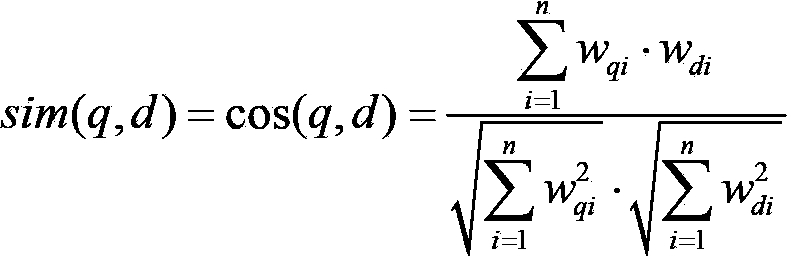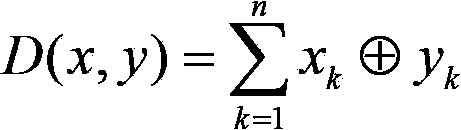Patents
Literature
931 results about "Hamming distance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
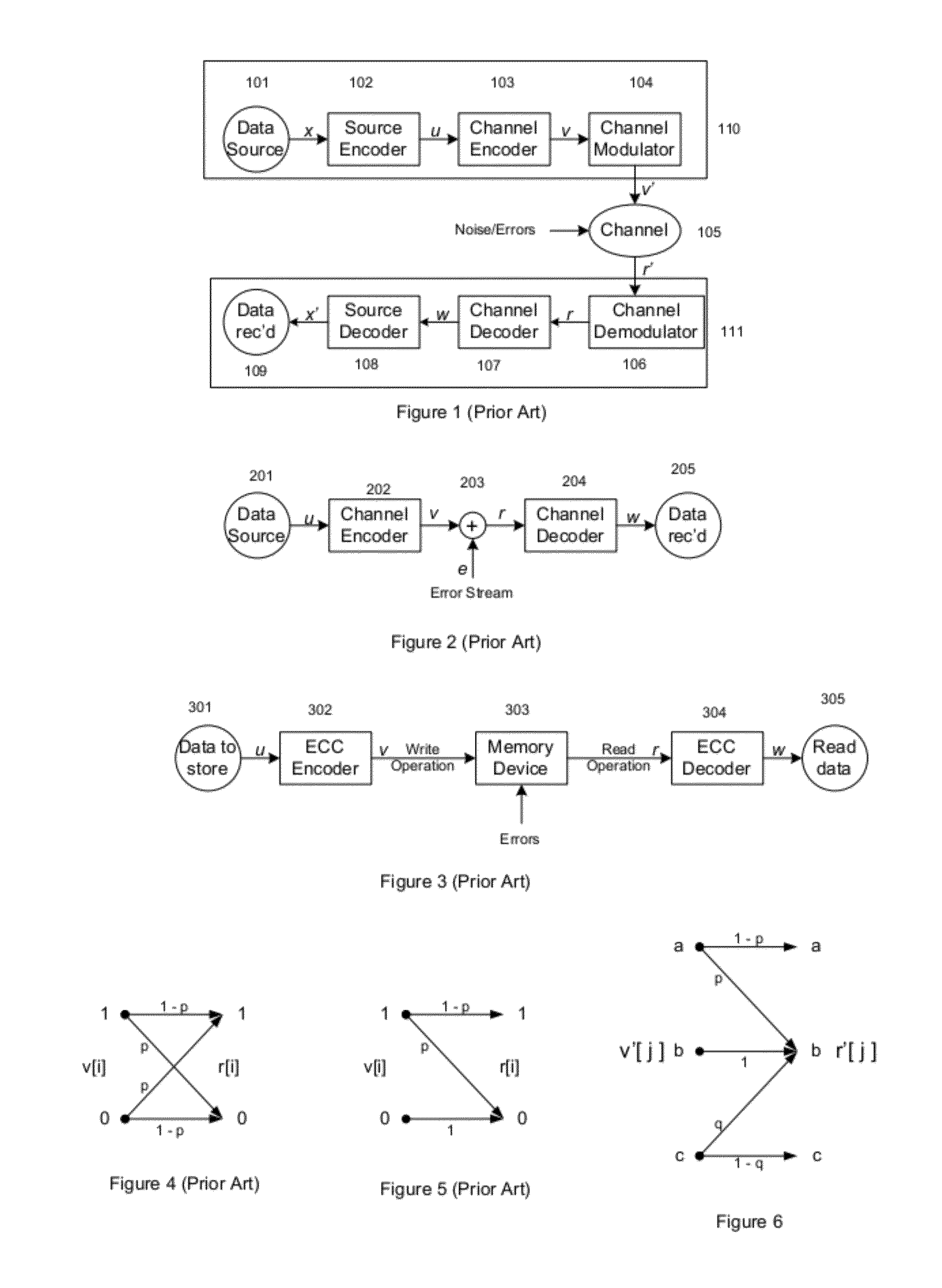
In information theory, the Hamming distance between two strings of equal length is the number of positions at which the corresponding symbols are different. In other words, it measures the minimum number of substitutions required to change one string into the other, or the minimum number of errors that could have transformed one string into the other. In a more general context, the Hamming distance is one of several string metrics for measuring the edit distance between two sequences. It is named after the American mathematician Richard Hamming.
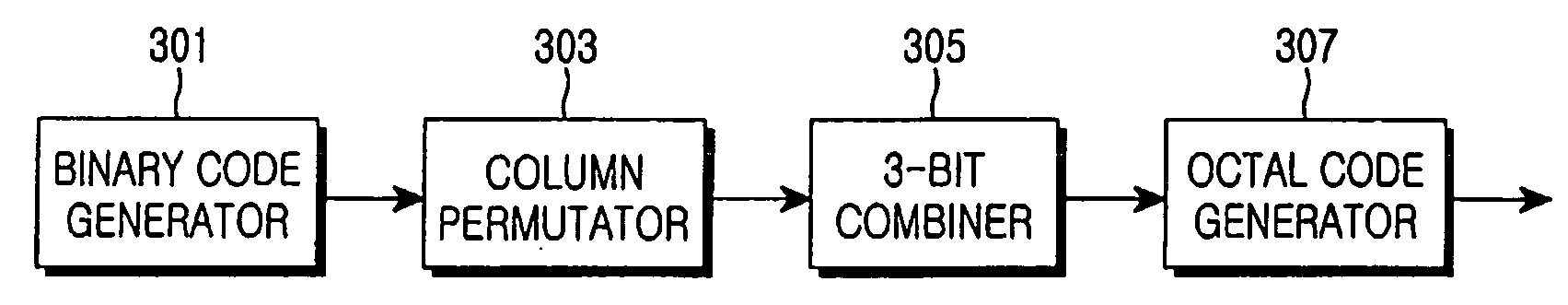
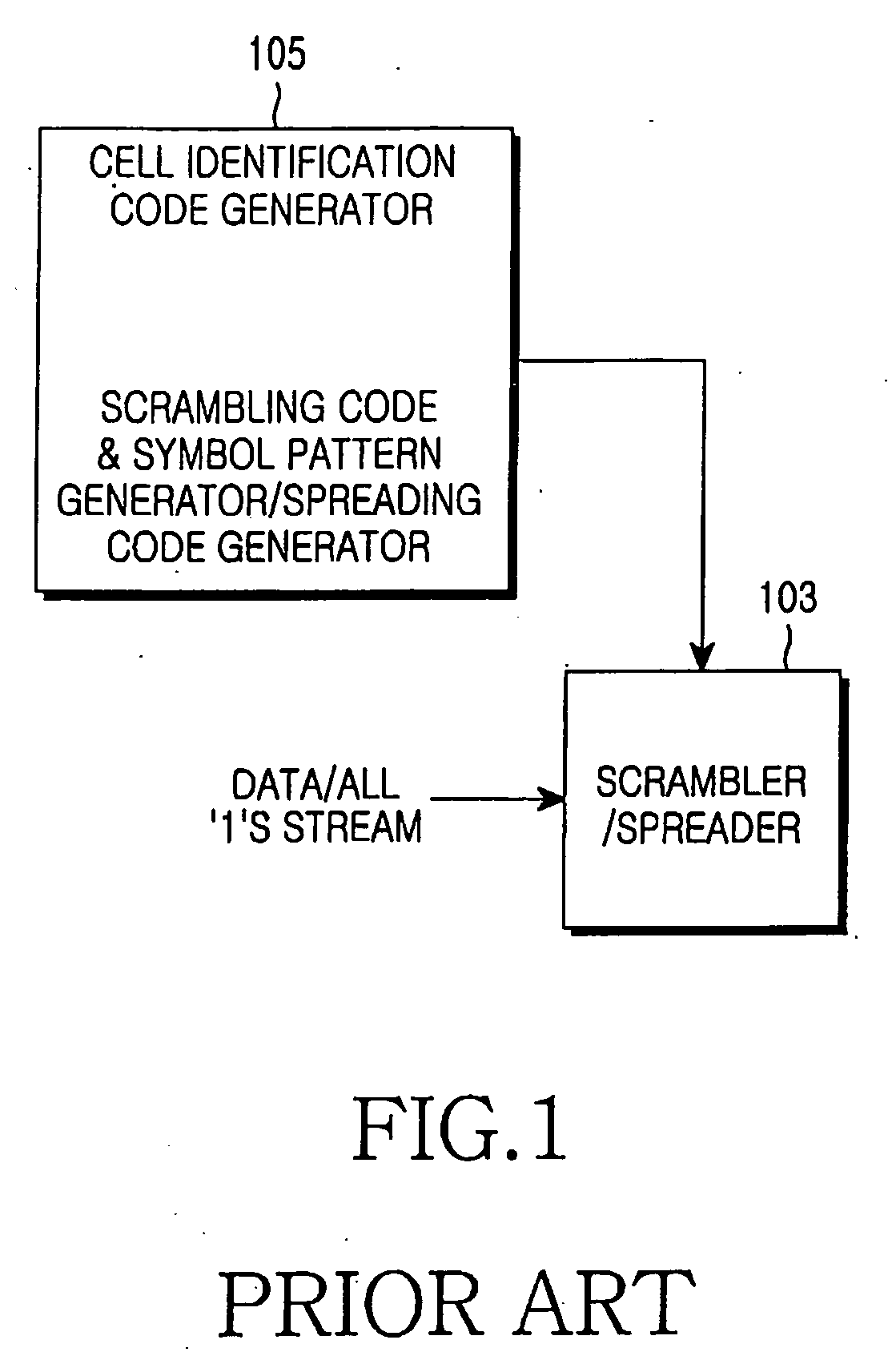
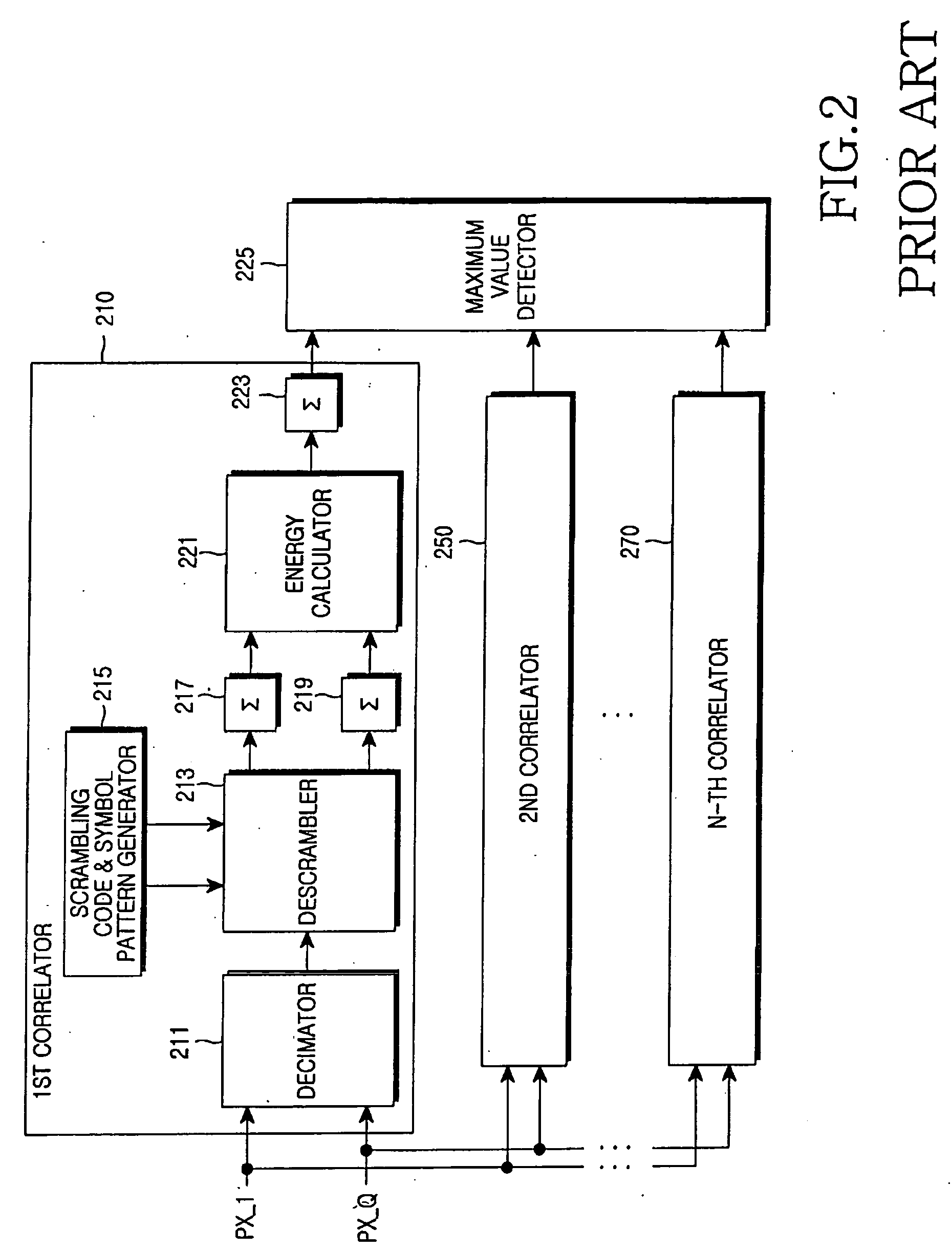
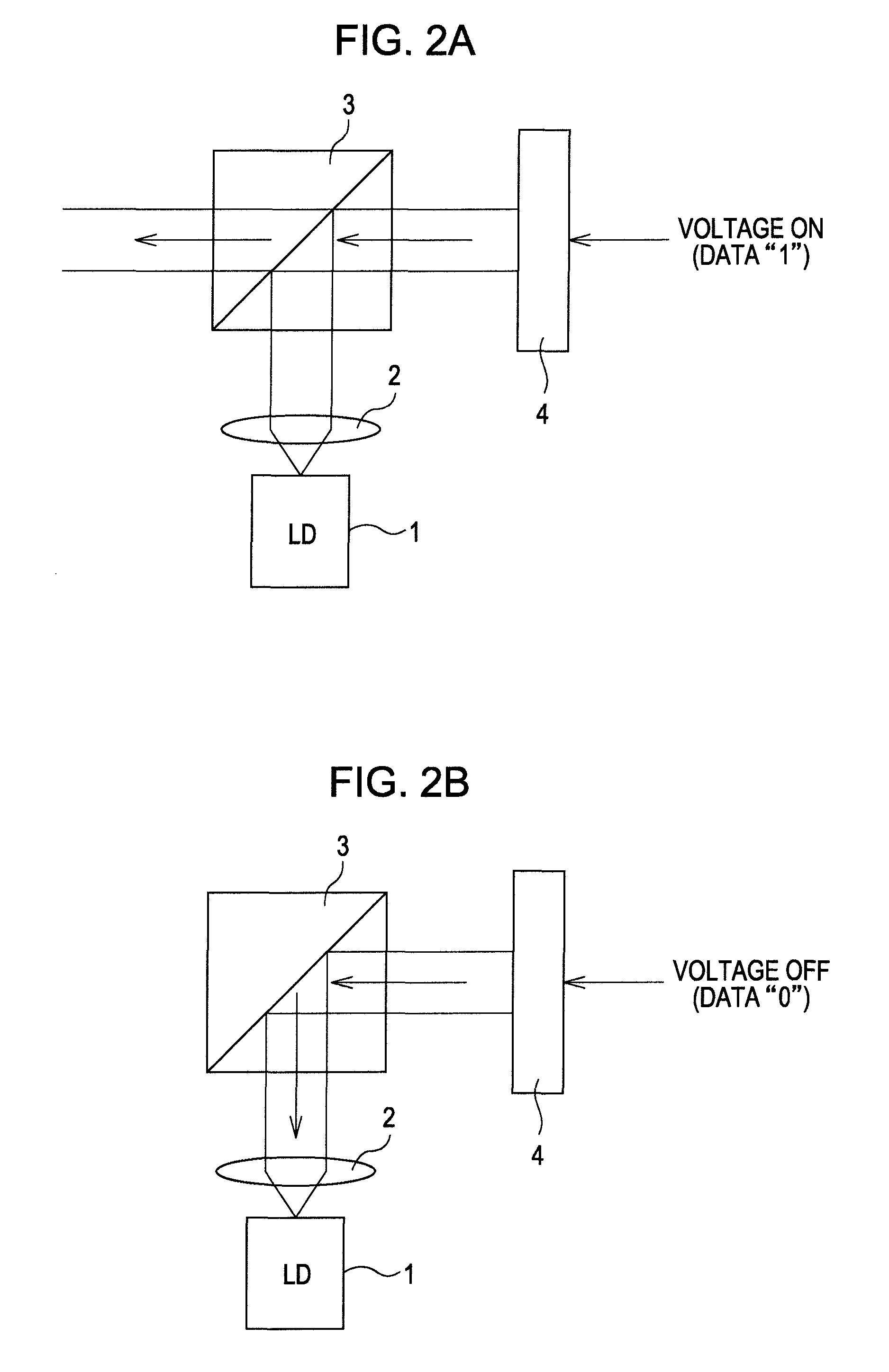
Apparatus and method for transmitting and receiving a cell identification code in a mobile communication system
ActiveUS20050265293A1Improve performanceTransmission control/equlisationFrequency-division multiplex detailsProgramming languageHamming distance
An apparatus and method for generating an octal code for identifying cells in a mobile communication system. In the octal code generating apparatus, a binary code generator generates a binary code with a predetermined minimum Hamming distance. A column permutator permutes the order of columns of the binary code in a predetermined interleaving method. A 3-bit combiner generates a plurality of codewords using the column-permuted binary code as a generator matrix and groups the bits of each of the codewords by threes. An octal code generator converts the 3-bit grouped binary codewords to octal code sequences.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
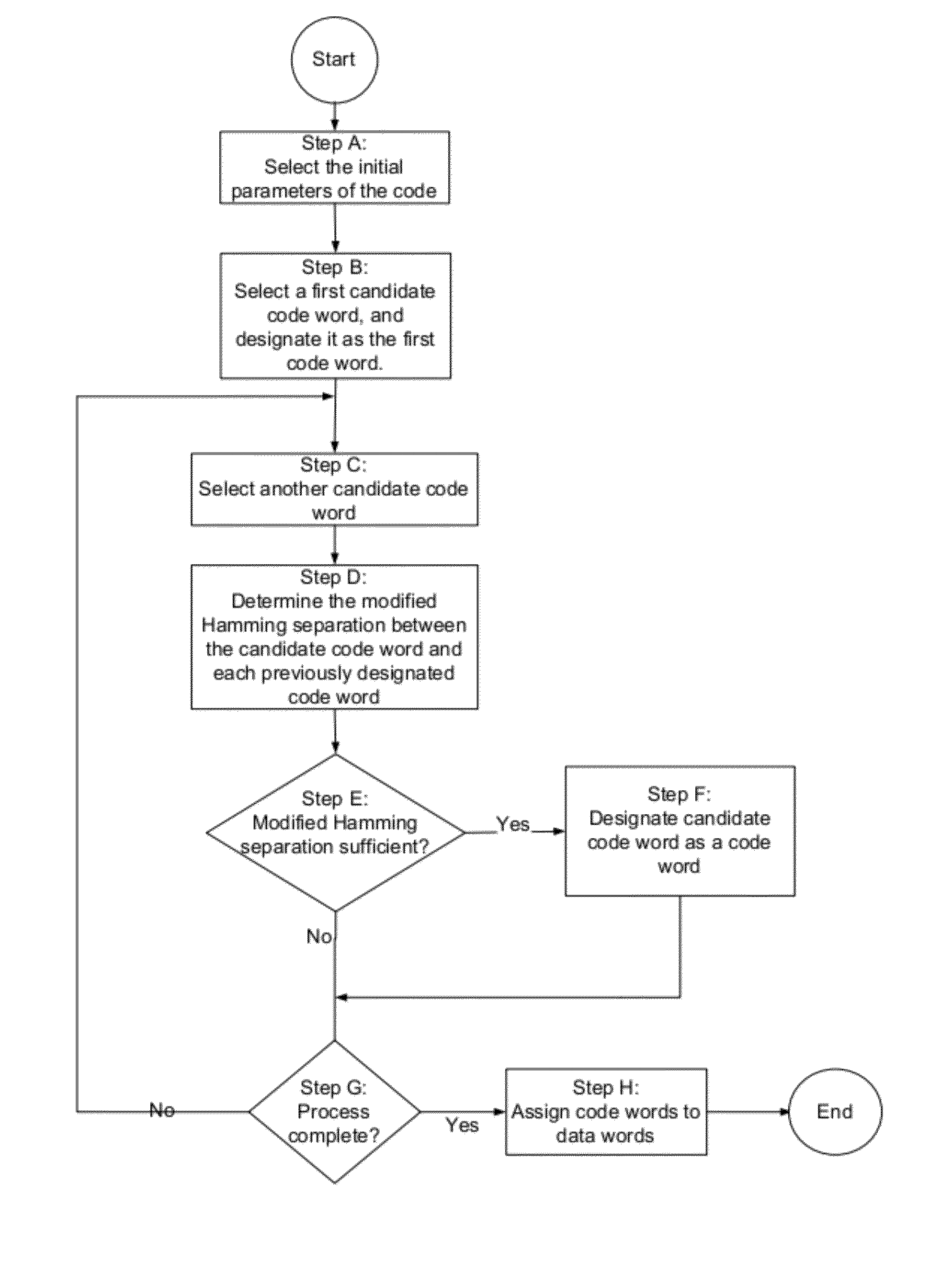
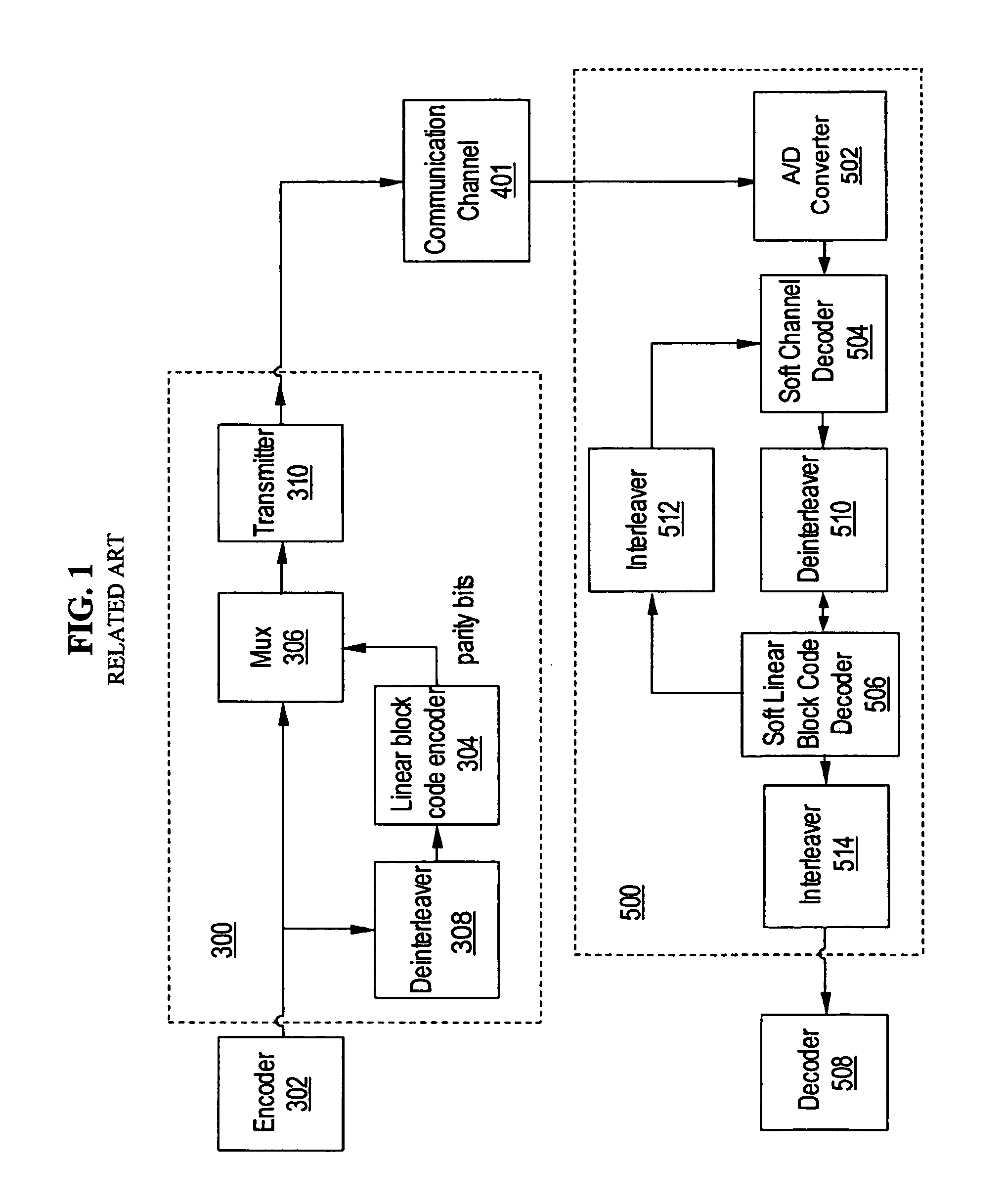
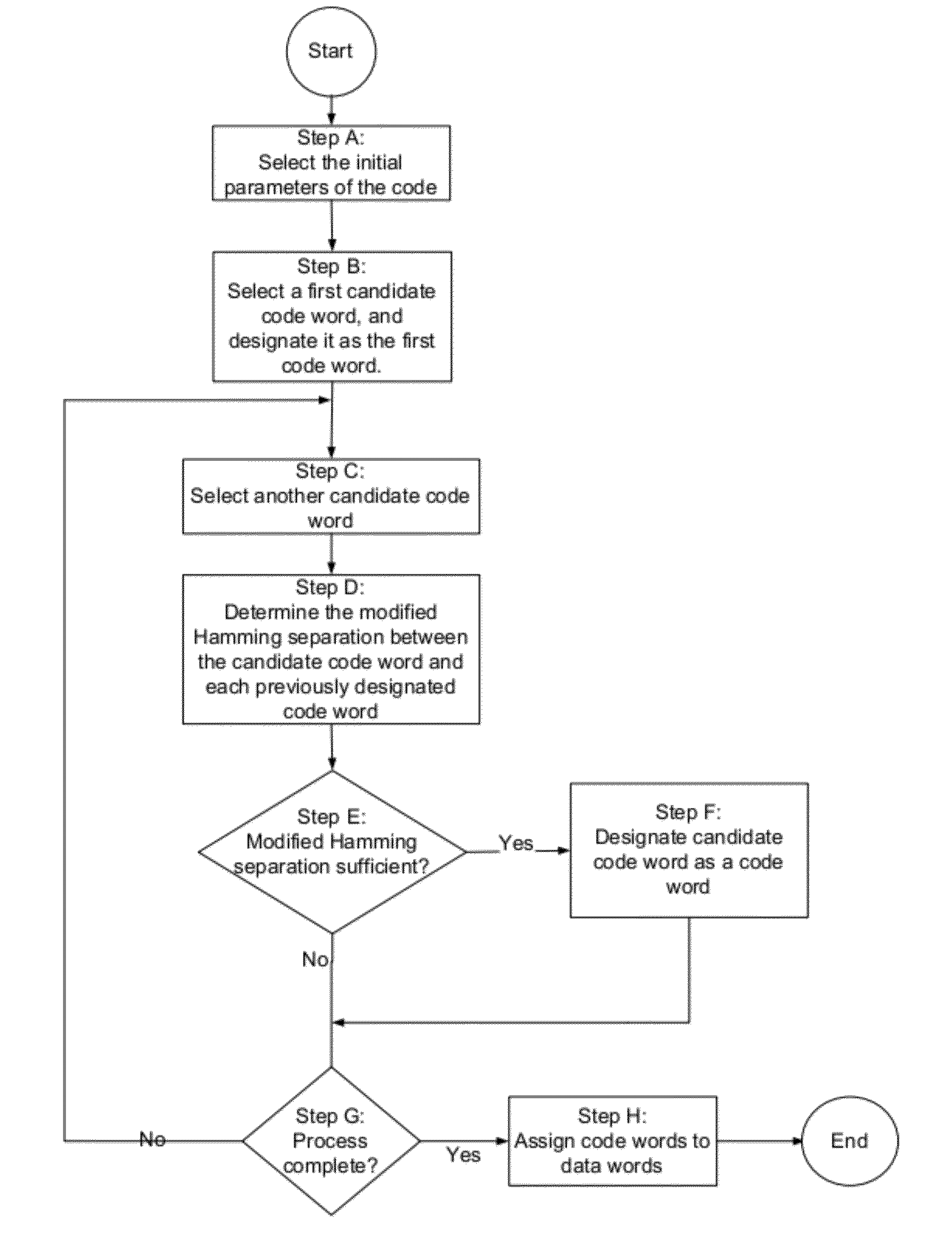
Error detection and correction codes for channels and memories with incomplete error characteristics
InactiveUS8429495B2Efficient error-correcting codeOther error detection/correction/protectionCode conversionParallel computingErrors and residuals
A channel has a first and a second end. The first end of the channel is coupled to a transmitter. The channel is capable of transmitting symbols selected from a symbol set from the first end to the second end. The channel exhibits incomplete error introduction properties. A code comprises a set of code words. The elements of the set of code words are one or more code symbols long. The code symbols are members of the symbol set. The minimum modified Hamming separation between the elements of the set of code words in light of the error introduction properties of the channel is greater than the minimum Hamming distance between the elements of the set of code words. A memory device, a method of using the channel, and a method of generating the code are also described.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
Data modulating device and method thereof
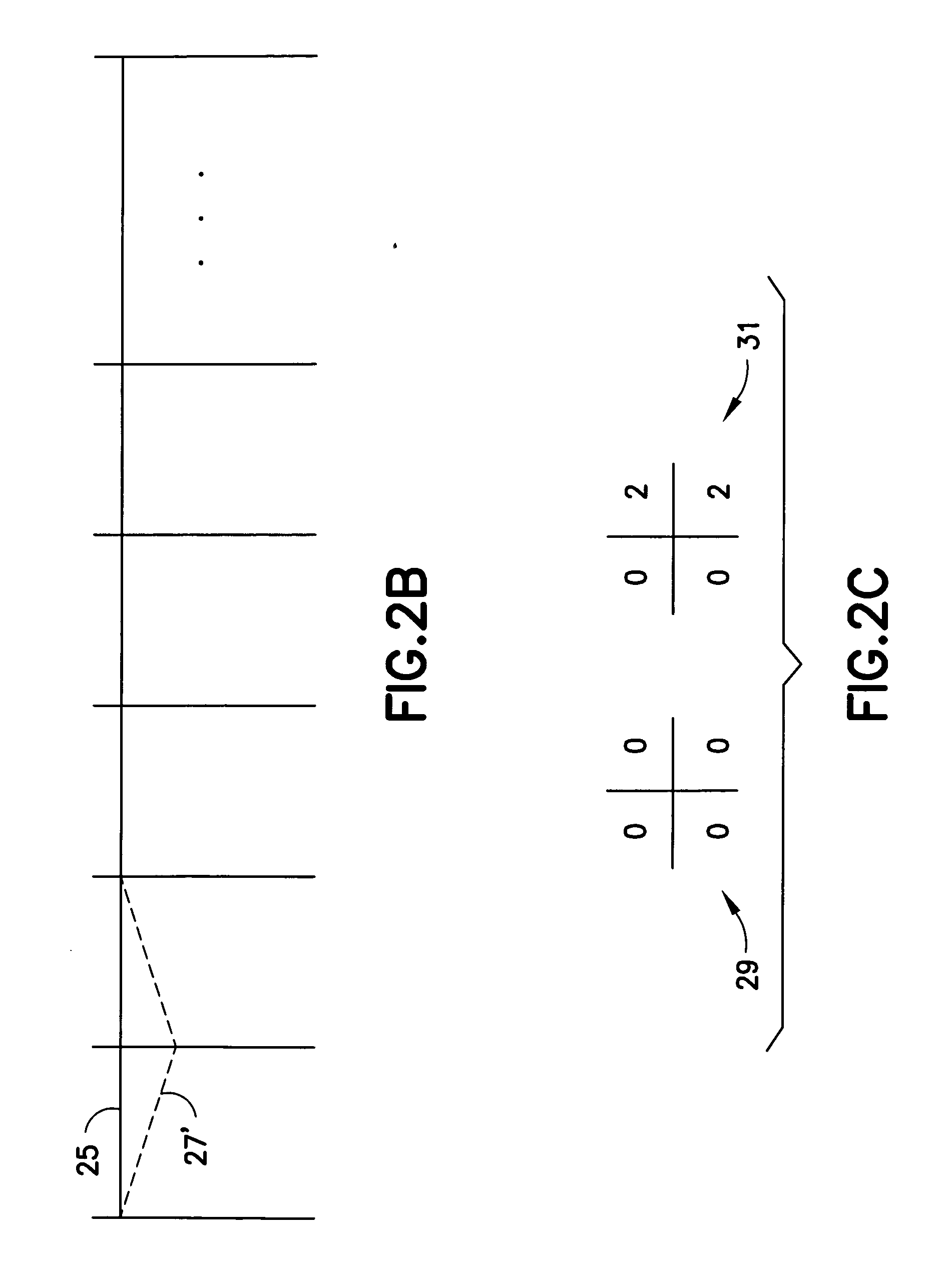
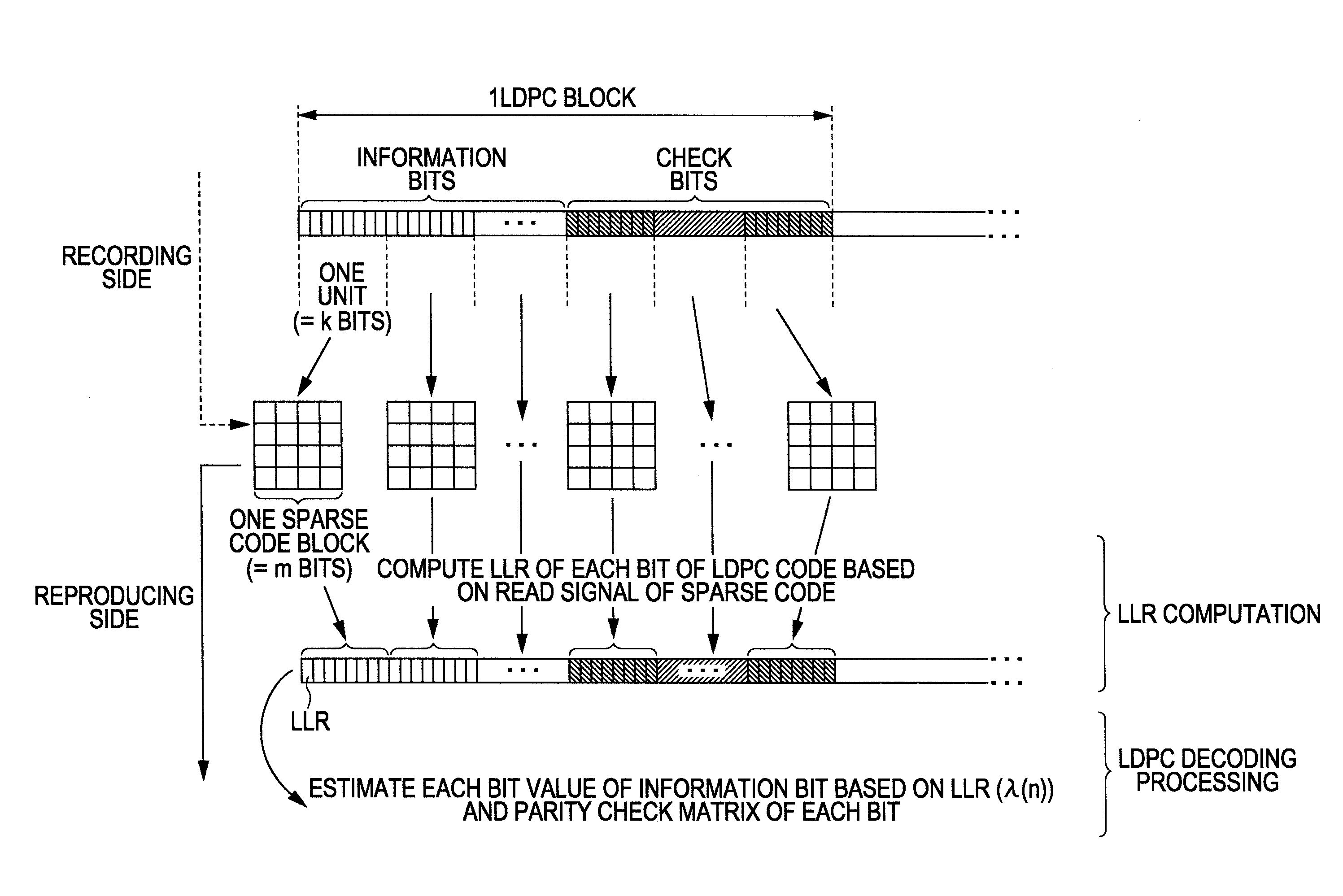
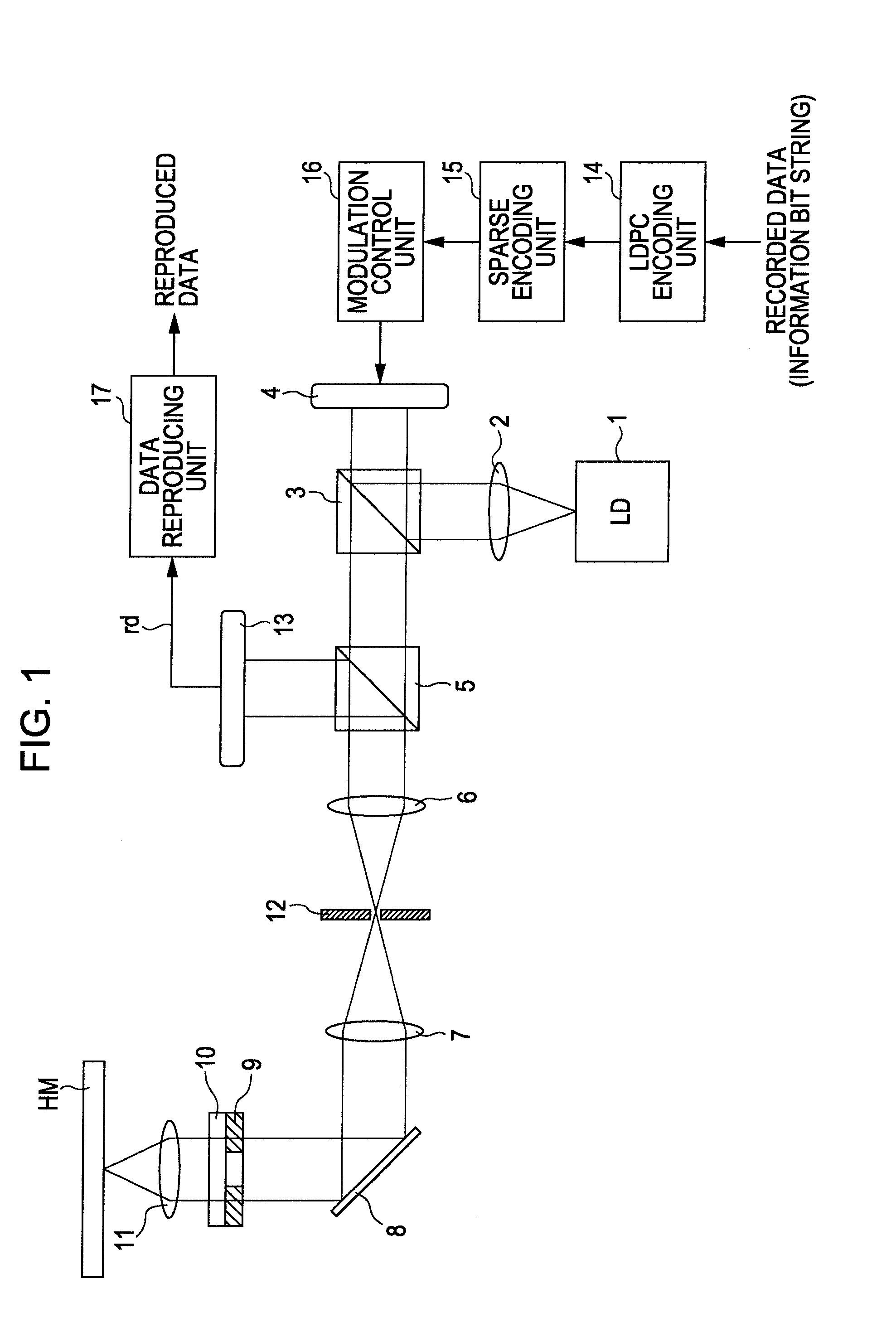
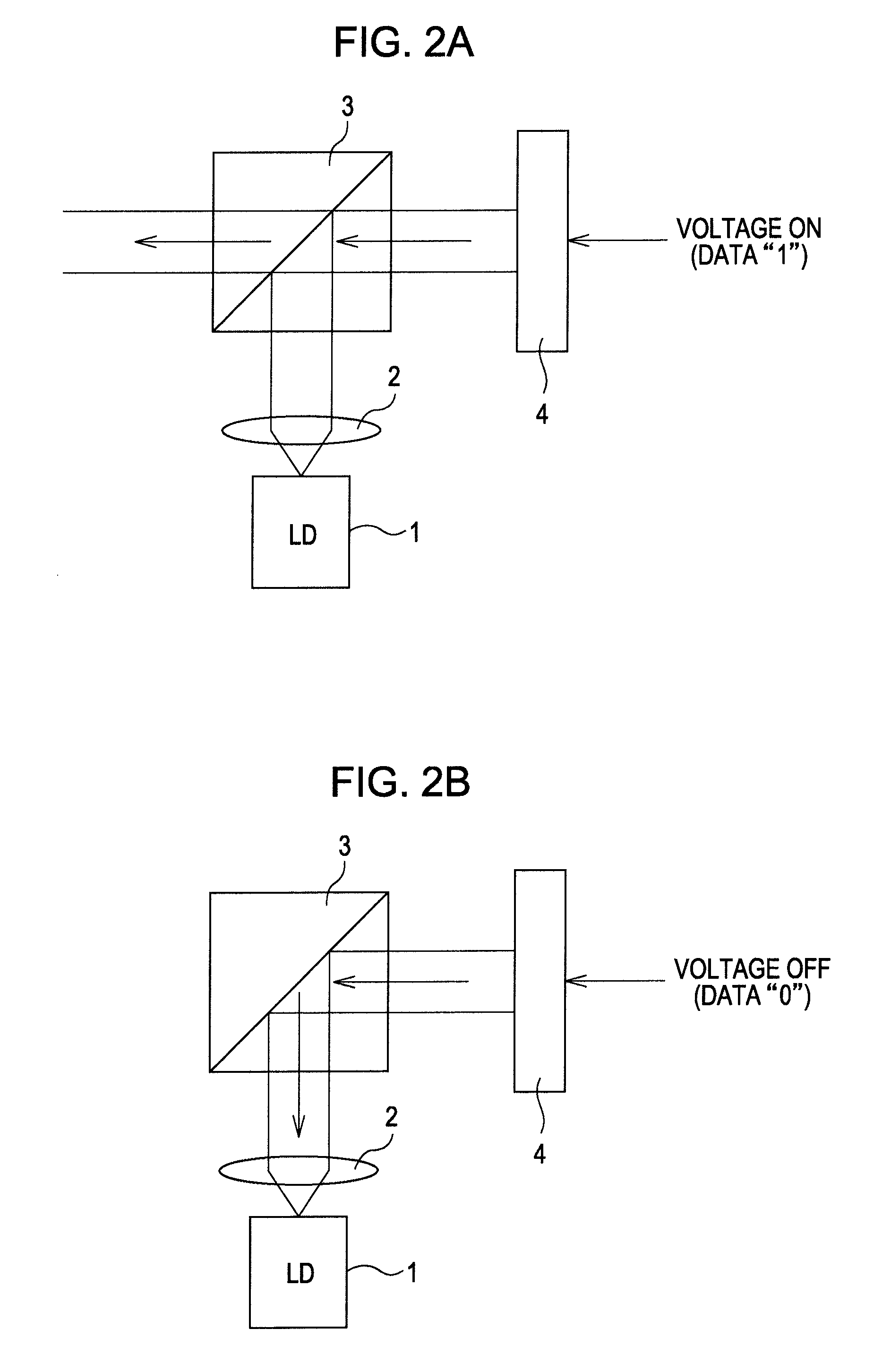
InactiveUS8365035B2Reliable valueGreat likelihoodError prevention/detection by using return channelJoint error correctionTheoretical computer scienceHamming distance
A data modulating device includes: an LDPC encoding unit configured to execute LDPC encoding; and a balance encoding unit configured to input a data string subjected to encoding by the LDPC encoding unit as data to be encoded, and convert k bits of this data to be encoded into balance code made up of m-bit block data; with the balance encoding unit executing balance encoding of said data to be encoded using a data conversion table subjected to mapping so that a set of the k-bit data patterns of which the Hamming distance is 1 corresponds to a set of block data of which the Hamming distance is 2.
Owner:SONY CORP
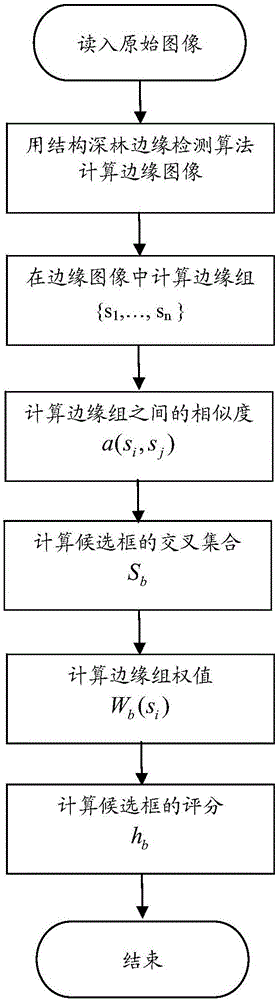
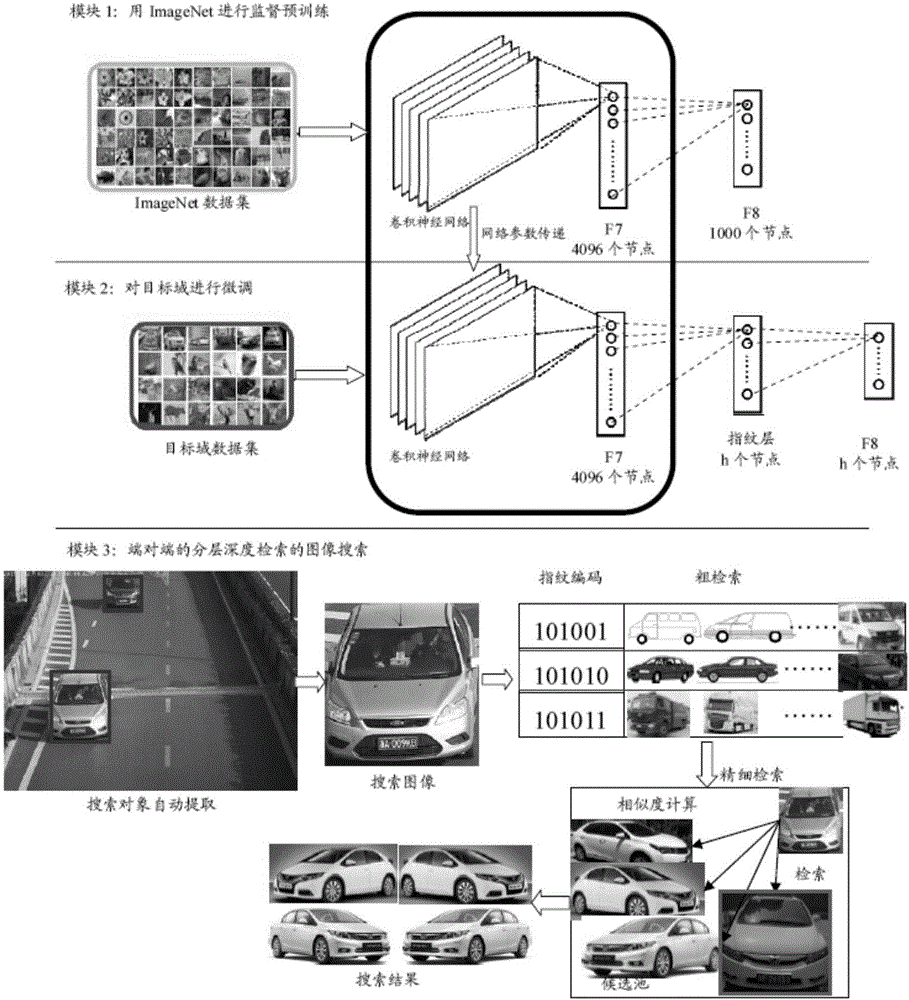
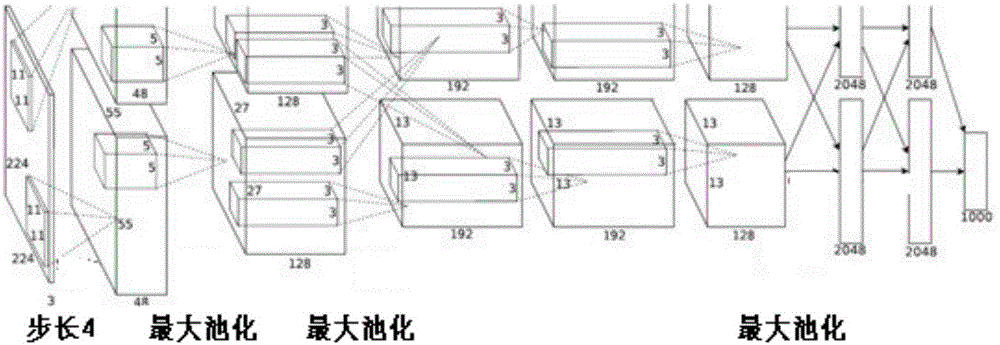
Deep convolutional neural network end-to-end based image retrieval method by layered deep searching
ActiveCN106227851ARealize automatic extractionMeet search needsCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsImage retrievalHamming distance
The invention discloses a deep convolutional neural network end-to-end based image retrieval method by layered deep searching. The method is characterized by mainly including a convolutional neural network used for deep learning, training and recognition, a rapid visual segmentation algorithm for searching image objects, a quick comparison method used for rough searching with a Hash method and Hamming distance fast images, and a precise comparison method for first k ranked images based on images from a candidate pool P. By the method, automation and intelligence level in searching images with images can be effectively heightened, search results can be acquired accurately, and demand of image retrieval in the big data era is satisfied with less storage space and high retrieval speed.
Owner:汤一平
Parity check matrix and method of forming thereof
InactiveUS7000177B1Data representation error detection/correctionError detection/correctionTransfer systemBlock code
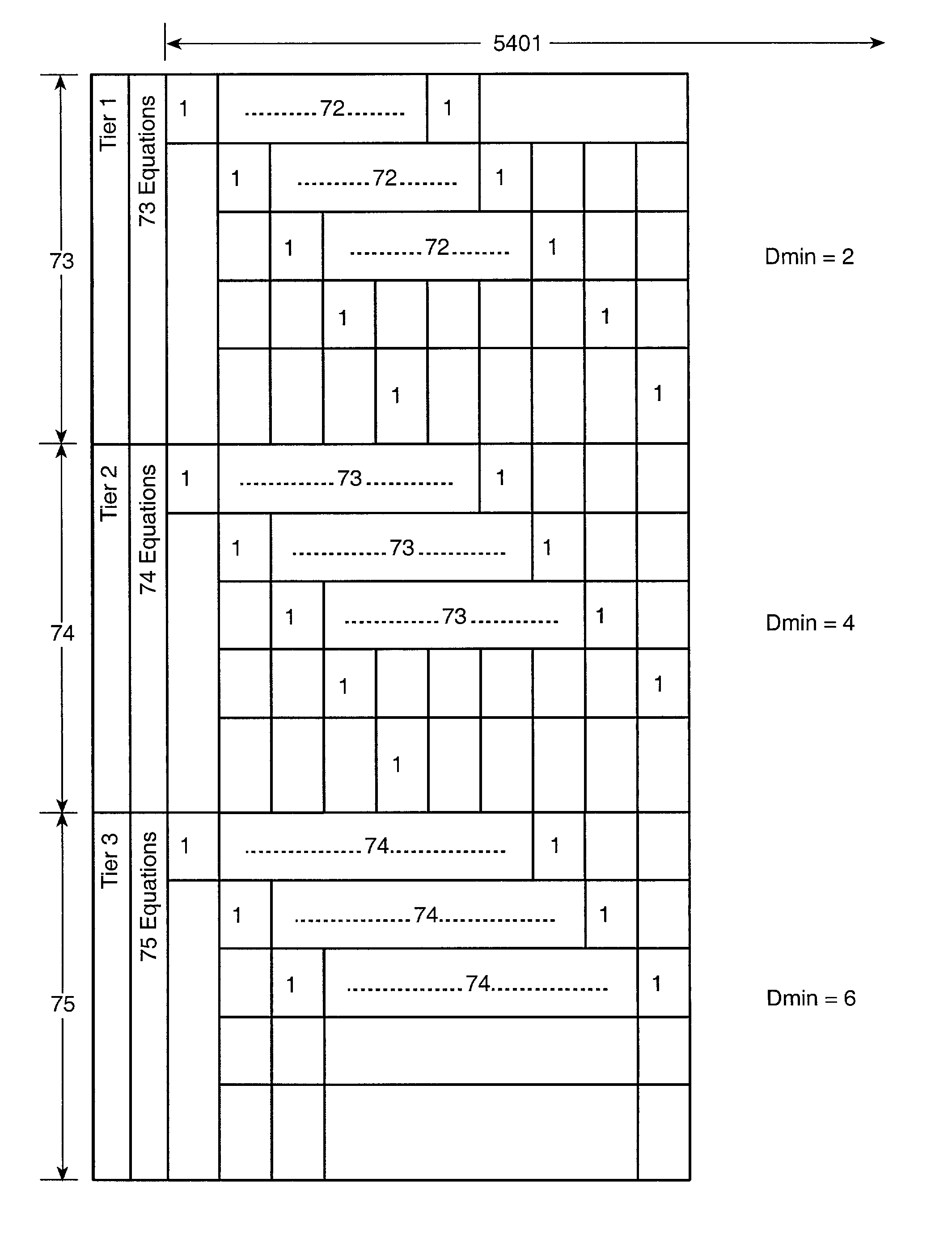
A data transmission system is provided for transmitting user data to and receiving data from a communication channel, including a parity check matrix having M tiers, wherein M≦2, Dmin=2*M for M=1 . . . 3 or 2*M≦Dmin≦6 for M>3, wherein Dmin is the minimum Hamming distance, tc=M, wherein tc is the column weight, and cycle−4=0. A linear block encoder encodes the user data in response to the parity check matrix, and a transmitter transmits an output of the linear block encoder to the communication channel. A soft channel decoder decodes data, and a soft linear block code decoder to decode data decoded by the soft channel decoder in response to the parity check matrix.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
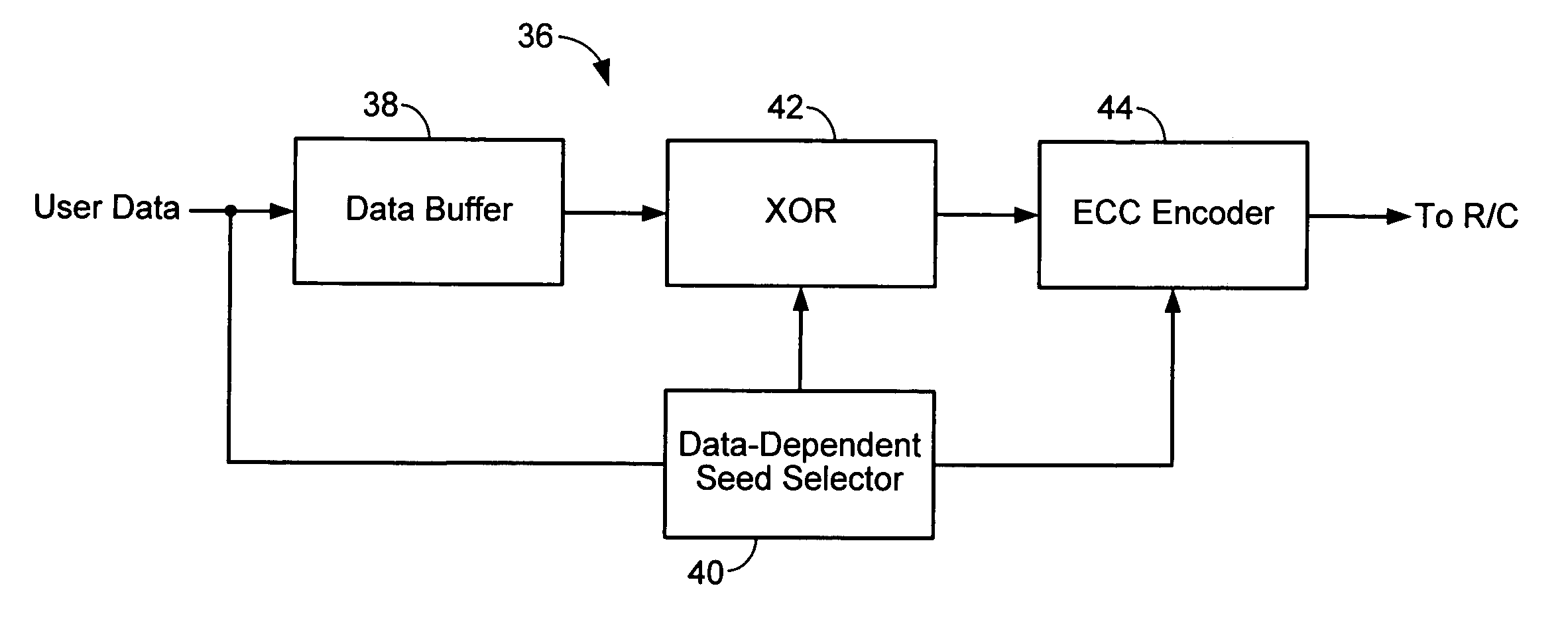
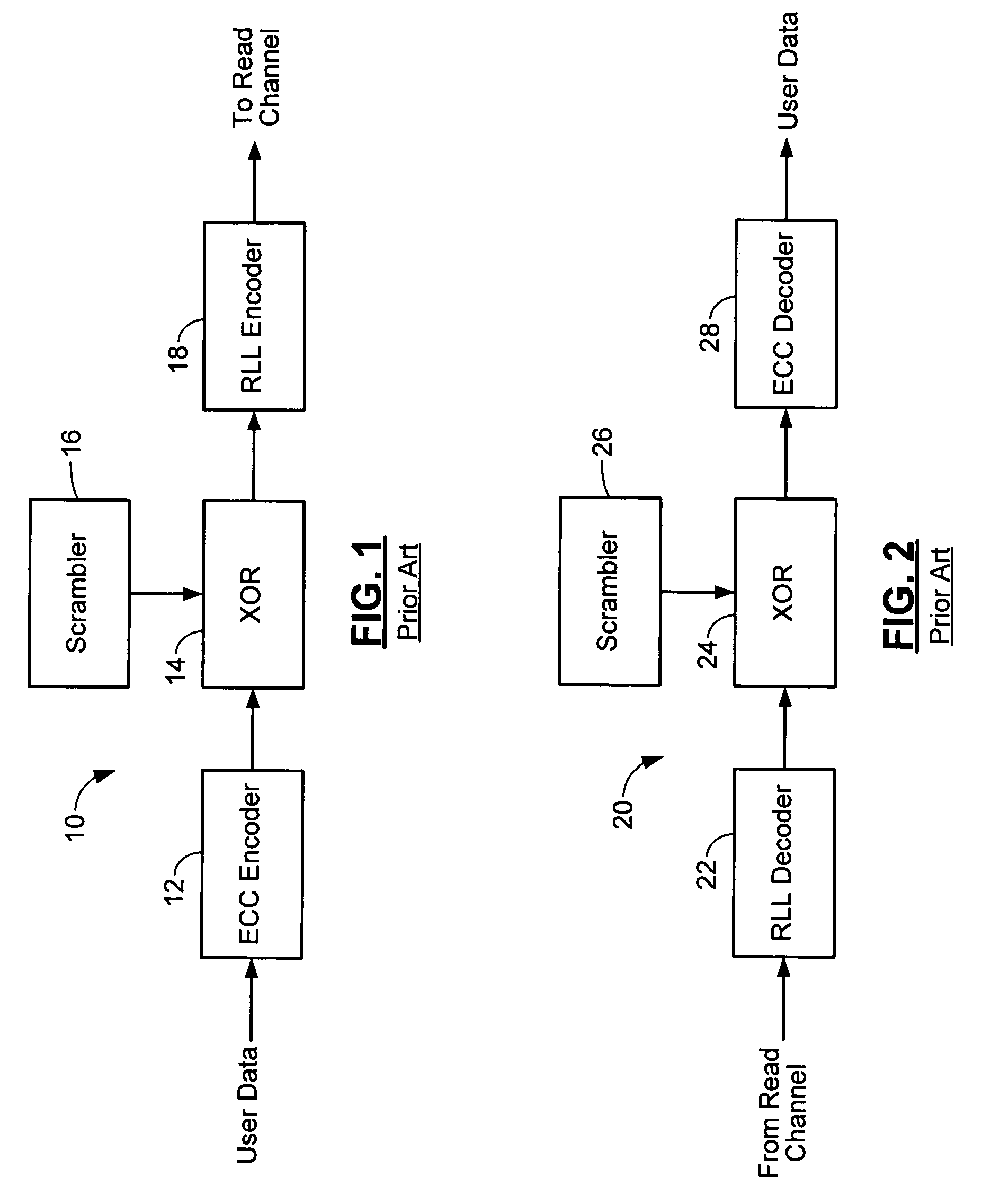
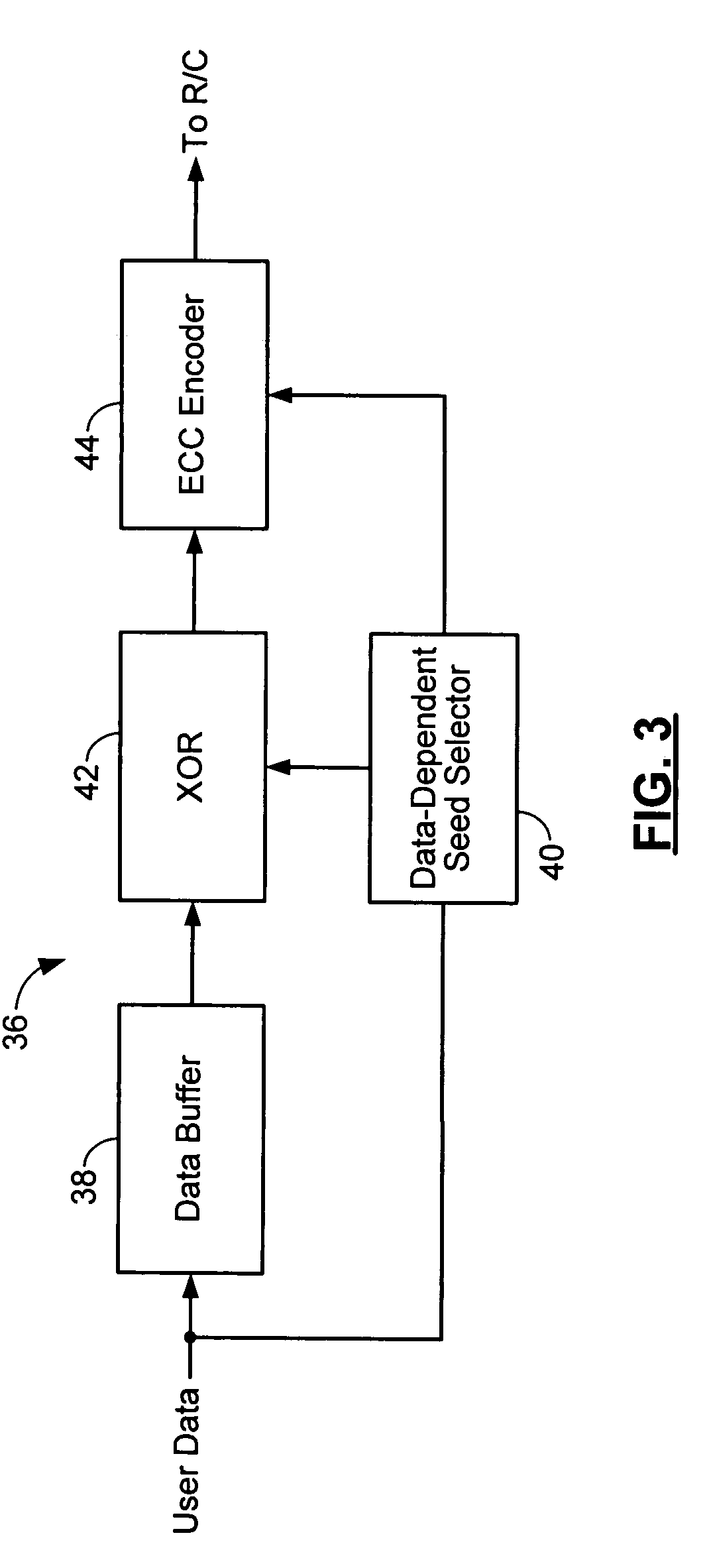
Method and apparatus for generating a seed set in a data dependent seed selector
InactiveUS7158058B1Modification of read/write signalsRecord information storageComputer networkHamming distance
A communications channel includes a buffer that receives user data symbols including a plurality of M-bit symbols. A seed selector receives the plurality of M-bit symbols, selectively removes symbols from a seed set based on Hamming distances between at least two of the M-bit symbols, and selects a scrambling seed from remaining symbols in the seed set. A scrambling device that communicates with the seed selector and the data buffer generates scrambled user data based on the user data symbols and the scrambling seed. The communications channel is implemented in a data storage system. The seed selector ensures a minimum Hamming weight of 15 percent in the scrambled user data. The seed selector compares first and second user data symbols in the plurality of M-bit symbols.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
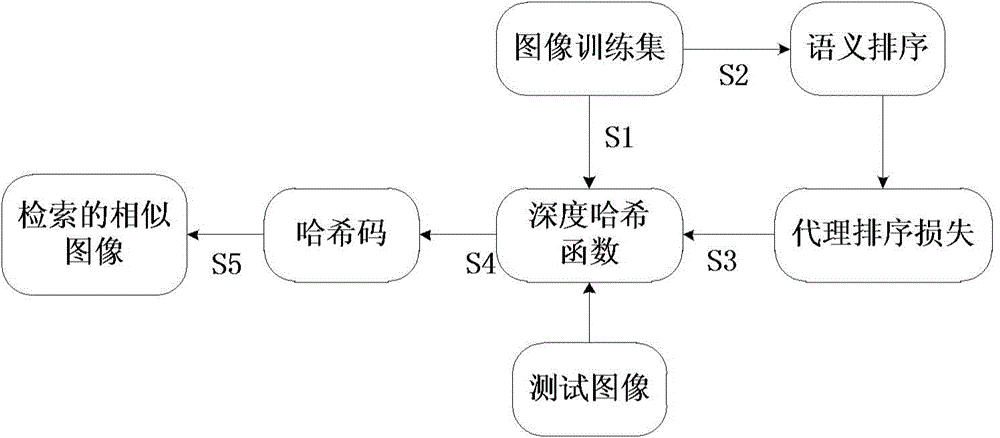
Image retrieval method utilizing deep semantic to rank hash codes
ActiveCN104834748APreserve multi-level similarityAvoid lostStill image data retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionStochastic gradient descentHash function
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
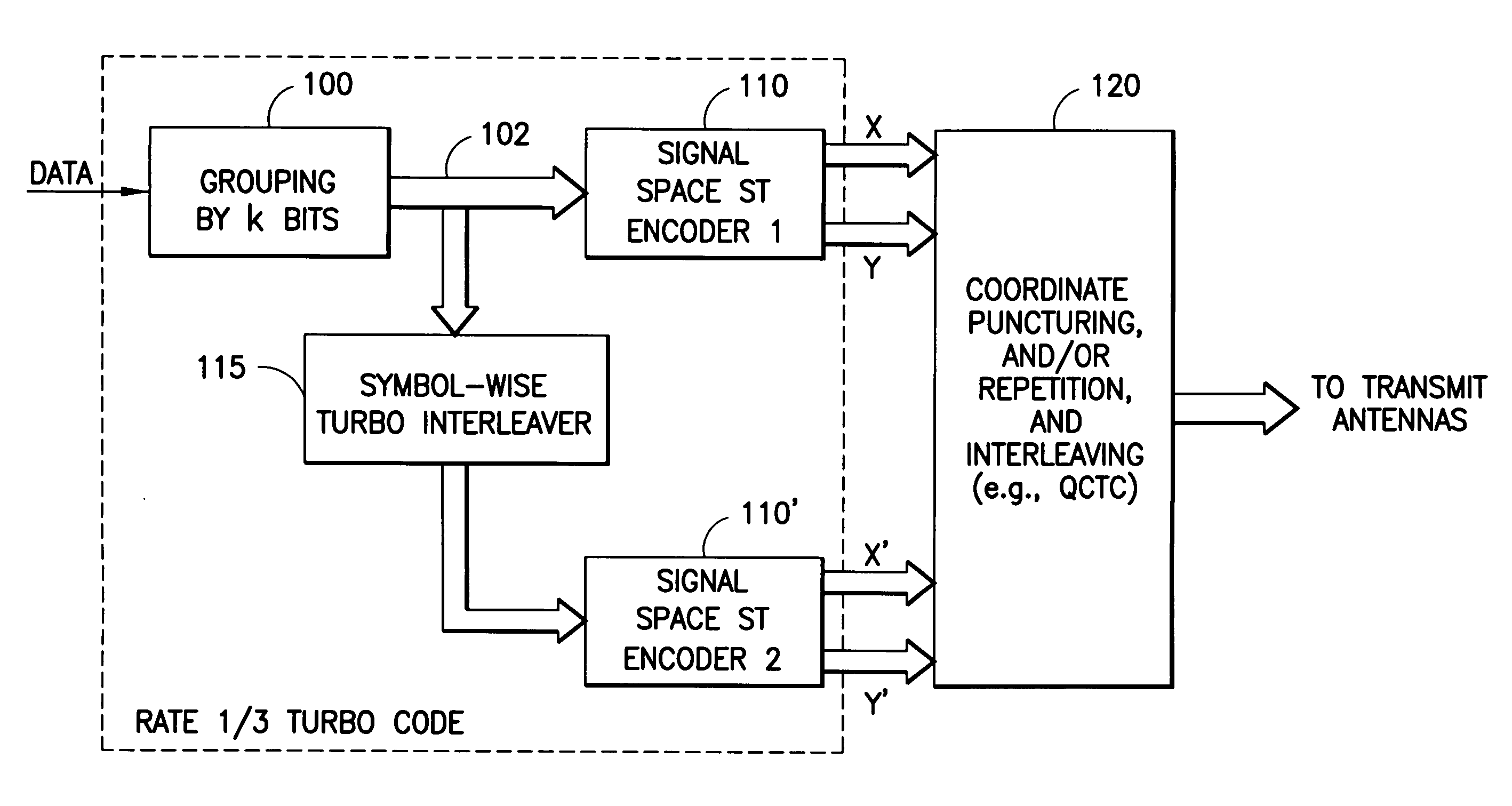
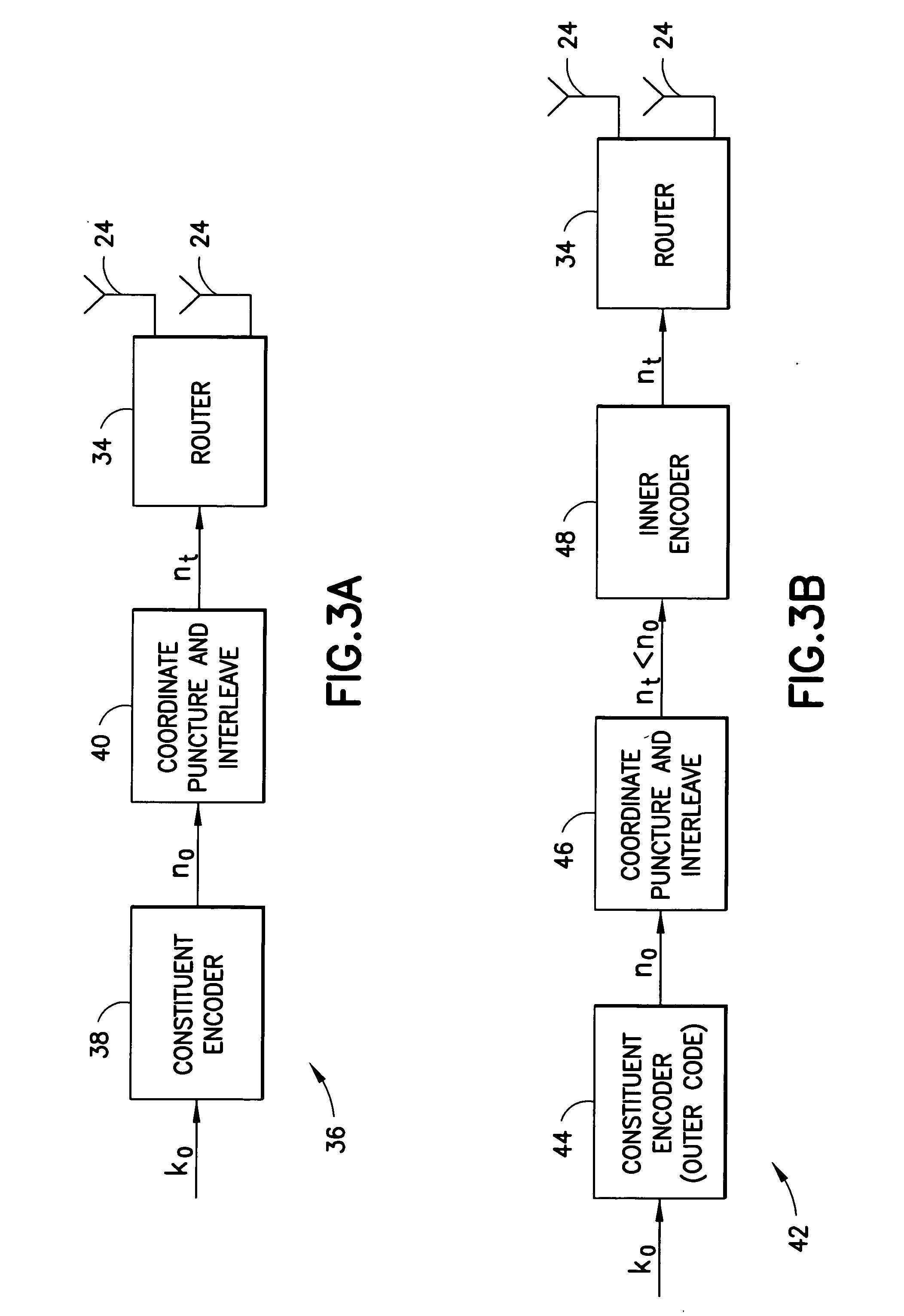
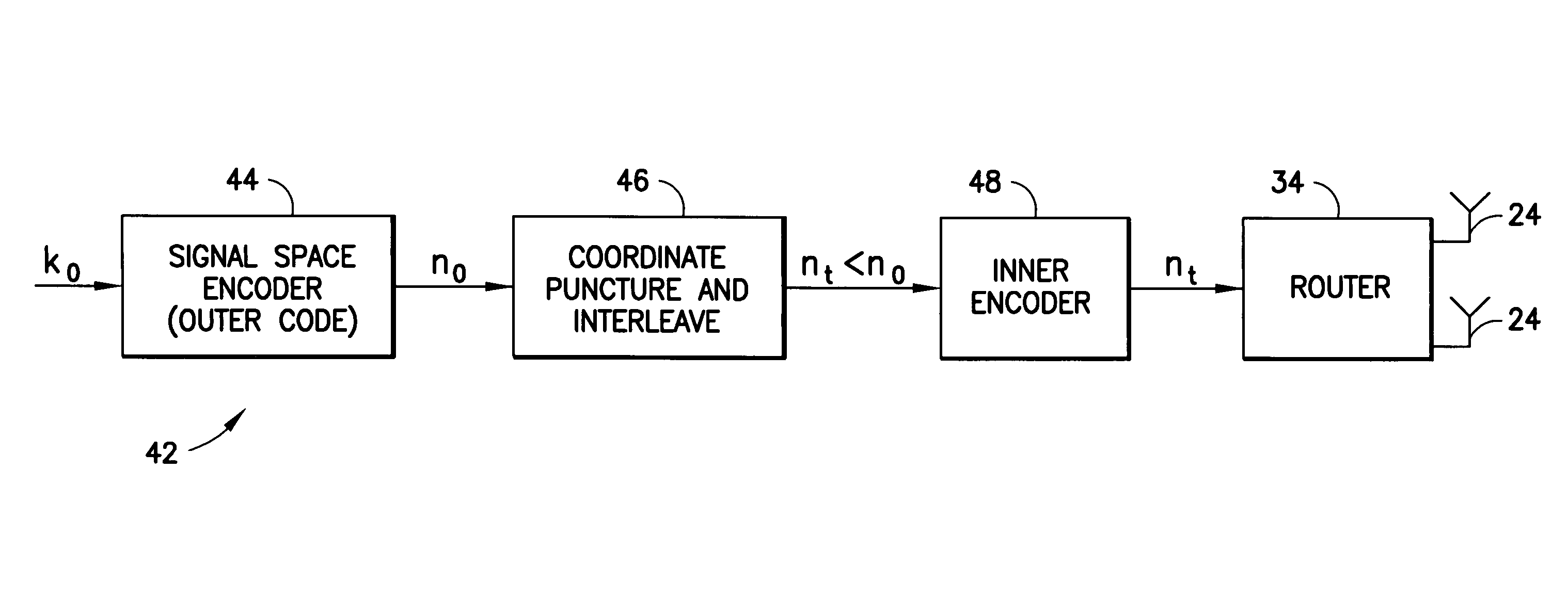
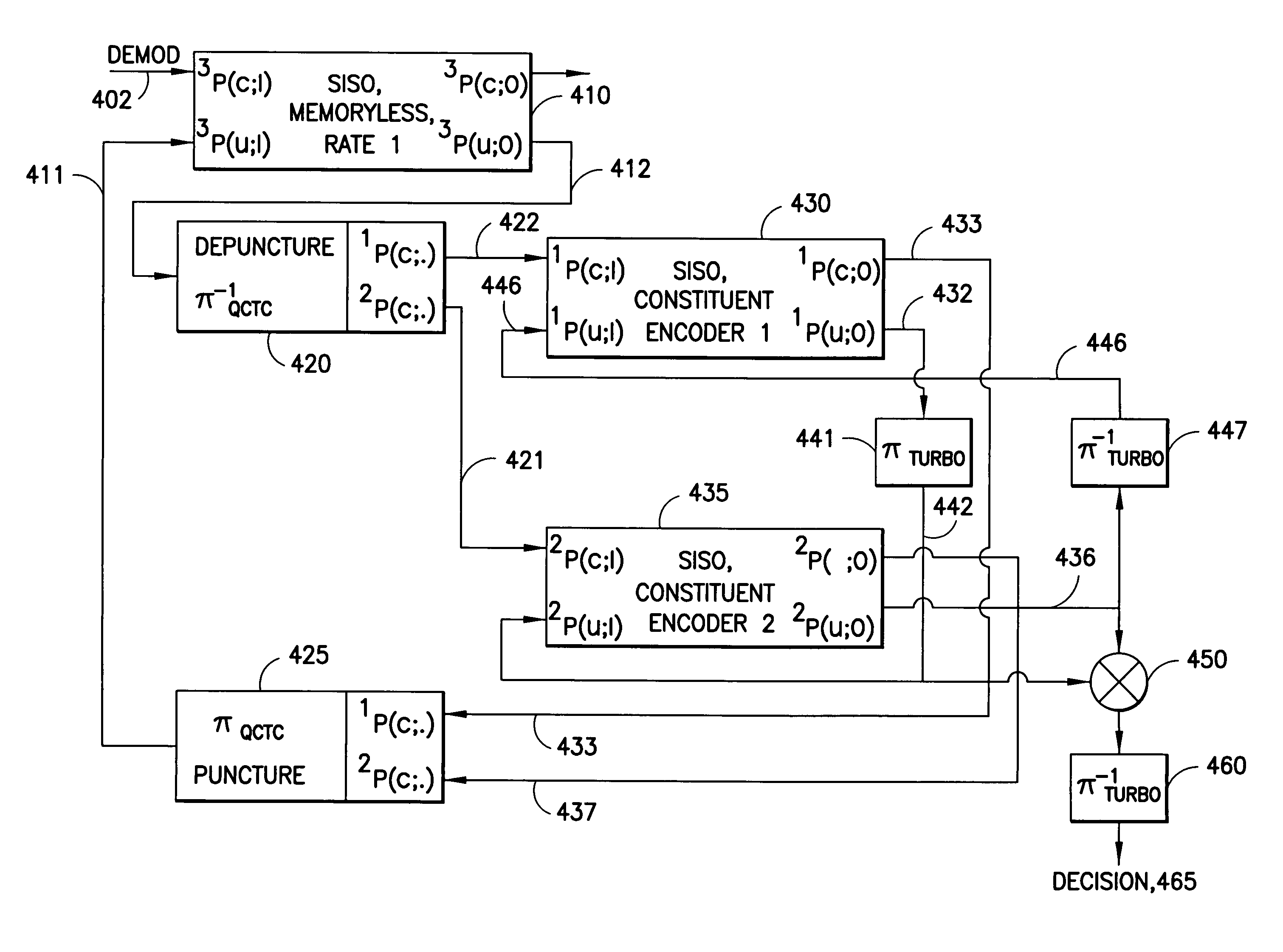
Apparatus using concatenations of signal-space codes for jointly encoding across multiple transmit antennas, and employing coordinate interleaving
InactiveUS20060159195A1Accommodate usageCode conversionError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresHamming distanceComputer science
A system for transmitting data over a MIMO channel has a transmitter and a receiver. In the transmitter, the input data is encoded over at least two pipes by a concatenation of at least two constituent signal-space encoders. Each constituent encoder is used to generate, in response to the input data, a sequence of symbols from a channel alphabet having at least one dimension. Each symbol of the channel alphabet includes at least one complex symbol having real and imaginary coordinates. The transmitter interleaves the coordinates of the sequence of channel alphabet symbols, and transmits (from at least two transmit antennas) the interleaved coordinates. Preferably, each constituent encoder maximizes a minimum coordinate-wise Hamming distance between members of all valid pairs of symbol sequences, maximizes a minimum Euclidean distance between members of all valid pairs of different codewords, and obeys an equal eigenvalue criterion.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Compiler apparatus and compilation method
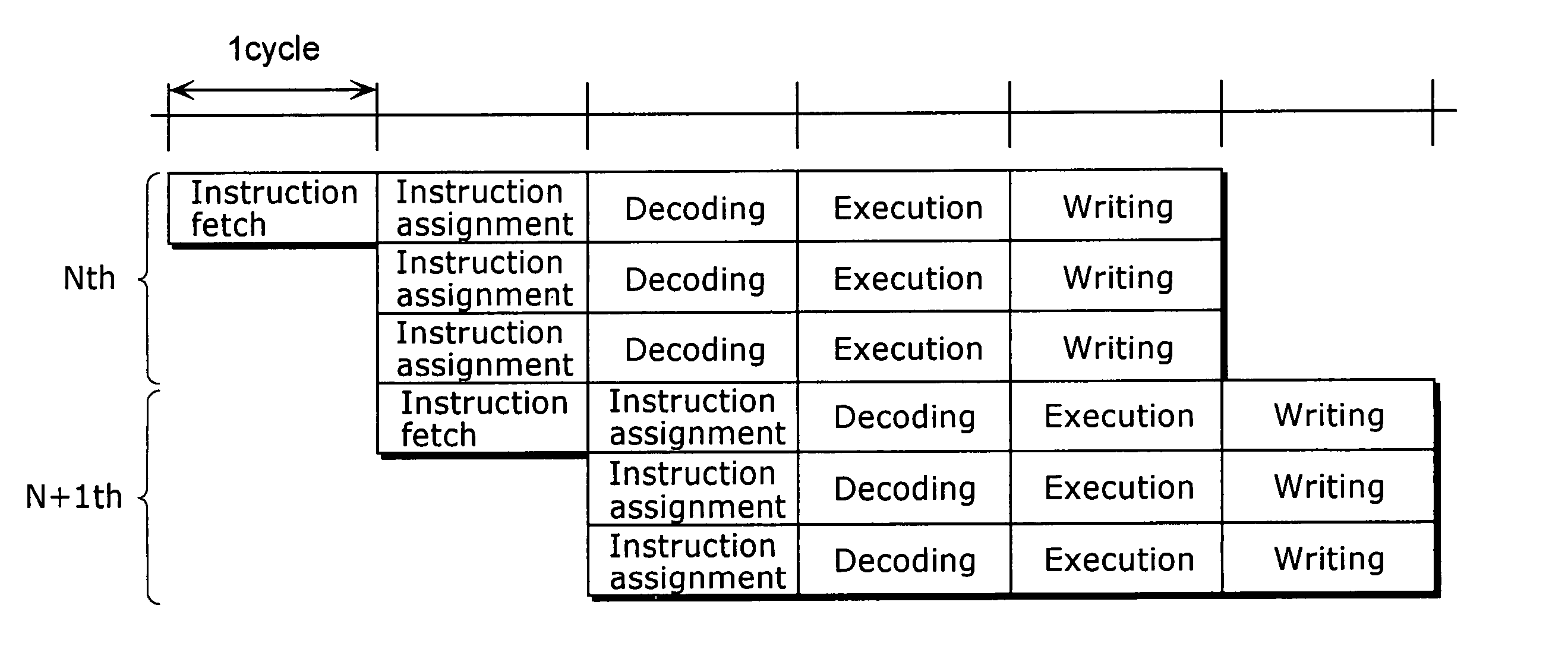
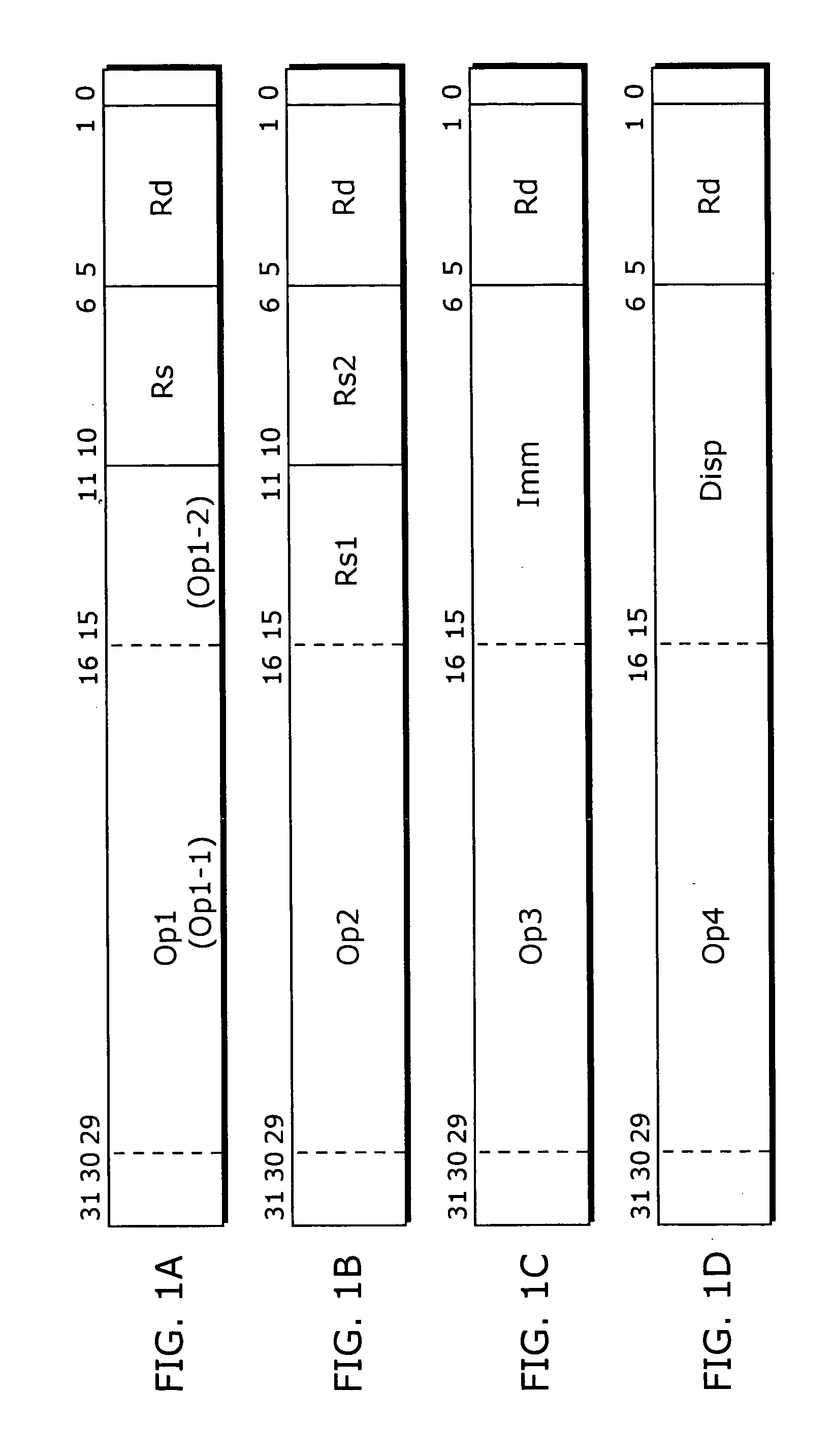
InactiveUS20040154006A1Avoid changeReduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTSoftware engineeringMachine instructionInstruction cycle
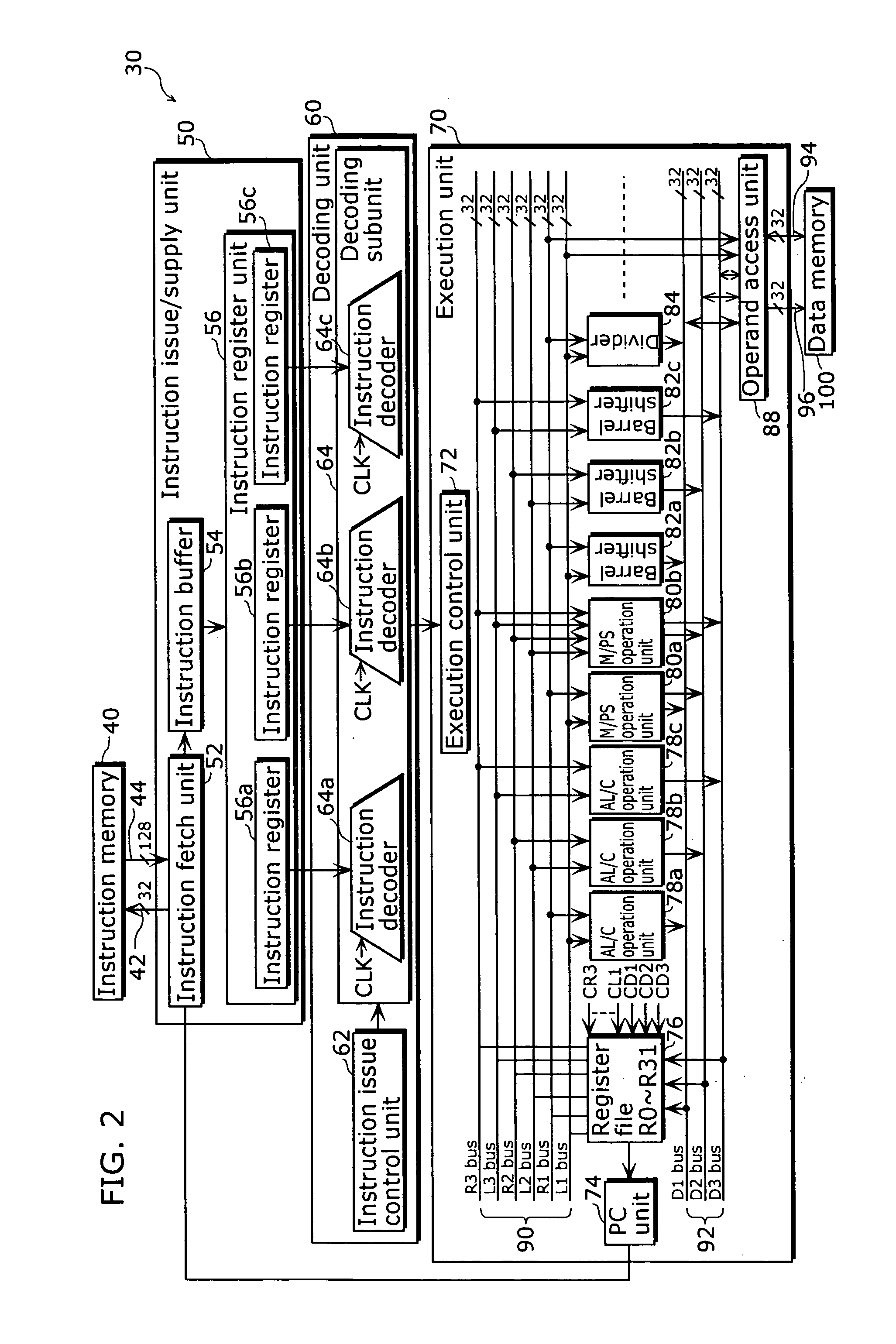
A compiler apparatus that is capable of generating instruction sequences for causing a processor with parallel processing capability to operate with lower power consumption is a compiler apparatus that translates a source program into a machine language program for the processor including a plurality of execution units which can execute instructions in parallel and a plurality of instruction issue units which issue the instructions executed respectively by the plurality of execution units, and includes: a parser unit operable to parse the source program; an intermediate code conversion unit operable to convert the parsed source program into intermediate codes; an optimization unit operable to optimize the intermediate codes so as to reduce a hamming distance between instructions placed in positions corresponding to the same instruction issue unit in consecutive instruction cycles, without changing dependency between the instructions corresponding to the intermediate codes; and a code generation unit operable to convert the optimized intermediate codes into machine language instructions.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
Text similarity computing method
The invention discloses a text similarity computing method. The method comprises the following steps of text representation and text similarity computing. The aim of text representation is that a text document of product description is converted into a vector for description. In the text similarity computing method, natural language processing technologies such as Chinese words segmentation, stop word removing, word frequency statistics and the like are used for converting all the description texts of products into vectors; the text similarity is computed by a method based on a Hamming distance, and the other advantage of the Hamming distance is that the computing speed is very high. Due to the fact that the method of statistical machine learning is used, so that the text similarity computing method is more stable and effective compared with a method based on rules.
Owner:DALIAN LINGDONG TECH DEV
Large-scale image library retrieving method based on image Hash
InactiveCN101710334AOvercome the problem of requiring more hash functionsSolve the problem of not being able to expand to kernel spaceCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsHash functionImage retrieval
The invention discloses a large-scale image library retrieving method based on image Hash, which belongs to the technical field of image retrieval and relates to an image retrieving method based on contents. The large-scale image library retrieving method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: selecting a training image which is relevant to a query image from an image library to be retrieved; respectively extracting Gist characteristics of an image to be retrieved, the training image and the query image; clustering the training characteristics into a C category by a K average value clustering method; calculating a hypersphere classified function of each category of sample characteristics to define a Hash function as a Hash sequence for calculating the characteristics of the image to be retrieved and the characteristics of the query image; calculating the Hamming distance between the Hash sequence of the query image and the Hash sequence of the image to be retrieved; setting a threshold value d and returning similar images. The invention overcomes the defect of more Hash functions of an LSH method, solves the problem that a spectrum Hash method and a semantic Hash method can not be expanded to the core space and the selecting problem on samples when the Hash function is calculated by a KLSH method simultaneously.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
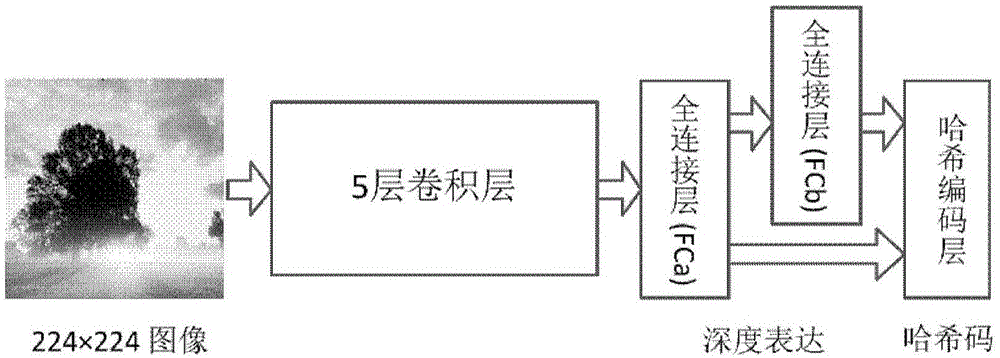
Image Hash indexing and establishing method based on deep learning
ActiveCN106503106AEffective hash expressionSolve the problem of insufficient discriminationSpecial data processing applicationsData setTest sample
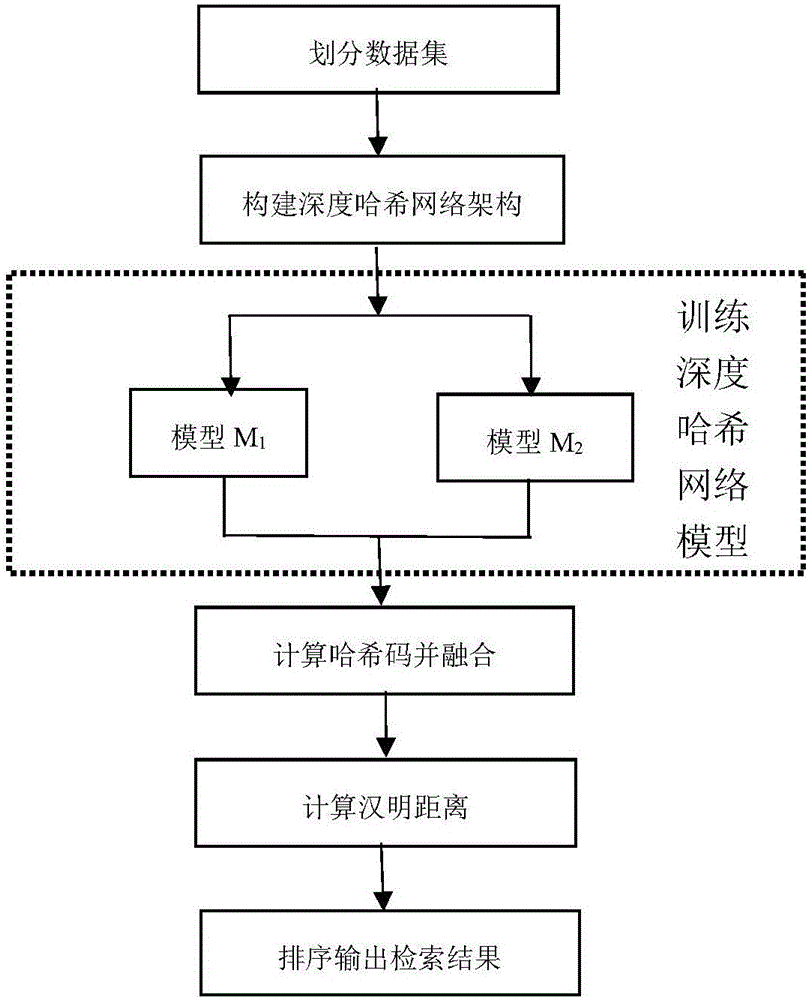
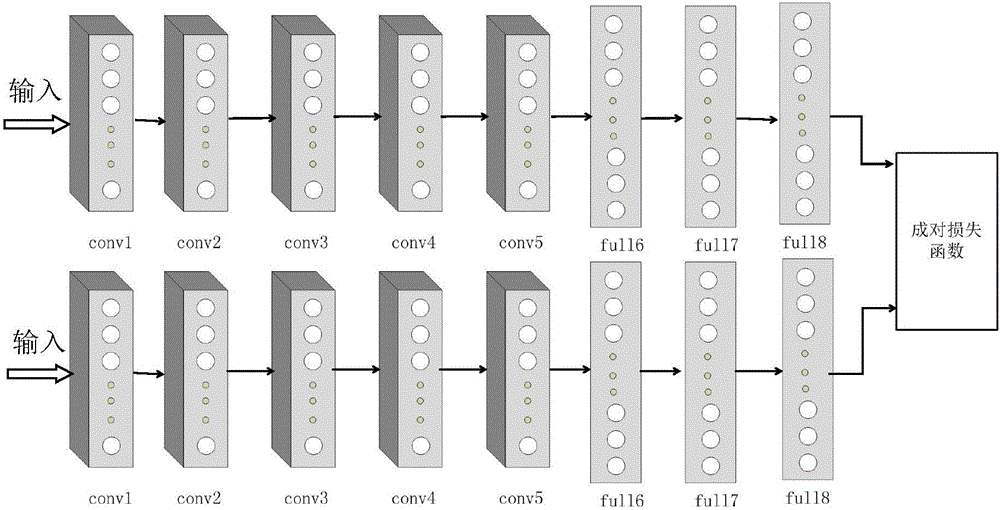
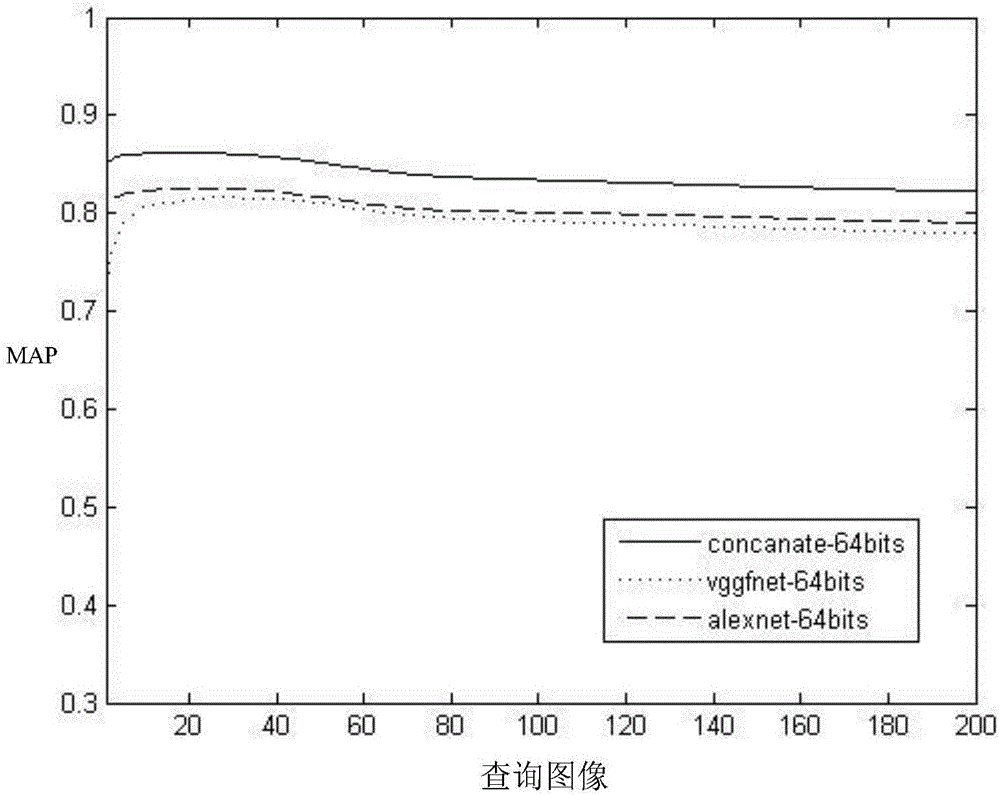
The invention discloses an image Hash indexing and establishing method based on deep learning and belongs to the technical field of image retrieval. The method comprises the steps that an image data set is firstly divided to obtain a test sample set, a training sample set and an image library, then the characteristic that depth characteristics extracted by a deep learning model have the very good expression capability to image semantic is fully utilized to establish different depth Hash network models of two deep convolution network structures, then each image in the test sample set and the image library undergoes forward propagations of the two models respectively, corresponding two groups of initial Hash codes are calculated, then two groups of initial Hash codes of the same image are spliced and fused to serve as fused Hash codes of the image, and similar image retrieval results are obtained by calculating and querying Hamming distances of the fused Hash codes of images and each image in the image library and arranging the Hamming distances from small to large. The image Hash indexing and establishing method makes large-scale image retrieval accurate and effective.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method and apparatus using coordinate interleaving to increase diversity in a MIMO system
InactiveUS7409001B2Increase diversityModulated-carrier systemsPolarisation/directional diversityAs elementEngineering
A method to increase diversity in MIMO fading channels interleaves coordinates of complex symbol(s) in a transmission frame after encoding and modulating. Specifically, an input signal is encoded and modulated into a codeword, jointly across at least two pipes, said pipes having space, time, frequency, or other nature, wherein the codeword spans a frame and is defined as at least one complex symbol whose complex values are all those to be transmitted during all channel uses covered by the frame. Each of the complex symbols have a first and second coordinate. After modulating, which may be combined with encoding in a signal space encoder, the coordinates are interleaved. In modulation, the complex symbols (typically two dimensional) may arise as elements of a multidimensional (typically greater than two dimensions) signal constellation, in which case those multidimensional constellation coordinates are the ones that are interleaved in the frame. The frame carrying the interleaved coordinates is transmitted by the first and at least second antennas, possible opposed sub-frames of the overall frame being transmitted separately by opposed antennas. A coset selector is used in some embodiments to maximize a minimum Hamming distance, and / or a minimum Euclidean distance, between coordinates within a coset to control diversity and / or coding gain. In some embodiments, the operation of the encoder and modulator is such as to maximize a minimum coordinate-wise Hamming distance, and / or a minimum Euclidean distance, between allowable codewords, and / or to provide additional structure for the allowable codewords. A method, transmitter, system, and mobile station are described.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
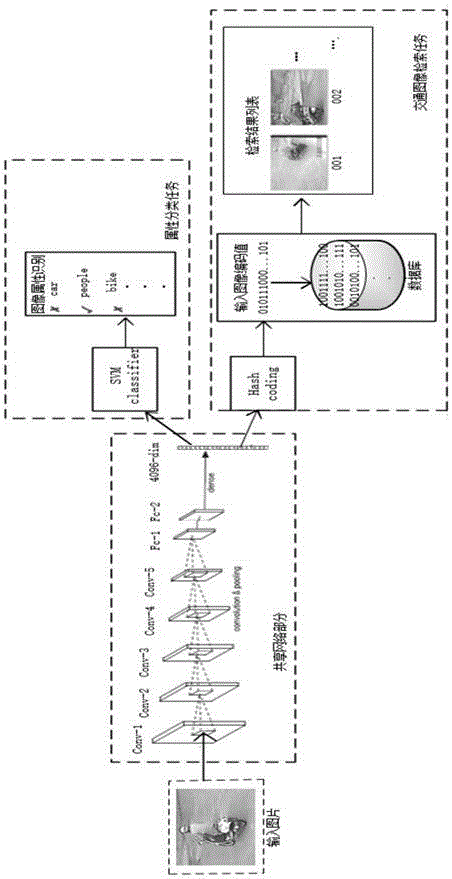
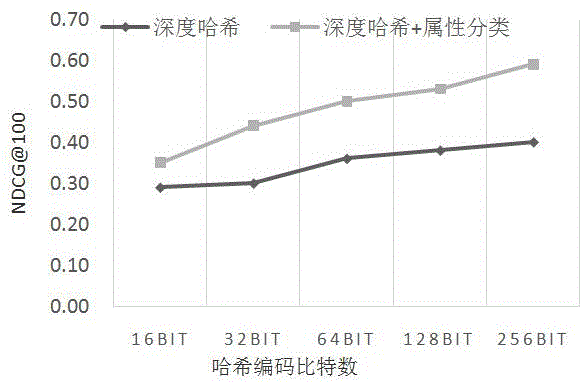
Traffic image retrieval method based on depth learning
ActiveCN106407352AHigh expressionSearch precise and effectiveSpecial data processing applicationsNeural learning methodsData setHash function
The invention provides a traffic image retrieval method based on depth learning in an intelligent traffic application scene for performing traffic monitoring video image retrieval through depth hash encoding. The method comprises the following steps: dividing a target data set into a training set and a test set; acquiring features and image hash codes of a target category and a target color by a depth convolutional neural network; optimizing a hash function by back-propagating of classification loss and hash encoding loss of the features of the category and the color; performing hash encoding on an image by the hash function, and calculating and inquiring a Hamming distance between the image and the has code of the image in the test data set to represent the similarity of the images; and performing similarity score sorting according to the size of the Hamming distance to retrieve images. According to the method provided by the invention, rich multistage semantic information in the images is retained in the image retrieval, the special attribute information of targets in the images is utilized, multiple tasks of retrieval and image attribute classification are accomplished by sharing a network structure, and the retrieval is assisted by a classification task.
Owner:SYSU CMU SHUNDE INT JOINT RES INST +1
Sparse dimension reduction-based spectral hash indexing method
InactiveCN101894130AImprove interpretabilityImprove search efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsSearch problemPrincipal component analysis
The invention discloses a sparse dimension reduction-based spectral hash indexing method, which comprises the following steps: 1) extracting image low-level features of an original image by using an SIFT method; 2) clustering the image low-level features by using a K-means method, and using each cluster center as a sight word; 3) reducing the dimensions of the vectors the sight words by using a sparse component analysis method directly and making the vectors sparse; 4) resolving an Euclidean-to-Hamming space mapping function by using the characteristic equation and characteristic roots of a weighted Laplace-Beltrami operator so as to obtain a low-dimension Hamming space vector; and 5) for an image to be searched, the Hamming distance between the image to be searched and the original image in the low-dimensional Hamming space and using the Hamming distance as the image similarity computation result. In the invention, the sparse dimension reduction mode instead of a spectral has principle component analysis dimension reduction mode is adopted, so the interpretability of the result is improved; and the searching problem of the Euclidean space is mapped into the Hamming space, and the search efficiency is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Apparatus, method and computer program product for reading information stored in storage medium, and storage medium for storing information based on charge amount
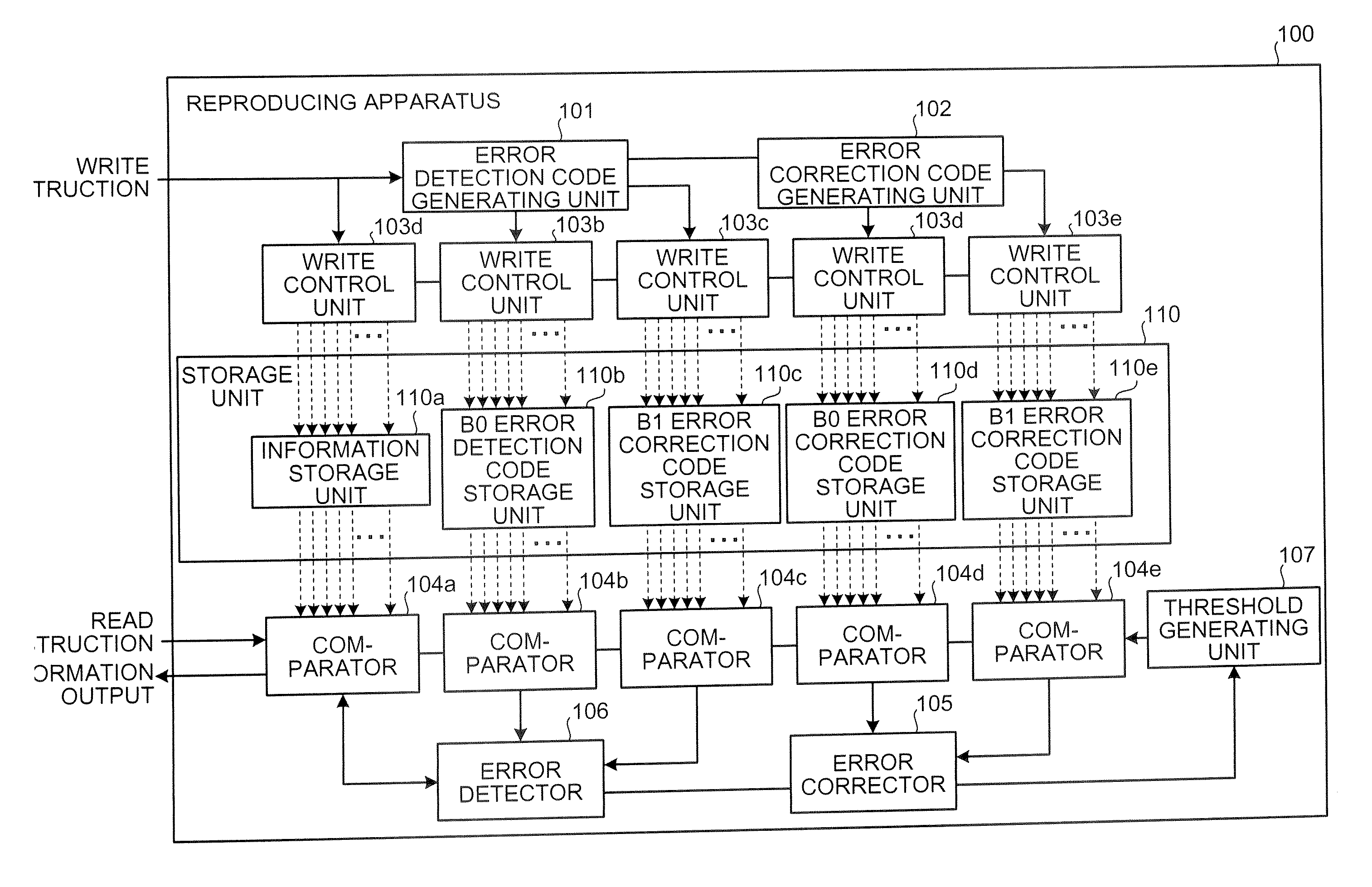
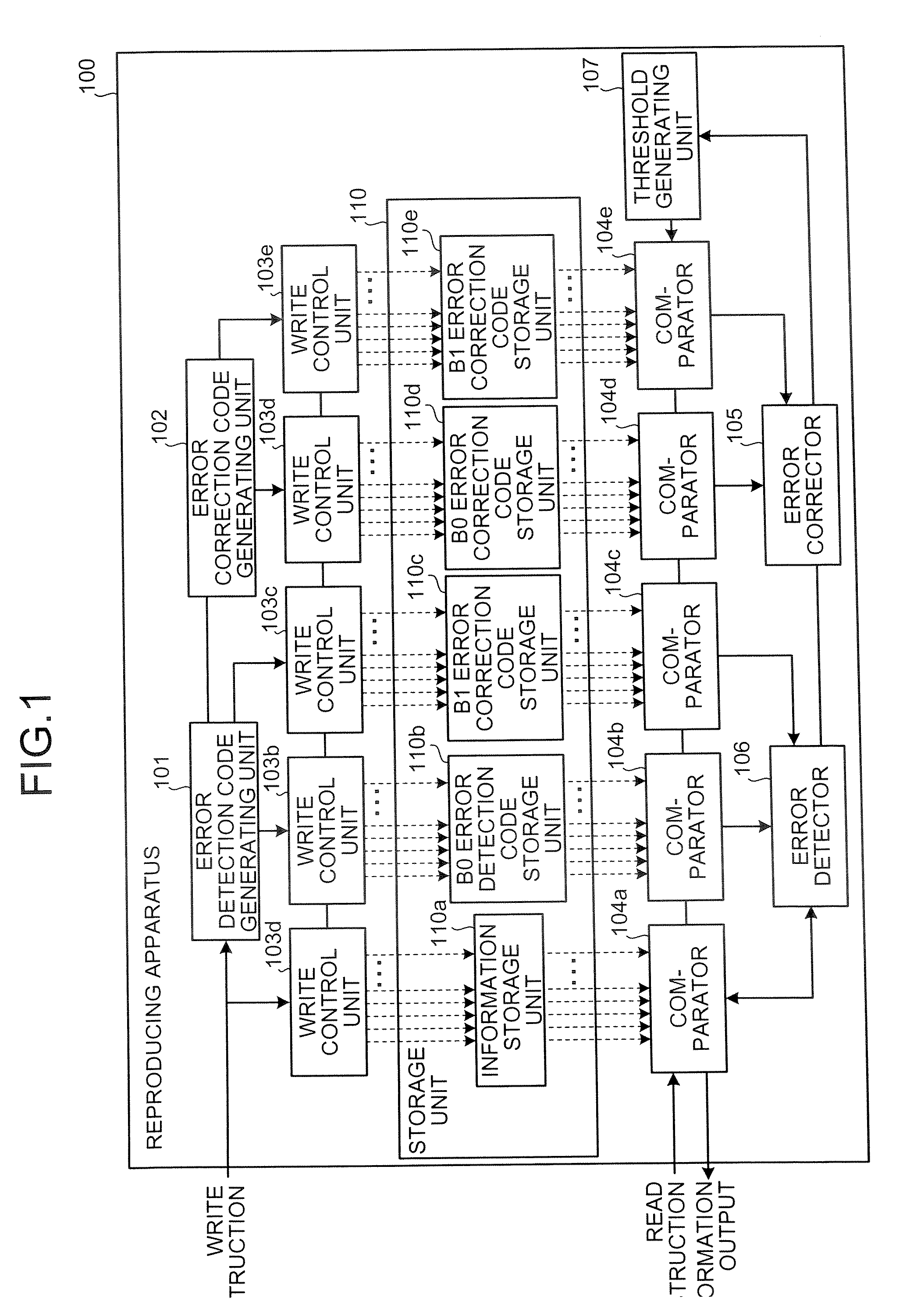
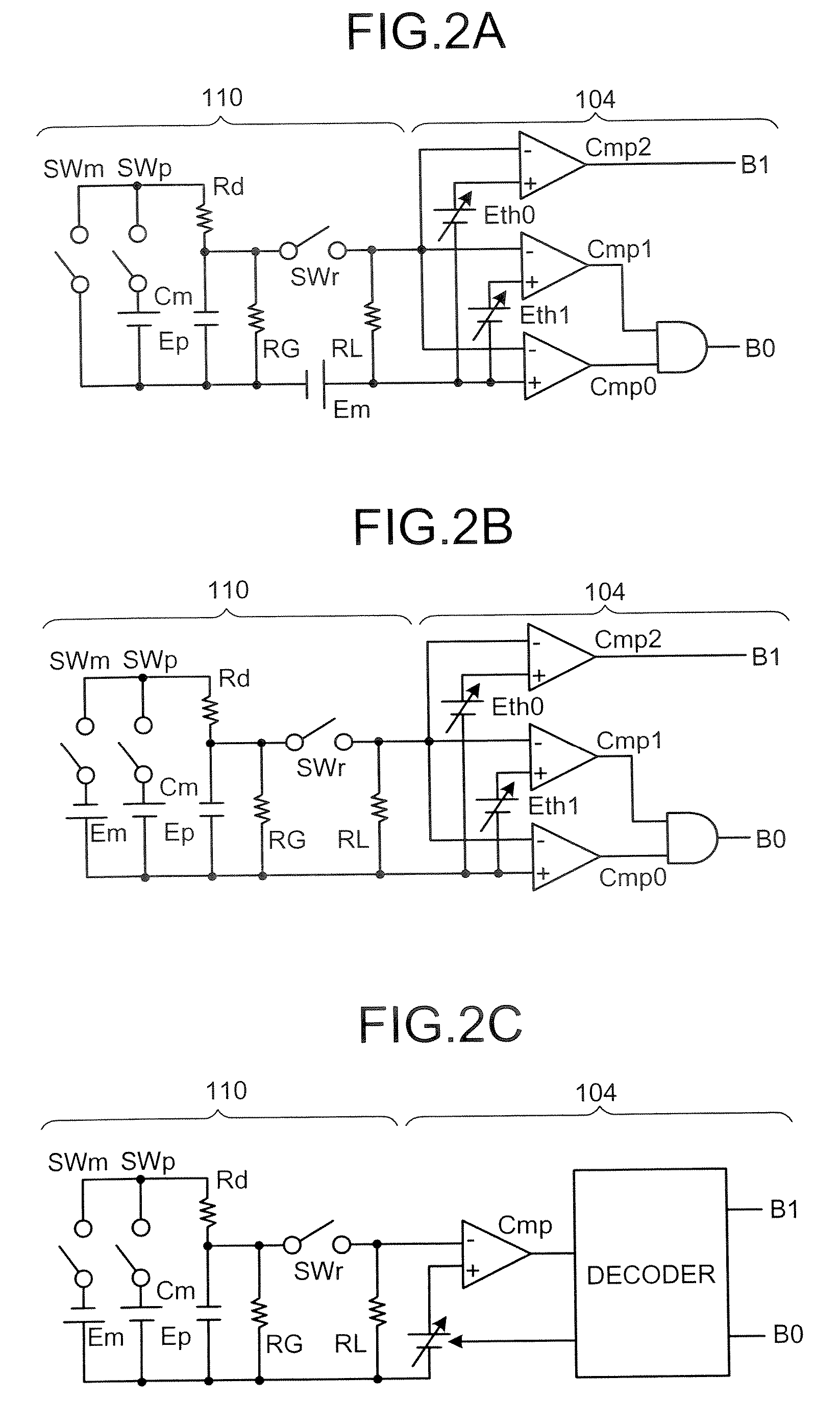
A reproducing apparatus includes a storage unit including a plurality of memory elements each capable of holding an electric charge, each memory element indicating a 2-bit code which is related to each other so that the Hamming distance between adjacent codes is unity in four ranges determined by a charge amount with respect to three threshold values with the minimum or maximum value thereof as a fixed value; a reading unit that reads each 2-bit code by the charge amount which is held in each memory element using the three threshold values corresponding to each memory element; an error detector that detects whether a first bit string consisting of right bits of the 2 bit codes read or a second bit string consisting of left bits of the 2 bit codes read has an error; and a threshold changing unit that, upon detection of the error, changes a threshold value corresponding to the bit string having the error other than a fixed threshold value to secure a correct bit string.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
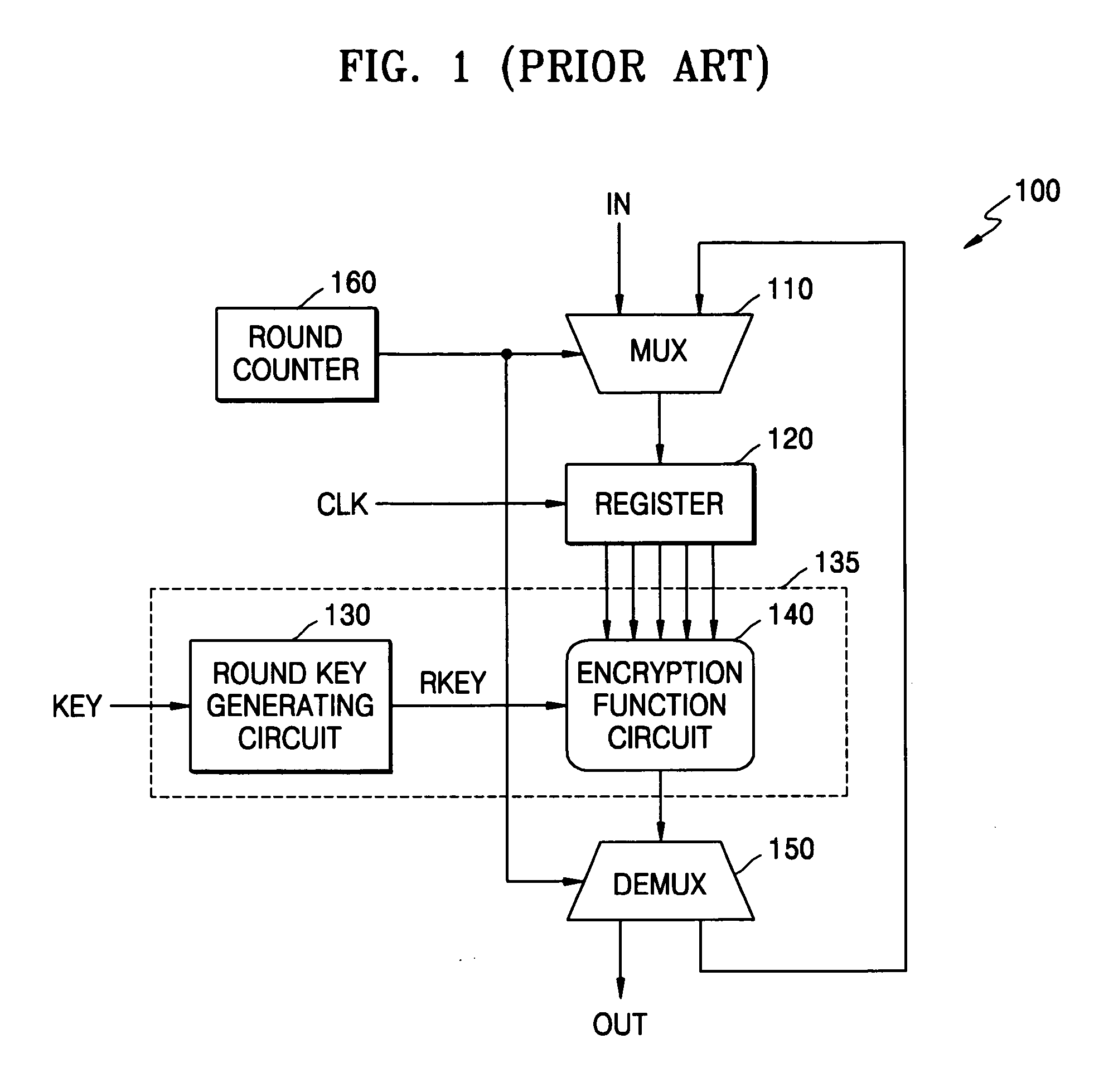
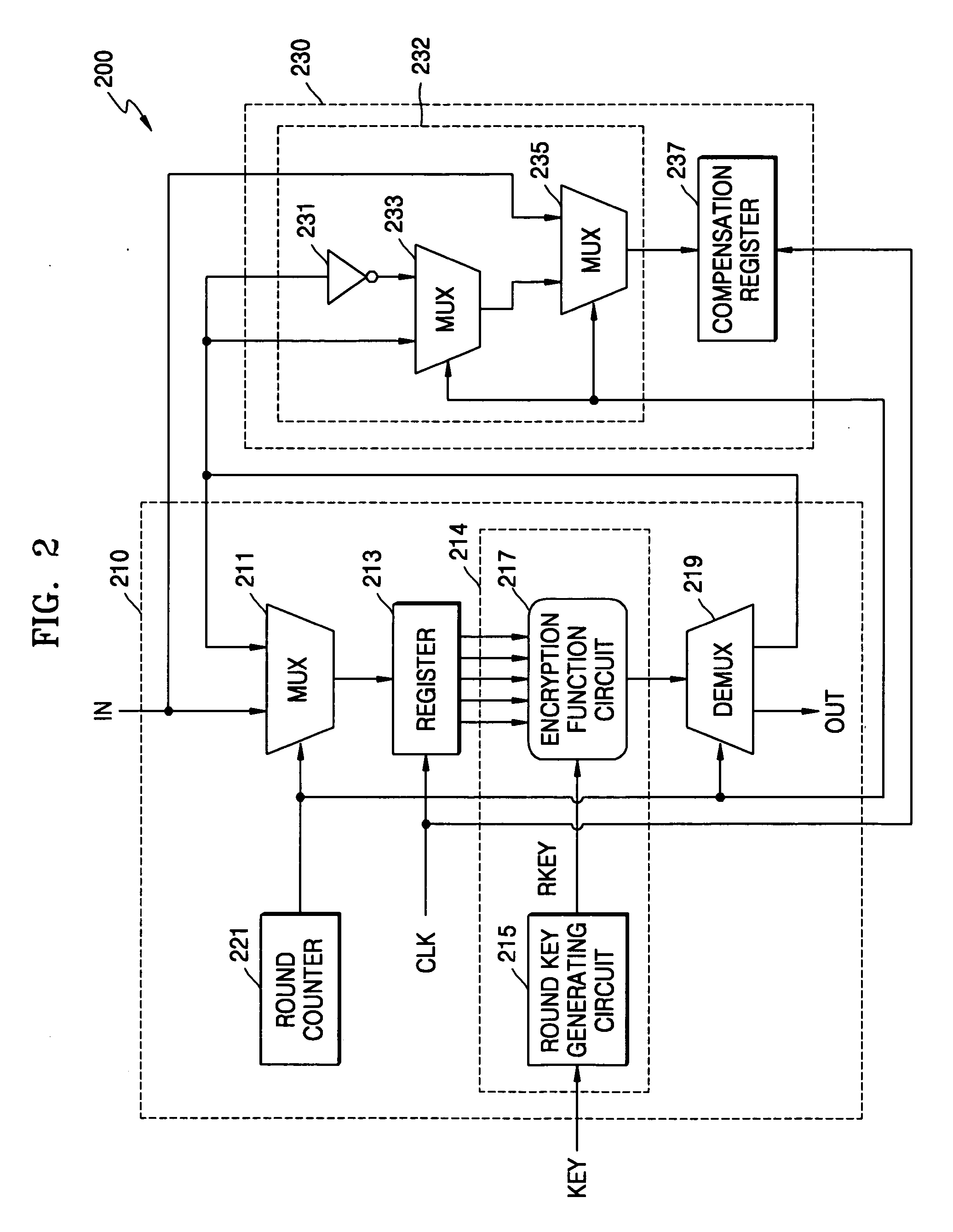
Cryptographic system and method for encrypting input data
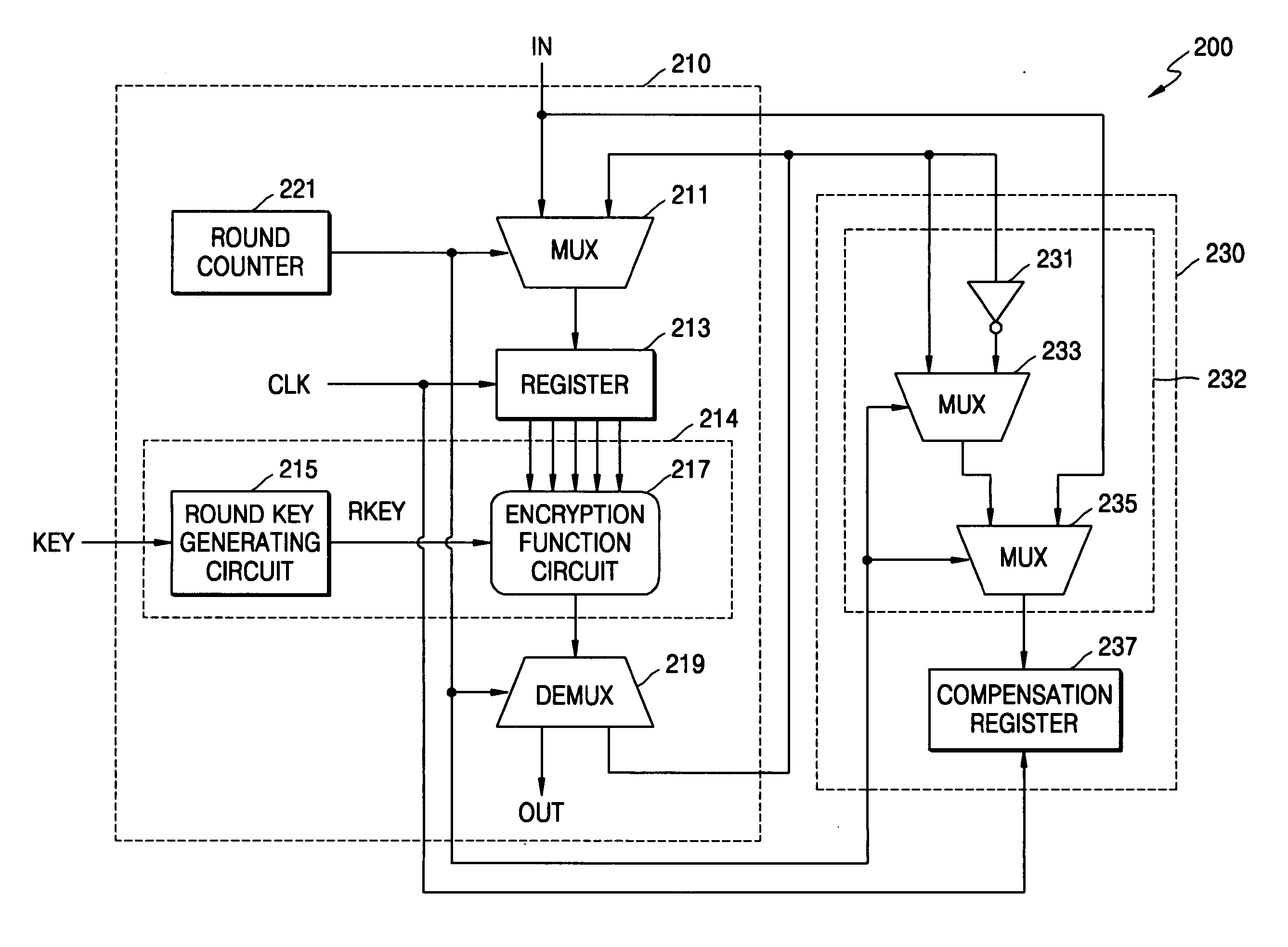
ActiveUS20070076864A1Key distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesComputer hardwareHamming distance
A cryptographic system for encrypting input data in accordance with an encryption algorithm having a repeated-round structure may include an encryption unit updating and storing encrypted data in accordance with the encryption algorithm in each given round, and outputting the encrypted data after executing the encryption for a given number of rounds. The system may include a compensation unit generating and storing compensation data so that a sum of a Hamming distance for the updated and stored data and a Hamming distance of the compensation data is maintained at a constant value.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus using coordinate interleaving to increase diversity in a MIMO system
InactiveUS20060034381A1Increase diversityPolarisation/directional diversityPhase-modulated carrier systemsAs elementEngineering
A method to increase diversity in MIMO fading channels interleaves coordinates of complex symbol(s) in a transmission frame after encoding and modulating. Specifically, an input signal is encoded and modulated into a codeword, jointly across at least two pipes, said pipes having space, time, frequency, or other nature, wherein the codeword spans a frame and is defined as at least one complex symbol whose complex values are all those to be transmitted during all channel uses covered by the frame. Each of the complex symbols have a first and second coordinate. After modulating, which may be combined with encoding in a signal space encoder, the coordinates are interleaved. In modulation, the complex symbols (typically two dimensional) may arise as elements of a multidimensional (typically greater than two dimensions) signal constellation, in which case those multidimensional constellation coordinates are the ones that are interleaved in the frame. The frame carrying the interleaved coordinates is transmitted by the first and at least second antennas, possible opposed sub-frames of the overall frame being transmitted separately by opposed antennas. A coset selector is used in some embodiments to maximize a minimum Hamming distance, and / or a minimum Euclidean distance, between coordinates within a coset to control diversity and / or coding gain. In some embodiments, the operation of the encoder and modulator is such as to maximize a minimum coordinate-wise Hamming distance, and / or a minimum Euclidean distance, between allowable codewords, and / or to provide additional structure for the allowable codewords. A method, transmitter, system, and mobile station are described.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
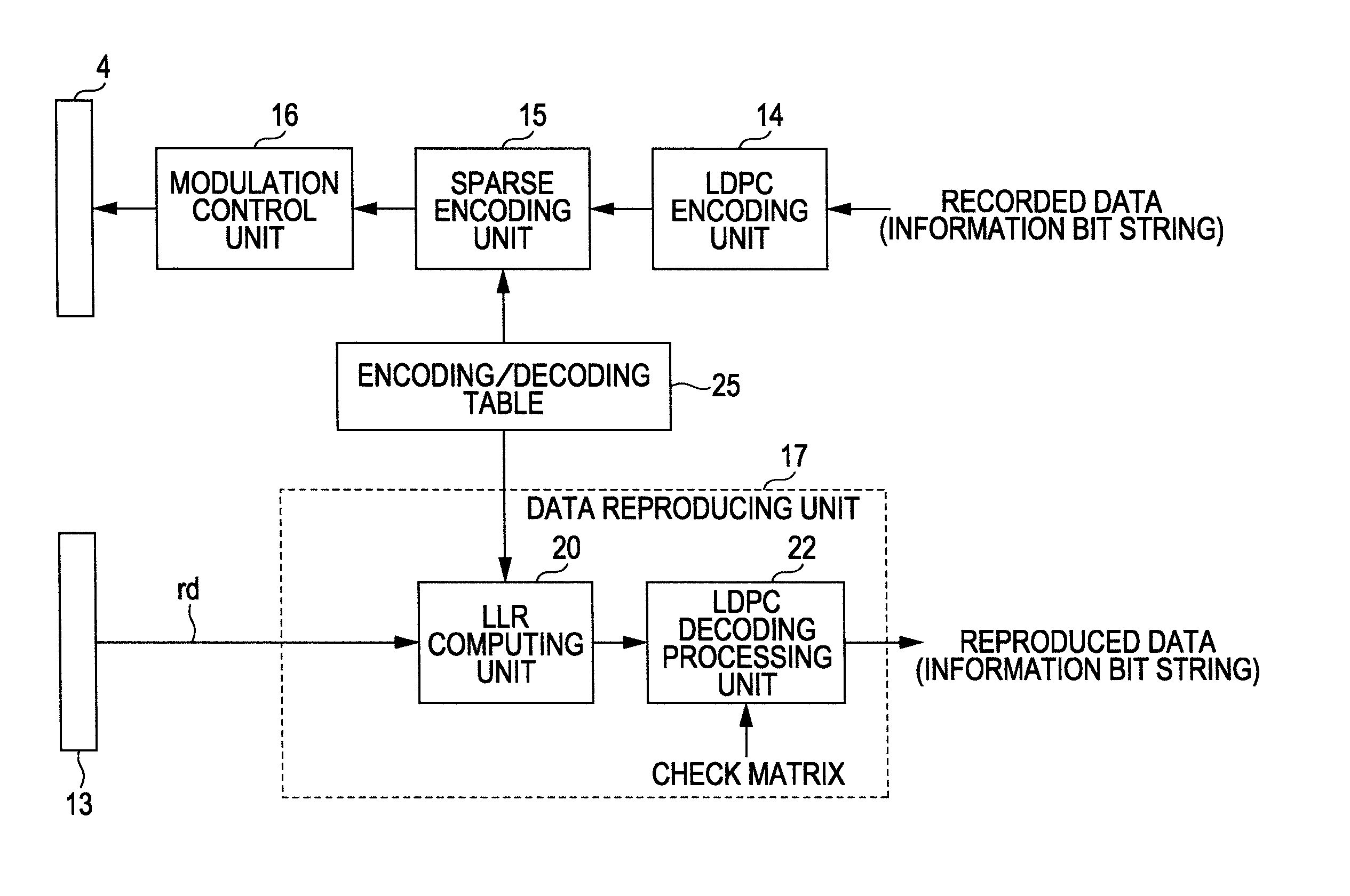
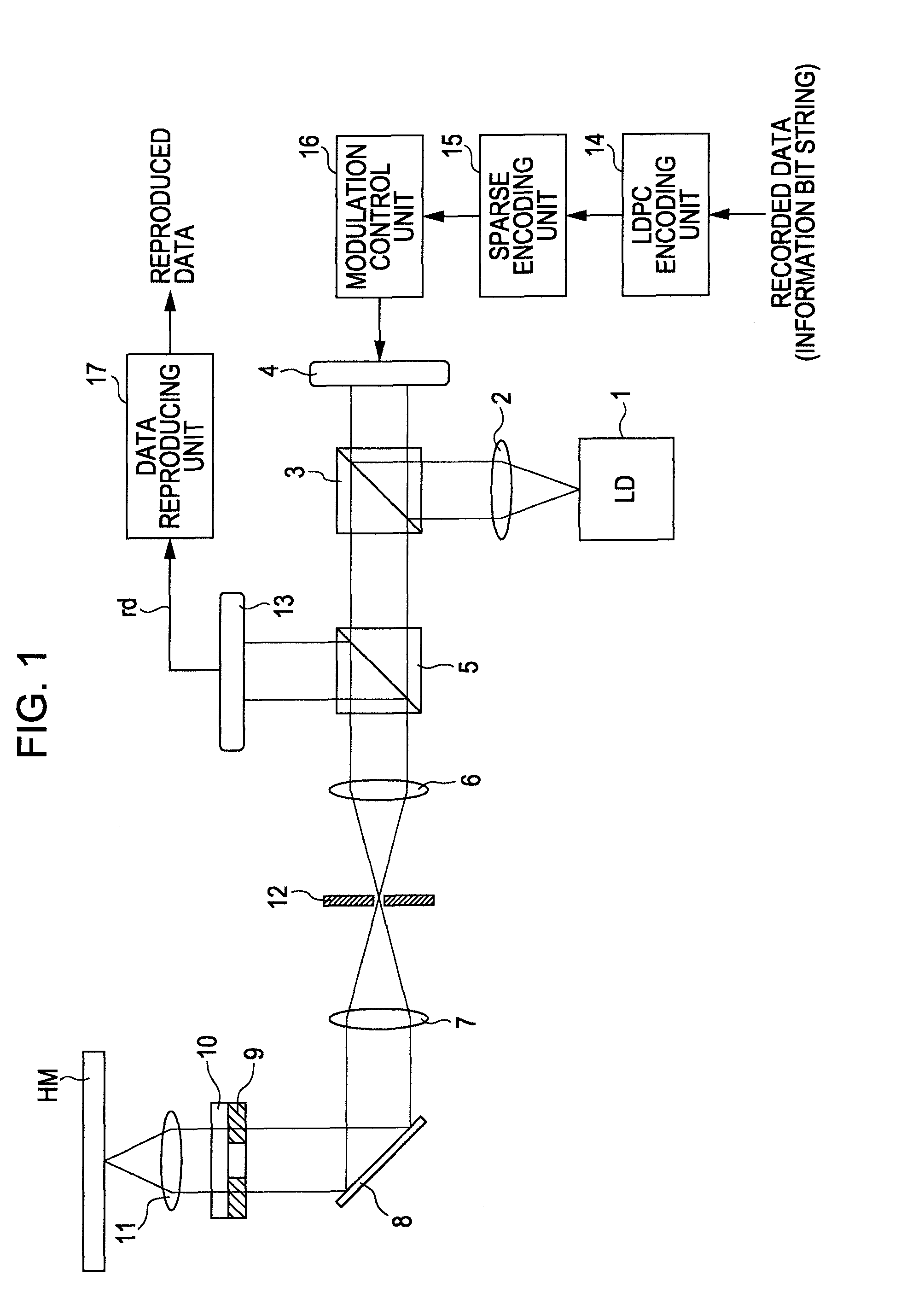
Data modulating device and method thereof
InactiveUS20100205506A1Improve decoding performanceReliable valueError prevention/detection by using return channelJoint error correctionData miningHamming distance
A data modulating device includes: an LDPC encoding unit configured to execute LDPC encoding; and a balance encoding unit configured to input a data string subjected to encoding by the LDPC encoding unit as data to be encoded, and convert k bits of this data to be encoded into balance code made up of m-bit block data; with the balance encoding unit executing balance encoding of said data to be encoded using a data conversion table subjected to mapping so that a set of the k-bit data patterns of which the Hamming distance is 1 corresponds to a set of block data of which the Hamming distance is 2.
Owner:SONY CORP
Error detection and correction codes for channels and memories with incomplete error characteristics
InactiveUS20120096330A1Efficient error-correcting codeOther error detection/correction/protectionCode conversionParallel computingHamming distance
A channel has a first and a second end. The first end of the channel is coupled to a transmitter. The channel is capable of transmitting symbols selected from a symbol set from the first end to the second end. The channel exhibits incomplete error introduction properties. A code comprises a set of code words. The elements of the set of code words are one or more code symbols long. The code symbols are members of the symbol set. The minimum modified Hamming separation between the elements of the set of code words in light of the error introduction properties of the channel is greater than the minimum Hamming distance between the elements of the set of code words. A memory device, a method of using the channel, and a method of generating the code are also described.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
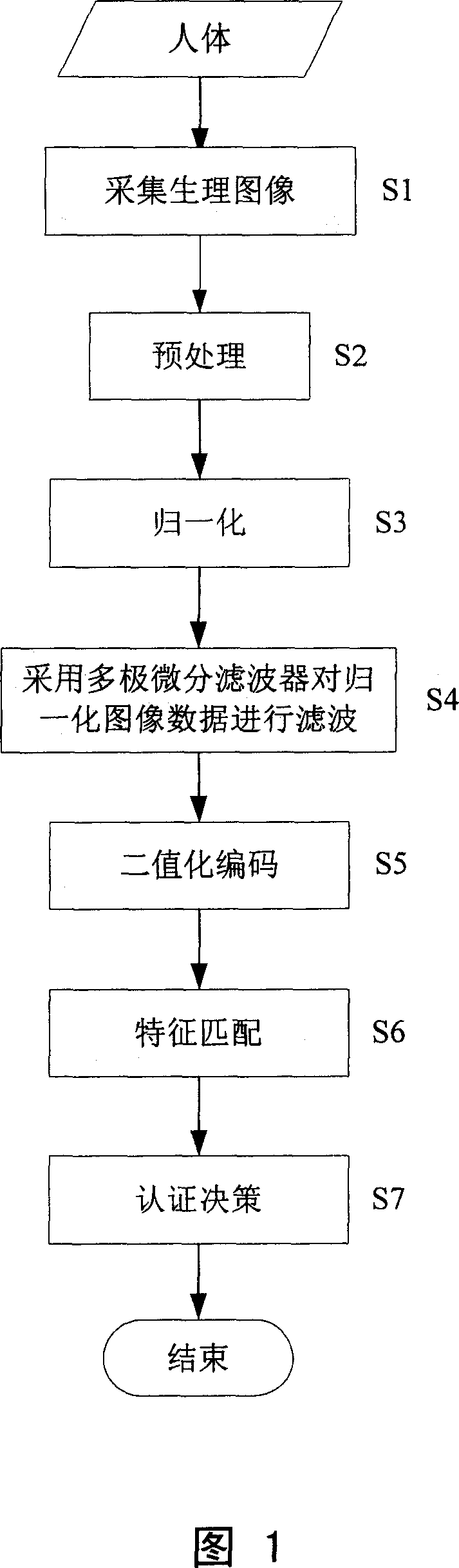
Automatic identity discriminating method based on human-body physiological image sequencing estimating characteristic
ActiveCN101030244AImprove recognition accuracyCalculation speedCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorHuman body
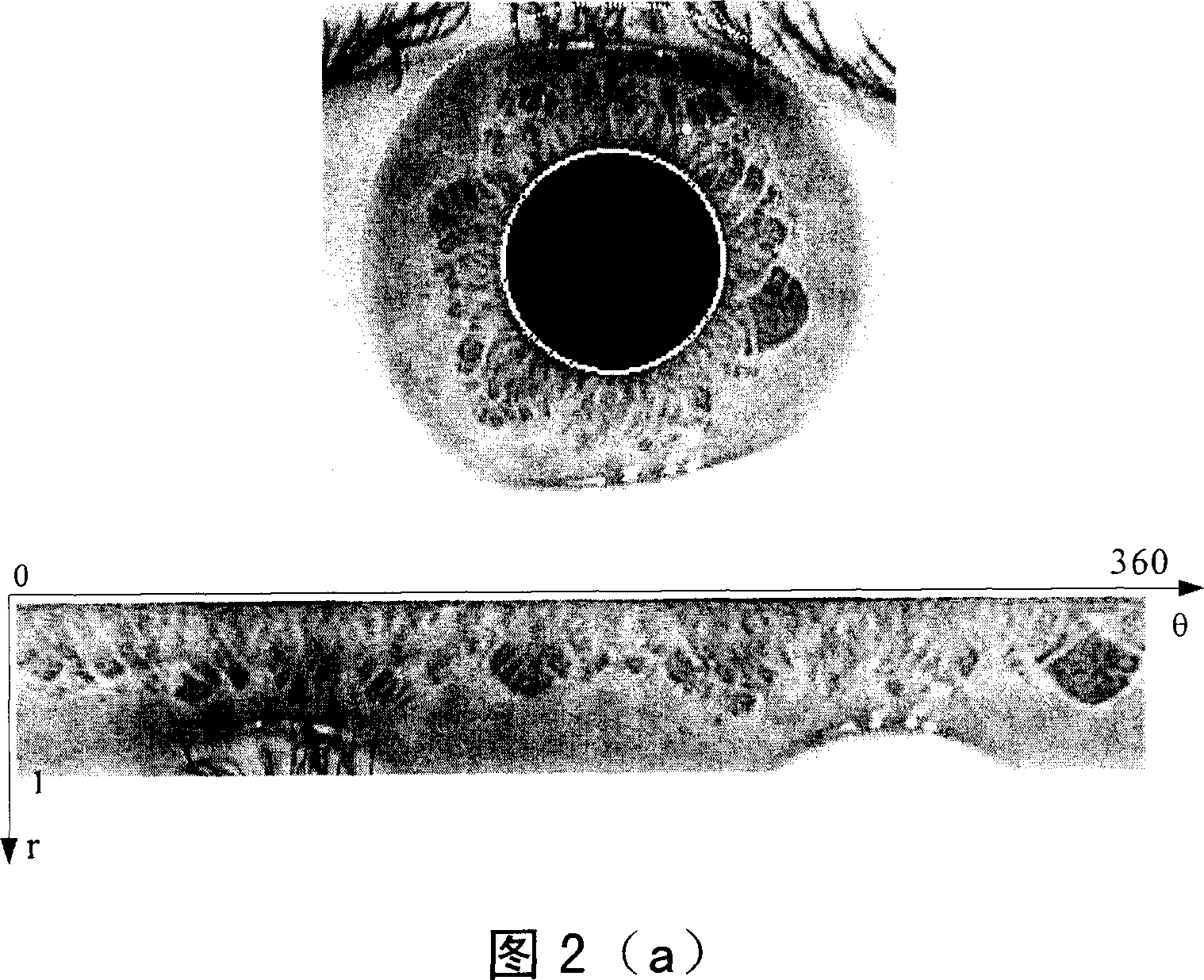
A method for automatically identifying status based on sequence measure character in human body physiological image includes preprocessing and normalizing collected physiological image, picking up sequence measure character in normalized image by multi-pole differential filter, coding sequence measure character to form two-valued character vector, calculating Hamming distance between character vectors in two frames of physiological images and judging whether two frame of physiological image are coming from one and the same person or not according to calculated Hamming distance.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
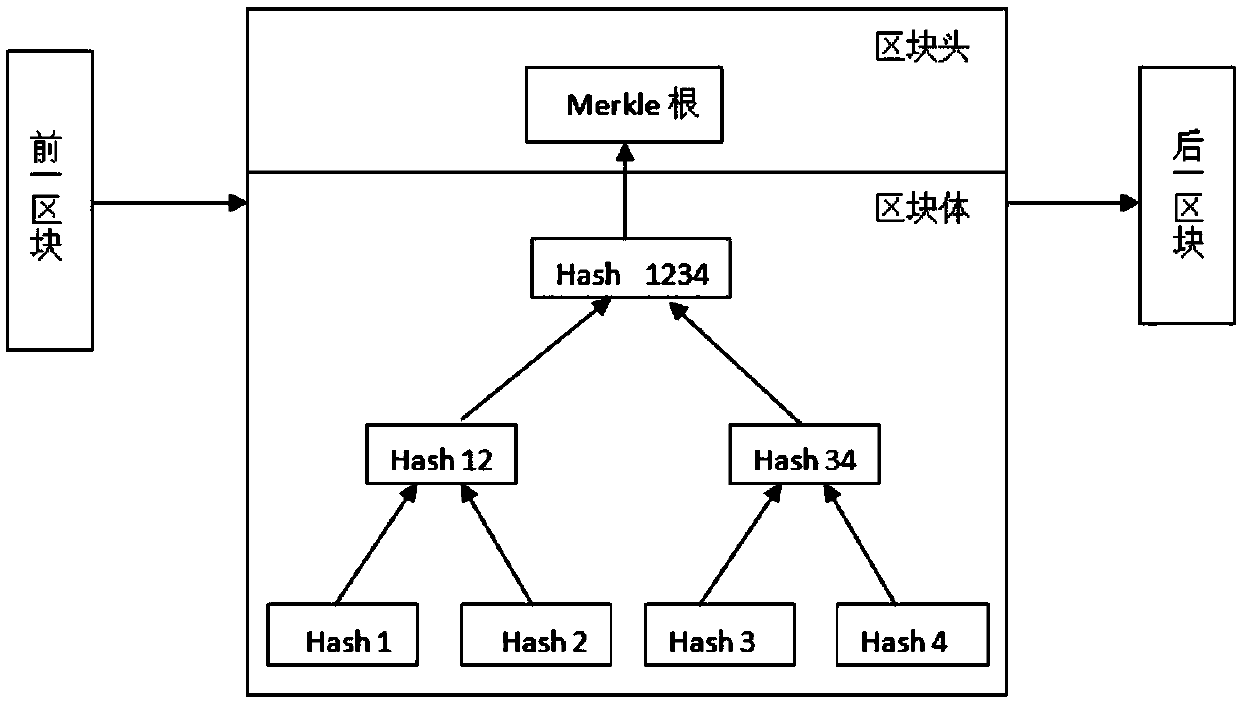
The invention discloses a cCopyright traceability protection framework and method based on a block chain
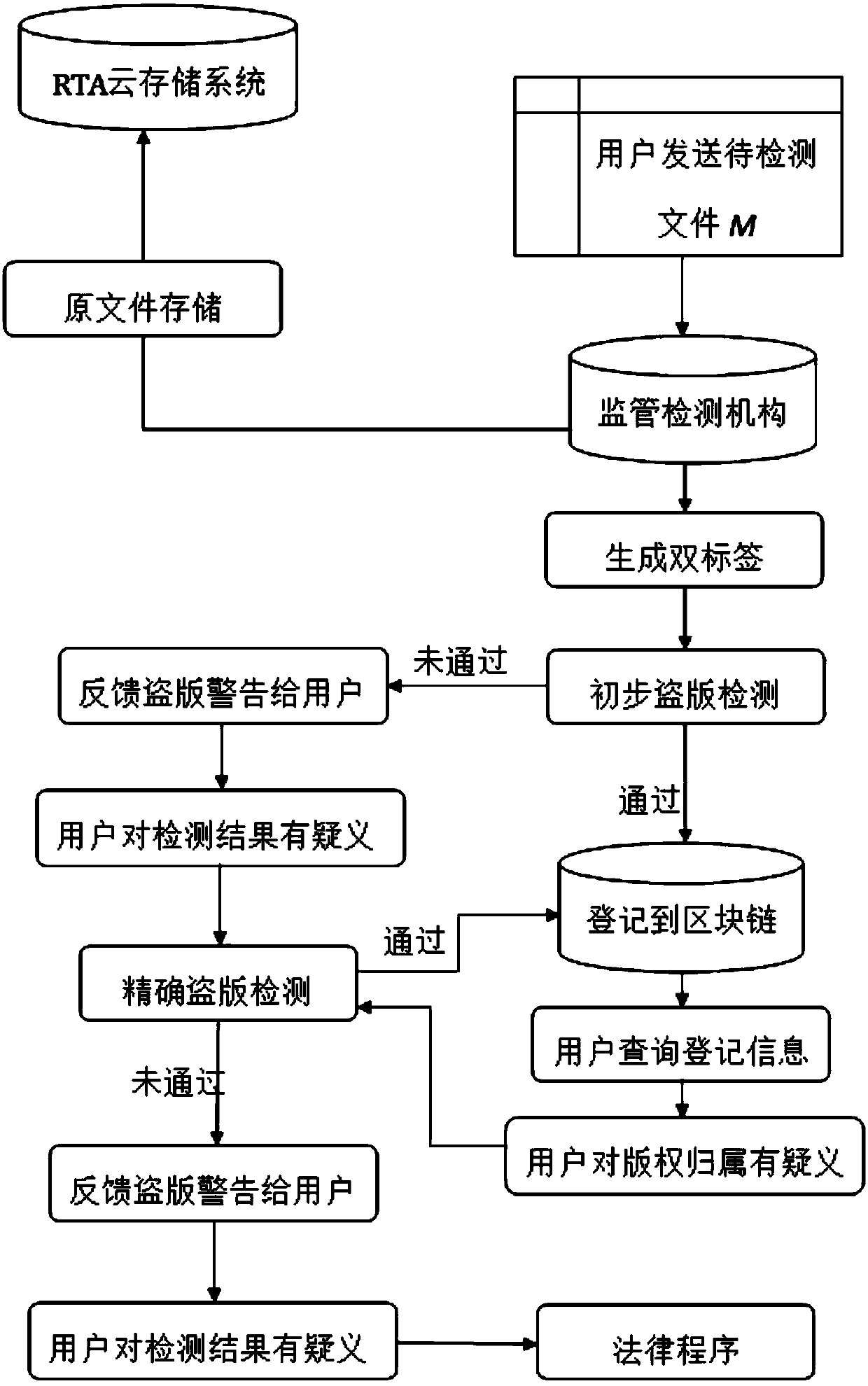
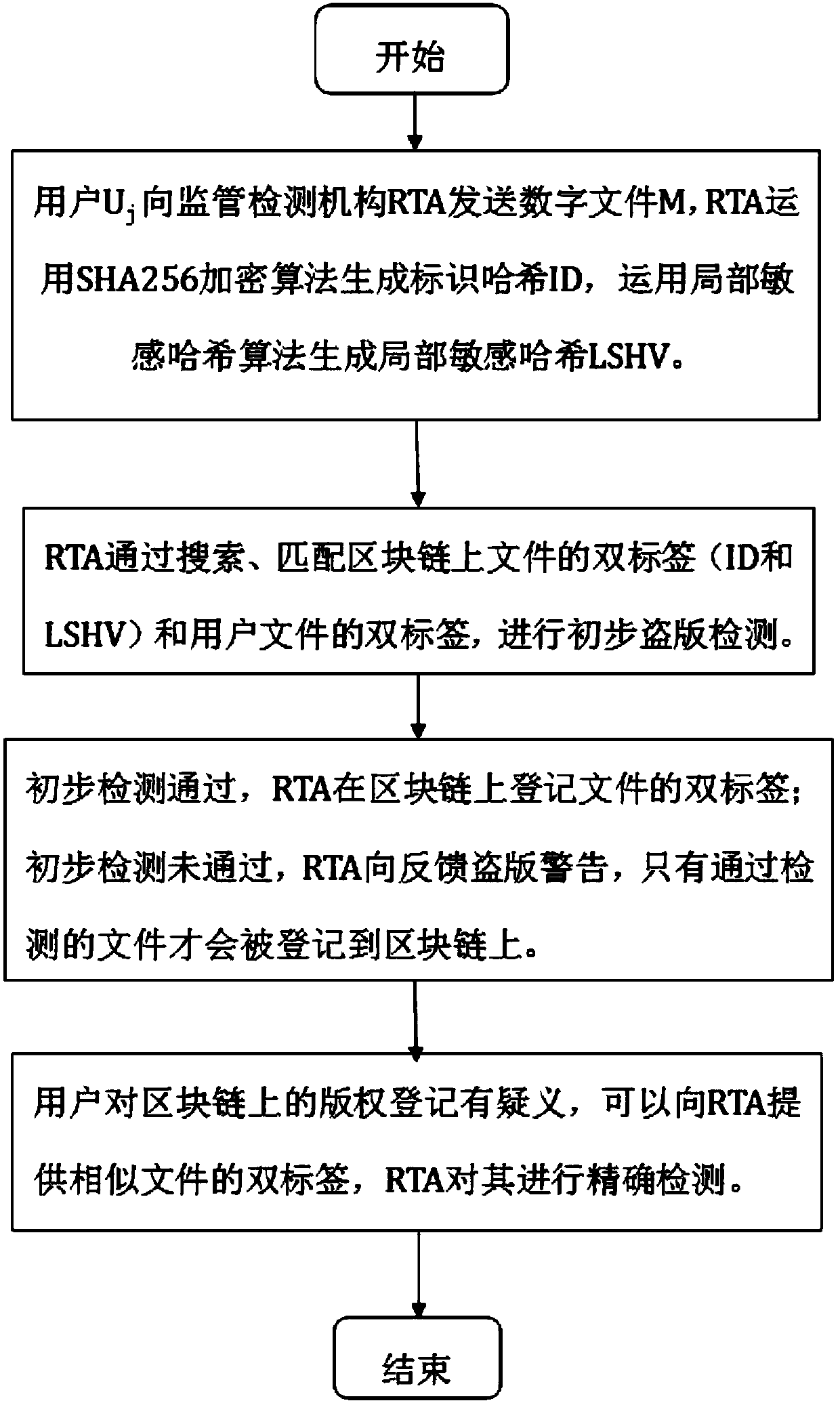
InactiveCN109614775ARelieve pressureThe registration process is transparent and credibleDigital data protectionProgram/content distribution protectionUnique identifierHamming distance
The invention discloses a copyright traceability protection method based on a block chain, which is applied to a network environment formed by a block chain with characteristics of decentralization, data non-tampering and time sequence block chain and a supervision and detection mechanism RTA and acting on n users. W; wherein Uj represents the jth user, j is greater than or equal to 1 and less than or equal to n, and the method comprises the following steps: S1, generating double tags; S; s2, a piracy detection stage; S; s3, a file registration stage; S; s4, a piracy warning stage is fed back;S; s5, a user feedback stage. The invention also discloses a copyright traceability protection framework based on the block chain. According to the invention, a supervision detection mechanism encrypts a file to generate a unique identifier hash; a local sensitive algorithm generates local sensitive hash, the file similarity is calculated in combination with the Hamming distance, it is confirmedthat the file is originally registered into a copyright block chain, the method effectively solves the problems that in the existing copyright protection process, the copyright fraud risk is low, anda copyright registration mechanism is low in efficiency, and safety, transparency and credibility of the registration process are achieved.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
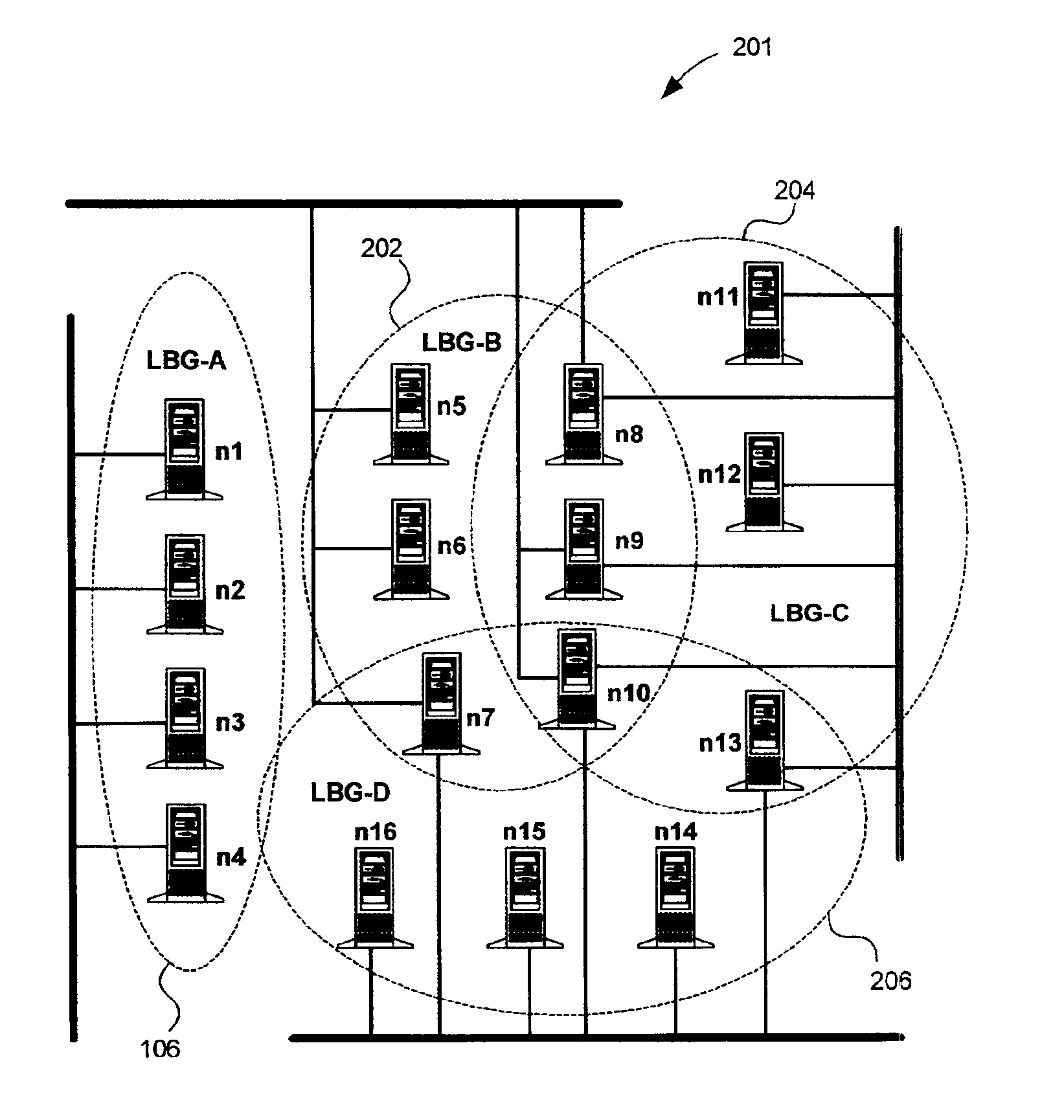
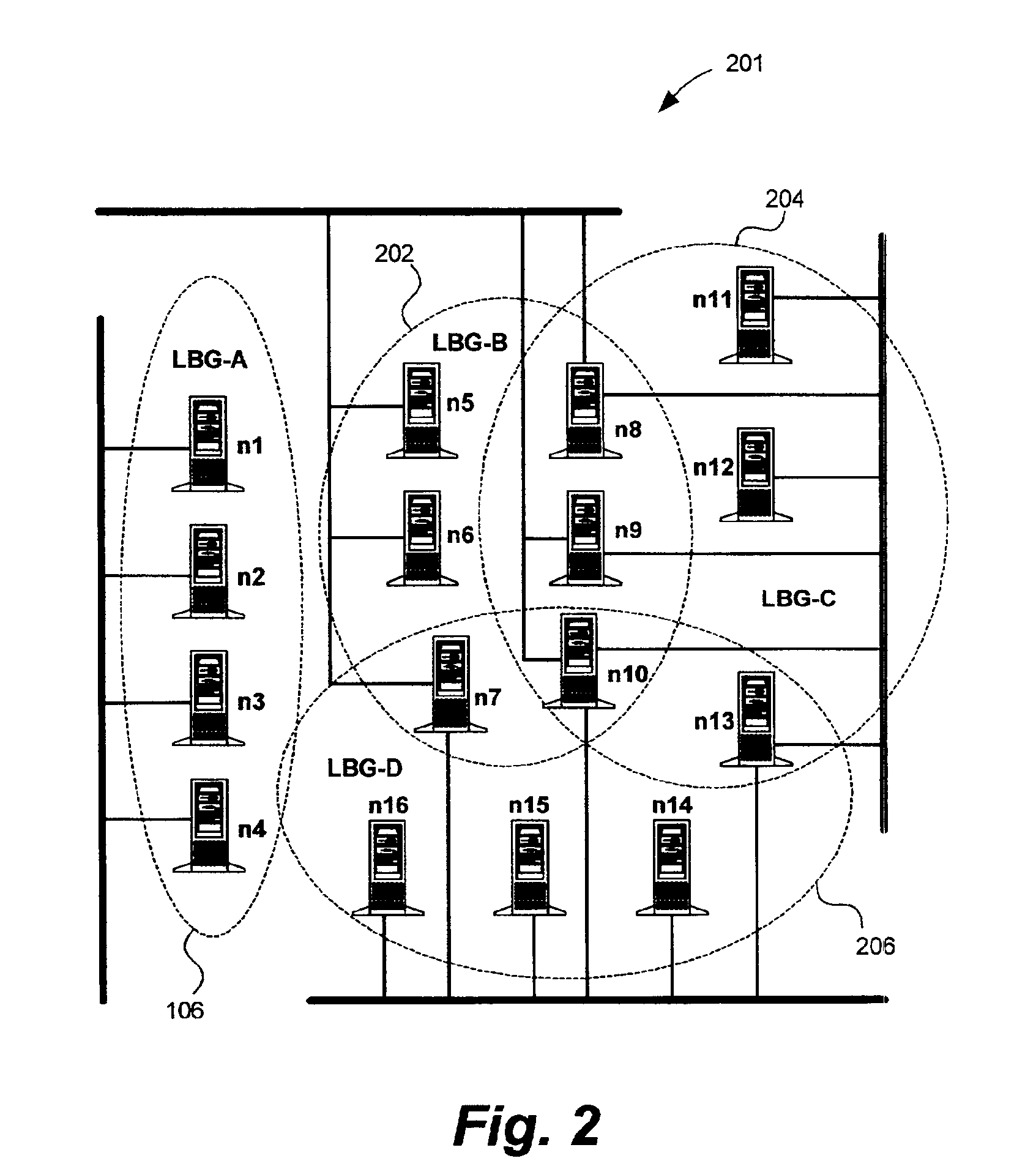
Master node selection in clustered node configurations
InactiveUS6950855B2Maximum total availability potentialImprove bindingData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsHamming distanceDistributed computing
A method and system for selecting master nodes to manage a target node group in a computer network having multiple nodes and overlapping node groups. The system includes determining a hamming distance for node pairs within the network. The node pair includes two node pair members and the hamming distance is the number of node groups the node pair members do not share in common. A participation index for nodes within the network is determined at a determining operation. The participation index is the number of node groups the node belongs to. An availability potential for node pairs is also determined. The availability potential is the sum of the participation indexes of the node pair members subtracted by the hamming distance of the node pair. An optimal combination of node pairs is found by searching for the maximum total availability potential for the network. A master node pair for the target node group is selected from the optimal combination of node pairs. If a master node pair does not exist for the target node group, a master node belonging to the target node group is selected for the target group.
Owner:IBM CORP
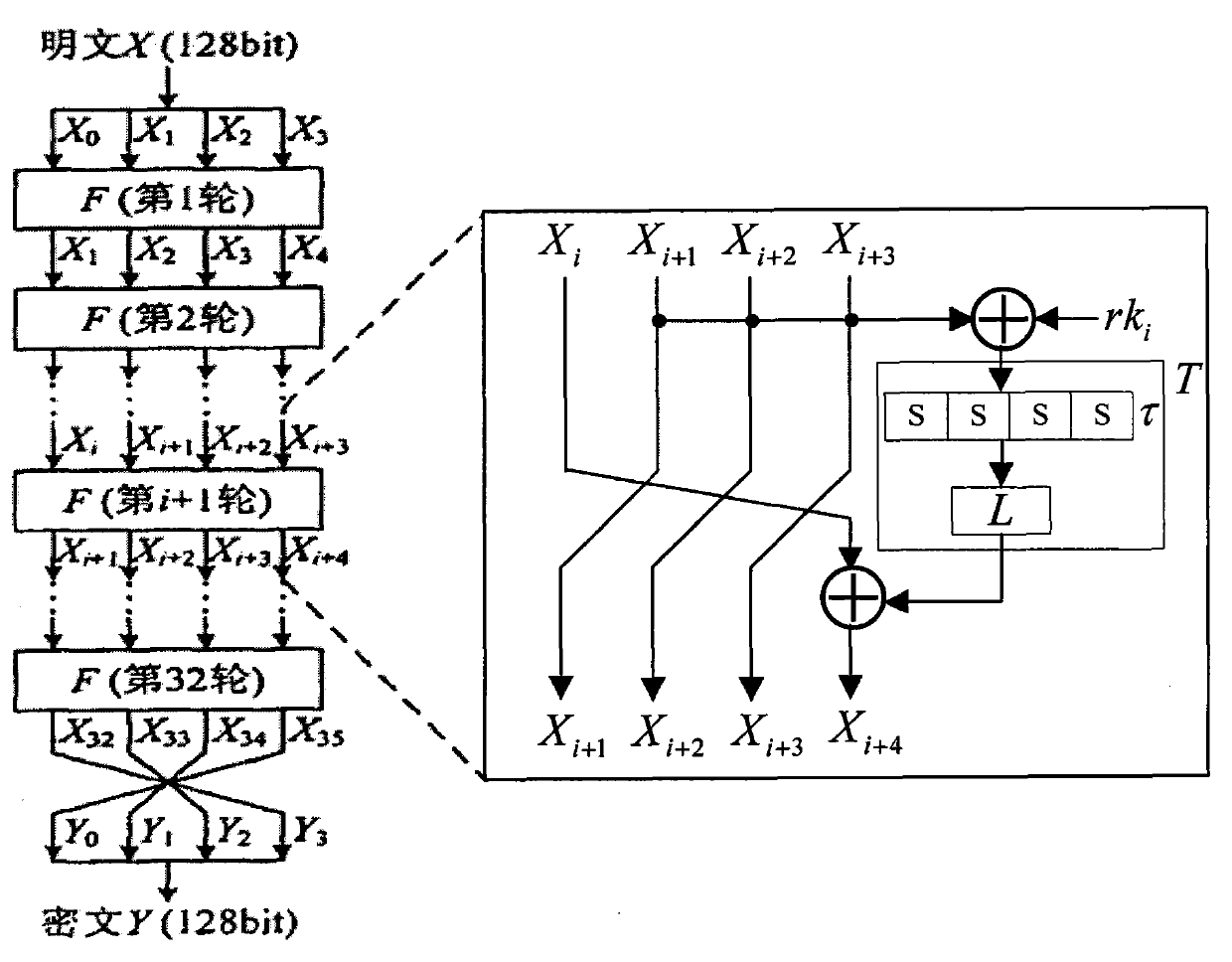
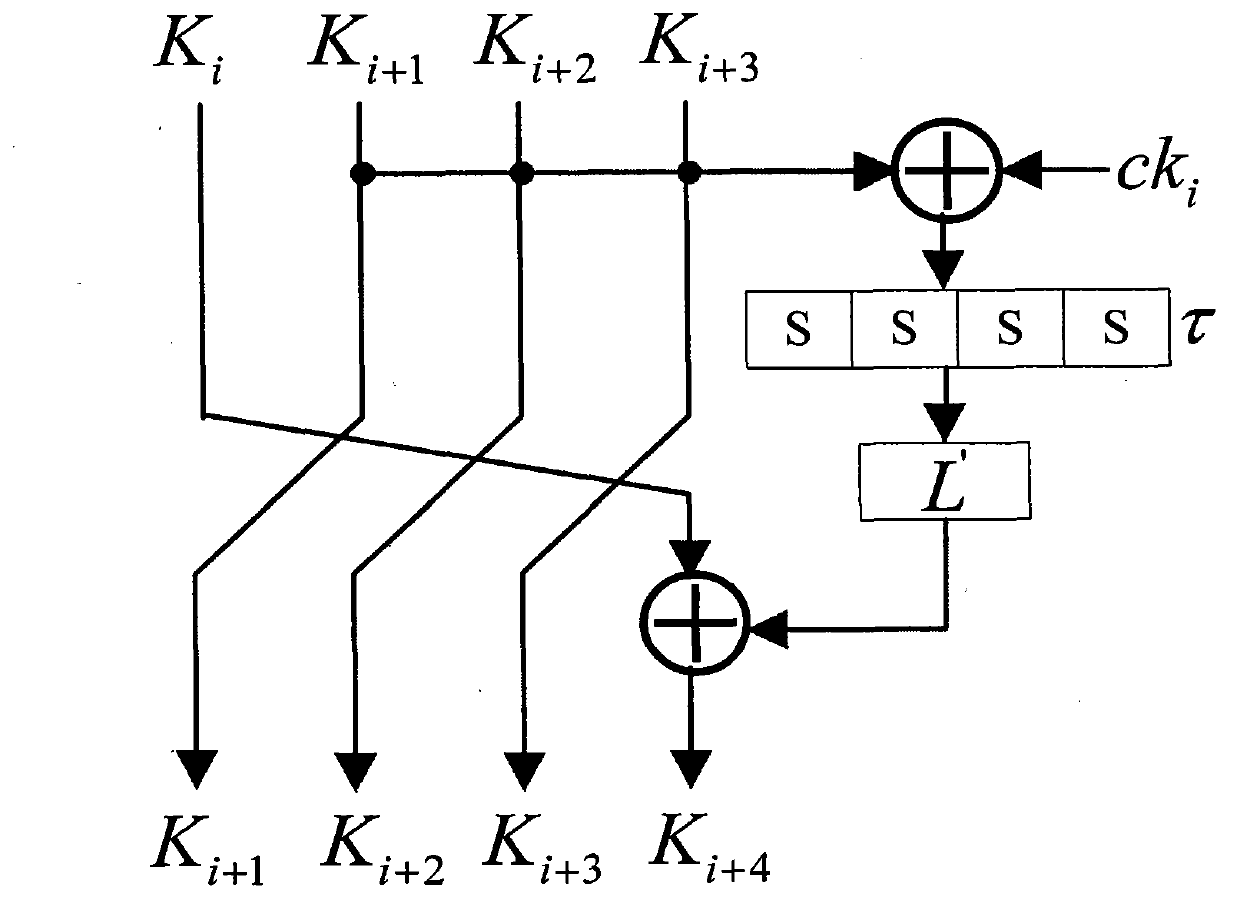
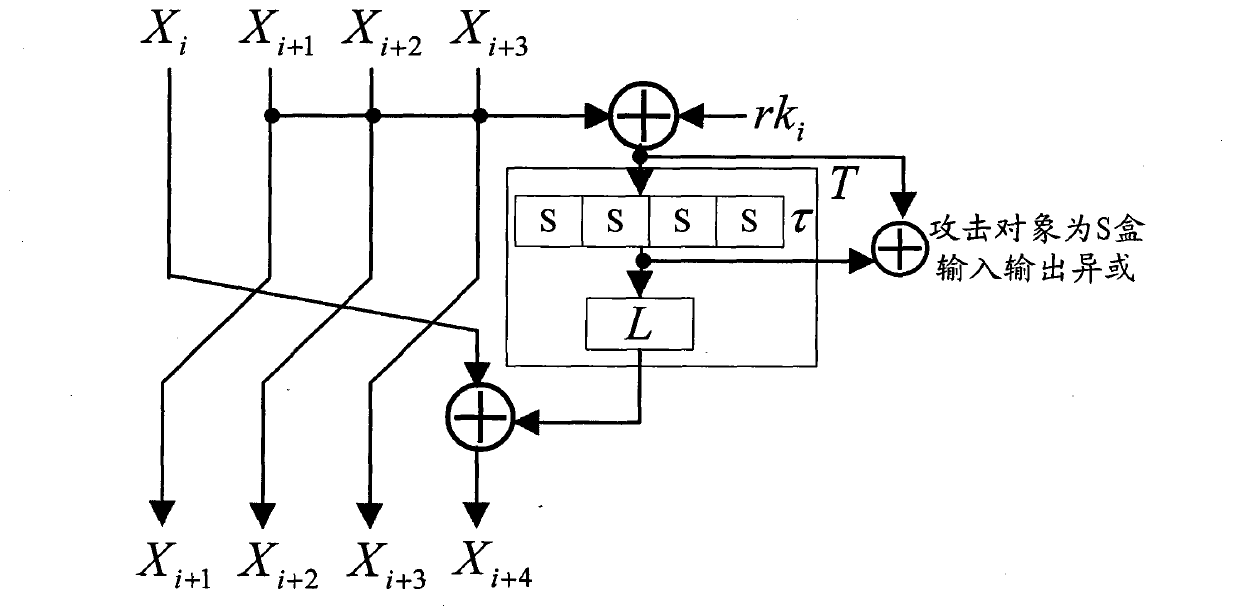
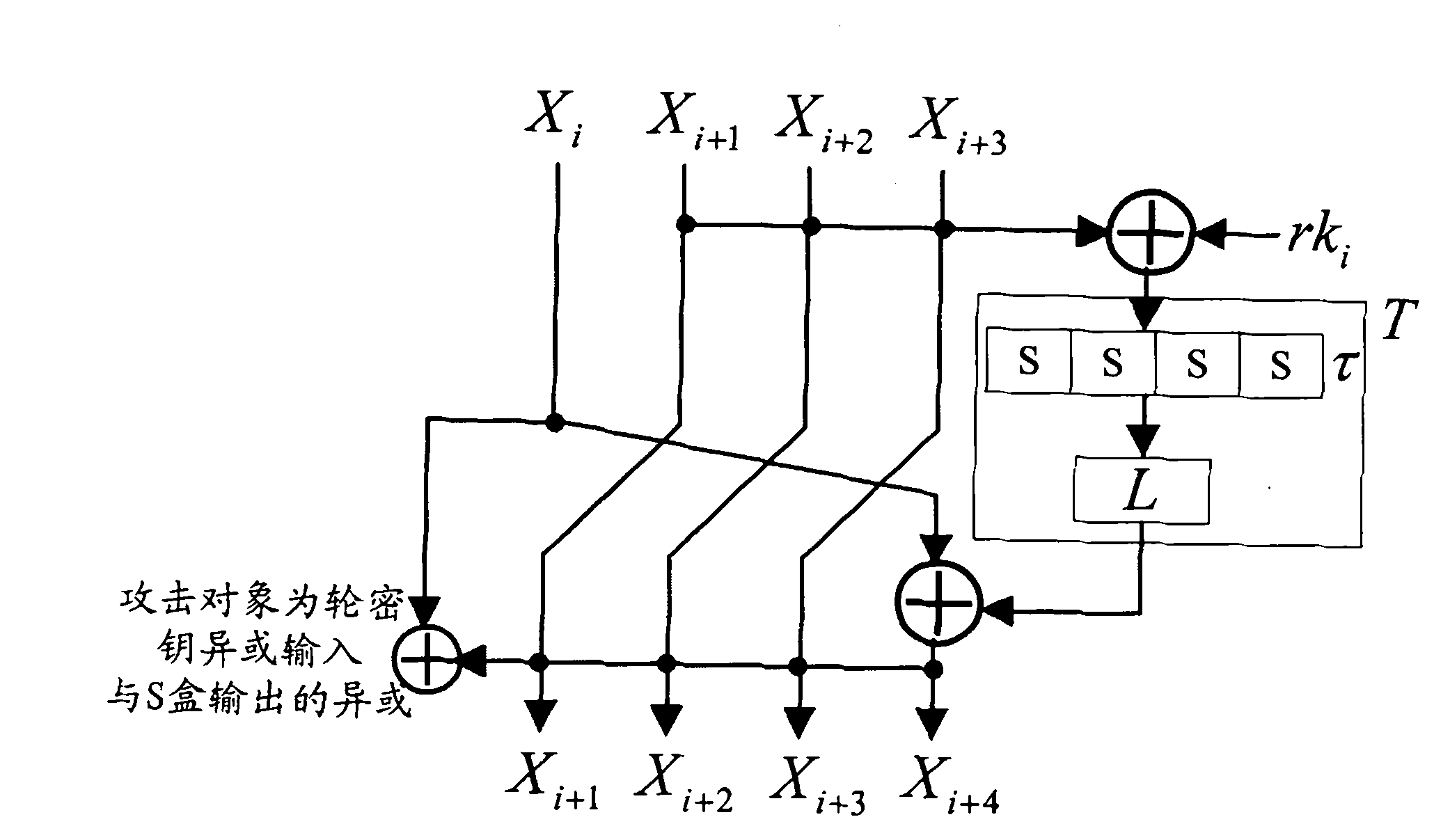
Application method of Hamming distance model on SM4 cryptographic algorithm lateral information channel energy analysis and based on S box input
ActiveCN103138917AExtended Side Channel Energy Analysis MethodEfficient analysisEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesPower analysisS-box
The invention discloses an application method of a Hamming distance model on SM4 cryptographic algorithm lateral information channel energy analysis and based on S box input. The application method is characterized in that the Hamming distance model is established by selecting an S box or a round function as an attacking point in the process that the SM4 cryptographic algorithm lateral information channel energy analysis is carried out, the input of the S box is used as an initial state v1 of the Hamming distance model, the output of the S box is used as subsequent state v2 of the Hamming distance (HD (v1, v2)) model when the S box is attacked, and the output / input of the round function is used as the subsequent state v2 of the Hamming distance (HD (v1, v2)) model when the round function is attacked. The method can be applied to CPA / DPA lateral information channel energy analysis of the SM4 cryptographic algorithm. Correlation between a correct guess secret key and energy information is improved, and validity and success rate of the analysis are enhanced.
Owner:国家密码管理局商用密码检测中心
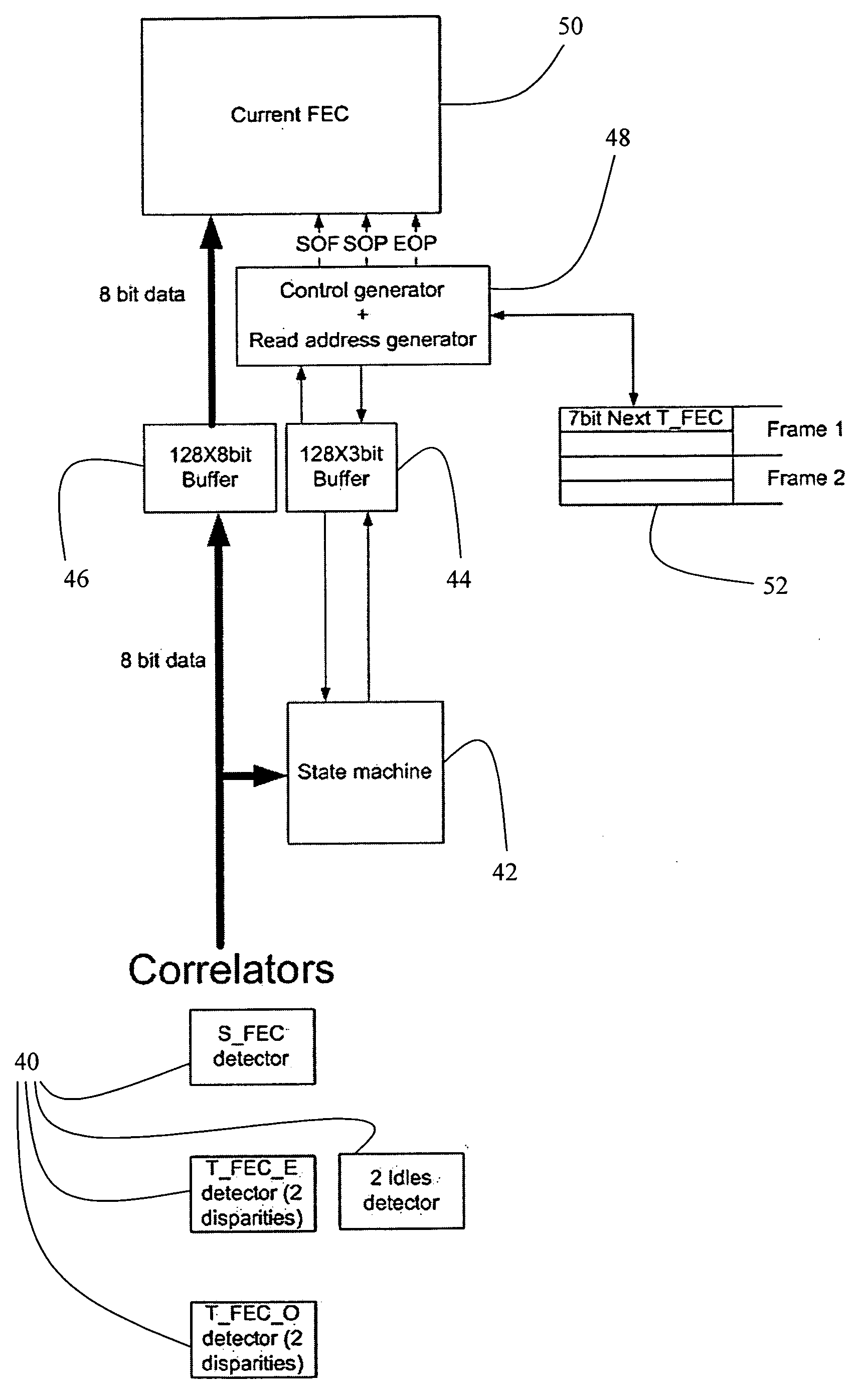
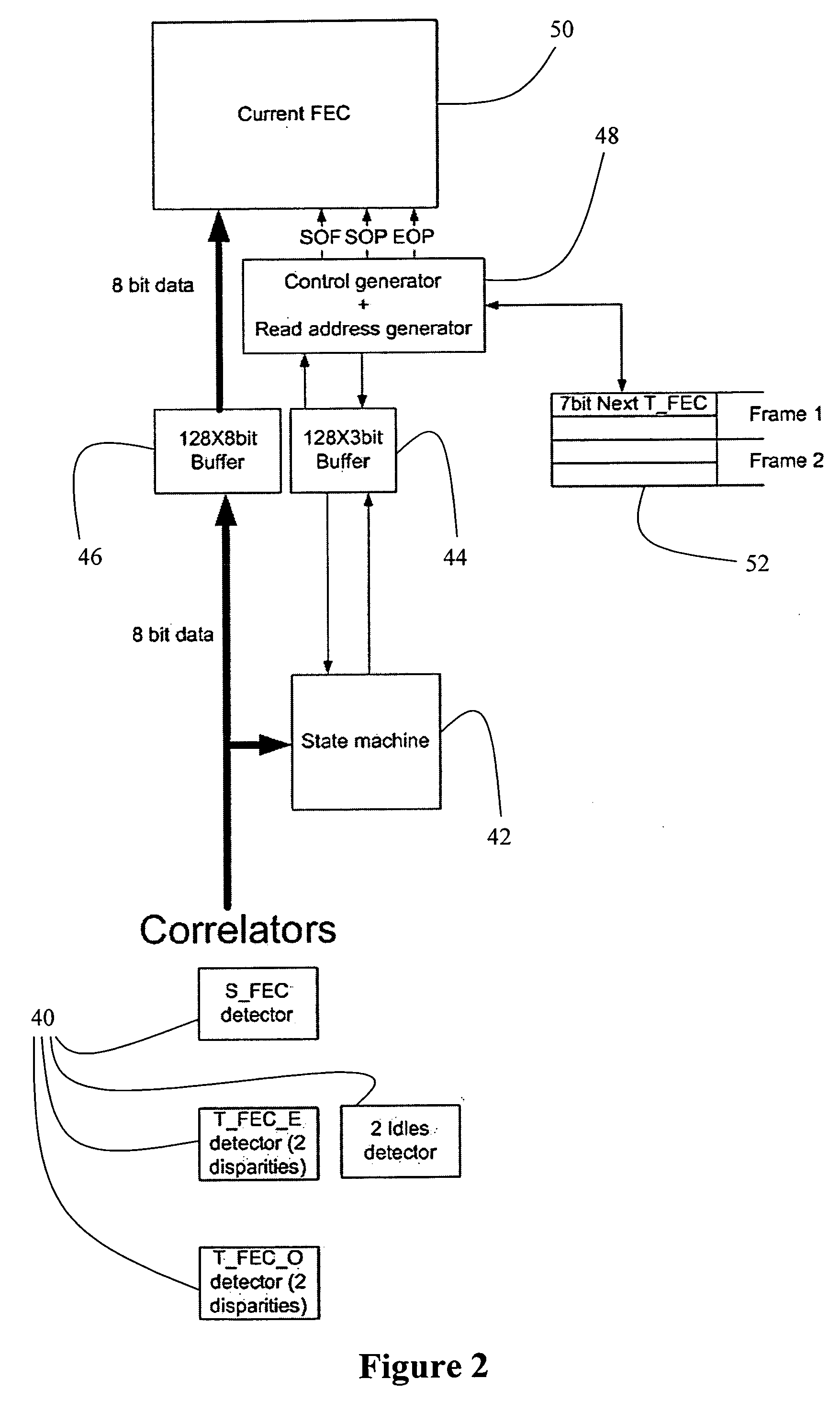
Enhancing the ethernet FEC state machine to strengthen correlator performance
InactiveUS20070206709A1Improving data correlationCode conversionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsMatch/mismatchHamming distance
The present invention discloses devices and methods for improving data correlation using a multiple-correlation state-machine, the method including the steps of: (a) pre-processing a data frame having a plurality of symbol sets, wherein each symbol set demarks a respective frame field of the frame, to provide a threshold-compared hamming-distance indicator; (b) comparing the threshold-compared hamming-distance indicator with at least one multiple-correlation threshold to provide a threshold-compared multiple-correlation indicator; and (c) combining the threshold-compared hamming-distance indicator and the threshold-compared multiple-correlation indicator to determine a match / no-match comparison indicative of the respective frame field. In some embodiments, the step of combining includes forming a logical-AND of the threshold-compared hamming-distance indicator and the threshold-compared multiple-correlation indicator. Preferably, the method further includes the step of: (d) prior to the step of combining, comparing a BER of the frame to a BER threshold. Also disclosed is a weighted-correlation method for improving data correlation.
Owner:PMC SIERRA ISRAEL
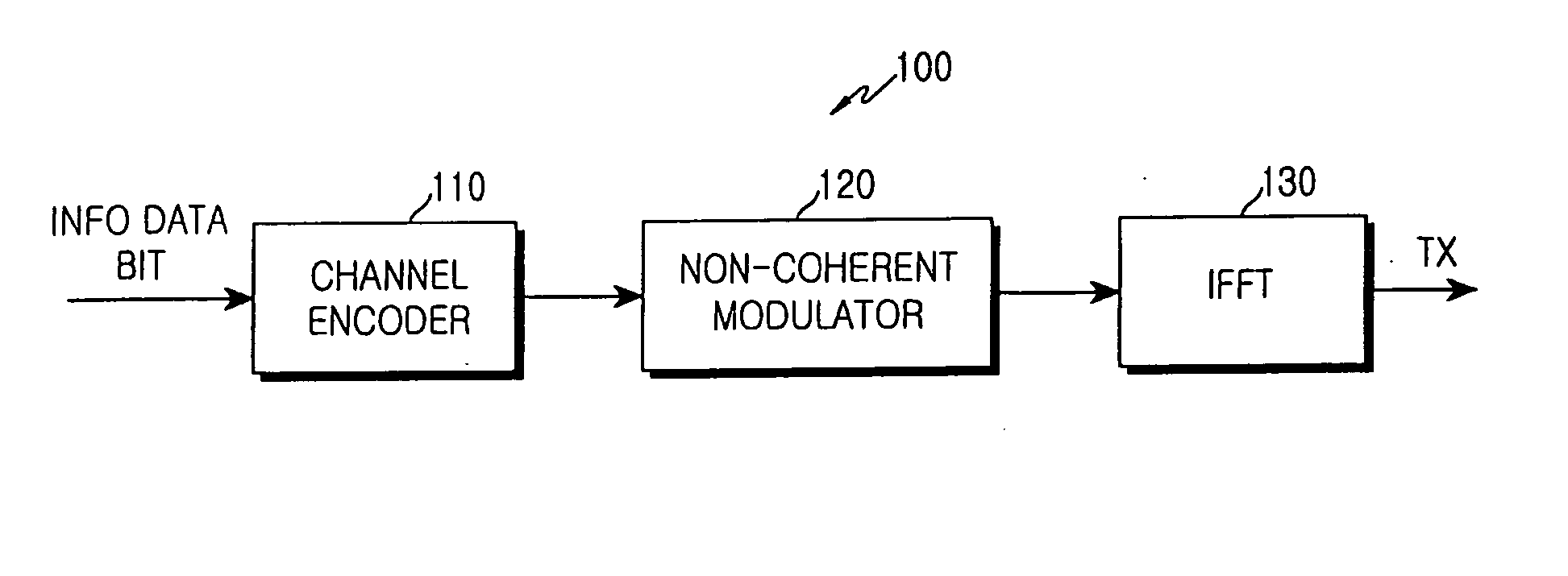
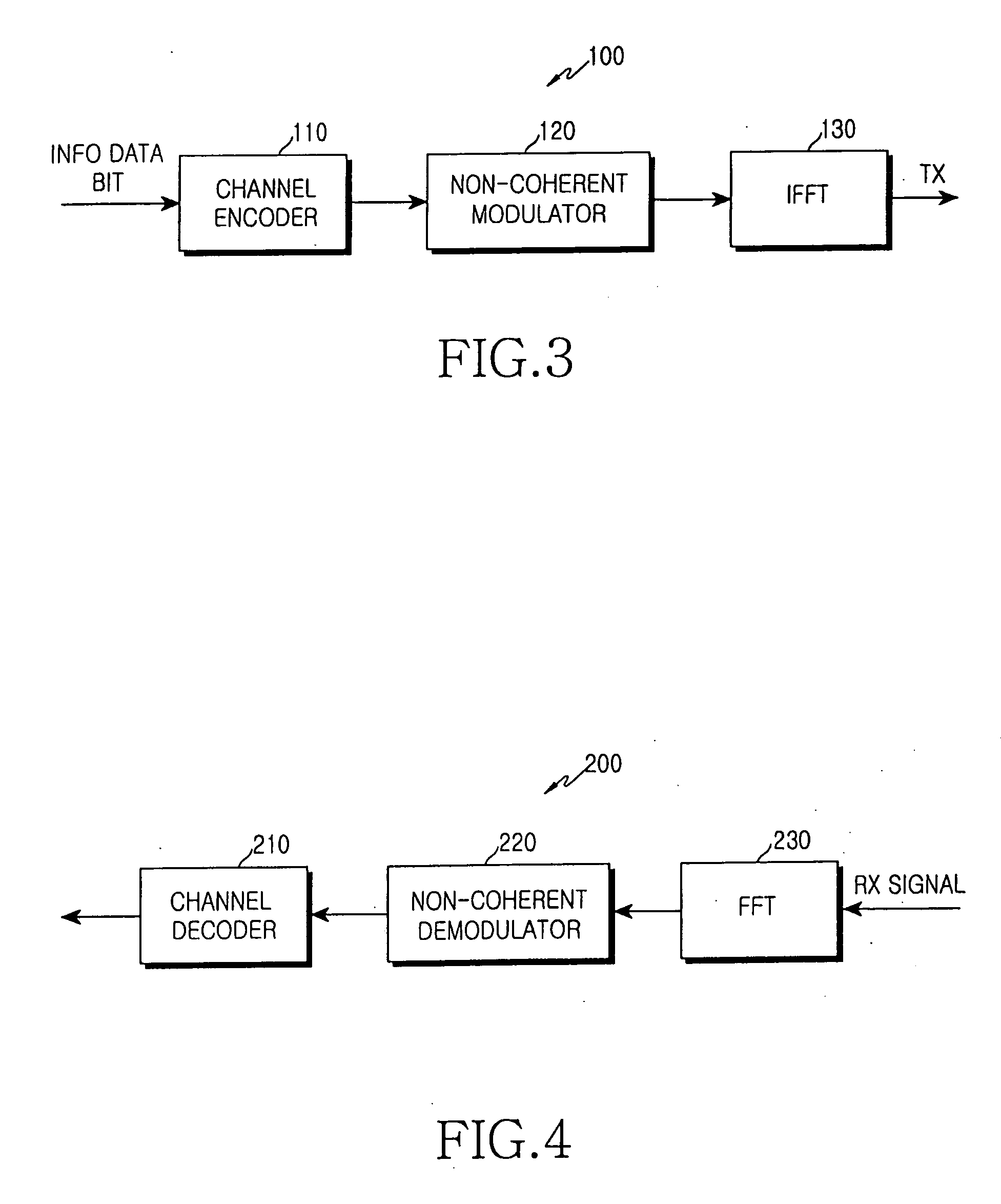
Method and apparatus for transmitting uplink fast feedback information in an OFDMA communication system
ActiveUS20050265227A1Guaranteed normal transmissionImprove accuracyTime-division multiplexRadio transmissionFast Fourier transformCommunications system
An apparatus and method for transmitting uplink fast feedback information using a fast feedback channel in an orthogonal frequency division multiple access (OFDMA) communication system. A channel encoder generates uplink fast feedback information to be transmitted, and outputs codewords designed such that a minimum Hamming distance between the codewords is maximized, according to the uplink fast feedback information. A non-coherent modulator performs orthogonal modulation on transmission symbols corresponding to the codewords and allocates the orthogonal-modulated transmission symbols to subcarrier cluster. An inverse fast Fourier transform (IFFT) block performs IFFT on a transmission signal having the subcarrier cluster and transmits the IFFT-processed transmission signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Apparatus using concatenations of signal-space codes for jointly encoding across multiple transmit antennas, and employing coordinate interleaving
InactiveUS8031793B2Code conversionError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresSymbol of a differential operatorSpatial encoding
A system for transmitting data over a MIMO channel has a transmitter and a receiver. In the transmitter, the input data is encoded over at least two pipes by a concatenation of at least two constituent signal-space encoders. Each constituent encoder is used to generate, in response to the input data, a sequence of symbols from a channel alphabet having at least one dimension. Each symbol of the channel alphabet includes at least one complex symbol having real and imaginary coordinates. The transmitter interleaves the coordinates of the sequence of channel alphabet symbols, and transmits (from at least two transmit antennas) the interleaved coordinates. Preferably, each constituent encoder maximizes a minimum coordinate-wise Hamming distance between members of all valid pairs of symbol sequences, maximizes a minimum Euclidean distance between members of all valid pairs of different codewords, and obeys an equal eigenvalue criterion.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Generalized parity stripe data storage array
InactiveUS20050086575A1Increased Hamming distanceIncrease distanceNon-binary linear block codesError detection/correctionOn columnTheoretical computer science
The Hamming distance of an array of storage devices is increased by generating a parity check matrix based on column equations that are formed using an orthogonal parity code and includes a higher-order multiplier that changes each column. The higher order multiplier is selected to generate a finite basic field of a predetermined number of elements. The array has M rows and N columns, such that M is greater than or equal to three and N is greater than or equal to three. Row 1 through row M-2 of the array each have n-p data storage devices and p parity storage devices. Row M-1 of the array has n-(p+1) data storage devices and (p+1) parity storage devices. Lastly, row M of the array has N parity storage devices.
Owner:IBM CORP
Application of selecting round key XOR input to perform side-channel power analysis of SM4 cryptographic algorithm
ActiveCN103227717AExtended Side Channel Energy Analysis MethodEfficient analysisEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesComputer hardwareChannel power
The invention discloses an application of selecting round key XOR input to perform side-channel power analysis of an SM4 cryptographic algorithm. The application is characterized in that in the process of the side-channel power analysis of the SM4 cryptographic algorithm, S boxes or round functions are selected to serve as attack points to establish a Hamming distance (HD) model, the round key XOR input is taken as a preceding state v1 of the HD model, and when the S boxes are attacked, the subsequent state v2 of the HD (v1, v2) model is S box output; and when the round functions are attacked, the subsequent state v2 of the HD (v1, v2) model is output / input of the round functions. The method can be applied to the side-channel power analysis of a CPA (correlation power analysis) and DPA (differential power analysis) of the SM4 cryptographic algorithm. With the adoption of the method, the correlation between a right guessing secret key and a power message is improved, the effectiveness of the analysis is enhanced, and the success rate is increased.
Owner:国家密码管理局商用密码检测中心
System and method for generating many ones codes with hamming distance after precoding
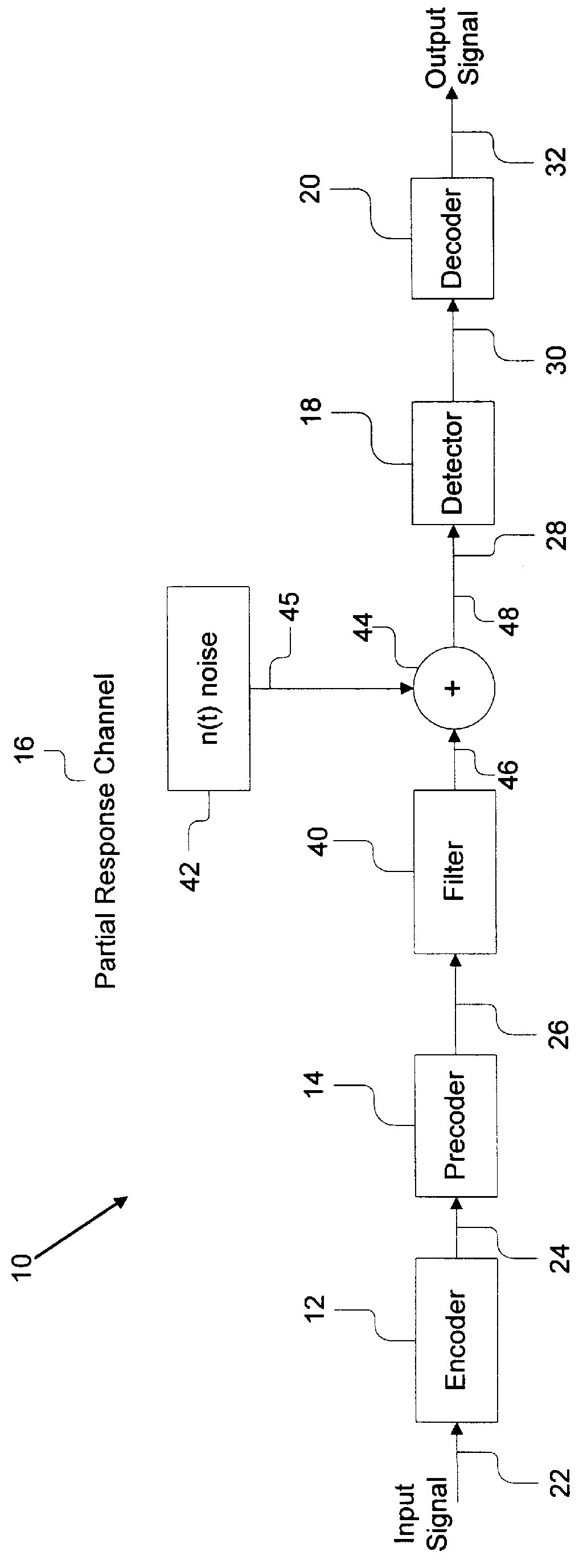
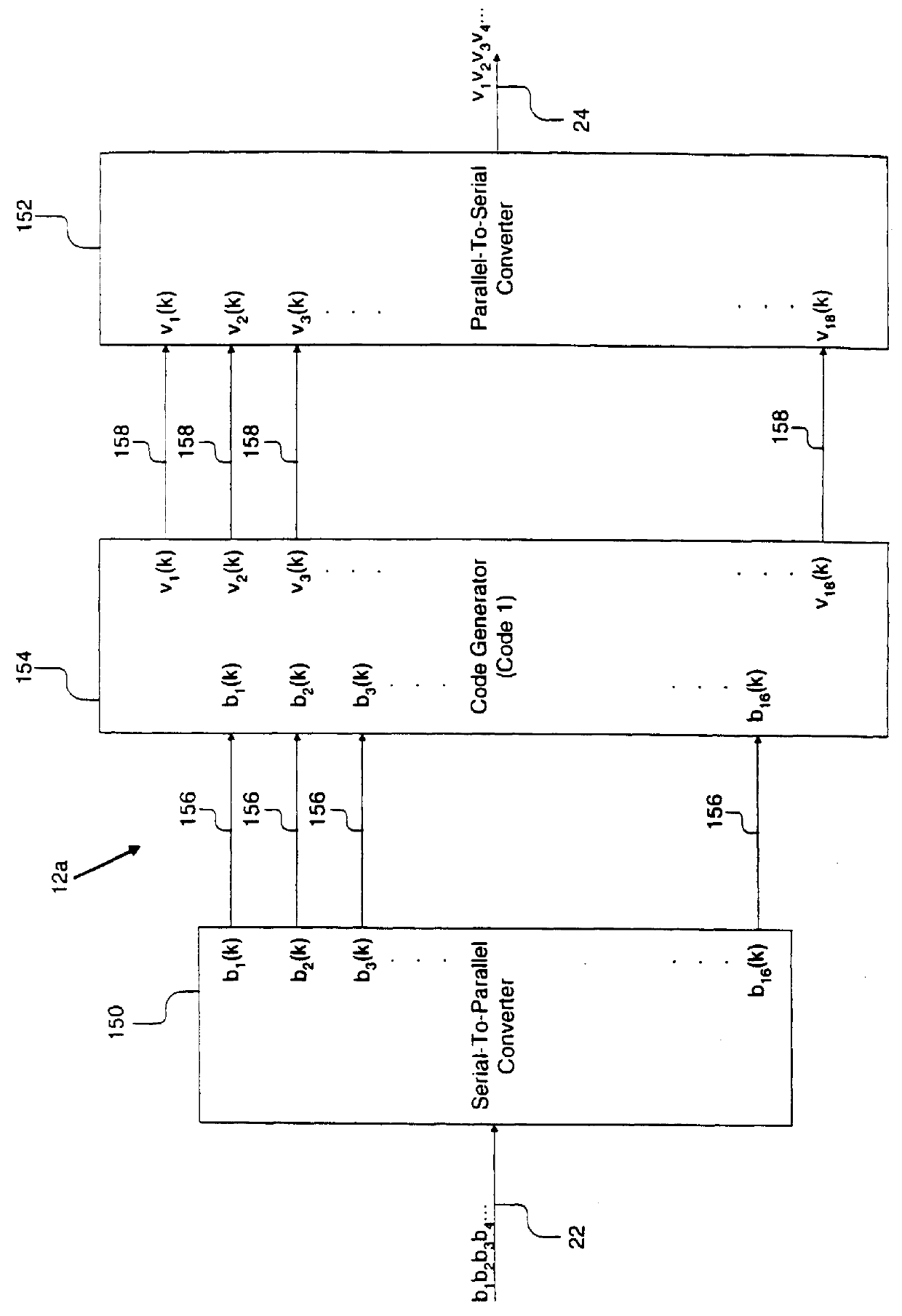
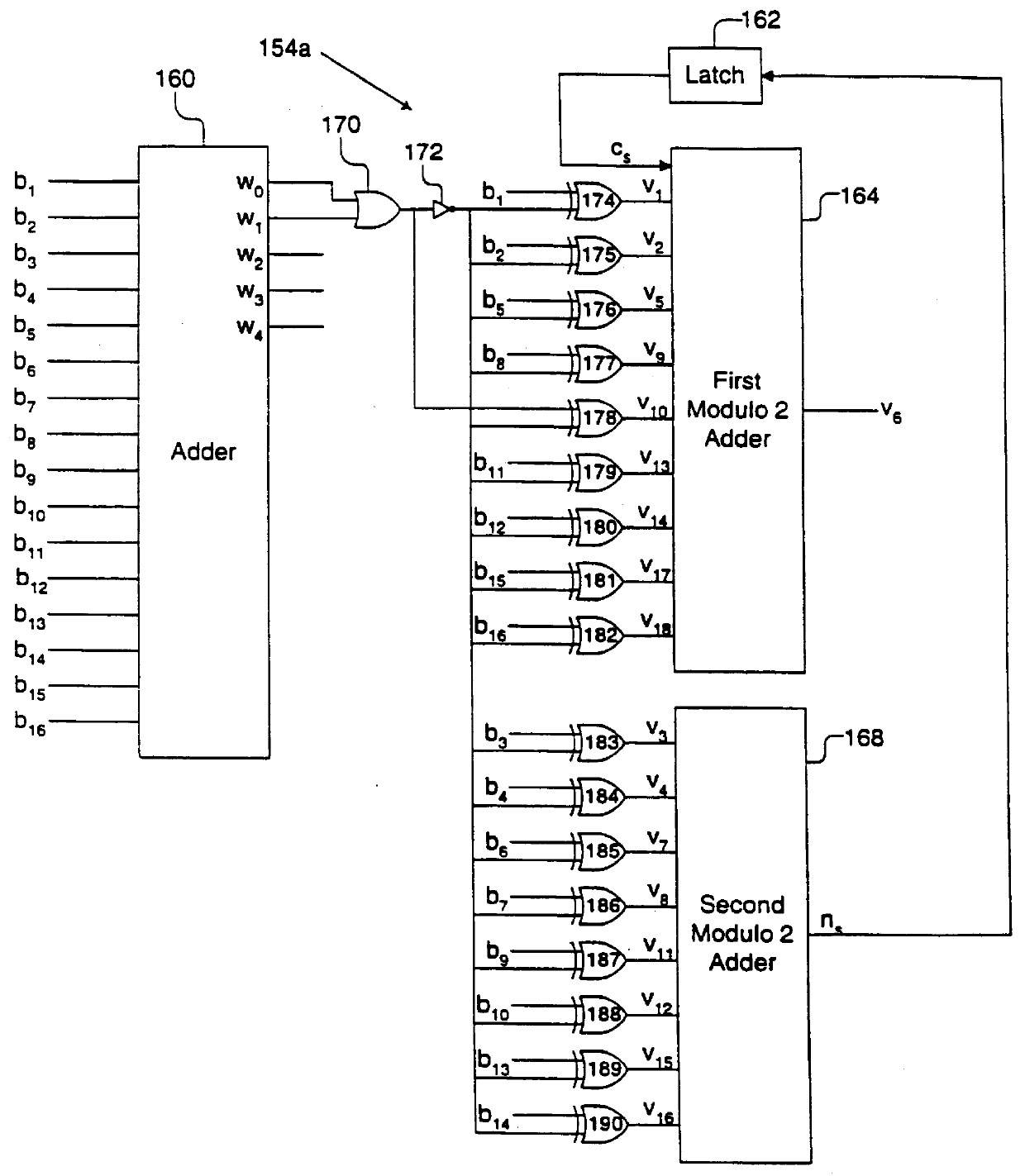
InactiveUS6084535AModification of read/write signalsRecord information storagePrecodingComputer hardware
A system comprises an encoder, a precoder, a PRML channel, a detector, and a decoder. An input signal is received by the encoder. The encoder generates a code string by adding one or more bits and outputs the code string to the precoder. The encoder applies encoding such that the code string after passing through the precoder has a Hamming distance greater than one to eliminate error events with a small distance at the output of the PRML channel. The present invention also provides codes that after precoding have Hamming distance of 2 and 0 mod 3 number of ones. These codes when used over a PRML channel in an interleaved manner preclude + / -( . . . 010-10 . . . ) error events and error events + / -( . . . 01000-10 . . . ). The code string also has a predetermined minimum number of ones at the output of the PRML channel to help derive a clock from the input signal. The encoder provides a "systematic" encoding scheme in which for many code strings the encoded bits are the same as the input bits used to generate the encoded bits. This systematic approach of the present invention provides an encoder that is easy to implement because a majority of the bits directly "feed through" and non-trivial logic circuits are only needed to generate the control bits. The systematic encoding also dictates a decoder that is likewise easy to construct and can be implemented in a circuit that simply discards the control bit. The encoder preferably comprises a serial-to-parallel converter, a code generator, and a parallel-to-serial converter. The code generator produces a rate 16 / 18 or 16 / 17 code. The present invention also includes a method that is directed to encoding bit strings and comprises the steps of: 1) converting the input strings to input bits, and 2) adding at least one bit to produce an encoded string with many ones and a Hamming distance greater than one after precoding.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com