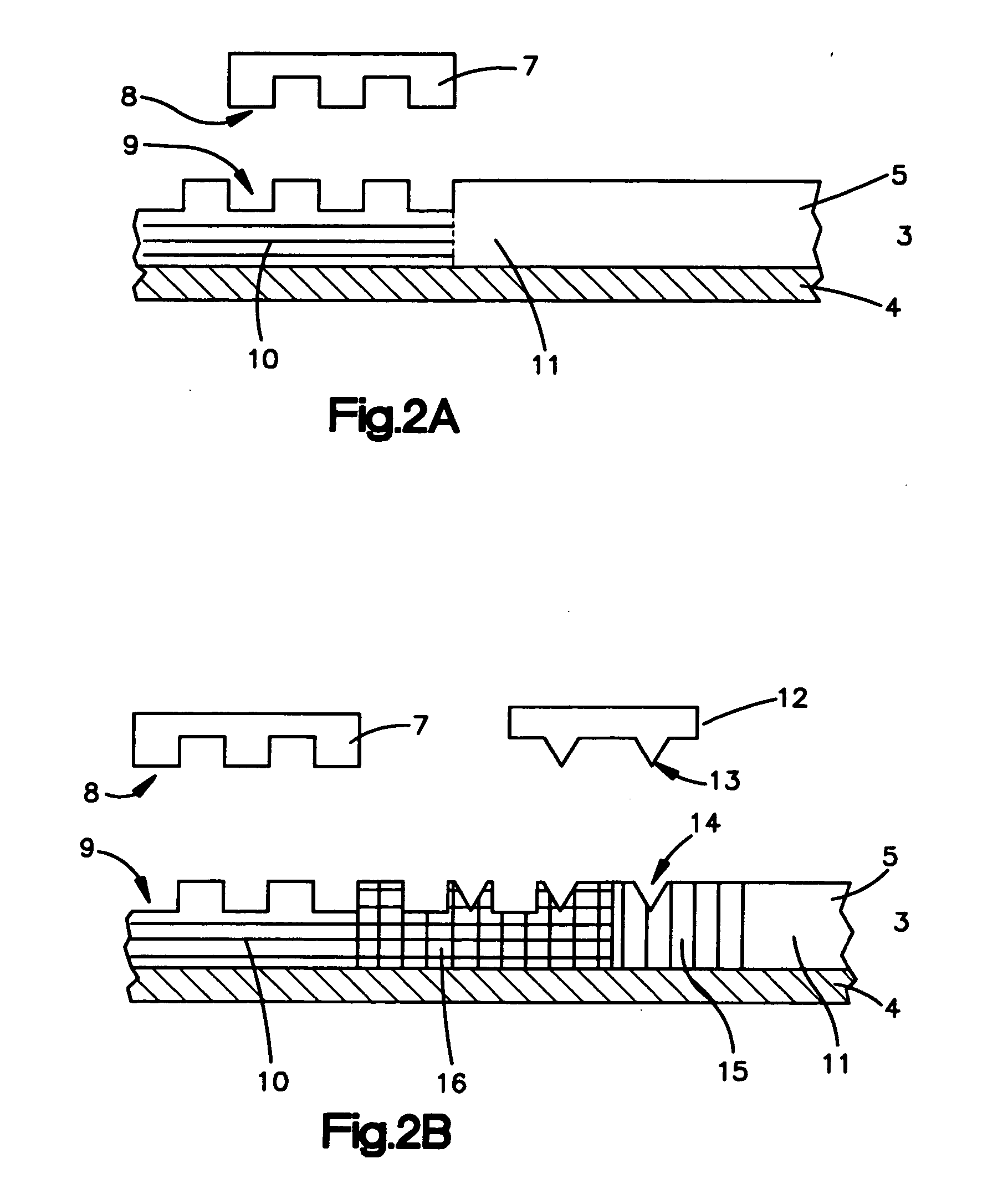
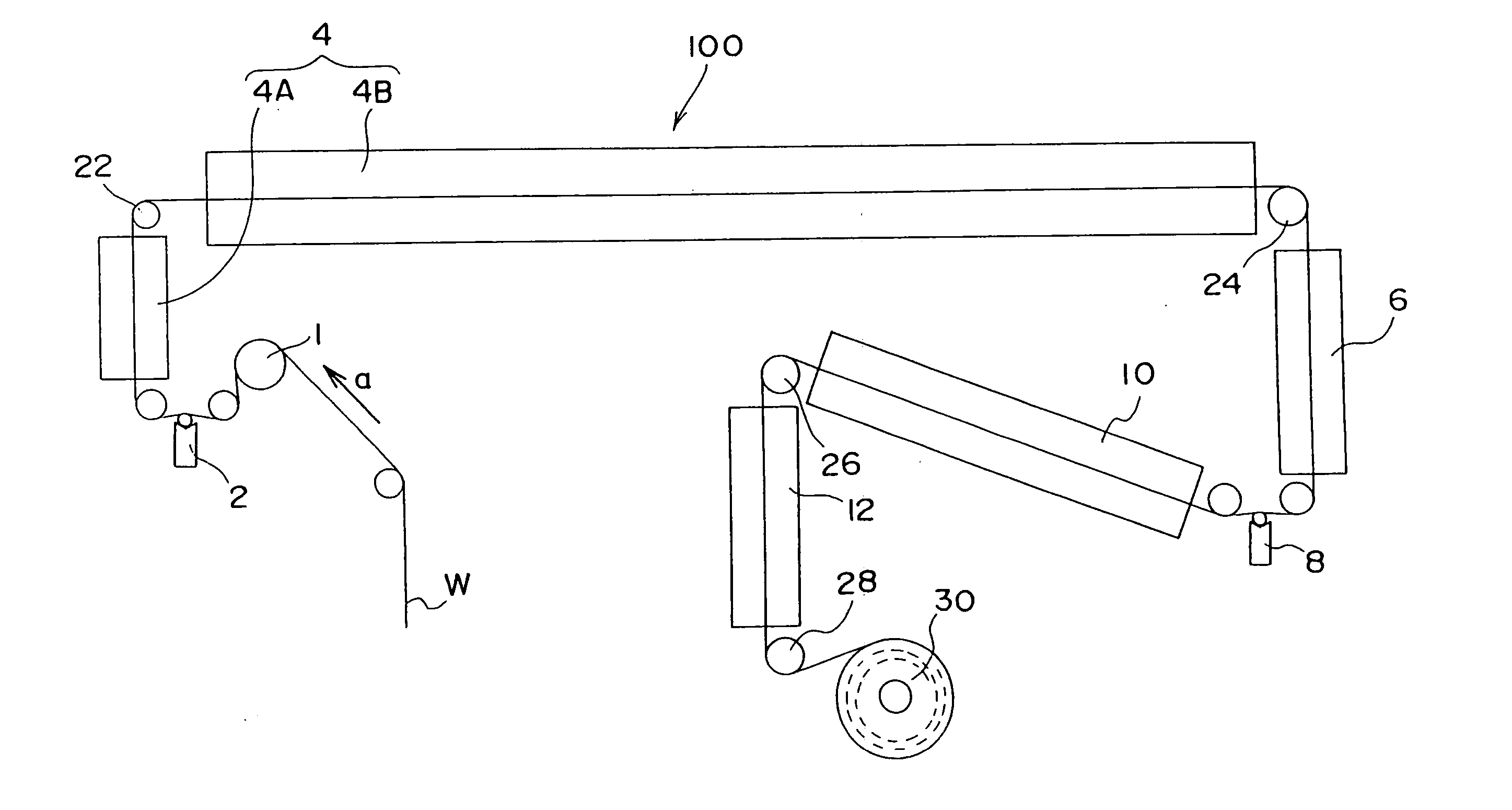
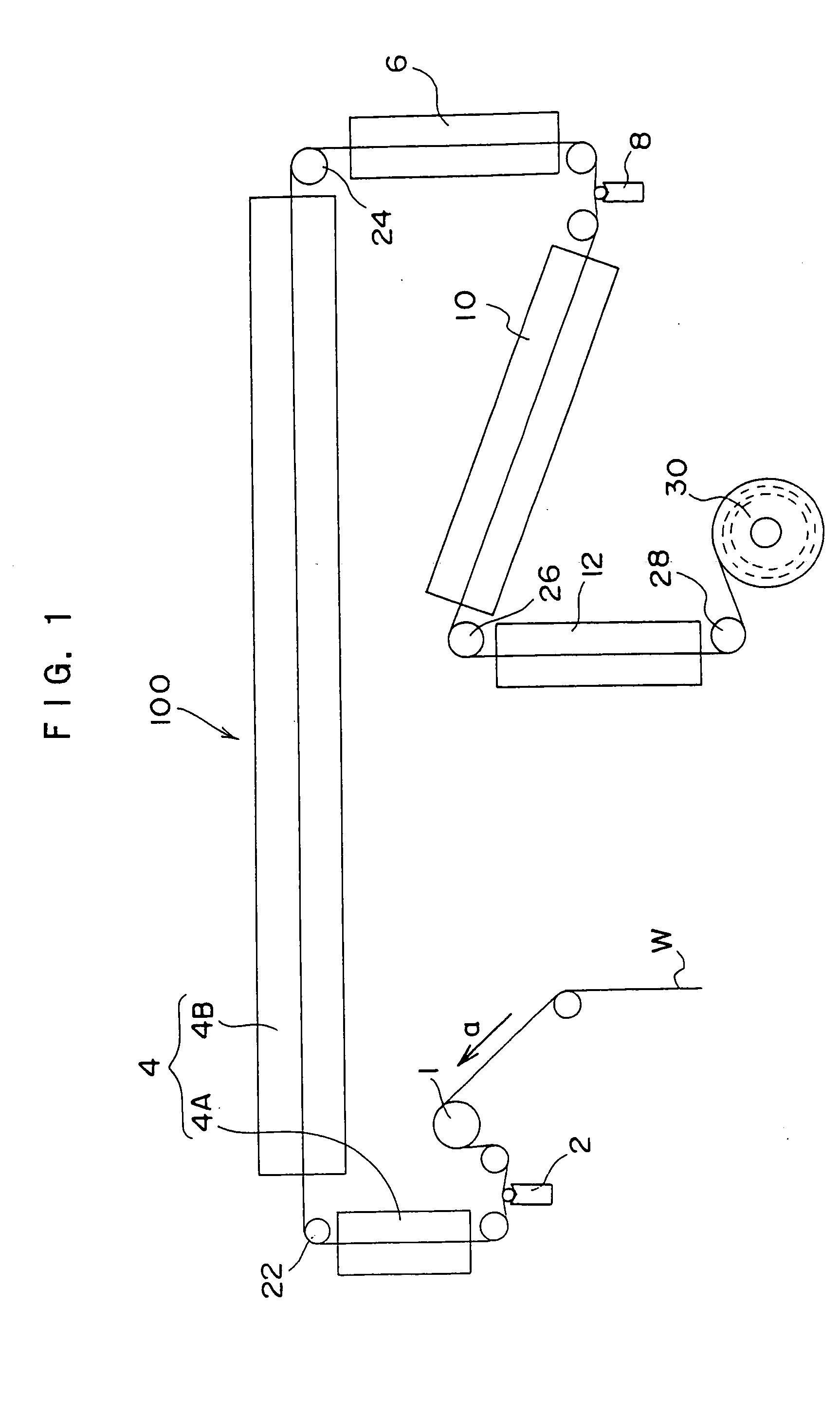
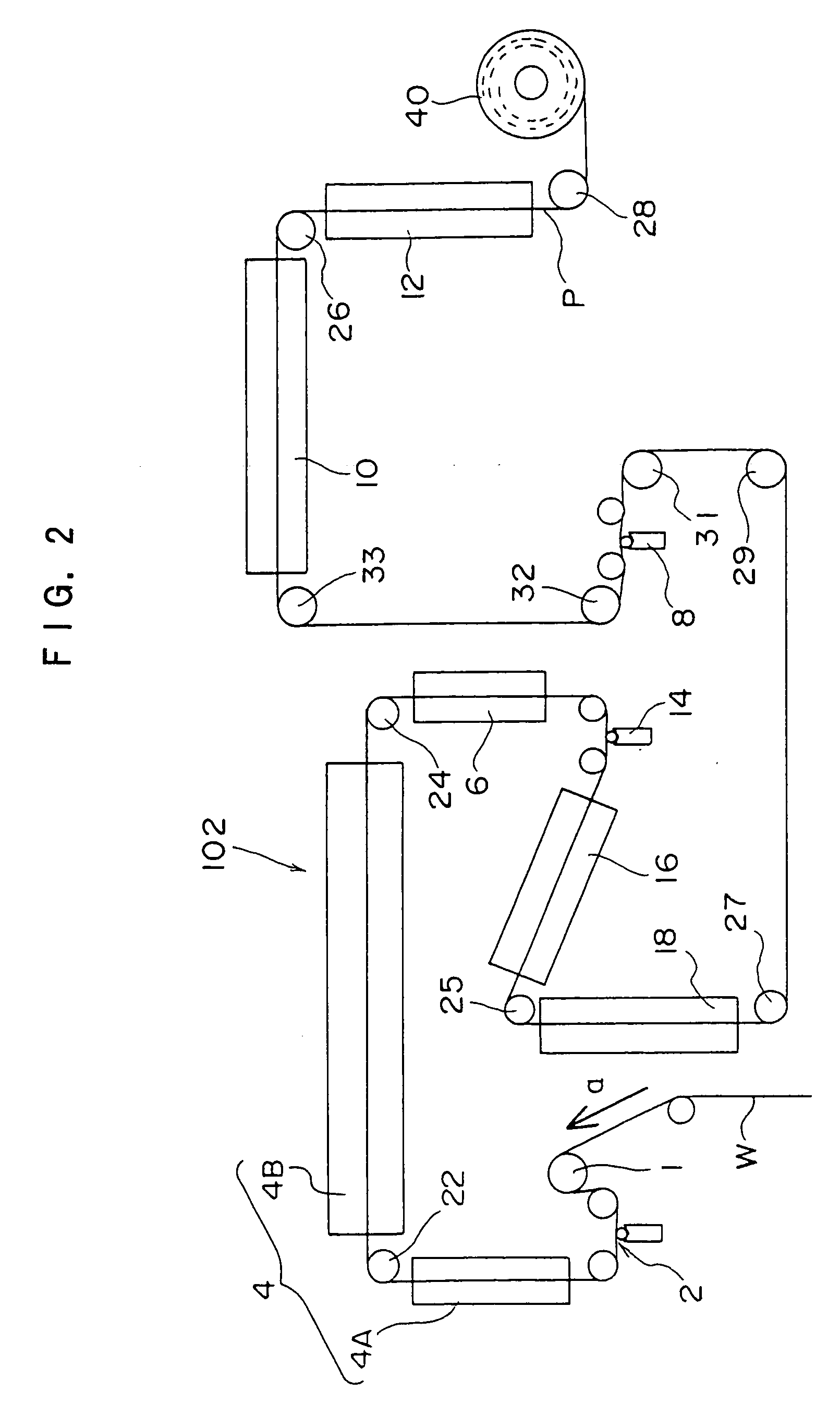
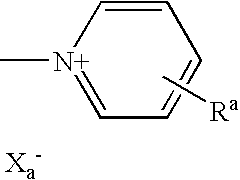
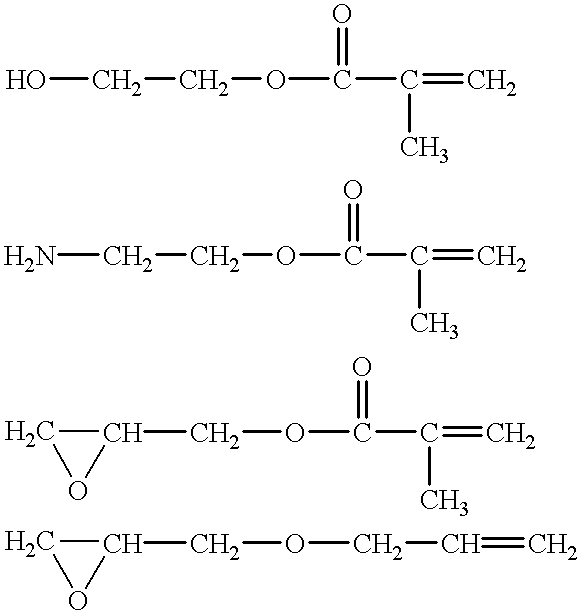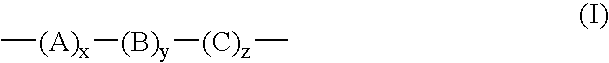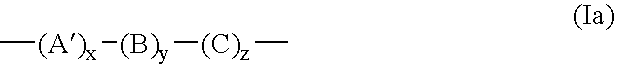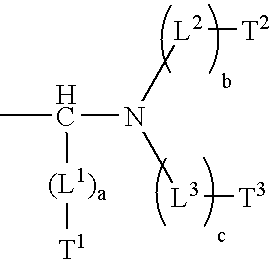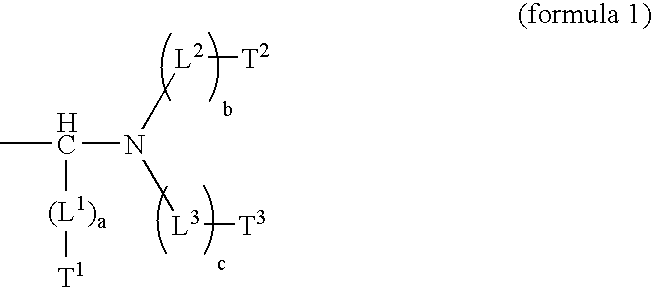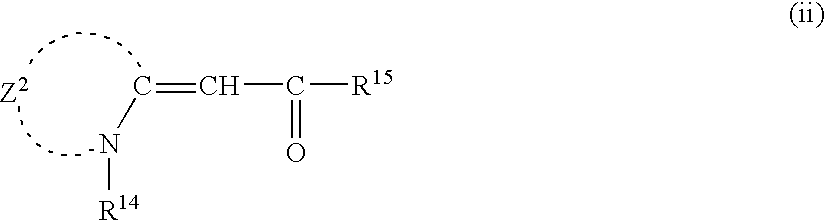Patents
Literature
2424 results about "Planographic printing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
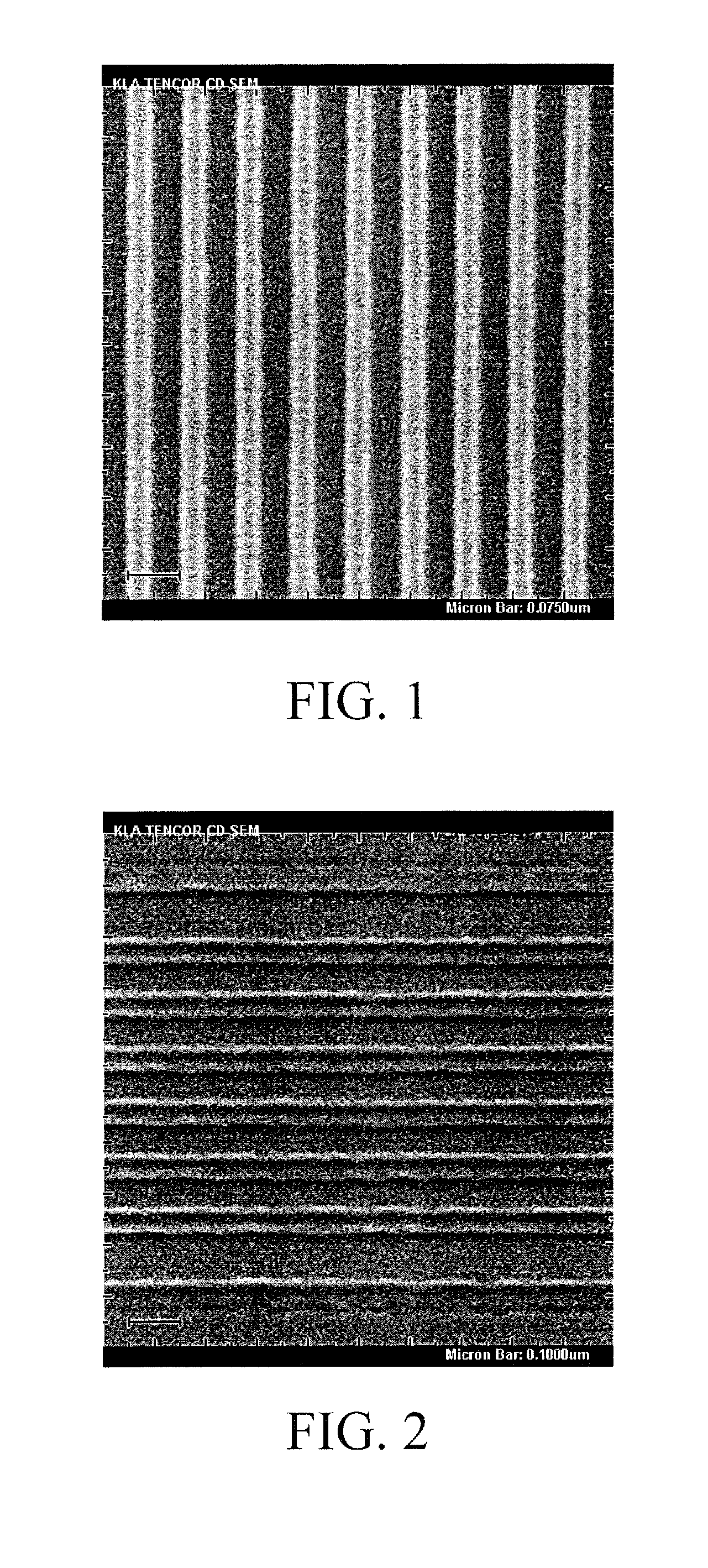
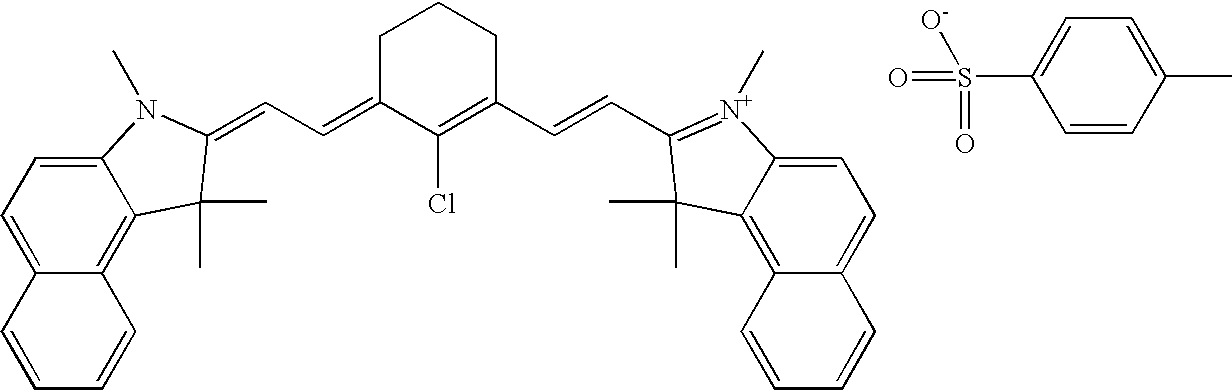
Planographic printing means printing from a flat surface, as opposed to a raised surface (as with relief printing) or incised surface (as with intaglio printing). Lithography and offset lithography are planographic processes that rely on the property that water will not mix with oil. The image is created by applying a tusche (greasy substance) to a plate or stone. (The term lithography comes from litho, for stone, and -graph to draw.) Certain parts of the semi-absorbent surface being printed on can be made receptive to ink while others (the blank parts) reject it.
Spin-on carbon compositions for lithographic processing
The invention described herein is directed towards spin-on carbon materials comprising polyamic acid compositions and a crosslinker in a solvent system. The materials are useful in trilayer photolithography processes. Films made with the inventive compositions are not soluble in solvents commonly used in lithographic materials, such as, but not limited to PGME, PGMEA, and cyclohexanone. However, the films can be dissolved in developers commonly used in photolithography. In one embodiment, the films can be heated at high temperatures to improve the thermal stability for high temperature processing. Regardless of the embodiment, the material can be applied to a flat / planar or patterned surface. Advantageously, the material exhibits a wiggling resistance during pattern transfer to silicon substrate using fluorocarbon etch.
Owner:BREWER SCI
Process window based optical proximity correction of lithographic images
InactiveUS6578190B2Maximize rangeCharacter and pattern recognitionPhotomechanical exposure apparatusProcess windowPlanographic printing
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Negative Working, Heat-Sensitive, Lithographic Printing Plate Precursor
ActiveUS20080213696A1Number of defectSize of defectPhotosensitive materialsDuplicating/marking methodsSimple Organic CompoundsPhosphoric acid
A heat-sensitive negative-working lithographic printing plate precursor includes on a grained and anodized aluminum support a coating including hydrophobic thermoplastic polymer particles, a hydrophilic binder, and an organic compound, wherein the organic compound includes at least one phosphonic acid group or at least one phosphoric acid group or a salt thereof.
Owner:AGFA OFFSET BV
Negative-acting no-process printing plates
InactiveUS6027857APhotosensitive materialsPhotosensitive material processingFunctional monomerOligomer
A photosensitive composition is prepared containing a polymer of the formula B(X)(Y) wherein B represents an organic backbone, each X independently is an acidic group or salt thereof and each Y independently is a photocurable group and a photoinitiating compound or compounds. Preferably, free-radically polymerizable multi-functional monomer and / or oligomer is added to the photosensitive composition. The photosensitive composition can be coated on a suitable substrate for planographic printing plate applications. Imagewise irradiation causes the light struck regions to photocure, becoming insoluble in aqueous and organic mediums, while the non-light struck regions remain highly soluble / dispersable. Printing plates of this construction do not require processing prior to being run on a press.
Owner:3M CO
High speed negative-working thermal printing plates
Negative working thermally imageable elements useful as lithographic printing plate precursors and methods for their use are disclosed. The elements have a substrate, a layer of imageable composition over the substrate, and, optionally, an overcoat layer over the layer of imageable composition. The imageable composition has an allyl-functional polymeric binder. Optimum resolution and on-press performance can be attained without a post-exposure bake. The elements do not require a post-exposure bake and can be used in on-press development applications.
Owner:KODAK POLYCHROME GRAPHICS
Method of making a photopolymer printing plate
ActiveUS20050266349A1High degree of polymerizationImage deteriorationPhotosensitive materialsDuplicating/marking methodsPhotopolymerEngineering
A method of making a lithographic printing plate comprising the steps of: a) providing a lithographic printing plate precursor comprising (i) a support having a hydrophilic surface or which is provided with a hydrophilic layer, (ii) a photopolymerizable coating on said support, b) image-wise exposing said coating in a plate setter, c) developing the precursor, thereby removing the non-exposed areas of the coating from the support, whereby the developing step is carried out off-press in a gumming unit by treating the coating of the precursor with a gum solution.
Owner:AGFA OFFSET BV
Negative-acting no-process printing plates
InactiveUS6171735B1Platen pressesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFunctional monomerOligomer
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Method of making a lithographic printing plate
ActiveUS8232043B2High degree of polymerizationQuality improvementPlaten pressesPhotosensitive materialsInter layerEngineering
A method of making a lithographic printing plate includes the steps of a) providing a lithographic printing plate precursor including (i) a support having a hydrophilic surface or which is provided with a hydrophilic layer, (ii) a coating on the support including a photopolymerizable layer, and, optionally, an intermediate layer between the photopolymerizable layer and the support, b) image-wise exposing the coating in a plate setter, c) optionally, heating the precursor in a preheating unit, and d) developing the precursor off-press in a gumming unit by treating the coating of the precursor with a gum solution, thereby removing the non-exposed areas of the coating from the support, wherein the coating further includes a compound capable of interacting with the support, the compound being present in the photopolymerizable layer and / or in the intermediate layer.
Owner:AGFA OFFSET BV
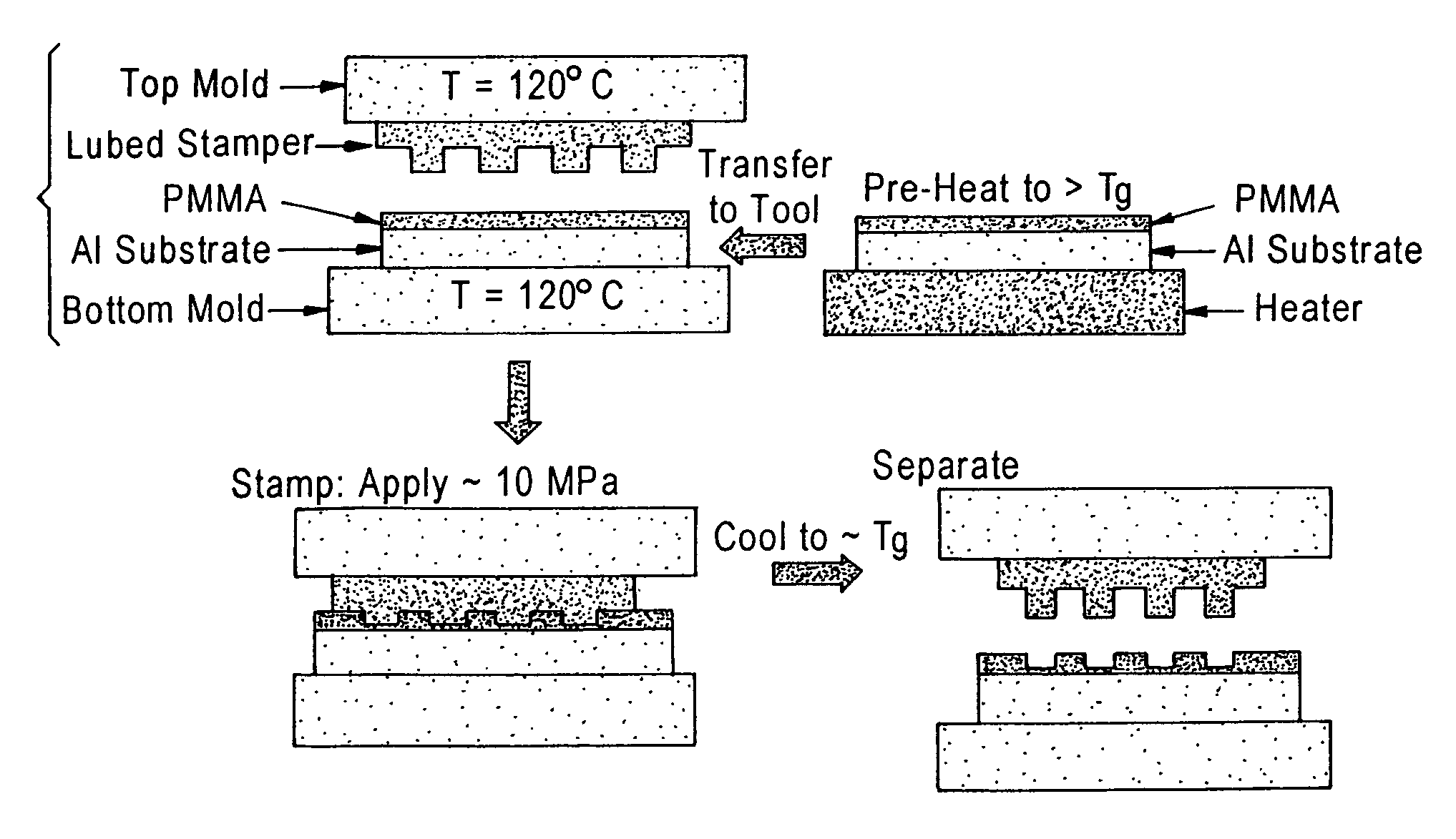
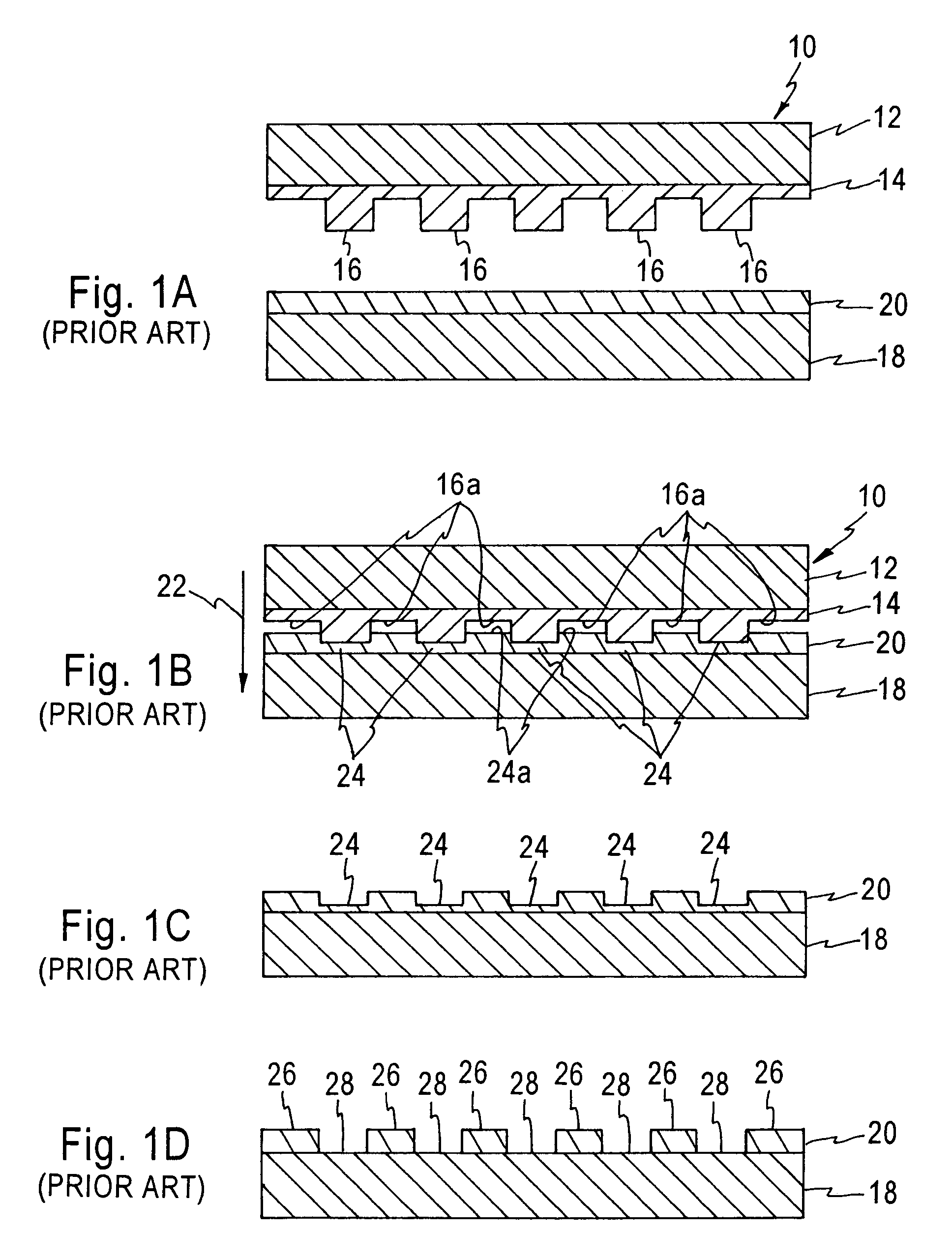
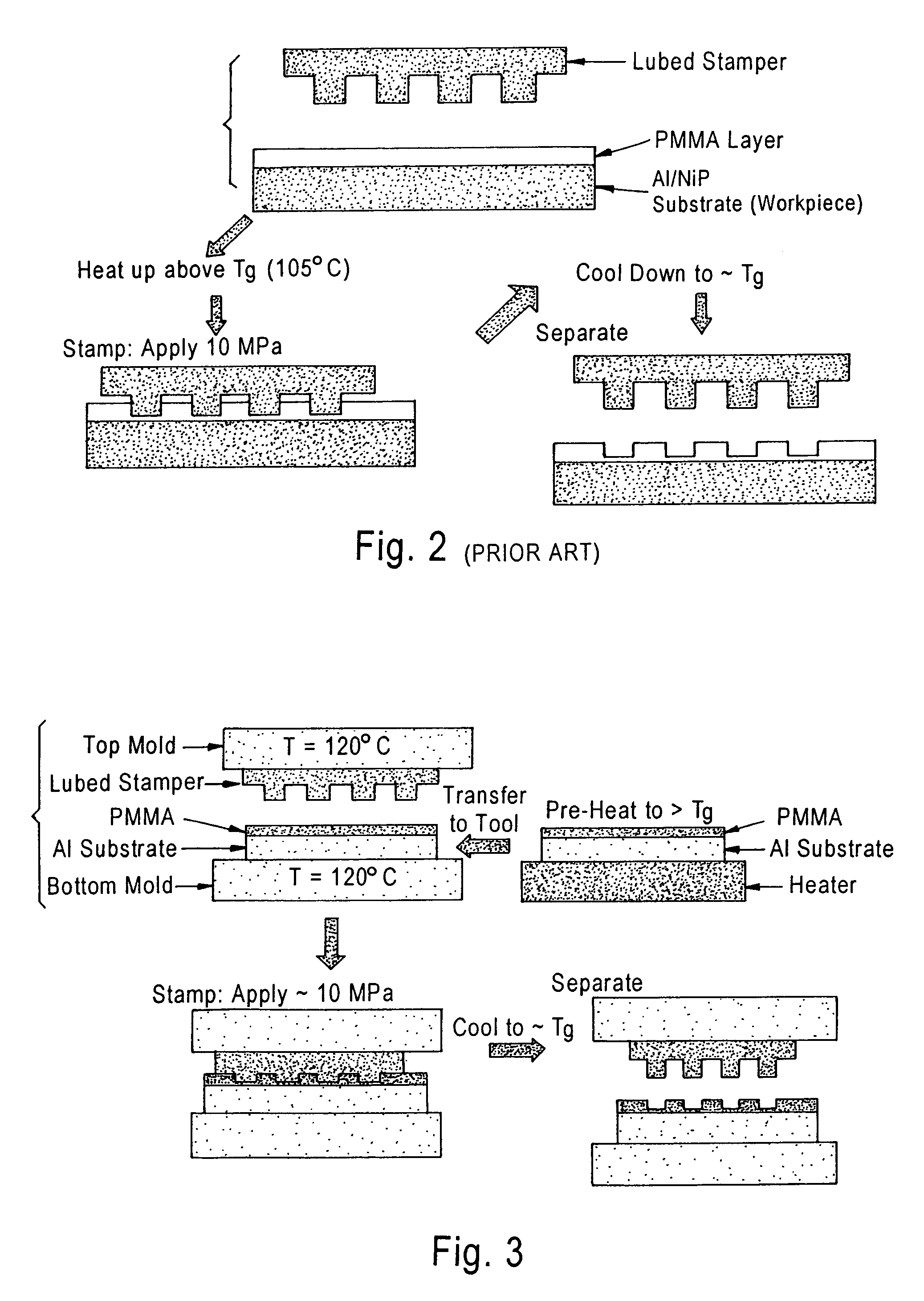
Heat-transfer-stamp process for thermal imprint lithography
InactiveUS6949199B1Eliminate disadvantagesSimple methodNanostructure manufactureDecorative surface effectsStamping processPlanographic printing
A method of performing thermal imprint lithography of a surface of a thermoplastic layer-coated workpiece for forming a pattern therein comprises pre-heating the workpiece to a pre-selected high temperature prior to inserting the workpiece in a stamping / imprinting tool maintained at a predetermined lower temperature, whereby the interval for thermal cycling of the stamping / imprinting tool between higher and lower temperatures is eliminated or at least reduced. Applications of the method include forming servo patterns in disk-shaped substrates for hard disk recording media.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Light-sensitive lithographic printing plate
InactiveUS20050214677A1High developing latitudeExcellent printing durabilityPhotosensitive materialsLithographyOrganic acidPlanographic printing
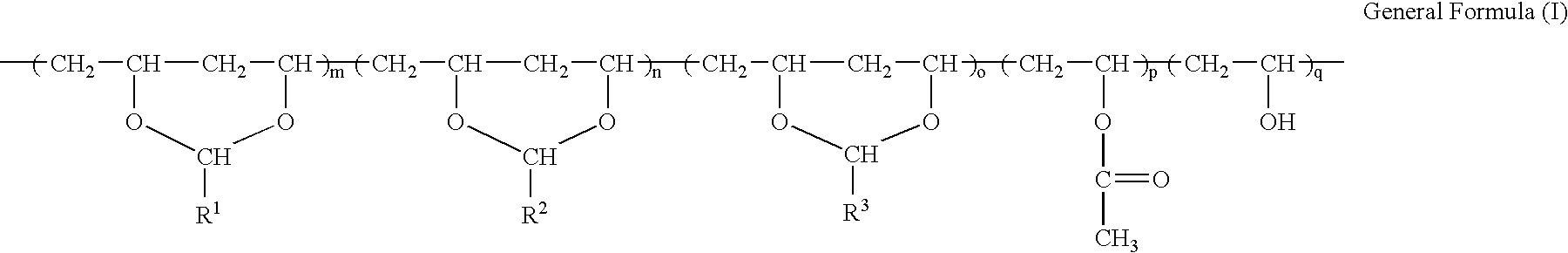
A light-sensitive lithographic printing plate comprising a hydrophilic substrate provided thereon with a layer sensitive to infrared light rays comprising (A) a polymer represented by the following general formula (I); (B) an organic acid and / or a cyclic acid anhydride; and (C) a light-heat conversion substance. The light-sensitive lithographic printing plate is excellent in the both printing durability and the developing latitude.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP
Printing form precursor and process for preparing a stamp from the precursor
The invention pertains to a printing form precursor and a method for preparing a stamp from the precursor for use in soft lithographic applications. The printing form precursor includes a composition layer of a fluorinated compound capable of polymerization upon exposure to actinic radiation and a flexible support transparent to the actinic radiation adjacent the composition layer.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Method for making a lithographic printing plate involving on press development
InactiveUS6030750AImprove printing effectSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPlate printingEngineeringPrinting press
The present invention provides a method for making a lithographic printing plate comprising the steps of: (1) image-wise exposing to light an imaging element comprising (i) on a hydrophilic surface of a lithographic base an image forming layer comprising hydrophobic thermoplastic polymer particles capable of coalescing under the influence of heat and dispersed in a hydrophilic binder and (ii) a compound capable of converting light to heat, said compound being comprised in said image forming layer or a layer adjacent thereto; (2) and developing a thus obtained image-wise exposed imaging element by mounting it on a print cylinder of a printing press and supplying an aqueous dampening liquid and / or ink to said image forming layer while rotating said print cylinder.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Lithographic printing plate precursor and lithographic printing method
InactiveUS20050170282A1Photomechanical apparatusPhotosensitive material auxillary/base layersLaser exposureEngineering
An on-press development or non-processing (non-development) type lithographic printing plate precursor capable of giving a printout image having a large lightness difference, and a lithographic printing method using this lithographic printing plate precursor are provided, a lithographic printing plate precursor comprising a support and a photosensitive-thermosensitive layer capable of recording an image by infrared laser exposure, the lithographic printing plate precursor being capable of performing a printing by loading on a printing press without passing through a development processing step after recording an image, or by recording an image after loading on a printing press, wherein said photosensitive-thermosensitive layer comprises (1) an infrared absorbent and (2) a discoloring agent or discoloration system capable of generating a color change upon exposure; and the lithographic printing method performing a printing using the above-described lithographic printing plate precursor.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Negative-working radiation-sensitive compositions and imageable materials
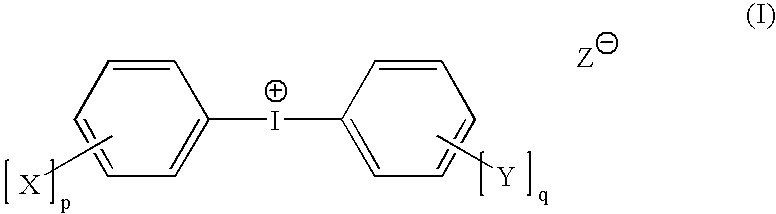
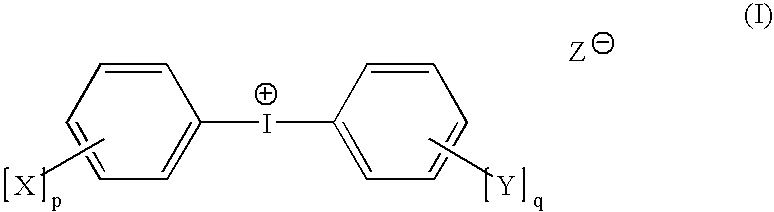
ActiveUS7524614B2Improve solubilityIncrease speedPhotosensitive materialsRadiation applicationsRadiation sensitivityPlanographic printing
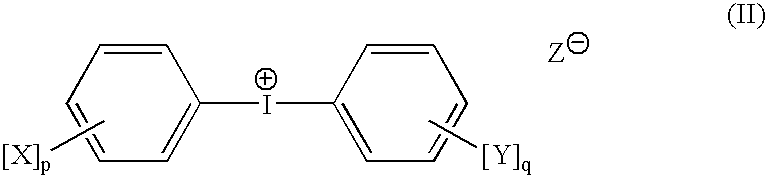
A radiation-sensitive composition includes a radically polymerizable component and an iodonium borate initiator composition capable of generating radicals sufficient to initiate polymerization of the free radically polymerizable component upon exposure to imaging radiation. The iodonium borate composition includes a particular diaryliodonium borate compound having organic substituents to provide a sum of at least 6 carbon atoms on the iodonium cation phenyl rings. This composition can be applied to a suitable substrate to provide a negative-working imageable element with improved digital speed and good shelf life and that can be imaged to provide lithographic printing plates. The imaged elements can be developed either on-press or off-press using alkaline developers.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
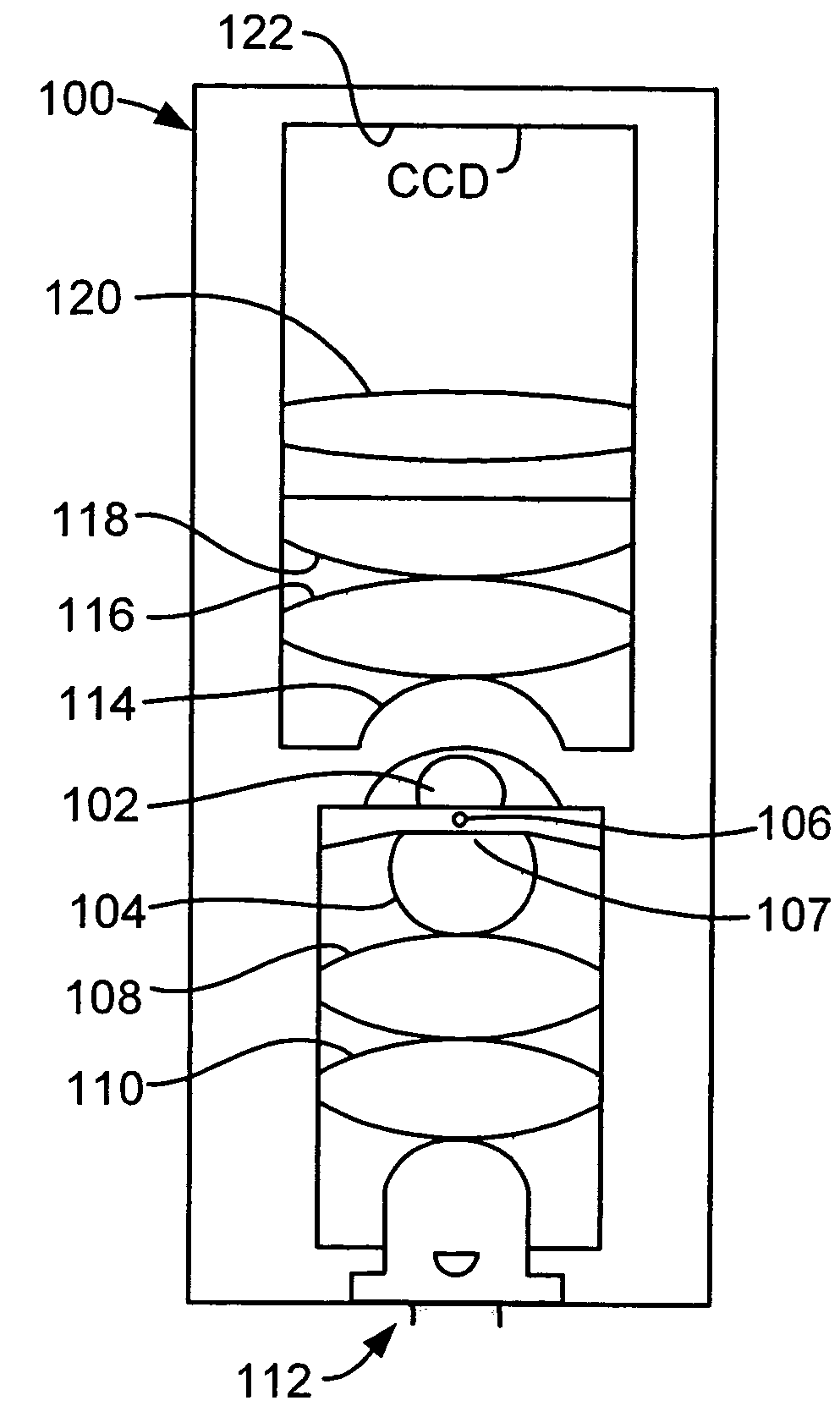
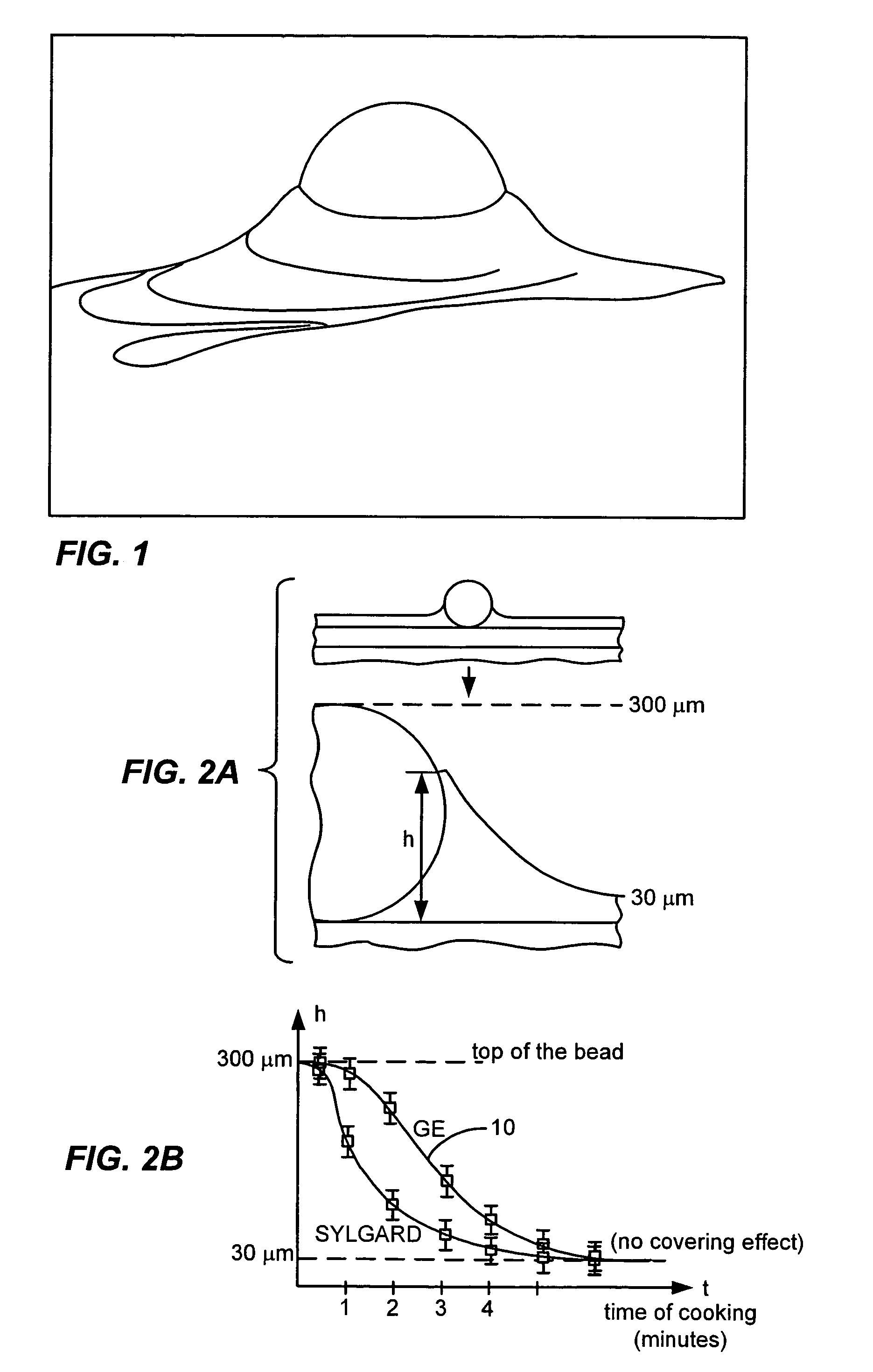
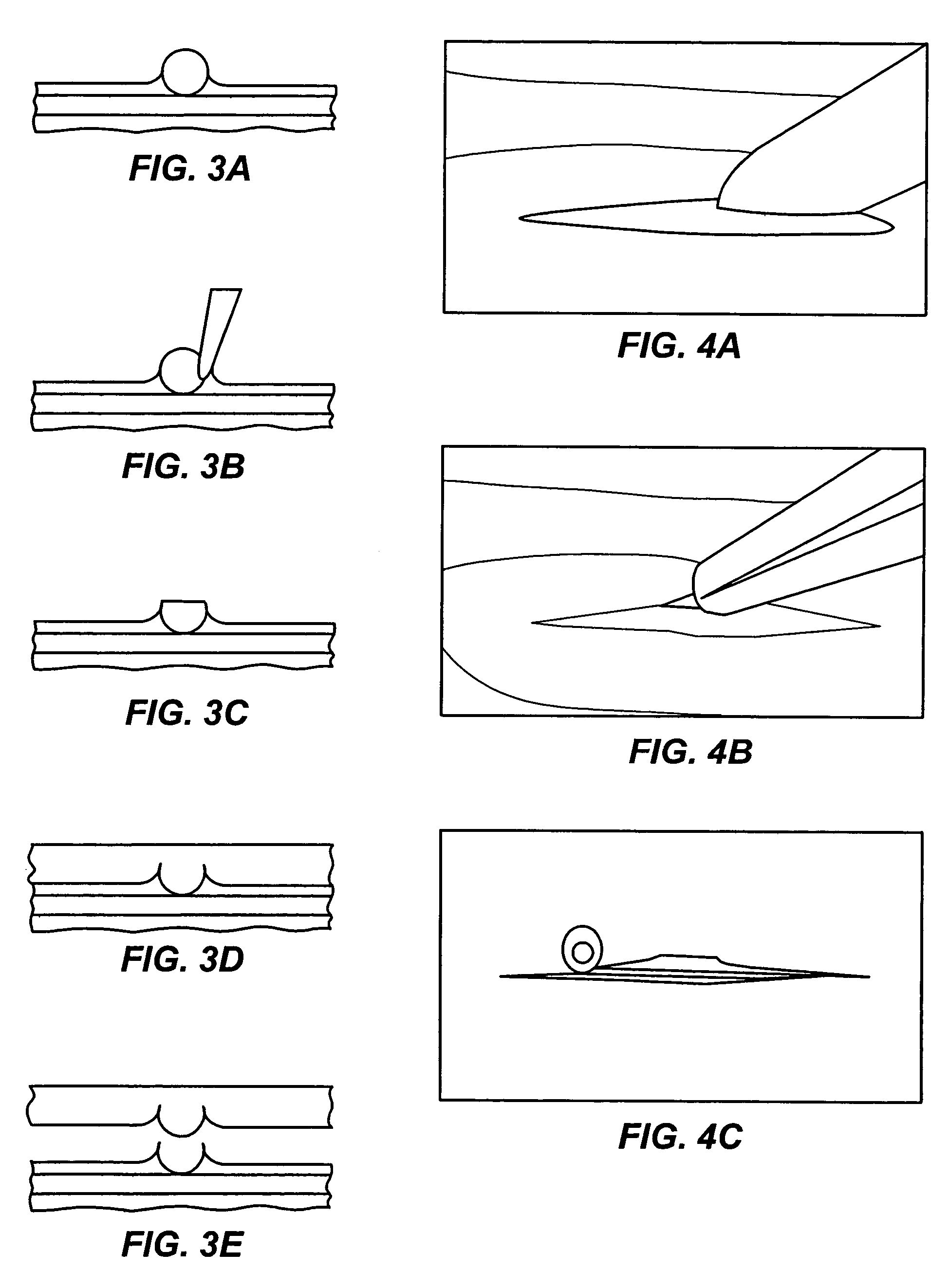
Microfabricated rubber microscope using soft solid immersion lenses
Soft lithography with surface tension control is used to microfabricate extremely efficient solid immersion lenses (SILs) out of rubber elastomeric material for use in microscope type applications. In order to counteract the surface tension of the mold material in a negative mold that causes creep on a positive mold, material such as RTV is partially cured before use in order to allow the reticulation of polymer chains to change the viscosity of the uncured material in a controllable manner. In a specific embodiment, the techniques of soft lithography with surface tension control are used to make molded SILs out of the elastomer polydimethylsiloxane. The lenses achieve an NA in the range of 1.25. The principle of compound lens design is used to make the first compound solid immersion lens, which is corrected for higher light gathering ability and has a calculated NA=1.32. An important application of these lenses is integrated optics for microfluidic devices, specifically in a handheld rubber microscope for microfluidic flow cytometry.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
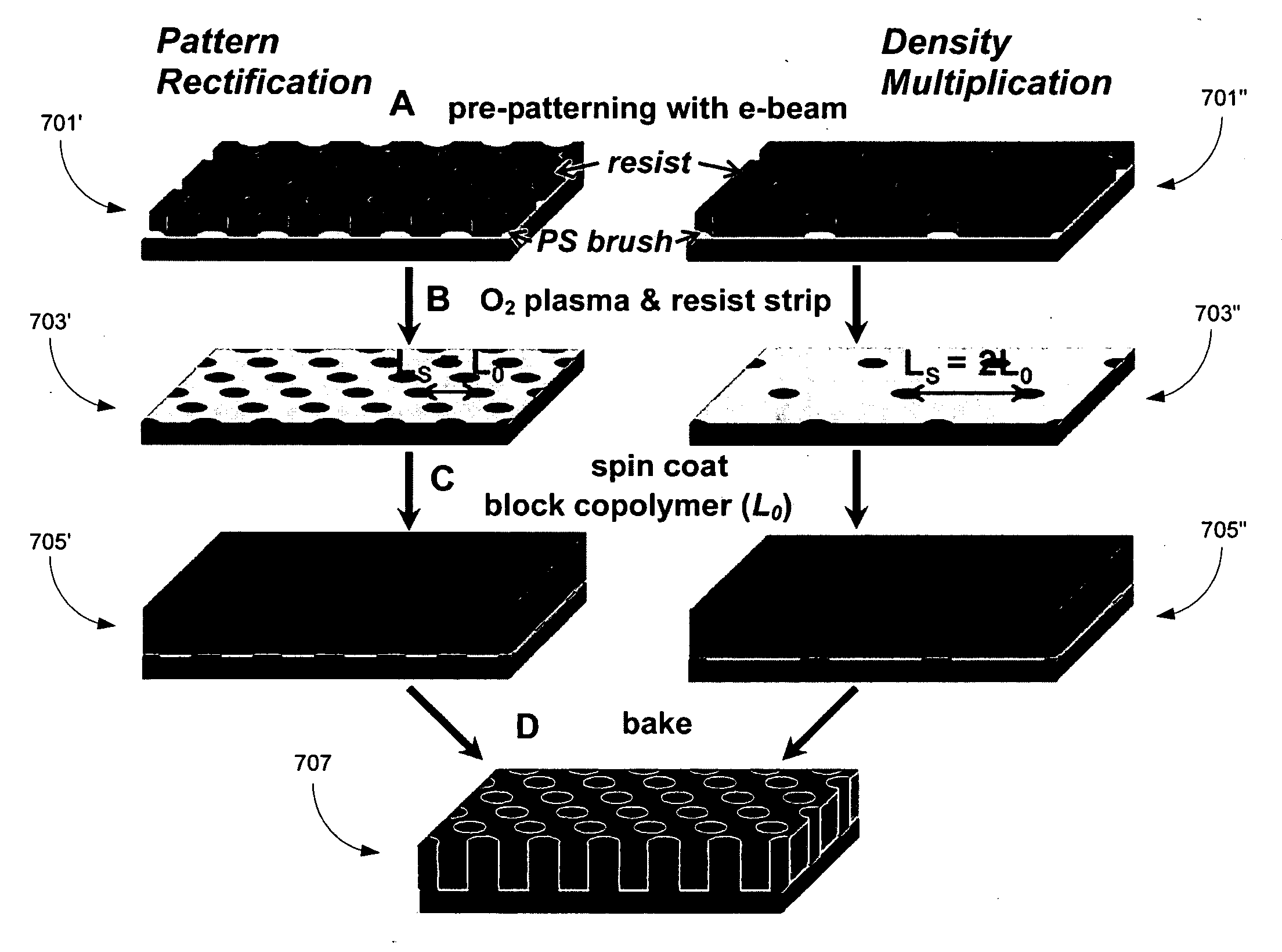
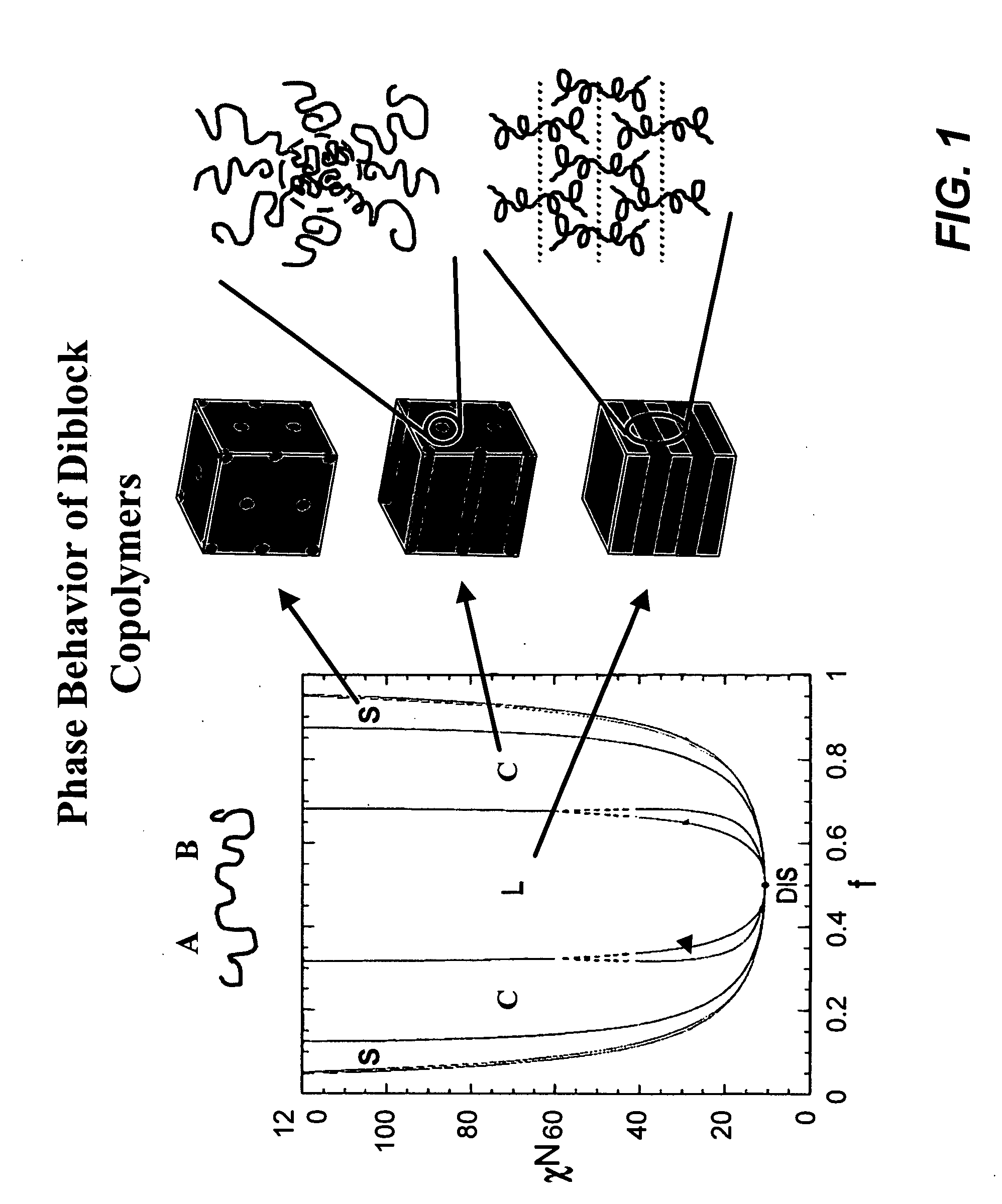
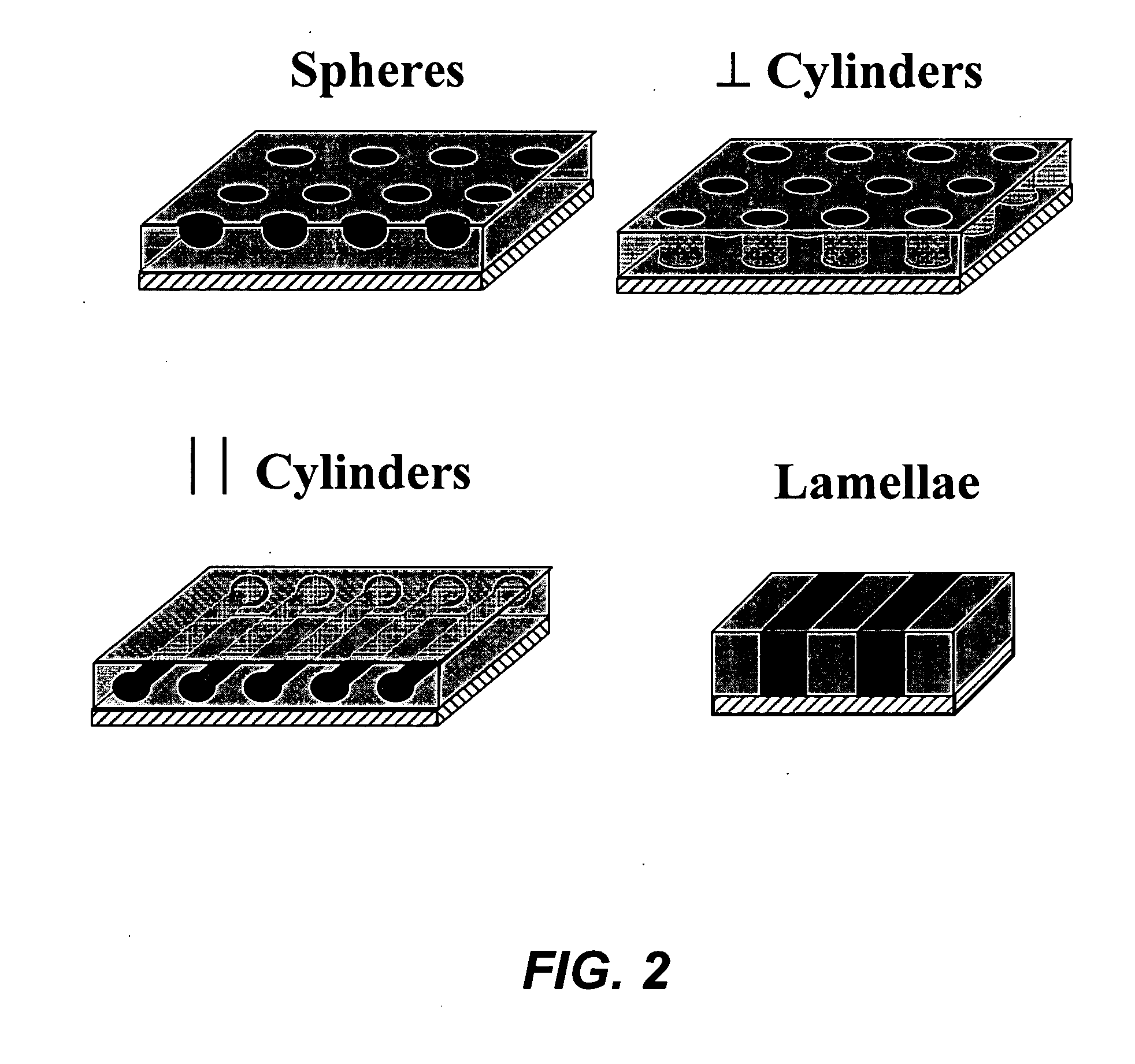
Density multiplication and improved lithography by directed block copolymer assembly
ActiveUS20090196488A1High densityQuality improvementMaterial nanotechnologyPatterned record carriersHigh densityPeriodic nanostructures
Methods to pattern substrates with dense periodic nanostructures that combine top-down lithographic tools and self-assembling block copolymer materials are provided. According to various embodiments, the methods involve chemically patterning a substrate, depositing a block copolymer film on the chemically patterned imaging layer, and allowing the block copolymer to self-assemble in the presence of the chemically patterned substrate, thereby producing a pattern in the block copolymer film that is improved over the substrate pattern in terms feature size, shape, and uniformity, as well as regular spacing between arrays of features and between the features within each array compared to the substrate pattern. In certain embodiments, the density and total number of pattern features in the block copolymer film is also increased. High density and quality nanoimprint templates and other nanopatterned structures are also provided.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND +1
Coated and imprinted medical devices and methods of making the same
InactiveUS20070110888A1Increase first surface areaIncrease surface areaSurgeryPharmaceutical containersInsertion stentPlanographic printing
The present invention relates generally to coated medical devices, preferably a stent, that has a drug-eluting surface completely or partially coated with a coating that is imprinted with an impression. In particular, the invention is directed to a coated medical device having a coating that comprises biologically active materials, polymers, or a combination thereof. The coating is imprinted with an impression by printing, molding, lithography, or embossing techniques. Preferably, the patterning imprinted on the coating is capable of releasing biologically active materials in different amounts, at different rates, and / or at different time periods. The invention also relates to methods of making and methods of using the coated medical device.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Planographic printing plate
InactiveUS6017677AHigh sensitivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotosensitive material processingSide chainPhotoacid generator
The present invention provide a planographic printing plate comprising a substrate having thereon a recording layer which comprises at least one of a polymer compound carrying on a side chain a functional group which generates sulfonic acid under influence of an acid, base or heating; and a photo acid-generating agent or acid-generating agent; thermal base-generating agent; or an infrared ray absorbing agent, and by this structure, a high sensitive positive type planographic printing plate which can be developed with water or requires no developing is provided.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Coating method and planographic printing plate
InactiveUS20050005794A1Low costImprove uniformityPretreated surfacesPhotomechanical coating apparatusPlanographic printingMaterials science
The present invention provides a method of coating a coating solution comprising: providing a web; providing a coating solution; coating the coating solution on at least one surface of the web; and drying the coating solution to form a coated layer, wherein a temperature of the web is maintained at 35° C. or more during coating. According to the coating method, a multi-layered planographic printing plate can be manufactured at low energy cost and running cost.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Planographic printing plate precursor and planographic printing method
ActiveUS7005234B2Excellent plate-wear resistanceAvoid small quantitiesPhotosensitive materialsRadiation applicationsPlanographic printingPhotochemistry
The present invention provides a planographic printing plate precursor comprising a photosensitive layer on a support, the photosensitive layer including an infrared absorbent, a radical polymerization initiator and a radical polymerizing compound, the photosensitive layer being recordable with irradiation with an infrared ray, and being at least one of soluble and dispersible in water.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Substrate for and a process in connection with the product of structures
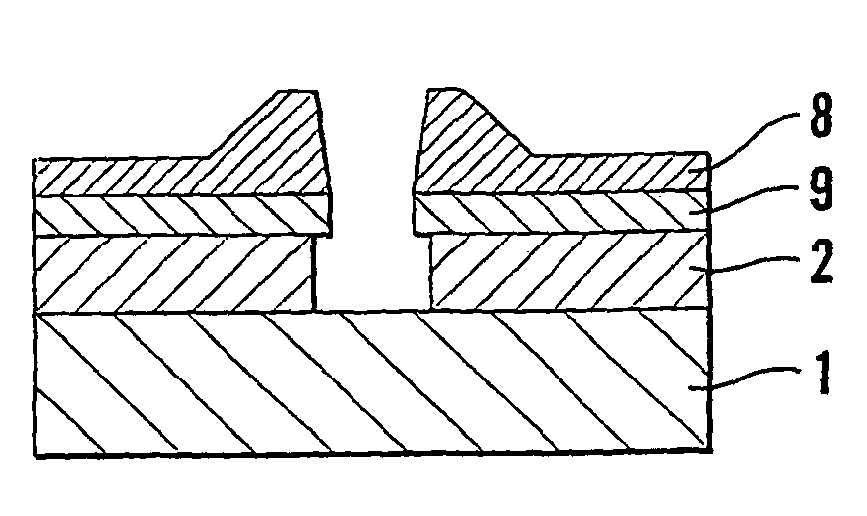
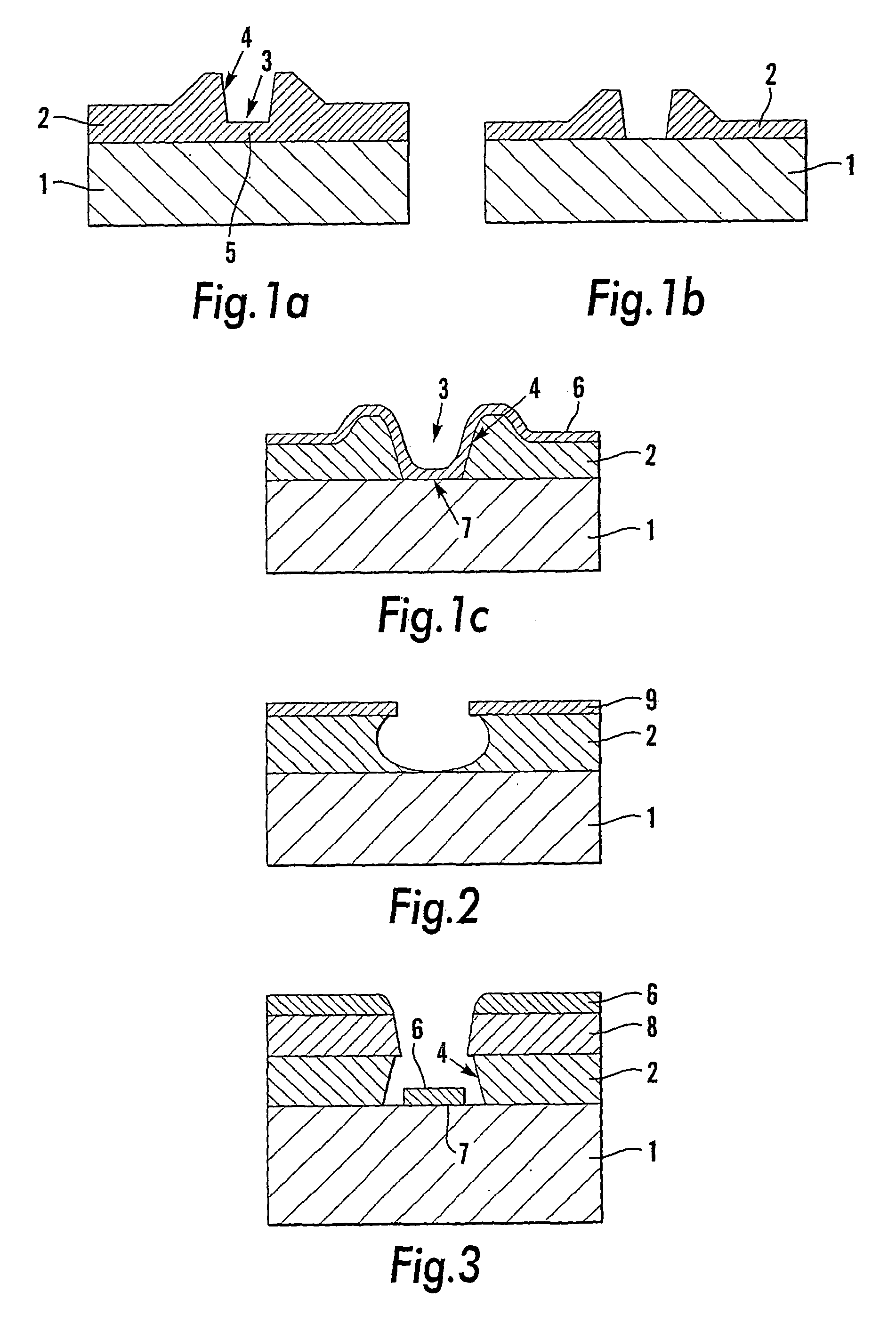
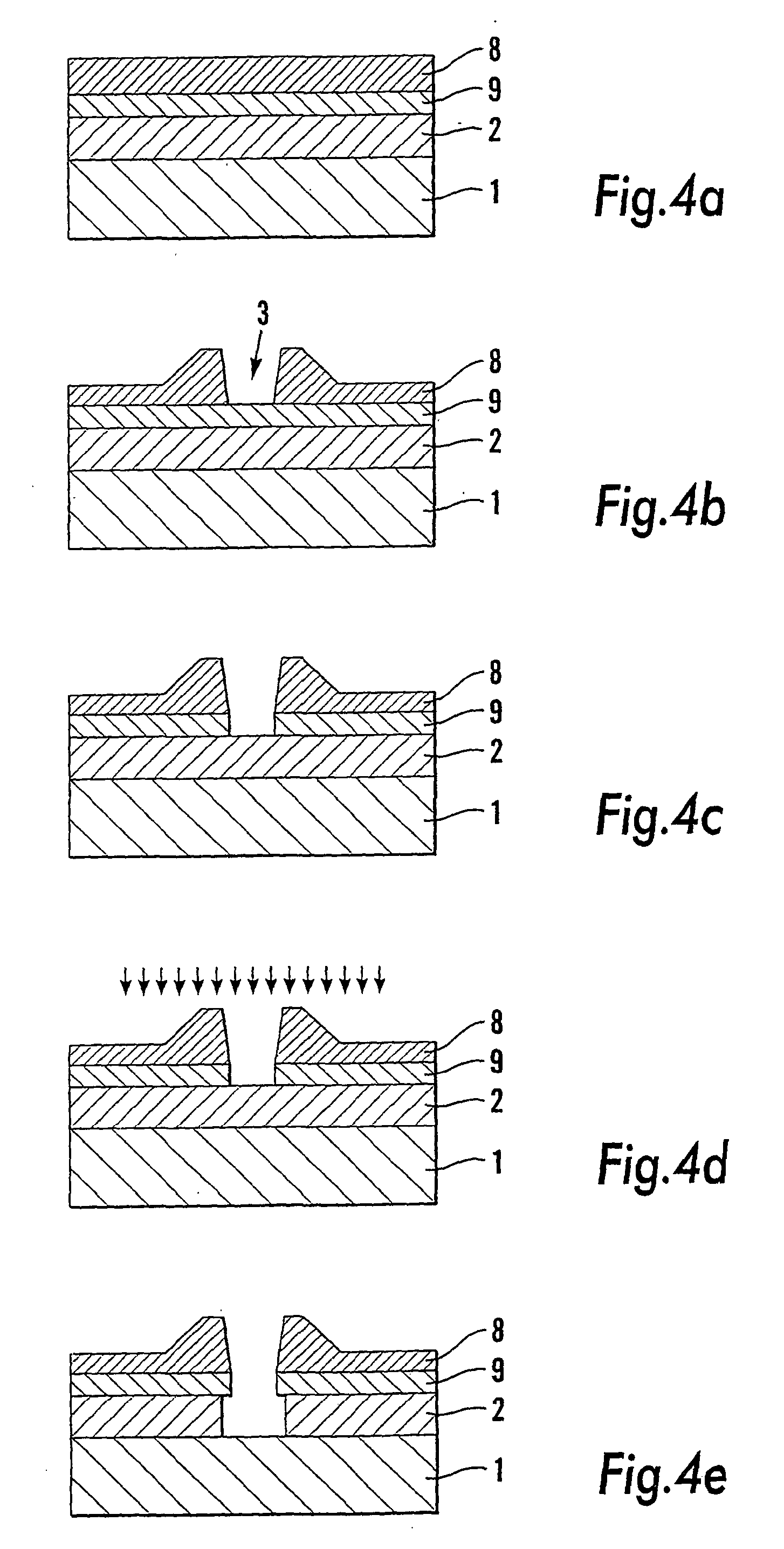
InactiveUS20040005444A1Easy to disassembleFacilitate NILSemi-permeable membranesFixed microstructural devicesResistMetallurgy
The invention relates to a substrate (1) comprising at least a first (2) and a second (8) coating layer on one surface of the substrate, for nanoimprint lithography, said first coating layer (2) consisting of a positive resist and said second (8) coating layer consisting of a negative resist. The invention also relates to a process in connection with nanoimprint lithography on the substrate (1), a pattern (3) of nanometre size being impressed in a first stage into the second coating layer (8) by means of a template (610), following which the first coating layer (2), in a second stage, is exposed to a chiefly isotropic developing method on surfaces thereof that have been exposed in connection with said first stage, a method for developing and material for said first and second coating layers being selected so that the first coating layer (2) is developed more quickly than the second coating layer (8), so that an undercut profile is obtained in the coating layers.
Owner:OBDUCAT AB SE
Negative-working radiation-sensitive compositions and imageable materials
InactiveUS7332253B1Good solvent resistanceEasy to attachPhotosensitive materialsRadiation applicationsRadiation sensitivitySolvent
A radiation-sensitive composition and negative-working imageable element includes a polymeric binder comprising pendant allyl ester groups to provide solvent resistance, excellent digital speed (sensitivity) and can be imaged and developed without a preheat step to provide lithographic printing plates. The polymeric binder can be prepared with a precursor polymer having pendant carboxy groups that are converted to allyl ester groups using an allyl-containing halide in the presence of a base in order to avoid gelation.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Planographic printing plate
InactiveUS20010041305A1High purityReduce surface roughnessPhotosensitive materialsRadiation applicationsAnodizingSolubility
A planographic printing plate precursor comprising: an aluminum substrate which has been subjected to a roughening treatment and an anodizing treatment; and a photosensitive layer which provided on a surface of said substrate, and which contains an infrared absorbing agent and a water-insoluble and alkali aqueous solution-soluble polymer compound, and whose solubility in an alkali developing solution varies by infrared laser exposure, wherein said substrate is obtained by electrochemically roughening an aluminum alloy plate which contains a trace amount of certain elements to an aluminum alloy of high purity.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Heat-sensitive lithographic printing plate precursor
InactiveUS20050037280A1Radiation applicationsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHeat sensitivePhenyl group
A heat-sensitive lithographic printing plate precursor is disclosed which comprises a hydrophilic support and an oleophilic coating comprising an infrared absorbing agent and a developer soluble polymer which comprises a phenolic monomeric unit wherein the phenyl group of the phenolic monomeric unit is substituted by a group Q, wherein Q has the structure and is covalently linked to a carbon atom of the phenyl group and wherein L1, L2 and L3 are linking groups, a, b and c are 0 or 1, and T1, T2 and T3 are terminal groups. The polymer, substituted by the group Q, increases the chemical resistance of the coating.
Owner:AGFA NV
Lithographic printing plate precursor and lithographic printing method
ActiveUS20050069811A1Excellent developabilityProlong lifeRadiation applicationsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingActinic RaysImage recording
A lithographic printing plate precursor comprising: a support; an image recording layer comprising (A) an actinic ray absorber, (B) a polymerization initiator, and (C) a polymerizable compound, wherein the image recording layer is capable of being removed with at least one of a printing ink and a fountain solution; and an overcoat layer comprising an inorganic laminar compound. And a lithographic printing method comprising: mounting a lithographic printing plate precursor on a printing press; imagewise exposing the lithographic printing plate precursor with laser beams; and feeding at least one of a printing ink and a fountain solution to the lithographic printing plate precursor to remove a laser beams non-exposed area in an image recording layer; and performing printing.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method and apparatus to apply surface release coating for imprint mold
In imprint lithography, the mold is coated with a surface release layer for a non-sticking separation. Bonding strength of the release layer to the mold depends on the cleanness of the surface and the process of release layer deposition. In accordance with the invention, the mold is disposed in an evacuable chamber, cleaned to remove surface organic contamination and coated with the surface release layer in a chamber, all without relocation or undesired time delay. The chamber encloses a support chuck for the mold or substrate, a surface cleaner unit adjacent the support, a heating source adjacent the support, and advantageously, sensors of measuring chamber pressure, vapor partial pressure and moisture concentration. A vapor source connected to the chamber supplies release surfactant vapor. The mold is cleaned, and the cleaning is followed by vapor phase deposition of the surfactant. The mold is advantageously heated. Typical ways of cleaning include exposure to ozone or plasma ion etch. Surfactant vapor may be generated by liquid surface vaporization, liquid injection or spray vaporization. A surface adhesion promoter can be coated on the substrate by a similar method with the same apparatus.
Owner:NANONEX
Planographic printing plate material, planographic printing plate, and printing process employing the same
InactiveUS20060019196A1Excellent printing durabilitySimplify the development processPhotomechanical apparatusPlate printingImage formationWater soluble
Disclosed is a planographic printing plate material comprising a plastic support and provided thereon, a subbing layer containing a water-soluble resin, a hydrophilic layer containing metal oxide particles with an average particle diameter of from 3 to 100 nm, and an image formation layer containing heat melting particles or heat fusible particles in that order, the planographic printing plate material being in the form of roll, wherein a dry coating amount of the water-soluble resin in the subbing layer is in the range of from 0.001 g / m2 to 3.0 g / m2.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA MEDICAL & GRAPHICS INC
Positive-working radiation-sensitive imageable elements
InactiveUS20110059399A1High sensitivityHigh image resolutionPlaten pressesPhotosensitive materialsImideAryl
Positive-working imageable elements having improved sensitivity, high resolution, and solvent resistance are prepared using a water-insoluble polymeric binder comprising vinyl acetal recurring units that have pendant hydroxyaryl groups, and recurring units comprising carboxylic acid aryl ester groups that are substituted with a cyclic imide group. These imageable elements can be imaged and developed to provide various types of elements including lithographic printing plates.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Aluminum substrates and lithographic printing plate precursors
ActiveUS20130052582A1Enhance layeringImprove adhesionPhotosensitive materialsLayered productsSide chainCarboxylic acid
An aluminum-containing substrate can be provided for use in lithographic printing plate precursors. Before radiation-sensitive layers are applied, a grained and sulfuric acid anodized aluminum-containing support is treated with an alkaline or acidic pore-widening solution to provide its outer surface with columnar pores. The diameter of the columnar pores at their outermost surface is at least 90% of the average diameter of the columnar pores. Directly on this treated surface, a hydrophilic layer is applied, which hydrophilic layer contains a non-crosslinked hydrophilic polymer having carboxylic acid side chains.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Method for preparation of lithographic printing plate and lithographic printing plate precursor
InactiveUS20070020563A1Improve discriminationHigh sensitivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotosensitive material processingHexaarylbiimidazolePlanographic printing
A method for preparation of a lithographic printing plate comprising: exposing a lithographic printing plate precursor comprising a hydrophilic support, a photosensitive layer containing (A) a sensitizing dye having an absorption maximum in a wavelength range of from 350 to 450 nm, (B) a hexaarylbiimidazole compound, (C) a polymerizable compound, (D) a hydrophobic binder polymer and (E) a chain transfer agent and a protective layer in this order, with a laser beam of from 350 to 450 nm; and rubbing a surface of the exposed lithographic printing plate precursor with a rubbing member in a presence of a developer having pH of from 2 to 10 in an automatic processor equipped with the rubbing member to remove the protective layer and an unexposed area of the photosensitive layer.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com