Patents
Literature
4988 results about "Network switch" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
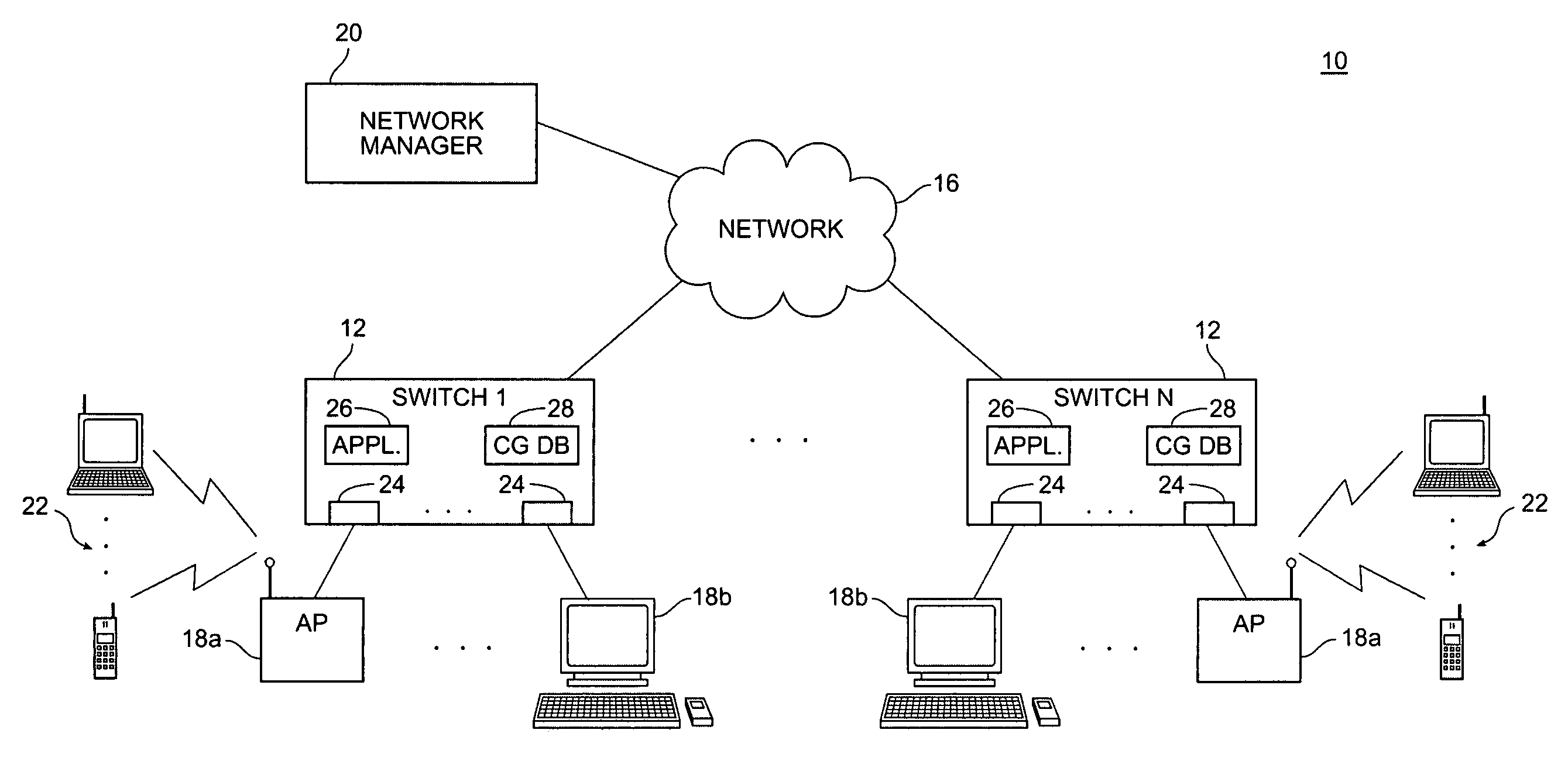
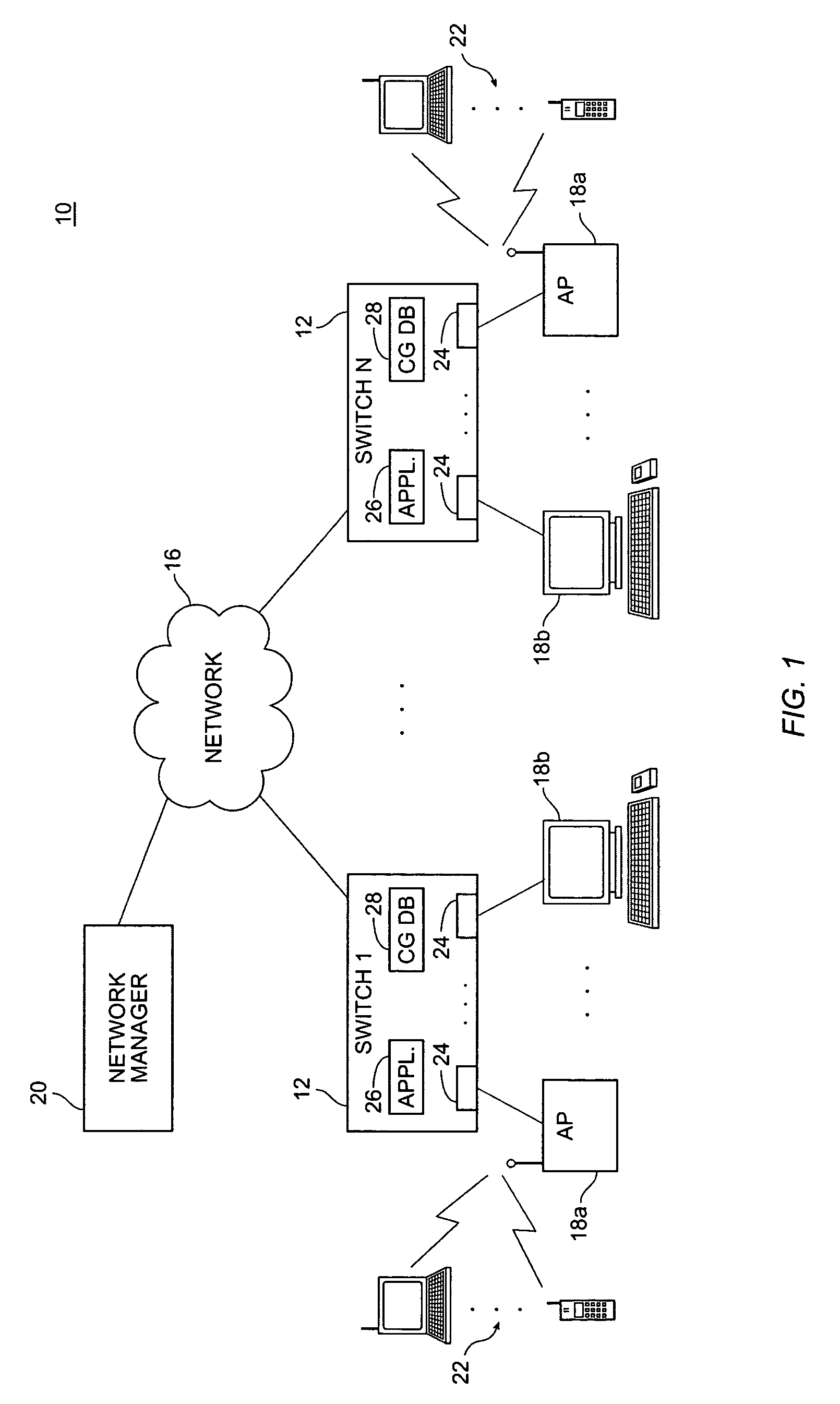
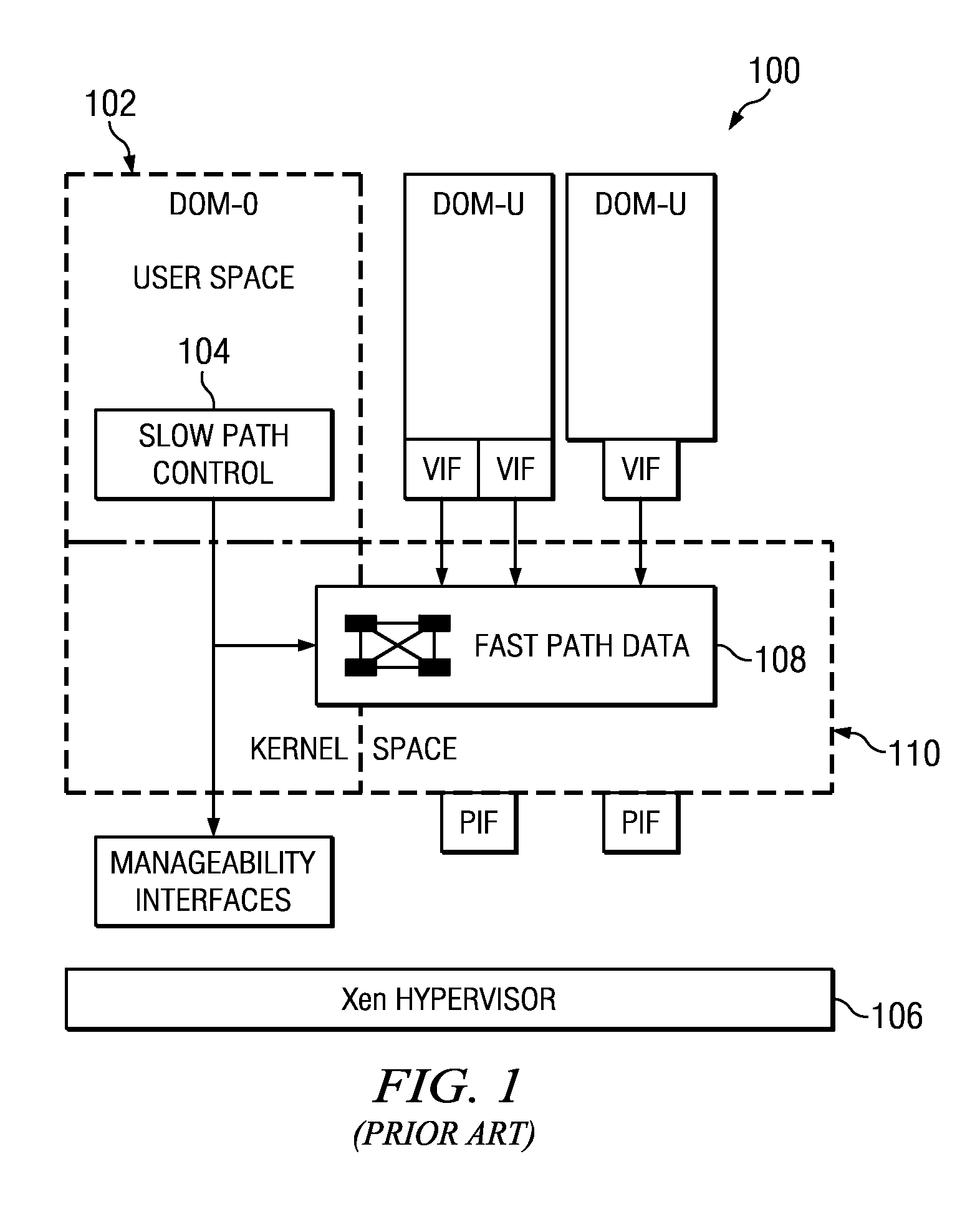
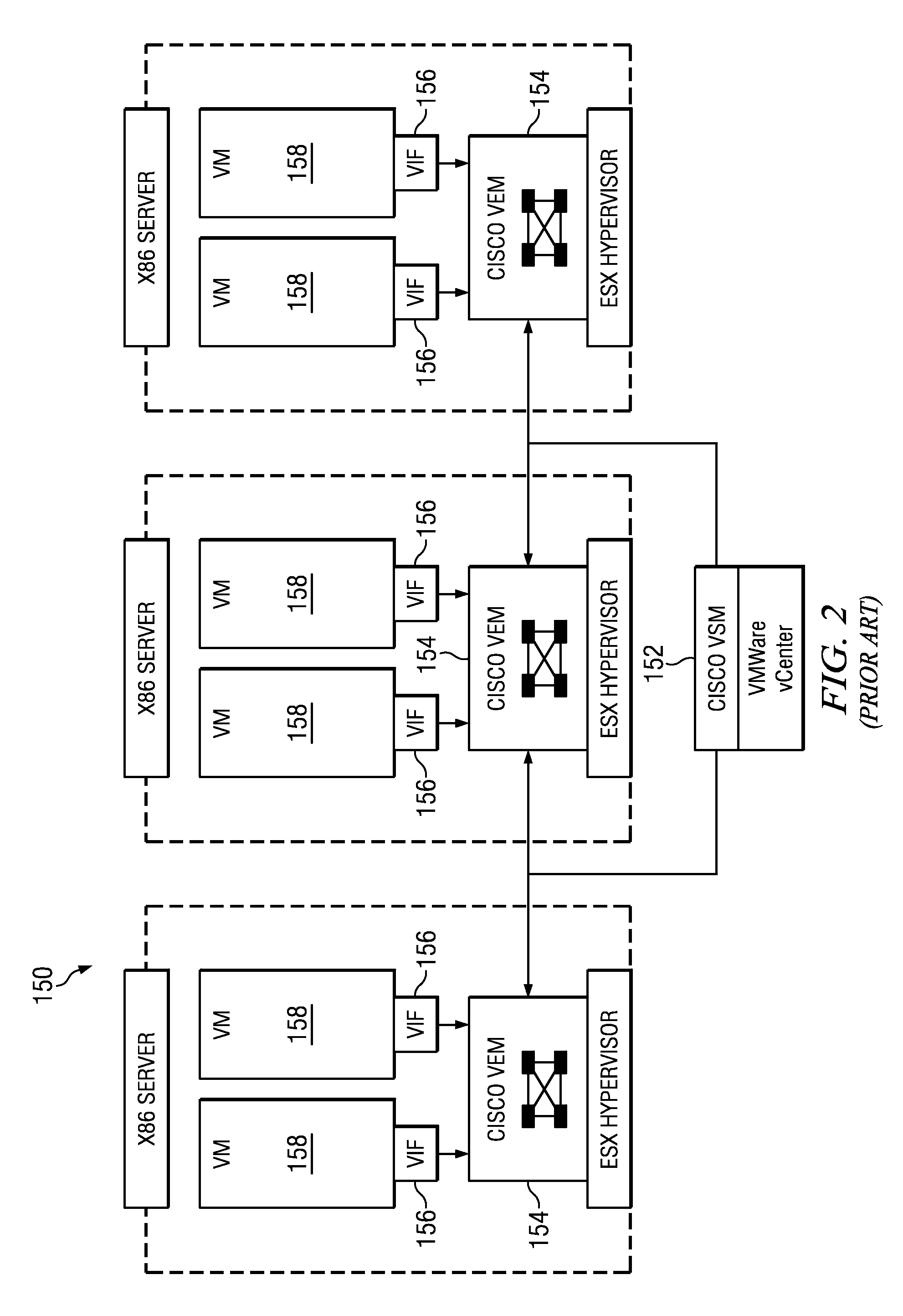
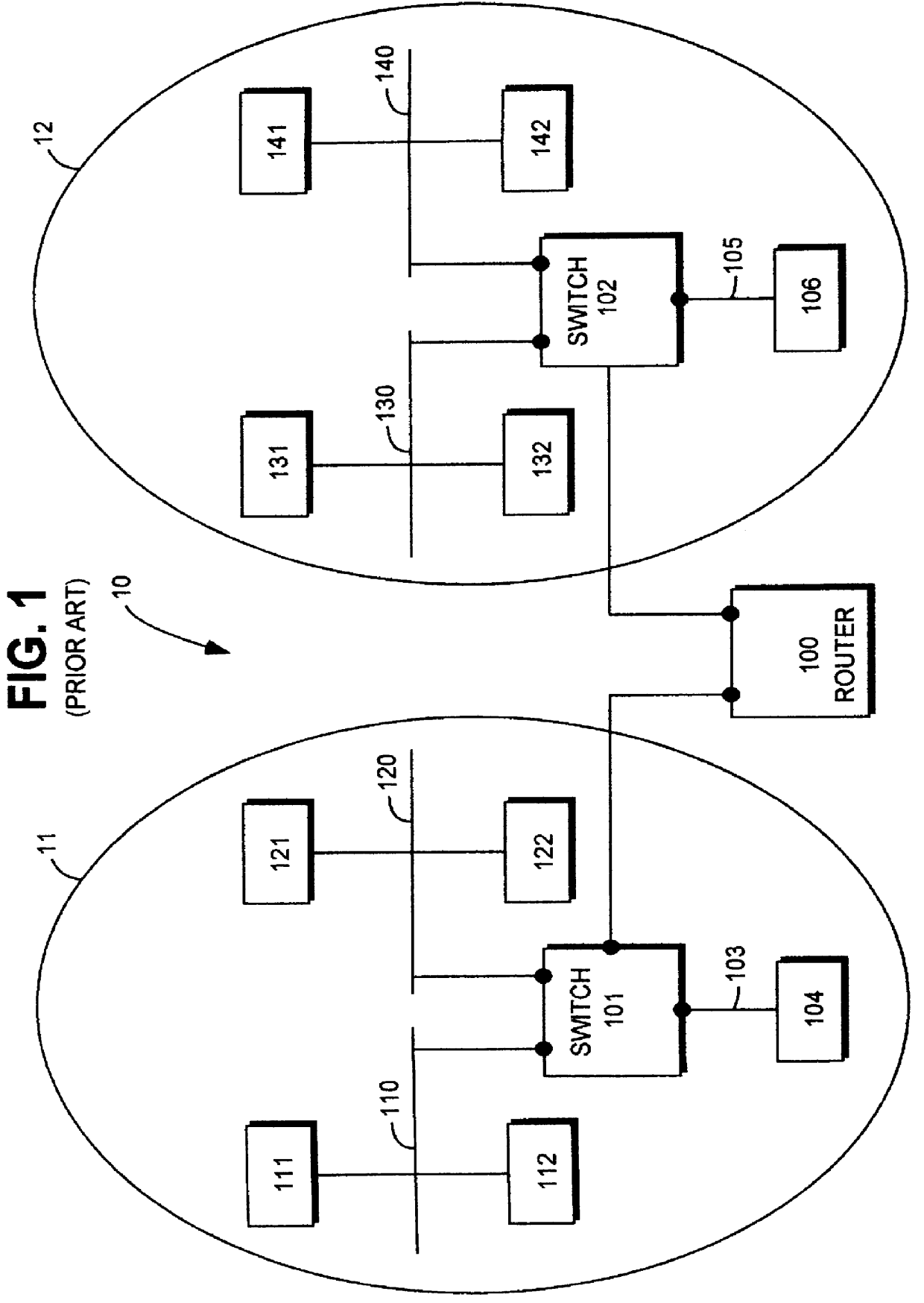
A network switch (also called switching hub, bridging hub, officially MAC bridge) is networking hardware that connects devices on a computer network by using packet switching to receive, and forward data to the destination device.
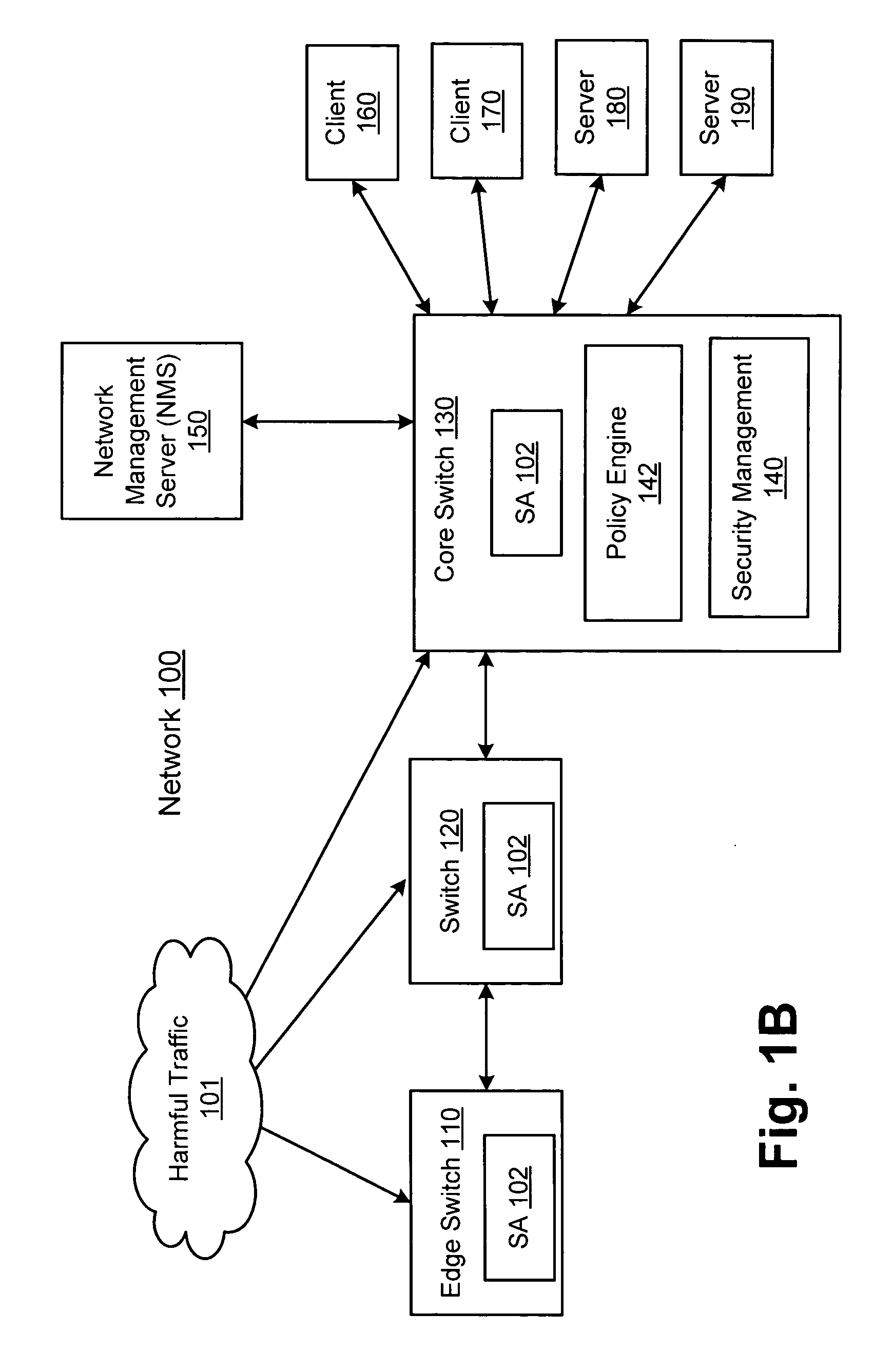
Secure network switching infrastructure
InactiveUS20080189769A1Reduces the trusted computing baseReduce overheadDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationNetwork packetNetwork control
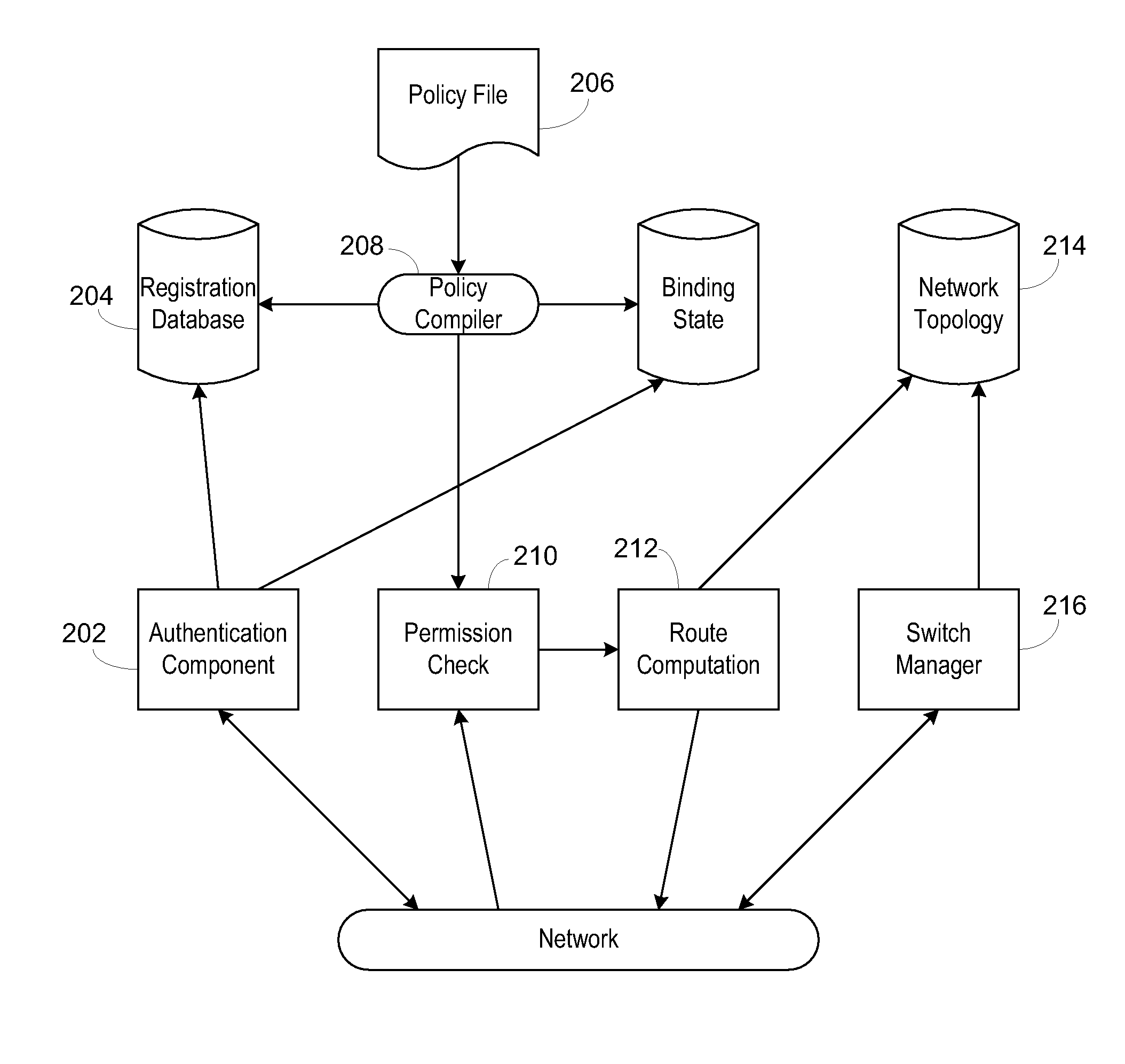
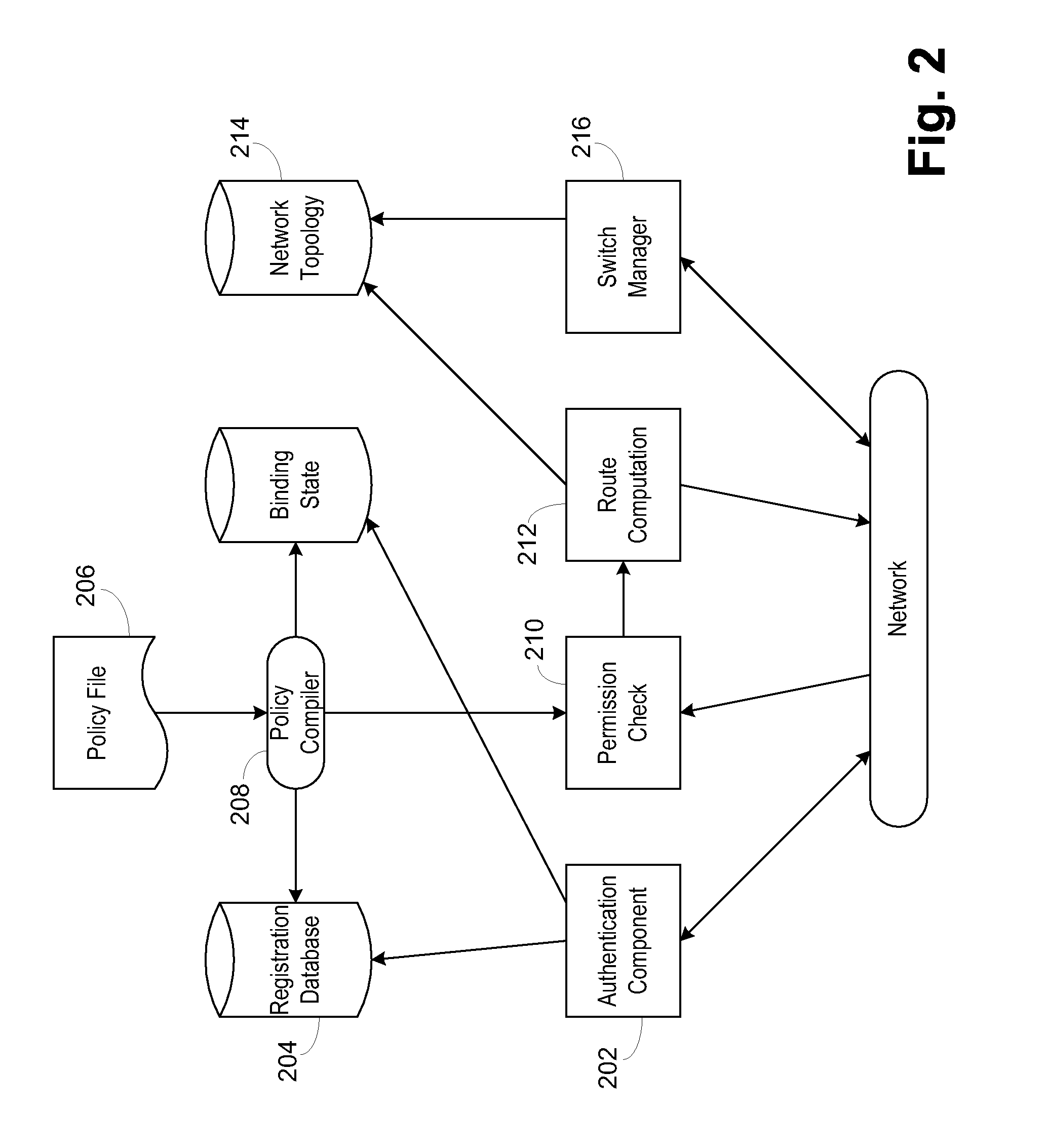
Use of a centralized control architecture in a network. Policy declaration, routing computation, and permission checks are managed by a logically centralized controller. By default, hosts on the network can only route to the network controller. Hosts and users must first authenticate themselves with the controller before they can request access to the network resources. The controller uses the first packet of each flow for connection setup. When a packet arrives at the controller, the controller decides whether the flow represented by that packet should be allowed. The switches use a simple flow table to forward packets under the direction of the controller. When a packet arrives that is not in the flow table, it is forwarded to the controller, along with information about which port the packet arrived on. When a packet arrives that is in the flow table, it is forwarded according to the controller's directive.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
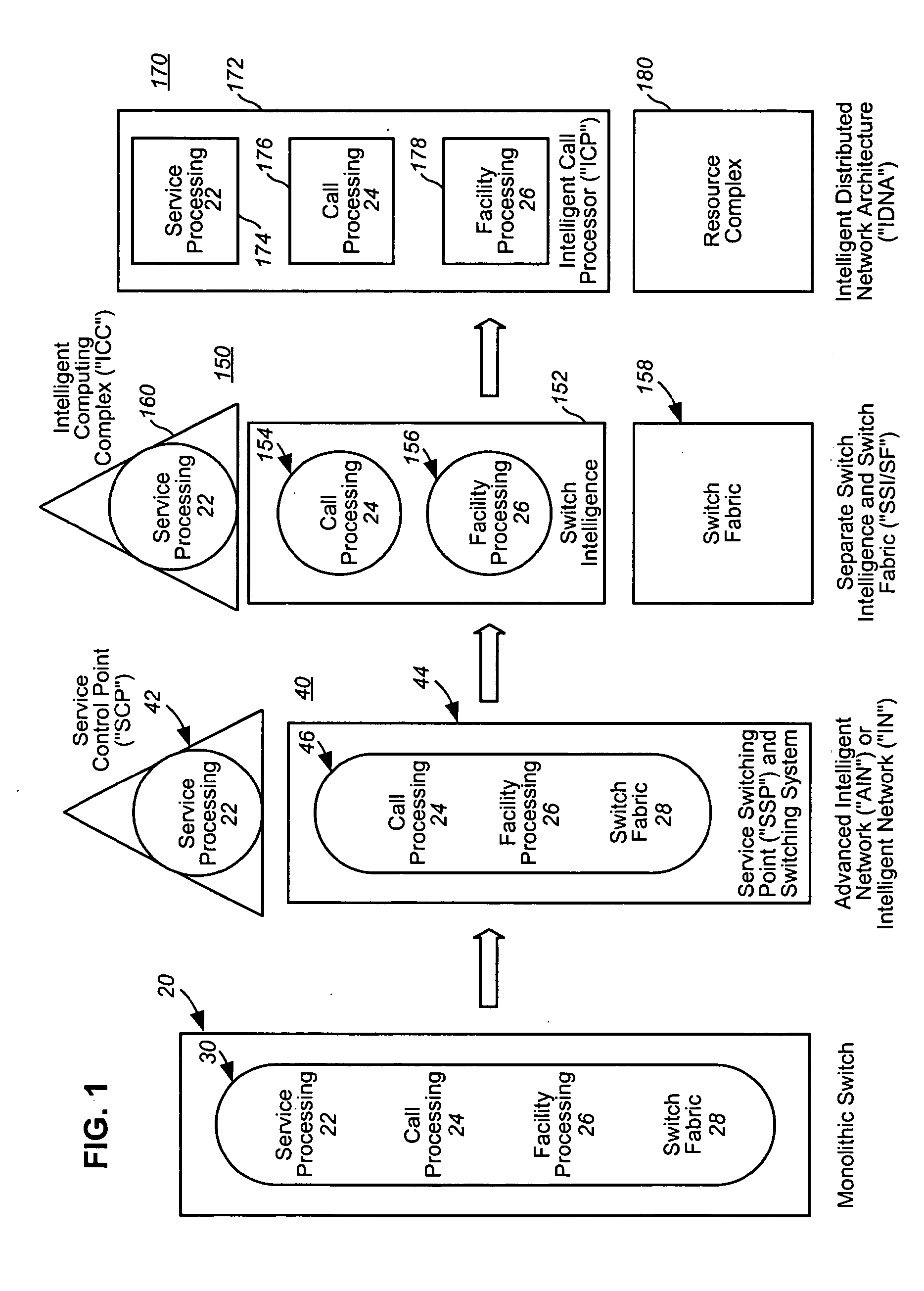
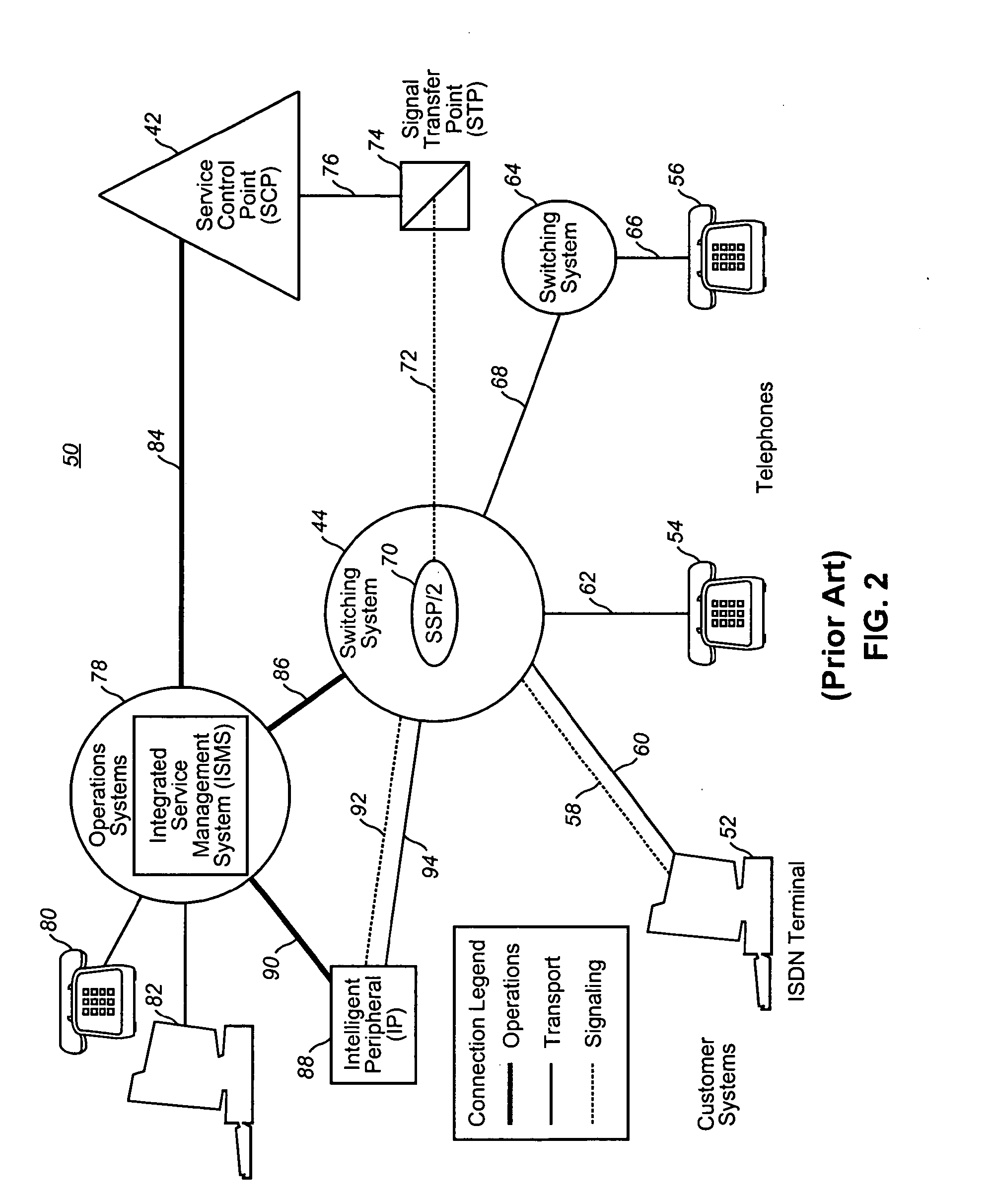
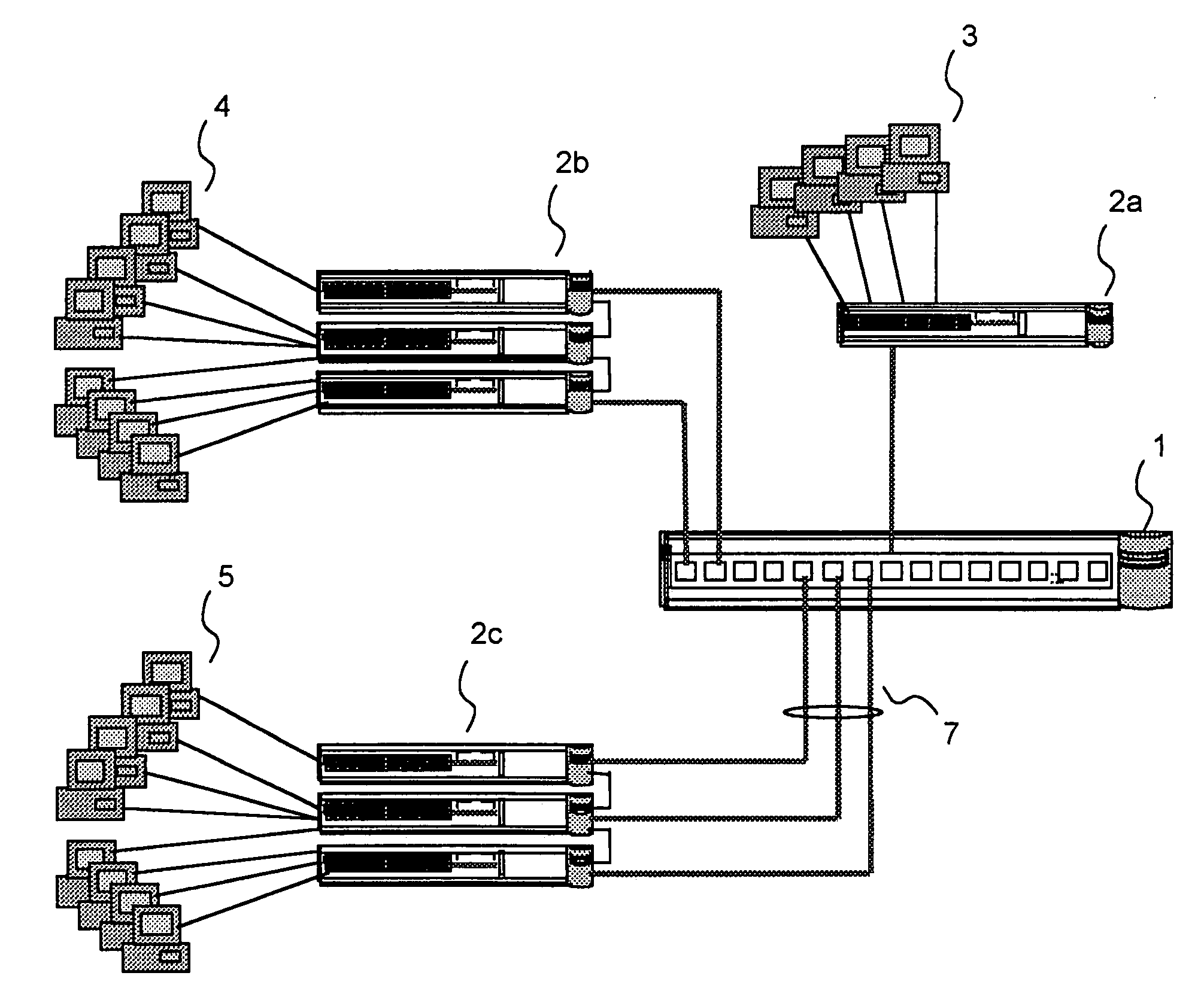
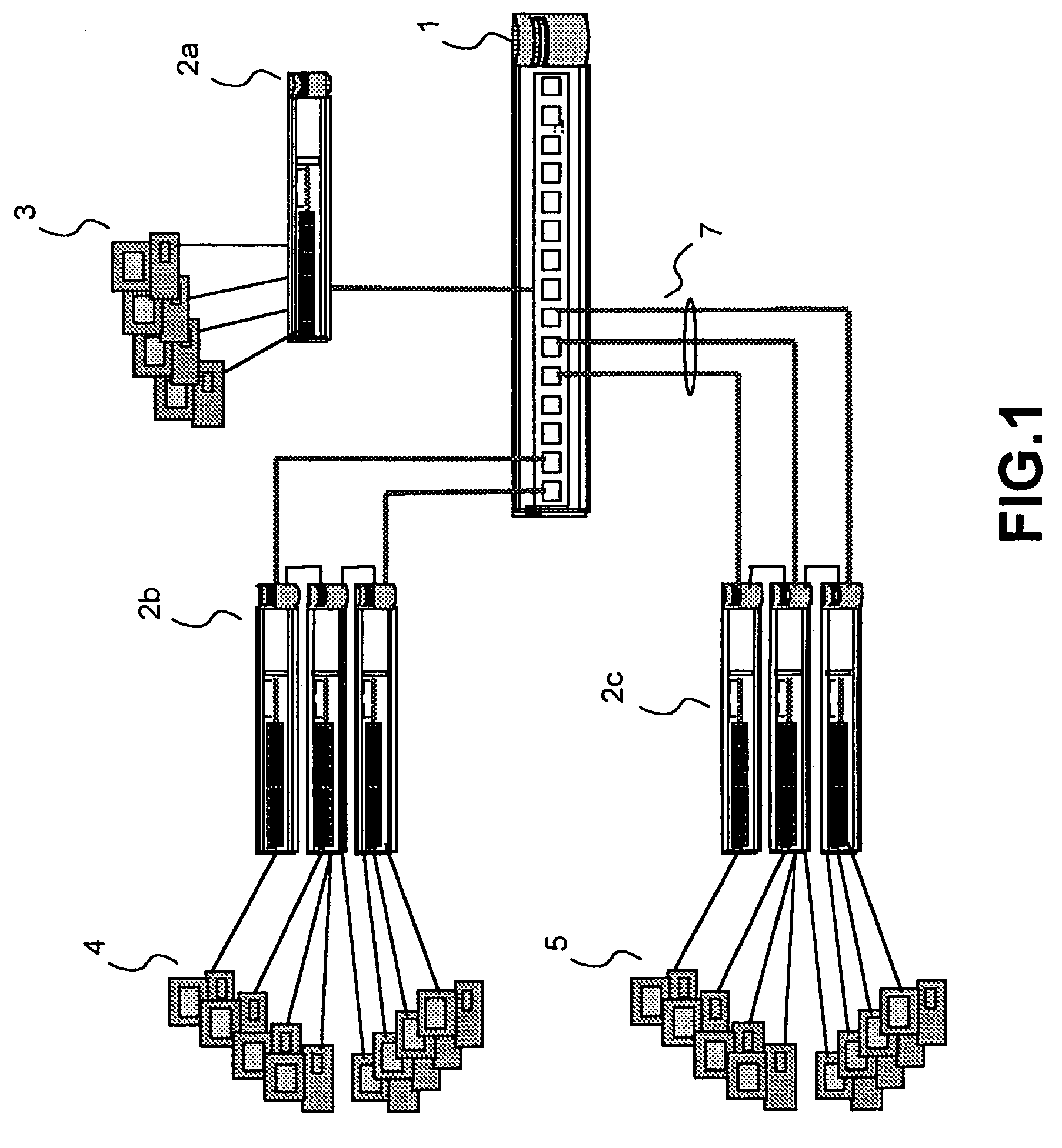
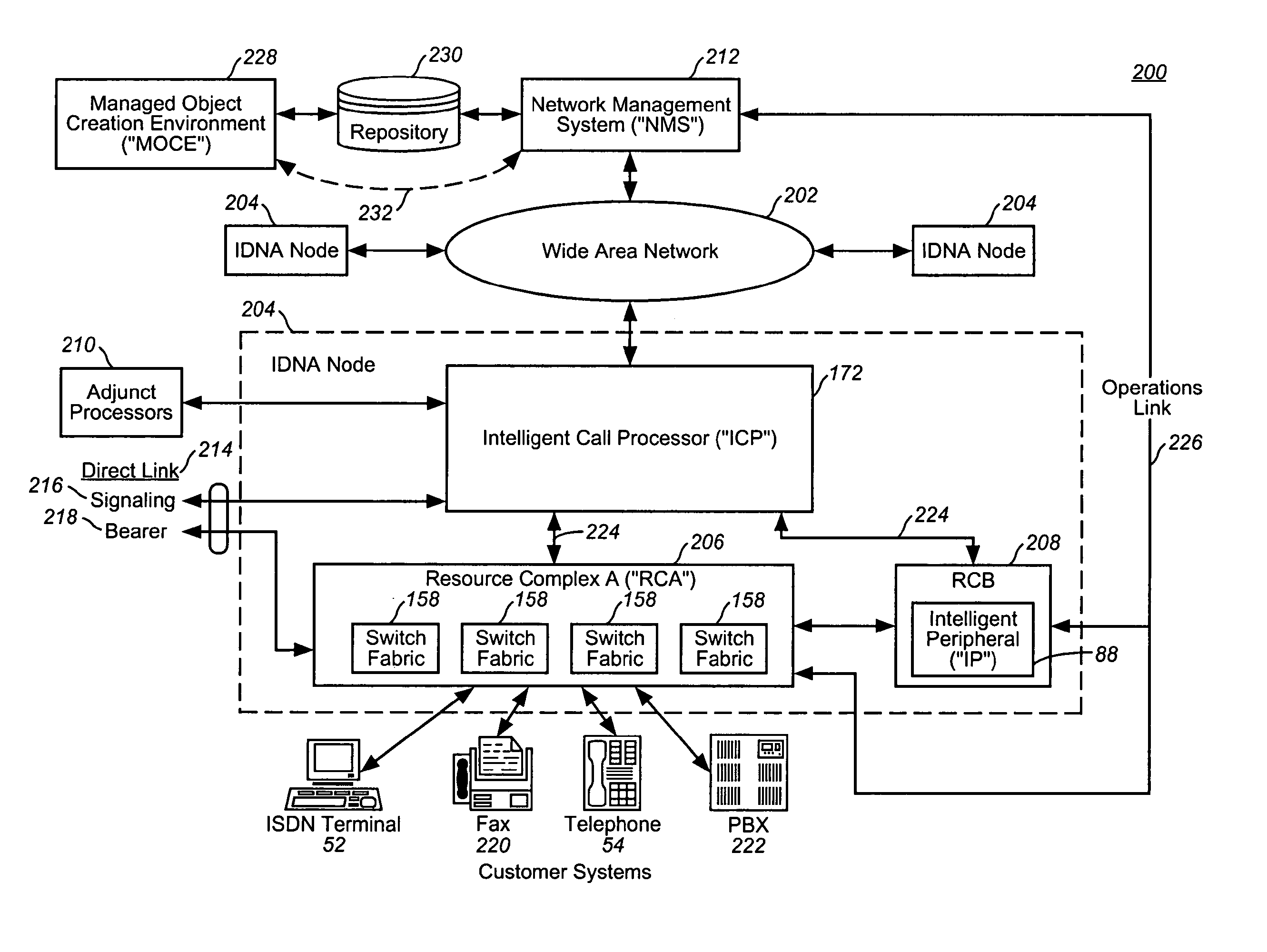
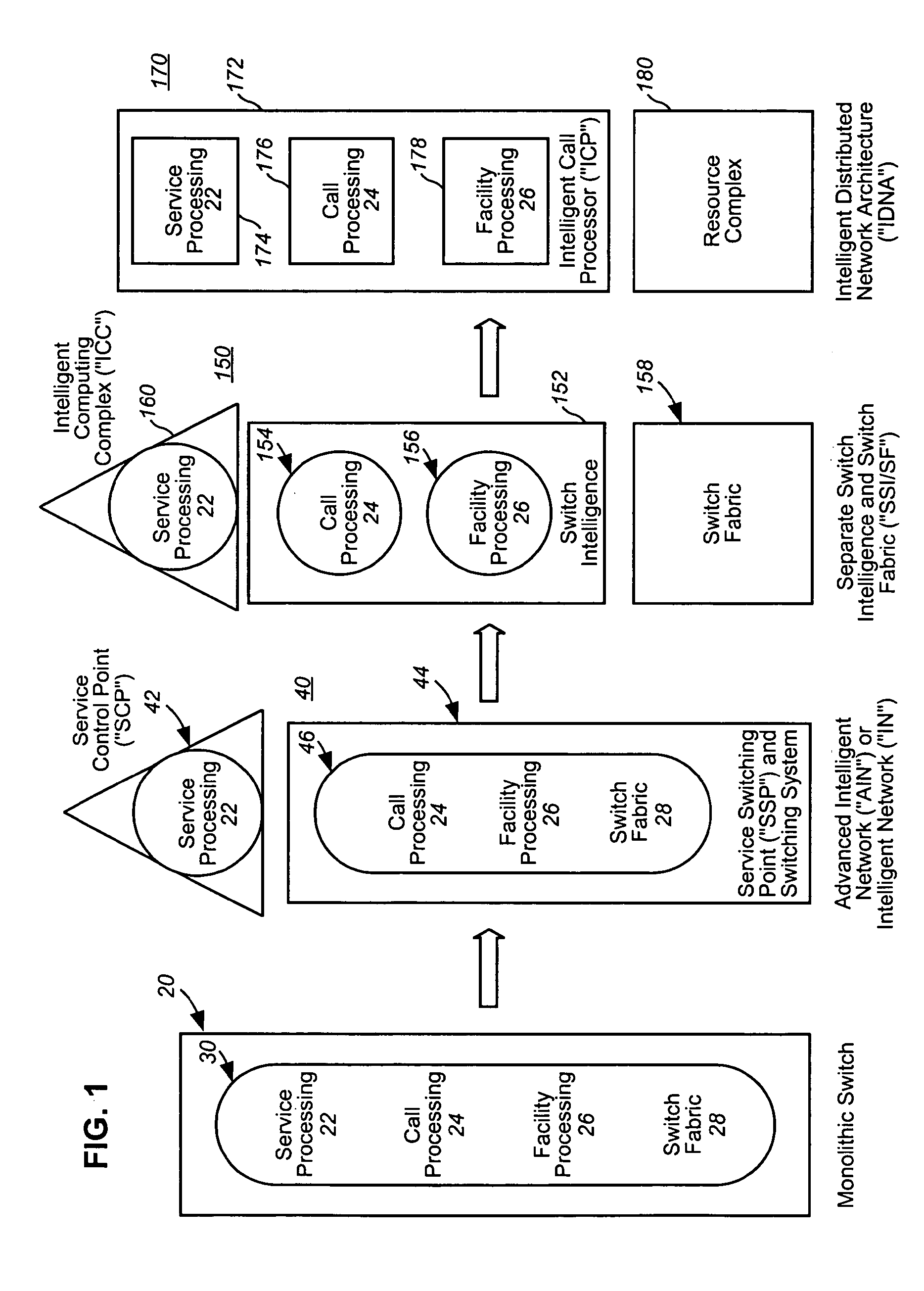
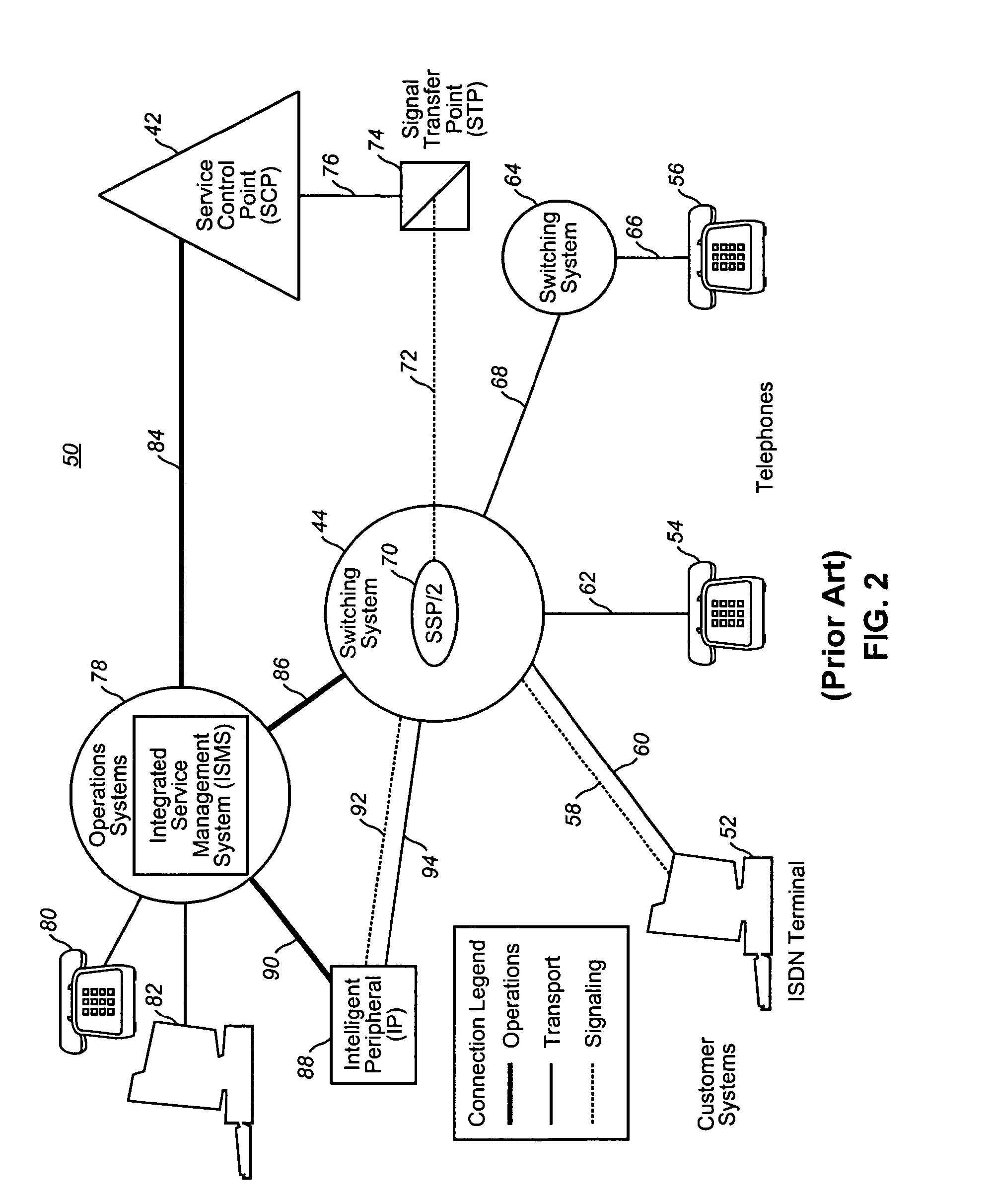
Intelligent network
InactiveUS20050021713A1Easy to handleEliminate dependenciesSpecial service for subscribersMultiple digital computer combinationsIntelligent NetworkCommunications system
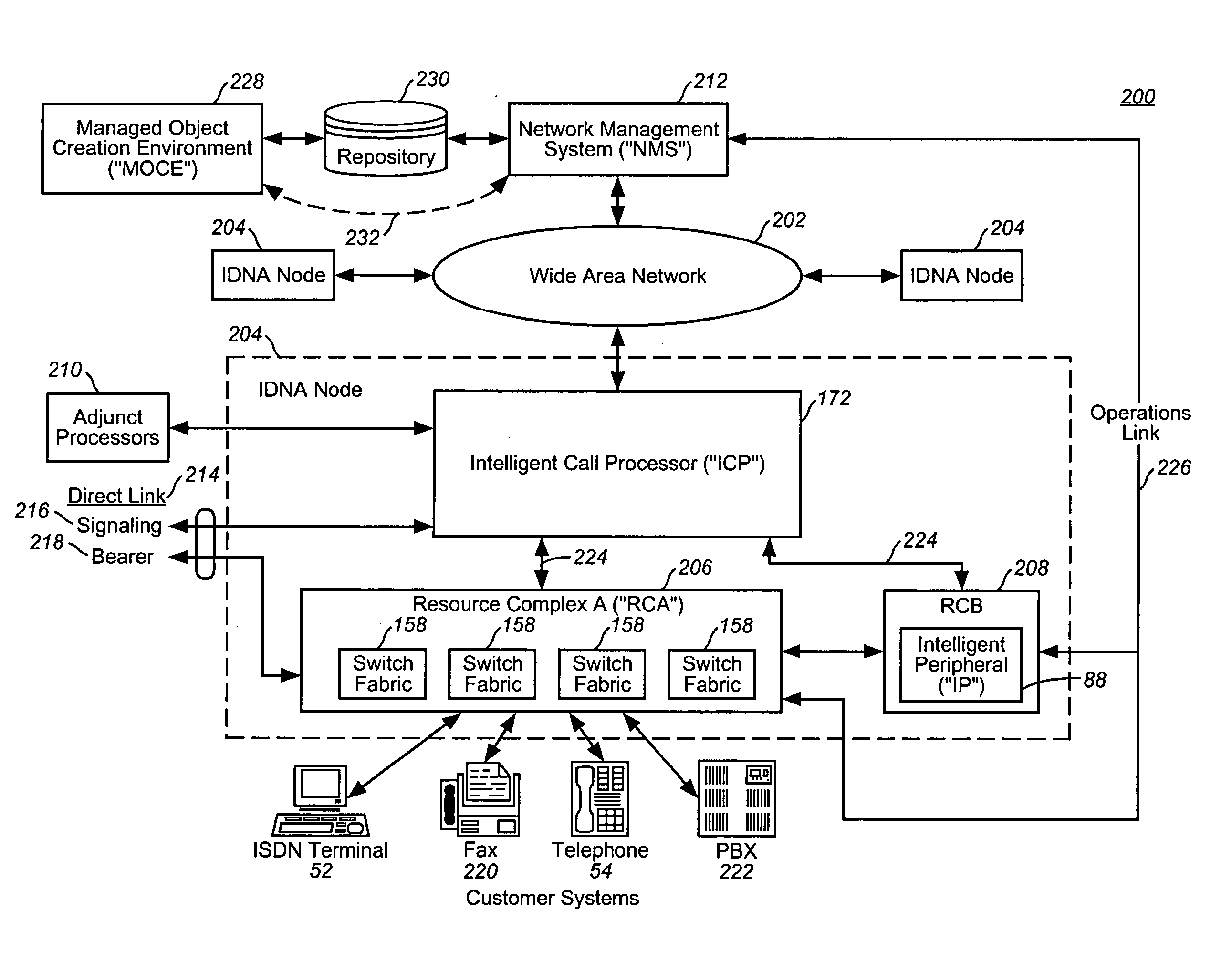
In a telecommunications switching network having a resource complex including network switches, an intelligent service platform for providing intelligent call processing and service execution for call events received at the switches and requiring call processing services. A centralized administration system is provided that comprises a system for storing one or more reusable business objects that each encapsulate a distinct call-processing function, and any associated data required by the business object; a system for distributing selected business objects and associated data to selected nodes in the switching network based on pre-determined node configuration criteria; and, a system for activating the business objects in preparation for real-time use. A computing platform is provided within each node for executing those business objects required to perform a service in accordance with an event received at the network switch. Also within a node is a storage and retrieval system for sorting and retrieving selected objects and any associated data distributed by the administration system, and making them locally available to the computing platform when required to perform a service. An underlying location-independent communication system is provided to coordinate interaction of one or more business objects to perform the service in response to needs of the received event.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
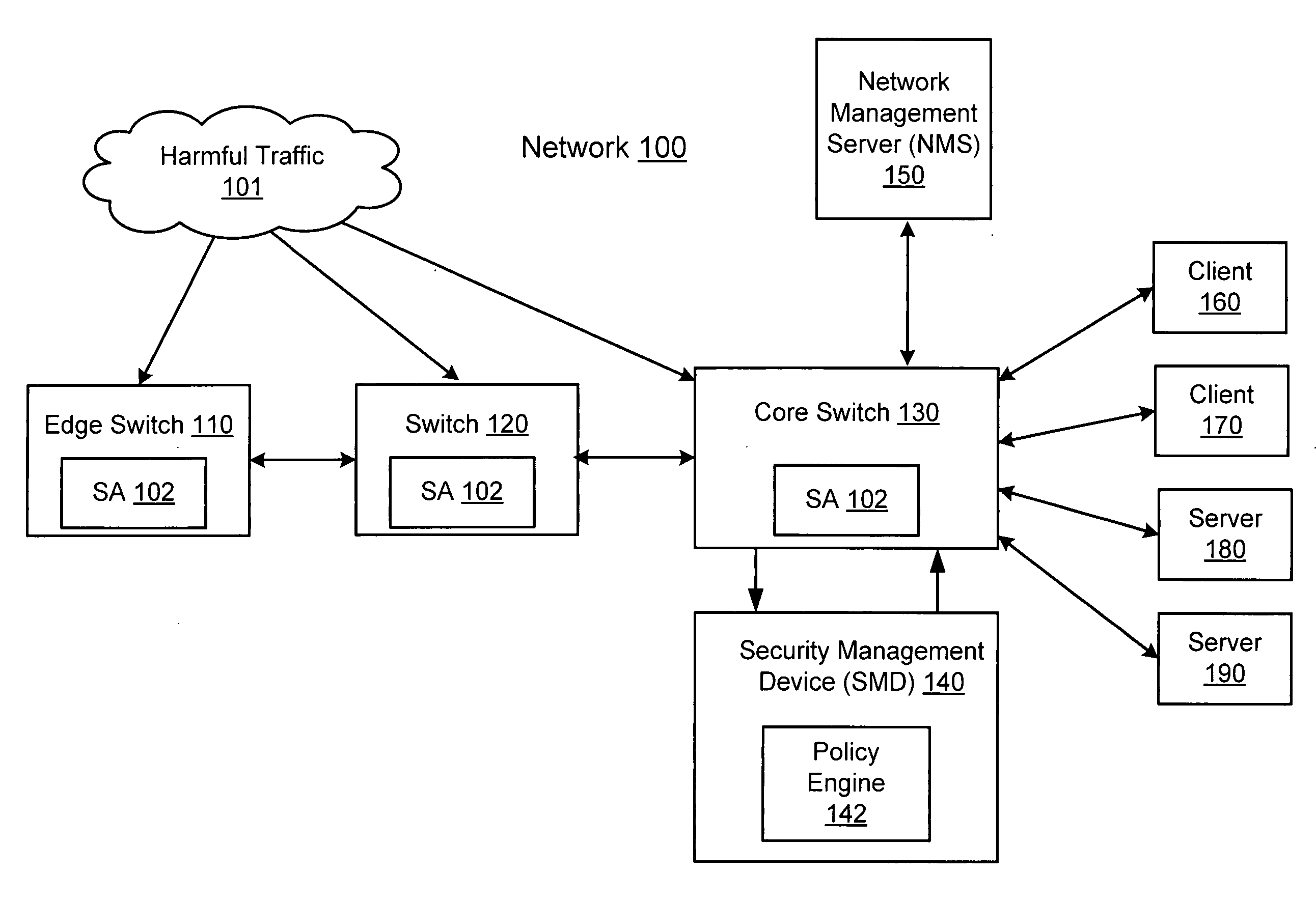
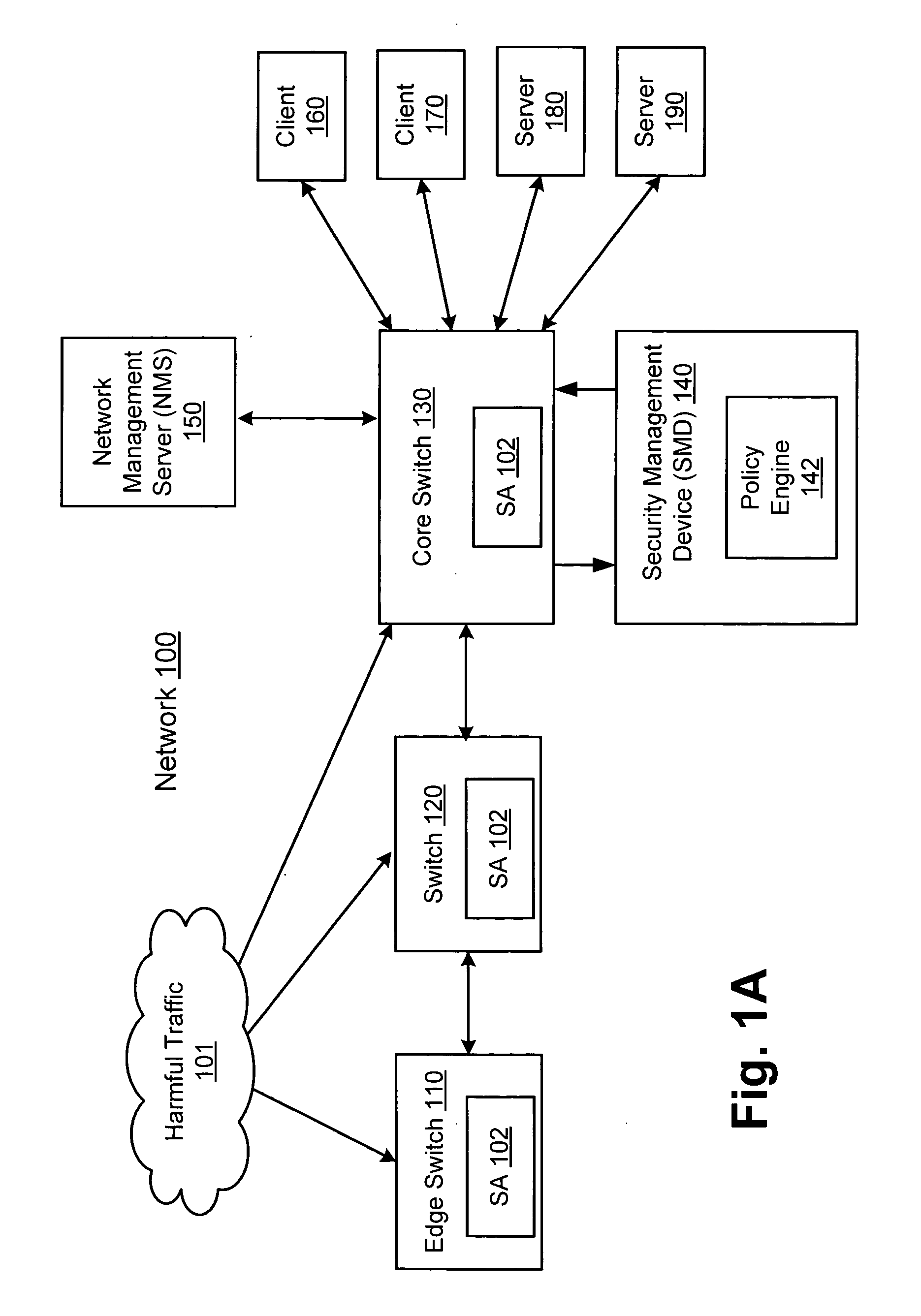
Network threat detection and mitigation
ActiveUS20070157306A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsInternet trafficNetwork switch
A network switch automatically detects undesired network traffic and mirrors the undesired traffic to a security management device. The security management device determines the source of the undesired traffic and redirects traffic from the source to itself. The security management device also automatically sends a policy to a switch to block traffic from the source.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
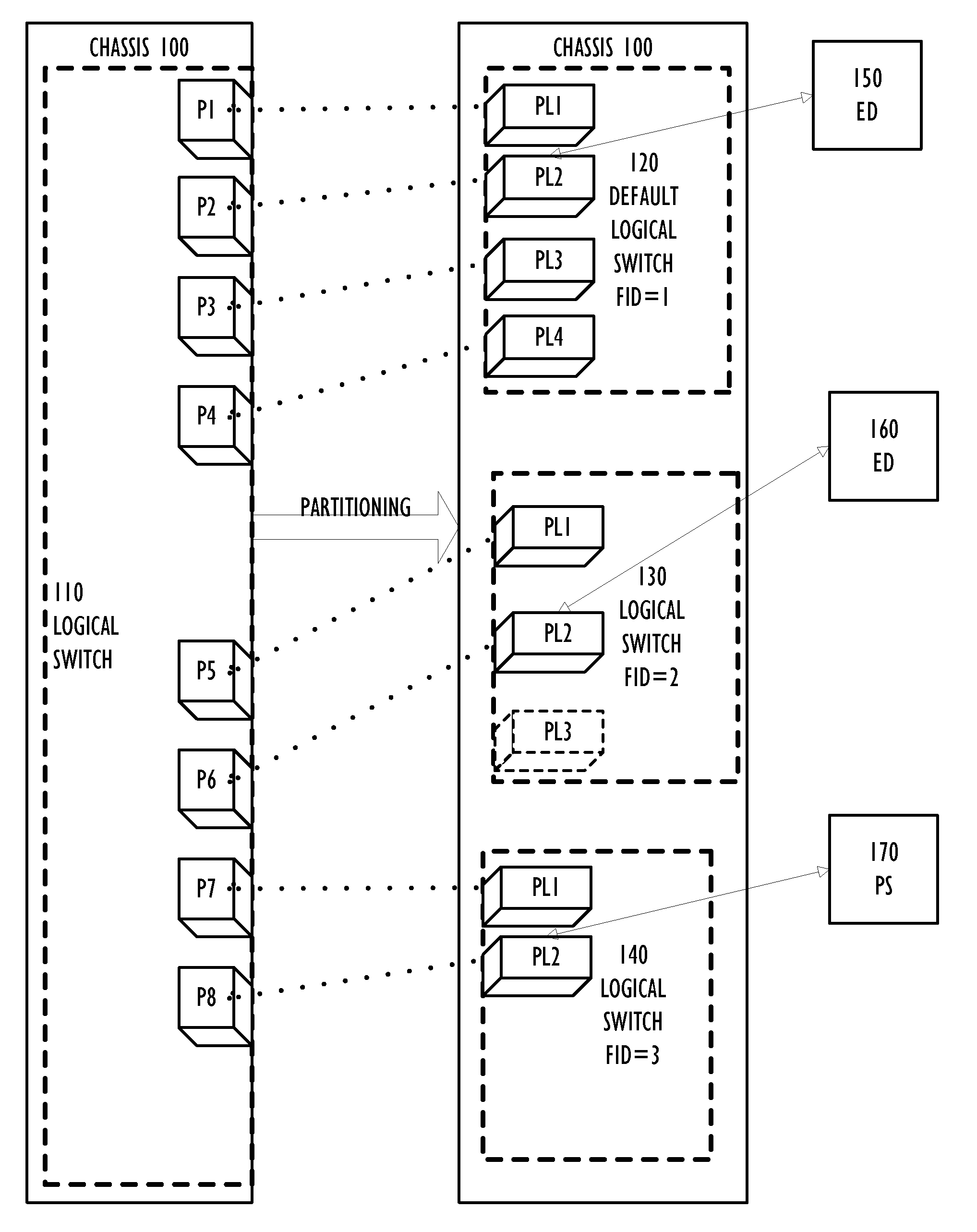
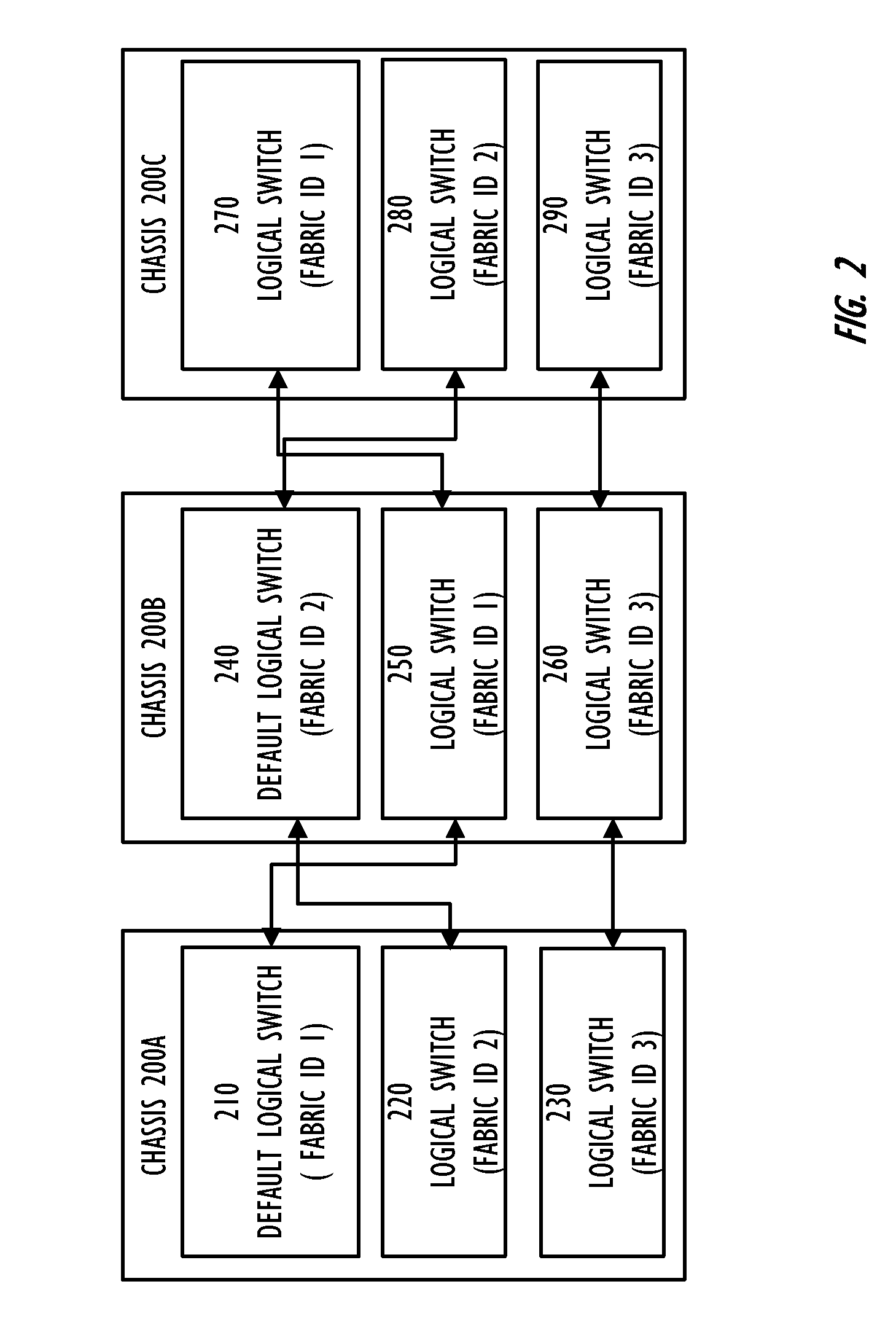
Defining an optimal topology for a group of logical switches
ActiveUS8339994B2Digital computer detailsData switching by path configurationTier 2 networkVirtual structure
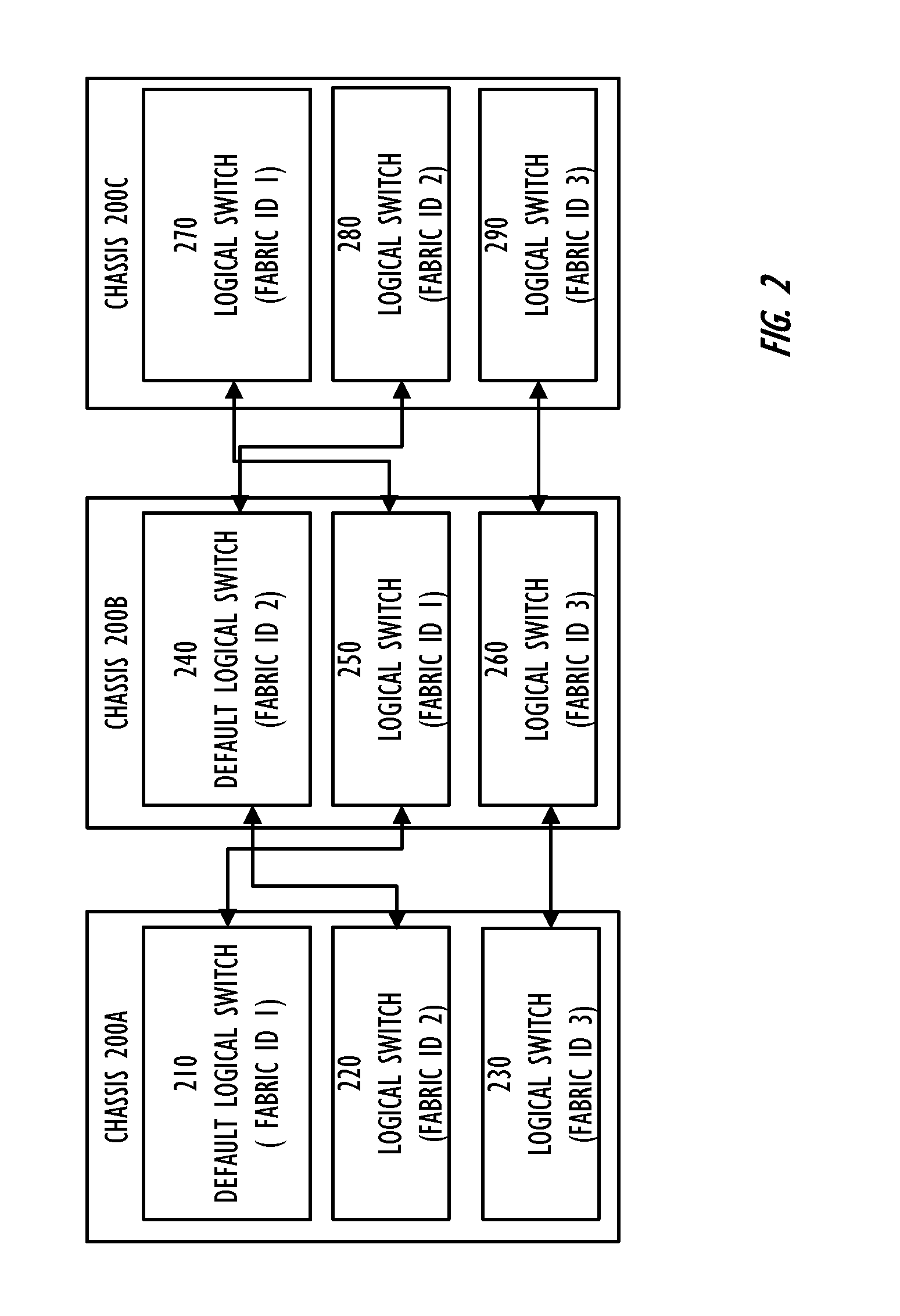
A Layer 2 network switch fabric is partitionable into a plurality of virtual fabrics. A network switch chassis is partitionable into a plurality of logical switches, each of which may be associated with one of the virtual fabrics, including a base switch. Logical switches in multiple network switch chassis are connected by logical connections, such as logical inter-switch links that use physical connections, such as extended inter-switch links between base switches, for data transport. A topology of logical connections is established that balances competing metrics, such as robustness and scalability, while maintaining alignment with the topology of the physical connections. A topology factor allows establishing different topologies with different balances between the competing metrics.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Virtual network management method, virtual network management program, virtual network management system, and virtual network means
InactiveUS7649851B2Lighten the taskDigital computer detailsData switching by path configurationManagement information baseNetwork management
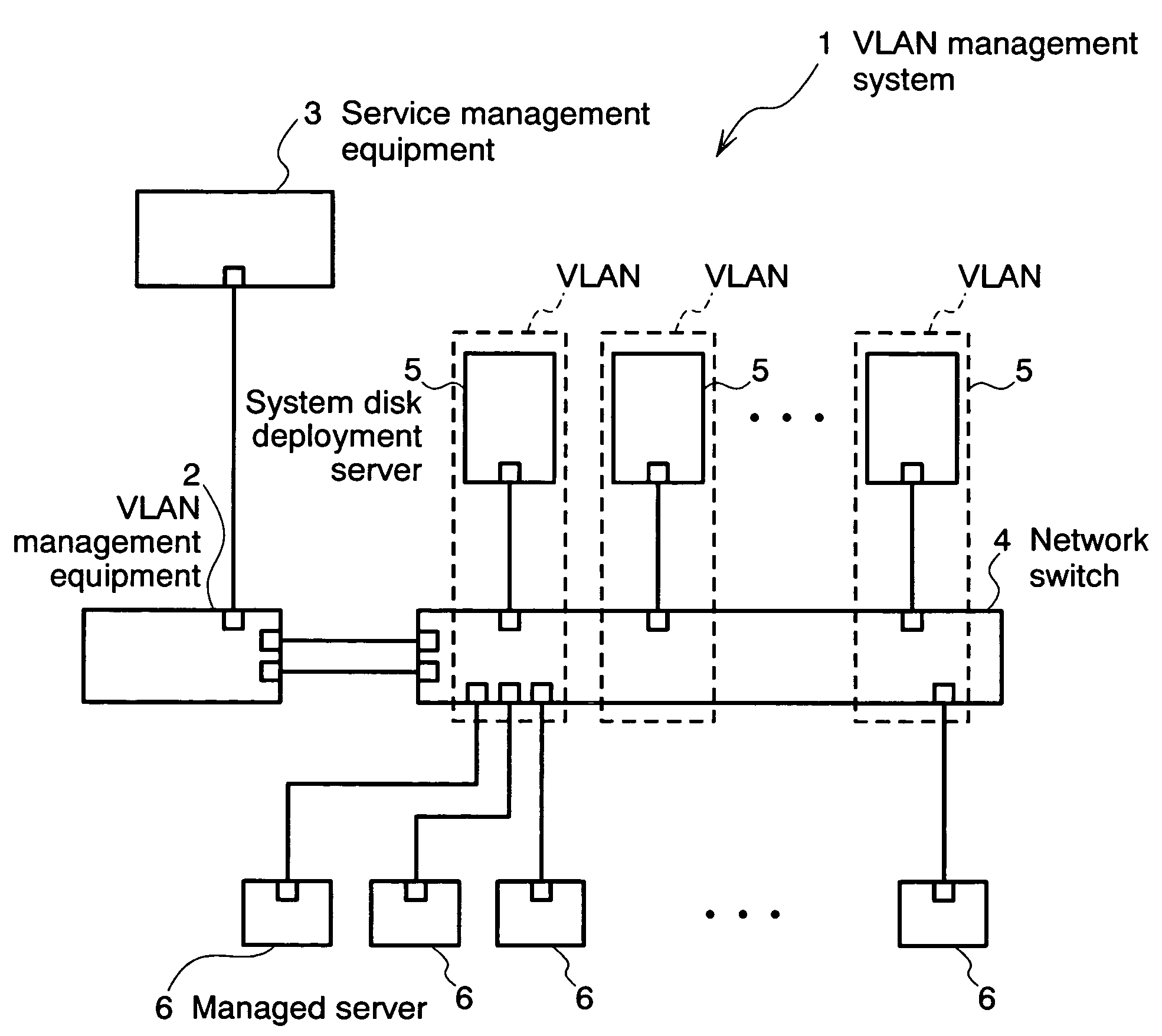
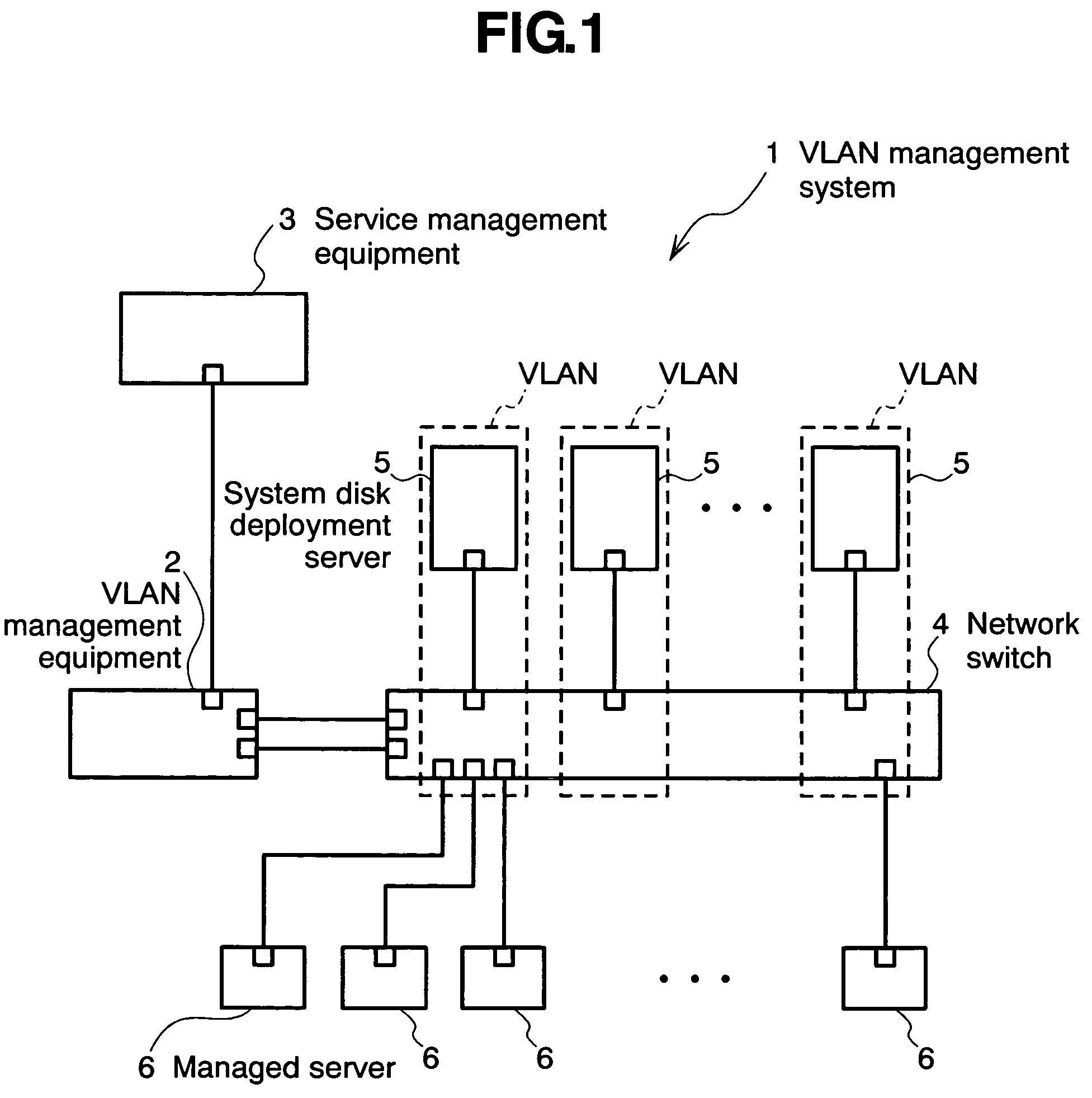
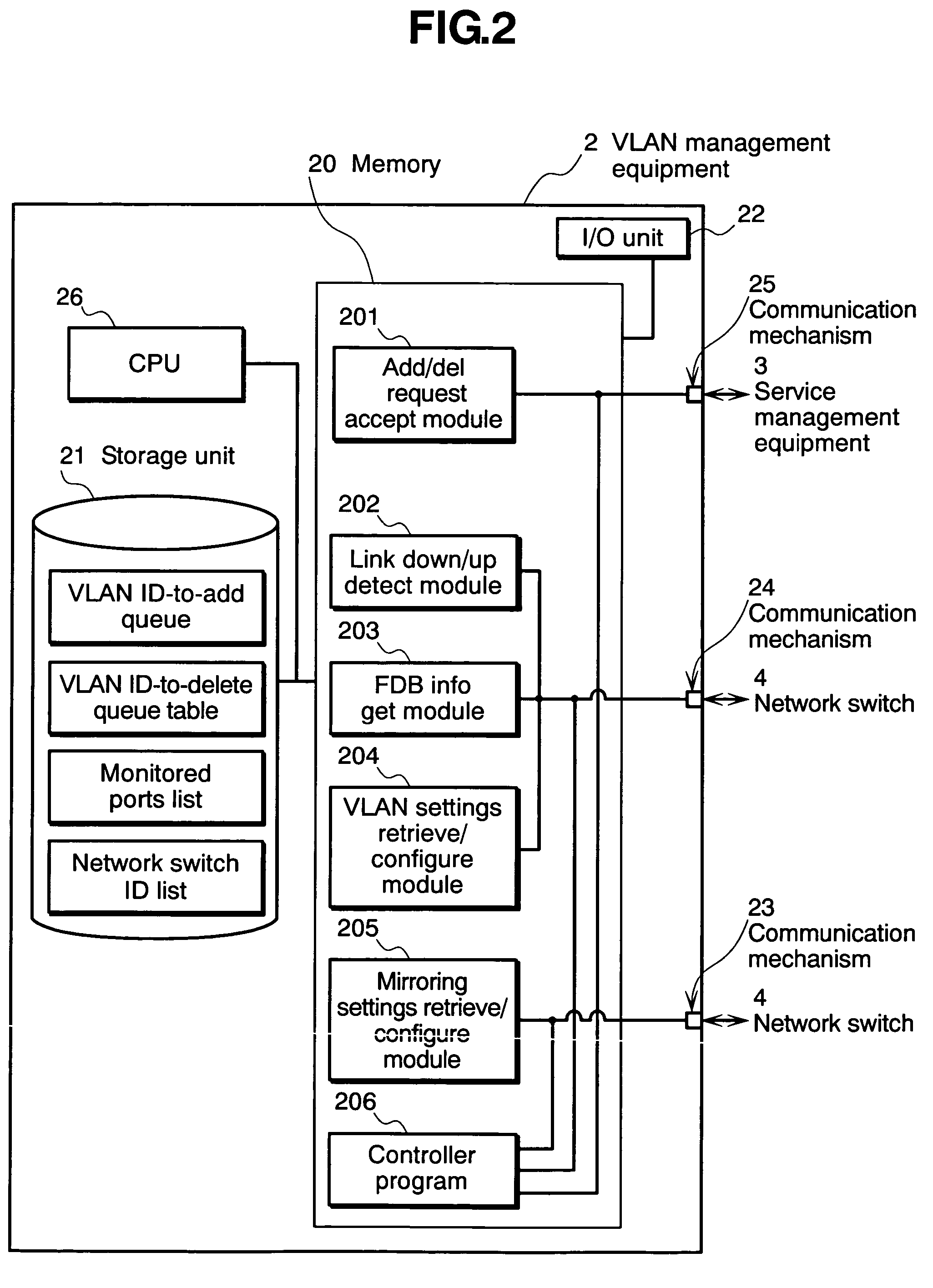
The invention relates to a network management method wherein: a service management equipment holds the mapping of services and virtual networks as management information; a managed server sends an advice to a VLAN management equipment when its status changes; and the VLAN management equipment receives the advice and refers to the information contained in the advice to thereby identify the managed server and the connection port of a network switch, and configures a virtual network belonging to the identified port of the network switch. The method alleviates the task of reconfiguration associated with the adding or deleting of servers.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
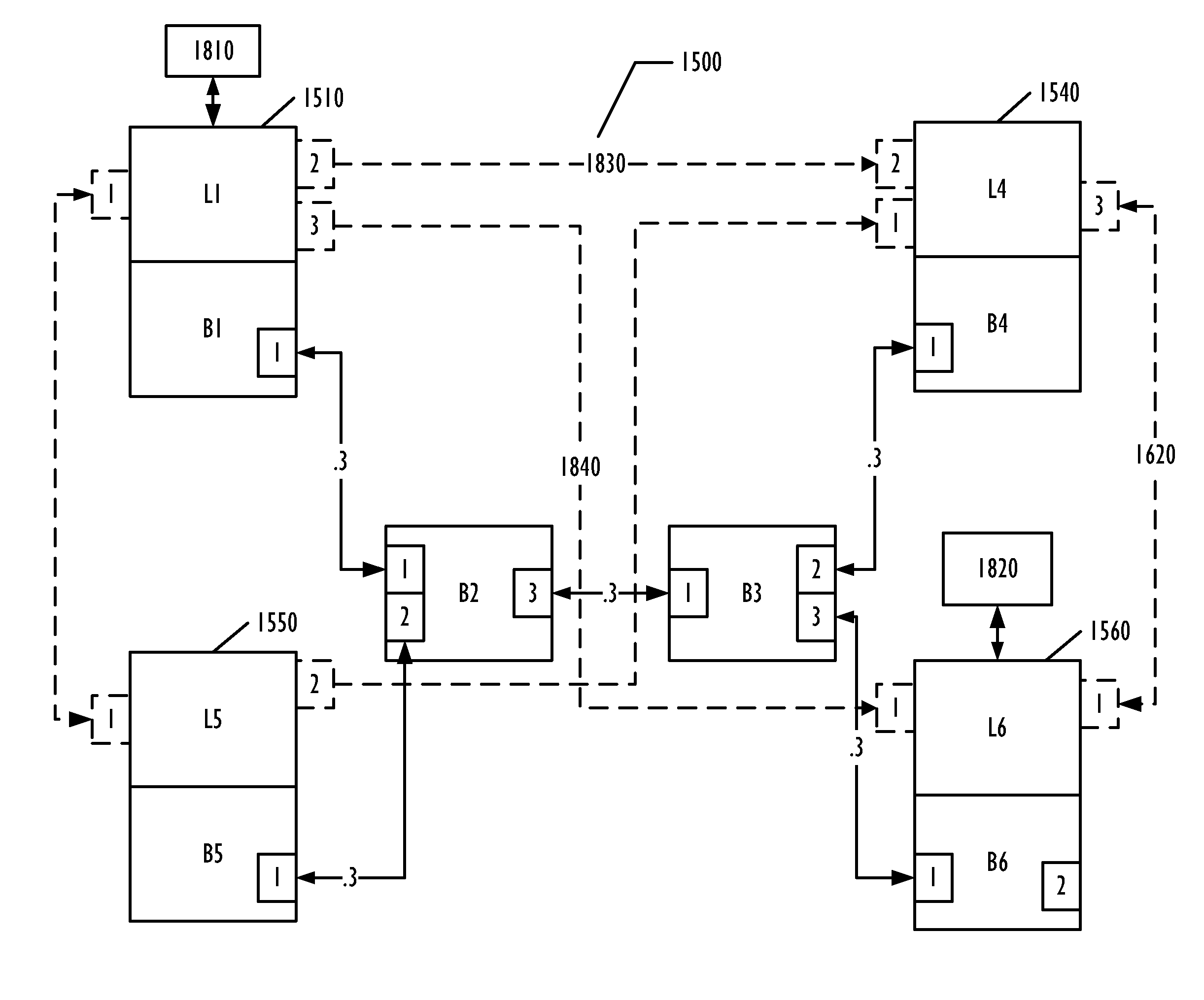
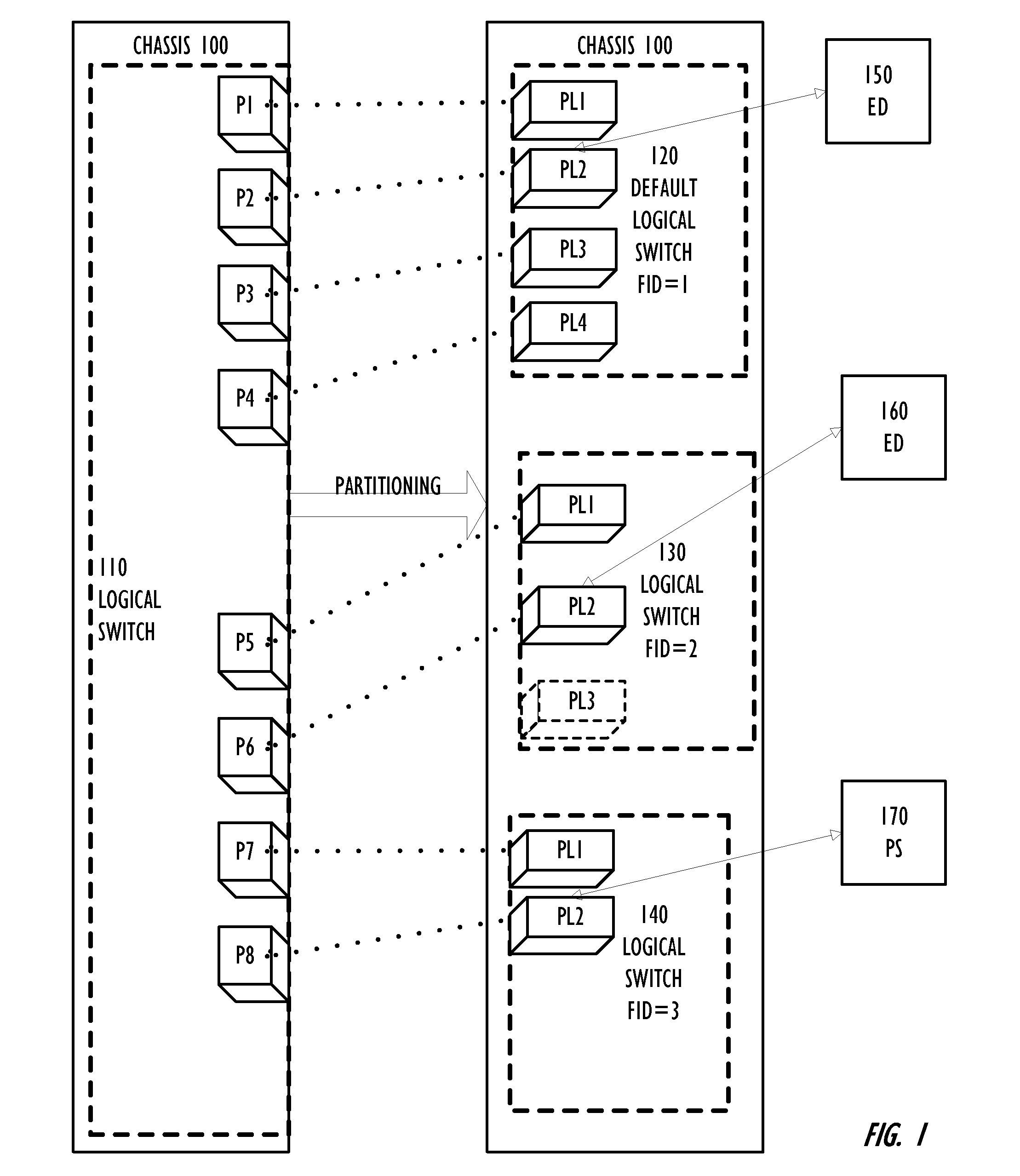
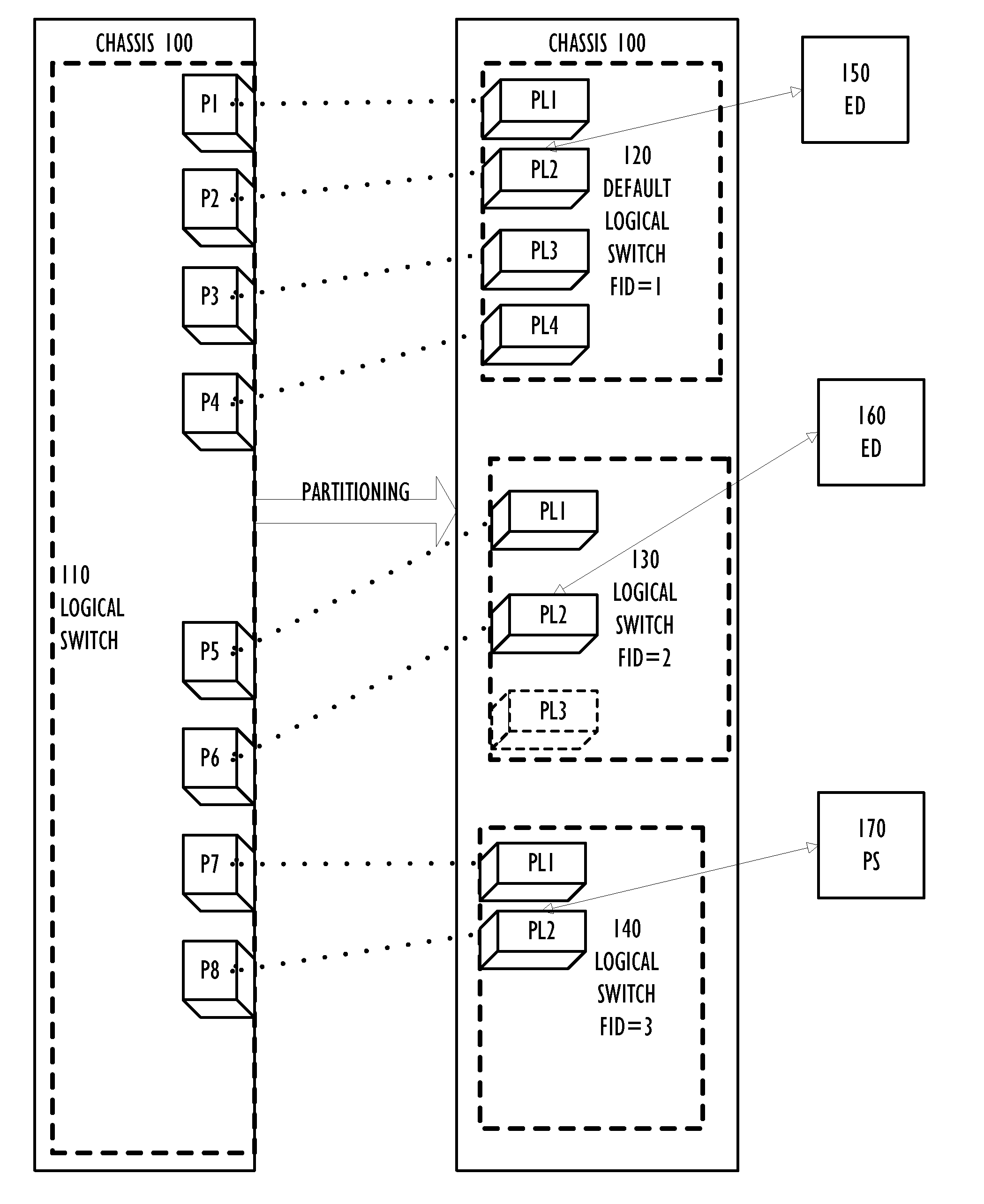
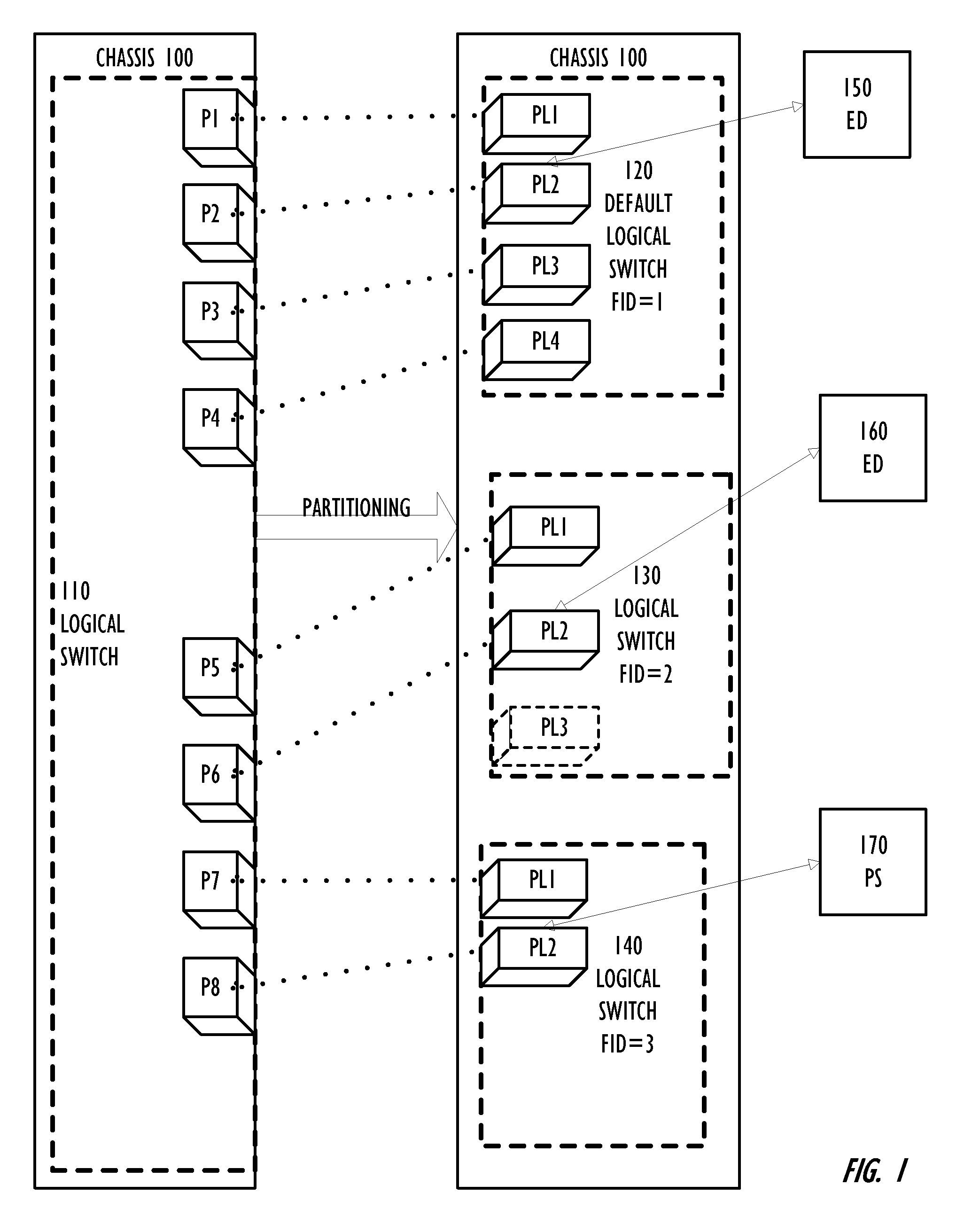
Partitioning of Switches and Fabrics into Logical Switches and Fabrics
A Layer 2 network switch is partitionable into a plurality of switch fabrics. The single-chassis switch is partitionable into a plurality of logical switches, each associated with one of the virtual fabrics. The logical switches behave as complete and self-contained switches. A logical switch fabric can span multiple single-chassis switch chassis. Logical switches are connected by inter-switch links that can be either dedicated single-chassis links or logical links. An extended inter-switch link can be used to transport traffic for one or more logical inter-switch links. Physical ports of the chassis are assigned to logical switches and are managed by the logical switch. Legacy switches that are not partitionable into logical switches can serve as transit switches between two logical switches.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Transit Switches in a Network of Logical Switches
ActiveUS20110085559A1Data switching by path configurationWireless commuication servicesComputer architectureTier 2 network
A Layer 2 network switch is partitionable into a plurality of switch fabrics. The single-chassis switch is partitionable into a plurality of logical switches, each associated with one of the virtual fabrics. The logical switches behave as complete and self-contained switches. A logical switch fabric can span multiple single-chassis switch chassis. Logical switches are connected by inter-switch links that can be either dedicated single-chassis links or logical links. An extended inter-switch link can be used to transport traffic for one or more logical inter-switch links. Physical ports of the chassis are assigned to logical switches and are managed by the logical switch. Legacy switches that are not partitionable into logical switches can serve as transit switches between two logical switches.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Virtual channels in a network switch
A system and method providing virtual channels with credit-based flow control on links between network switches. A network switch may include multiple input ports, multiple output ports, and a shared random access memory coupled to the input ports and output ports by data transport logic. Two network switches may go through a login procedure to determine if virtual channels may be established on a link. A credit initialization procedure may be performed to establish the number of credits available to the virtual channels. Credit-based packet flow may then begin on the link. A credit synchronization procedure may be performed to prevent the loss of credits due to errors. On detecting certain error conditions, a virtual channel may be deactivated. In one embodiment, the link is a Gigabit Ethernet link, and the packets are Gigabit Ethernet packets. The packets may encapsulate storage format (e.g. Fiber Channel) frames.
Owner:NISHAN SYST
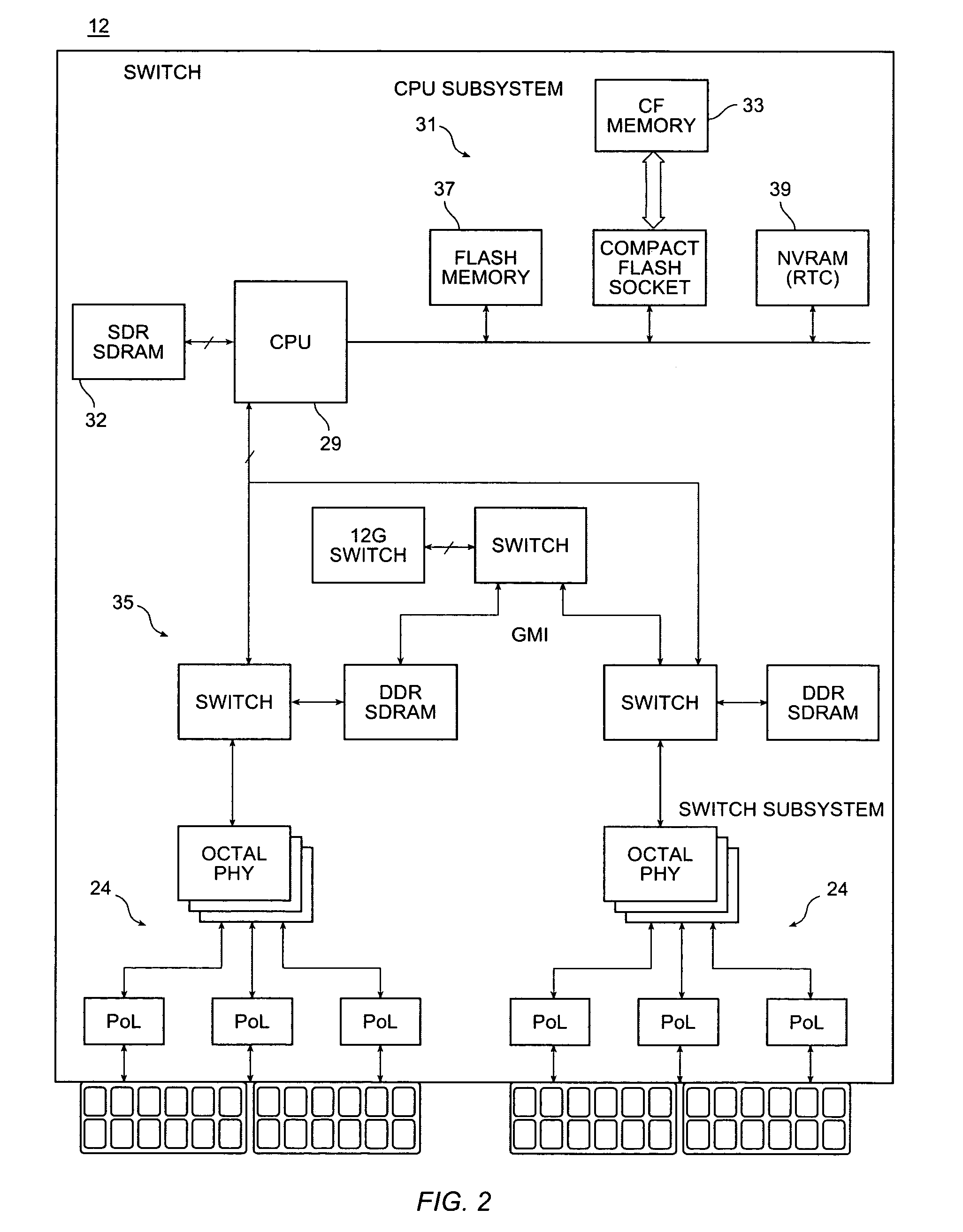
Hardware abstraction layer
ActiveUS20060193266A1Eliminate needData switching by path configurationInformation repositoryComputer hardware
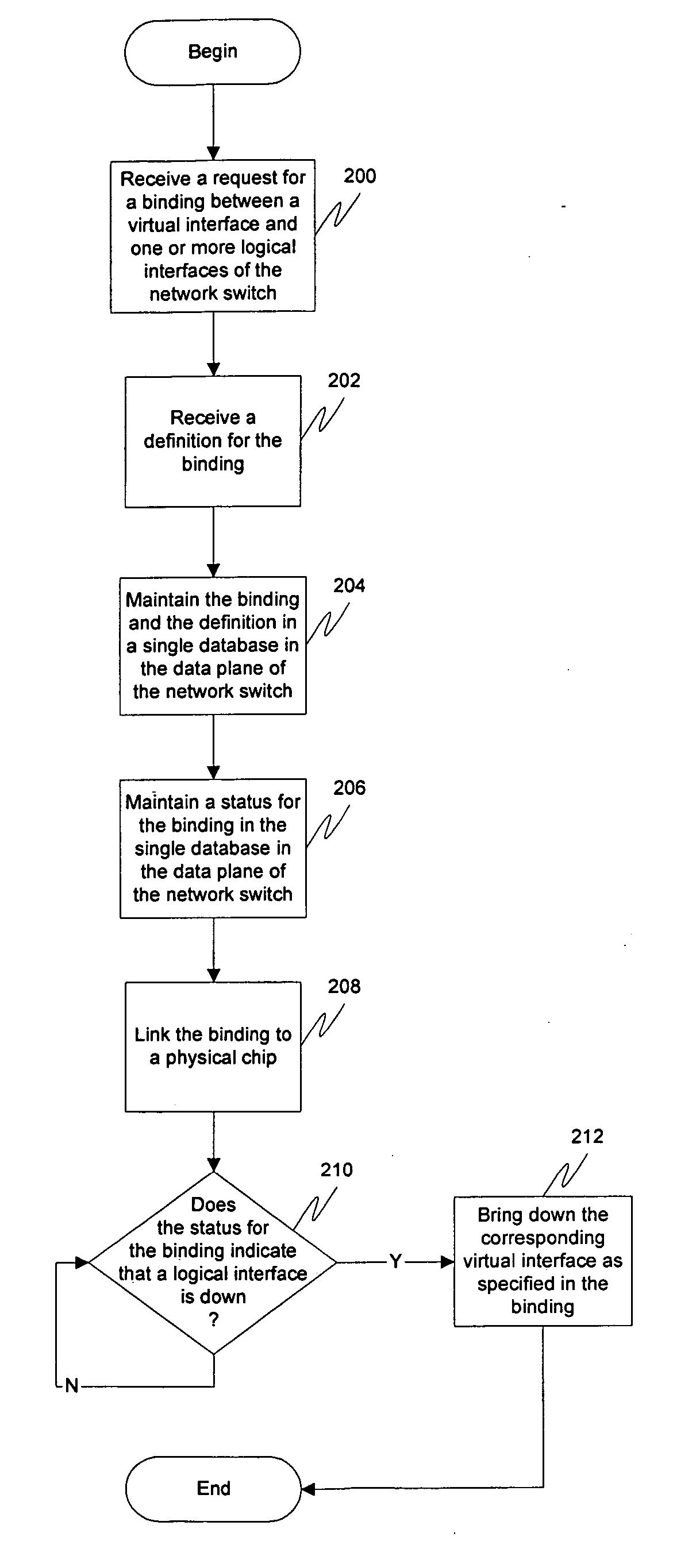
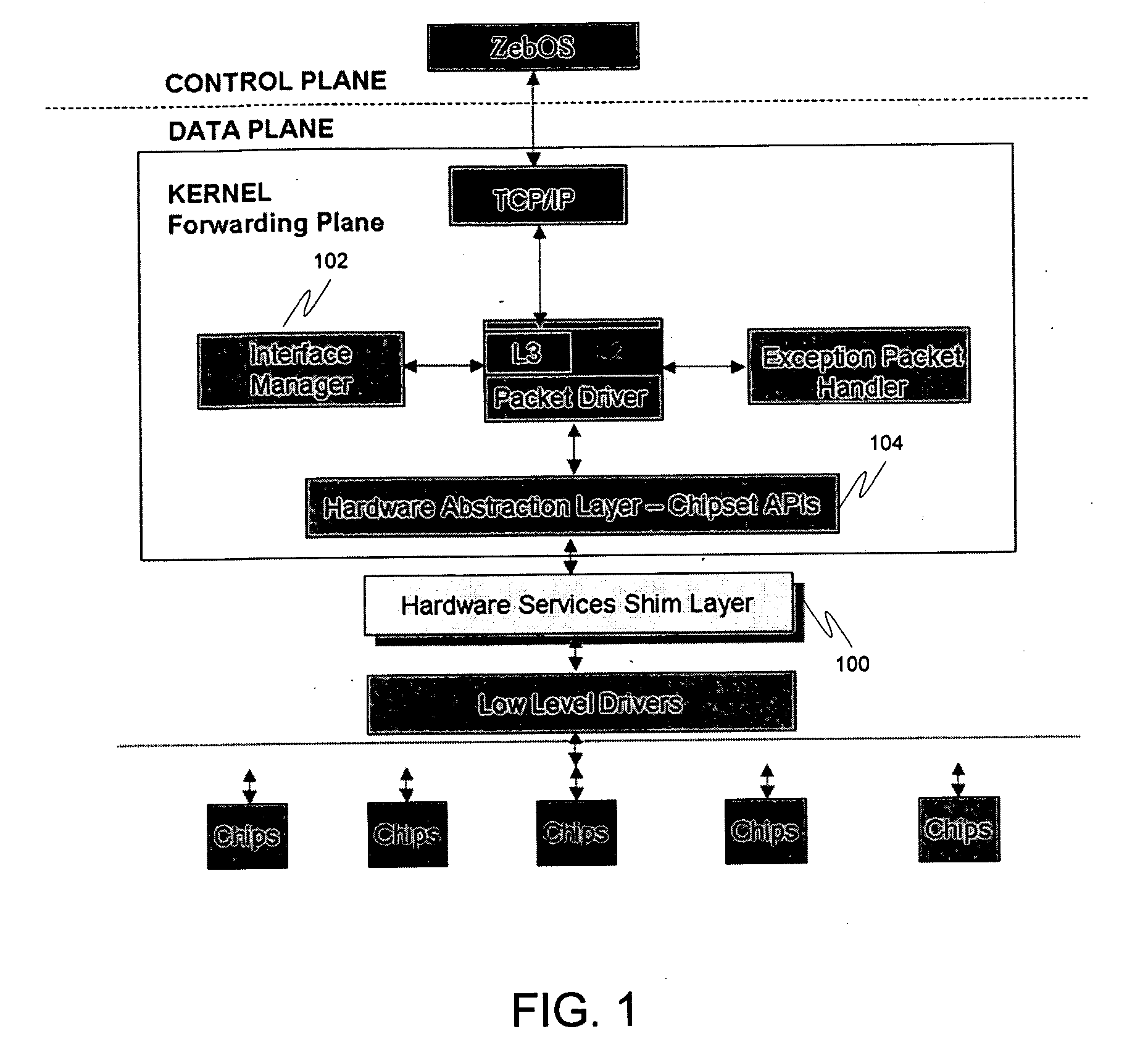
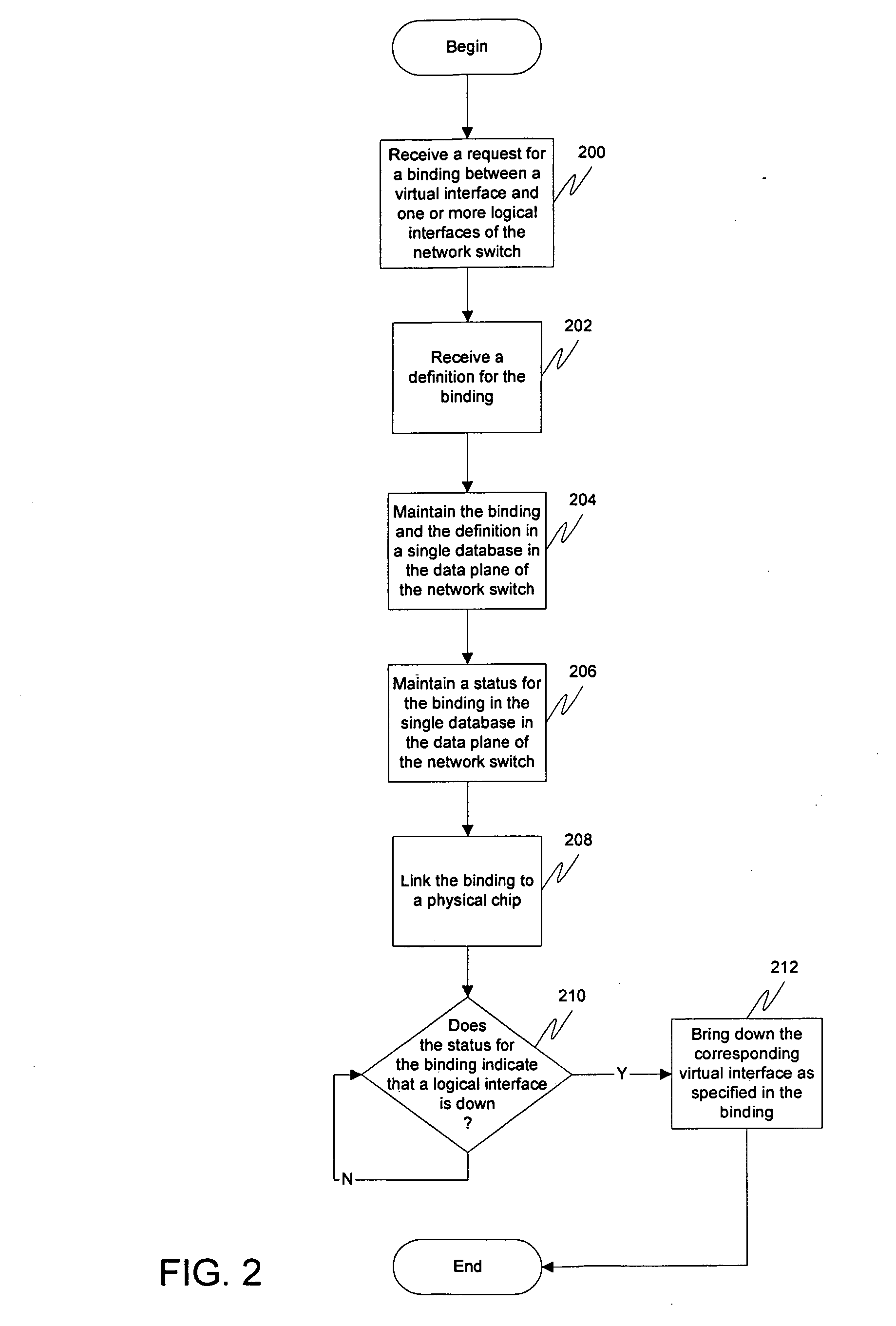
Switching and routing functions may be provided in a data plane of a network switch by having all functions and algorithms needed to handle all related interface, logical and physical, under one interface manager to keep track of bindings between virtual interfaces and logical interfaces, as well as maintain the statuses of ports that belong to the virtual interface and the actual logical ports. When the actual interface goes down, the virtual interface may go down along with it. The bindings may also include definitions. All of these bindings may be located in a single routing information base (RIB) database, eliminating the need for multiple bindings to be kept in various places. Furthermore, a hardware abstraction layer in the control plane can also then be mirrored in the data plane, eliminating the need for the customer to create a layer performing the same tasks.
Owner:IP INFUSION INC
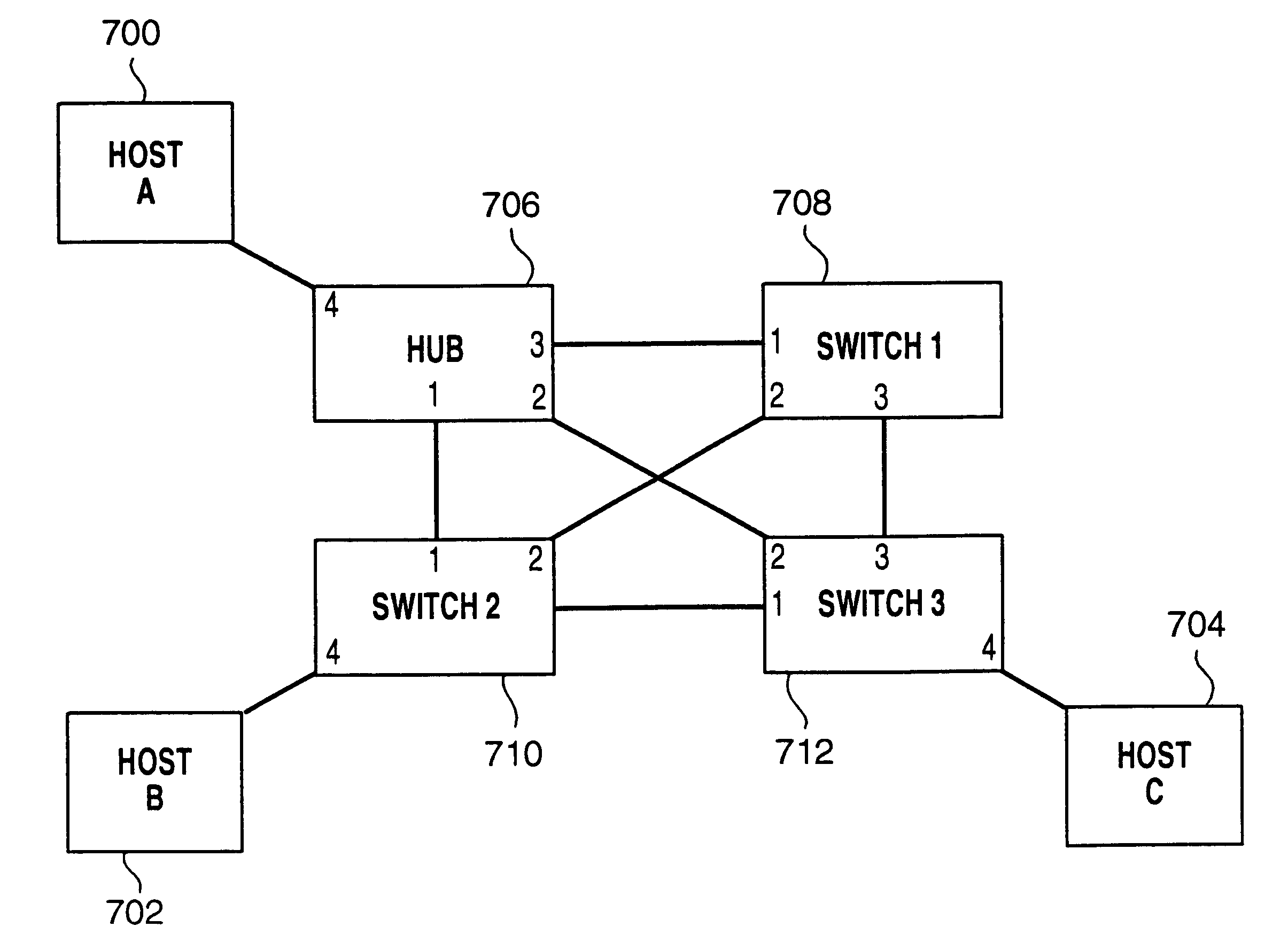
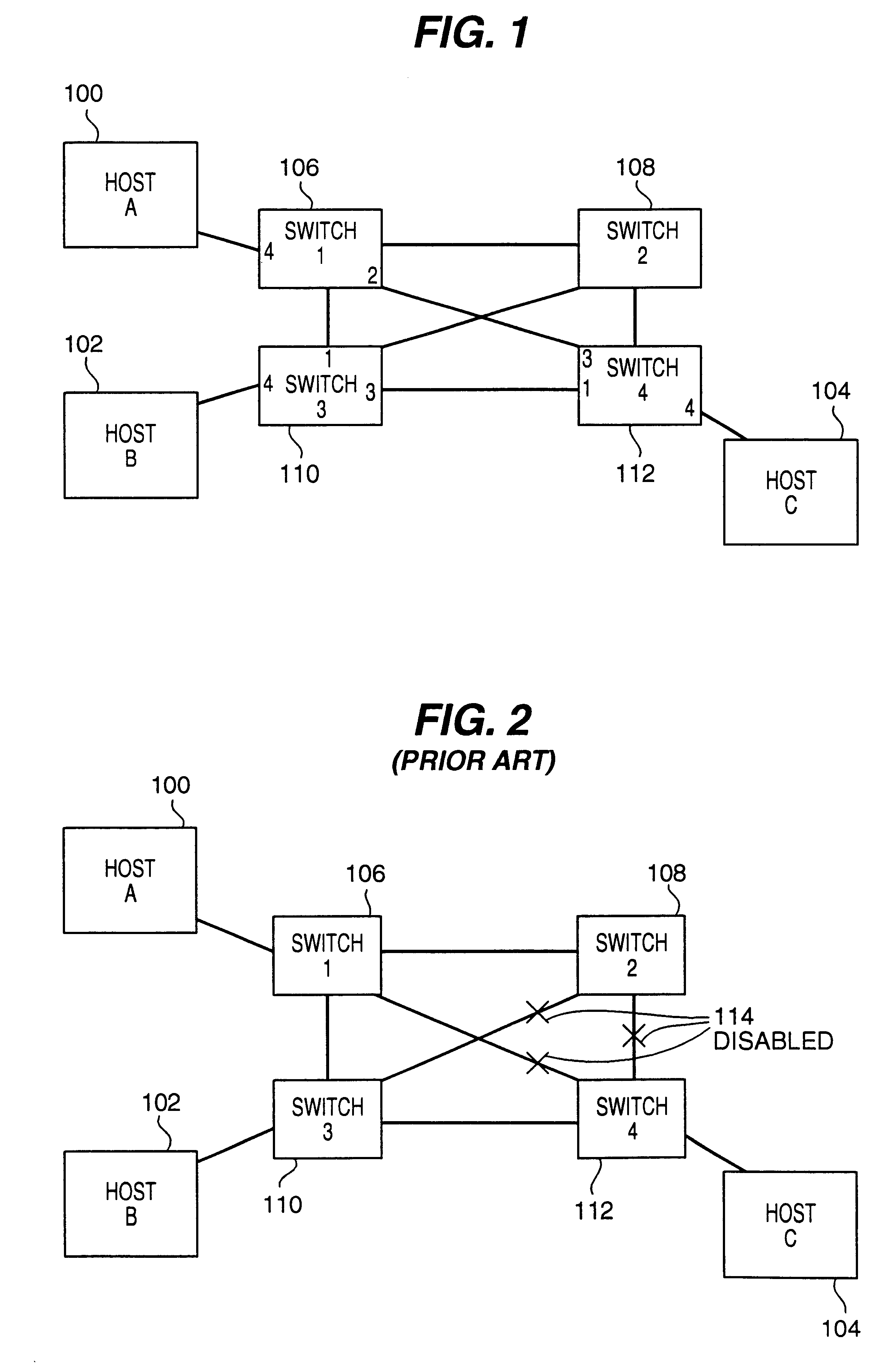
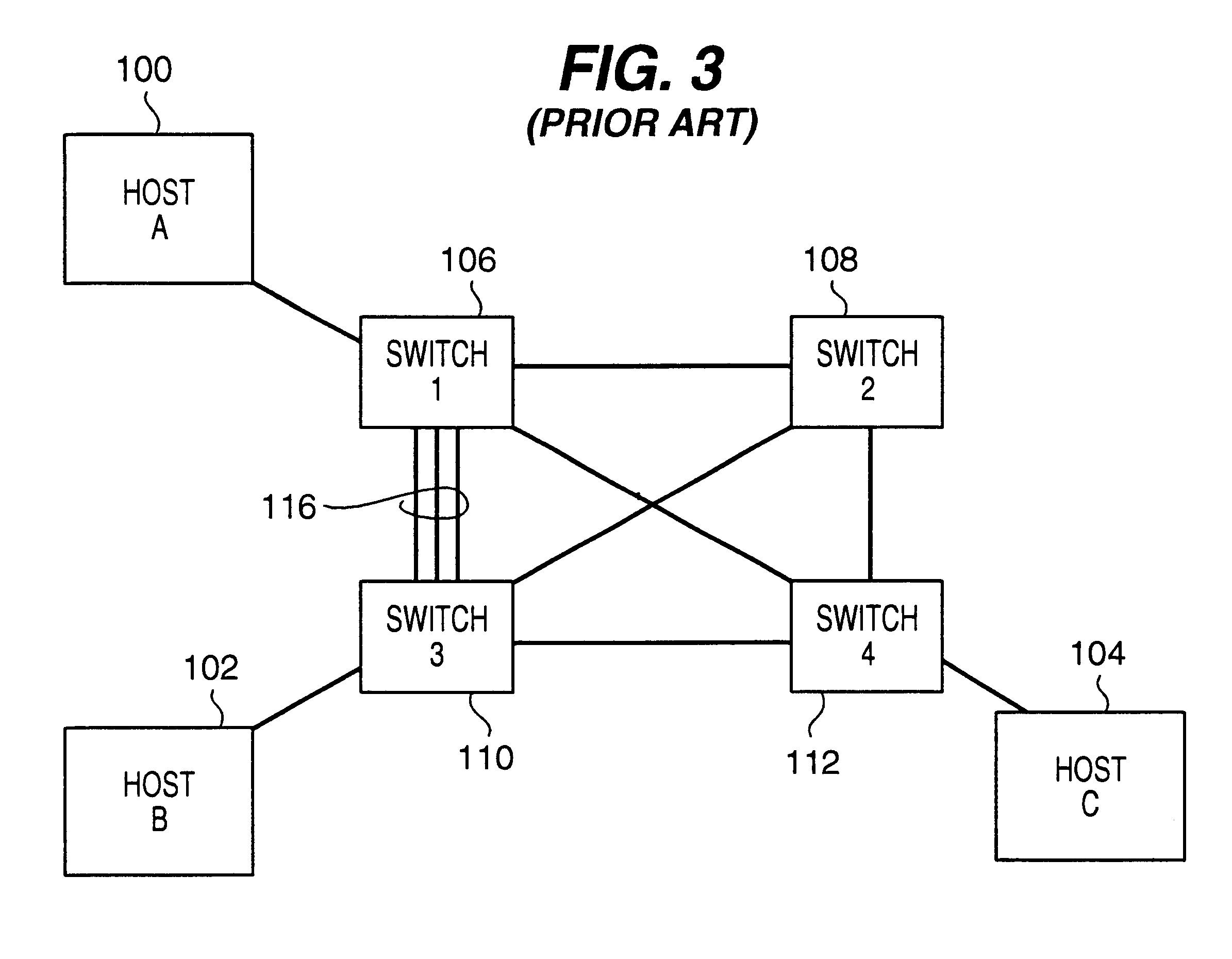
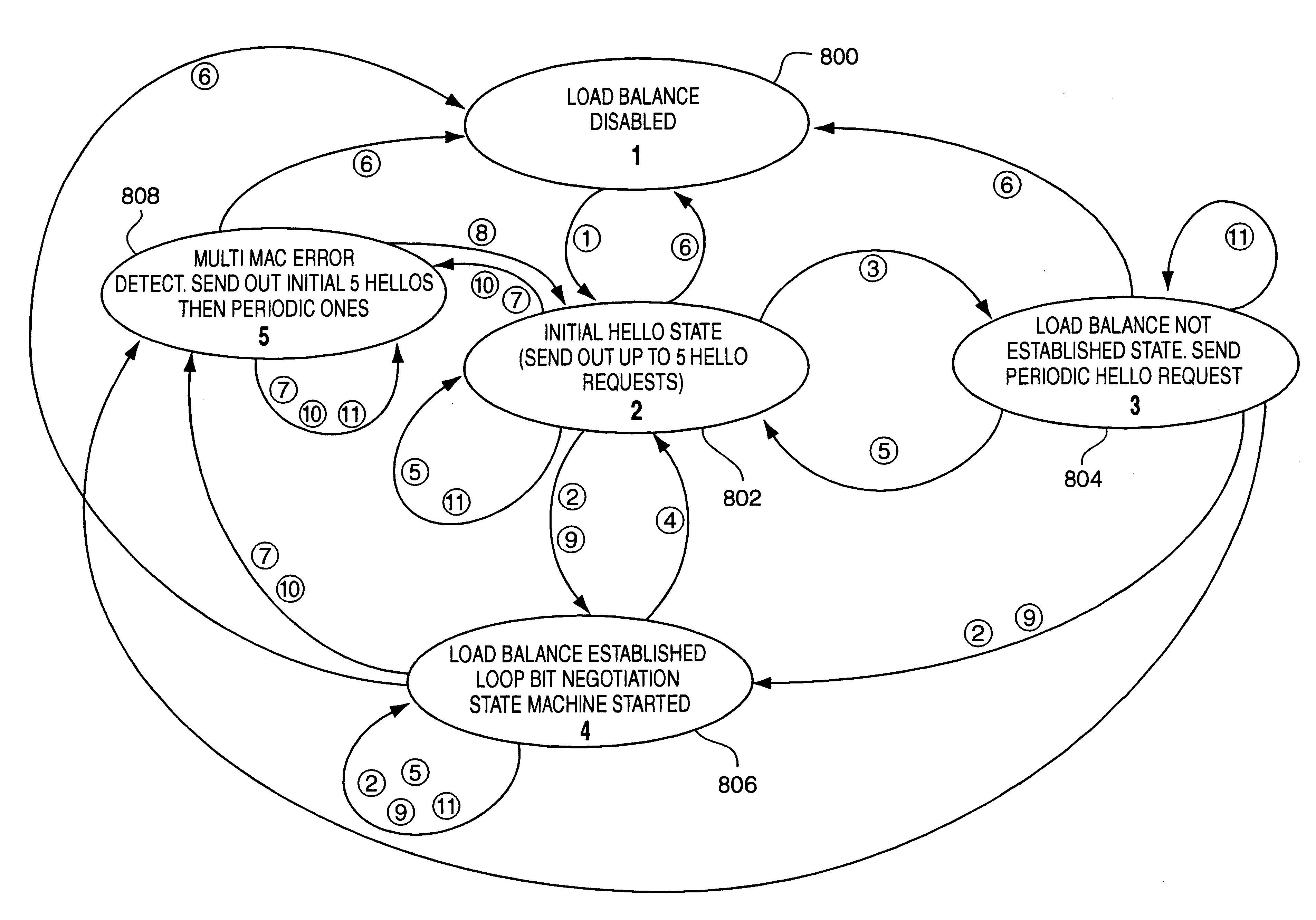
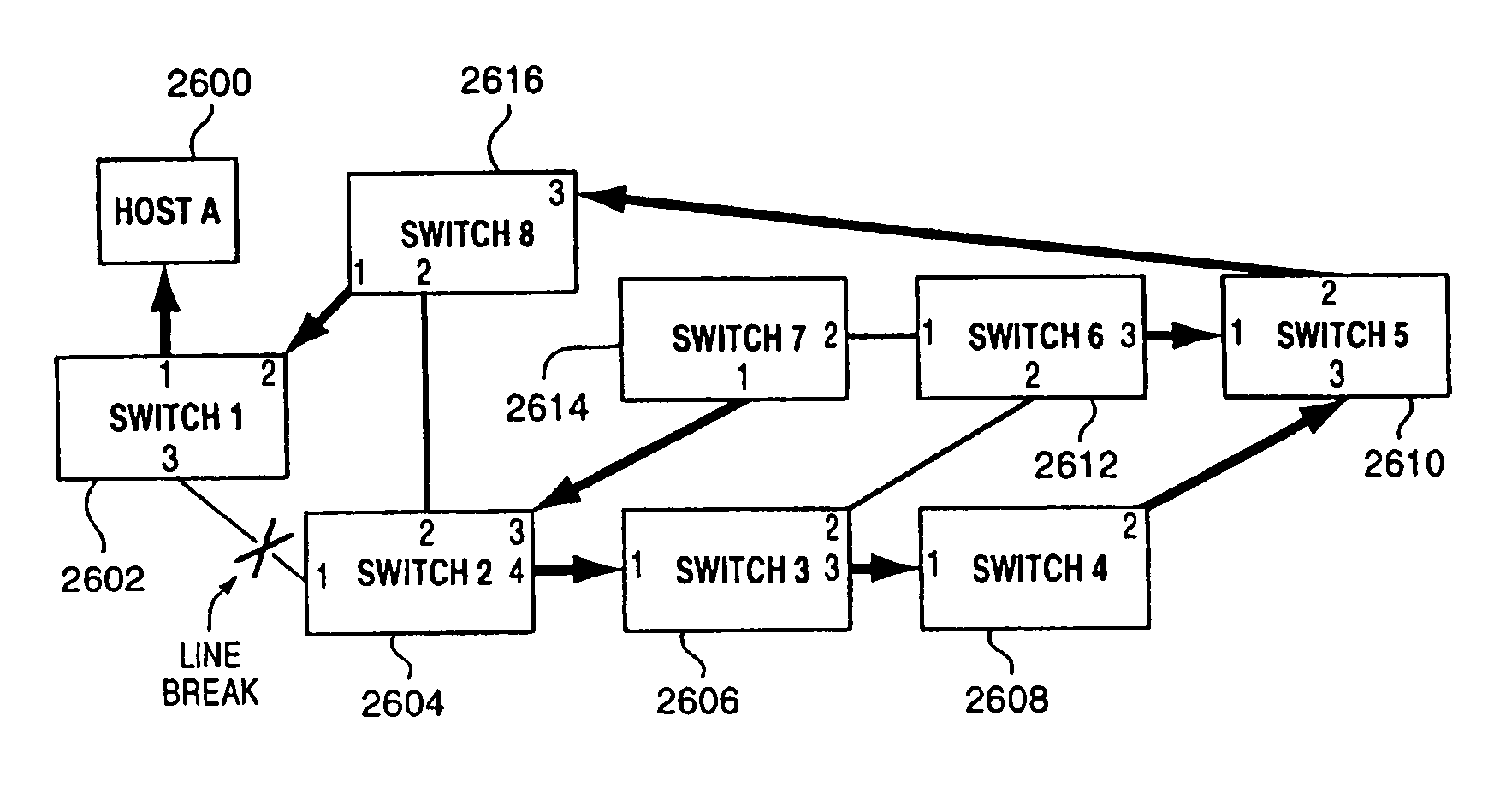
Path recovery on failure in load balancing switch protocols
InactiveUS20030016624A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsBackup pathNetwork switch
A method for managing multiple active paths among a plurality of network switches to identify and select an alternate path in response to failure of a path from a switch to a device. Load balancing protocols of the present invention enable the simultaneous use of multiple paths between network devices through a mesh of compliant network switches. When a port of a network switch fails (or the link connected to a port fails), a switch in accordance with the present invention selects an alternate port which may be used for forwarding packets to devices normally reached through the failed port. Networks switches operable in accordance with the structures and protocols of the present invention exchange messages to identify potential alternate paths. A potential alternate path is used to send a query message to a neighboring network switch to determine if a path to the identified devices is available through the neighboring network switch. Such query messages are propagated through all intermediate network switches between the switch sensing the failed port up to the identified network device. Acknowledgment messages are returned to verify potential availability of an alternate path. Where an intermediate network switch determines that the complete path is not available through it to the identified device, or where a potentially better path exists, a regenerated query message so indicating is returned along the path that initiated the query message.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Method and mechanism for port redirects in a network switch
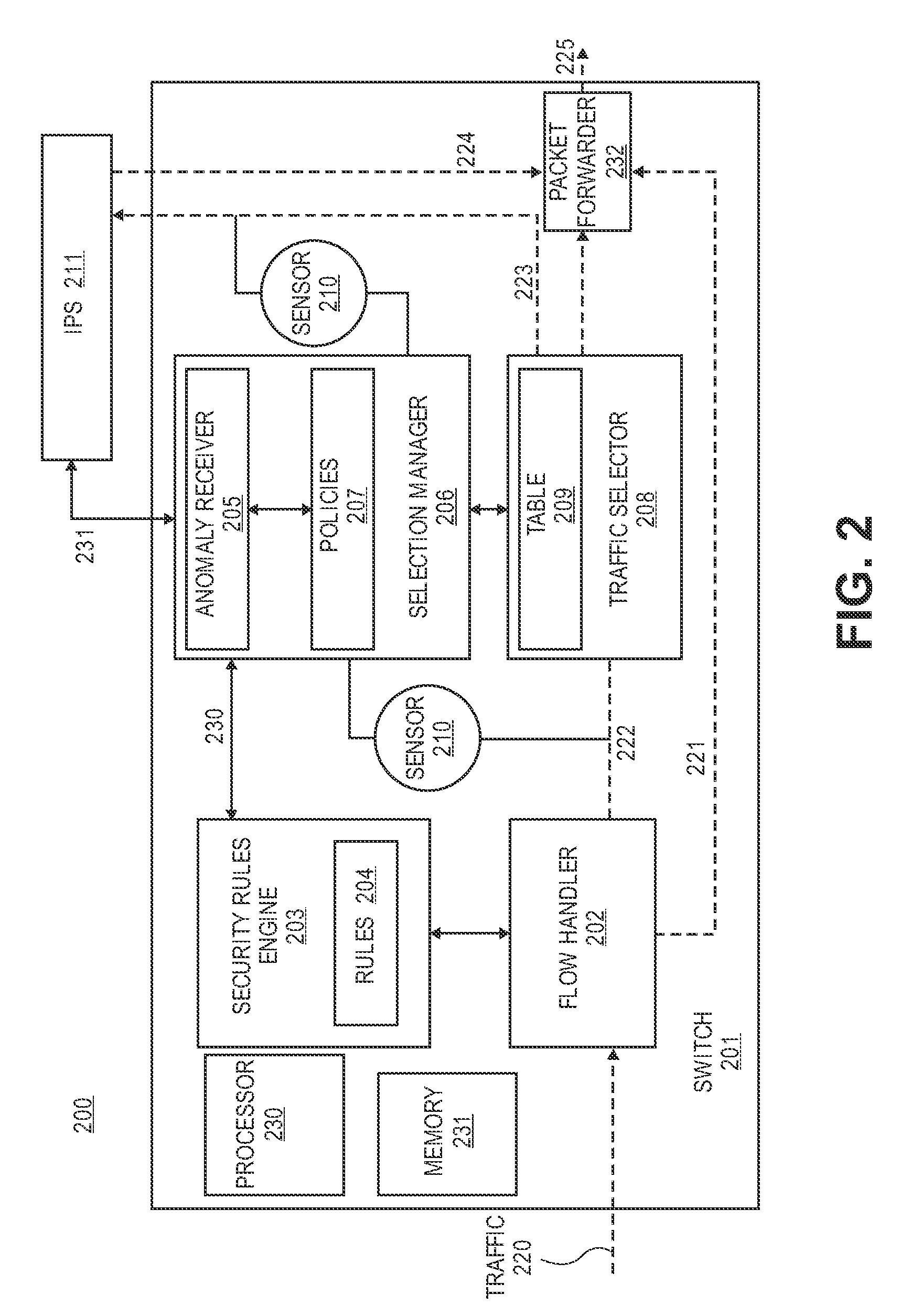
ActiveUS20090003317A1Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionNetwork switchSecurity analysis
A method for selectively redirecting a data packet to a port on a switching device which is associated with a corresponding network service. In one embodiment, the data packet is redirected to an intrusion prevention service (IPS) for security analysis of the data packet. In another embodiment, the switching device performs a data link layer redirecting of the data packet based at least in part on whether the data packet is to be flooded from the switching device.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
Centralized base station system based on advanced telecommunication computer architecture platform
InactiveUS20090149221A1Type of reductionSaving slotSubstation equipmentTransmissionNetwork switchControl switch
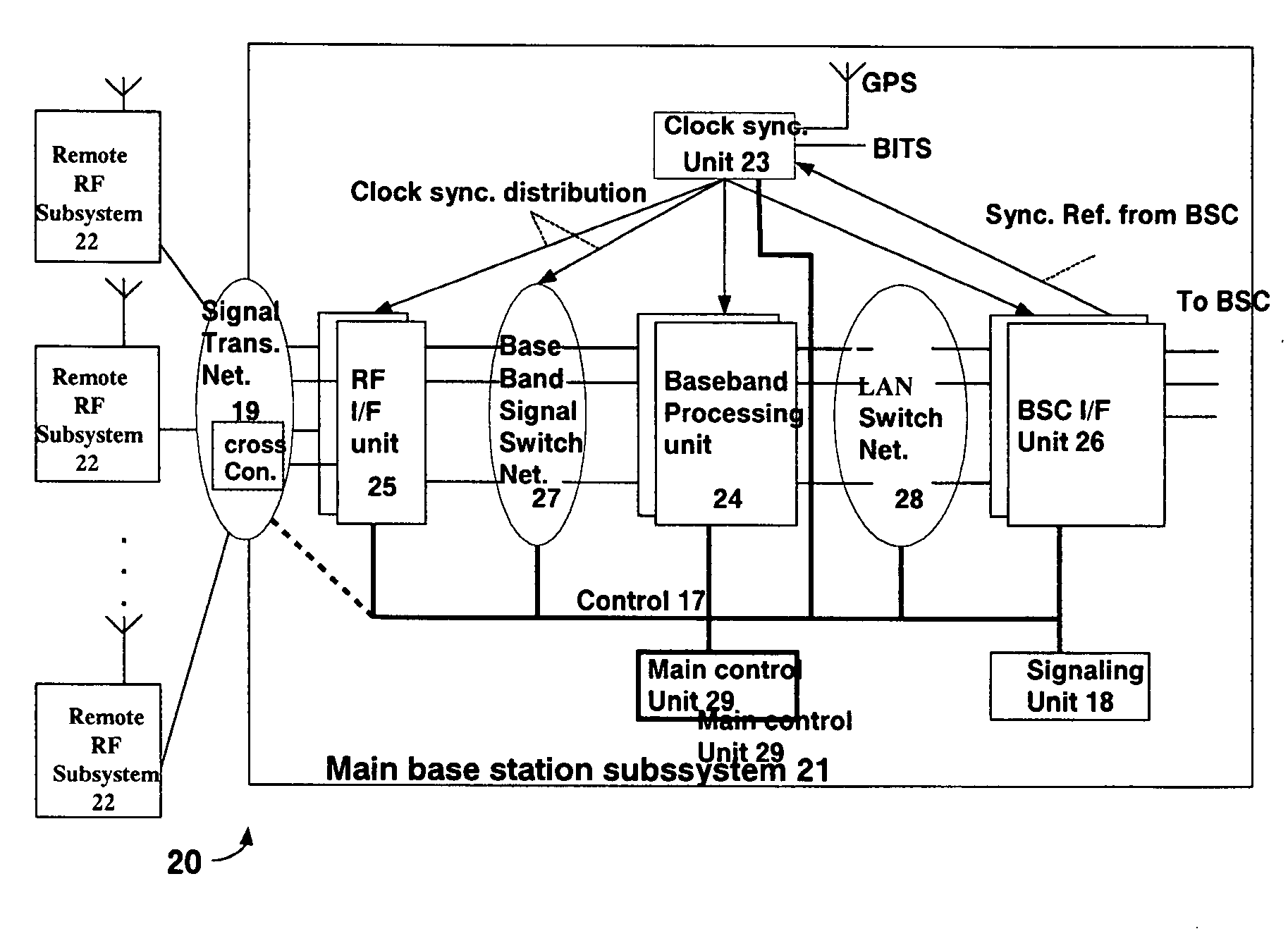
A centralized base station system based on ATCA, comprising a main base station subsystem and one or more remote radio frequency subsystems, the main base station subsystem comprising: one or more shelves based on ATCA platform, each shelf comprising at least one control switch module of ATCA board form; one or more base station controller interface module; a signaling module; one or more baseband processing modules; one or more remote radio frequency interface modules; a first switch network comprising first switch network shelf back board BASE interface link, a control switch module and a first network switch unit; a second switch network comprising a shelf back board FABRIC interface link, a control switch module and a second network switch unit; a clock synchronization network comprising a shelf back board clock synchronization bus, a control switch module and a clock unit; and a signal transmission network, wherein the second network switch unit and the clock unit are further connected to the first network switch unit, one of the control switch modules of all the shelves is the main control module.
Owner:UTSTARCOM TELECOM CO LTD
Unified, configurable, adaptive, network architecture
ActiveUS7310664B1Reduce the burden onReduce operating costsDigital computer detailsTransmissionAdaptive managementNetwork architecture
A network switch having a unified, adaptive management paradigm for wireless network devices is disclosed. The switch includes configurable ports for connecting devices. A software application running on the switch allows a network administrator to selectively configure each port to support either a wired device or wireless device. Configuration information and software images that are needed for operation of the wireless device are associated with the port. When a wireless device is first plugged into the switch port, it downloads its configuration directly from the switch port. By storing the configuration information and images at the switch and automatically downloading them to the wireless devices, the task of configuring the devices is greatly simplified for the network administrator. This is particularly advantageous in heterogeneous network environments that support both wired and wireless devices, and where wireless device are readily moved to different ports.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
MAC address learning and propagation in load balancing switch protocols
InactiveUS6556541B1Special service provision for substationError preventionNetwork switchMAC address
A method for disseminating MAC addresses for discovered network devices through a plurality of network switches which cooperate to enable maintaining multiple active paths between such devices. Where a plurality of network switches cooperate through load balancing protocols to enable simultaneous use of multiple paths between, protocols of the present invention permit newly discovered MAC addresses attached to ports of an edge switch to be disseminated through the network switches. When an edge switch detects a device having a previously unknown MAC address, a MAC address information packet is generated and disseminated from the edge switch the other switched of the same load balance domain. The packet is preferably, in effect, broadcast using the pruned broadcast tree constructed and maintained by other protocols related to the present invention.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Discovery of unknown MAC addresses using load balancing switch protocols
InactiveUS6456597B1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityNetwork switch
A method for discovering addressing information within a network switch for an unknown MAC address received as a destination address of a packet. Where prior techniques flooded the network with the received packet, switch to switch protocols of the present invention reduce the volume of such overhead network traffic required to discover the addressing information. In particular, the present invention propagates query messages through network switches in a load balance domain (a group of switches cooperable in accordance with the protocols described herein). The query messages are propagated using a pruned broadcast tree to reduce the number of transmissions required to reach all switches in the load balance domain. The propagated query message eventual elicits a response from the device which owns the previously unknown destination address. Switches and devices outside the load balance domain are similarly probed for the unknown destination address using link level test messages which elicit a response from the device owning the unknown address without impacting the network higher layer protocols. These techniques reduce the volume of network traffic required to obtain the desired addressing information by forcing the response from the device owning the previously unknown destination address and constructing a unicast path to that device. Creating the unicast path obviates the need to flood the unknown destination address on the network.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Method and apparatus for input based control of discards in a lossy packet network
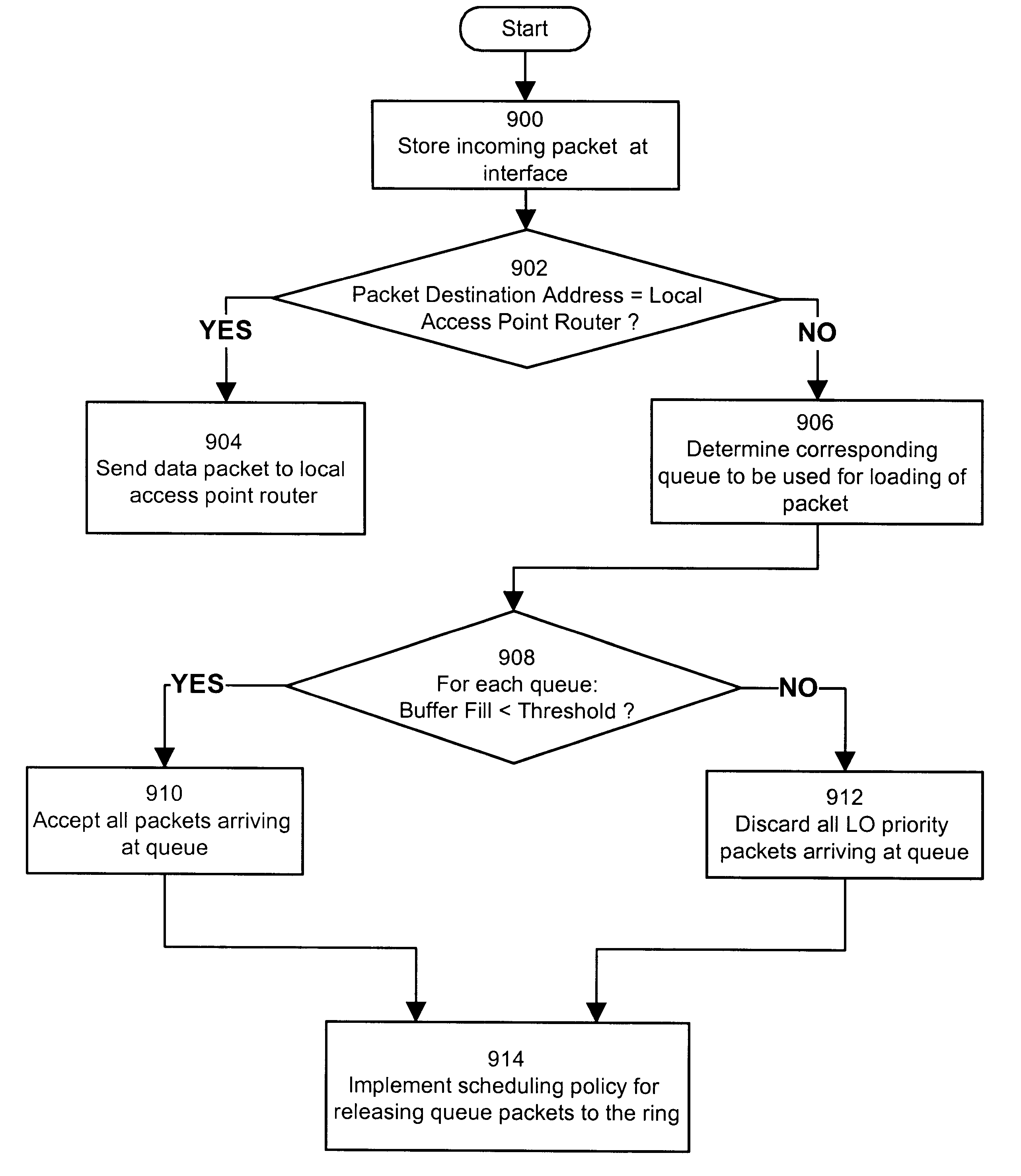
InactiveUS6304552B1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsReal-time computingSwitched fabric
The present invention relates to a lossy switch for processing data units, for example IP data packets. The switch can be implemented as a contained network that includes a plurality of input ports, a plurality of output ports and a lossy switch fabric capable of establishing logical pathways to interconnect a certain input port with a certain output port. A characterizing element of the switch is its ability to control the discard of data packets at a transport point within the switch. This control mechanism prevents and reduces congestion which may occur within the switch fabric and at the level of the input and output ports. The system also supports priorities, routing HI priority request data packets over the switch fabric before LO priority request data packets, and discarding LO priority data packets first when controlling congestion.
Owner:AVAYA INC
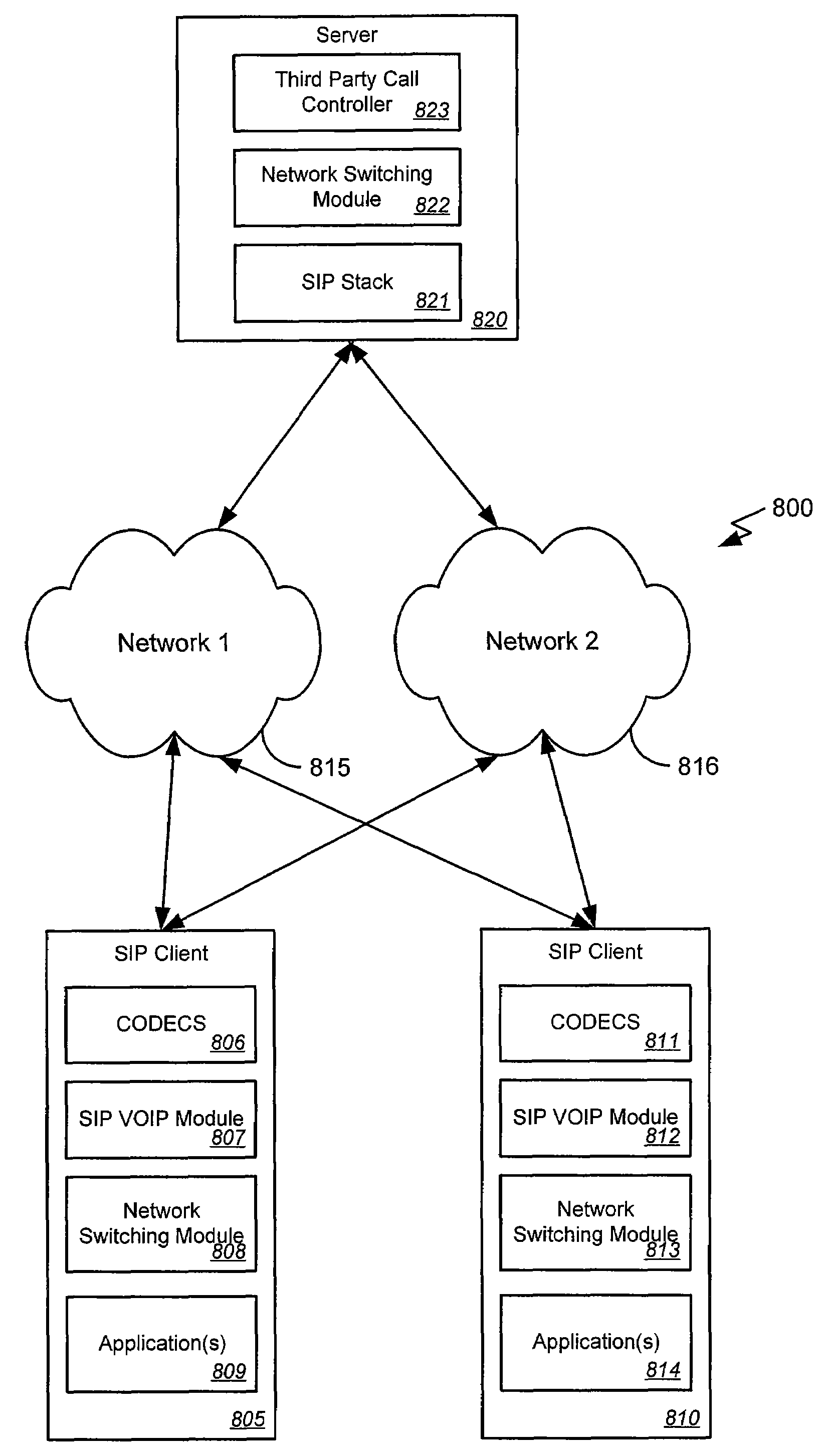
System using session initiation protocol for seamless network switching in a media streaming session
ActiveUS7711848B2Digital computer detailsWireless network protocolsStreaming dataSession Initiation Protocol
Systems, methods, and machine-readable media are disclosed for switching a media streaming session between a plurality of networks. In one embodiment, a method of switching networks in a media streaming session can comprise detecting a plurality of networks available for communication of streaming data. The plurality of networks can include a first network providing a first streaming session and a second network. A determination can be made as to whether to switch the first streaming session from the first network. Determining to switch the first streaming session from the first network to the second network can be based on detecting a loss of the first network, detecting a lower cost alternative to the first network, etc. In response to determining to switch the first streaming session from the first network, the first streaming session can be switched from the first network to the second network.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
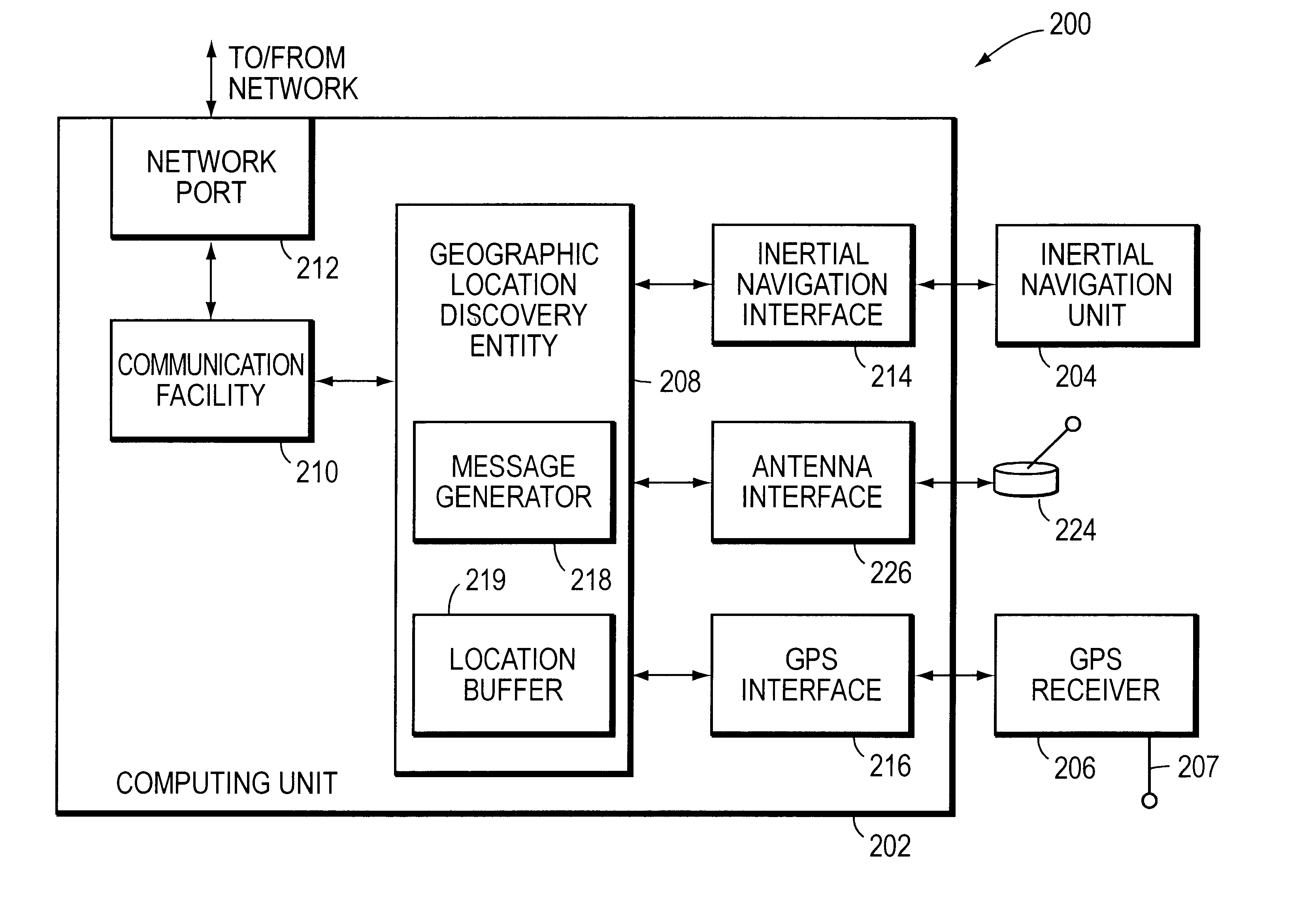
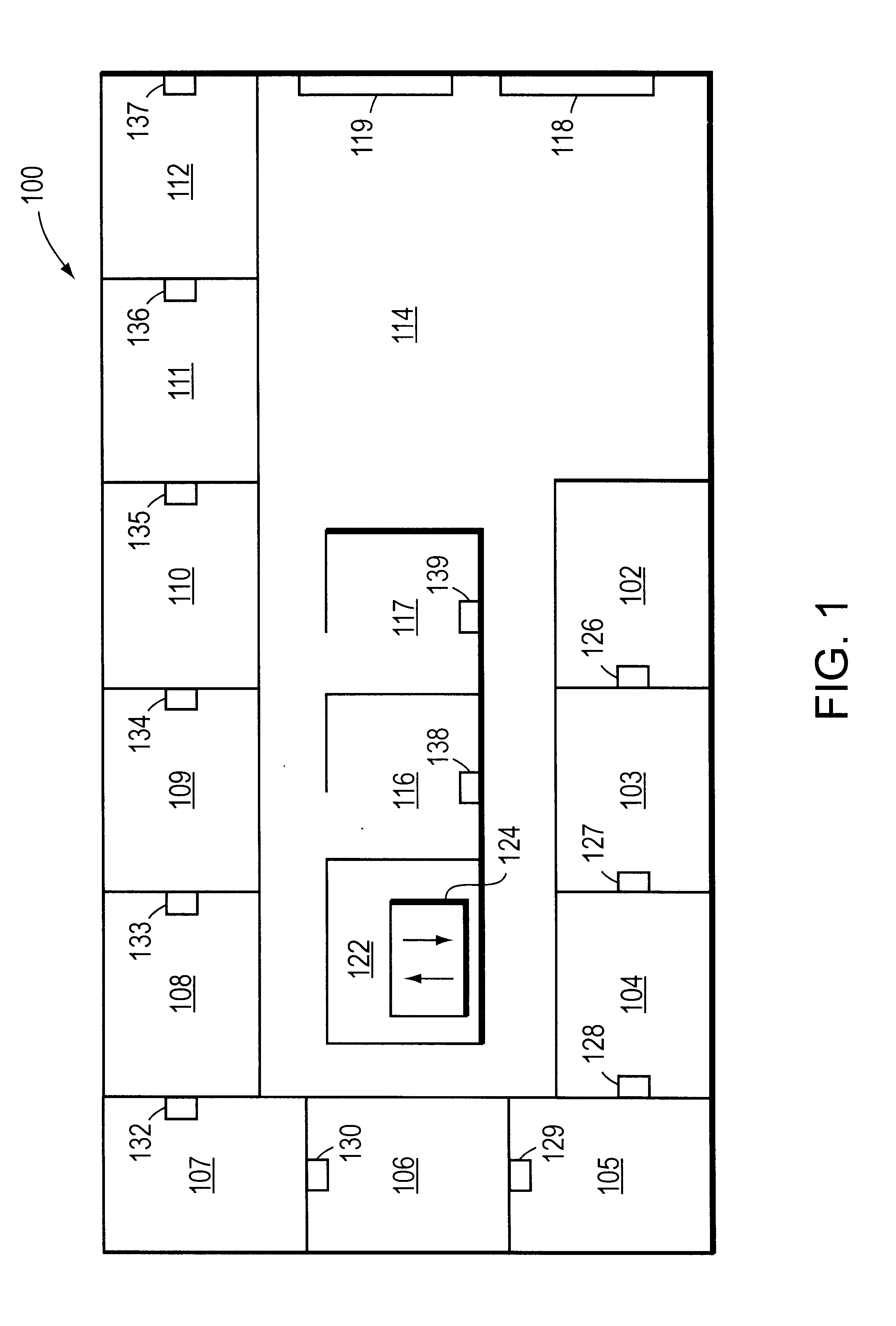
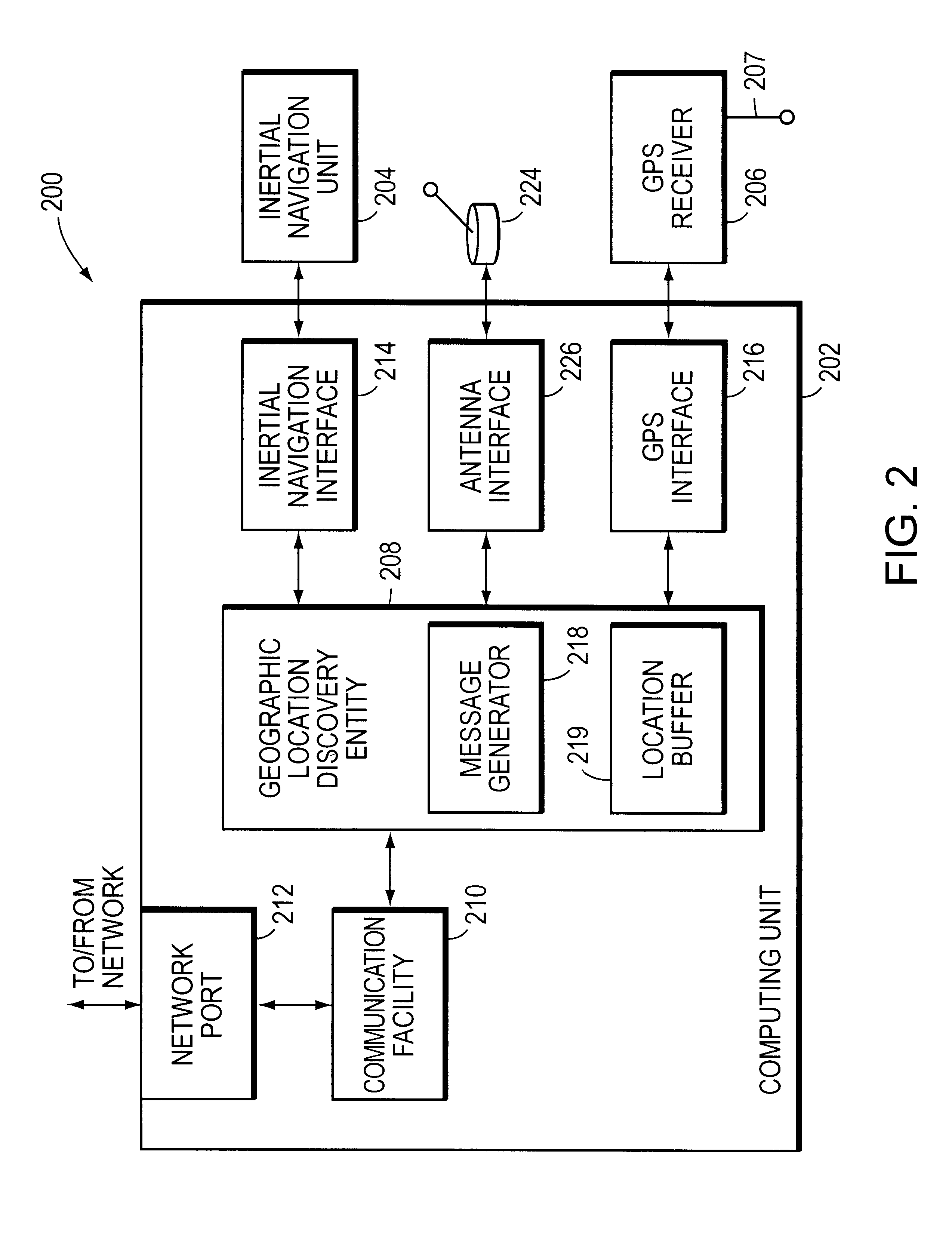
System for discovering and maintaining geographic location information in a computer network to enable emergency services
InactiveUS6665611B1Promote generationPosition fixationTelephonic communicationGps receiverGeolocation
A system automatically discovers and maintains geographic location information for entities and devices making up a computer network. The system preferably includes a computing unit and a geographic location generator, such as a Global Positioning System (GPS) receiver. The computing unit includes a location discovery entity and a message generator. The GPS receiver, which is mounted to and in communication with the computing unit, may be augmented with an inertial navigation unit to facilitate the generation of location information inside of buildings where GPS signals can be difficult to receive. The computing unit further includes a network communications facility so that it can communicate with one or more network devices, such as a network switch. The switch includes a location recording / reporting entity and a location database. Physical coordinates of network entities or devices are obtained by the GPS receiver and / or-inertial navigation unit and transmitted to the network switch, and the recording / reporting entity stores the physical coordinates at the location database.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
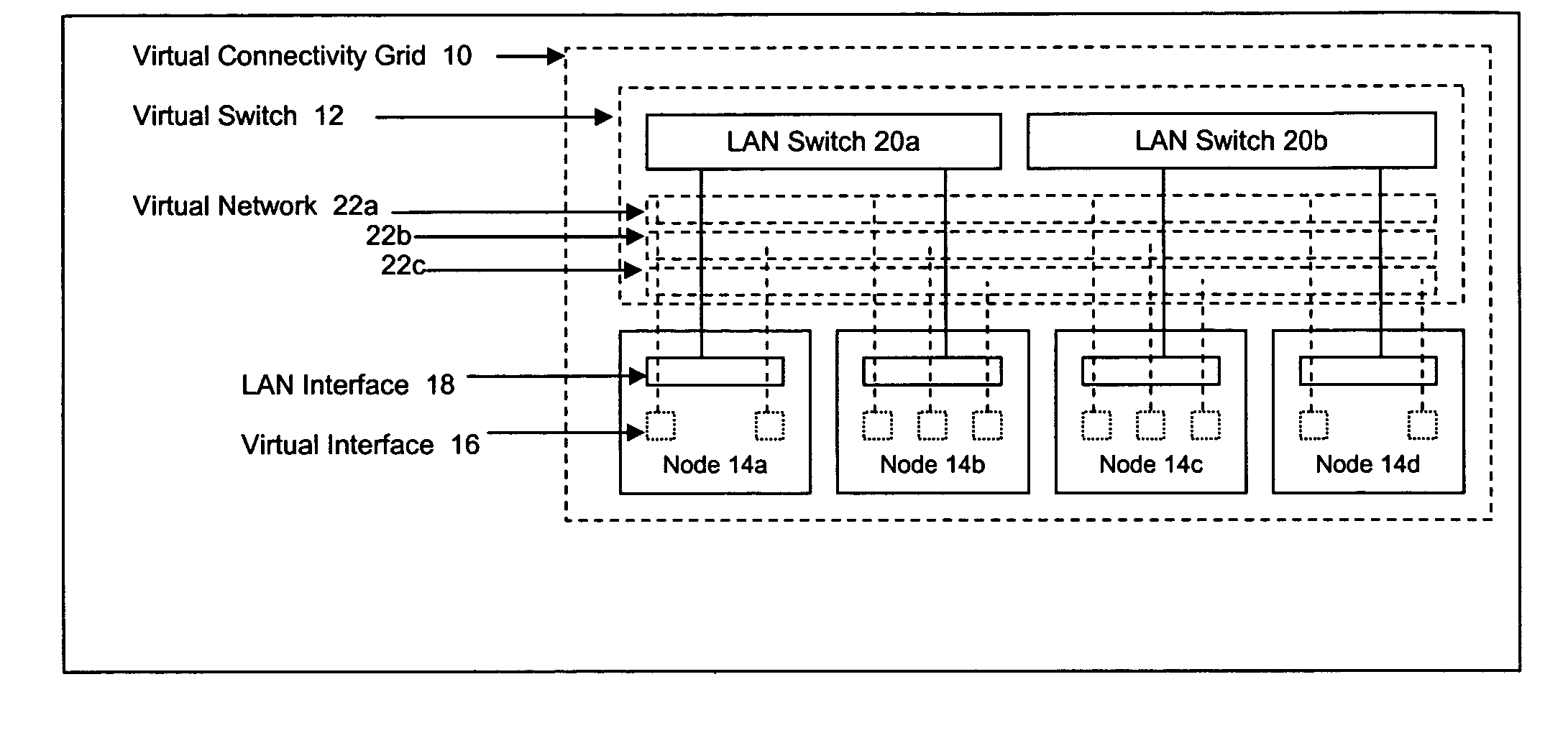
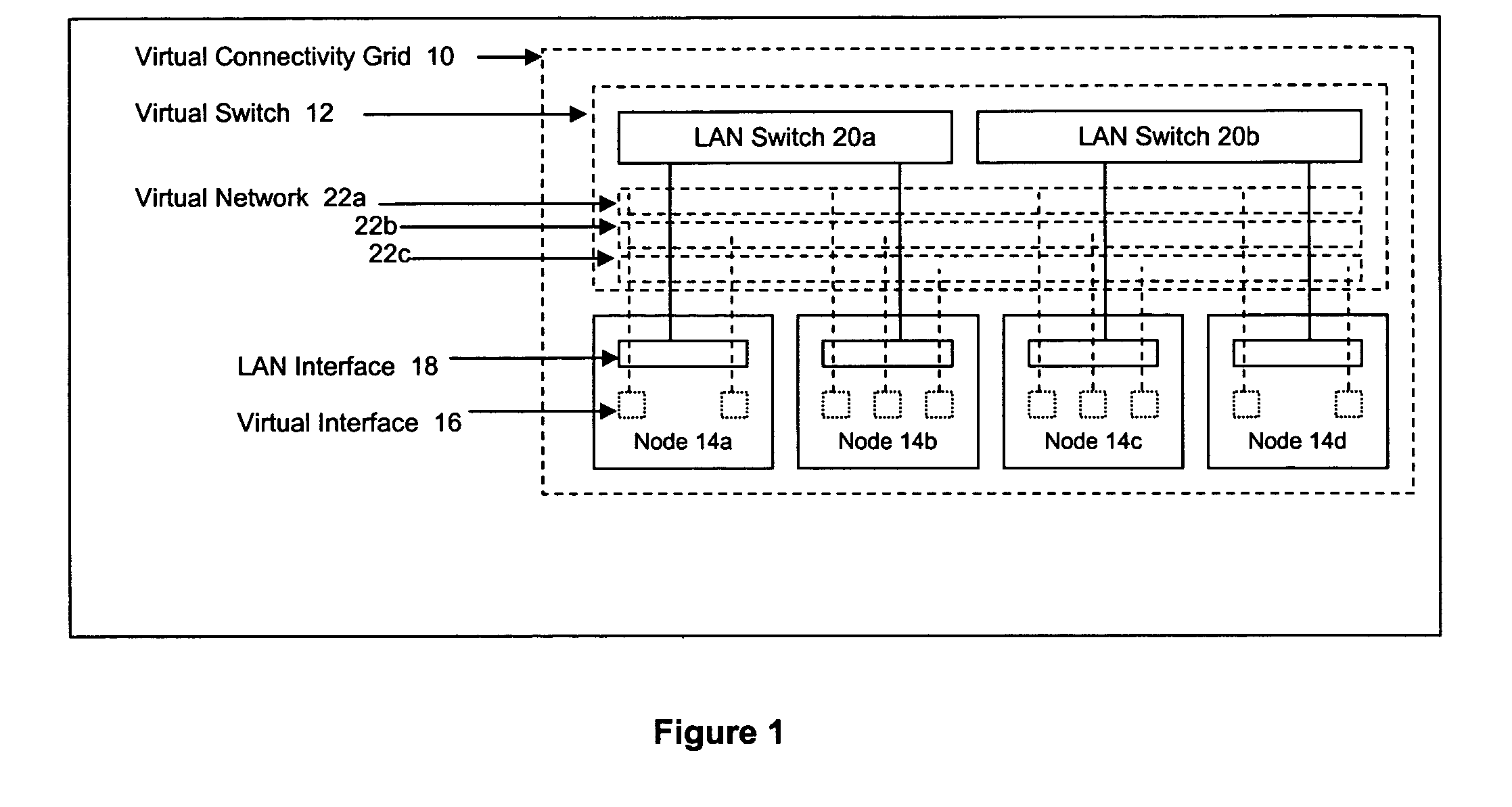
Method and apparatus for achieving dynamic capacity and high availability in multi-stage data networks using adaptive flow-based routing
ActiveUS20050091396A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionSystems managementHigh availability
Methods and systems for determining paths for flows within a multi-stage network made up of clusters of processing nodes. The flow paths may be determined without knowledge of whether or not packets of a particular flow will actually traverse specific ones of the clusters within the multi-stage network. In various implementations, the nodes of the multi-stage network may be coupled to one or more physical network switches through respective physical interfaces and a virtual connectivity grid superimposed thereon and configured through the use of a flow routing framework and system management framework to group the nodes into a number of clusters. The nodes of each cluster are configured to perform similar packet processing functions and the clusters are interconnected through virtual networks to which the nodes are communicatively coupled via virtual interfaces overlaid on top of the physical network interfaces.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
Method and system for managing time division multiplexing (TDM) timeslots in a network switch
InactiveUS20030026287A1Time-division multiplexRadio transmissionStatistical time division multiplexingFibre Channel
A system and method for managing the allocation of Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) timeslots in a network switch. The network switch may use a TDM cycle comprising multiple timeslots to manage shared resources and to schedule data ingress and egress through the ports of the current configuration, wherein each port is assigned one or more timeslots. The network switch may be reprogrammed to support one of multiple timeslot assignment schemes for one of multiple port configurations. The network switch may support configurations with varying numbers of ports, e.g. 8- and 16-port configurations. A network switch may also support configurations where two or more ports are combined to form one port, for example, a 2 Gbs Fibre Channel port. To meet the requirements of the various configurations, the timeslot assignment scheme may be reprogrammed to meet the scheduling requirements of each of the possible port configurations.
Owner:BROCADE COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMS
System and method for the management of power supplied over data lines
ActiveUS20040230846A1Configuring power of Ethernet devicesSpecial service provision for substationVolume/mass flow measurementNetwork switchEthernet
A system for providing power over data lines, particularly Ethernet data lines, comprises a network switch including a multiplicity of ports each of which is capable of supplying power in addition to data packets, a controllable power source which is coupled to said ports for supplying power thereto and a processor which is coupled to control the supply of power by the power source. The processor is programmed to guarantee the supply of power to selected ports and to allow or inhibit the supply of power to ports other than the selected ports, having regard to a specified limit on the supply of power by the controllable power source and the total guaranteed power to the selected ports.
Owner:VALTRUS INNOVATIONS LTD +1
Intelligent network
InactiveUS7209964B2Easy to handleEliminate dependenciesInterconnection arrangementsSpecial service for subscribersExchange networkBusiness object
In a telecommunications switching network having a resource complex including network switches, an intelligent service platform for providing intelligent call processing and service execution for call events received at the switches and requiring call processing services. A centralized administration system is provided that comprises a system for storing one or more reusable business objects that each encapsulate a distinct call-processing function, and any associated data required by the business object; a system for distributing selected business objects and associated data to selected nodes in the switching network based on pre-determined node configuration criteria; and, a system for activating the business objects in preparation for real-time use. A computing platform is provided within each node for executing those business objects required to perform a service in accordance with an event received at the network switch. Also within a node is a storage and retrieval system for sorting and retrieving selected objects and any associated data distributed by the administration system, and making them locally available to the computing platform when required to perform a service. An underlying location-independent communication system is provided to coordinate interaction of one or more business objects to perform the service in response to needs of the received event.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
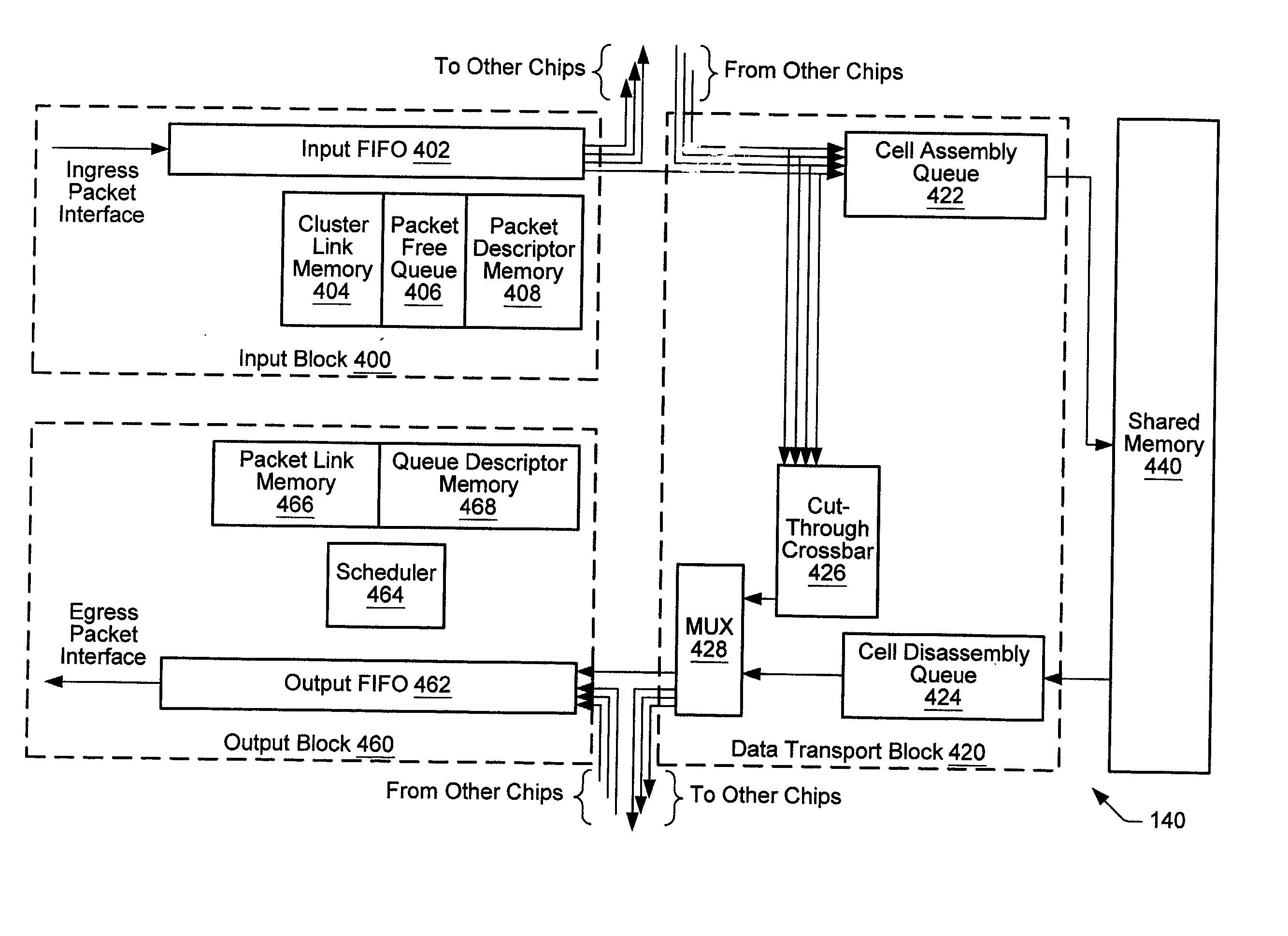
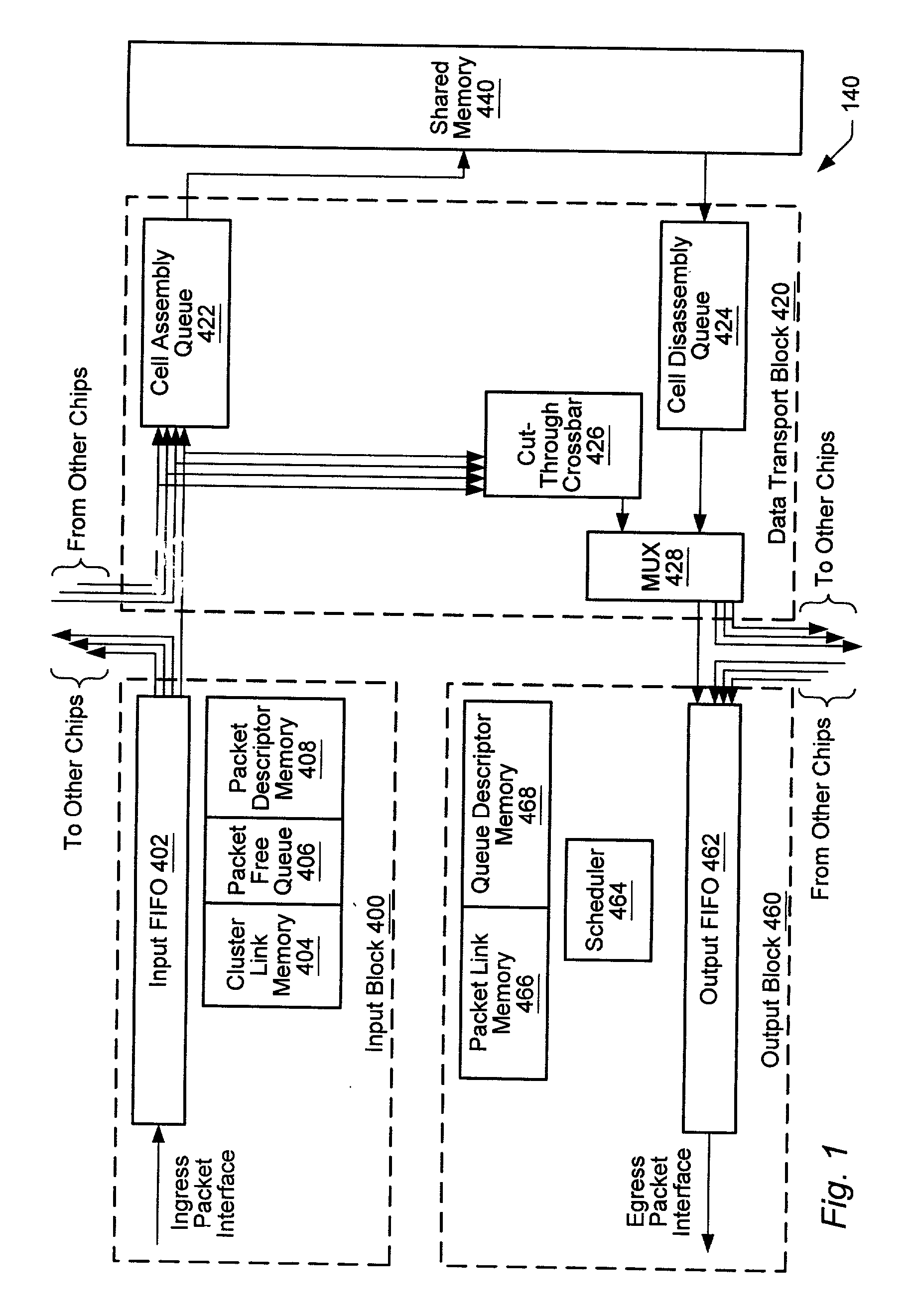
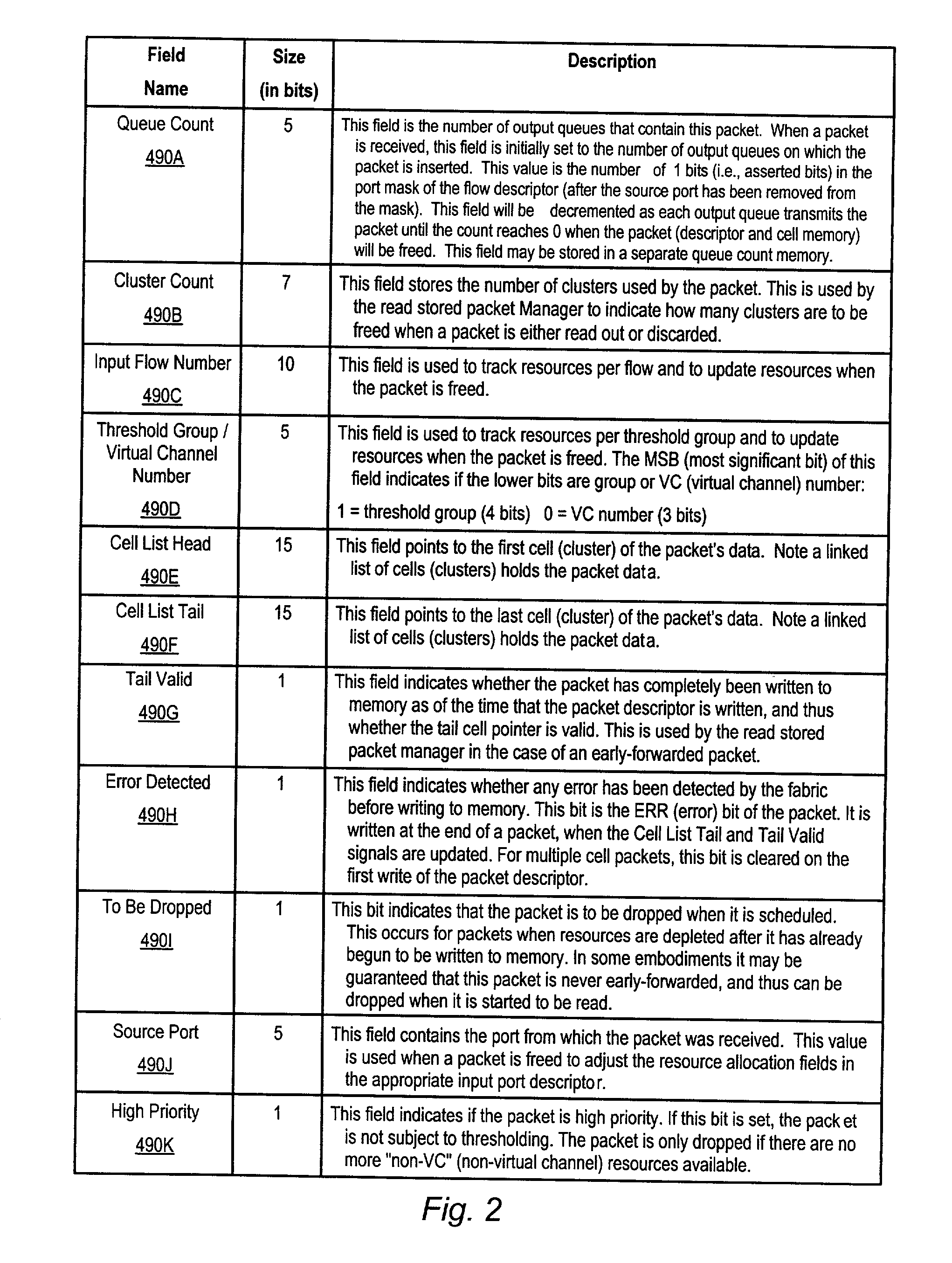
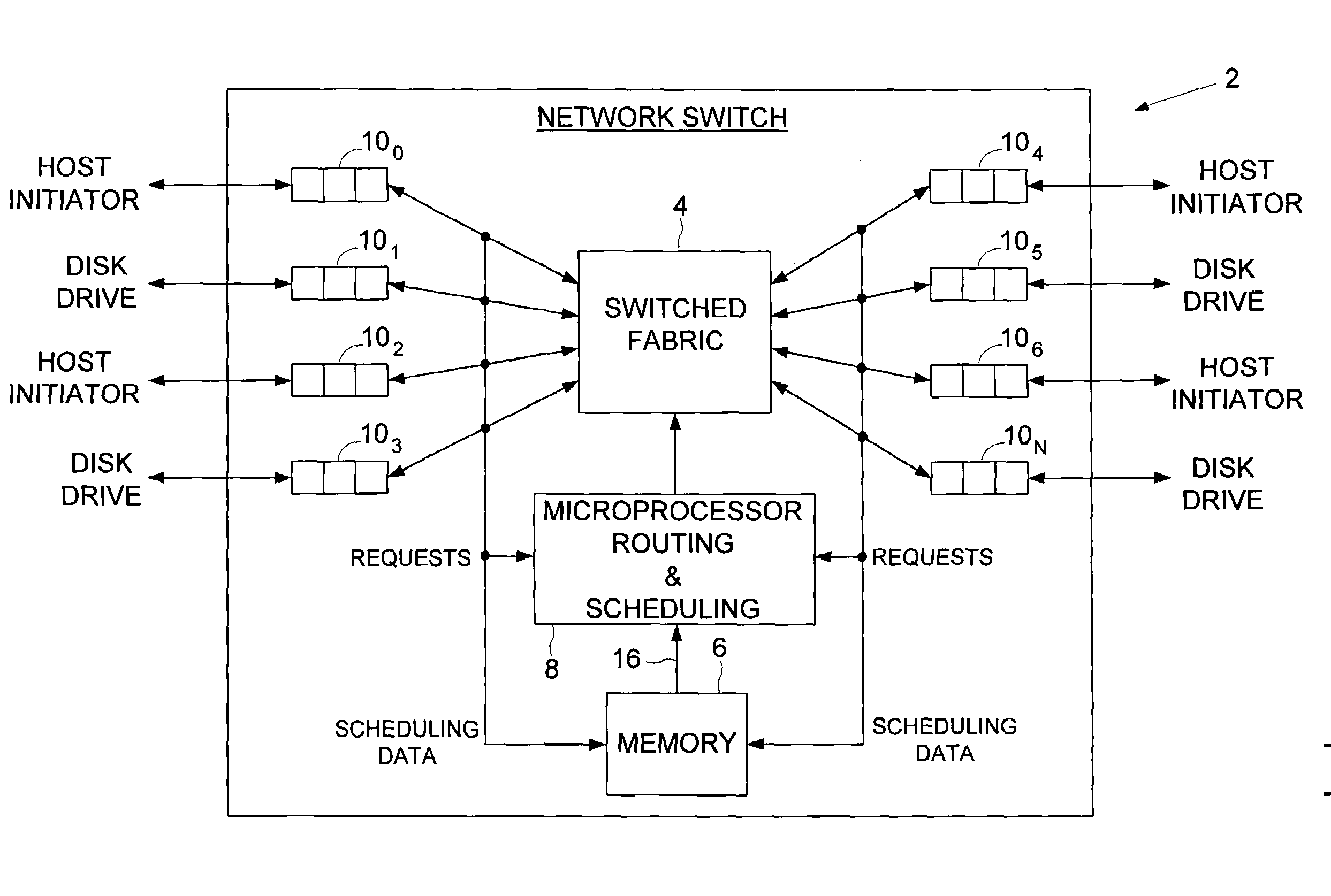
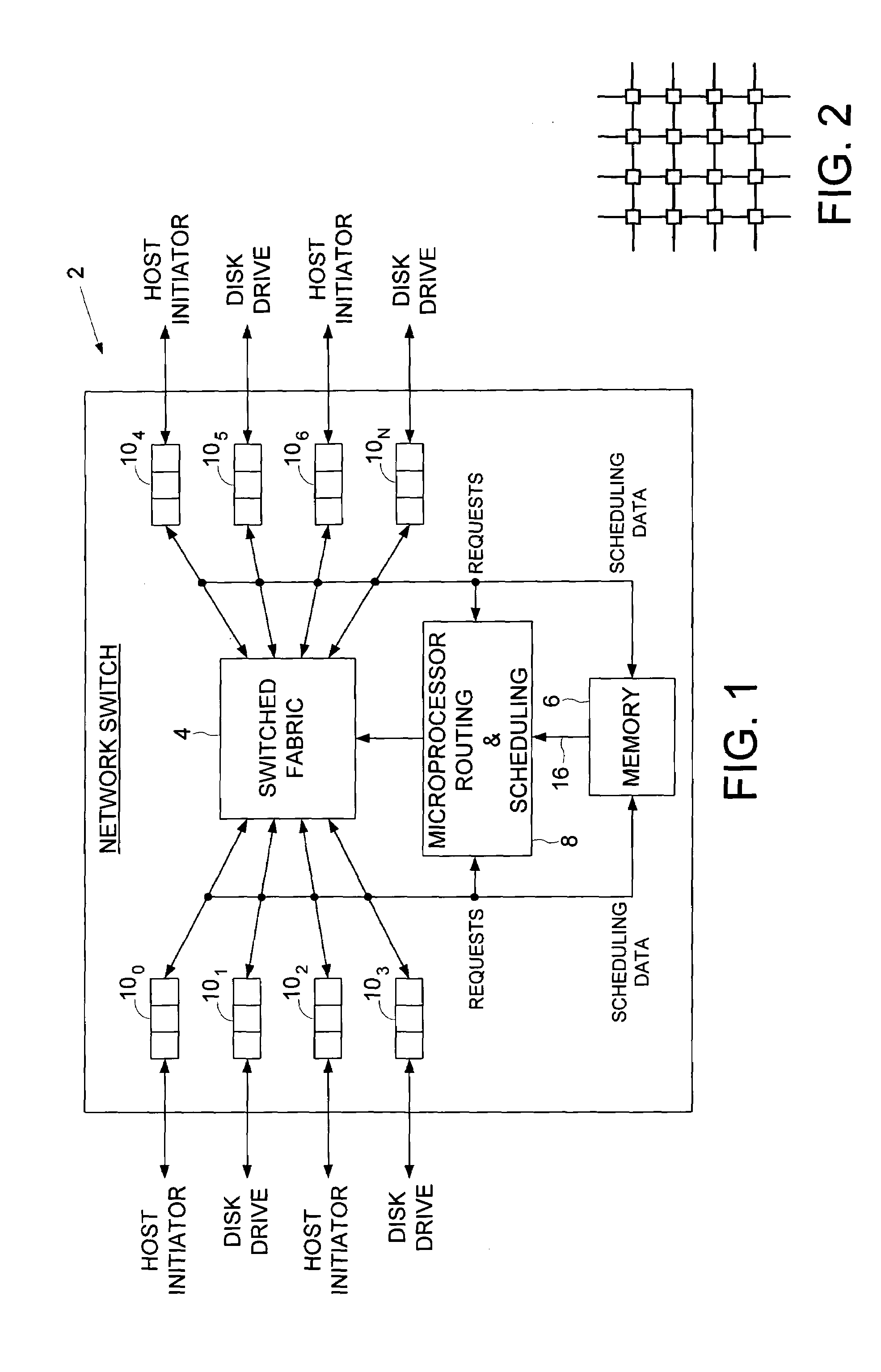
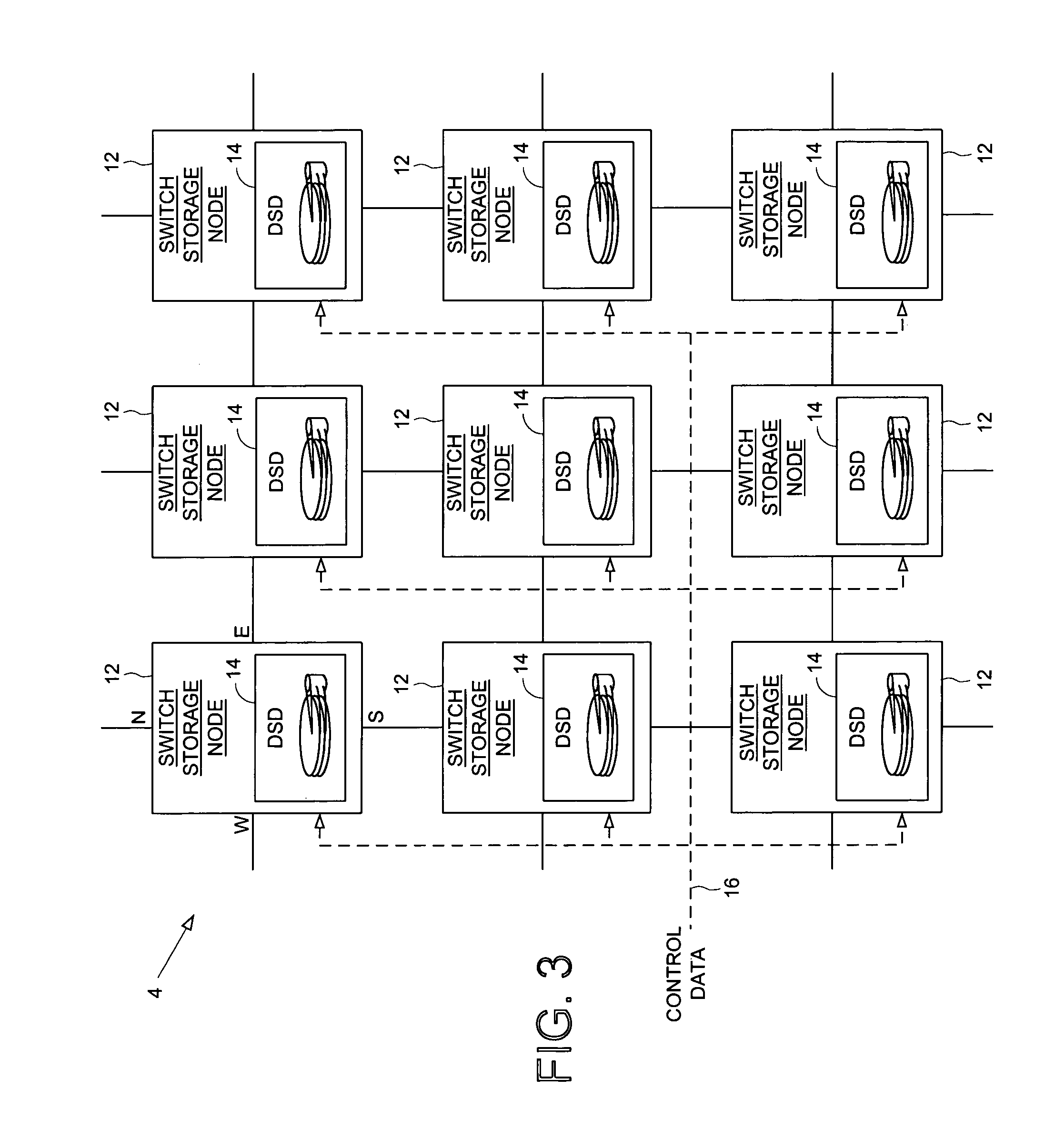
Transferring scheduling data from a plurality of disk storage devices to a network switch before transferring data associated with scheduled requests between the network switch and a plurality of host initiators
InactiveUS6928470B1Input/output to record carriersMultiple digital computer combinationsControl dataNetwork switch
A network switch is disclosed for resolving requests from a plurality of host initiators by scheduling access to a plurality of disk storage devices. The network switch comprises a switched fabric comprising a plurality of switching elements. Each switching element comprises a plurality of bi-directional switched fabric ports, and a control input connected to receive switch control data for selectively configuring the switching element in order to interconnect the bi-directional switched fabric ports. The network switch further comprises a memory for storing a routing and scheduling program, and a microprocessor, responsive to the requests, for executing the steps of the routing and scheduling program to generate the switch control data to transmit scheduled requests through the bi-directional switched fabric ports. At least one of the plurality of switching elements comprises a disk storage interface for connecting to a selected one of the disk storage devices. The microprocessor schedules access to the plurality of disk storage devices through the disk storage interface. The disk storage interface receives scheduling data from the selected one of the storage devices, and the memory stores the scheduling data received via the bi-directional switched fabric ports of a selected number of the switching elements. The scheduling data is processed according to a priority such that the selected switching elements transfer the scheduling data through the bi-directional switched fabric ports before transferring data associated with the scheduled requests.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Path recovery on failure in load balancing switch protocols
InactiveUS7430164B2Increase profitQuick identificationError preventionTransmission systemsBackup pathNetwork switch
A method for managing multiple active paths among a plurality of network switches to identify and select an alternate path in response to failure of a path from a switch to a device. Load balancing protocols of the present invention enable the simultaneous use of multiple paths between network devices through a mesh of compliant network switches. When a port of a network switch fails (or the link connected to a port fails), a switch in accordance with the present invention selects an alternate port which may be used for forwarding packets to devices normally reached through the failed port. Networks switches operable in accordance with the structures and protocols of the present invention exchange messages to identify potential alternate paths. A potential alternate path is used to send a query message to a neighboring network switch to determine if a path to the identified devices is available through the neighboring network switch. Such query messages are propagated through all intermediate network switches between the switch sensing the failed port up to the identified network device. Acknowledgment messages are returned to verify potential availability of an alternate path. Where an intermediate network switch determines that the complete path is not available through it to the identified device, or where a potentially better path exists, a regenerated query message so indicating is returned along the path that initiated the query message.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
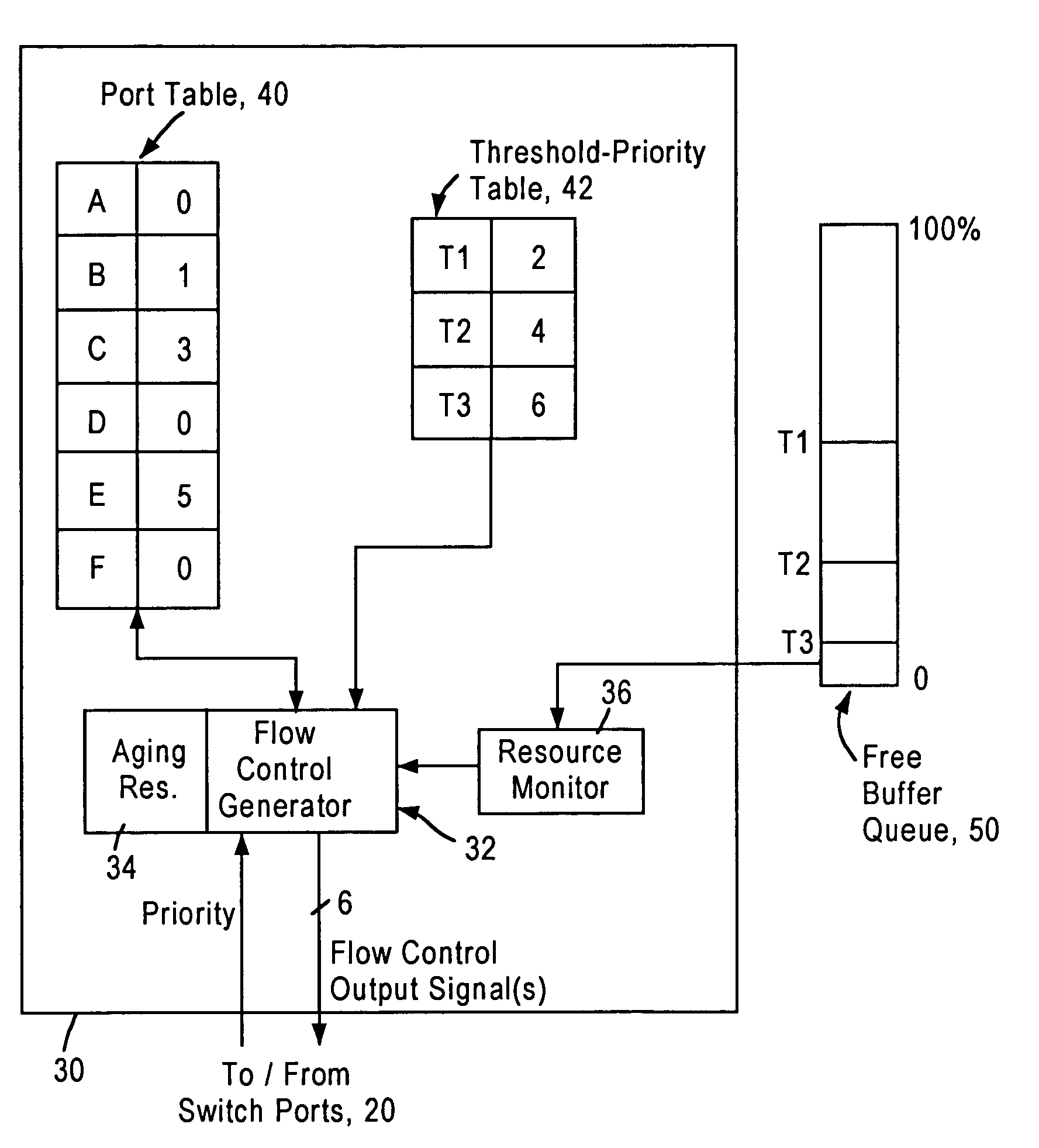
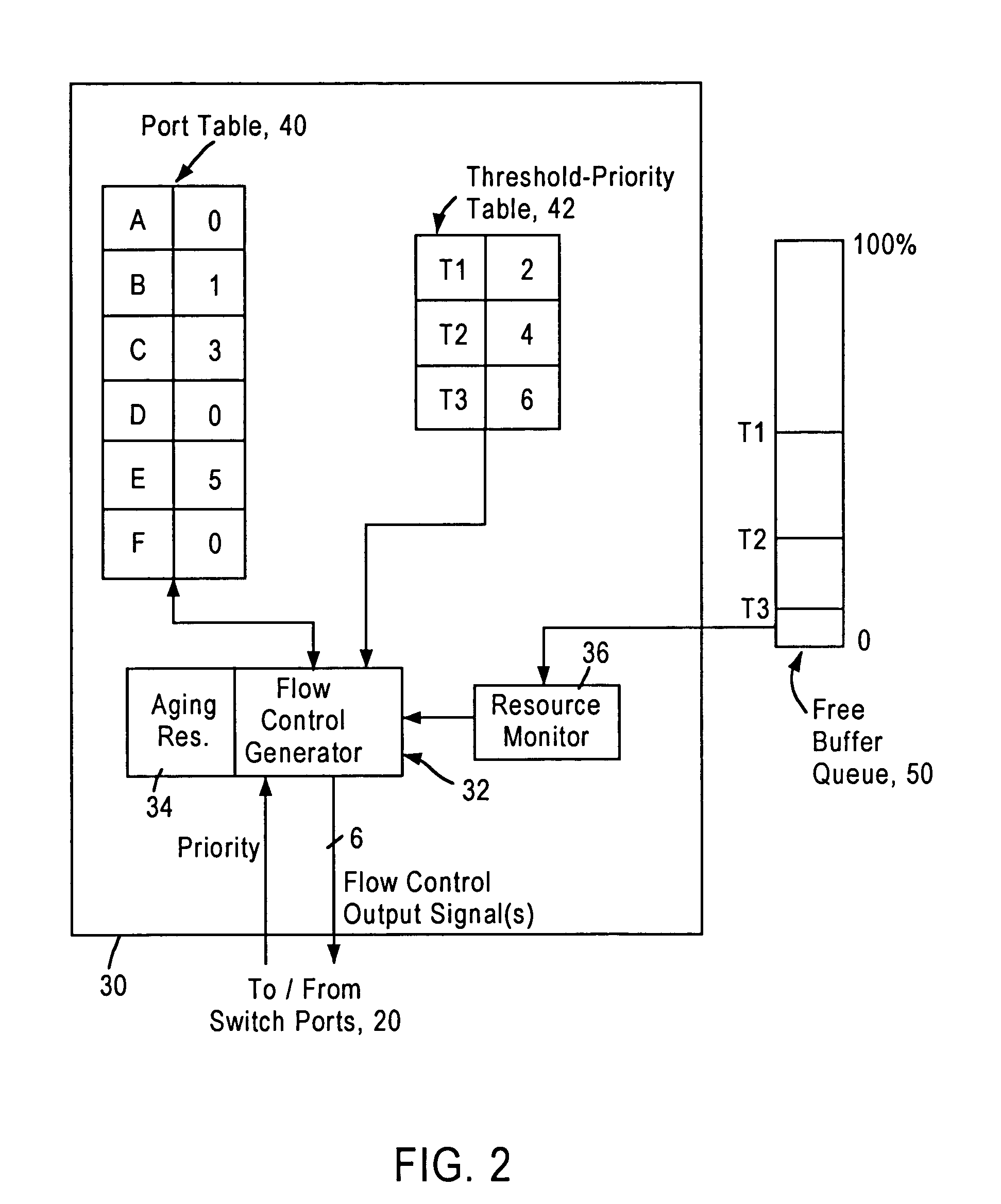
Flow control arrangement in a network switch based on priority traffic
InactiveUS6981054B1Avoid congestionMaintain reliabilityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityFrame based
A network switch includes network switch ports, each including a port filter configured for detecting user-selected attributes from a received layer 2 frame. Each port filter, upon detecting a user-selected attribute in a received layer 2 frame, sends a signal to a switching module indicating the determined presence of the user-selected attribute, for example whether the data packet has a prescribed priority value. The network switch includes a flow control module that determines which of the network switch ports should output a flow control frame based on the determined depletion of network switch resources and based on the corresponding priority value of the network traffic on each network switch port. Hence, any network switch port that receives high priority traffic does not output a flow control frame to the corresponding network station, enabling that network station to continue transmission of the high priority traffic. In most cases, the congestion and depletion of network switch resources can be alleviated by sending flow control frames on only those network switch ports that receive lower priority traffic, enabling the network switch to reduce congestion without interfering with high priority traffic.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
System and Method for an In-Server Virtual Switch
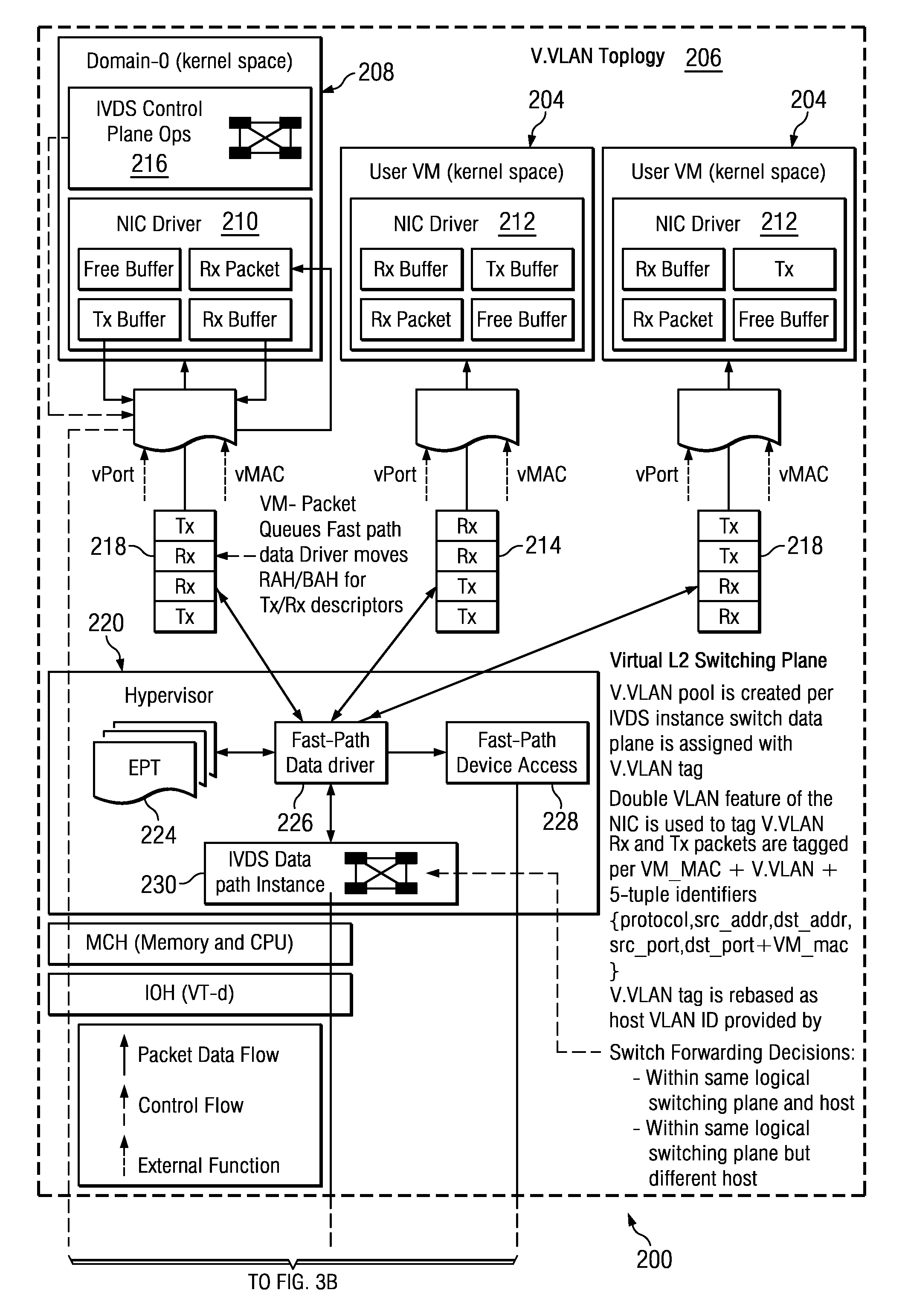
ActiveUS20120324442A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionData processing systemNetwork interface device
In accordance with an embodiment, a data processing system includes a processor, a memory, and an interface port configured to be coupled to a hardware network interface device. The processor is configured to run a process that maps network switching functions of each of a plurality of virtual machines to the hardware network interface device.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
VLAN frame format
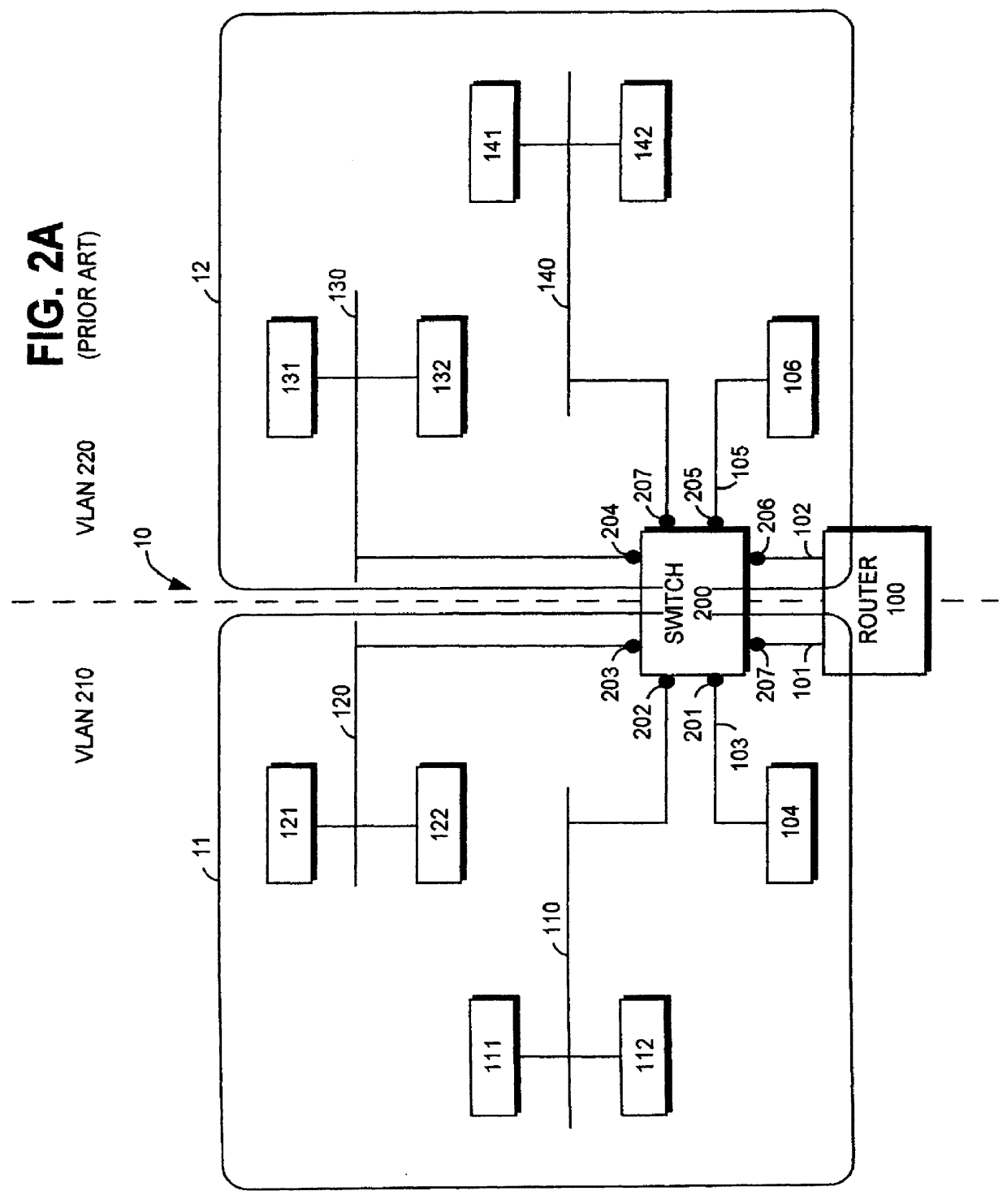
InactiveUS6111876AReduce decreaseAvoid ambiguityNetwork topologiesTime-division multiplexVirtual LANNetwork switch
In a network device such as a network switch having a port coupled to a communications medium dedicated to a single virtual local area network and another port coupled to a communications medium shared among multiple virtual local area networks for transmitting data frames between the dedicated communications medium and the shared communications medium, a method of identifying the virtual network associated with each data frame received by the network switch when transmitting the data frames over the shared communications medium. The method comprises receiving data frames from the dedicated communications medium coupled to one port, and, with respect to each data frame so received, inserting a new type field and a virtual network identifier field. The contents of the new type field indicate the data frame comprises a virtual network identifier field. The method further includes placing a value in the virtual network identifier field identifying the virtual network associated with the data frame and transmitting the data frame over the shared communications medium. Upon receipt of the data frames from over the shared communications medium, another network device can discern from the virtual network identifier field in each data frame the virtual network from which the data frames were received and determine whether to forward the data frames accordingly.
Owner:INT LICENSE EXCHANGE OF AMERICA LLC
Method and system for power control based on application awareness in a packet network switch
Certain aspects of a method and system for a power control based on application awareness in a packet network switch are provided. Data communication flow may be monitored in ports in a packet network switch based on packet classification. Ports where data flow is not detected may have at least some functionality disabled to reduce power consumption. In this regard, a power saving mode may be utilized for disabling at least some functionality in a switch port, such as Ethernet ports, for example. A partially disabled port may be fully enabled when monitoring detects active data communication flow in that port. Port functionality may be enabled or disabled sequentially, for example. In some instances, a physical layer portion of the packet network switch may be utilized to adjust power in a port based on the data communication flow.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
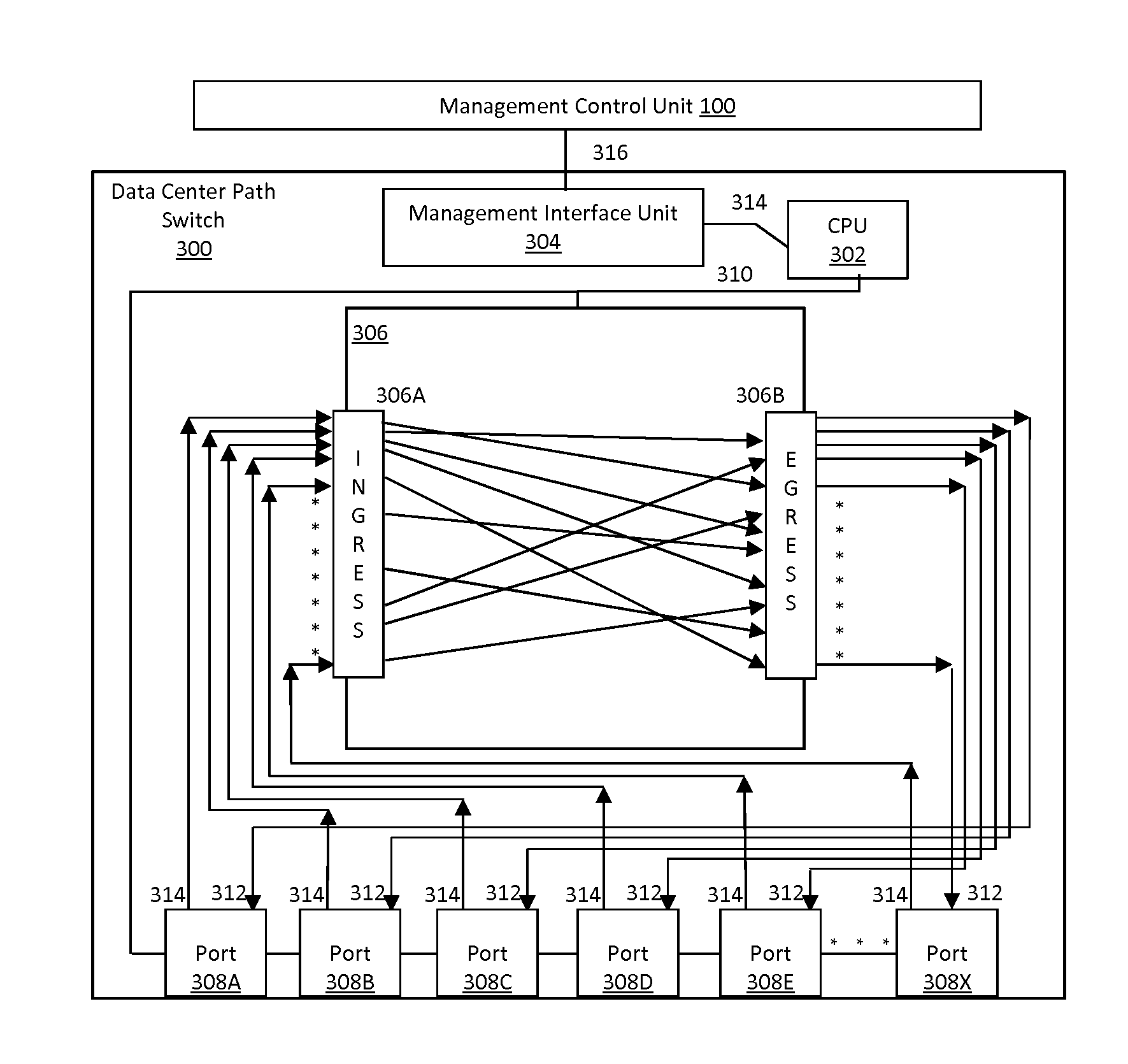
Data center path switch with improved path interconnection architecture
ActiveUS20160007102A1Easy to controlSimplifying interconnectionMultiplex system selection arrangementsOptical multiplexData centerSwitching signal
A data center path switch architecture permits path switching of the signal path of incoming signals to one or more output paths in real time without the need for manual intervention, and without delays associated with current data center network switches. In this architecture, a switching core capable of switching signals directly from the ingress of the switching core to alternate destination ports in real time, either under software or hardware control.
Owner:FIBER MOUNTAIN INC
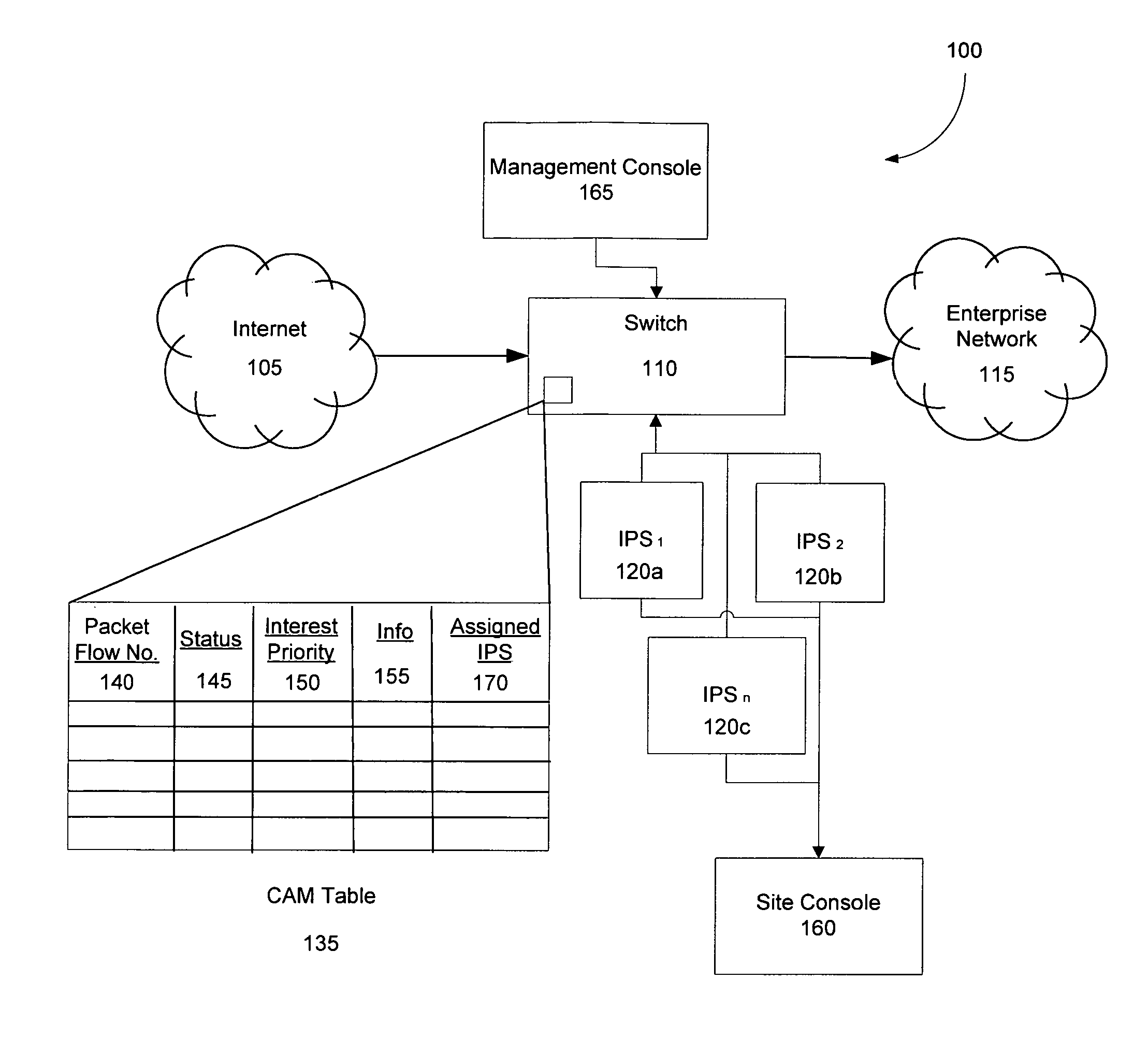
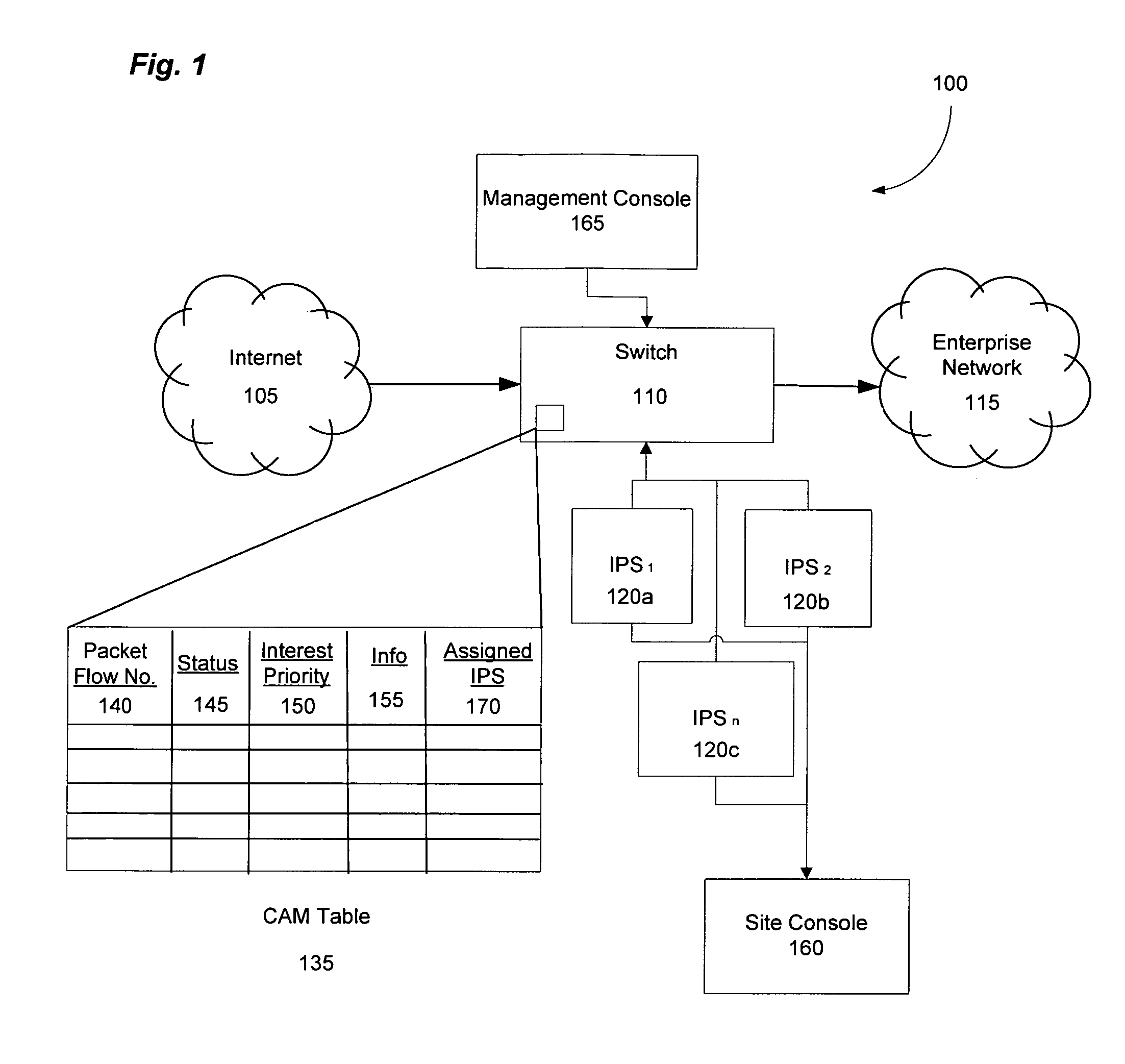
Fast network security utilizing intrusion prevention systems
InactiveUS7808897B1Avoid OverloadingIncrease the number ofError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityNetwork data
Intrusion Prevention Systems (“IPSs”) are used to detect and / or prevent intrusion events from infiltrating a computer network. However, in large computer networks the IPSs cannot conduct their analysis on network data traffic quickly enough in the network core to meet the demand placed on them by the computer networks, thereby causing delays in the transmission of network data traffic from a source to a destination. To prevent this delay, the IPSs can be configured to intelligently communicate with a high-capacity network switch. The IPSs conduct the initial inspection of the network data traffic flows to determine if an intrusion event is present. However, after the initial inspection, the IPS can inform the switch of what actions to take for future traffic flows including determining which future traffic flows are inspected by the IPSs and which future traffic flows are allowed to be blocked or transmitted to their destination by the switch.
Owner:LINKEDIN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com