Patents
Literature
197 results about "Optical routing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
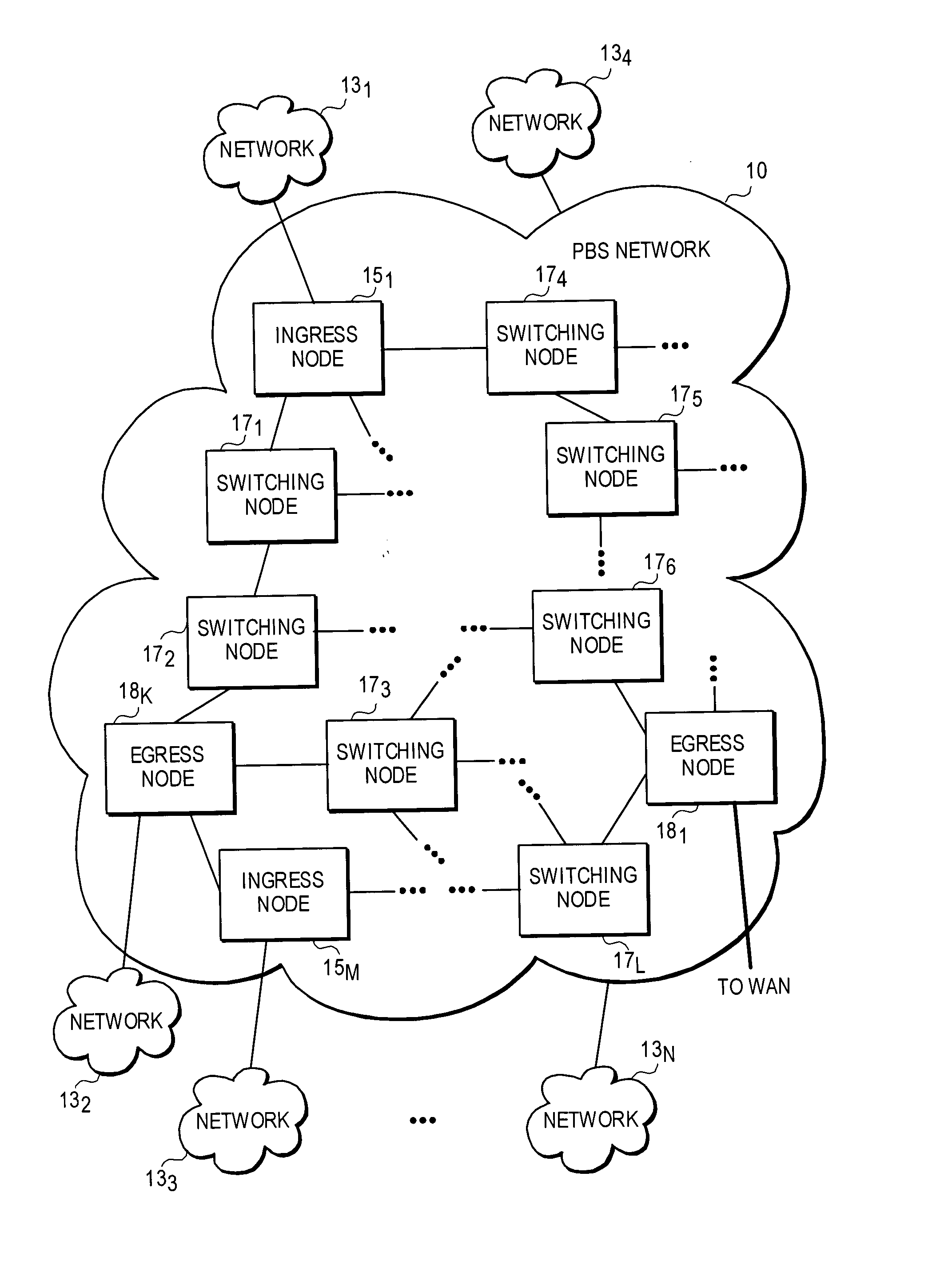
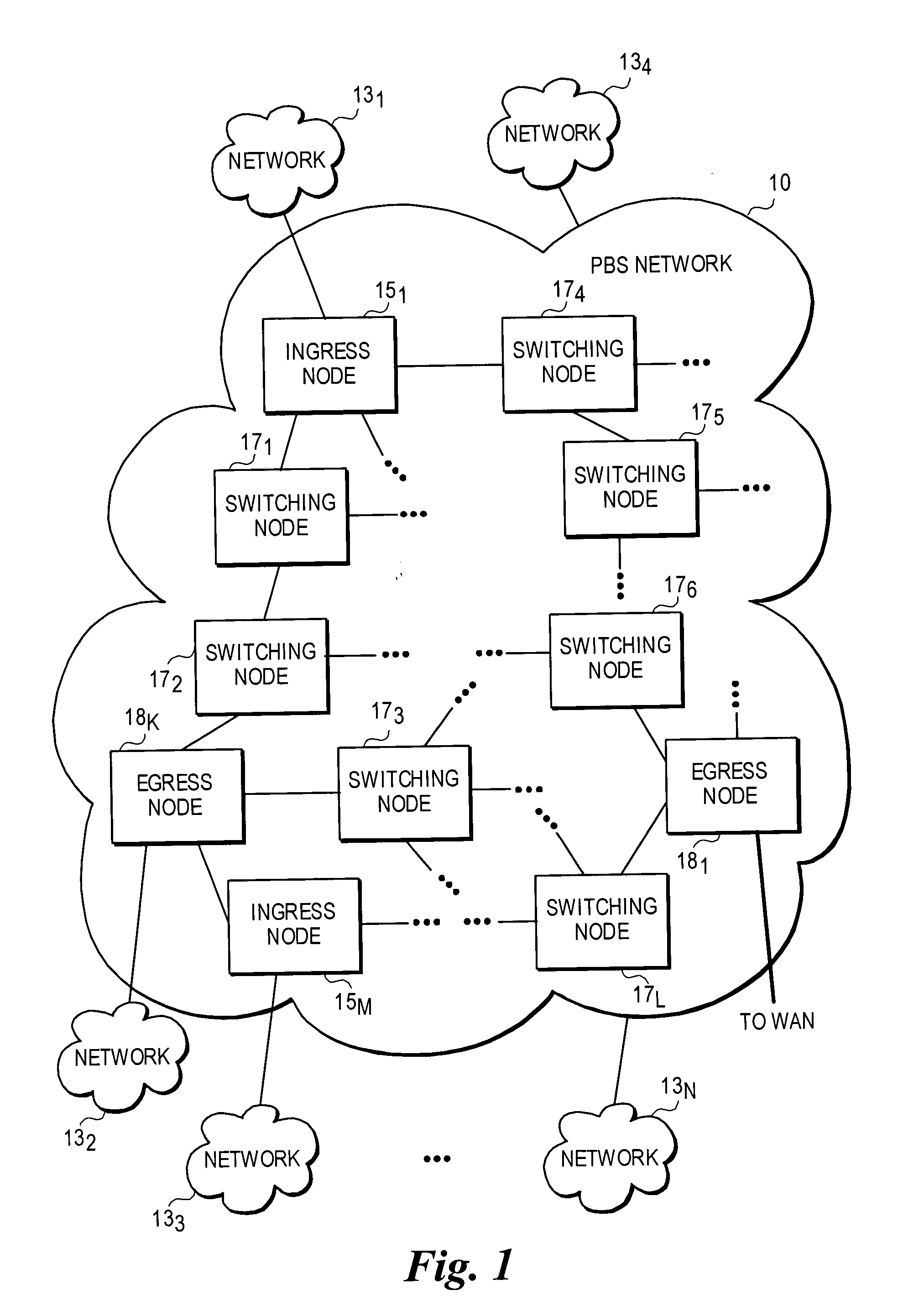
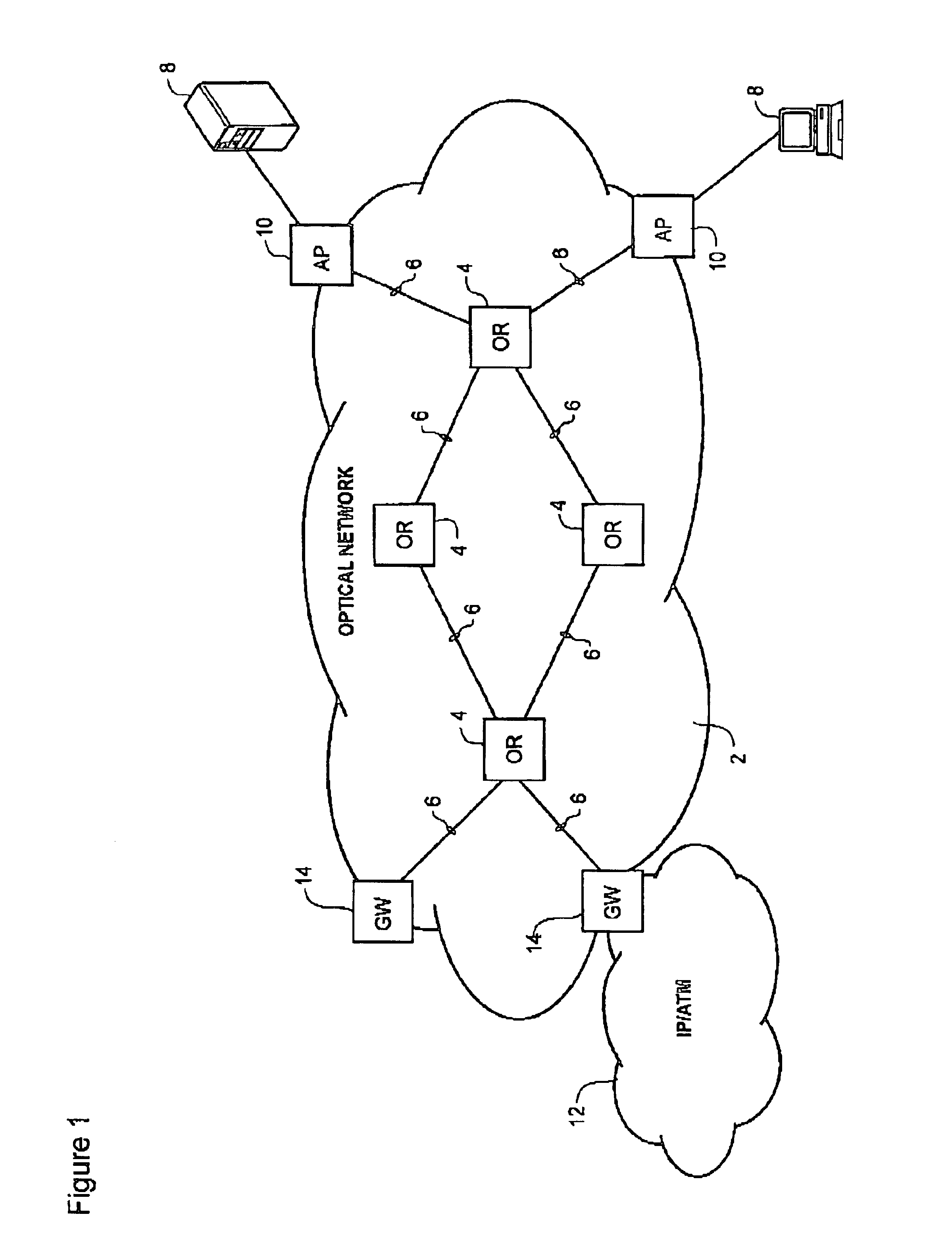
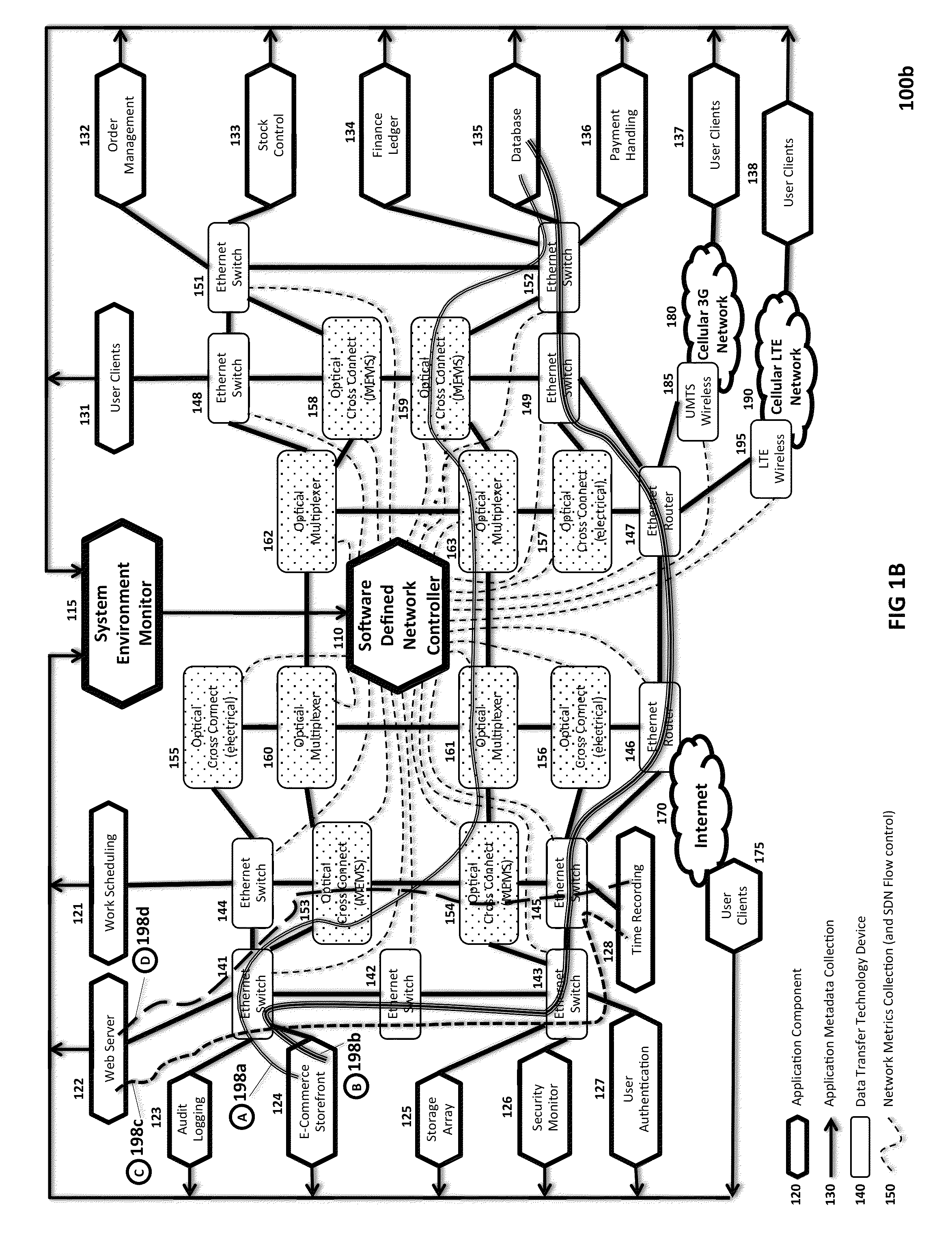
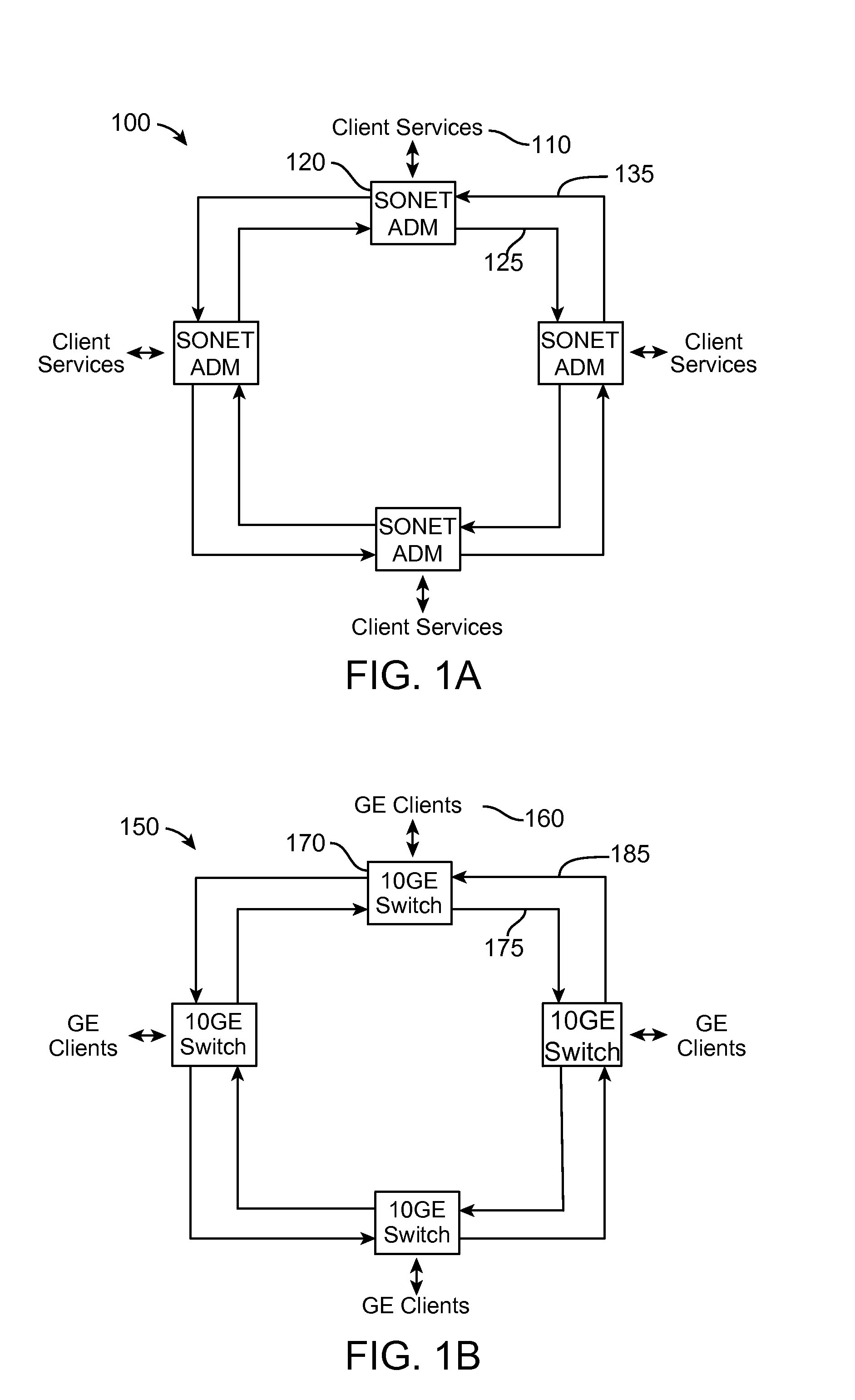
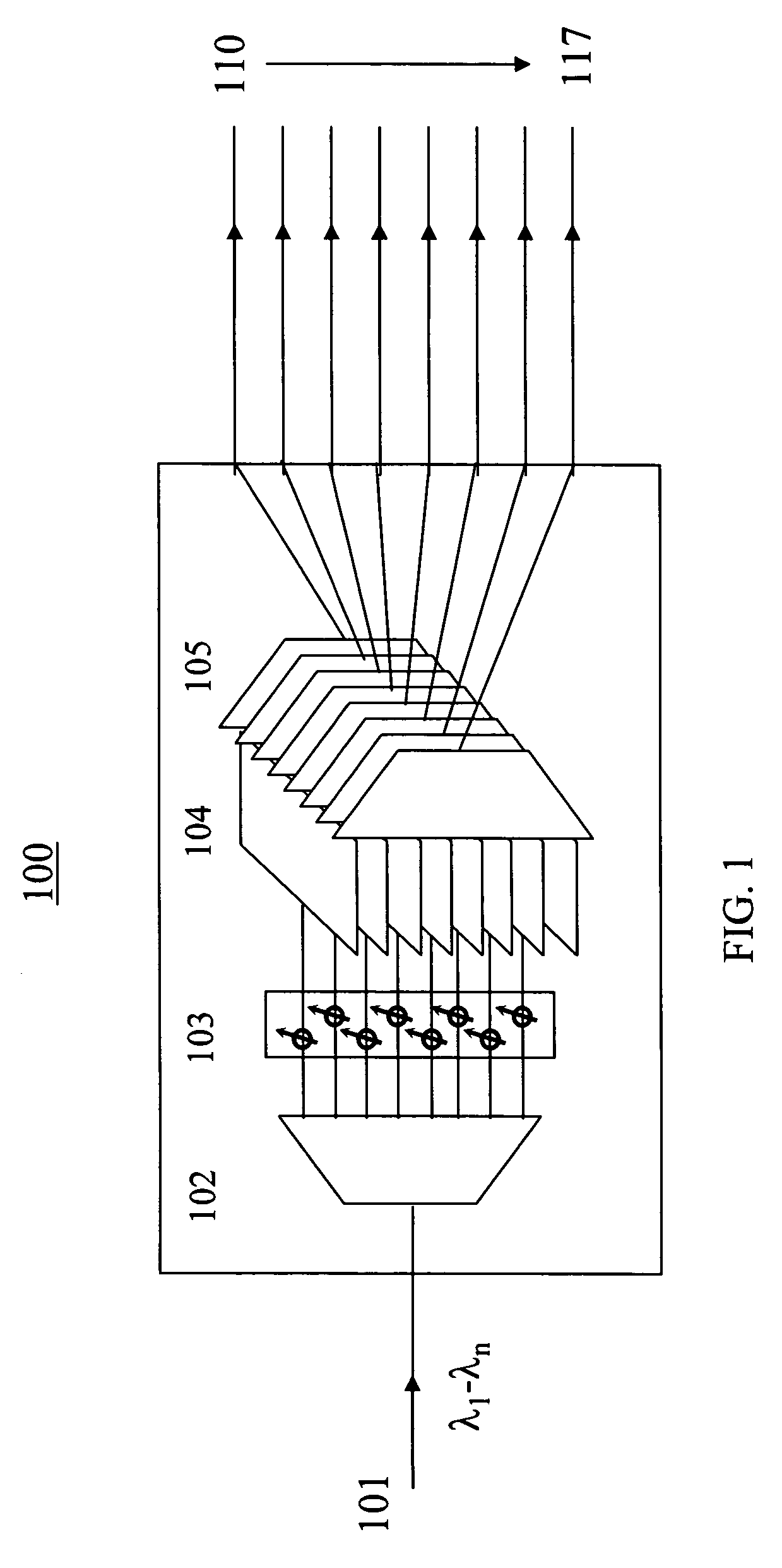
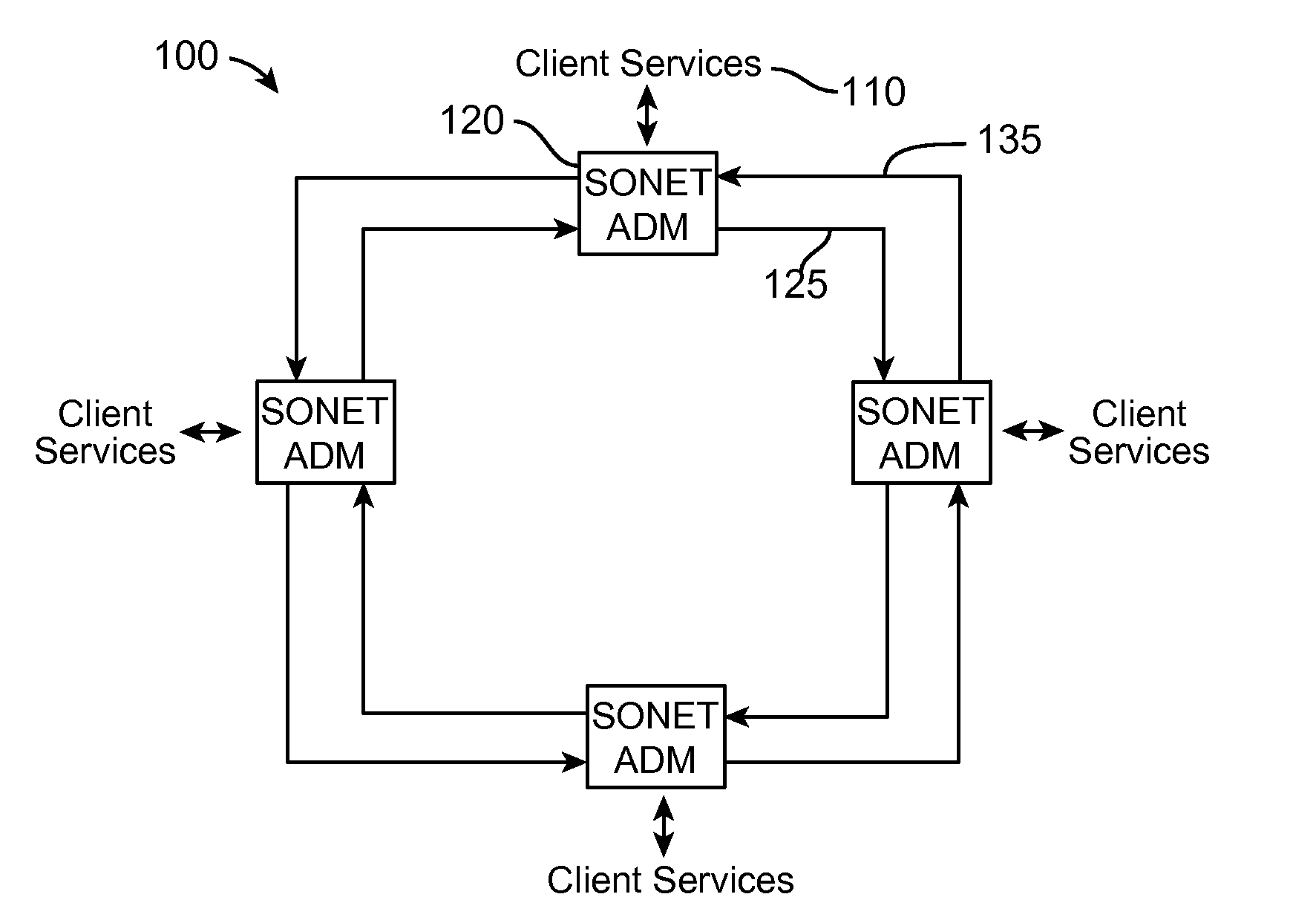
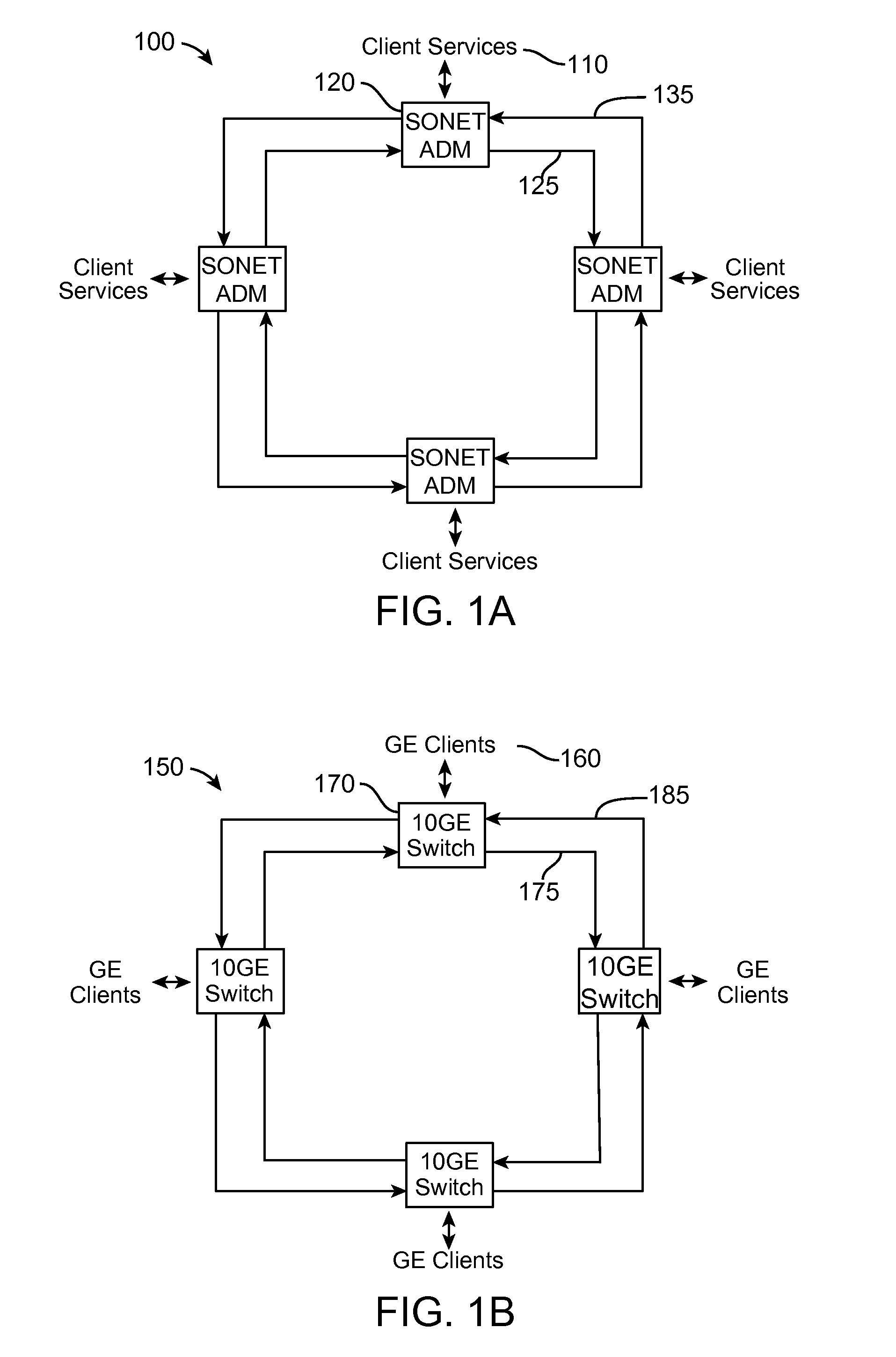
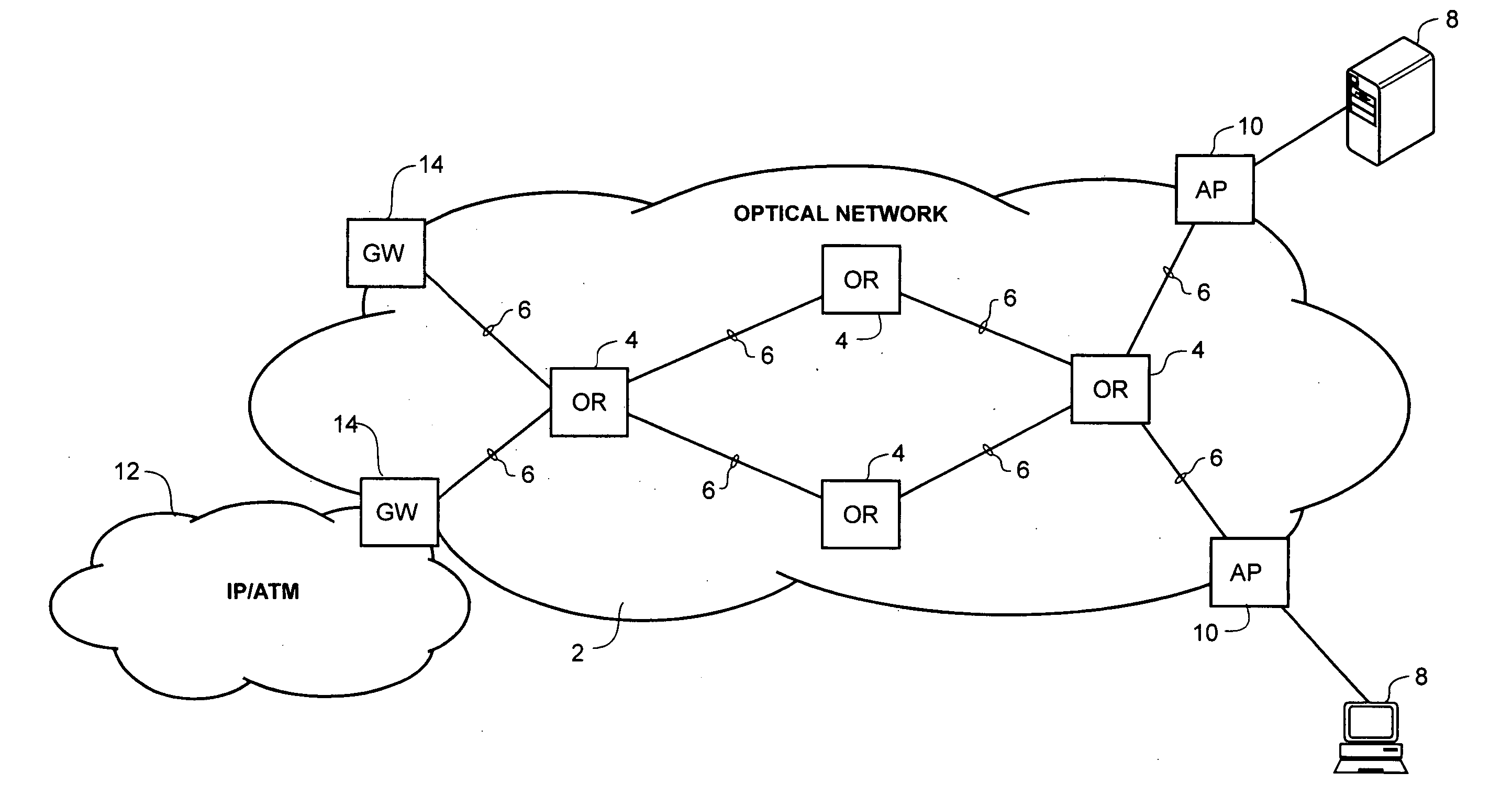
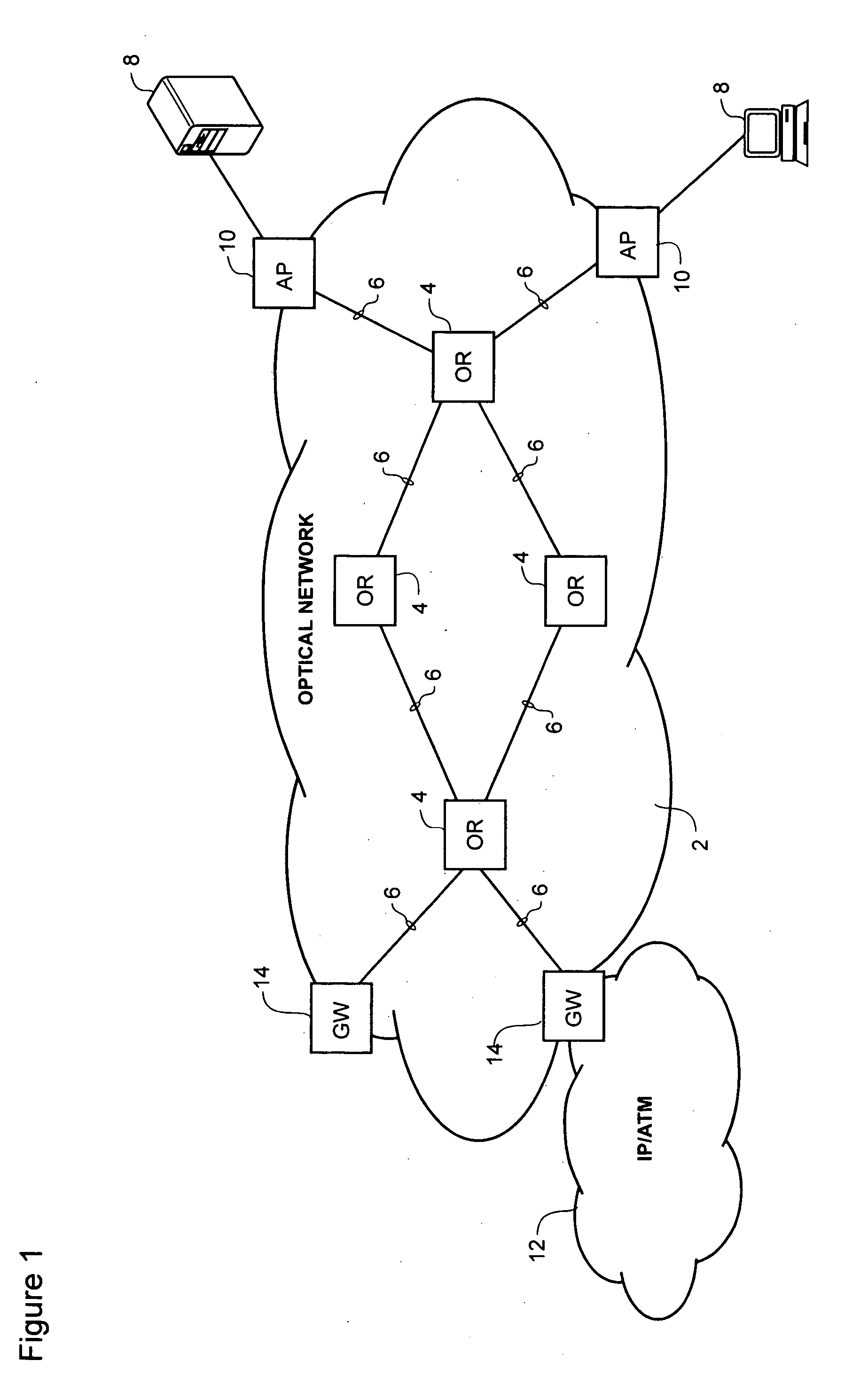
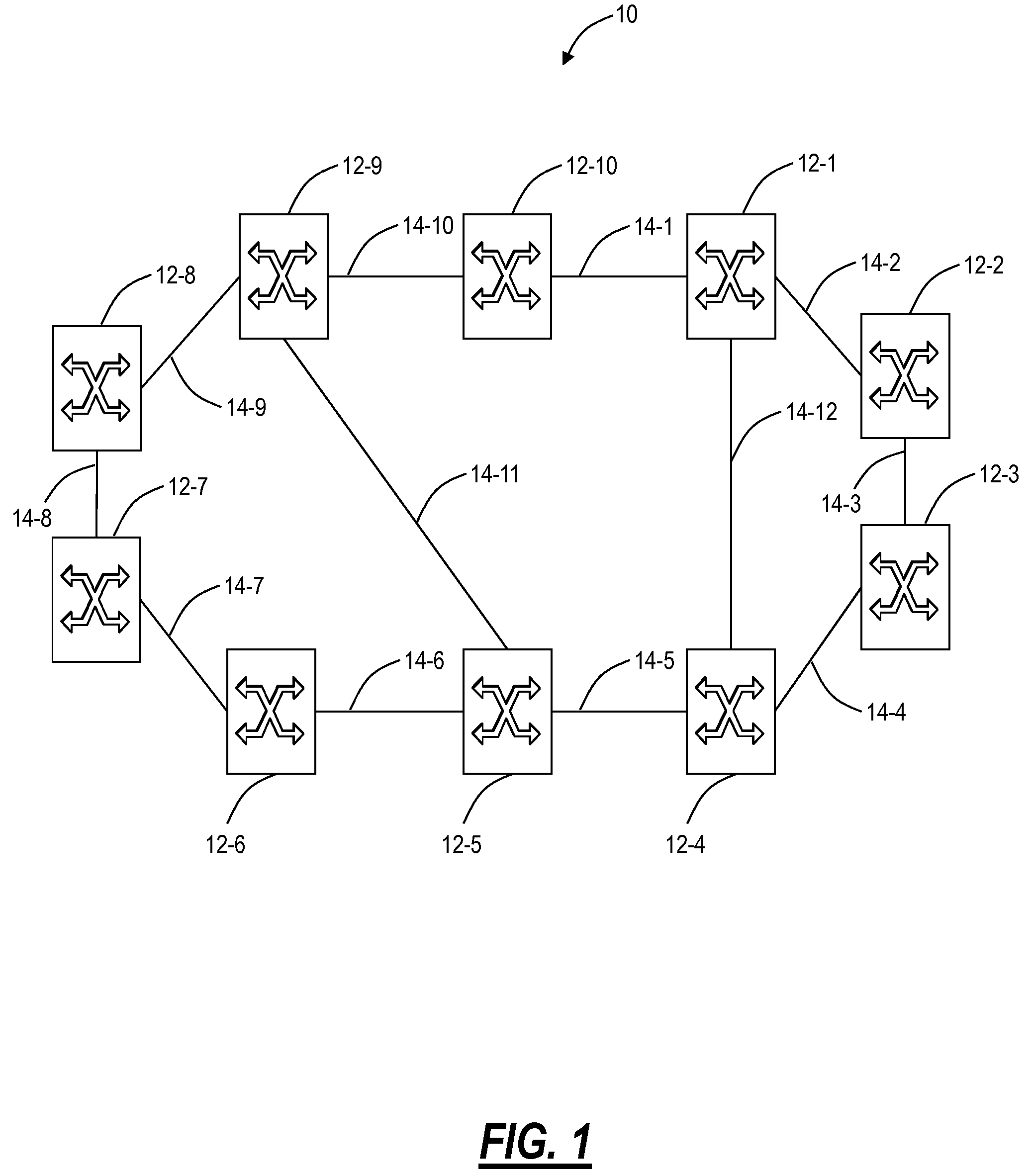
Optical-switched (OS) network to OS network routing using extended border gateway protocol
InactiveUS20050068968A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationBorder Gateway ProtocolRouting table
Routing mechanisms for routing data via a plurality of optical switched (OS) networks, such as optical burst-switched (OBS) networks. A plurality of OBS networks are connected to form an enterprise network, which may further include non-OBS networks such as LANs and the like. Each of the OBS networks is modeled as an autonomous system (AS), and one or more edge nodes of each OBS network are designated as external gateway protocol (EGP) routers. Each EGP router maintains a routing table identifying routes that may be used to reach destination networks. The routing table is dynamically updated via update messages that comprise an extension to the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) and account for optical routing considerations particular to OBS networks. In response to a routing request, data is sent from an internal node using an internal routing protocol to a BGP router edge node. The BGP router edge node then determines a next network hop based on current routing information in its routing table, and the data is routed using an external routing protocol. At the same time, data is routed within an individual OBS network using an internal routing protocol under which data are sent as data bursts via reserved lightpaths.
Owner:INTEL CORP
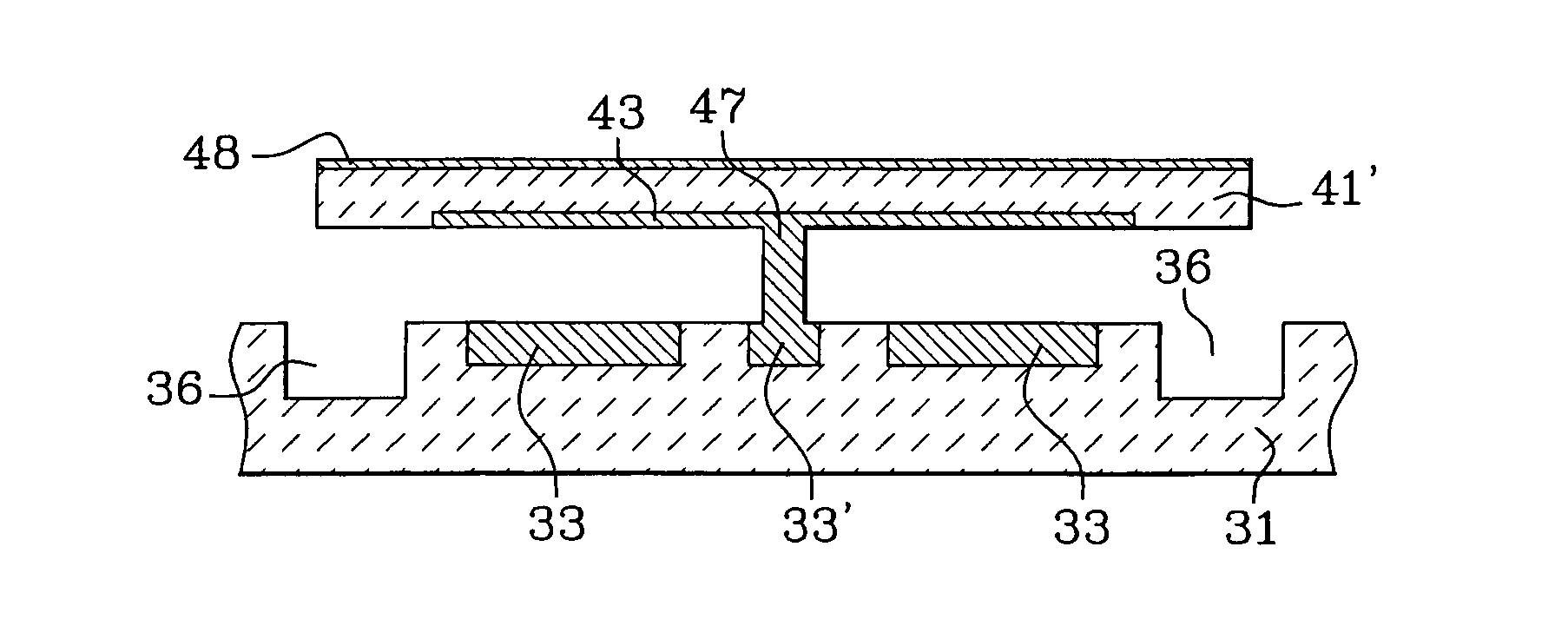
Build-up structures with multi-angle vias for chip to chip interconnects and optical bussing
InactiveUS6919508B2Improve performanceIncrease speedTelevision system detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesAnisotropic conductive filmCopper interconnect
A build-up structure for chip to chip interconnects and System-In-Package utilizing multi-angle vias for electrical and optical routing or bussing of electronic information and controlled CTE dielectrics including mesocomposites to achieve optimum electrical and optical performance of monolithic structures. Die, multiple die, Microelectromechanical Machines (MEMs) and / or other active or passive components such as transducers or capacitors can be accurately positioned on a substrate such as a copper heatsink and multi-angle stud bumps can be placed on the active sites of the components. A first dielectric layer is preferably placed on the components, thereby embedding the components in the structure. Through various processes of photolithography, laser machining, soft lithography or anisotropic conductive film bonding, escape routing and circuitry is formed on the first metal layer. Additional dielectric layers and metal circuitry are formed utilizing multi-angle vias to form escape routing from tight pitch bond pads on the die to other active and passive components. Multi-angle vias can carry electrical or optical information in the form of digital or analog electromagnetic current, or in the form of visible or non-visible optical bussing and interconnections.
Owner:CAPITALSOURCE FINANCE
Ring architecture for an optical satellite communication network with passive optical routing
InactiveUS6912075B1Reduce power consumptionReduce weightSatellite communication transmissionOptical multiplexFiberLength wave
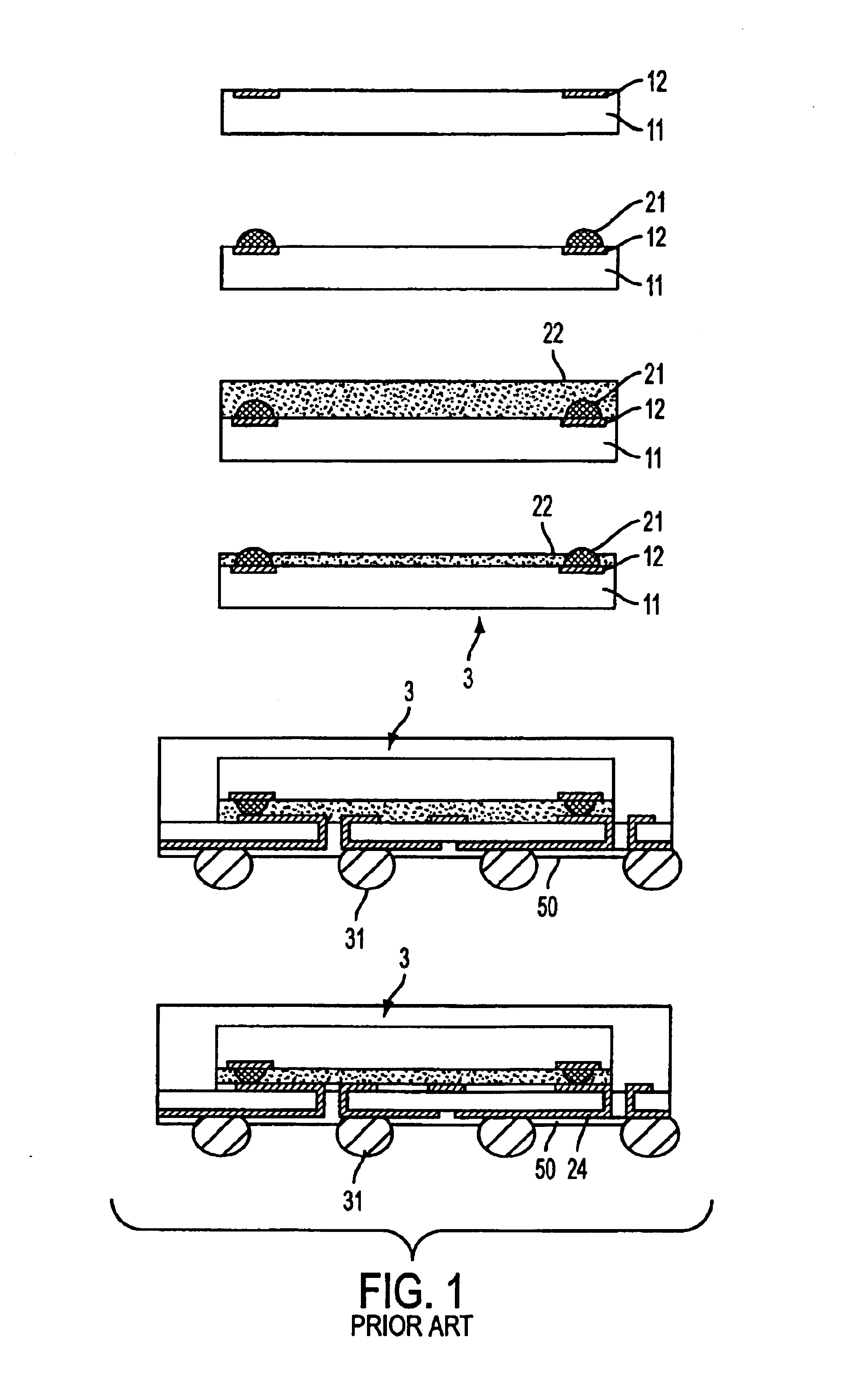
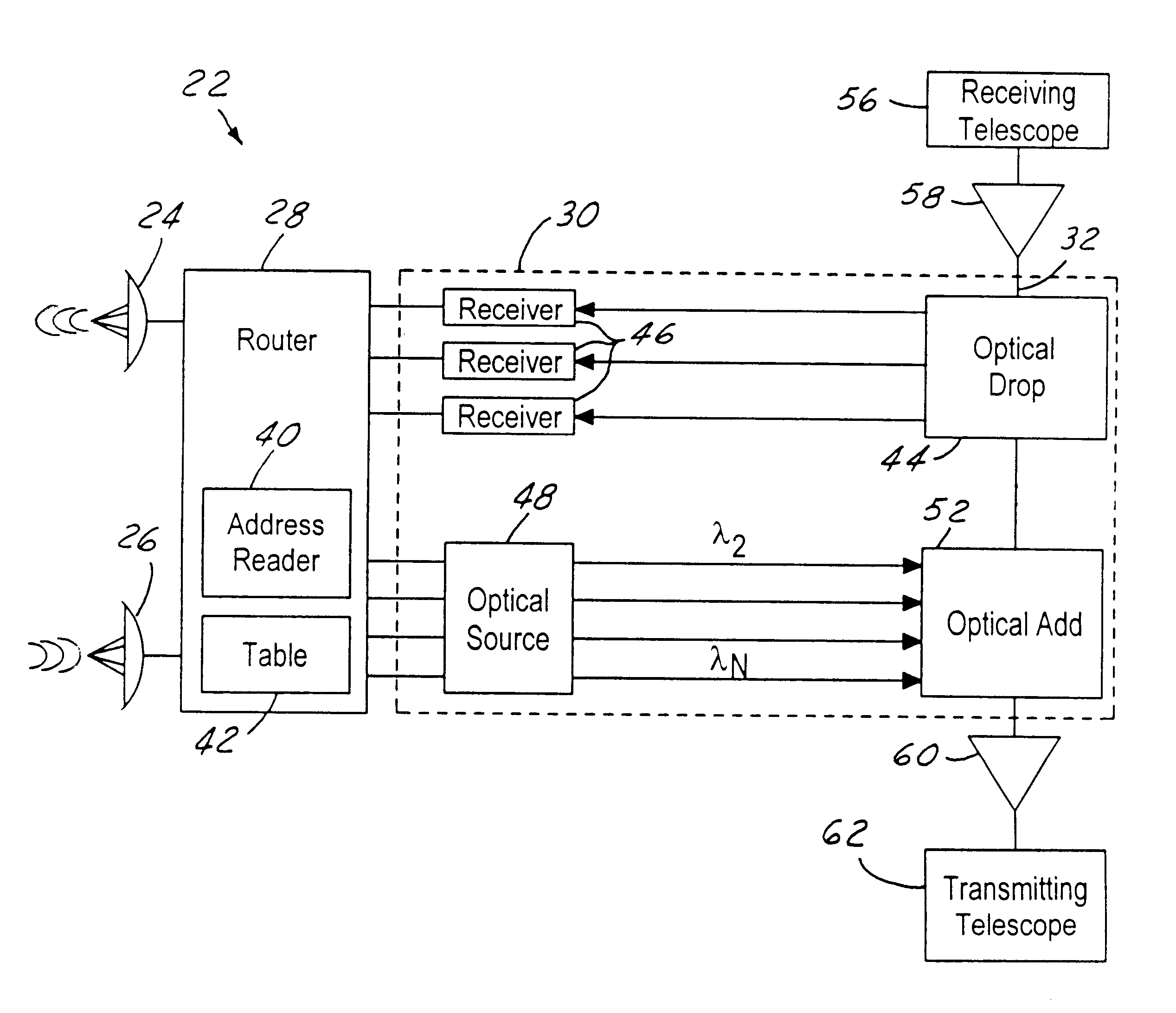
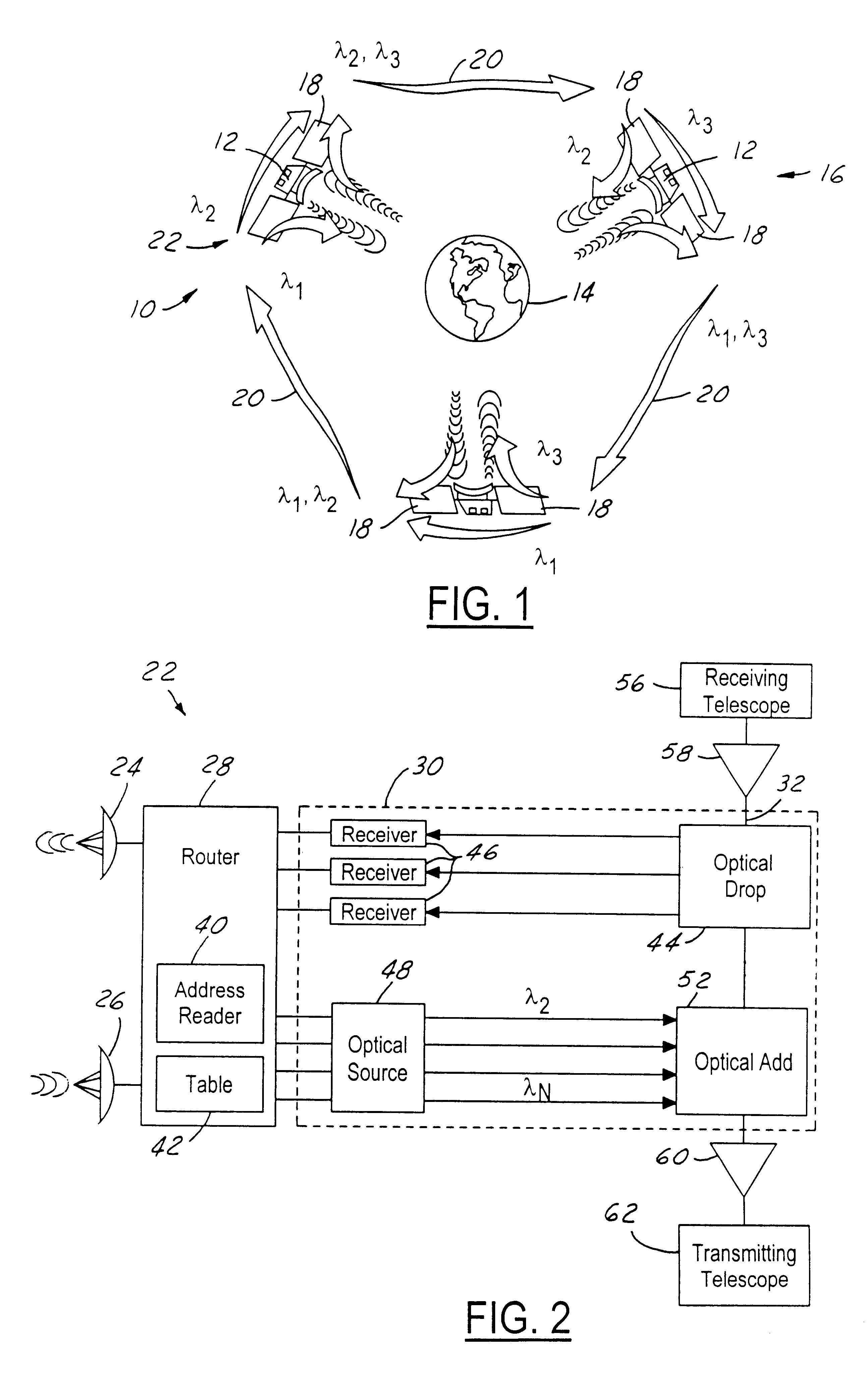
A node for satellite system communications between a ground station and a satellite includes a fiber optic bus on the satellite. An optical drop is coupled to the bus. The optical drop resolves an optical signal destined to the given satellite from the optical bus. An uplink and downlink receive and transmit communications from a ground terminal. A router is coupled to the optical drop and the uplink and downlink. An address reader and a table are used by the router to determine the destination of the received RF signals. The received RF signals are converted to optical signals by an optical source. The optical source has a wavelength that corresponds with the destination satellite. The optical signals are transmitted to an adjacent satellite by an optical transmitter such as a transmitting telescope.
Owner:HUGHES ELECTRONICS
Build-up structures with multi-angle vias for chip to chip interconnects and optical bussing
InactiveUS20050087356A1Enhanced signalReduce in quantityTelevision system detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesAnisotropic conductive filmEngineering
A build-up structure for chip to chip interconnects and System-In-Package utilizing multi-angle vias for electrical and optical routing or bussing of electronic information and controlled CTE dielectrics including mesocomposites to achieve optimum electrical and optical performance of monolithic structures. Die, multiple die, Microelectromechanical Machines (MEMs) and / or other active or passive components such as transducers or capacitors can be accurately positioned on a substrate such as a copper heatsink and multi-angle stud bumps can be placed on the active sites of the components. A first dielectric layer is preferably placed on the components, thereby embedding the components in the structure. Through various processes of photolithography, laser machining, soft lithography or anisotropic conductive film bonding, escape routing and circuitry is formed on the first metal layer. Additional dielectric layers and metal circuitry are formed utilizing multi-angle vias to form escape routing from tight pitch bond pads on the die to other active and passive components. Multi-angle vias can carry electrical or optical information in the form of digital or analog electromagnetic current, or in the form of visible or non-visible optical bussing and interconnections.
Owner:CAPITALSOURCE FINANCE
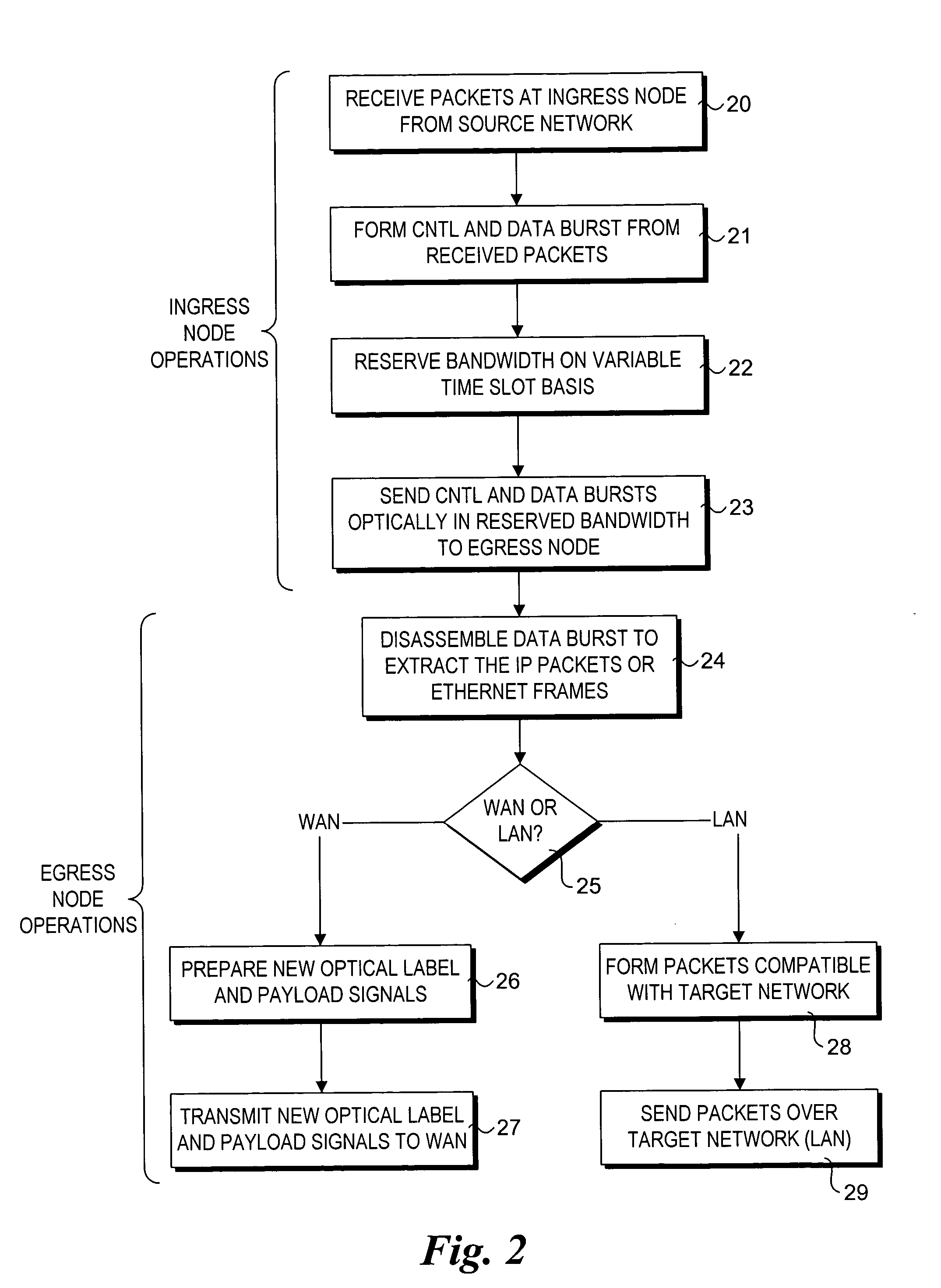
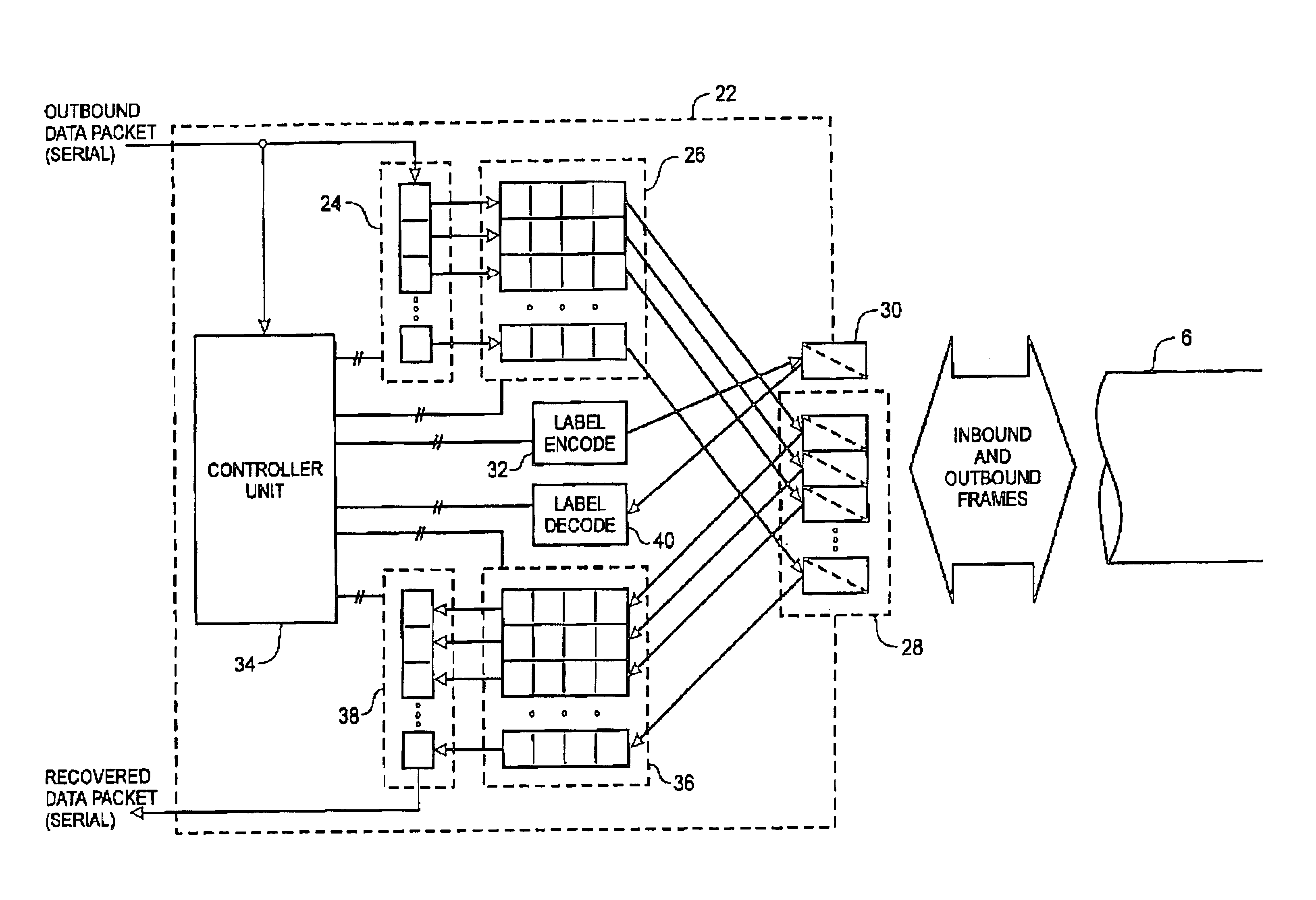
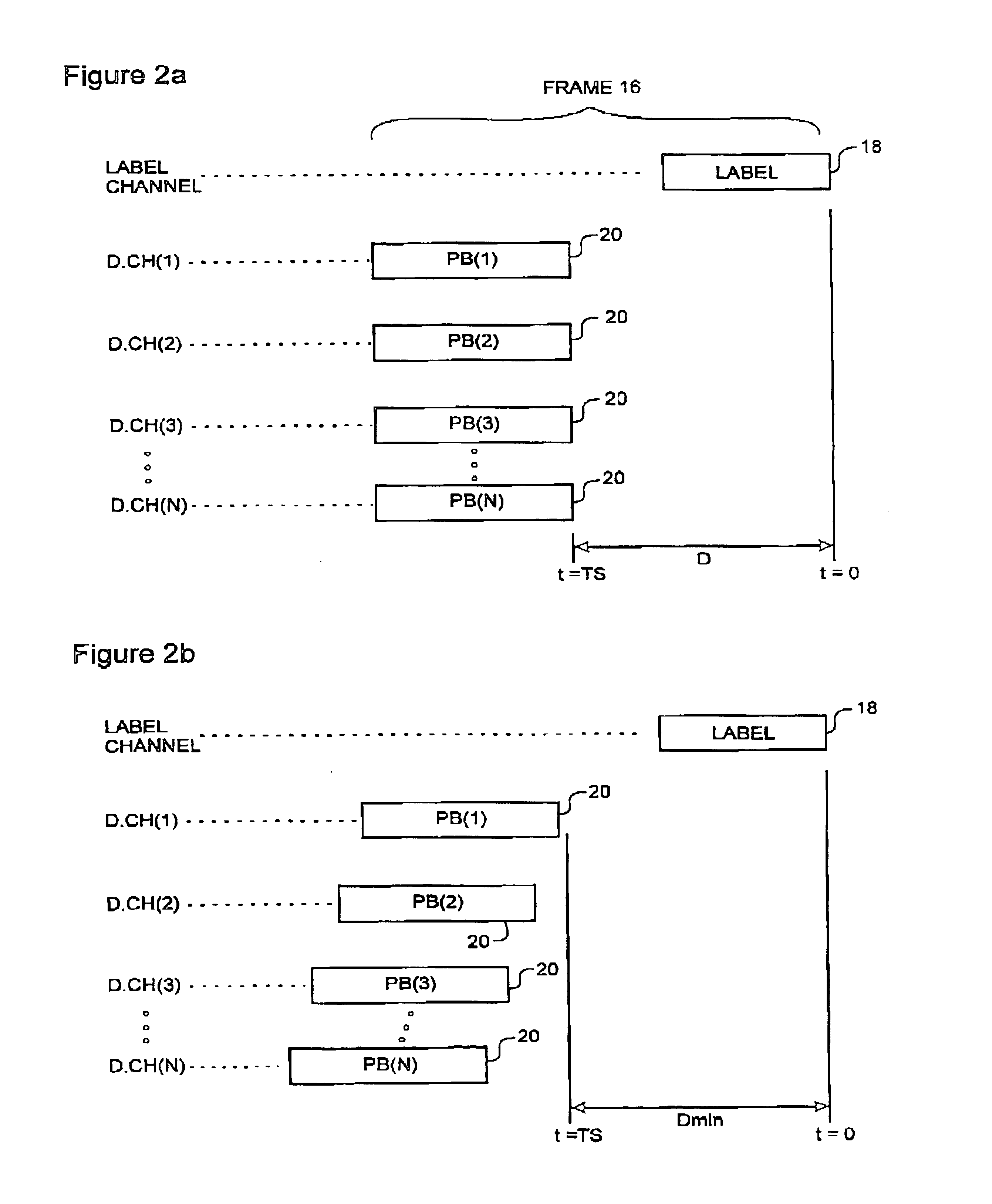
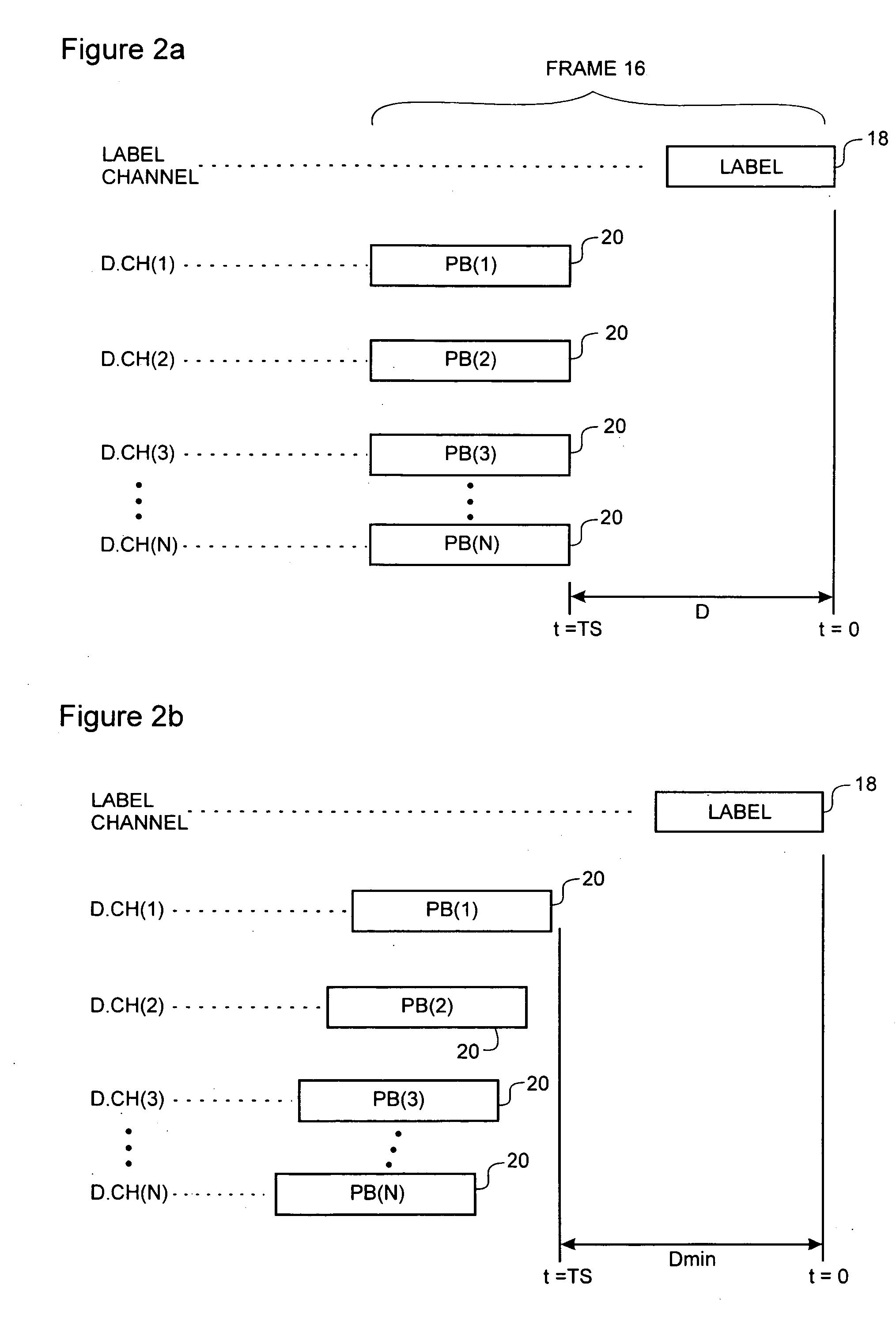
Method and system for optical routing of variable-length packet data
InactiveUS6839322B1Facilitates full optical routingMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionMultiplexingStart time
A method and system of routing variable-length packet data across a wave division multiplex (WDM) communications network having a plurality of data communications channels comprises inverse-multiplexing each data packet into a respective frame. Each frame includes a label block containing label information of the frame, and two or more respective payload blocks having a predetermined length. The label block contains encoded routing information, a start time, and, possibly an end time, and is transmitted over a label channel of the communications network. The start time preferably indicates a delay between launching a first bit of the label clock and the first bit of the payload blocks. The end time may be a bit count indicative of the location of the last bit of the data packet within the frame. The data packet is divided into a plurality of data segments, each of which is transported across the network within a respective payload block. Each payload block is transmitted over a respective separate data channel of the communications network. Routing control of the frame may be handled using the multi-protocol label switch (MPLS) protocol.
Owner:BIOSPHERICS
Subchannel security at the optical layer
InactiveUS20140193154A1Facilitate decision-makingMinimize network congestionWavelength-division multiplex systemsSecret communicationComputer scienceConcatenation
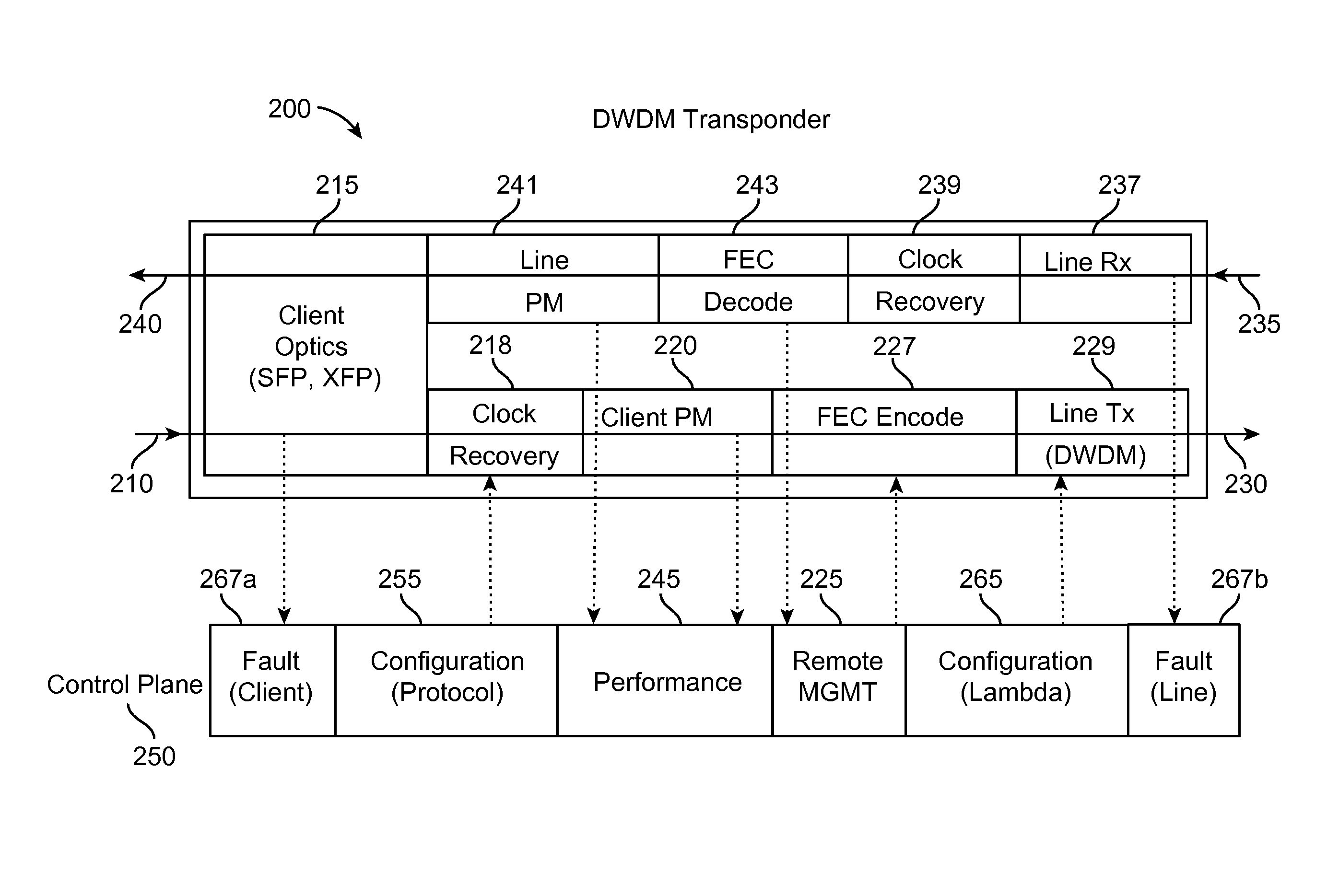
The present invention includes various novel systems and methods for dynamically modifying WDM transmission and receive steps (individually or in combination), including encoding client signals, mapping them to subchannels within or across ITU channels, modulating them onto subcarrier frequencies, and multiplexing them together for optical transmission. By dynamically modifying one or more of these processing steps over time (as well as encrypting underlying client signals), additional security is provided at the physical (optical) layer of an optical network, thereby greatly enhancing overall network security. Tunable lasers are employed to generate respective subcarrier frequencies, which represent subchannels of an ITU channel to which client signals are mapped. Client circuits are divided and combined with one another before being mapped to individual subchannels within and across ITU channels, thereby facilitating desired optical routing, switching, concatenation and protection of the client circuits mapped to those subchannels across the nodes of a WDM network.
Owner:SONUS NETWORKS
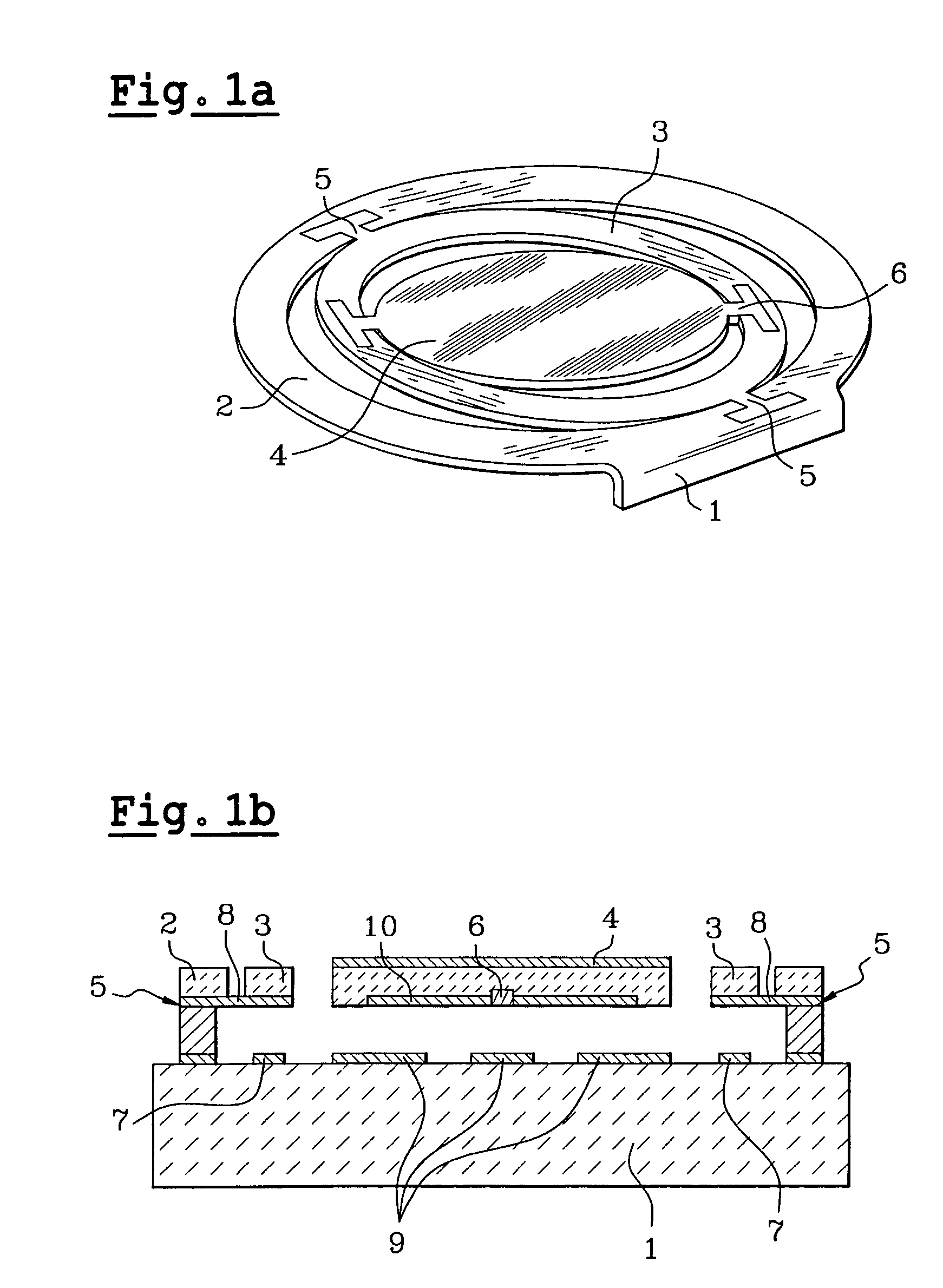
Method for making an optical micromirror and micromirror or array of micromirrors obtained by said method
InactiveUS7022249B2Overcome limitationsGreat freedomDecorative surface effectsOptical articlesProjection systemMicromirror array
A method for manufacturing an optical micro-mirror including a fixed part and a moveable part, with a reflection device connected to the fixed part by an articulation mechanism. This method realizes a stack including a mechanical substrate, a first layer of thermal oxidation material, and at least one second layer of material for forming the moveable part, realizes the articulation mechanism, realizes the reflection device on the second layer, realizes the moveable part by etching of at least the second layer of material, and eliminates the thermal oxidation layer to liberate the moveable part. Such an optical micro-mirror may find possible applications to optical routing or image projection systems.
Owner:TEEM PHOTONICS
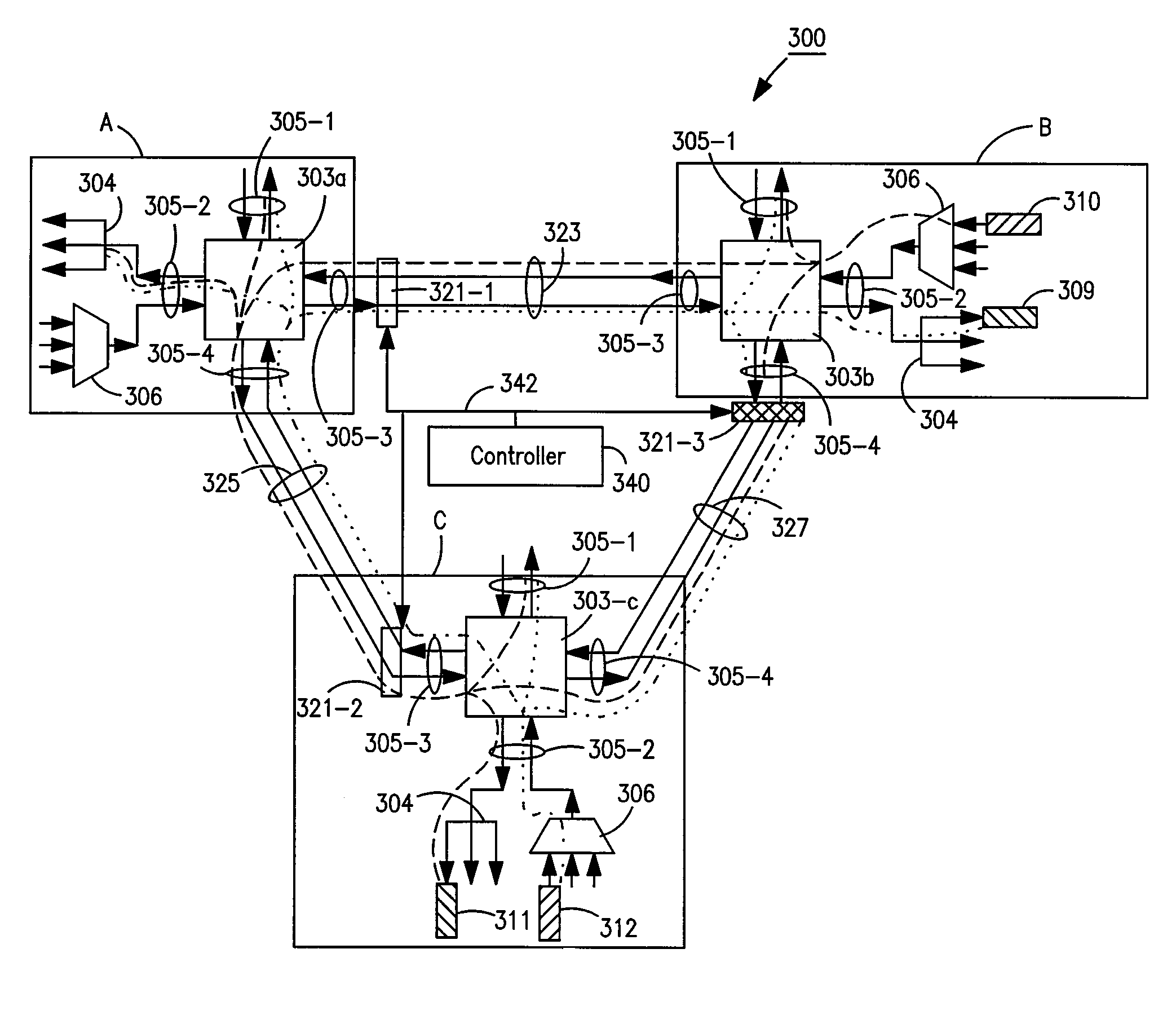
Colorless, directionless, and gridless optical network, node, and method
ActiveUS20120183294A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsEngineeringOptical routing
An optical node includes an optical routing apparatus including N ports, N is an integer greater than 2, the optical routing apparatus configured to direct light that is input to each of the N ports to all of the other N ports, and a configurable optical blocking element located in line with at least one of the N ports. A method includes broadcasting a plurality of optical signals over a plurality of ports using a broadcast element, selectively receiving a desired signal from all of the plurality of optical signals at one of the plurality of ports, and blocking the plurality of signals via a blocking element in line with one of the plurality of ports thereby preventing a multiple path of the broadcast plurality of optical signals.
Owner:CIENA
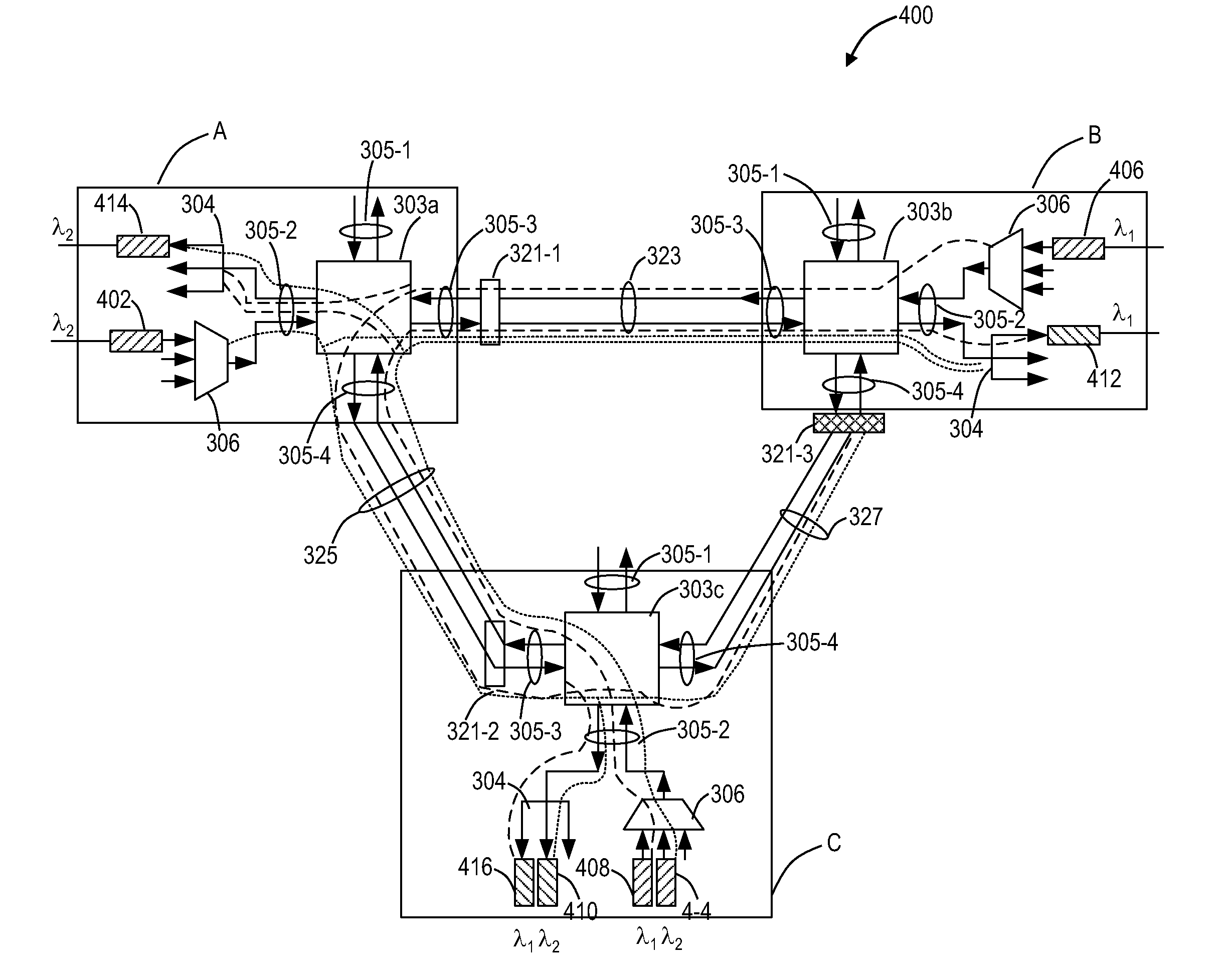
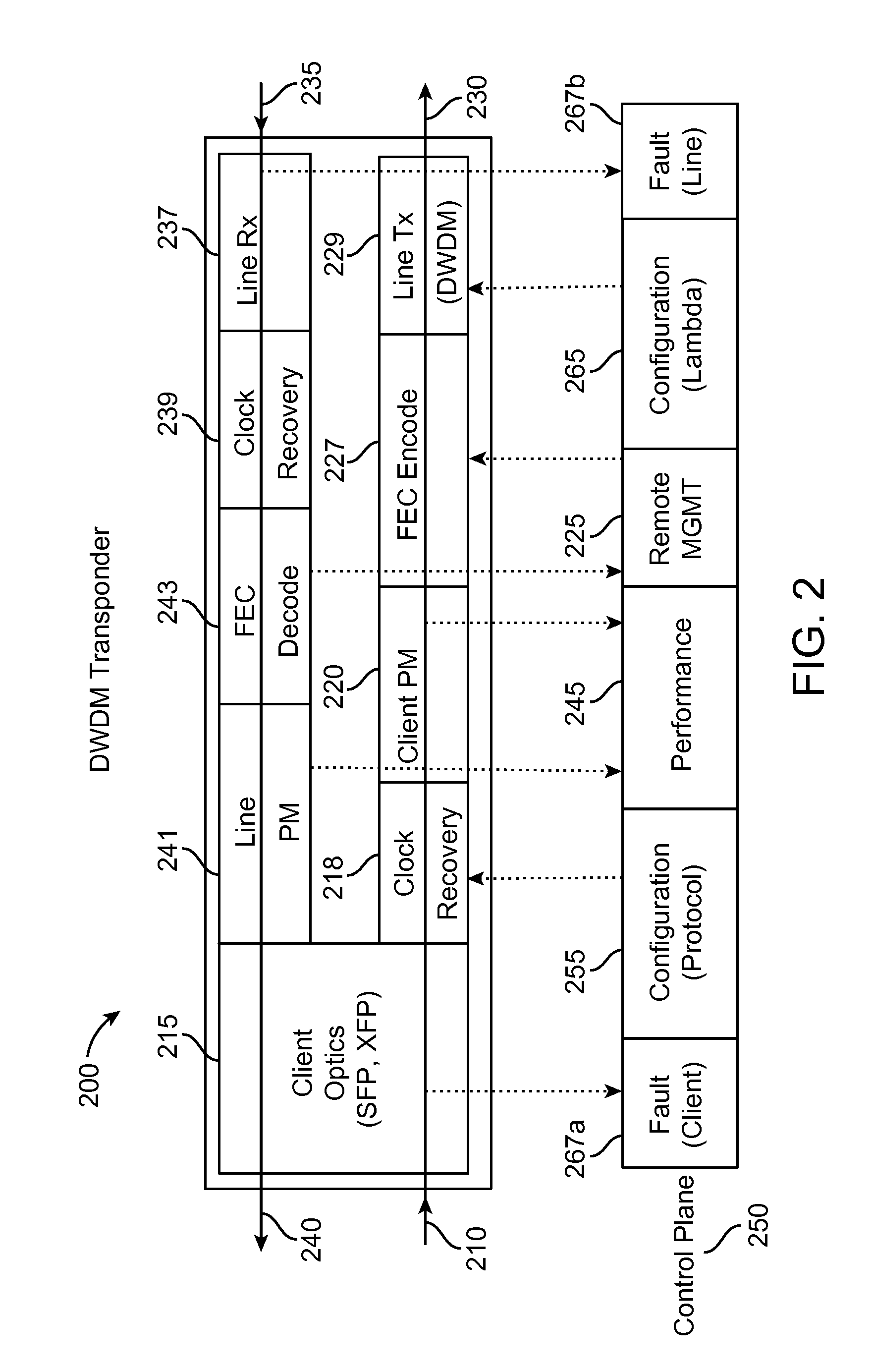
Optical Subchannel Routing, Protection Switching and Security
ActiveUS20110135305A1Easy mappingMaintaining full visibilityMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsNetwork architectureEngineering
The present invention includes novel techniques, apparatus, and systems for optical WDM communications. Tunable lasers are employed to generate subcarrier frequencies representing subchannels of an ITU channel to which client signals can be mapped. Client circuits can be divided and combined before being mapped, independent of one another, to individual subchannels within and across ITU channels. Subchannels may be independently routed to a single subchannel receiver filter, such that each subchannel detected at the receiver may come from a different source location. Network architectures and subchannel transponders, muxponders and crossponders are disclosed, and techniques are employed (at the subchannel level / layer), to facilitate the desired optical routing, switching, concatenation and protection of client circuits mapped to these subchannels across the nodes of a WDM network. Subchannel hopping may also be used to increase the optical network security.
Owner:SNELL HLDG LLC +1
Build-up structures with multi-angle vias for chip to chip interconnects and optical bussing
InactiveUS20050269687A1Improve performanceIncrease speedTelevision system detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesAnisotropic conductive filmEngineering
A build-up structure for chip to chip interconnects and System-In-Package utilizing multi-angle vias for electrical and optical routing or bussing of electronic information and controlled CTE dielectrics including mesocomposites to achieve optimum electrical and optical performance of monolithic structures. Die, multiple die, Microelectromechanical Machines (MEMs) and / or other active or passive components such as transducers or capacitors can be accurately positioned on a substrate such as a copper heatsink and multi-angle stud bumps can be placed on the active sites of the components. A first dielectric layer is preferably placed on the components, thereby embedding the components in the structure. Through various processes of photolithography, laser machining, soft lithography or anisotropic conductive film bonding, escape routing and circuitry is formed on the first metal layer. Additional dielectric layers and metal circuitry are formed utilizing multi-angle vias to form escape routing from tight pitch bond pads on the die to other active and passive components. Multi-angle vias can carry electrical or optical information in the form of digital or analog electromagnetic current, or in the form of visible or non-visible optical bussing and interconnections.
Owner:CAPITALSOURCE FINANCE
Combined optical fiber wheel, beamsplitter, switch, and logic gate
A machine that can pass, reflect, filter, or block light along multiple paths. The specific portions of light that can be passed, reflected, blocked, or filtered, are controlled by an optical routing subassembly. This optical routing subassembly can be manipulated to direct specific portions of light to specific paths.
Owner:KEYSTREAM LABS LLC
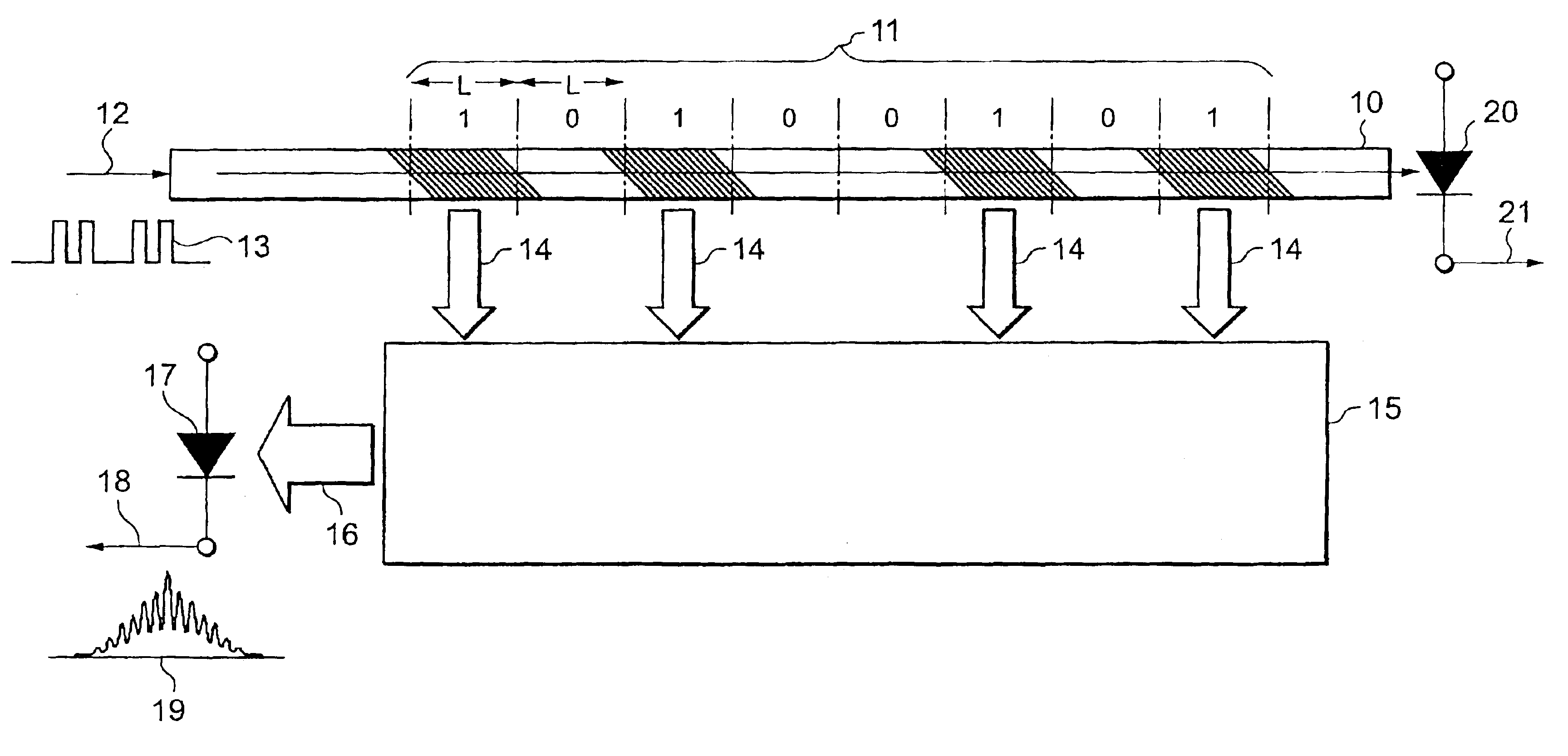
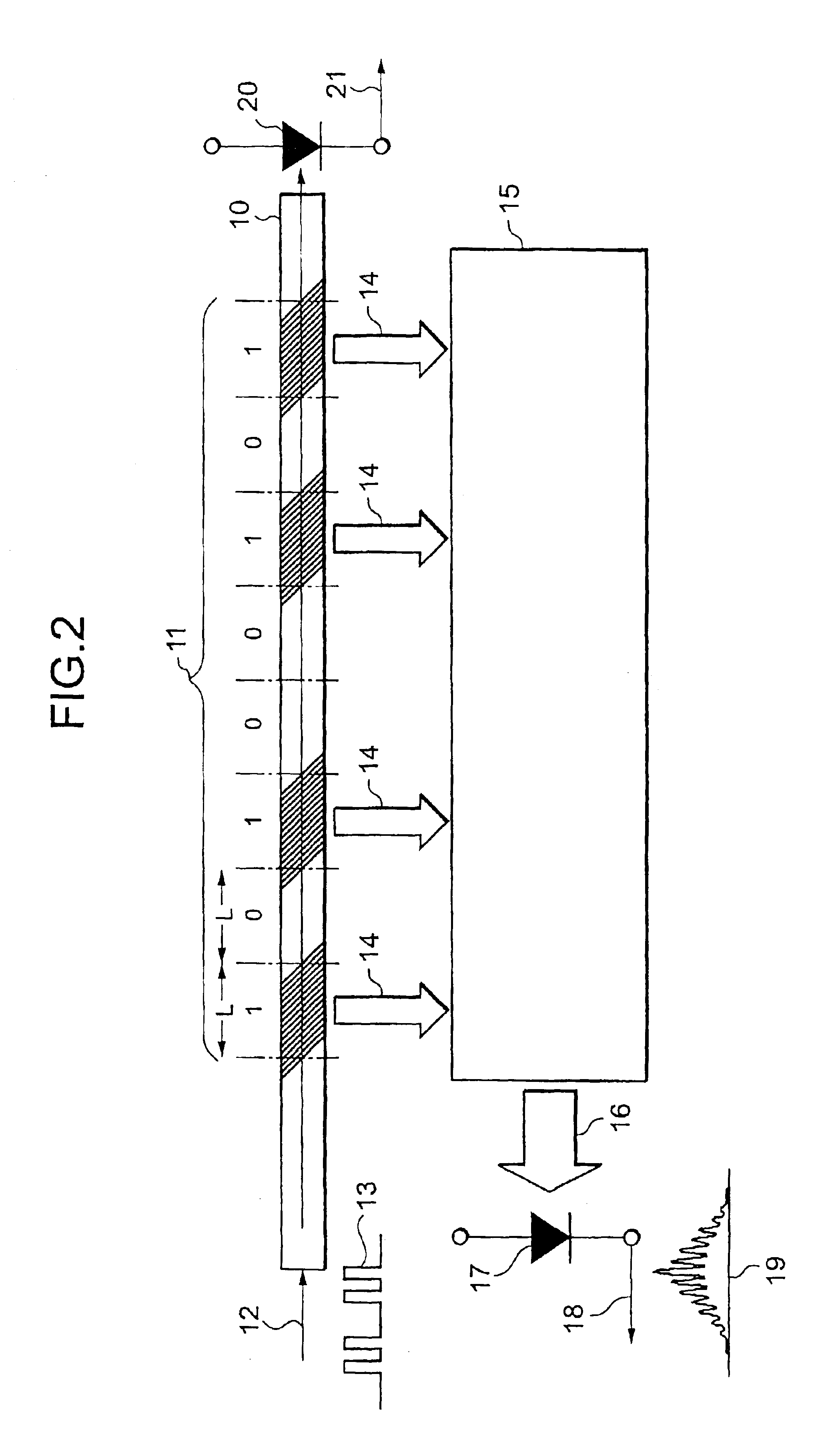
Optical packet header identifier, optical router incorporating the same therein, and optical routing method using the router
InactiveUS6892001B2Simple configurationReduce power consumptionMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsGratingOptical packet
An optical packet header identifier having a simplified configuration and being superior in reliability, stability, and economical efficiency, an optical router incorporating the identifier therein, and a routing method using the optical router are provided. The optical packet header identifier includes an optical waveguide, optical focusing elements, and a photo receiver. Tilted gratings for diffracting an incident optical beam and emitting the beams as diffracted optical beams to the outside of the waveguide are formed within the optical waveguide. The tilted gratings are not formed uniformly in a longitudinal direction of a core of the optical waveguide, but are arranged at intervals. The length of a portion containing a set of gratings and the length of a portion containing no gratings can be defined in increments of length “L”. “L” equals to the spatial length which 1 bit in an optical signal occupies.
Owner:LASERFRONT TECH
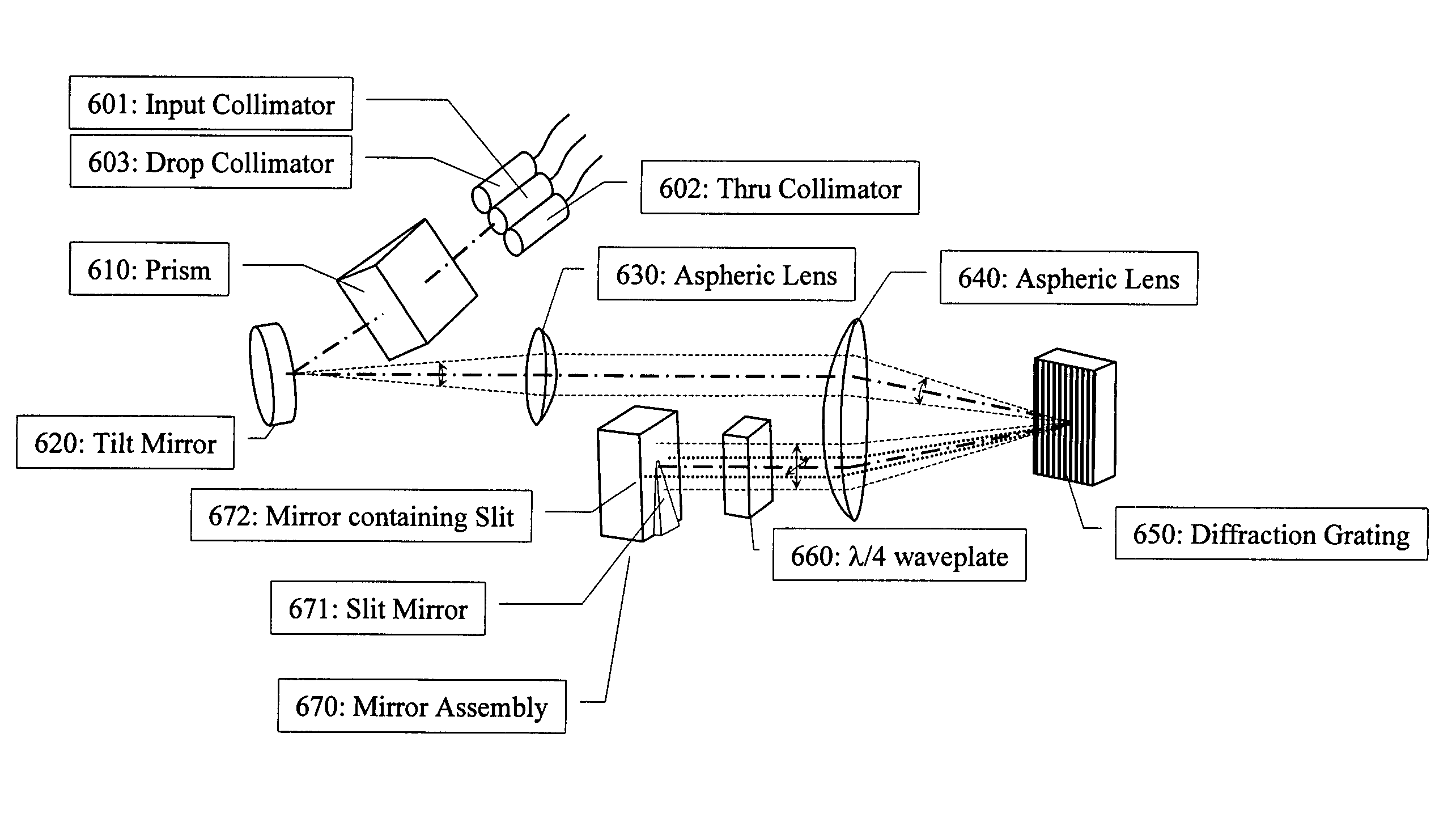
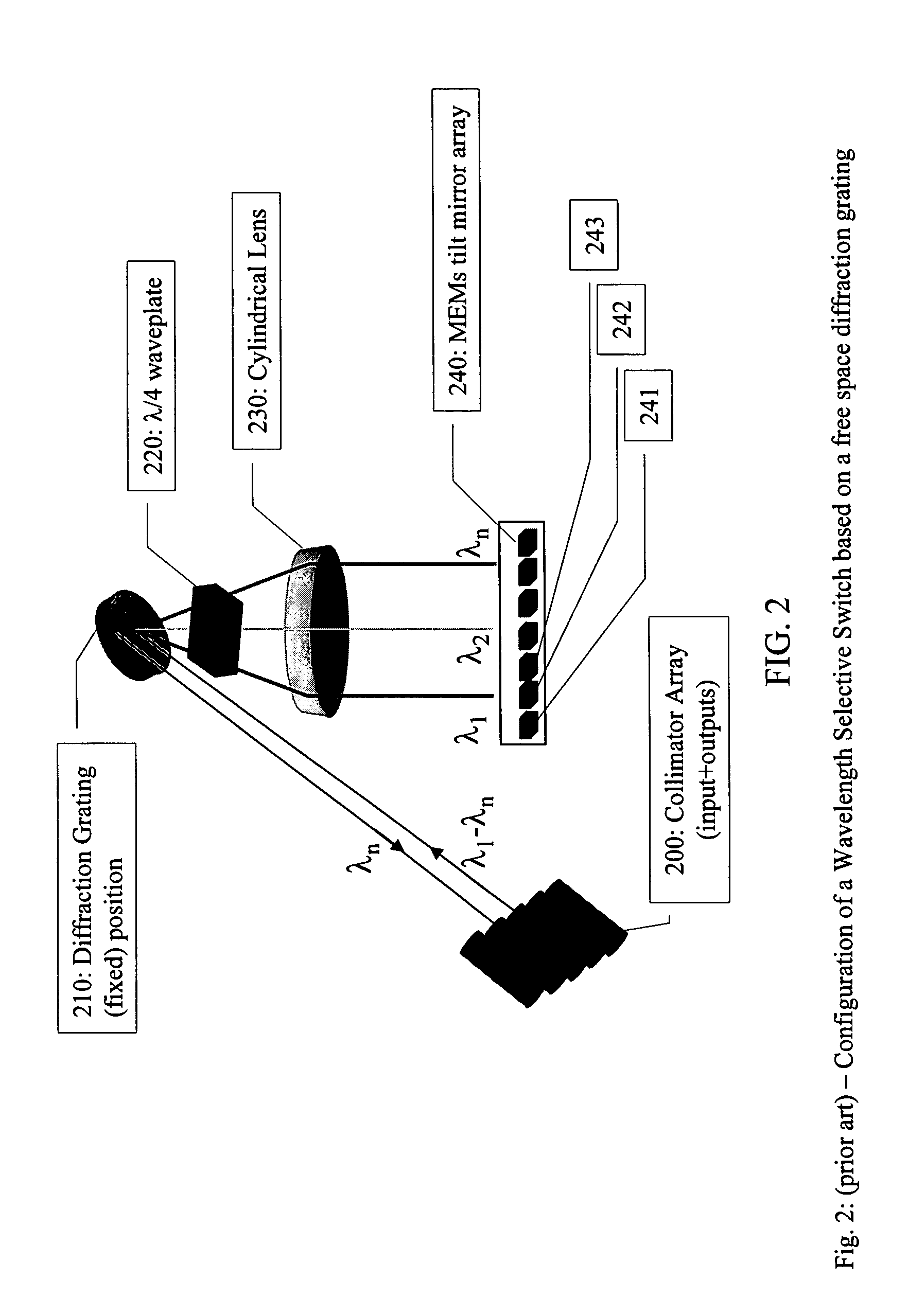
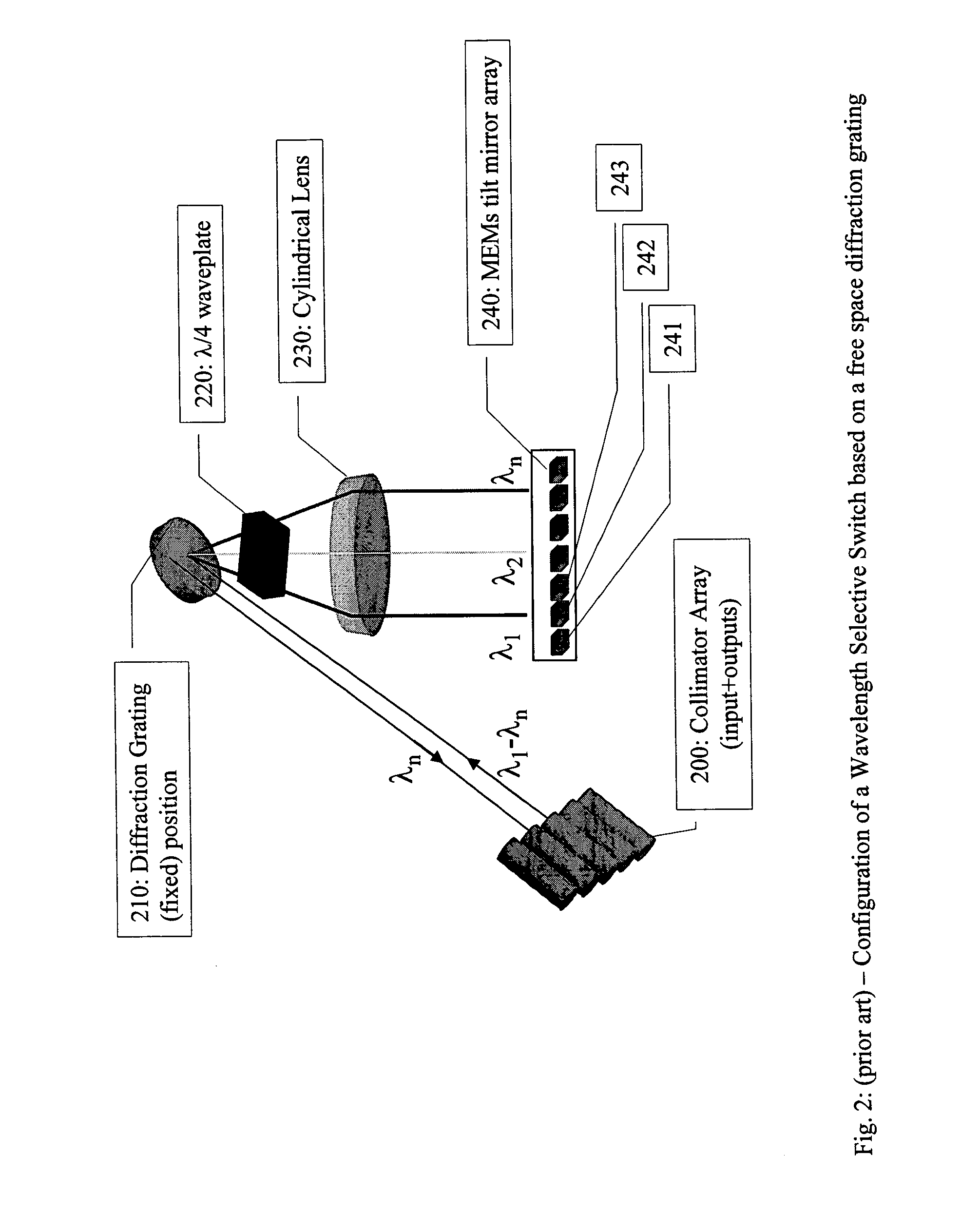
Tunable optical routing systems
Owner:MOLEX INC
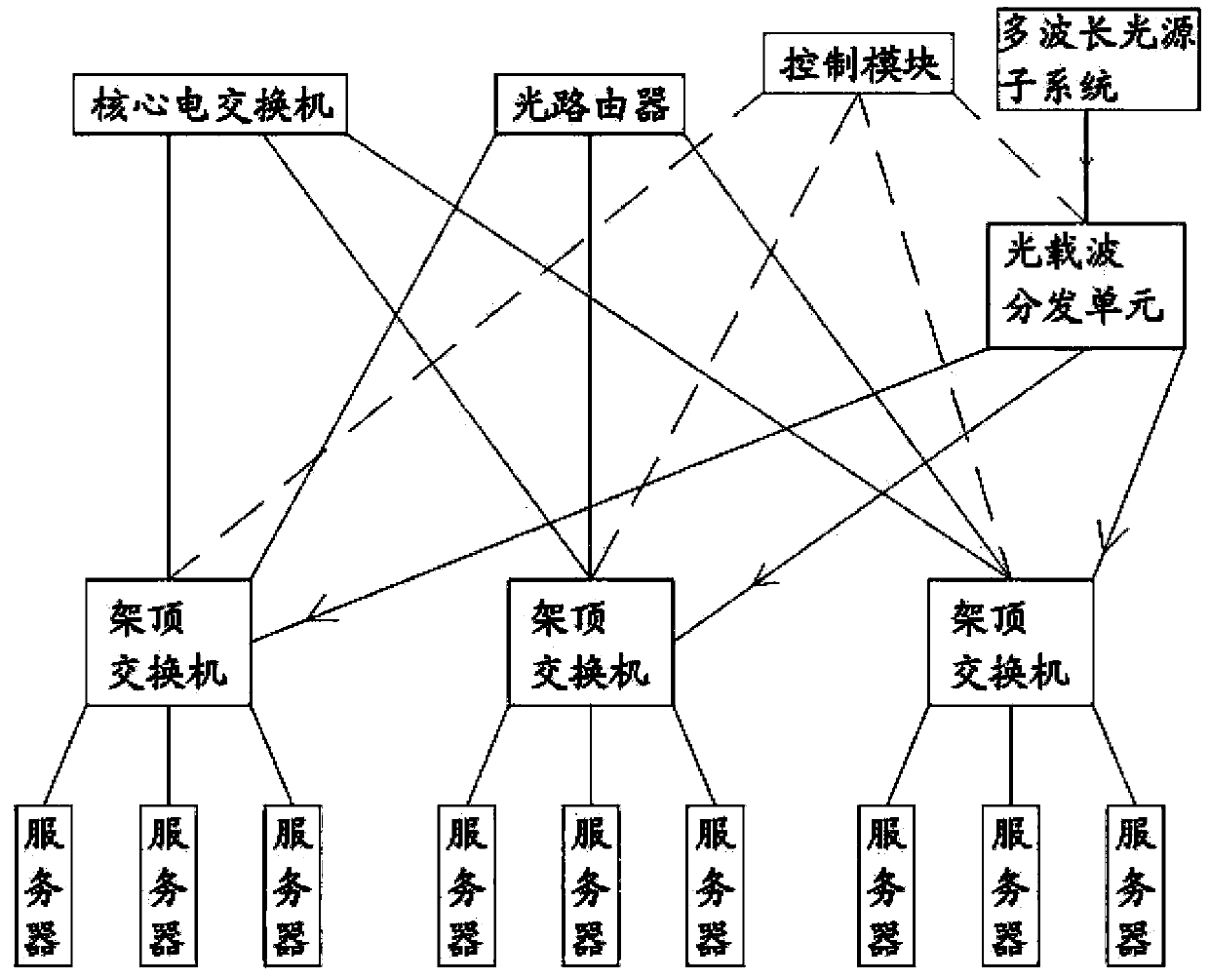
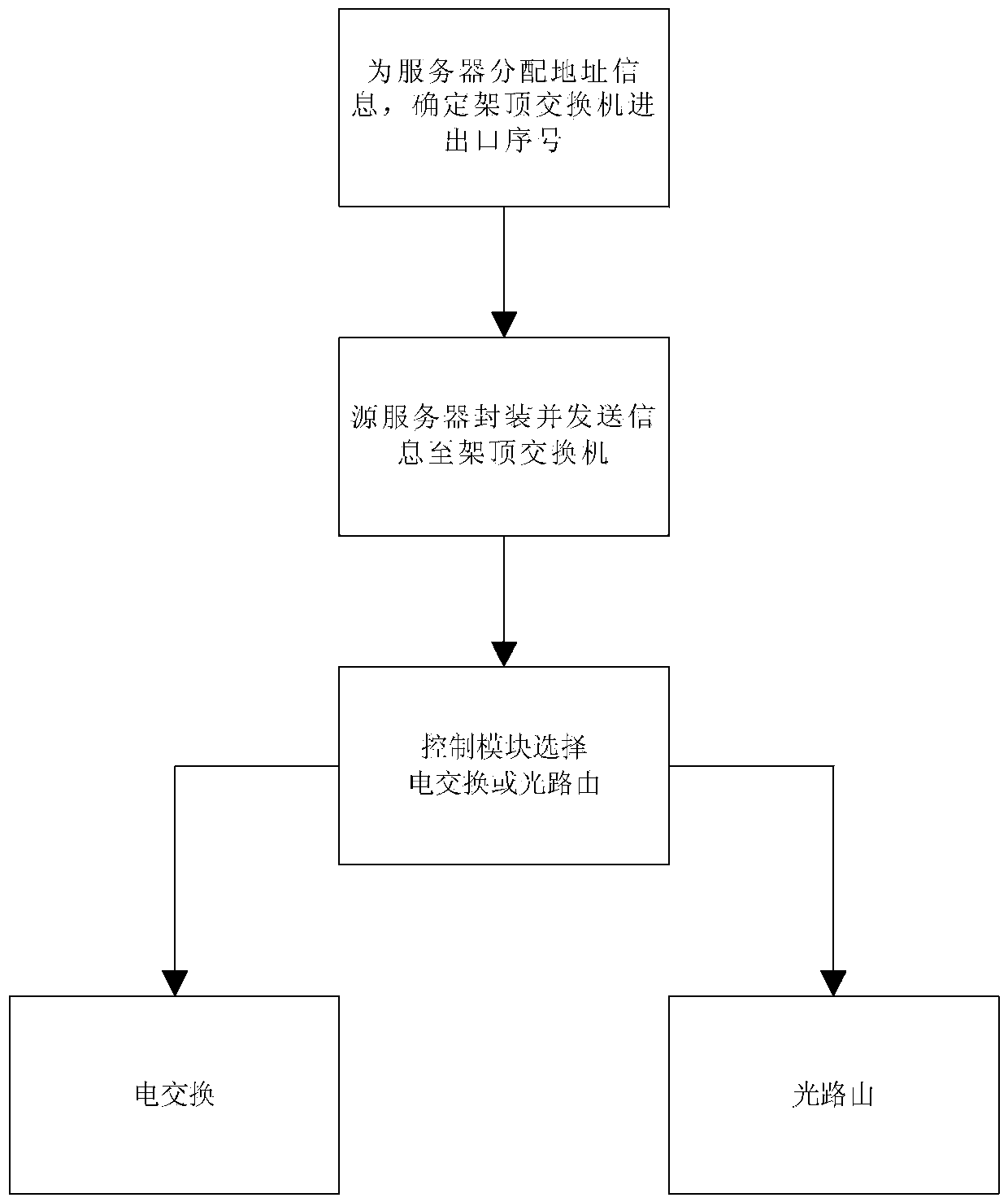
Data center network system and data communication method based on software definition
ActiveCN103441942AReduce energy consumptionEmission reductionMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching networksTraffic characteristicData center
The invention provides a data center network system and data communication method based on software definition and relates to the technical field of cloud calculating data centers. The data center network system structurally comprises a core electric switch, an optical router, a top-of-rack switch, servers, a control module, an optical carrier wave distribution unit and a multi-wavelength light source subsystem. In data communication, communication optical carrier waves are allocated according to the address of the destination server of data and the traffic of the data; the data are sent to the top-of-rack switch after being packaged by the source server; the control module determines and selects an electric switching path or an optical routing path to forward the data according to the address of the destination server and the traffic characteristics of the data information and the corresponding routing algorithm. The top-of-rack switch performs light modulation on the data according to instructions of the control module and forwards the data to the corresponding electric switching or optical routing path. The data center network system and data communication method based on software definition have very good energy saving effect, are low in construction cost and improve the management efficiency of a data center network and the performance of the network.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
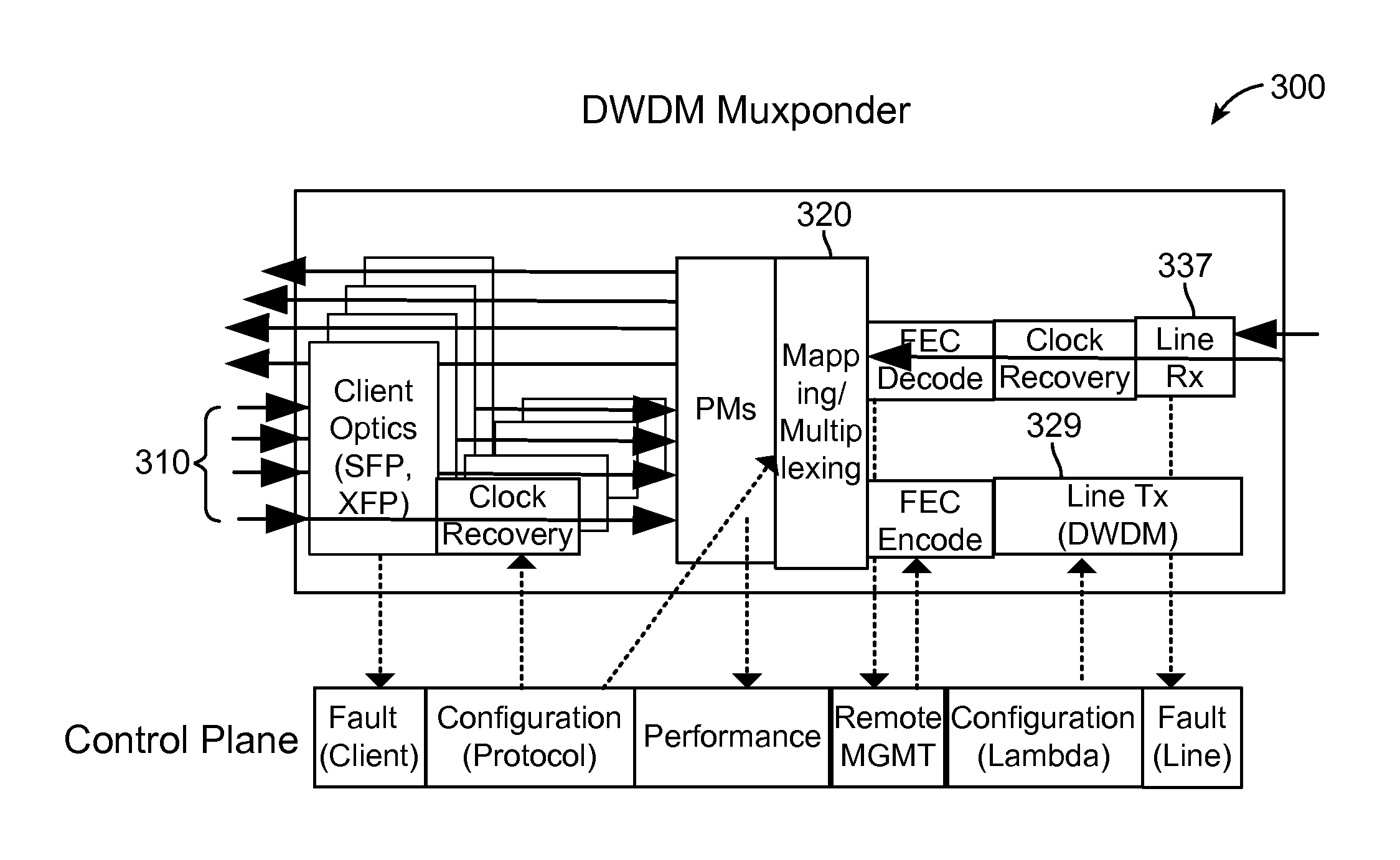
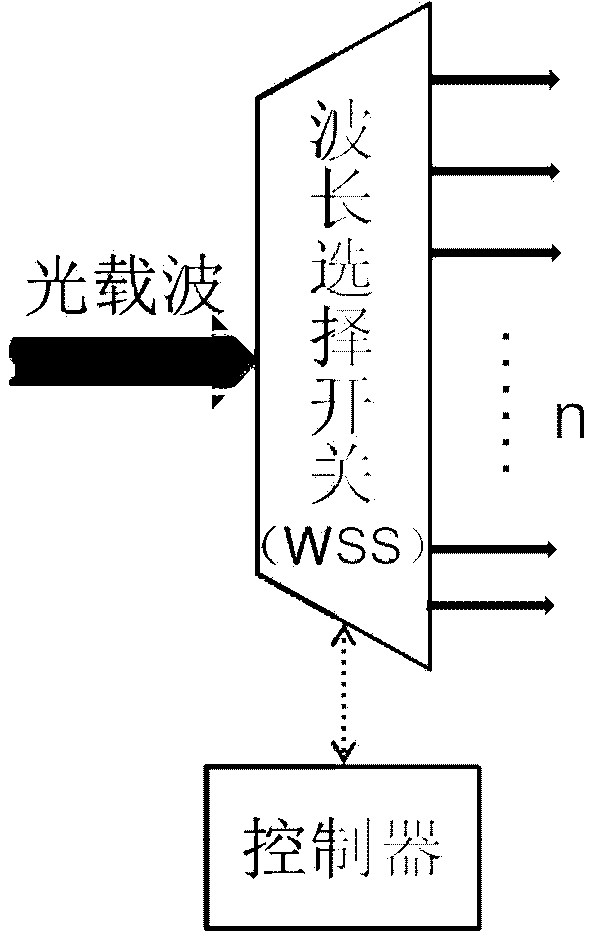
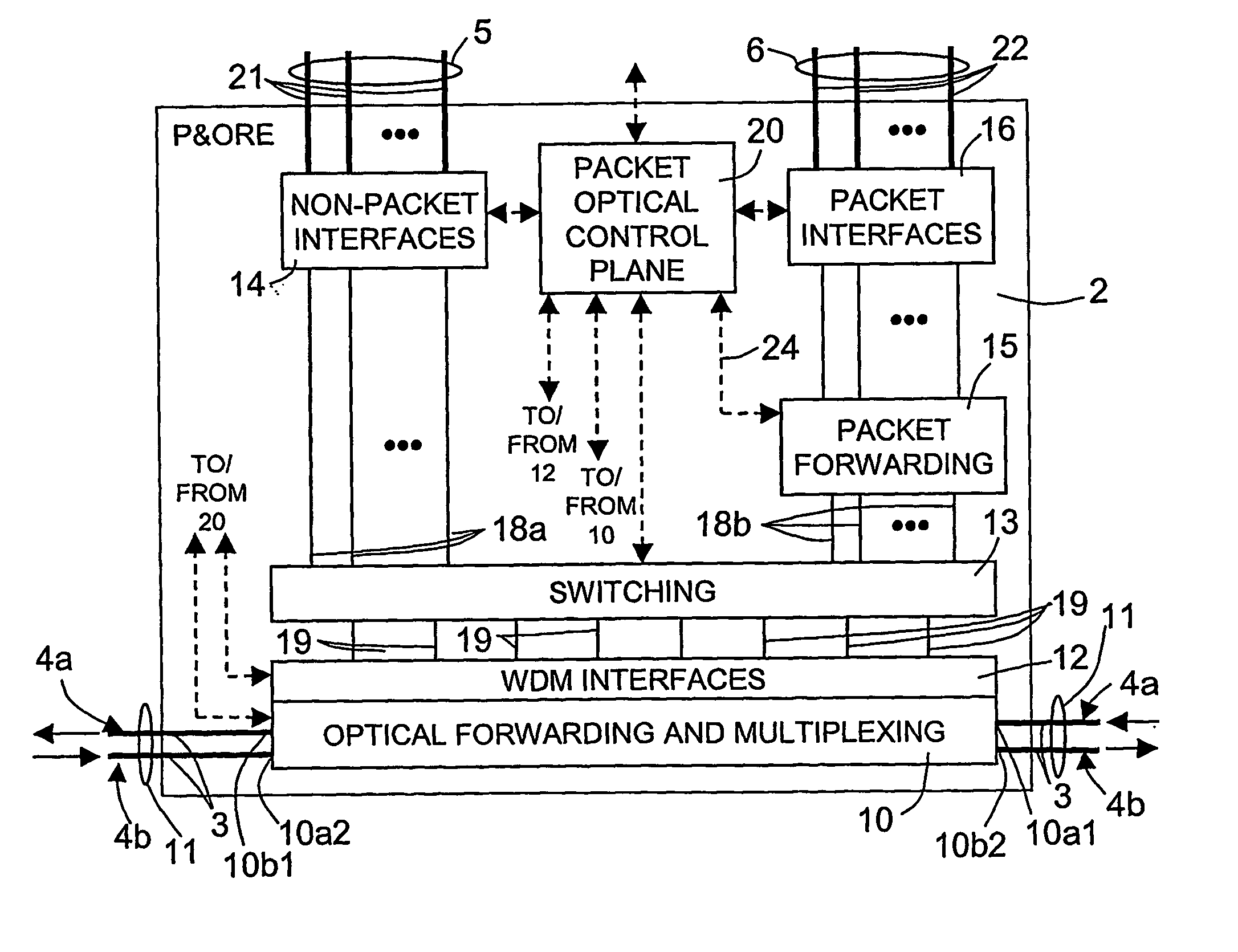
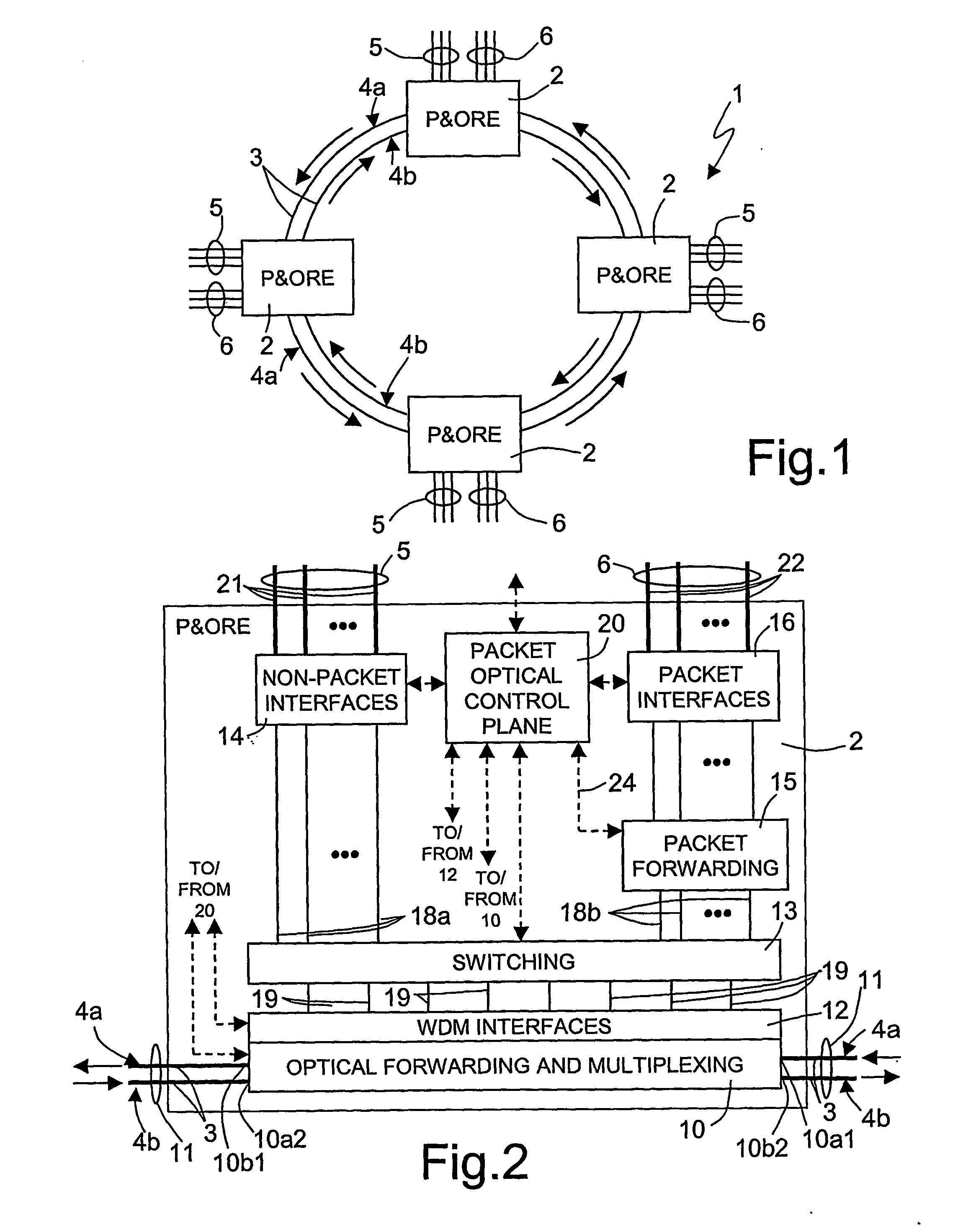
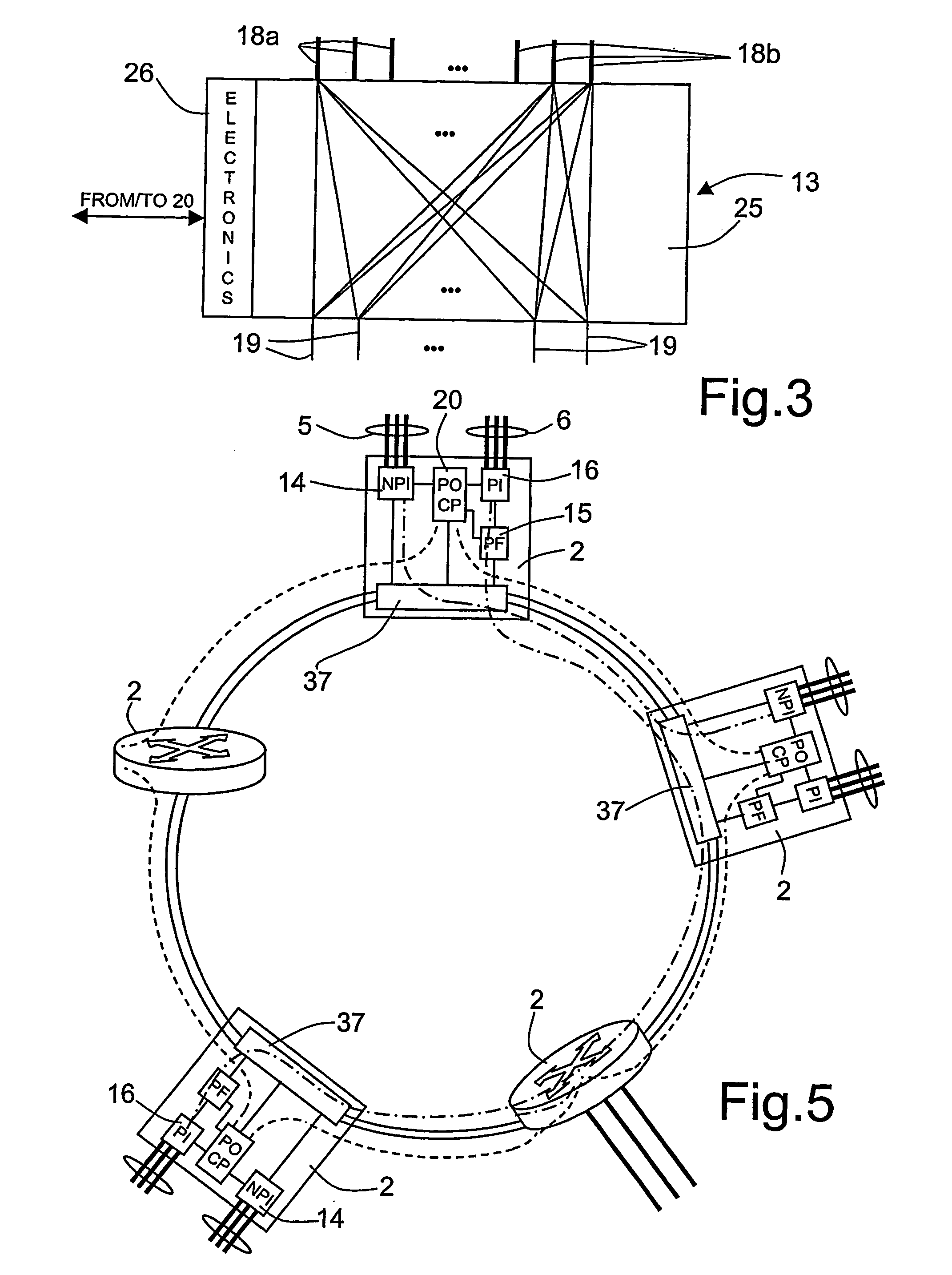
Packet and optical routing equipment and method
InactiveUS20060257143A1Savings in implementationSavings in operationMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultiplexingElectricity
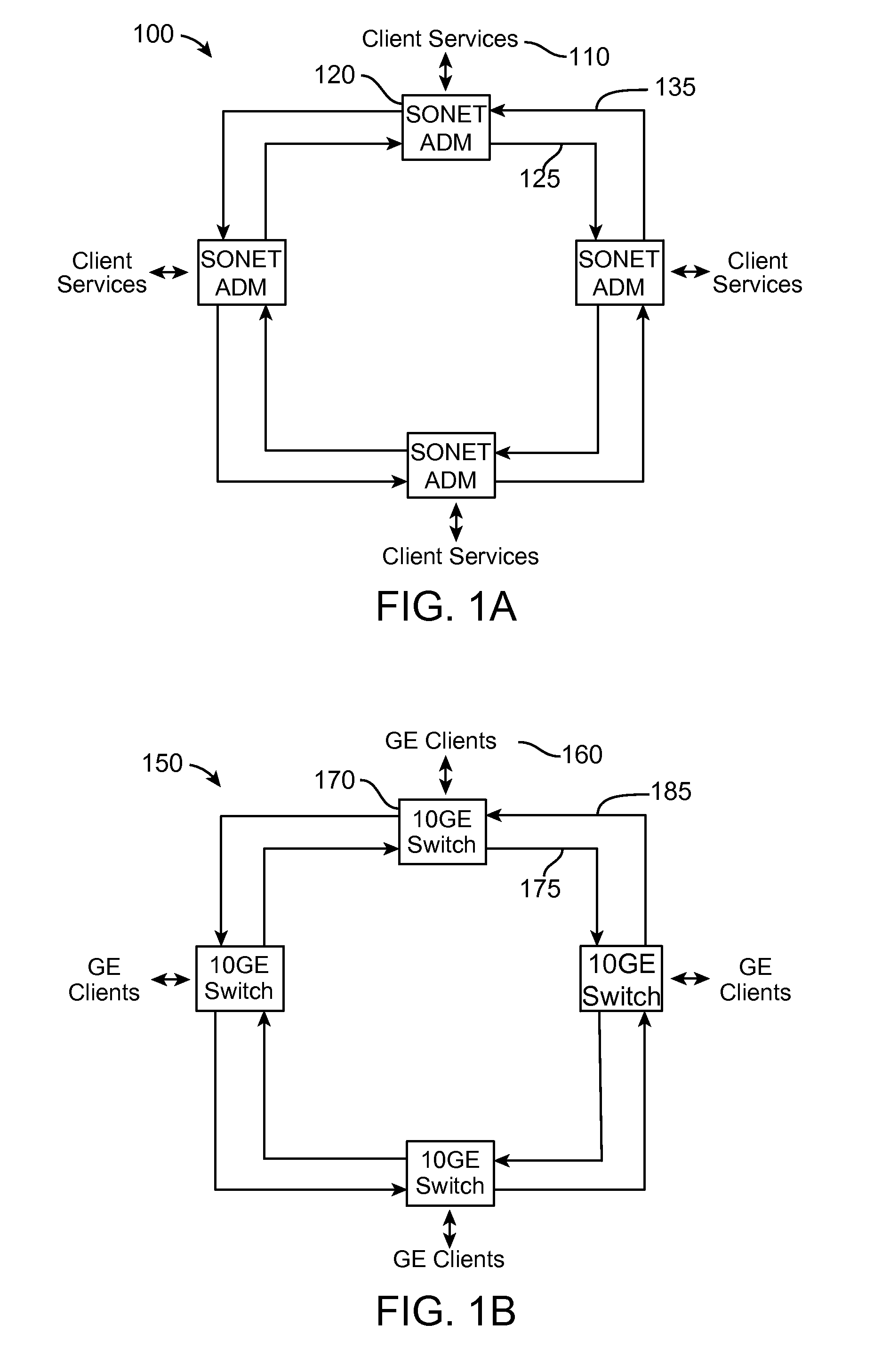
A packet and optical routing equipment exchanges multiplexed optical signals with other equipment in a network and exchanges branch non-packet and packet signals with client equipment. The entering branch non-packet signals are converted into electric signals by a non-packet interface and supplied directly to an electric switching unit, the entering packet branch signals are converted into electric signals, supplied to a packet forwarding module and routed to the electric switching unit. The electric switching unit switches the electric signals toward a WDM interface that converts them into optical signals at selected wavelengths that are added to the multiplexed optical signals. The entering multiplexed optical signals that should be terminated in the equipment are extracted, converted into electrical signals, and electrically switched toward the non-packet interface or the packet forwarding module according to whether they are of non-packet or of a packet type. The switching unit is of configurable type and may switch a variable ratio of electric non-packet and packet signals according to the traffic requirements.
Owner:TELECOM ITALIA SPA +1
Optical Subchannel-Based Cyclical Filter Architecture
InactiveUS20110158658A1Easy to switchIncrease the number ofMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultiplexingNetwork architecture
The present invention includes novel techniques, apparatus, and systems for optical WDM communications. Tunable lasers are employed to generate respective subcarrier frequencies which represent subchannels of an ITU channel to which client signals can be mapped. In one embodiment, subchannels are polarization interleaved to reduce crosstalk. In another embodiment, polarization multiplexing is used to increase the spectral density. Client circuits can be divided and combined with one another before being mapped, independent of one another, to individual subchannels within and across ITU channels. A crosspoint switch can be used to control the client to subchannel mapping, thereby enabling subchannel protection switching and hitless wavelength switching. Network architectures and subchannel transponders, muxponders and crossponders are disclosed, and techniques are employed (at the subchannel level / layer), to facilitate the desired optical routing, switching, concatenation and protection of the client circuits mapped to these subchannels across the nodes of a WDM network.
Owner:SNELL HLDG LLC +1
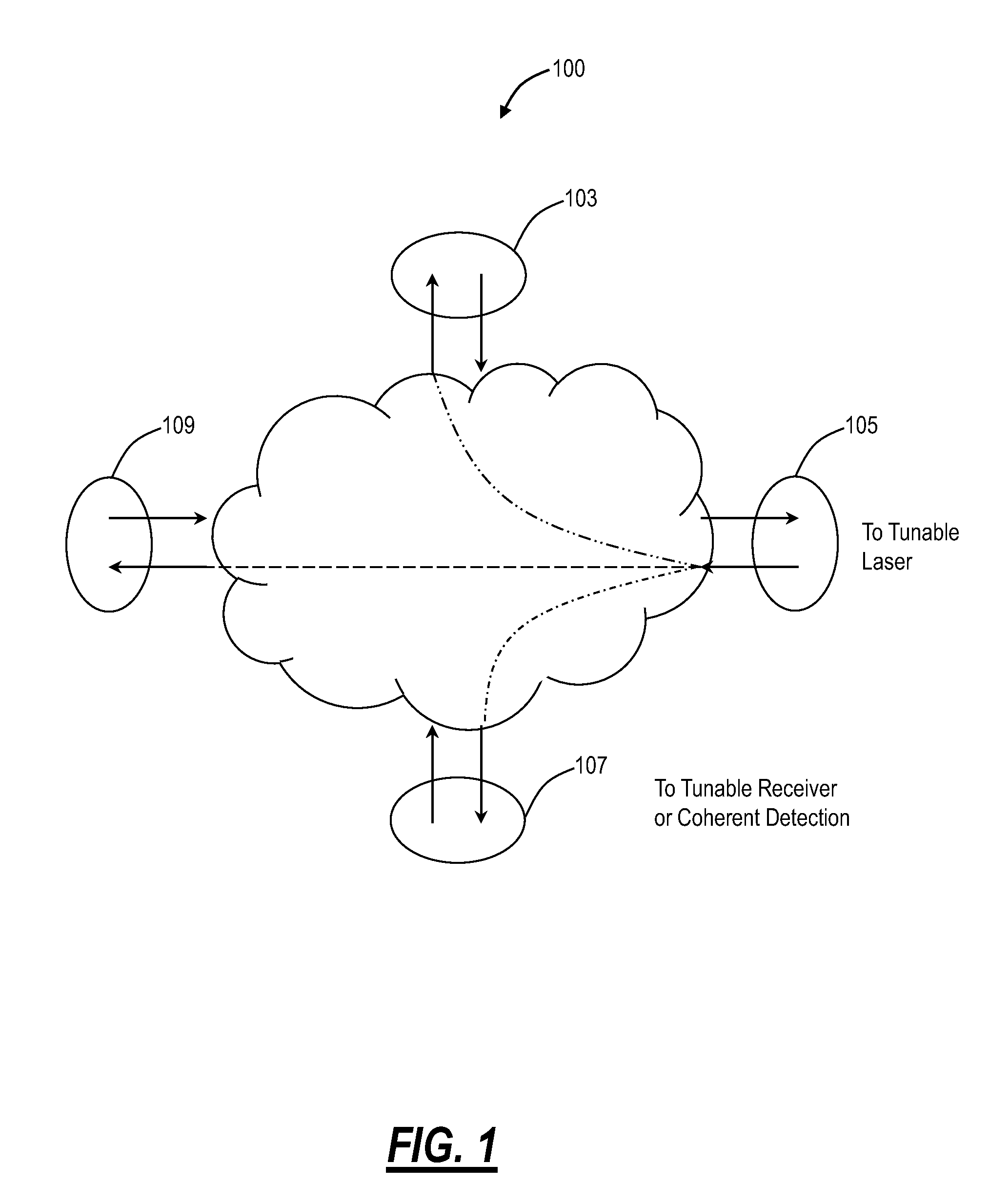
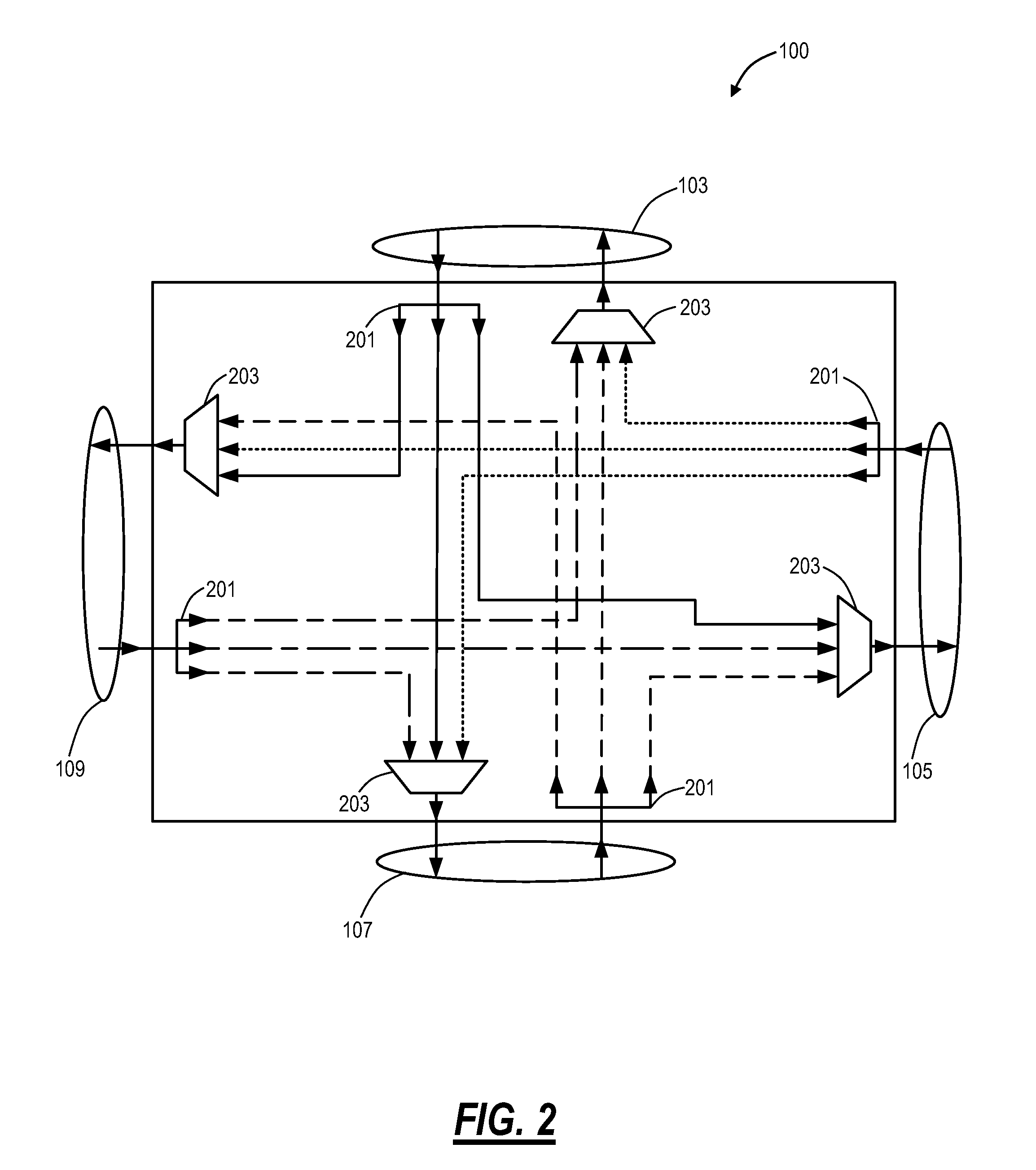
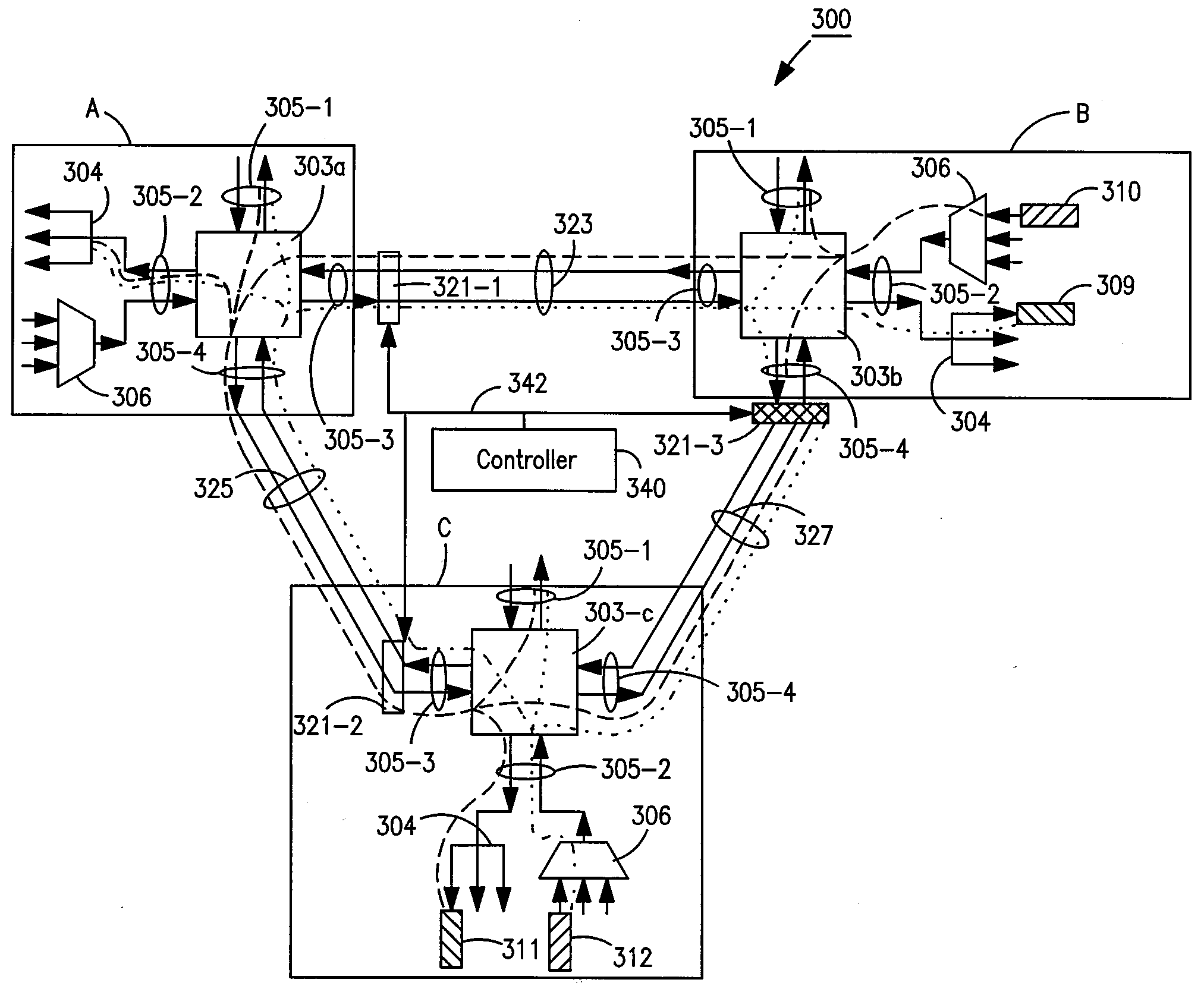
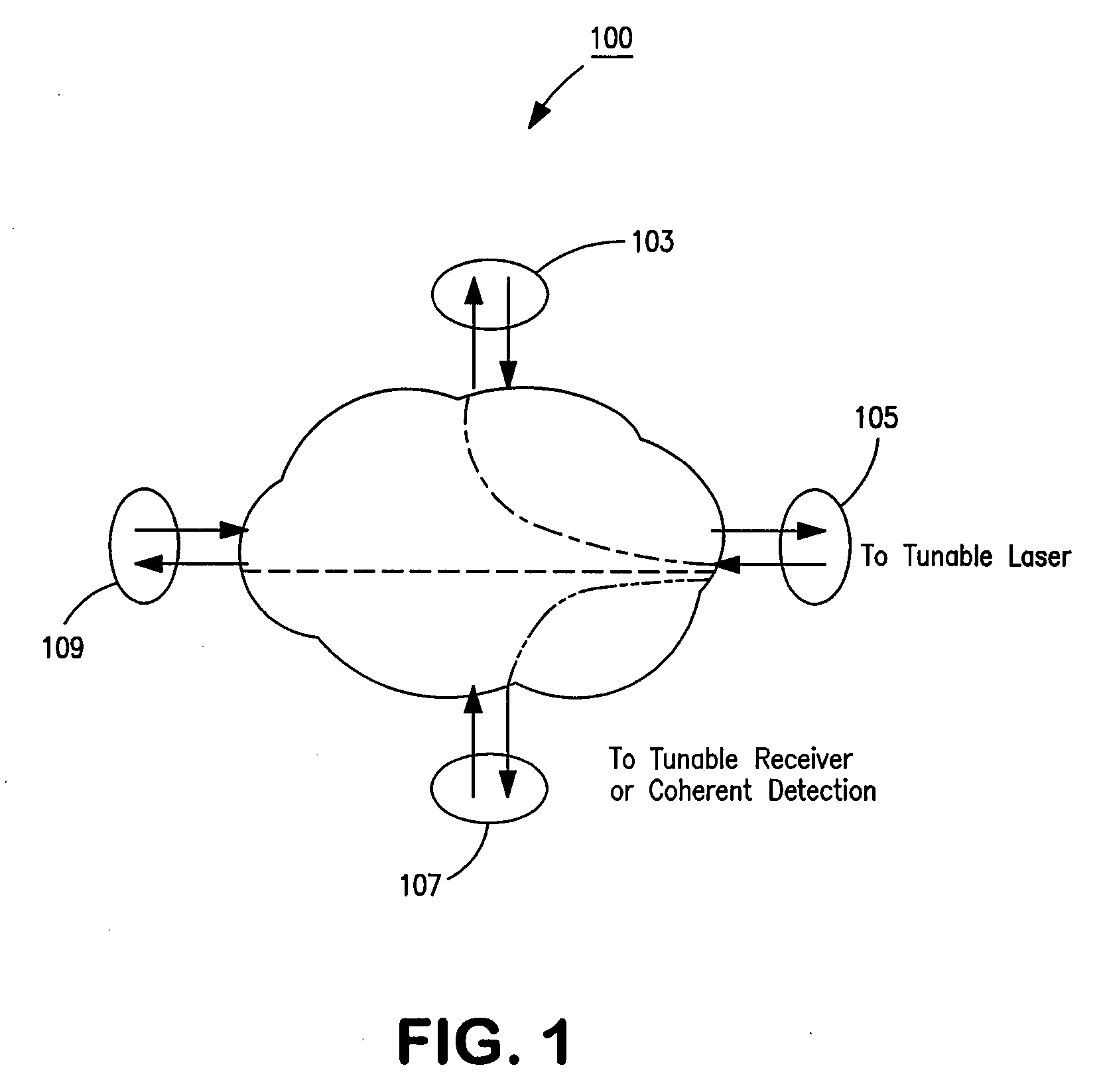
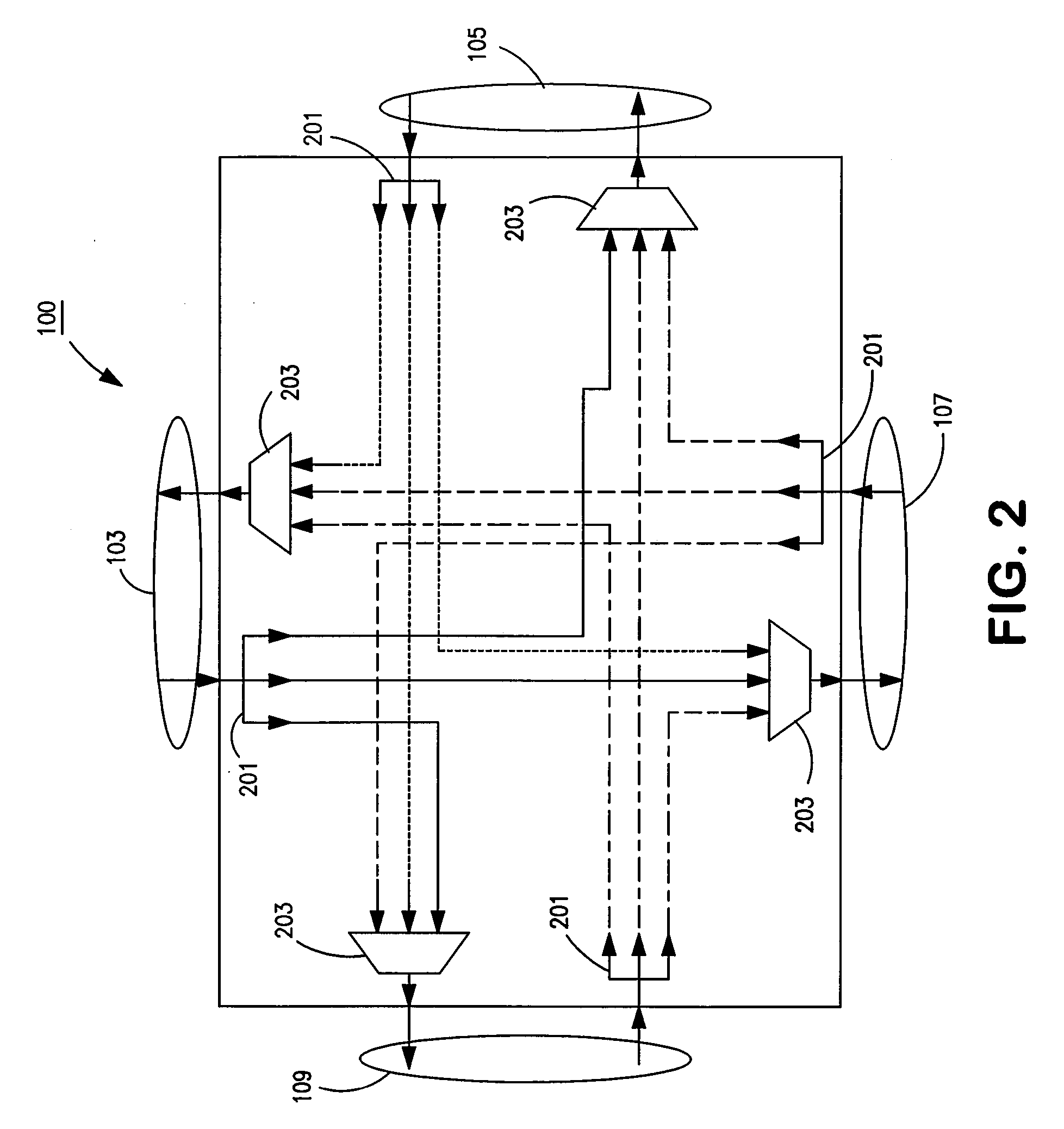
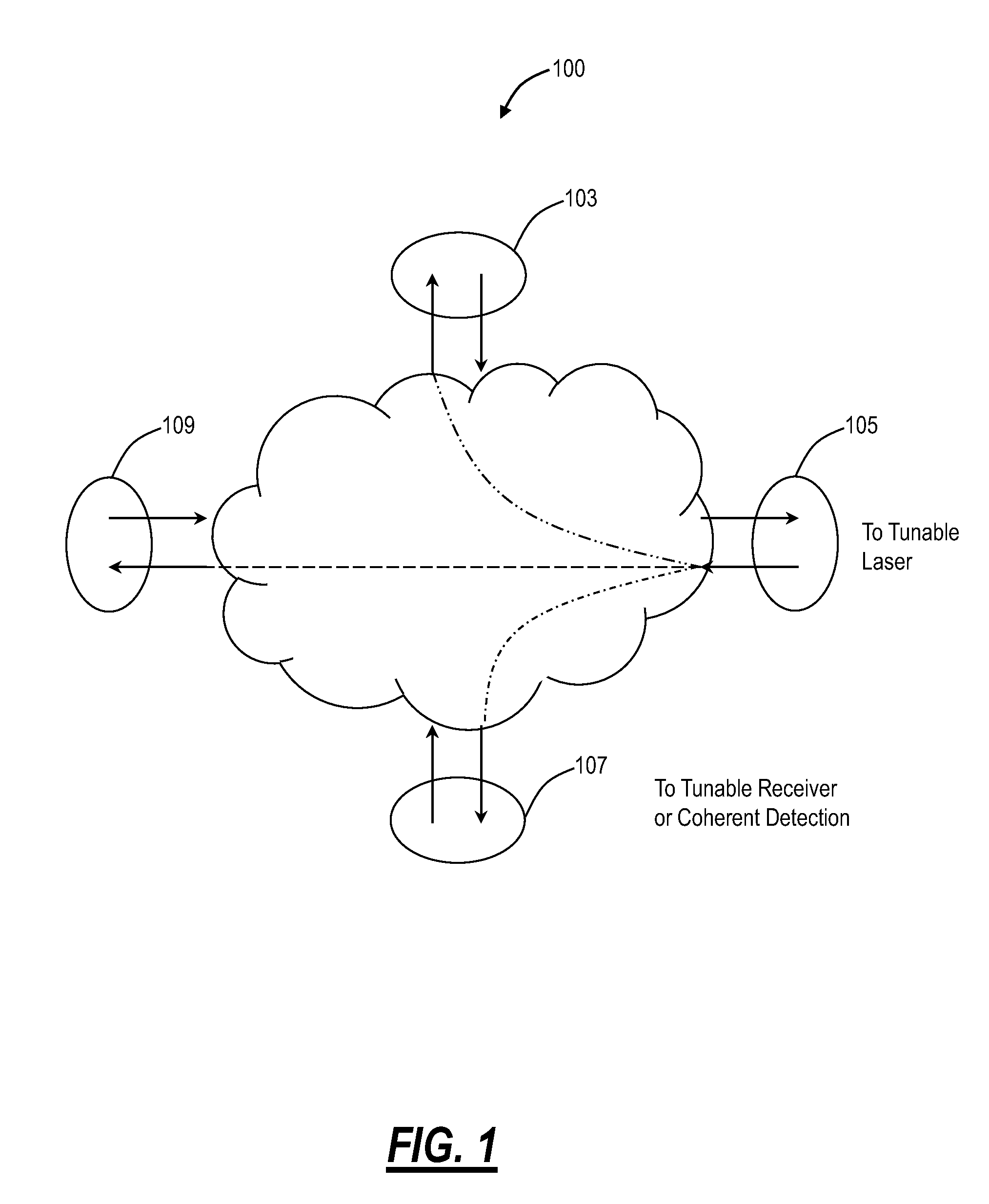
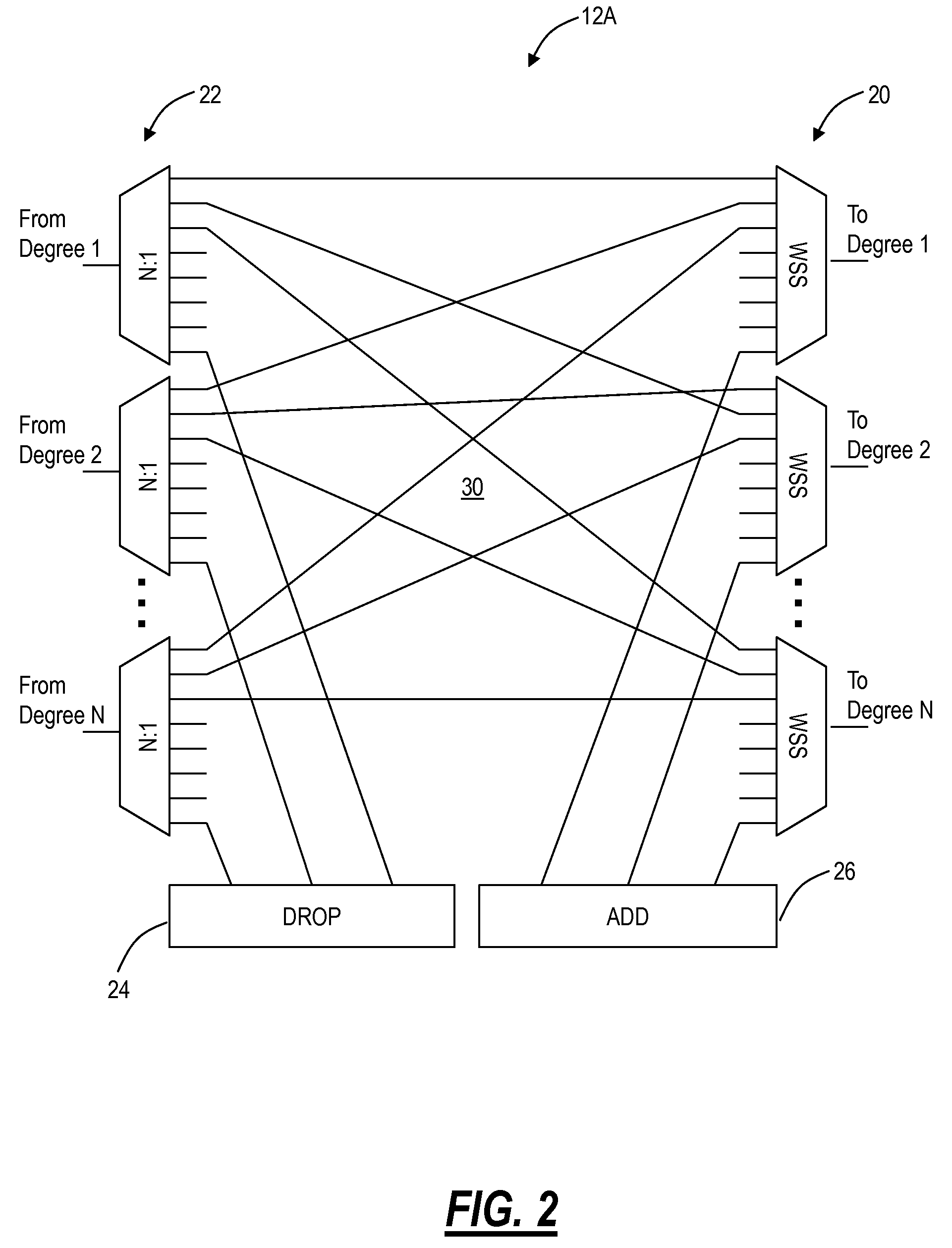
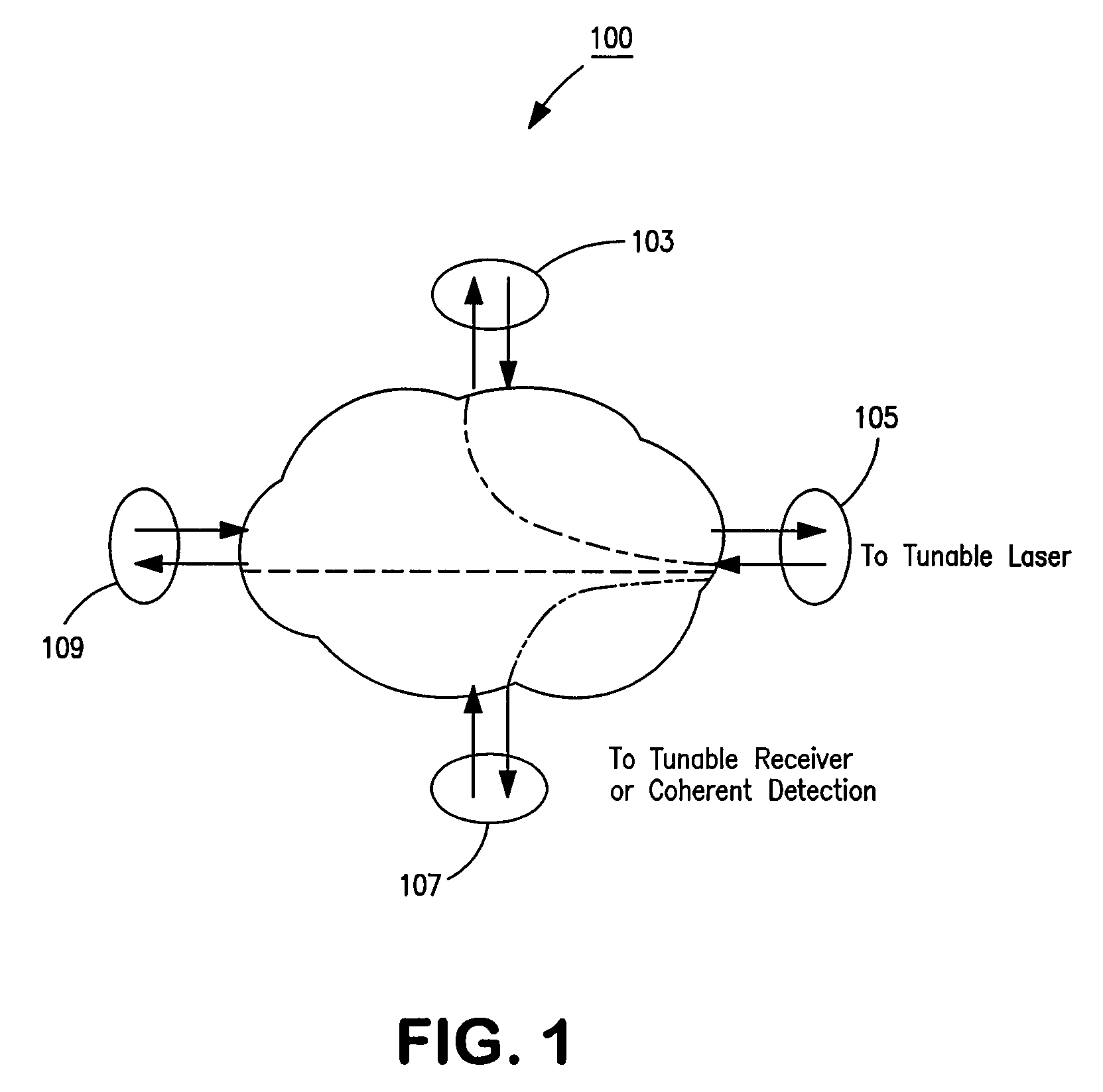
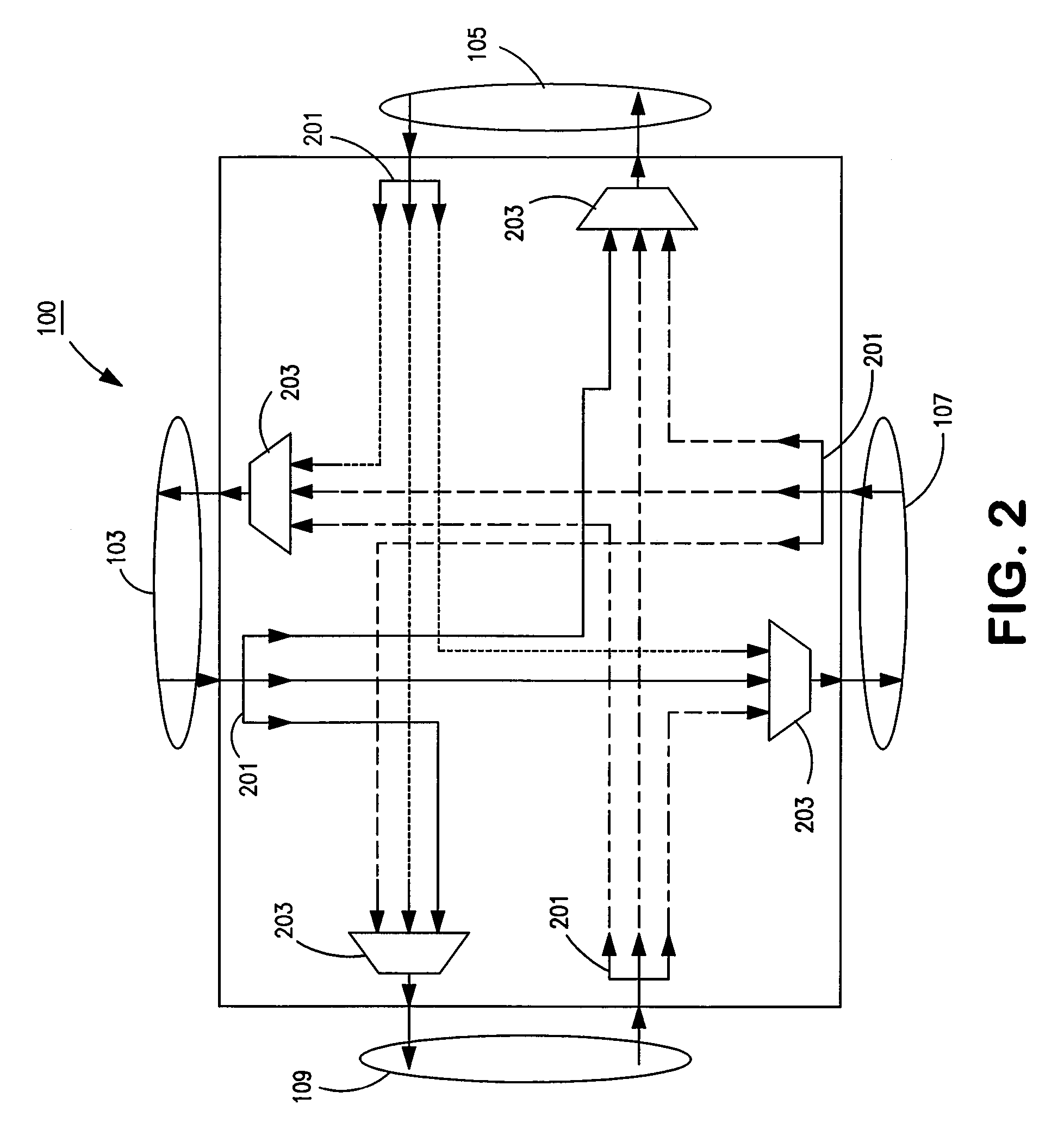
Optical routing device and optical network using same
ActiveUS20100284691A1Blocking in networkMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical couplerOptical routing
The invention pertains to methods, apparatus, and systems optical of networking using tunable receivers, optical blocking elements selectively placed in the network, and optical routing elements comprised of passive elements, such as optical couplers and splitters. The routing elements have a plurality of ports and comprise passive elements such as couplers and splitters configured so that input light received at any port of the element is output from each of the other ports of the element, but not at port at which it was input.
Owner:CIENA
Colorless, directionless, and gridless optical network, node, and method
An optical node includes an optical routing apparatus including N ports, N is an integer greater than 2, the optical routing apparatus configured to direct light that is input to each of the N ports to all of the other N ports, and a configurable optical blocking element located in line with at least one of the N ports. A method includes broadcasting a plurality of optical signals over a plurality of ports using a broadcast element, selectively receiving a desired signal from all of the plurality of optical signals at one of the plurality of ports, and blocking the plurality of signals via a blocking element in line with one of the plurality of ports thereby preventing a multiple path of the broadcast plurality of optical signals.
Owner:CIENA
Tunable optical routing systems
ActiveUS7408639B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsRadiation pyrometryAngle of incidenceActuator
An optical spectral detection device utilizing free space optical beam propagation is provided. The device includes at least one optical fiber input, at least one opto-electronic detection device, an optical element having an actuator with at least one tilt axis, and a diffraction element having a surface thereon. The device also includes an optical beam transfer arrangement positioned between the optical element and the diffraction element such that tilt actuation of the optical element elicits a proportional change in an angle of incidence of the optical beam onto the diffraction element, wherein the center of rotation for the angular change is the surface of the diffraction element. The spectral properties of the optical beam that are detected are selected by selectively positioning the optical element about at least one of the tilt axes.
Owner:CHRISTOPHER S KOEPPEN +1
Method and system for optical routing of variable-length packet data
InactiveUS20050047392A1Facilitates full optical routingMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionData segmentStart time
A method and system of routing variable-length packet data across a wave division multiplex (WDM) communications network having a plurality of data communications channels comprises inverse-multiplexing each data packet into a respective frame. Each frame includes a label block containing label information of the frame, and two or more respective payload blocks having a predetermined length. The label block contains encoded routing information, a start time, and, possibly an end time, and is transmitted over a label channel of the communications network. The start time preferably indicates a delay between launching a first bit of the label clock and the first bit of the payload blocks. The end time may be a bit count indicative of the location of the last bit of the data packet within the frame. The data packet is divided into a plurality of data segments, each of which is transported across the network within a respective payload block. Each payload block is transmitted over a respective separate data channel of the communications network. Routing control of the frame may be handled using the multi-protocol label switch (MPLS) protocol.
Owner:BIOSPHERICS
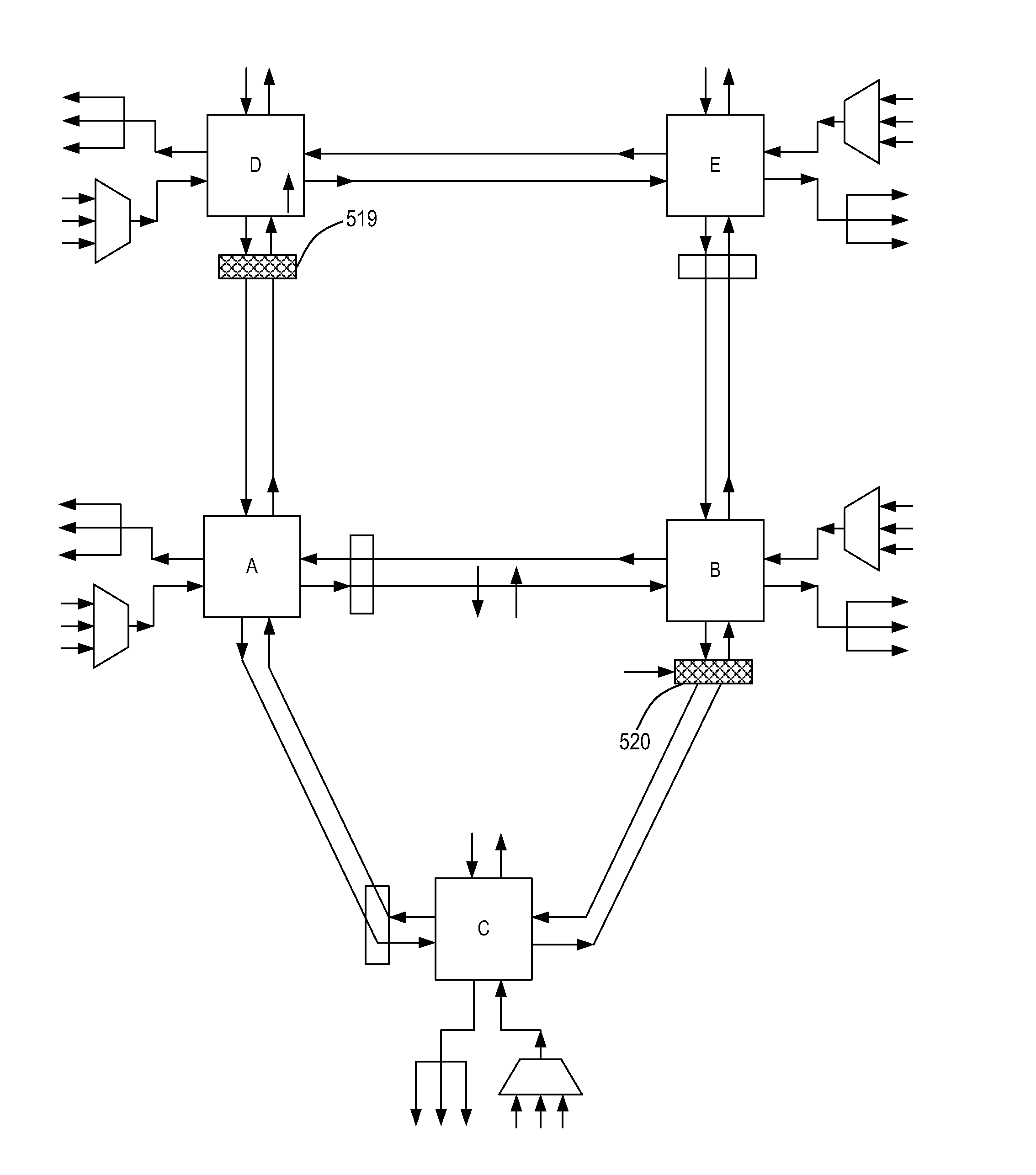
Photonic routing systems and methods for loop avoidance
A photonic network includes a plurality of nodes each supporting add and drop of at least Y wavelengths, a plurality of optical links interconnecting the plurality of nodes, the plurality of optical links support up to X wavelengths and Y≦X, an optical routing protocol configured to compute a loop-free path through the plurality of nodes on the plurality of links, the loop-free path is computed for one of the X wavelengths or a group of the X wavelengths using routing constructs adapted to a photonic domain, and optical components at each of the plurality of nodes configured to selectively block at least one of the X wavelengths based on the computed loop-free path. A photonic routing method and photonic node are also disclosed.
Owner:CIENA
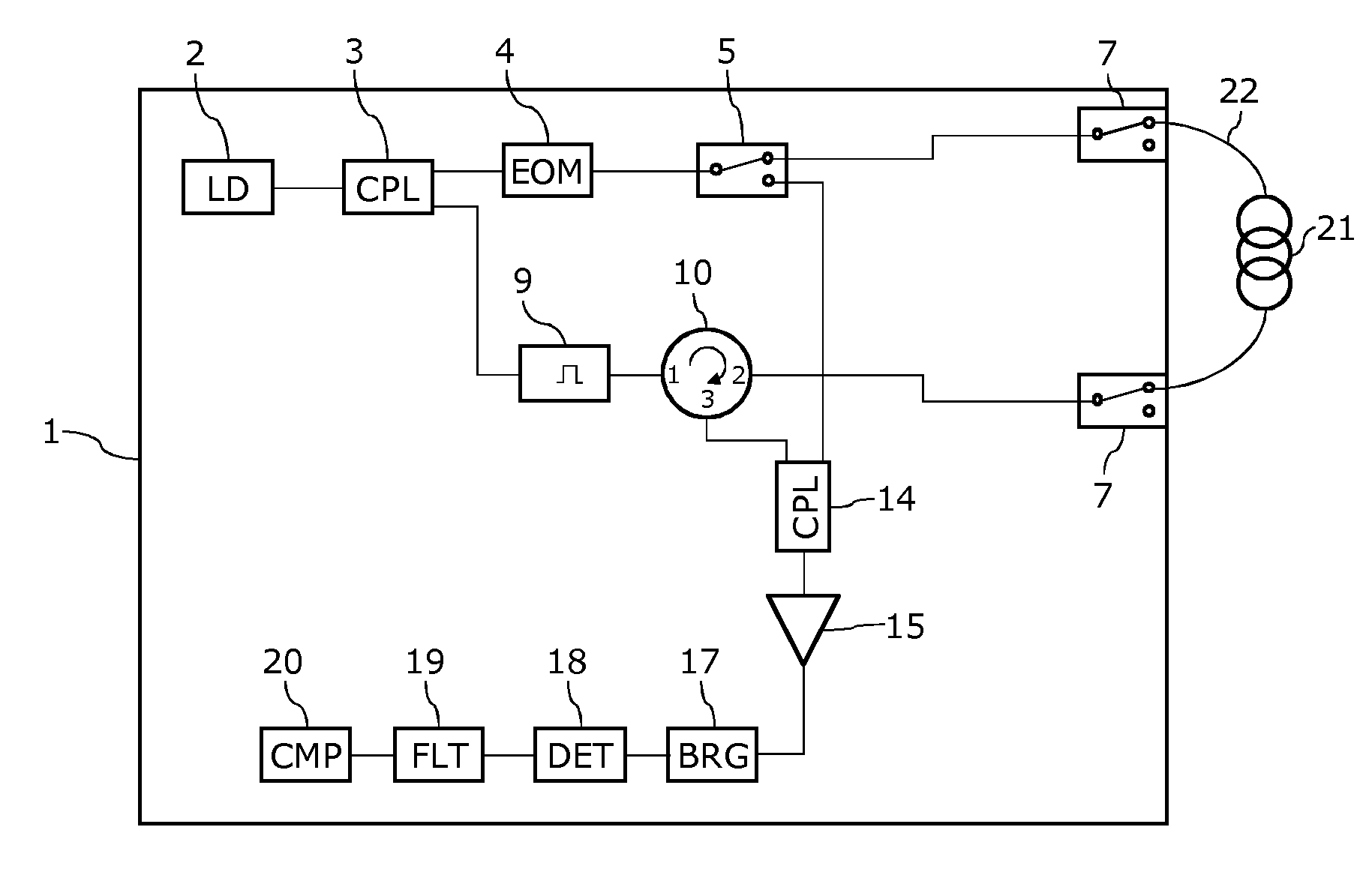
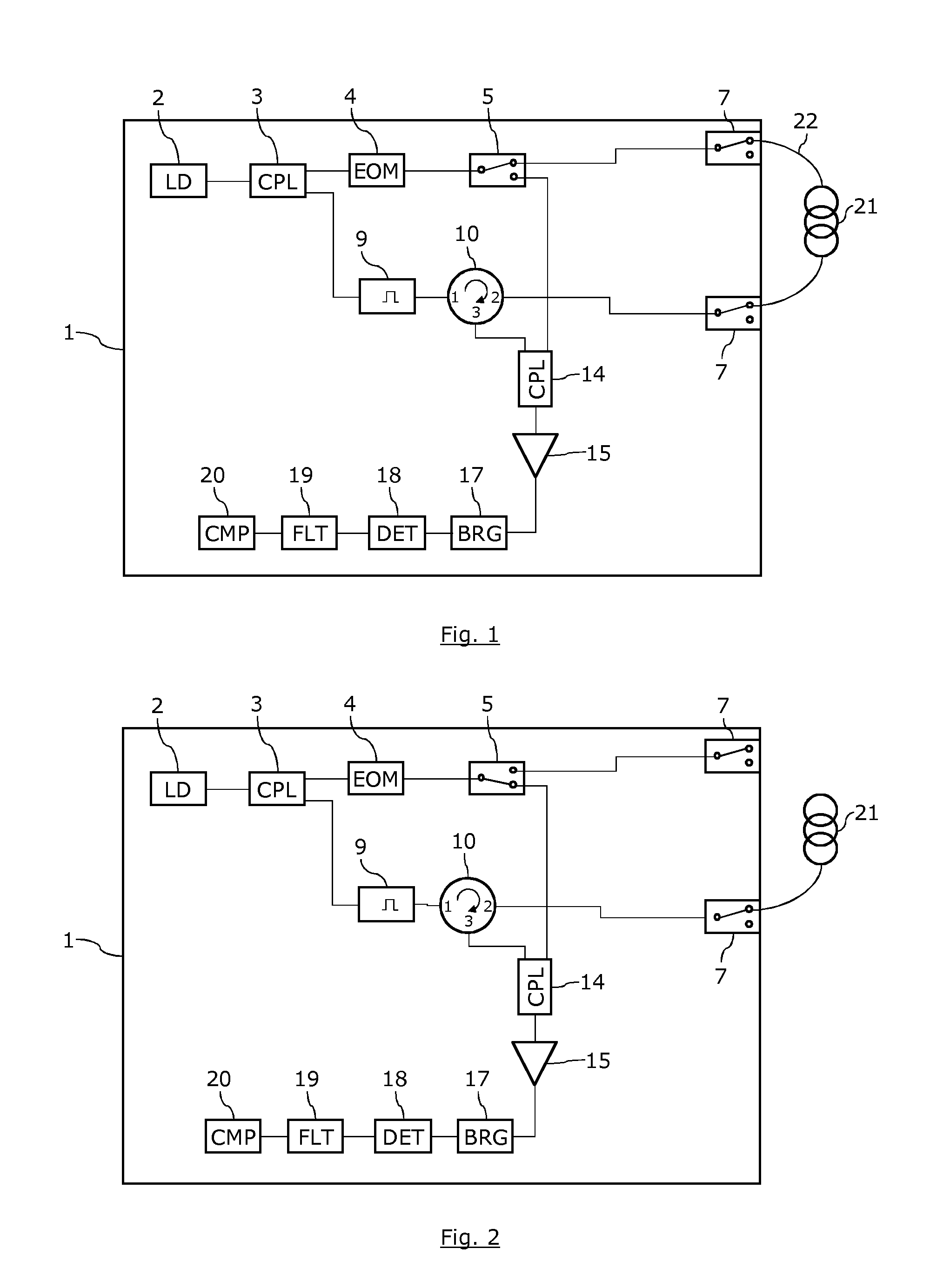
Brillouin optical distributed sensing device and method with improved tolerance to sensor failure
ActiveUS20160025524A1Easy to reconfigureAvoid excessive complexityForce measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical probingOptical measurements
A Brillouin optical distributed sensing device and method includes a structure for generating an optical pulsed signal and an optical probe signal. Includes is a circulation component for directing the optical pulsed signal to a sensing optical fiber and for directing an optical measurement signal with Brillouin scattering information arising from the sensing optical fiber toward a detection apparatus. Also included is an optical routing component for configuring the device to allow generating: (i) according to a first configuration, an optical measurement signal with stimulated Brillouin scattering information resulting from the interaction of the optical pulsed signal, and an optical probe signal propagating in the sensing optical fiber in a direction opposite to the optical pulsed signal, or (ii) according to a second configuration, an optical measurement signal with spontaneous Brillouin scattering information resulting from the propagation of the optical pulsed signal in the sensing optical fiber.
Owner:OMNISENS
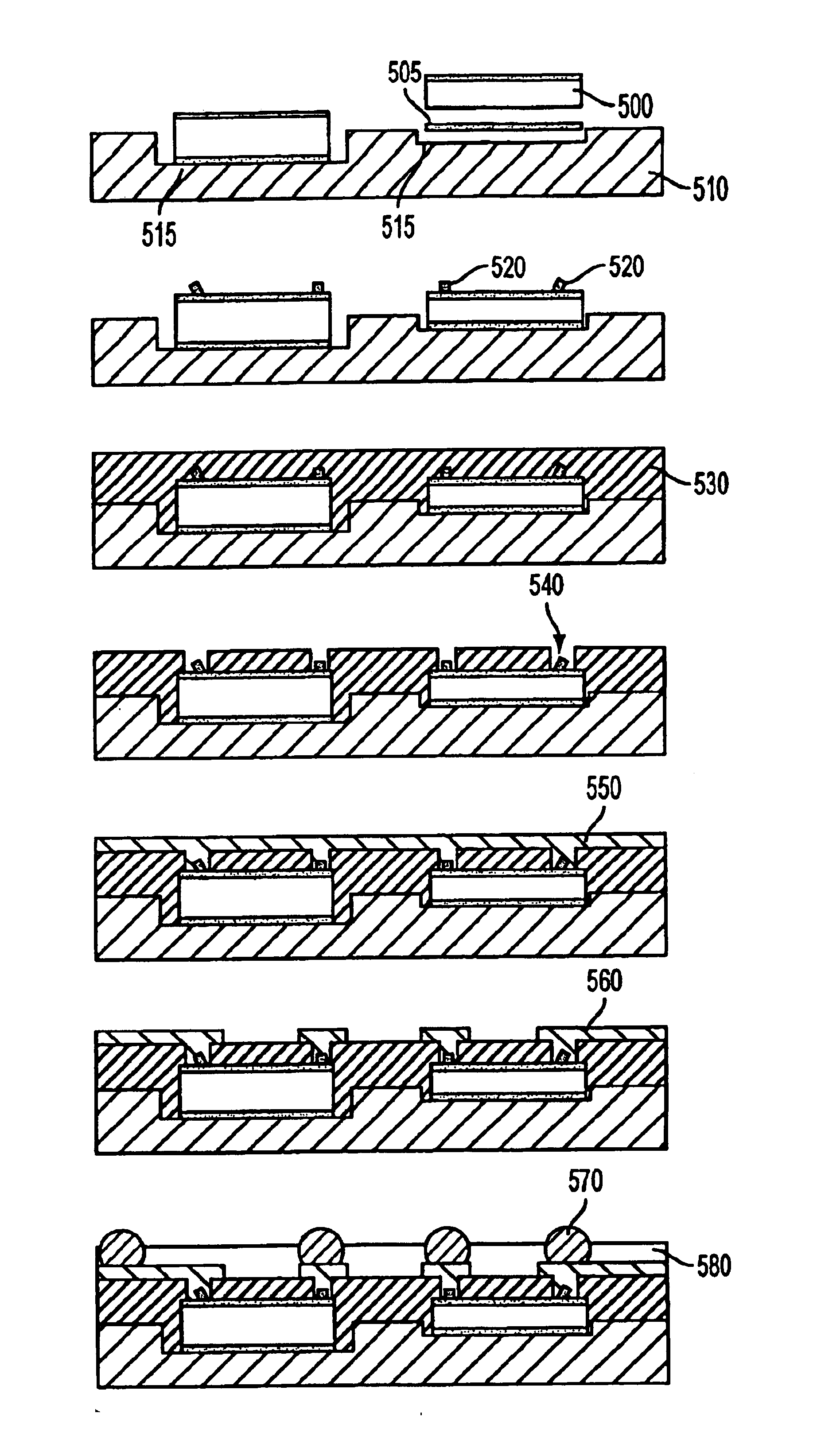
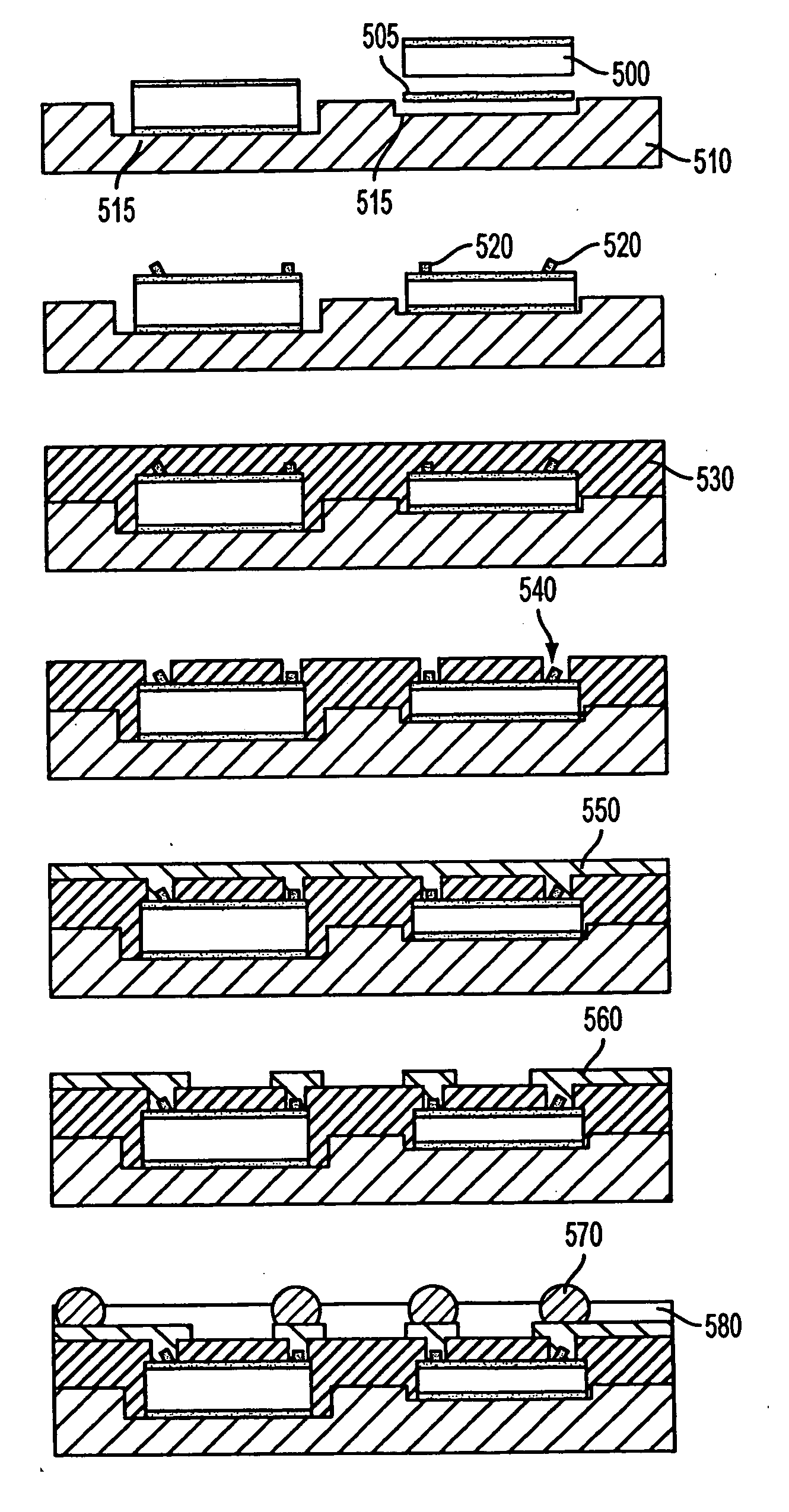
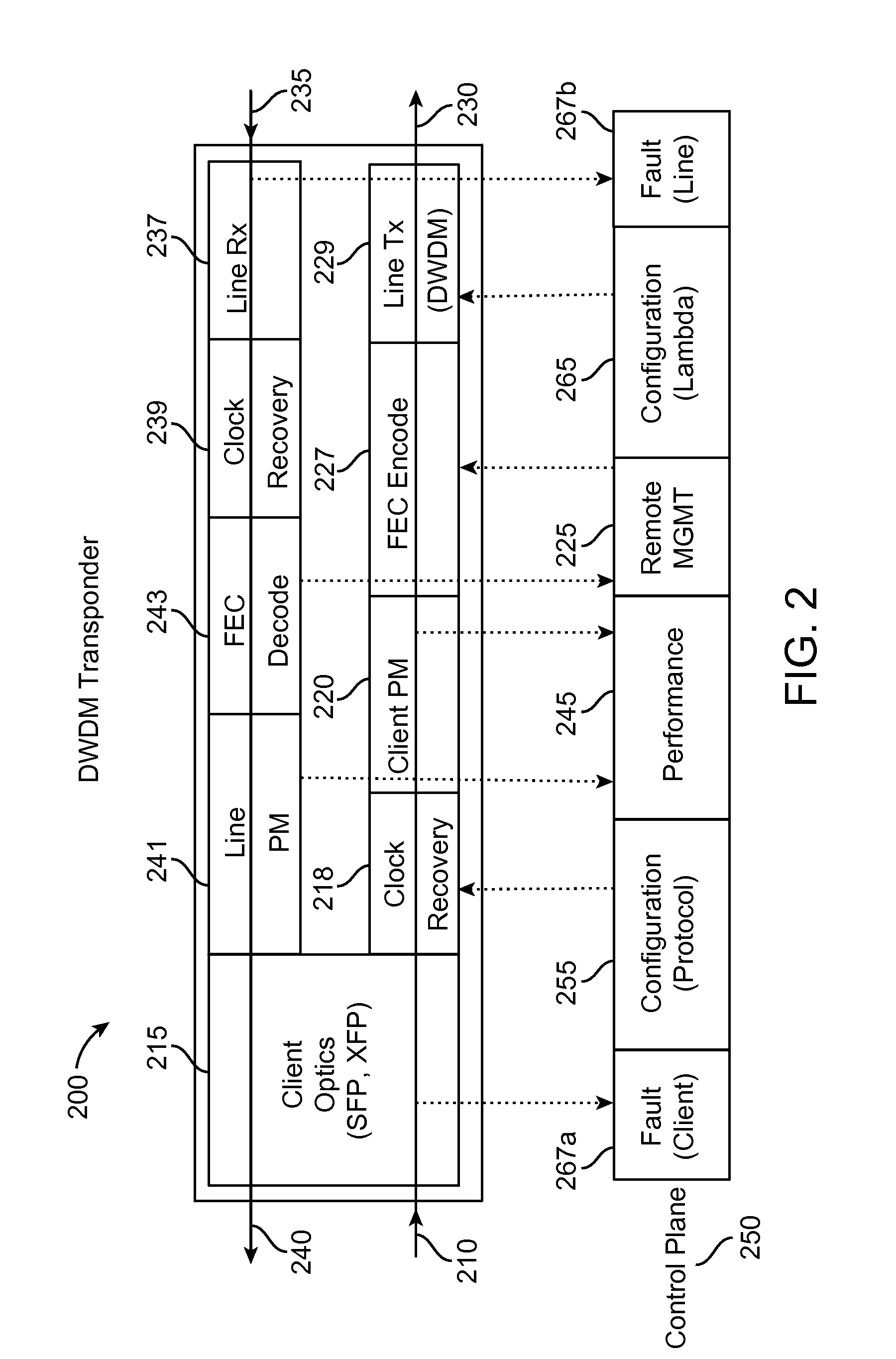
Optical-routing boards for opto-electrical systems and methods and apparatuses for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS7224857B2Low degree of optical birefringence and dispersionHigh densityCircuit optical detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansLight beamEngineering
Disclosed are optical-routing boards for opto-electrical systems having optical waveguides embedded in non-laminated optical substrates that enable optical signals to be routed among opto-electric components mounted on the top surfaces of the optical substrates. Methods for making the optical-routing boards are also disclosed. The waveguides are formed by focused pulse-laser writing, with the focal point of the pulsed-laser beam being moved in a three-dimensional manner through the non-laminated substrate. Bevel surfaces are preferably formed in the substrate to facilitate bending of the waveguides.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Optical routing device and optical network using same
ActiveUS8131149B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationEngineeringOptical coupler
The invention pertains to methods, apparatus, and systems optical of networking using tunable receivers, optical blocking elements selectively placed in the network, and optical routing elements comprised of passive elements, such as optical couplers and splitters. The routing elements have a plurality of ports and comprise passive elements such as couplers and splitters configured so that input light received at any port of the element is output from each of the other ports of the element, but not at port at which it was input.
Owner:CIENA
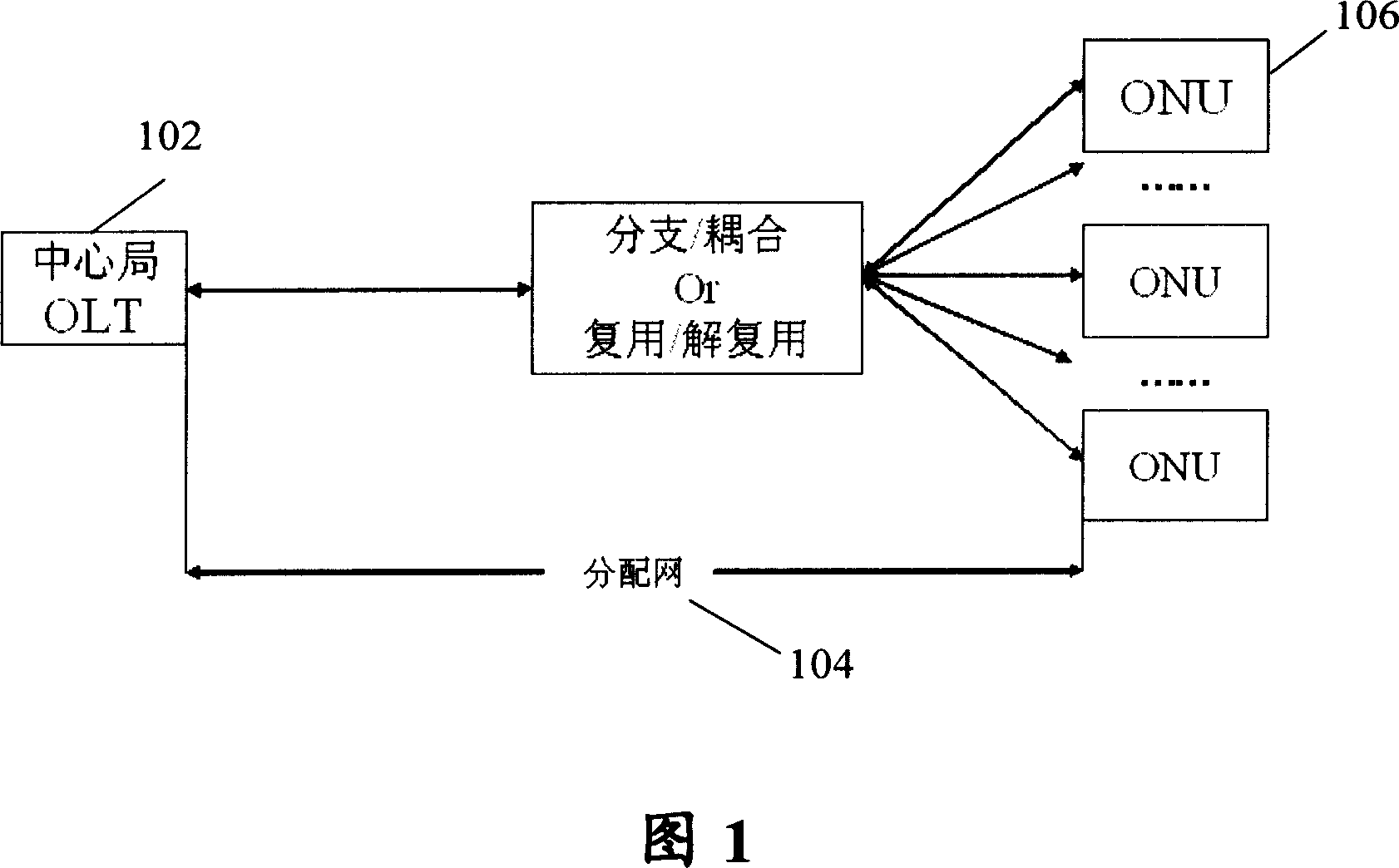
Passive optical network system and method of optical routing device and application optical routing device
ActiveCN101087174AAchieve universalFacilitate business distributionWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmissionGeneral purposeEngineering
The invention discloses an optical route device, which can output the input optical signal with different wavelength at arbitrary output end, and it includes: uniting / splitting wave device, which is used to unite and split the received optical signal; several splitters, and one port connects with several second uniting / splitting wave devices, which is used to distributing / combining the received optical signal; and routing device, connects with ports of several splitters, which is used to switch between the different output ports, and the optical signal can be sent to any output ports. The invention also discloses wireless optical network system and method which use the optical route device. Using the invention, it can realize the general purpose of optical network unit, and it is convenient for providing service for vendor.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Generic optical routing information base support
ActiveUS6947669B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionComputer hardwareInformation repository
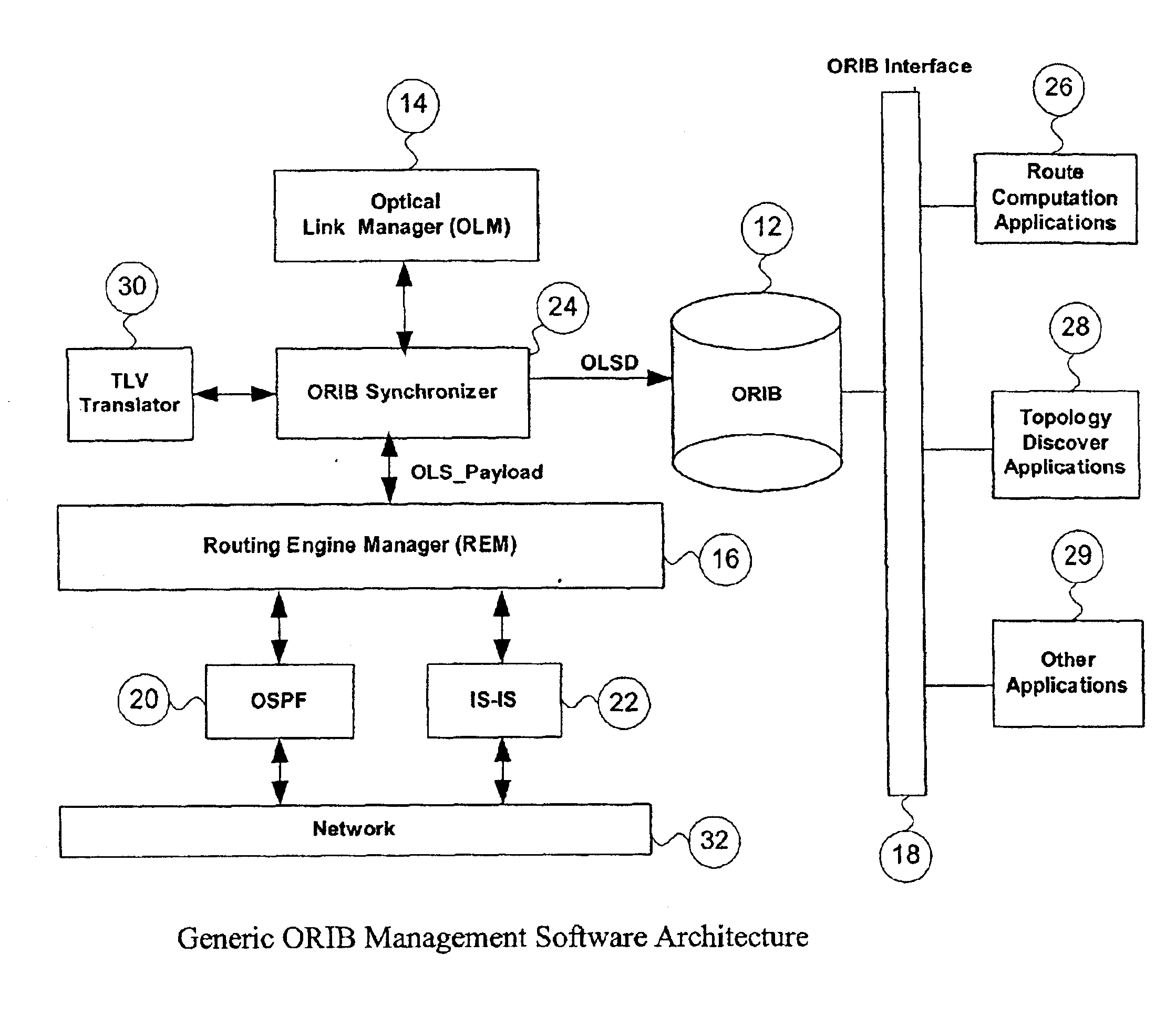
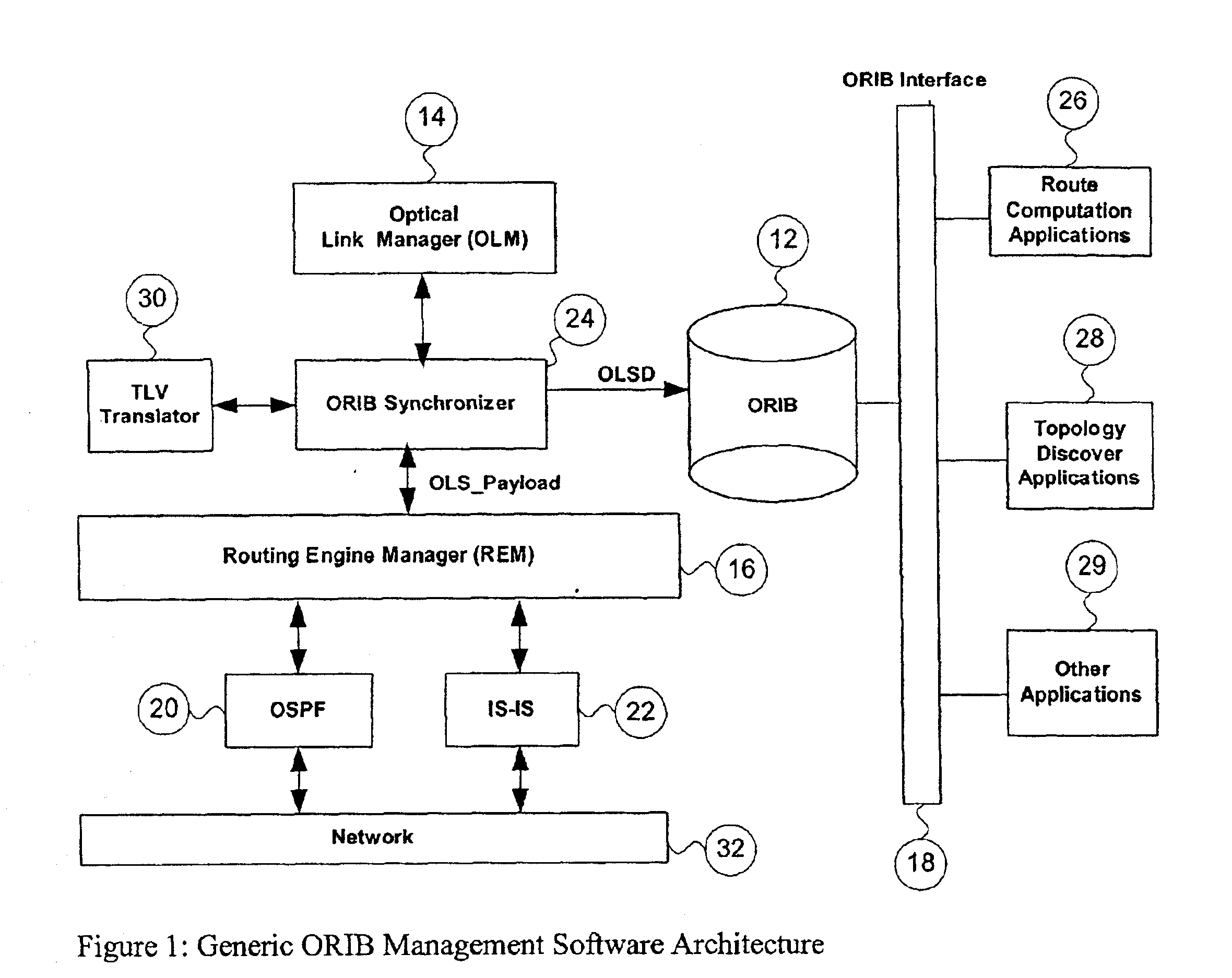
This application proposes a solution that makes access to the Optical Link State (OLS) information more efficient for use by upper level applications. Applications are independent of underlying routing protocols. This solution applies to all Link State based IGP protocols with the extension to optical networks, including OSPF and IS-IS.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
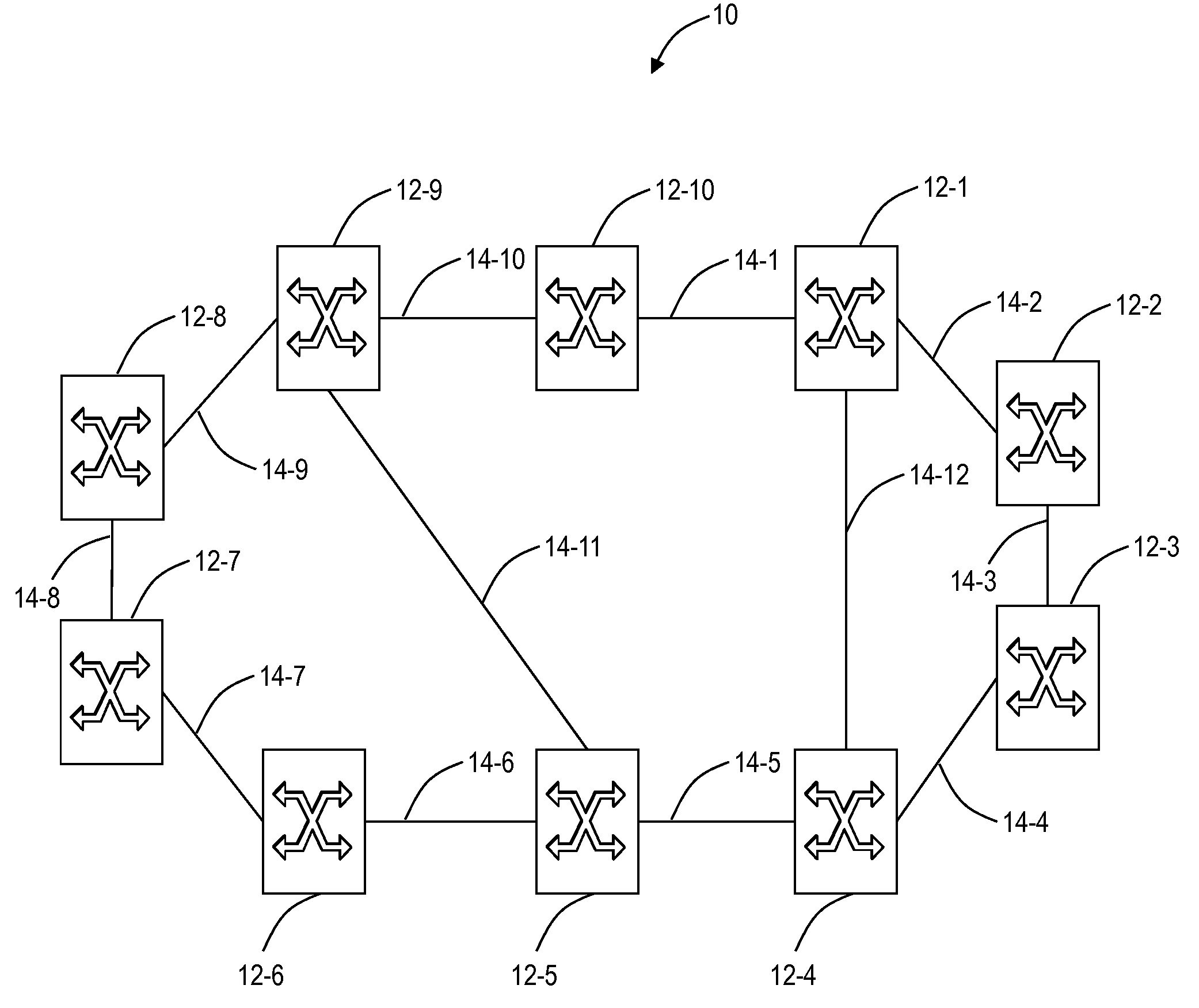
Physically-diverse routing in heterogeneous optical networks
Systems and methods are described that provide a two-step, physically-diverse optical routing. A diverse routing is formulated using Integer Linear Programming (ILP) to find feasible routes having a minimum estimated cost, and post-processing the feasible routes on an auxiliary cost graph to optimize regenerator and terminal Optical Transponder (OT) placement and wavelength assignment.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Centralized monitoring method for optical cable resource
ActiveCN102412895APerfect monitoring methodScientific monitoring methodTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsFailure rateComputer module
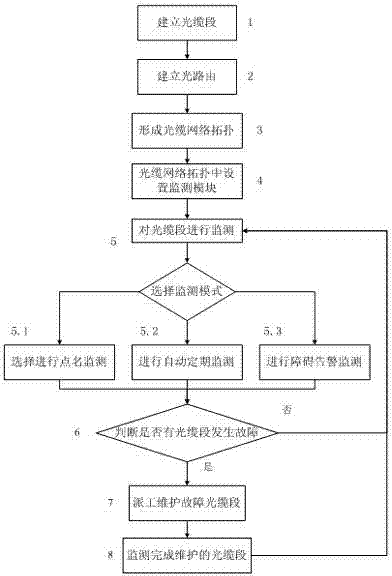
The invention discloses a centralized monitoring method for the optical cable resource. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, establishing an optical cable section; 2, establishing optical routing; 3, forming optical cable network topology; 4, setting a monitoring module for a network; 5, selecting a monitoring mode, skipping to a step 5.1 in a roll-call monitoring mode, skipping to a step 5.2 in an automatic periodic monitoring mode, and skipping to a step 5.3 in a barrier alarm monitoring mode; 5.1, performing roll-call monitoring at the optical cable section; 5.2, automatically and periodically monitoring the optical cable section; 5.3, performing barrier alarm monitoring at the optical cable section; 6, monitoring central analysis testing data, judging whether a fault occurs, skipping to a step 7 if the fault occurs, and skipping to the step 5 if no fault occurs; 7, assigning a person to maintain the failed optical cable section; and 8, monitoring the maintained optical cable section by using the monitoring module, and skipping to the step 5. In the method, online monitoring, analysis and real-time fault alarm are performed on a communication optical cable and communication equipment, so that the line communication and maintenance efficiencies are increased, the line failure rate is lowered, and the fault time is shortened.
Owner:SHANGHAI MUNICIPAL ELECTRIC POWER CO +1
Subchannel Photonic Routing, Switching and Protection with Simplified Upgrades of WDM Optical Networks
ActiveUS20110158641A1Easy to switchIncrease the number ofMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsNetwork architecturePhotonics
The present invention includes novel techniques, apparatus, and systems for optical WDM communications. Tunable lasers are employed to generate respective subcarrier frequencies which represent subchannels of an ITU channel to which client signals can be mapped. In one embodiment, subchannels are polarization interleaved to reduce crosstalk. In another embodiment, polarization multiplexing is used to increase the spectral density. Client circuits can be divided and combined with one another before being mapped, independent of one another, to individual subchannels within and across ITU channels. A crosspoint switch can be used to control the client to subchannel mapping, thereby enabling subchannel protection switching and hitless wavelength switching. Network architectures and subchannel transponders, muxponders and crossponders are disclosed, and techniques are employed (at the subchannel level / layer), to facilitate the desired optical routing, switching, concatenation and protection of the client circuits mapped to these subchannels across the nodes of a WDM network.
Owner:VELLO SYST +1
Two-by-two optical routing element using two-position MEMS mirrors
InactiveUS7177498B2Flexible routingCoupling light guidesBundled fibre light guideOptoelectronicsOptical routing
Retroreflecting elements adapted for use in two-by-two optical routing elements. Each retroreflecting element is configured to selectively retroreflect two optical rays. A first reflective surface, such as may be provided by a mirror, is inclined with respect to a reference plane. A second reflective surface, such as may also be provided by a mirror, is opposed to and inclined with respect to the first reflective surface. The two surfaces are configured for rotation about an axis to multiple positions such that in a first position, a first ray is retroreflected along a first path and second ray is reflected along a second path, and in a second position, the first ray is reflected along the second path and the second ray is reflected along the first path.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com