Patents
Literature
357 results about "Exact match" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Auto playlist generator
ActiveUS6993532B1Simplifies list generationEfficient use ofGearworksMetadata audio data retrievalInformation retrievalMetadatabase
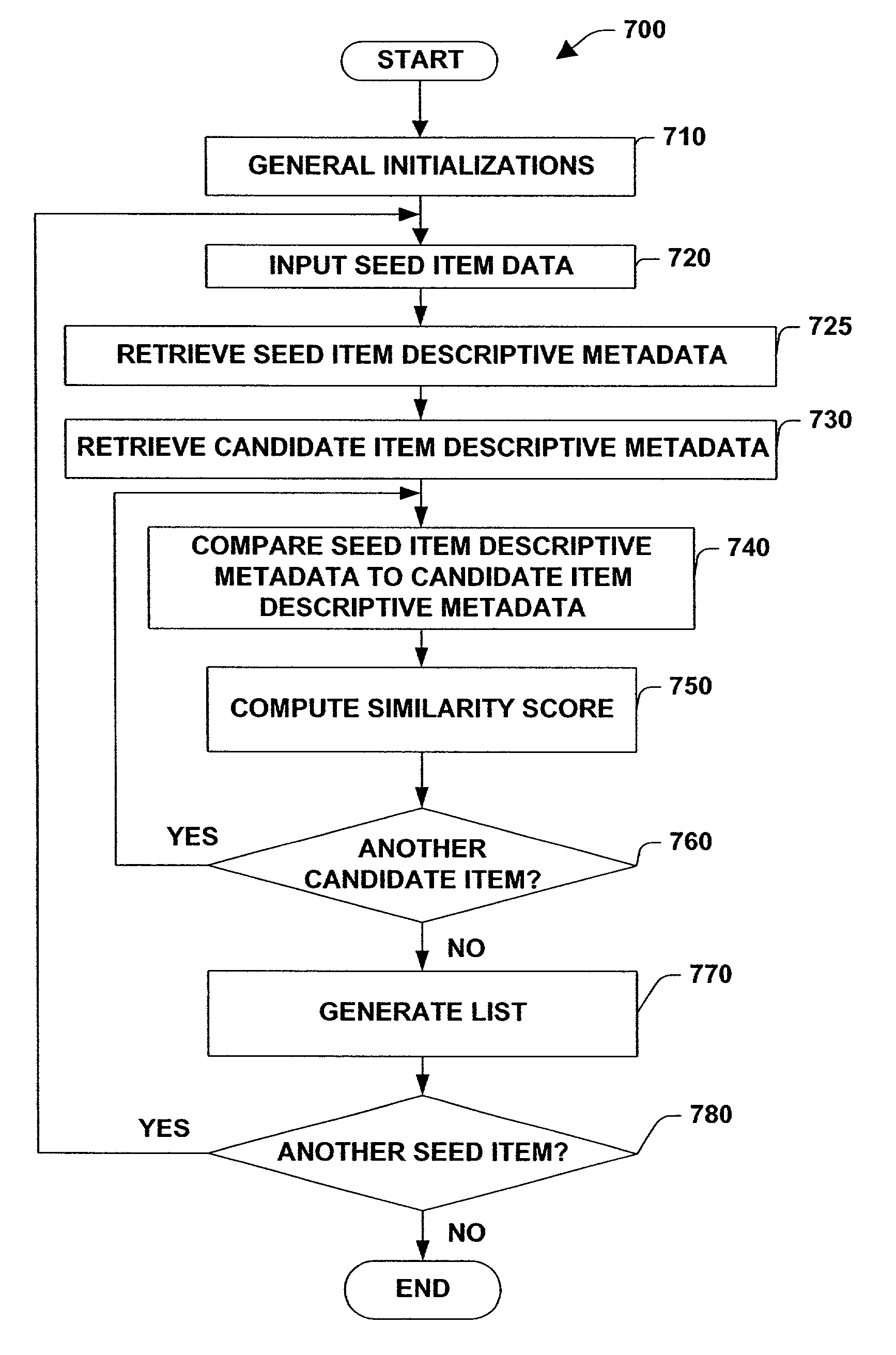
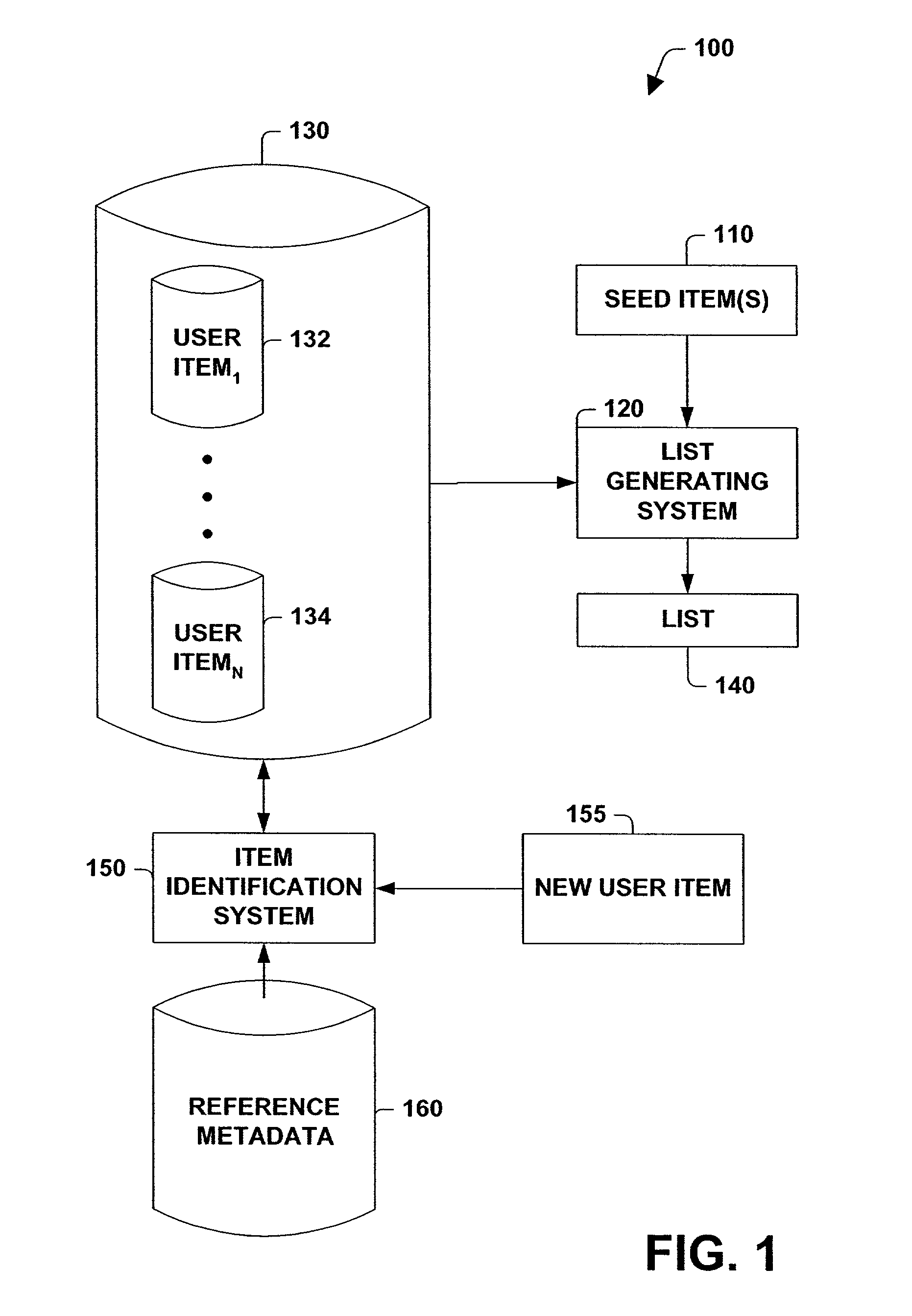
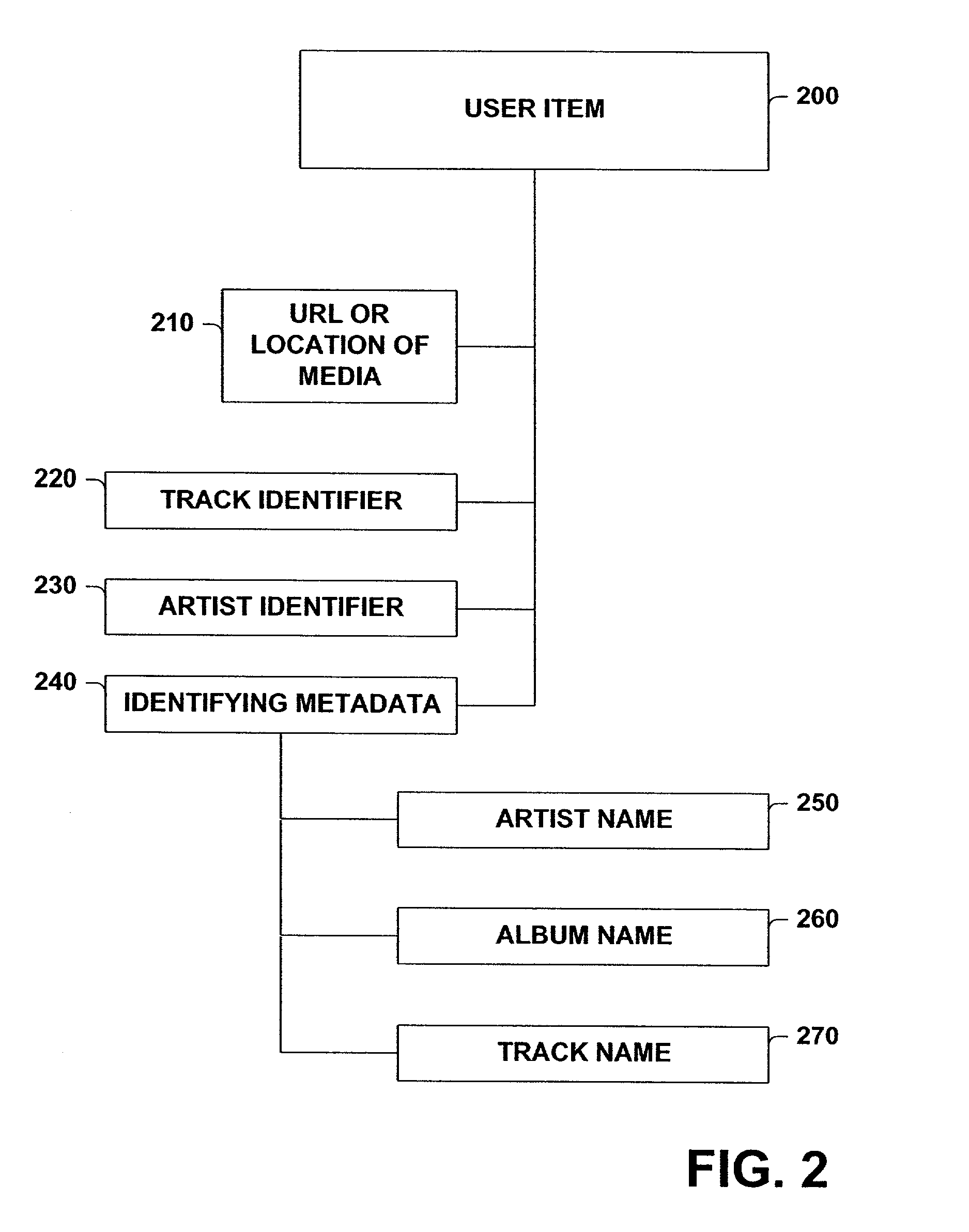
A system and method for generating a list is provided. The system includes a seed item input subsystem, an item identifying subsystem, a descriptive metadata similarity determining subsystem and a list generating subsystem that builds a list based, at least in part, on similarity processing performed on seed item descriptive metadata and user item descriptive metadata and user selected thresholds applied to such similarity processing. The method includes inexact matching between identifying metadata associated with new user items and identifying metadata stored in a reference metadata database. The method further includes subjecting candidate user items to similarity processing, where the degree to which the candidate user items are similar to the seed item is determined, and placing user items in a list of items based on user selected preferences for (dis)similarity between items in the list and the seed item.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
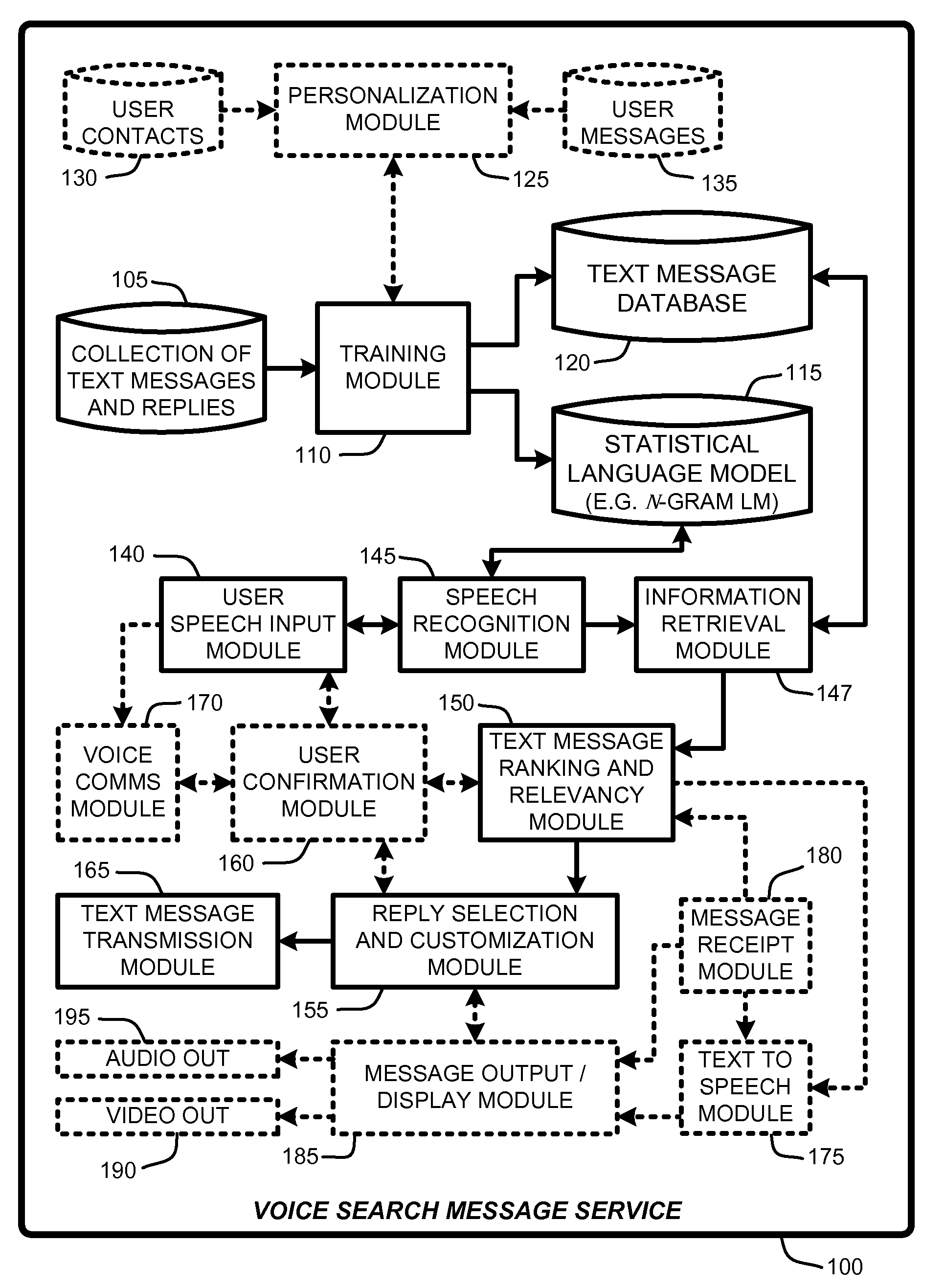
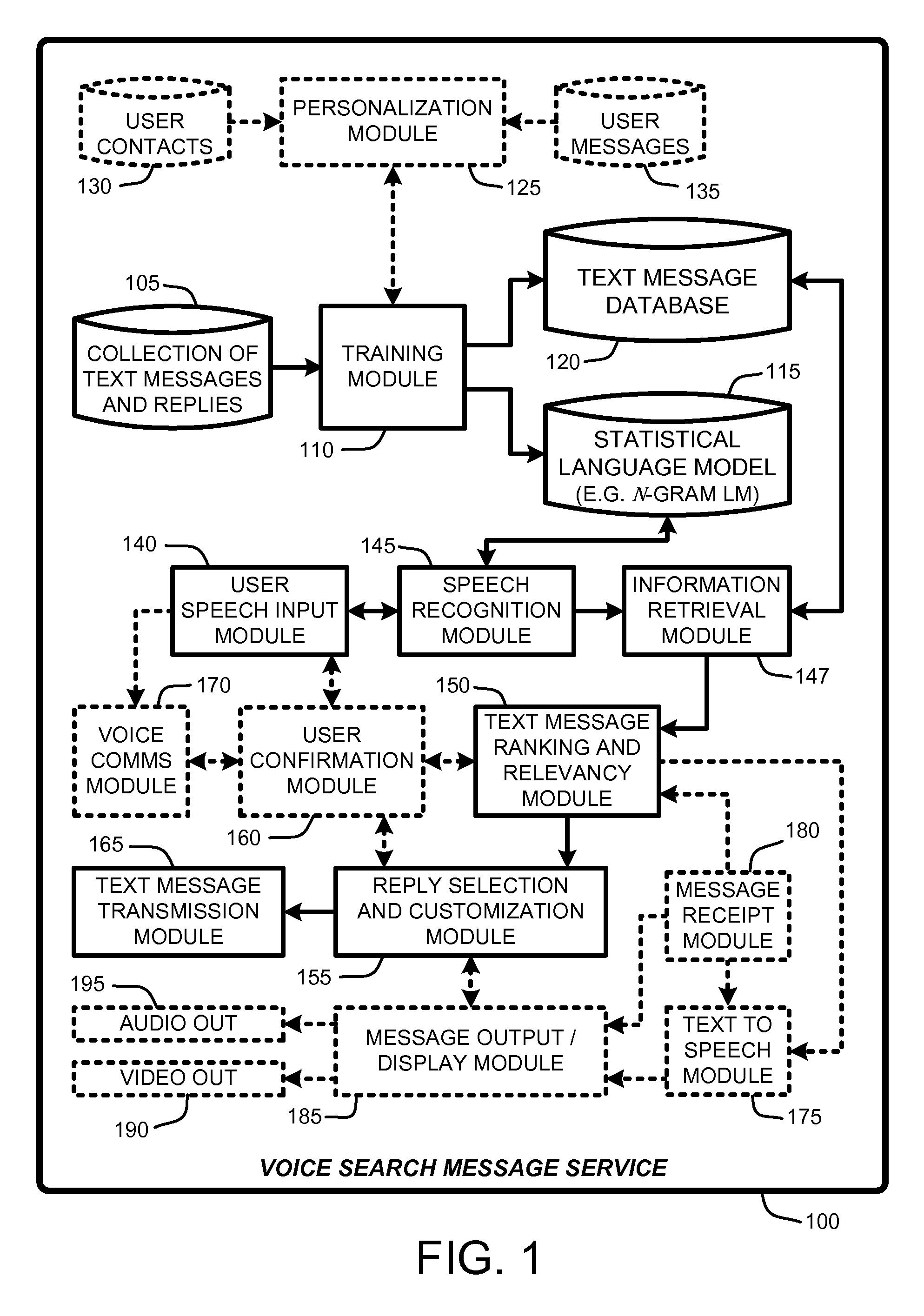
Replying to text messages via automated voice search techniques
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and method for automatic weight generation for probabilistic matching
InactiveUS20080005106A1Not easy to make mistakesImprove performanceDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsExact matchGeneration process
Embodiments of the invention provide a system and method of automatically generating weights for matching data records. Each field of a record may be compared by an exact match and / or close matches and each comparison can result in a mathematical score which is the sum of the field comparisons. To sum up the field scores accurately, the automatic weight generation process comprises an iterative process. In one embodiment, initial weights are computed based upon unmatched-set probabilities and default discrepancy weights associated with attributes in the comparison algorithm. A bulk cross-match is performed across the records using the initial weights and a candidate matched set is computed for updating the discrepancy probabilities. New weights are computed based upon the unmatched probabilities and the updated discrepancy probabilities. Test for convergence between the new weights and the old weights. Repeat with the new weight table until the weights converge to their final value.
Owner:IBM CORP
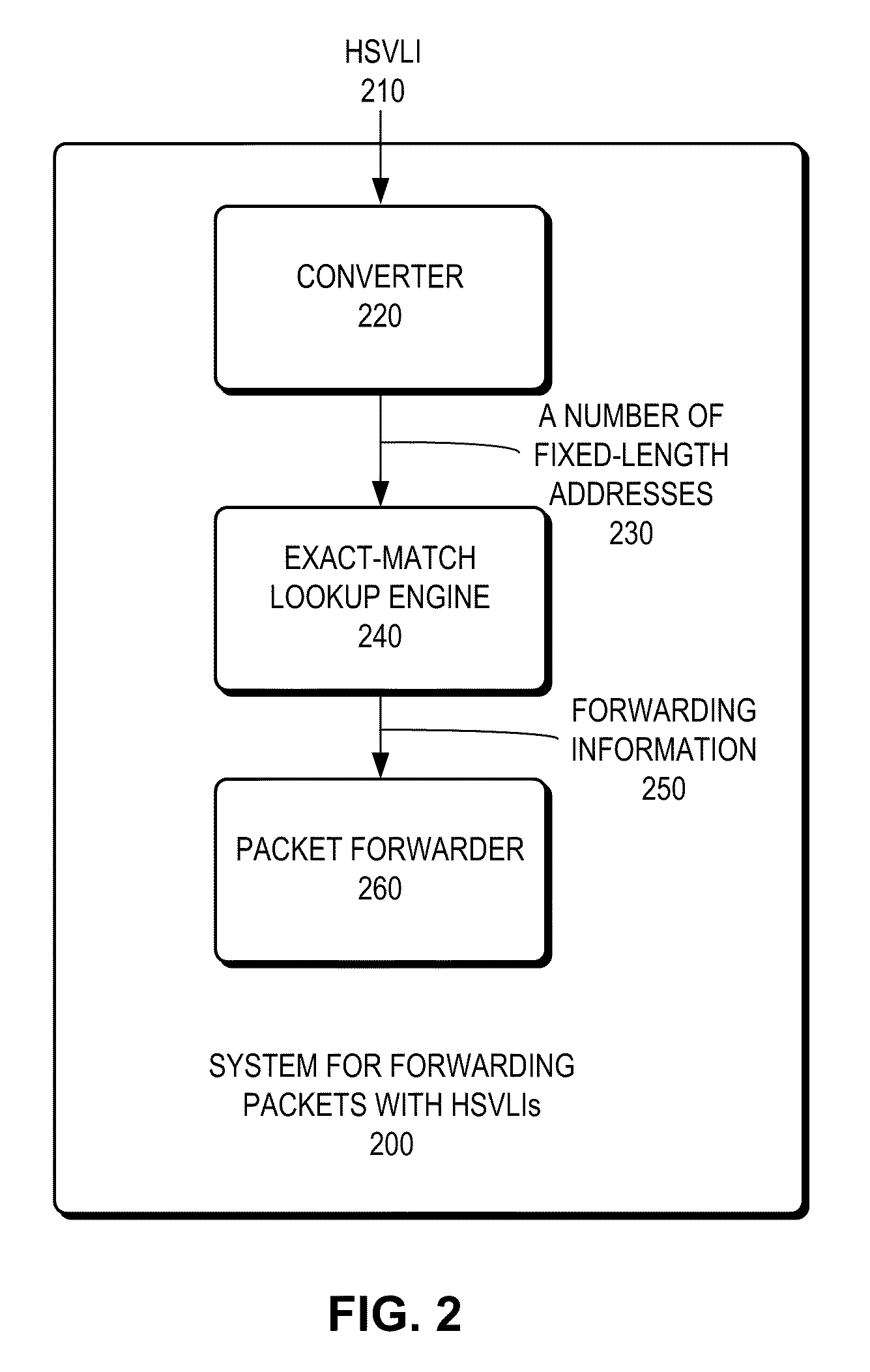
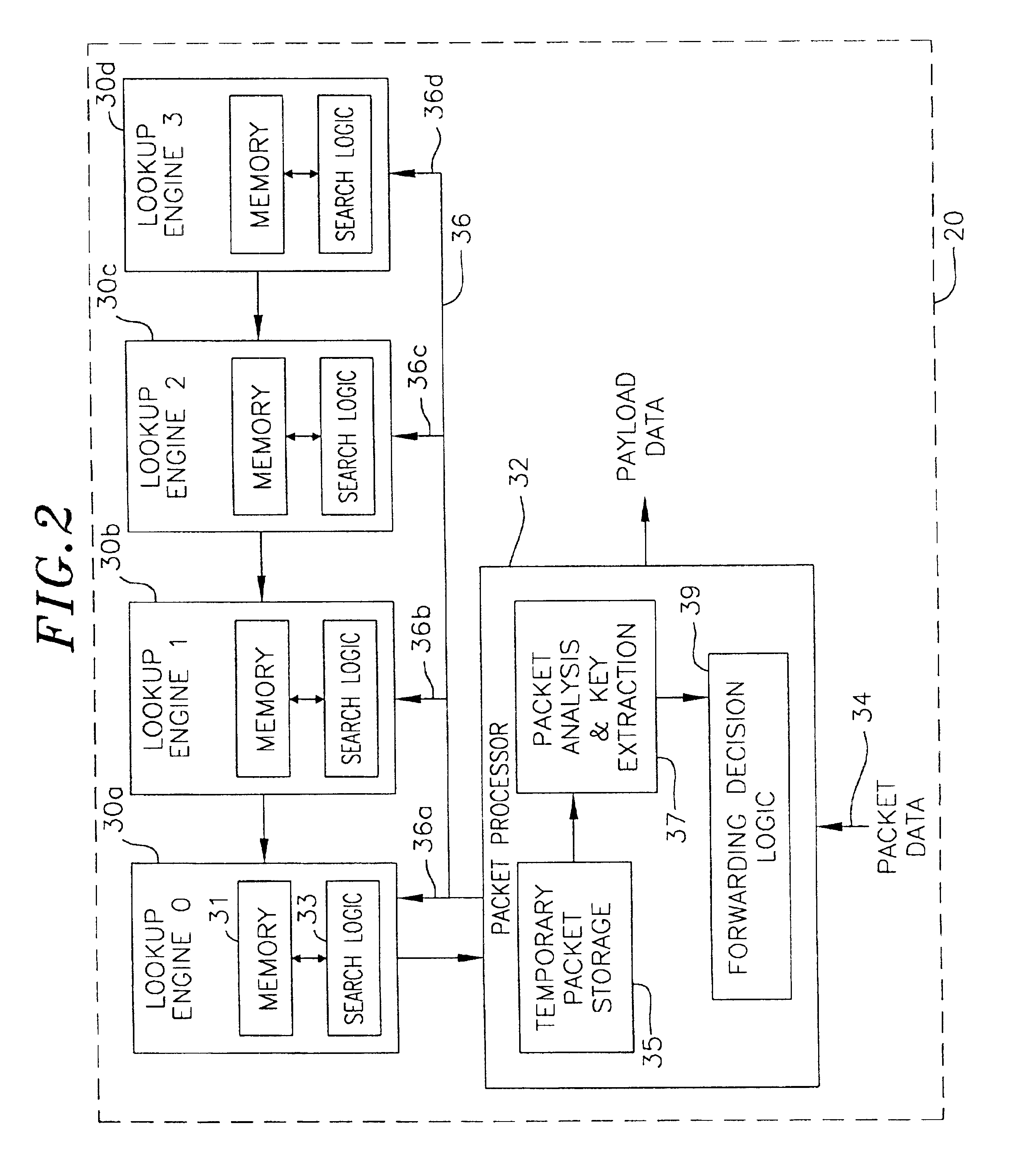
System for forwarding packets with hierarchically structured variable-length identifiers using an exact-match lookup engine
ActiveUS20100195654A1Easy to find laterReduce chanceCoin-freed apparatus detailsData switching by path configurationExact matchVariable length
One embodiment provides a system for forwarding packets with hierarchically structured variable-length identifiers (HSVLIs), wherein the computer includes a processor. During operation, the system converts an HSVLI into a number of fixed-length addresses, wherein the HSVLI indicates a piece of content and is hierarchically structured, and comprises contiguous components ordered from a most general level to a most specific level. In addition, the length of a respective HSVLI is not fixed. The system further performs an effective longest-prefix-match lookup by performing multiple exact-match lookups based at least on the fixed-length addresses.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
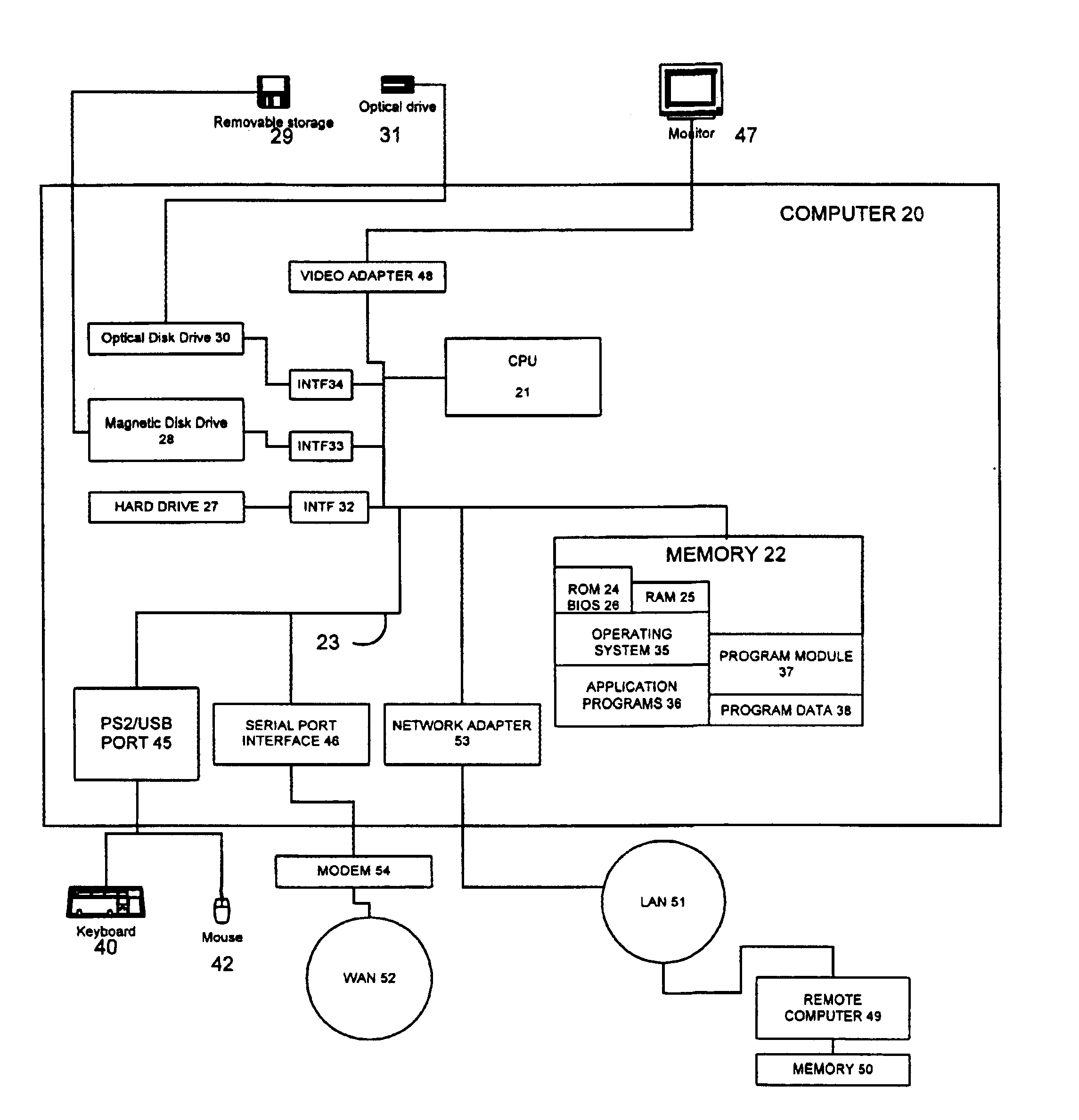
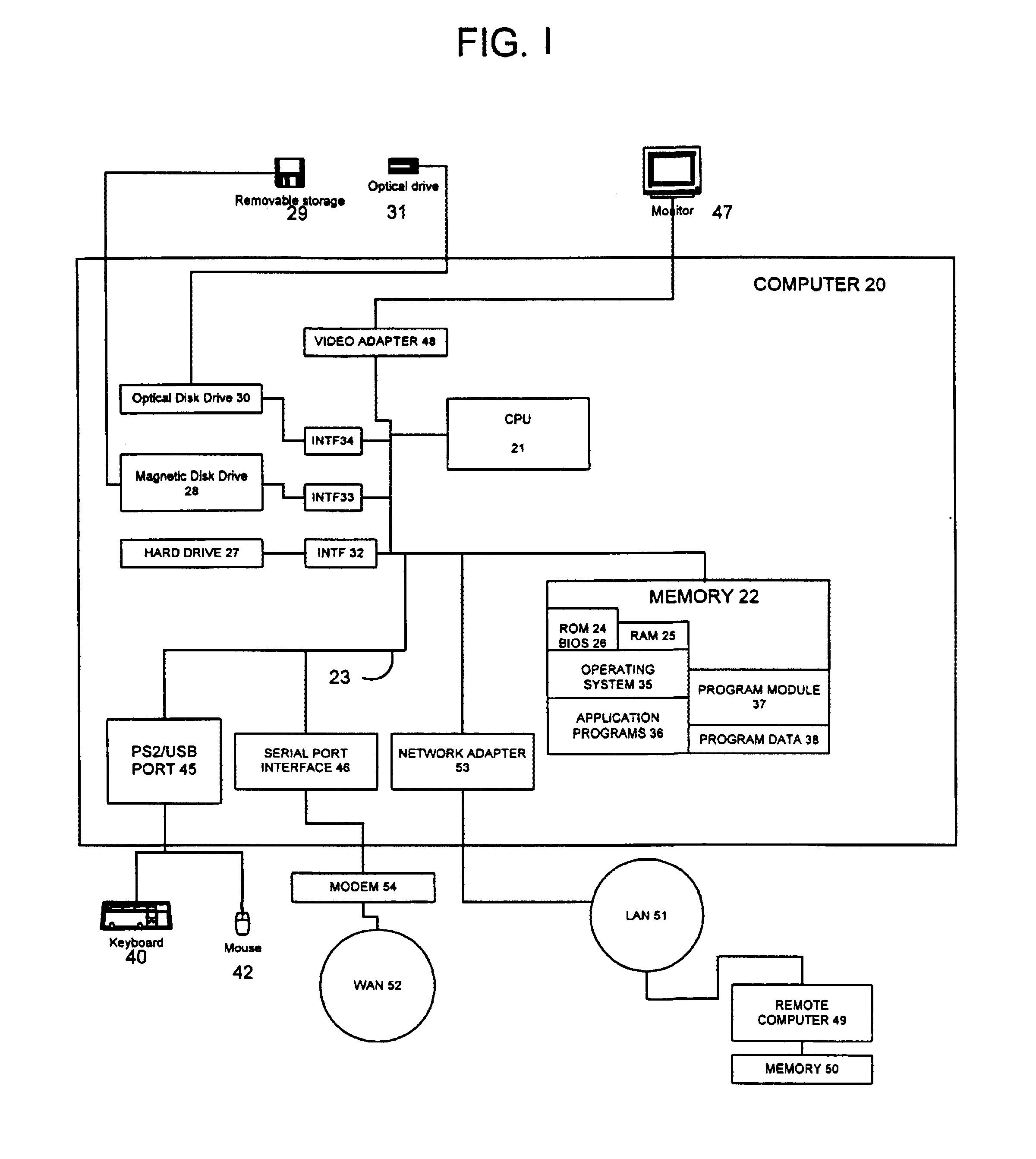
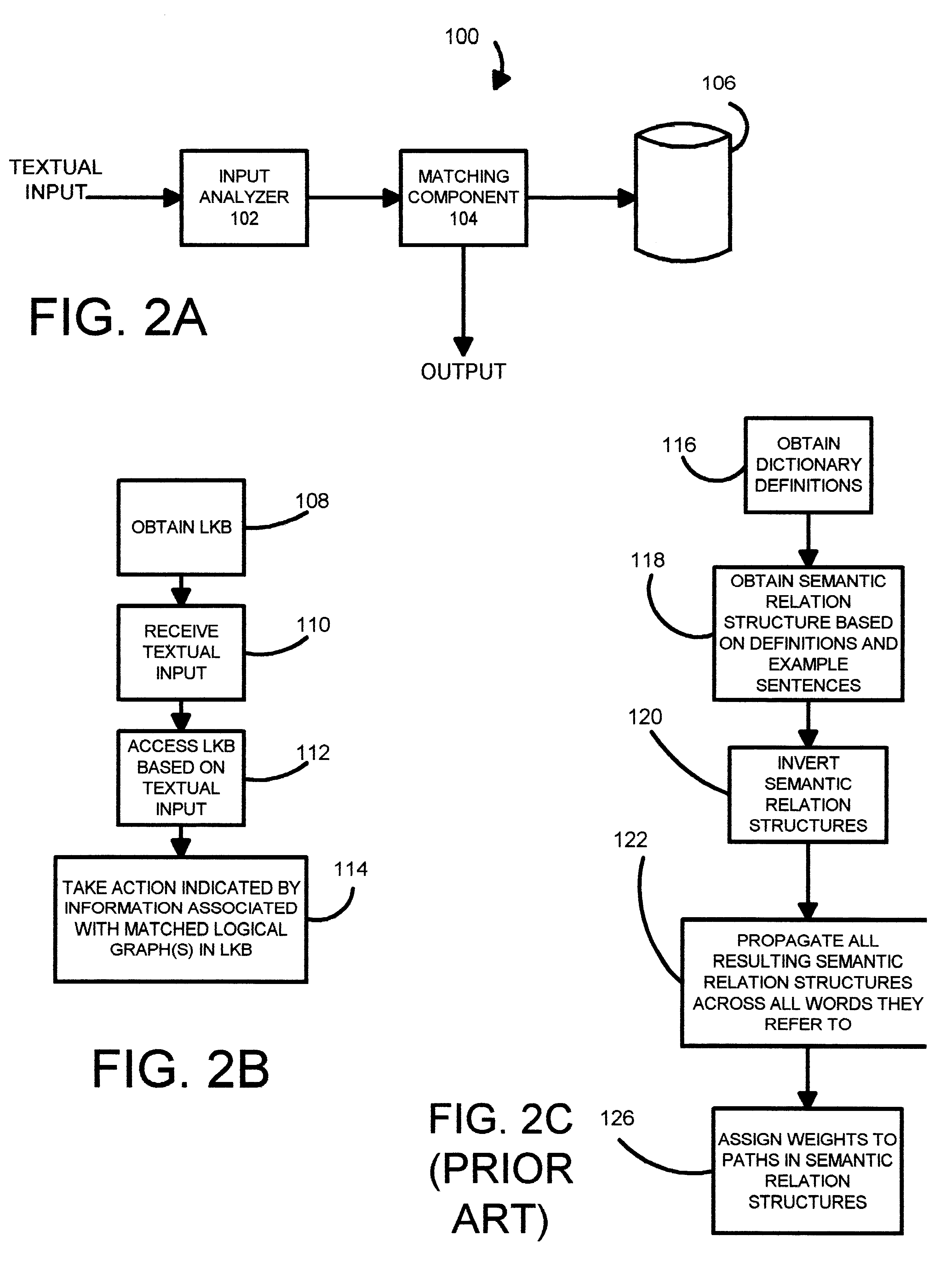
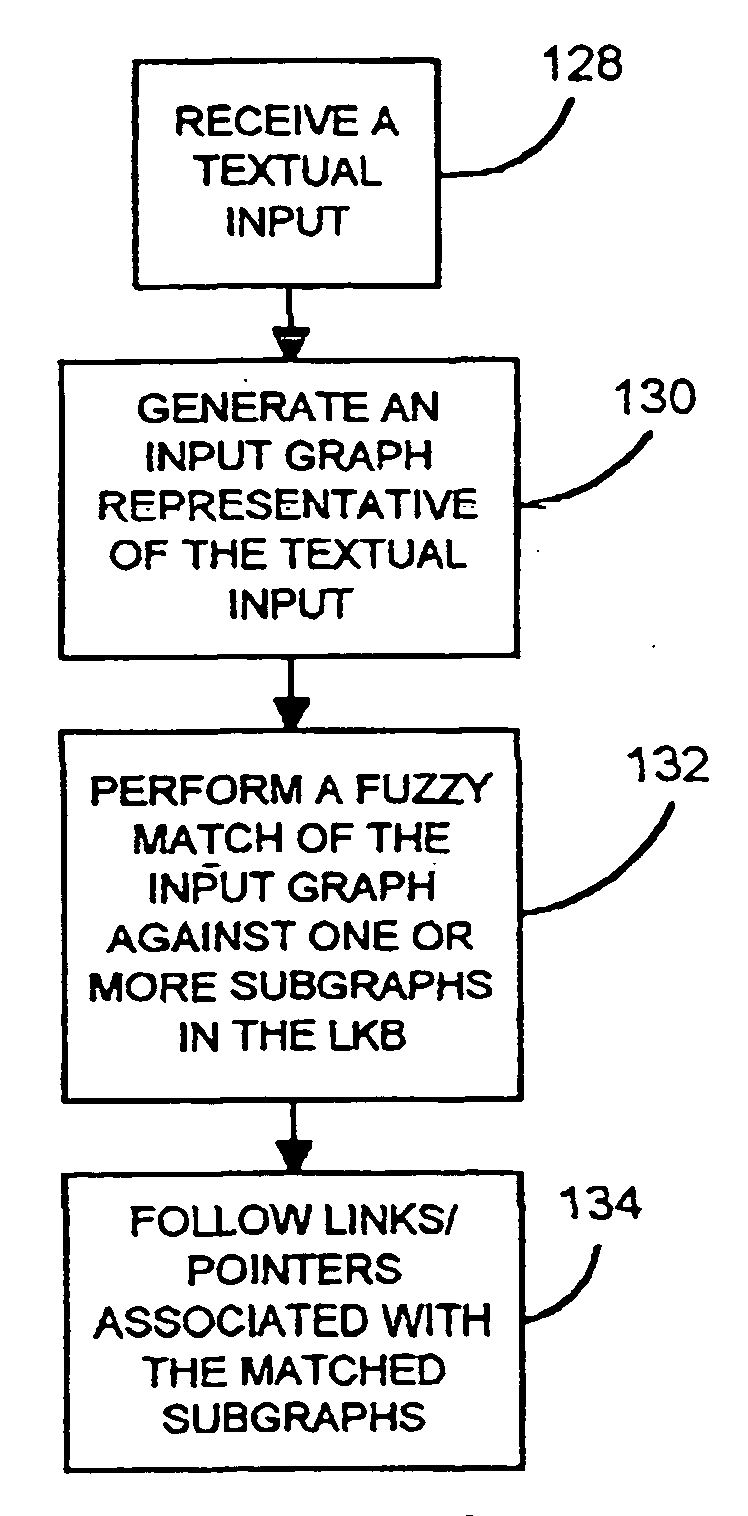
System and method for matching a textual input to a lexical knowledge base and for utilizing results of that match
InactiveUS6871174B1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalExact matchText entry
The present invention can be used in a natural language processing system to determine a relationship (such as similarity in meaning) between two textual segments. The relationship can be identified or determined based on logical graphs generated from the textual segments. A relationship between first and second logical graphs is determined. This is accomplished regardless of whether there is an exact match between the first and second logical graphs. In one embodiment, the first graph represents an input textual discourse unit. The second graph, in one embodiment, represents information in a lexical knowledge base (LKB). The input graph can be matched against the second graph, if they have similar meaning, even if the two differ lexically or structurally.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
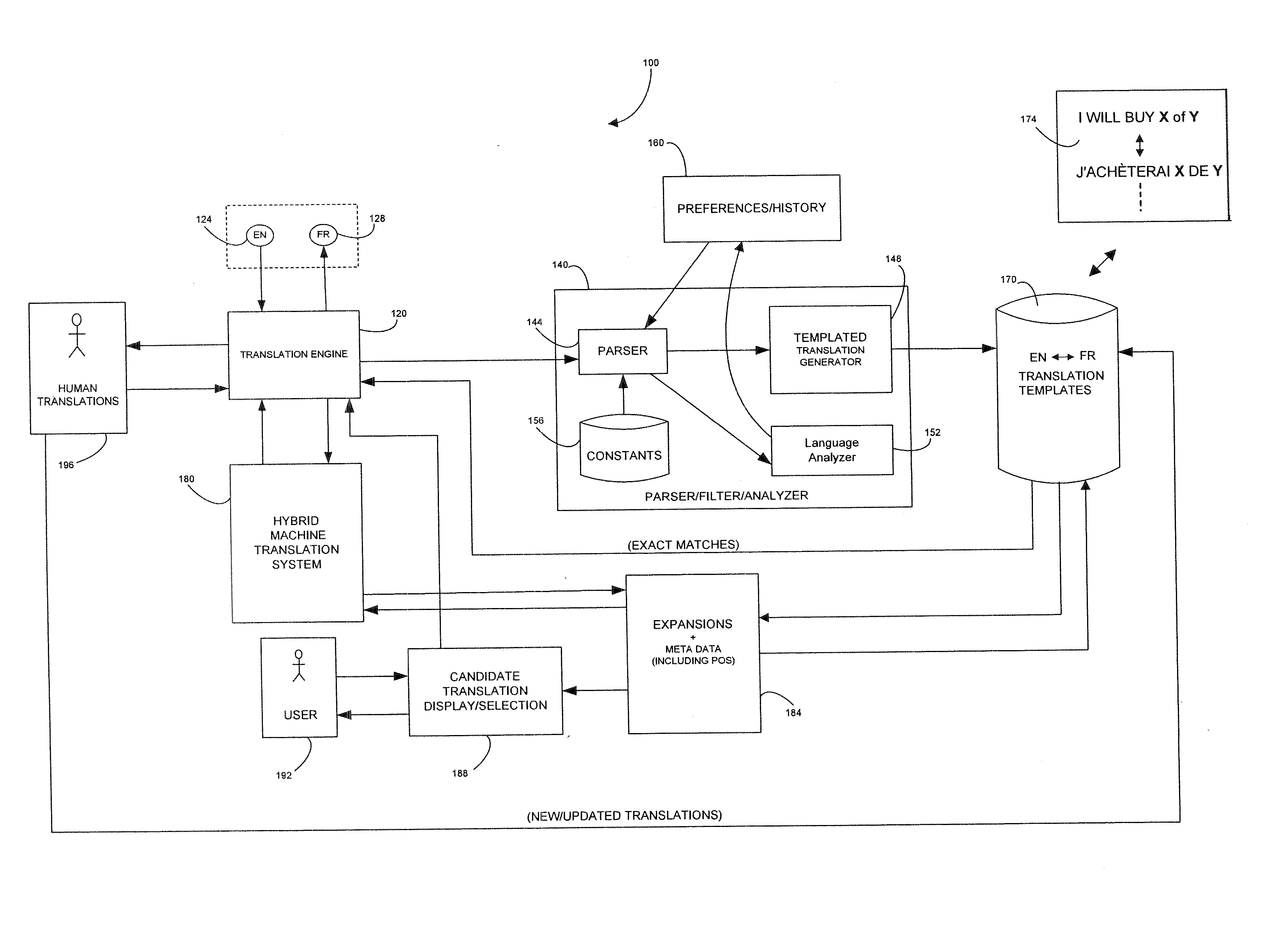
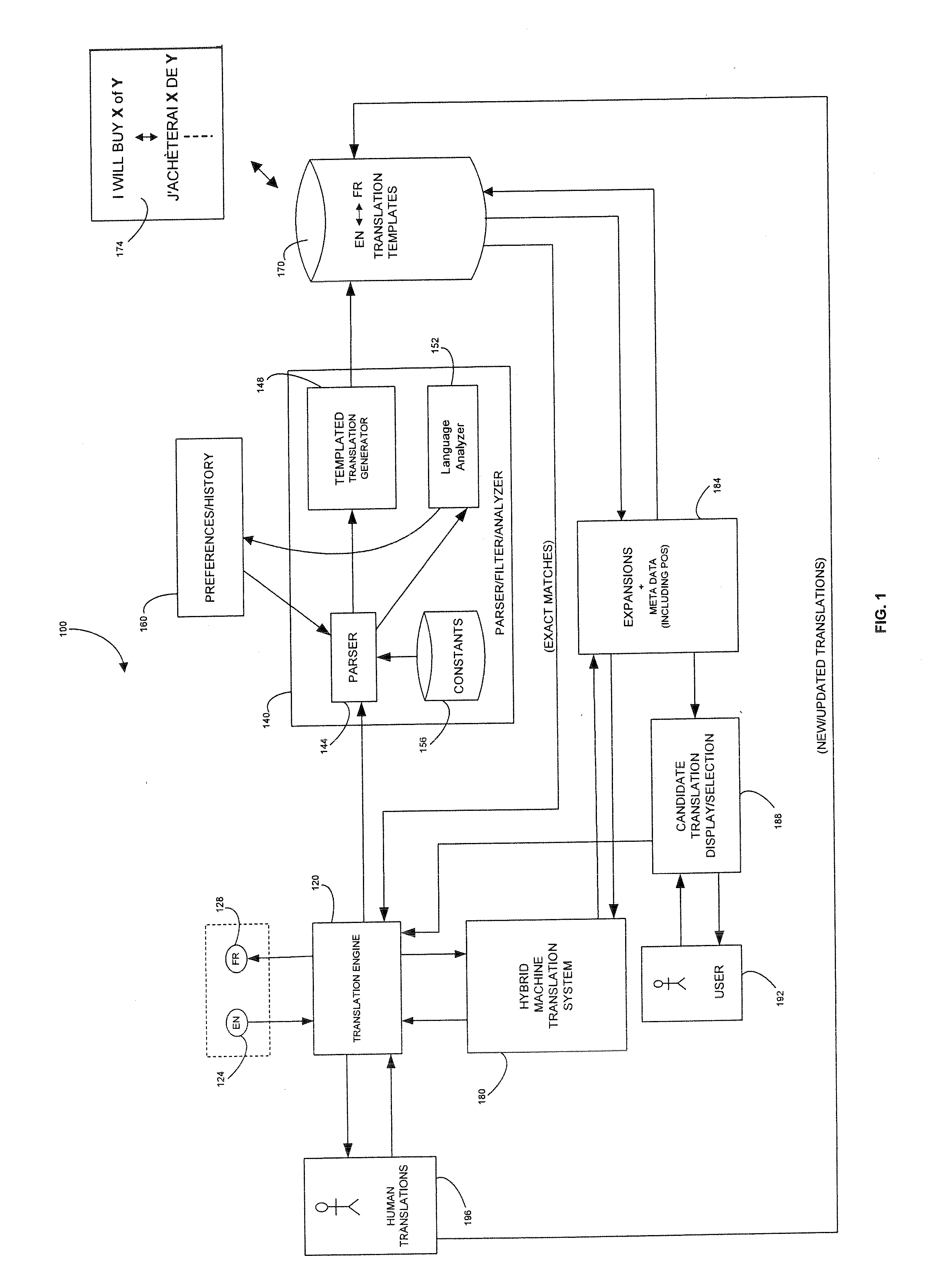
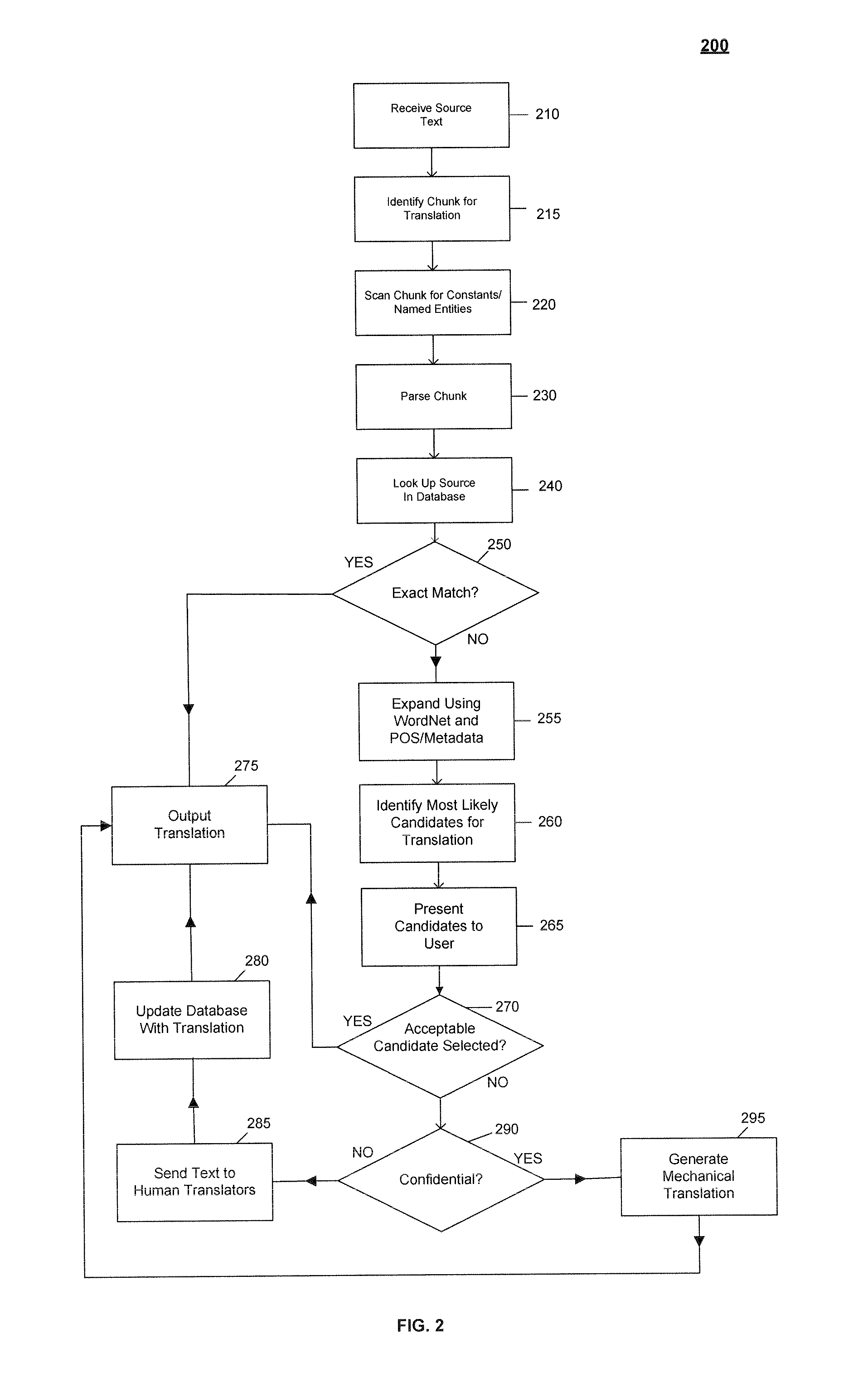
System and Method for Interactive Auromatic Translation
ActiveUS20130173247A1Improve accuracyLimit its incremental updatingNatural language translationSpecial data processing applicationsExact matchComputerized system
Embodiments of the invention relate to computerized systems and methods for automatically translating text between natural languages. Text for translation may be broken into segments, which may themselves be templates including placeholders. If an exact match for a segment is found in a translation database, the segment may be matched with its translation from the database. Otherwise, alternate source language text, corresponding to the segment, for which an exact translation is available, may be identified and presented to the user for selection. Text selected by the user may replace the original segment and be matched with its translation.Translation of a segment may be influenced by other translated segments. Additionally, translations may be modified as the user interactively enters and edits text.
Owner:BLOOMBER FINANCE LP
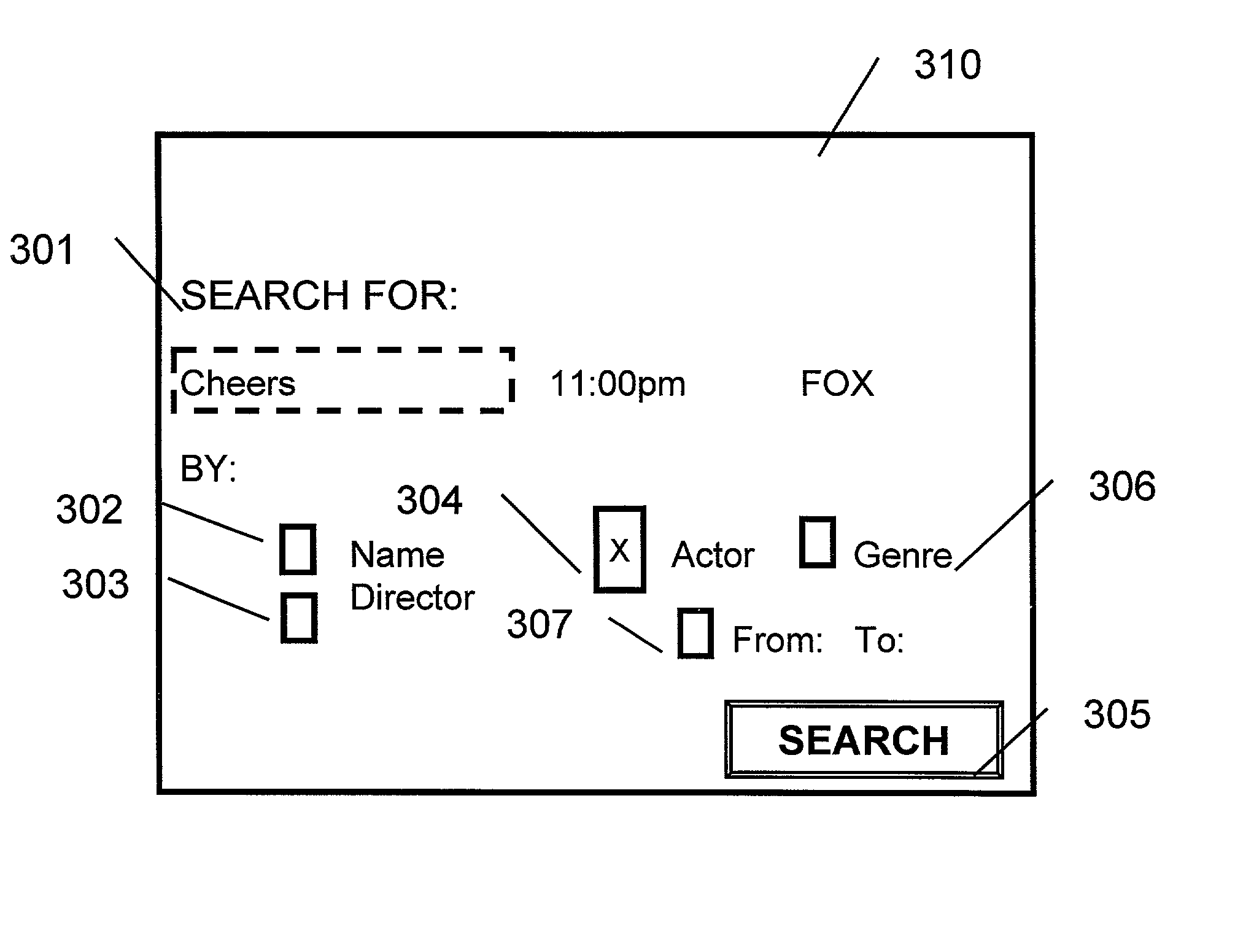
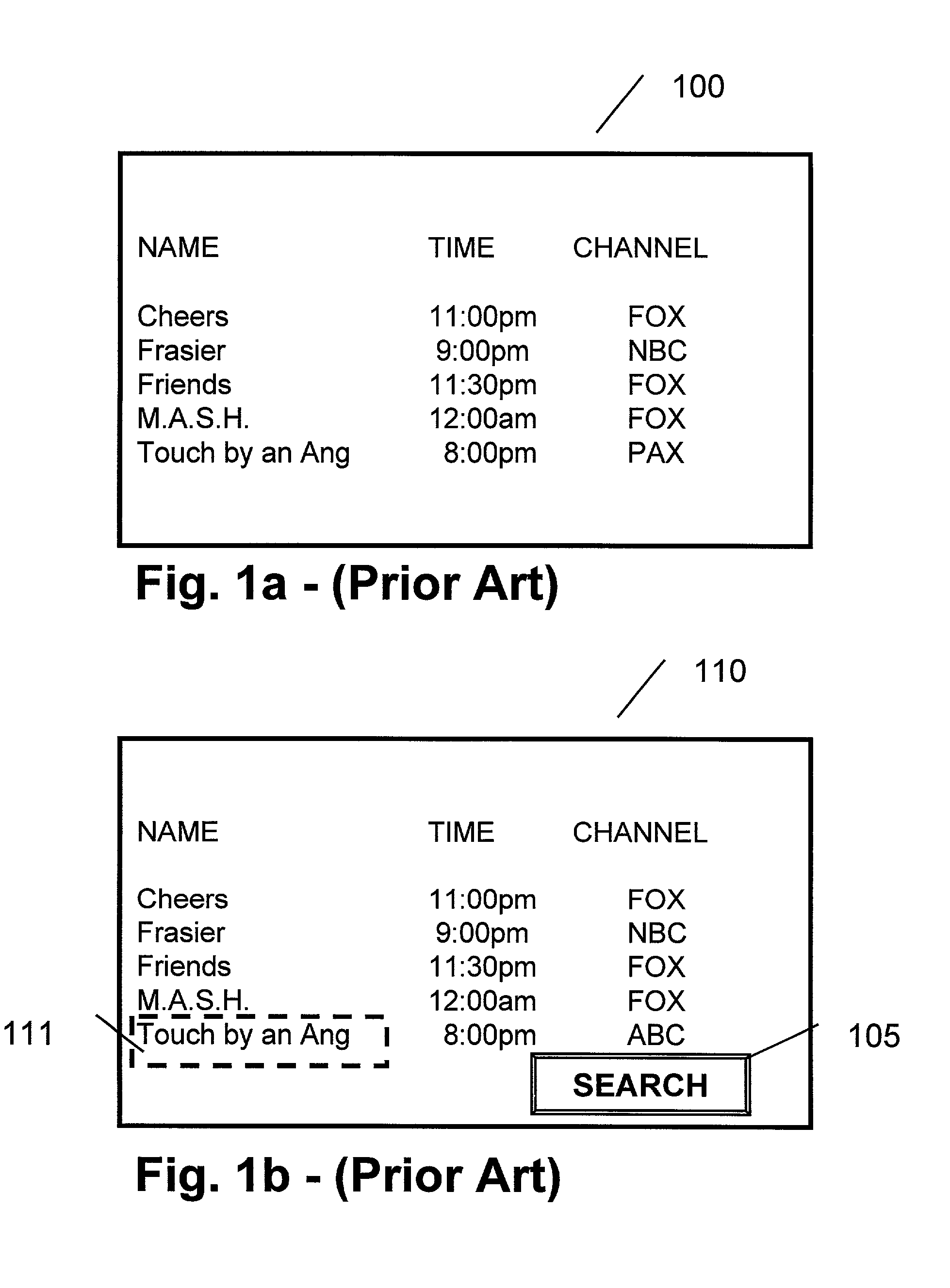
Method and apparatus for finding the same of similar shows
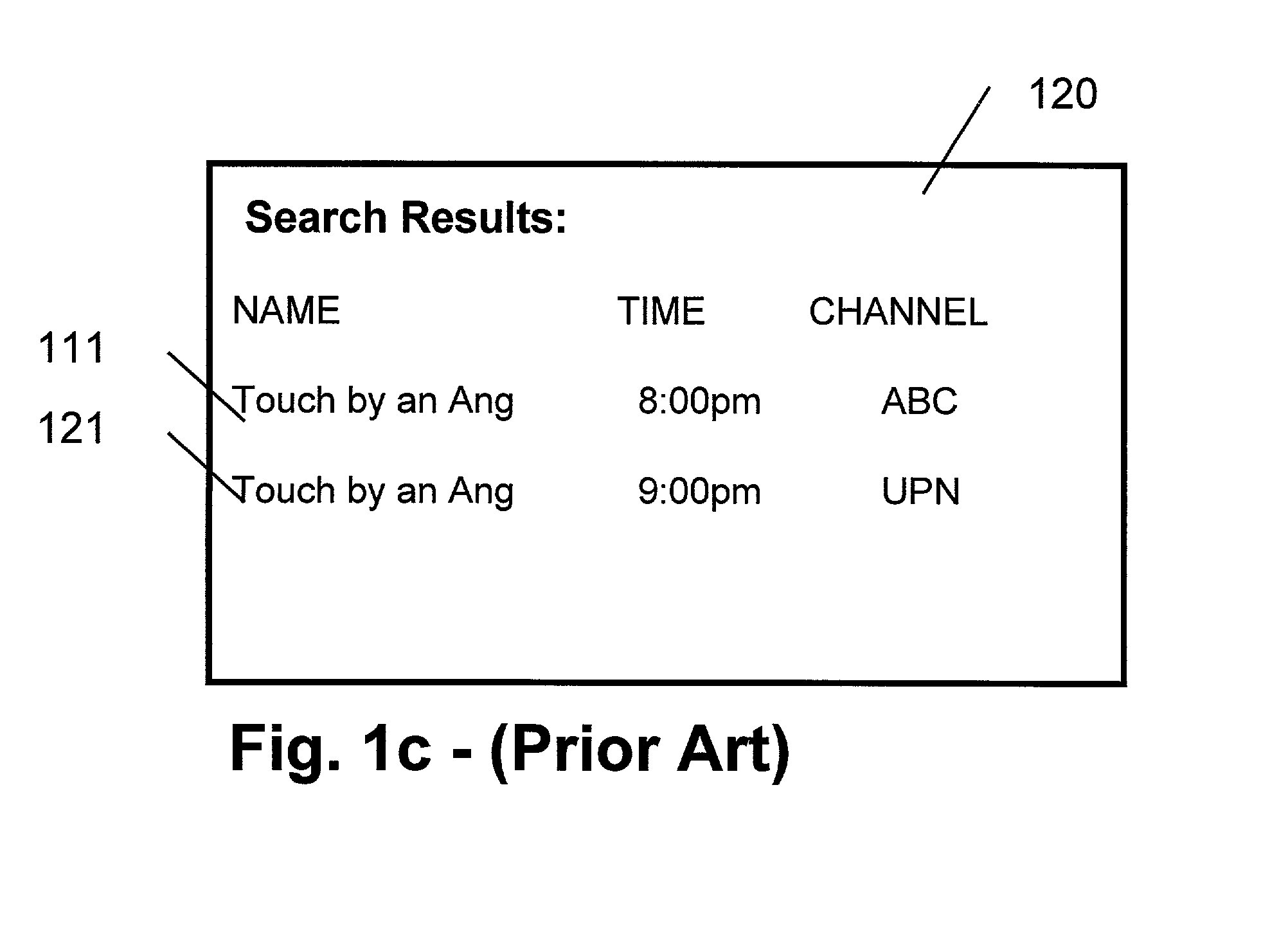
InactiveUS7213256B1Television system detailsColor television detailsExact matchElectronic program guide
A method and apparatus providing for expanded search functionality in an electronic program guide (EPG) for television is described. The expanded search function finds show titles that are the same or similar to the show title of the program data currently displayed by the EPG. The expanded search function also finds shows similar to the one currently displayed by the EPG by using additional search elements based on the descriptive part of the EPG program data, such as actors, director, genre, etc., as well as search parameters based on the show time, channel, etc. Rather than only finding exact matches, the expanded search function uses fuzzy logic to find near matches and prioritizes the results according to the search elements and parameters as specified by the viewer.
Owner:JLB VENTURES LLC
Associative database scanning and information retrieval
InactiveUS7181437B2Threshold may be loweredRaise the importanceData processing applicationsInput/output to record carriersMass storageExact match
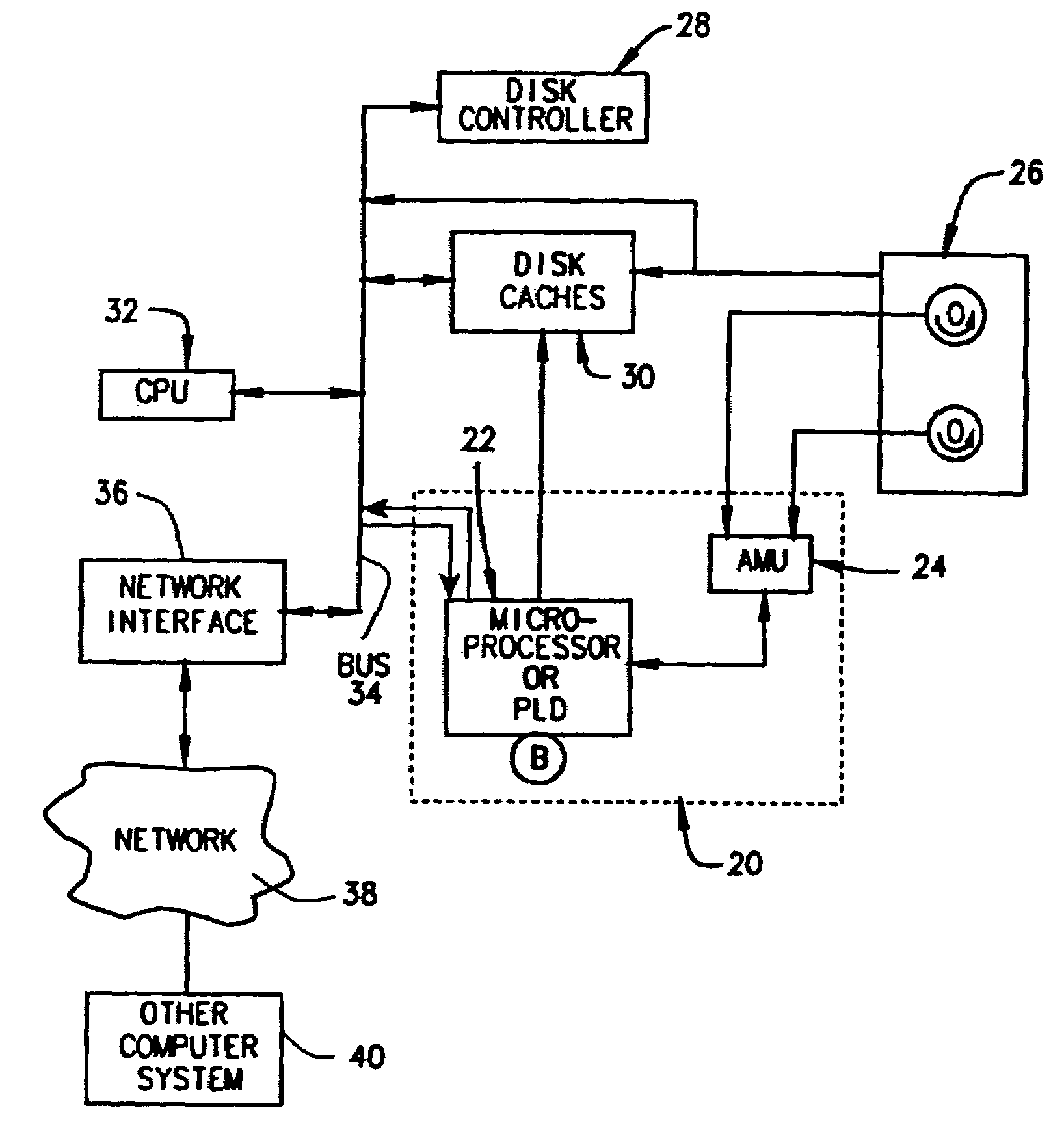
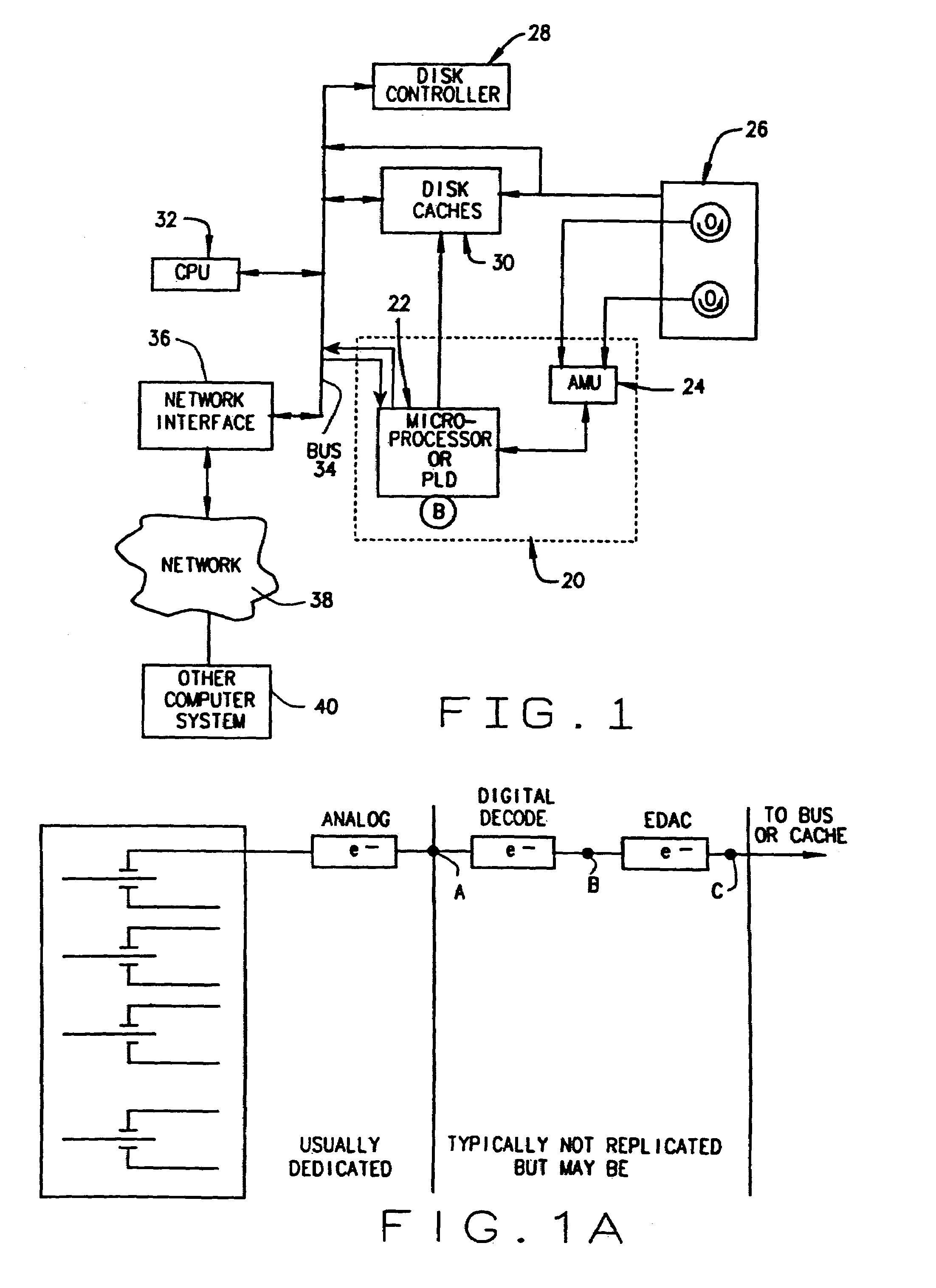
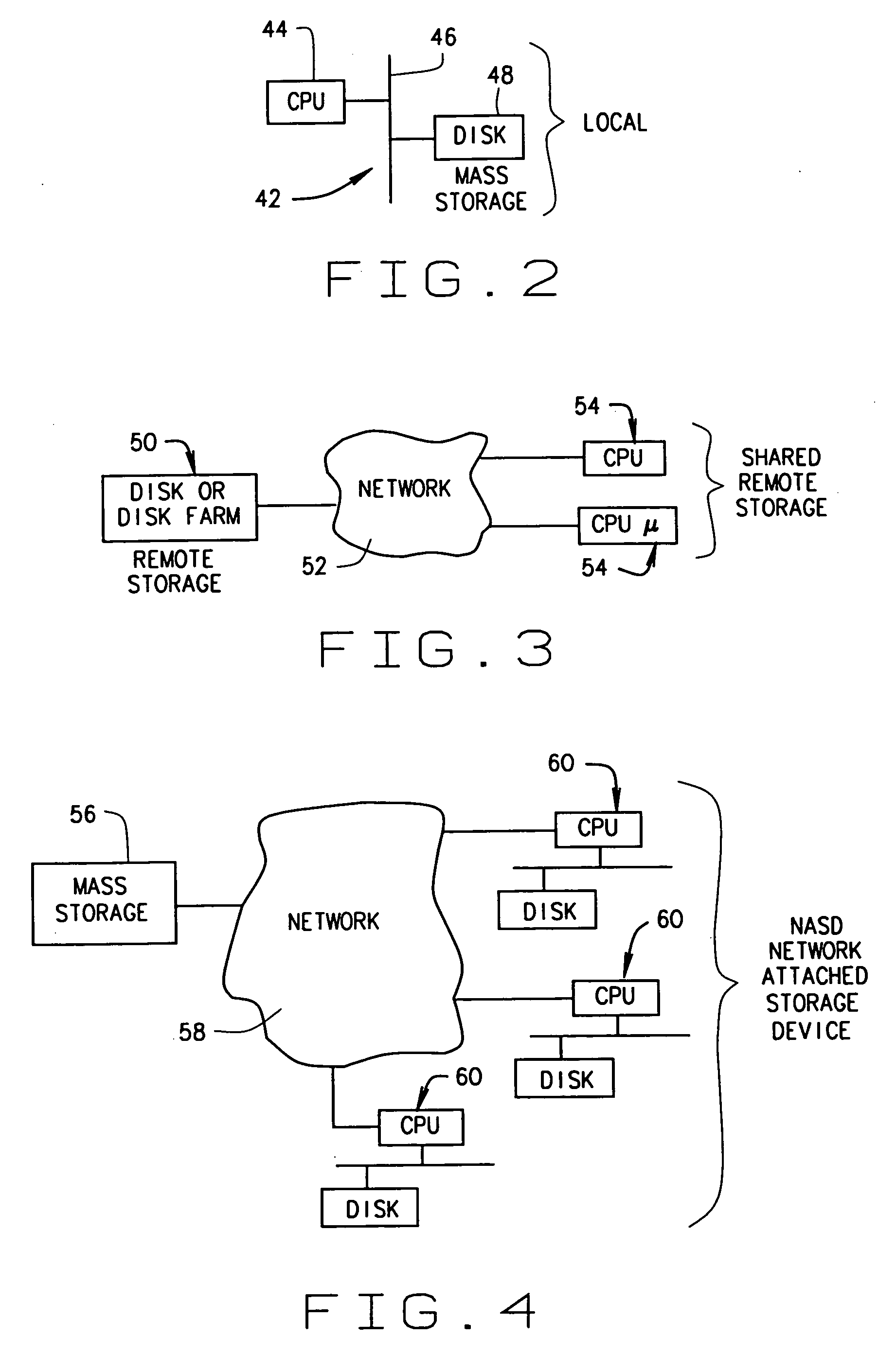
A method and device are disclosed for an associative and approximate, analog or digital scanning of databases that allows for the asynchronous accessing of data from a mass storage medium. The invention includes providing dedicated analog and digital circuitry and decision logic at the mass storage medium level for determining a key identifying the data of interest, continuously comparing the key to a signal generated from a reading of the data from the mass storage medium with an approximate or exact matching circuit to determine a pattern match, determining a correlation value between the key and the data as it is read in a continuous fashion, and determining a match based upon a preselected threshold value for the correlation value. The pattern matching technique eliminates any need to compare data based on its intrinsic structure or value, and instead is based on an analog or digital pattern. The key and data may be either analog or digital. This device and method may be provided as part of a stand-alone computer system, embodied in a network attached storage device, or can otherwise be provided as part of a computer LAN or WAN.
Owner:IP RESERVOIR
Method of building a validation database
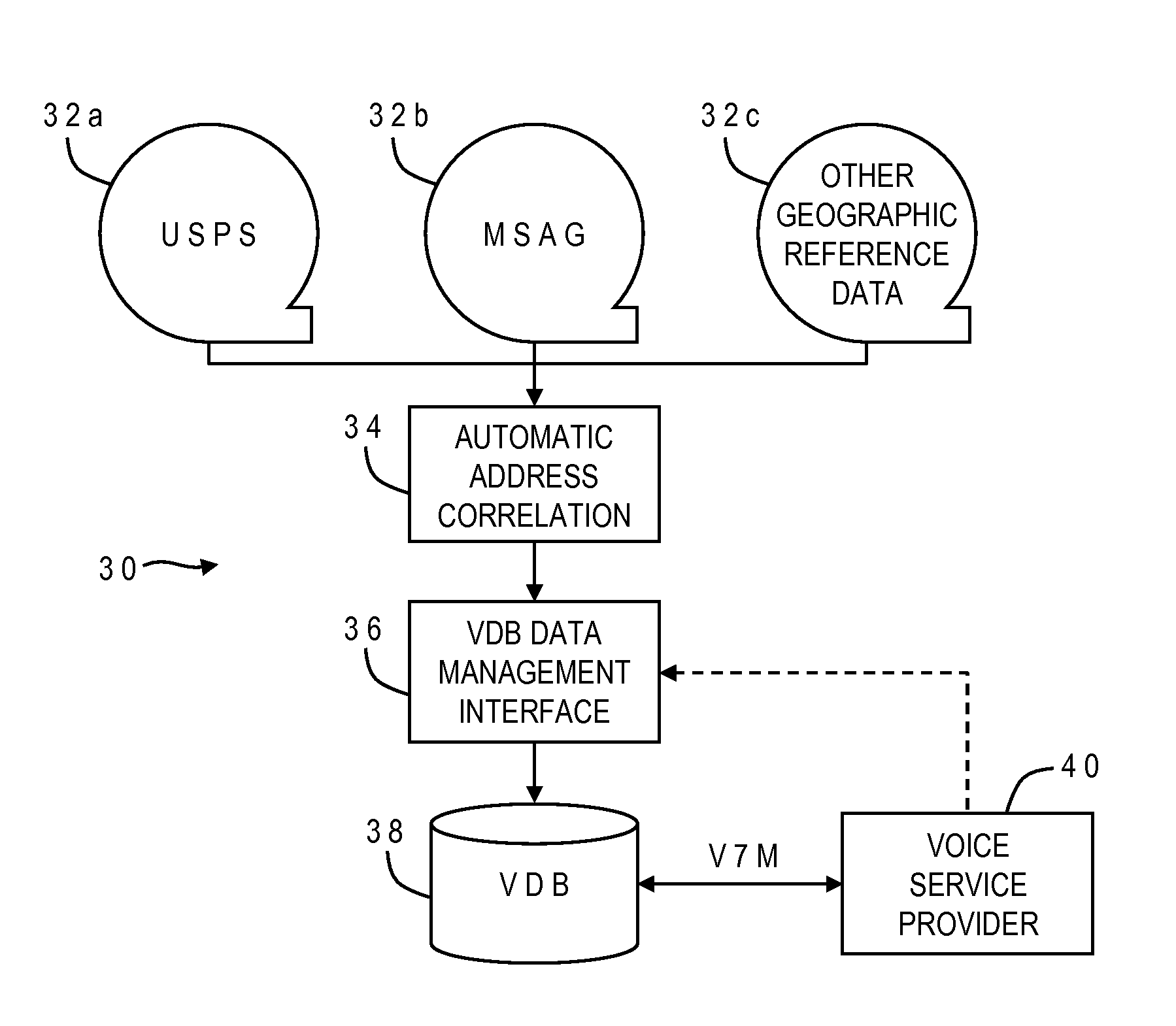
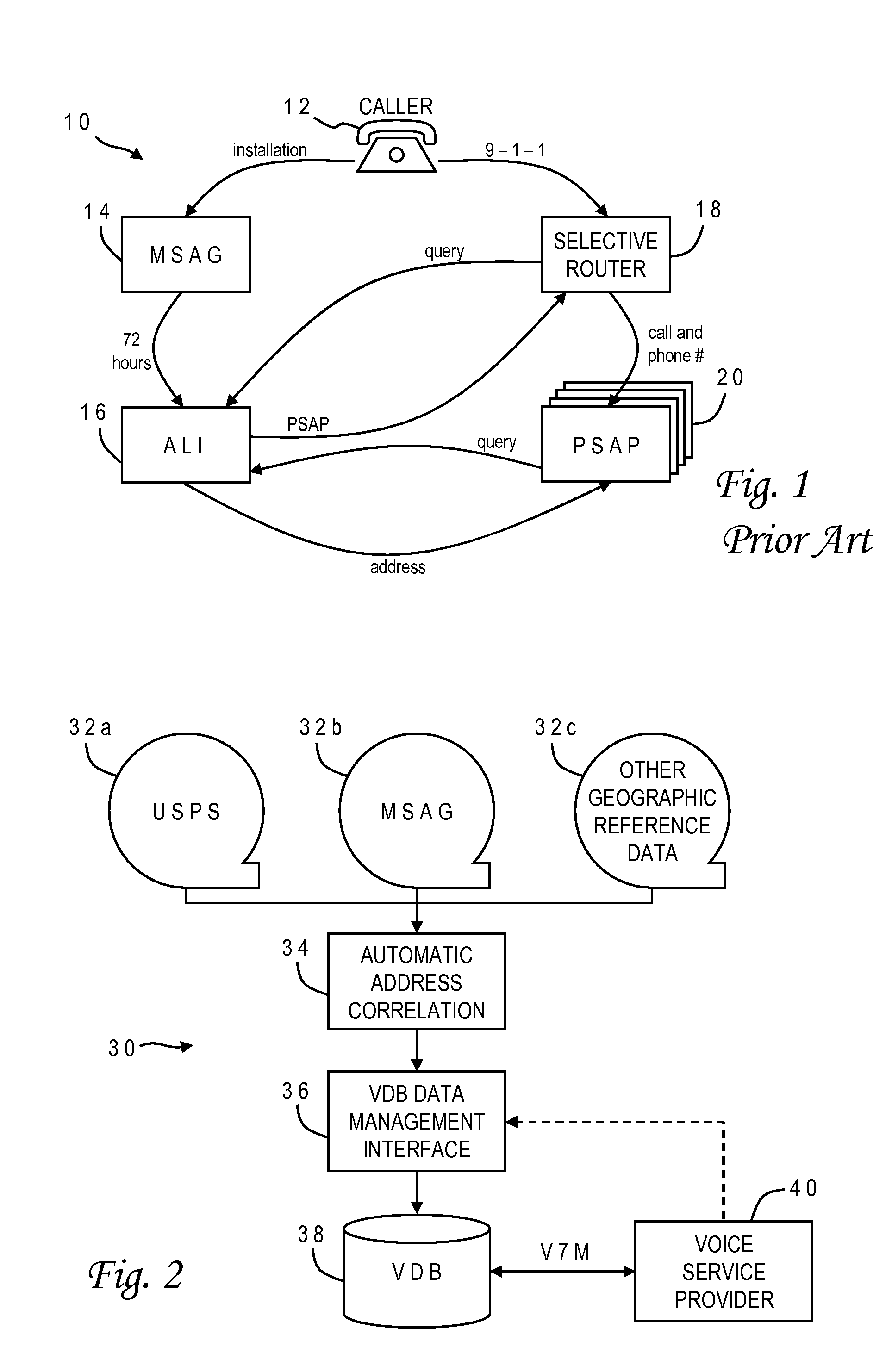
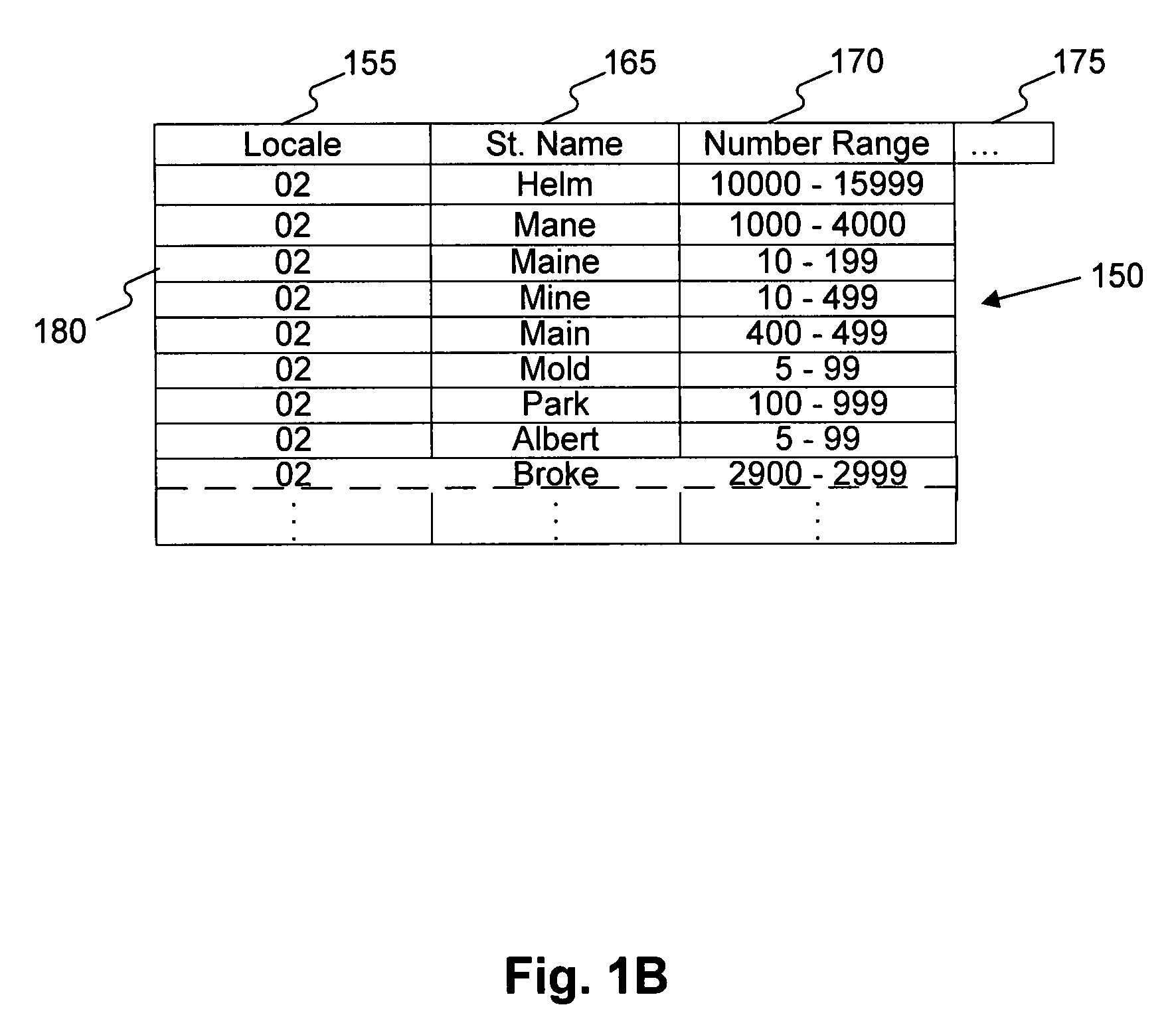
InactiveUS20090094270A1Easy and quick correctionValid matchGeographical information databasesSpecial data processing applicationsExact matchData source
A validation database (VDB) is built from geographic reference data sources such as MSAG and USPS using automatic address correlation, and links between the records are stored in the VDB. The automatic address correlation employs multiple correlation algorithms, and a score is assigned to each link representing a confidence level. The score is based on a combination of results from the different algorithms. Links having a score representing a partial or exact match are used for address validation purposes. A management interface allows the VDB agent to edit master records and the links, including the score. A remote subscriber can request validation of a proposed address from the VDB, and may include match criteria with the request. If any matches are found, a validation reply is sent from the VDB to the subscriber with the corresponding MSAG records.
Owner:WEST SAFETY SERVICES INC
Point cloud automatic registration method based on normal vector
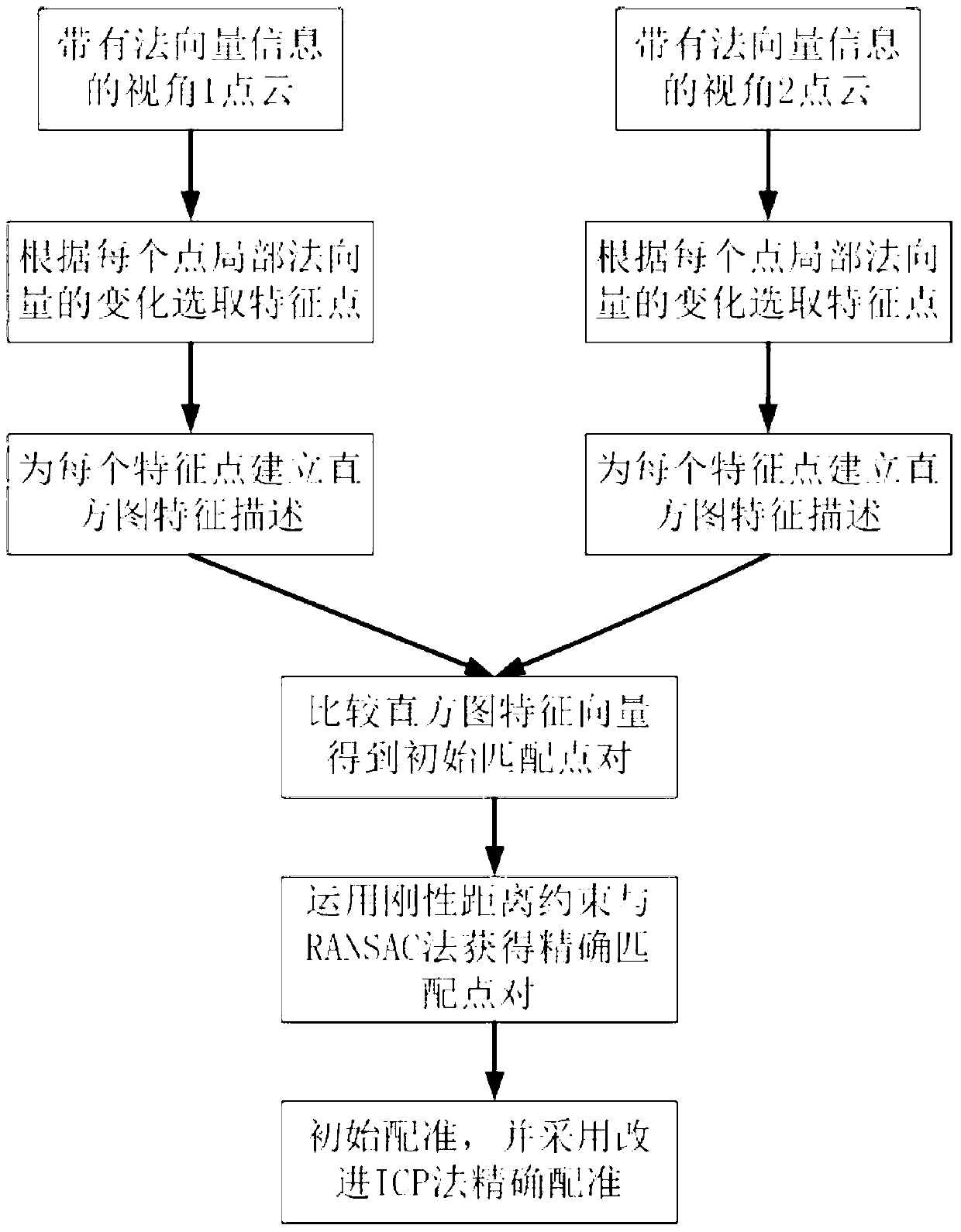
ActiveCN103236064AMeet registration requirementsRealize automatic registrationImage analysisFeature vectorExact match
The invention relates to a point cloud automatic registration method based on normal vector. According to the method, processing objects are two or more than two pieces of three-dimensional point cloud data, wherein overlapped part exists every two pieces of adjacent three-dimensional point cloud data. The method comprises the following processing steps that (1) feature points are selected according to the point cloud local normal vector changes; (2) the histogram feature quantity is designed for carrying out feature description on each obtained feature point; (3) the initial matching dot pair is obtained through comparing the histogram feature vector of the feature points; (4) the precise matching dot pair is obtained through applying the rigid distance constraint condition and combining a RANSAC (random sample consensus) algorithm, and in addition, the initial registration parameters are obtained through calculation by using a four-element method; and (5) an improved ICP (iterative closest point)) algorithm is adopted for carrying out point cloud precise registration. The point cloud can be automatically registered according to the steps. The method has the advantages that feature description is simple, identification degree is high, higher robustness is realized, and registration precision and speed are improved to a certain degree.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
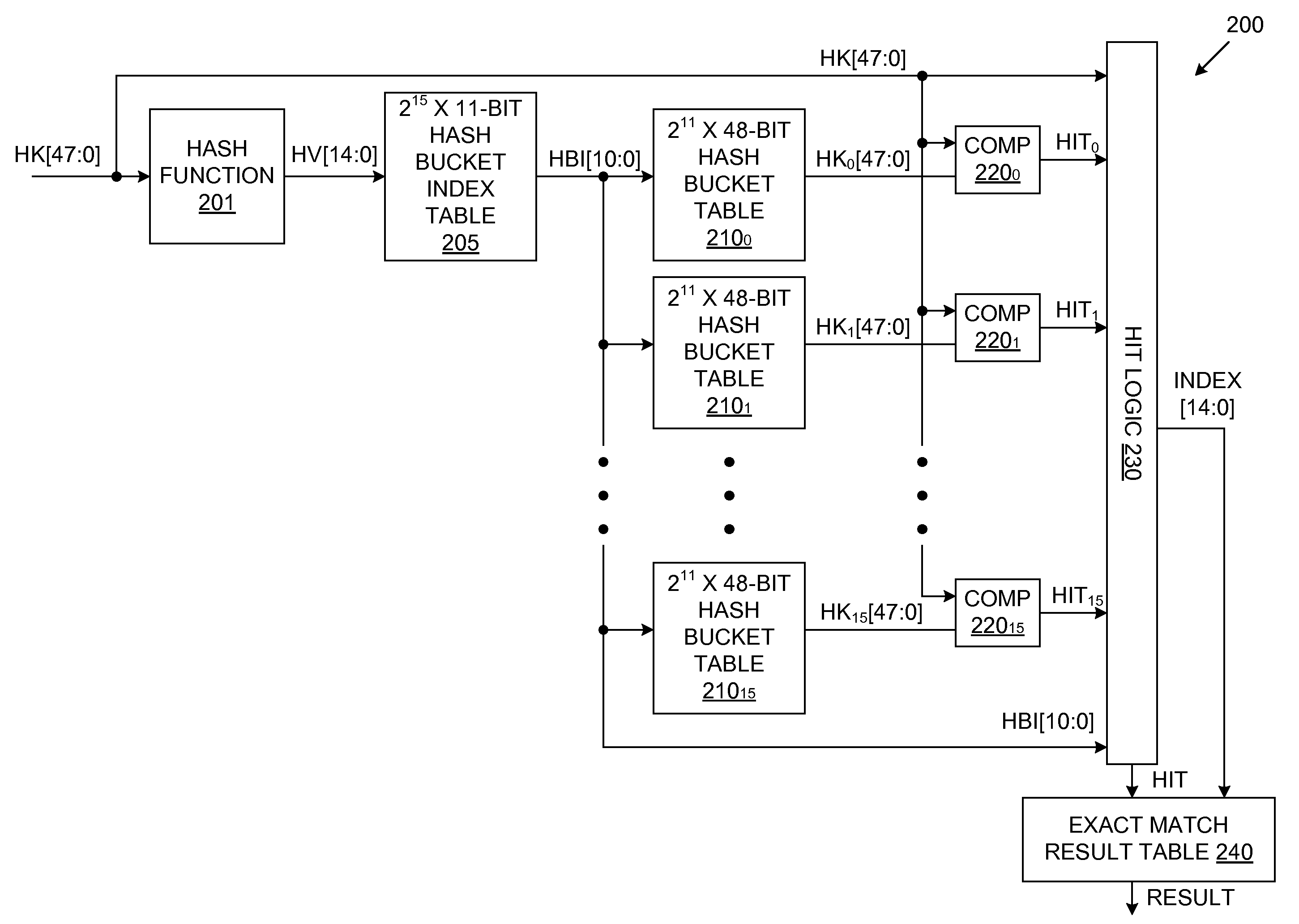
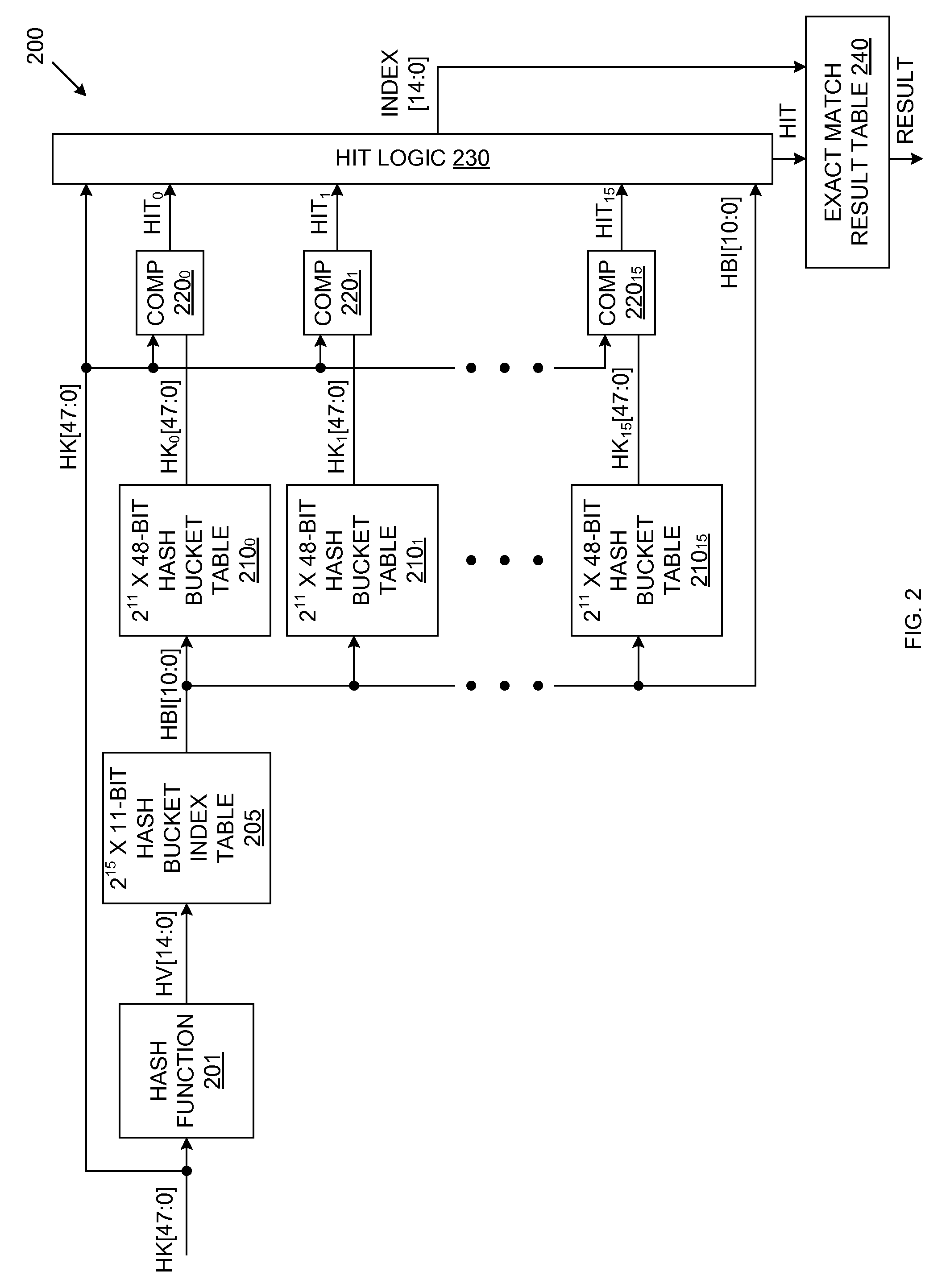
Exact Match Lookup Scheme
InactiveUS20110060876A1Digital data information retrievalData switching networksExact matchHash table
An exact match lookup system includes a hash function that generates a hash value in response to an input hash key. The hash value is used to retrieve a hash bucket index value from a hash bucket index table. The hash bucket index value is used to retrieve a plurality of hash keys from a plurality of hash bucket tables, in parallel. The retrieved hash keys are compared with the input hash key to identify a match. Hit logic generates an output index by concatenating the hash bucket index value with an address associated with the hash bucket table that provides the matching hash key. An exact match result is provided in response to the output index. A content addressable memory (CAM) may store hash keys that do not fit in the hash bucket tables.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
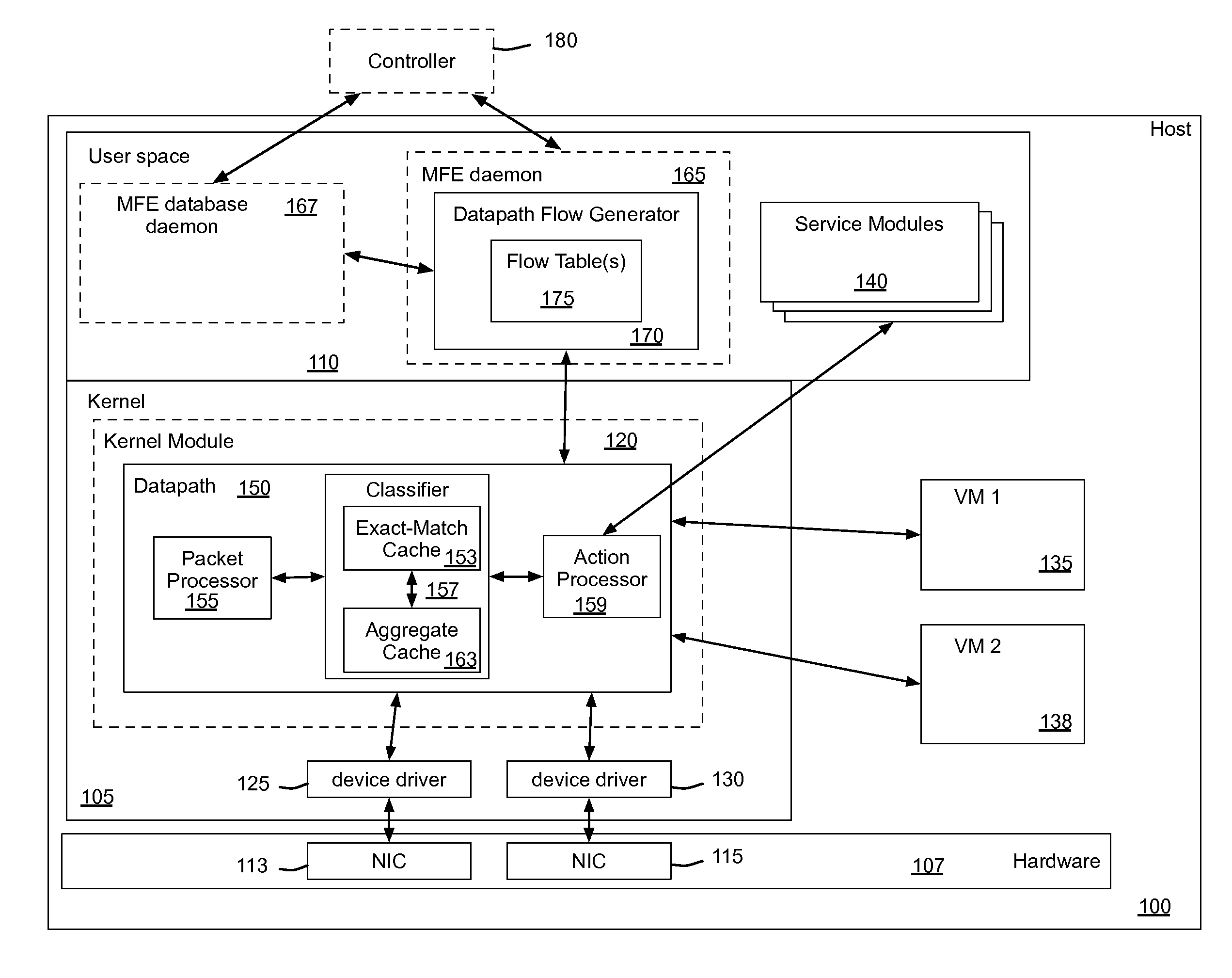
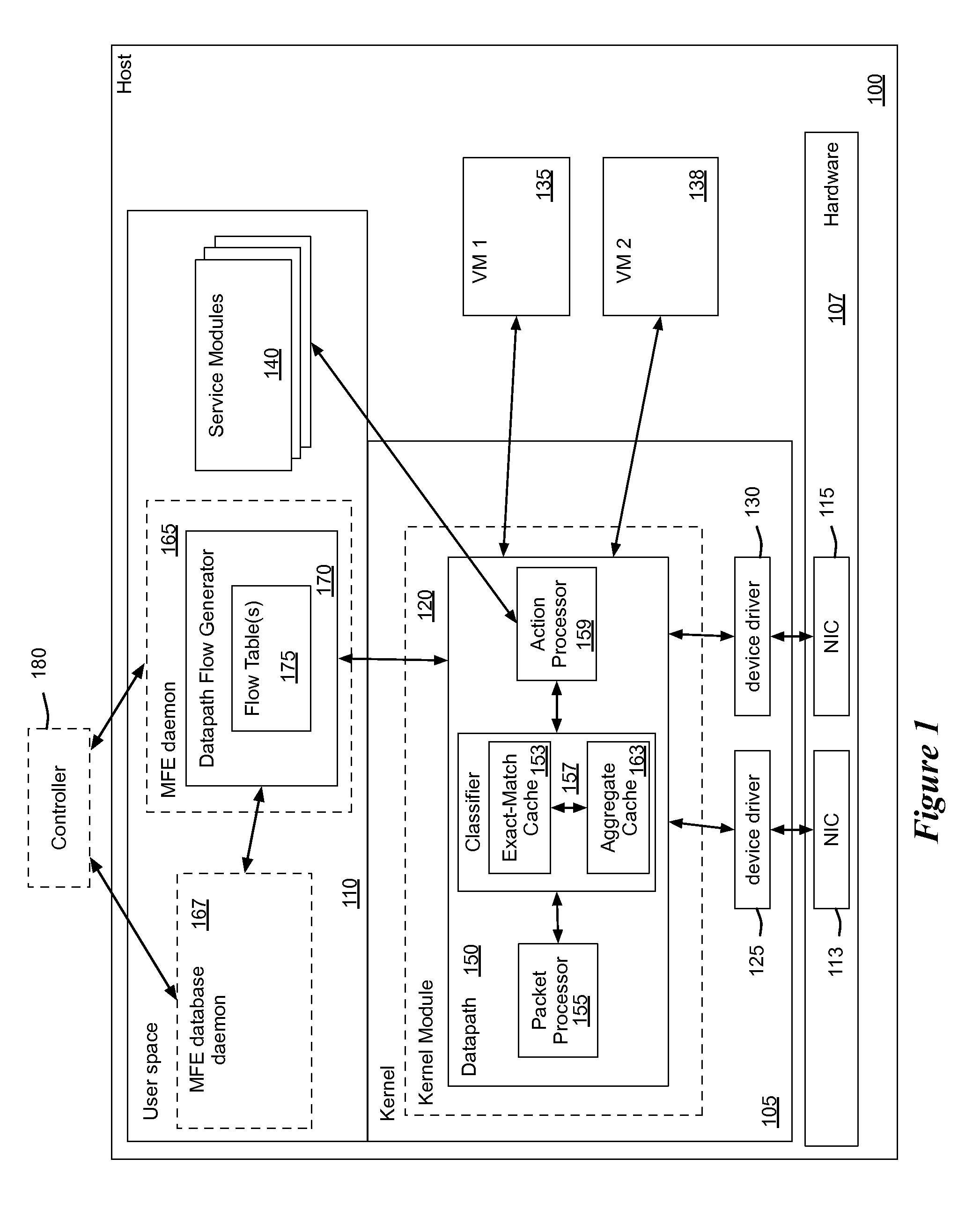
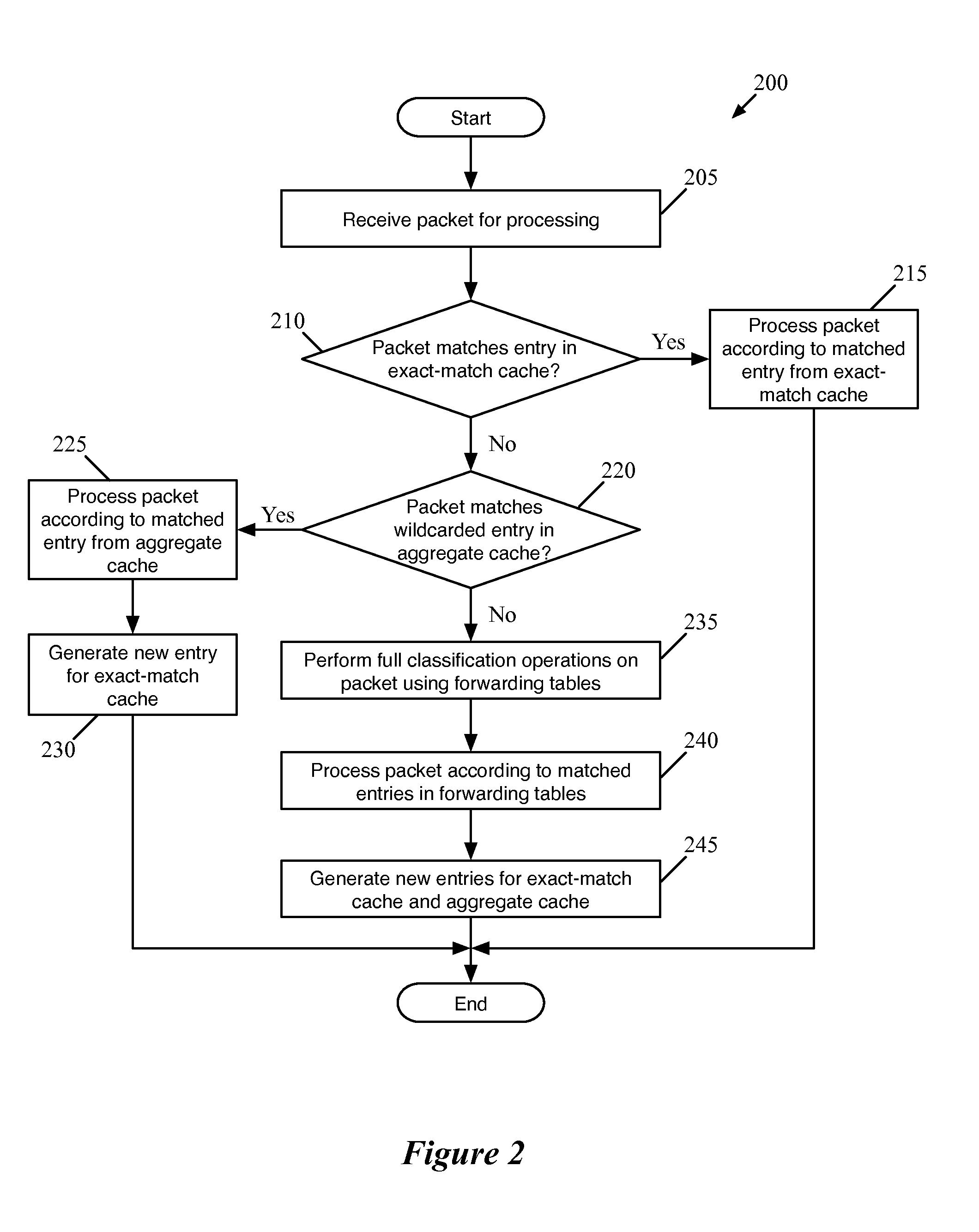
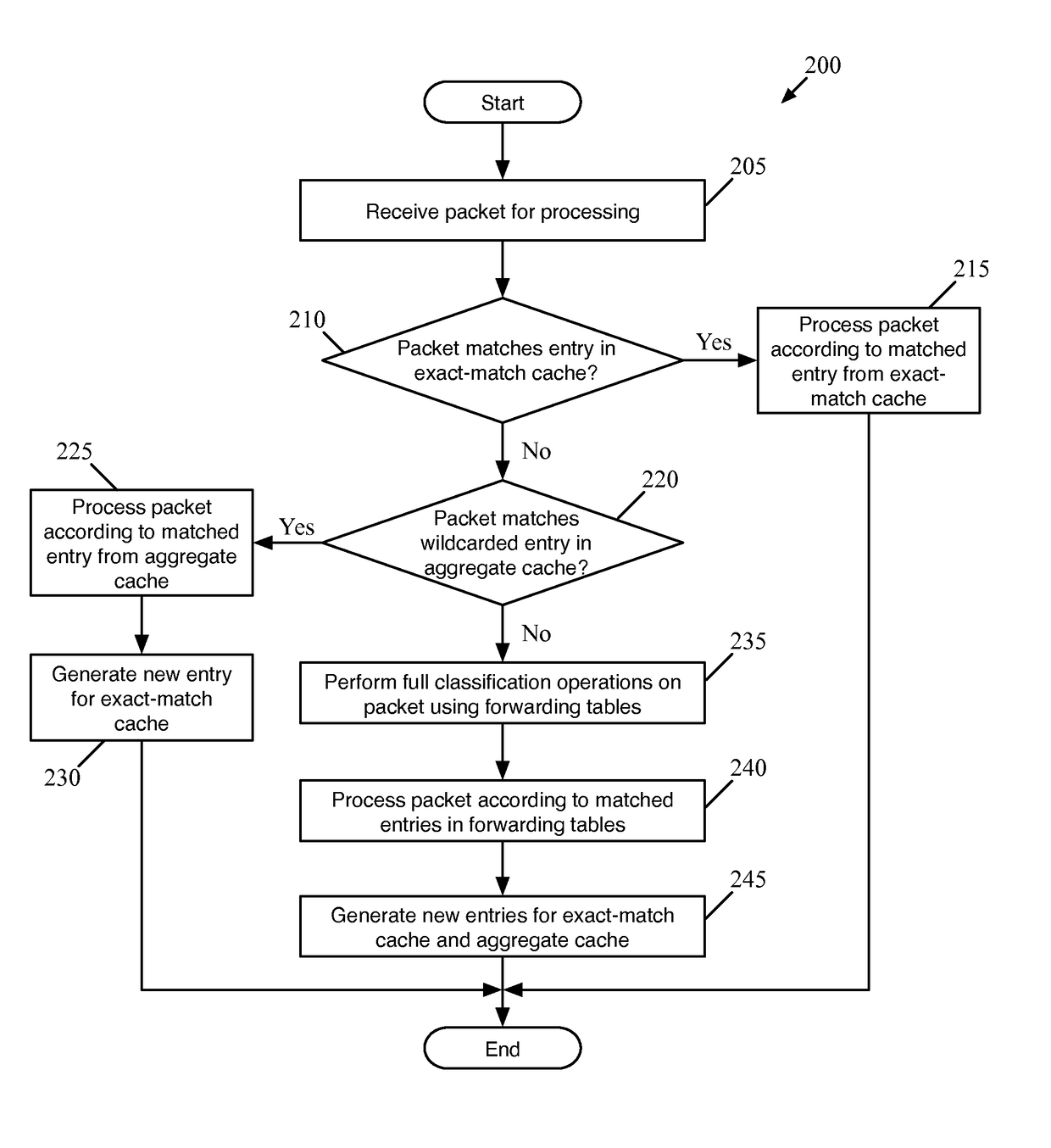
Flow Cache Hierarchy
ActiveUS20150281098A1Save computing resourcesSave a lot of timeMemory architecture accessing/allocationError preventionExact matchCache hierarchy
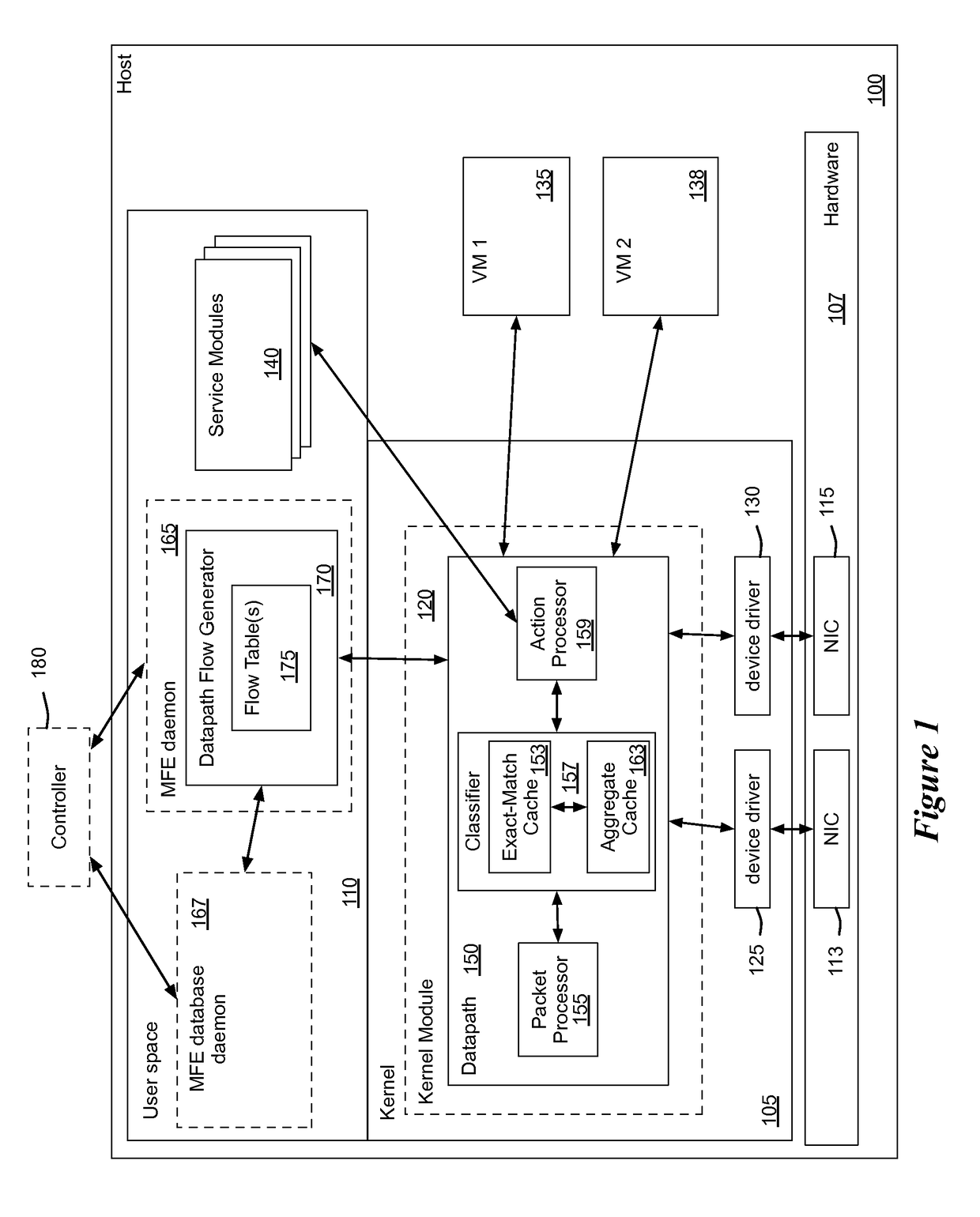
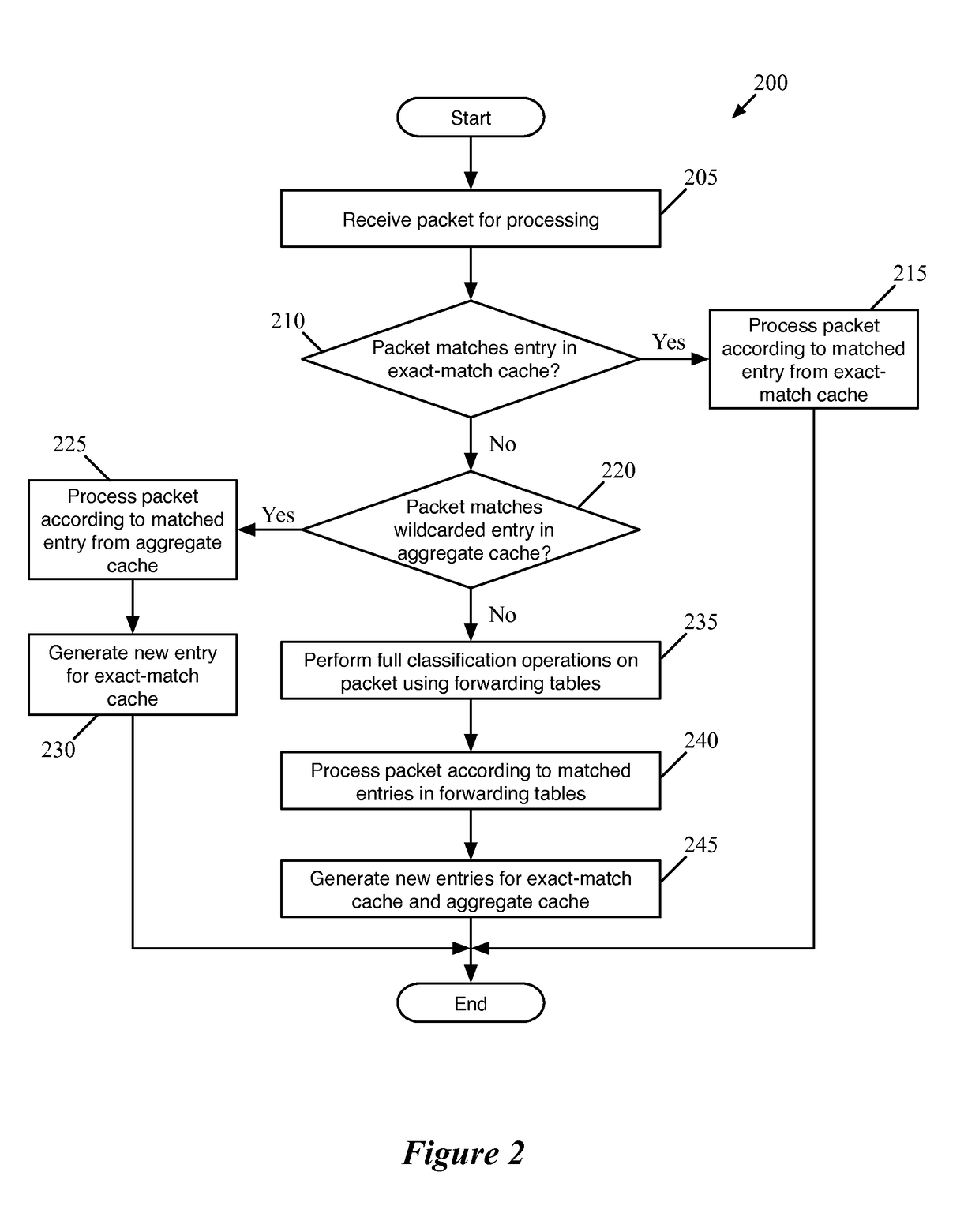
Some embodiments provide a managed forwarding element (MFE that includes a set of flow tables including a first set of flow entries for processing packets received by the MFE. The MFE includes an aggregate cache including a second set of flow entries for processing packets received by the MFE. Each of the flow entries of the second set is for processing packets of multiple data flows. At least a subset of packet header fields of the packets of the multiple data flows have a same set of packet header field values, and a same set of operations is applied to said packets. The MFE includes an exact-match cache including a third set of flow entries for processing packets received by the MFE. Each of the flow entries of the third set is for processing packets for a single data flow having a unique set of packet header field values.
Owner:NICIRA
Collection synchronization using equality matched network names
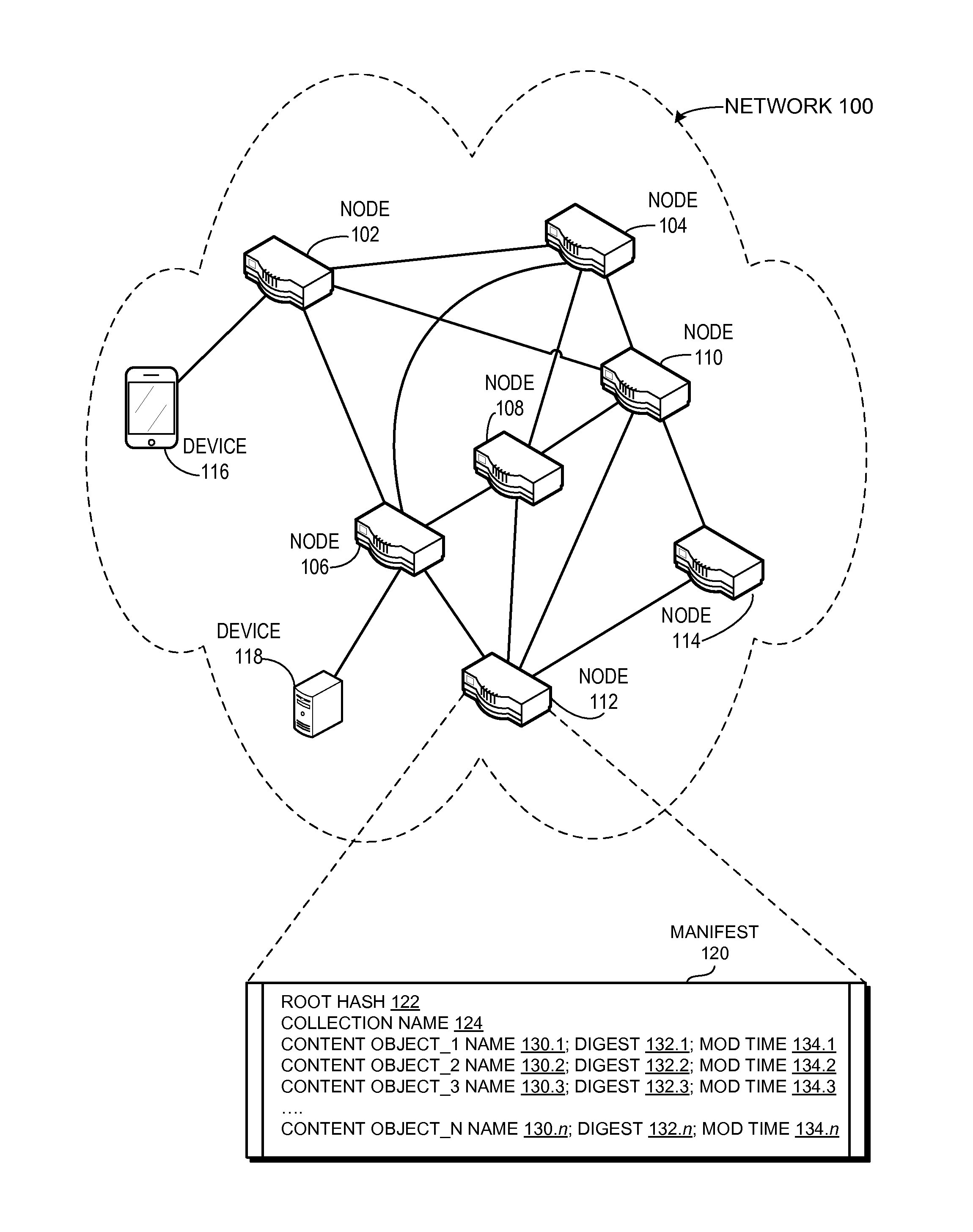
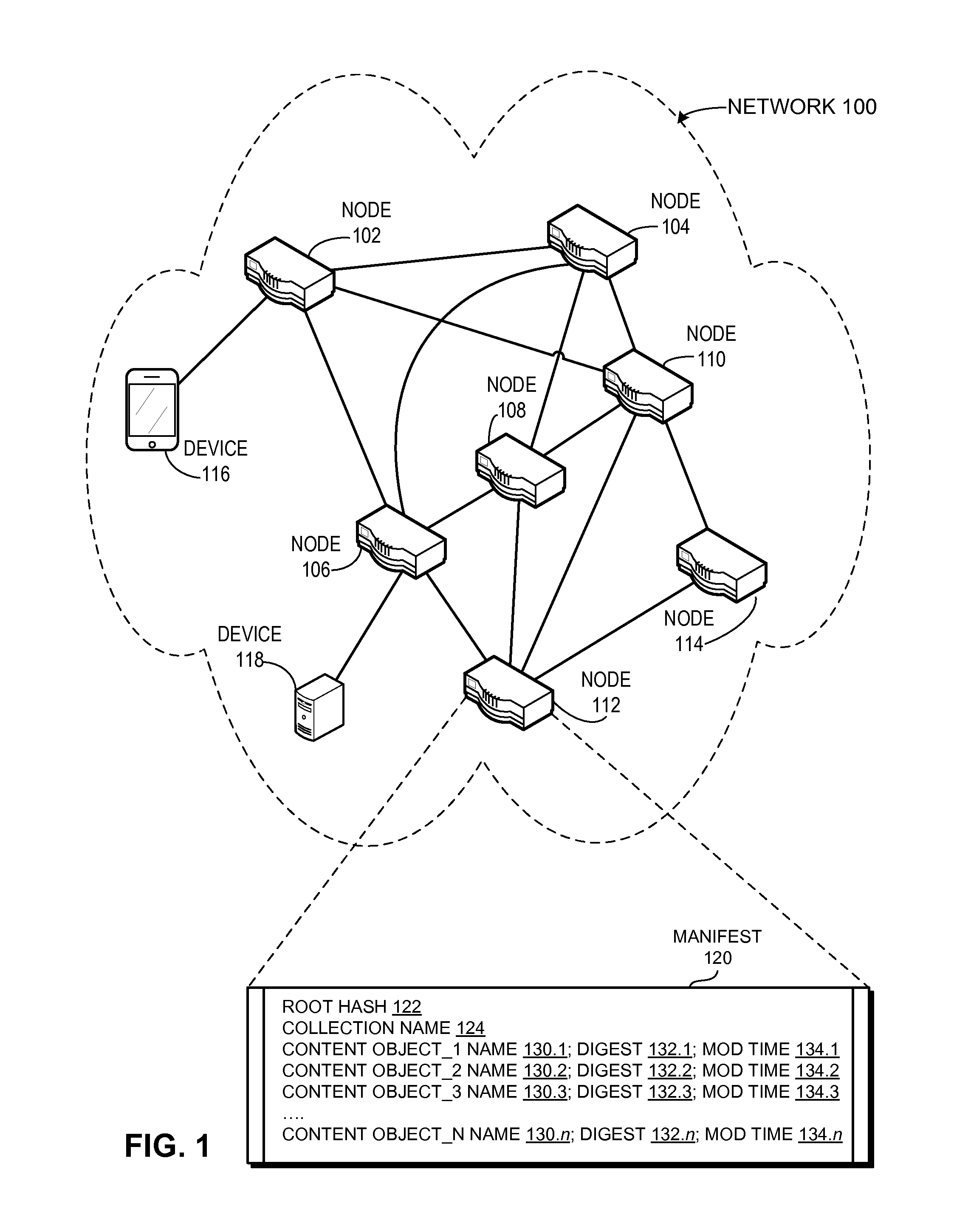
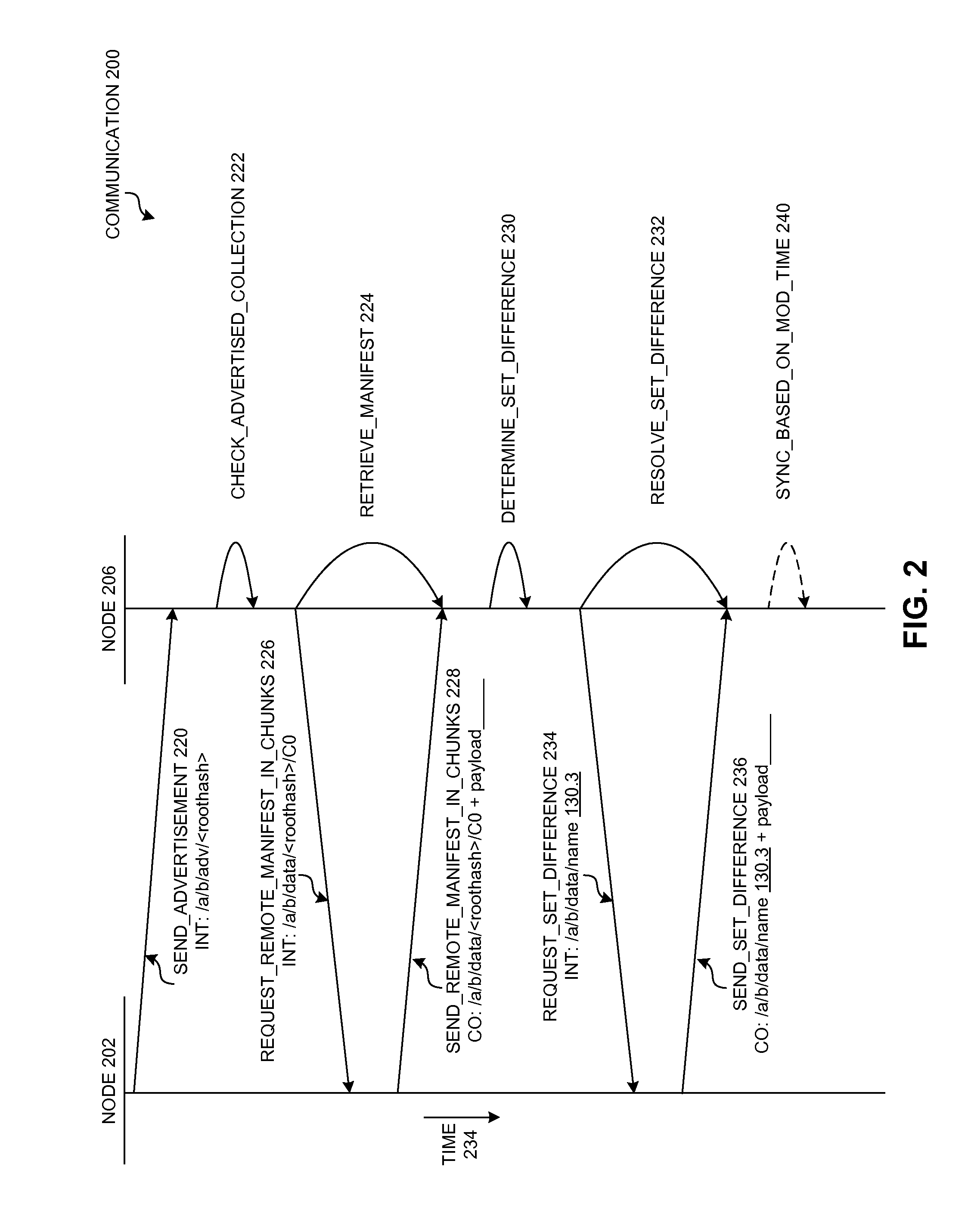
ActiveUS20150288755A1Good synchronizationIncrease contentMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionExact matchDistributed computing
One embodiment provides a system that facilitates synchronization collections of data between a local and a remote node by using exact match names. During operation, a local node receives an advertisement corresponding to a remote manifest at a remote node. A manifest represents a collection of content objects at a node. In some embodiments, a manifest corresponds to a root hash value that identifies the content objects of the collection. The local node determines that the local manifest and the remote manifest both indicate the same collection of content objects. The local node then determines if the content of the collections are different by comparing the root hash value of the local manifest with the root hash value of the remote manifest. Responsive to determining that the root hash values of the manifests are different, the local node retrieves the remote manifest by sending a request for the remote manifest. The local node determines which content objects identified in the remote manifest are different from the content objects identified in the local manifest. The local node transmits a set of interests for the content objects that are different and receives the requested set of content objects, thereby facilitating synchronization of content objects associated with the manifests at both the local and remote node.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
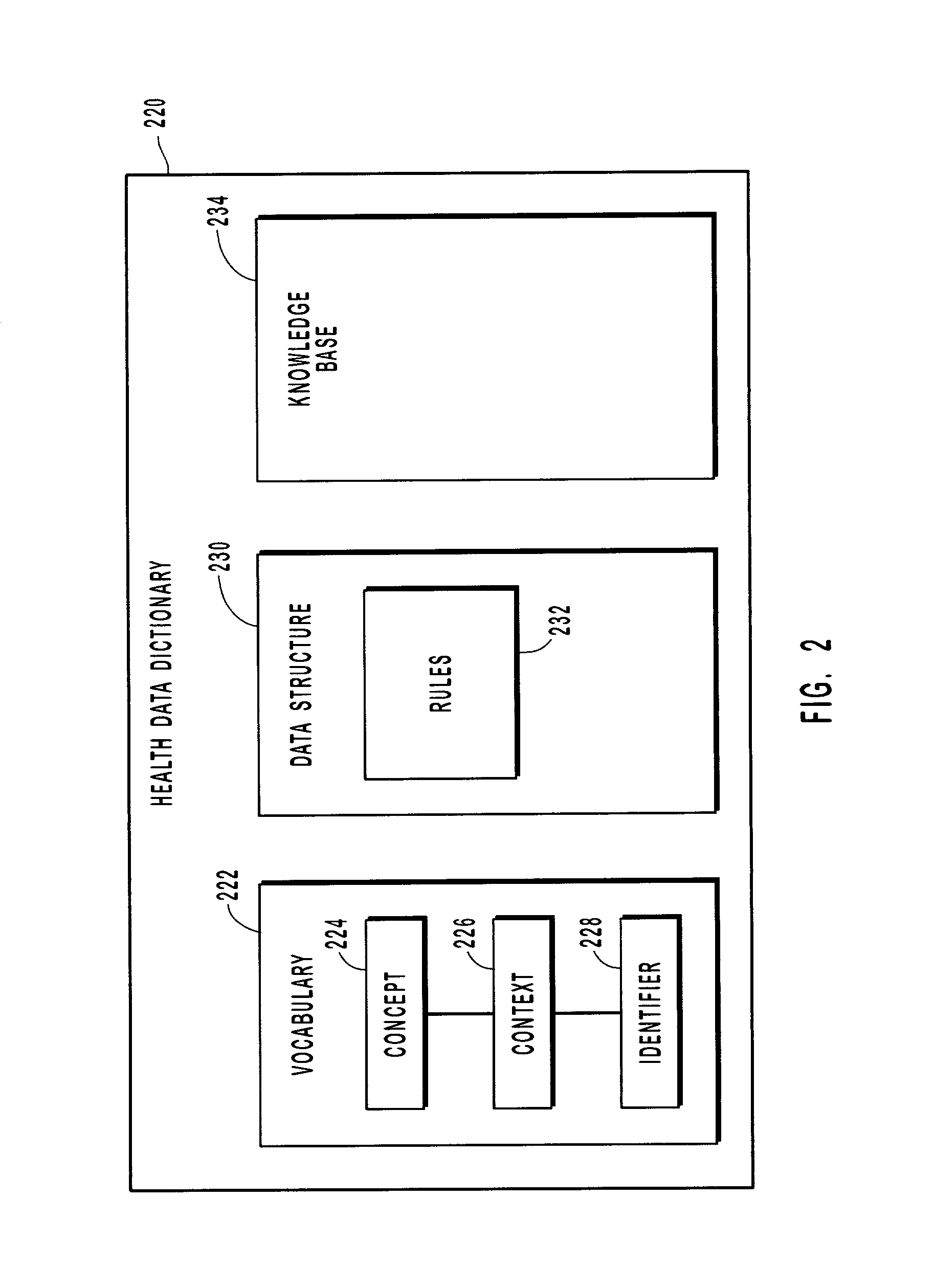
Mapping clinical data with a health data dictionary
InactiveUS20020128861A1Automate processingOffice automationMedical practises/guidelinesExact matchDrug compound
Systems, methods, and computer program products for mapping clinical data including insurance data and pharmaceutical data with a health data dictionary. The health data dictionary provides a vocabulary that identifies insurance companies and pharmaceutical compounds including drugs in a normalized and standard form. The clinical data generated at a legacy system is compared with standard clinical data stored in the health data dictionary. Based on this comparison a partial or exact match is identified for the clinical data. After a match is selected, the normalized clinical data can be stored in a data repository. For unmatched clinical data, new concepts can be created and added to the health data dictionary for future use.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
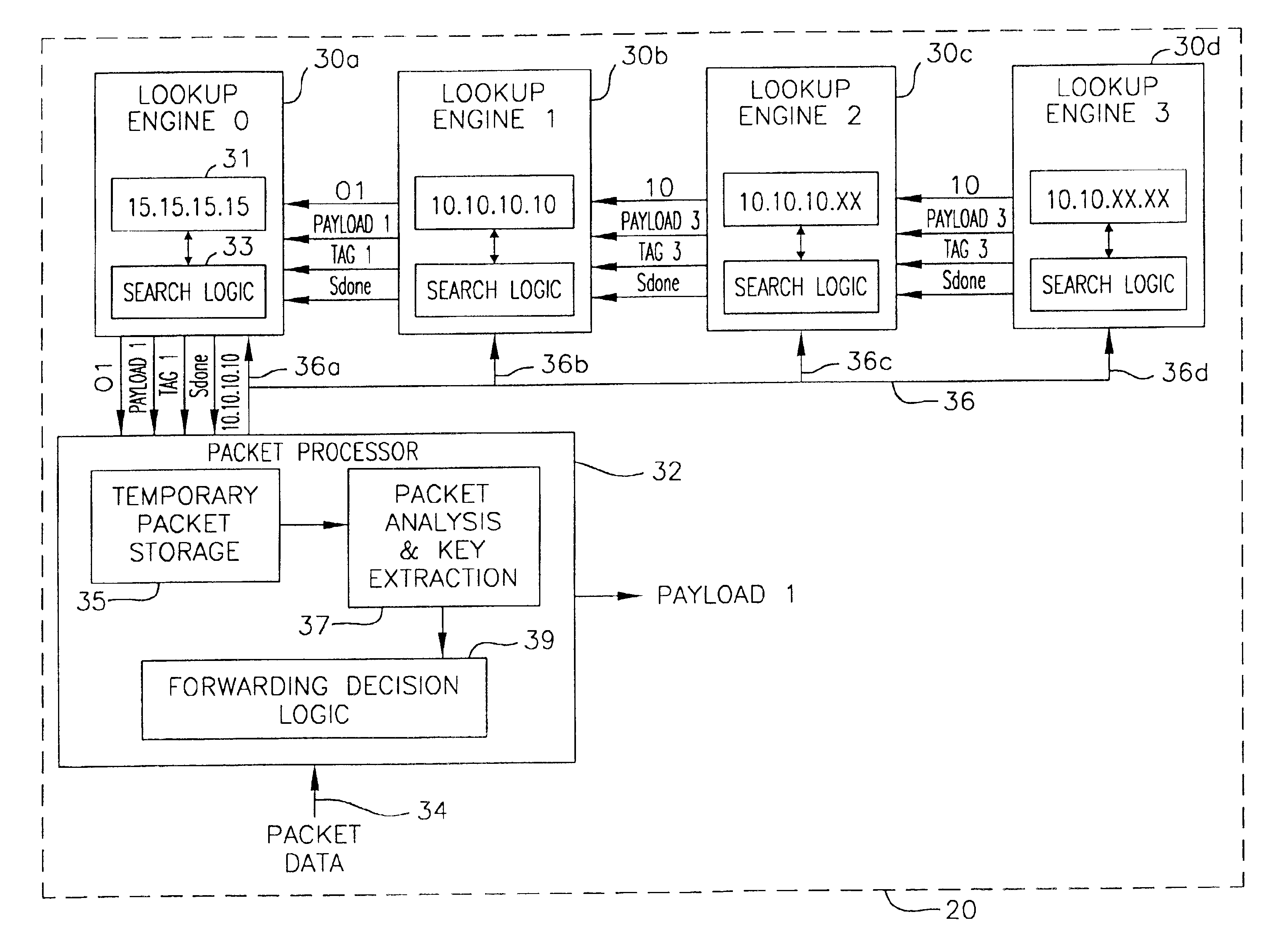
Stackable lookup engines
InactiveUS6957272B2Increase in sizeDigital computer detailsData switching by path configurationExact matchComputer science
Owner:ALCATEL INTERNETWORKING PE
Longest prefix match (LPM) algorithm implementation for a network processor
InactiveUS6947931B1Reduce storage spaceSimple and efficient implementationData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalExact matchTheoretical computer science
Novel data structures, methods and apparatus for finding the longest prefix match search when searching tables with variable length patterns or prefixes. To find the exact match or the best matching prefix, patterns have to be compared a bit at a time until the exact or first match is found. This requires “n” number of comparisons or memory accesses to identify the closest matching pattern. The trees are built in such a way that the matching result is guaranteed to be a best match, whether it is an exact match or a longest prefix match. Using the trail of all the birds and associated prefix lengths enables determination of the correct prefix result from the trail. By construction, the search tree provides the best matching prefix at or after the first compare during walking of the trail or tree.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
System and method for matching a textual input to a lexical knowledge based and for utilizing results of that match
InactiveUS20050065777A1Digital data information retrievalData processing applicationsExact matchText entry
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
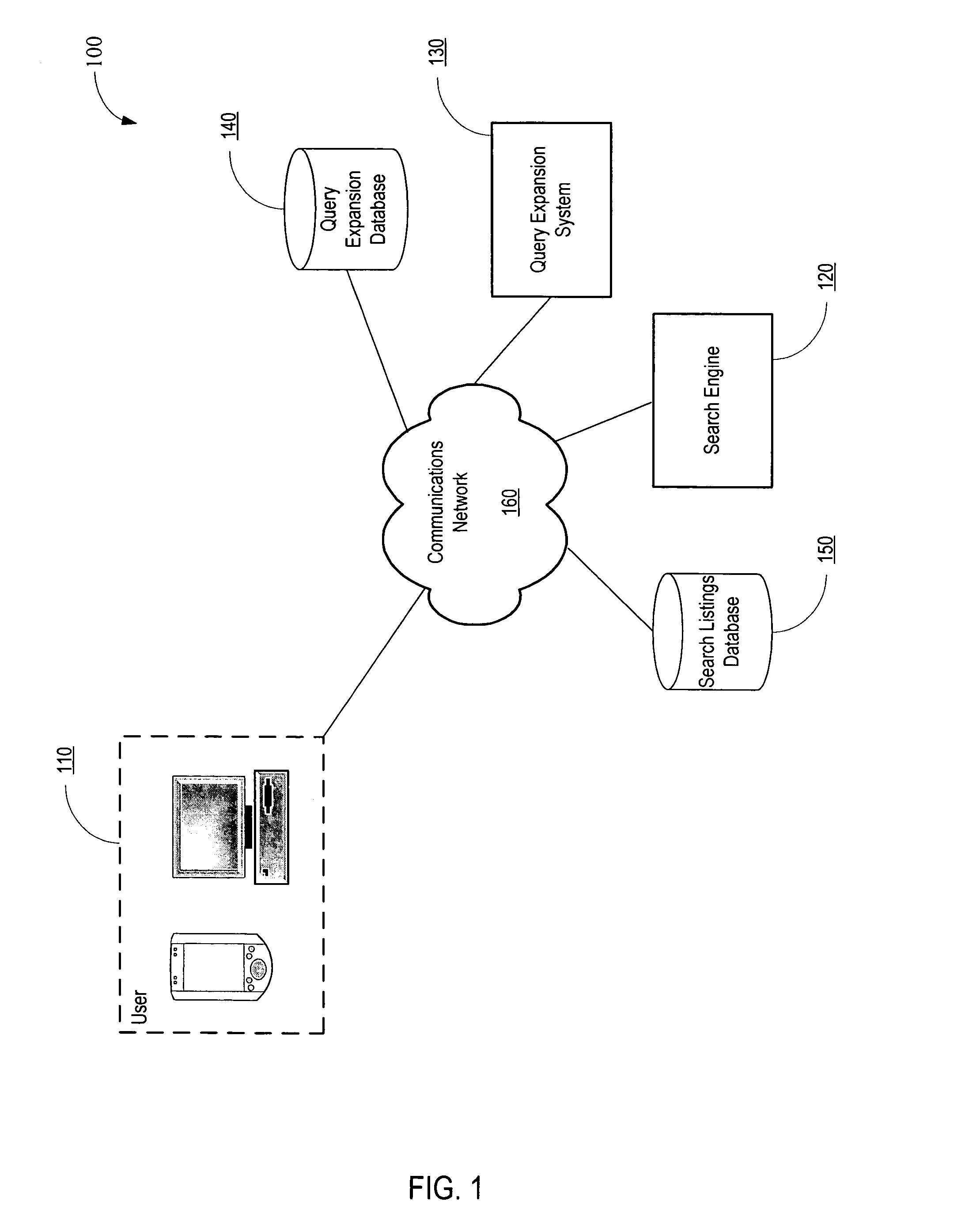
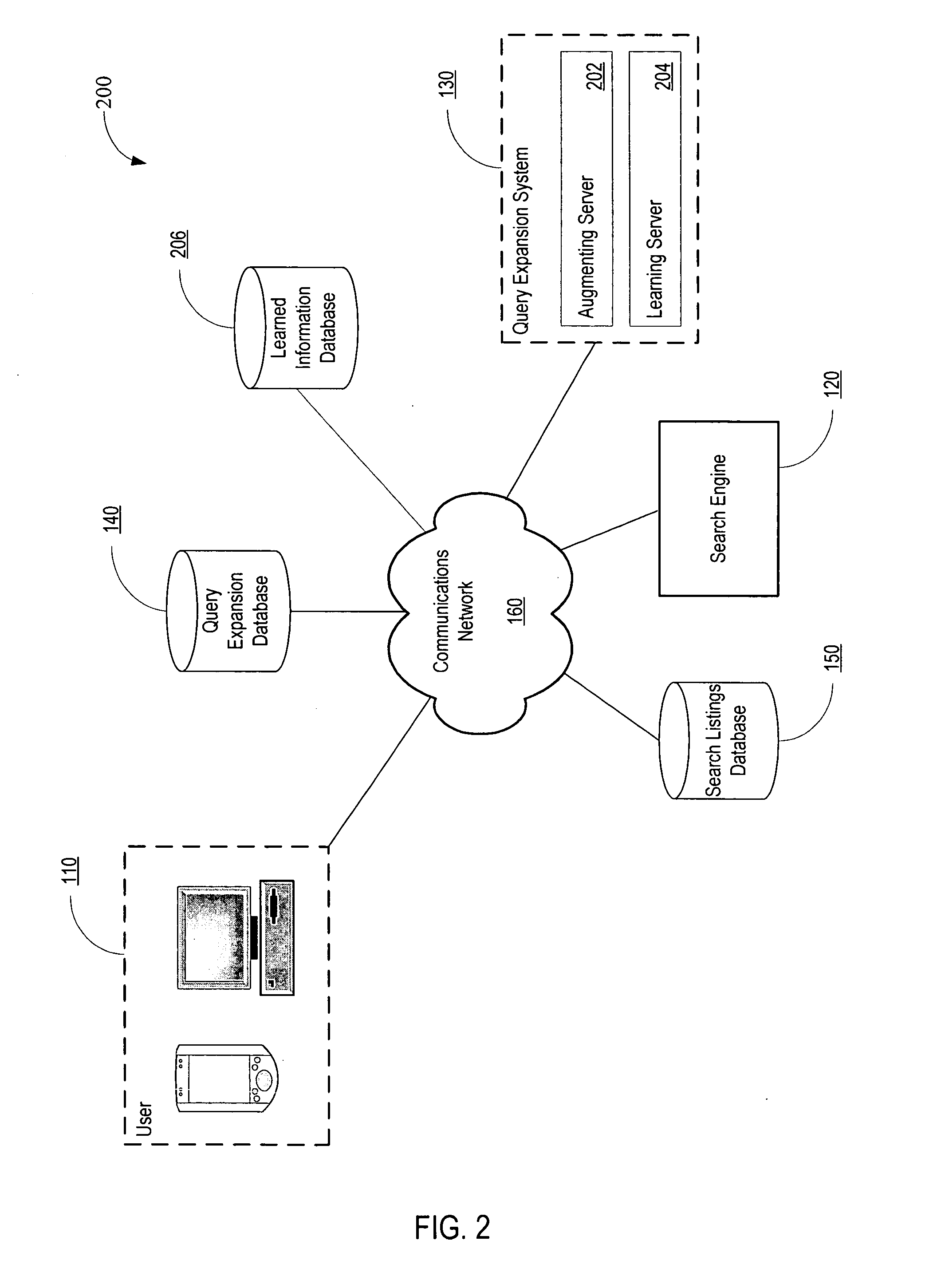
System and method for query expansion
InactiveUS20080154856A1Raise the possibilityData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalExact matchRanking
A system is disclosed for expanding a user query based on user learned popularity rankings. User queries often have no exact match, resulting in a user having to refine or abandon the search. The disclosed system obtains popularity rankings based on the content of a user query. The system expands the user query based on the popularity rankings. Thereafter, query results based on the expanded user query may be provided to the user. The system also regularly learns from user behavior and adapts the popularity rankings according to the learned information.
Owner:R2 SOLUTIONS
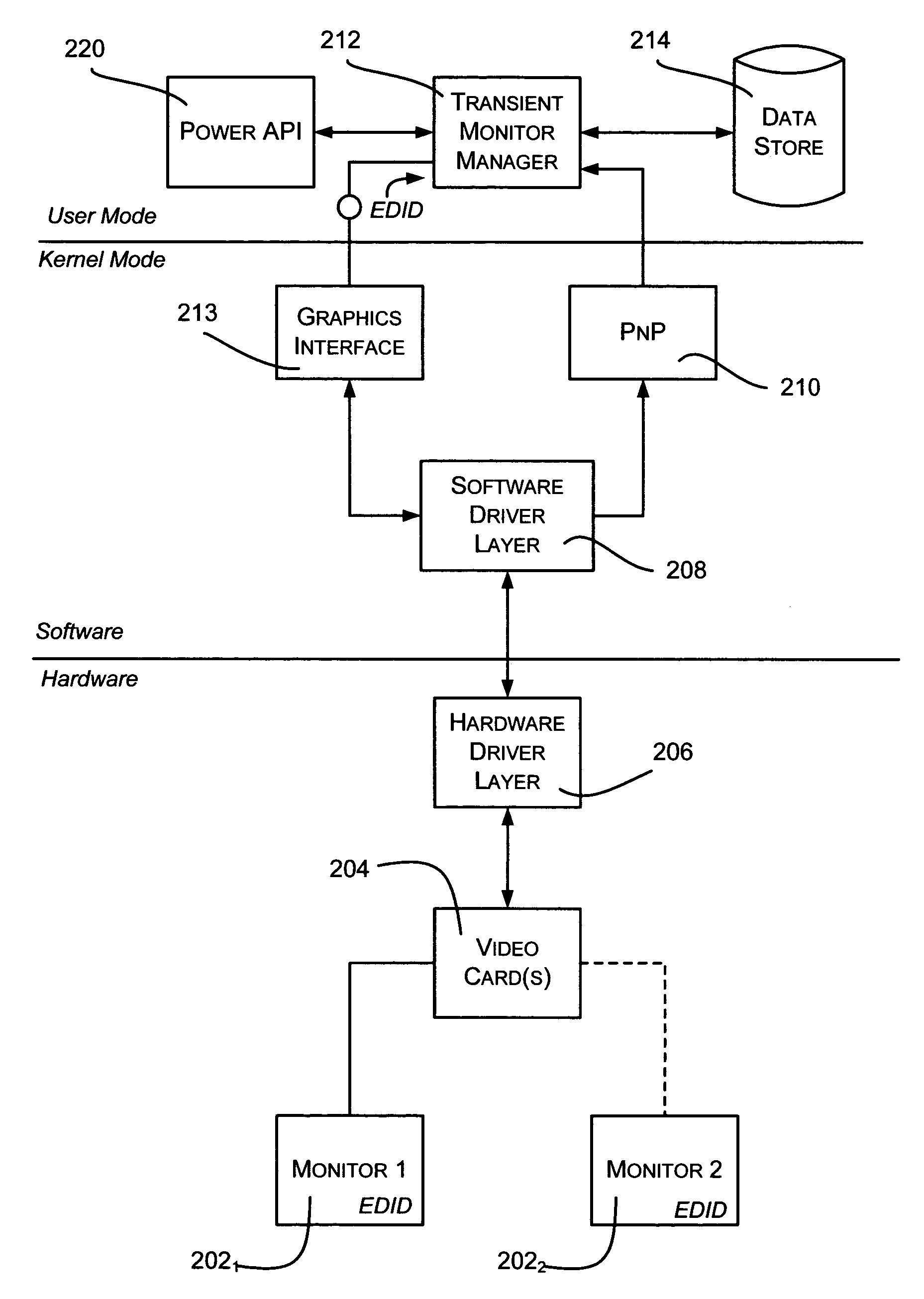
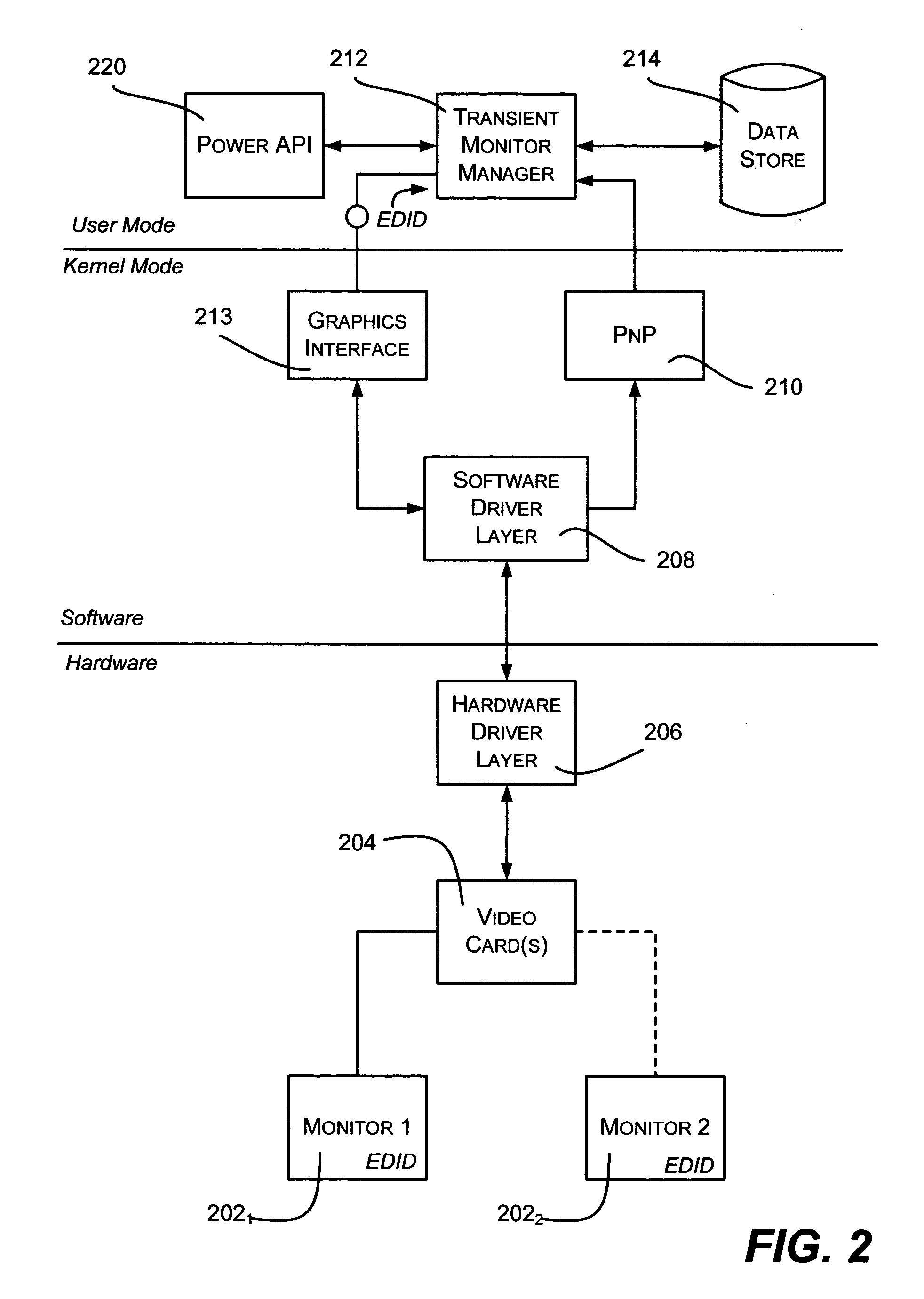
System and method for managing computer monitor configurations
Described is a method and system a system and method for dynamically and intelligently configuring a computer system's video-related settings upon connection of a monitor, and / or reconfiguring upon disconnection. A monitor configuration may include one or more display mechanisms, their video settings, relative positioning, and may include power scheme data. When a monitor is plugged into or unplugged from a computer system, a monitor manager component is notified and determines the current configuration, such as based on monitor identifiers. The current configuration is searched against persisted monitor configurations seeking a match. If previous monitor configuration data is found, the previous monitor configuration is applied. If not an exact match, configuration data is constructed based on similar configuration data that is persisted, or by querying for capabilities and iterating as necessary to find a video mode that the video card and monitor can use.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
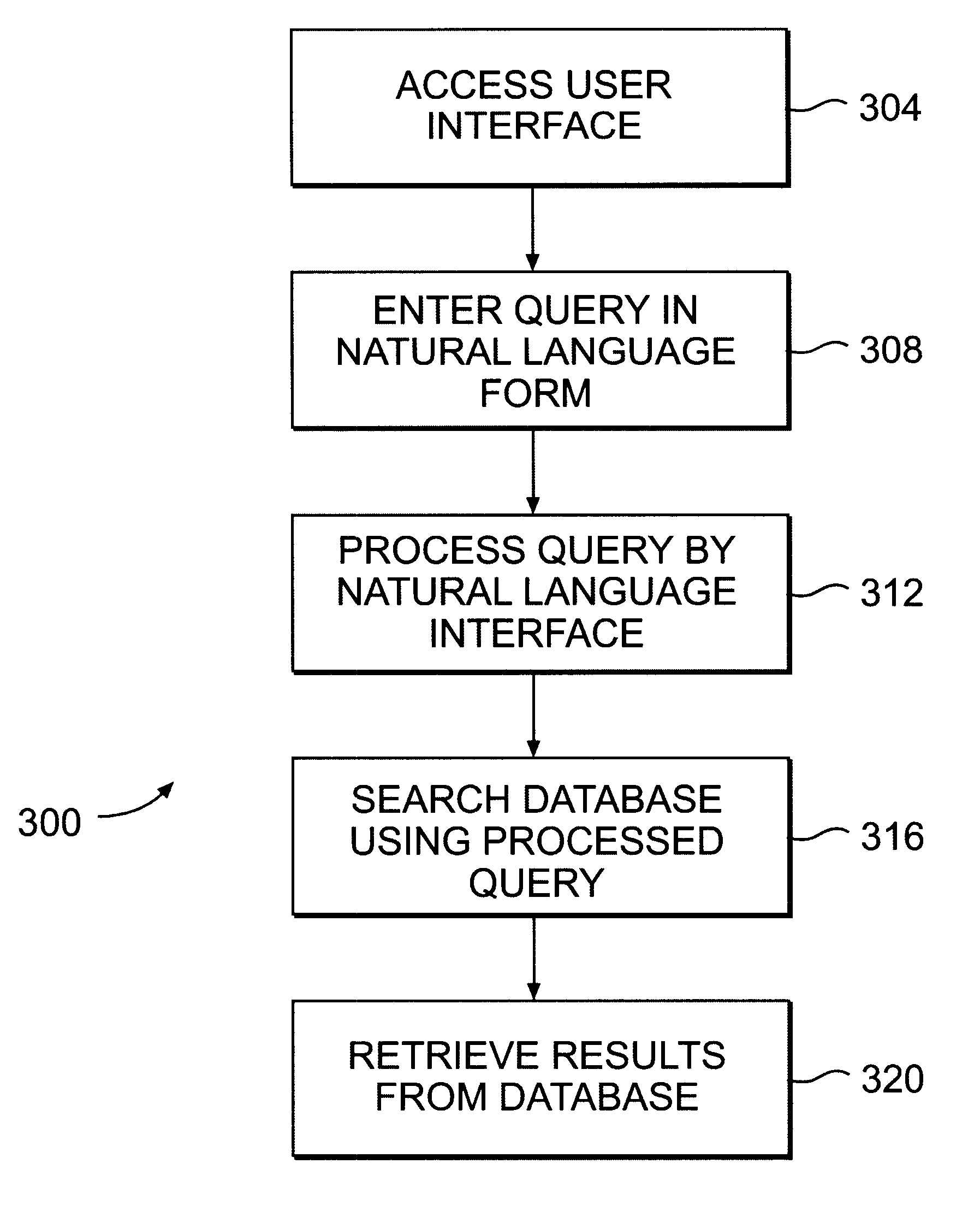
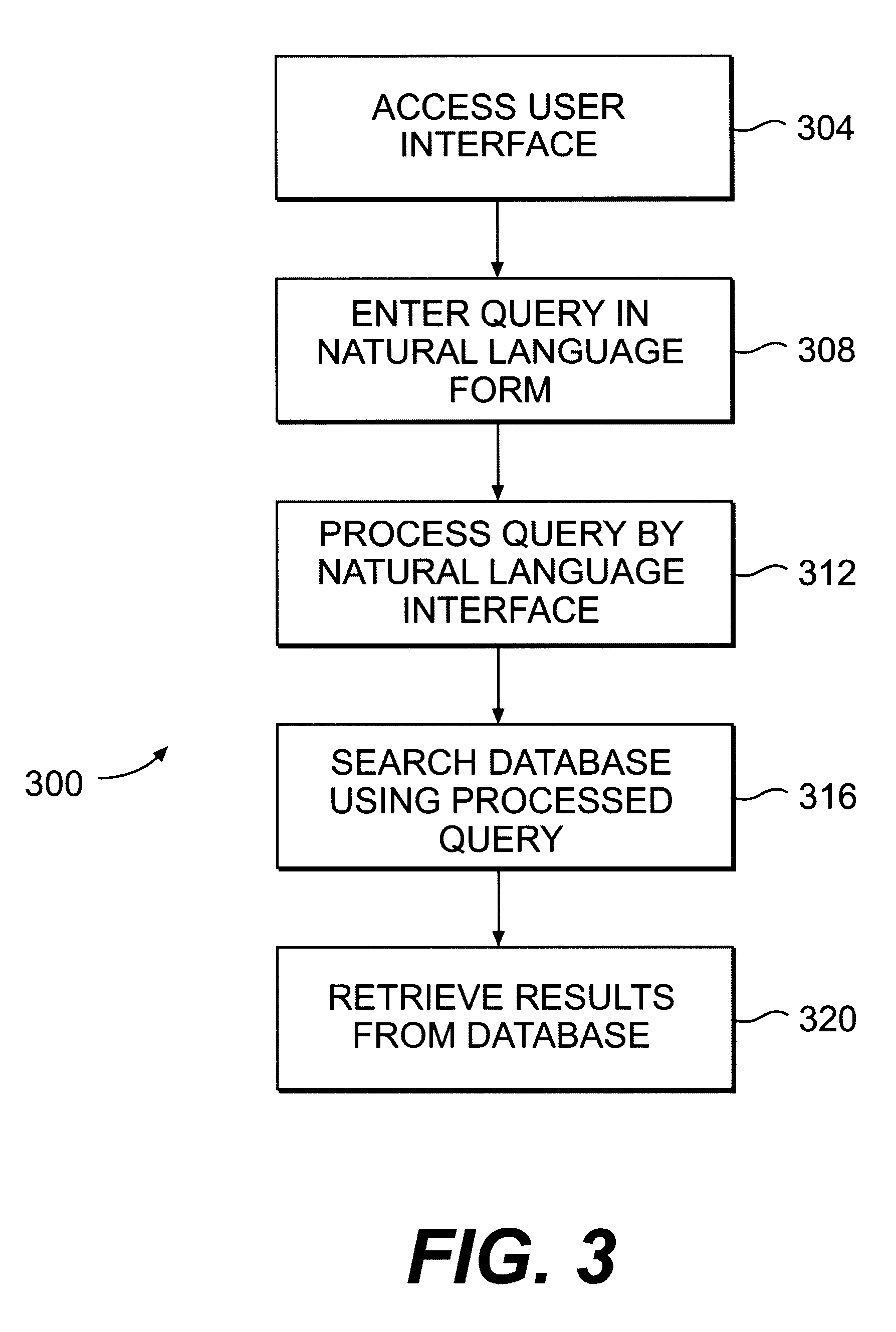
System and method for enhancing e-commerce using natural language interface for searching database
InactiveUS6446064B1Digital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsSearch wordsExact match
A system and method for enhancing e-commerce using a natural language interface. The natural language interface allows the user to formulate a query in a natural language form, rather than in conventional search terms. The natural language interface provides the user with a "user friendly" interface. The natural language interface can process a query even if there is not an exact match between the user formulated search words and the content in the database. Furthermore, the natural language interface is capable of processing misspelled queries or queries having syntax errors. The method for enhancing e-commerce using a natural language interface comprises the steps of accessing a user interface provided by a service provider, entering a query using a natural language interface, the query being formed in a natural language, processing the query by the natural language interface, searching a database using the processed query, retrieving results from the database, and providing the results to the user. The system for enhancing e-commerce on the Internet comprises a user interface for receiving a query in a natural language form, a natural language interface coupled to the user interface for processing the query, a service provider coupled to the user interface for receiving the processed query, and one or more databases coupled to the user interface for storing information, wherein the system searches the databases using the processed query and provides the results to the user through the user interface.
Owner:GO ALBERT FRANCE
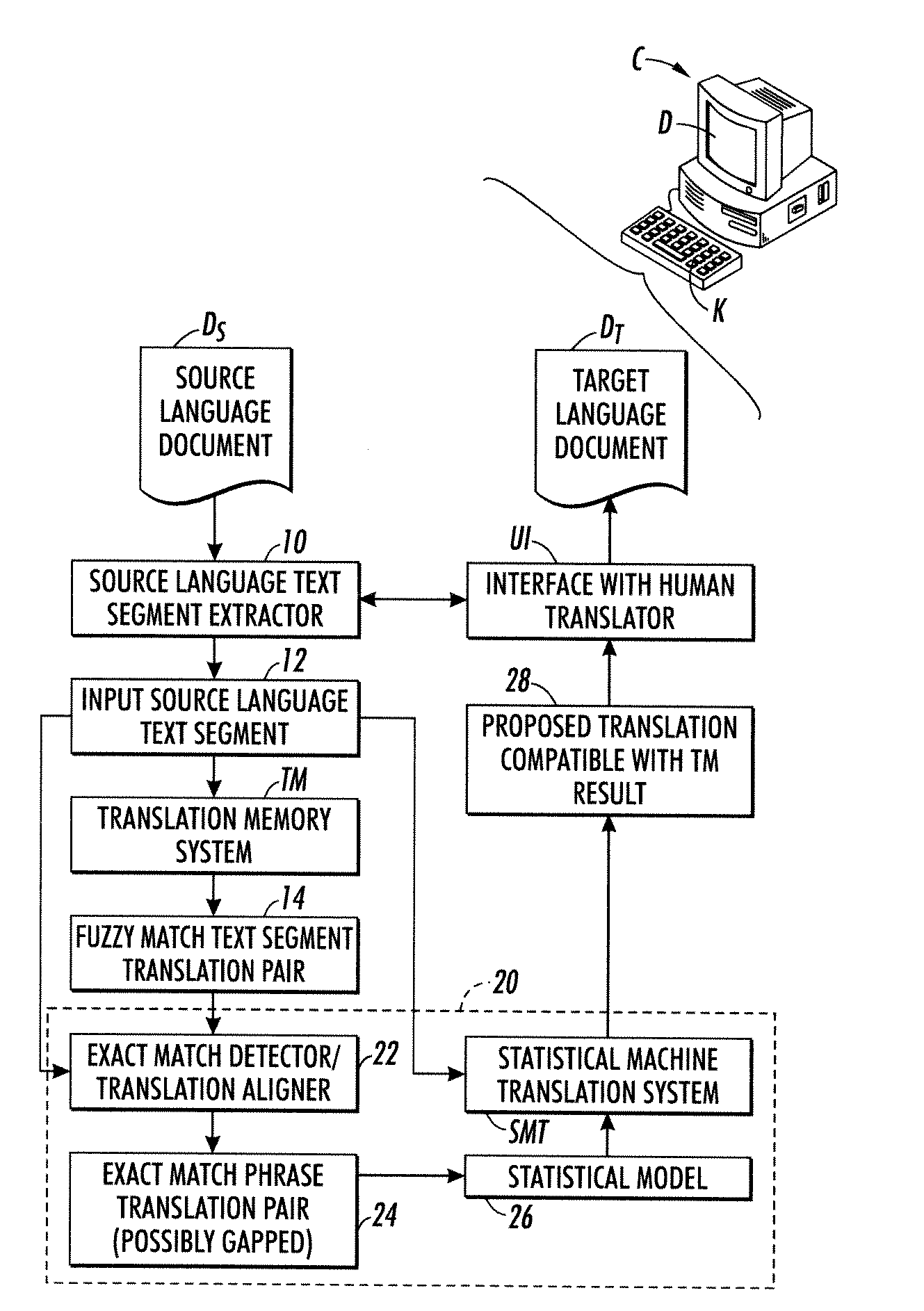
Dynamic translation memory using statistical machine translation
InactiveUS20100138213A1High statistical probabilityNatural language translationFuzzy logic based systemsExact matchTranslation memory
A translation method comprises: retrieving a fuzzy match text segment translation pair from a translation memory (TM) for an input source language text segment, the fuzzy match text segment translation pair comprising a fuzzy source language text segment having a fuzzy match to the input source language text segment and a corresponding translated target language text segment; extracting from the fuzzy match text segment translation pair an exact match phrase pair comprising a source language phrase that exactly matches a phrase of the input source language text segment and a corresponding translated target language phrase; and invoking a statistical machine translation (SMT) system to generate a proposed translation of the input source language text segment based on a statistical translation model that is enriched by the exact match phrase pair with the exact match phrase pair assigned a high statistical probability.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Flow cache hierarchy
ActiveUS9686200B2Save a lot of timeOperation is necessaryMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationCache hierarchyExact match
Some embodiments provide a managed forwarding element (MFE that includes a set of flow tables including a first set of flow entries for processing packets received by the MFE. The MFE includes an aggregate cache including a second set of flow entries for processing packets received by the MFE. Each of the flow entries of the second set is for processing packets of multiple data flows. At least a subset of packet header fields of the packets of the multiple data flows have a same set of packet header field values, and a same set of operations is applied to said packets. The MFE includes an exact-match cache including a third set of flow entries for processing packets received by the MFE. Each of the flow entries of the third set is for processing packets for a single data flow having a unique set of packet header field values.
Owner:NICIRA
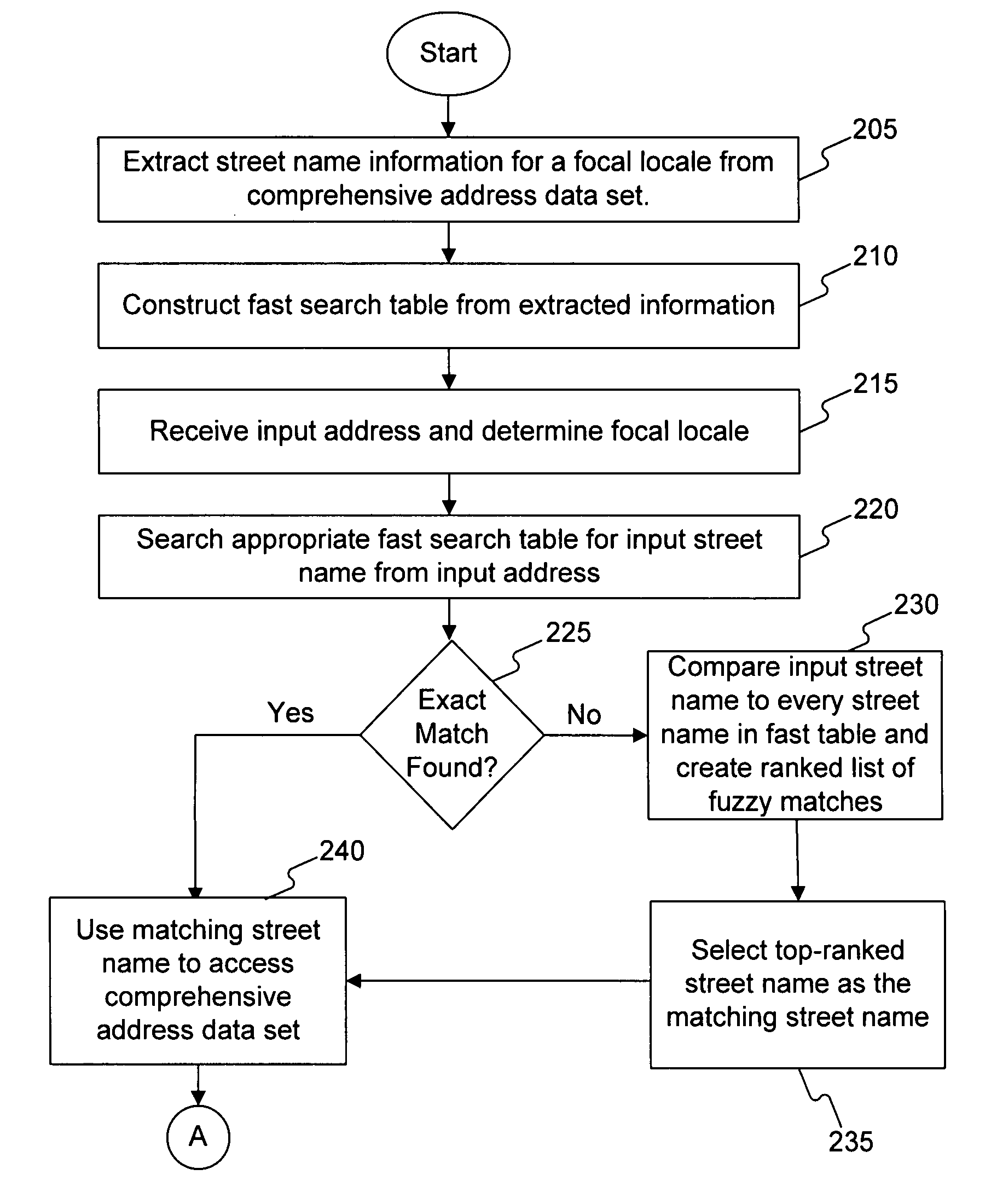
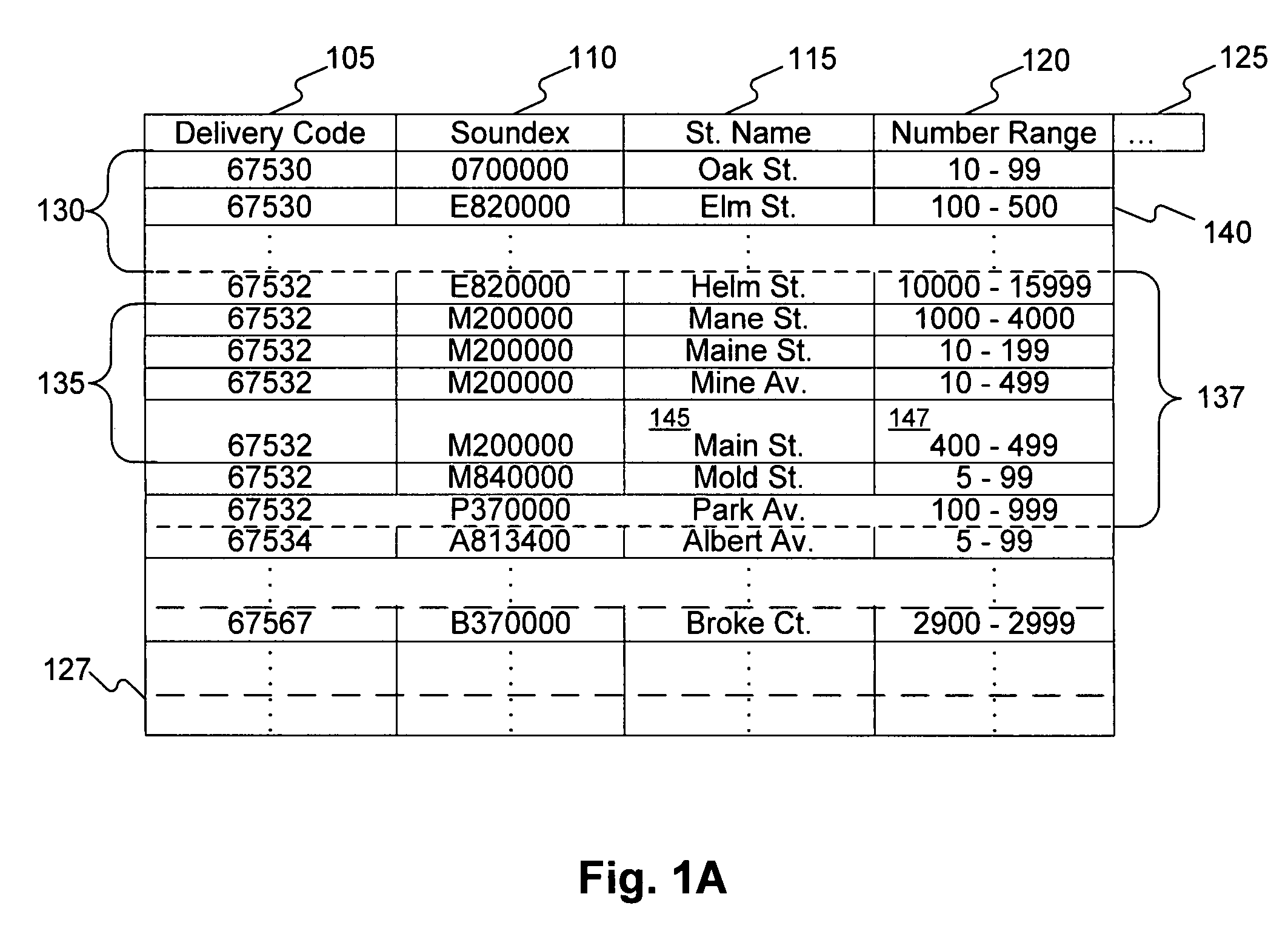
Systems and methods for validating an address
Systems, methods, and software determine whether a field of an input digital representation of information, such as the street name field in an address, is correct by quickly comparing the field to a list of valid choices for that field. The list of valid choices is generated based on information from the input digital representation, such as a character string. If an exact match is not found, a fuzzy match comparison determines the most closely matching valid choice. If a suitable fuzzy match is not found, then the input information is invalid. Otherwise, another field of the input information, such as the building number field of an address, is tested for validity. If the second field passes the validity check, then the fuzzy match (or exact match) for the field is valid. A fuzzy matching field may replace the input field, thereby correcting the input information.
Owner:US POSTAL SERVICE
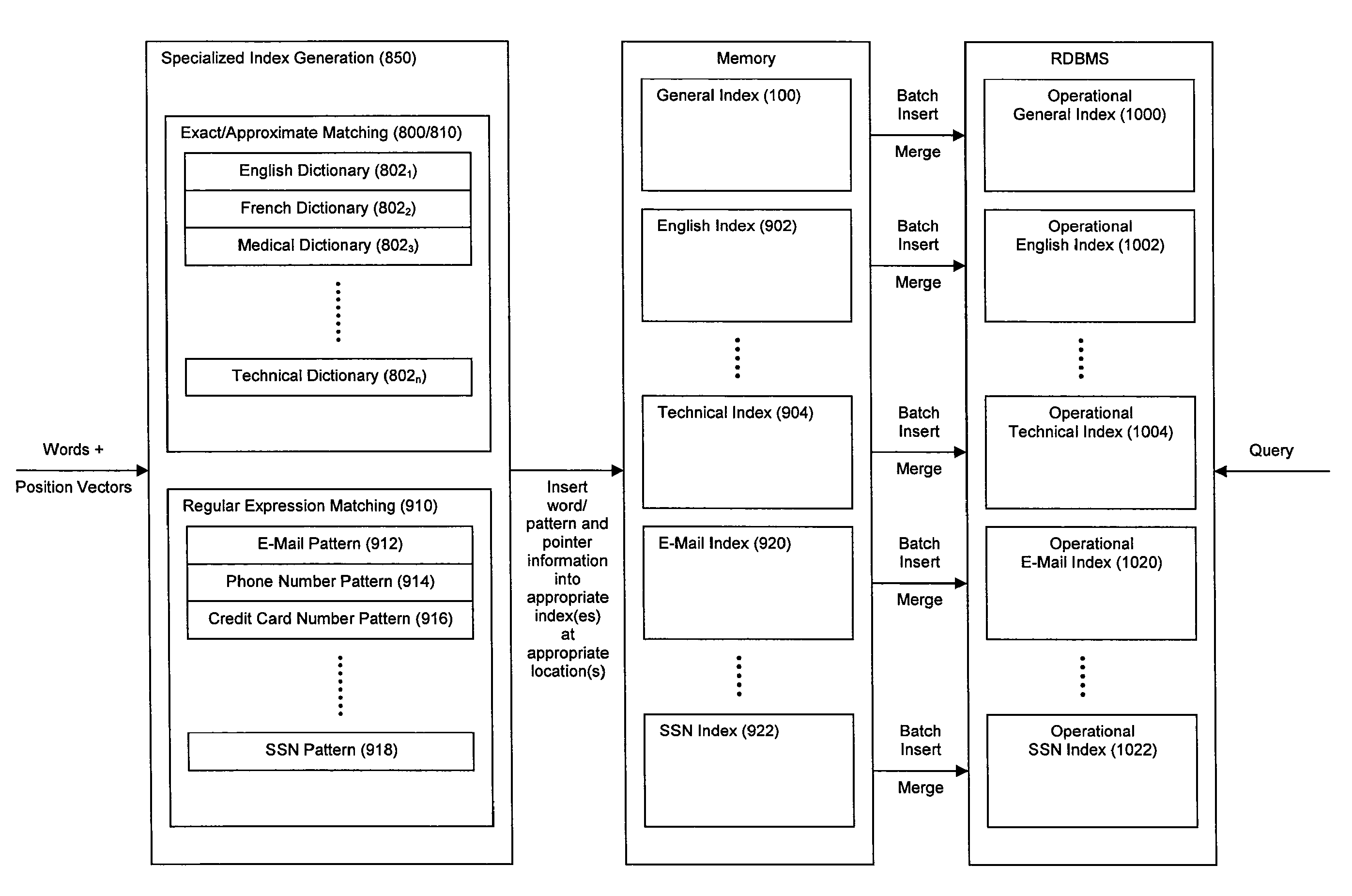
Method and system for high performance data metatagging and data indexing using coprocessors
ActiveUS8326819B2Robust and high performance data searchingHigh indexWeb data indexingDigital data processing detailsData streamCoprocessor
Disclosed herein is a method and system for hardware-accelerating the generation of metadata for a data stream using a coprocessor. Using these techniques, data can be richly indexed, classified, and clustered at high speeds. Reconfigurable logic such a field programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) can be used by the coprocessor for this hardware acceleration. Techniques such as exact matching, approximate matching, and regular expression pattern matching can be employed by the coprocessor to generate desired metadata for the data stream.
Owner:IP RESERVOIR
Longest Prefix Match Scheme
ActiveUS20130031077A1Effectively reduces quantization lossComparison of digital valuesTransmissionExact matchIPv4
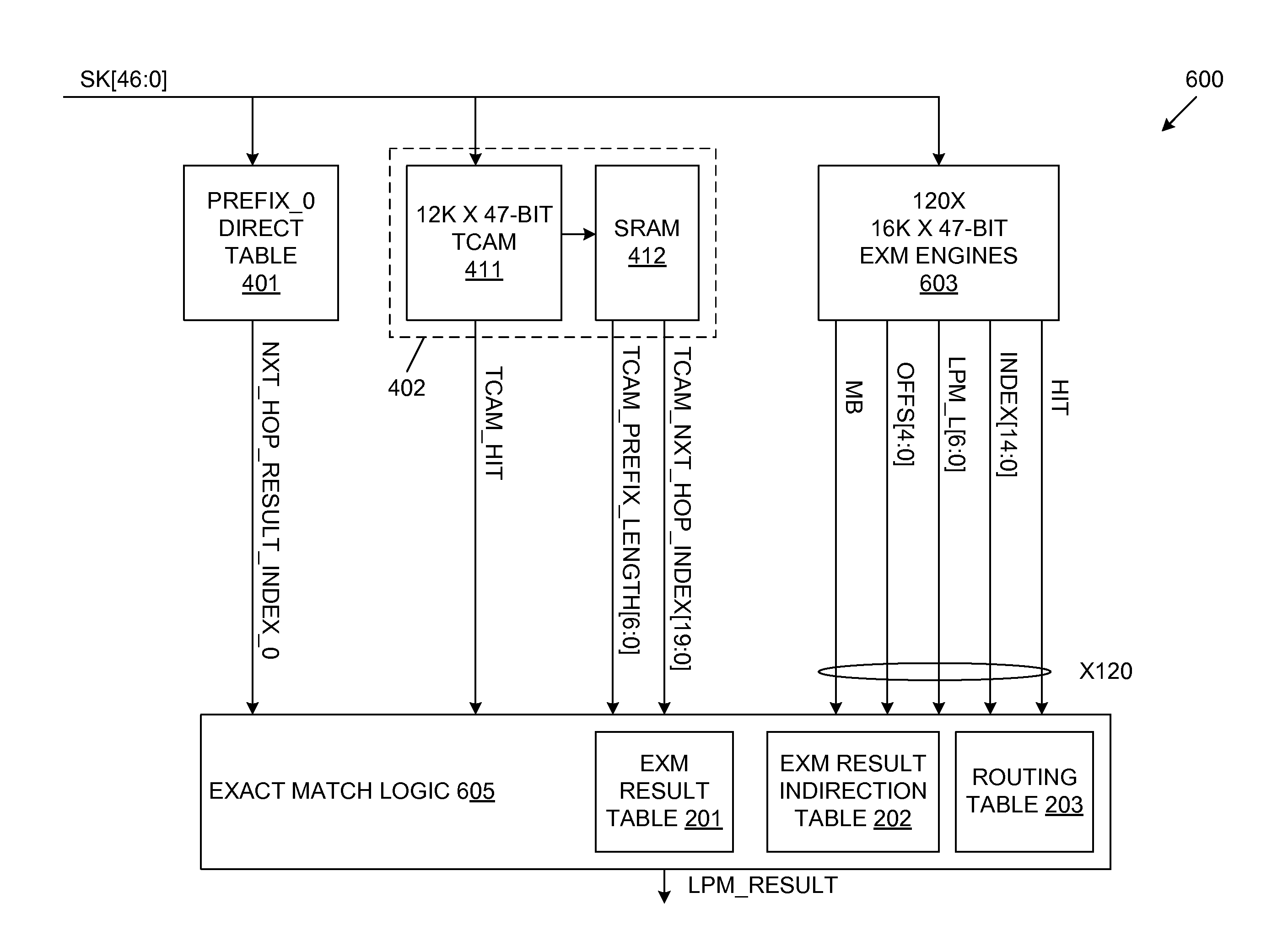
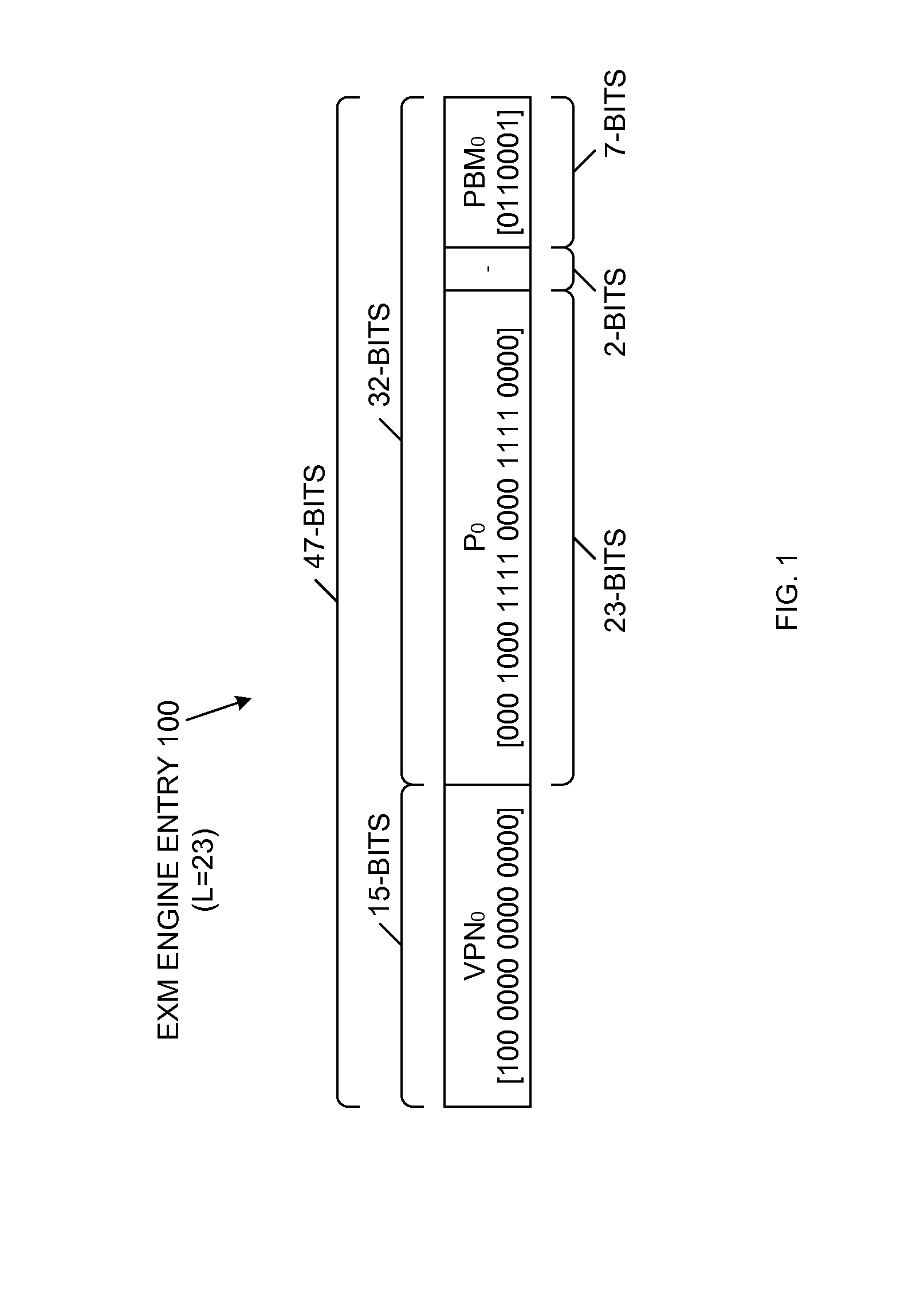
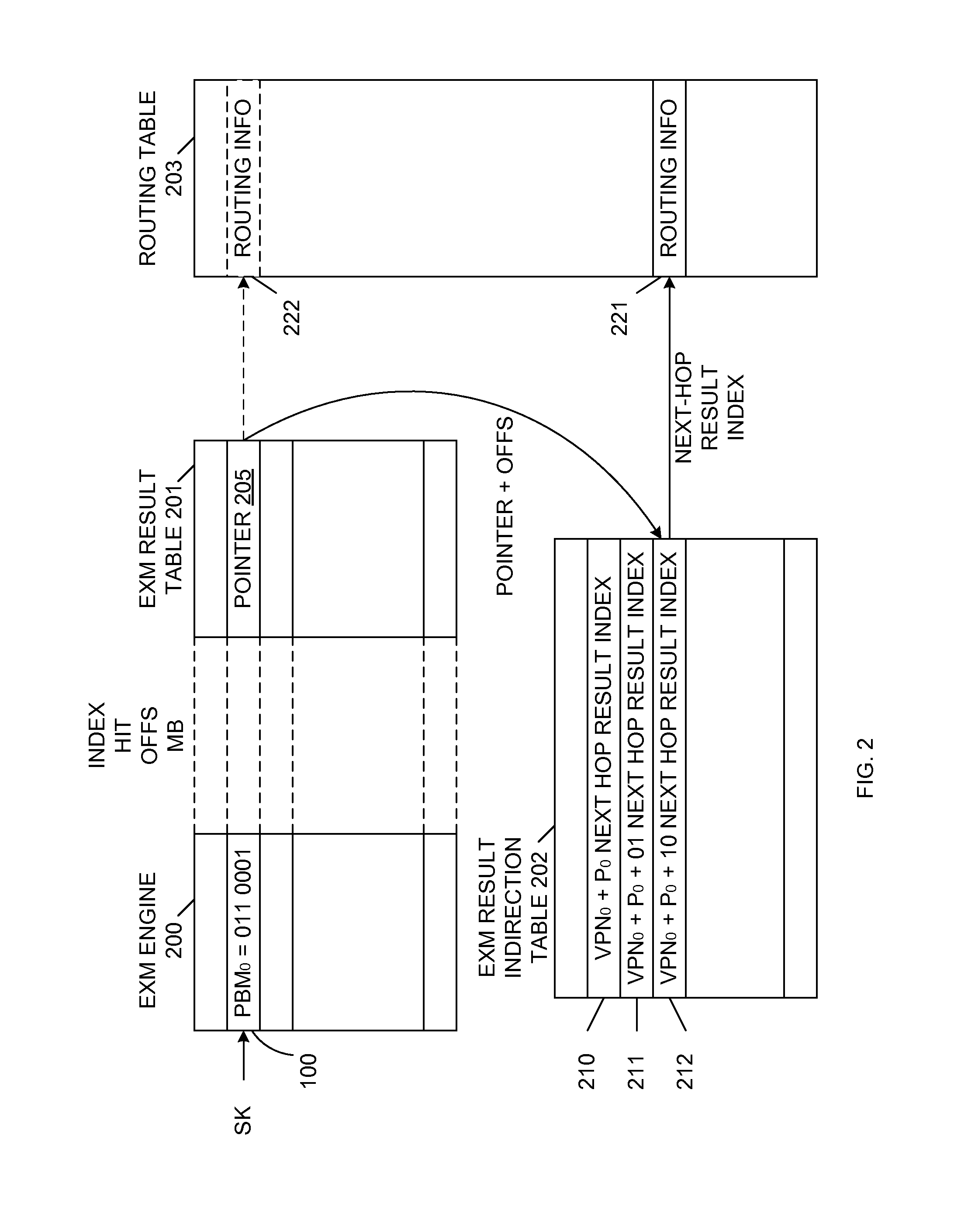
A LPM search engine includes a plurality of exact match (EXM) engines and a moderately sized TCAM. Each EXM engine uses a prefix bitmap scheme that allows the EXM engine to cover multiple consecutive prefix lengths. Thus, instead of covering one prefix length L per EXM engine, the prefix bitmap scheme enables each EXM engine to cover entries having prefix lengths of L, L+1, L+2 and L+3, for example. As a result, fewer EXM engines are potentially underutilized, which effectively reduces quantization loss. Each EXM engine provides a search result with a determined fixed latency when using the prefix bitmap scheme. The results of multiple EXM engines and the moderately sized TCAM are combined to provide a single search result, representative of the longest prefix match. In one embodiment, the LPM search engine supports 32-bit IPv4 (or 128-bit IPv6) search keys, each having associated 15-bit level 3 VPN identification values.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
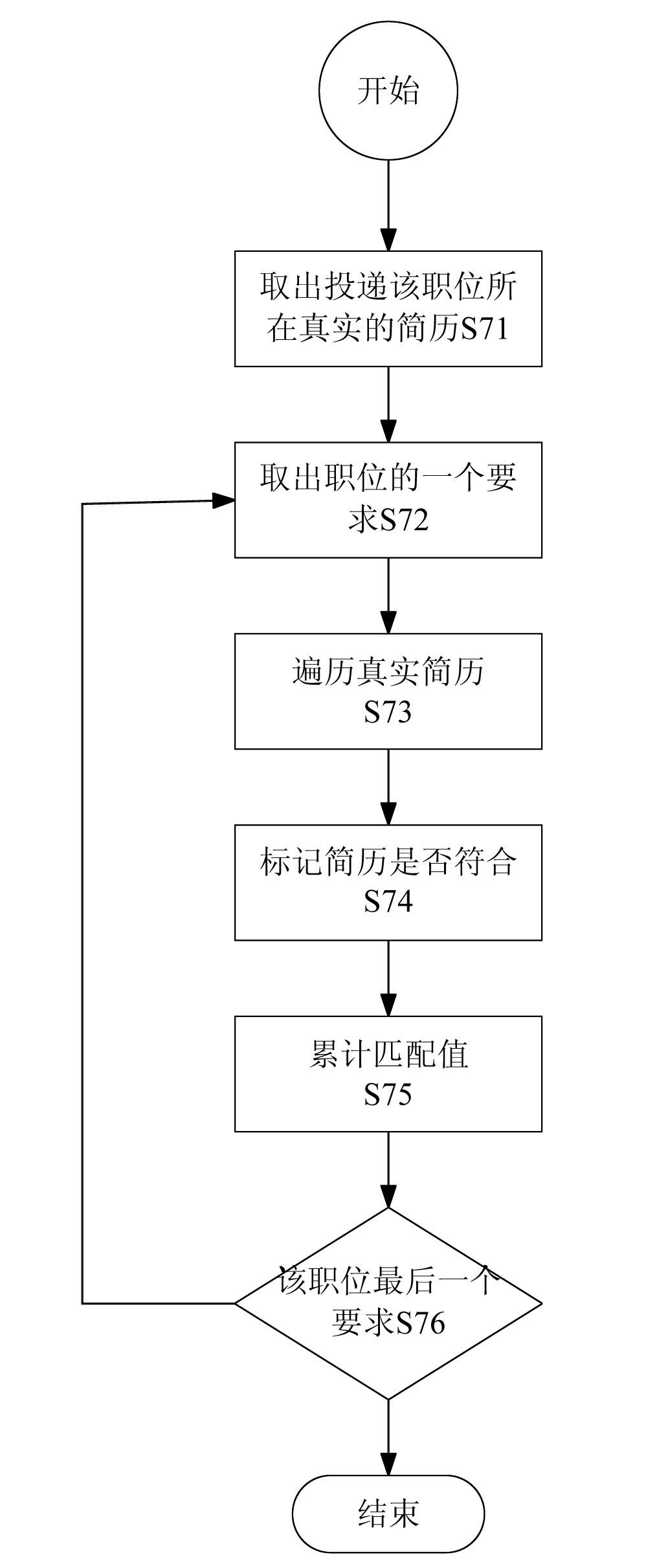
Job seeker resume recommendation processing method and system
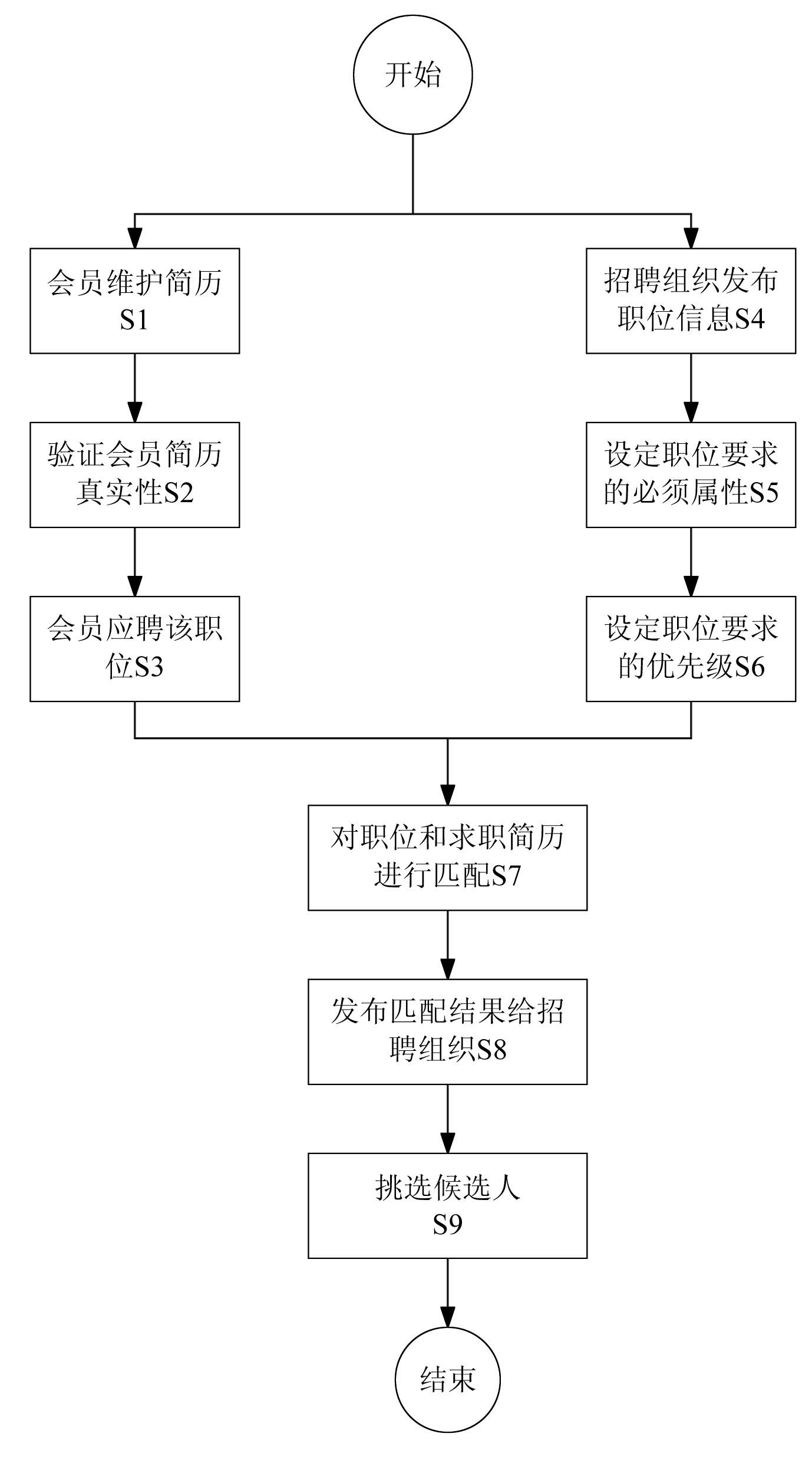
InactiveCN102117323AGuarantee authenticityResolution timeResourcesSpecial data processing applicationsExact matchRecruitment methods
The invention discloses a processing method and a processing system for accurately recommending resumes. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a member resume database and the recruitment information of an enterprise, setting whether vacant position requirements are necessarily met or not, and setting priorities; and sequentially performing accurate matching with key attributes of the job seeker resumes in combination with rules of matching the position requirements with the resumes according to whether the vacant position requirements are necessarily met or not and the priorities, and accurately pushing the job seeker resumes meeting the requirements to a recruitment group according to a matching degree sequence. By the method and the system, the recruitment group can accurately screen corresponding candidates, the recruitment efficiency can be improved, the recruitment cost can be reduced, and simultaneously, the job seeker resumes meeting the requirements may not be omitted.
Owner:SHENZHEN AISI OUNA INFORMATION CONSULTING
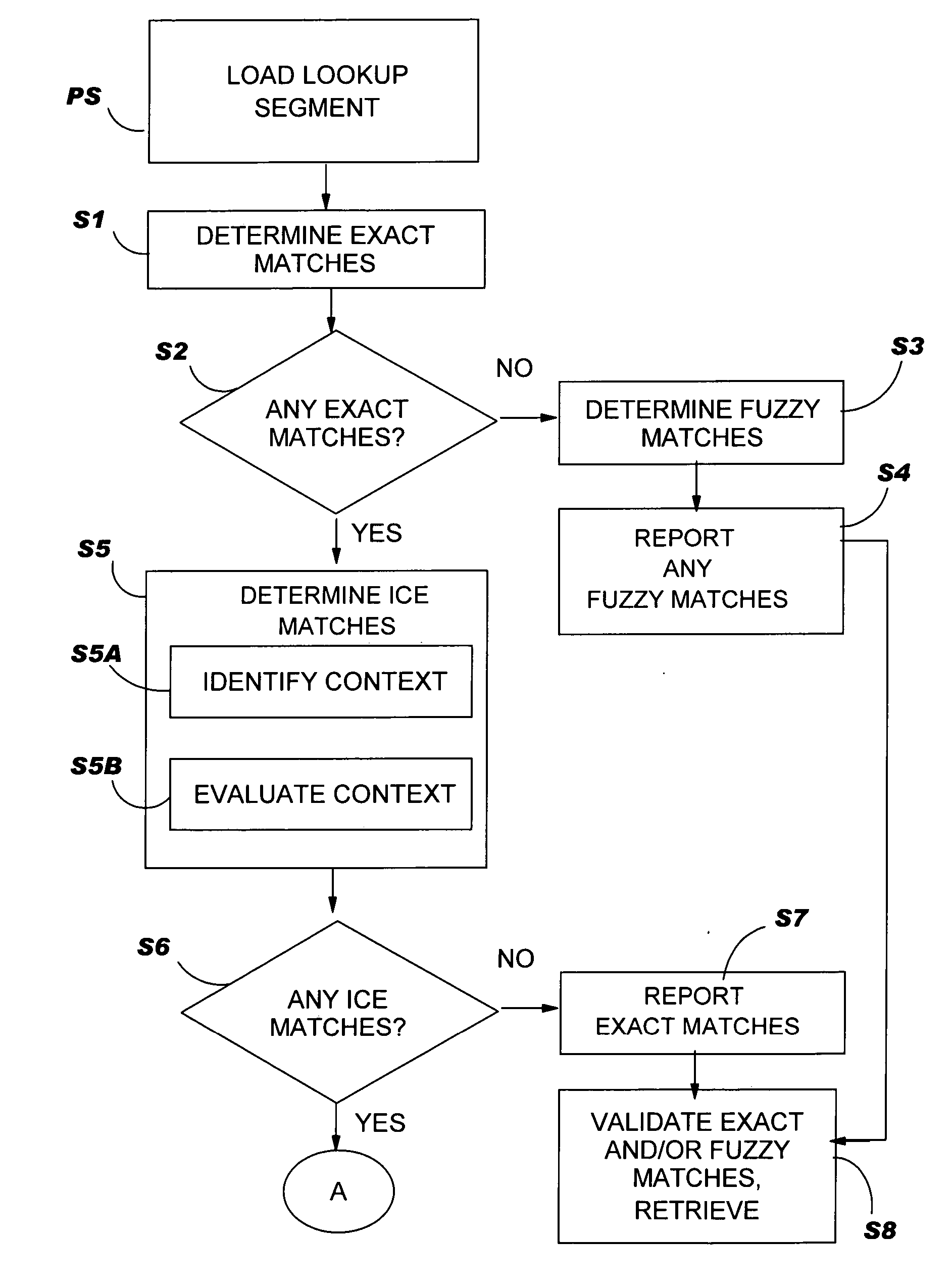
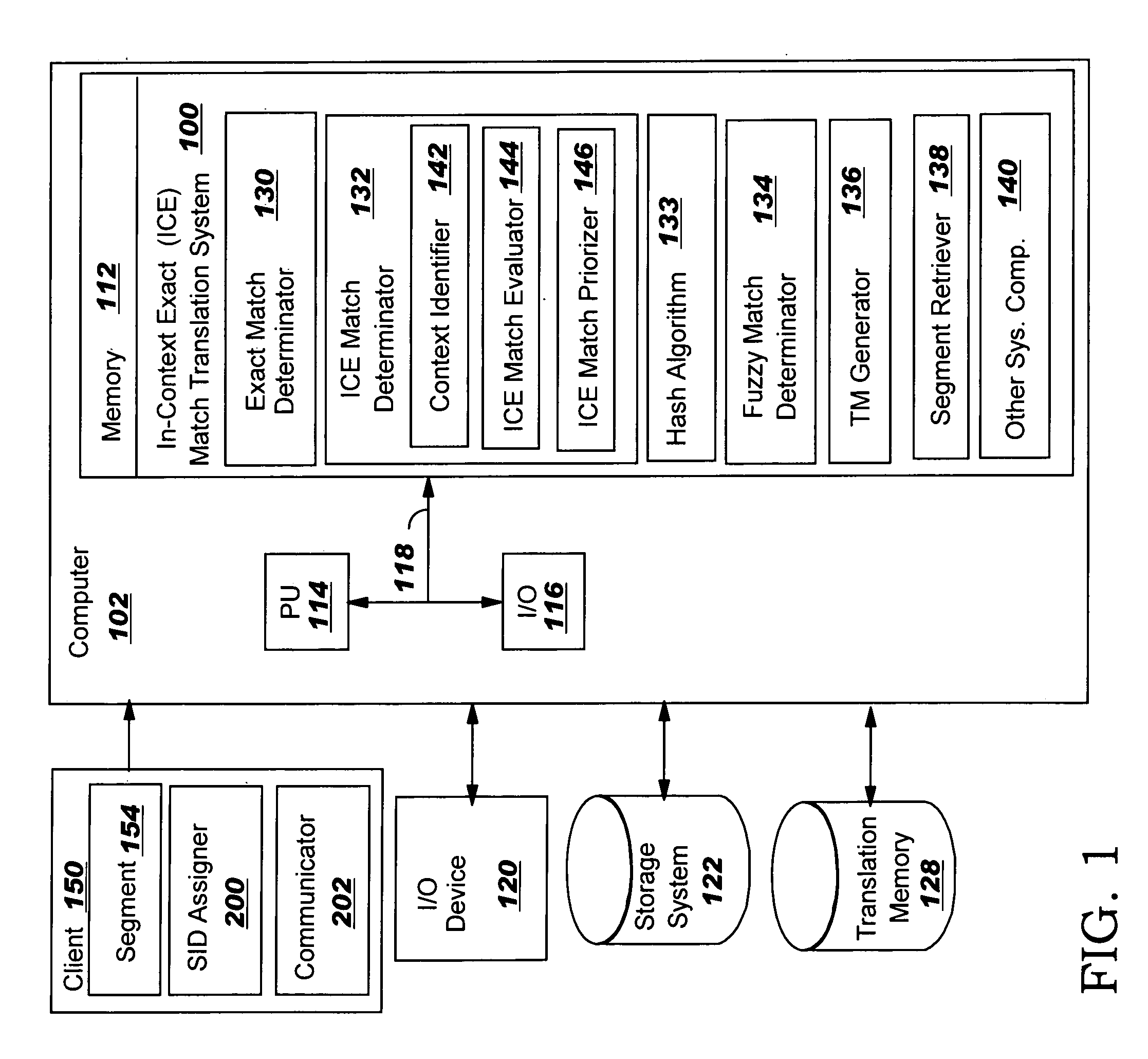
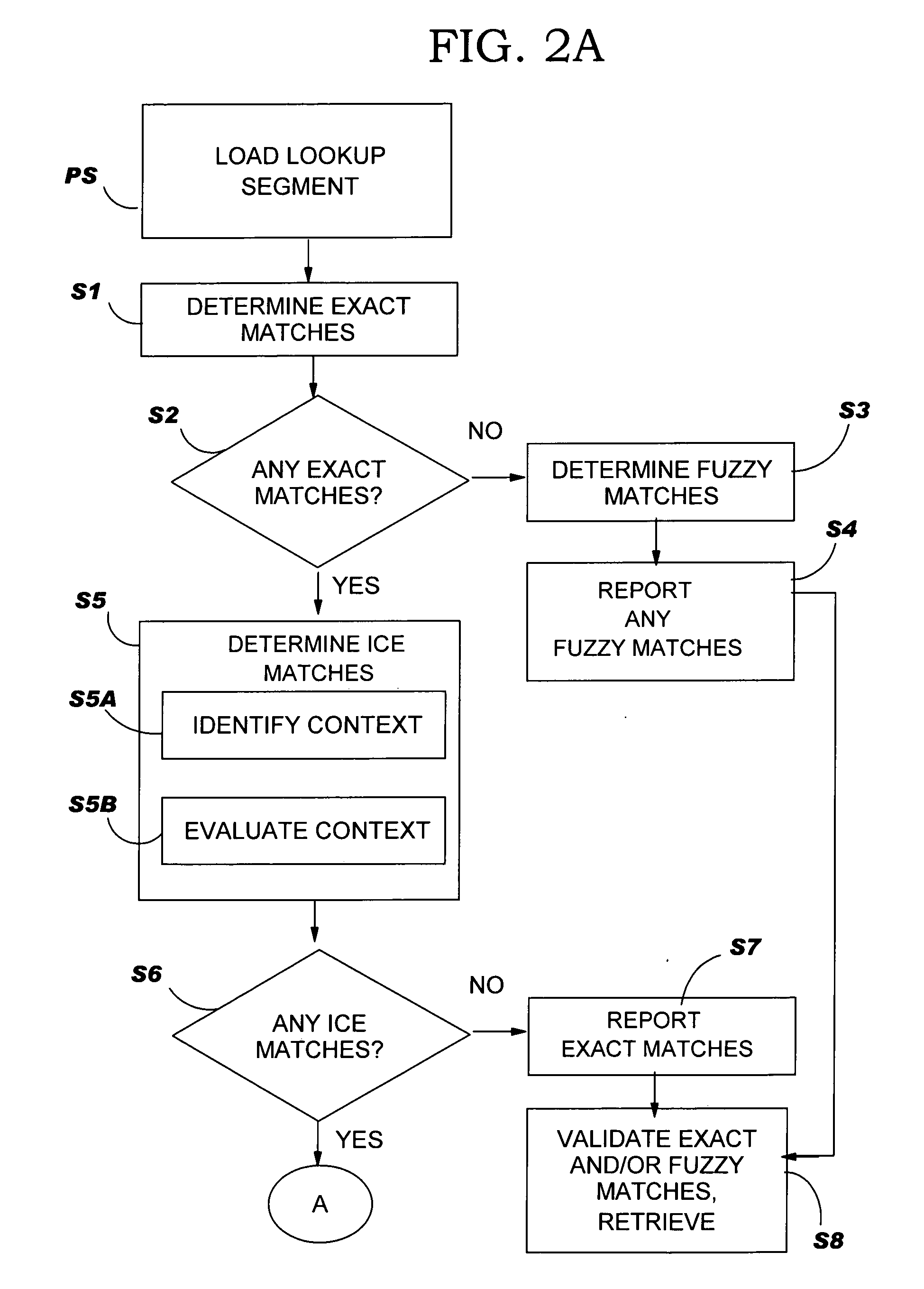
In-context exact (ICE) matching
ActiveUS20050197827A1Reduces translator interventionReduce interventionNatural language translationDigital data information retrievalExact matchTranslation memory
Methods, systems and program product are disclosed for determining a matching level of a text lookup segment with a plurality of source texts in a translation memory in terms of context. In particular, the invention determines any exact matches for the lookup segment in the plurality of source texts, and determines, in the case that at least one exact match is determined, that a respective exact match is an in-context exact (ICE) match for the lookup segment in the case that a context of the lookup segment matches that of the respective exact match. The degree of context matching required can be predetermined, and results prioritized. The invention also includes methods, systems and program products for storing a translation pair of source text and target text in a translation memory including context, and the translation memory so formed. The invention ensures that content is translated the same as previously translated content and reduces translator intervention.
Owner:SDL INK
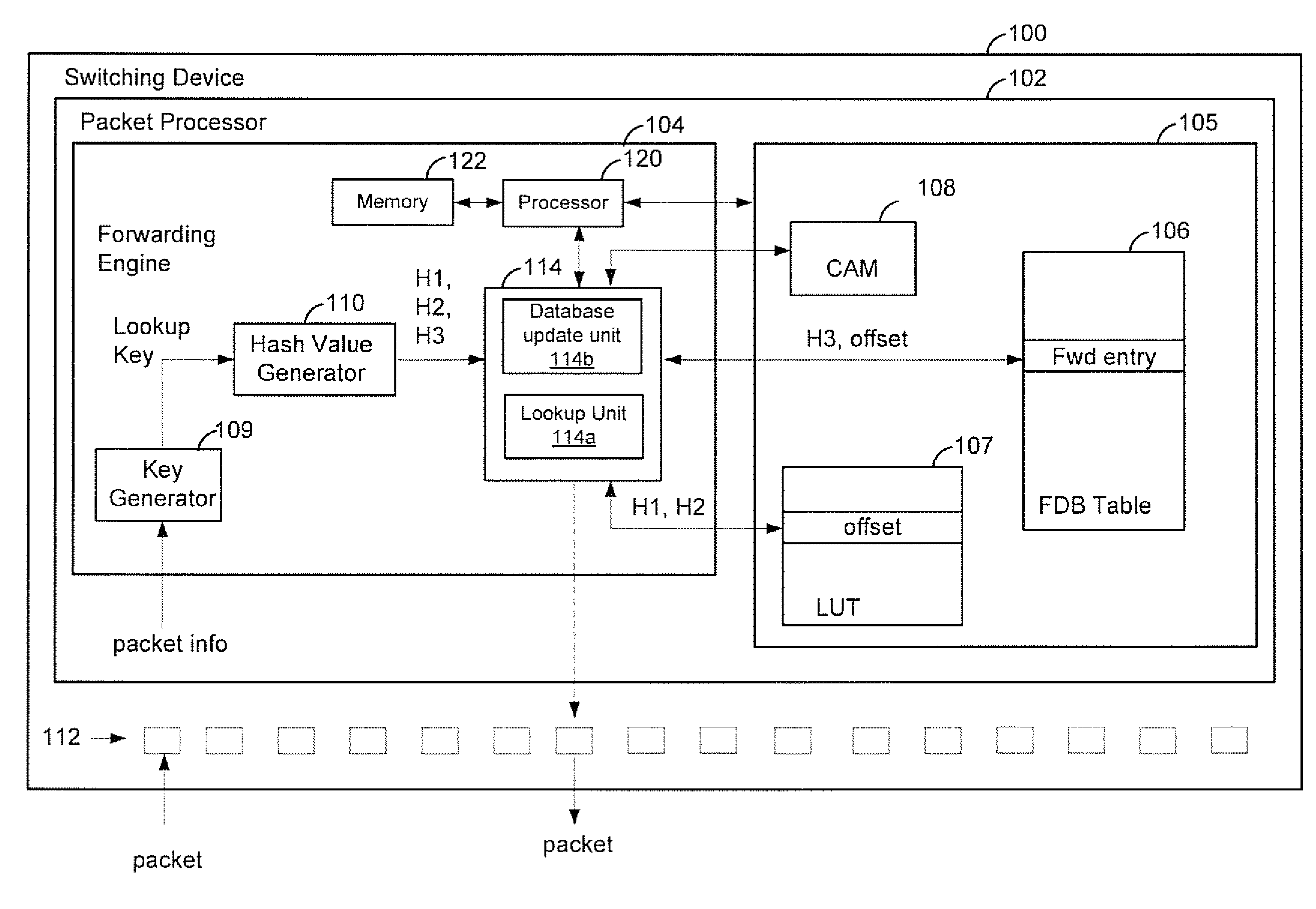
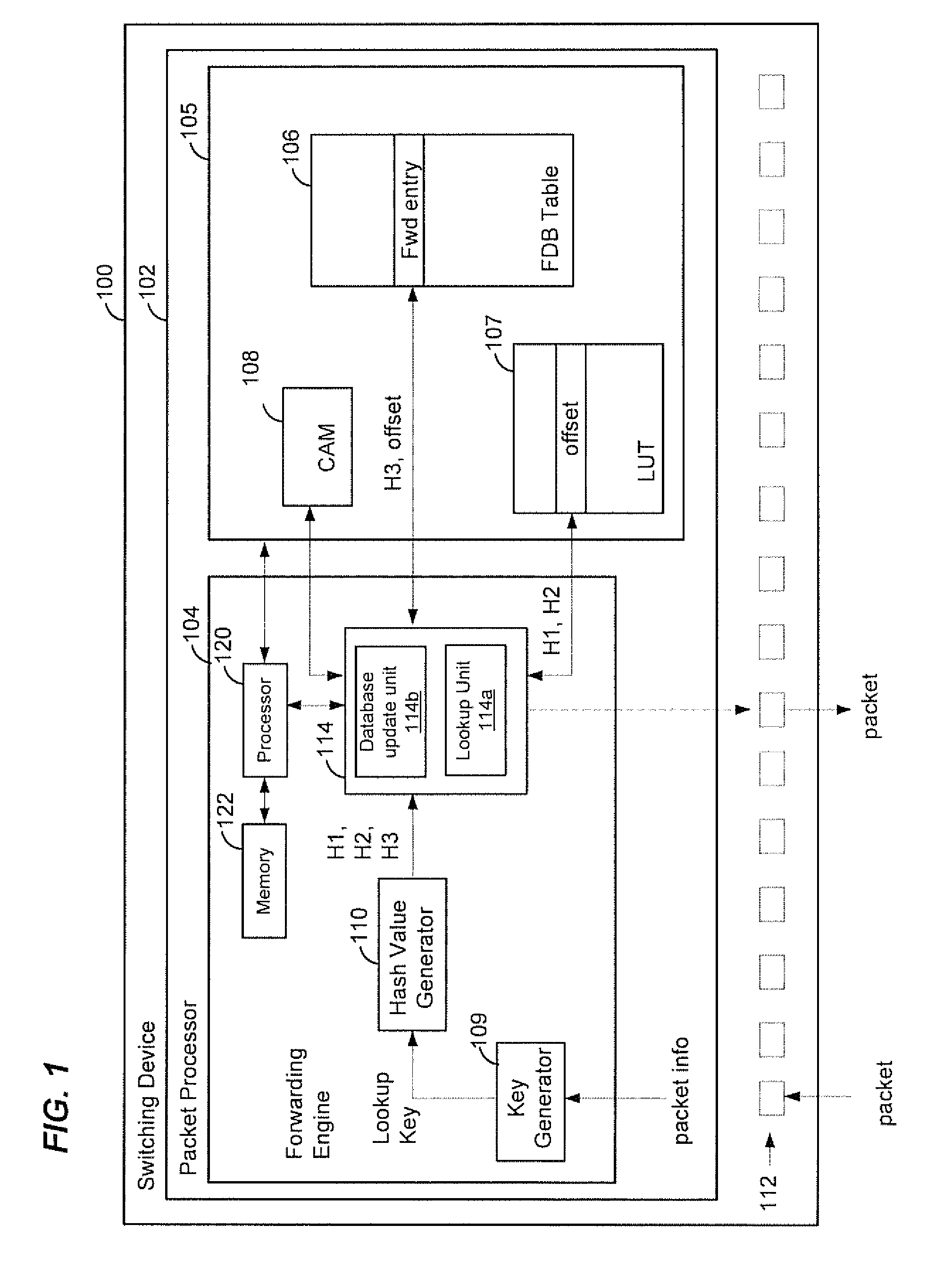
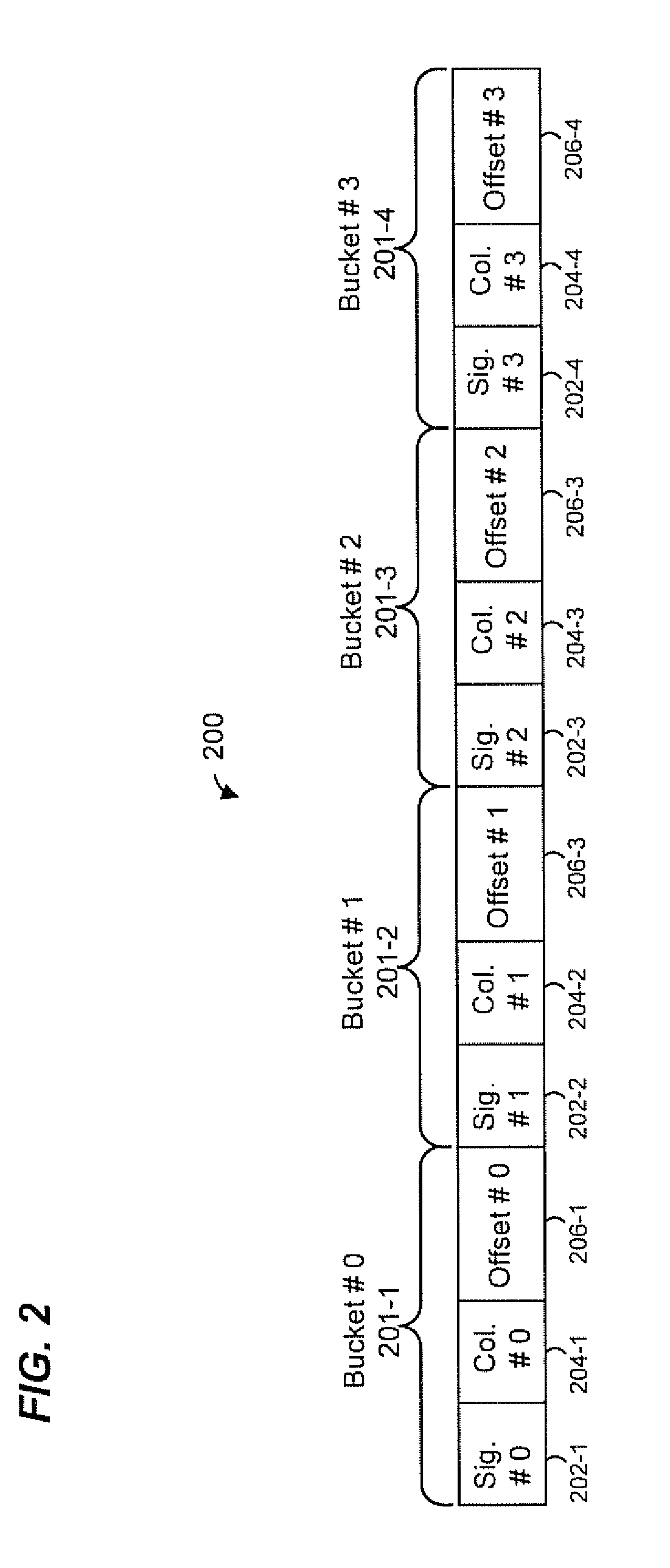
Exact match hash lookup databases in network switch devices
ActiveUS20140301394A1Data switching by path configurationSpecial data processing applicationsExact matchComputer hardware
In a method for forwarding packets in a network device a plurality of hash values is generated based on a lookup key. The plurality of hash values includes at least a first hash value generated using a first hash function, a second hash value generated using a second hash function and a third hash value generated using a third hash function. The third hash function is different from the first hash function and the second hash function. A lookup table is searched using the first hash value and the second hash value to determine an offset for the lookup key. Then, a forwarding table is searched using the third hash value and the offset determined for the lookup key to select a forwarding entry corresponding to the lookup key. The packet is forwarded to one or more ports of the network device based on the selected forwarding entry.
Owner:MARVELL ISRAEL MISL
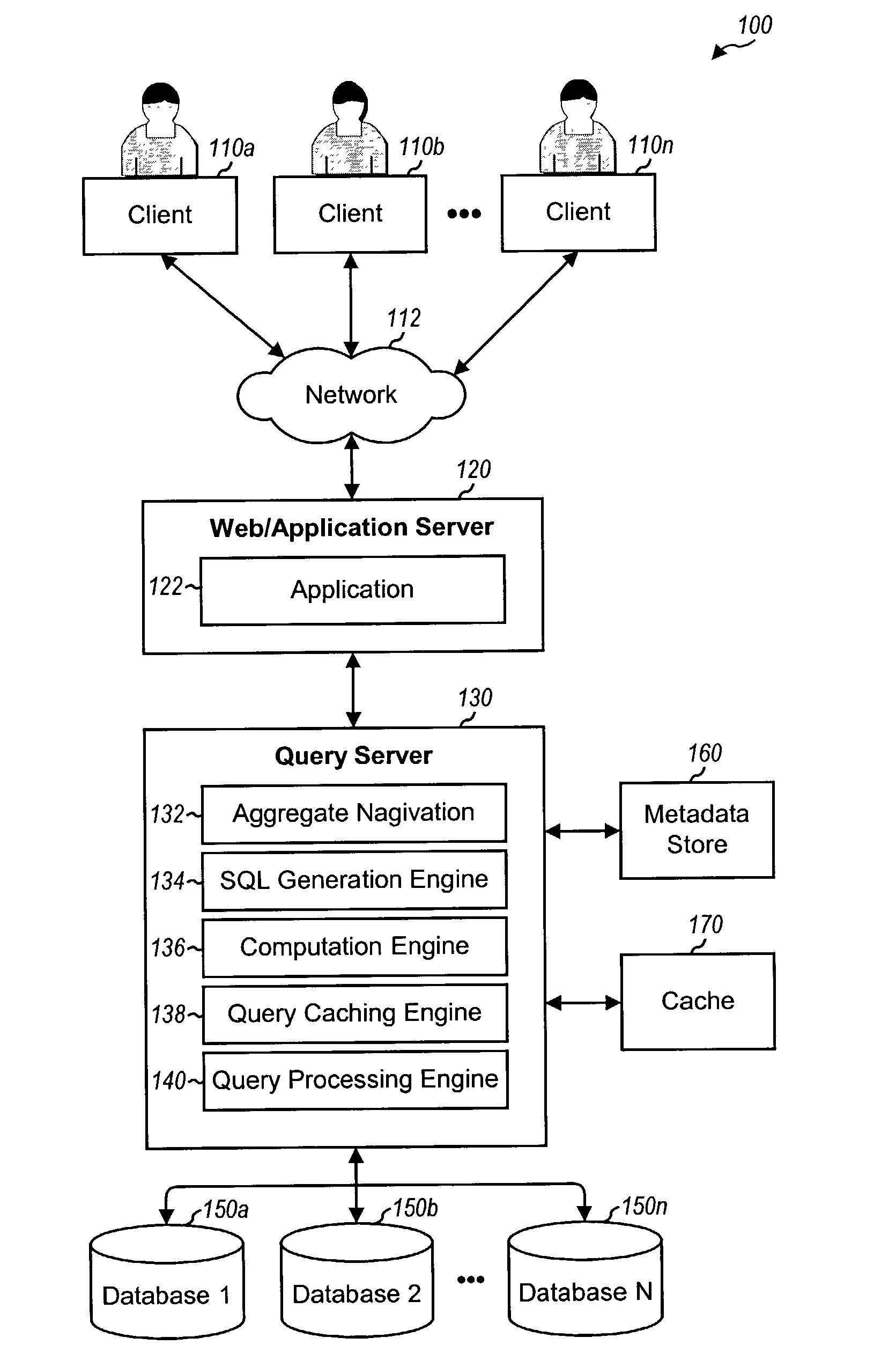
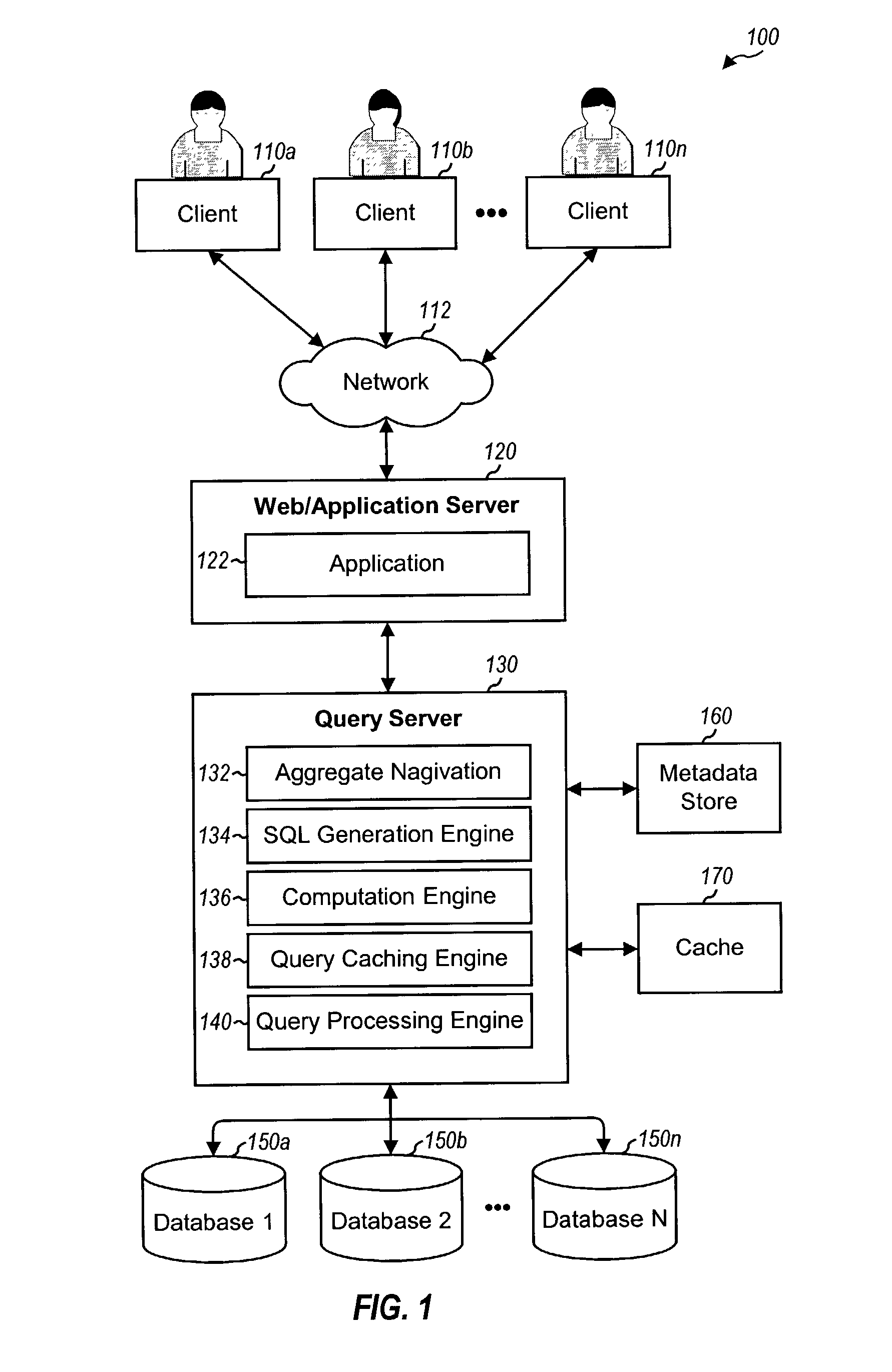
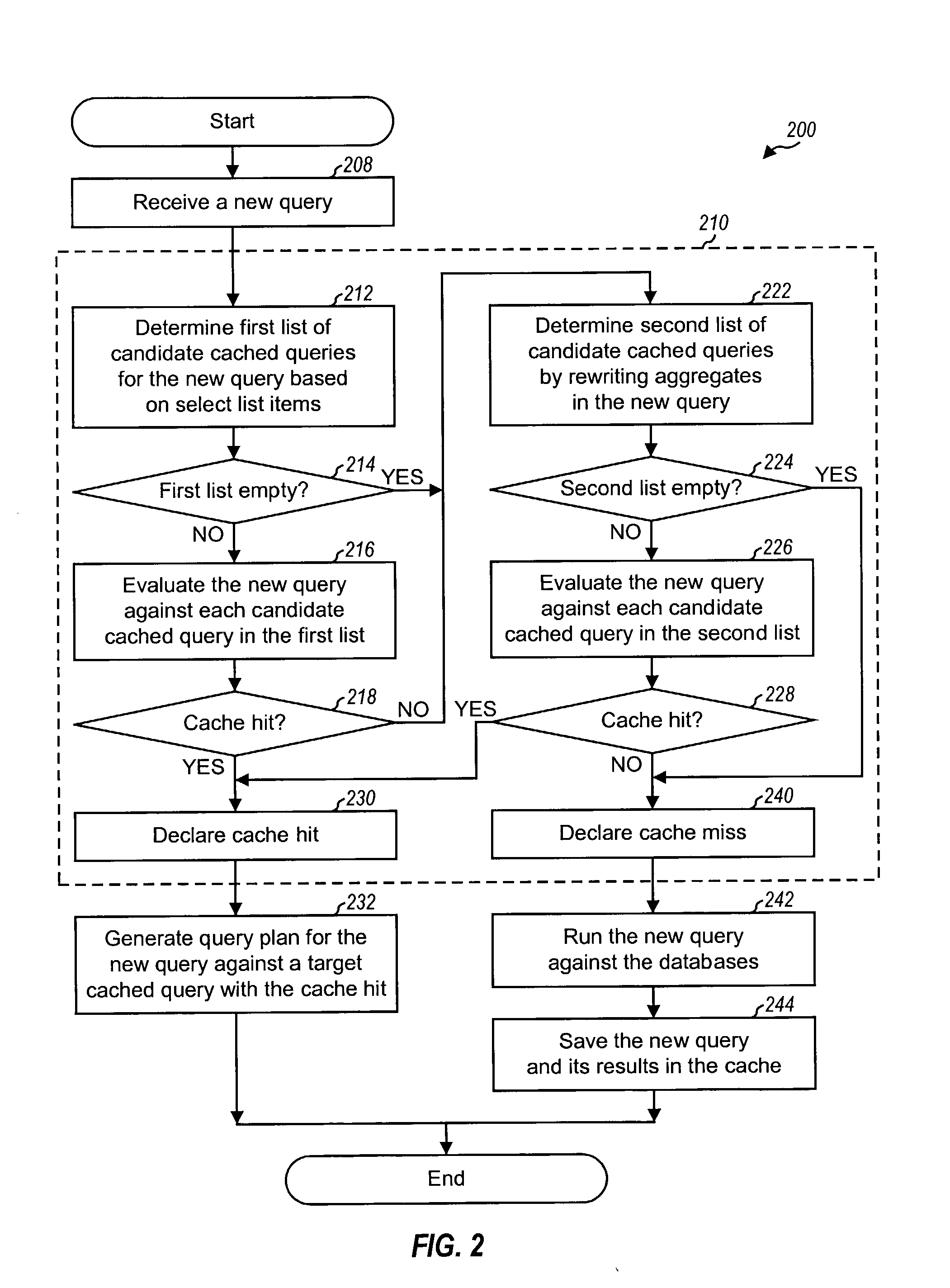
Detecting and processing cache hits for queries with aggregates
ActiveUS20070208690A1EfficientlyImprove query caching performanceData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalExact matchQuery plan
Techniques to improve query caching performance by efficiently selecting queries stored in a cache for evaluation and increasing the cache hit rate by allowing for inexact matches. A list of candidate queries stored in the cache that potentially could be used to answer a new query is first determined. This list may include all cached queries, cached queries containing exact matches for select list items, or cached queries containing exact and / or inexact matches. Each of at least one candidate query is then evaluated to determine whether or not there is a cache hit, which indicates that the candidate query could be used to answer the new query. The evaluation is performed using a set of rules that allows for inexact matches of aggregates, if any, in the new query. A query plan is generated for the new query based on a specific candidate query with a cache hit.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
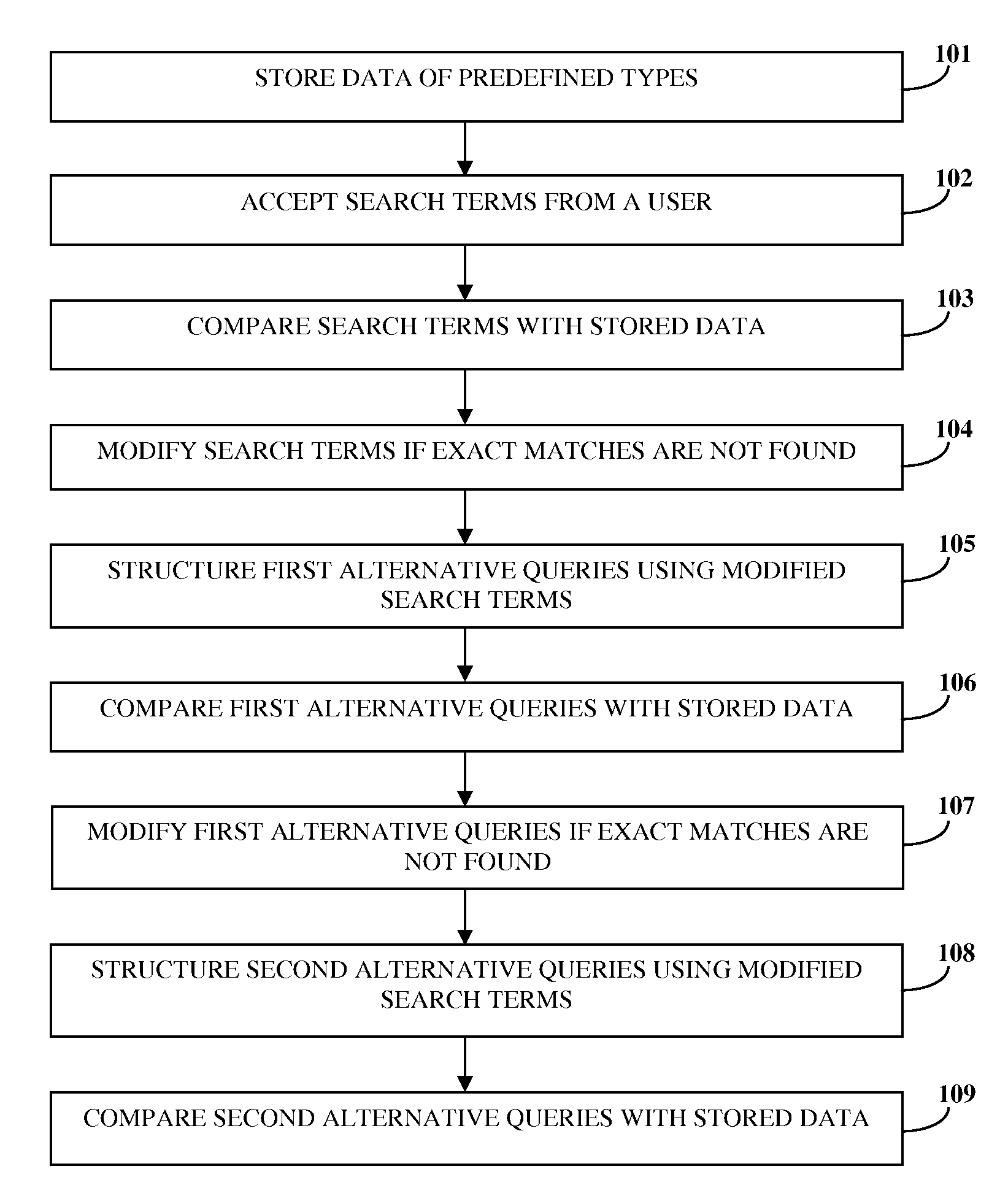
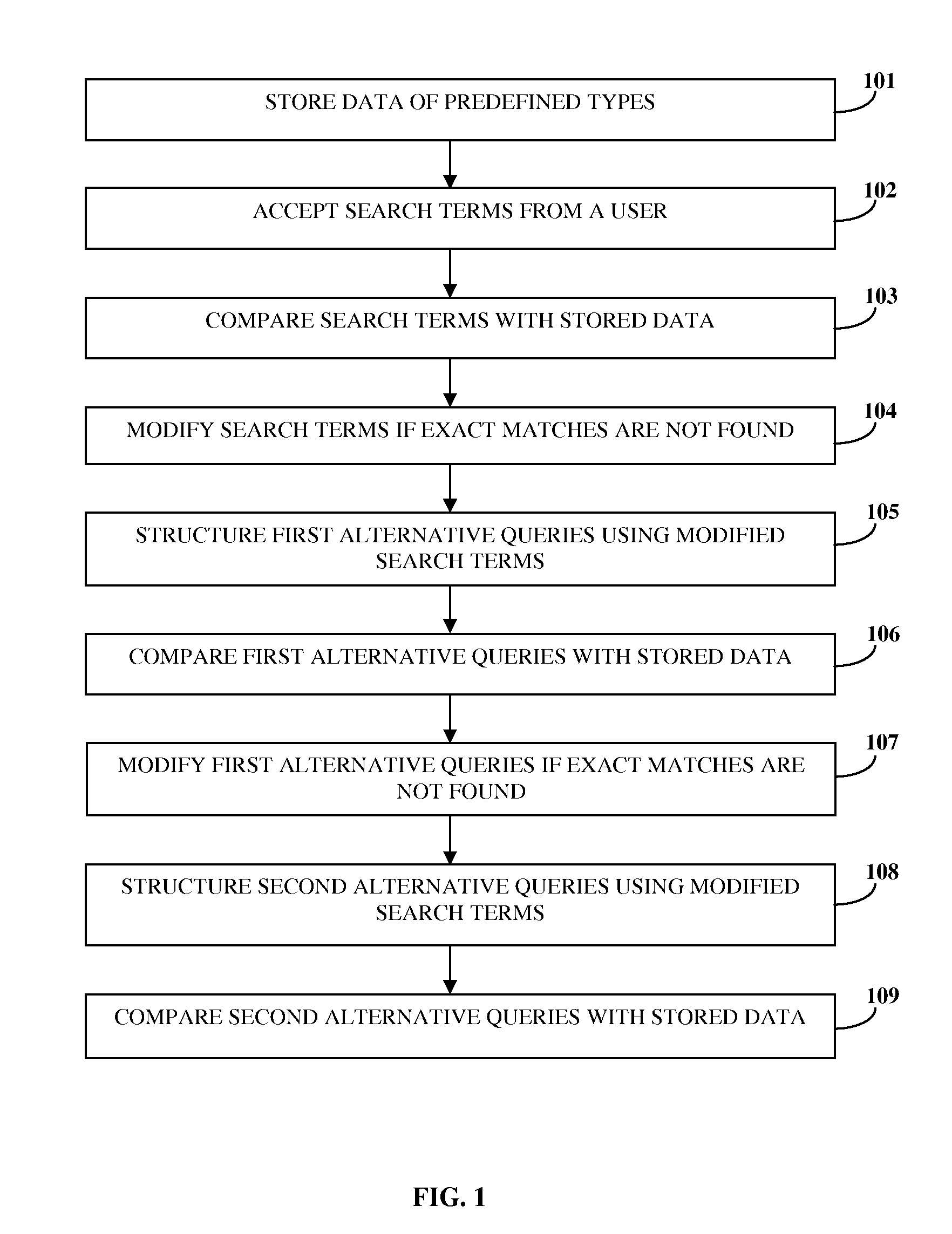
Fuzzy search using progressive relaxation of search terms
Disclosed herein is a computer implemented method and system that progressively relaxes search terms provided by a user. Data of predefined types is stored in a database. The data is obtained by uniquely modifying data previously stored in the database, based on the predefined types. Search terms of predefined types are accepted from the user. The search terms are compared with the stored data to find exact matches, if length of the search terms exceeds a predefined value. On not finding exact matches, the accepted search terms are modified uniquely based on the predefined types to structure first alternative queries. The first alternative queries are compared with the stored data to find exact matches. On not finding exact matches, the first alternative queries are modified based on the predefined types to structure second alternative queries. The second alternative queries are compared with the stored data to find approximate matches.
Owner:DEEM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com