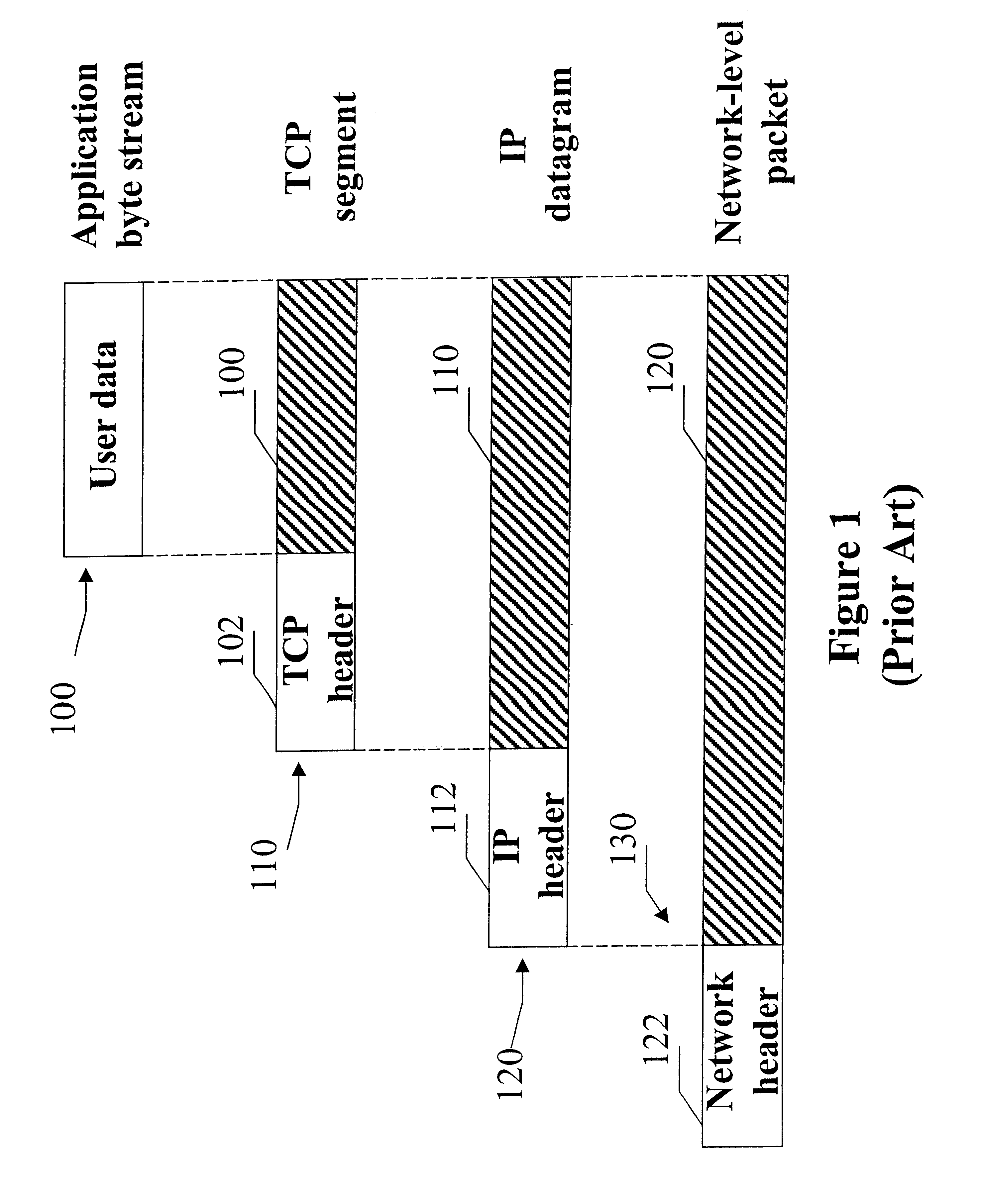
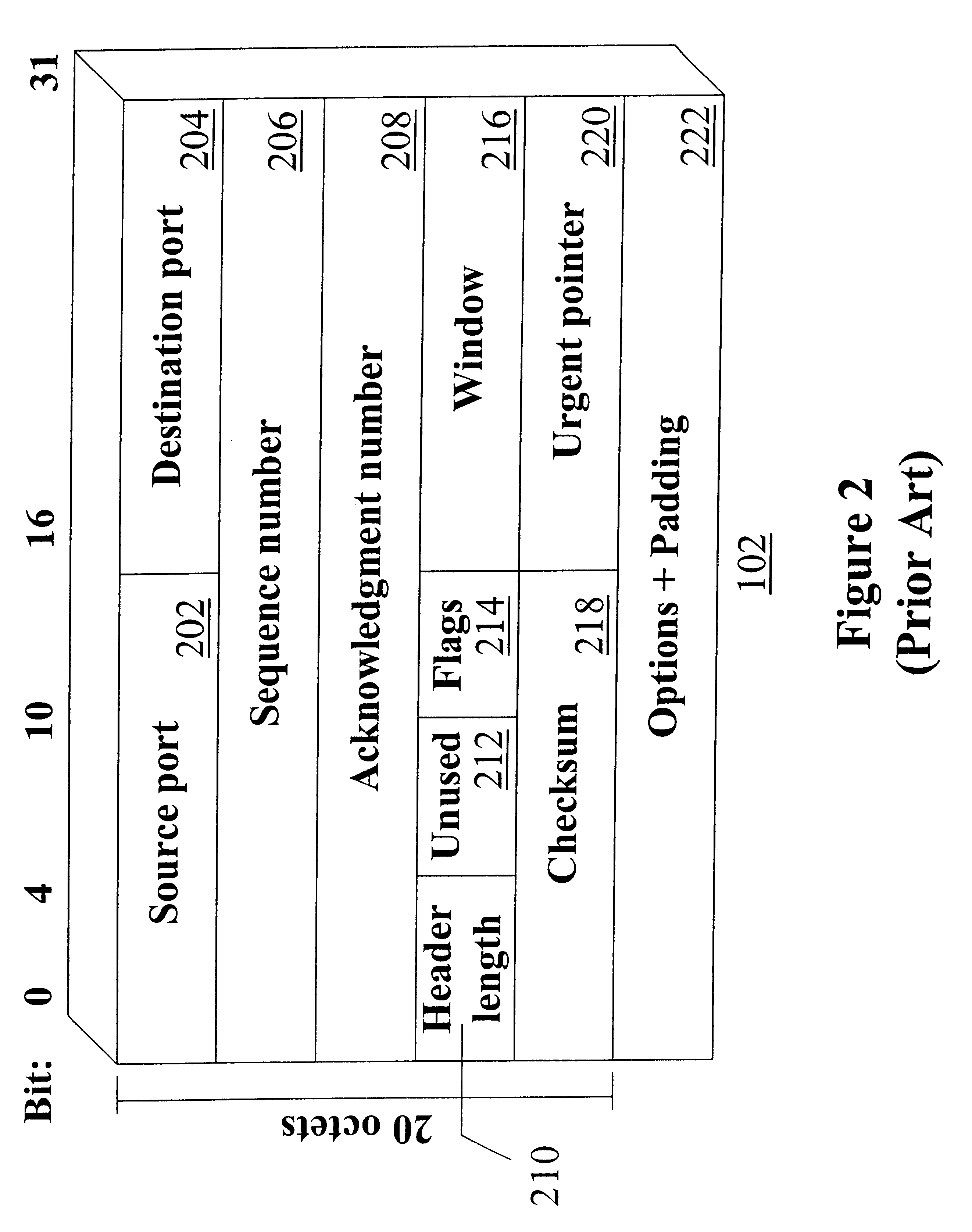
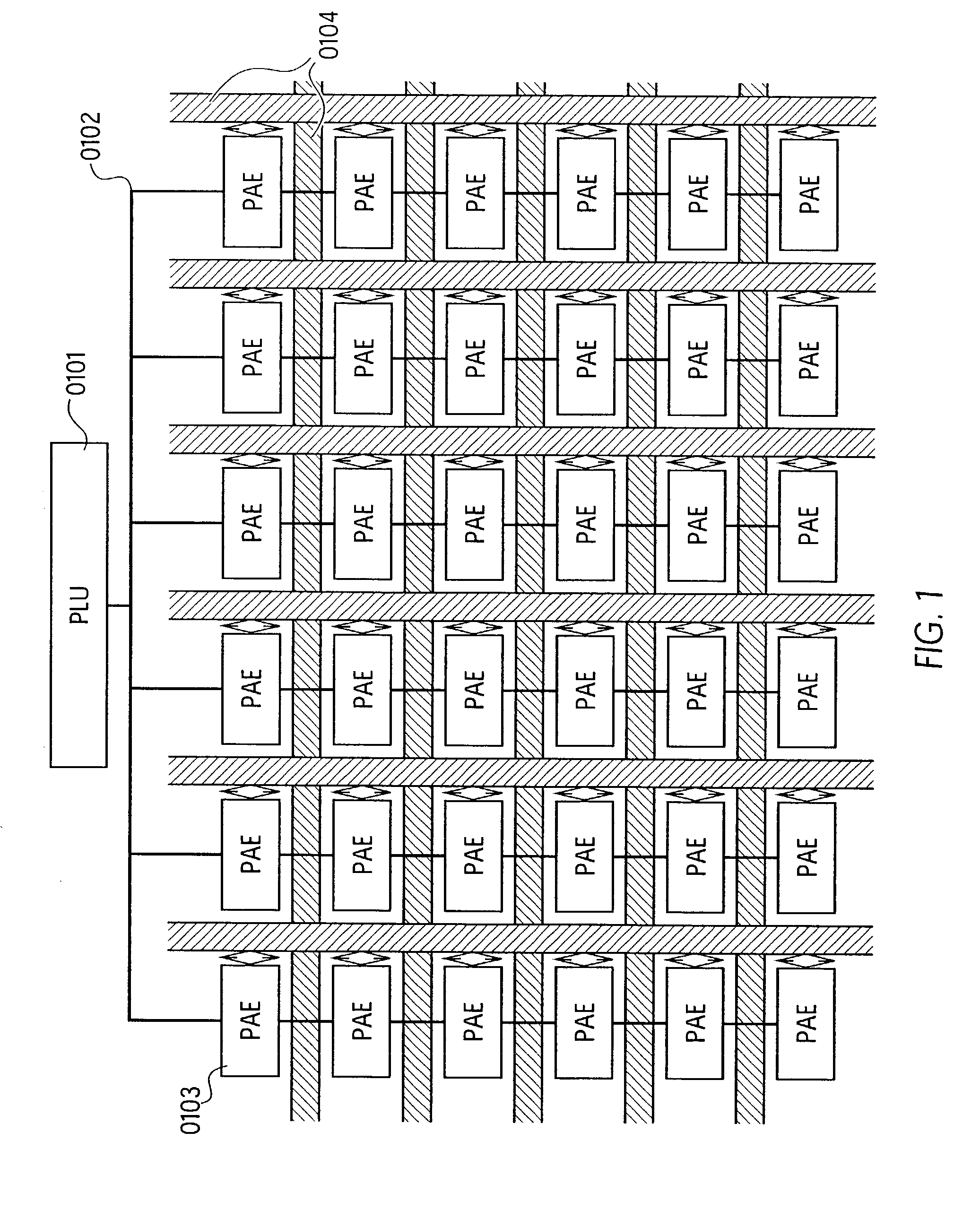
Patents
Literature
2149 results about "Logical operations" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
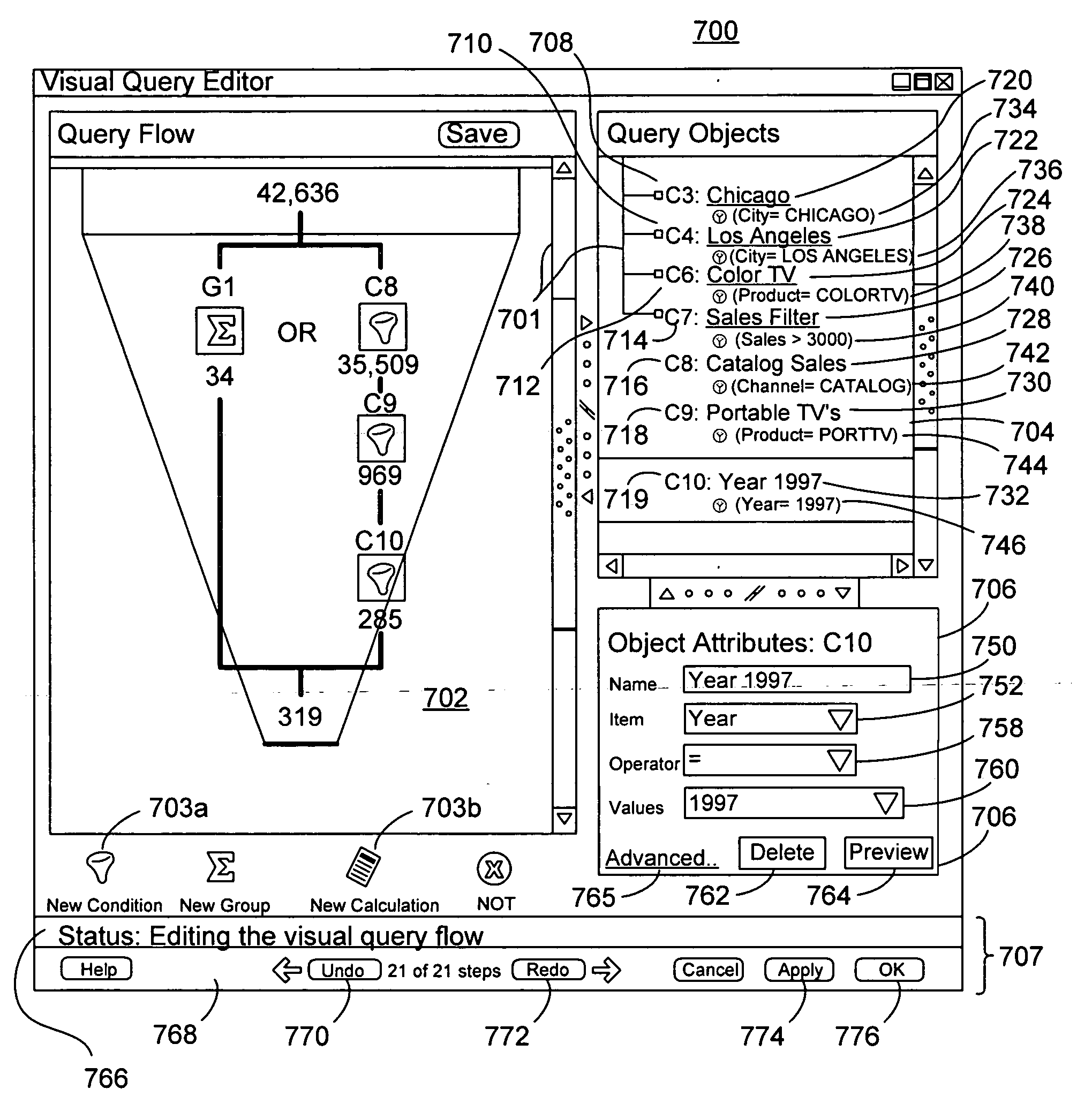
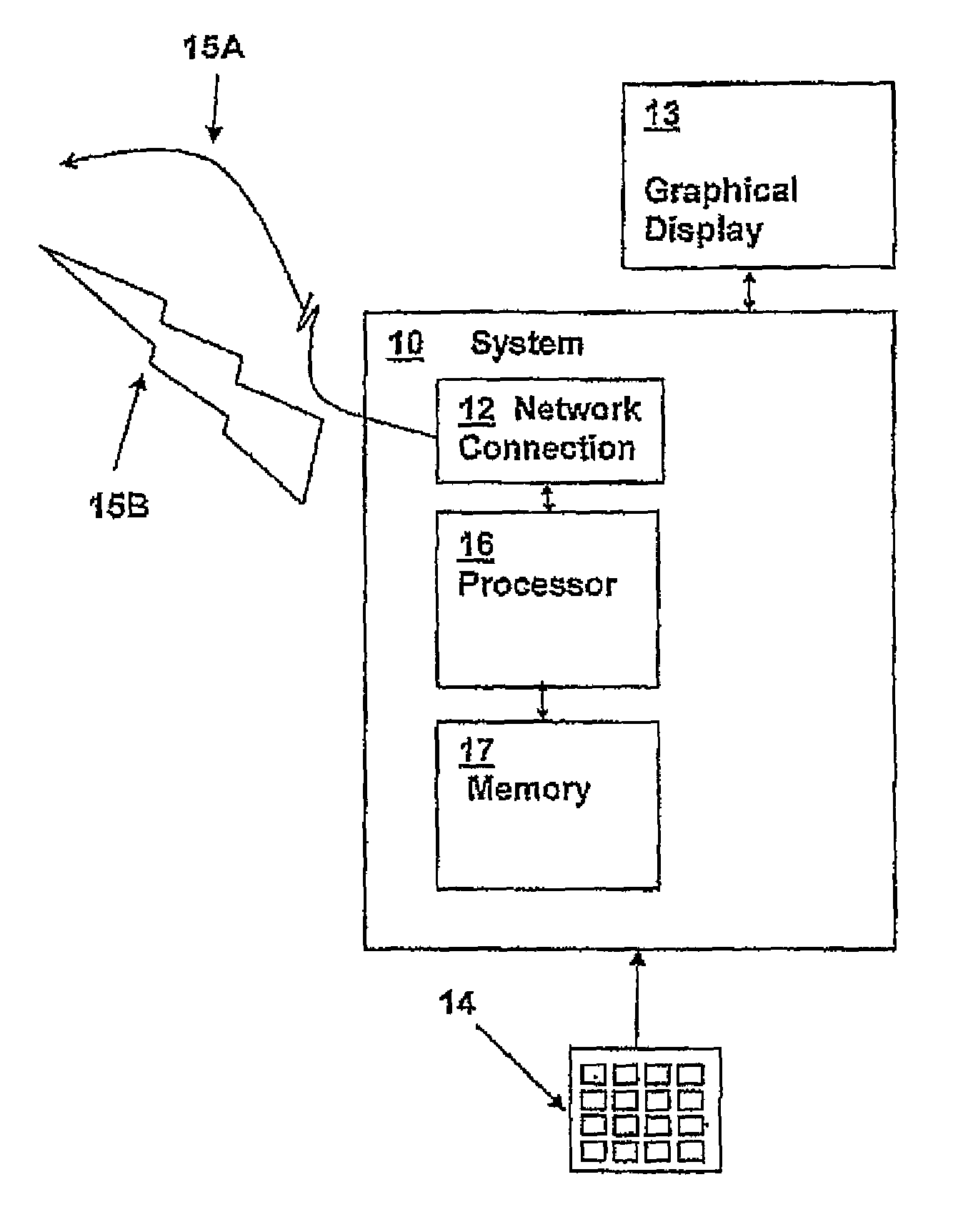
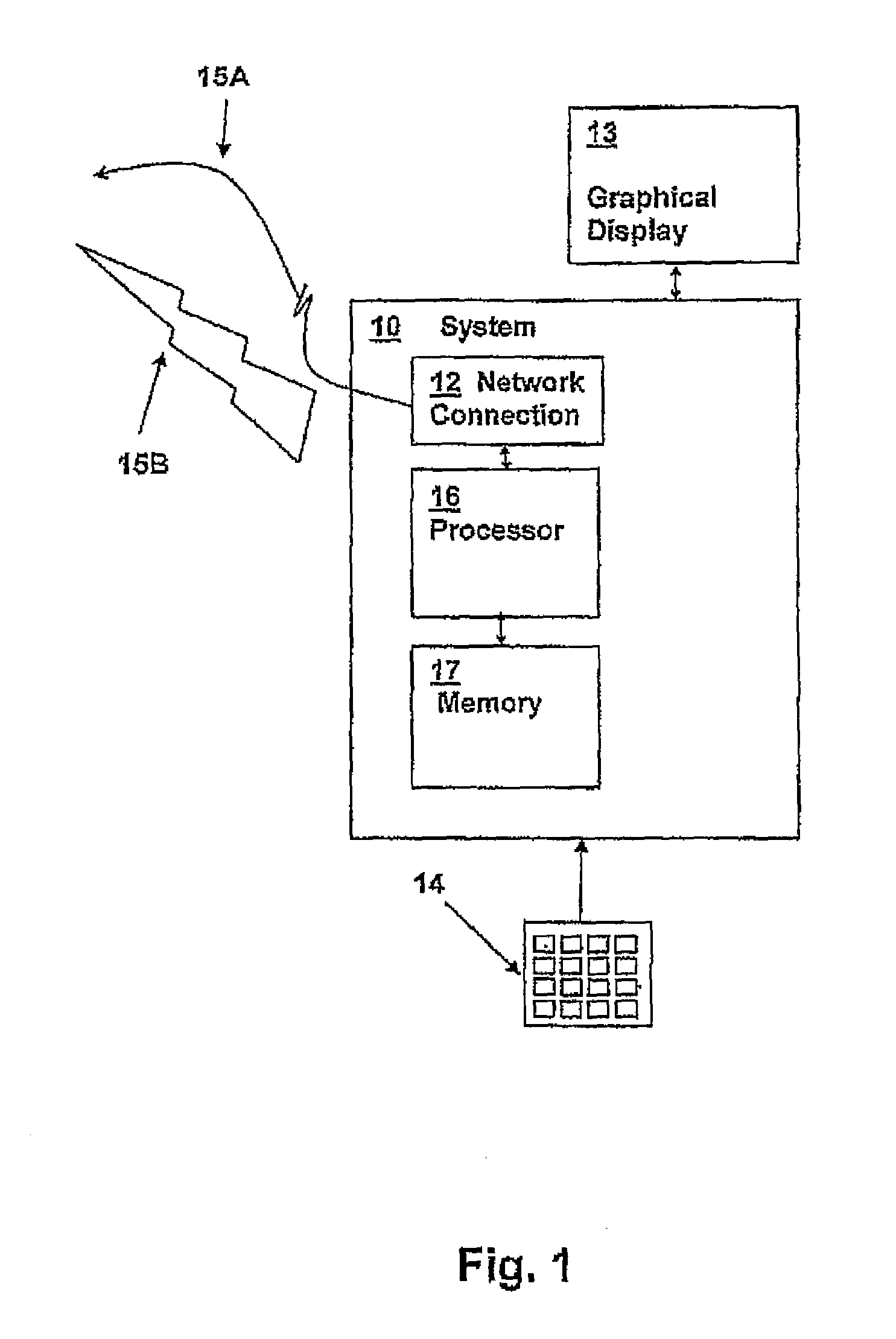
Graphical condition builder for facilitating database queries
ActiveUS20050004911A1Digital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsDatabase query
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
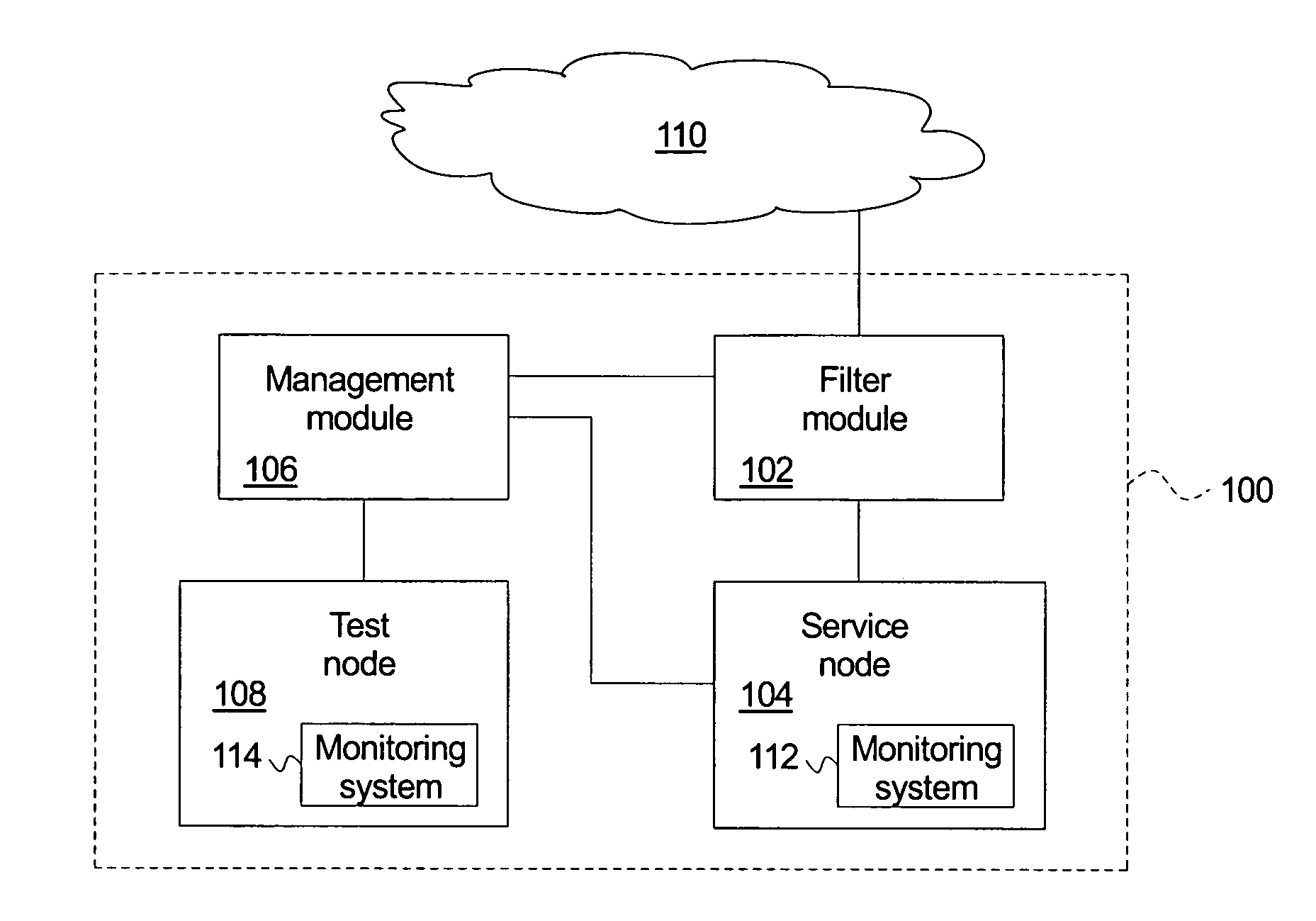
Automatically protecting network service from network attack
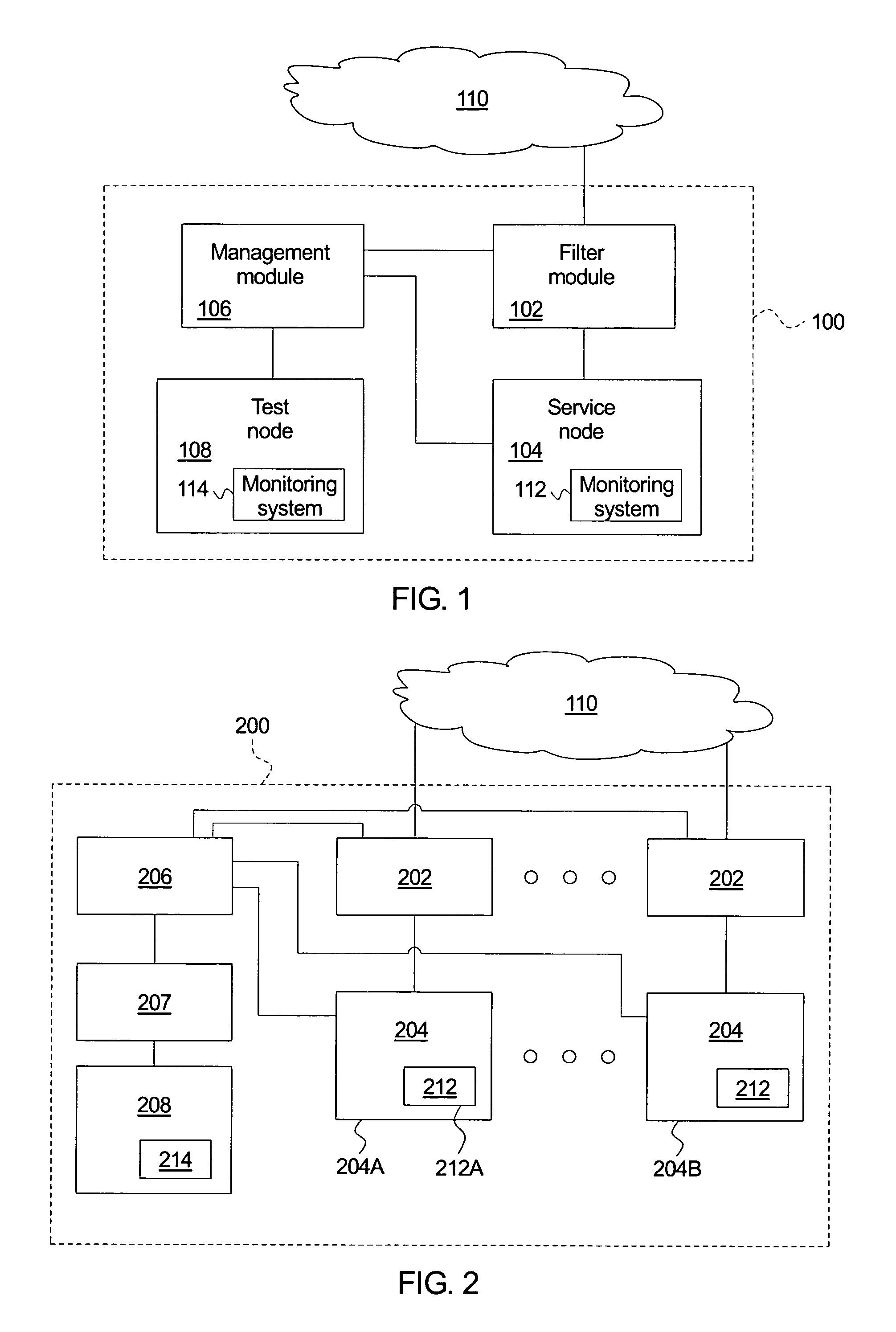
A system for detecting and responding to an attack comprises a filter module, a node, a management module, and a test node. The filter module allows questionable messages to proceed. The node receives the questionable messages and maintains logical operations associated with the questionable messages within a restricted region. The management module resets the service node upon a network attack. The test node replays the node questionable messages to identify a new attack. A method of protecting against a network attack logs questionable messages and directs the questionable messages to a node. The method maintains logical operations associated with the questionable messages within a restricted region and identifies a network attack upon the node, which triggers an intrusion response. The intrusion response resets the node, replays the questionable messages within a test node to identify a new attack message, and adds the new attack message to the known attack messages.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Object code logic analysis and automated modification system and method
InactiveUS6071317ALow costImprove automationSoftware maintainance/managementProgram loading/initiatingOperational systemObject code
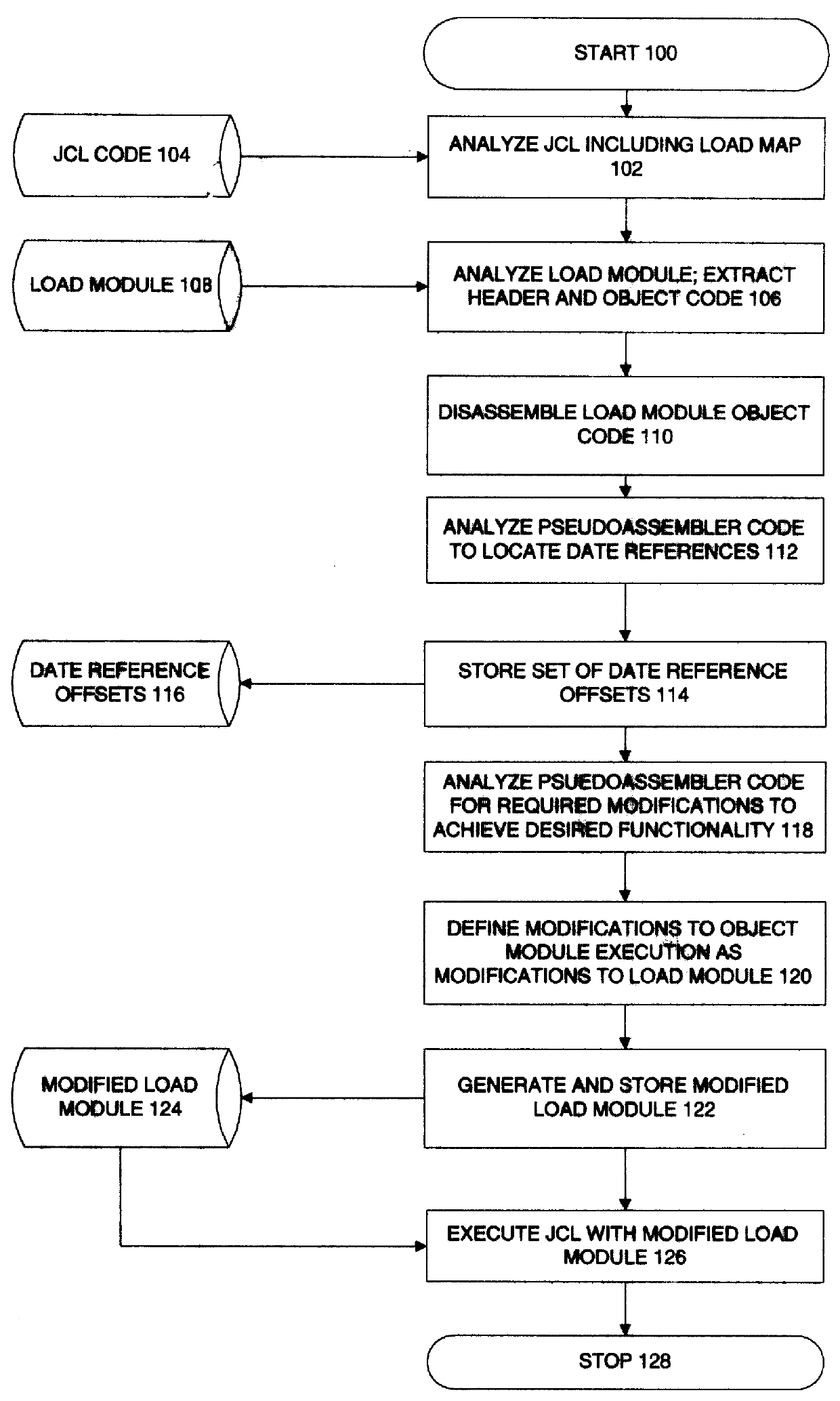
A method and system for modifying computer program logic with respect to a predetermined aspect, comprising (a) before run time: analyzing compiled computer program logic of a module for processes involving the predetermined aspect before run time, substantially without decompilation or reference to computer program source code; and storing a set of modifications relating to computer program logic modifications of the module relating to the predetermined aspect; and (b) at run time: based on the stored set of modifications, selectively transferring program control from the module to a separate logical structure, executing modified logical operations with respect to the predetermined aspect, and subsequently returning program control to the module. The predetermined aspect may be, for example, a data type, algorithm type, or interface specification. In a preferred embodiment, the predetermined aspect is date related data, and more particularly, to logical operations relating to date related data which are flawed. The system preferably operates in a mainframe environment, wherein the compiled computer program constitutes one or more load modules, executing under an operating system, wherein the computer program logic modifications preferably comprise program flow control diversions in an original object module, which selectively transfer logical control to a separate object module to effect modifications to the computer program logic, followed by a return of control to the original object module.
Owner:HANGER SOLUTIONS LLC +1
Machine fault information detection and reporting
InactiveUS7142990B2Quick identificationEasy to installAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceComputer controlCavitationLogical operations
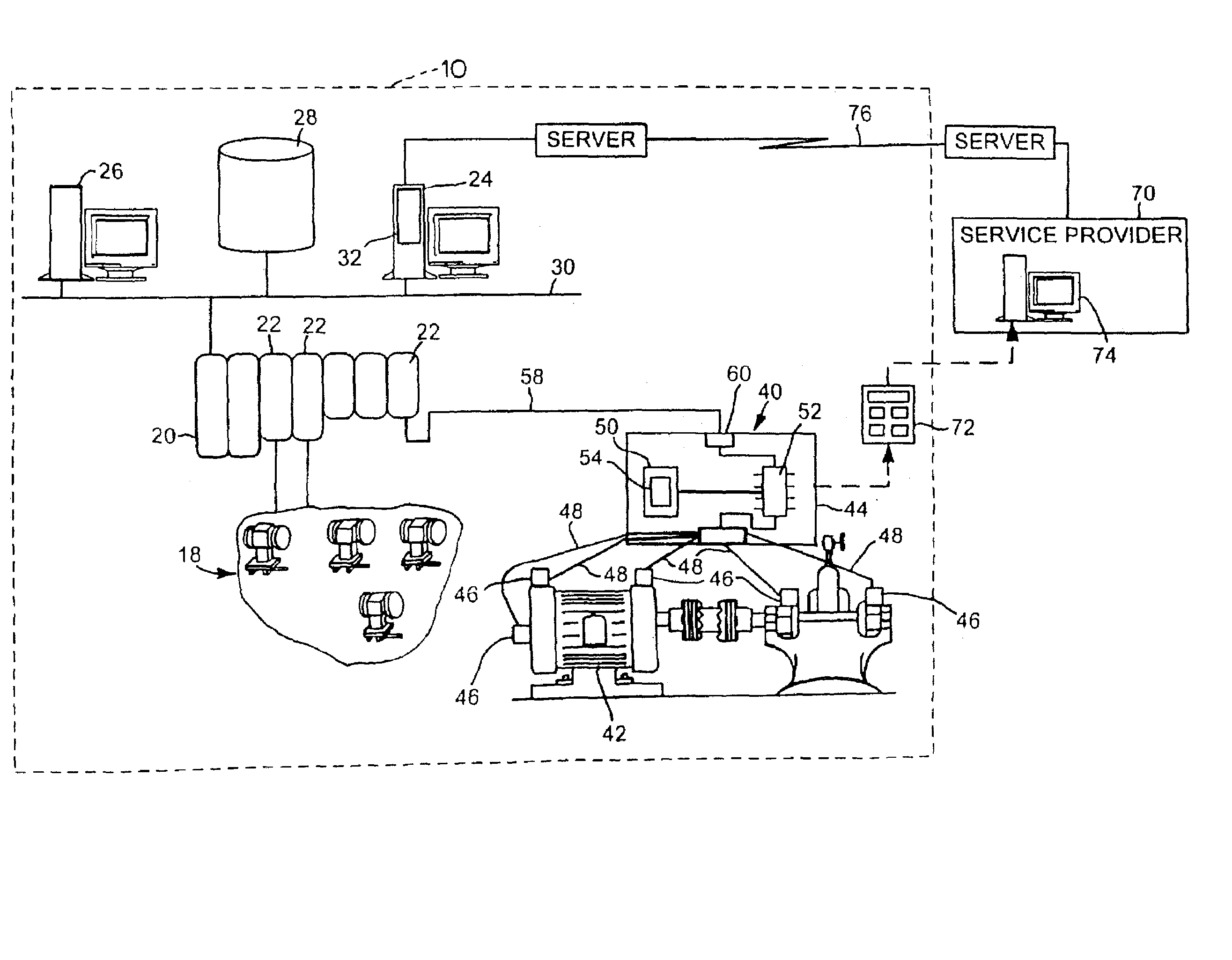
Sensors detect machine parameters such as vibration, turning speed, and temperature, and a local processor performs logic operations based on the parameters and inference rules to produce fault information that is reported to a system processor, which selectively uses the fault information to control the plant machines. The inference rules include rules for determining faults as to balance, alignment, bearing condition, electrical condition, and cavitation. The inference rules are contained in rules code that is separate from the analysis code that performs the logical operations. Thus, the inference rules may be easily changed without changing other code, such as the analysis code.
Owner:COMPUTATIONAL SYST
Logic circuit utilizing pass transistors and logic gate
InactiveUS6084437ATransistorReliability increasing modificationsCmos logic circuitsLogical operations
A logic circuit combines a plurality of pass-transistor logic trees and a multiple-input logic gate for receiving intermediate logic signals from the respective pass-transistor logic trees, and can express a complex logical operation while decreasing the number of stages in pass-transistor logic trees and improving operation speed. Even a logical operation that cannot be expressed efficiently by a known or conventional pass-transistor logic circuit can be expressed efficiently with performance higher than that of a known CMOS logic circuit. Furthermore, when a static feedthrough current of the multiple-input logic gate is suppressed, power consumption can be reduced. In some embodiments, since circuitry for suppressing a static feedthrough current of the multiple-input logic gate is arranged so that a probability of occurrence of logical collision with a preceding stage will decrease or will be nil, power consumption can further be reduced.
Owner:KAWASAKI MICROELECTRONICS
Method and apparatus for data hierarchy maintenance in a system for mask description
InactiveUS6453452B1Data augmentationReduce processing speedCAD circuit designProgram controlComputer architectureLogical operations
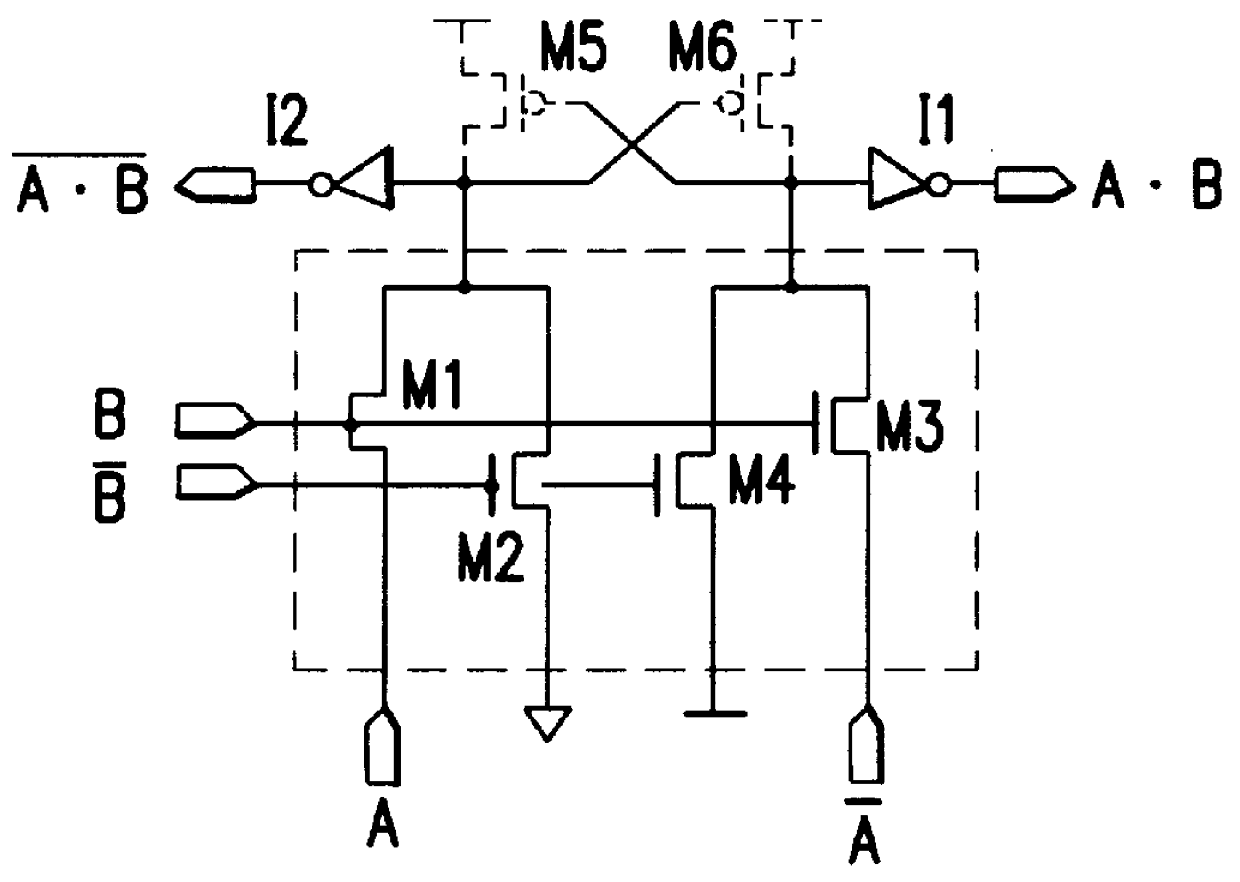
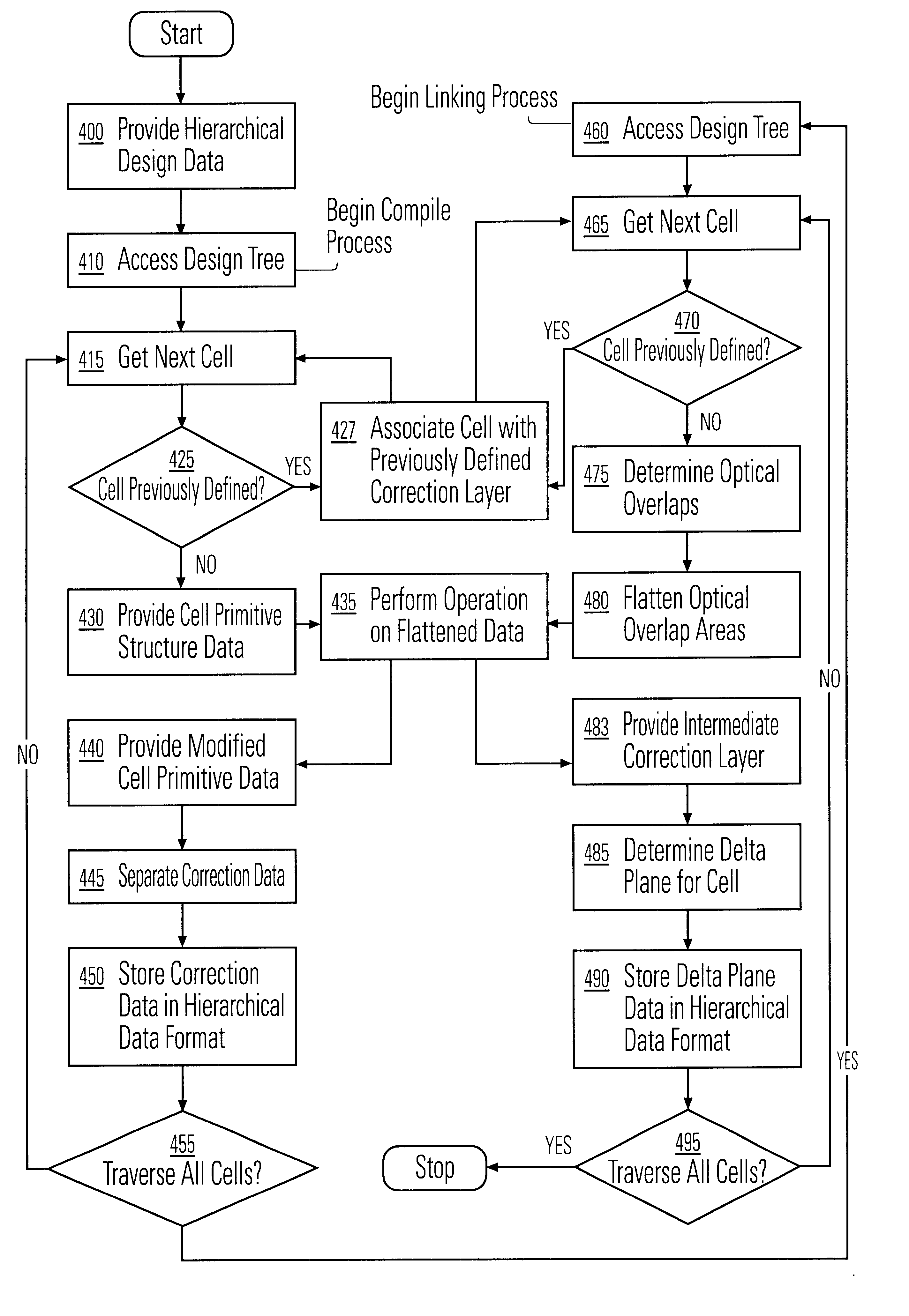
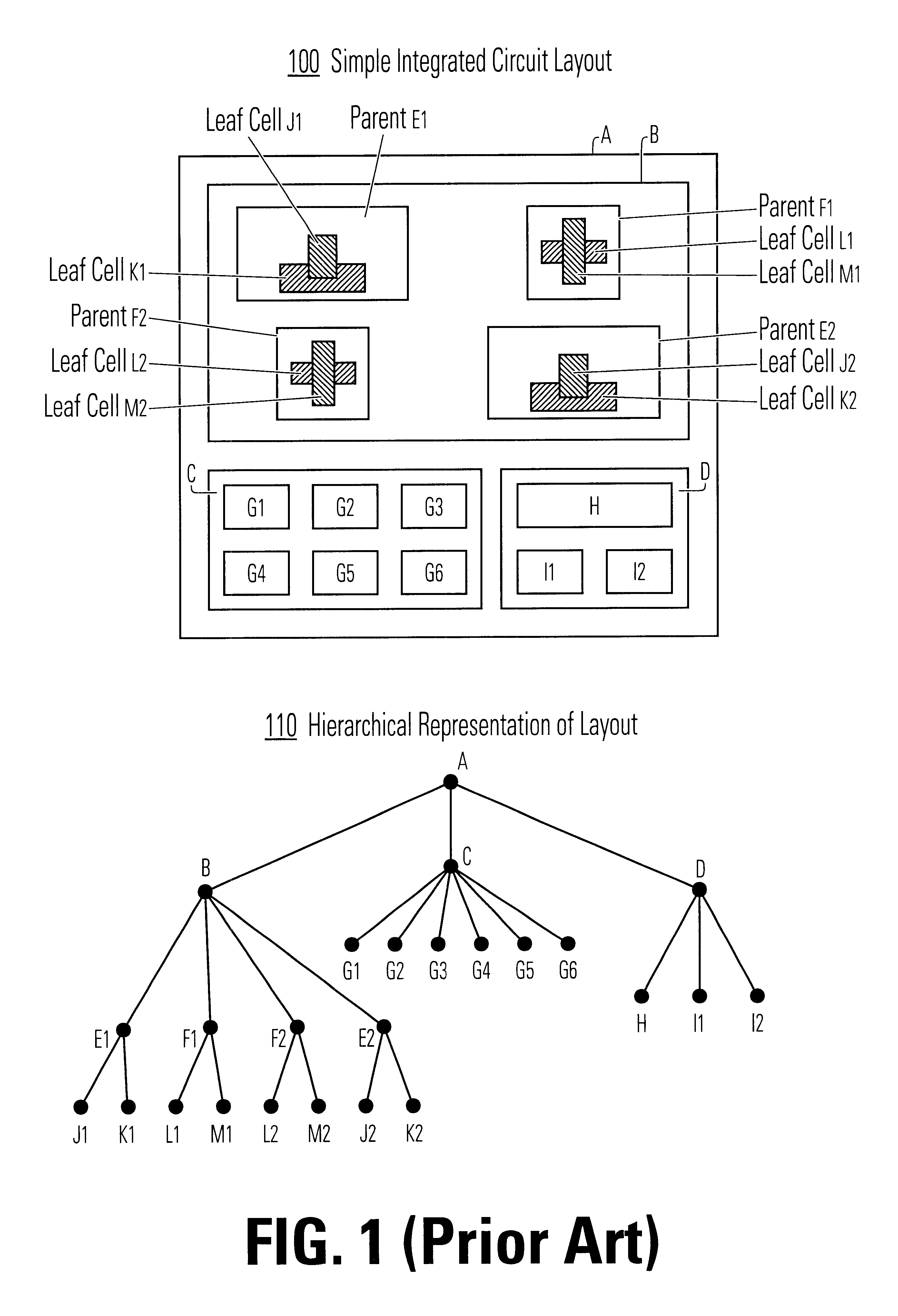
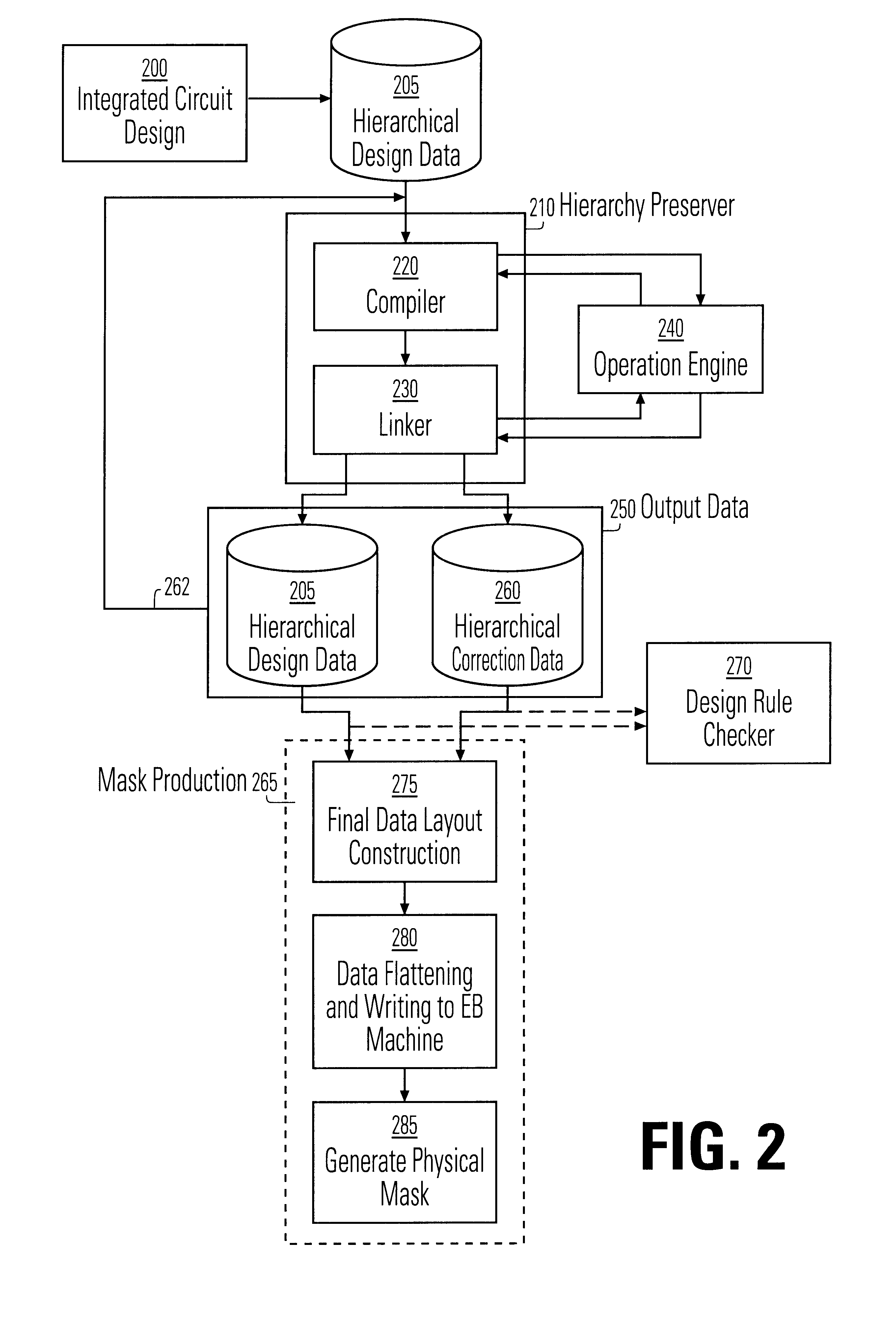
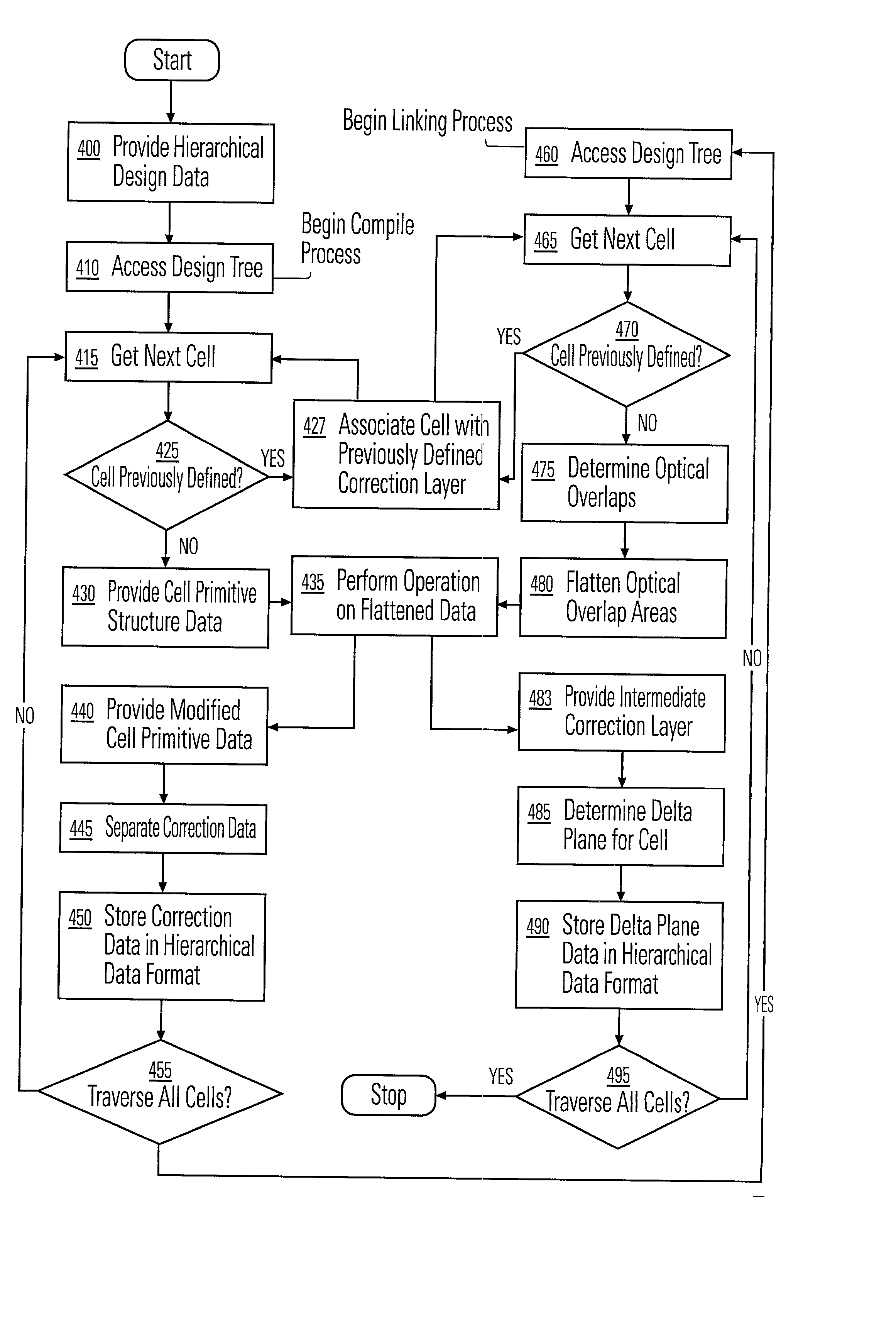
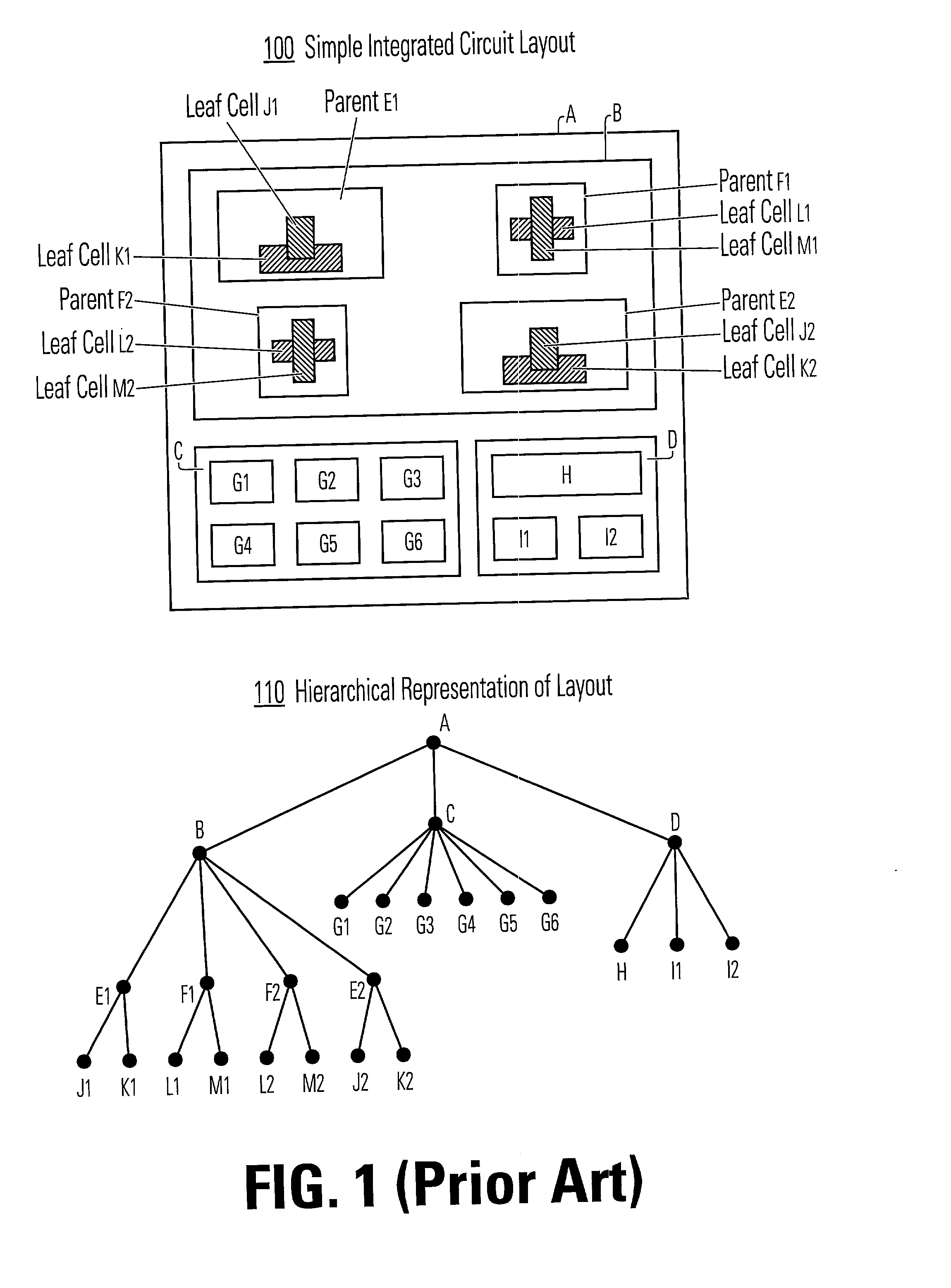
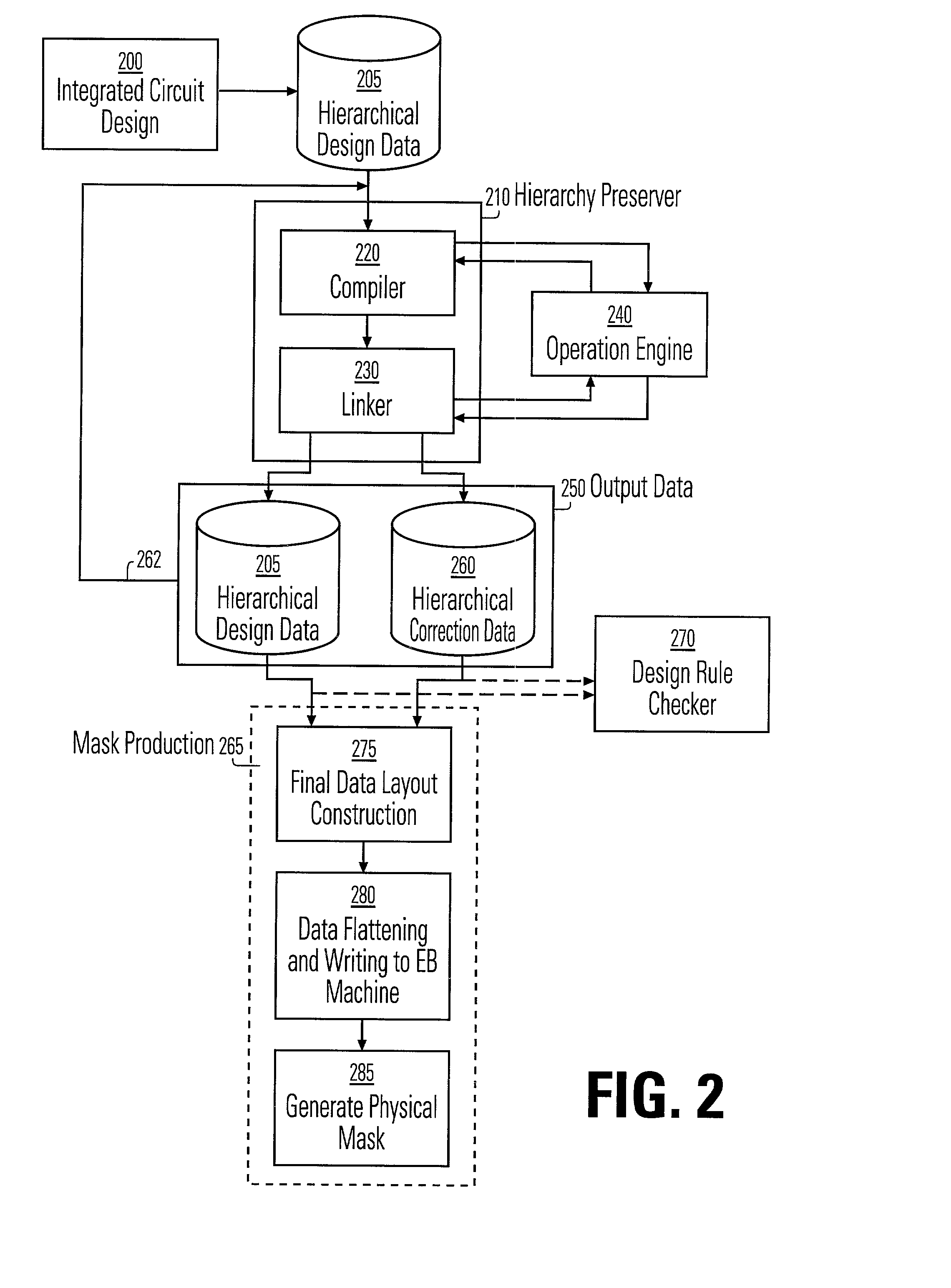
A method and apparatus for performing an operation on hierarchically described integrated circuit layouts such that the original hierarchy of the layout is maintained is provided. The method comprises providing a hierarchically described layout as a first input and providing a particular set of operating criteria corresponding to the operation to be performed as a second input. The mask operation, which may include operations such as OPC and logical operations such as NOT and OR, is then performed on the layout in accordance with the particular set of operating criteria. A first program data comprising hierarchically configured correction data corresponding to the hierarchically described layout is then generated in response to the layout operation such that if the first program data were applied to the flattened layout an output comprising data representative of the result of performing the operation on the layout would be generated. As the first program data is maintained in a true hierarchical format, layouts which are operated upon in accordance with this method are able to be processed through conventional design rule checkers. Further, this method is capable of being applied to all types of layouts including light and dark field designs and phase shifting layouts.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Non-volatile semiconductor memory
InactiveUS6937510B2Large storage capacityWider marginRead-only memoriesDigital storageSensing dataData retrieval
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
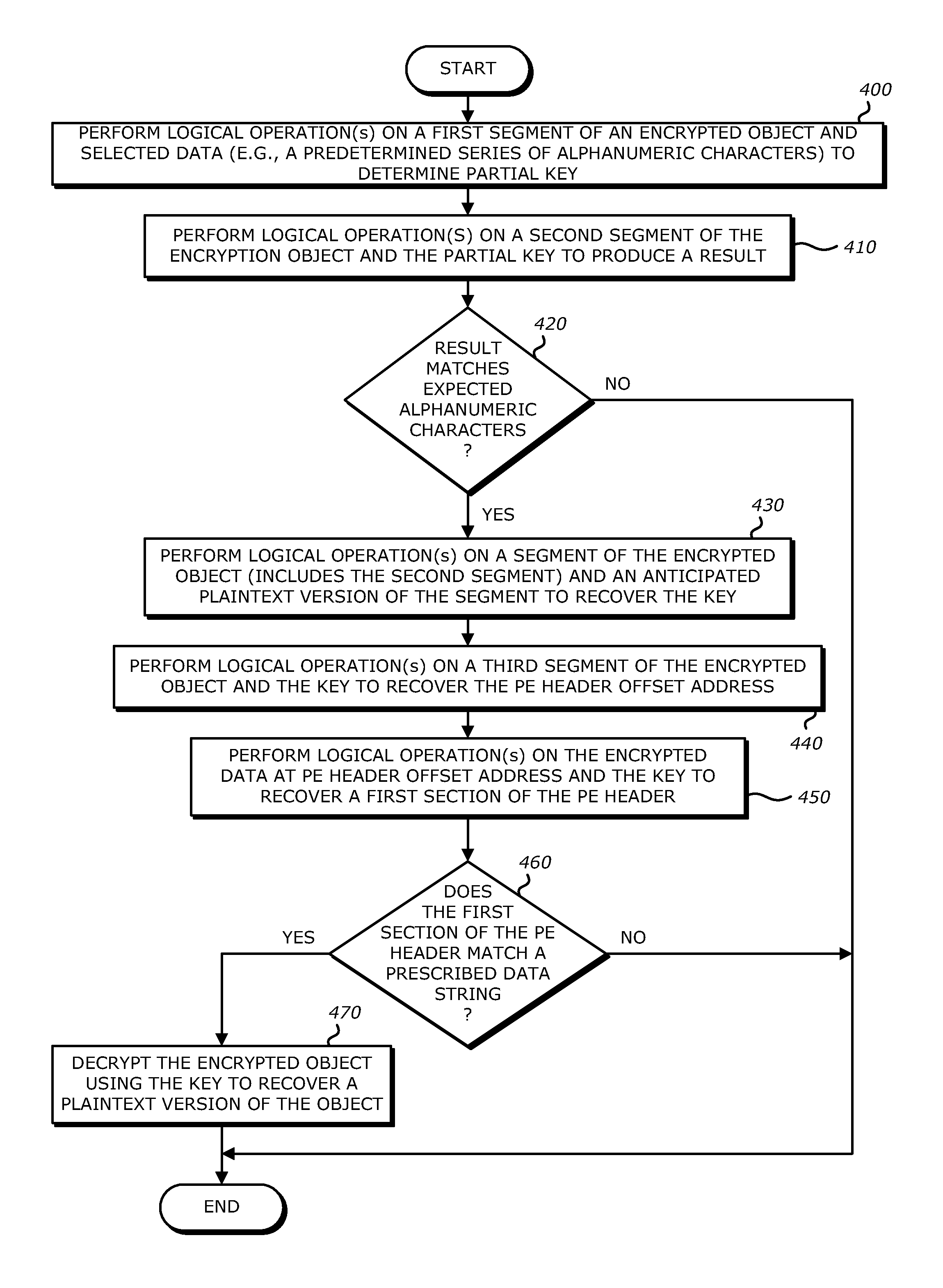
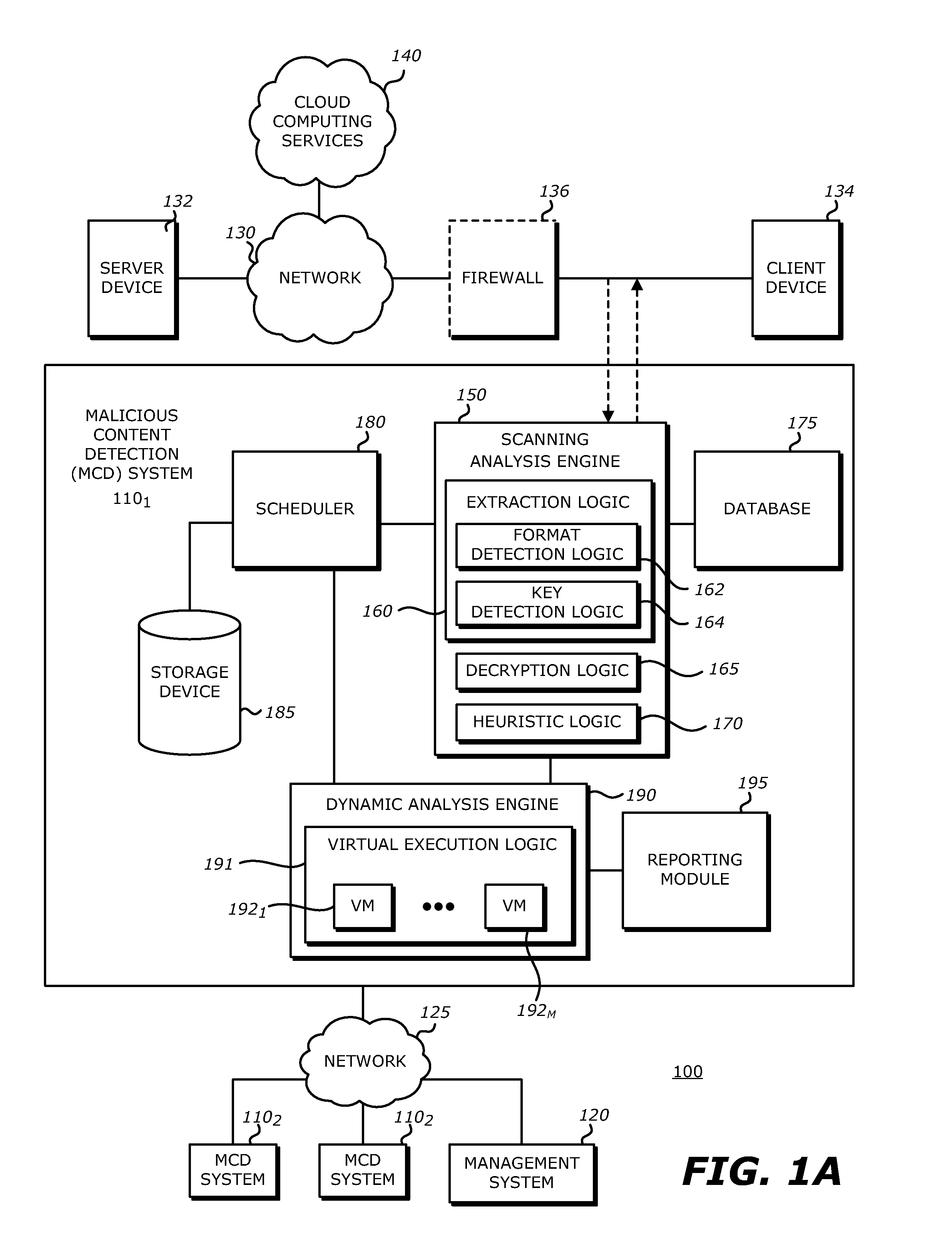
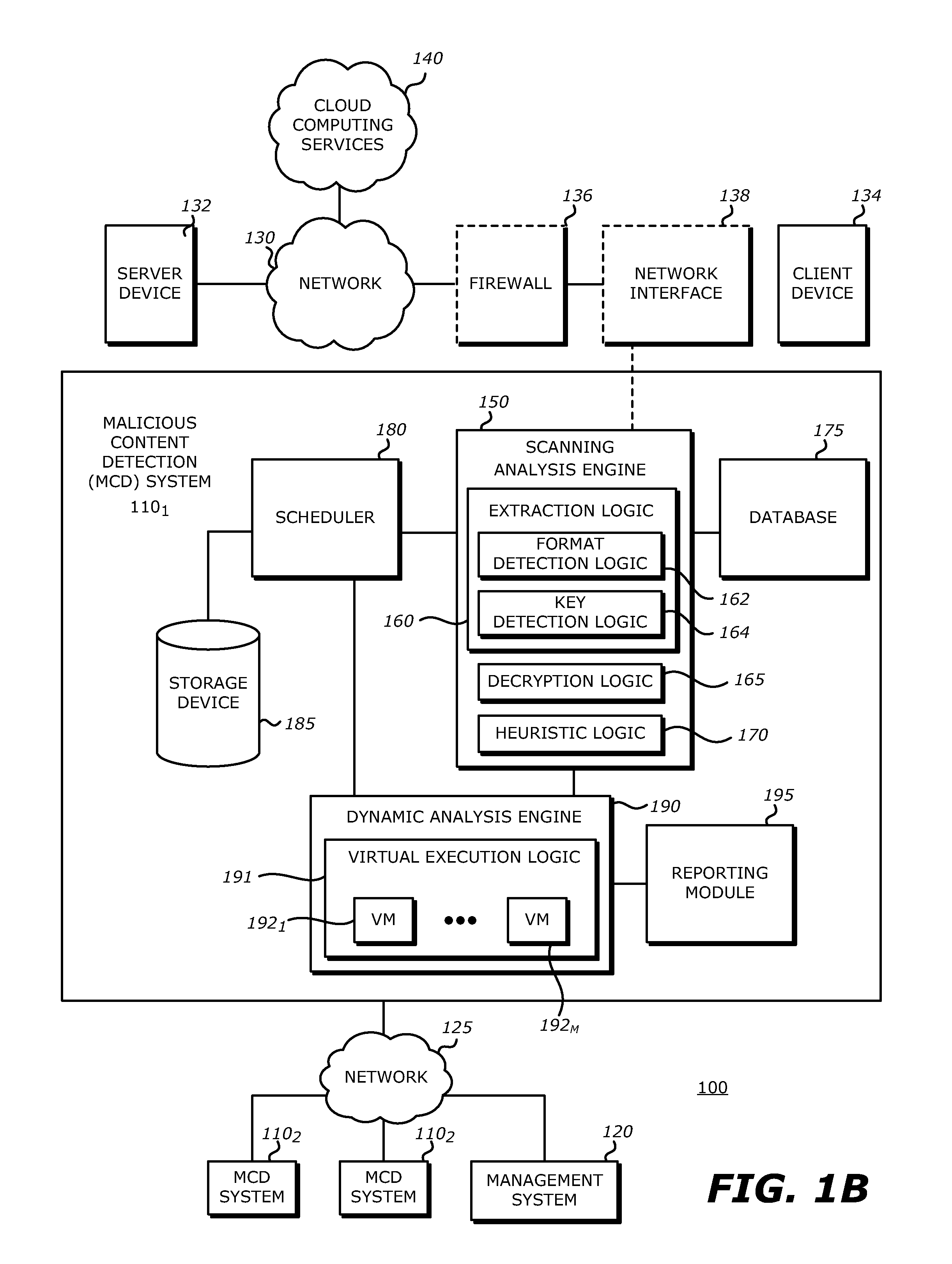
System, apparatus and method for conducting on-the-fly decryption of encrypted objects for malware detection
ActiveUS9560059B1Key distribution for secure communicationData stream serial/continuous modificationComputer hardwareLogical operations
A decryption scheme for recover of a decrypted object without a cryptographic key is described. First, logical operation(s) are conducted on data associated with a first data string expected at a first location within an object having the predetermined format and data within the encrypted object at the first location to recover data associated with a portion of a cryptographic key from the encrypted object. Thereafter, logical operation(s) are conducted on that data and a first portion of the encrypted object at a second location to produce a result. Responsive to the result including data associated with the plaintext version of the second data string, logical operation(s) are conducted on a second portion of the encrypted object and the data associated with the plaintext version of the second data string to recover data associated with the cryptographic key. Thereafter, the encrypted object may be decrypted using the cryptographic key.
Owner:FIREEYE SECURITY HLDG US LLC +1
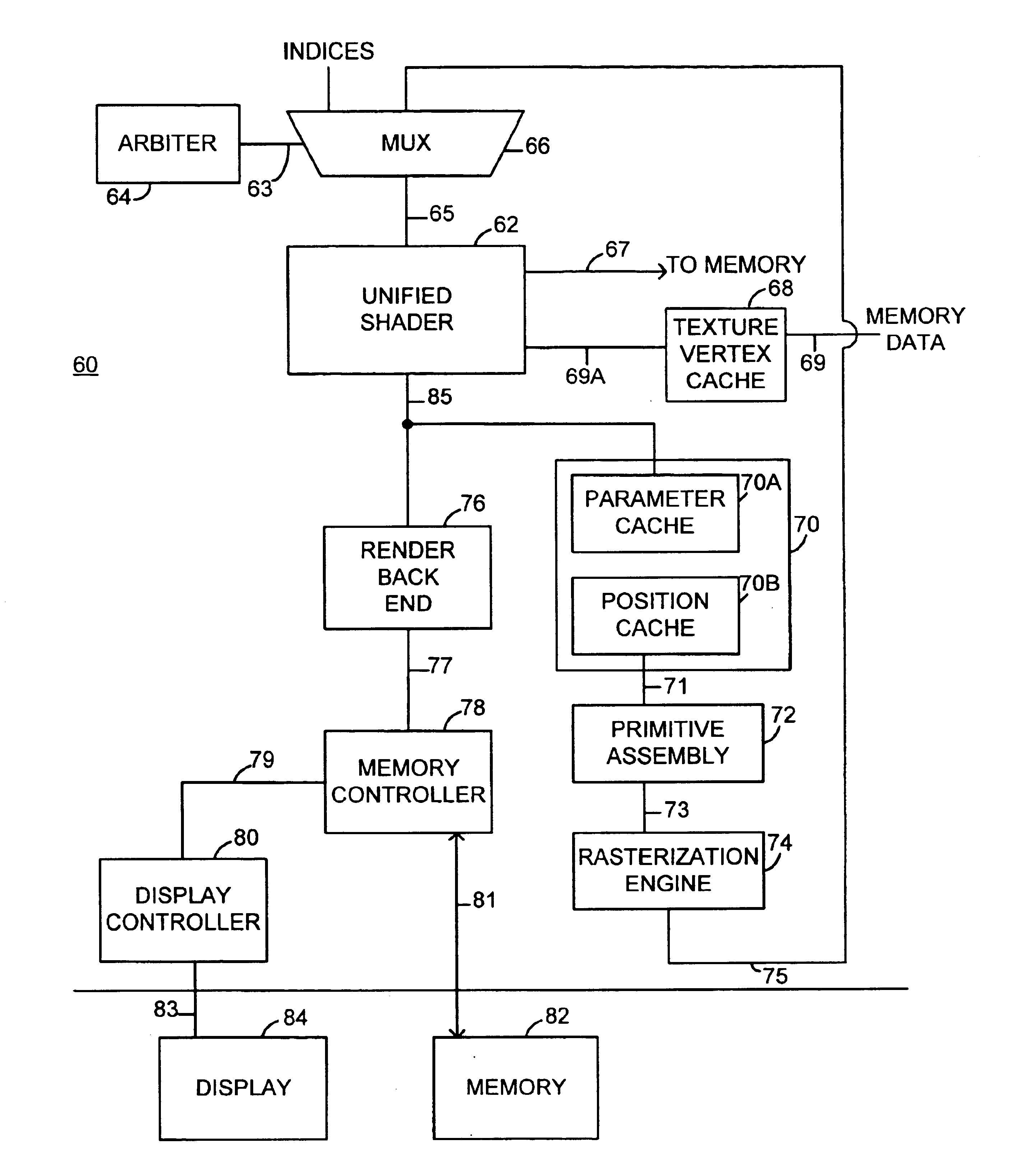
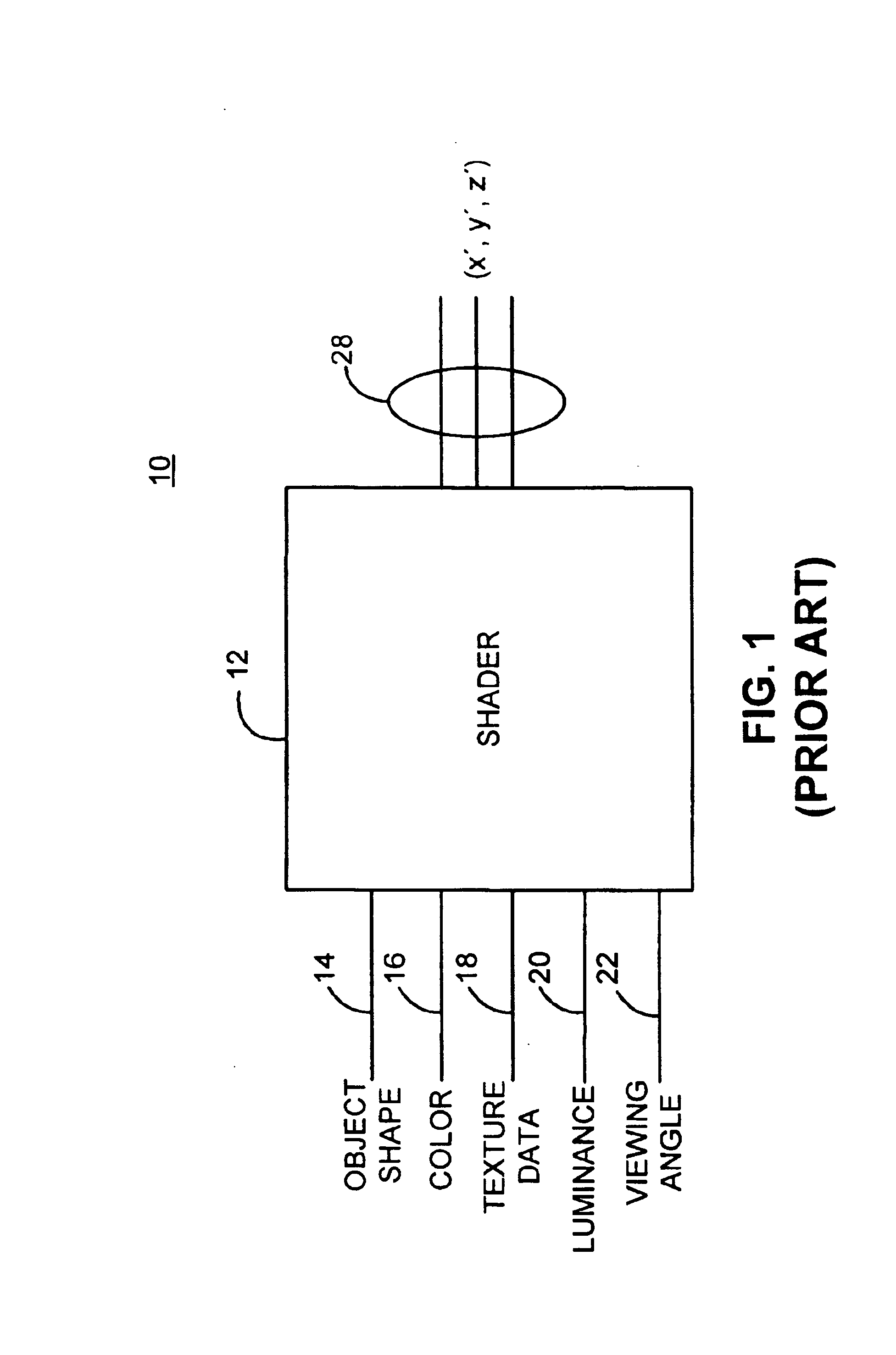
Graphics processing architecture employing a unified shader
ActiveUS6897871B1More computationally efficientFlexiblyDigital computer detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsControl signalLogical operations
A graphics processing architecture employing a single shader is disclosed. The architecture includes a circuit operative to select one of a plurality of inputs in response to a control signal; and a shader, coupled to the arbiter, operative to process the selected one of the plurality of inputs, the shader including means for performing vertex operations and pixel operations, and wherein the shader performs one of the vertex operations or pixel operations based on the selected one of the plurality of inputs. The shader includes a register block which is used to store the plurality of selected inputs, a sequencer which maintains vertex manipulation and pixel manipulations instructions and a processor capable of executing both floating point arithmetic and logical operations on the selected inputs in response to the instructions maintained in the sequencer.
Owner:ATI TECH INC
Nonvolatile memory device and method of operating the same
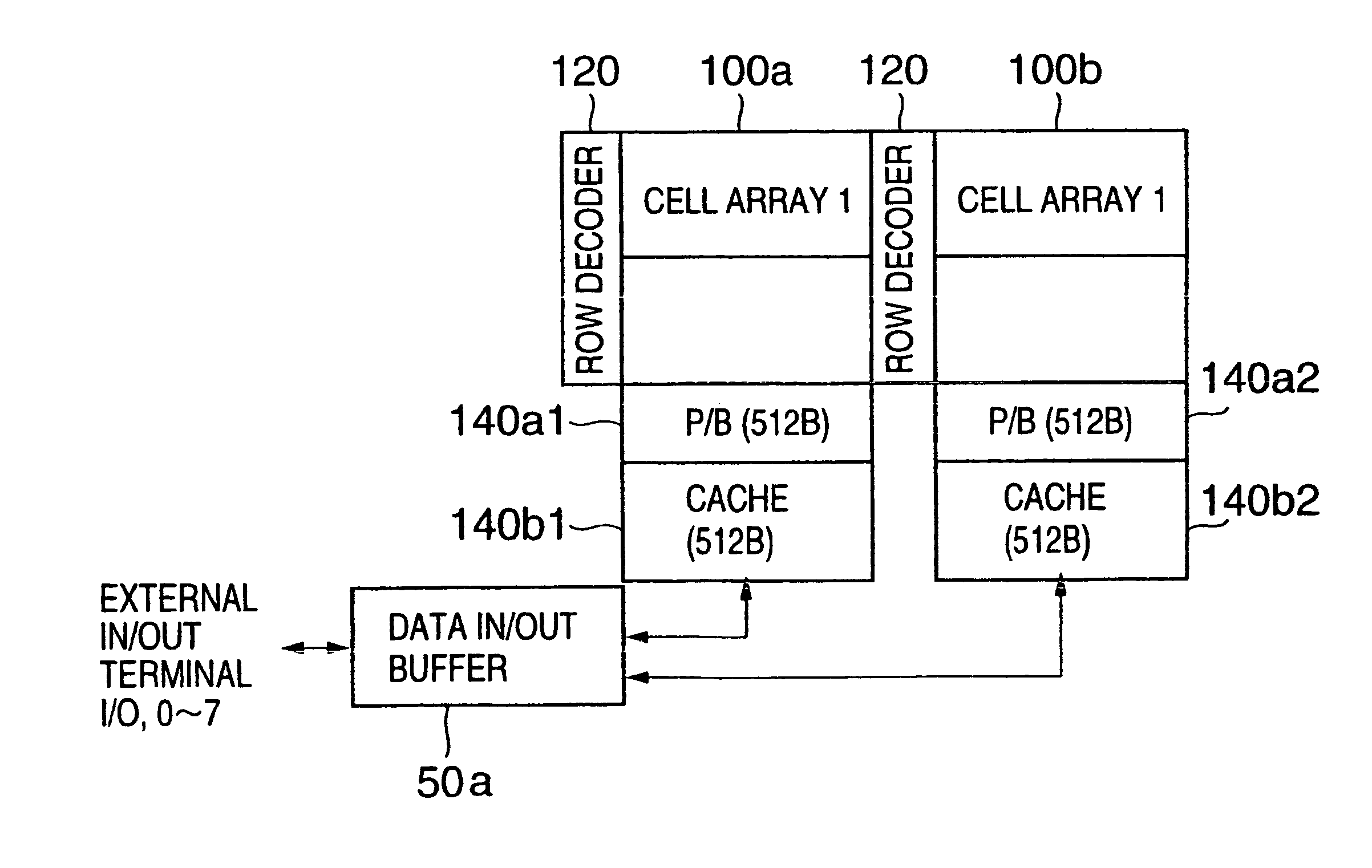
ActiveUS20100199138A1Correction errorError preventionTransmission systemsLogical operationsError detection coding
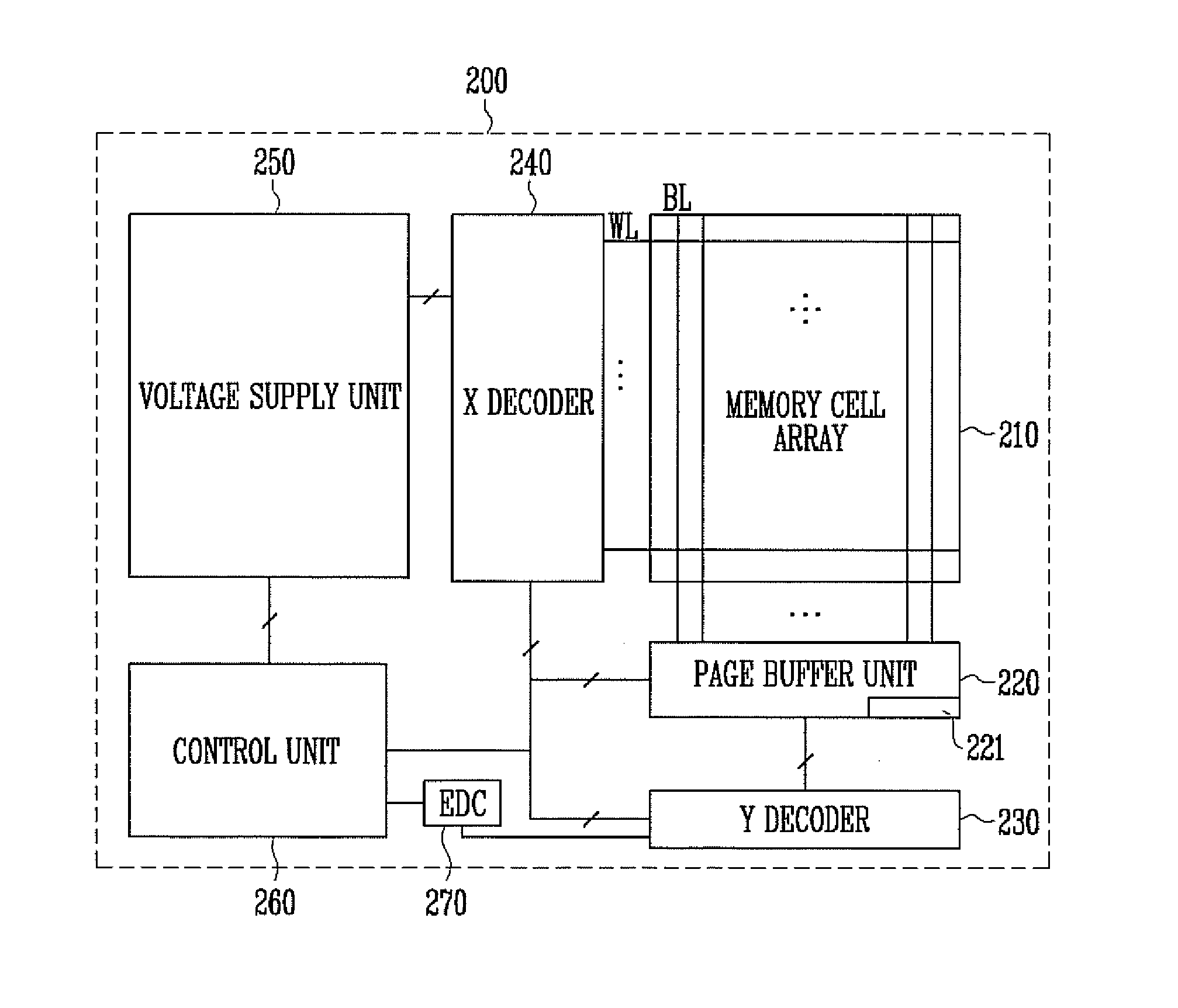
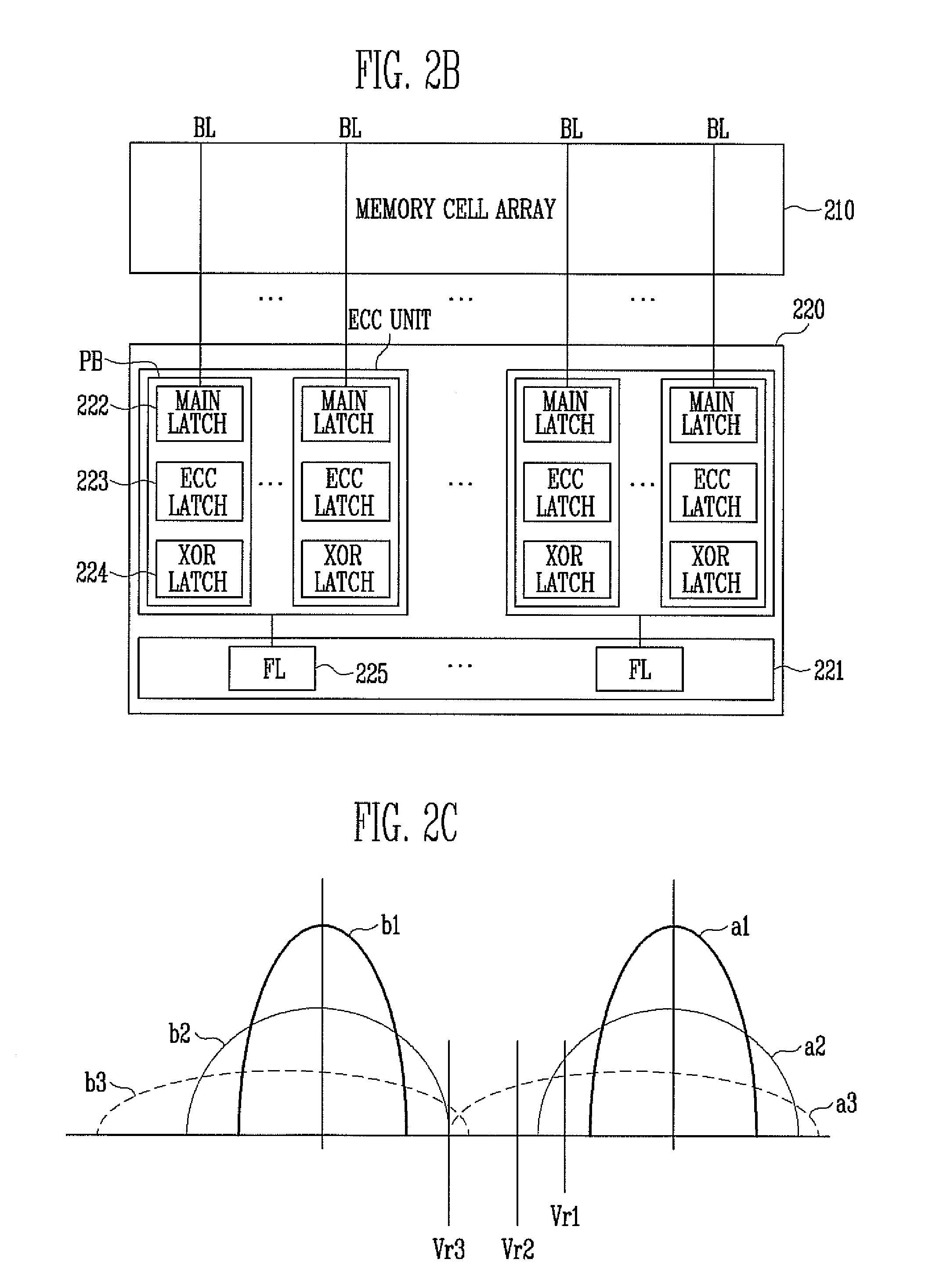
A nonvolatile memory device includes a memory cell array configured to comprise memory cells coupled by bit lines and word lines, a page buffer unit configured to comprise page buffers and flag latches, wherein the page buffers, coupled to one or more of the bit lines, each are configured to comprise a plurality of latches for storing logic operation results for error correction and configured to store data read using a read voltage, and the flag latches each are configured to classify the page buffers into some page buffer groups each having a predetermined number and to store flag information indicating whether an error has occurred in each group, and an error detection code (EDC) checker configured to determine whether an error has occurred in each of the page buffer groups.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
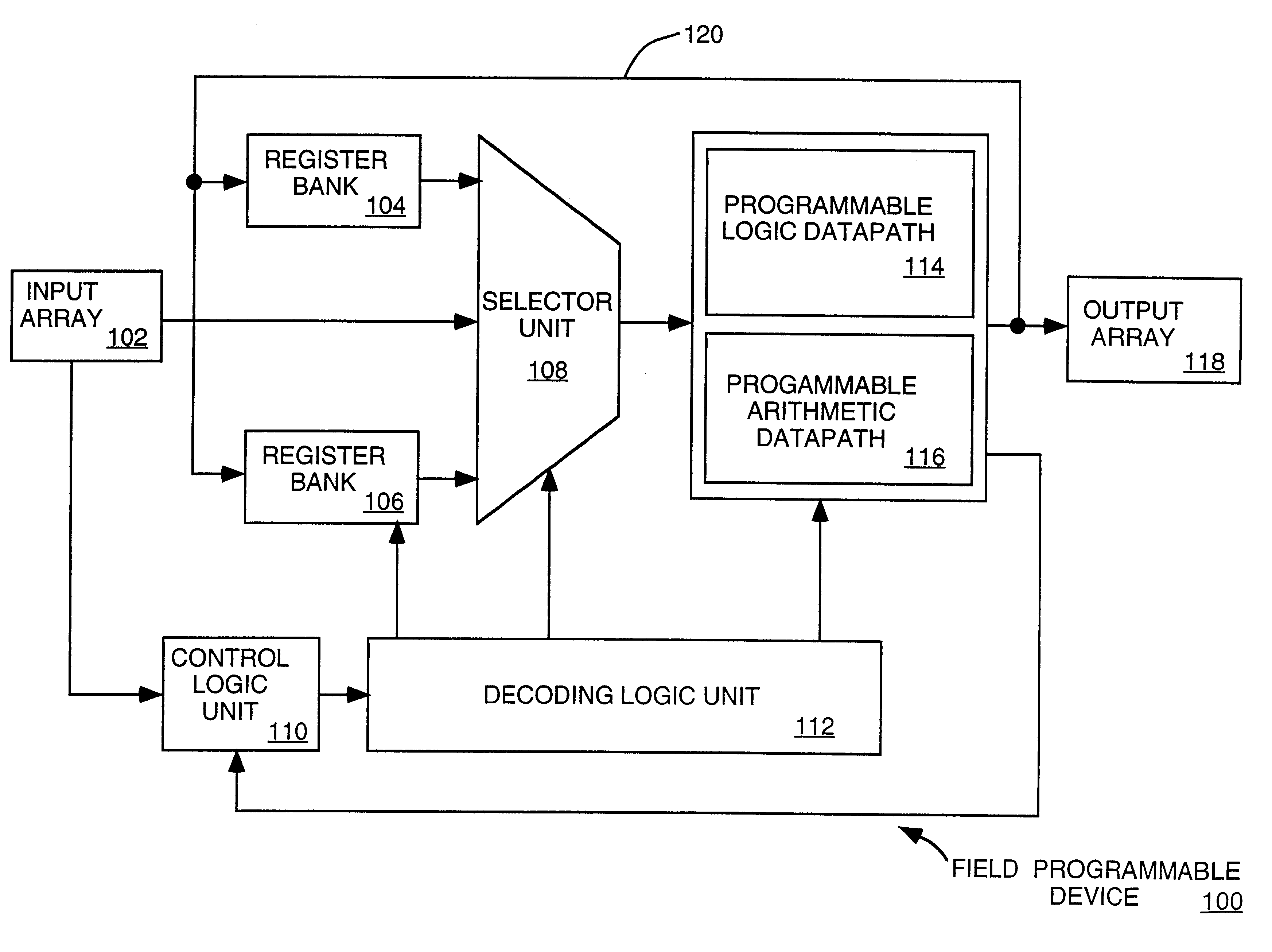
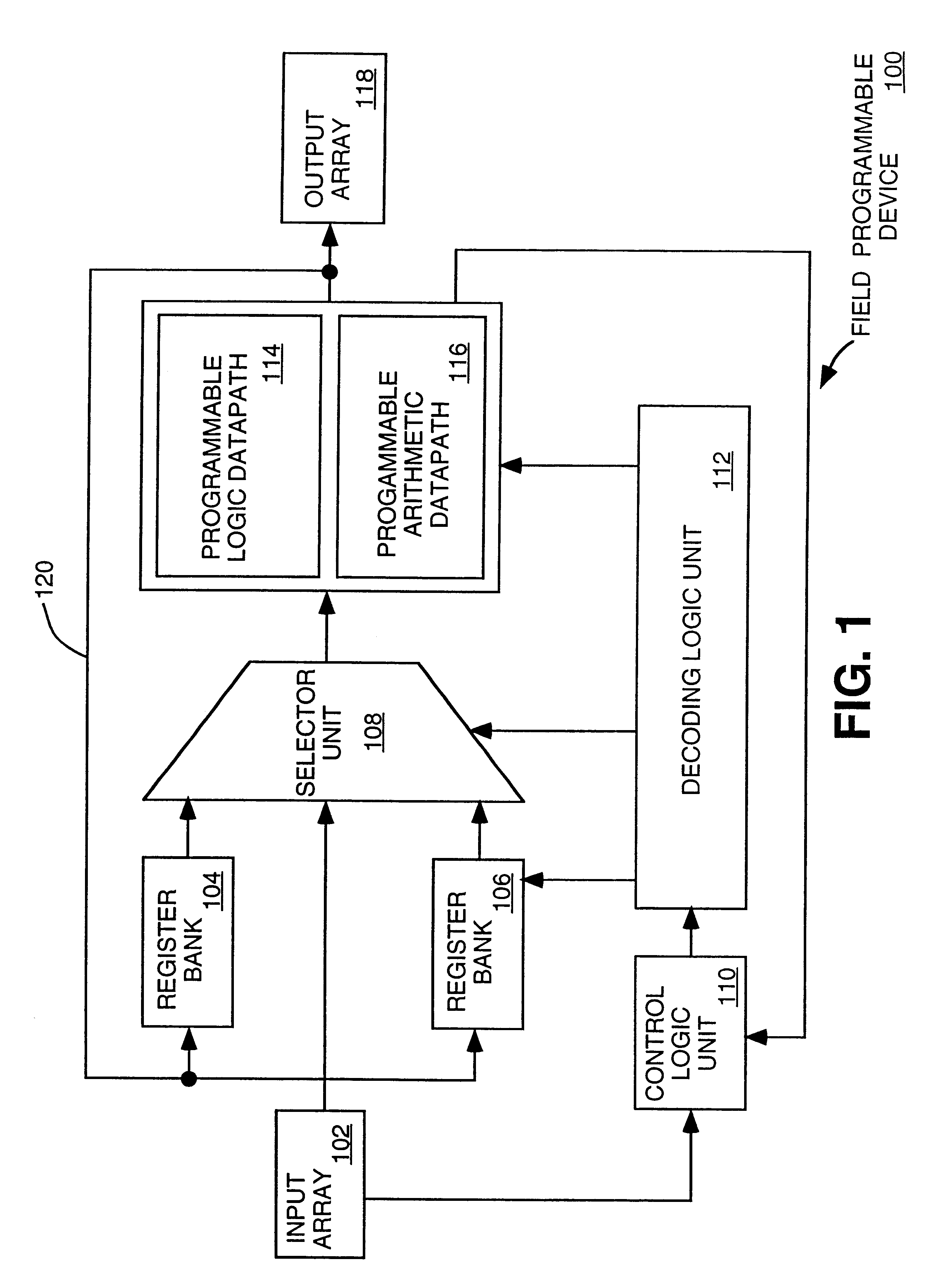
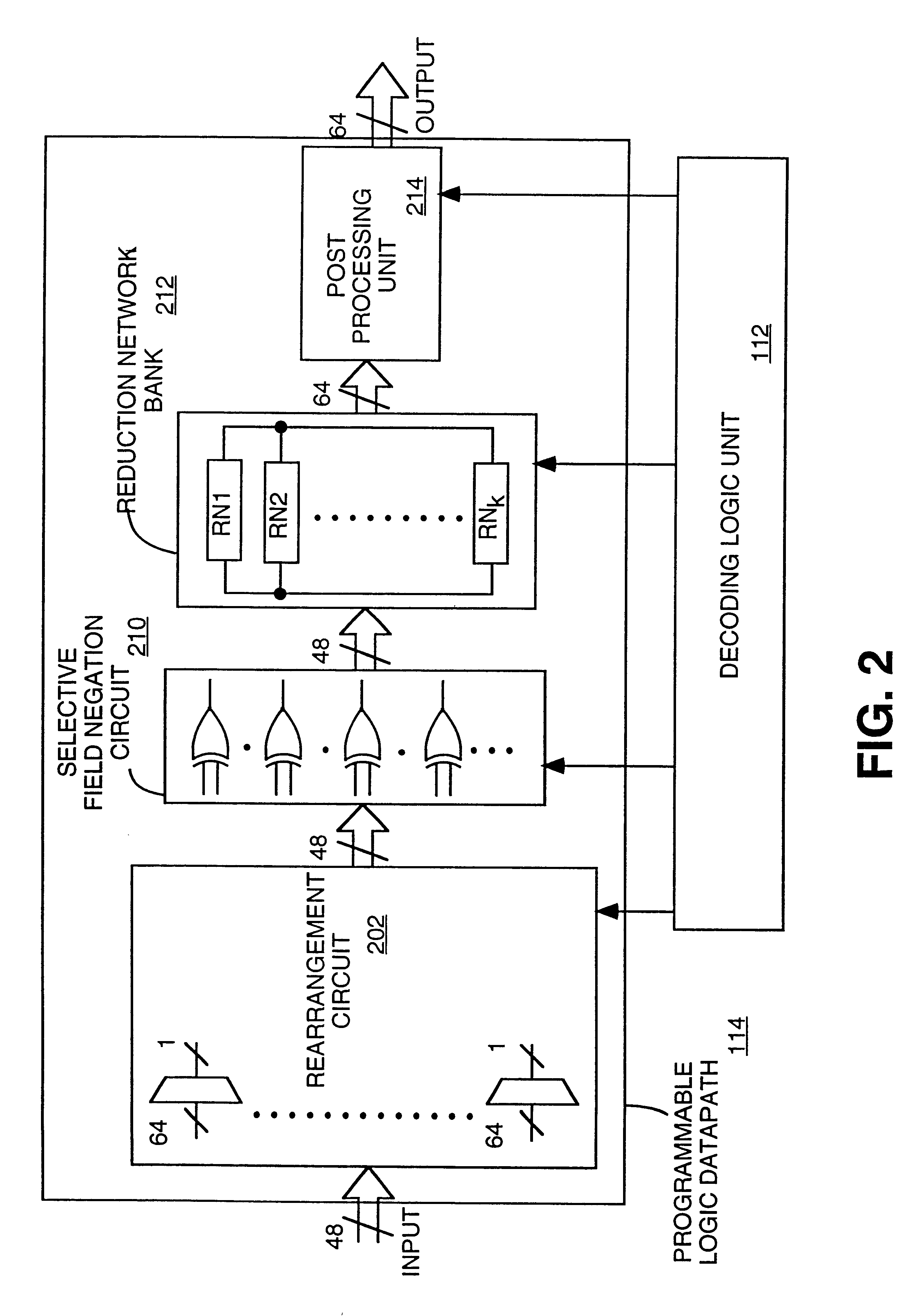
Programmable logic datapath that may be used in a field programmable device
A method and apparatus for providing a programmable logic datapath that may be used in a field programmable device. According to one aspect of the invention, a programmable logic datapath is provided that includes a plurality of logic elements to perform various (Boolean) logic operations. The programmable logic datapath further includes circuitry to selectively route and select operand bits between the plurality of logic elements (operand bits is used hereinafter to refer to input bits, logic operation result bits, etc., that may be generated within the logic datapath). In one embodiment, by providing control bits concurrently with operand bits to routing and selection (e.g., multiplexing) circuitry, the programmable logic datapath of the invention can provide dynamic programmability to perform a number of logic operations on inputs of various lengths on a cycle-by-cycle basis.
Owner:PMC-SIERRA
Methods and apparatus for fairly arbitrating contention for an output port
InactiveUS6487213B1Data switching by path configurationStore-and-forward switching systemsComputer architectureComputer network
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INST OF NEW YORK
Unit for processing numeric and logic operations for use in central processing units (CPUS), multiprocessor systems, data-flow processors (DSPS), systolic processors and field programmable gate arrays (FPGAS)
InactiveUS20030056085A1The process is convenient and fastSimplifies (re)configurationEnergy efficient ICTMultiple digital computer combinationsBus masteringBroadcasting
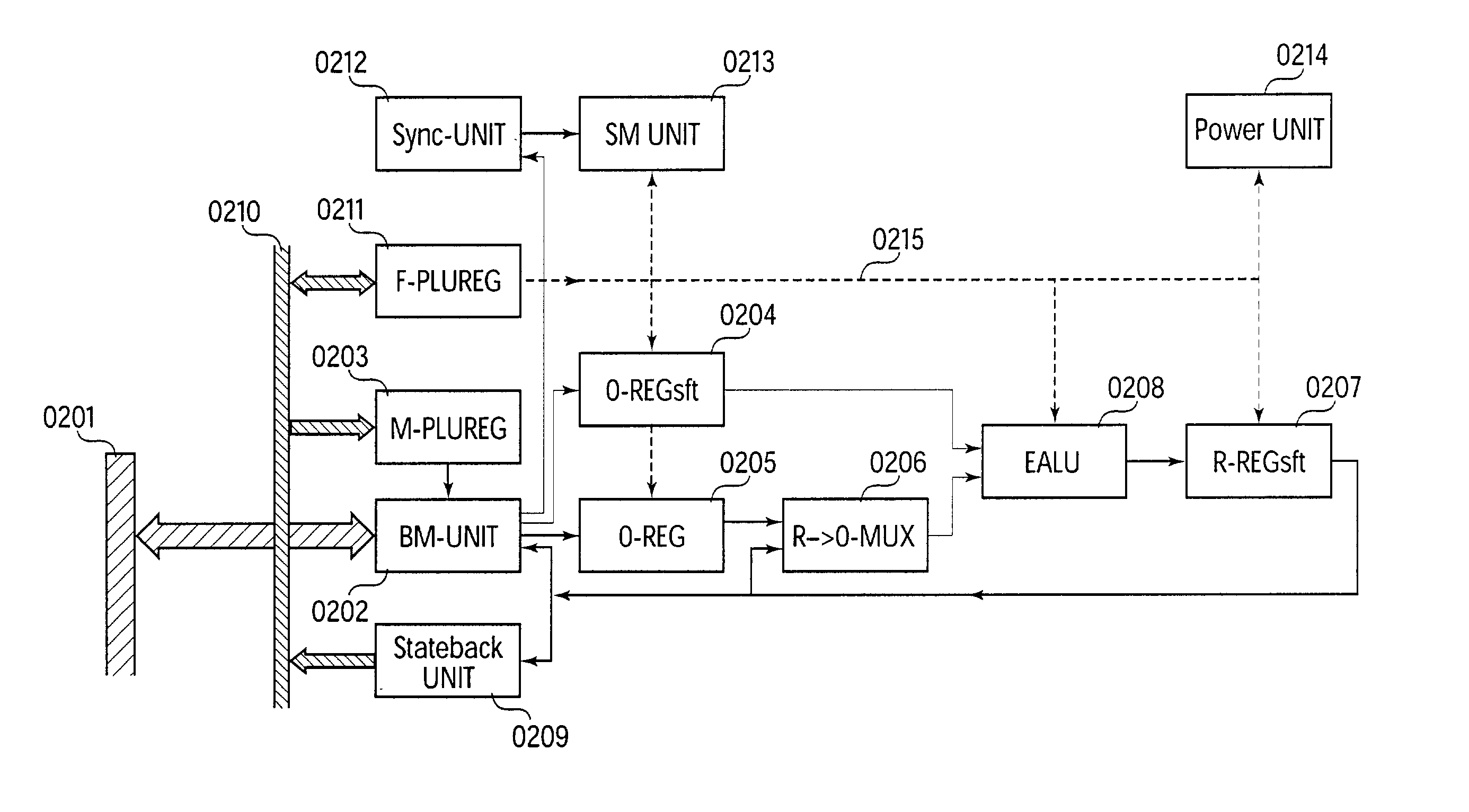
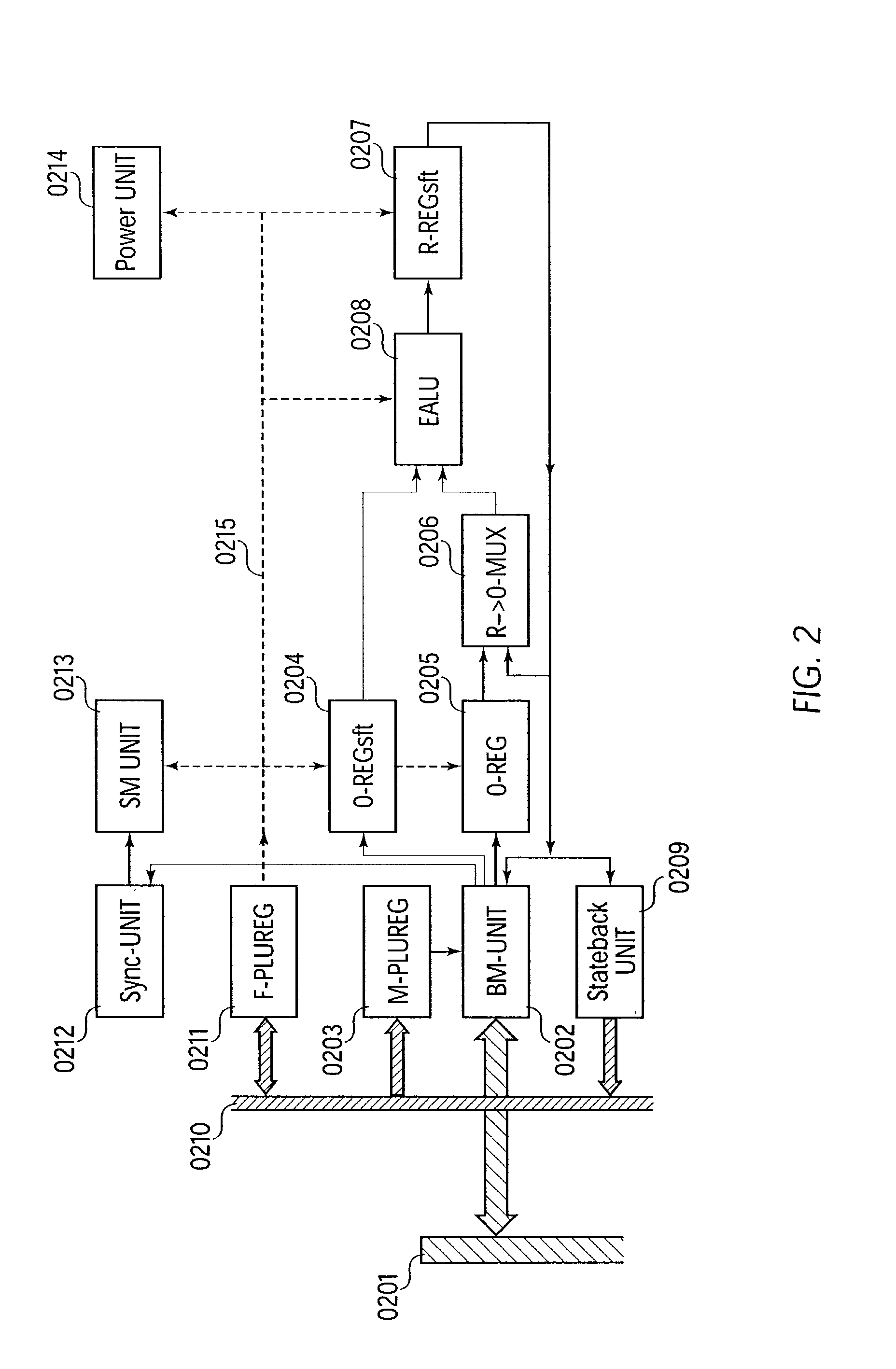
An expanded arithmetic and logic unit (EALU) with special extra functions is integrated into a configurable unit for performing data processing operations. The EALU is configured by a function register, which greatly reduces the volume of data required for configuration. The cell can be cascaded freely over a bus system, the EALU being decoupled from the bus system over input and output registers. The output registers are connected to the input of the EALU to permit serial operations. A bus control unit is responsible for the connection to the bus, which it connects according to the bus register. The unit is designed so that distribution of data to multiple receivers (broadcasting) is possible. A synchronization circuit controls the data exchange between multiple cells over the bus system. The EALU, the synchronization circuit, the bus control unit, and registers are designed so that a cell can be reconfigured on site independently of the cells surrounding it. A power-saving mode which shuts down the cell can be configured through the function register; clock rate dividers which reduce the working frequency can also be set.
Owner:PACT +1
Systems and methods for communication, storage, retrieval, and computation of simple statistics and logical operations on encrypted data
InactiveUS20110264920A1Unauthorized memory use protectionHardware monitoringLogical queryData system
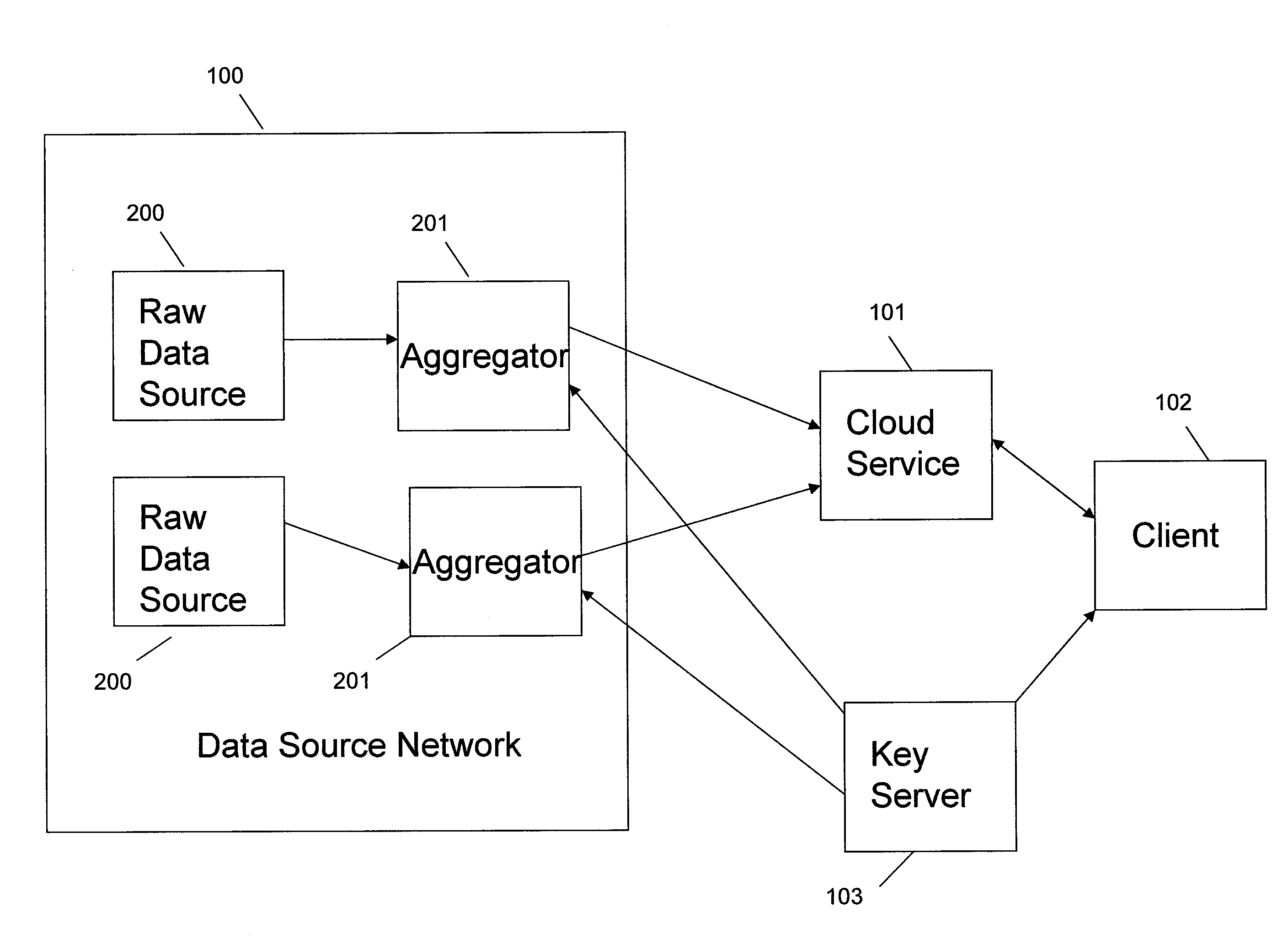
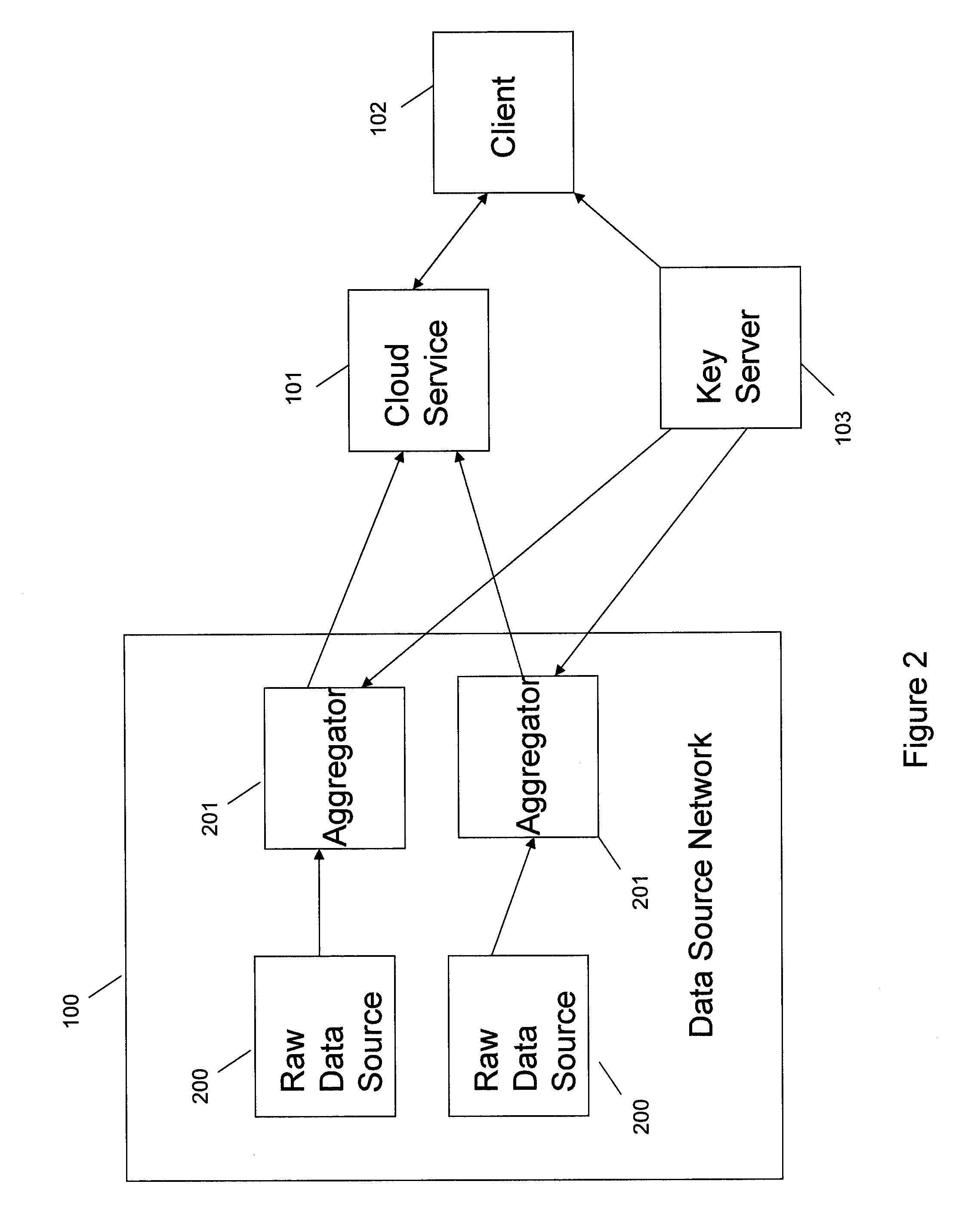
Systems and methods provide for a symmetric homomorphic encryption based protocol supporting communication, storage, retrieval, and computation on encrypted data stored off-site. The system may include a private, trusted network which uses aggregators to encrypt raw data that is sent to a third party for storage and processing, including computations that can be performed on the encrypted data. A client on a private or public network may request computations on the encrypted data, and the results may then be sent to the client for decryption or further computations. The third party aids in computation of statistical information and logical queries on the encrypted data, but is not able to decrypt the data on its own. The protocol provides a means for a third party to aid in computations on sensitive data without learning anything about those data values.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
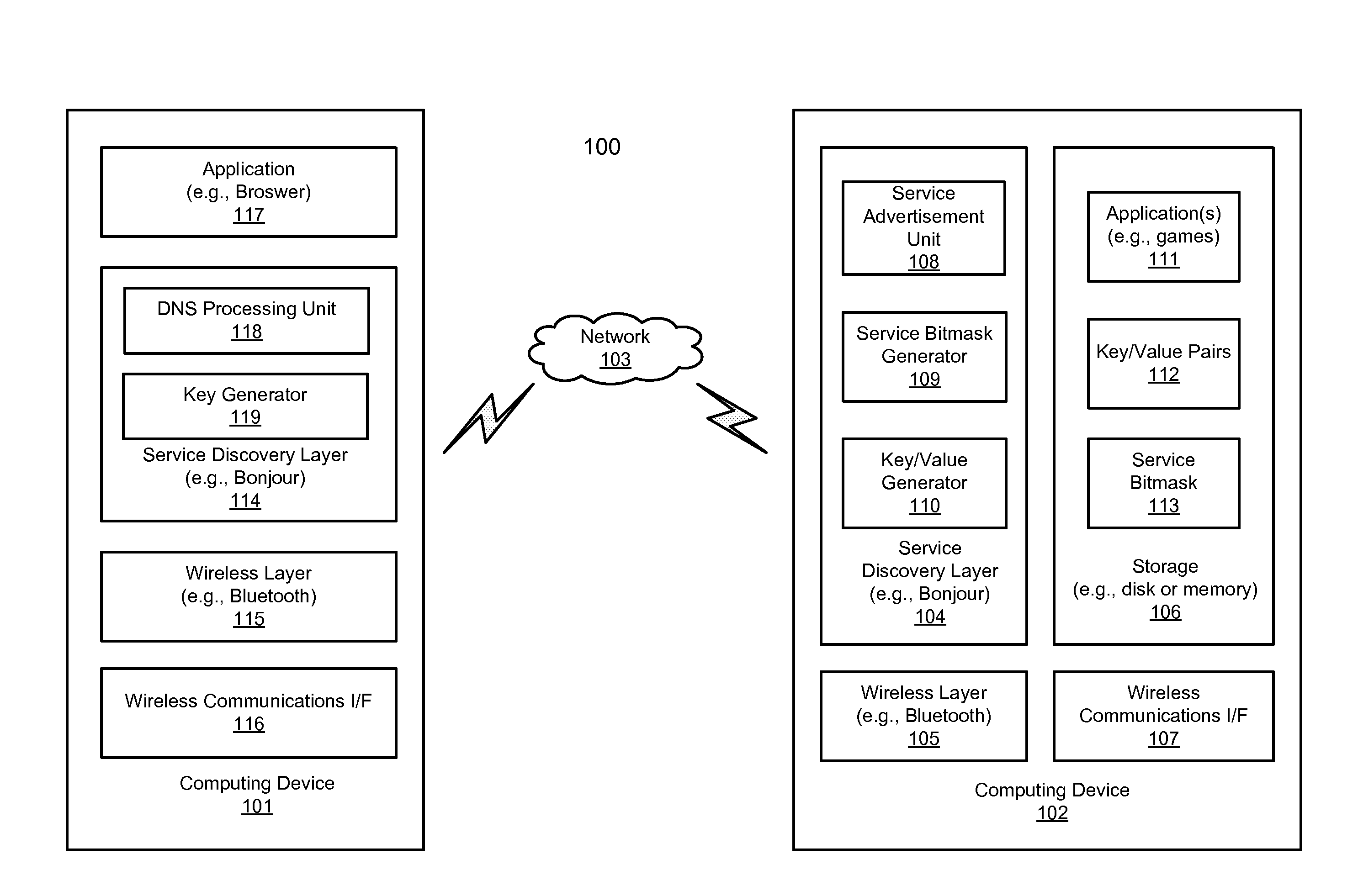
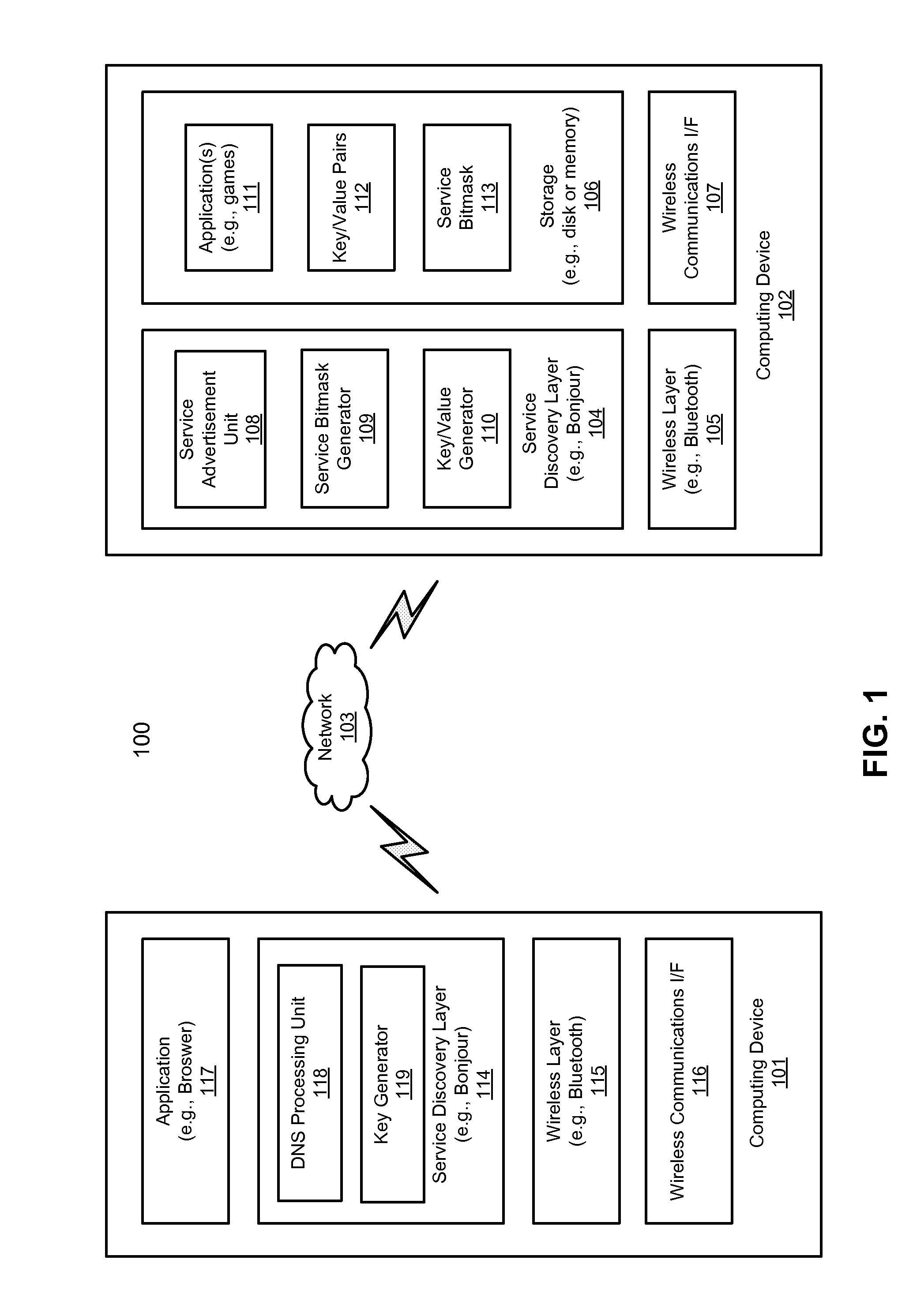
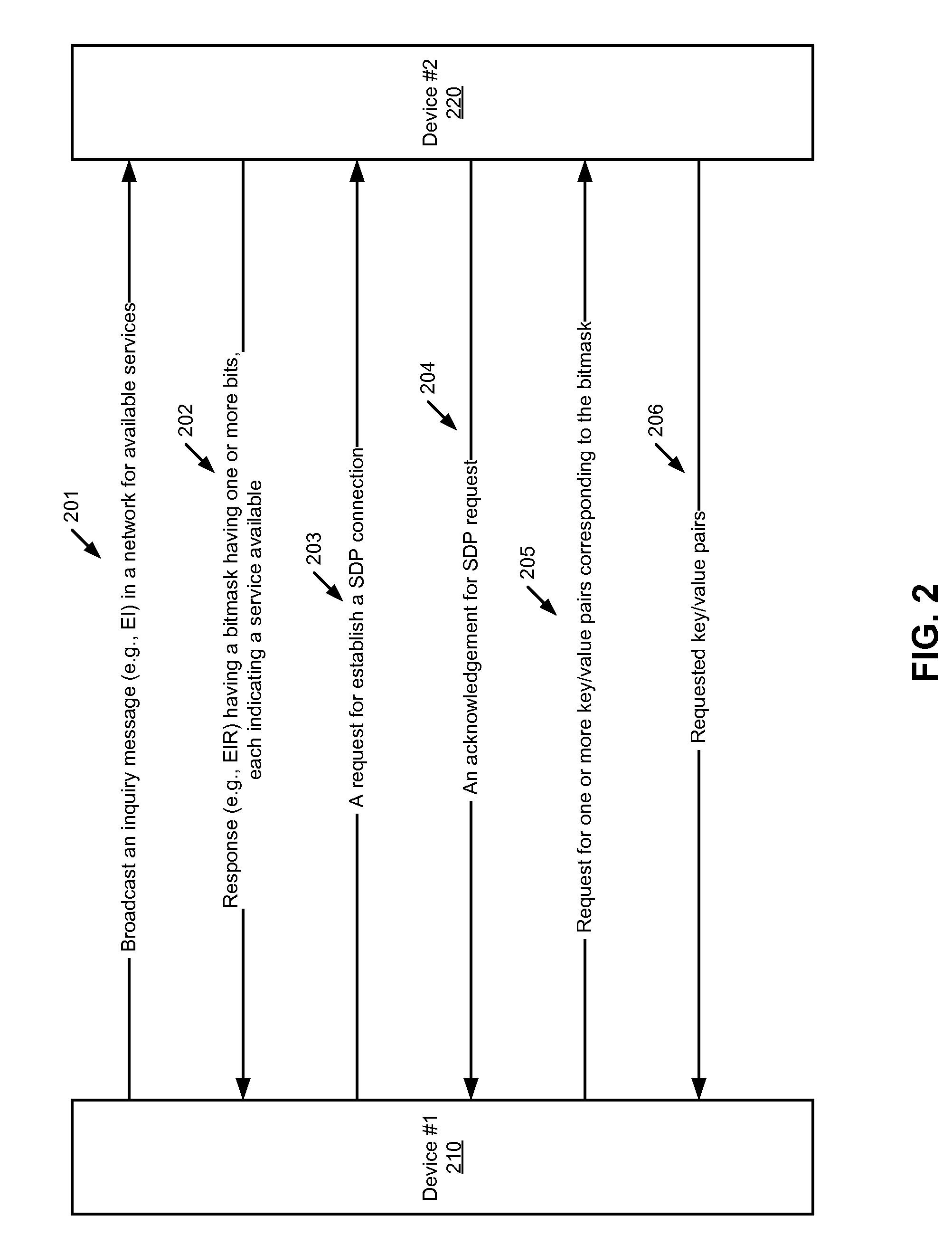
Efficient service discovery for peer-to-peer networking devices
Techniques for discovering and / or advertising services are described herein. A first bitmask is received from a remote device over a wireless network, the first bitmask having one or more bits that have a predetermined logical value. Each bit represents a particular service provided by the remote device. A logical operation is performed between the first bitmask and a second bitmask locally generated within a local device, where the second bitmask represents a service being searched by the local device. It is determined whether the remote device is potentially capable of providing the service being searched by the local device based on a result of the logical operation.
Owner:APPLE INC
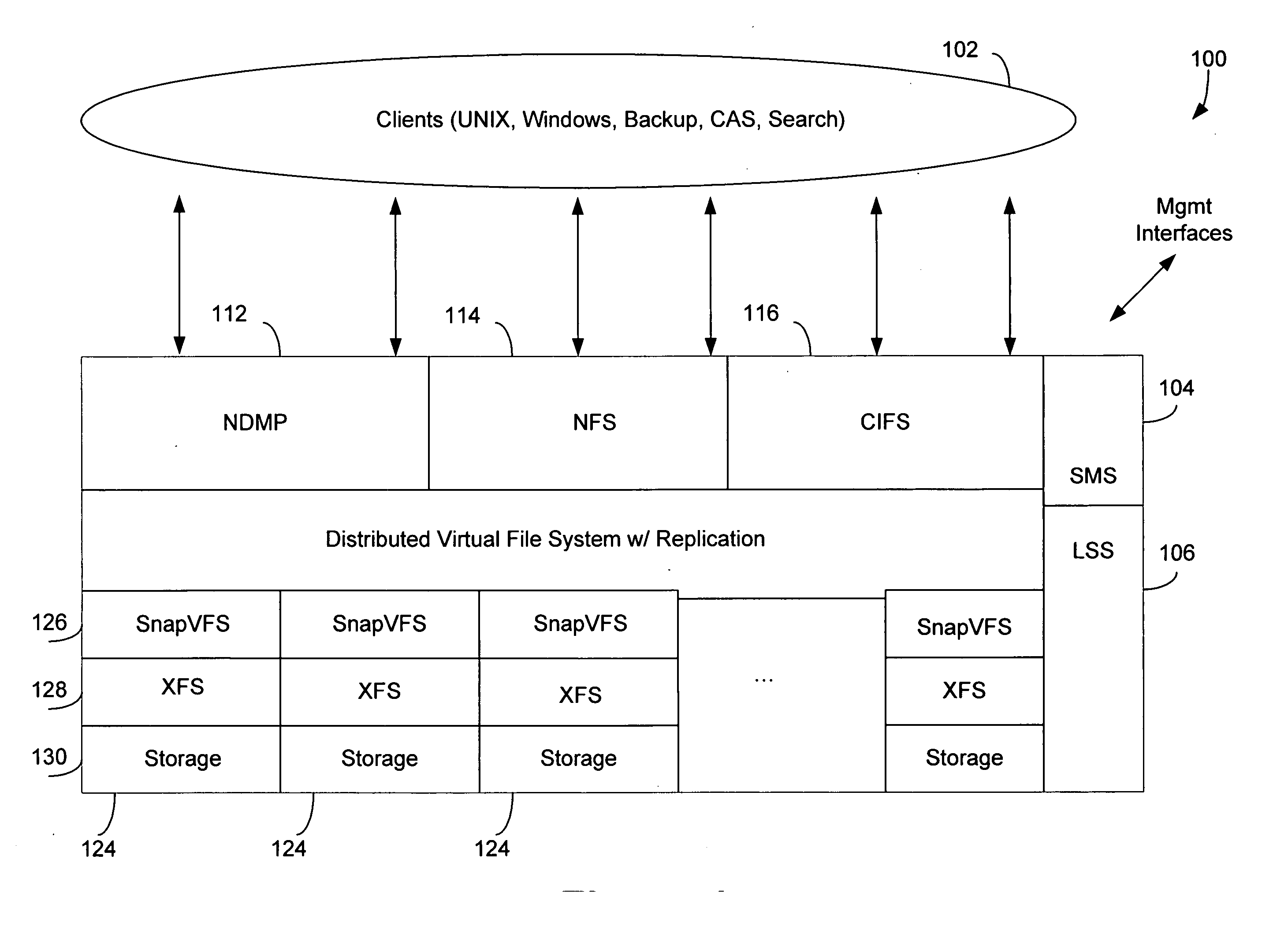
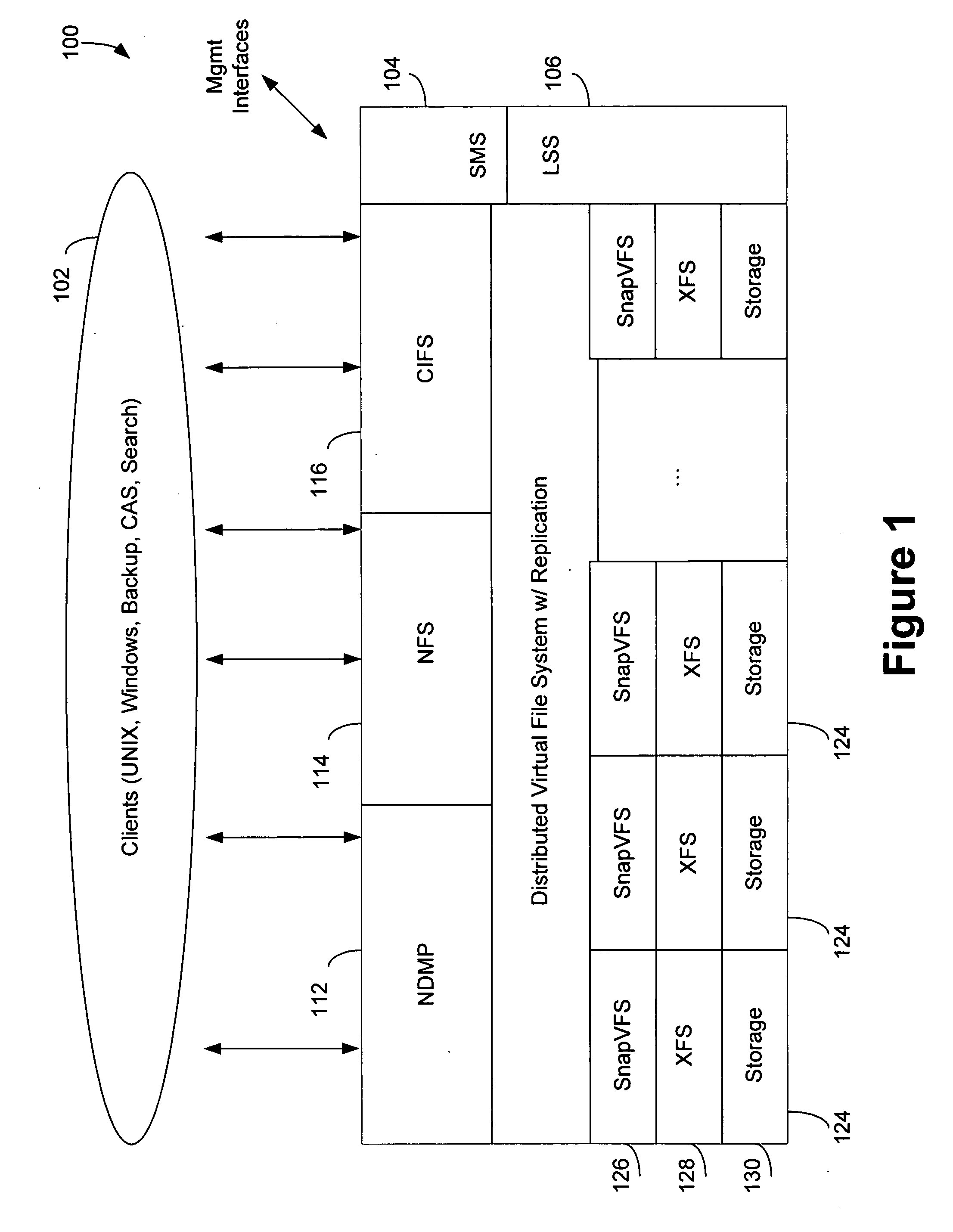
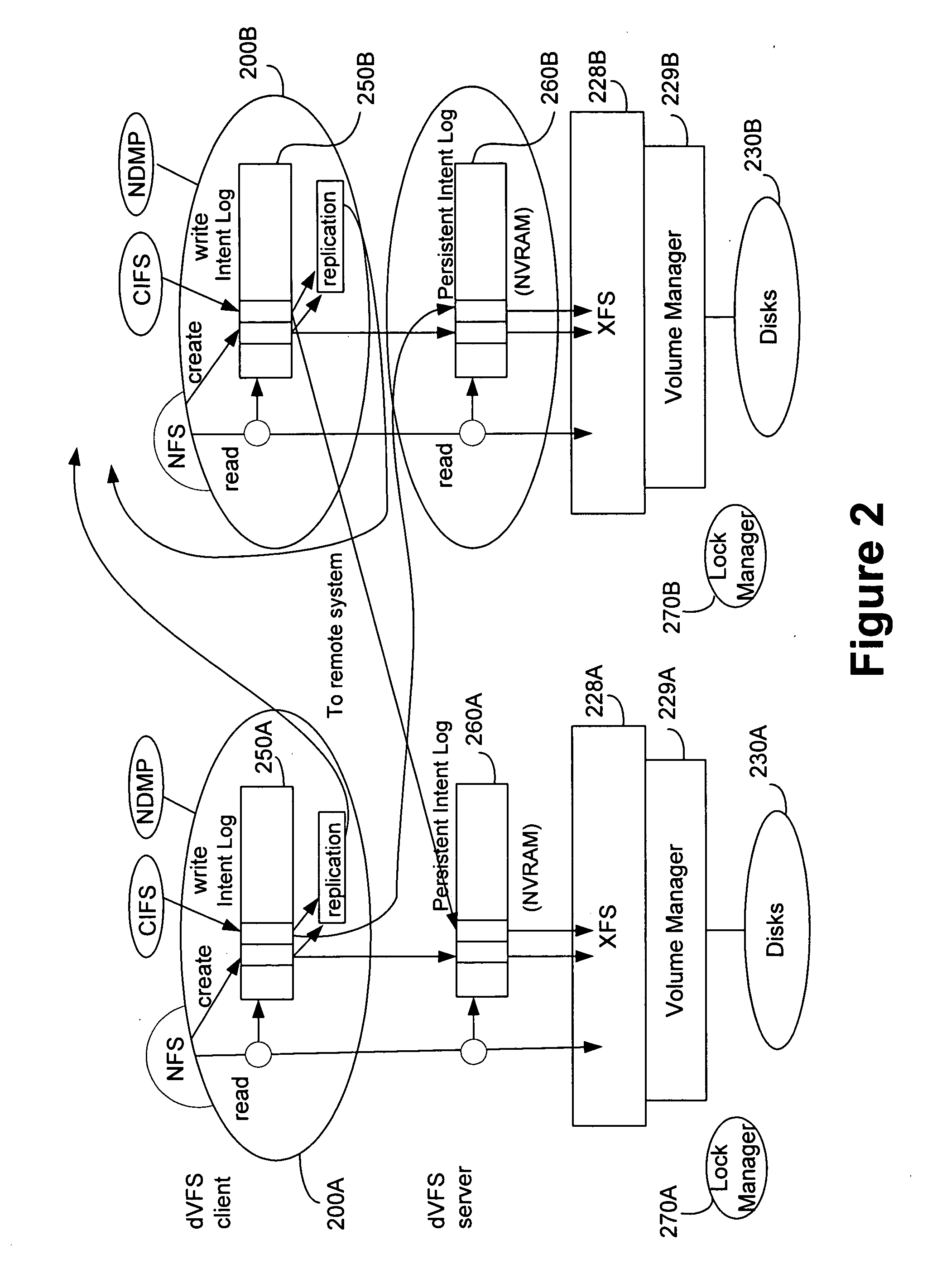
Method and apparatus for implementing a file system
InactiveUS20050289152A1Efficient implementationDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsVirtual file systemFile system
A system and method for efficiently implementing a local or distributed file system is disclosed. The system may include a distributed virtual file system (“dVFS”) that utilizes a persistent intent log (“PIL”) to record transactions to be applied to the file system. The PIL is preferably implemented in stable storage, so that a logical operation may be considered complete as soon as the log record has been made stable. This allows the dVFS to continue immediately, without waiting for the operation to be applied to a local or real file system. The dVFS may further incorporate replication to one or more remote file systems as an integral facility.
Owner:AGAMI SYSTEMS
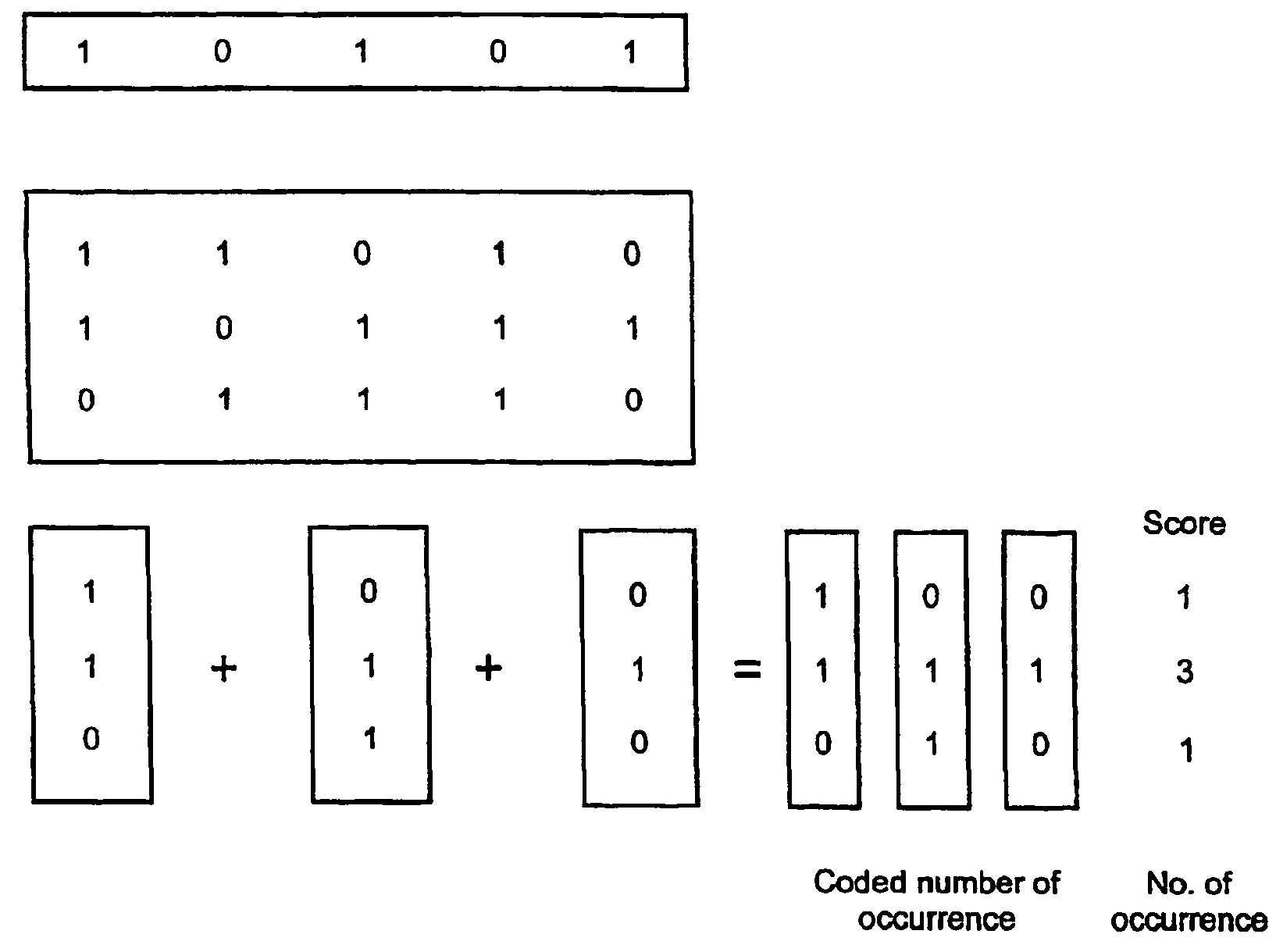
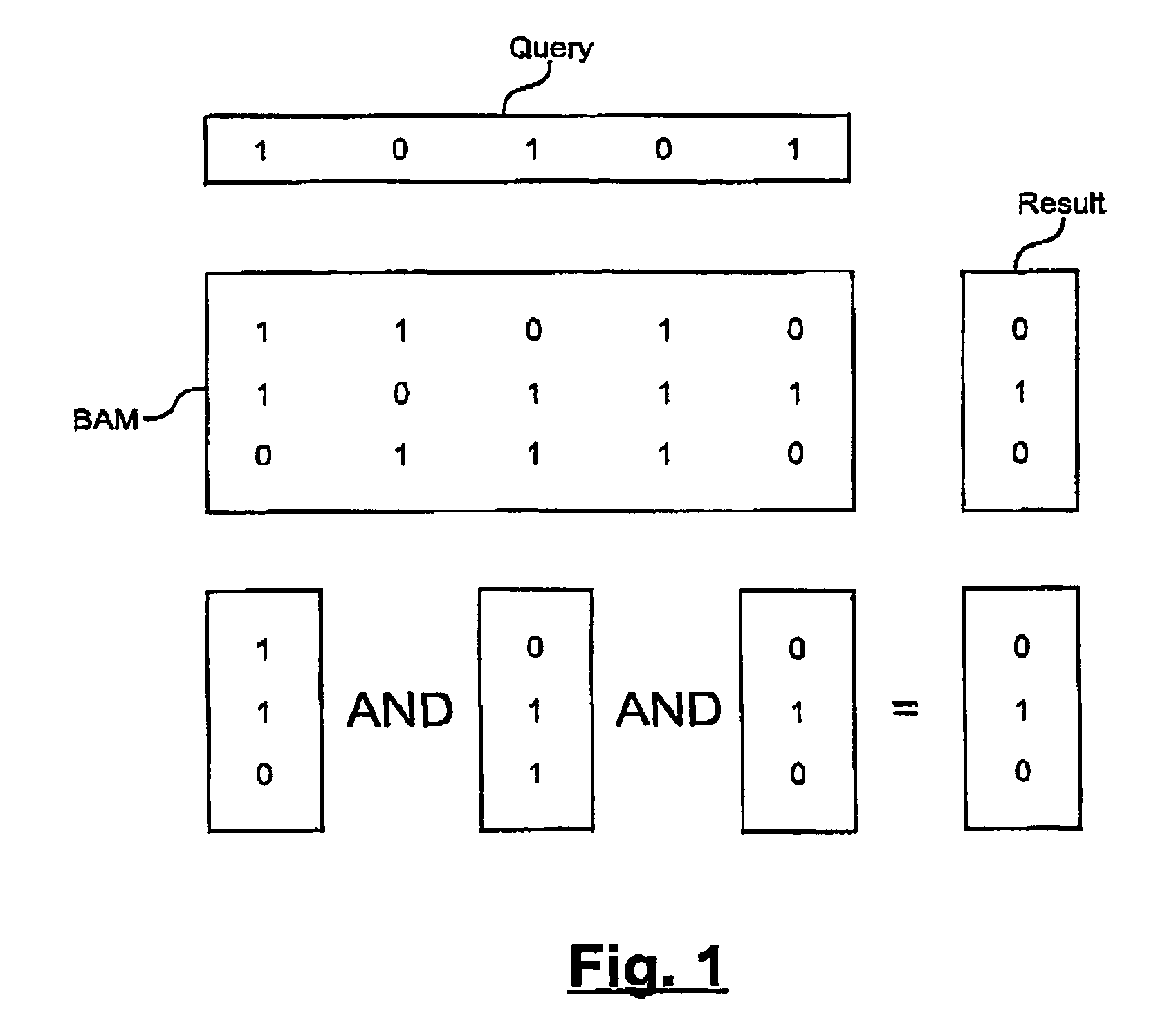
Associative memory
InactiveUS6983345B2Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalFeature vectorLogical operations
A computer-implemented method of realizing an associative memory capable of storing a set of documents and retrieving one or more stored documents similar to an inputted query document, said method comprising: coding each document or a part of it through a corresponding feature vector consisting of a series of bits which respectively code for the presence or absence of certain features in said document; arranging the feature vectors in a matrix; generating a query feature vector based on the query document and according to the rules used for generating the feature vectors corresponding to the stored documents such that the query vector corresponds in its length to the width of the matrix; storing the matrix column-wise; for those columns of the matrix where the query vector indicates the presence of a feature, bitwise performing one or more of preferably hardware supported logical operations between the columns of the matrix to obtain one or more additional result columns coding for a similarity measure between the query and parts or the whole of the stored documents; and said method further comprising one or a combination of the following: retrieval of one or more stores documents based on the obtained similarity measure; and or storing a representation of a document through its feature vector into the above matrix.
Owner:HYLAND SWITZERLAND SARL
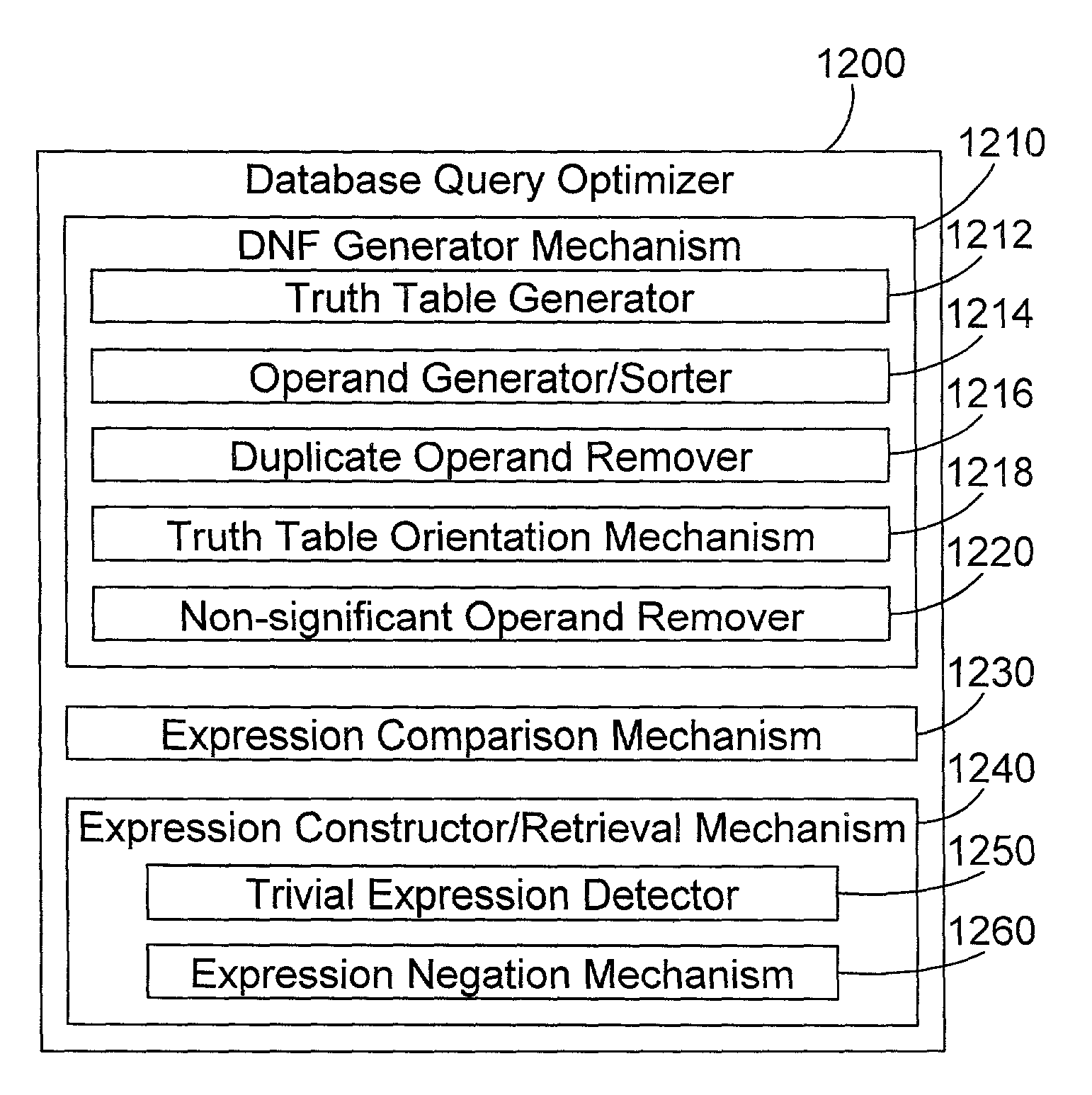
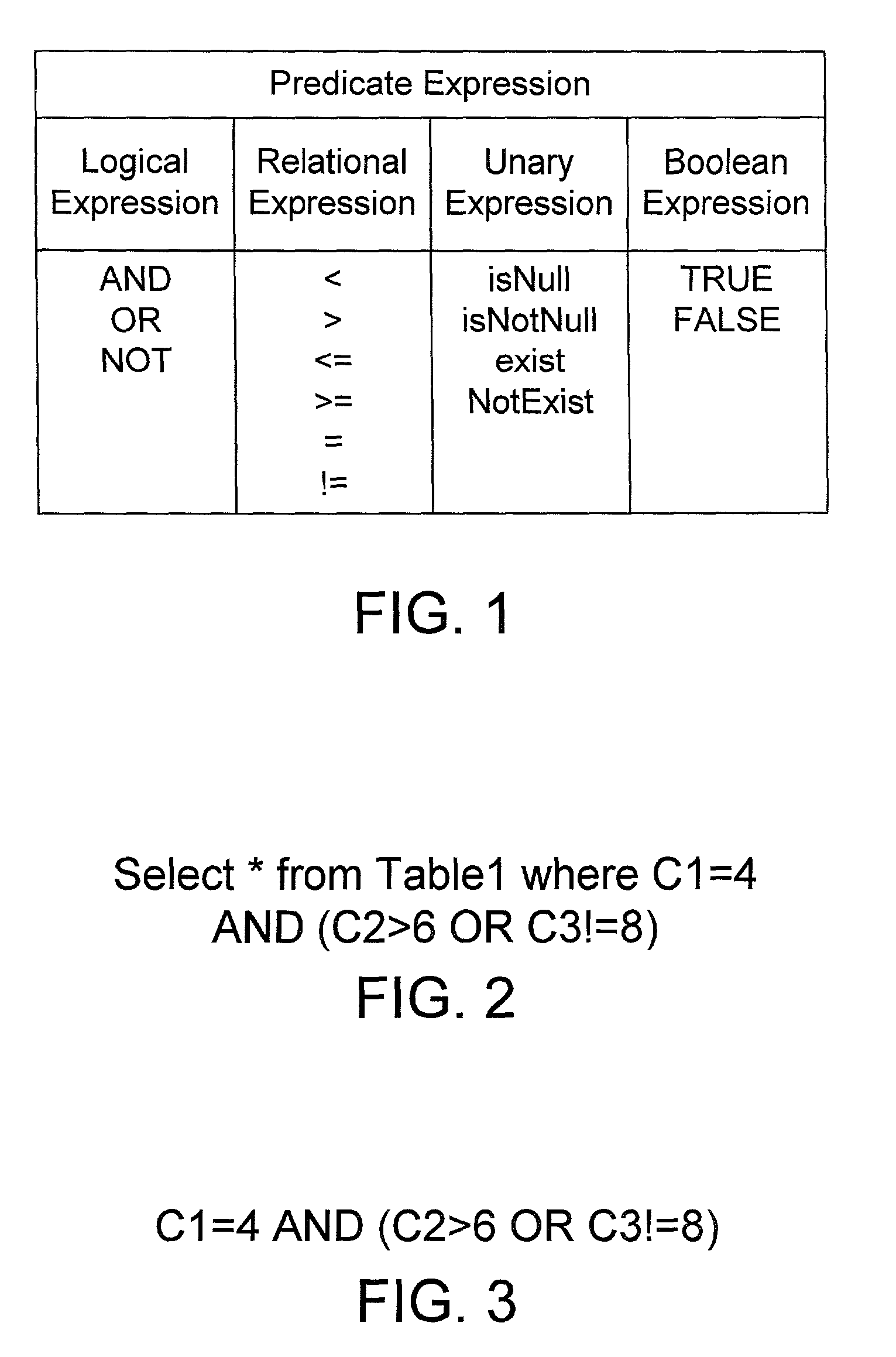
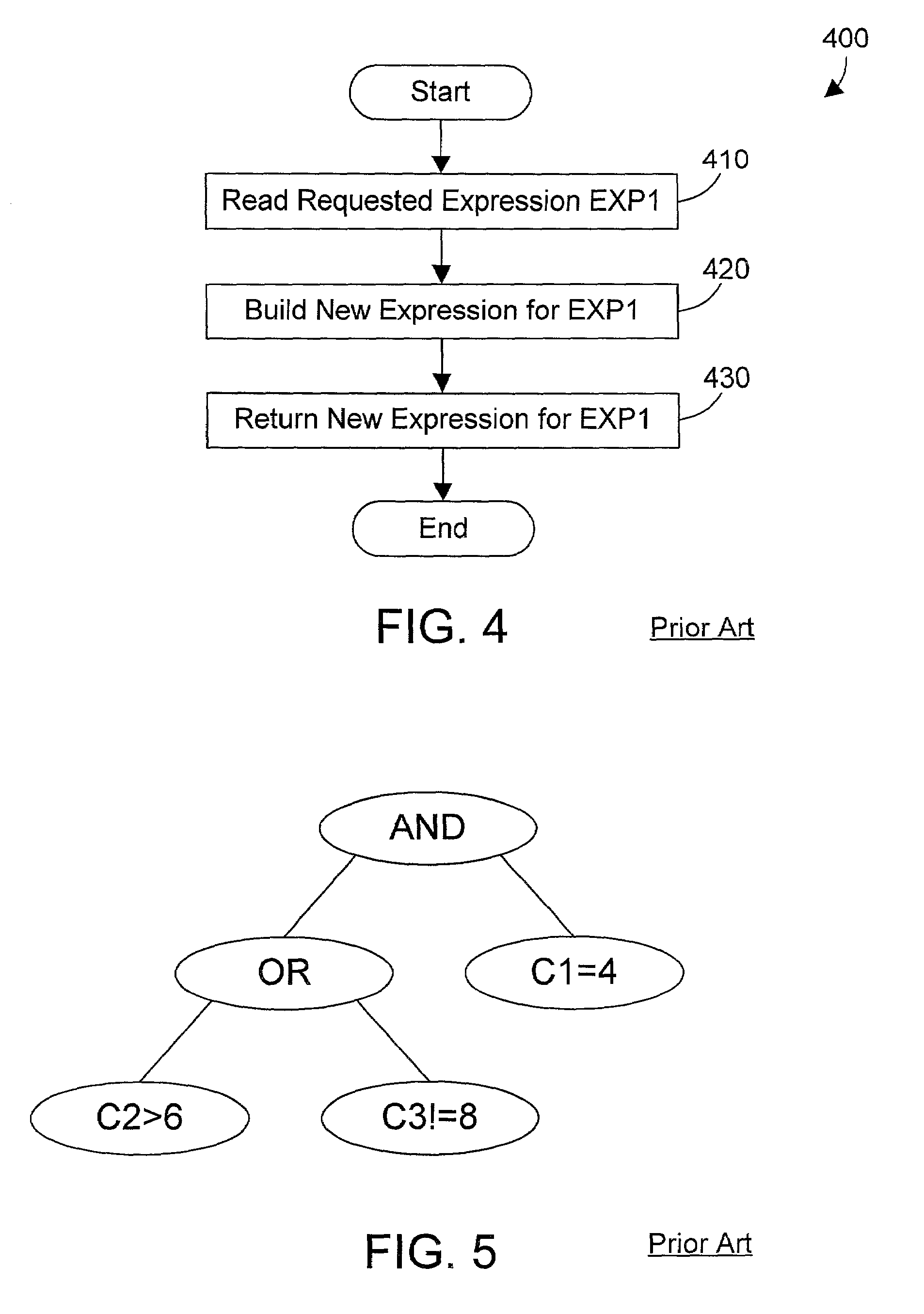
Database query optimization apparatus and method
InactiveUS6968330B2Easy constructionData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalDatabase queryTruth value
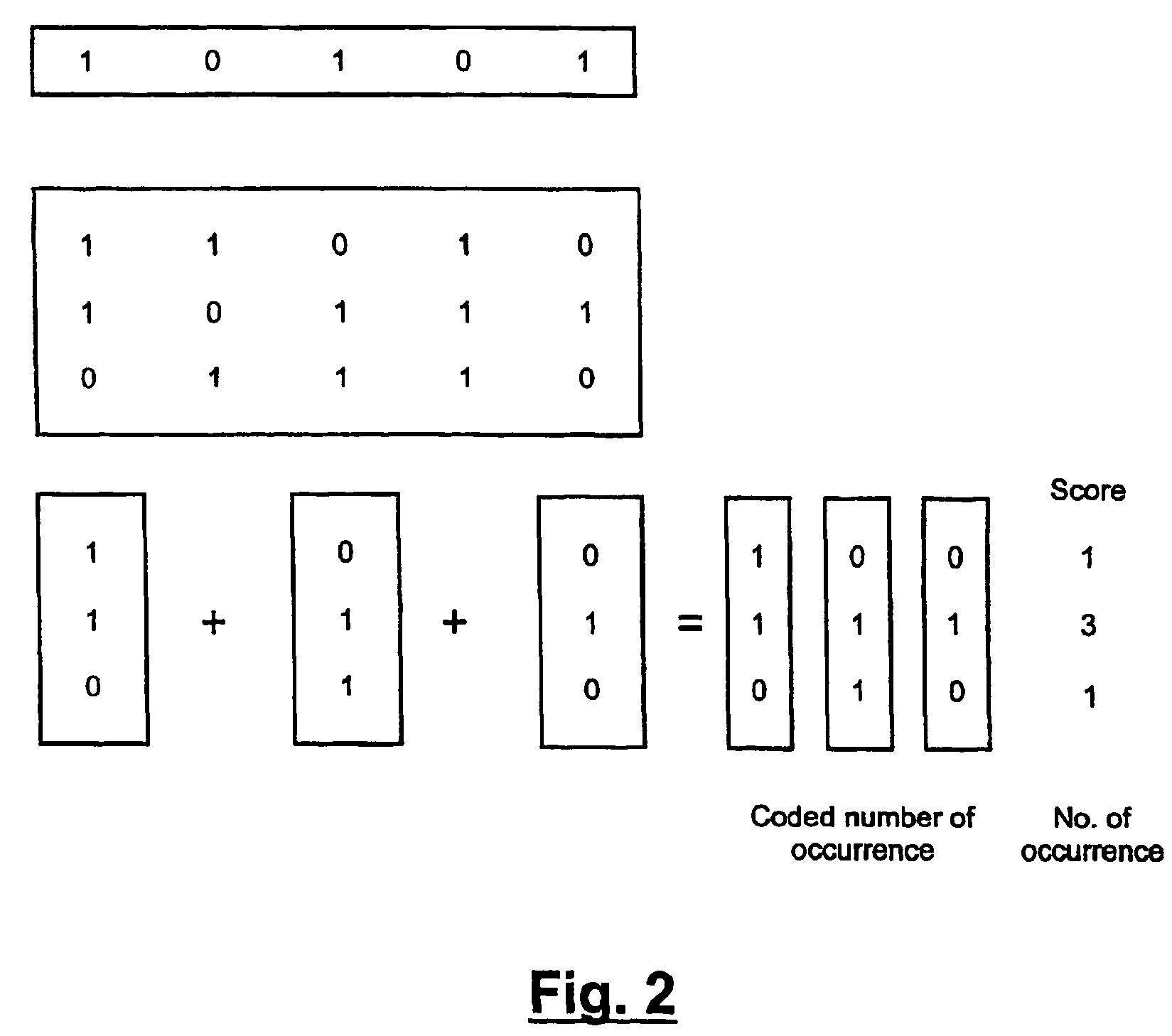
A database query optimizer processes an expression in a database query, and generates therefrom an operand list and a corresponding truth table that may be represented by a list of binary characters, where the operand list and corresponding truth table represent a disjunct normal form for the expression. Each expression is stored once it is processed into its operand list and corresponding list of binary characters. New queries are processed into component expressions, and each expression is checked to see if the expression was previously processed and stored as a processed expression. If so, the operand list and list of binary characters for the previously-stored expression may be used in processing the current expression. If there is no previously-stored expression that corresponds to the current expression, the previously-stored expressions are checked to see if any correspond to a complement of the current expression. If so, a new expression is easily constructed for the current expression by retrieving the list of binary characters that correspond to the complement expression, and inverting the bits in the list of binary characters. If there is no previously-stored expression that corresponds to the current expression or its complement, an operand list and corresponding list of binary characters are generated for the current expression. Logical operations between predicates in a query may be performed by performing mathematical operations on the lists of binary characters corresponding to each predicate expression. The end result is an operand list and corresponding list of binary characters that represents the entire expression in a query.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Using atomic sets of memory locations
InactiveUS7716645B2Software engineeringSpecific program execution arrangementsLogical operationsHuman language
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Apparatus, method and system for a synchronicity independent, resource delegating, power and instruction optimizing processor
InactiveUS20050235134A1Improve cache hit ratioMemory architecture accessing/allocationResource allocationLogical operationsPower usage
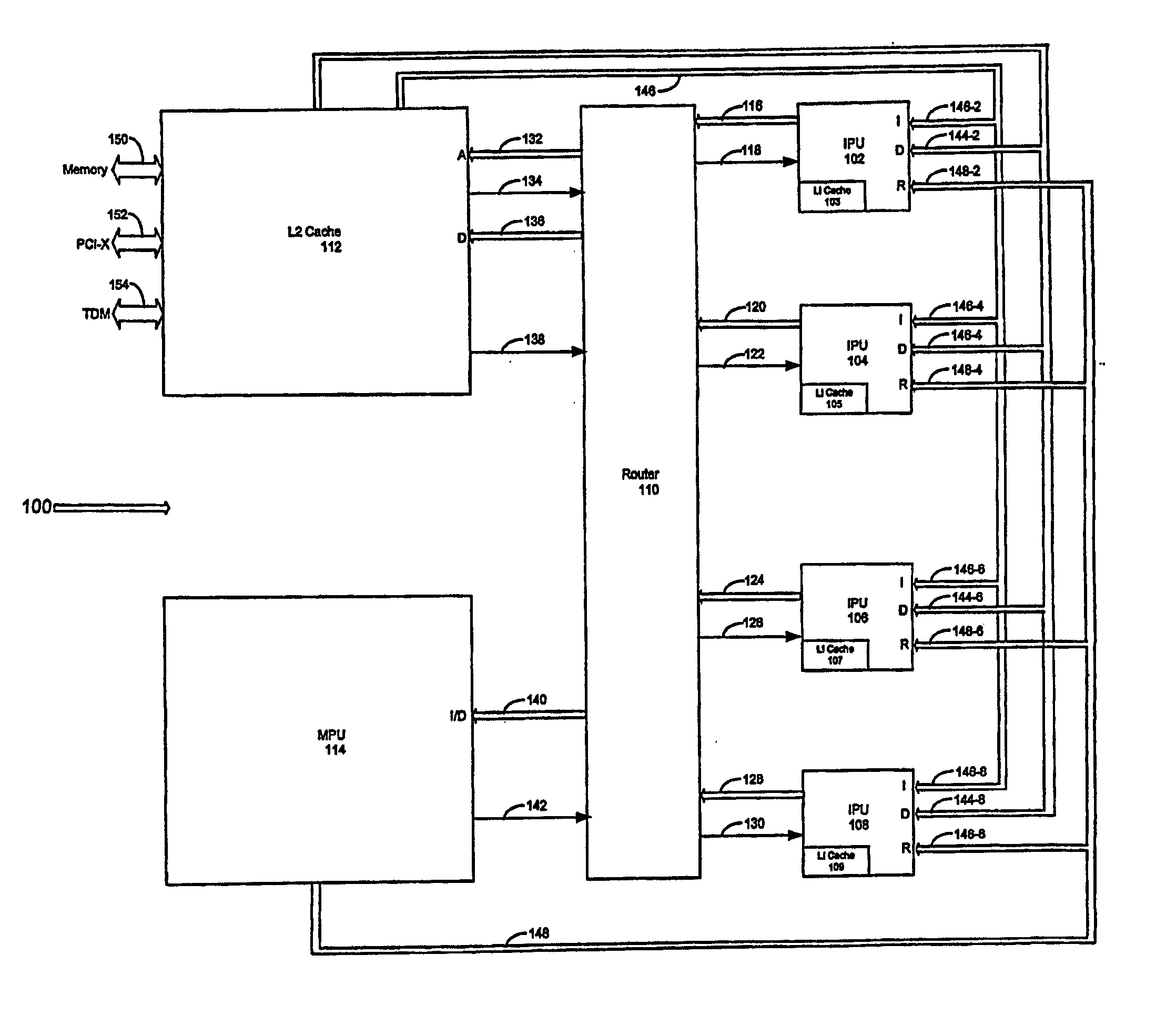
An apparatus, method, and system for synchronicity independent, resource delegating, power and instruction optimizing processor is provided where instructions are delegated between various processing resources of the processor. An Integer Processing Unit (IPU) of the processor delegates complicated mathematical instructions to a Mathematical Processing Unit (MPU) of the processor. Furthermore, the processor puts underutilized processing resources to sleep thereby increasing power usage efficiency. A cache of the processor is also capable of accepting delegated operations from the IPU. As such, the cache performs various logical operations on delegated requests allowing it to lock and share memory without requiring extra processing cycles by the entire processor. With the processor, execution instructions are optimized reducing the complexity of the processor, throughput is increased as delegation to multiple processing resources is scalable, and power usage efficacy is increased as underutilized and / or waiting processing resources may sleep when not active.
Owner:MMAGIX TECH
Secure Flash-based Memory System with Fast Wipe Feature
ActiveUS20120166715A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationError detection/correctionEmergent systemsLogical operations
A Flash-based storage system, card, and / or module comprises a Flash controller configured to encrypt the data pages of a page stripe by shuffling the data pages, including loading each data page into a data shuffling buffer in a sequential order relative to other data pages in the page stripe, and thereafter unloading each data page in a non-sequential order relative to other data pages in the page stripe. The Flash controller is also configured to scramble the data pages of the page stripe by performing a bitwise logical operation on the data pages that are unloaded from the data shuffling buffer. A user key and one or more system keys are used to perform the shuffling and scrambling. The Flash controller is further configured to flush the user key by bypassing the system's backup power supply and performing an emergency system shutdown without backing up system data.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method for obscuring bit-wise and two's complement integer computations in software
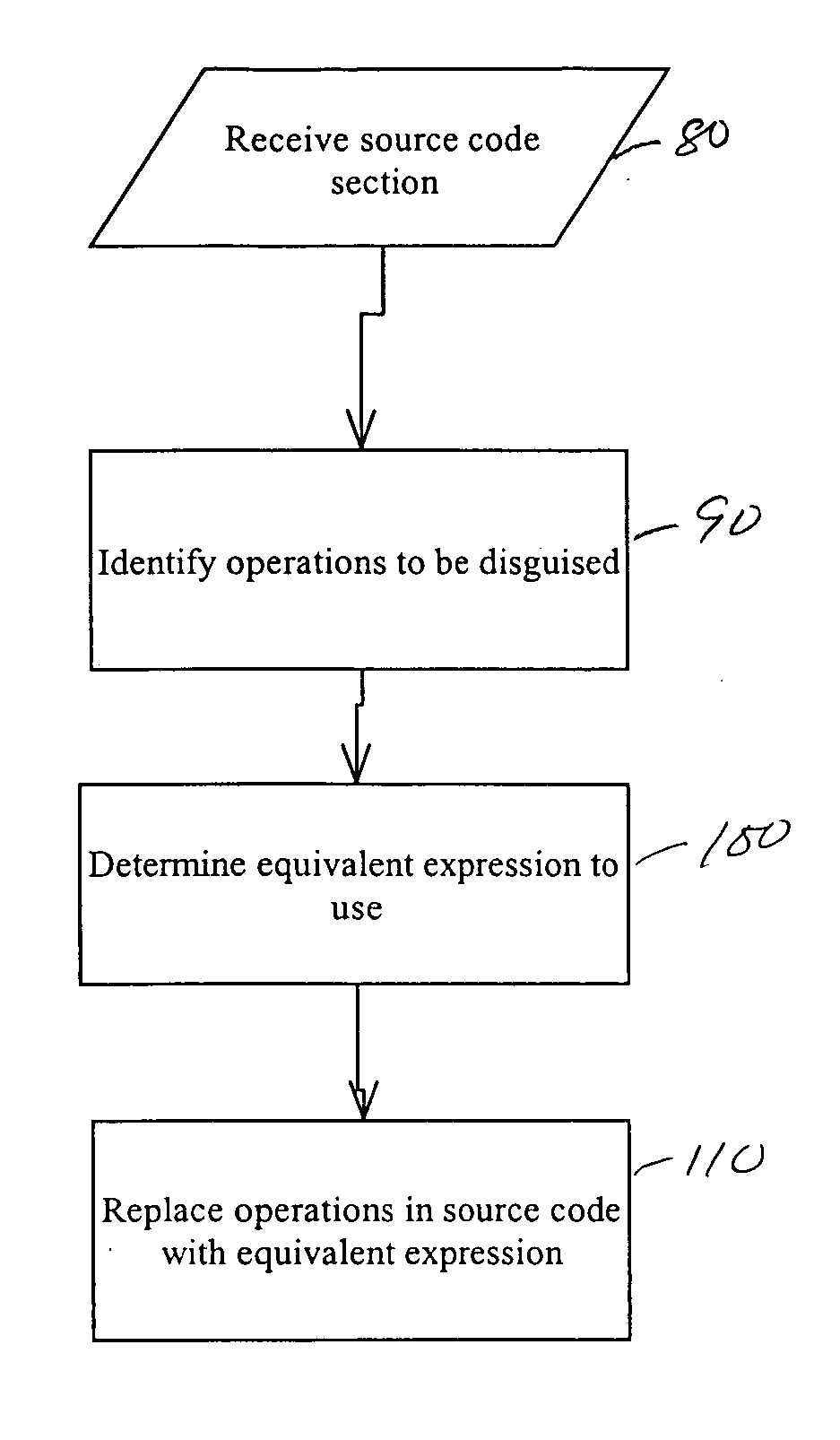
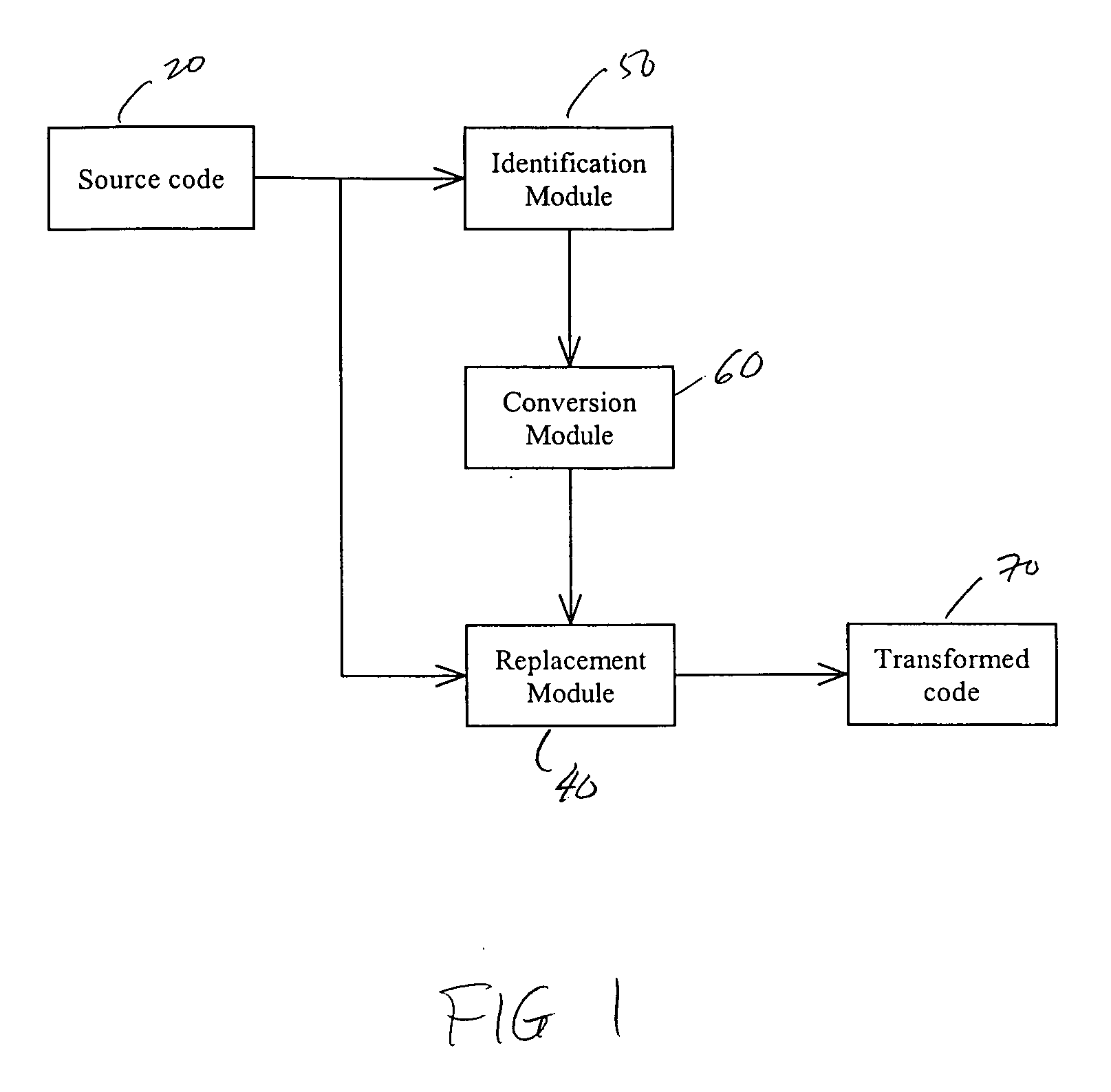
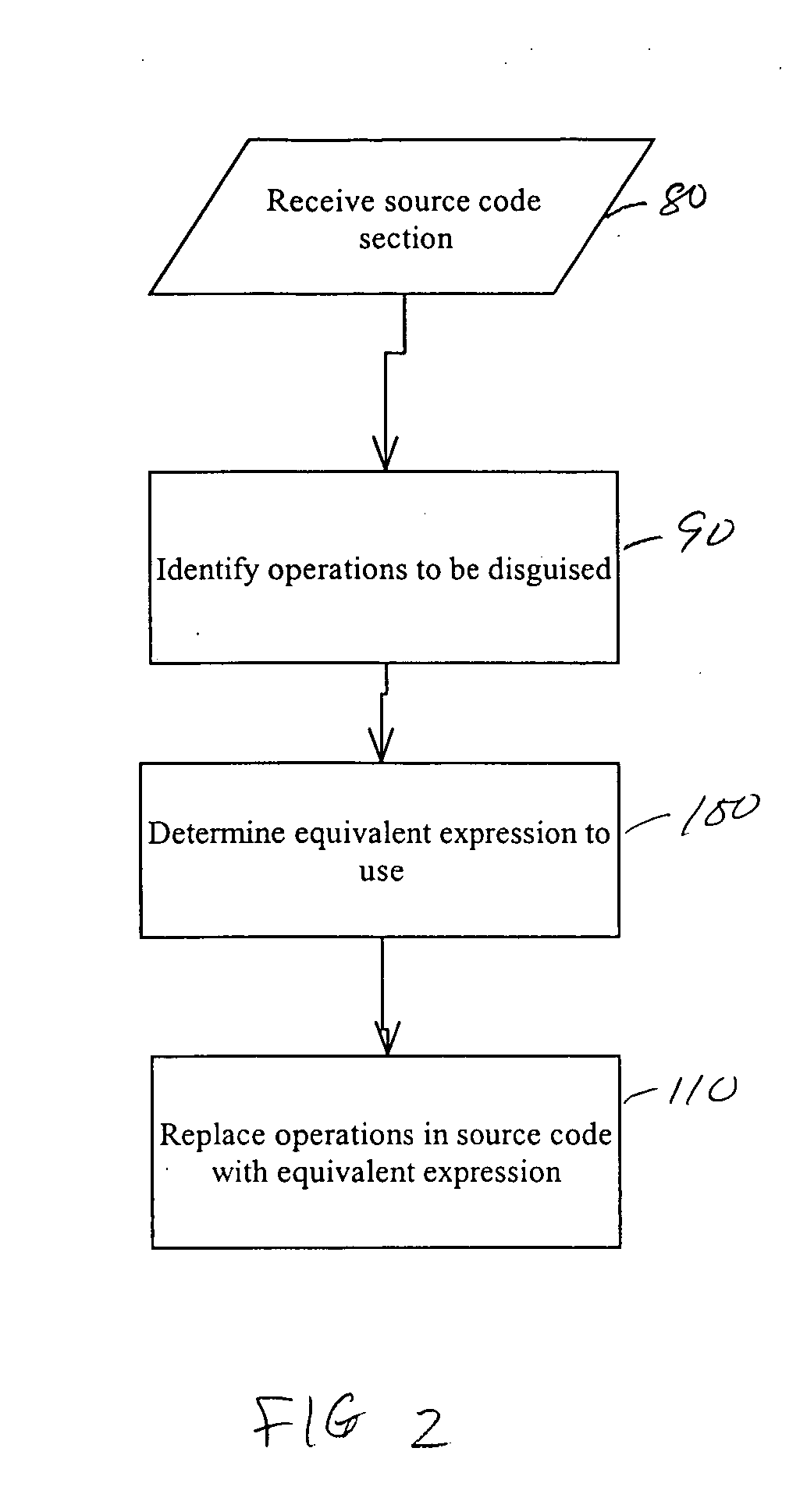
ActiveUS20050166191A1True natureDigital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionSoftware systemTheoretical computer science
Systems and methods related to concealing mathematical and logical operations in software. Mathematical and logical operations are disguised by replacing them with logically equivalent expressions. Each equivalent expression has at least two expression constants whose values are based on scaling and bias constants assigned to variables in the original mathematical or logical operation. Each of the expression constants may also be based on additive or multiplicative inverses modulo n of the scaling and bias constants. By replacing the original operations with more complex but logically equivalent expressions containing variables that also involve more operations, the true nature of the original operations is disguised.
Owner:IRDETO ACCESS +1
Encryption/decryption system, encryption/decryption equipment, and encryption/decryption method
InactiveUS20050149745A1Adverse of arithmetic operationAdverse effect of loadRandom number generatorsData stream serial/continuous modificationComputer hardwareLogical operations
An object of the present invention is to provide an encryption / decryption system and encryption / decryption equipment which suppress the adverse effect of a load on arithmetic and logic operations to be performed by a computer, whose cipher system is hard to infer, which provide great security, and which eliminate the labor of managing keys or entering a key. A security key that encrypts or decrypts data using random numbers generated by a thermal noise random number generator is detachably attached to a personal computer. When attached to the personal computer, the security key autonomously encrypts or decrypts data to be handled by the personal computer. In other words, encryption / decryption equipment employing the thermal noise random number generator is detachably attached to a computer. The encryption / decryption equipment can be used as easily as keystrokes are made, and great security can be guaranteed.
Owner:BUFFALO CORP LTD
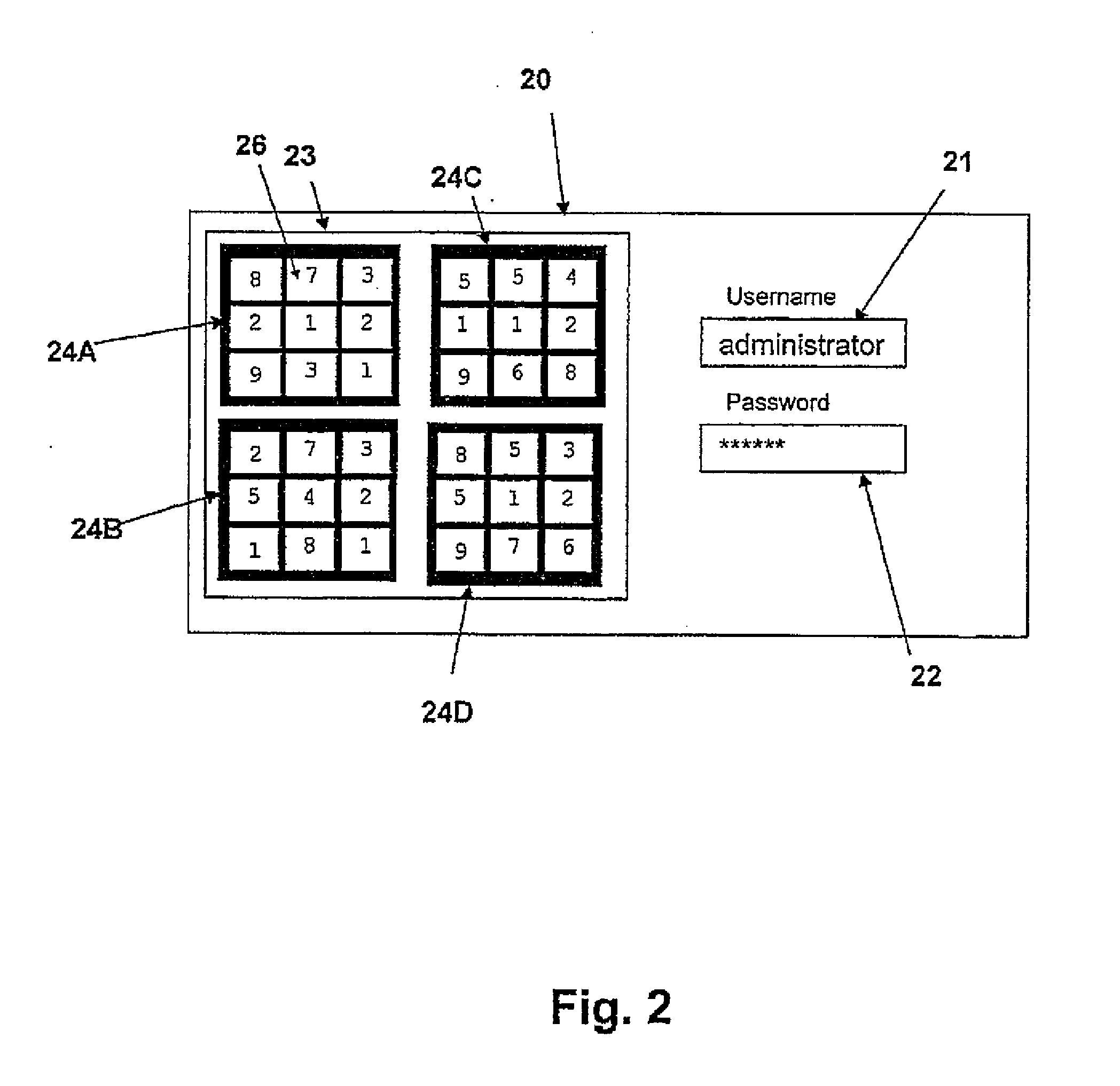
Secure Access by a User to a Resource
InactiveUS20140143844A1Shorten the lengthDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsArray data structureUser input
A method for allowing user access to a resource includes a large number of arrays of elements which are generated and stored for each user for use in a series of log-in sessions. A user input token is calculated by identifying a subset of the array by a pattern of the elements in the array, combined in an operation on the elements selected using one or more mathematical, relational and / or logical operations. The arrays are stored in a table with the tokens calculated from those arrays and withdrawn in a random pattern for use in the sessions for that user. Each array includes multiple possible solutions including the actual solution using the pattern and calculation of that user and these other possible solutions act as hacker traps to indicate the presence of a hacker who has calculated a solution but found the wrong solution
Owner:PASSRULES CANADIAN SECURITY
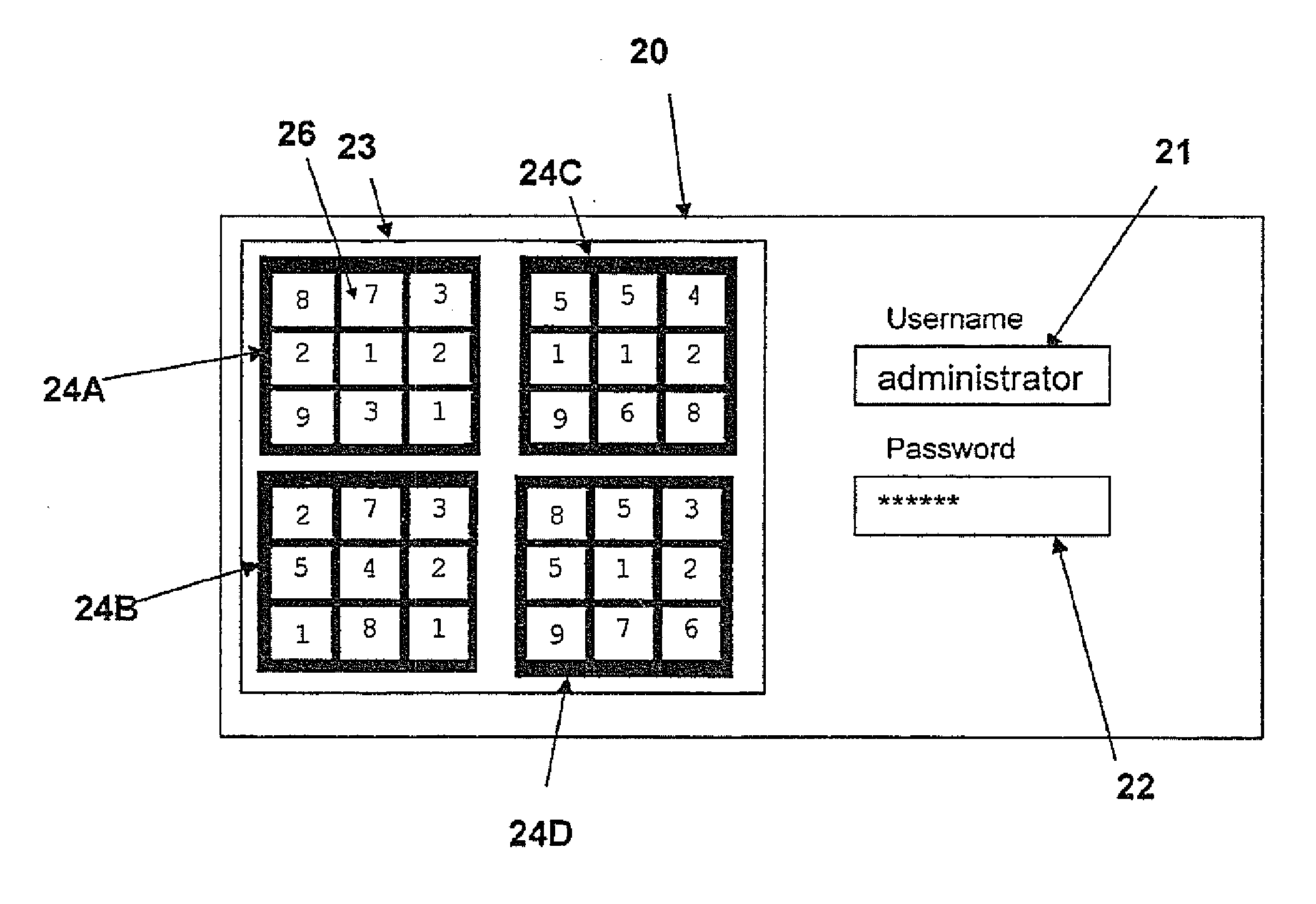
Secure Access by a User to a Resource
InactiveUS20110191592A1Shorten the lengthDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsArray data structureUser input
A method for allowing user access to a resource includes a large number of arrays of elements which are generated and stored for each user for use in a series of log-in sessions. A user input token is calculated by identifying a subset of the array by a pattern of the elements in the array, combined in an operation on the elements selected using one or more mathematical, relational and / or logical operations. The arrays are stored in a table with the tokens calculated from those arrays and withdrawn in a random pattern for use in the sessions for that user. Each array includes multiple possible solutions including the actual solution using the pattern and calculation of that user and these other possible solutions act as hacker traps to indicate the presence of a hacker who has calculated a solution but found the wrong solution
Owner:PASSRULES CANADIAN SECURITY
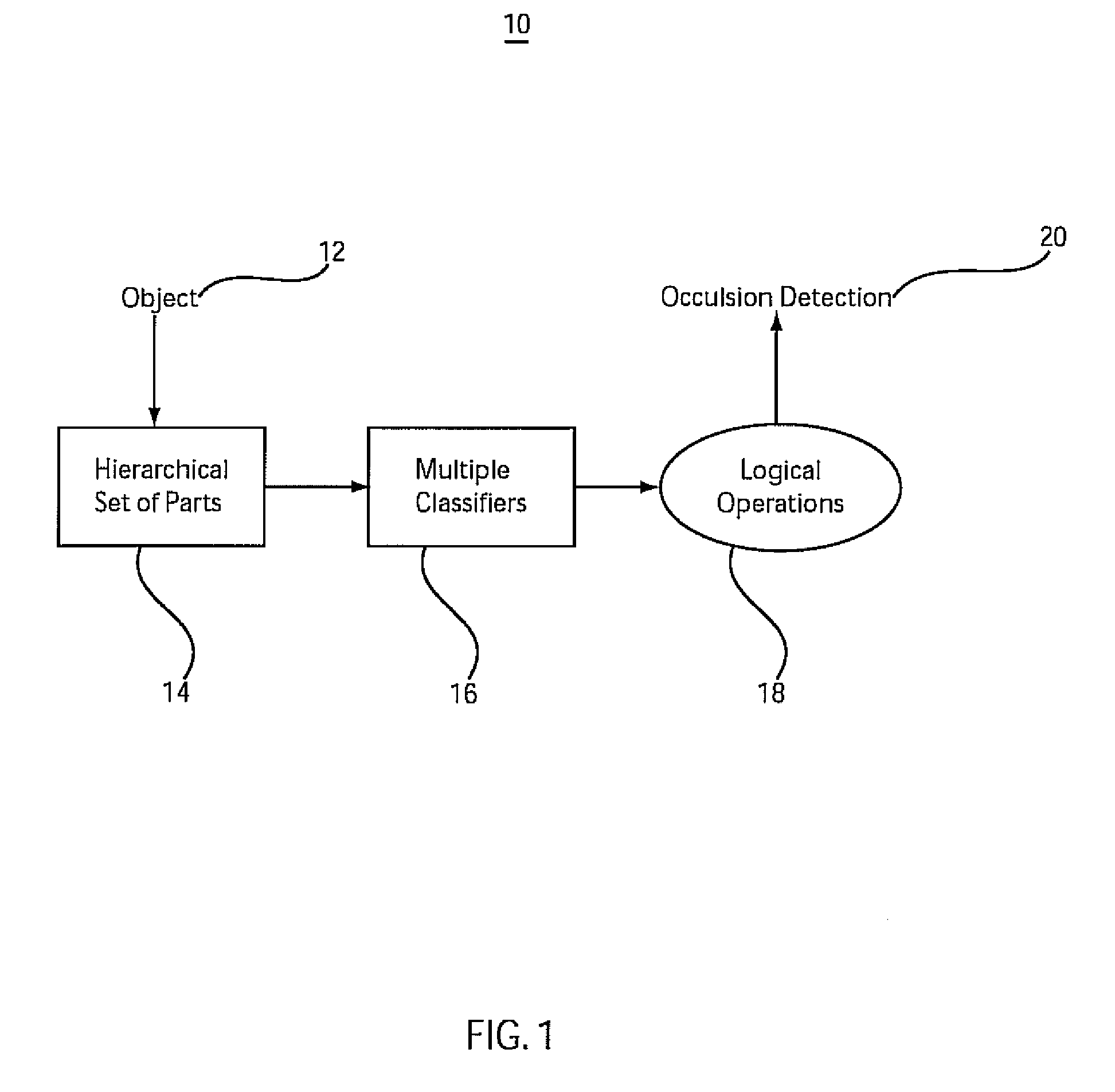
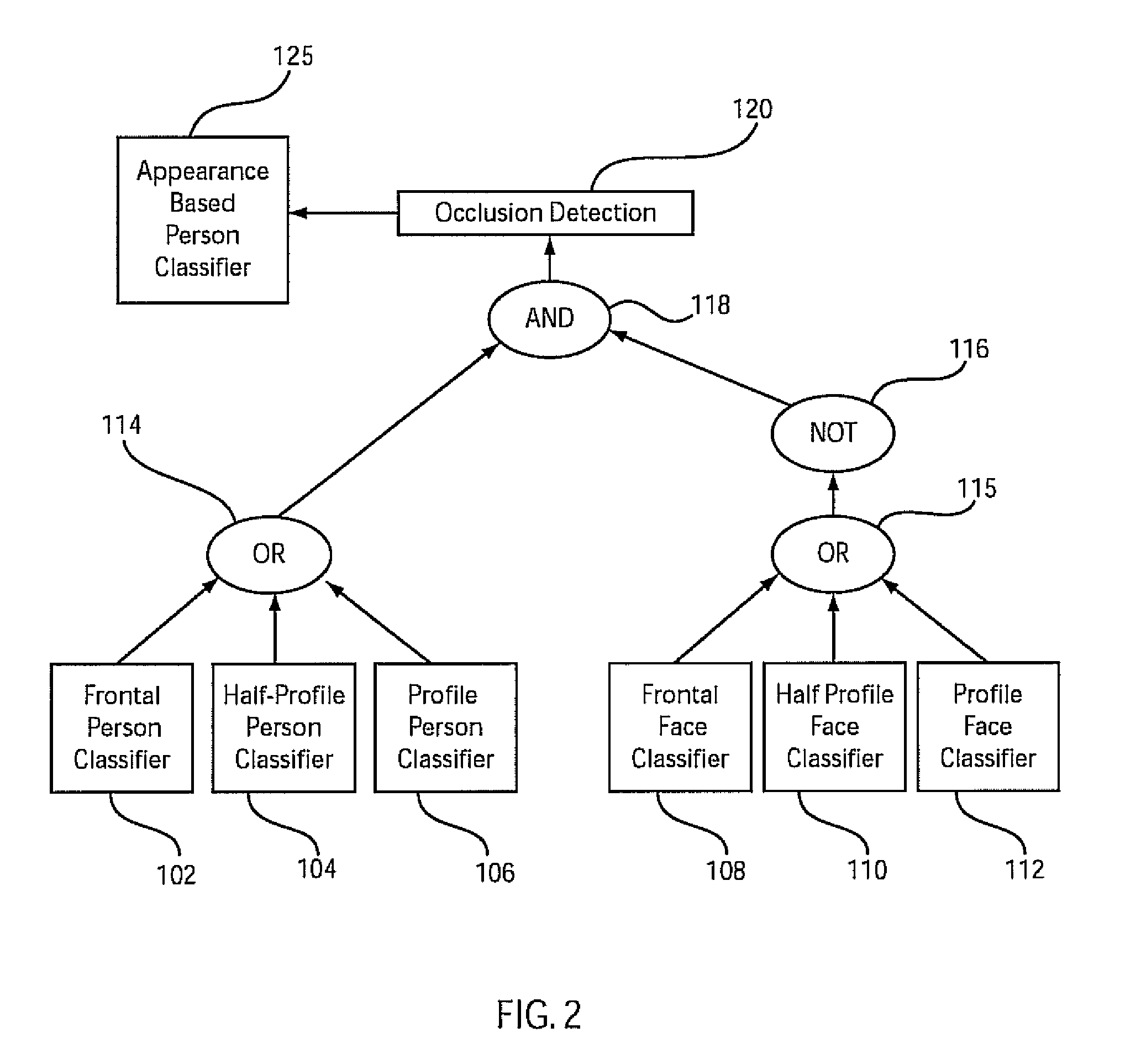
Rule-based combination of a hierarchy of classifiers for occlusion detection
ActiveUS20080247609A1Reduce in quantityCharacter and pattern recognitionImage data processing detailsLogical operationsOcclusion detection
An occlusion detection system and method include a decomposer configured to decompose an image into a set of hierarchical parts. A hierarchy of classifiers is employed to detect features in the image and the hierarchical parts. A logical operation is configured to logically combine a classification result from at least two of the classifiers to detect an occlusion state of the image.
Owner:IBM CORP
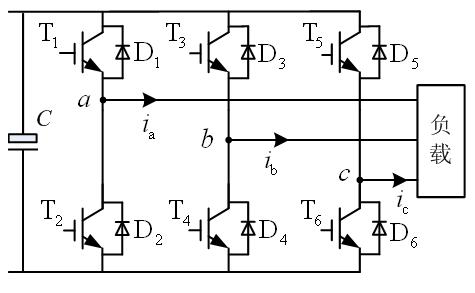
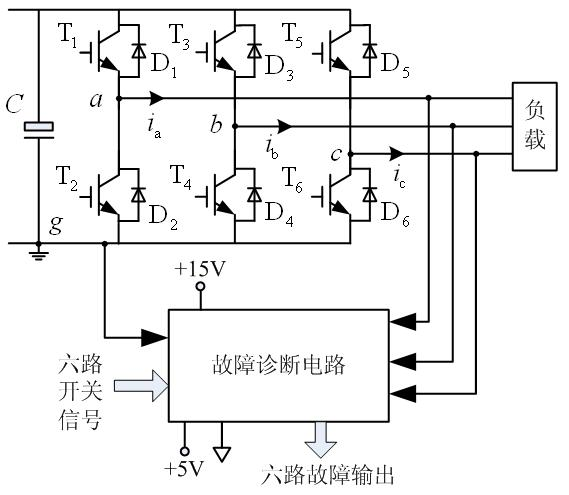
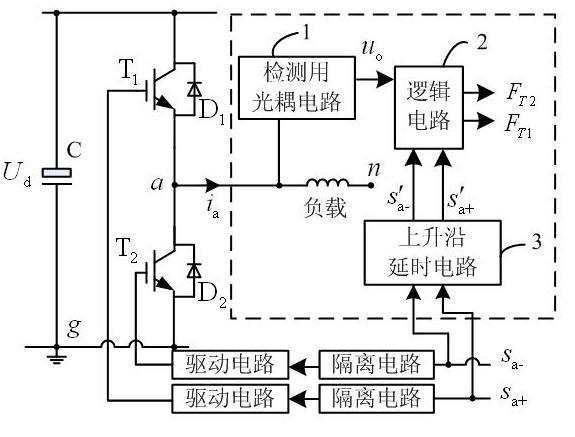
On-line detection device and detection method for open-circuit fault of power tubes of inverter
InactiveCN101793938ADoes not affect effectivenessEasy to implementElectrical testingMotor driveTime delays
The invention discloses an on-line detection device for open-circuit fault of power tubes of an inverter and a detection method thereof, relates to the field of on-line detection, and solves the problem of low detection speed existing in the conventional detection method and detection device. The detection device consists of three on-line detection circuits for the open-circuit fault of the power tubes; the circuit is used for detecting the open-circuit fault state of two power tubes in a bridge-arm circuit, and consists of a photocoupler circuit for detection, a logic circuit and a rising-edge delay circuit, wherein the rising-edge delay circuit receives a switch signal for time delay to acquire a time-delay switch signal, and sends the time-delay switch signal to the logic circuit; meanwhile, the photocoupler circuit for detection receives the switch signal controlled lower output signal, and transforms the output signal into a logic signal and sends the logic signal to the logic circuit; and logical operation is carried out to obtain the fault state, when the logical operation result is zero, the power unit correspondingly controlled by the switch signal is in a open-circuit fault state, otherwise, the power unit is normal. The invention is applicable to the open-circuit fault diagnosis of the single pipe or bridge arm of the inverter in various controlled motor drive systems and power-supply systems with current-open or close loop.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method and apparatus for data hierarchy maintenance in a system for mask description
A method and apparatus for performing an operation on hierarchically described integrated circuit layouts such that the original hierarchy of the layout is maintained is provided. The method comprises providing a hierarchically described layout as a first input and providing a particular set of operating criteria corresponding to the operation to be performed as a second input. The mask operation, which may include operations such as OPC and logical operations such as NOT and OR, is then performed on the layout in accordance with the particular set of operating criteria. A first program data comprising hierarchically configured correction data corresponding to the hierarchically described layout is then generated in response to the layout operation such that if the first program data were applied to the flattened layout an output comprising data representative of the result of performing the operation on the layout would be generated. As the first program data is maintained in a true hierarchical format, layouts which are operated upon in accordance with this method are able to be processed through conventional design rule checkers. Further, this method is capable of being applied to all types of layouts including light and dark field designs and phase shifting layouts.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
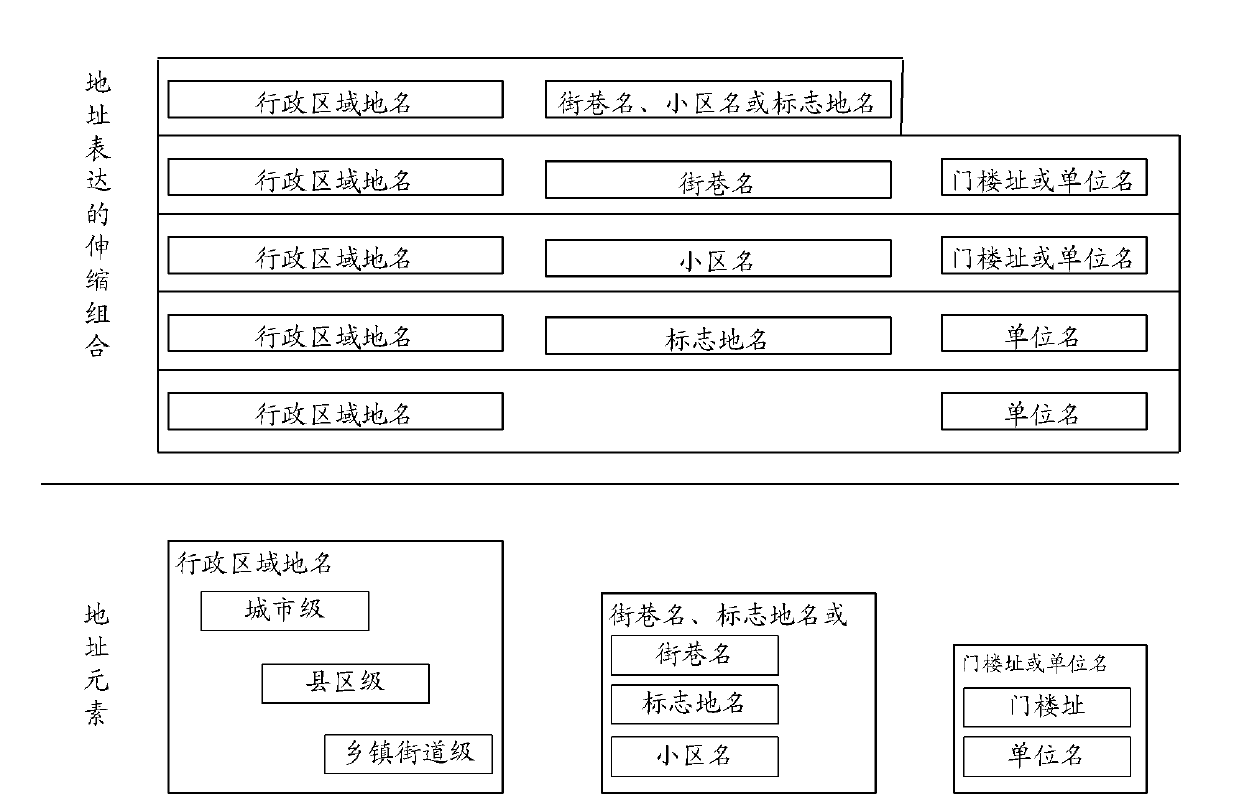
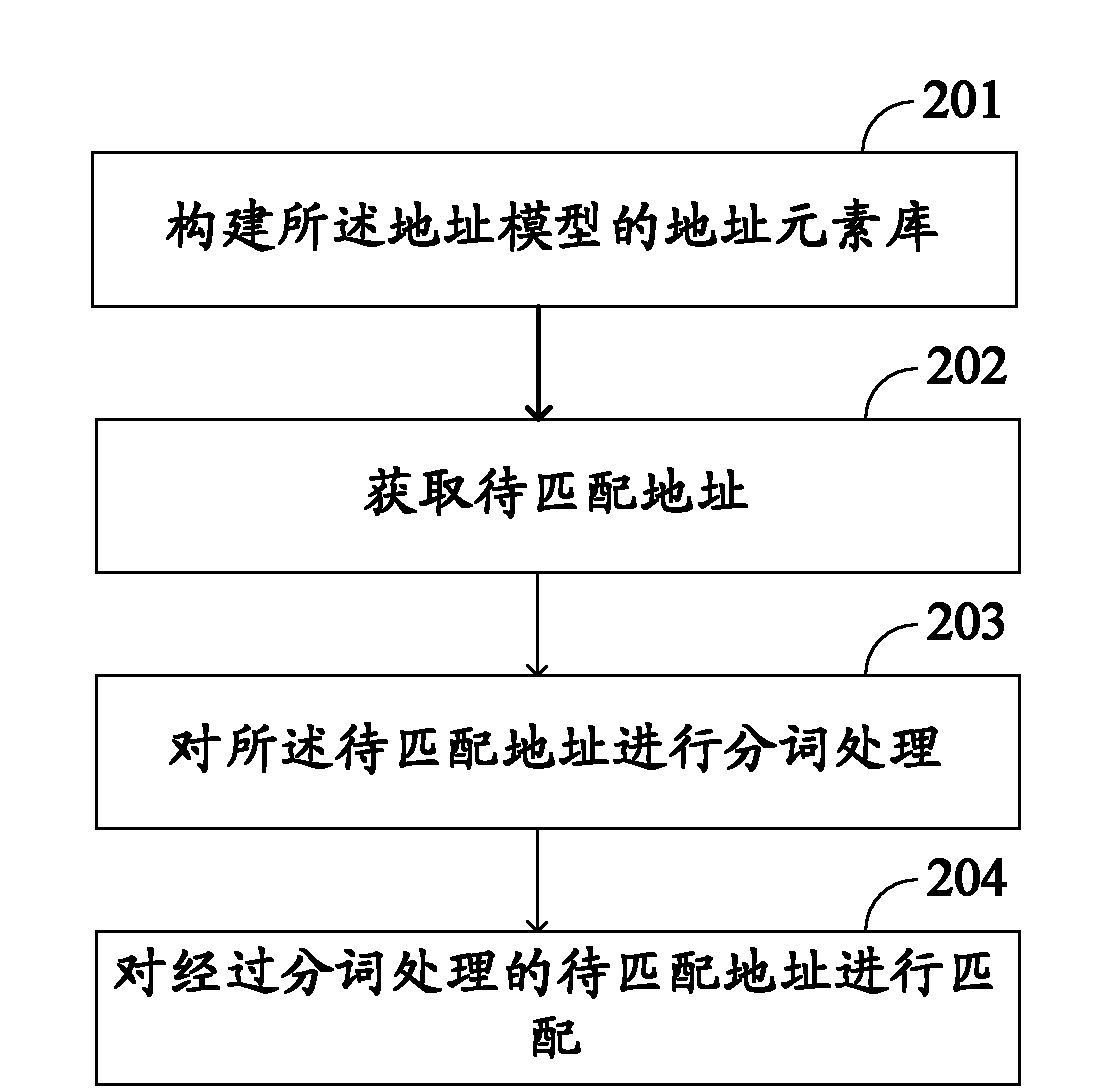
Address model constructing method and address matching method and system
InactiveCN102169498AFlexible matchingValid matchSpecial data processing applicationsTheoretical computer scienceLogical operations
The invention provides an address model constructing method. The method comprises the following steps of: A, defining description granularity in different levels for an address; and B, combining and constructing address models according to the description granularity in the different levels. In an address matching method for the address models, an address element library is established according to the address models. The method comprises the following steps of: M, acquiring addresses to be matched; N, performing participle processing on the addresses to be matched to generate different address elements; and O, matching the different address elements in the address element library through logical operation. The invention also provides an address matching system, which comprises a terminal, the address element library, a comparison table database and an operation server. By the methods and the system, the effective matching and space orientation of address information in various presentation modes are realized.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF SURVEYING & MAPPING
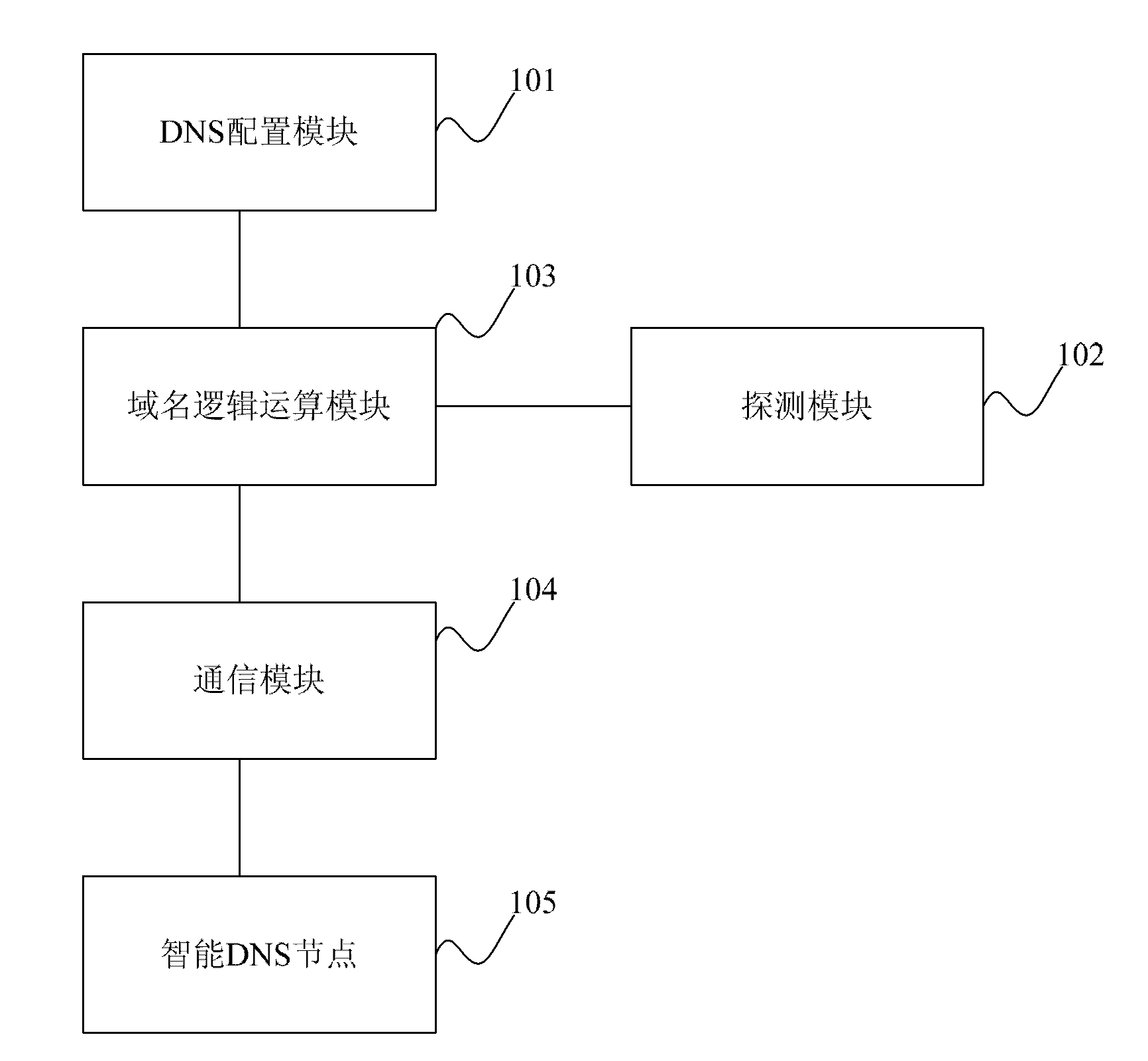
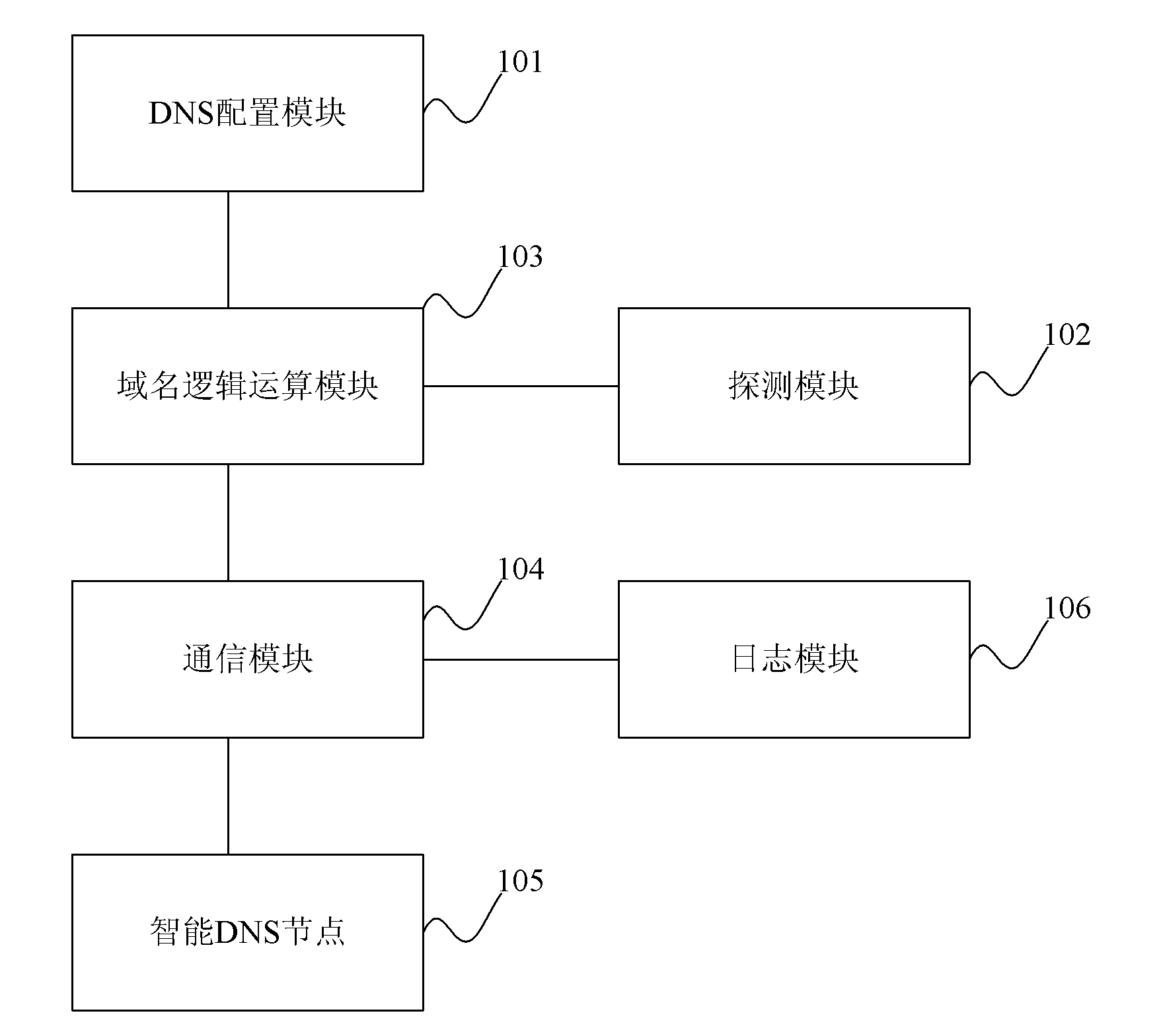
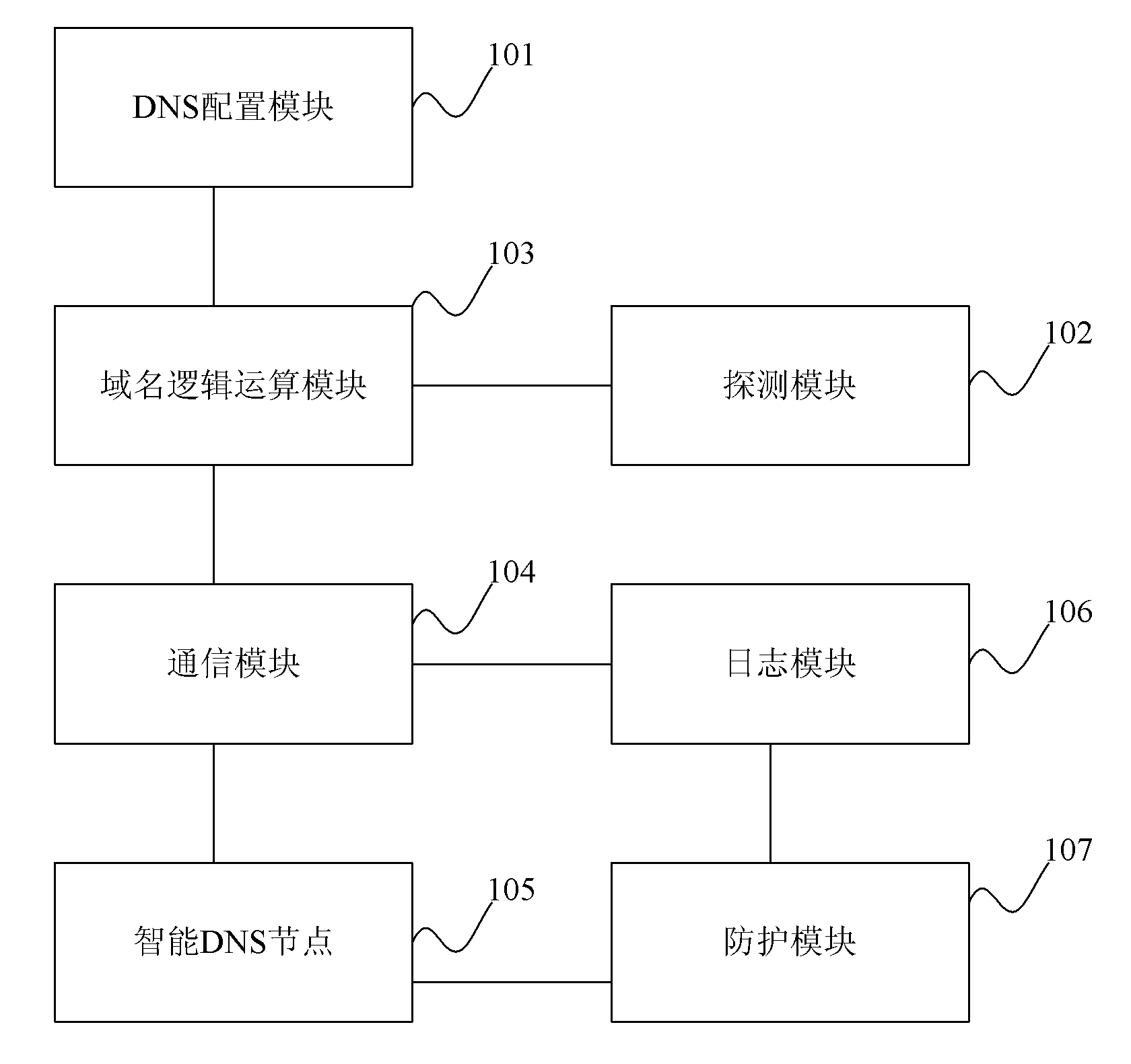
Distributed intelligent DNS (domain name server) library system
The invention discloses a distributed intelligent DNS (domain name server) library system which comprises a DNS configuration module, a domain name logical operation module, a detection module, a communication module and a plurality of intelligent DNS nodes. By the distributed intelligent DNS library system provided by the embodiment of the invention, through the mutual cooperation of modules, when the DNS of a user passes the local DNS server request to the intelligent DNS nodes, the intelligent DNS nodes return the user DNS request result, thus the user can nearby access a CDN (content distribution network) node with the best performance.
Owner:上海蓝云网络科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com