Patents
Literature
1151 results about "Instruction sequence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Instruction sequencing The order in which the instructions in a program are carried out. Normally the sequence proceeds in a linear fashion through the program, and the address of the instructions is obtained from the program counter in the control unit.
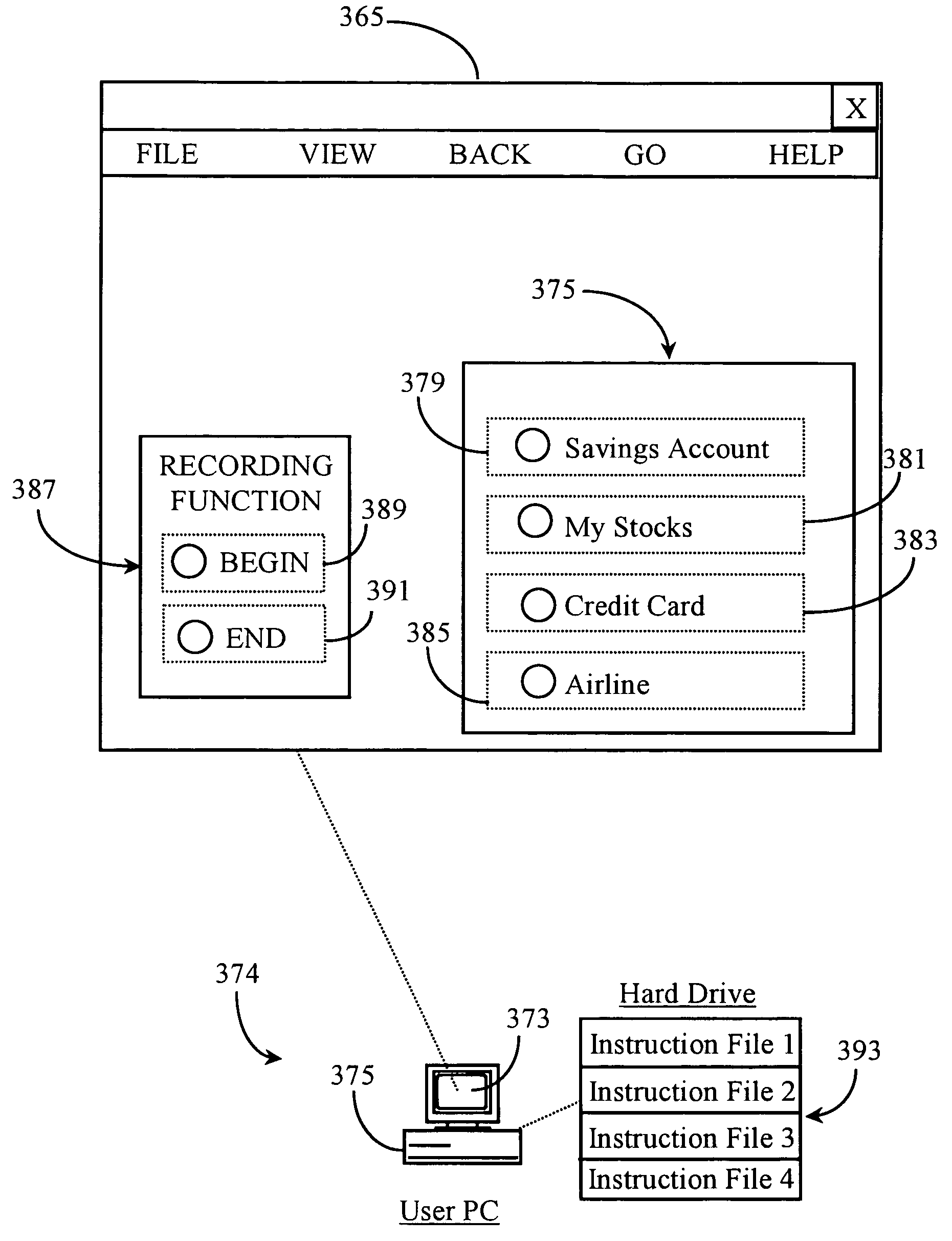
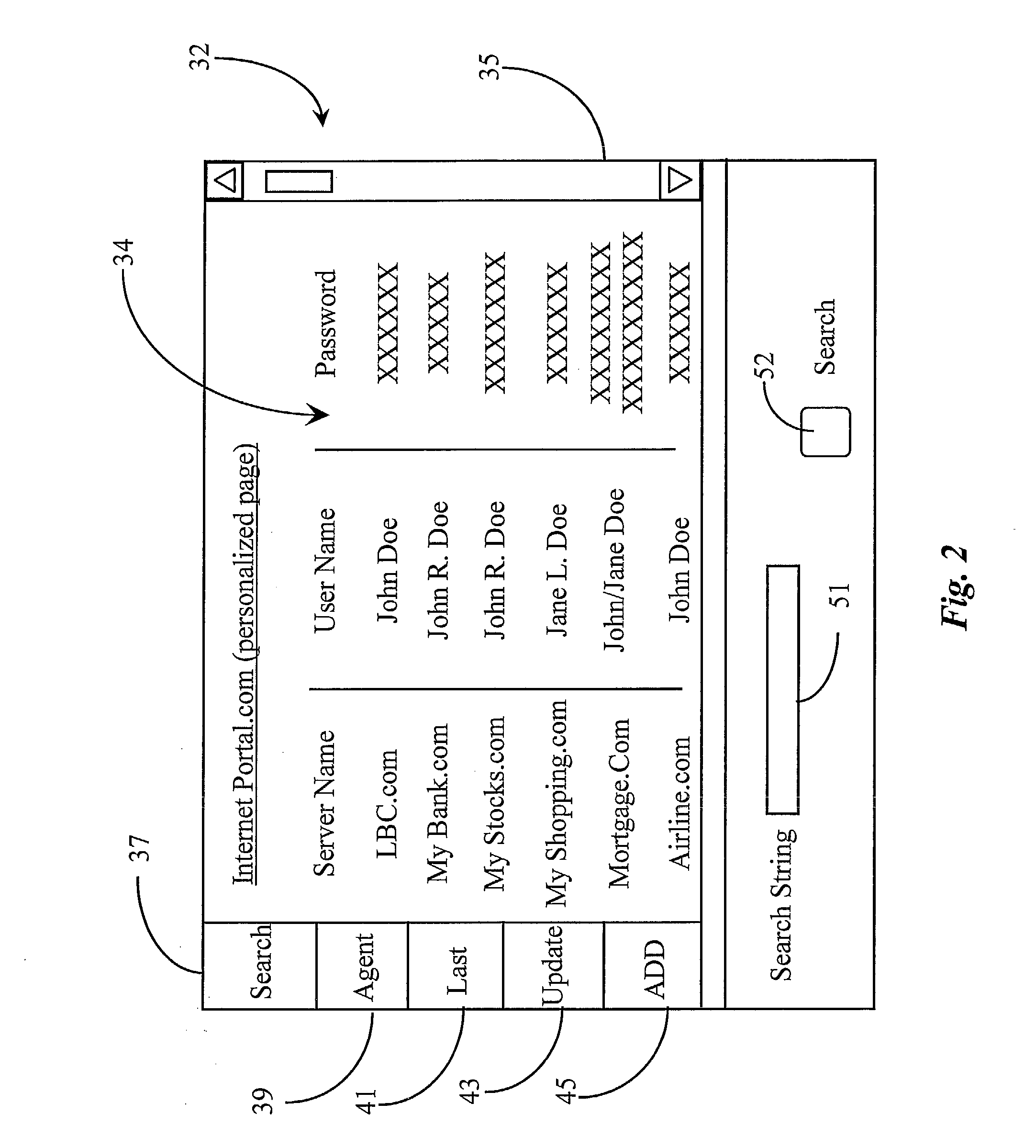
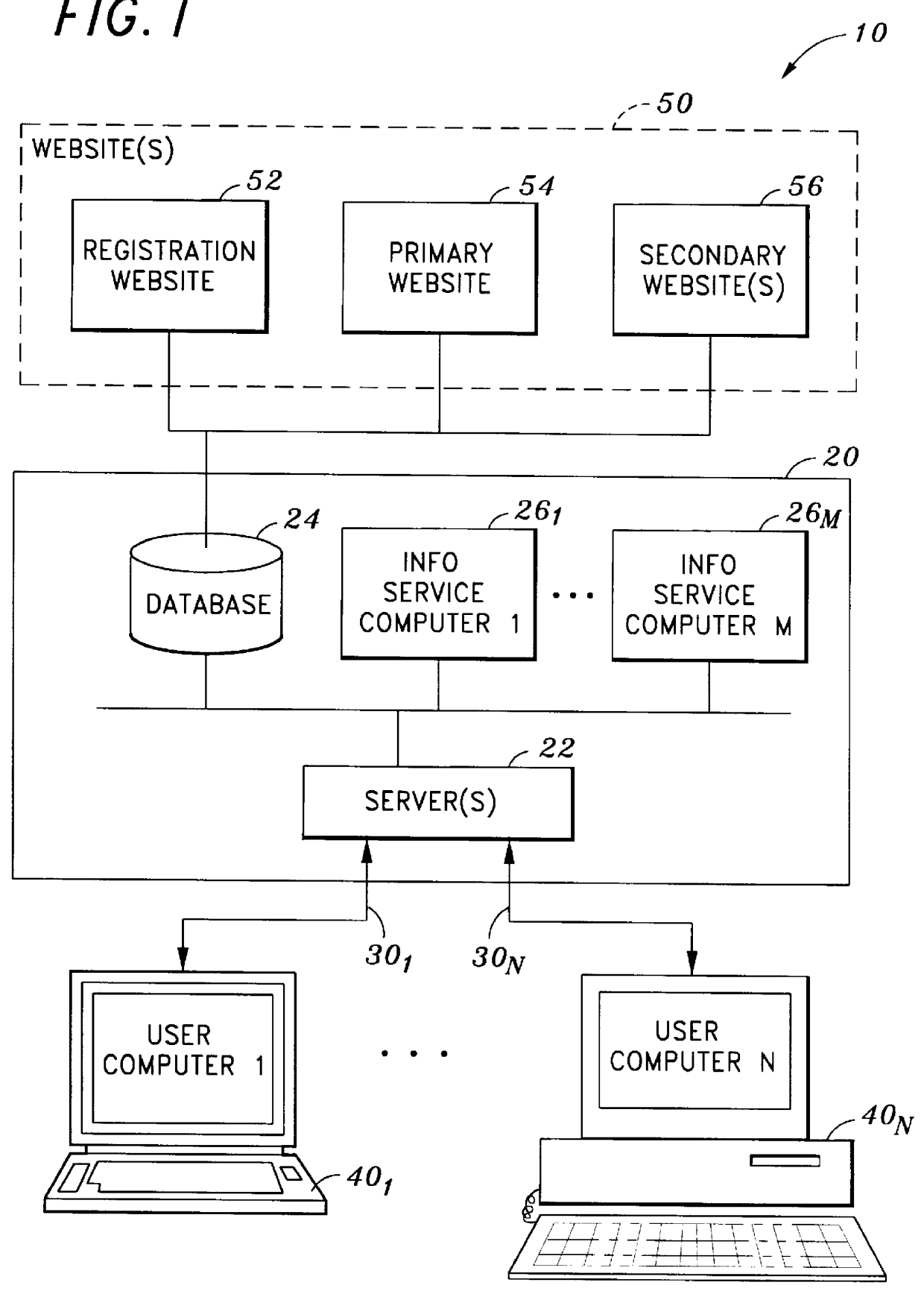
Method and apparatus for providing automation to an internet navigation application
InactiveUS7200804B1Reduce manual inputLower capability requirementsWeb data indexingNatural language data processingComputer moduleThe Internet
A software application for enabling creation and execution of an automated browser navigation sequence is provided. The software application comprises a session recording module for recording parameters associated with a manual navigation sequence, a file creation module for converting data of a manual session into data comprising an executable sequence of instructions for conducting an automated navigation sequence, and an application-program-interface module for integrating a functional capability with the automated navigation sequence. The automated navigation sequence is characterized in that a completely automated browser-navigation sequence performed by the browser application is enabled through execution of the executable instruction sequence created from the recorded parameters of the manual navigation sequence.
Owner:YODLEE COM INC
Methods and apparatus for fault-detecting and fault-tolerant process control
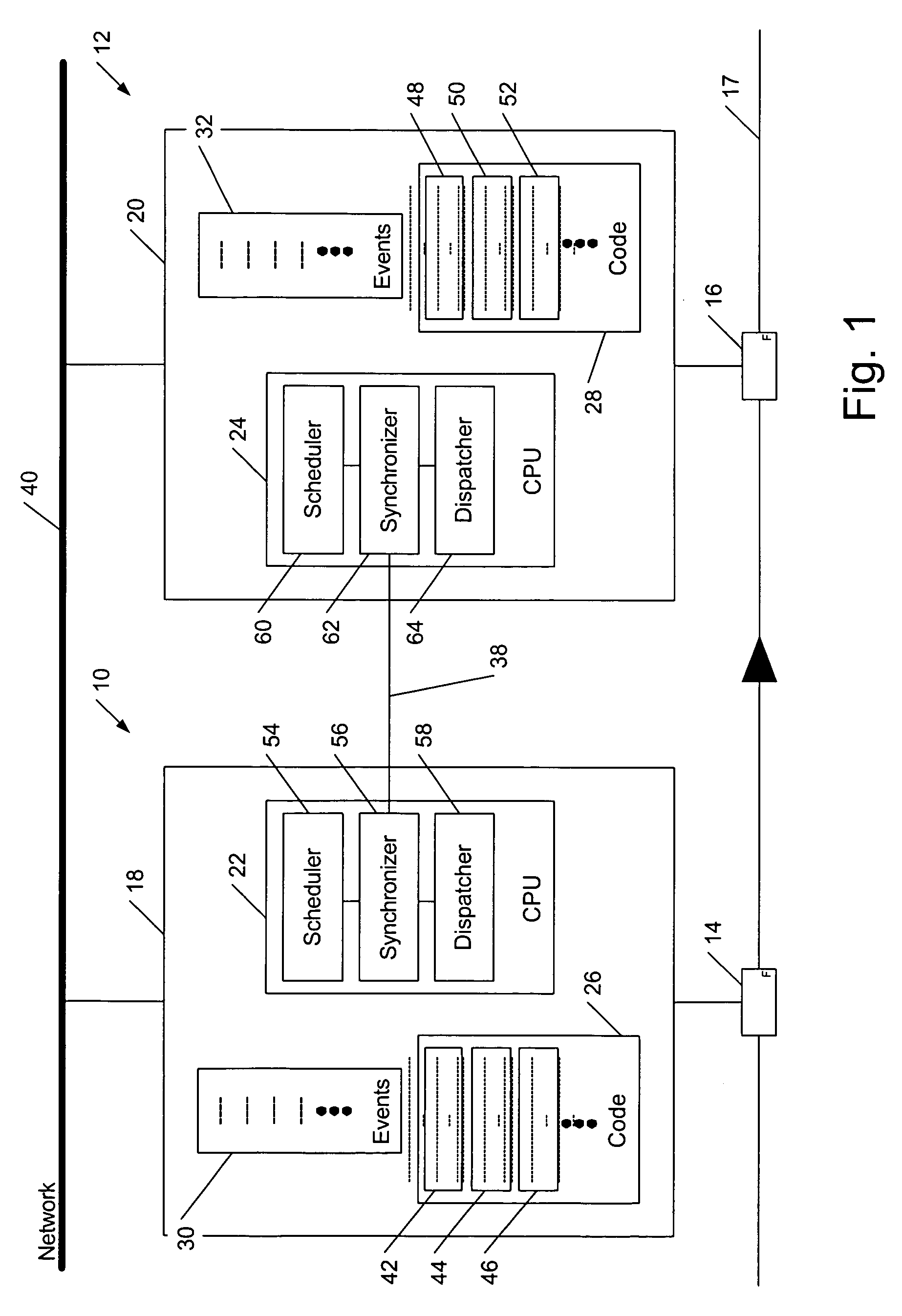
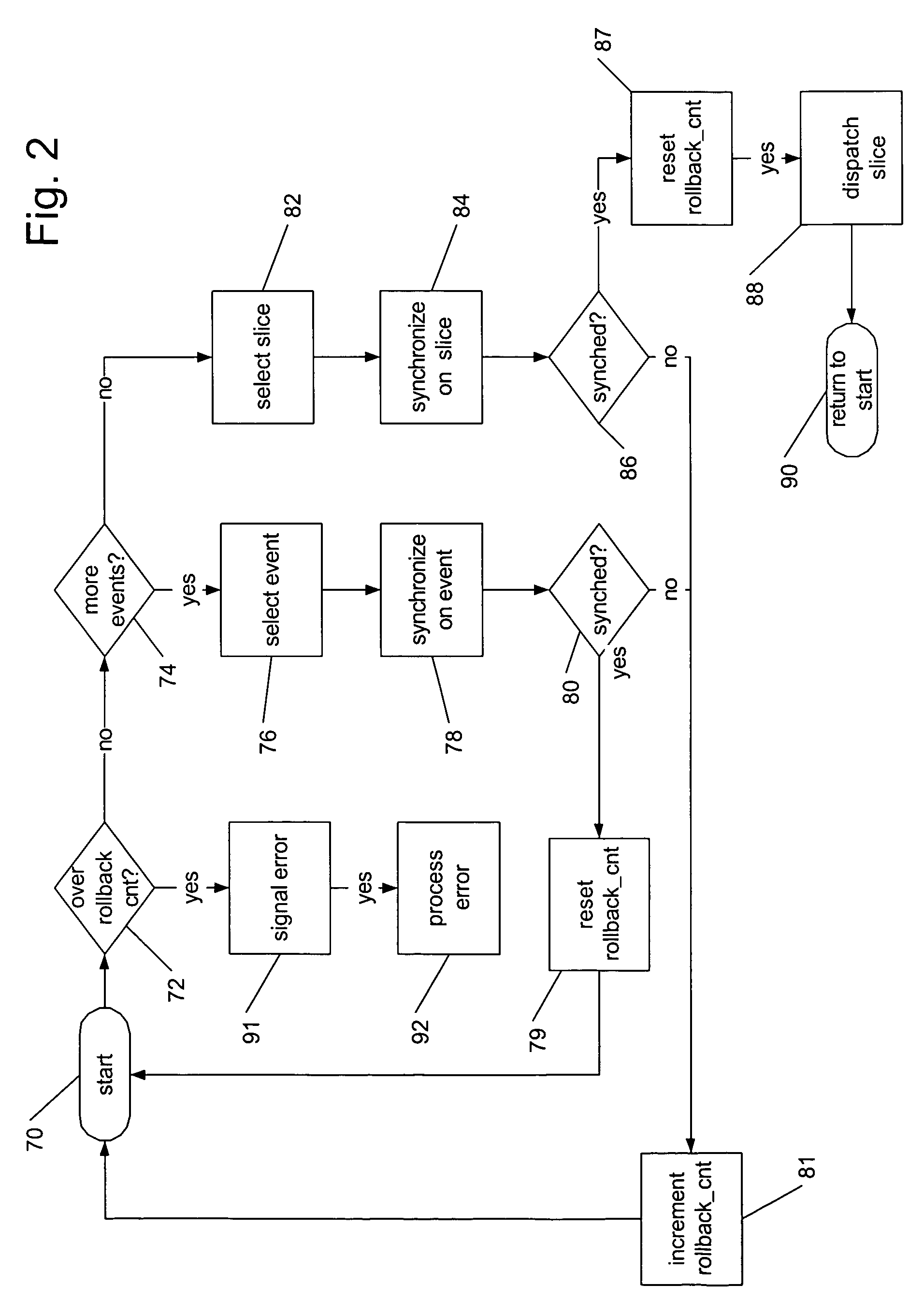
A method of process, industrial, environmental or other control includes executing a first sequence of instructions in a first process (or thread) and executing a second sequence of instructions in a second process (or thread) that is loosely coupled with the first. States of the first and second processes are compared following their respective completions of the first and second instruction sequences. The comparison can cover registers, memory, flags, interrupts, tasks, and / or events in each of the respective processes. Execution of further instruction sequences by either process is delayed pending a favorable comparison of the process states. If the process achieve comparable states, the first process can take up execution of a third sequence, while the second process takes up execution of a fourth sequence. In the event that one of the processes does not complete its respective instruction sequence within a set period of time, or if the process states do not otherwise favorably compare after execution of the respective sequences, the method calls for signaling an error. A device for process, industrial, environmental or other control operates in accord with such a method.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC SYST USA INC
Method and Apparatus for Providing Automation to an Internet Navigation Application
InactiveUS20070180380A1Reduce manual inputLower capability requirementsWeb data indexingDigital computer detailsThe InternetInstruction sequence
A software application for enabling creation and execution of an automated browser navigation sequence is provided. The software application comprises a session recording module for recording parameters associated with a manual navigation sequence, a file creation module for converting data of a manual session into data comprising an executable sequence of instructions for conducting an automated navigation sequence, and an application-program-interface module for integrating a functional capability with the automated navigation sequence. The automated navigation sequence is characterized in that a completely automated browser-navigation sequence performed by the browser application is enabled through execution of the executable instruction sequence created from the recorded parameters of the manual navigation sequence.
Owner:YODLEE COM INC
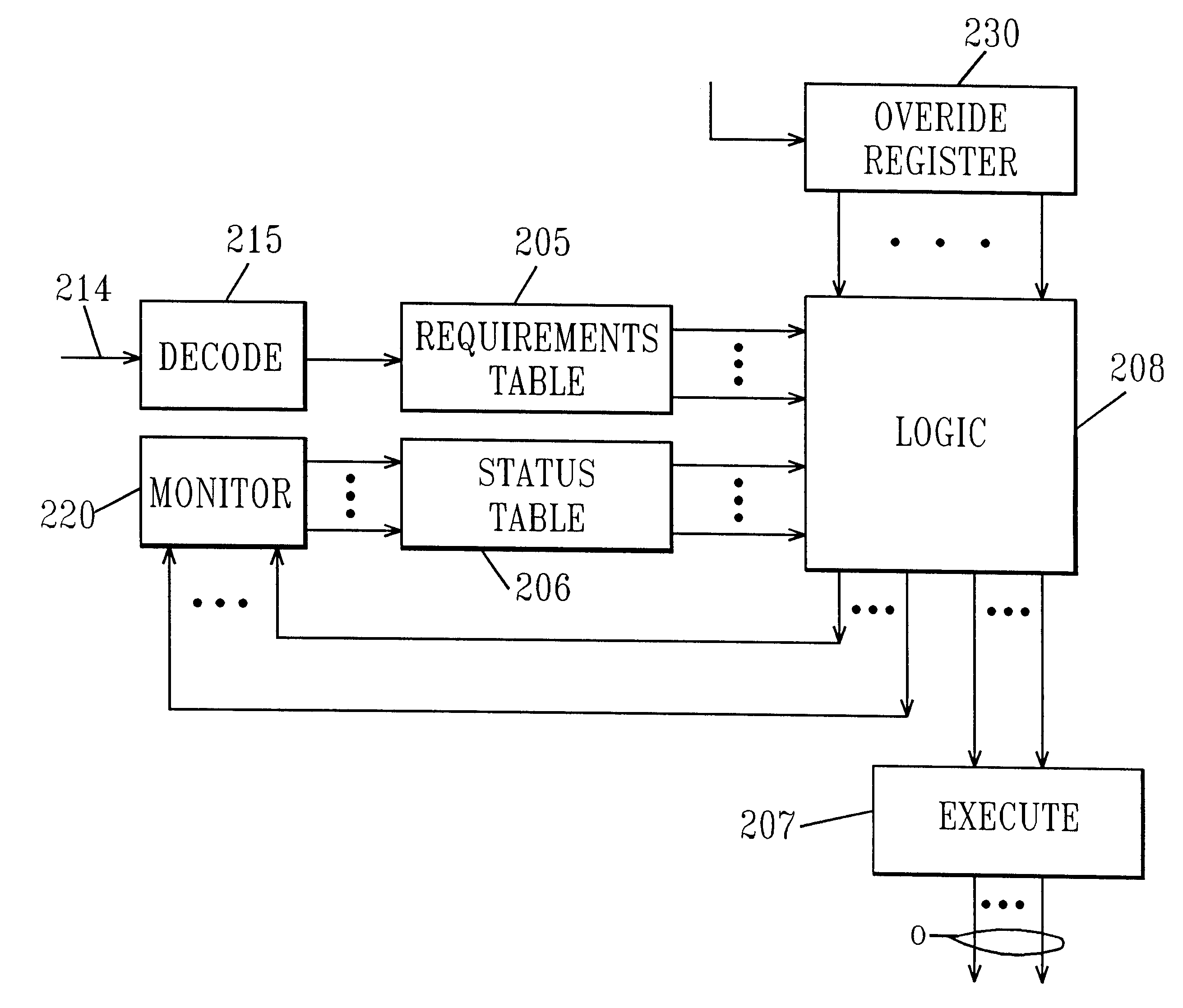
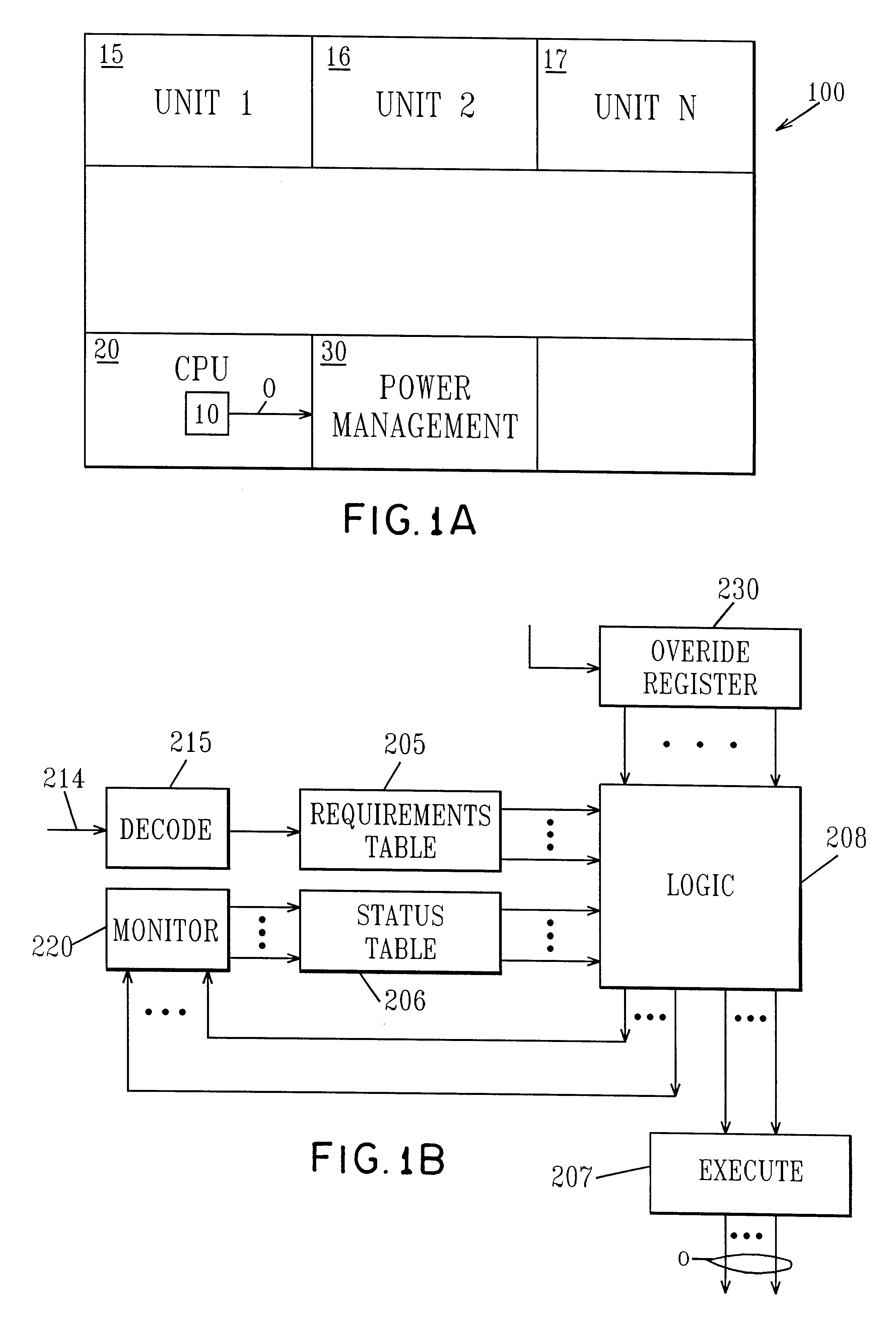
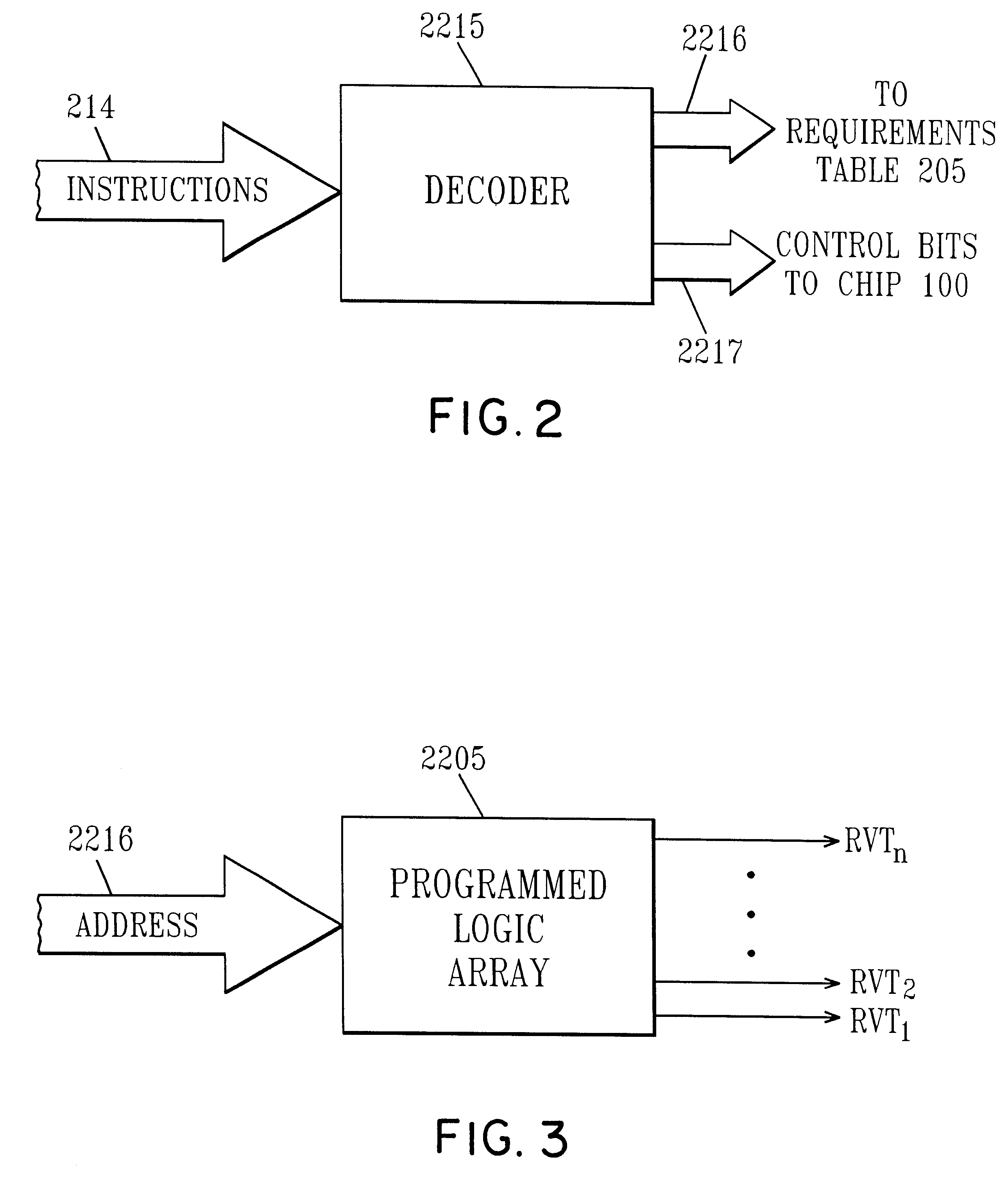
Managing Vt for reduced power using a status table
InactiveUS6345362B1Improve performanceReduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementHemt circuitsLow power dissipation
An integrated circuit includes a CPU, a power management unit and plural functional units each dedicated to executing different functions. The power management unit controls the threshold voltage of the different functional units to optimize power / performance operation of the circuit and intelligent power management control responds to the instruction stream and decodes each instruction in turn. This information identifies which of the functional units are required for the particular instruction and by comparing that information to power status, the intelligent power control determines whether the functional units required to execute the command are at the optimum power level. If they are, the command is allowed to proceed, otherwise the intelligent power control either stalls the instruction sequence or modifies process speed.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Cycle segmented prefix circuits
InactiveUS6609189B1Improve performanceAvoid performanceComputation using non-contact making devicesGeneral purpose stored program computerExtensibilityScalar processor
The poor scalability of existing superscalar processors has been of great concern to the computer engineering community. In particular, the critical-path delays of many components in existing implementations grow quadratically with the issue width and the window size. This patent presents a novel way to reimplement these components and reduce their critical-path delay growth. It then describes an entire processor microarchitecture, called the Ultrascalar processor, that has better critical-path delay growth than existing superscalars. Most of our scalable designs are based on a single circuit, a cyclic segmented parallel prefix (cspp). We observe that processor components typically operate on a wrap-around sequence of instructions, computing some associative property of that sequence. For example, to assign an ALU to the oldest requesting instruction, each instruction in the instruction sequence must be told whether any preceding instructions are requesting an ALU. Similarly, to read an argument register, an instruction must somehow communicate with the most recent preceding instruction that wrote that register. A cspp circuit can implement such functions by computing for each instruction within a wrap-around instruction sequence the accumulative result of applying some associative operator to all the preceding instructions. A cspp circuit has a critical path gate delay logarithmic in the length of the instruction sequence. Depending on its associative operation and its layout, a cspp circuit can have a critical path wire delay sublinear in the length of the instruction sequence.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Compiler for optimizing memory instruction sequences by marking instructions not having multiple memory address paths
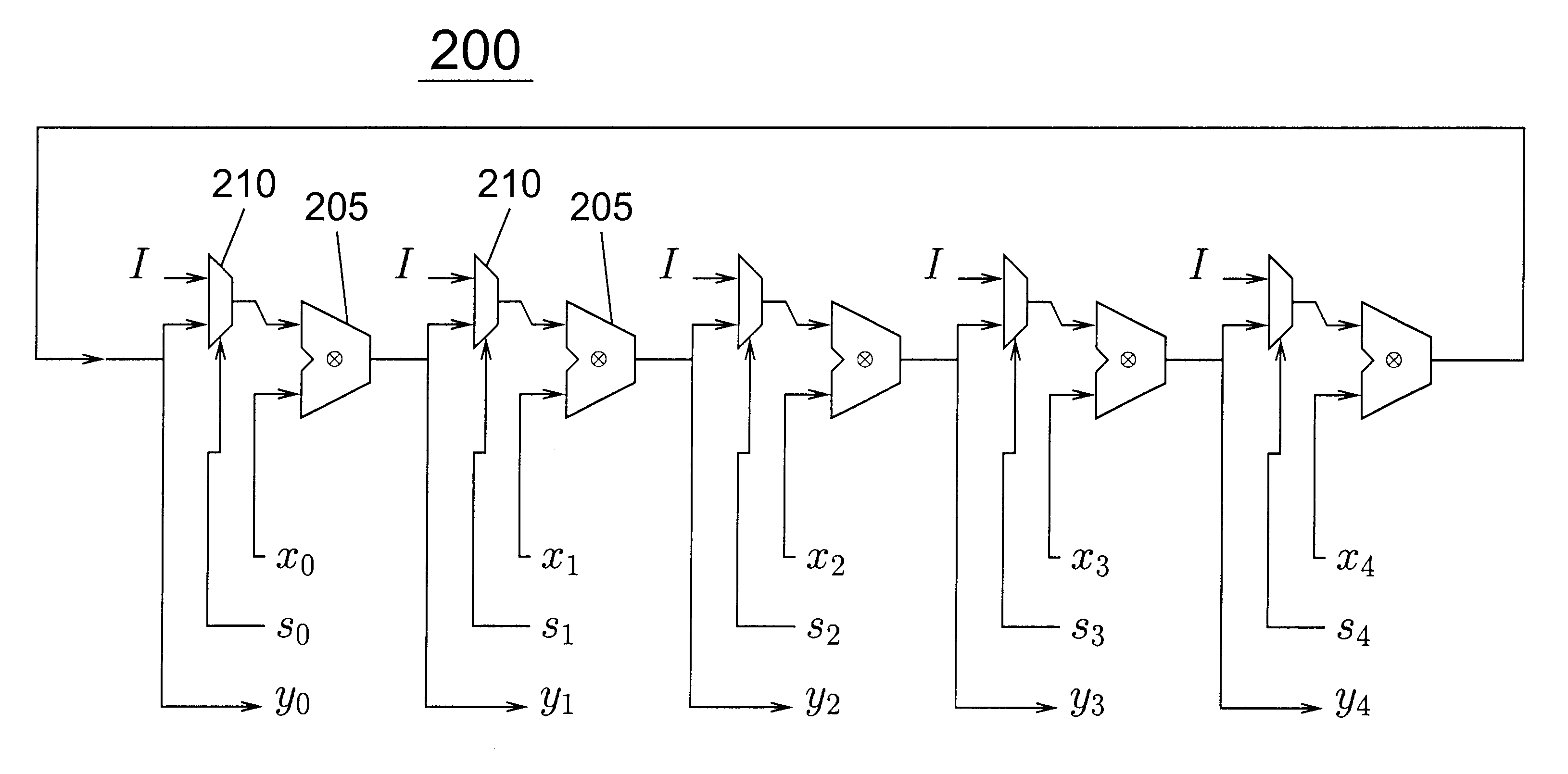
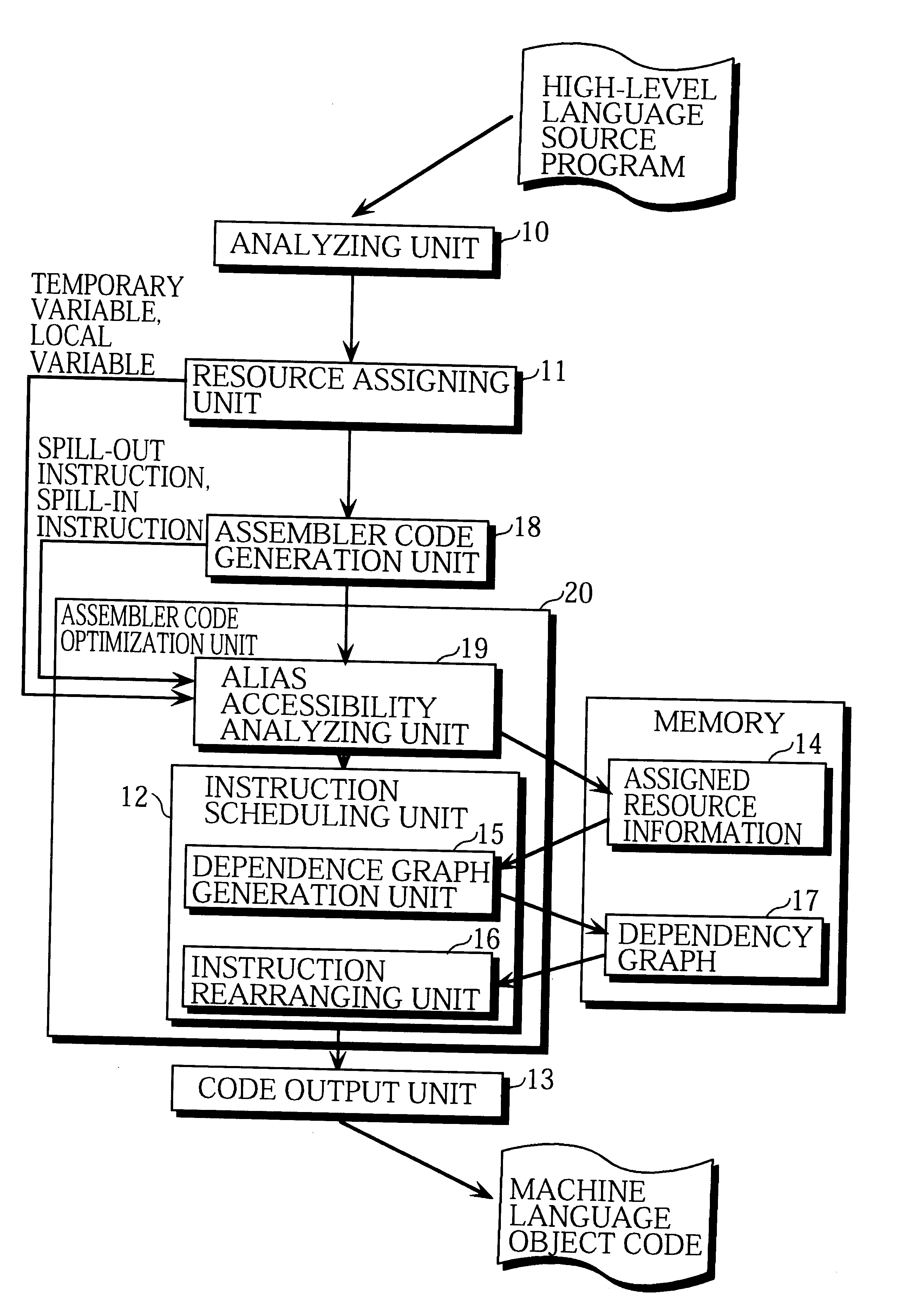
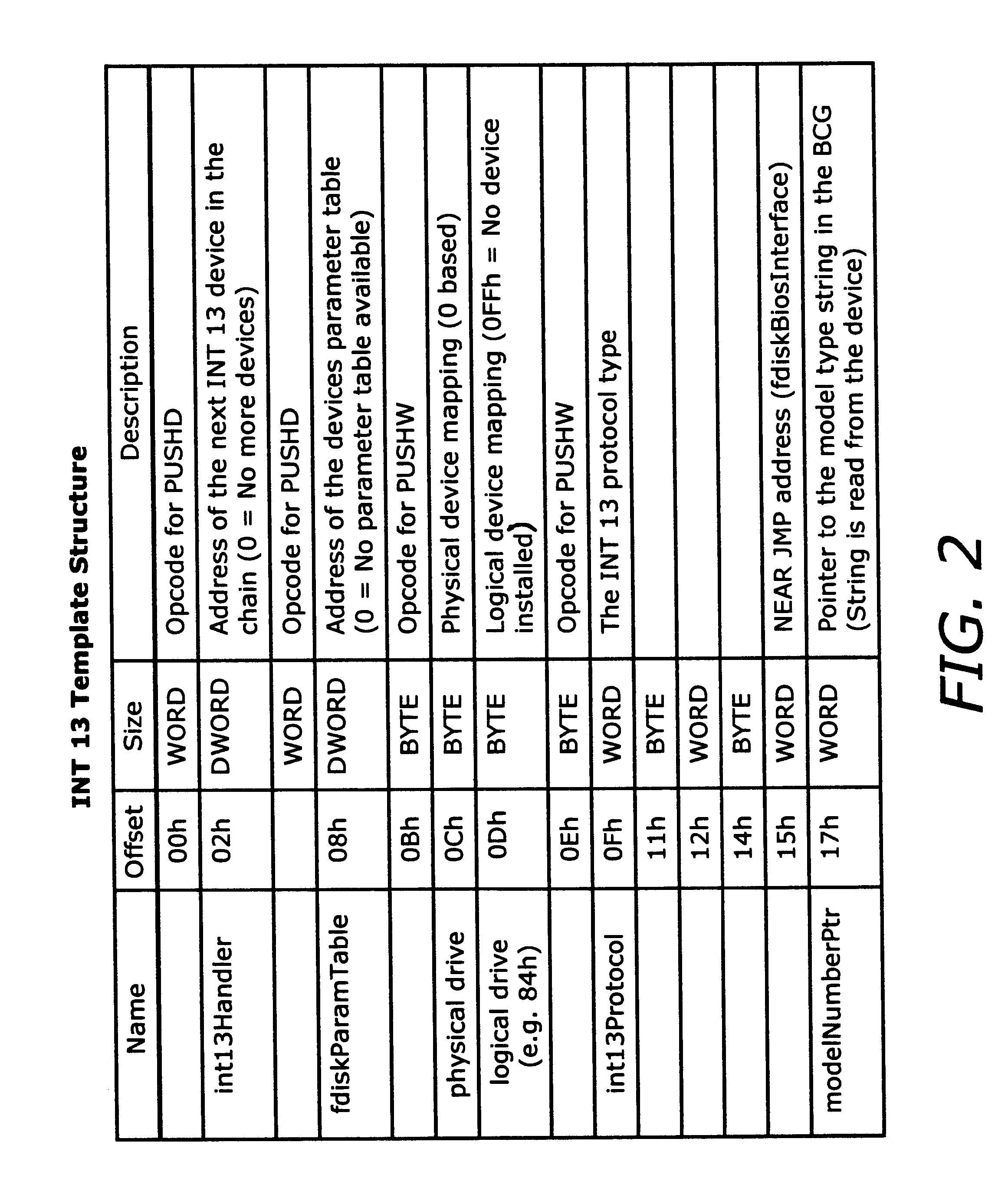
Internal variables generated by a compiler are assigned to machine resources such as registers and memory by the resource assigning unit 11, and when the assembler code generation unit 18 has outputted an instruction sequence, the alias accessibility analyzing unit 19 registers memory access instructions in the instruction sequence in the assigned resource information 14 according to whether the instructions have a possibility of access by alias. The assembler code optimization unit 20 refers to the assigned resource information 14 and performs optimization at assembler level, thereby reducing the program size and execution time of the instruction sequence.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
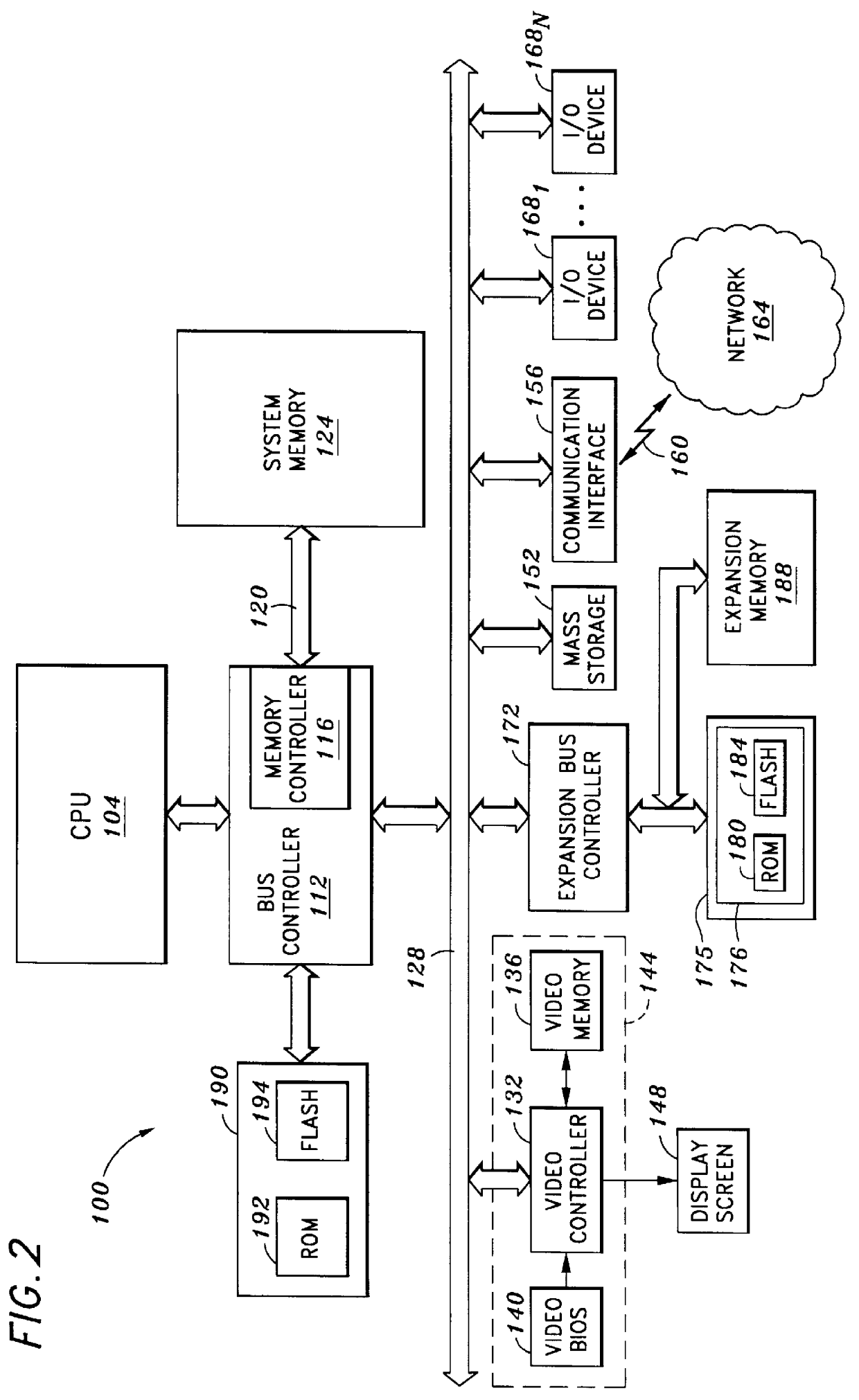
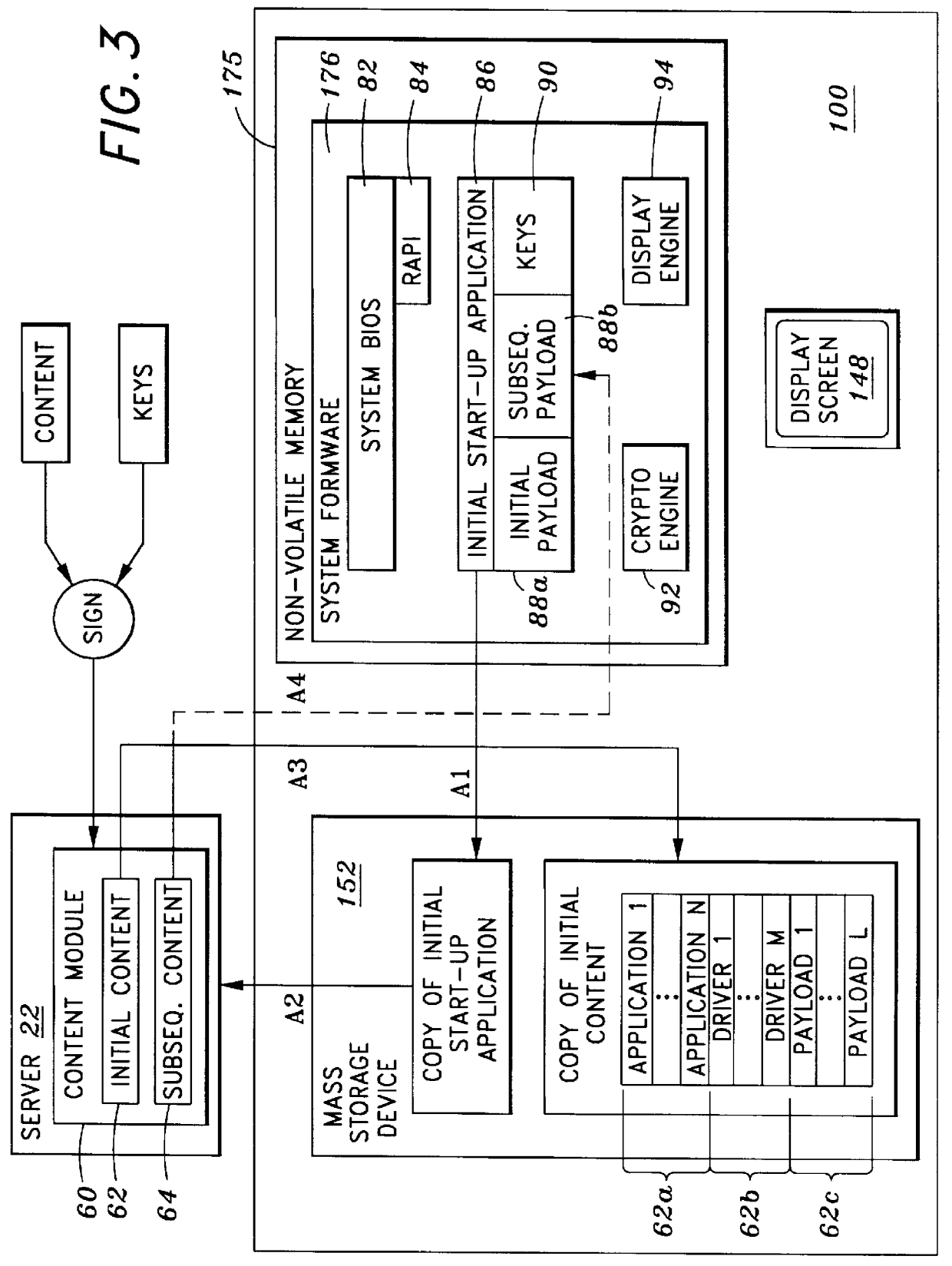
System and method for securely utilizing basic input and output system (BIOS) services
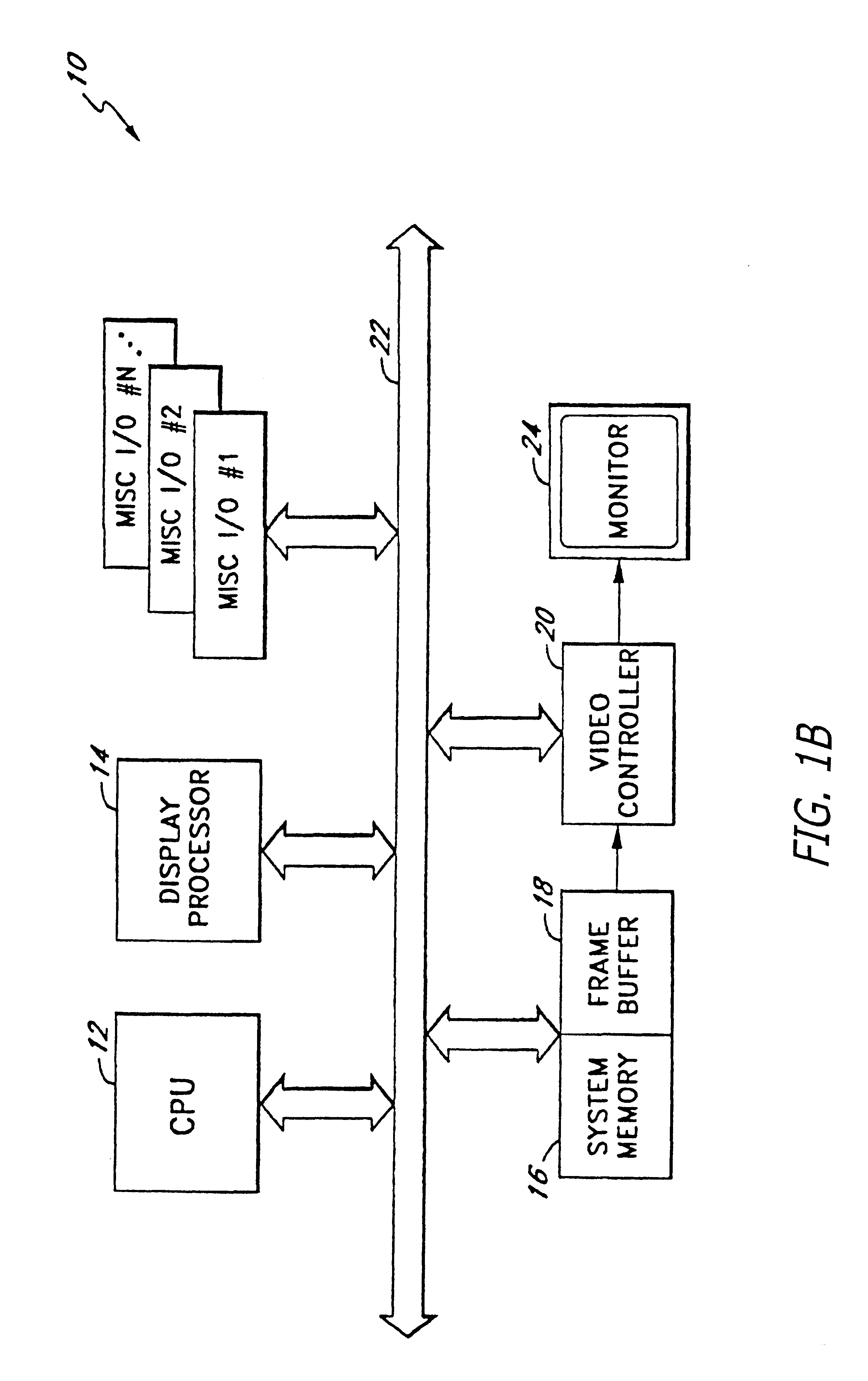
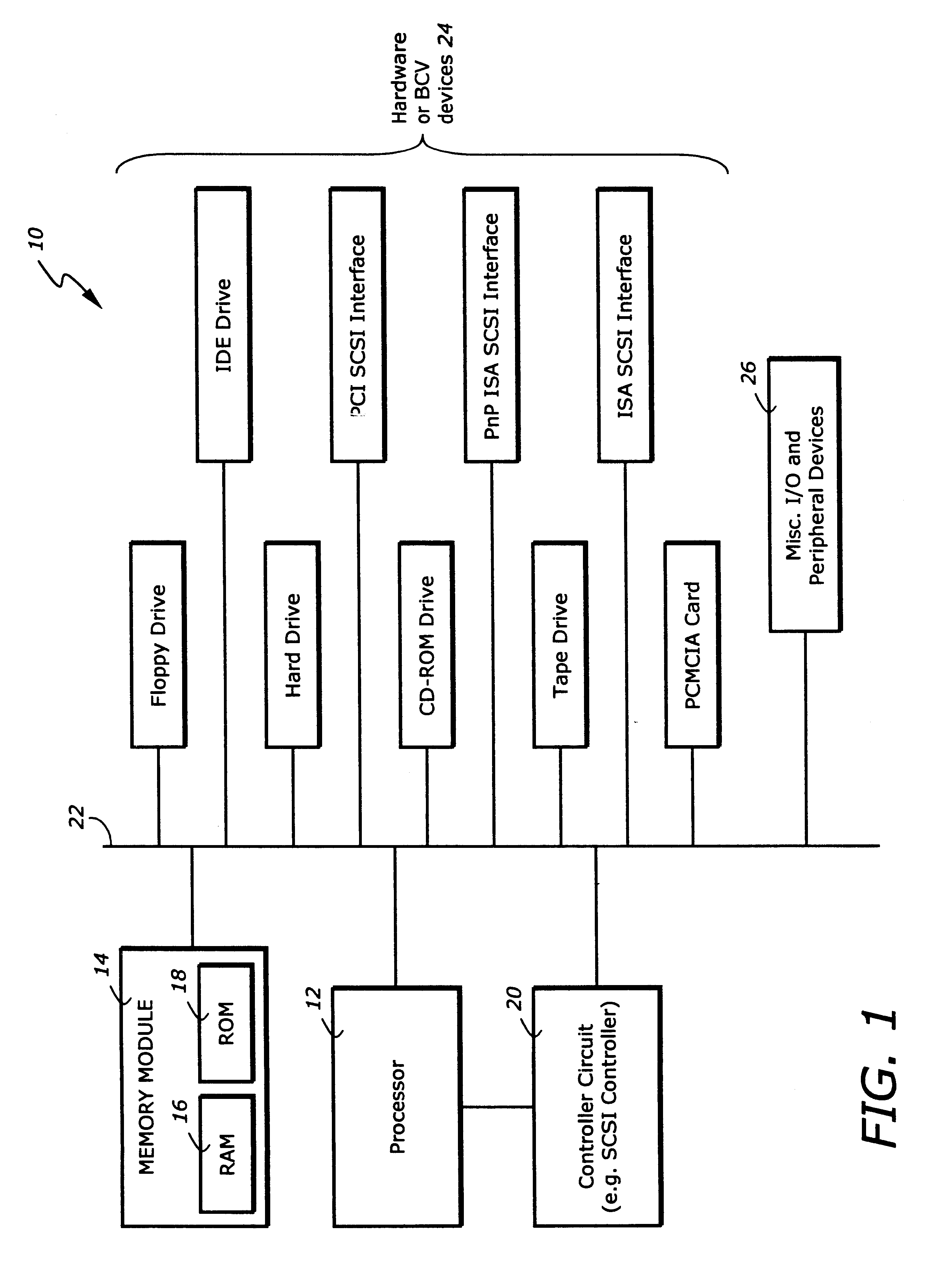
InactiveUS6148387AResource allocationDigital data processing detailsVirtual memorySoftware engineering
In accordance with one aspect of the current invention, the system comprises a memory for storing instruction sequences by which the processor-based system is processed, where the memory includes a physical memory and a virtual memory. The system also comprises a processor for executing the stored instruction sequences. The stored instruction sequences include process acts to cause the processor to: map a plurality of predetermined instruction sequences from the physical memory to the virtual memory, determine an offset to one of the plurality of predetermined instruction sequences in the virtual memory, receive an instruction to execute the one of the plurality of predetermined instruction sequences, transfer control to the one of the plurality of predetermined instruction sequences, and process the one of the plurality of predetermined instruction sequences from the virtual memory. In accordance with another aspect of the present invention, the system includes an access driver to generate a service request to utilize BIOS services such that the service request contains a service request signature created using a private key in a cryptographic key pair. The system also includes an interface to verify the service request signature using a public key in the cryptographic key pair to ensure integrity of the service request.
Owner:KINGLITE HLDG INC
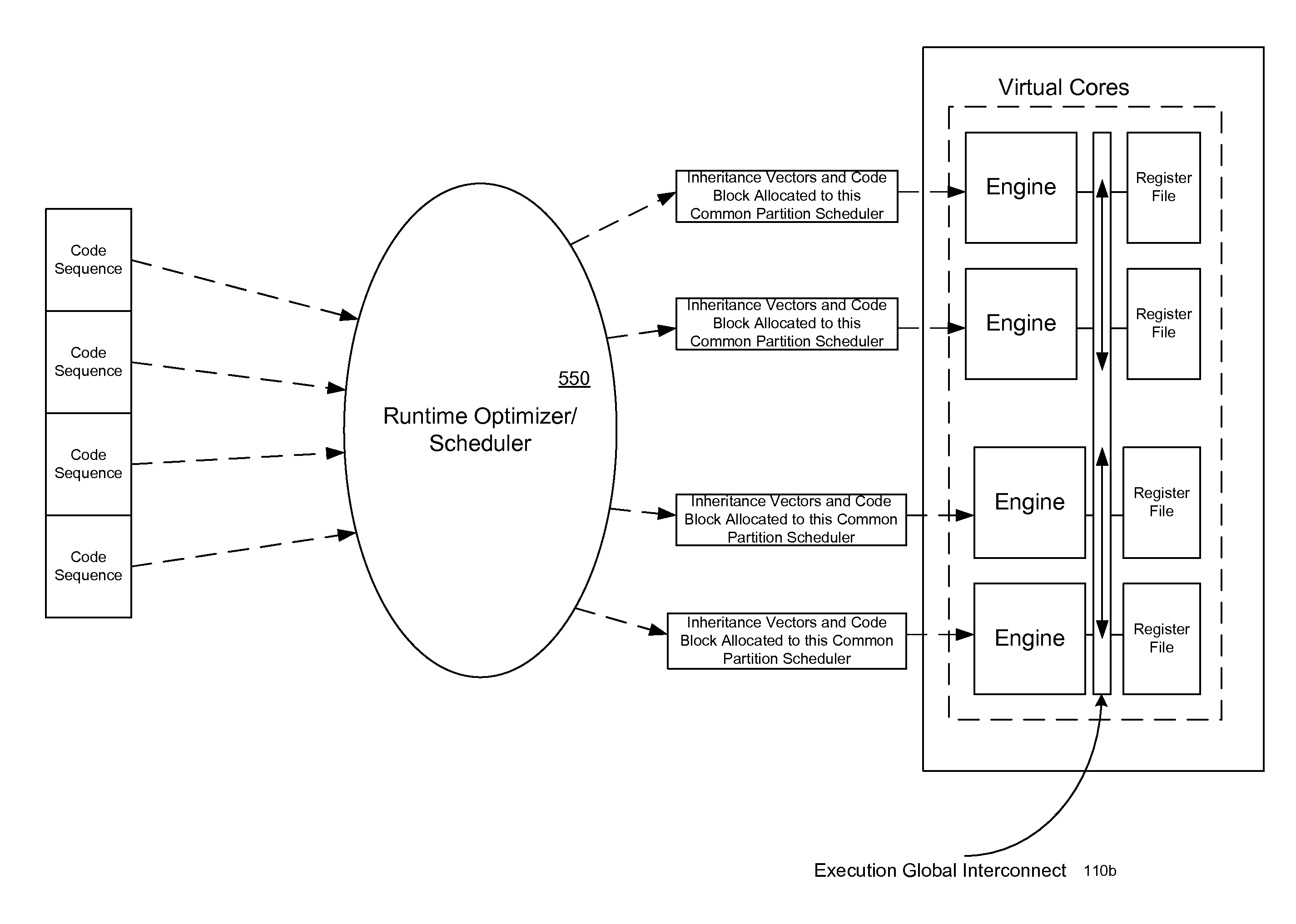
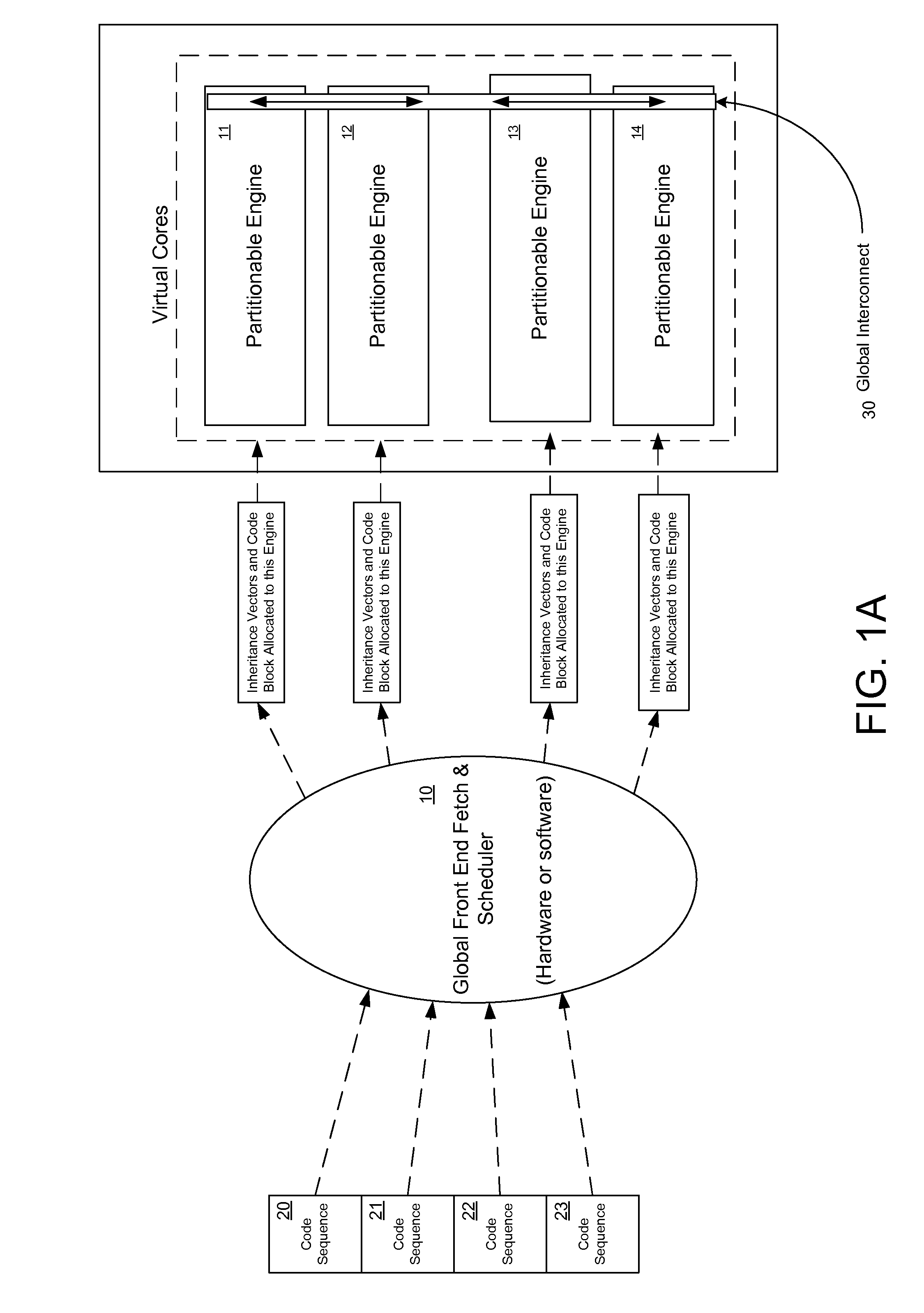
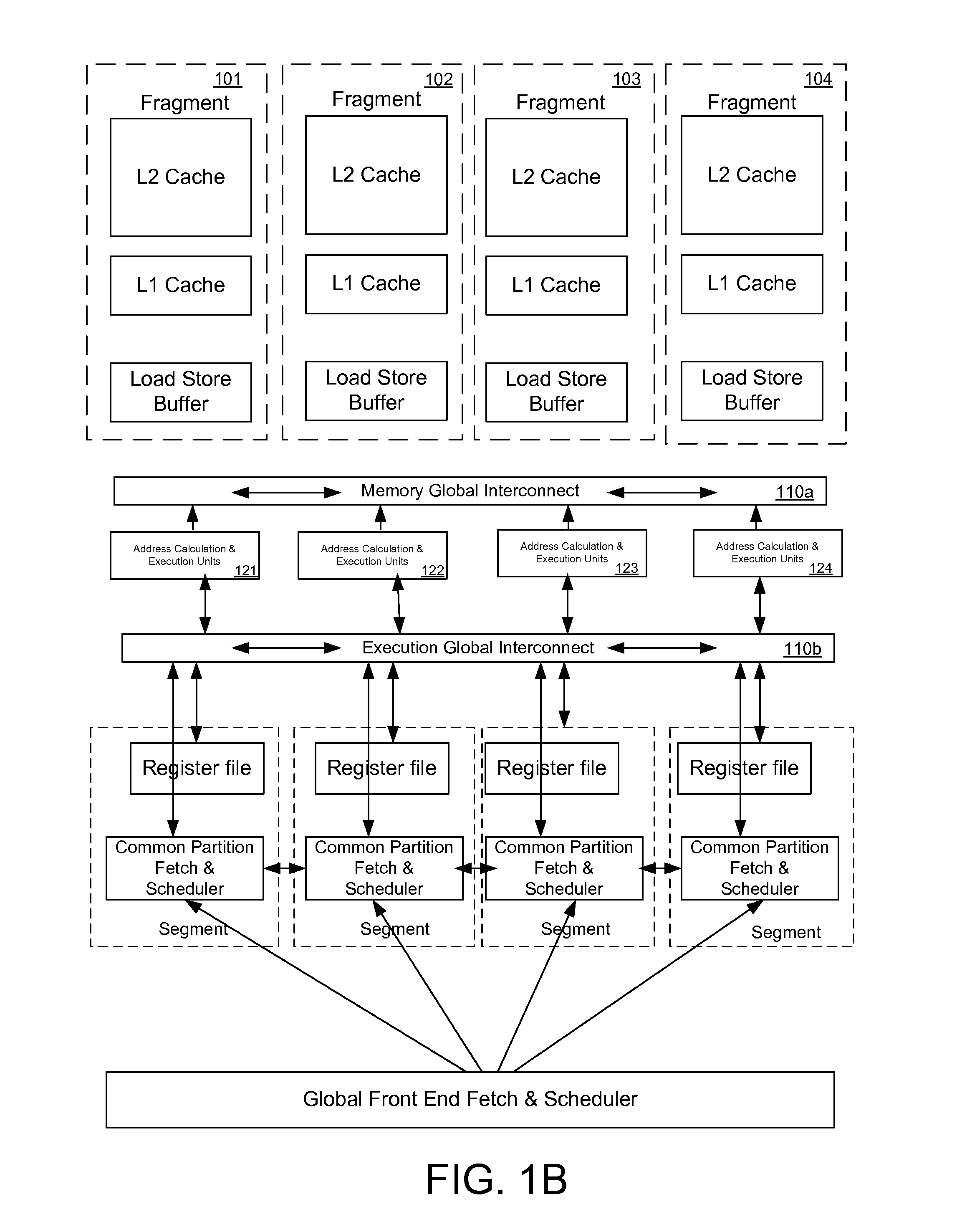
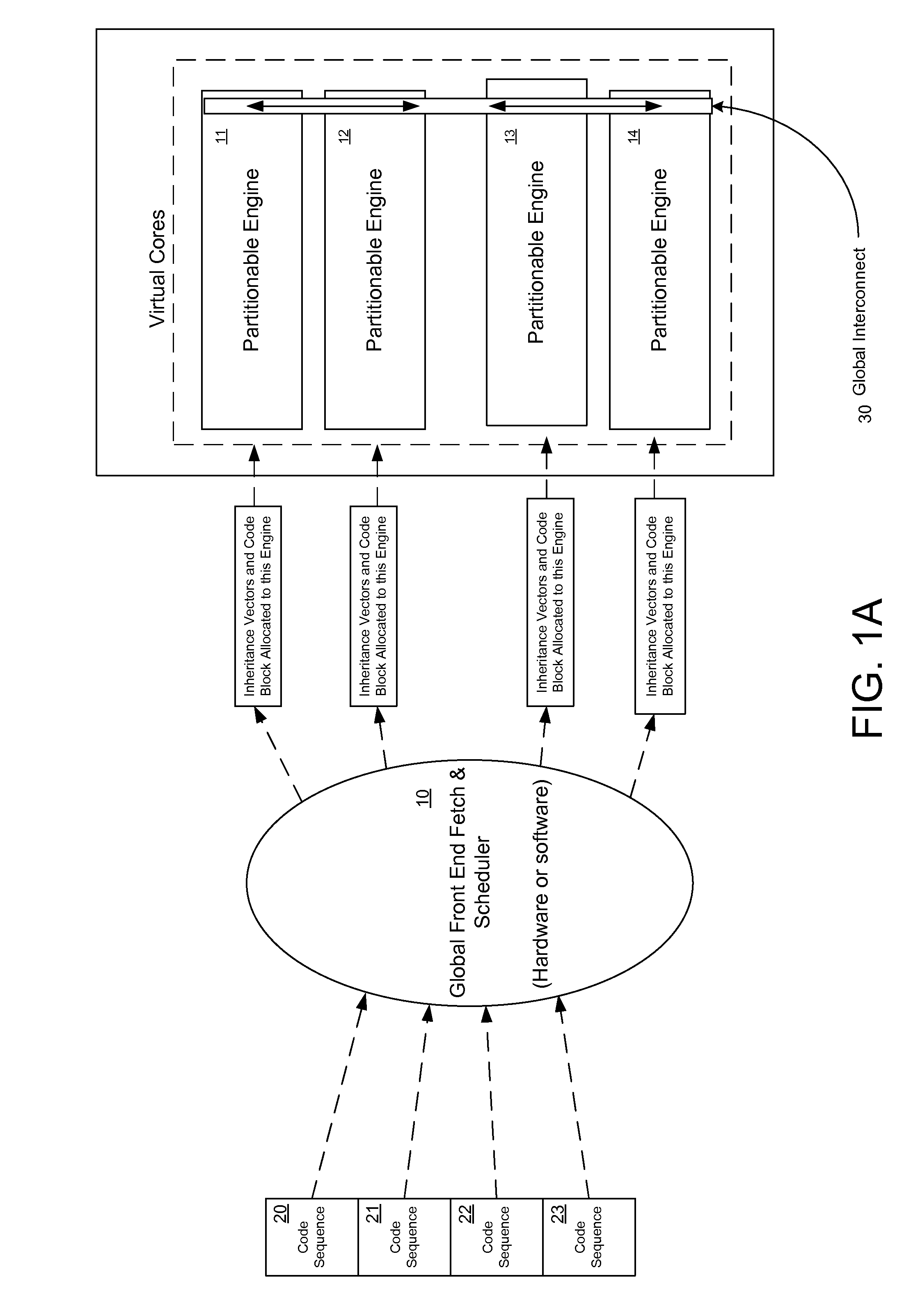
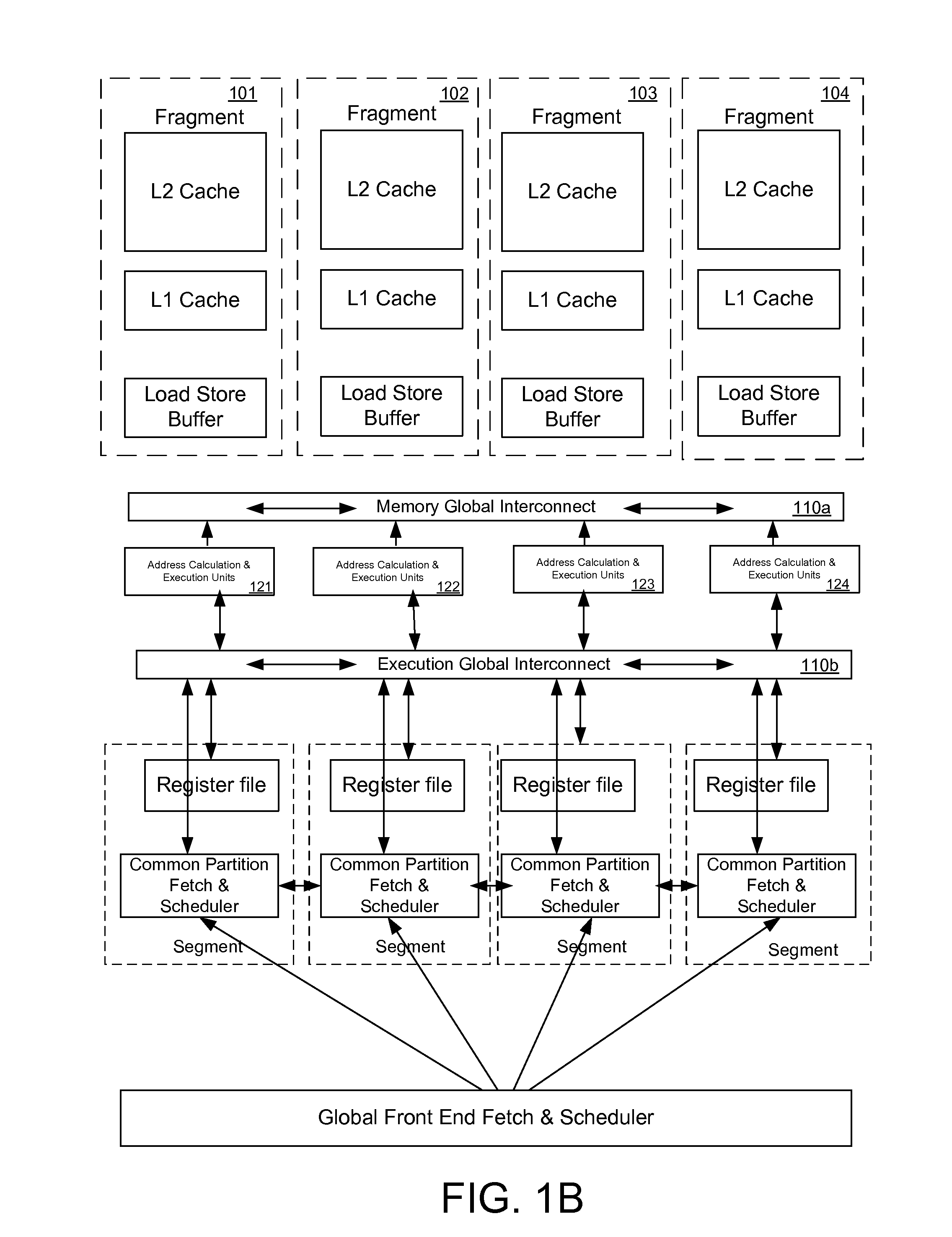
Register file segments for supporting code block execution by using virtual cores instantiated by partitionable engines
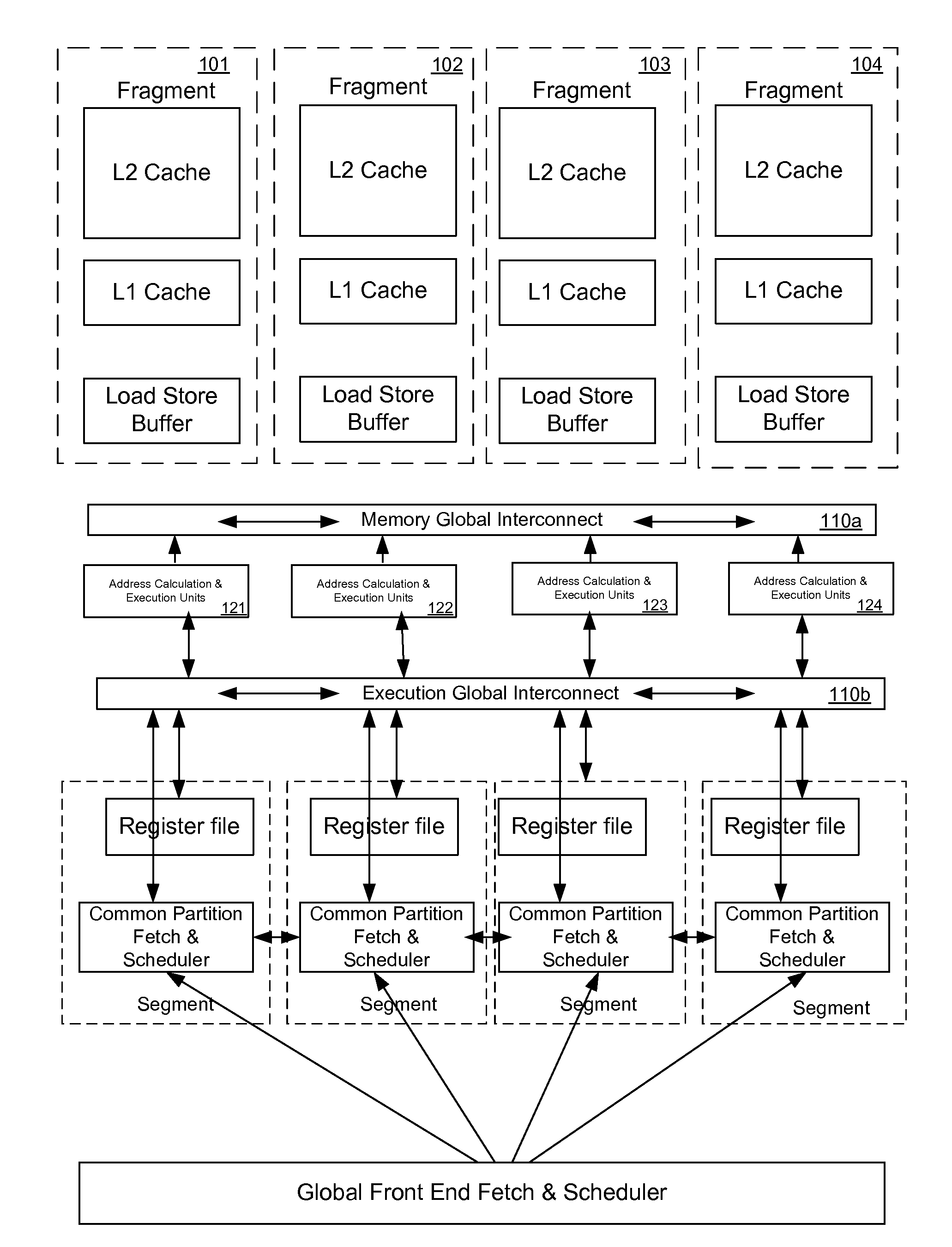
ActiveUS20120246450A1ScalingMemory architecture accessing/allocationProgram control using stored programsCoding blockProcessor register
A system for executing instructions using a plurality of register file segments for a processor. The system includes a global front end scheduler for receiving an incoming instruction sequence, wherein the global front end scheduler partitions the incoming instruction sequence into a plurality of code blocks of instructions and generates a plurality of inheritance vectors describing interdependencies between instructions of the code blocks. The system further includes a plurality of virtual cores of the processor coupled to receive code blocks allocated by the global front end scheduler, wherein each virtual core comprises a respective subset of resources of a plurality of partitionable engines, wherein the code blocks are executed by using the partitionable engines in accordance with a virtual core mode and in accordance with the respective inheritance vectors. A plurality register file segments are coupled to the partitionable engines for providing data storage.
Owner:INTEL CORP
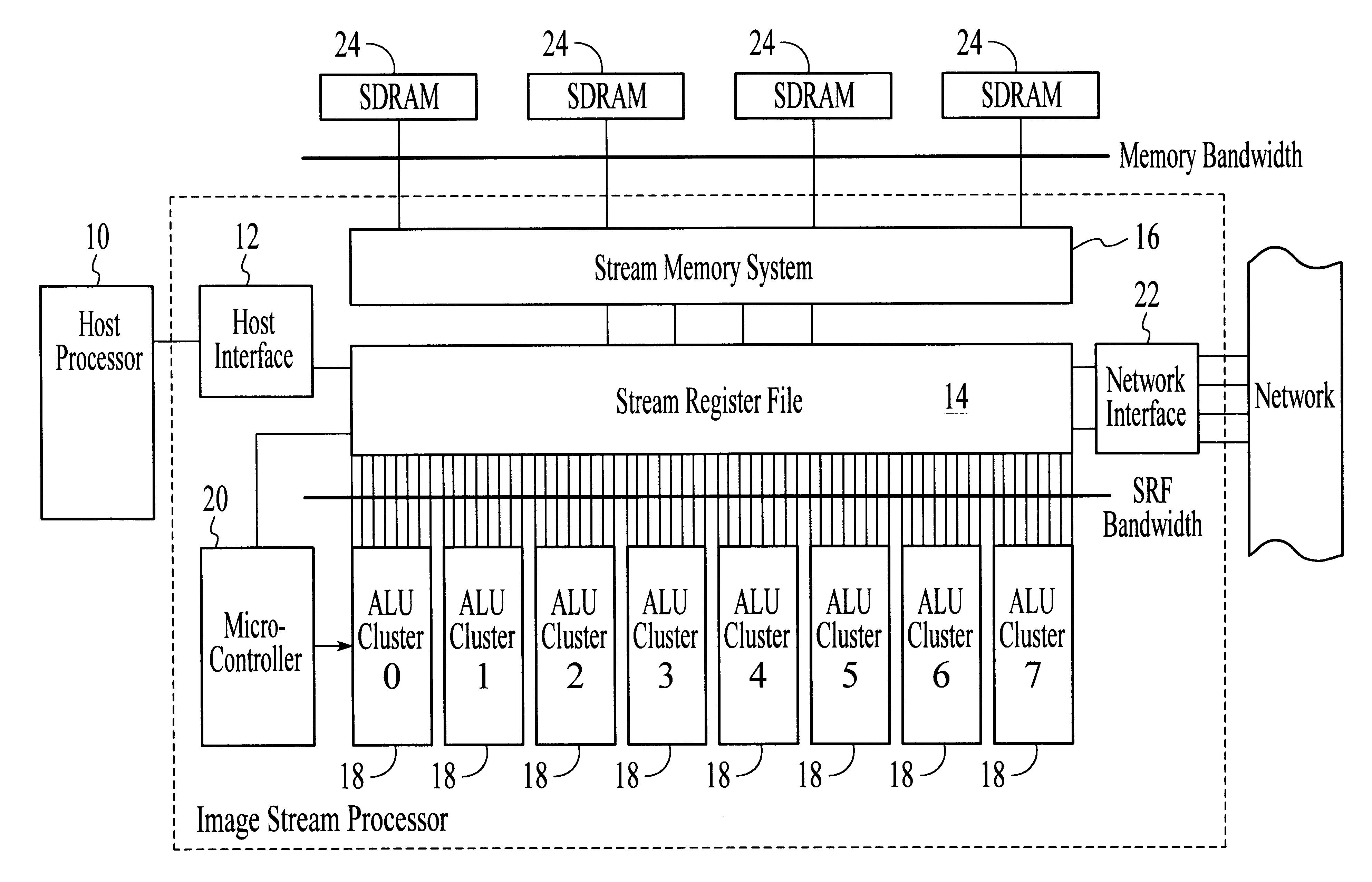
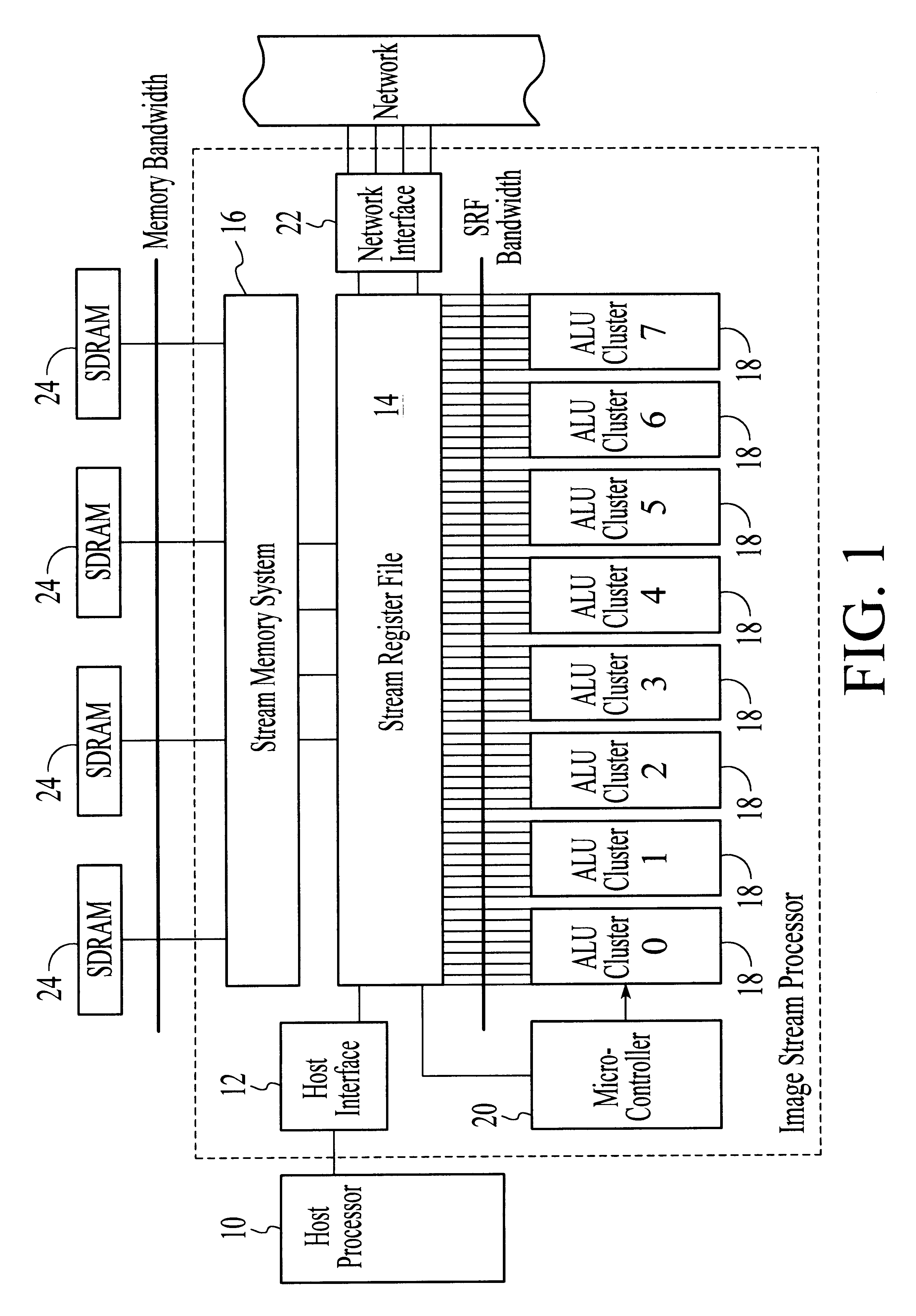
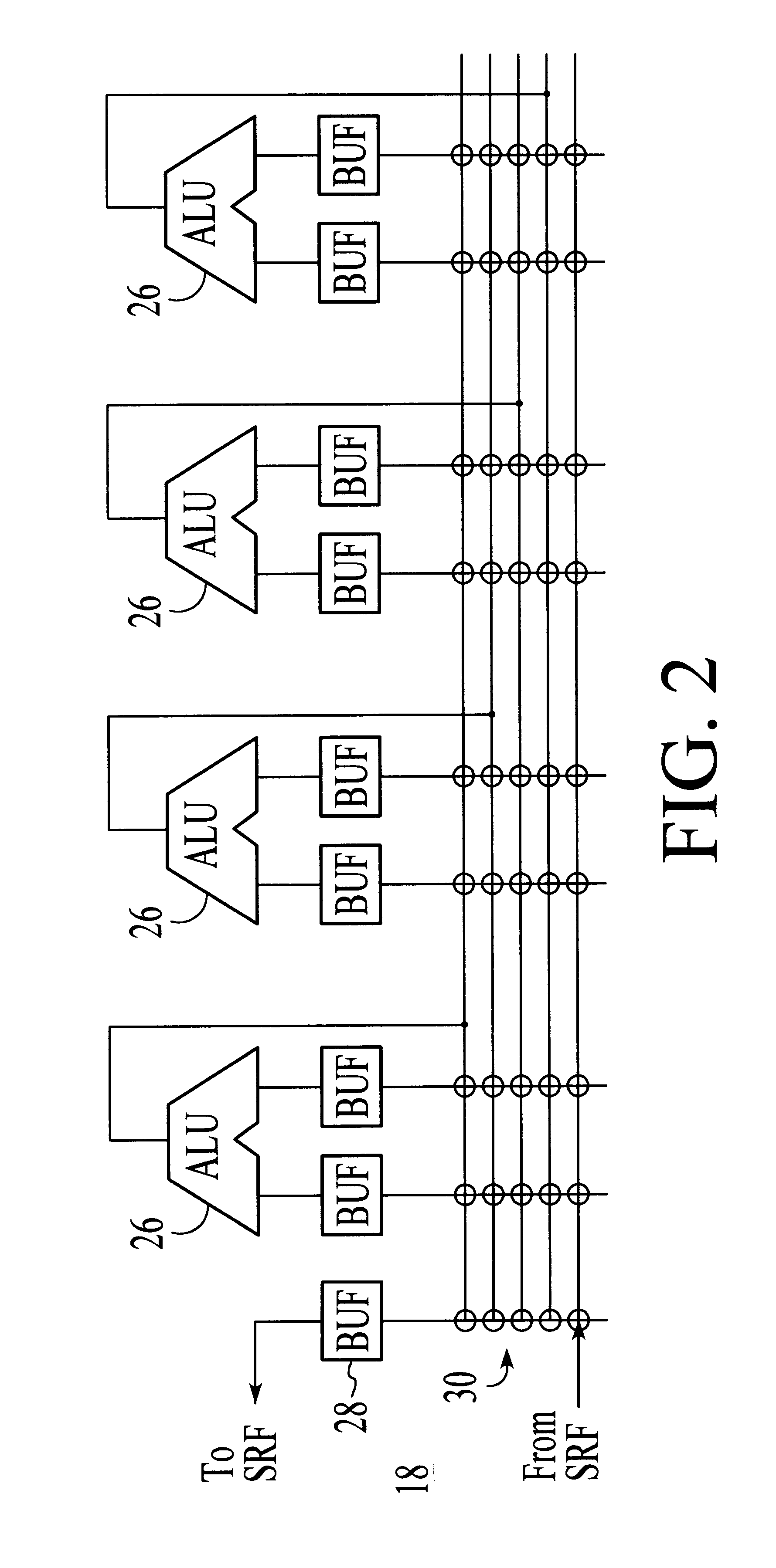
System and method for performing compound vector operations
InactiveUS6192384B1Reduce bandwidth requirementsMinimize the numberOperational speed enhancementRegister arrangementsOperating instructionImaging processing
A processor particularly useful in multimedia applications such as image processing is based on a stream programming model and has a tiered storage architecture to minimize global bandwidth requirements. The processor has a stream register file through which the processor's functional units transfer streams to execute processor operations. Load and store instructions transfer streams between the stream register file and a stream memory; send and receive instructions transfer streams between stream register files of different processors; and operate instructions pass streams between the stream register file and computational kernels. Each of the computational kernels is capable of performing compound vector operations. A compound vector operation performs a sequence of arithmetic operations on data read from the stream register file, i.e., a global storage resource, and generates a result that is written back to the stream register file. Each function or compound vector operation is specified by an instruction sequence that specifies the arithmetic operations and data movements that are performed each cycle to carry out the compound operation. This sequence can, for example, be specified using microcode.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND +1
Emulator-enabled network connectivity to a device
InactiveUS7209874B2Television system detailsInput/output to record carriersNetwork controlInstruction sequence
An emulator is capable of connecting to an information interface that can communicate information from an information source to an information sink in a format native to the information sink. The emulator comprises an emulation controller capable of coupling to the information interface, a network controller coupled to the emulation controller and capable of coupling to an external network, and a storage. The storage holds an instruction sequence executable on the emulation controller. The instruction sequence comprises a code for receiving network information from the external network and a code capable of converting the network information to the native format for transfer to the information sink.
Owner:CSR TECH INC
Apparatus and method for power performance monitors for low-power program tuning
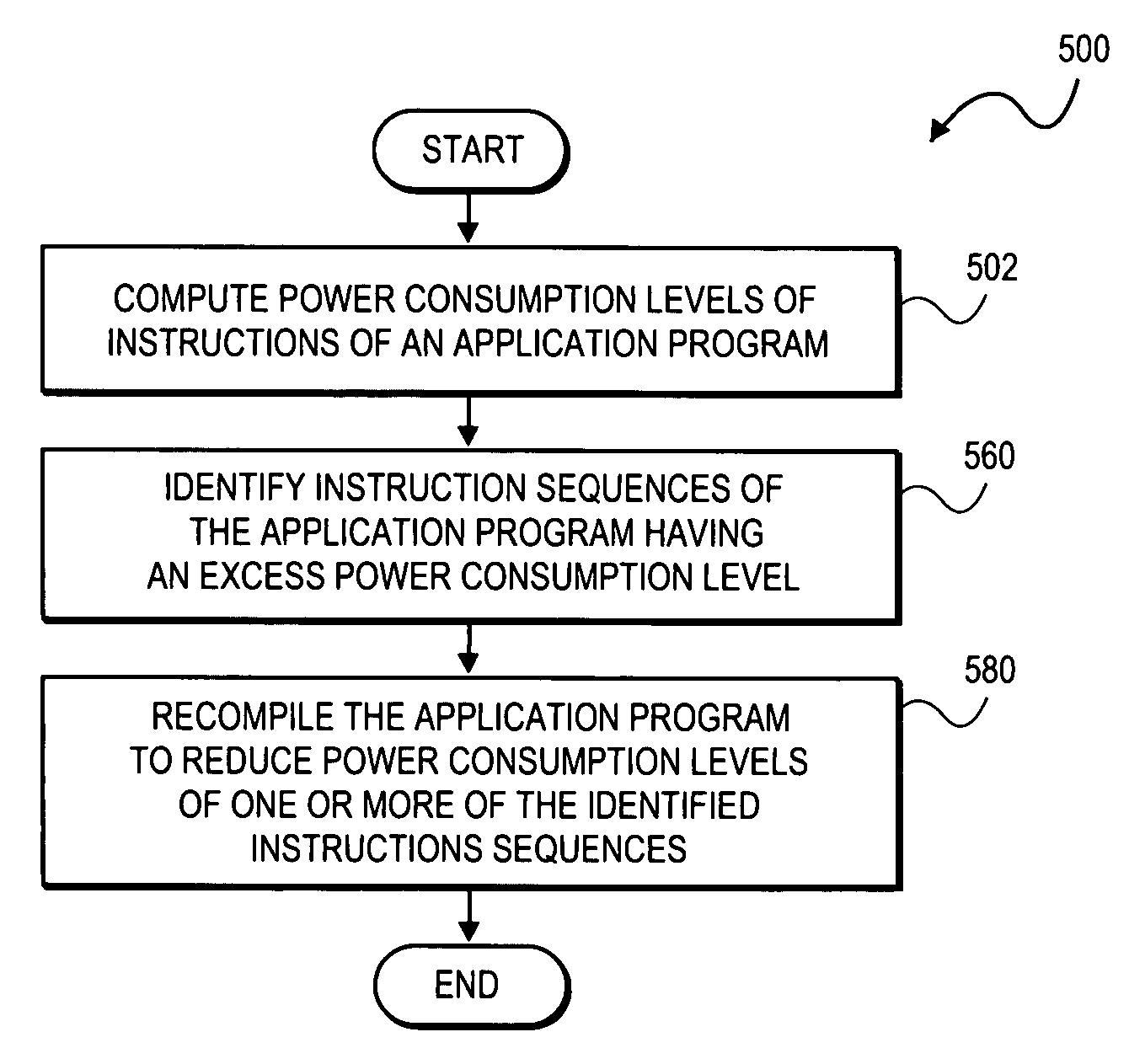
In some embodiments, a method and apparatus for power performance monitors for low-power program tuning are described. In one embodiment, the method includes the computation of power consumption levels of instructions of an application. Once consumption levels are computed, instruction sequences of the application are identified that exhibit an excess power consumption level. For the identified instruction sequences, the application program is recompiled to reduce power consumption levels of one or more of the identified instruction sequences. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Hardware-based packet filtering accelerator
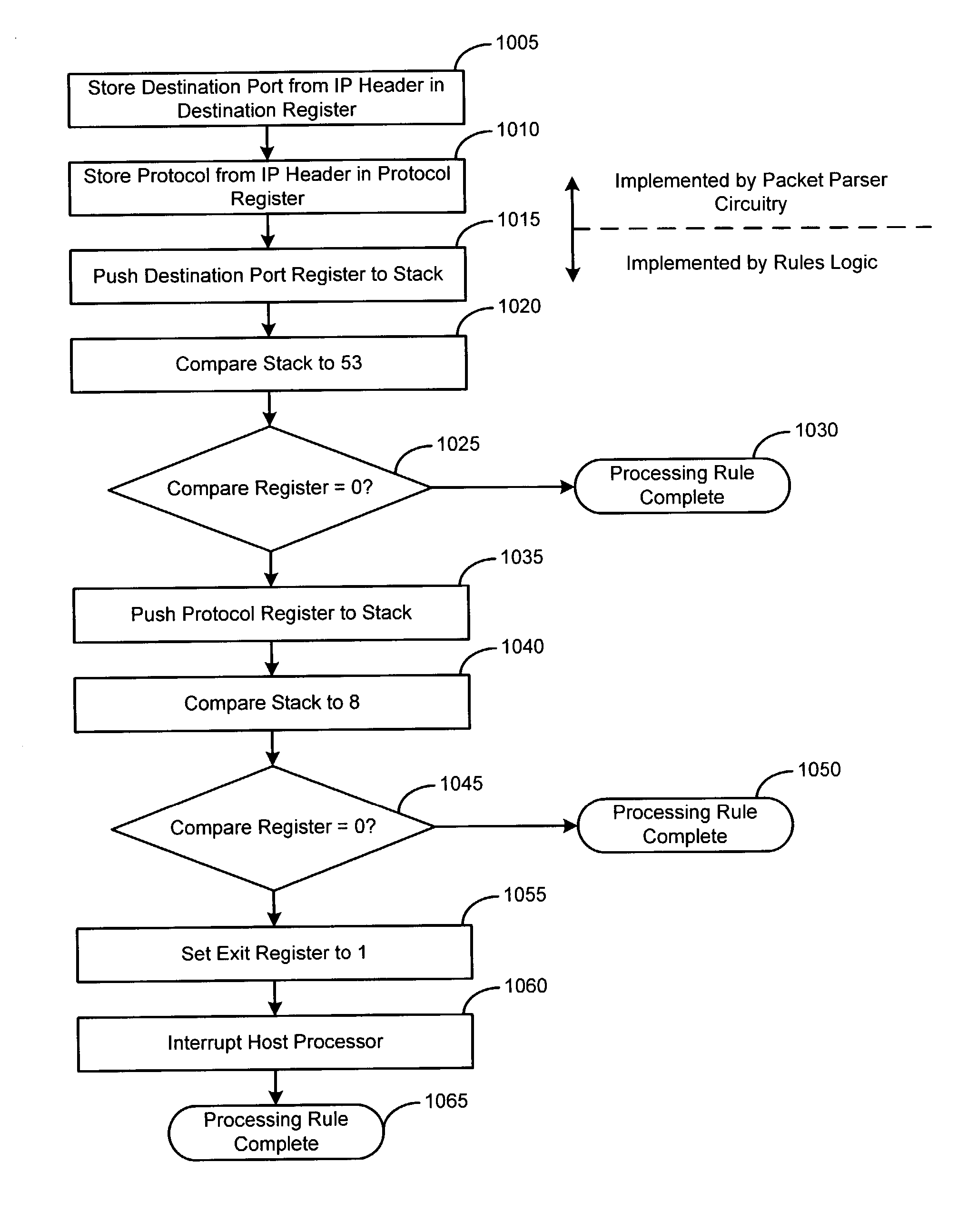
InactiveUS20040039940A1Digital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionProcessor registerParallel computing
A data packet filtering accelerator processor operates in parallel with a host processor and is arranged on an integrated circuit with the host processor. The accelerator processor classifies data packets by executing a sequence machine code instructions converted directly from a set of rules. Portions of data packets are passed to the accelerator processor from the host processor. The accelerator processor includes packet parser circuit for parsing the data packets into relevant data units and storing the relevant data units in memory. A packet analysis circuit executes the sequence of machine code instructions converted directly from the set of rules. The machine code instruction sequence operates on the relevant data units to classify the data packet. The packet analysis circuit returns the results of the classification to the host processor by storing the classification results in a register accessible by the host processor.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Optimized cache allocation algorithm for multiple speculative requests
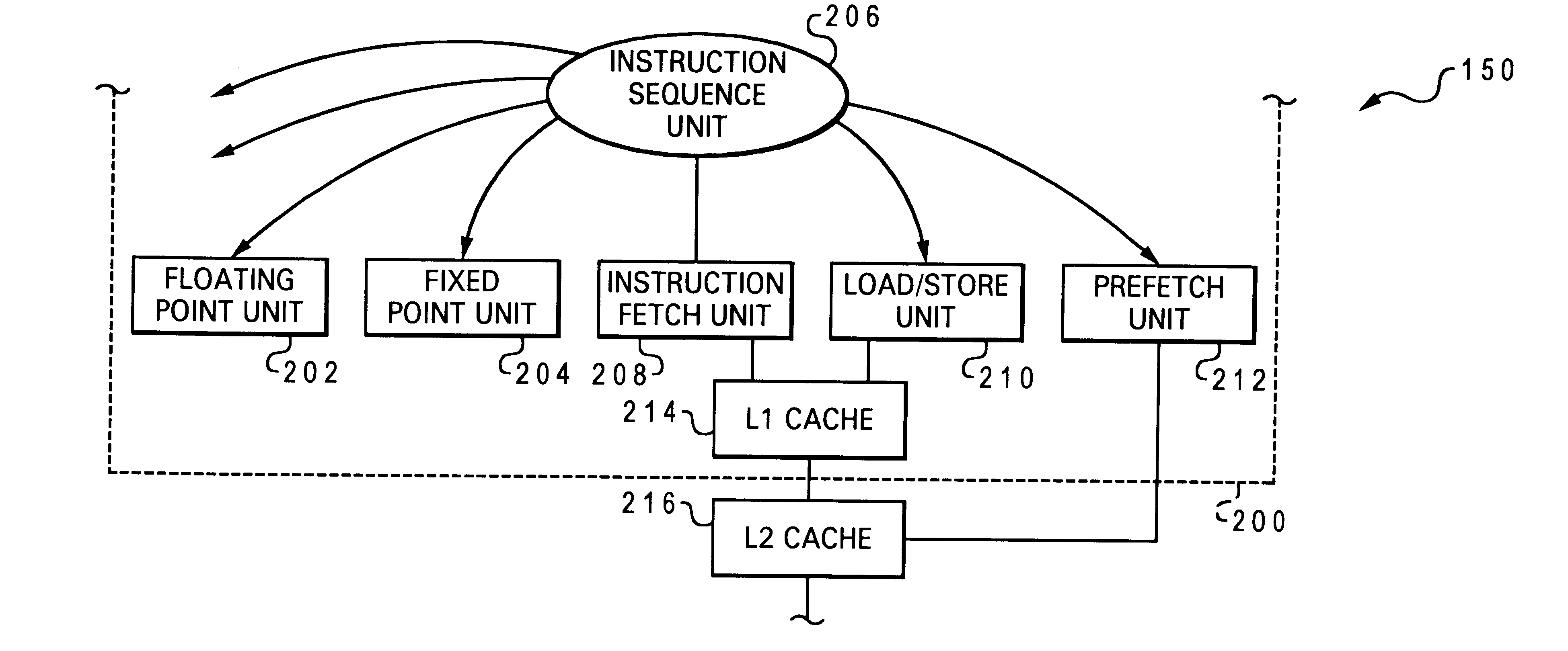
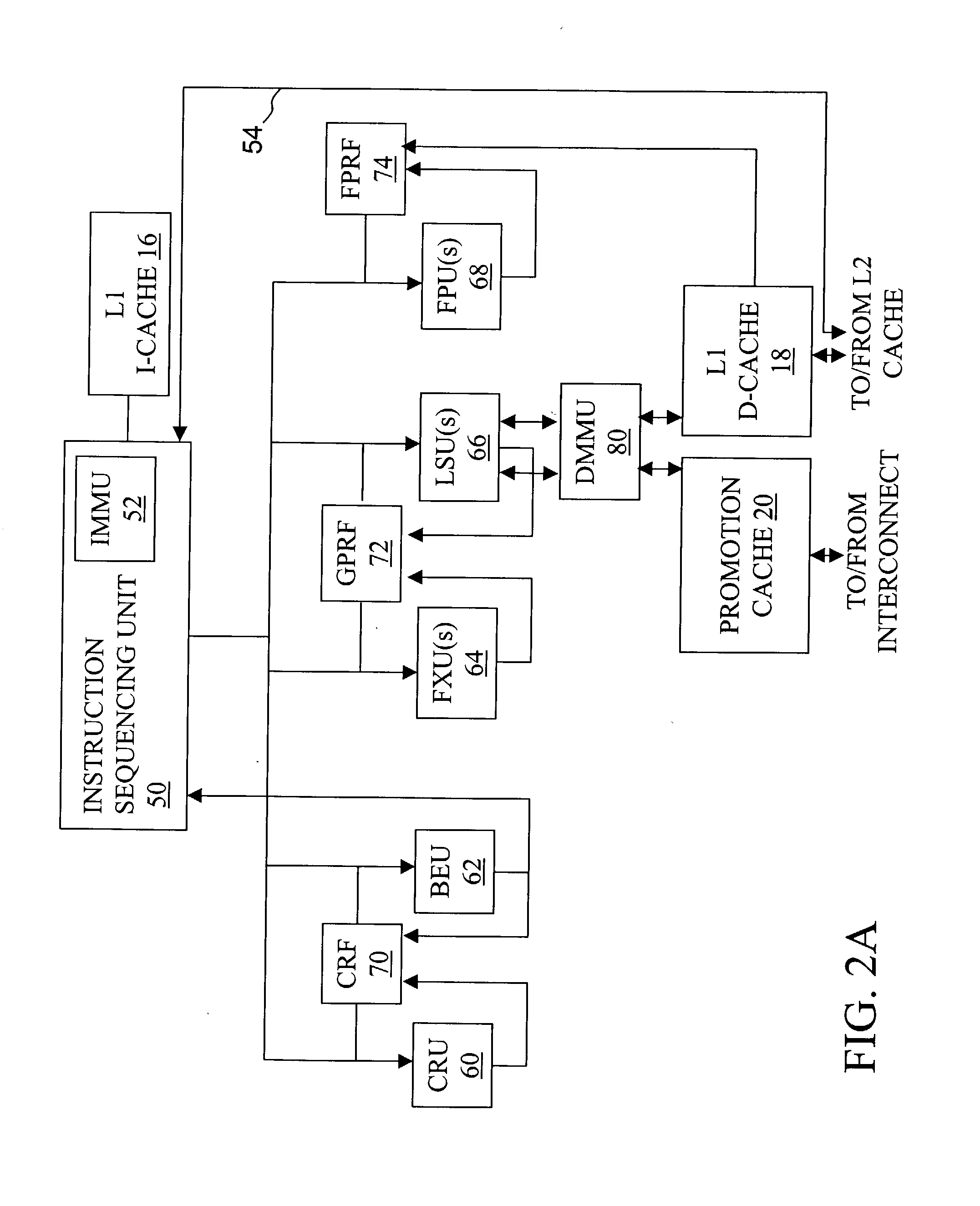
A method of operating a computer system is disclosed in which an instruction having an explicit prefetch request is issued directly from an instruction sequence unit to a prefetch unit of a processing unit. In a preferred embodiment, two prefetch units are used, the first prefetch unit being hardware independent and dynamically monitoring one or more active streams associated with operations carried out by a core of the processing unit, and the second prefetch unit being aware of the lower level storage subsystem and sending with the prefetch request an indication that a prefetch value is to be loaded into a lower level cache of the processing unit. The invention may advantageously associate each prefetch request with a stream ID of an associated processor stream, or a processor ID of the requesting processing unit (the latter feature is particularly useful for caches which are shared by a processing unit cluster). If another prefetch value is requested from the memory hiearchy and it is determined that a prefetch limit of cache usage has been met by the cache, then a cache line in the cache containing one of the earlier prefetch values is allocated for receiving the other prefetch value.
Owner:IBM CORP
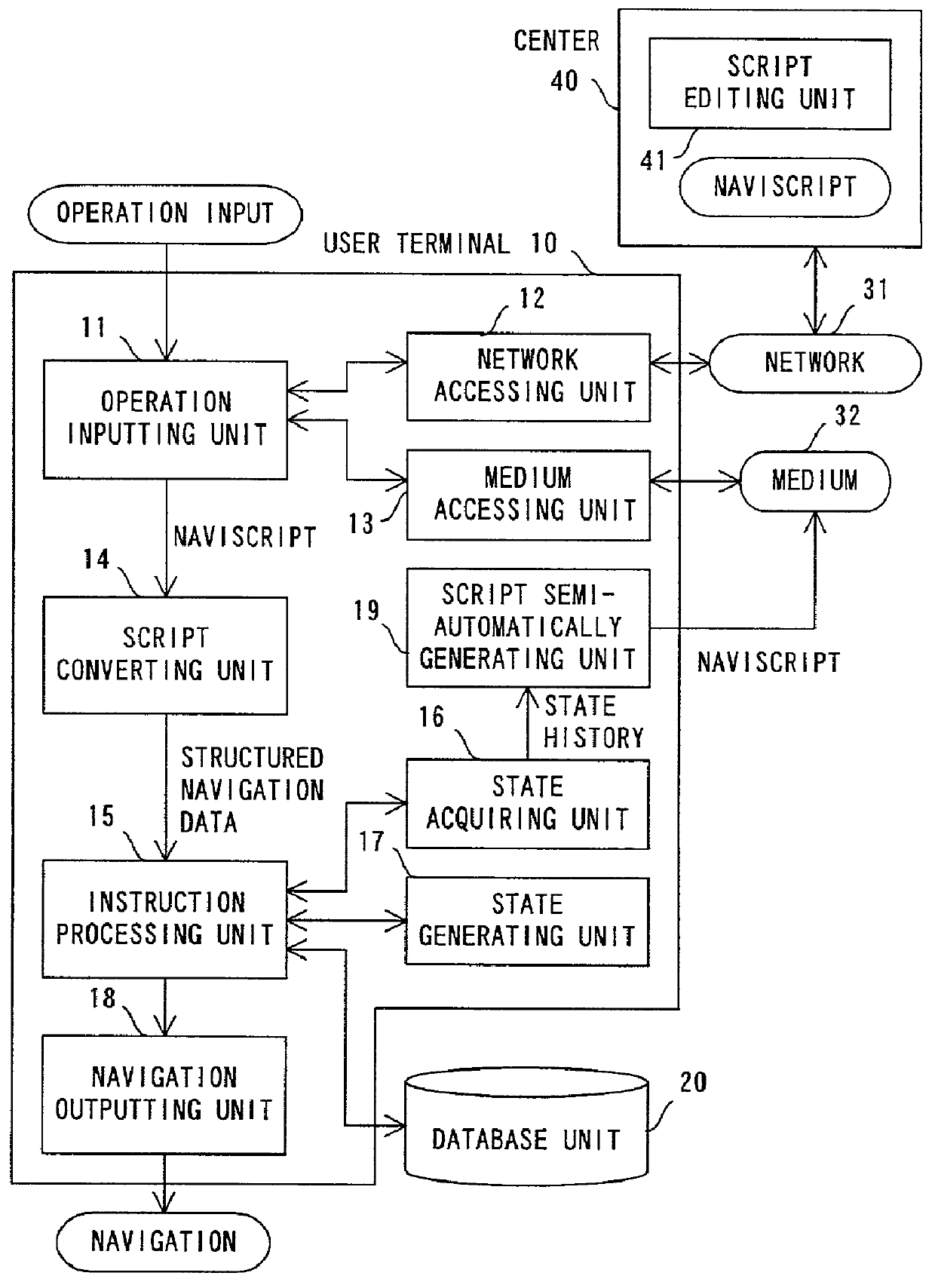
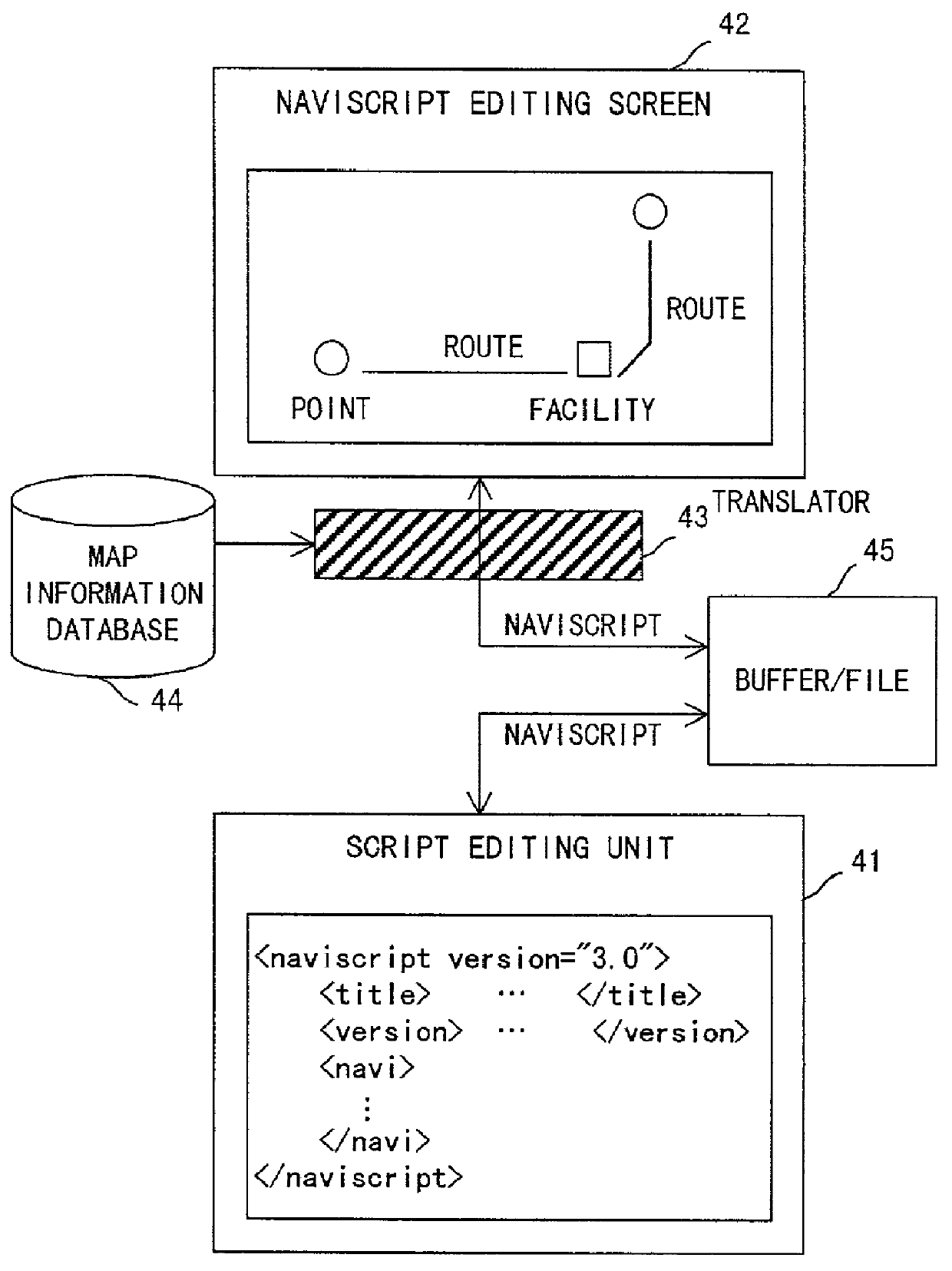
Apparatus and method for presenting navigation information based on instructions described in a script
InactiveUS20010056443A1Instruments for road network navigationDigital data processing detailsTime series representationInstruction sequence
A navigation script includes time and point information for navigation and information for guidance, and describes an instruction sequence which can represent these information in time series in a mark-up language. According to the structured data generated from the navigation script, an instruction corresponding to a current time or point is executed, so that information for guidance to be presented is output.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
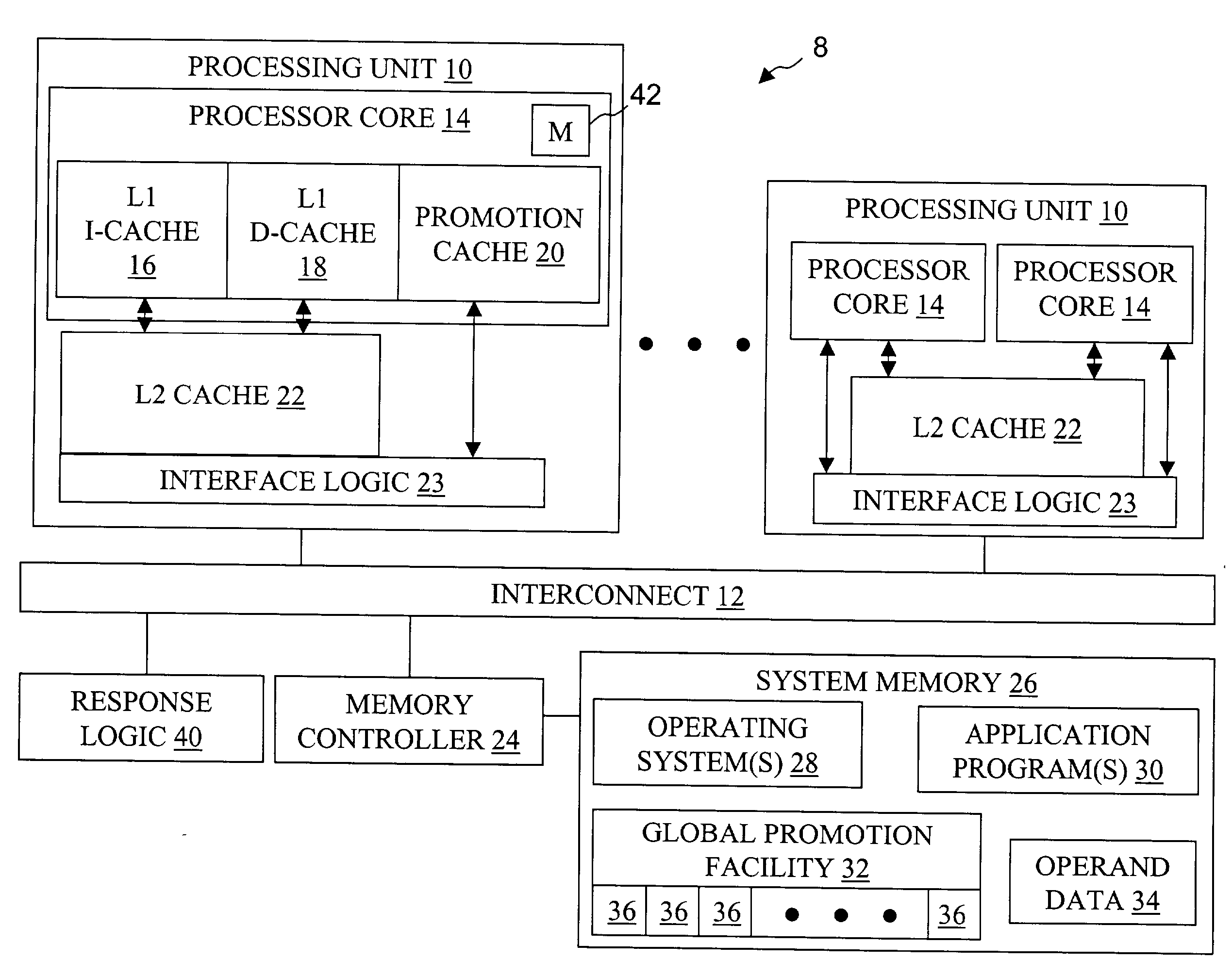
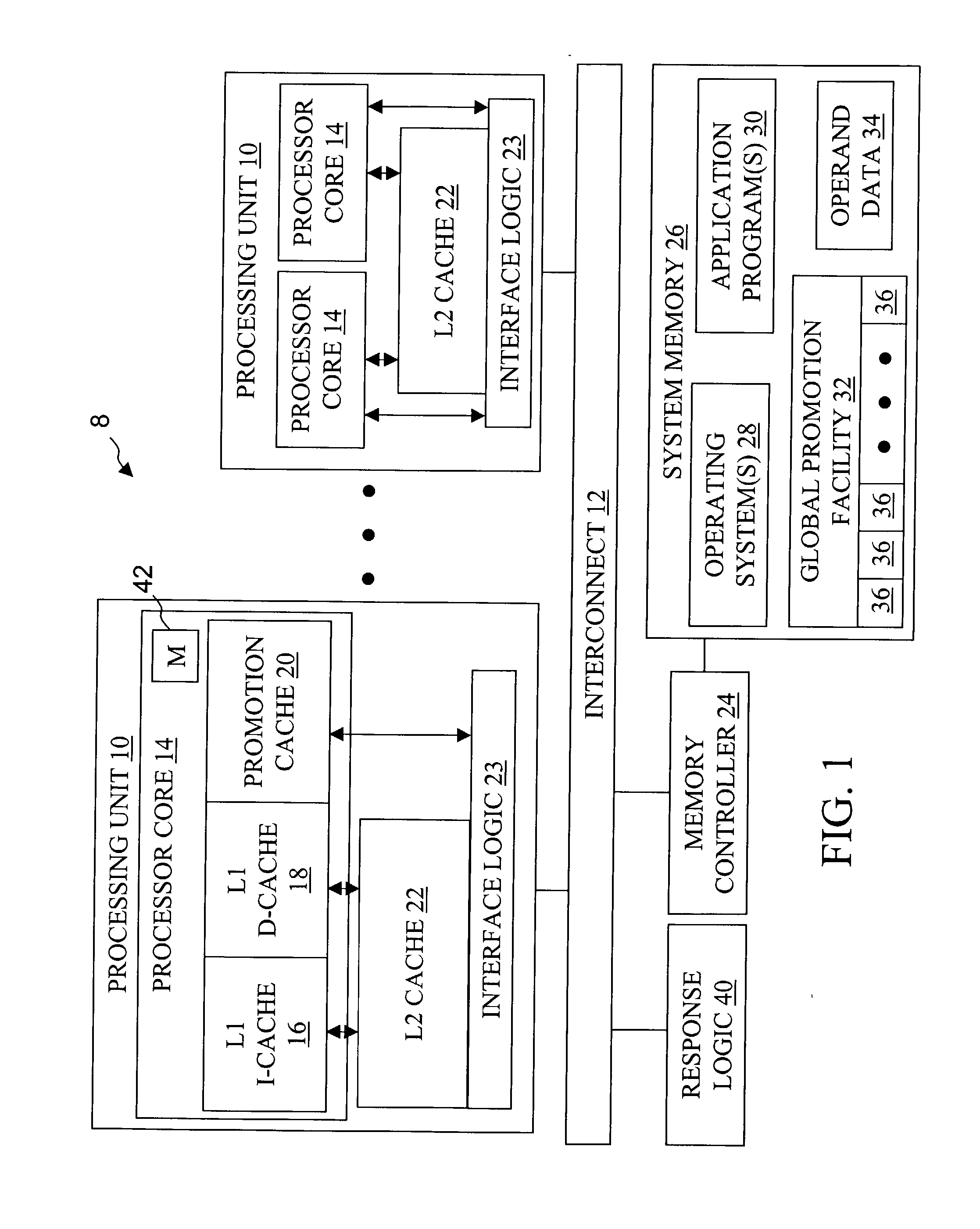
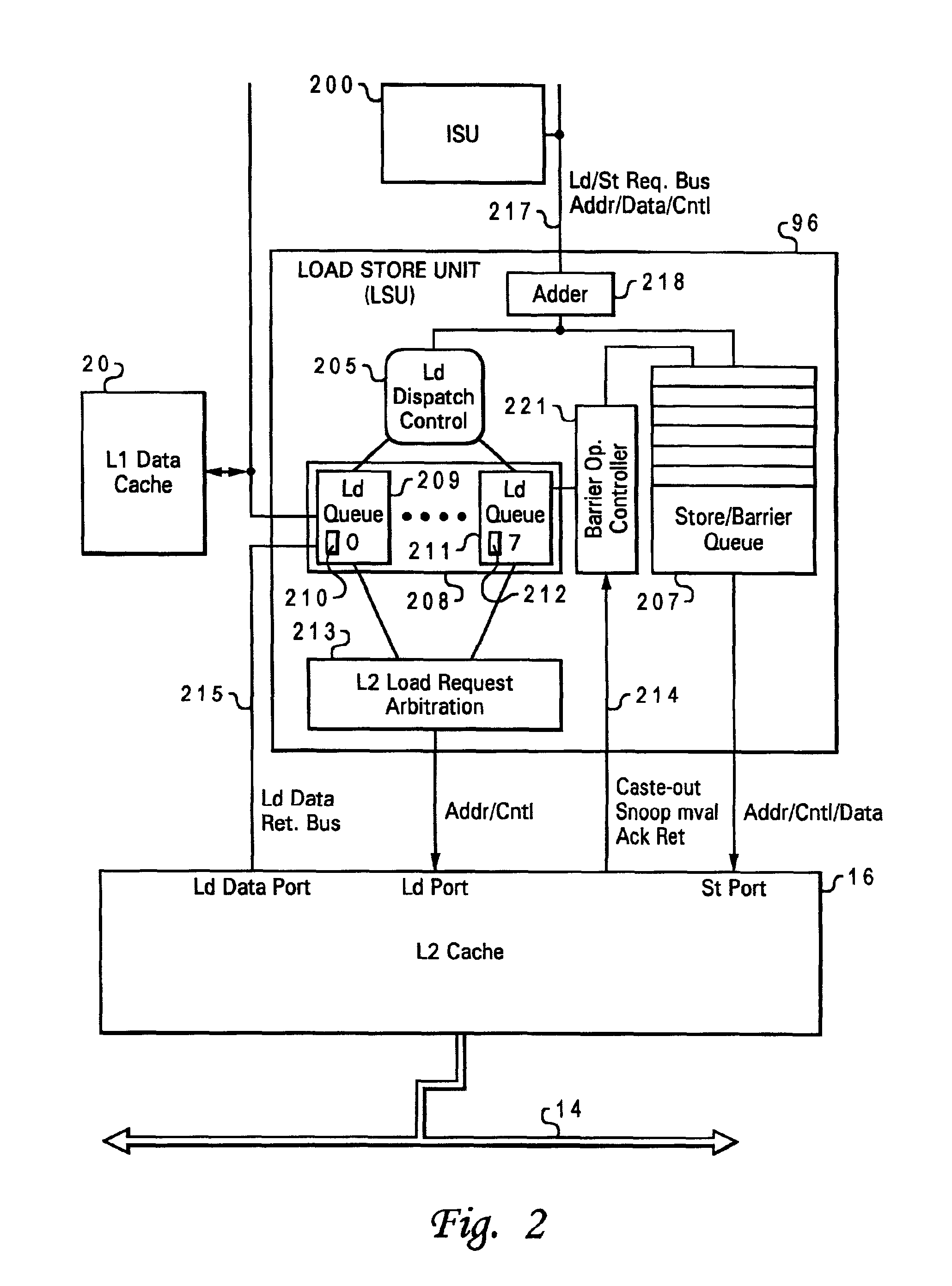
High speed promotion mechanism suitable for lock acquisition in a multiprocessor data processing system
InactiveUS20040073909A1Program synchronisationUnauthorized memory use protectionData processing systemBit field
A multiprocessor data processing system includes a plurality of processors coupled to an interconnect and to a global promotion facility containing at least one promotion bit field. A first processor executes a high speed instruction sequence including a load-type instruction to acquire a promotion bit field within the global promotion facility exclusive of at least a second processor. The request may be made visible to all processors coupled to the interconnect. In response to execution of the load-type instruction, a register of the first processor receives a register bit field indicating whether or not the promotion bit field was acquired by execution of the load-type instruction. While the first processor holds the promotion bit field exclusive of the second processor, the second processor is permitted to initiate a request on the interconnect. Advantageously, promotion bit fields are handled separately from data, and the communication of promotion bit fields does not entail the movement of data cache lines.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and apparatus for providing remote access, control of remote systems and updating of display information
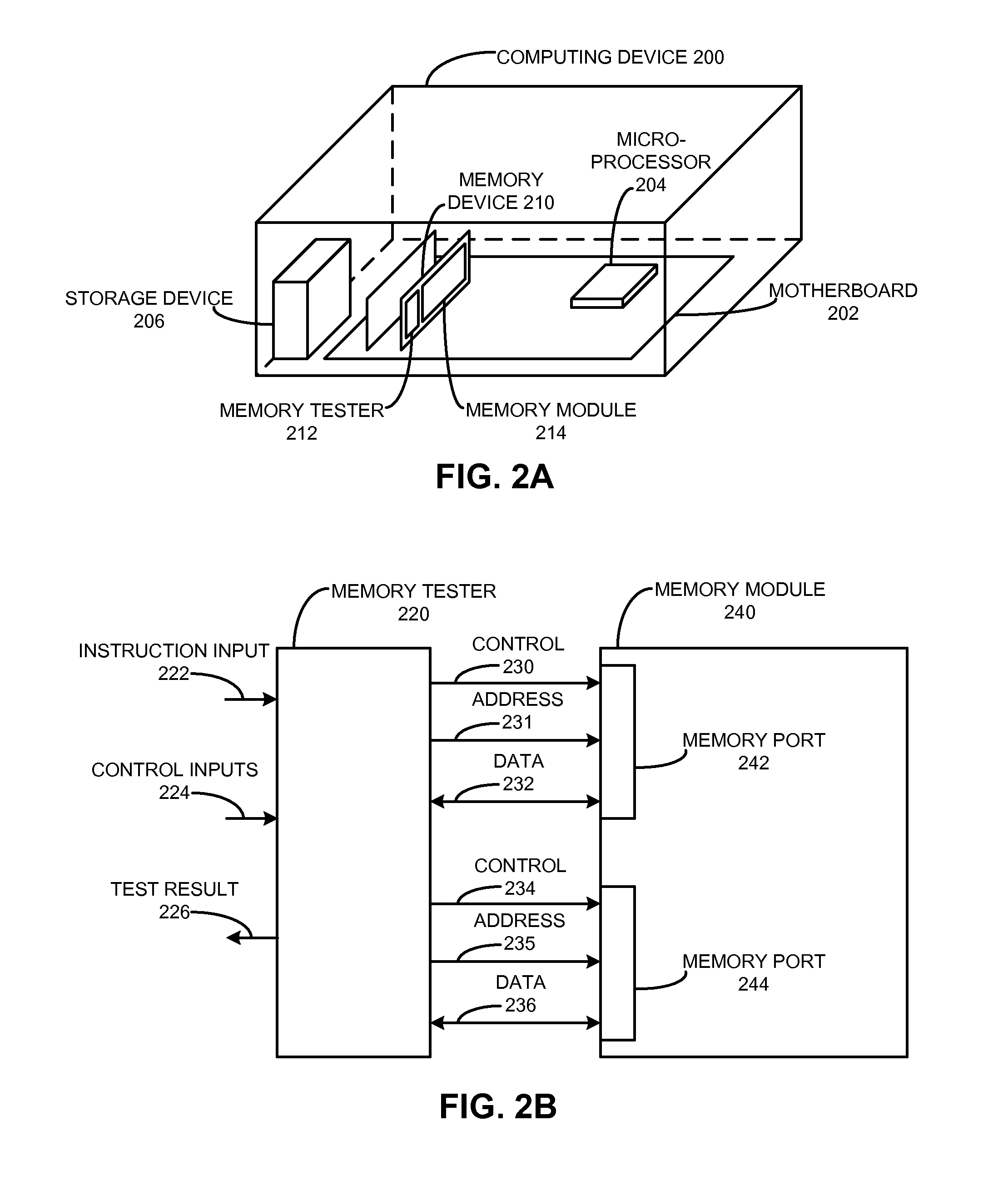
InactiveUS6331855B1Static indicating devicesMultiple digital computer combinationsRemote systemInstruction sequence
The present invention is a system and method for controlling information displayed on a first processor-based system, from a second processor-based system. The apparatus comprises a memory to store instruction sequences by which the second processor-based system is processed, and a processor coupled to the memory. The stored instruction sequences cause the processor to: (a) examine, at a predetermined interval, a location of a currently displayed image; (b) compare the location with a corresponding location of a previously displayed image to determine if the previously displayed image has changed; (c) transmitting location information representing the change; and (d) storing the changed information on the first processor-based system. Various embodiments are described.
Owner:GETGO INC
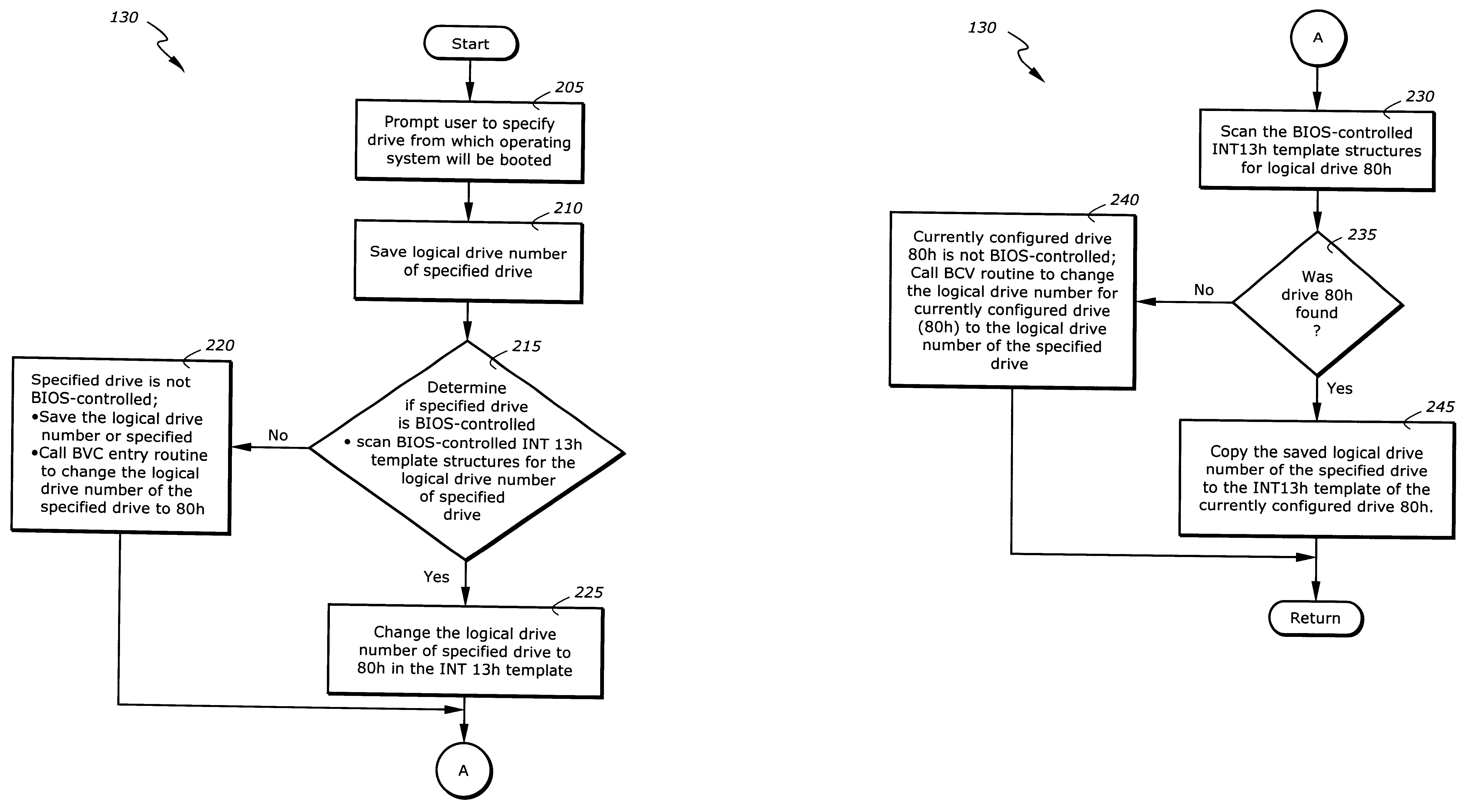
System for reconfiguring a boot device by swapping the logical device number of a user selected boot drive to a currently configured boot drive
The present invention is an apparatus and method for specifying operation of a boot device in a processor-based system. The apparatus comprises a memory for storing instruction sequences by which the processor-based system is processed and a processor for executing the stored instruction sequences. The stored instruction sequences cause the processor to: (a) determine if a boot process should proceed from a currently specified drive; (b) if not, specify a drive from which the boot process will proceed; and (c) initiate the boot process.
Owner:KINGLITE HLDG INC
Compiler apparatus and compilation method
InactiveUS20040154006A1Avoid changeReduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTSoftware engineeringMachine instructionInstruction cycle
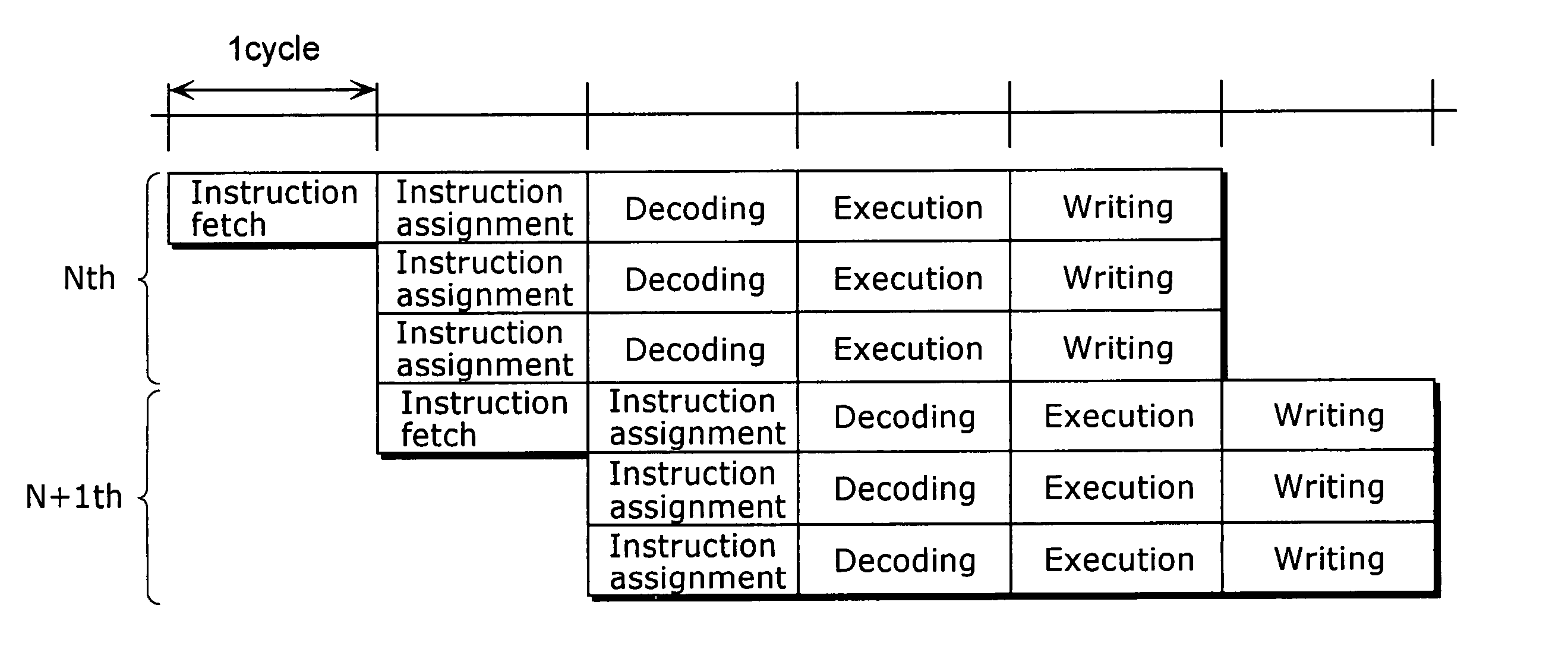
A compiler apparatus that is capable of generating instruction sequences for causing a processor with parallel processing capability to operate with lower power consumption is a compiler apparatus that translates a source program into a machine language program for the processor including a plurality of execution units which can execute instructions in parallel and a plurality of instruction issue units which issue the instructions executed respectively by the plurality of execution units, and includes: a parser unit operable to parse the source program; an intermediate code conversion unit operable to convert the parsed source program into intermediate codes; an optimization unit operable to optimize the intermediate codes so as to reduce a hamming distance between instructions placed in positions corresponding to the same instruction issue unit in consecutive instruction cycles, without changing dependency between the instructions corresponding to the intermediate codes; and a code generation unit operable to convert the optimized intermediate codes into machine language instructions.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
Method for extracting malicious code behavior characteristic
InactiveCN102054149AComprehensive information extractionImprove anti-interference abilityPlatform integrity maintainanceData dependency graphSingle sample
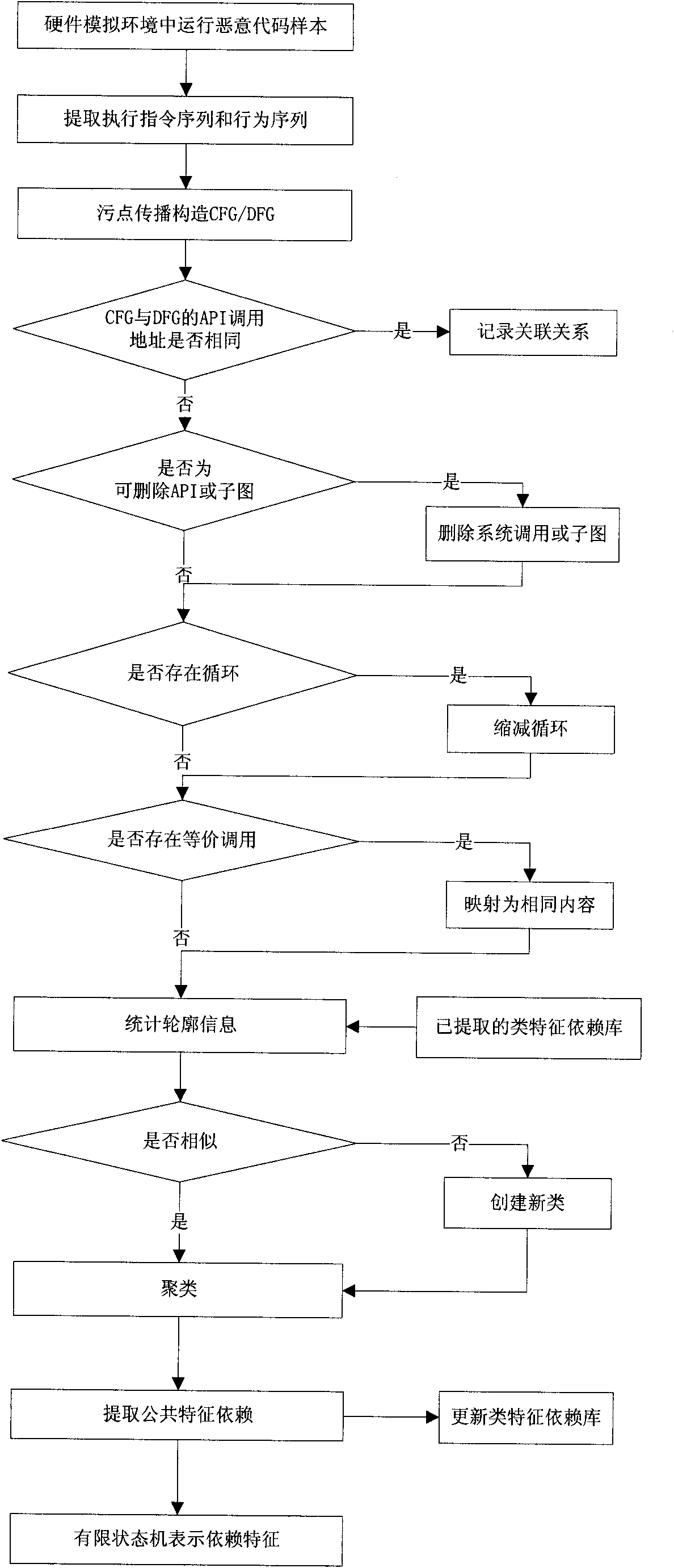
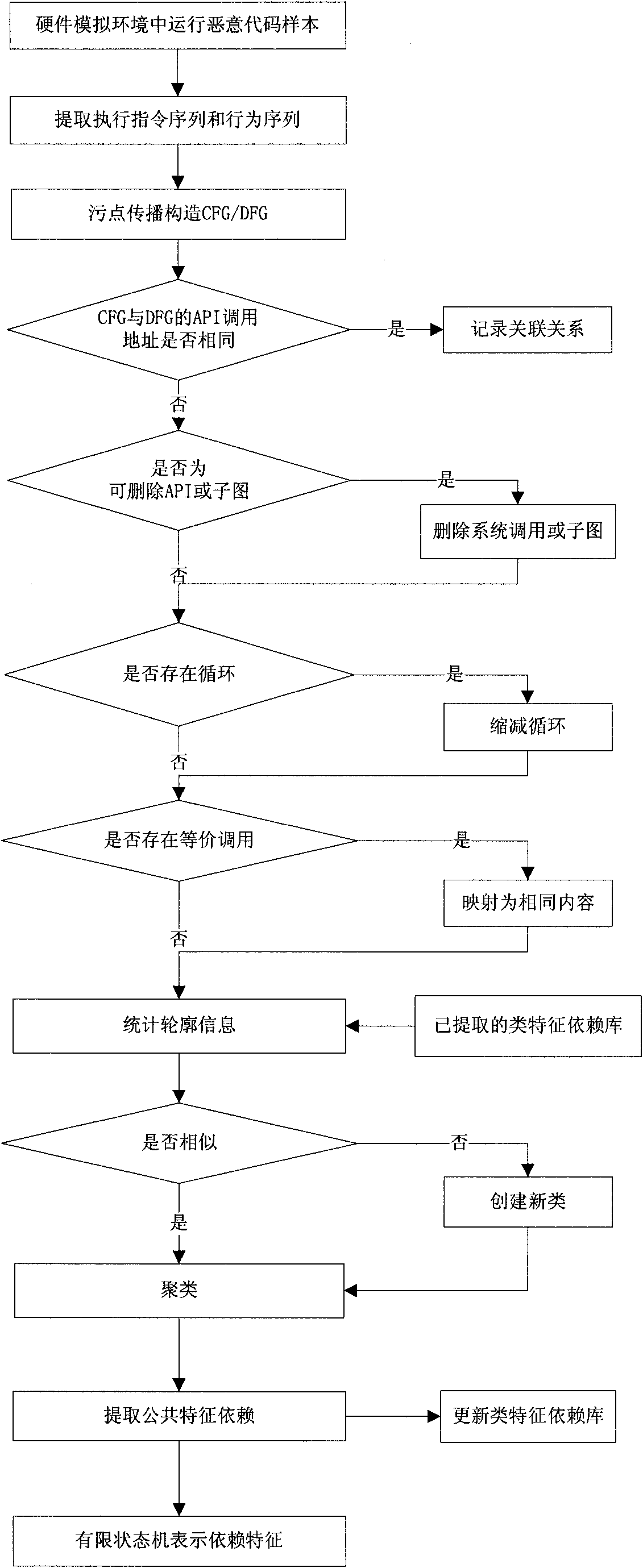
The invention discloses a method for extracting a malicious code behavior characteristic, which belongs to the technical field of network security. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) running a malicious code and extracting executive information of the malicious code, wherein the executive information comprises an executive instruction sequence and a behavior sequence of the maliciouscode; 2) constructing a control dependence graph and a data dependence graph for executing the code according to the executive information; 3) comparing relevance of the control dependence graph and the data dependence graph and recording related relevance information; and 4) comparing the control dependence graphs and the data dependence graphs of different malicious codes and extracting characteristic dependency of each type of samples according to similarity clustering. Compared with the prior art, the method has the characteristics of complete information extraction, high anti-interference performance, certain applicability to varieties of a single sample characteristic, small-sized characteristic library and wide application range.
Owner:GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI GSCAS
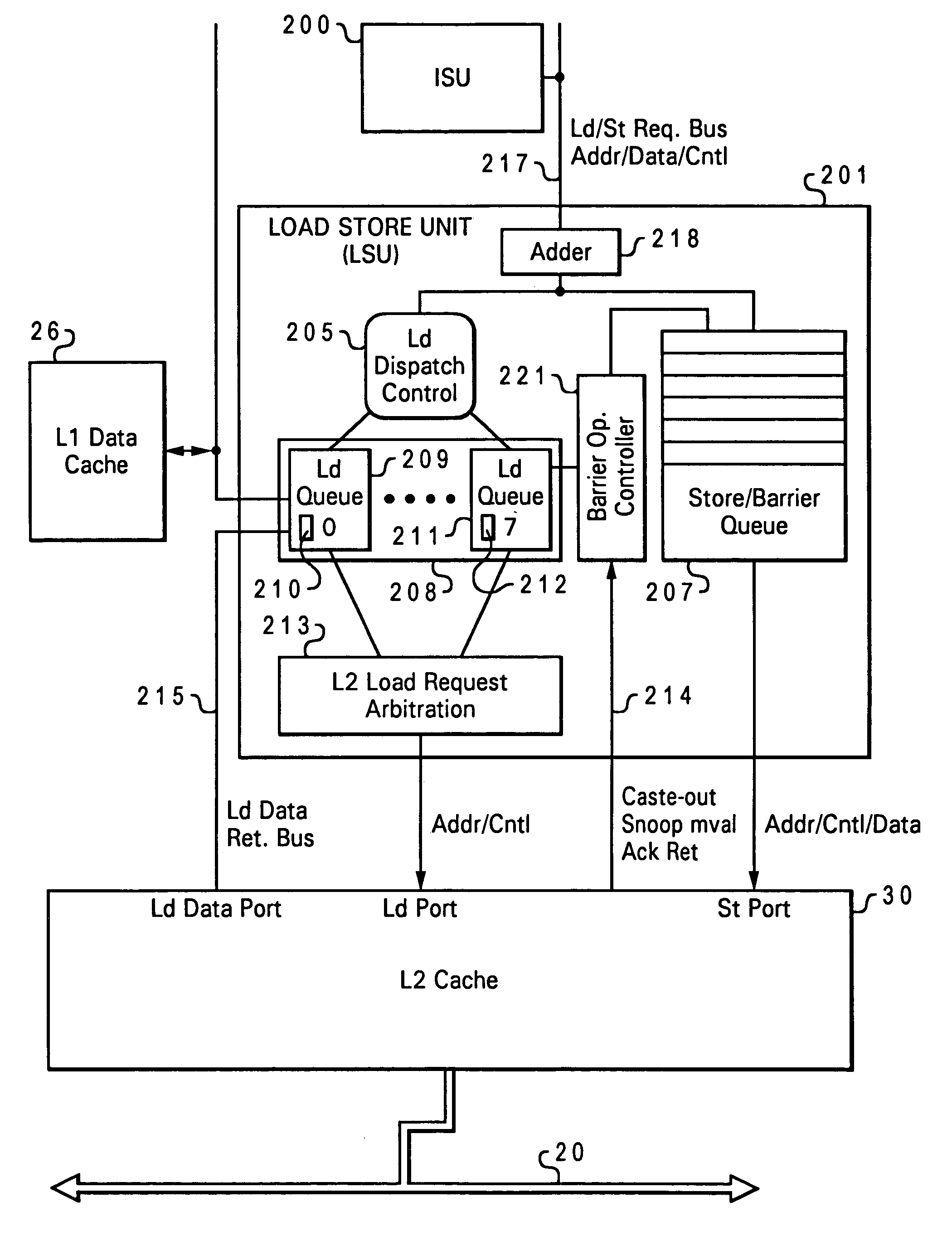
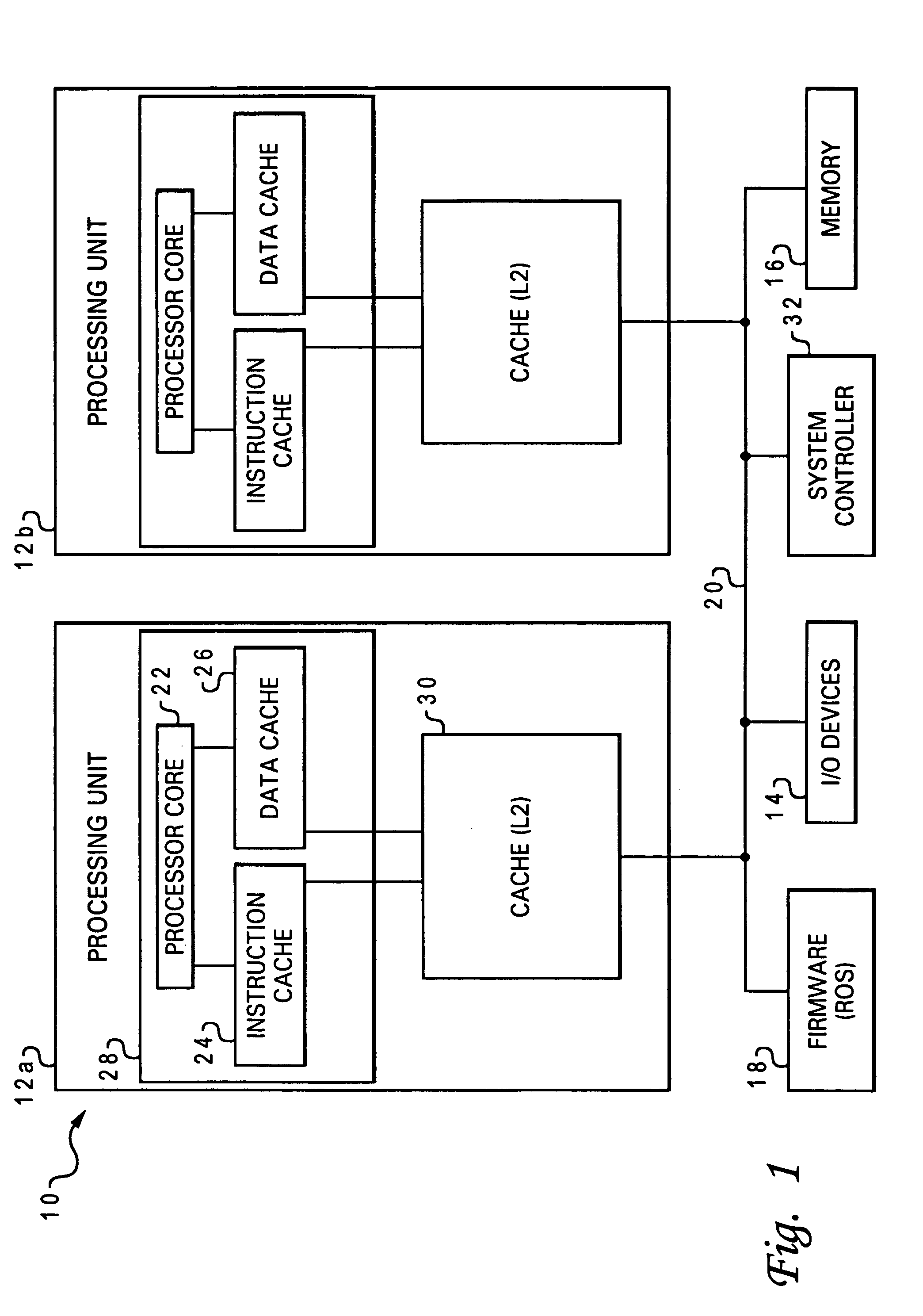
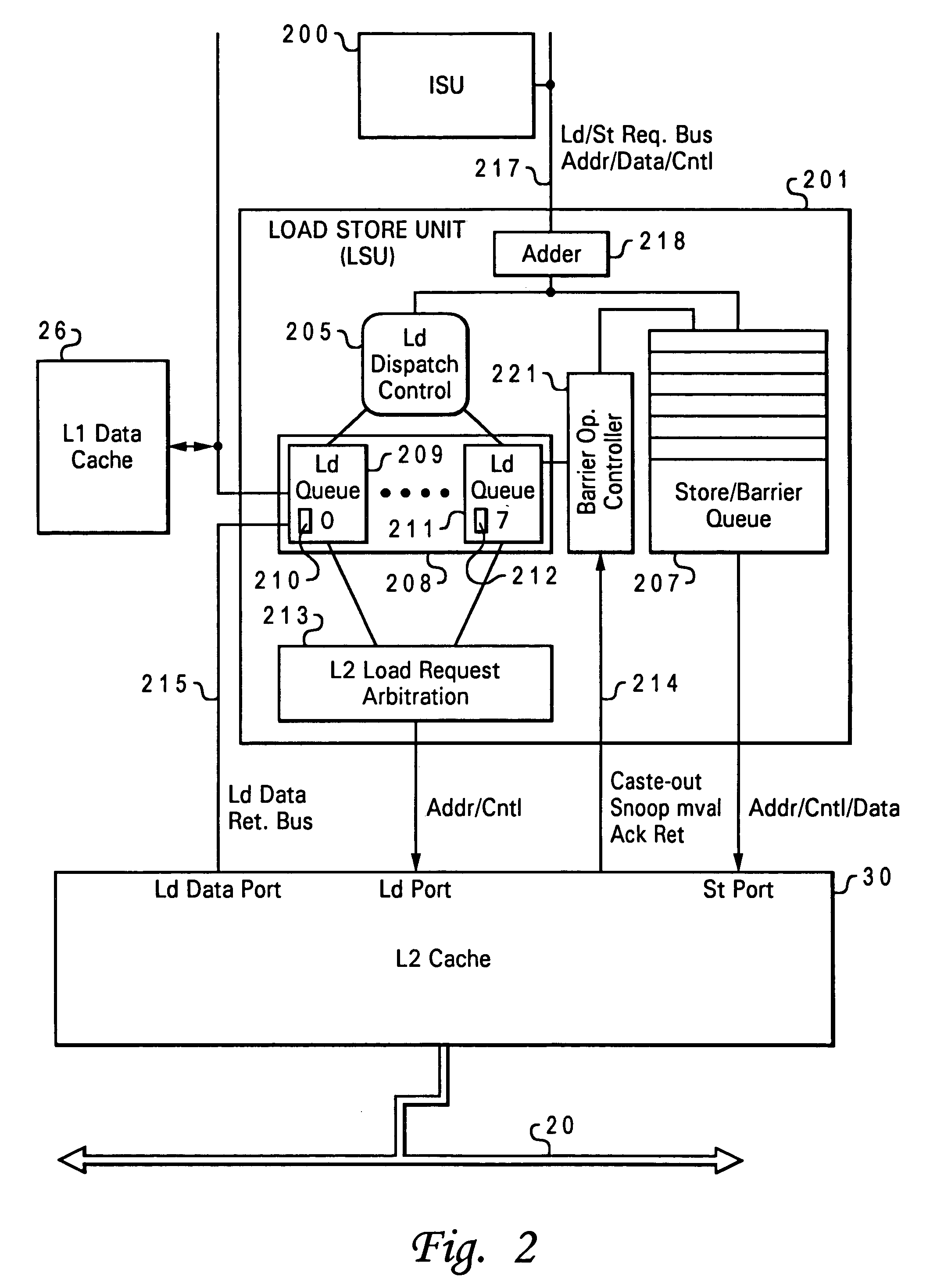
Speculative execution of instructions and processes before completion of preceding barrier operations
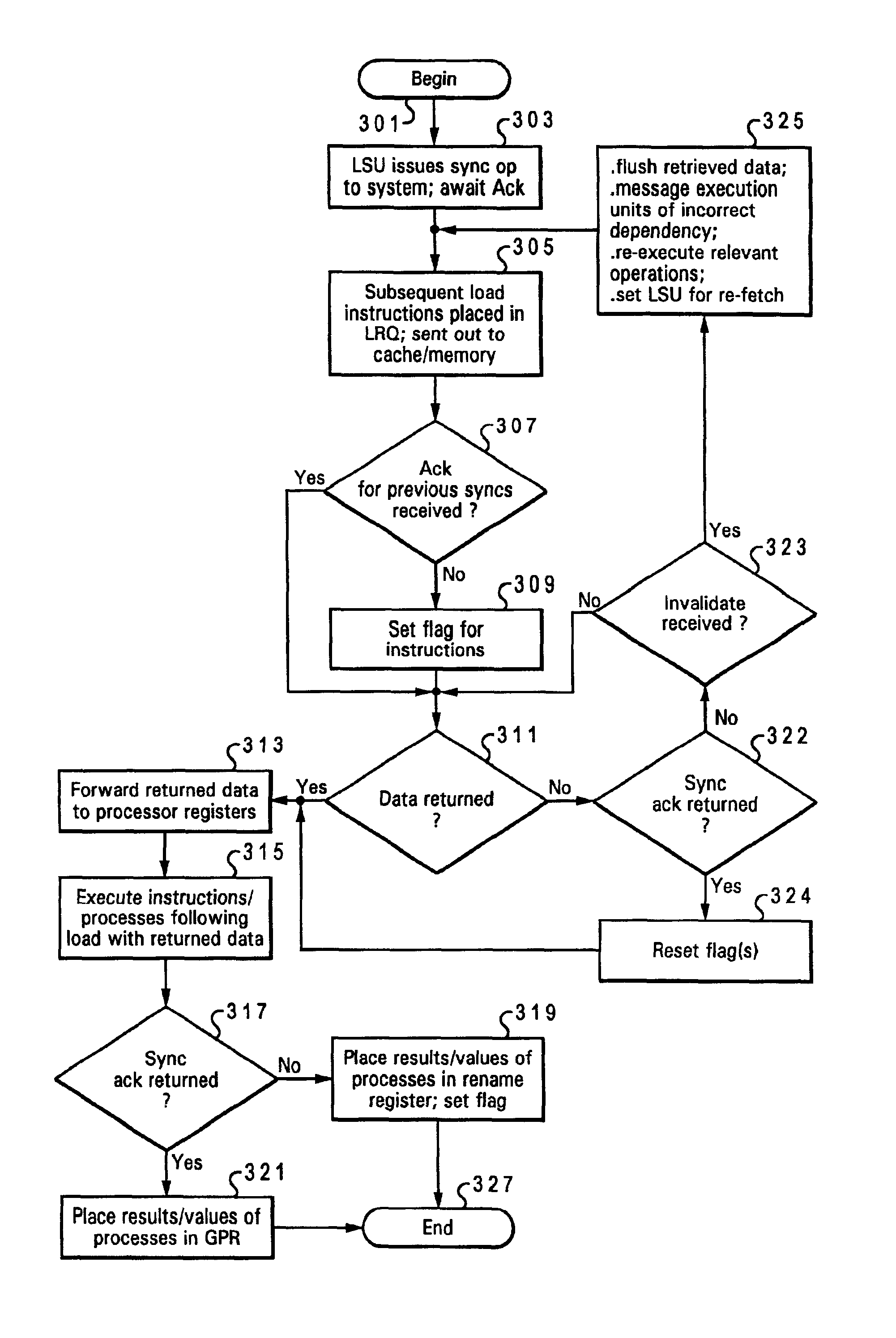
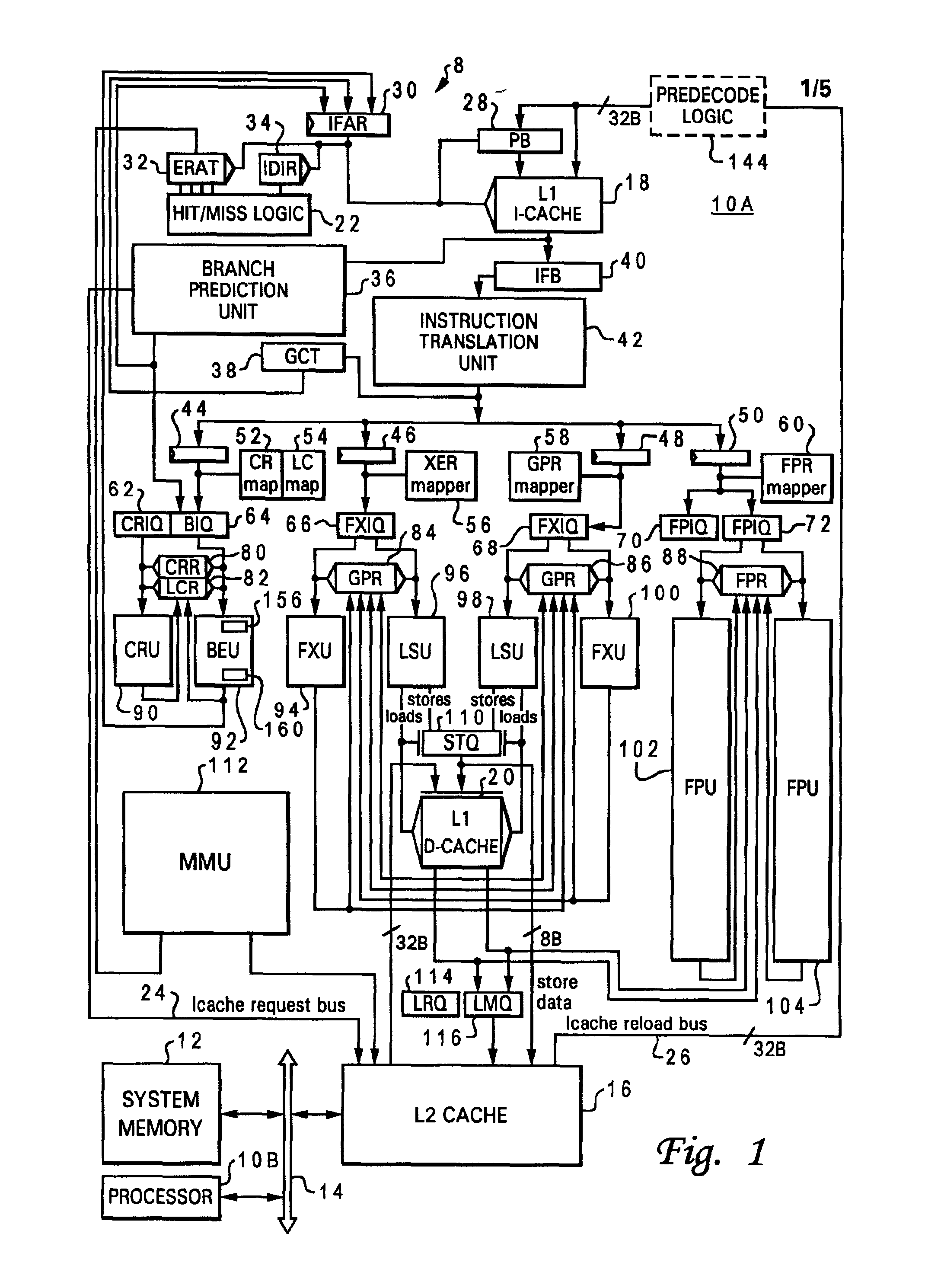
InactiveUS6880073B2Digital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionData processing systemSpeculative execution
Described is a data processing system and processor that provides full multiprocessor speculation by which all instructions subsequent to barrier operations in a instruction sequence are speculatively executed before the barrier operation completes on the system bus. The processor comprises a load / store unit (LSU) with a barrier operation (BOP) controller that permits load instructions subsequent to syncs in an instruction sequence to be speculatively issued prior to the return of the sync acknowledgment. Data returned is immediately forwarded to the processor's execution units. The returned data and results of subsequent operations are held temporarily in rename registers. A multiprocessor speculation flag is set in the corresponding rename registers to indicate that the value is “barrier” speculative. When a barrier acknowledge is received by the BOP controller, the flag(s) of the corresponding rename register(s) are reset.
Owner:IBM CORP
High speed promotion mechanism suitable for lock acquisition in a multiprocessor data processing system
InactiveUS7213248B2Reduce percentageReduce the amount requiredProgram synchronisationUnauthorized memory use protectionData processing systemBit field
A multiprocessor data processing system includes a plurality of processors coupled to an interconnect and to a global promotion facility containing at least one promotion bit field. A first processor executes a high speed instruction sequence including a load-type instruction to acquire a promotion bit field within the global promotion facility exclusive of at least a second processor. The request may be made visible to all processors coupled to the interconnect. In response to execution of the load-type instruction, a register of the first processor receives a register bit field indicating whether or not the promotion bit field was acquired by execution of the load-type instruction. While the first processor holds the promotion bit field exclusive of the second processor, the second processor is permitted to initiate a request on the interconnect. Advantageously, promotion bit fields are handled separately from data, and the communication of promotion bit fields does not entail the movement of data cache lines.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Method and apparatus for dynamic branch prediction utilizing multiple stew algorithms for indexing a global history
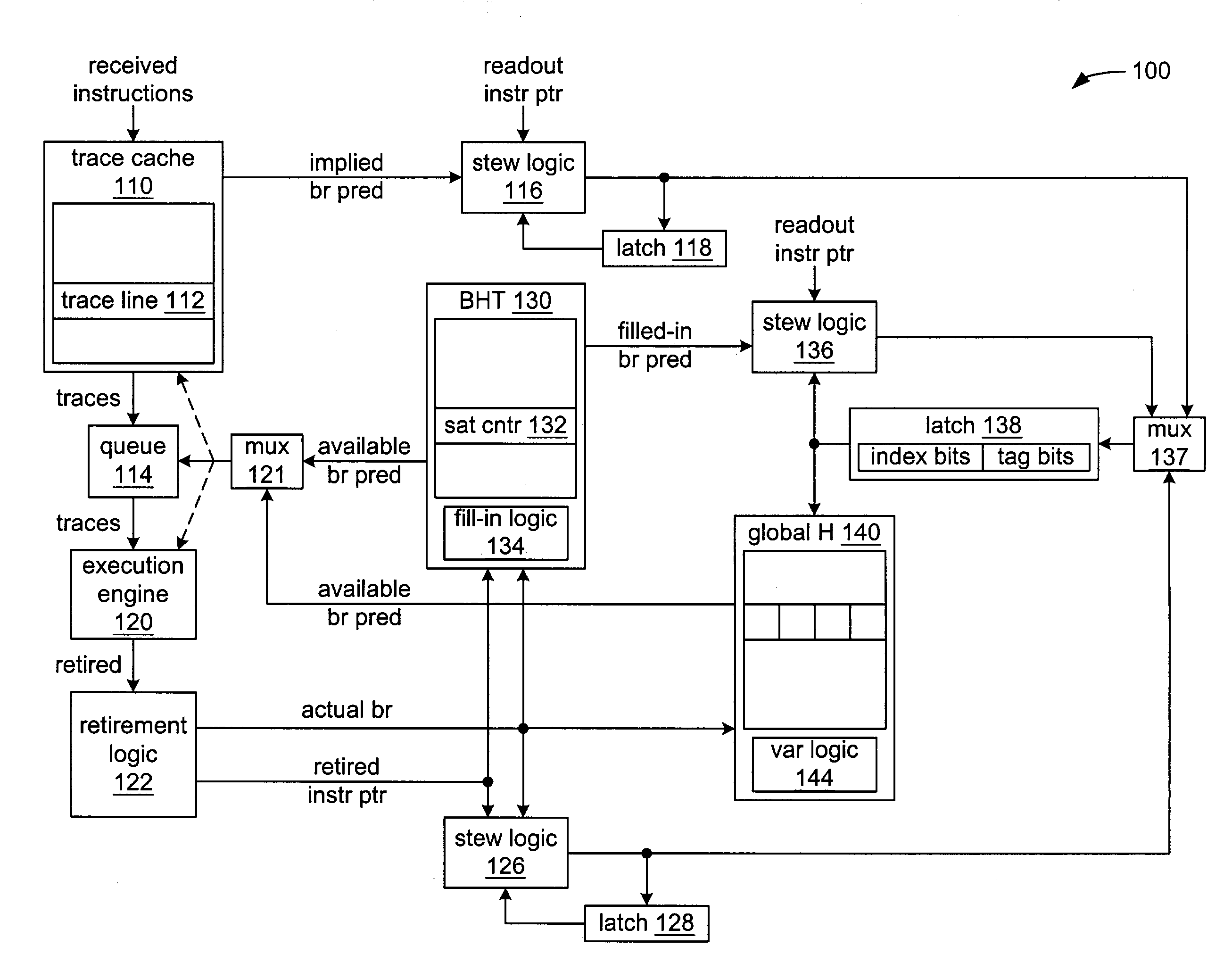
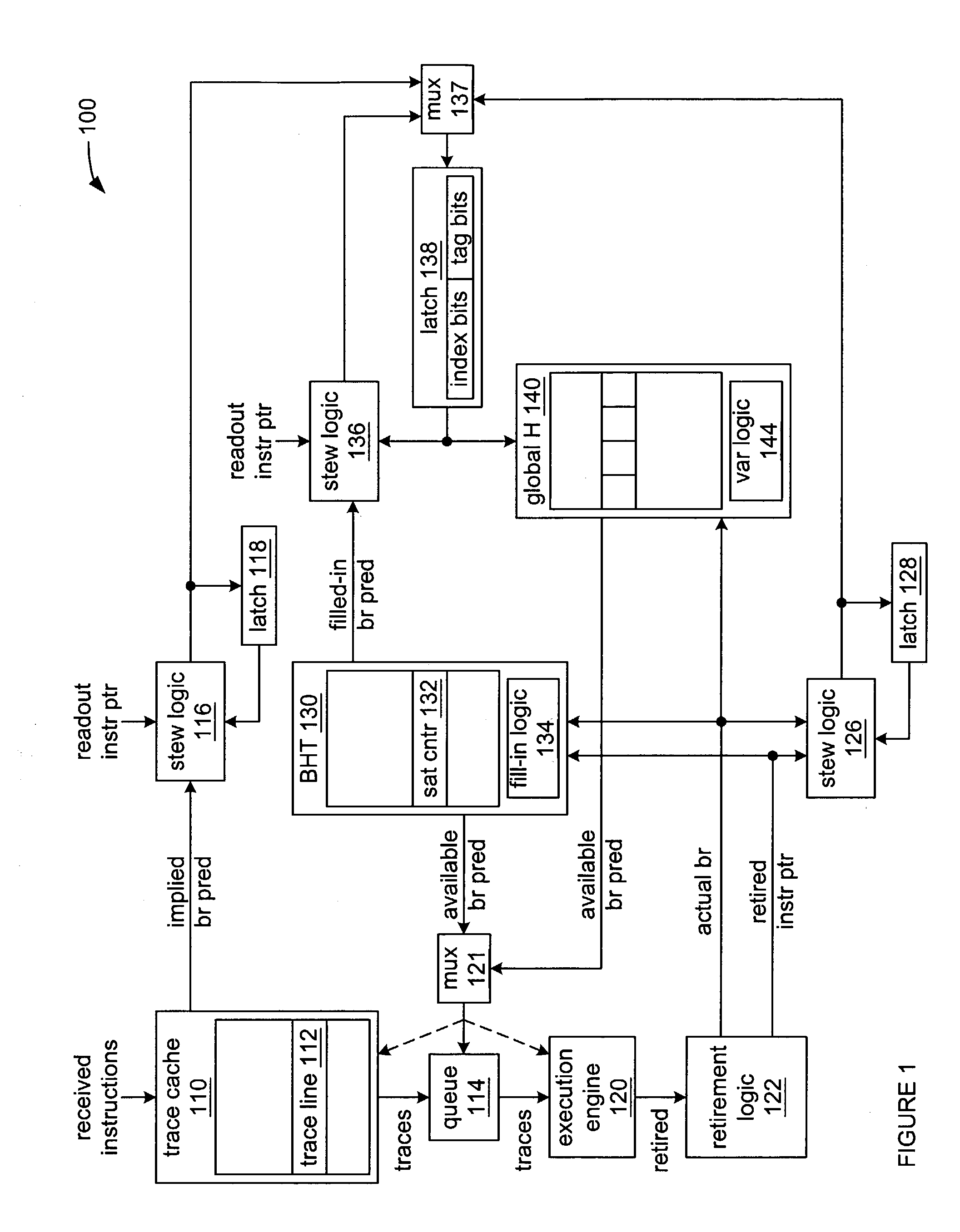
InactiveUS7143273B2Digital computer detailsNext instruction address formationParallel computingInstruction sequence
Toggling between accessing an entry in a global history with a stew created from branch predictions implied by the ordering of instructions within a trace of a trace cache when a trace is read out of a trace cache, and accessing an entry in a global history with repeatable variations of a stew when there is more than branch instruction within a trace within the trace cache and at least a second branch instruction is read out.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Executing instruction sequence code blocks by using virtual cores instantiated by partitionable engines
ActiveUS20120246657A1ScalingProgram control using stored programsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationCoding blockParallel computing
A method for executing instructions using a plurality of virtual cores for a processor. The method includes receiving an incoming instruction sequence using a global front end scheduler, and partitioning the incoming instruction sequence into a plurality of code blocks of instructions. The method further includes generating a plurality of inheritance vectors describing interdependencies between instructions of the code blocks, and allocating the code blocks to a plurality of virtual cores of the processor, wherein each virtual core comprises a respective subset of resources of a plurality of partitionable engines. The code blocks are executed by using the partitionable engines in accordance with a virtual core mode and in accordance with the respective inheritance vectors.
Owner:INTEL CORP
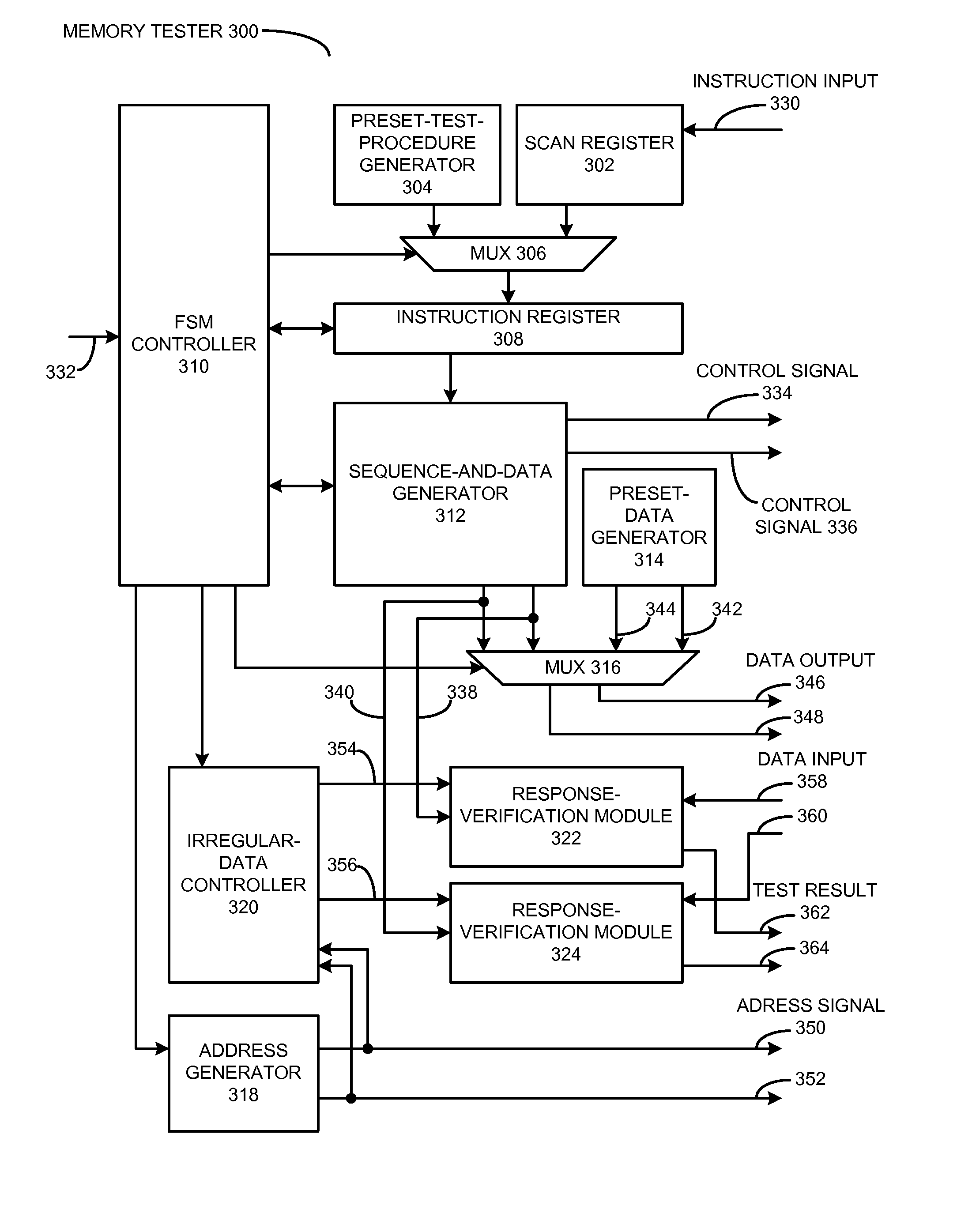
Runtime programmable BIST for testing a multi-port memory device
One embodiment provides a runtime programmable system which comprises methods and apparatuses for testing a multi-port memory device to detect a multi-port memory fault, in addition to typical single-port memory faults that can be activated when accessing a single port of a memory device. More specifically, the system comprises a number of mechanisms which can be configured to activate and detect any realistic fault which affects the memory device when two simultaneous memory access operations are performed. During operation, the system can receive an instruction sequence, which implements a new test procedure for testing the memory device, while the memory device is being tested. Furthermore, the system can implement a built-in self-test (BIST) solution for testing any multi-port memory device, and can generate tests targeted to a specific memory design based in part on information from the instruction sequence.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
System and method for enabling weak consistent storage advantage to a firmly consistent storage architecture
InactiveUS6963967B1Efficient processingDigital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionData processing systemProcessing Instruction
Disclosed is a method of processing instructions in a data processing system. An instruction sequence that includes a memory access instruction is received at a processor in program order. In response to receipt of the memory access instruction a memory access request and a barrier operation are created. The barrier operation is placed on an interconnect after the memory access request is issued to a memory system. After the barrier operation has completed, the memory access request is completed in program order. When the memory access request is a load request, the load request is speculatively issued if a barrier operation is pending. Data returned by the speculatively issued load request is only returned to a register or execution unit of the processor when an acknowledgment is received for the barrier operation.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and apparatus for advancing load operations
InactiveUS6658559B1Digital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionLoad instructionPhysical address
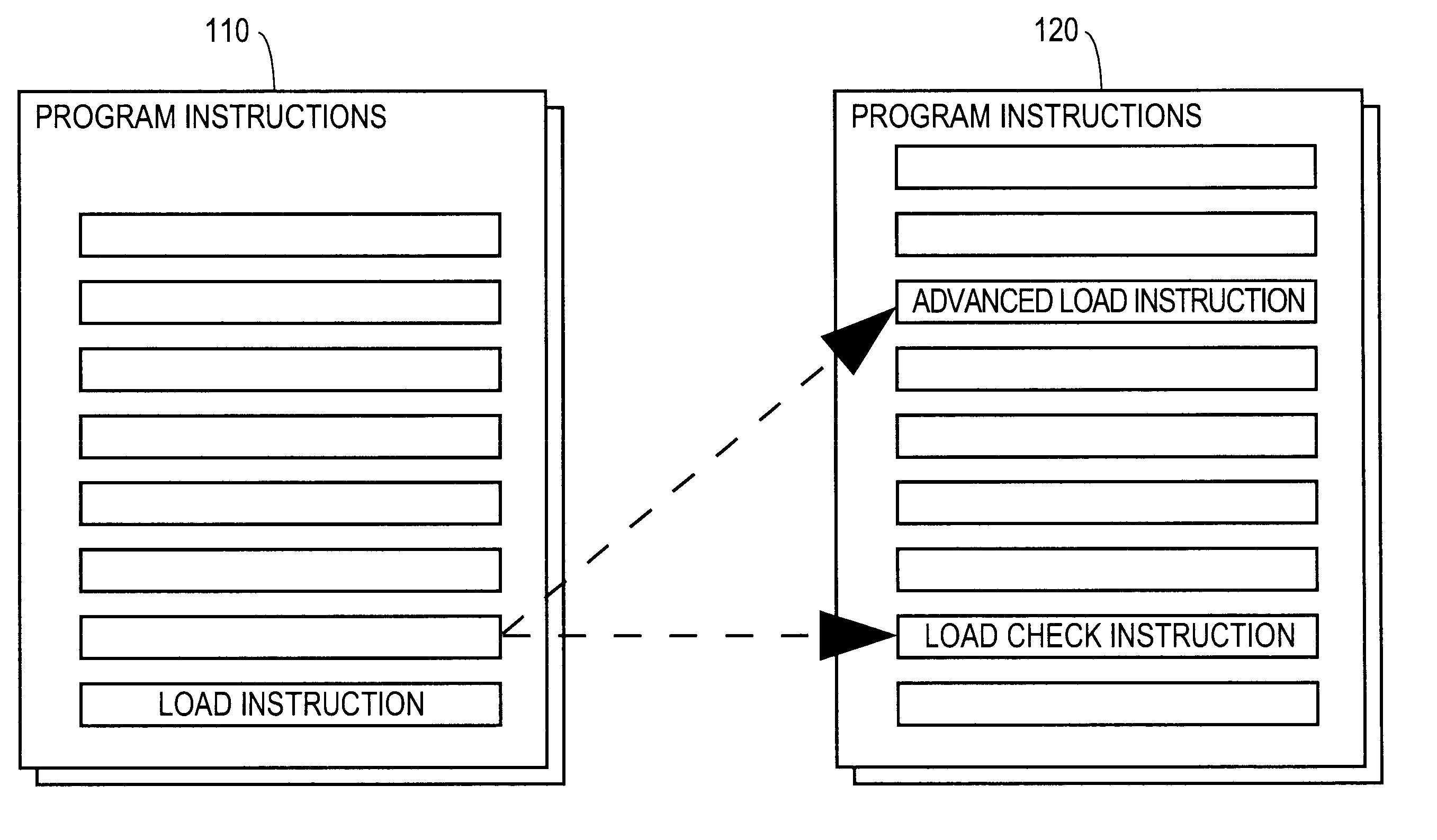
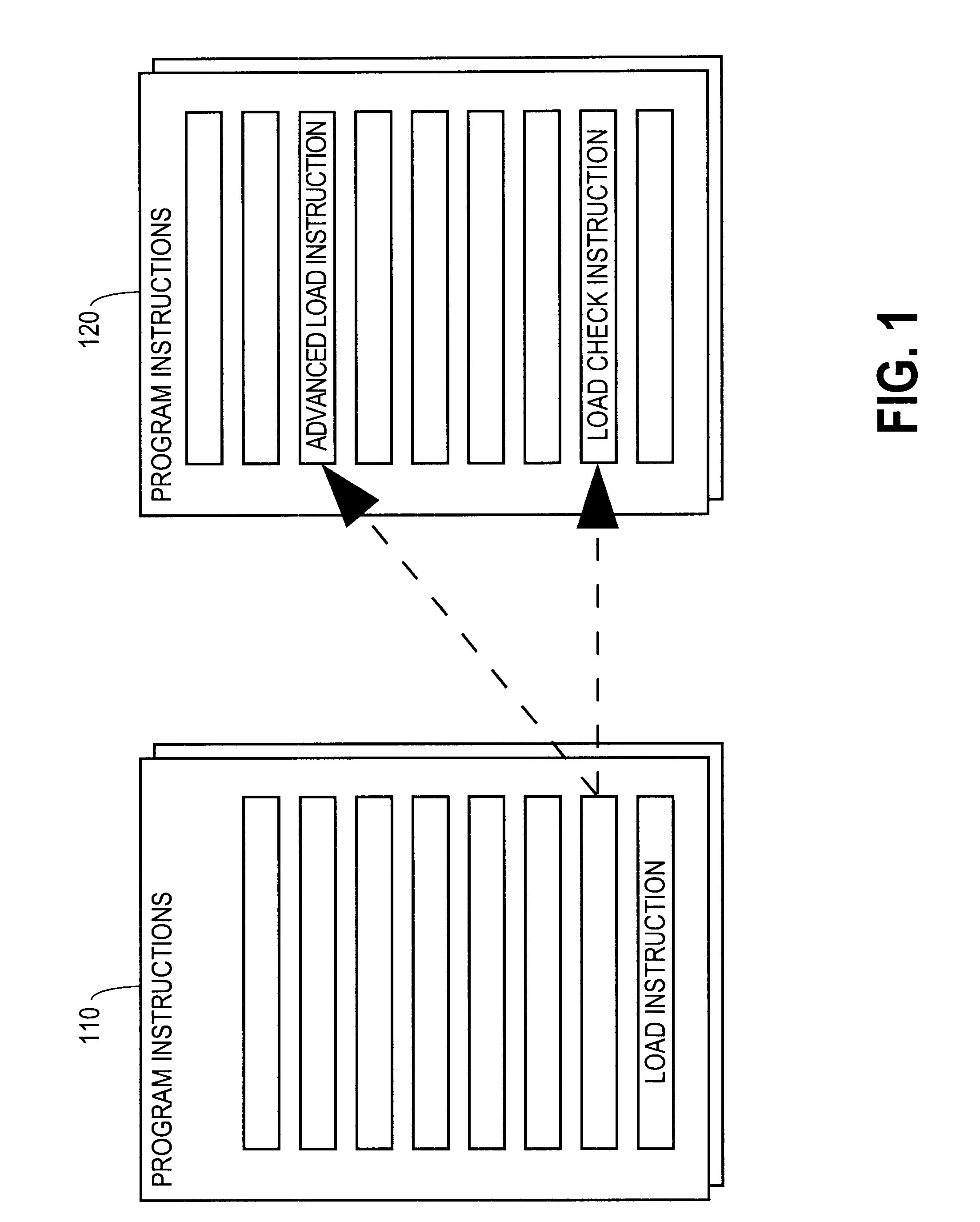
A computer product, method, and apparatus for causing a computer to perform load operations in a particular way are disclosed. The computer is made to replace a load instruction at a particular location in a computer program instruction sequence with two instructions, an advanced load instruction and a load check instruction. The advanced load instruction is inserted into the instruction sequence up-stream from where the original load instruction was located, and may be inserted above store instructions. The load check instruction is inserted into the instruction sequence after the store instructions. An Advanced Load Address Table (ALAT) structure, containing physical address data and validity data for each non-speculative advanced load, is updated with data about each advanced load and each store instruction executed, and queried on execution of each load check instruction about whether or not a particular advanced load is safe to use. An advanced load speculative pipeline and speculative invalidation pipeline are similarly queried regarding speculative advanced loads.
Owner:INTEL CORP
An AGV navigation control method based on two-dimension code image tags
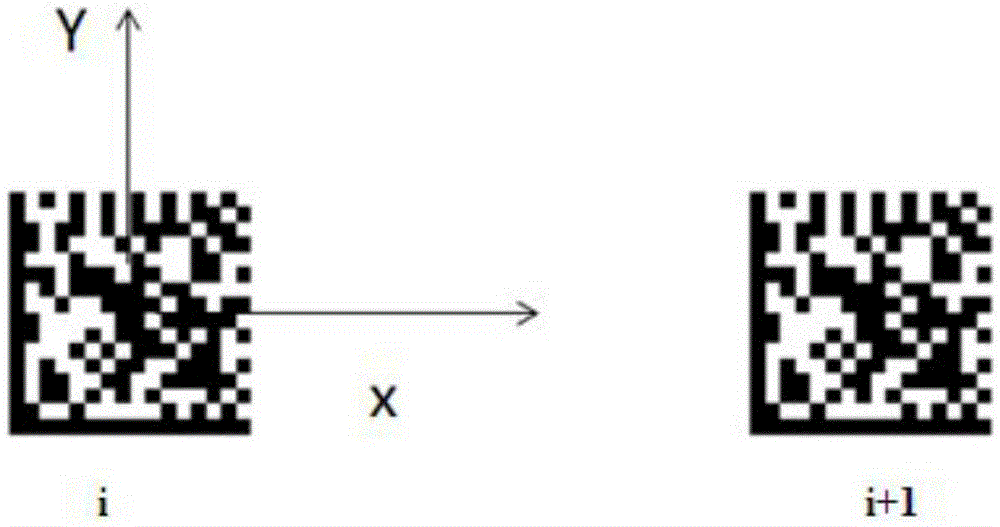
ActiveCN105388899AImprove flexibilityReduce manufacturing costPosition/course control in two dimensionsInstruction sequenceMarine navigation
The invention discloses an AGV navigation control method based on two-dimension code image tags. The AGV navigation control method comprises the following steps: 1) obtaining the range of each pixel point in scanned images of two-dimension code tag scanners; 2) obtaining corresponding IDs and positions of the two-dimension code image tags in a coordinate system of the images themselves according to the scanned images of the two-dimension code tag scanners; 3) an AGV receiving navigation path instructions sent by a scheduling center; 4) the AGV sequentially establishing local navigation coordinate systems according to the navigation path instructions and calculating initial positions of the AGV in the local navigation coordinate systems; 5) planning an arc track between two two-dimension code image tags of the AGV in sequence; and 6) calculating the control quantity of the AGV according to the planed arc radius to enable the AGV to drive to each two-dimension code image tag in a navigation path instruction sequence in sequence, and thus the navigation path instruction is finished. The method can reduce production cost, reduce on-site implementation difficulty and improve guiding flexibility.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High speed virtual instruction execution mechanism
InactiveUS20040139304A1Digital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionParallel computingExecution unit
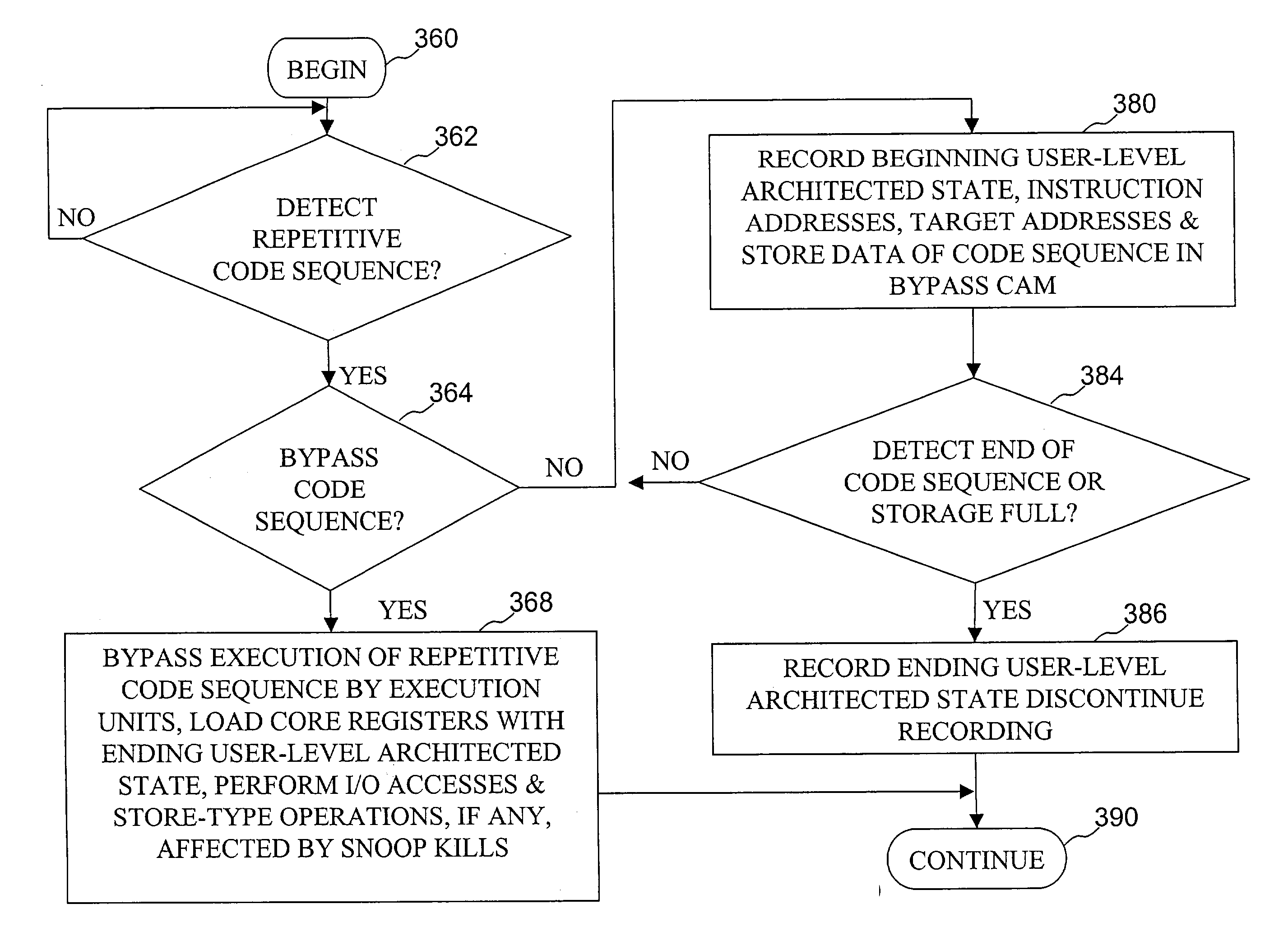
Execution of code within a processor is accelerated through hardware bypass of repetitive code sequences. In accordance with a preferred method, an instruction sequence including a plurality of instructions is executed within one or more execution units of a processor to generate and store a data result. The processor records instruction addresses and target addresses of selected instructions within the instruction sequence. After recording the instruction addresses and target addresses, any operation affecting the instruction sequence is detected. Thereafter, in response to detecting an intended execution of the instruction sequence by the processor, the processor bypasses execution of the plurality of instructions within the instruction sequence in response to failing to detect an operation affecting particular instructions within the instruction sequence after the recording.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for dependency broadcasting through a block organized source view data structure
ActiveUS20140282601A1Conditional code generationProgram initiation/switchingParallel computingInstruction sequence
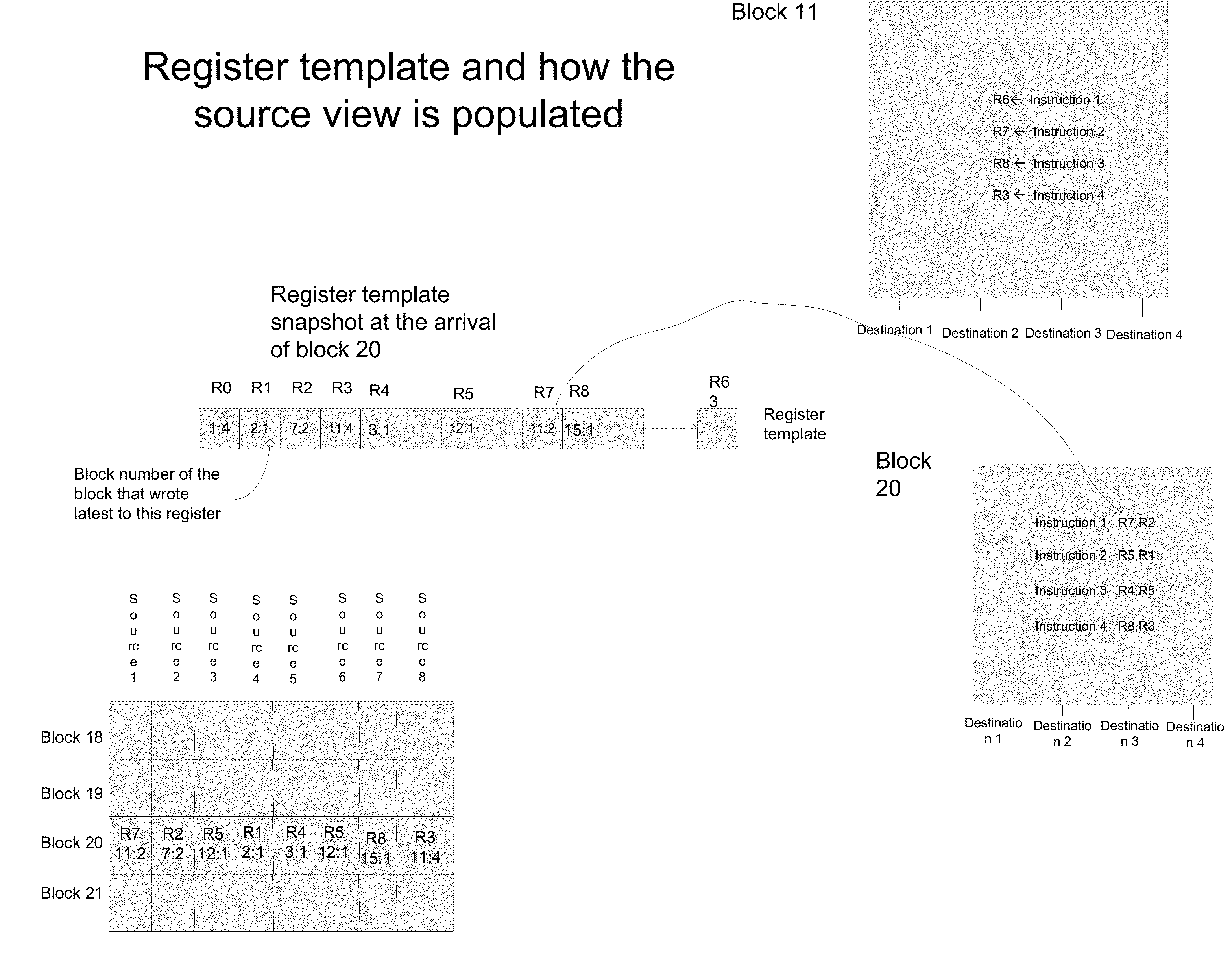
A method for dependency broadcasting through a block organized source view data structure. The method includes receiving an incoming instruction sequence using a global front end; grouping the instructions to form instruction blocks; using a plurality of register templates to track instruction destinations and instruction sources by populating the register template with block numbers corresponding to the instruction blocks, wherein the block numbers corresponding to the instruction blocks indicate interdependencies among the blocks of instructions; populating a block organized source view data structure, wherein the source view data structure stores sources corresponding to the instruction blocks as recorded by the plurality of register templates; upon dispatch of one block of the instruction blocks, broadcasting a number belonging to the one block to a column of the source view data structure that relates that block and marking the column accordingly; and updating the dependency information of remaining instruction blocks in accordance with the broadcast.
Owner:INTEL CORP
High speed virtual machine and compiler
InactiveUS20030191792A1Multiprogramming arrangementsConcurrent instruction executionData setProcessor register
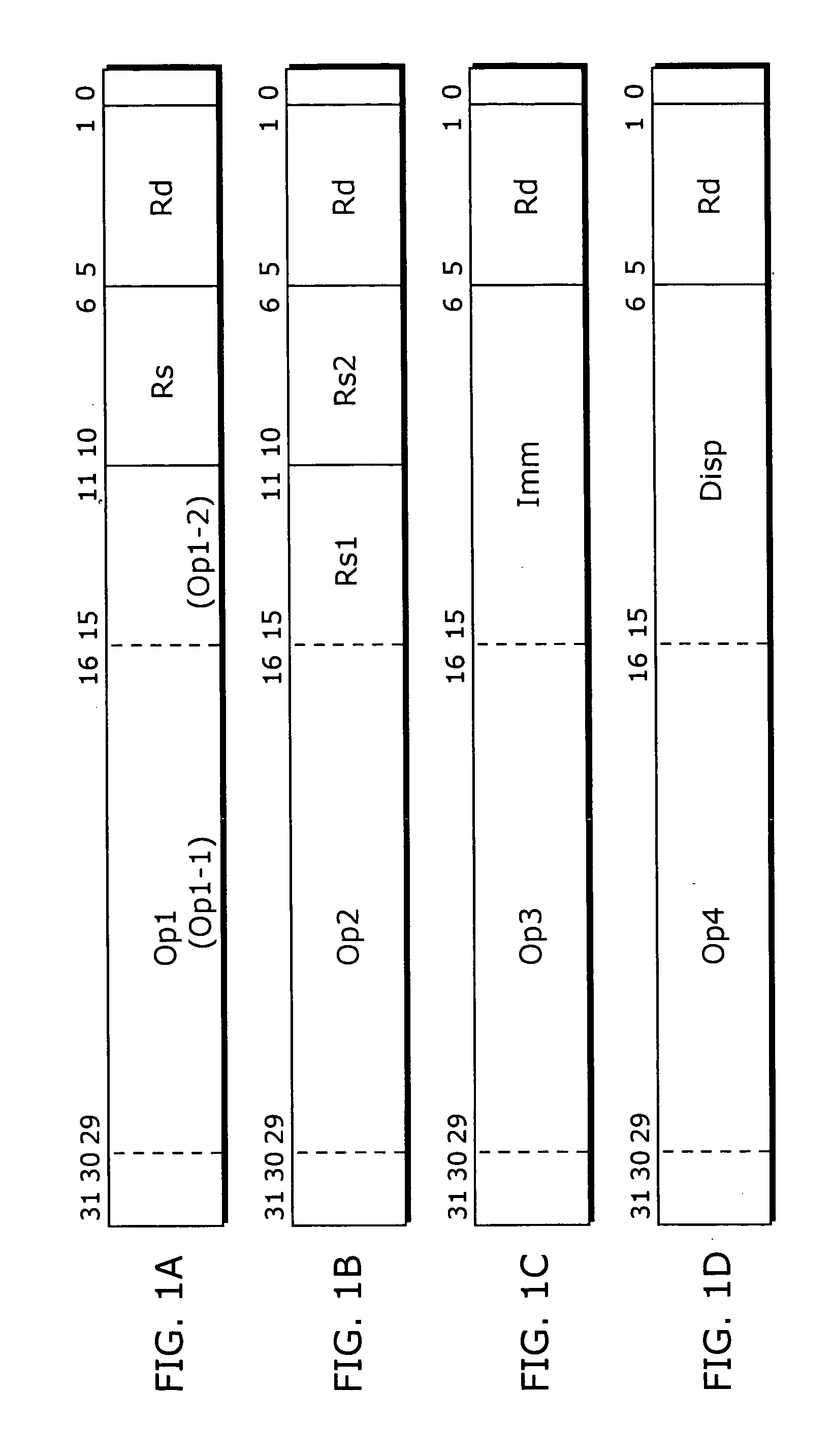
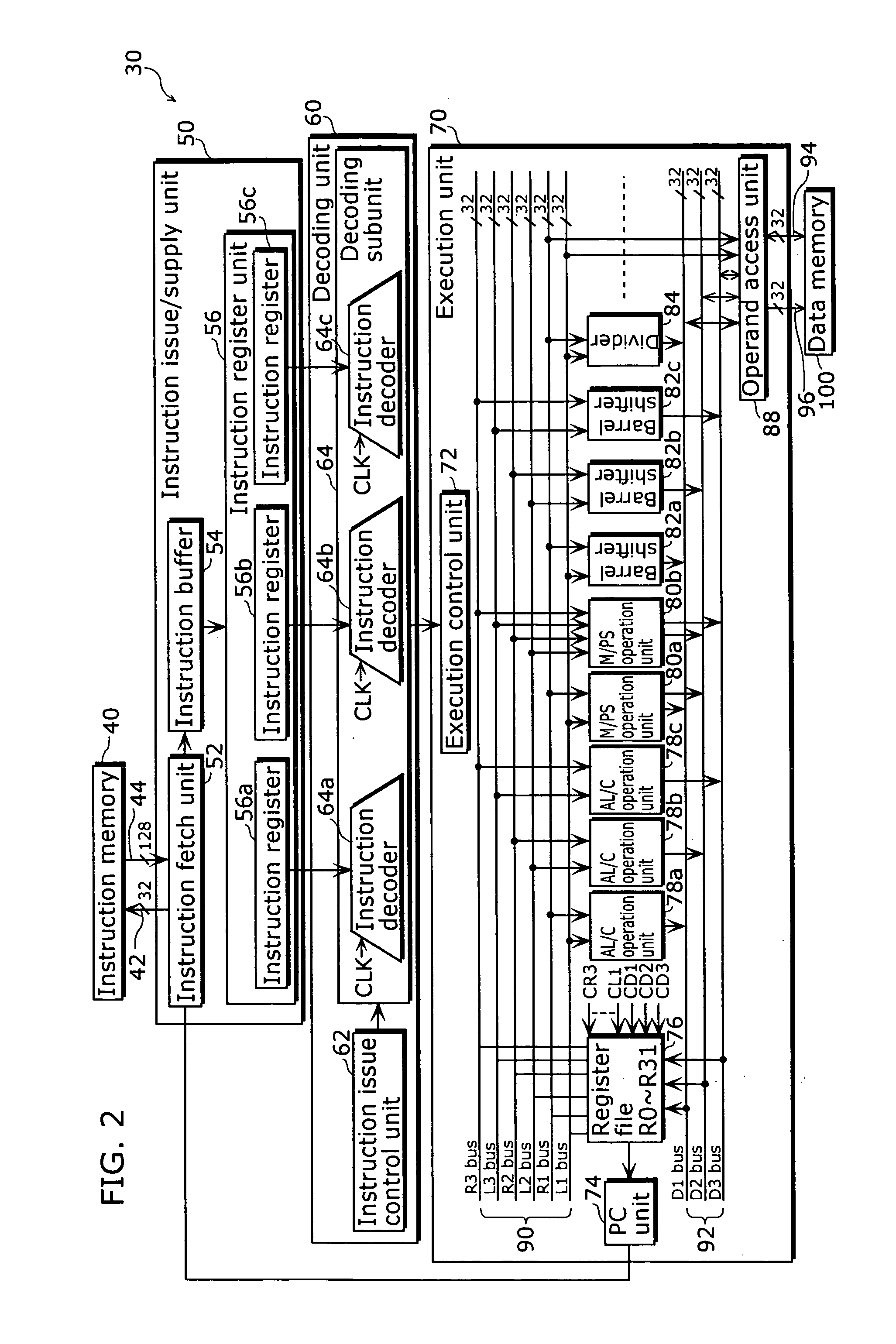
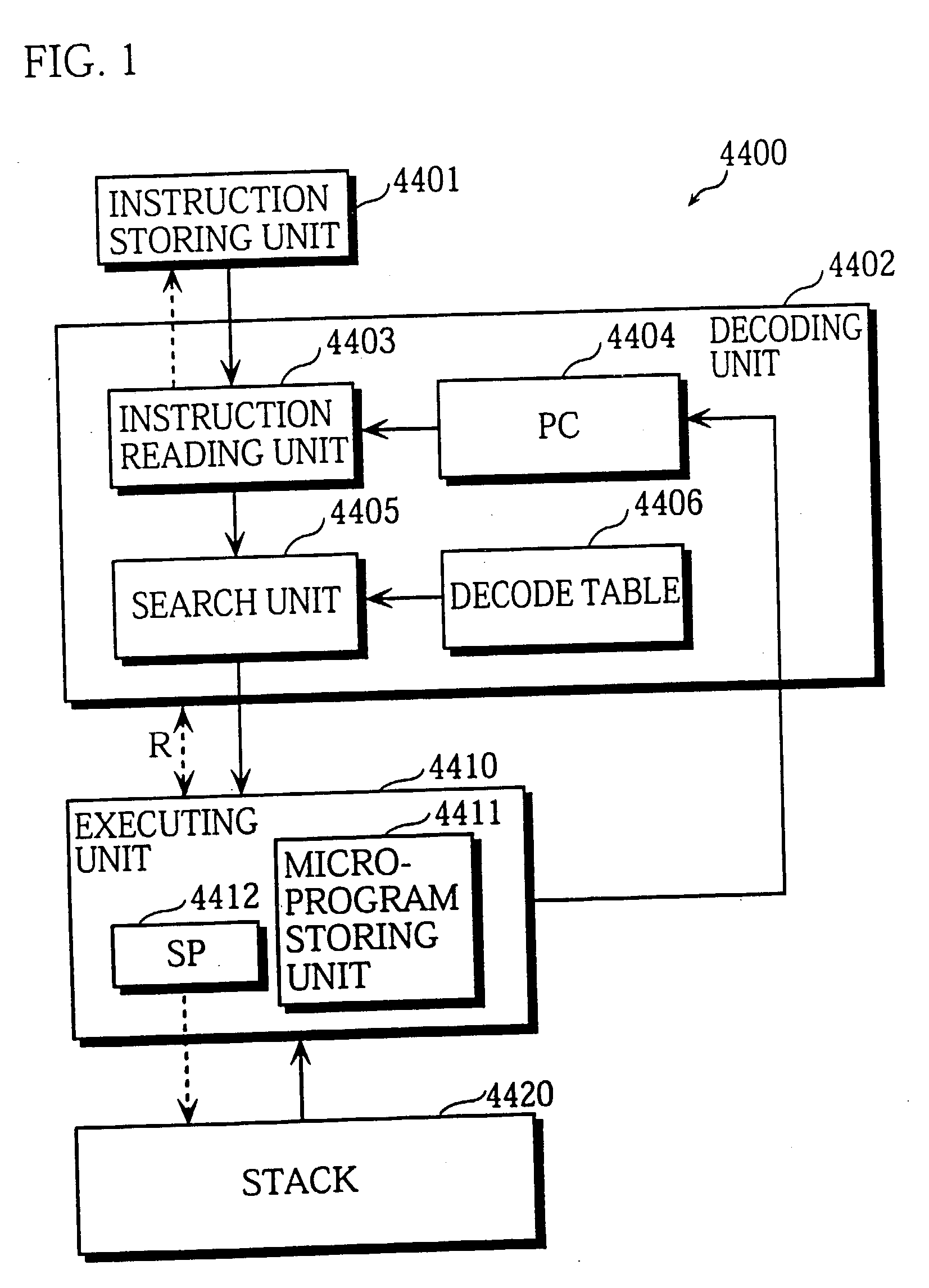
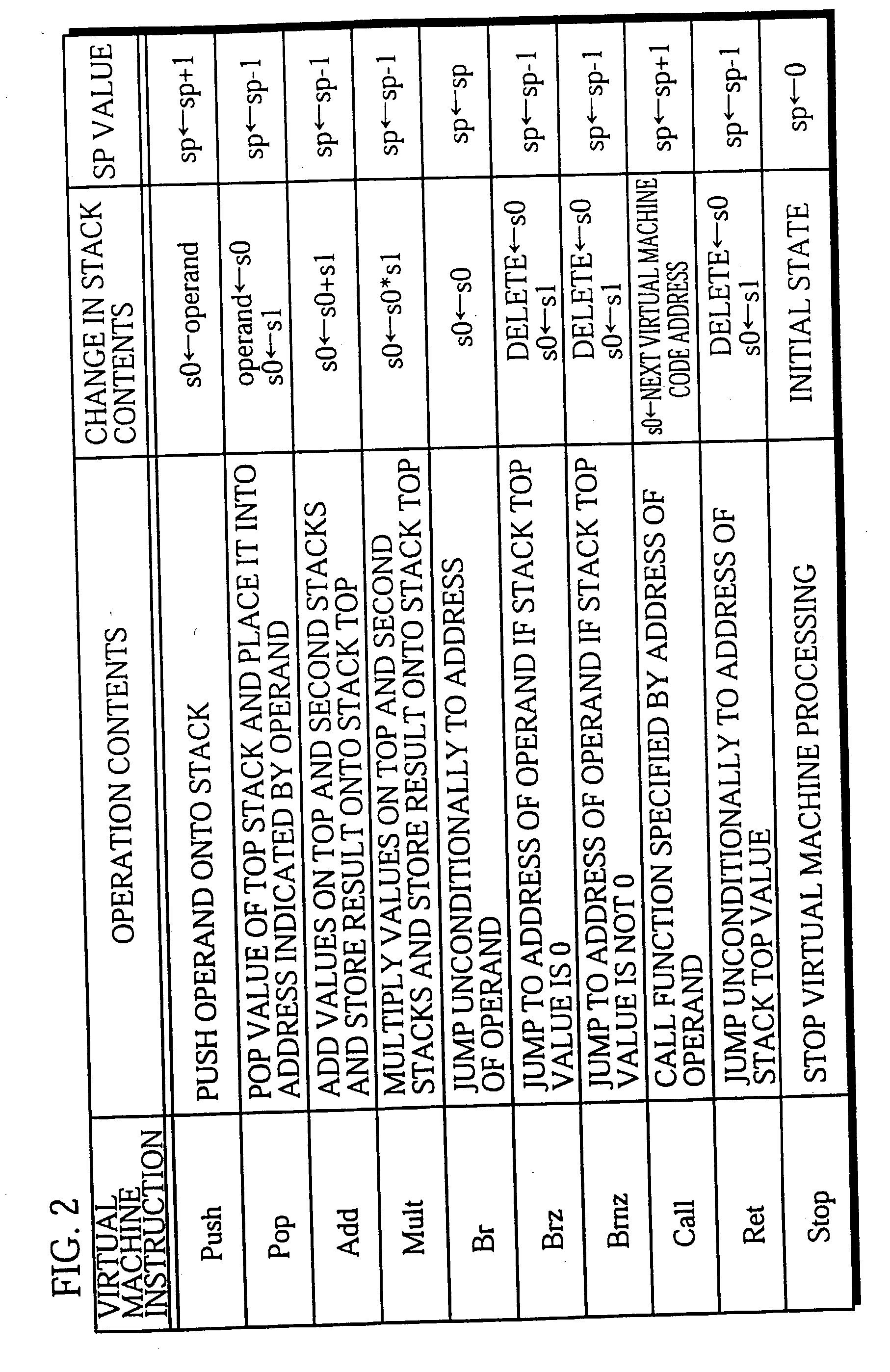
A virtual machine with a stack architecture includes: a stack 120 whose top level (TOS) and the second level from the top (SOS) are mapped to registers of a real machine 201; an instruction storing unit 102 for storing a virtual machine instruction sequence to be executed; next instruction information storing unit 101 for storing a plurality of sets of next instruction information that are each associated with a different virtual machine instruction in the virtual machine instruction sequence, the set of next instruction information for a given virtual machine instruction indicating a change in a number of sets of data stored in the stack 120 due to execution of a virtual machine instruction executed after the given virtual machine instruction; a decoding unit 103 for decoding a virtual machine instruction and an associated set of next instruction information after reading them from the instruction storing unit 102 and the next instruction information storing unit 101; and an executing unit 110 for executing the decoded virtual machine instruction and performing a stack handling in. the stack 120 in advance for a virtual machine instruction that is to be executed next based on the set of next instruction information.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com