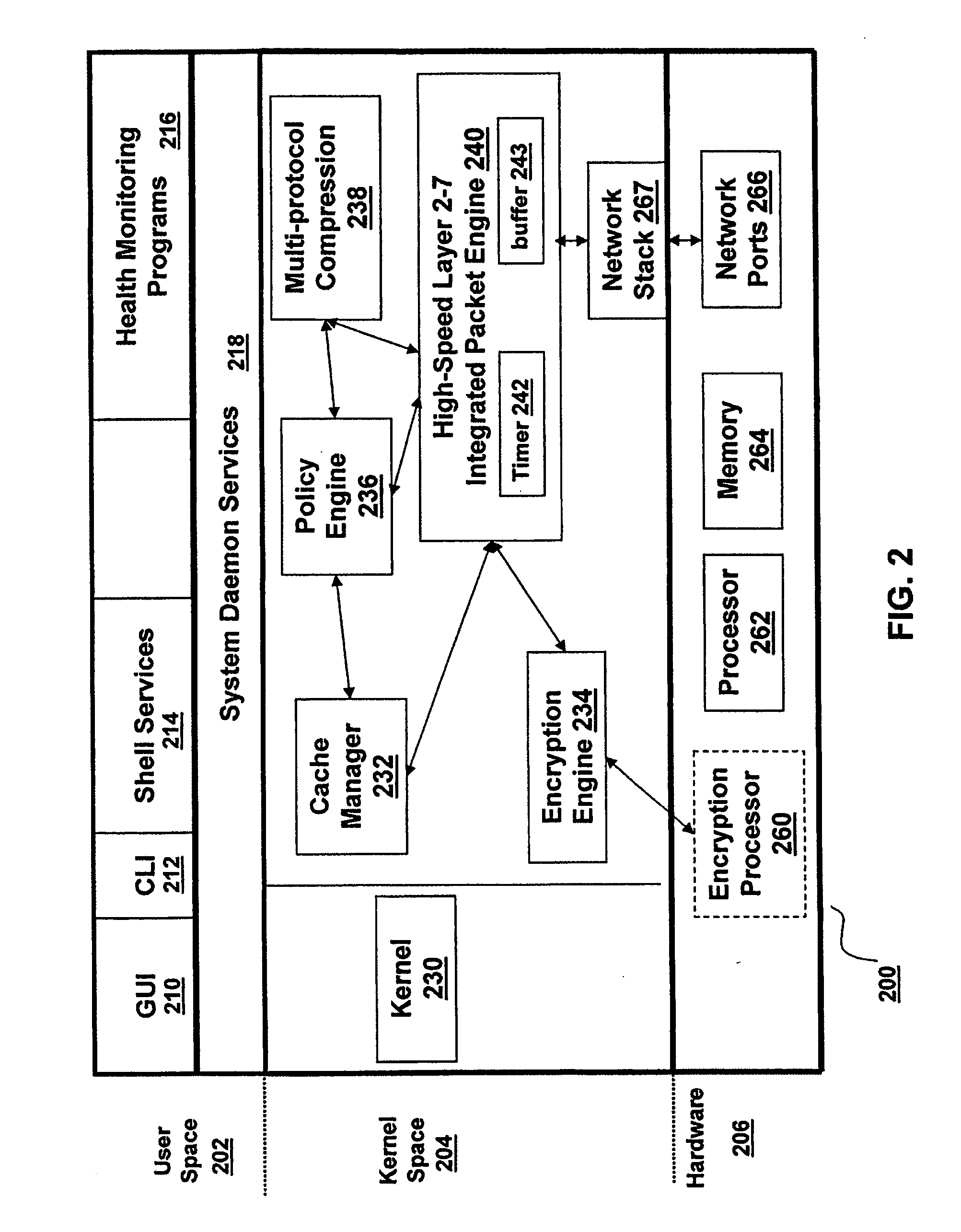
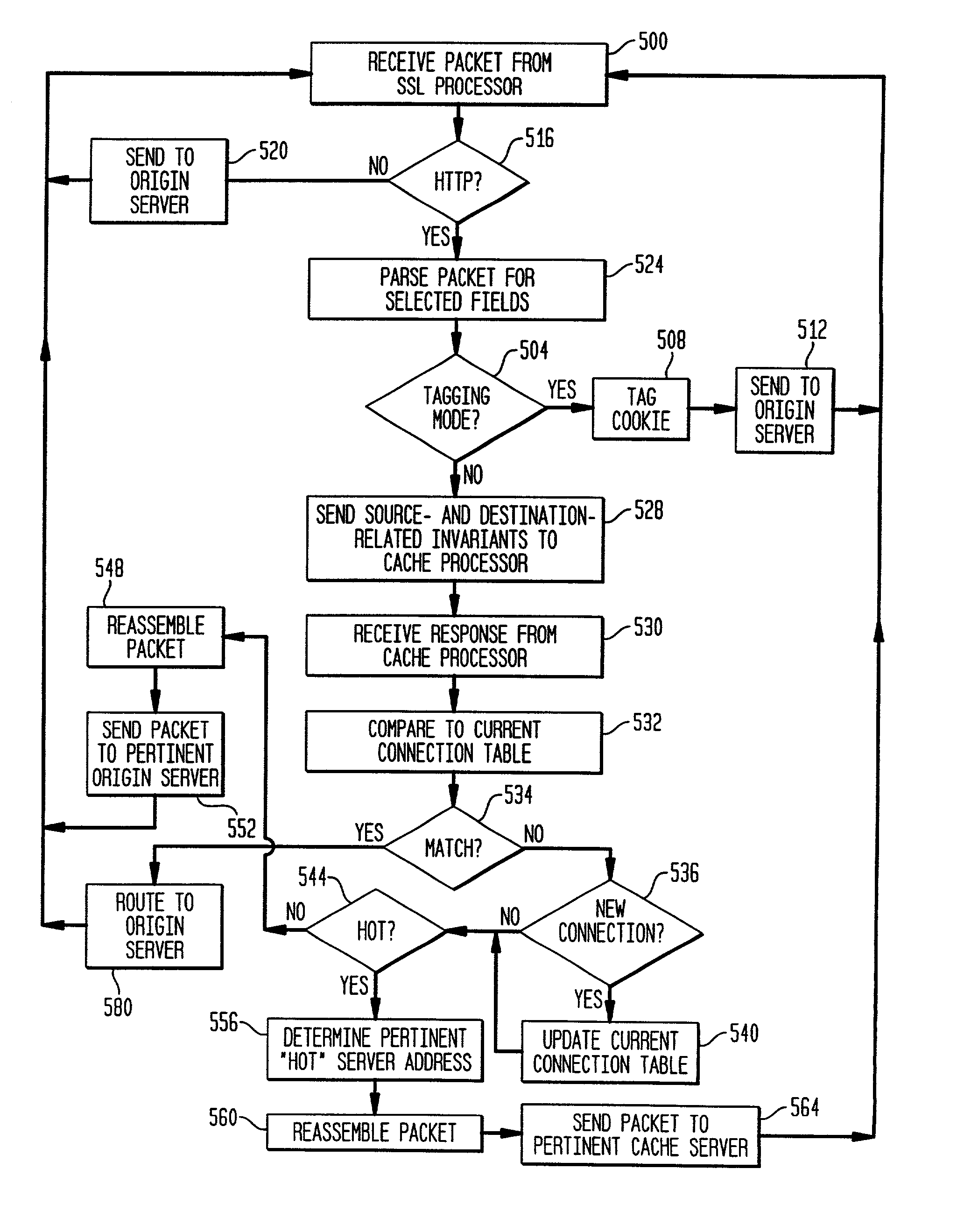
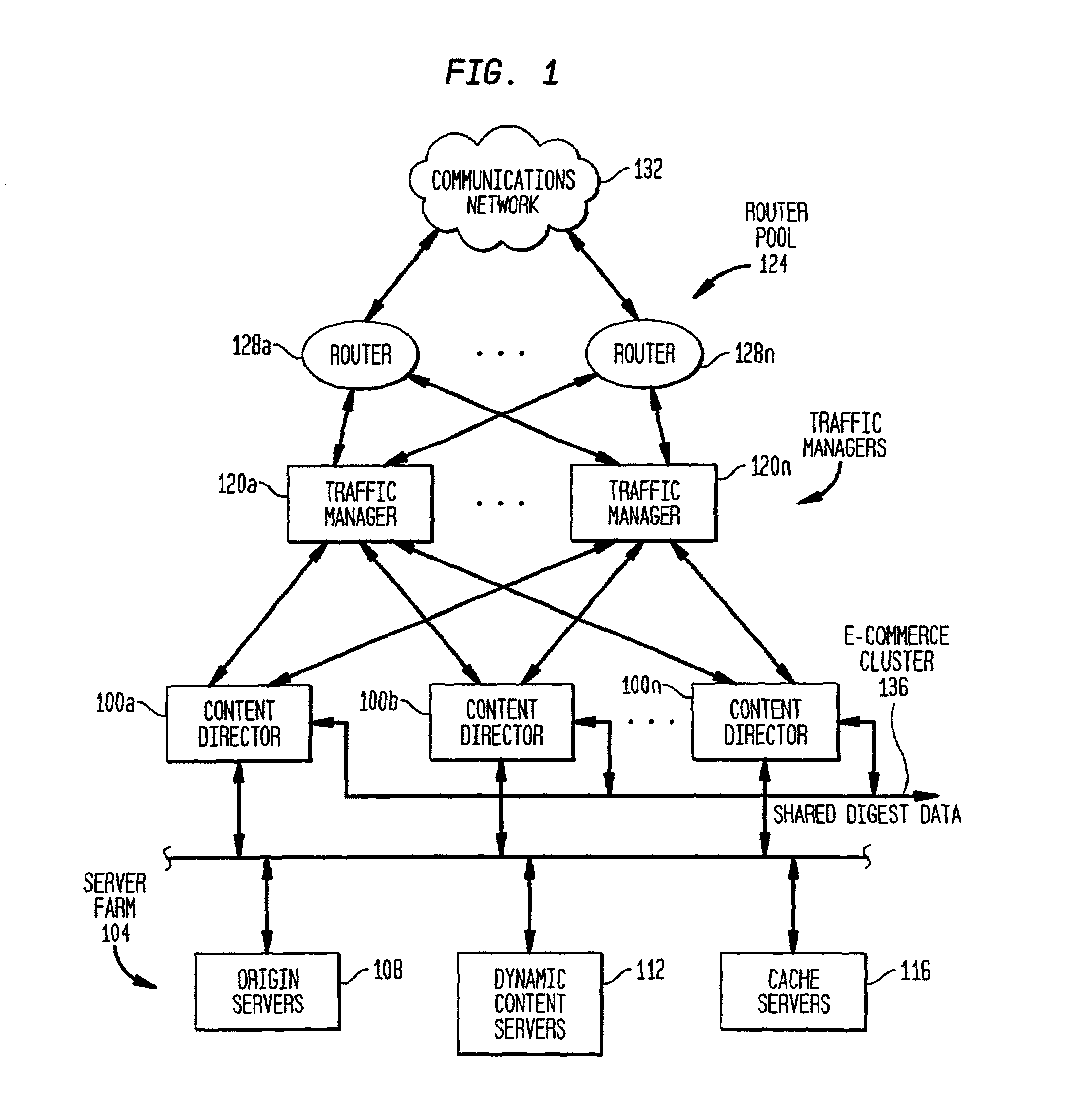
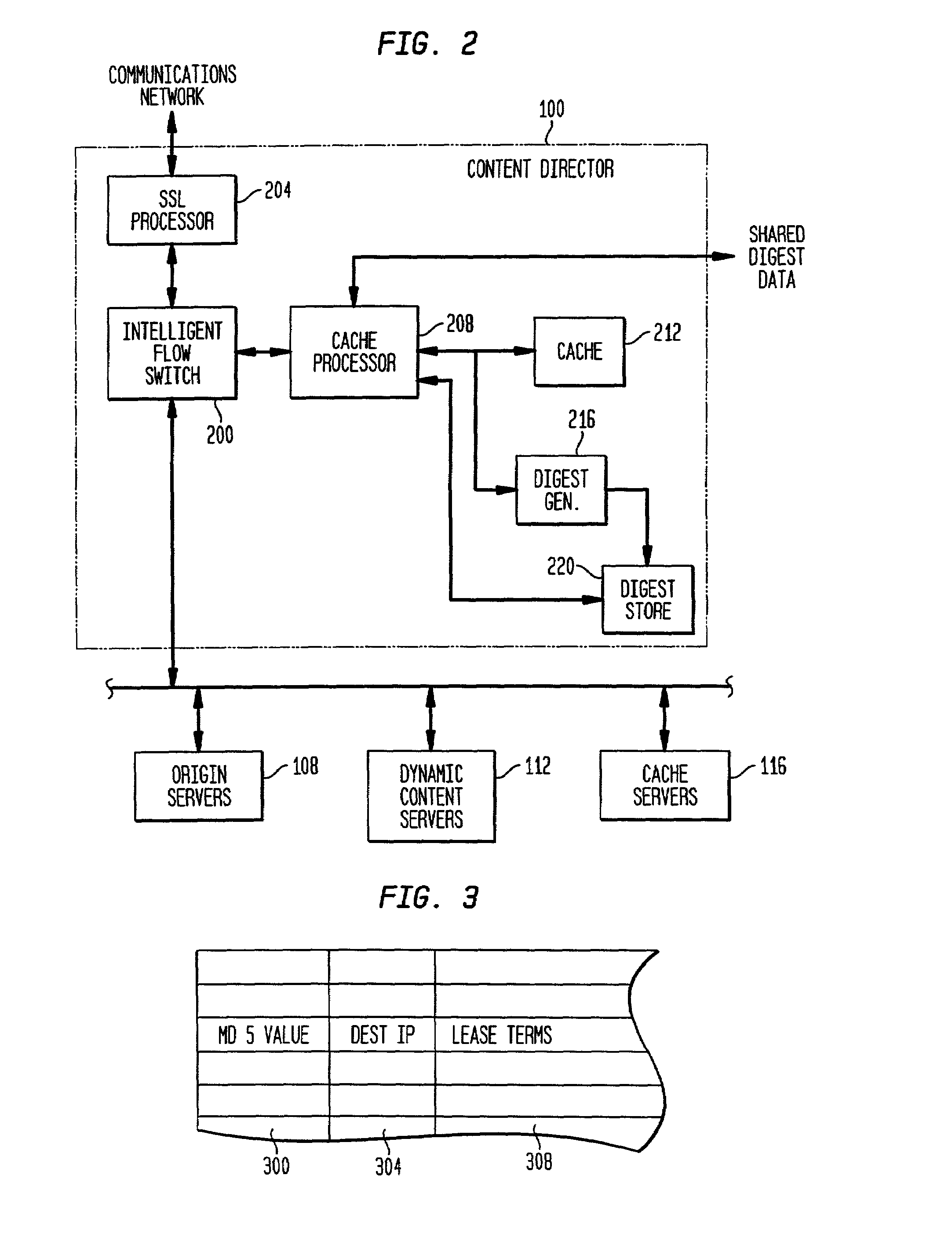
Patents
Literature
356results about How to "Improve cache hit ratio" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
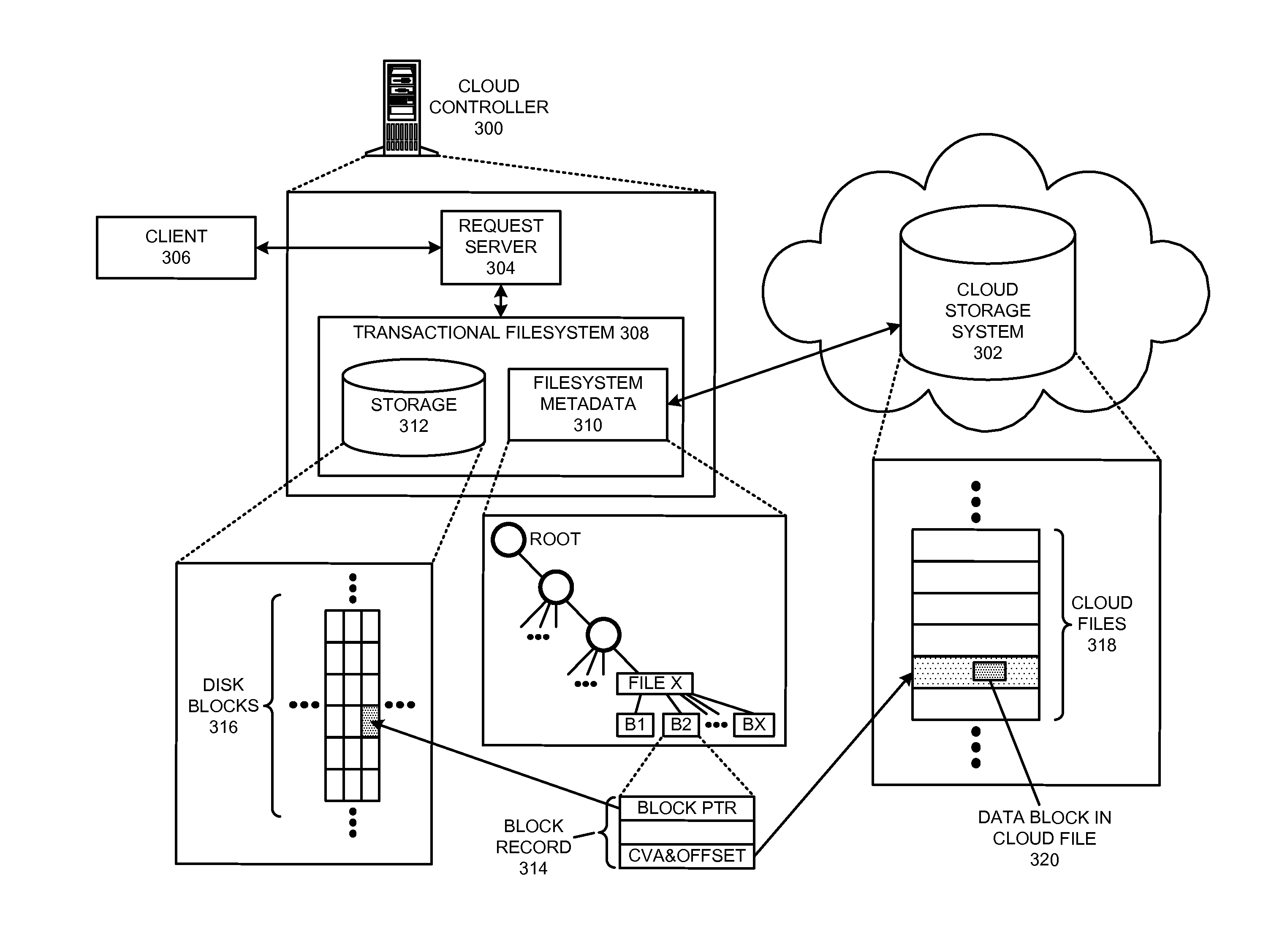
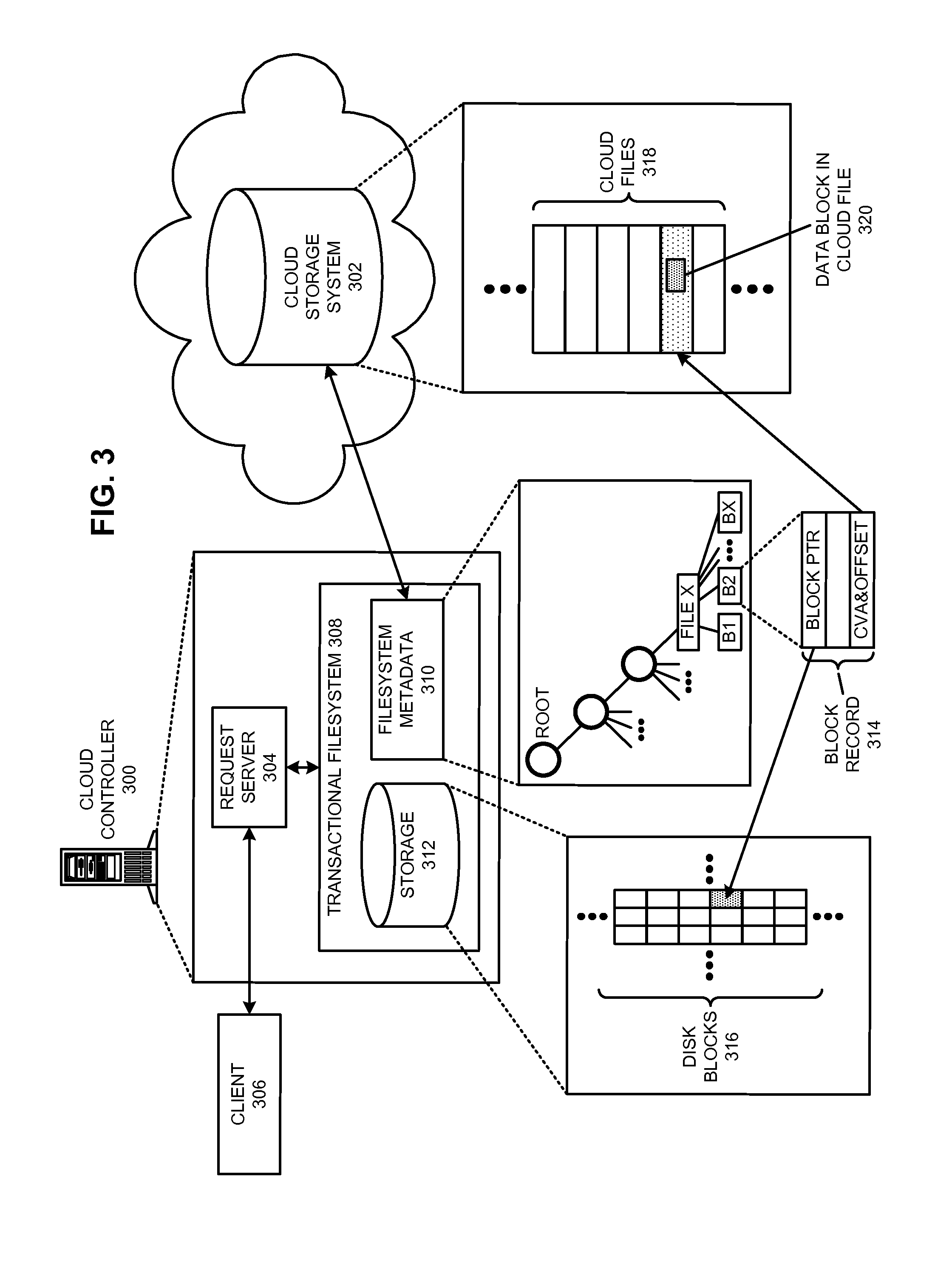
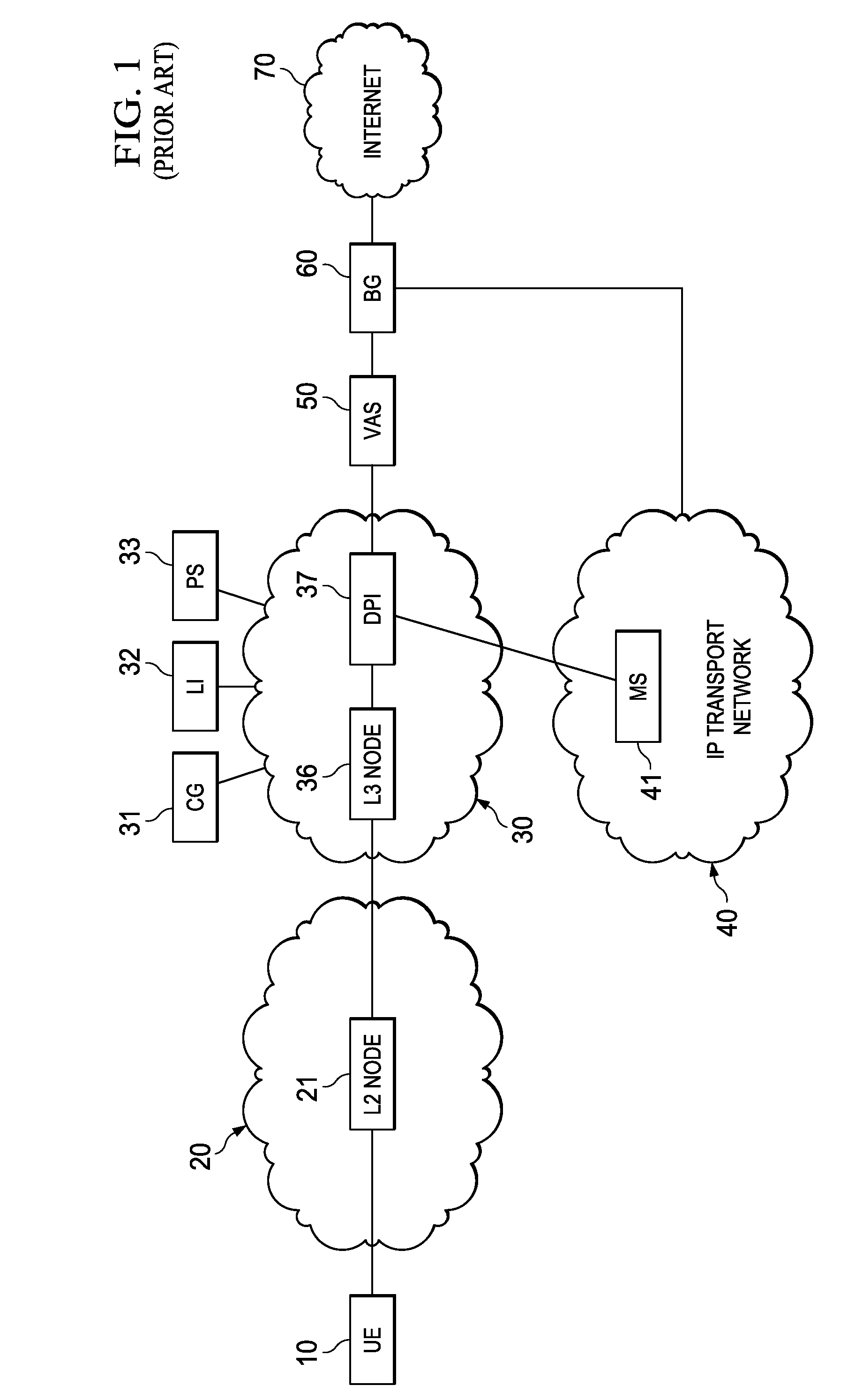
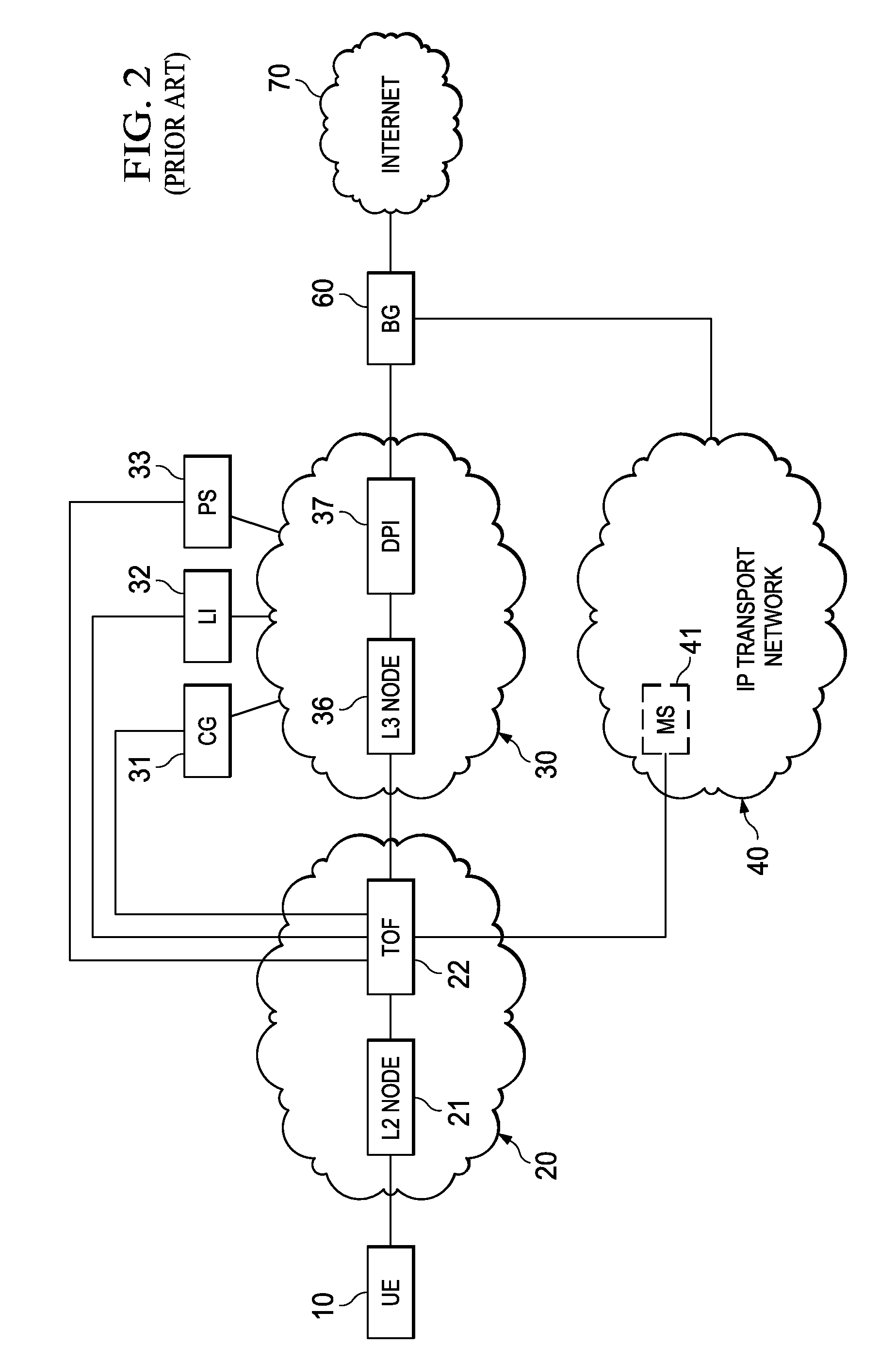
Managing a global namespace for a distributed filesystem
ActiveUS20140006465A1Outweigh additional overheadIncreasing file access performanceDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsFile systemCloud storage system
The disclosed embodiments disclose techniques for managing a global namespace for a distributed filesystem. Two or more cloud controllers collectively manage distributed filesystem data that is stored in a cloud storage system; the cloud controllers ensure data consistency for the stored data, and each cloud controller caches portions of the distributed filesystem. Furthermore, a global namespace for the distributed filesystem is also split across these cloud controllers, with each cloud controller “owning” (e.g., managing write accesses for) a distinct portion of the global namespace and maintaining a set of namespace mappings that indicate which portion of the namespace is assigned to each cloud controller. During operation, an initial cloud controller receives a request from a client system to access a target file in the distributed system. This initial cloud controller uses the namespace mappings for the global namespace to determine a preferred cloud controller that will handle the request.
Owner:PANZURA LLC
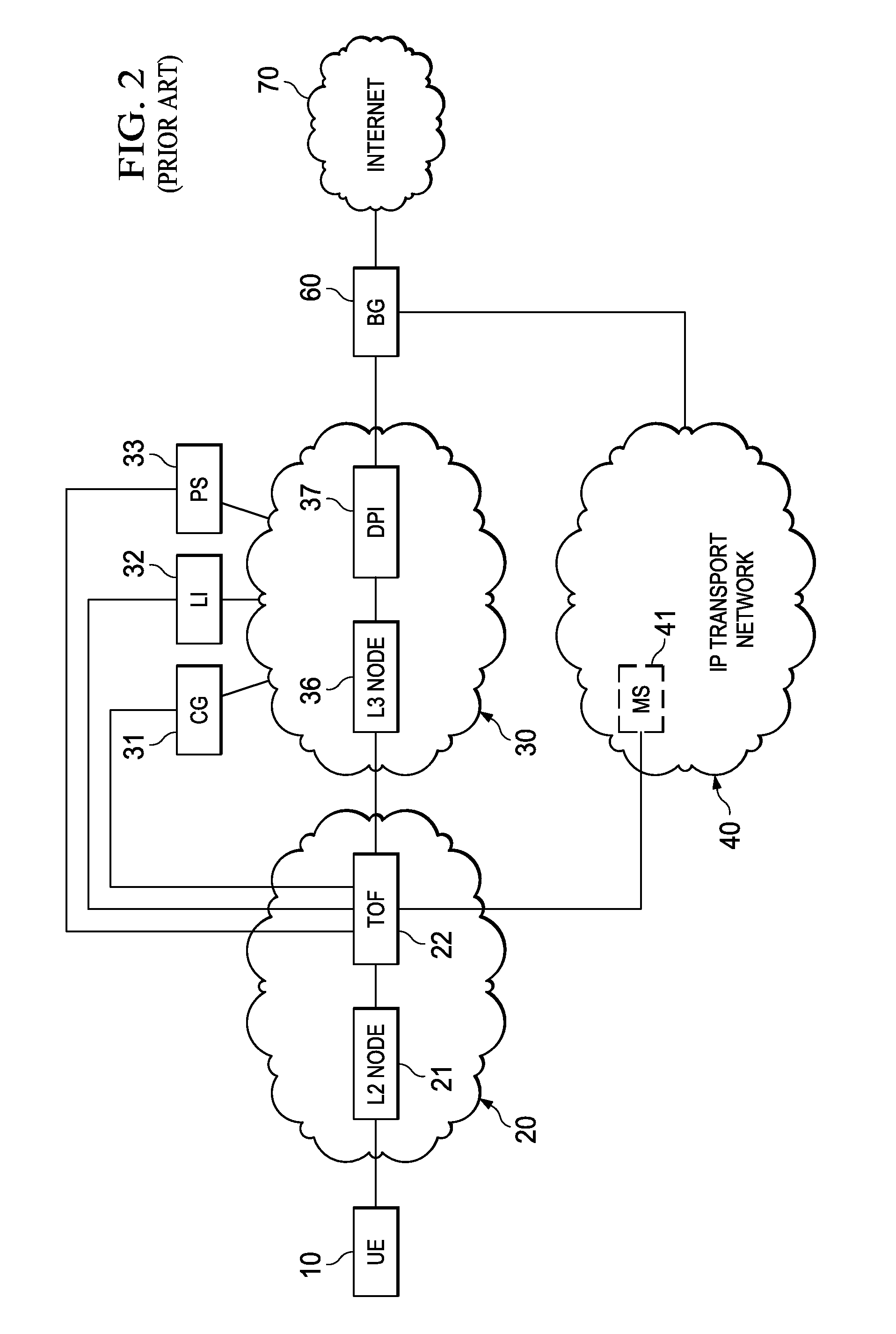
System, Apparatus for Content Delivery for Internet Traffic and Methods Thereof
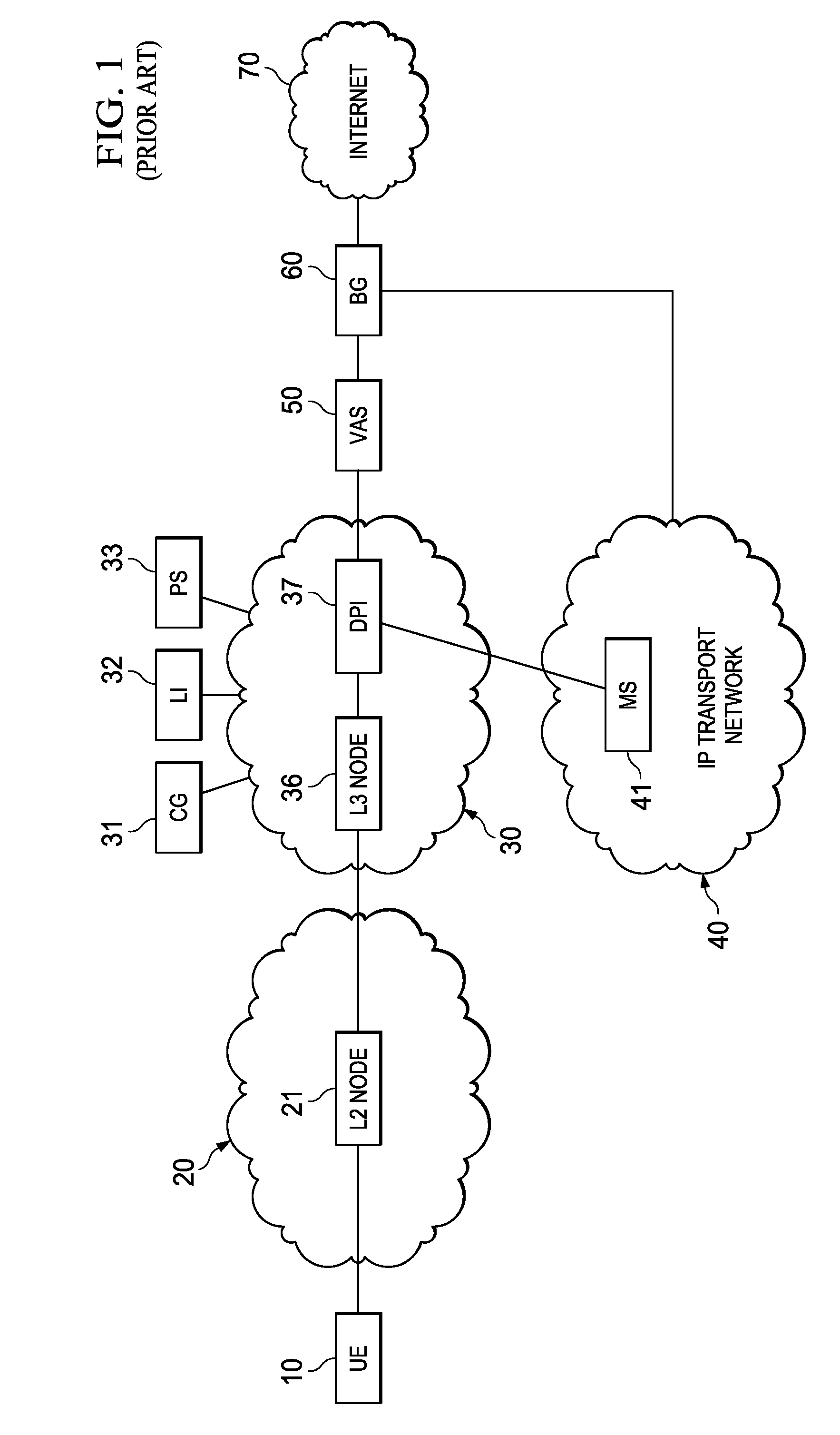
ActiveUS20110280143A1Effective decouplingImprove cache hit ratioDigital data information retrievalMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsAccess networkInternet traffic
In one embodiment, a method of serving media includes receiving a delivery log of traffic use after every first time interval for an user equipment. The user equipment is part of a hot billing class of users. The traffic use comprises data usage by the user equipment during communication with a media server in a layer2 access network. A user traffic information computed from the delivery log is transmitted to a billing center. A account status information is received from the billing center. The account status information is received if the user equipment exceeds a user account metric. A session termination information based on the account status information is transmitted.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
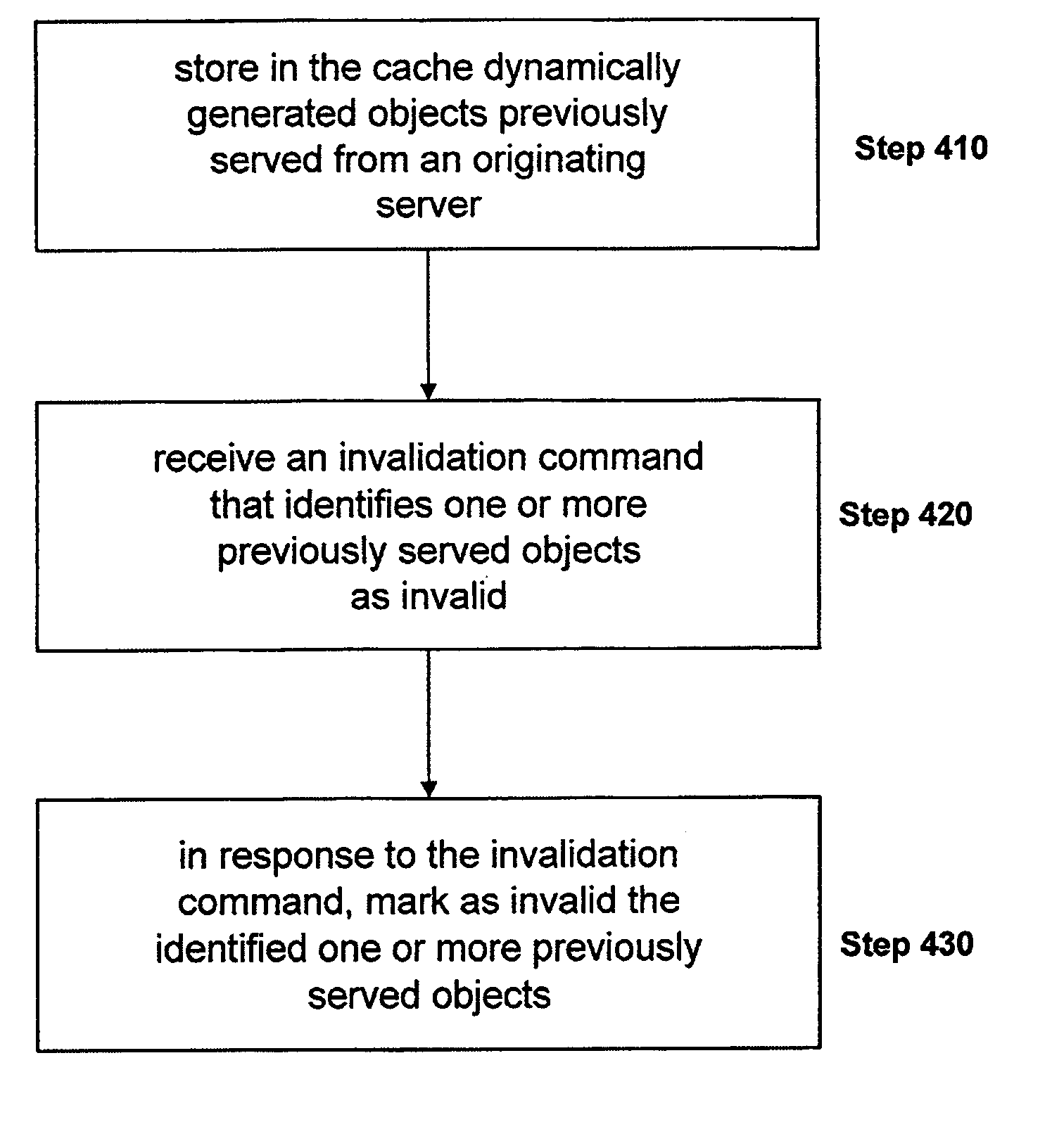
System and method for performing flash caching of dynamically generated objects in a data communication network
ActiveUS20070156876A1Improve cache hit ratioQuick changeMultiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsObject storeClient-side
The present invention is directed towards a method and system for providing a technique referred to as flash caching to respond to requests for an object, such as a dynamically generated object, from multiple clients. This technique of the present invention uses a dynamically generated object stored in a buffer for transmission to a client, for example in response to a request from the client, to also respond to additional requests for the dynamically generated object from other clients while the object is stored in the buffer. Using this technique, the present invention is able to increase cache hit rates for extremely fast changing dynamically generated objects that may not otherwise be cacheable.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Non-intrusive multiplexed transaction persistency in secure commerce environments
InactiveUS7177945B2Efficiently cachedEfficiently segregatedDigital computer detailsData switching by path configurationMultiplexingCache server
The present invention is directed to a network switch that determines when specific content is hot and directs flow to one or more cache servers. The architecture of the present invention includes a decryption processor for authenticating clients and decrypting and encrypting transaction requests before the transaction requests are routed by the switch.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
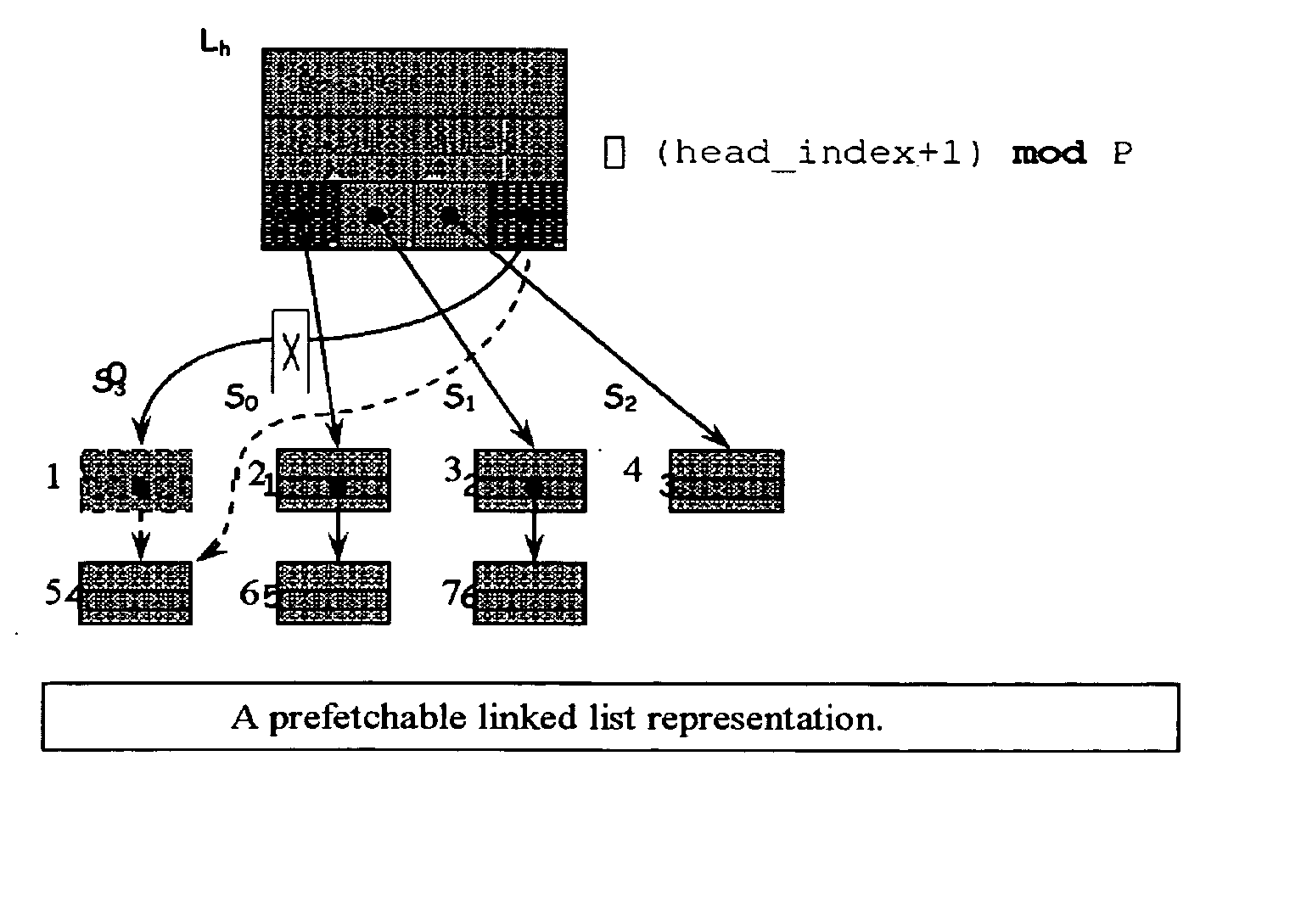
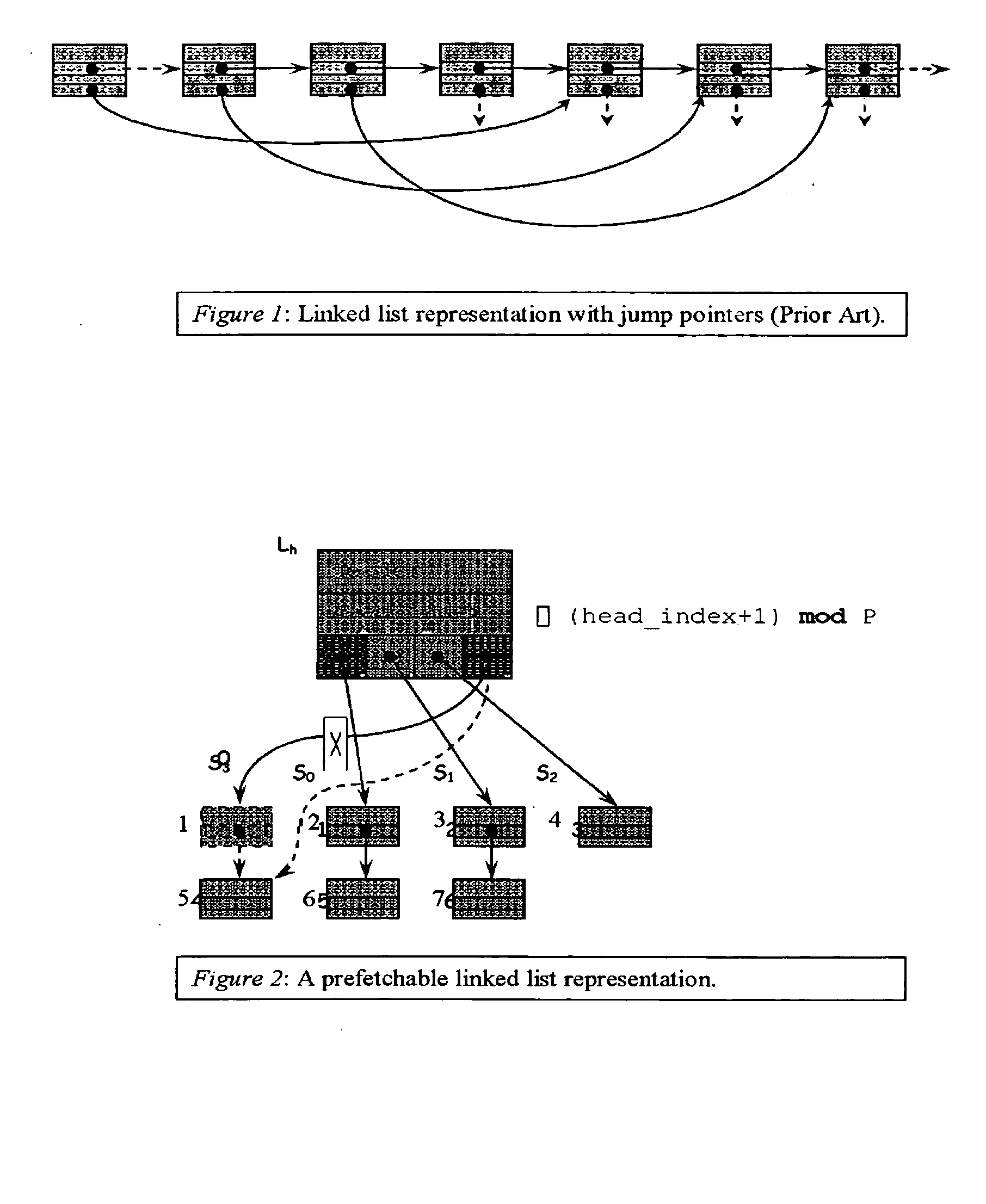
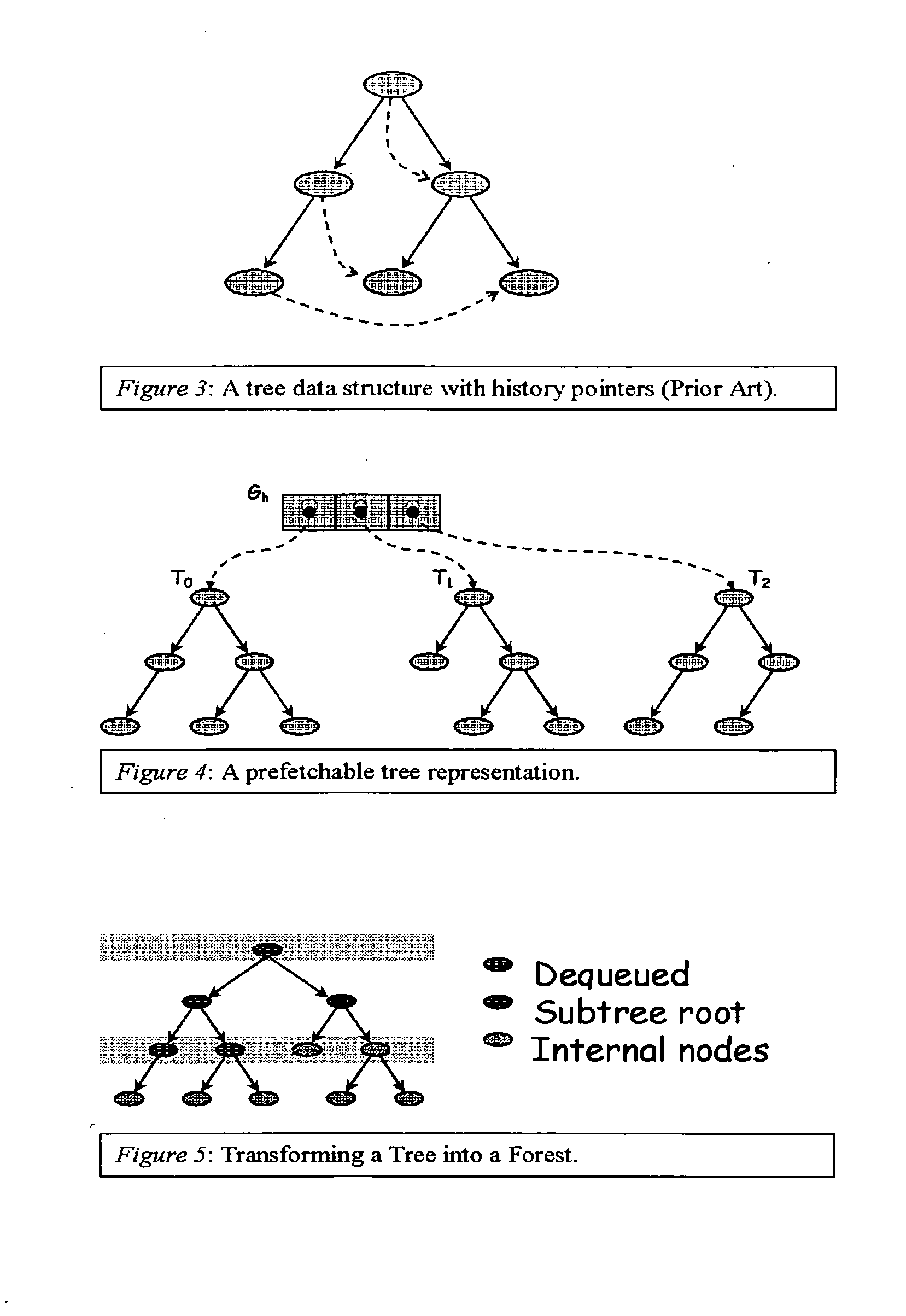
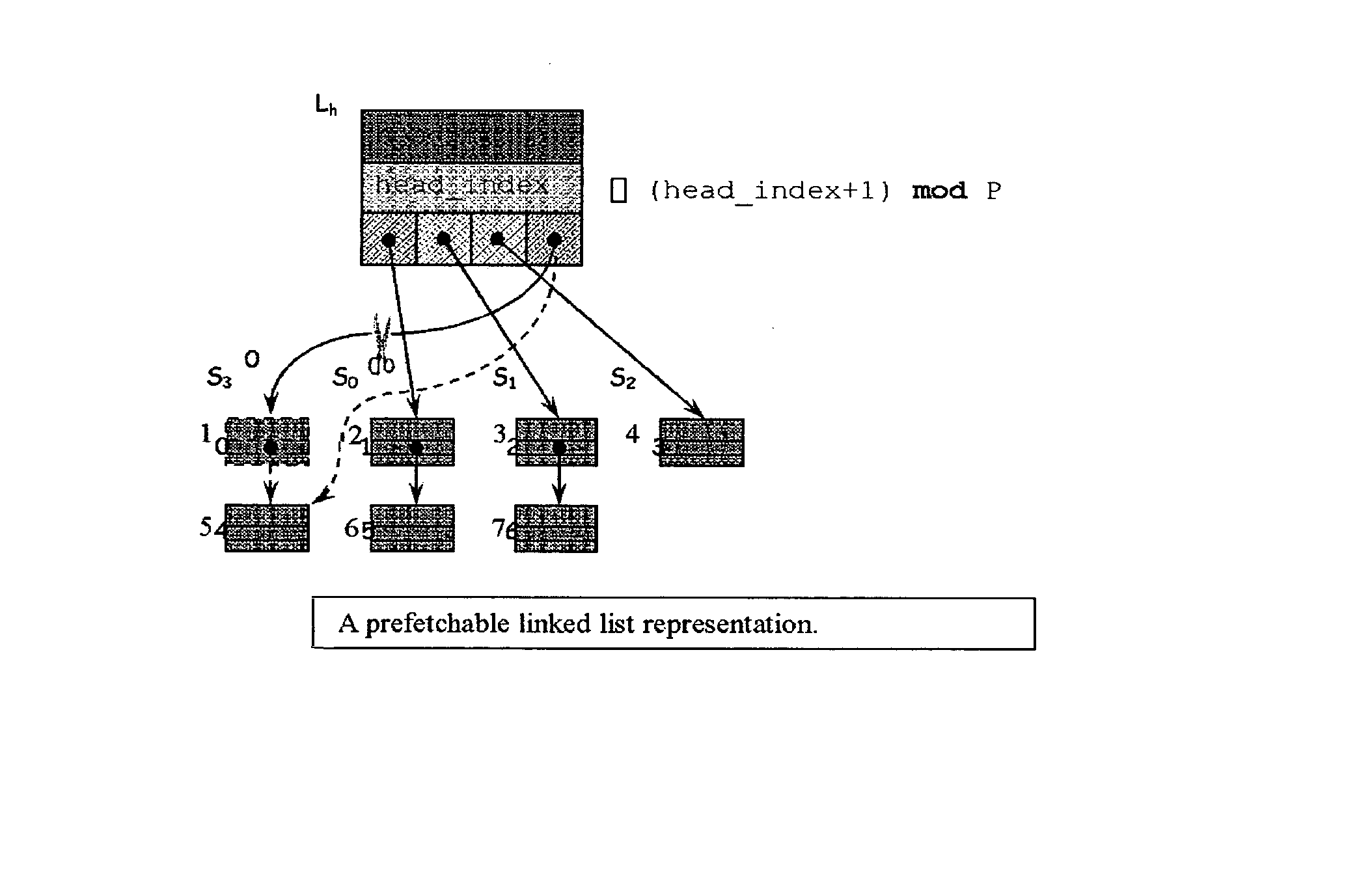
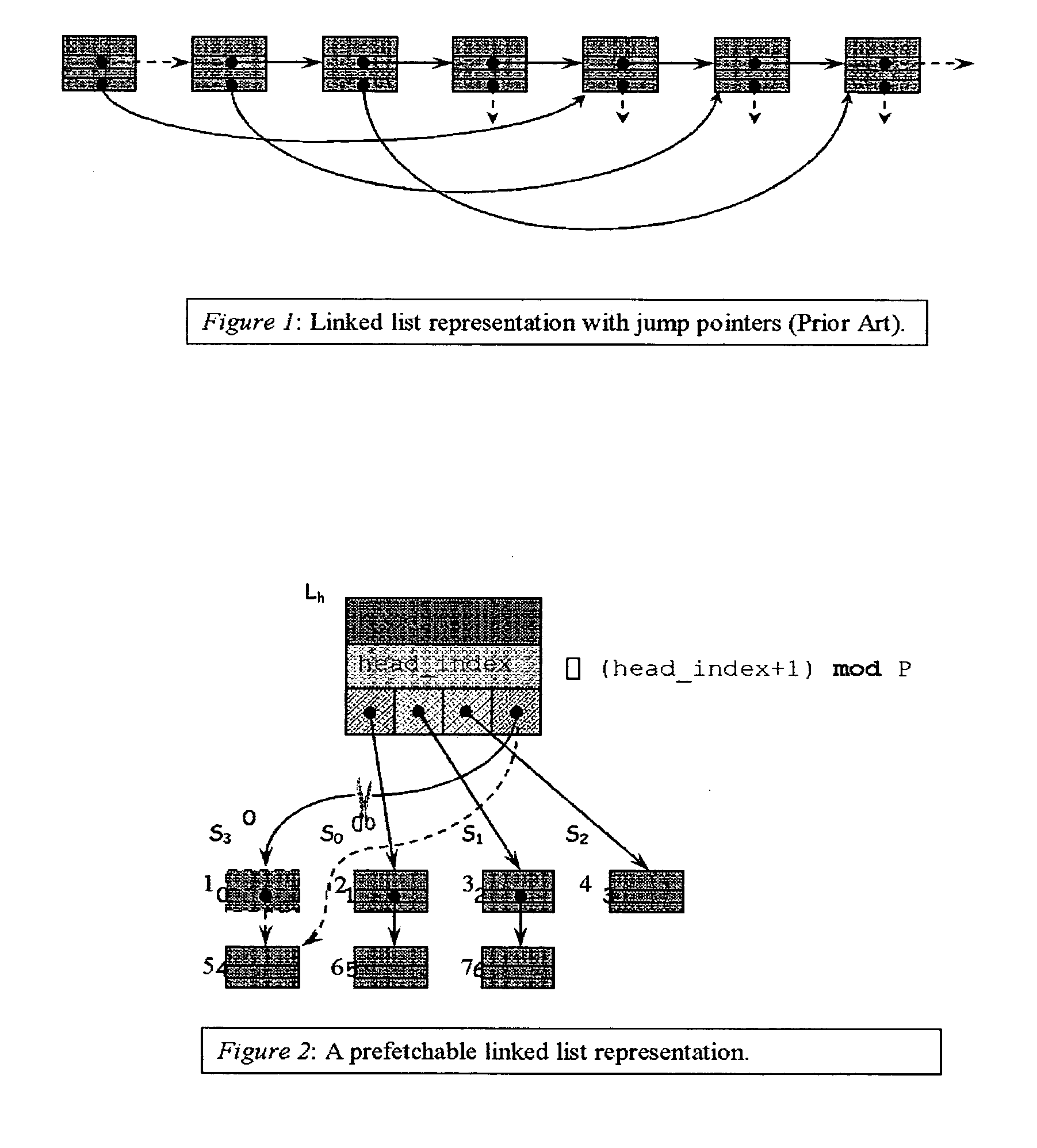
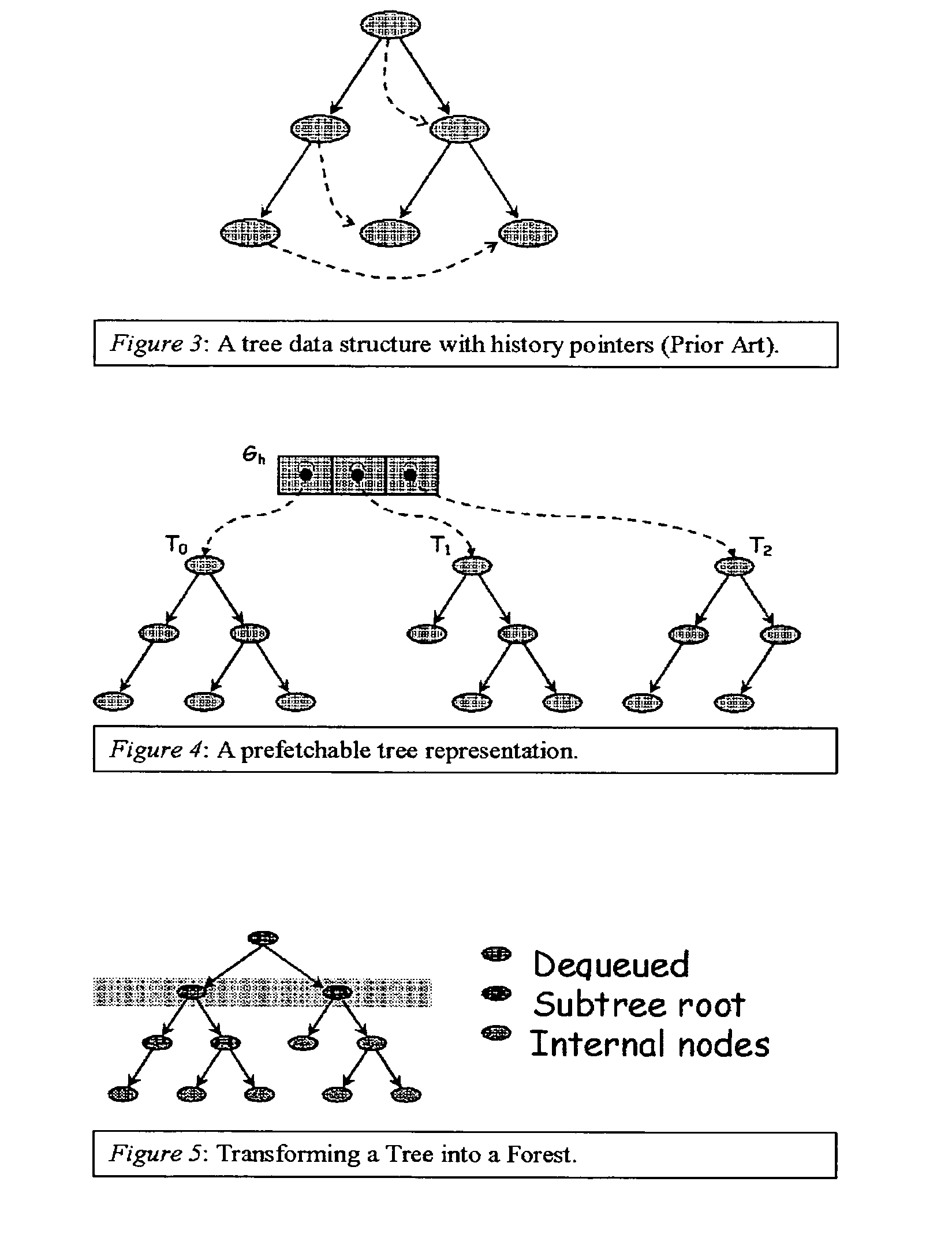
Method for prefetching recursive data structure traversals
InactiveUS20050102294A1Improve cache hit ratioPotential throughput of the computer systemDigital data information retrievalData processing applicationsOperational systemTerm memory
Computer systems are typically designed with multiple levels of memory hierarchy. Prefetching has been employed to overcome the latency of fetching data or instructions from or to memory. Prefetching works well for data structures with regular memory access patterns, but less so for data structures such as trees, hash tables, and other structures in which the datum that will be used is not known a priori. In modern transaction processing systems, database servers, operating systems, and other commercial and engineering applications, information is frequently organized in trees, graphs, and linked lists. Lack of spatial locality results in a high probability that a miss will be incurred at each cache in the memory hierarchy. Each cache miss causes the processor to stall while the referenced value is fetched from lower levels of the memory hierarchy. Because this is likely to be the case for a significant fraction of the nodes traversed in the data structure, processor utilization suffers. The inability to compute the address of the next address to be referenced makes prefetching difficult in such applications. The invention allows compilers and / or programmers to restructure data structures and traversals so that pointers are dereferenced in a pipelined manner, thereby making it possible to schedule prefetch operations in a consistent fashion. The present invention significantly increases the cache hit rates of many important data structure traversals, and thereby the potential throughput of the computer system and application in which it is employed. For data structure traversals in which the traversal path may be predetermined, a transformation is performed on the data structure that permits references to nodes that will be traversed in the future be computed sufficiently far in advance to prefetch the data into cache.
Owner:DIGITAL CACHE LLC
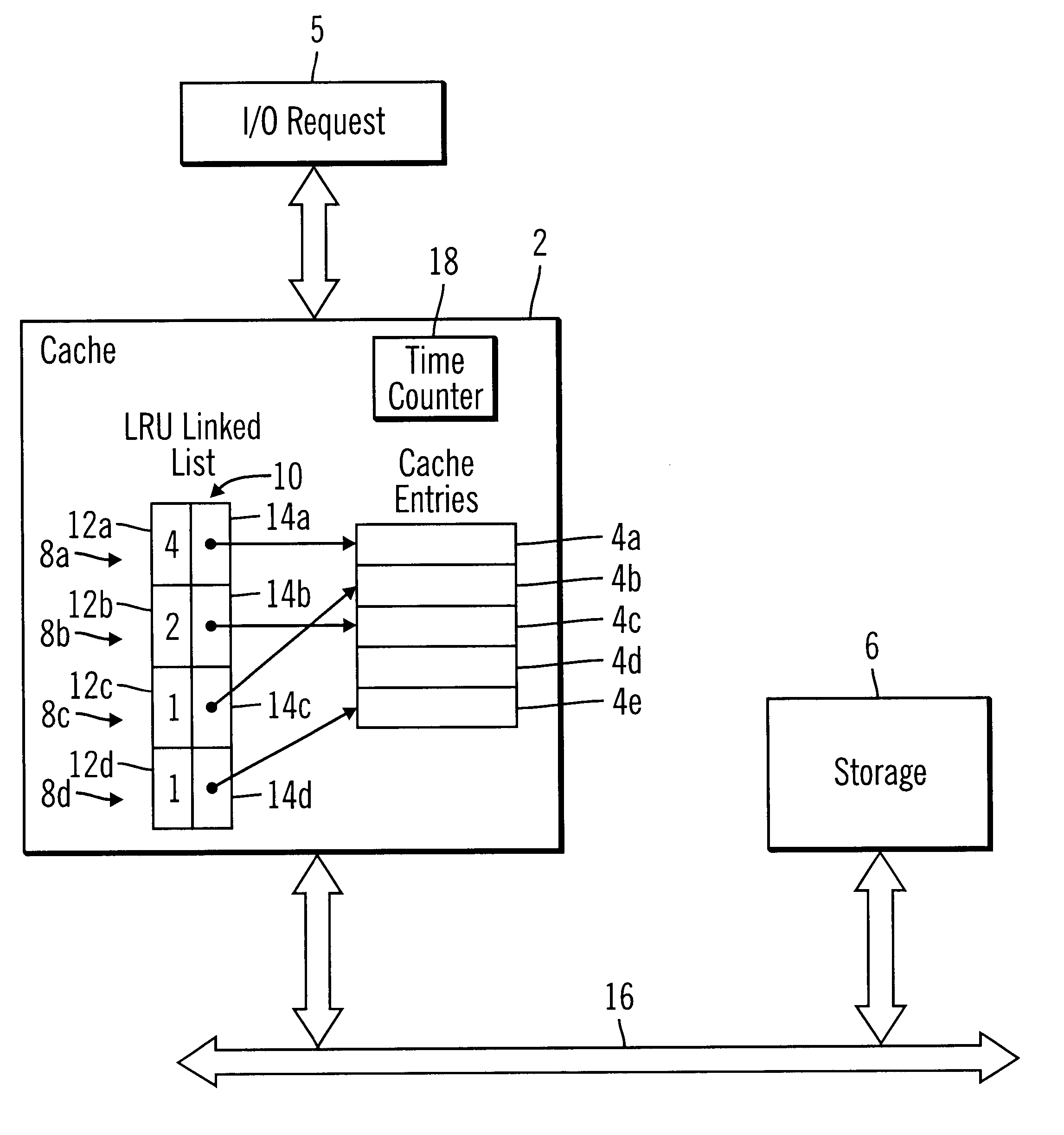
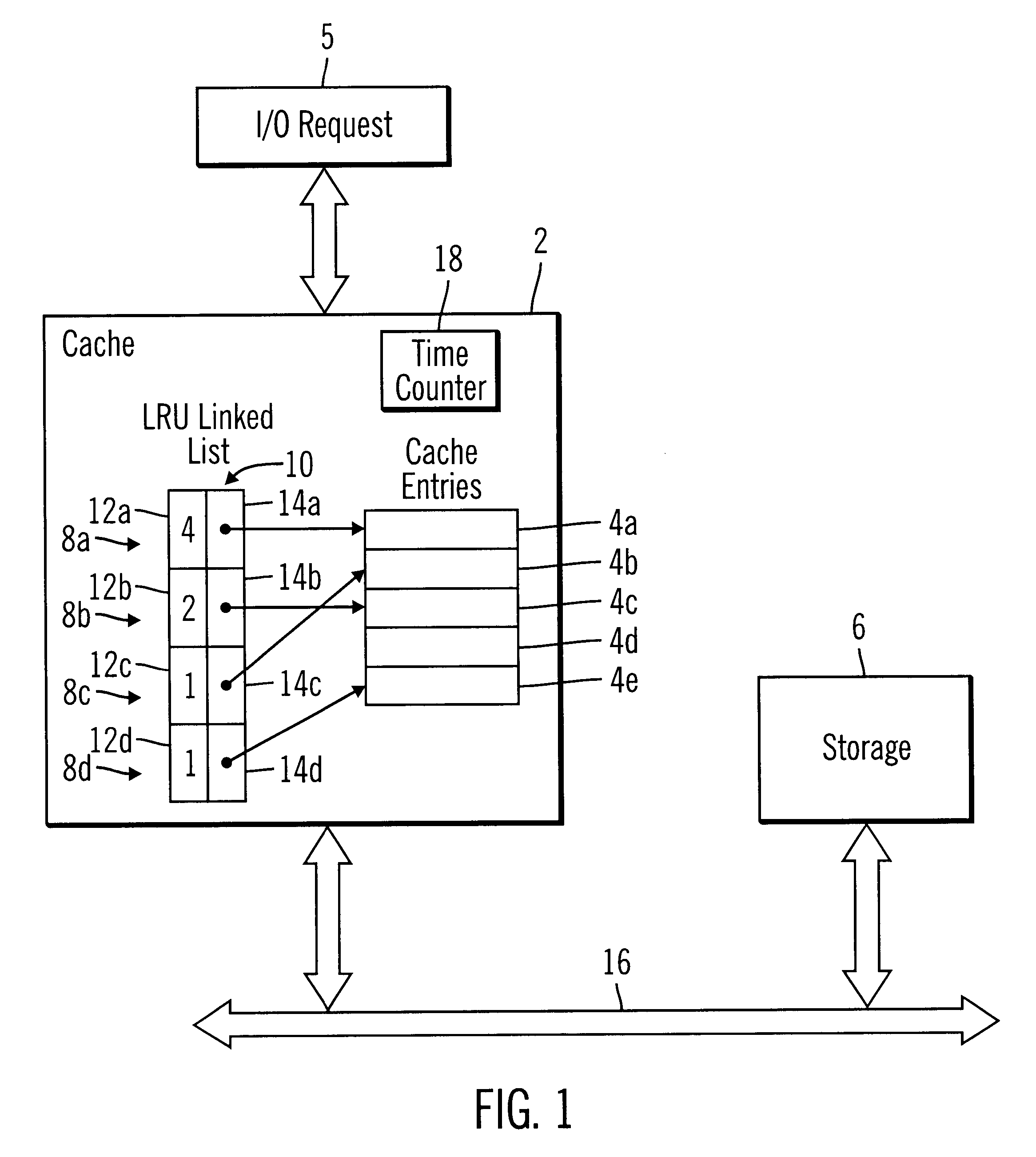
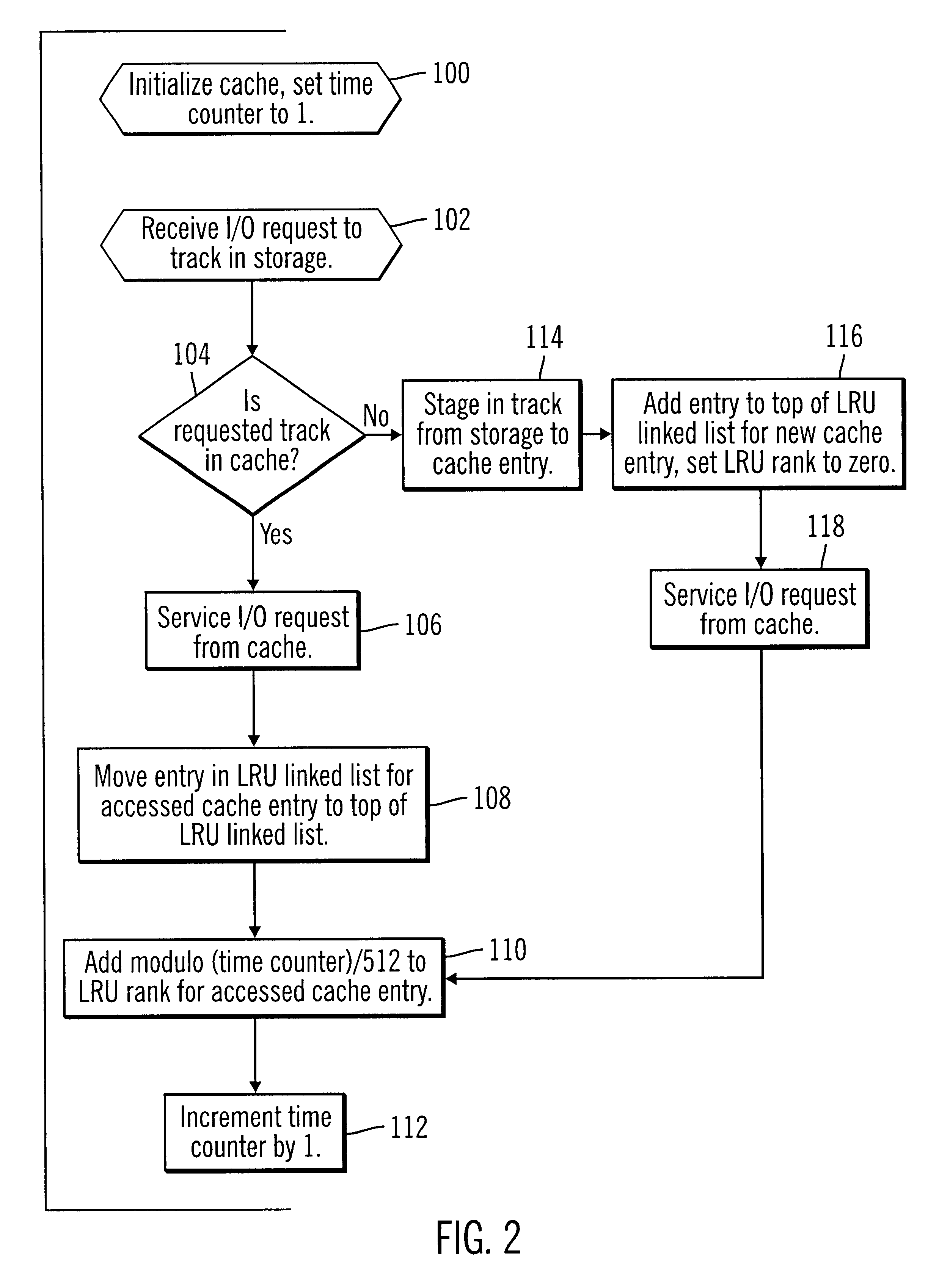
Method, system, and program for demoting data from cache based on least recently accessed and least frequently accessed data
InactiveUS6738865B1Improve cache hit ratioRaise the possibilityMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMicro-instruction address formationParallel computingVolatile memory
Disclosed is a method, system, and program for caching data. Data from a device, such as a volatile memory device or non-volatile storage device, is maintained in entries in a cache. For each entry in cache, a variable indicates both a time when the cache entry was last accessed and a frequency of accesses to the cache entry.The variable is used in determining which entry to denote from cache to make room for subsequent entries.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
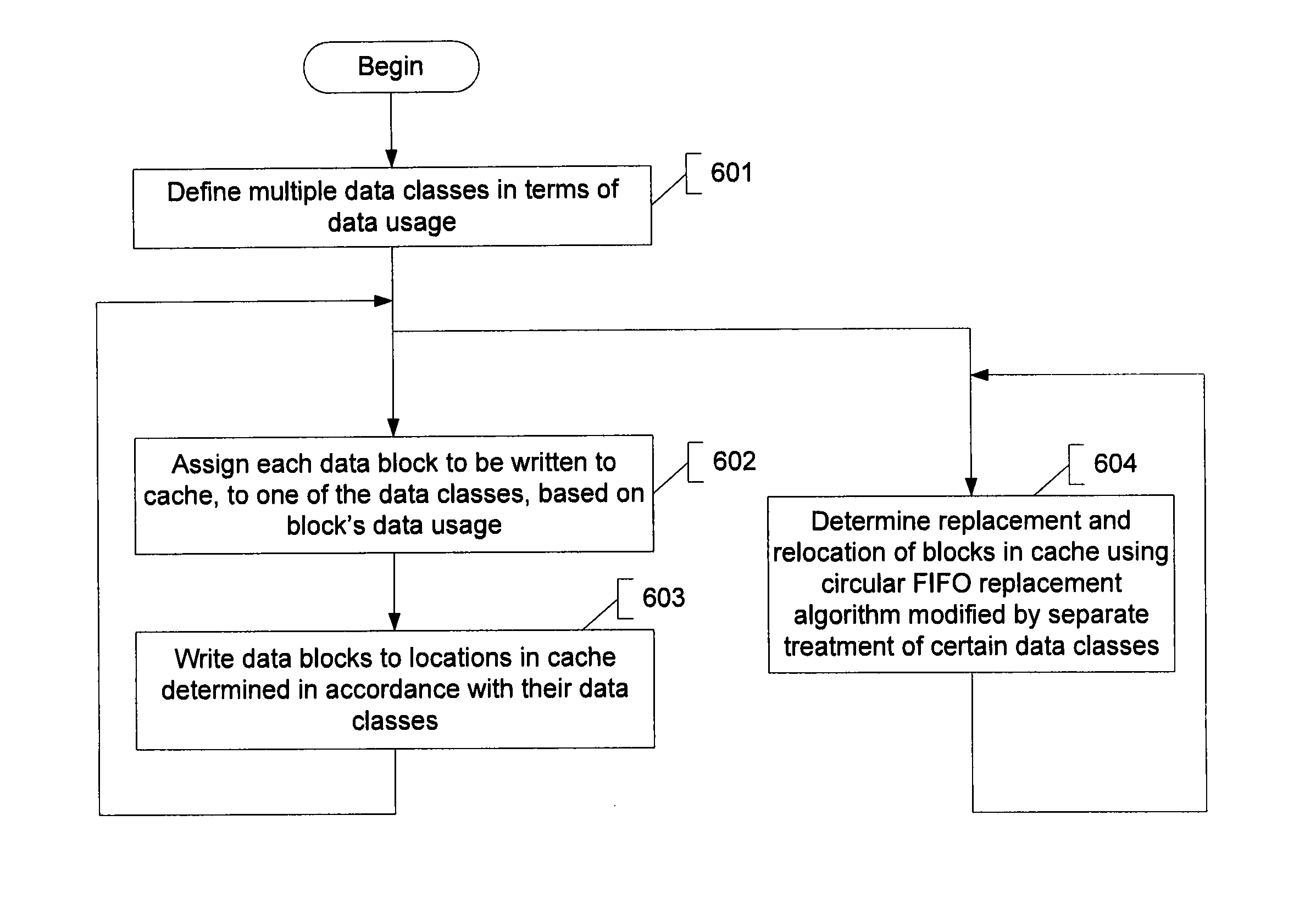
Concurrent content management and wear optimization for a non-volatile solid-state cache
ActiveUS8621145B1Good wear levelingImprove caching capacityMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationParallel computingContent management
Described is a technique for managing the content of a nonvolatile solid-state memory data cache to improve cache performance while at the same time, and in a complementary manner, providing for automatic wear leveling. A modified circular first-in first-out (FIFO) log / algorithm is generally used to determine cache content replacement. The algorithm is used as the default mechanism for determining cache content to be replaced when the cache is full but is subject to modification in some instances. In particular, data are categorized according to different data classes prior to being written to the cache, based on usage. Once cached, data belonging to certain classes are treated differently than the circular FIFO replacement algorithm would dictate. Further, data belonging to each class are localized to designated regions within the cache.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Mixed storage system and method for supporting solid-state disk cache dynamic distribution
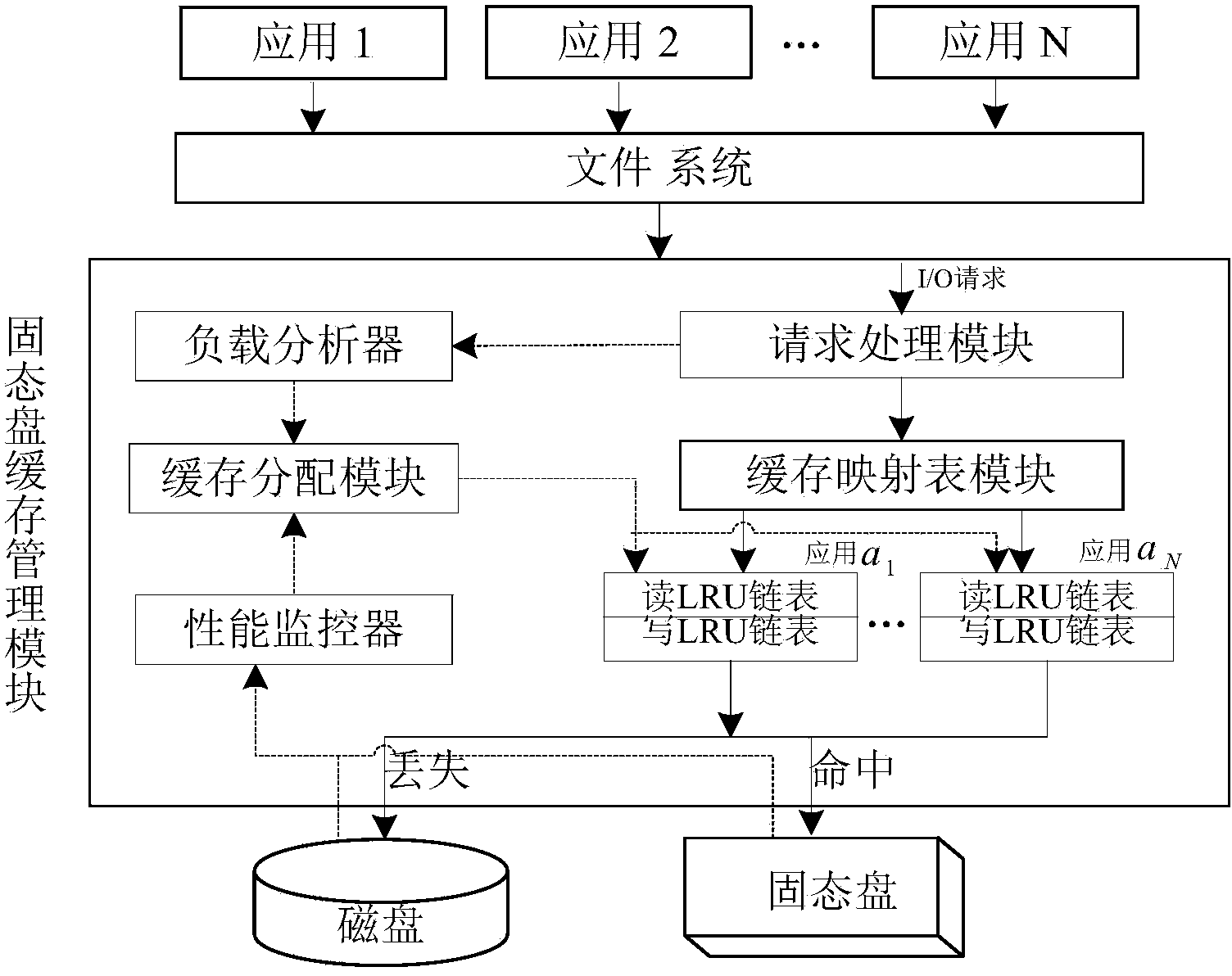
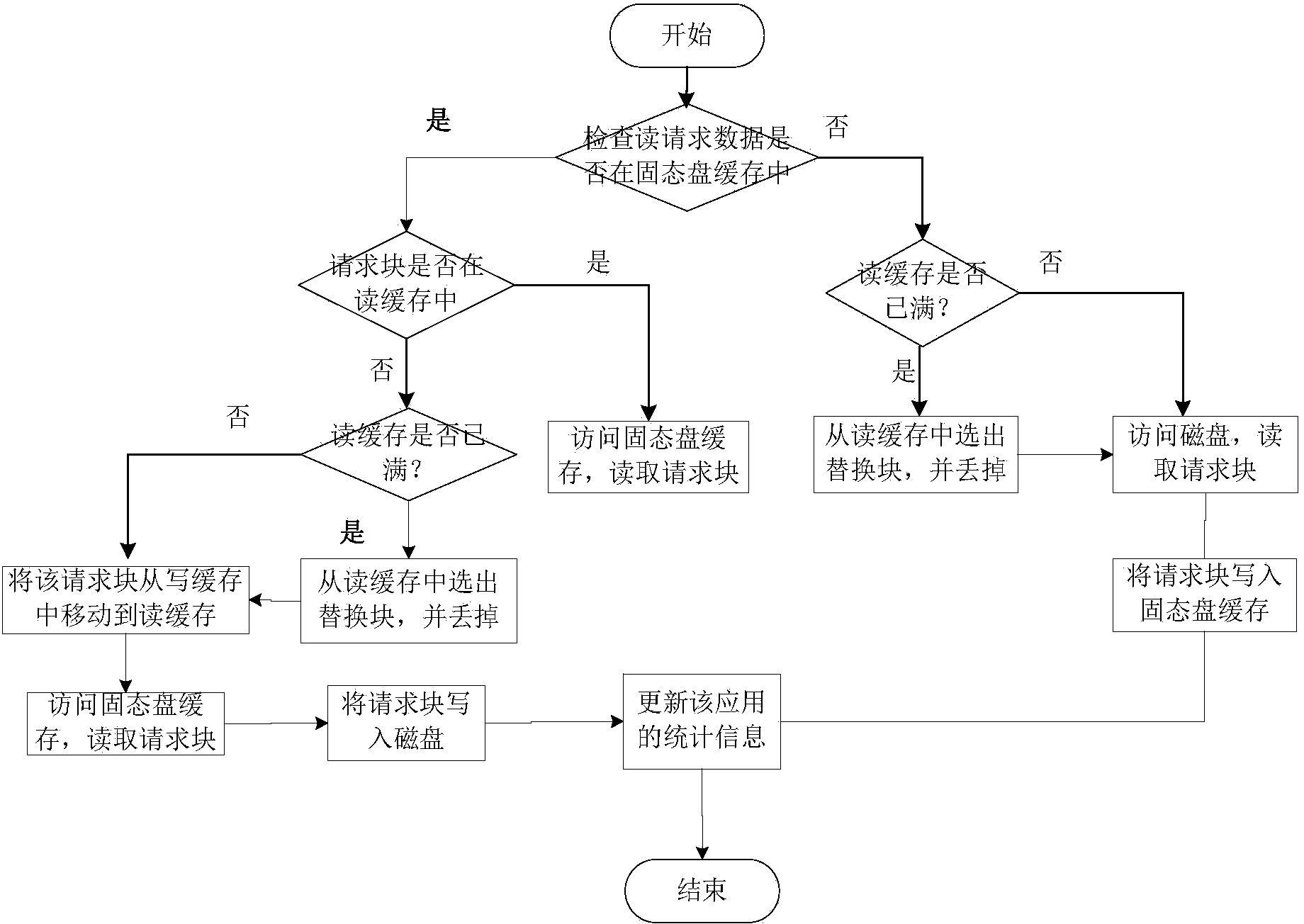
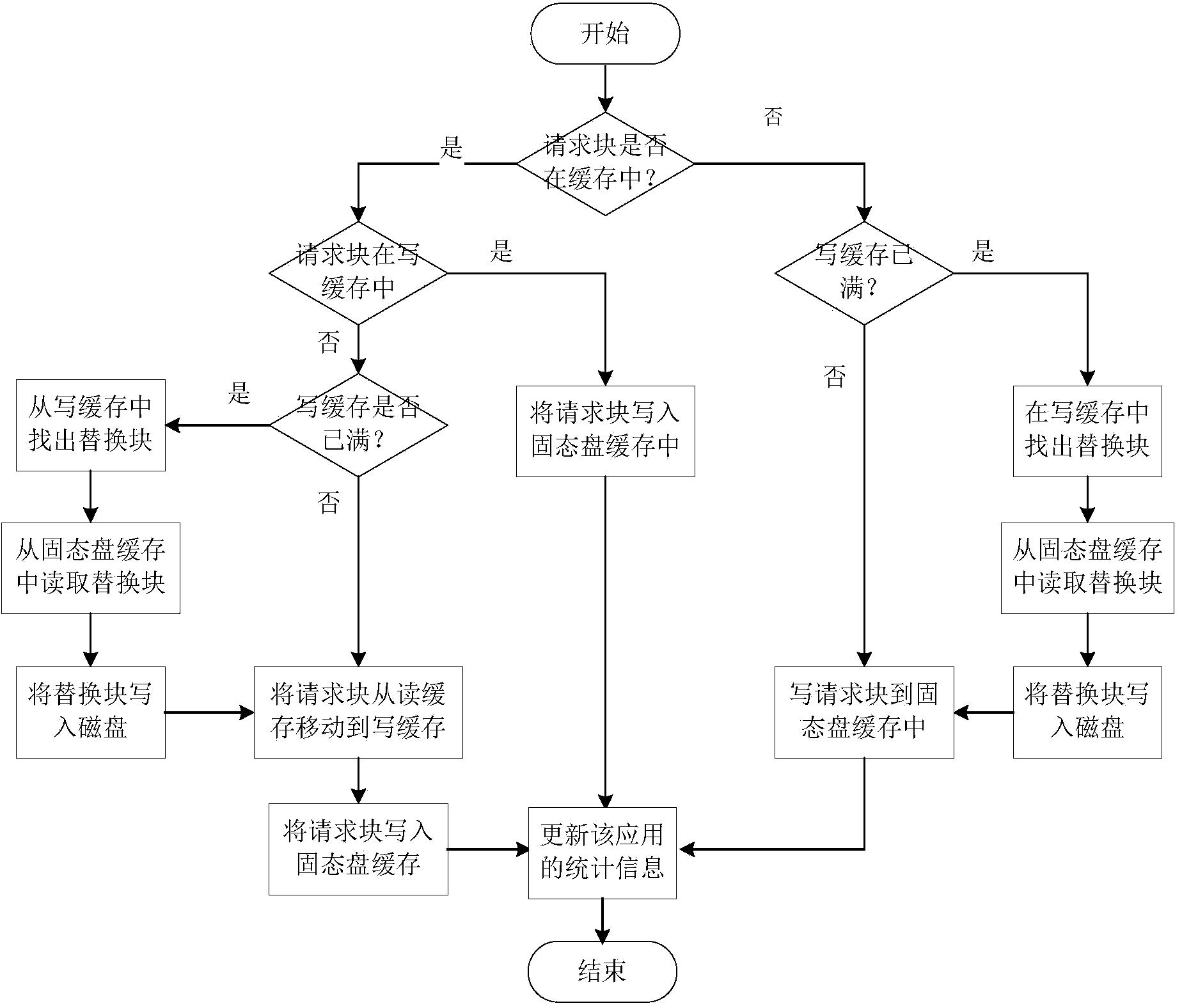
ActiveCN103902474AEfficient use ofAvoid performance degradationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDifferentiated servicesDirty data
The invention provides a mixed storage system and method for supporting solid-state disk cache dynamic distribution. The mixed storage method is characterized in that the mixed storage system is constructed through a solid-state disk and a magnetic disk, and the solid-state disk serves as a cache of the magnetic disk; the load characteristics of applications and the cache hit ratio of the solid-state disk are monitored in real time, performance models of the applications are built, and the cache space of the solid-state disk is dynamically distributed according to the performance requirements of the applications and changes of the load characteristics. According to the solid-state disk cache management method, the cache space of the solid-state disk can be reasonably distributed according to the performance requirements of the applications, and an application-level cache partition service is achieved; due to the fact that the cache space of the solid-state disk of the applications is further divided into a cache reading section and a cache writing section, dirty data blocks and the page copying and rubbish recycling cost caused by the dirty data blocks are reduced; meanwhile, the idle cache space of the solid-state disk is distributed to the applications according to the cache use efficiency of the applications, and therefore the cache hit ratio of the solid-state disk of the mixed storage system and the overall performance of the mixed storage system are improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
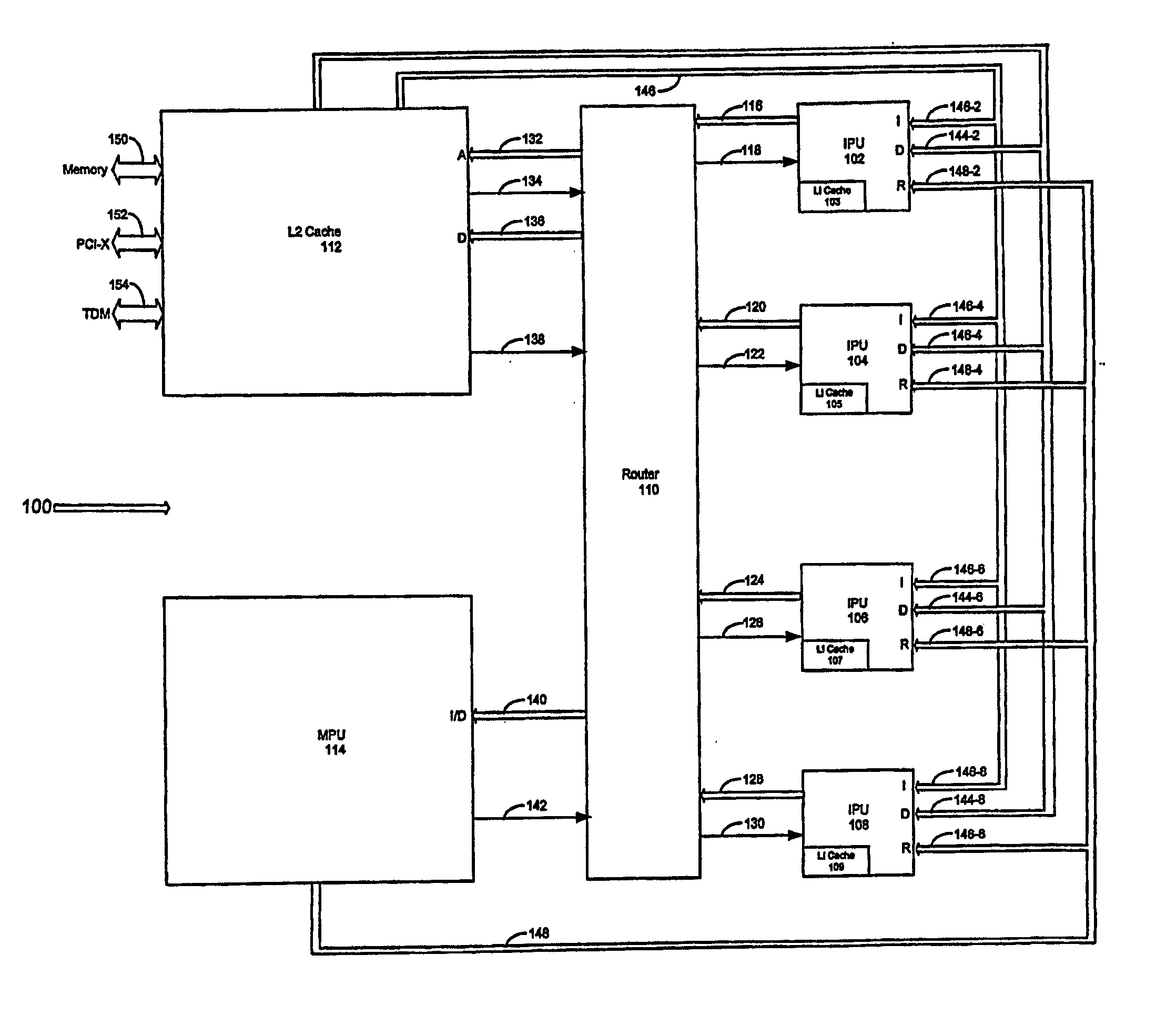
Apparatus, method and system for a synchronicity independent, resource delegating, power and instruction optimizing processor
InactiveUS20050235134A1Improve cache hit ratioMemory architecture accessing/allocationResource allocationLogical operationsPower usage
An apparatus, method, and system for synchronicity independent, resource delegating, power and instruction optimizing processor is provided where instructions are delegated between various processing resources of the processor. An Integer Processing Unit (IPU) of the processor delegates complicated mathematical instructions to a Mathematical Processing Unit (MPU) of the processor. Furthermore, the processor puts underutilized processing resources to sleep thereby increasing power usage efficiency. A cache of the processor is also capable of accepting delegated operations from the IPU. As such, the cache performs various logical operations on delegated requests allowing it to lock and share memory without requiring extra processing cycles by the entire processor. With the processor, execution instructions are optimized reducing the complexity of the processor, throughput is increased as delegation to multiple processing resources is scalable, and power usage efficacy is increased as underutilized and / or waiting processing resources may sleep when not active.
Owner:MMAGIX TECH
System, Apparatus for Content Delivery for Internet Traffic and Methods Thereof
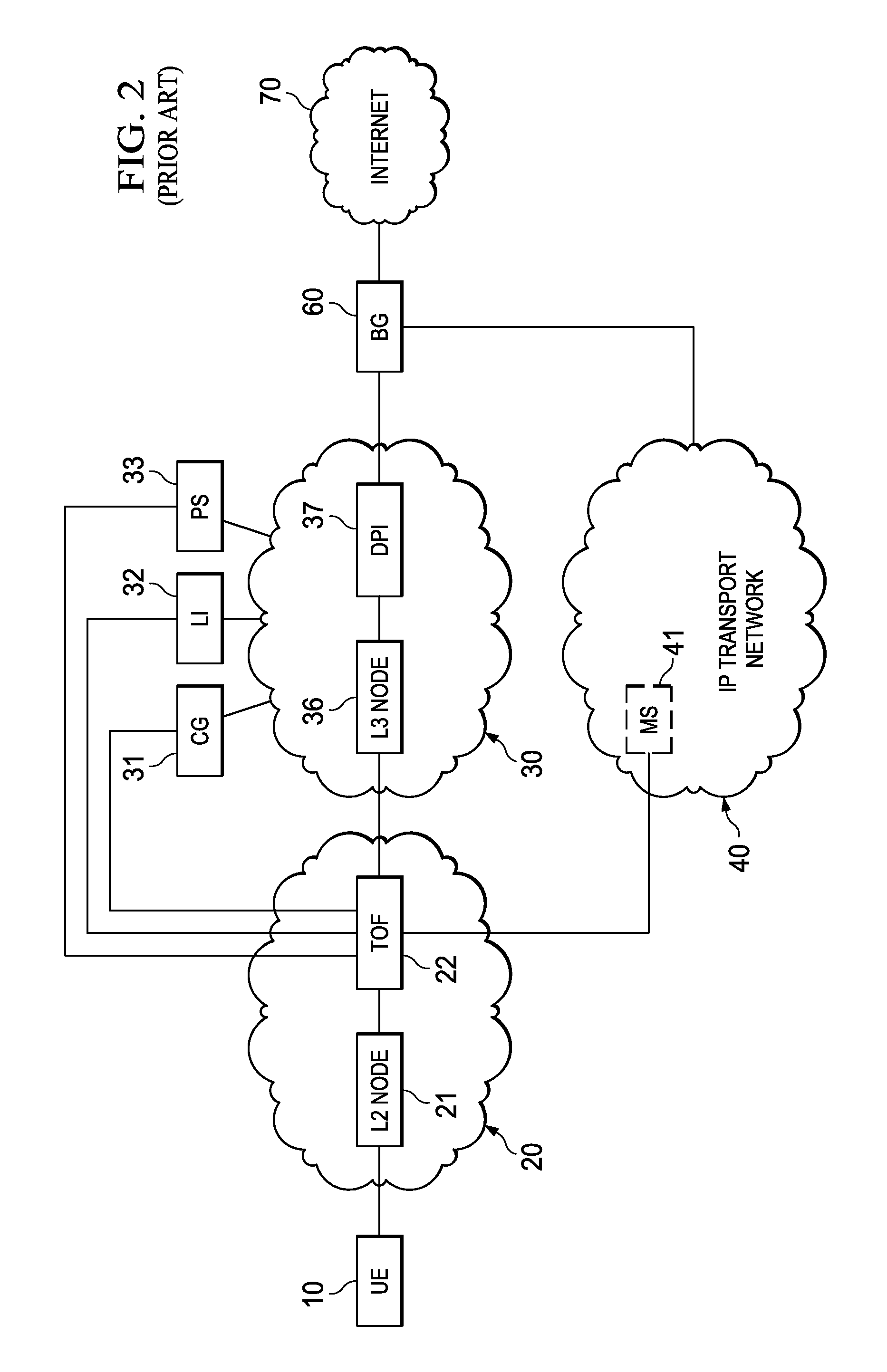
ActiveUS20110280216A1Effective decouplingImprove cache hit ratioDigital data information retrievalMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsAccess networkInternet traffic
In one embodiment, a method of serving media includes receiving a request to serve a cacheable media content to a user equipment at a second media server deployed in a second layer2 access network. The request is received around when the user equipment is handed-off from a first layer2 node in a first layer2 access network to a second layer2 node in the second layer2 access network and when a streaming session of the cacheable media content to the user equipment from a first media server is terminated. The method further includes determining if the cacheable media content is stored in a cache of the second media server, and serving the cacheable media content from the cache of the second media server to the user equipment if the media content is stored in the cache of the second media server.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
Directed least recently used cache replacement method
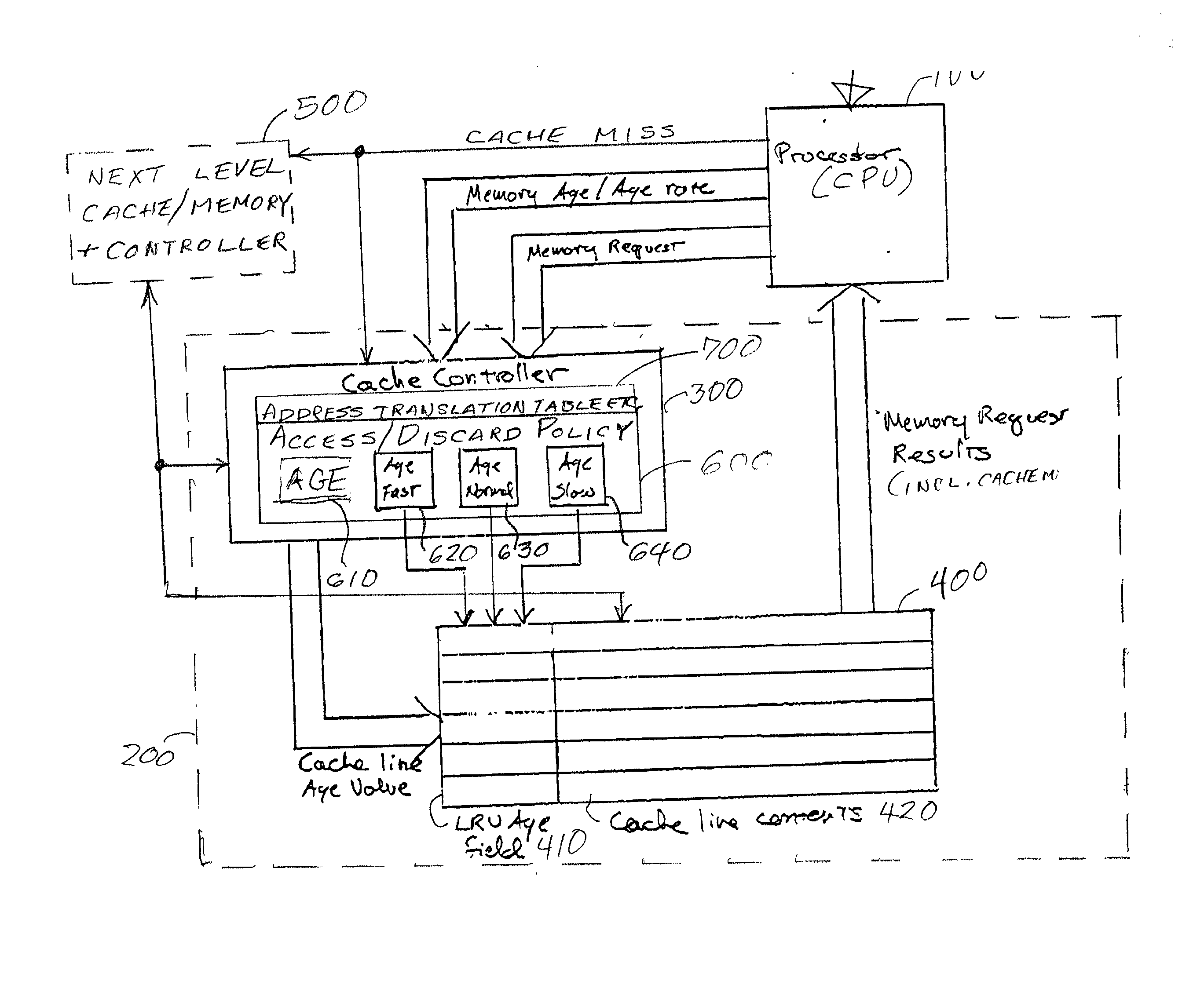
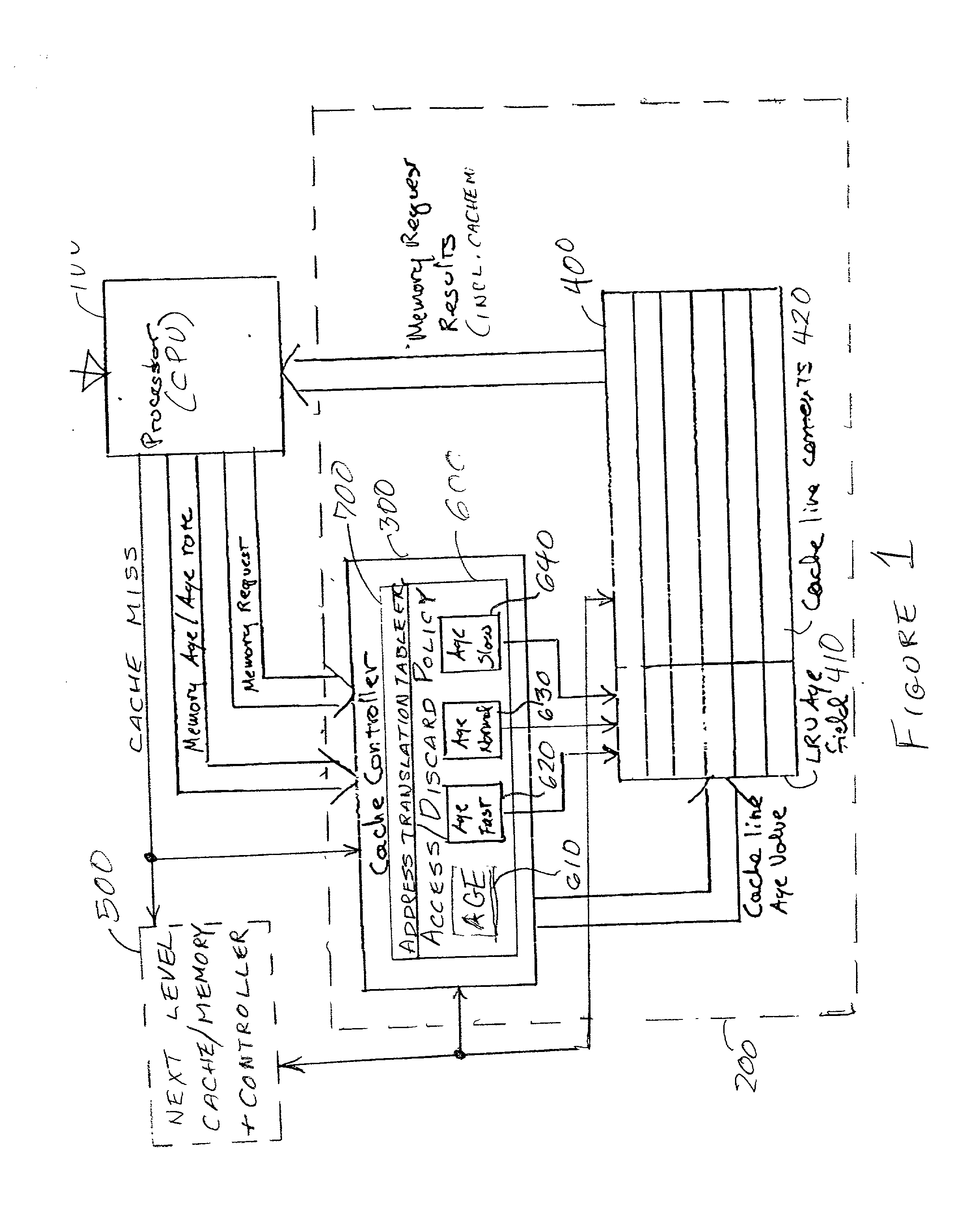
InactiveUS20020152361A1Performance maximizationImprove cache hit ratioEnergy efficient ICTMemory adressing/allocation/relocationParallel computingLeast recently frequently used
Fine grained control of cache maintenance resulting in improved cache hit rate and processor performance by storing age values and aging rates for respective code lines stored in the cache to direct performance of a least recently used (LRU) strategy for casting out lines of code from the cache which become less likely, over time, of being needed by a processor, thus supporting improved performance of a processor accessing the cache. The invention is implemented by the provision for entry of an arbitrary age value when a corresponding code line is initially stored in or accessed from the cache and control of the frequency or rate at which the age of each code is incremented in response to a limited set of command instructions which may be placed in a program manually or automatically using an optimizing compiler.
Owner:IBM CORP
Storage controller, data processing method and computer program product for reducing channel processor overhead by effcient cache slot management
InactiveUS20080270689A1Speed-up of the Fibre Channel interfaceReduce overheadMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationControl storeParallel computing
Owner:HITACHI LTD
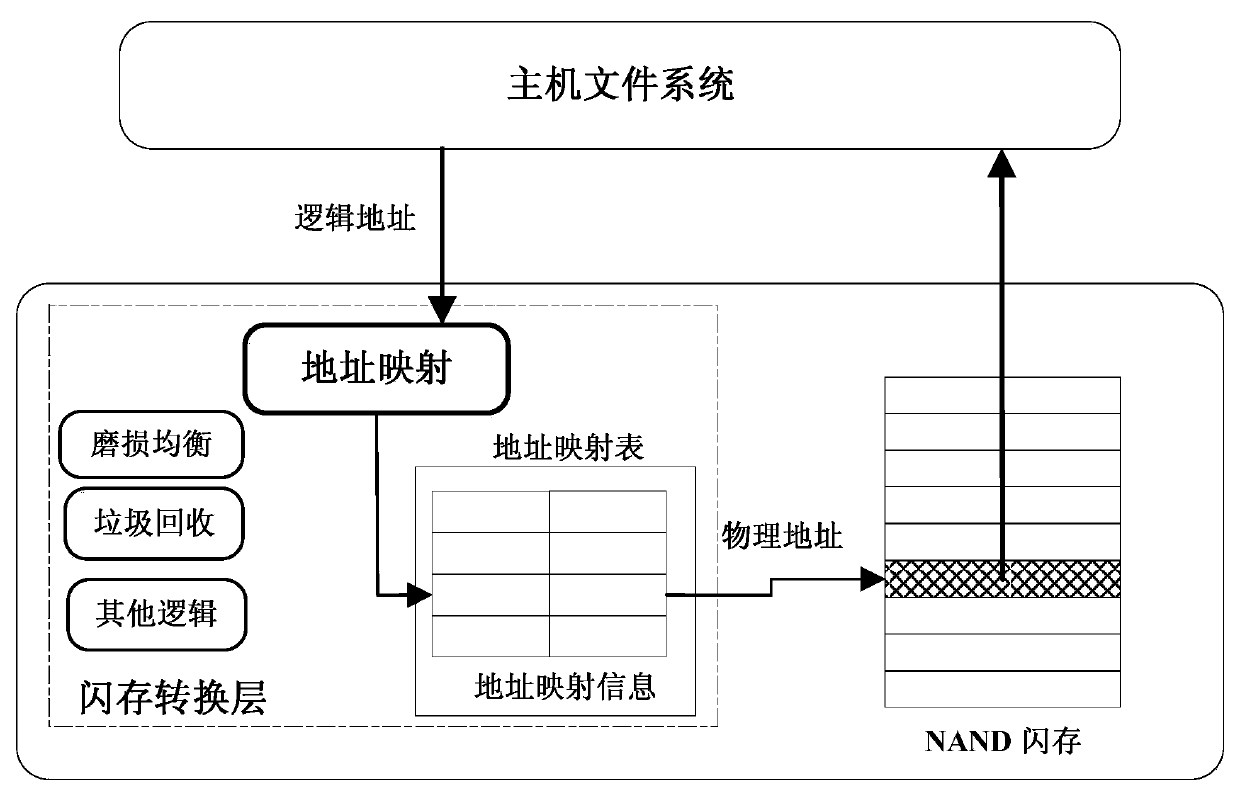
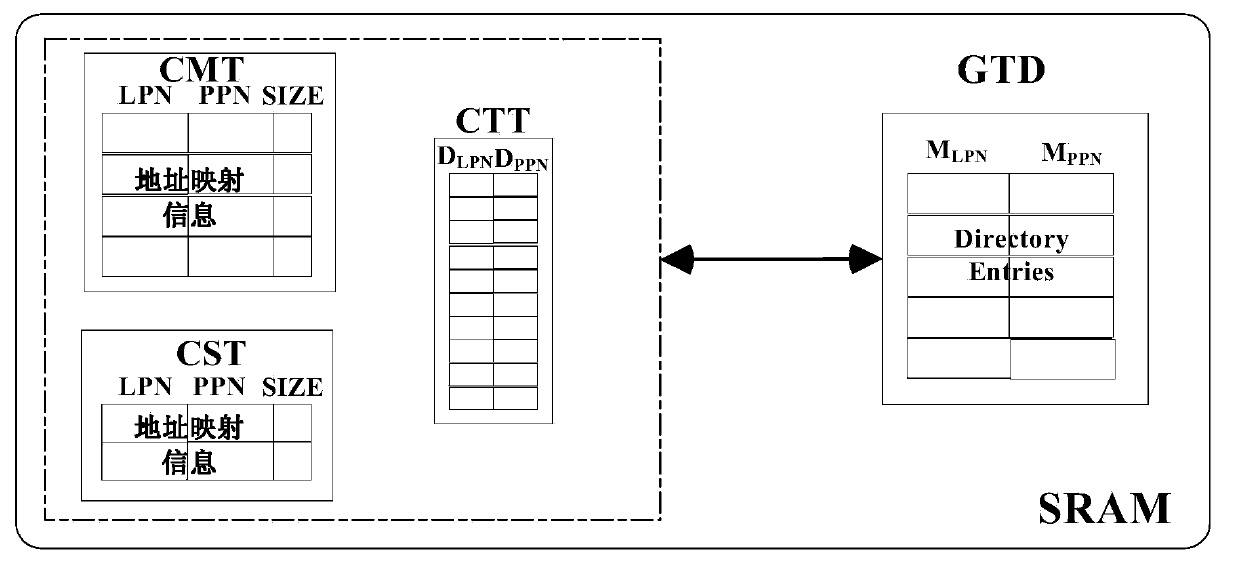
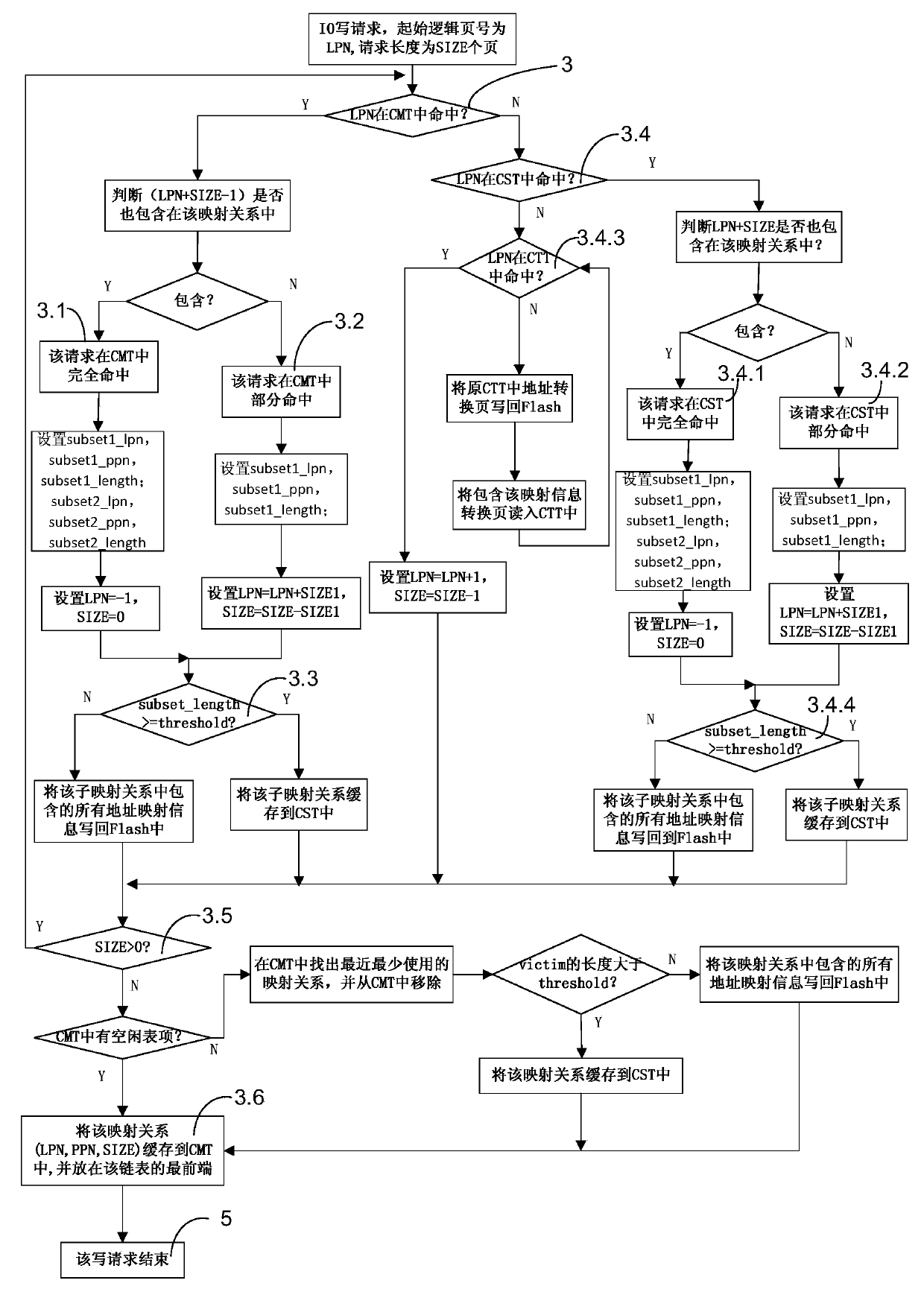
Address mapping method for flash translation layer of solid state drive
ActiveCN103425600AImprove random write performanceImprove hit rateMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationStatic random-access memorySolid-state drive
The invention discloses an address mapping method for a flash translation layer of a solid state drive. The method comprises the following steps of (1) establishing a cached mapping table, a cached split table, a cached translation table and a global translation directory in an SRAM (static random access memory) in advance; (2) receiving an IO (input / output) request, turning to a step (3) if the IO request is a write request, otherwise turning to a step (4); (3) preferentially and sequentially searching the tables in the SRAM for the hit condition of the current IO request, finishing write operation according to hit mapping information, and caching the mapping information according to a hit type and a threshold value; (4) preferentially searching the tables in the SRAM for the hit condition of the current IO request, and finishing read operation according to the hit mapping information in the SRAM. The method has the advantages that the random write performance of the solid state drive can be improved, the service life of the solid state drive can be prolonged, the efficiency of the flash translation layer is high, the hit ratio of address mapping information in the SRAM is high, and less additional read-write operation between the SRAM and the solid state drive Flash is realized.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
System, Apparatus for Content Delivery for Internet Traffic and Methods Thereof
ActiveUS20110283011A1Quality of experience for equipmentEffective decouplingMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsDigital data information retrievalAccess networkInternet traffic
In one embodiment, a method of serving media includes receiving user profiles from a layer3 node in an access network, and receiving a request to serve media content to a user equipment. The user profiles include information relating to user account and / or network characteristics of the user equipment. The method further includes using an user equipment information from the user profiles, assigning a first media server from a hierarchical set of media servers to serve the user equipment if the media content to be served is cacheable. The hierarchical set of media servers include a plurality of first type of media servers deployed in a plurality of layer2 (L2) access networks. The user equipment is coupled to a content delivery network through a layer2 access network of the plurality of layer2 access networks.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
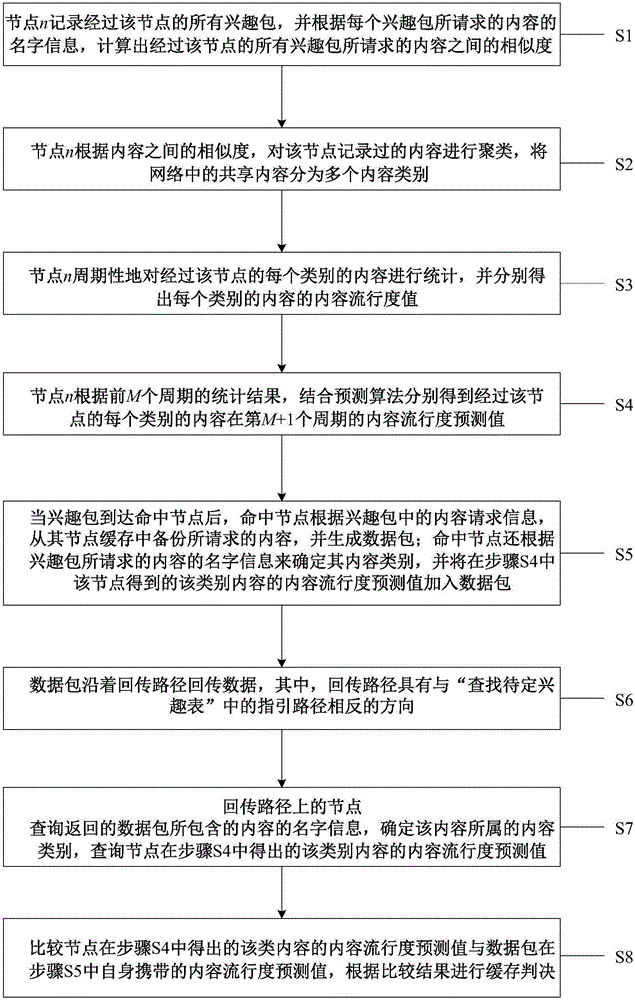
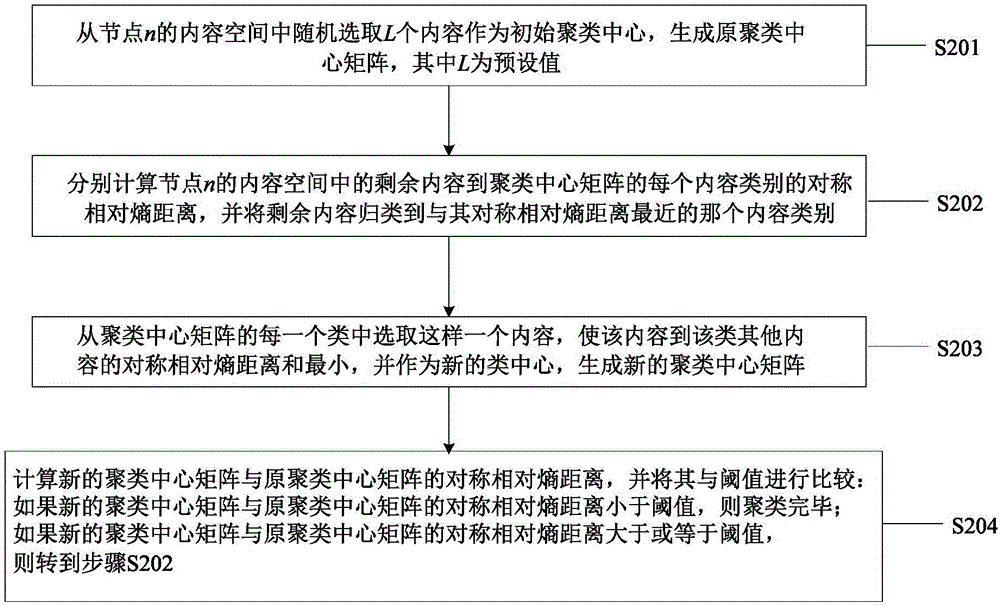
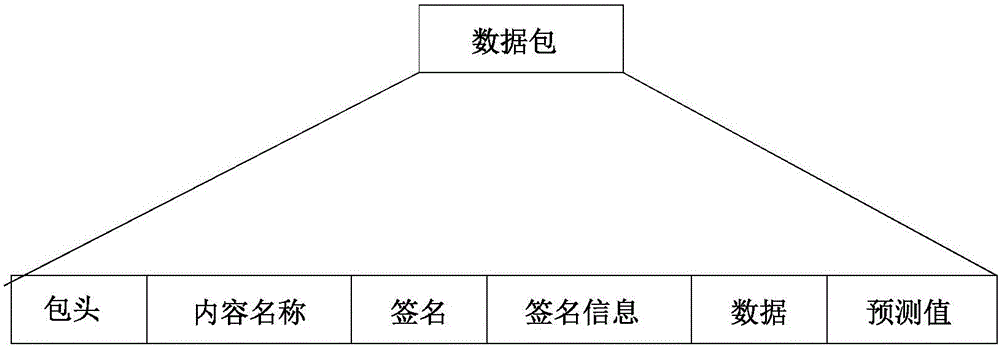
Information centric networking caching method based on content popularity prediction
ActiveCN106453495AReduce computational overheadReduce cache redundancy issuesData processing applicationsCharacter and pattern recognitionCache accessPrediction algorithms
The invention provides an information centric networking caching method based on content popularity prediction, relates to the technical field of communication network data processing, solves a caching redundancy problem in the prior art of information centric networking caching, and improves the sharing efficiency of cached contents. In the method, each node records the content names of all request contents received by each node, and similarities among all contents are calculated and are clustered; the content popularity value of each class of contents which pass through the node is calculated and is subjected to periodic statistics; and a prediction algorithm is used for predicting the content popularity value of each class of contents of a future moment of the node, and the content popularity value is added into the data packet of a hit node; and in a data packet returning process, a content popularity prediction value carried by the data packet is compared with a local content popularity prediction value to determine whether the contents are added into a node cache or not. The method is used for optimizing the cache access of content-based information centric networking.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM +1
Method, device and system for cache regulation
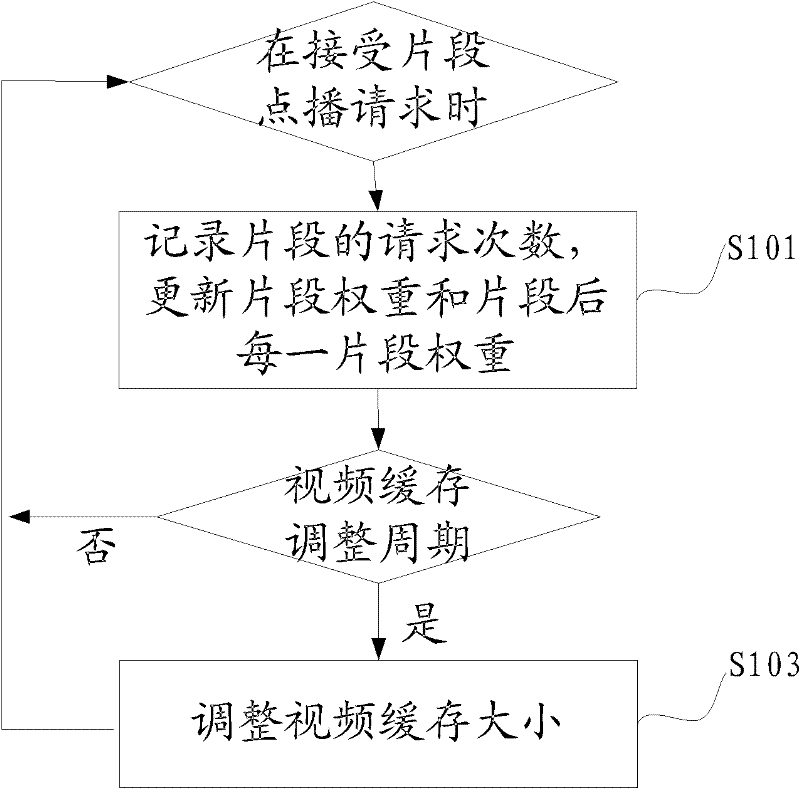
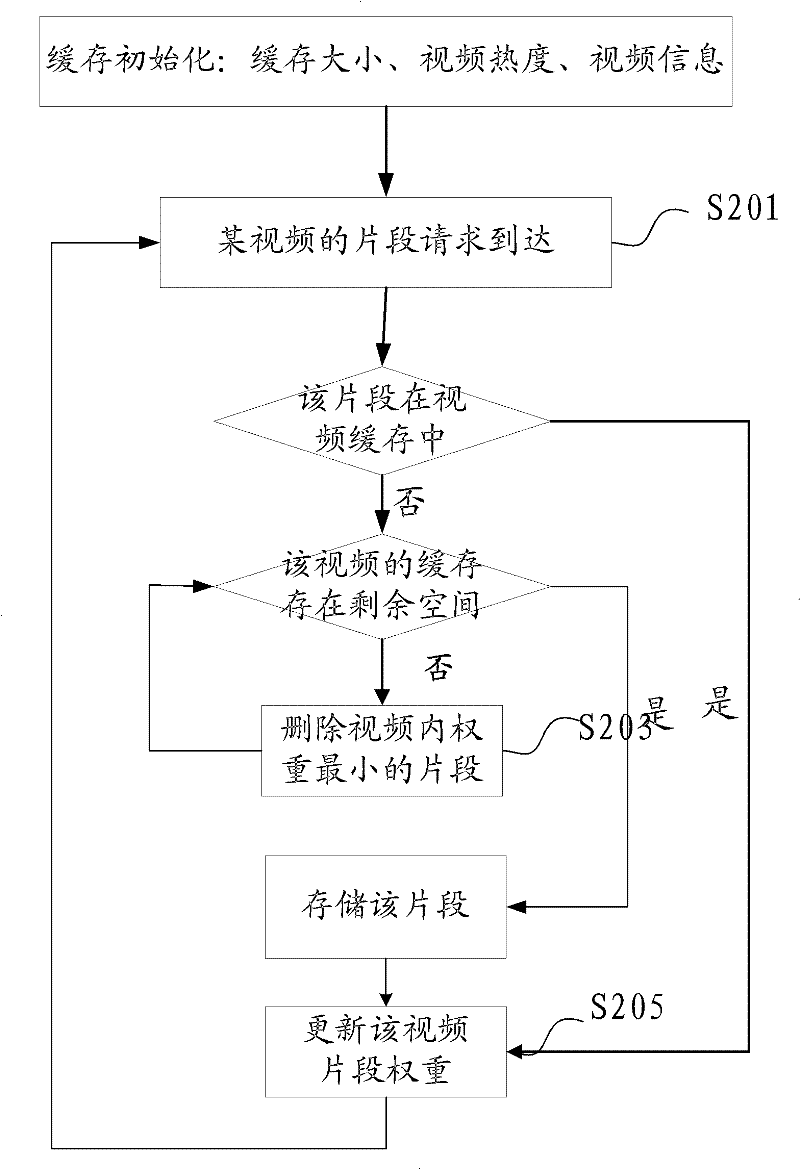
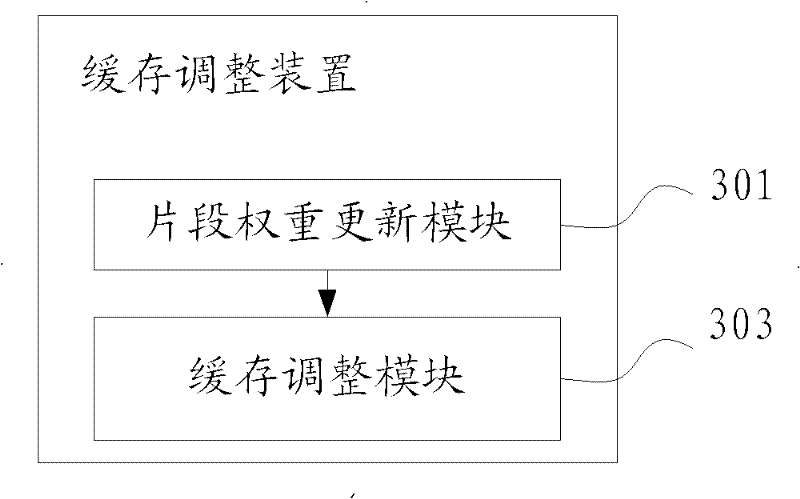
InactiveCN102447973AImprove visual experienceImprove cache hit ratioSelective content distributionComputer graphics (images)Video on demand
The embodiment of the invention provides a method and a device for video on demand (VoD) cache replacement based on predicted weight. The method comprises the steps of: recording request times for a video segment when a VoD request of a user on the video segment is received, and updating the segment weight of the video segment and the segment weight of each video segment after the video segment in a video according to the request times of the video segment; and in a cache regulation period of the video, regulating the cache size of the video according to the video weight of the video, the sum of the video weights of all the videos on a server and the cache size of the server. According to the invention, more hot videos and hot segments can be cached, so that the vision experience for user VoD is promoted.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD +1
Apparatus, method, computer program and mobile terminal for processing information
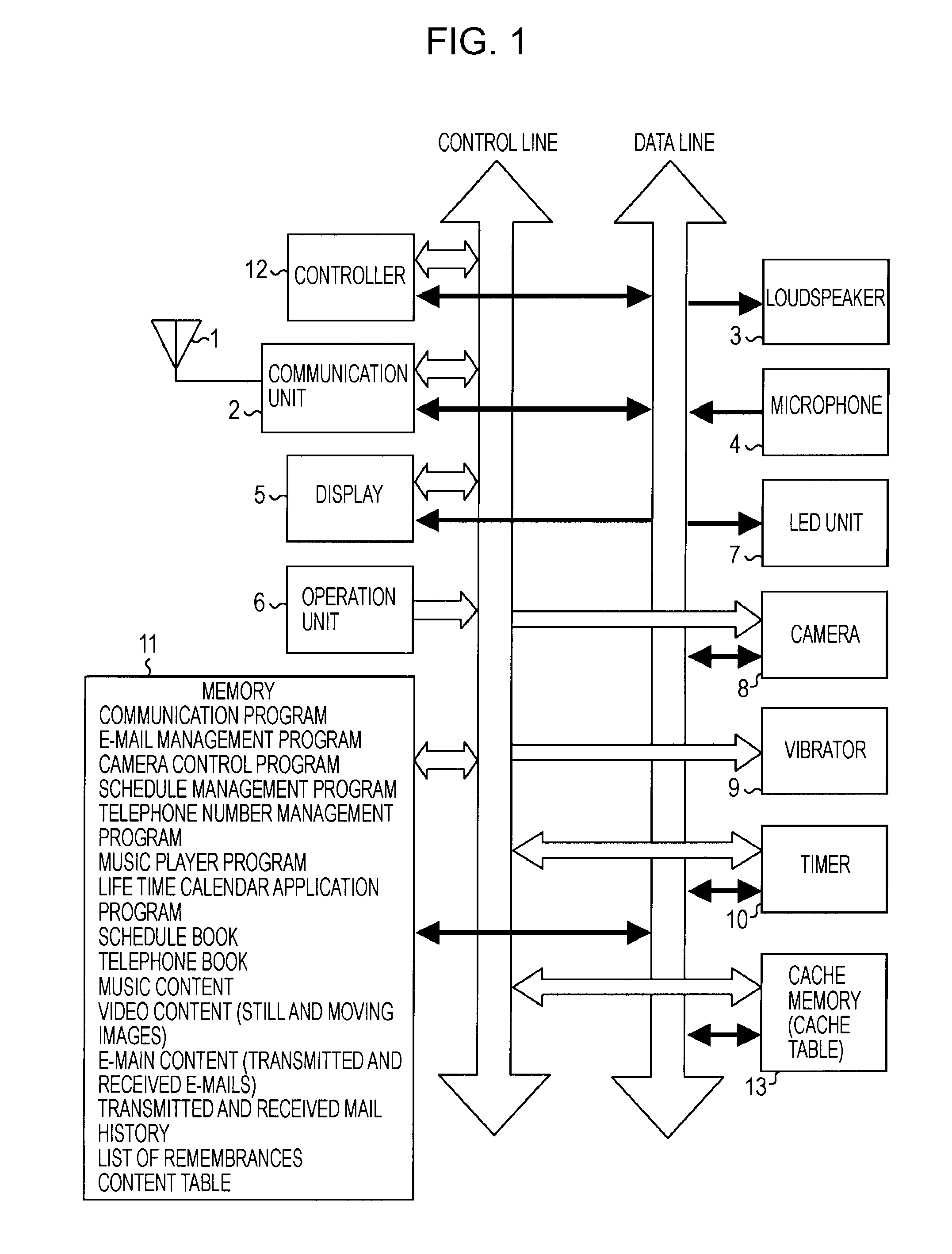
InactiveUS20080005087A1Increase speedImprove cache hit ratioSubstation equipmentSpecial data processing applicationsTemporal informationDisplay device
An apparatus for processing information, includes a memory storing a plurality of content items different in type and metadata containing time information of the content items, a cache processor for fetching from the memory the content item and the metadata of the content item to be displayed on a display and storing the fetched content item and the metadata thereof on a cache memory, a display controller for displaying on the display the metadata of the content items from the cache memory arranged in accordance with the time information and a selection operator selecting metadata corresponding to a content item desired to be processed, out of the metadata displayed, and a content processor for fetching from the cache memory a content item corresponding to the metadata selected by the selection operator by referencing the cache memory in response to the selected metadata, and for performing a process responsive to the fetched content item.
Owner:SONY MOBILE COMM INC
System and method for performing entity tag and cache control of a dynamically generated object not identified as cacheable in a network
ActiveUS20060195660A1Improve cache hit ratioMemory loss protectionAssess restrictionParallel computingClient-side
The present invention is directed towards a method and system for modifying by a cache responses from a server that do not identify a dynamically generated object as cacheable to identify the dynamically generated object to a client as cacheable in the response. In some embodiments, such as an embodiment handling HTTP requests and responses for objects, the techniques of the present invention insert an entity tag, or “etag” into the response to provide cache control for objects provided without entity tags and / or cache control information from an originating server. This technique of the present invention provides an increase in cache hit rates by inserting information, such as entity tag and cache control information for an object, in a response to a client to enable the cache to check for a hit in a subsequent request.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
System, Apparatus for Content Delivery for Internet Traffic and Methods Thereof
ActiveUS20110280153A1Effective decouplingImprove cache hit ratioDigital data information retrievalMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsAccess networkInternet traffic
In one embodiment, a method of serving media includes receiving a request to serve media content to an user equipment, and receiving caching information regarding the media content. The caching information includes information regarding whether the media content requested by the user equipment is cacheable. A first media server is assigned from a hierarchical set of media servers to serve the user equipment if the media content to be served is cacheable. The hierarchical set of media servers includes a plurality of first type of media servers deployed in a plurality of layer2 (L2) access networks. The user equipment is coupled to the content delivery network through a layer2 access network of the plurality of L2 access networks.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
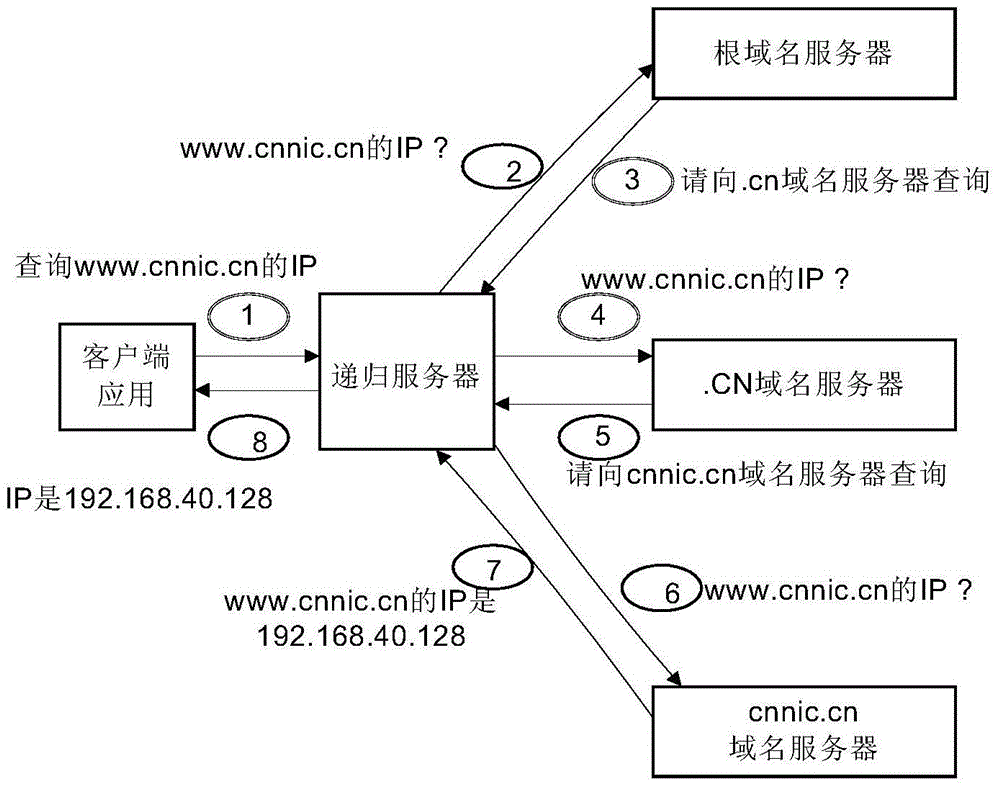
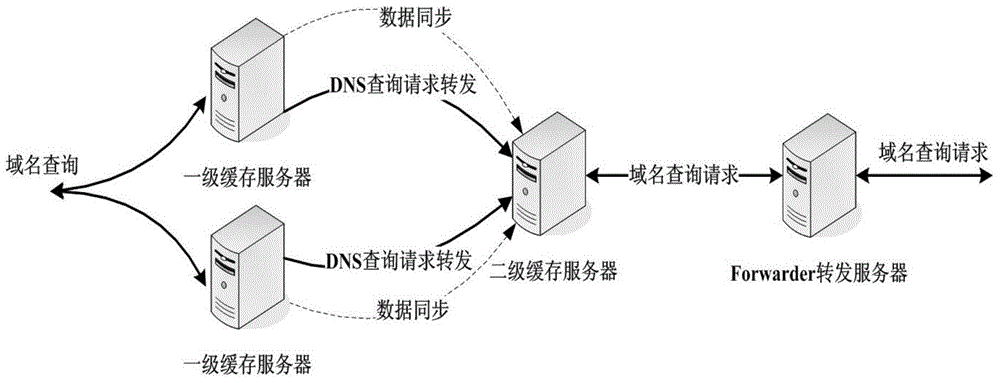
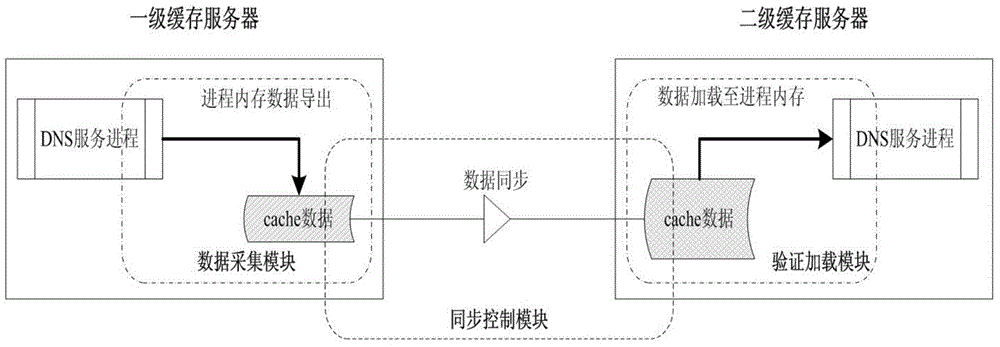
Recursive domain name service system and method of multi-level shared cache
The invention relates to a recursive domain name service system and method of multi-level shared cache. The system comprises first-level cache servers, a second-level cache server and a forward server. The second-level cache server is used for collecting cache records of all first-level cache servers at a front end through a consistency cache sharing mechanism, and establishing a relatively large cache region; and checking a local server cache region after receiving a domain name query request forwarded by the first-level cache server; and directly returning data to the first-level cache server if a requested resource record exists in the local cache region, or forwarding the domain name query name to the forward server; and then the forward server is used for iteratively querying to obtain a query result. Furthermore, the system comprises a data acquisition module, a synchronous control module and a verification loading module. The sharing of cache resource records between different cache servers can be realized, the domain name cache hit ratio is obviously improved, and the domain name analysis time delay is shortened.
Owner:CHINA INTERNET NETWORK INFORMATION CENTER
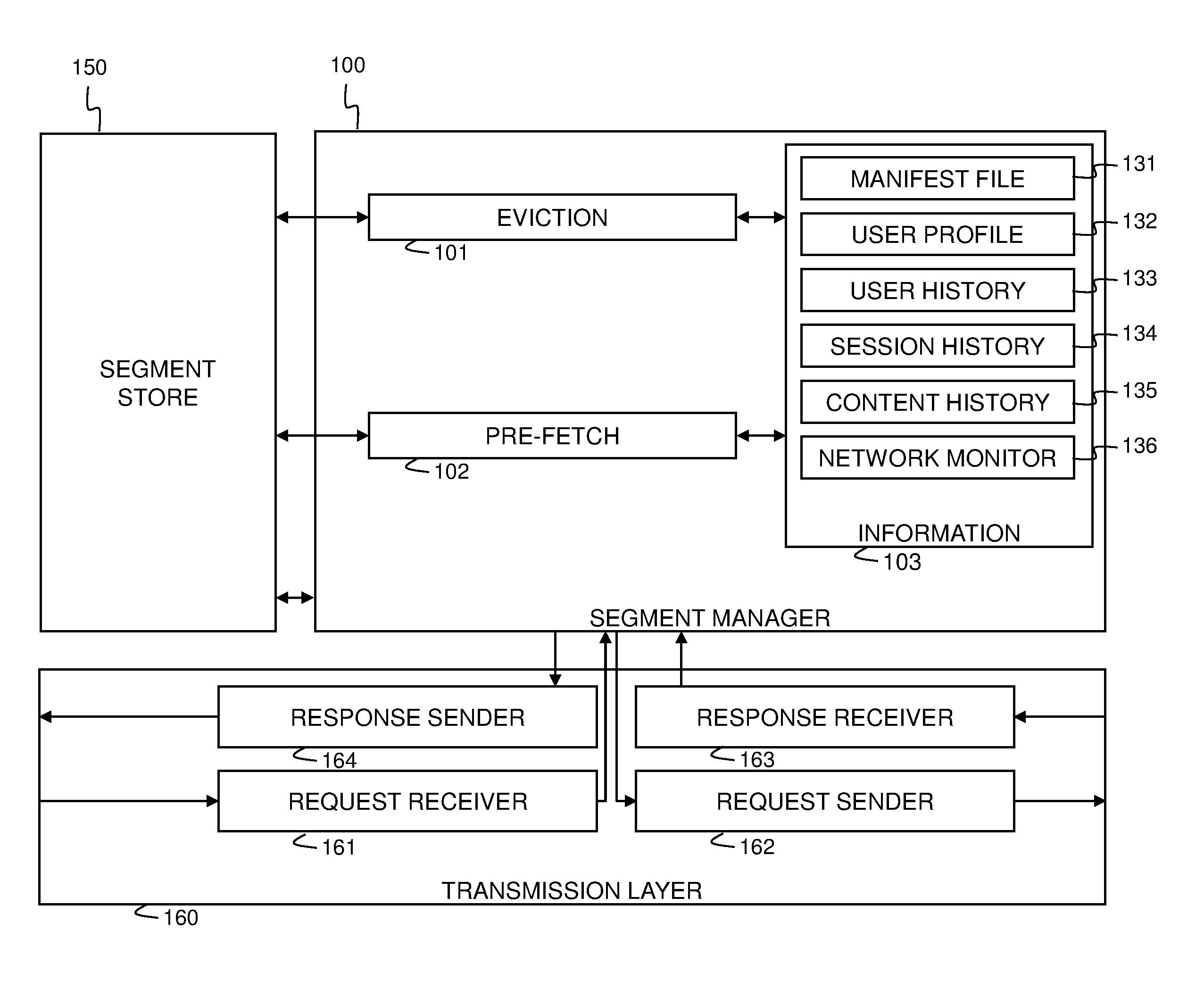
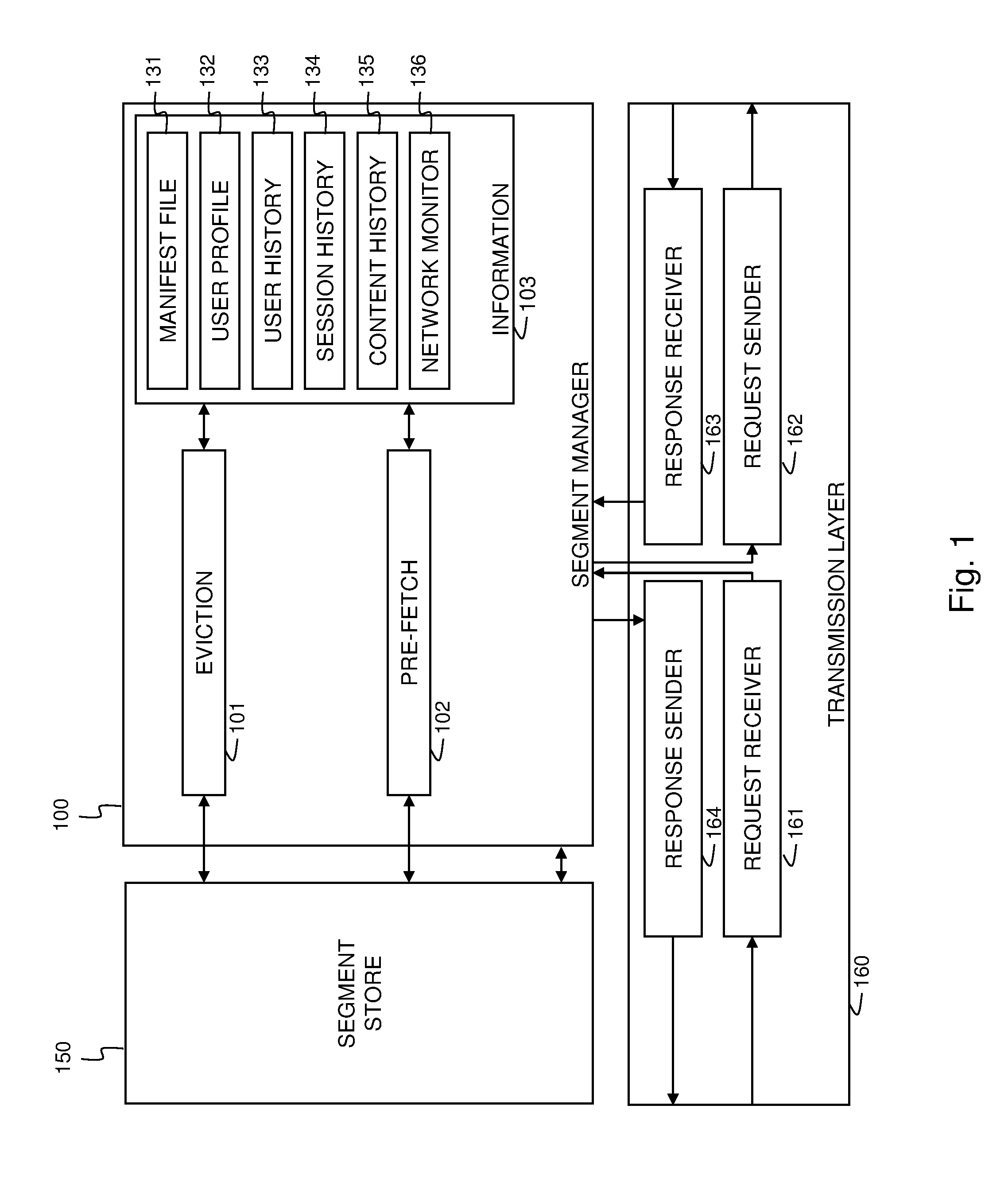
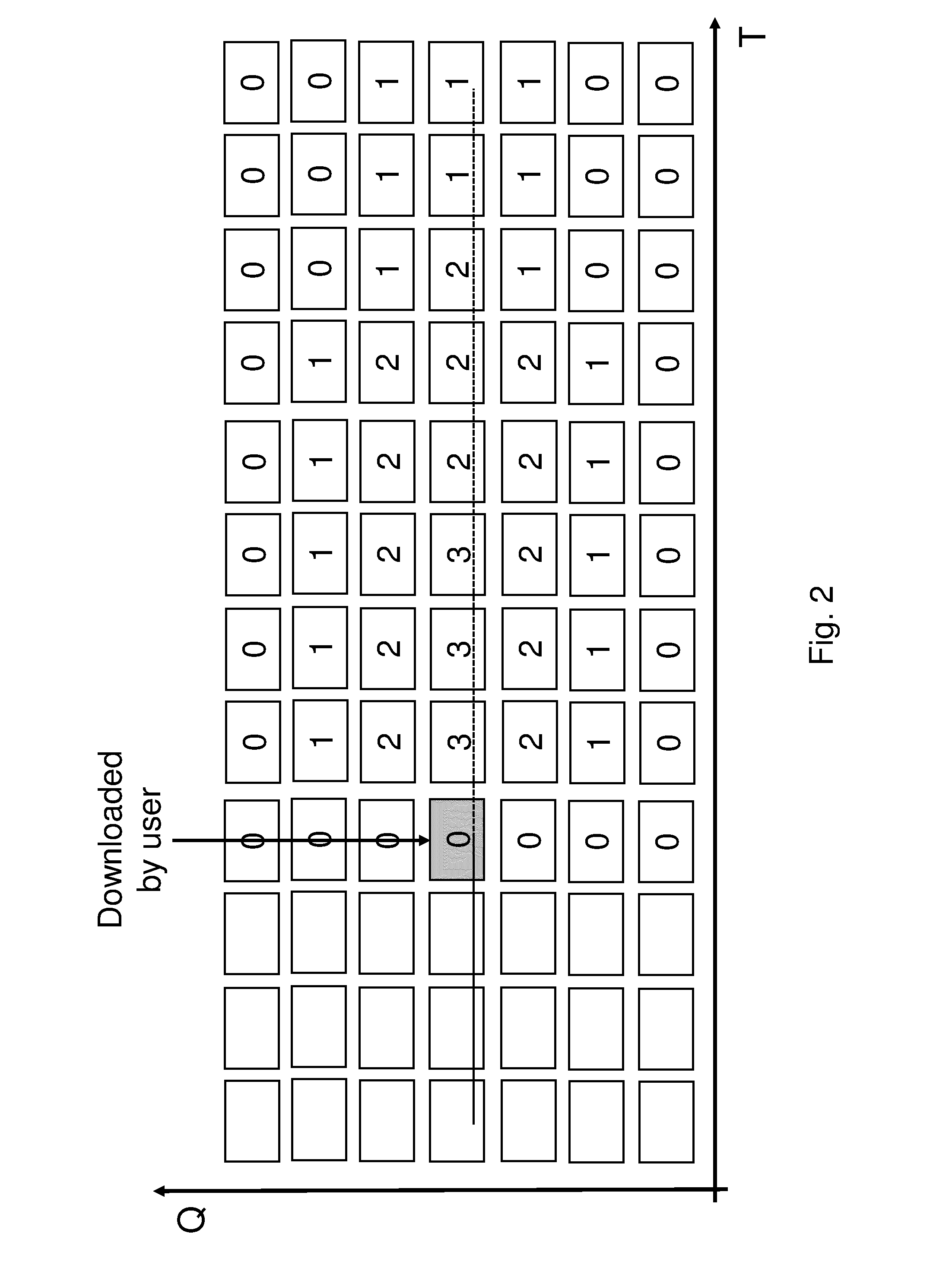
Cache manager for segmented multimedia and corresponding method for cache management
ActiveUS20140032849A1Raise the possibilityImprove usabilityMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSpecial data processing applicationsParallel computingCache management
The invention concerns a cache manager (100) for managing the intermediate caching of segmented multimedia items. Multiple versions are available of each multimedia item, each version representing the multimedia item with a different quality. The cache manager (100) comprises control means (101, 102) to control the pre-fetching and eviction of segments. The control means (101, 102) are at least responsive to temporal and quality related inter-segment relationships (131).
Owner:RPX CORP
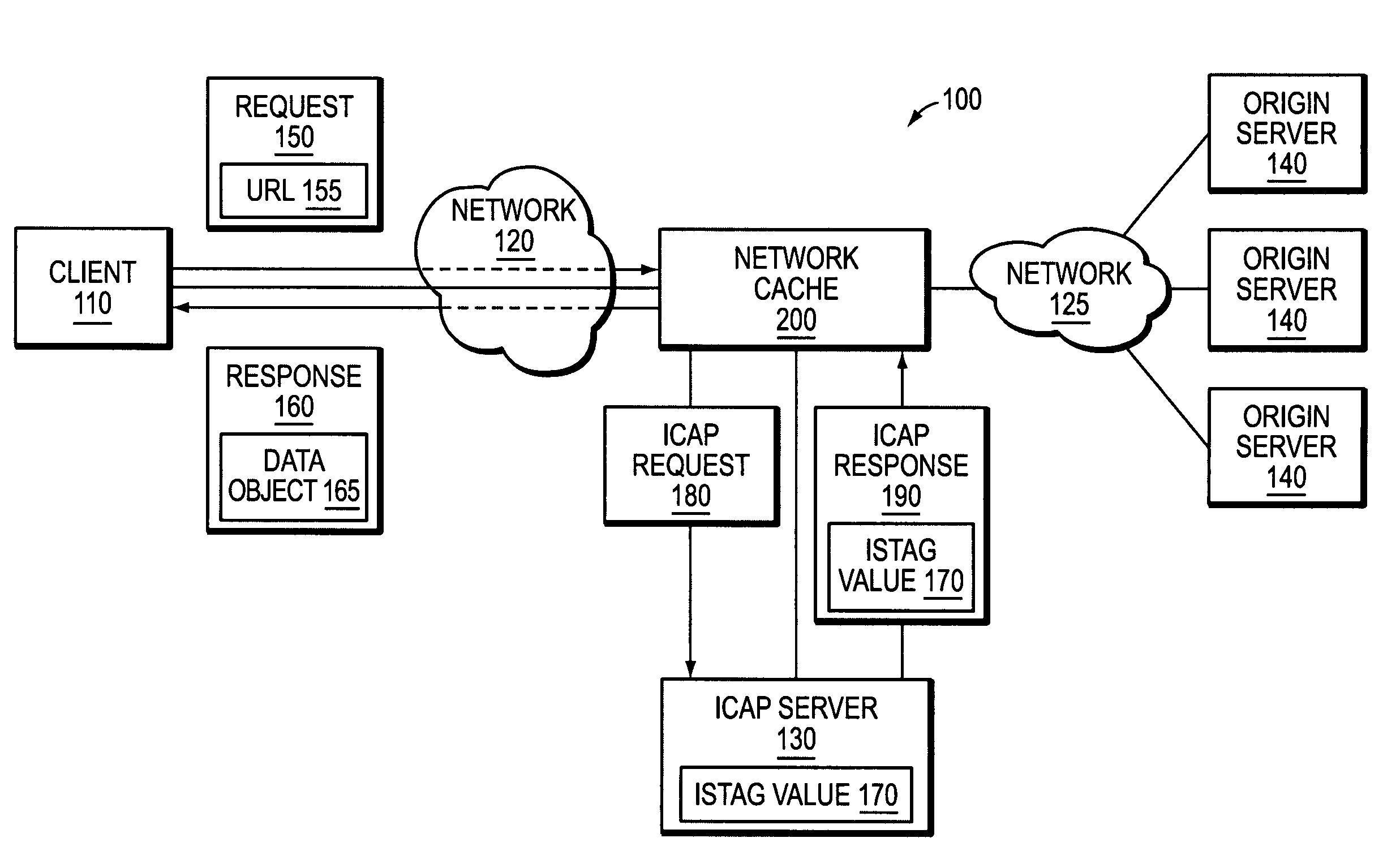
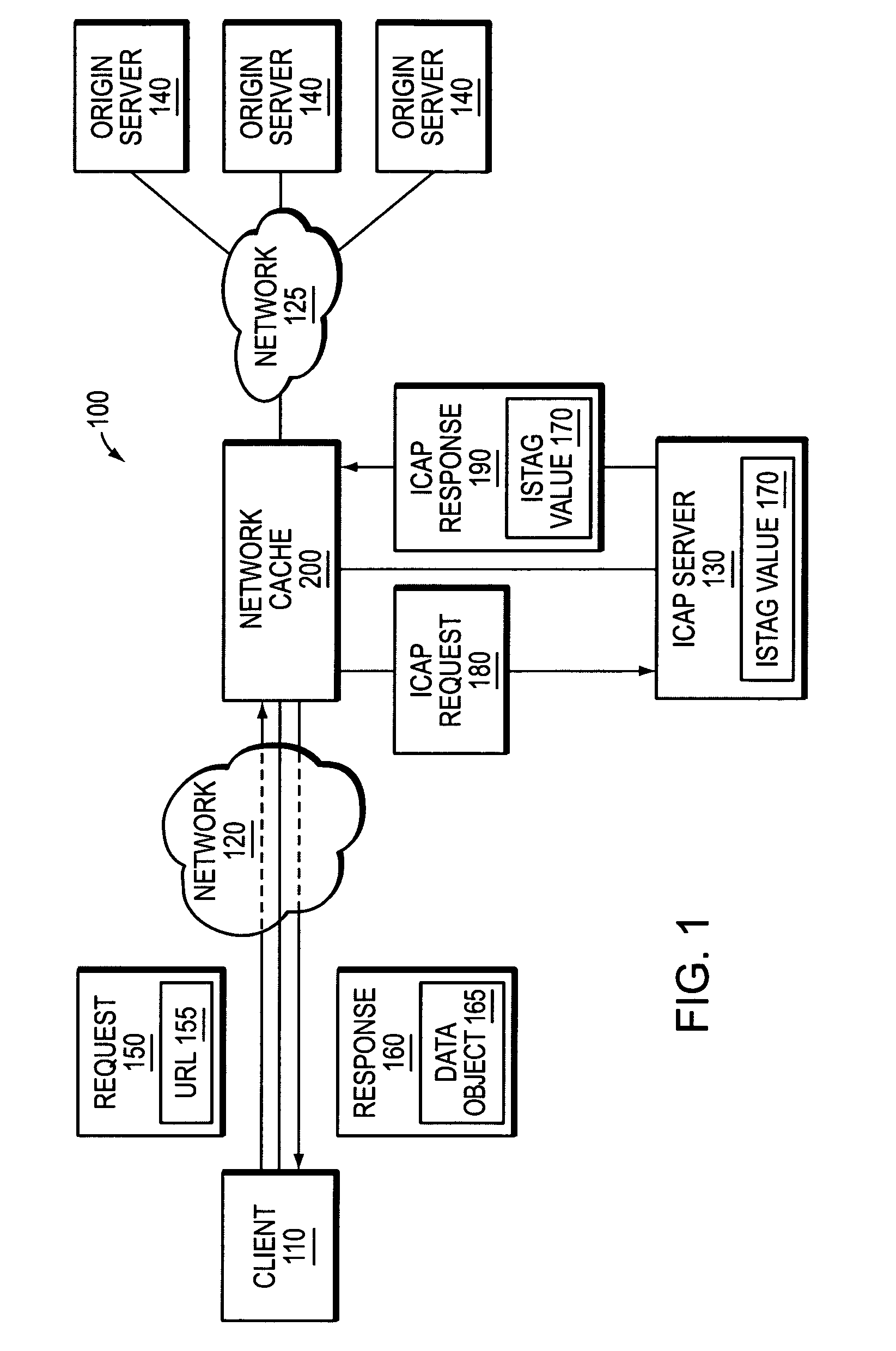
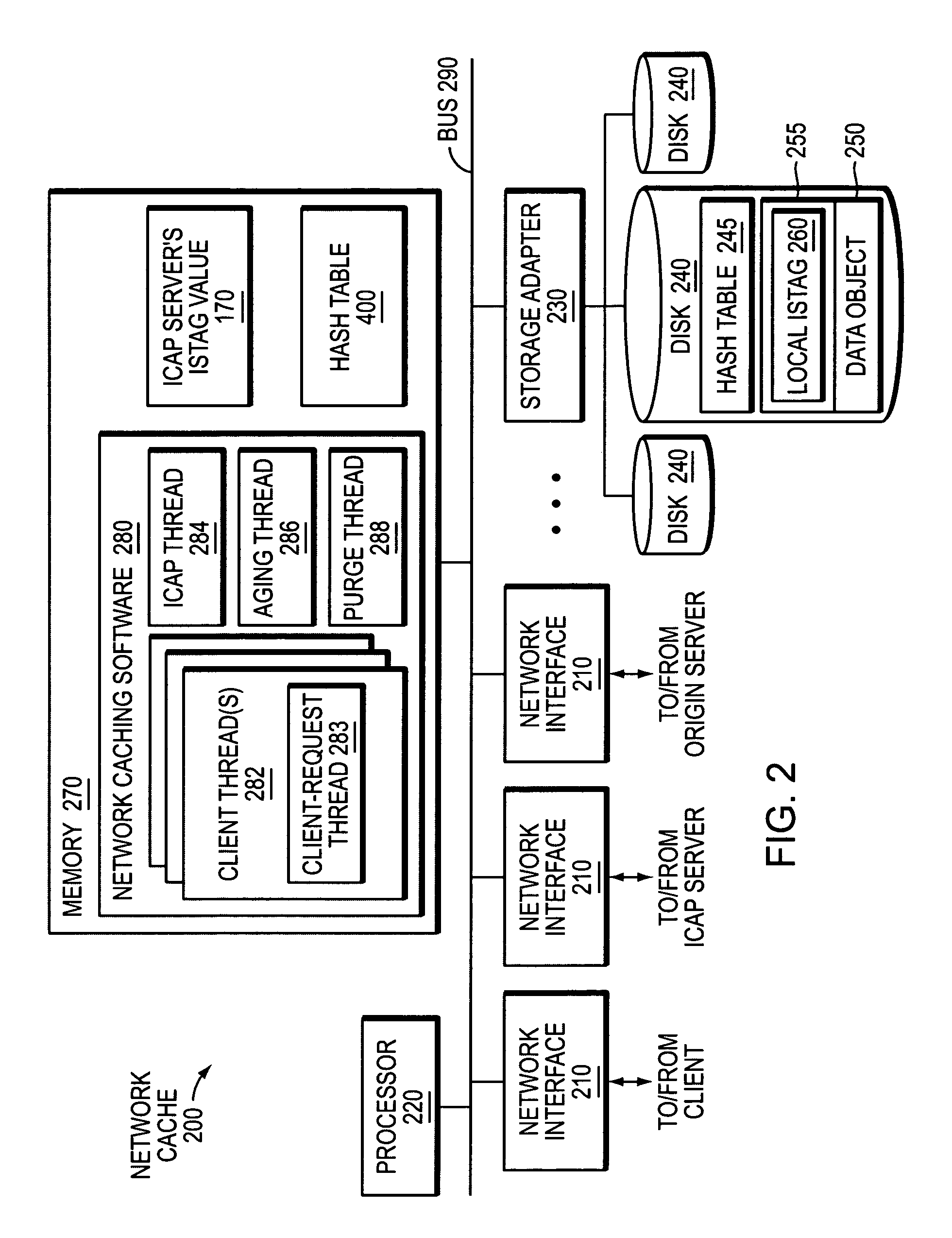
Object cacheability with ICAP
ActiveUS7647417B1Improve cache hit ratioConsume network bandwidthDigital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsObject storeClient-side
A novel system and method is provided for improving object cacheability in an ICAP-configured network cache. Unlike prior implementations, the present invention does not require the network cache to invalidate every data object in its object store in response to receiving an updated ISTag value from an ICAP server. Rather, the network cache invalidates data objects on an object-by-object basis after receiving the updated ISTag value. Specifically, the network cache invalidates a data object if the following conditions are satisfied: (1) the network cache has received an updated ISTag value, (2) the data object is requested by a client and (3) the requested data object requires transformation by the ICAP server. When each of these conditions is satisfied, the data object is invalidated and replaced with its transformed version. Because not every client-requested data object necessarily requires ICAP transformation after an updated ISTag value is received, the network cache may invalidate fewer data objects than in prior implementations.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
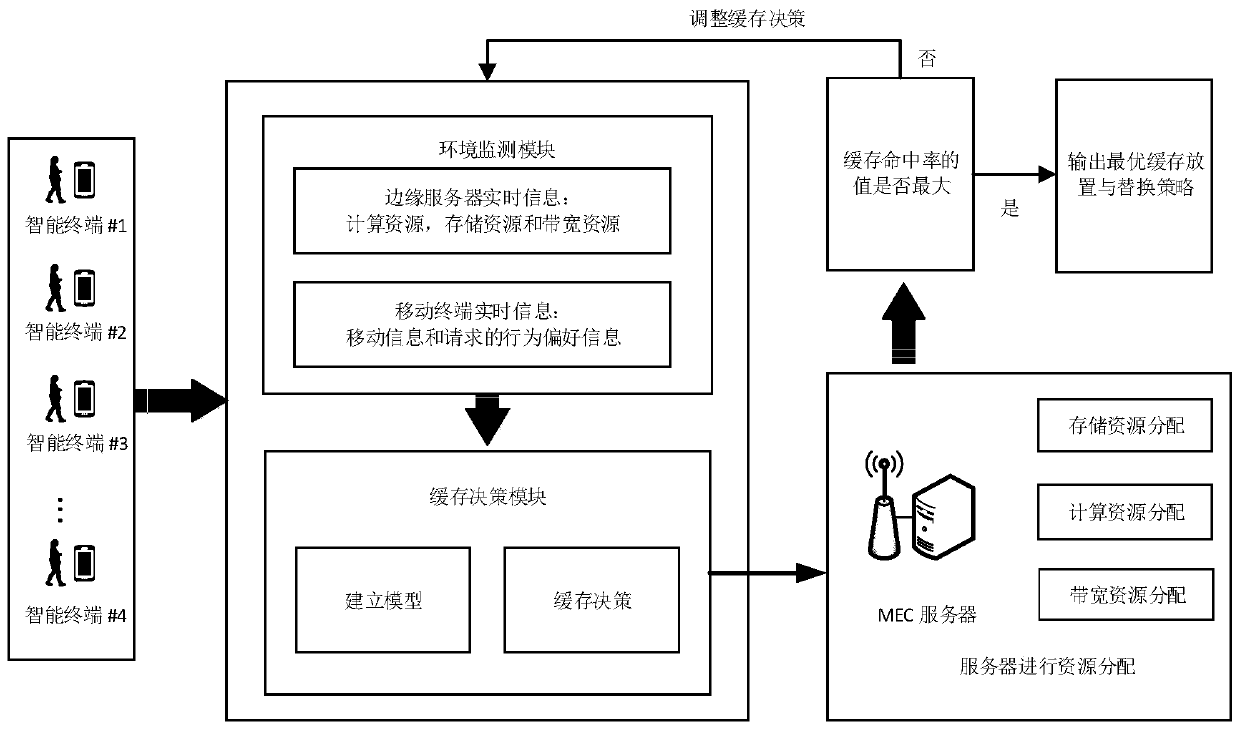
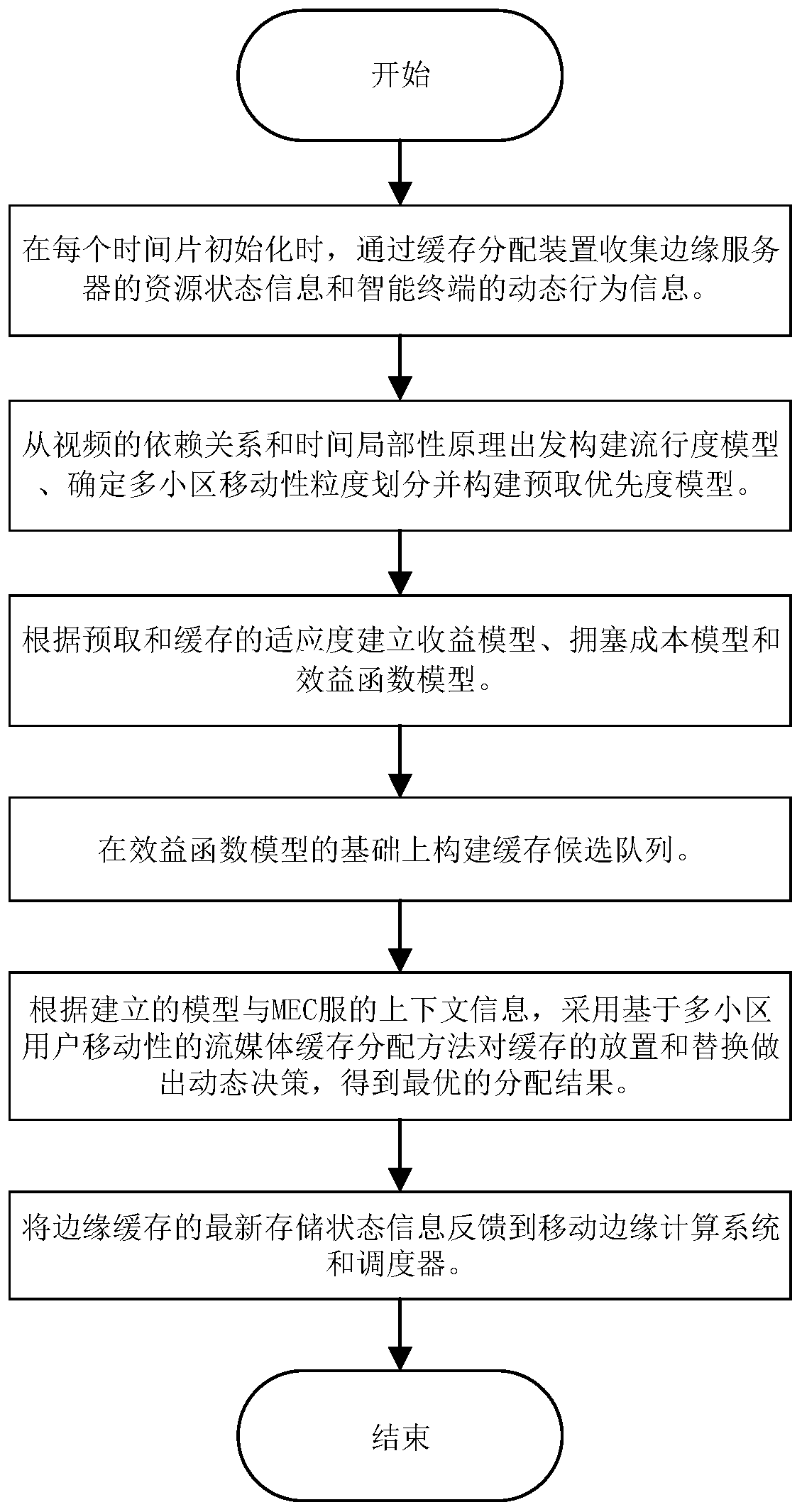
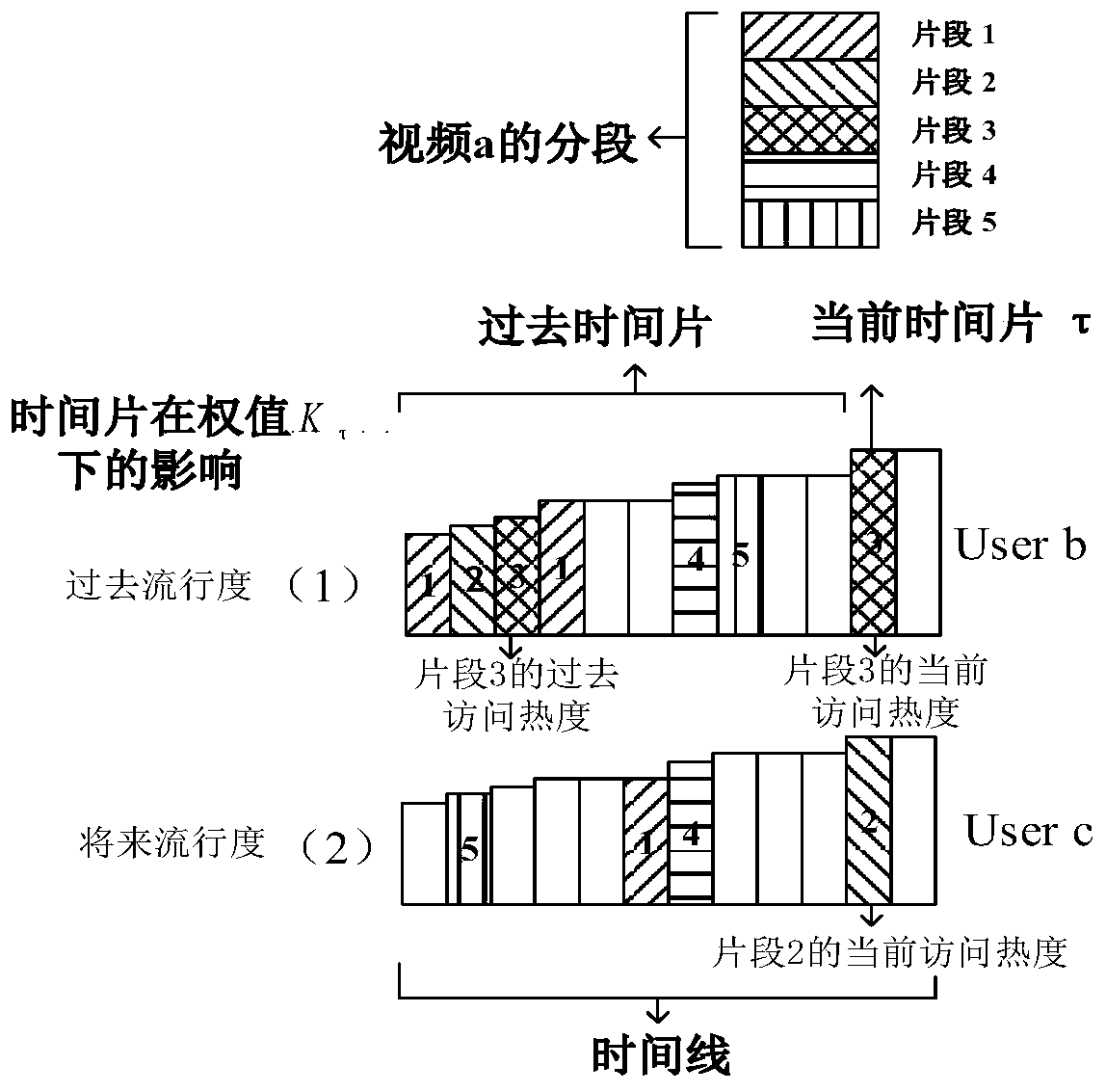
Streaming media cache distribution device based on multi-cell user mobility and working method thereof
ActiveCN110213627AExcellent distribution resultCongestion cost reductionSelective content distributionEdge serverEdge computing
The invention belongs to the field of mobile edge computing, and provides a streaming media cache distribution device based on a dynamic programming algorithm and a multi-cell user mobility and a working method thereof, and the device can collect context perception information of an edge server, and the context perception information comprises a movement track of a user in a cell, a request mode of a terminal, a current network load and a distribution state of server resources. According to the method, a space-time locality principle is considered to carry out abstract analysis on a multi-celloverlapping switching probability of a user, and a popularity cache model and a motion sensing prefetching model are established. On the premise of meeting the constraints of storage, bandwidth and computing resources, an optimization target of maximizing cache benefits is established. An optimal cache placement and replacement decision is made for the server through dynamic programming, and theoverall cache benefit is improved from three aspects of popularity statistics, mobility perception and cost management. According to the device and the method, the average access delay of the terminaland the congestion cost of resources can be effectively reduced, and the cache performance of an edge computing system is improved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Highly-available application operation method and system, and method and system of changing application version on line
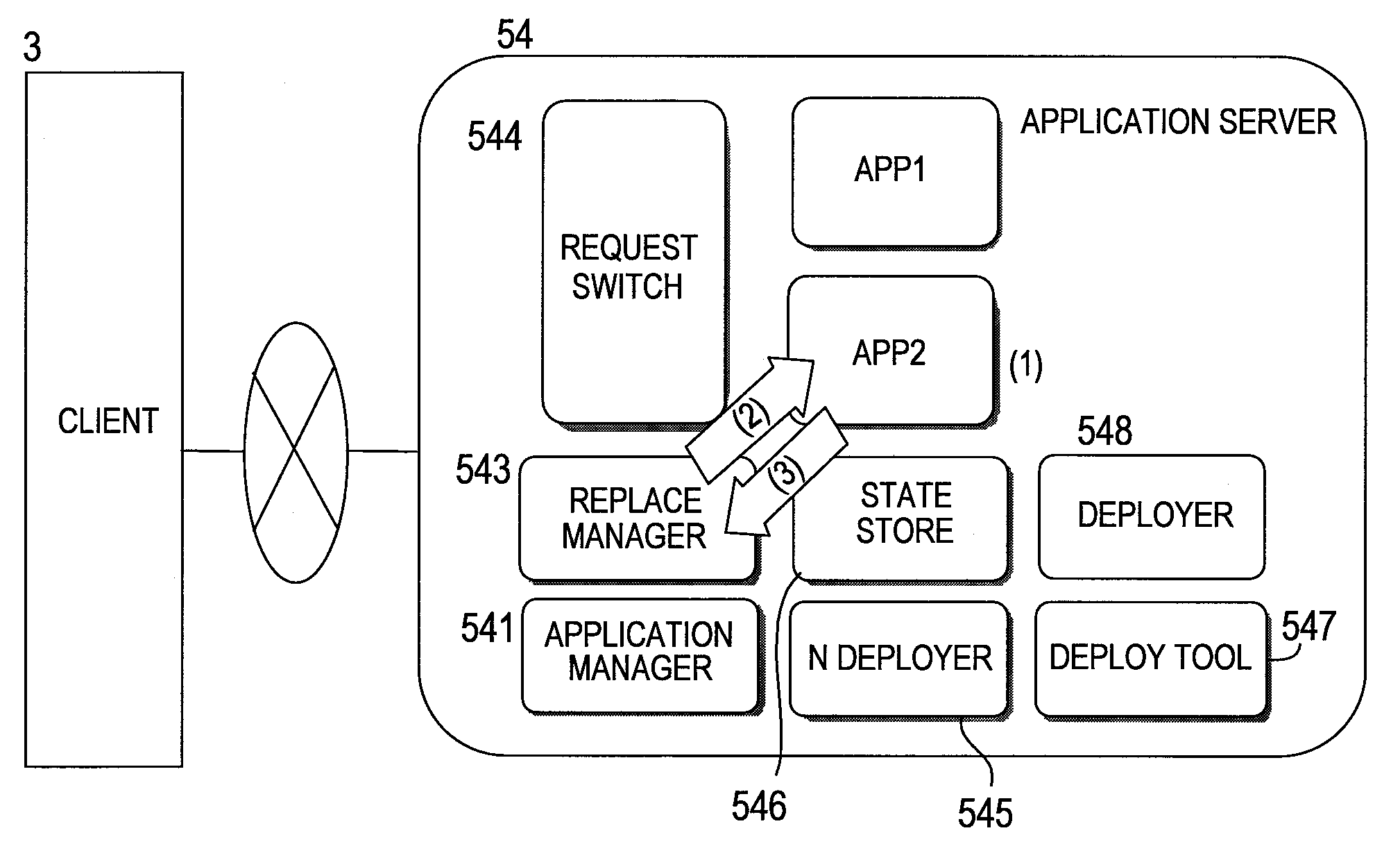
InactiveUS20080282255A1Minimizes lowering of cache hit ratePerformance degradation can be preventedError detection/correctionApplication softwareOperating system
By releasing a part of execution environment that contains a leaked resource, a failure is avoided while the remaining part of execution environment in a memory and the like prevents performance degradation that results from a cold cache. This invention provides a highly available application operation method for replacing a first application (App1) which receives a processing request with a second application (App2). The method includes the steps of: invoking the first application (App1) and forwarding the processing request to the first application (App1); when a given condition is met, invoking the second application (App2) and forwarding a new processing request to the second application (App2); and, when the first application (App1) completes the processing request after the second application (App2) is invoked, stopping the first application (App1).
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method for prefetching recursive data structure traversals
InactiveUS7058636B2Improve cache hit ratioPotential throughput of the computer systemData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalOperational systemParallel computing
Computer systems are typically designed with multiple levels of memory hierarchy. Prefetching has been employed to overcome the latency of fetching data or instructions from or to memory. In modern transaction processing systems, database servers, operating systems, and other commercial and engineering applications, information is frequently organized in trees, graphs, and linked lists. Lack of spatial locality results in a high probability that a miss will be incurred at each cache in the memory hierarchy. The present invention significantly increases the cache hit rates of many important data structure traversals, and thereby the potential throughput of the computer system and application in which it is employed. For data structure traversals in which the traversal path may be predetermined, a transformation is performed on the data structure that permits references to nodes that will be traversed in the future be computed sufficiently far in advance to prefetch the data into cache.
Owner:DIGITAL CACHE LLC
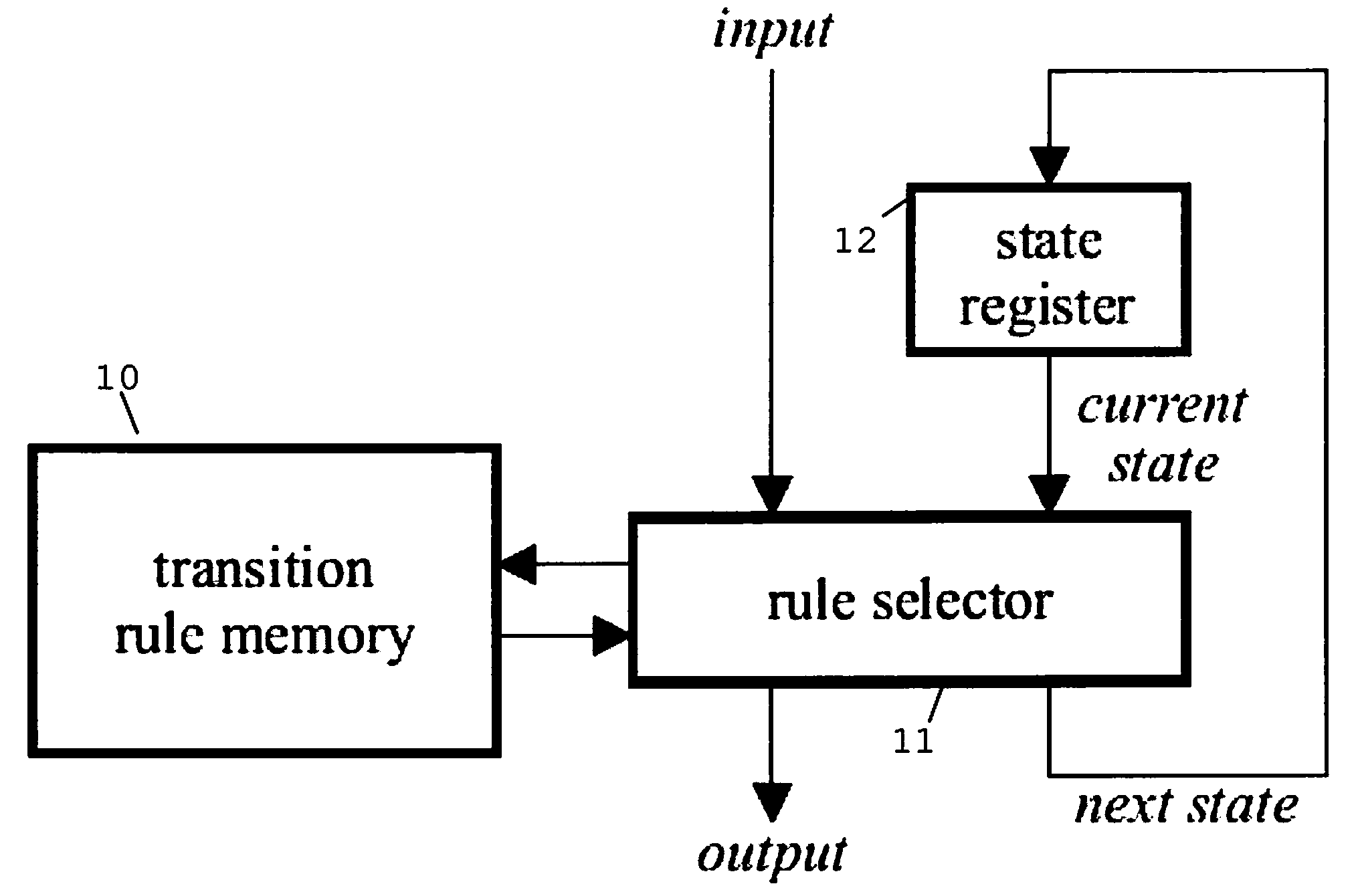
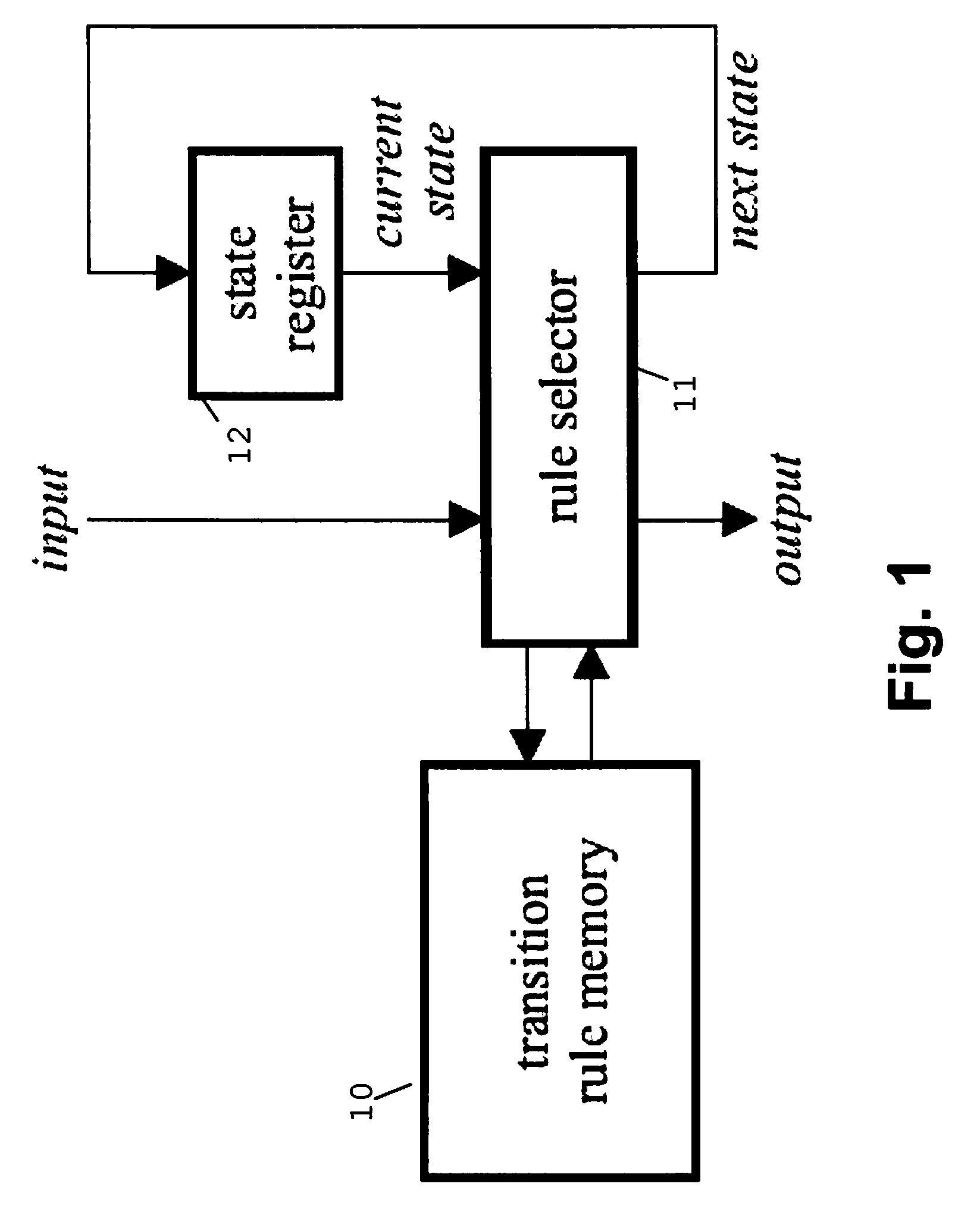
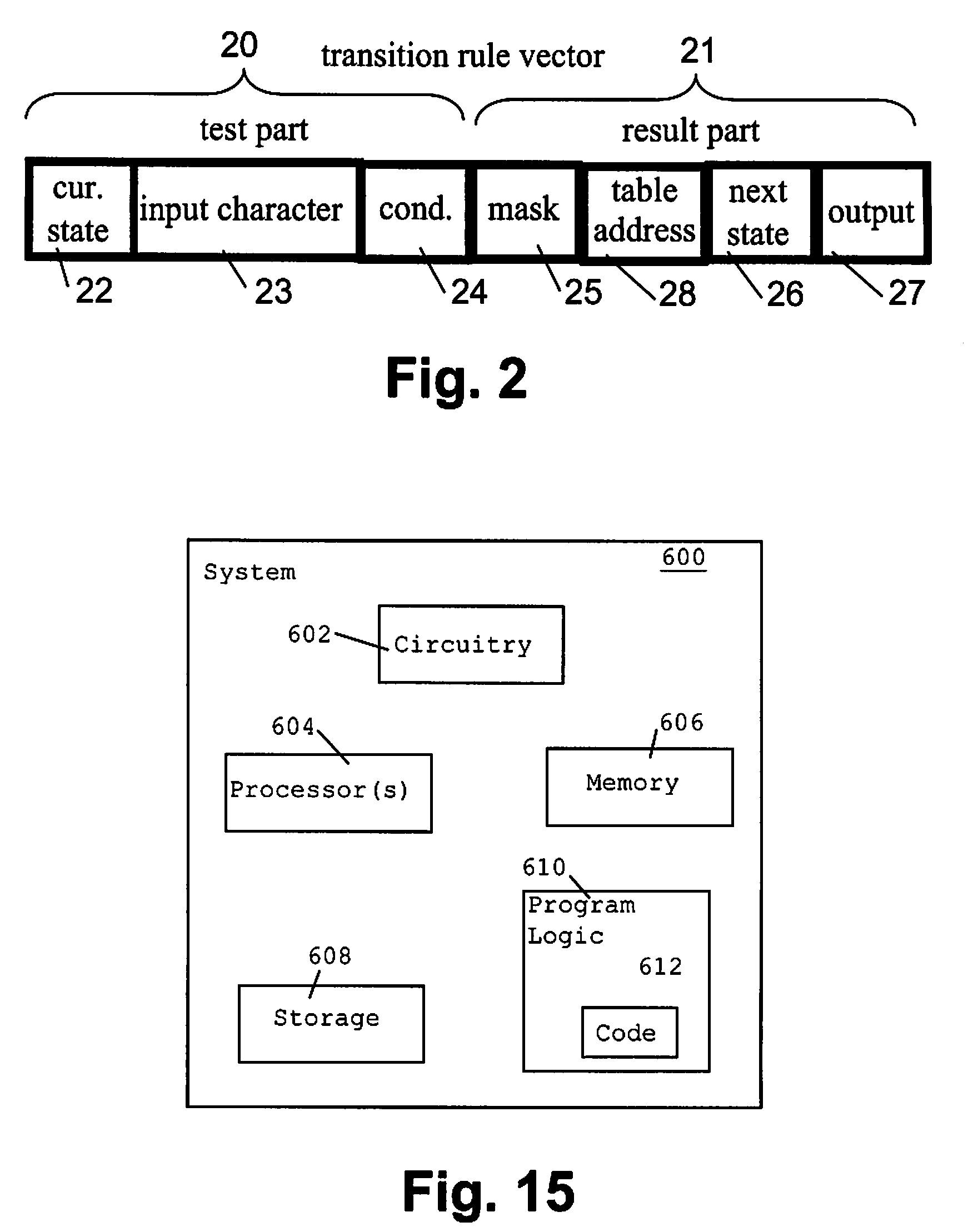
Method and System for Changing a Description for a State Transition Function of a State Machine Engine
InactiveUS20070282573A1Improve performanceImprove cache hit ratioNatural language data processingComputation using non-denominational number representationState switchingCache hit rate
The invention relates to a method of optimizing a state transition function specification for a state machine engine based on a probability distribution for the state transitions. For the preferred embodiment of the invention, a B-FSM state machine engine accesses a transition rule memory using a processor cache. The invention allows improving the cache hit rate by exploiting the probability distribution. The N transition rules that comprise a hash table entry will be loaded in a burst mode from the main memory, from which the N transition rules are transferred to the processor cache. Because the comparison of the actual state and input values against each of the transition rules can immediately start after each of these rules has been received, the overall performance is improved as the transition rule that is most likely to be selected is the first to be transferred as part of the burst access.
Owner:IBM CORP
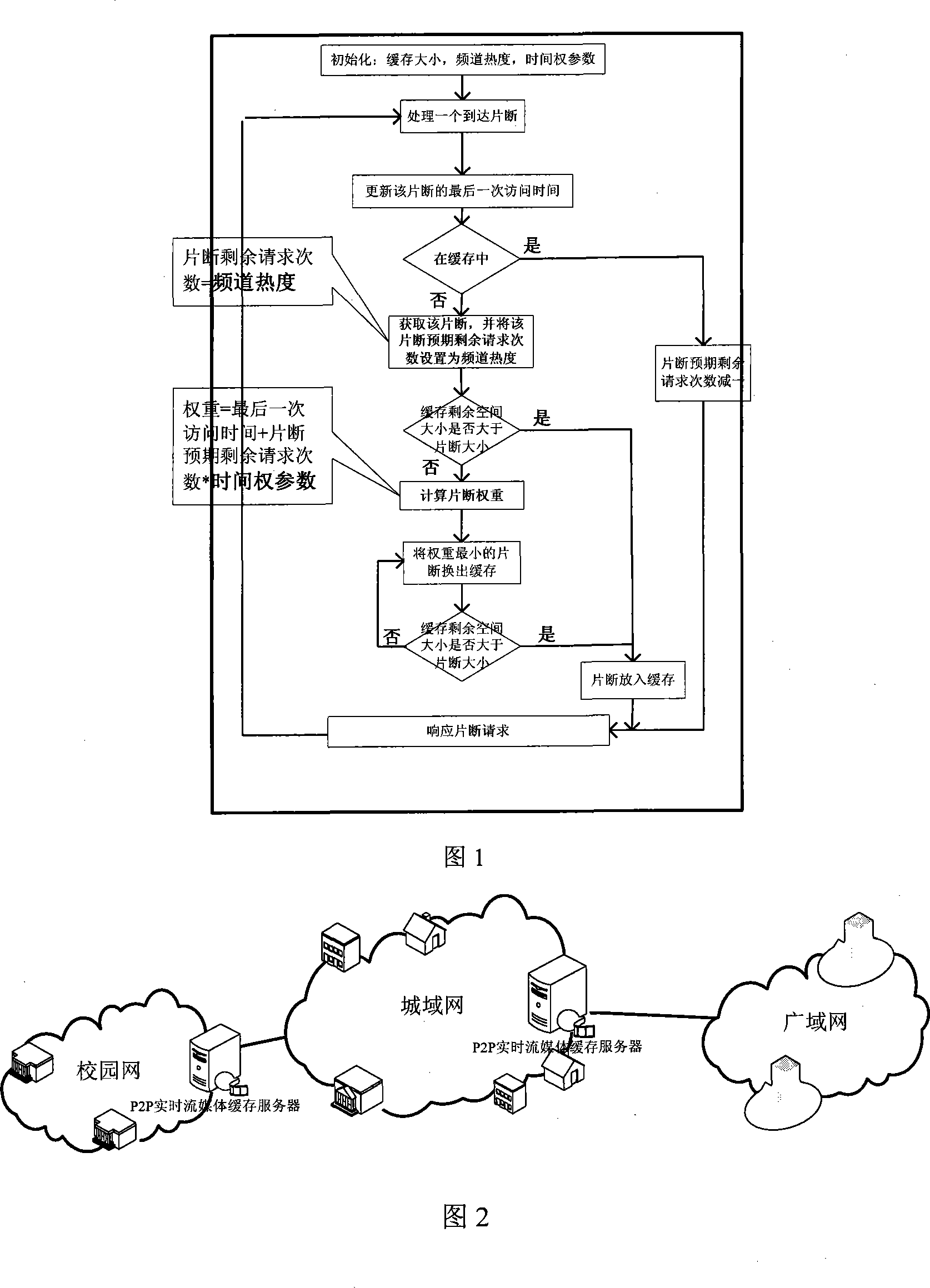
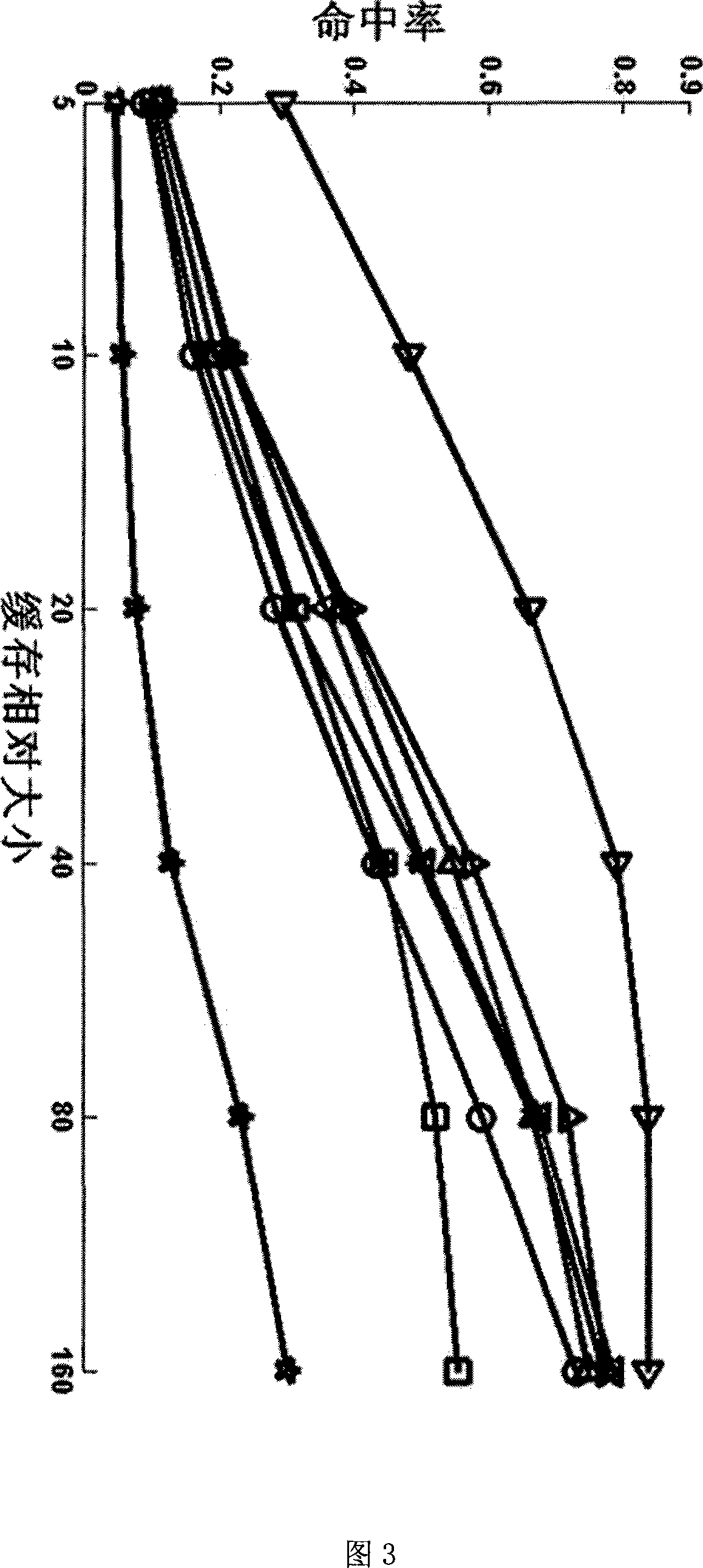
P2P real time stream media buffer replacing method based on time weight parameter
InactiveCN101232464AImprove cache hit ratioTwo-way working systemsSelective content distributionWeight coefficientAccess time
A time-weighted-coefficient-based real-time streaming media cache replacement method (TOW-Time Over Weight) belongs to the technical field of internet P2P real hyphen time media and cache replacement and is characterized in that the time characteristic of real-time synchronization of P2P real-time streaming media application users is analyzed with TOW method and meanwhile the effect of the last access time and the expected residual request of fragments on the cache are considered. The TOW algorithm can differentiate 'hot and cold' channels and 'cold or hot' fragments in the same channel and remain the 'hot' fragments in the cache to improve cache hit ratio. The cache effect of the method in the invention is confirmed better than the effect of common cache replacement method, suitable for P2P real-time streaming media application.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Filter cache method and device, and cache system
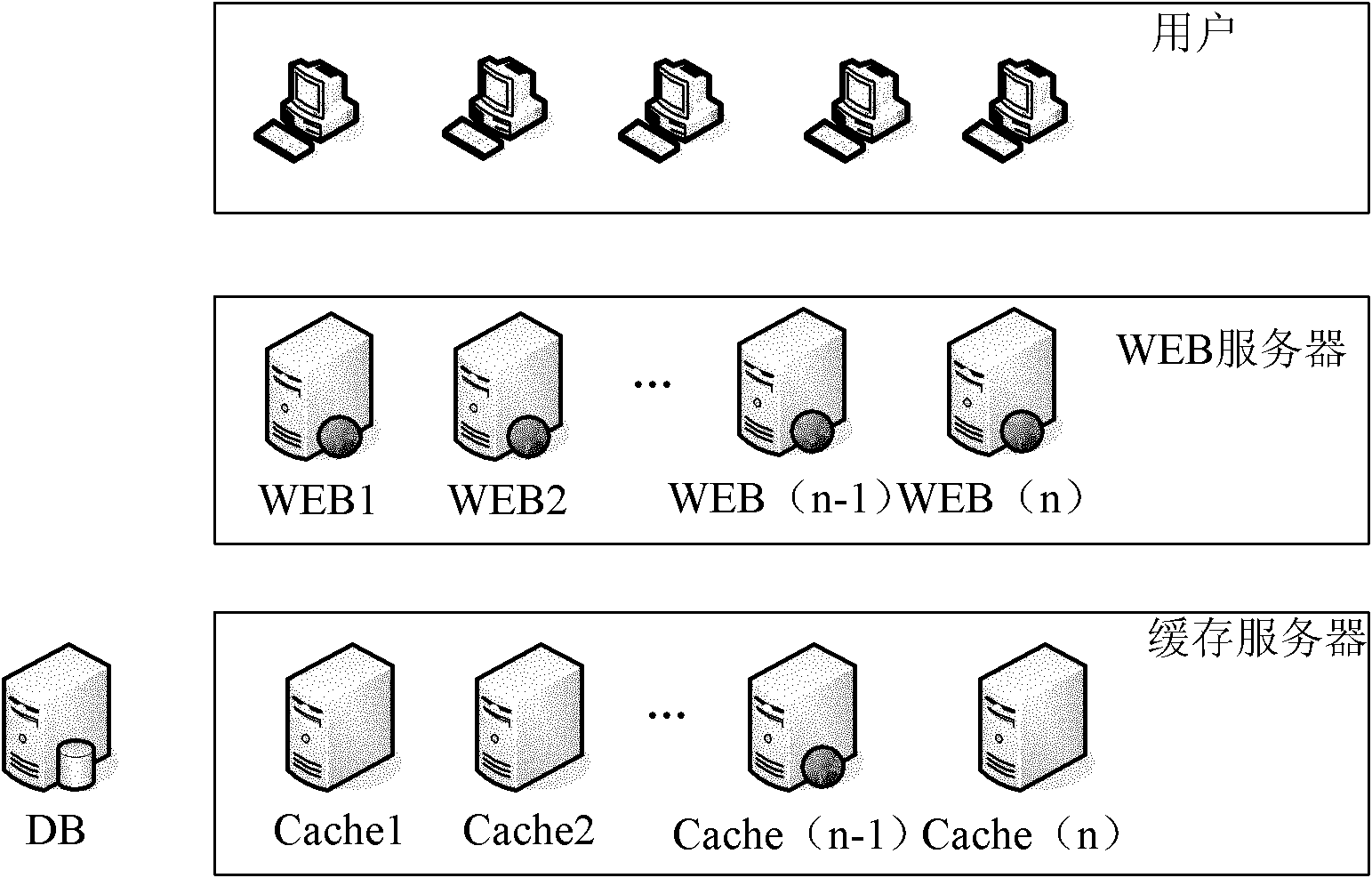
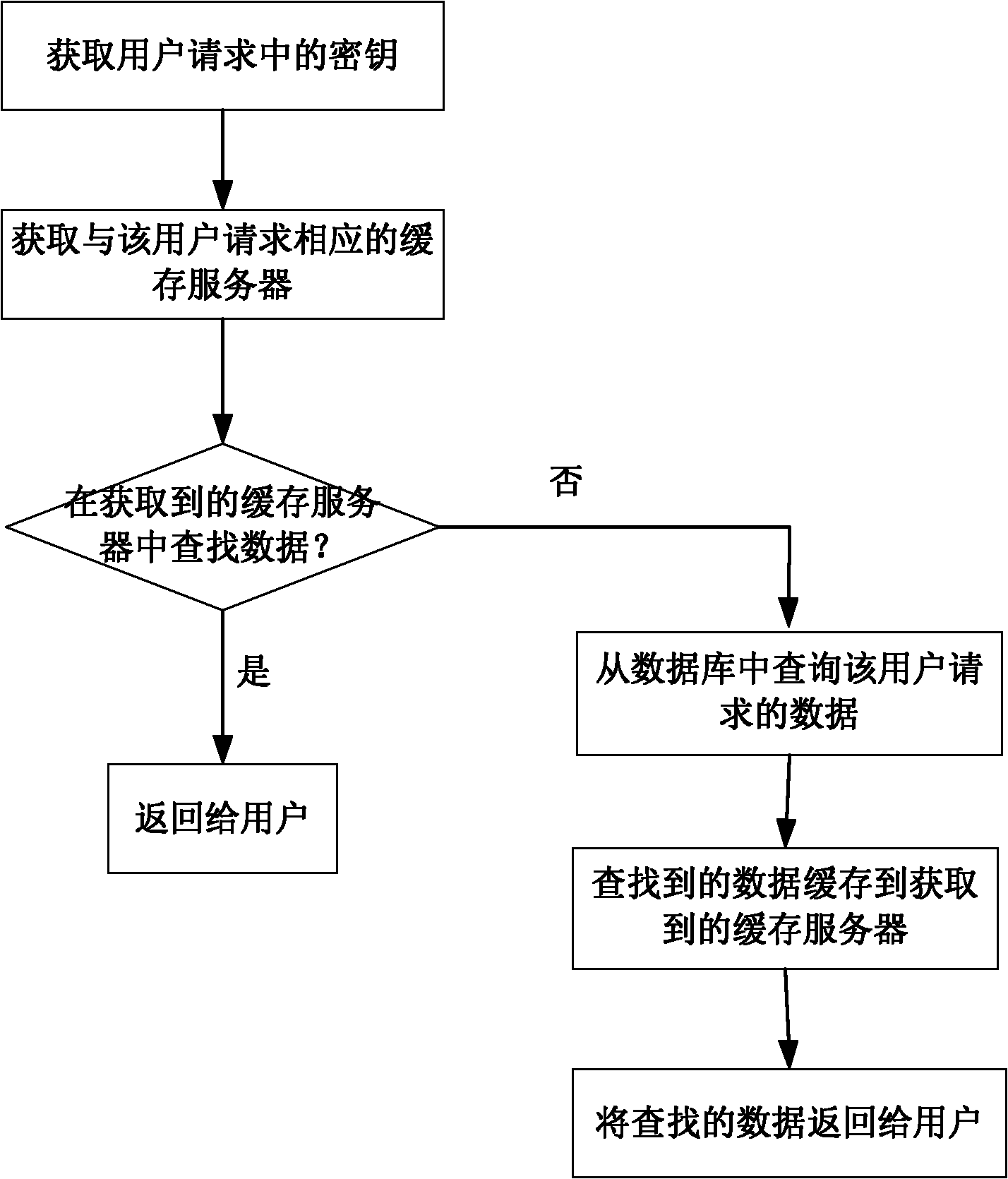
InactiveCN102012931AImprove scalabilityImprove cache hit ratioSpecial data processing applicationsCache serverFilter cache
The invention discloses a filter cache method and a filter cache device, and a cache system. The filter cache method comprises the following steps of: 1, acquiring a key in a user request according to the user request; 2, selecting a cache server corresponding to the user request according to the key; and 3, querying data requested by a user from the selected cache server, and directly returning the searched data to the user. The filter cache method can improve the cache data hit rate and the cache expansibility.
Owner:BEIJING RUIXIN ONLINE SYST TECH
Systems and methods for data caching
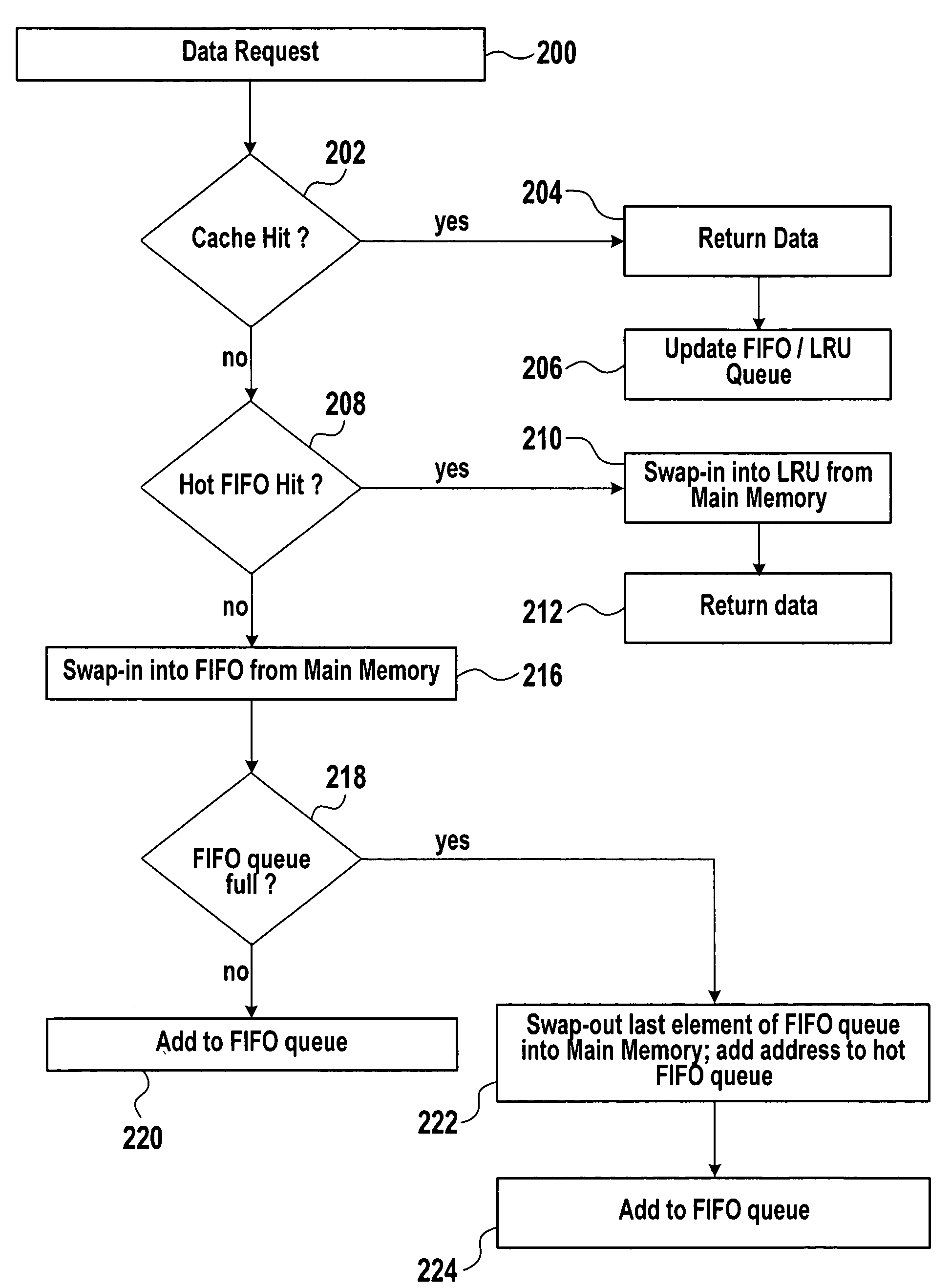
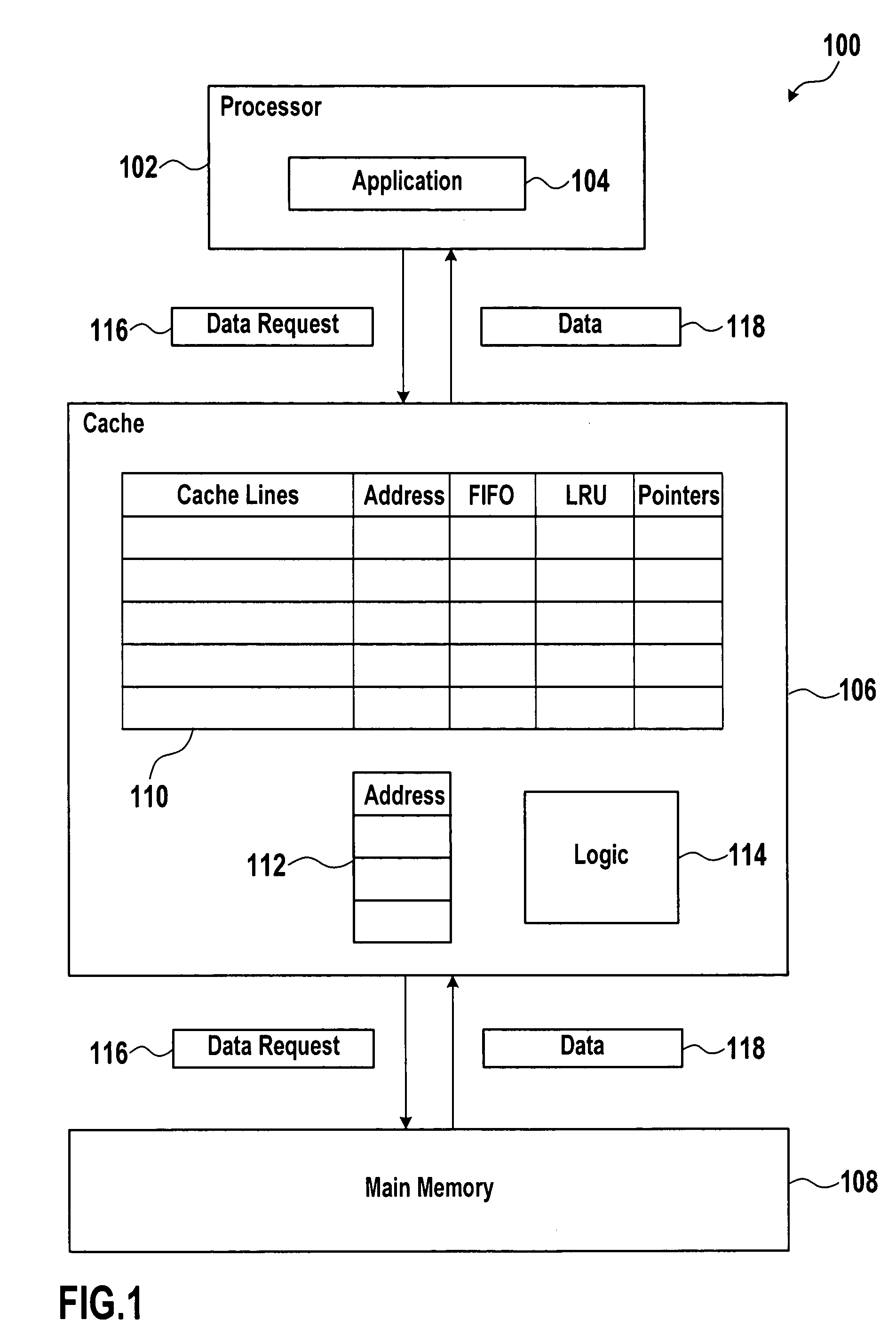
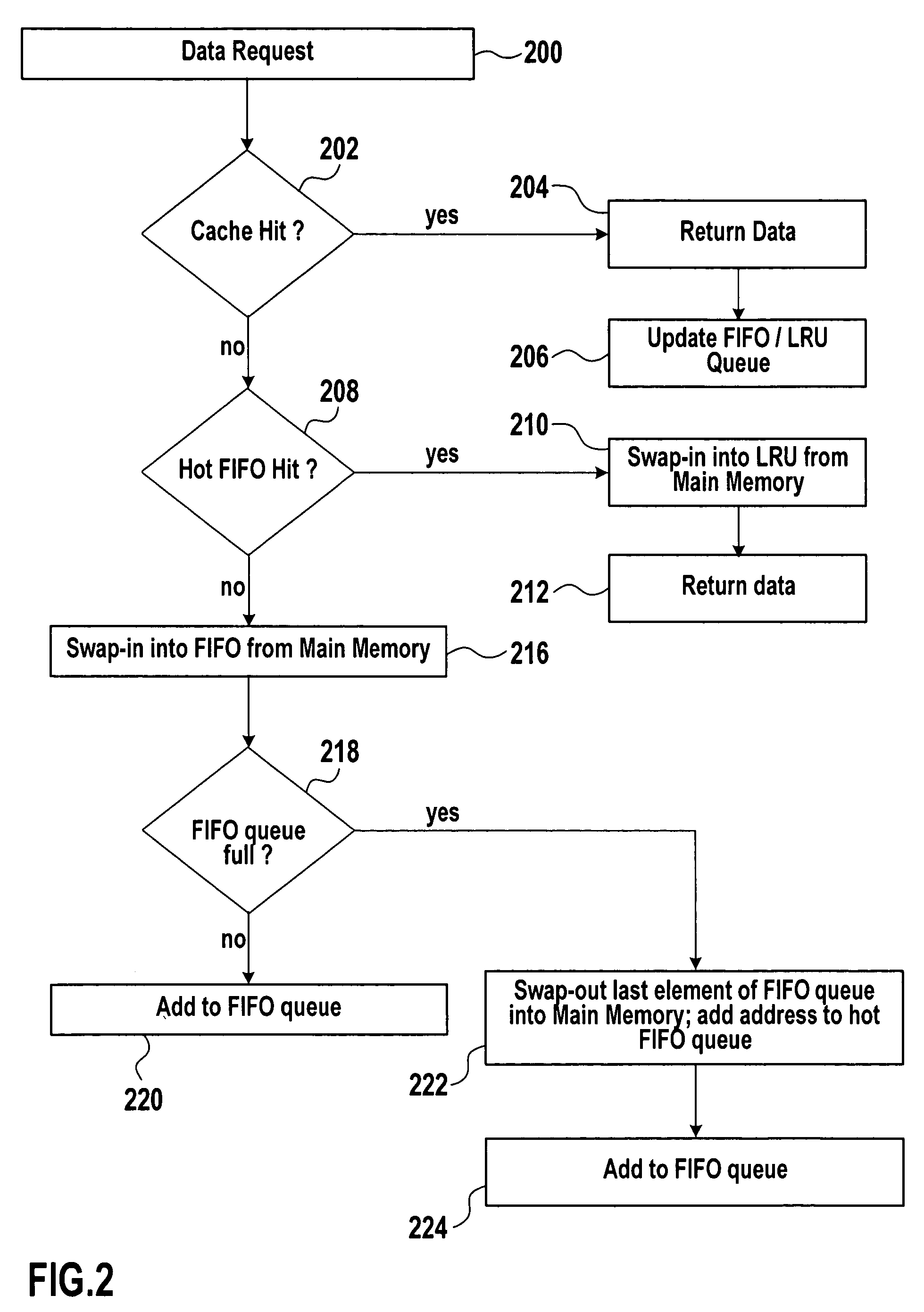
ActiveUS7284096B2Positively performanceImprove cache hit ratioMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationExternal storageData exchange
Systems and methods are provided for data caching. An exemplary method for data caching may include establishing a FIFO queue and a LRU queue in a cache memory. The method may further include establishing an auxiliary FIFO queue for addresses of cache lines that have been swapped-out to an external memory. The method may further include determining, if there is a cache miss for the requested data, if there is a hit for requested data in the auxiliary FIFO queue and, if so, swapping-in the requested data into the LRU queue, otherwise swapping-in the requested data into the FIFO queue.
Owner:SAP AG
Detecting and processing cache hits for queries with aggregates
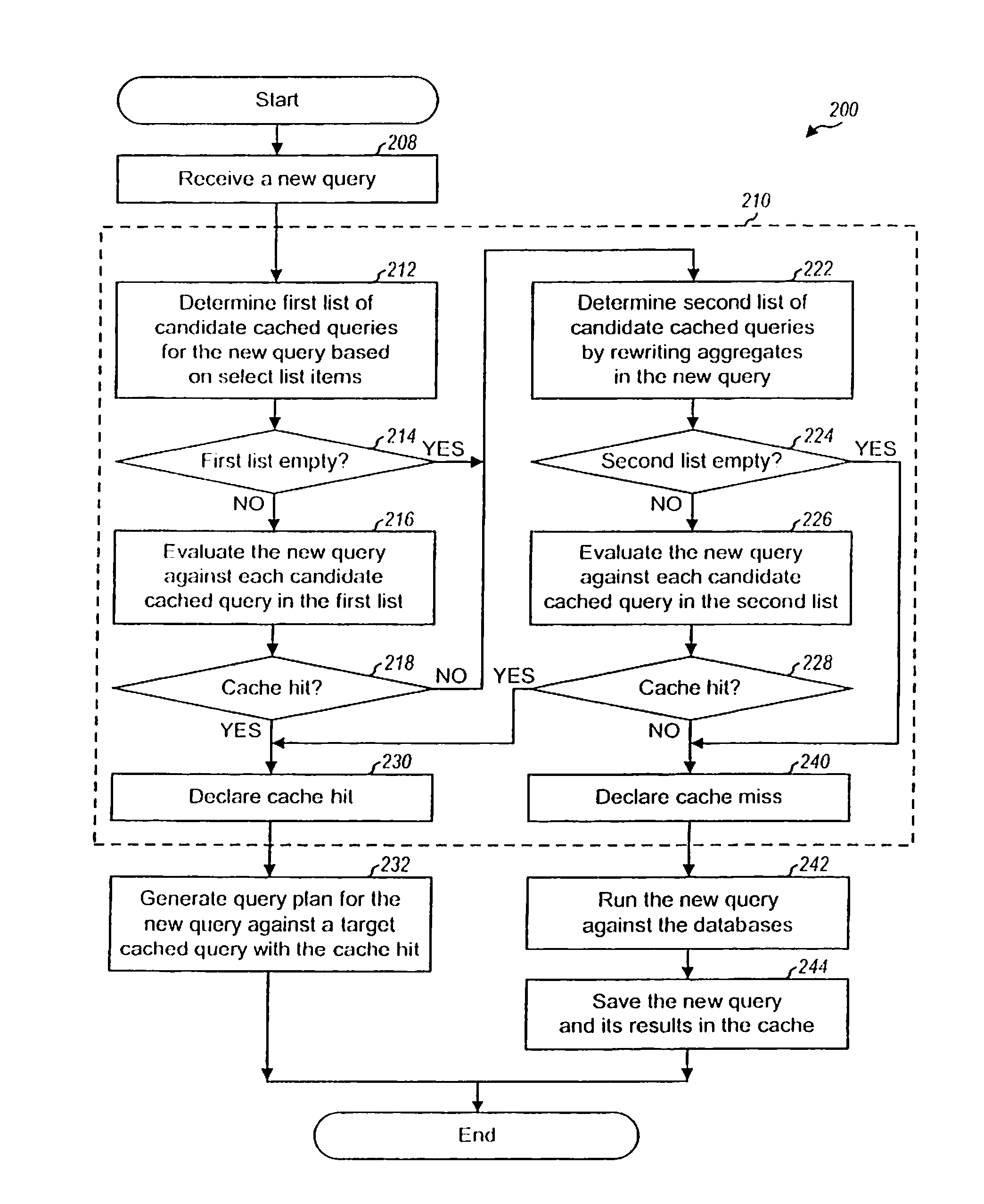
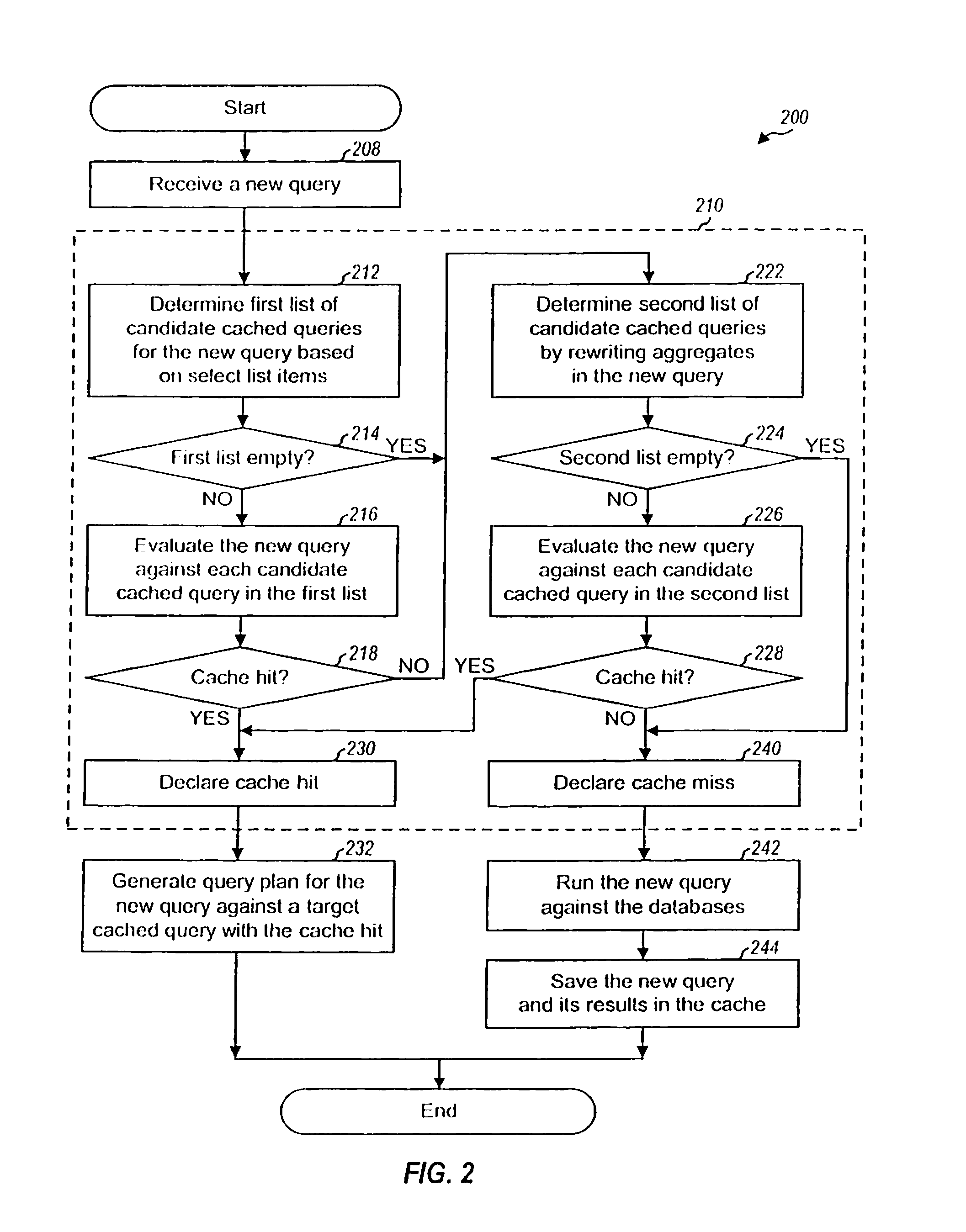
ActiveUS20080077557A1Valid choiceEfficiently determinedData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalExact matchQuery plan
Techniques to improve query caching performance by efficiently selecting queries stored in a cache for evaluation and increasing the cache hit rate by allowing for inexact matches. A list of candidate queries stored in the cache that potentially could be used to answer a new query is first determined. This list may include all cached queries, cached queries containing exact matches for select list items, or cached queries containing exact and / or inexact matches. Each of at least one candidate query is then evaluated to determine whether or not there is a cache hit, which indicates that the candidate query could be used to answer the new query. The evaluation is performed using a set of rules that allows for inexact matches of aggregates, if any, in the new query. A query plan is generated for the new query based on a specific candidate query with a cache hit.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com