Patents
Literature
2016 results about "Logic level" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In digital circuits, a logic level is one of a finite number of states that a digital signal can inhabit. Logic levels are usually represented by the voltage difference between the signal and ground, although other standards exist. The range of voltage levels that represents each state depends on the logic family being used.
Dual function data register
ActiveUS20090290434A1Reduce disadvantagesRead-only memoriesDigital storageProcessor registerTheoretical computer science
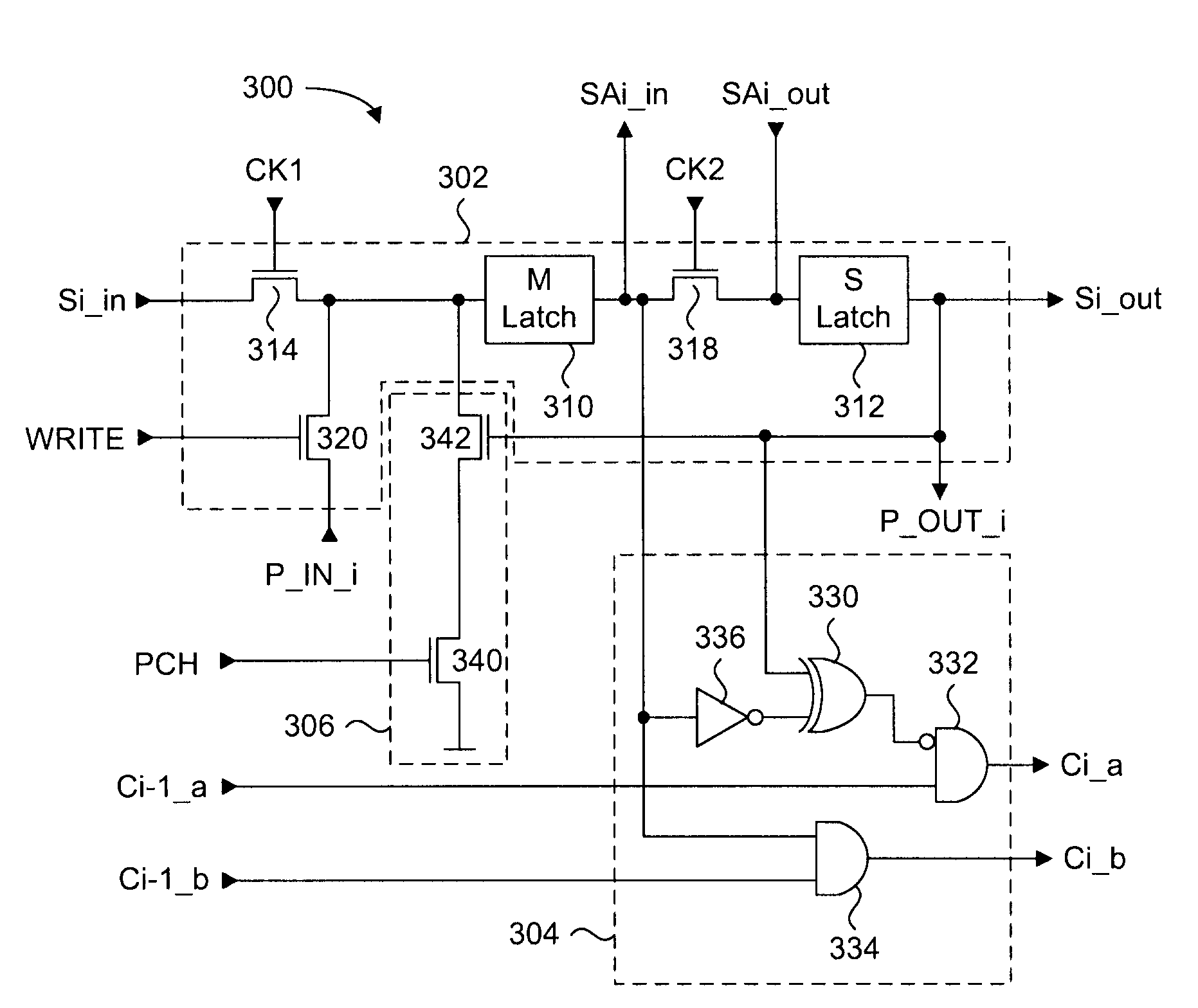
A dual function serial and parallel data register with integrated program verify functionality. The master and slave latching circuits of the dual function data register can concurrently store two different words of data. In a program verify operation, the master latch stores program data and the slave latch will receive and store read data. Comparison logic in each register stage will compare the data of both latches, and integrate the comparison result to that of the previous register stage. The final single bit result will indicate the presence of at least one bit that has not been programmed. Automatic program inhibit logic in each stage will prevent successfully programmed bits from being re-programmed in each subsequent reprogram cycle. Either data word can be serially clocked out by selectively starting the shift operations on either the low or high active logic level of a clock signal.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
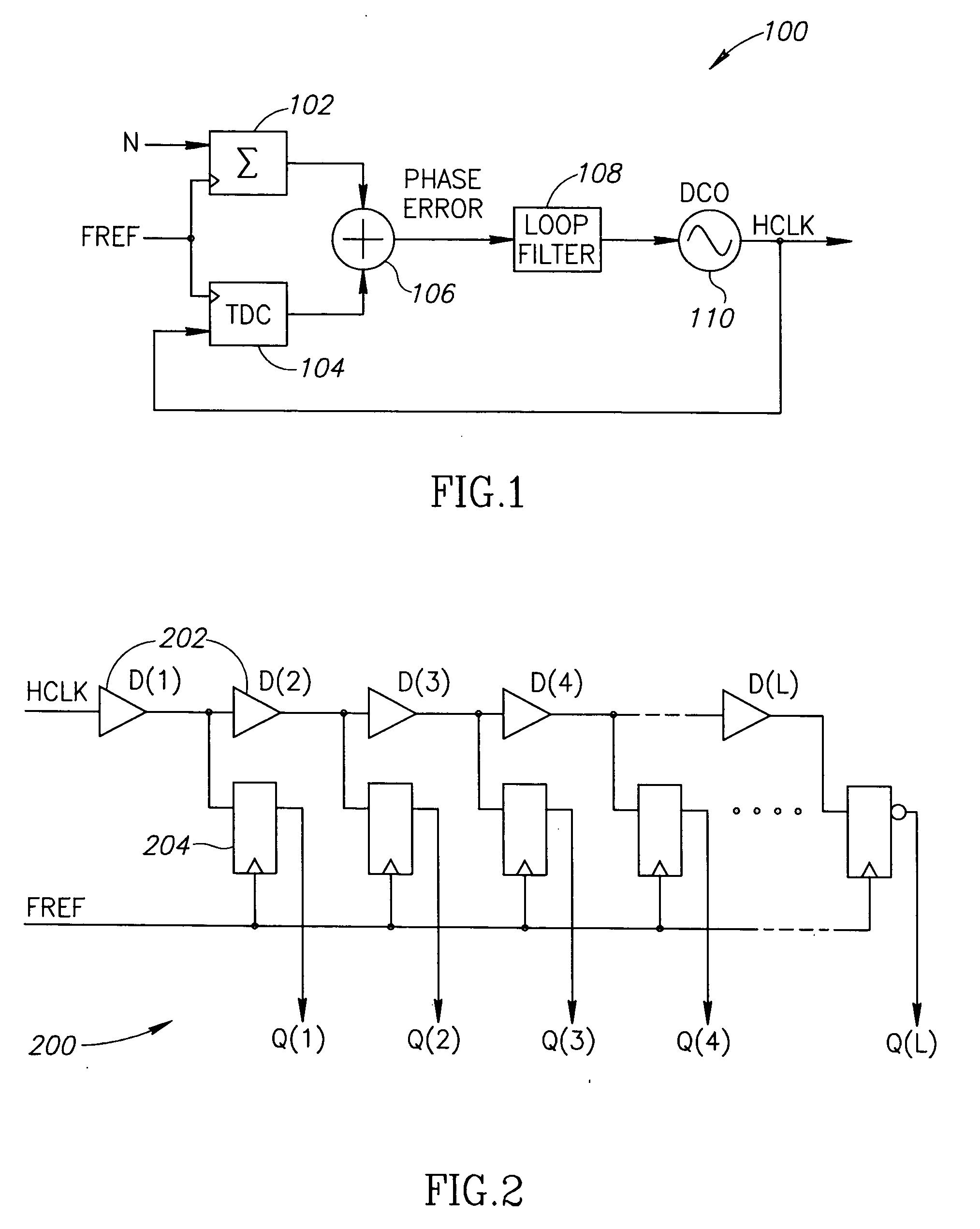
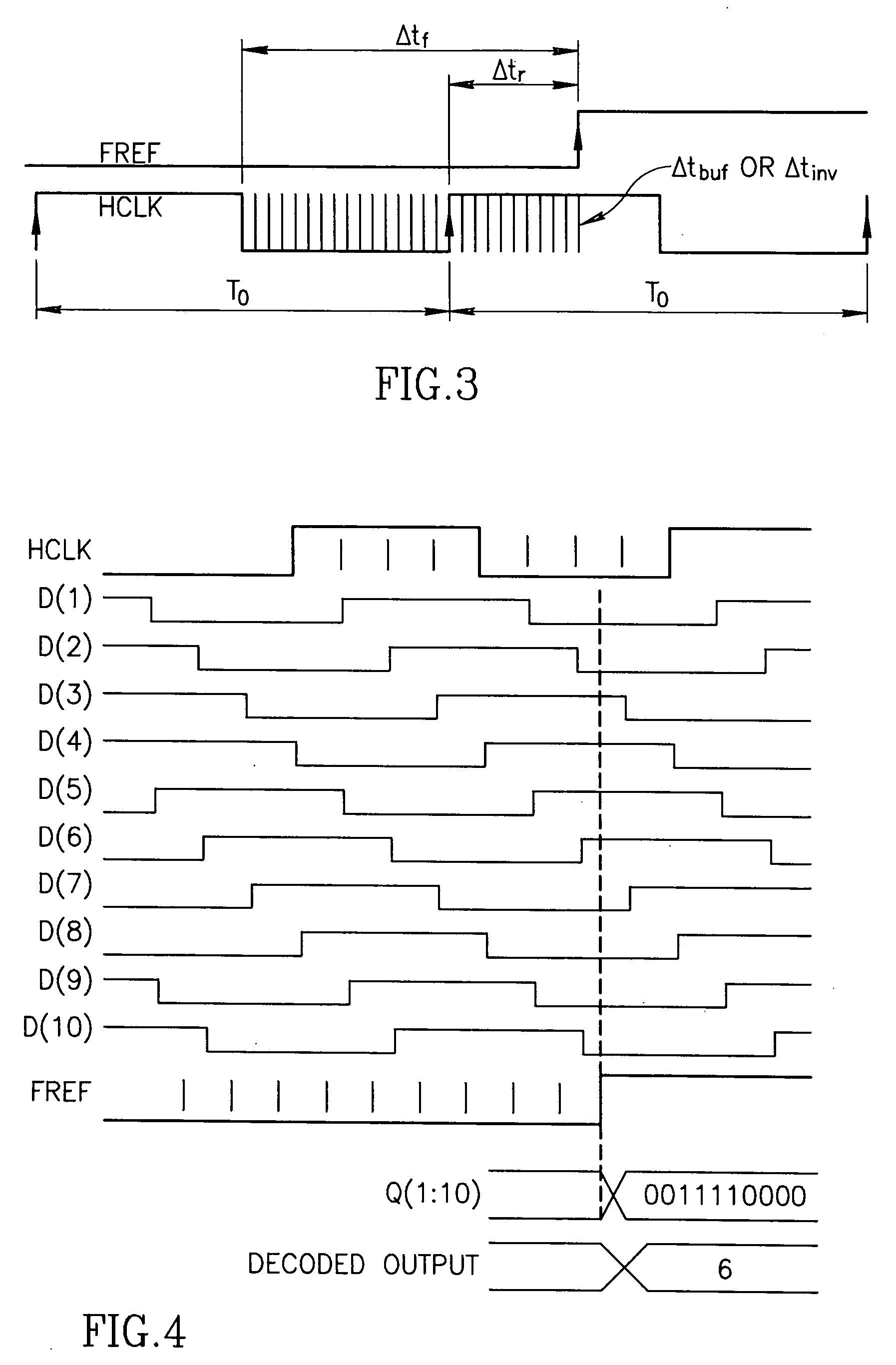
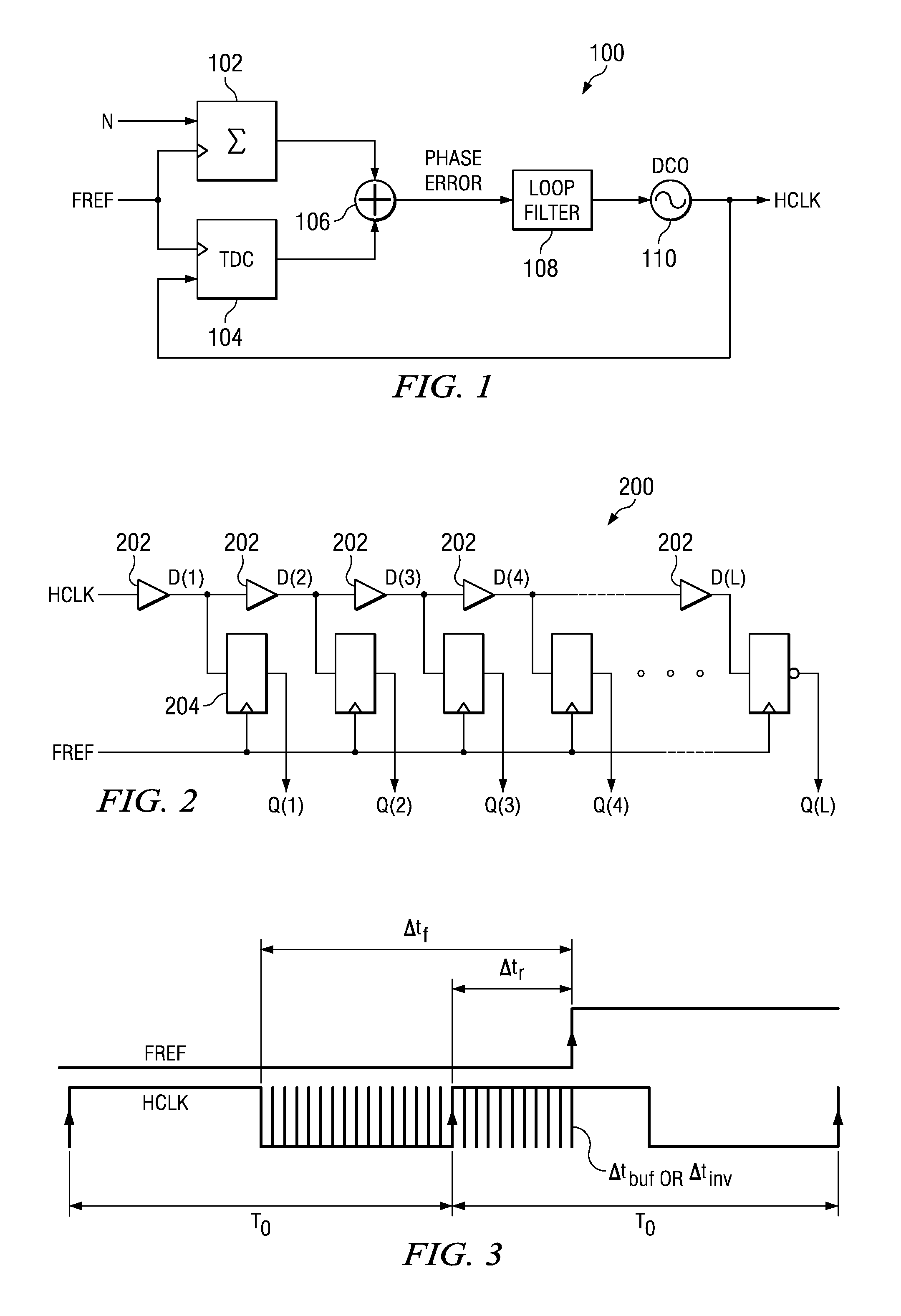
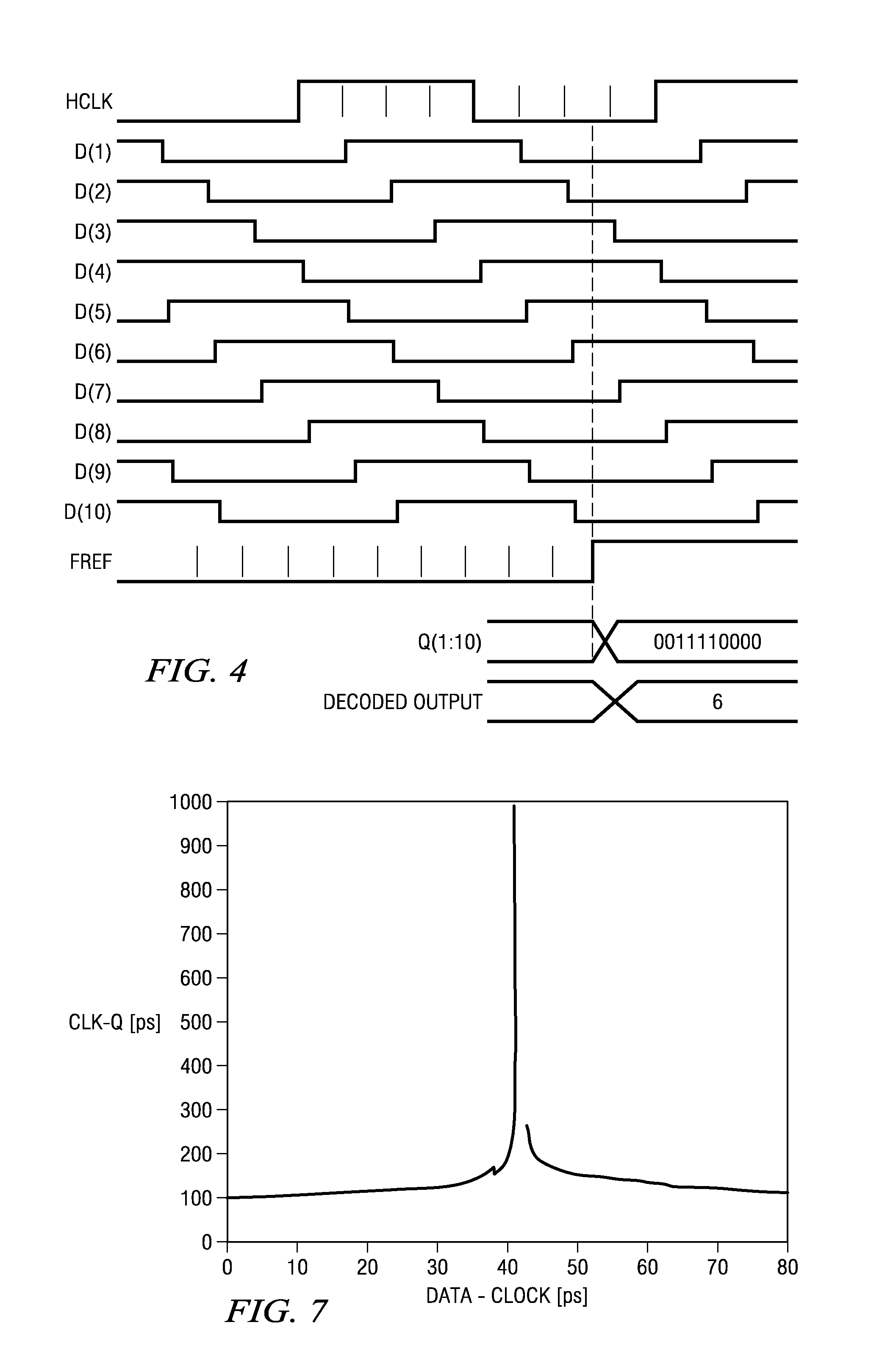
Circuit for high-resolution phase detection in a digital RF processor
ActiveUS20060103566A1Less sensitiveReduce power consumptionElectric signal transmission systemsPulse automatic controlEngineeringDigital converter
A novel time-to-digital converter (TDC) used as a phase / frequency detector and charge pump replacement in an all-digital PLL within a digital radio processor. The TDC core is based on a pseudo-differential digital architecture making it insensitive to NMOS and PMOS transistor mismatches. The time conversion resolution is equal to an inverter propagation delay, e.g., 20 ps, which is the finest logic-level regenerative timing in CMOS. The TDC is self calibrating with the estimation accuracy better than 1%. The TDC circuit can also serve as a CMOS process strength estimator for analog circuits in large SoC dies. The circuit also employs power management circuitry to reduce power consumption to a very low level.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
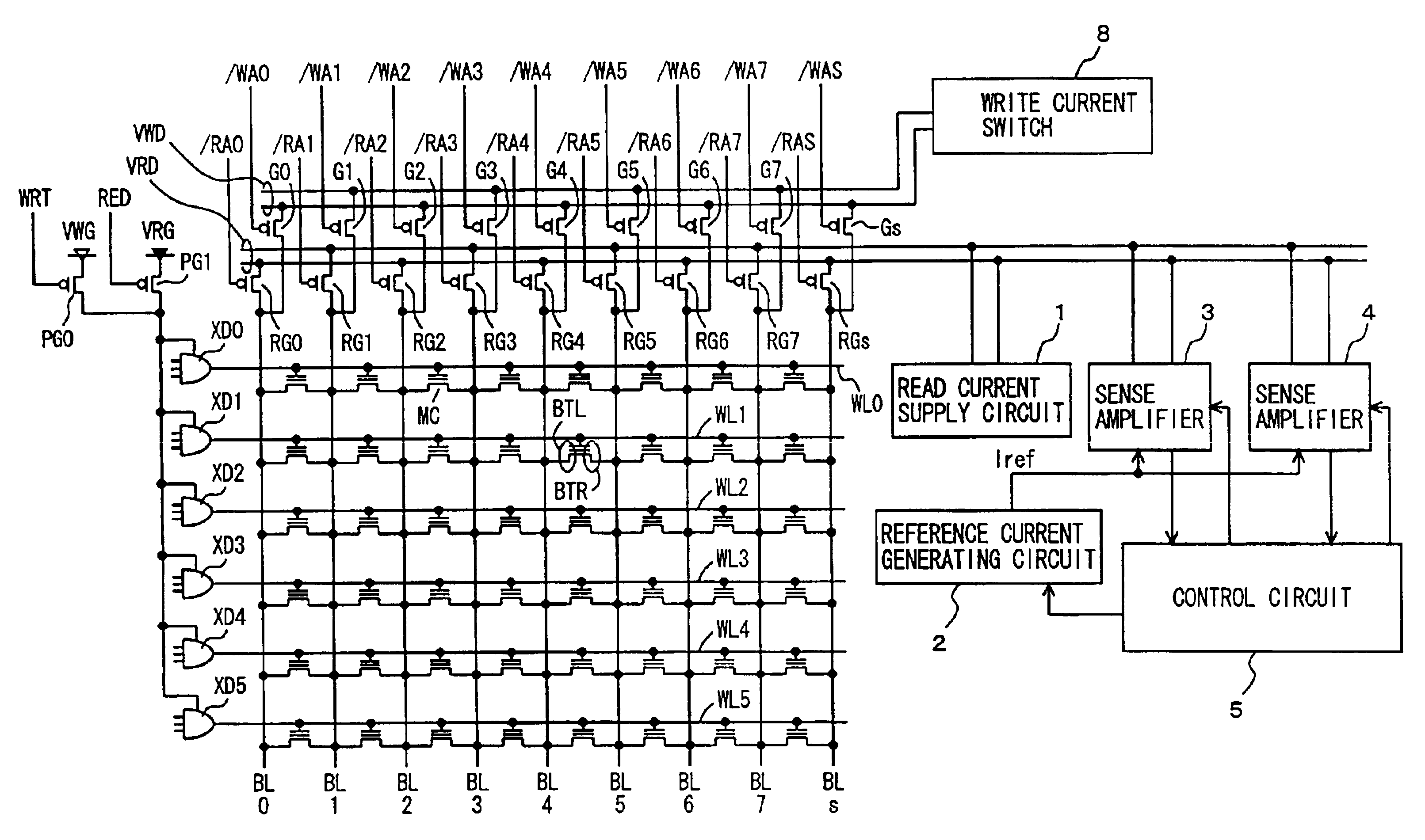
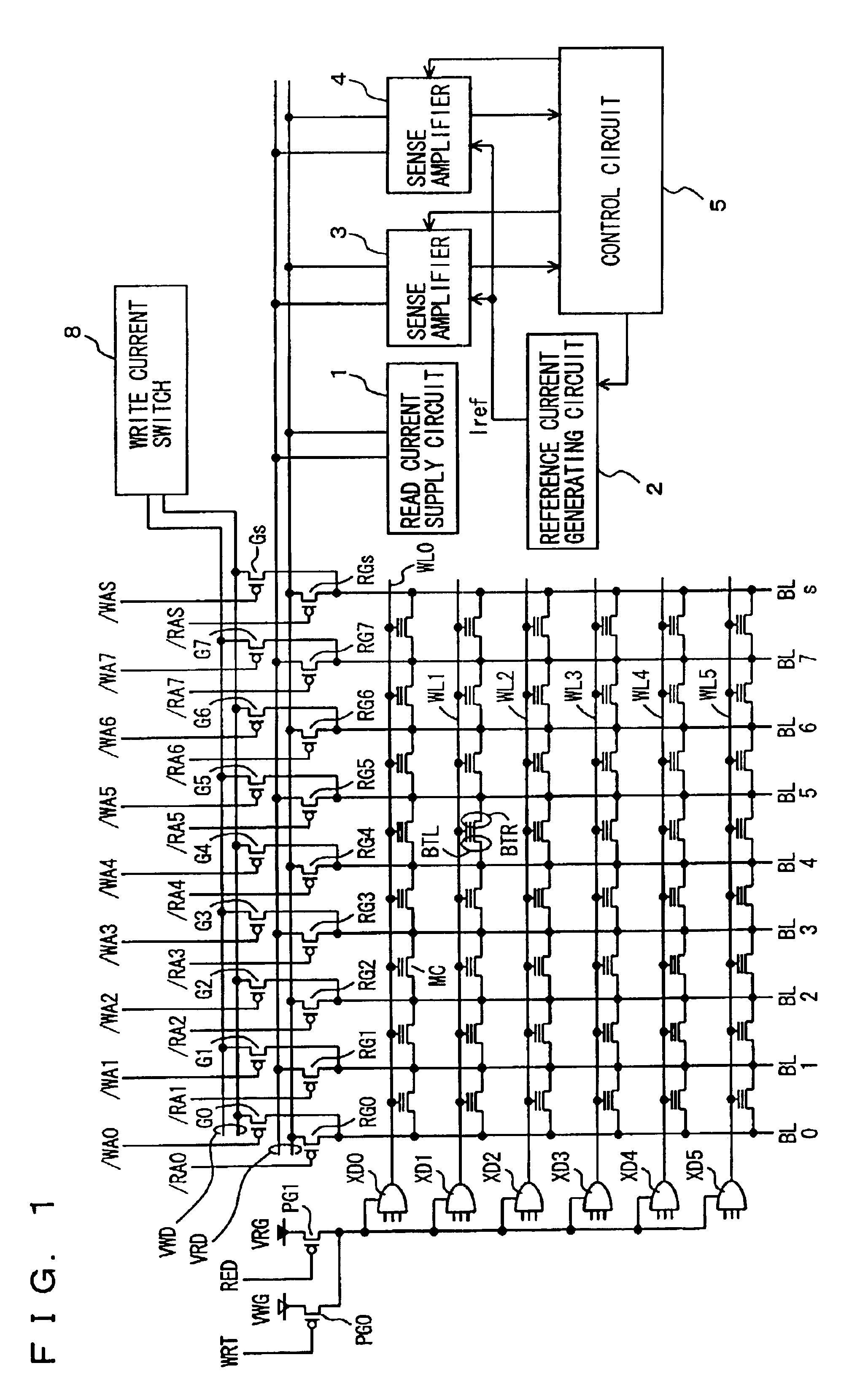
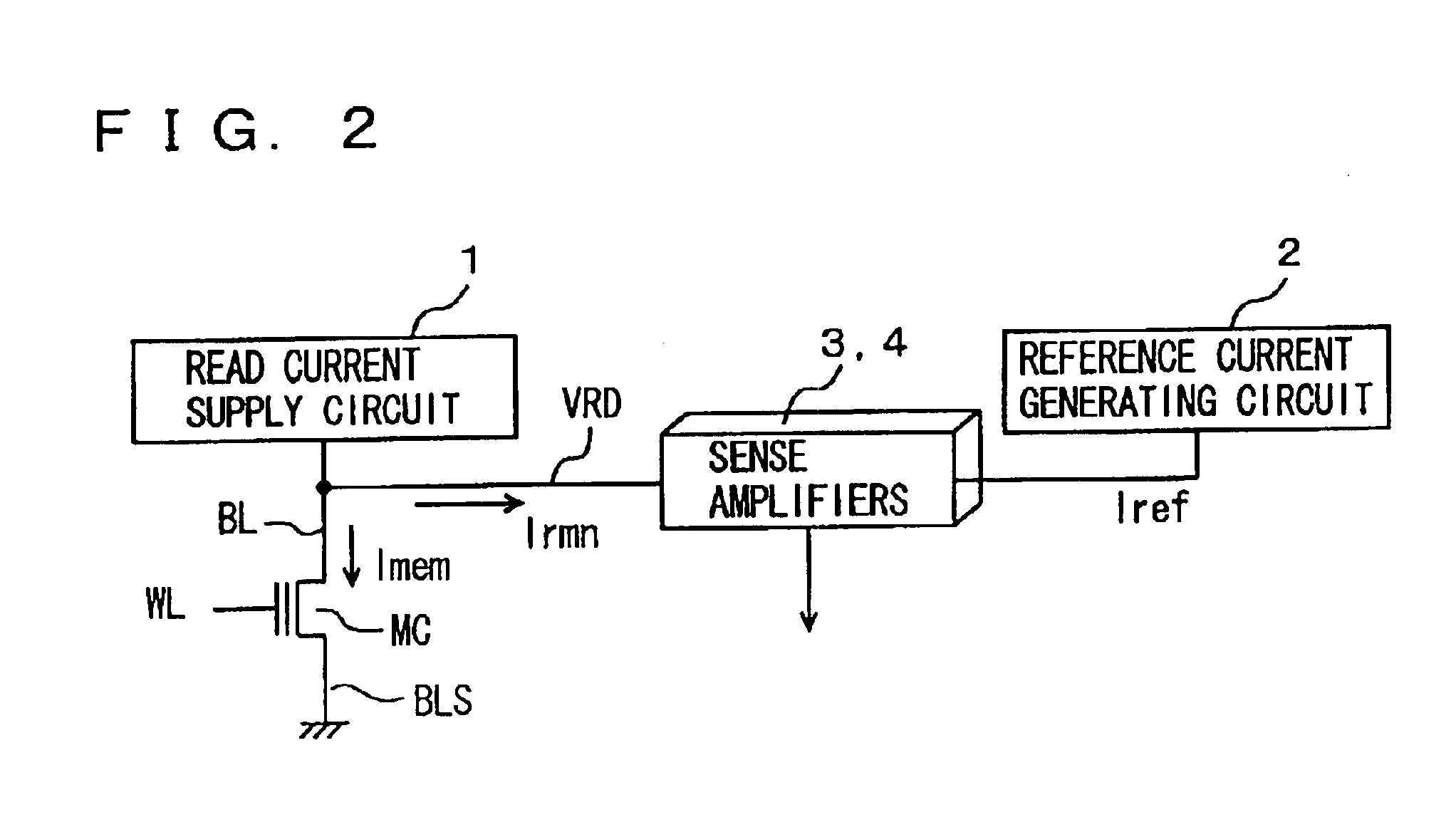
Semiconductor memory device
A plurality of sense amplifiers are connected to a selected bit line. Each sense amplifier is supplied with a residual current corresponding to a current flowing in a memory cell and a reference current serving as a reference for a threshold voltage of the memory cell to sense the currents. Operations of the sense amplifiers are controlled such that different sense margins are provided to different sense amplifiers and a margin failure is detected according to coincidence / non-coincidence in logical level between output signals of the sense amplifiers. The address of a memory cell with the margin failure is registered. With such a construction, a threshold voltage defect of a non-volatile memory cell is compensated for to enable internal reading of memory cell data with correctness.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
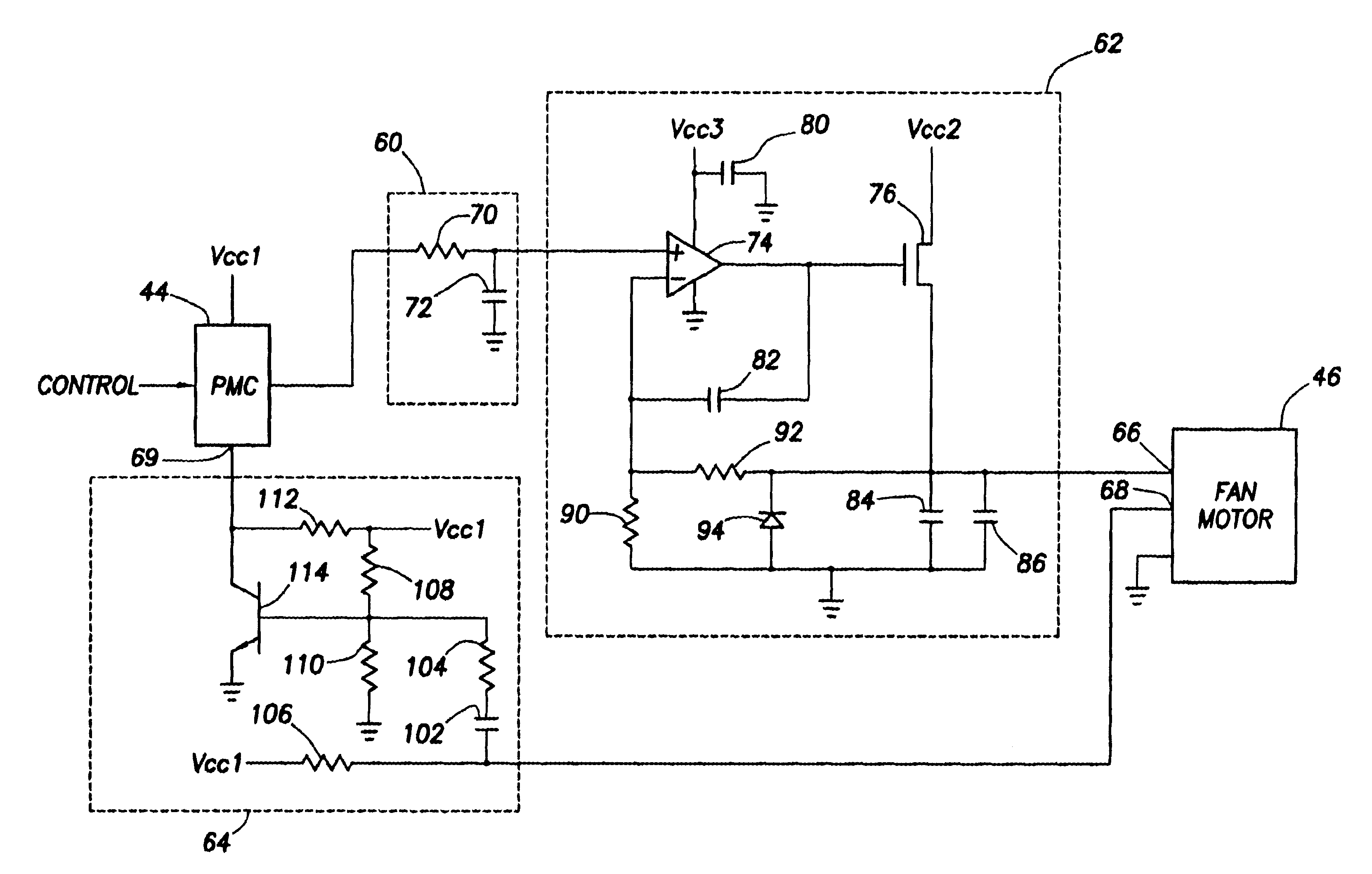
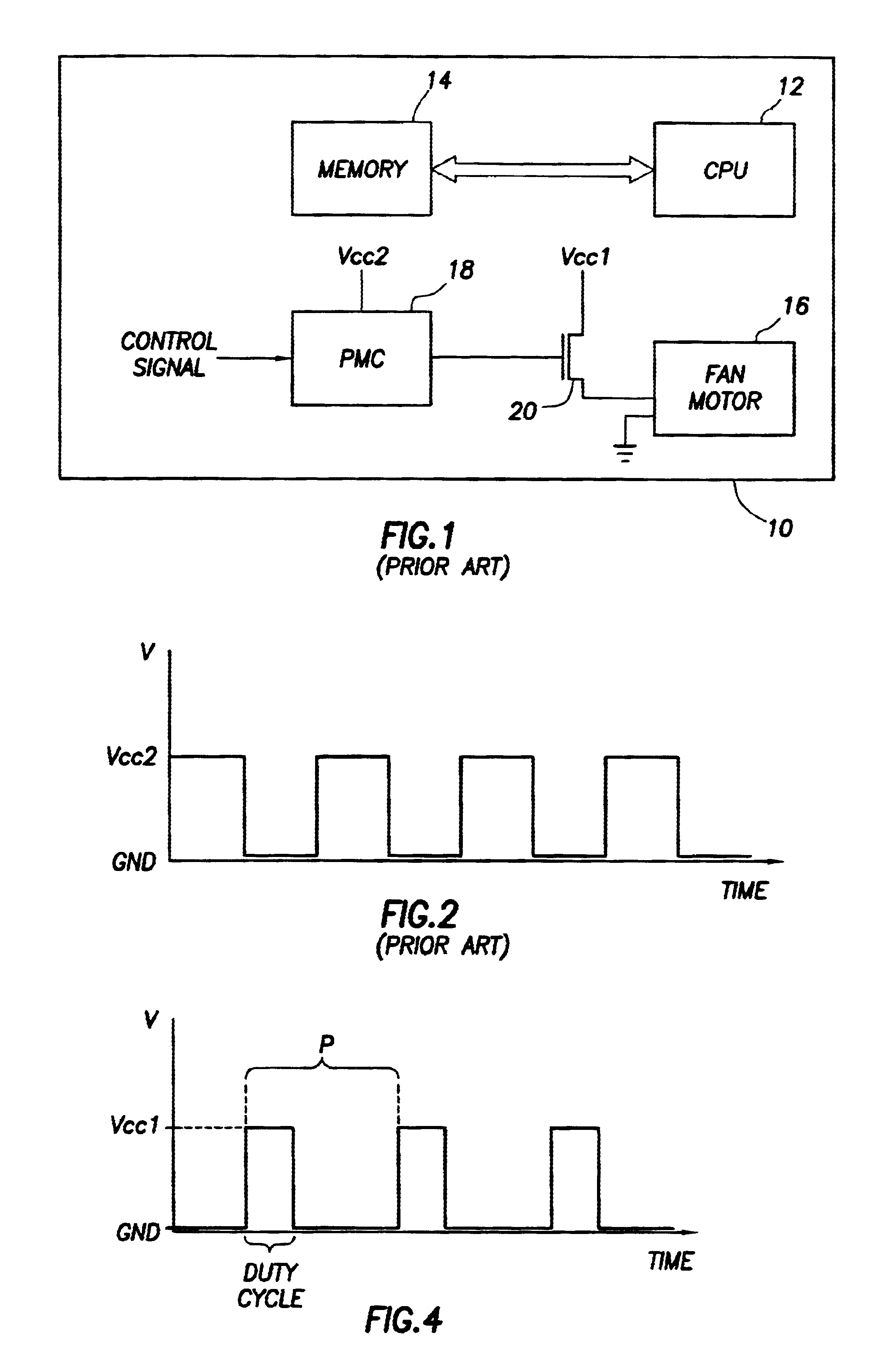
Fan speed controller with conditioned tachometer signal
The speed of a fan motor is controlled by varying a DC voltage to the fan motor. A series pass transistor is used to vary the DC voltage to the fan motor. A power management controller sets the fan motor speed by outputting pulses to a pulse-to-DC voltage converter that changes the pulses to a proportional DC control voltage for controlling the series pass transistor. A tachometer output amplifier circuit is used to remove DC components and amplify to useful logic levels a low level tachometer output signal from the fan motor. The amplified tachometer signal is used by the power management controller in controlling the rotational speed of the fan motor.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
Circuit for high-resolution phase detection in a digital RF processor
ActiveUS7205924B2Less sensitiveReduce power consumptionElectric signal transmission systemsModulated-carrier systemsDigital converterCmos process
A novel time-to-digital converter (TDC) used as a phase / frequency detector and charge pump replacement in an all-digital PLL within a digital radio processor. The TDC core is based on a pseudo-differential digital architecture making it insensitive to NMOS and PMOS transistor mismatches. The time conversion resolution is equal to an inverter propagation delay, e.g., 20 ps, which is the finest logic-level regenerative timing in CMOS. The TDC is self calibrating with the estimation accuracy better than 1%. The TDC circuit can also serve as a CMOS process strength estimator for analog circuits in large SoC dies. The circuit also employs power management circuitry to reduce power consumption to a very low level.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Endurance and retention flash controller with programmable binary-levels-per-cell bits identifying pages or blocks as having triple, multi, or single-level flash-memory cells
InactiveUS9123422B2Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationTruth valueRetention time
An retention flash controller reads assigned-level bits from a bad block / erase count table or from a page status table that indicate when flash memory cells operate as Triple-Level-Cell (TLC), Multi-Level-Cell (MLC), or Single-Level-Cell (SLC). Pages that fail as TLC or MLC are downgraded for use as SLC pages by changing the assigned-level bits. The level bits adjust truth tables used by translation logic that receives inputs from voltage comparators reading a bit line. The range of voltages for each logic level may be adjusted by the truth tables or by programmable registers. The programming voltage or programming pulses may be adjusted to increase endurance and the number of permitted program-erase cycles while reducing retention times before a refresh is needed of the flash cells. Mixed configurations of flash memory have MLC blocks and MLC as SLC blocks, or other combinations.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
Semiconductor memory device and methods thereof
A semiconductor memory device and methods thereof. The example semiconductor memory device may include a semiconductor substrate, a first source line and a second source line oriented in a first direction, the first and second source lines not in contact with each other, at least one bit line oriented in the first direction and at least one drain positioned between the first and second source lines and the at least one bit line. A first example method may include applying a first voltage to a source line, connected to the memory cell, during a write operation of the memory cell and applying a second voltage to the source line during a read operation of the memory cell, the first and second voltages not being the same and the second voltage not being a ground voltage. A second example method may include applying a first positive voltage to a word line, applying a second positive voltage to a source line, detecting a voltage at a bit line, the detected bit line voltage based on the applied first and second positive voltages and determining whether the memory cell stores data at a first logic level or a second logic level based on the detected bit line voltage.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
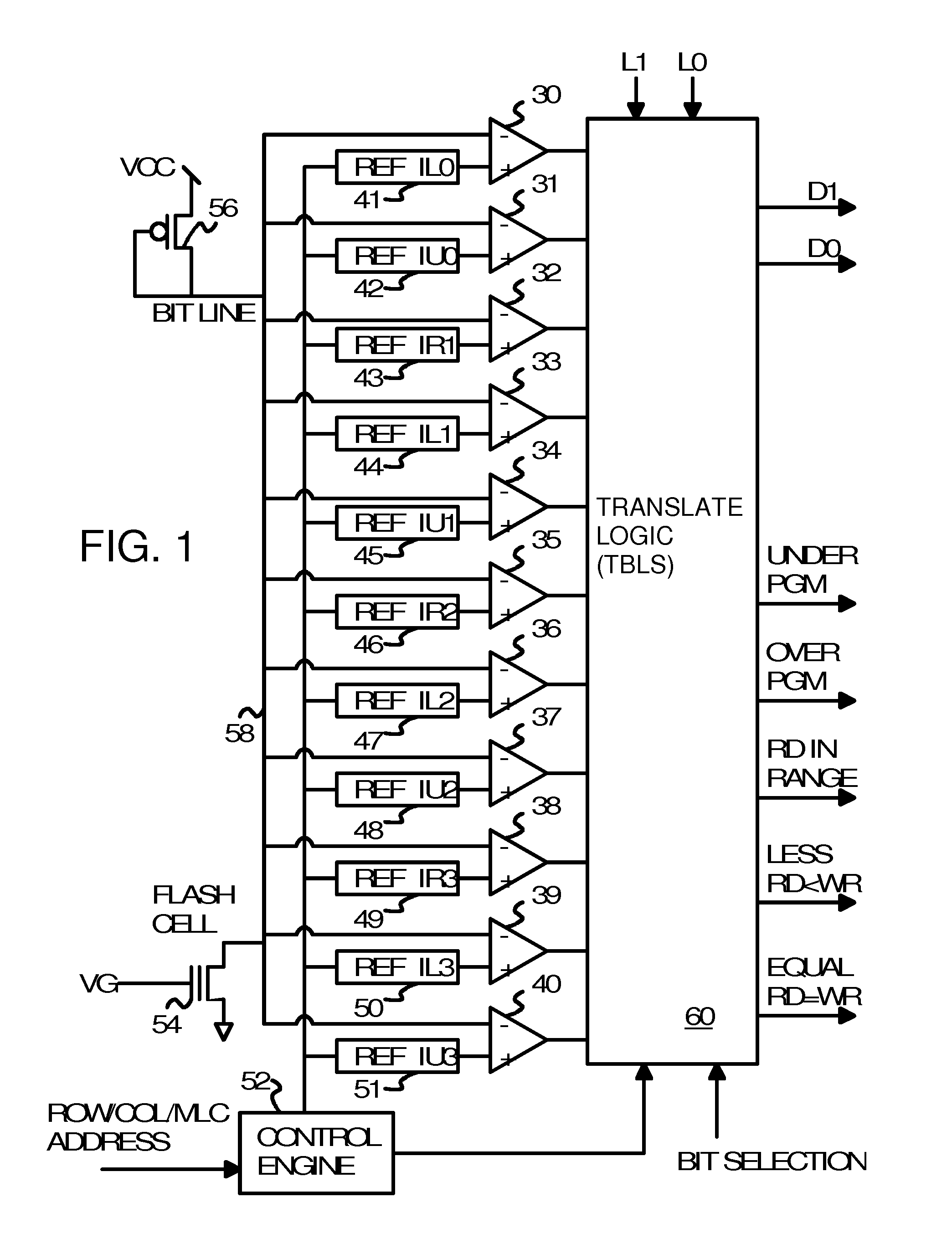
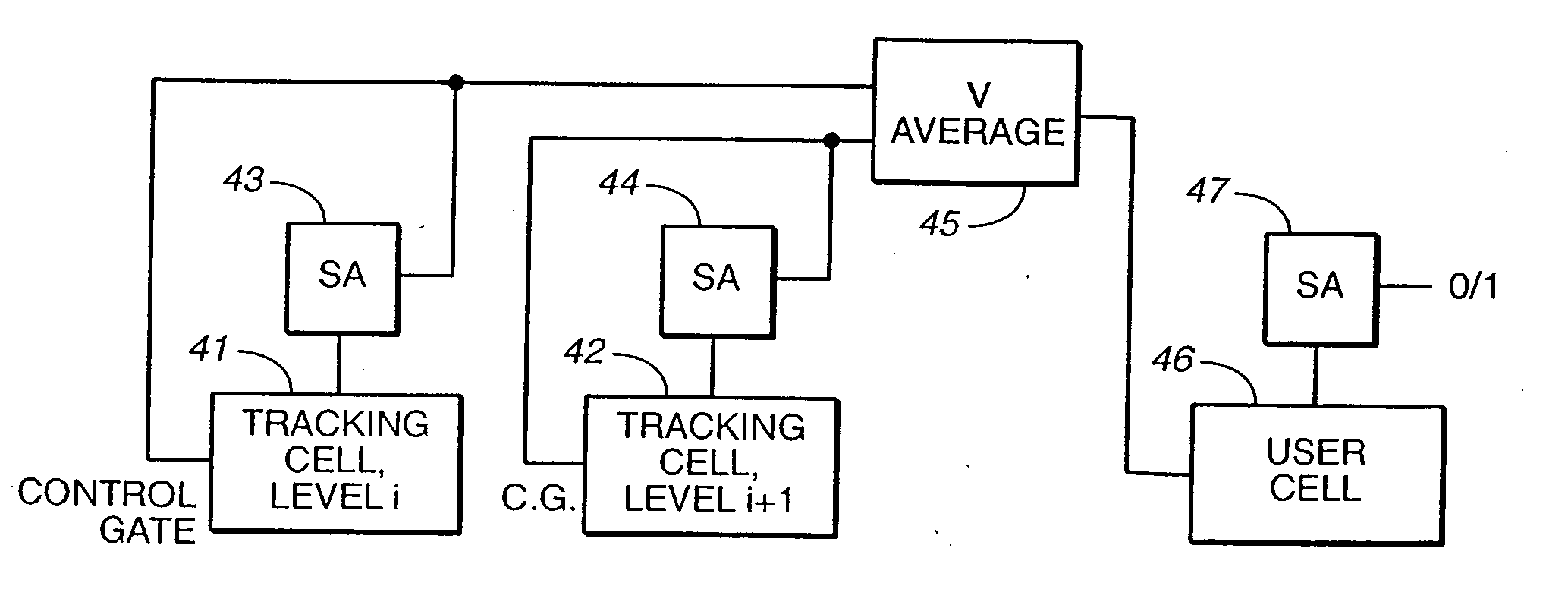
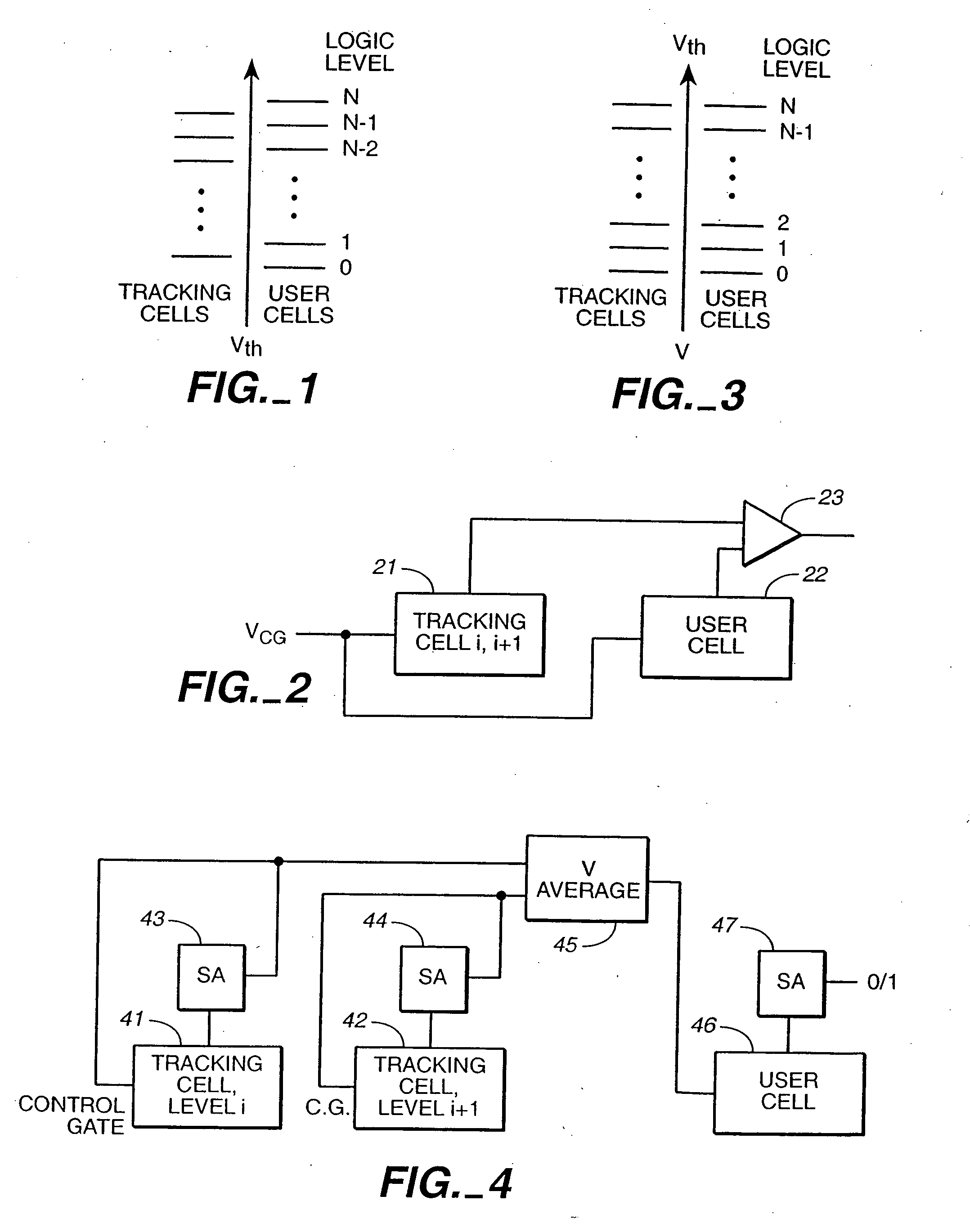
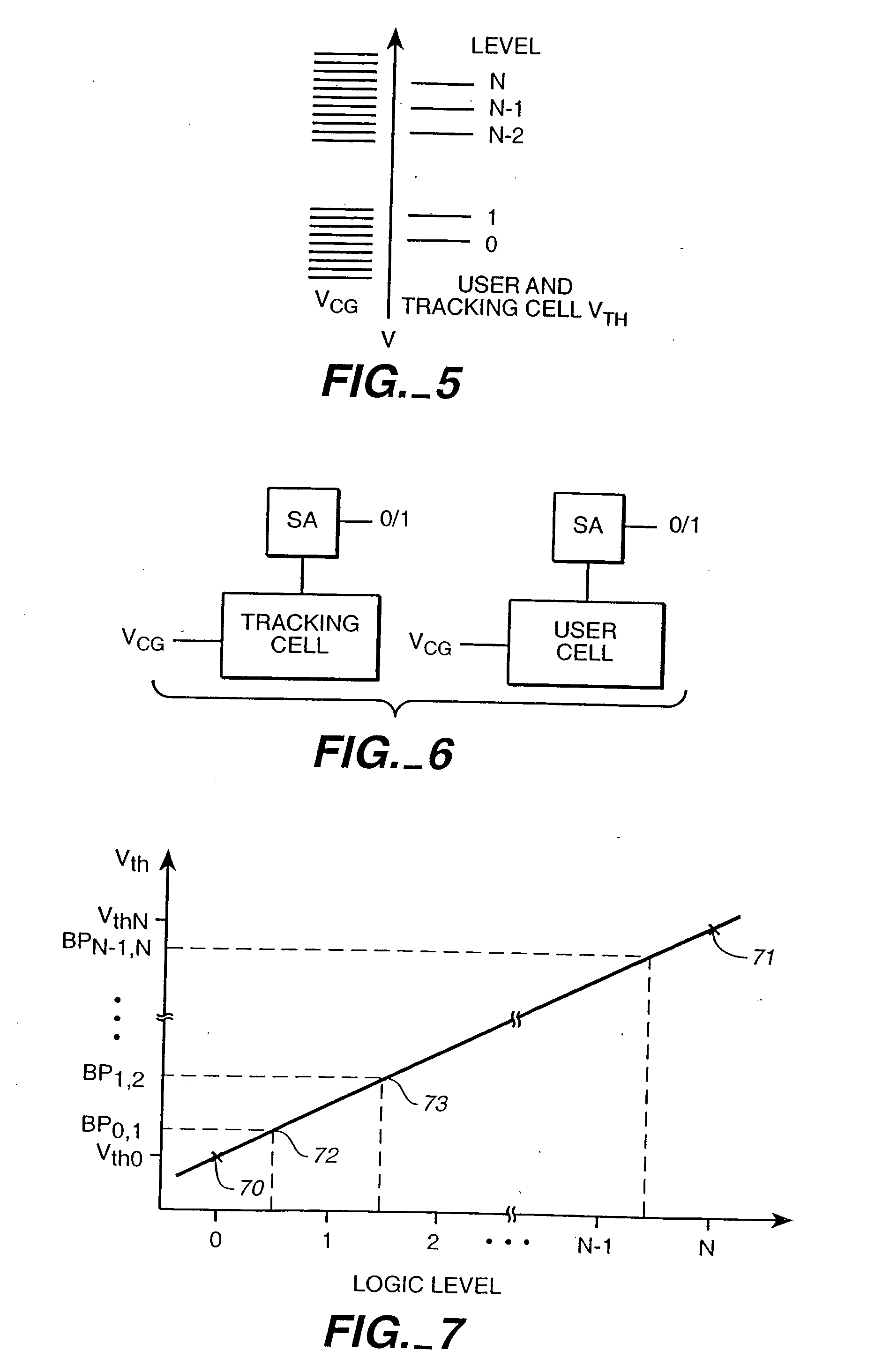
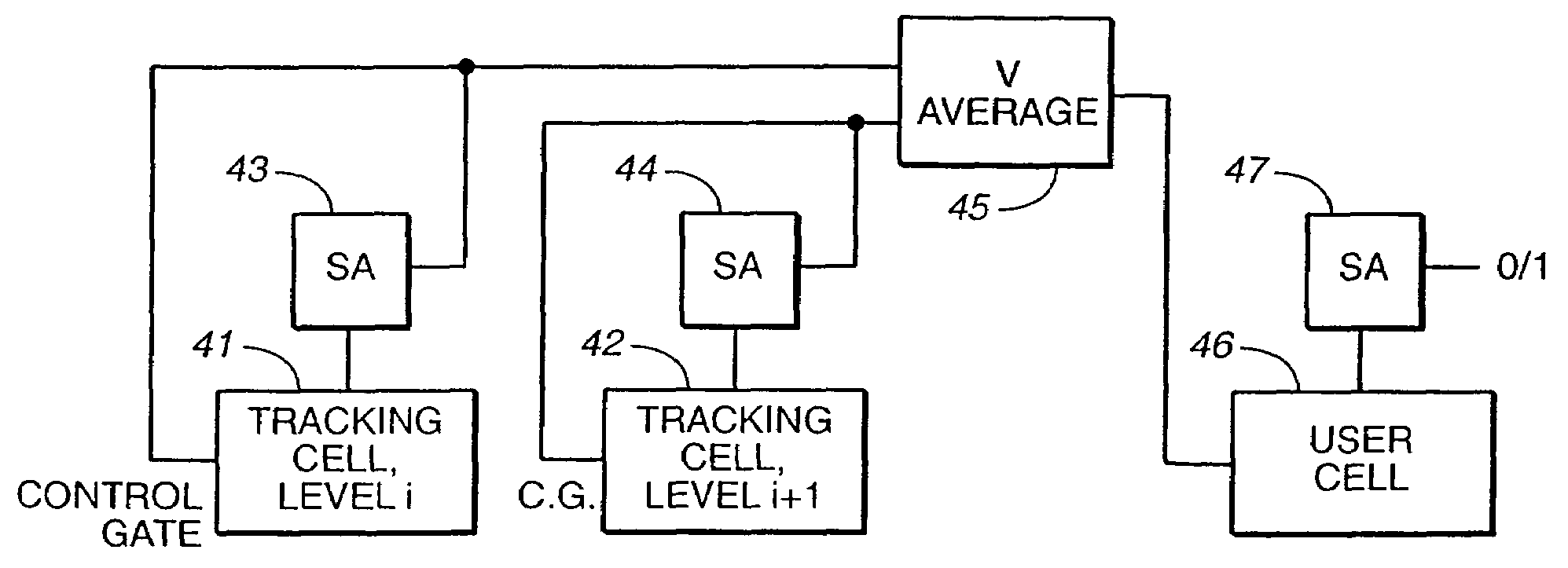
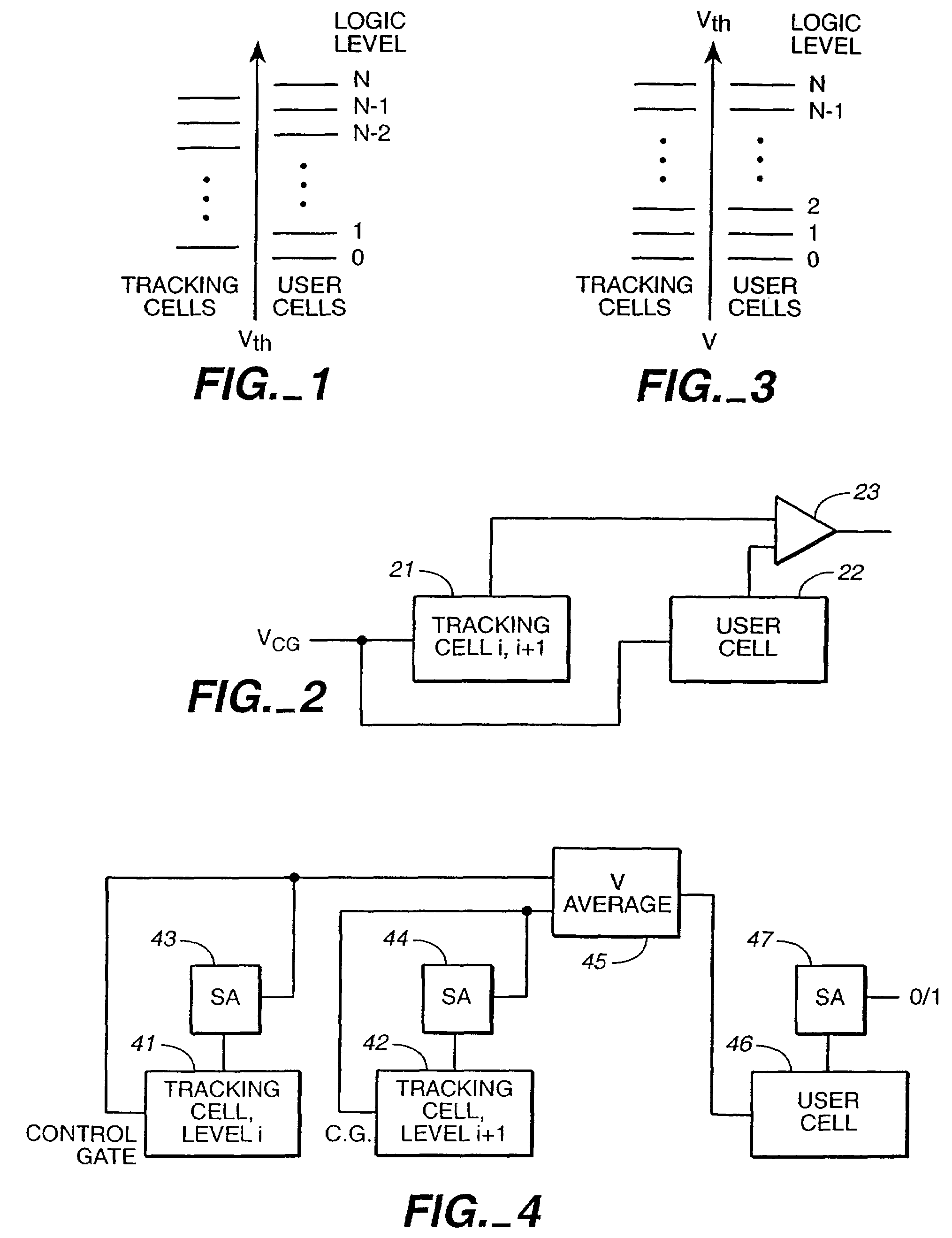
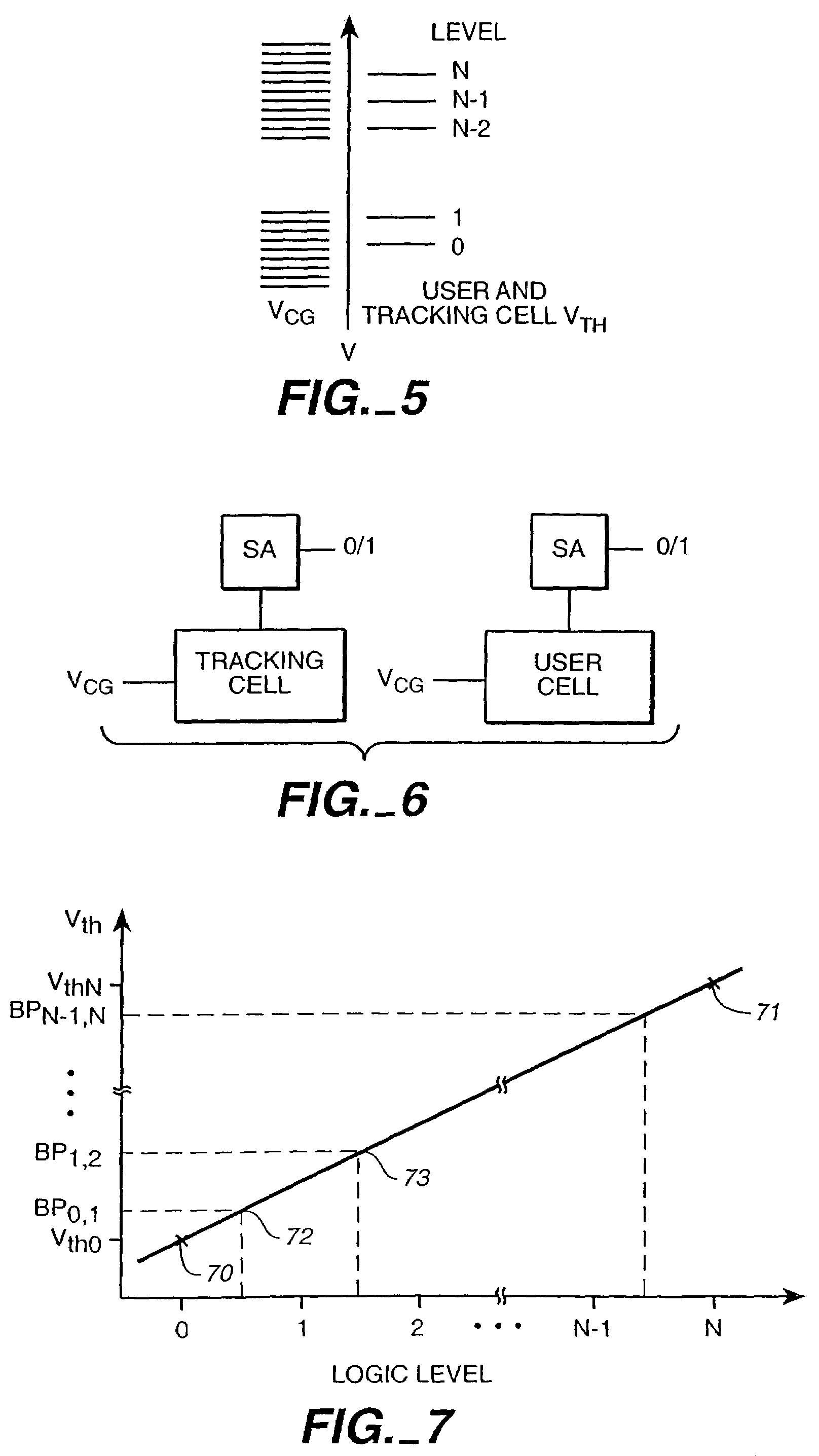
Writable tracking cells
ActiveUS20050169051A1Less uncertaintyReduce reference cell threshold uncertaintyElectric analogue storesRead-only memoriesComputer scienceThreshold voltage
The present invention presents several techniques for using writable tracking cells. Multiple tracking cells are provided for each write block of the memory. These cells are re-programmed each time the user cells of the associated write block are written, preferably at the same time, using the same fixed, global reference levels to set the tracking and user cell programmed thresholds. The threshold voltages of the tracking cells are read every time the user cells are read, and these thresholds are used to determine the stored logic levels of the user cells. In one set of embodiments, populations of one or more tracking cells are associated with different logic levels of a multi-state memory. These tracking cell populations may be provided for only a subset of the logic levels. The read points for translating the threshold voltages are derived for all of the logic levels based upon this subset. In one embodiment, two populations each consisting of multiple tracking cells are associated with two logic levels of the multi-bit cell. In an analog implementation, the user cells are read directly using the analog threshold values of the tracking cell populations without their first being translated to digital values. A set of alternate embodiments provide for using different voltages and / or timing for the writing of tracking cells to provide less uncertainty in the tracking cells' final written thresholds.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Writable tracking cells
InactiveUS7301807B2Less uncertaintyReduced referenceElectric analogue storesRead-only memoriesComputer scienceThreshold voltage
The present invention presents several techniques for using writable tracking cells. Multiple tracking cells are provided for each write block of the memory. These cells are re-programmed each time the user cells of the associated write block are written, preferably at the same time, using the same fixed, global reference levels to set the tracking and user cell programmed thresholds. The threshold voltages of the tracking cells are read every time the user cells are read, and these thresholds are used to determine the stored logic levels of the user cells. In one set of embodiments, populations of one or more tracking cells are associated with different logic levels of a multi-state memory. These tracking cell populations may be provided for only a subset of the logic levels. The read points for translating the threshold voltages are derived for all of the logic levels based upon this subset. In one embodiment, two populations each consisting of multiple tracking cells are associated with two logic levels of the multi-bit cell. In an analog implementation, the user cells are read directly using the analog threshold values of the tracking cell populations without their first being translated to digital values. A set of alternate embodiments provide for using different voltages and / or timing for the writing of tracking cells to provide less uncertainty in the tracking cells' final written thresholds.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory circuit utilizing a mis transistor as a memory cell
ActiveUS20090316477A1Lower threshold voltagePotential differenceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHemt circuitsMemory circuits
A memory circuit includes a latch having a first node and a second node to store data such that a logic level of the first node is an inverse of a logic level of the second node, a MIS transistor having a gate node, a first source / drain node, and a second source / drain node, the first source / drain node coupled to the first node of the latch, and a control circuit configured to control the gate node and second source / drain node of the MIS transistor in a first operation such that a lingering change is created in transistor characteristics of the MIS transistor in response to the data stored in the latch, wherein the MIS transistor includes a highly-doped substrate layer, a lightly-doped substrate layer disposed on the highly-doped substrate layer, diffusion regions formed in the lightly-doped substrate layer, a gate electrode, sidewalls, and an insulating film.
Owner:NSCORE
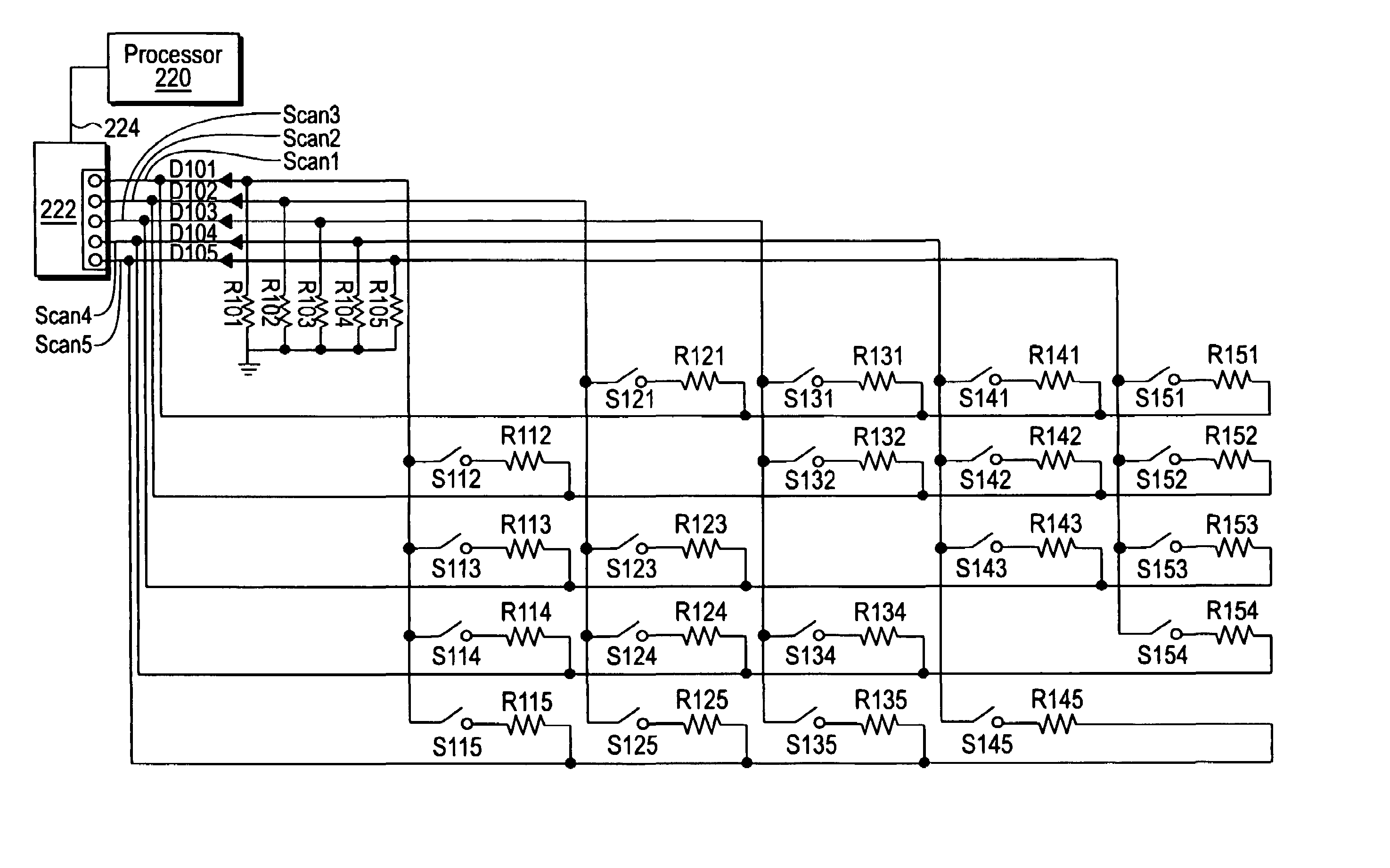
Circuit and method for a switch matrix and switch sensing
Aspects of a switch matrix circuit are provided. In accordance with a circuit aspect, a plurality of switches are organized in a row and column configuration. Coupled to the plurality of switches is a current sensing circuit. The current sensing circuit includes a transistor and at least one resistor per column of the plurality of switches. Current amplified by the transistor and converted by the at least one resistor in a column is sensed as a logic level indicative of a switch status within the column for a selected row. The current sensing arrangement may also be used in an embodiment utilizing bi-directional signal control to minimize the number of I / O lines required to scan the switch matrix. The bi-directional signal scanning may also be implemented in another embodiment that senses voltage levels to determine switch closures.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
Self-aligned clock recovery circuit with proportional phase detector
InactiveUS6347128B1Pulse automatic controlGenerating/distributing signalsPhase differenceContinuous data
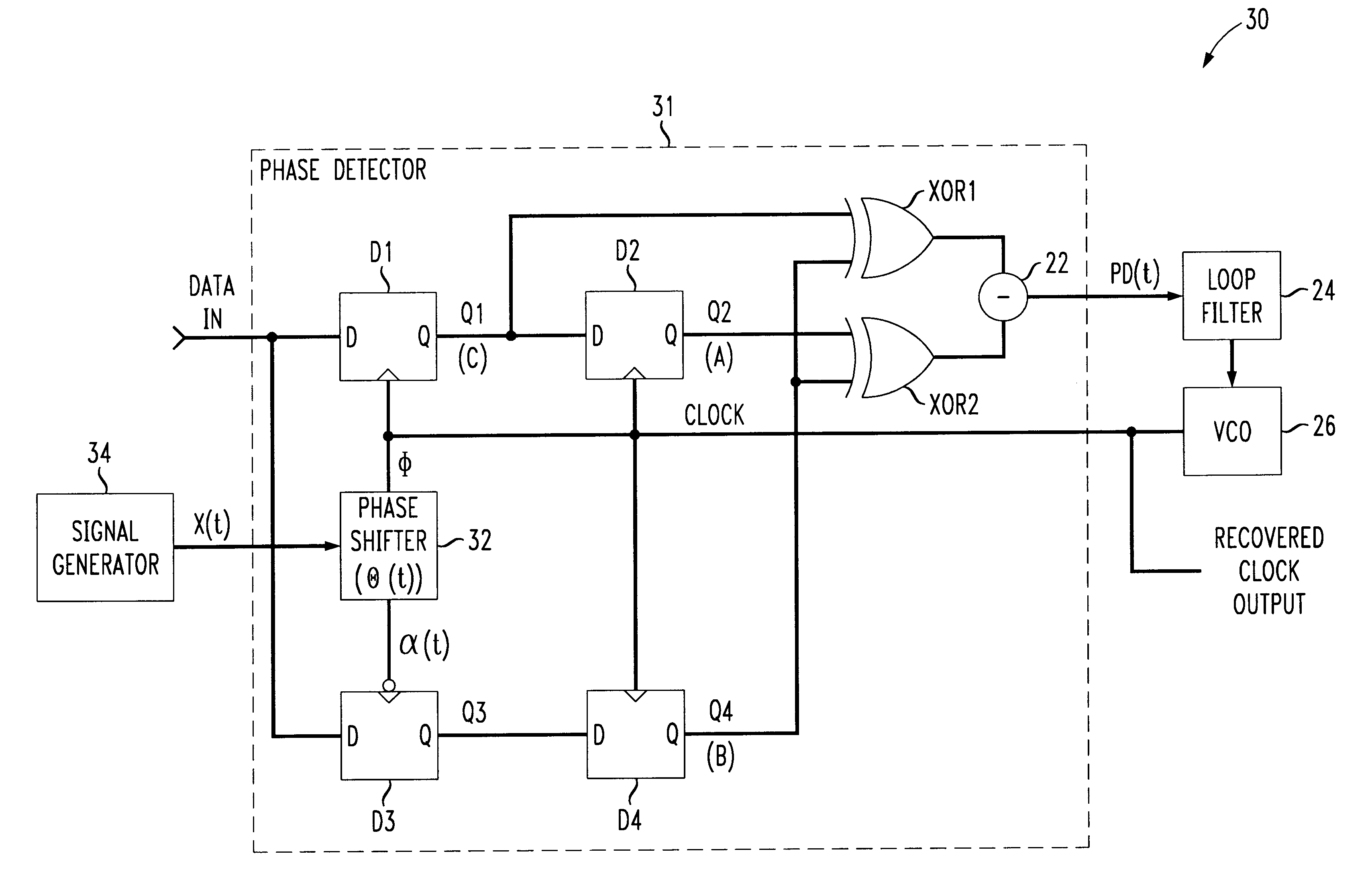
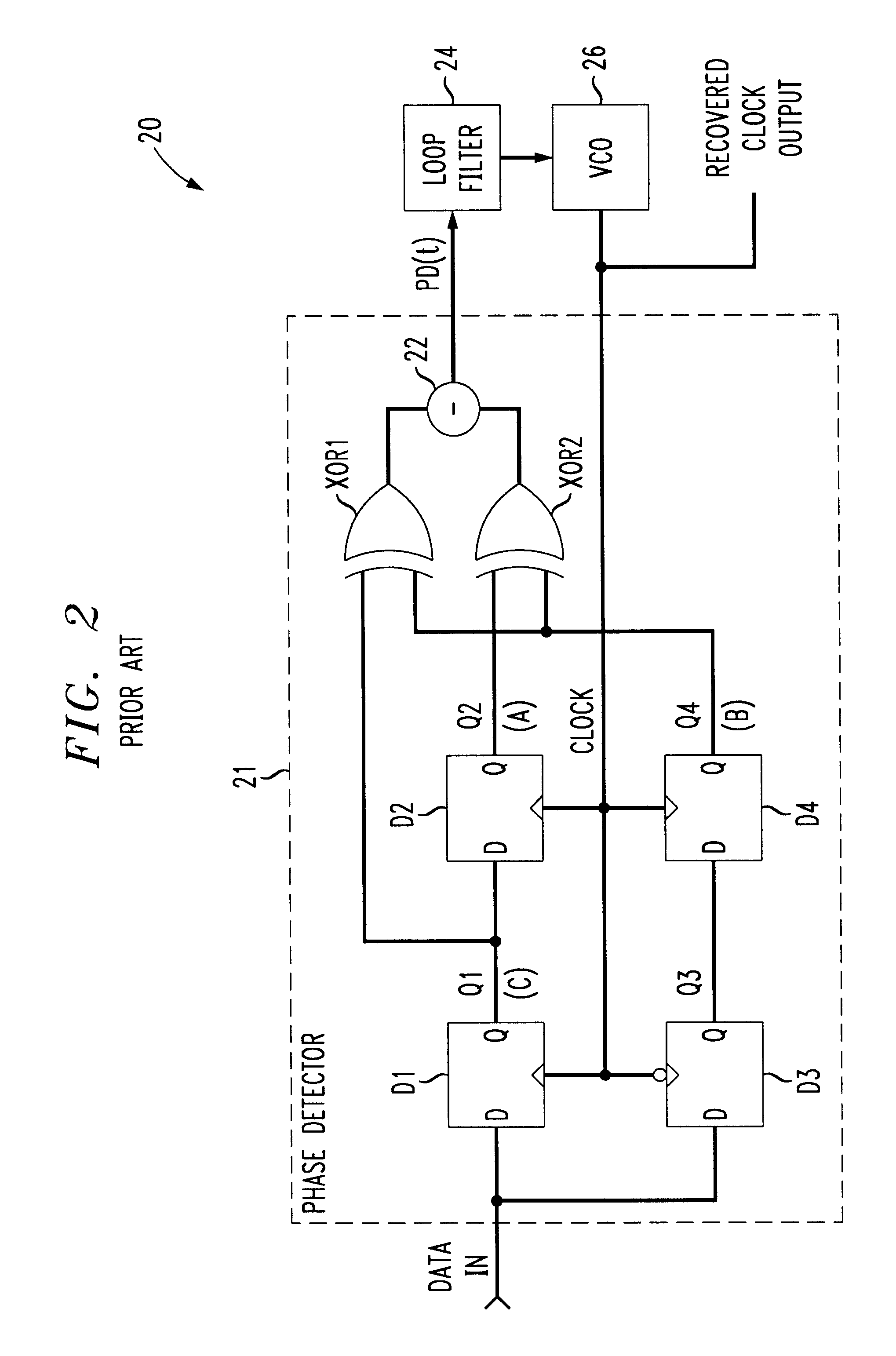
A self-aligned clock recovery circuit for synchronizing a local clock with an input data signal includes a sampling type phase detector for generating an output signal based on the phase difference between the local clock and the data signal timing. The phase detector obtains samples of consecutive data symbols at sampling times corresponding to transitions of the local clock, and obtains a data crossover sample at a sampling instant in between those of the consecutive data symbol samples. A phase shifter is employed to phase shift the local clock by an amount corresponding to a time varying modulation signal so as to obtain each data crossover sample at a variable sampling instant relative to the associated consecutive symbol samples. Logic circuitry determines whether the local clock appears to be early or late based on a comparison of the logic levels of the symbol samples and the associated data crossover sample, and provides a corresponding output signal through a filter to the local clock to adjust the clock accordingly. Since the relative sampling instants of successive data crossover samples are varied with time, the phase detector output signal amplitude is substantially proportional to the amount of phase error between the local clock and the symbol timing, thereby improving jitter properties of the clock recovery circuit.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Sensing Circuit For Programmable Resistive Device Using Diode as Program Selector
ActiveUS20120044748A1Low costSmall sizeSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesHemt circuitsEngineering
A sensing circuit for programmable resistive device using diode as program selector is disclosed. The sensing circuit can have a reference and a sensing branch. In one embodiment, each branch can have a first type of MOS with the source coupled to a first supply voltage, the drain coupled to the drain of a second type of MOS, which can have the gate coupled to a bias supply voltage. The sources of the second type of MOS in the reference and sensing branches can be coupled to a reference resistor and a programmable resistance element, respectively, and they are further coupled to a second supply voltage through their diodes. The gate of the first type of MOS in the sensing branch can be coupled to the gate of the first type of MOS in the reference branch, which can have the drain coupled to the gate. The resistance difference between the reference resistor and the programmable resistive element can be sensed through the drain of the first type of MOS in the sensing branch into a logic level.
Owner:ATTOPSEMI TECH CO LTD
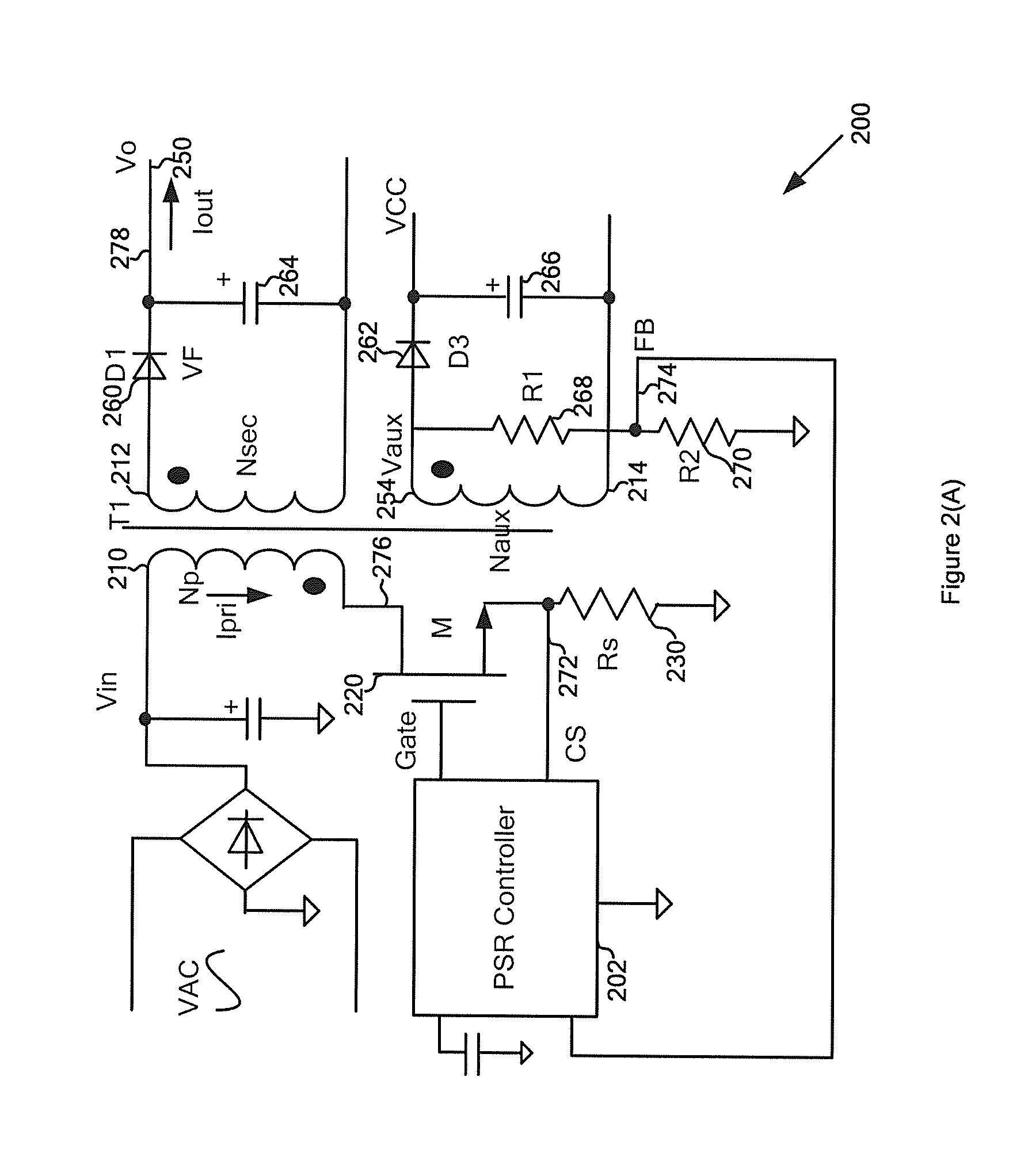
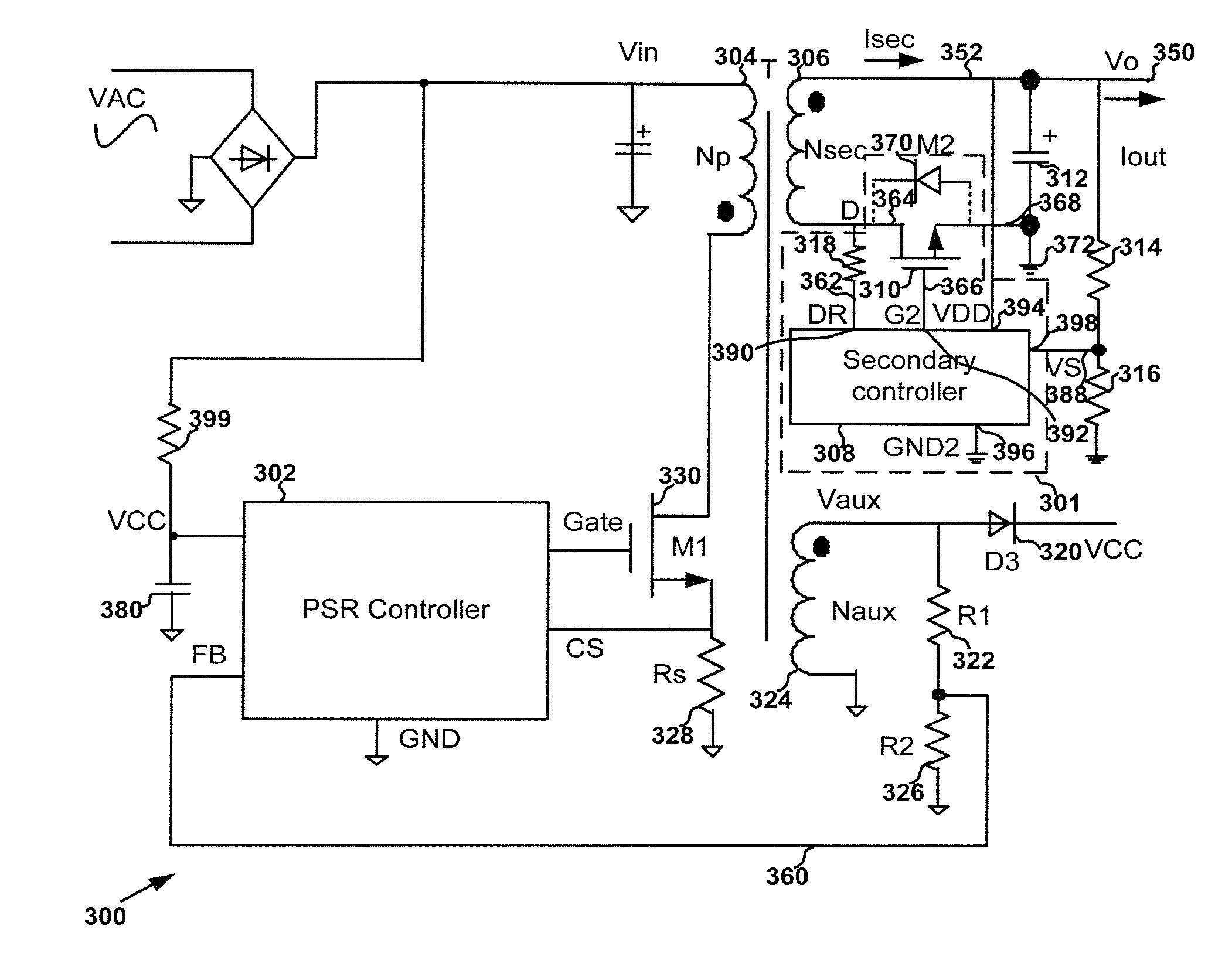
Systems and methods for regulating power conversion systems with output detection and synchronized rectifying mechanisms
ActiveUS20130272036A1Efficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionSignal correlationEngineering
System and method for regulating a power conversion system. A system controller for regulating a power conversion system includes a first controller terminal and a second controller terminal. The system controller is configured to receive at least an input signal at the first controller terminal, and generate a gate drive signal at the second controller terminal based on at least information associated with the input signal to turn on or off a transistor in order to affect a current associated with a secondary winding of the power conversion system. The system controller is further configured to, if the input signal is larger than a first threshold, generate the gate drive signal at a first logic level to turn off the transistor.
Owner:ON BRIGHT ELECTRONICS SHANGHAI
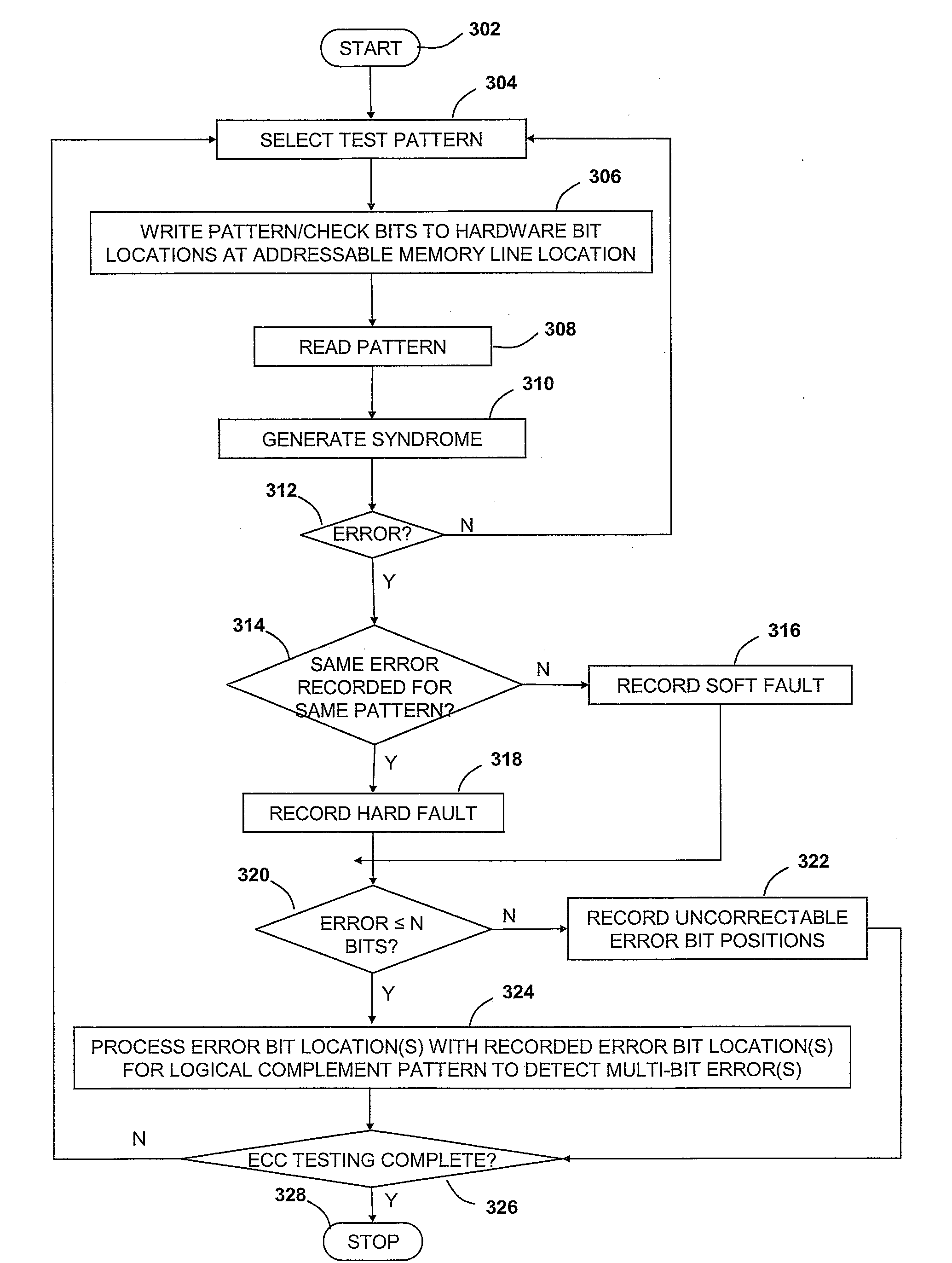
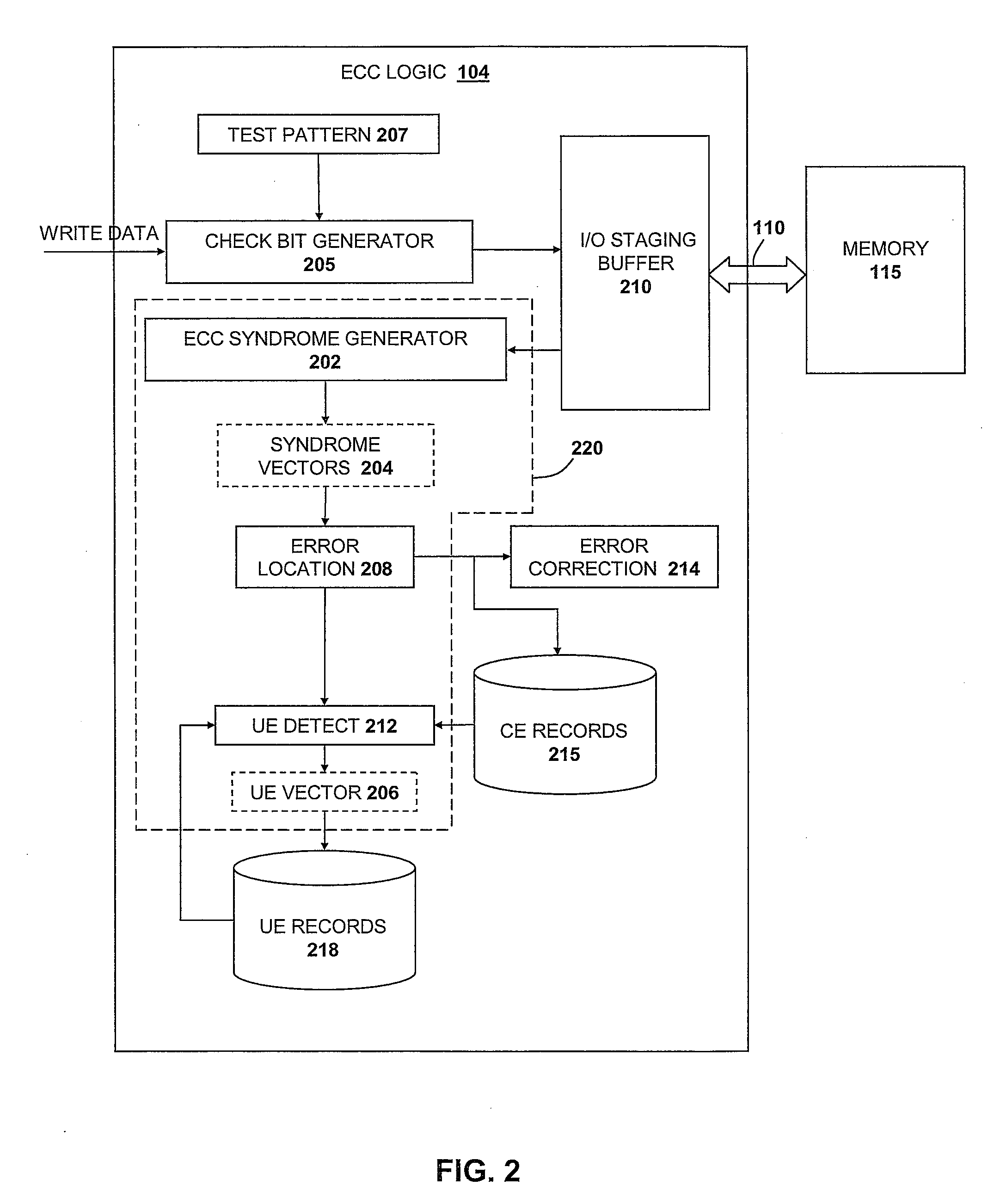
Method and system for uncorrectable error detection
InactiveUS20080201620A1Electronic circuit testingError detection/correctionComputer hardwareComputer science
A system, method and program product for utilizing error correction code (ECC) logic to detect multi-bit errors. In one embodiment, a first test pattern and a second test pattern are applied to a set of hardware bit positions. The first and second patterns are multiple logic level patterns and the second test pattern is the logical complement of the first test pattern. The first and second test patterns are utilized by the ECC logic to detect correctable errors having n or fewer bits. One or more bit positions of a first correctable error occurring responsive to applying the first test pattern are determined and one or more bit positions of a second correctable error occurring responsive to applying the second test pattern are determined. The determined bit positions of the first and second correctable errors are processed to identify a multiple-bit error within the set of hardware bit positions.
Owner:IBM CORP
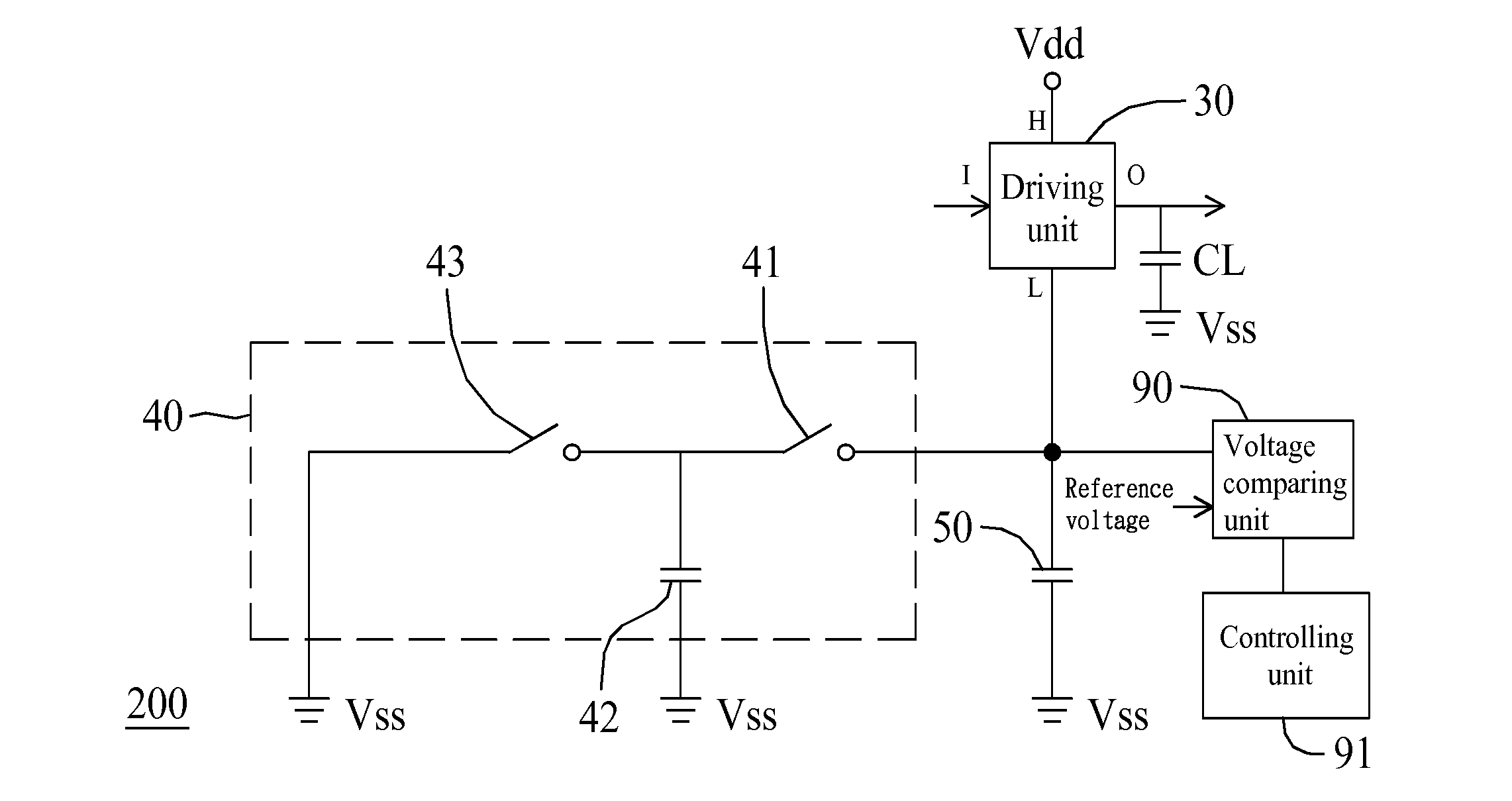
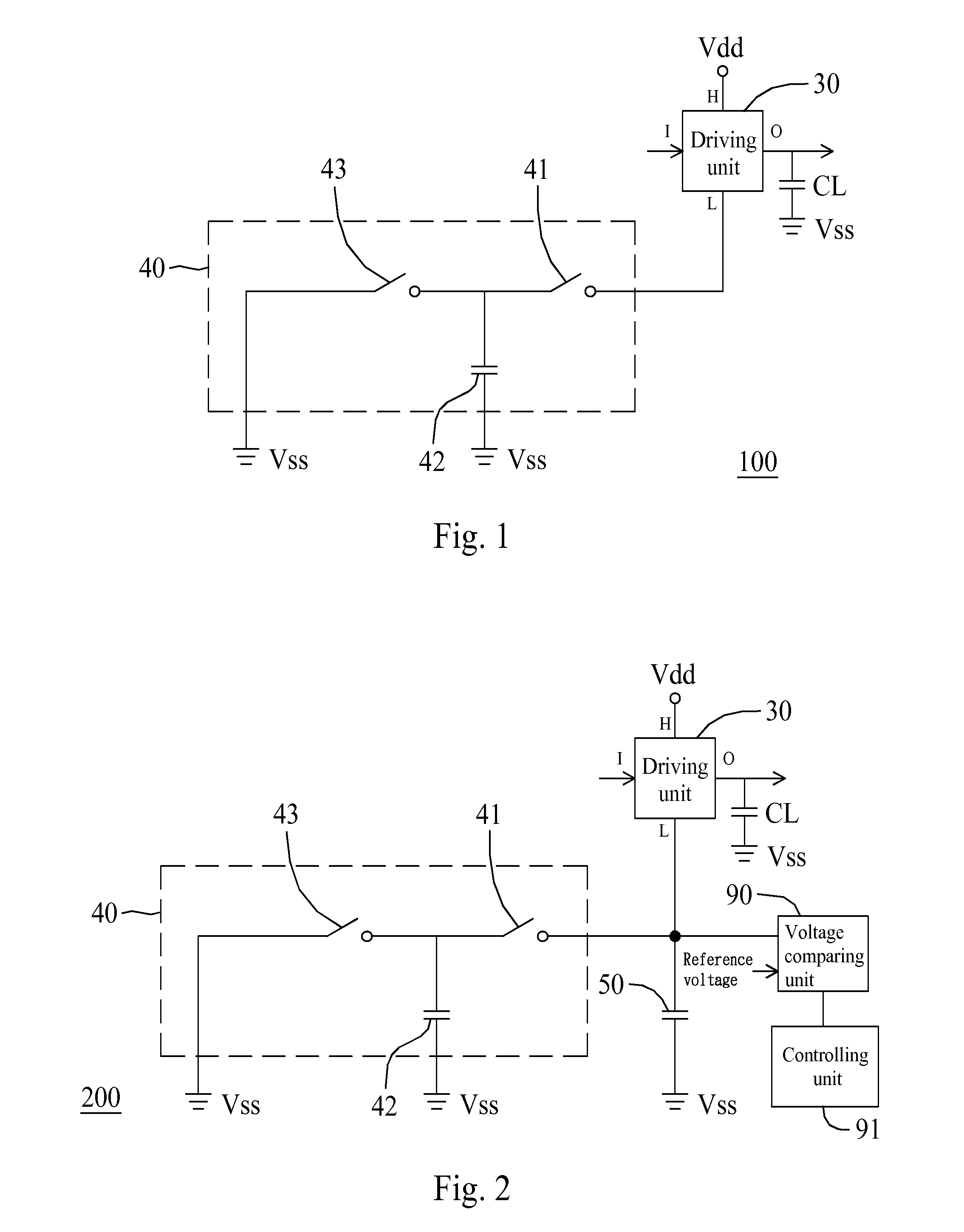
Voltage generating circuit
A voltage generating circuit includes: (1) a driving unit having an input terminal and an output terminal, wherein the input terminal is configured to receive an input signal, wherein when the input signal is at a first logic level, power is configured to be charged from a first voltage terminal to the output terminal, and when the input signal is at a second logic level, power is configured to be discharged from the output terminal to a second voltage terminal; (2) a first switch configured to couple the second voltage terminal to a capacitance-compensating terminal based on the input signal; (3) a compensating capacitor configured to be coupled between the capacitance-compensating terminal and a third voltage terminal; and (4) a second switch configured to couple the capacitance-compensating terminal to a fourth voltage terminal based on the input signal.
Owner:M31 TECH
Hand-held data capture system with interchangeable modules
InactiveUS20050087603A1Avoid defectsLow costEnergy efficient ICTCredit registering devices actuationTransceiverData acquisition
A data capture system includes a data collection terminal and a wireless communications module comprising a transceiver arranged to transmit and receive radio frequency signals to and from a remote station in the data capture system. At least one flat antenna embedded within the communications module, and a pair of flat antennas may be included. A connector is arranged to removably couple the communications module with the data collection terminal and to transmit signals. A microprocessor is coupled with the connector and is arranged to standardize the logic levels and the format of the signals transmitted over the connector such that the data collection terminal may be engaged by the communications module through the connector without adjustment of the communications module.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory circuit utilizing a MIS transistor as a memory cell
ActiveUS7821806B2Many problemReduce adverse effectsSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesHemt circuitsMemory circuits
A memory circuit includes a latch having a first node and a second node to store data such that a logic level of the first node is an inverse of a logic level of the second node, a MIS transistor having a gate node, a first source / drain node, and a second source / drain node, the first source / drain node coupled to the first node of the latch, and a control circuit configured to control the gate node and second source / drain node of the MIS transistor in a first operation such that a lingering change is created in transistor characteristics of the MIS transistor in response to the data stored in the latch, wherein the MIS transistor includes a highly-doped substrate layer, a lightly-doped substrate layer disposed on the highly-doped substrate layer, diffusion regions formed in the lightly-doped substrate layer, a gate electrode, sidewalls, and an insulating film.
Owner:NSCORE
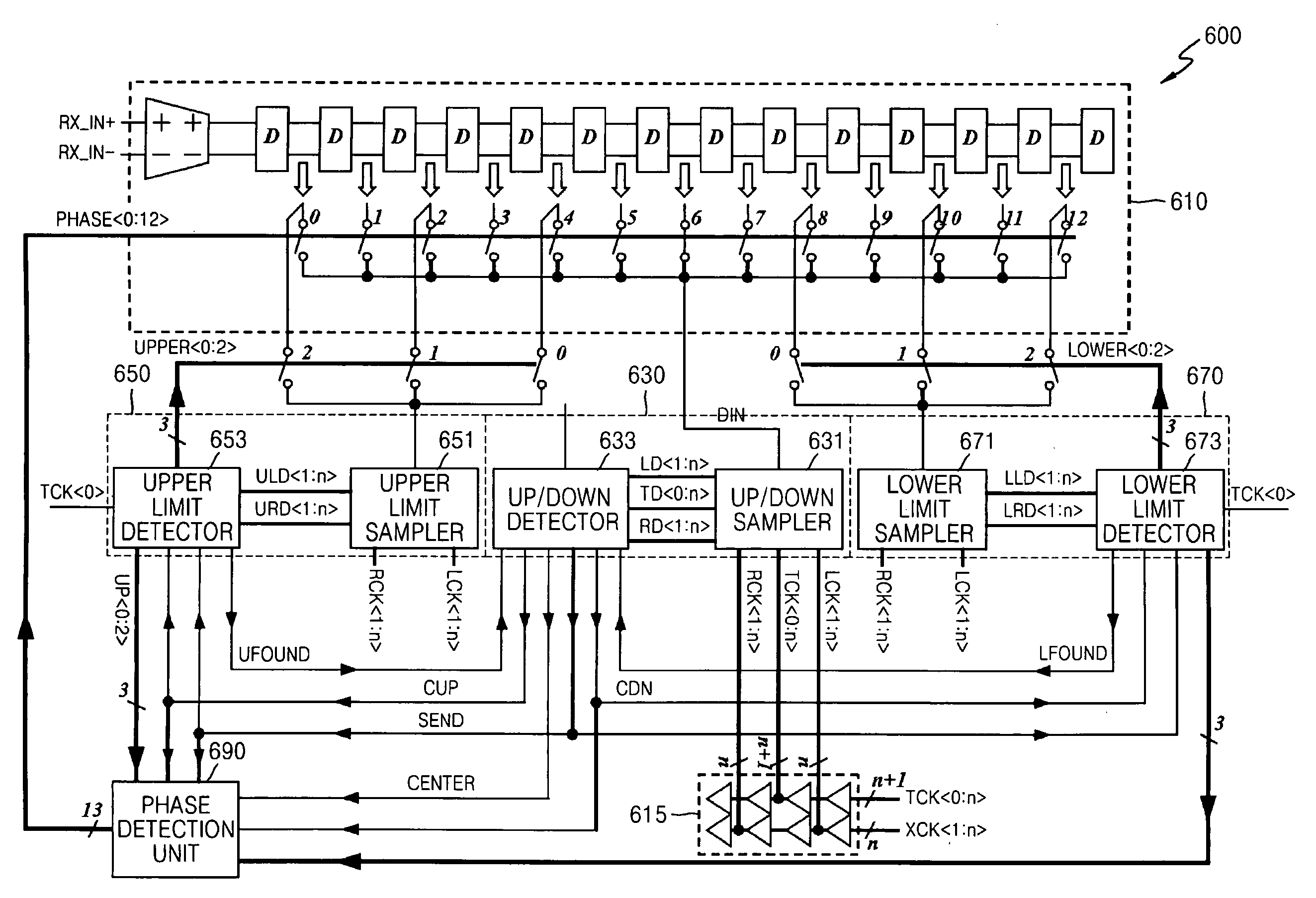
Deskewing method and apparatus, and data reception apparatus using the deskewing method and apparatus
InactiveUS20070297551A1Pulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionLower limitData signal
Deskewing method and apparatus, and a data reception apparatus using the deskewing method and apparatus, in which the deskewing apparatus includes an up / down detection unit, a lower limit detection unit, an upper limit detection unit, a phase detection unit, and a buffer unit. The up / down detection unit samples a received data signal in response to a data sampling clock signal, a first edge sampling clock signal, and a second edge sampling clock signal and determines in which of first through third areas of the data signal the logic level of the data signal transitions by using the result of the sampling, wherein the data sampling clock signal, the first edge sampling clock signal, and the second edge sampling clock signal are sequentially activated. The lower limit detection unit detects a lower limit of the first area if the logic level of the data signal transitions in the first area. The upper limit detection unit detects an upper limit of the third area if the logic level of the data signal transitions in the third area. The phase detection unit determines a delay amount indicating the amount by which the data signal is to be delayed according to the upper limit detected by the upper limit detection unit and the lower limit detected by the lower limit detection unit. The buffer unit delays the data signal by the delay amount determined by the phase detection unit. The deskewing apparatus can optimize data sampling by efficiently reducing data skew. In addition, the deskewing apparatus can minimize data restoration errors by reducing an accumulation of jitter.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Systems and methods for regulating power conversion systems with output detection and synchronized rectifying mechanisms
ActiveUS20140218976A1Increase the switching frequencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionConductor CoilControl theory
System and method for regulating a power conversion system. An example system controller includes: a first controller terminal and a second controller terminal. The system controller is configured to: receive an input signal at the first controller terminal and generate a first drive signal at the second controller terminal based on at least information associated with the input signal to turn on or off a transistor to affect a current associated with a secondary winding of the power conversion system. The system controller is further configured to: in response to the input signal changing from a first value larger than a first threshold to a second value smaller than the first threshold, change the first drive signal from a first logic level to a second logic level to turn on the transistor.
Owner:ON BRIGHT ELECTRONICS SHANGHAI
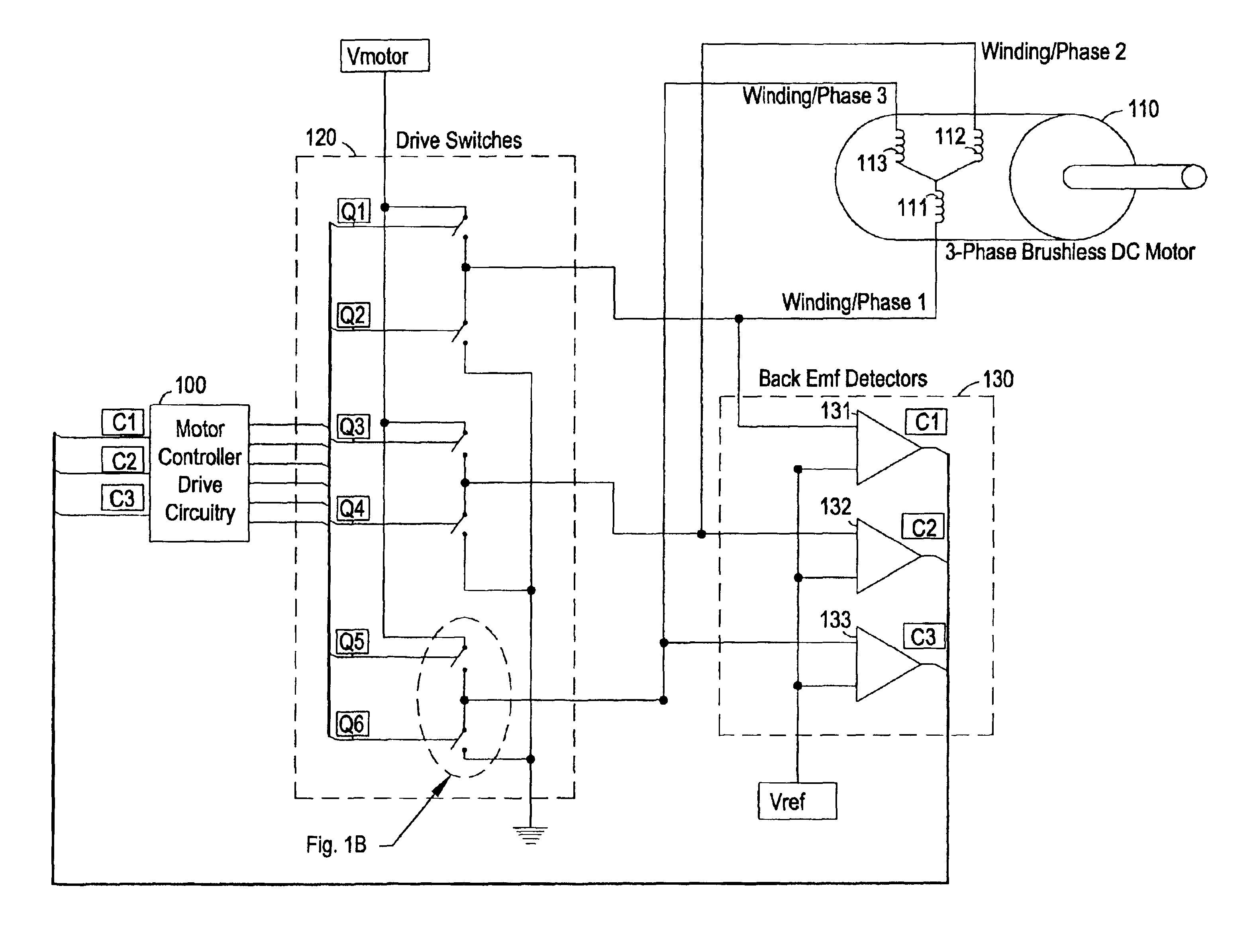
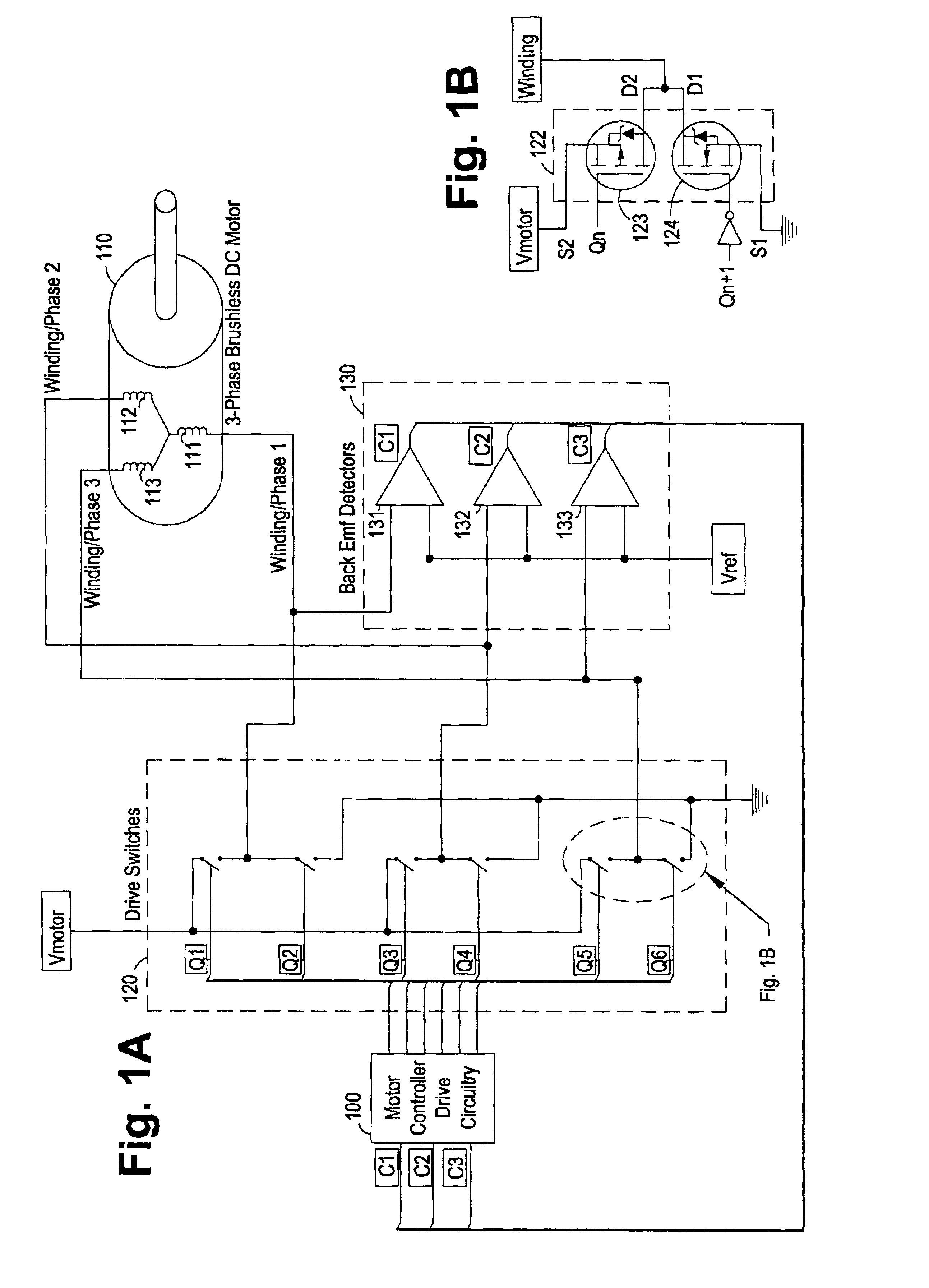
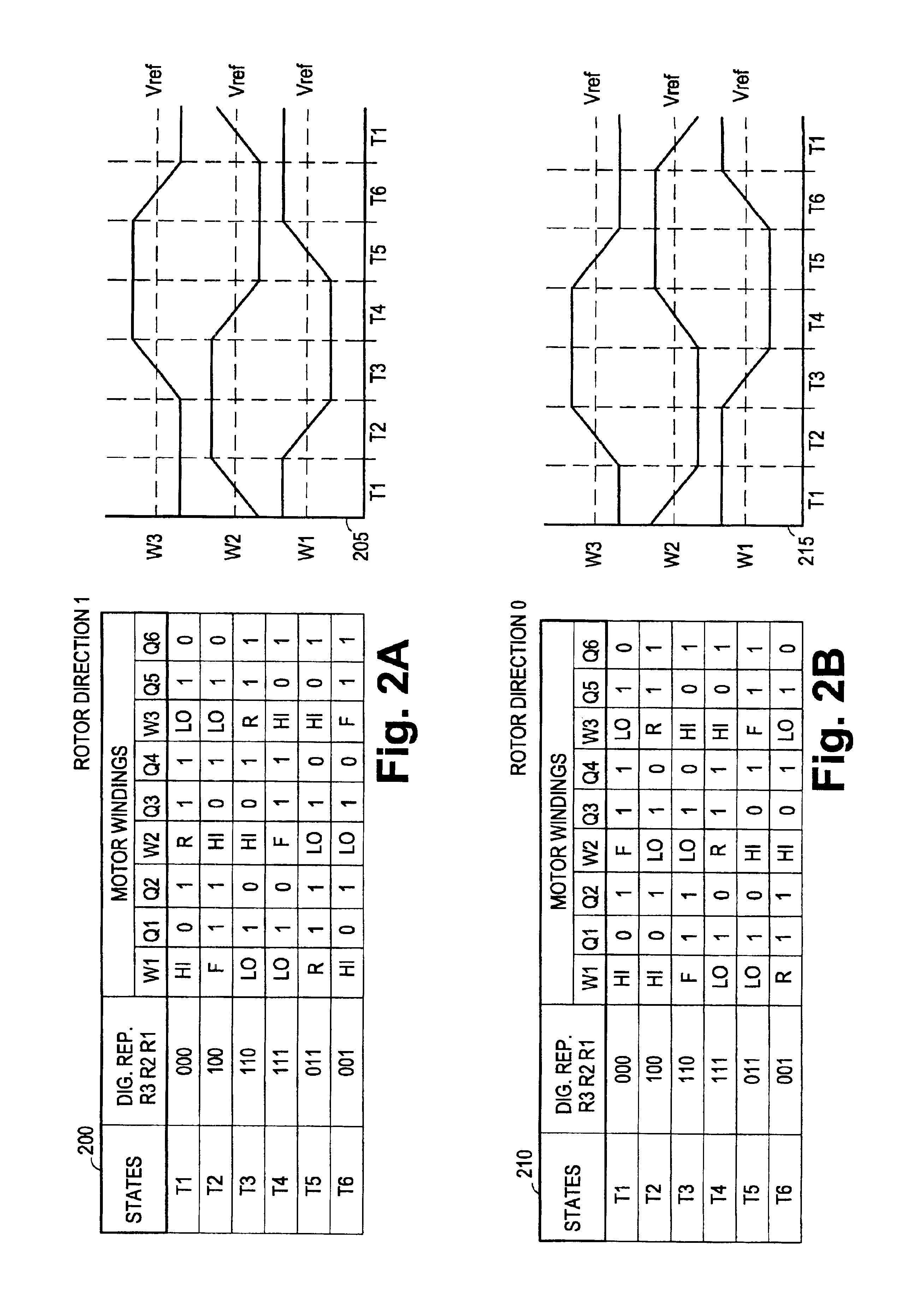
Digital adaptive sensorless commutational drive controller for a brushless DC motor
InactiveUS6901212B2Efficient startMotor/generator/converter stoppersCommutation monitoringControl signalProgrammable logic device
A digitally adaptive controller circuit for commutating a brushless, sensorless, DC motor in either of two directions adapted to receive digital back electromotive force (BEMF) detector signals. The digital circuit is driven by an input clock that is adjustable to configure the motor controller for use with a broad range of DC motors. The circuit includes commutational logic that decodes a current commutational state and a user-definable binary direction input into logic levels for digital control signals for controlling motor drive switches. The circuit also includes a signature analyzer to compare logic levels in the BEMF detector signals with expected logic levels based on an expected rotor position and direction of rotation. The digital circuit commutates the motor if the logic levels in the BEMF detector signals are at the expected logic levels. The digital circuit is compact and simple enough to be deployed onto a single programmable logic device.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
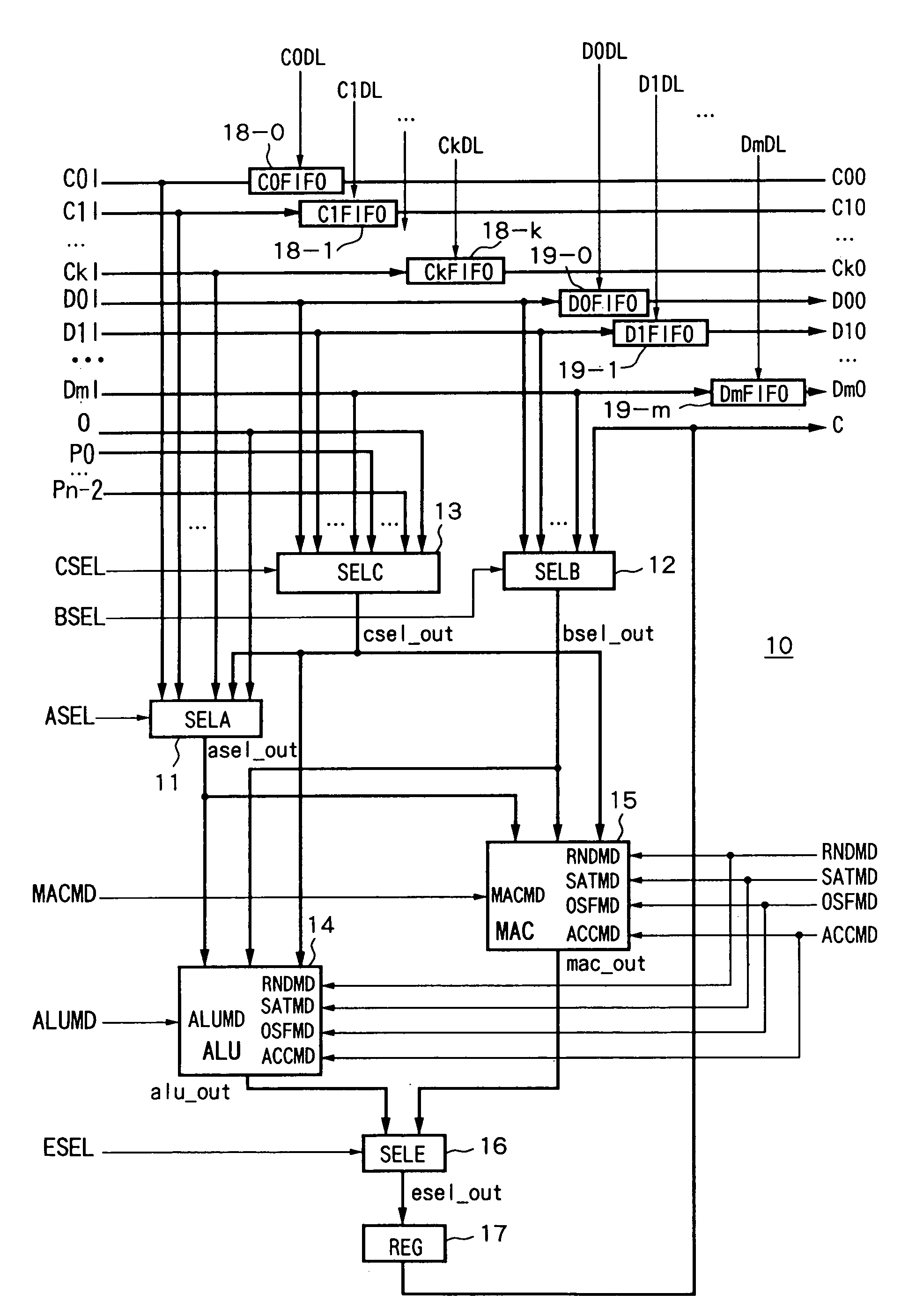
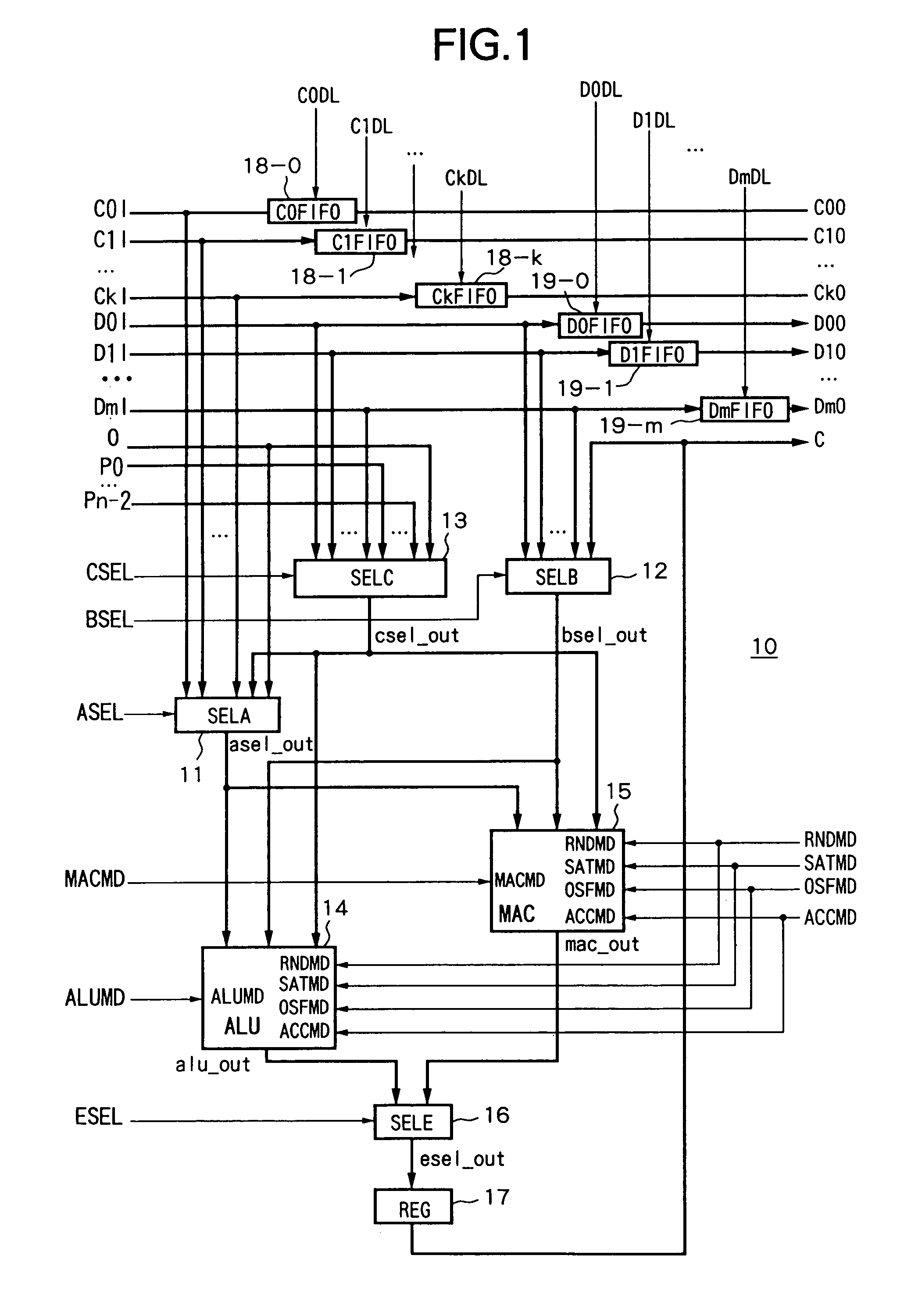
Reconfigurable arithmetic device and arithmetic system including that arithmetic device and address generation device and interleave device applicable to arithmetic system
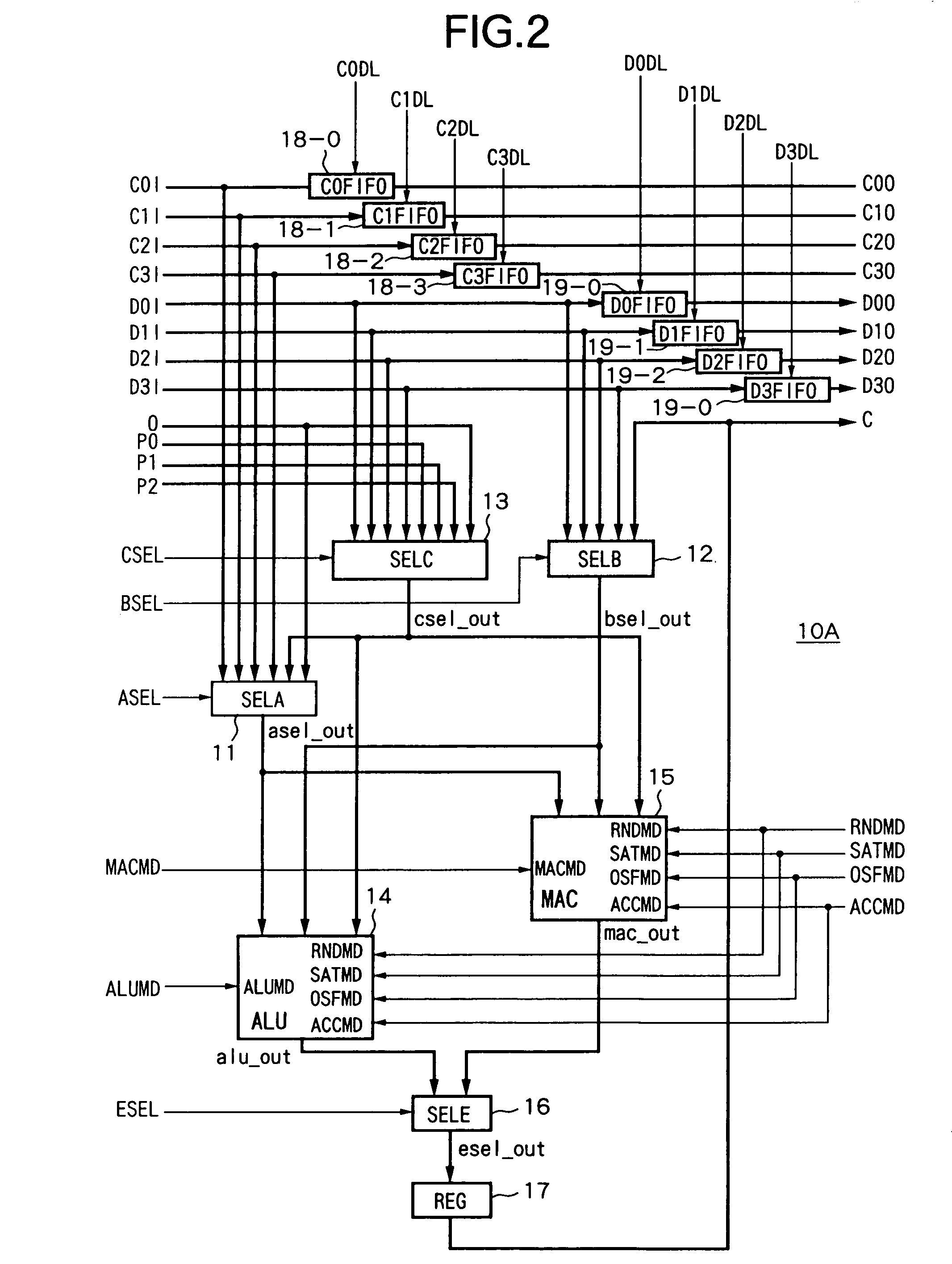
ActiveUS7020673B2Level of optimizationAvoid elevationComputation using denominational number representationControl signalLogical operations
An arithmetic device able to optimize the logic level, able to prevent an increase in the component data, able to prevent the area efficiency as an integrated operation efficiency, and circuit, achieving an improvement in the achieving a reduction power consumption, provided with a first selection device for selecting coefficient inputs C0I to CkI in accordance with a control signal ASEL, a second selection device for selecting data inputs D0I to DmI in accordance with a control signal BSEL, a third selection device for selecting cascade inputs P0 to Pn−2 in accordance with a control signal CSEL, an ALU for receiving as input the output signal of the first to third selection devices and performing a logic operation in accordance with instructions of the control signals ALUMD etc., a MAC for receiving as input the output signals of the first to third selection devices and performing operation in accordance with instructions of
Owner:SONY CORP
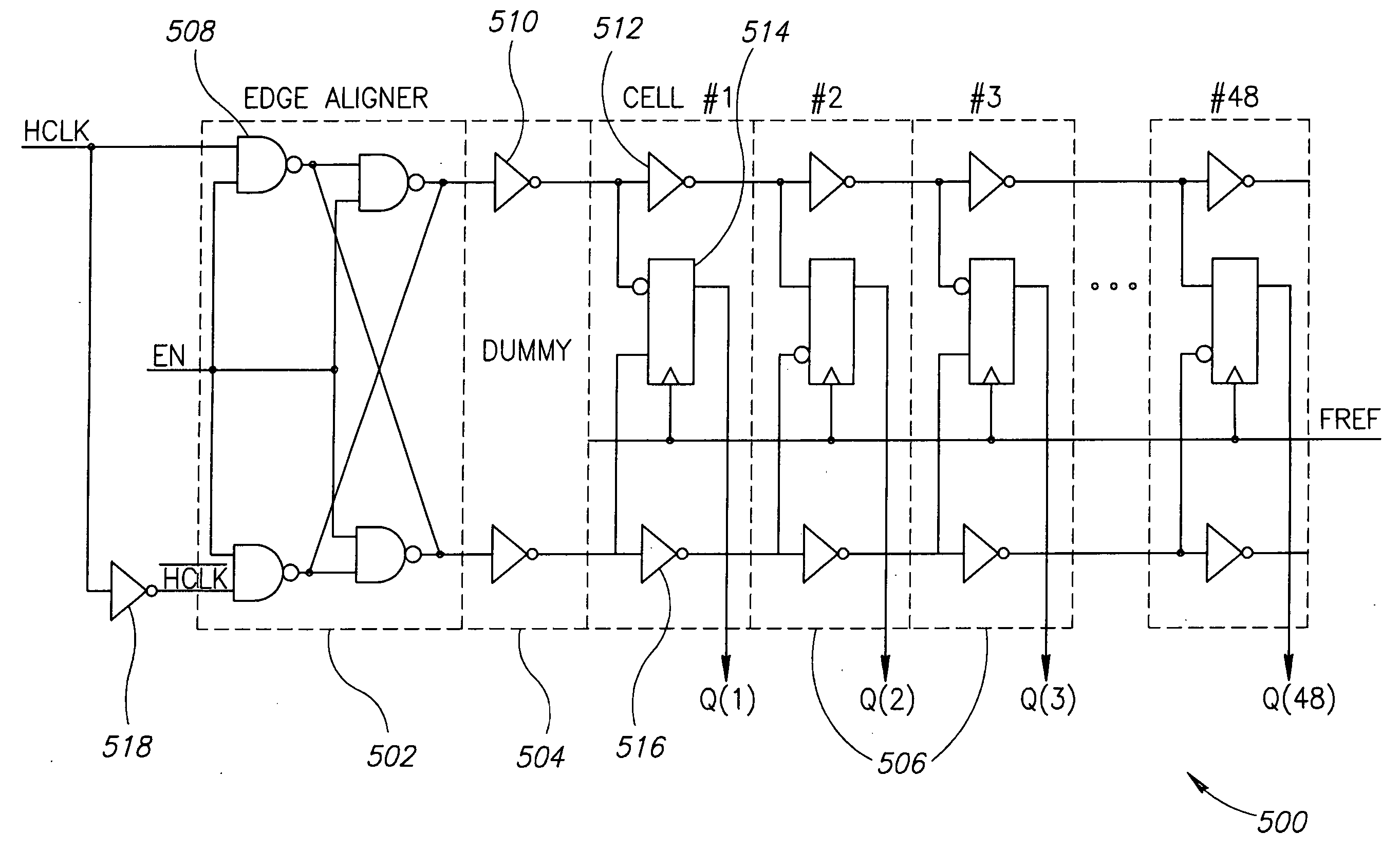
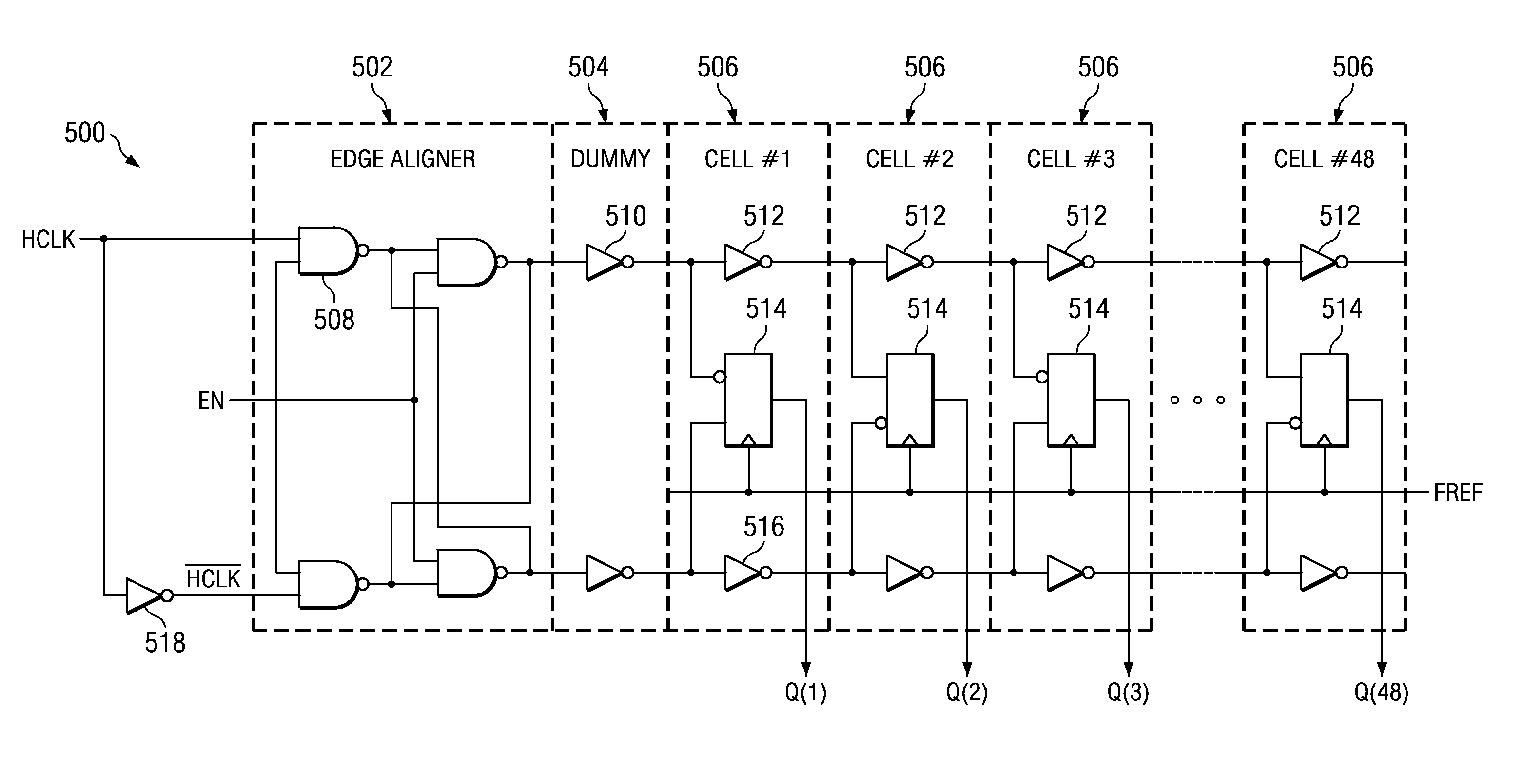
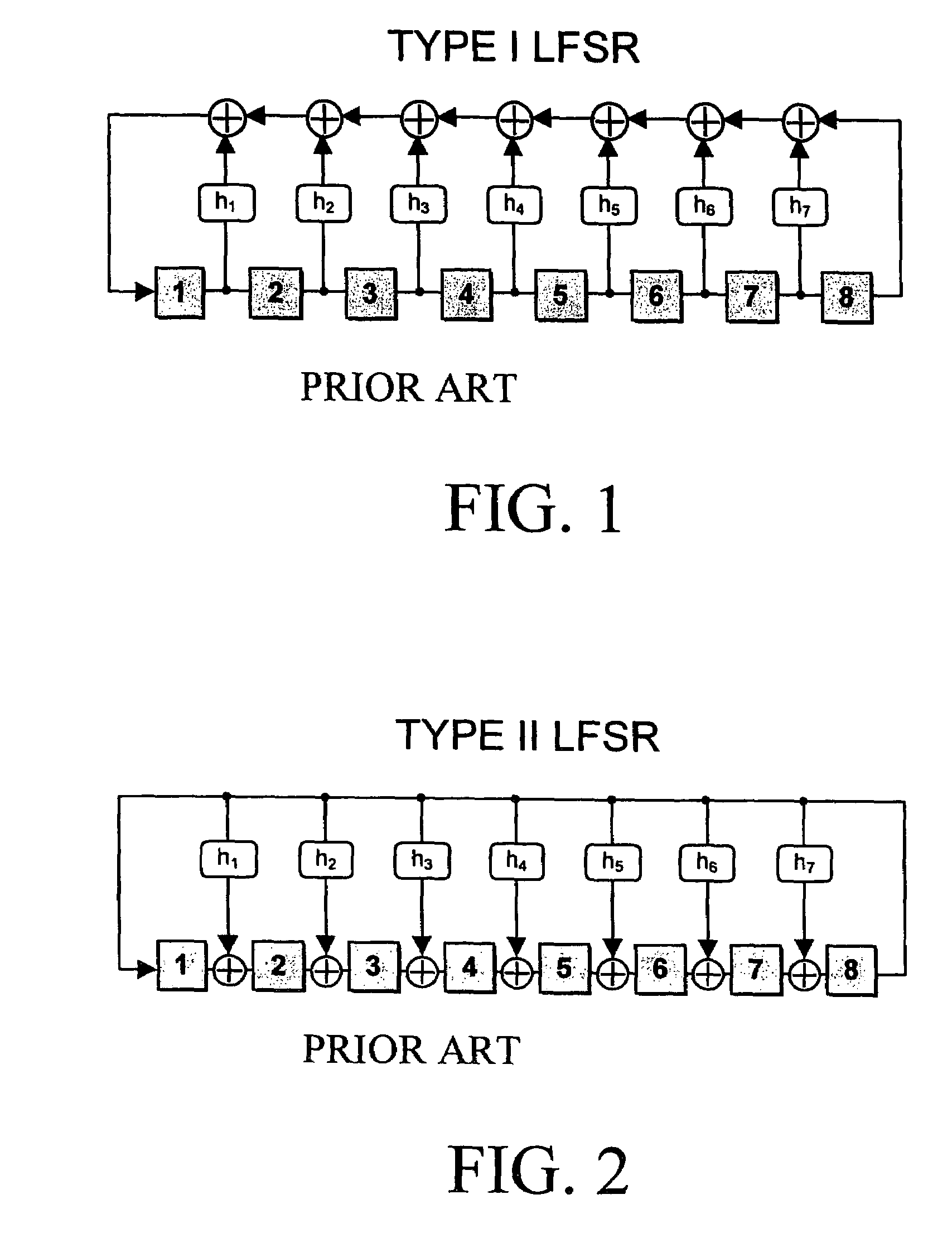
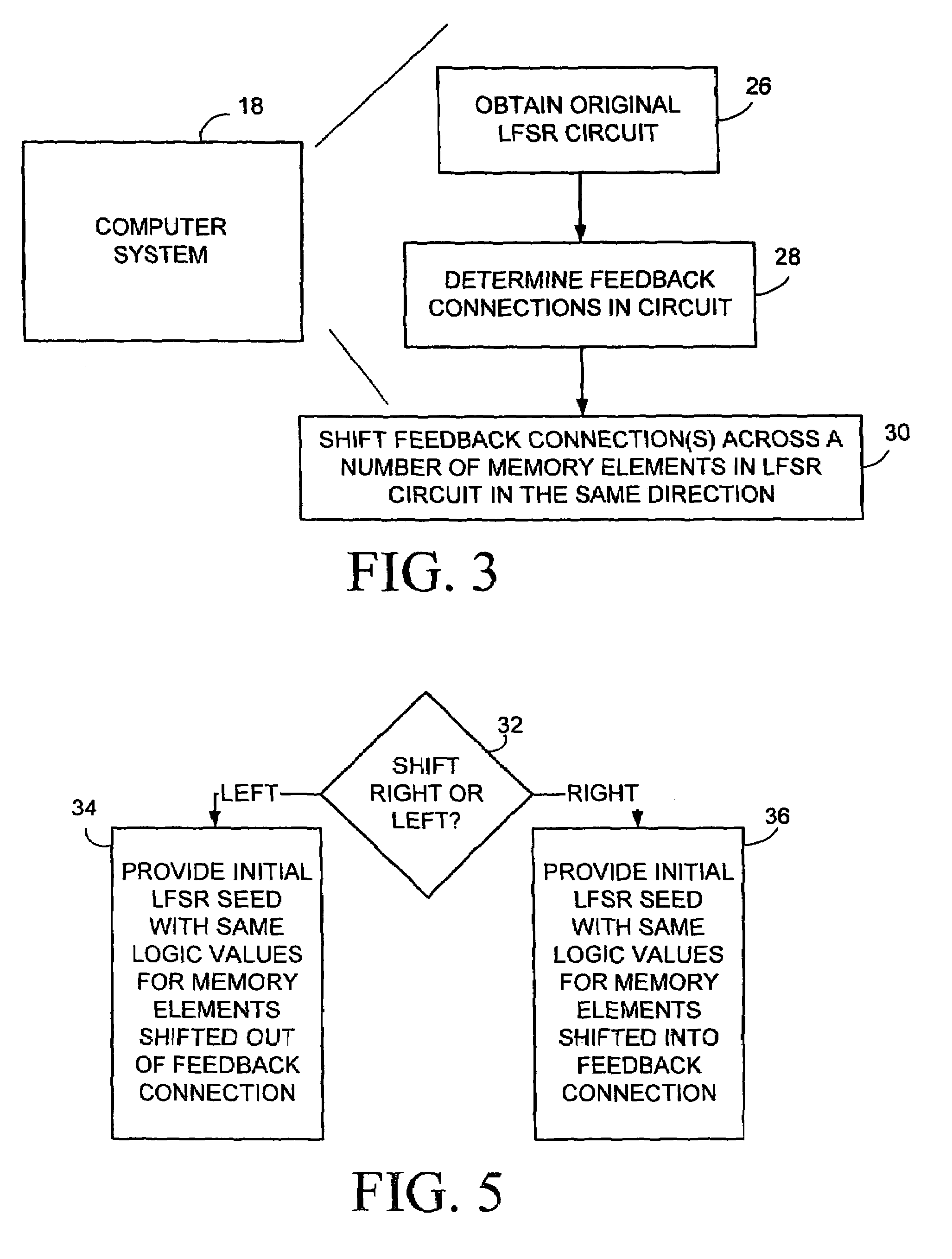
Method for synthesizing linear finite state machines
InactiveUS7260591B2Random number generatorsDigital function generatorsCellular automationVirtual finite-state machine
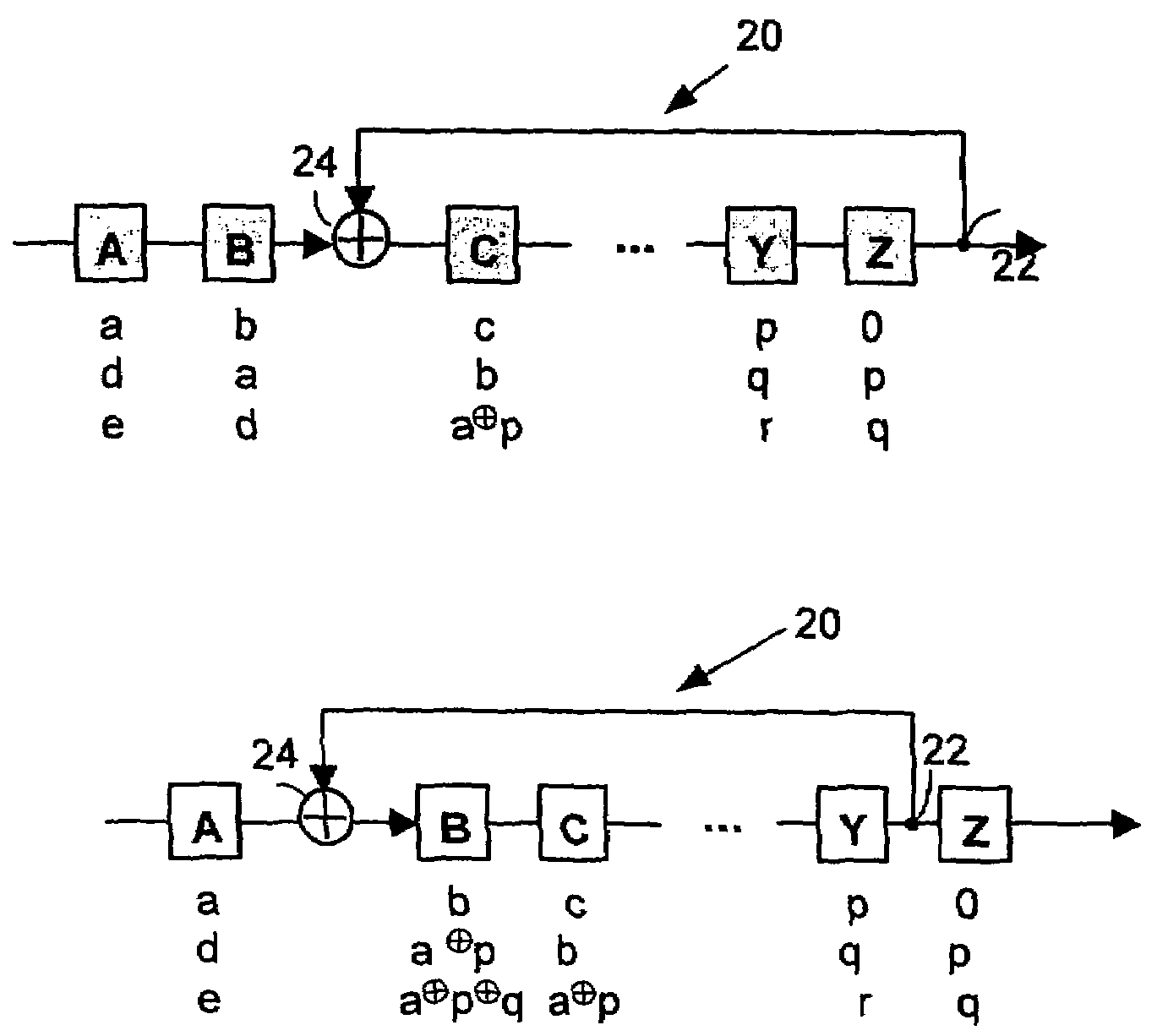
Method and apparatus for synthesizing high-performance linear finite state machines (LFSMs) such as linear feedback shift registers (LFSRs) or cellular automata (CA). Given a characteristic polynomial for the circuit, the method obtains an original LFSM circuit such as a type I or type II LFSR. Feedback connections within the original circuit are then determined. Subsequently, a number of transformations that shift the feedback connections can be applied in such a way that properties of the original circuit are preserved in a modified LFSM circuit. In particular, if the original circuit is represented by a primitive characteristic polynomial, the method preserves the maximum-length property of the original circuit in the modified circuit and enables the modified circuit to produce the same m-sequence as the original circuit. Through the various transformations, a modified LFSM circuit can be created that provides higher performance through shorter feedback connection lines, fewer levels of logic, and lower internal fan-out.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
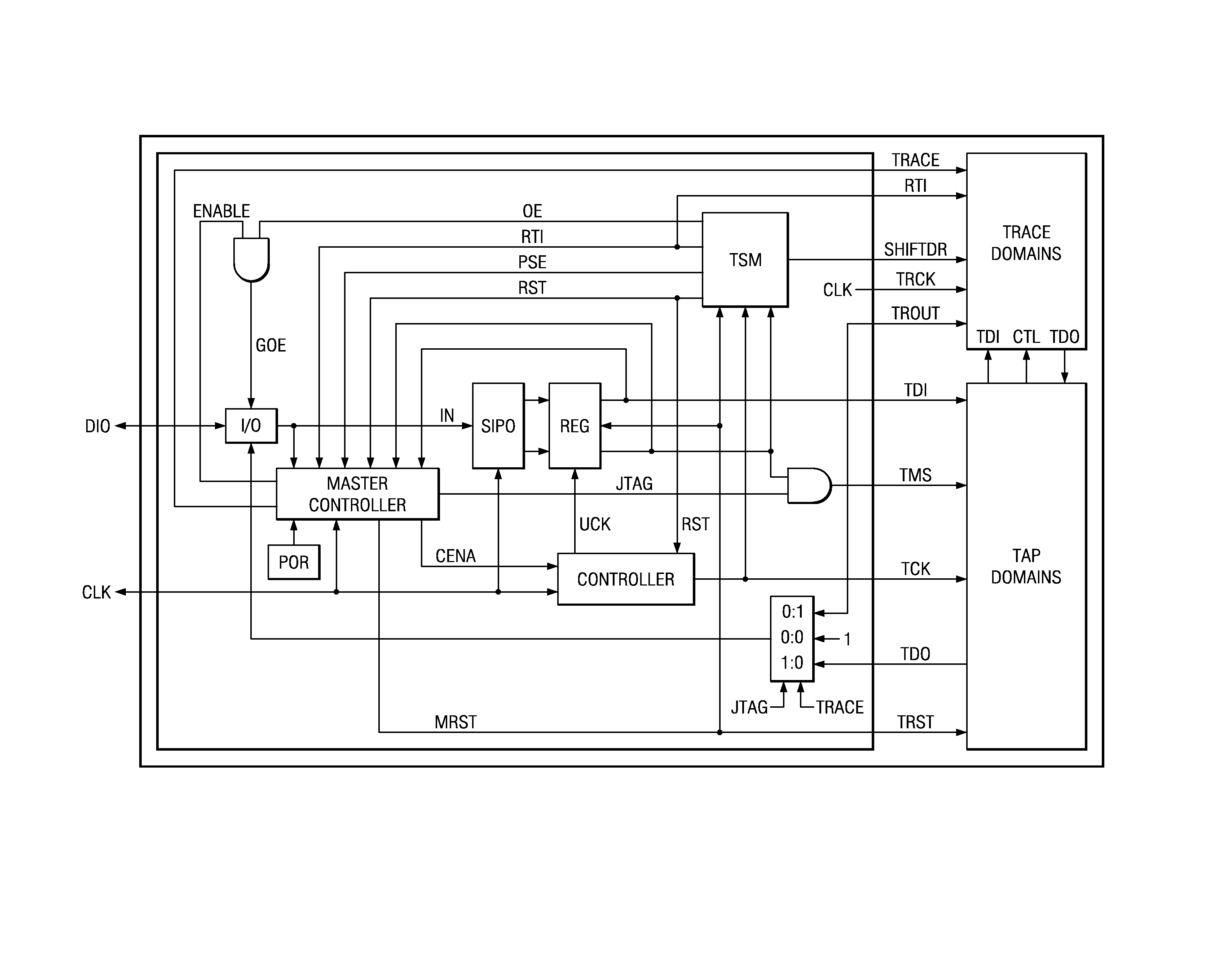
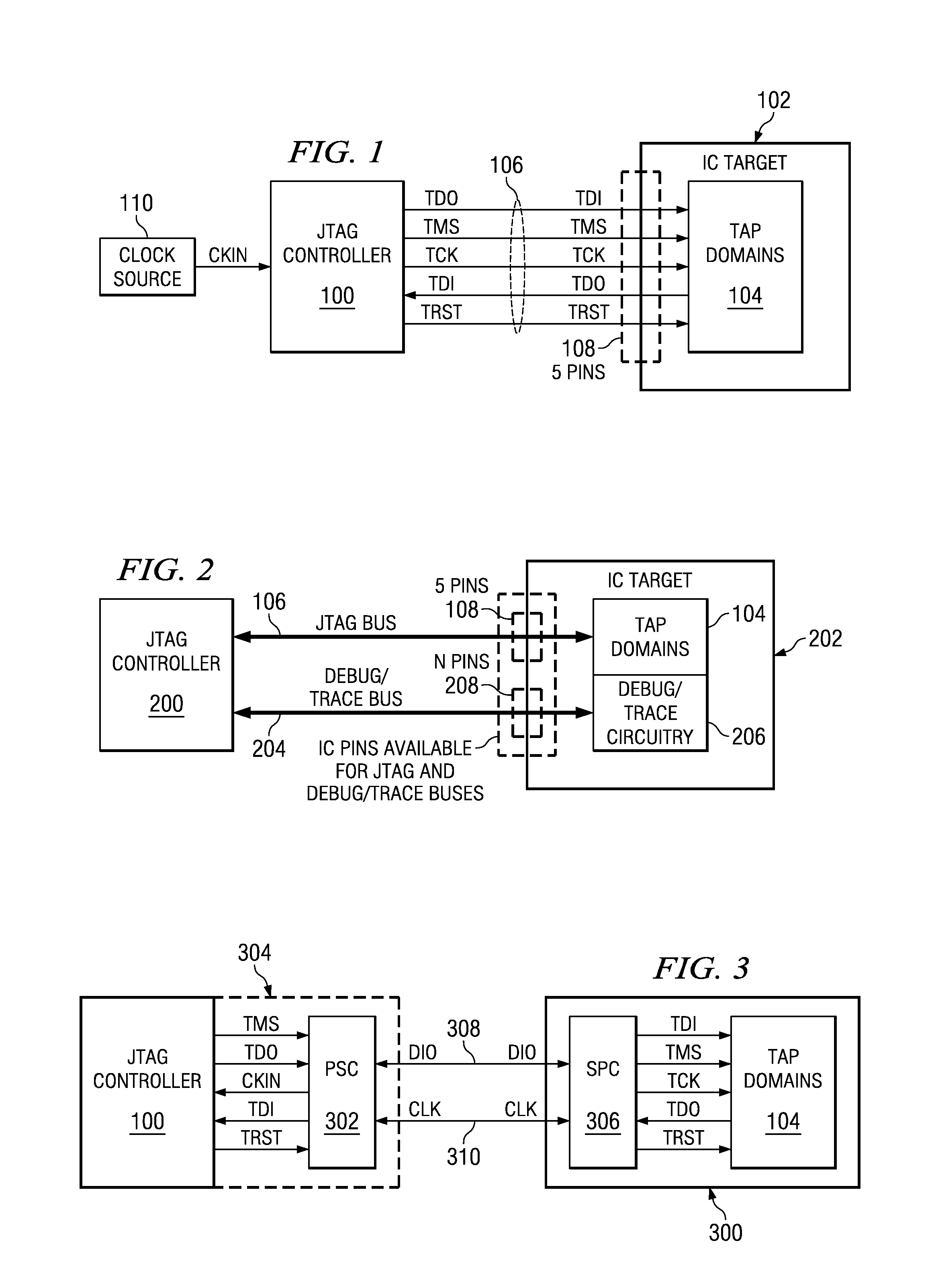
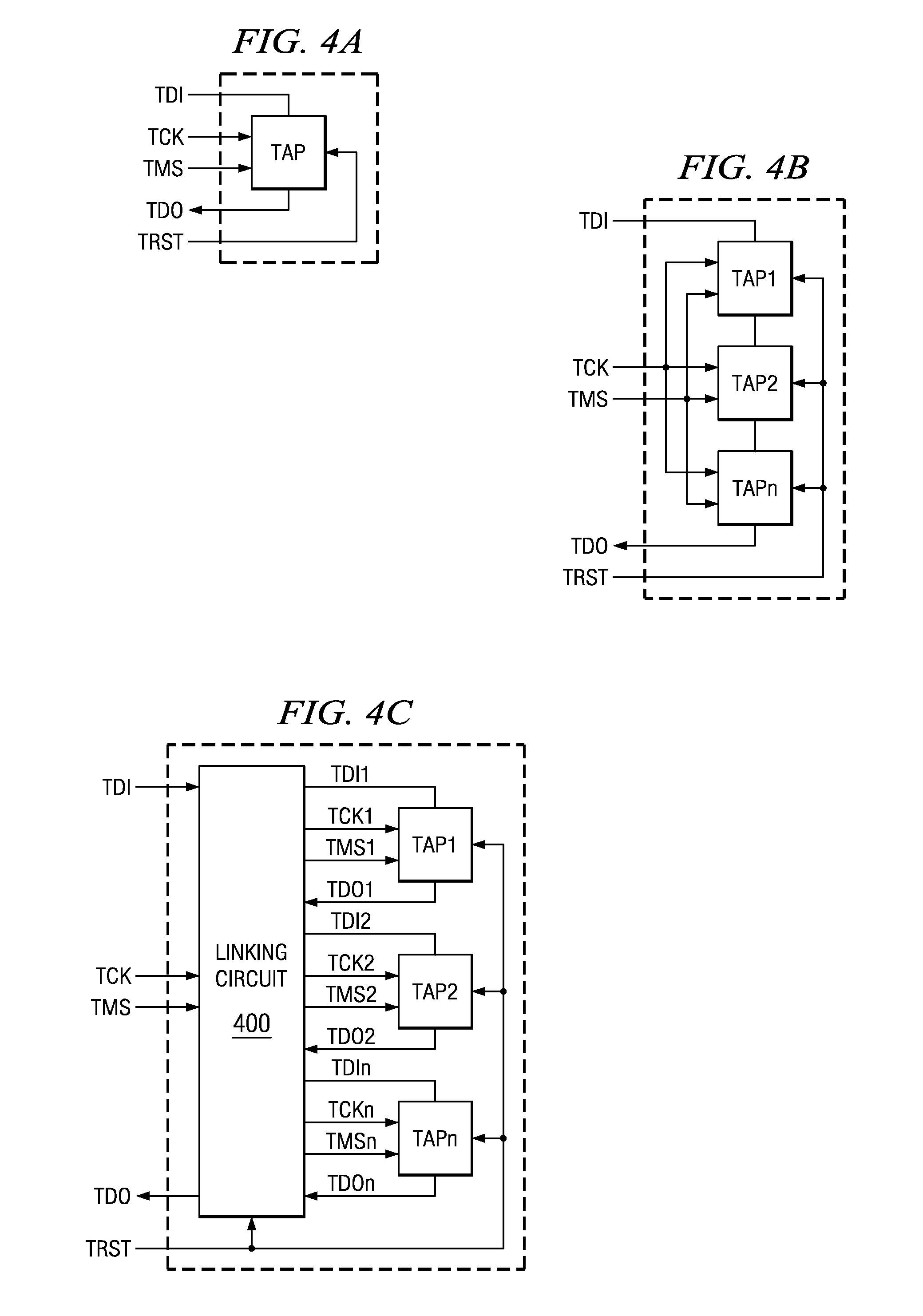
Selectable JTAG or trace access with data store and output
ActiveUS7571364B2Electronic circuit testingFunctional testingJoint Test Action GroupData transmission
An addressable interface selectively enables JTAG TAP domain operations or Trace domain operations within an IC. After being enabled, the TAP receives TMS and TDI input from a single data pin. After being enabled, the Trace domain acquires data from a functioning circuit within the IC in response to a first clock and outputs the acquired data from the IC in response to a second clock. An addressable two pin interface loads and updates instructions and data to a TAP domain within the IC. The instruction or data update operations in multiple ICs occur simultaneously. A process transmits data from an addressed target device to a controller using data frames, each data frame comprising a header bit and data bits. The logic level of the header bit is used to start, continue, and stop the data transmission to the controller. A data and clock signal interface between a controller and multiple target devices provides for each target device to be individually addressed and commanded to perform a JTAG or Trace operation. Trace circuitry within an IC can operate autonomously to store and output functional data occurring in the IC. The store and output operations of the trace circuitry are transparent to the functional operation of the IC. An auto-addressing RAM memory stores input data at an input address generated in response to an input clock, and outputs stored data from an output address generated in response to an output clock.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
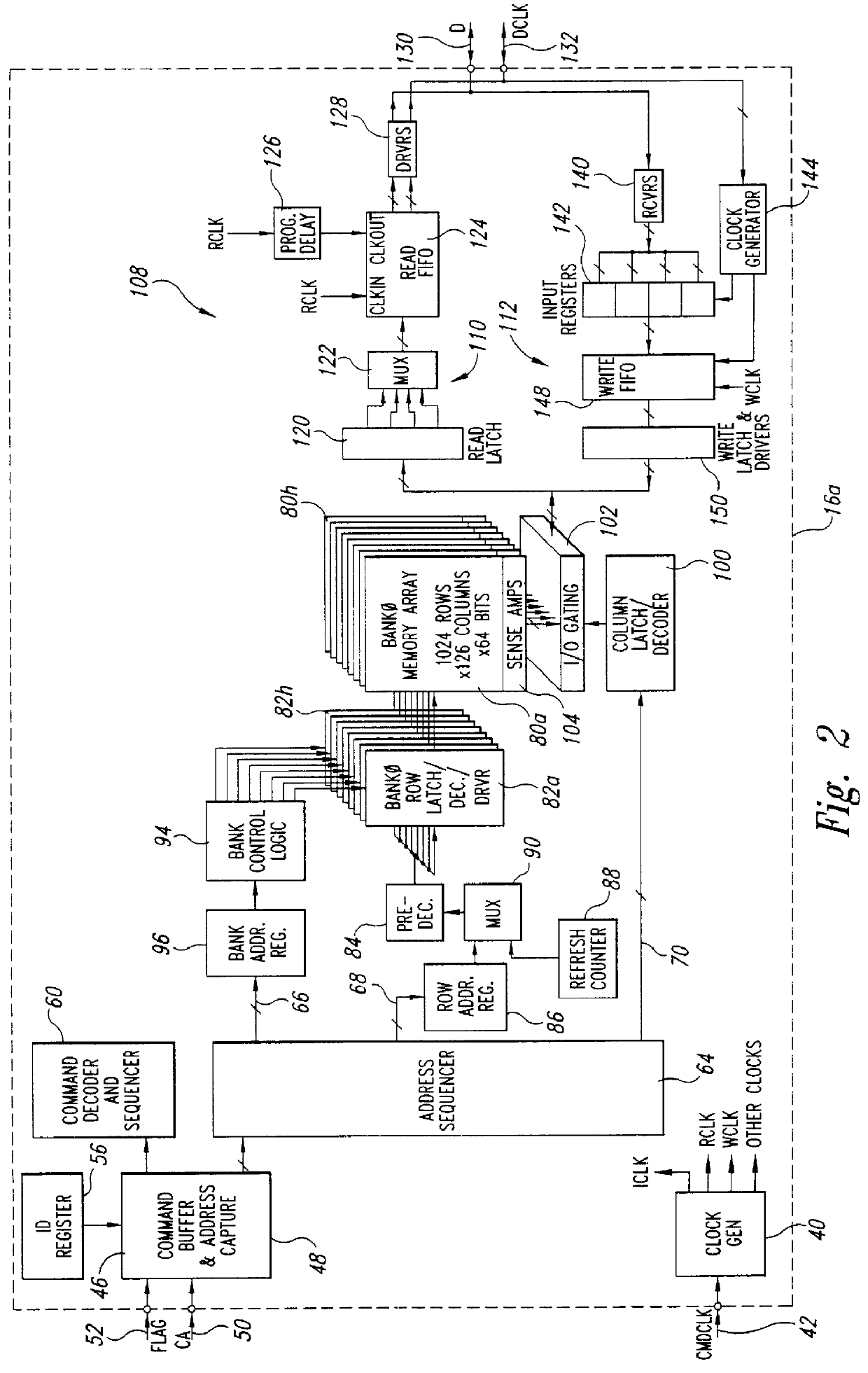
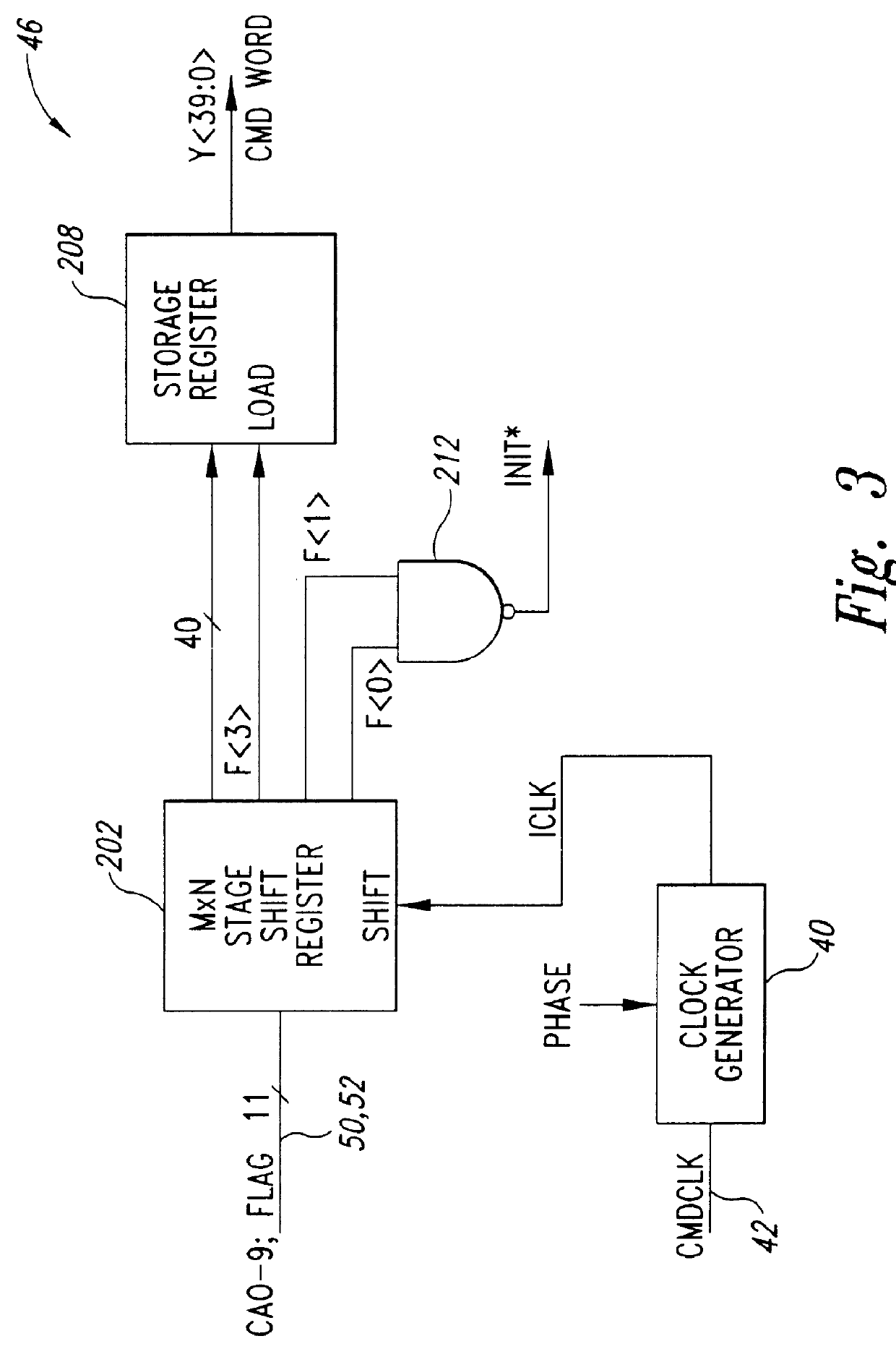
Method and apparatus for detecting an initialization signal and a command packet error in packetized dynamic random access memories
InactiveUS6167495AIncrease chanceMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionShift registerNAND gate
A system for detecting an initialization flag signal and distinguishing it from a normal flag signal having half the duration of the initialization flag signal. The initialization flag detection system may be included in the command buffer of a packetized DRAM that is used in a computer system. In one embodiment, the initialization flag detection system includes a pair of shift registers receiving the flag signal at their respective data inputs. One of the shift registers is clocked by a signal corresponding to an externally applied to command clock signal, while the other shift register is clocked by a quadrature clock signal. Together, the shift registers store a number of samples taken over a duration that is longer than the duration of the normal flag signal. The outputs of the shift registers are applied to a logic circuit, such as a NAND gate, that generates an initialization signal when all of the samples stored in the shift registers correspond to the logic levels of the flag signal. In another embodiment, the initialization flag detection system includes a plurality of latches receiving the flag signals at their data inputs. The latches are clocked by respective strobe signals corresponding to the command clock signal, but having phases that differ from each other. The outputs of the latches are applied to a logic circuit, such as a NAND) gate. Finally, in another embodiment of the invention, the bits of the command packet are sampled along with the flag signal and compared to the samples of the flag signal to detect when a command packet having a predetermined pattern does not correspond to a flag signal having a predetermined pattern.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
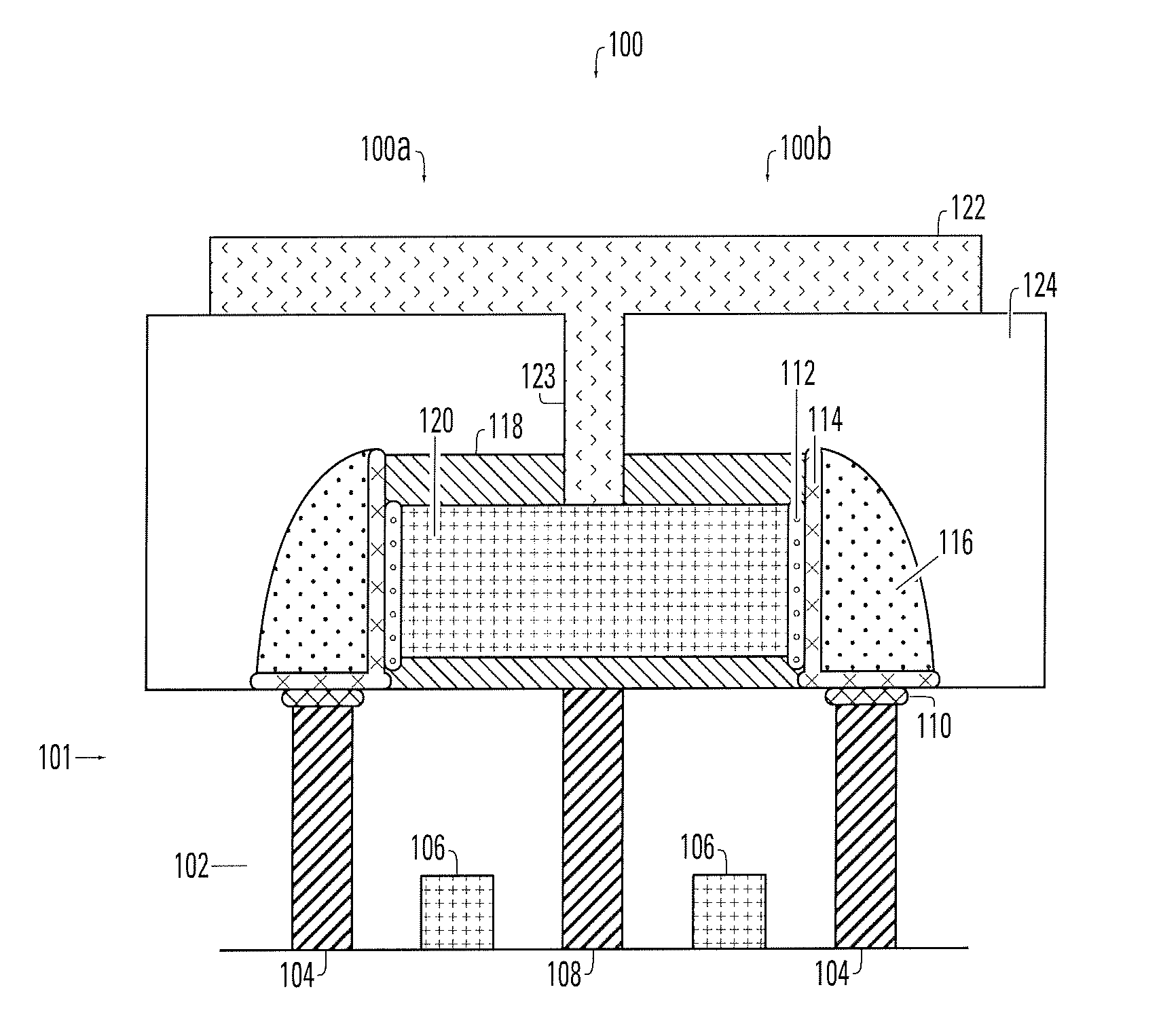
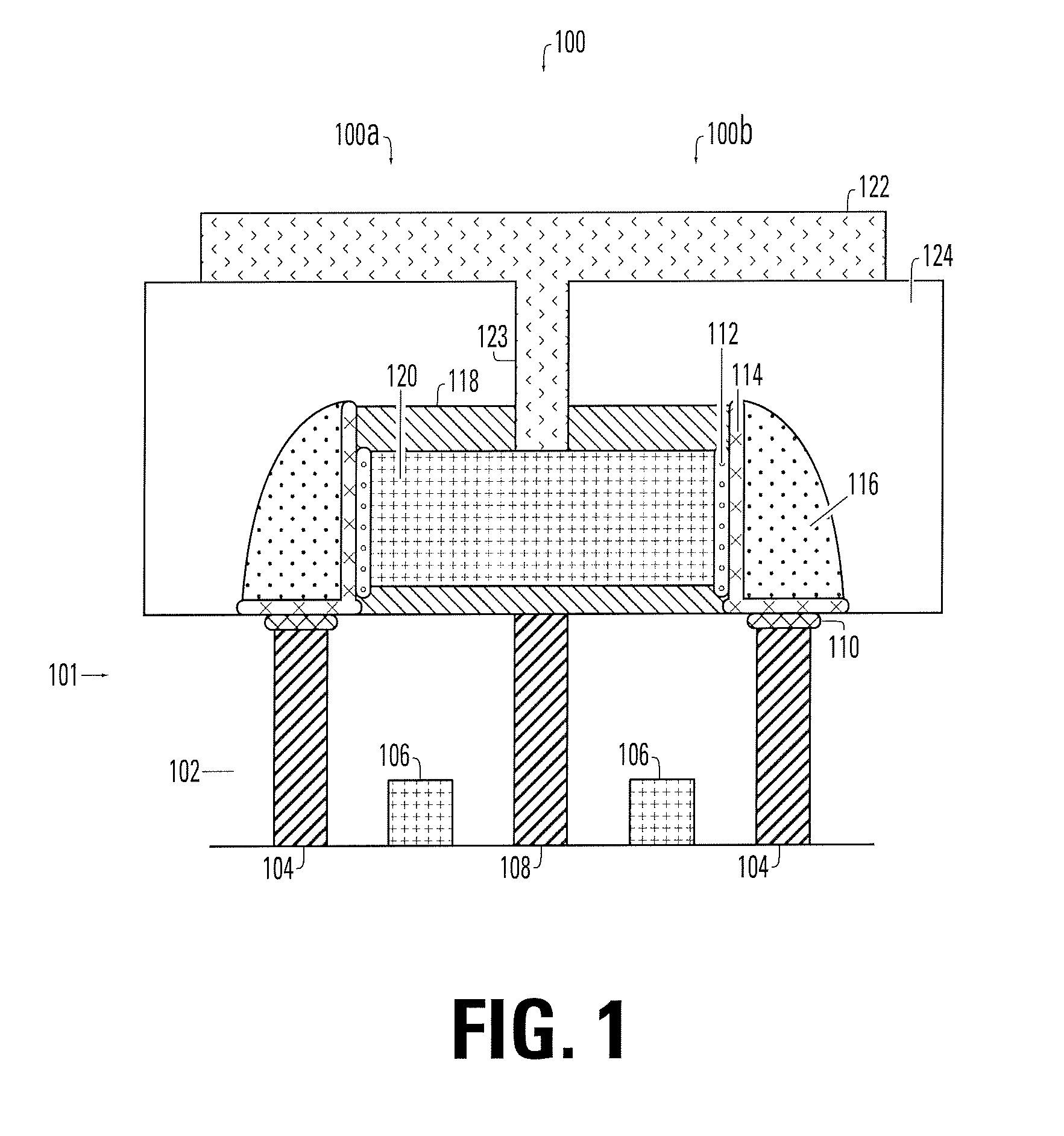
Method and Apparatus for Non-Volatile Multi-Bit Memory
A memory device that selectably exhibits first and second logic levels. A first conductive material has a first surface with a first memory layer formed thereon, and a second conductive material has a second surface with a second memory layer formed thereon. A connective conductive layer joins the first and second memory layers and places the same in electrical contact. The structure is designed so that the first memory layer has a cross-sectional area less than that of the second memory layer.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Circuit for providing a logical output signal in accordance with crossing points of differential signals
InactiveUS6448806B1Increase currentMinimal numberMultiple input and output pulse circuitsDigital circuit testingAudio power amplifierDifferential signaling
A circuit provides an output signal in accordance with crossing points of a differential signal, which includes a normal input signal and a complementary input signal. The circuit includes a first amplifier for amplifying a first signal difference between the normal input signal and a first threshold value, and for providing as a first output signal the amplified first signal difference. The circuit includes a second amplifier for amplifying a second signal difference between the complementary input signal and a second threshold value, and for providing as a second output signal the amplified second signal difference. The circuit also includes a first comparator for providing a first logical level when a third signal difference between the first output signal and the second output signal is greater than a third threshold value, and for providing a second logical level when the third signal difference is smaller than the third threshold value.
Owner:ADVANTEST CORP
Semiconductor device and test method thereof
ActiveUS20120092943A1Reduce in quantityShorten the timeSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesSemiconductorElectrical current
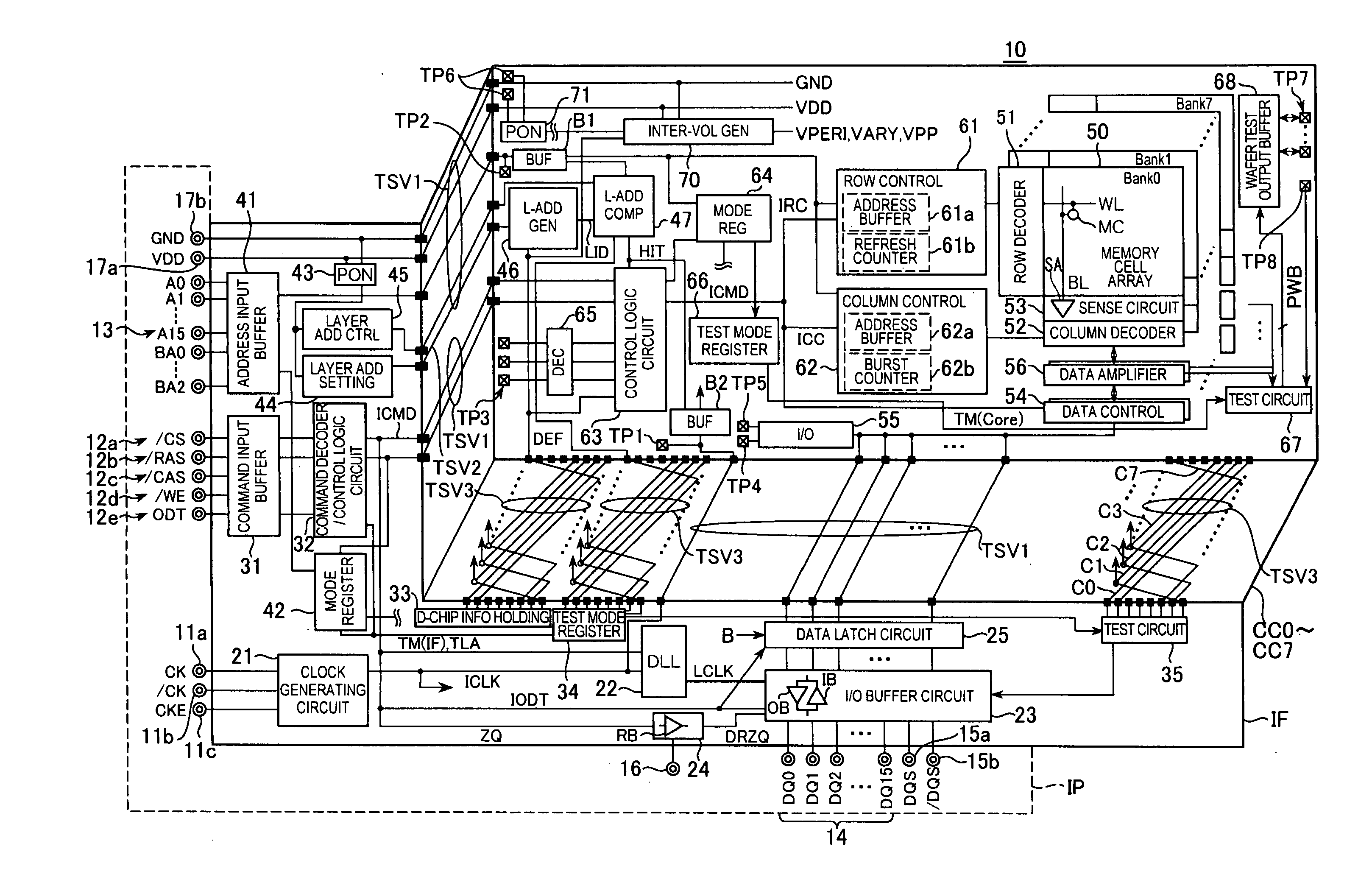
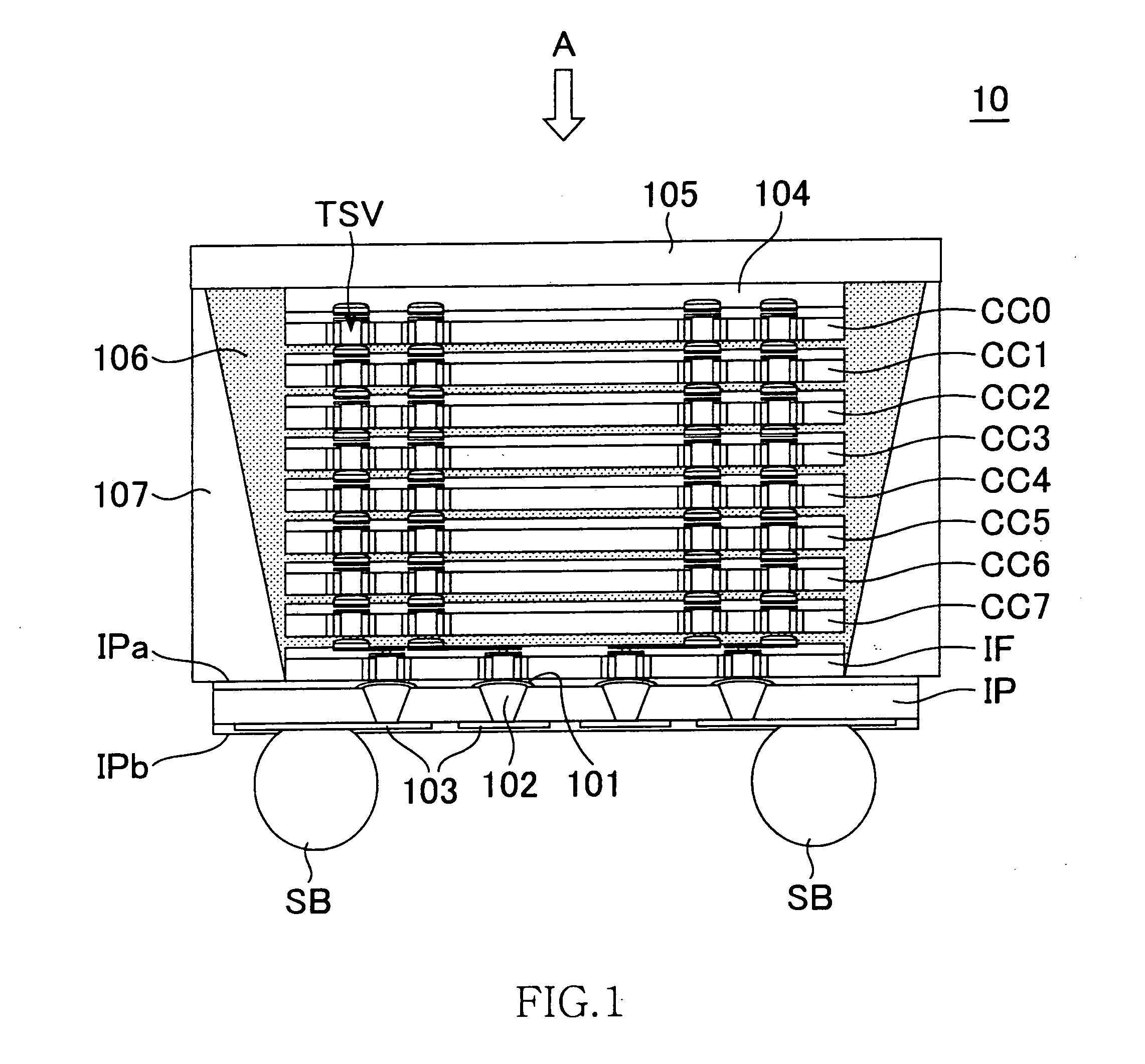
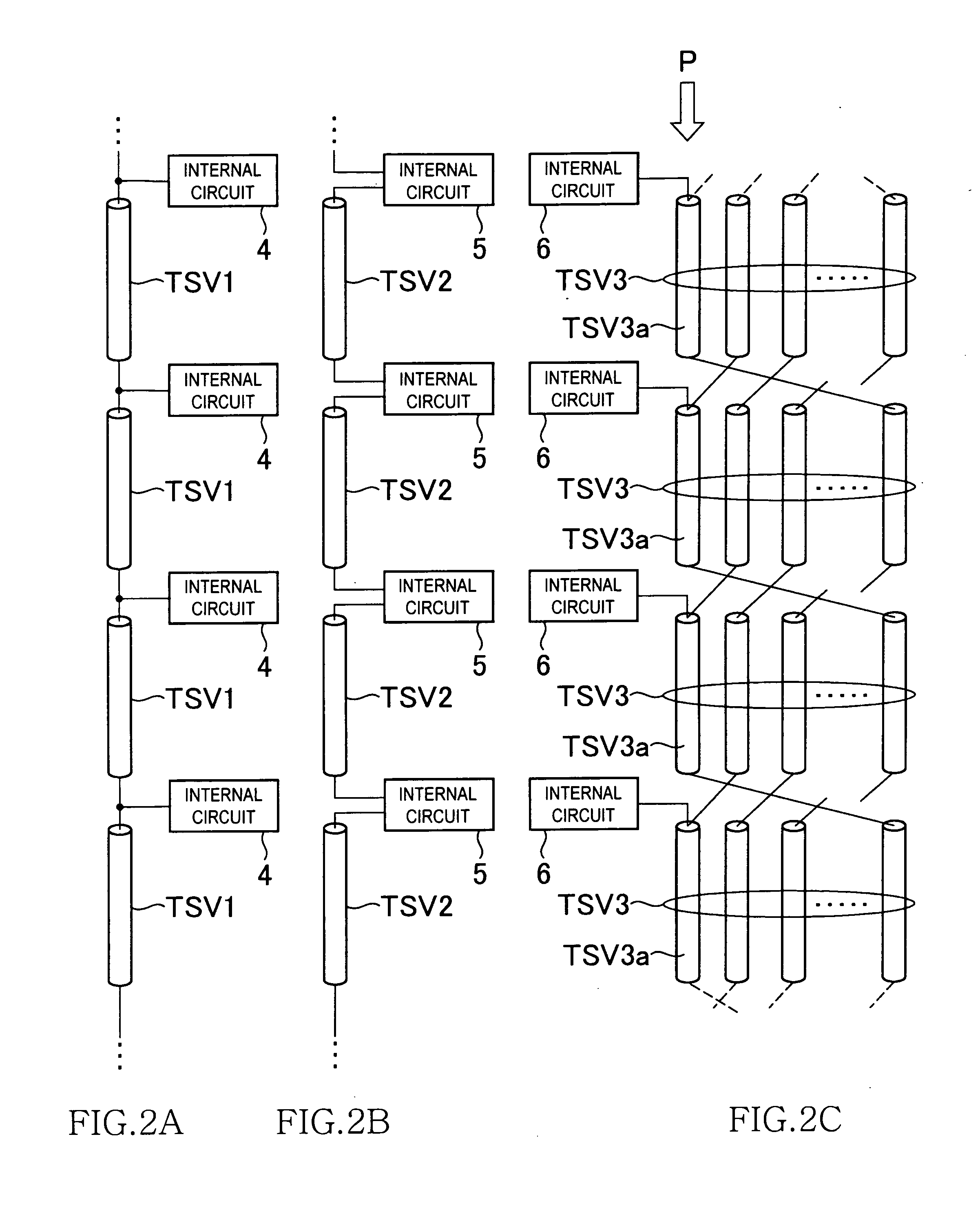
plurality of core chips to which chip identification information different from each other is allocated and an interface chip are layered, the plurality of core chips are commonly connected to the interface chip through a first current path including at least a through silicon via, the interface chip serially supplies an enable signal to the plurality of core chips through the first current path, and the plurality of core chips are activated based on a logic level of a bit corresponding to the chip identification information among a plurality of bits configuring the enable signal. The present invention can reduce the number of through silicon vias required to supply an enable signal.
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
Phase-change random access memory and programming method
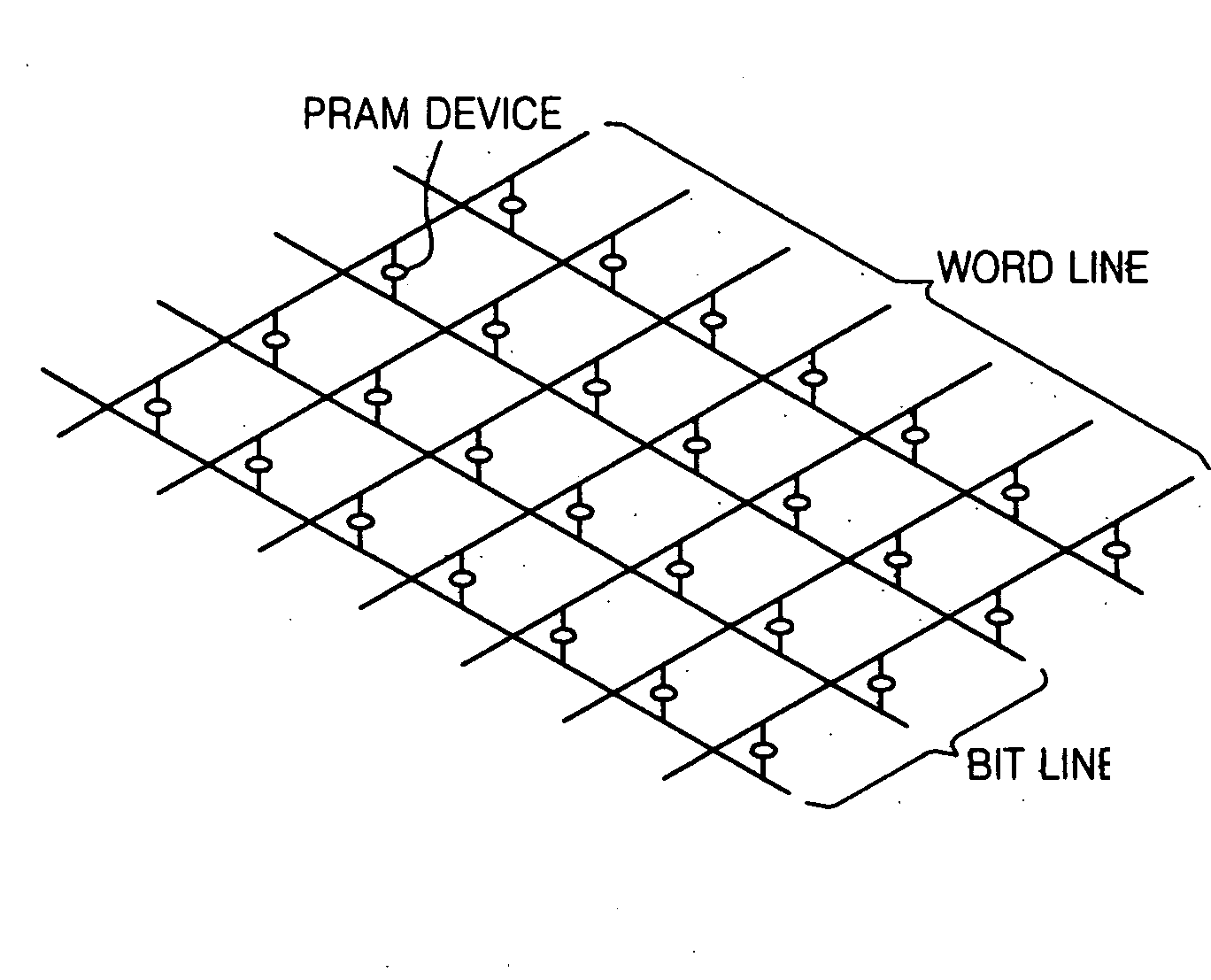
ActiveUS20070189065A1Improve reliabilityEffective controlRead-only memoriesDigital storageRandom access memoryTheoretical computer science
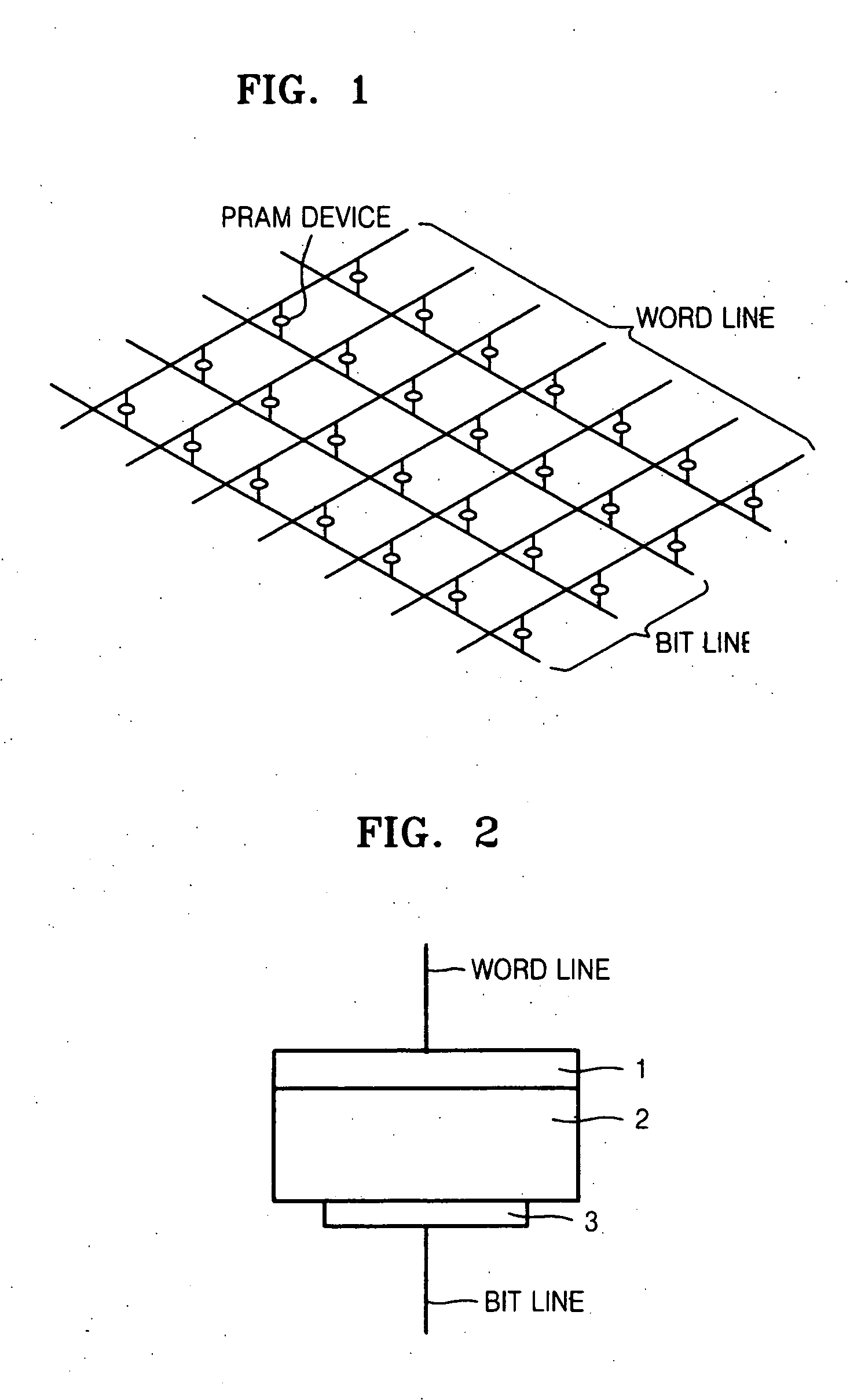
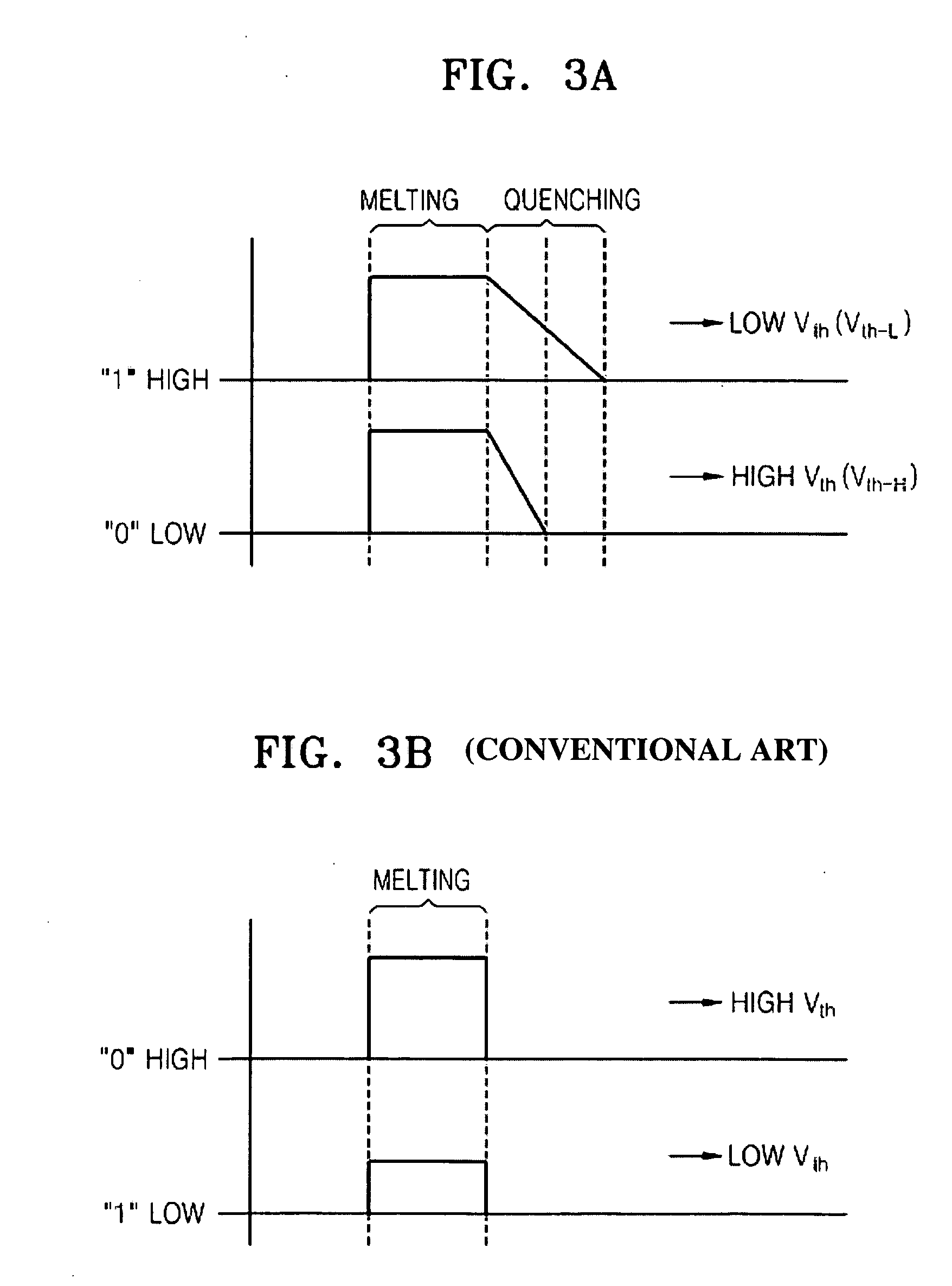
A programming method for a phase-change random access memory (PRAM) may be provided. The programming method may include determining an amorphous state of a chalcogenide material using programming pulses to form programming areas having threshold voltages corresponding to logic high and logic low, and / or controlling a trailing edge of programming pulses during programming to control a quenching speed of the chalcogenide material so as to adjust a threshold voltage of the chalcogenide material. Accordingly, programming pulses corresponding to logic low or logic high may have uniform magnitudes regardless of a corresponding logic level. Accordingly, reliability of a PRAM device may be improved.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
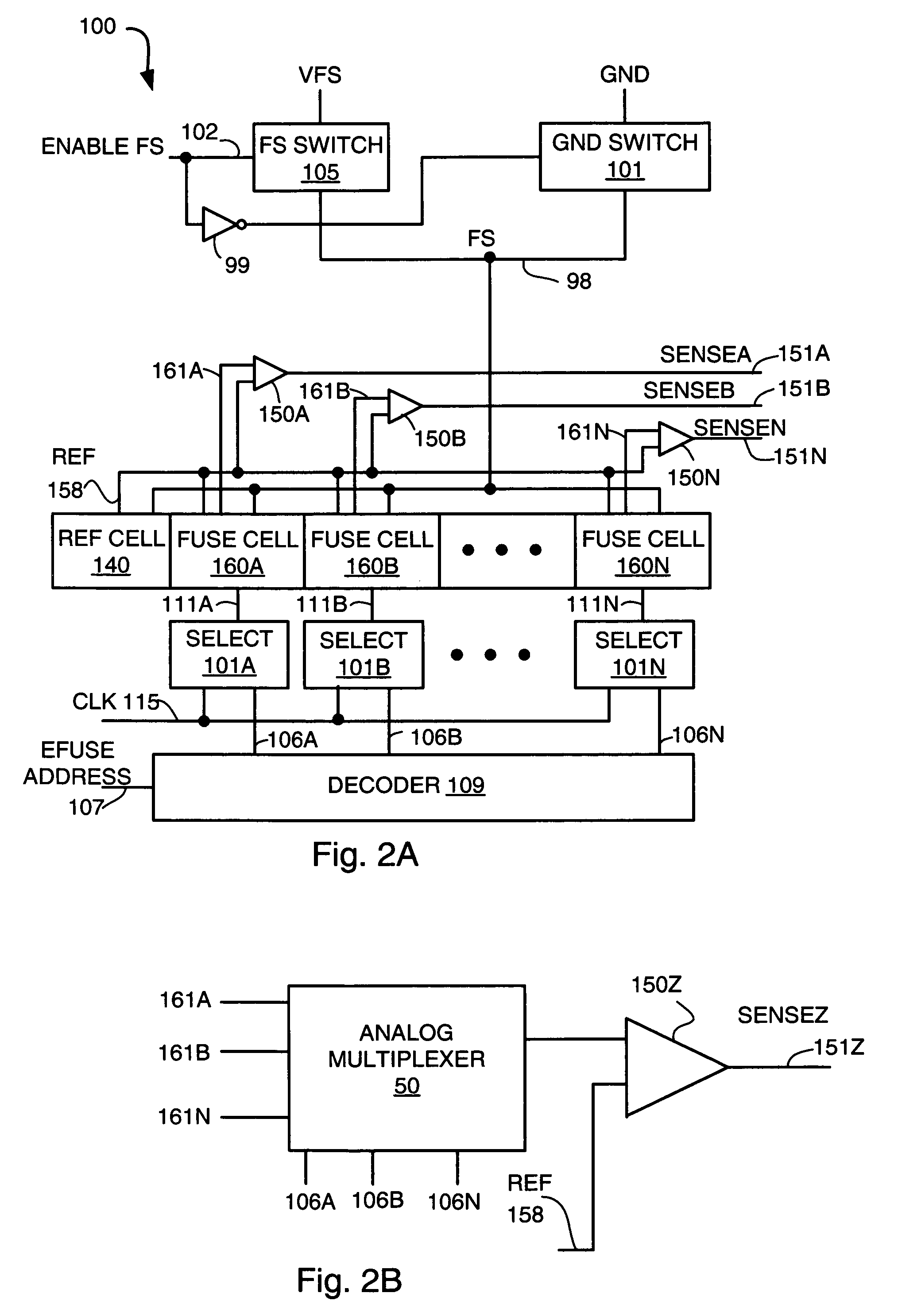
eFuse sense circuit
InactiveUS7224633B1Reliable sensingQuick fixRead-only memoriesDigital storageReference currentHemt circuits
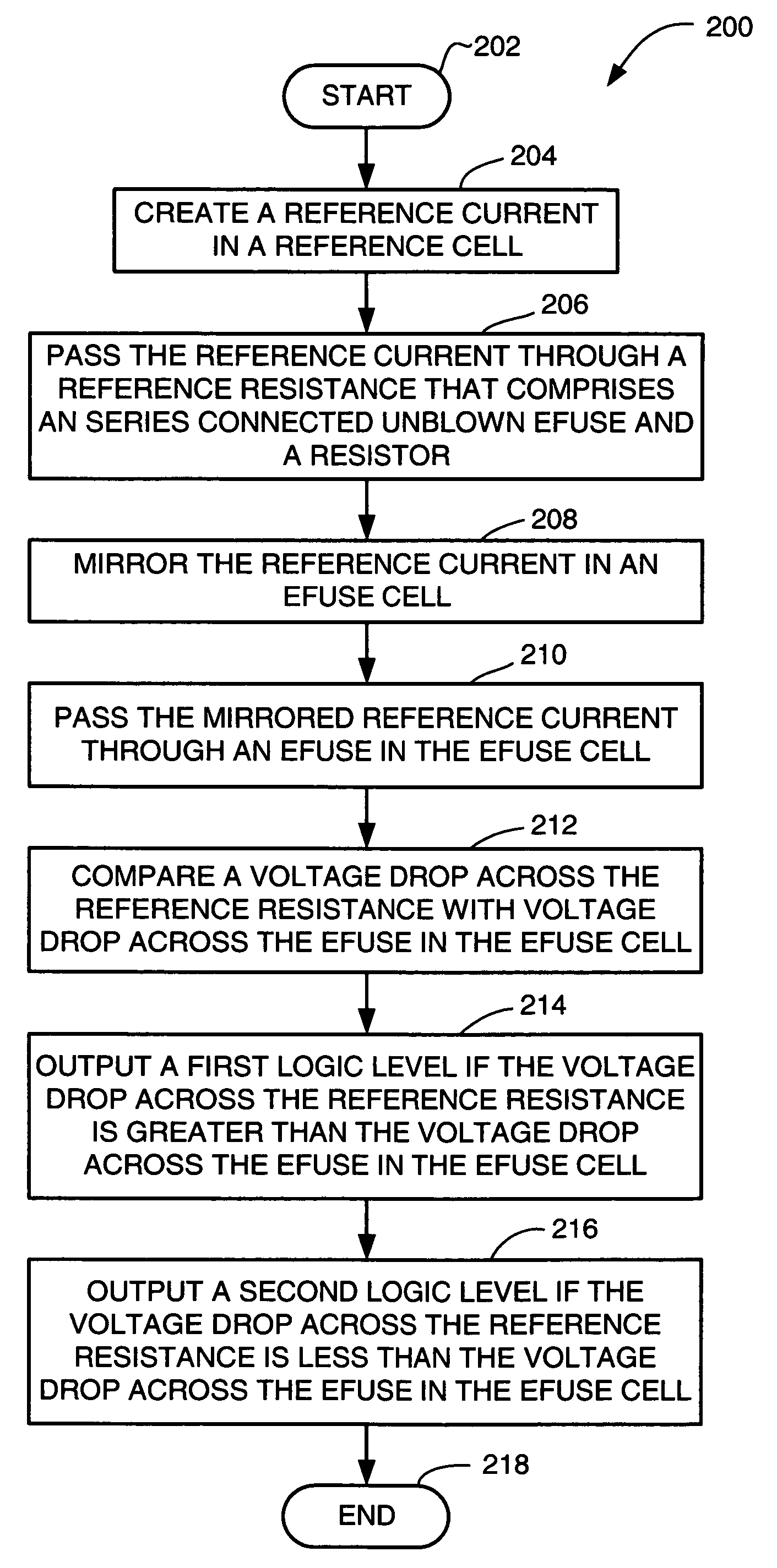
An eFuse reference cell on a chip provides a reference voltage that is greater than a maximum voltage produced by an eFuse cell having an unblown eFuse on the chip but less than a minimum voltage produced by an eFuse cell having a blown eFuse on the chip. A reference current flows through a resistor and an unblown eFuse in the eFuse reference cell, producing the reference voltage. The reference voltage is used to create a mirrored copy of the reference current in the eFuse cell. The mirrored copy of the reference current flows through an eFuse in the eFuse cell. A comparator receives the reference voltage and the voltage produced by the eFuse cell. The comparator produces an output logic level responsive to the voltage produced by the eFuse cell compared to the reference voltage.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com