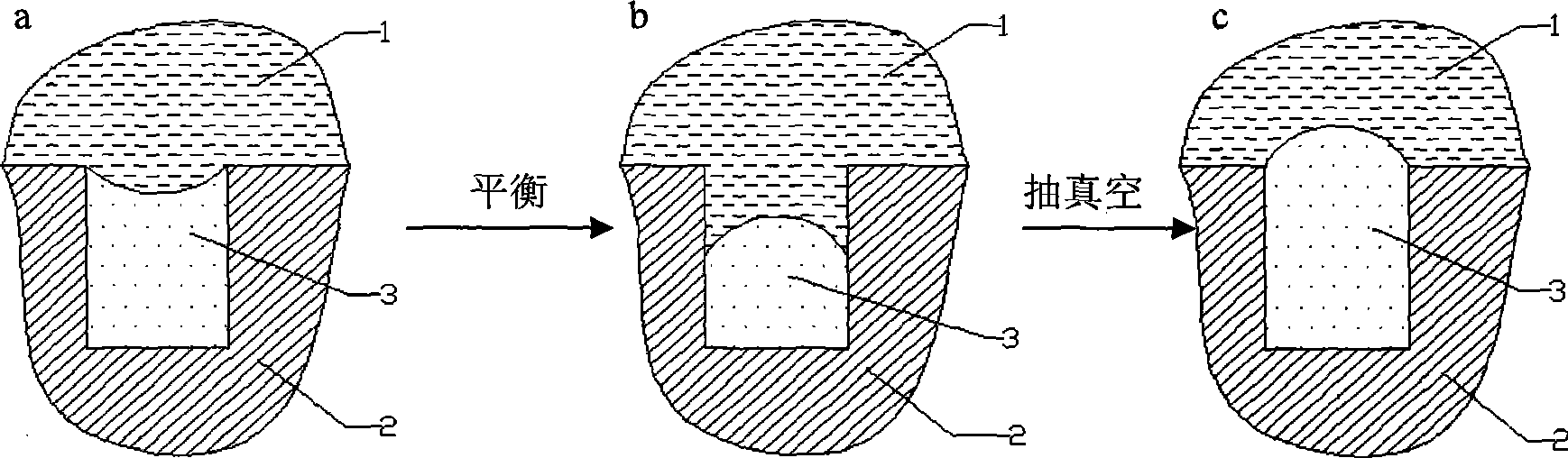
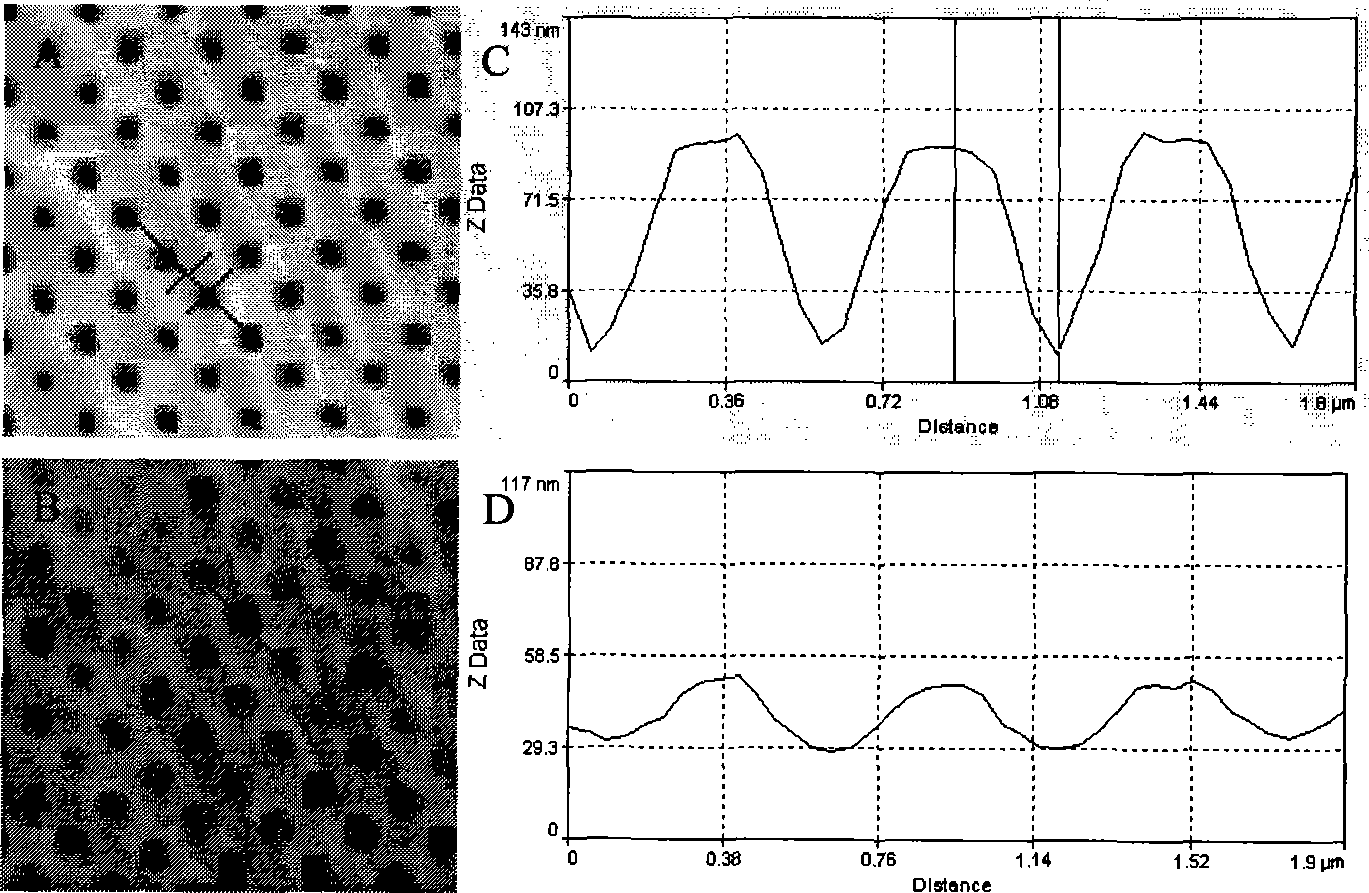
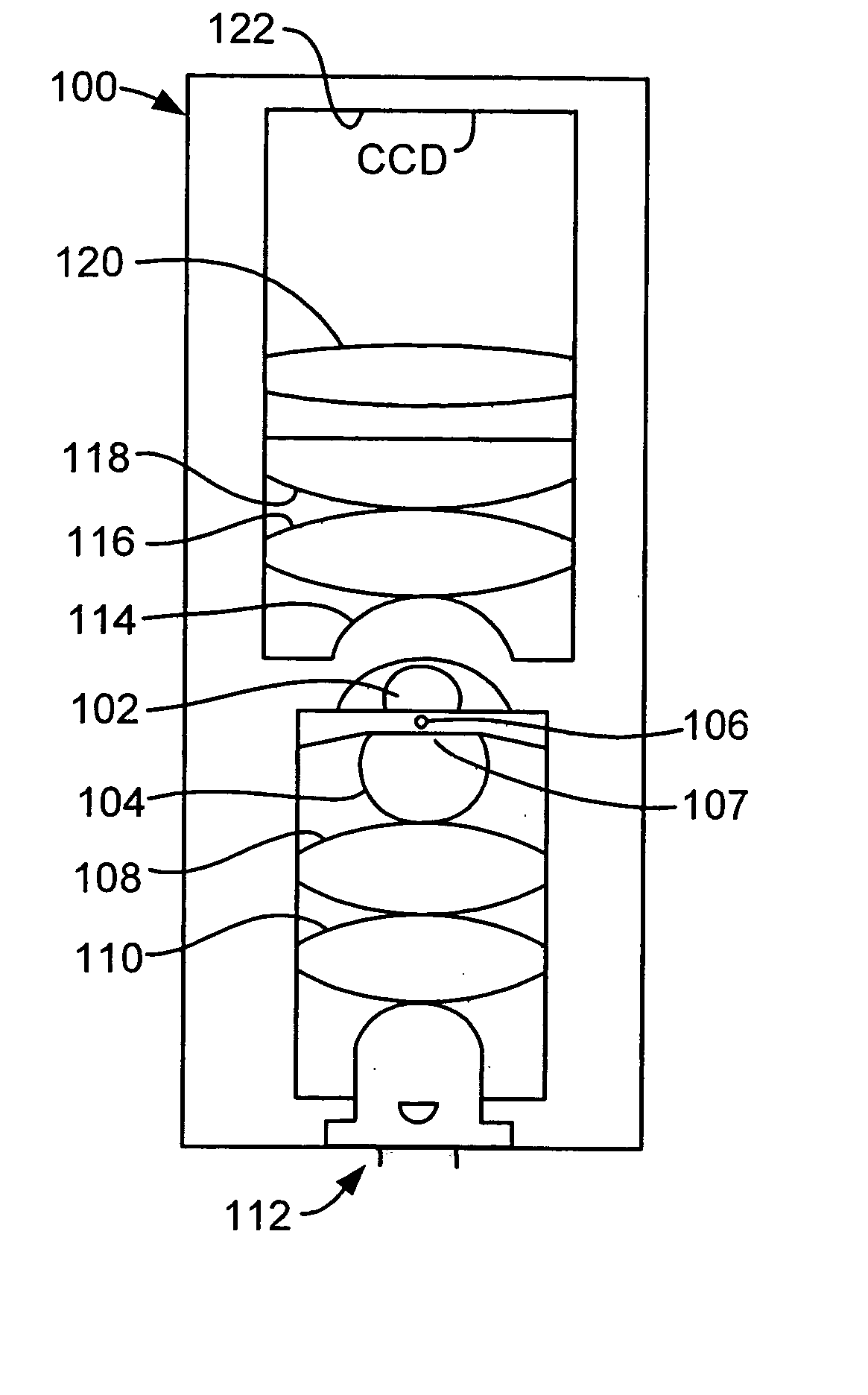
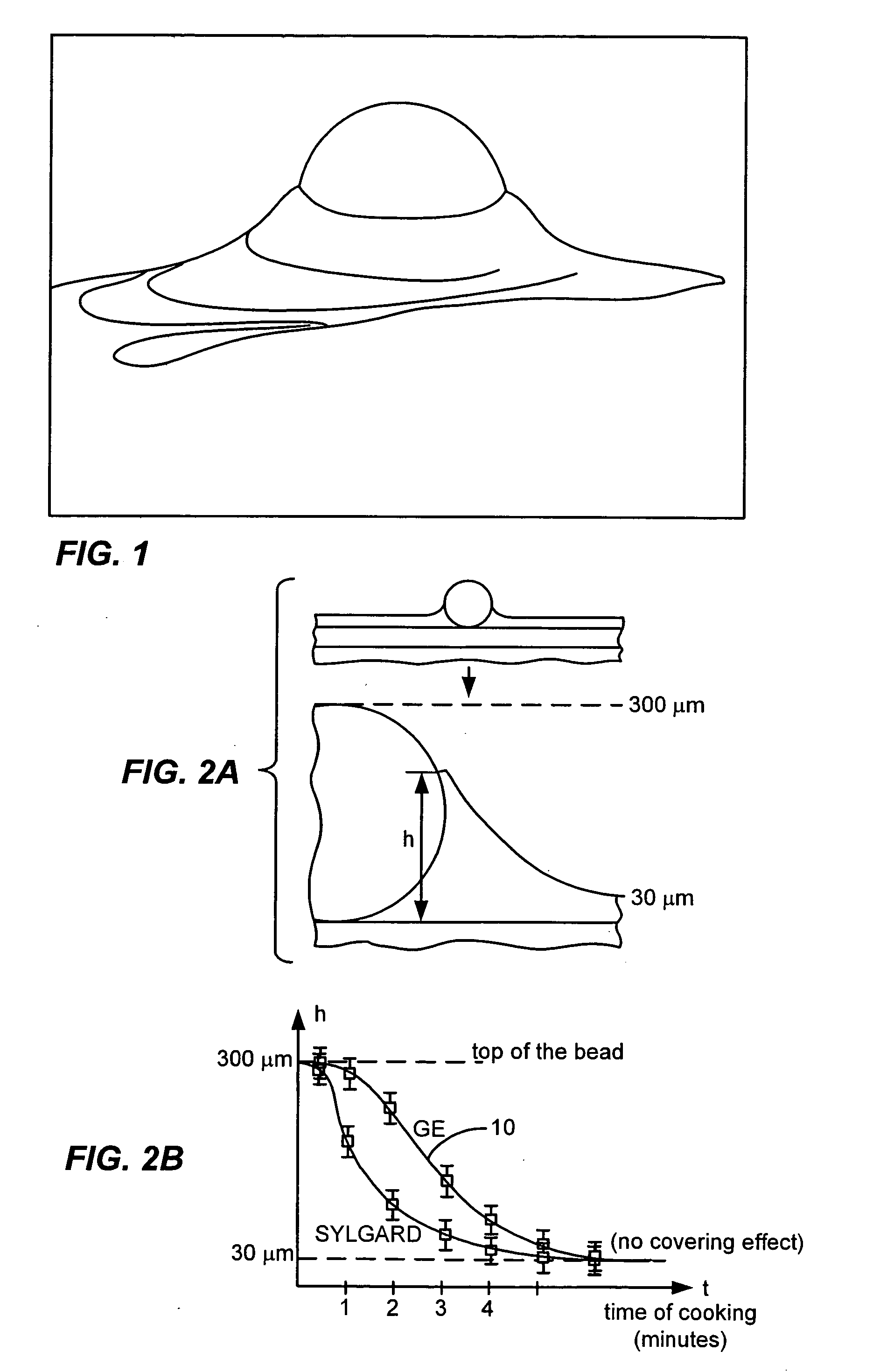
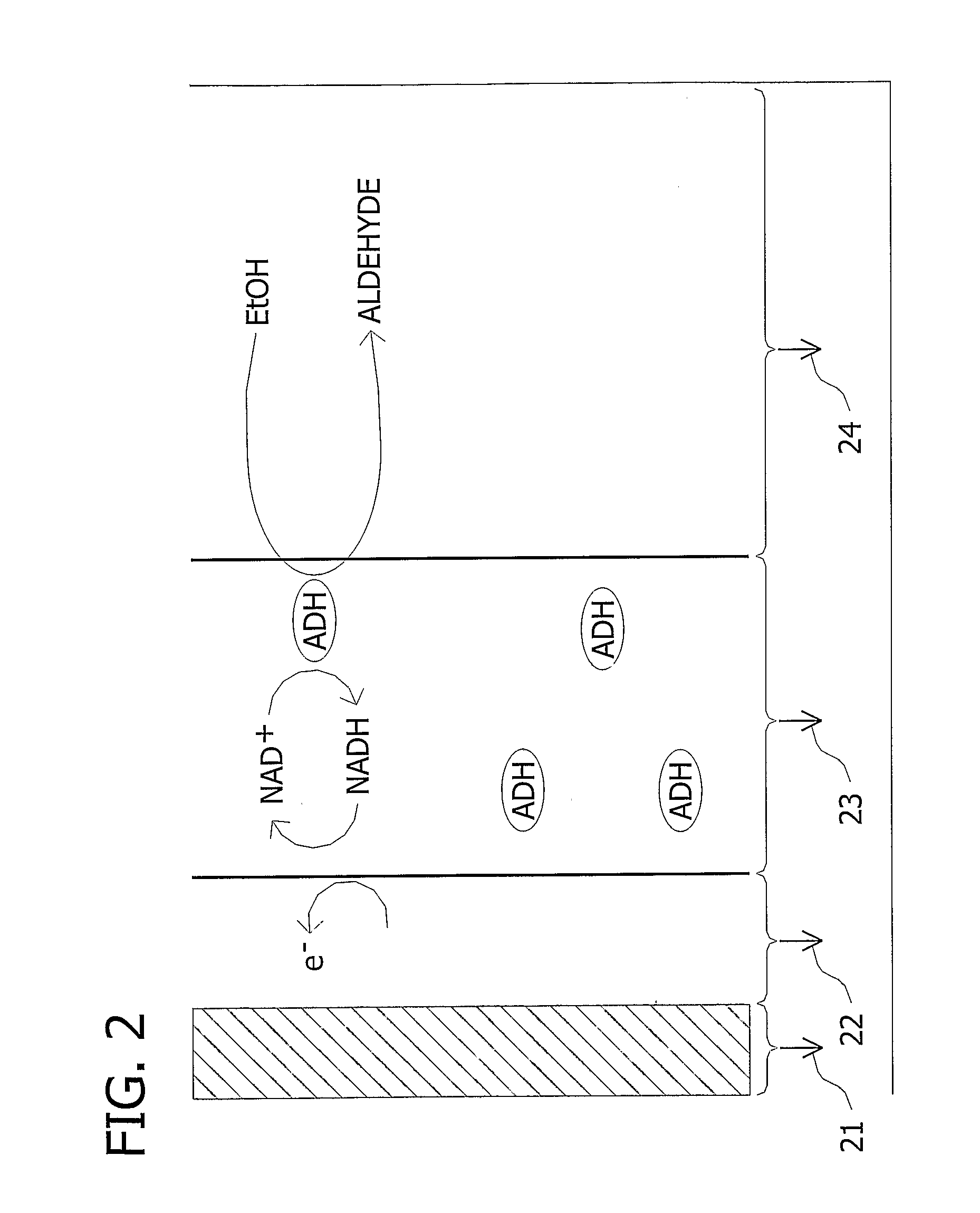
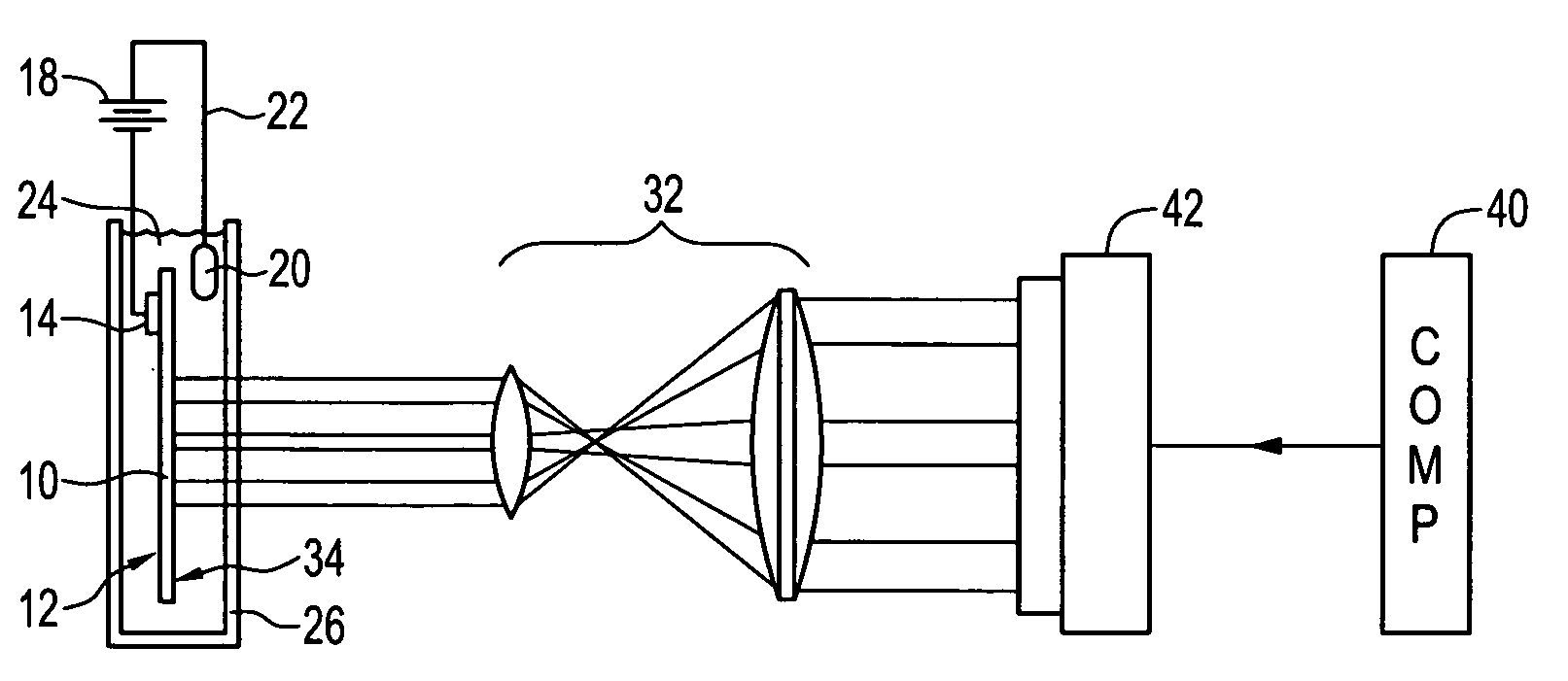
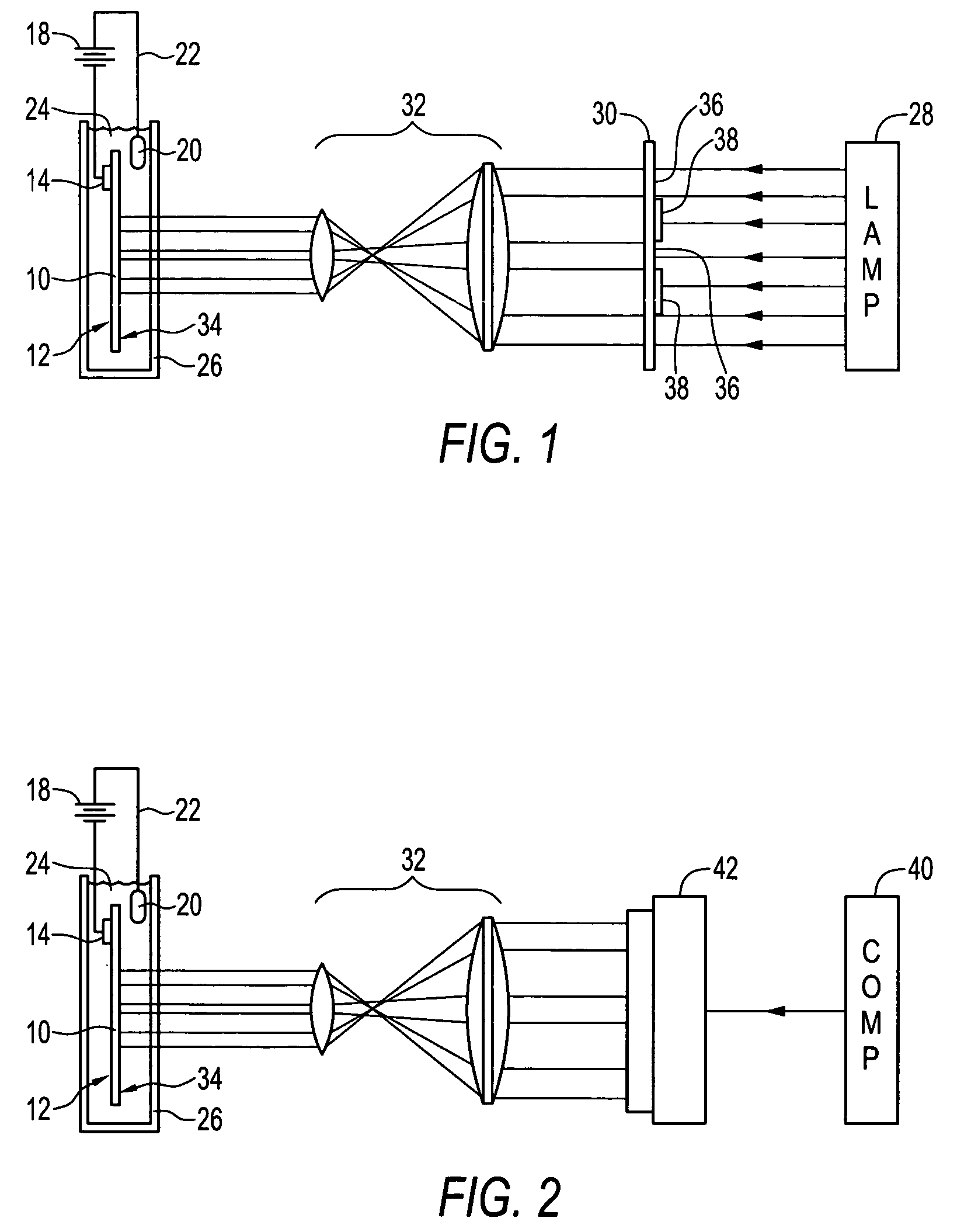
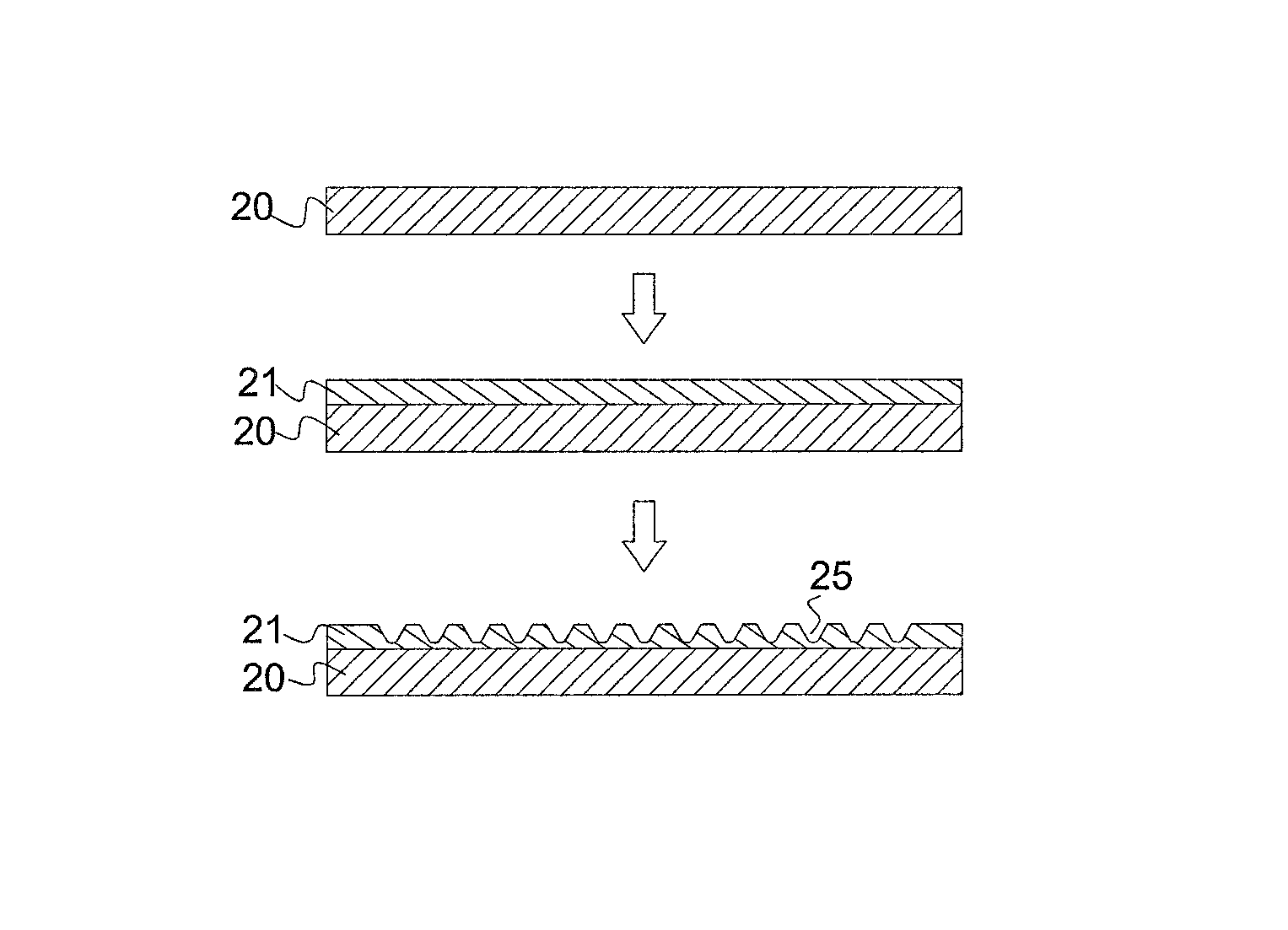
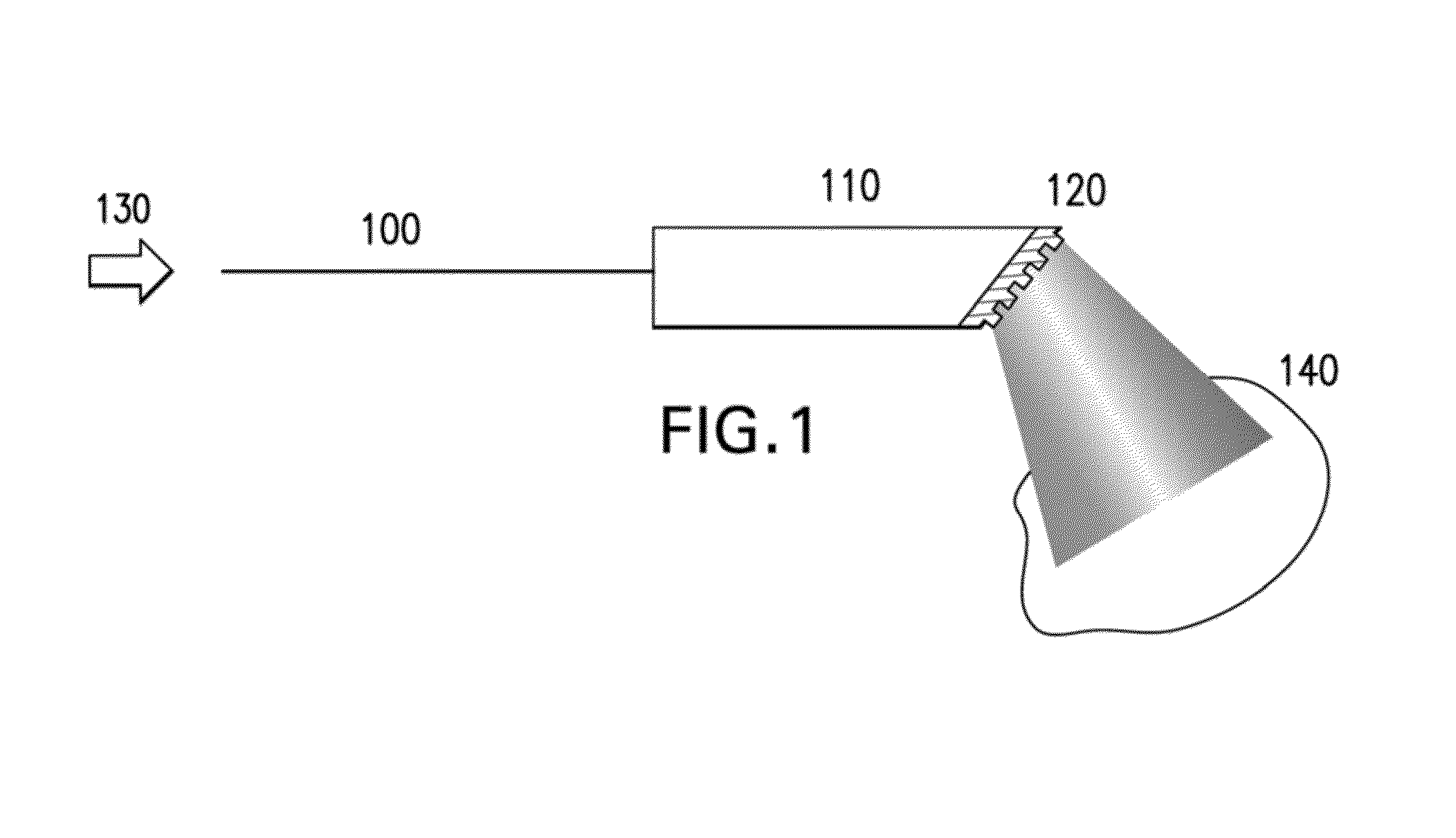
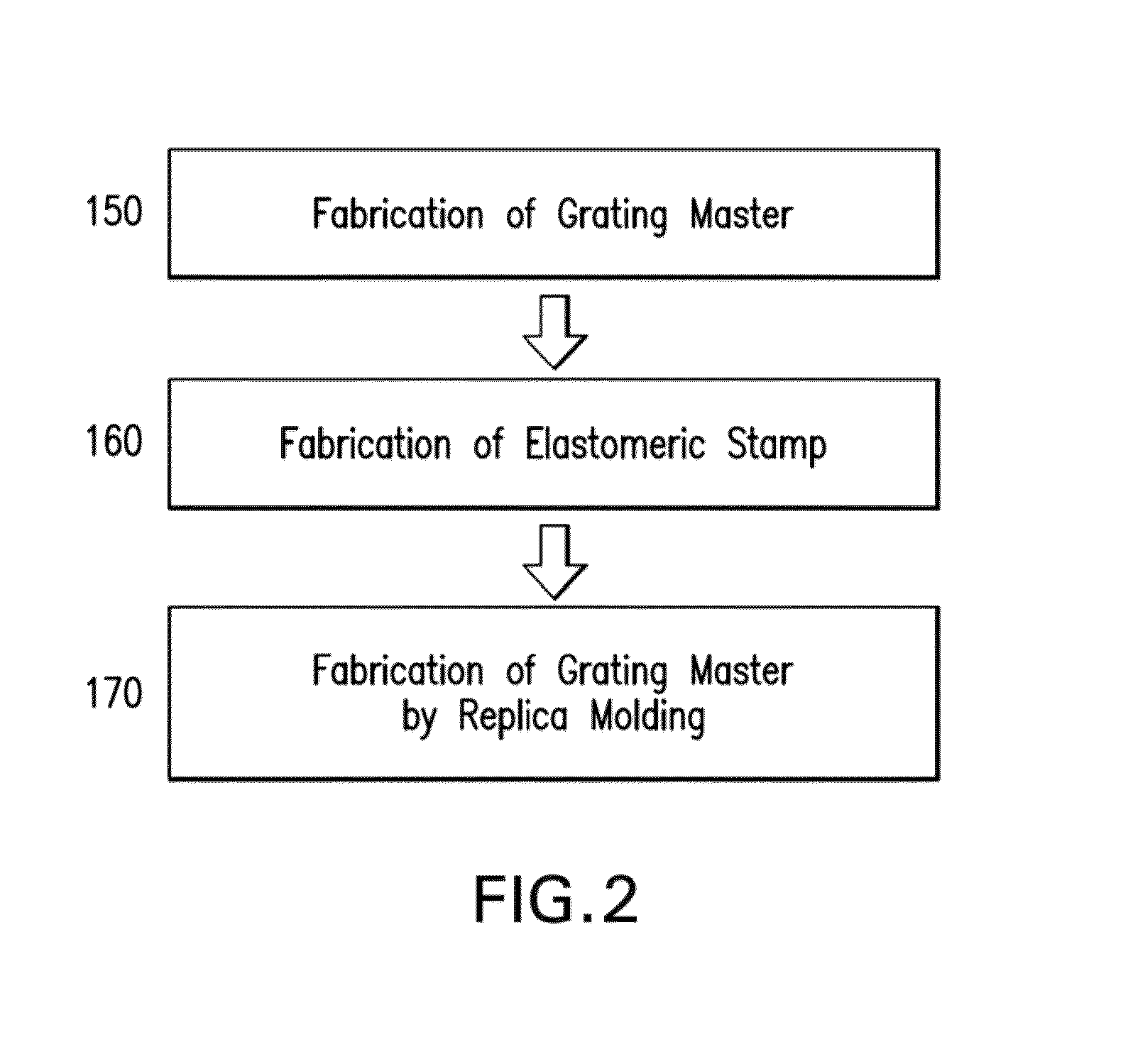
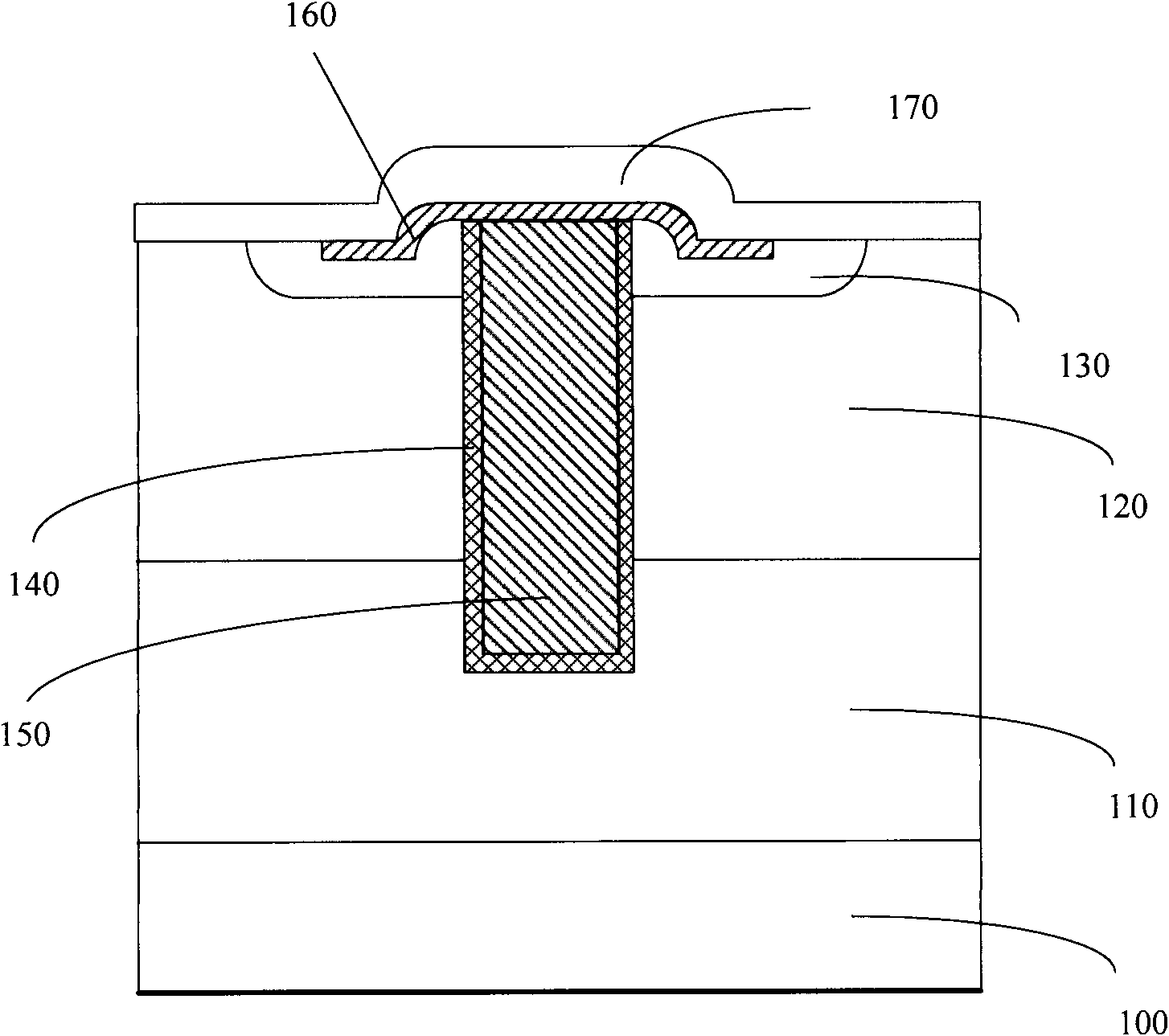
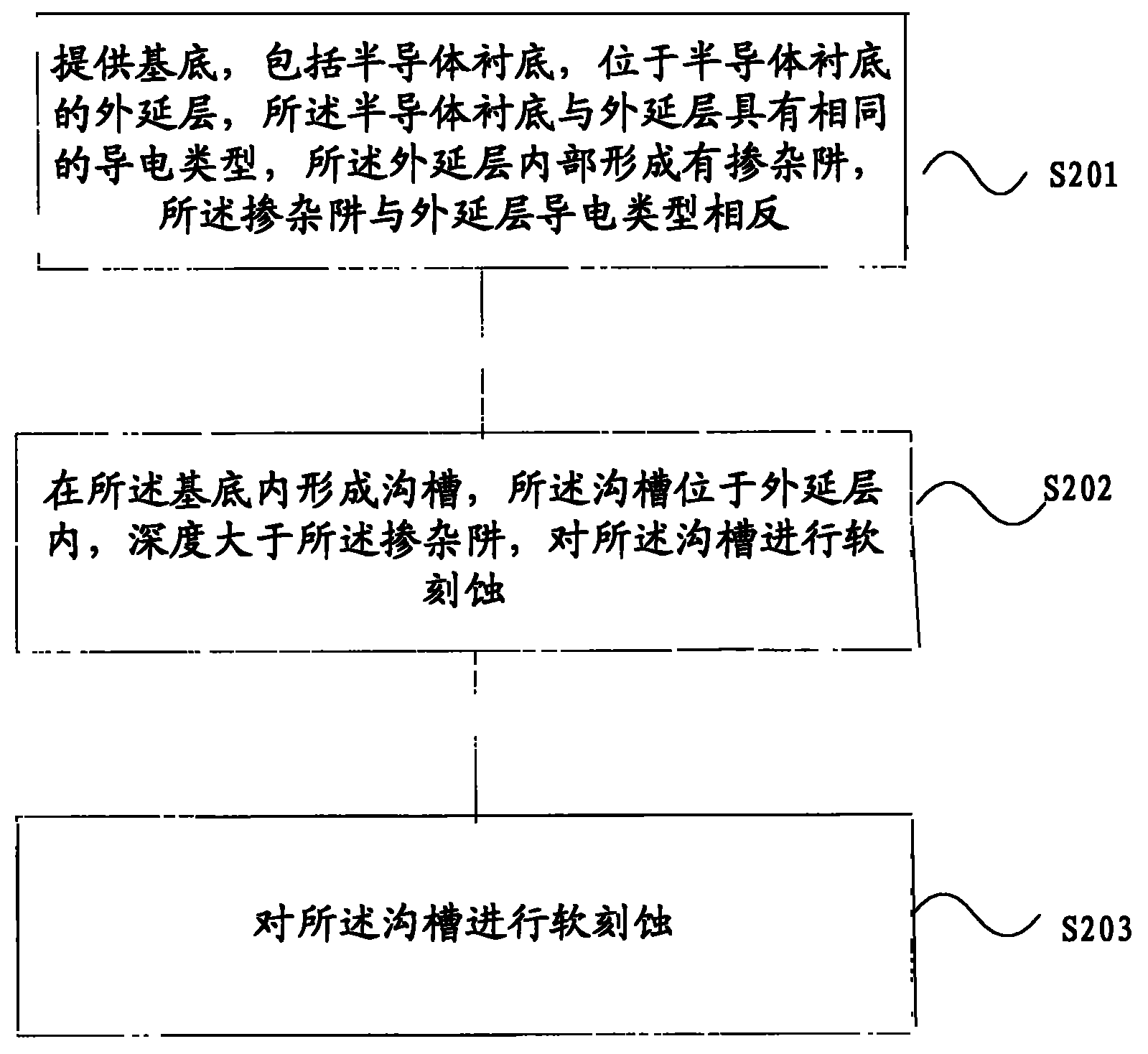
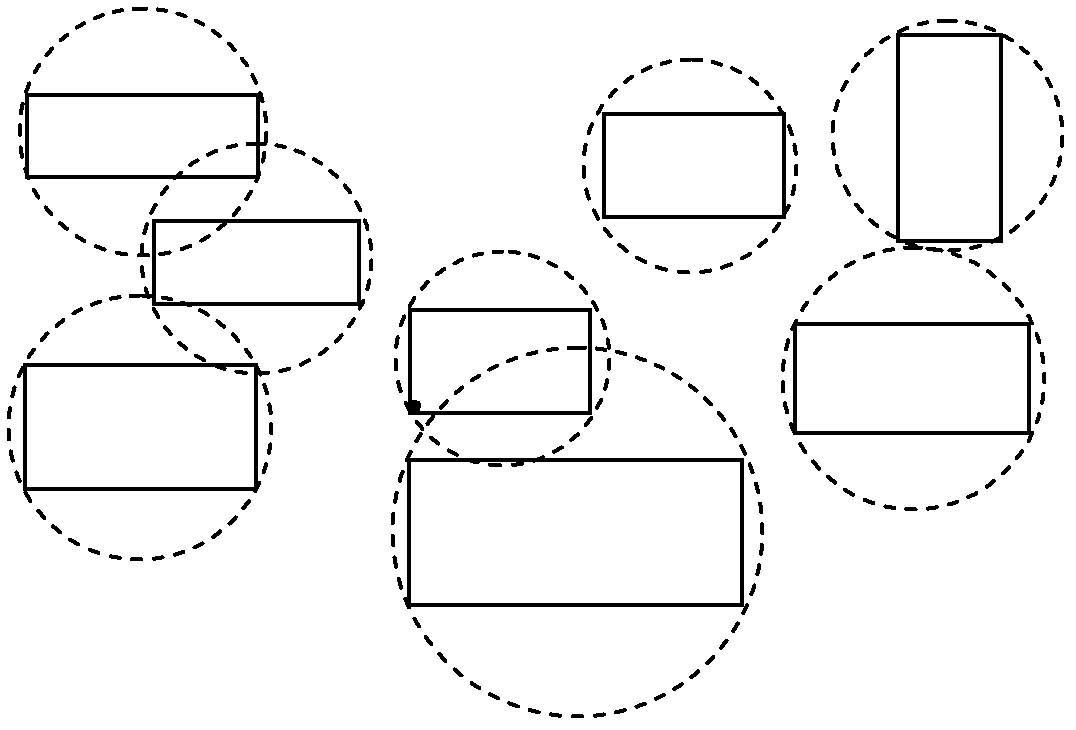Patents
Literature
162 results about "Soft lithography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In technology, soft lithography is a family of techniques for fabricating or replicating structures using "elastomeric stamps, molds, and conformable photomasks". It is called "soft" because it uses elastomeric materials, most notably PDMS.
Composite patterning devices for soft lithography
ActiveUS7195733B2Improve fidelityIncrease resistanceMaterial nanotechnologyNanoinformaticsNano sizeYoung's modulus
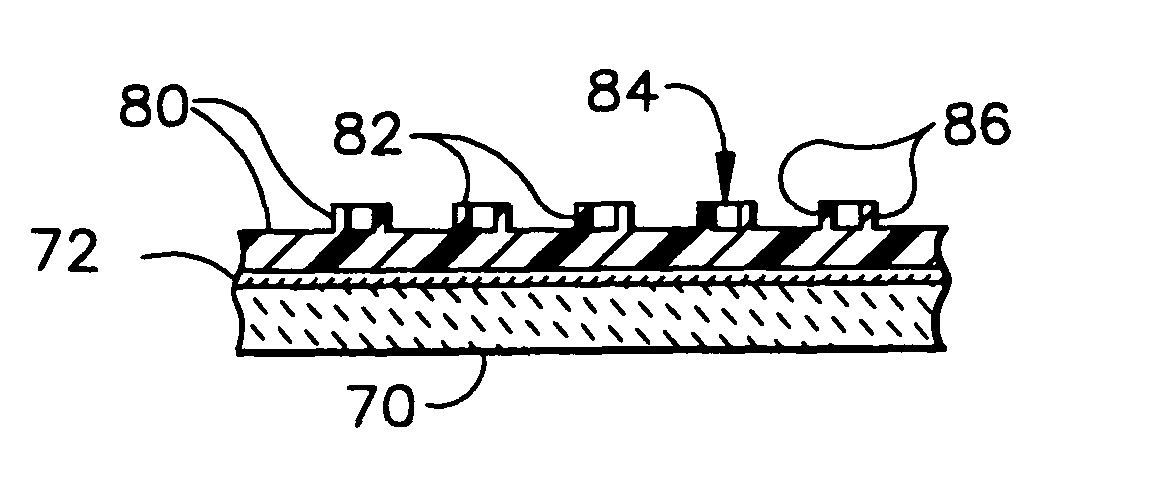
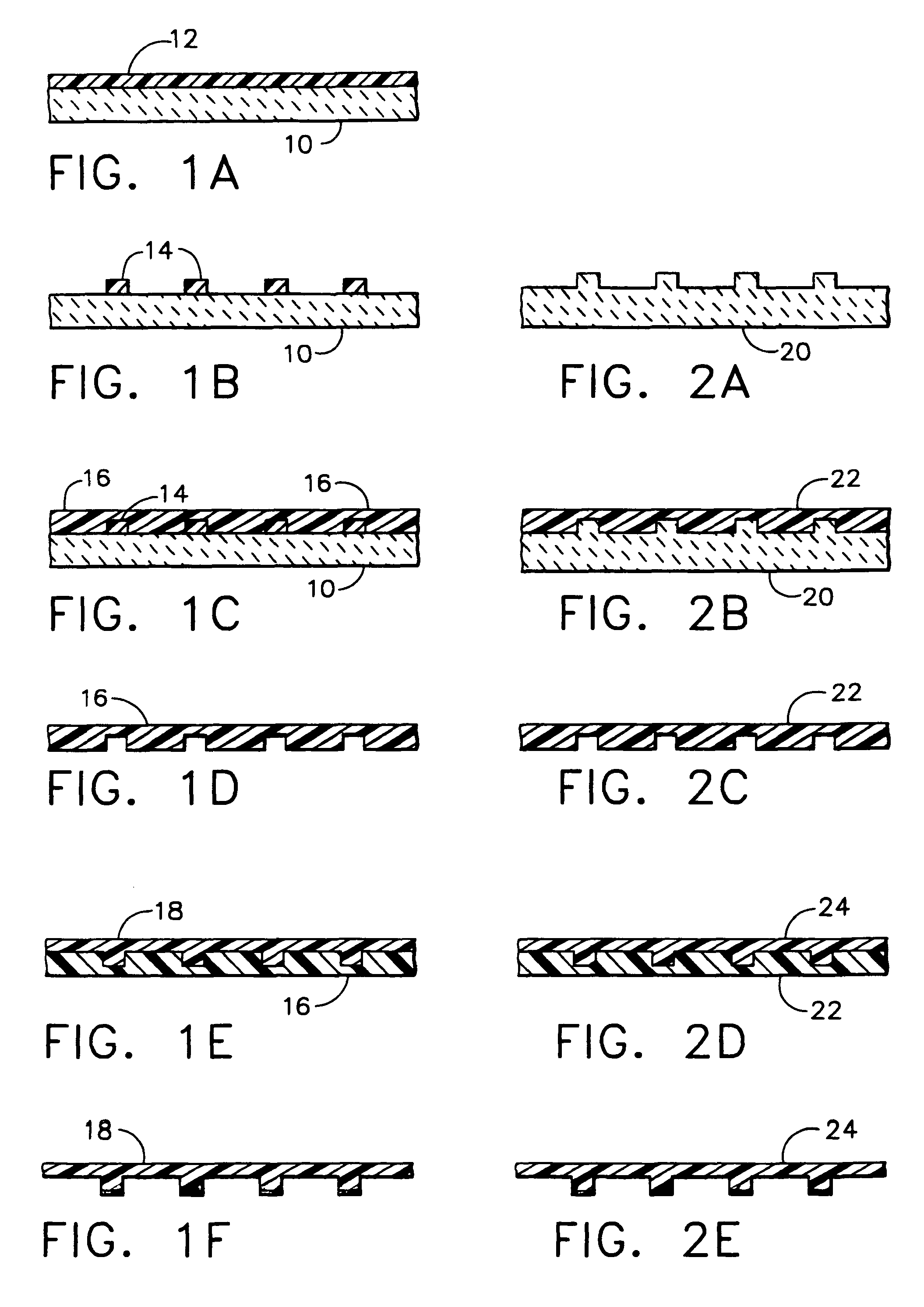
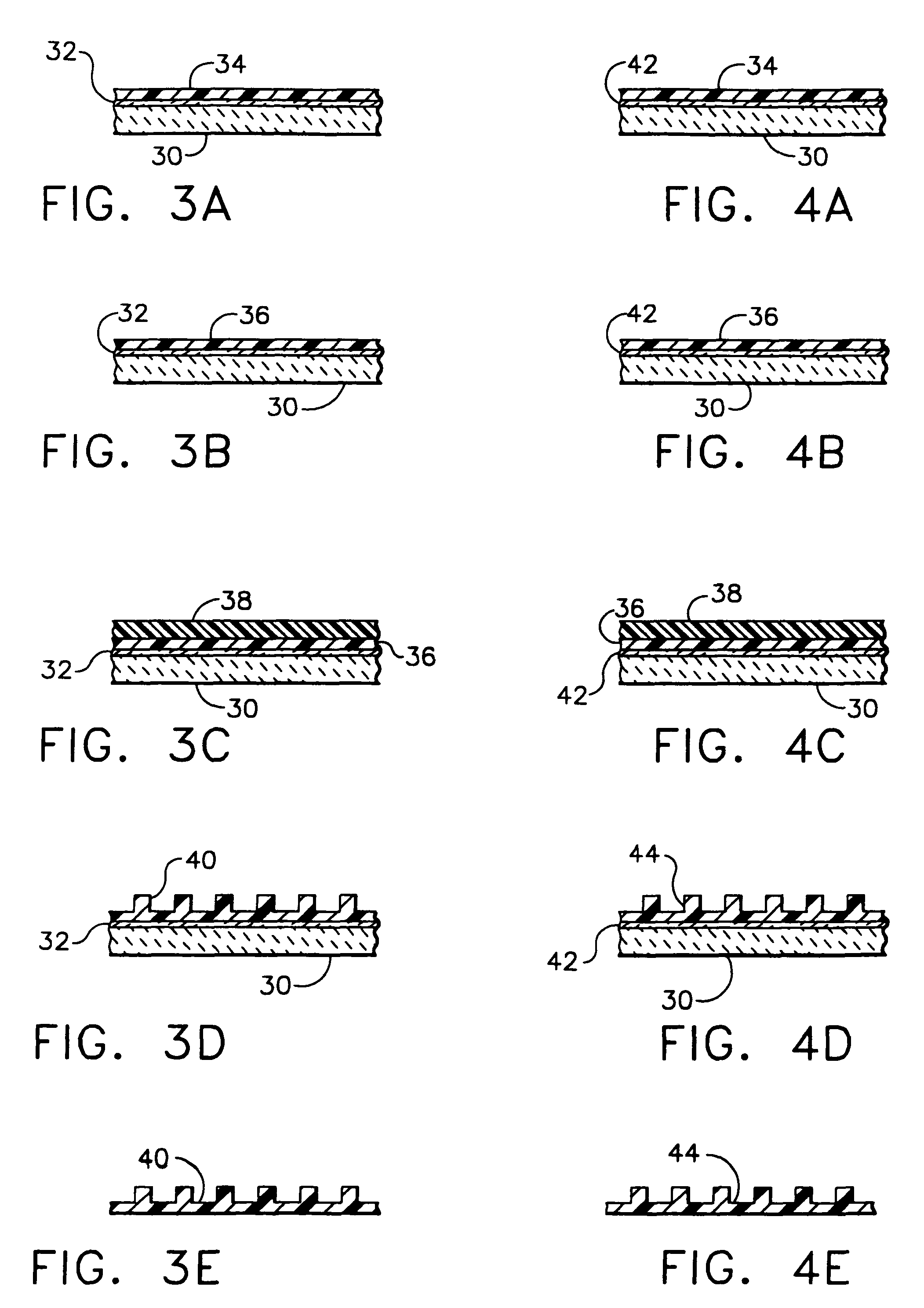
The present invention provides methods, devices and device components for fabricating patterns on substrate surfaces, particularly patterns comprising structures having microsized and / or nanosized features of selected lengths in one, two or three dimensions. The present invention provides composite patterning devices comprising a plurality of polymer layers each having selected mechanical properties, such as Young's Modulus and flexural rigidity, selected physical dimensions, such as thickness, surface area and relief pattern dimensions, and selected thermal properties, such as coefficients of thermal expansion, to provide high resolution patterning on a variety of substrate surfaces and surface morphologies.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Composite patterning devices for soft lithography
ActiveUS20050238967A1High resolutionImprove placement accuracyMaterial nanotechnologyNanoinformaticsEngineeringThermal expansion
The present invention provides methods, devices and device components for fabricating patterns on substrate surfaces, particularly patterns comprising structures having microsized and / or nanosized features of selected lengths in one, two or three dimensions. The present invention provides composite patterning devices comprising a plurality of polymer layers each having selected mechanical properties, such as Young's Modulus and flexural rigidity, selected physical dimensions, such as thickness, surface area and relief pattern dimensions, and selected thermal properties, such as coefficients of thermal expansion, to provide high resolution patterning on a variety of substrate surfaces and surface morphologies.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Thermotherapy device
InactiveUS7549987B2Prevent drynessControlled lateral marginsSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments using microwavesThermal energyNeurosurgery
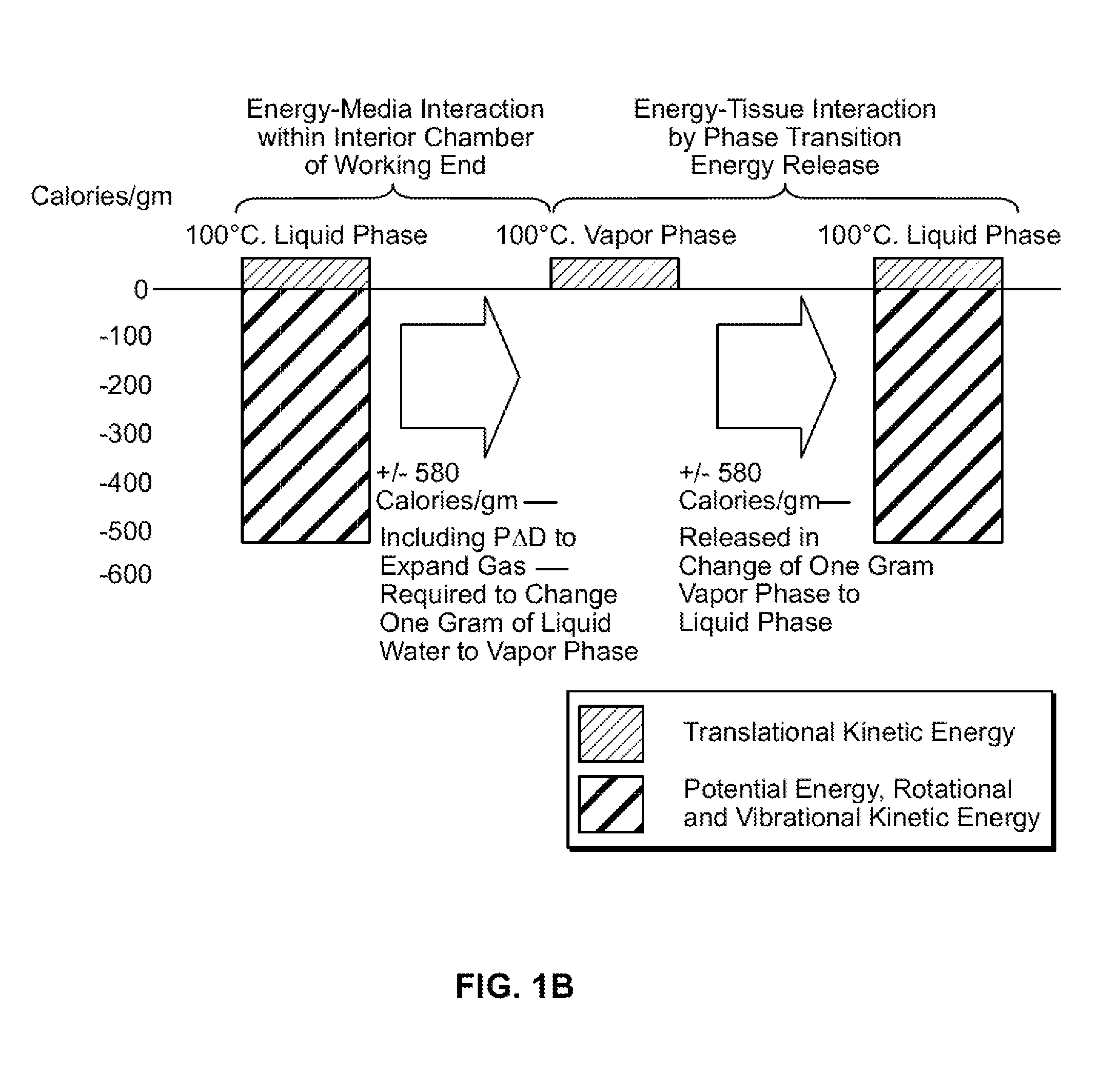
This invention relates to the working end of a medical instrument that applies energy to tissue. In one embodiment, the instrument has a microfluidic tissue-engaging surface fabricated by soft lithography means together with optional superlattice cooling means that allows for very precise control of energy application, for example in neurosurgery applications. The tissue-engaging surface can eject a high-heat content vapor into the engaged tissue for treating tissue, while the superlattice cooling structure can prevent collateral thermal damage. Also, the superlattice cooling structure can be used to localize heat at a selected depth in tissue and prevent surface ablation. Also, the superlattice cooling structure can be used to prevent tissue sticking to a thermal energy delivery surface. In another embodiment, the tissue-engaging surface can be used in a jaw structure for sealing tissue together with hydrojet means for transecting the tissue.
Owner:TSUNAMI MEDTECH
Microfabricated rubber microscope using soft solid immersion lenses
Soft lithography with surface tension control is used to microfabricate extremely efficient solid immersion lenses (SILs) out of rubber elastomeric material for use in microscope type applications. In order to counteract the surface tension of the mold material in a negative mold that causes creep on a positive mold, material such as RTV is partially cured before use in order to allow the reticulation of polymer chains to change the viscosity of the uncured material in a controllable manner. In a specific embodiment, the techniques of soft lithography with surface tension control are used to make molded SILs out of the elastomer polydimethylsiloxane. The lenses achieve an NA in the range of 1.25. The principle of compound lens design is used to make the first compound solid immersion lens, which is corrected for higher light gathering ability and has a calculated NA=1.32. An important application of these lenses is integrated optics for microfluidic devices, specifically in a handheld rubber microscope for microfluidic flow cytometry.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Build-up structures with multi-angle vias for chip to chip interconnects and optical bussing
InactiveUS6919508B2Improve performanceIncrease speedTelevision system detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesAnisotropic conductive filmCopper interconnect
A build-up structure for chip to chip interconnects and System-In-Package utilizing multi-angle vias for electrical and optical routing or bussing of electronic information and controlled CTE dielectrics including mesocomposites to achieve optimum electrical and optical performance of monolithic structures. Die, multiple die, Microelectromechanical Machines (MEMs) and / or other active or passive components such as transducers or capacitors can be accurately positioned on a substrate such as a copper heatsink and multi-angle stud bumps can be placed on the active sites of the components. A first dielectric layer is preferably placed on the components, thereby embedding the components in the structure. Through various processes of photolithography, laser machining, soft lithography or anisotropic conductive film bonding, escape routing and circuitry is formed on the first metal layer. Additional dielectric layers and metal circuitry are formed utilizing multi-angle vias to form escape routing from tight pitch bond pads on the die to other active and passive components. Multi-angle vias can carry electrical or optical information in the form of digital or analog electromagnetic current, or in the form of visible or non-visible optical bussing and interconnections.
Owner:CAPITALSOURCE FINANCE
Build-up structures with multi-angle vias for chip to chip interconnects and optical bussing
InactiveUS20050087356A1Enhanced signalReduce in quantityTelevision system detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesAnisotropic conductive filmEngineering
A build-up structure for chip to chip interconnects and System-In-Package utilizing multi-angle vias for electrical and optical routing or bussing of electronic information and controlled CTE dielectrics including mesocomposites to achieve optimum electrical and optical performance of monolithic structures. Die, multiple die, Microelectromechanical Machines (MEMs) and / or other active or passive components such as transducers or capacitors can be accurately positioned on a substrate such as a copper heatsink and multi-angle stud bumps can be placed on the active sites of the components. A first dielectric layer is preferably placed on the components, thereby embedding the components in the structure. Through various processes of photolithography, laser machining, soft lithography or anisotropic conductive film bonding, escape routing and circuitry is formed on the first metal layer. Additional dielectric layers and metal circuitry are formed utilizing multi-angle vias to form escape routing from tight pitch bond pads on the die to other active and passive components. Multi-angle vias can carry electrical or optical information in the form of digital or analog electromagnetic current, or in the form of visible or non-visible optical bussing and interconnections.
Owner:CAPITALSOURCE FINANCE
Direct patterning of silicon by photoelectrochemical etching
ActiveUS20050009374A1High resolutionComplex detailDecorative surface effectsAnalogue computers for chemical processesPhotoelectrochemical etchingSoft lithography
The invention is directed to methods for direct patterning of silicon. The invention provides the ability to fabricate complex surfaces in silicon with three dimensional features of high resolution and complex detail. The invention is suitable, for example, for use in soft lithography as embodiments of the invention can quickly create a master for use in soft lithography. In an embodiment of the invention, electrochemical etching of silicon, such as a silicon wafer, for example, is conducted while at least a portion of the silicon surface is exposed to an optical pattern. The etching creates porous silicon in the substrate, and removal of the porous silicon layer leaves a three-dimensional structure correlating to the optical pattern.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Build-up structures with multi-angle vias for chip to chip interconnects and optical bussing
InactiveUS20050269687A1Improve performanceIncrease speedTelevision system detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesAnisotropic conductive filmEngineering
A build-up structure for chip to chip interconnects and System-In-Package utilizing multi-angle vias for electrical and optical routing or bussing of electronic information and controlled CTE dielectrics including mesocomposites to achieve optimum electrical and optical performance of monolithic structures. Die, multiple die, Microelectromechanical Machines (MEMs) and / or other active or passive components such as transducers or capacitors can be accurately positioned on a substrate such as a copper heatsink and multi-angle stud bumps can be placed on the active sites of the components. A first dielectric layer is preferably placed on the components, thereby embedding the components in the structure. Through various processes of photolithography, laser machining, soft lithography or anisotropic conductive film bonding, escape routing and circuitry is formed on the first metal layer. Additional dielectric layers and metal circuitry are formed utilizing multi-angle vias to form escape routing from tight pitch bond pads on the die to other active and passive components. Multi-angle vias can carry electrical or optical information in the form of digital or analog electromagnetic current, or in the form of visible or non-visible optical bussing and interconnections.
Owner:CAPITALSOURCE FINANCE
Hydroxy-amino thermally cured undercoat for 193 NM lithography
InactiveUS6323287B1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPlate printingCross-linkSoft lithography
The present invention is directed to a thermally curable polymer composition, and a photolithographic substrate coated therewith, the composition comprising a hydroxyl-containing polymer, an amino cross-linking agent and a thermal acid generator. The thermally curable polymer composition may be dissolved in a solvent and used as an undercoat layer in deep UV lithography.
Owner:ARCH CHEM INC
Microfluidic Biofuel Cell
InactiveUS20070287034A1Great current densityIncrease current densityElectrolysis componentsActive material electrodesChemical physicsFuel cells
Microfluidic biofuel cells comprising a bioanode and / or a biocathode are formed using microfluidic principles and soft lithography. The enzymes utilized in the redox reactions at the bioanode and / or the biocathode are stabilized in a micellar or inverted micellar structure. The biofuel cell is used to produce high power densities.
Owner:SAINT LOUIS UNIVERSITY
Method of manufacturing microneedle structures using photolithography
ActiveUS7763203B2Fast preparationUse directlyFixed microstructural devicesVolume/mass flow measurementSoft lithographyMicrofabrication
Owner:CORIUM PHARMA SOLUTIONS INC
Preparation of micro-nano lens array
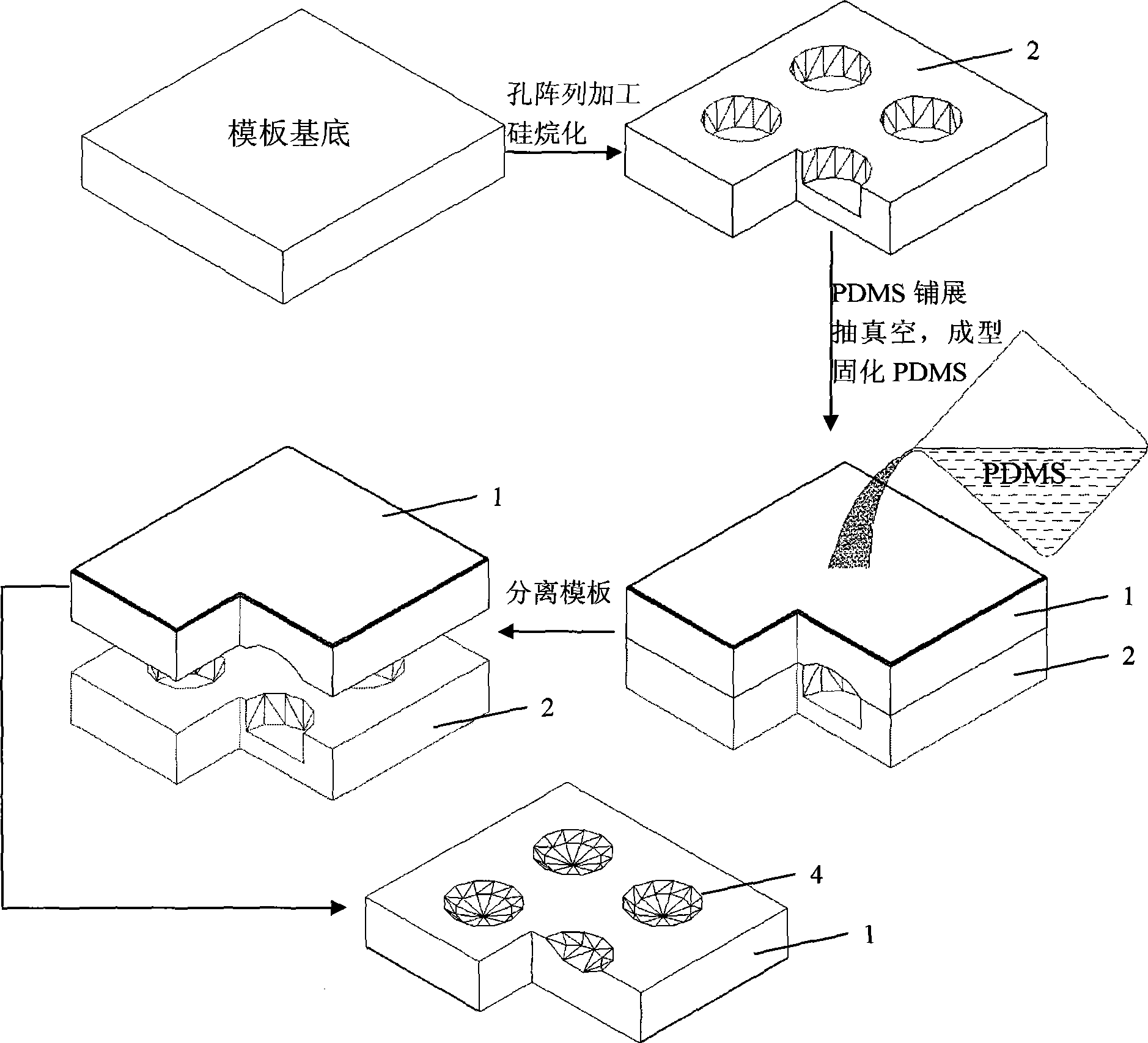
InactiveCN101481079ALower manufacturing requirementsQuality improvementNanostructure manufactureDecorative surface effectsMicro nanoSoft lithography
The invention relates to a micronano device preparing technique which relates to the technical field of soft lithography, in particular to a technical method and a technique process for preparing a micronano lens array by adopting the soft lithography technique. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, preparing the micronano hole array by a conventional method on a template; secondly, performing silanization process to the prepared template; thirdly, adding the molding material PDMS on the surface of the template, placing the template coated with the PDMS inside a vacuum drying box so as to mold the PDMS fluid; solidifying the PDMS; and finally, separating the template from the PDMS and obtaining a PDMS membrane provided with the micro lens array. The method relieves the contradiction between the lens quality and the Millipore, easily controls the lens focus and has simple preparation technique and low requirement on the equipment.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Microfabricated rubber microscope using soft solid immersion lenses
Soft lithography with surface tension control is used to microfabricate extremely efficient solid immersion lenses (SILs) out of rubber elastomeric material for use in microscope type applications. In order to counteract the surface tension of the mold material in a negative mold that causes creep on a positive mold, material such as RTV is partially cured before use in order to allow the reticulation of polymer chains to change the viscosity of the uncured material in a controllable manner. In a specific embodiment, the techniques of soft lithography with surface tension control are used to make molded SILs out of the elastomer polydimethylsiloxane. The lenses achieve an NA in the range of 1.25. The principle of compound lens design is used to make the first compound solid immersion lens, which is corrected for higher light gathering ability and has a calculated NA=1.32. An important application of these lenses is integrated optics for microfluidic devices, specifically in a handheld rubber microscope for microfluidic flow cytometry.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Method for preparing graphene gas sensors in batches based on nano soft lithography
InactiveCN102680527AImprove performanceRegular shapeMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSoft lithographyCvd graphene
The invention provides a method for preparing graphene gas sensors in batches based on nano soft lithography, belonging to the field of preparation of graphene sensors. In order to solve the problems in the existing graphene sensor preparation technology that the graphene shapes and sizes are difficult to control, and the prepared graphene sensors have inconsistent performances, thus being not beneficial to micro / nano graphene sensor integration, the method comprises the following steps: 1. preparation of a graphene film; 2. preparation of graphenes (including graphenes prepared by a reduction-oxidation method and a CVD (chemical vapor deposition) method) in regular shapes; 3. modification of graphenes; and 4. preparation of the graphene gas sensors in batches. The method is mainly used for preparing the graphene gas sensors in batches. The method has the following advantages: the advantages of nano soft lithography and the two-dimensional material graphene are given full play to; and the prepared strip graphene sensors have the same properties, laying a foundation for wide application and industrialization of the graphene sensors.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
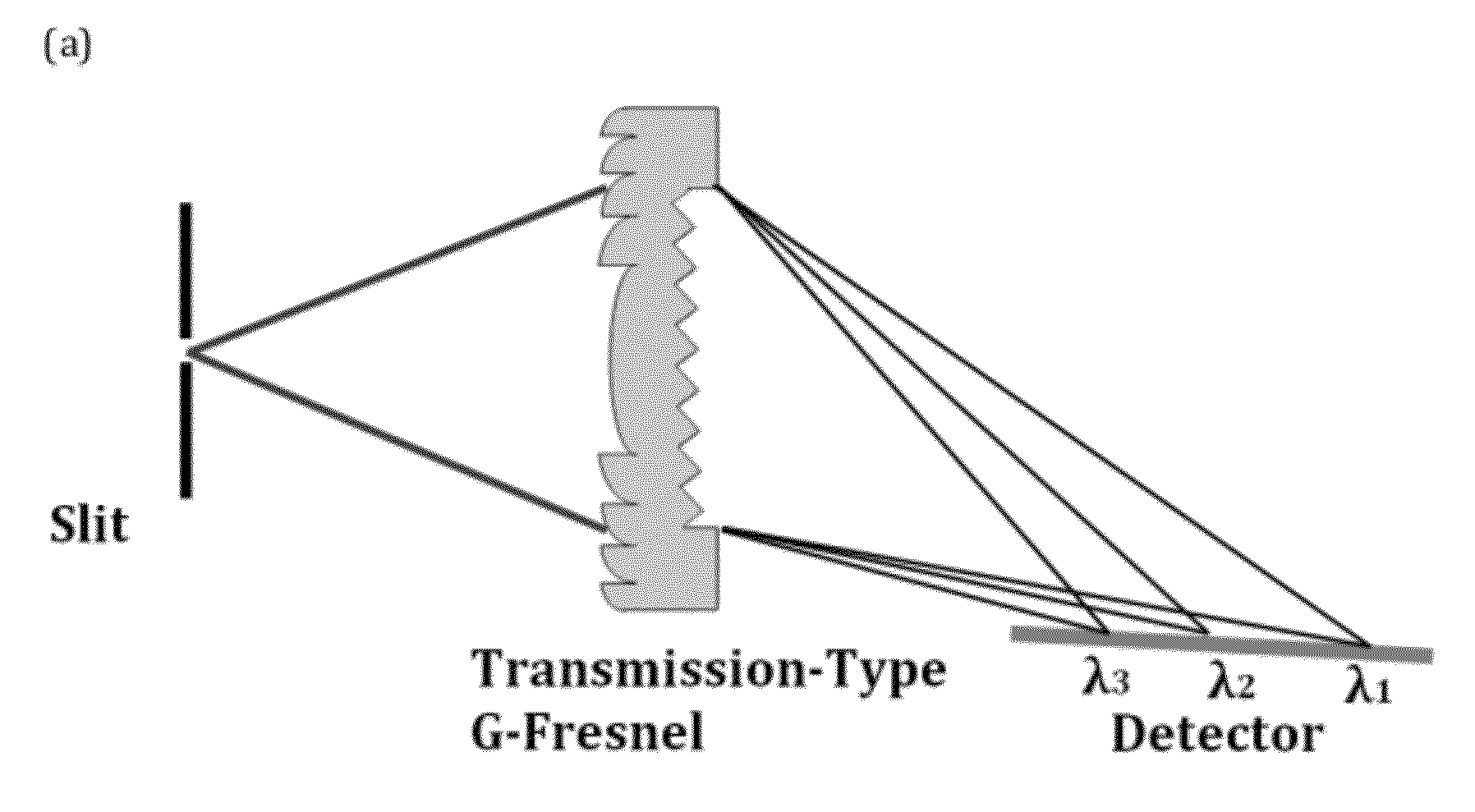
Compact Spectrometer Including a Diffractive Optical Element with Dual Dispersion and Focusing Functionality
ActiveUS20120038918A1Low cost mass productionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationSoft lithographyMillimeter
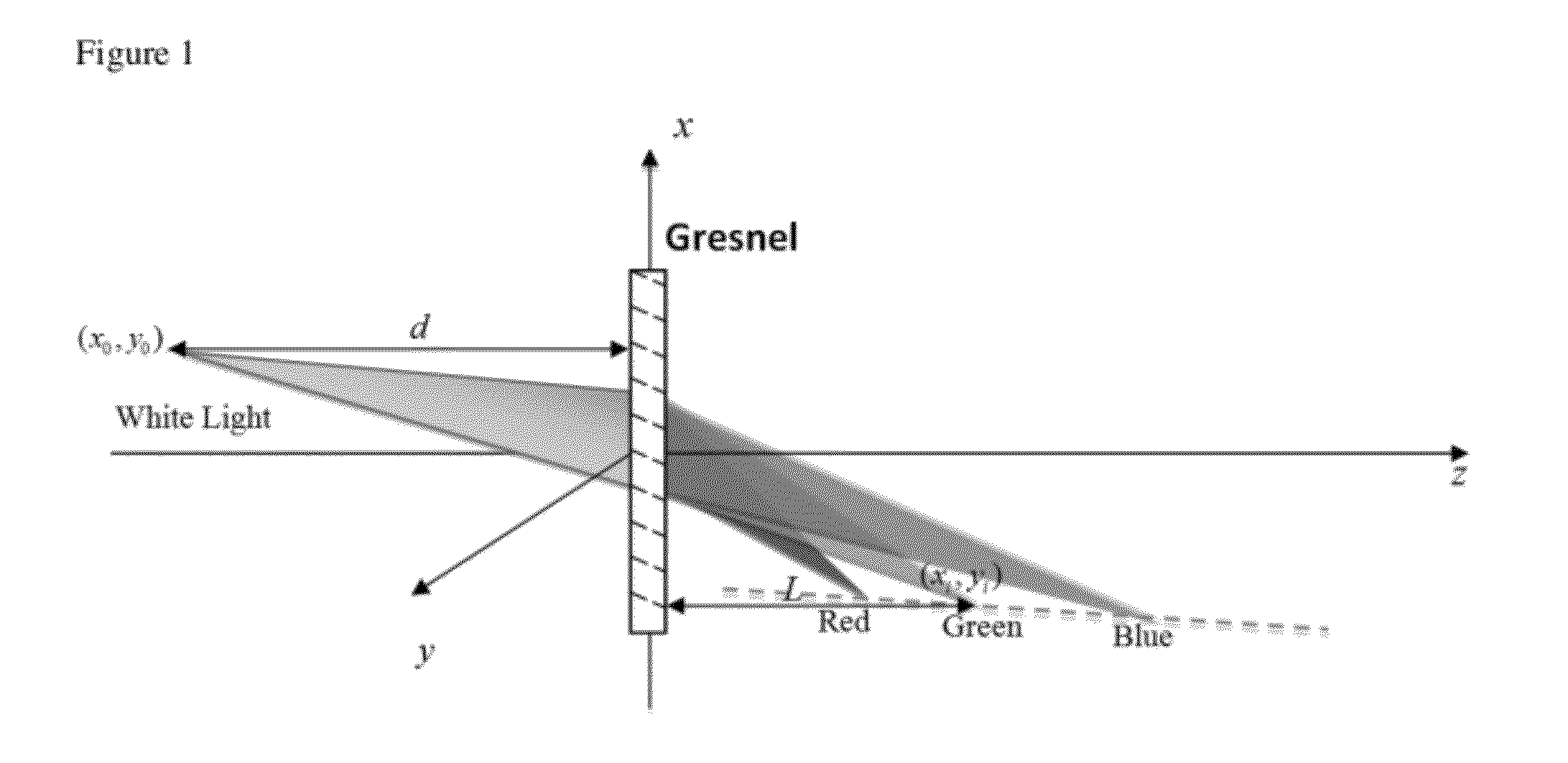
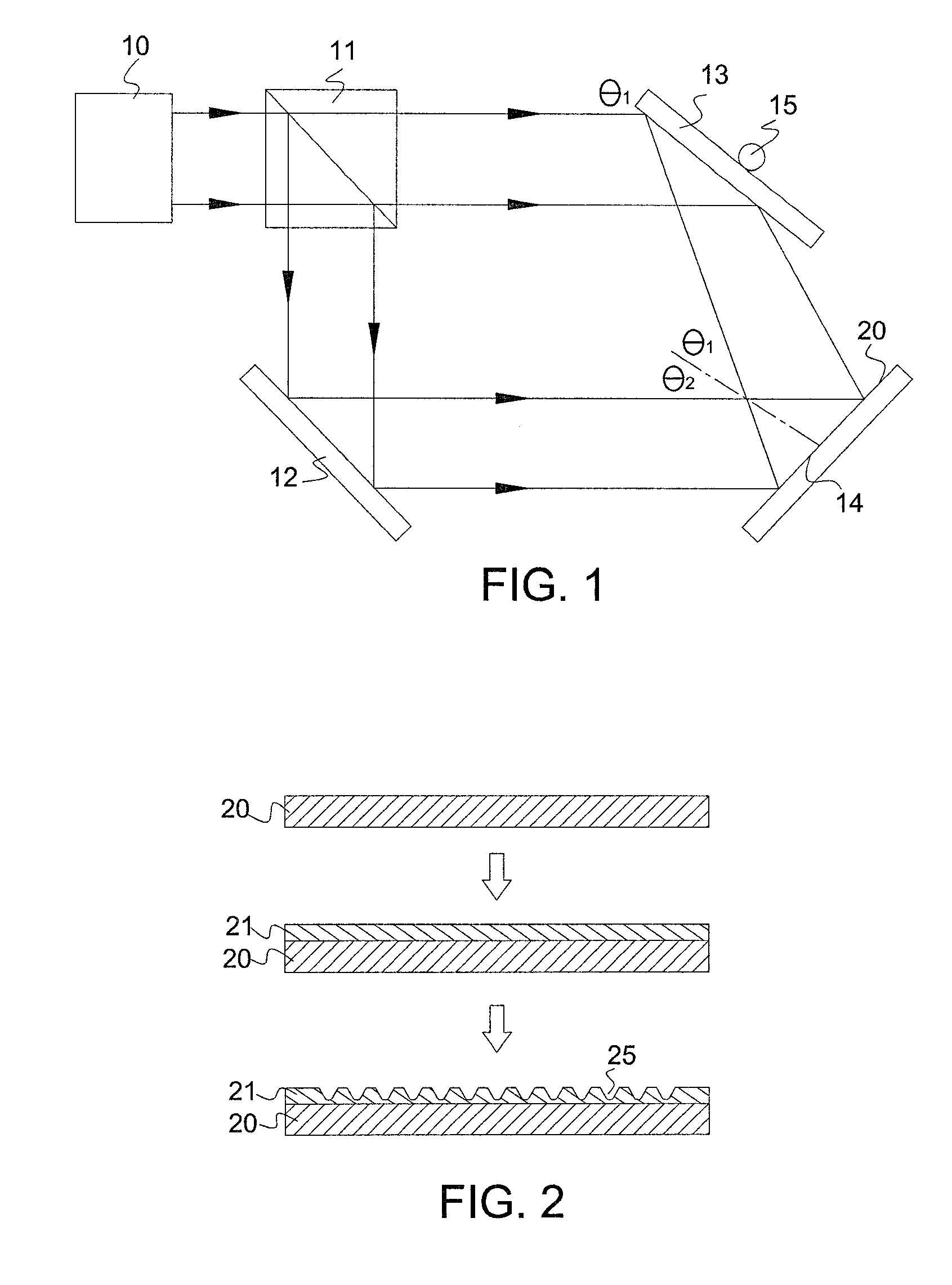
Embodiments of the invention provide a device called a “G-Fresnel” device that performs the functions of both a linear grating and a Fresnel lens. We have fabricated the G-Fresnel device by using PDMS based soft lithography. Three-dimensional surface profilometry has been performed to examine the device quality. We have also conducted optical characterizations to confirm its dual focusing and dispersing properties. The G-Fresnel device can be useful for the development of miniature optical spectrometers as well as emerging optofluidic applications. Embodiments of compact spectrometers using diffractive optical elements are also provided. Theoretical simulation shows that a spectral resolution of approximately 1 nm can be potentially achieved with a millimeter-sized G-Fresnel. A proof-of-concept G-Fresnel-based spectrometer with subnanometer spectral resolution is experimentally demonstrated.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
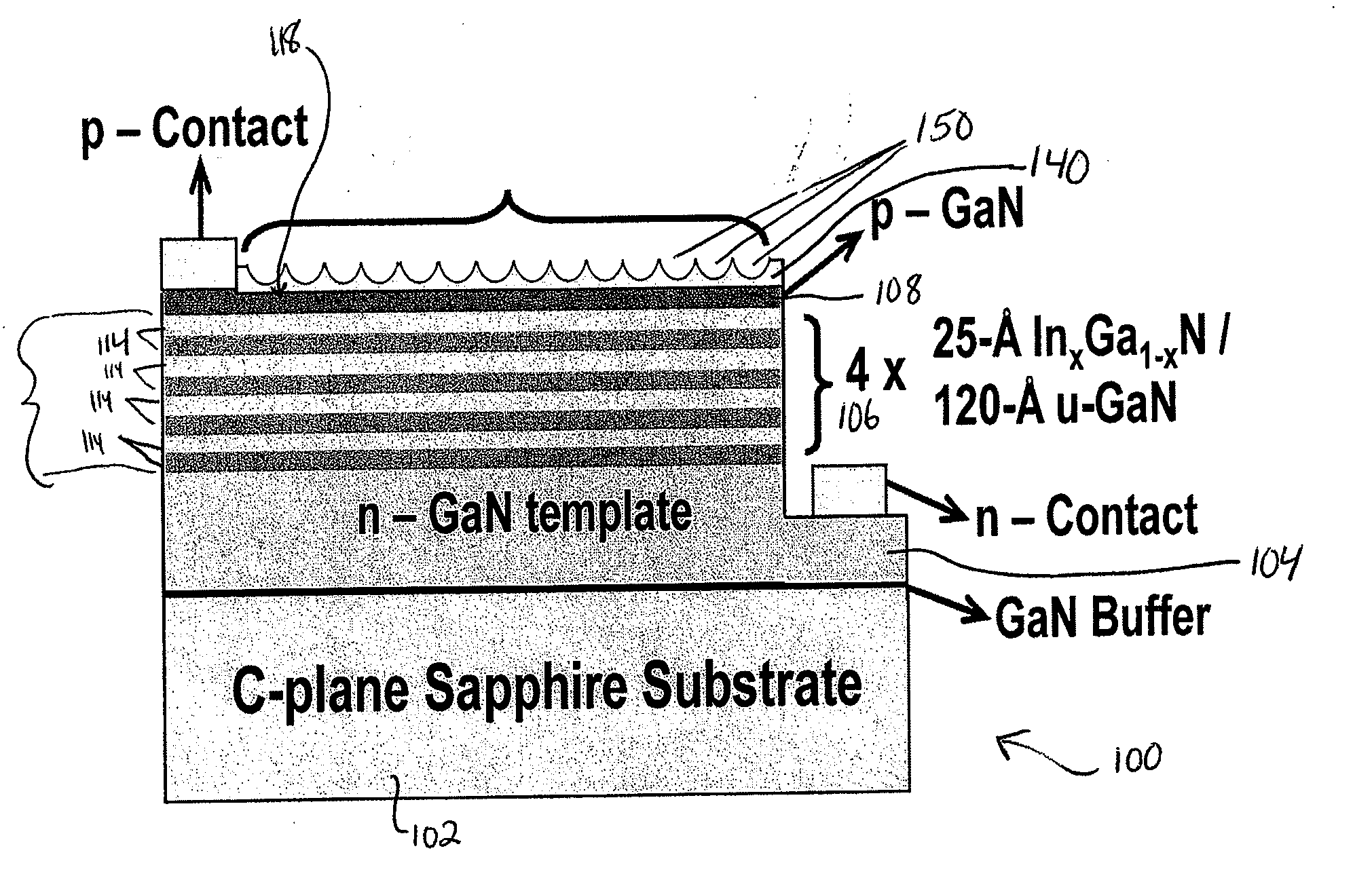
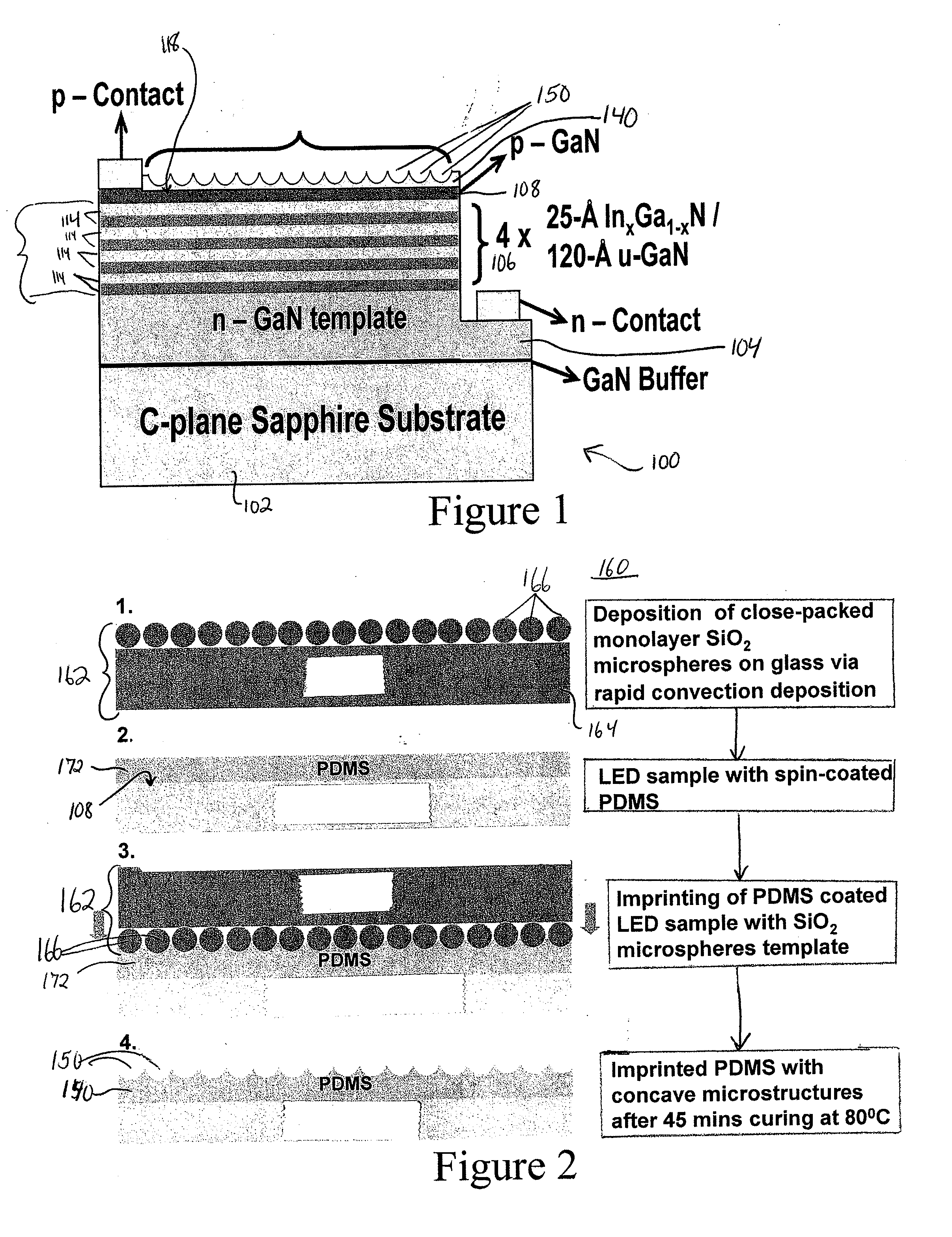
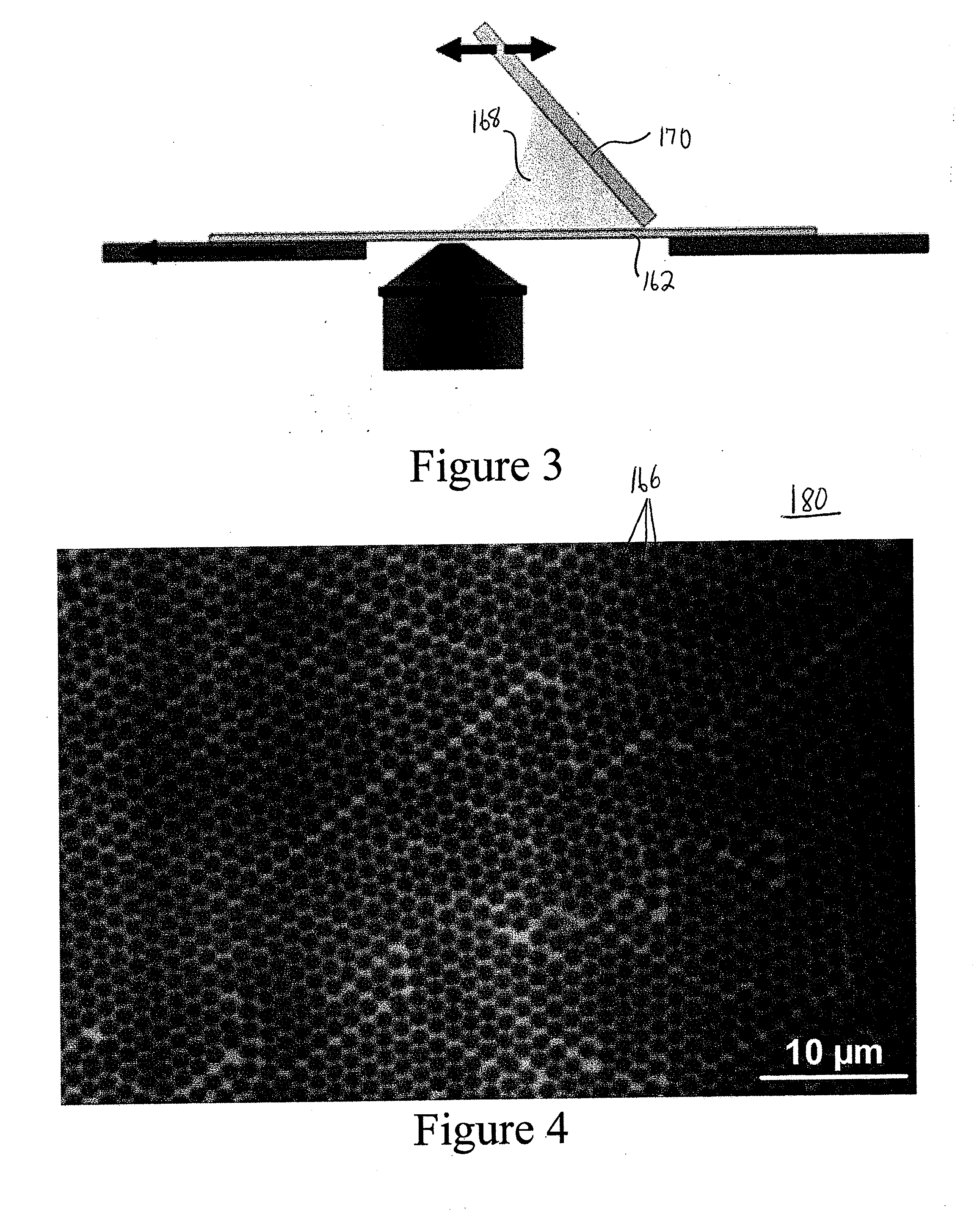
Semiconductor light-emitting devices having concave microstructures providing improved light extraction efficiency and method for producing same
ActiveUS20110155999A1Light extraction efficiency can be improvedIncrease light escape coneSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMicrosphereQuantum well
A conventional semiconductor LED is modified to include a microlenslayer over its light-emitting surface. The LED may have an active layer including at least one quantum well layer of InGaN and GaN. The microlens layer includes a plurality of concave microstructures that cause light rays emanating from the LED to diffuse outwardly, leading to an increase in the light extraction efficiency of the LED. The concave microstructures may be arranged in a substantially uniform array, such as a close-packed hexagonal array. The microlens layer is preferably constructed of curable material, such as polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), and is formed by soft-lithography imprinting by contacting fluid material of the microlens layer with a template bearing a monolayer of homogeneous microsphere crystals, to cause concave impressions, and then curing the material to fix the concave microstructures in the microlens layer and provide relatively uniform surface roughness.
Owner:LEHIGH UNIVERSITY
Method and device for detecting and separating HP (helicobacter pylori) ELISA (enzyme-linked immuno sorbent assay)
InactiveCN103278628AOvercoming Abundant MedicineOvercoming demandsFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceMagnetic bead
The invention discloses a method and a device for detecting and separating HP ELISA. According to the method, a prepared magnetic bead provided with HP, an enzyme-labeled antibody, an enzyme reaction substrate, a gastric juice sample and a cleaning fluid are placed in different liquid storage tanks on a micro-fluidic chip by the aid of an electric fluid force, and flow of liquids in the different liquid storage tanks is electrically controlled , so that ELISA is fully and automatically detected; and a detected fluorescence signal is taken as a trigger signal, so that an HP sample is fully and automatically separated. The device comprises a platform structure, the micro-fluidic chip and an electric cabinet, wherein the micro-fluidic chip comprises a glass sheet, a PDMS (polydimethylsiloxane) square plate and a driving electrode, a micro channel, a mixed channel and a detection area are formed in the surface of the PDMS square plate in a photoetching manner by the aid of a soft lithography technology, and the liquid storage tanks are arranged on the PDMS square plate. The device for detecting and separating the HP ELISA has the advantages as follows: the device is small in size, light in weight, convenient to carry and operate and low in construction cost and can be handheld for field detection, thereby facilitating popularization and application.
Owner:QIQIHAR MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Microfluidic biofuel cell
InactiveUS7709134B2Great current densityIncrease current densityElectrolysis componentsActive material electrodesFuel cellsChemical physics
Microfluidic biofuel cells comprising a bioanode and / or a biocathode are formed using microfluidic principles and soft lithography. The enzymes utilized in the redox reactions at the bioanode and / or the biocathode are stabilized in a micellar or inverted micellar structure. The biofuel cell is used to produce high power densities.
Owner:SAINT LOUIS UNIVERSITY
Direct patterning of silicon by photoelectrochemical etching
ActiveUS7433811B2High resolutionComplex detailDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotoelectrochemical etchingSoft lithography
The invention is directed to methods for direct patterning of silicon. The invention provides the ability to fabricate complex surfaces in silicon with three dimensional features of high resolution and complex detail. The invention is suitable, for example, for use in soft lithography as embodiments of the invention can quickly create a master for use in soft lithography. In an embodiment of the invention, electrochemical etching of silicon, such as a silicon wafer, for example, is conducted while at least a portion of the silicon surface is exposed to an optical pattern. The etching creates porous silicon in the substrate, and removal of the porous silicon layer leaves a three-dimensional structure correlating to the optical pattern.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Optical filters based on polymer asymmetric bragg couplers and its method of fabrication
InactiveUS8396341B2Avoid unwanted overlap of transmission spectrumEasy to controlOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingCoupling light guidesSoft lithographyWaveguide
The present invention discloses a method for fabricating an optical filter based on polymer asymmetric bragg couplers using holographic interference techniques, soft lithography, and micro molding, which comprises following steps: prepare a UV polymer with gratings; coating photo-resister film on the UV polymer, and exposed by UV light to obtain a photo-resister mold with two grooves each having gratings; coating diluted PDMS film on the photo-resister mold, and baking the PDMS film to obtain a PDMS mold having two waveguides with gratings; placing glass substrate over the PDMS mold to form a first tunnel; injecting a precure UV polymer into the first tunnel to from a cladding layer with two grooves having gratings pattern at its bottom; placing glass slide over the cladding layer and injecting a mixed UV polymer into the grooves to form waveguide cores; placing a second glass substrate over the cladding layer, and injecting UV polymer to form an upper cladding layer laminated with the cladding layer to obtain the optical filter based on polymer asymmetric bragg couplers.
Owner:CHINA UNIV SCI & TECH
Hydroxy-amino thermally cured undercoat for 193 nm lithography
InactiveUS20020007018A1Ornamental textile articlesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCross-linkSoft lithography
The present invention is directed to a thermally curable polymer composition, and a photolithographic substrate coated therewith, the composition comprising a hydroxyl-containing polymer, an amino cross-linking agent and a thermal acid generator. The thermally curable polymer composition may be dissolved in a solvent and used as an undercoat layer in deep UV lithography.
Owner:ARCH CHEM INC
Silicone rubber material for soft lithography
ActiveUS20110094403A1High incubation temperatureHigh incubation temperature is avoidedPlaten pressesDuplicating/marking methodsPolymer scienceLithography process
The present invention relates to a silicone rubber like material and a printing device including a stamp layer (100;201) comprising such a material. The material is suitable for use in soft lithography as it enables stable features having mensions in the nanometer range to be obtained on a substrate, and also allows for the accommodation onto rough and non-flat substrate surfaces. The invention also relates to methods for manufacturing the silicone rubber like material and stamp layer (100;201) and use thereof in lithographic processes.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Rapid intersection method for STL (stereo lithography) models of products
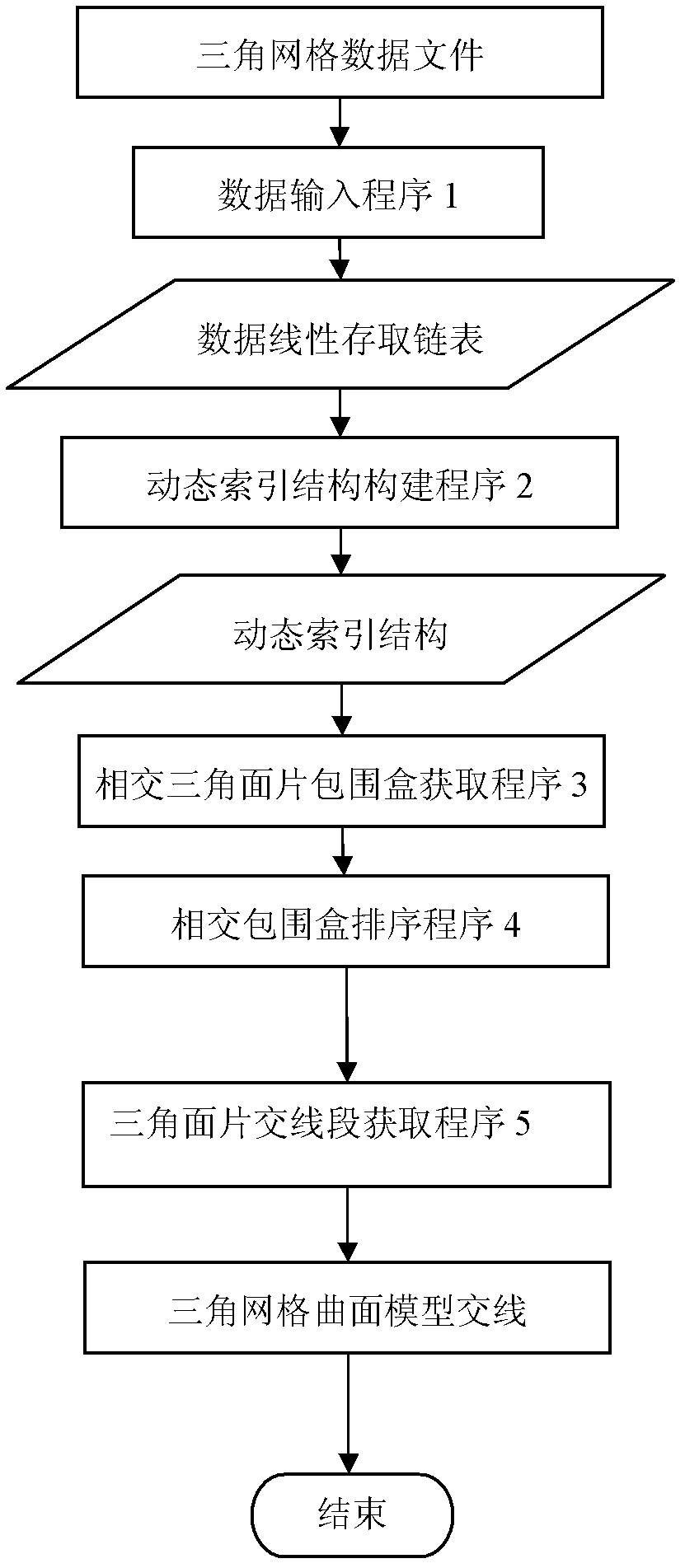
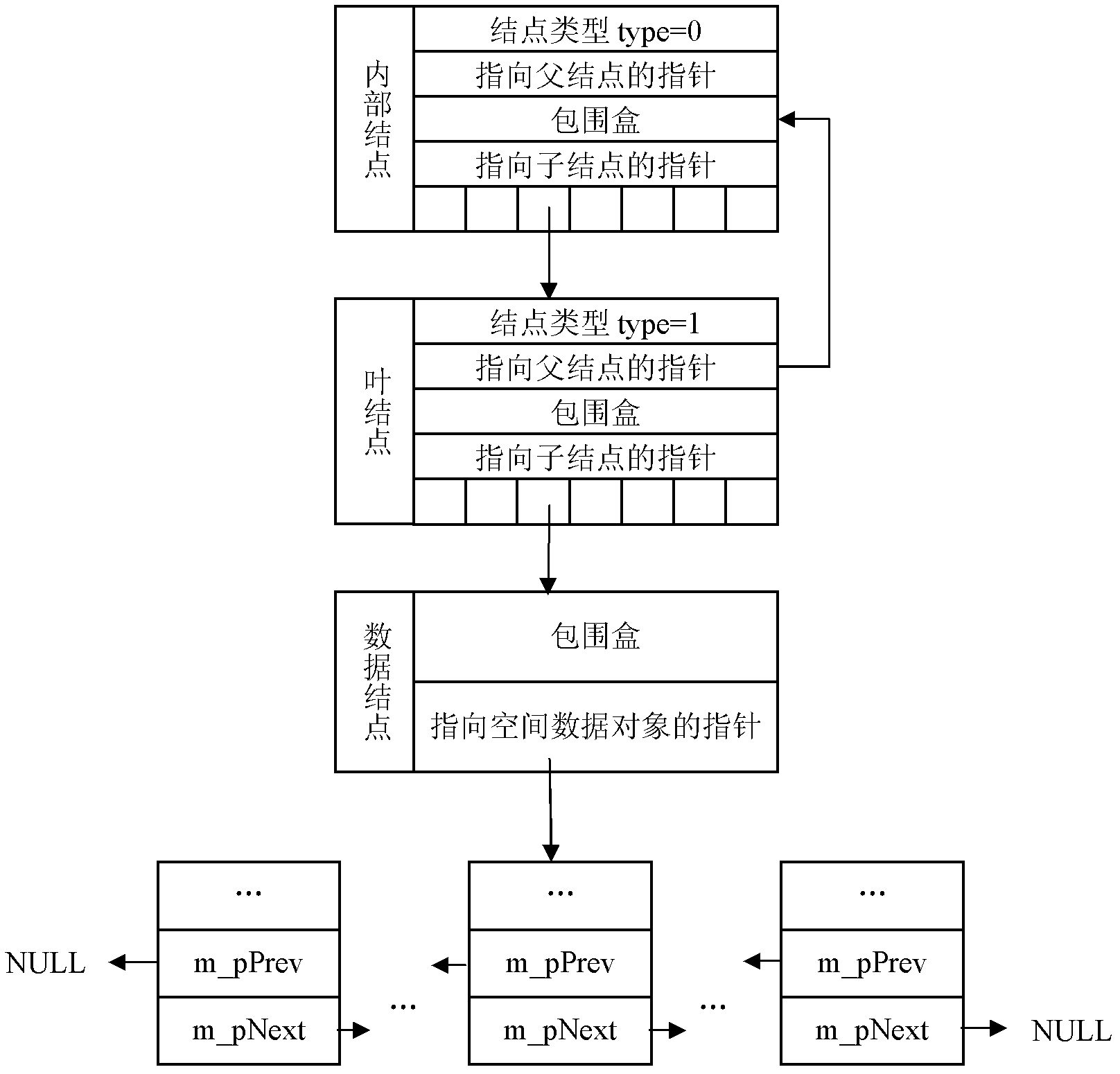
InactiveCN102508973AImprove cross-seeking efficiencyQuick extractionSpecial data processing applicationsModel dynamicsLithographic artist
The invention provides a rapid intersection method for STL (stereo lithography) models of products, and belongs to the technical field of reverse engineering of products. The method is characterized in that an STL model dynamic index structure is built based on the R*-tree; the intersection range is rapidly narrowed through the intersection detection of index node bounding boxes; an intersecting triangle patch bounding box set is accurately positioned, and topological K-nearest neighbor sorting of the set is carried out; and the intersecting line sections of triangular mesh surface models in all the bounding boxes are connected in sequence, so as to rapidly extract the intersecting lines of the surface models. Examples prove that the method can effectively improve the intersection efficiency of STL surface models with intensive data and complicated shapes, and is of great significance for the clipping and splicing of the triangular mesh surface models and numerically-controlled tool path generation in reverse engineering.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
Anti-reflective coating forming composition for lithography containing polymer having ethylenedicarbonyl structure
ActiveUS7632626B2Effective absorptionStrong absorption capacityPhotosensitive materialsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAnti-reflective coatingLithography process
There is provided an anti-reflective coating forming composition for lithography comprising a polymer having an ethylenedicarbonyl structure and a solvent; an anti-reflective coating formed from the composition; and a method for forming photoresist pattern by use of the composition. The anti-reflective coating obtained from the composition can be used in lithography process for manufacturing a semiconductor device, has a high preventive effect for reflected light, causes no intermixing with photoresists, and has a higher etching rate than photoresists.
Owner:NISSAN CHEM CORP
Construction method of micro point array in microchannel
InactiveCN101274469ASimple interfaceConvenient inspectionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicrofluidicsShell molding
The invention provides a method for establishing a micro-point array in a micro-channel which relates to the technical field of processing of micro-channels. In the method, the main steps of arrangement, casting, etc. are adopted to cure microfilament arrays contacted in a cross manner in polymer and then the steps of demoulding, filament removal, etc. are adopted to entirely form micro-points or micro-point arrays in the micro-channel. The method of the invention is based on a molding process belonging to the soft lithography category without relying on a costly and stringent photoetching process; in addition, the method can also flexibly and differently create various surfaces, geometric shapes and sizes of different micro-point materials in different micro-flowing channels through combining and arranging material composition, geometric shapes and sizes of the crossed filaments, which results in that basic technical types of the micro-flowing and the micro-array can be closely integrated as a whole to provide a flexible and low-cost processing and manufacturing approach for the integration of the techniques of micro-fluidic control and micro-solid control.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Preparation of micro-nano structure bionics valve, surface congeal-resistance and drag reduction testing method thereof
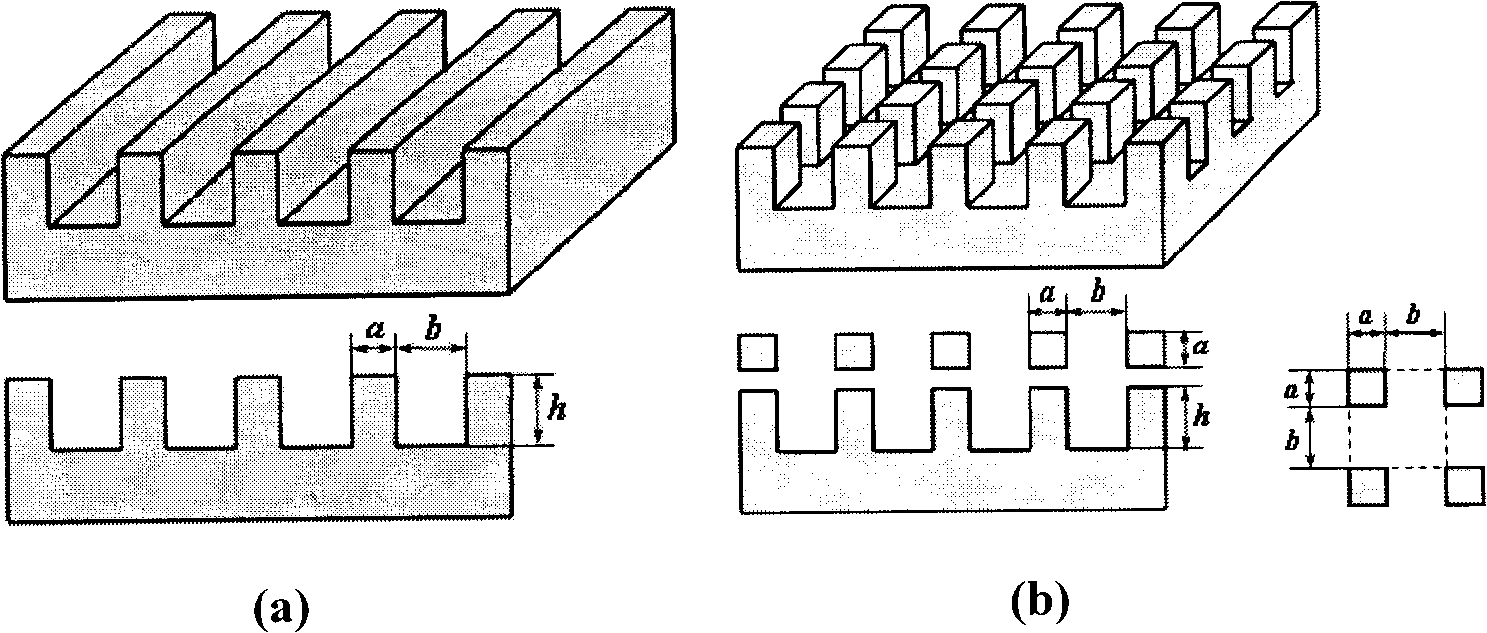
InactiveCN101254137AStable structureNot easy to damageHeart valvesMaterial resistanceFine structureMicro nano
The invention relates to a medical graft, which is applied to various artificial prosthesis cardiac valves. A fine structure form on the surface of an artificial cardiac valve is designed through determining the structural geometric parameters that are a, b, and h according to a biological prototype of the cardiac valve, the apparent contact angle calculation formula of the surface which is denoted by the geometric parameters is deduced, the proper fine structural geometric parameters are determined according to the calculation formula to lead the apparent contact angle on the cardiac valve surface to be larger than 150 degrees, so as to gain a more ideal super-hydrophobic surface; then a template which is provided with a fine structure surface is processed by utilizing the technology of femtosecond laser machining, and is washed, dried and processed through the silanization treatment; a PDMS valve surface which has the same fine structure with the template is copied by using a soft lithography method. The valve surface structure made by the invention is stable, has obvious characteristics of anticoagulation resistance and drag-reduction, effectively prevents the thrombosis, is hard to be damaged when being used for a long time, and is reusable without damage and deformation. Therefore, the mass production can be completed. In addition, the test method is simple and reliable.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
SLA (stereo lithography) technology of light curing stereo homocentric sphere
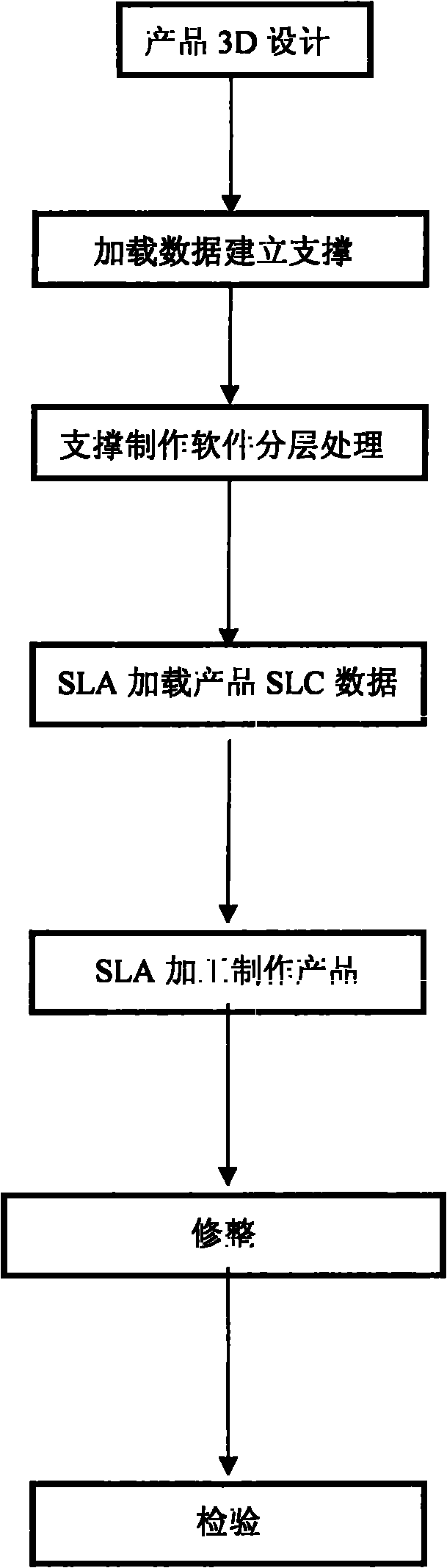
The invention discloses an SLA (stereo lithography) technology of a light curing stereo homocentric sphere which is characterized by comprising the following steps: 1) designing product; 2) loading data and establishing support; 3) carrying out layering treatment on an RPDate; 4) loading SLC data based on SLA; 5) processing and manufacturing products based on SLA; 6) clearing; and 7) inspecting. In the invention, hollow sphere manufactured after process improvement has a bright and clean surface and is convenient to post process, furthermore, the cost is low, the product surface is beautified, and the product hardness is increased.
Owner:JIANGSU WENGUANG VEHICLE ACCESSORIES
System, method, and computer-accessible medium for fabrication miniature endoscope using soft lithography
Exemplary method and system can be implemented and / or used for providing a diffractive configuration in an optical arrangement can be provided. For example, an elastomeric material can be provided with at least one patterned surface. The elastomeric material can be connected with at least one portion of a waveguide arrangement using a pre-polymer adhesive composition. Further, the pre-polymer adhesive composition can be caused to polymerize so as to form the diffractive configuration which at least approximately replicate a structure or at least one feature of an elastomeric mold.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
Method for treating groove and forming UMOS (U-shaped groove Metal Oxide Semiconductor) transistor
InactiveCN102013395AImprove flatnessImprove uniformitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBiochemical engineeringSoft lithography
The invention relates to a method for treating a groove and forming a UMOS (U-shaped groove Metal Oxide Semiconductor) transistor, wherein the method for treating the groove comprises the step of carrying out soft lithography on the groove. The invention improves the uniformity of the dielectric layers of the side wall and the bottom of the groove; the process complexity is not increased obviously, and the production cost and the capacity are not changed obviously.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP +1
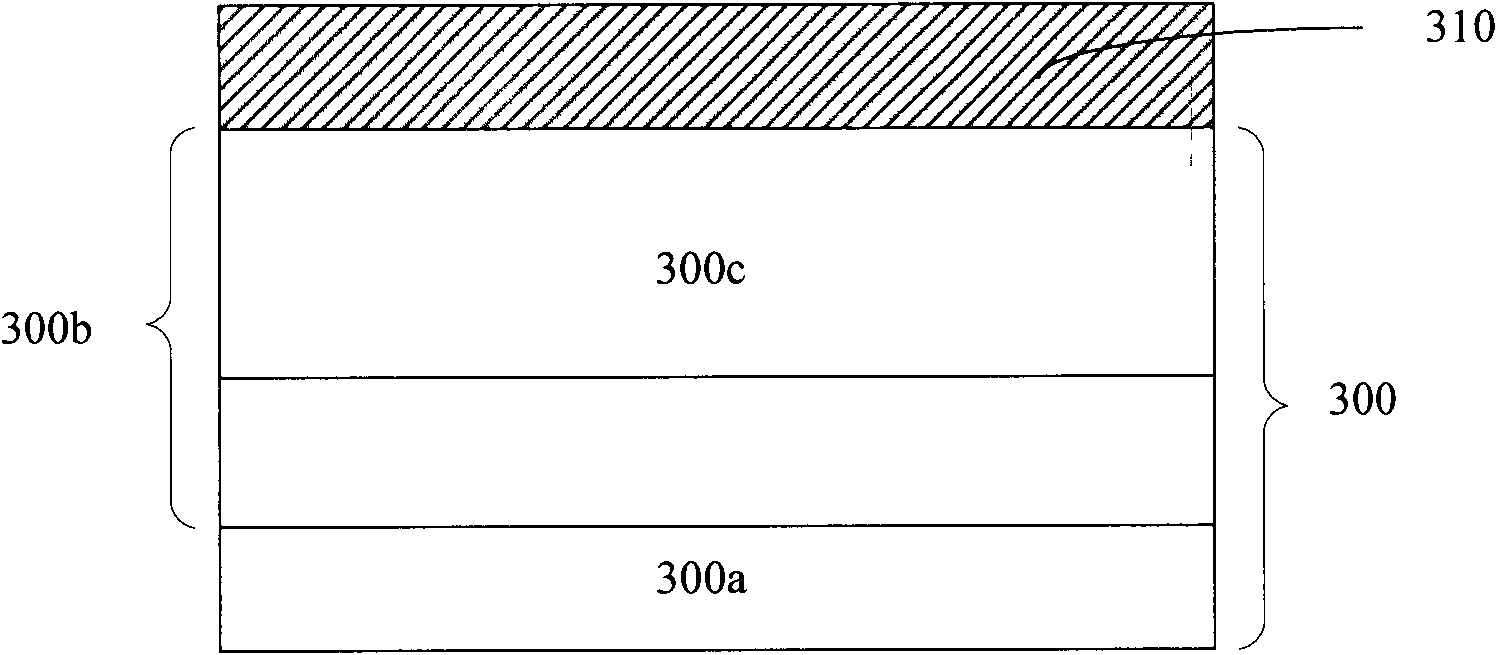
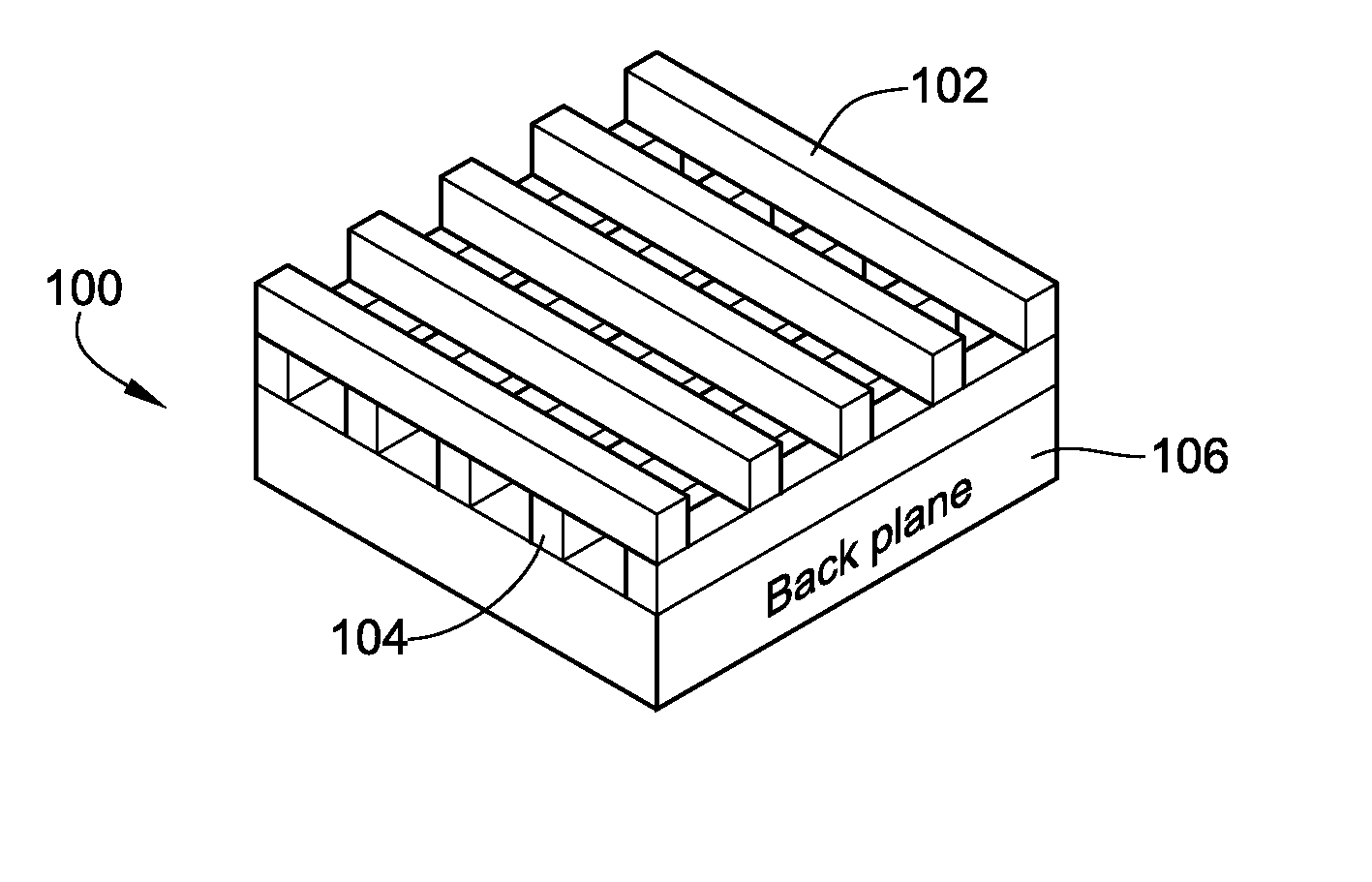
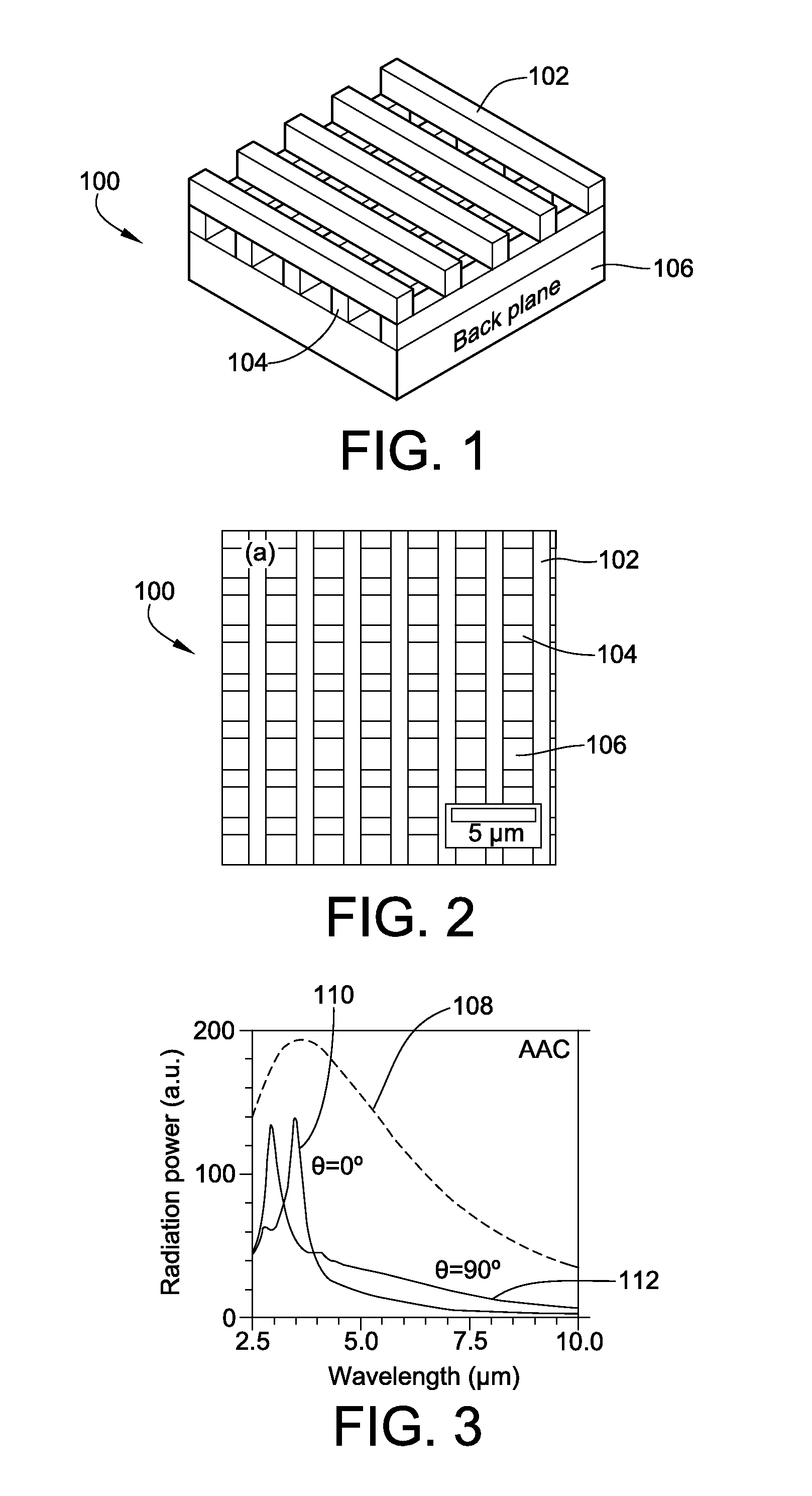
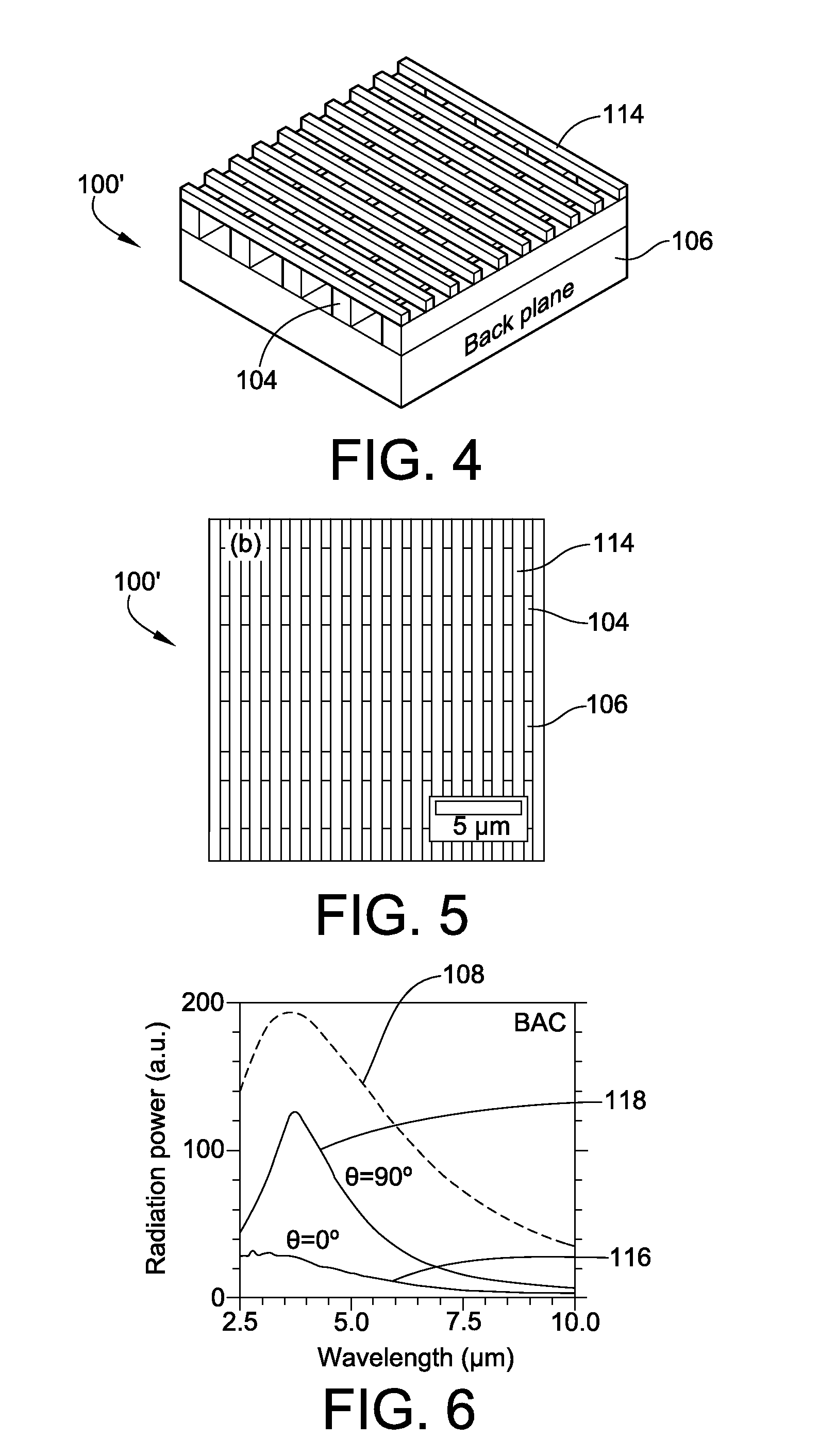
Metallic Layer-by-Layer Photonic Crystals for Linearly-Polarized Thermal Emission and Thermophotovoltaic Device Including Same
ActiveUS20100294325A1Overcome problemsIncreased Radiation PowerRadiation pyrometryPV power plantsGratingPhotonics
Metallic thermal emitters consisting of two layers of differently structured nickel gratings on a homogeneous nickel layer are fabricated by soft lithography and studied for polarized thermal radiation. A thermal emitter in combination with a sub-wavelength grating shows a high extinction ratio, with a maximum value close to 5, in a wide mid-infrared range from 3.2 to 7.8 μm, as well as high emissivity up to 0.65 at a wavelength of 3.7 μm. All measurements show good agreement with theoretical predictions. Numerical simulations reveal that a high electric field exists within the localized air space surrounded by the gratings and the intensified electric-field is only observed for the polarizations perpendicular to the top sub-wavelength grating. This result suggests how the emissivity of a metal can be selectively enhanced at a certain range of wavelengths for a given polarization.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com