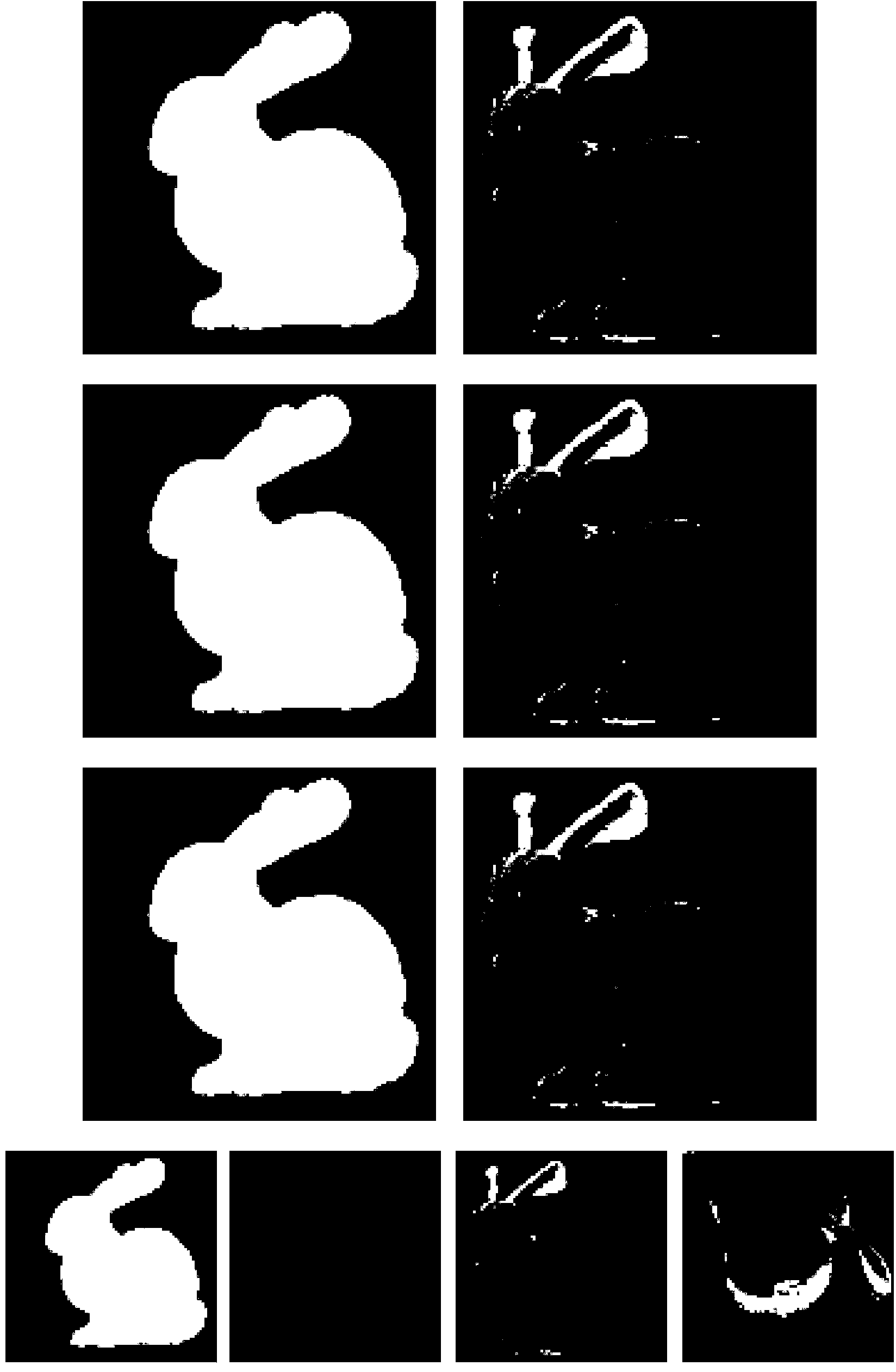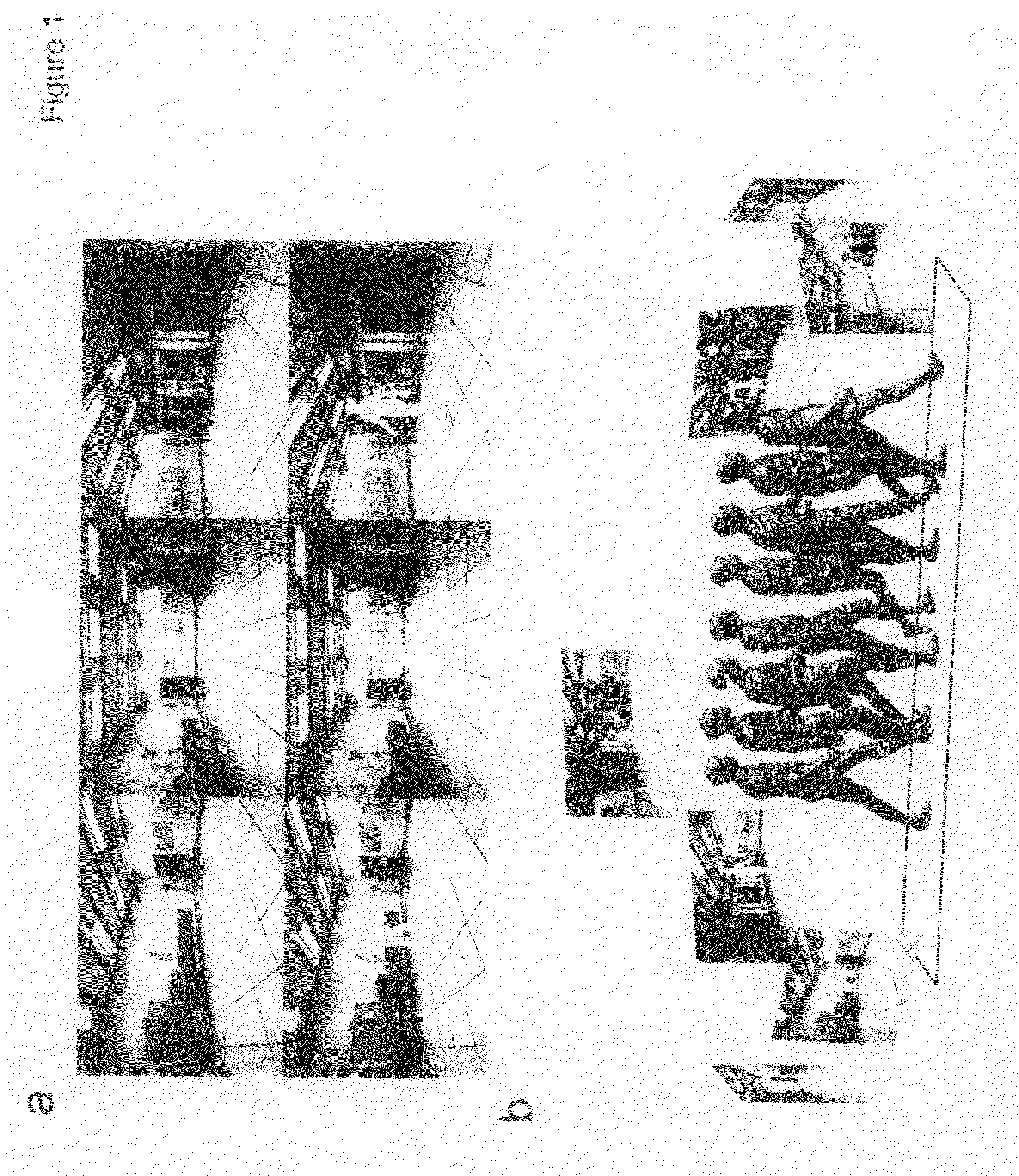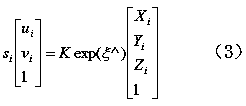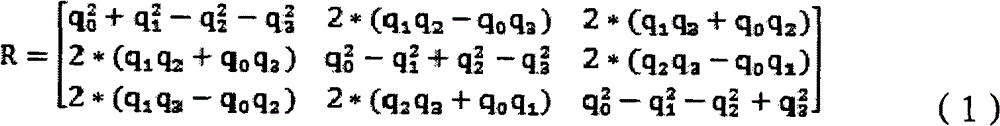Patents
Literature
270 results about "Iterative closest point" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
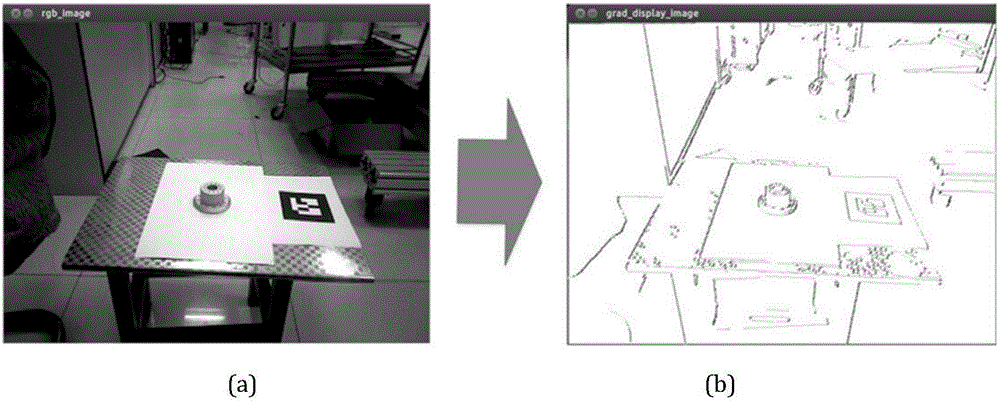
Iterative closest point (ICP) is an algorithm employed to minimize the difference between two clouds of points. ICP is often used to reconstruct 2D or 3D surfaces from different scans, to localize robots and achieve optimal path planning (especially when wheel odometry is unreliable due to slippery terrain), to co-register bone models, etc.
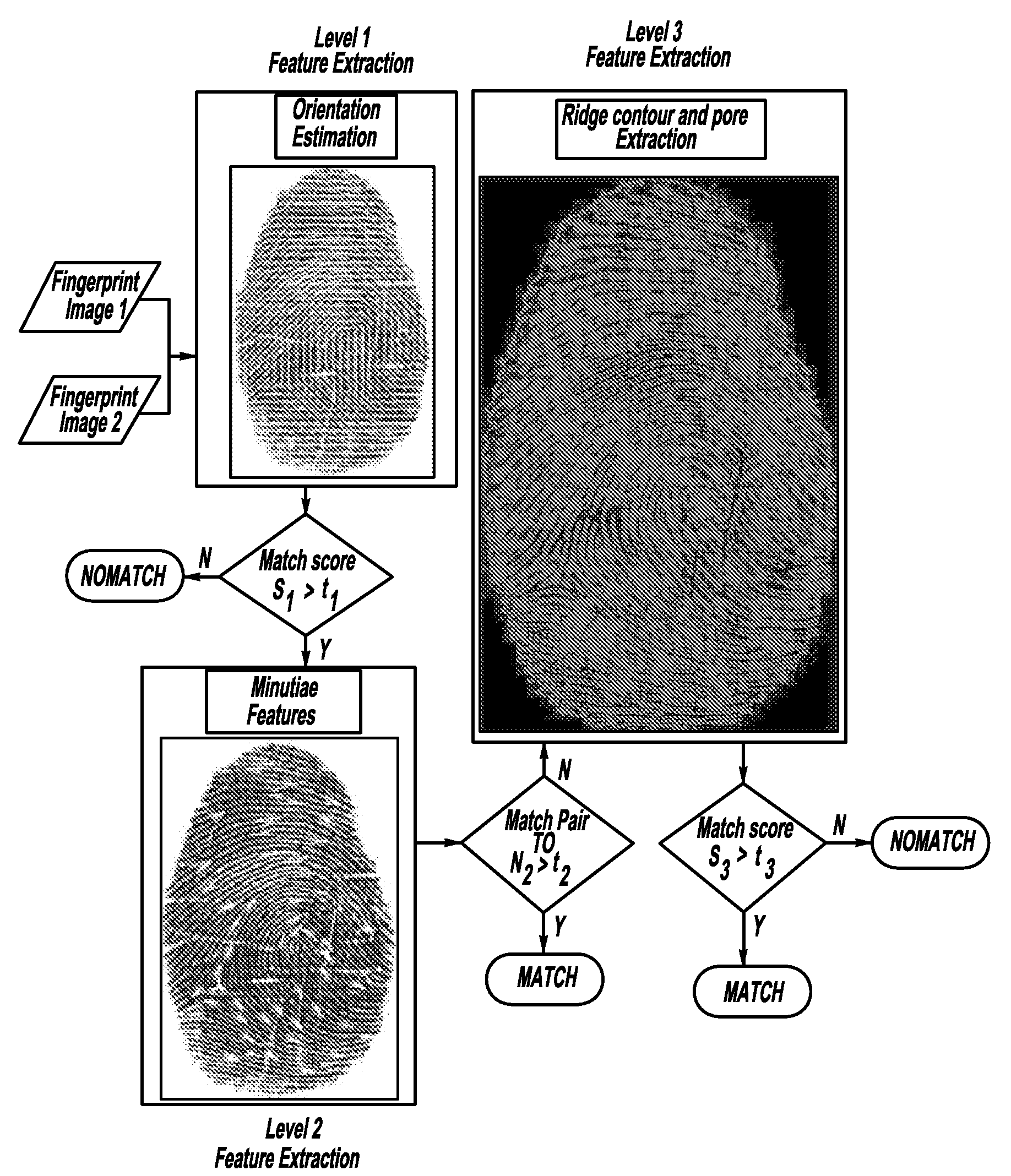
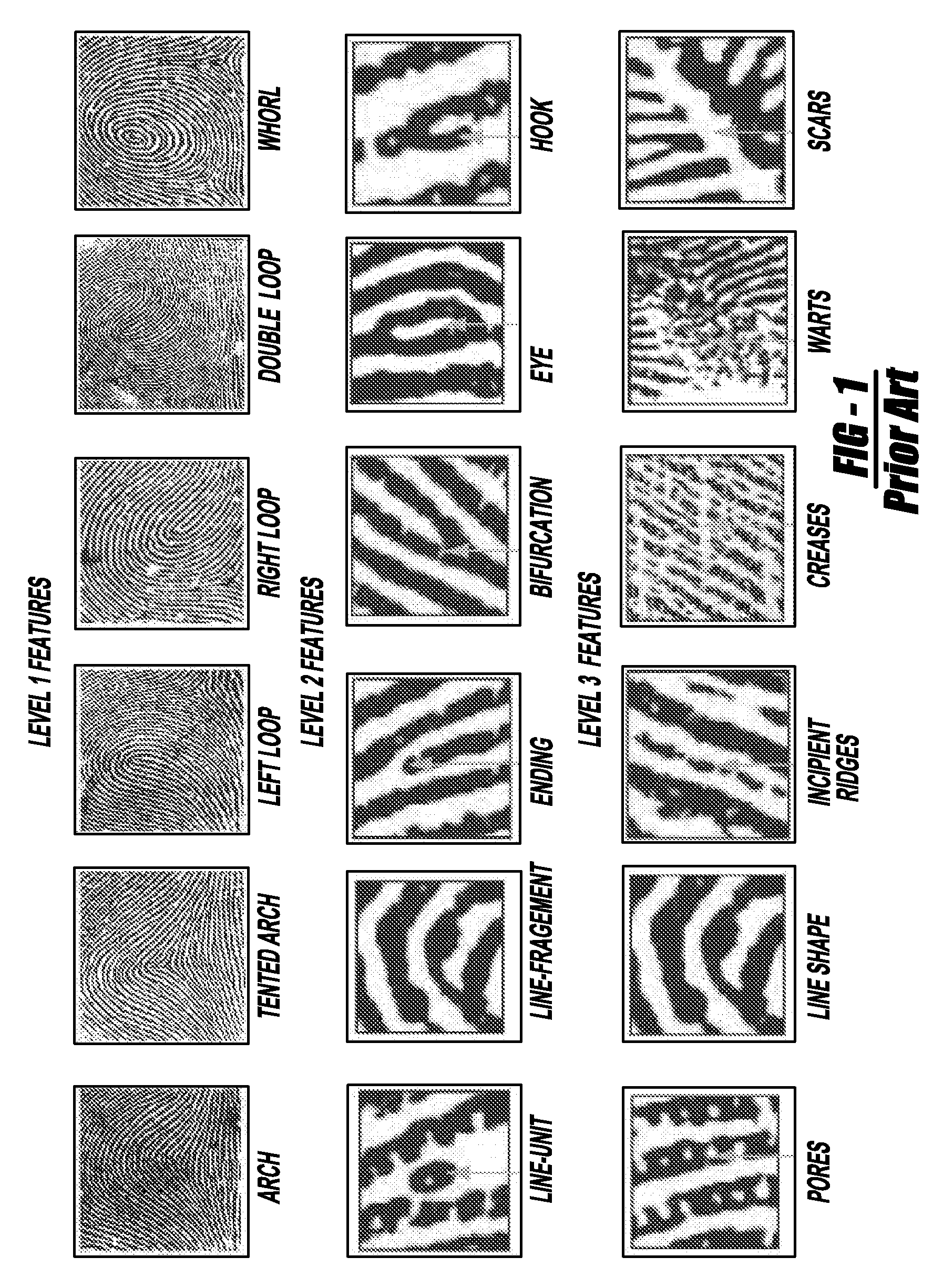
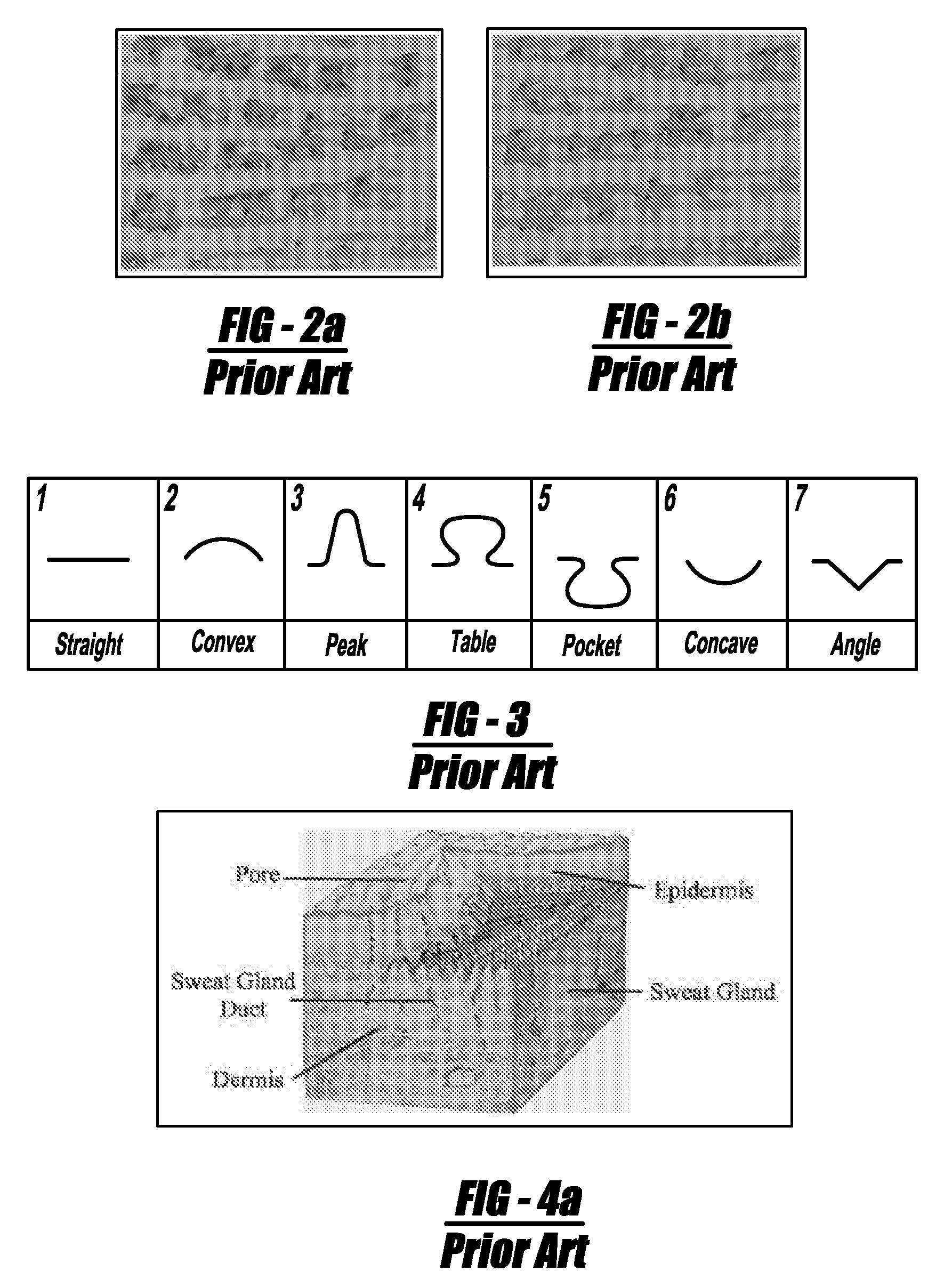
Level 3 features for fingerprint matching
Fingerprint recognition and matching systems and methods are described that utilize features at all three fingerprint friction ridge detail levels, i.e., Level 1, Level 2 and Level 3, extracted from 1000 ppi fingerprint scans. Level 3 features, including but not limited to pore and ridge contour characteristics, were automatically extracted using various filters (e.g., Gabor filters, edge detector filters, and / or the like) and transforms (e.g., wavelet transforms) and were locally matched using various algorithms (e.g., the iterative closest point (ICP) algorithm). Because Level 3 features carry significant discriminatory and complementary information, there was a relative reduction of 20% in the equal error rate (EER) of the matching system when Level 3 features were employed in combination with Level 1 and Level 2 features, which were also automatically extracted. This significant performance gain was consistently observed across various quality fingerprint images.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
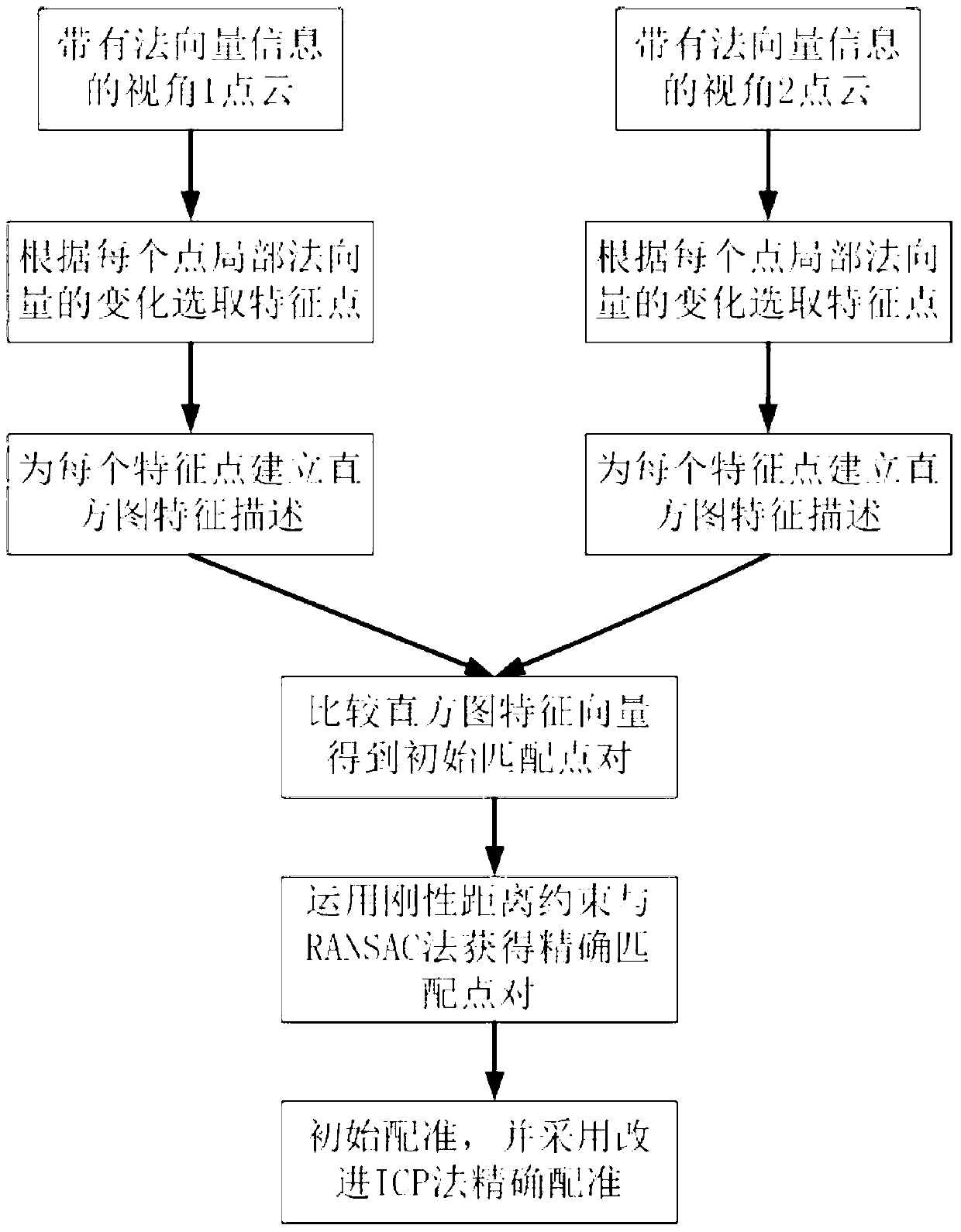
Point cloud automatic registration method based on normal vector
ActiveCN103236064AMeet registration requirementsRealize automatic registrationImage analysisFeature vectorExact match
The invention relates to a point cloud automatic registration method based on normal vector. According to the method, processing objects are two or more than two pieces of three-dimensional point cloud data, wherein overlapped part exists every two pieces of adjacent three-dimensional point cloud data. The method comprises the following processing steps that (1) feature points are selected according to the point cloud local normal vector changes; (2) the histogram feature quantity is designed for carrying out feature description on each obtained feature point; (3) the initial matching dot pair is obtained through comparing the histogram feature vector of the feature points; (4) the precise matching dot pair is obtained through applying the rigid distance constraint condition and combining a RANSAC (random sample consensus) algorithm, and in addition, the initial registration parameters are obtained through calculation by using a four-element method; and (5) an improved ICP (iterative closest point)) algorithm is adopted for carrying out point cloud precise registration. The point cloud can be automatically registered according to the steps. The method has the advantages that feature description is simple, identification degree is high, higher robustness is realized, and registration precision and speed are improved to a certain degree.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Precise registration method of multilook point cloud
InactiveCN101645170ACalculation speedImprove registration accuracyImage analysisMatch algorithmsIterative closest point
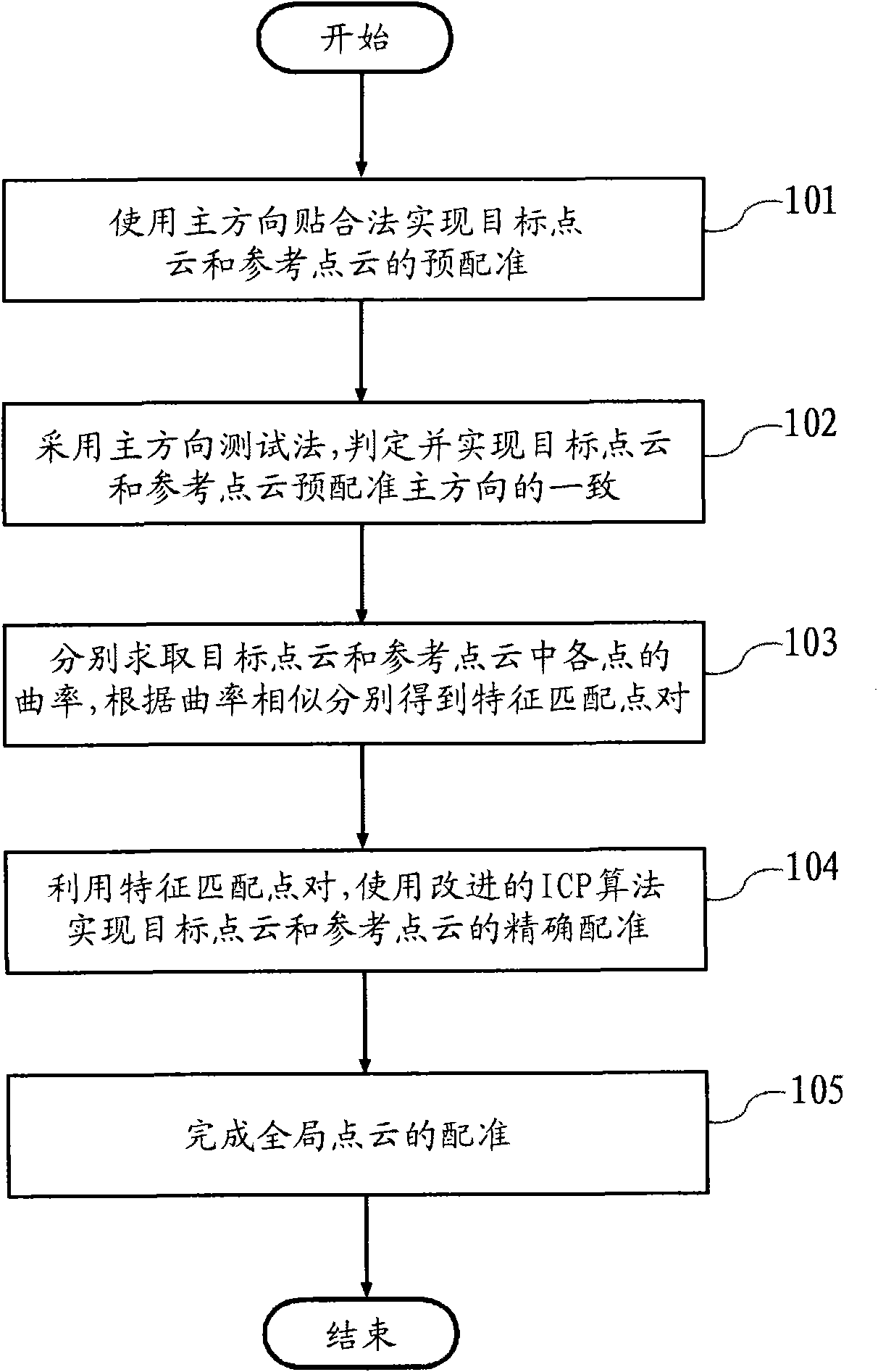
The invention provides a precise registration method of multilook point cloud, comprising the following steps: respectively selecting one piece of point cloud overlapping approximately from two piecesof global point cloud to be registered to serve as the target point cloud and the reference point cloud; utilizing a principle direction bonding method to realize the preregistration of the target point cloud and the reference point cloud; utilizing the principle direction test method to judge and realize the consistency of the preregistration principle directions of the target point cloud and the reference point cloud; respectively calculating the curvature of each point in the target point cloud and the reference point cloud; respectively obtaining characteristic matching point symetries P0and Q0 according to curvature similarity; using the iterative closest point matching algorithm to realize the precise registration of the target point cloud and the reference point cloud by utilizingthe characteristic matching point symetries P0 and Q0; and completing the registration of the two pieces of global point cloud. The method is characterized by high computation speed and high registration precision, thus being capable of realizing good registration effect.
Owner:BEIJING INFORMATION SCI & TECH UNIV
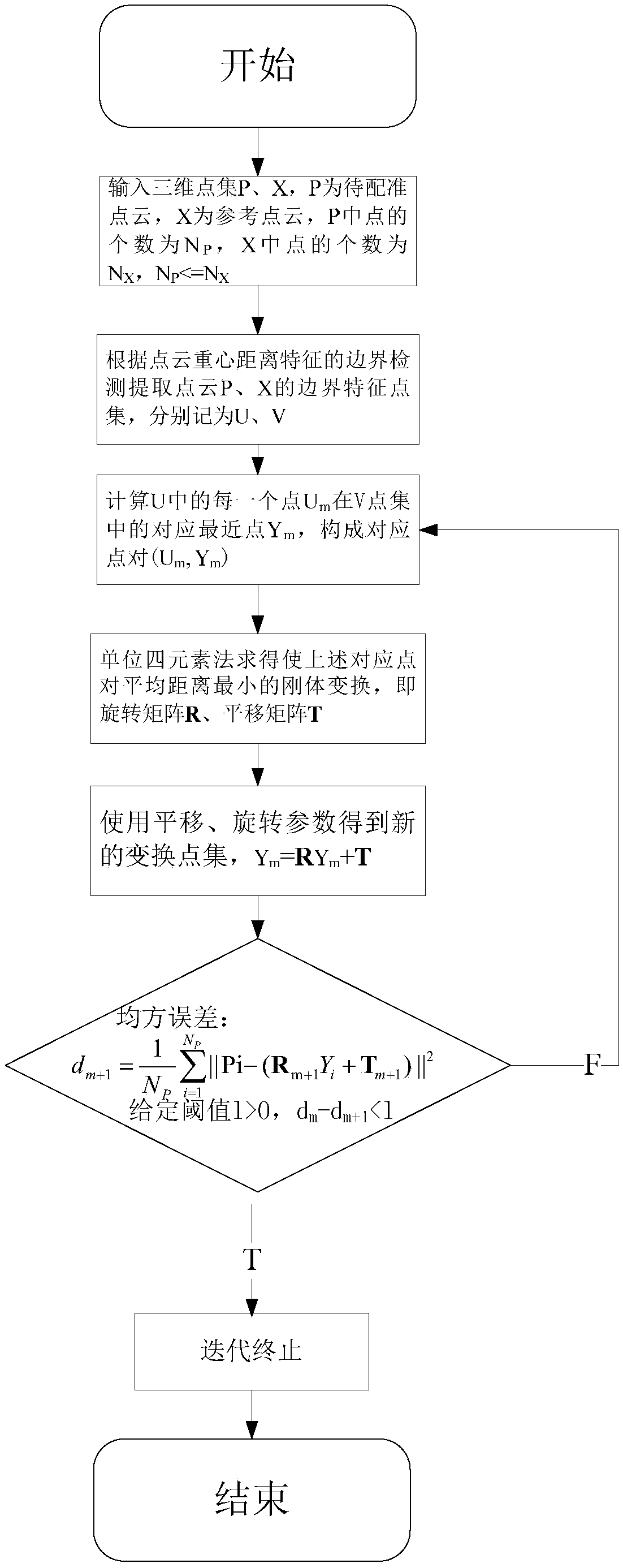
Boundary feature point registering method for point cloud splicing in three-dimensional scanning system
InactiveCN103955939AQuick registrationAccurate registration effectImage analysisMeasurement devicesGravity centerData needs
The invention discloses a boundary feature point registering method for point cloud splicing in a three-dimensional scanning system. The method comprises the following steps that (1) a three-dimensional laser scanner acquires space sampling points on the surfaces of a real object in different view angles; (2) a boundary detecting method of a point cloud gravity center distance feature is used for extracting point cloud boundary feature points in different viewing angles; (3) an improved iterative closest point (ICP) algorithm is used for registering point cloud according to the extracted point cloud boundary feature points; (4) the registering precision is evaluated according to a registering error standard, and whether a registering result meets a registering request or not is verified. According to the boundary feature point registering method for point cloud splicing in the three-dimensional scanning system, boundary feature point extraction is conducted on the point cloud to be registered, the defect that all points in point cloud data need to be traversed to search for the corresponding points in a traditional ICP algorithm is overcome, on the basis that the registering precision is guaranteed, the complexity of the algorithm is effectively lowered, and meanwhile the efficiency of point cloud registering is obviously improved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
Ground three-dimensional laser scanning point cloud and image fusion and registration method
InactiveCN105931234AImprove noise immunityEnsuring rotation invarianceImage enhancementImage analysisLaser scanningImage fusion
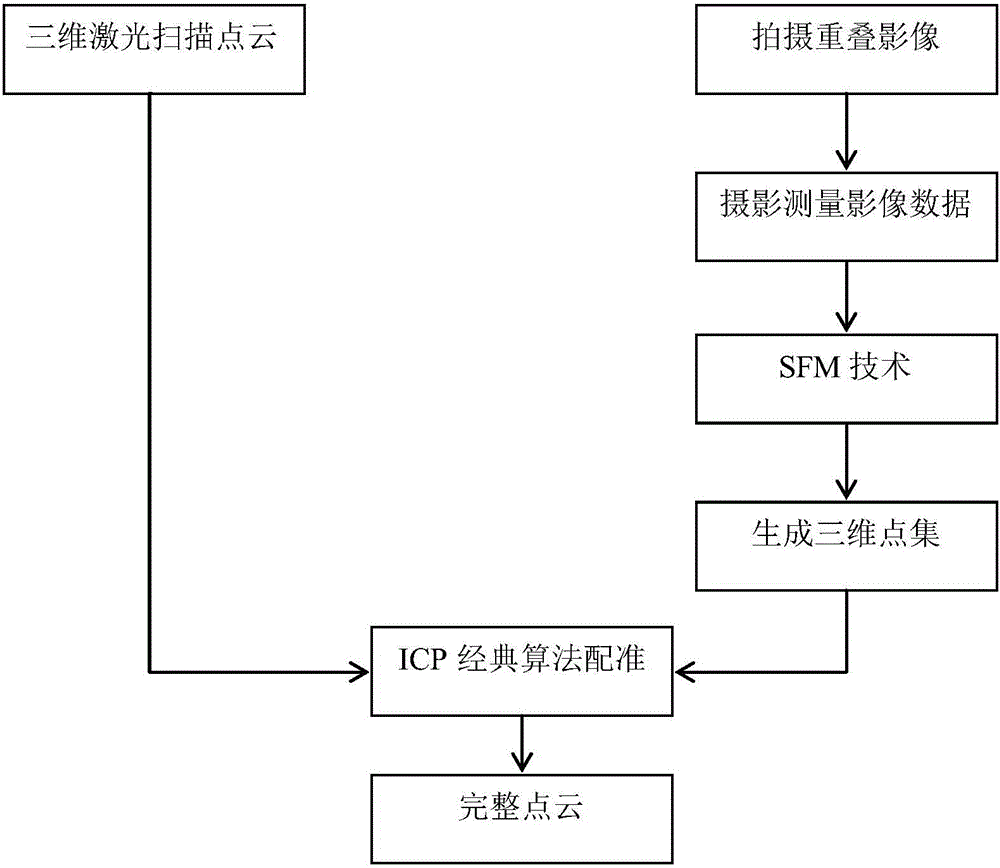
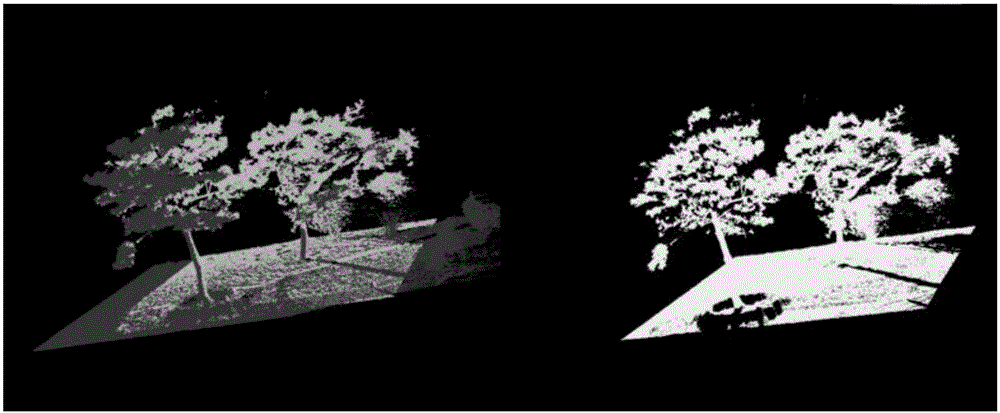
The present invention provides a ground three-dimensional laser scanning point cloud and image fusion and registration method, and the limitation of the scanning of the ground three-dimensional laser scanning technology is overcome. The point cloud data obtained by ground three-dimensional laser scanning often comprises various areas which can not be measured, point cloud holes are generated, and thus local area information of a scanned object is lost. The holes cause that a model can not realize visualization correctly, and model subsequent processing is influenced too. For the above problems, the invention aims to solve the problems through the following technical scheme that an SIFT image is used to carry out mosaic processing of collected image photos by means of an algorithm to obtain a panoramic image, the intensive reconstruction is carried out through the panoramic image to obtain the 3D point cloud data generated by the image photo, and an iterative closest point algorithm (ICP) is used to realize the registration working of laser scanning point cloud and image data generation point cloud.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Markerless motion capture system
ActiveUS7804998B2Level accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionNon-surgical orthopedic devicesBiomechanicsThree dimensional kinematics
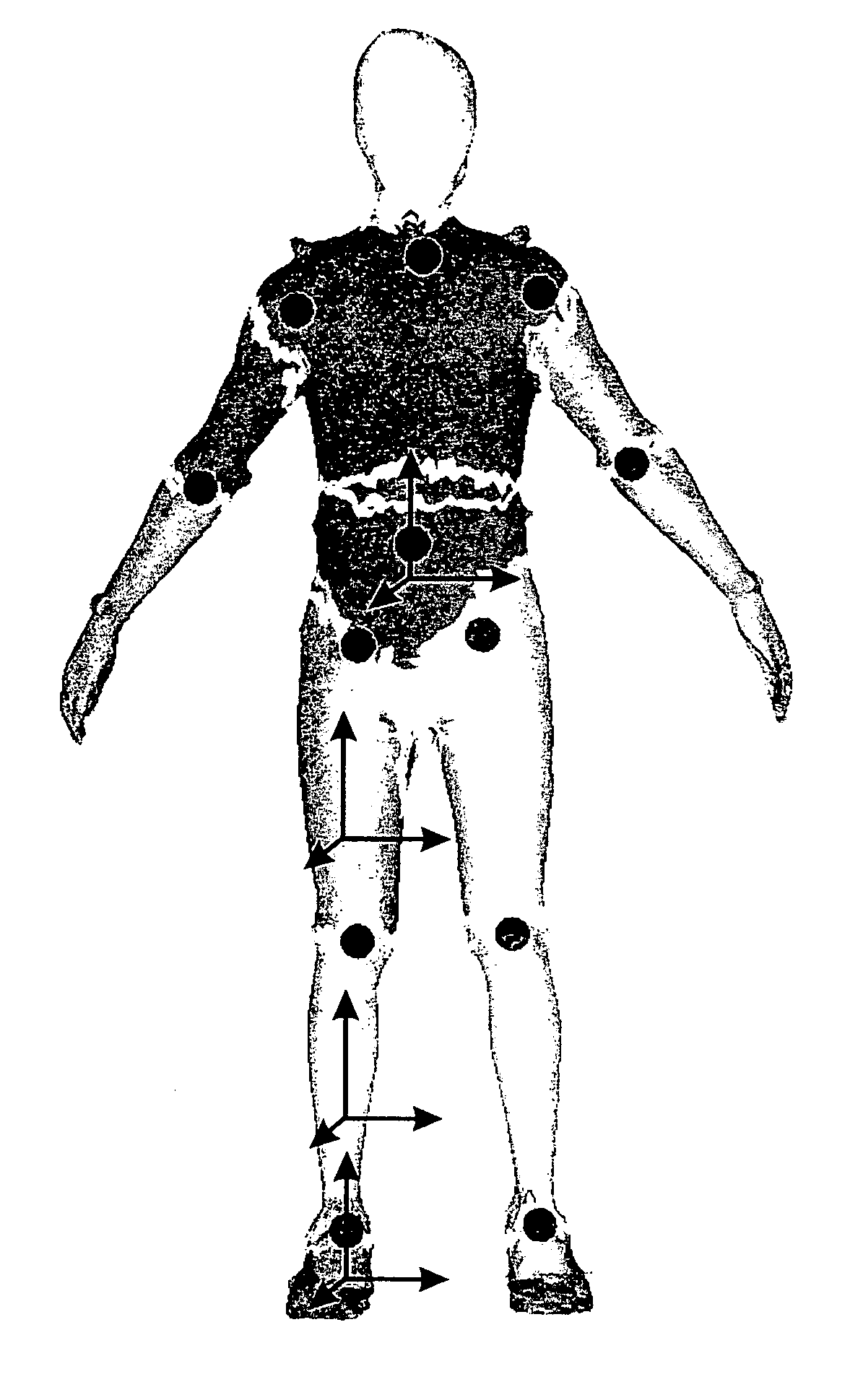
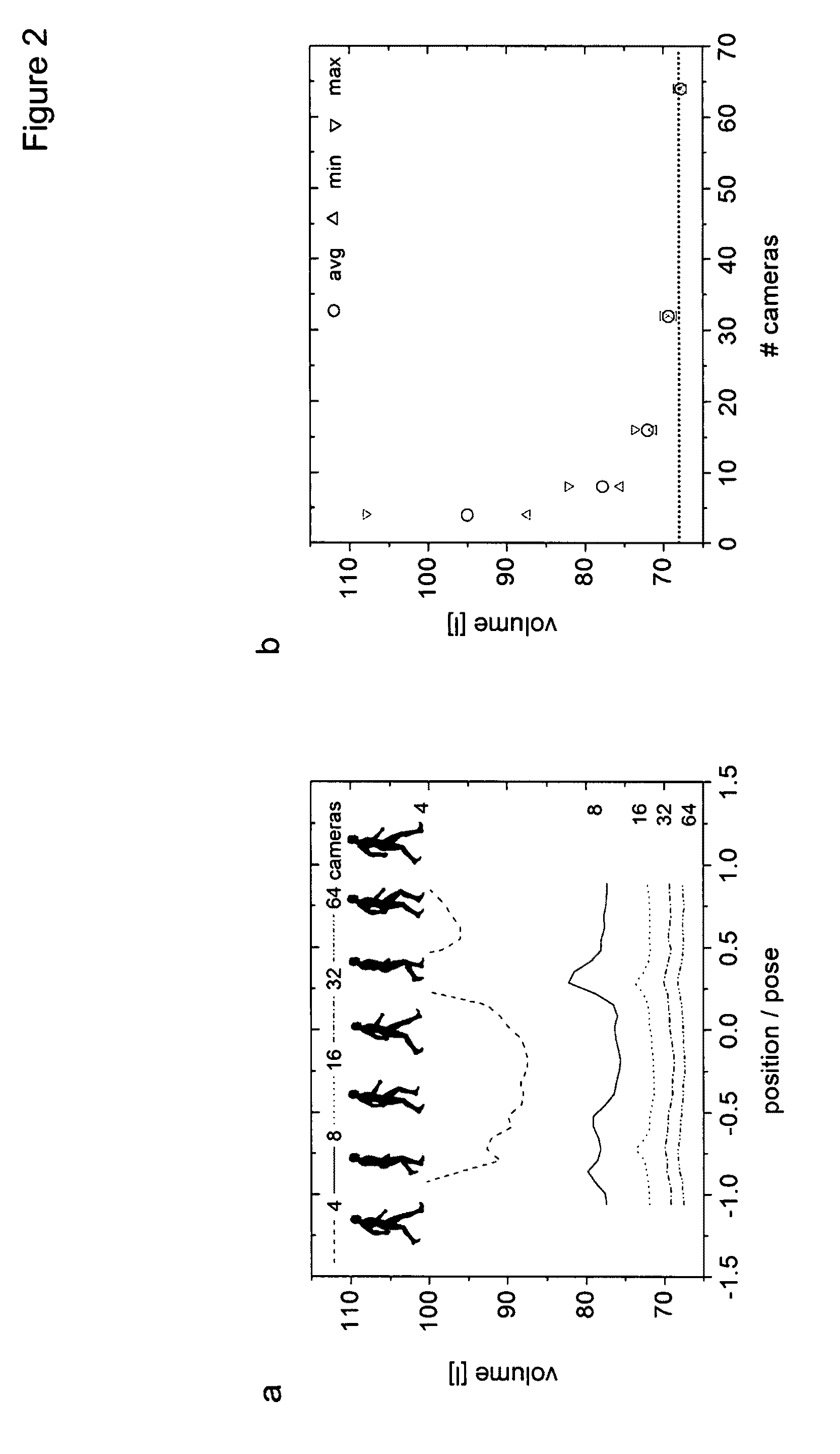
A markerless motion capture system is provided for measurements accurate enough for biomechanical, clinical, sport, entertainment, animation, game and movie, design, ergonomics, surveillance applications. The system has multiple cameras distributed around a viewing volume. The cameras allow for the creation of three-dimensional mesh representations of an object dynamically moving within the viewing volume. A model of the object that incorporates specific morphological and kinematic model information (including soft joint constraints) is then matched to the captured three-dimensional mesh representations. The matching routine aims to embed the model into each of the three-dimensional representations using (i) iterative closest point or simulated annealing algorithms and (ii) using soft joint constraints. This unique combination of routines offers a simple, time-efficient, accurate and thus more meaningful assessment of movements. The system further offers feasibility of accurately and precisely measuring three-dimensional kinematics of the dynamically moving object or human.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
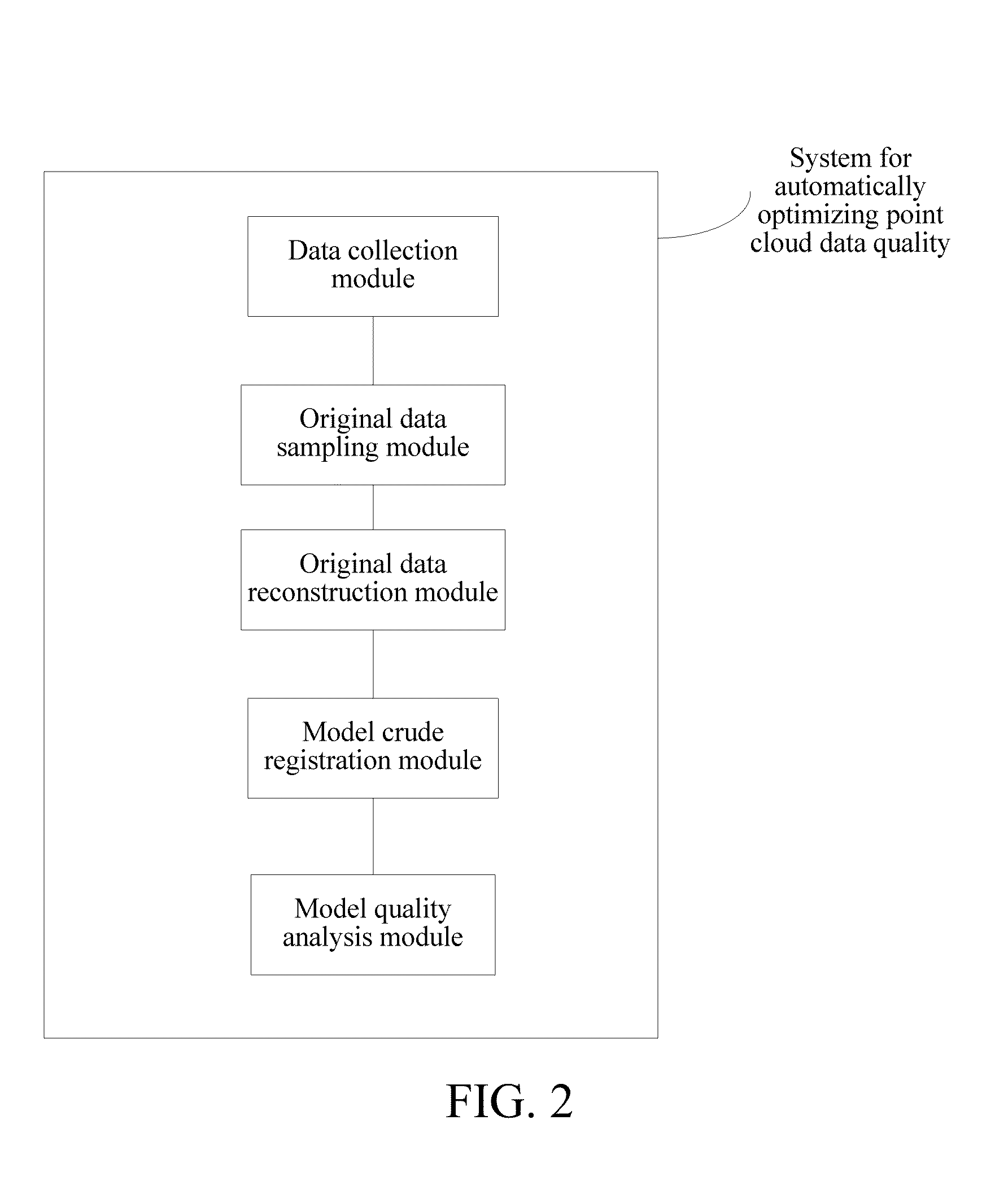
Method and system for automatically optimizing quality of point cloud data
Disclosed is a method for automatically optimizing point cloud data quality, including the following steps of: acquiring initial point cloud data for a target to be reconstructed, to obtain an initial discrete point cloud; performing preliminary data cleaning on the obtained initial discrete point cloud to obtain a Locally Optimal Projection operator (LOP) sampling model; obtaining a Possion reconstruction point cloud model by using a Possion surface reconstruction method on the obtained initial discrete point cloud; performing iterative closest point algorithm registration on the obtained Possion reconstruction point cloud model and the obtained initial discrete point cloud; and for each point on a currently registered model, calculating a weight of a surrounding point within a certain radius distance region of a position corresponding to the point for the point on the obtained LOP sampling model, and comparing the weight with a threshold, to determine whether a region where the point is located requires repeated scanning. Further disclosed is a system for automatically optimizing point cloud data quality.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Indoor and independent drone navigation method based on three-dimensional vision SLAM
ActiveCN108303099AAvoid complex processSolve complexityNavigational calculation instrumentsUncrewed vehicleGlobal optimization
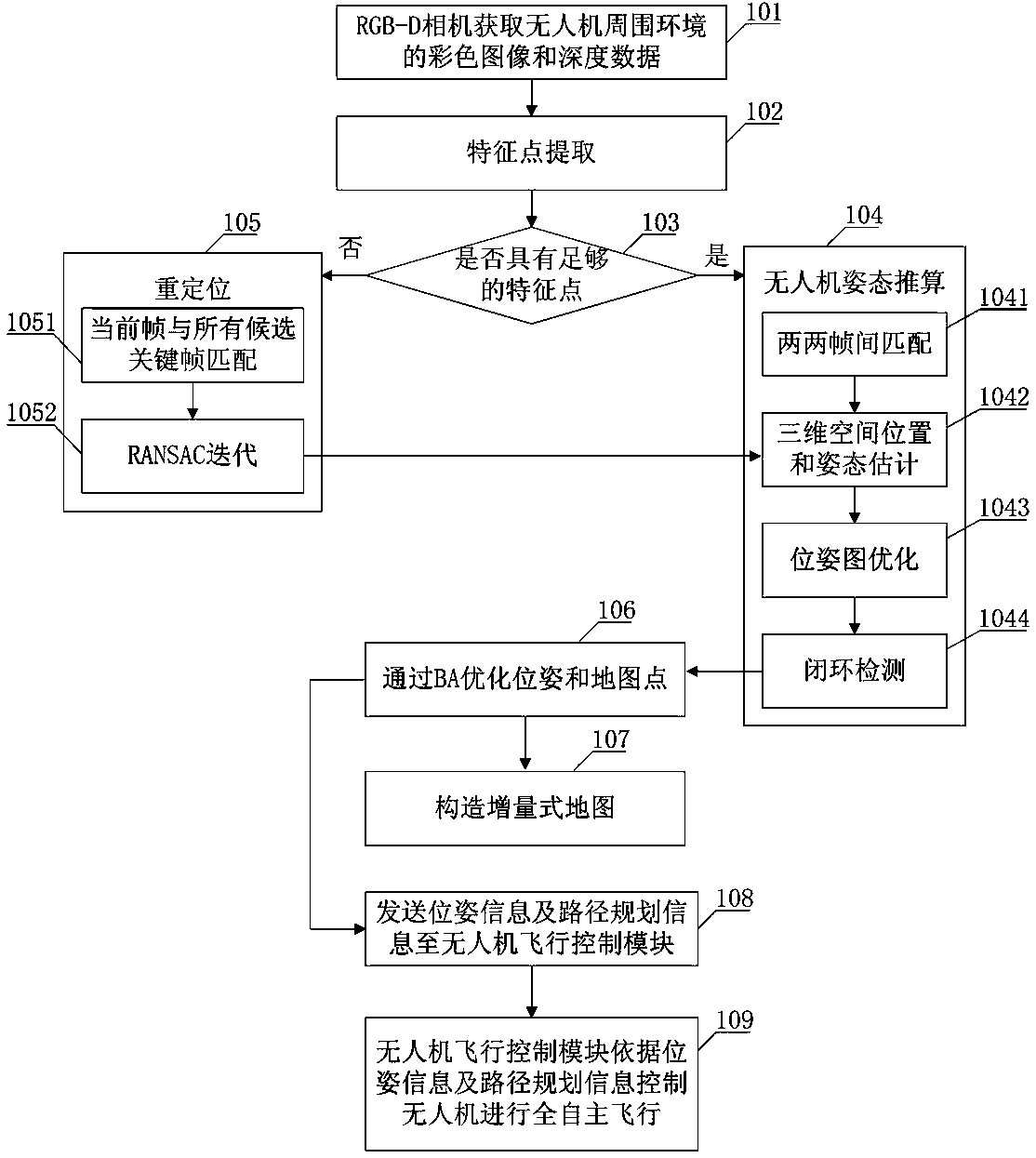
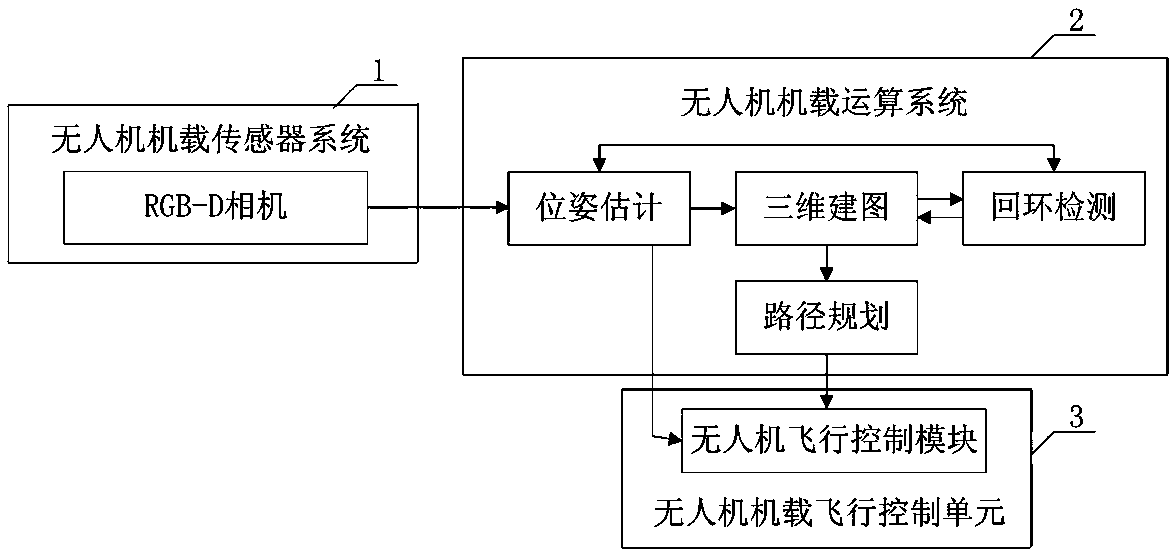
The invention provides an indoor and independent drone navigation method based on three-dimensional vision SLAM. The indoor and independent drone navigation method comprises the steps that an RGB-D camera obtains a colored image and depth data of a drone surrounding environment; a drone operation system extracts characteristic points; the drone operation system judges whether enough characteristicpoints exist or not, if the quantity of the characteristic points is larger than 30, it shows that enough characteristic points exist, the drone attitude calculation process is conducted, or, relocating is conducted; a bundling optimizing method is used for global optimization; an incremental map is built. Drone attitude information is given with only one RGB-D camera, a three-dimensional surrounding environment is rebuilt, the complex process that a monocular camera solves depth information is avoided, and the problems of complexity and robustness of a matching algorithm in a binocular camera are solved; an iterative nearest-point method is combined with a reprojection error algorithm, so that drone attitude estimation is more accurate; a drone is located and navigated and independentlyflies indoors and in other unknown environments, and the problem that locating cannot be conducted when no GPS signal exists is solved.
Owner:江苏中科智能科学技术应用研究院
Point cloud registering method based on iterative closest point algorithm
InactiveCN104700451AImprove registration accuracyOvercome the shortcomings of single registration method and poor registration accuracy3D modellingReference spaceAlgorithm
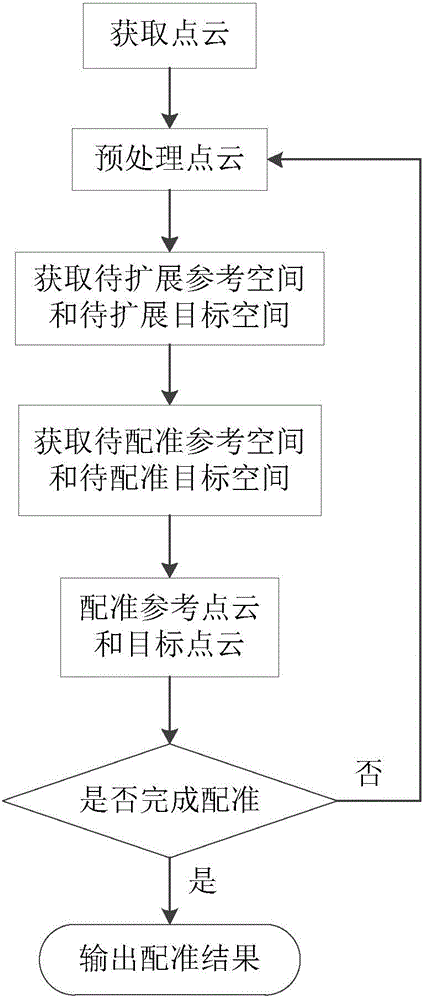
The invention discloses a point cloud registering method based on an iterative closest point algorithm. The point cloud registering method based on the iterative closest point algorithm is implemented through the steps of (1) obtaining a point cloud; (2) preprocessing the point cloud; (3) obtaining a reference space to be expanded and a target space to be expanded; (4) obtaining a reference space to be registered and a target space to be registered; (5) registering a reference point cloud and a target point cloud; (6) if determining that all segmented point clouds complete registration, performing the step (7), if not, returning to the step (2); (7) outputting a registration result. According to the point cloud registering method based on the iterative closest point algorithm, the point cloud to be registered is obtained according to scenes and through different scanning manners; then through the steps of rough registration, precise registration, corresponding point maximization and the like as well as registration score correction, the possibility of falling into local solution can be reduced, and the robustness and the registering precision can be improved. Therefore, the point cloud registering method based on the iterative closest point algorithm can be applied to registering point clouds of complex scenes.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
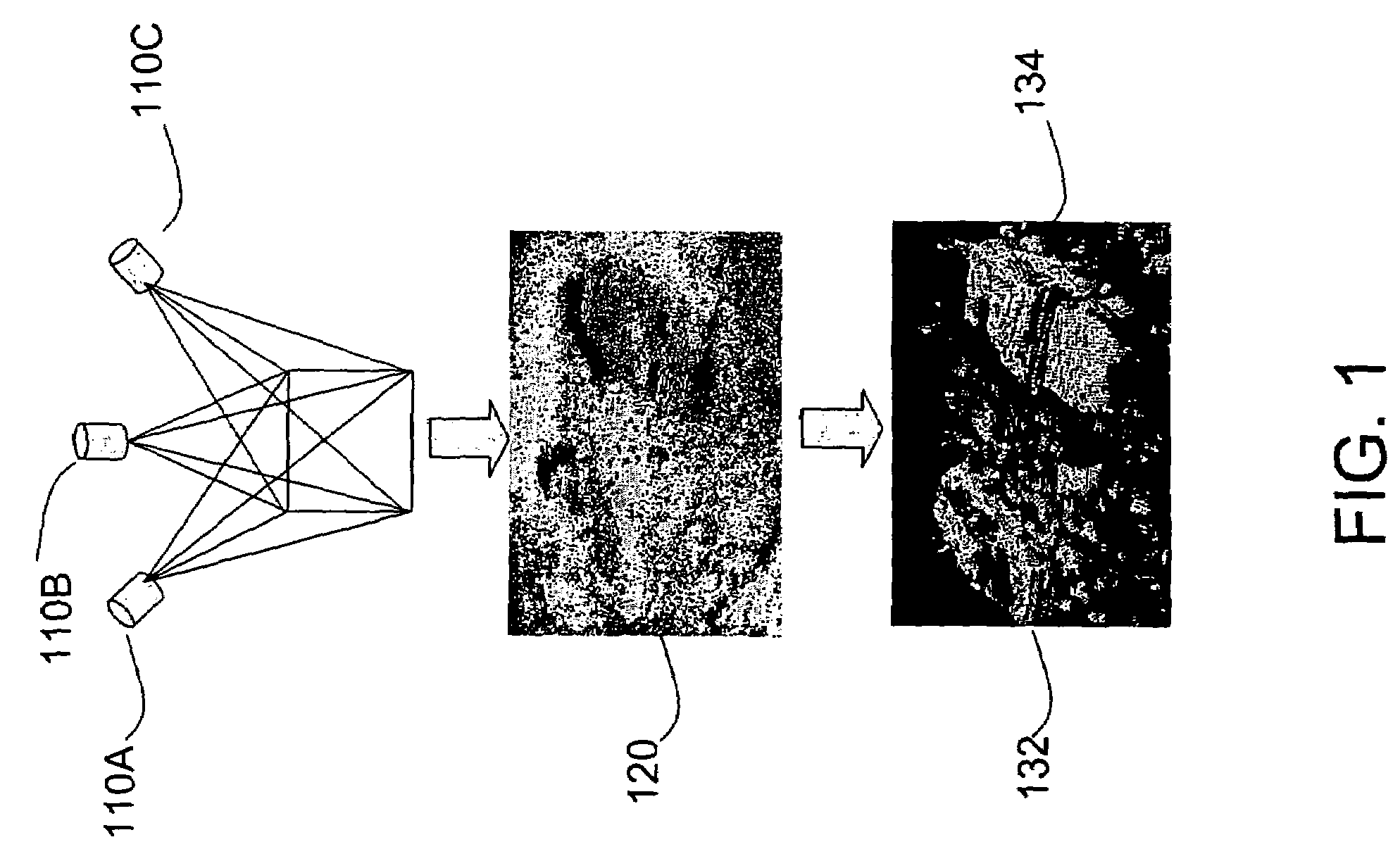
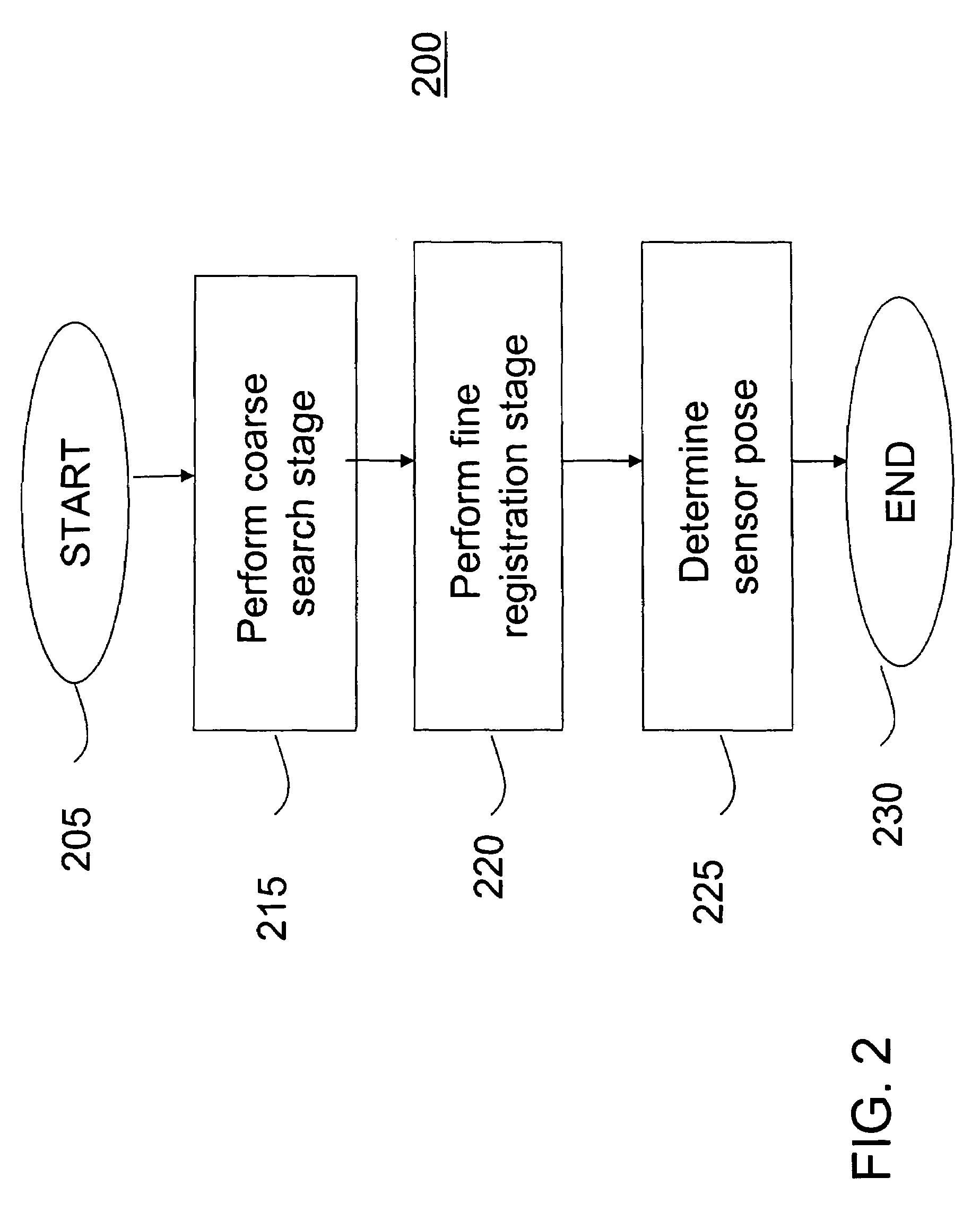
Method and apparatus for automatic registration and visualization of occluded targets using ladar data
A method and apparatus for high-resolution 3D imaging ladar system which can penetrate foliage and camouflage to sample fragments of concealed surfaces of interest is disclosed. Samples collected while the ladar moves can be integrated into a coherent object shape. In one embodiment, a system and method for automatic data-driven registration of ladar frames, comprises a coarse search stage, a pairwise fine registration stage using an iterated closest points algorithm, and a multi-view registration strategy. After alignment and aggregation, it is often difficult for human observers to find, assess and recognize objects from a point cloud display. Basic display manipulations, surface fitting techniques, and clutter suppression to enhance visual exploitation of 3D imaging ladar data may be utilized.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
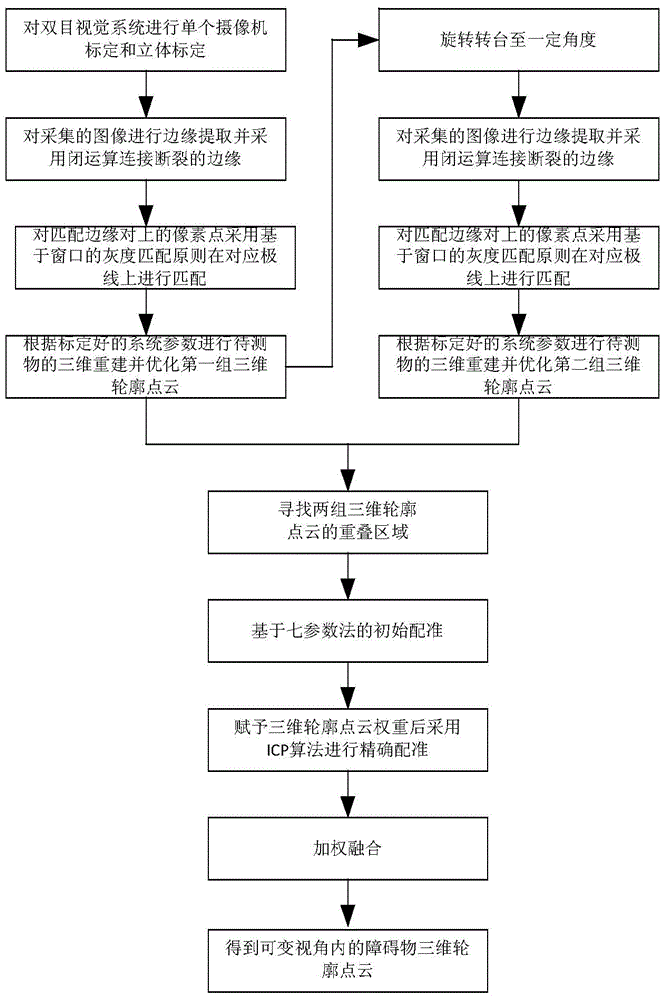
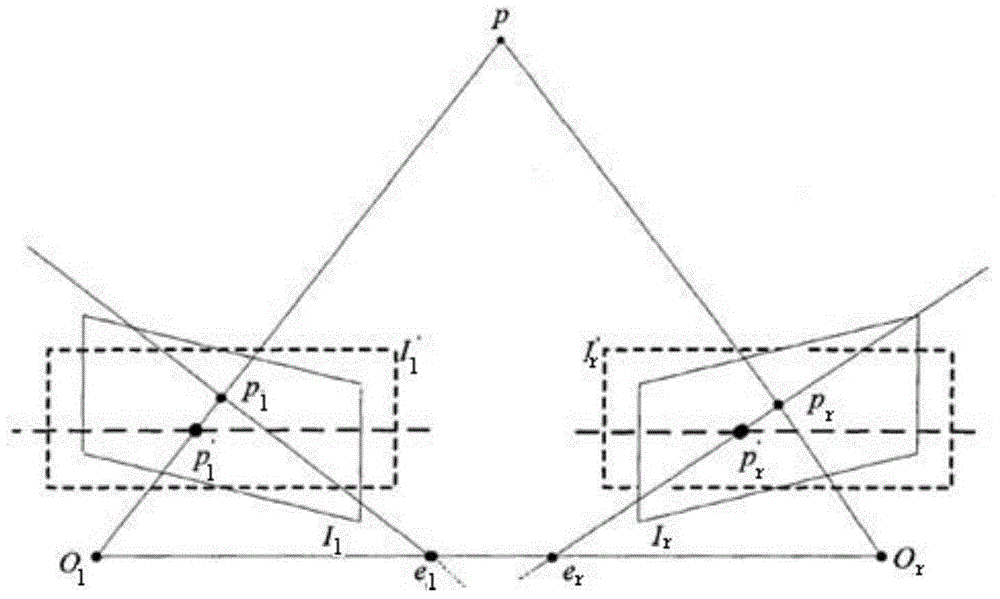
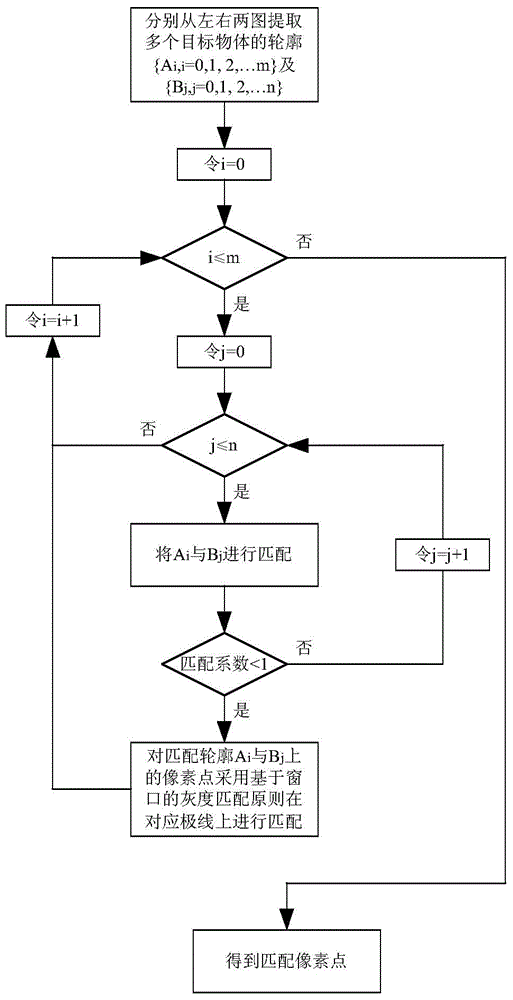
Variable-viewing angle obstacle detection method for robot based on outline recognition
ActiveCN104484648AQuick stitchingSmall amount of calculationImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
The invention discloses a variable-viewing angle obstacle detection method for a robot based on outline recognition. The method comprises the following steps: (1) calibrating a binocular visual system by using a calibration plate; (2) simultaneously shooting the same scene by virtue of two video cameras, carrying out epipolar rectification on left and right images, then extracting edges and connecting the edges; (3) searching an outline of a target object, and matching the outline; (4) rebuilding three-dimensional point clouds of the outline, and optimizing three-dimensional outline point clouds; (5) rotating a turntable at a certain angle, ensuring an overlapping region in two times of shooting, carrying out three-dimensional rebuilding in another direction; (6) searching the overlapping region of two groups of three-dimensional outline point clouds; (7) carrying out initial registration on the two groups of three-dimensional outline point clouds by adopting a seven-parameter method; (8) providing corresponding point weights of the overlapping region, carrying out iterative closest point operation on the three-dimensional outline point clouds of the overlapping region, and finishing accurate registration of the three-dimensional outline point clouds. The method disclosed by the invention is high in registration accuracy, small in operand and relatively high in instantaneity.
Owner:湖州度信科技有限公司
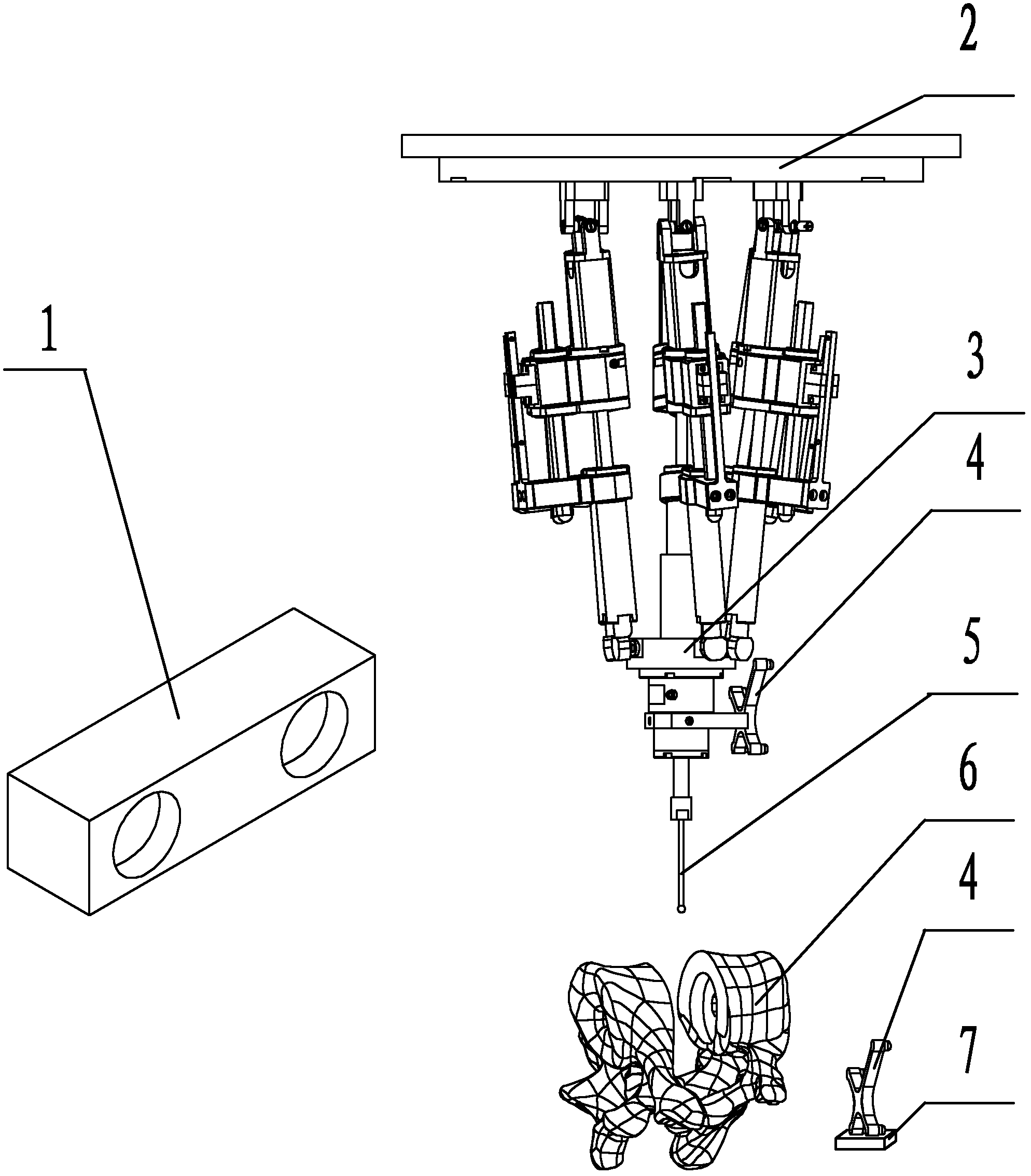
Image navigation-based parallel robot-assisted artificial cervical intervertebral disc replacement surgery positioning method
InactiveCN102429726AAchieve positioningSolve the lack of precisionDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsPatient modelSurgical operation
The invention discloses an image navigation-based parallel robot-assisted artificial cervical intervertebral disc replacement surgery positioning method, which belongs to application of a parallel robot in the field of surgical operation and is used for making sure that the pose relation between a practical surgery abrasive drilling and a patient is consistent with the pose relation between a virtual abrasive drilling and a patient model determined by a doctor in a virtual environment. According to technical key points, the method comprises the following steps of: performing three-dimensional reestablishment on a CT (Computerized Tomography) image by using a VTK (Visualization Tool Kit) software package to obtain a three-dimensional model of the silk cervical vertebra of a patient; introducing the virtual abrasive drilling into an image space and making the doctor complete virtual positioning on a computer; establishing a position and pose mapping relation among the image, the patient and the robot by using an optical positioning system and an ICP (Iterative Closest Point) algorithm; and controlling the parallel robot to move to finally complete positioning of the abrasive drilling of the parallel robot and the patient.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
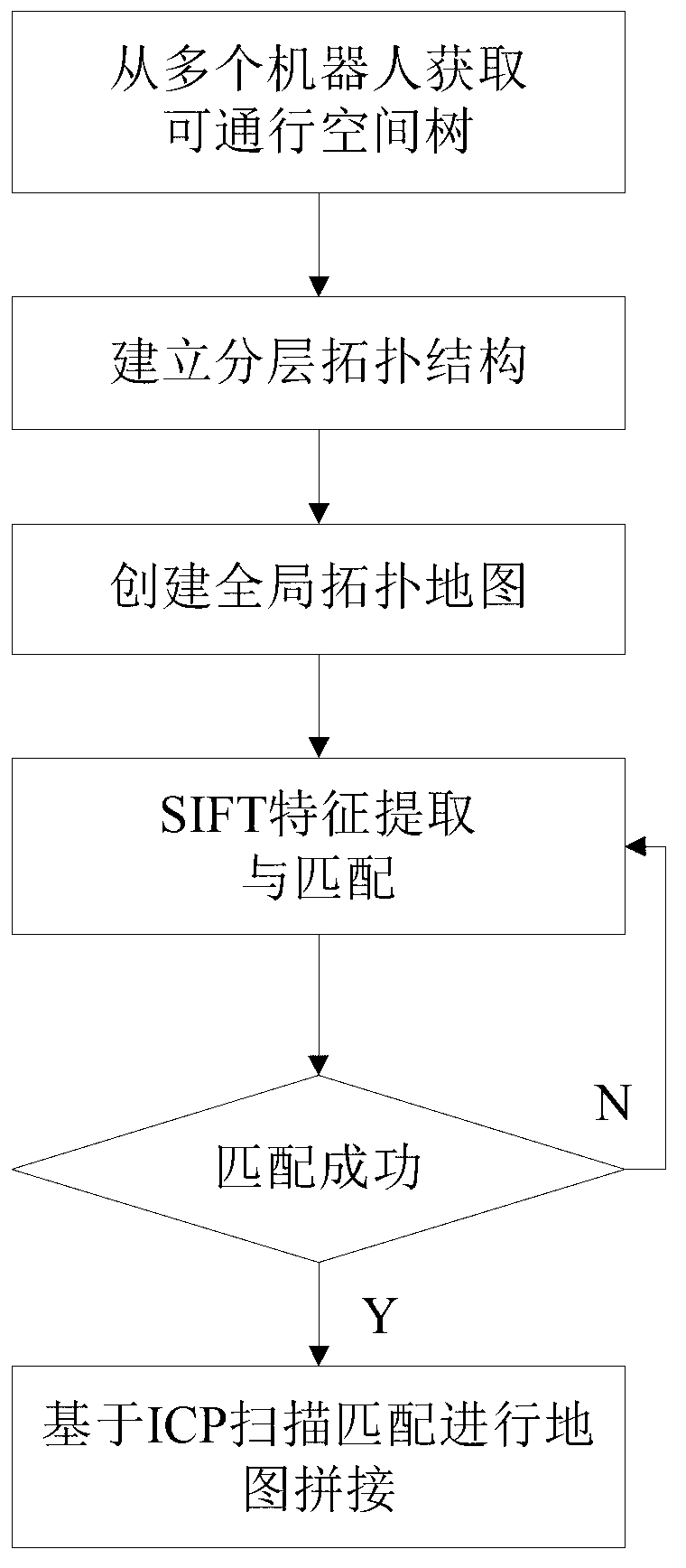
Layered topological structure based map splicing method for multi-robot system
InactiveCN103247040AImprove accuracySolve the problem of creating efficiencyImage enhancementScale-invariant feature transformMultirobot systems
The invention belongs to the field of intelligent movable robots, and discloses a layered topological structure based map splicing method for a multi-robot system in an unknown environment and solves the map splicing problem of the multi-robot system in case the position and posture are unknown. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring an accessible space tree, building a layered topological structure, creating a global topological map, extracting SIFT (Scale Invariant Feature Transform) features and performing feature matching, and performing map splicing based on ICP (Iterative Closest Point) scanning matching. According to the invention, under the condition that the relative positions and gestures of robots are unknown, a layered topological structure merging SIFT features is provided, the global topological map is created in an increment manner, and the map splicing of the multi-robot system under large scale unknown environment is realized according to the SIFT information among the nodes, in combination with a scanning matching method; and the splicing accuracy and real-time performance are effectively improved. Therefore, the method is suitable for the field of intelligent mobile robots related to map creation and map splicing.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Dual bootstrap iterative closest point method and algorithm for image registration
ActiveUS7177486B2Fewer initial correspondencesAvoid ambiguityImage enhancementImage analysisFeature mappingIterative method
An iterative method and associated algorithm for performing image registration to map features in a first image to corresponding features in a second image in accordance with a transformation model. Upon convergence of a parameter vector associated with the model, a current bootstrap region includes and exceeds an initial bootstrap region that is initially established. During the iterations, the parameter vector is estimated by minimizing an objective function with respect to the parameter vector. Each iteration generates a next bootstrap region that minimally includes the current bootstrap region and may exceed the current bootstrap region. The model may change in successive iterations.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
An improved ICP object point cloud splicing method for fusing fast point characteristic histogram
ActiveCN109345620AImprove processing efficiencyImprove processing precisionImage enhancementImage analysisLocal optimumGrating
The invention discloses an improved ICP object point cloud splicing method for fusing fast point characteristic histogram. The method comprises the steps of projecting a standard sinusoidal digital grating onto the surface of the object to be measured, photographing stripe images of the surface of the object projected with the standard sinusoidal digital grating from different angles of view by aCCD camera, and obtaining photographing point clouds from multiple angles of view; for two image point clouds that need to be stitched together, building a k-D tree and interpolate to obtain that interpolated point cloud; for the two interpolated point clouds to be spliced, computing the fast point feature histogram, and obtaining the point cloud by random sampling consistent transformation; usingthe improved iterative nearest point method to obtain the first interpolated point cloud which is precisely registered; overlaying point cloud and mesh to realize the mosaic of two different angles of view of the shooting point cloud. The invention has low requirement for the initial position of the splice point cloud, the robustness is remarkably improved, the local optimization is not easy to fall into, the splice accuracy is improved, and the precise splicing of the point cloud under multi-view angles is realized, so that the practical industrial application requirements can be met.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
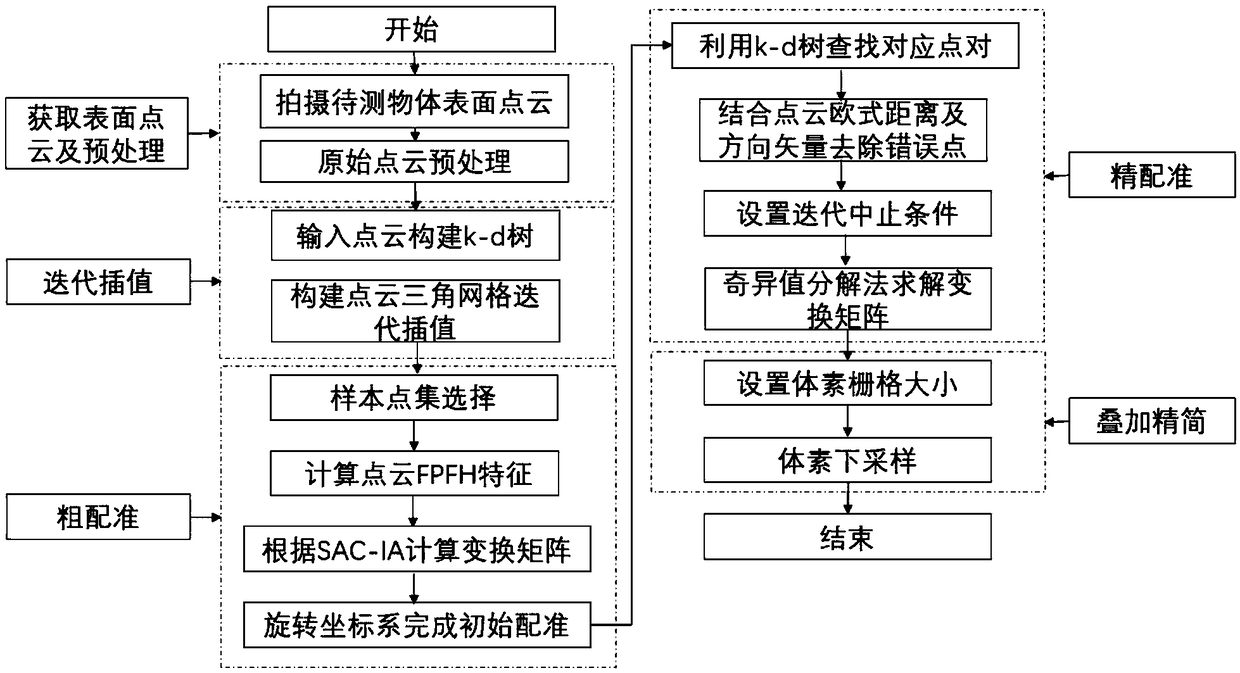
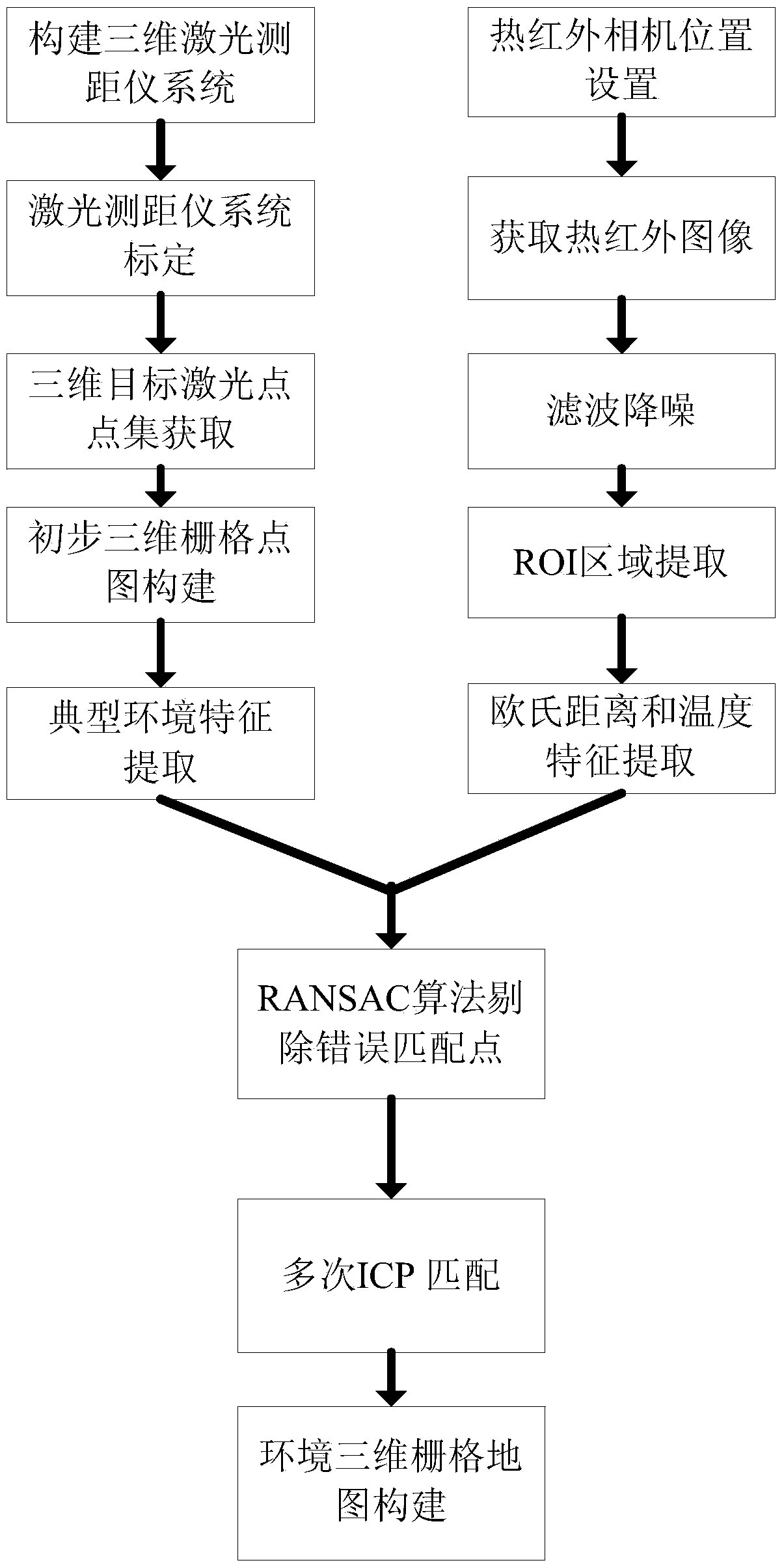
Map building method based on thermal infrared camera and laser range finder
ActiveCN103512579AImprove reliabilityFixes an issue where maps would not build correctlyInstruments for road network navigationMaps/plans/chartsLaser rangingEuclidean distance
The invention relates to a map building method based on a thermal infrared camera and a laser range finder. The method is characterized in that the problem that in the prior art, a map cannot be correctly built under the conditions of poor light condition and existence of a shielding object is effectively solved by acquiring a thermal infrared image of a target instead of acquiring the visible image of the target, and a rectangular frame containing the target is obtained by taking a variance weighted information entropy for interest area extracting, so as to reduce the learning space and remove huge noise jamming. According to the invention, the matched corresponding points of Euclidean distance and temperature are high in reliability, an RANSAC (random sample consensus) algorithm filters the corresponding points, so that the reliability of the corresponding points is improved to the greatest extent, and the matching calculation speed based on an ICP (iterative closest point) algorithm is high.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
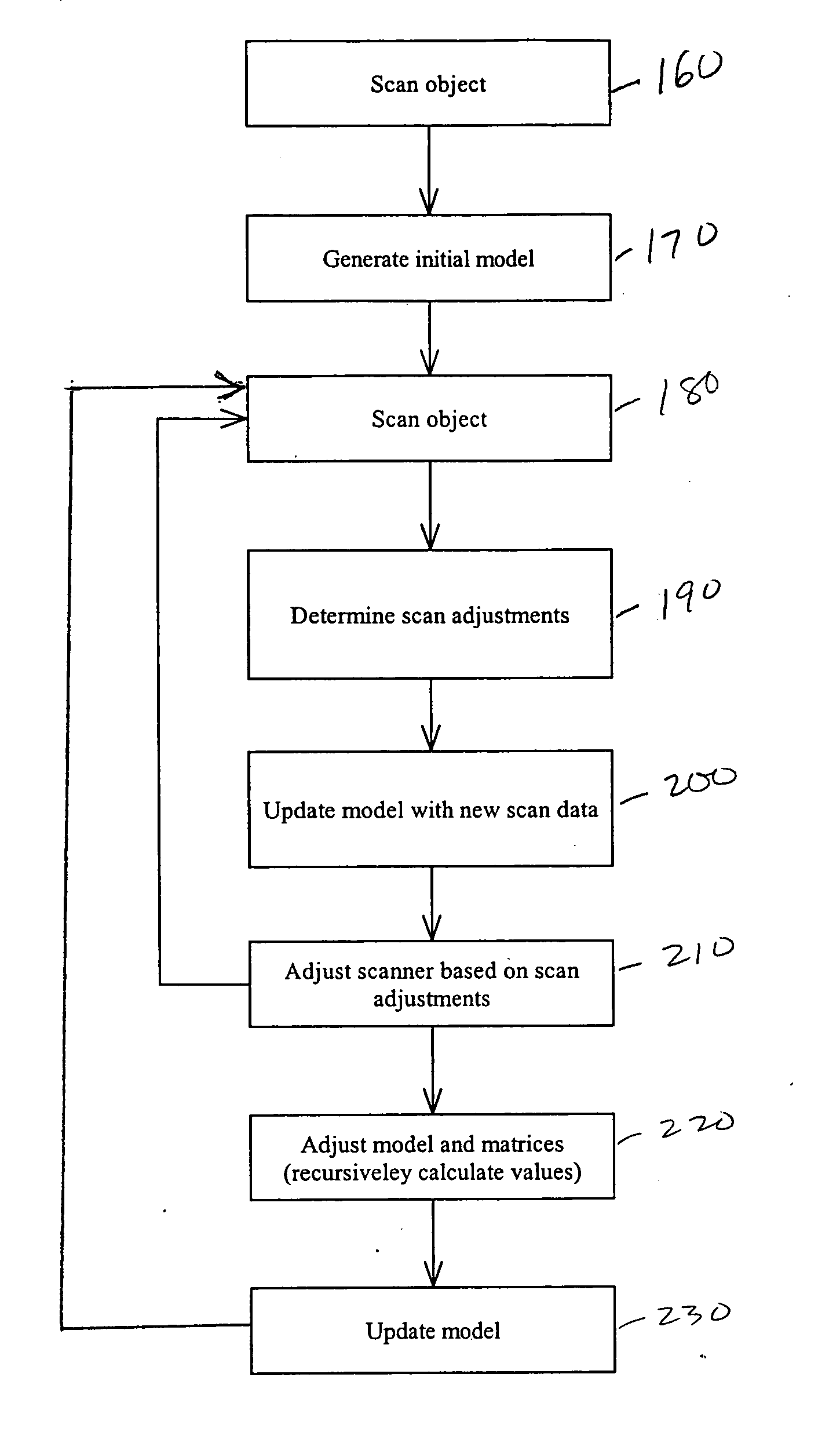
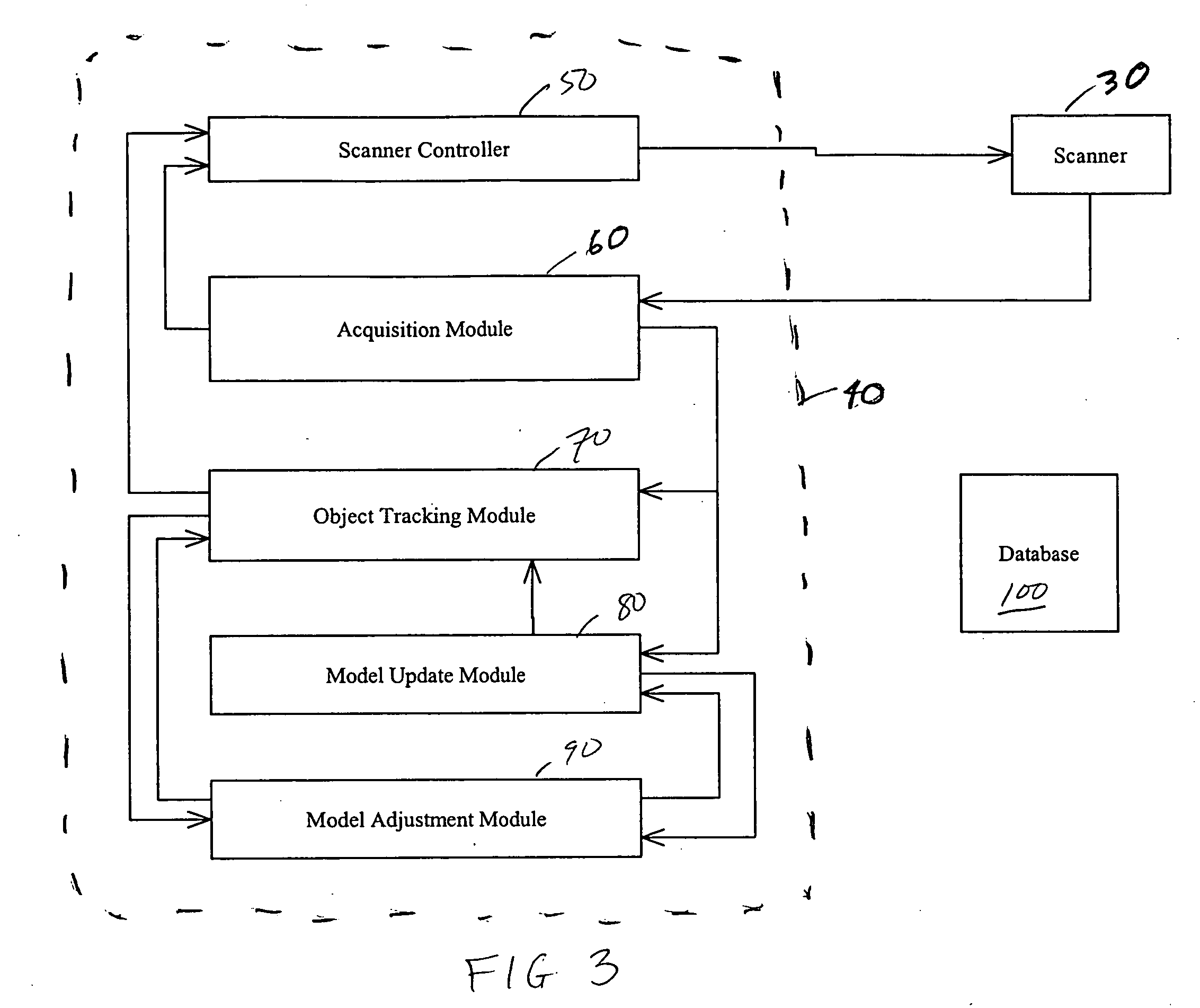
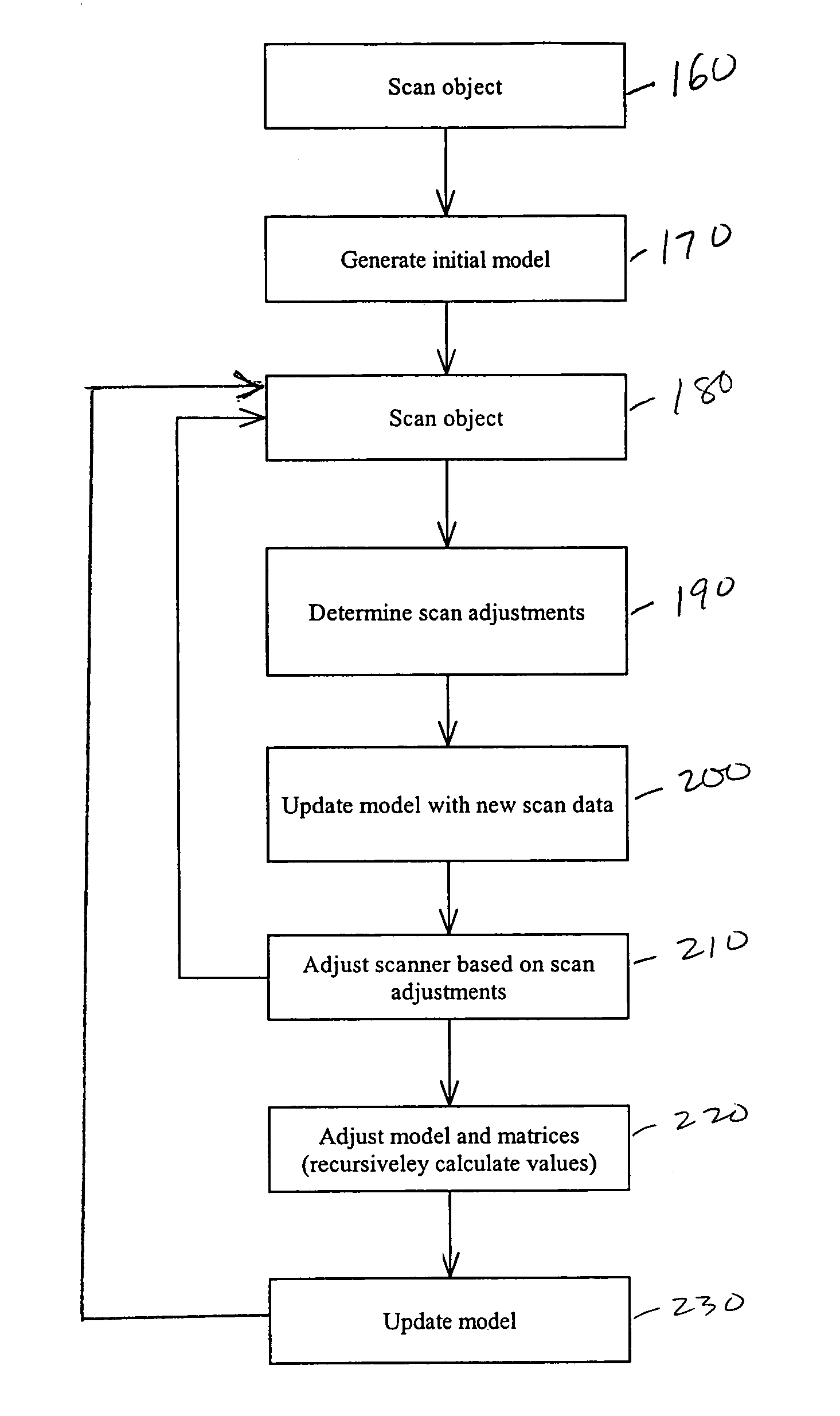
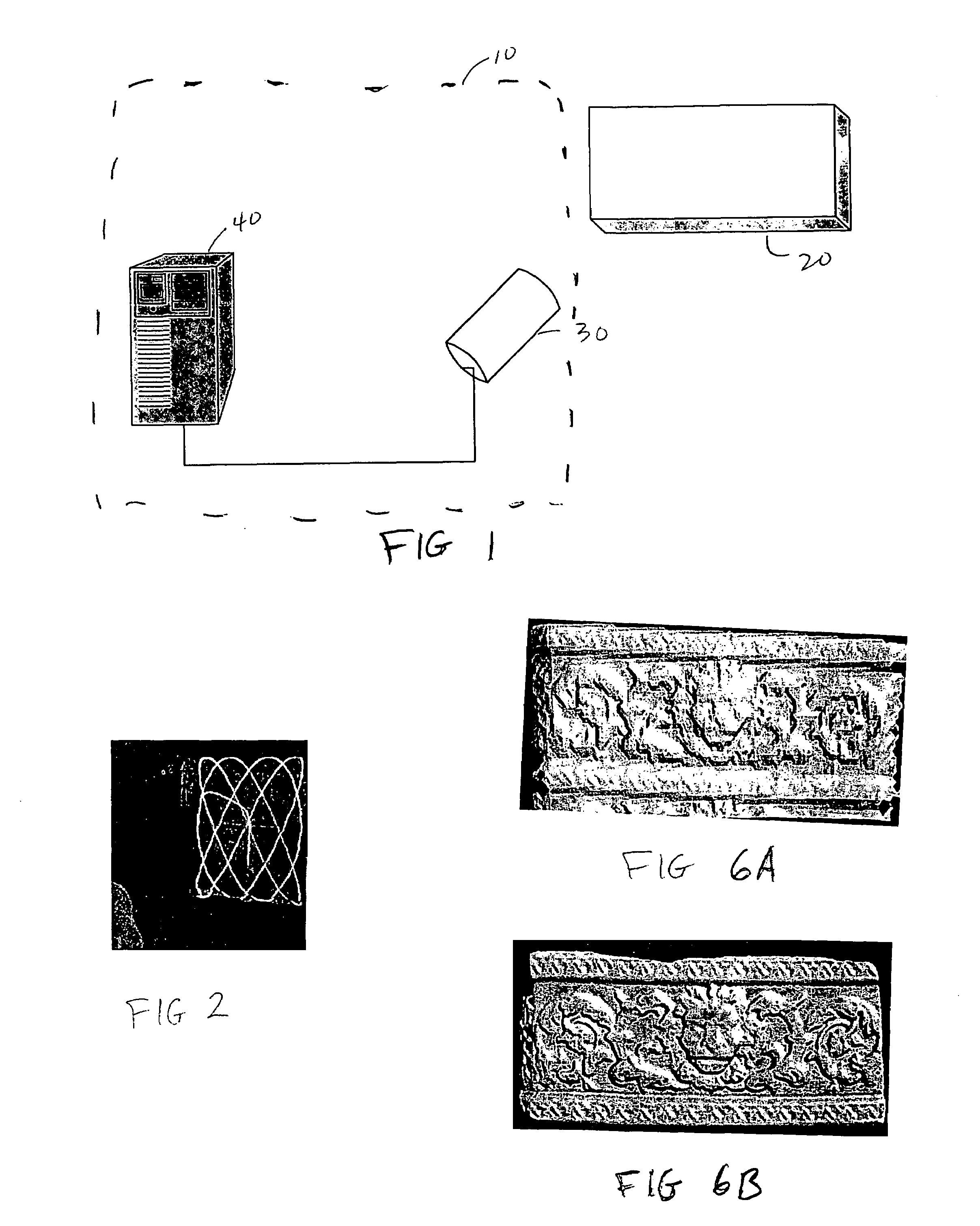
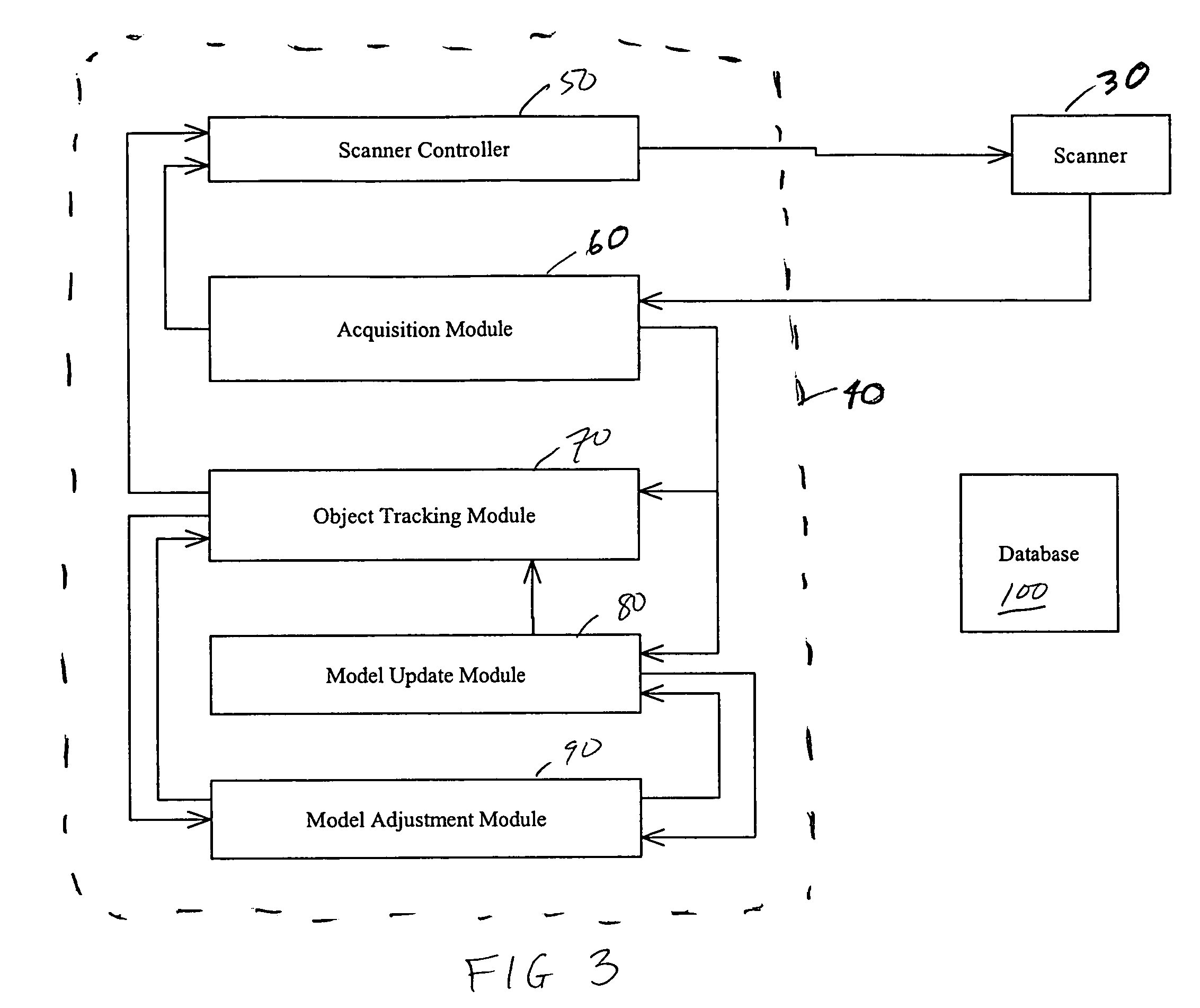
Recursive 3D model optimization
Systems and methods for generating and optimizing 3D models of objects. A laser scanner is controlled by a data processing subsystem that controls the scanning and processes the data generated. From an initial model, either a raster scan of the object or an initial scan, the system scans the object multiple times, each time adjusting the laser scanner to maximize a correlation between the data generated and the model. The model is also updated using the scan data and taking into account the adjustments which were applied to the laser scanner. Other adjustments, such as those which would remove the effect of relative motion on the scan data, are also accounted for when incorporating scan data into the model. The model is recursively adjusted and optimized using previous scan data (both pre-recorded and fresh scan data) and previous adjustments. The model may be modified and adjusted using previous scan data and an Iterative Closest Point method. The method and systems may be used in uncontrolled environments where unpredictable motions and vibrations can occur. The invention may be used with scanners mounted on a robotic arm, scaffolding, unstable tripods, at the tips of booms or lifts, or the scanners may be simply held by hand.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
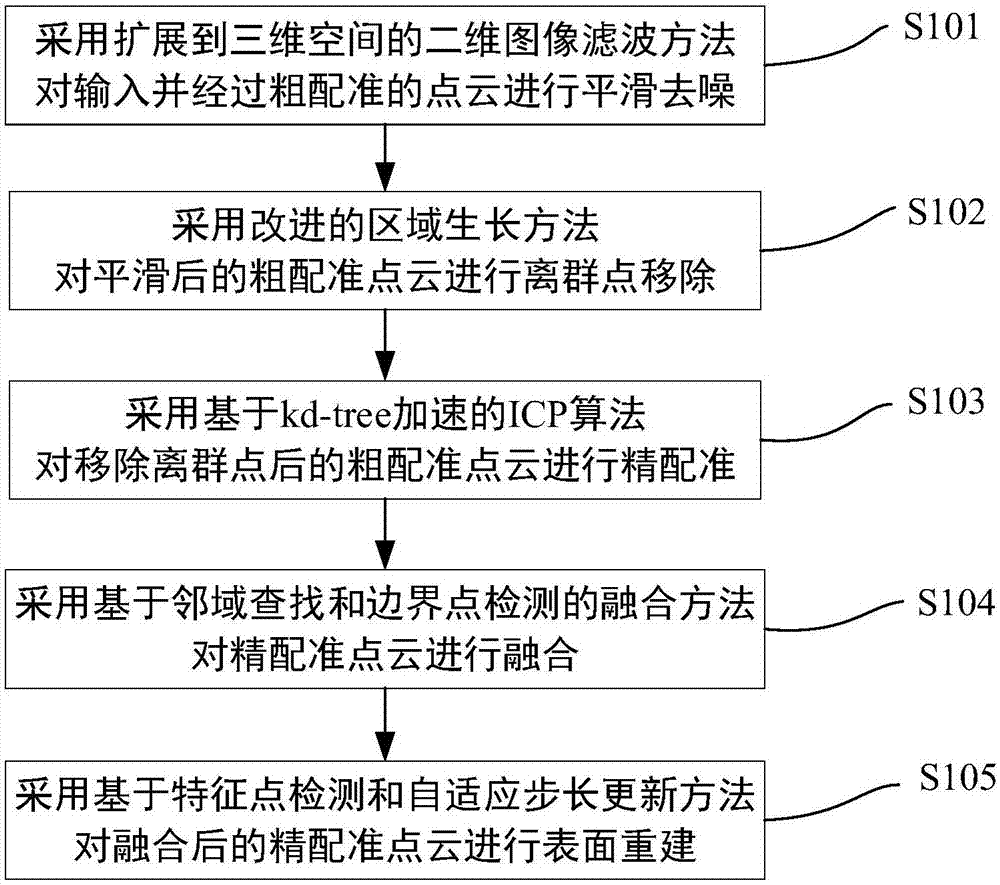
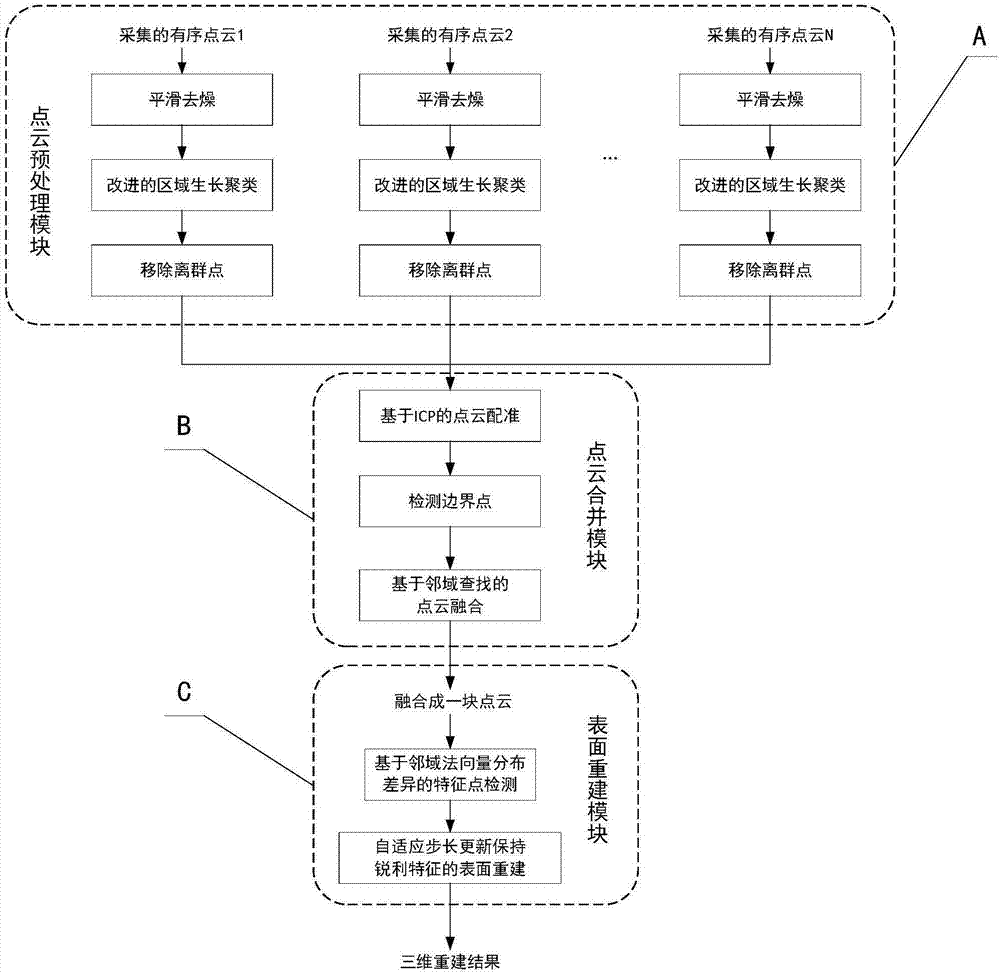
Three-dimensional reconstruction method and system capable of maintaining sharp features
The present invention discloses a three-dimensional reconstruction method and system capable of maintaining sharp features. The method includes the following steps that: 1) a two-dimensional image filtering method extended to a three-dimensional space is adopted to perform smoothing de-noising on inputted roughly-registered point cloud; 2) an improved region growth method is adopted to perform outlier removal on the smoothed roughly-registered point cloud; 3) a kd-tree (k-dimensional tree) acceleration-based ICP (iterative closest point) algorithm is adopted to perform precise registration on the outlier-removed roughly-registered point cloud; 4) a neighborhood search and boundary point detection-based fusion method is adopted to fuse the precisely-registered point cloud; and 5) a feature point detection and adaptive step size update-based method is adopted to perform surface reconstruction on the fused precisely-registered point cloud. The three-dimensional reconstruction system is composed of a point cloud preprocessing module, a point cloud combining module and a surface reconstruction module. The three-dimensional reconstruction system which is realized based on the method of the invention can maintain the sharp features of the edge of a reconstructed model, and therefore, reconstruction speed is considered with accuracy ensured.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for filling indoor light detection and ranging (LiDAR) missing data based on Kinect
InactiveCN102938142AIntegrity can be maintainedRealize collection workImage enhancementImage analysisMissing dataScale-invariant feature transform
The invention relates to a method for filling indoor LiDAR missing data based on Kinect. The method comprises extracting a key frame in a Kinect scanning process to obtain sparse scanned data; using a scale invariant feature transform (SIFT) algorithm to perform feature extraction on a RGB-D image collected by a Kinect device, and rejecting abnormal feature matching points through a random sample concensus (RANSAC) operator; merging the extracted features; extracting features of an LiDAR image, matching the features with the features of the Kinect device roughly to obtain a transfer matrix; using an improved iterative closest point (ICP) algorithm to achieve fine match of the LiDAR image with the RGB-D image of the Kinect; and performing the missing data fusion between an LiDAR model and the part scanned by the Kinect. The method for filling indoor LiDAR missing data based on Kinect has the advantages that the device cost is low, the acquisition process is flexible, scene depth and image information can be obtained, partial or missing data of indoor complex scenes can be acquired and filled rapidly.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
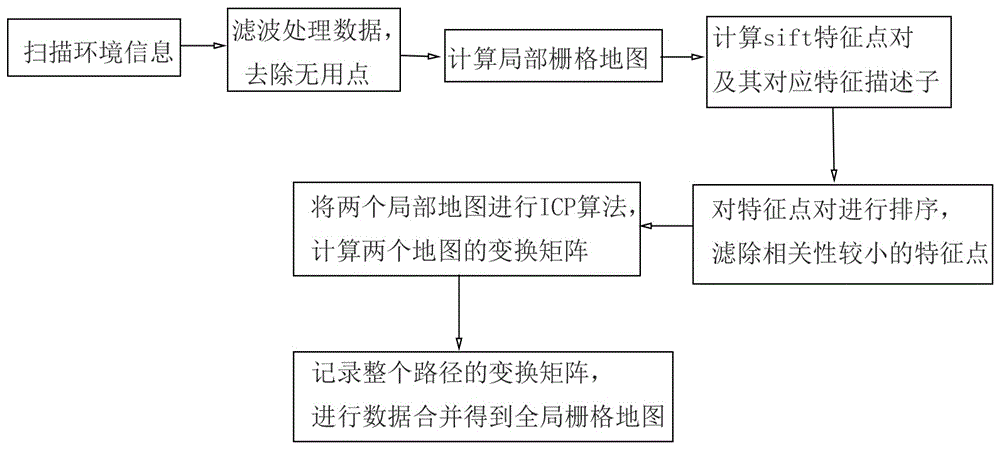
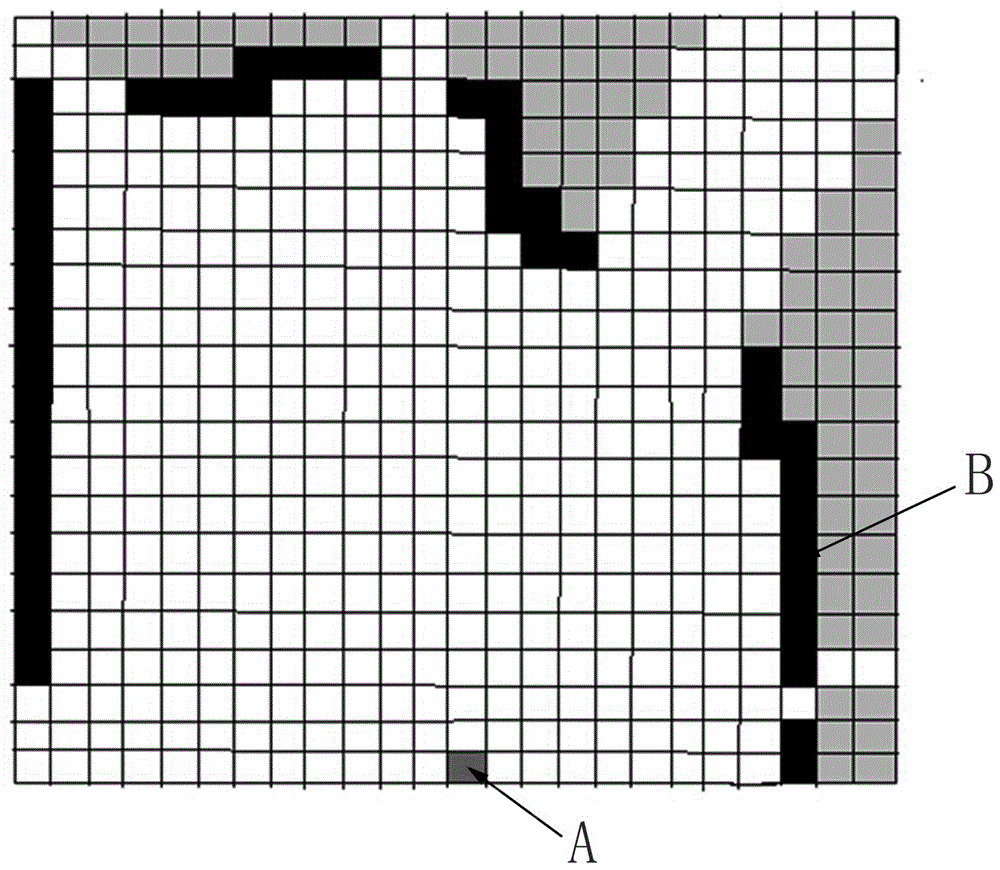
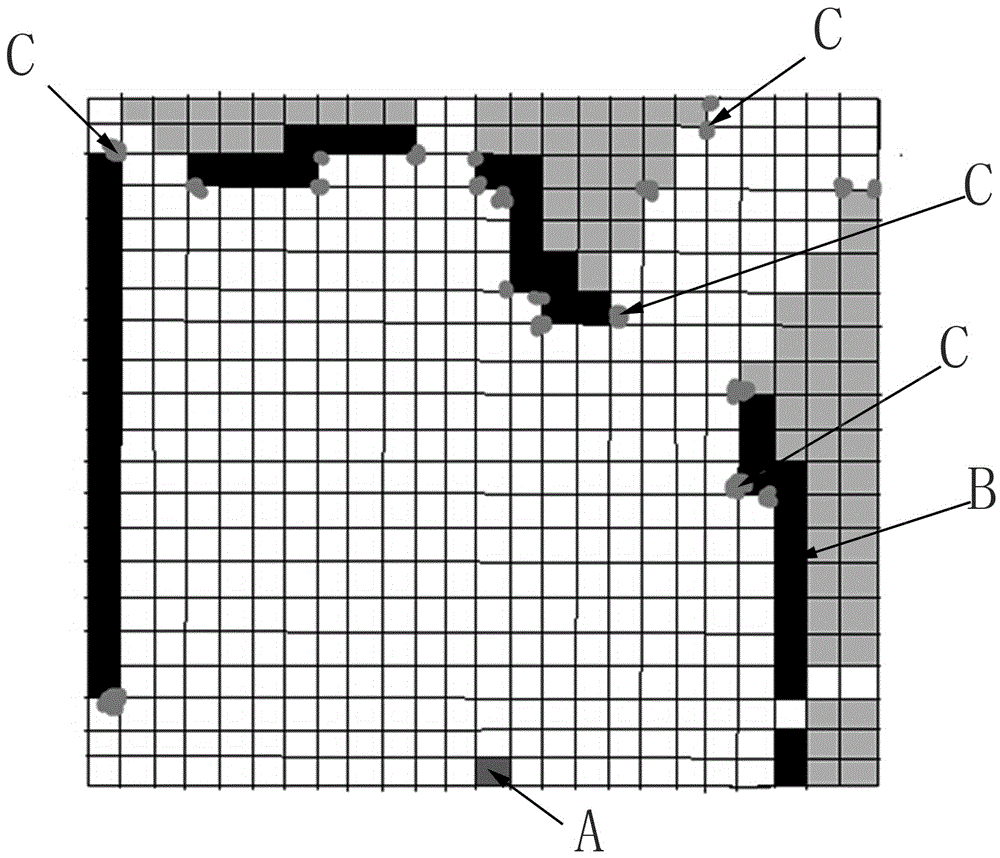
Raster map building method based on local map splicing
ActiveCN105806344ANo estimation biasReduce cumulative errorNavigational calculation instrumentsGeometric image transformationLaser dataLaser sensor
The invention discloses a raster map building method based on local map splicing.The method comprises the following steps that 1, a robot scans and records environment information; 2, scanning data points are filtered to remove useless points; 3, local raster maps are calculated based on the filtered data through a ray tracking method; 4, sift feature points and corresponding feature descriptors of the local raster maps under two adjacent poses are calculated; 5, according to relevancy of the feature descriptors, the feature points are ranked, and feature points with small feather feature descriptors are filtered away; 6, the two local maps are subjected to iterative closest point algorithm ICP, and a transformation matrix of the two local maps is calculated; 7, the steps 1-6 are repeated, a transformation matrix of the whole path is recorded and completed, and finally data is merged to obtain a global raster map.The map is built through one-time laser data, so that the estimation error of the map is mainly the observation error of a laser sensor, and no estimation error exits.
Owner:HANGZHOU SHENHAO TECH
Method for quickly measuring topography by using ground laser scanner based on CORS (Continuous Operational Reference System) and ICP (Iterative Closest Point) algorithms
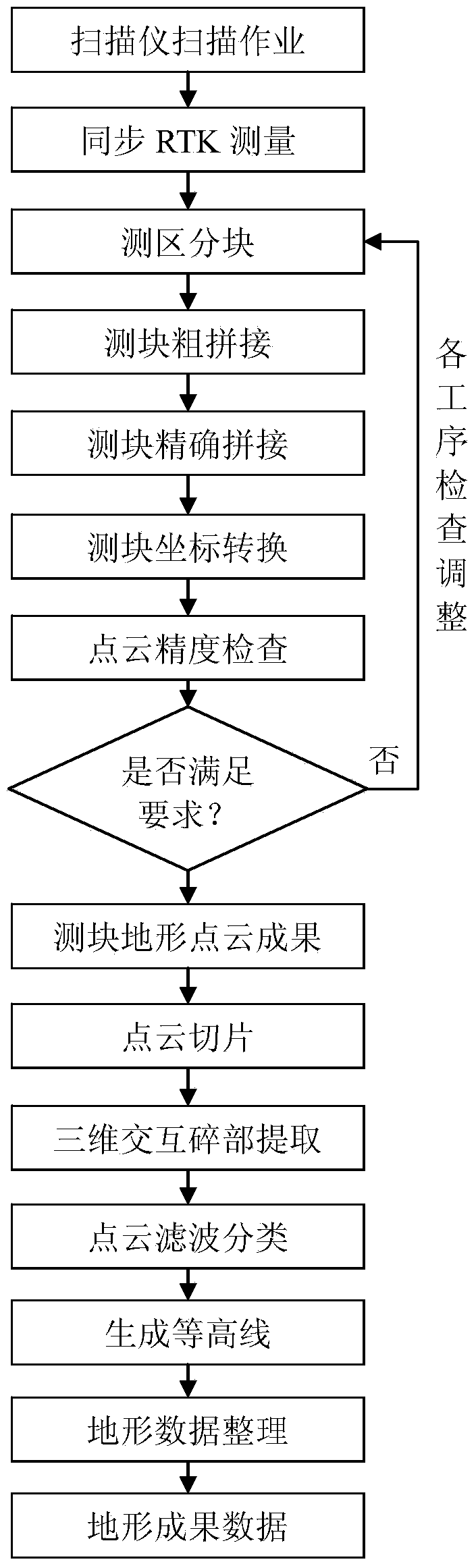
The invention discloses a method for quickly measuring topography by using a ground laser scanner based on CORS (Continuous Operational Reference System) and ICP (Iterative Closest Point) algorithms. The method comprises the following steps: 1, coaxially connecting a GPS (Global Position System) antenna with the scanner; 2, mounting the scanner at the top of a vehicle; 3, scanning in 360 degrees through the scanner during operating; 4, synchronously measuring a topocentric geodetic coordinate of the scanner by using a GPS carrier phase dynamic real-time difference method on the basis of CORS; 5, partitioning large measuring regions into blocks along roads and rivers; 6, roughly registering measurement blocks by using public planimetric points between measuring stations; 7, carrying out multi-station cloud accurate splicing in the measurement blocks by using an iterative closest point algorithm from a point to a tangent plane; 8, converting point cloud of the measurement blocks to the geodetic coordinate by using the topocentric geodetic coordinate; 9, dividing a three-dimensional point cloud into ground points and non-ground points and generating a contour line by using the ground points; 10, measuring and drawing a terrain landform line graph by using a method of collecting man-machine interaction details and slicing point cloud based on the three-dimensional point cloud; and 11, carrying out field investigation and plotting, mending and measuring, and editing and finishing a terrain line graph to obtain a topography result.
Owner:GUANGZHOU URBAN PLANNING & DESIGN SURVEY RES INST
Weak-texture workpiece, and method and system for recognizing and detecting three-dimensional pose
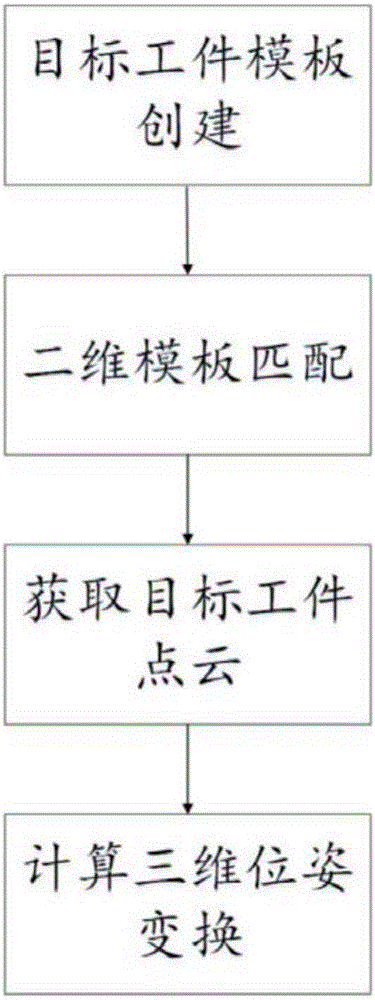
InactiveCN106251353AEasy to operateImproving the accuracy of 3D pose estimationImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionColor image
The invention discloses a weak-texture workpiece, and a method and a system for recognizing and detecting the three-dimensional pose. After a color image of a target workpiece acquired by an RGB-D sensor and a gradient pattern template library are subjected to image pyramid search based on a similarity evaluation function, a three-dimensional point cloud is built on a depth image according to a matching result, and finally, through filtering and iterative closest point computation on the three-dimensional point cloud, the precise three-dimensional pose of the target workpiece is obtained. An industrial robot can accurately and intelligently recognize the weak-texture workpiece and acquire the three-dimensional pose information, and tasks such as grinding and assembling on the workpiece can be completed.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
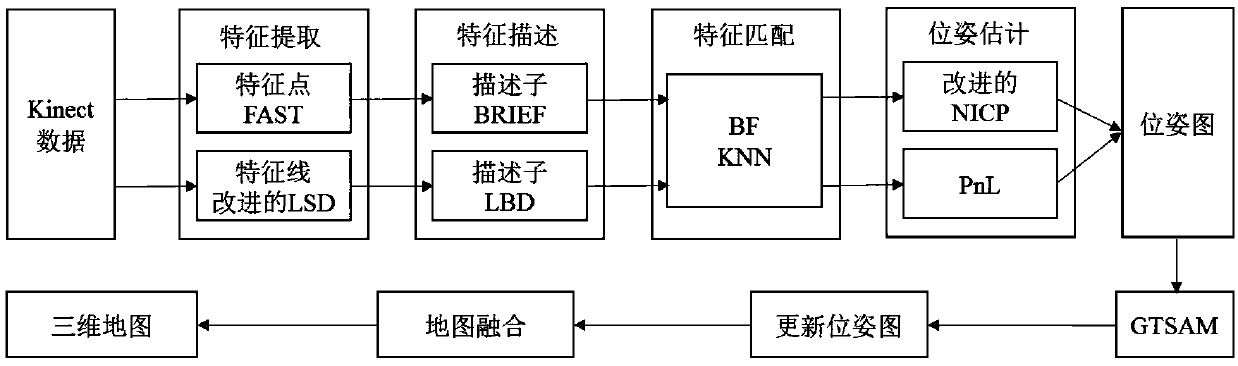
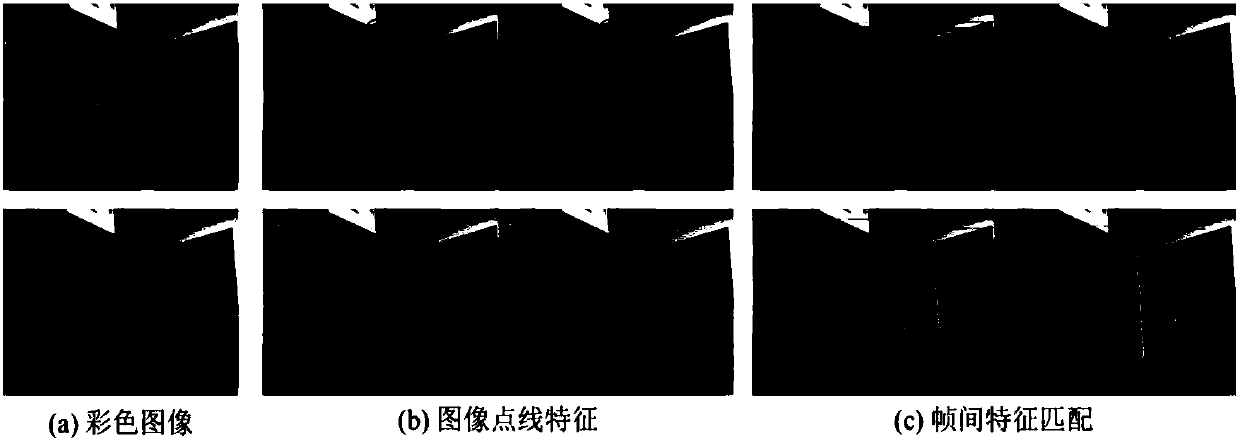
VSLAM method based on multi-characteristic visual odometer and graph optimization model
The invention discloses a VSLAM method based on a multi-characteristic visual odometer and a graph optimization model, and belongs to the robot SLAM field; the method comprises the following steps: firstly using a FAST (features from accelerated segment test) and an improved LSD algorithm to extract point and line features in a color image; further using different descriptors to describe characteristics; then carrying out characteristic matching; finally using an improved NICP (normal iterative closest point) algorithm and a PnL (perspective n line) algorithm to estimate a robot initial posture. The method can extract image line features so as to enlarge algorithm application scenes, can obtain a well robot initial posture, uses a Bayes network to express a multi-characteristic visual odometer, obtains a factor graph on the basis of the Bayes network, uses a maximum posterior probability to estimate a robot global posture in the factor graph, and uses a Gauss-Newton method to solve themaximum posterior probability to obtain the updated posture graph; finally, the posture graph and three dimensional points of corresponding frames are fused to obtain a reconstructed three dimensional map.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
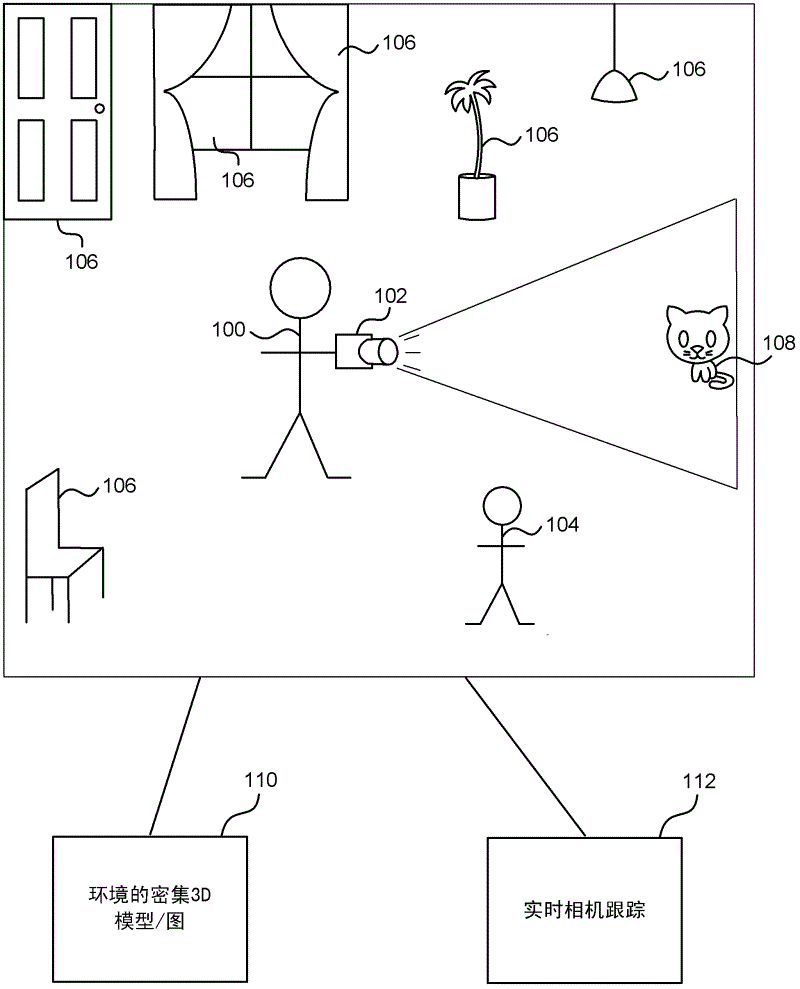
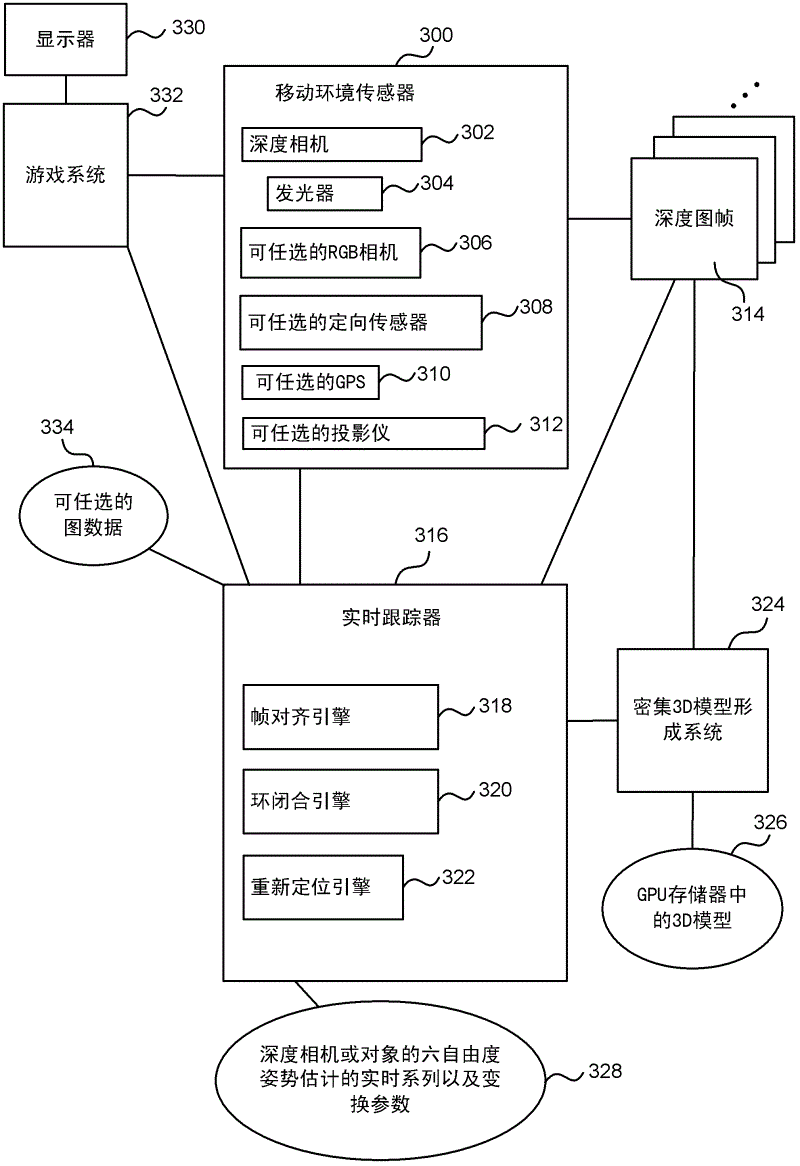
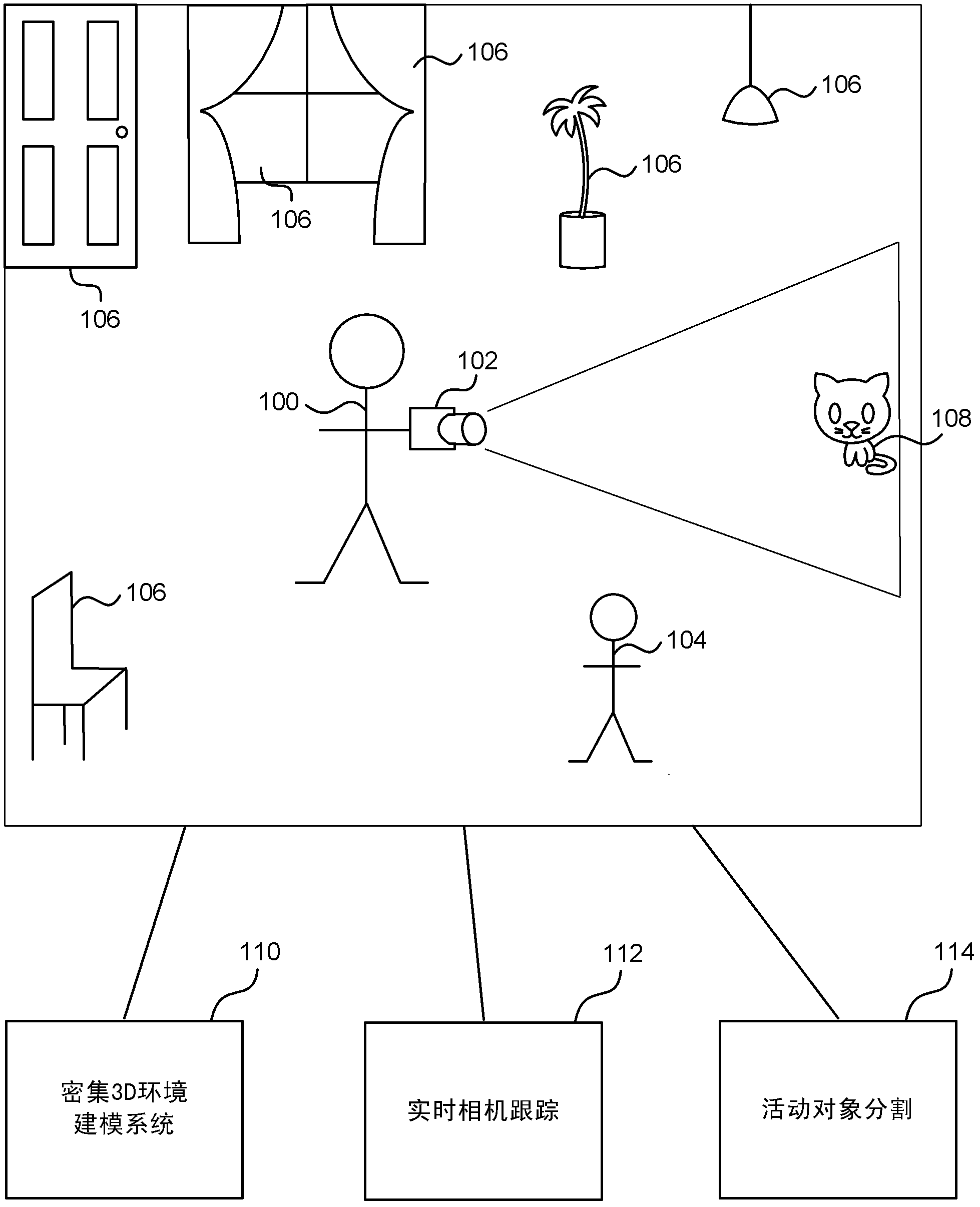
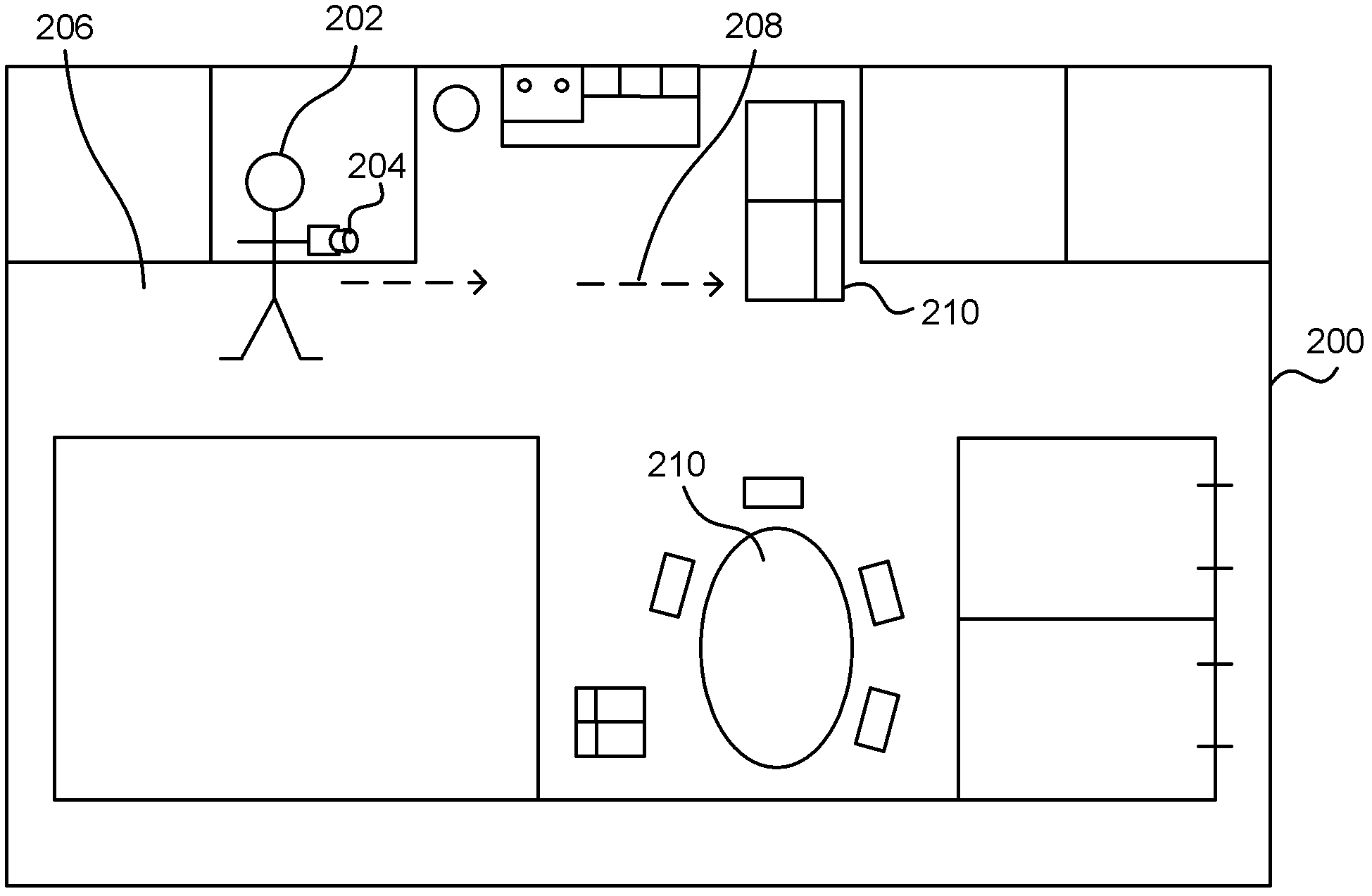
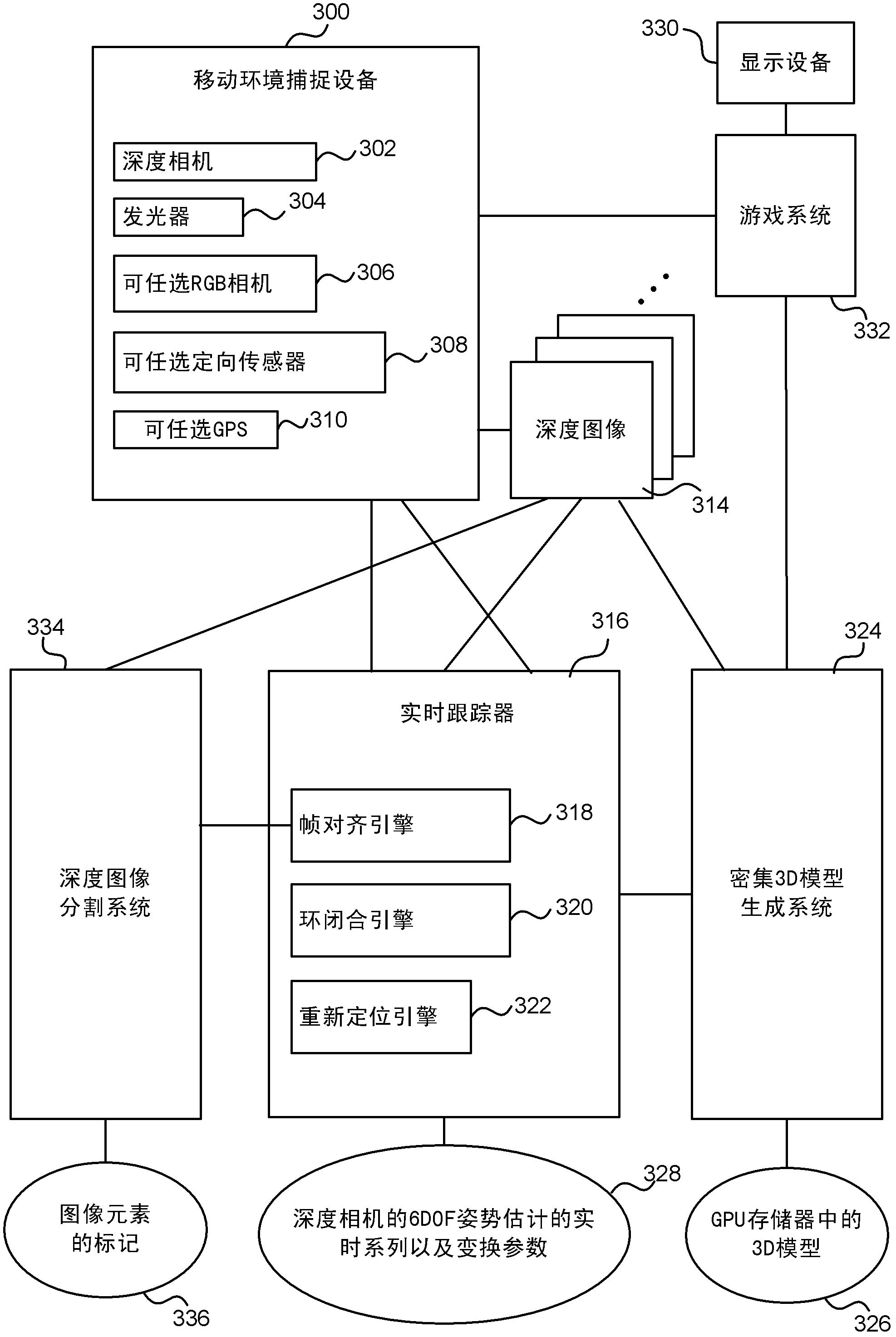
Real-time camera tracking using depth maps
Real-time camera tracking using depth maps is described. In an embodiment depth map frames are captured by a mobile depth camera at over 20 frames per second and used to dynamically update in real-time a set of registration parameters which specify how the mobile depth camera has moved. In examples the real-time camera tracking output is used for computer game applications and robotics. In an example, an iterative closest point process is used with projective data association and a point-to-plane error metric in order to compute the updated registration parameters. In an example, a graphics processing unit (GPU) implementation is used to optimize the error metric in real-time. In some embodiments, a dense 3D model of the mobile camera environment is used.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
OCT eye fundus image data registration method
InactiveCN106447708AAdvantage time complexityAdvantage Registration AccuracyImage enhancementImage analysisSingular value decompositionTime complexity
The invention discloses an OCT eye fundus image data registration method, which comprises the following steps: at first, extracting retina edges of an OCT eye fundus image by virtue of a Canny edge detection method, and collecting the edges in a format of point cloud data; then, extracting characteristic points of the point cloud data by adopting a space grid division method; next, calculating a transformation matrix of point clouds to be registered to eliminate obvious position errors by virtue of an SVD (singular value decomposition) algorithm; finally, performing accurate registration by virtue of an improved iterative closest point algorithm, and applying an obtained rotation matrix and translation matrix to the original OCT eye fundus image to obtain a final result. When a dense point cloud with a relatively large volume of data is processed, the method has obvious advantages in terms of time complexity and registration accuracy. Under most conditions, the efficiency of a conventional iterative closest point algorithm is improved by 70 percent by the method, not only can the OCT eye fundus image be effectively registered and spliced, but also the accuracy of a large-vision eye fundus retina accuracy is ensured.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
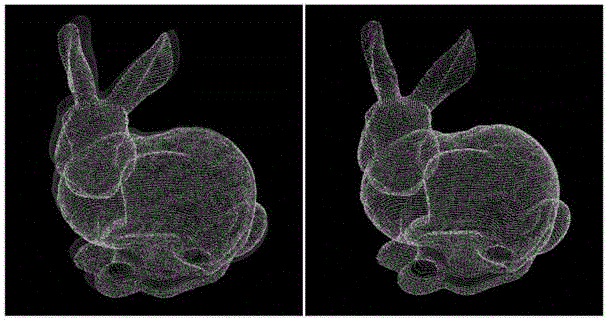
Moving object segmentation using depth images
Moving object segmentation using depth images is described. In an example, a moving object is segmented from the background of a depth image of a scene received from a mobile depth camera. A previous depth image of the scene is retrieved, and compared to the current depth image using an iterative closest point algorithm. The iterative closest point algorithm includes a determination of a set of points that correspond between the current depth image and the previous depth image. During the determination of the set of points, one or more outlying points are detected that do not correspond between the two depth images, and the image elements at these outlying points are labeled as belonging to the moving object. In examples, the iterative closest point algorithm is executed as part of an algorithm for tracking the mobile depth camera, and hence the segmentation does not add substantial additional computational complexity.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
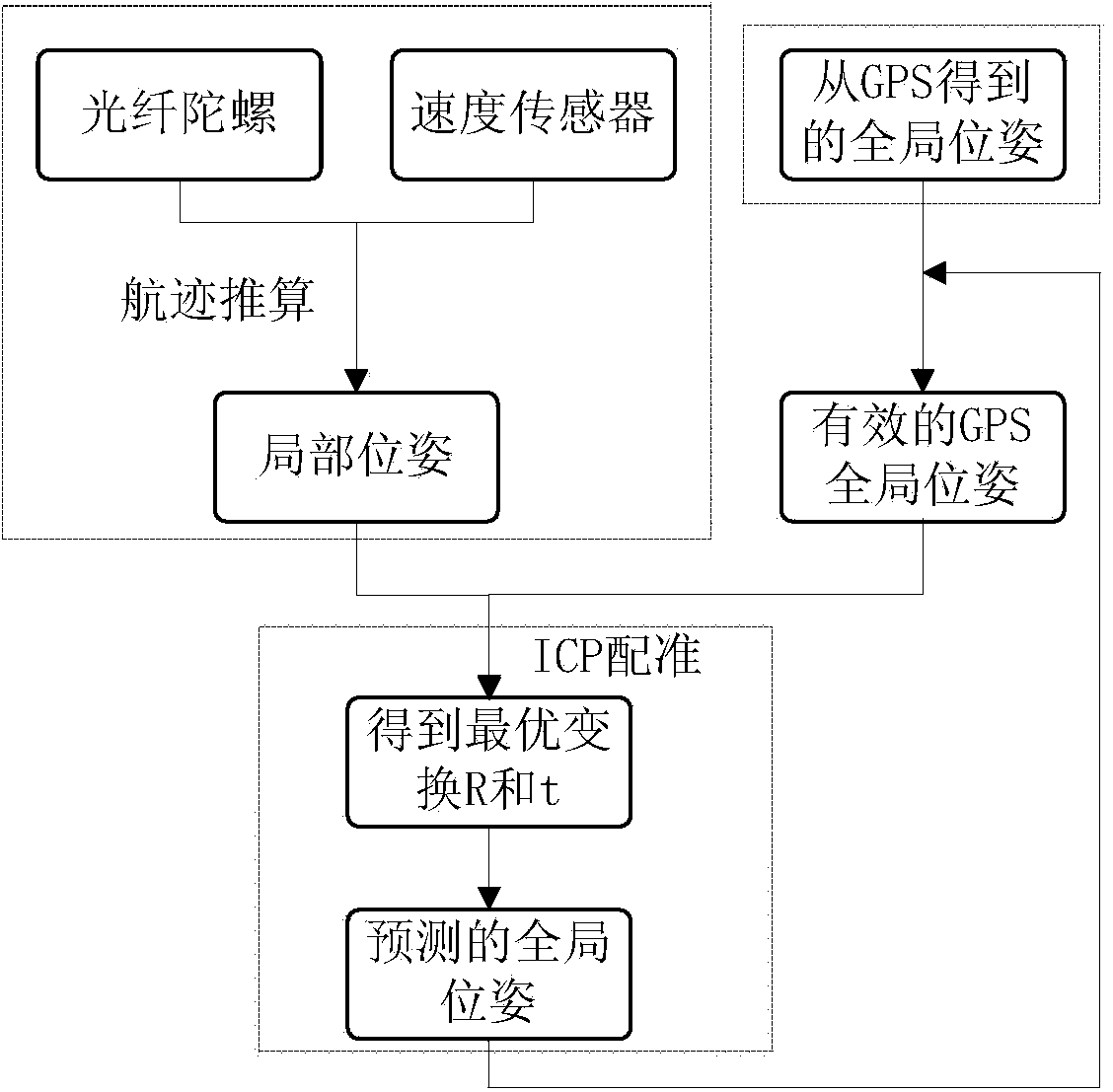
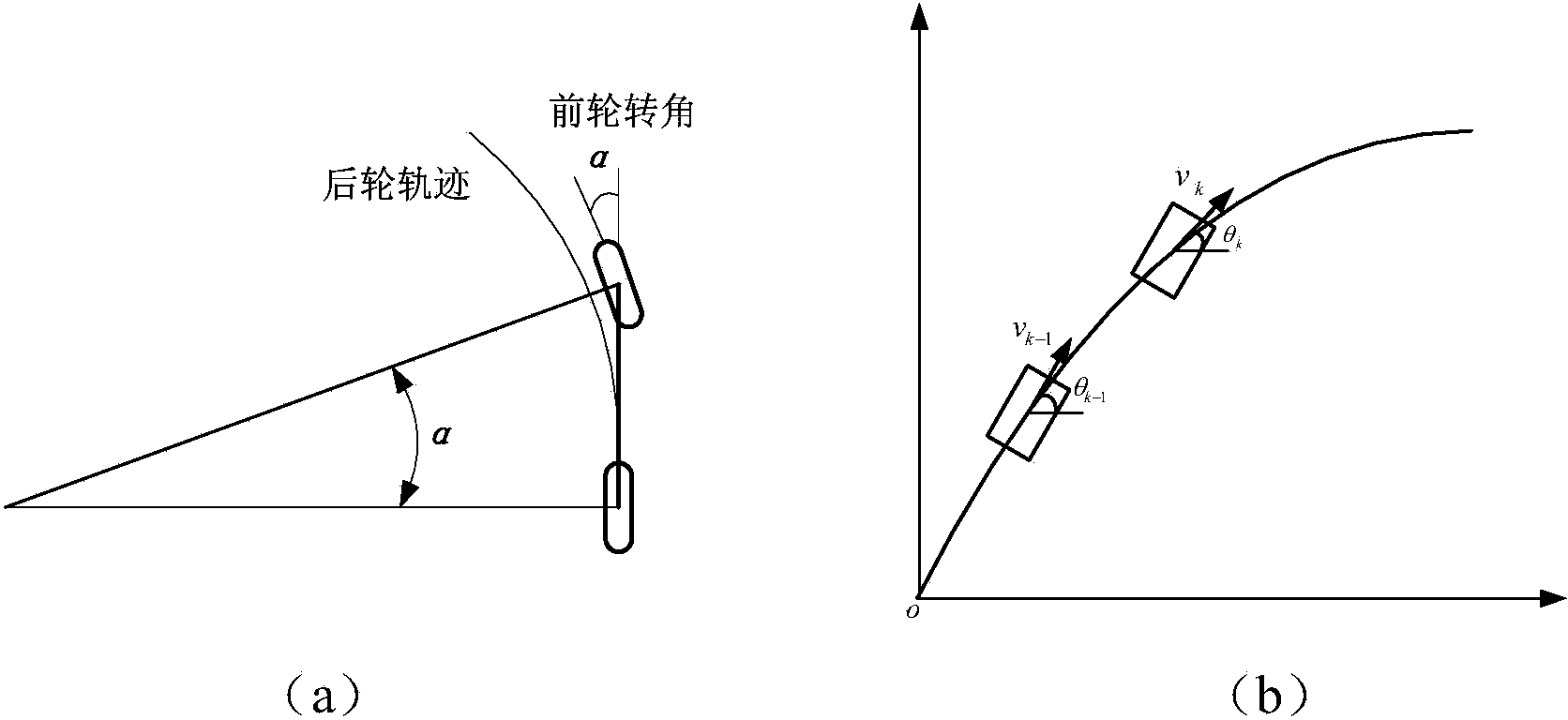
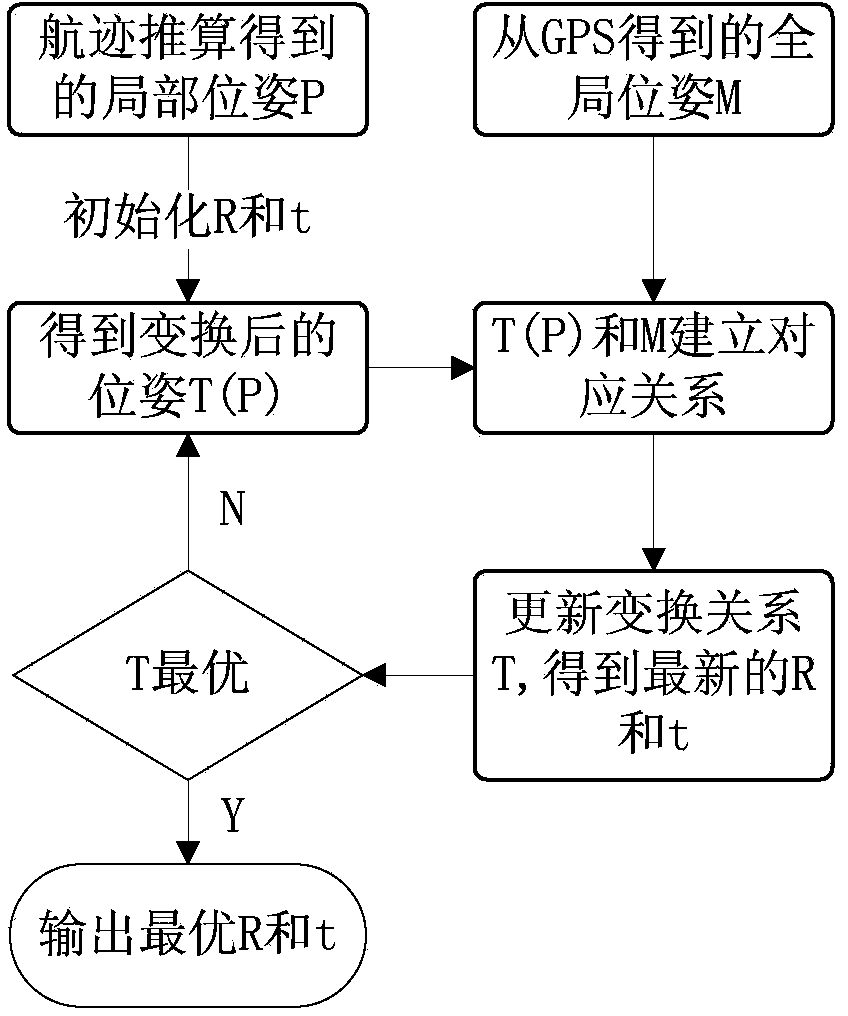
Real-time and accurate pose estimation method based on fiber-optic gyroscope, speed sensor and GPS
InactiveCN103777220ARemove random noiseCorrect cumulative errorNavigation instrumentsSatellite radio beaconingFiberGyroscope
The invention provides a real-time and accurate pose estimation method based on a fiber-optic gyroscope, a speed sensor and a GPS. The unmanned vehicle local locating algorithm based on a vehicle body motion model is mainly based on the two-dimensional plane dead reckoning principle, the vehicle body current local pose is estimated through the vehicle body sensor speed and course information estimation at the previous time, and the gyroscope course accumulative error is compensated through a linear model, so the accuracy of the local locating system can be improved; and by using the iterative closet point algorithm to register GPS and the local pose measuring system pose estimation method, the local locating accumulative error can be corrected, so the random noise of the GPS can be effectively eliminated, and the pose accuracy can be maintained when the GPS is in complete failure condition or failed, and the running test result shows that the method provided in the invention can be used to well fuse multi-sensor information, and provide reliable and continuous locating information for unmanned vehicles in multi-tree and multi-building urban environments. Moreover, the method has the advantage of good real-time performance.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
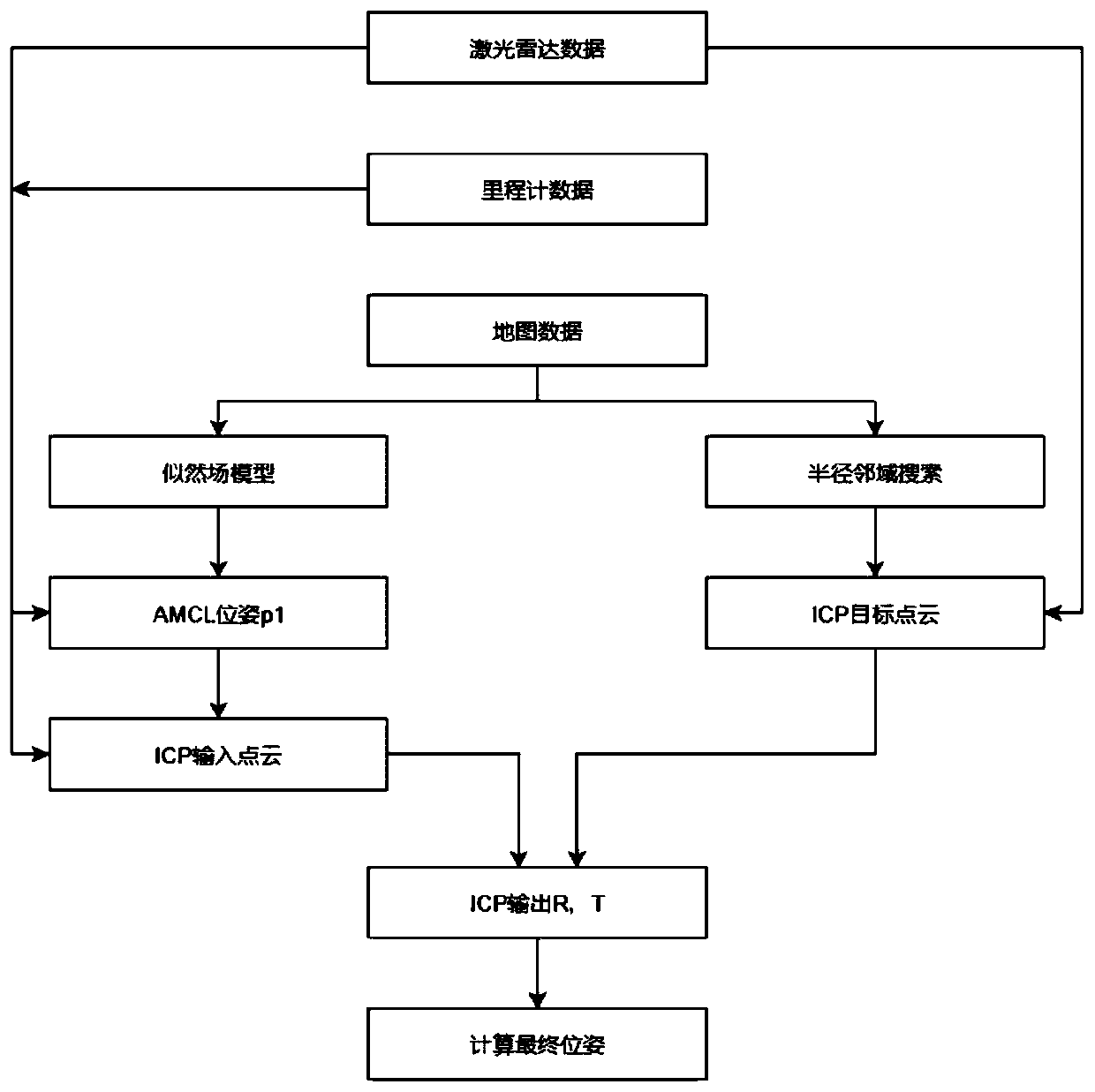
Mobile robot positioning method
PendingCN110927740AImprove matching speedHigh positioning accuracyNavigation instrumentsElectromagnetic wave reradiationReal-time dataComputer graphics (images)
The invention discloses a mobile robot positioning method, which belongs to the technical field of mobile robot positioning, and comprises the steps of placing a robot carrying a two-dimensional laserradar in a current positioning environment, and obtaining map point cloud of an obstacle; estimating the current pose of the robot by adopting a self-adaptive Monte Carlo positioning algorithm; converting the real-time data of the two-dimensional laser radar into point cloud PTCloud under the same coordinate system as the map point cloud by using the current pose of the robot; taking each frame of point cloud PTCloudscan as an input of an iterative closest point to obtain a rotation matrix R and a translation matrix T of the current frame of point cloud PTCloudscan relative to the map point cloud; and calculating the final pose of the robot according to the rotation matrix R and the translation matrix T. The pose obtained by adopting the adaptive Monte Carlo positioning algorithm is usedas the reference value to transform the point cloud coordinate system of the two-dimensional laser radar, so that the point cloud coordinate system is close enough to the current map point cloud, thematching speed of the iterative closest point is accelerated, and the positioning precision is improved.
Owner:HEFEI CSG SMART ROBOT TECH CO LTD
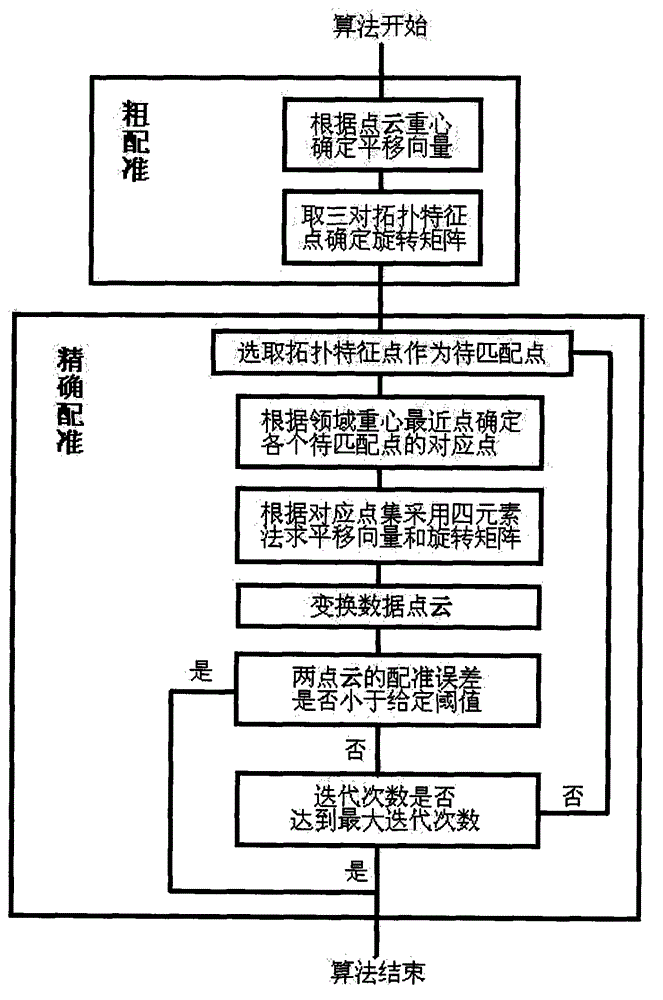
Point cloud registration algorithm based on topological characteristic
InactiveCN103150747ASmall amount of calculationImprove robustness3D-image renderingClosest pointRotation matrix
The invention provides a point cloud registration algorithm based on a topological characteristic. Topological characteristic points (border characteristic points and highlight characteristic points) of the point cloud are extracted and are used for calculating an initial rotation matrix and an initial translation vector at the initial point cloud registration stage of the algorithm. A basic idea of an iterative closest point (ICP) algorithm is adopted at the accurate registration stage, and the method of choosing a registration element and determining a corresponding point set is improved. The registration element chooses the topological characteristic points, and the closest point of a neighbor center of gravity is chosen as the corresponding point when the corresponding point set is determined. The method introduces the topological characteristic, reduces the number of the extracted points and ensures matching effect because the topological characteristic contains abundant point cloud characteristics. The method takes the neighbor characteristic into consideration when determining the corresponding points, thereby enhancing robustness of the algorithm to noises.
Owner:PCI TECH GRP CO LTD
Recursive 3D model optimization
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com