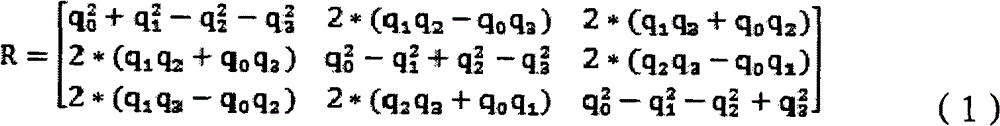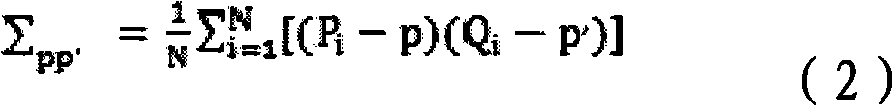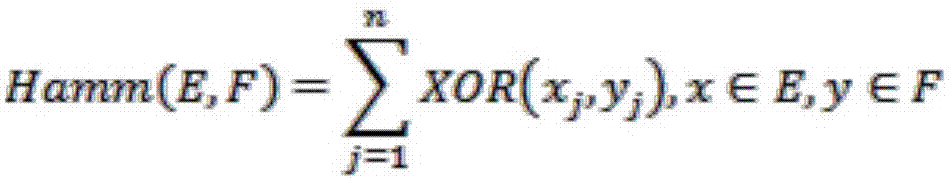Patents
Literature
270 results about "Closest point" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Collision avoidance method and system using stereo vision and radar sensor fusion
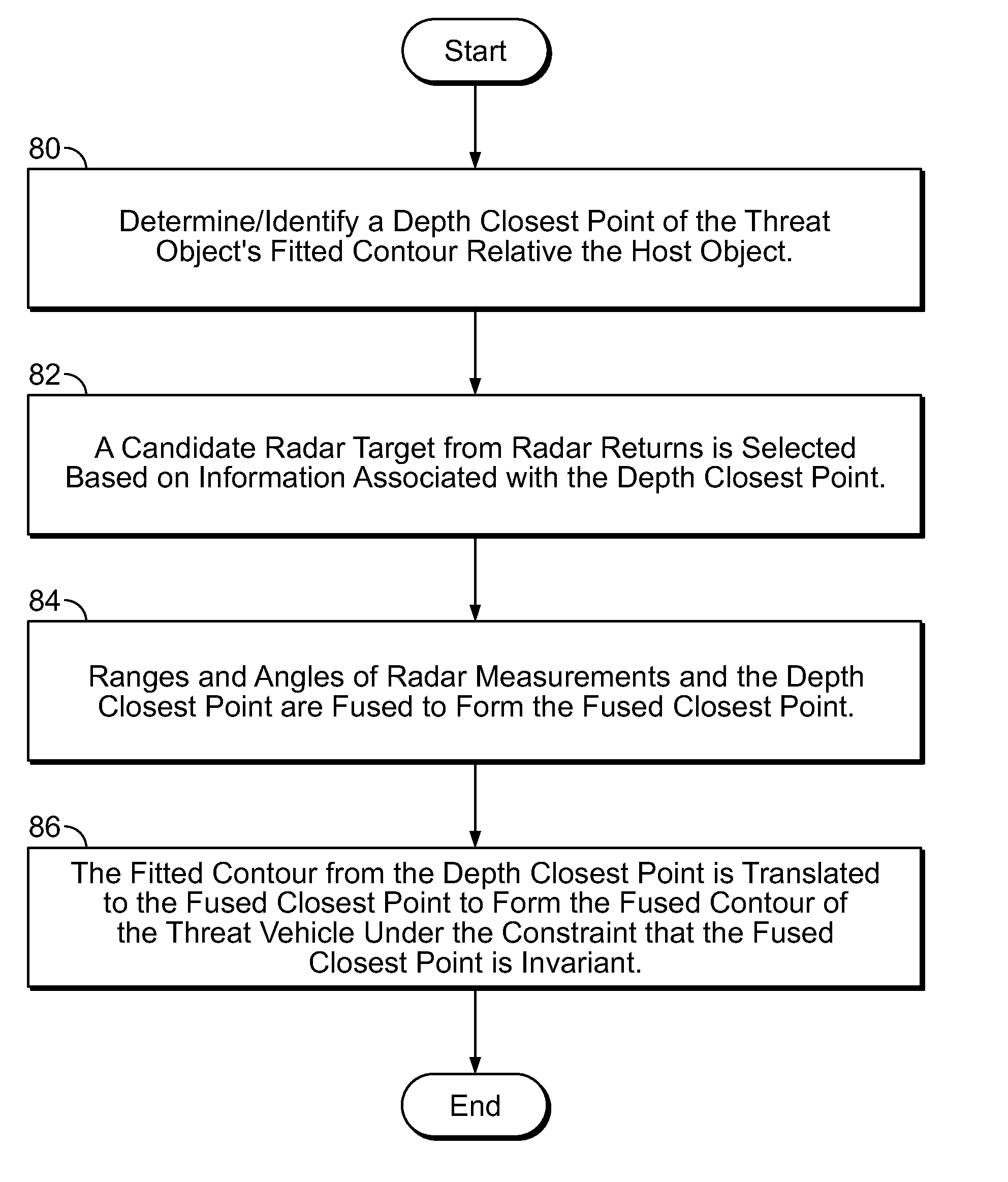
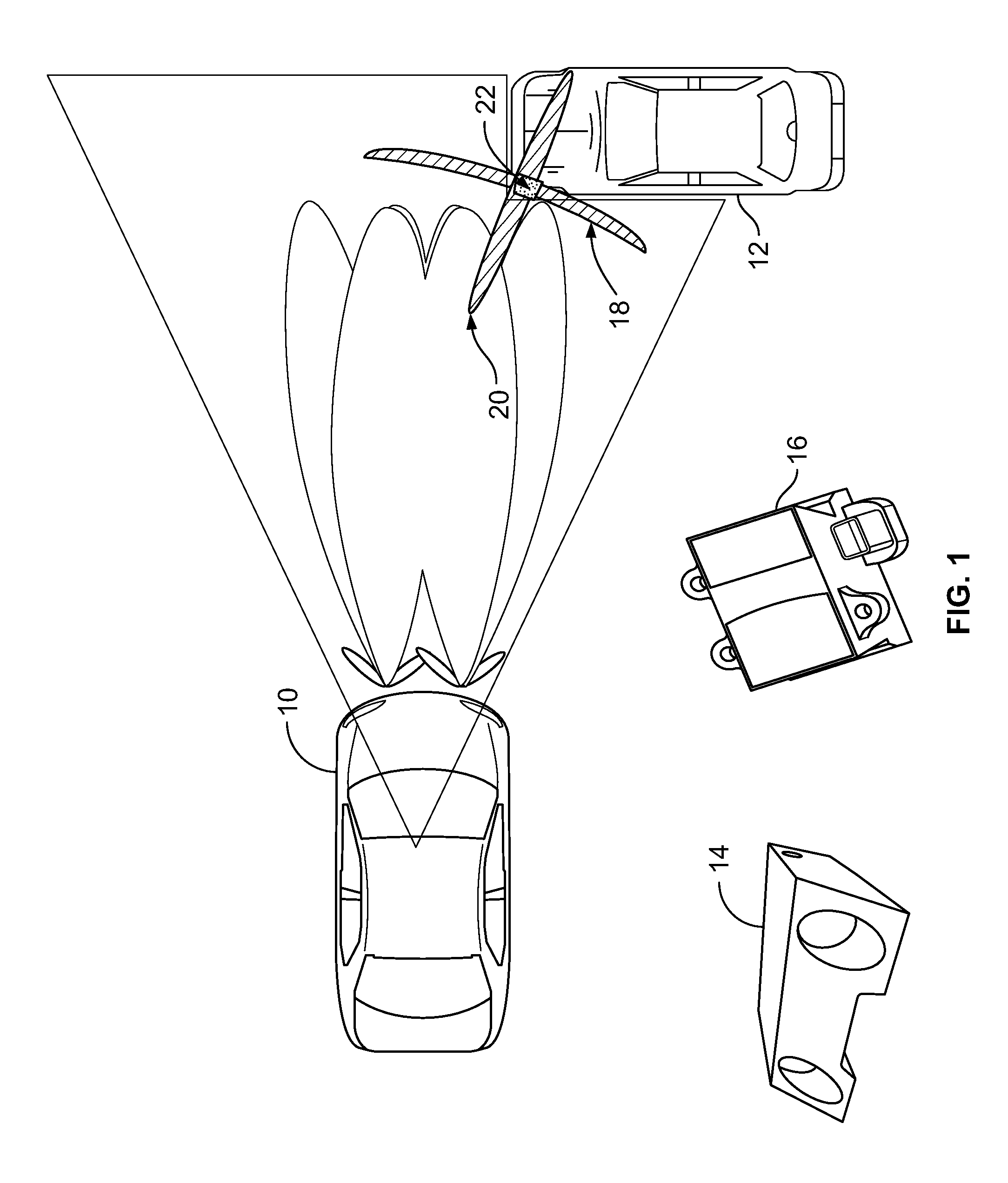
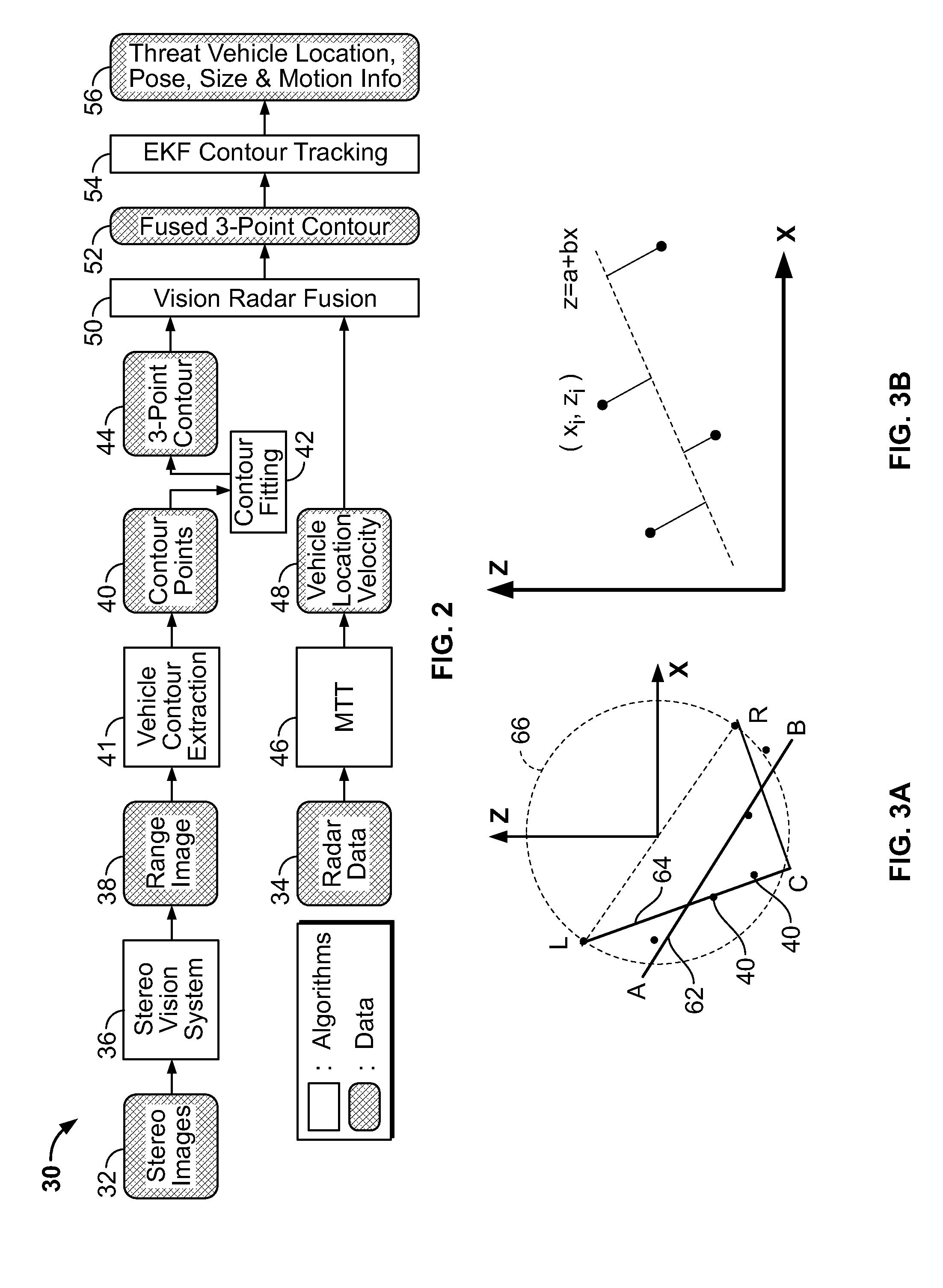
A system and method for fusing depth and radar data to estimate at least a position of a threat object relative to a host object is disclosed. At least one contour is fitted to a plurality of contour points corresponding to the plurality of depth values corresponding to a threat object. A depth closest point is identified on the at least one contour relative to the host object. A radar target is selected based on information associated with the depth closest point on the at least one contour. The at least one contour is fused with radar data associated with the selected radar target based on the depth closest point to produce a fused contour. Advantageously, the position of the threat object relative to the host object is estimated based on the fused contour. More generally, a method is provided for aligns two possibly disparate sets of 3D points.
Owner:SARNOFF CORP
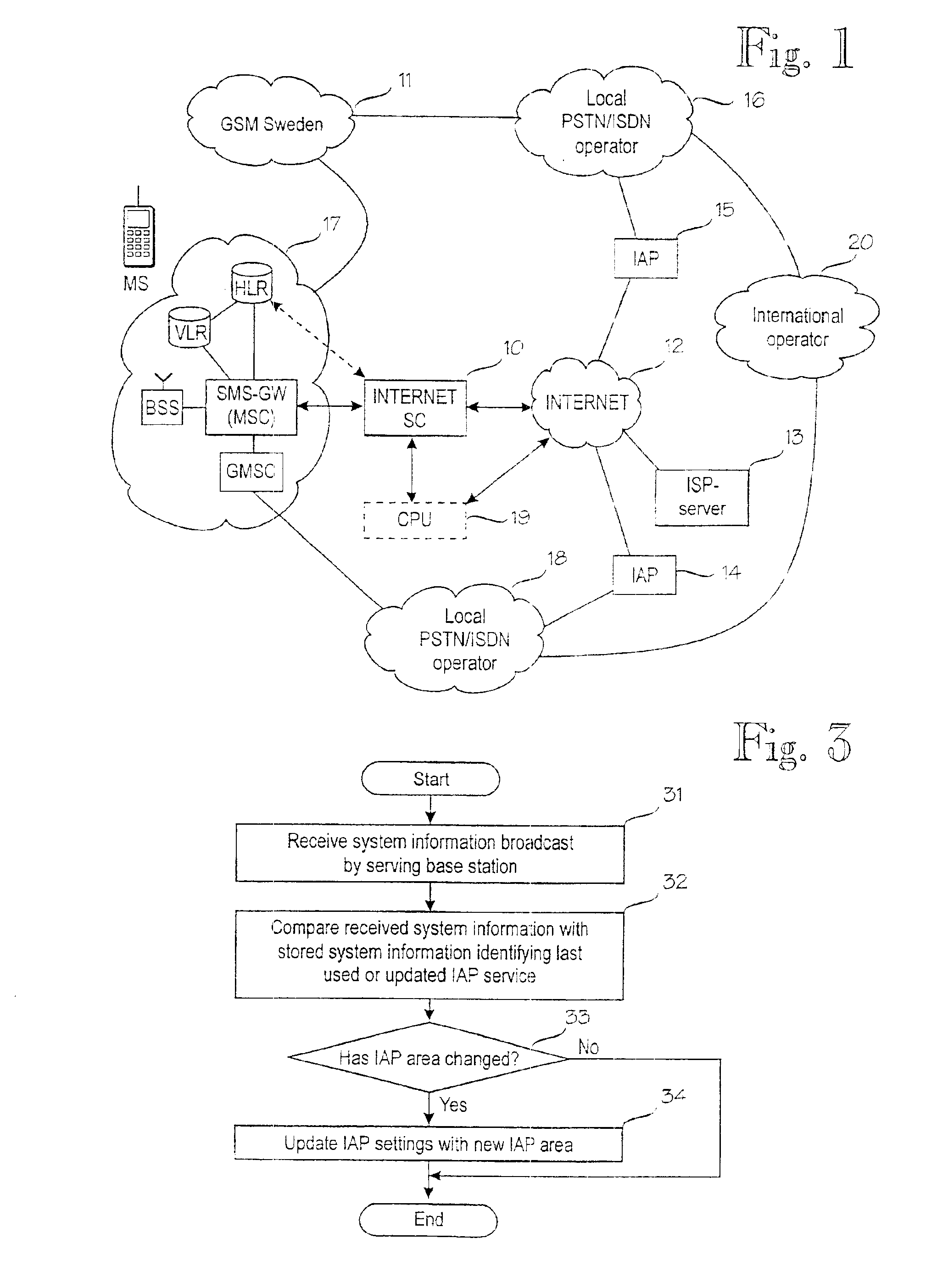
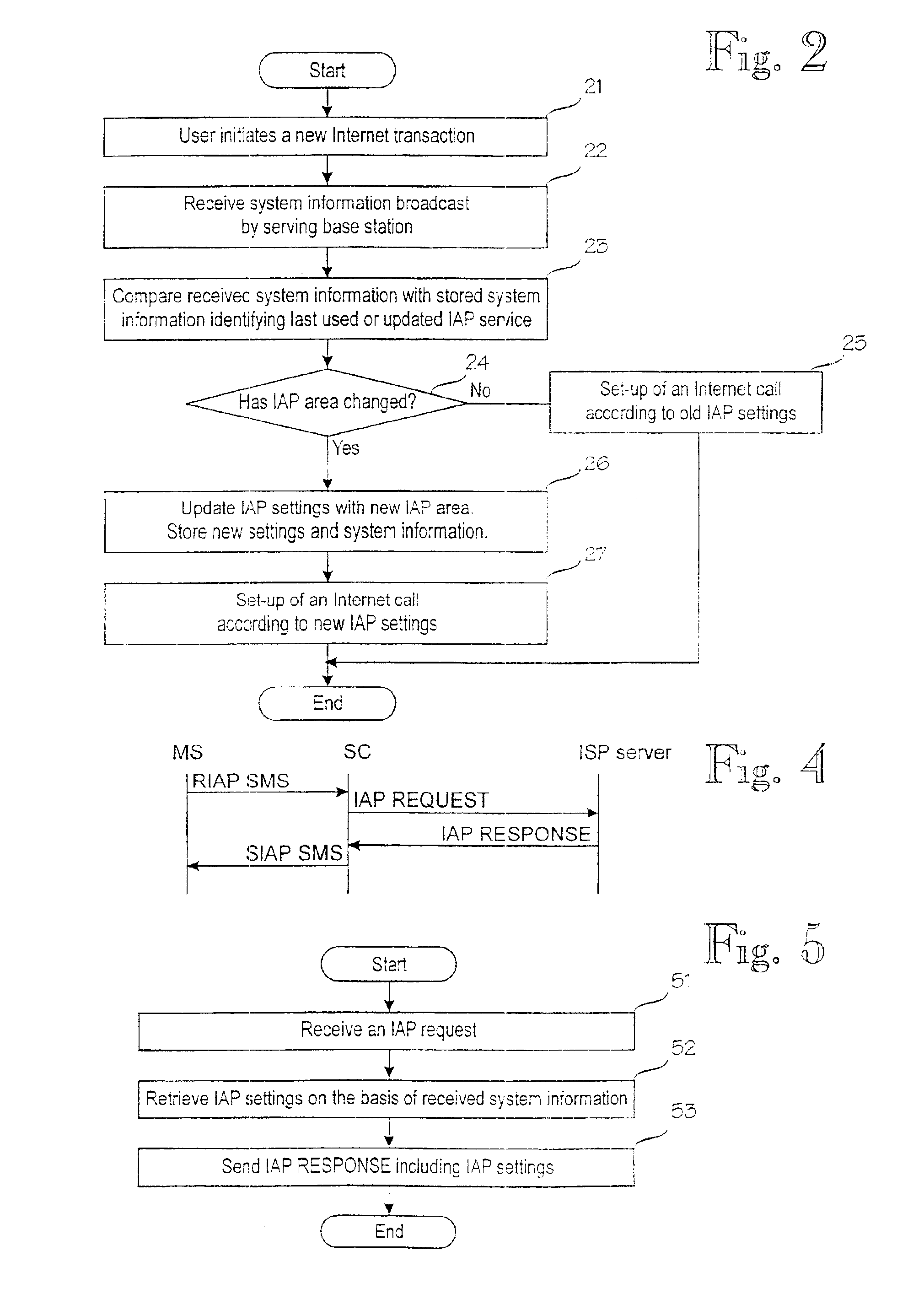
Updating of internet access point settings in a mobile communication system
InactiveUS6904026B1Reduce call costsMinimal amount of workBroadcast service distributionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsClosest pointInternet access
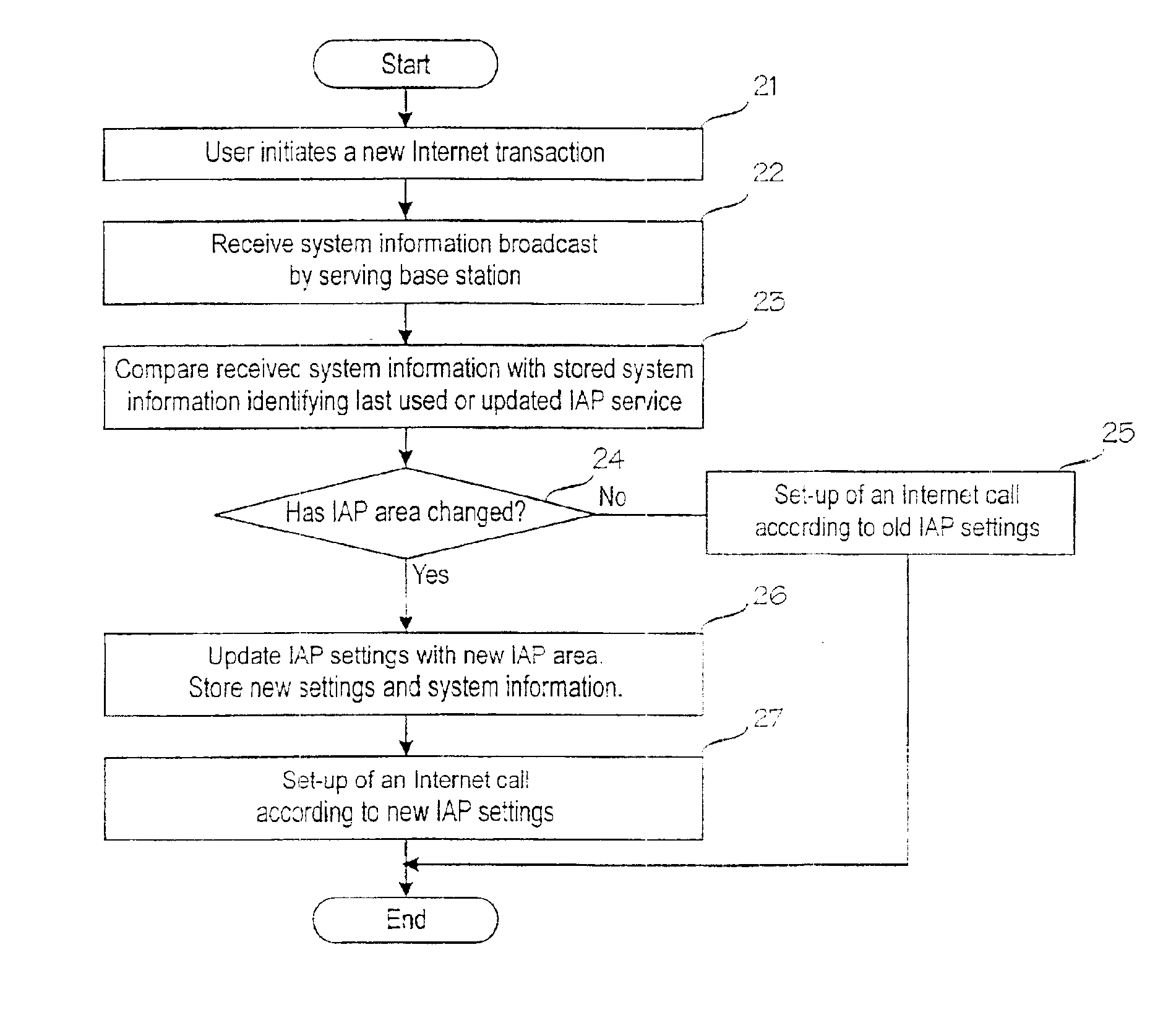
A digital mobile communication system is provided with a facility by means of which it can establish a connection to the Internet network (12) via an Internet access point (14, 15). IAP settings needed for establishing a connection are stored in a mobile station (MS). When a mobile station (MS) roams, the closest point may, however, change, and IAP settings should be updated in the mobile station (MS). The invention comprises dividing the mobile communication system into IAP areas, which are given preferred IAPs. An IAP area may be e.g. a mobile communication network (11, 17). Mobile communication networks broadcast system information on the basis of which a mobile station may detect that the IAP area has changed and start a procedure for updating IAP settings. Updating may comprise retrieval of IAP settings from a special server (13) in the network maintained by an Internet service provider. Retrieval can be done e.g. via a short message service center (10). In one embodiment the mobile communication network broadcasts messages giving recommended IAP settings to mobile stations.
Owner:COMCAST CABLE COMM LLC
Methods and systems for mapping a virtual model of an object to the object
Systems, apparati and methods for mapping a virtual model of a real object, such as a body part, to the real object are presented. Such virtual model can be generated, for example, from an imaging scan of the object, for example, using MRI, CT, etc. A camera with a probe fixed thereto can be moved relative to the object until a video image of the object captured by the camera appears to coincide on a video screen with the virtual model which is shown fixed on that screen. The position of the camera in a real coordinate system can be sensed, and the position in a virtual coordinate system of the virtual model relative to a virtual camera, by which the view of the virtual model on the screen is notionally captured, can be predetermined and known. From this, the position of the virtual model relative to the object can be mapped and a transform generated to position the object in the virtual coordinate system to approximately coincide with the virtual model. After completion of such an initial registration process, a second, refined, registration process can be initiated. Such refined registration process can include acquiring a large number of real points on the surface of the object. Such points can, for example, then be processed using an iterative closest point measure to generate a second, more accurate transform between the object and its virtual model. Further, the refined registration processing can be iterated and more and more accurate transforms generated until a termination condition is met and a final transform generated. Using the final transform generated by this process the virtual model can be positioned in the real coordinate system to substantially exactly coincide with the object.
Owner:BRACCO IMAGINIG SPA
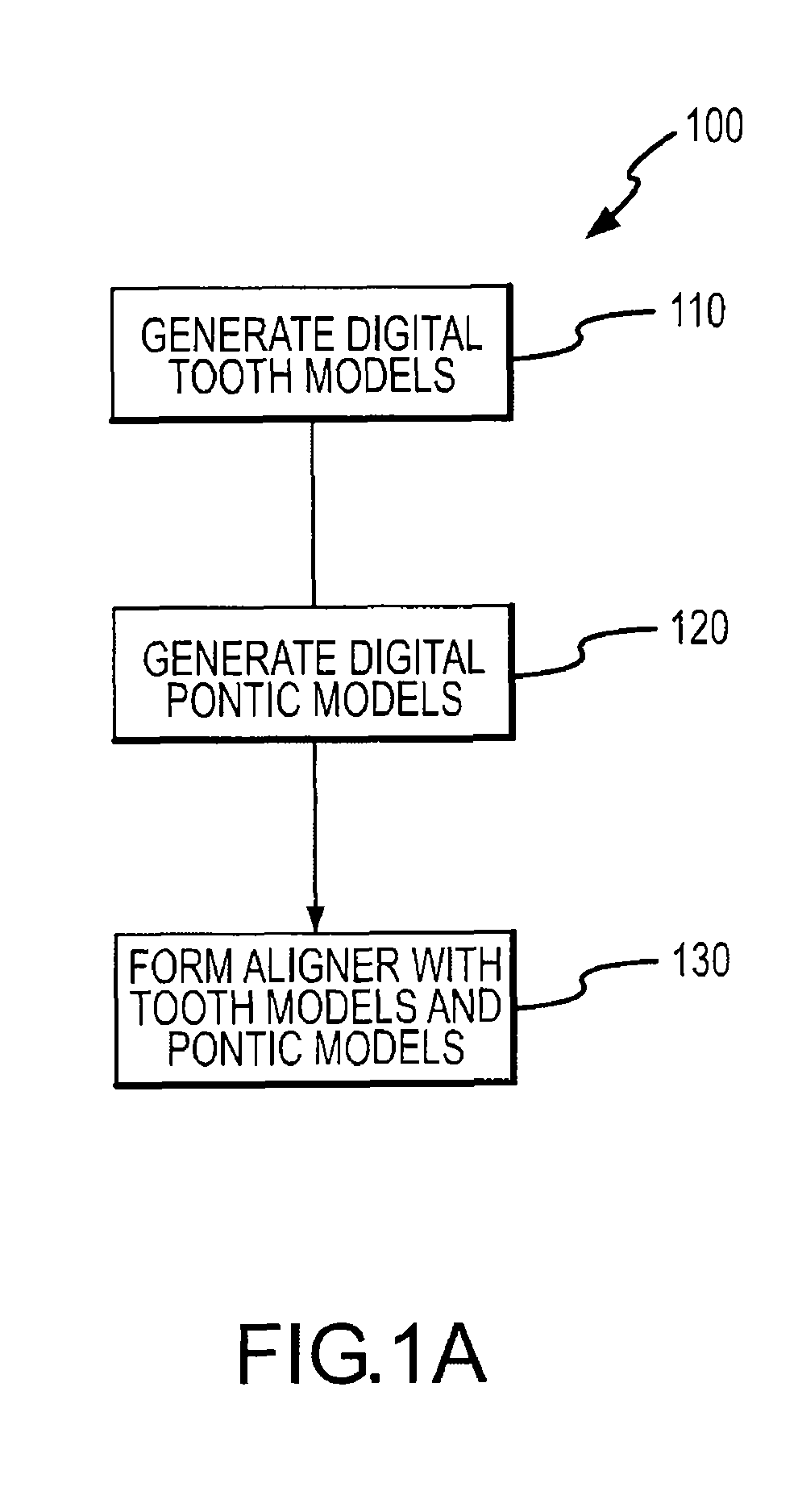
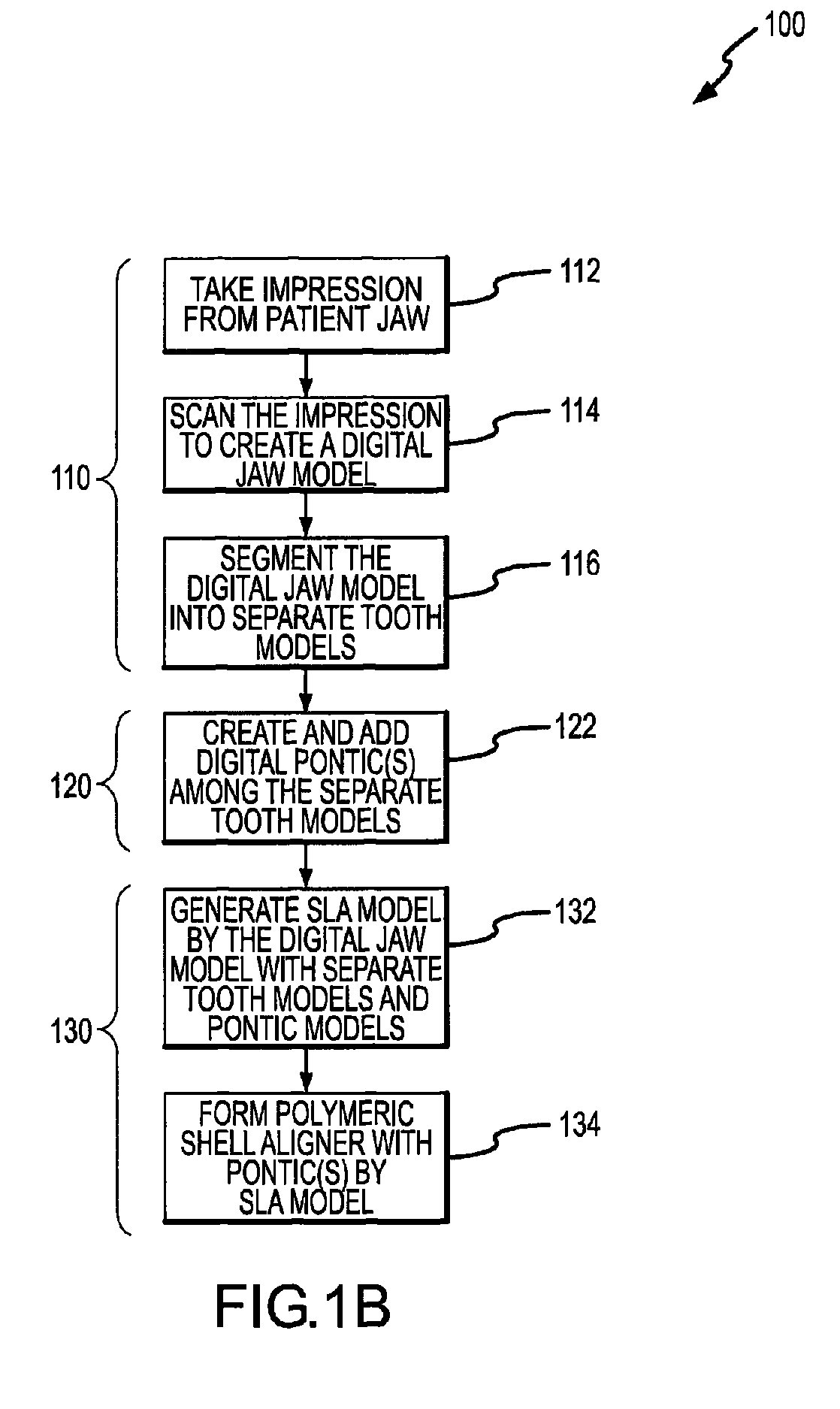
System and method for representation, modeling and application of three-dimensional digital pontics
Modeling pontics at successive treatment stages includes: (1) calculating space measurements between first and second teeth by getting first and second tooth transformations at a treatment stage i; (2) applying the first and second tooth transformations to get positions of the first and second teeth at the stage i; (3) calculating a direction vector of the space measurements at the stage i; (4) calculating a reference plane using the direction vector as a normal; (5) determining whether the space is available for a pontic by measuring the distance from the closest point on each of the first and second teeth to the reference plane; (6) generating an original pontic geometry for a first treatment stage; and (7) generating pontic geometries at each successive stage by calculating deformation parameters based on the original pontic geometry and size characteristics of the space and of the first and second teeth at each stage.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
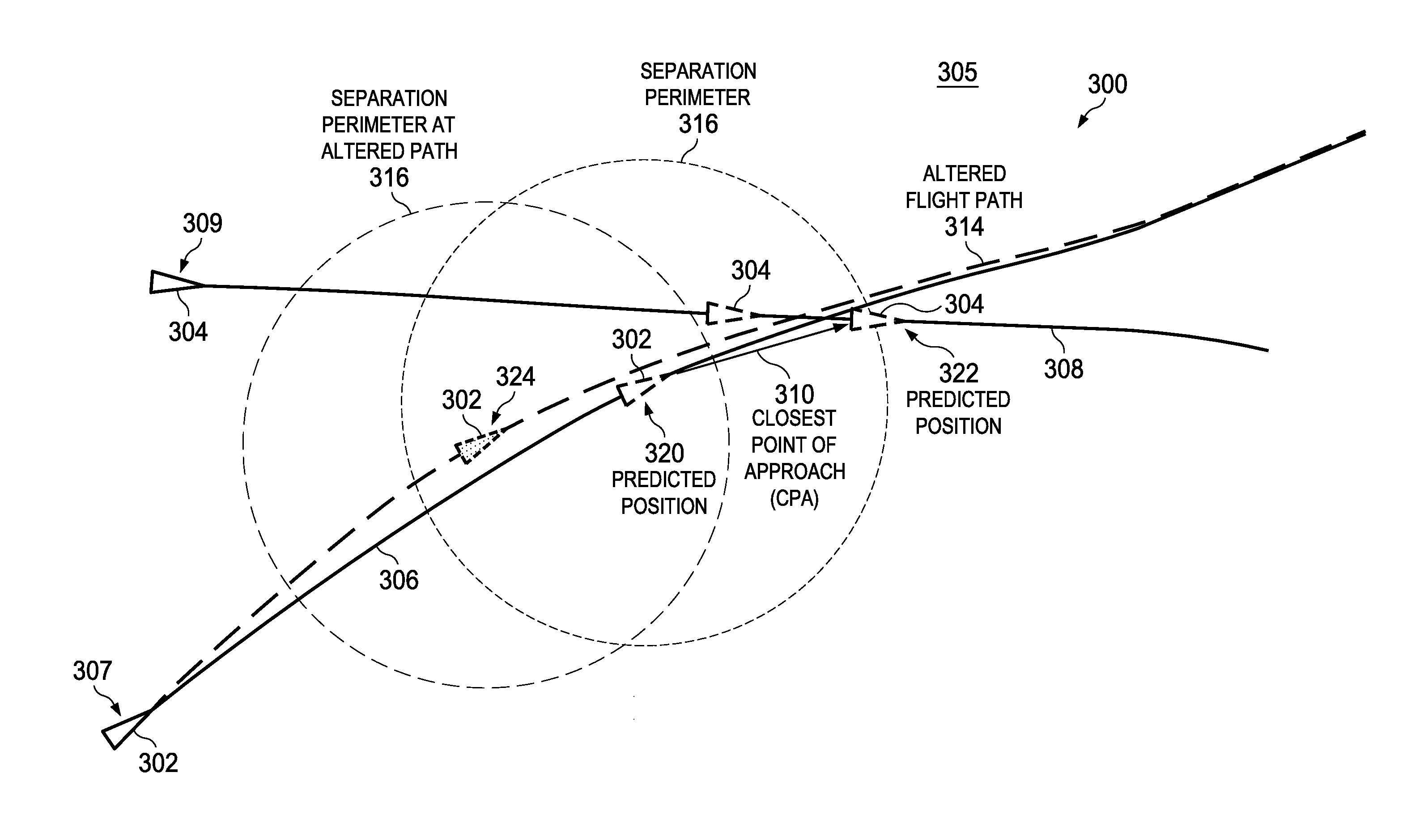
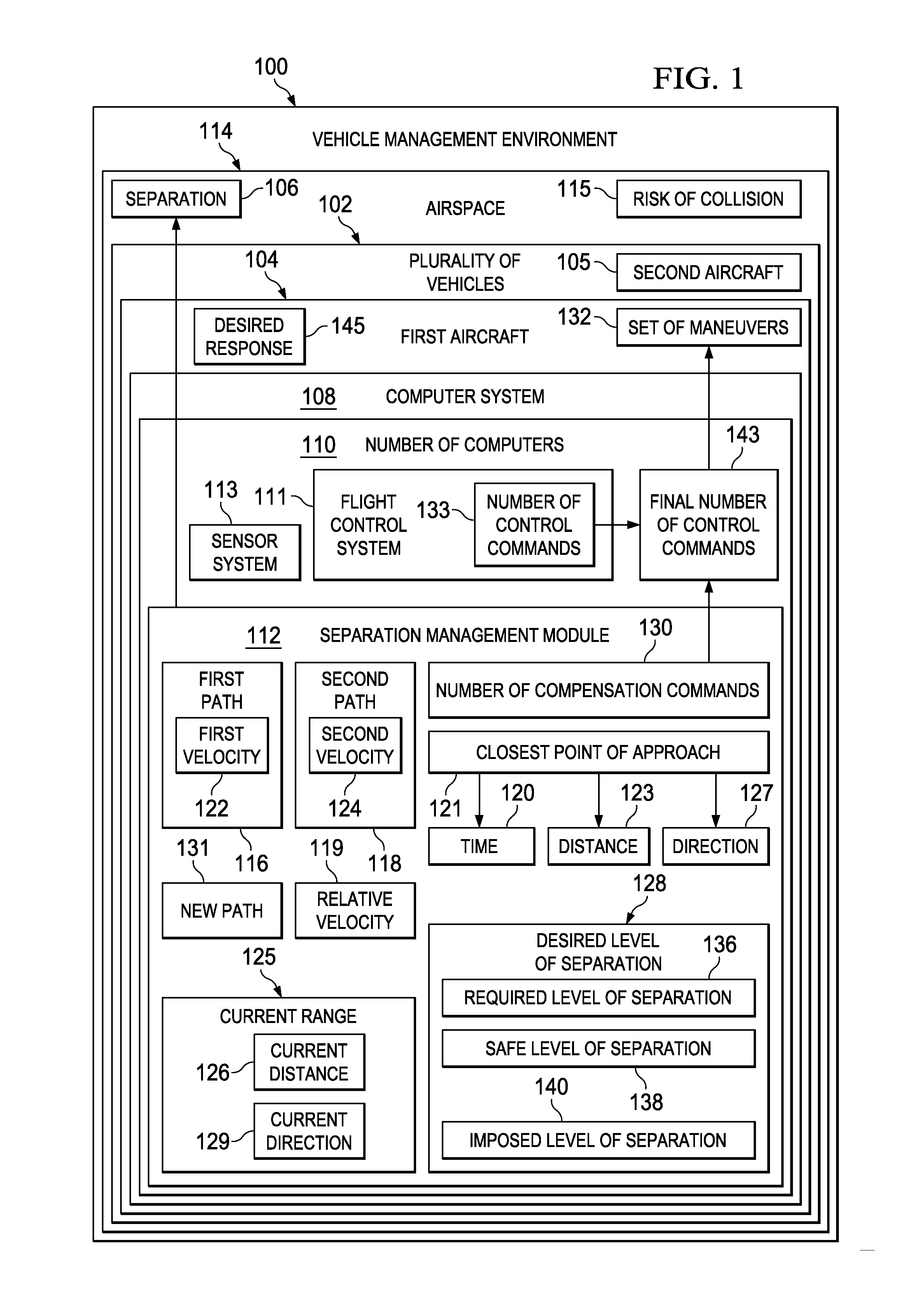
Aircraft Traffic Separation System
ActiveUS20120209457A1Maintain standardAnalogue computers for vehiclesCosmonautic vehiclesClosest pointEngineering
A method and apparatus for managing separation between vehicles. A closest point of approach between a first vehicle traveling along a first path and a second vehicle traveling along a second path is predicted. A number of compensation commands for altering the first path of the first vehicle are generated using the closest point of approach and a desired level of separation between the first vehicle and the second vehicle. The number of compensation commands is integrated with a number of control commands for the first vehicle to form a final number of control commands configured to maneuver the first vehicle to substantially maintain the desired level of separation between the first vehicle and the second vehicle. A response of the first vehicle to the final number of control commands is a desired response.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
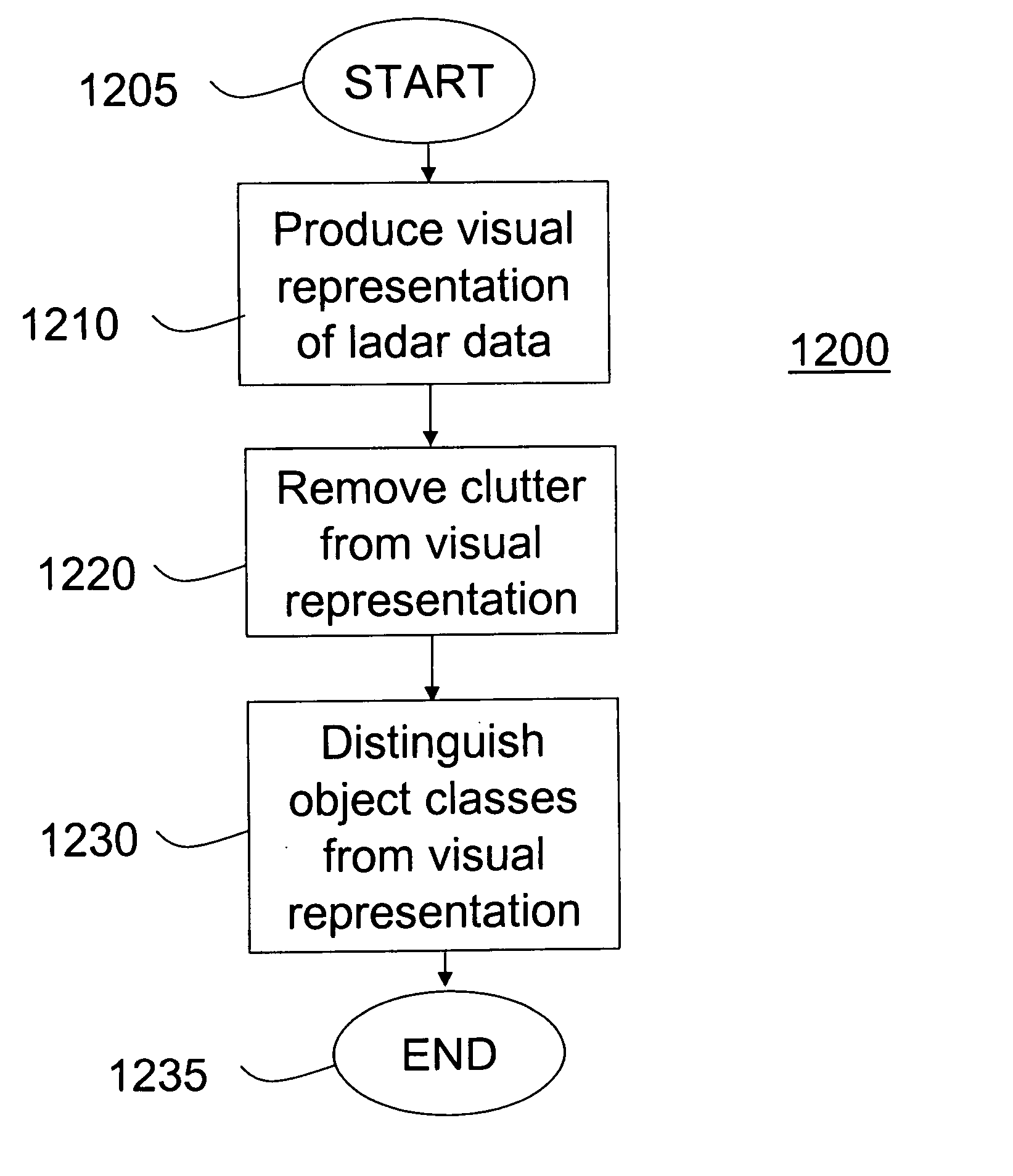
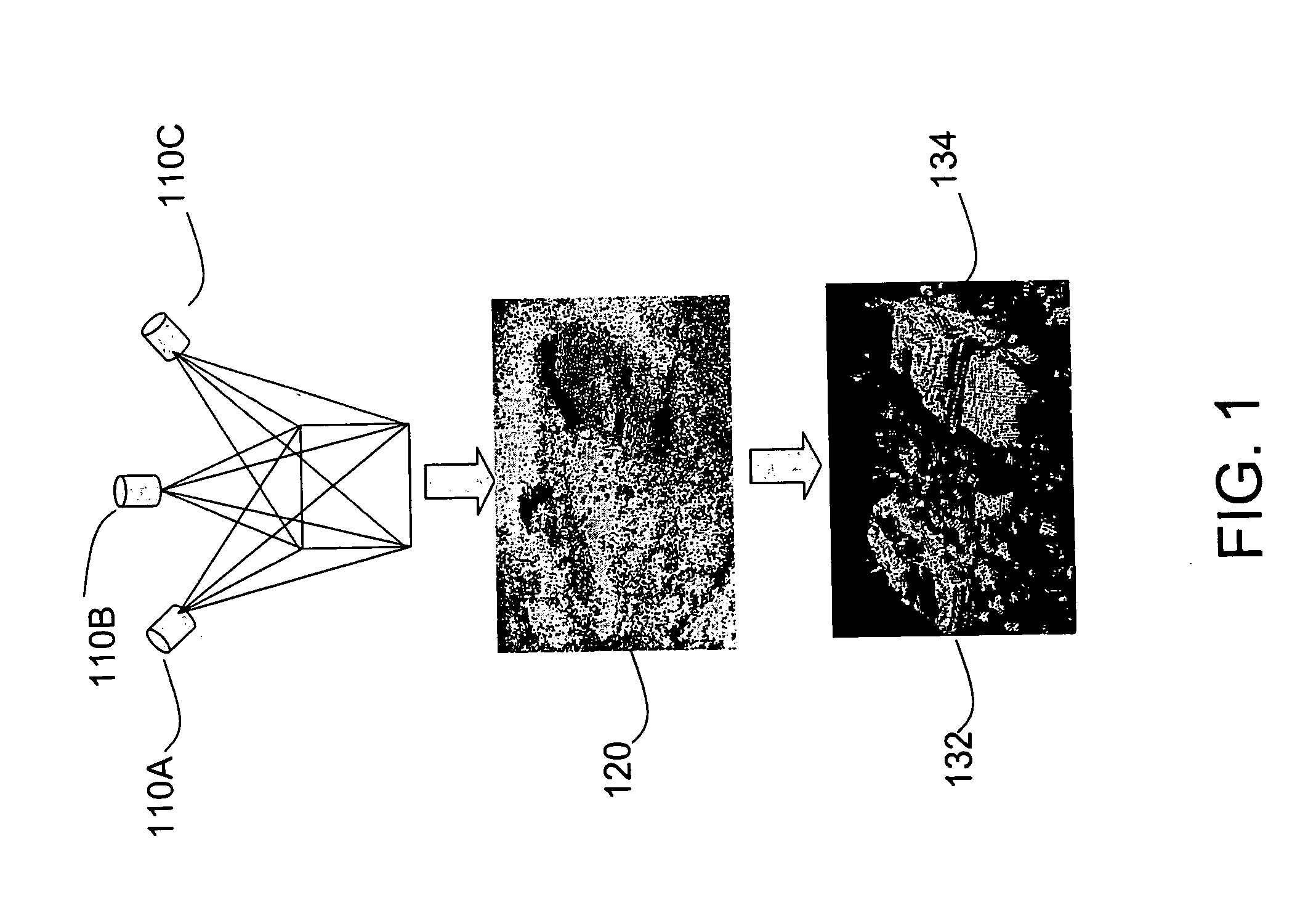
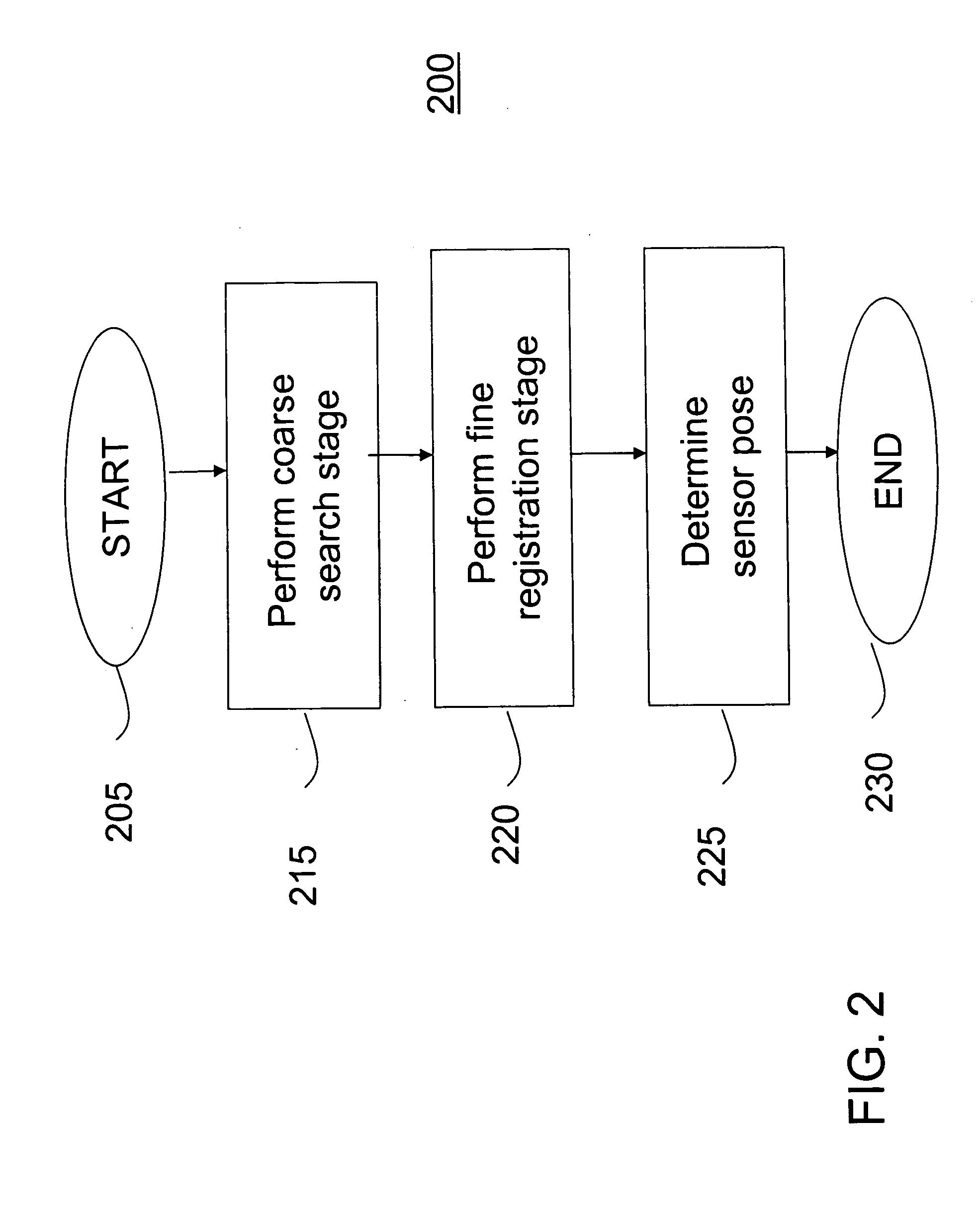
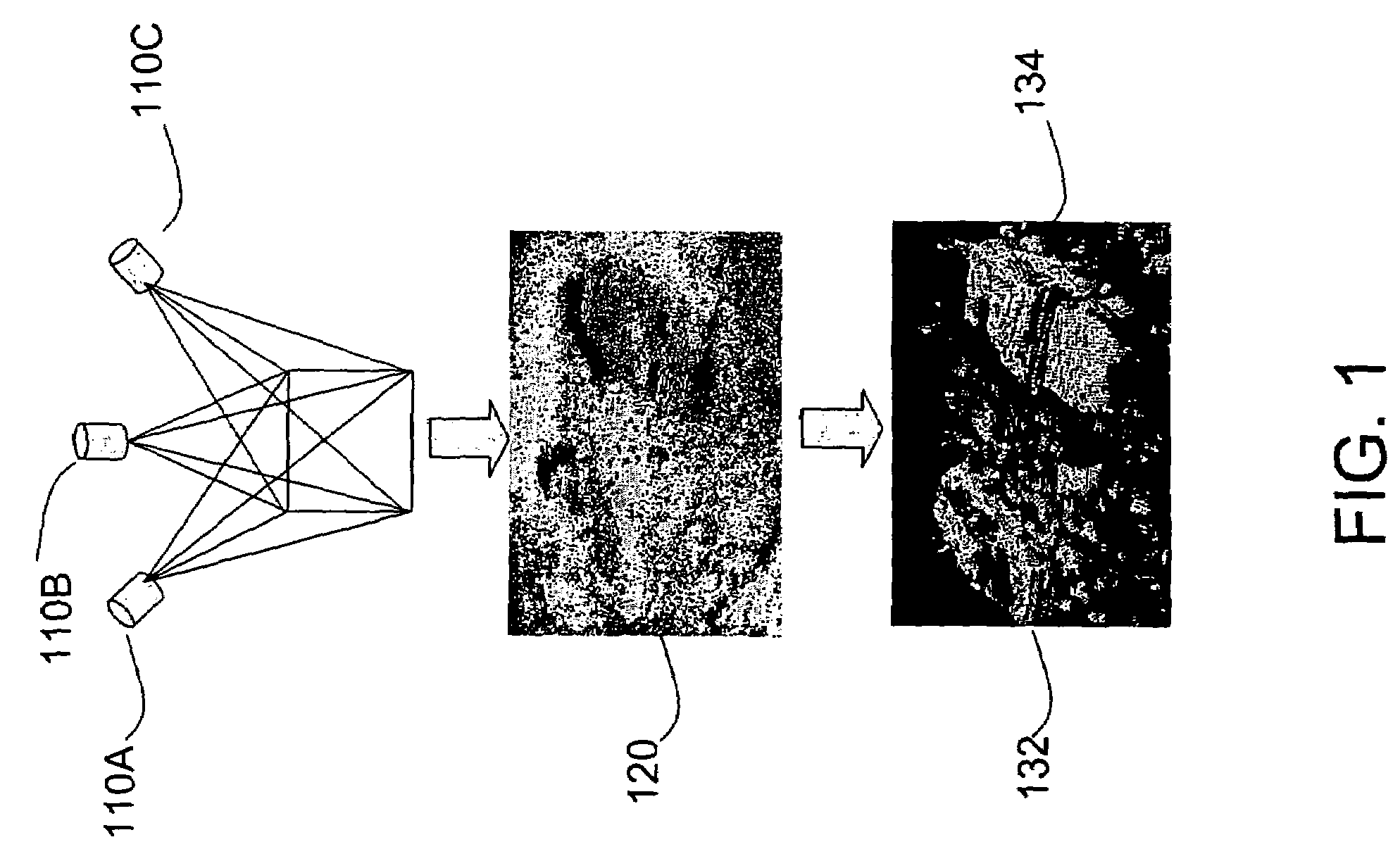
Method and apparatus for automatic registration and visualization of occluded targets using ladar data
ActiveUS20050243323A1Enhancing visual exploitationImage enhancementRadiation pyrometryClosest pointPoint cloud
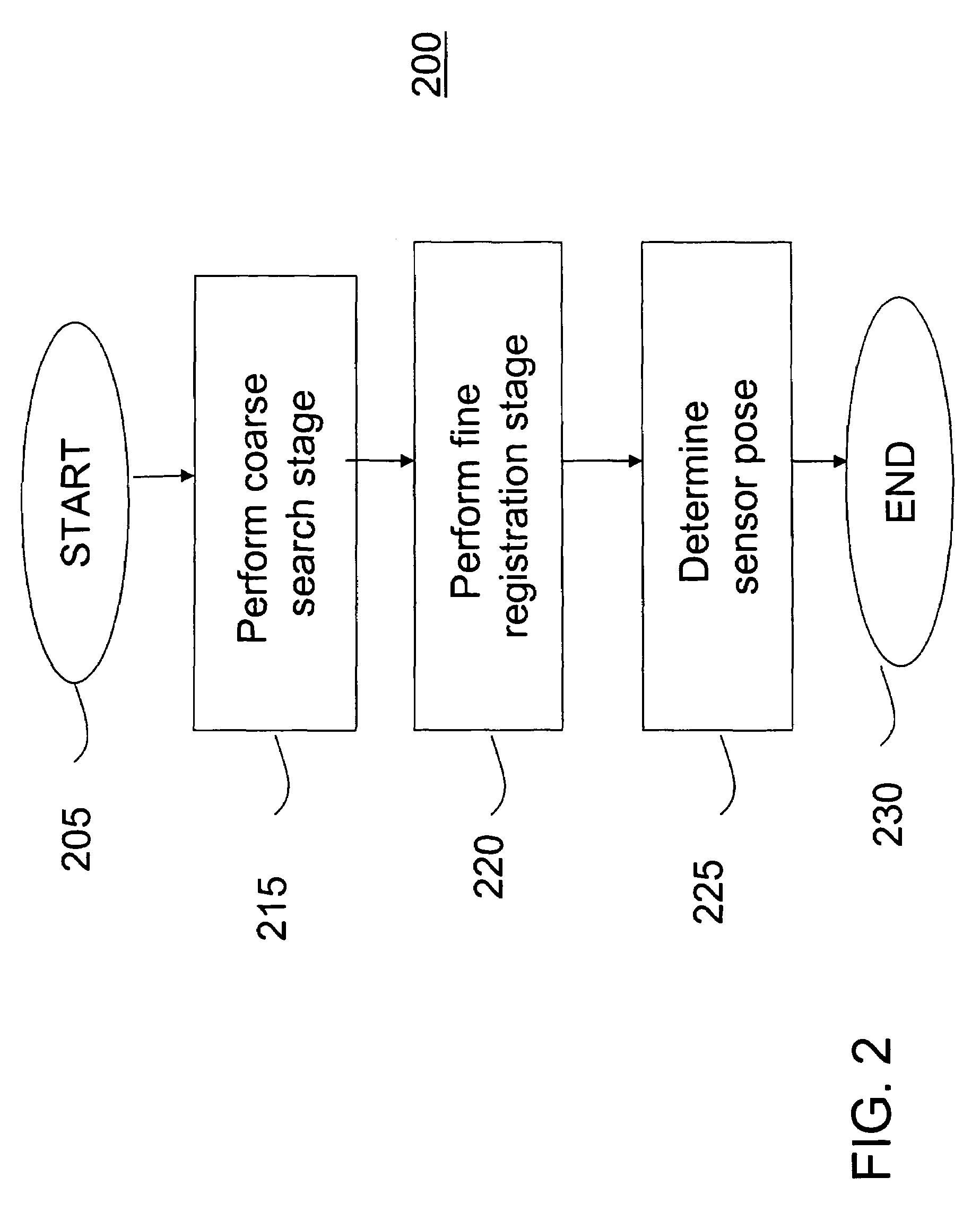
A method and apparatus for high-resolution 3D imaging ladar system which can penetrate foliage and camouflage to sample fragments of concealed surfaces of interest is disclosed. Samples collected while the ladar moves can be integrated into a coherent object shape. In one embodiment, a system and method for automatic data-driven registration of ladar frames, comprises a coarse search stage, a pairwise fine registration stage using an iterated closest points algorithm, and a multi-view registration strategy. After alignment and aggregation, it is often difficult for human observers to find, assess and recognize objects from a point cloud display. Basic display manipulations, surface fitting techniques, and clutter suppression to enhance visual exploitation of 3D imaging ladar data may be utilized.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
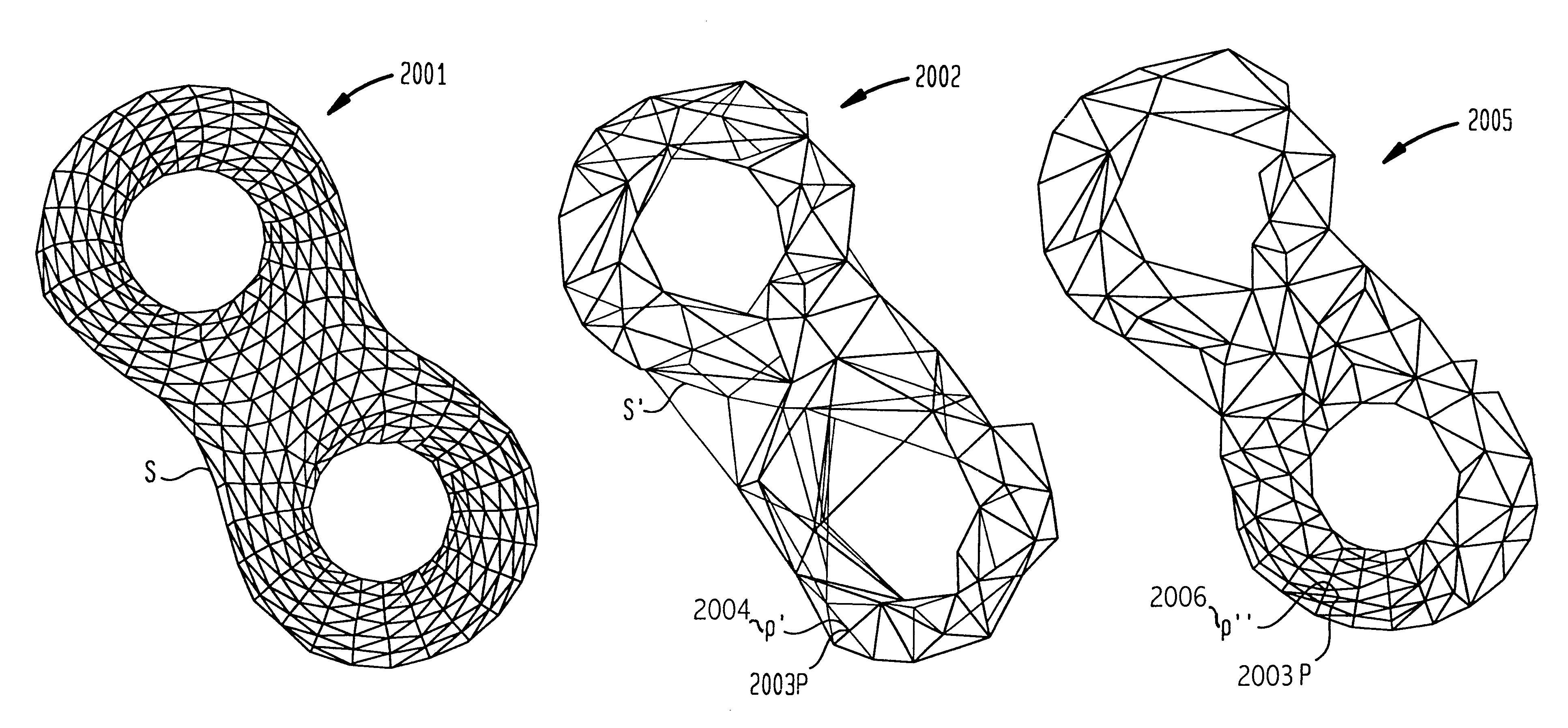
System and method for finding the distance from a moving query point to the closest point on one or more convex or non-convex shapes
The present invention is a computer system and method for determining the closest point on a shape (2 dimensional or 3 dimensional surface) to any general query point. The system has one or more central processing units (CPUs), one or more memories, and one or more geometric model portions stored in one or more of the memories. The geometric model portions have a plurality of line segments (polygons), each of the line segments (polygons) being between a first and a second endpoint (having a polygon boundary). The line segments and end points (polygons and polygon boundaries) are connected to form a shape (in 3 dimensions, a surface) with one or more parameters. Parameters can include geometric position, time, temperature, pressure, flow, color, texture, or any other descriptive value. A multiresolution process that creates one or more models of the shape (surface). The models having a hierarchy of resolutions. Each model has one or more model line segments (model polygons) that approximate one or more of the line segments (polygons). Each model line segment (model polygons) is associated with an error. A distance process, for every model line segment (polygon), determines a distance between a closest point on one or more of the model line segments and a query point. The distance represents one or a combination of two or more of the parameters. The process further determines a confidence level in terms of an upper bound and a lower bound of an envelope enclosing the segment (polygon). The closest point is within the envelope-the upper bound representing an upper limit of the parameter in the envelope determined by an upper error of the respective model containing the model line segment and the lower bound representing a lower limit of the parameter in the envelope determined by a lower error of the respective model. A priority process orders the model line segments (polygons) according to their respective lower bounds and if a maximum error for every one of the model line segments is less than a threshold. The priority process also selects the smallest distance as the minimum distance between the query point and the shape.
Owner:UNILOC 2017 LLC
Reduced-size apparatus for non-intrusively inspecting an object
InactiveUS7027554B2Radiation/particle handlingX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentClosest pointReduced size
Owner:MORPHO DETECTION INC
Method and system for generating detail-in-context lens presentations for elevation data
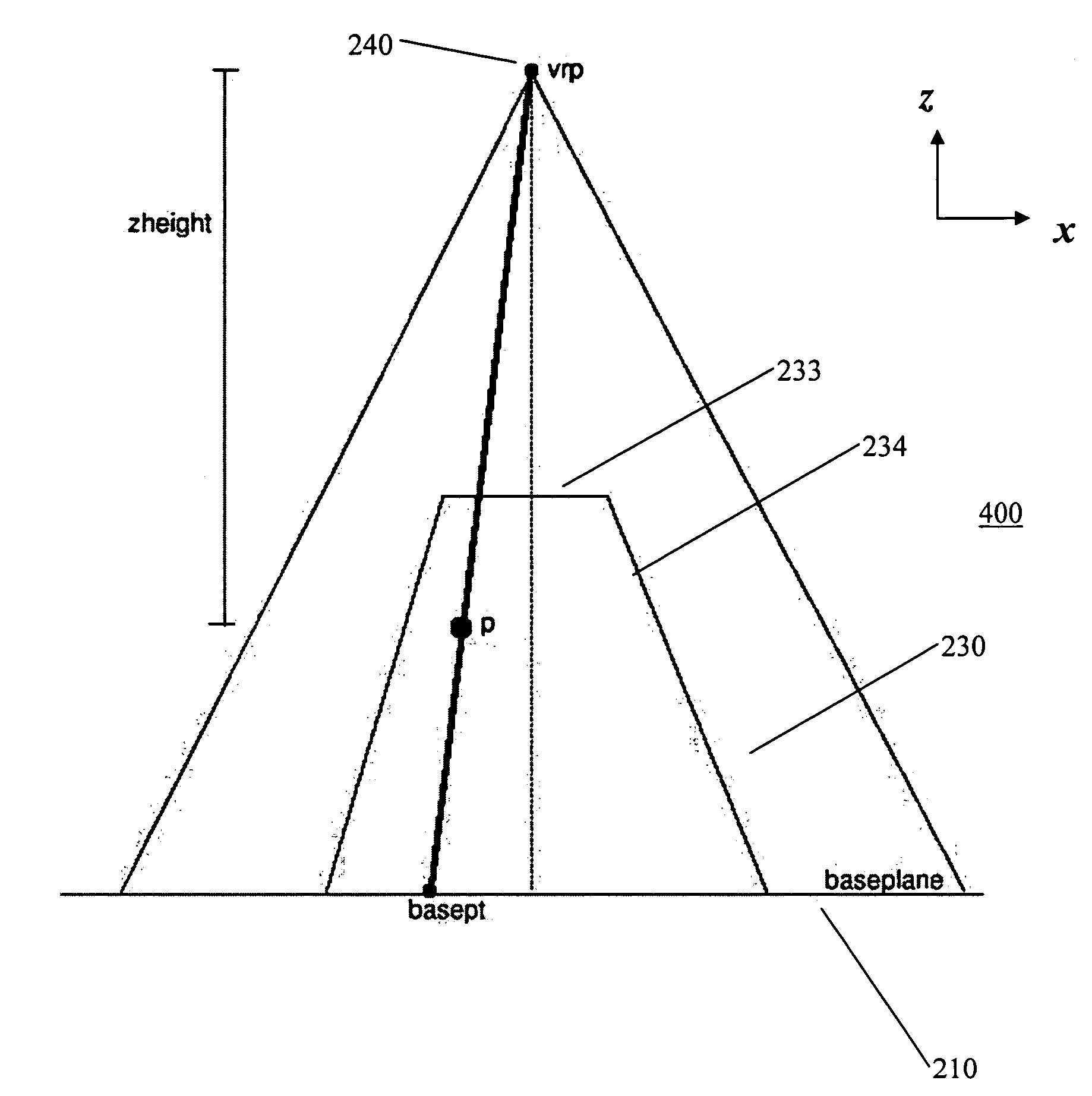
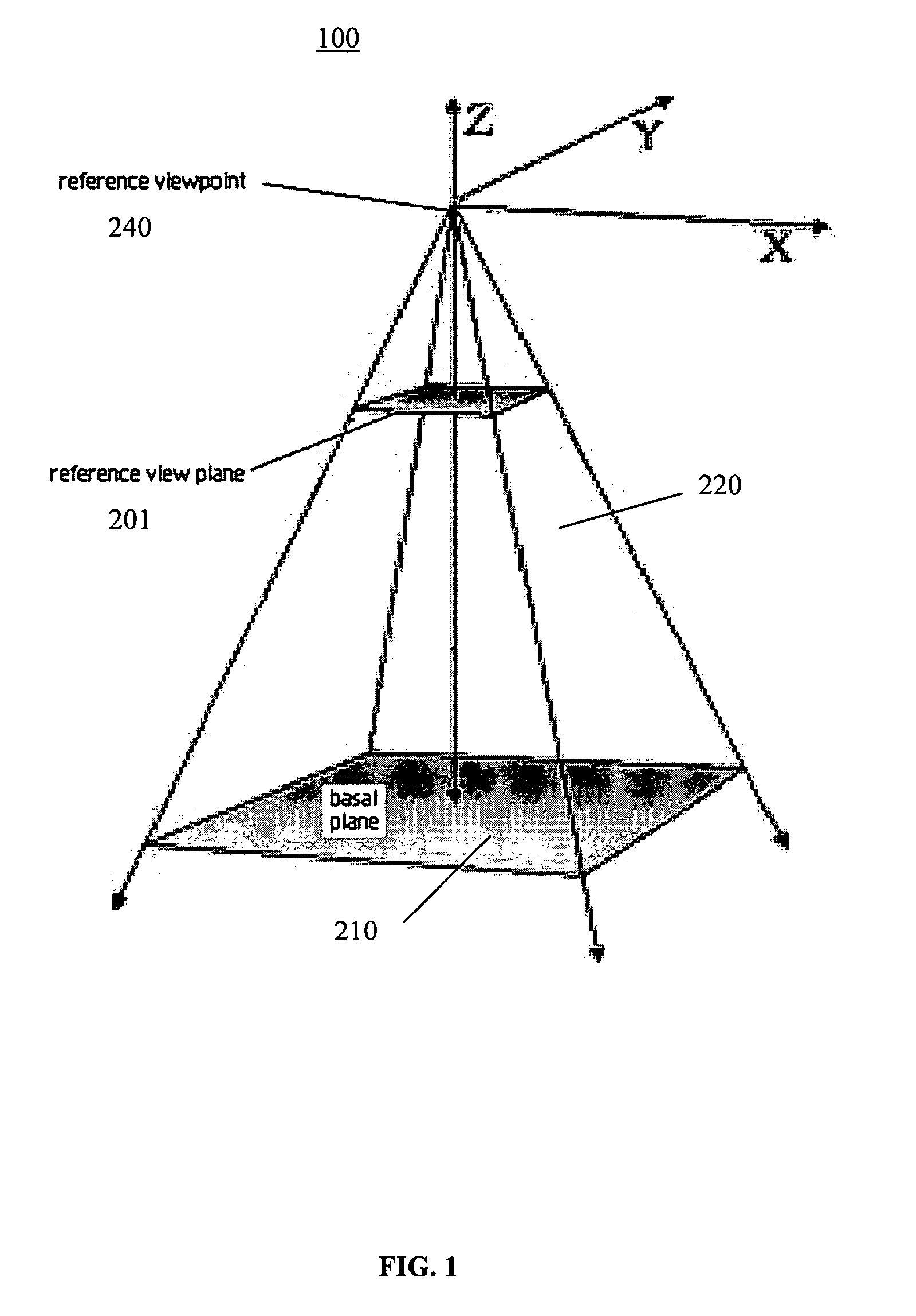
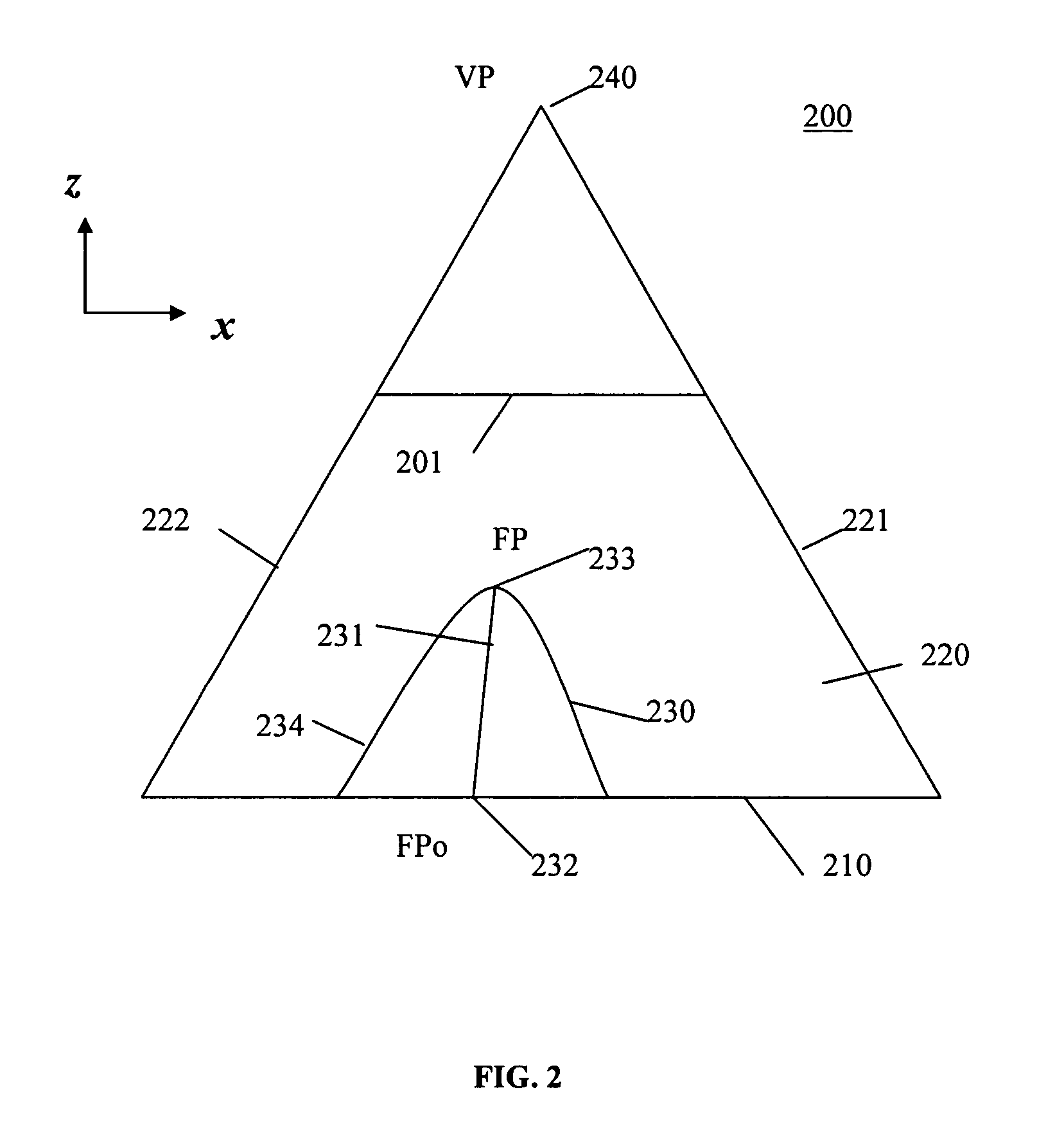
A method for generating a presentation of a region-of-interest in an elevation data representation for display on a display screen, comprising: calculating a displacement height for at least one point in the representation falling within a lens by inversely scaling a vertical height of the point from a viewpoint for the presentation by a magnification for the lens; if the point is within a shoulder region of the lens, scaling the displacement height by a value of the shoulder function evaluated at a value given by a distance between a projection point in the basal plane and a closest point on a perimeter of a focal region as projected onto the basal plane, the distance being scaled by a distance between the closest point and an intersection point on a perimeter of the shoulder region; and, displacing the point by the displacement height to generate the presentation.
Owner:NOREGIN ASSETAB N V L L C
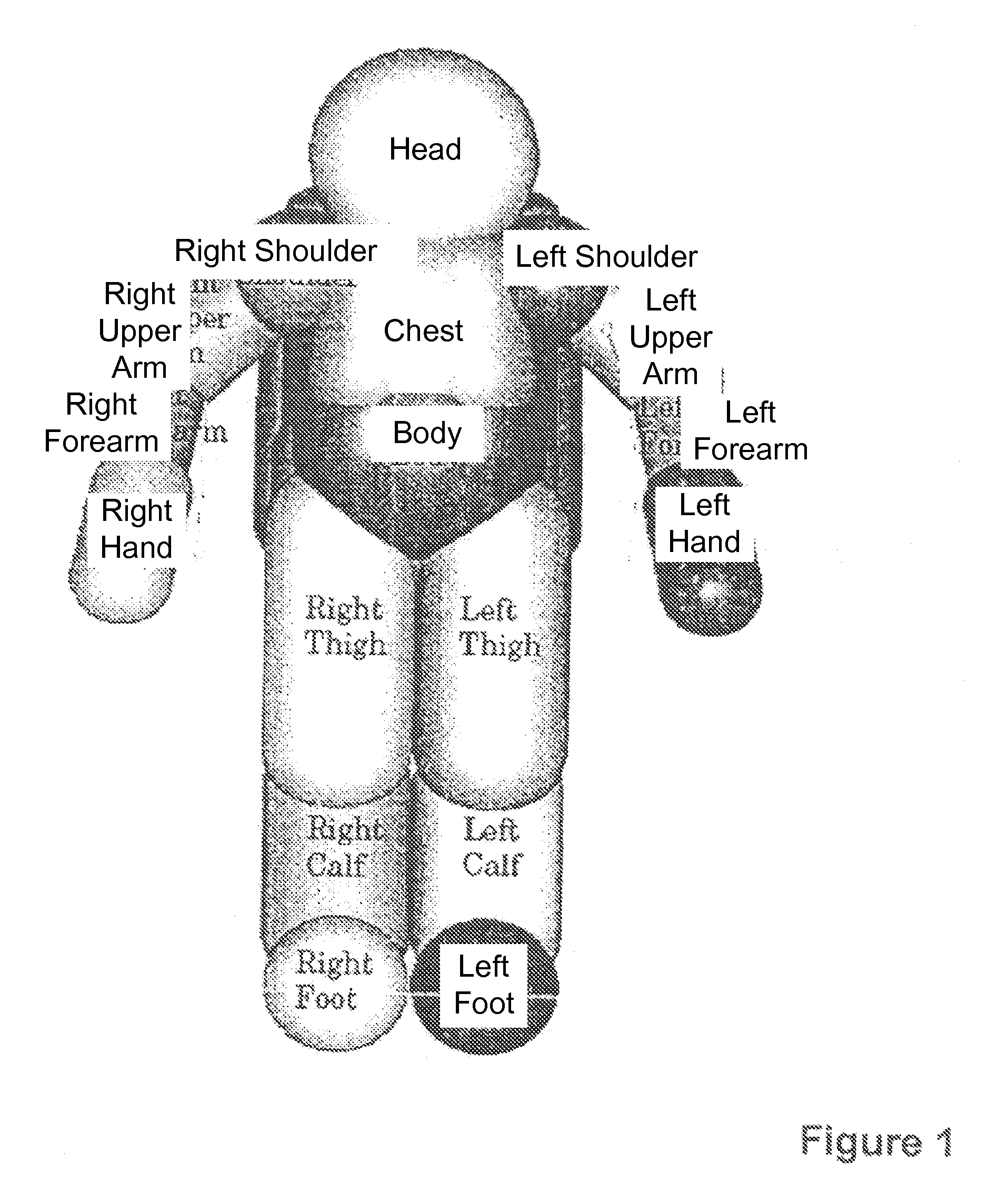
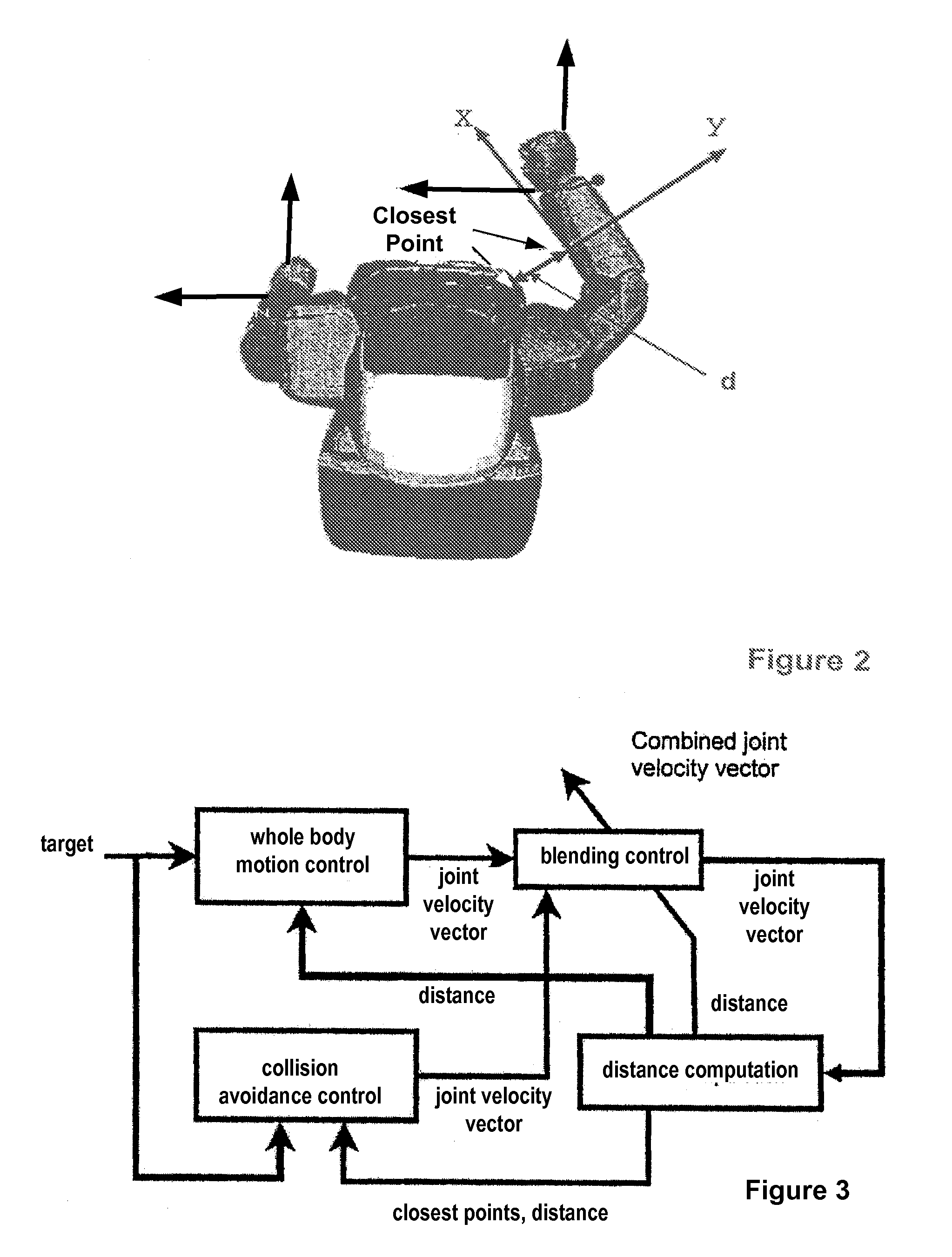
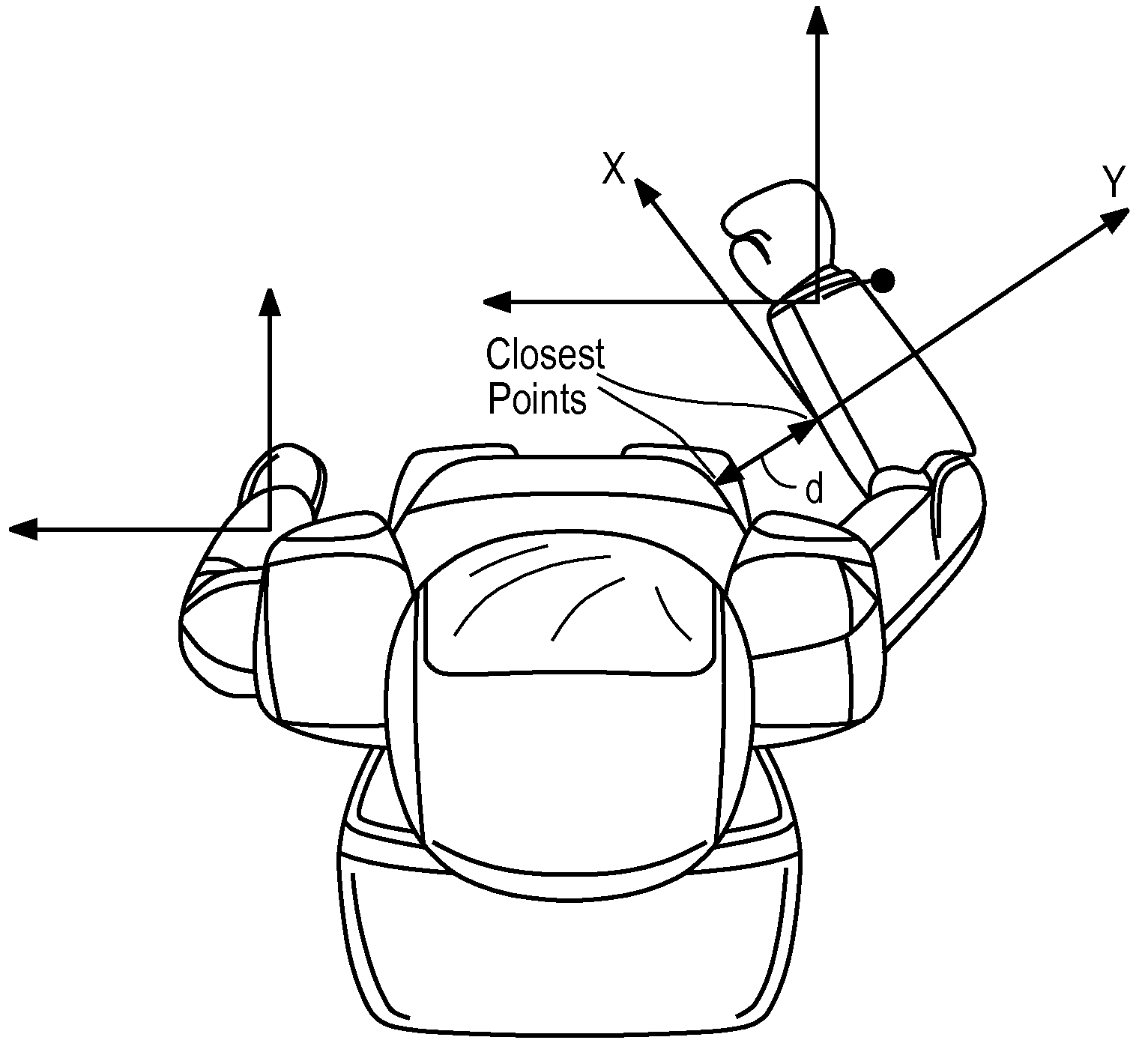
Robots with Occlusion Avoidance Functionality
ActiveUS20080312771A1Avoid occlusionWeight of the motion control output signal is higherProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorClosest pointControl signal
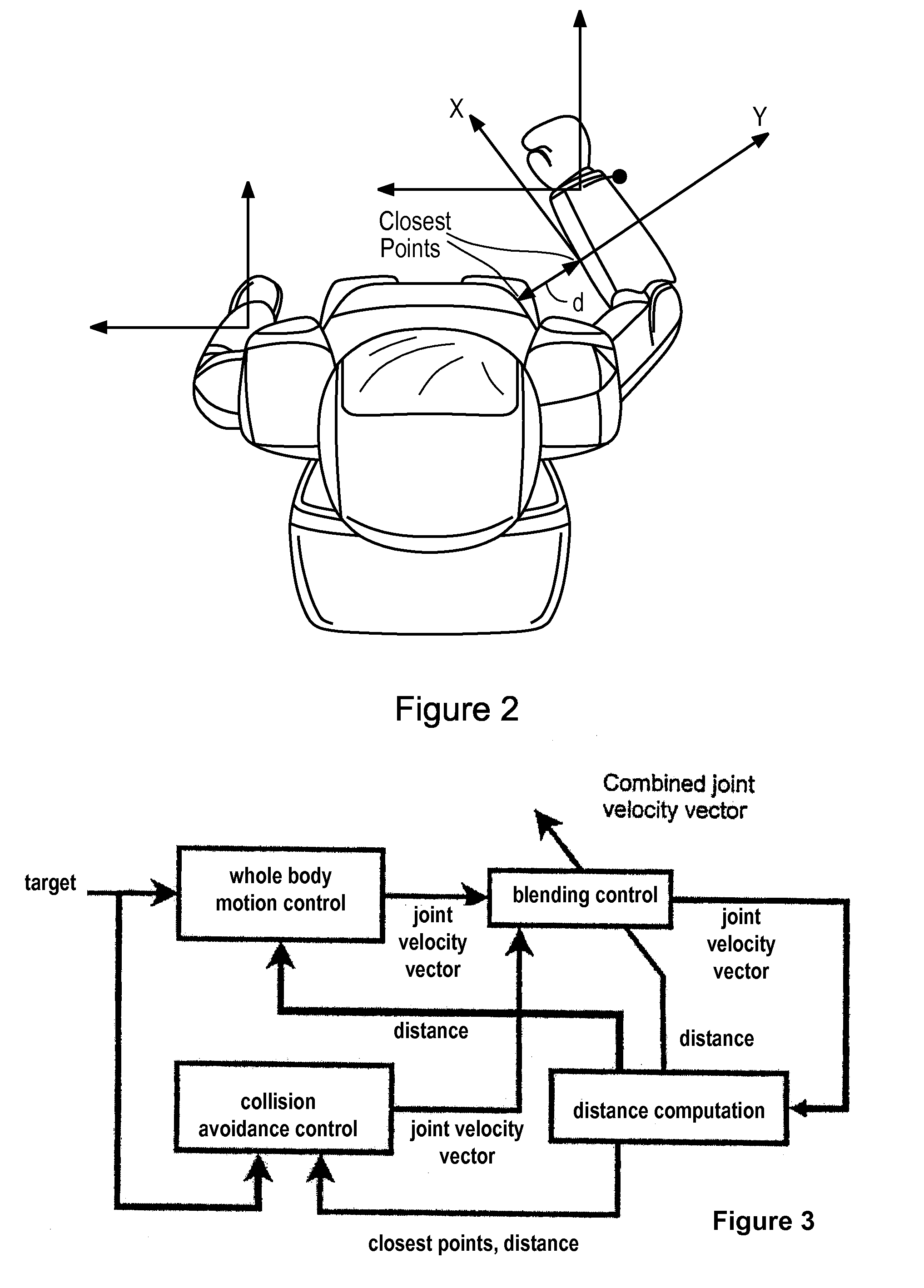
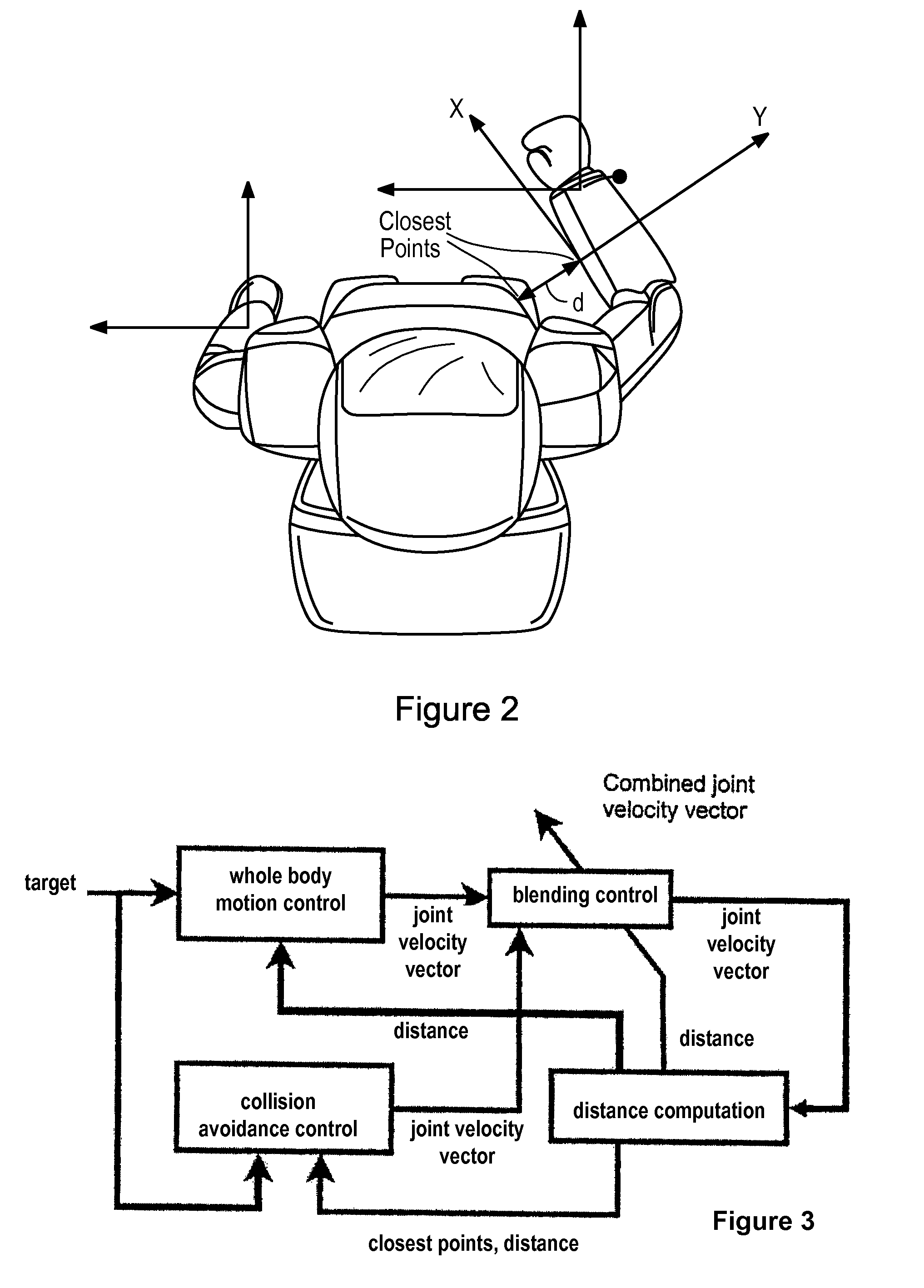
A method for controlling a robot having at least one visual sensor. A target for a motion of the robot is defined. A motion control signal adapted for the robot reaching the target is calculated. A collision avoidance control signal based on the closest points of segments of the robot and a virtual object between the visual sensing means and the target is calculated. The motion control signal and the collision avoidance control signal are weighted and combined. The weight of the motion control signal is higher when a calculated collision risk is lower. The motion of the robot is controlled according to the combined signal so that no segment of the robot enters the space defined by the virtual object.
Owner:HONDA RES INST EUROPE
Method and apparatus for automatic registration and visualization of occluded targets using ladar data
A method and apparatus for high-resolution 3D imaging ladar system which can penetrate foliage and camouflage to sample fragments of concealed surfaces of interest is disclosed. Samples collected while the ladar moves can be integrated into a coherent object shape. In one embodiment, a system and method for automatic data-driven registration of ladar frames, comprises a coarse search stage, a pairwise fine registration stage using an iterated closest points algorithm, and a multi-view registration strategy. After alignment and aggregation, it is often difficult for human observers to find, assess and recognize objects from a point cloud display. Basic display manipulations, surface fitting techniques, and clutter suppression to enhance visual exploitation of 3D imaging ladar data may be utilized.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Target movement situation information data association strategy-based target tracking method
ActiveCN106249232AImplement adaptive switchingSmall amount of calculationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionClosest pointAlgorithm
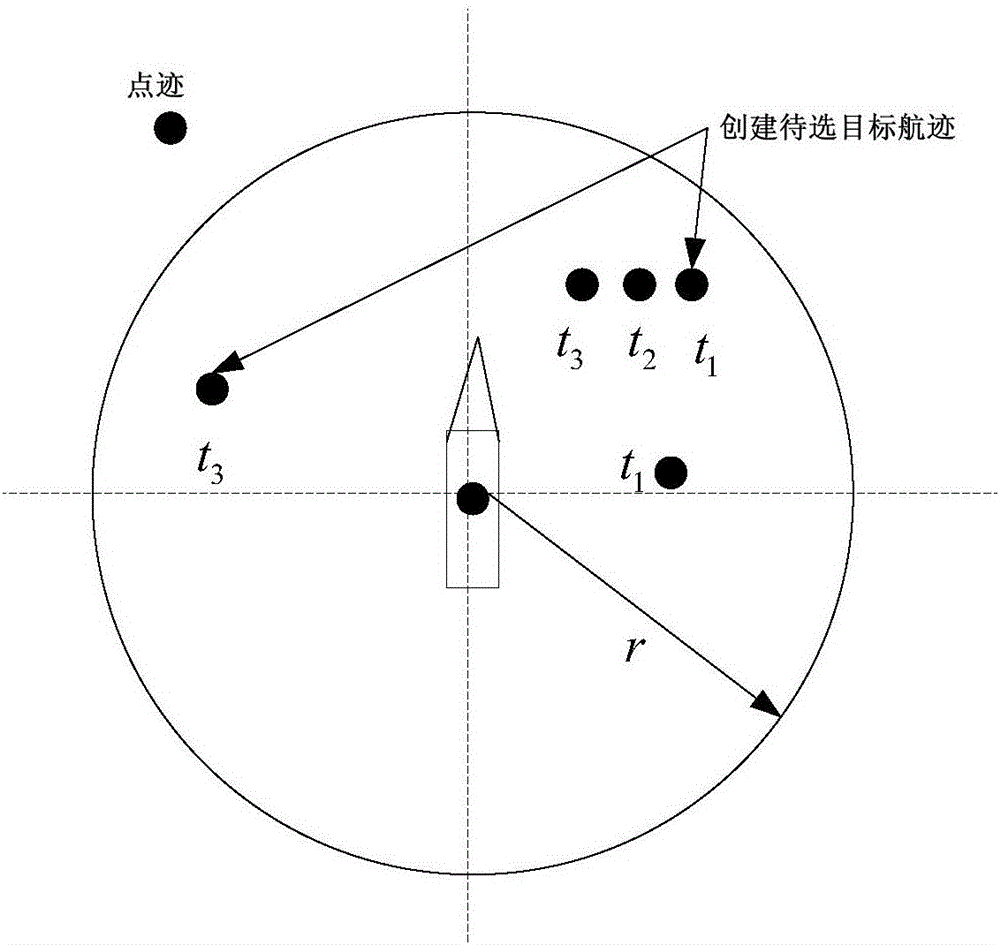
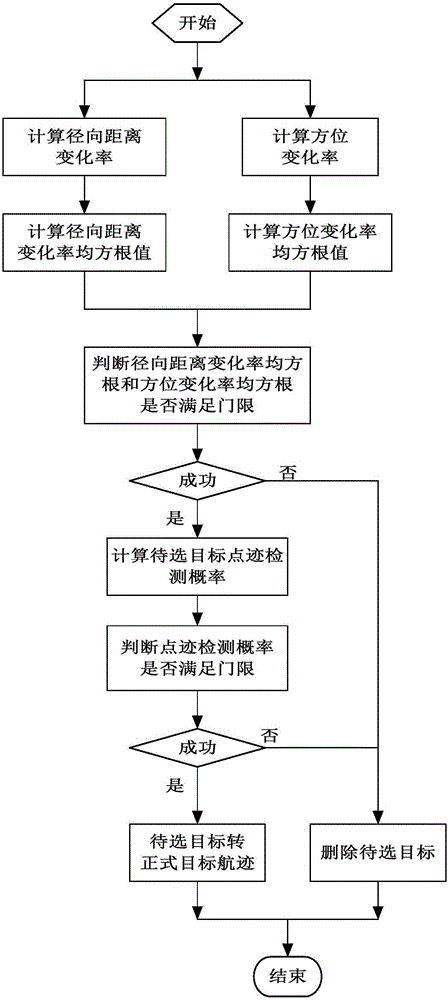
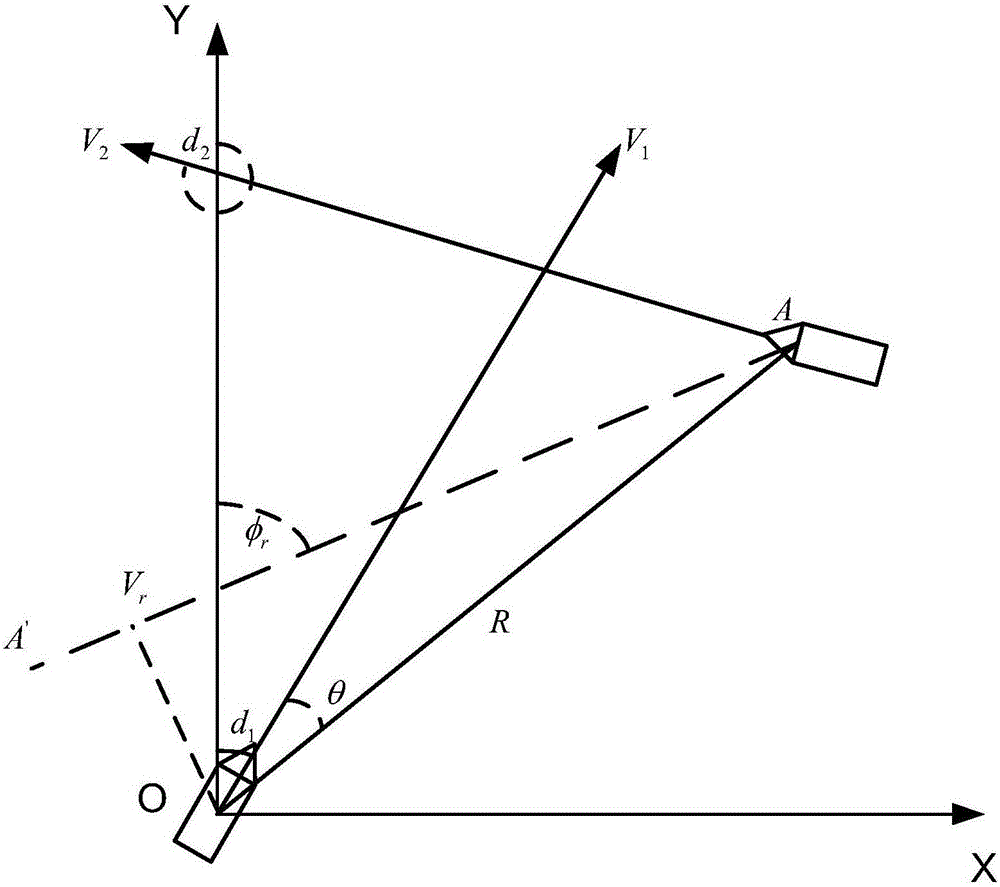
The invention discloses a target movement situation information data association strategy-based target tracking method. The method includes the following steps that: step 1, the track of a target to be selected is created; step 2, tracking processing is carried out on the track of the target to be selected, a reasonable track of a formal target is established according to a target starting condition; and step 3, a Kalman filtering model is used to carry out filtering estimation processing on the tracks of a tracked target and the formal target, so that a track state estimation value can be obtained, the time to closest point of approach (TCPA) of the tracked target and the formal target is calculated according to a ship collision avoidance radar measurement model and a TCPA value is compared with a target separation time threshold, a target approach time threshold and a target overlap time threshold, so that the movement state information of the targets can be obtained; and step 4, and the association strategy and associated algorithm of the trace points and tracks of the tracked target are determined according to the movement state information of the targets, and the association relation of the tracked target and the trace points can be obtained.
Owner:THE 28TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP
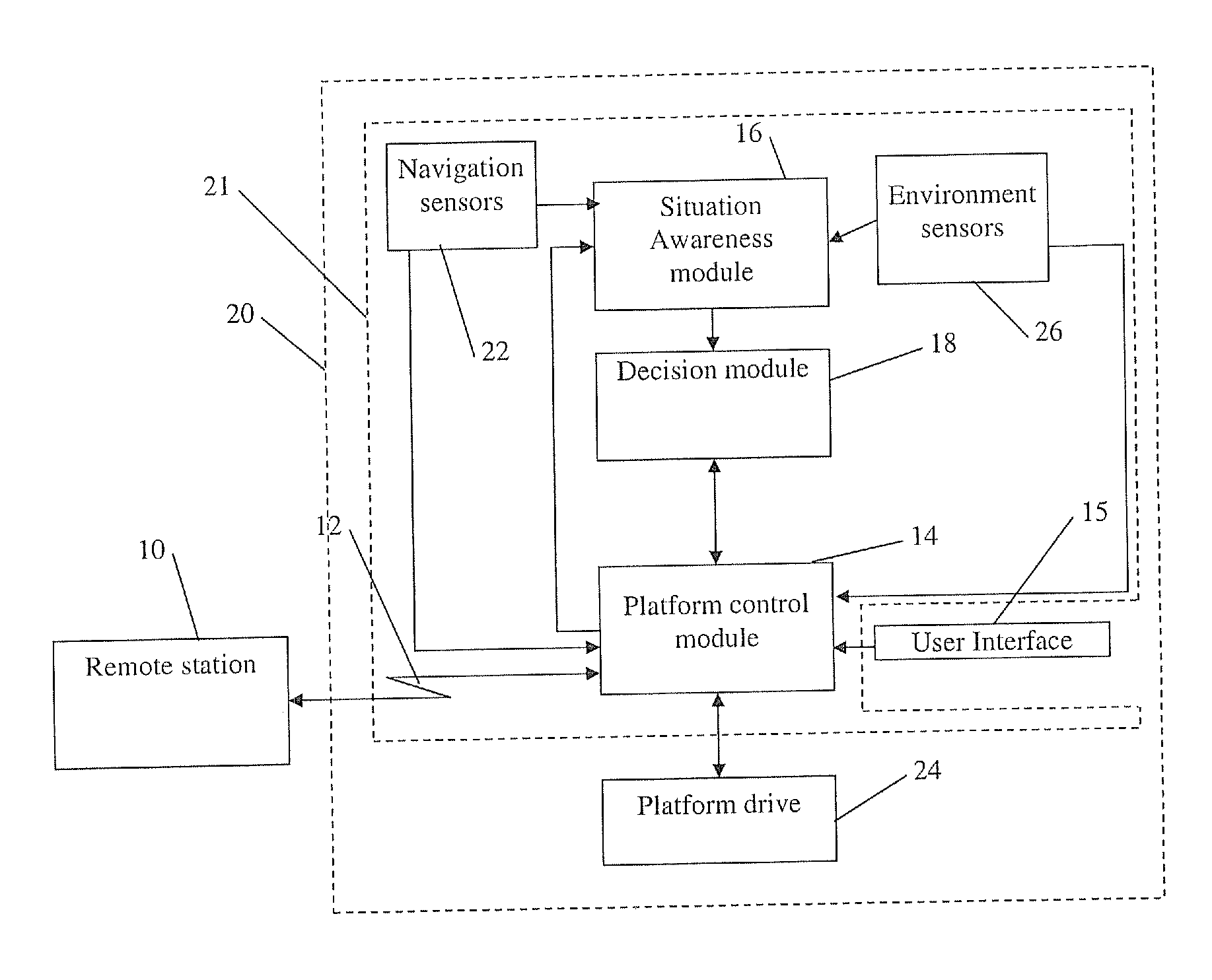
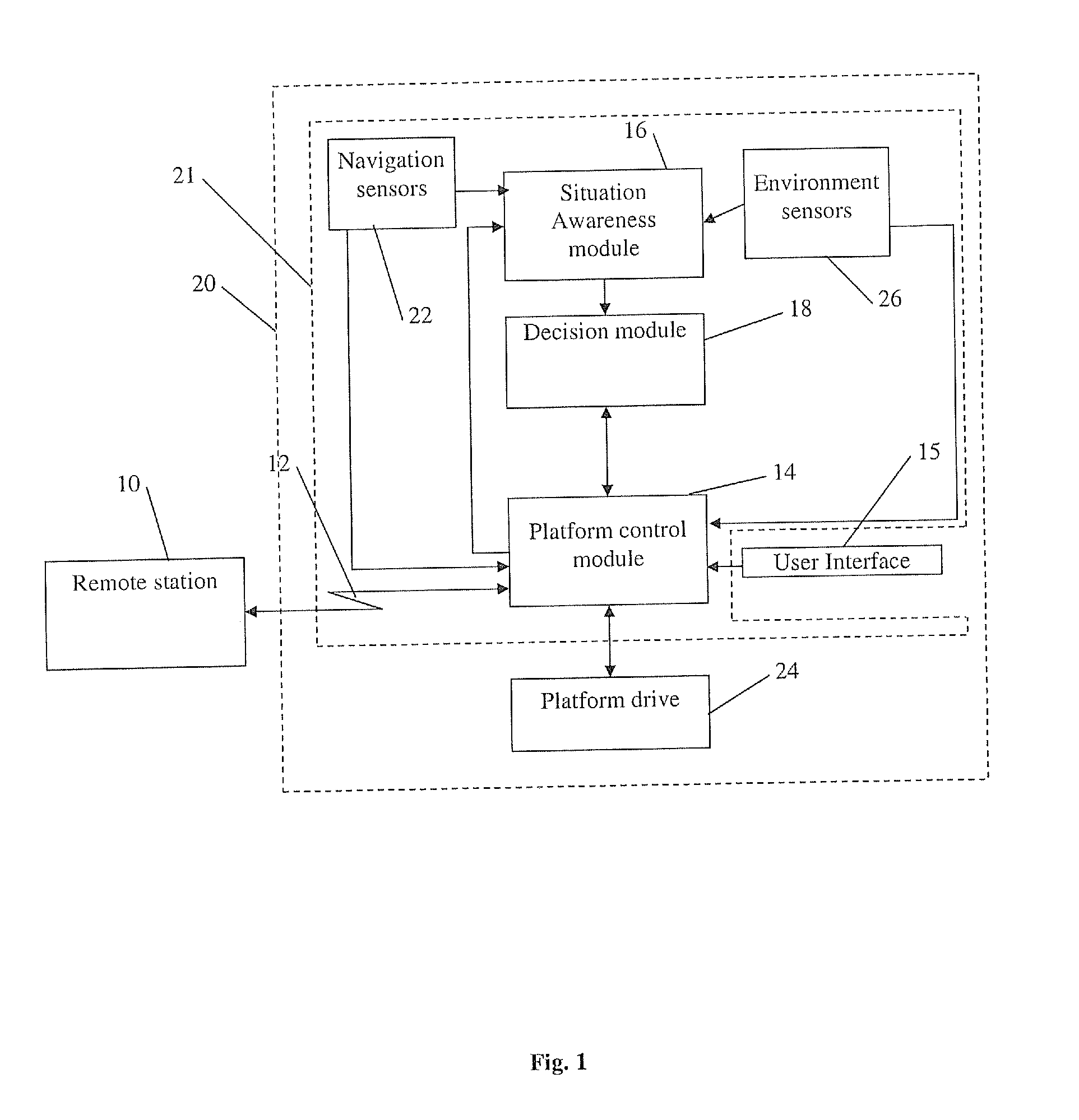
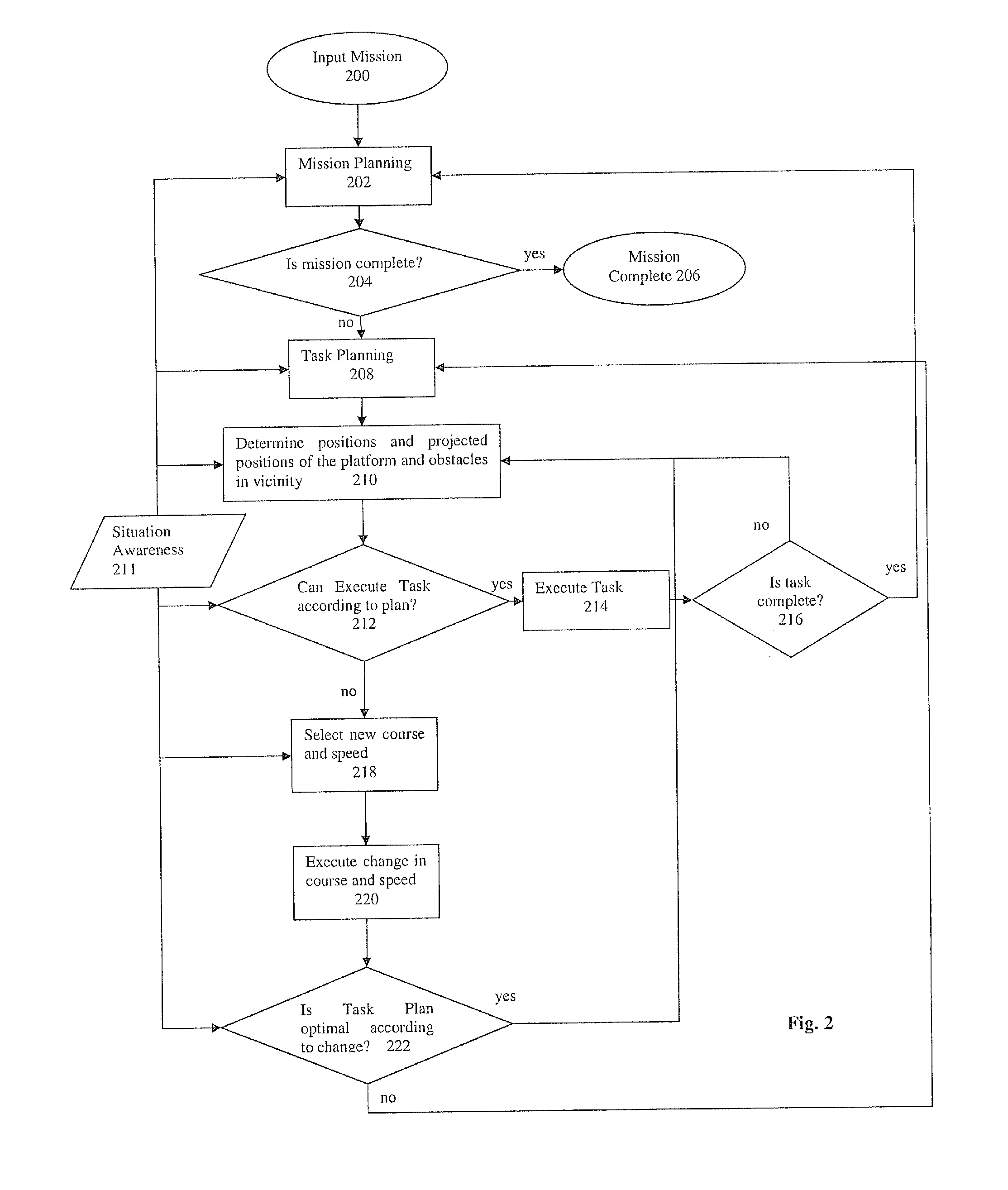
Autonomous navigation system and method for a maneuverable platform
ActiveUS20140195095A1Avoid collisionLarge speed changePosition/course control in two dimensionsDistance measurementAutonomous Navigation SystemClosest point
Owner:ELBIT SYST LTD
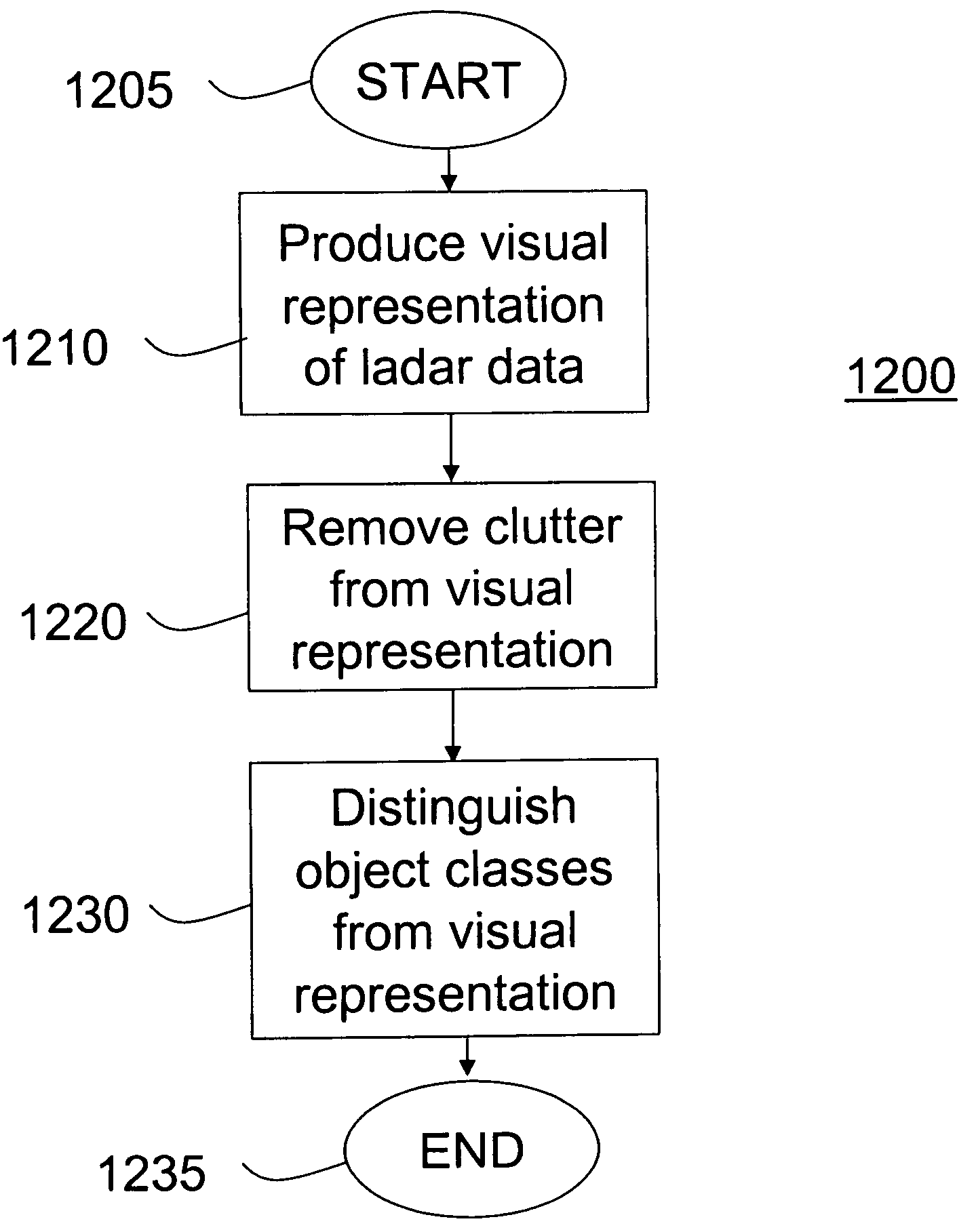
Robots with Collision Avoidance Functionality
InactiveUS20080234864A1Interference minimizationMinimize interferenceProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlClosest pointControl signal
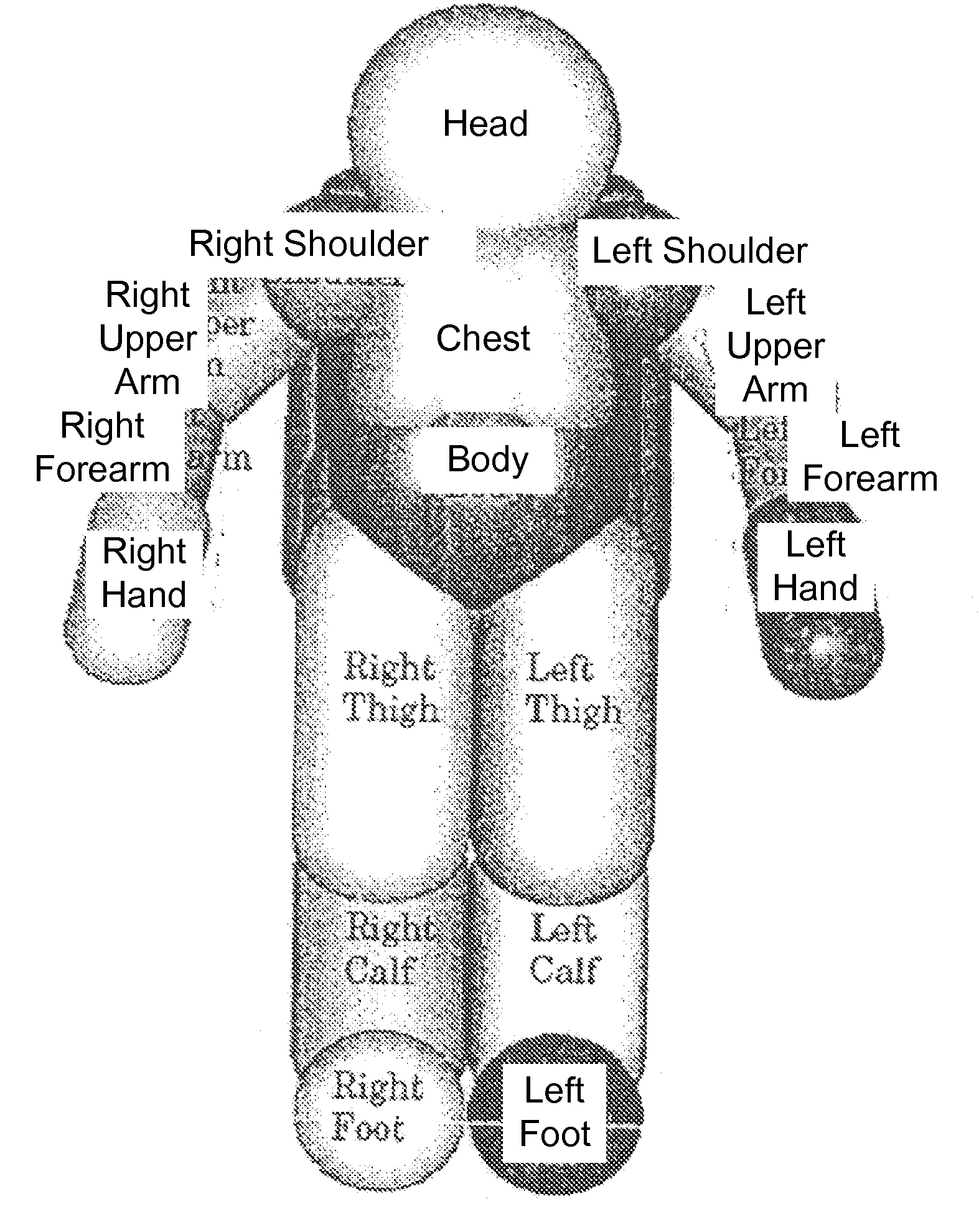
A robot is provided with a motion control unit that avoids collision between segments of the robot or between segments of the robot and other objects. The motion control unit of the robot comprises a distance computing module, a whole body control module, a collision avoidance module, and a blending control unit. The distance computing module calculates two closest points of different segments of the robot connected to each other via at least one joint or a segment of the robot and another object. The collision avoidance module is provided with the information about the two closest points. The blending control unit combines the weighted output control signals of the whole body control module and the collision avoidance control module. The weight of the whole body control output signal is higher when the risk of collision is lower. The weight of the collision avoidance control output signal is higher when the risk of collision is higher. The collision avoidance module is designed to control a collision avoidance action only in the direction parallel to a line connecting between the two closest points.
Owner:HONDA RES INST EUROPE +1
Rescue robot three-dimensional environment map real-time construction method
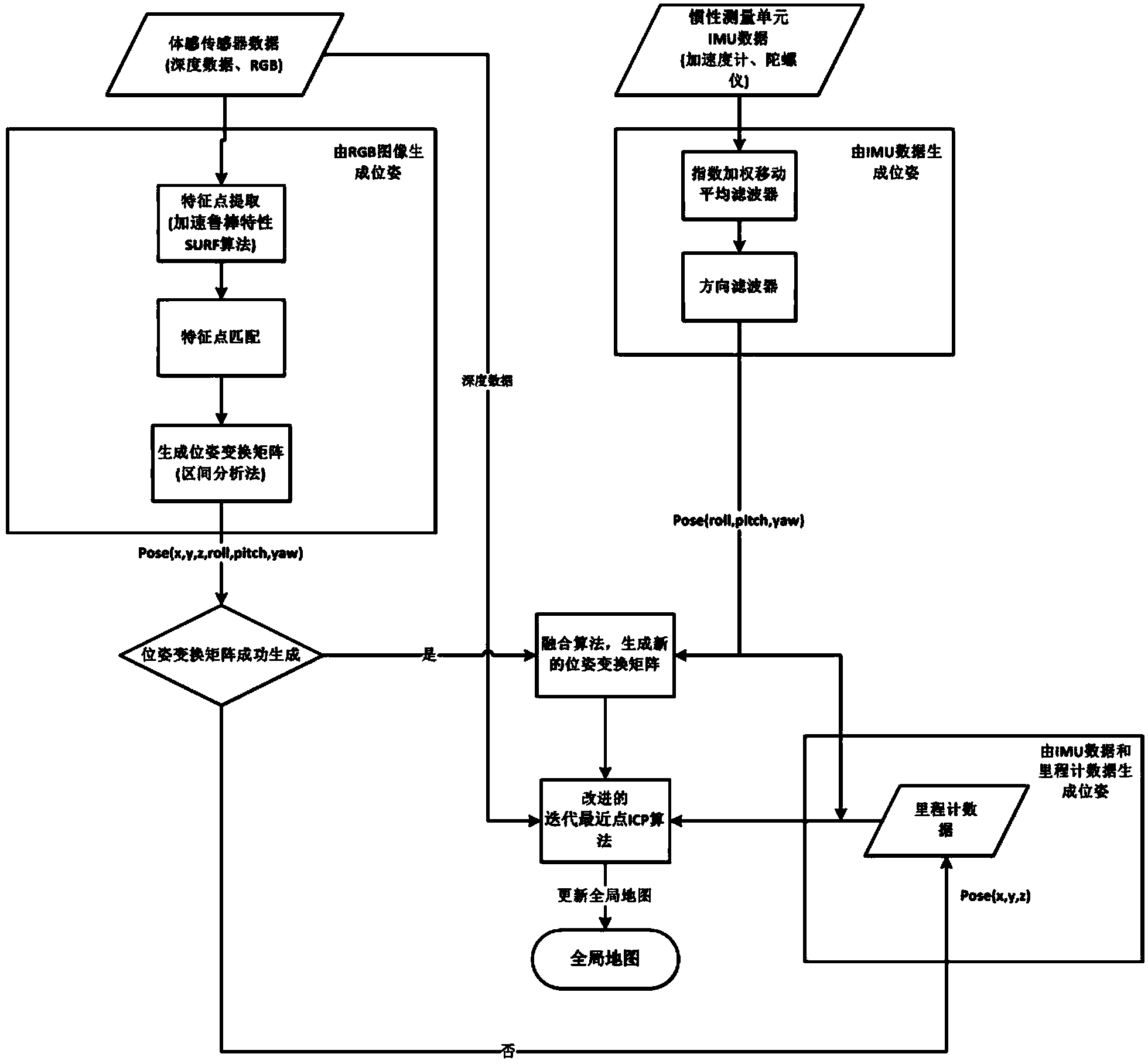
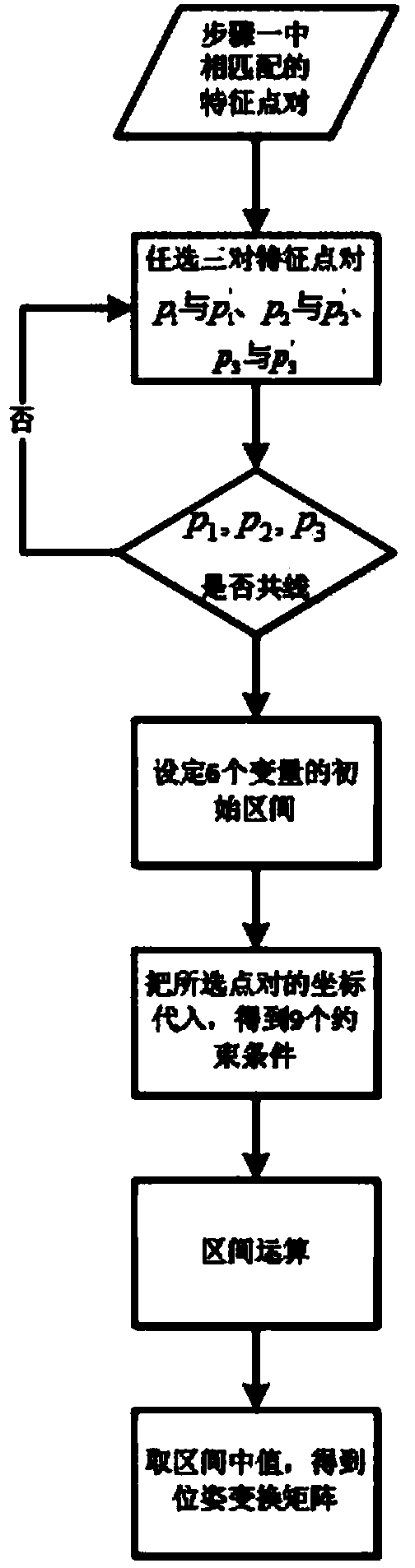
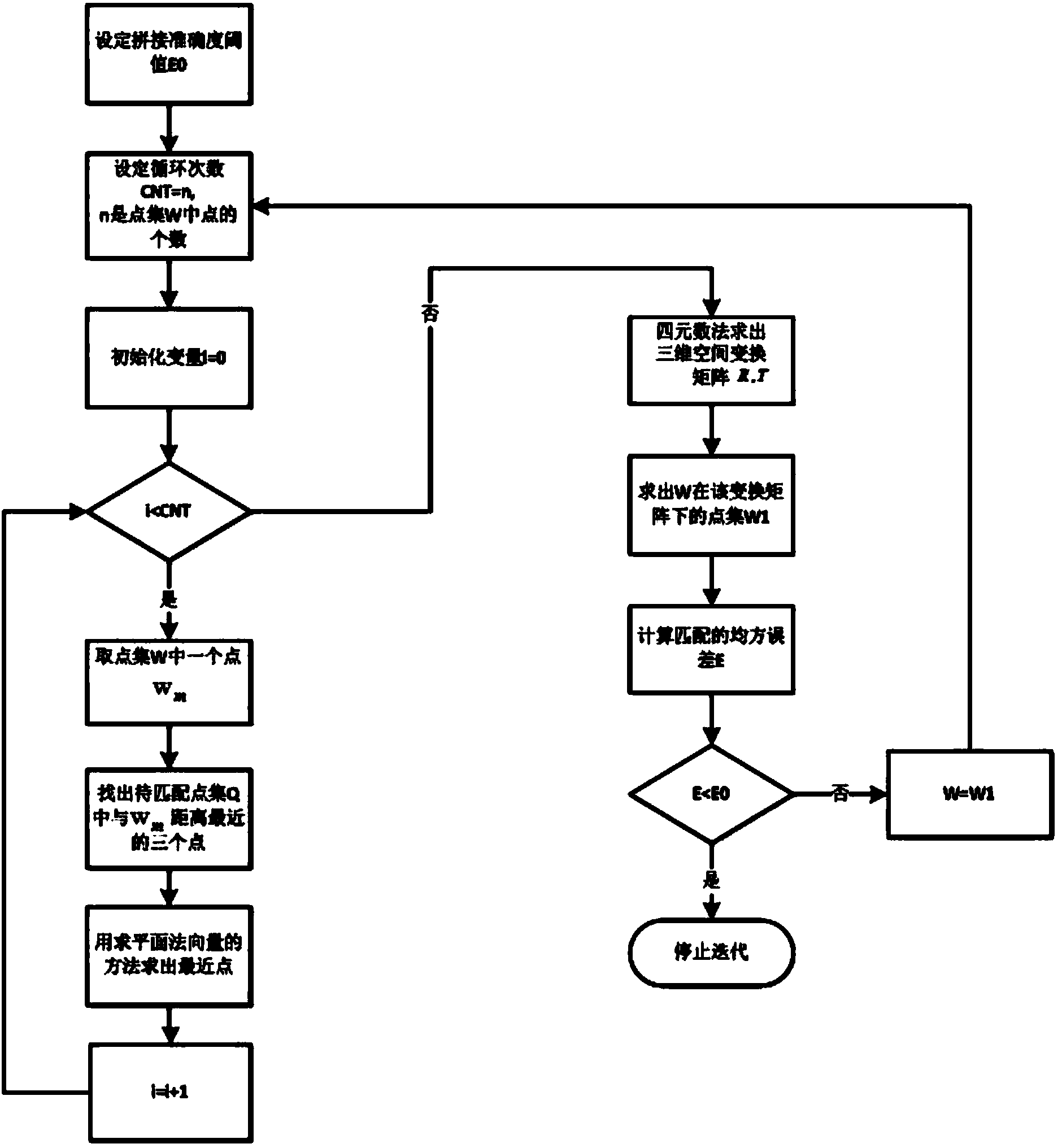
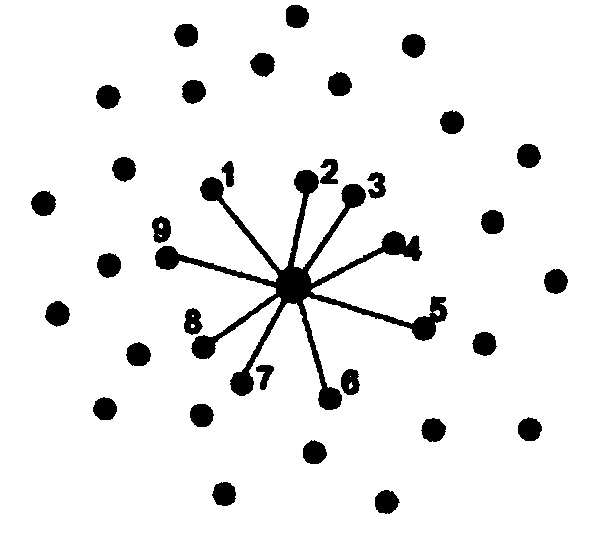
The invention discloses a rescue robot three-dimensional environment map real-time construction method. According to the method, an efficient speeded up robust feature (SURF) algorithm is adopted to carry out recognition and matching of feature points; next, an interval analysis method is proposed, roughly matched pose transformation matrixes are generated. The method has good robustness and can contain all possible values under the situation that one set of constraint conditions are given. In order to overcome the defect that the iterative process probably can not converge the globally optimal solution through an ICP algorithm, an improved closest point select method is proposed: for a measure point in a point cloud A, three points, closest to the measure point, in a point cloud B are solved to form a plane, an intersection of normal vector passing the measurement point in the plane and the plane is regarded as the closest point, and consequently the accuracy of the algorithm is well improved. In addition, the approach combining an inertial management unit (IMU), odometer data and the pose transformation matrixes is adopted, so that the algorithm has better robustness, and accurate location can be achieved under the condition that feature point matching is unsuccessful or the environment dynamically changes.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Robots with collision avoidance functionality
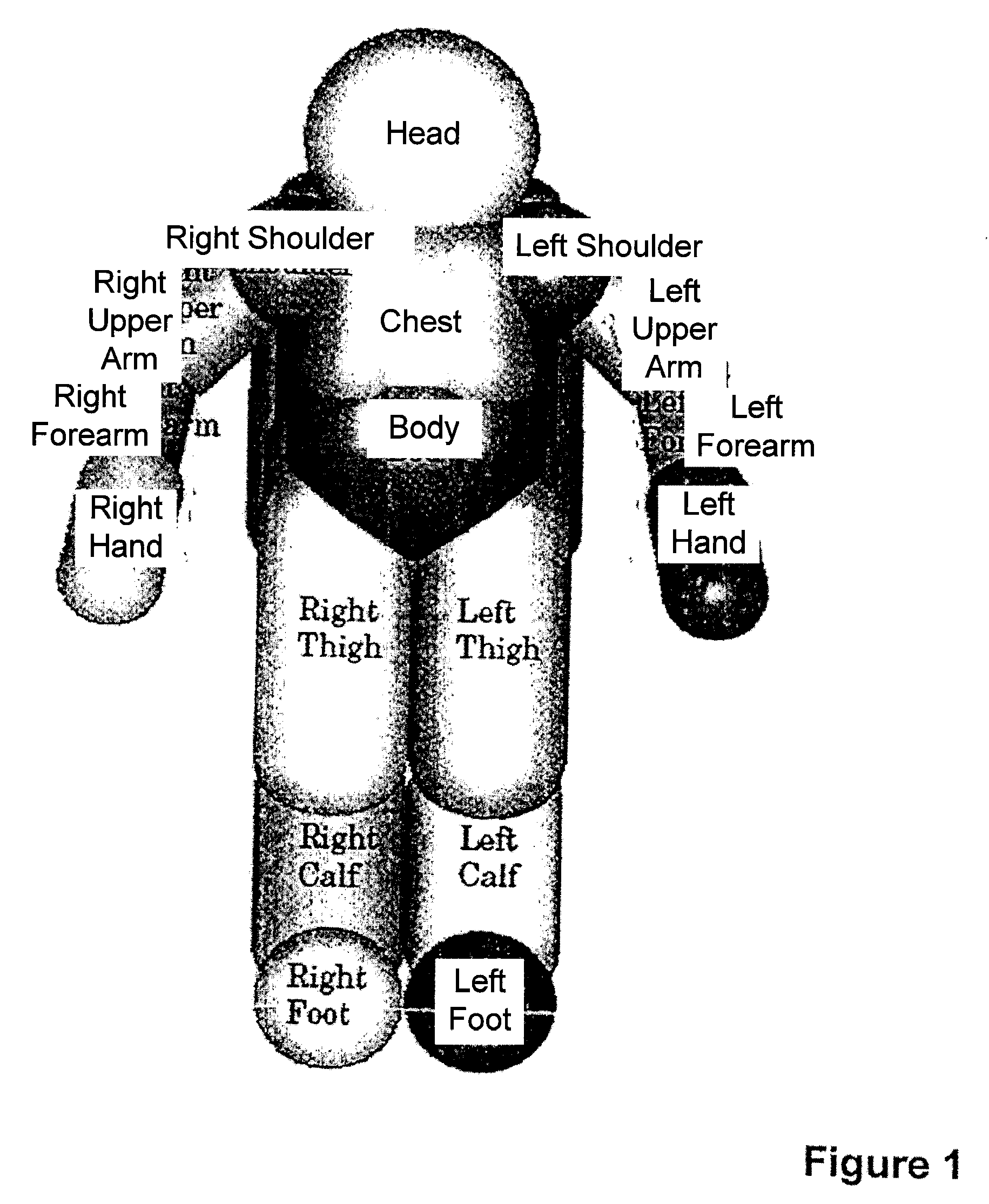
InactiveUS8311731B2Minimize interferenceTechnique have been hamperedProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlClosest pointWhole body
Owner:HONDA RES INST EUROPE +1
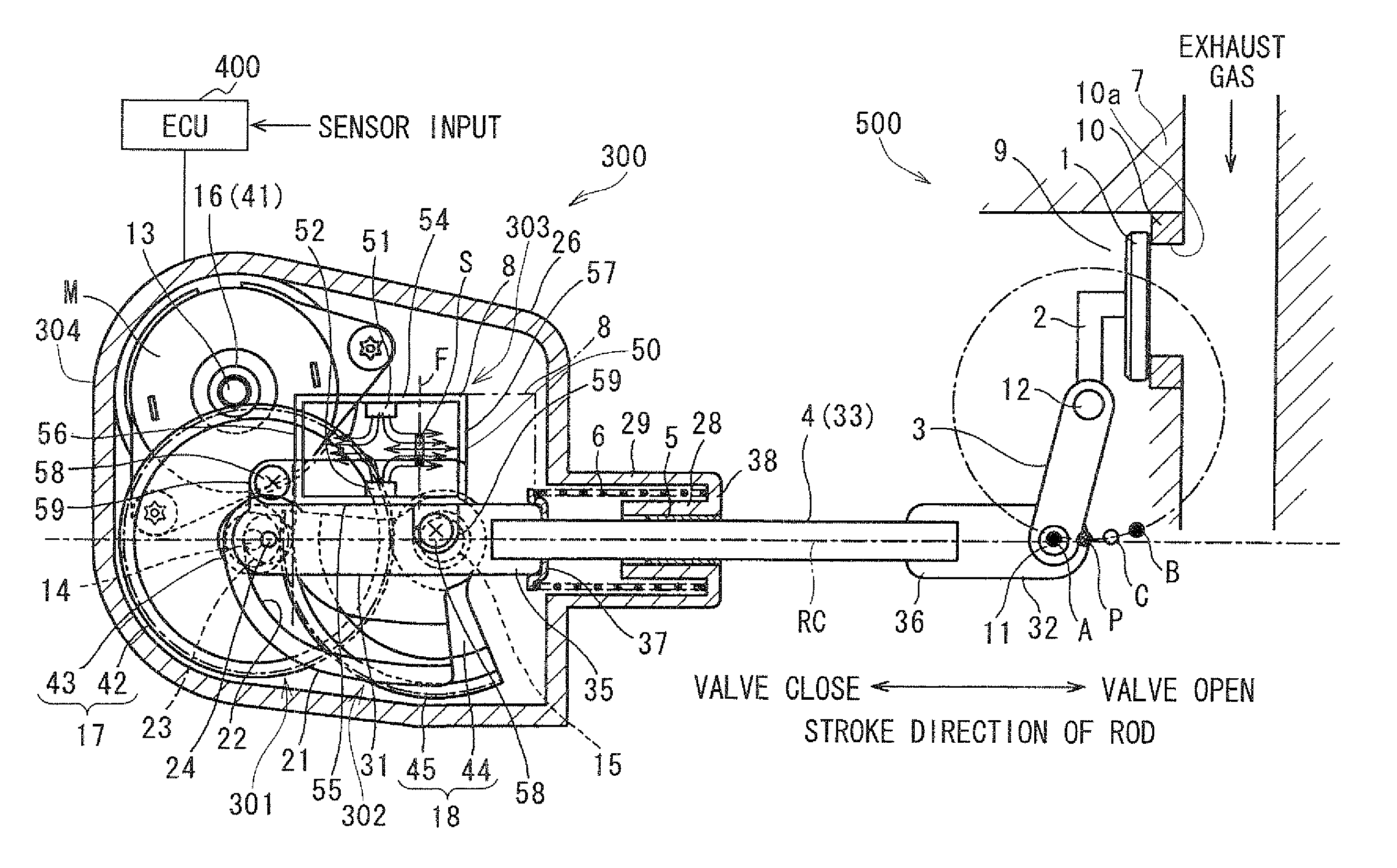
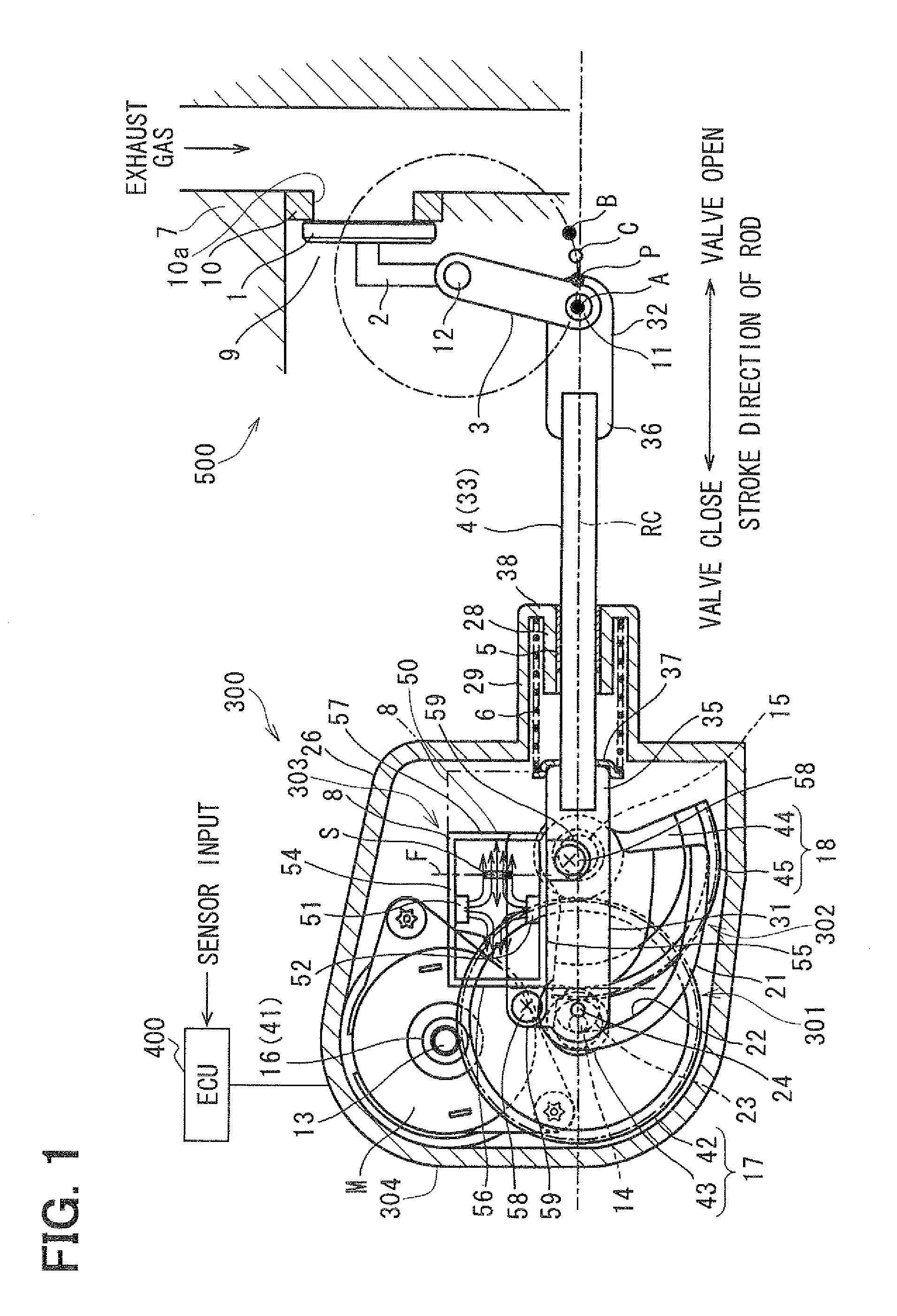
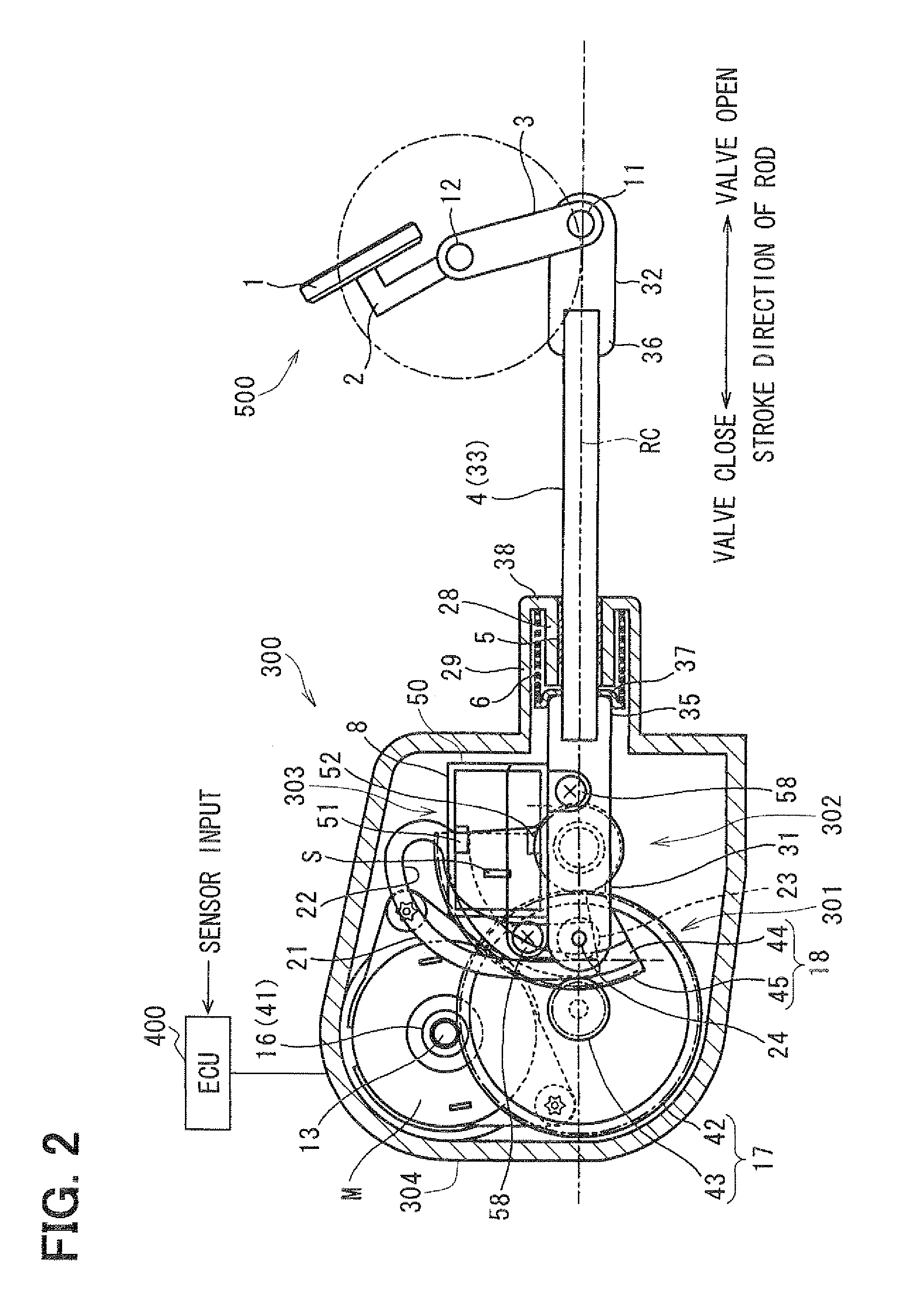
Valve control apparatus
InactiveUS20120001111A1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesInternal combustion piston enginesClosest pointEngineering
Owner:DENSO CORP
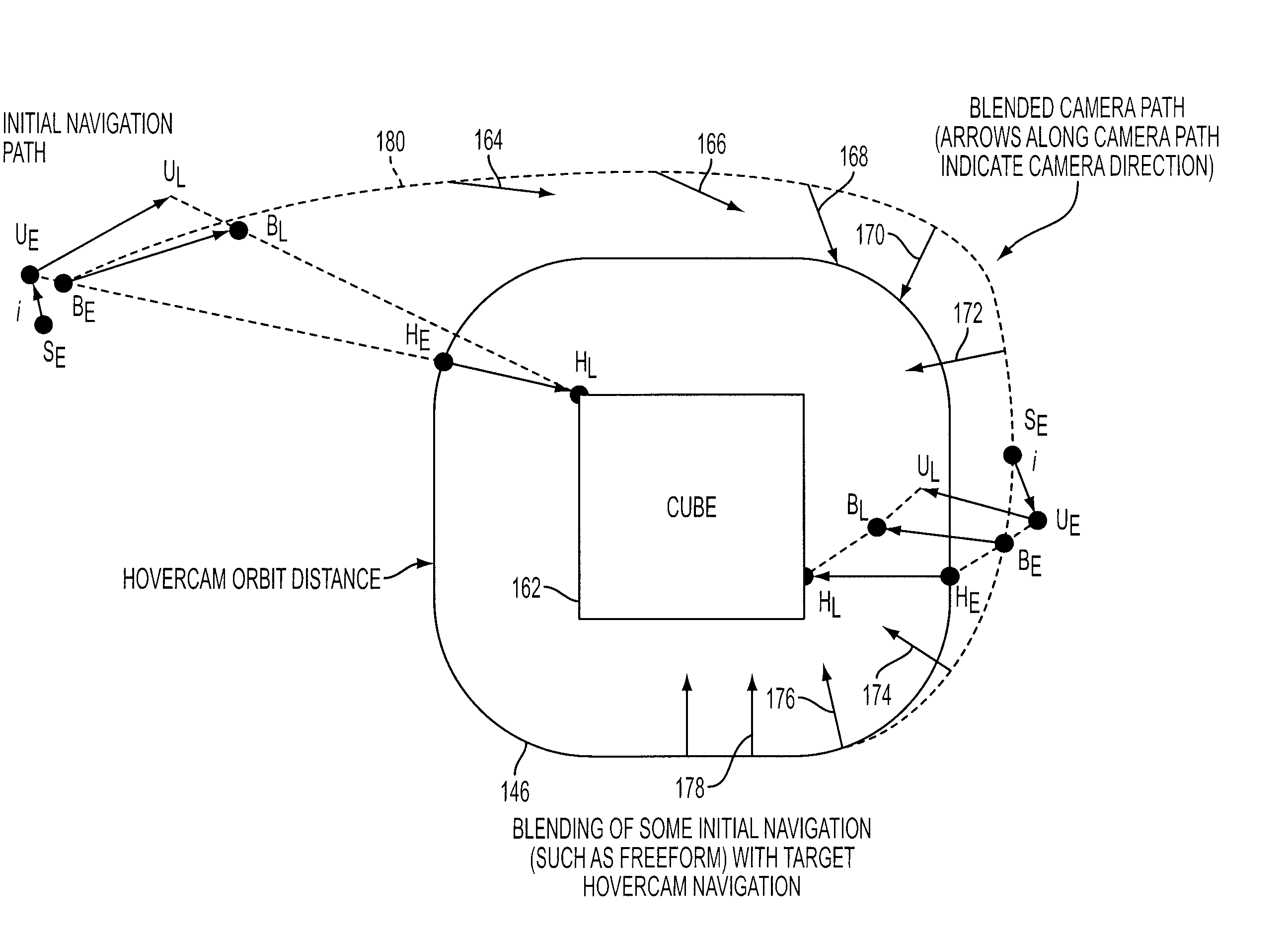
System for interactive 3D navigation for proximal object inspection
ActiveUS20060227134A1Reduce processing timeGeometric image transformationCathode-ray tube indicatorsClosest pointProximal point
A system that transitions from freeform camera motion to surface following motion as a surface of an object is approached by clipping the vectors for closest point and look-at point. When the surface is reached and while following the surface the user can designate an up model that sets an up vector to conform the view to a users expectations while the system operates using a local up vector for computations. A restricted surface field of view along with an obstacle field of view can be used by the system to allow the view to traverse cavities and maintain a specified surface following distance from an obstacle, from a wall and from a floor.
Owner:AUTODESK INC
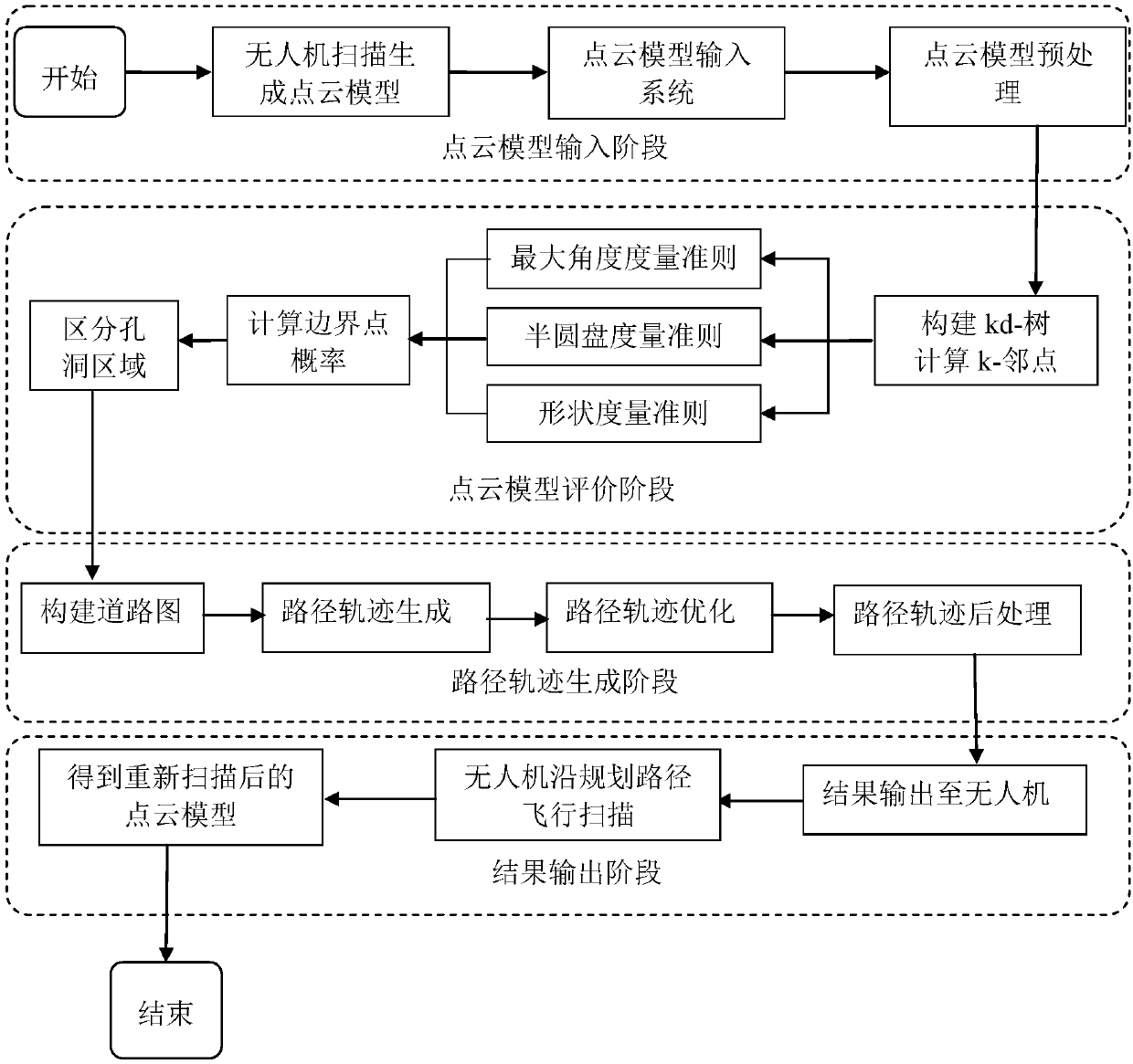
Point cloud quality evaluating and unmanned aerial vehicle track planning method for unmanned aerial vehicle scanning reconstruction
ActiveCN107749079AReduce blind spotsThe final data is accurateNavigational calculation instruments3D modellingVisibilityClosest point
The invention discloses a point cloud quality evaluating and unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) track planning method for UAV scanning reconstruction, which includes the following steps: the original pointcloud model of a scene is acquired and reconstructed through scanning by a UAV; the points of the point cloud model are classified by using a kd tree; for each point in the point cloud model, the probability that the point is a hole boundary point is estimated based on three criteria respectively, and weighted averaging is carried out on the three probabilities to comprehensively judge whether the point is a hole boundary point; a hole boundary line is generated by searching for closest points, in order to distinguish between different holes; a road map with visibility information is constructed in a point cloud model scene through a ball filling method; an optimal rescanning track of the UAV is generated; and finally, a result is output, a generated path is fed back to the UAV, the UAV flies along the planned path, and the hole area of the point cloud model is repaired. The method can assist an UAV in quickly and automatically rescanning a scene to be reconstructed and generating a more accurate building model, so as to reduce the hole area with texture missing in a building point cloud model.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for automatically partitioning tree point cloud data
InactiveCN101839701AThe segmentation result is accurateAccurate segmentationUsing optical meansClosest pointPoint cloud
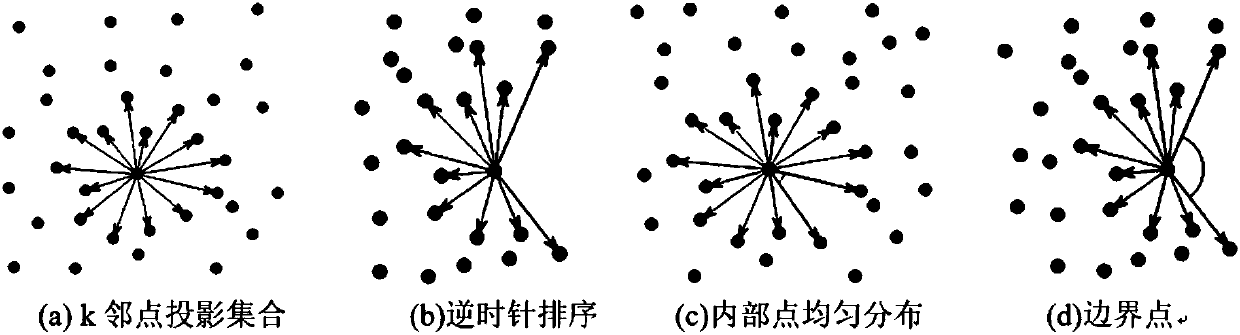
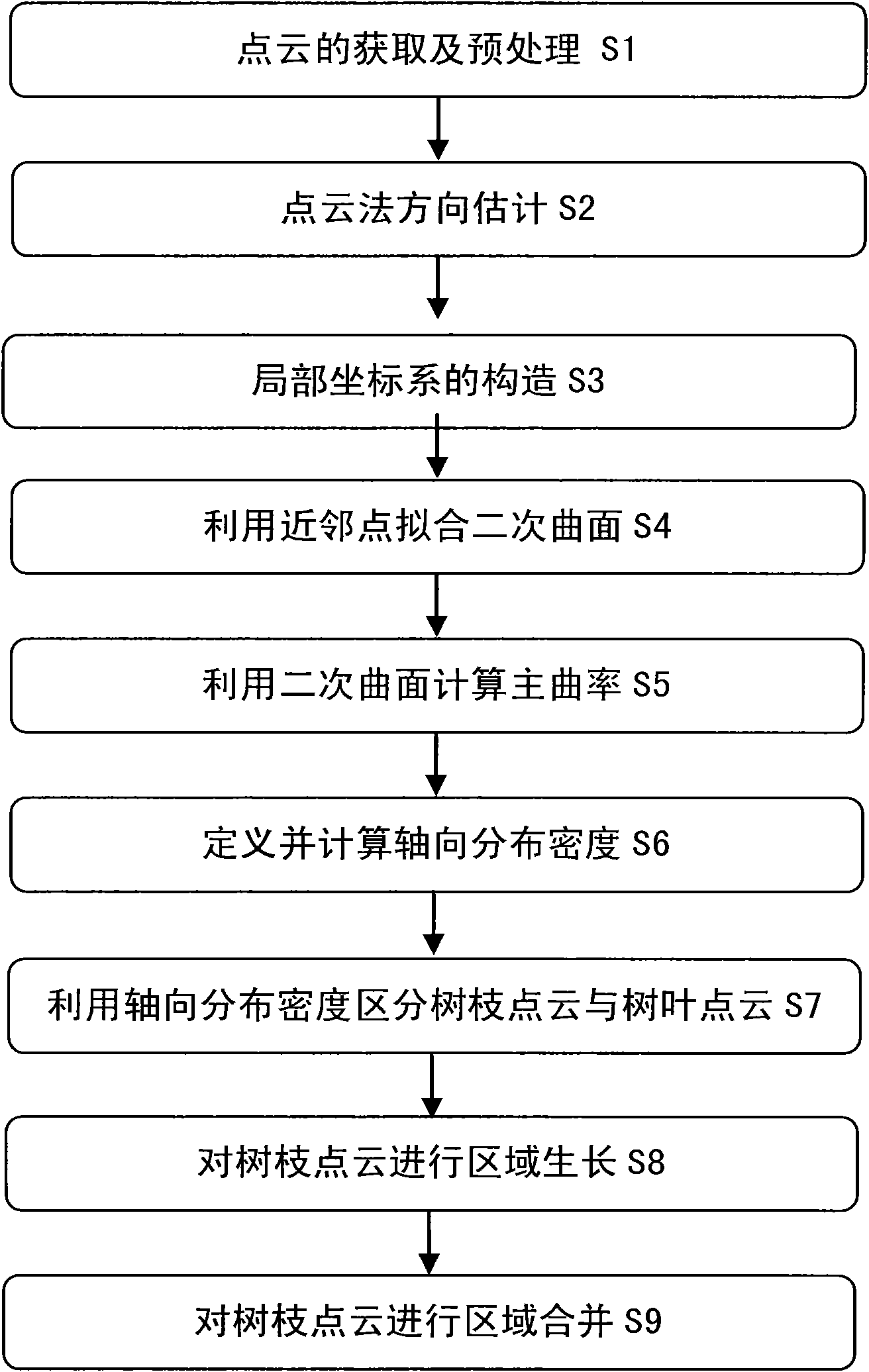
The invention relates to a method for automatically partitioning tree point cloud data. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring and preprocessing point cloud, estimating the direction by a point cloud process, constructing a local coordinate system, fitting a conicoid by using a closest point process, calculating the principal curvature by using the conicoid, defining and calculating the axial distribution density, distinguishing the branch point cloud and the leaf point cloud by using the axial distribution density, carrying out region growing on the branch point cloud, and carrying out region merging on the branch point cloud. By using the tree scanning data of a laser scanner and the estimated principal curvature, the invention partitions the tree scanning point cloud according with the actual organ distribution conditions. The method automatically partitions the tree point cloud scanning data among different organs through the local direction of principal curvature, and has the advantages of simple algorithm and accurate calculation result. The calculation result has important application value in the fields of tree point cloud 3D reconstruction, forest measurement, tree point cloud registration and the like.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Point cloud registration algorithm based on topological characteristic
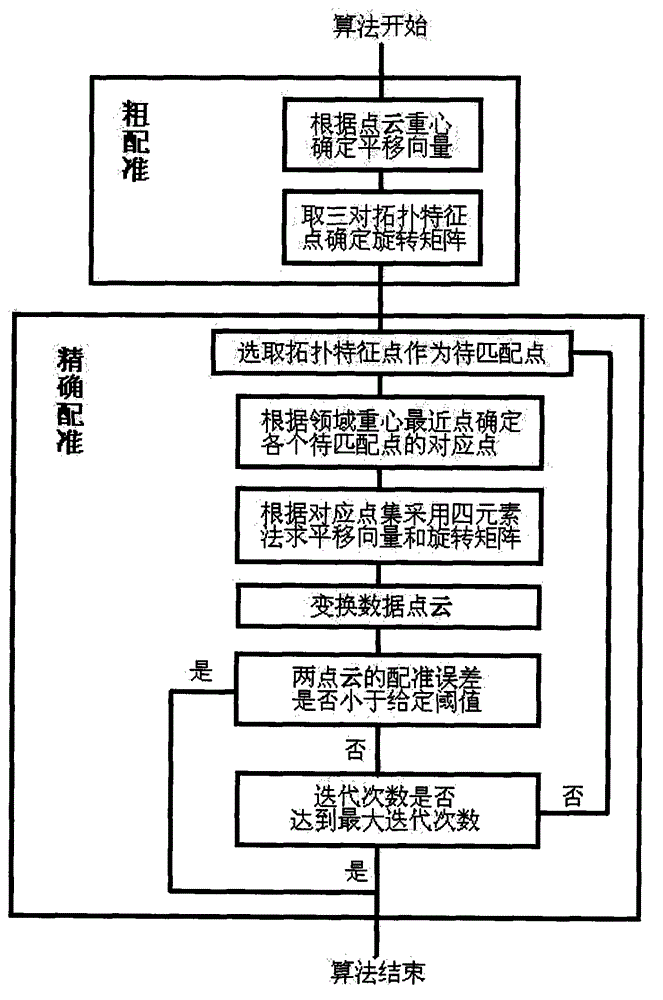
InactiveCN103150747ASmall amount of calculationImprove robustness3D-image renderingClosest pointRotation matrix
The invention provides a point cloud registration algorithm based on a topological characteristic. Topological characteristic points (border characteristic points and highlight characteristic points) of the point cloud are extracted and are used for calculating an initial rotation matrix and an initial translation vector at the initial point cloud registration stage of the algorithm. A basic idea of an iterative closest point (ICP) algorithm is adopted at the accurate registration stage, and the method of choosing a registration element and determining a corresponding point set is improved. The registration element chooses the topological characteristic points, and the closest point of a neighbor center of gravity is chosen as the corresponding point when the corresponding point set is determined. The method introduces the topological characteristic, reduces the number of the extracted points and ensures matching effect because the topological characteristic contains abundant point cloud characteristics. The method takes the neighbor characteristic into consideration when determining the corresponding points, thereby enhancing robustness of the algorithm to noises.
Owner:PCI TECH GRP CO LTD
Visual positioning system and method based on high-precision three-dimensional map
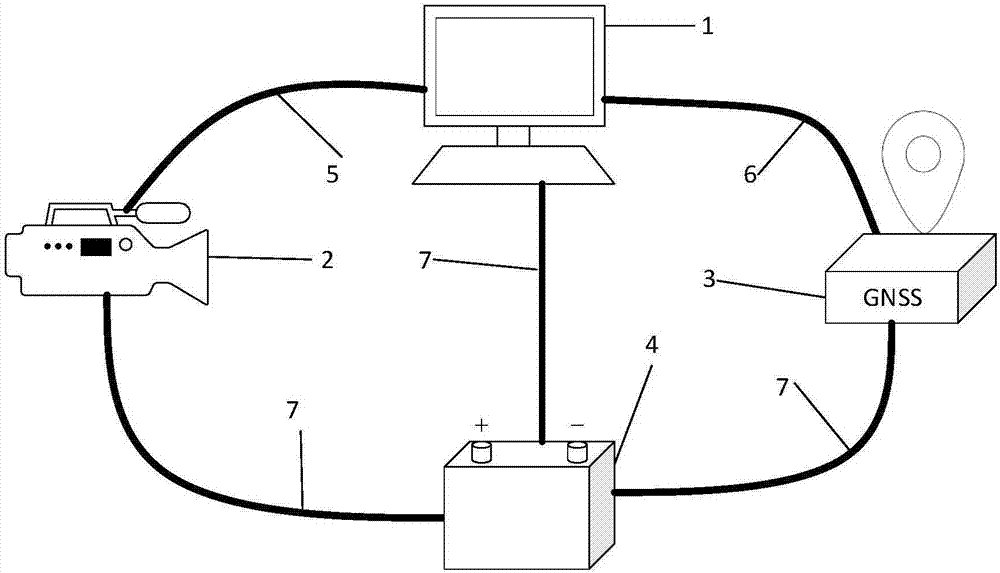
ActiveCN107084727AHigh precisionIncrease costInstruments for road network navigationSatellite radio beaconingData matchingClosest point
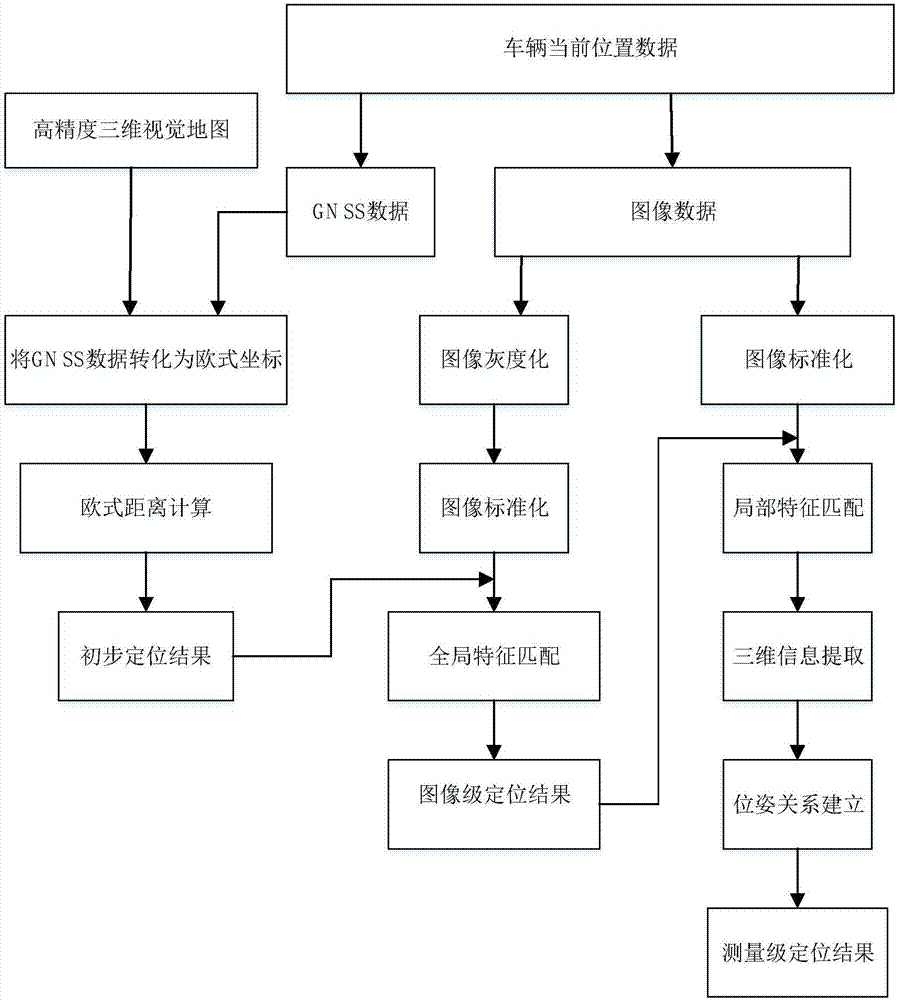
The invention discloses a visual positioning system and method based on a high-precision three-dimensional map. The system comprises a data acquisition module which is used for acquiring the image data and GNSS data of a current position, an acquisition aiding module which is used for data transmission, a power supply module which is used for supplying power to a system module, and a data processing module which is used for storing visual map information, processing the acquired GNSS data and image data and eventually realizing a positioning function, wherein the processing comprises GNSS data matching and feature point extraction and matching. The method is based on the high-precision three-dimensional map and comprises the following steps: carrying out preliminary positioning via matching of GNSS information; then carrying out image-level positioning via matching of global features; and finally carrying out measurement-level positioning and calculation via matching of three-dimensional local features so as to obtain the closest point in the map and the pose of a vehicle in the map, thereby realizing positioning of the vehicle. The system and method provided by the invention improves the precision of vehicle positioning and reduces positioning cost without great increase of hardware cost.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Image matching method, program, and image matching system
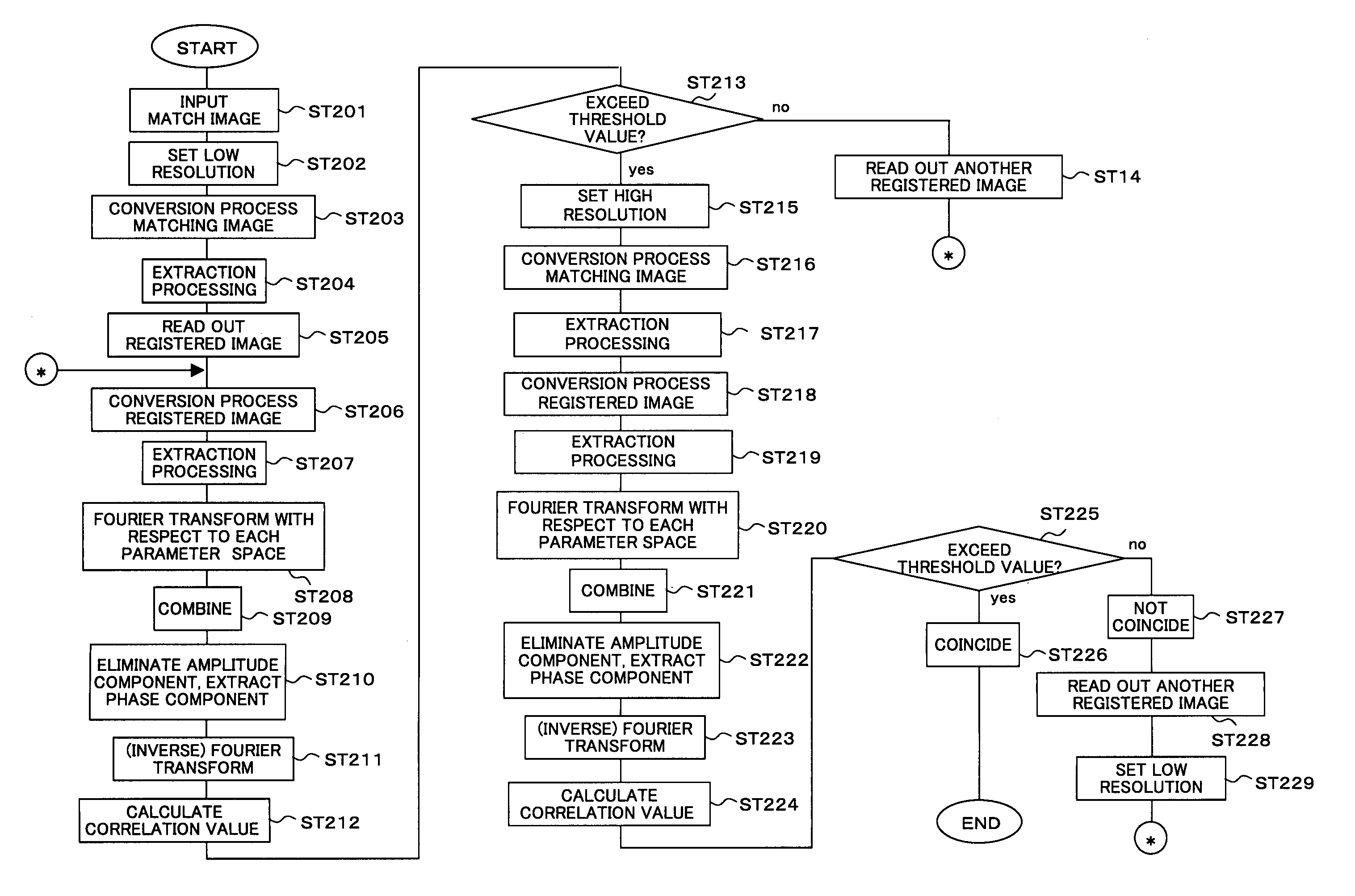
InactiveUS7720307B2Improve accuracyImage analysisGeometric image transformationClosest pointLinear component
An image matching method capable of matching images with a high precision and a program and an image matching system for the same, providing a conversion unit for performing image processing based on a registered image and a match image for converting points in each image to patterns of curves based on a distance from a reference position to the closest point on a straight line passing through each point in the image from the reference position and an angle formed by a straight line passing through the reference position and the closest point and an x-axis as a reference axis including the reference position, converting linear components in the images to patterns of a plurality of overlapped curves, and generating converted images, a correlation value generation unit for performing correlation processing based on the converted images and generating a correlation value, and a matching unit for performing the matching based on a signal indicating the correlation value generated by the correlation value generation unit.
Owner:SONY CORP
Methods, apparatuses and computer program products for three dimensional segmentation and textured modeling of photogrammetry surface meshes
ActiveUS9613388B2Improve accuracyImage enhancementDetails involving processing stepsClosest pointGeographic object
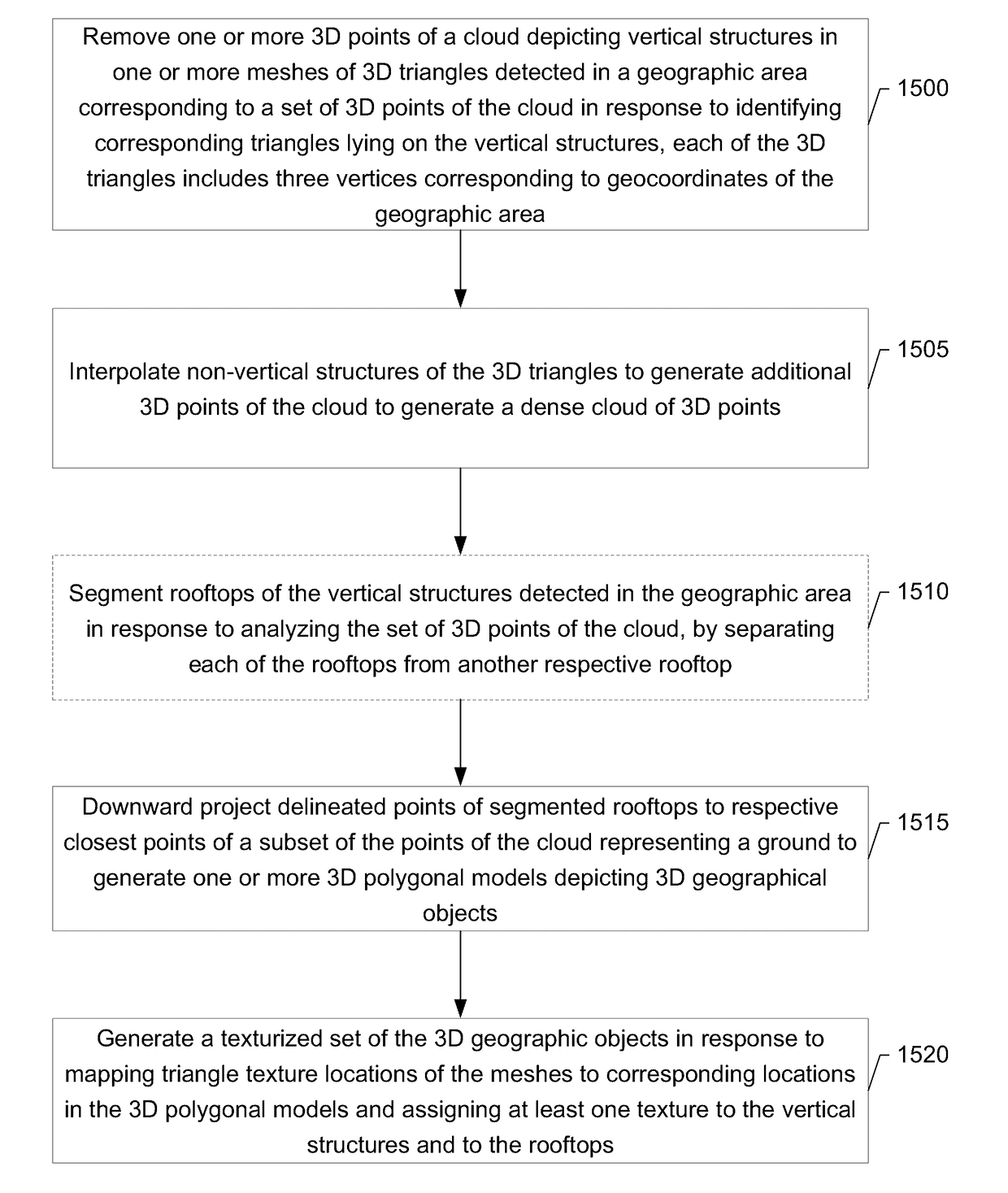
An apparatus for generating 3D geographical models includes a processor and memory storing executable computer program code causing the apparatus to at least perform operations including removing points of a cloud depicting vertical structures in meshes of triangles detected in an area corresponding to a set of 3D points responsive to identifying triangles on vertical structures. The triangles include vertices corresponding to geocoordinates. The program code further causes the apparatus to interpolate non-vertical structures of triangles to generate a dense cloud of points. The program code further causes the apparatus to downward project delineated points of segmented rooftops to closest points of a ground to generate 3D polygonal models depicting geographical objects. The program code further causes the apparatus to generate texturized objects responsive to mapping triangle locations to the 3D polygonal models and assign texture to vertical structures and rooftops. Corresponding methods and computer program products are also provided.
Owner:HERE GLOBAL BV
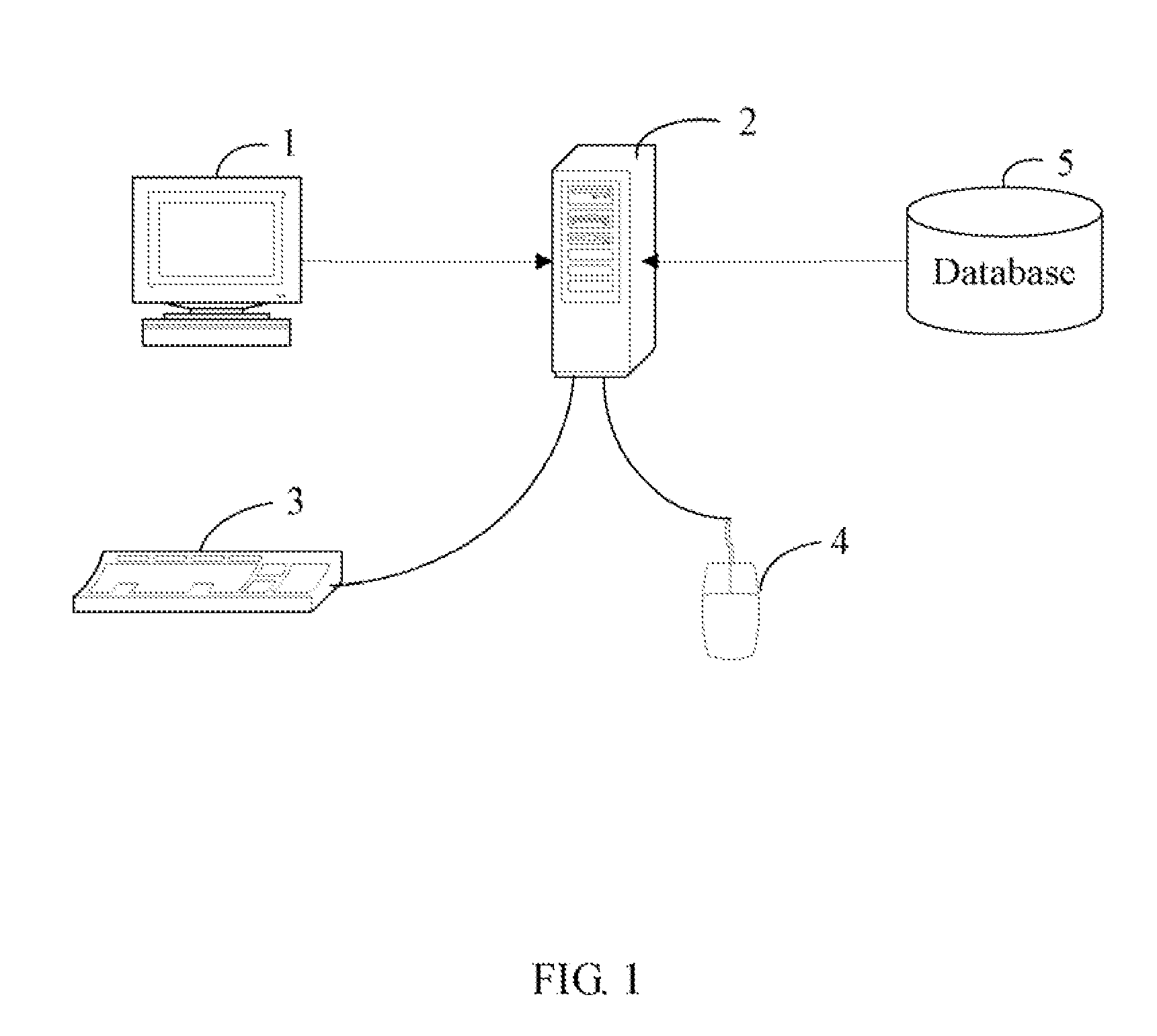
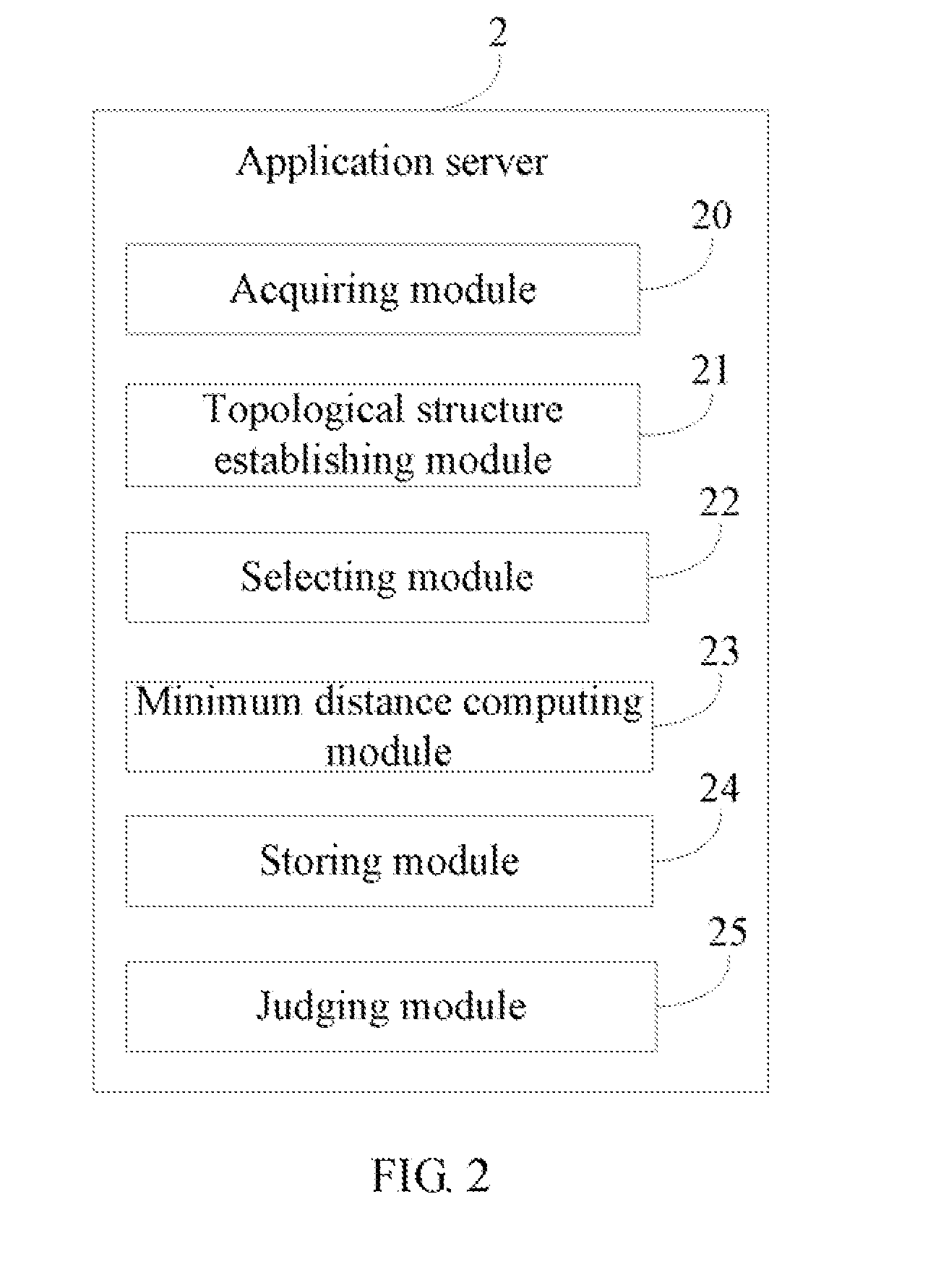
System and method for computing minimum distances between two point clouds
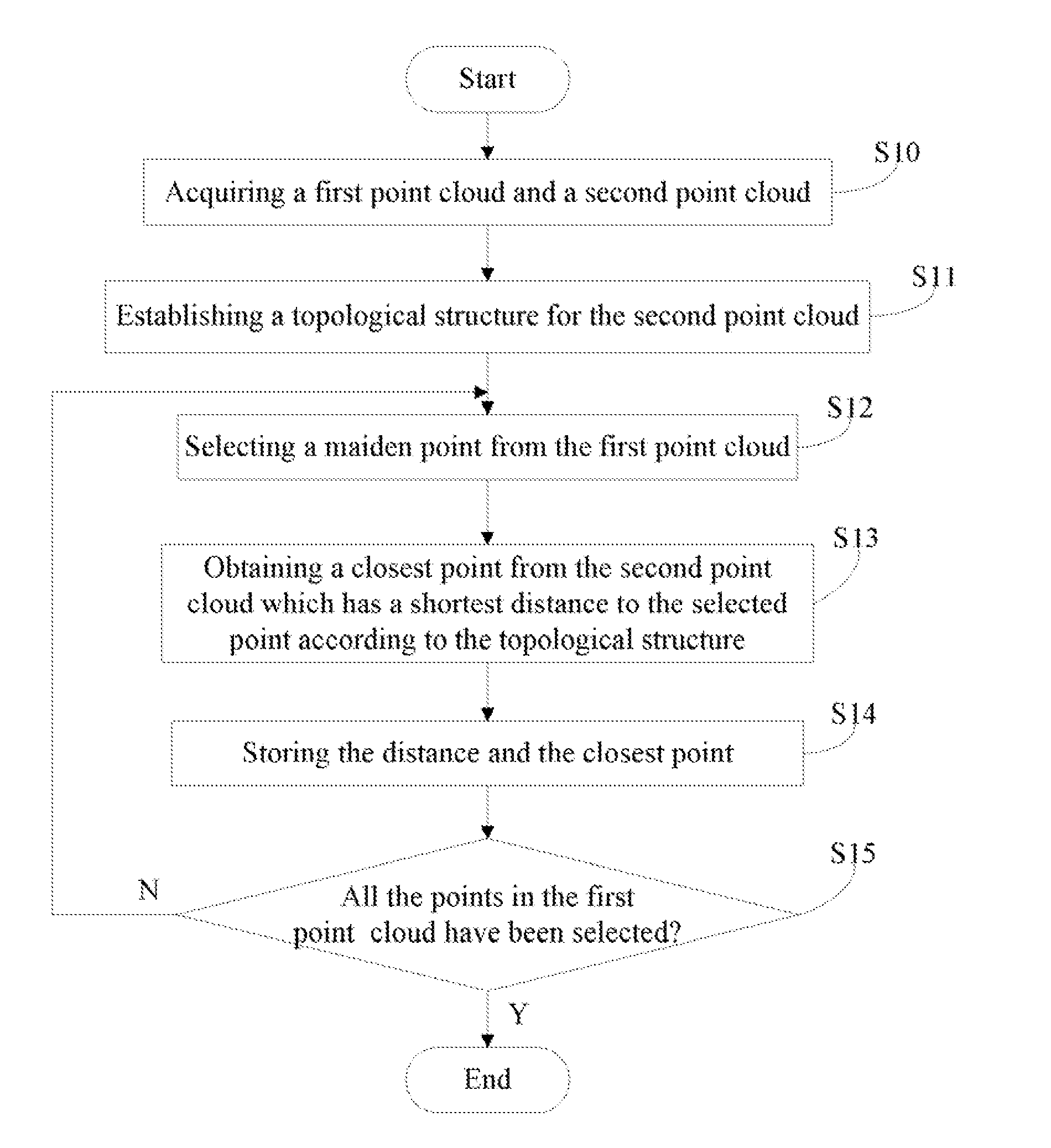
A method for computing minimum distances between two point clouds is provided. The method includes: (a) acquiring a first point cloud and a second point cloud; (b) establishing a topological structure for the second point cloud to make points of the second point cloud confined in a plurality of related cubical grids; (c) selecting a point from the first point cloud; (d) searching one or more cubical grids from the related cubical grids according to the topological structure and computing a distance between the selected point and each of points which belong to the second point cloud and in the searched cubical grids to obtain a closest point from the second point cloud, which has a shortest distance to the selected point; (e) repeating steps from (c) to (d) until all the points in the first point cloud have been selected. A related system is also provided.
Owner:HONG FU JIN PRECISION IND (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
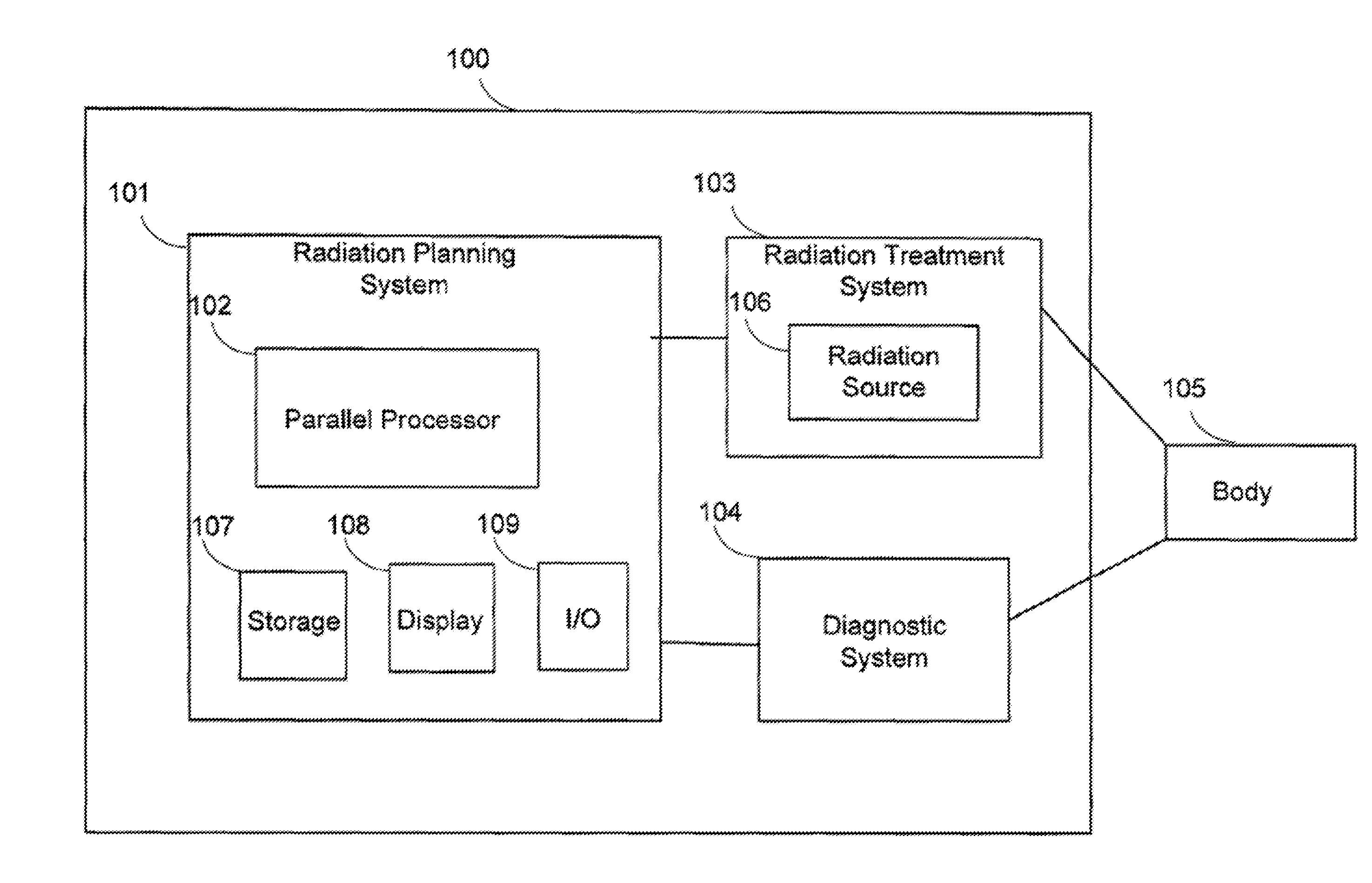
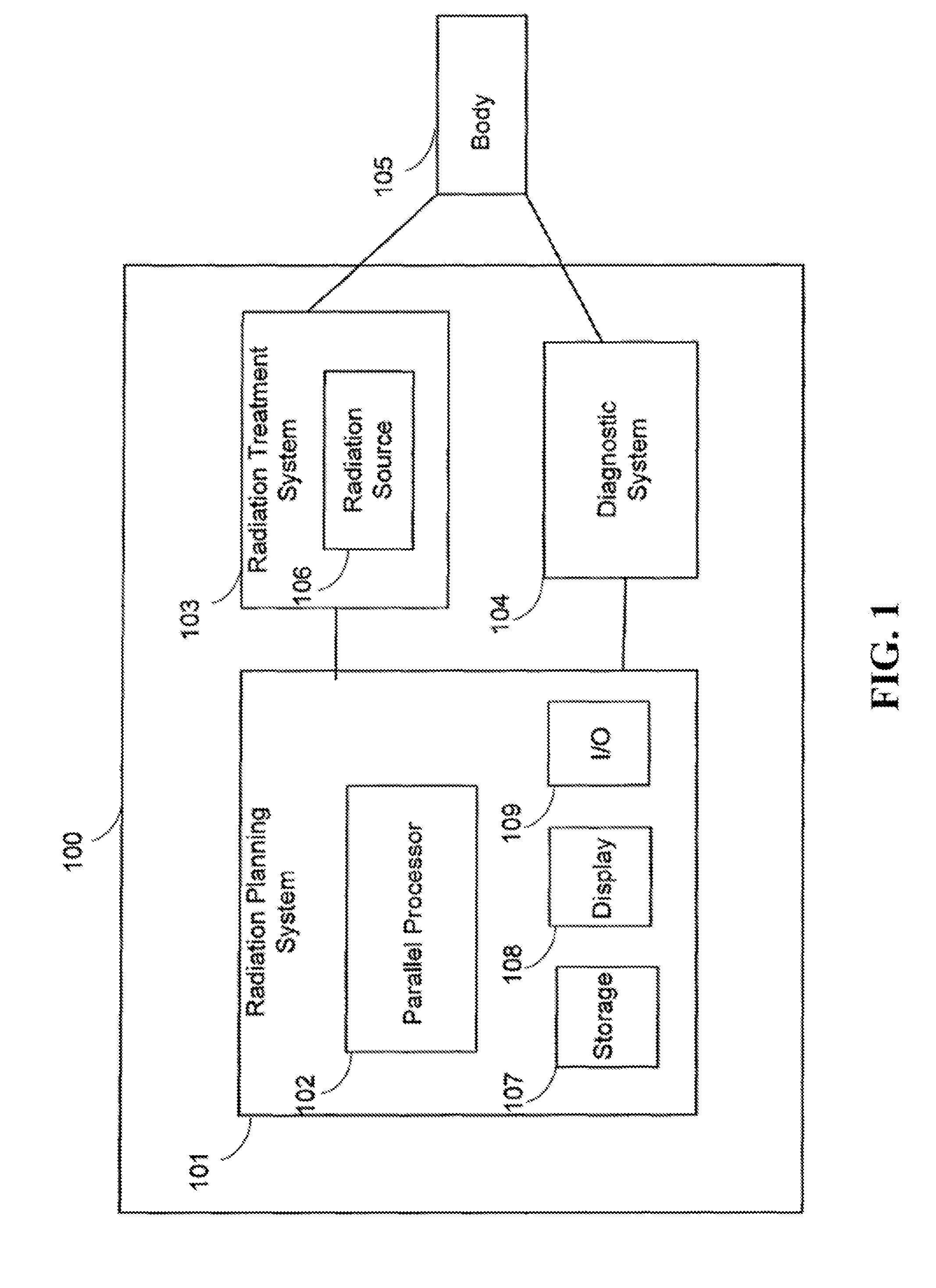
Multi-Criteria Optimization in Particle Beam Dose Optimization
InactiveUS20150202464A1Minimizes a weighted norm of the total irradiationSatisfy constraintsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesMedical automated diagnosisClosest pointParticle beam
A method optimizes a dose of radiation for a radio-therapy treatment subject to constraints on diagnostic parameters of the radio-therapy treatment. The method determines a point of a polytope arranged in a coordinate system of the diagnostic parameters, such that a position of the point in the coordinate system is determined at least in part by values of each diagnostic parameter. The polytope is convex with boundaries formed by intersecting half-spaces of feasible values of each diagnostic parameter specified by the constraints. The point is the closest point of the polytope to an origin of the coordinate system with regard to a weighted Euclidean distance norm. The method determines a distribution of the dose of radiation for the radio-therapy treatment using the values of the diagnostic parameters corresponding to the position of the point.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
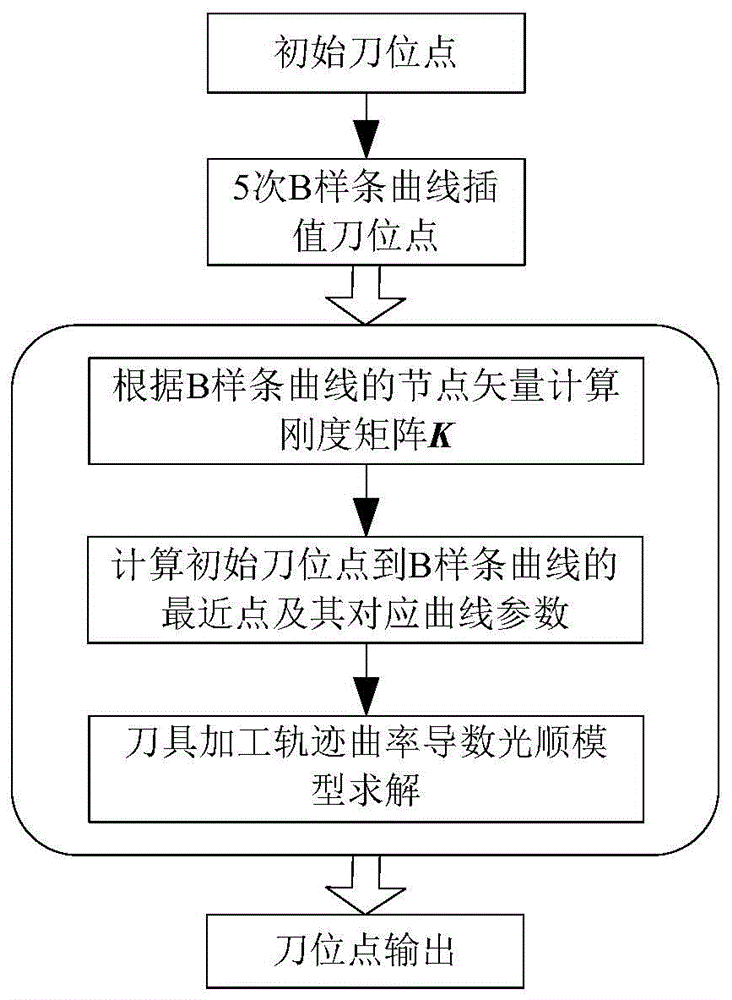
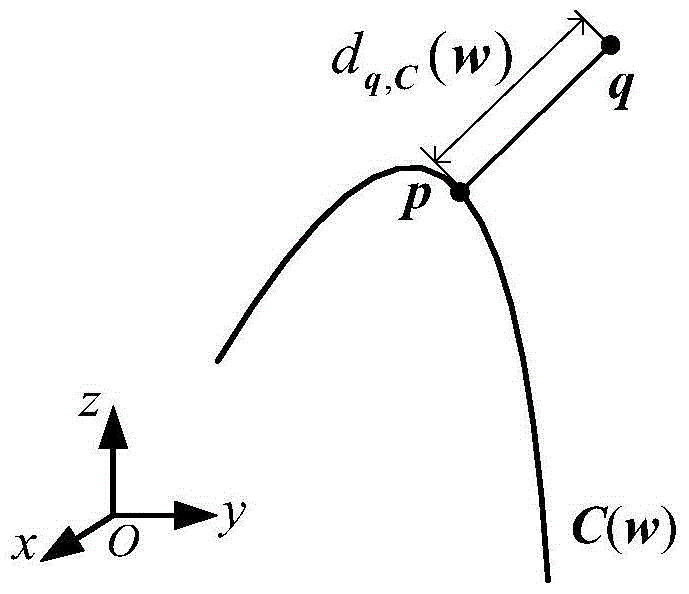
Curvature fairing method for high-speed numerical control processing track
InactiveCN105700466ASolve the trajectory problemSolve the problem of tool path in high-speed NC machiningNumerical controlNumerical controlClosest point
The invention provides a curvature fairing method for a high-speed numerical control processing track. The curvature fairing method comprises the steps of: inputting tool location points of an initial processing track; interpolating the initial tool location points by utilizing B-spline curve repeatedly to obtain a tool processing track line, and representing the tool processing track line by using the B-spline curve; calculating a stiffness matrix of a track curve according to node vectors of the B-spline curve; calculating a closest point from each initial tool location point to the B-spline curve and curve parameters corresponding to the closet points, and calculating a first-order derivative of a distance (from the initial tool location points to the closest points of the B-spline curve) to control points of the B-spline curve; solving a tool processing track curvature derivative fairing model by adopting a sequence linear method to obtain a processing track after fairing optimization; and outputting tool locating points of the tool processing track after fairing optimization. The curvature fairing method solves the problem of generating the high-speed numerical control processing tool track with fair curvature, and is suitable for generating a 2.5-axis cavity high-speed processing track.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
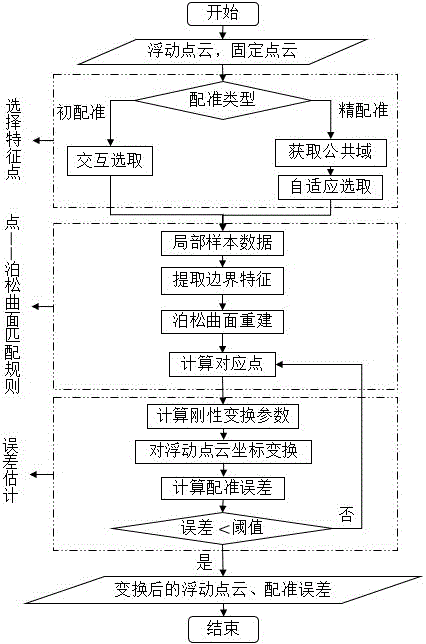
Point cloud rigid registration method based on local Poisson curved surface reconstruction
InactiveCN106023298AImprove robustnessImprove initial registration accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisClosest pointPoint cloud
The invention discloses a point cloud rigid registration method based on local sample Poisson curved surface reconstruction to find a corresponding point, and belongs to the field of digital design and manufacturing. The method is characterized by, in crude registration, mutually selecting feature point pairs from a floating point cloud and a fixed point cloud, and establishing a Poisson curved surface based on a neighborhood point set of feature points of the fixed point cloud; establishing a KD tree of the curved surface; searching a closest point of a sample point of the floating point cloud in the KD tree, and serving the closest point as a reference point; serving the closest point from the sample point to a reference point ring domain surface patch as the corresponding point, and establishing a measure function based on a corresponding point pair and calculating transformation parameters through an SVD method; and on the basis of crude registration, in precise registration, obtaining feature point pairs in a self-adaptive manner based on a public domain, and establishing error metric by utilizing the minimum distance from the point to the Poisson curved surface, so that transformation parameters can be calculated, and registration precision is further improved. In crude registration, higher registration precision can be achieved, and the precise registration can quickly converge to the global optimum and has higher robustness.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
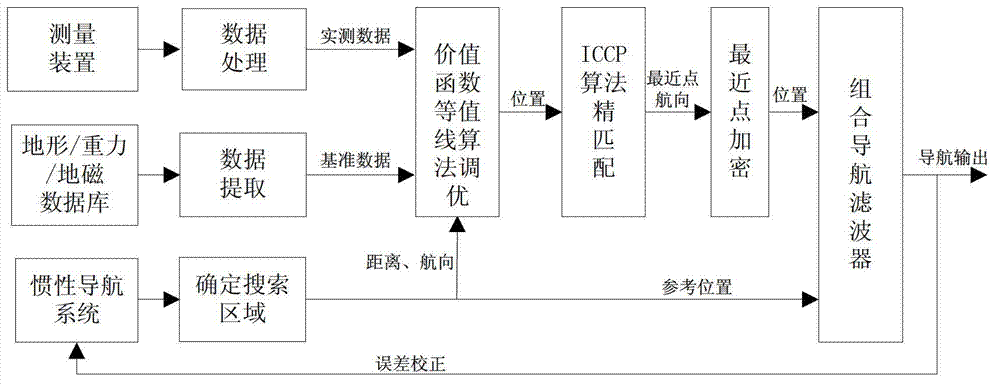
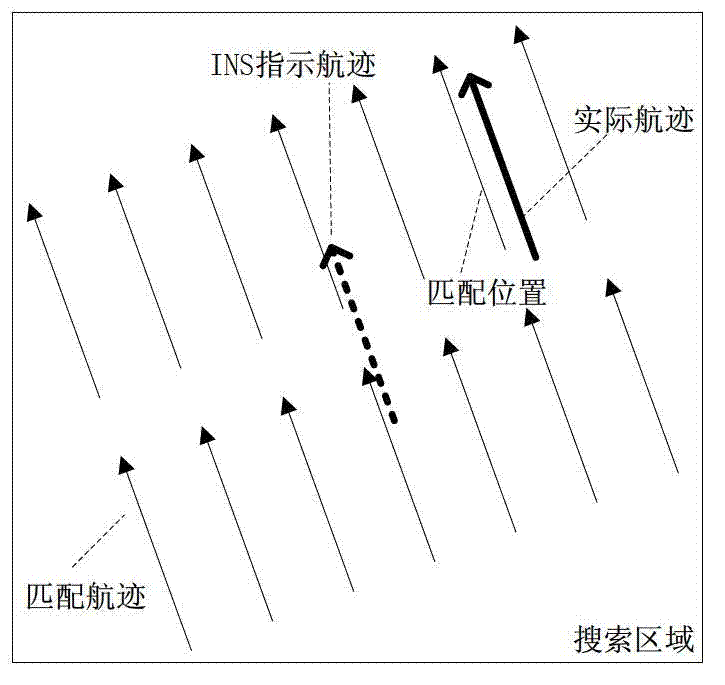
Isoline-based assistant navigation positioning method
InactiveCN102809376AImprove matching accuracyHigh positioning accuracyNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsClosest pointComputer vision
The invention discloses an isoline-based assistant navigation positioning method. The method specifically comprises the following steps: finding out a track relatively close to an actual track within a confidence region by utilizing an isoline matching algorithm based on a value function under relatively high initial matching error when an aircraft is started to perform topography / gravity / terrestrial magnetism matching, so as to reduce the initial positioning error of an inertial navigation system (INS); and then obtaining a course made good and the sequence information of the closet points based on the rotating and translation of an ICCP (iterative closest contour point) algorithm; and finally obtaining the optimum matching track from the isoline by utilizing an encrypting method based on the obtained course made good and the information of the closest point. By adopting the isoline-based assistant navigation positioning method disclosed by the invention, the problem that the assistant navigation system is easily subjected to diffusion under a high initial positioning error in the current assistant navigation system can be solved, and the precision and the reliability of the assistant navigation system can be improved; and the method is specially suitable for being applied to assisting the navigation positioning in the presence of a blind zone.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
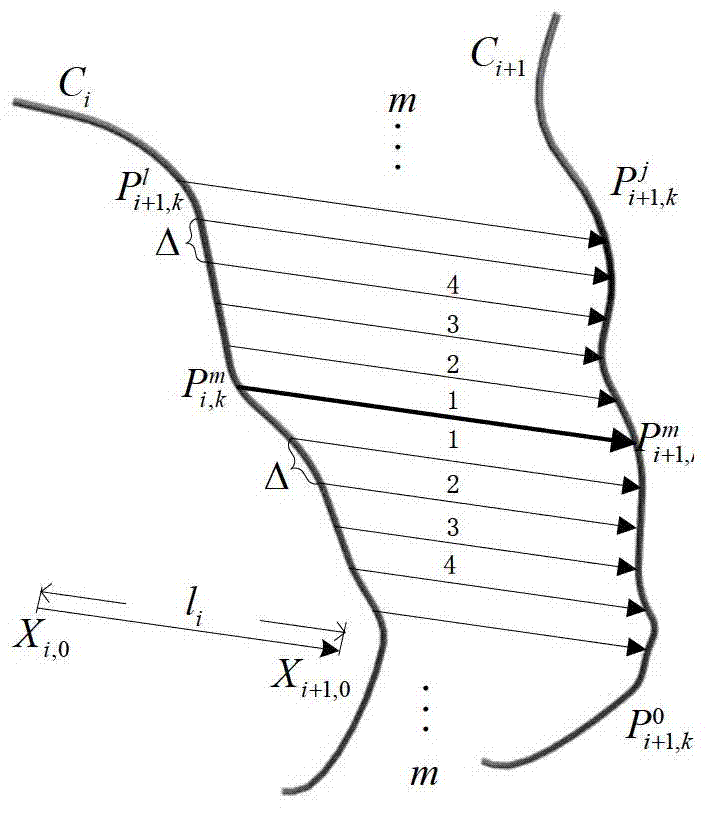
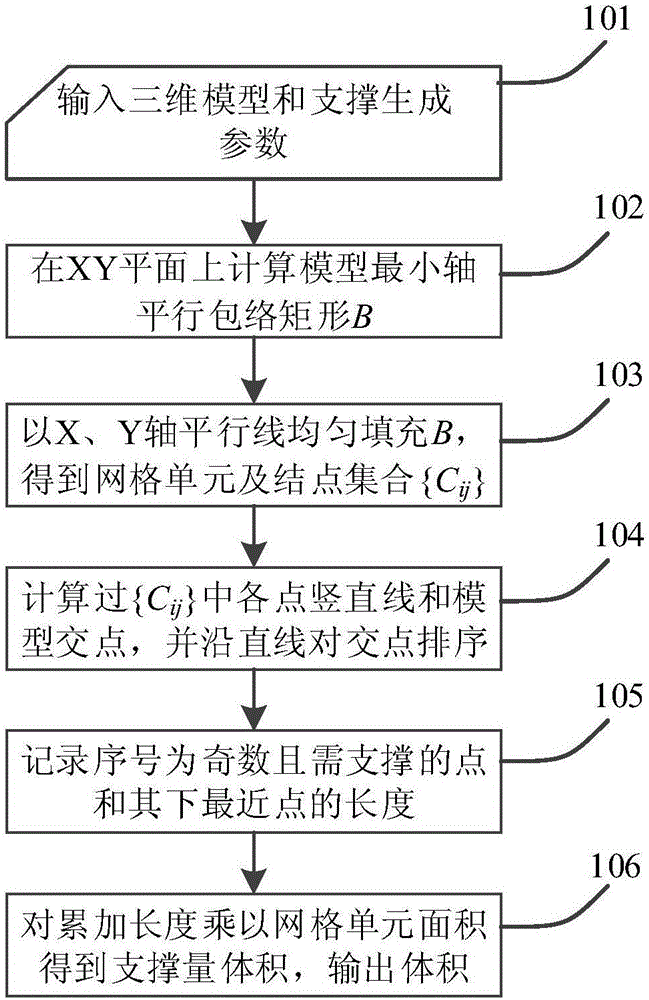
Three-dimensional printing model placing required support amount rapid estimation method
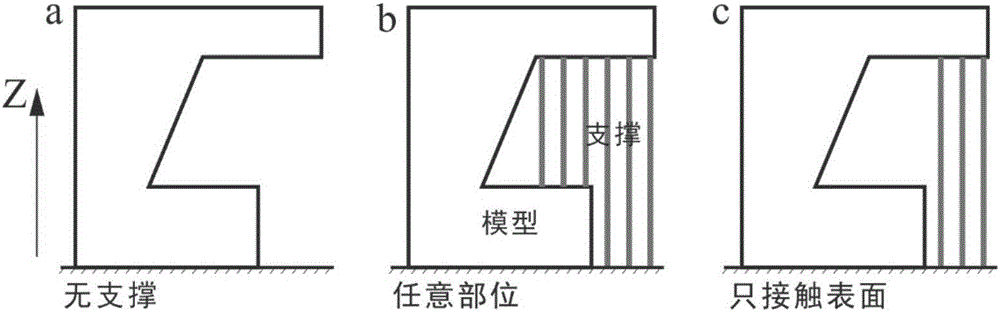
The invention discloses a three-dimensional printing model placing required support amount rapid estimation method. The method comprises the following steps: inputting a three-dimensional model file, needing estimation of support amount, and support generation parameters; if the model grows along the Z axis, calculating a minimum axis parallel envelope rectangle B in an XY plane; making equidistant parallel filling lines of the X axis and the Y axis in the B and with d being an interval to obtain a series of grid units and nodes; making vertical straight lines passing the nodes respectively, calculating intersection points of the lines and the model, recording normal direction of each surface patch, where each intersection point locates, and ranking the intersection points on each line from small to big based on the Z coordinates; for the intersection points, the serial number of which is odd, if the inclination angle of one surface patch corresponding to one intersection point is smaller than a critical value, recording the distance between the point and the closest point therebelow; and accumulating the recorded line length, and multiplying the total line length and grid unit area to obtain support amount volume and outputting the support amount. The method can estimate the model required support amount quickly, and is especially suitable for model intelligent optimization placing calculation needing a lot of iteration.
Owner:SUZHOU ZIJINGANG INTELLIGENT MFG EQUIP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com