1), a photoacid generator, and a crosslinker. In formula (1), X is alkyl or alkoxy, R1 and R2 are H, OH, alkyl, substitutable alkoxy or halogen, R3 and R4 are H or CH3, n is an integer of 1 to 4, m and k are an integer of 1 to 5, p, q and r are positive numbers. The composition has a high contrast of alkali dissolution rate before and after exposure, high sensitivity, high resolution and good etching resistance.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Photoresist composition for deep ultraviolet lithography comprising a mixture of photoactive compounds
InactiveUS6991888B2Reduce edge roughnessAcceptable photosensitivityOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationResistUltraviolet
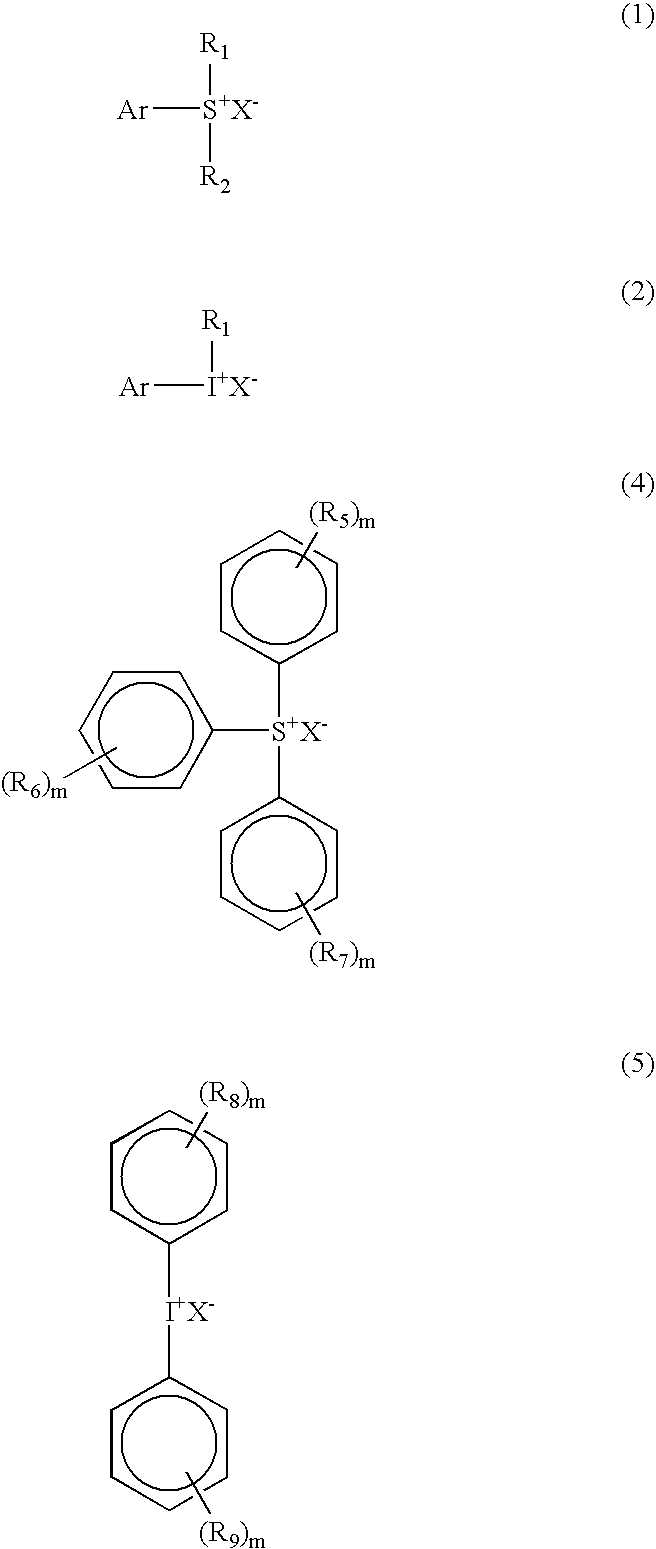
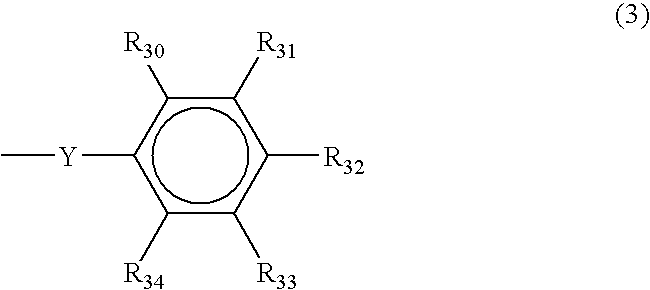
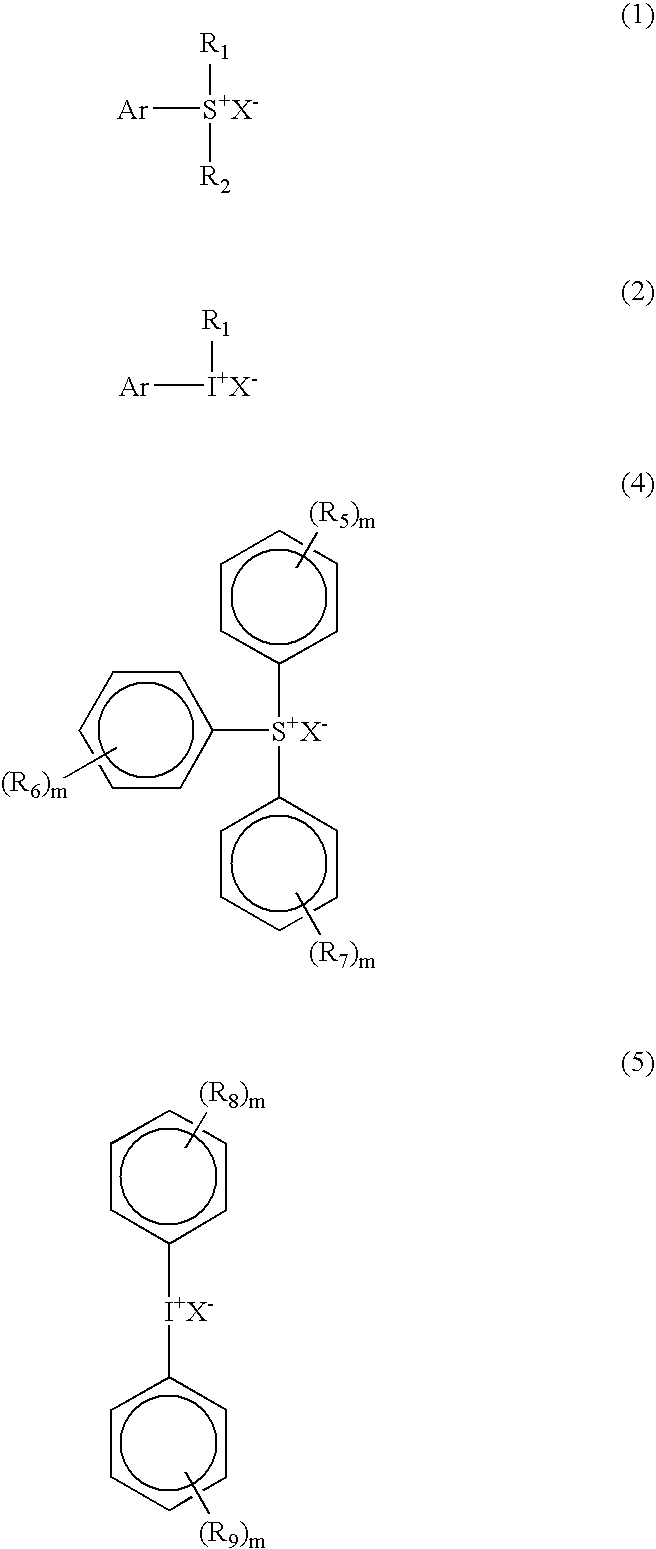
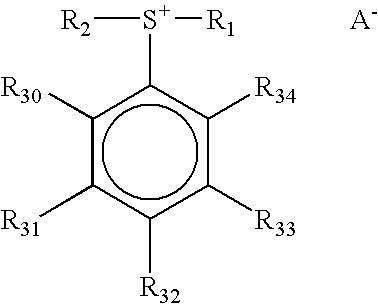
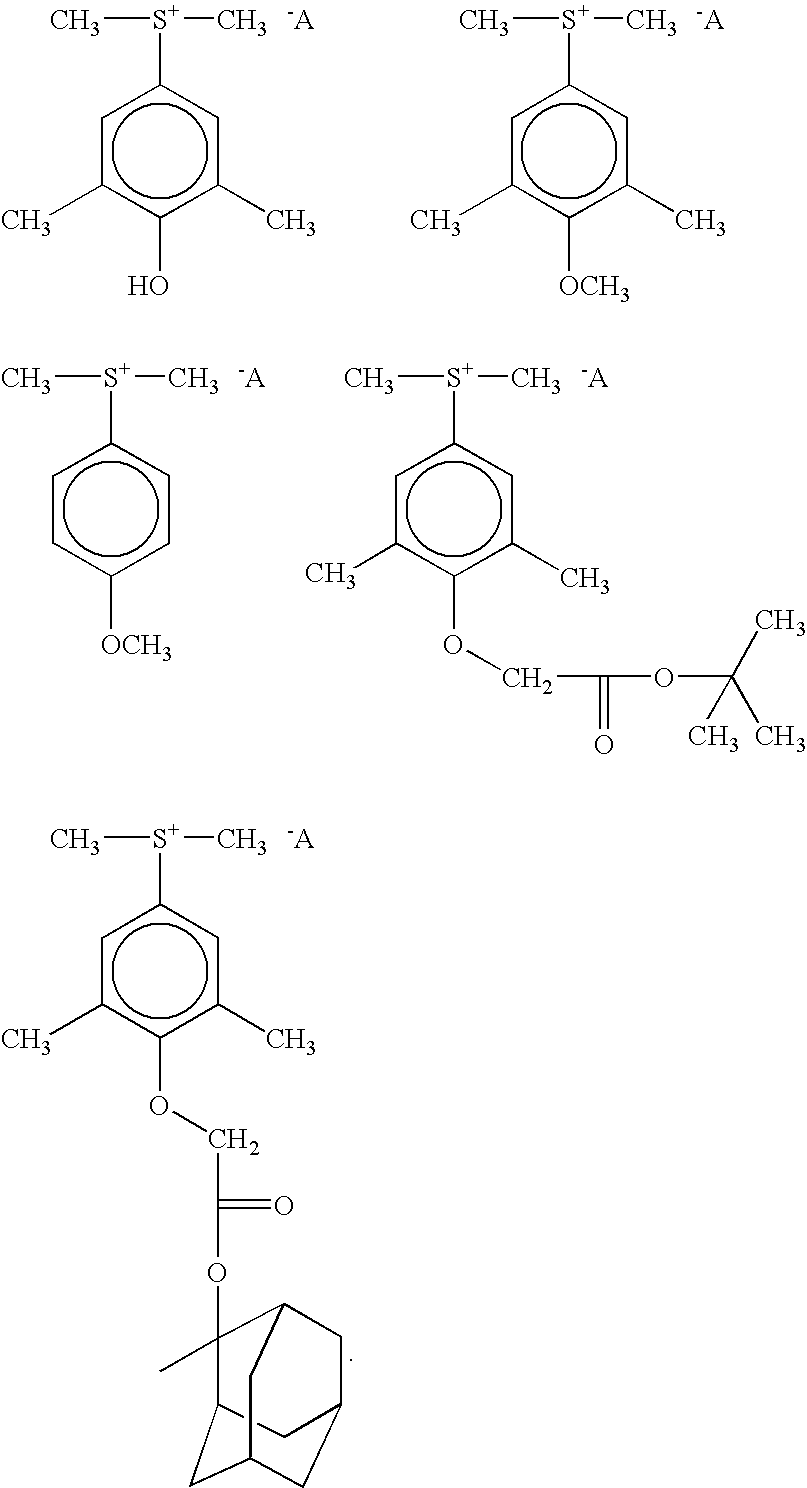
The present invention relates to a novel photoresist composition that can be developed with an aqueous alkaline solution, and is capable of being imaged at exposure wavelengths in the deep ultraviolet. The invention also relates to a process for imaging the novel photoresist as well as novel photoacid generators.The novel photoresist comprises a) a polymer containing an acid labile group, and b) a novel mixture of photoactive compounds, where the mixture comprises a lower absorbing compound selected from structure 1 and 2, and a higher absorbing compound selected from structure 4 and 5, where, R1 and R2 R5, R6, R7, R8, and R9 are defined herein; m=1–5; X− is an anion, and Ar is selected from naphthyl, anthracyl, and structure 3, where R30, R31, R32, R33, and R34 are defined herein.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Radiation sensitive resin composition
Positive as well as negative radiation sensitive resin compositions that, in addition to being capable of providing excellent resolution and pattern profile, are particularly excellent in avoiding the problems of "nano-edge roughness" or "coating surface roughness". The positive type radiation sensitive resin composition comprises (A) (a) an acid-decomposable group-containing resin, or (b) an alkali-soluble resin and an alkali dissolution controller, and (B) a photoacid generator comprising "a compound that upon exposure to radiation generates a carboxylic acid having a boiling point of 150.degree. C. or higher", and "a compound that upon exposure to radiation generates an acid other than a carboxylic acid". The negative type radiation sensitive resin composition comprises (C) an alkali-soluble resin, (D) a cross-linking agent, and the component (B) as described above.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON
Compound for Photoacid Generator, Resist Composition Using the Same, and Pattern-Forming Method
ActiveUS20100035185A1Stable structureImprove solubilityOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationResistOrganic group
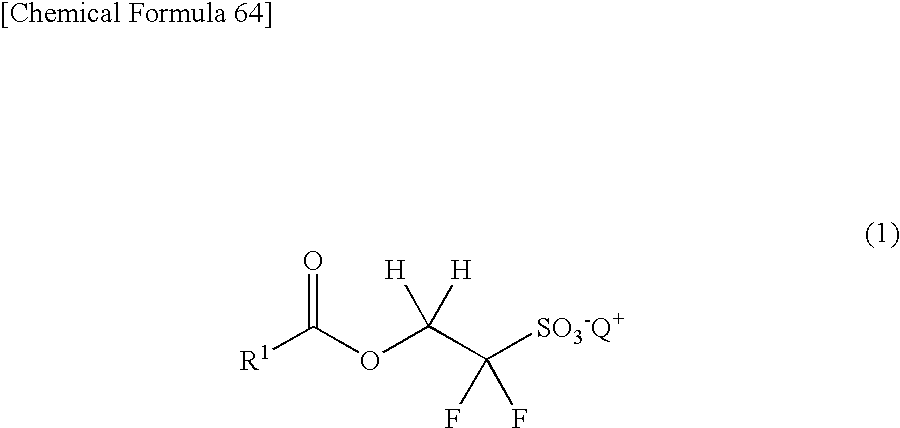
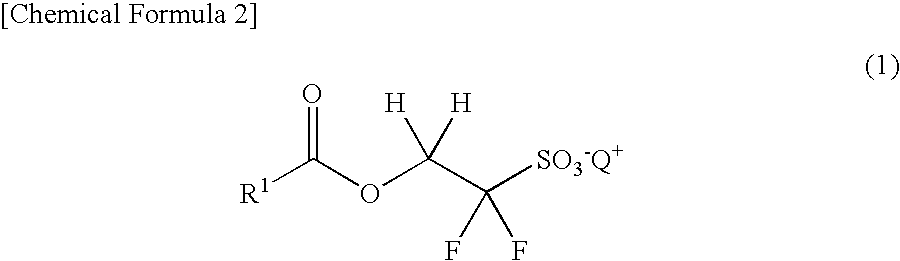
A sulfonic acid onium salt represented by the following formula (1) can be used as a superior radiosensitive acid generator for resist compositions. It is possible to form a good pattern by using a resist composition containing this sulfonic acid onium salt.In formula (1), R1 represents a monovalent organic group, and Q+ represents a sulfonium cation or iodonium cation.
Owner:CENT GLASS CO LTD
Planographic printing plate
InactiveUS6017677AHigh sensitivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotosensitive material processingSide chainPhotoacid generator
The present invention provide a planographic printing plate comprising a substrate having thereon a recording layer which comprises at least one of a polymer compound carrying on a side chain a functional group which generates sulfonic acid under influence of an acid, base or heating; and a photo acid-generating agent or acid-generating agent; thermal base-generating agent; or an infrared ray absorbing agent, and by this structure, a high sensitive positive type planographic printing plate which can be developed with water or requires no developing is provided.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Photoacid generators for use in photoresist compositions
A photoacid compound having the following general structure:R—O(CF2)nSO3X wherein n is an integer between about 1 to 4; R is selected from the group consisting of: substituted or unsubstituted C1-C12 linear or branched alkyl or alkenyl, substituted or unsubstituted araalkyl, substituted or unsubstituted aryl, substituted or unsubstituted bicycloalkyl, substituted or unsubstituted tricycloalkyl, hydrogen, alkyl sulfonic acid, substituted or unsubstituted perfluoroalkyl, the general structure F((CF2)pO)m(CF2)q— wherein p is between about 1 to 4, m is between about 0 to 3 and q is between about 1 to 4, and substituted or unsubstituted partially fluorinated alkyl, halofluoroalkyl, perfluoroalkylsulfonic, or glycidyl; and X is selected from the group consisting of: organic cations and covalently bonded organic radicals.
Owner:FUJIFILM ELECTRONICS MATERIALS US
Polymer resin composition, related method for forming a pattern, and related method for fabricating a capacitor
InactiveUS20070249117A1Reduce in quantityReduce processing timeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCross-link(Hydroxyethyl)methacrylate
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Photoimageable coating composition and composite article thereof
InactiveUS20050266335A1Photosensitive materialsPhotomechanical coating apparatusResistPhotoacid generator
A photoimagable composition suitable for use as a negative photoresist comprising: (A) at least one epoxidized polyfunctional bisphenol A formaldehyde novolak resin; (B) at least one polycaprolactone polyol reactive diluent, wherein the amount of component (A) is from about 95% to about 75% by weight of the sum of (A) and (B) and the amount of component (B) is from about 5% to about 25% by weight of the sum of (A) and (B); (C) at least one photoacid generator in an amount from about 2.5 to about 12.5 parts per hundred parts of resin and reactive diluent, which initiates polymerization upon exposure to actinic radiation; and (D) a sufficient amount of solvent to dissolve (A), (B) and (C); wherein the solvent comprises 2-pentanone, 3-pentanone, and 1,3-dioxolane and mixtures thereof.
Owner:MICROCHEM CORP +1
Photoacid generators and lithographic resists comprising the same
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
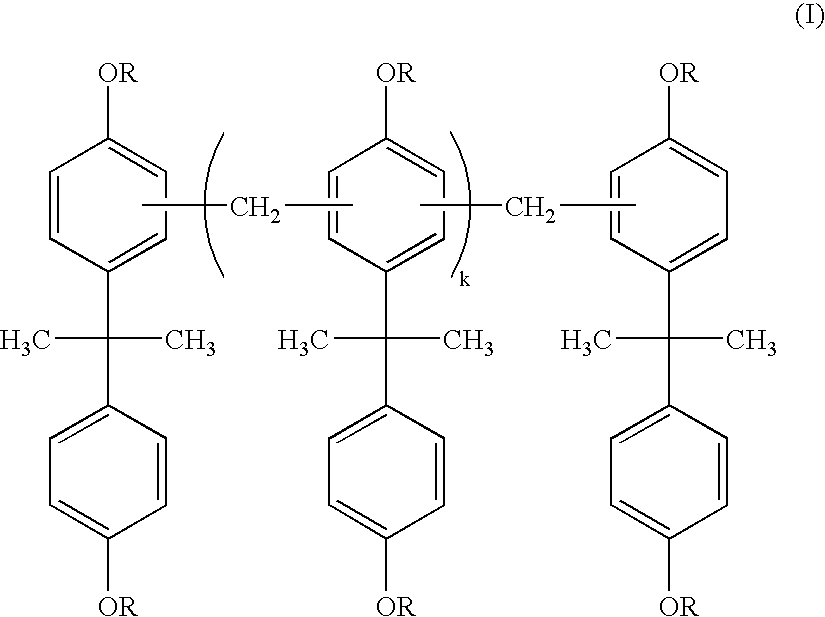
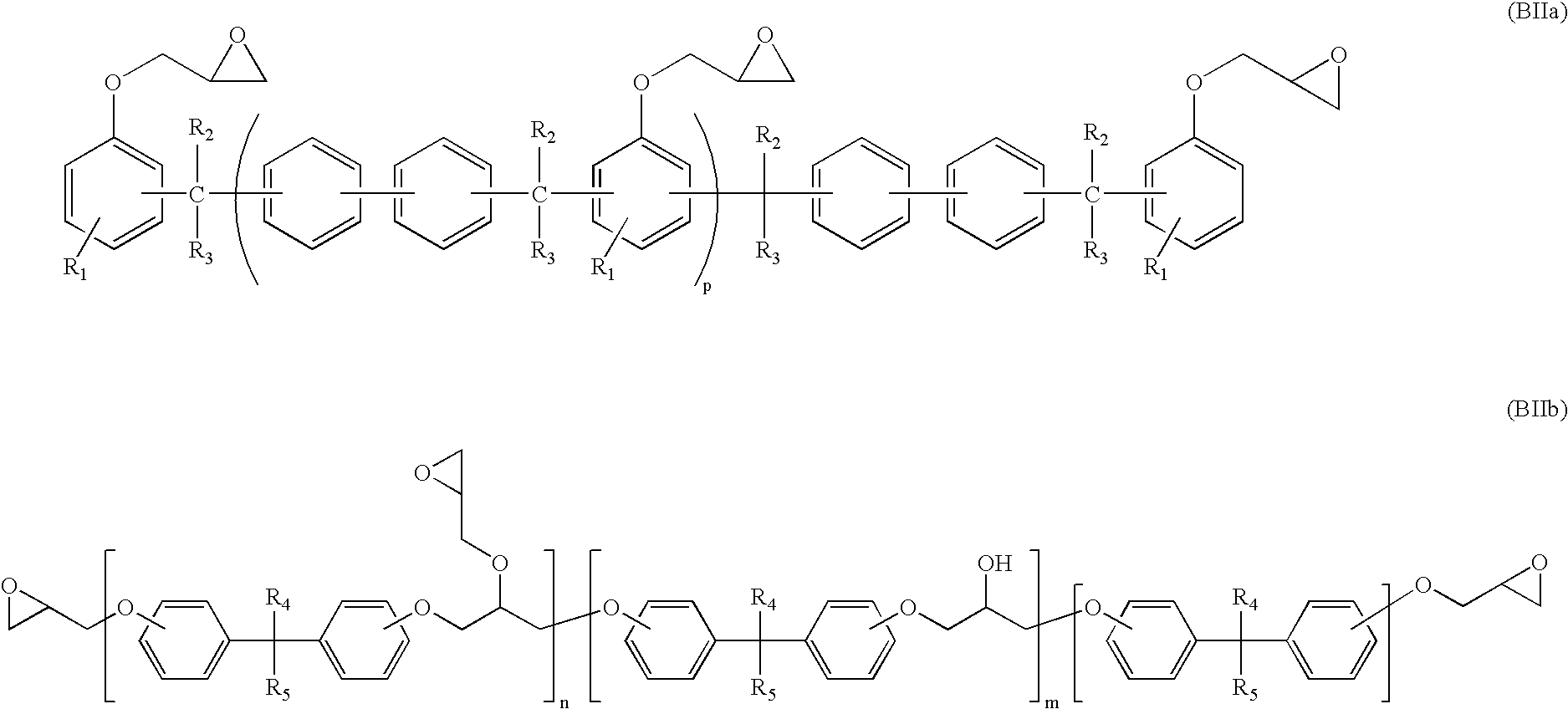
Permanent resist composition, cured product thereof, and use thereof
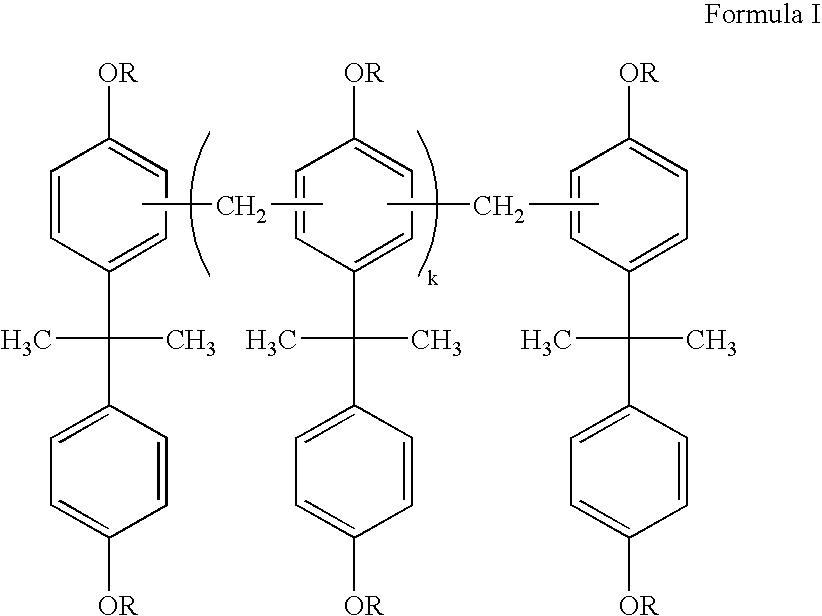
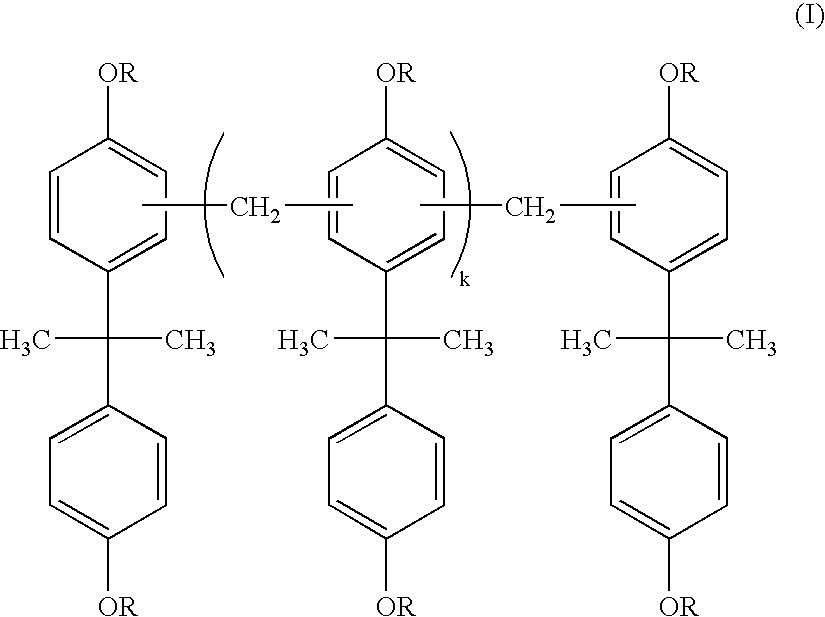
InactiveUS20050260522A1High densityImprove film adhesionNanoinformaticsPhotomechanical apparatusPolymer sciencePhotoacid generator
A permanent photoresist composition comprising: (A) one or more bisphenol A-novolac epoxy resins according to Formula I; wherein each group R in Formula I is individually selected from glycidyl or hydrogen and k in Formula I is a real number ranging from 0 to about 30; (B) one or more epoxy resins selected from the group represented by Formulas BIIa and BIIb; wherein each R1, R2 and R3 in Formula BIIa are independently selected from the group consisting of hydrogen or alkyl groups having 1 to 4 carbon atoms and the value of p in Formula BIIa is a real number ranging from 1 to 30; the values of n and m in Formula BIIb are independently real numbers ranging from 1 to 30 and each R4 and R5 in Formula BIIb are independently selected from hydrogen, alkyl groups having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, or trifluoromethyl; (C) one or more cationic photoinitiators (also known as photoacid generators or PAGs); and (D) one or more solvents.
Owner:MICROCHEM CORP +1
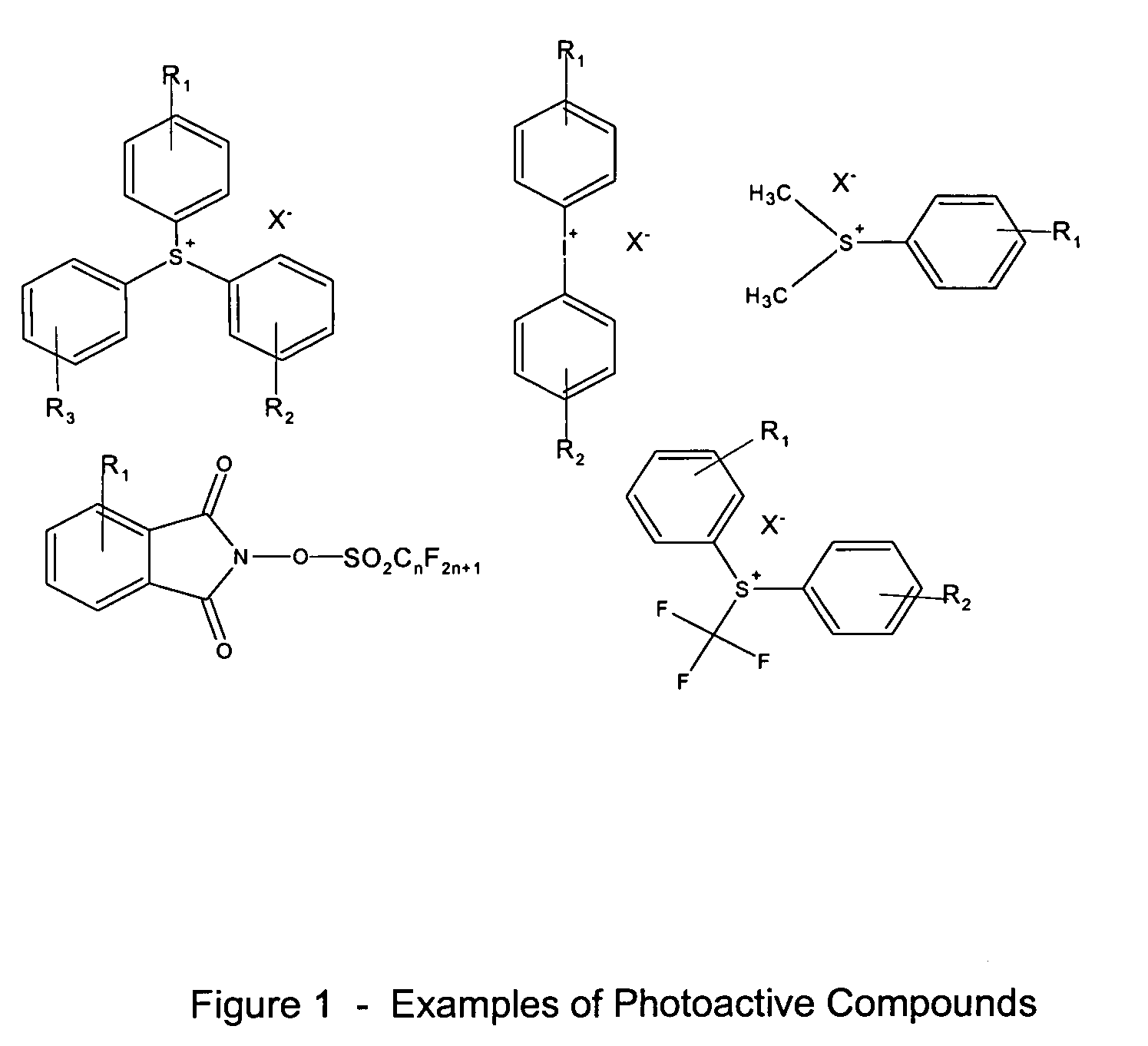
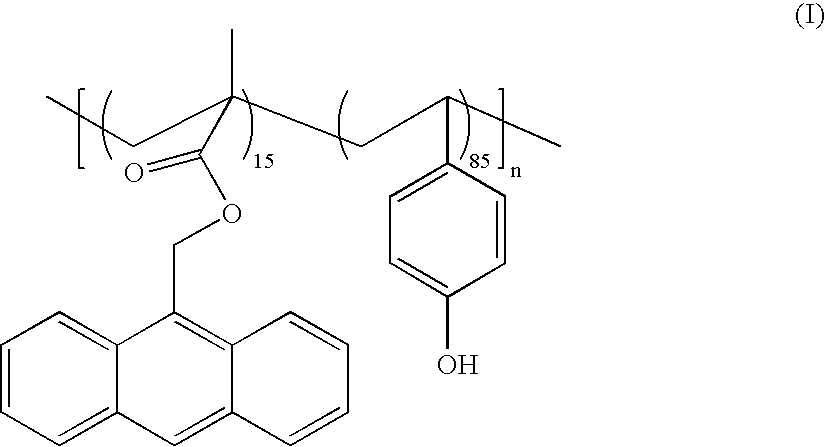
Photoactive compounds
Owner:AZ ELECTRONICS MATERIALS USA CORP
Ionic photoacid generators with segmented hydrocarbon-fluorocarbon sulfonate anions
InactiveUS6841333B2Improve solubilitySolubility in organic compoundsOrganic compound preparationPhotosensitive materialsSolubilityAcid catalyzed
Photoacid generator salts comprising photoactive cationic moieties and segmented, highly fluorinated-hydrocarbon anionic moieties are disclosed which provide high photoacid strength and can be tailored for solubility and polarity. The present invention further relates to photoacid generators as they are used in photoinitiated acid-catalyzed processes for uses such as photoresists for microlithography and photopolymerization.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Resist composition and patterning process
A resist composition comprising (A) an organic solvent; (B) at least two polymers with weight average molecular weights of 1,000-500,000, which have at least one type of acid labile group and are crosslinked within a molecule and / or between molecules with crosslinking groups having C-O-C linkages; and (C) a photoacid generator is sensitive to high-energy radiation, has excellent sensitivity, resolution, and plasma etching resistance, and provides resist patterns of outstanding thermal stability and reproducibility. Patterns obtained with this resist composition are less prone to overhanging and have excellent dimensional controllability. The resist composition is suitable as a micropatterning material for VLSI fabrication because it has a low absorption at the exposure wavelength of a KrF excimer laser, thus enabling the easy formation of a finely defined pattern having sidewalls perpendicular to the substrate.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Resist composition and patterning process
ActiveUS20100266957A1Readily availableEasy to handlePhotosensitive materialsElectric discharge tubesResistOrganic solvent
An additive polymer comprising recurring units of formula (1) is added to a resist composition comprising a base resin, a photoacid generator, and an organic solvent. R1 is hydrogen or methyl, R2 is alkylene or fluoroalkylene, and R3 is fluoroalkyl. The additive polymer is highly transparent to radiation with wavelength of up to 200 nm. Water repellency, water slip, acid lability, hydrolysis and other properties of the polymer may be adjusted by a choice of polymer structure.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Anti-reflective coatings using vinyl ether crosslinkers
InactiveUS20070207406A1High percent solubilityReduce production processOrganic chemistrySilver halide emulsionsVinyl etherAnti-reflective coating
Novel, developer soluble anti-reflective coating compositions and methods of using those compositions are provided. The compositions comprise a polymer and / or oligomer having acid functional groups and dissolved in a solvent system along with a cross linker, a photoacid generator, and optionally a chromophore. The preferred acid functional group is a carboxylic acid, while the preferred crosslinker is a vinyl ether crosslinker. In use, the compositions are applied to a substrate and thermally crosslinked. Upon exposure to light (and optionally a post exposure bake), the cured compositions will decrosslink, rendering them soluble in typical photoresist developing solutions (e.g., alkaline developers). In one embodiment, the compositions can be used to form ion implant areas in microelectronic substrates.
Owner:BREWER SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com