Patents
Literature
409 results about "Content-addressable memory" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
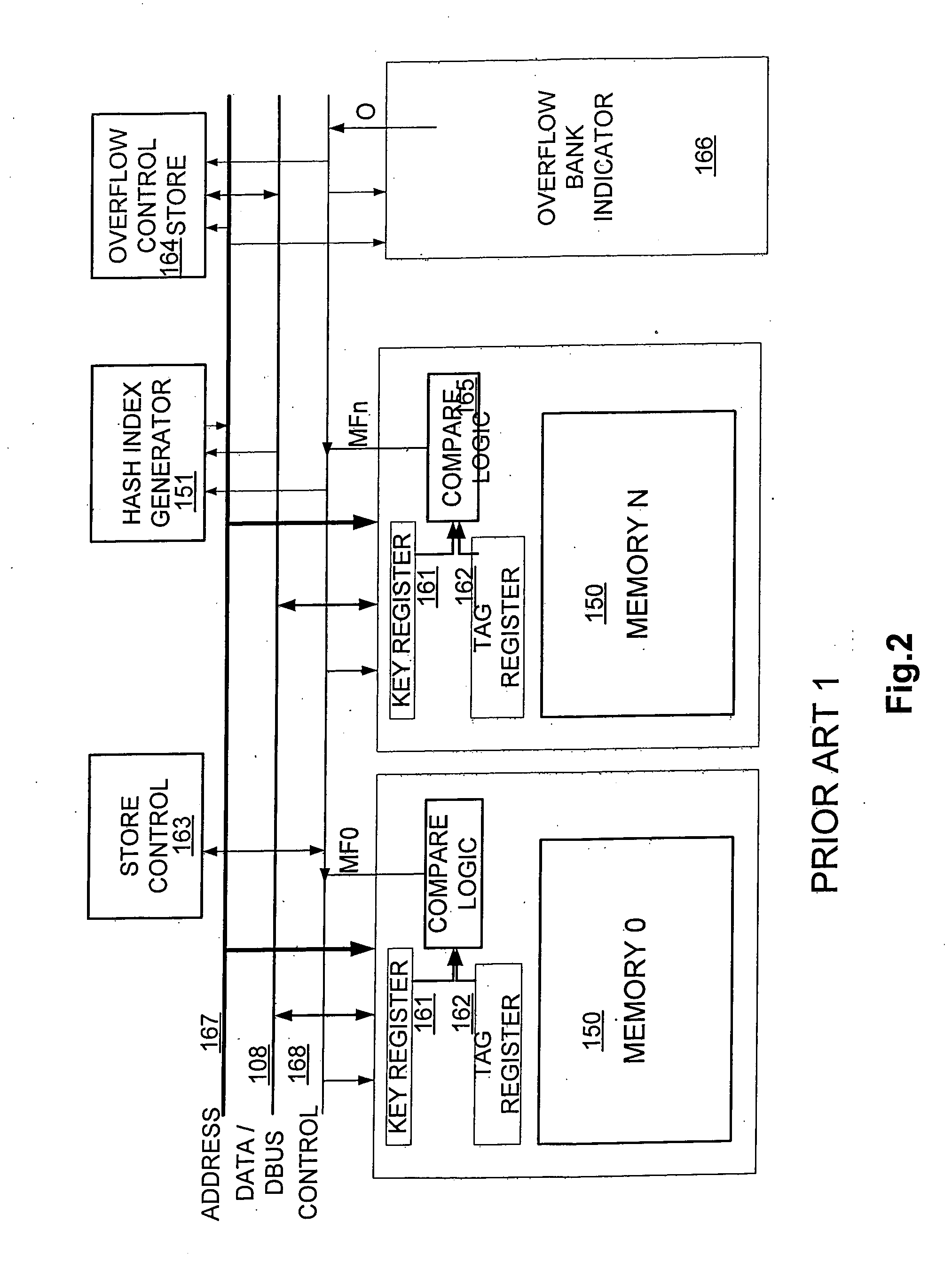
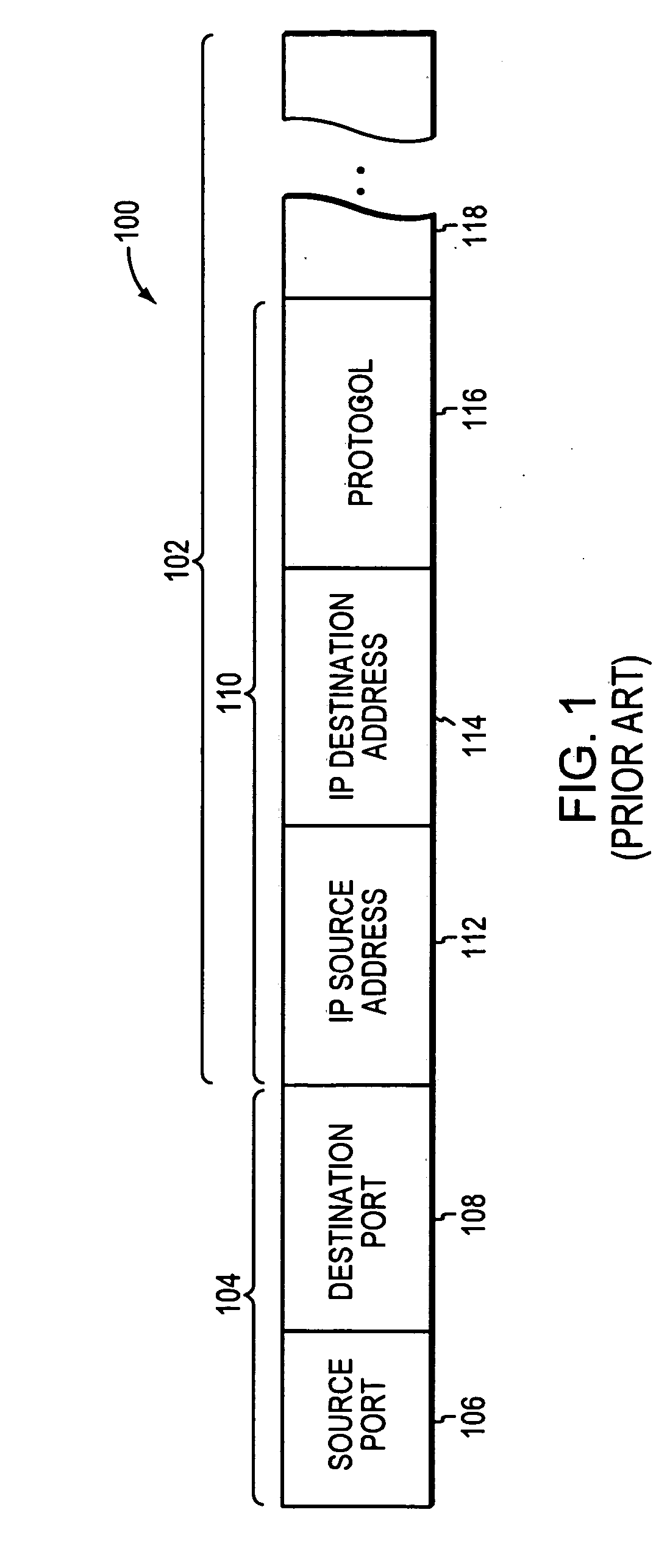
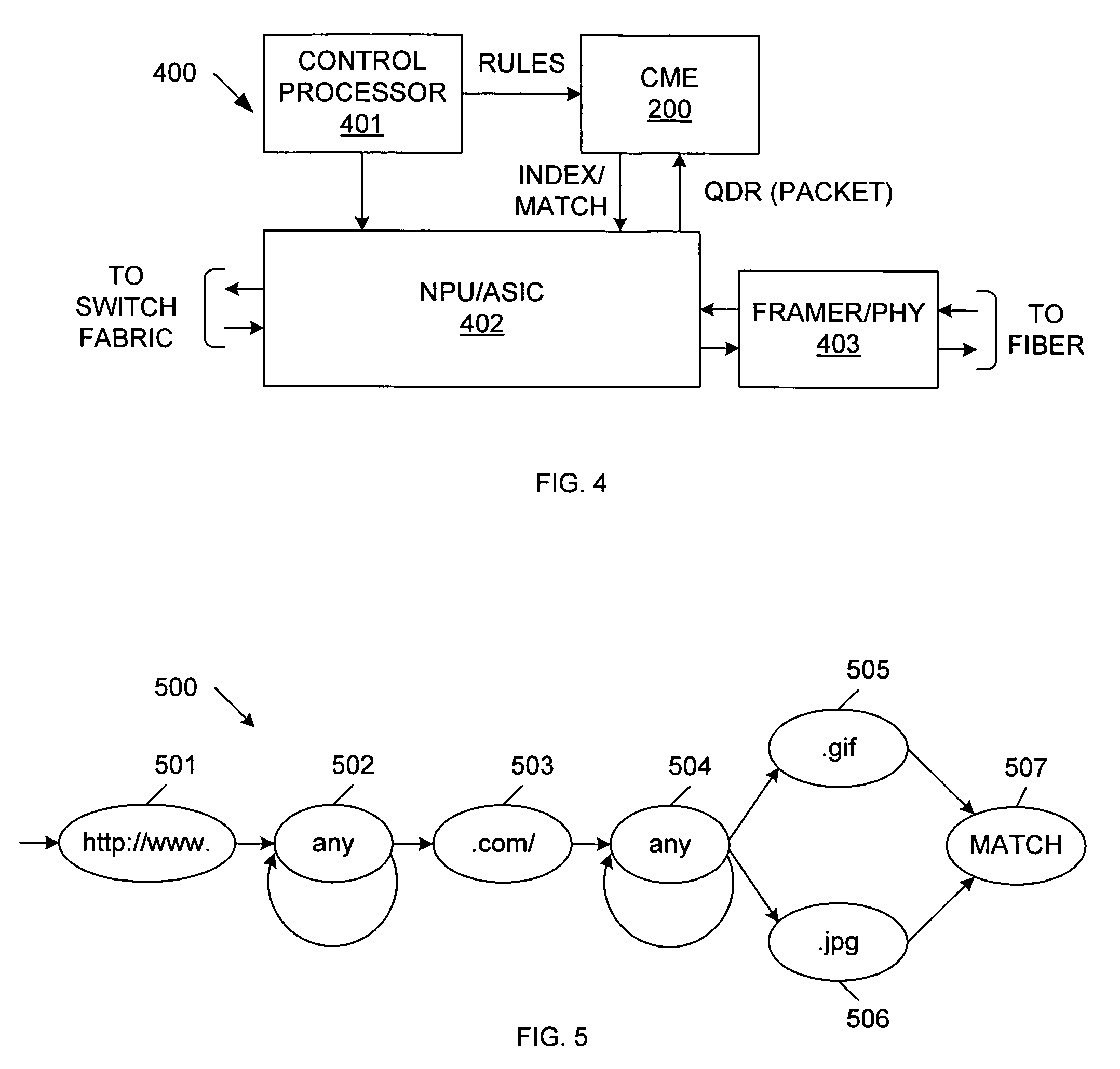
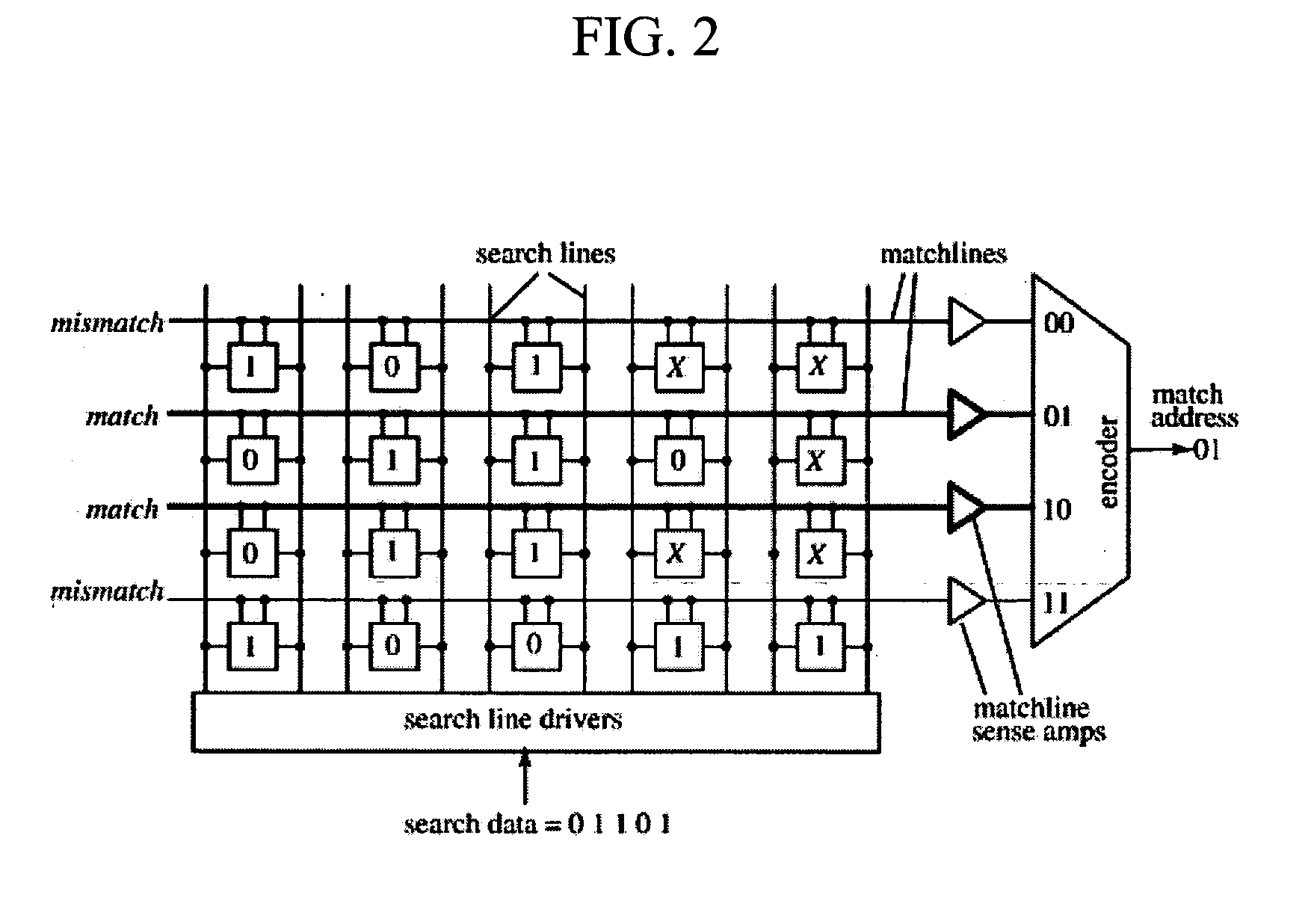
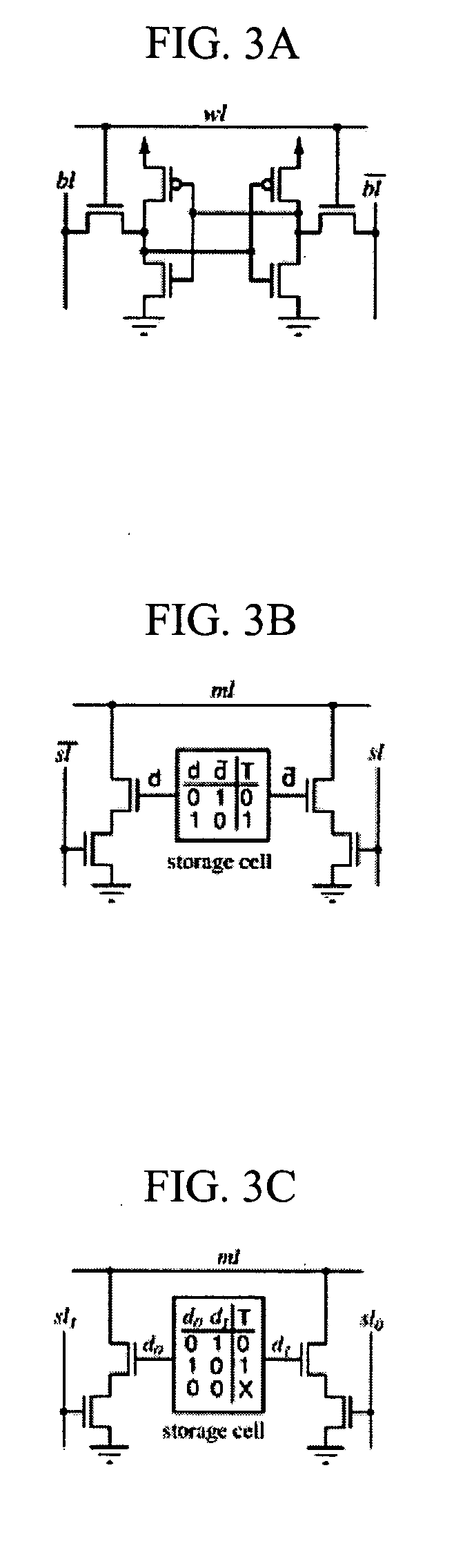
Content-addressable memory (CAM) is a special type of computer memory used in certain very-high-speed searching applications. It is also known as associative memory or associative storage and compares input search data (tag) against a table of stored data, and returns the address of matching data (or in the case of associative memory, the matching data).
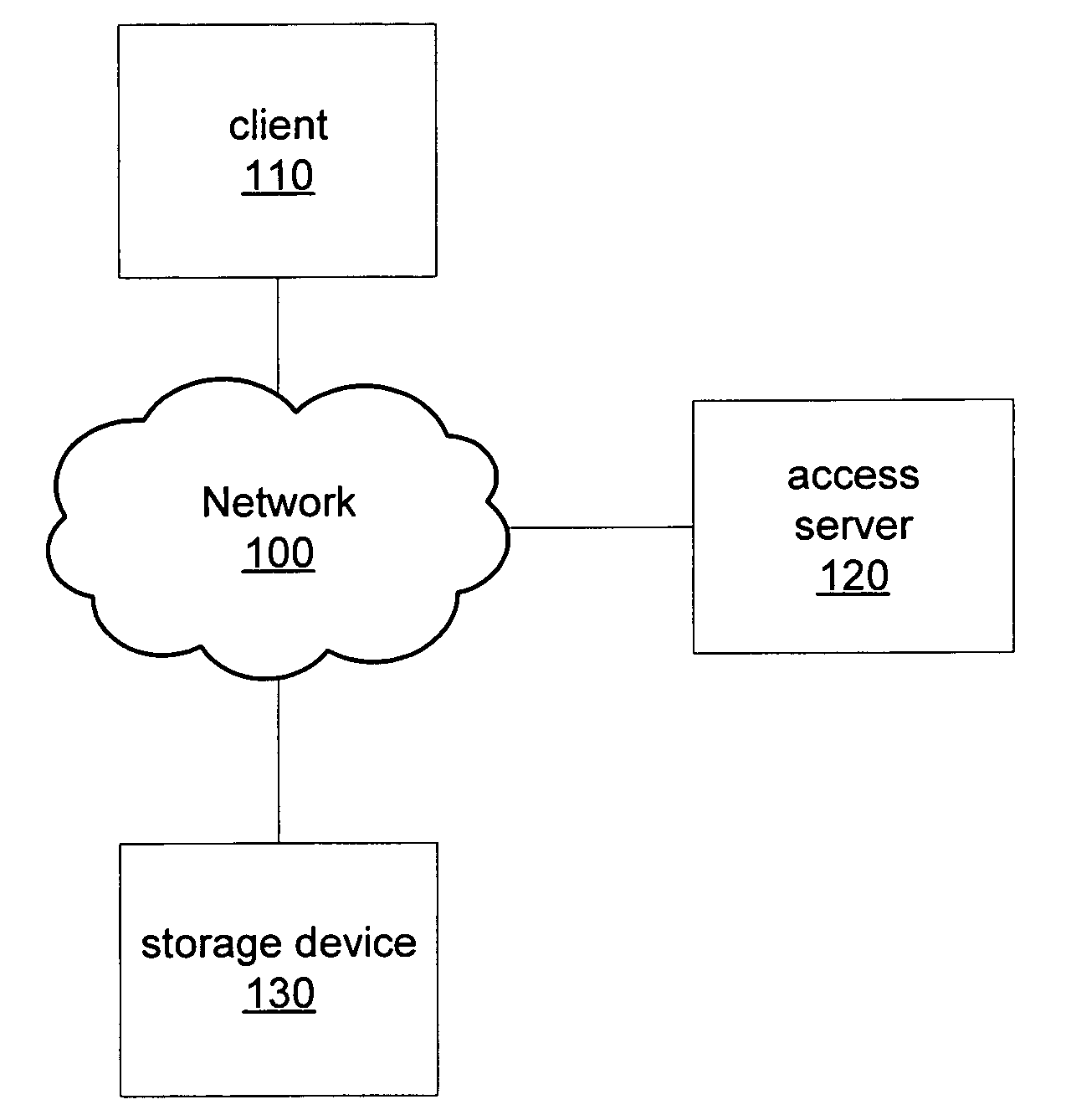
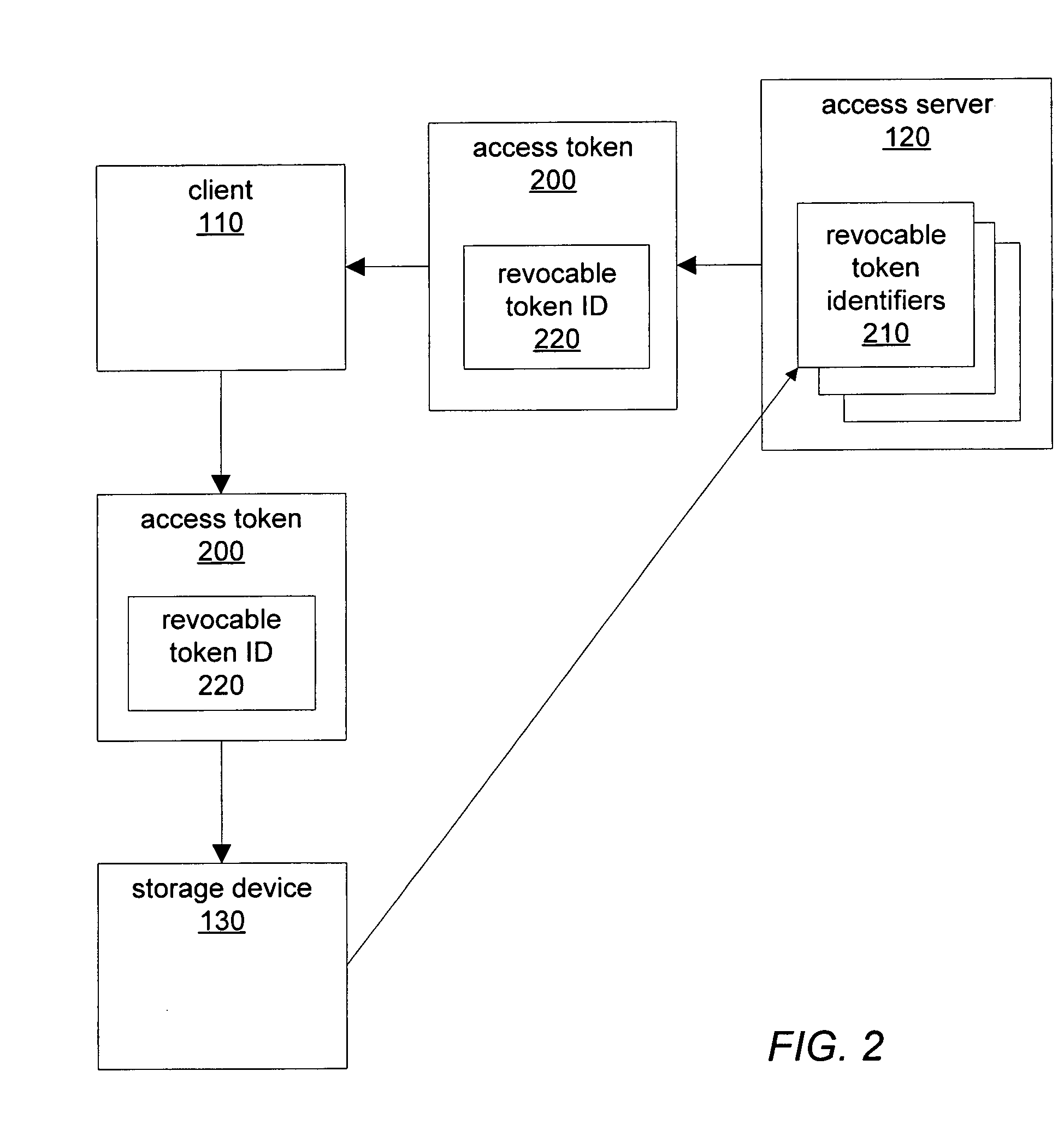
Secure storage access using third party capability tokens
ActiveUS8042163B1Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsThird partyClient-side
A method for revocable token identifiers may be employed in a shared storage environment. An access server may generate access tokens and include revocable token identifiers previously obtained from storage devices. When clients present access tokens to storage devices during storage requests, storage devices may check the validity of access tokens by verifying that the revocable token identifiers were previously issued to the access server. An access server may request that the storage device revoke revocable token identifiers. Storage devices may deny any future storage requests including revoked token identifiers. Additionally, an access token may include instructions specifying operations for a storage device to perform in conjunction with a storage request. A trusted server may issue grantor tokens granting permissions for access servers to use when issuing access tokens. An access server may then include such a grantor token in access tokens that it generates and issues to clients.
Owner:CA TECH INC
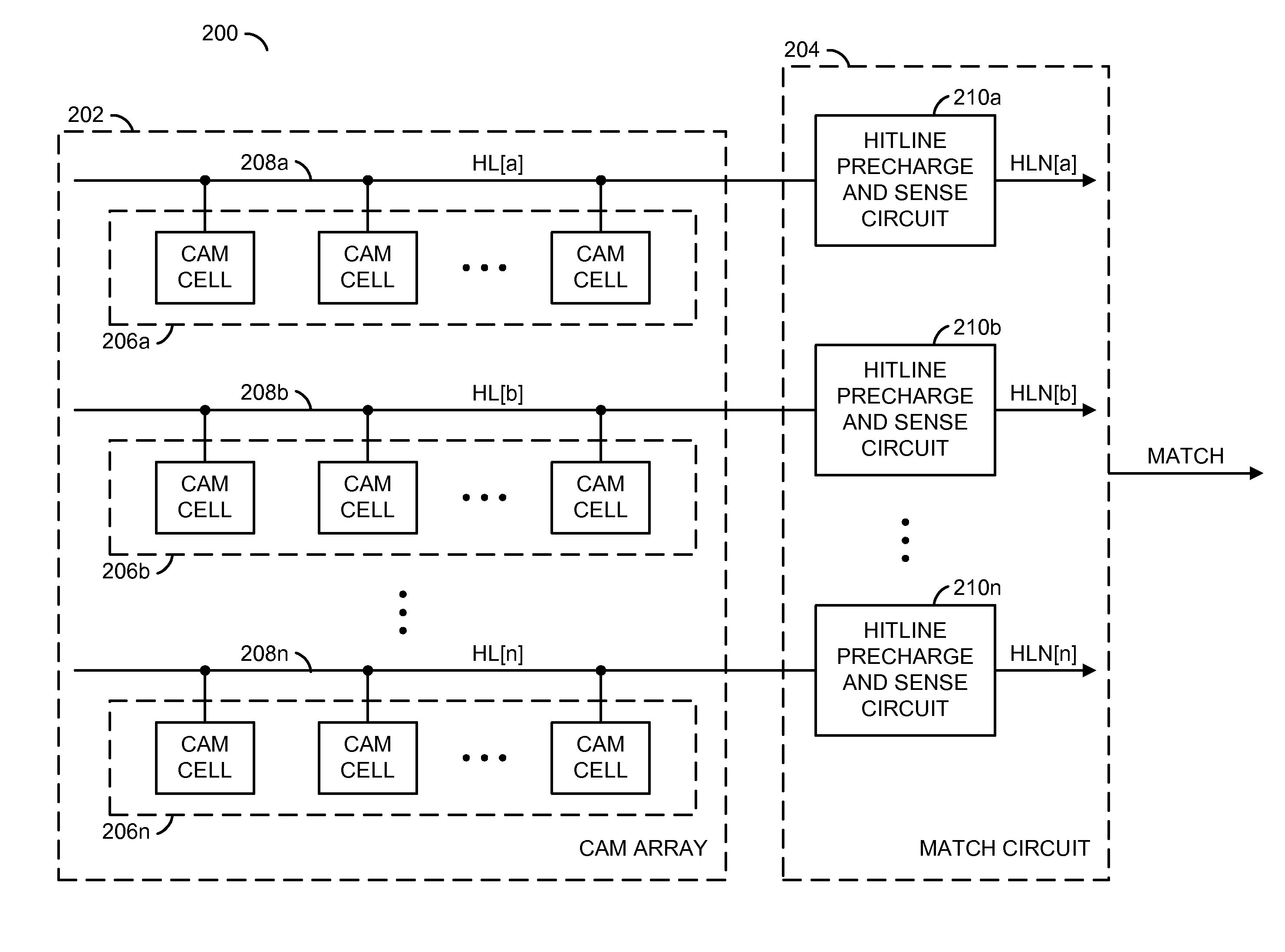
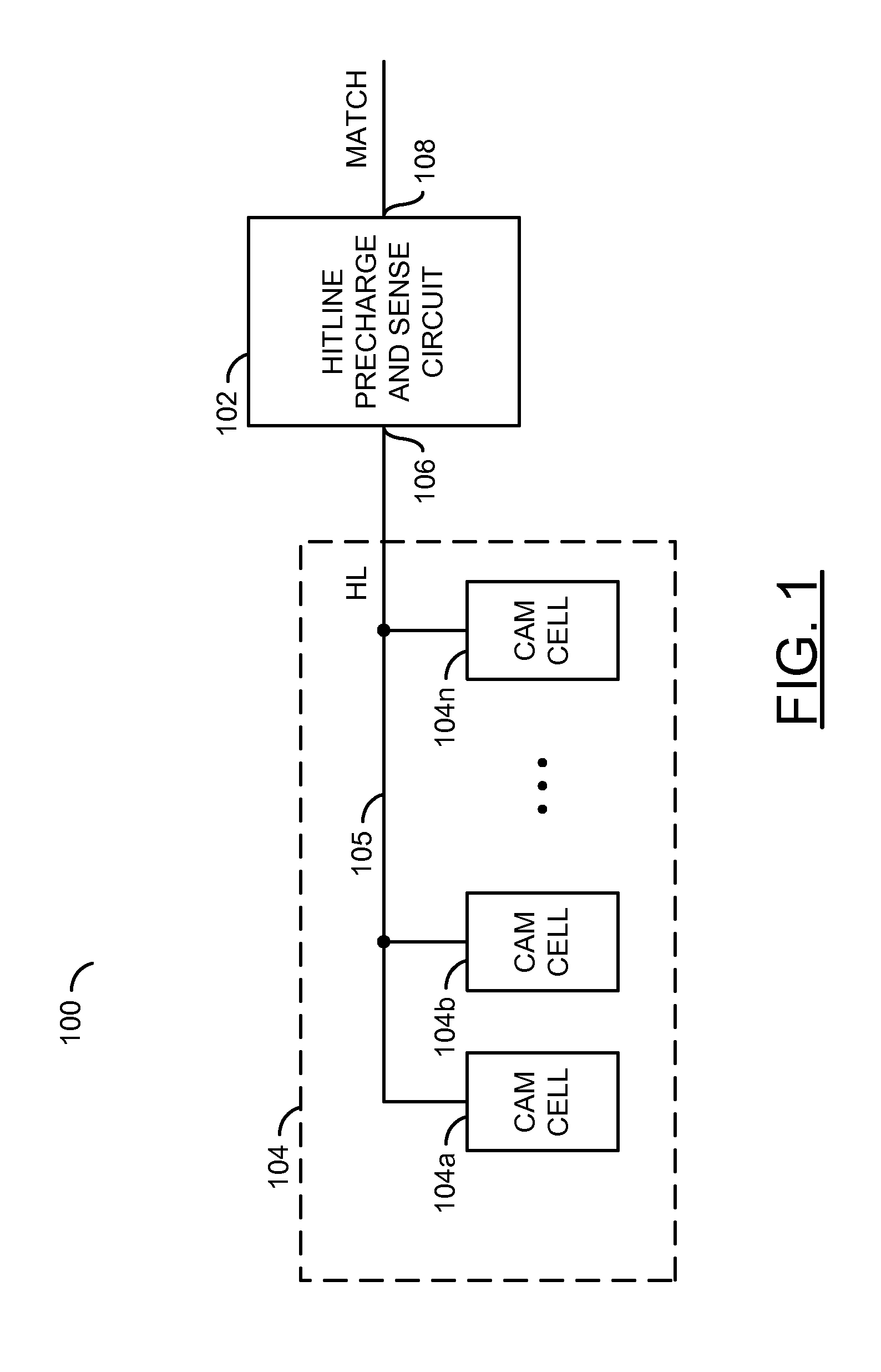
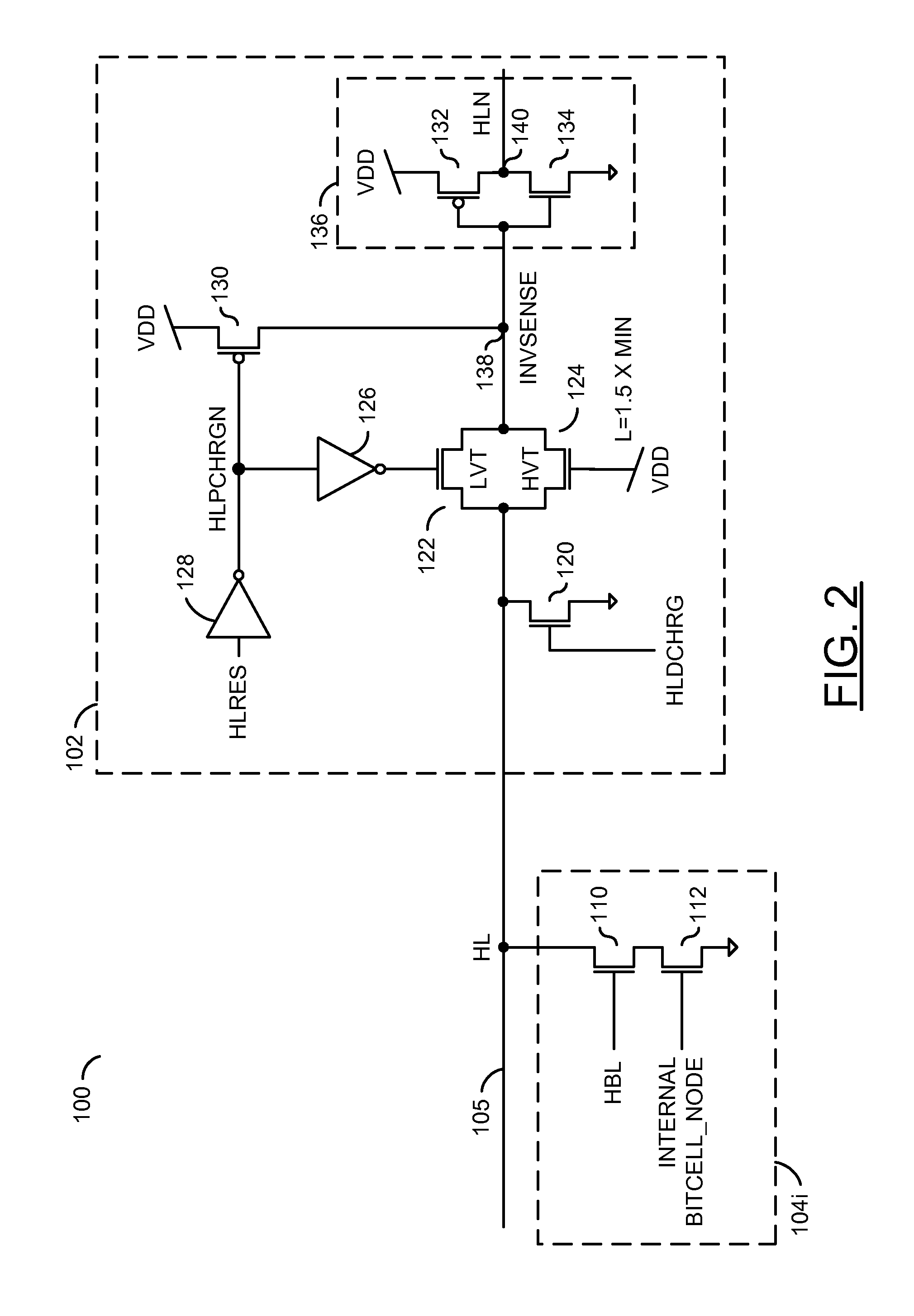
Low power content addressable memory hitline precharge and sensing circuit
An apparatus and a method of operating the apparatus. The apparatus includes a driver circuit and a memory circuit. The driver circuit may be configured to precharge a hitline in response to a predetermined voltage level and a control signal and sense a result of a compare operation based upon a hitline signal on the hitline. The driver circuit generally precharges the hitline to a voltage level lower than the predetermined voltage level and senses the result of the compare operation using the full predetermined voltage level. The memory circuit may be configured to perform the compare operation using the hitline.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
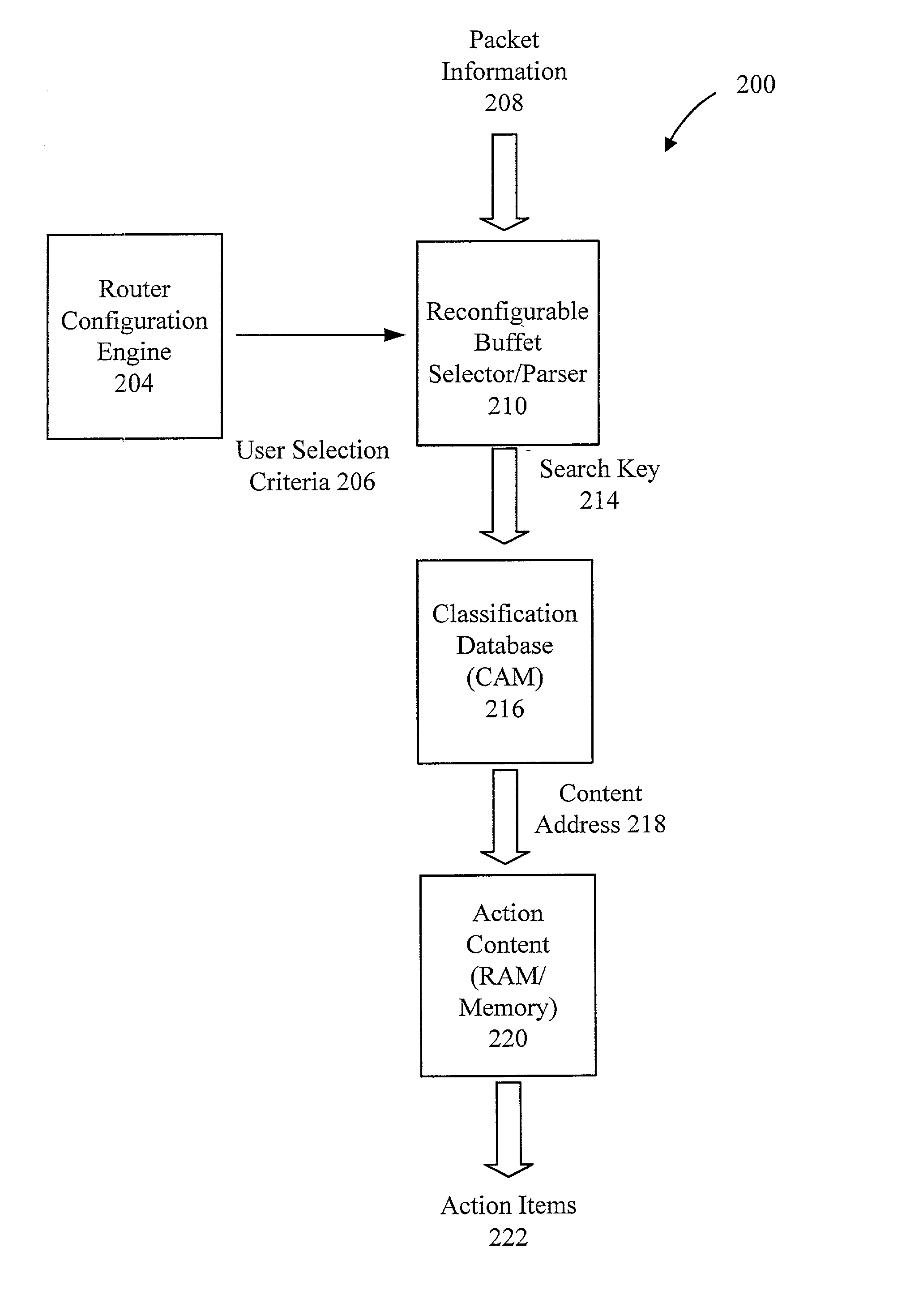
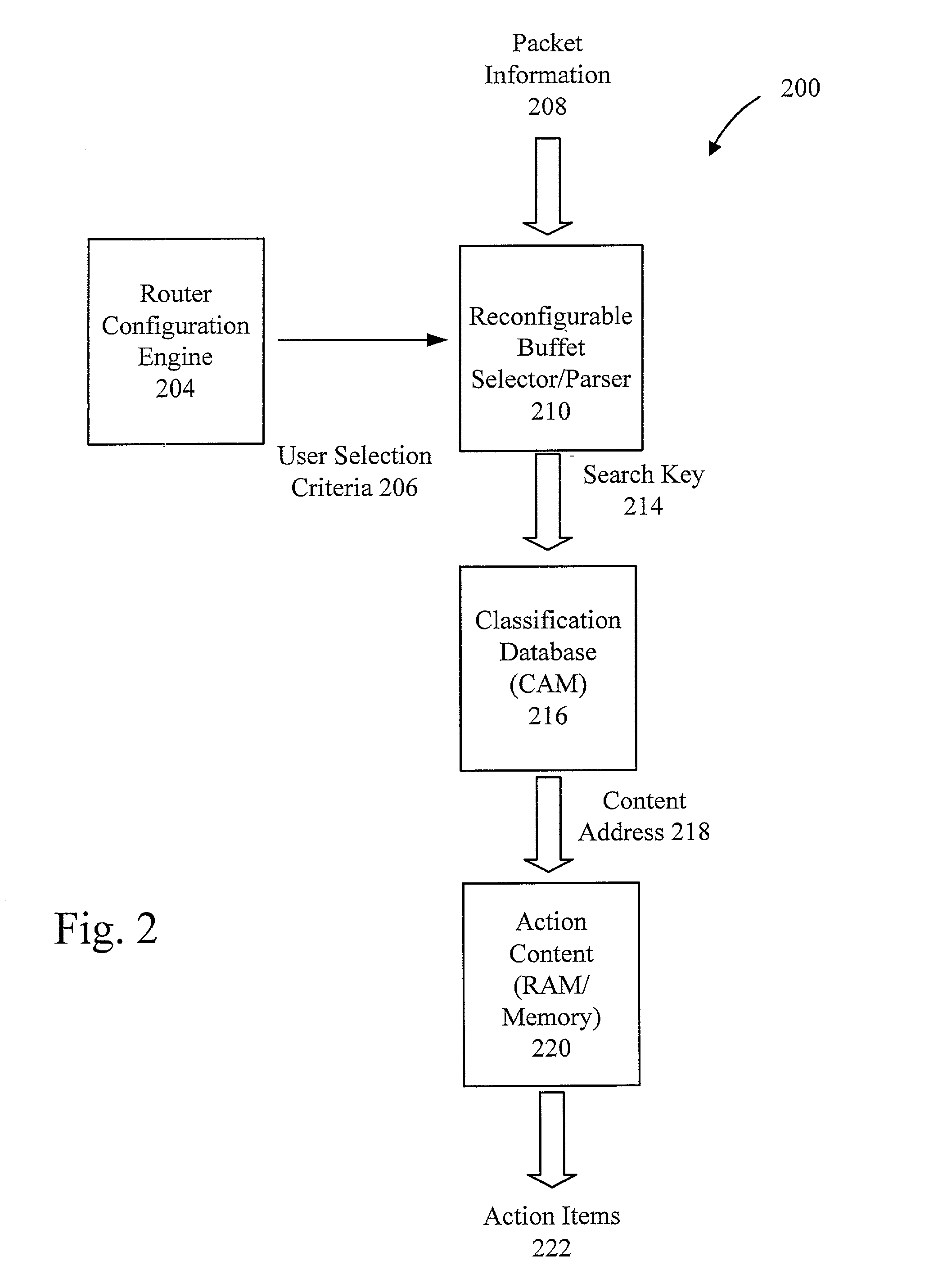
Method and apparatus for a flexible and reconfigurable packet classifier using content addressable memory
InactiveUS20020126672A1Low costFlexibility of deploymentData switching by path configurationSecuring communicationCustomer requirementsTernary content addressable memory
The present invention provides for a reconfigurable packet classifier using CAM. The invention is directed to packet classification for switching / routing systems where the router's system resources are limited and the customer requirements from the router are variable. The invention addresses the CAM constraint (e.g. search key width) problems of CAM-based classification systems, by allowing a reconfigurable selection of packet fields and / or payload bits to be used in the definition of the search key. For any given incoming packet, a subset of that incoming packet may be statically chosen to fit that particular CAM architecture and to create a particular CAM search key. This provides router deployment flexibility within networks and, thus, cuts costs.
Owner:ACUTE COMM CORP
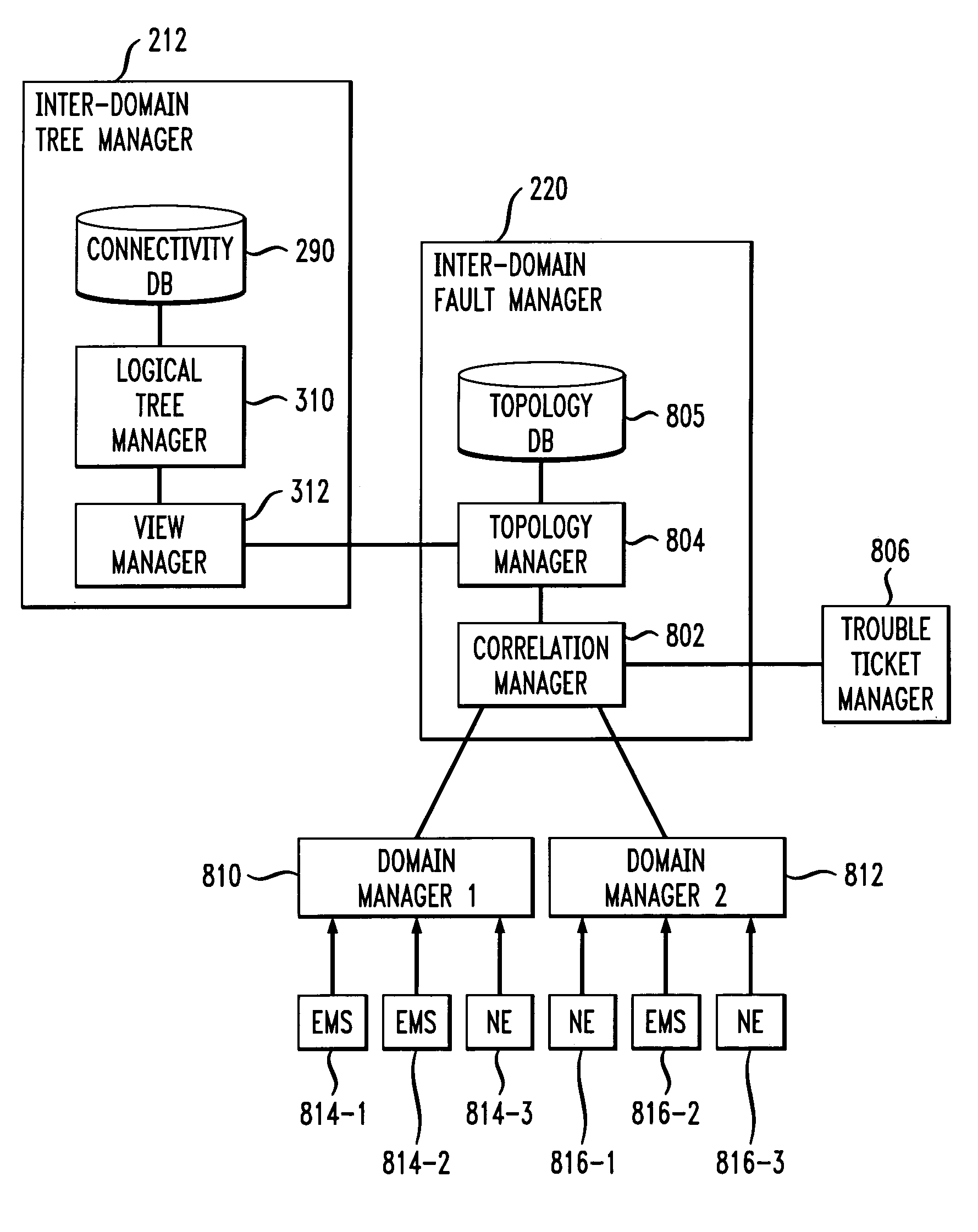
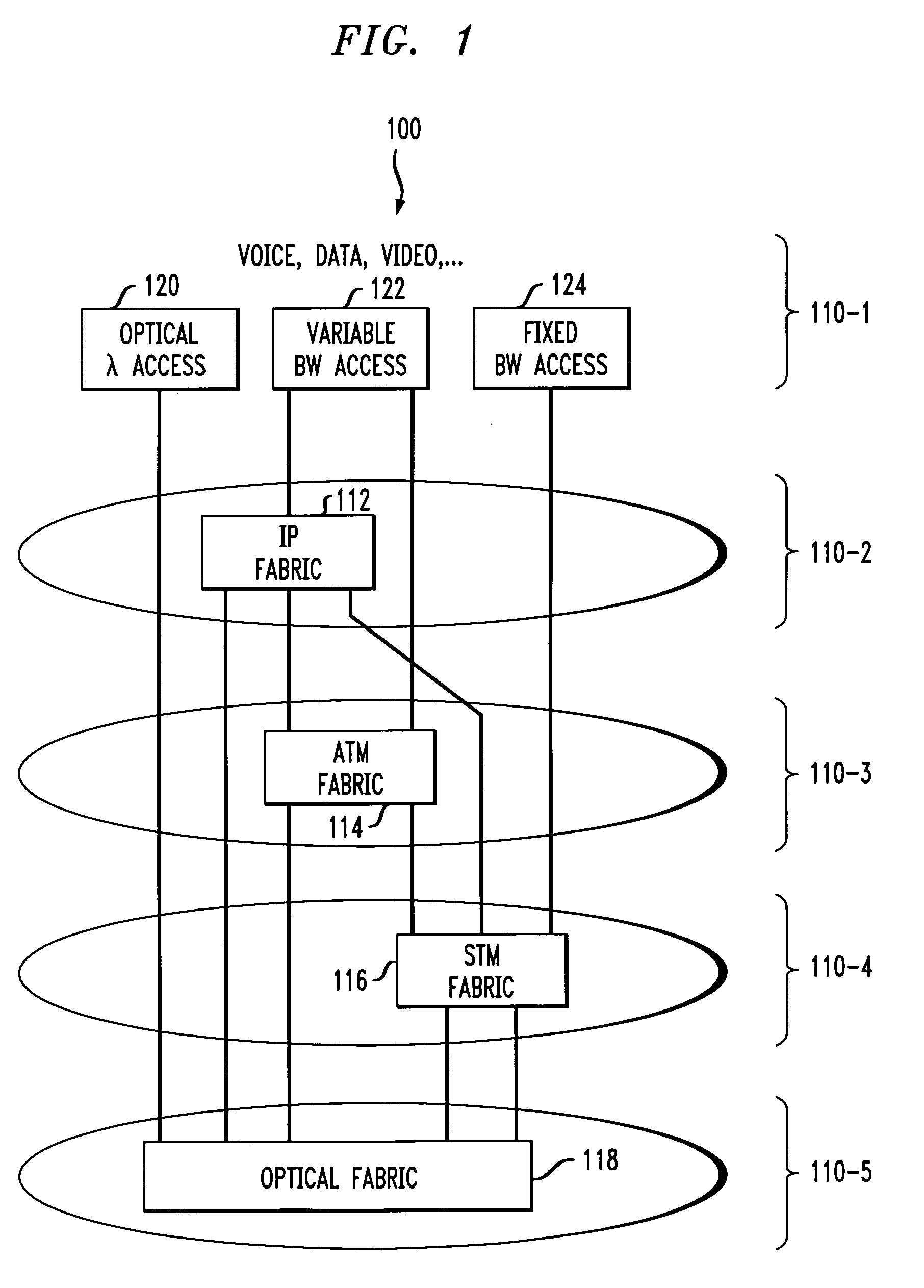
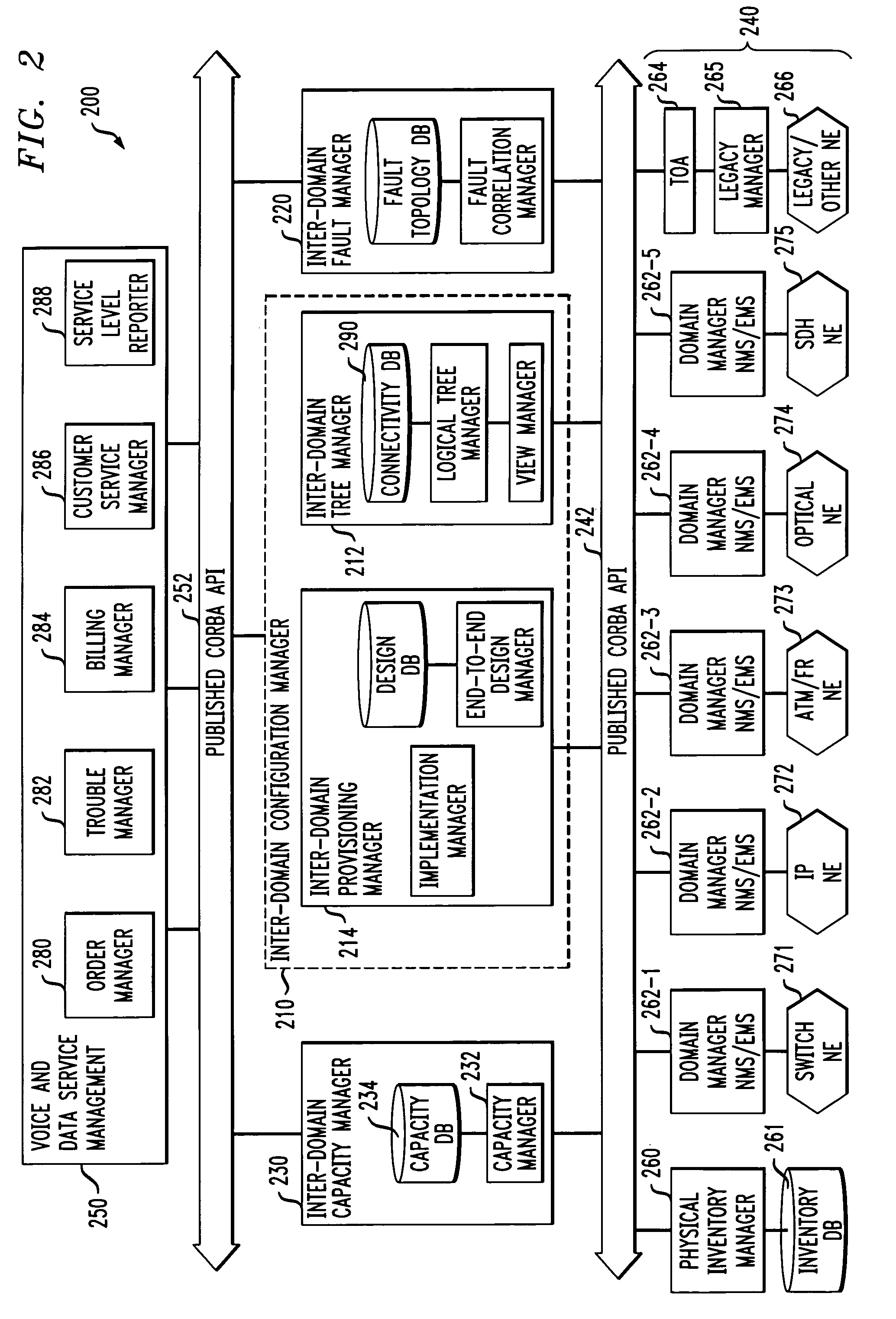
Inter-domain network management system for multi-layer networks
InactiveUS7197546B1High activityEasy maintenanceData processing applicationsTime-division multiplexNetwork managementApplication software
A network management system for a multi-layer network having multiple architectural or technological domains includes an inter-domain configuration manager arranged between a set of one or more network service management applications and a set of network element domain managers, each of the domain managers being associated with a particular domain of the multi-layer network. The configuration manager implements network service design and provisioning functions across the domains of the network in conjunction with stored connectivity information characterizing the multi-layer network. The network management system further includes an inter-domain fault manager and an inter-domain capacity manager, which provide respective fault management and transport capacity management functions across the domains of the multi-layer network. The inter-domain configuration manager, inter-domain fault manager and inter-domain capacity manager may be interfaced to the set of network service management applications and the set of network element domain managers through corresponding published Common Object Request Broker Architecture (CORBA) Application Programming Interfaces (APIs).
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
Method and apparatus for performing link aggregation
ActiveUS20070280258A1Reduce in quantityEnergy efficient ICTData switching by path configurationComputer networkLink aggregation
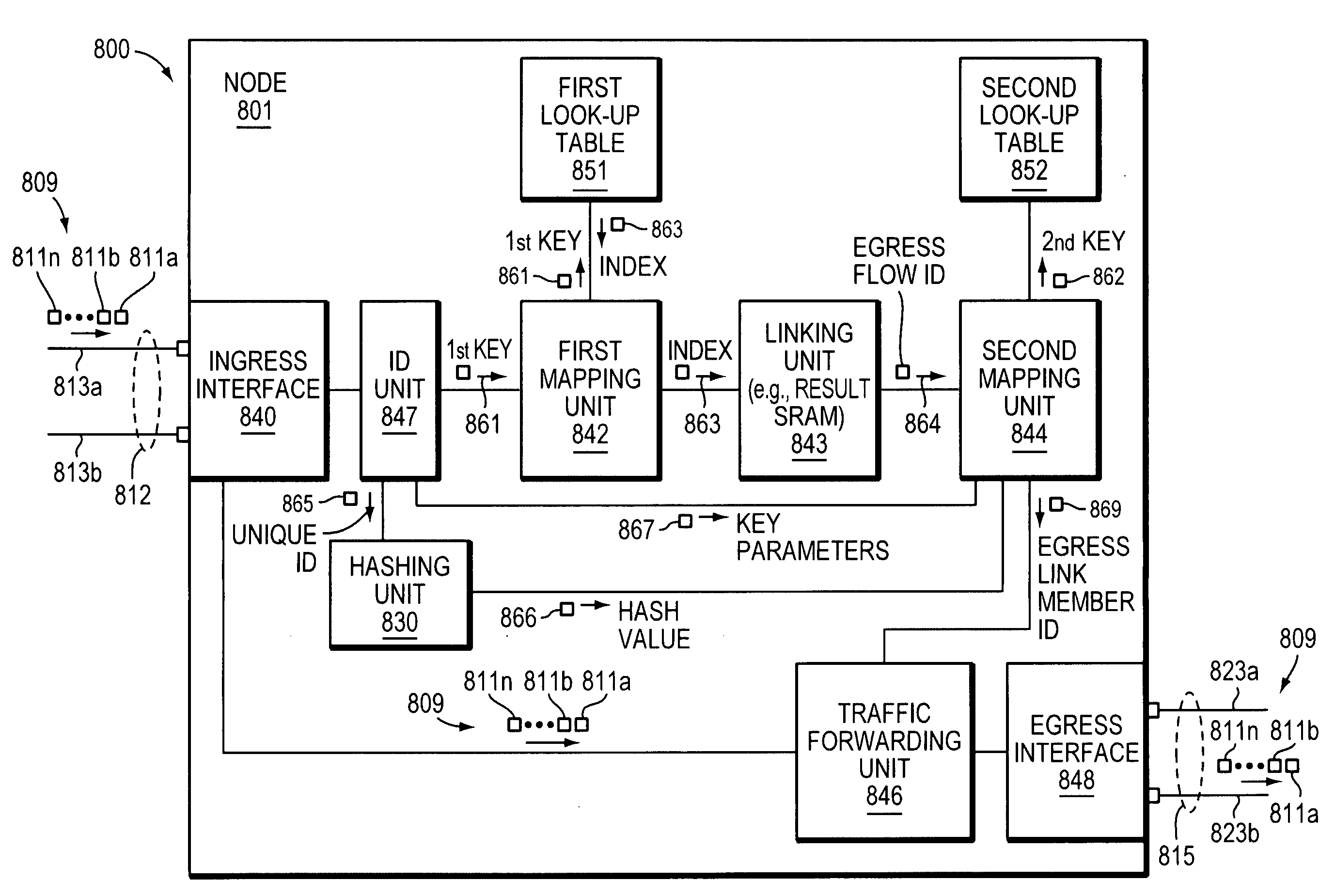
A network node or corresponding method of performing link aggregation reduces a number of Content Addressable Memory (CAM) entries required to make a forwarding decision for a given ingress flow, reducing cost, size, and power consumption of the CAM and accompanying static RAM. In one embodiment, an ingress flow is mapped to an egress flow identifier. Subsequently, the egress flow identifier is mapped to a member of an aggregated group associated with an egress interface based on information available in a given ingress flow. Finally, the given ingress flow is forwarded to the member of the aggregated group associated with the egress interface. A hashing technique or two lookups may be used alone or in combination in mapping the ingress flow to the egress flow identifier to reduce CAM memory usage.
Owner:TELLABS OPERATIONS
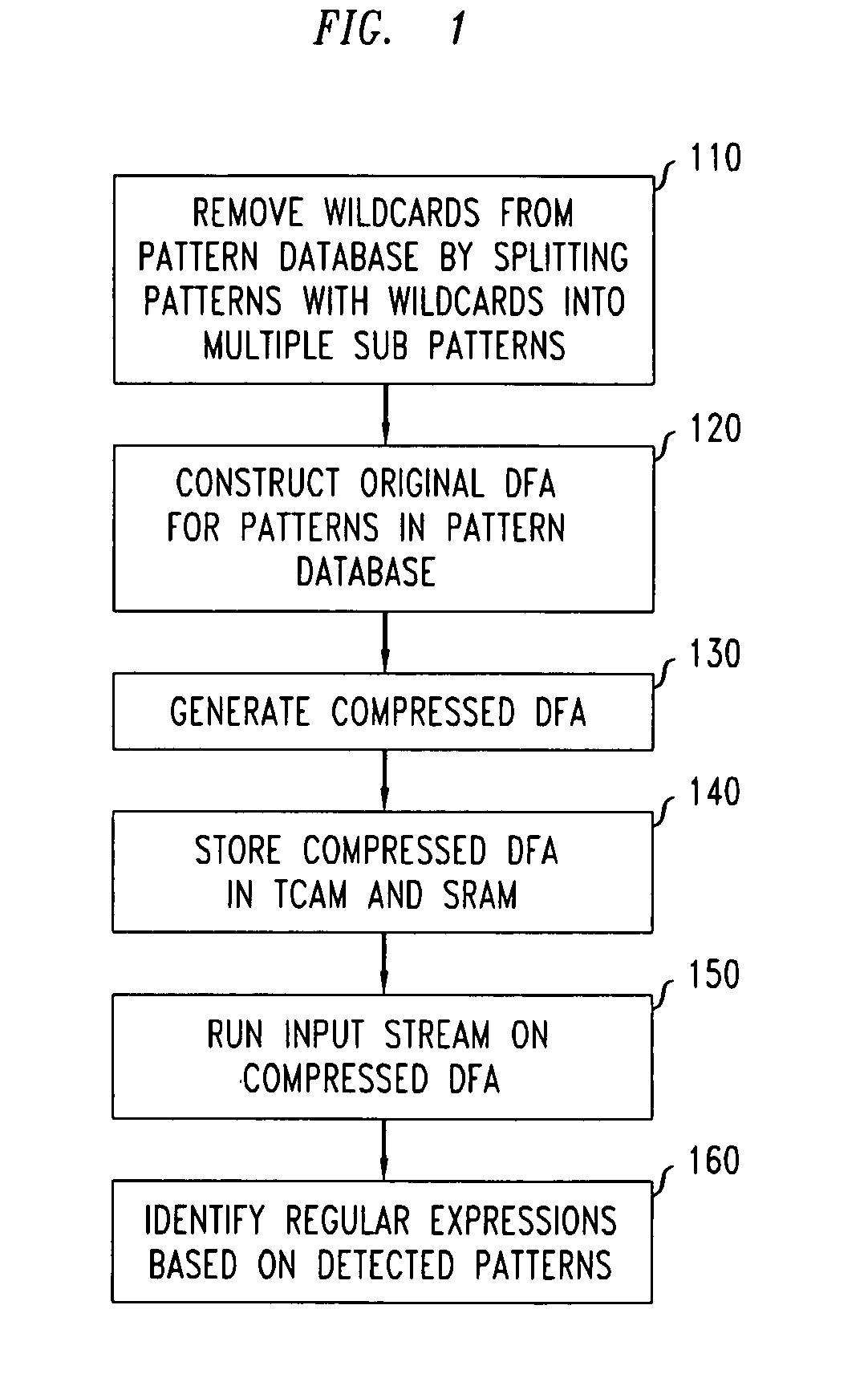
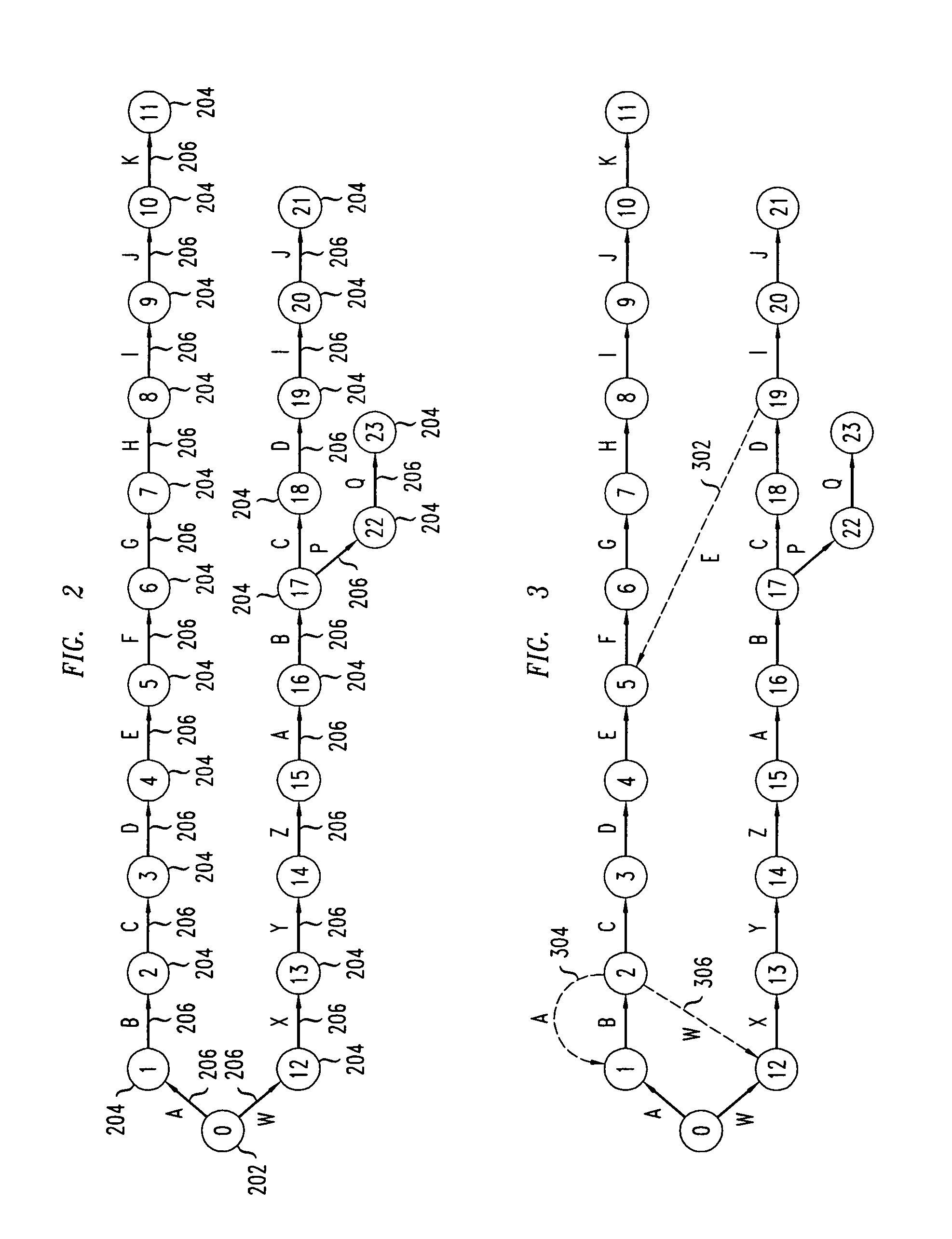
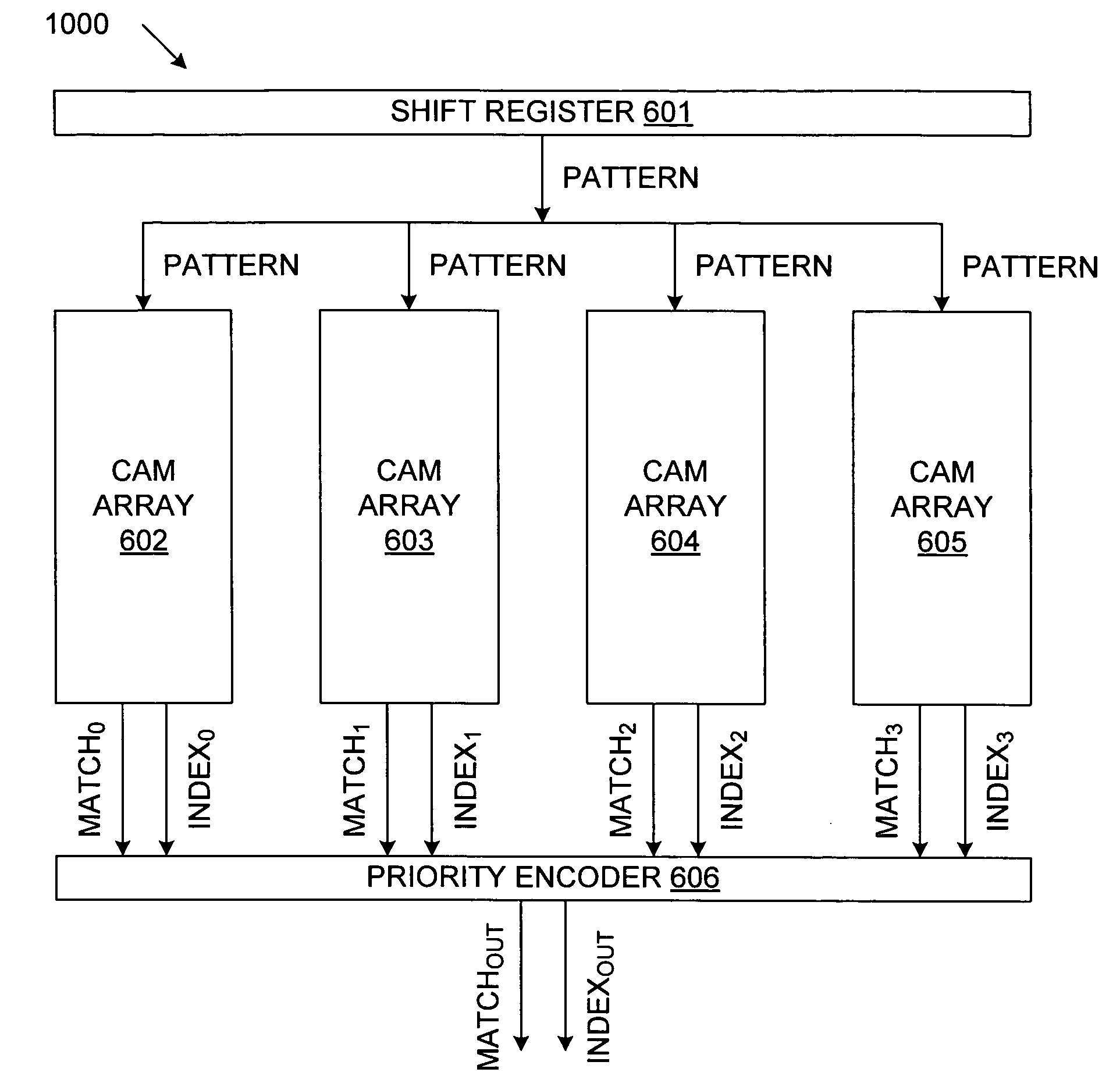
Method and system for multi-character multi-pattern pattern matching
ActiveUS20080046423A1High pattern matching speedEasy to implementData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalPattern matchingTernary content addressable memory
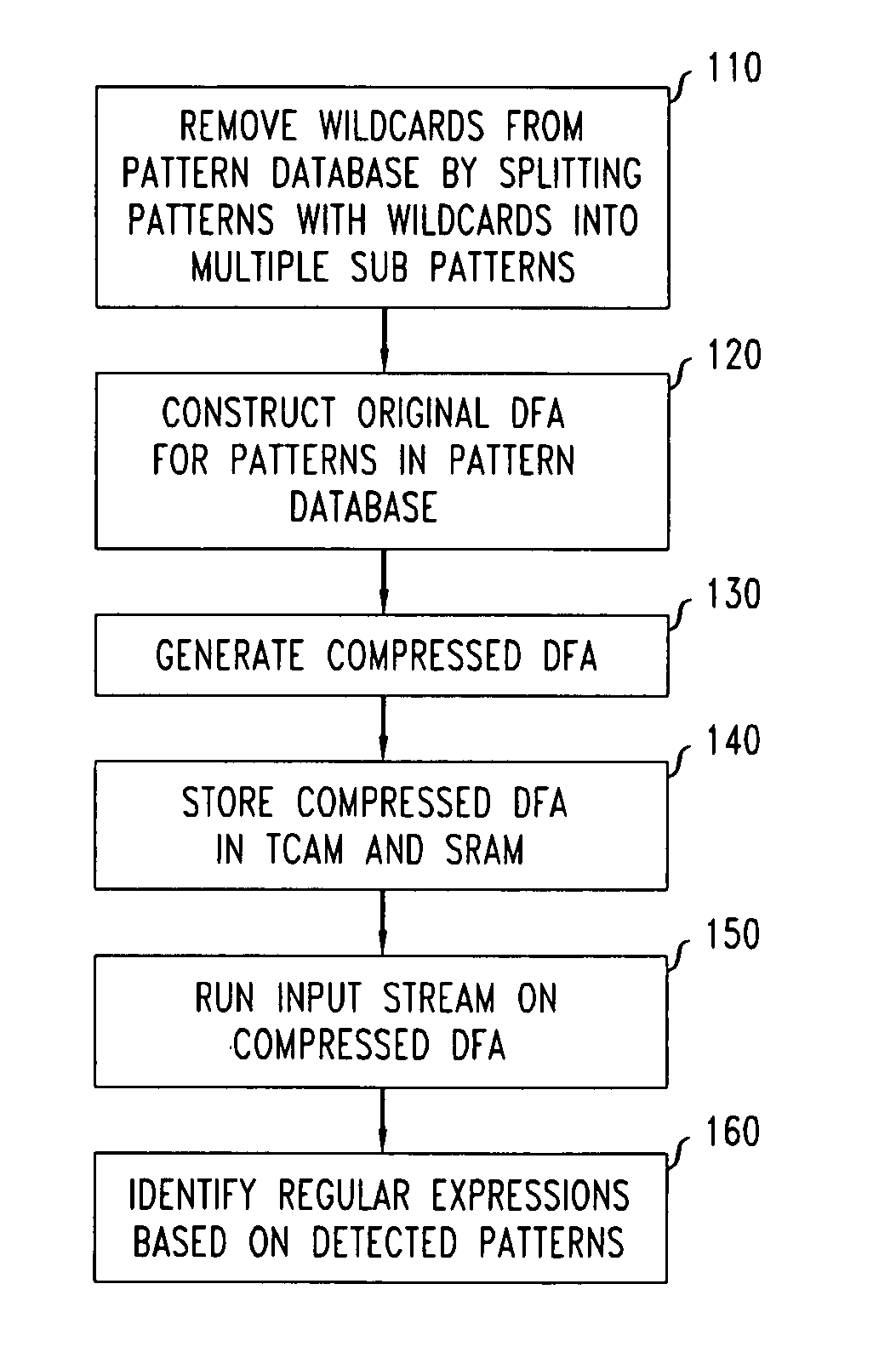
Disclosed is a method and system for multi-character multi-pattern pattern matching. In the multi-character multi-pattern pattern matching method, patterns in an input stream are detected by transitioning between states of a “compressed deterministic finite state automaton (DFA)”, with each transition based on multiple characters of the input stream. The compressed DFA is created by compressing an original DFA, such as an Aho-Corasick DFA, such that each state of the compressed DFA represents multiple consecutive states of the original DFA and each transition between the states of the compressed DFA is a combination of all of the transitions between the multiple consecutive states of the original DFA. This method can be implemented using a Ternary Content-Addressable Memory (TCAM) to store the transitions of the compressed DFA and compares the transitions with multiple characters of an input stream at a time to detect patterns in the input stream.
Owner:ALGOGENE FINANCIAL TECHNOLOGY COMPANY LIMITED
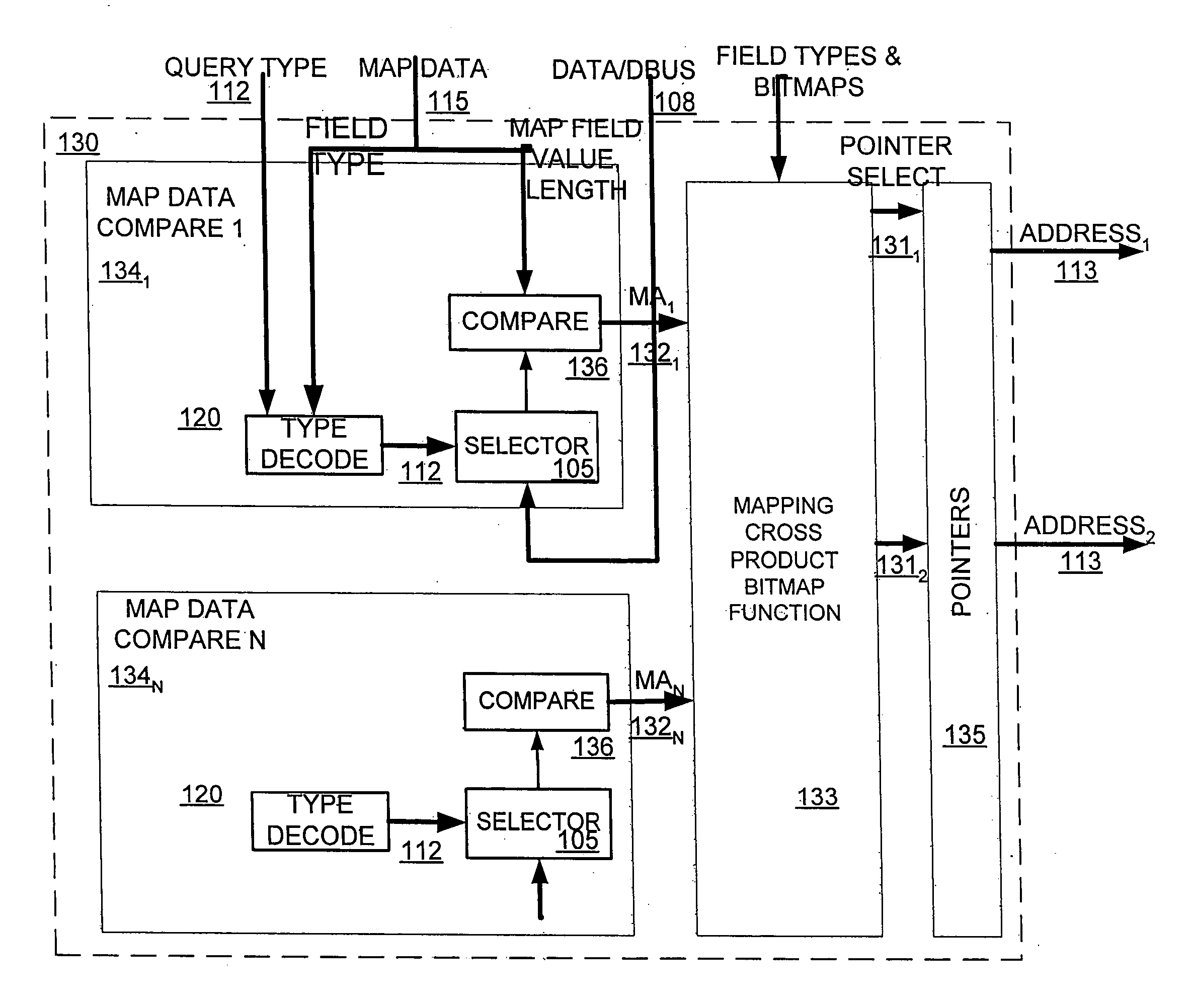
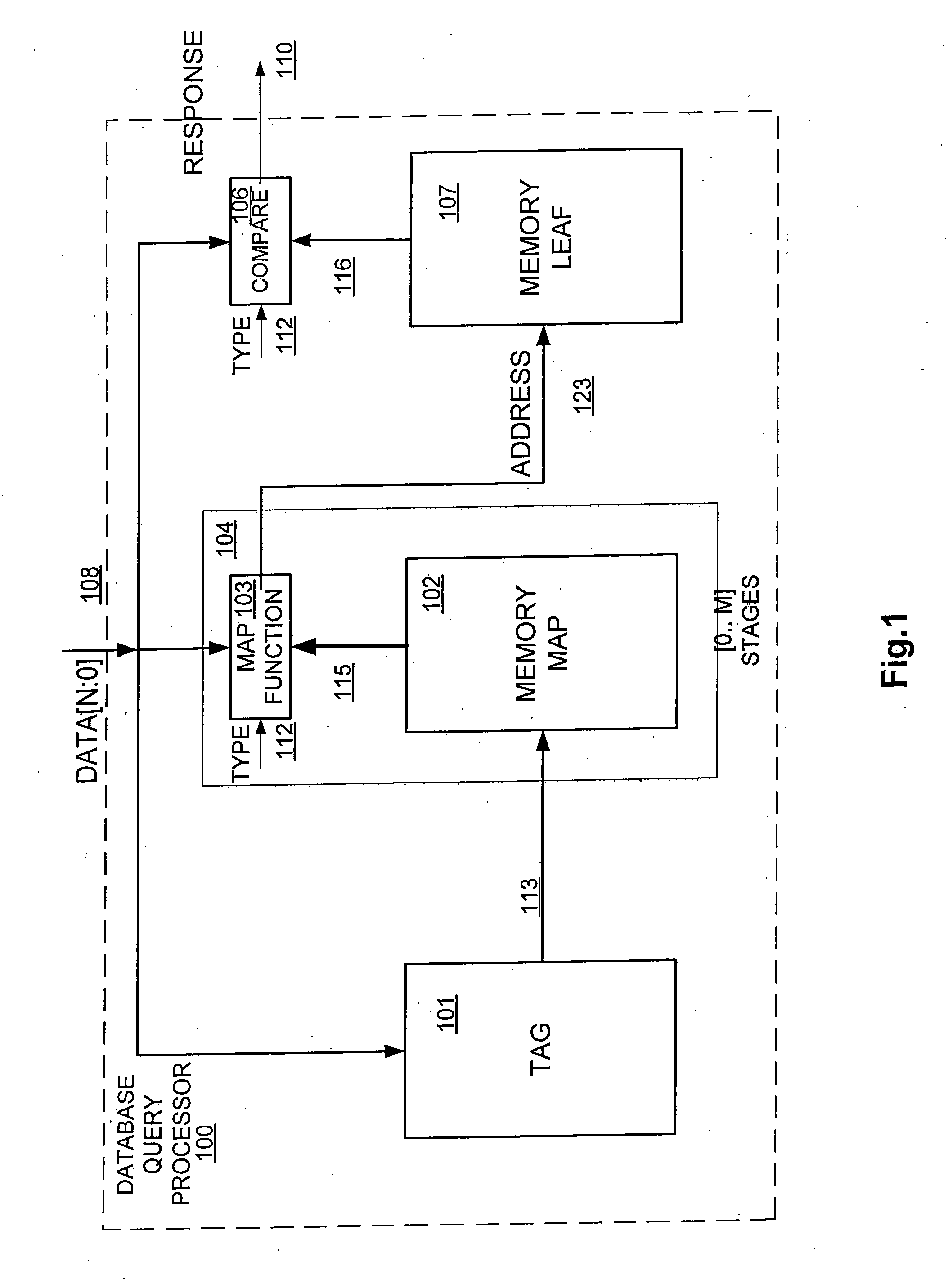
Database query processor
InactiveUS20060155915A1High utilityQuick searchUnauthorized memory use protectionTransmissionTheoretical computer scienceMulti dimensional data
Disclosed is an associative content or memory processor for wirespeed query of routing, security string or multi-dimensional lookup tables or databases, which enables high utilization of memory resources and fast updates. The device can operate as binary or ternary CAM (content addressable memory). The device applies parallel processing with spatial and data based partitioning to store multi-dimensional databases with high utilization. One or more CAM blocks are coupled directly to leaf memory or indirectly through mapping stages. The contents of mapping memory are processed by the mapping logic block. The mapping logic processes the stored crossproduct bitmap information to traverse a path to one or more leaf memory storage blocks. The compare block compares the contents of the leaf memory with the search or query key. The output response includes match result, associated data address and associated data.
Owner:GRACENOTE
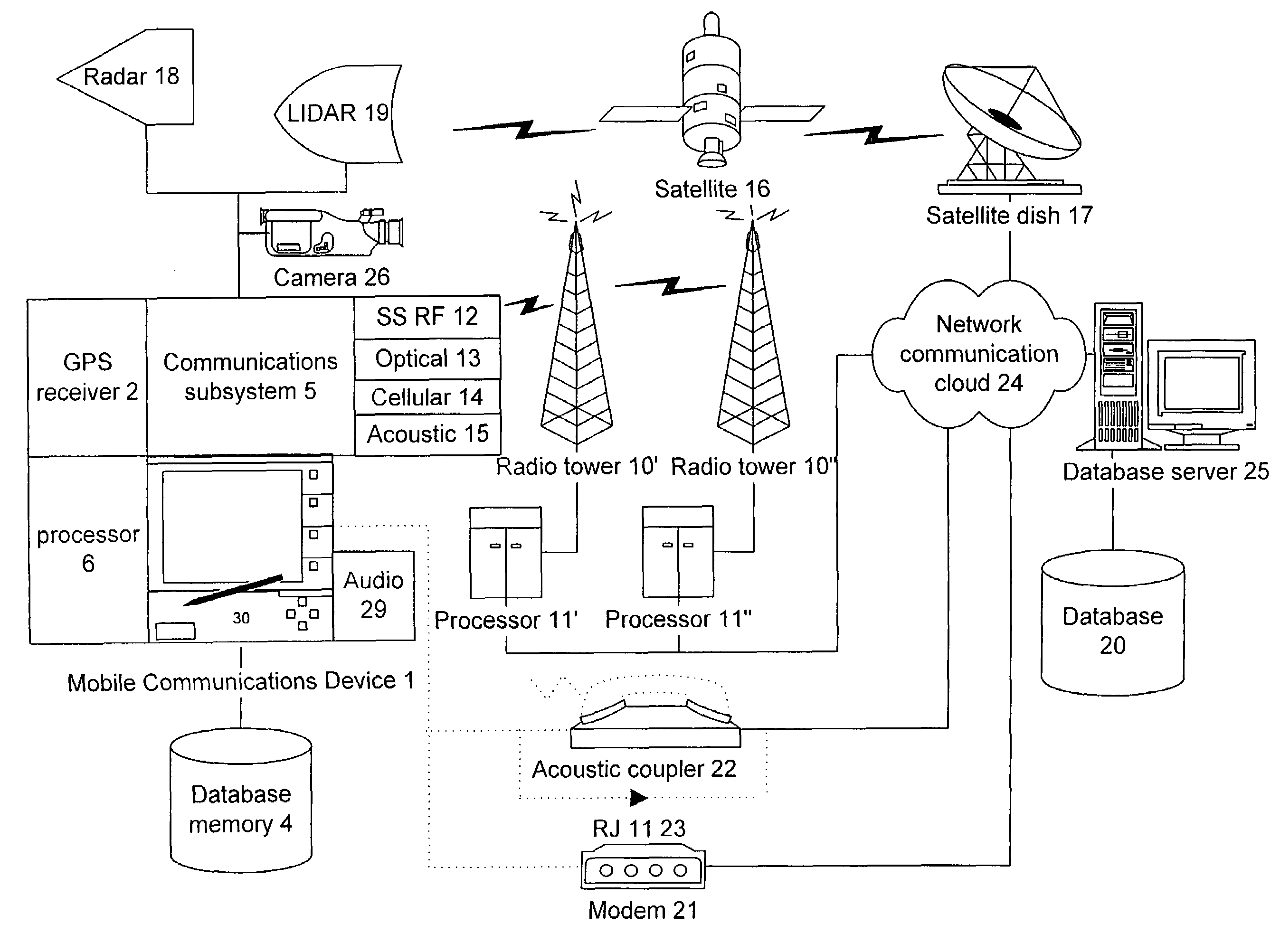
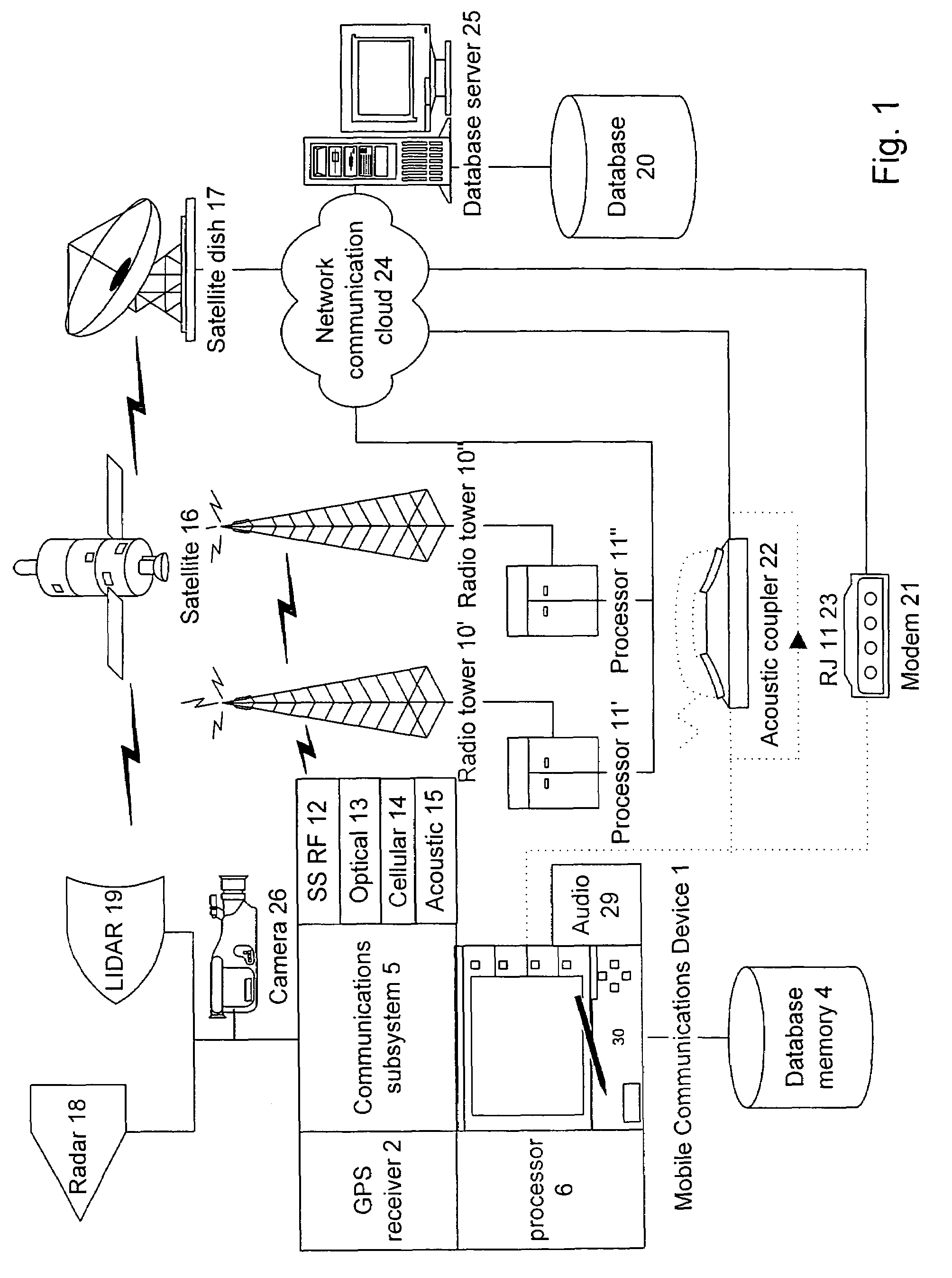
Mobile communication device
InactiveUS7268700B1Improve accuracyLow costAnalogue computers for vehiclesInstruments for road network navigationRemote systemCommunication device
A mobile communications device comprising a location sensing system, producing a location output; a memory, storing a set of locations and associated events: a telecommunications device, communicating event and location information between a remote system and said memory; and a processor, processing said location output in conjunction with said stored locations and associated events in memory, to determine a priority thereof.
Owner:HOFFBERG STEVEN M
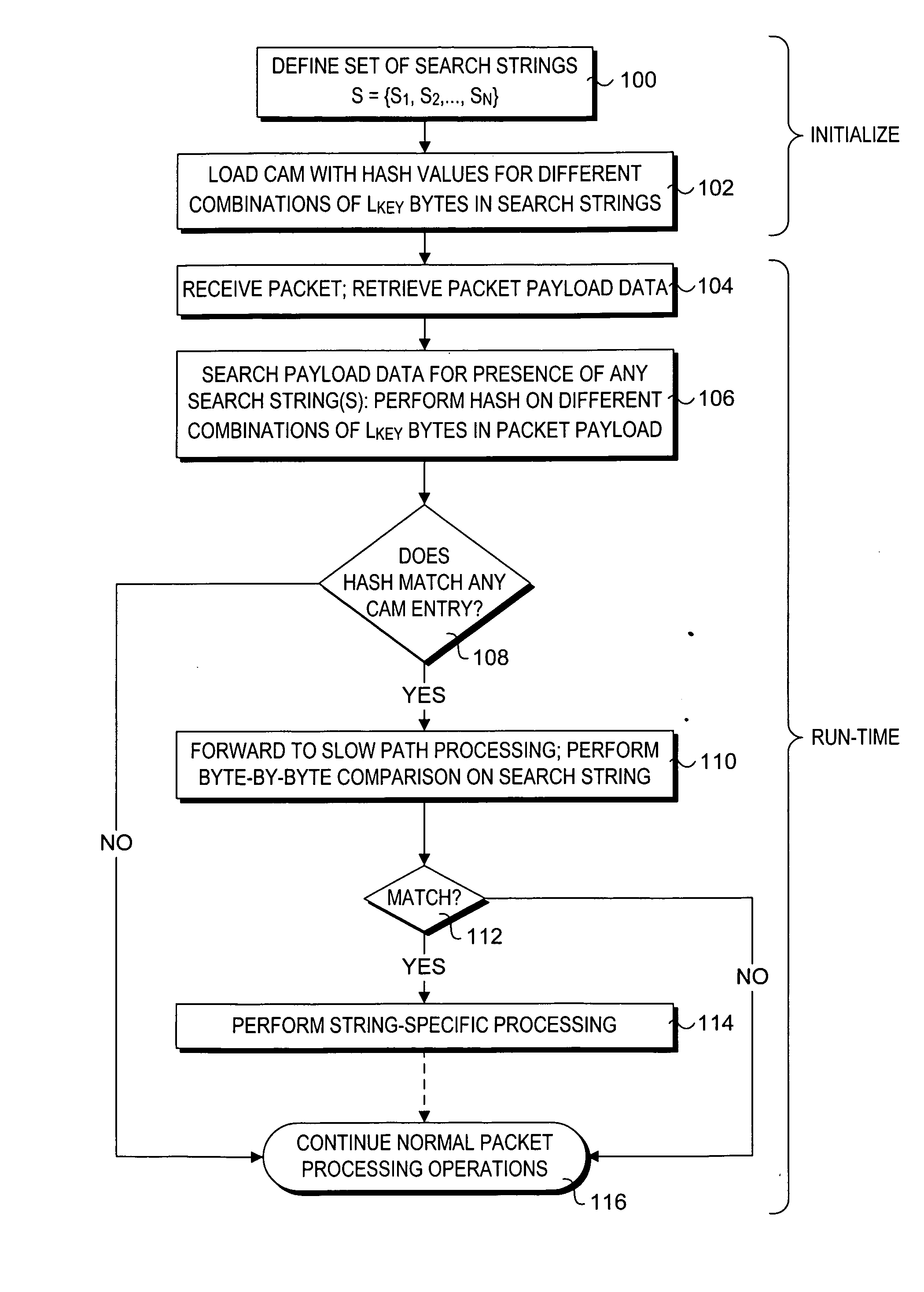
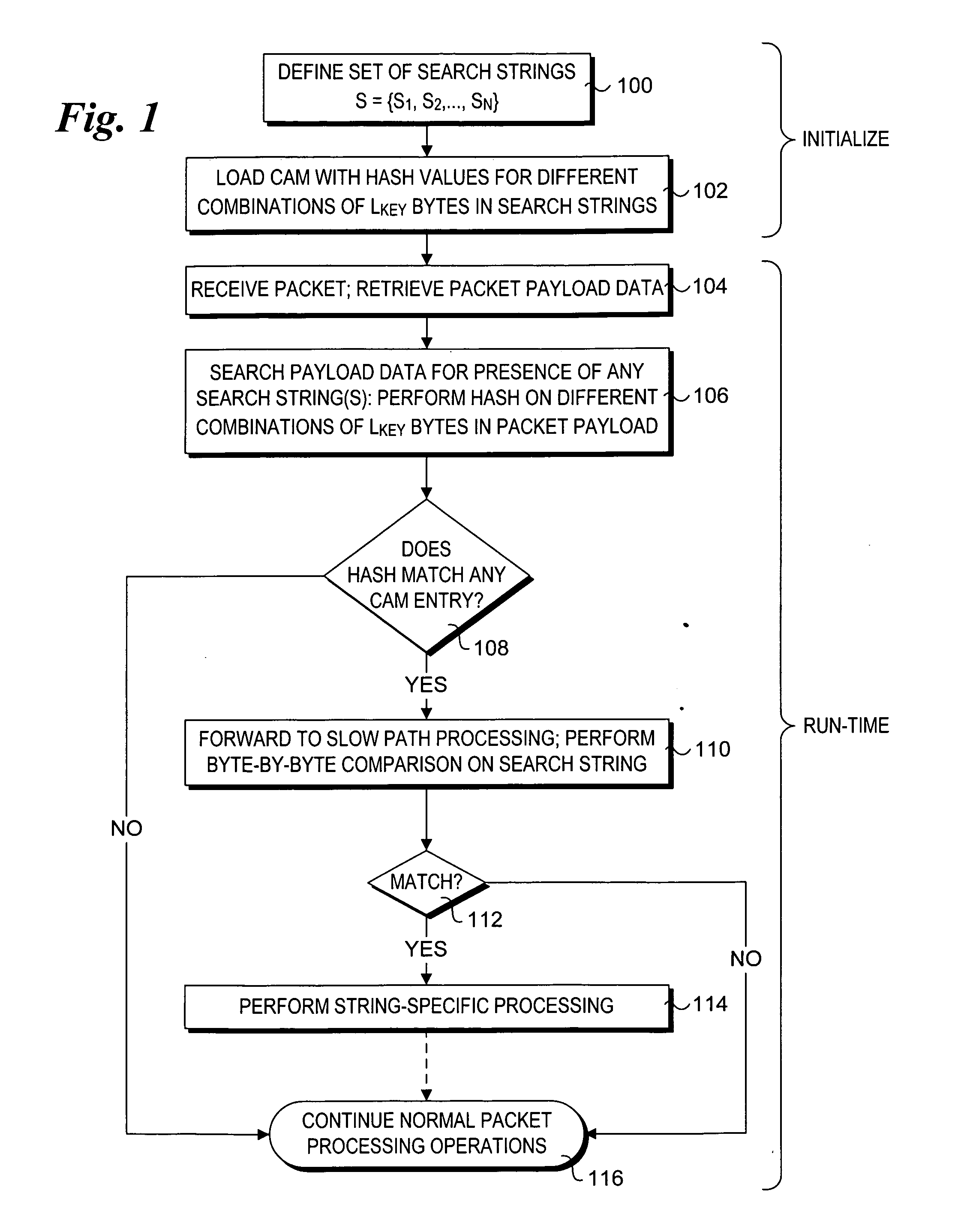
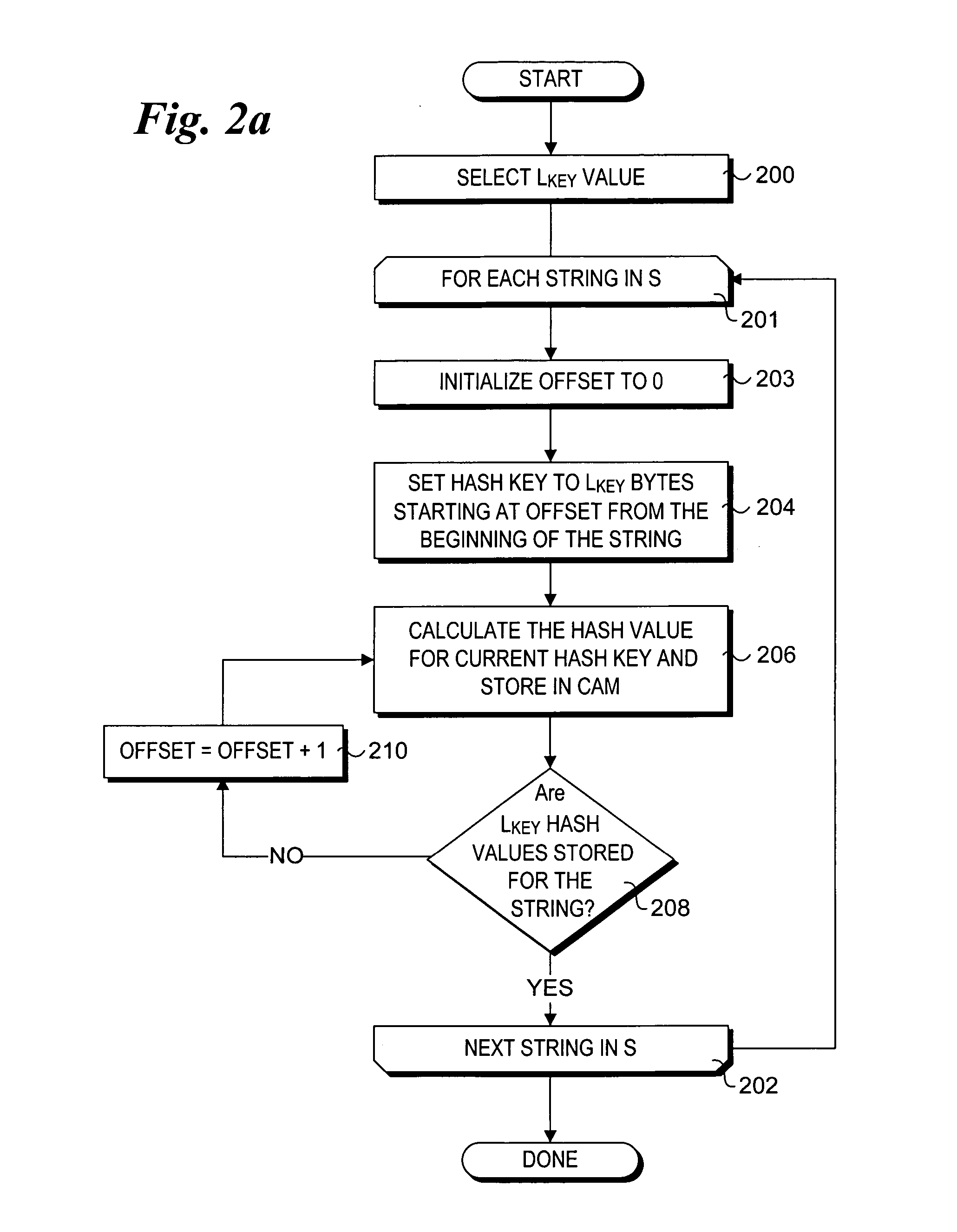
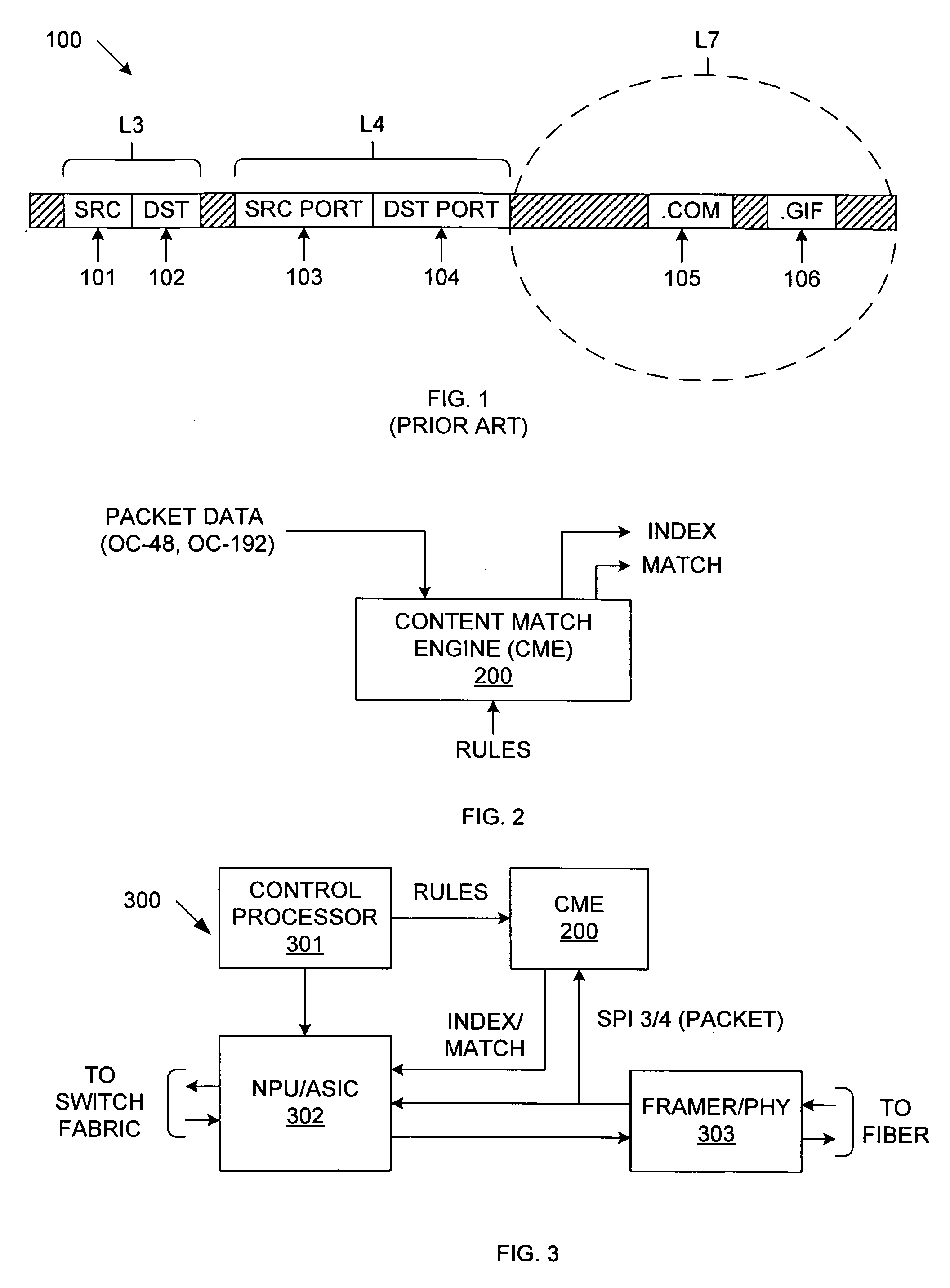
Efficient CAM-based techniques to perform string searches in packet payloads
InactiveUS20060212426A1TransmissionSpecial data processing applicationsData packTheoretical computer science
Efficient Content Addressable Memory (CAM)-based techniques for performing string searches in packet payloads. Hashes are performed on hash keys comprising overlapping sub-strings in one or more search strings. The resulting hash values are stored in a CAM. During packet processing operations, a search of the packet payload data is made to determine if any of the search strings are present. Hashes are performed on non-overlapping sub-strings in the payload data, and the hash results are submitted to the CAM for comparison with the previously-generated search string hash values. If no CAM hits result, the payload data does not contain any of the search strings, while a CAM hit indicates that at least one of the search strings might be present in the payload data. In this instance, a full string comparison is made between the search strings (or an identified search string) and strings in the payload data to verify whether a search string is actually present.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Hierarchical associative memory-based classification system
ActiveUS20060155875A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionTheoretical computer scienceCam
A system and method for efficiently searching long strings of data, such as network messages, is described. The system preferably includes an associative memory structure, having a plurality of content addressable memories (CAMs). The CAMs are hierarchically arranged such the output of at least one CAM is used as the input to a second CAM. Preferably, a top-level CAM receives only a selected portion of the data string or network message as its input. The output of the top-level CAM is then joined with some or all of the remaining portions of the data string to form a new output that is provided to the CAM at the next lower level. The top-level CAM is programmed such that its output is substantially smaller (e.g., has fewer bits) than the selected data string portion that is input to the top-level CAM. The system can thus search data strings that are on the whole far longer than the widths of the respective CAMs forming the memory structure.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
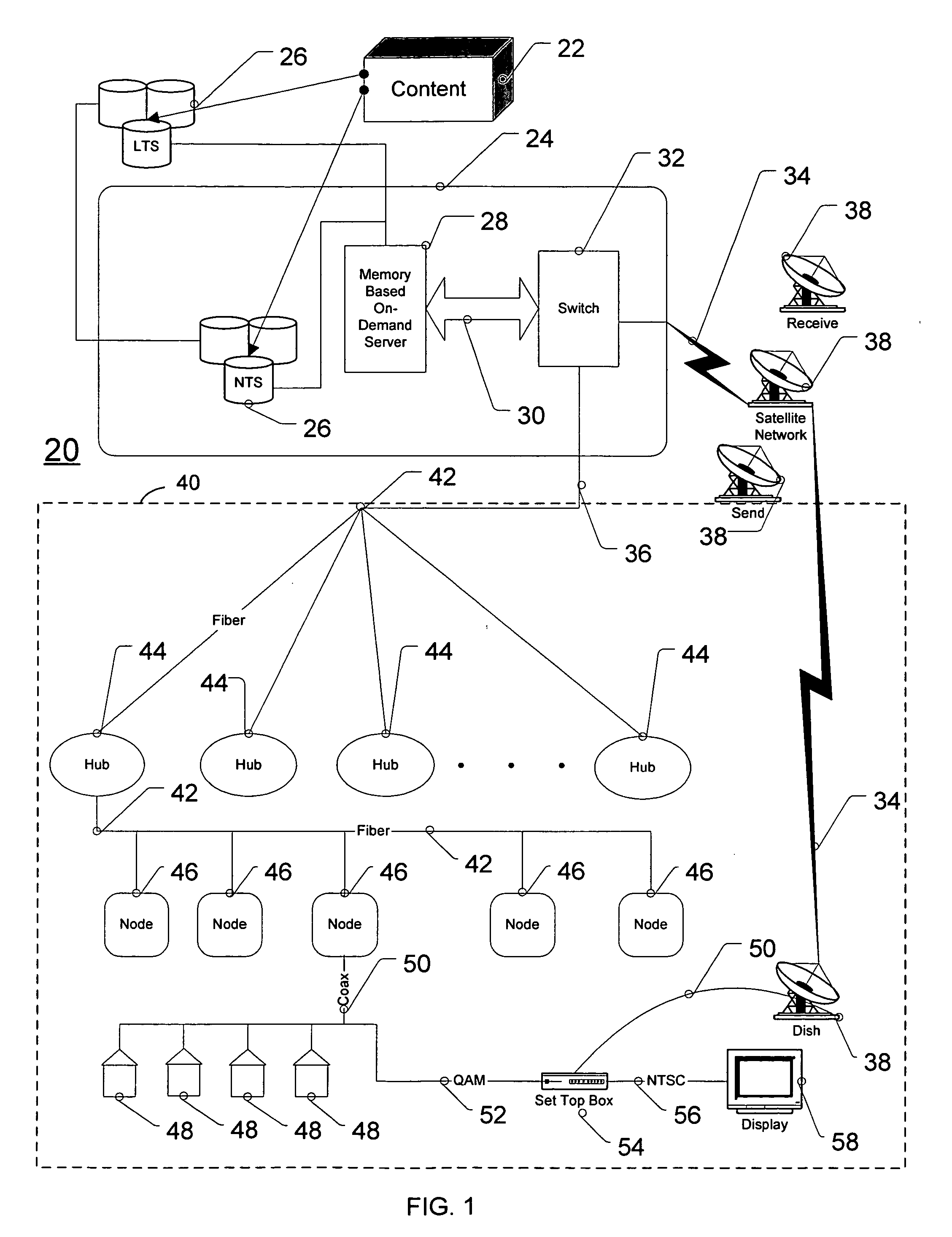
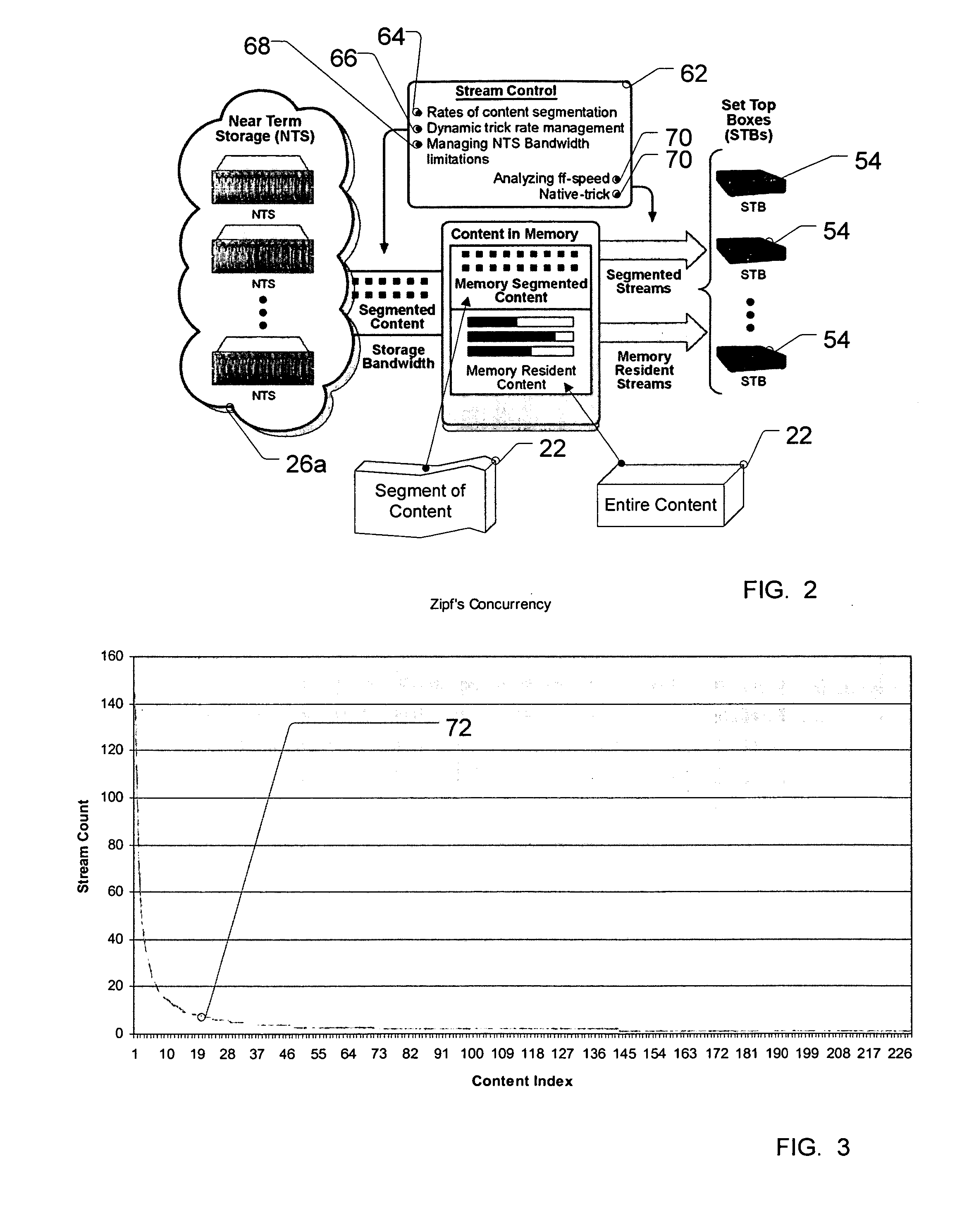
Method and system for resource management in a video on-demand server
ActiveUS20050267948A1Minimizes disk accessImprove overall utilizationMultiple digital computer combinationsTwo-way working systemsOut of memoryResource management
An on-demand server configured to dynamically control and optimize memory utilization while minimizing access to disk storage by monitoring content addressable memory (CAM) usage so as to remove the content from resident CAM memory and page the same adaptively and to eliminate creating separate files for trick playback of content streamed to a customer. The method and system dynamically uses the current concurrency count of the contents to optimize memory utilization so as to swap content in and out of memory as the concurrency values change in conjunction with an on-demand memory based server to provided advantages of optimizing the usage of server resources.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Dram CAM cell with hidden refresh
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Data processing apparatus
ActiveUS20100293342A1Simple structureSmall spacingConditional code generationRegister arrangementsInstruction setContent-addressable memory
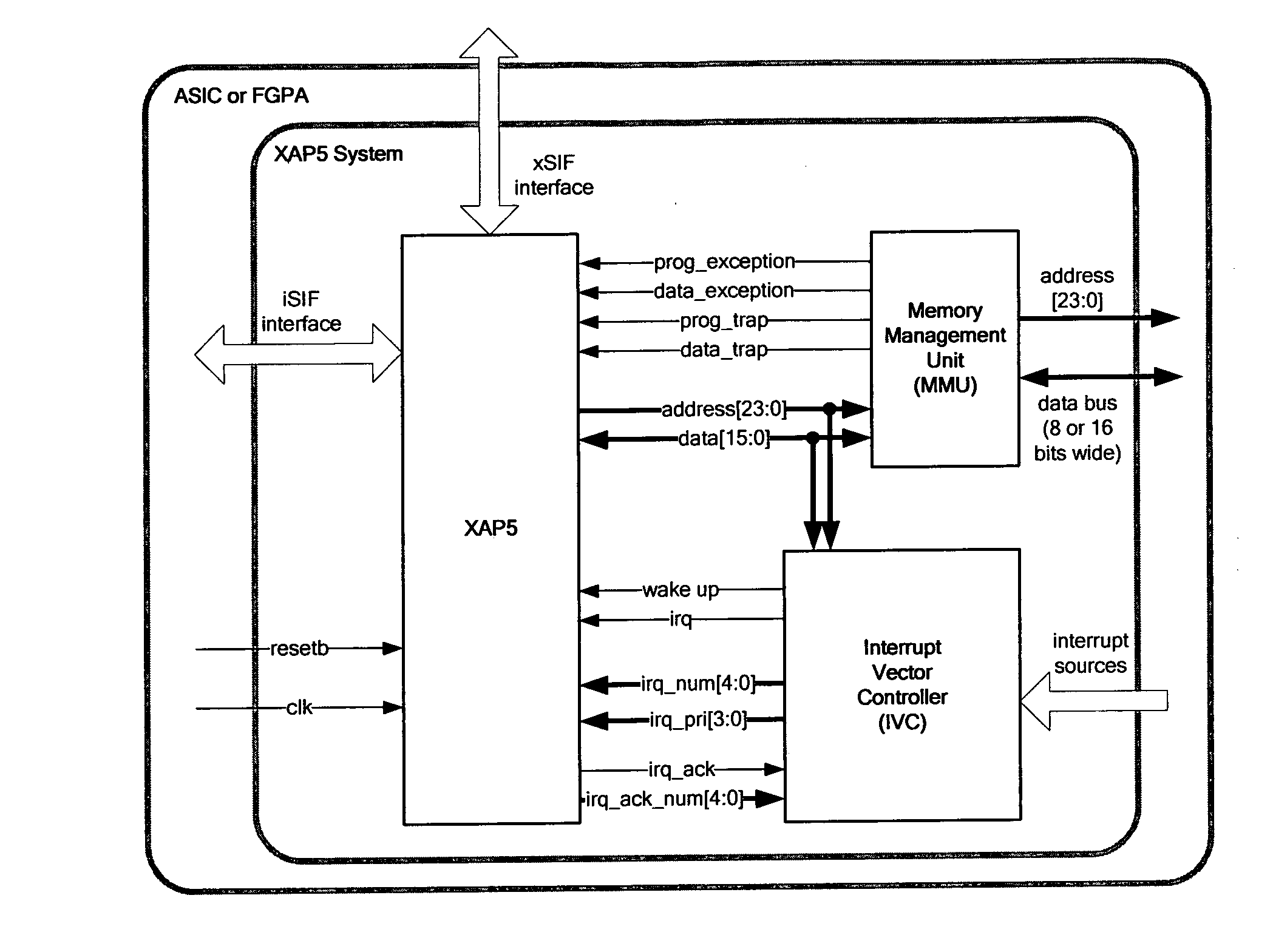
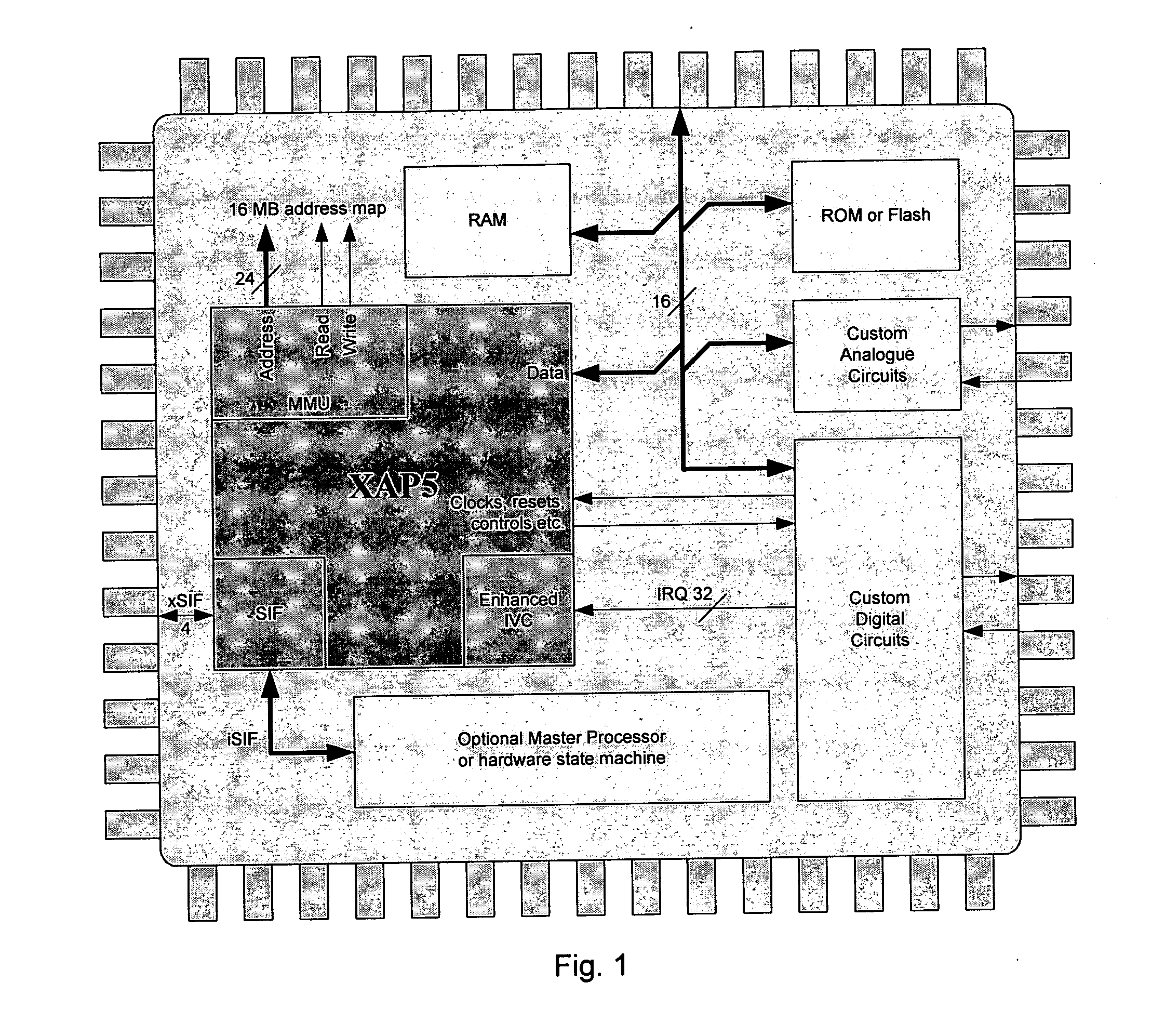
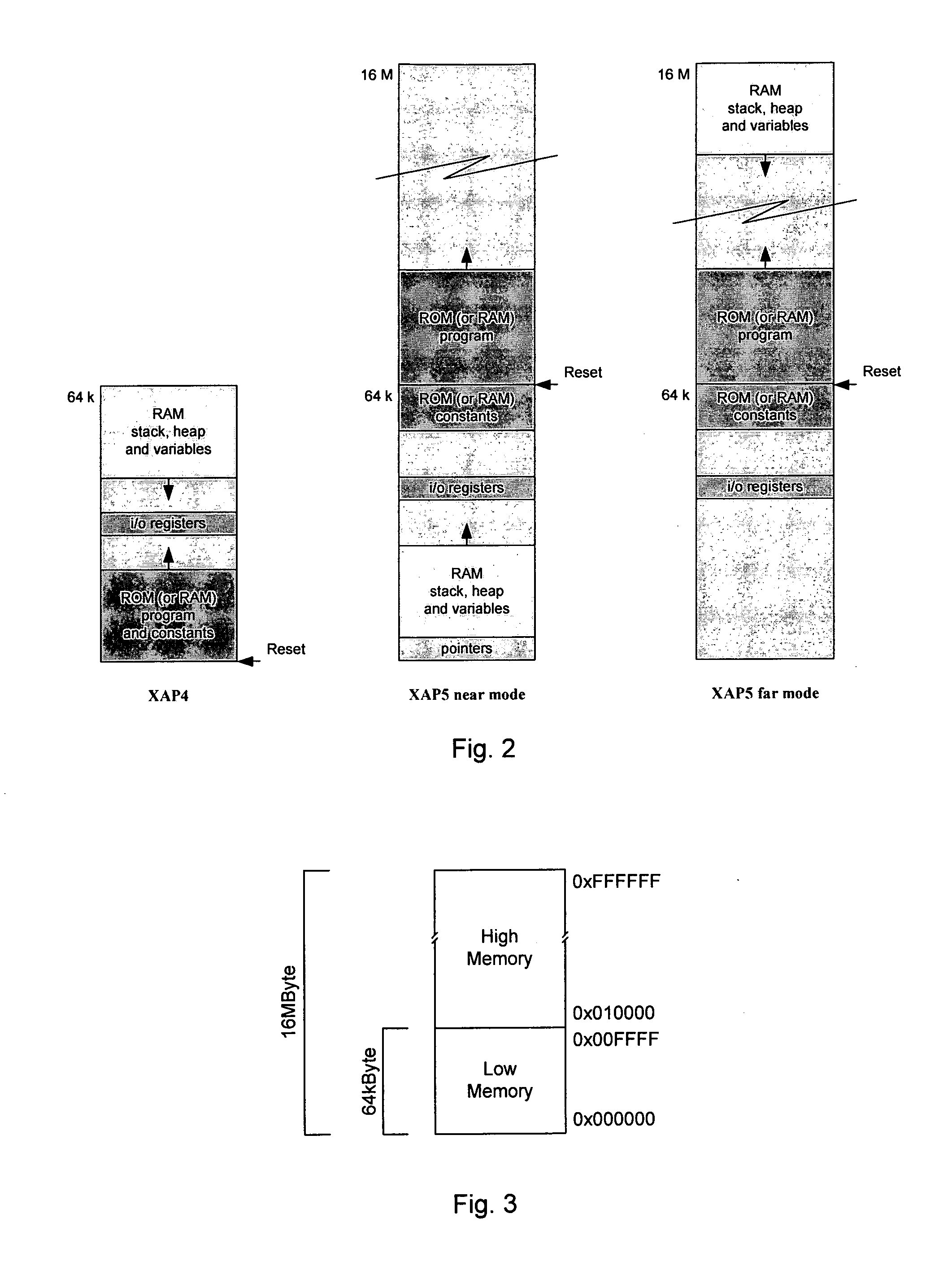
Apparatus comprises a processor configured for operation under a sequence of instructions from an instruction set, wherein said processor comprises: means for conditionally inhibiting at least one type of trap, interrupt or exception (TIE) event, wherein, when operating under a sequence of instructions, said inhibition means is inaccessible by said instructions to inhibit the or each type of TIE event, without interrupting said sequence. A data processing apparatus includes a processor adapted to operate under control of program code comprising instructions selected from an instruction set, the apparatus comprising: a predefined memory space providing a predefined addressable memory for storing program code and data, a larger memory space providing a larger addressable memory, means for accessing program code and data within the predefined memory space, and means for controlling the access means so as to enable the access means to access program code located within the larger memory space.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE CONSULTANTS LTD
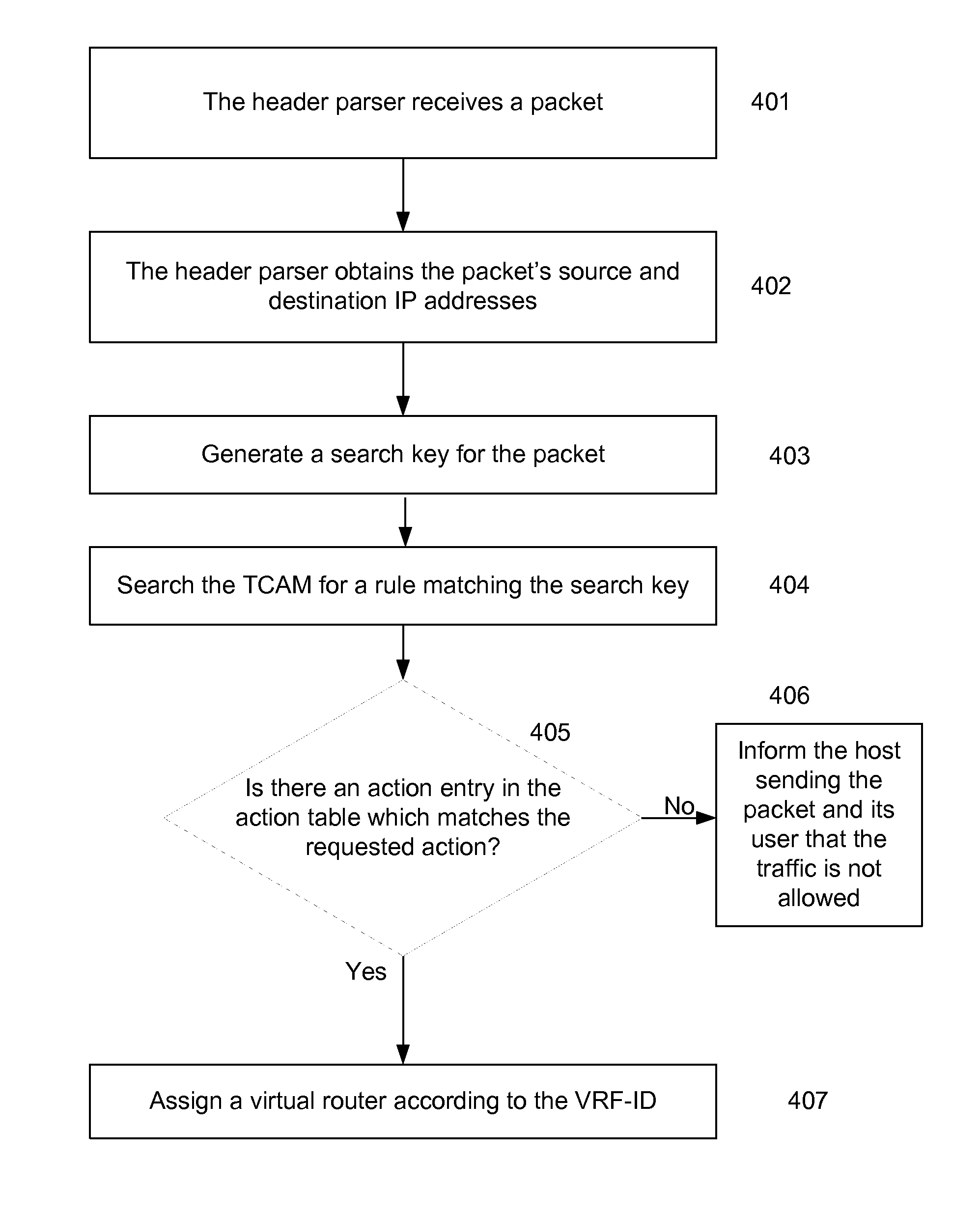
Policy-based virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) assignment
A method for increasing resolution of virtual router assignment in a computer network. An incoming packet may be parsed to obtain its source and destination IP addresses. With the obtained IP addresses, and in some cases other information about the packet, a classification engine may perform a multi-field classification in a memory such as a TCAM (Ternary Content-Addressable Memory). The classification result may point to an action entry in an action table in a memory, e.g., an SRAM (Static random access memory). The action entry may indicate policy-based setting of the virtual router, and the VRF-ID. A virtual router is then assigned according to the VRF-ID. A group based classification in layer 3 of the present invention may avoid using a table to define segregation policies between hosts pair by pair.
Owner:MARVELL ISRAEL MISL
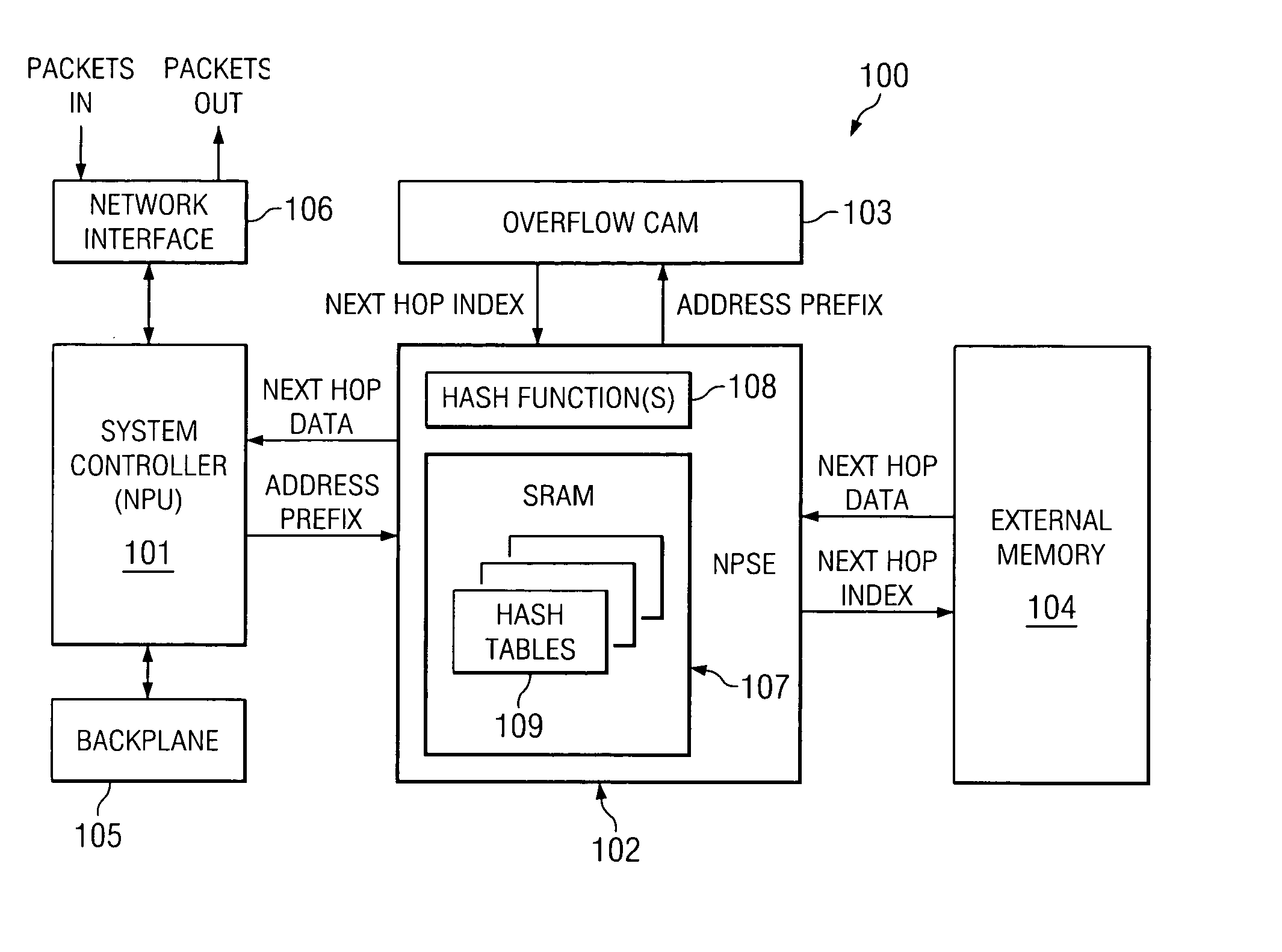
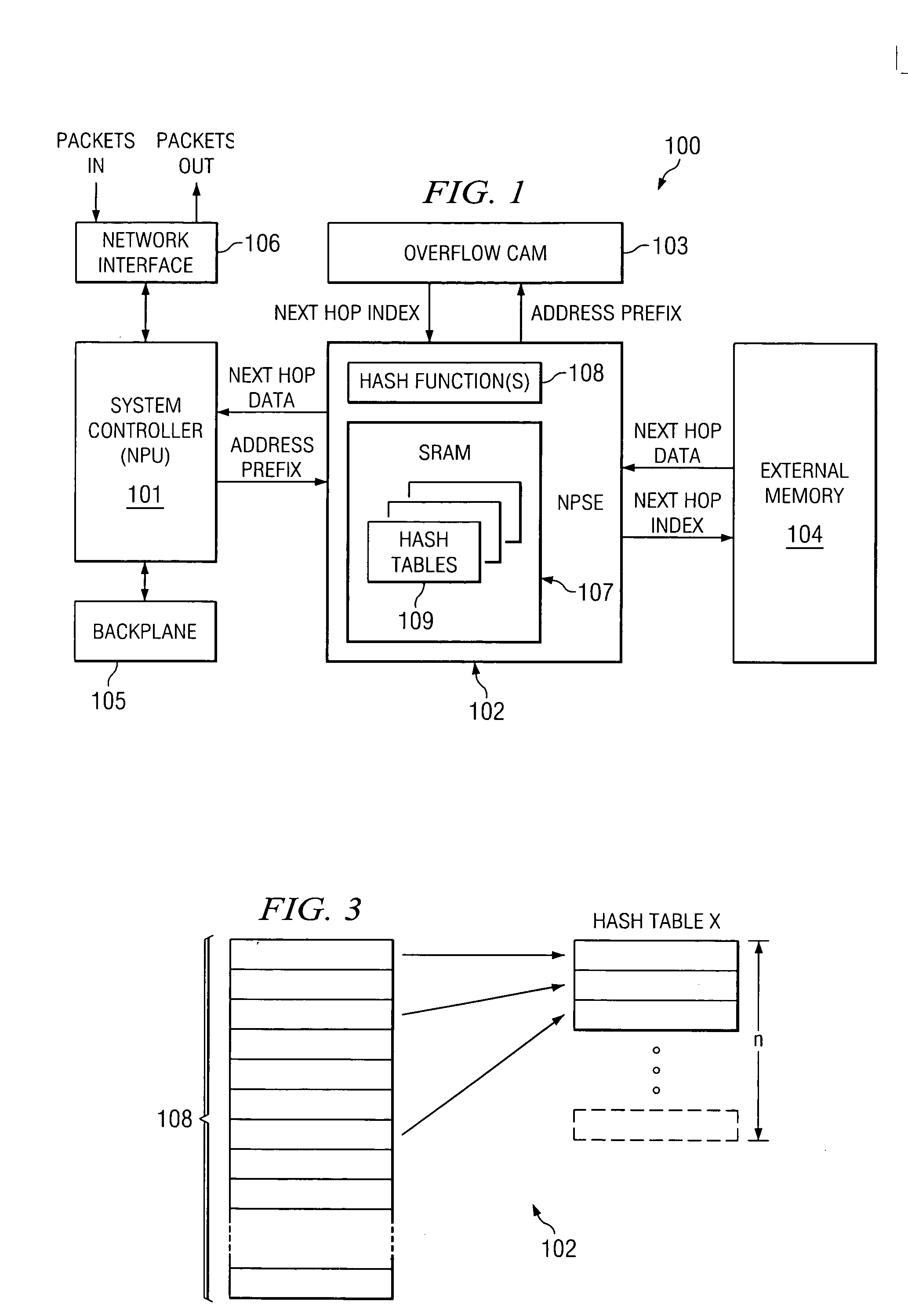
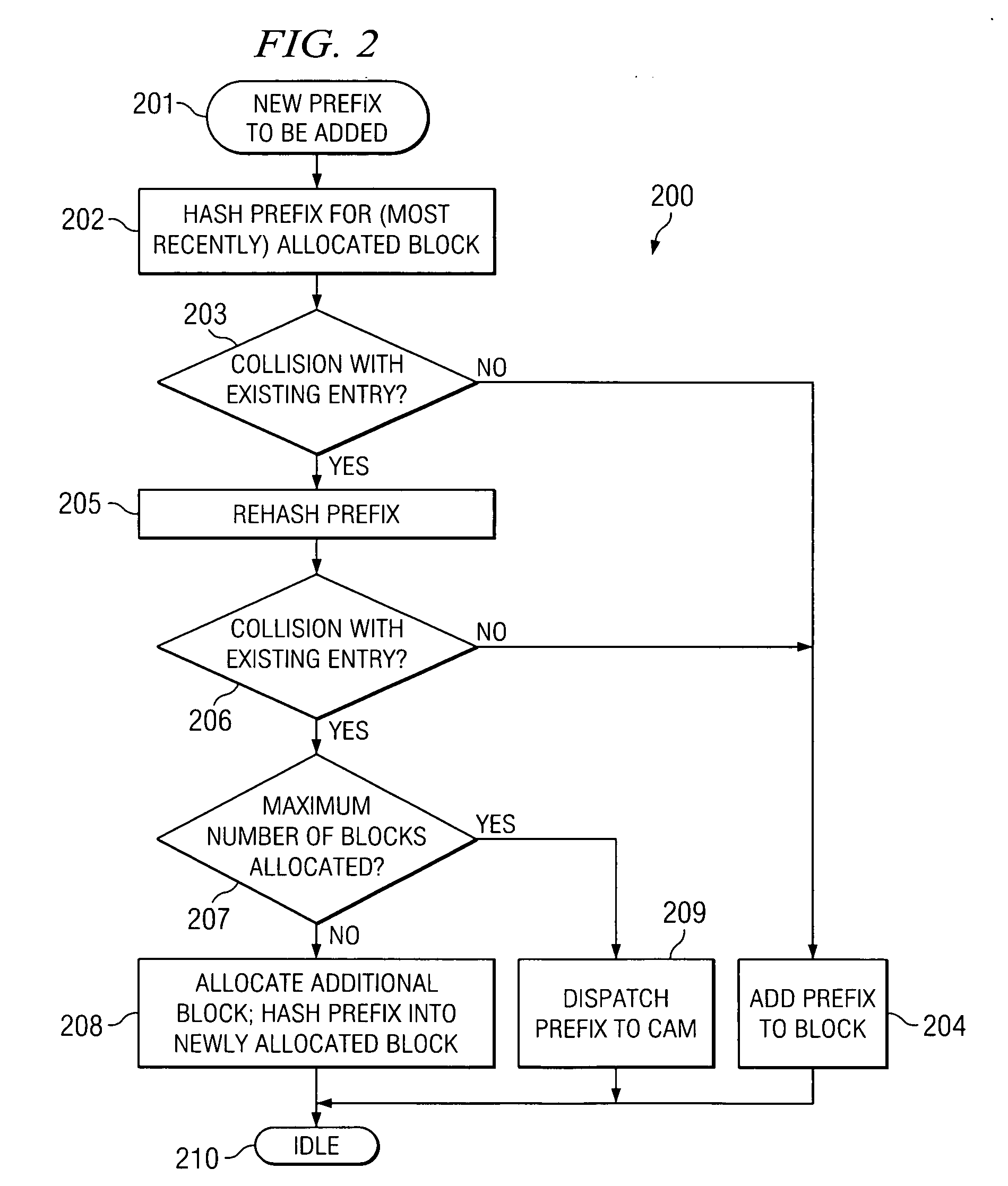
Apparatus and method using hashing for efficiently implementing an IP lookup solution in hardware
ActiveUS20050141519A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsCircuit switching systemsHash tableContent-addressable memory
Internet Protocol address prefixes are hashed into hash tables allocated memory blocks on demand after collisions occur for both a first hash and a single rehash. The number of memory blocks allocated to each hash table is limited, with additional prefixes handled by an overflow content addressable memory. Each hash table contains only prefixes of a particular length, with different hash tables containing prefixes of different lengths. Only a subset of possible prefix lengths are accommodated by the hash tables, with a remainder of prefixes handled by the content addressable memory or a similar alternate address lookup facility.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
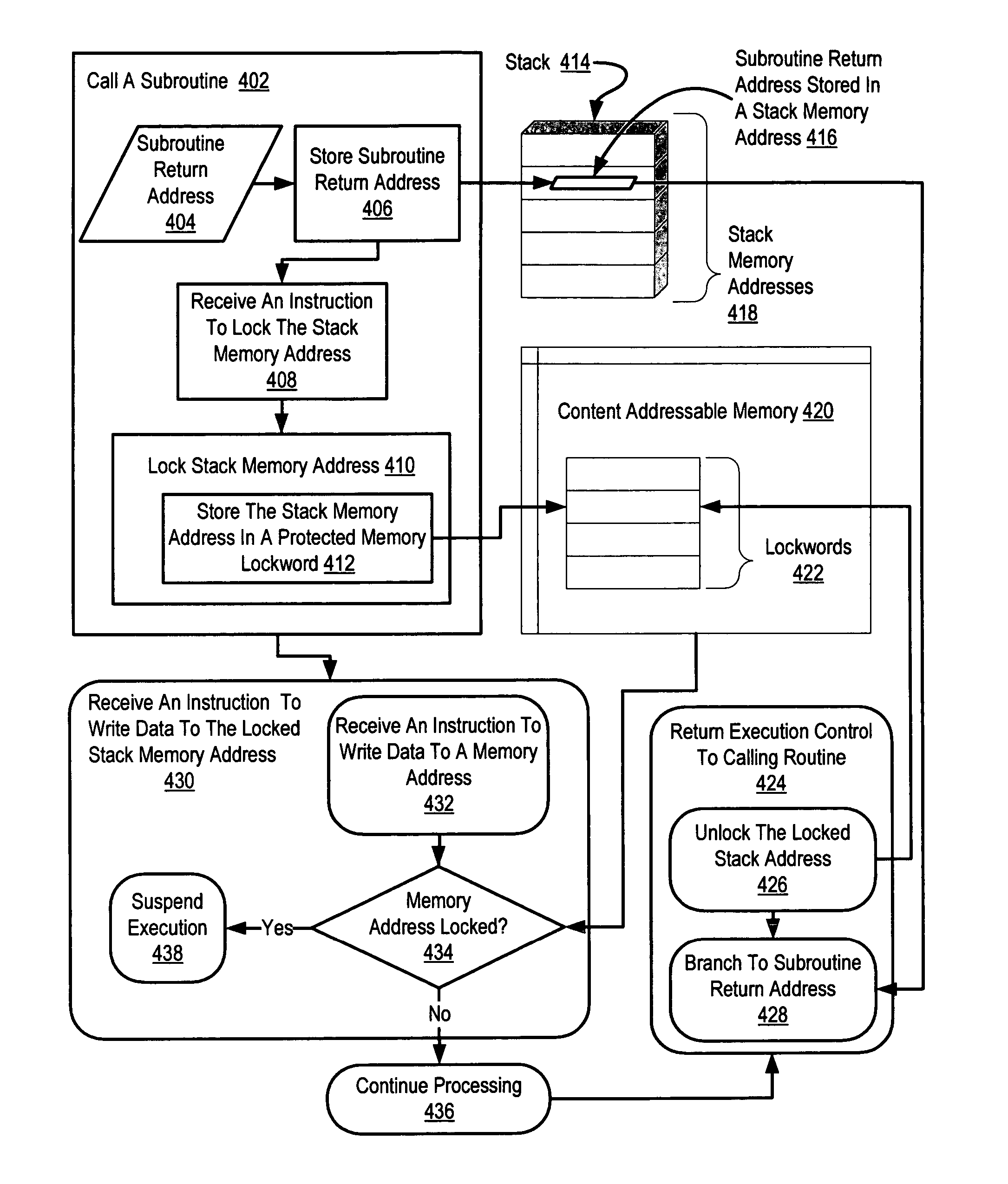
Write protection of subroutine return addresses
Exemplary methods, systems, and products are described that operate generally by moving subroutine return address protection to the processor itself, in effect proving atomic locks for subroutine return addresses stored in a stack, subject to application control. More particularly, exemplary methods, systems, and products are described that write protect subroutine return addresses by calling a subroutine, including storing in a stack memory address a subroutine return address and locking, by a computer processor, the stack memory address against write access. Calling a subroutine may include receiving in the computer processor an instruction to lock the stack memory address. Locking the stack memory address may be carried out by storing the stack memory address in a protected memory lockword. A protected memory lockword may be implemented as a portion of a protected content addressable memory.
Owner:IBM CORP
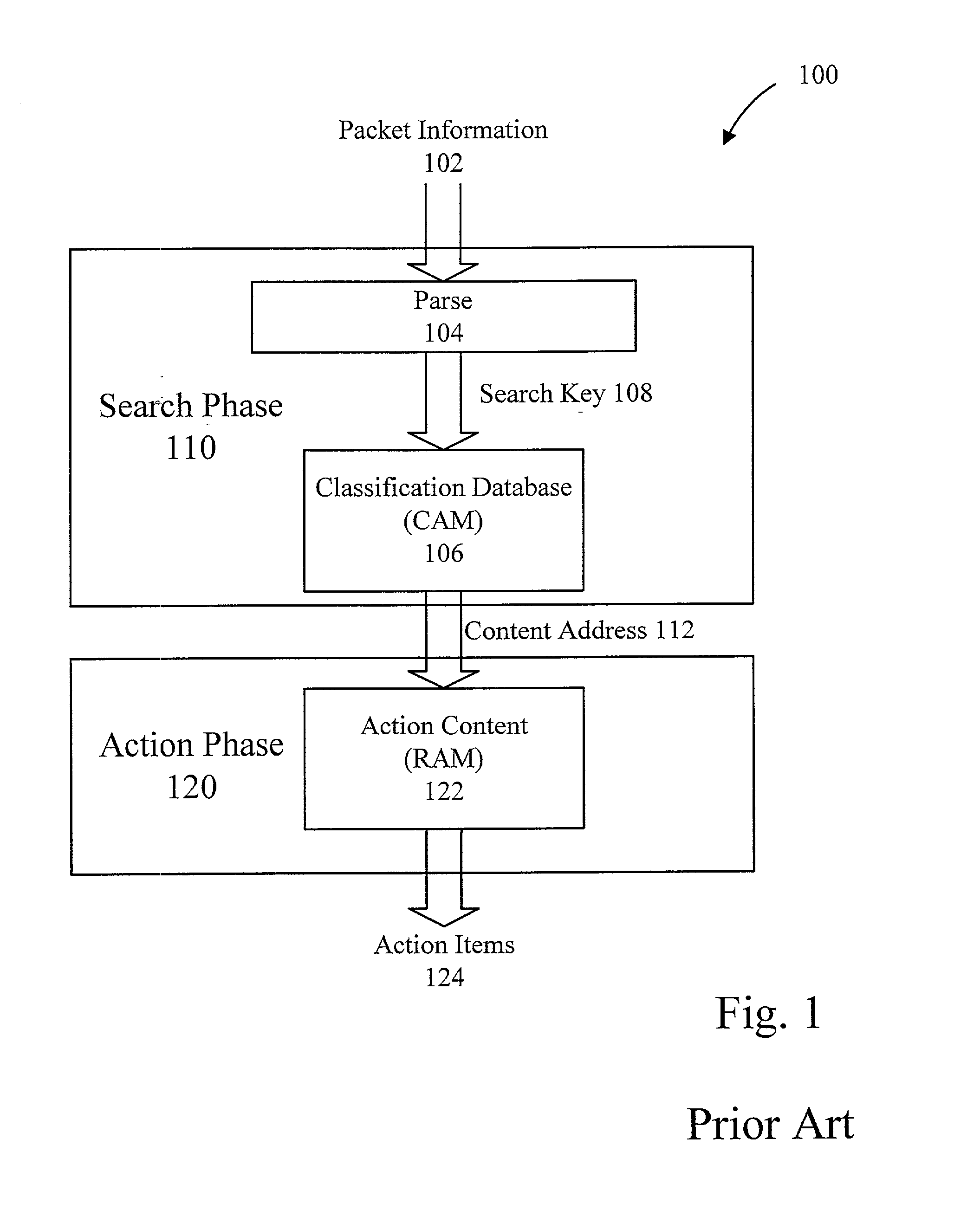
Packet classification
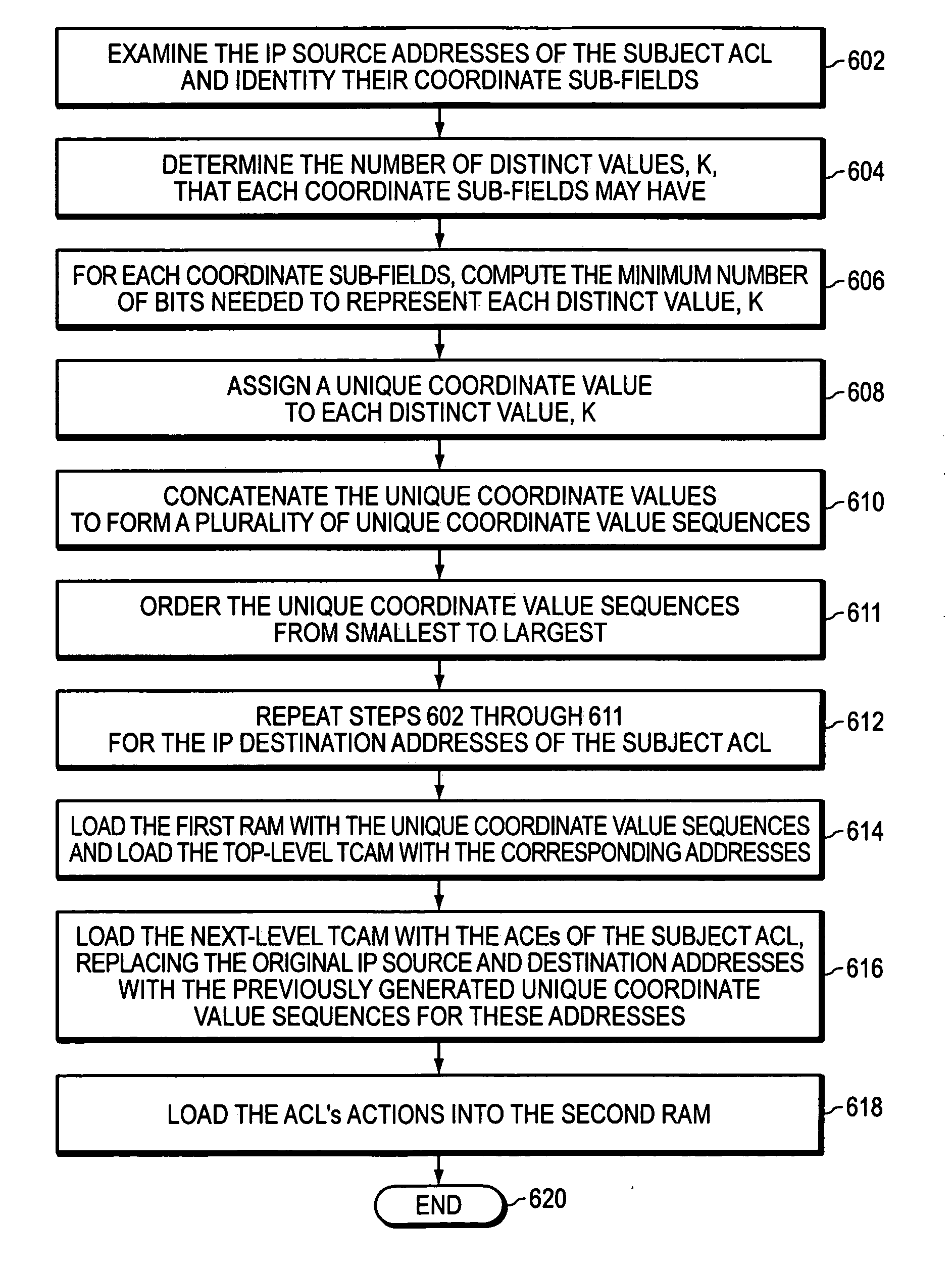
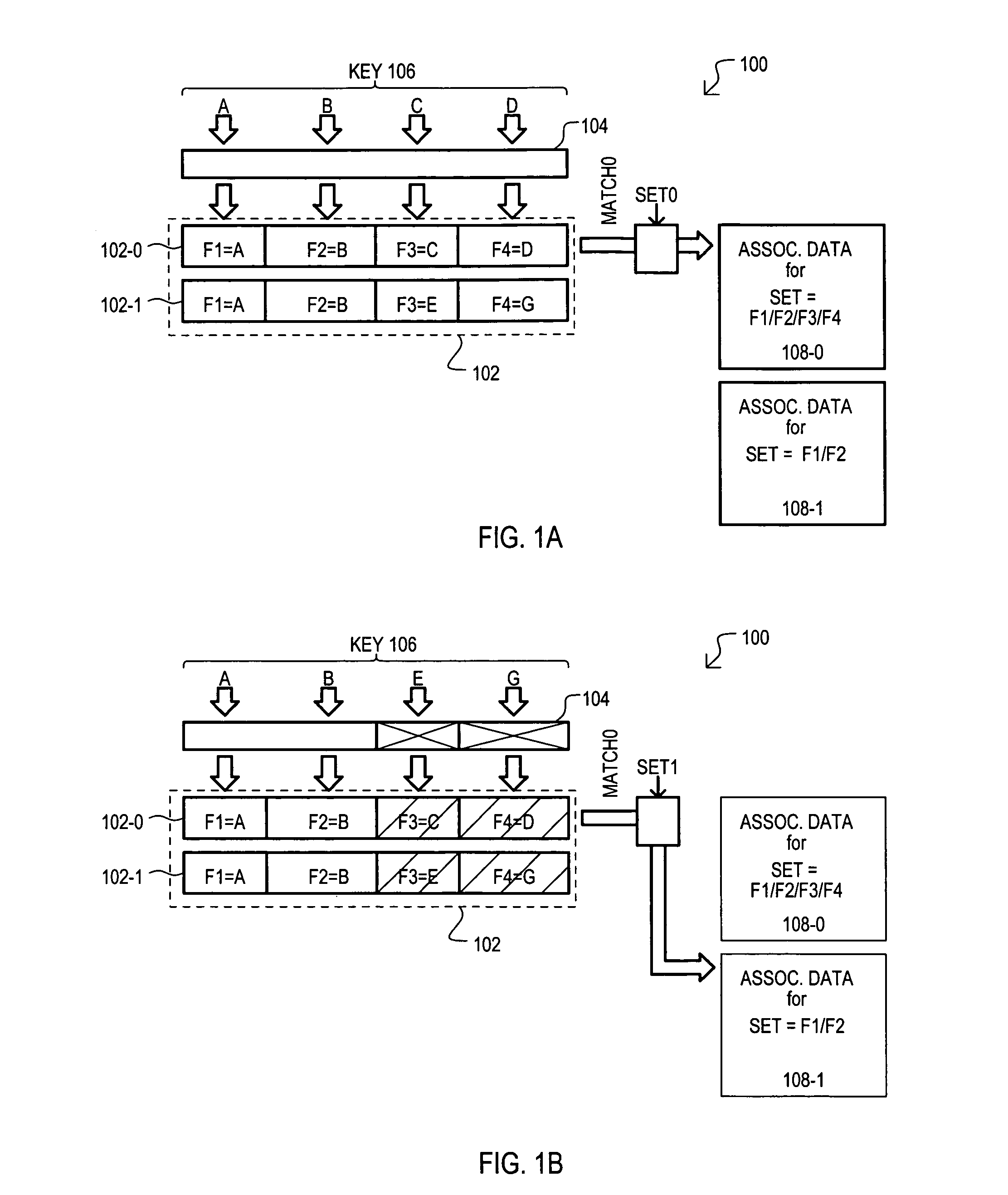
InactiveUS7193997B2Efficient use ofEffective structureData switching by path configurationSecuring communicationData processing systemClassification methods
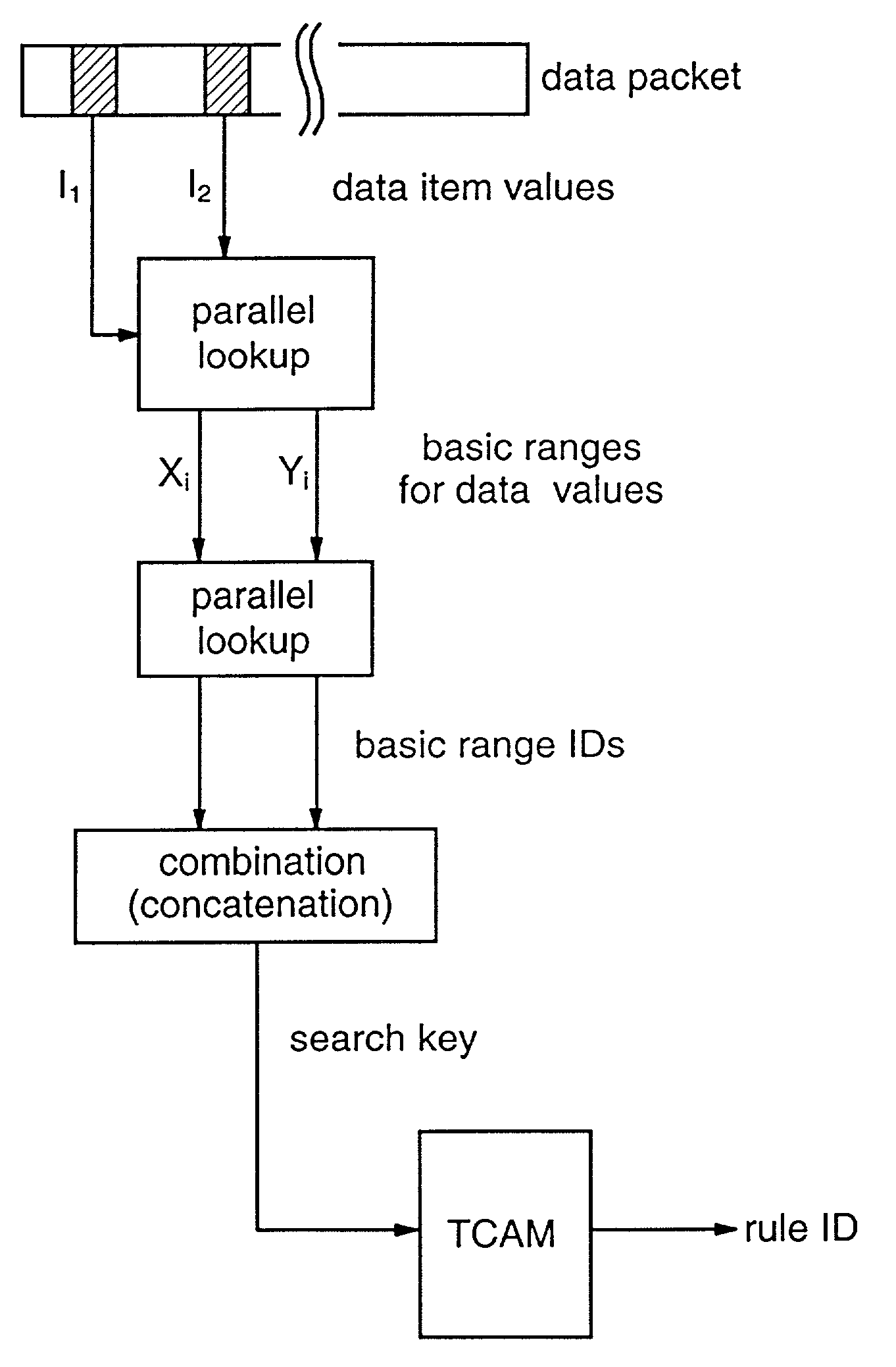
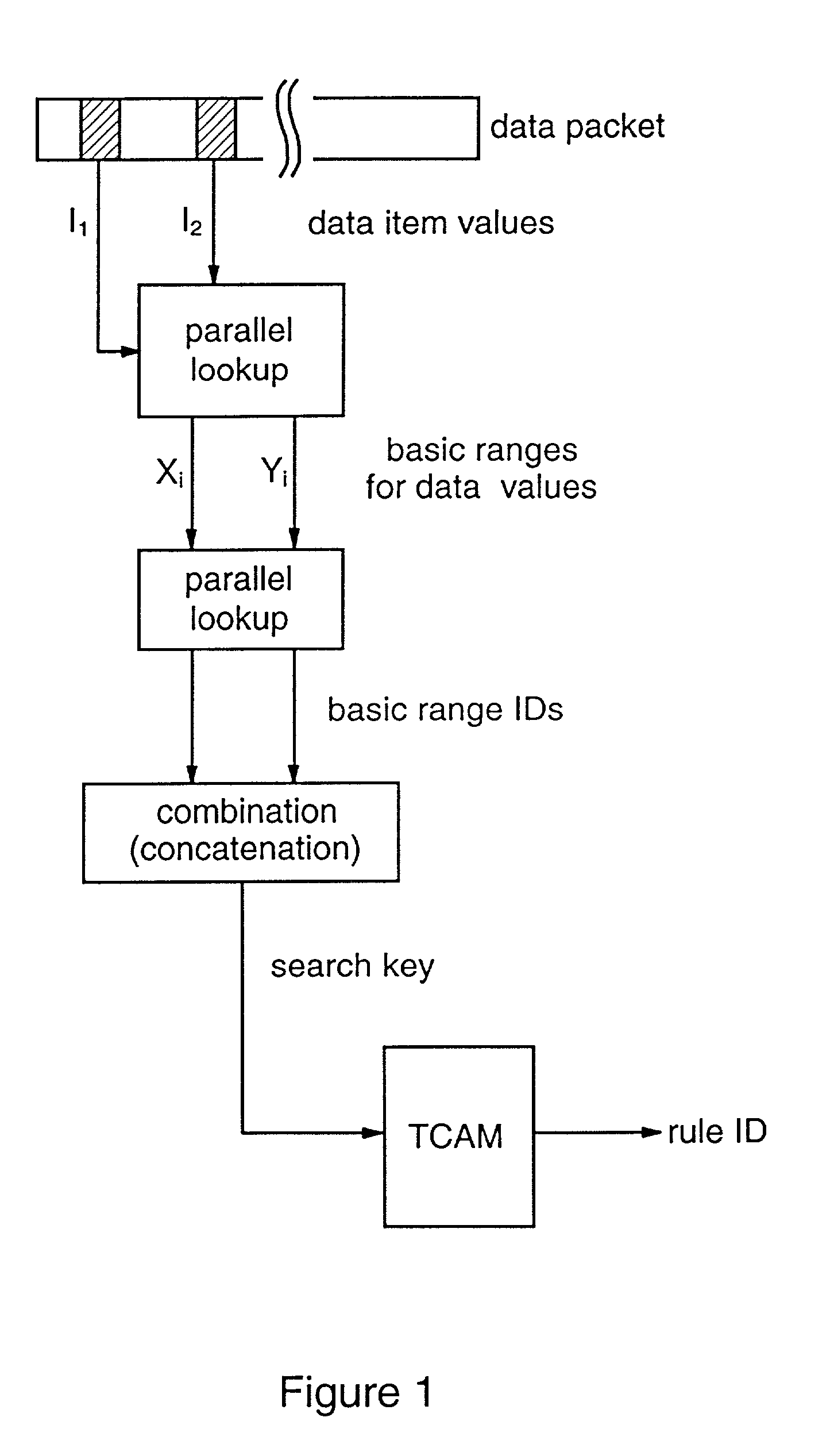
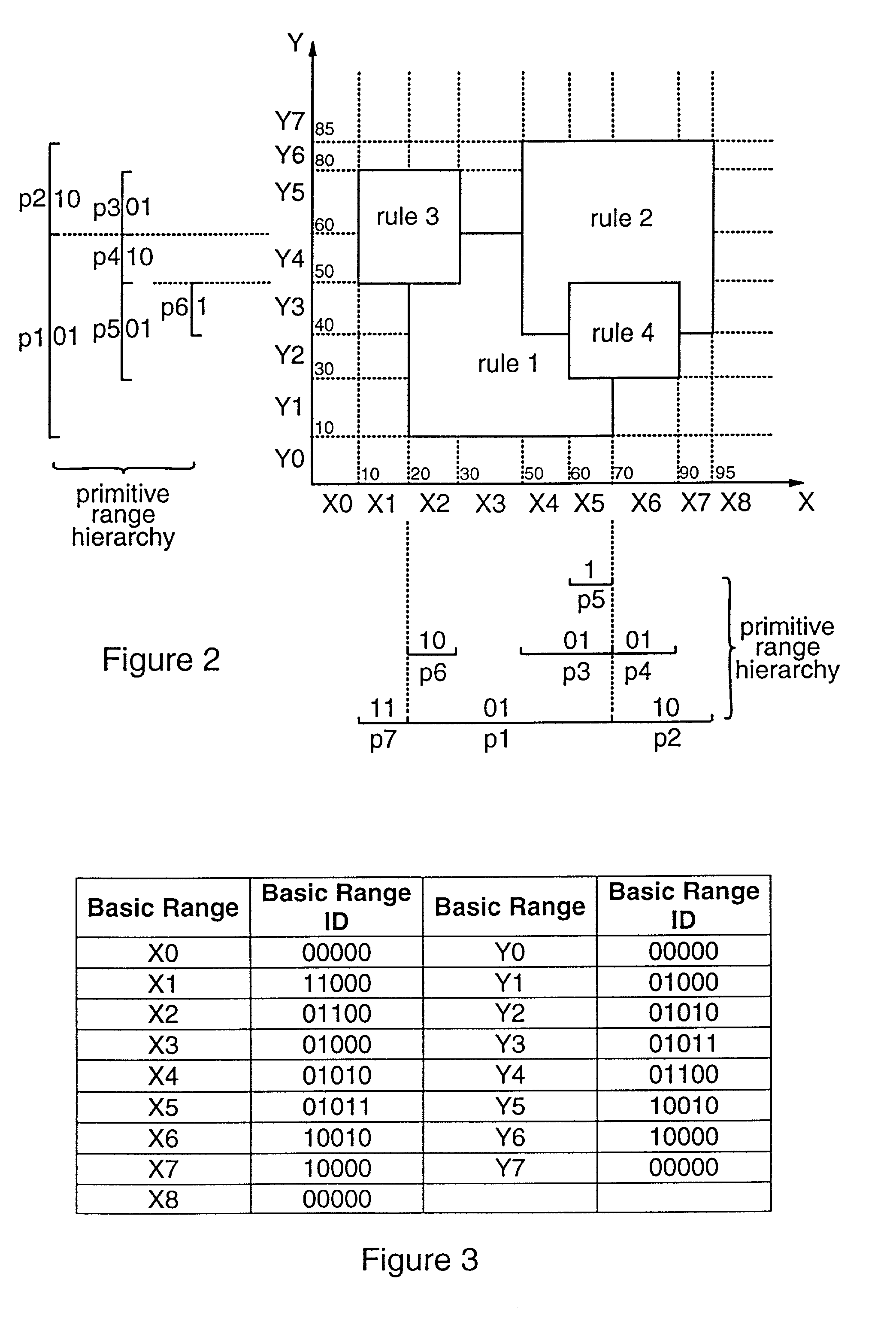
Methods and apparatus are provided for classifying data packets in data processing systems. A first packet classification method determines which of a plurality of predefined processing rules applies to a data packet, where each rule is associated with a range of possible data values in each of a plurality of dimensions (X,Y) corresponding to respective data items in the packet format. For each dimension (X,Y), it is determined which of a set of predefined basic ranges contains the corresponding data value (I1, I2) from the packet, where the basic ranges correspond to respective non-overlapping value ranges between successive rule range boundaries in the dimension. For the basic range so determined for each dimension, a corresponding basic range identifier is selected from a set of predefined basic range identifiers corresponding to respective basic ranges in that dimension. For each of at least two dimensions (X,Y), the basic range identifiers comprise respective pD-bit strings generated independently for that dimension by a process of deriving a primitive range hierarchy based on the rule ranges in that dimension. The resulting basic range identifiers, one for each dimension, are then combined to produce a search key which is supplied to a ternary content-addressable memory (5). In the memory (5), the search key is compared with a set of ternary rule vectors, each associated with a particular rule and derived for that rule from the aforementioned hierarchies, to identify at least one rule which applies to the data packet. A second method classifies data packets according to the values in respective data packets of a single, predetermined data item (DA) in the data packet format, where a plurality of classification results are predefined for respective ranges of values of the data item (DA). Here the data item (DA) in the packet is first segmented. The resulting segments are then equated to different dimensions (X,Y) of a multidimensional packet classification problem and are processed in a similar manner to identify a classification result for the packet.
Owner:IBM CORP
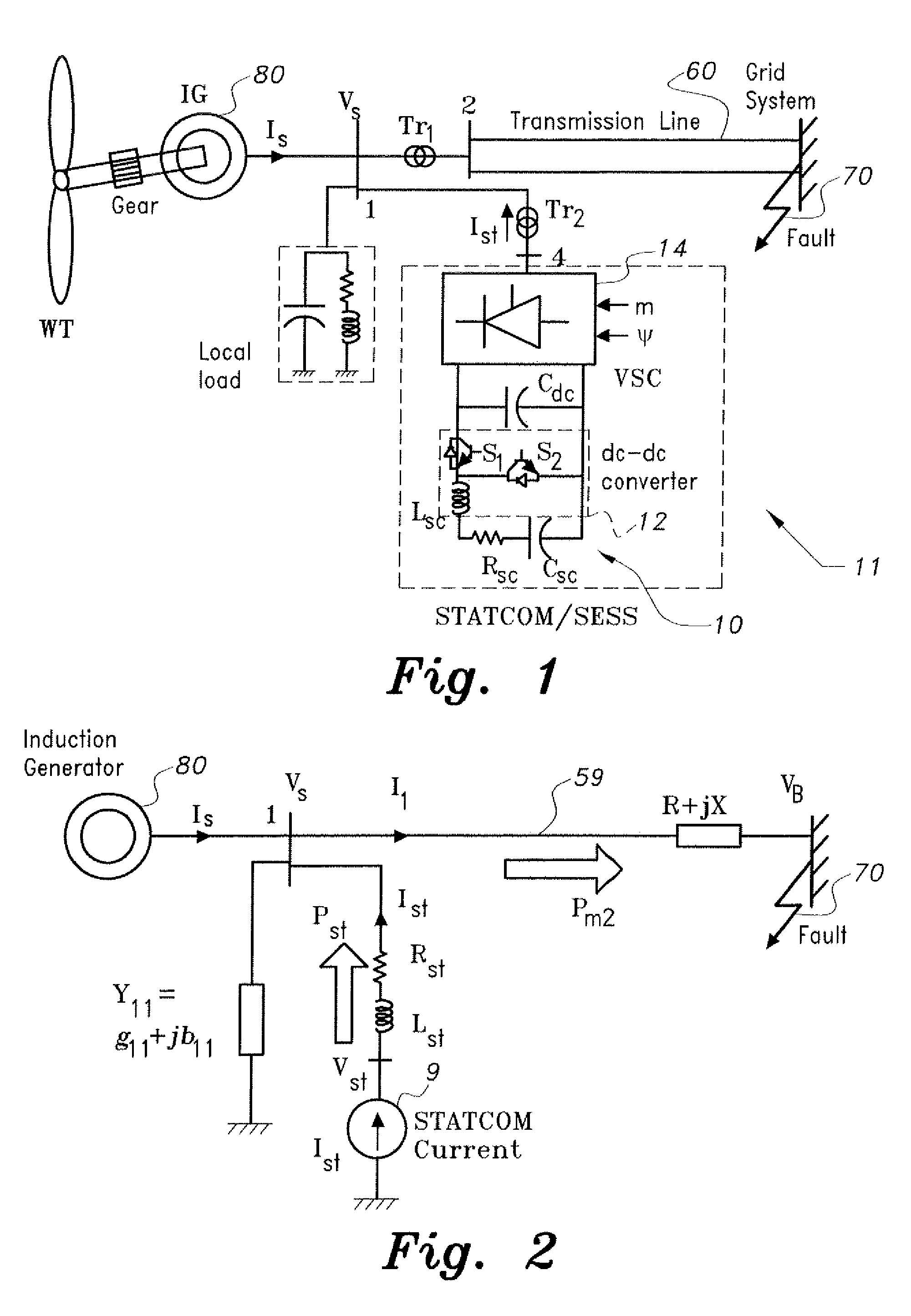
Supercapacitor-based grid fault ride-through system
InactiveUS20120280569A1Improve power densityImprove efficiencyFlexible AC transmissionBatteries circuit arrangementsDynamic modelsEngineering
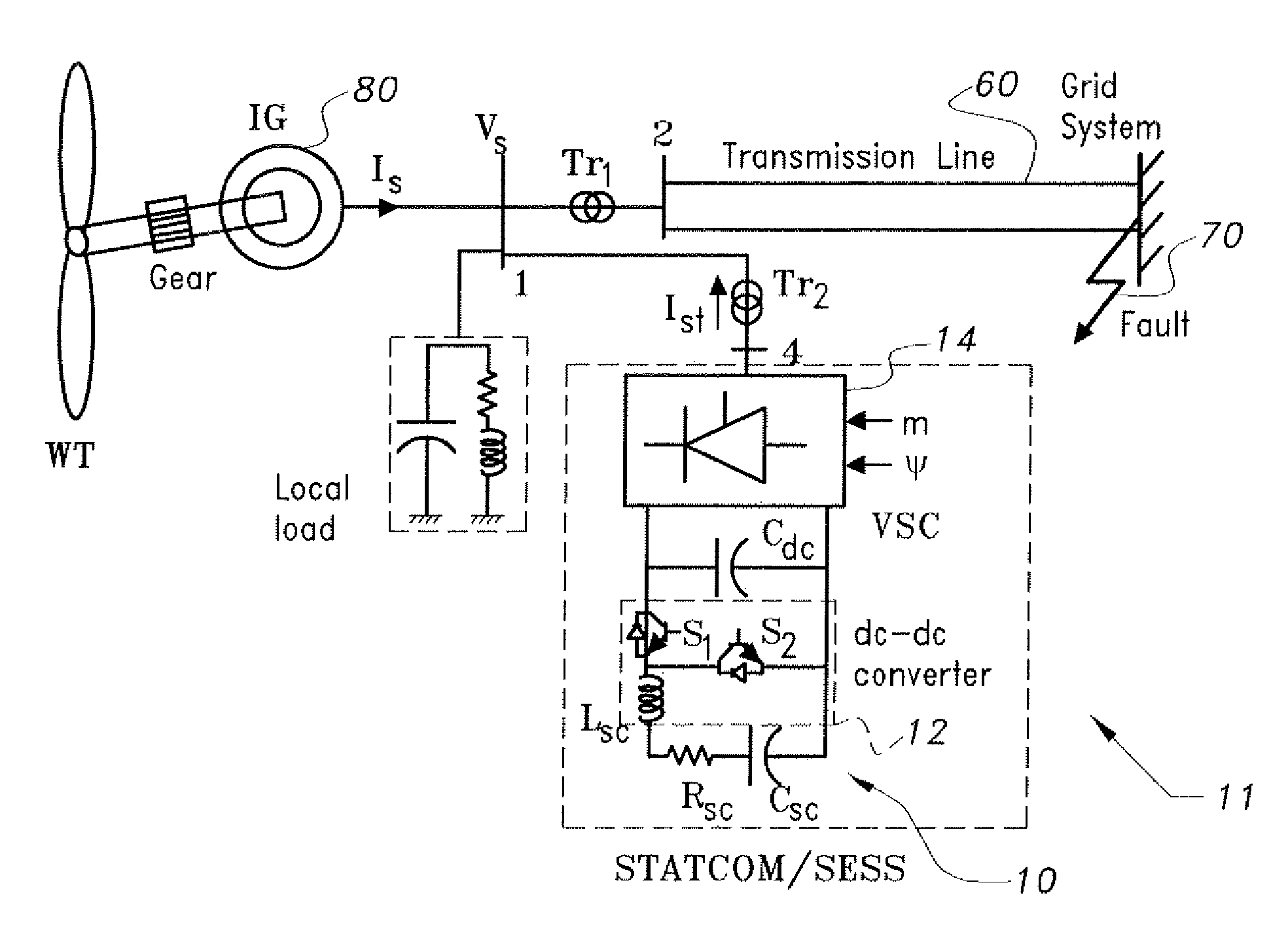
The supercapacitor-based grid fault ride-through system provides a dynamic model of a wind generation system including a Voltage Source Converter (VSC), which functions as a Static Compensator (STATCOM). The power control capability of the STATCOM is extended by incorporating energy stored in a supercapacitor. The system implements a vector control technique based on the decoupling of real and reactive power. Simulation results show that a fixed speed induction generator is capable of withstanding a significant grid fault when aided by the supercapacitor-based grid fault ride-through system. Moreover, the induction generator regains its pre-fault status immediately after the fault is cleared.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
Switching circuit implementing variable string matching
InactiveUS20070083646A1Preventing subsequent erroneous matchReduce processing timeDigital storageMultiple digital computer combinationsData packTheoretical computer science
A content matching engine (CME) uses a content addressable memory (CAM) array that stores a plurality of strings in separate entries. The strings define one or more rules to be matched. The strings of each rule are linked, thereby providing a required order. The strings of each rule can be linked by per-entry counters associated with each string, or by a state machine. The strings in the CAM array are compared with a packet, which is shifted one symbol at a time (because the strings can start on any boundary). When the CAM detects a match, the CAM skips over the string that resulted in the match, thereby preventing erroneous matches. The CAM allows parallel matching to be performed for multiple rules. If the contents of a packet match all of the strings of a rule, in order, then the CME asserts a match / index signal that identifies the matched rule.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Methods for nucleic acid and polypeptide similarity search employing content addressable memories
InactiveUS20060020397A1Character and pattern recognitionBiological testingBiopolymerContent-addressable memory
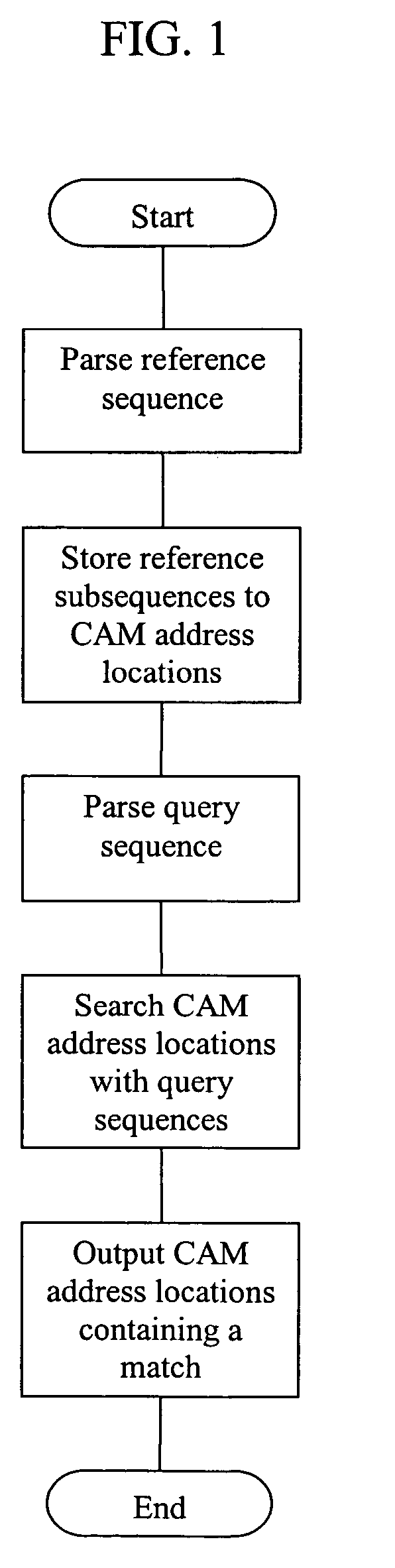
This invention is directed to systems and methods for comparing the similarity of biopolymer sequences. Algorithms useful in the systems and methods of the invention include (a) parsing one or more biopolymer reference sequences to produce a plurality of reference subsequences; (b) storing the plurality of reference subsequence to a plurality of CAM address locations; (c) parsing a query sequence to produce a plurality of query subsequences; (d) searching the plurality of reference subsequences stored in the plurality of CAM address locations with the plurality of query subsequences, and (e) producing an output of CAM address locations containing at least one match, the at least one match indicating sequence similarity between the reference subsequence stored in the CAM address location and the query subsequence producing the at least one match.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
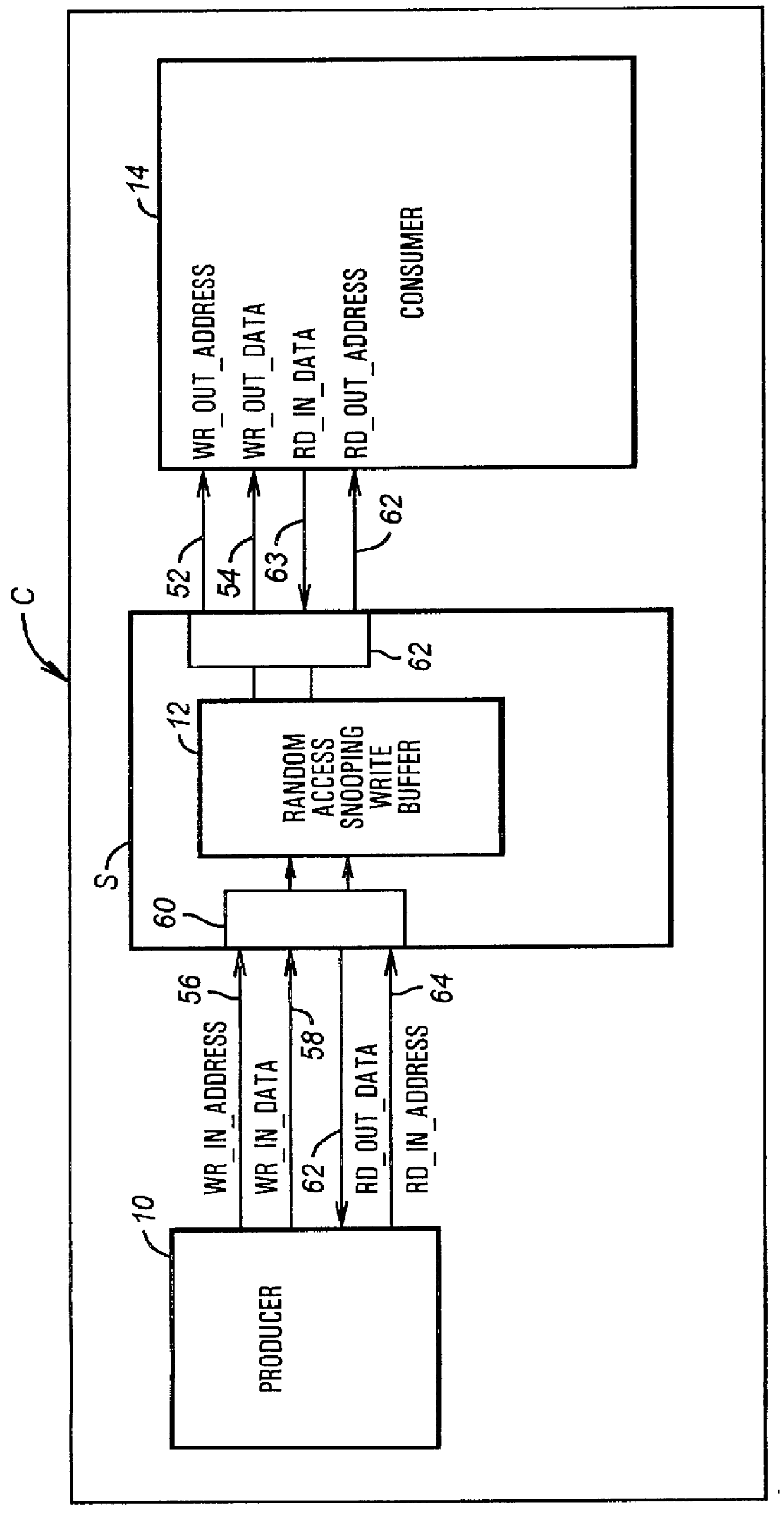
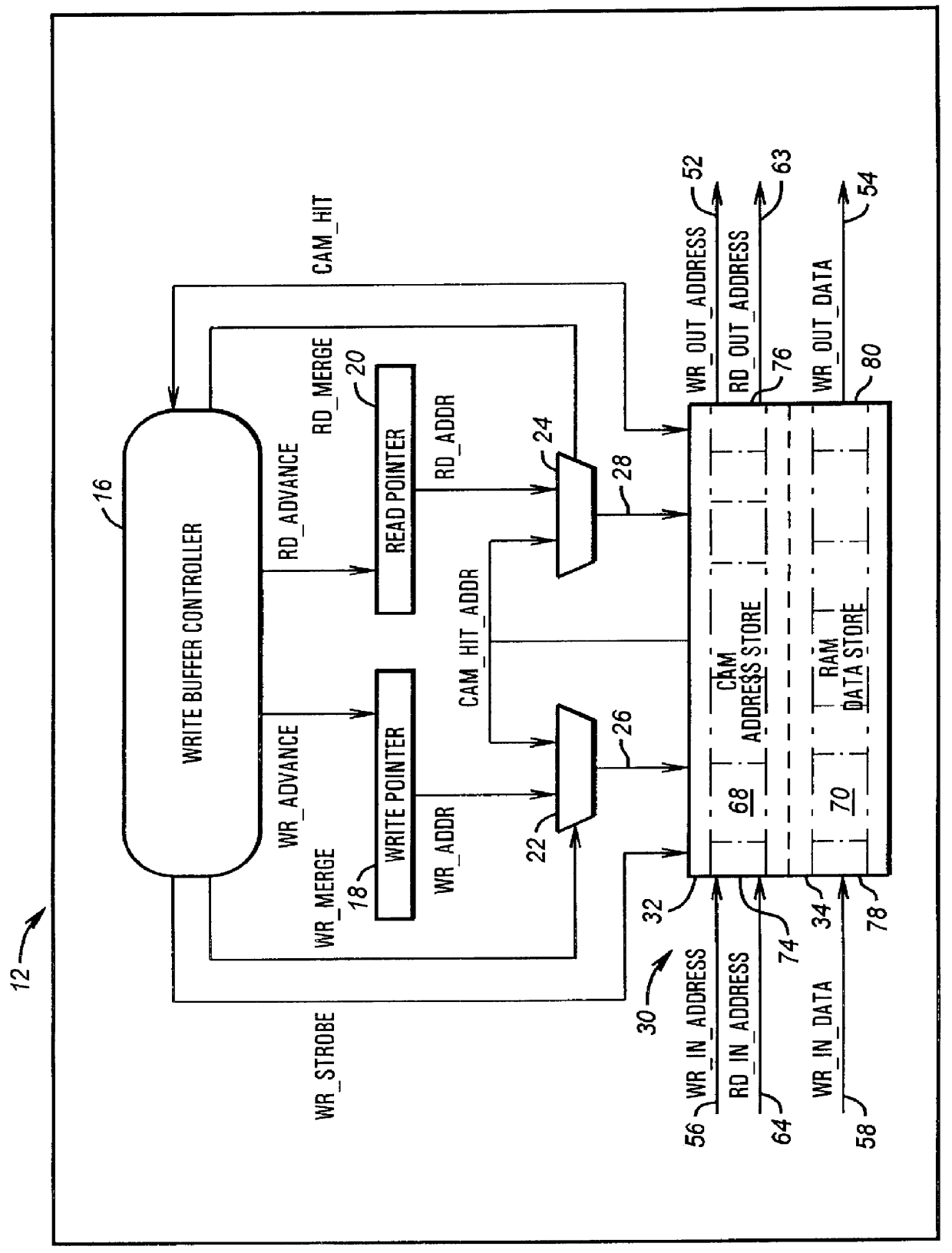
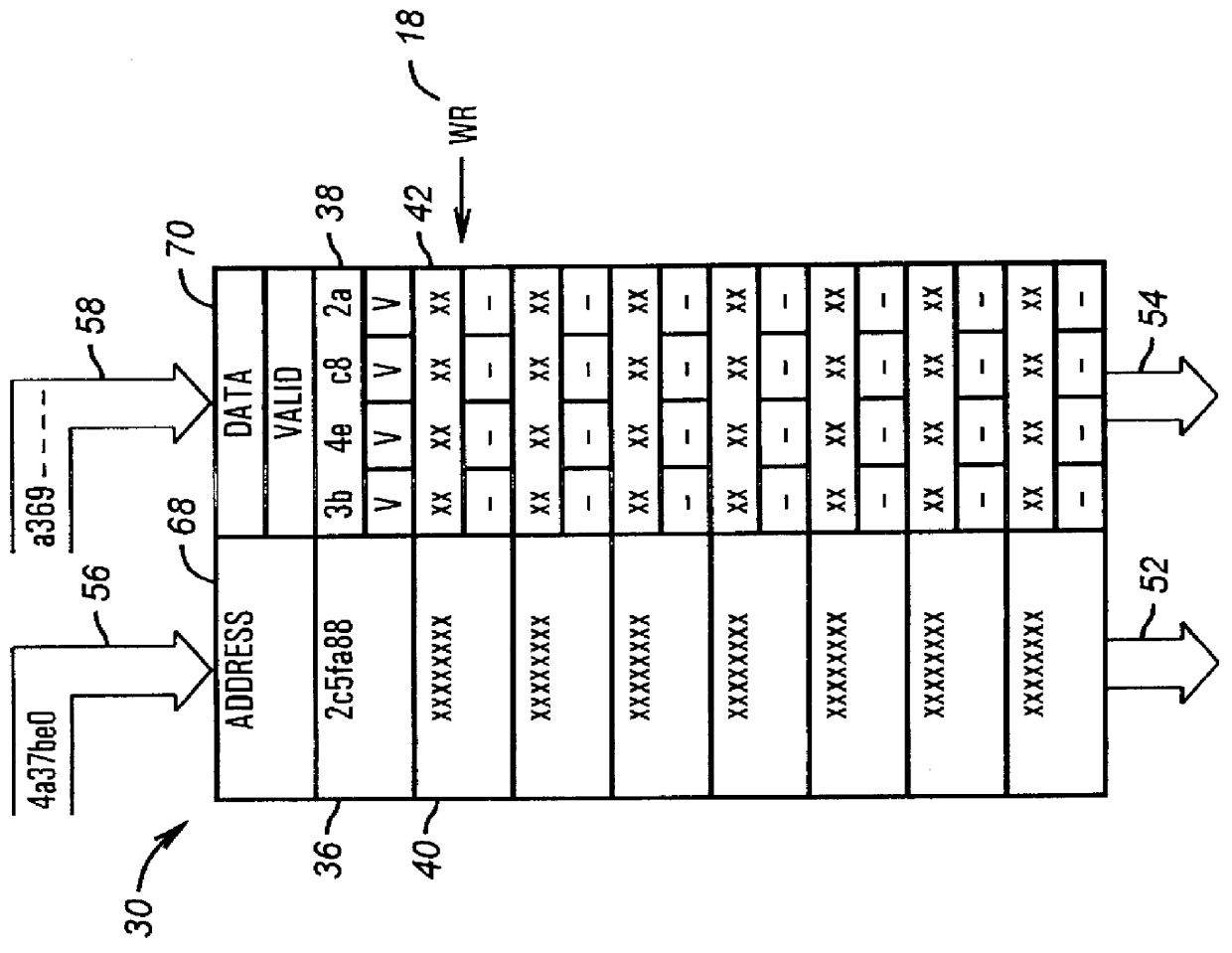
Write-buffer FIFO architecture with random access snooping capability
A system provides a write buffer with random access snooping capability. A random access write buffer includes a write buffer controller and a random access memory (RAM) containing a content addressable memory (CAM) address store and a random access memory data store. The CAM compares an input write address from a producer to the addresses present in the address store. If the input write address is "related" to an address present in the address store, the CAM detects an address hit. The indication of an address hit is provided to the write buffer controller which signals the data store to store the input write data in the existing rank of the data store associated with the "related" address detected by the CAM. The CAM also detects whether an input read address provided by a producer to a consumer is "related" to an address in the address store. If the input read address is "related" to an address in the address store, the read data at the "related" address in the address store is retrieved and merged with the read data from the consumer to produce valid read data. The valid read data is then provided to the producer. The write buffer thus enhances a general FIFO function with write merging, write collapsing, and read merging.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Linear associative memory-based hardware architecture for fault tolerant ASIC/FPGA work-around
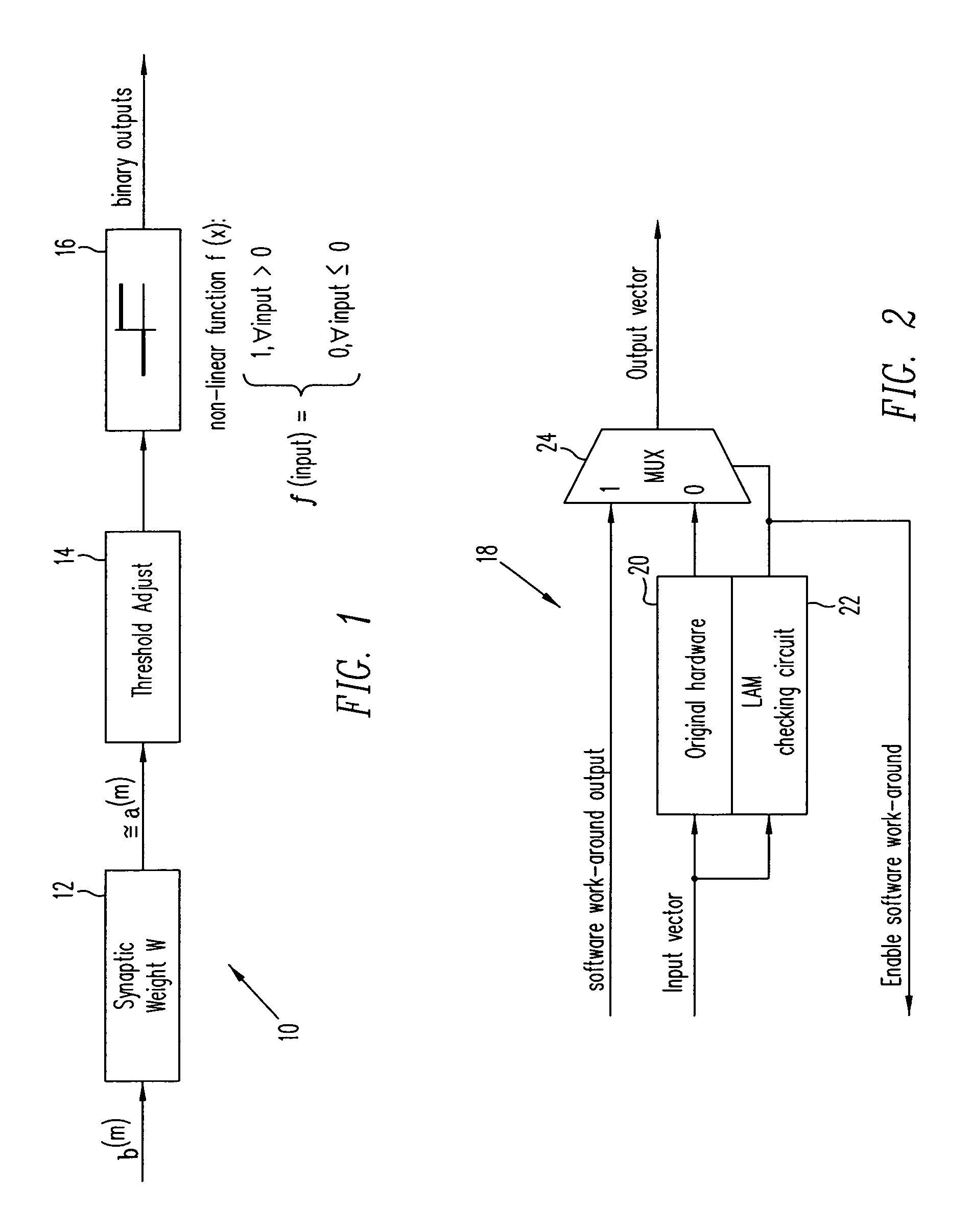
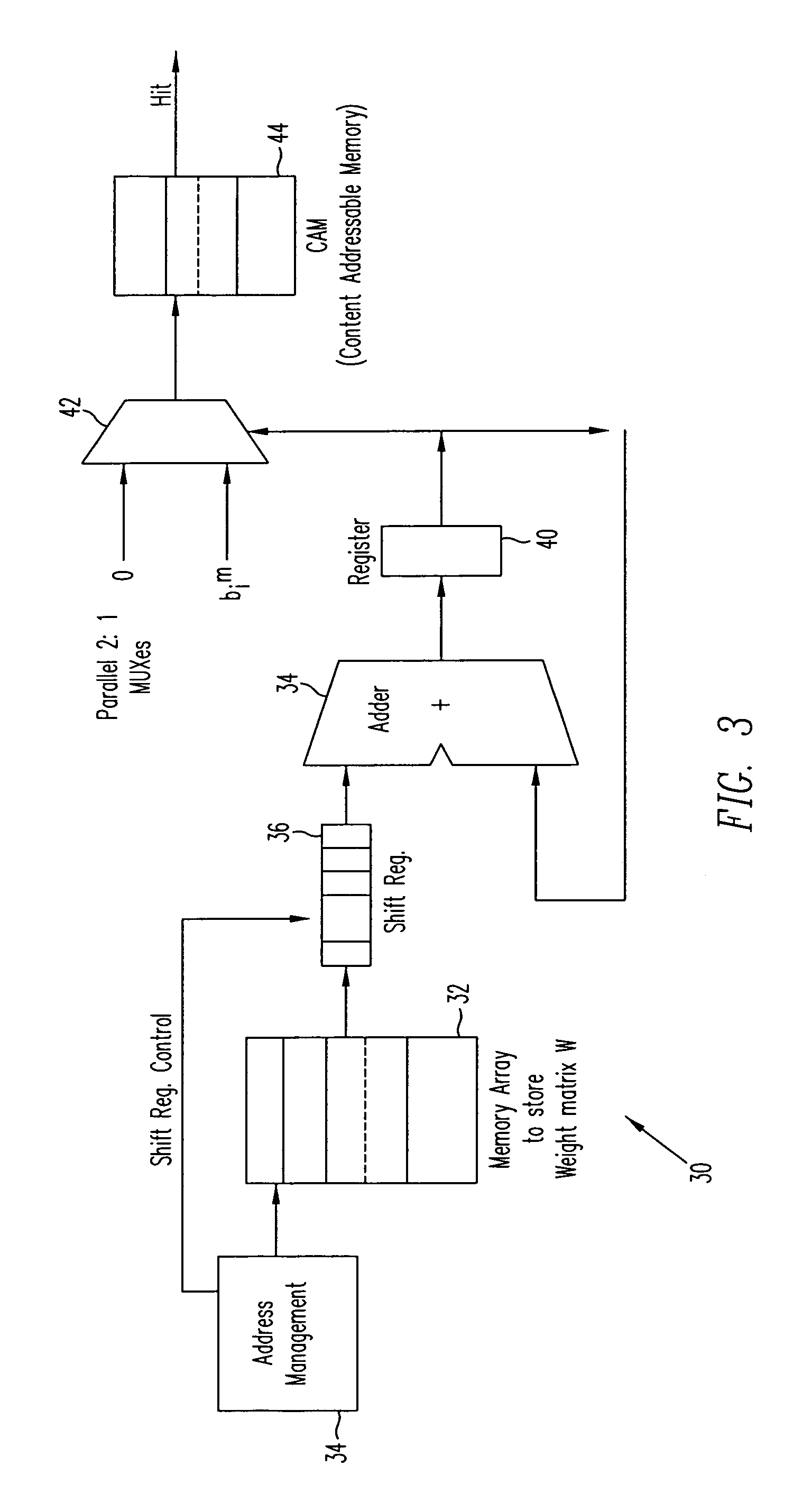
A programmable logic unit (e.g., an ASIC or FPGA) having a feedforward linear associative memory (LAM) neural network checking circuit which classifies input vectors to a faulty hardware block as either good or not good and, when a new input vector is classified as not good, blocks a corresponding output vector of the faulty hardware block, enables a software work-around for the new input vector, and accepts the software work-around input as the output vector of the programmable logic circuit. The feedforward LAM neural network checking circuit has a weight matrix whose elements are based on a set of known bad input vectors for said faulty hardware block. The feedforward LAM neural network checking circuit may update the weight matrix online using one or more additional bad input vectors. A discrete Hopfield algorithm is used to calculate the weight matrix W. The feedforward LAM neural network checking circuit calculates an output vector a(m) by multiplying the weight matrix W by the new input vector b(m), that is, a(m)=wb(m), adjusts elements of the output vector a(m) by respective thresholds, and processes the elements using a plurality of non-linear units to provide an output of 1 when a given adjusted element is positive, and provide an output of 0 when a given adjusted element is not positive. If a vector constructed of the outputs of these non-linear units matches with an entry in a content-addressable memory (CAM) storing the set of known bad vectors (a CAM hit), then the new input vector is classified as not good.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and device for virtualization of multiple data sets on same associative memory
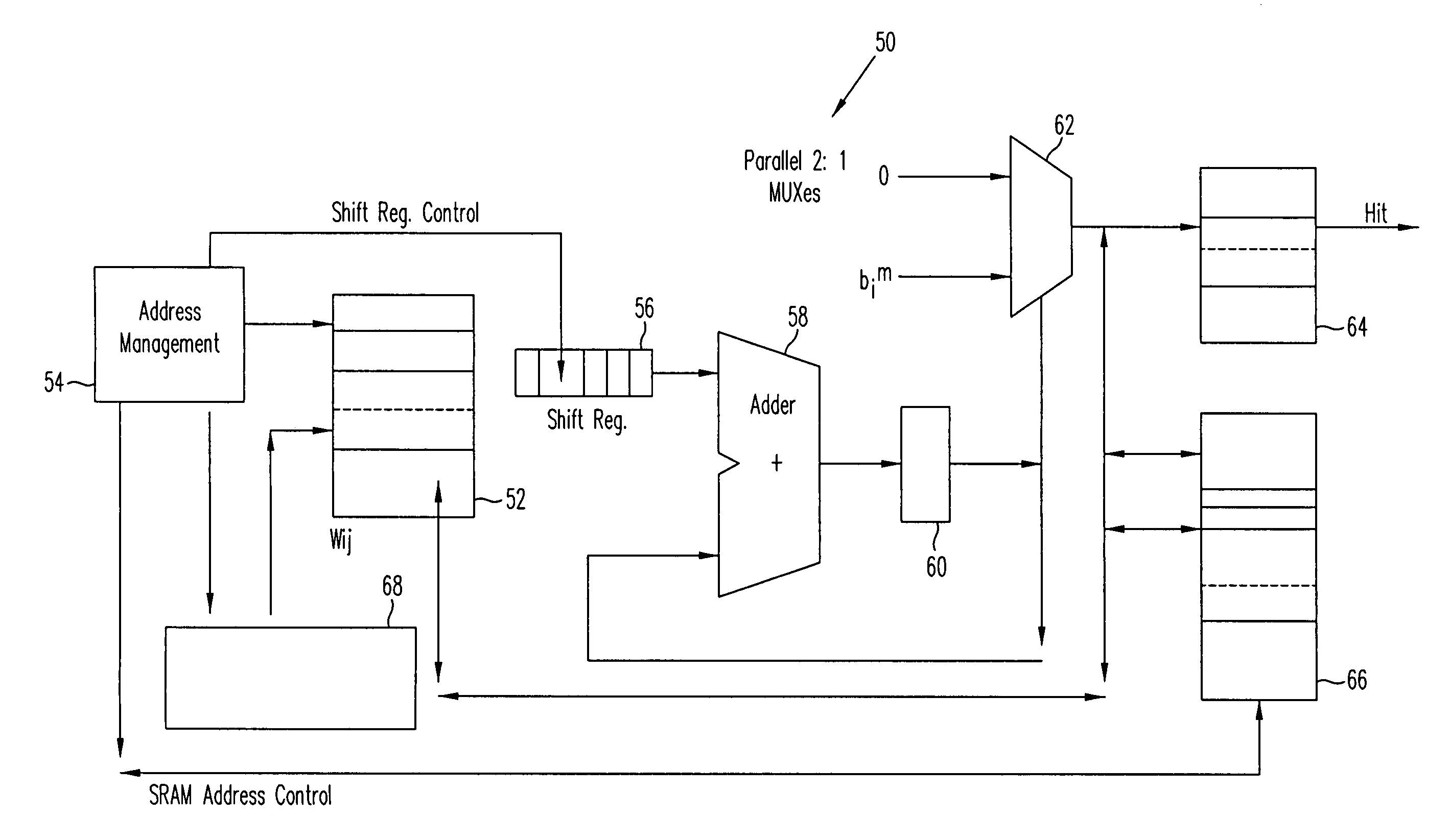
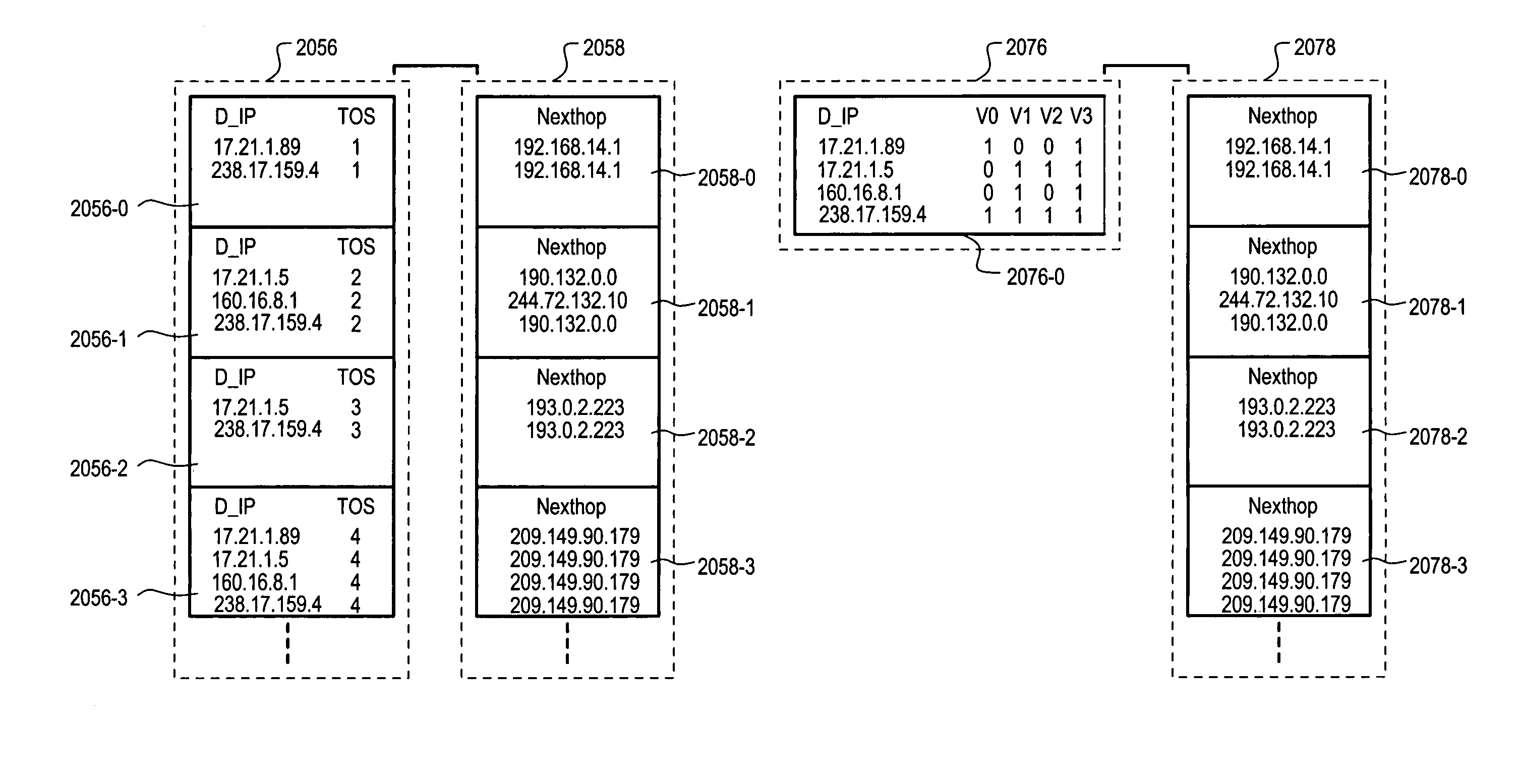
InactiveUS7281085B1Easy accessData can be usedError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsScheme valueVirtualization
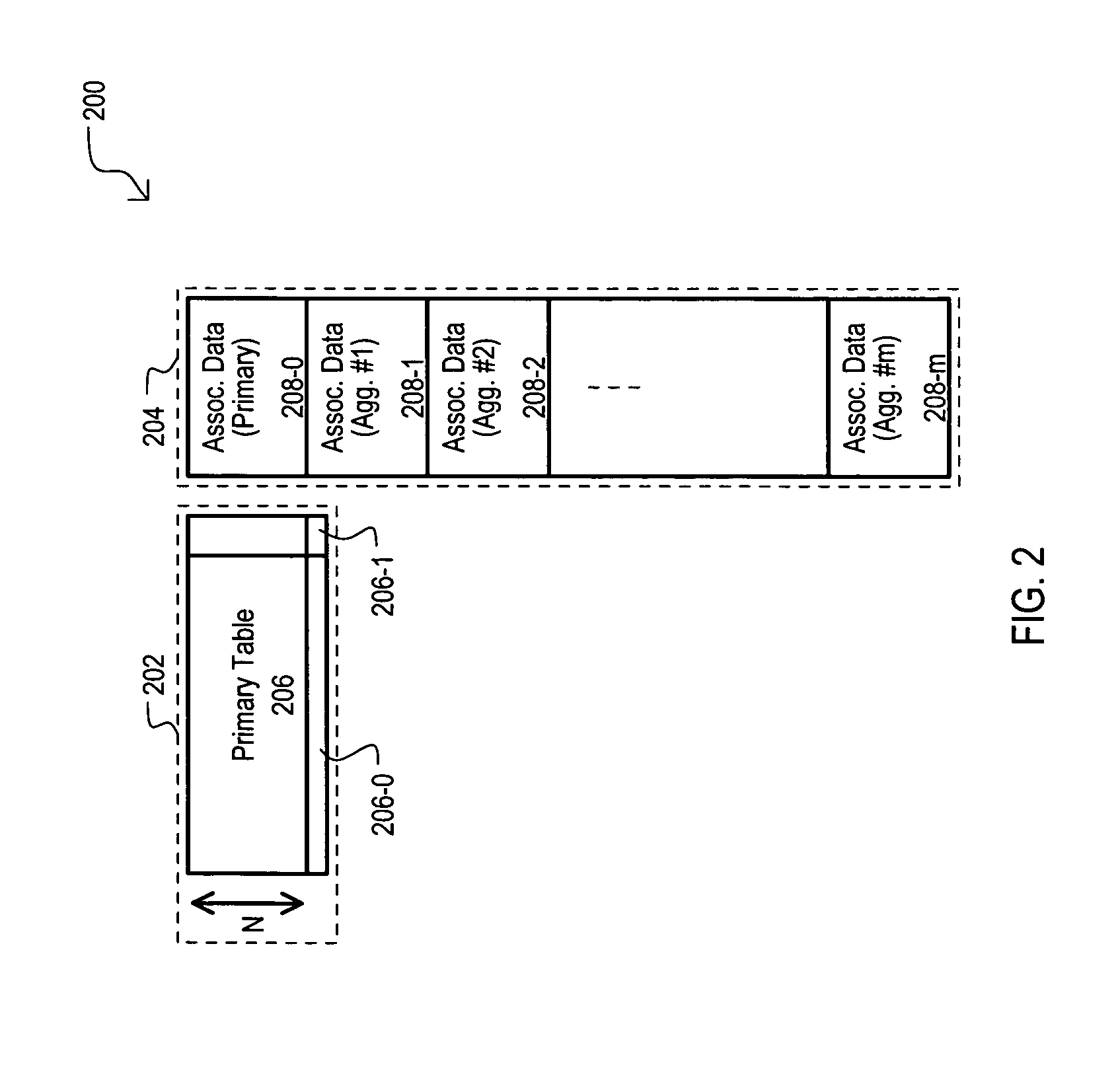
A system (200) can provide data aggregation with a single primary table (206) formed in a content addressable memory (CAM) section (202). Within a primary table (206) CAM entries can be part of a primary table, one or more aggregate tables, or both. In one arrangement, valid bits in each CAM entry can indicate which particular schemes a CAM entry belongs to (primary table, or any of the aggregate tables). Associated data for each table can be stored in a RAM section (204) and can be accessed according to an offset address generated according to a scheme value (i).
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Content addressable memory (CAM) devices having multi-block error detection logic and entry selective error correction logic therein
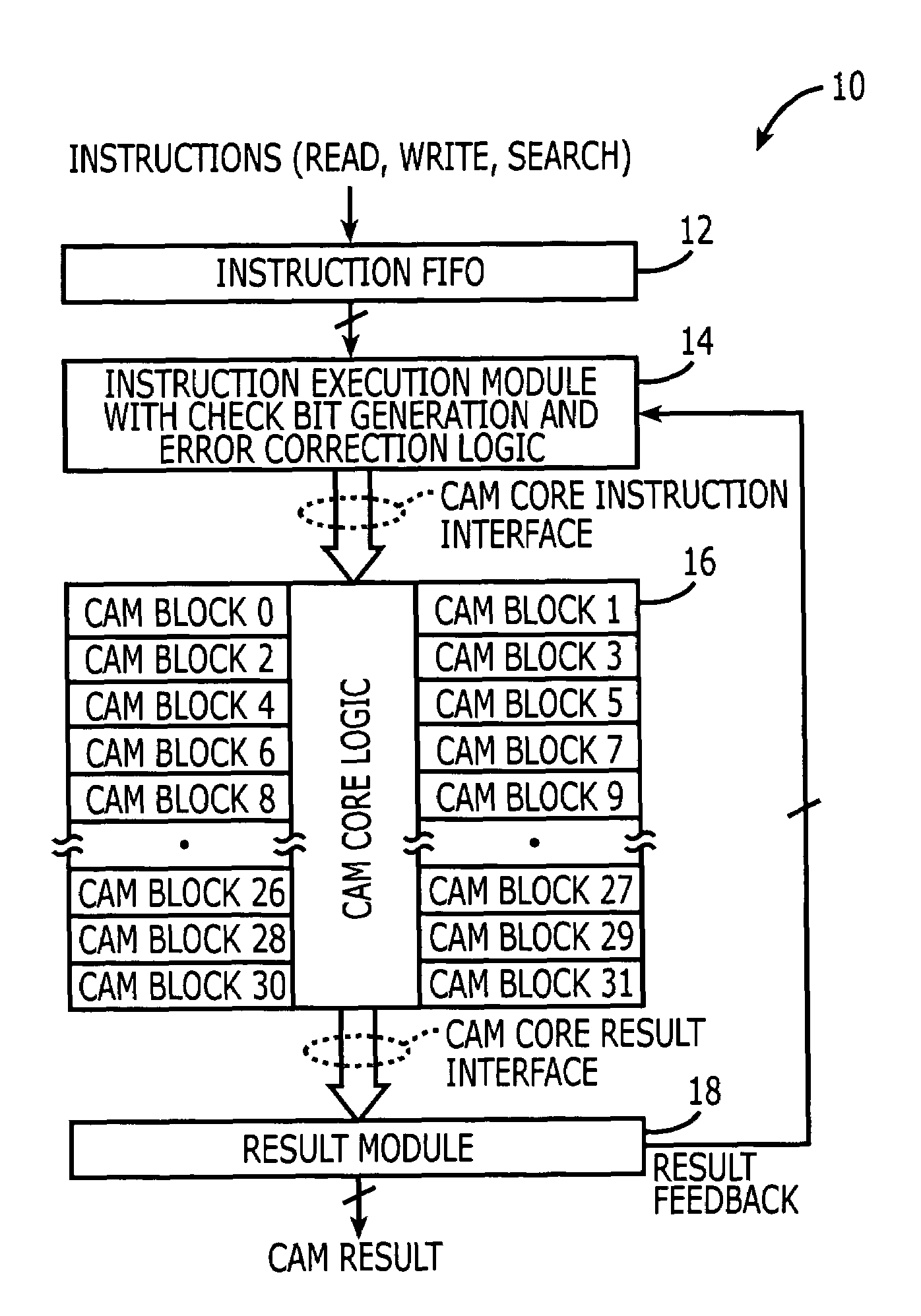
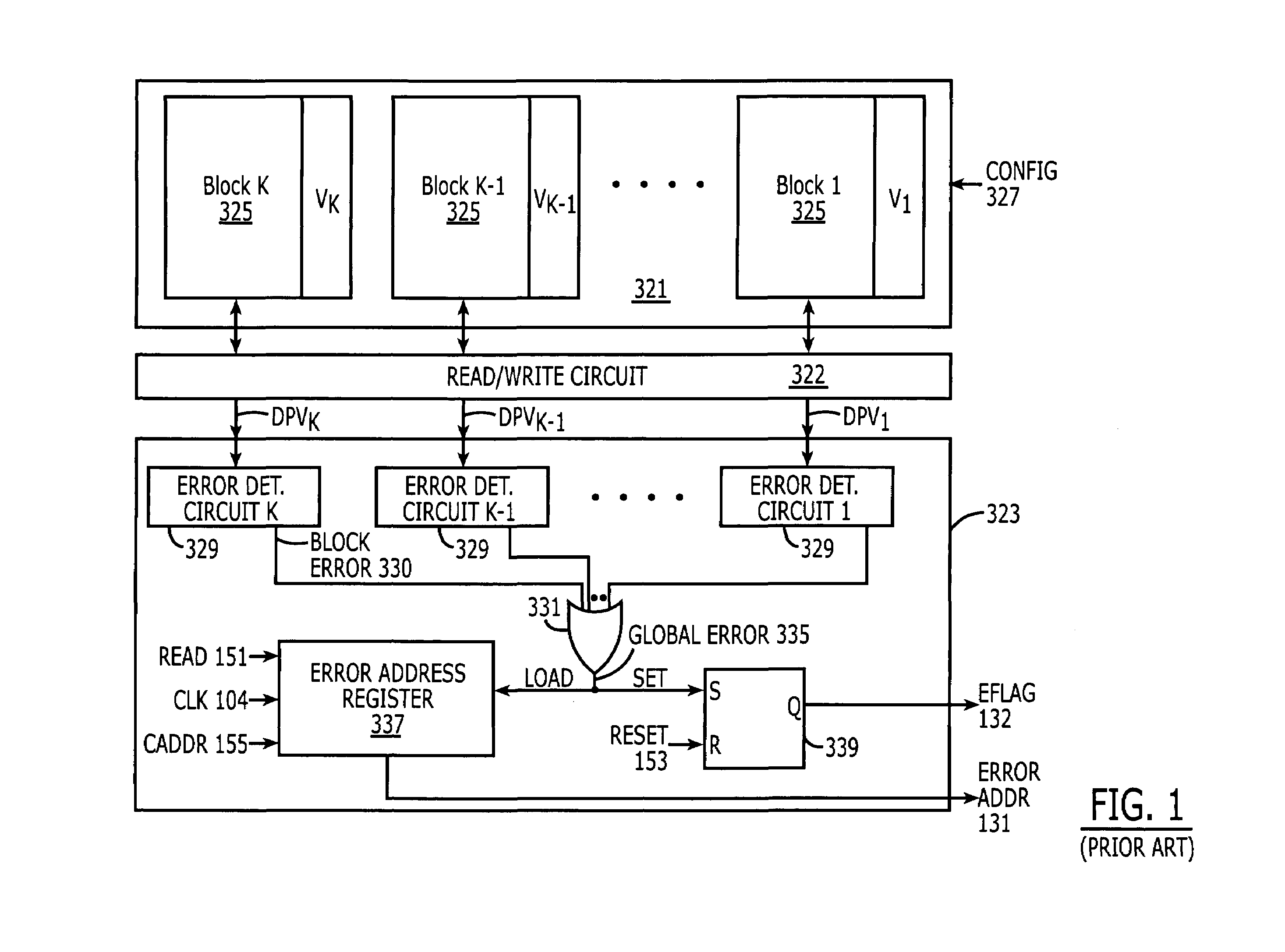
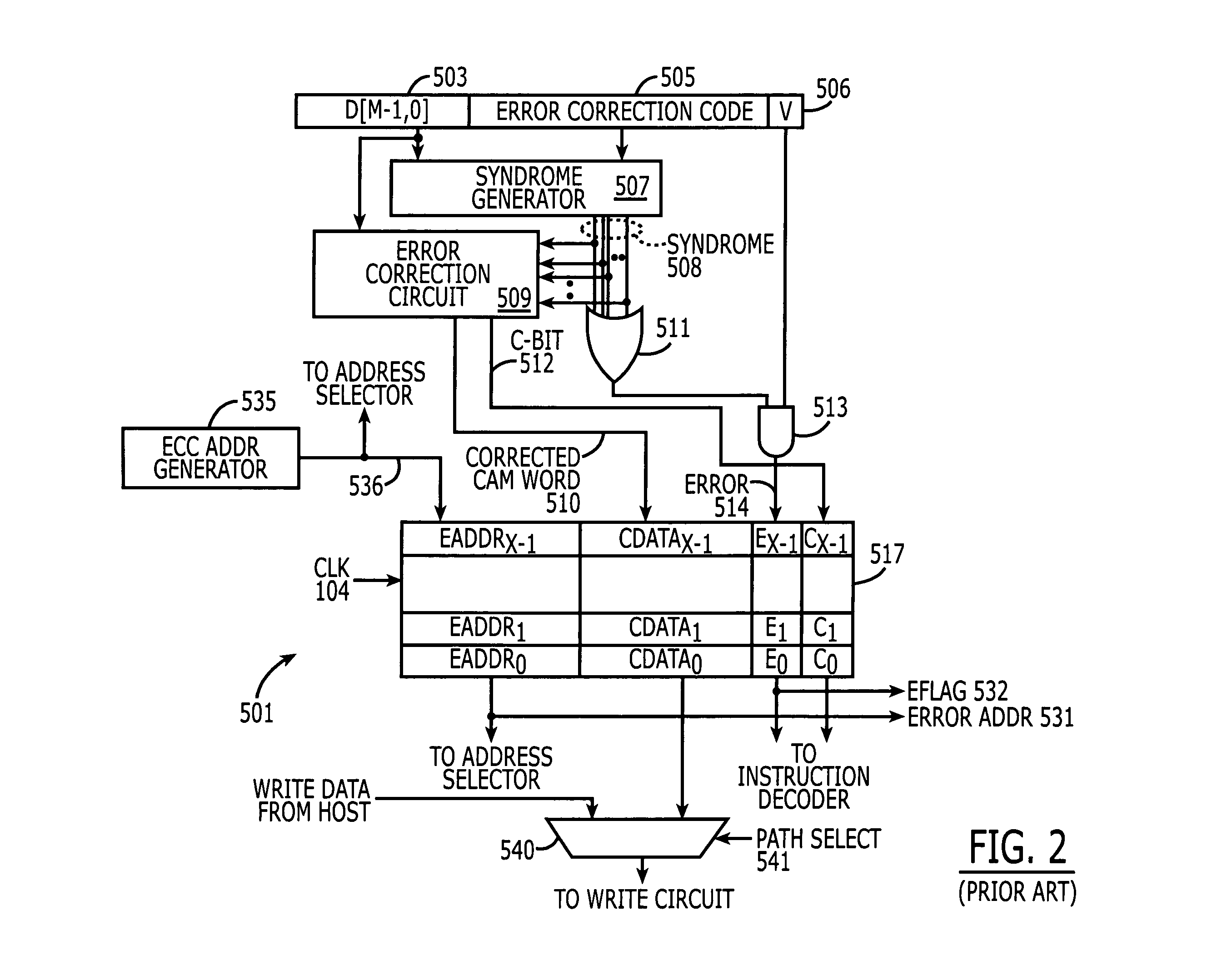
Search engine devices include a content addressable memory (CAM) core having a plurality of CAM array blocks therein and a control circuit that is electrically coupled to the CAM core. The control circuit is configured to support internal error detection and correction operations using modified Hamming code words. These operations are performed without significant impact on the compare bandwidth of the search engine device, even when operations to read entries from the CAM core are performed as foreground operations that may block concurrent search operations. The control circuit may perform the error detection and correction operations by issuing multiple read instructions. These instructions include a first instruction (e.g., error check instruction) to read at least a first entry into the CAM core for the purpose of error detection and then, in response to detecting the first entry as erroneous, issuing a second instruction to read the first entry from the CAM core. The entry is then corrected and written back into the CAM core.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
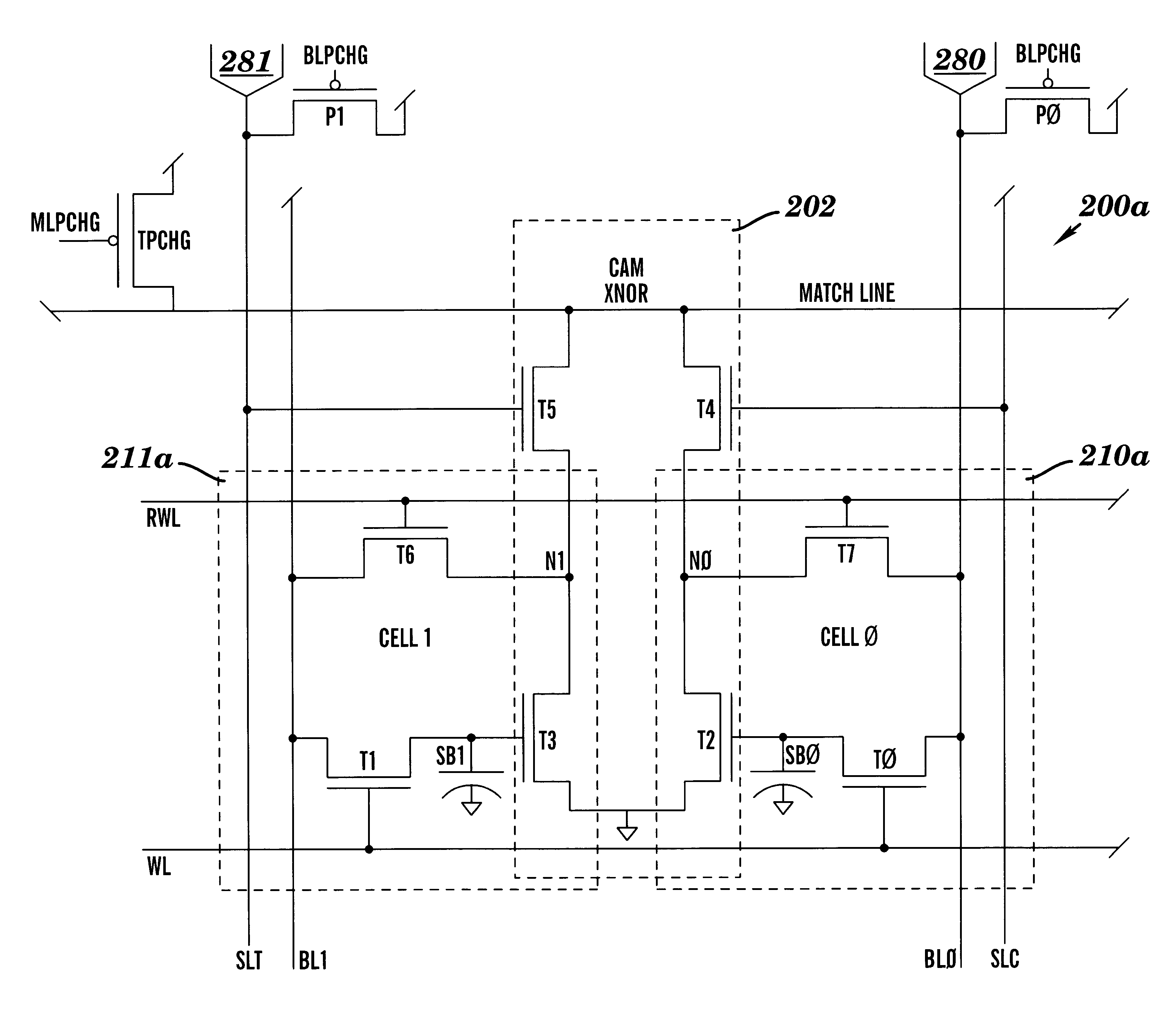
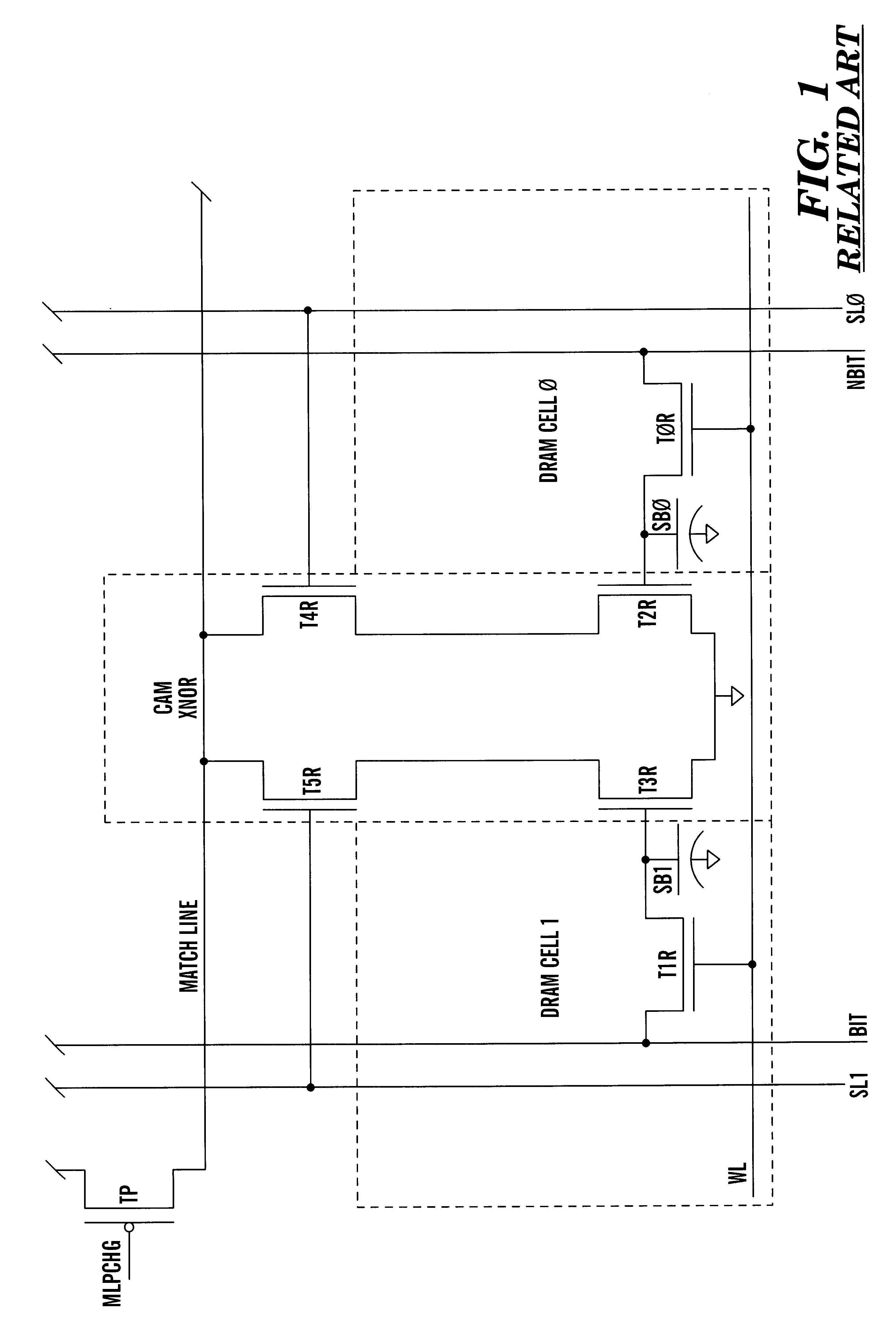
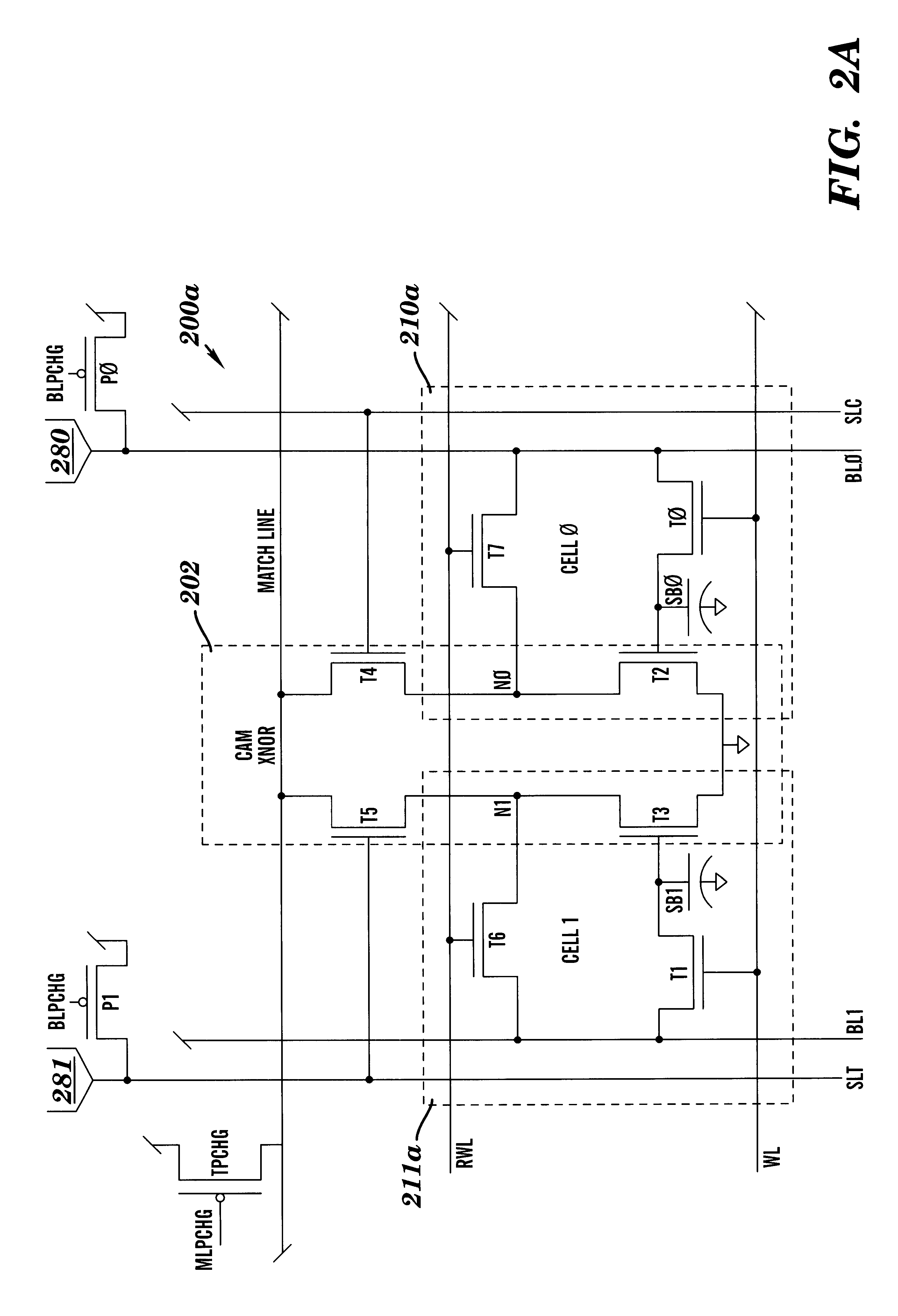
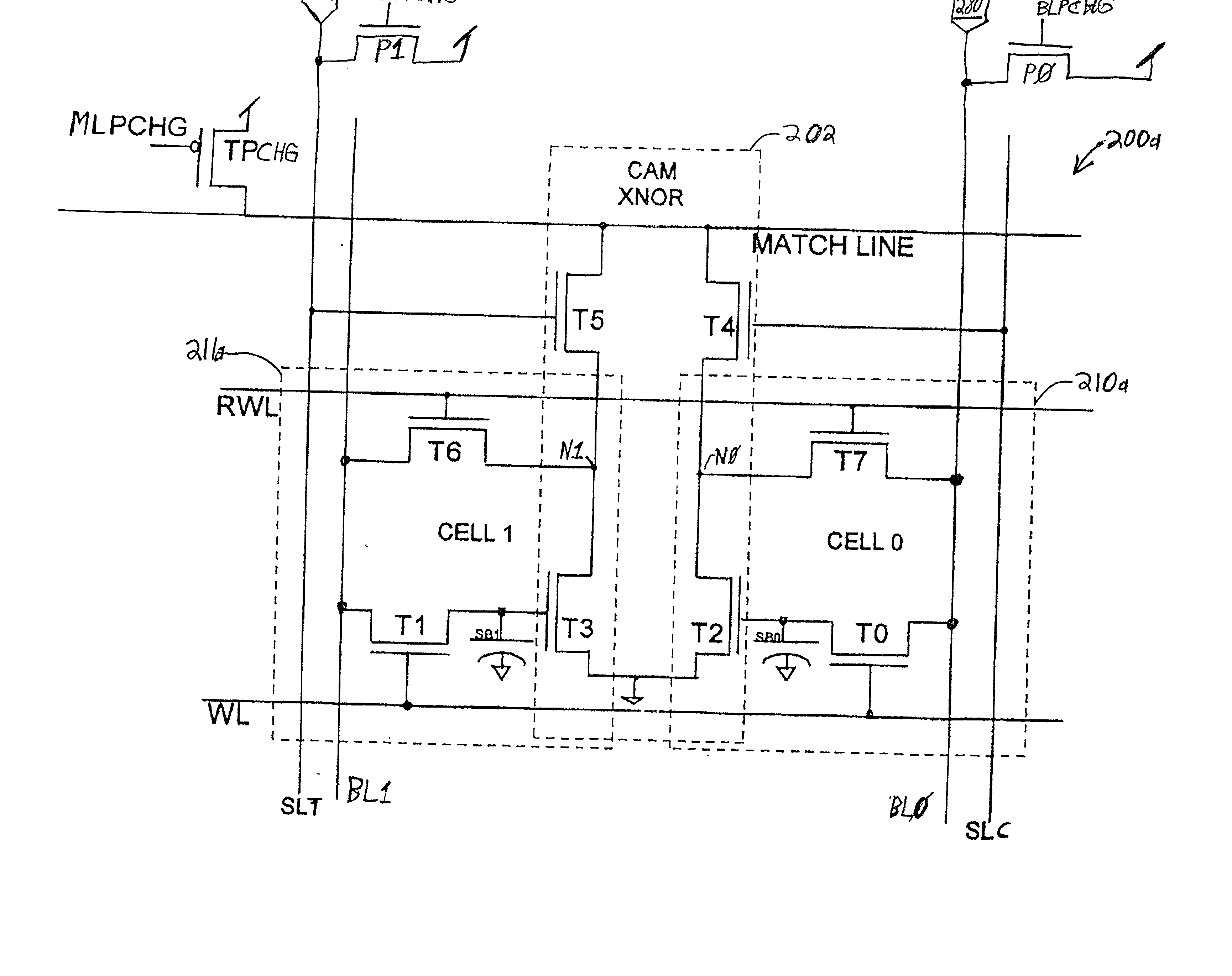
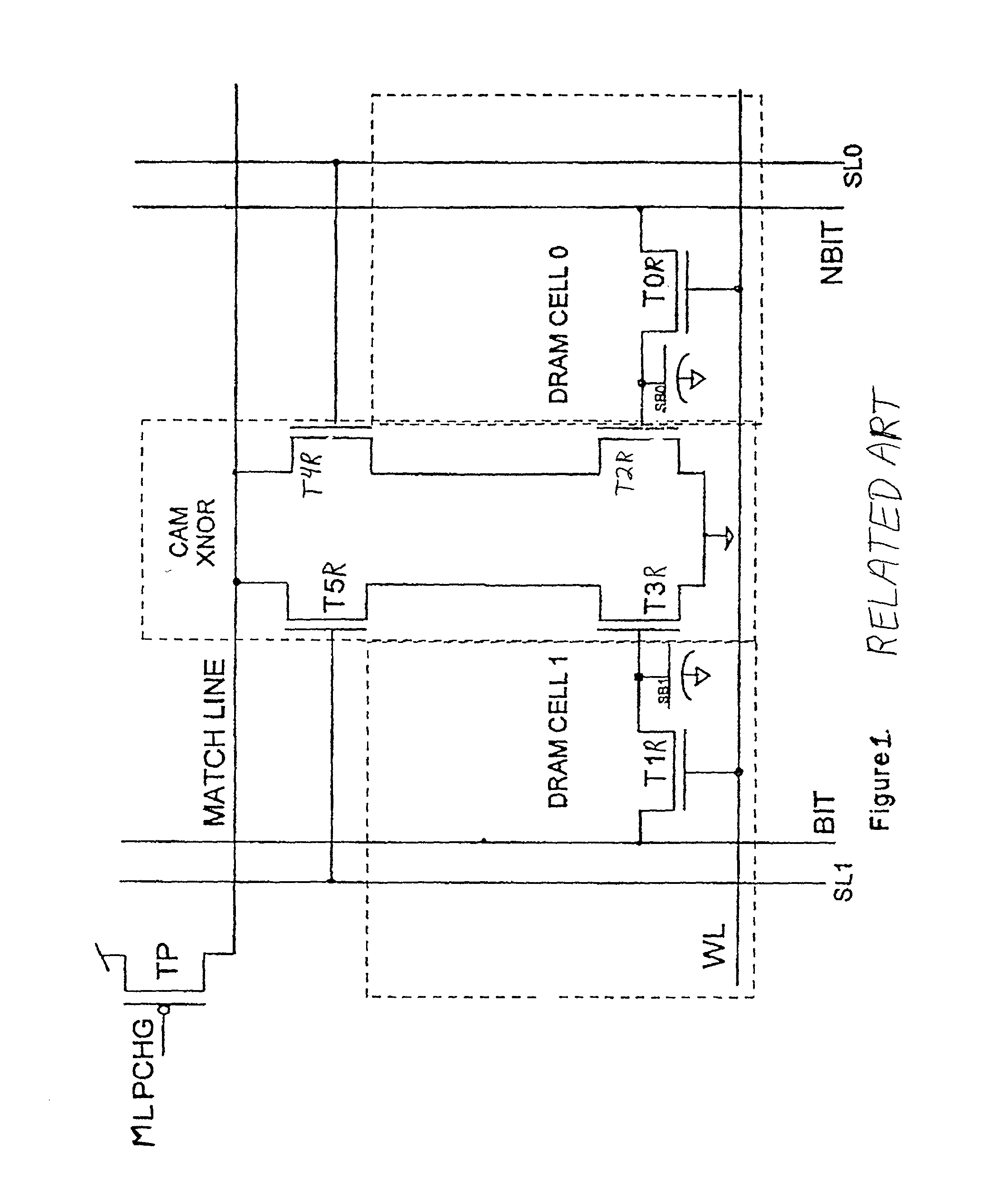
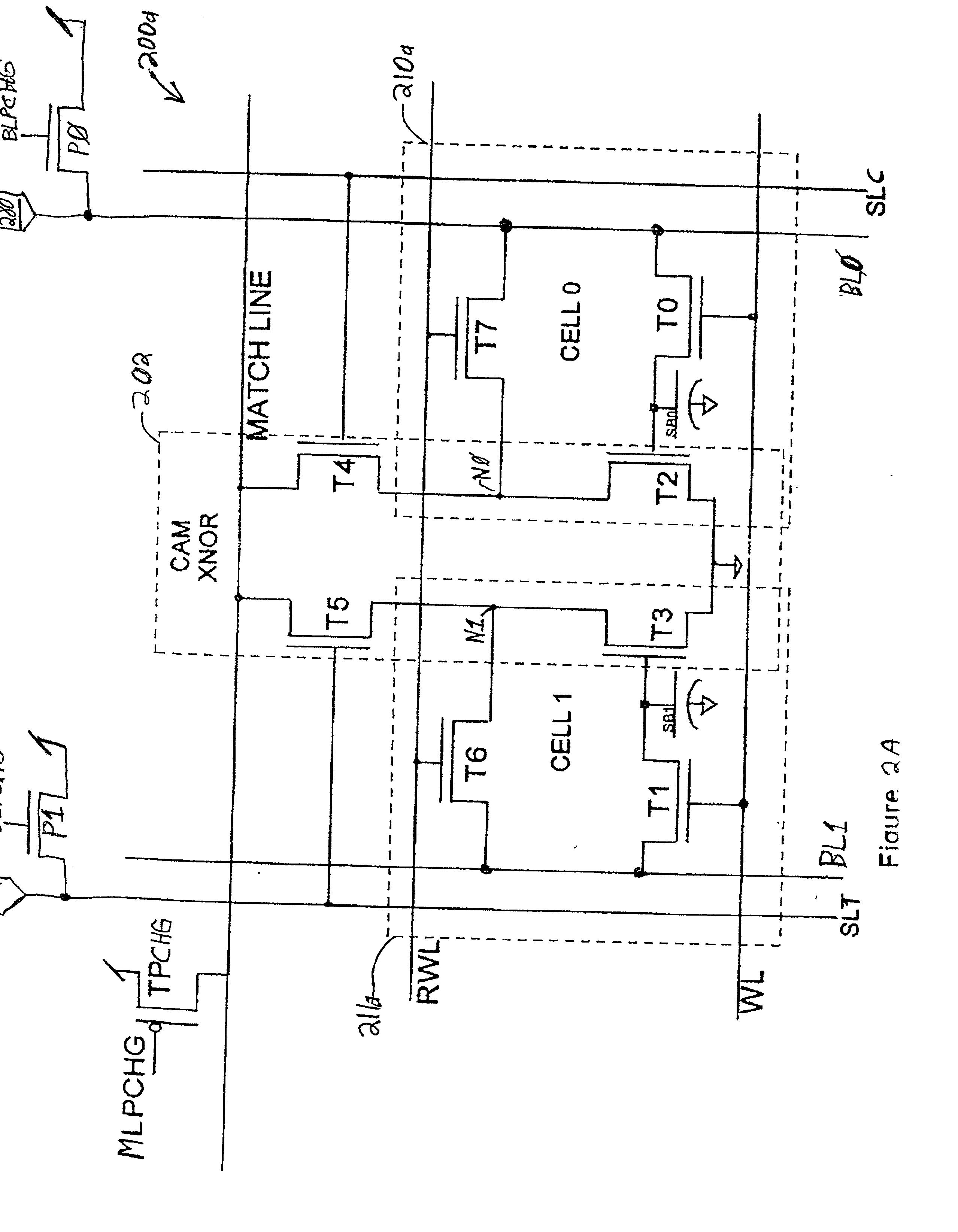
Dram cam cell with hidden refresh
A Dynamic Content Addressable Memory (DCAM) cell topology that contains fewer that can perform a "hidden" refresh of stored data that does not delay nor interrupt the CAM search cycle, thereby providing SCAM-like performance. A non-destructive read operation, is performed such that the stored-data does not have to be written back because of a refresh-read operation. A reliable CAM search can be performed after a read operation and before or even while the refresh-data is being written back. Soft-error detection processes can be performed on each CAM entry during the pendency of the refresh cycle. The DCAM cell can be used in a digital system such as a digital computer and a Network Router.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
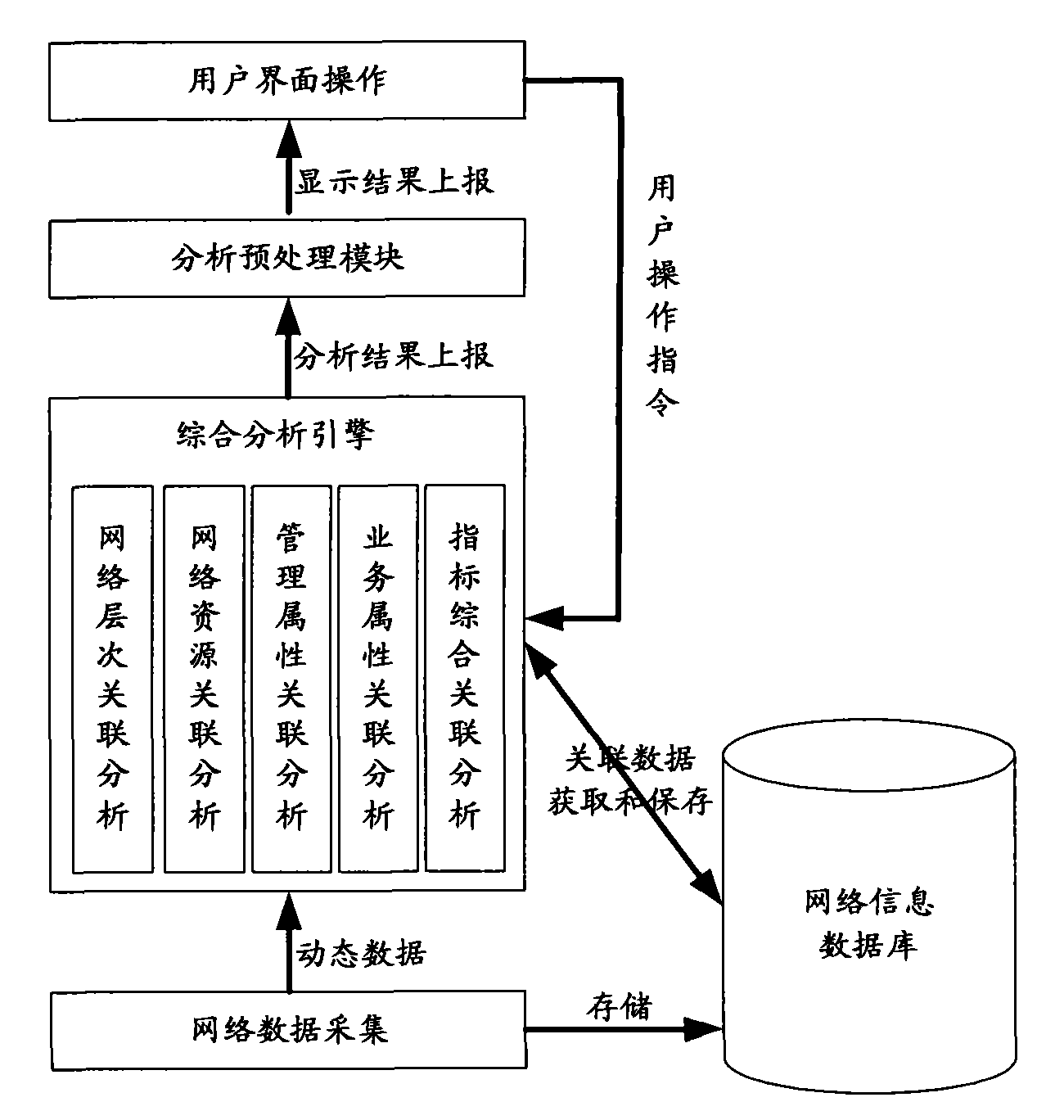
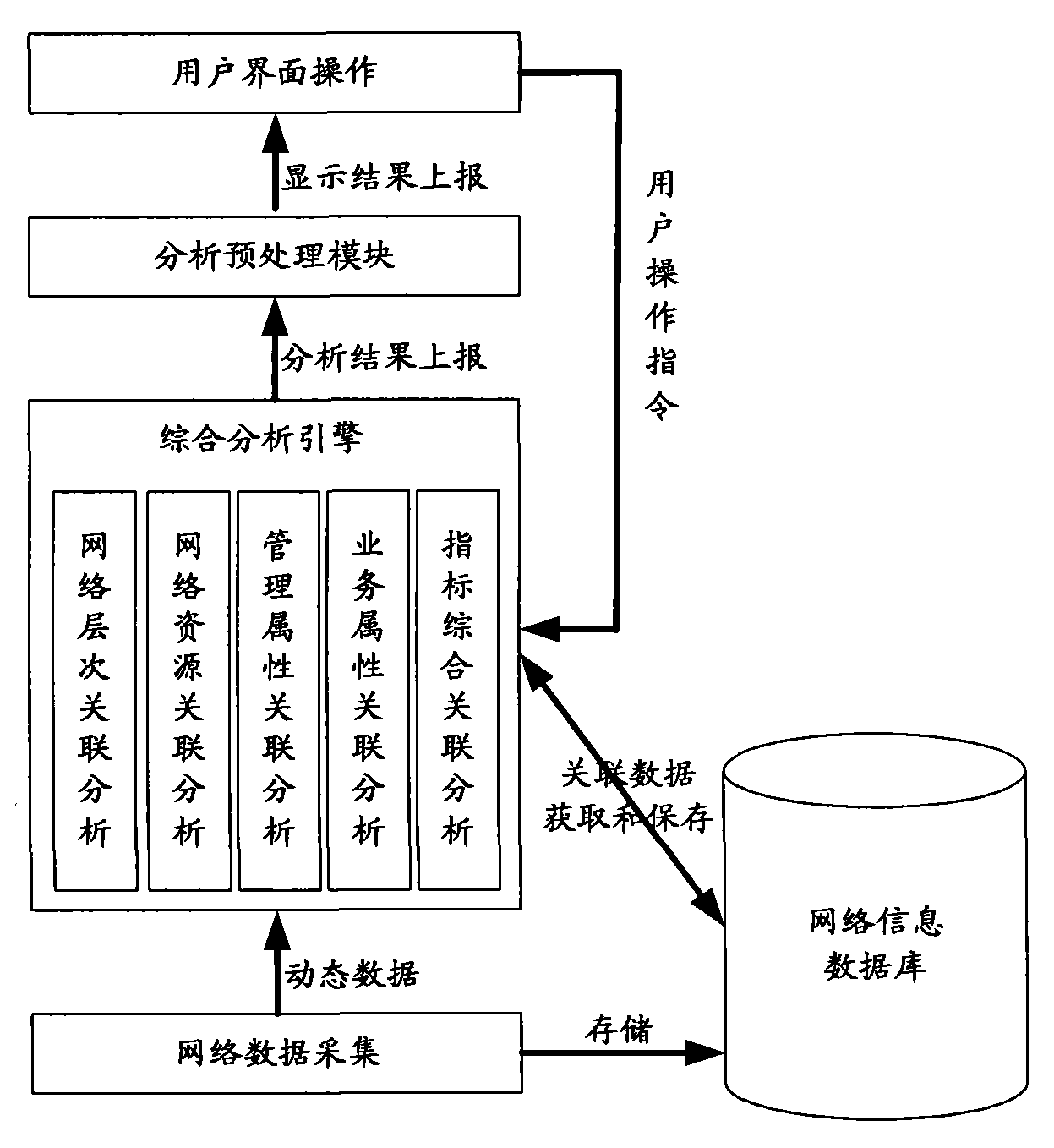
Multidimensional comprehensive situation display system based on degree of association
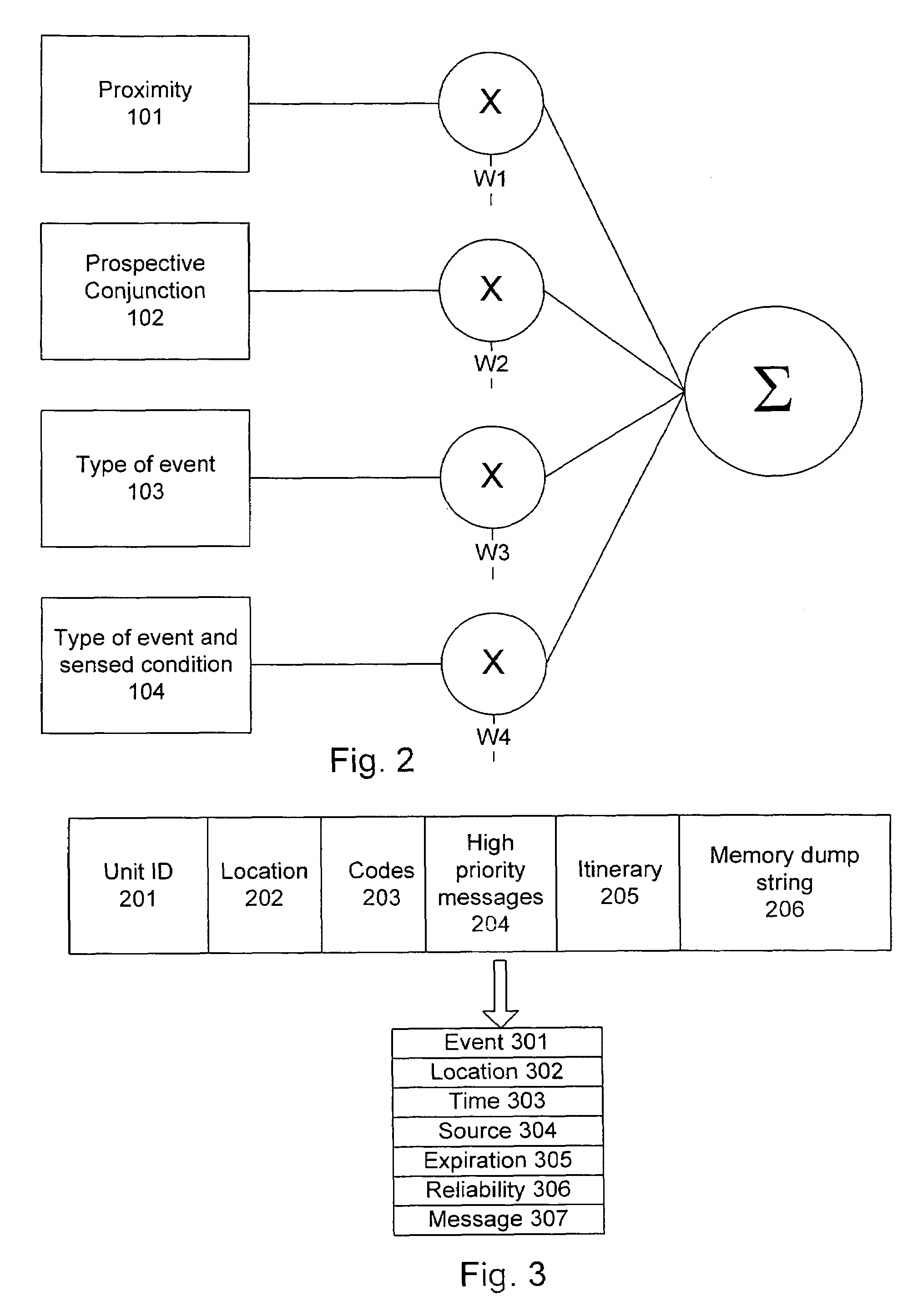
The invention provides a multidimensional comprehensive situation display system based on degree of association, which comprises a network management data acquisition module, a network management information comprehensive analysis engine, an analysis result preprocessing module and an interface display module, wherein the network management data acquisition module is used for acquiring data on the network, storing the acquired network dynamic operating data and static data to a database, and reporting dynamic operating data to the network management information comprehensive analysis engine in real time; after receiving the dynamic operating data or a data acquisition command and parameter configuration control command transmitted by a user through an interface, the network management information comprehensive analysis engine is used for carrying out analysis according to the static data stored in the database and transmitting the analysis result to the analysis result preprocessing module; and the analysis result preprocessing module is used for carrying out display data model reestablishment and data organization on the analysis result so as to be uniformly displayed by the interface display module. The invention can be used for displaying the topological situation by carrying out comprehensive monitoring on the communication network by multiple visual display means.
Owner:NO 30 INST OF CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP
Time diversity voice channel data communications
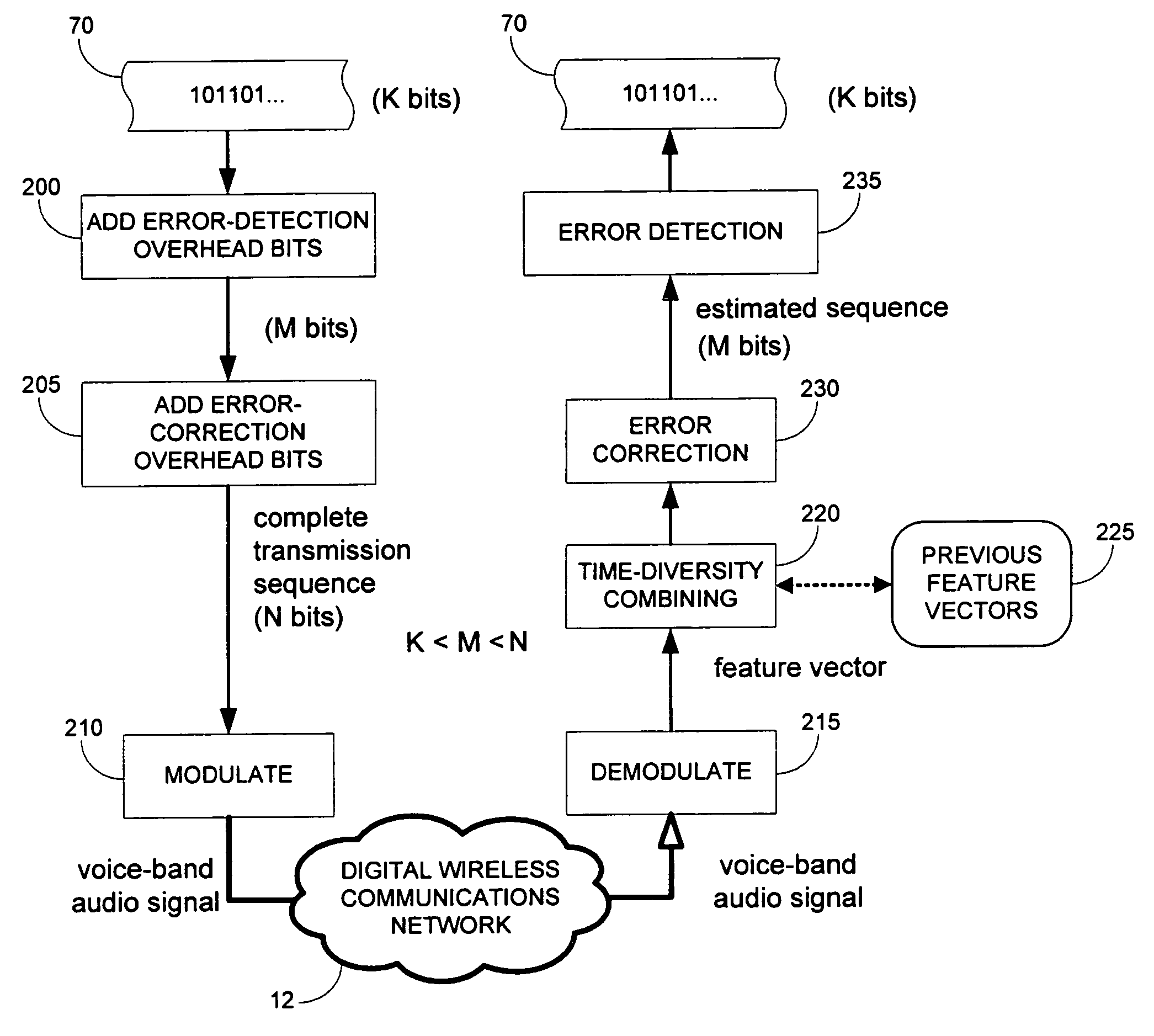
InactiveUS7924934B2Data representation error detection/correctionError preventionDigital dataFeature vector
A receiver with a time diversity combining component recovers a digital data signal transmitted over a voice channel of a digital wireless telecommunications network. A feature extraction module receives an audio frequency waveform encoding the digital data signal and generates a feature vector representing the digital data signal. A bit sequence estimation module analyzes the feature vector and generates an estimated bit sequence corresponding to the digital data signal. A memory stores the feature vector if the estimated bit sequence contains errors. A time diversity combining component generates a second estimated bit sequence by analyzing the first feature vector in combination with one or more feature vectors stored in the memory.
Owner:AIRBIQUITY INC
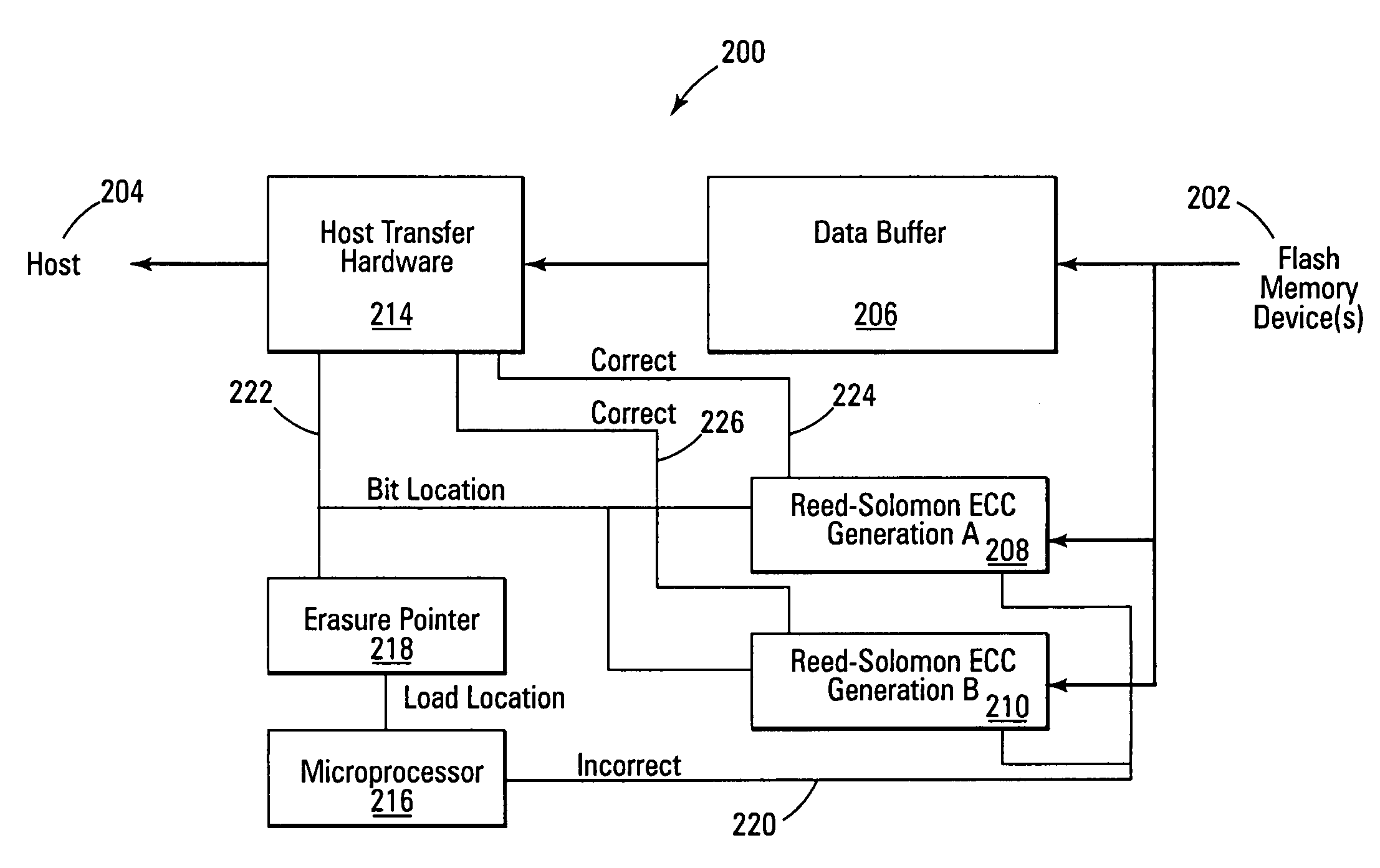
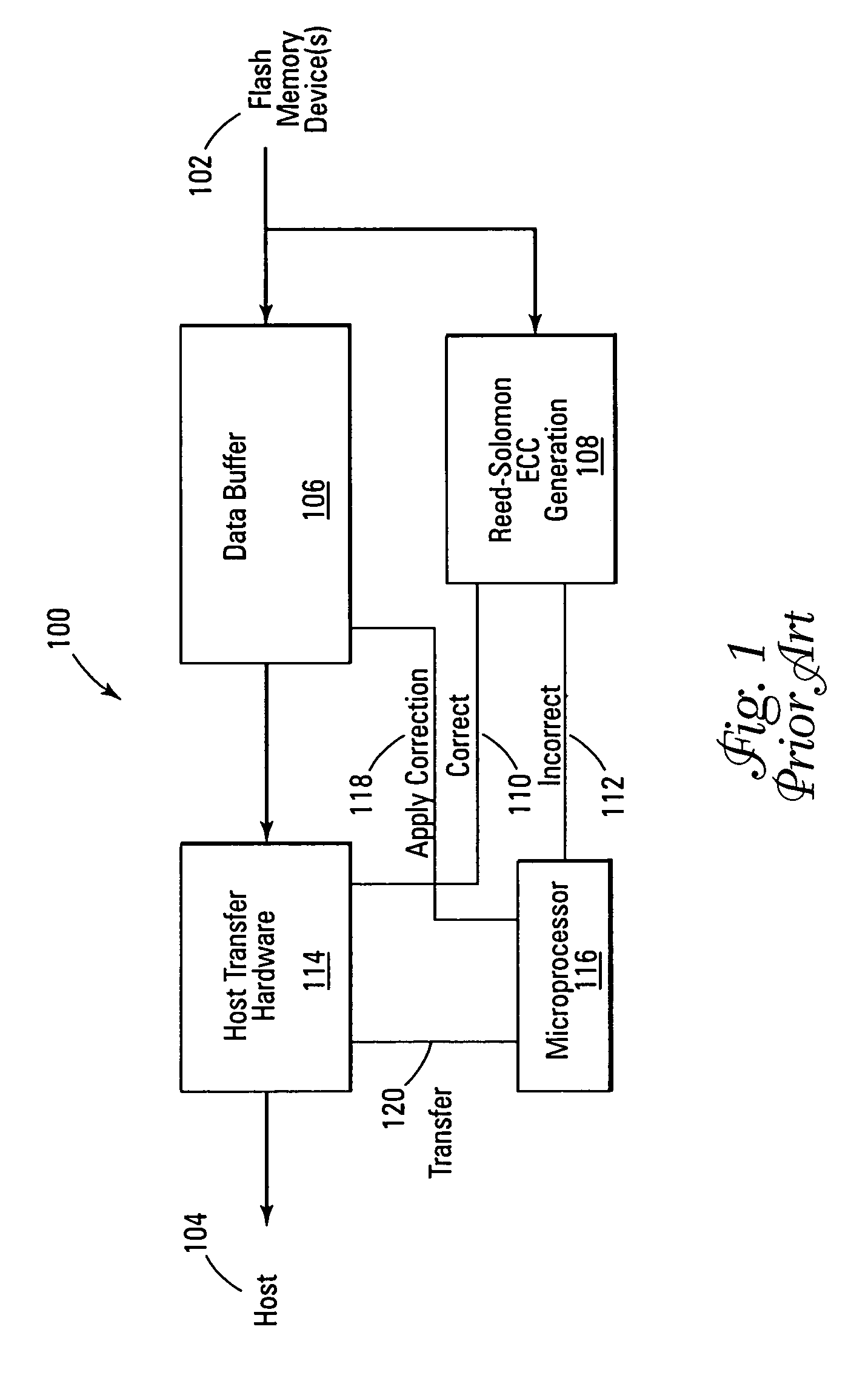
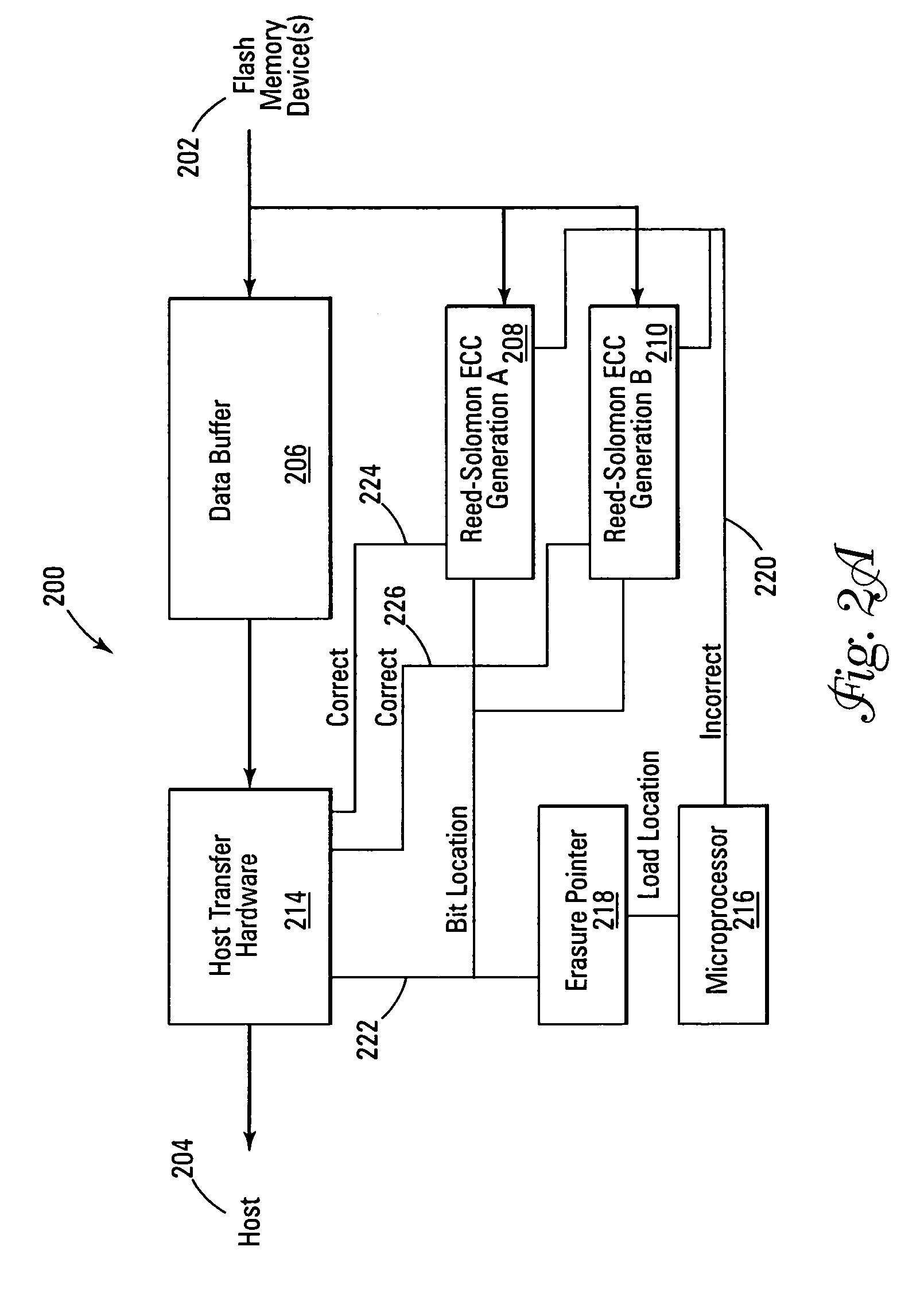
Erasure pointer error correction
ActiveUS7322002B2Easy to handleEffective correctionAlgebraic geometric codesCode conversionMemory systemsContent-addressable memory
Improved memory devices, circuitry, and data methods are described that facilitate the detection and correction of data in memory systems or devices in combination with a stored record of known flaws, errors, or questionable data bits of a read memory row or block to allow for more efficient processing and correction of these errors. An embodiment of the present invention utilizes an erasure pointer that can store the location of N bad or questionable bits in the memory segment that is currently being read, where for each bit stored by the erasure pointer the embodiment also contains 2N ECC generators to allow the read data to be quickly checked with the know bad bits in each possible state. This allows the read data to then be easily corrected on the fly before it is transferred by selecting the bad bit state indicated by the ECC generator detecting an uncorrupted read.
Owner:OVONYX MEMORY TECH LLC
Conditional execution via content addressable memory and parallel computing execution model
ActiveUS20060277392A1Improve performanceOptimize calculation speedProgram control using stored programsDigital data processing detailsConcurrent computationWhile loop
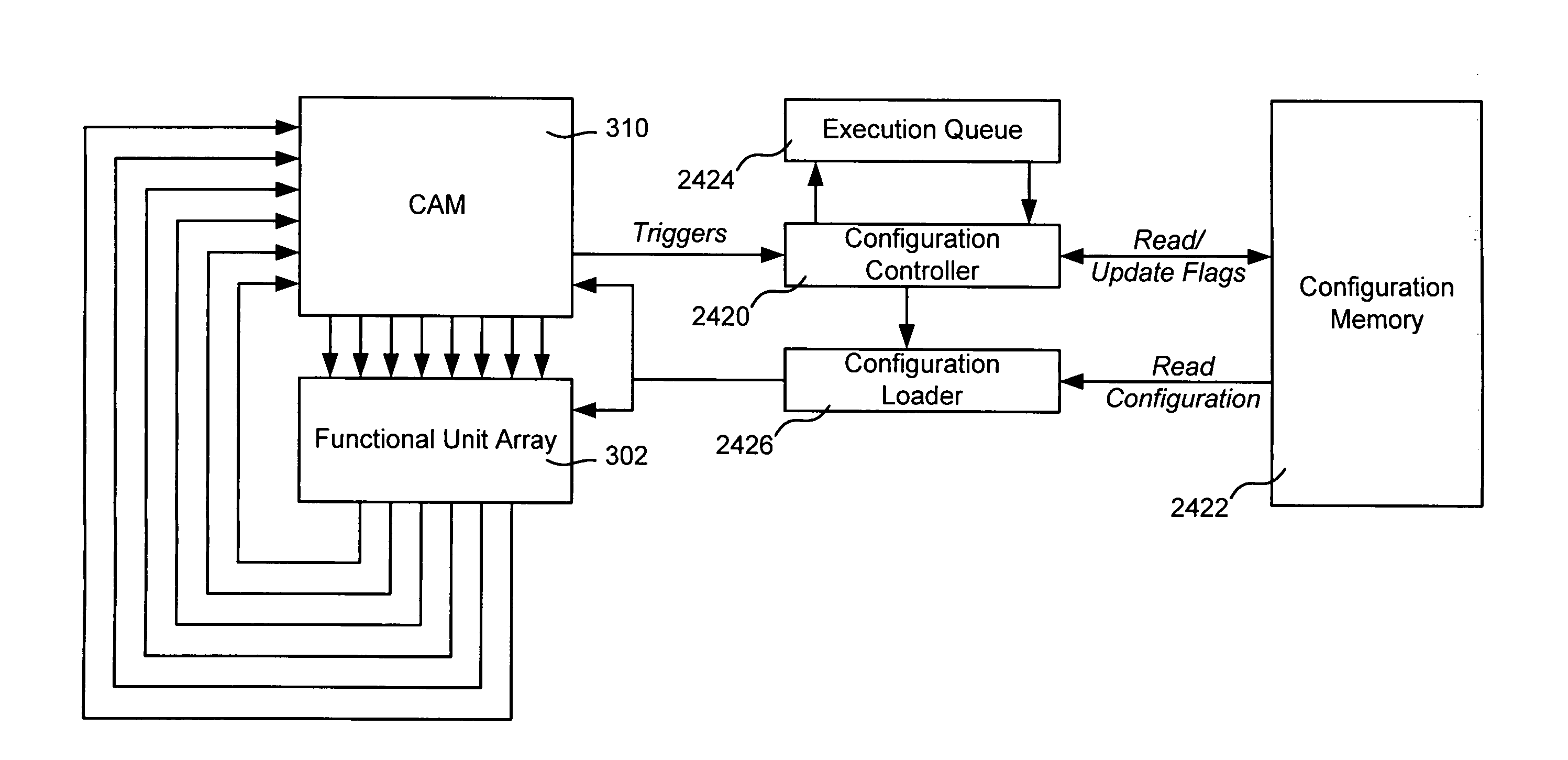
The use of a configuration-based execution model in conjunction with a content addressable memory (CAM) architecture provides a mechanism that enables performance of a number of computing concepts, including conditional execution, (e.g., If-Then statements and while loops), function calls and recursion. If-then and while loops are implemented by using a CAM feature that emits only complete operand sets from the CAM for processing; different seed operands are generated for different conditional evaluation results, and that seed operand is matched with computed data to for an if-then branch or upon exiting a while loop. As a result, downstream operators retrieve only completed operands. Function calls and recursion are handled by using a return tag as an operand along with function parameter data into the input tag space of a function. A recursive function is split into two halves, a pre-recursive half and a post-recursive half that executes after pre-recursive calls.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
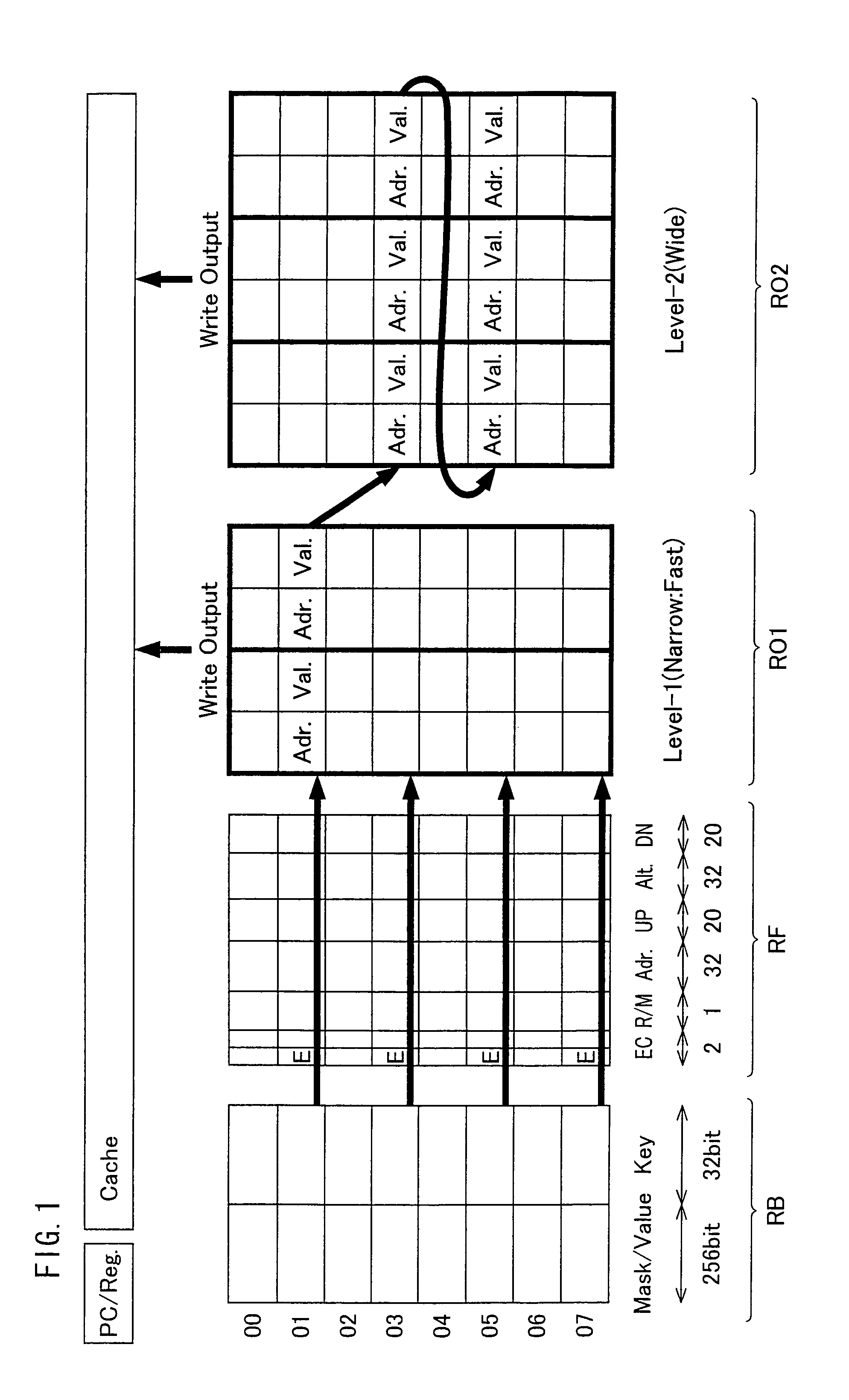
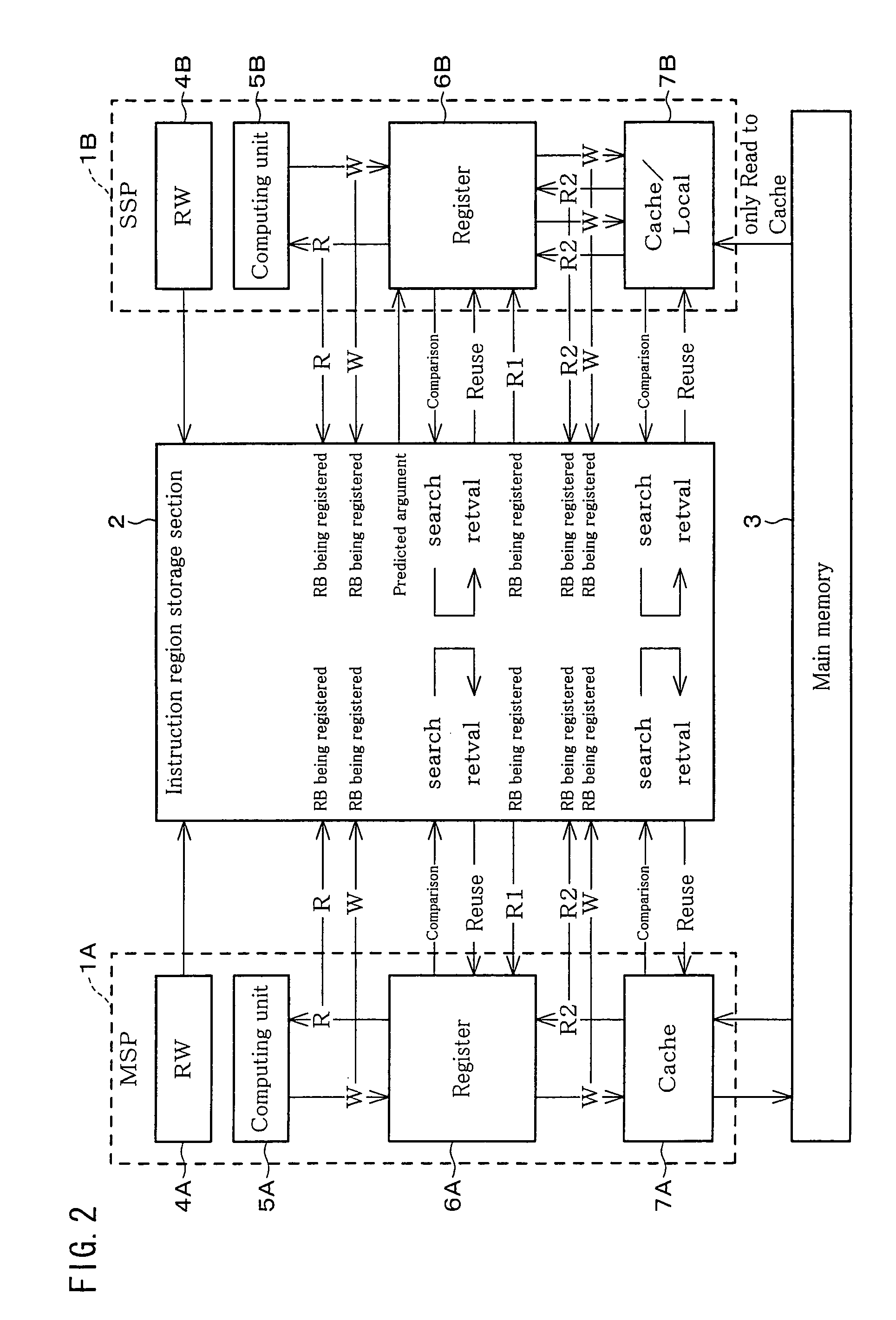
Data processing device for implementing instruction reuse, and digital data storage medium for storing a data processing program for implementing instruction reuse
ActiveUS8055885B2Improve forecast accuracyProgram control using stored programsDigital computer detailsComputer architectureEngineering
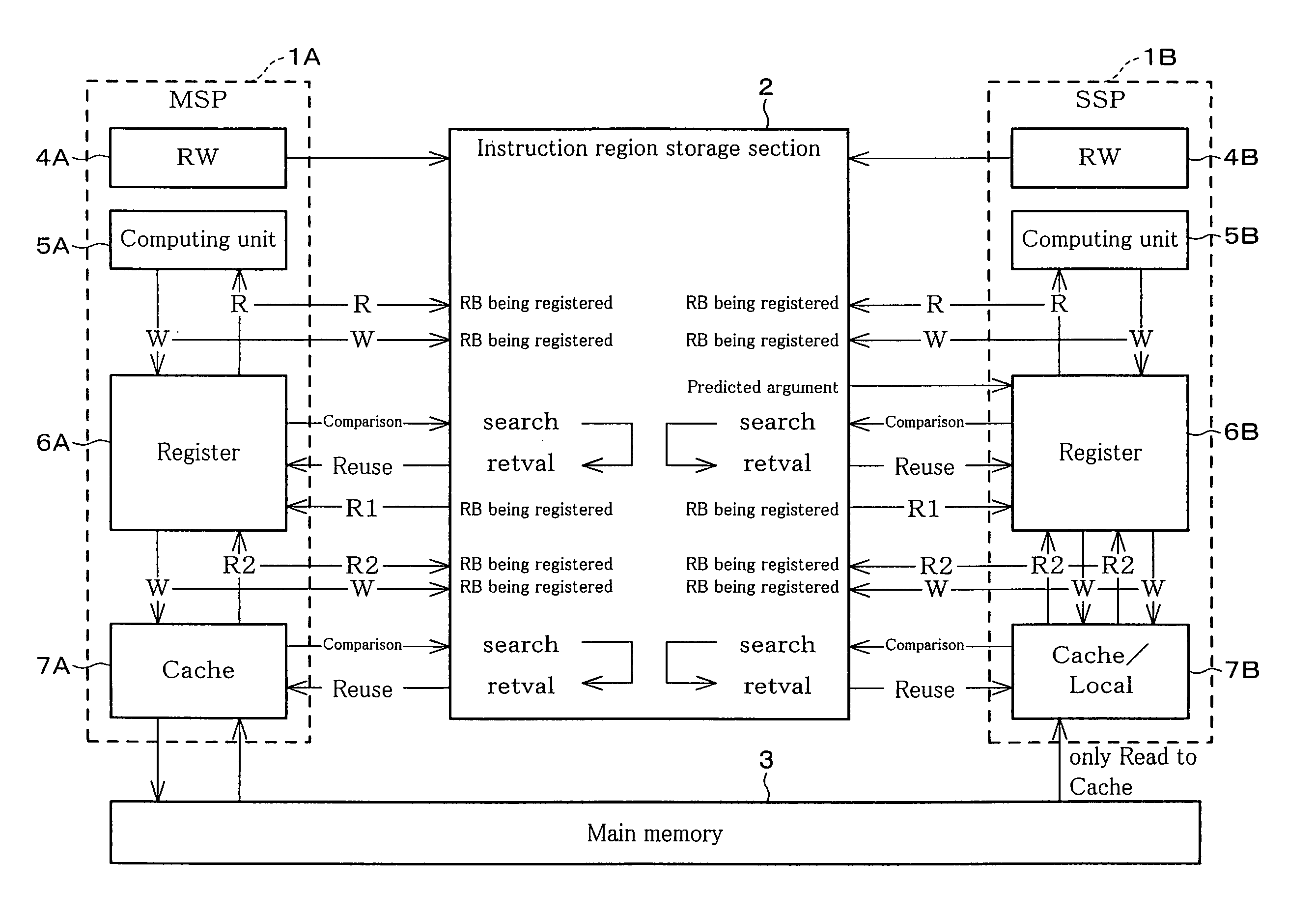
A method and apparatus is provided for significantly speeding-up program execution in a data processing device. The data processing device is provided with a specialized instruction region storage section comprising content addressable memory (CAM) and random access memory (RAM) that operatively functions as an instruction sequence reuse table which is capable of registering / storing sequences of program instructions and corresponding instruction sequence output data as input / output (I / O) groups for potential future use in place of re-executing identical portions of program code. The data processing device includes at least one instruction stream processor which includes a computing unit for executing instructions and a dependency relationship analysis unit or “reuse window” unit (RW) that analyzes instruction sequence patterns from regions of instructions stored in a main memory to determine if the patterns can be divided up into smaller partitions that have no interdependencies and hence are potential candidates for reuse.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com