Patents
Literature
4803 results about "Reference plane" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
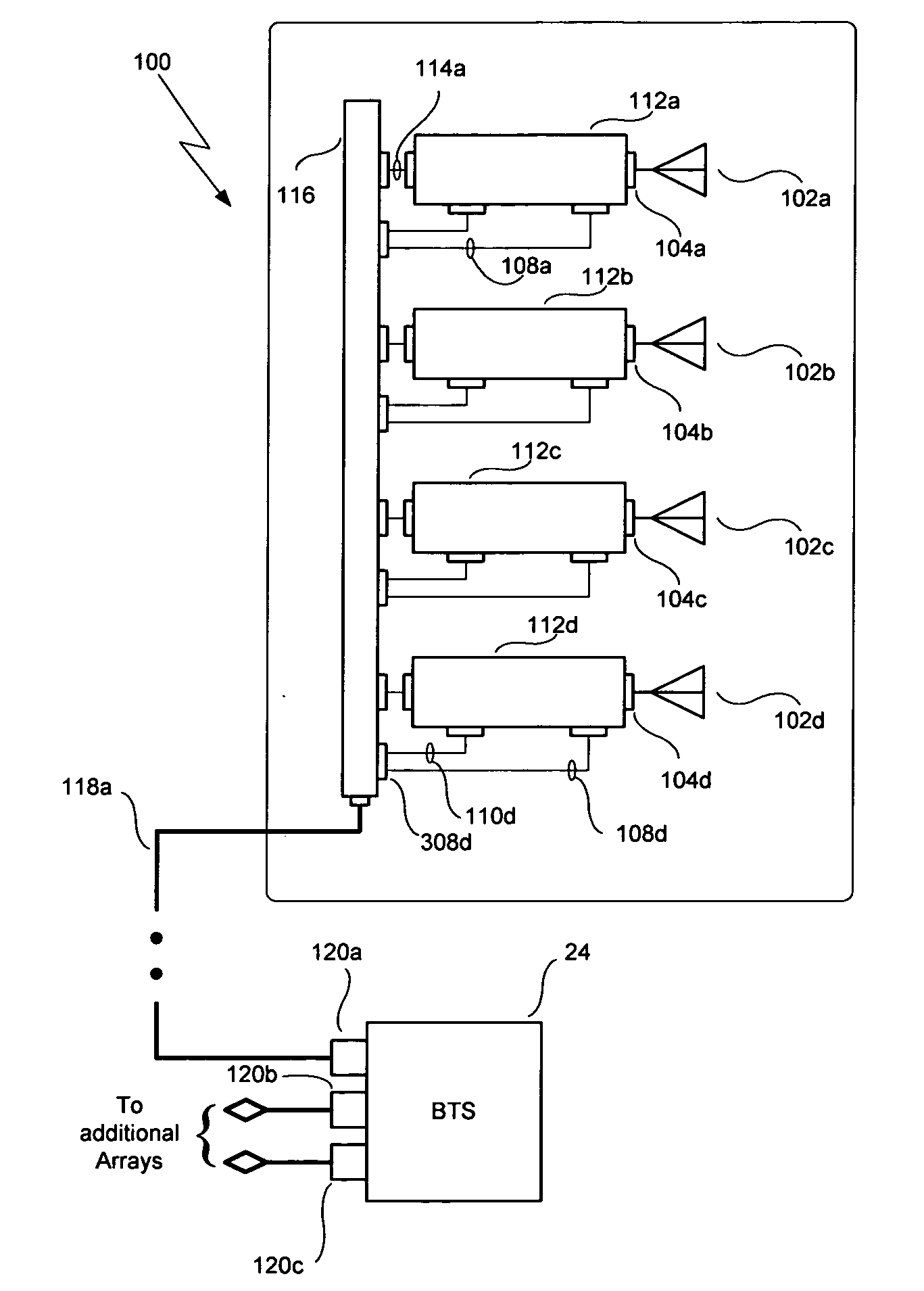
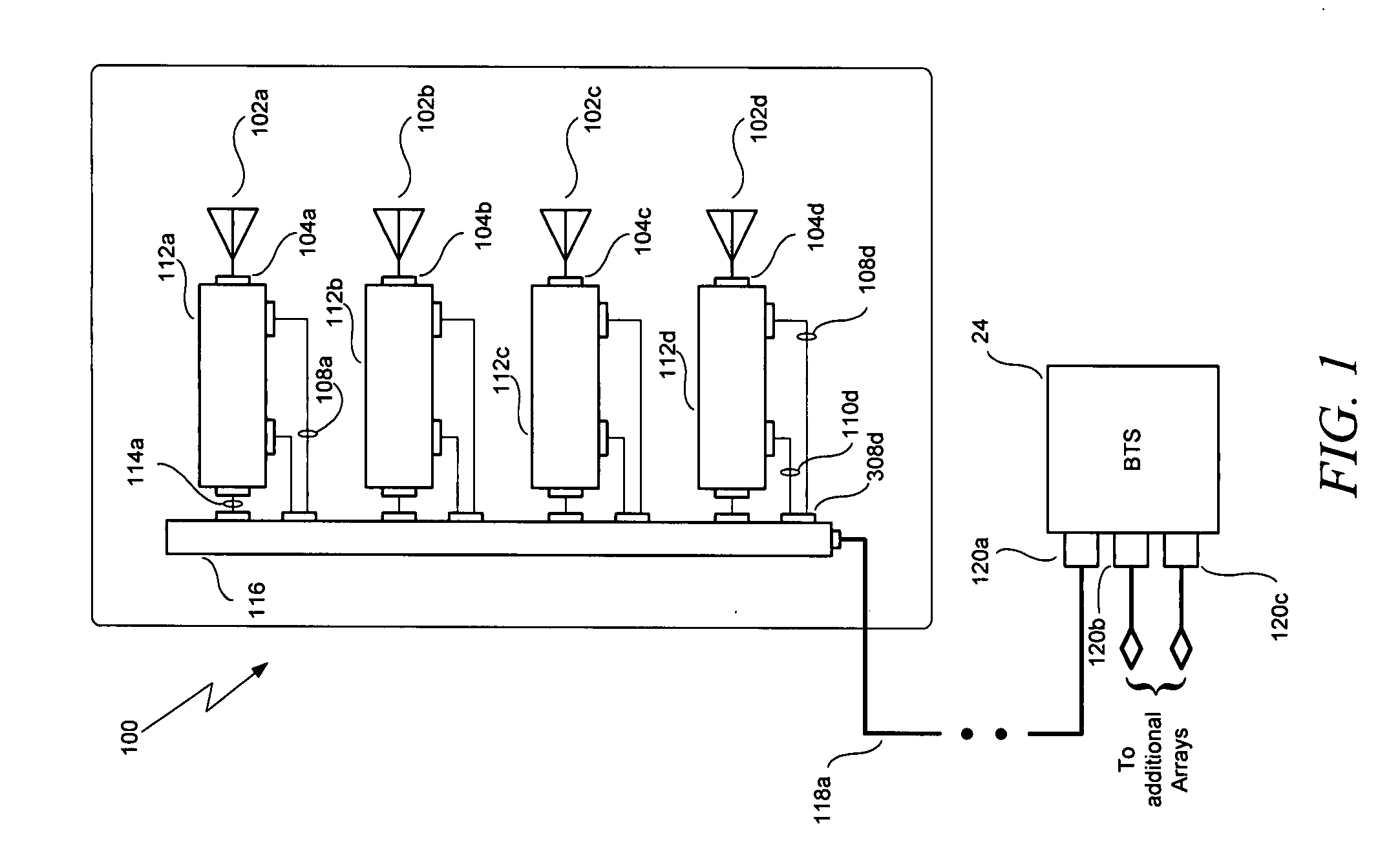
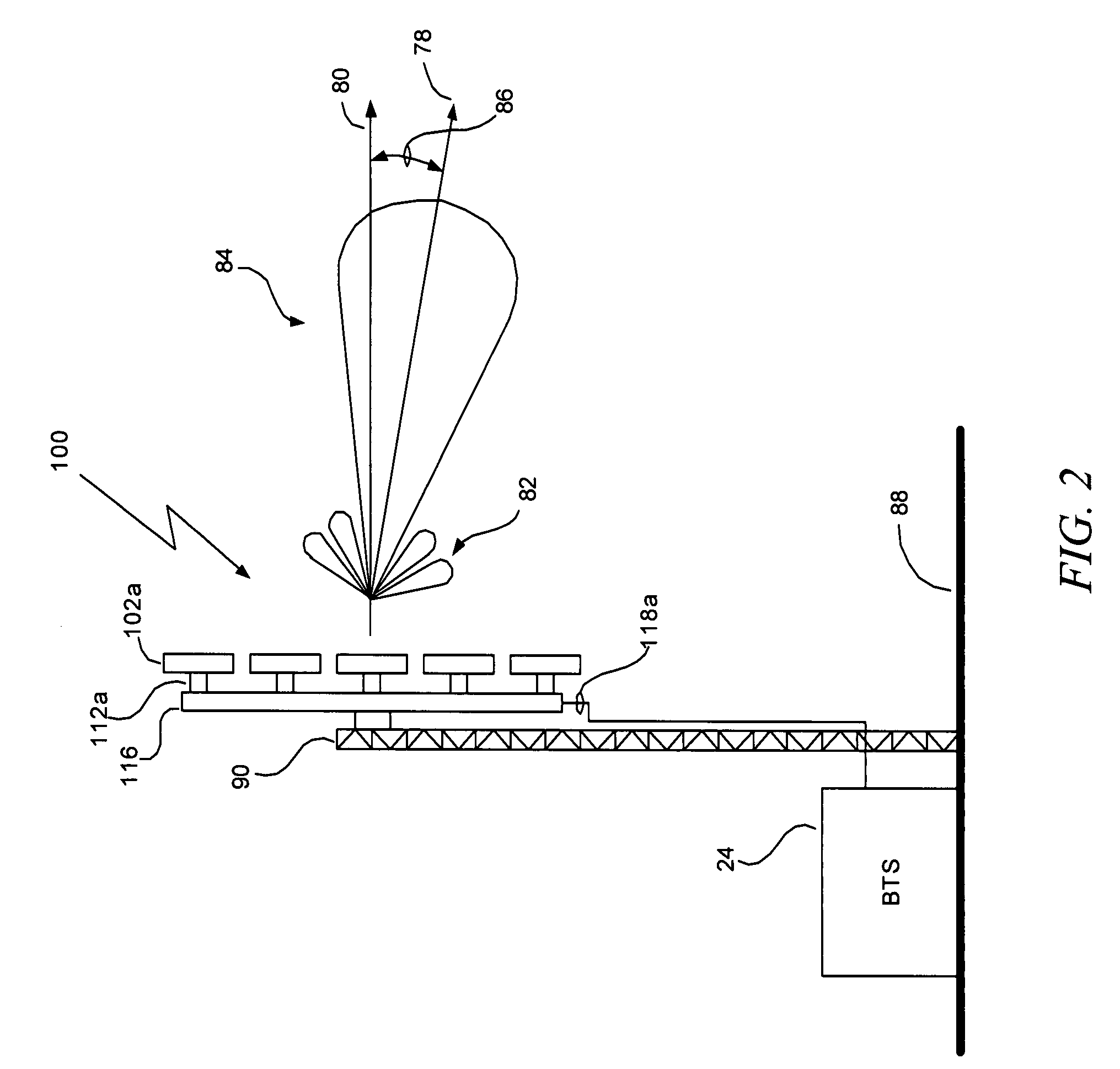
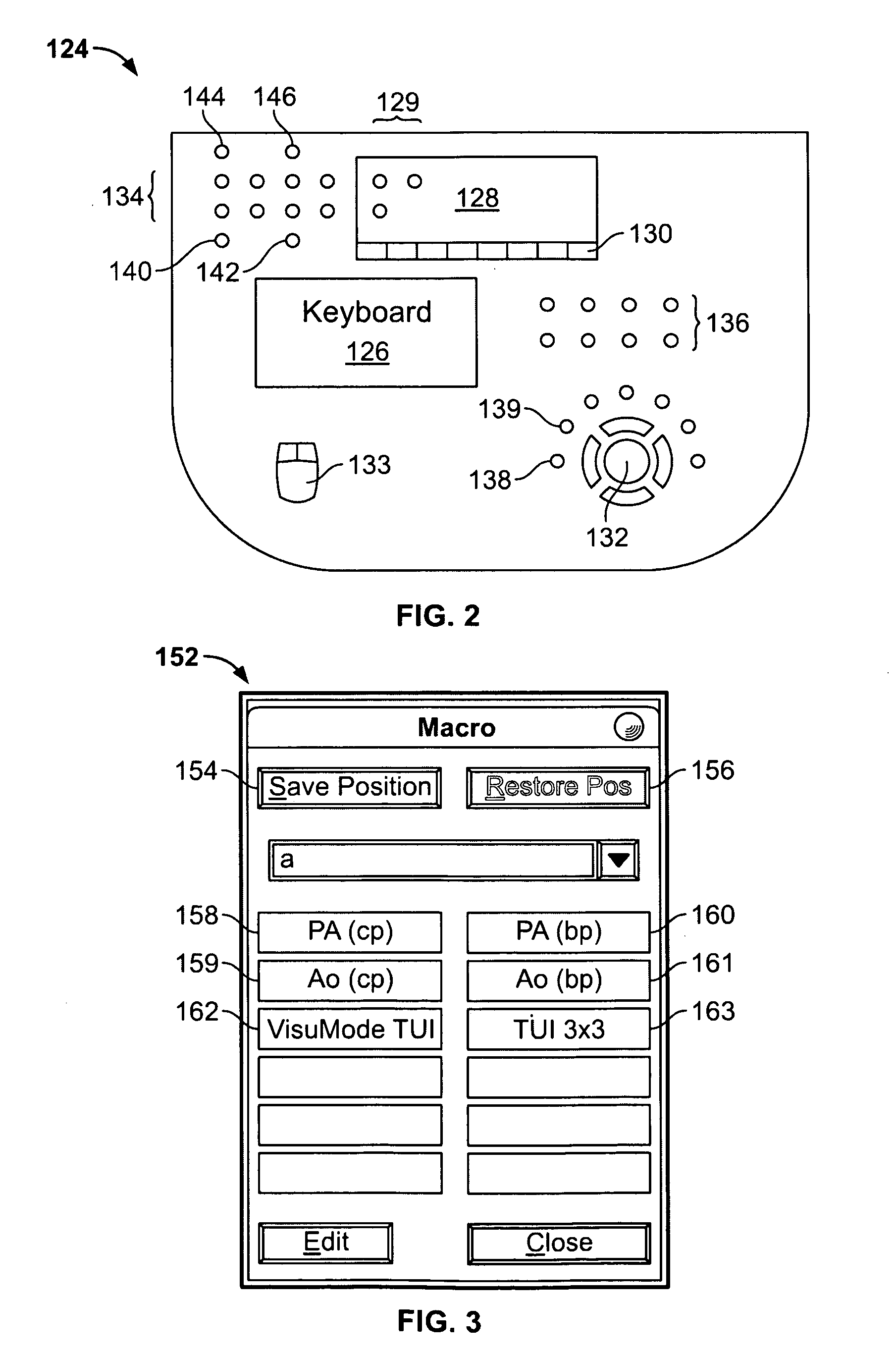
Substrate-supporting device
ActiveUS7691205B2Improve controllabilityStable and satisfactory controllabilityVacuum evaporation coatingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSupport surfaceCHEEK DIMPLES
A substrate-supporting device for CVD having a substrate-supporting region includes: a substrate-supporting surface which is a continuous surface defining a reference plane on which a substrate is placed; and multiple dimples having bottom surfaces lower than the reference plane. The respective dimples are isolated from each other by a portion of the substrate-supporting surface.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
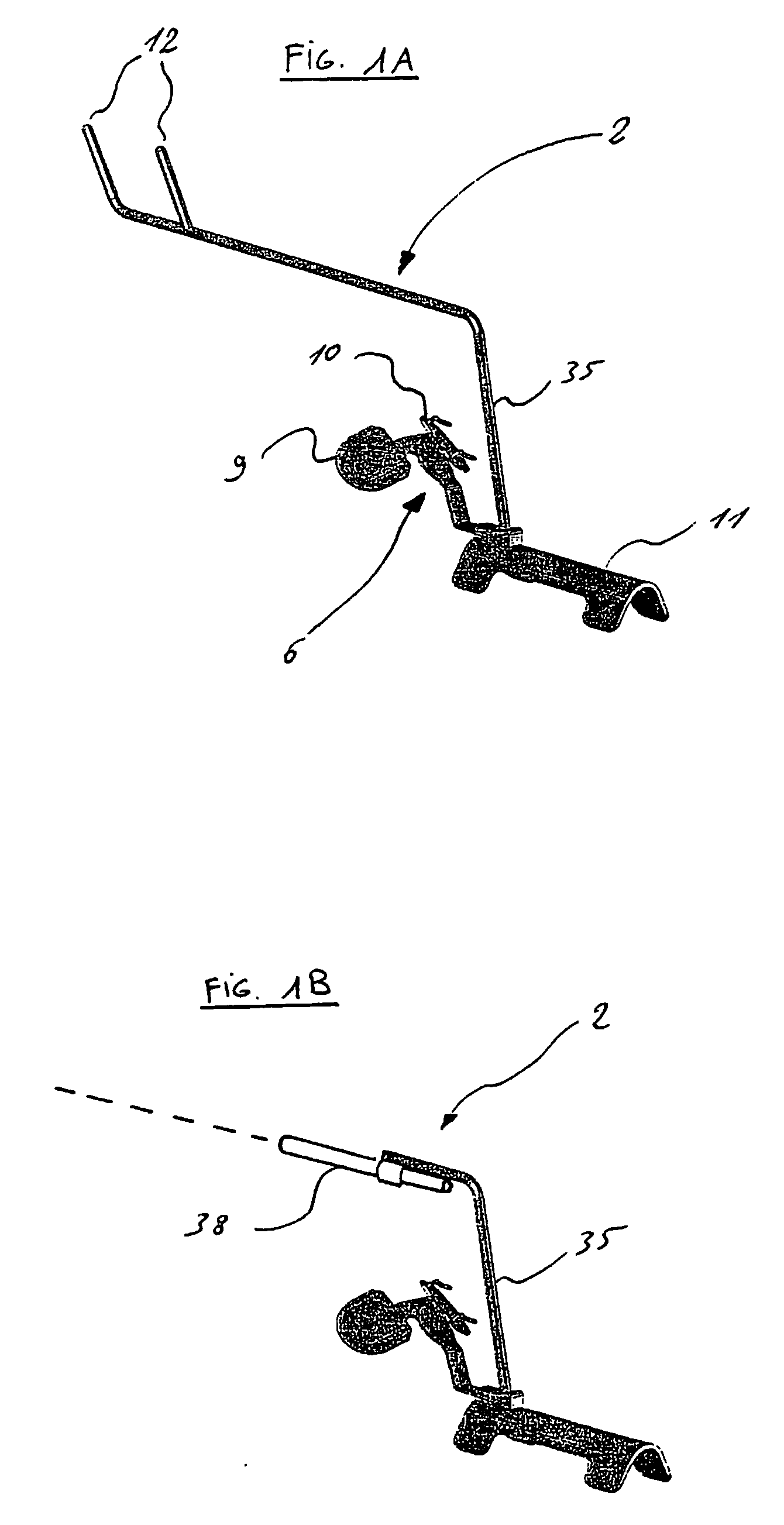
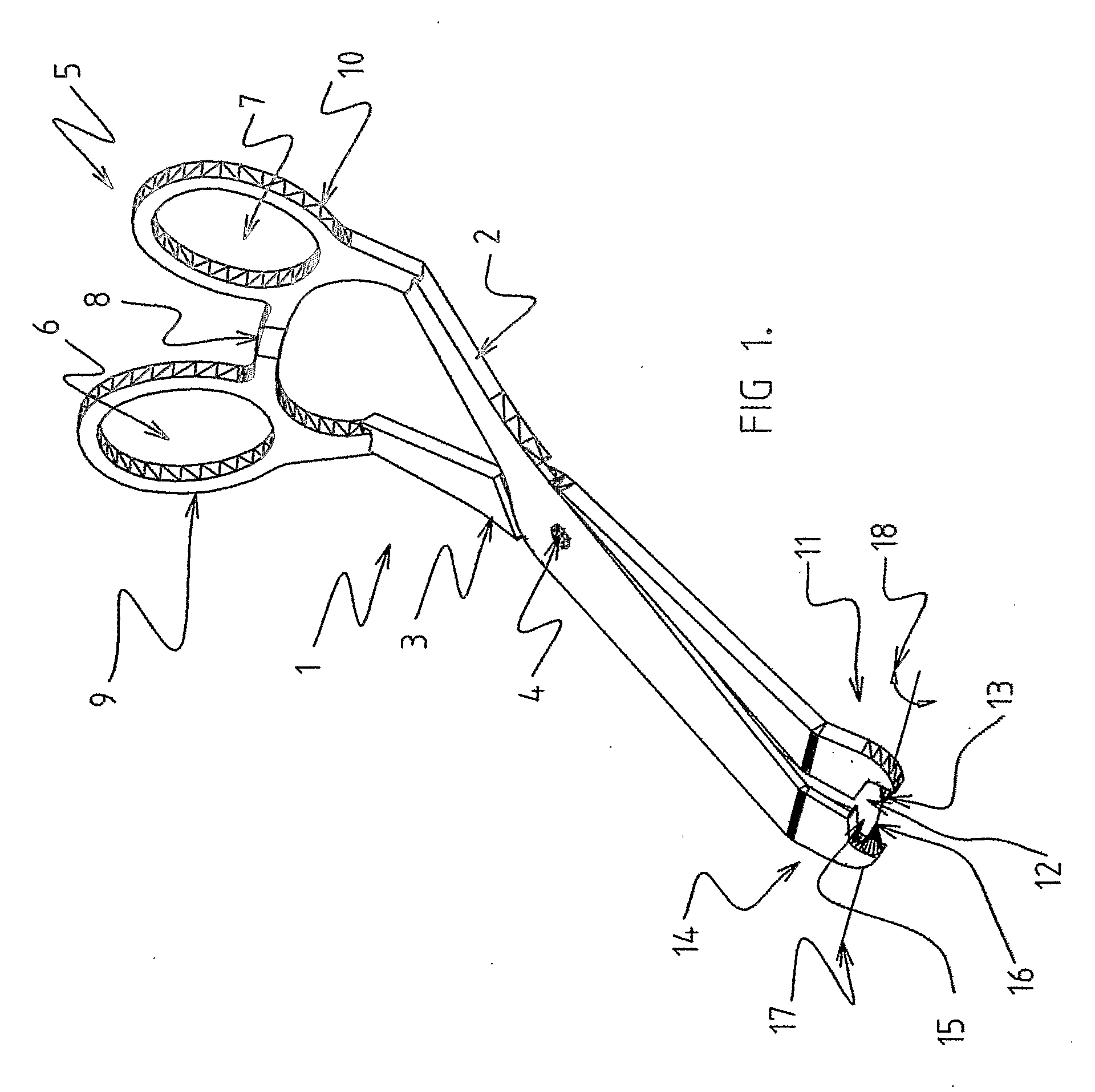
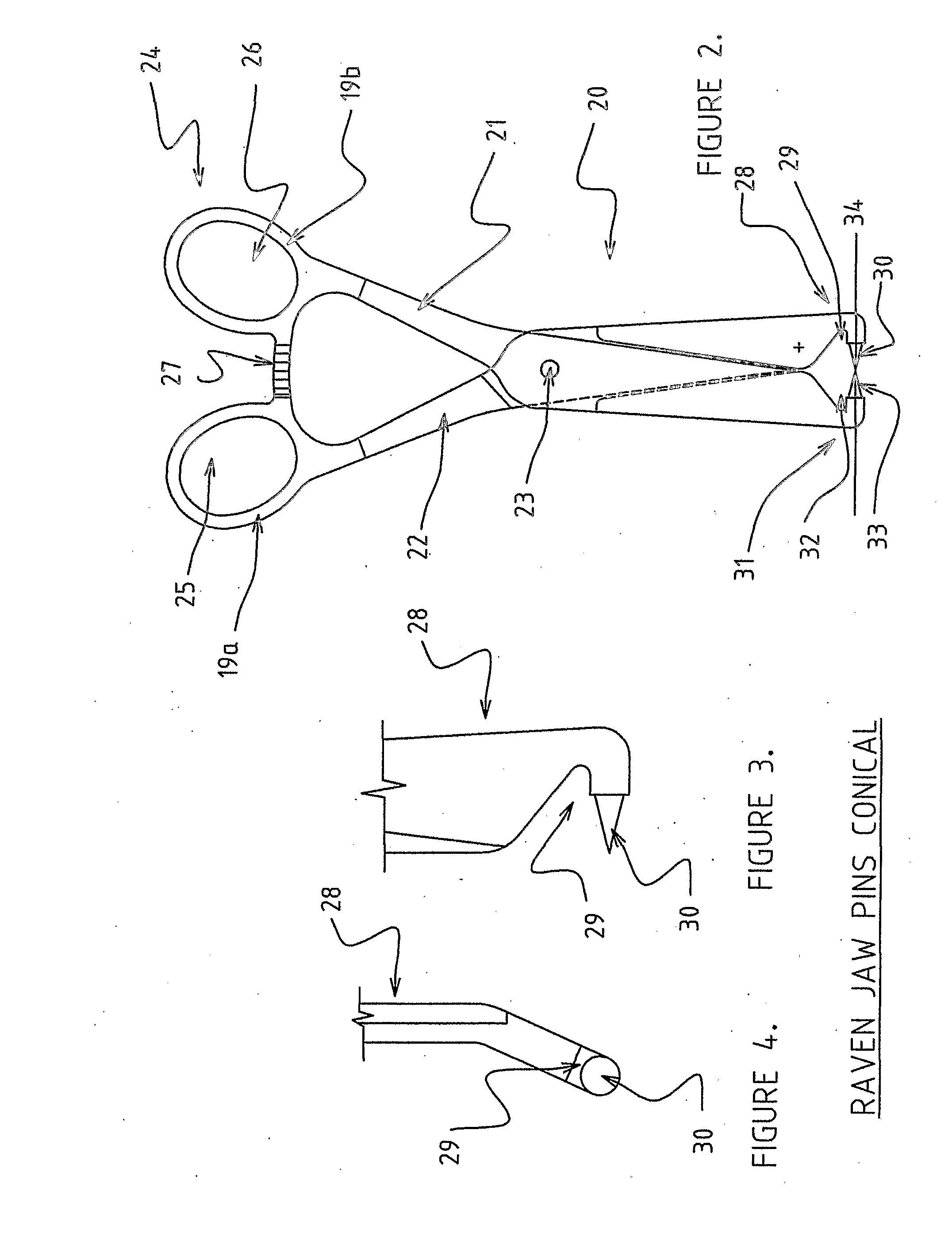
Orientation device for surgical implement
InactiveUS20060184177A1Improve objectivityFacilitates and improves trainingDiagnosticsJoint implantsSurgical operationPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
Orientation device for surgical use includes a frame and a level device attached to the frame. The feature may be oriented with a reference such as the Antero Superior Iliac Spine, the acetabulum or the operating table to position the pelvis or the device. The level device is adapted to define a reference plane. The device thus allows precise orientation with respect to the pelvis through use of a reference plane.
Owner:SAN TECH SURGICAL
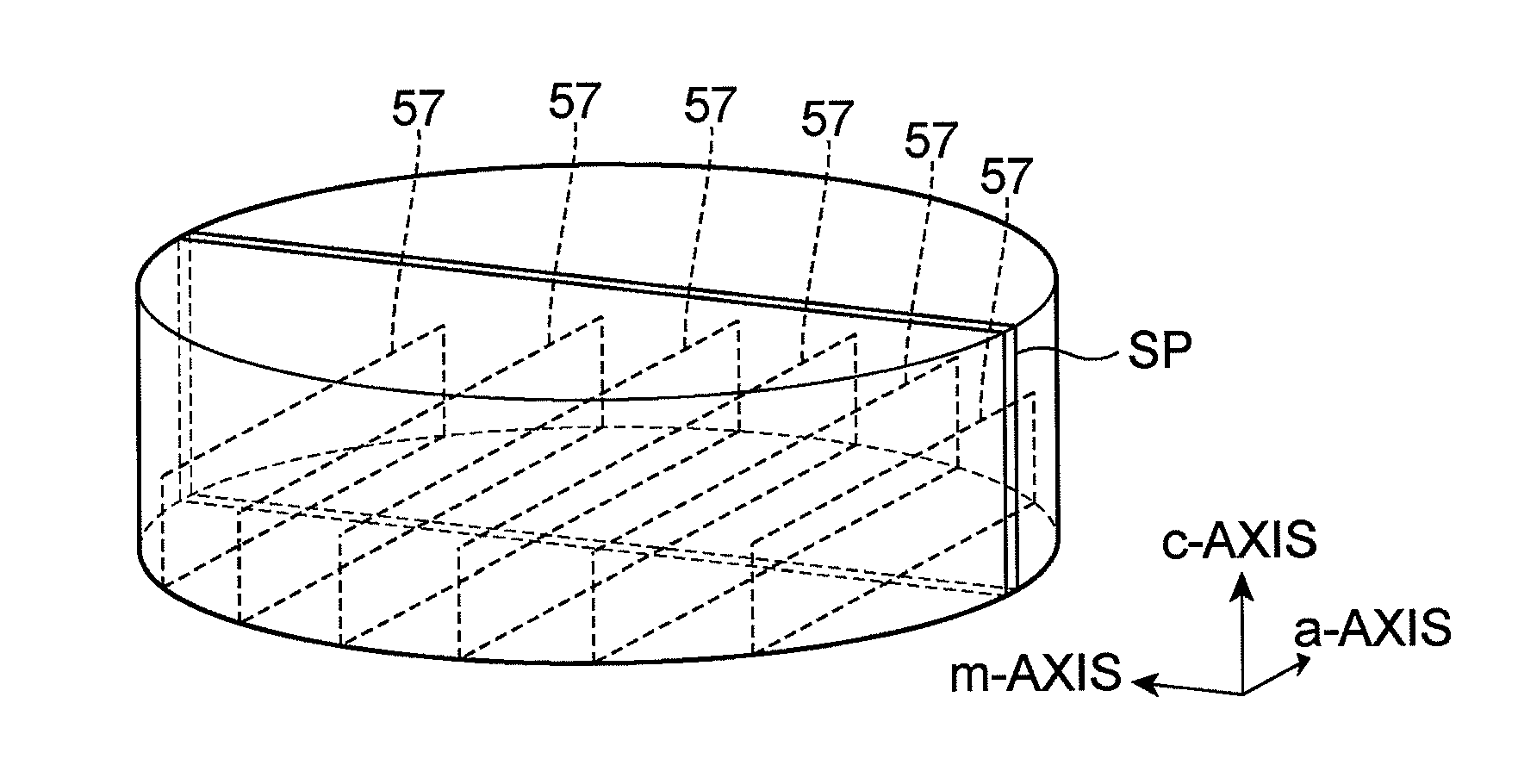
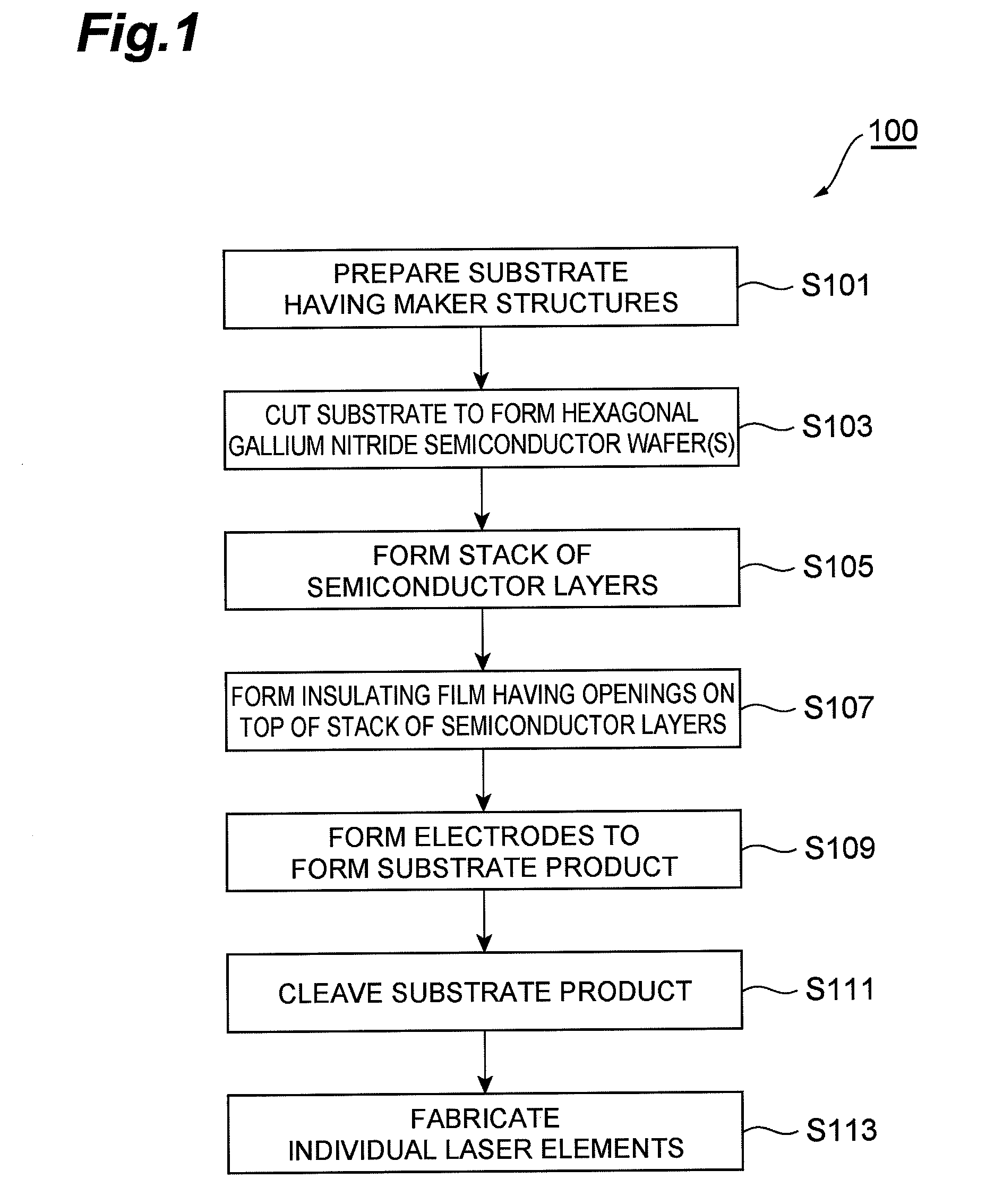
Method of fabricating nitride semiconductor laser
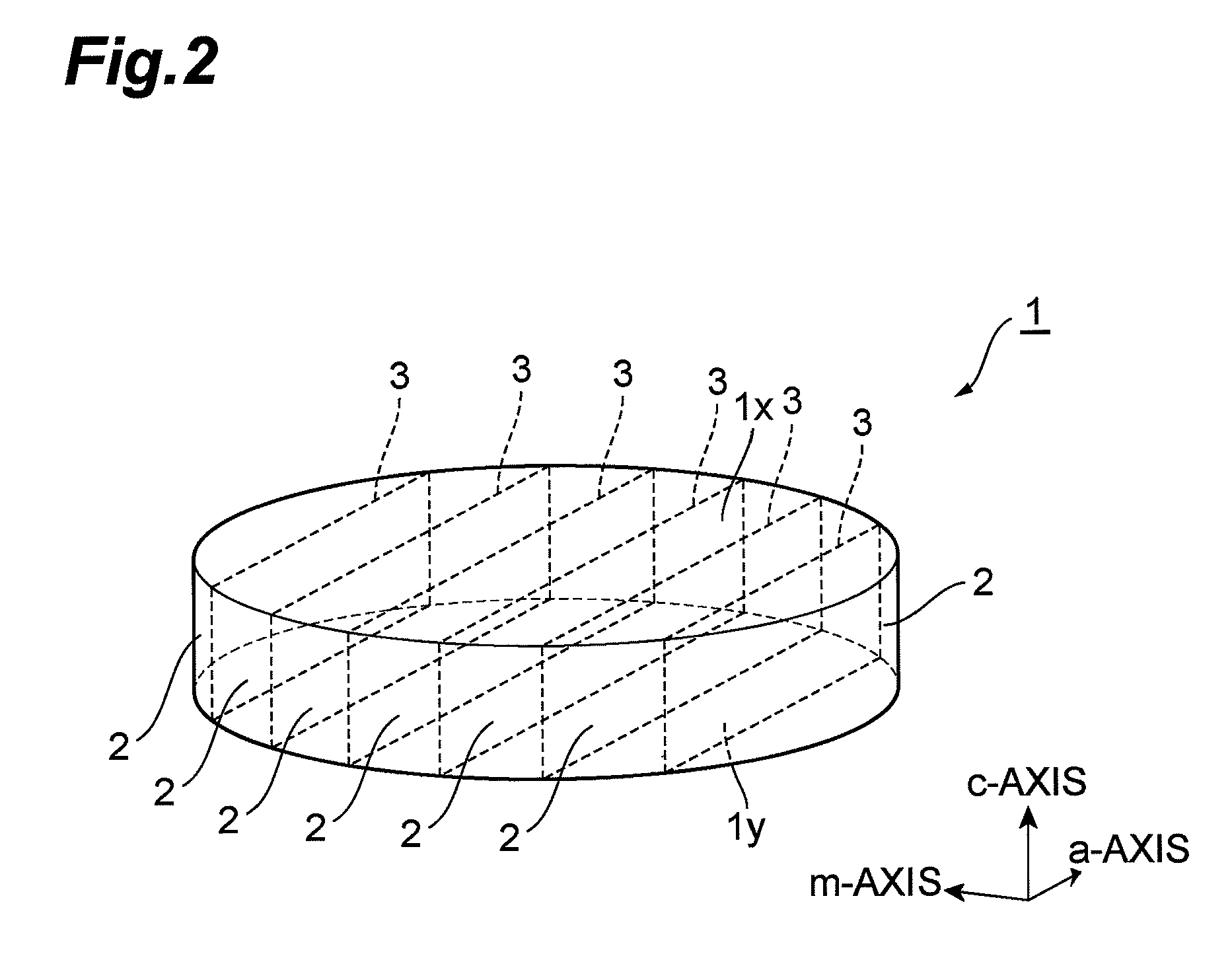
InactiveUS7939354B2Good orientationLarge caliberSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSemiconductor laser structural detailsGallium nitrideNitride semiconductors
A method of fabricating a nitride semiconductor laser comprises preparing a substrate having a plurality of marker structures and a crystalline mass made of a hexagonal gallium nitride semiconductor. The primary and back surfaces of the substrate intersect with a predetermined axis extending in the direction of a c-axis of the hexagonal gallium nitride semiconductor. Each marker structure extends along a reference plane defined by the c-axis and an m-axis of the hexagonal gallium nitride semiconductor. The method comprises cutting the substrate along a cutting plane to form a wafer of hexagonal gallium nitride semiconductor, and the cutting plane intersects with the plurality of the marker structures. The wafer has a plurality of first markers, each of which extends from the primary surface to the back surface of the wafer, and each of the first markers comprises part of each of the marker structures. The primary surface of the wafer is semipolar or nonpolar. The method comprises growing a number of gallium nitride based semiconductor layers for a semiconductor laser. The method comprises cleaving the substrate product at a cleavage plane of the hexagonal gallium nitride semiconductor, after forming a substrate product in an electrode forming step.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
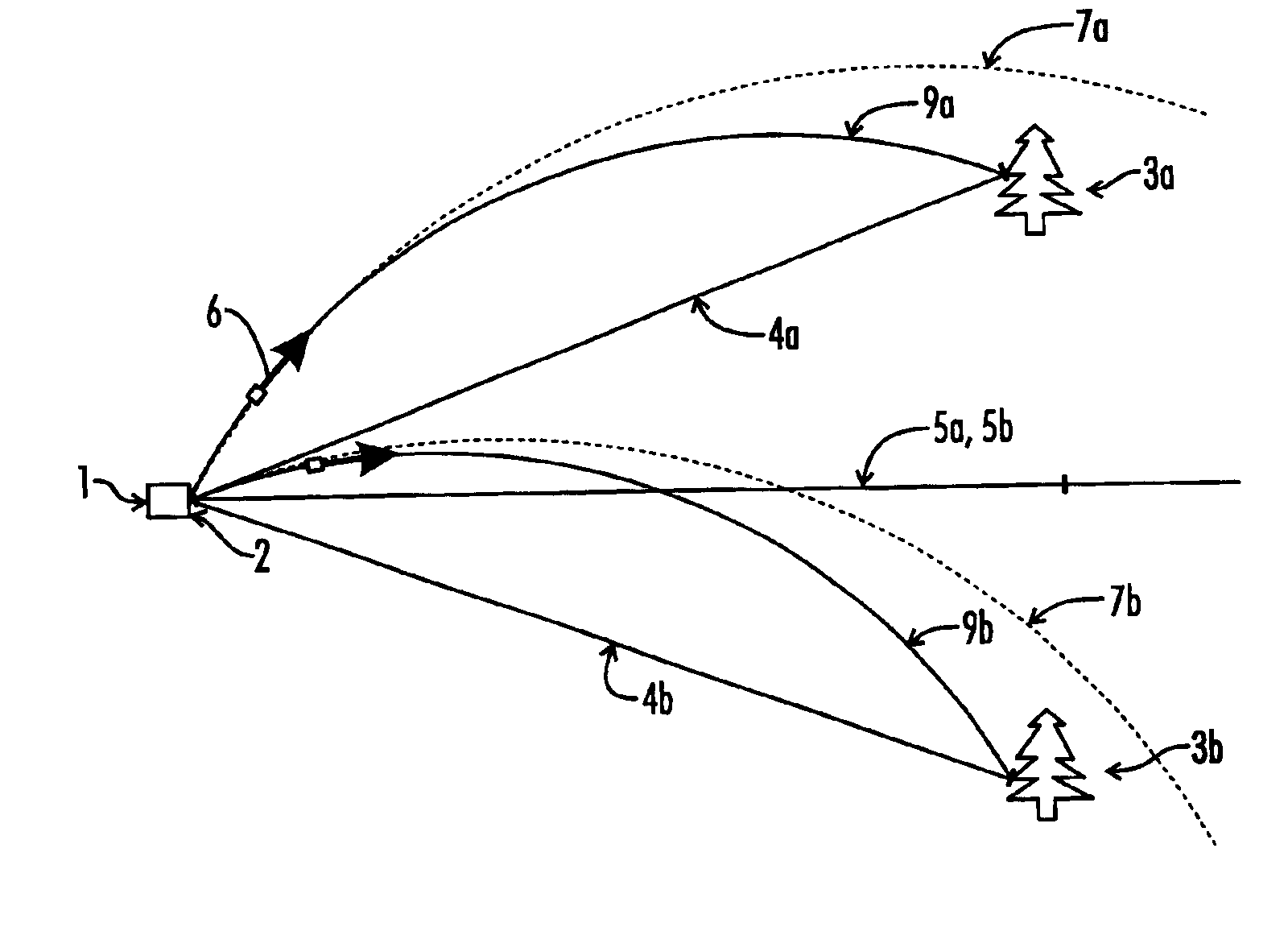
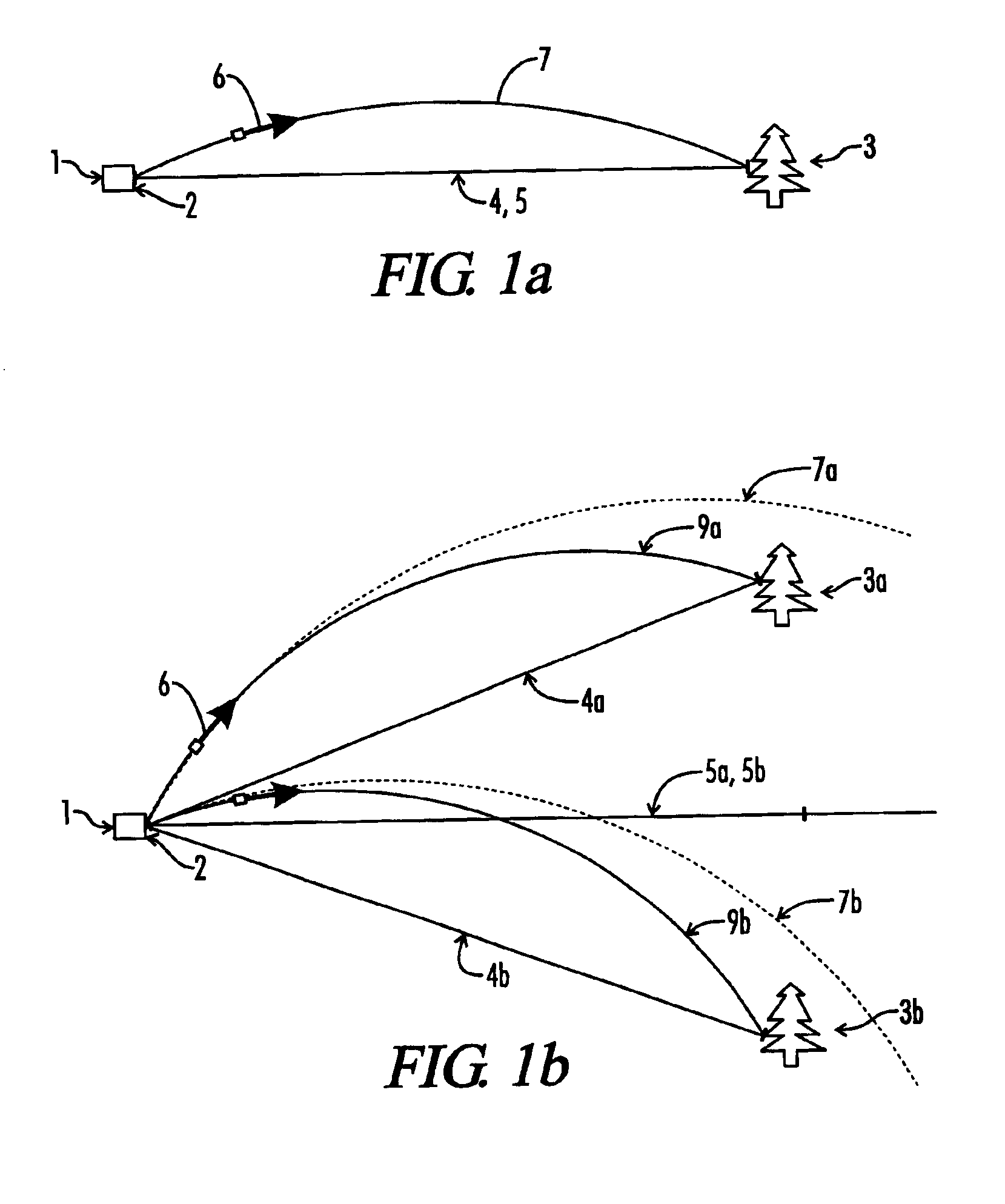
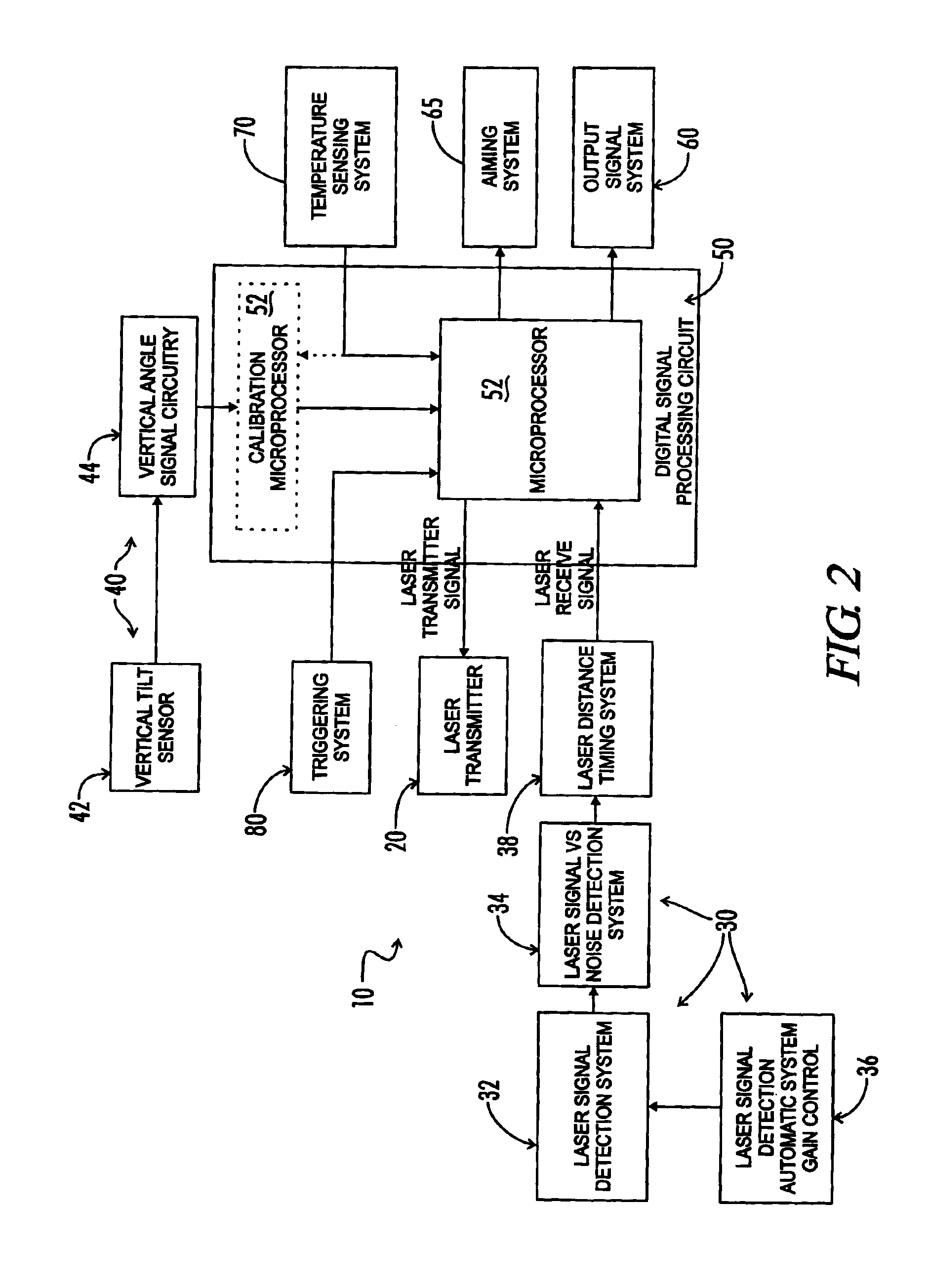
Tilt-compensated laser rangefinder
InactiveUS6873406B1Minimize impactError minimizationAngle measurementOptical rangefindersDigital signal processingInternal temperature
The present invention is a laser ranging device that incorporates an internal tilt sensor, an internal temperature sensor, and an internal pressure sensor. The tilt sensor is used to measure the target's vertical angle relative to the horizontal reference plane. Digital signal processing circuitry controls the firing of the laser pulse, calculation of time-of-flight range, measurement of the vertical angle of the tilt sensor, measurement of ambient temperature and storage of tilt sensor and temperature sensor calibration data. The digital signal processing circuitry then provides the user temperature corrected ballistic ranging information, including horizontal range. Additionally, an automatic gain control system minimizes the effects of target to target variance in reflectivity and its associated errors. It is also an object of this invention to electronically minimize errors in the measurement of a vertical angle caused by housing vibration and by temperature variance errors.
Owner:OPTI LOGIC CORP
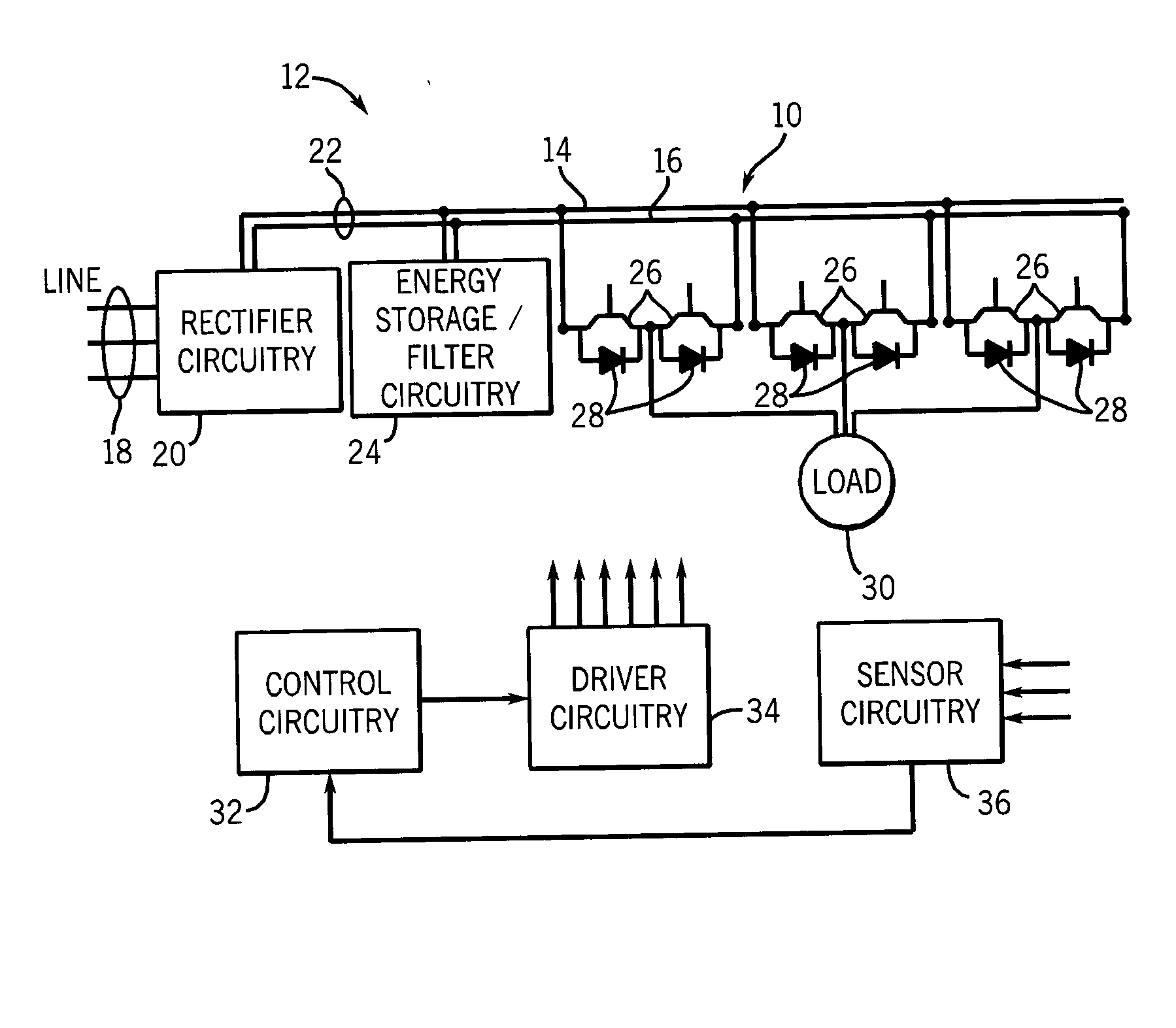
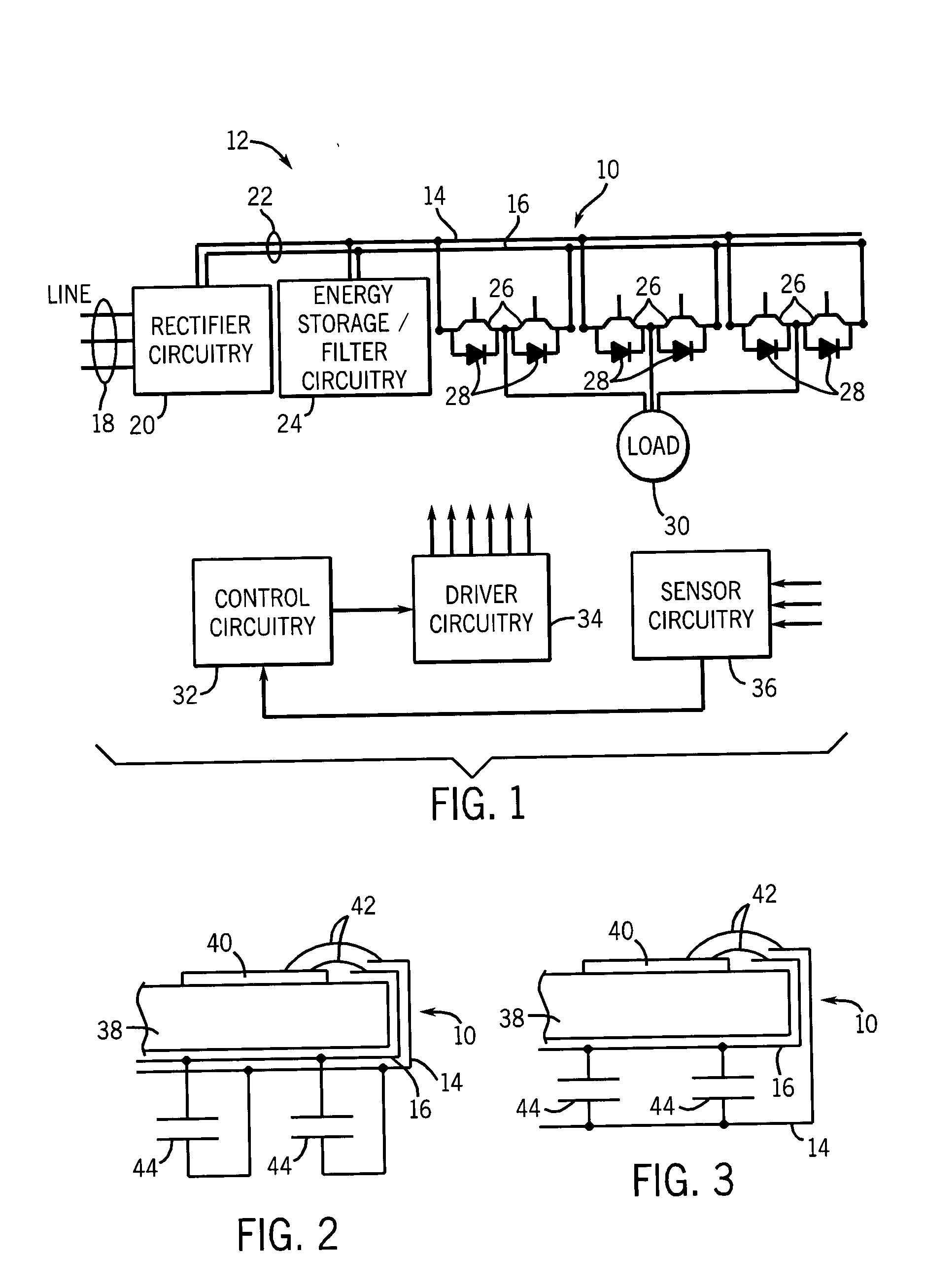
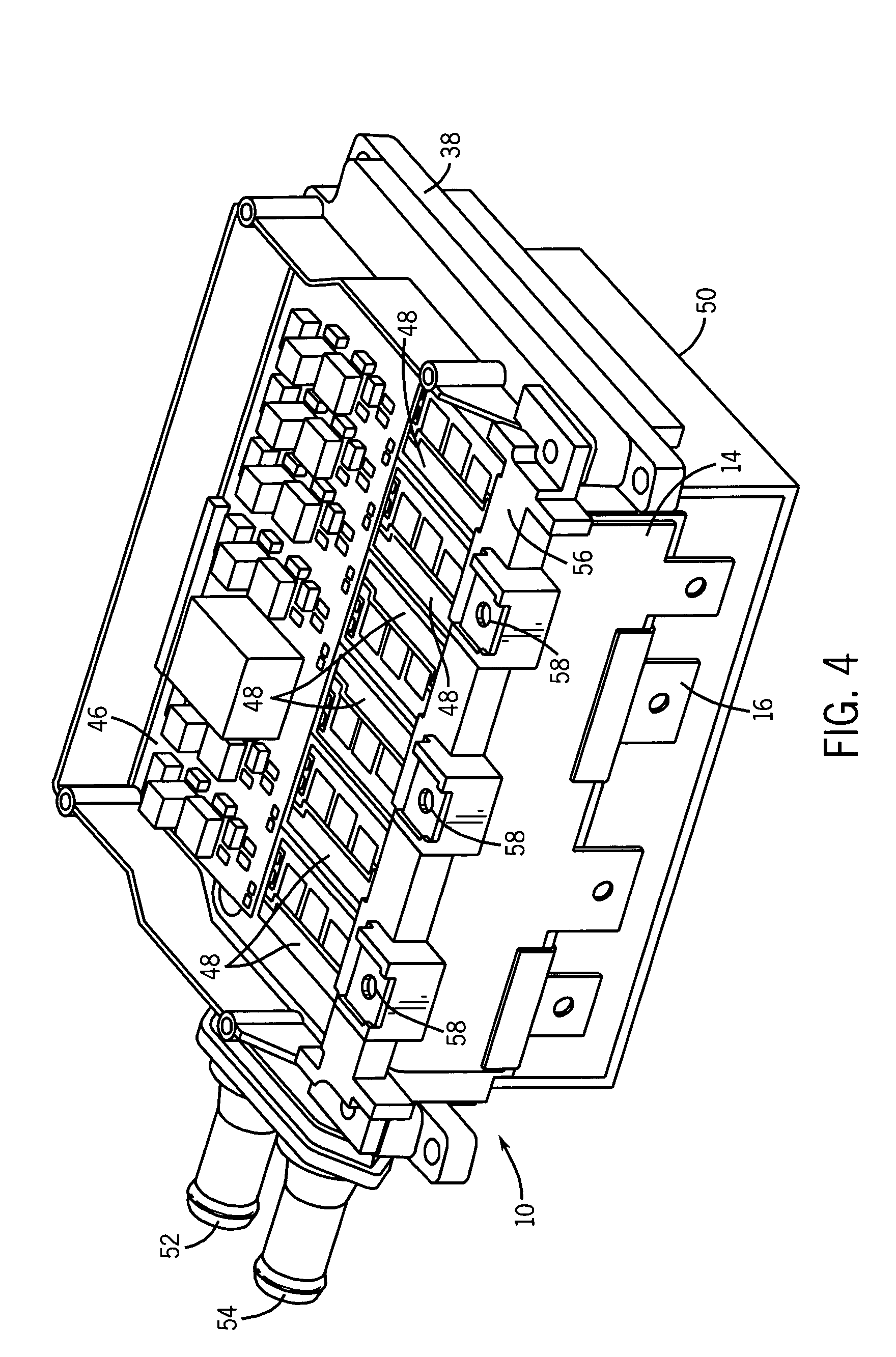
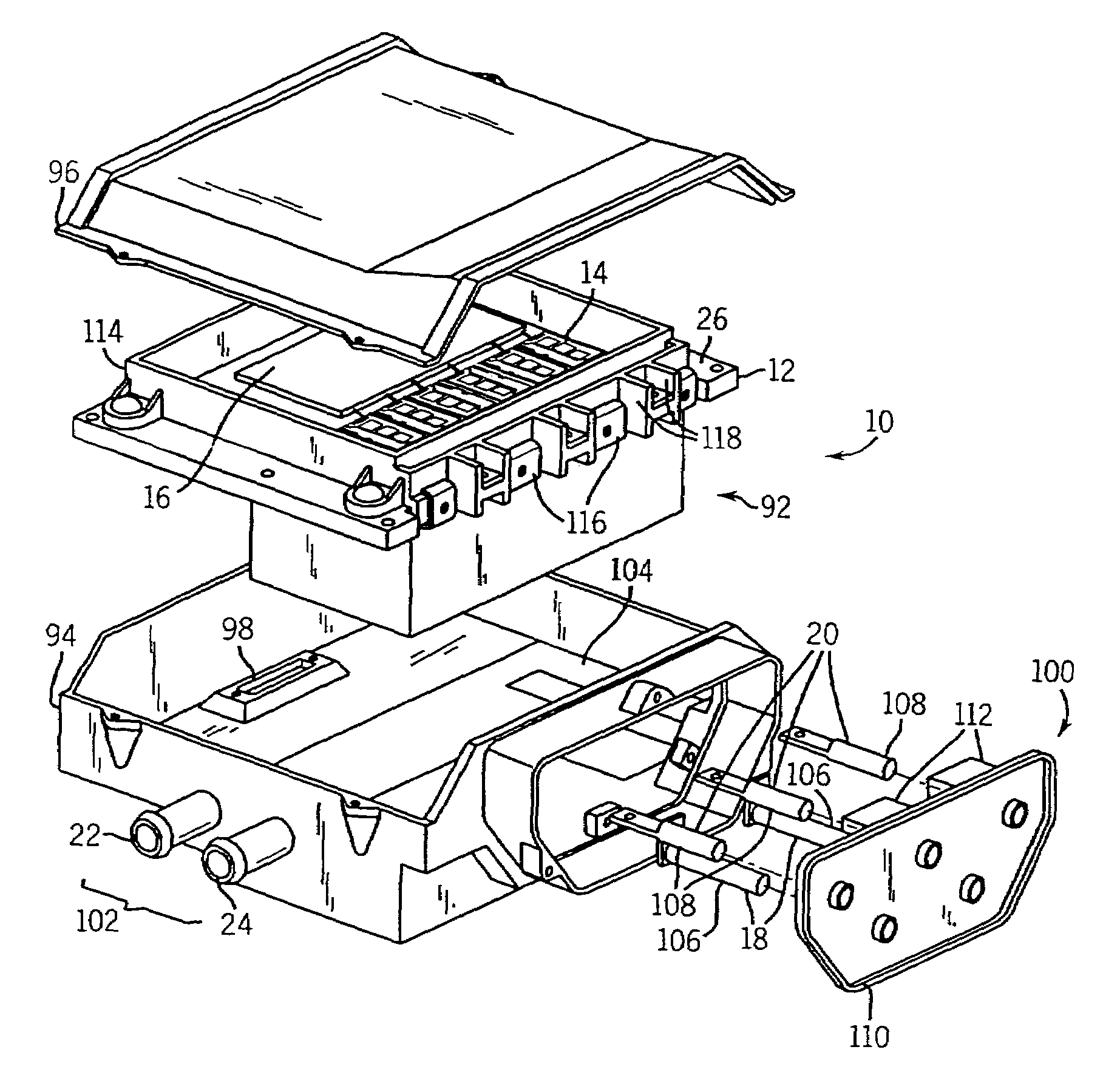
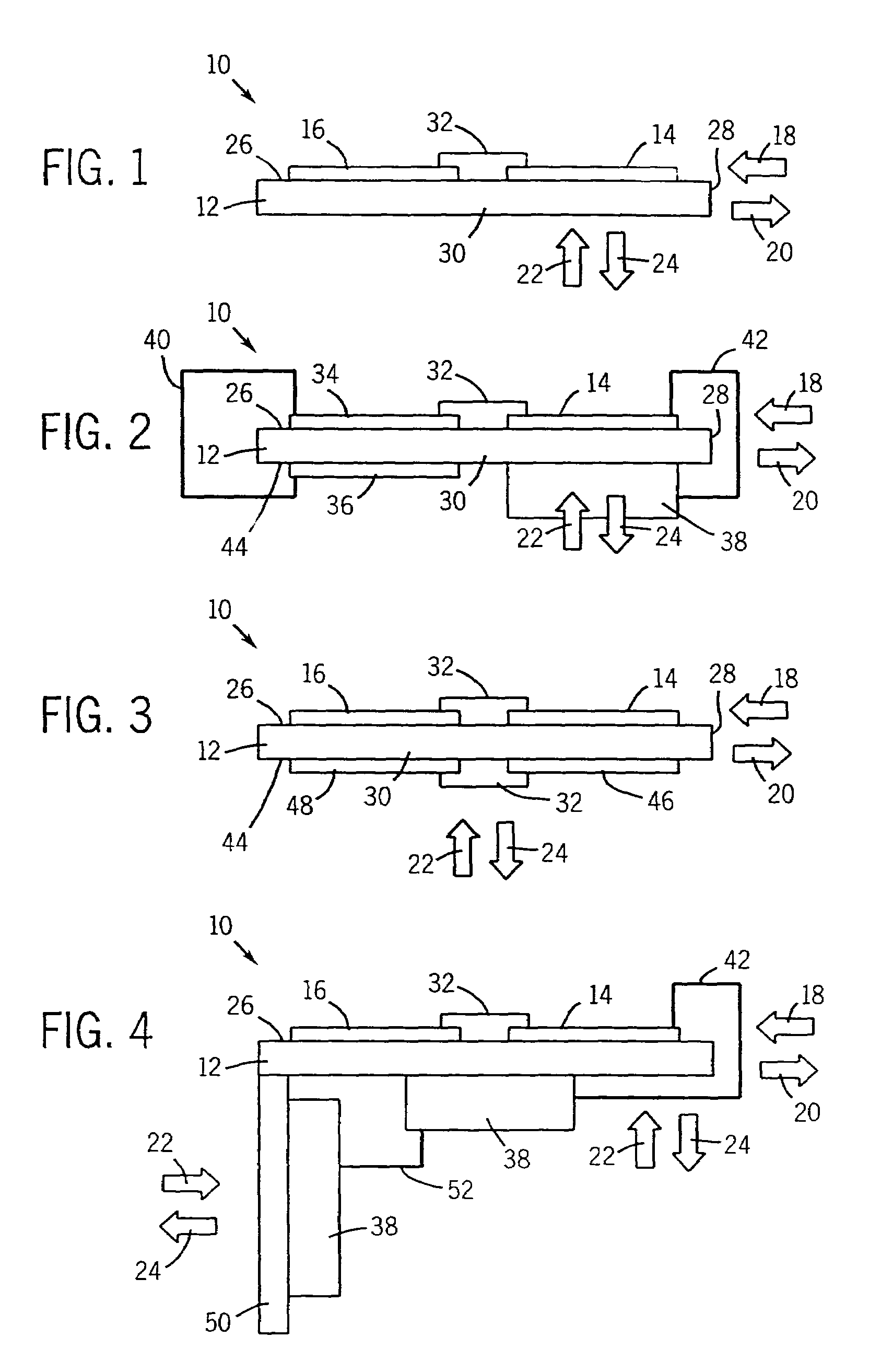
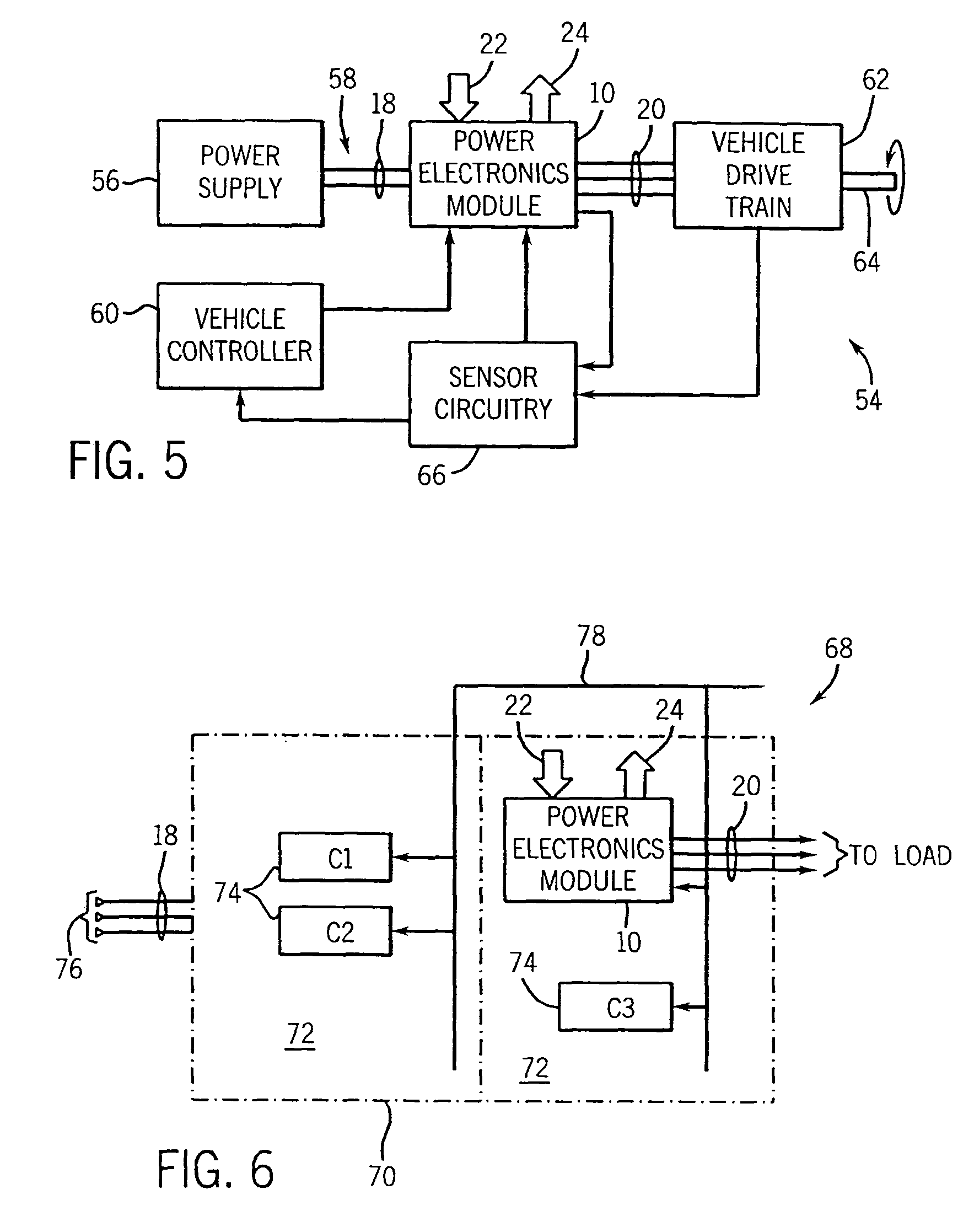
Bus structure for power switching circuits
ActiveUS20050068820A1Easy to optimizeReduction in parasitic conductanceBus-bar/wiring layoutsConversion constructional detailsElectricityPower switching
A bus system is disclosed for use with switching devices, such as power electronic devices. The system includes generally parallel bus elements that define electrical reference planes, such as for a dc bus. The bus elements are separated from one another by insulative layers, with additional insulative layers being available for separating the system from other circuit components. Portions of the bus elements are extended or exposed to permit connection to the circuit elements, including packaged switching circuits and energy storage or filtering circuits. The bus system may be conformed to a variety of geometric configurations, and substantially reduces parasitic inductance and total loop inductance in the resulting circuitry.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH +1
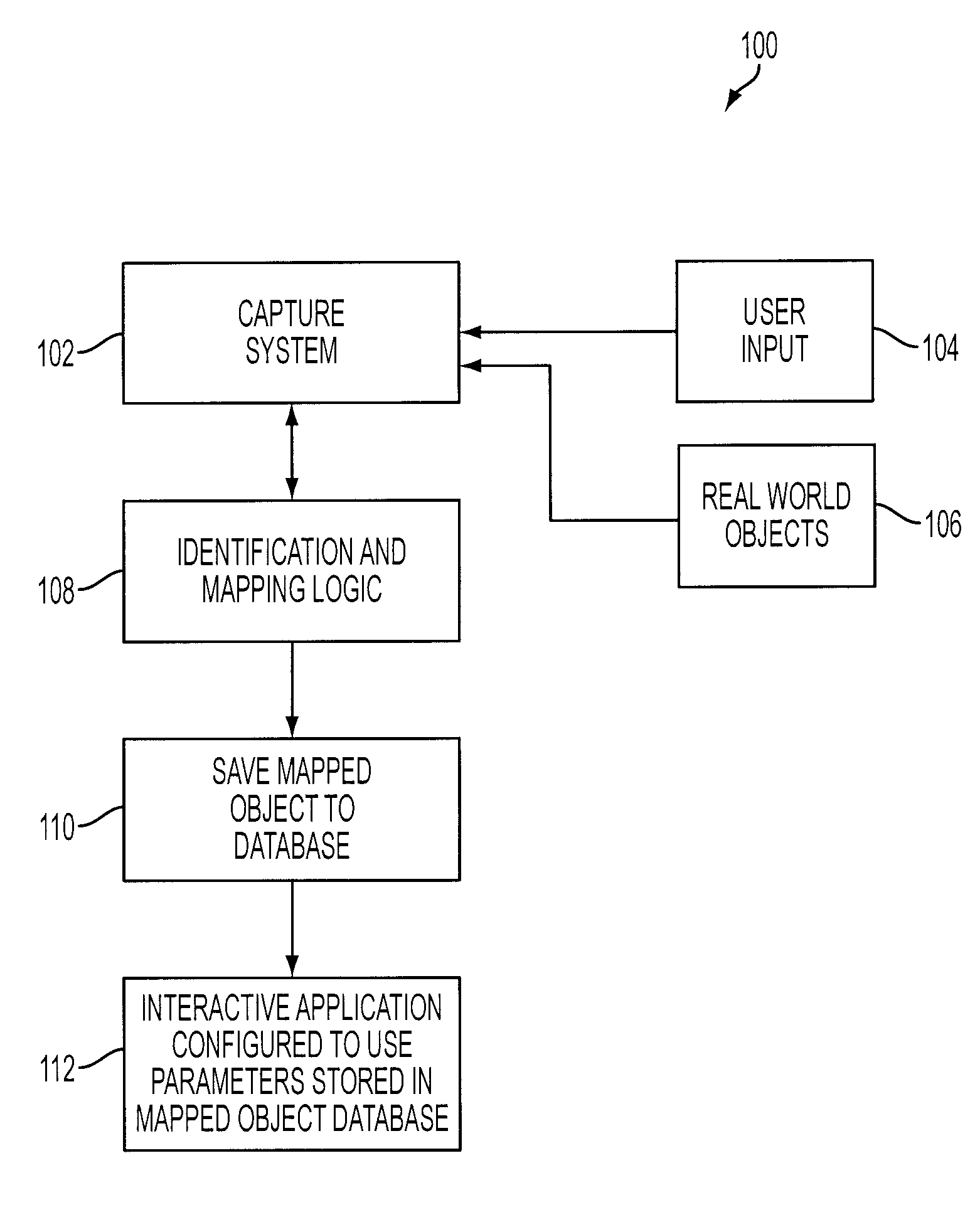
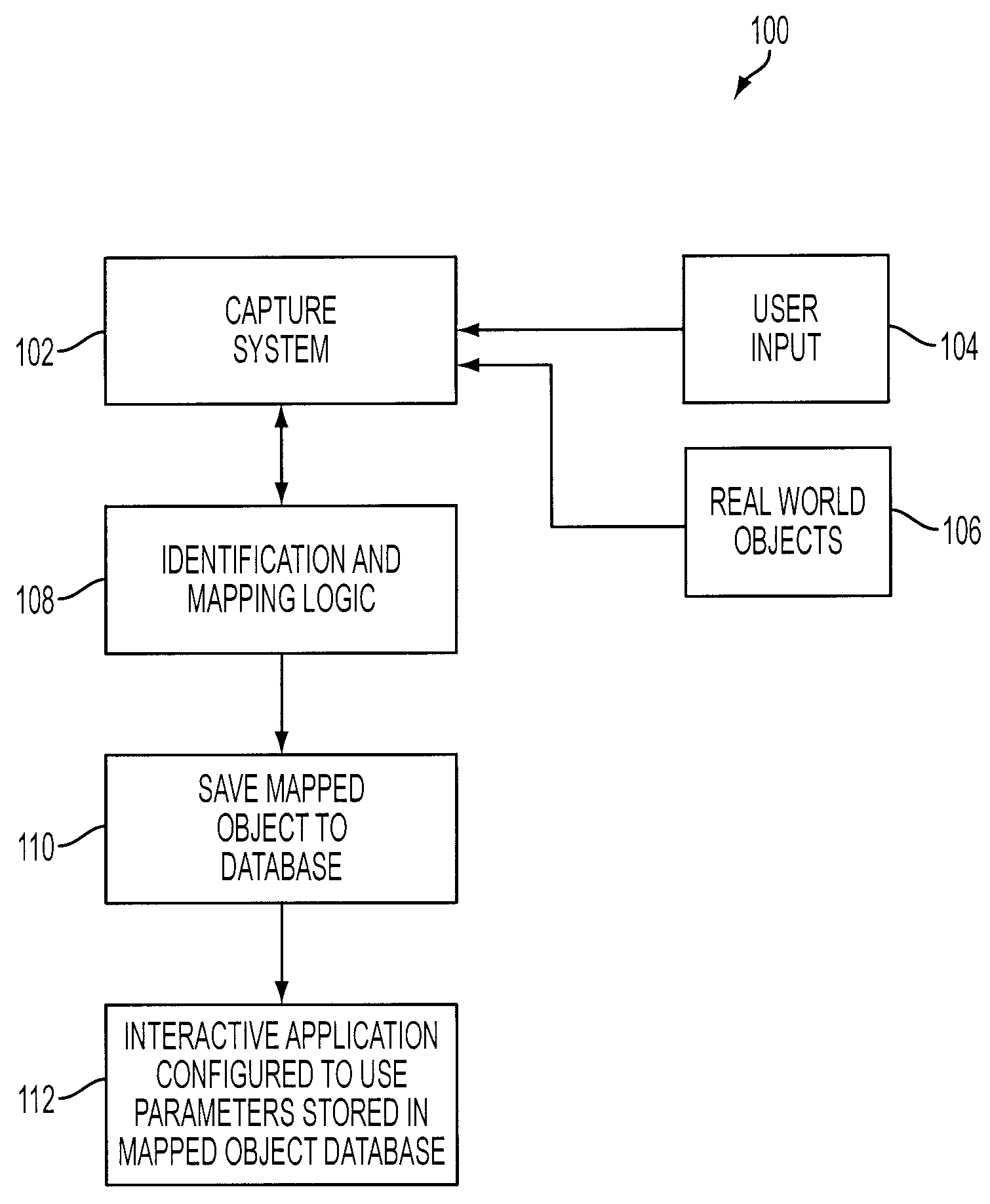
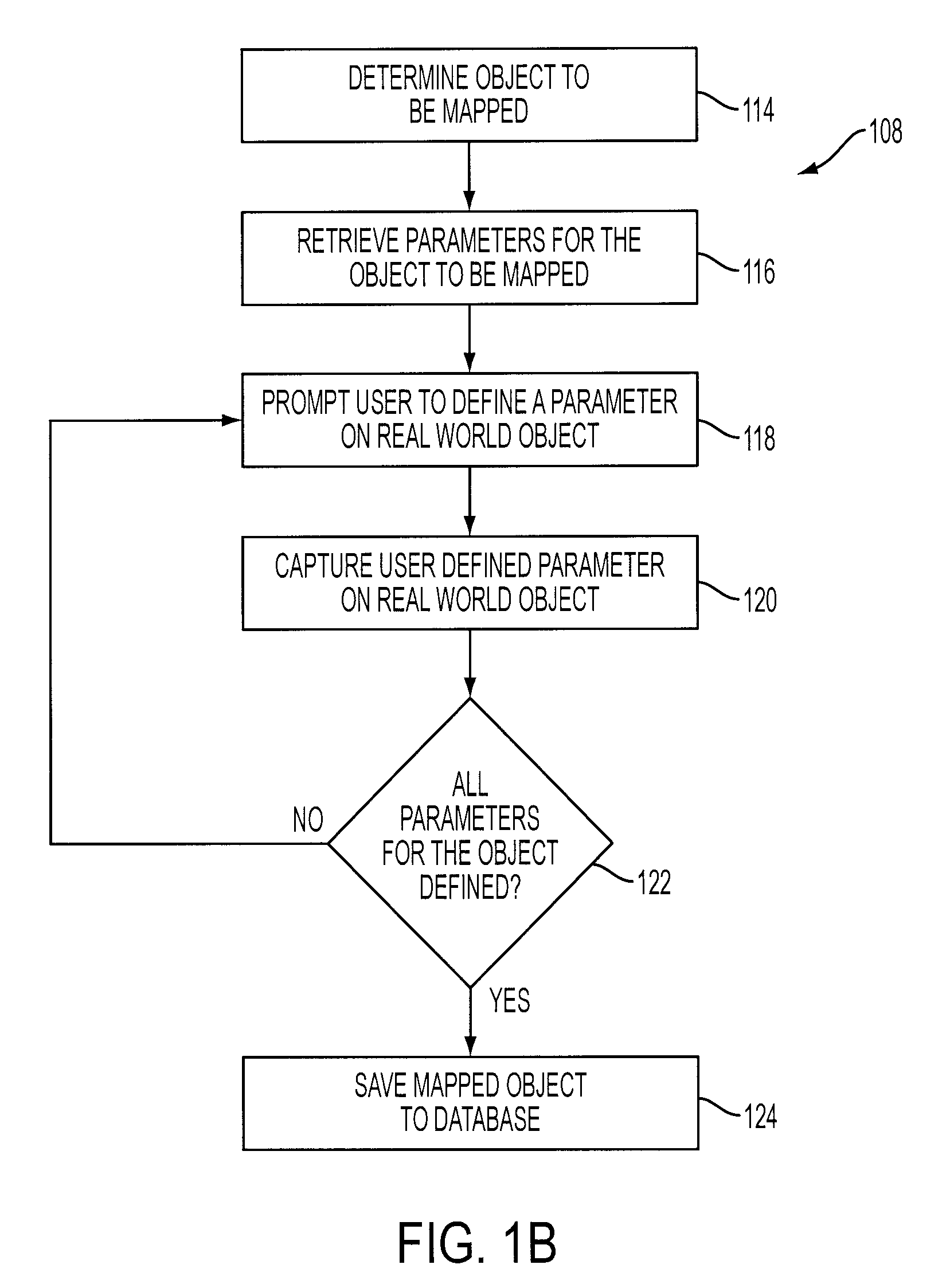
Selective interactive mapping of real-world objects to create interactive virtual-world objects
A method for interactively defining a virtual-world space based on real-world objects in a real-world space is disclosed. In one operation, one or more real-world objects in the real-world space is captured to define the virtual-world space. In another operation, one of the real-world objects is identified, the identified object is to be characterized into a virtual-world object. In yet another operation, a user is prompted for user identification of one or more object locations to enable extraction of parameters for real-world object, and the object locations are identified relative to an identifiable reference plane in the real-world space. In another operation, the extracted parameters of the real-world object may be stored in memory. The virtual-world object can then be generated in the virtual world space from the stored extracted parameters of the real-world object.
Owner:SONY COMP ENTERTAINMENT EURO +1
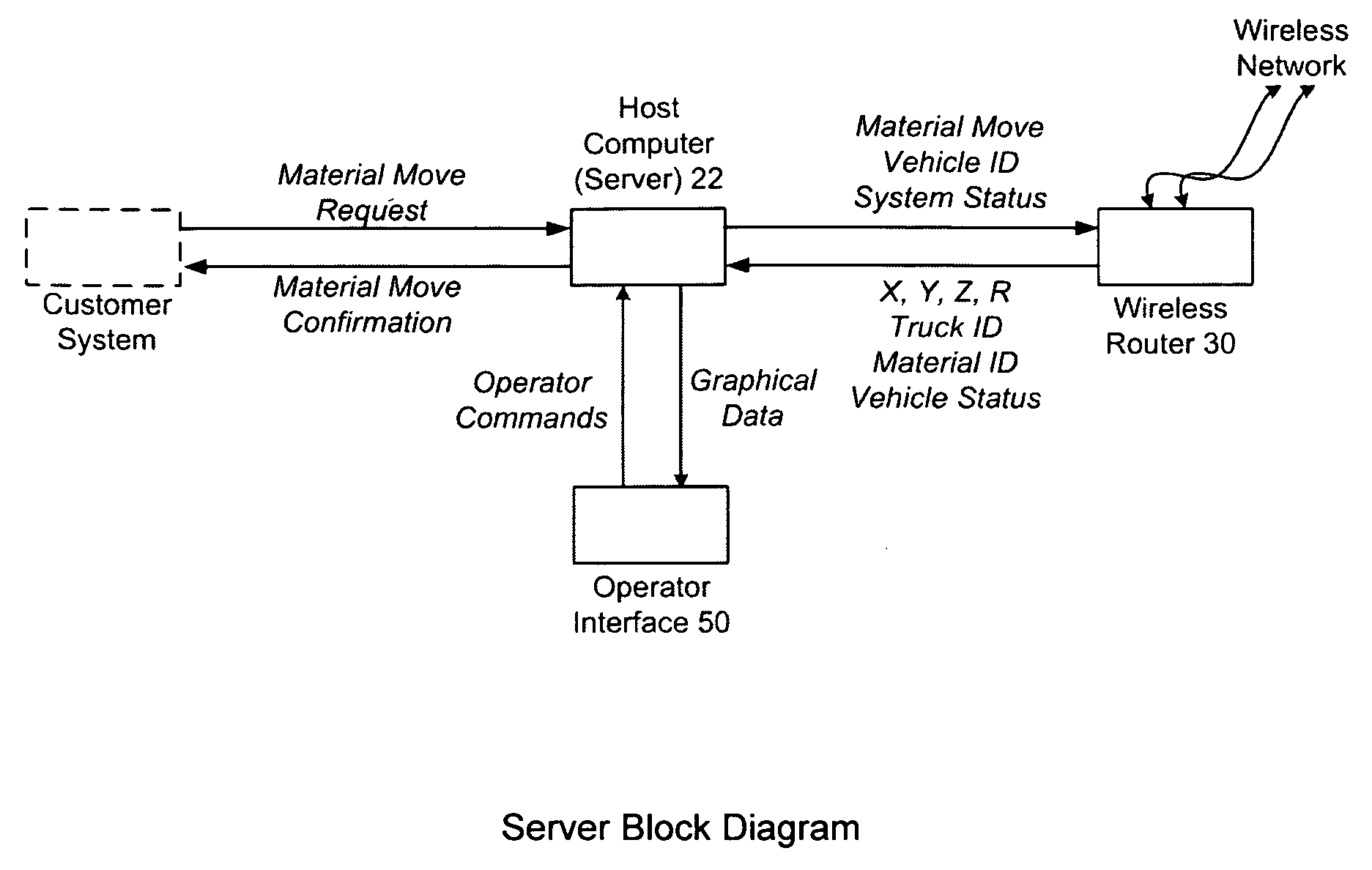
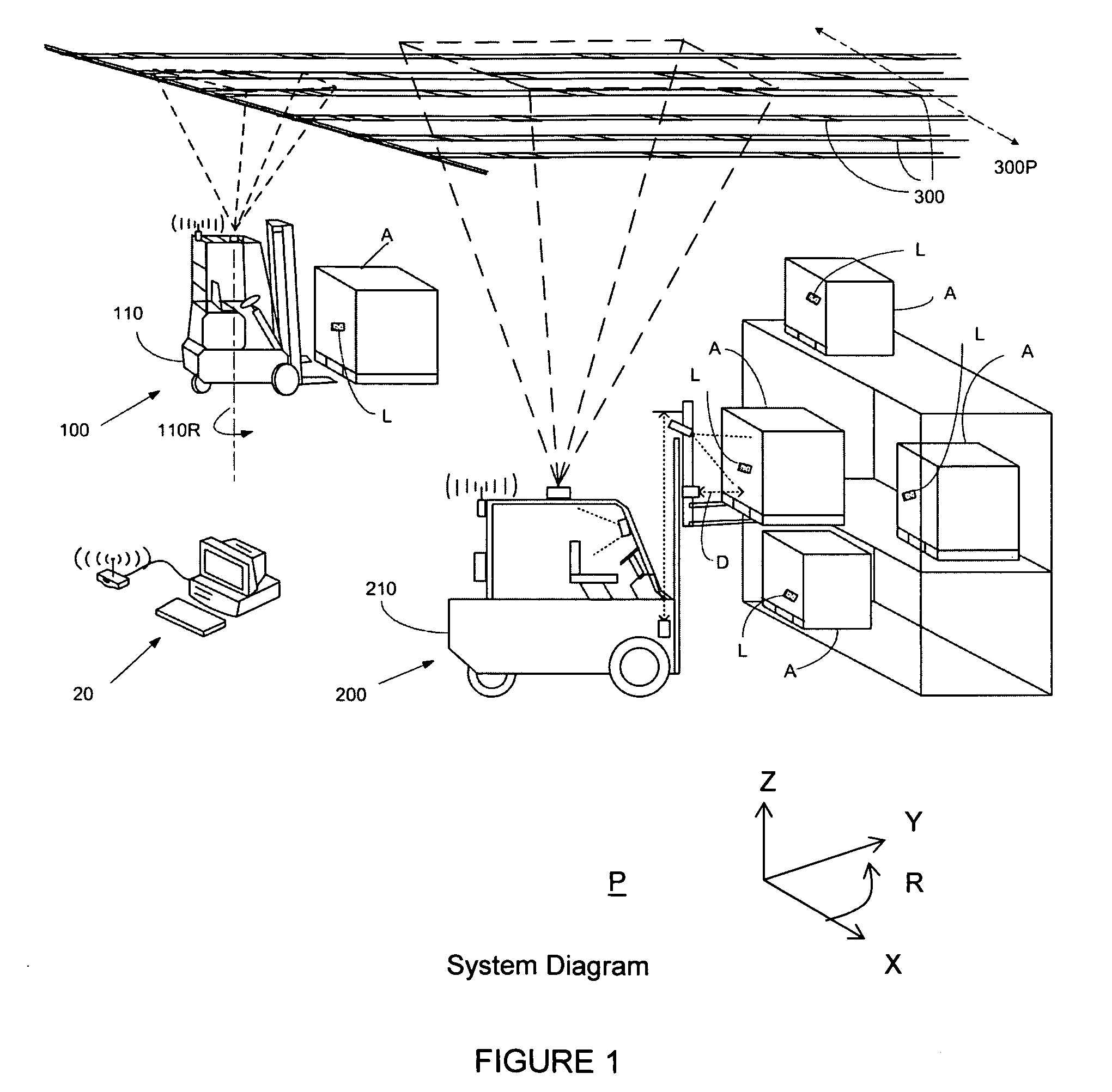
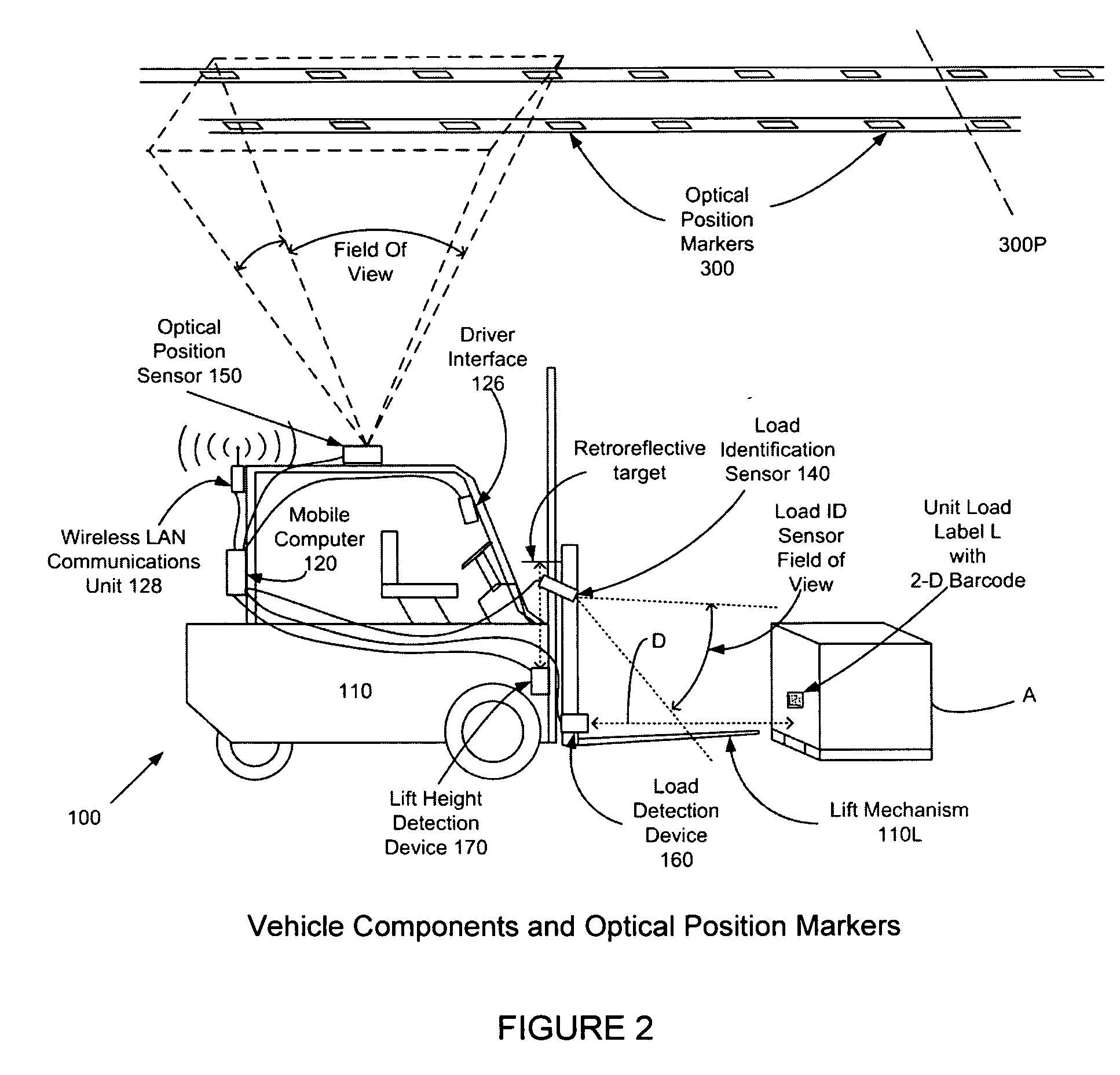
Apparatus and method for asset tracking
An apparatus and method for tracking the location of one or more assets, comprising an integrated system that identifies an asset, determines the time the asset is acquired by a conveying vehicle, determines the position, elevation and orientation of the asset at the moment it is acquired, determines the time the asset is deposited by the conveying vehicle, and determines the position, elevation and orientation of the asset at the time the asset is deposited, each position, elevation and orientation being relative to a reference plane. Mobile subsystems, each on a conveying vehicle, identify the location and orientation of that conveying vehicle using an optical position sensor unit viewing an array of optical position markers, determine the identity of the asset from a label, confirm acquisition of the asset, determine the elevation of the asset relative to the reference plane and communicate the tracking information to a fixed-base subsystem.
Owner:TOTALTRAX
Head worn computer display systems
ActiveUS20160246055A1Improve cooling effectIncrease airflowDetails for portable computersImage data processingOptical mountDisplay device
Aspects of the present disclosure relate to mounting electronics and optical systems in head-worn see-through computer displays. In embodiments, a head worn computer includes an optical chassis with a rigid open box structure configured to provide a stable optical mounting reference plane and a plurality of image source reference planes. The head worn computer further includes a first image source mounted on one of the image source reference planes to project first image light through a first hole in the optical mounting reference plane and a second image source mounted on a second of the image source reference planes and configured to project second image light through a second hole in the optical mounting reference plane. An outer frame holds the optical chassis such that, when worn by a user, the first and second image light is aligned with the eyes of the user.
Owner:OSTERHOUT GROUP INC
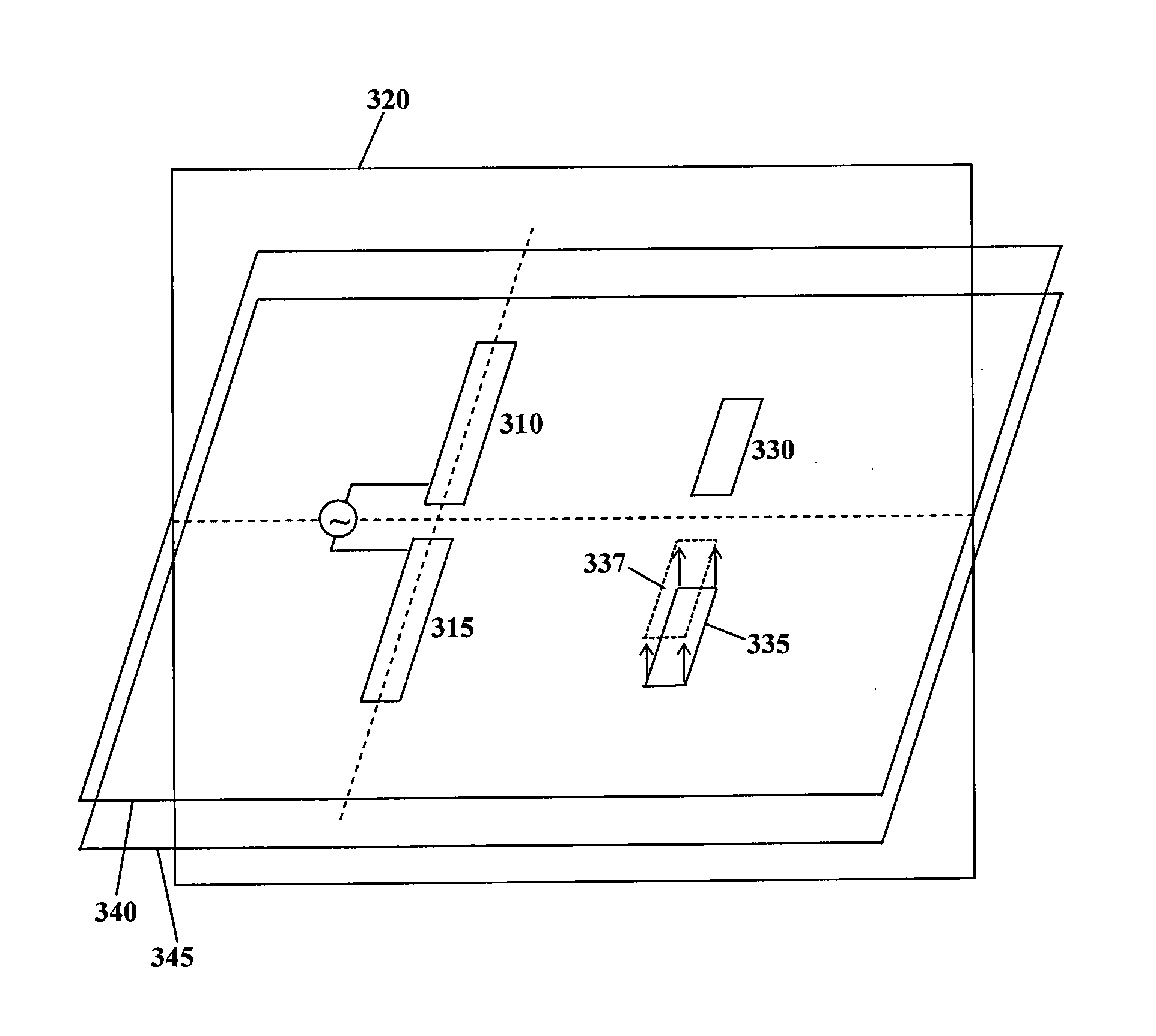
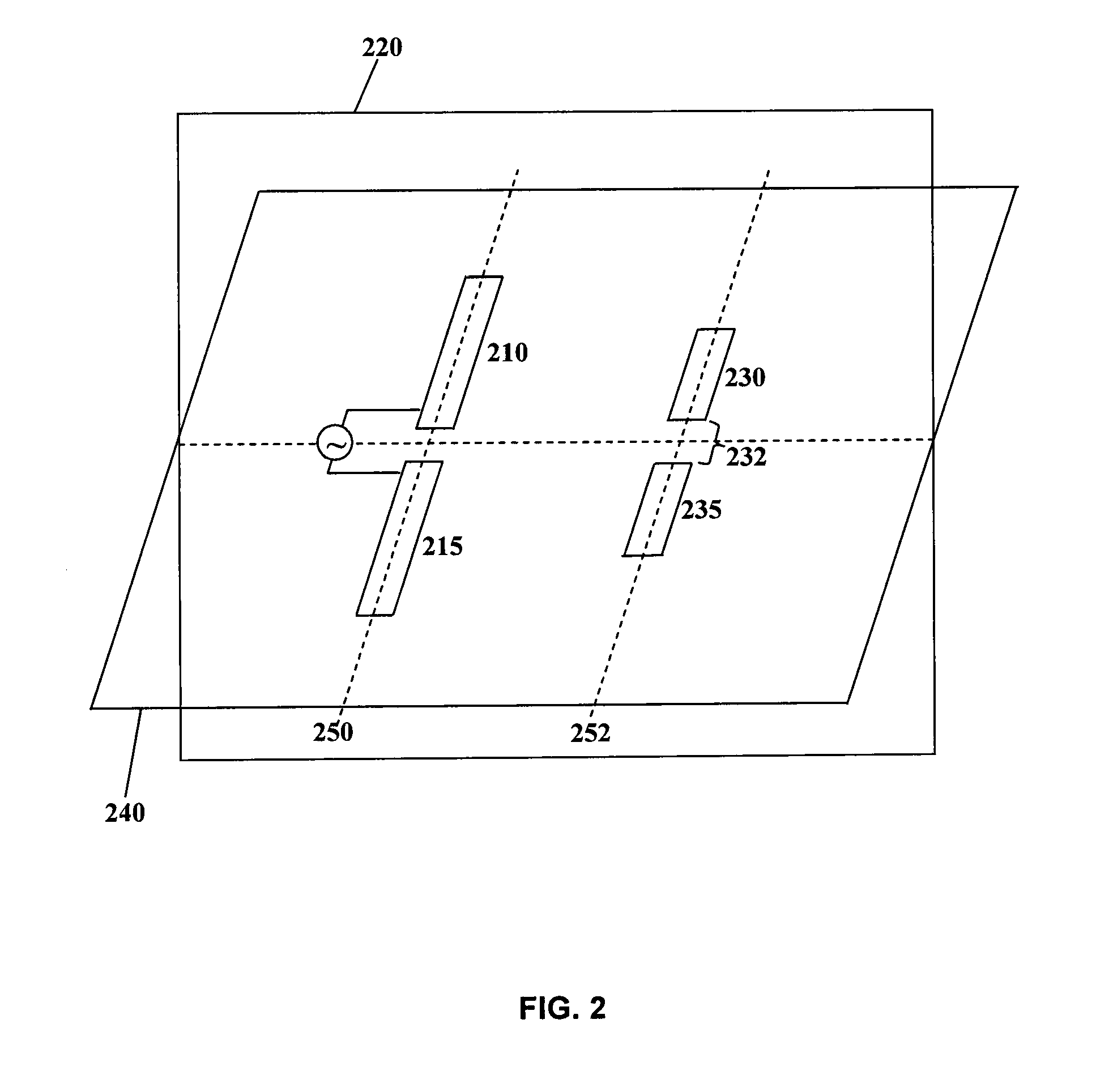
Antenna having split directors and antenna array comprising same
InactiveUS20140266953A1Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna feed intermediatesDirectional antennaEngineering
An antenna is provided comprising a pair of driven elements and a pair of passive elements. The driven elements are disposed on opposite sides of a reference plane, and the passive elements are also disposed on opposite sides of the reference plane. One or both passive elements may be provided in a different plane than the driven elements. By varying placement of the passive elements the antenna radiation pattern can be altered. An antenna array is also provided, comprising two or more oppositely directed directional antennas at least one of which is as described above. The passive elements of the antennas can be adjusted for a desired coverage pattern of the array, such as an azimuthal omnidirectional pattern, for example through simulation. The antenna or array may be embodied on a printed circuit board.
Owner:SIERRA WIRELESS
Repeatable reference for positioning sensors and transducers in drill pipe
InactiveUS6888473B1Precise positioningReliable indicationSurveyDrilling rodsTransmitted powerData acquisition
A drill pipe having a box end having a tapered thread, and an internal shoulder and an external face for engagement with a drill pipe pin end having a tapered mating thread, and an external shoulder and an external face adapted for data acquisition or transmission. The relative dimensions of the box and pin ends are precisely controlled so that when the tool joint is made up, a repeatable reference plane is established for transmitting power and tuning downhole sensors, transducers, and means for sending and receiving data along the drill string. When the power or data acquisition and transmission means are located in the tool joint, the dimensions of the tool joint are further proportioned to compensate for the loss of cross-sectional area in order maintain the joints ability to sustain nominal makeup torque.
Owner:INTELLISERV
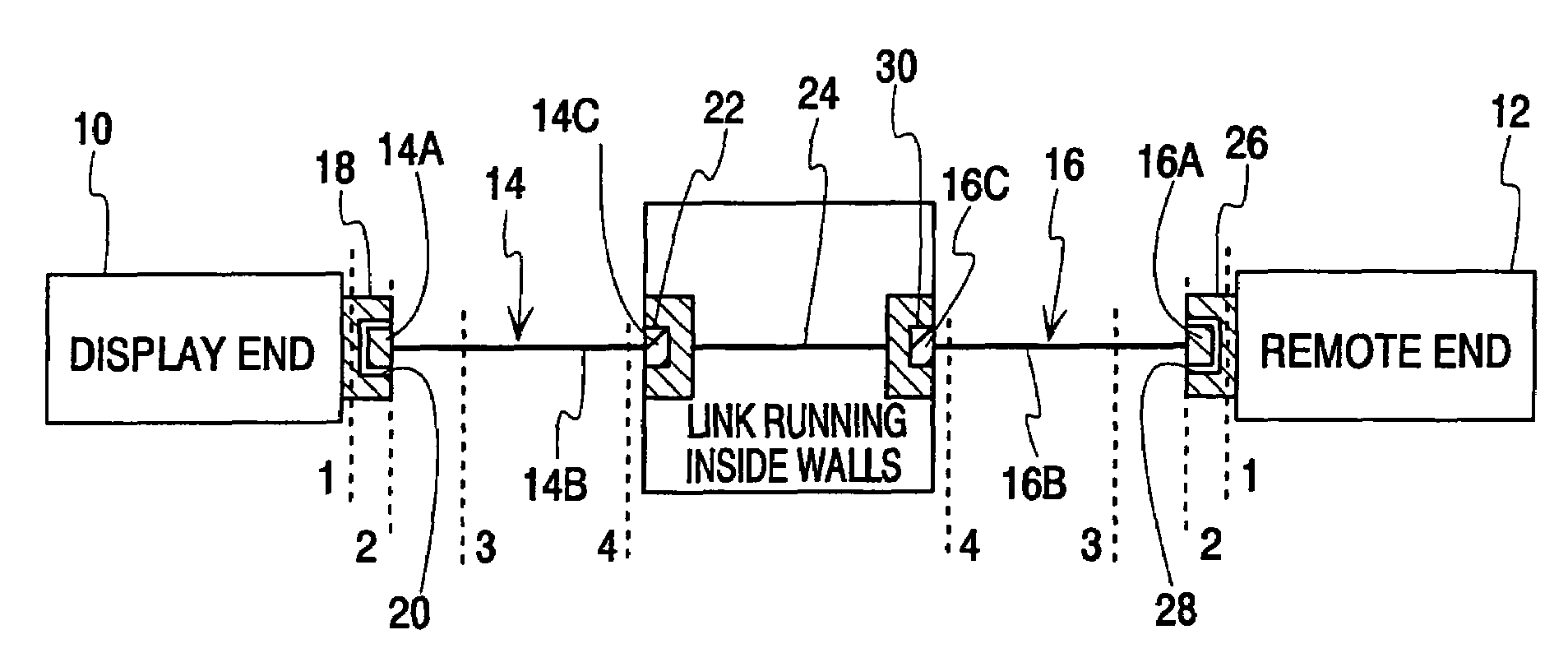
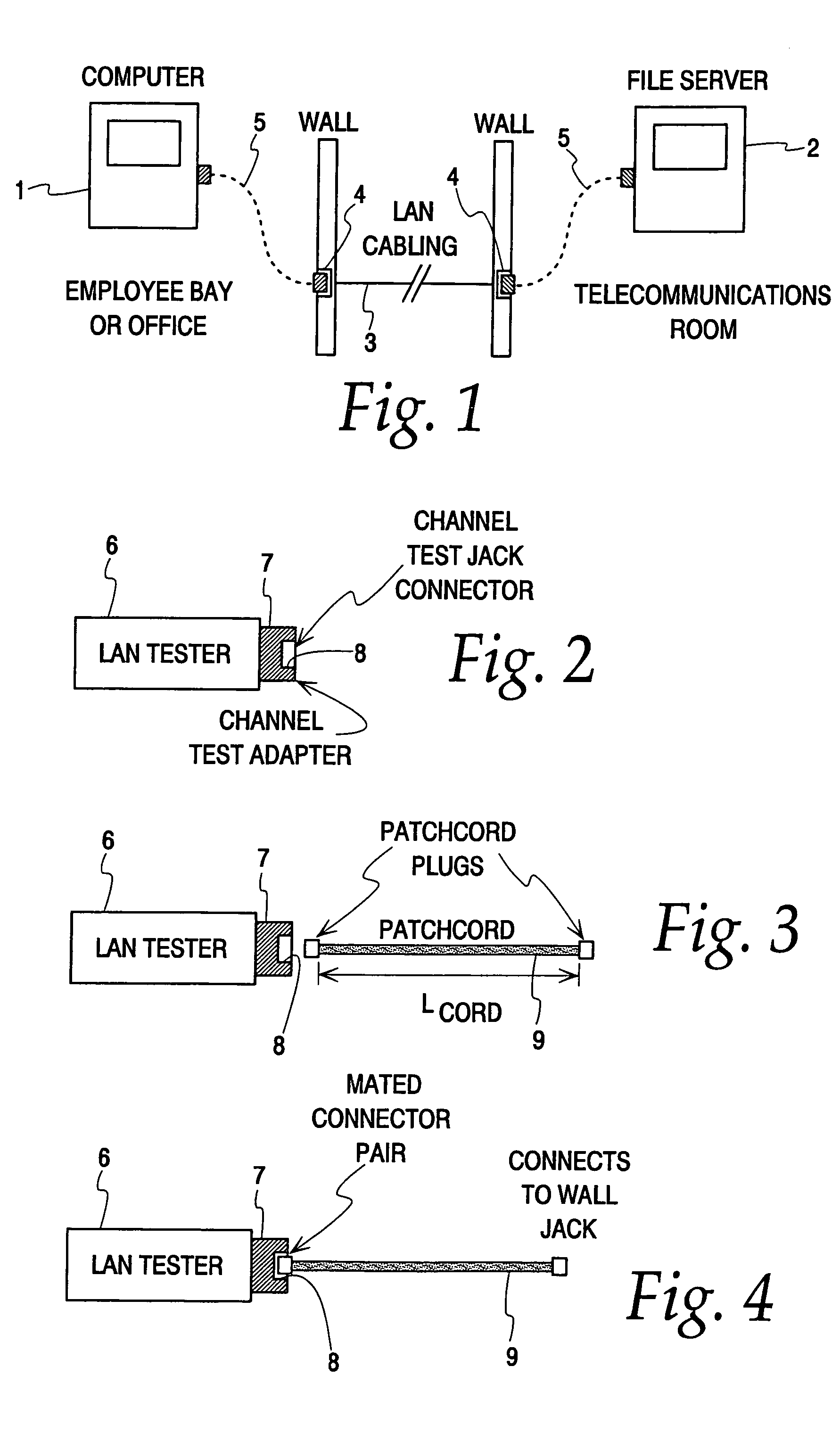
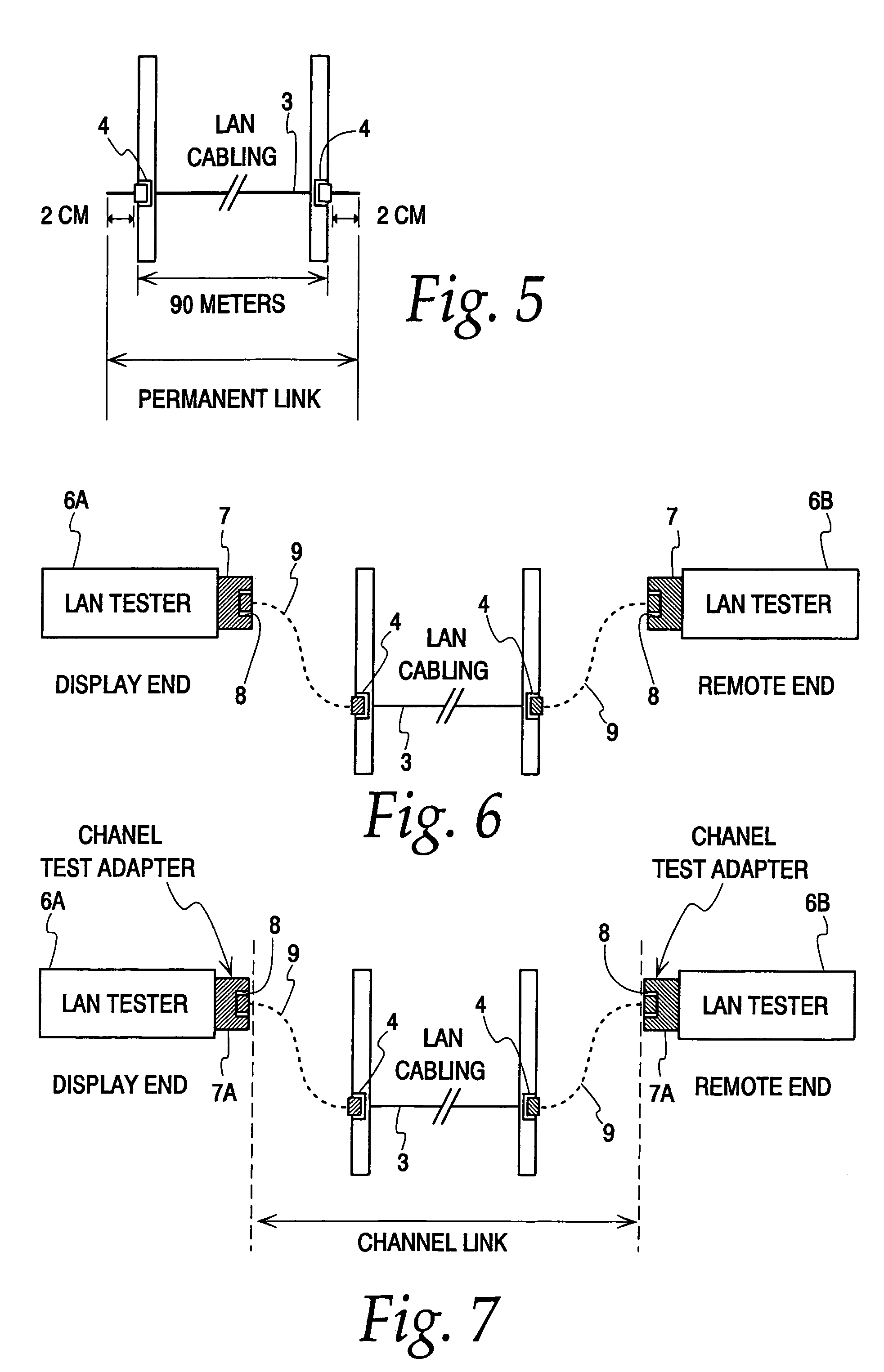
Hand-held tester and method for local area network cabling
InactiveUS7479776B2Simple processLow costError preventionTransmission systemsTester deviceDisplay device
A LAN tester has display and remote units each having a connector jack attached to an adapter board for connection to the plug of a patch cord. Both the display and remote units have circuits which are capable of measuring the phase between a drive signal voltage and the corresponding coupled or reflected signal due to the drive signal. Scattering parameters for the mated connector pairs and the patch cord itself are measured during a field calibration. A computer in one or both of the tester units stores the measured scattering parameters and uses the scattering parameters to move the reference plane to any desired location along the patch cord. Channel link or permanent link tests can be conducted using the same equipment.
Owner:IDEAL IND NETWORKS LTD
Surgical retractor and retractor assembly
Retractor for insertion in an incision of a patient includes a frame defining a central opening and a reference plane, and at least one blade disposed within the central opening The blade operatively coupled to the frame by a support structure for movement in a first direction generally laterally with the reference plane between an unretracted position and a retracted position, a second direction at an angle extending through and relative to the reference plane for adjustment of the blade depth, and a third direction rotationally relative to the reference plane Additionally, the frame includes a track in mating relationship with the support structure for sliding movement therebetween in a defined relationship relative to the reference plane. Retractor assembly includes the retractor as previously described, in combination with an adjustment tool or an insertion tool.
Owner:ZIMMER BIOMET SPINE INC +1
Smart antenna array over fiber
InactiveUS20080007453A1Improve performanceQuality improvementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsModular arraysFiberSmart antenna
A smart antenna system includes a plurality of antennas, a plurality of Transmit—Receive Modules (TRMs) coupled respectively to the plurality of antennas, and a beam steering module coupled to the plurality of TRMs and providing radiation beam steering for the plurality of TRMs. The beam steering module includes a pilot generator for generating a pilot signal and providing it to the TRMs to calibrate a receive (RX) reference plane. The pilot signal is injected at a first location before the receiver section into the RX path, and the pilot signal is sampled at a second location after the receiver section. The TRMs and the beam steering module can also be used to calibrate a transmit (TX) reference plane by sampling output signals from the TRMs. The output signals have a pilot signal component, and are sampled at the first location in the TX path after the transmitter section.
Owner:POWERWAVE TECH INC
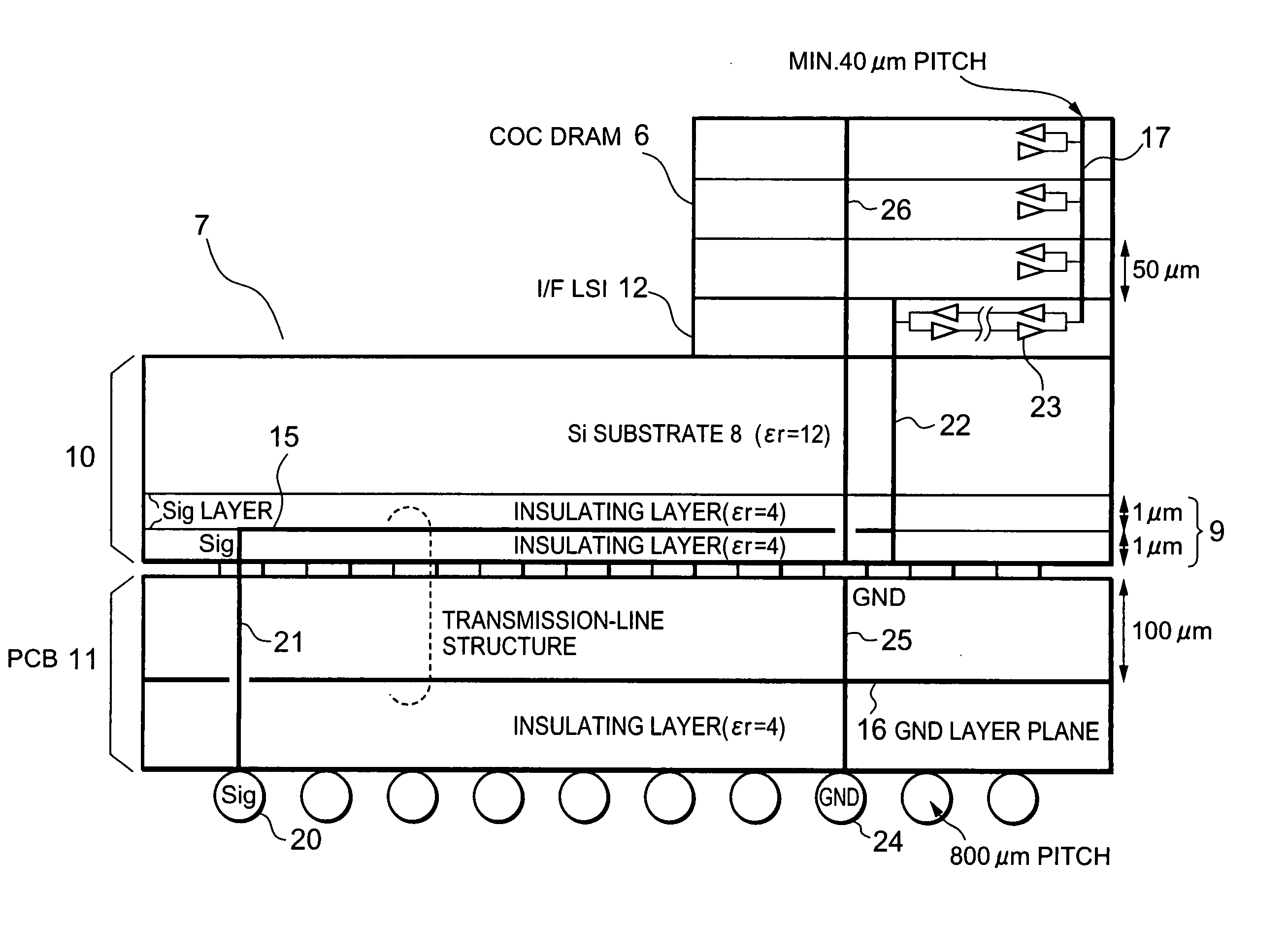
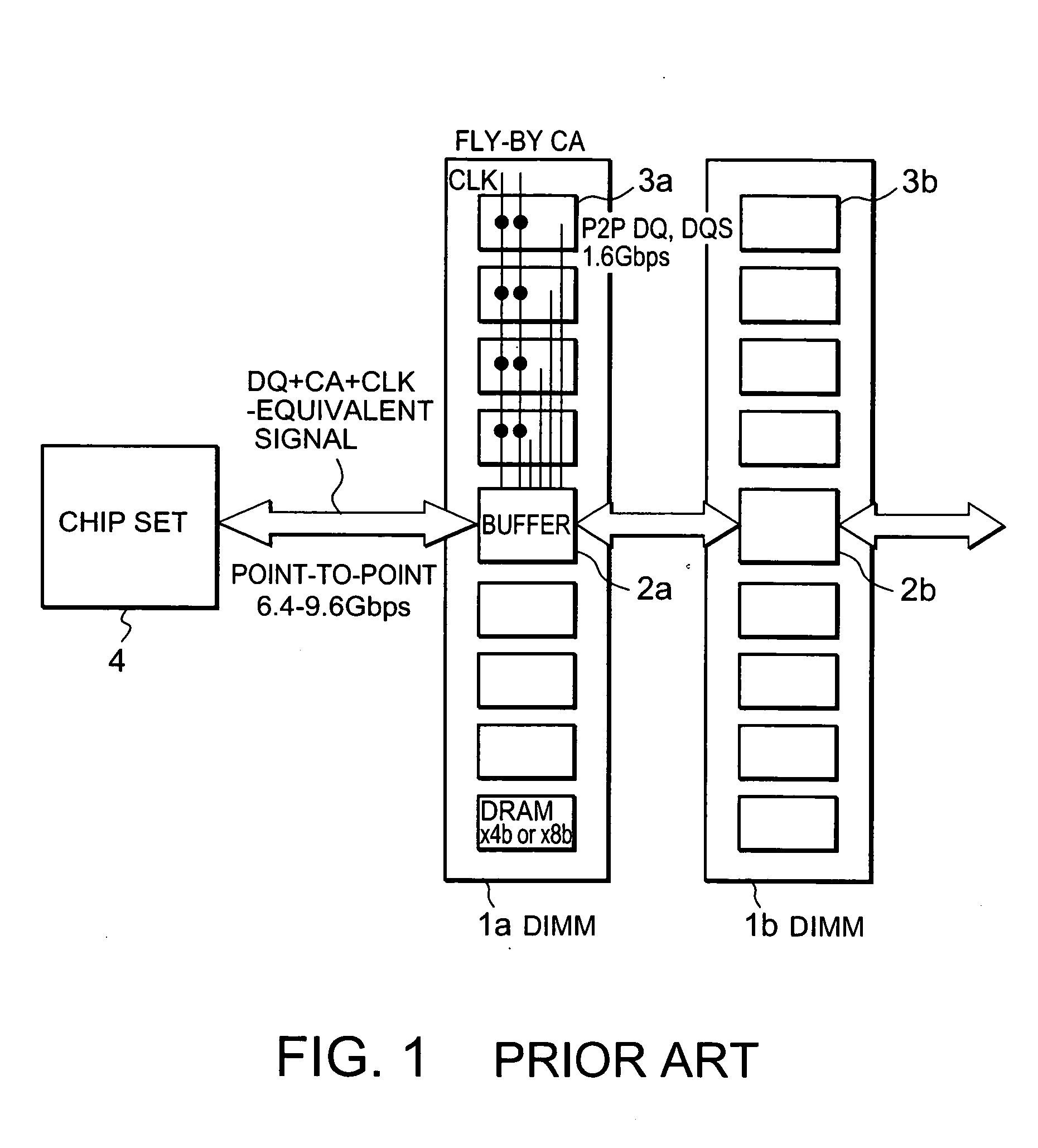
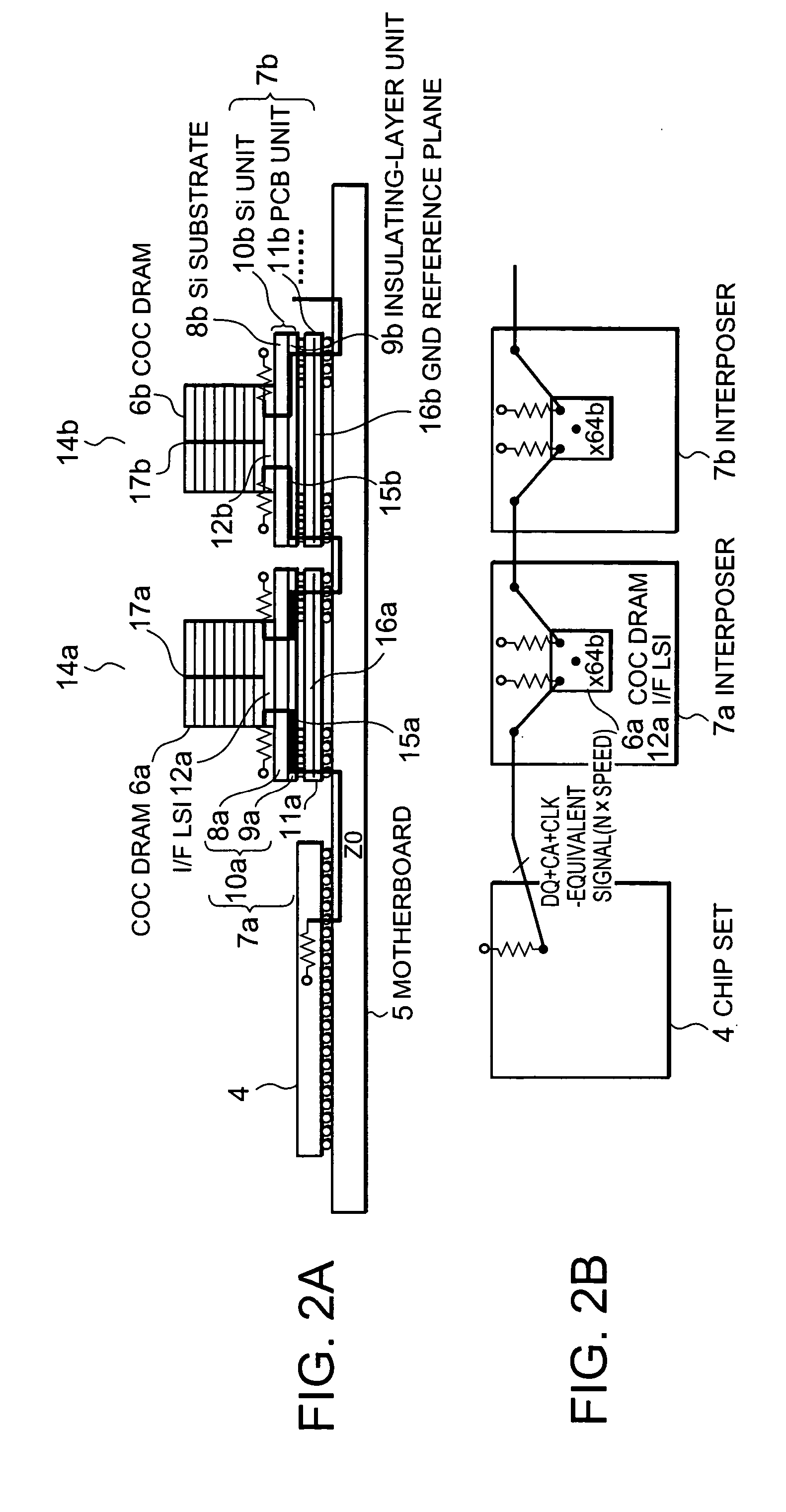
Semiconductor integrated circuit device
InactiveUS20050139977A1Easy impedance matchingReduce signalingTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsInterposerChipset
A COC DRAM including a plurality of stacked DRAM chips is mounted on a motherboard by using an interposer. The interposer includes a Si unit and a PCB. The Si unit includes a Si substrate and an insulating-layer unit in which wiring is installed. The PCB includes a reference plane for the wiring in the Si unit. The wiring topology between a chip set and the COC DRAM is the same for every signal. Accordingly, a memory system enabling a high-speed operation, low power consumption, and large capacity is provided.
Owner:PS4 LUXCO SARL
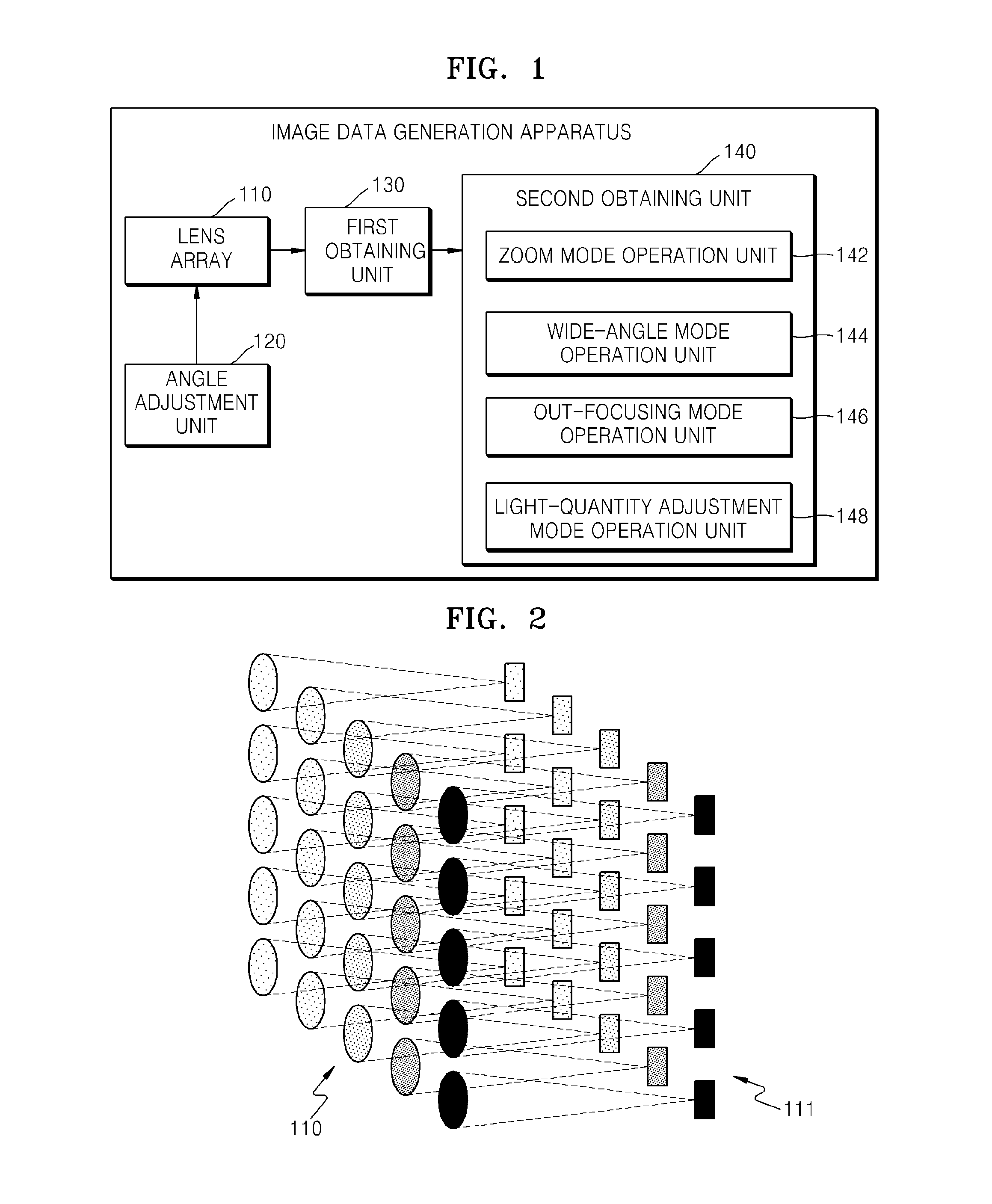
Method of generating image data by an image device including a plurality of lenses and apparatus for generating image data
InactiveUS9019426B2Weakening rangeIncreases magnitudeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsComputer graphics (images)Imaging equipment
A method for generating image data includes adjusting an angle formed by each of a plurality of lenses attached to the imaging device relative to a reference plane based on a photography mode, obtaining at least one first image data using the plurality of adjusted lenses, and generating second image data corresponding to the photography mode using the at least one first image data.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
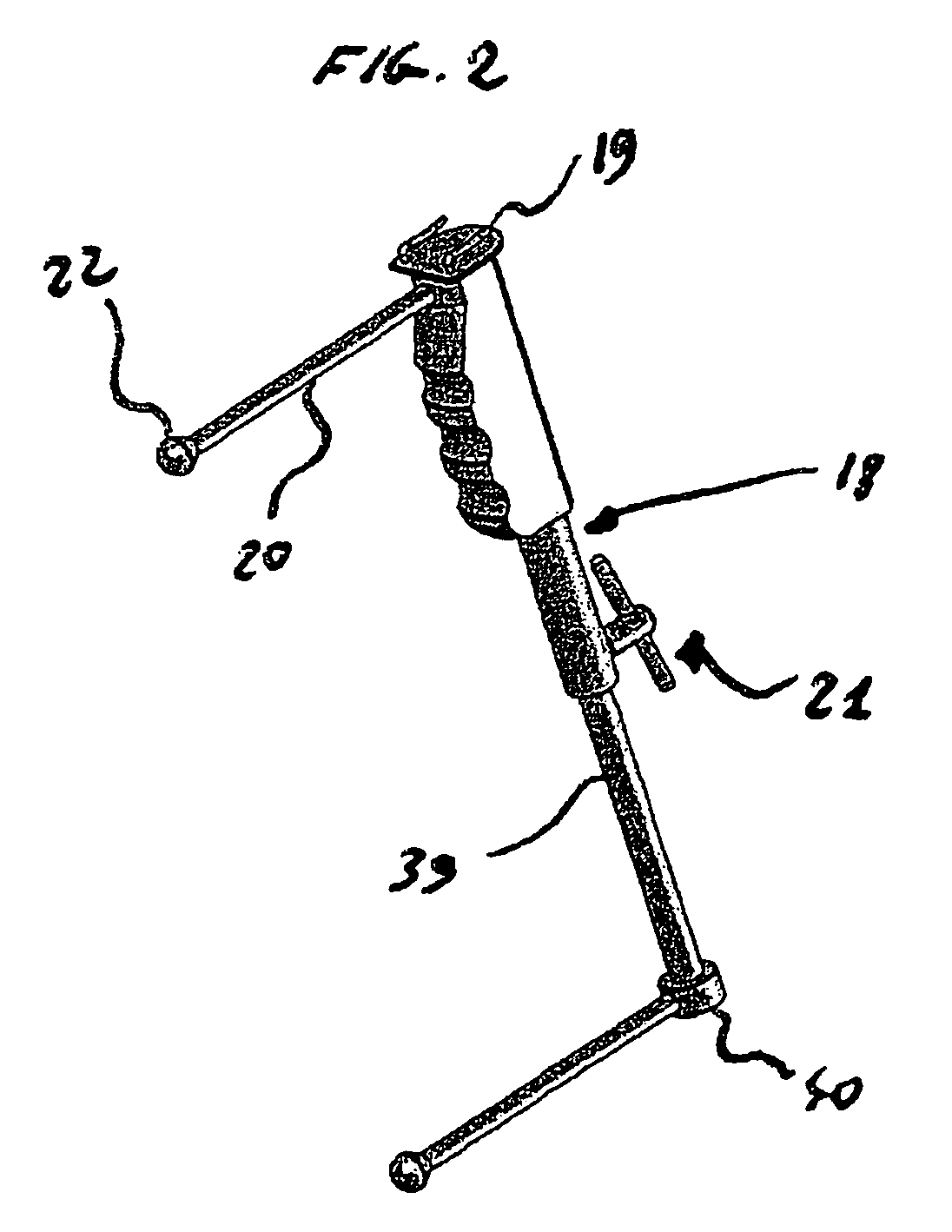
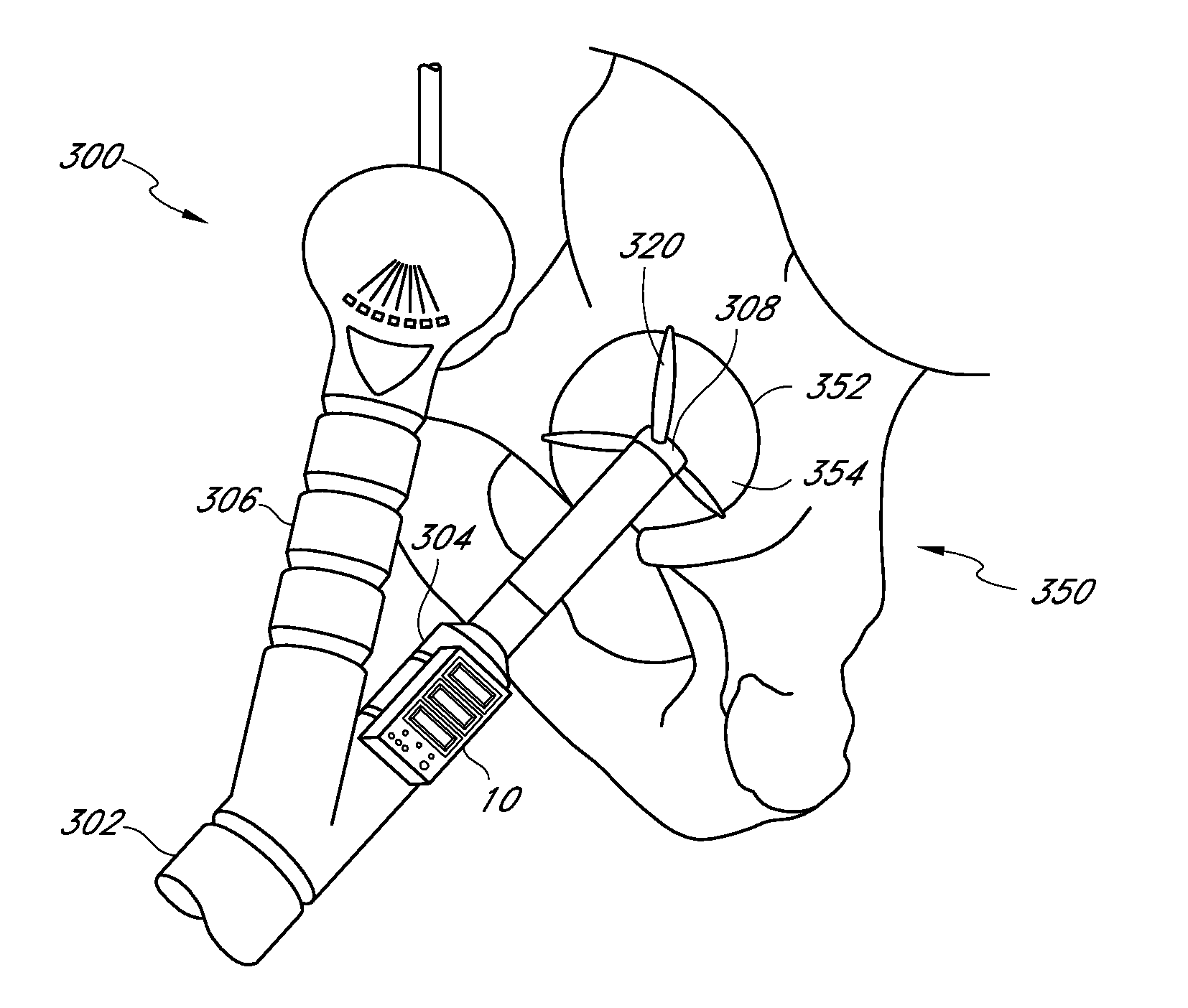
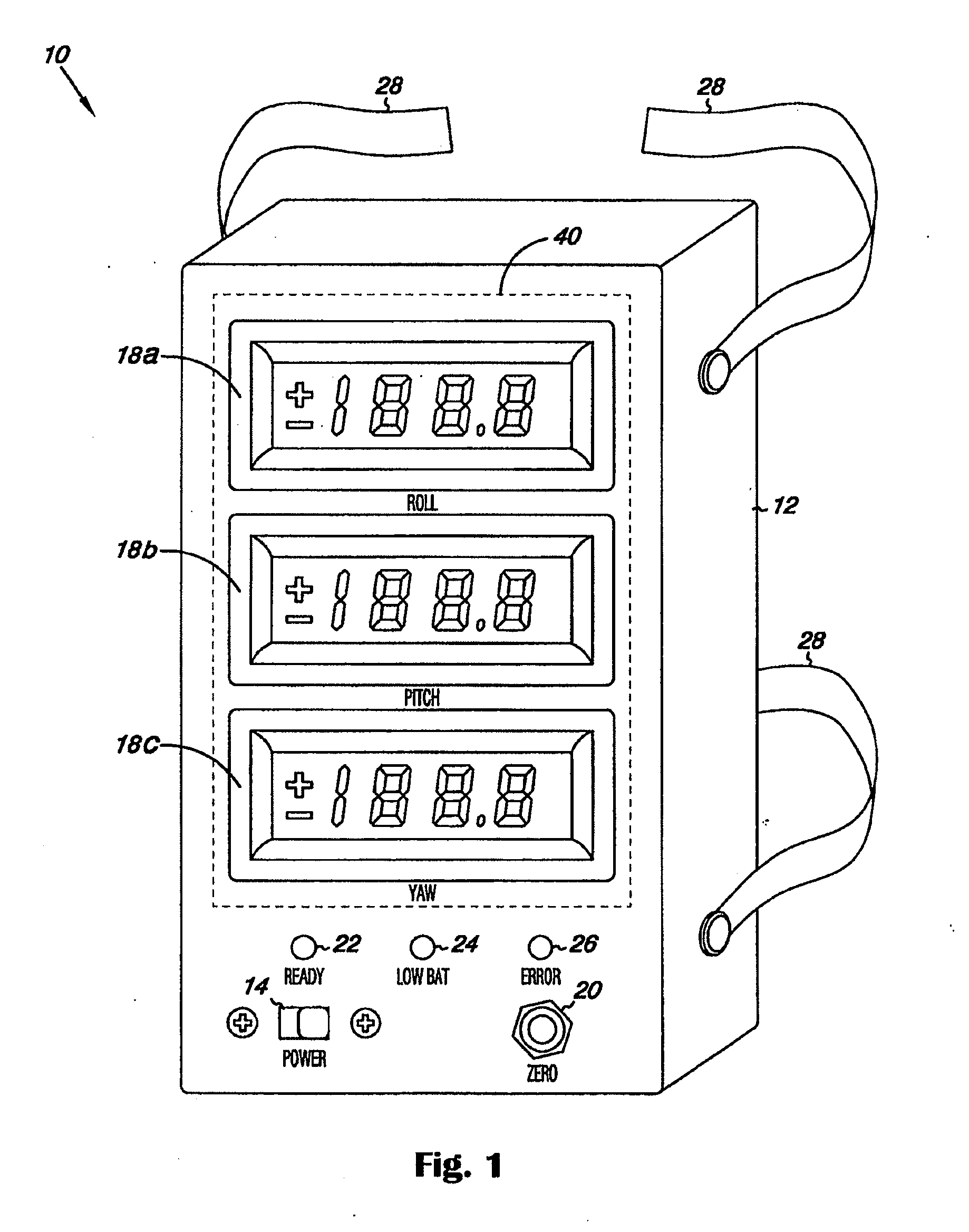
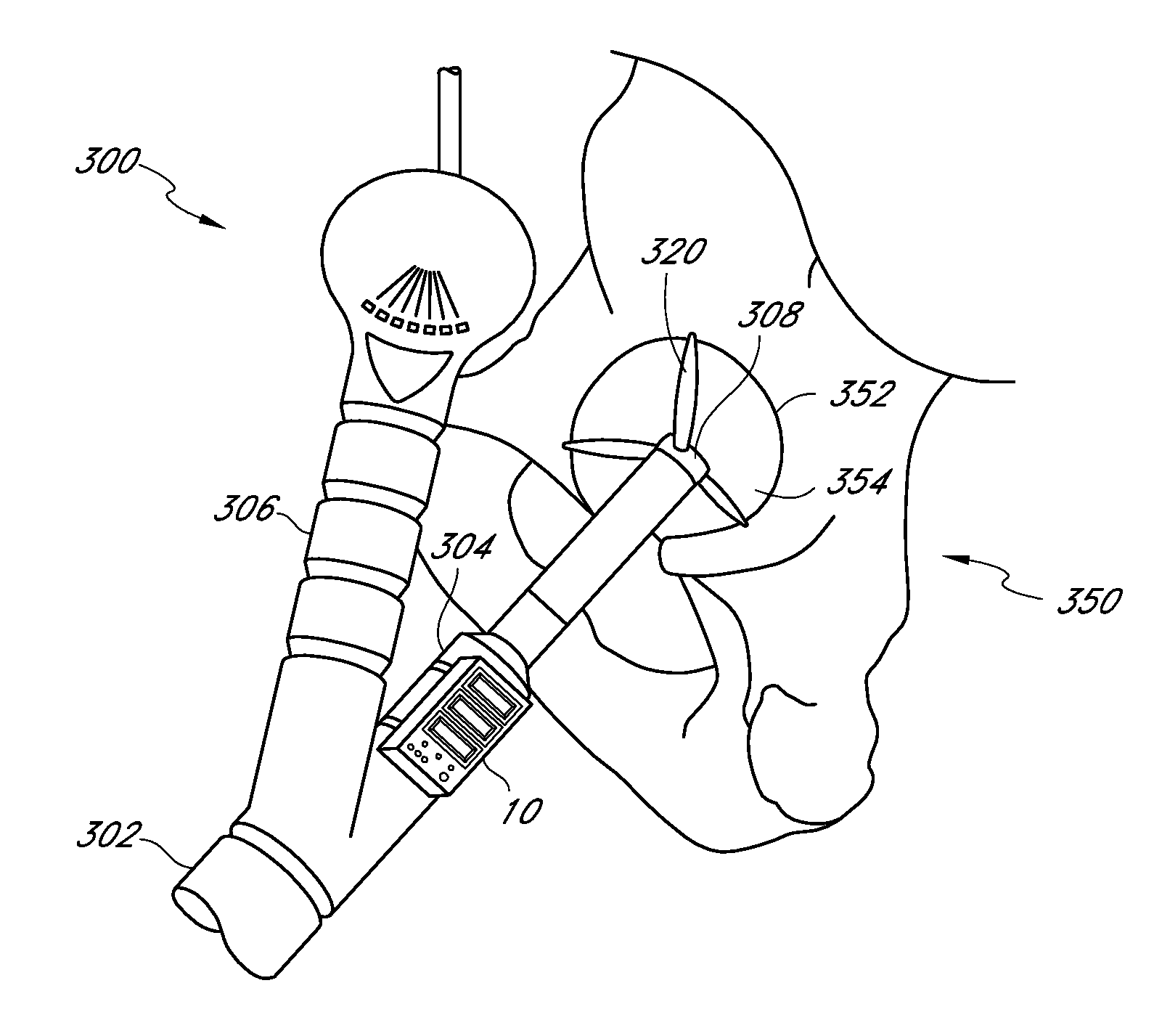
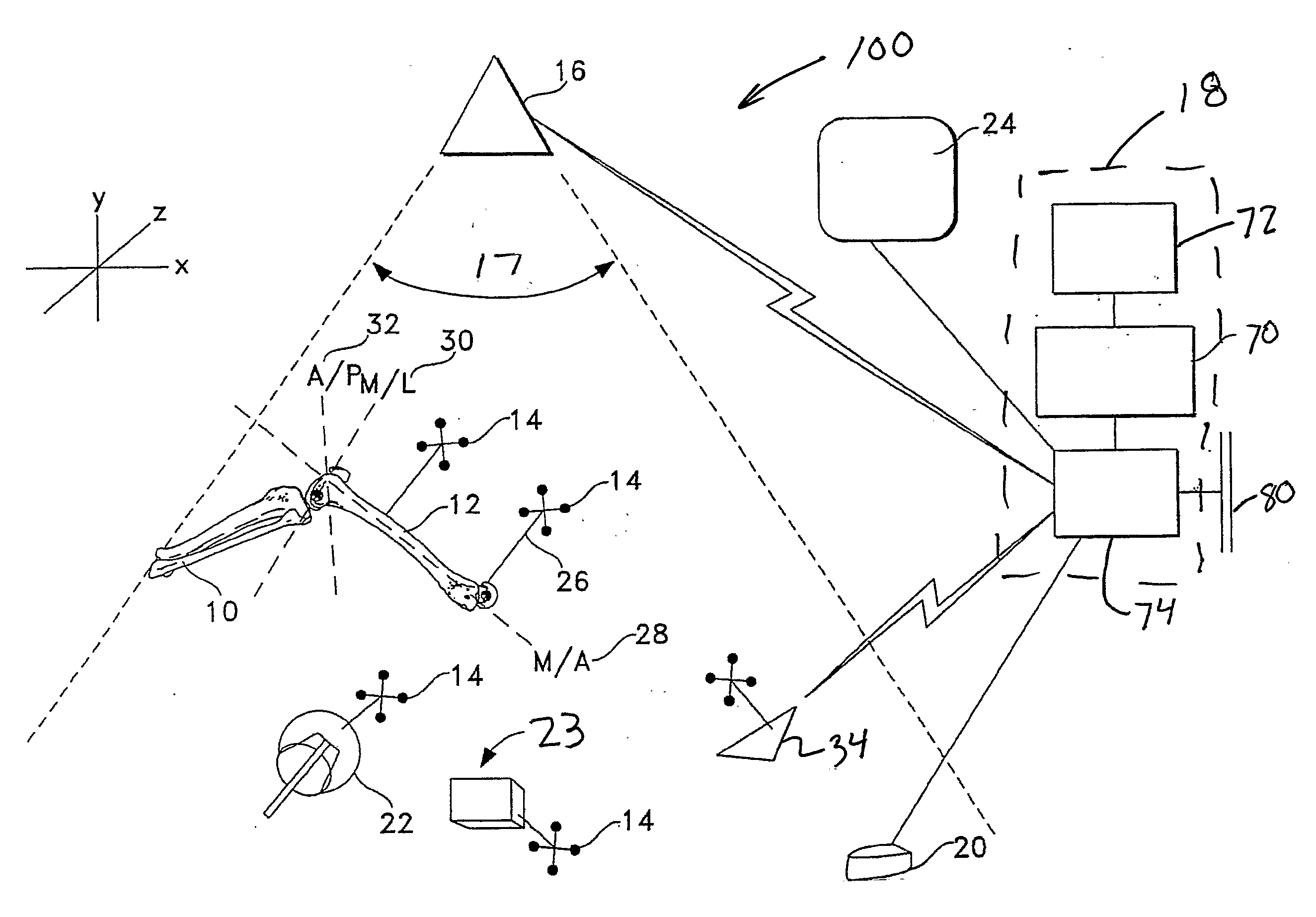
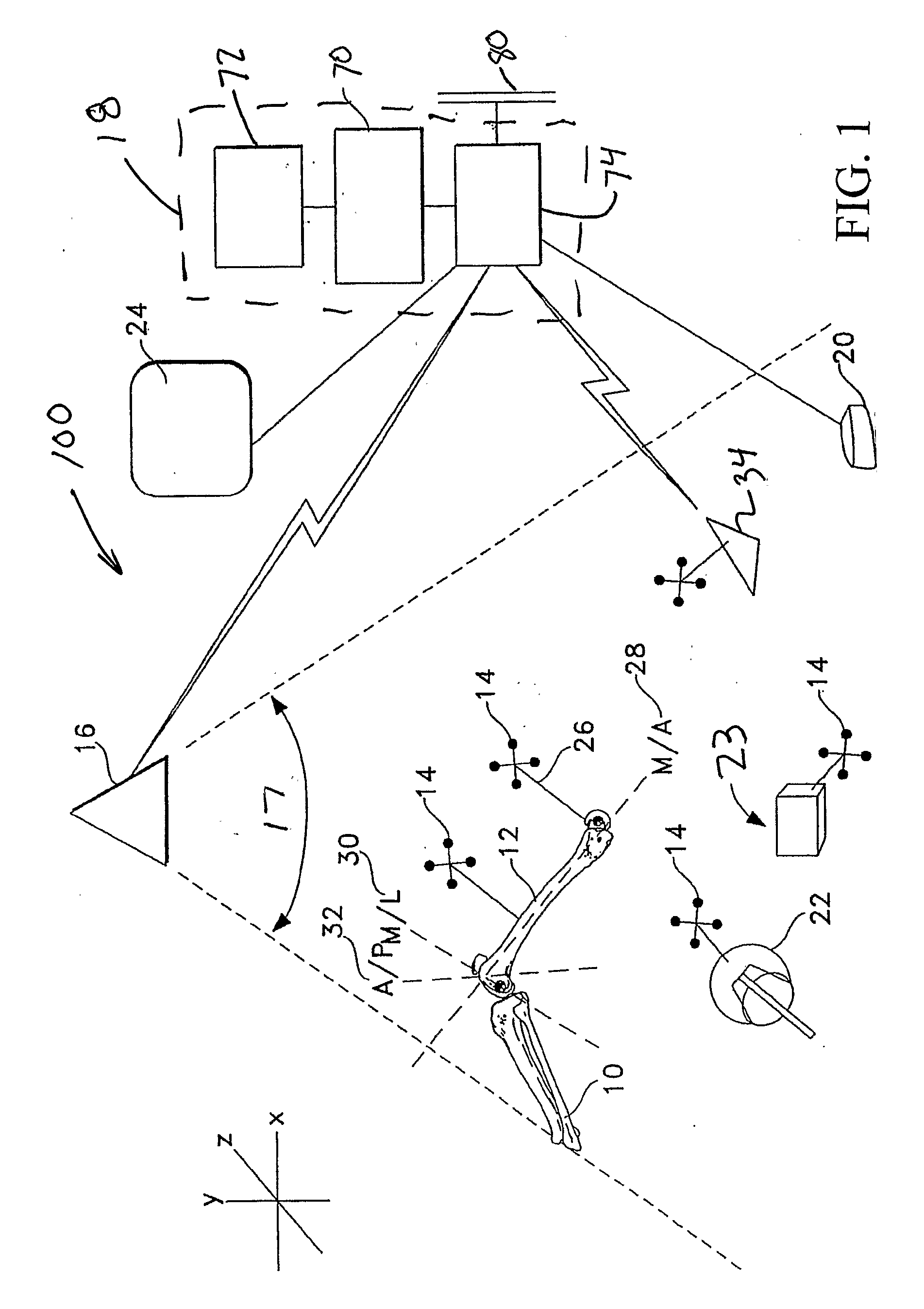
Surgical orientation system and method
A system and method for detecting and measuring changes in angular position with respect to a reference plane is useful in surgical procedures for orienting various instruments, prosthesis, and implants with respect to anatomical landmarks. One embodiment of the device uses dual orientation devices of a type capable of measuring angular position changes from a reference position. One such device provides information as to changes in position of an anatomical landmark relative to a reference position. The second device provides information as to changes in position of a surgical instrument and / or prosthesis relative to the reference position.
Owner:ORTHALIGN
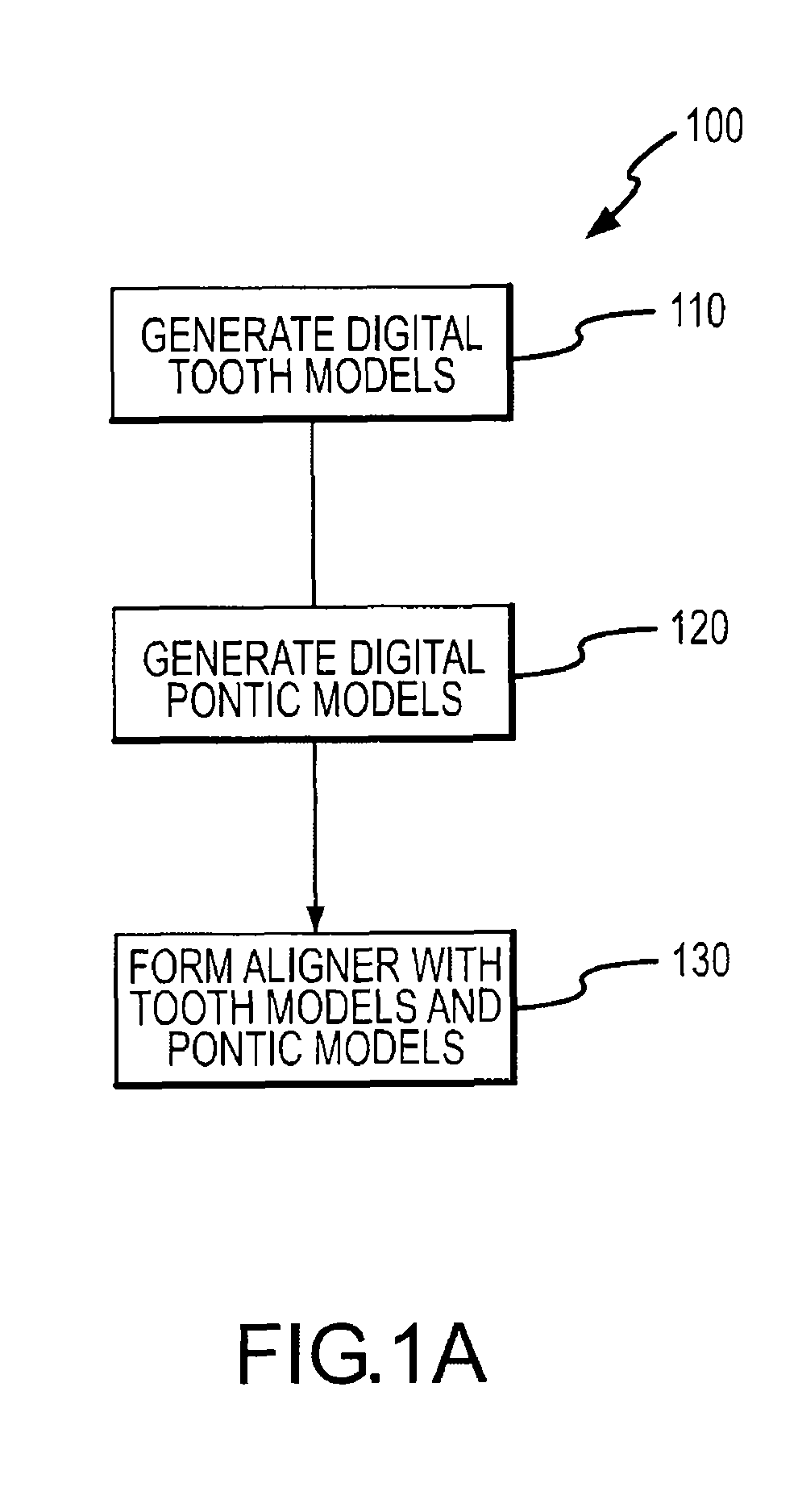
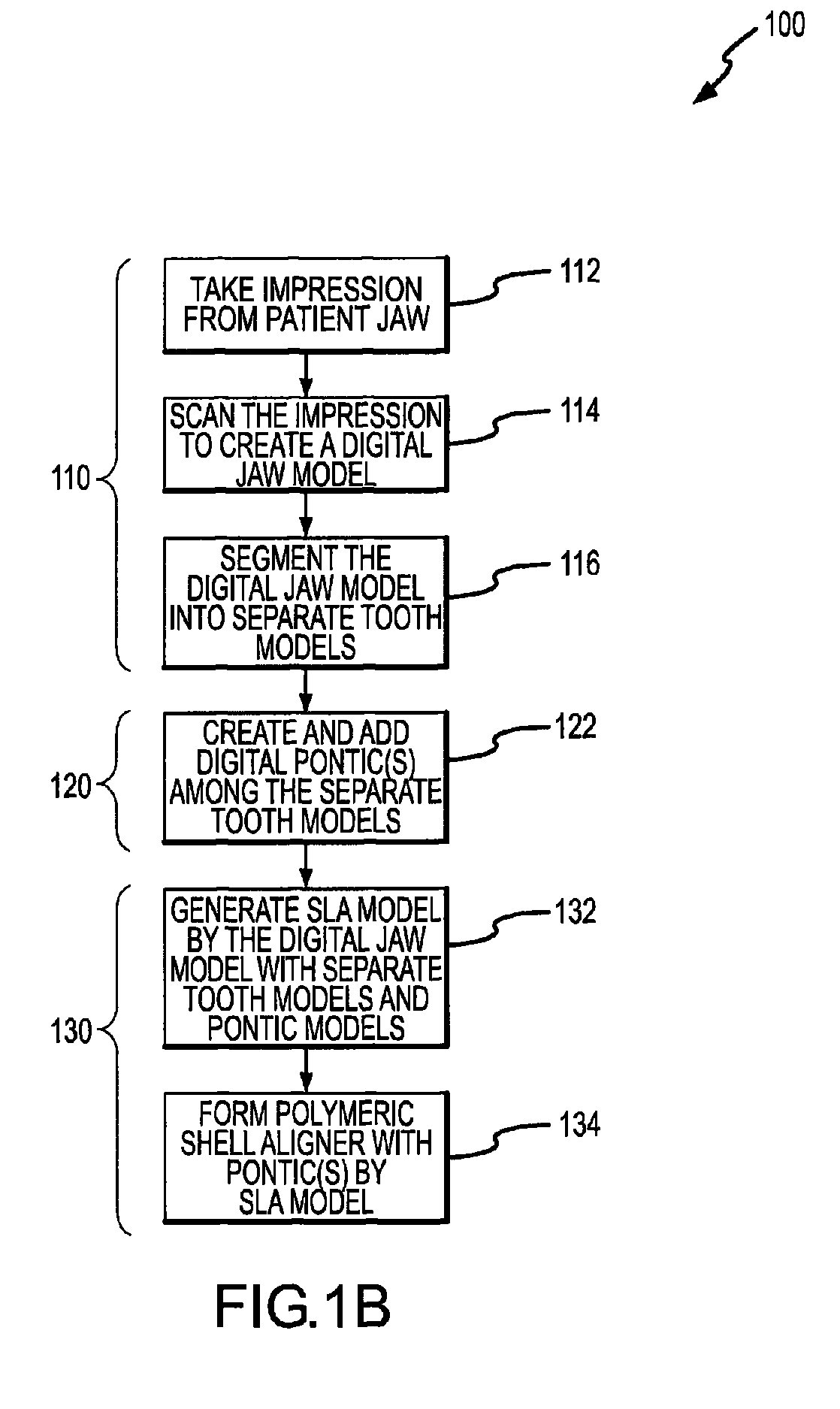
System and method for representation, modeling and application of three-dimensional digital pontics
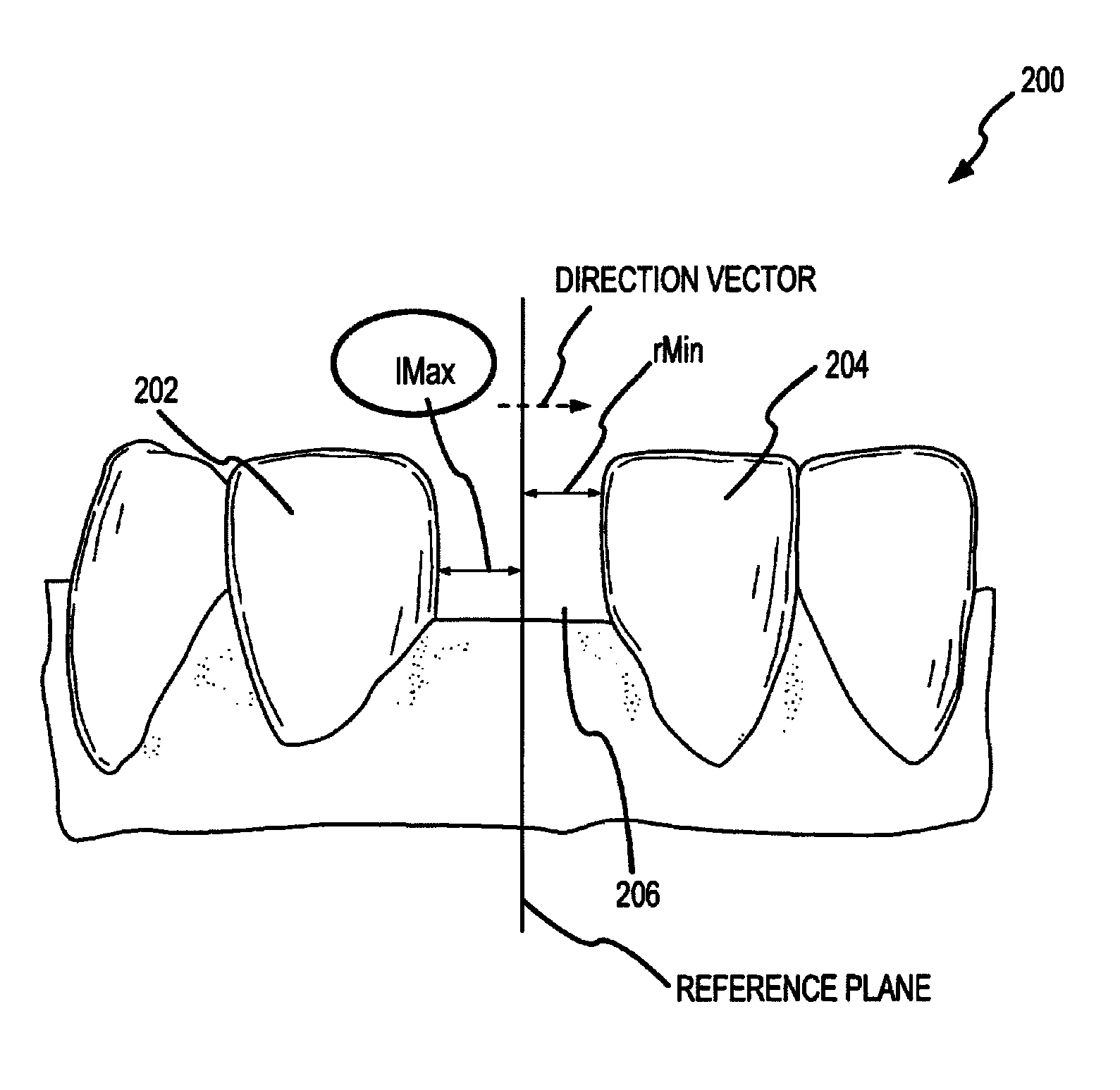
Modeling pontics at successive treatment stages includes: (1) calculating space measurements between first and second teeth by getting first and second tooth transformations at a treatment stage i; (2) applying the first and second tooth transformations to get positions of the first and second teeth at the stage i; (3) calculating a direction vector of the space measurements at the stage i; (4) calculating a reference plane using the direction vector as a normal; (5) determining whether the space is available for a pontic by measuring the distance from the closest point on each of the first and second teeth to the reference plane; (6) generating an original pontic geometry for a first treatment stage; and (7) generating pontic geometries at each successive stage by calculating deformation parameters based on the original pontic geometry and size characteristics of the space and of the first and second teeth at each stage.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
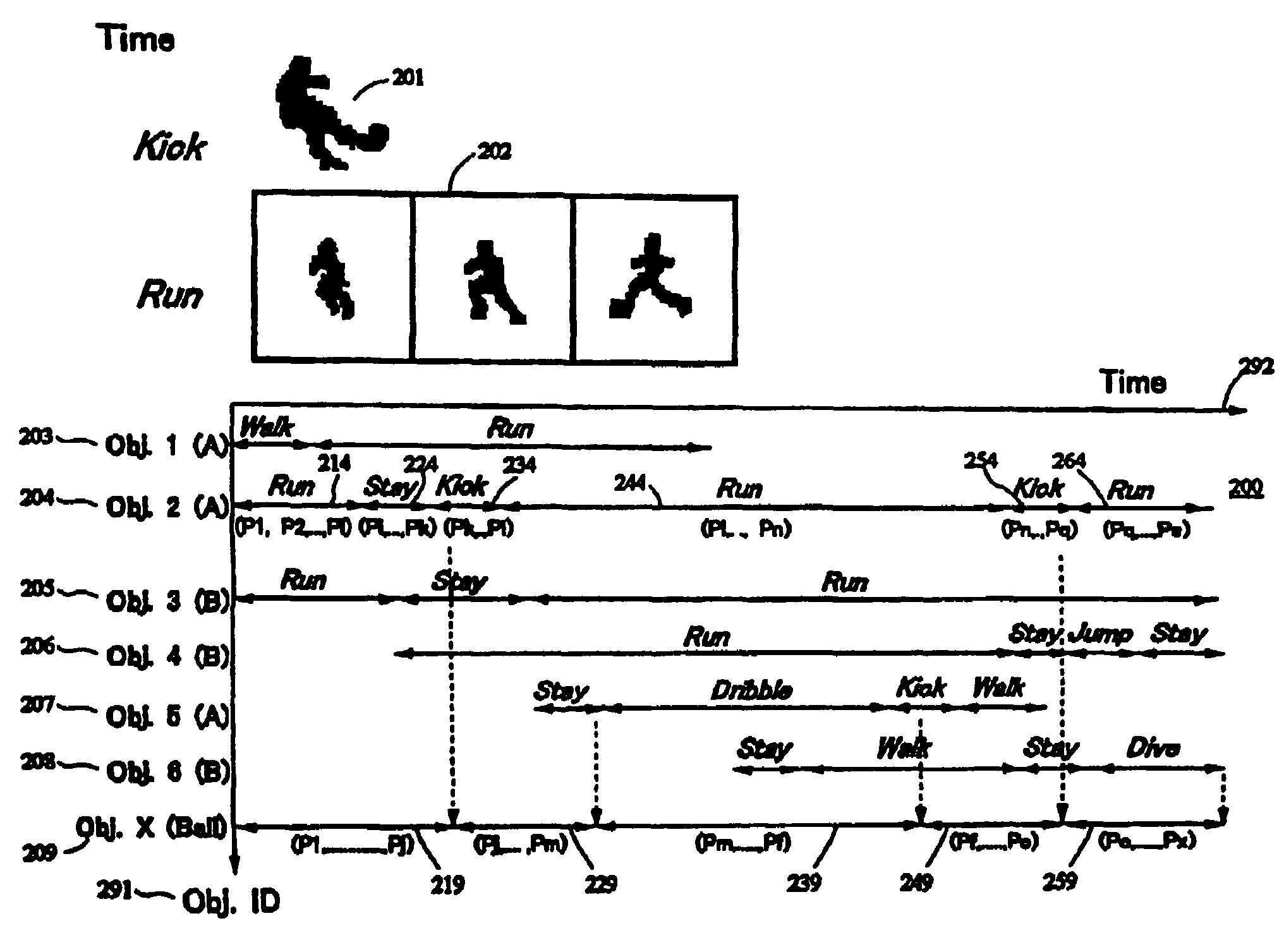
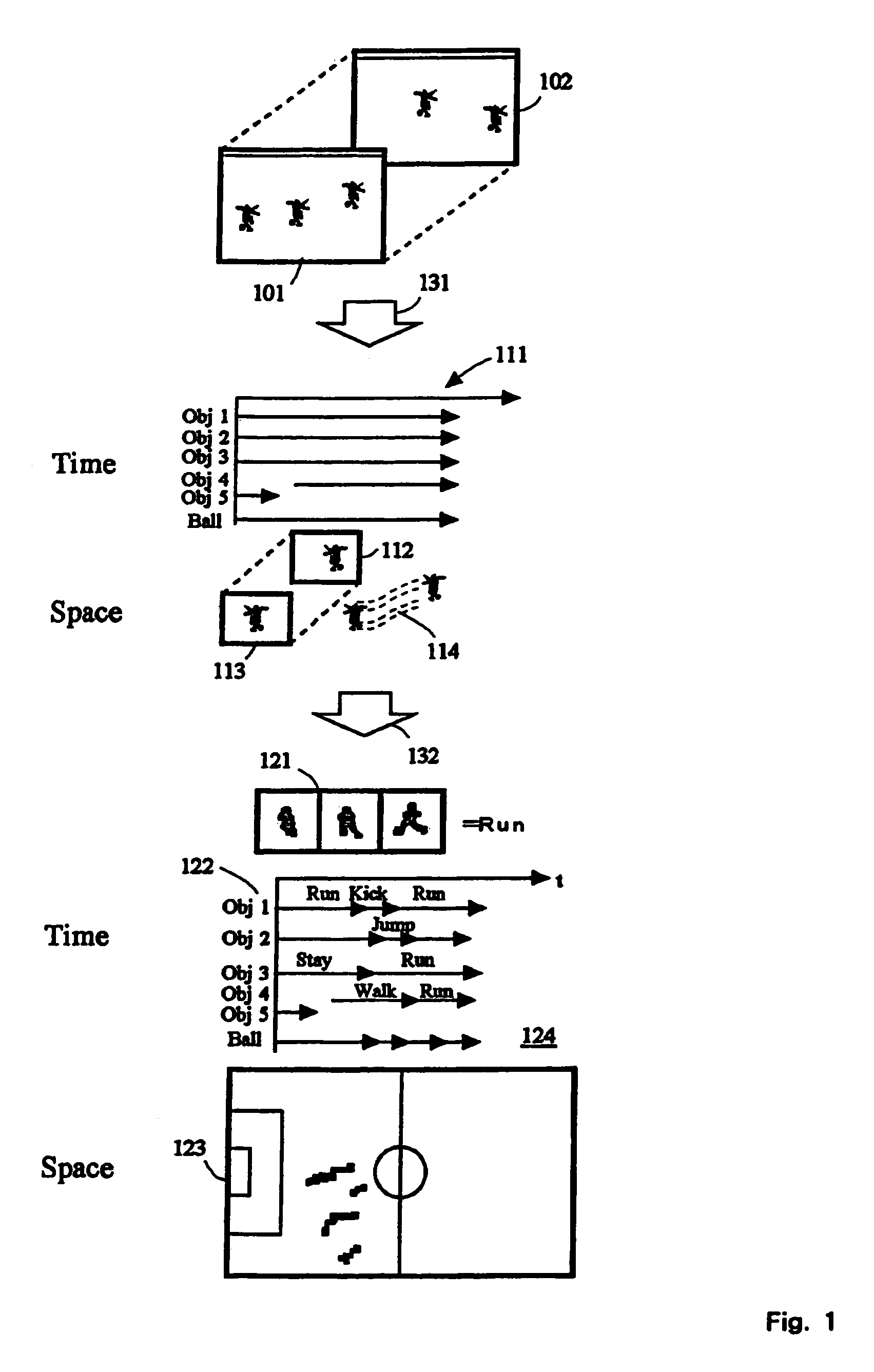
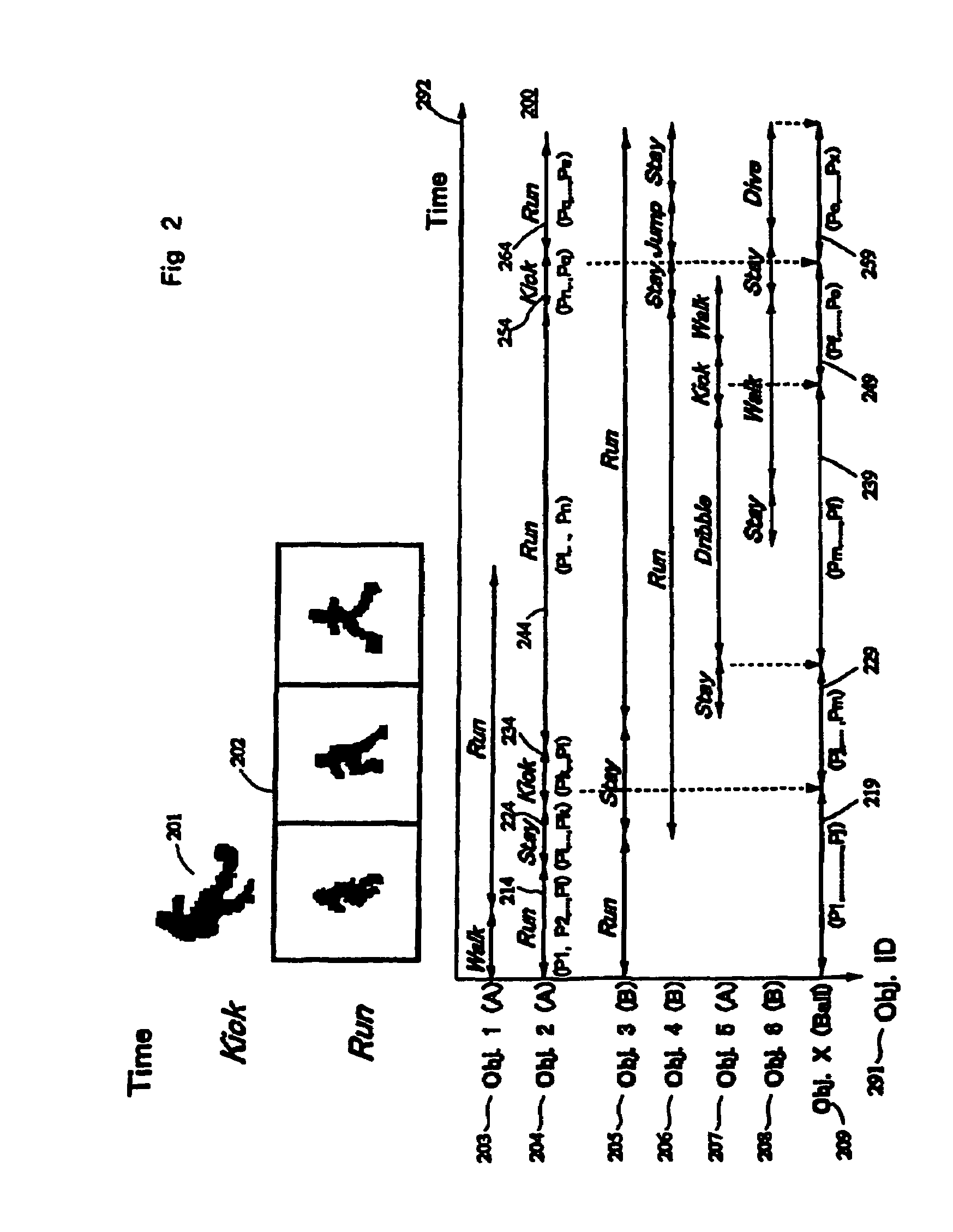
Method and device for describing video contents
An object of the present invention is to provide a description method for efficiently representing contents of motion picture with a small data volume. The organization of the present invention (1) represents a trajectory of how each object has moved over time by using reference plane representing position information of each object, (2) sets a description unit based on a type of action of each object by using changes in shape of each object, (3) has actions of each object represented as each behavioral section, and (4) comprises a description facility capable of reading and interpreting definition of an object dependent on video contents, definition of classes of actions, and definition of interpretation of a scene by interaction of plural objects.
Owner:IBM CORP
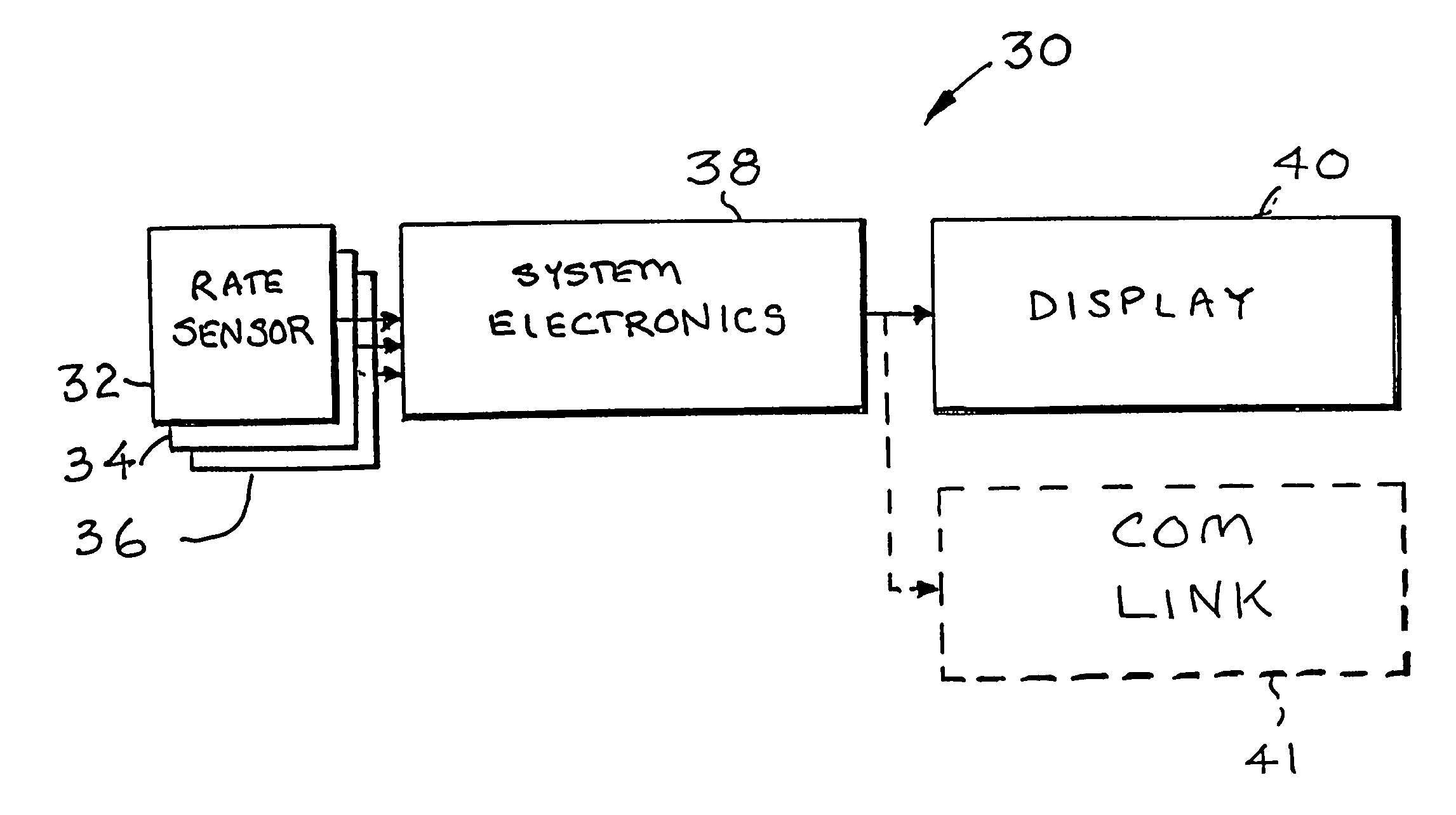
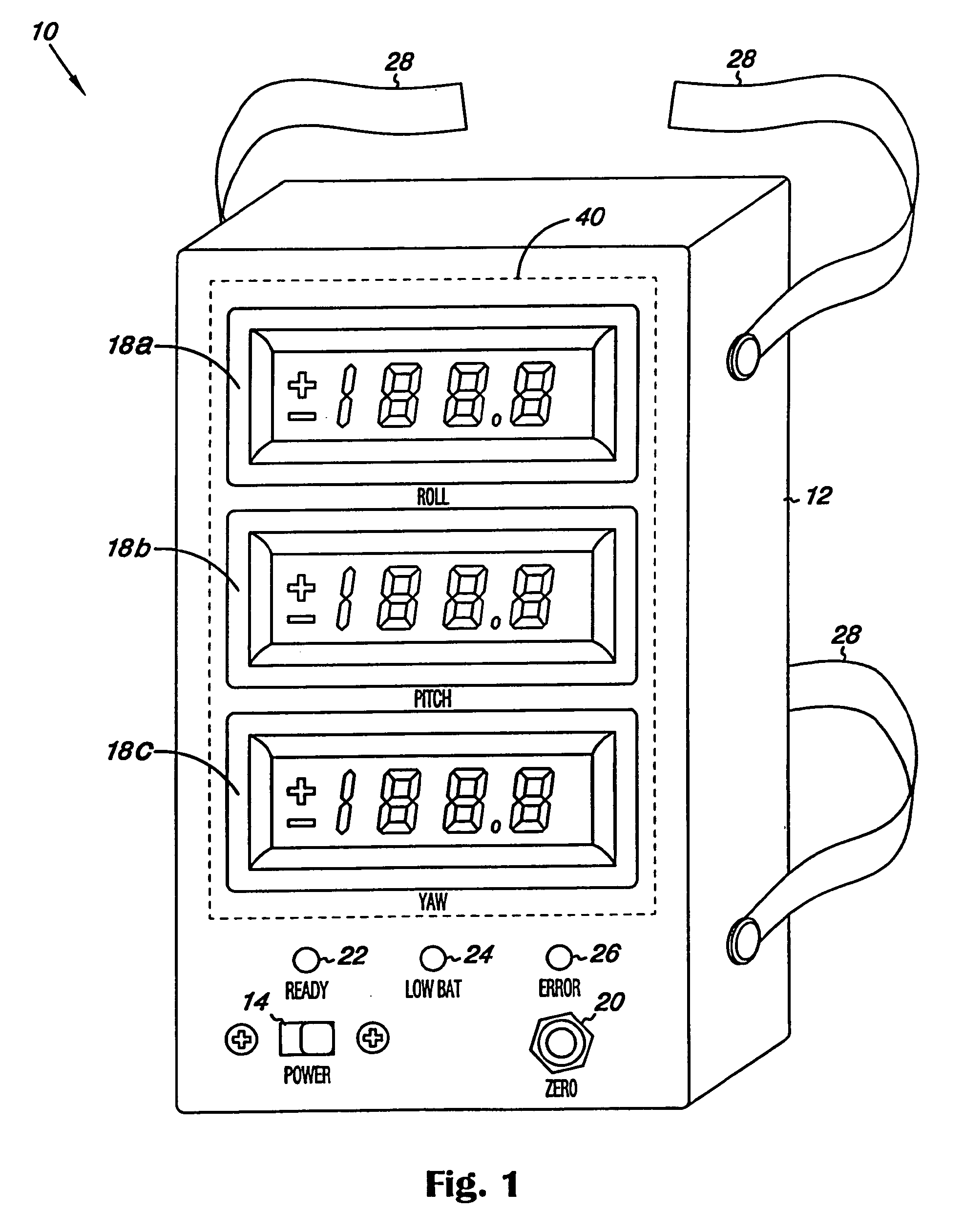
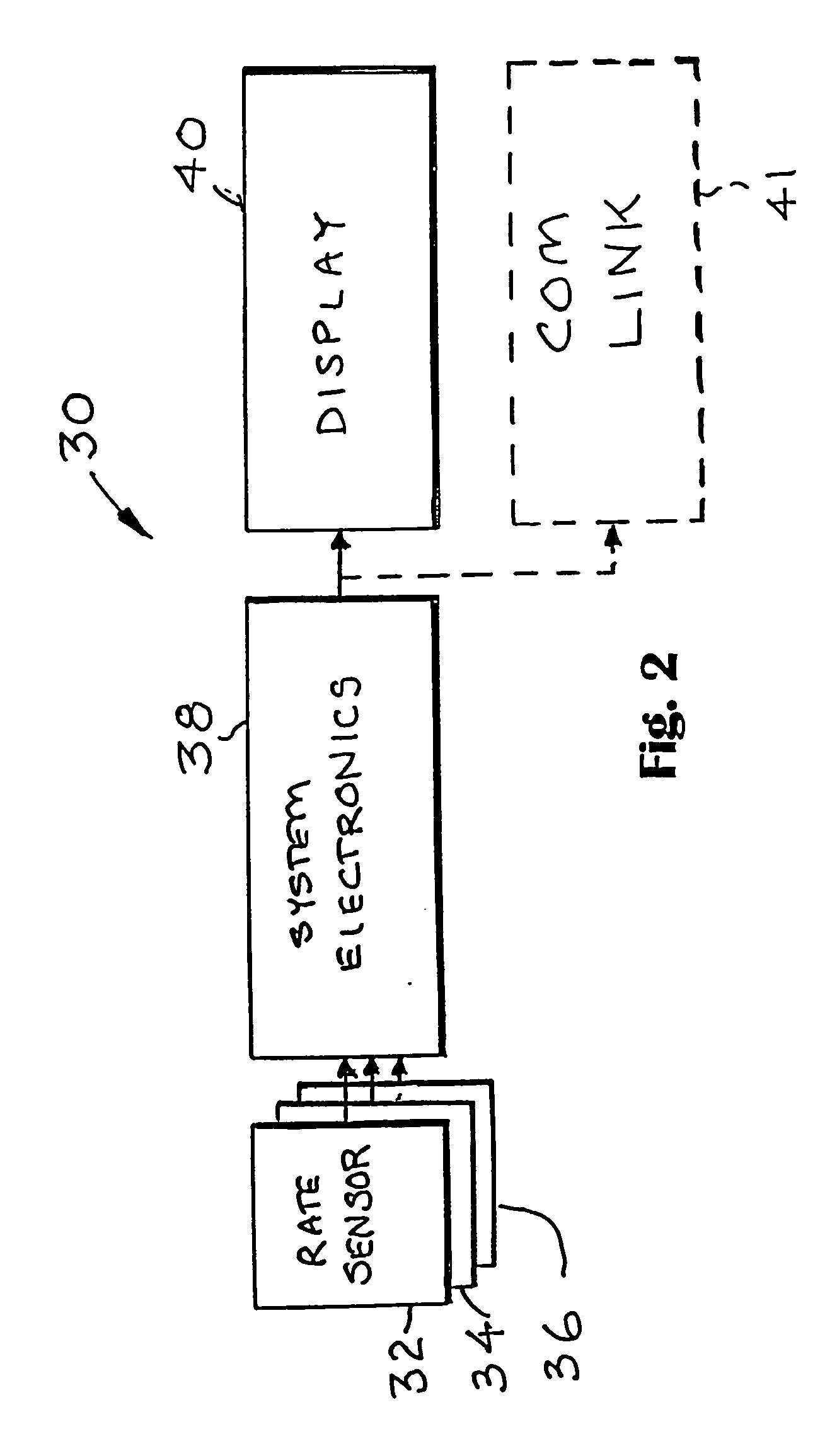
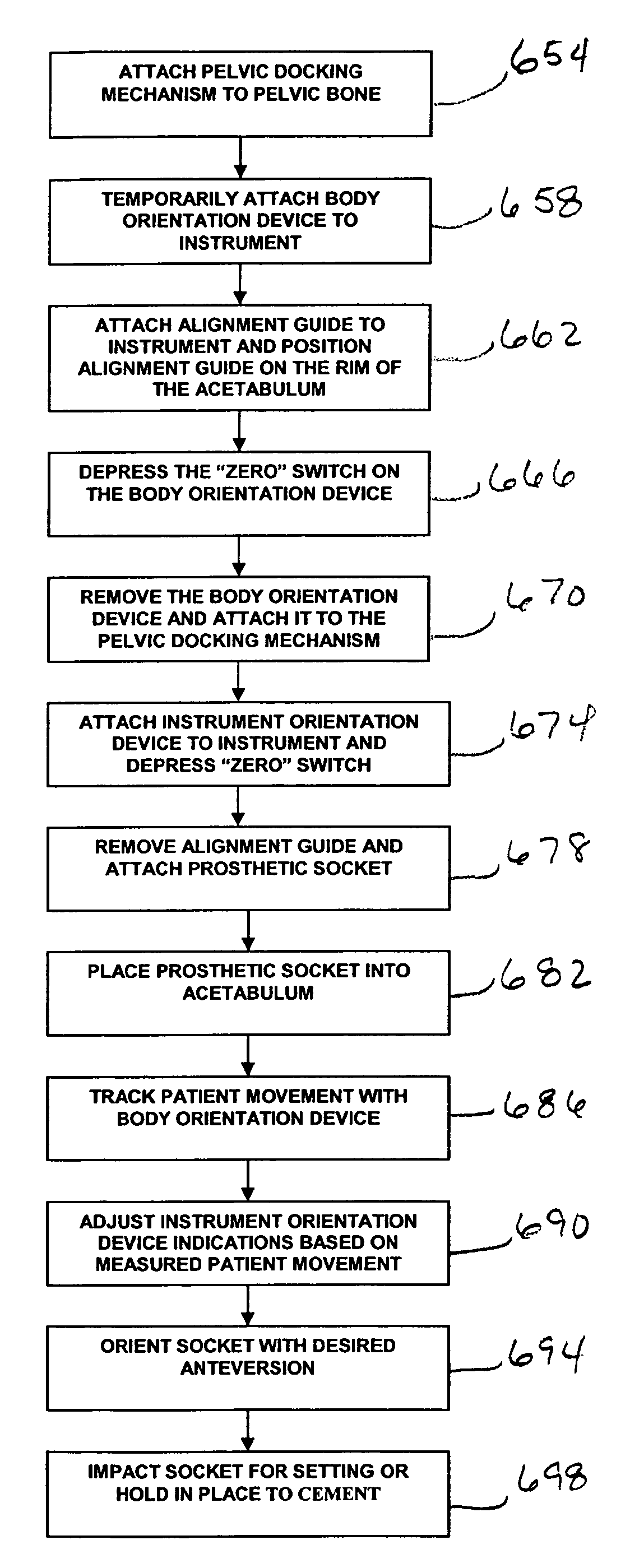
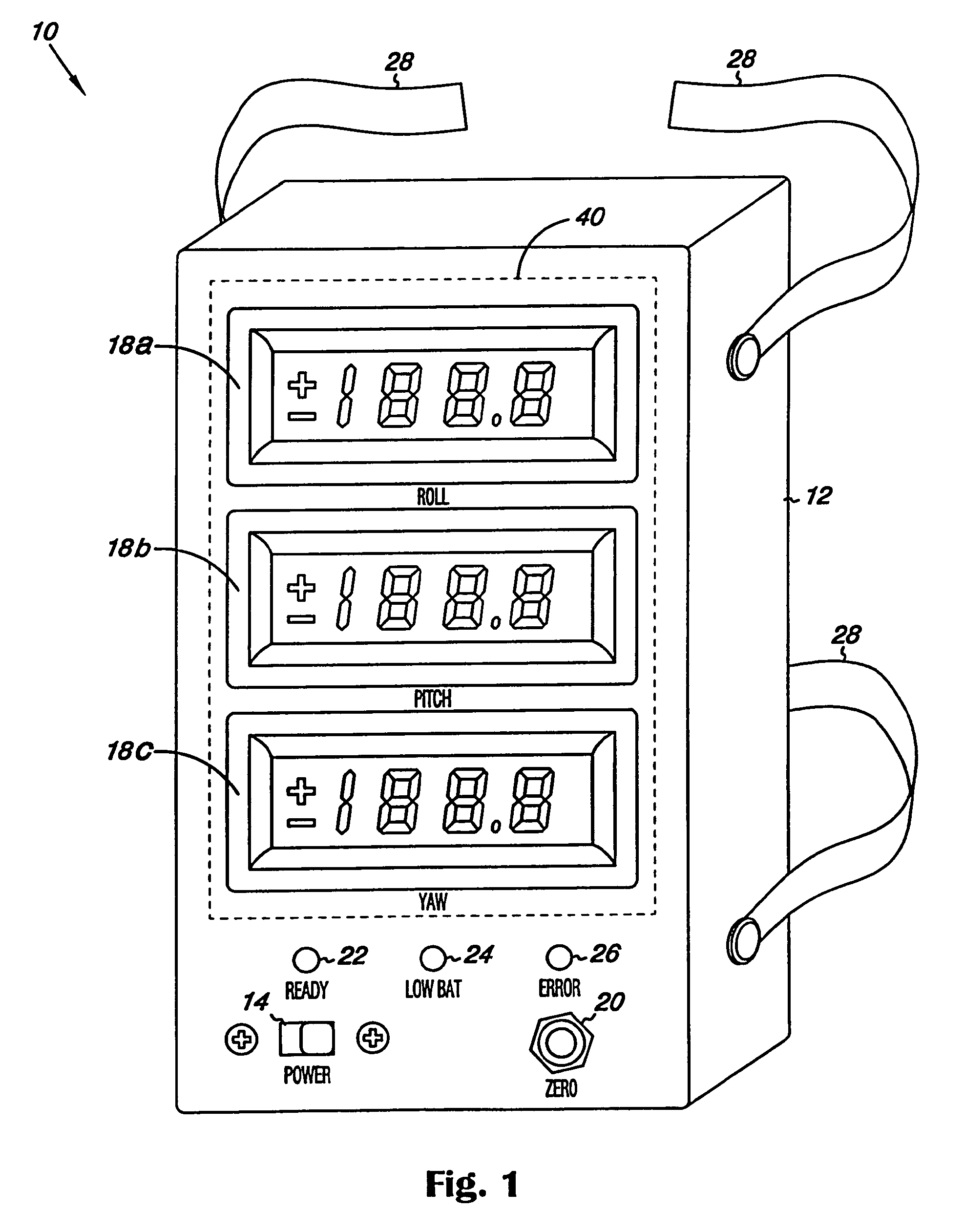
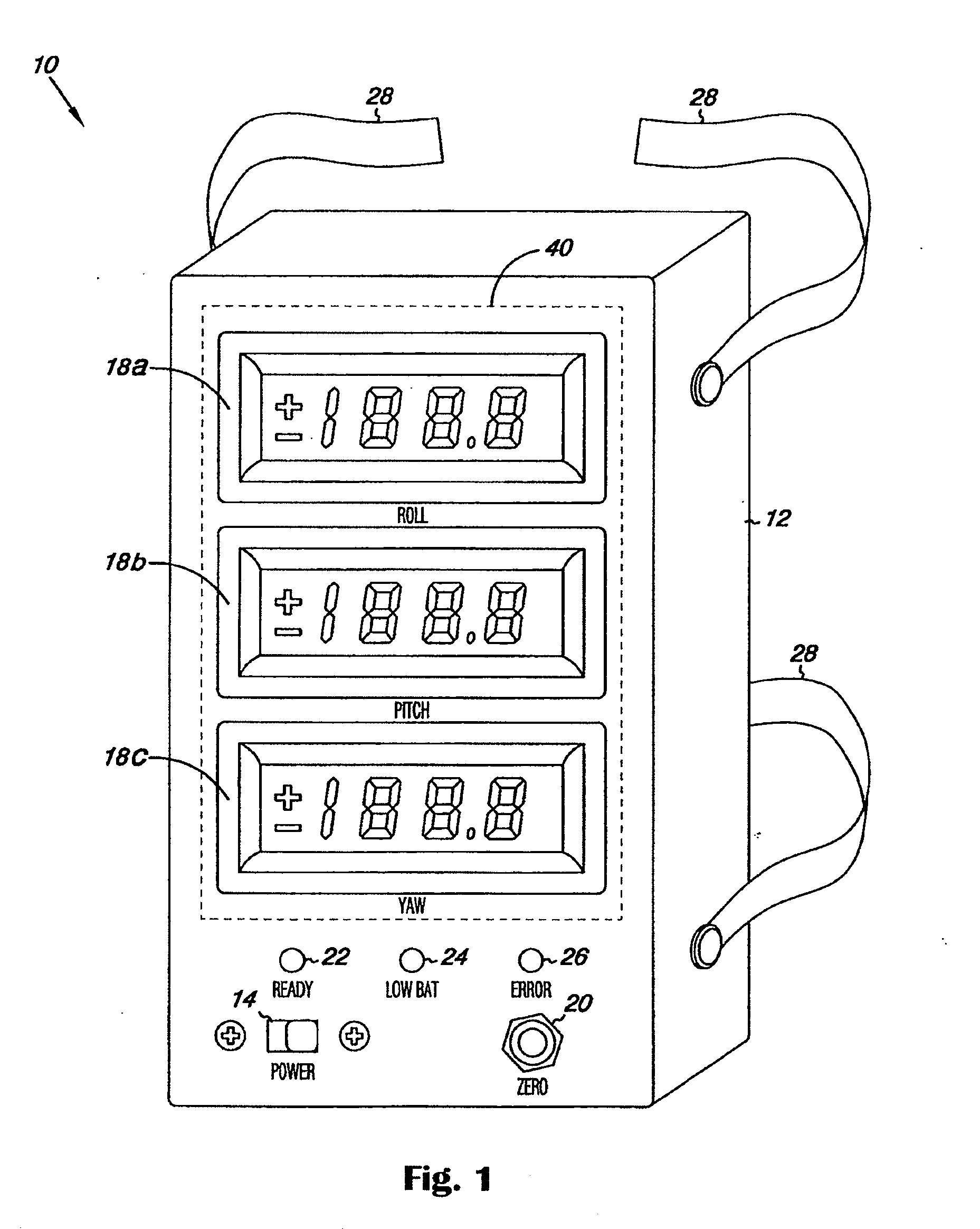
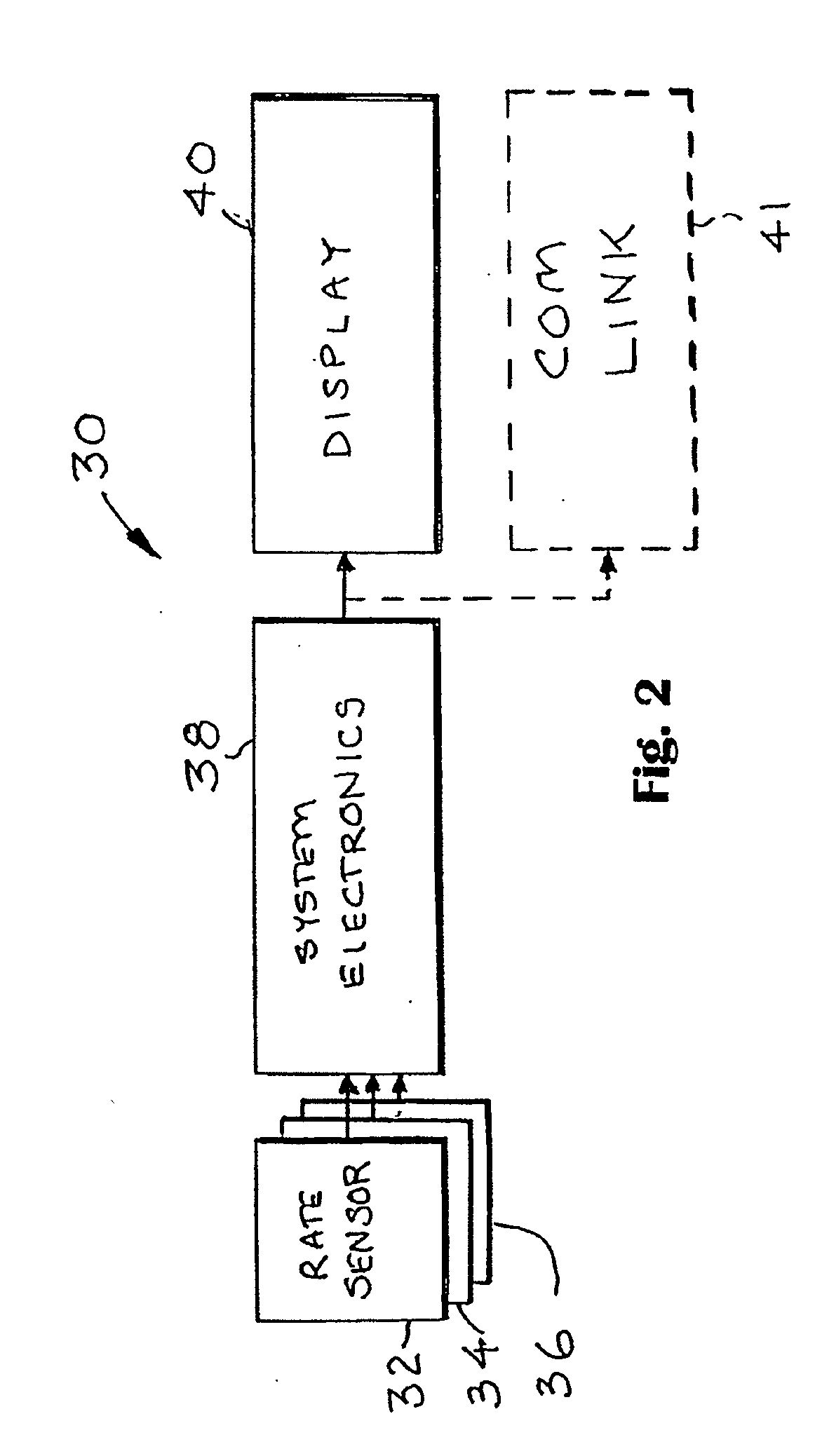
Surgical orientation device and method
A device for detecting and measuring a change in angular position with respect to a reference plane is useful in surgical procedures for orienting various instruments, prosthesis, and implants with respect to anatomical landmarks. One embodiment of the device uses three orthogonal rate sensors, along with integrators and averagers, to determine angular position changes using rate of change information. A display provides position changes from a reference position. Various alignment guides are useful with surgical instruments to obtain a reference plane.
Owner:ORTHALIGN
Apparatus and method for generating an overview image of a plurality of images using a reference plane
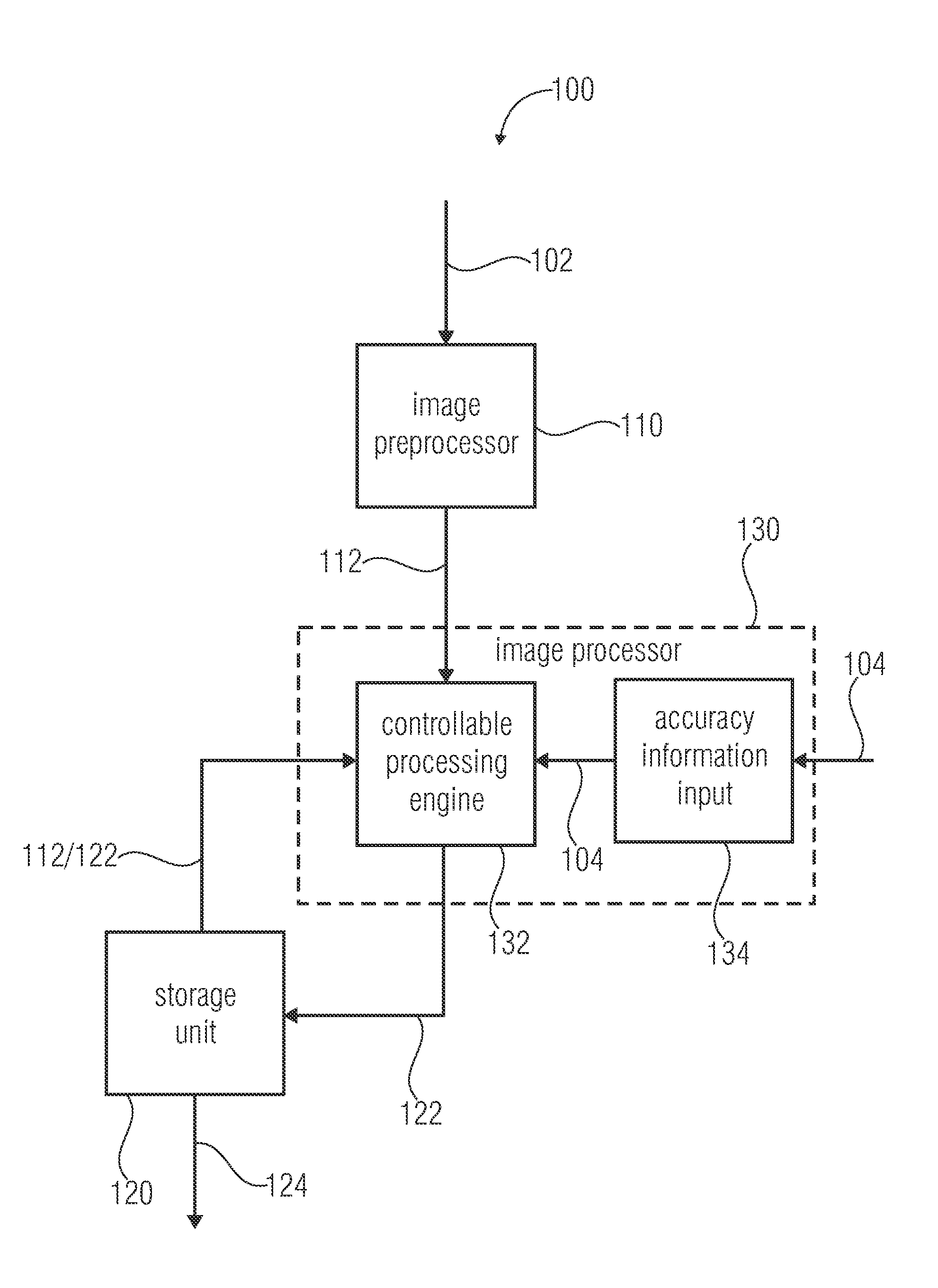
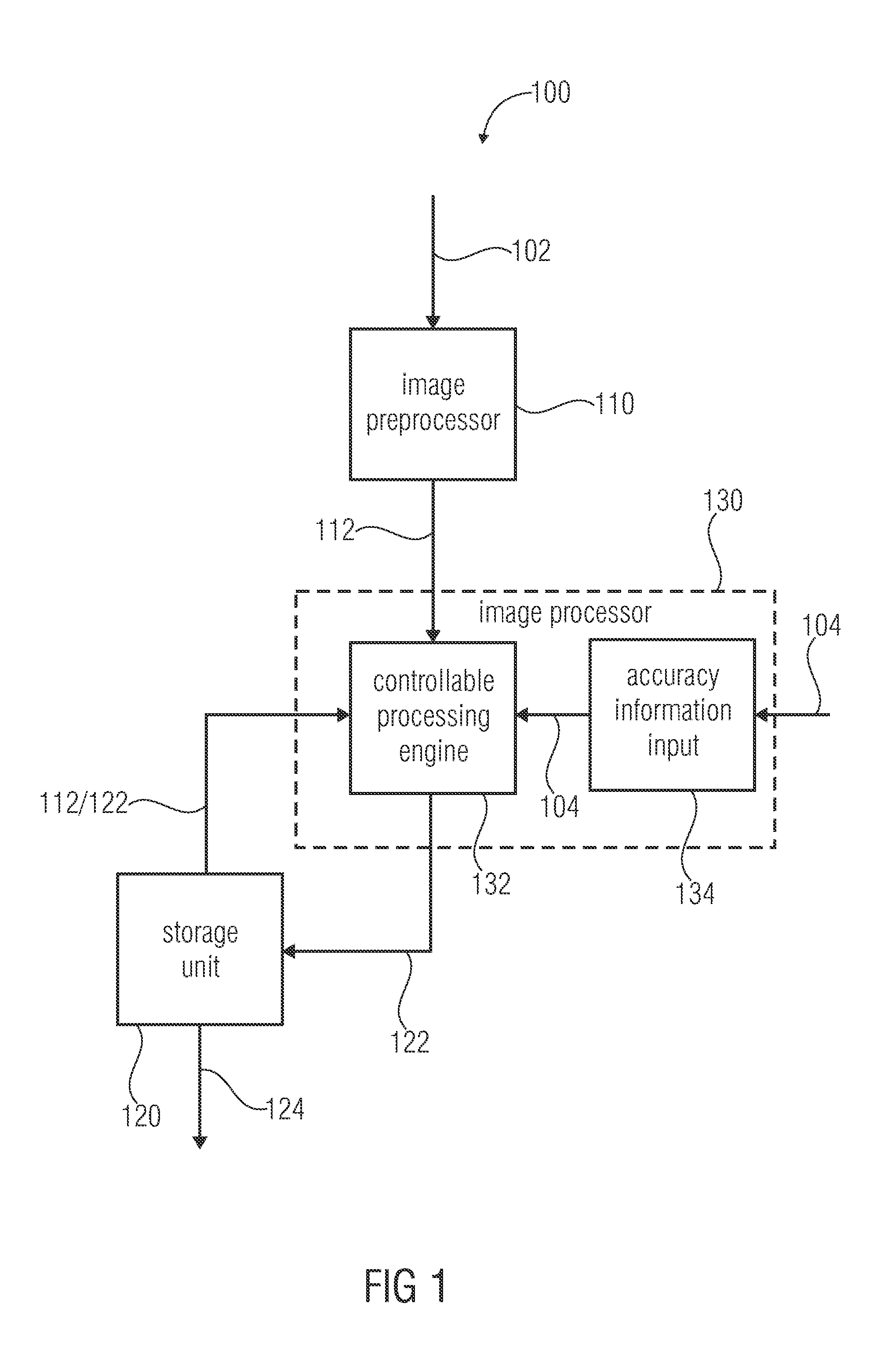
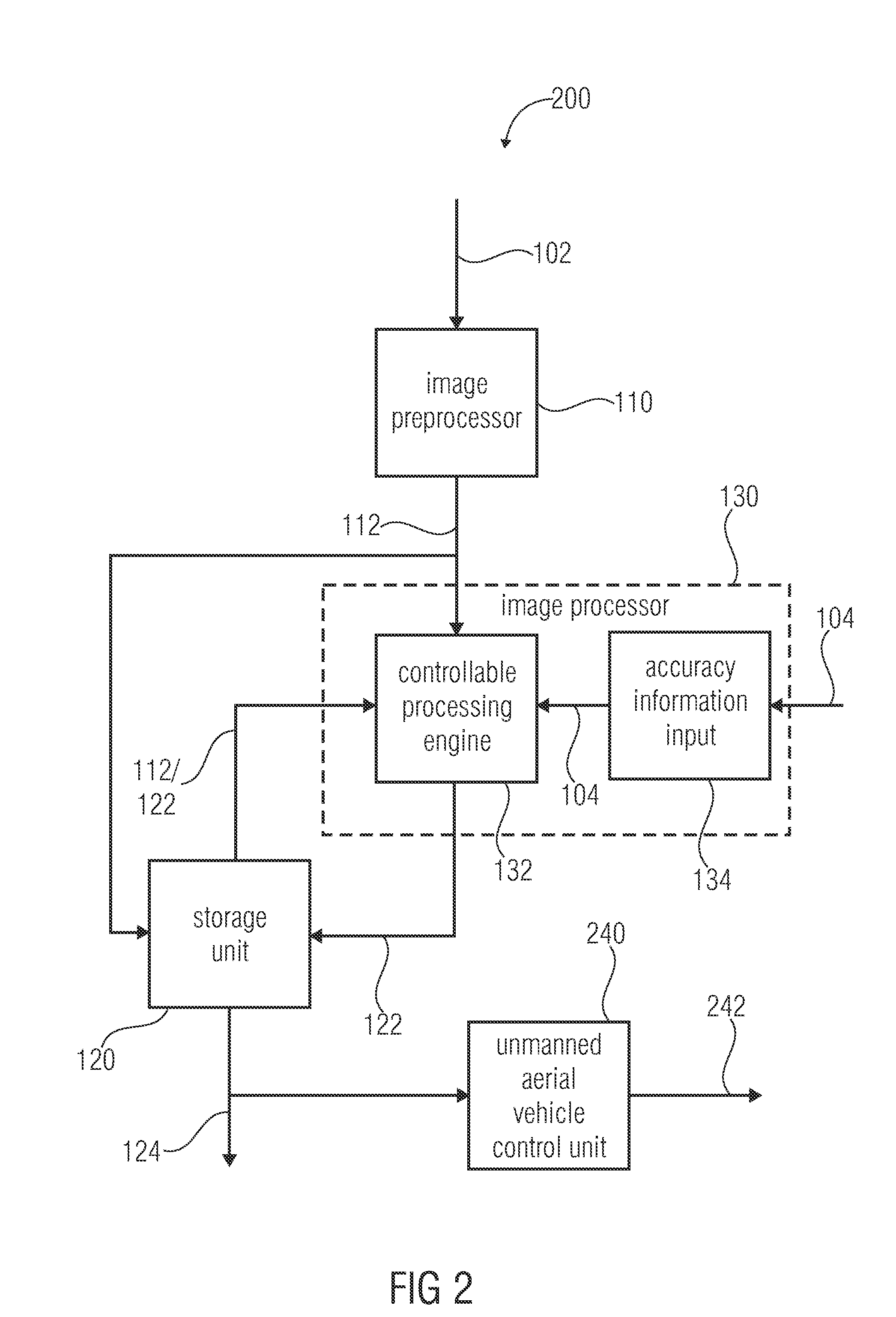
InactiveUS20120050525A1Quick buildImprove smoothnessImage enhancementImage analysisImage processorImage based
An apparatus for generating an overview image of a plurality of images comprises a storage unit and an image processor. The storage unit stores a plurality of processed images of the overview image and is able to provide the overview image containing the plurality of processed images at their assigned positions for displaying. The image processor determines feature points of a new image and compares the determined feature points of the new image with feature points of a stored processed image to identify common feature points and to obtain 3-dimensional positions of the common feature points. Further, the image processor determines common feature points located within a predefined maximum distance of relevance to a reference plane based on the 3-dimensional positions of the common feature points to identify relevant common feature points. Further, the image processor processes the new image by assigning the new image to a position in the overview image based on a comparison of an image information of each relevant common feature point of the new image with an image information of each corresponding relevant common feature point of the stored processed image without considering common feature points located beyond the predefined maximum distance of relevance to the reference plane.
Owner:LAKESIDE LAB
Surgical orientation system and method
A system and method for detecting and measuring changes in angular position with respect to a reference plane is useful in surgical procedures for orienting various instruments, prosthesis, and implants with respect to anatomical landmarks. One embodiment of the device uses dual orientation devices of a type capable of measuring angular position changes from a reference position. One such device provides information as to changes in position of an anatomical landmark relative to a reference position. The second device provides information as to changes in position of a surgical instrument and / or prosthesis relative to the reference position.
Owner:ORTHALIGN
Surgical orientation device and method
A device for detecting and measuring a change in angular position with respect to a reference plane is useful in surgical procedures for orienting various instruments, prosthesis, and implants with respect to anatomical landmarks. One embodiment of the device uses three orthogonal rate sensors, along with integrators and averagers, to determine angular position changes using rate of change information. A display provides position changes from a reference position. Various alignment guides are useful with surgical instruments to obtain a reference plane.
Owner:ORTHALIGN
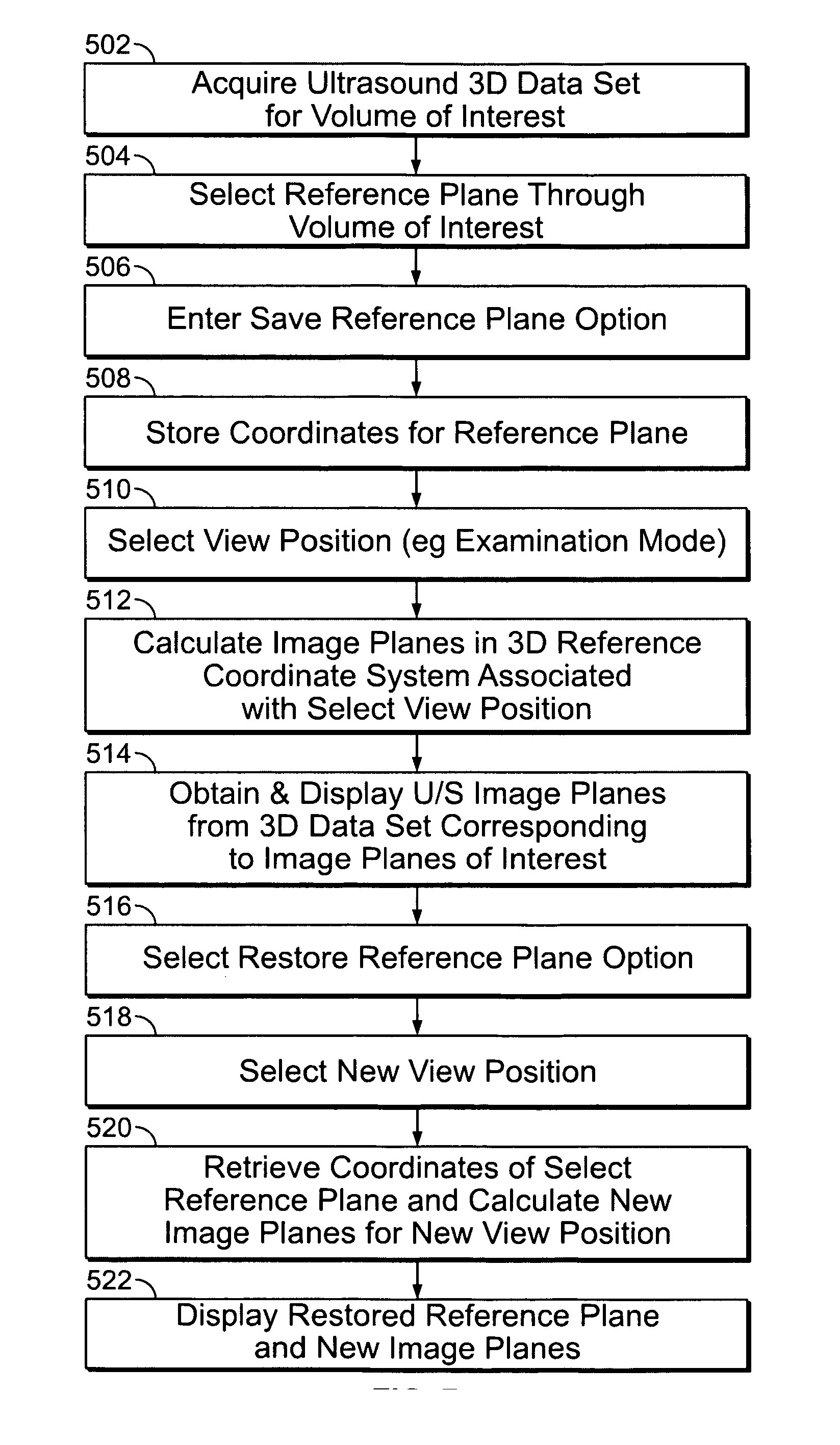
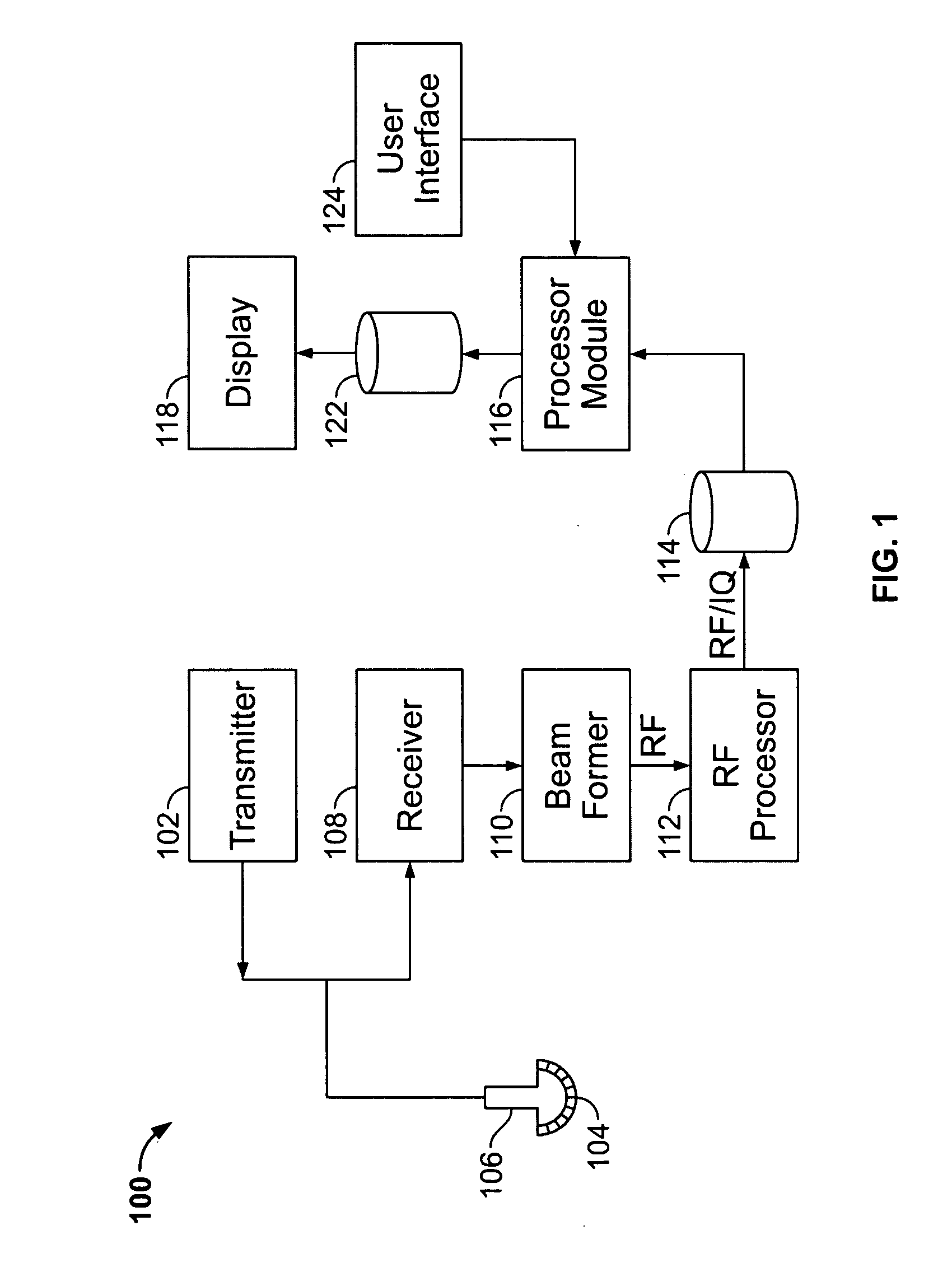
User interface for automatic multi-plane imaging ultrasound system
InactiveUS20070255139A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCharacter and pattern recognitionData setSonification
A diagnostic ultrasound system is provided for automatically displaying multiple planes from a 3-D ultrasound data set. The system comprises a user interface for designating a reference plane, wherein the user interface provides a safe view position option and a restore reference plane option. A processor module maps the reference plane into a 3D ultrasound data set and automatically calculates image planes based on the reference plane for a current view position and a prior view position. A display is provided to selectively display the image planes associated with the current and prior reference planes. Memory stores the prior reference plane in response to selection of the save reference plane option, while the display switches from display of the current reference plane to restore the prior reference plane in response to selection of the restore reference plane option. Optionally, the memory may store coordinates in connection with the current and prior reference planes.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
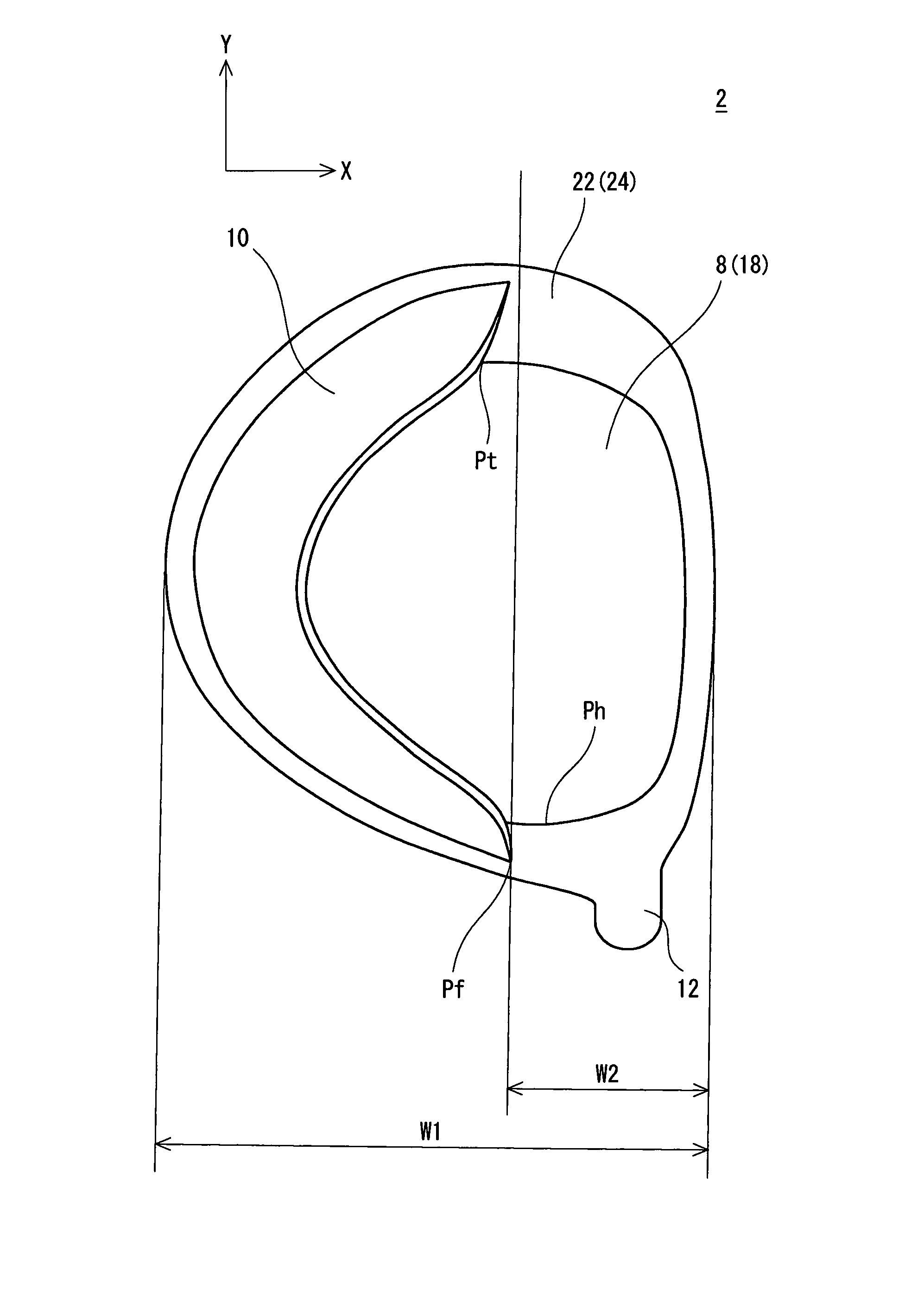
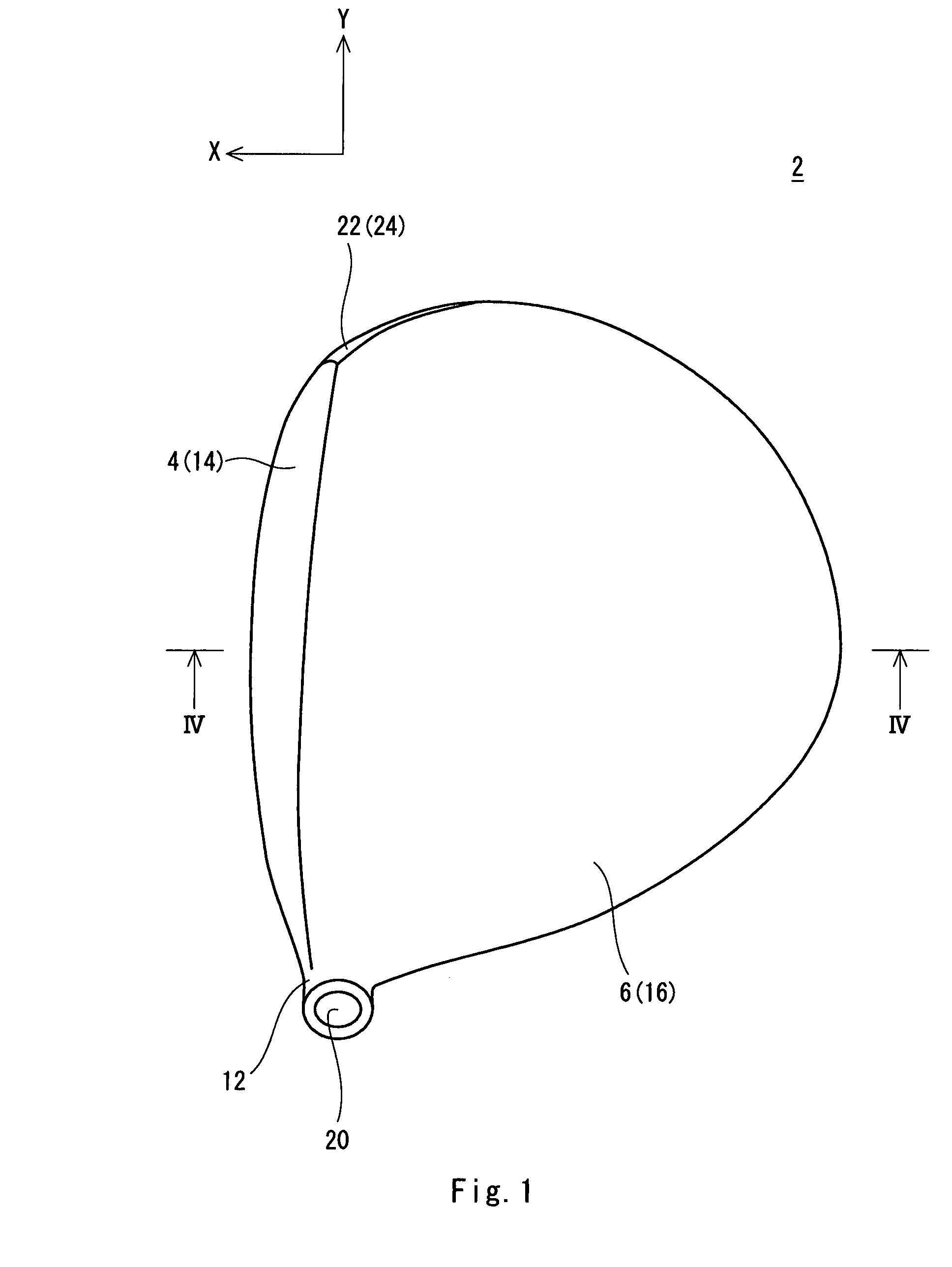
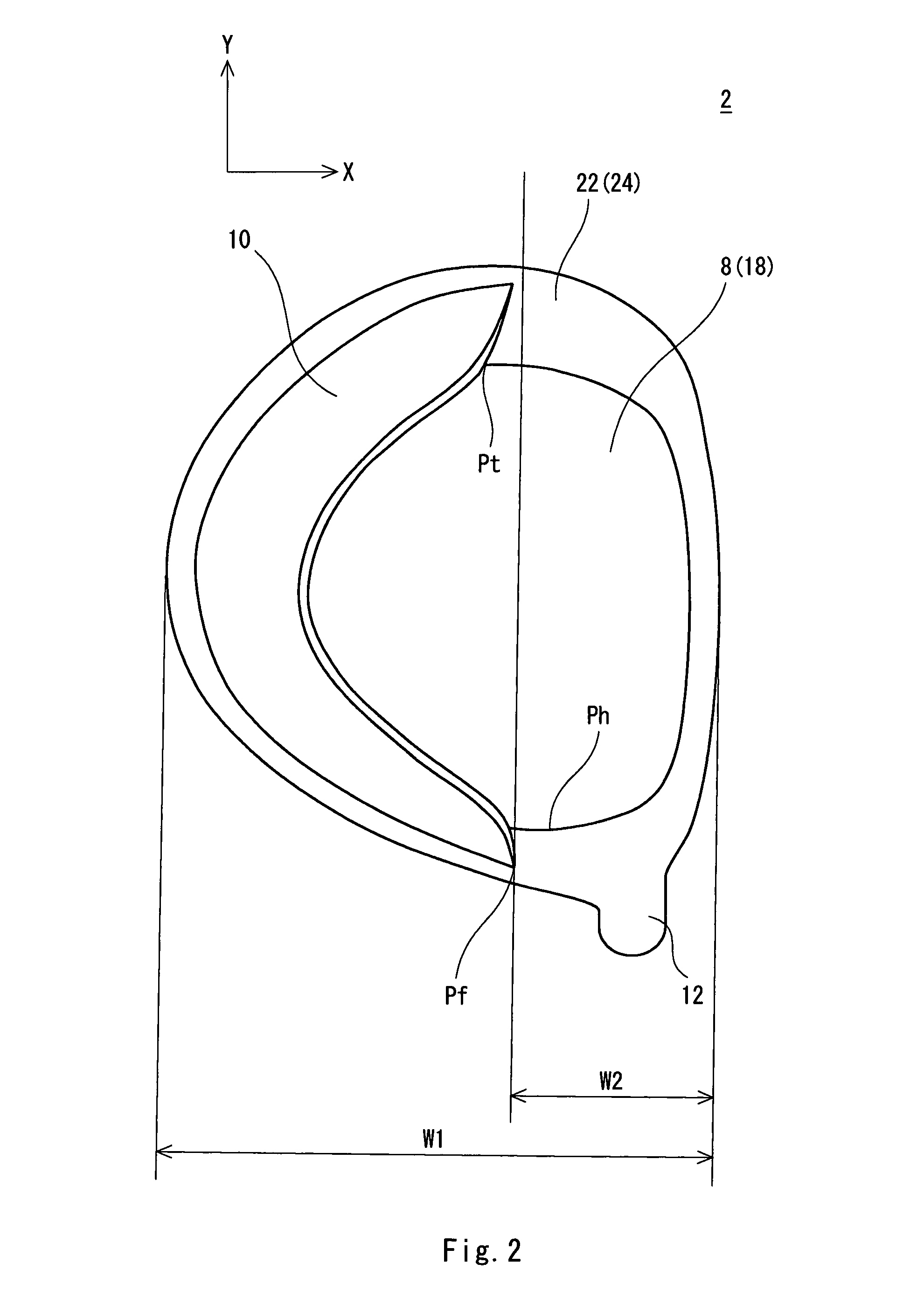
Golf club head
InactiveUS7934998B2Improve performanceImprovement of hitting soundGolf clubsGolfing accessoriesProject areaGolf Ball
Golf club head 2 is provided including face member 4, crown member 6, sole member 8 and recessed part 10. The recessed part 10 is provided around the sole member 8. The recessed part 10 has a maximum height Hm of equal to or greater than 10 mm. The projected area S1 of the sole member 8 projected on the reference plane accounts for 40% or more and 65% or less of the projected area S2 of the crown member 6 projected on the reference plane. The head 2 is hollow. Preferably, the maximum angle θm formed between the margin F1 of the recessed part 10 and the sole edge E1 in proximity thereto is equal to or greater than 45 degrees. Preferably, the curvature radius of the sole face in a toe-heel direction is 9.0 cm or greater and 11.5 cm or less. Preferably, the head 2 has a volume of 400 cc or more and 500 cc or less.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Power converter connection configuration
InactiveUS7450388B2Small and light and efficient configurationImprove performanceMagnetic/electric field screeningDigital data processing detailsModular unitModularity
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
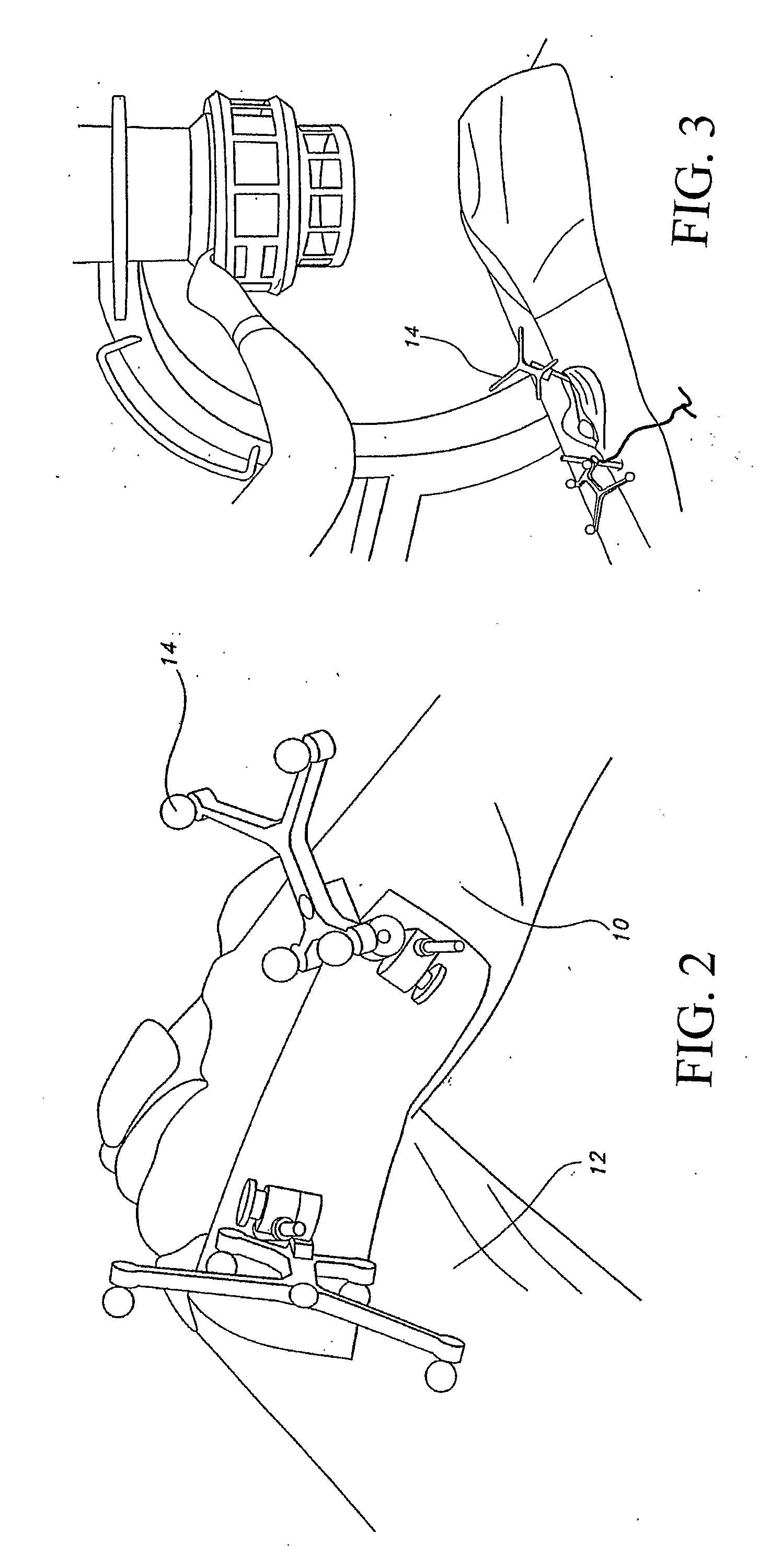
System and Method For Determining Tibial Rotation
InactiveUS20080208081A1Improved accuracy over the artEasy to repeatSurgical navigation systemsPerson identificationComputer visionArtificial intelligence
A system and method for determining tibial rotation is disclosed. The system includes a first fiducial, a second fiducial, a position and orientation sensor, a computer, and a monitor. The first fiducial is connected to a first part, and the second fiducial is connected to a second part. The position and orientation sensor tracks the first fiducial and the second fiducial. The computer has a memory, a processor, and an input / output device. The input / output device receives data from the position and orientation sensor. The processor processes the data to identify a first axis of the first part and a second axis of the second part. The processor constructs a reference plane through the second axis and orthogonal to the first axis. The monitor is connected to the input / output device and displays a rendering of the reference plane.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Method and apparatus for measuring the shape and thickness variation of polished opaque plates
InactiveUS6847458B2Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementInterferometersClassical mechanicsFizeau interferometer
The present invention consists of a technique and device for measuring the thickness variation and shape of wafers or other polished opaque plates. A combination of two improved phase-shifting Fizeau interferometers is used to simultaneously measure the single-sided distance maps between each side of the wafer and the corresponding reference flat, with the thickness variation and shape being calculated from these data. Provisions are made to determine and eliminate the shape and tilt of the reference surfaces, and also to facilitate the correct overlay of the two single-sided measurements for the calculation of thickness variation and shape.
Owner:PHASE SHIFT TECH
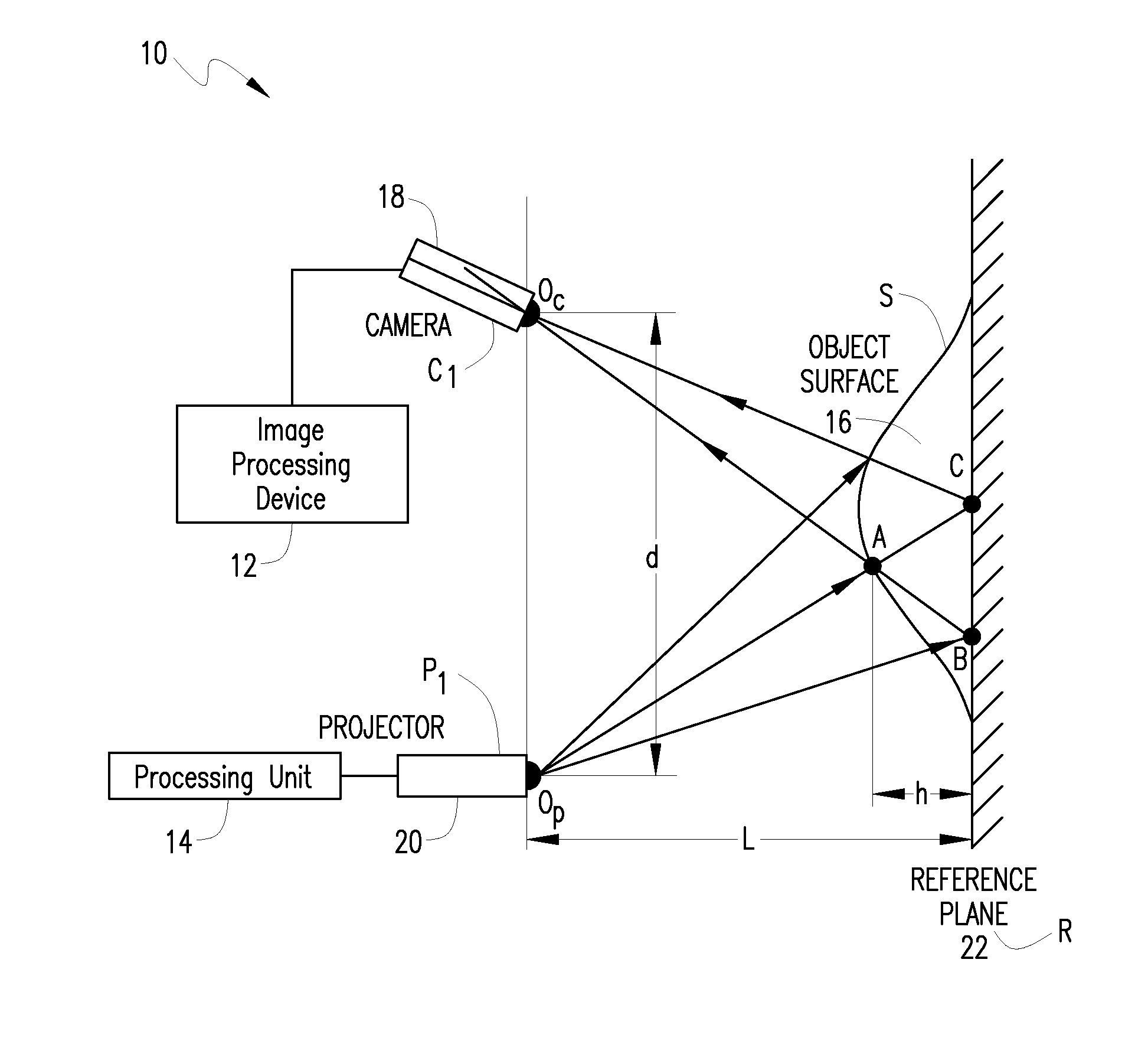
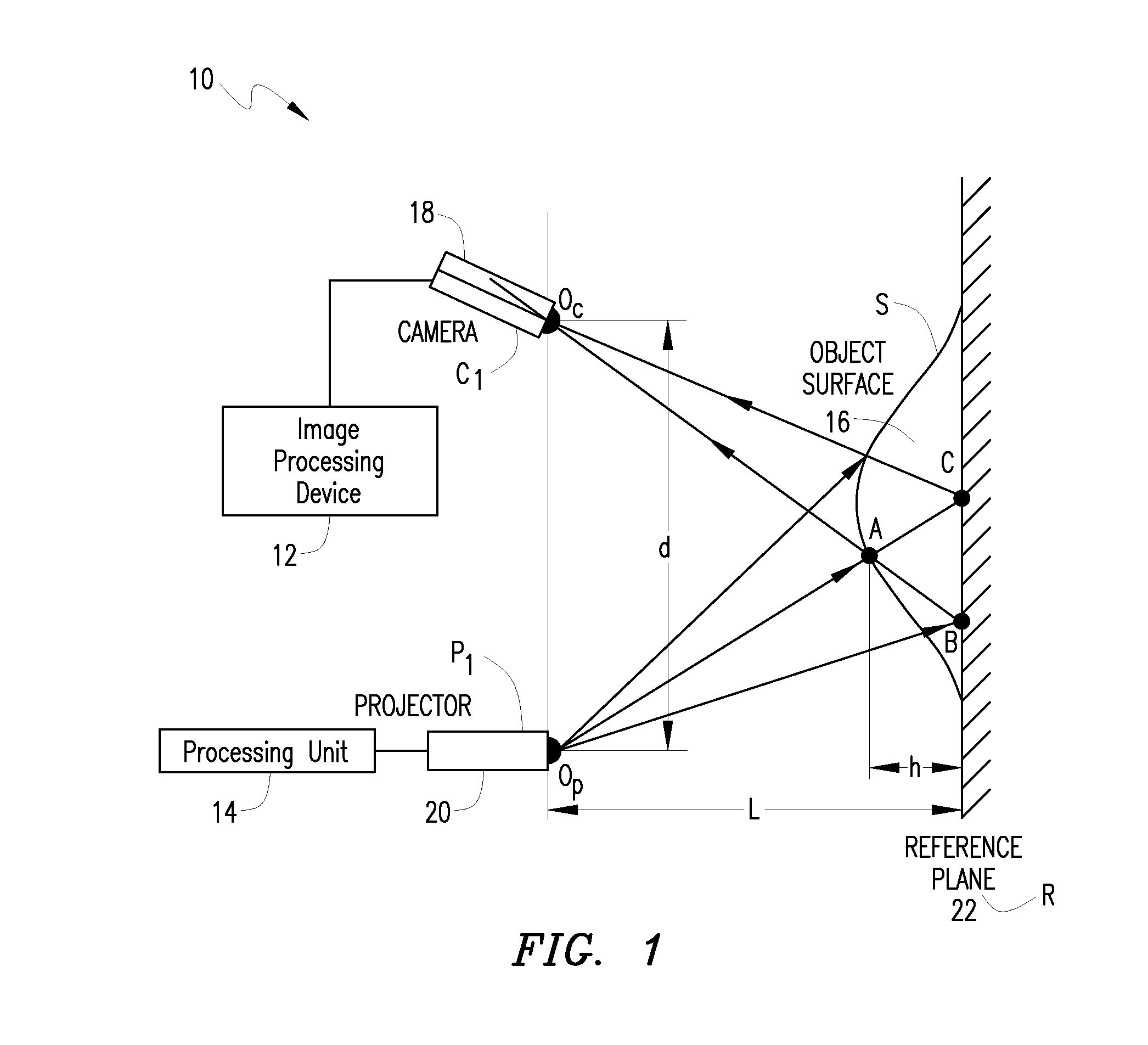
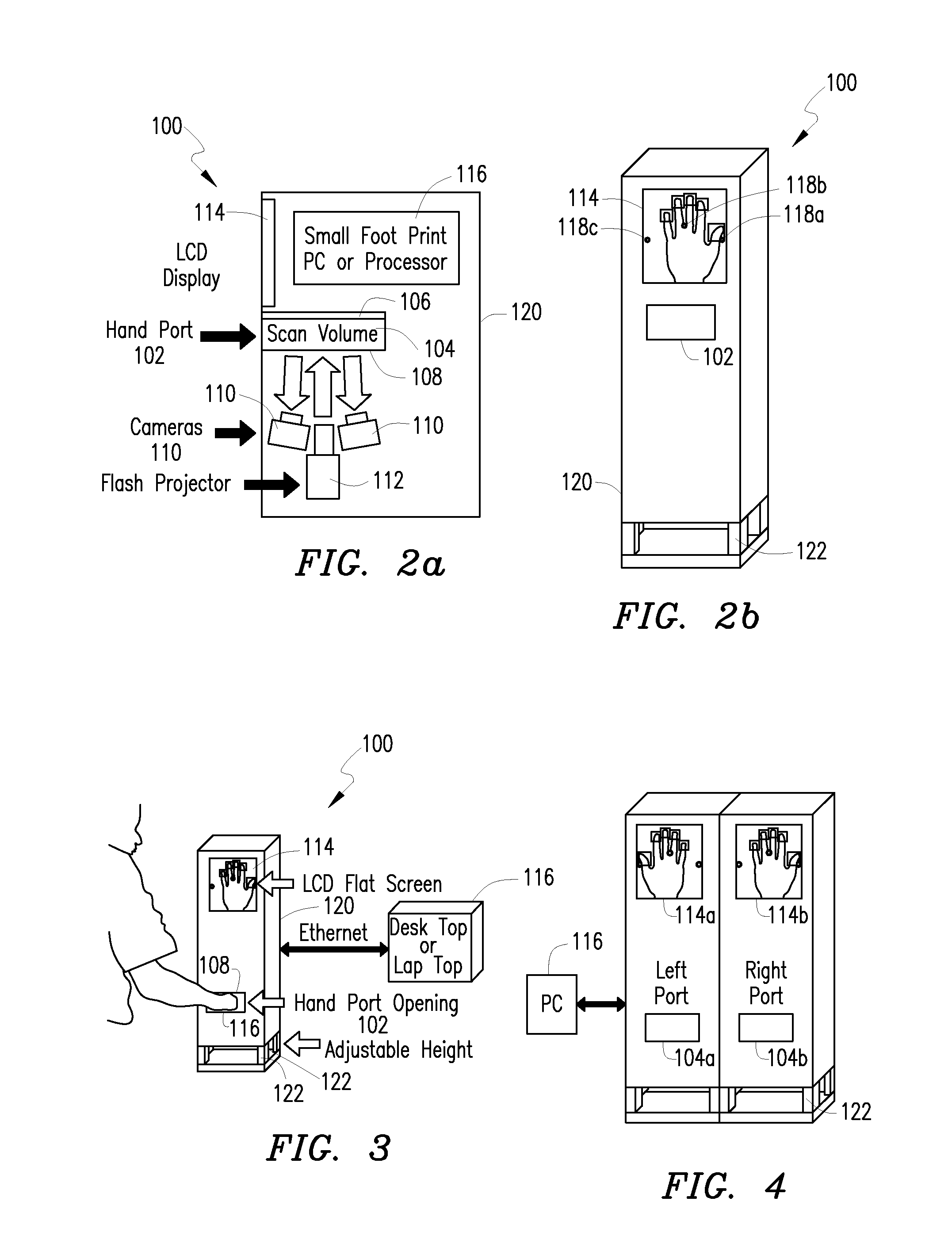
System and method for 3D imaging using structured light illumination
InactiveUS8224064B1Acquisition speed is fastMore robust to extremely worn ridges of the fingersImage enhancementImage analysisRandom noiseComputer science
A biometrics system captures and processes a handprint image using a structured light illumination to create a 2D representation equivalent of a rolled inked handprint. The biometrics system includes an enclosure with a scan volume for placement of the hand. A reference plane with a backdrop pattern forms one side of the scan volume. The backdrop pattern is preferably a random noise pattern and the coordinates of the backdrop pattern are predetermined at system provisioning. The biometrics system further includes at least one projection unit for projecting a structured light pattern onto a hand positioned in the scan volume on or in front of the backdrop pattern and at least two cameras for capturing a plurality of images of the hand, wherein each of the plurality of images includes at least a portion of the hand and the backdrop pattern. A processing unit calculates 3D coordinates of the hand from the plurality of images using the predetermined coordinates of the backdrop pattern to align the plurality of images and mapping the 3D coordinates to a 2D flat surface to create a 2D representation equivalent of a rolled inked handprint. The processing unit can also adjust calibration parameters for each hand scan from calculating coordinates of the portion of backdrop pattern in the at least one image and comparing with the predetermined coordinates of the backdrop pattern.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
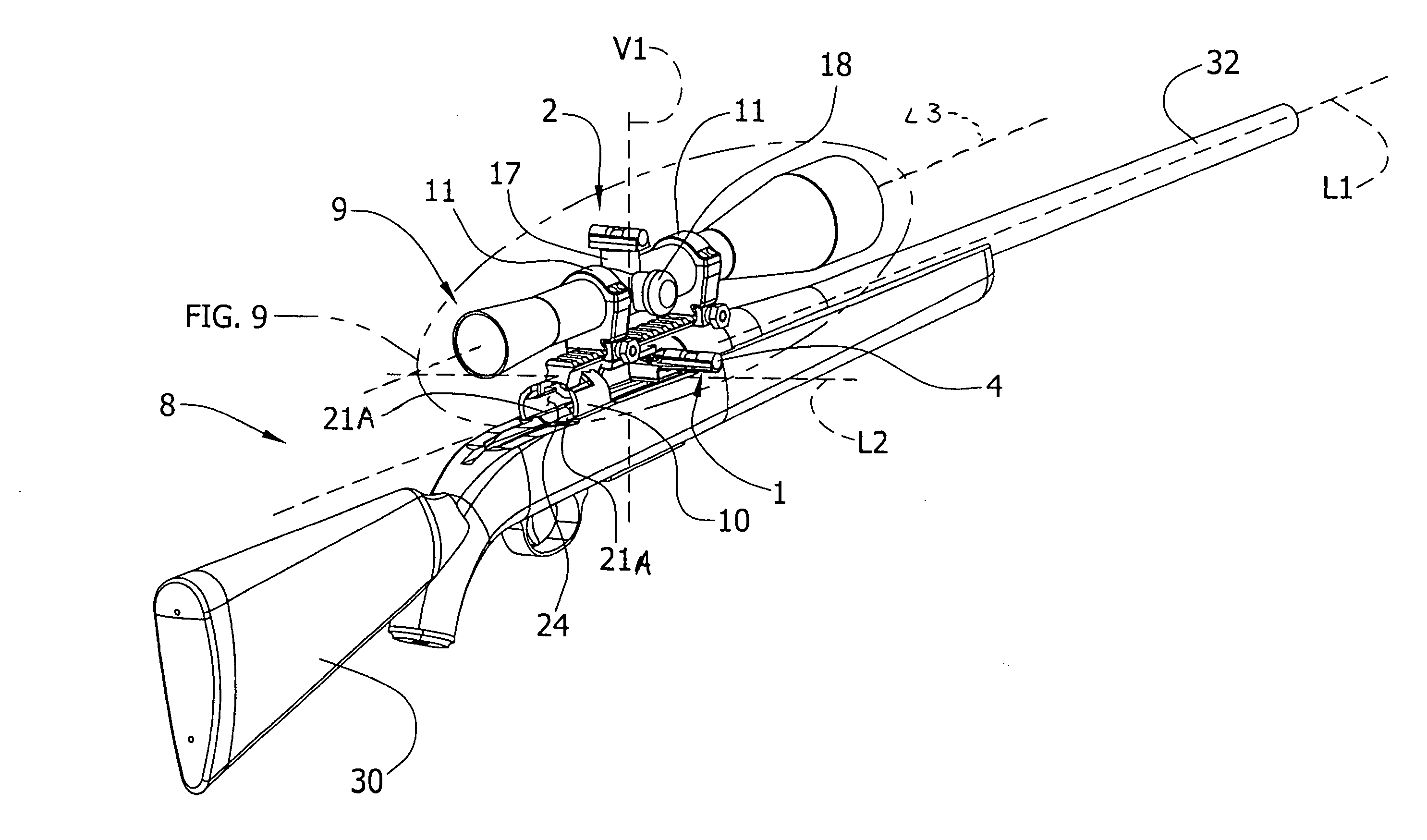
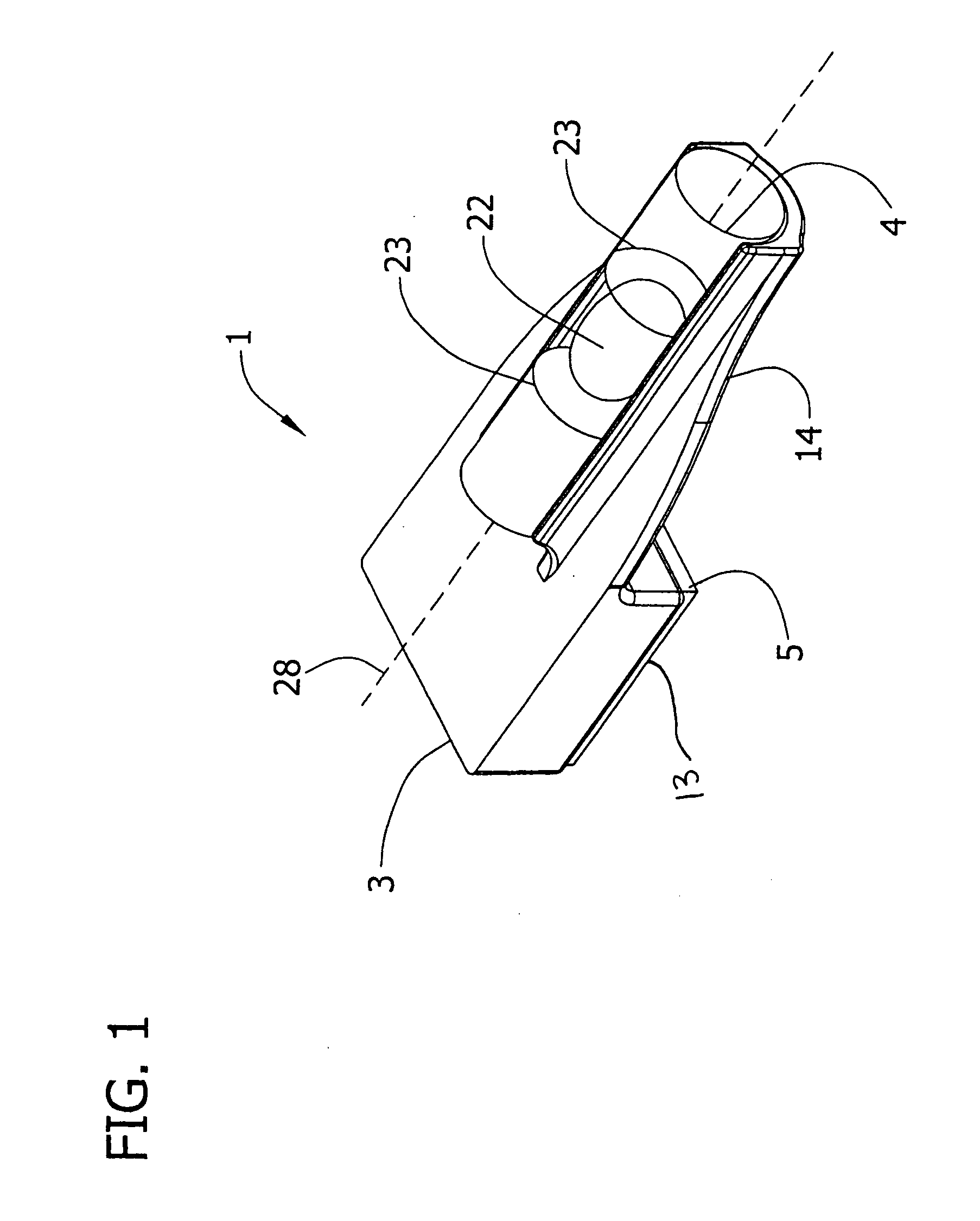
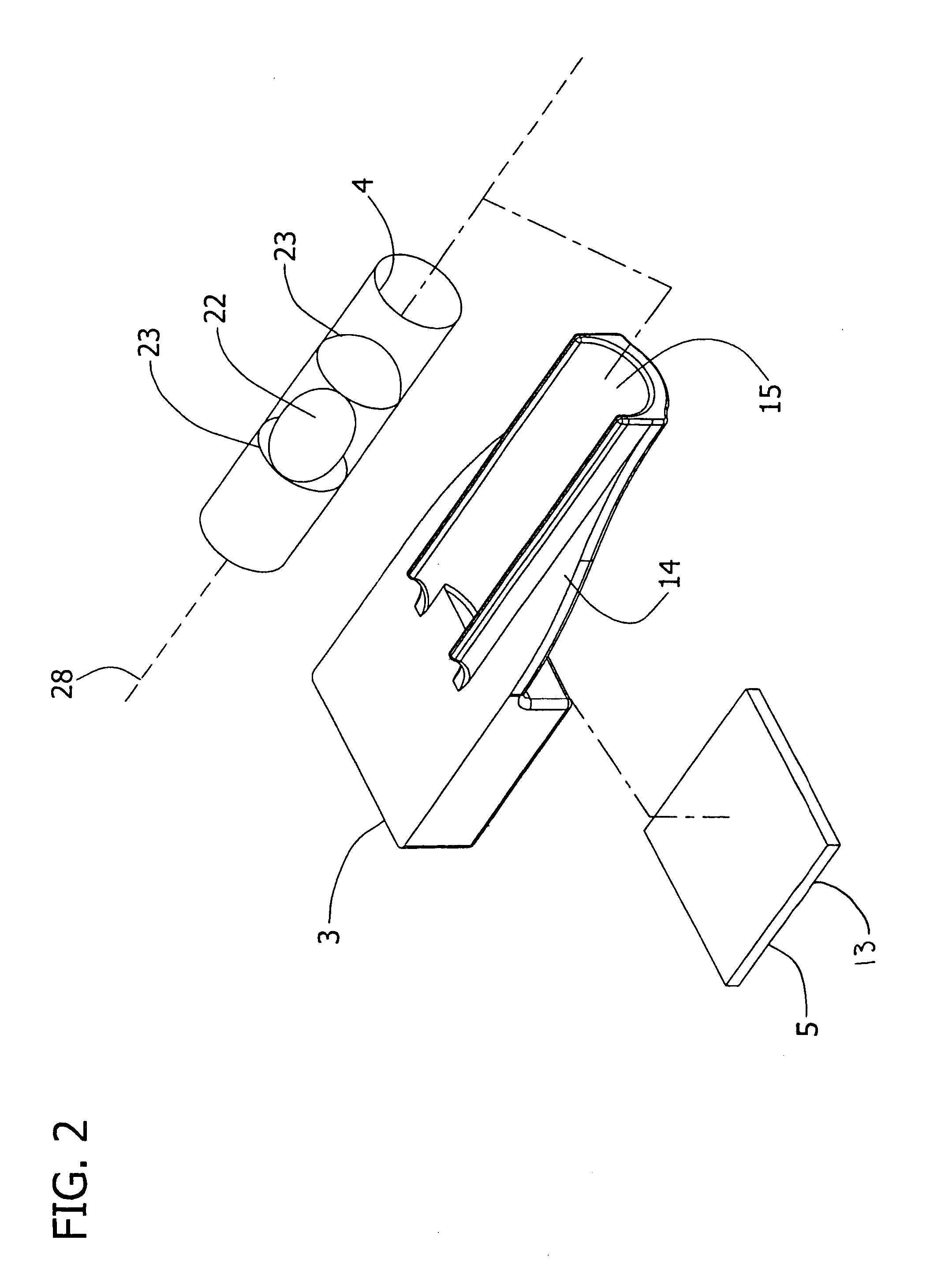
Method and apparatus for alignment of firearm sights
An apparatus for aligning a sighting device mounted on a firearm. The apparatus has a first indicating device adapted to be positioned on a surface of the firearm to determine a rotational position of the firearm relative to a reference plane and a second indicating device adapted to be positioned on a surface of the sighting device to determine a rotational position of the sighting device relative to the reference plane.
Owner:BATTENFELD TECH
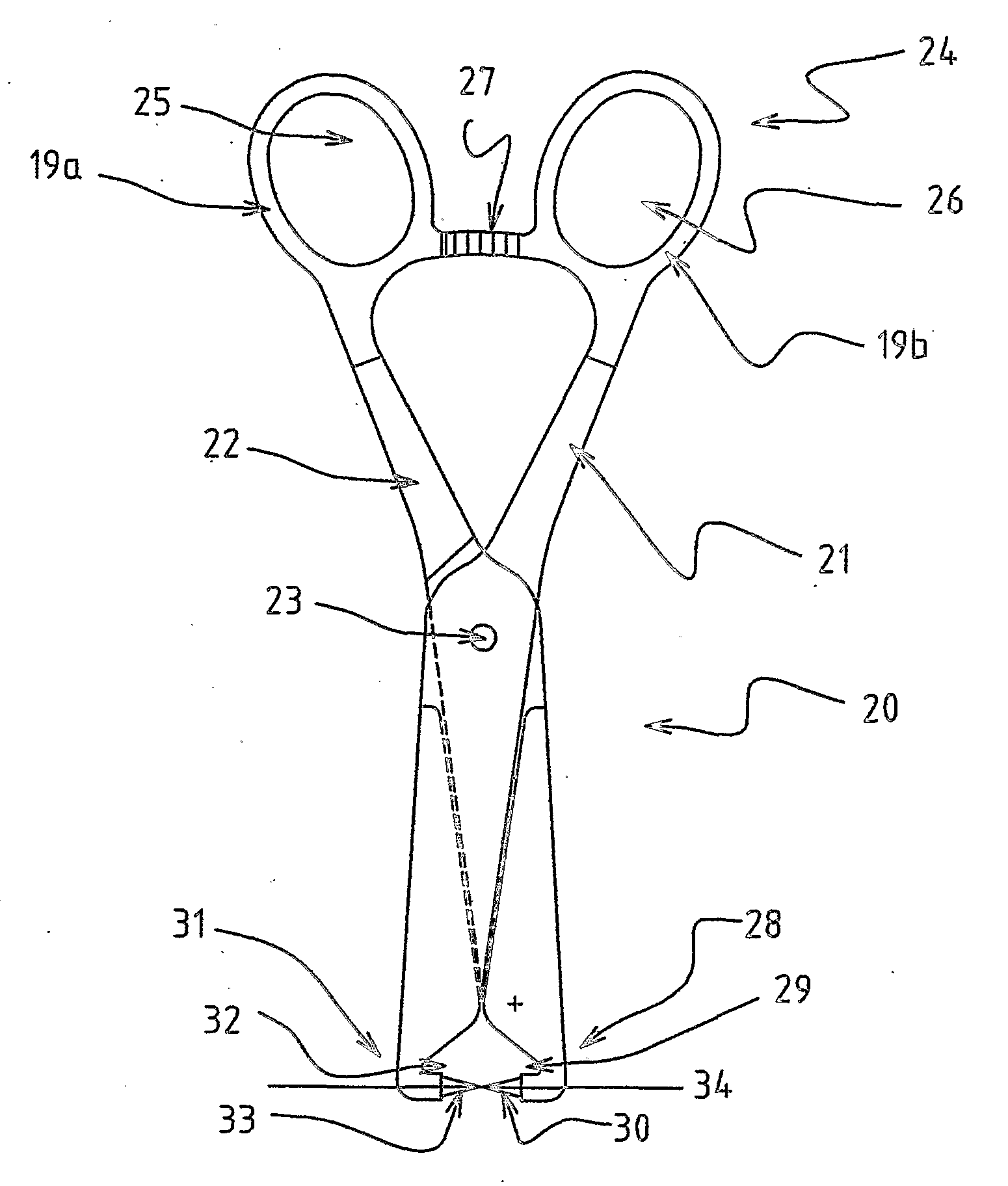
Distraction and retraction assemblies
An assembly (40) allowing retraction of soft tissue away from a reference plane; the assembly including at least one retracting element (51) each comprising a distal end having a formation allowing anchorage of the at least one retracting element (51). The assembly also includes a proximal end (50) of the at least one retracting element capable of movement through at least one degree of freedom relative to said anchorage.
Owner:SEEX KEVIN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com