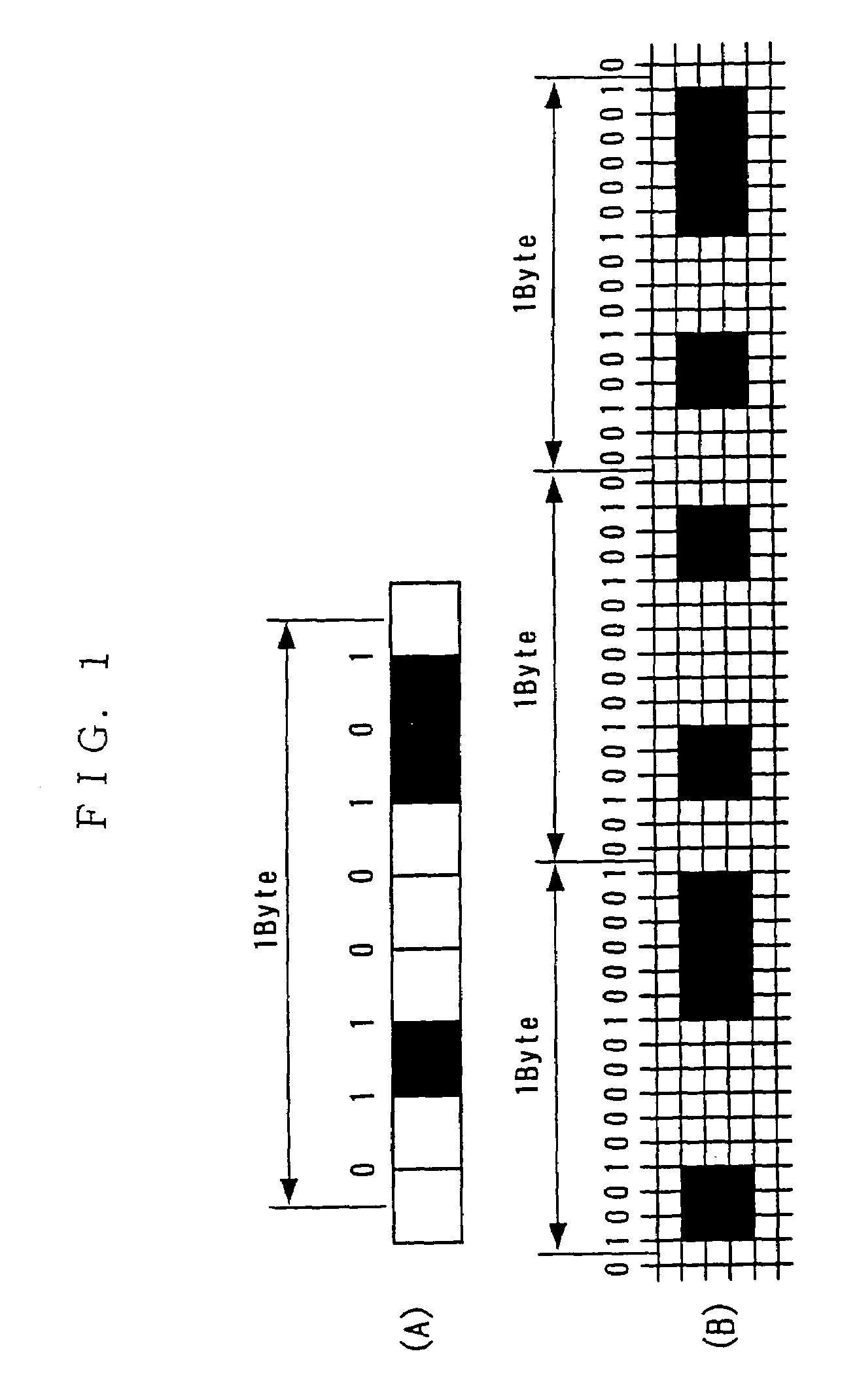
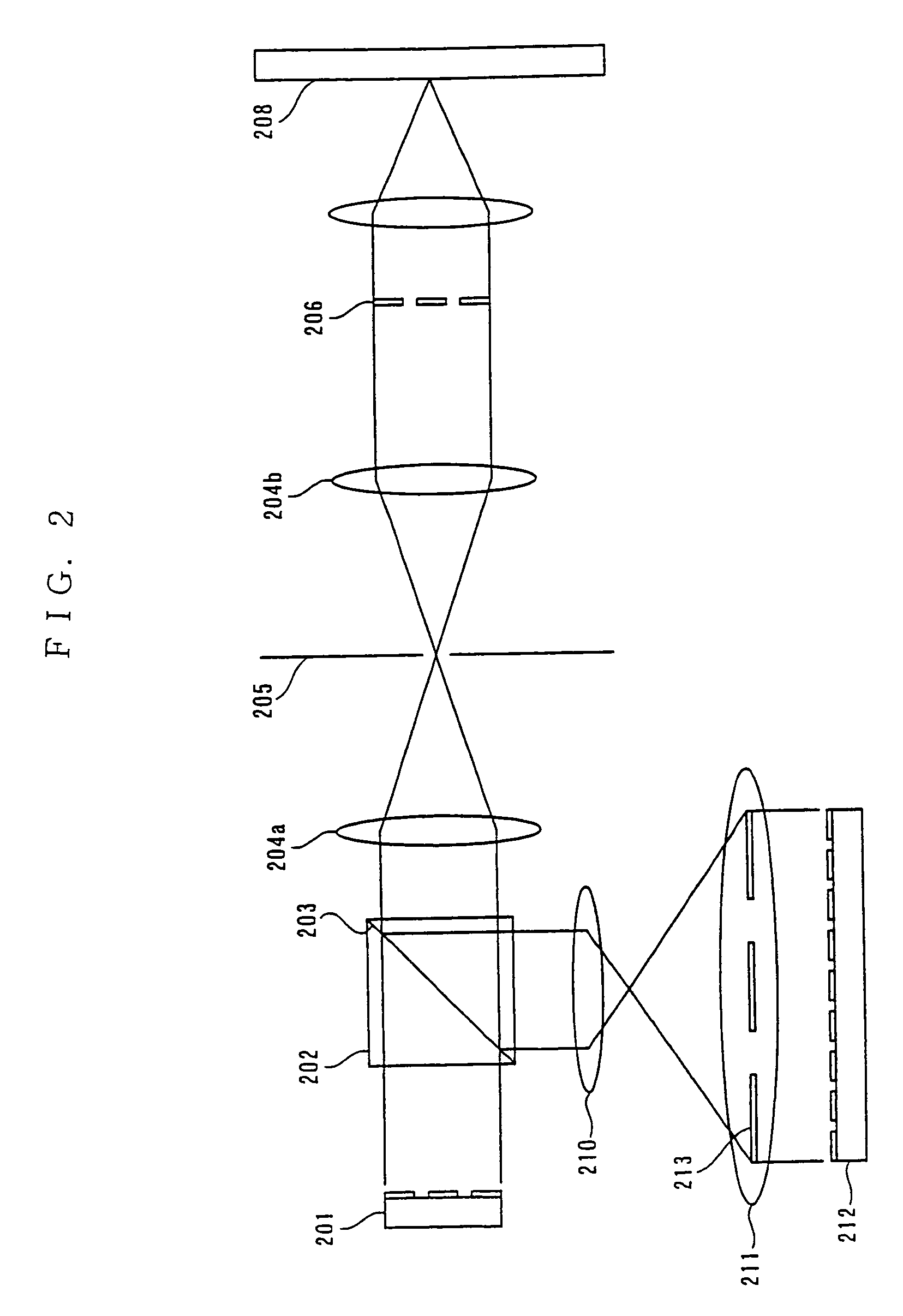
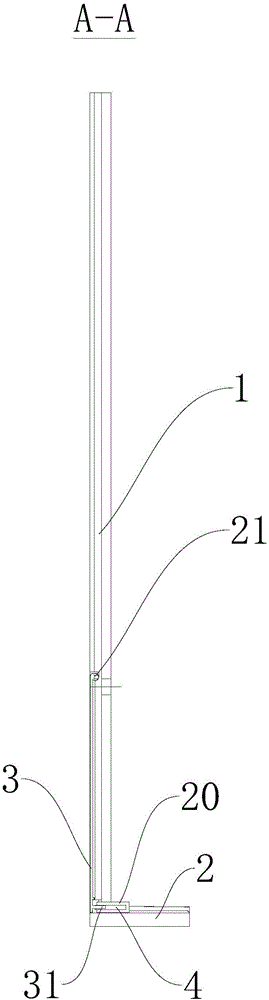
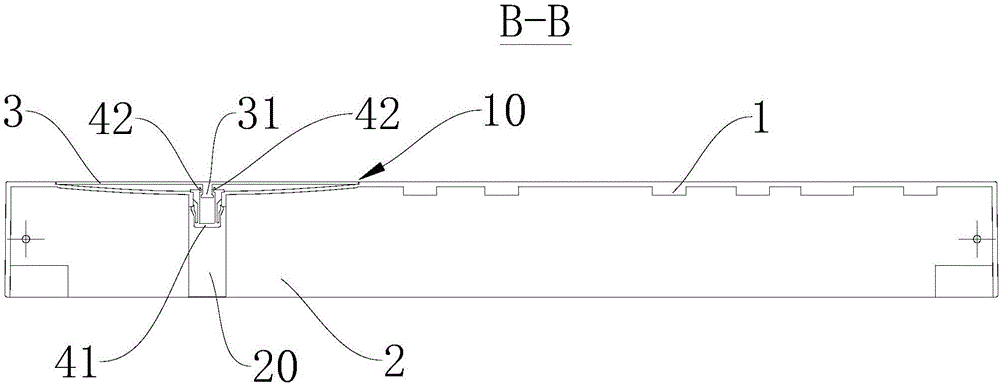
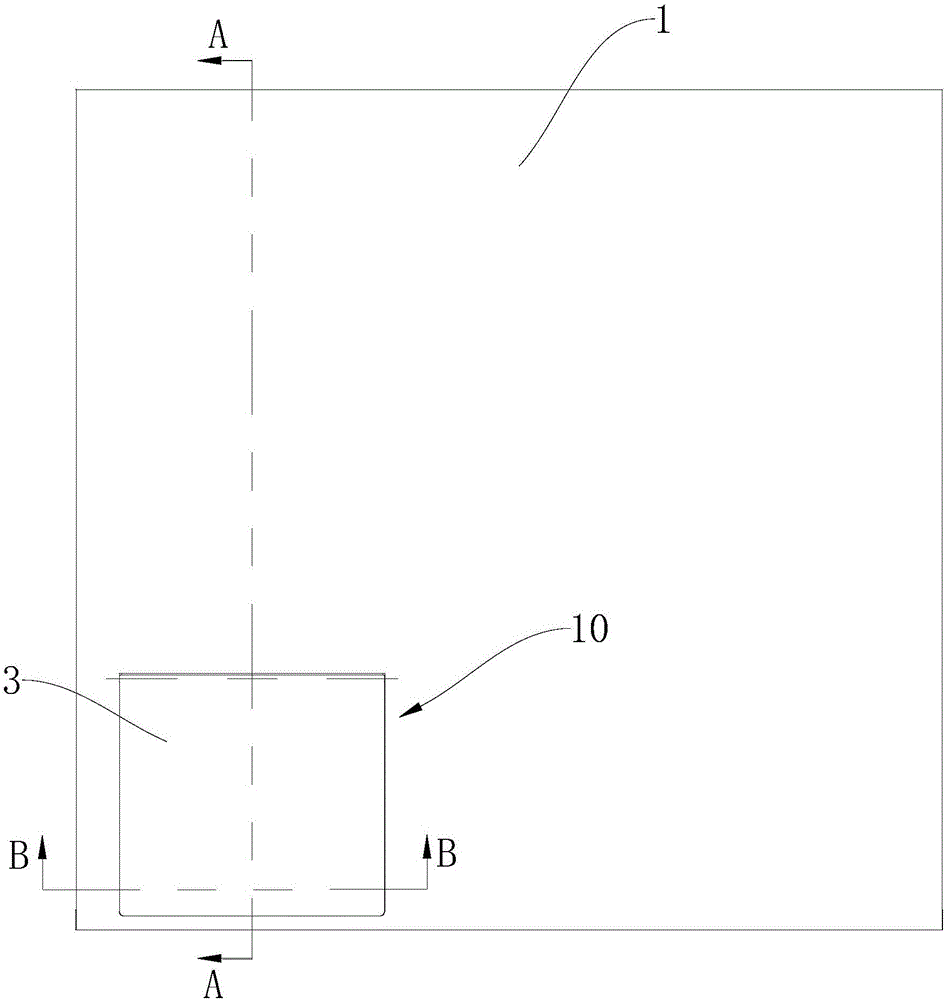Patents
Literature
31 results about "Match/mismatch" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The match/mismatch hypothesis (MMH) was first described by David Cushing (1969). The MMH "seeks to explain recruitment variation in a population by means of the relation between its phenology—the timing of seasonal activities such as flowering or breeding - and that of species at the immediate lower level", see Durant et al. (2007). In essence it is a measure of reproductive success due to how well the phenology of the prey is able to meet the requirements of its predator. In ecological studies, a few examples include; the seasonal occurrence of breeding bird species to that of their primary prey (Visser et al. 1998, Strode 2003), the interactions between herring fish reproduction and copepod spawning (Cushing 1990), or the relationship between winter moth egg hatching, and the timing of oak bud bursting (Visser & Holleman 2001).
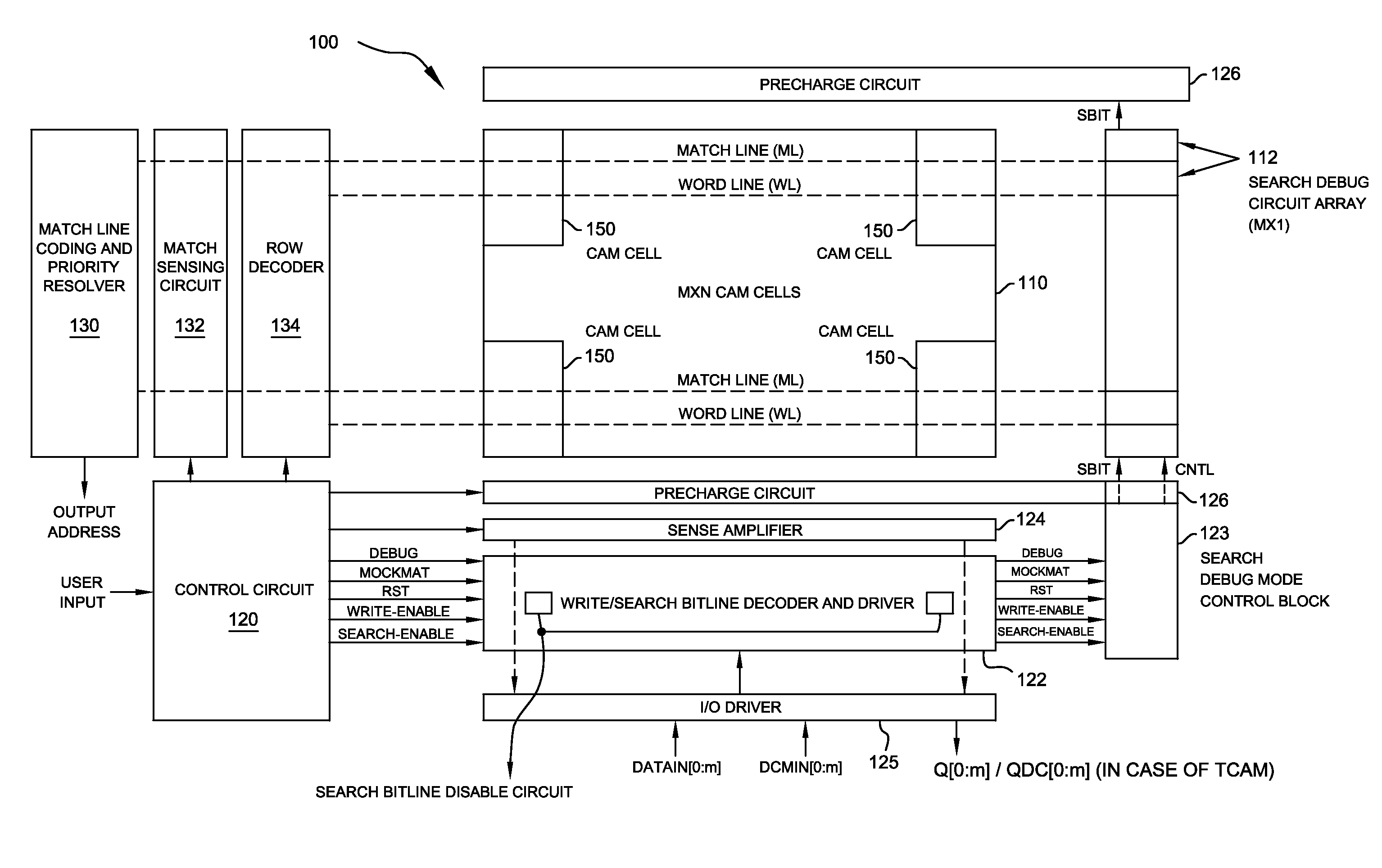
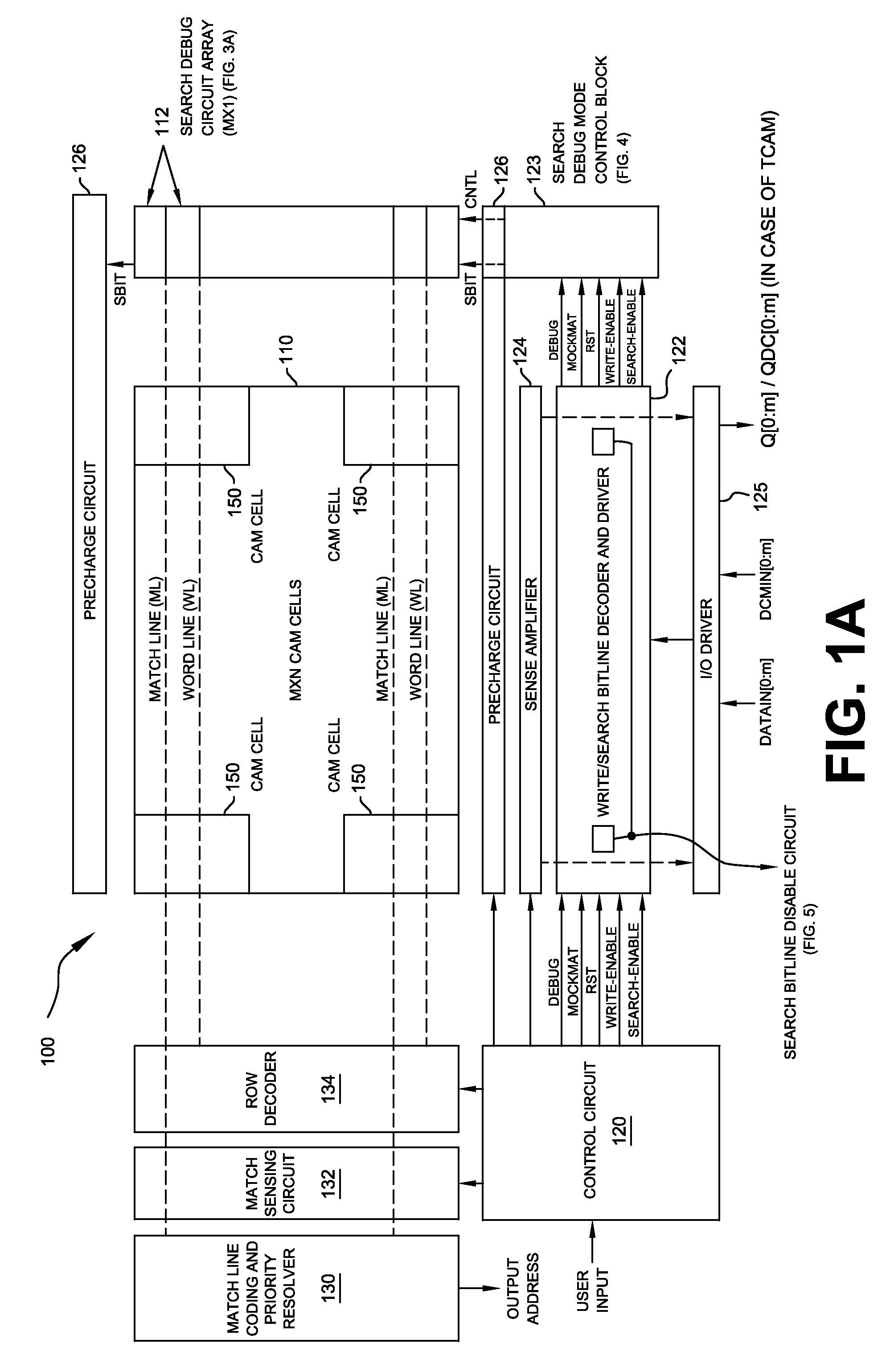
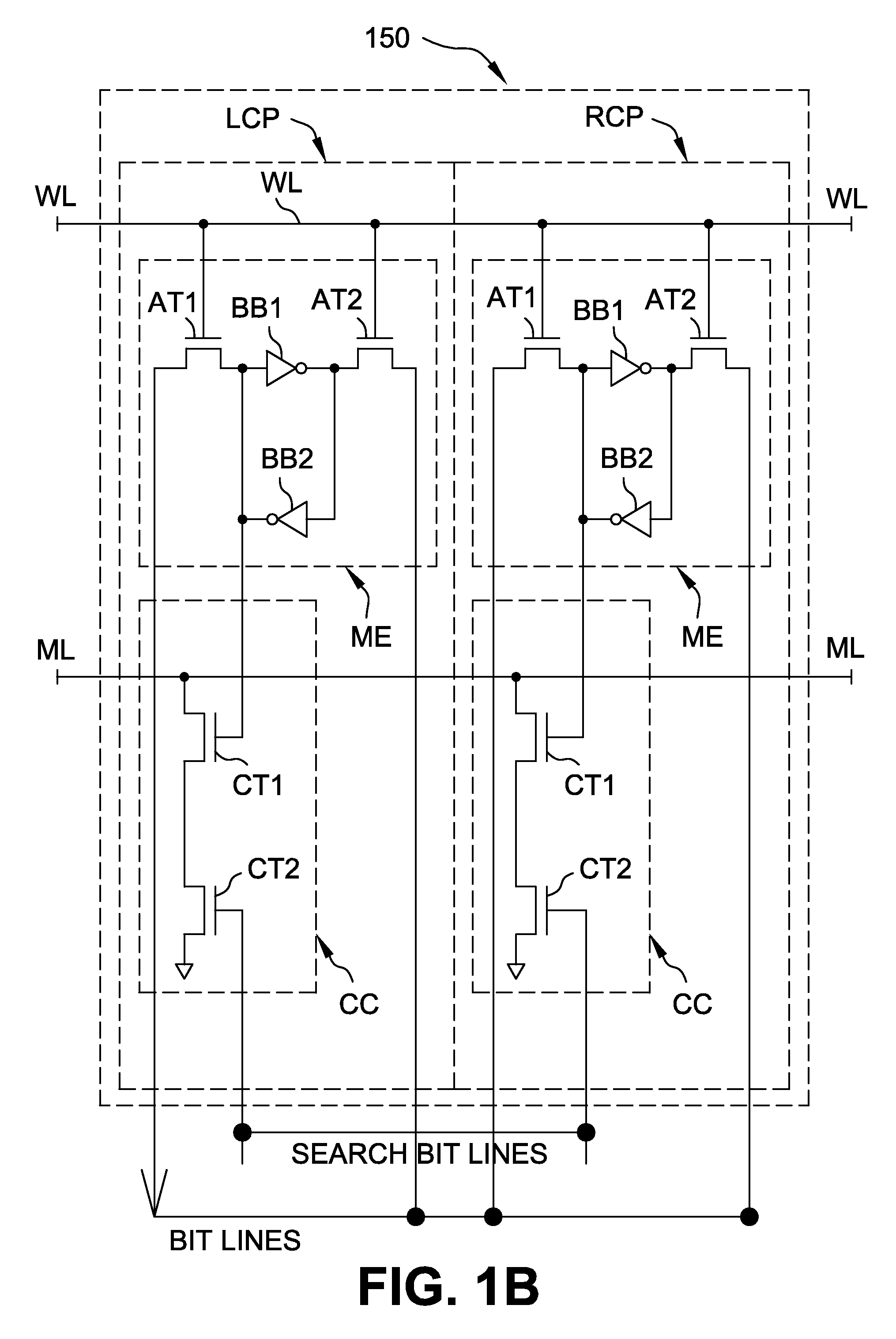
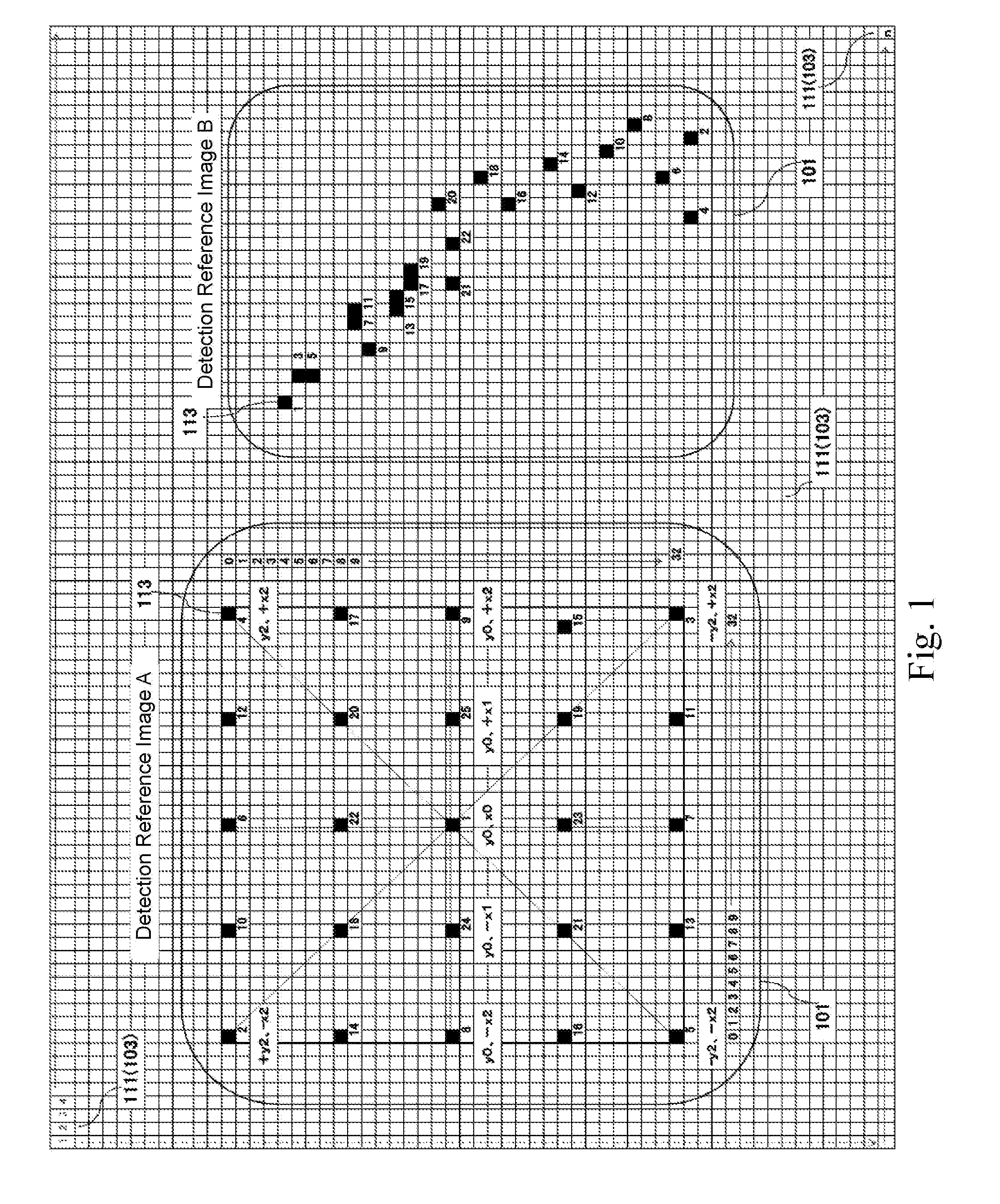
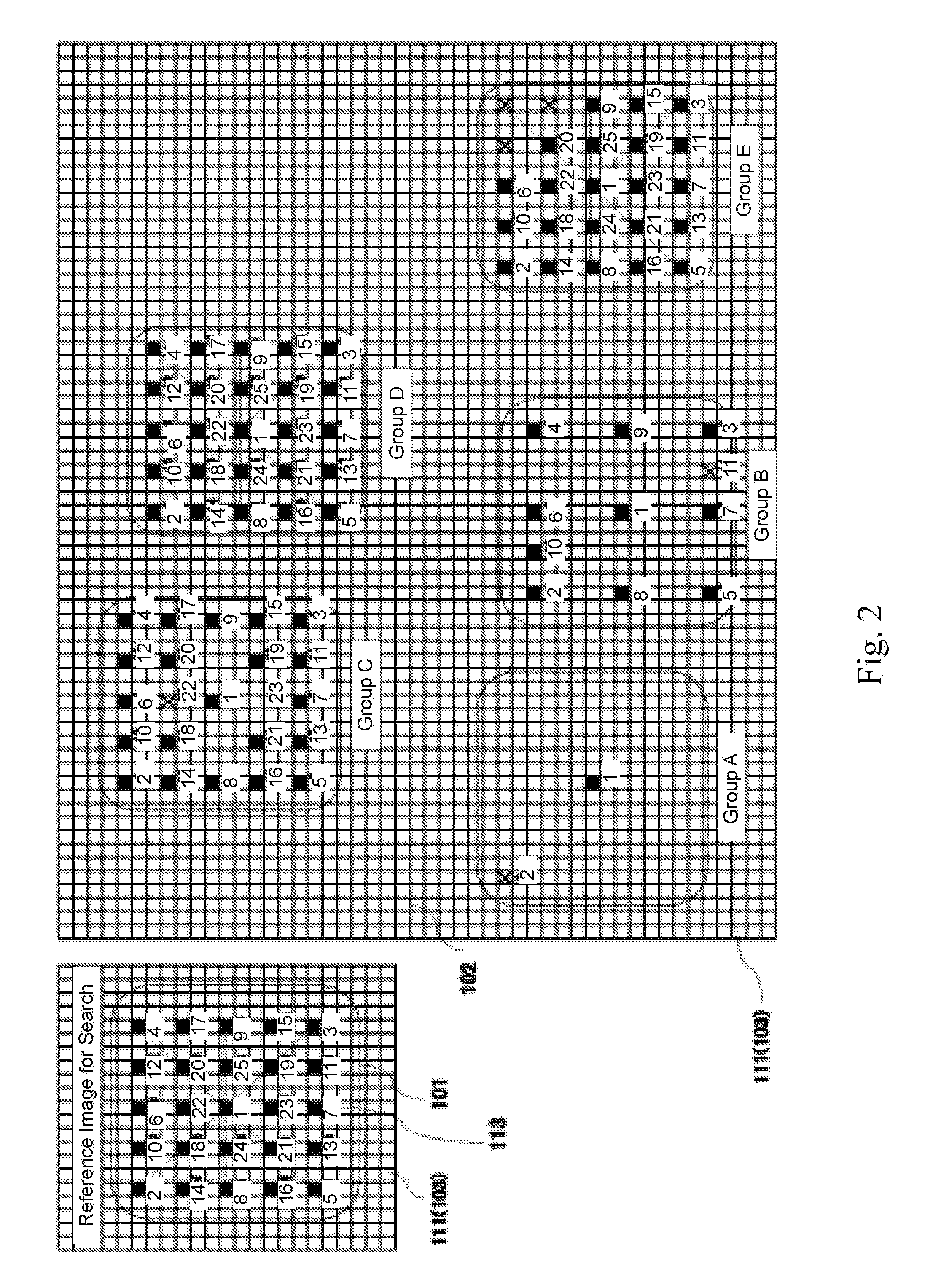
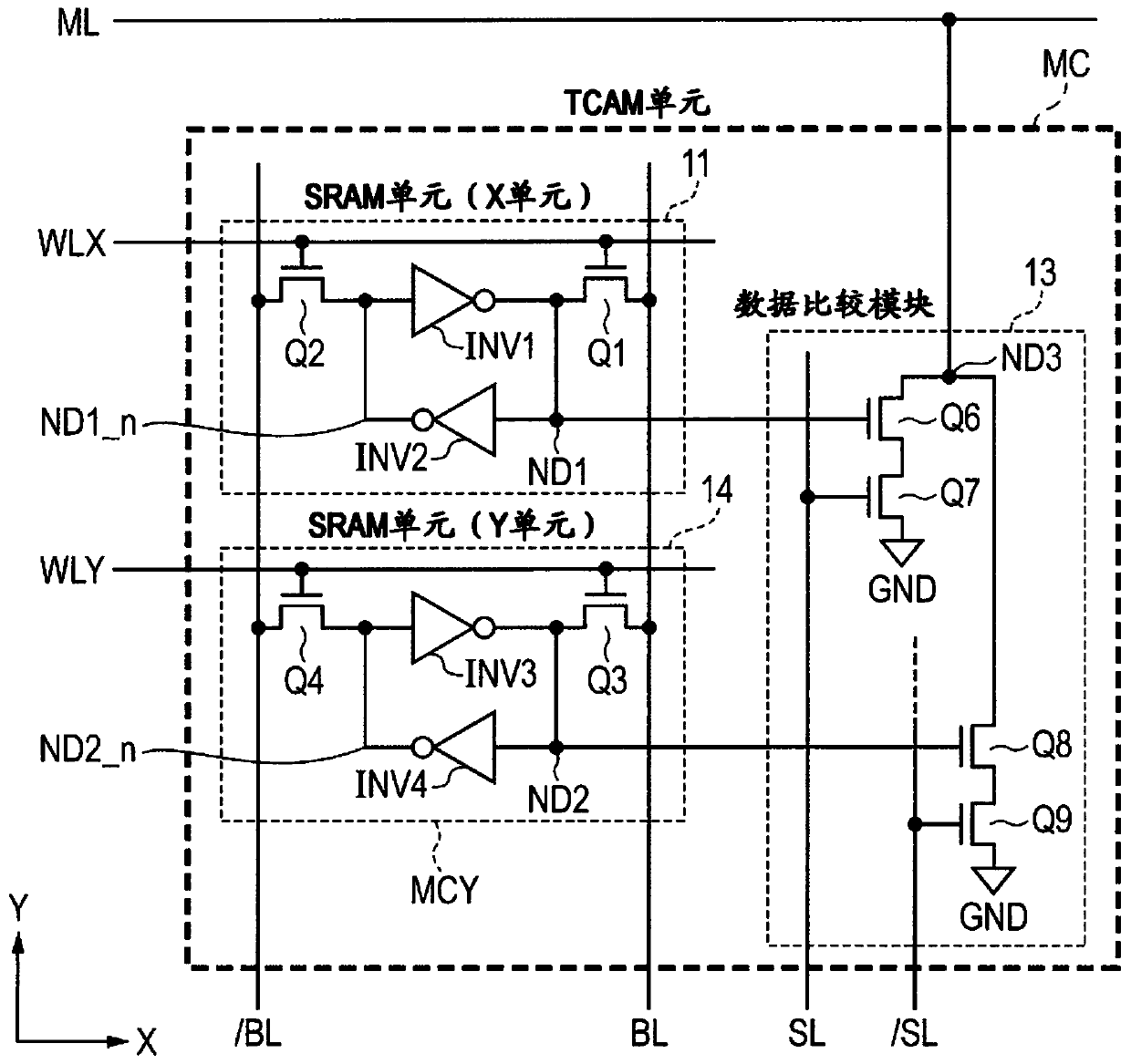
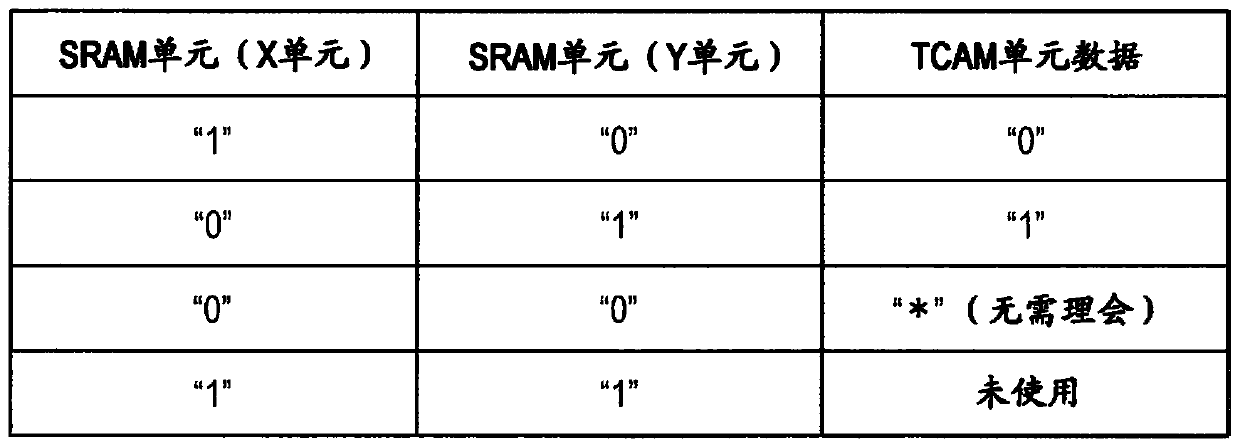
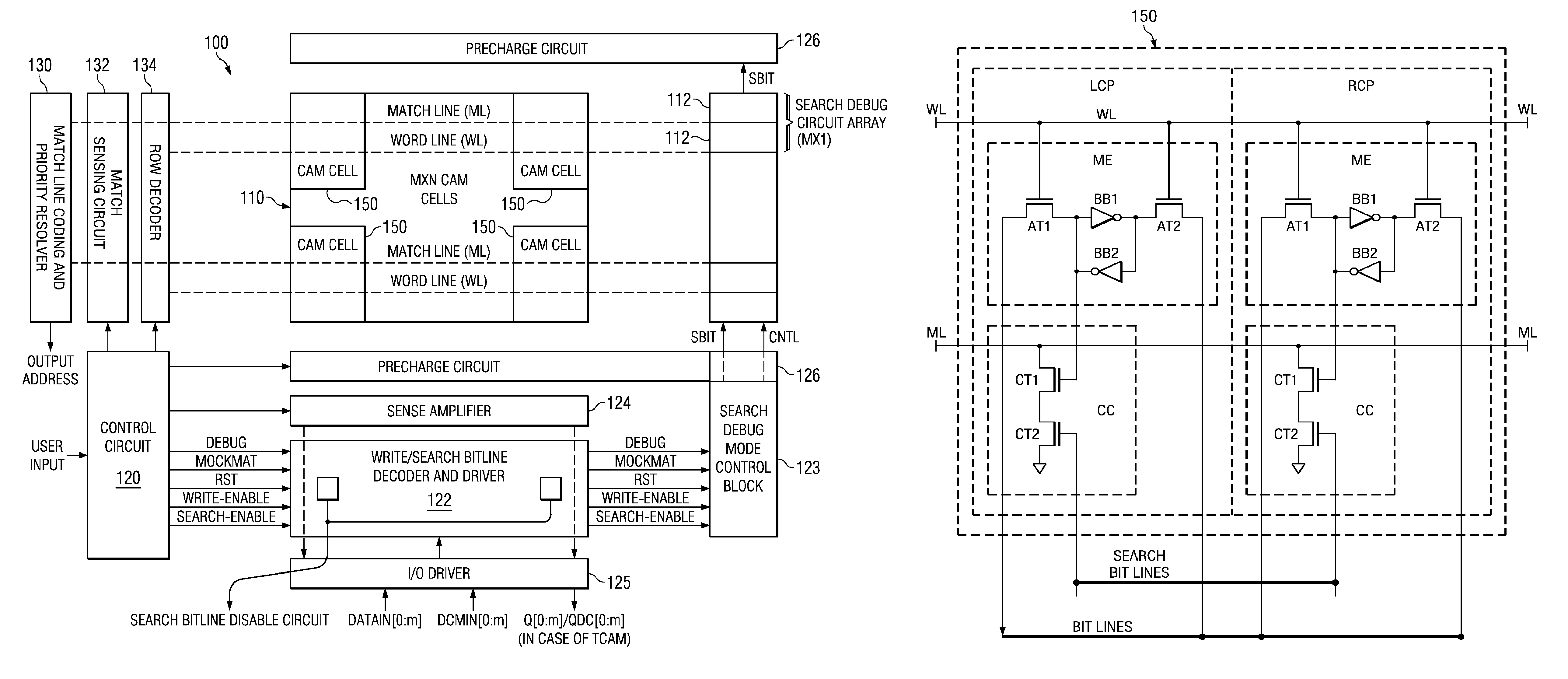
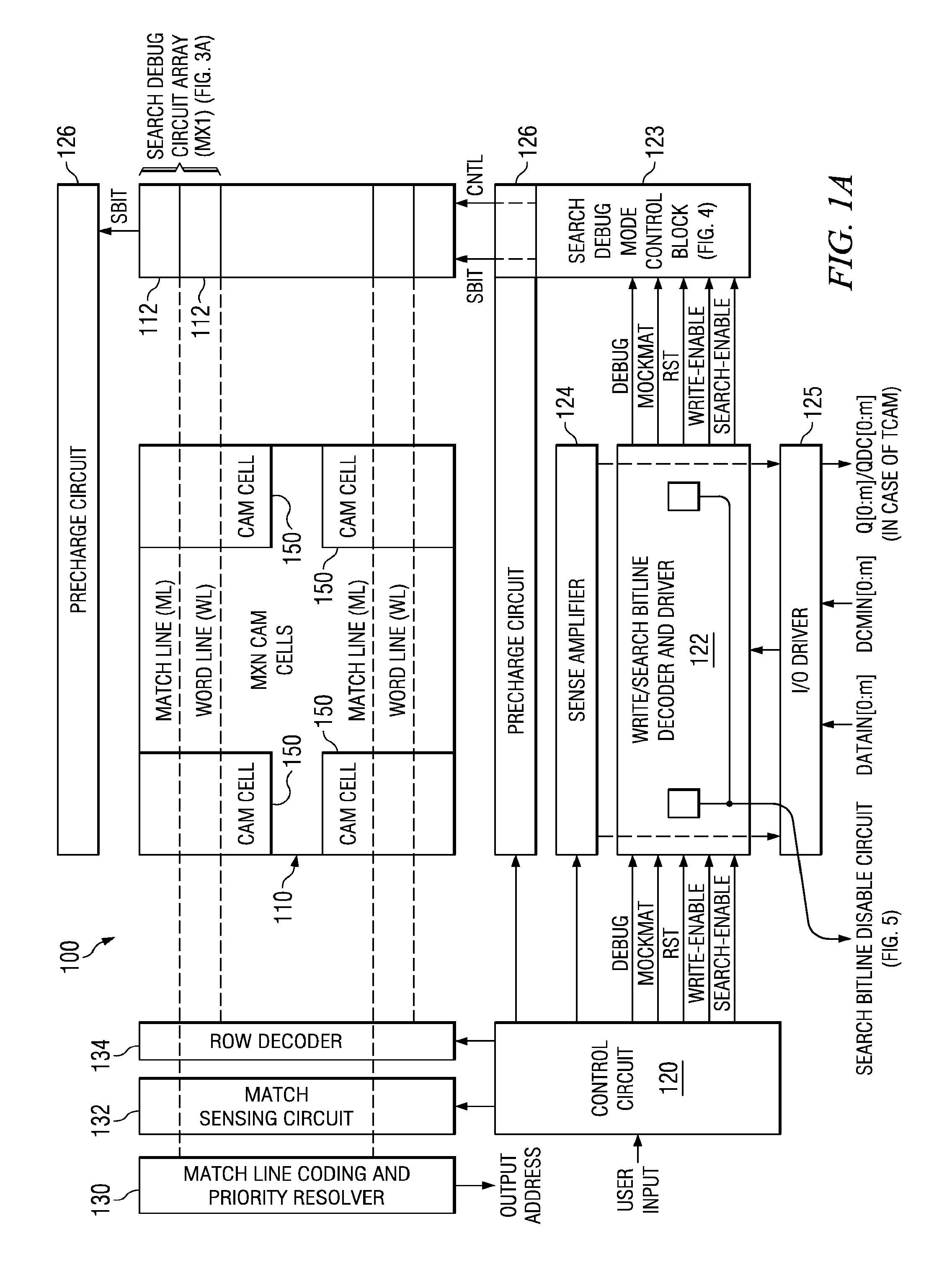
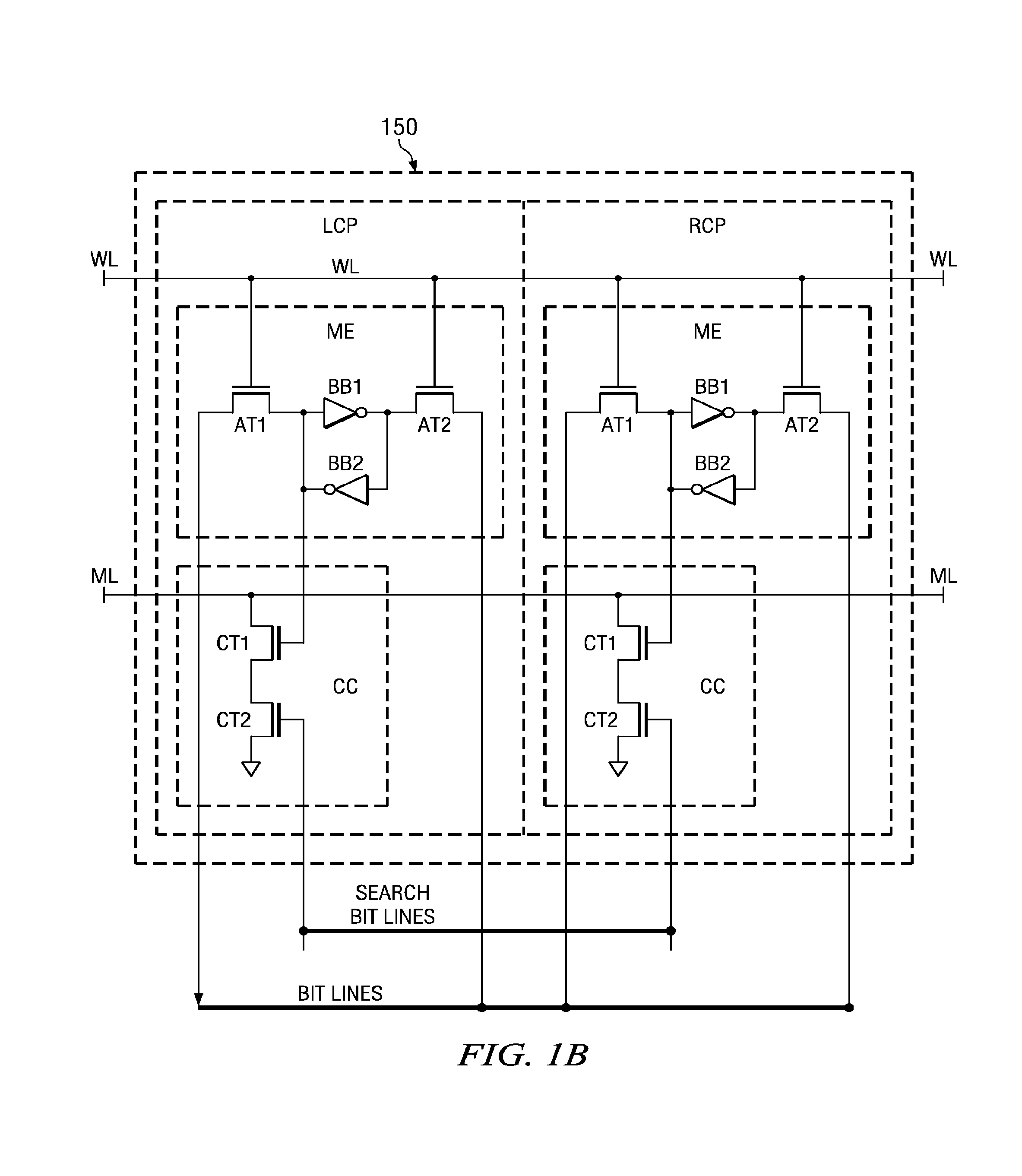
Novel match mismatch emulation scheme for an addressed location in a cam
A novel match / mismatch emulation scheme for an addressed location in a CAM system that includes a plurality of CAM blocks. The plurality of CAM blocks are organized into at least one rectangular array having rows each having a plurality of CAM blocks, a group of CAM cells and associated read / write bit lines connecting the group of CAM cells to an addressed search circuit. During debug mode, where the individual array cells do not participate in search, all the cells in the debug column behave the same way to emulate a match / mismatch on all words. The circuit provides a control input to include address evaluation of a debug cell in a row. The circuit also provides simultaneous switching noise analysis on an evaluating row. The resulting CAM cell provides a circuit to test individual rows for defects and noise analysis.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Information recording method, reproducing method, and recording/reproducing method utilizing holography
InactiveUS7321541B2Improve recording densityIncrease recording capacityRecord information storageDigital storageSpatial light modulatorRecording density
A method for recording information on a recording medium utilizing an interference pattern by interference between an information light modulated spatially with digital pattern information displayed on a spatial light modulator having multiple pixels and a reference light for recording. In order to provide a novel recording method capable of enhancing the recording density and the transfer rate furthermore, digital information to be recorded is represented by match / mismatch of the attributes of adjacent pixels in the spatial light modulator to produce digital pattern information.
Owner:OPTWARE
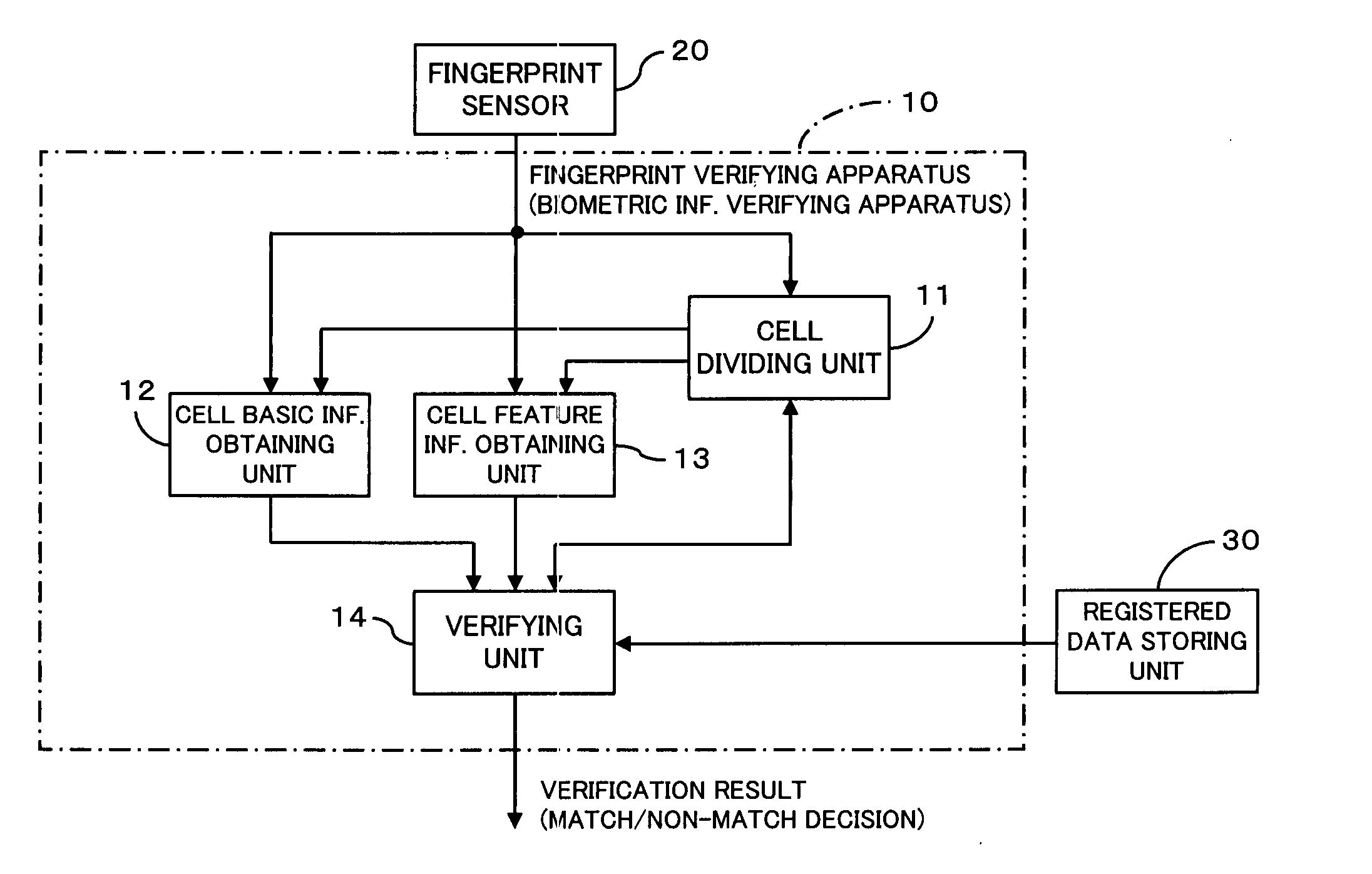
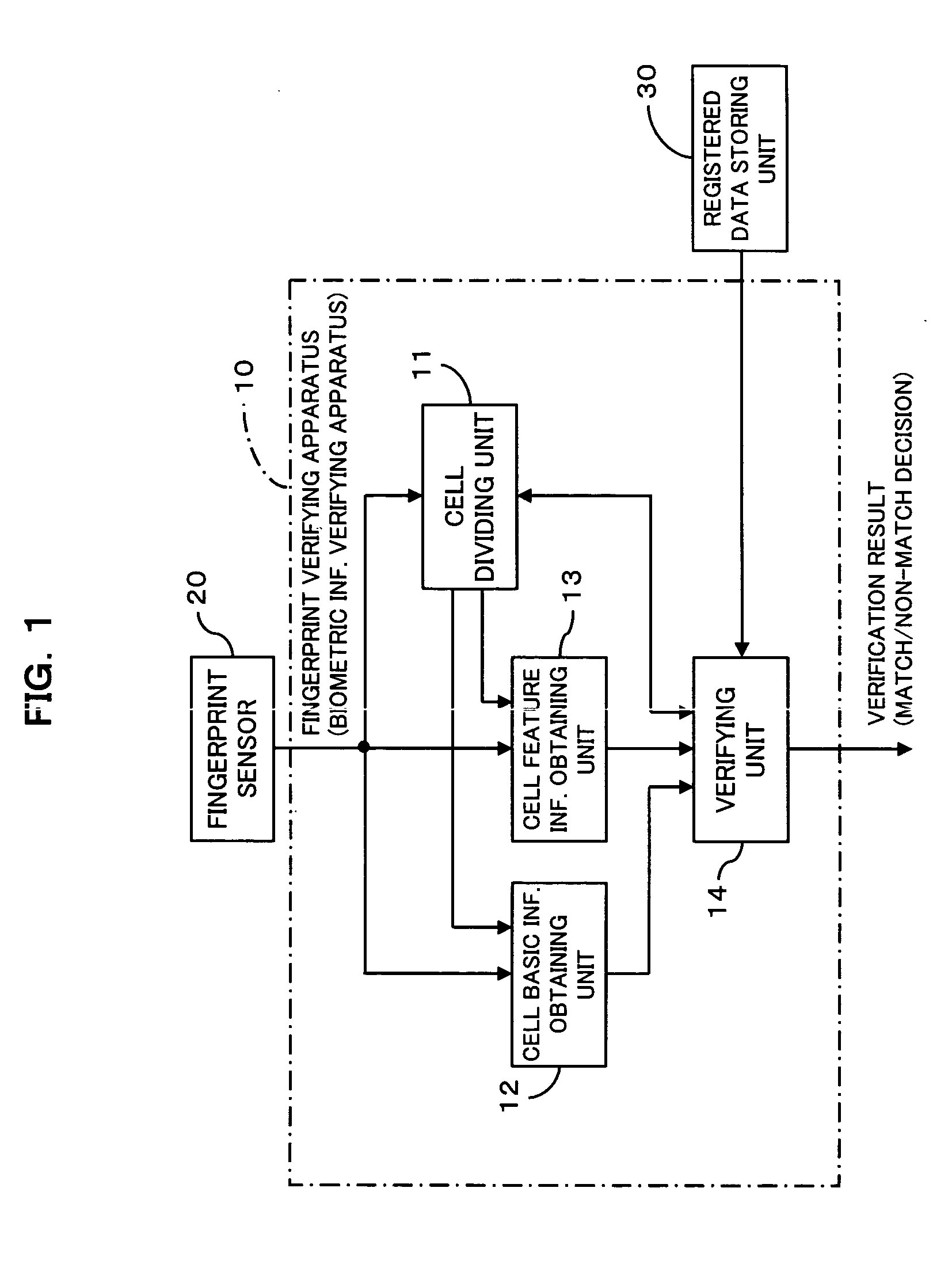
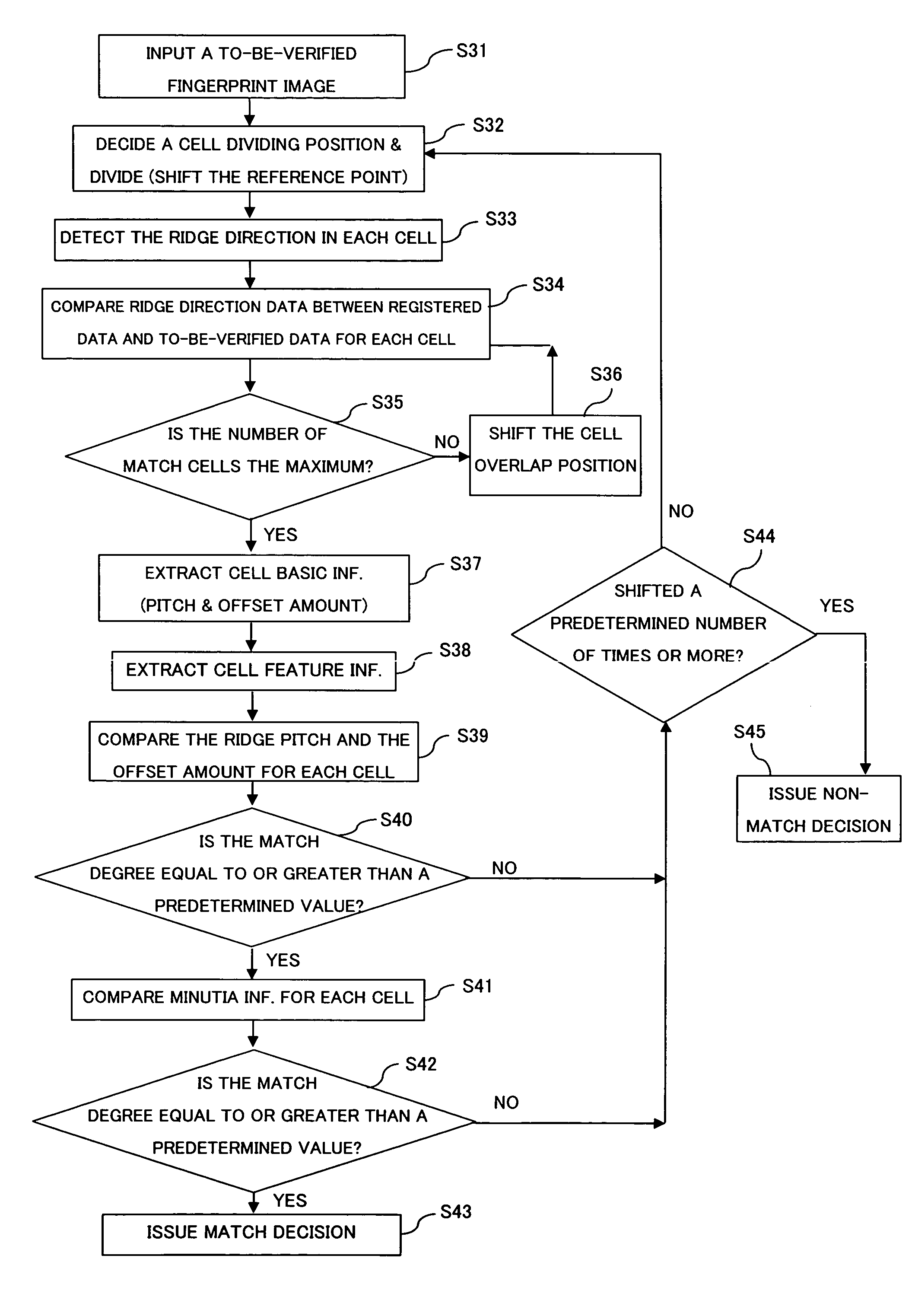
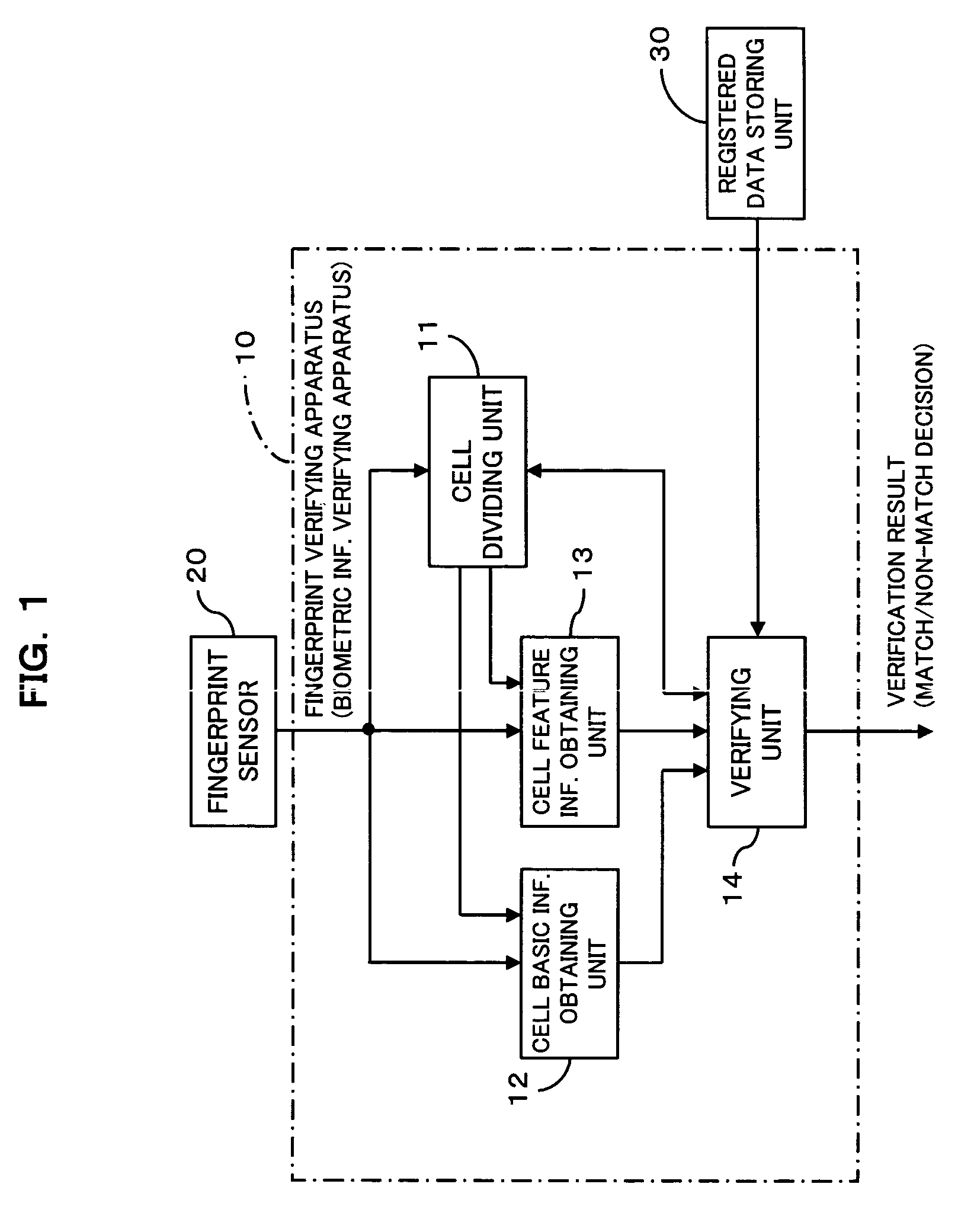
Biometric information verifying apparatus
InactiveUS20050175225A1Decreases false verification rateReduce data volumeImage analysisPerson identificationUser verificationPalm print
The apparatus greatly reduces the registered data amount and the verification computation amount required for user verification, in comparison with the verification using image information itself, and also decreases the false verification rate. The apparatus divides a biometric information image into cells, and extracts minutia information as well as cell basic information from the individual cells. After comparison of direction information of the individual cells of the registered data with direction information of the individual cells of the to-be-verified data, thereby aligning the registered fingerprint image and the to-be-verified fingerprint image, the apparatus compares the minutia information of corresponding cells between the registered data and the to-be-verified data to make a match / non-match decision. Such an apparatus is applicable to systems that employ pattern matching type image verification to perform user verification utilizing biometric information such as fingerprints, palm prints, blood vessel patterns, iris patterns, and facial images.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
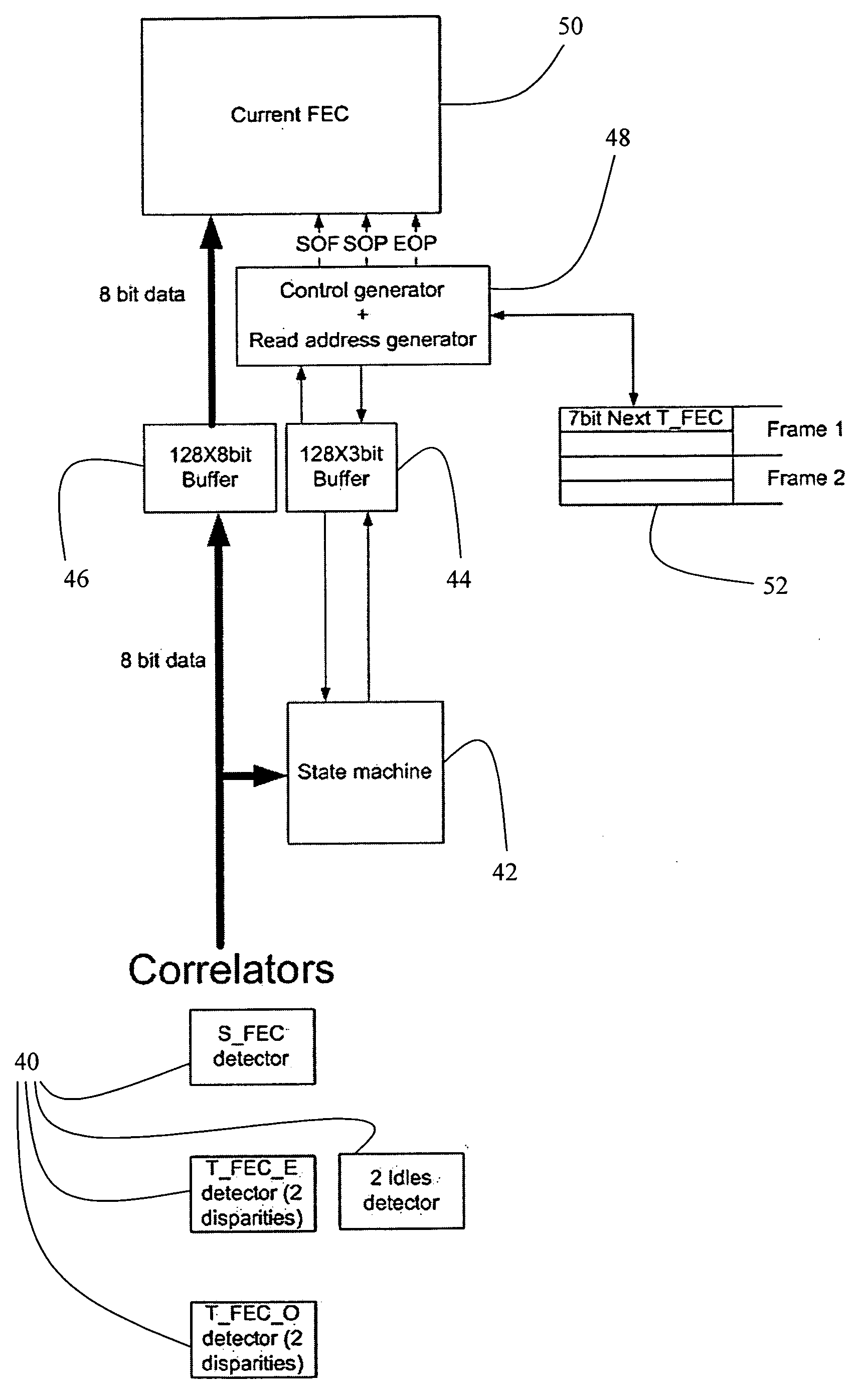
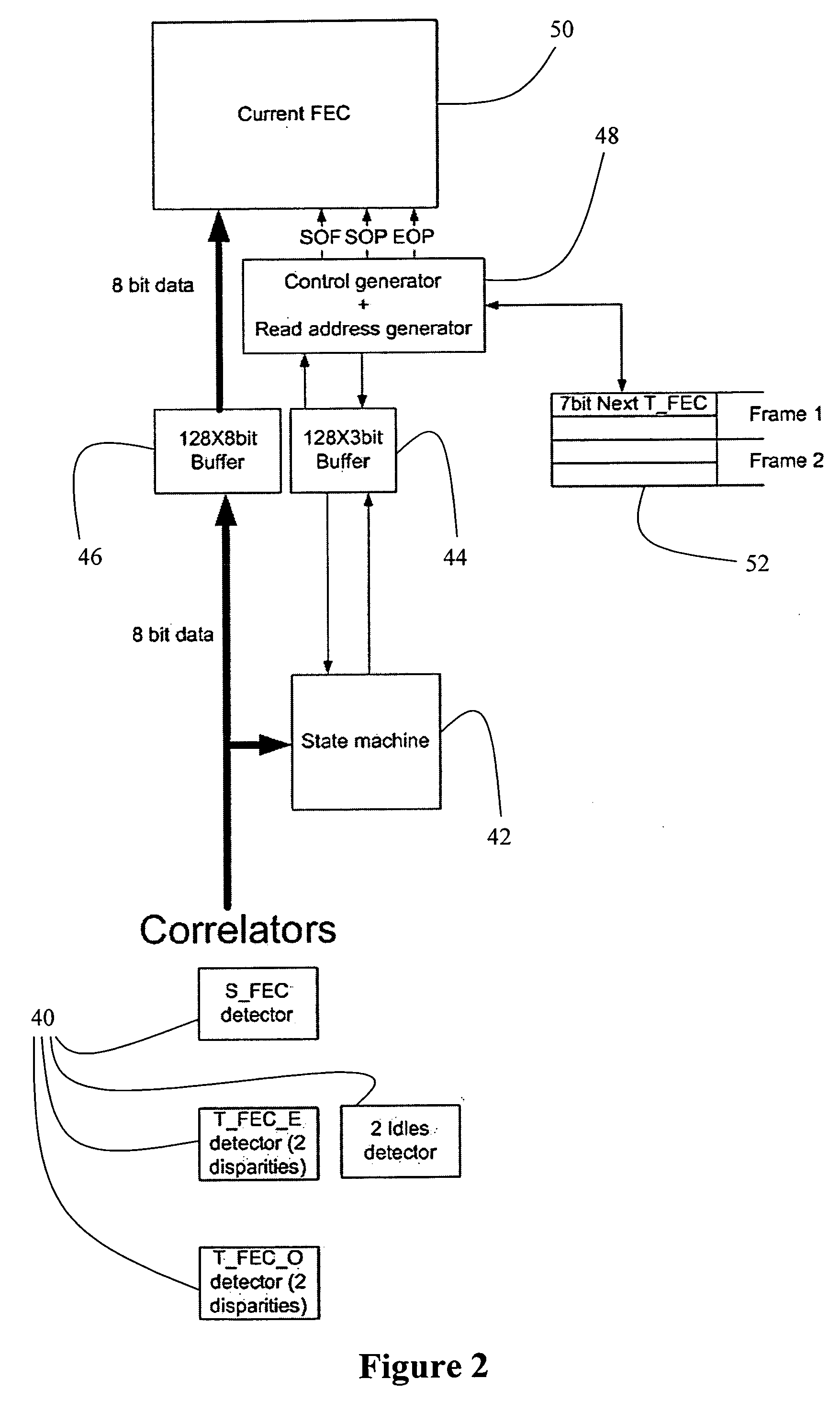
Enhancing the ethernet FEC state machine to strengthen correlator performance
InactiveUS20070206709A1Improving data correlationCode conversionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsMatch/mismatchHamming distance
The present invention discloses devices and methods for improving data correlation using a multiple-correlation state-machine, the method including the steps of: (a) pre-processing a data frame having a plurality of symbol sets, wherein each symbol set demarks a respective frame field of the frame, to provide a threshold-compared hamming-distance indicator; (b) comparing the threshold-compared hamming-distance indicator with at least one multiple-correlation threshold to provide a threshold-compared multiple-correlation indicator; and (c) combining the threshold-compared hamming-distance indicator and the threshold-compared multiple-correlation indicator to determine a match / no-match comparison indicative of the respective frame field. In some embodiments, the step of combining includes forming a logical-AND of the threshold-compared hamming-distance indicator and the threshold-compared multiple-correlation indicator. Preferably, the method further includes the step of: (d) prior to the step of combining, comparing a BER of the frame to a BER threshold. Also disclosed is a weighted-correlation method for improving data correlation.
Owner:PMC SIERRA ISRAEL
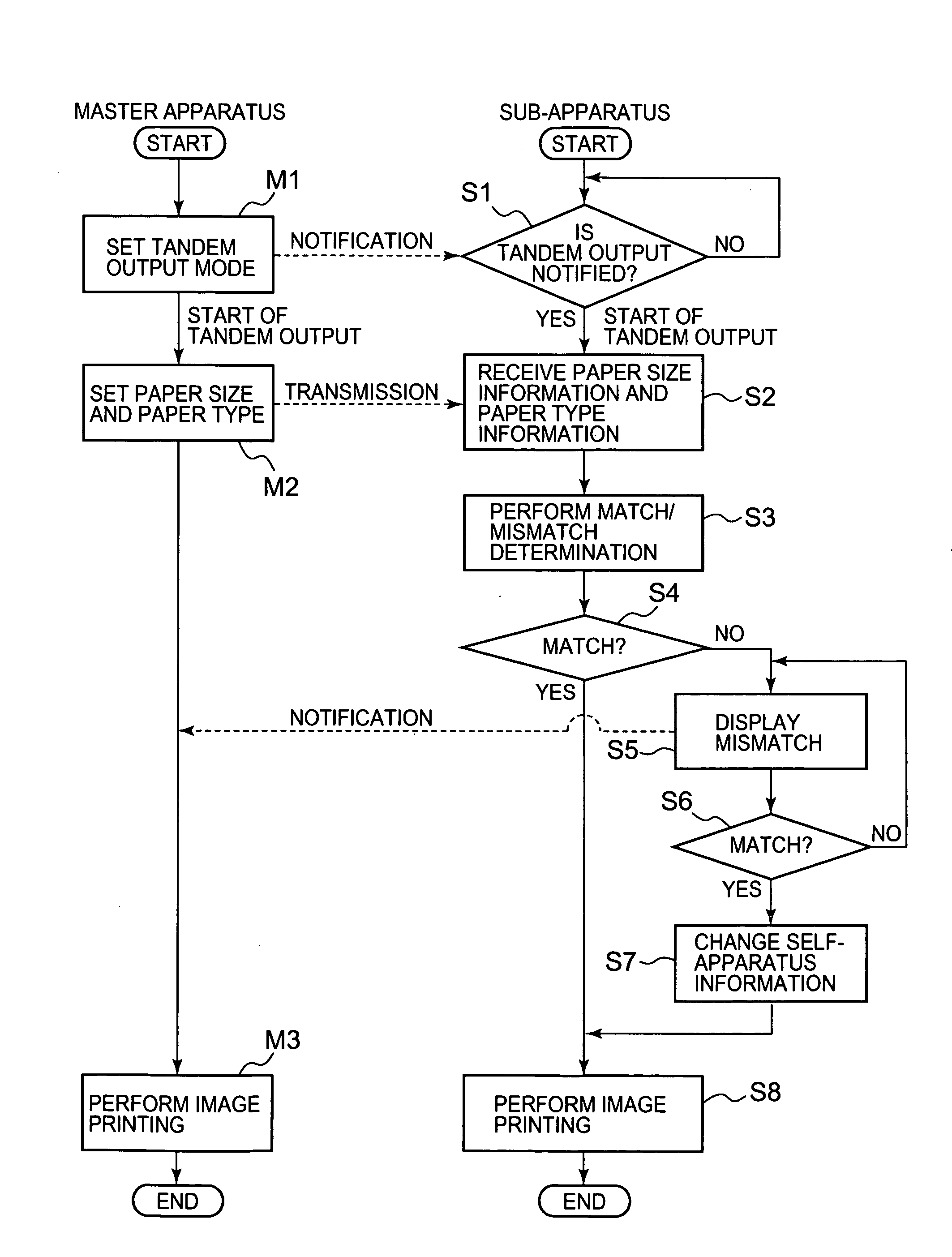
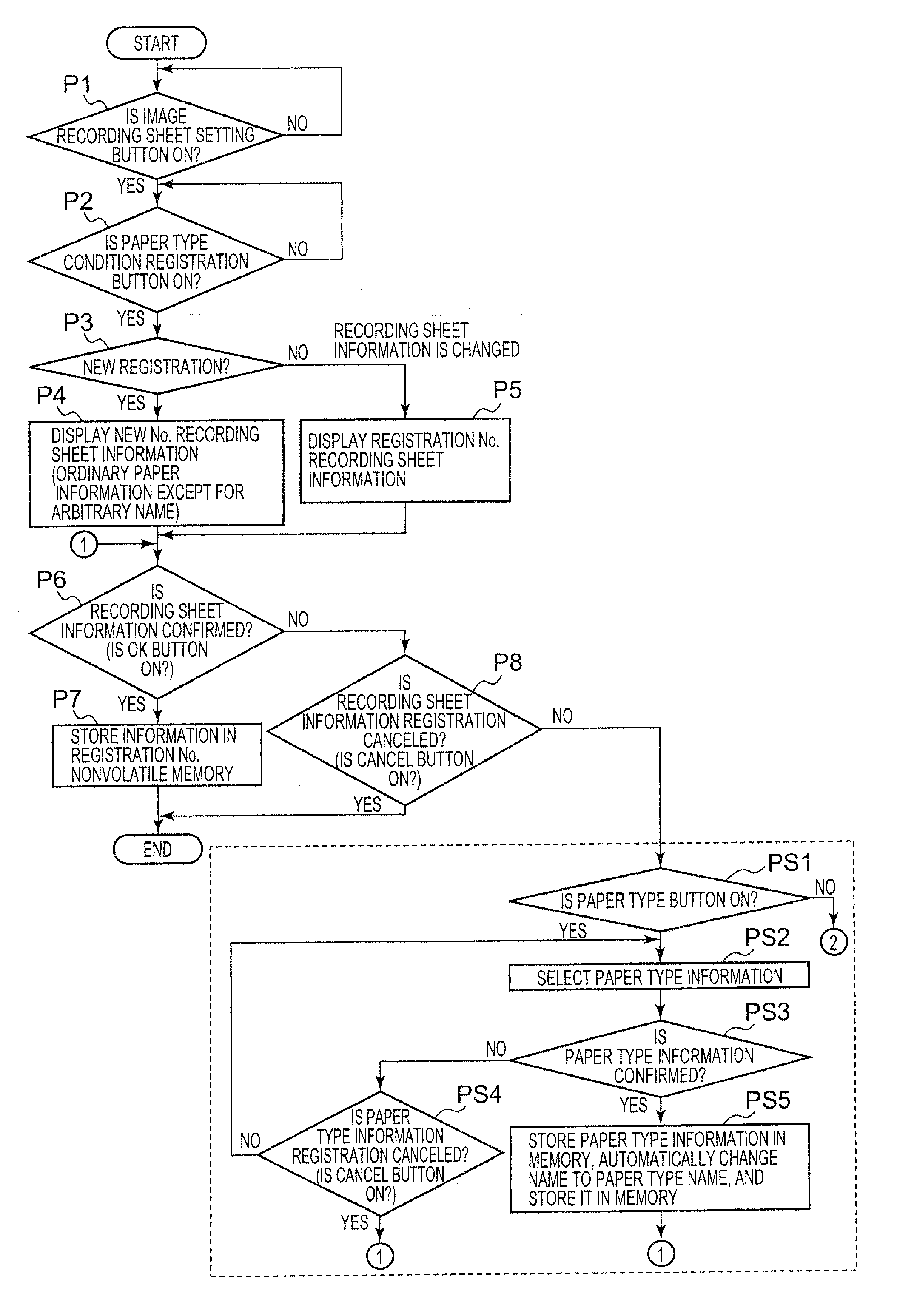
Image printing apparatus and tandem image printing method
InactiveUS20060262337A1Reliable outputEasy to knowDigital output to print unitsCommunication unitPulp and paper industry
This invention provides an image printing apparatus including a communication unit which communicatively connects to at least another image printing apparatus, a tandem output mode, a paper feed unit which feeds recording sheets, a comparison and determination unit which compares the information of recording sheets which can be fed from the paper feed unit with paper size information and paper type information in another image printing apparatus which has received by the communication unit in the tandem output mode, and determines a paper size match / mismatch and a paper type match / mismatch, and a mismatch notification unit which notifies a mismatch when one or both of the paper size and the paper type exhibits a mismatch upon receiving a determination result from the comparison and determination unit.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA BUSINESS TECH INC
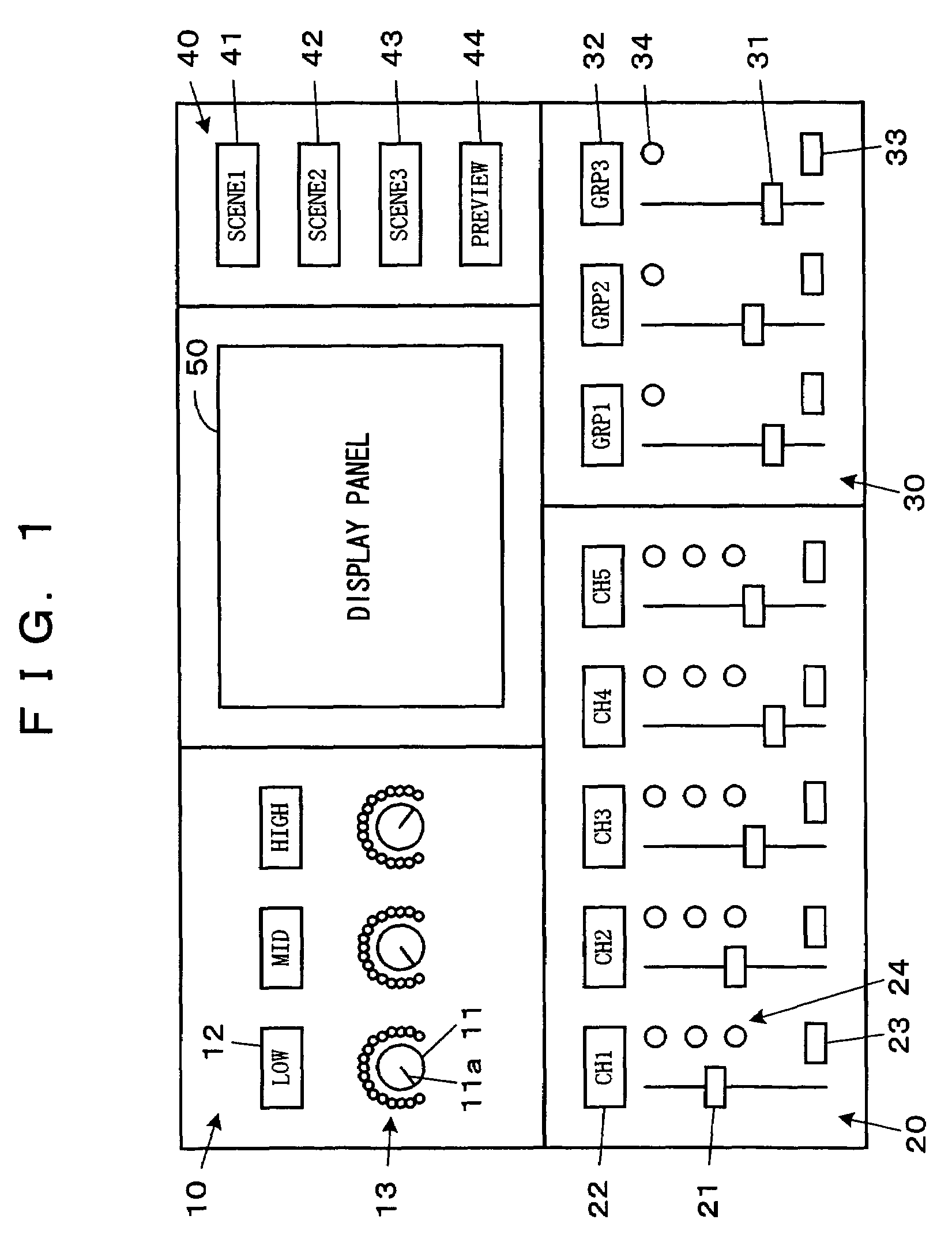
Audio signal processing device
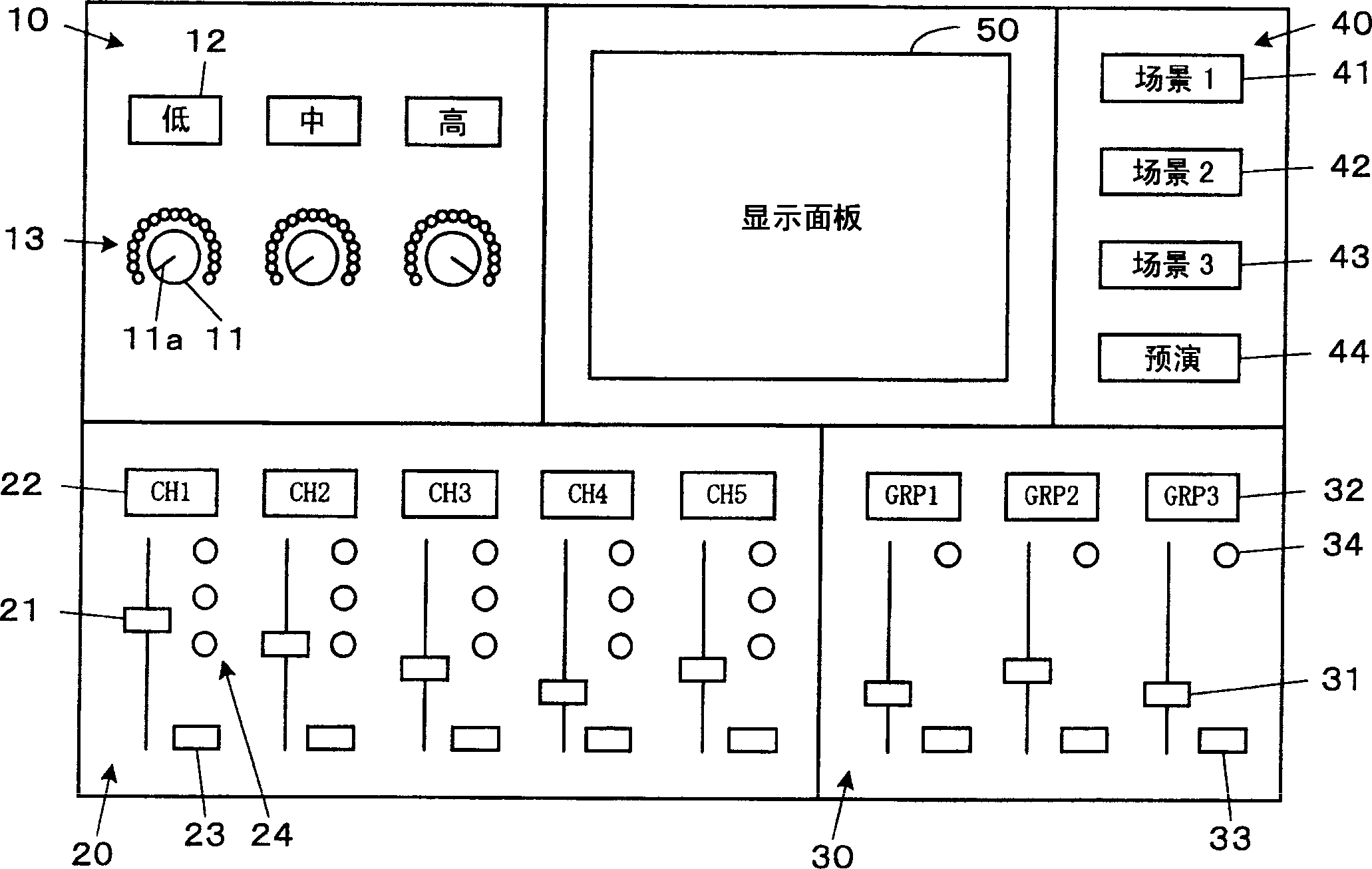
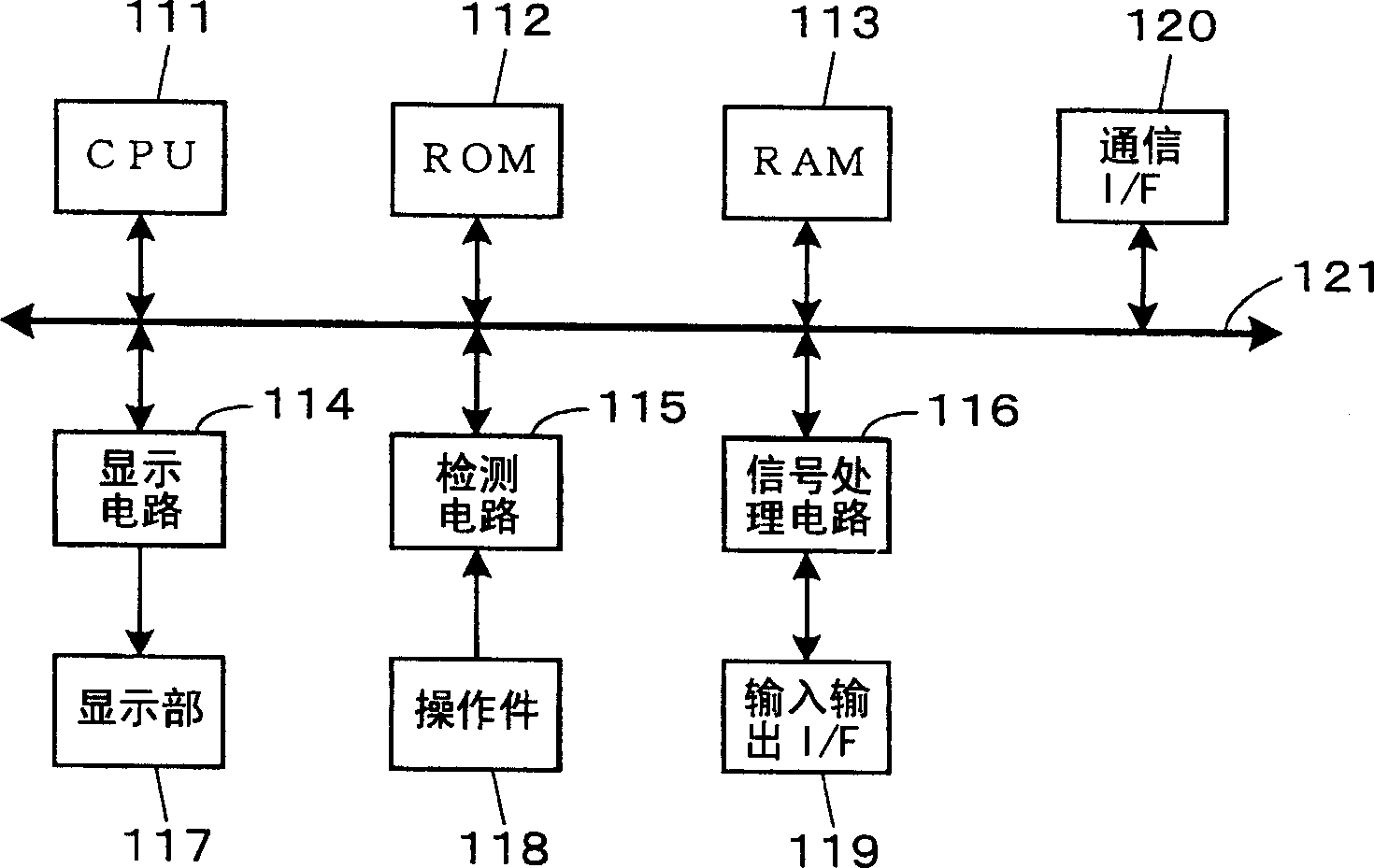
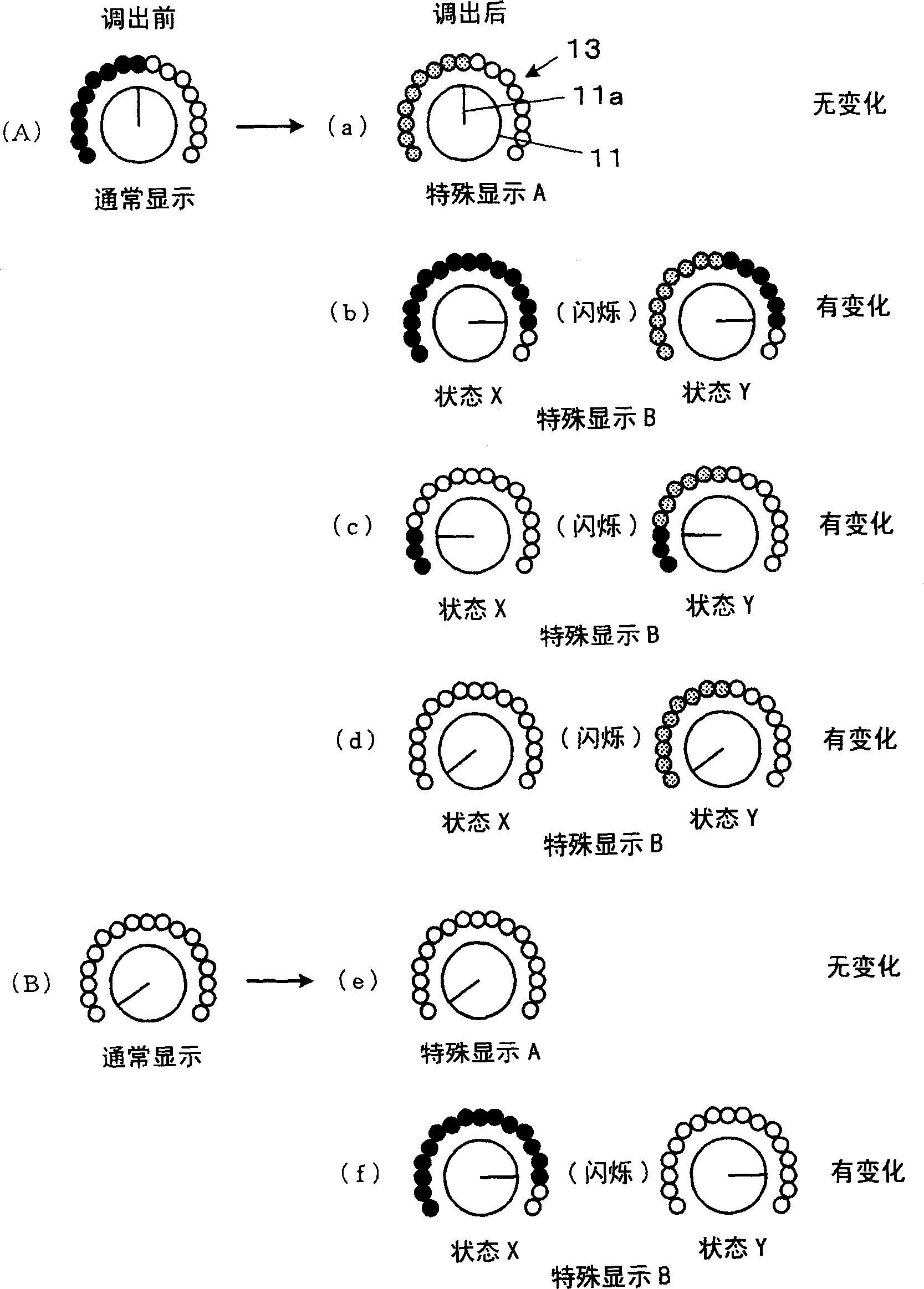
In an audio signal processing device which processes audio signals and outputs the audio signals, setting controls, such as filter controls, for setting values of parameters for the signal processing and a display for presenting information by the presence or absence and the style of lighting of LEDs is provided, in which when scene data stored in a scene memory is loaded, the display style of the display is made different in accordance with match / mismatch between a current set value of the parameter and the value of the parameter relating to the loaded scene data. Alternatively, the display is made to simultaneously present the loaded value and the value at the time of the loading in different display styles.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
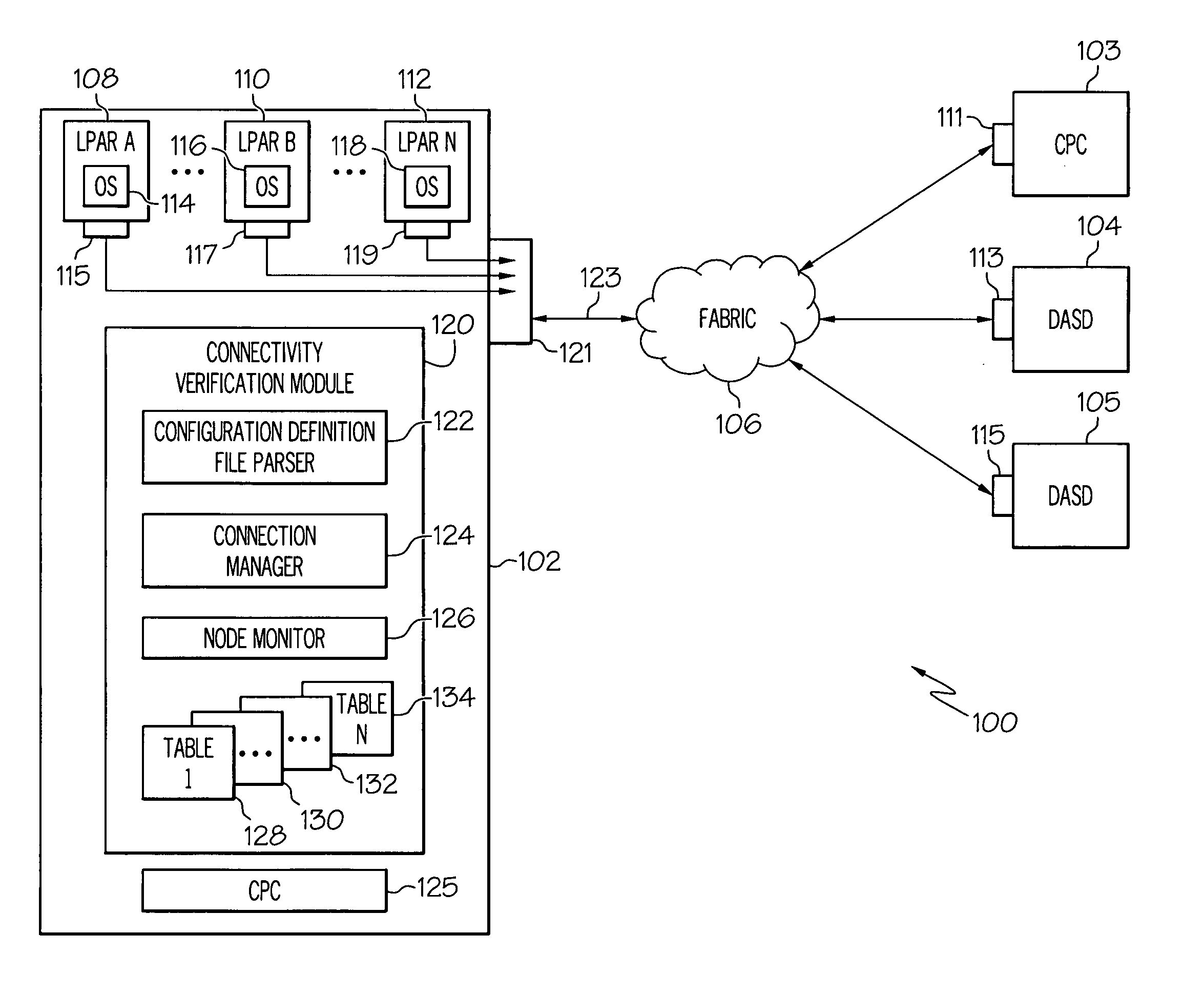
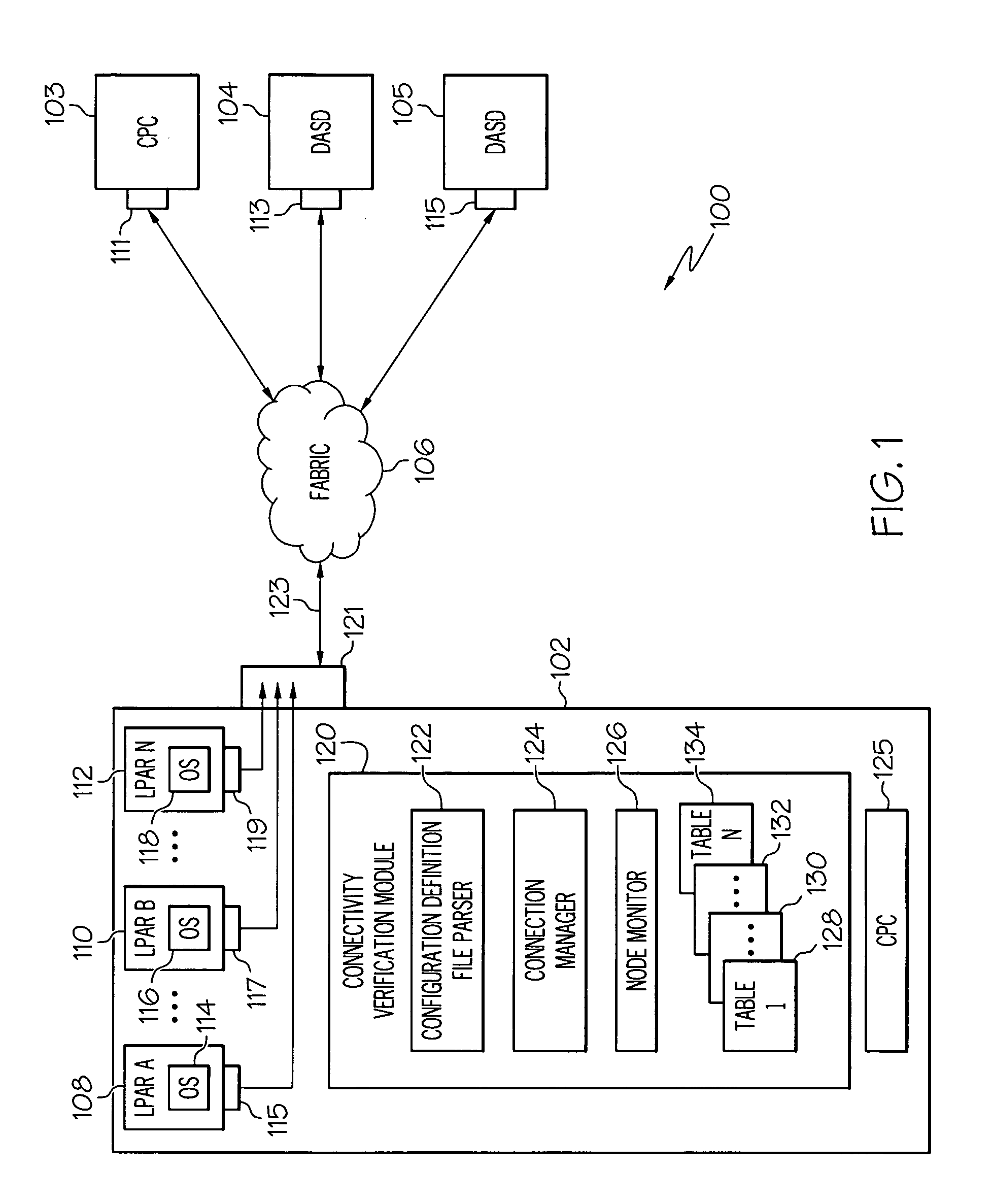
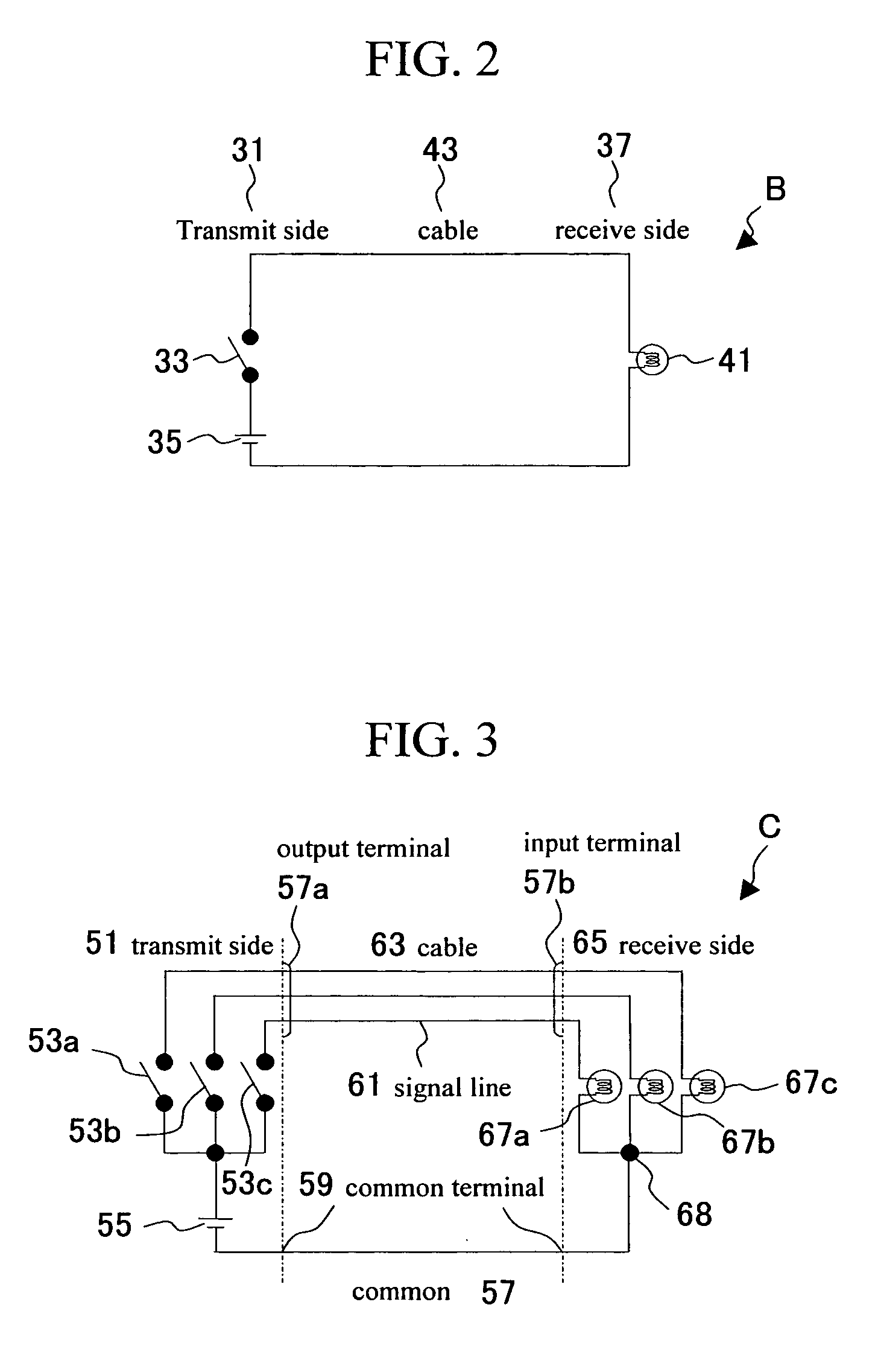
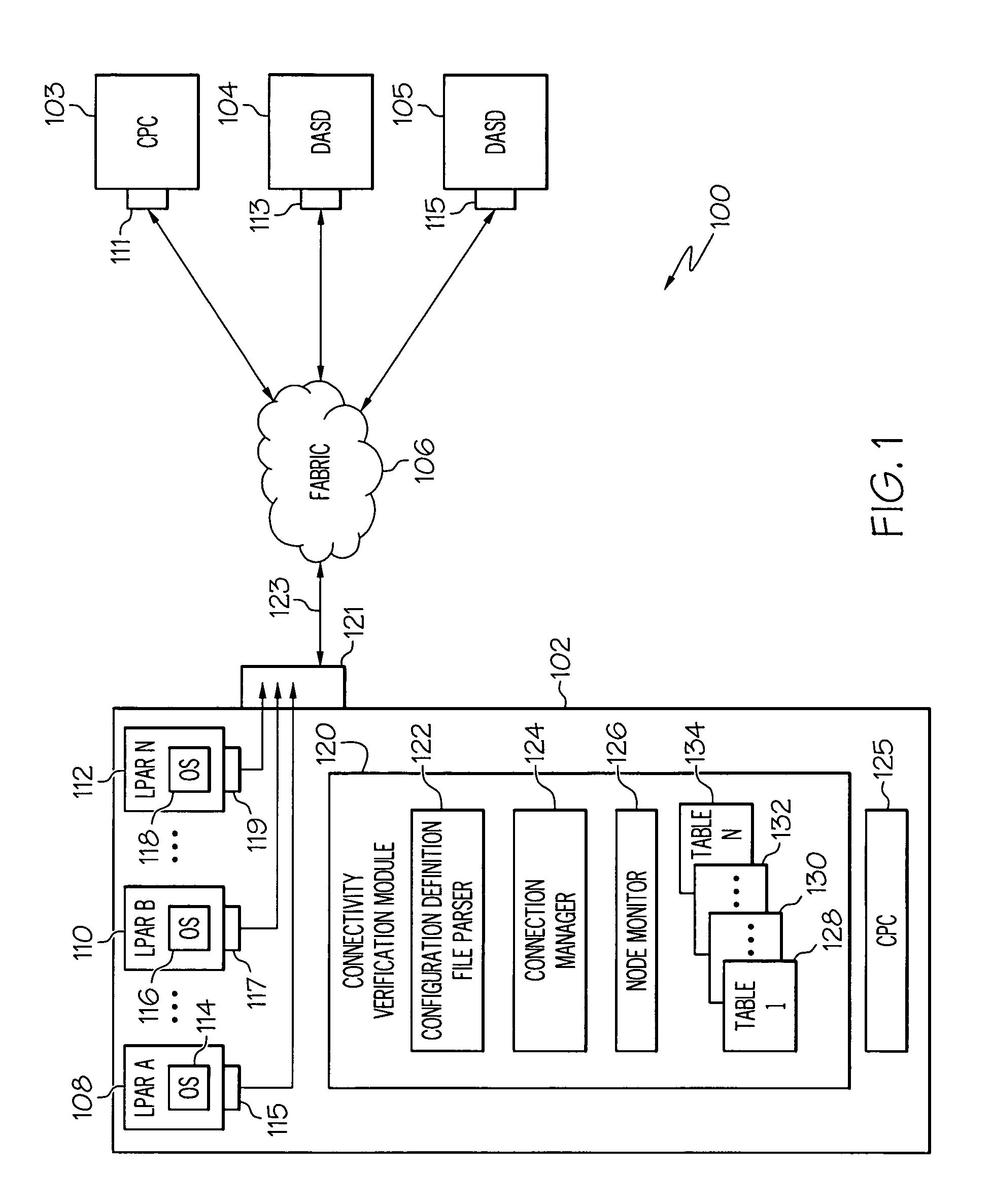
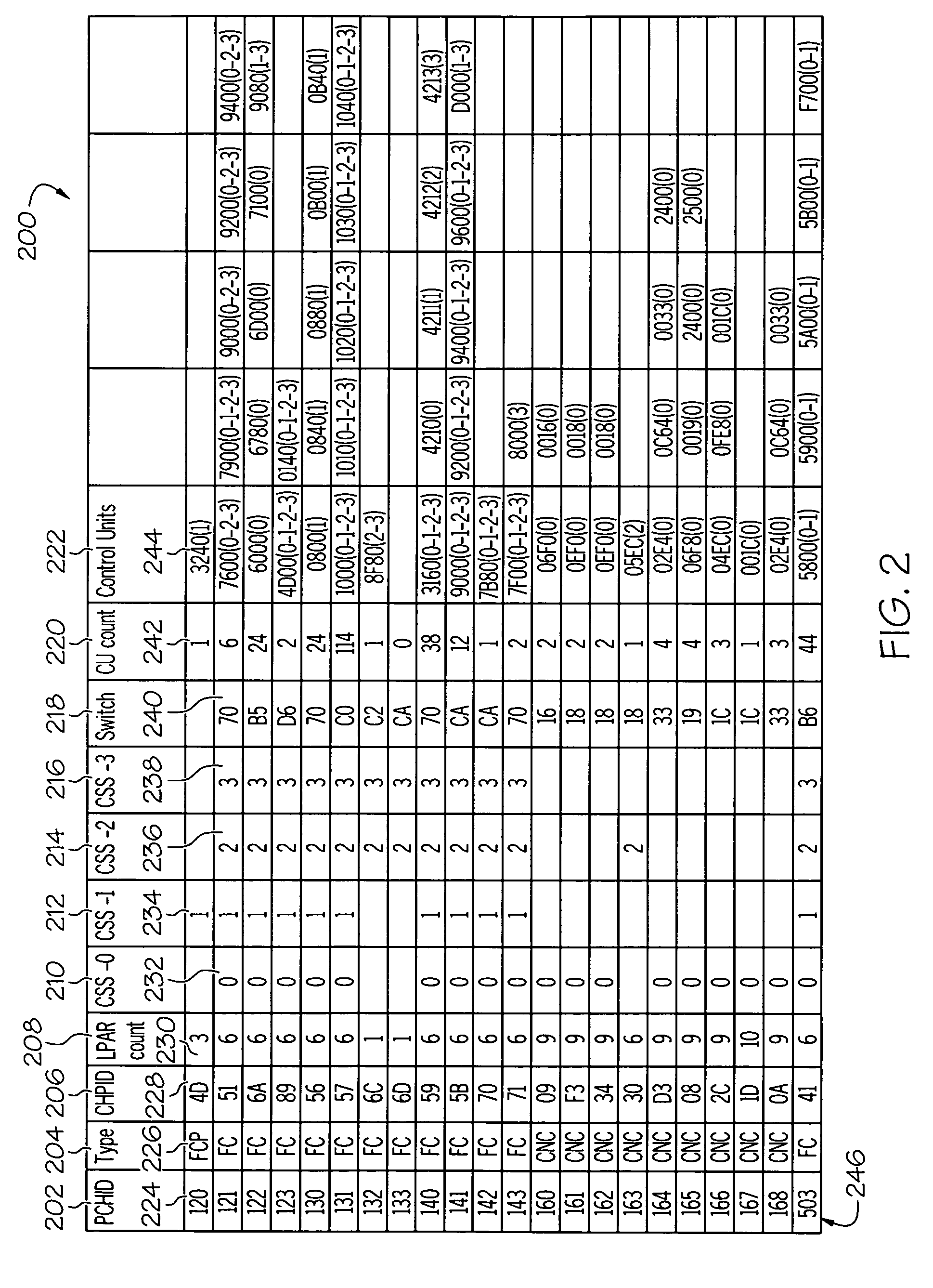
Logical to physical connectivity verification in a predefined networking environment
InactiveUS20090217103A1Error detection/correctionDigital computer detailsComputer hardwareMatch/mismatch
A method, information system, and computer readable storage medium verify predefined connectivity for I / O devices. Current predefined logical connection data and actual physical connection data is gathered. The predefined logical connection data and the actual physical connection data are formatted into a plurality of sortable tables. At least a portion of the predefined logical connection data is formatted into a predefined channels table and at least a portion of the actual physical connection data is formatted into a node information table. The portion of the predefined logical connection data is compared with the portion of the actual physical connection data. The portion of the predefined logical connection data is determined to substantially match / not match the portion of the actual physical connection data. At least one predefined logical connection associated with the predefined logical connection data that fails to substantially match the actual physical connection data is displayed to a user.
Owner:IBM CORP
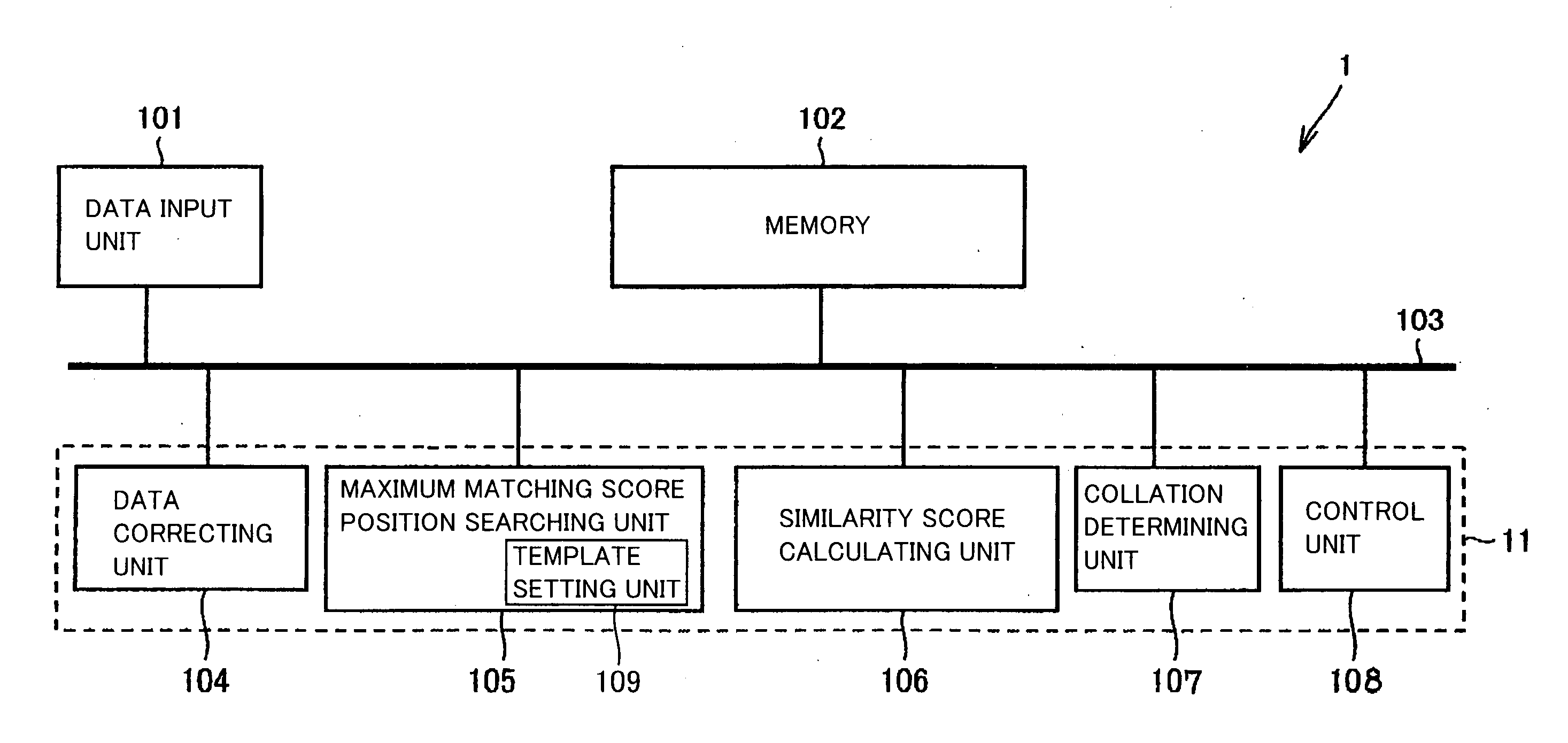
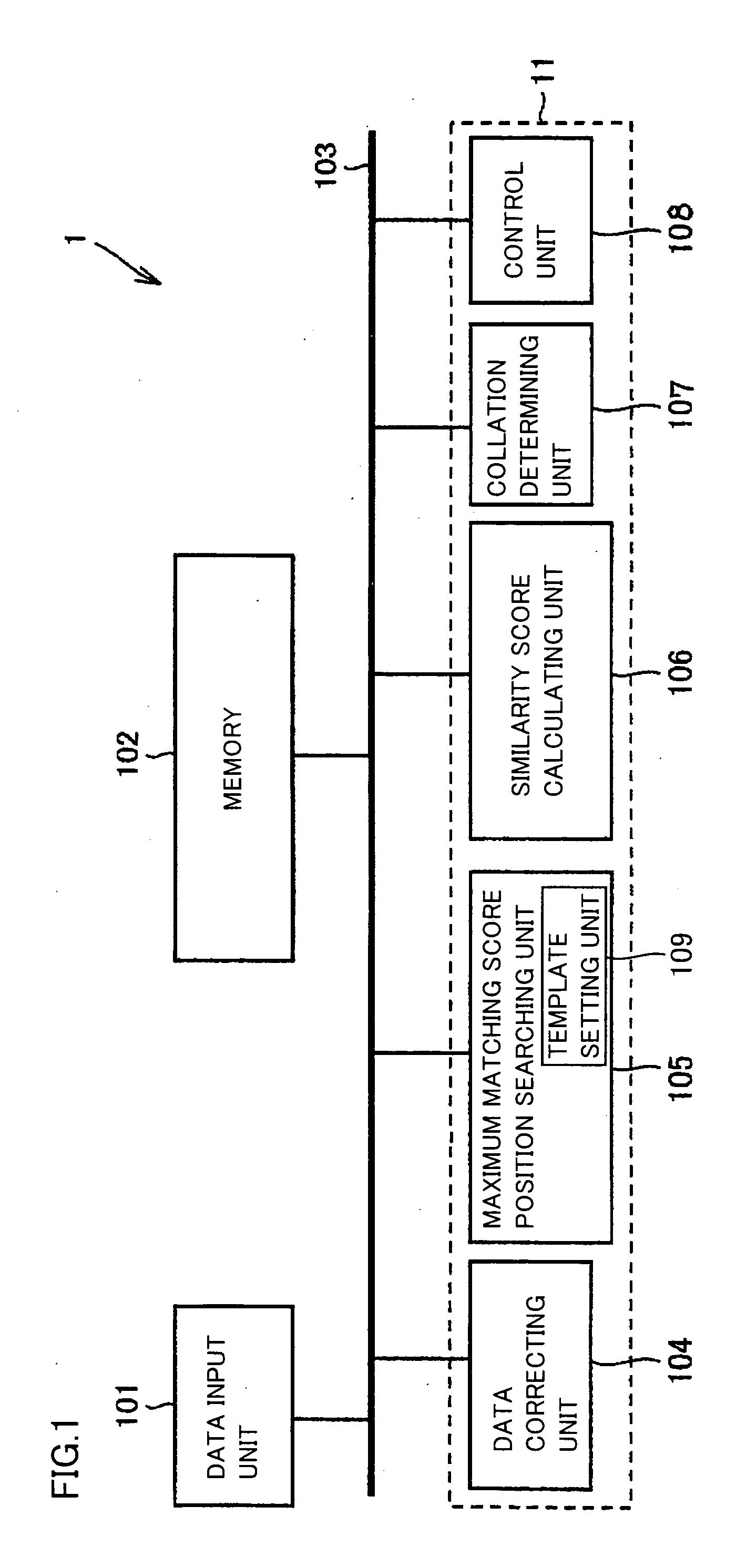
Apparatus, method and program performing image collation with similarity score as well as machine readable recording medium recording the program
InactiveUS20060045350A1Guaranteed accuracyIncrease storage capacityMatching and classificationTemplate matchingMatch/mismatch
Rectangular partial areas “Ri” for use in template matching in a process of determining match / mismatch between fingerprint images are spread adjacently to each other in one of the images. A boundary-including partial area is set in a portion including a crossing point of cross-shaped boundaries defined by the four neighboring partial areas. The plurality of partial areas formed of the neighboring partial areas and the boundary-including partial area are used as a template so that the number of the partial areas can be increased while ensuring a certain size of the partial area. Further, the boundary-including partial area covers the boundary between the neighboring partial areas so that continuity of image data at the boundary between the neighboring partial areas can be reflected in the determination of the match / mismatch between the images.
Owner:SHARP KK
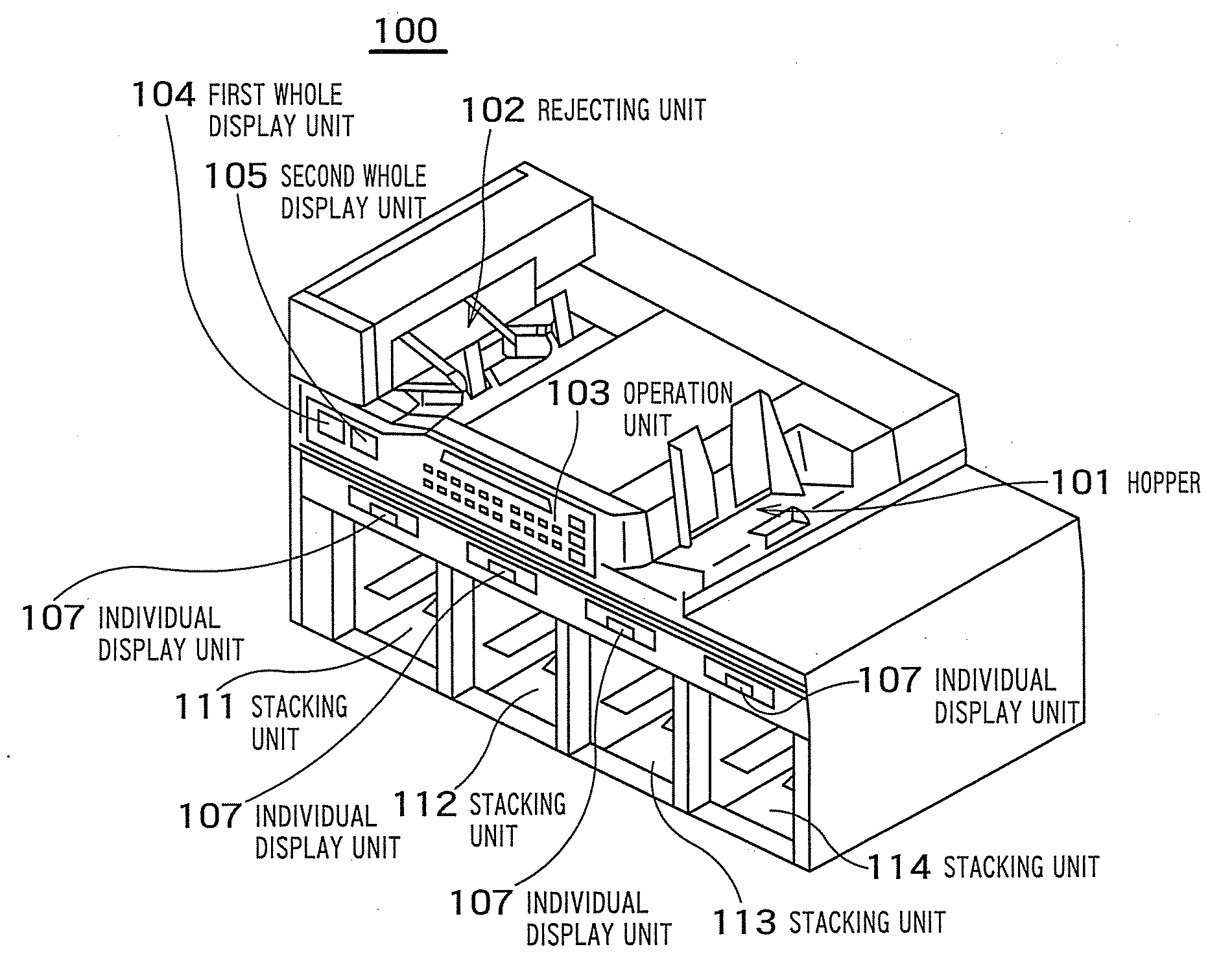
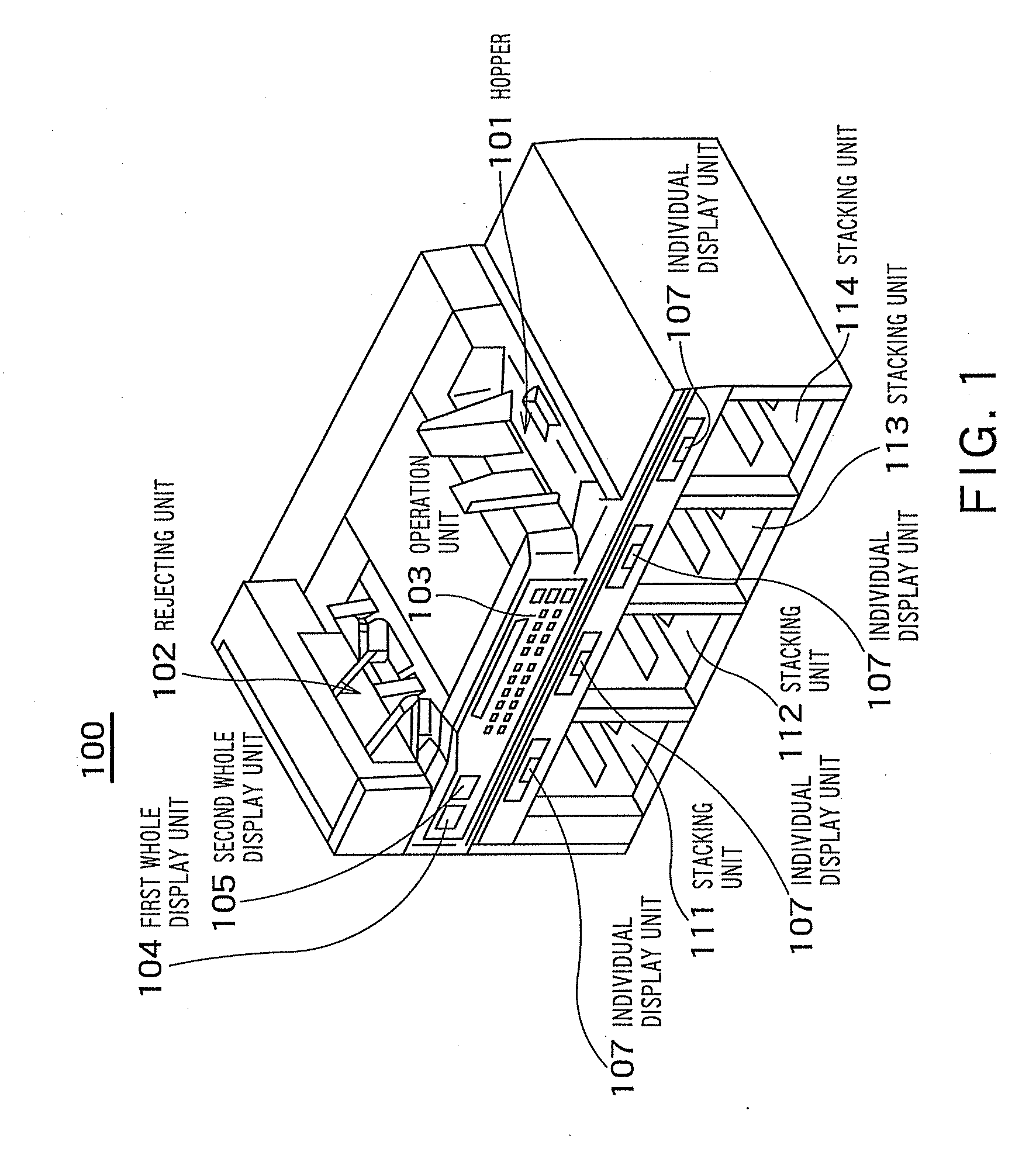
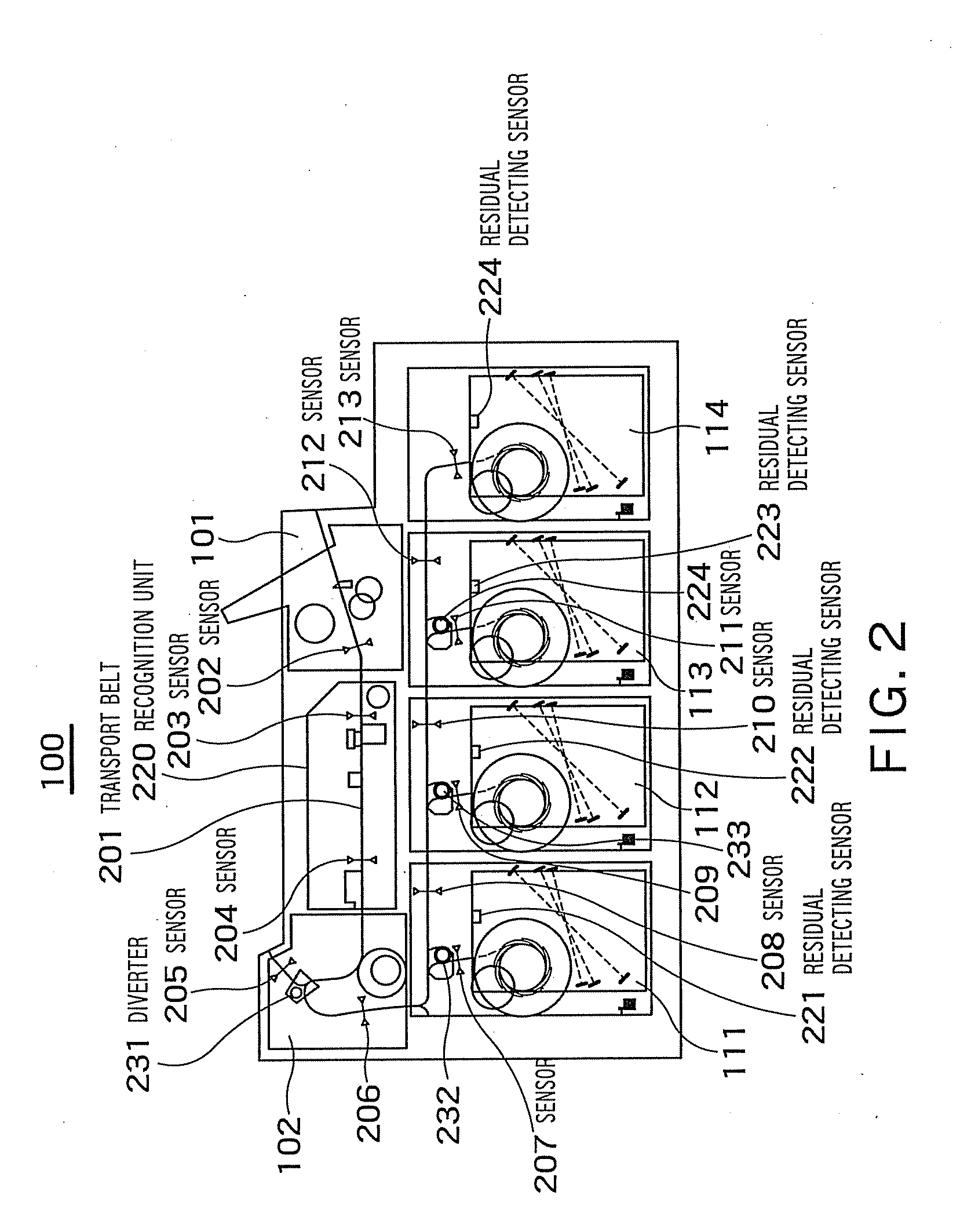
Banknote handling apparatus
InactiveUS8074806B2Improve reliabilityImprove conveniencePaper-money testing devicesCoin/currency accepting devicesMatch/mismatchComputer science
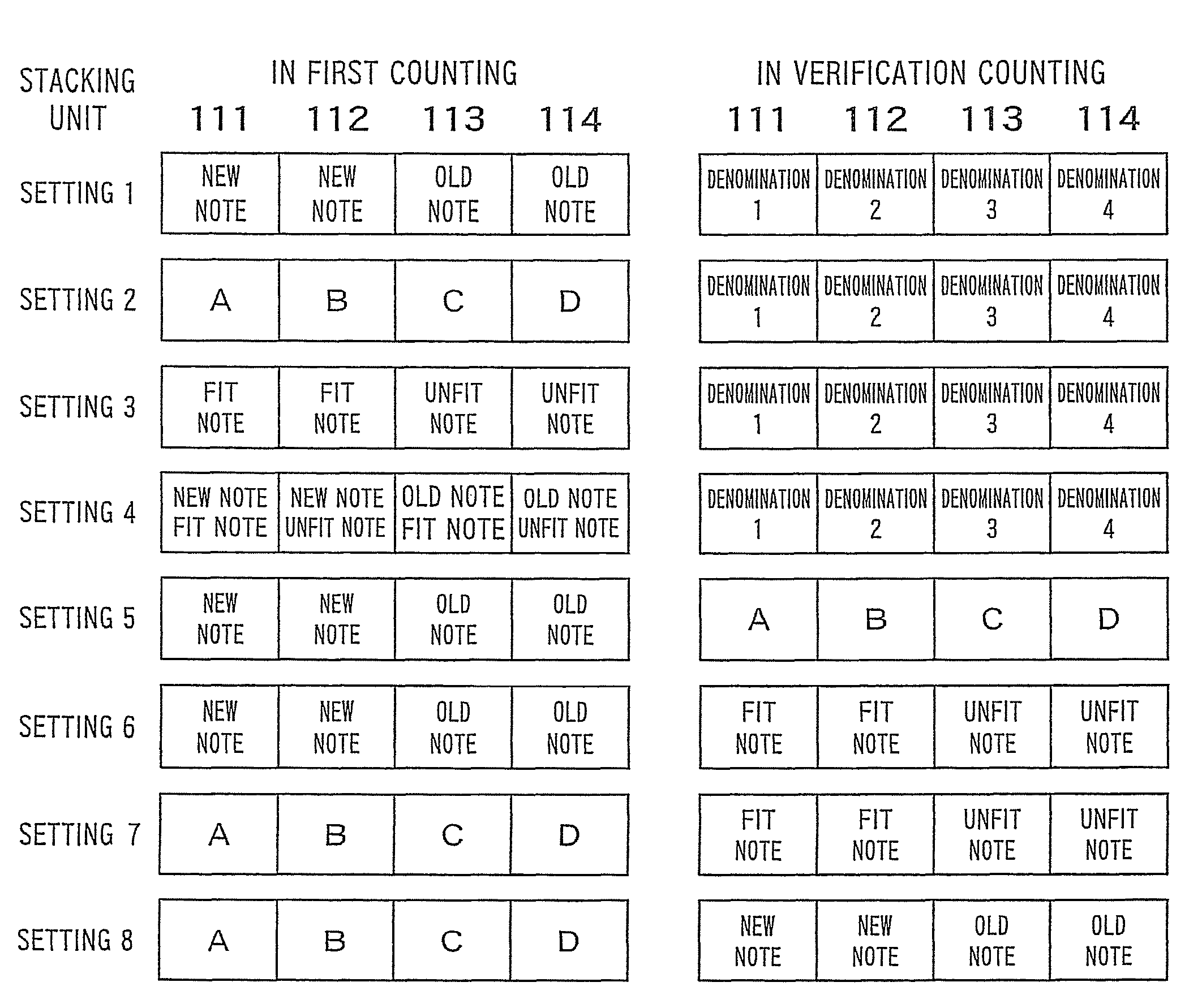
A banknote handling apparatus including a receiving unit that receives banknotes to be counted, a recognition unit that recognizes attributes of the banknotes, a storing unit that stores the banknotes sorted based on a recognition result by the recognition unit, an operation unit for selecting a counting mode and a setting for stacking, and a verification counting process control unit that executes a first counting process when the operation unit selects a verification mode as the counting mode, stores the banknotes in stacking units in a designated first setting for stacking, executes a verification counting process to the banknotes stacked in the first setting for stacking, stores the banknotes in stacking units in a designated second setting for stacking that is different from the first setting for stacking, and determines match / mismatch of the number of banknotes of each denomination in the first counting process and the verification counting process.
Owner:GLORY KOGYO KK
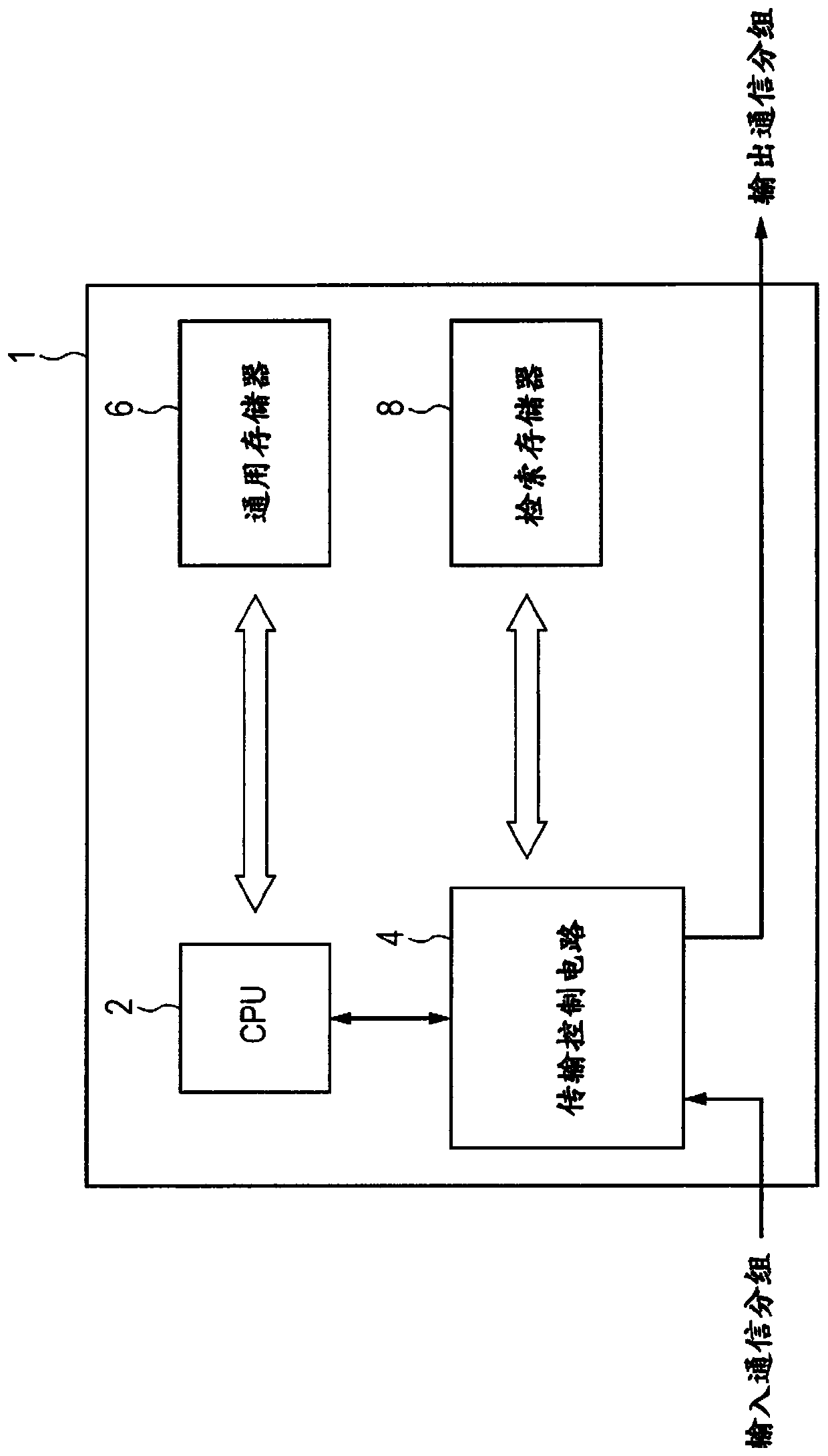
Memory Having information Refinement Detection Function, Information Detection Method Using Memory, Device Including Memory, Information Detection Method, Method For Using Memory, And Memory Address Comparison Circuit
ActiveUS20120324204A1Fast analysisQuick checkDigital storageSpecial data processing applicationsComputer hardwareMemory address
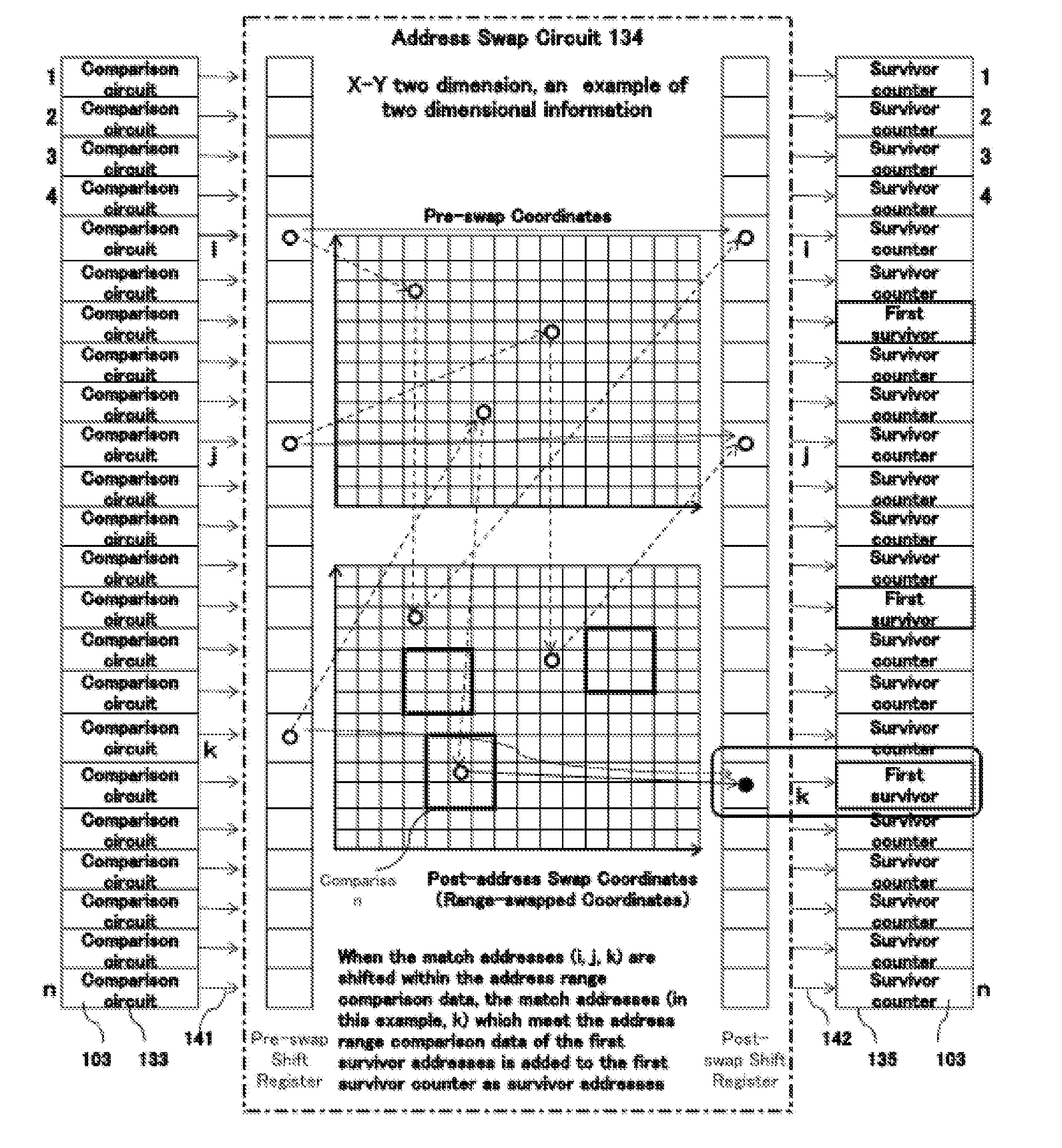
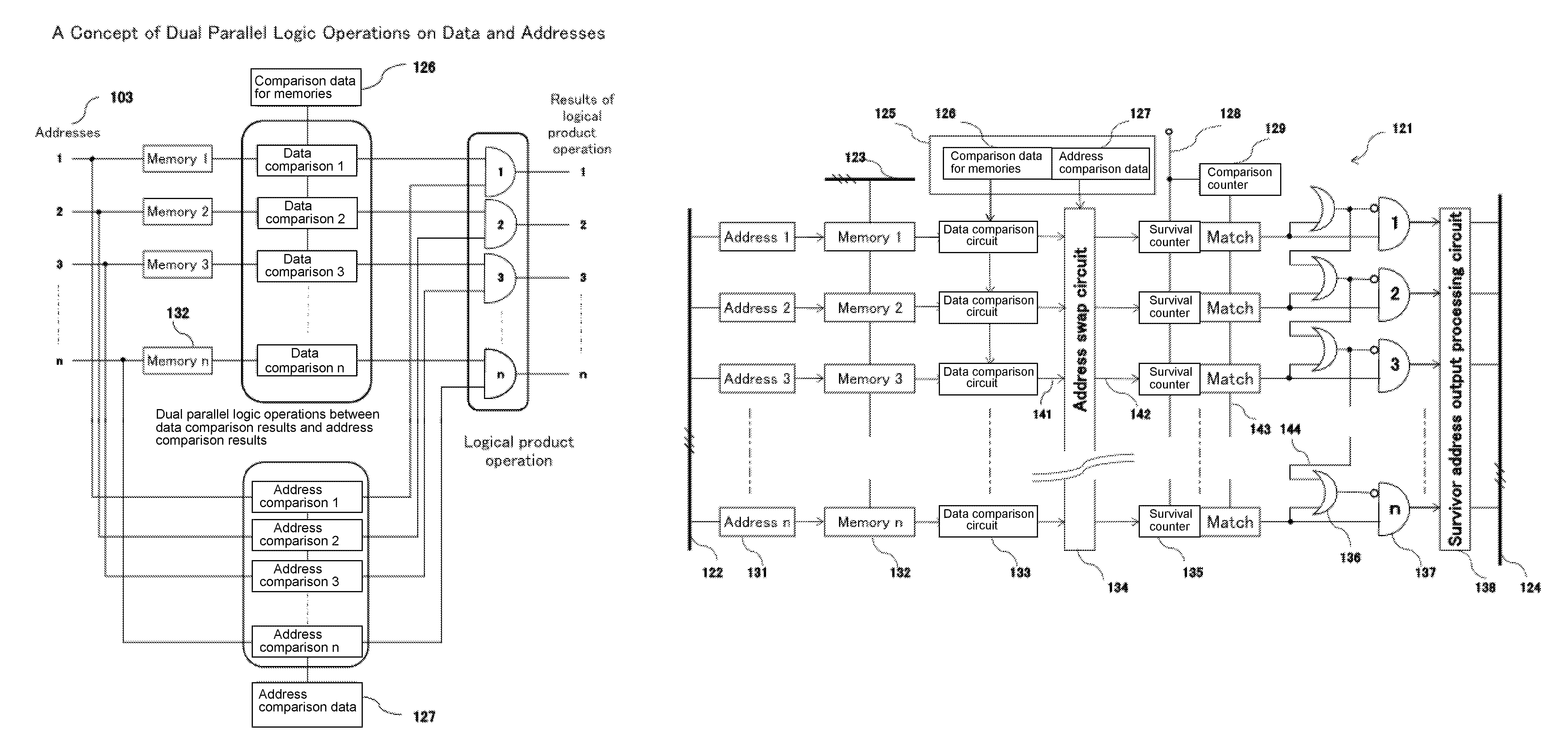
There is provided an externally readable memory for storing information in each memory address, and this memory is provided with an information refinement detection function; this memory comprises: an input means for entering first input data for comparing data items stored in the memory and second input data for comparing addresses in the memory, wherein the first and second comparison data are externally; means for determining matches / mismatches of both data items stored in the memory and addresses of the memory according to both of the input data provided by the input means, and further performing logic operations on both of the match / mismatch determination results; and means for outputting addresses with positive results of the logic operations. This memory may be applicable in a broad range of fields including intelligent information search as well as artificial intelligence.
Owner:INOUE KATSUMI
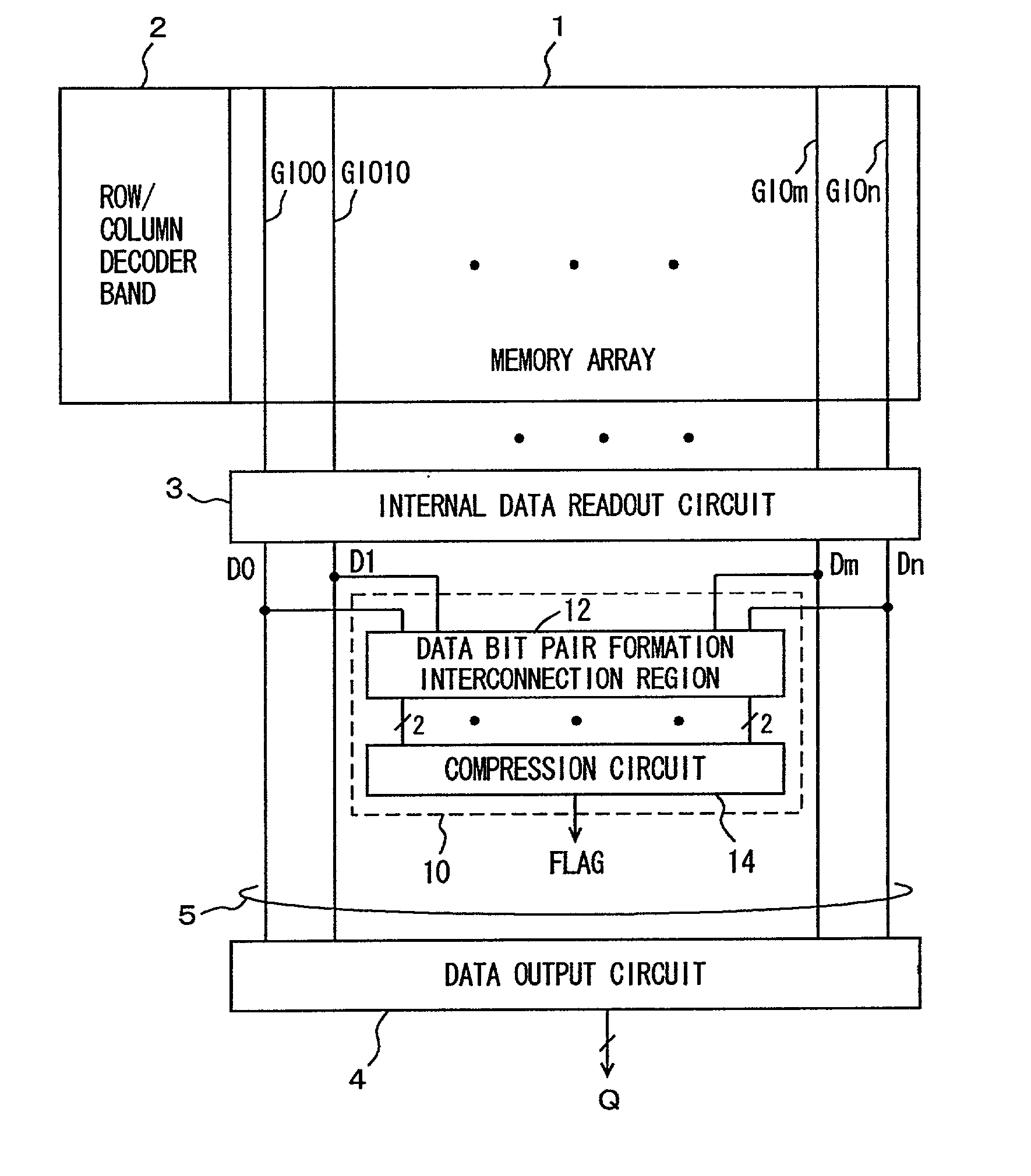
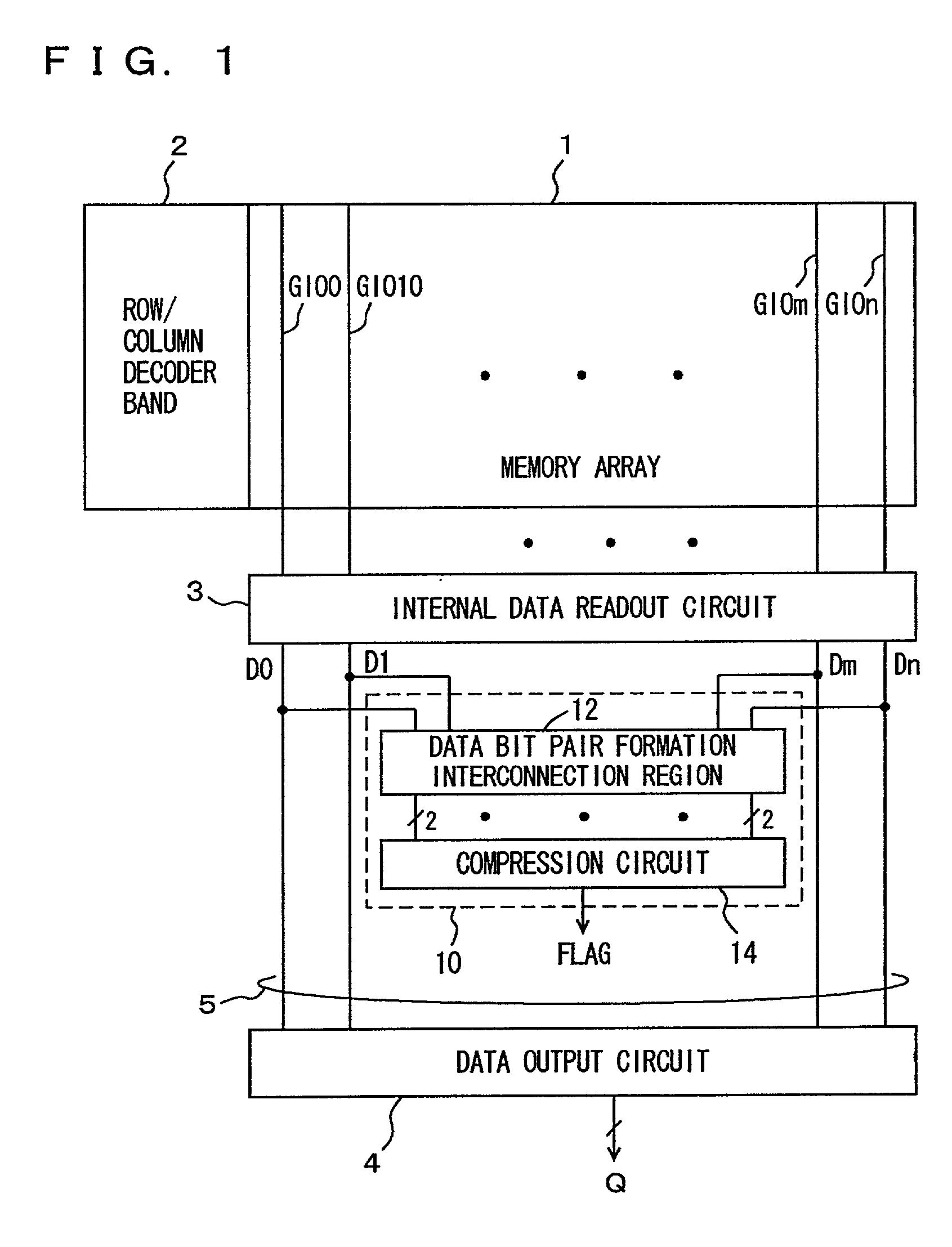
Multi-bit test circuit
InactiveUS20020129308A1Fast timeShorten interconnect lengthElectronic circuit testingDigital storageBit TestMatch/mismatch
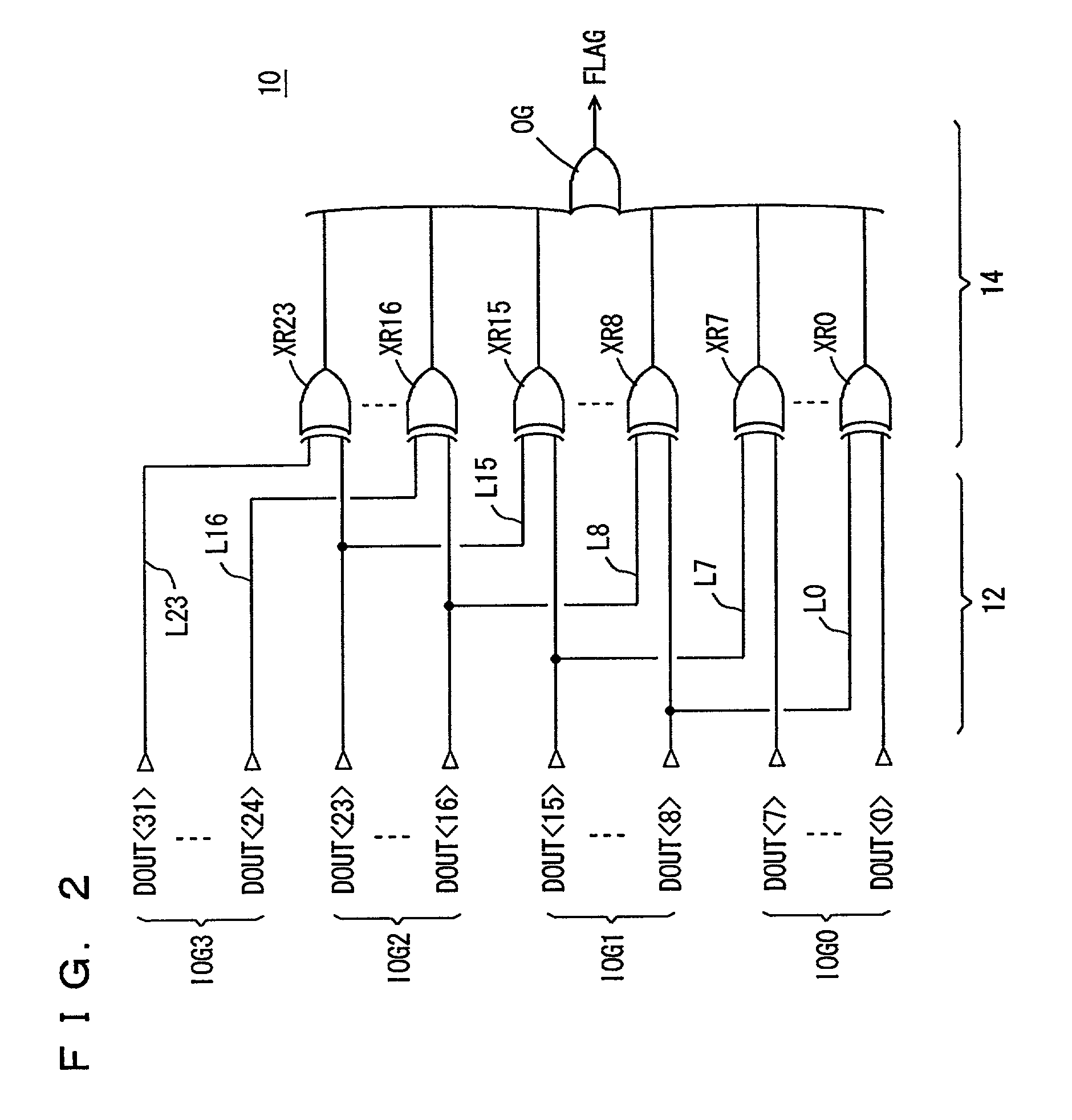
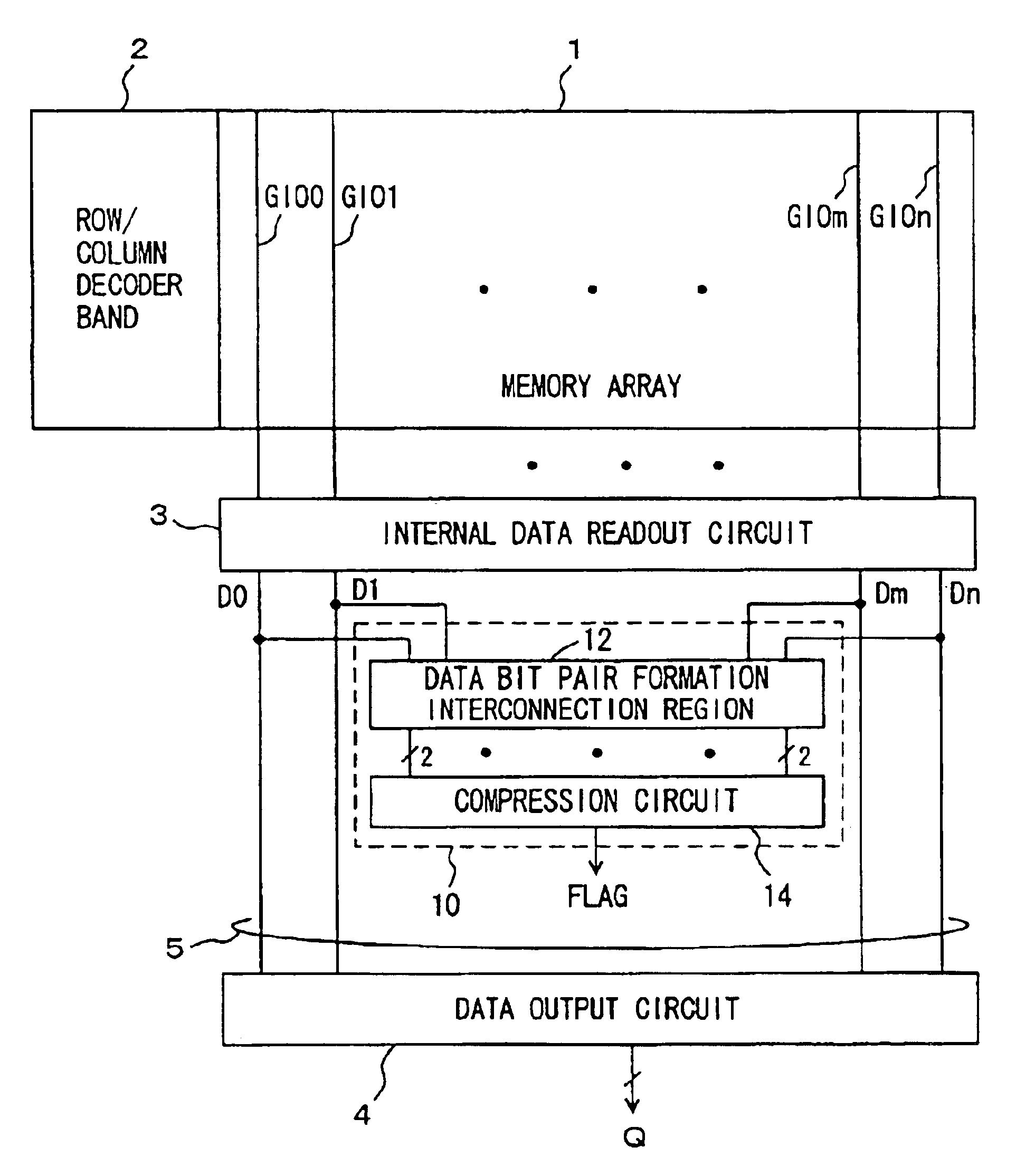
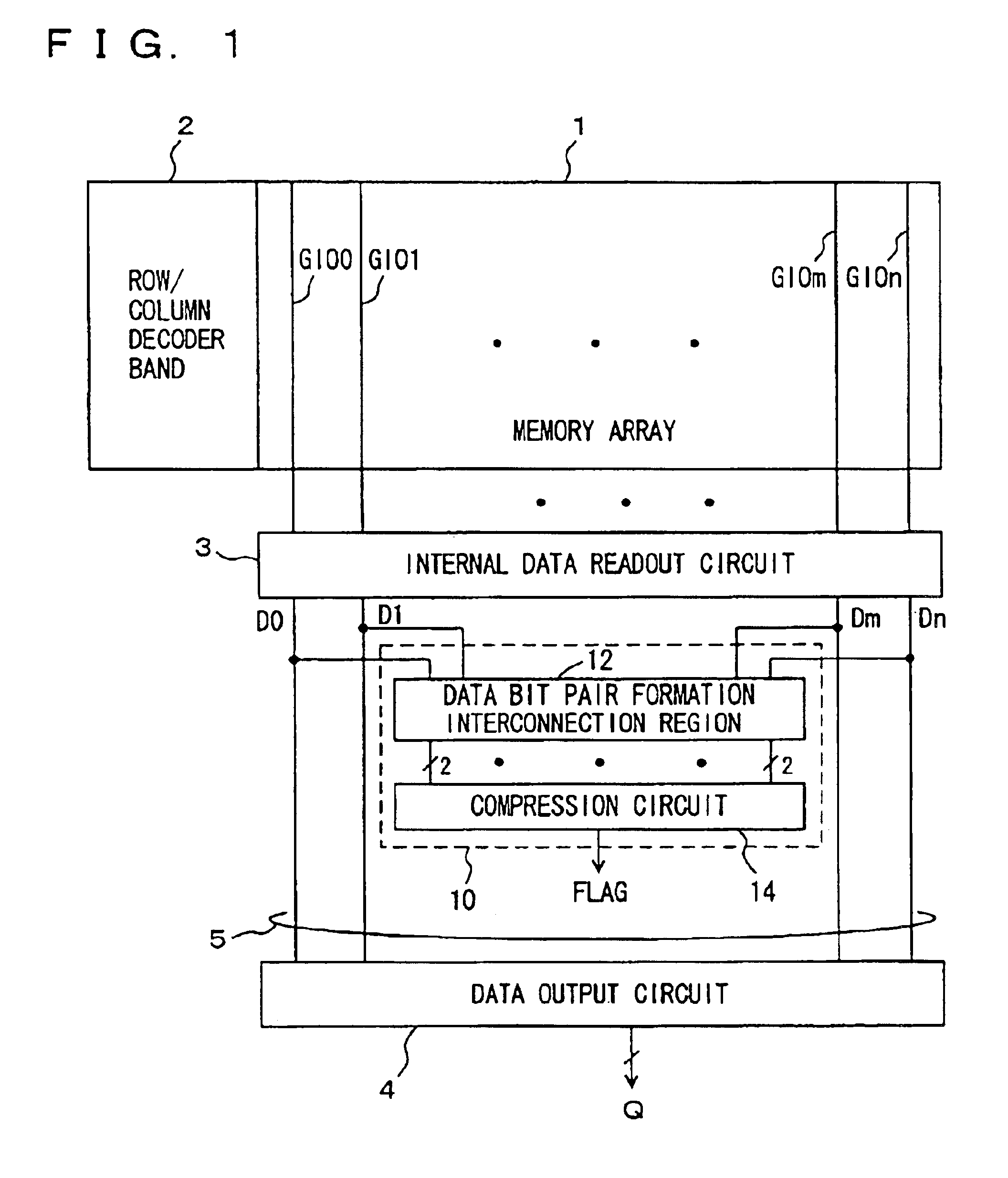
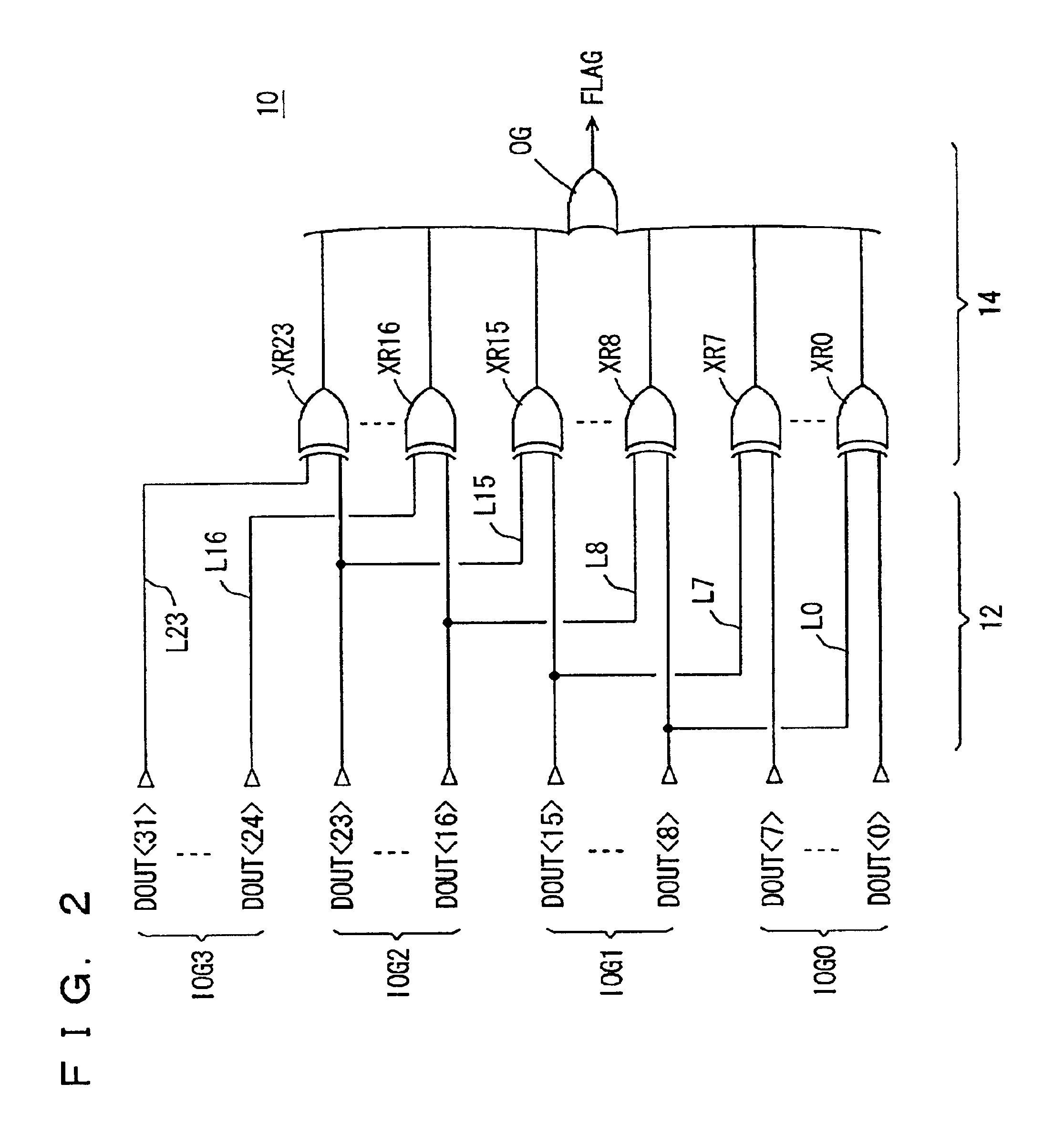
Internal read out data bits are divided into a plurality of data groups, and data bits in corresponding positions in different data groups are paired off. A determination gate is provided to each pair of data bits, and determining operation is performed in each pair to compress the result of determination to finally generate a 1-bit flag indicating a match / mismatch in logic level among the internal read out data. Consequently, a multi-bit test circuit that has a reduced layout area and can perform high-speed multi-bit determination is provided.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Multi-bit test circuit
InactiveUS6854078B2Fast timeShorten interconnect lengthElectronic circuit testingDigital storageBit TestMatch/mismatch
Internal read out data bits are divided into a plurality of data groups, and data bits in corresponding positions in different data groups are paired off. A determination gate is provided to each pair of data bits, and determining operation is performed in each pair to compress the result of determination to finally generate a 1-bit flag indicating a match / mismatch in logic level among the internal read out data. Consequently, a multi-bit test circuit that has a reduced layout area and can perform high-speed multi-bit determination is provided.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Banknote handling apparatus
InactiveUS20100032352A1Simple processImproving credibility in countingPaper-money testing devicesCoin/currency accepting devicesMatch/mismatchComputer science
A banknote handling apparatus including a receiving unit that receives banknotes to be counted, a recognition unit that recognizes attributes of the banknotes, a storing unit that stores the banknotes sorted based on a recognition result by the recognition unit, an operation unit for selecting a counting mode and a setting for stacking, and a verification counting process control unit that executes a first counting process when the operation unit selects a verification mode as the counting mode, stores the banknotes in stacking units in a designated first setting for stacking, executes a verification counting process to the banknotes stacked in the first setting for stacking, stores the banknotes in stacking units in a designated second setting for stacking that is different from the first setting for stacking, and determines match / mismatch of the number of banknotes of each denomination in the first counting process and the verification counting process.
Owner:GLORY KOGYO KK
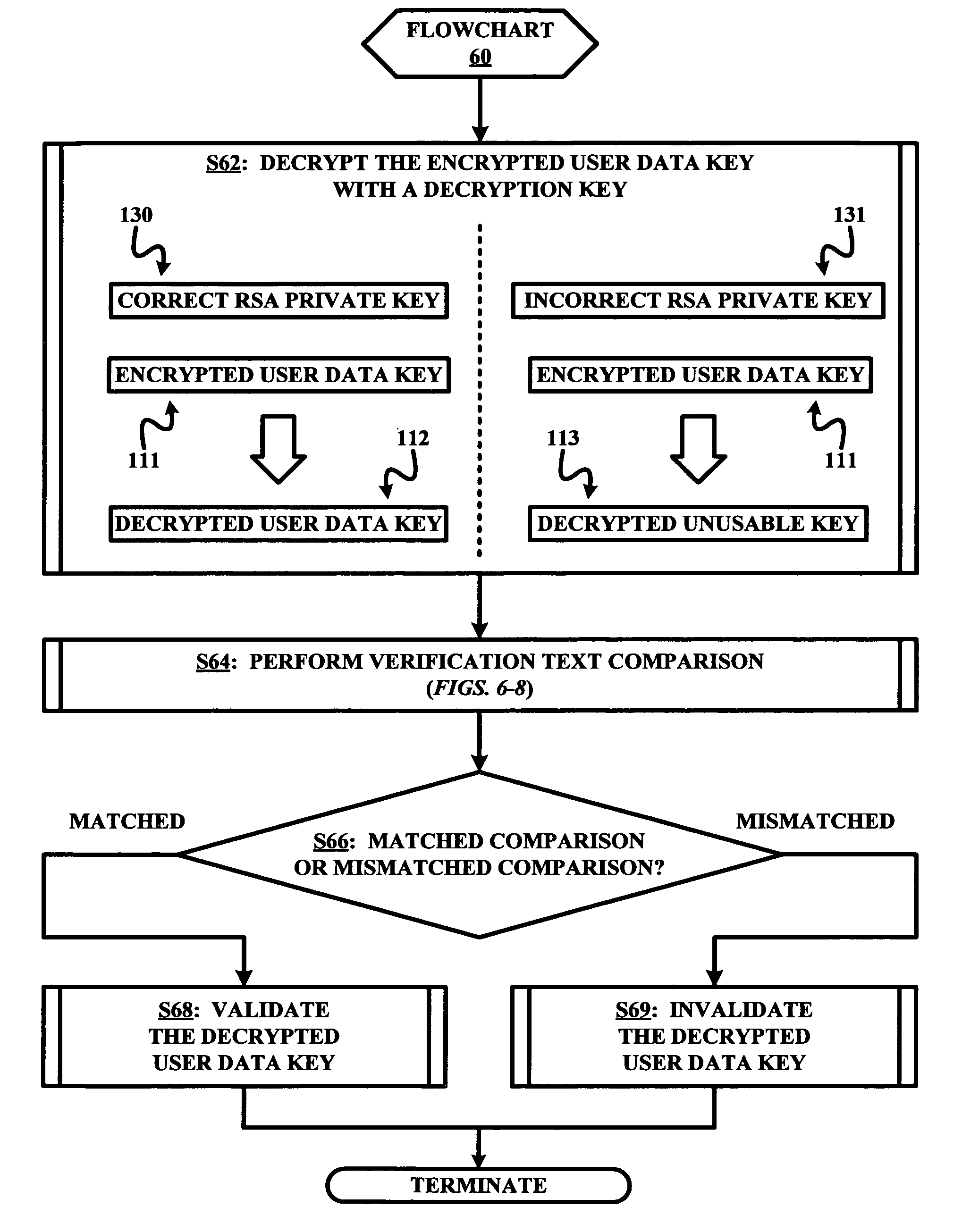
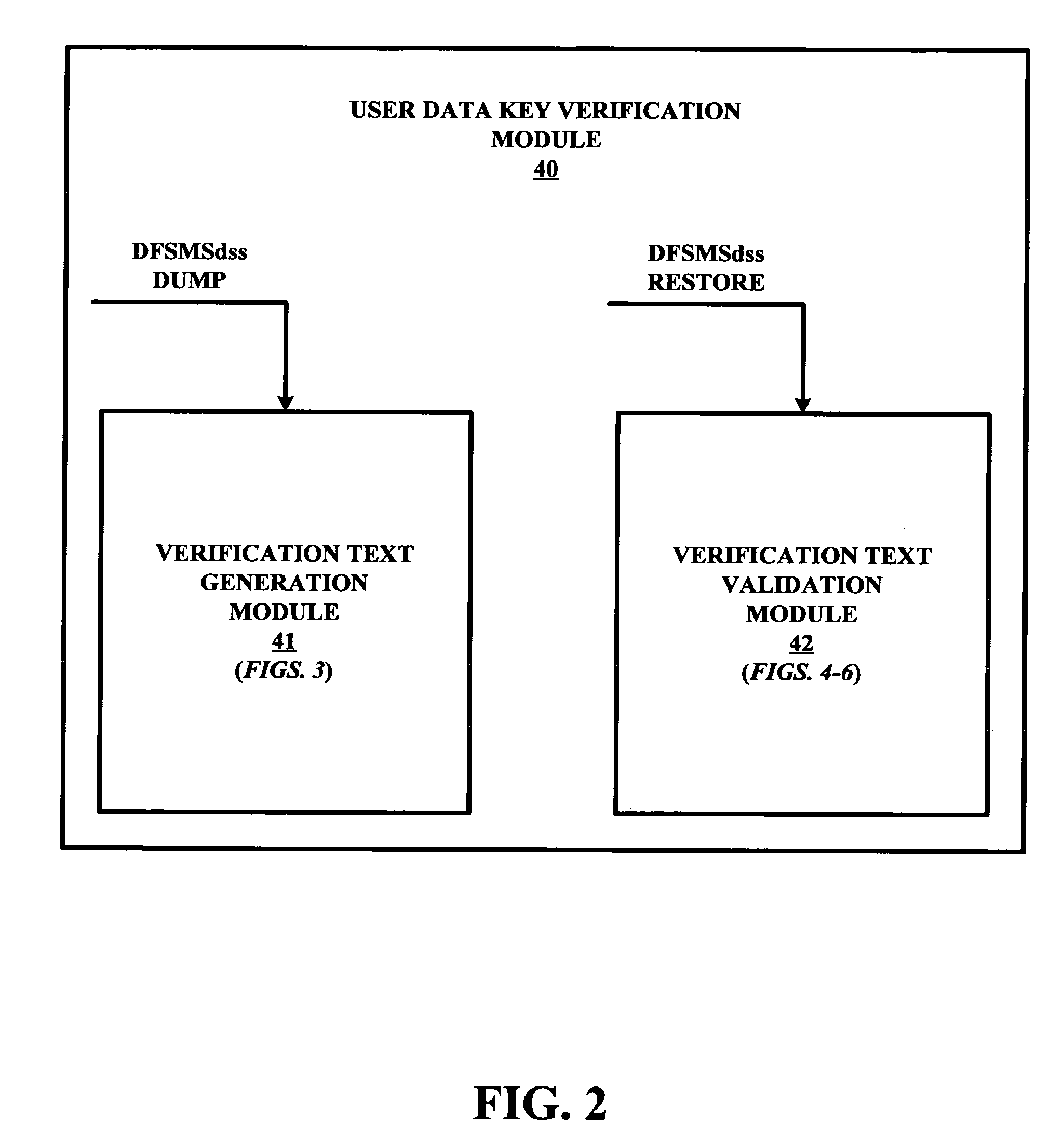
Cipher method and system for verifying a decryption of an encrypted user data key
InactiveUS7499552B2Key distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationMatch/mismatchRandom text
A cipher method for verifying a decryption of an encrypted user data key used to encrypt user data prior to an encryption of the user data key with an encryption key. The cipher method involves a decryption of the encrypted user data key with a decryption key in response to an initiation of a decryption of the encrypted user data with the user data key as decrypted with the description key, a decryption of the verification text with the user data key as decrypted with the decryption key, and a validation / invalidation of a use of the user data key as decrypted with the decryption key to decrypt the encrypted user data in response to a matched / unmatched comparison of the verification text as decrypted with the user data key and an intermixing of a known text and a random text.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Biometric information verifying apparatus
InactiveUS7778449B2Reduce rateReduce data volumeImage analysisPerson identificationUser verificationPalm print
The apparatus greatly reduces the registered data amount and the verification computation amount required for user verification, in comparison with the verification using image information itself, and also decreases the false verification rate. The apparatus divides a biometric information image into cells, and extracts minutia information as well as cell basic information from the individual cells. After comparison of direction information of the individual cells of the registered data with direction information of the individual cells of the to-be-verified data, thereby aligning the registered fingerprint image and the to-be-verified fingerprint image, the apparatus compares the minutia information of corresponding cells between the registered data and the to-be-verified data to make a match / non-match decision. Such an apparatus is applicable to systems that employ pattern matching type image verification to perform user verification utilizing biometric information such as fingerprints, palm prints, blood vessel patterns, iris patterns, and facial images.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
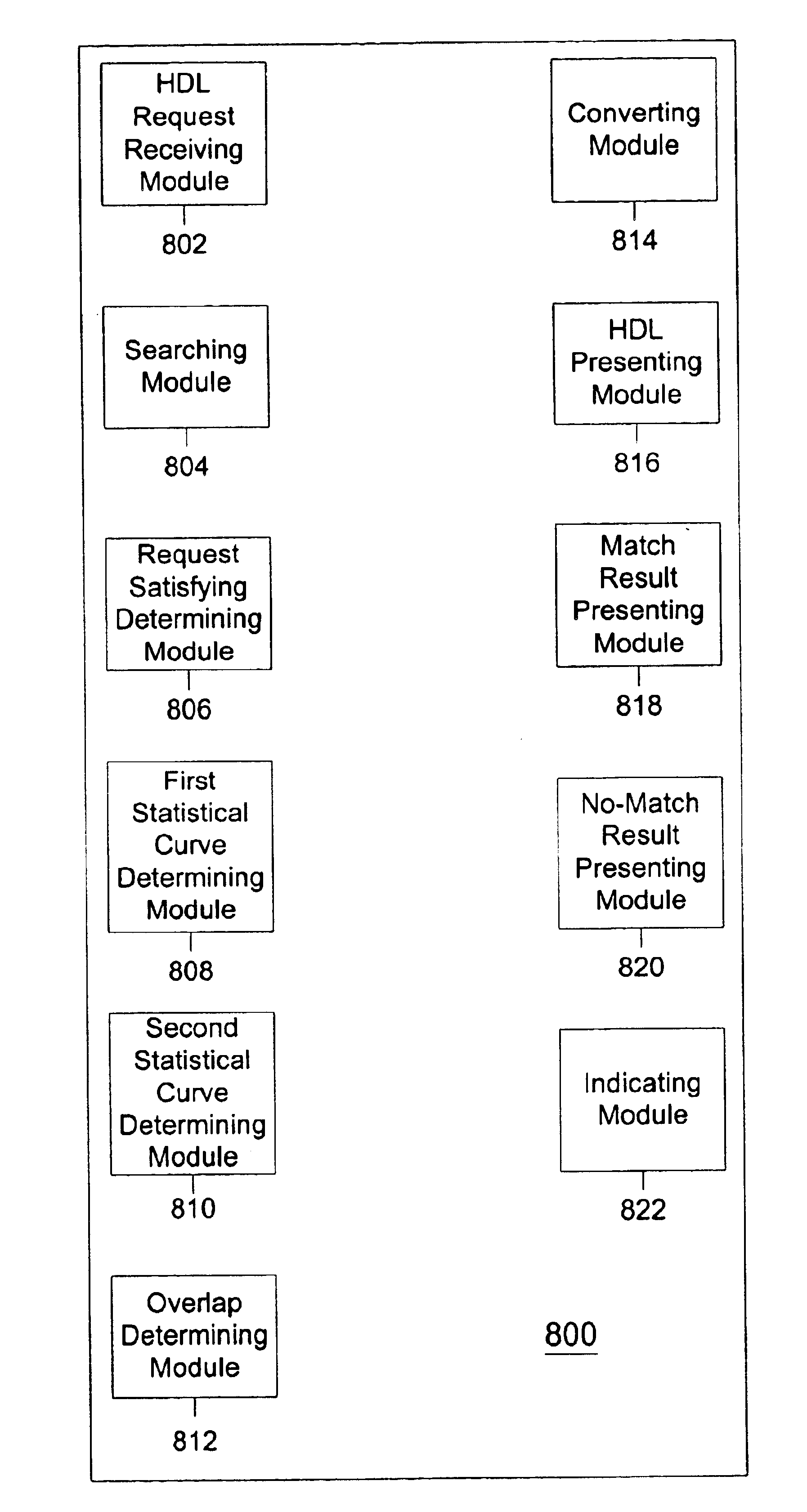
System and method for enabling statistical matching
InactiveUS6931393B1Sufficient storageSufficient retrievalData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalMatch/mismatchData mining
A system and method for statistical matching that determines statistical curves for data described in a data request and stored data that satisfies the request. The system may determine the statistical curves for each data type and determine whether any overlap exists between the statistical curves. A user may specify a particular acceptable percentage of data that may be used to satisfy the request. The data satisfying the request may be presented to the user or, alternatively, a match / no-match result may be presented indicating whether any data that satisfies the request exists.
Owner:IBM CORP
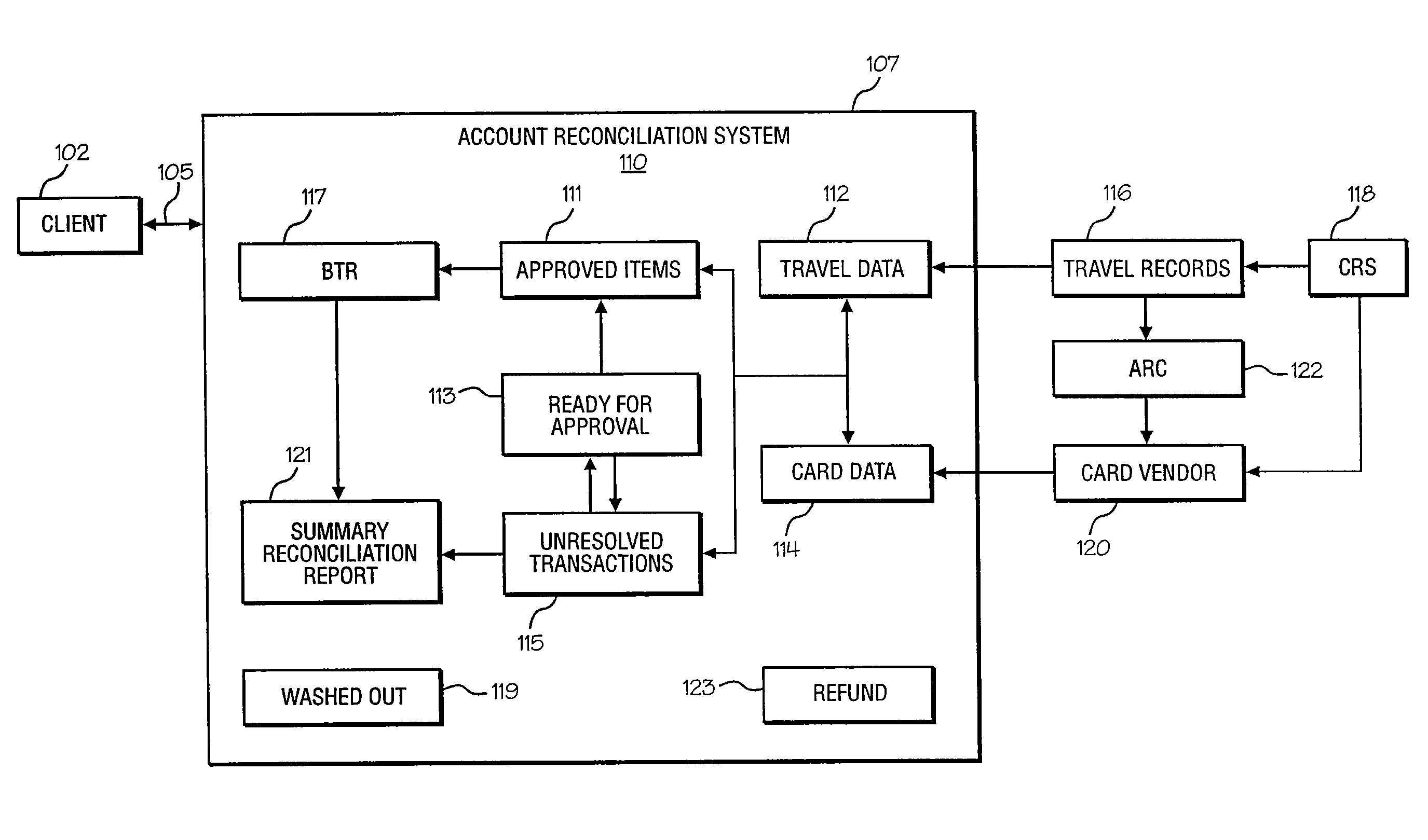
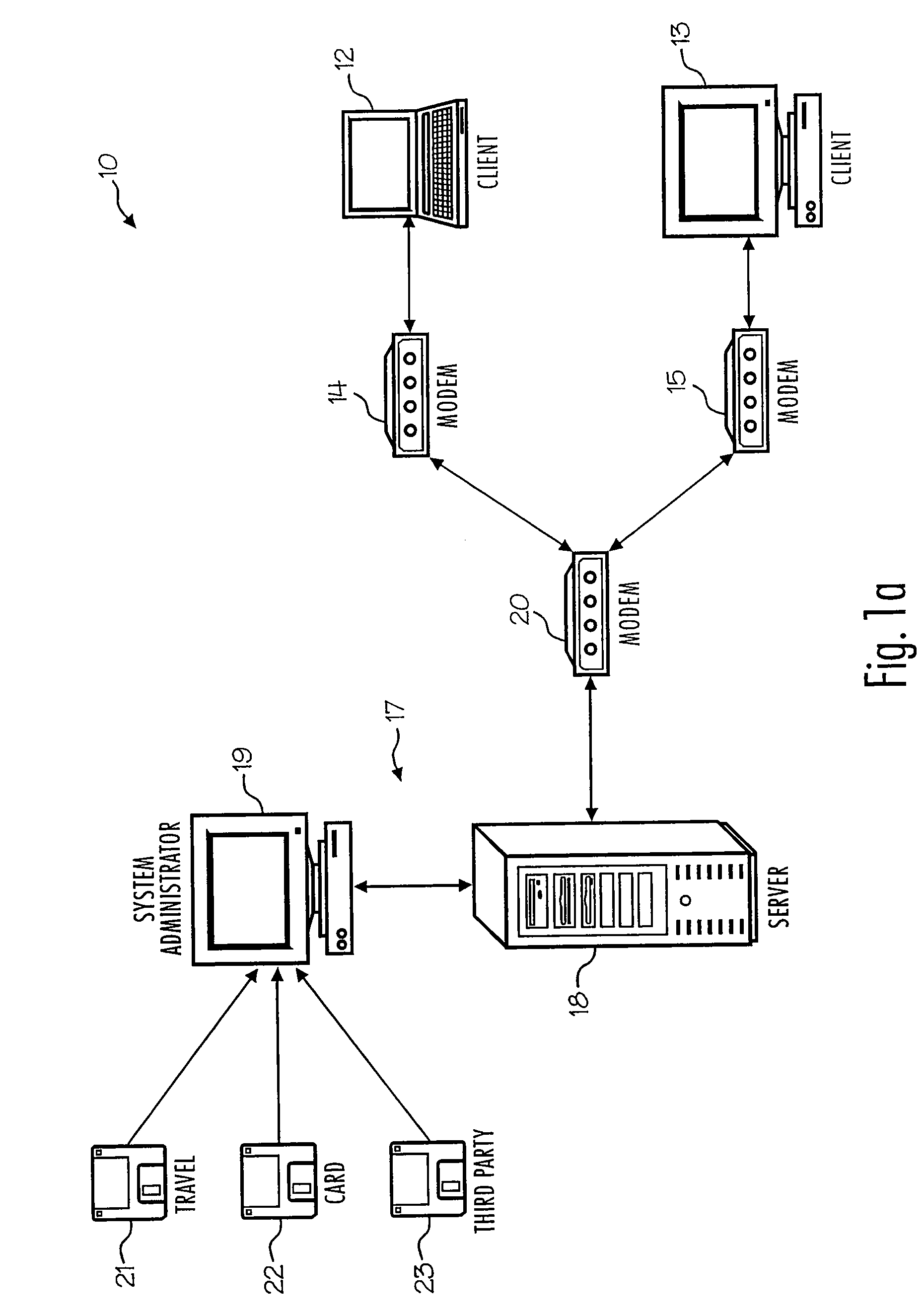
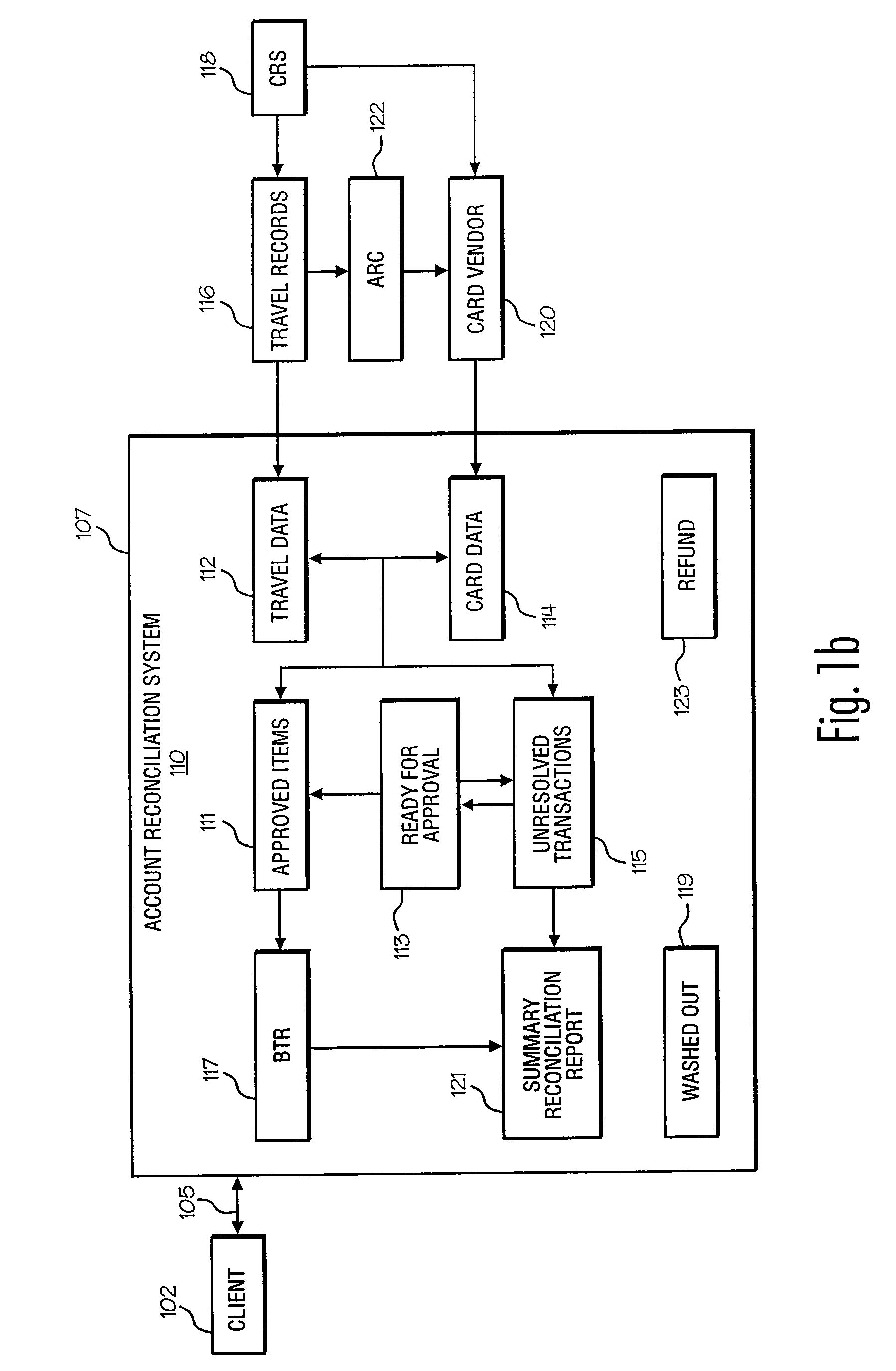
System and method for account reconciliation
An account reconciliation system having a particular usefulness in the reconciliation of centrally billed accounts and more specifically, in the reconciliation of centrally billed accounts in the travel industry is provided. The system and methods of the present invention expand on the traditional match / non-match techniques and provide complete transaction management for every item on a client's account. In another sense, reconciliation is redefined to include each and every transaction on an account regardless of it's reconciliation status, i.e., matched, unresolved, pending, etc. Consequently, the present invention reconciles the client's account to the account balance.
Owner:LIBERTY PEAK VENTURES LLC
Power supply controller
InactiveUS20070016313A1Small sizeLow costTesting/monitoring control systemsElectric controllersMicrocomputerCommunications system
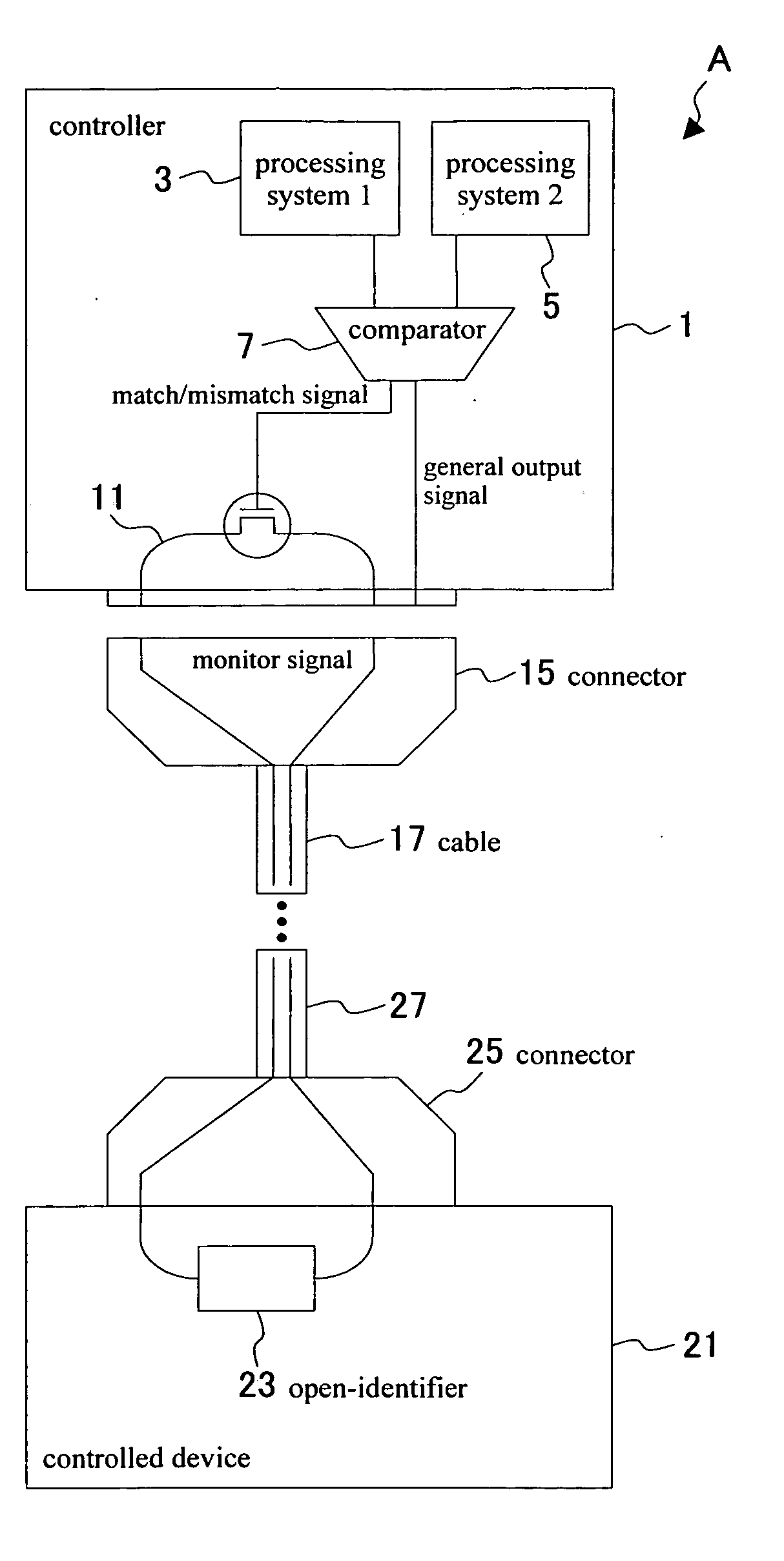
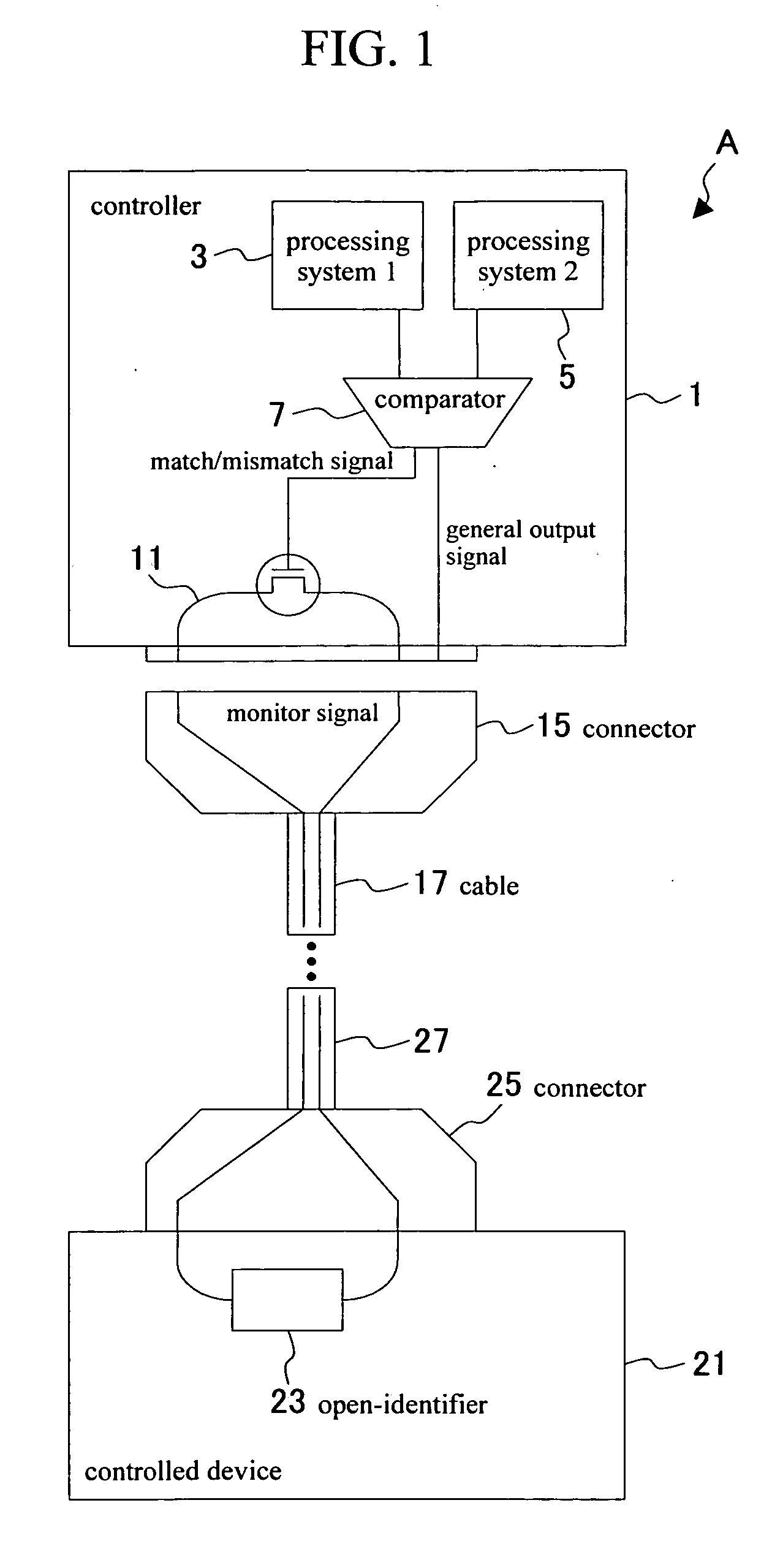
A power supply controller with a function to identify whether or not a signal that was output is reliable and to perform the necessary processing on the input side when an unreliable signal was sent that might adversely affect the input side in communication systems. A controller 1 and a controlled device 21 are connected at both ends of a cable 17 (27) with connectors. The controller contains a first processing system 1, a second processing system 2, and a comparator 7. The first processing system and the second processing system 2 are for example equivalent to microcomputers, etc. The comparator 7 compares the outputs of these two processors and generates a match / mismatch signal according to whether the outputs are a match or not. When the two outputs are a match then the outputs of these processors are reliable. However if the outputs are a mismatch then it signifies there is an error in one of these processing systems. Either of these processors outputs a general output signal separate from the match / mismatch signal. The general output signal may be output from either the first processing system or the second processing system without passing through the comparator. The general output signal is converted to a contact signal. The match / mismatch signal functions to turn the monitor signal on the monitor signal line on and off. The actual connection for this (output signal line) is shown in the drawings. The monitor signal line forms a loop on the monitor signal line for the signal to move back and forth between the controller and the controlled device. The controlled device contains an internal open-identifier for sensing whether the control signal line is open or closed.
Owner:HITACHI COMPUTER PERIPHERALS CO LTD
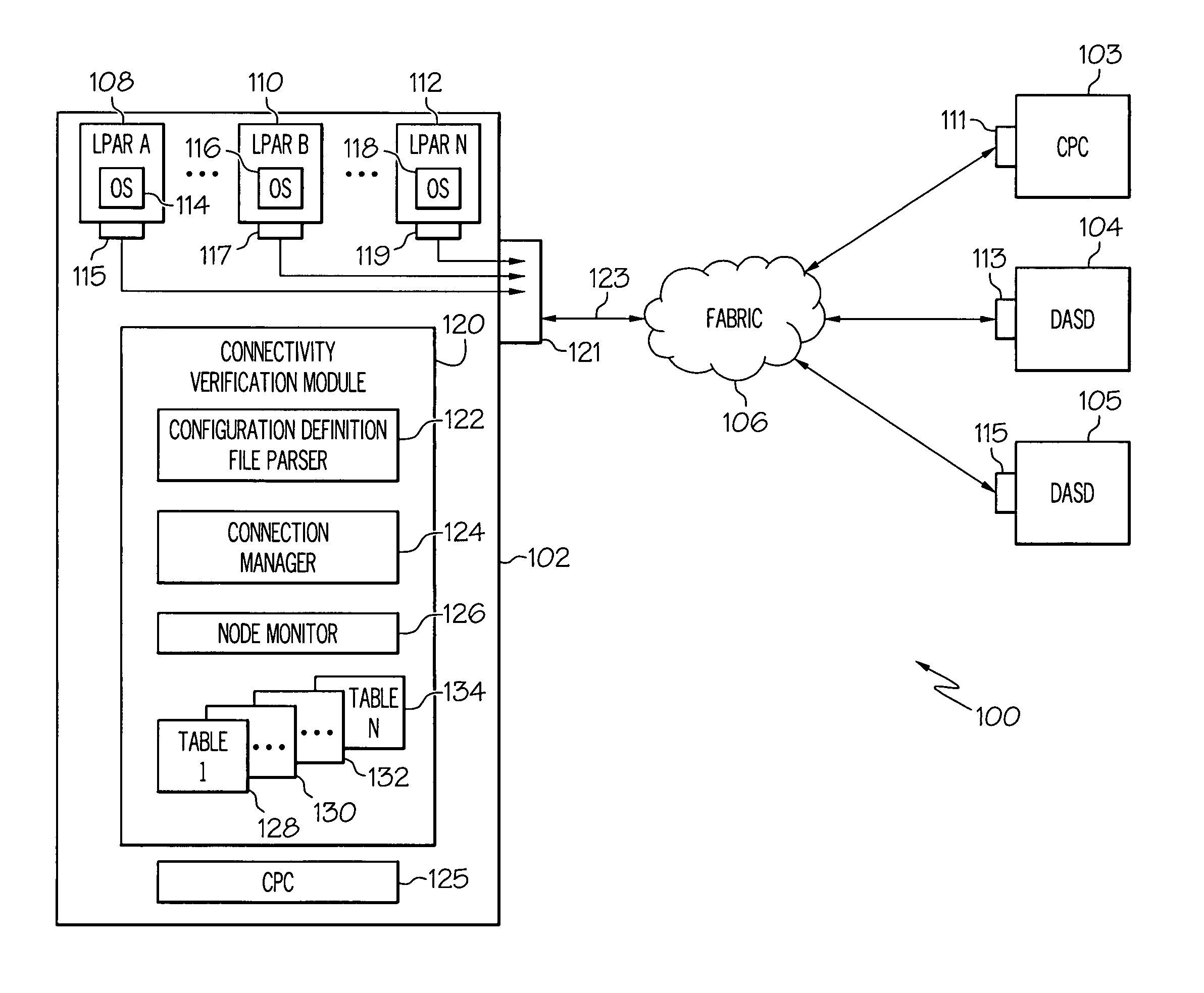
Logical to physical connectivity verification in a predefined networking environment
InactiveUS7930600B2Error detection/correctionDigital computer detailsComputer hardwareMatch/mismatch
A method, information system, and computer readable storage medium verify predefined connectivity for I / O devices. Current predefined logical connection data and actual physical connection data is gathered. The predefined logical connection data and the actual physical connection data are formatted into a plurality of sortable tables. At least a portion of the predefined logical connection data is formatted into a predefined channels table and at least a portion of the actual physical connection data is formatted into a node information table. The portion of the predefined logical connection data is compared with the portion of the actual physical connection data. The portion of the predefined logical connection data is determined to substantially match / not match the portion of the actual physical connection data. At least one predefined logical connection associated with the predefined logical connection data that fails to substantially match the actual physical connection data is displayed to a user.
Owner:IBM CORP
Roller washing machine
ActiveCN106222954APrevent accidental openingSimple structureOther washing machinesTextiles and paperMatch/mismatchMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a roller washing machine which comprises a body, a box, and a cover capable of opening and closing a feed hole, wherein the feed hole is formed in the top surface of the body; the box is arranged in the body and positioned below the feed hole; a first lock matching part is arranged on the box; the cover is movably arranged at the feed hole between an opening position and a closing position; the cover is provided with a second lock matching part which is matched / mismatched with the first lock matching part; and the first lock matching part is matched with the second lock matching part so as to lock the cover when the cover is positioned at the closing position. According to the roller washing machine disclosed by the embodiment of the invention, the cover can be opened from the upper part of the body, and leakage of detergents can be avoided when the cover is opened. Moreover, the cover can be prevented from being accidentally opened, and the roller washing machine is simple in structure, high in reliability and convenient to operate.
Owner:WUXI LITTLE SWAN ELECTRIC CO LTD
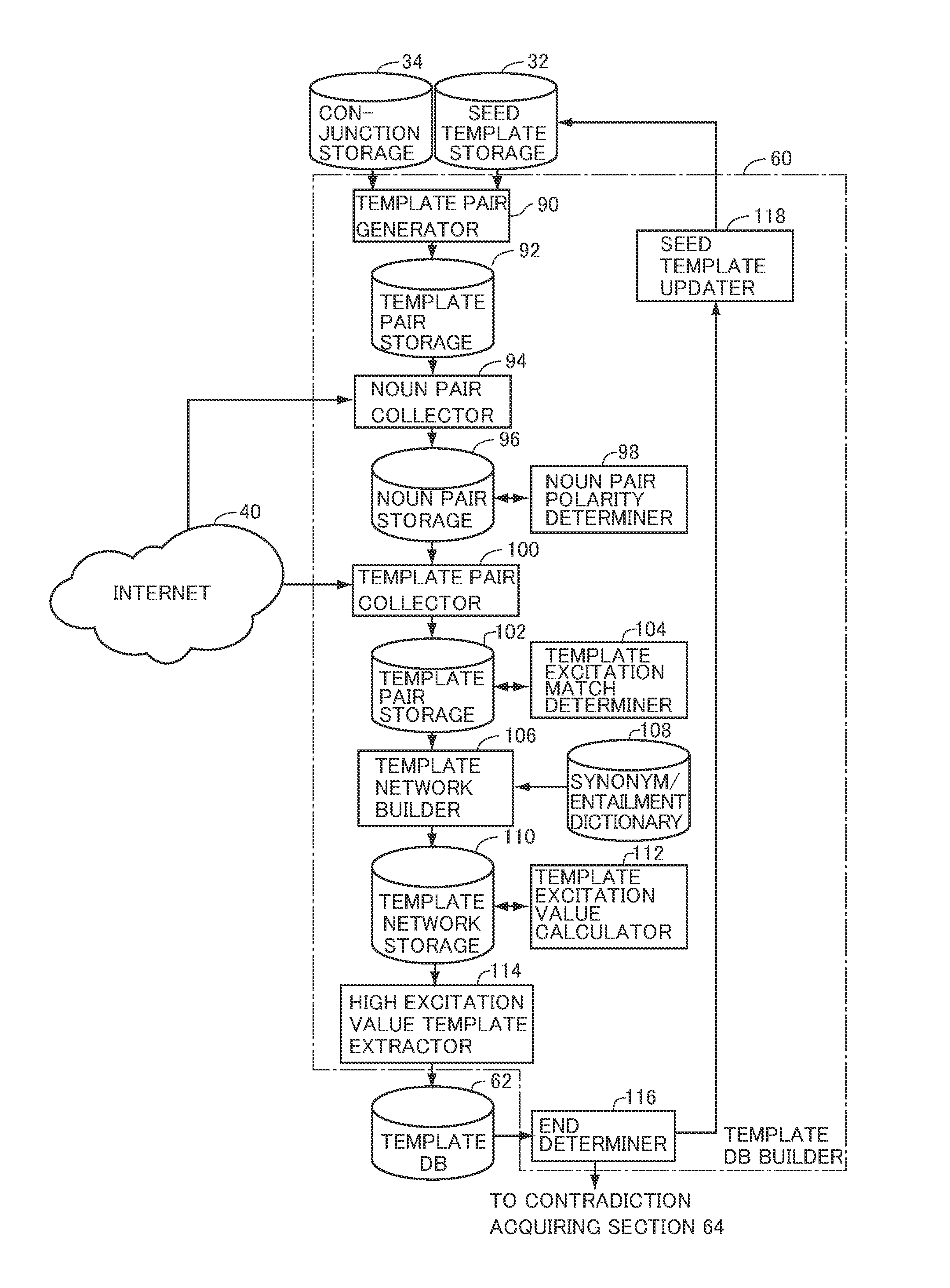
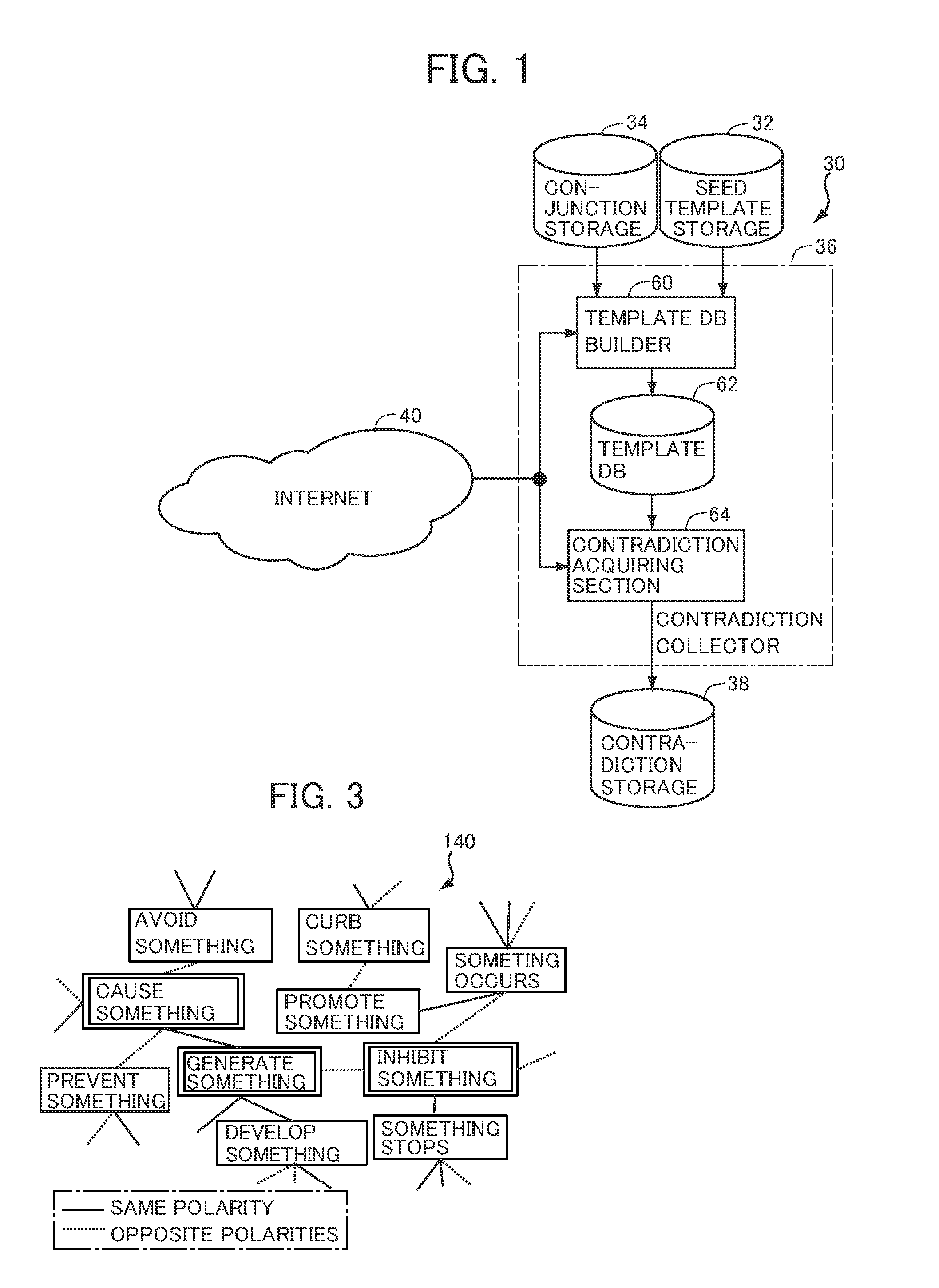
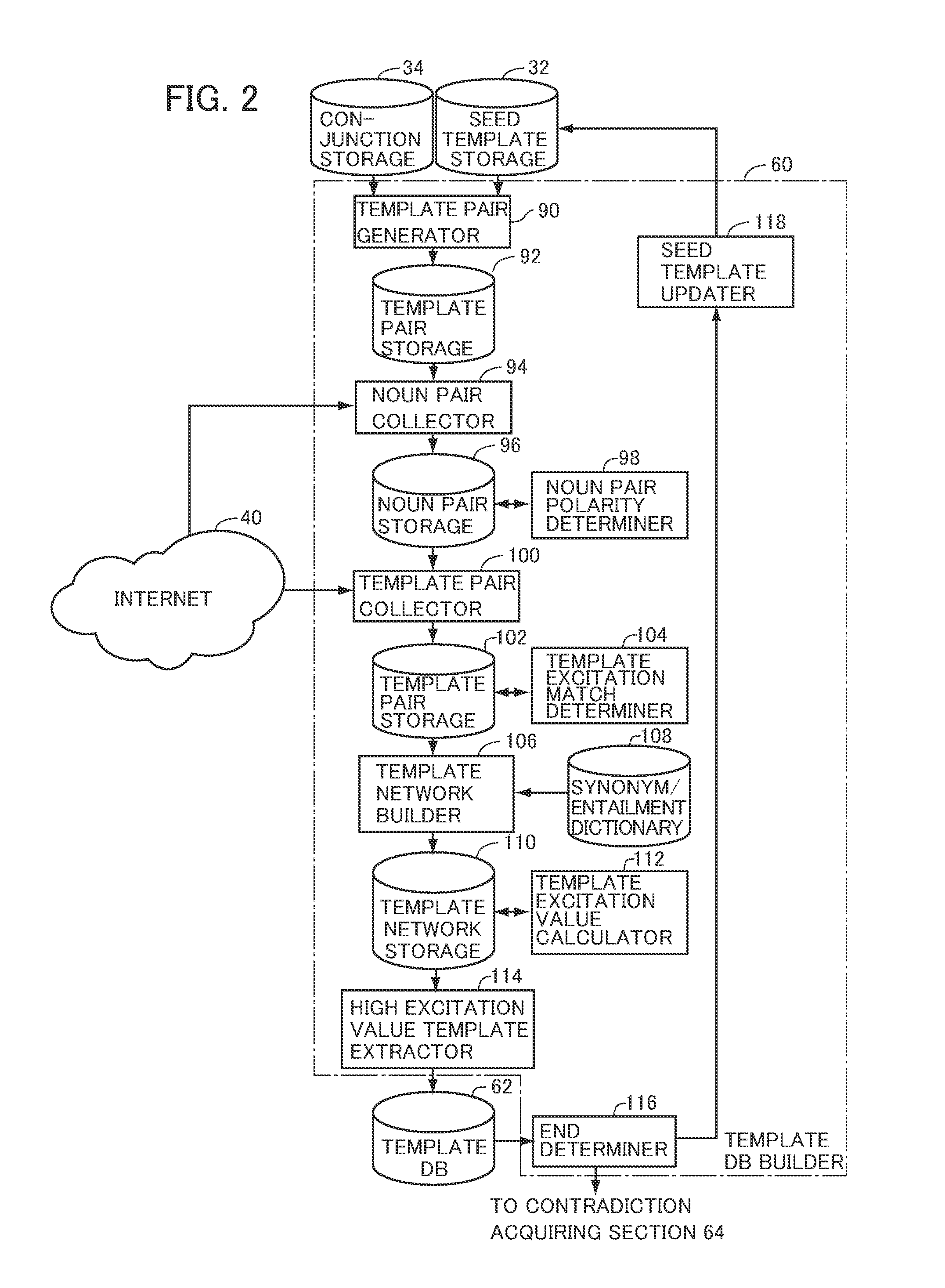
Predicate template collecting device, specific phrase pair collecting device and computer program therefor
InactiveUS9582487B2Efficiently and automatically and highly accurately recognizingNatural language analysisSemantic analysisNODALElectrical polarity
A predicate template collector allowing efficient and automatic recognition of predicate templates is adapted to include: a noun pair collector 94 and a noun pair polarity determiner 98 for collecting noun pairs co-occurring with predicate template pairs and determining polarity of relation between nouns, using conjunctions and seed templates; a template pair collector 100, collecting template pairs co-occurring with noun pairs and determining, based on the relation of noun pairs co-occurring with the predicate template pairs and the conjunctions between predicate templates pairs, whether the polarity of excitatory class of predicate template pair is the same or not; a template network builder 106 building a template network connecting predicate templates based on the predicate template pairs and match / mismatch of excitatory class thereof; and a template excitation value calculator 112 calculating excitation value to be assigned to each node, using the excitation value of seed templates and the relation between each of the nodes in the network.
Owner:NAT INST OF INFORMATION & COMM TECH
Image printing apparatus and tandem image printing method
InactiveUS20100178068A1Reliable outputPerformed quicklyElectrographic process apparatusInput/output processes for data processingCommunication unitPulp and paper industry
This invention provides an image printing apparatus including a communication unit which communicatively connects to at least another image printing apparatus, a tandem output mode, a paper feed unit which feeds recording sheets, a comparison and determination unit which compares the information of recording sheets which can be fed from the paper feed unit with paper size information and paper type information in another image printing apparatus which has received by the communication unit in the tandem output mode, and determines a paper size match / mismatch and a paper type match / mismatch, and a mismatch notification unit which notifies a mismatch when one or both of the paper size and the paper type exhibits a mismatch upon receiving a determination result from the comparison and determination unit.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA BUSINESS TECH INC
Content addressable memory capable of changing priority in priority encoder
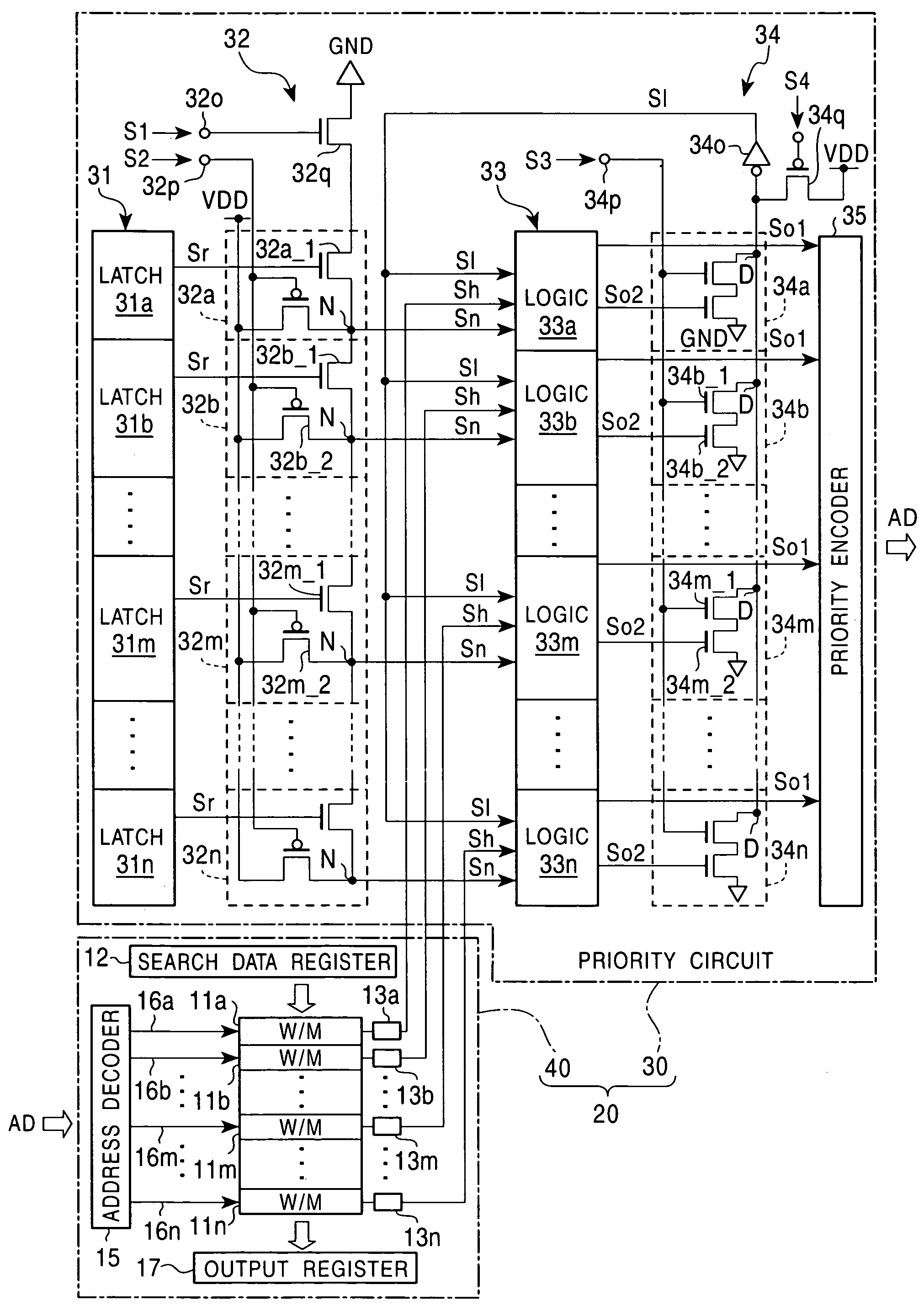
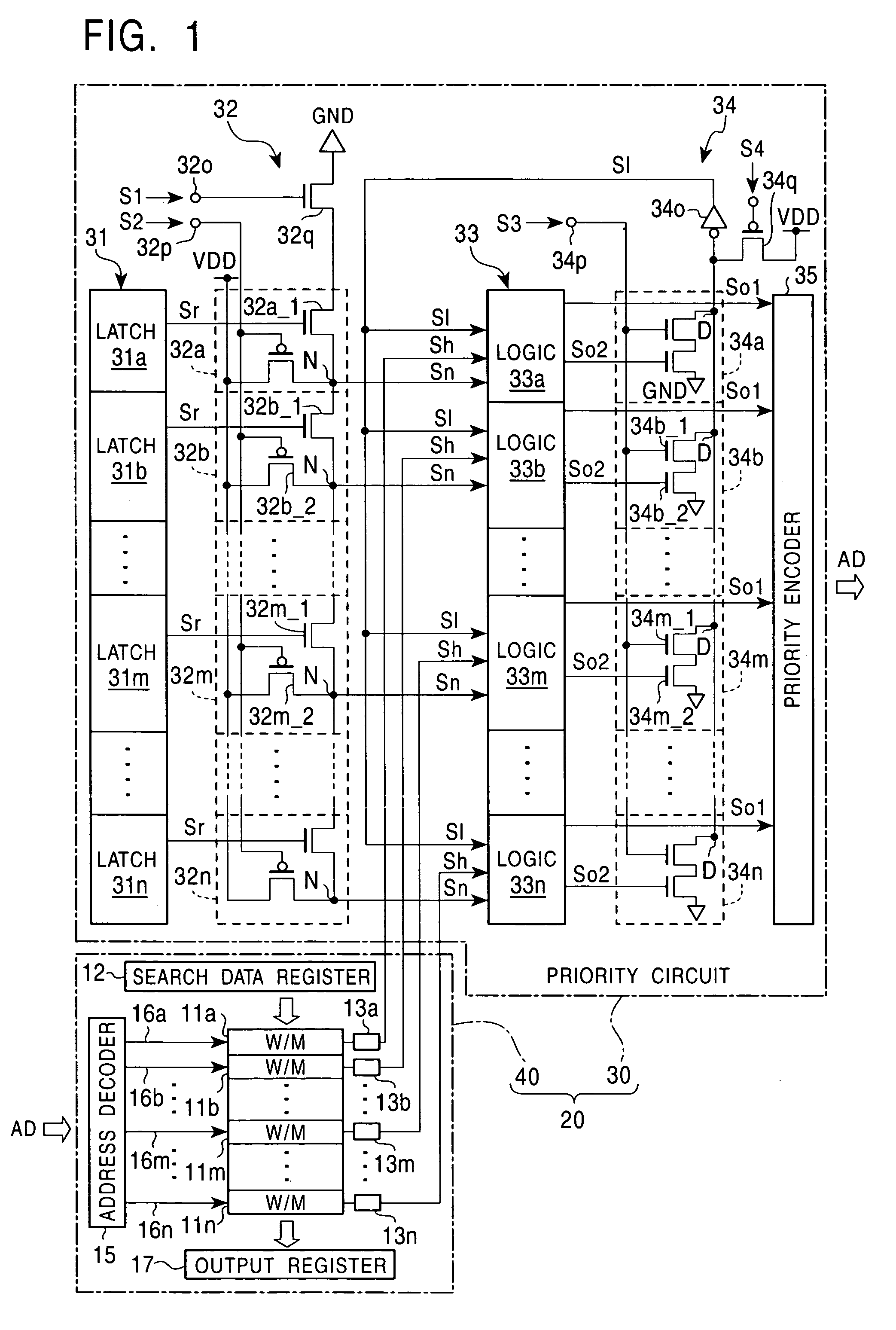
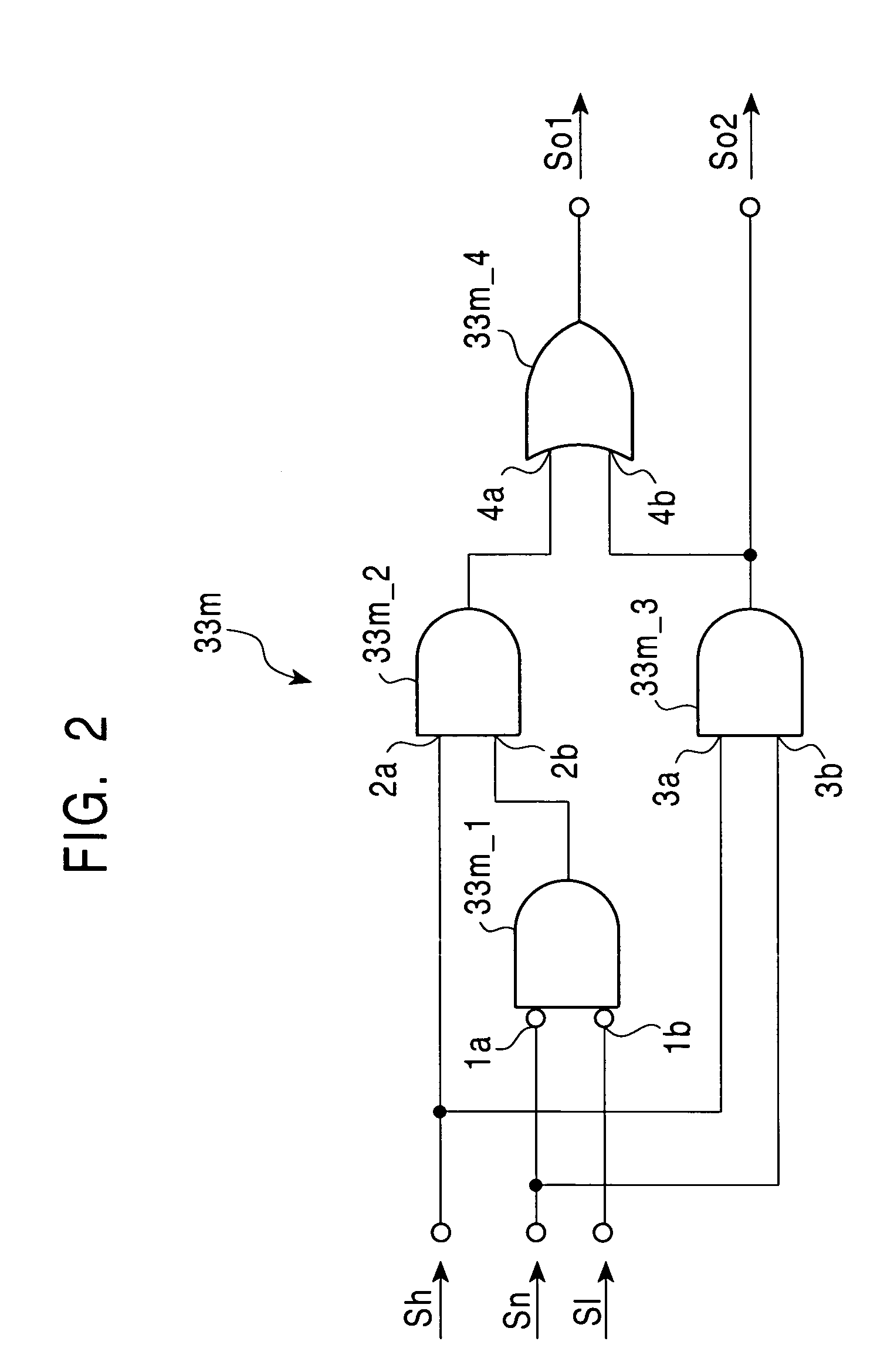
InactiveUS7257671B2Data facilitatedResults facilitatedDigital storageMemory systemsNO storageComputer hardware
A content addressable memory includes a plurality of word memories which respectively have assigned addresses, and each outputs a match / mismatch signal representing storage or no storage of a data item matching search data in a search mode, a priority encoder which output addresses of word memories which output the match signals in the search mode in predetermined fixed priority order, a first prior word-memory setting section for setting a first prior word memory, and a priority changing part which masks the match signals output from upper-positional word memories of the word memories, which correspond to word memories having upper positions compared with the first prior word memory in the fixed priority order in the priority encoder, and transmits signals representing that the word memories having the upper positions output no match signals to the priority encoder.
Owner:KAWASAKI MICROELECTRONICS
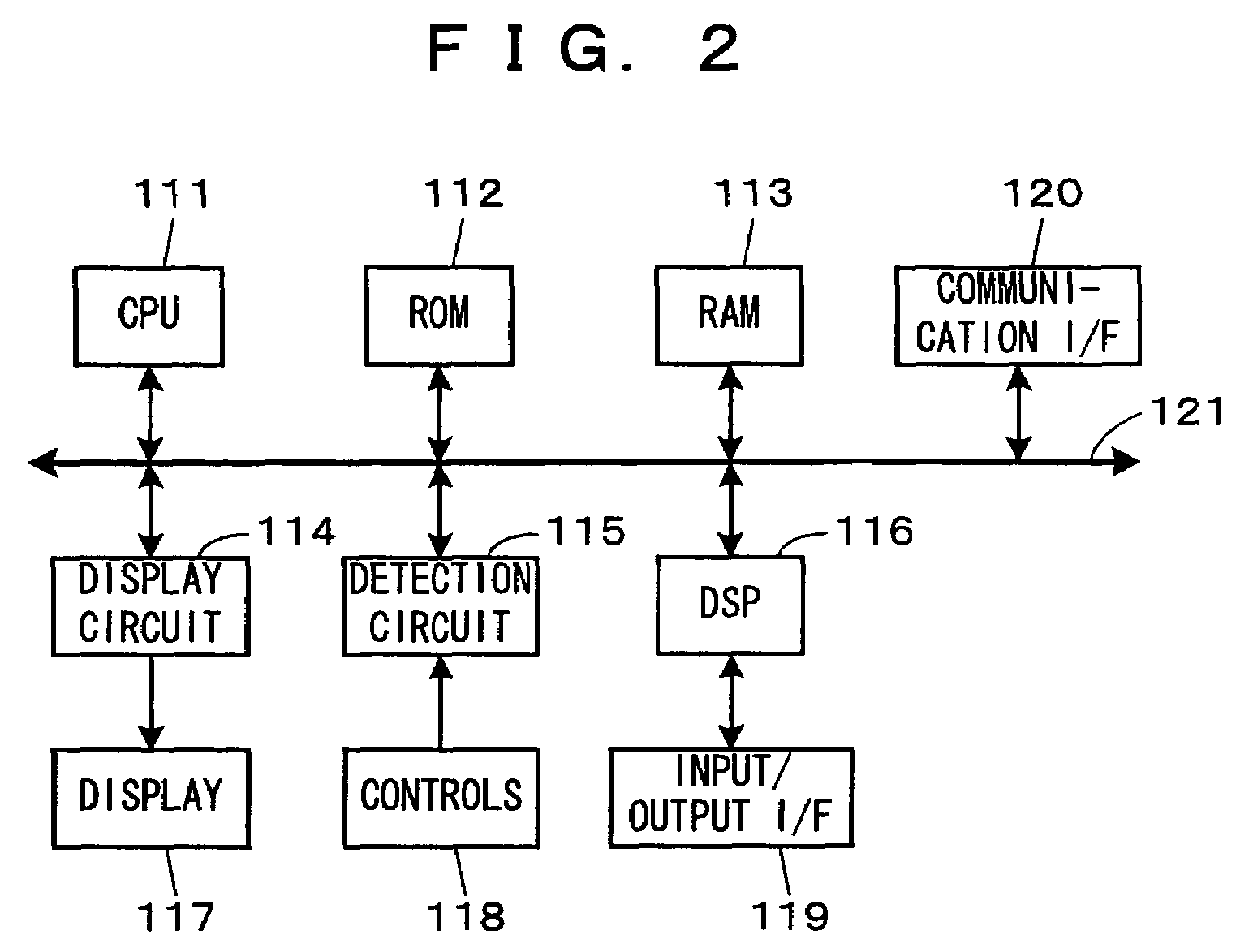
Sound signal processor
In an audio signal processing device which processes audio signals and outputs the audio signals, setting controls (118), such as filter controls (11), for setting values of parameters for the signal processing and a display (13, 24, 34) for presenting information by the presence or absence and the style of lighting of LEDs is provided, in which when scene data stored in a scene memory is loaded, the display style of the display (13, 24, 34) is made different in accordance with match / mismatch between a current set value of the parameter and the value of the parameter relating to the loaded scene data. Alternatively, the display (13, 24, 34) is made to simultaneously present the loaded value and the value at the time of the loading in different display styles.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
Memory having information refinement detection function by applying a logic operation in parallel for each memory address to the match/mismatch results of data items and memory addresses, information detection method using memory, and memory address comparison circuit for the memory
ActiveUS9275734B2Reduce in quantityIncrease speedDigital data information retrievalDigital storageMemory addressWide area
There is provided an externally readable memory for storing information in each memory address, and this memory is provided with an information refinement detection function; this memory comprises: an input means for entering first input data for comparing data items stored in the memory and second input data for comparing addresses in the memory, wherein the first and second comparison data are externally; means for determining matches / mismatches of both data items stored in the memory and addresses of the memory according to both of the input data provided by the input means, and further performing logic operations on both of the match / mismatch determination results; and means for outputting addresses with positive results of the logic operations. This memory may be applicable in a broad range of fields including intelligent information search as well as artificial intelligence.
Owner:INOUE KATSUMI
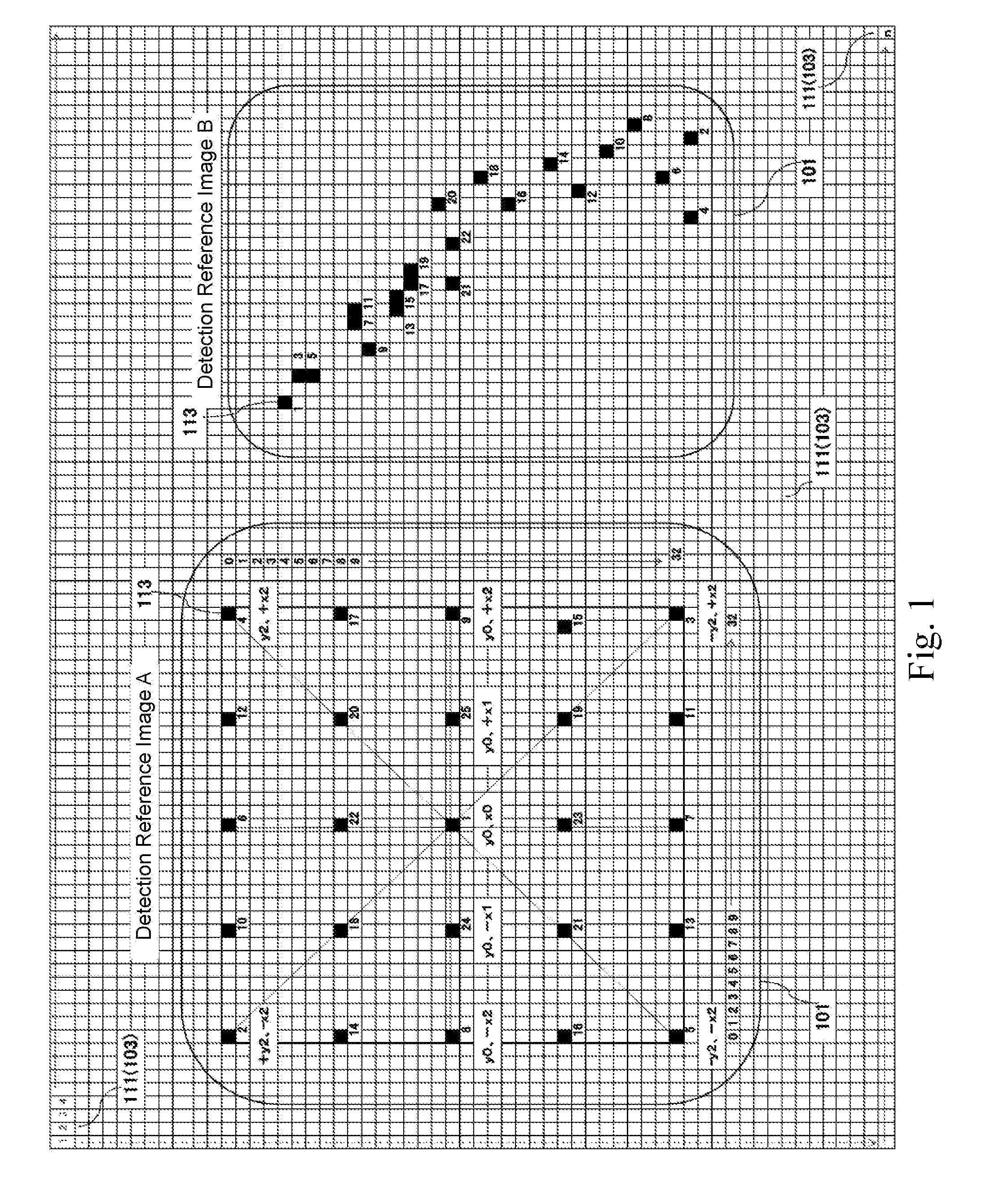
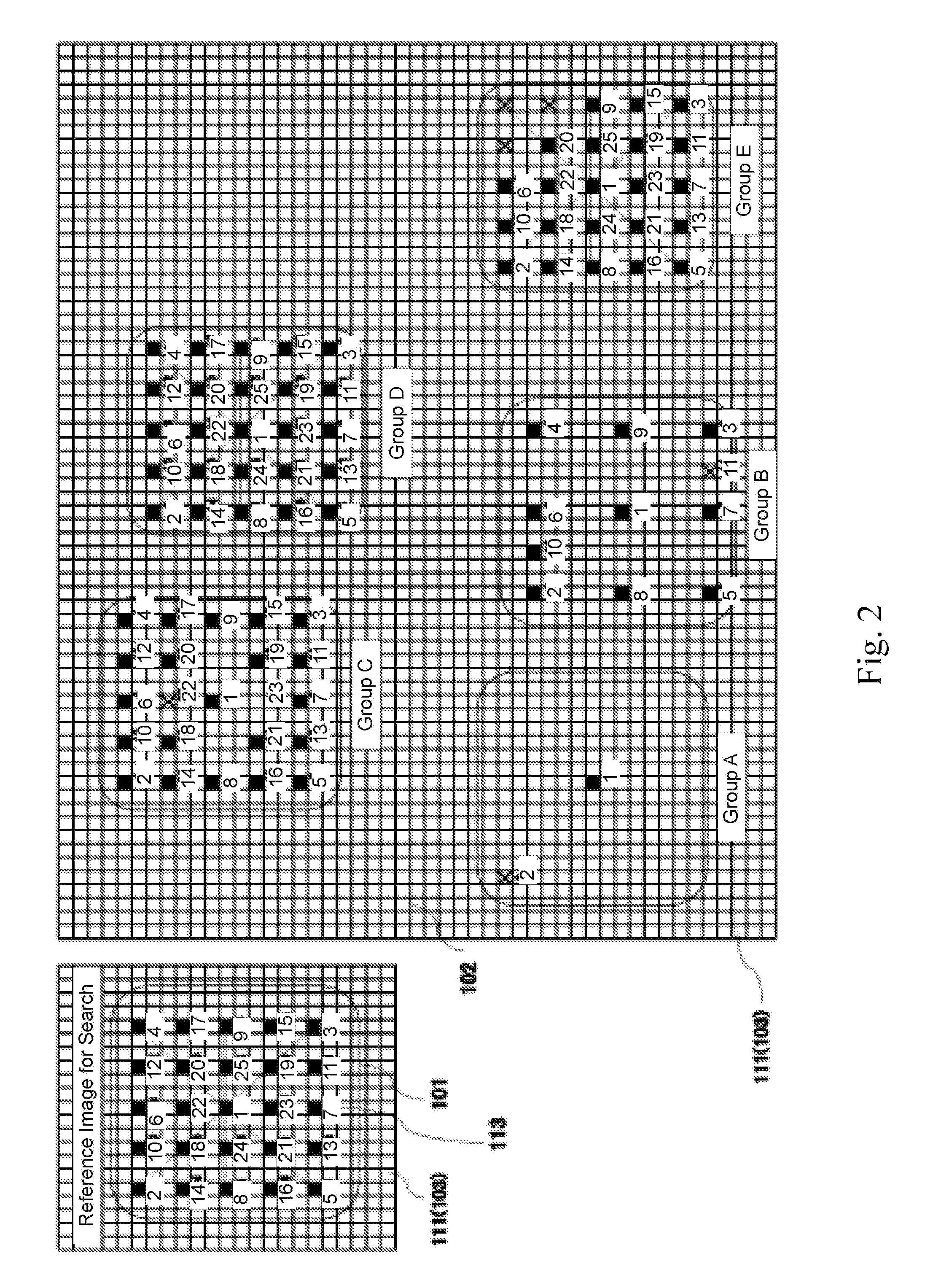
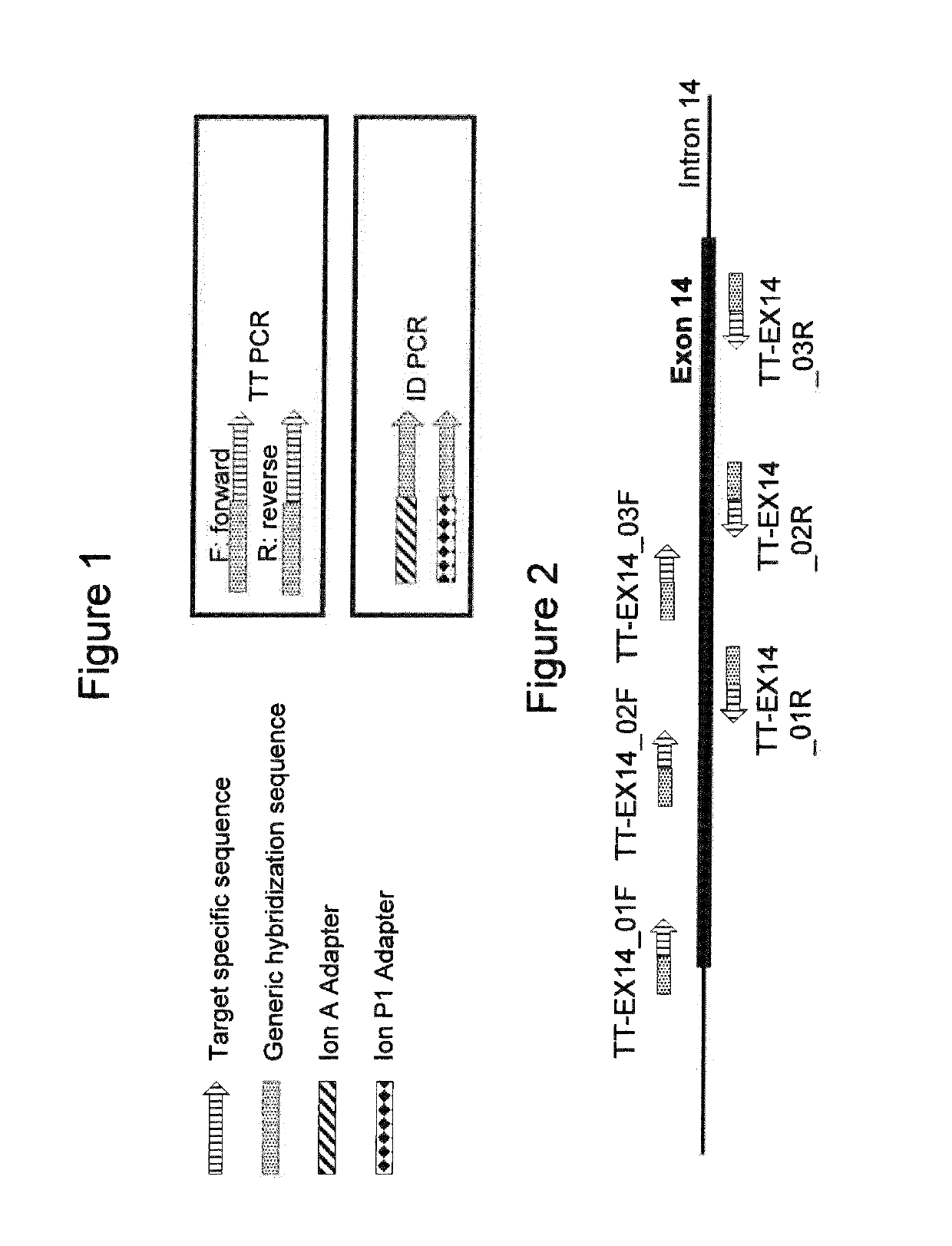
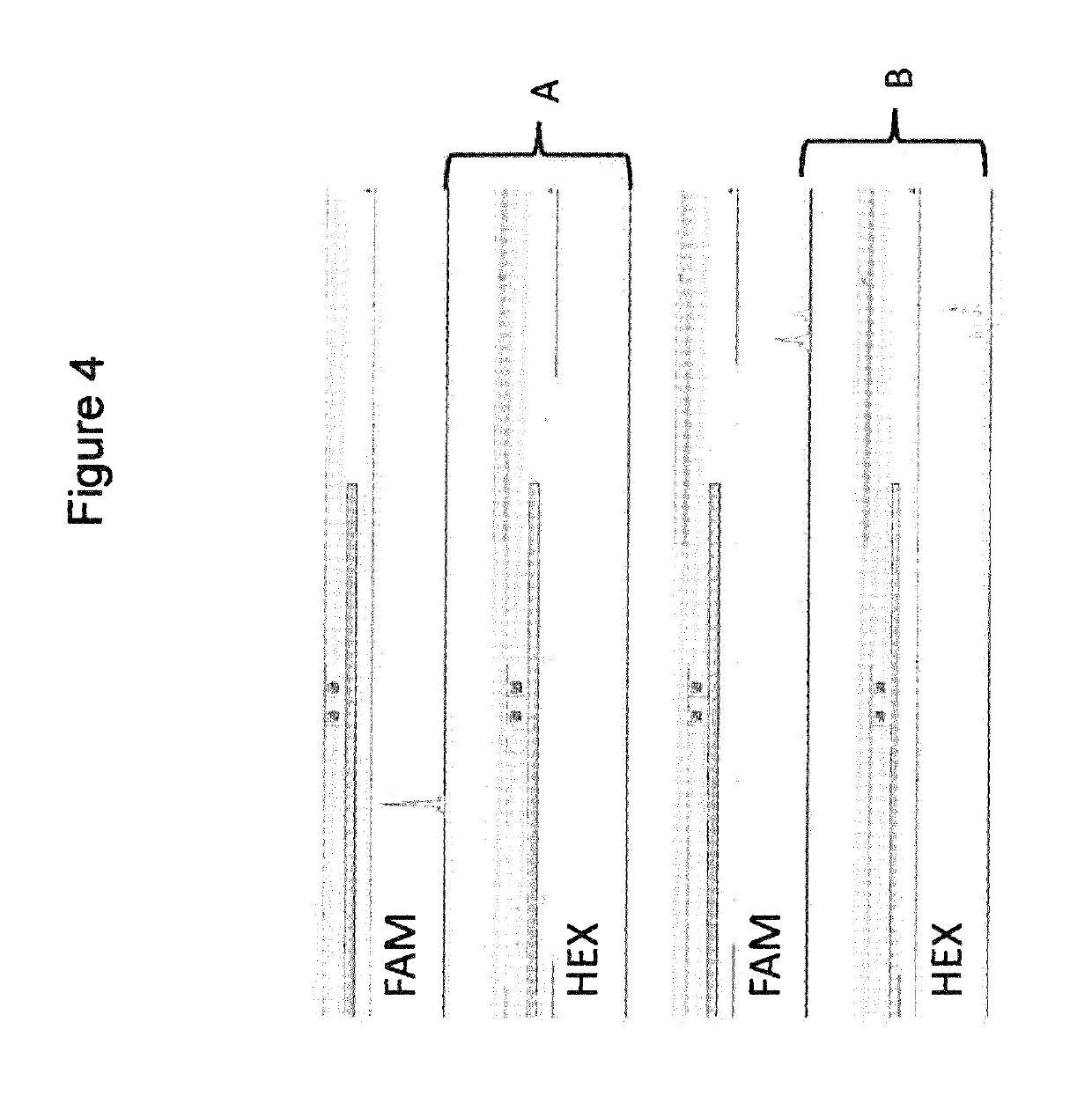
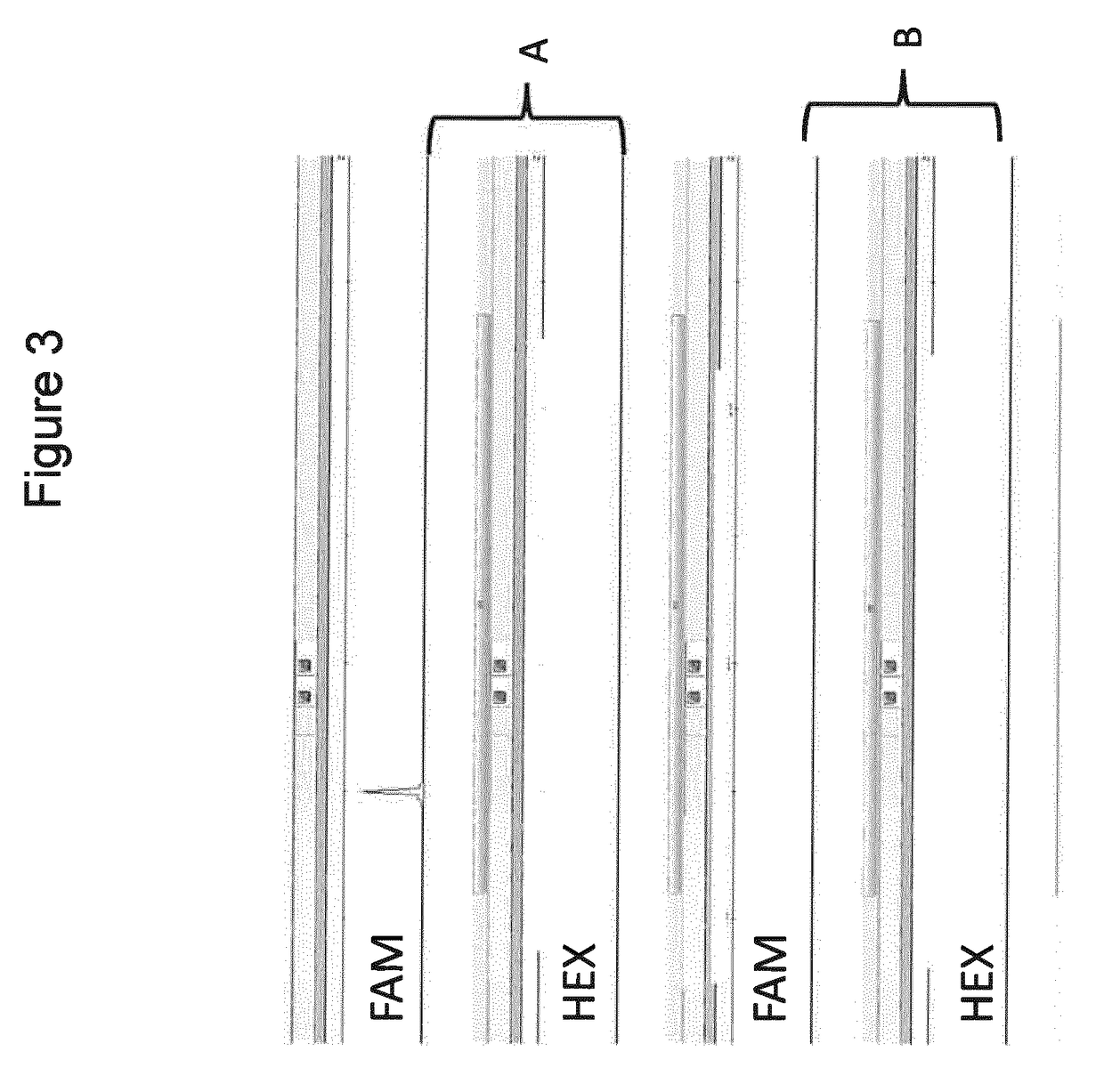
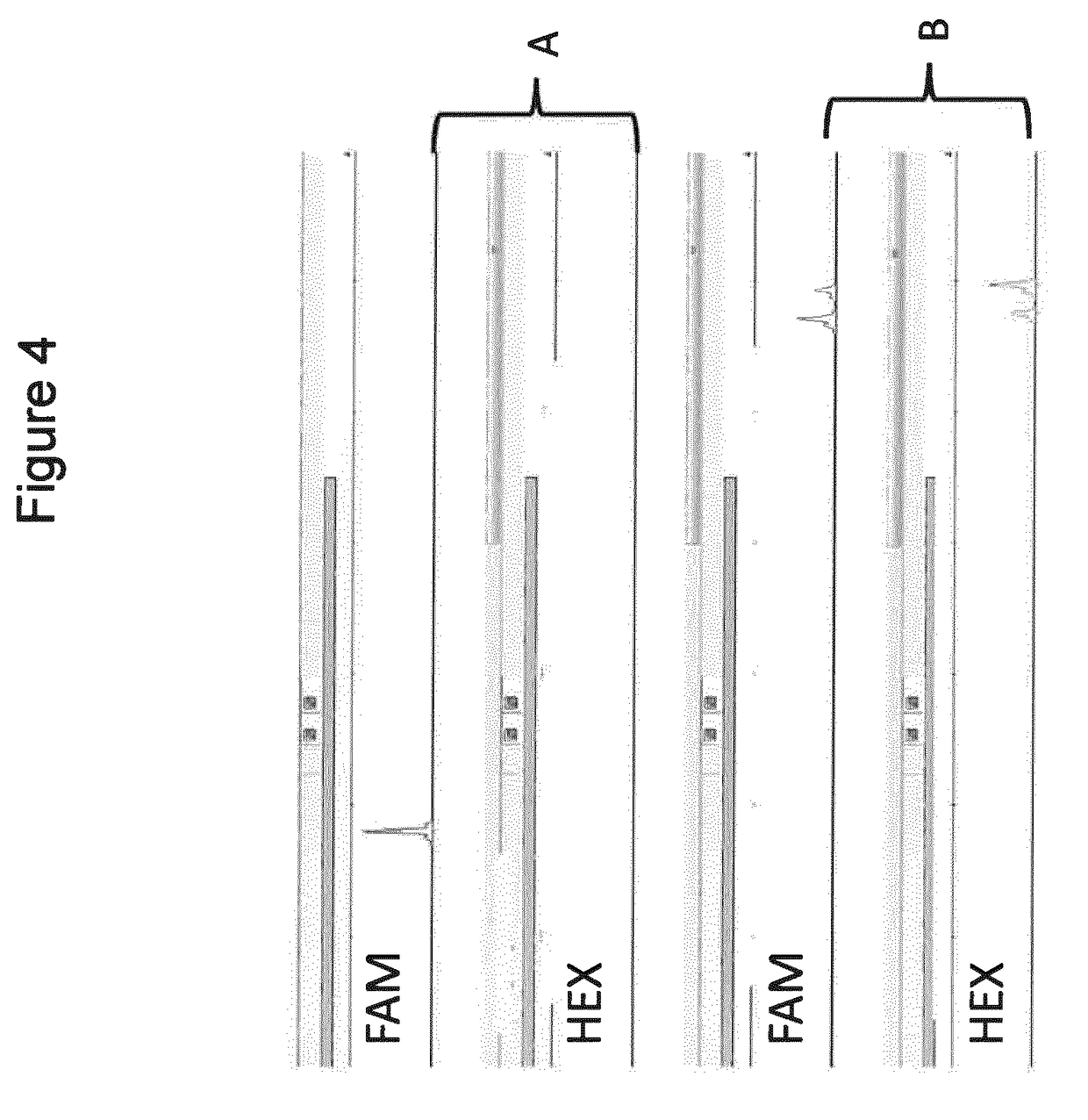
Selective amplification of desired nucleic acid regions in a target sequence
ActiveUS10246740B2Short sequenceLong sequenceMicrobiological testing/measurementInverse polymerase chain reactionMatch/mismatch
A method and kit for selective amplification of desired amplicons in a two-stage polymerase chain reaction is provided. The method and kit uses target primers comprising mismatch control sequences; wherein any pair of primers that flank a desired amplicon sequence have non-matching mismatch control sequences. and any pair of primers that flank an undesired amplicon sequence have matching mismatch control sequences.
Owner:DEVYSER HLDG
Semiconductor device
The present invention provides a semiconductor device that can reduce the power consumption, including: a plurality of search memory cells arranged in a matrix; a plurality of match lines provided corresponding to each memory cell row to determine match / mismatch between data stored in the search memory cell and search data; a plurality of match line retention circuits provided corresponding to each of the match lines; a storage unit for storing information relating to the state of each of the match lines; and a selection circuit for selectively activating the match line retention circuits based on the information stored in the storage unit.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Match mismatch emulation scheme for an addressed location in a CAM
A novel match / mismatch emulation scheme for an addressed location in a CAM system that includes a plurality of CAM blocks. The plurality of CAM blocks are organized into at least one rectangular array having rows each having a plurality of CAM blocks, a group of CAM cells and associated read / write bit lines connecting the group of CAM cells to an addressed search circuit. During debug mode, where the individual array cells do not participate in search, all the cells in the debug column behave the same way to emulate a match / mismatch on all words. The circuit provides a control input to include address evaluation of a debug cell in a row. The circuit also provides simultaneous switching noise analysis on an evaluating row. The resulting CAM cell provides a circuit to test individual rows for defects and noise analysis.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Selective amplification of desired nucleic acid regions in a target sequence
ActiveUS20180371528A1Short hybridization sequenceLong sequenceMicrobiological testing/measurementInverse polymerase chain reactionMatch/mismatch
A method and kit for selective amplification of desired amplicons in a two-stage polymerase chain reaction is provided. The method and kit uses target primers comprising mismatch control sequences; wherein any pair of primers that flank a desired amplicon sequence have non-matching mismatch control sequences. and any pair of primers that flank an undesired amplicon sequence have matching mismatch control sequences.
Owner:DEVYSER HLDG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com