Patents
Literature
373 results about "Backup path" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
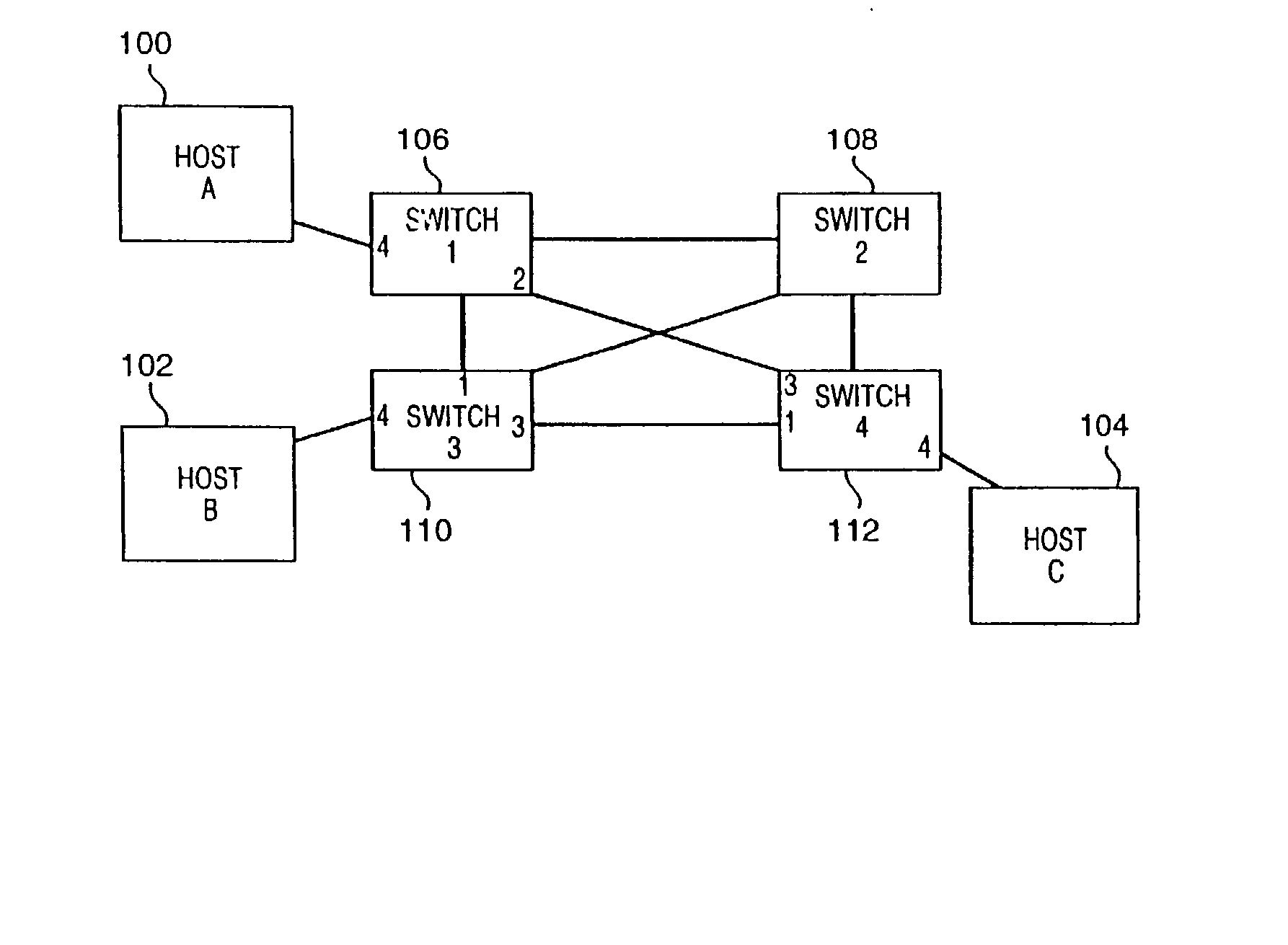
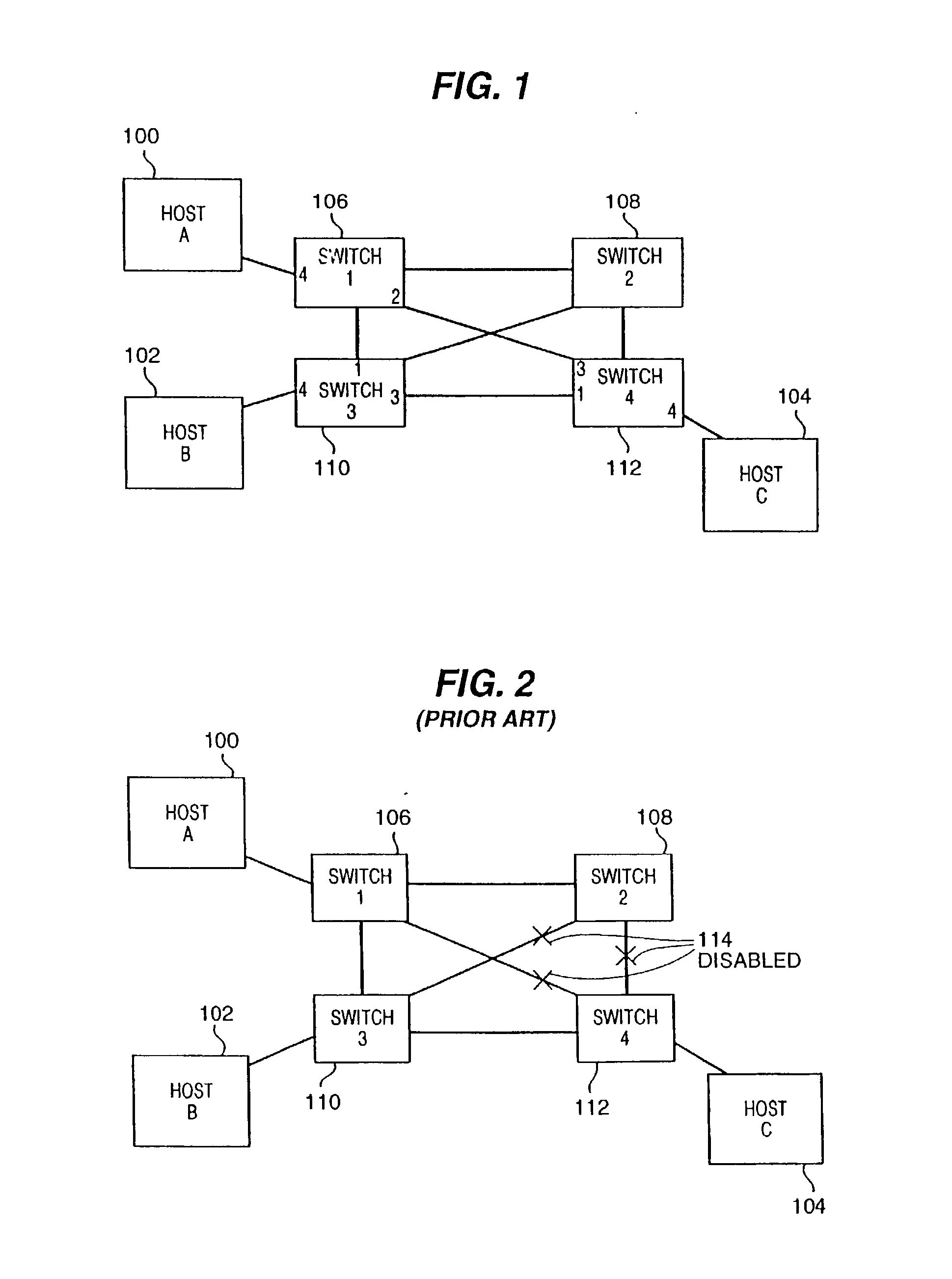
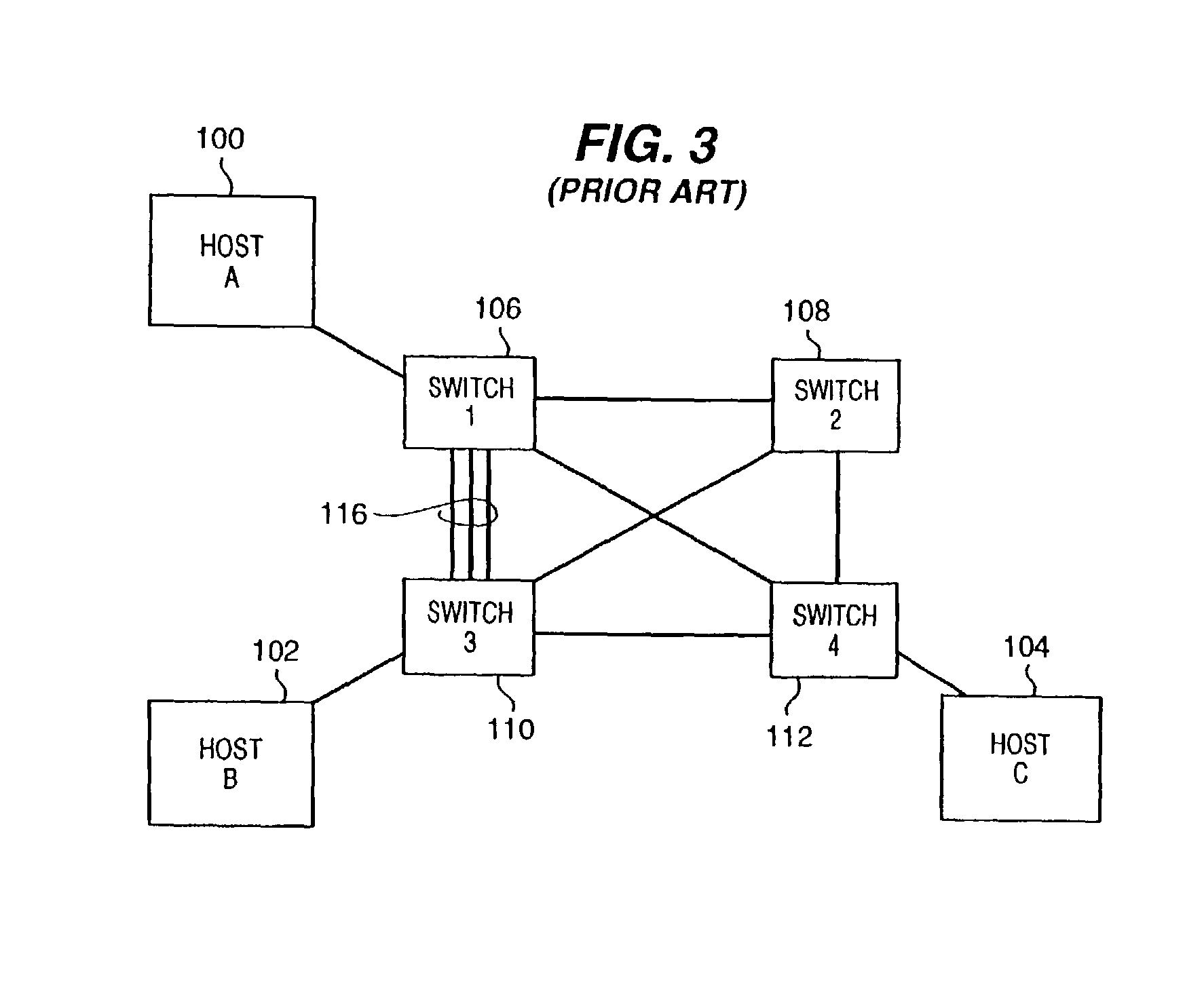
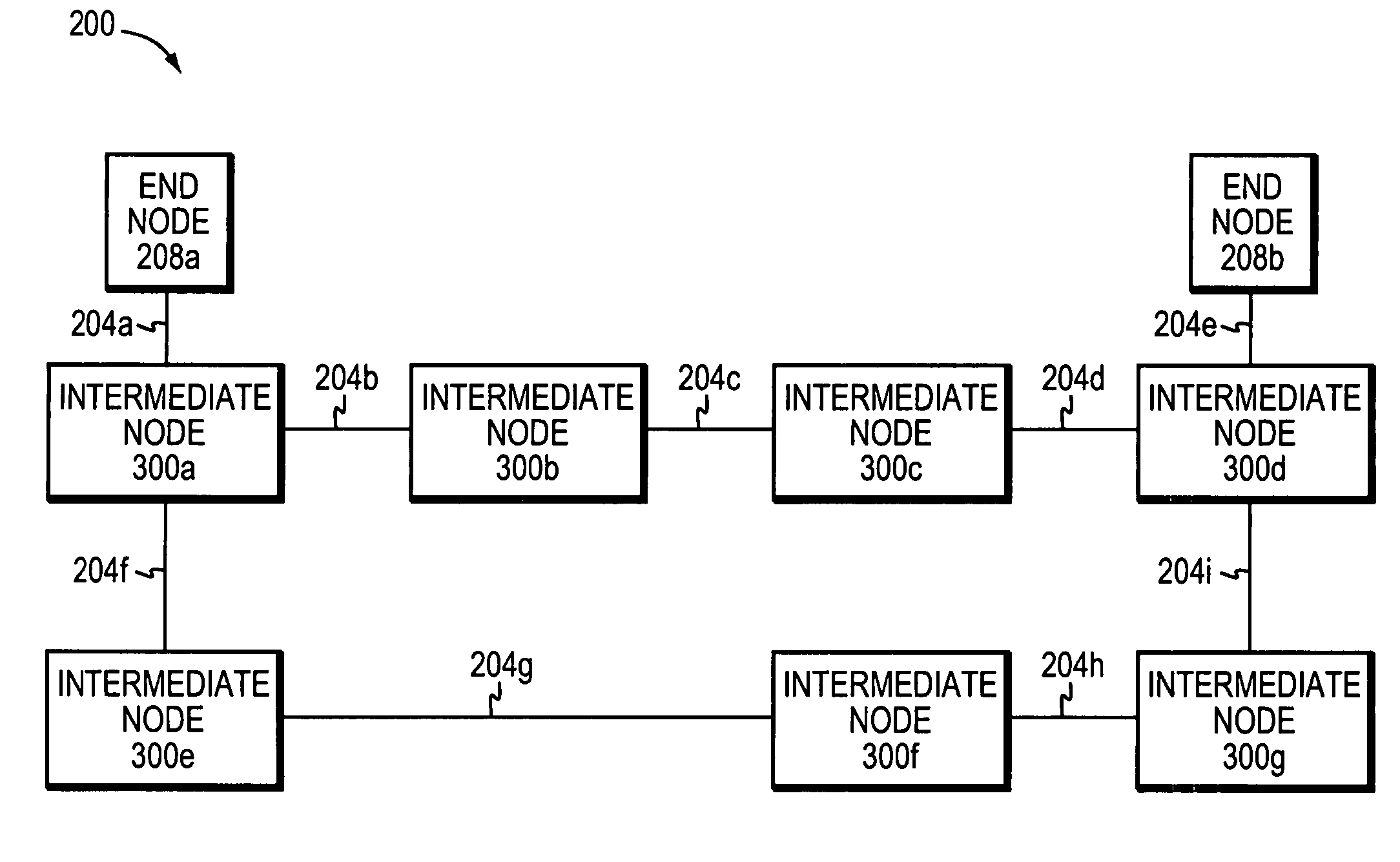
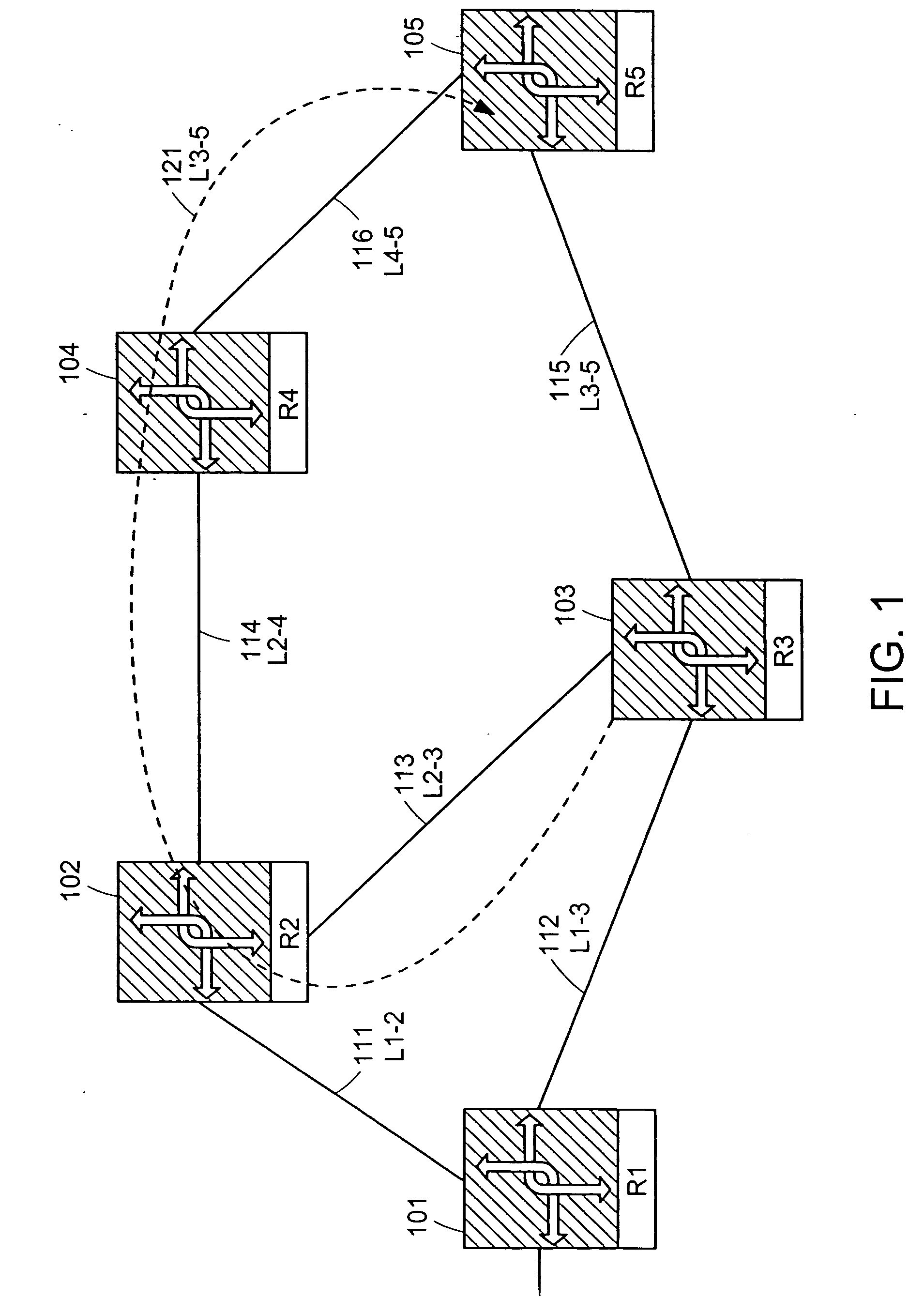
Path recovery on failure in load balancing switch protocols
InactiveUS20030016624A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsBackup pathNetwork switch
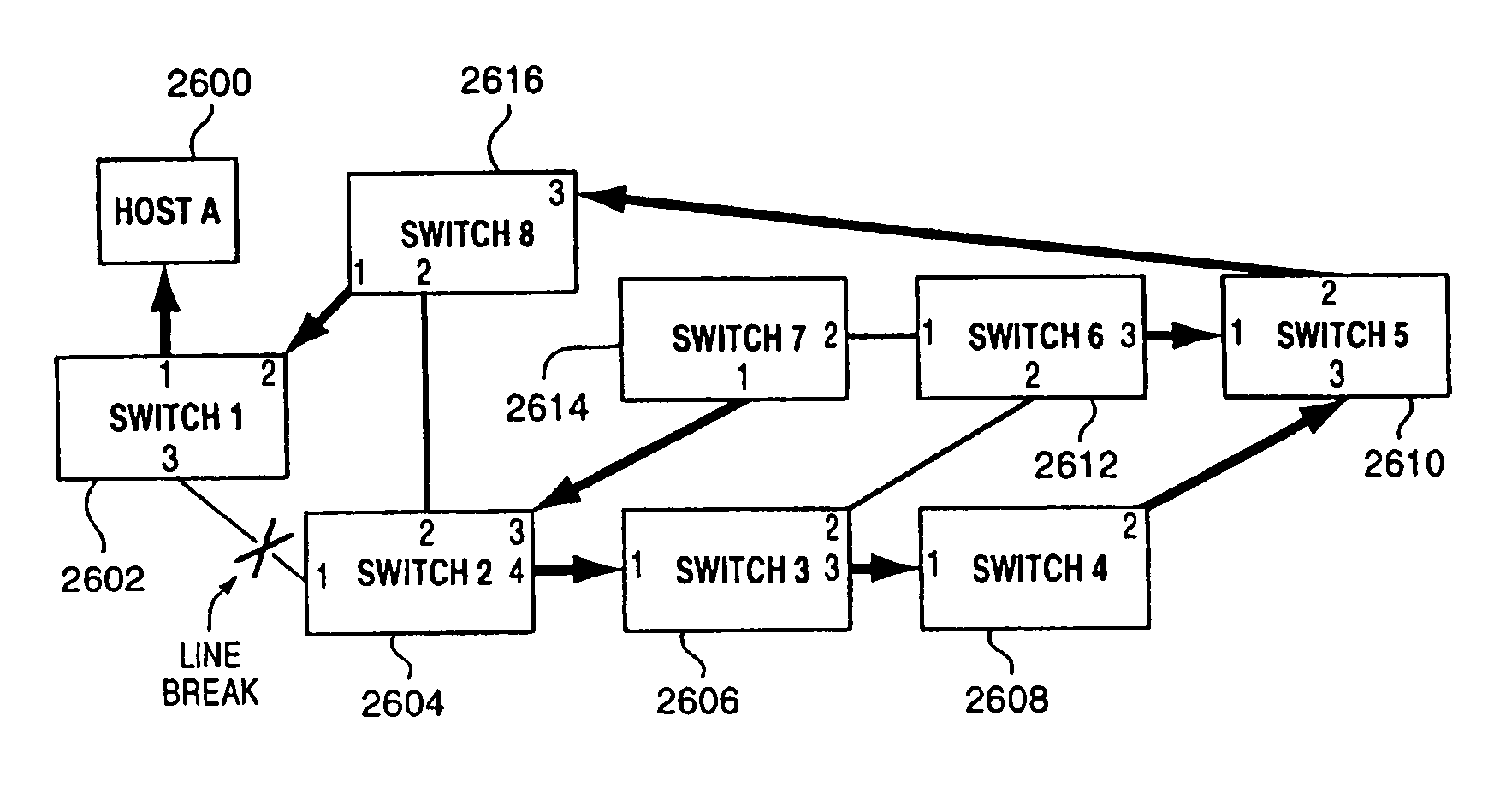
A method for managing multiple active paths among a plurality of network switches to identify and select an alternate path in response to failure of a path from a switch to a device. Load balancing protocols of the present invention enable the simultaneous use of multiple paths between network devices through a mesh of compliant network switches. When a port of a network switch fails (or the link connected to a port fails), a switch in accordance with the present invention selects an alternate port which may be used for forwarding packets to devices normally reached through the failed port. Networks switches operable in accordance with the structures and protocols of the present invention exchange messages to identify potential alternate paths. A potential alternate path is used to send a query message to a neighboring network switch to determine if a path to the identified devices is available through the neighboring network switch. Such query messages are propagated through all intermediate network switches between the switch sensing the failed port up to the identified network device. Acknowledgment messages are returned to verify potential availability of an alternate path. Where an intermediate network switch determines that the complete path is not available through it to the identified device, or where a potentially better path exists, a regenerated query message so indicating is returned along the path that initiated the query message.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
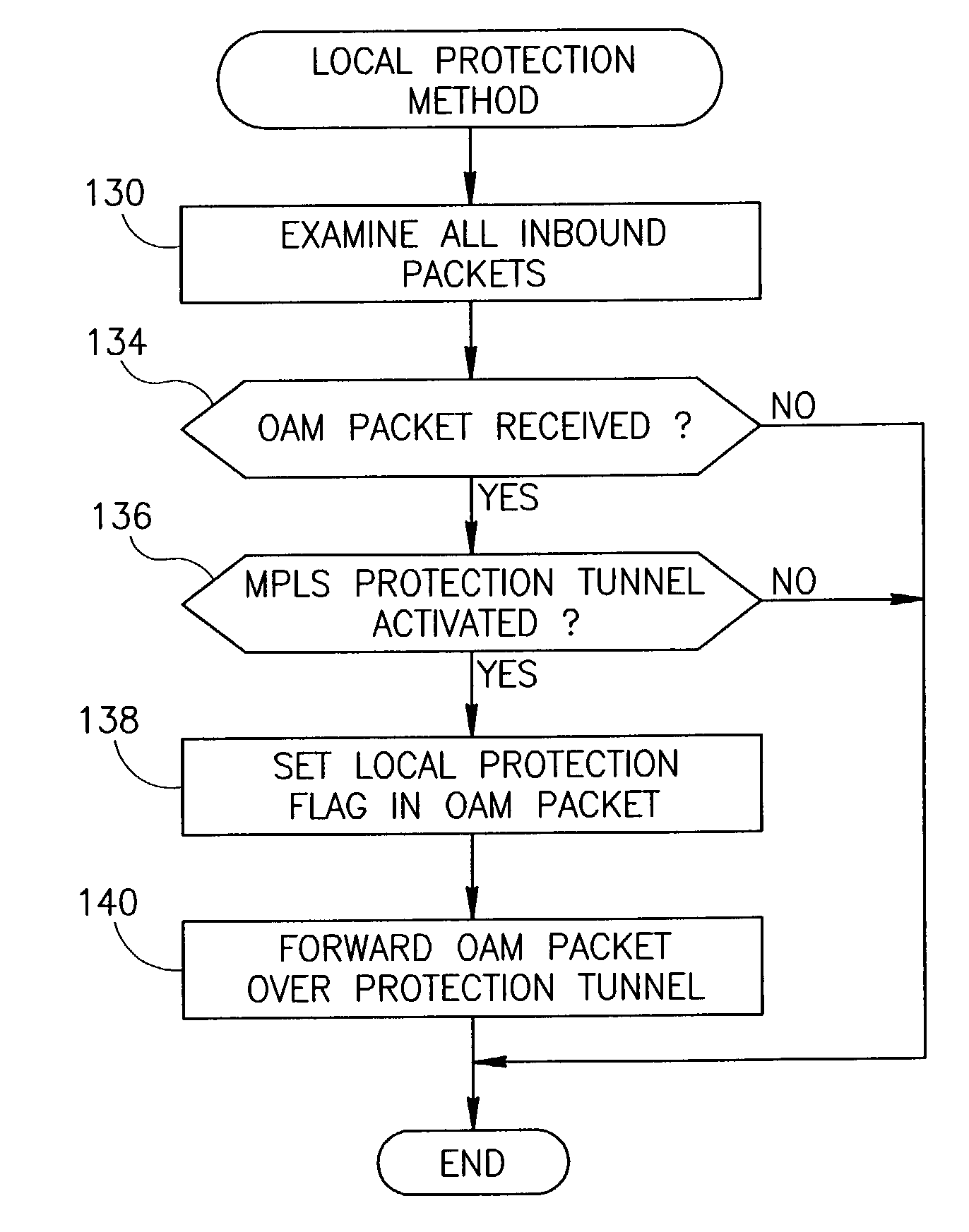
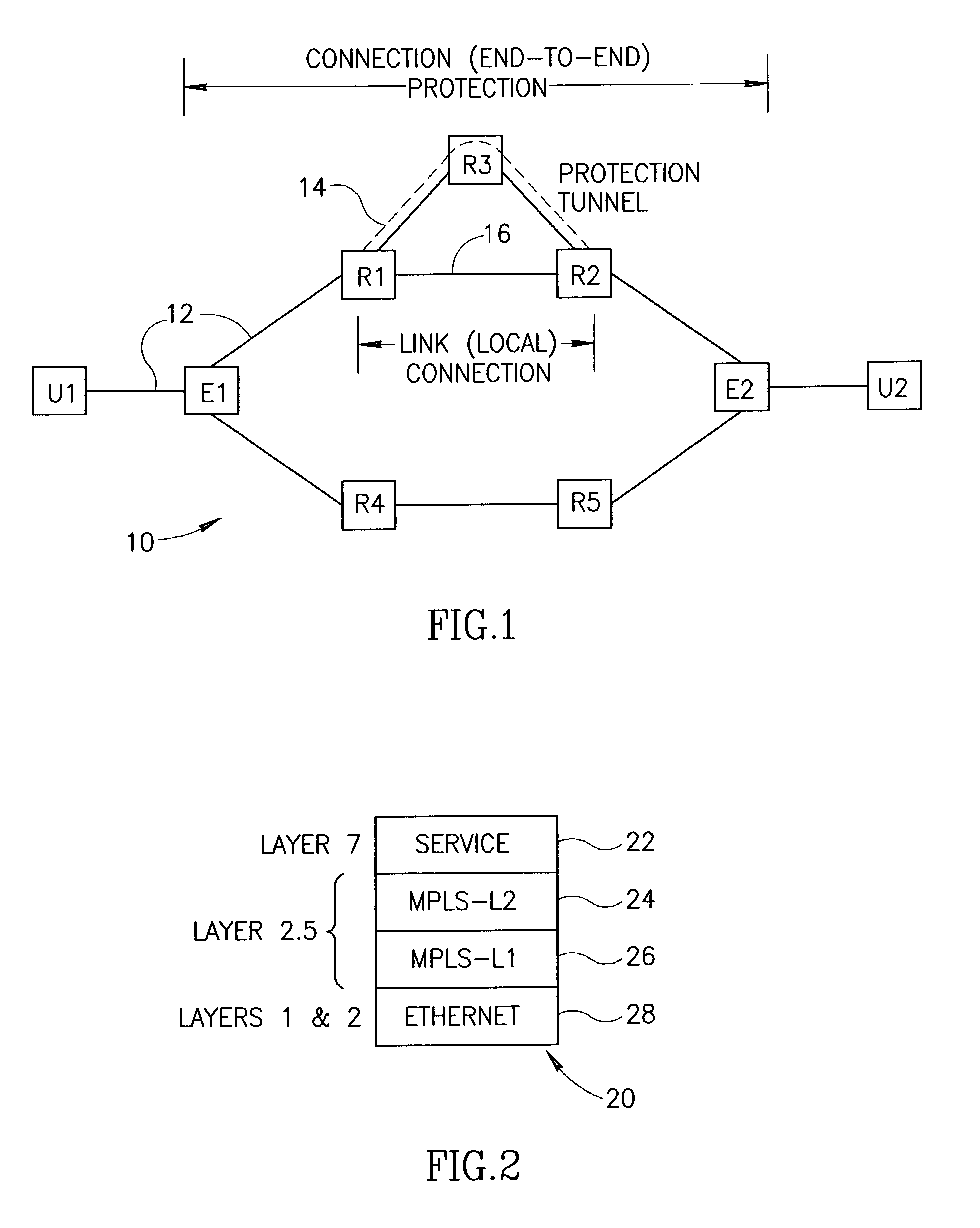
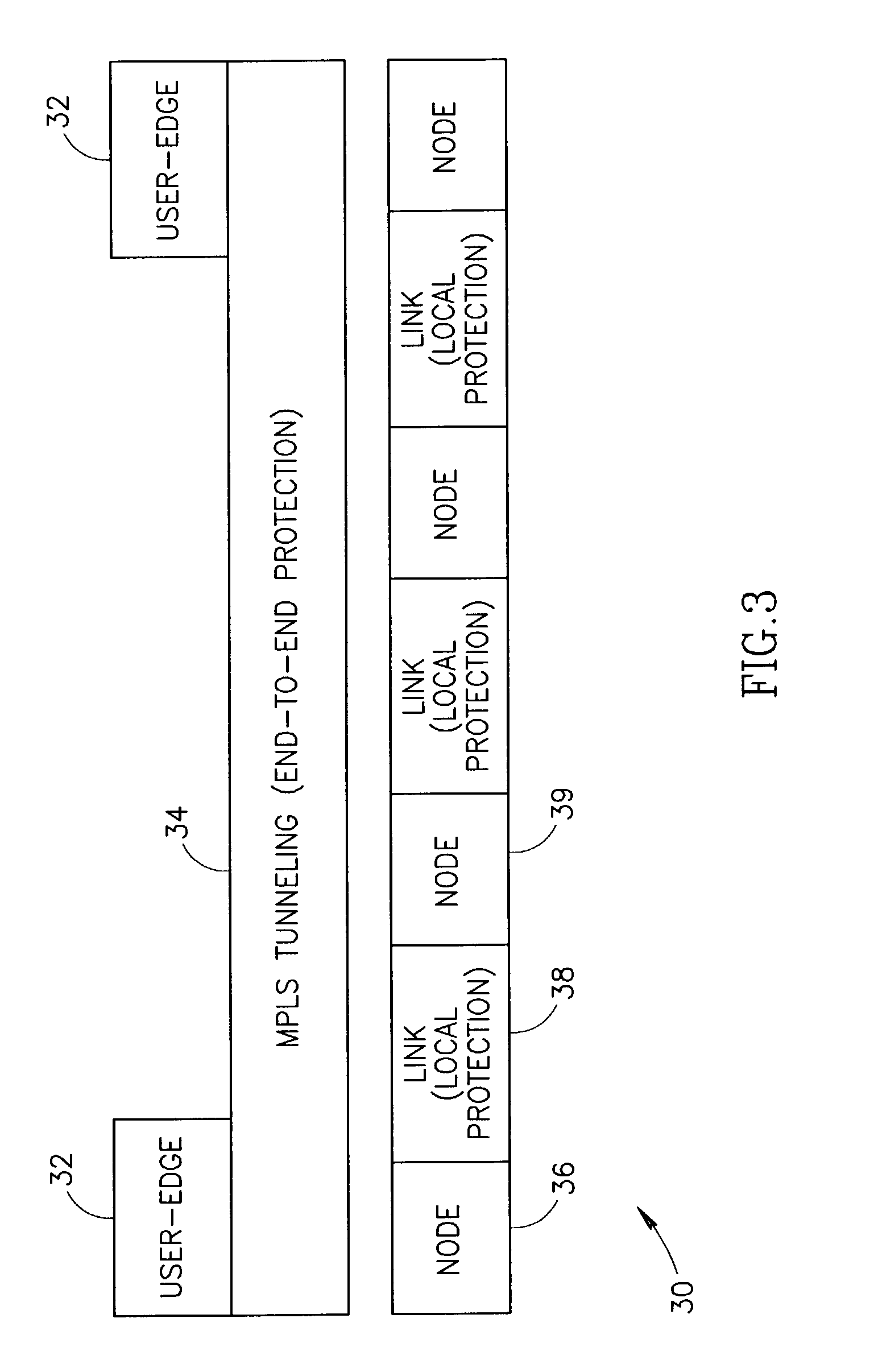
End-to-end notification of local protection using OAM protocol
ActiveUS7197008B1Lower performance requirementsMinimum interruptionError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityCommitted information rate
An end-to-end monitoring mechanism whereby edge nodes are notified that a particular path flows through a local protection tunnel along the way. The notification mechanism utilizes OAM packets which include a link protection indication that are transmitted on the Ethernet service layer. The link protection indication may be represented by one or more flags to indicate that local protection is in place along the path. The mechanism enables fast local protection to be used with slower end-to-end protection by informing the latter when local protection is activated. In an implementation in which local-protection does not preserve the CIR of the protected traffic, the invention provides minimal interruption of Committed Information Rate (CIR) connections by minimizing the time traffic is diverted through local protection tunnels. Notification of the edge node that local protection is in use occurs very quickly, thus allowing the edge node to rapidly switch to a backup path.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
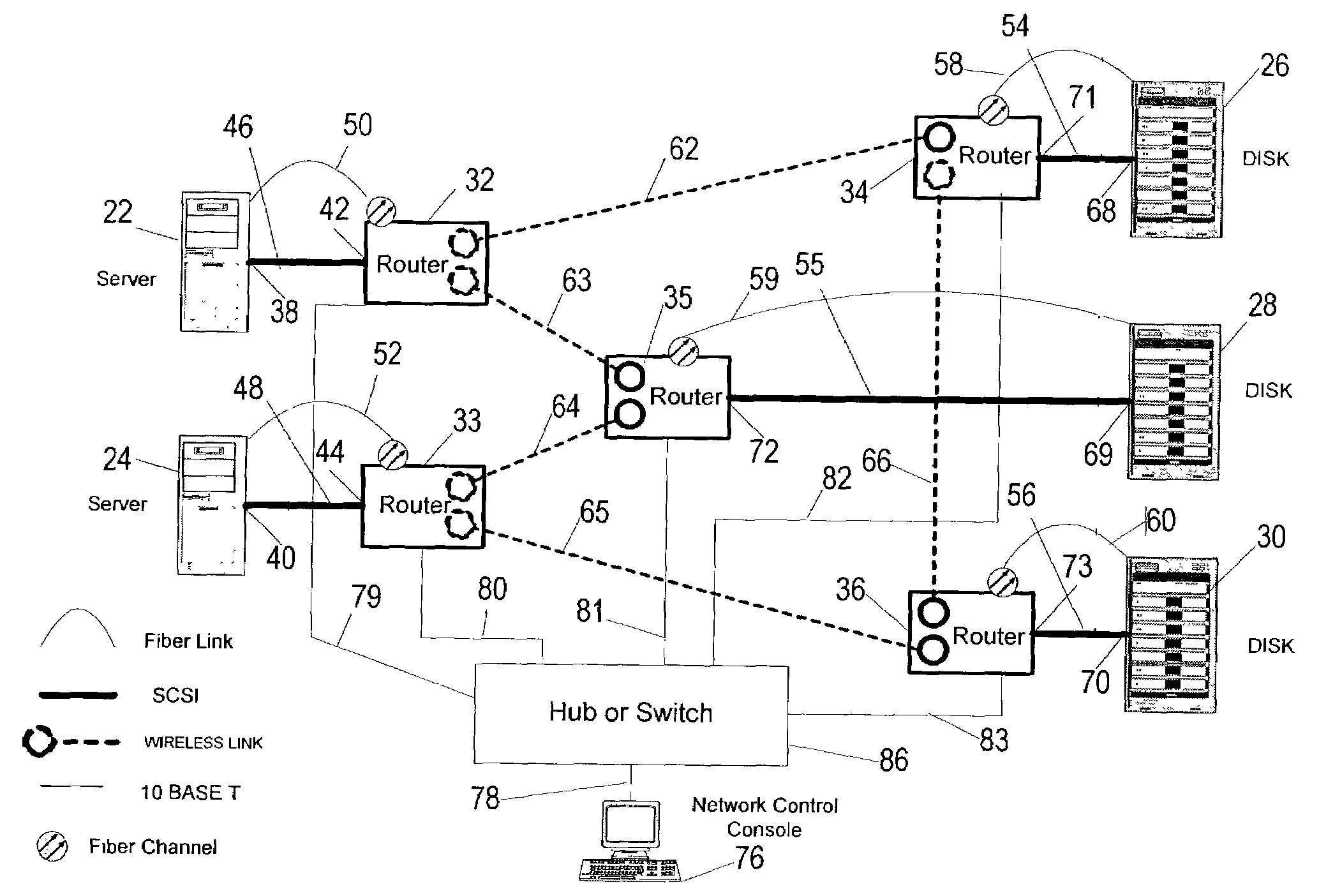
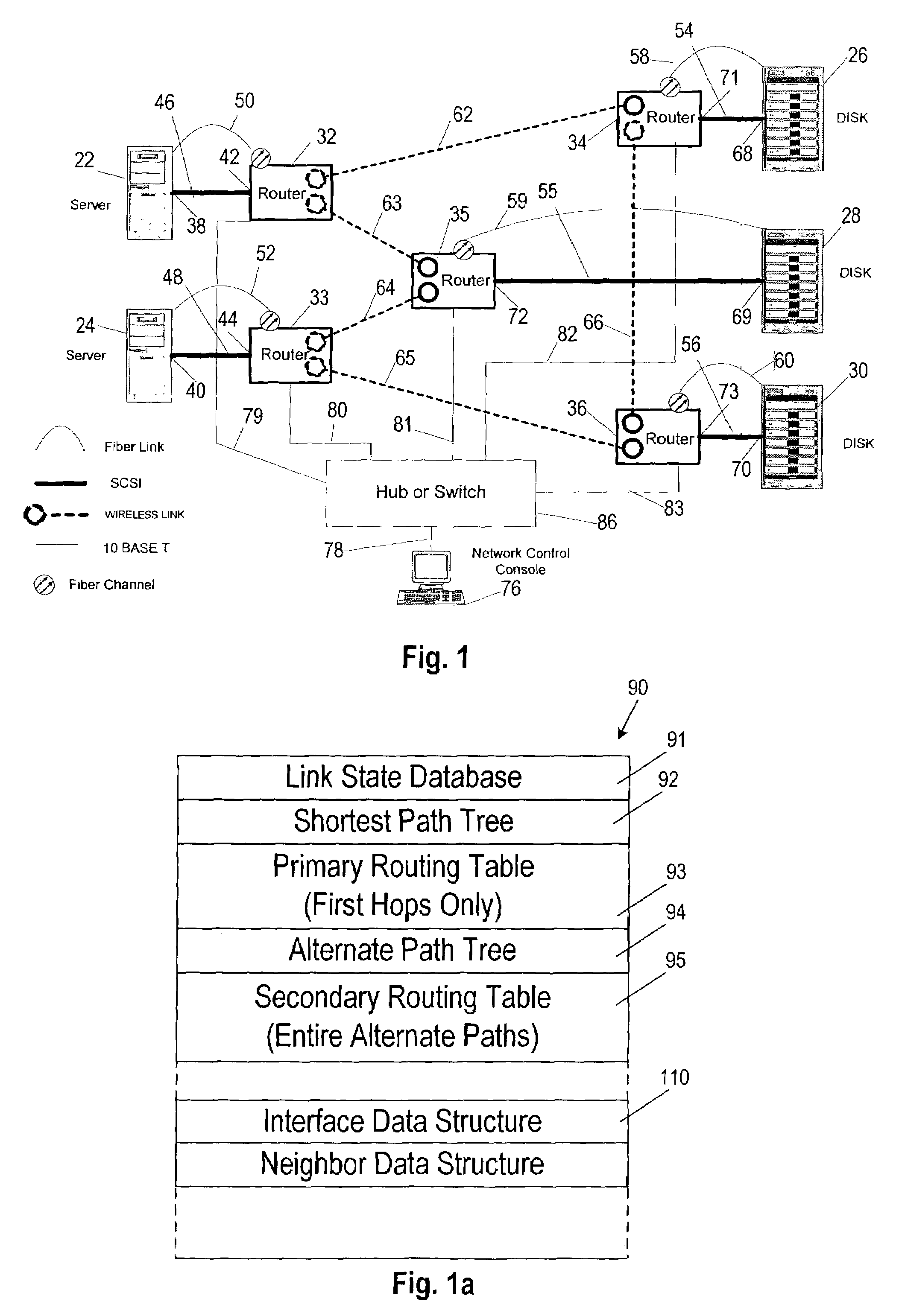
Agile digital communication network with rapid rerouting
ActiveUS7362709B1Low reliabilityImprove reliabilityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsUser deviceBackup path
An agile digital communications network has a number of routers that serve as nodes in a mesh network communicating between a user device (e.g., computer, server, etc.) and a target device (e.g., disc storage cabinets, tape, jukebox, etc.). The routers operate on an open shortest path first protocol, each router having two or more interfaces or links to other routers. When a link connected to a router is down and is in the shortest path to another router identified in a communication packet, the packet is forwarded to the identified router on a precalculated alternate route that does not use the unavailable link. IP tunneling assures that routing loops do not occur and send the packet back to the router with the unavailable link because it would have been in the shortest path of an intermediate router. A tunneling technique is provided that maximizes the levels of encapsulation needed at two, regardless of the size or configuration of the network. An unavailable link is not broadcast immediately throughout the network, giving the link an opportunity to be restored before all of the routers are called on to recalculate the shortest paths and alternate paths. During a short interval following the discovery of an unavailable link, then, a router connected to that link is in a state identified as the Use Alternate Path state, and the link is repeatedly checked for availability. Each router calculates and stores the alternative paths to each other router after first calculating the shortest path to each other router. The alternate paths are pulled up and used when an unavailable link is detected. Dijkstra's algorithm is used to calculate the shortest paths. A new algorithm called the iterative dynamic Dijkstra's algorithm is used to calculate the alternative routes.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
Path recovery on failure in load balancing switch protocols
InactiveUS7430164B2Increase profitQuick identificationError preventionTransmission systemsBackup pathNetwork switch
A method for managing multiple active paths among a plurality of network switches to identify and select an alternate path in response to failure of a path from a switch to a device. Load balancing protocols of the present invention enable the simultaneous use of multiple paths between network devices through a mesh of compliant network switches. When a port of a network switch fails (or the link connected to a port fails), a switch in accordance with the present invention selects an alternate port which may be used for forwarding packets to devices normally reached through the failed port. Networks switches operable in accordance with the structures and protocols of the present invention exchange messages to identify potential alternate paths. A potential alternate path is used to send a query message to a neighboring network switch to determine if a path to the identified devices is available through the neighboring network switch. Such query messages are propagated through all intermediate network switches between the switch sensing the failed port up to the identified network device. Acknowledgment messages are returned to verify potential availability of an alternate path. Where an intermediate network switch determines that the complete path is not available through it to the identified device, or where a potentially better path exists, a regenerated query message so indicating is returned along the path that initiated the query message.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
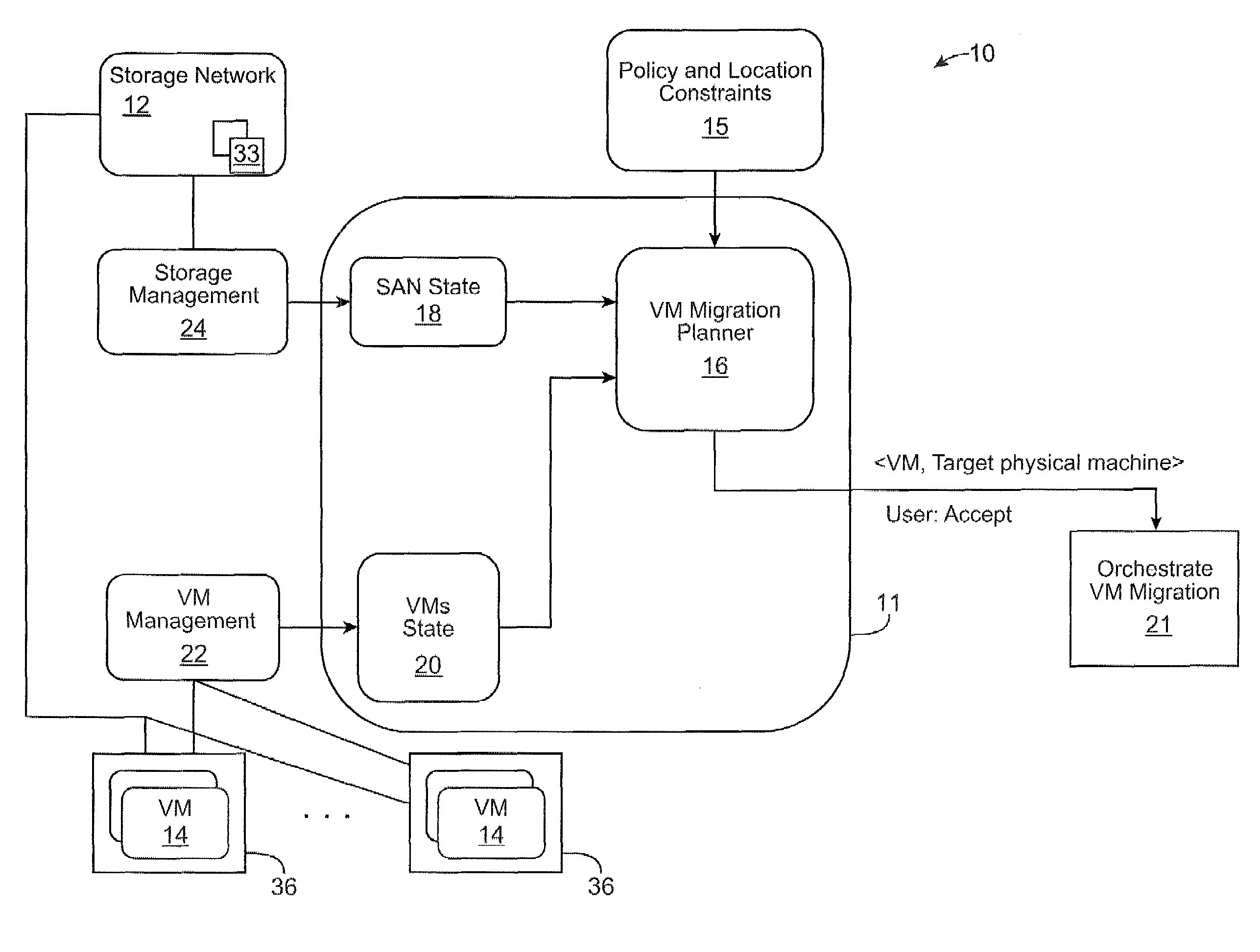
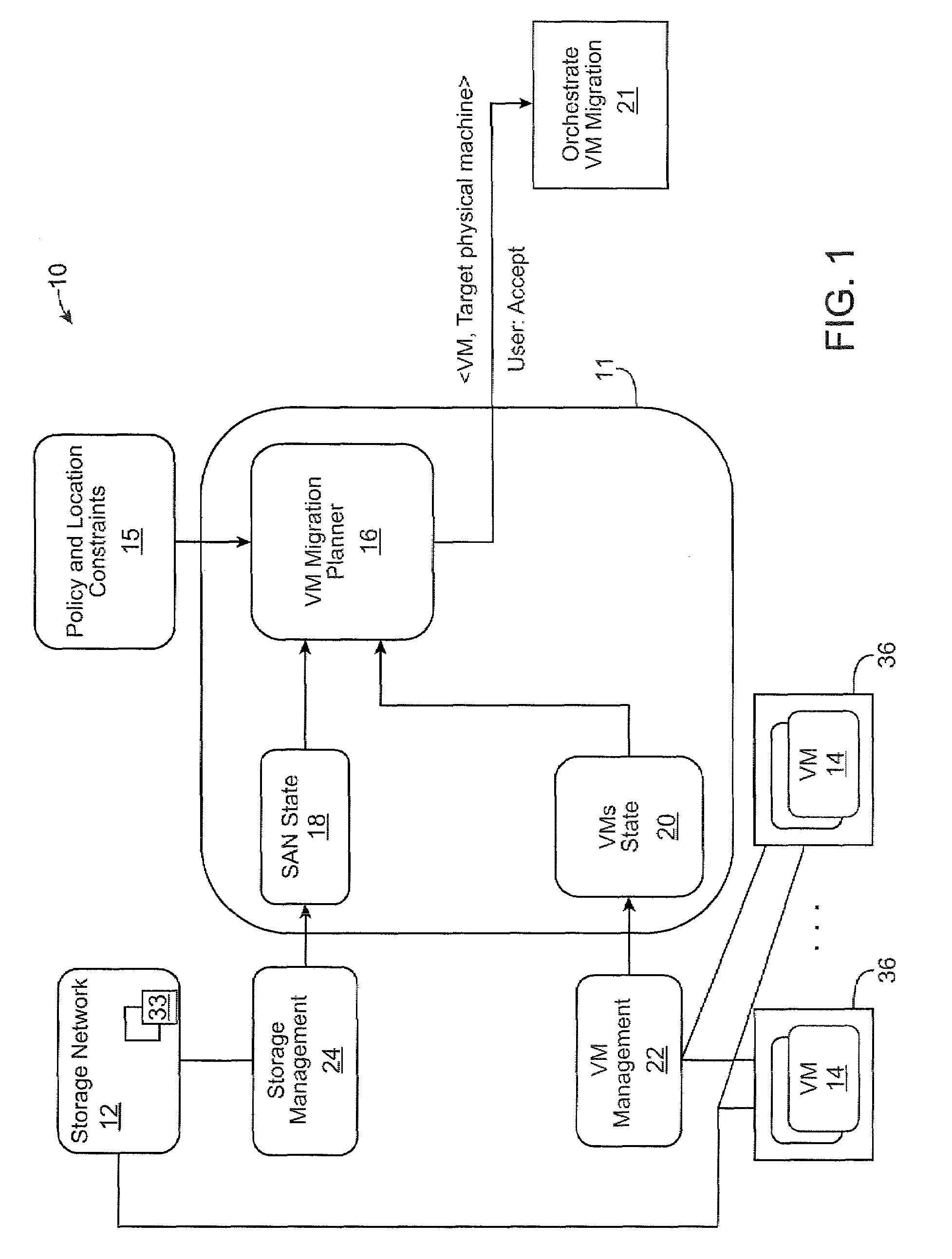
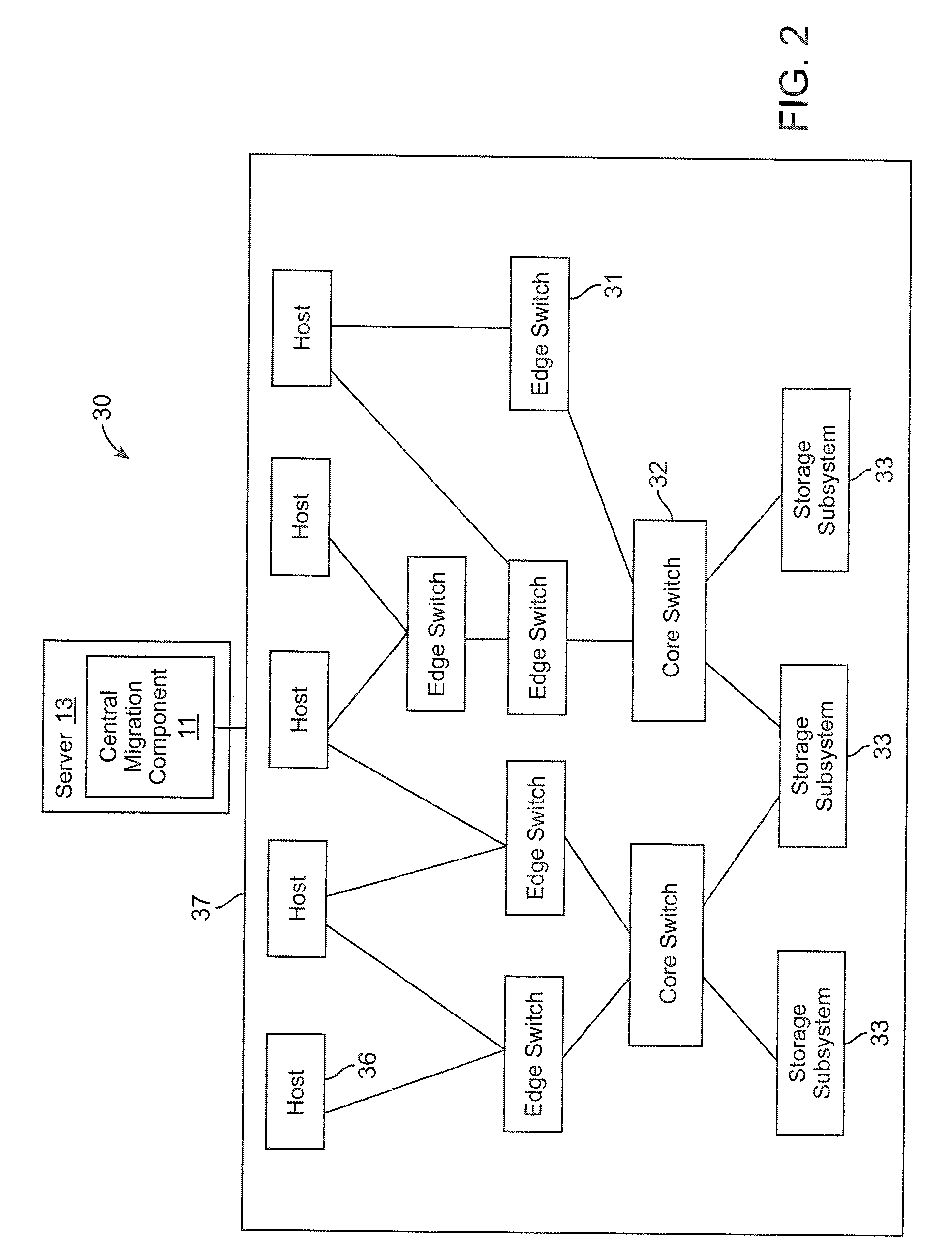
Server and storage-aware method for selecting virtual machine migration targets
ActiveUS20090228589A1Lower latencyLarge capacityMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionComputer architectureBackup path
A method and system selecting a target physical machine for a virtual machine (VM) migration is provided. Selecting a target physical machine for a VM migration involves determining storage volume connectivity and spare path capacity of one or more candidate physical machines, and preferentially selecting among the candidate physical machines a migration target with storage volume connectivity and spare path capacity to satisfy storage volume access requirements of the VM.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Nexthop fast rerouter for IP and MPLS
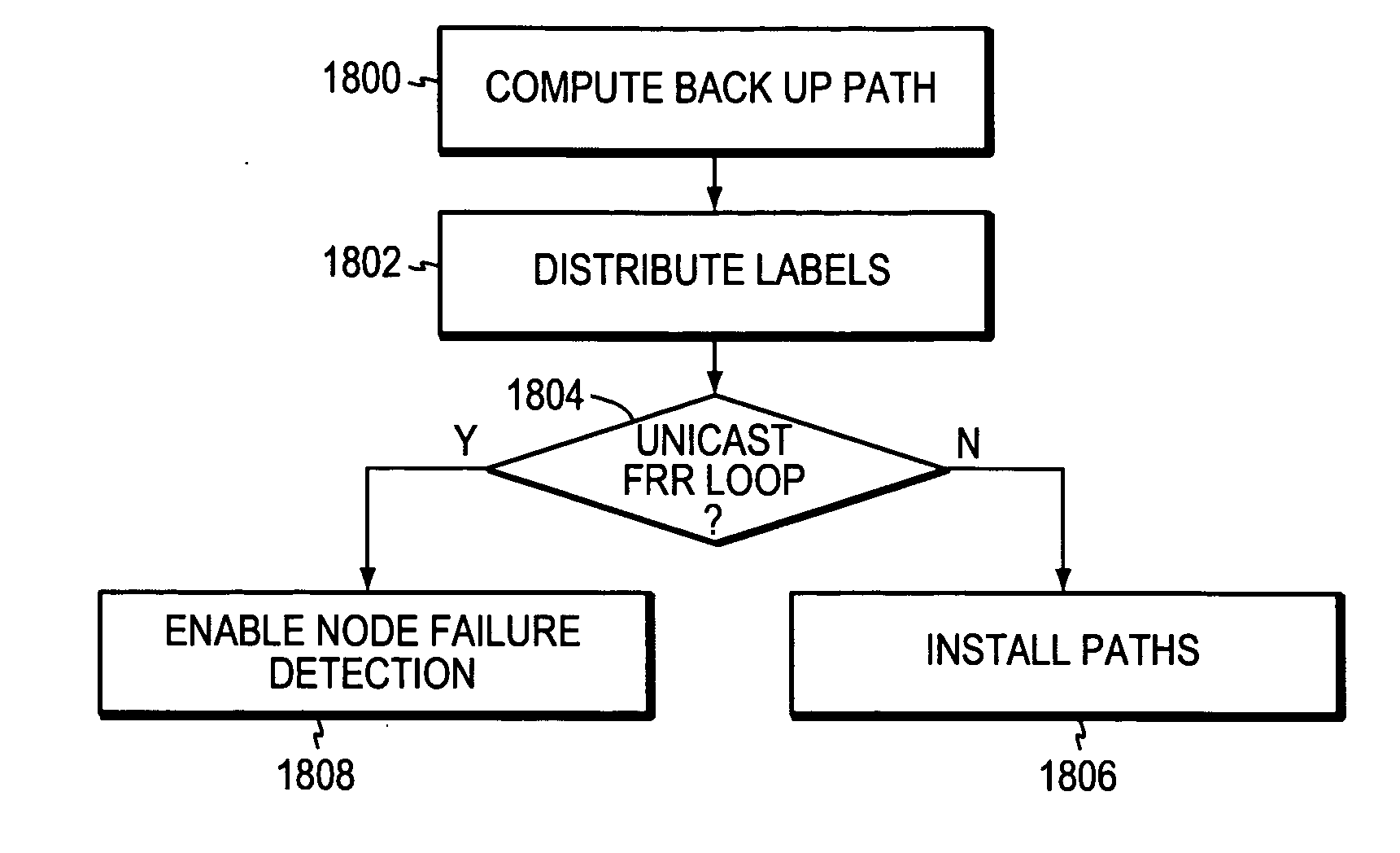
Methods and apparatus for rerouting network traffic are described herein. In one embodiment, an example of process includes maintaining as a part of a routing table of a network element information regarding one or more backup links leading to a node using label switched protocols (LSPs), the node being adjacent to the network element, and in response to a failure of a primary link coupling the network element to the node, the network element rerouting network traffic to the node via the one or more backup paths without having to notifying and waiting for a response from a headend node that originates the network traffic. Other methods and apparatuses are also described.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
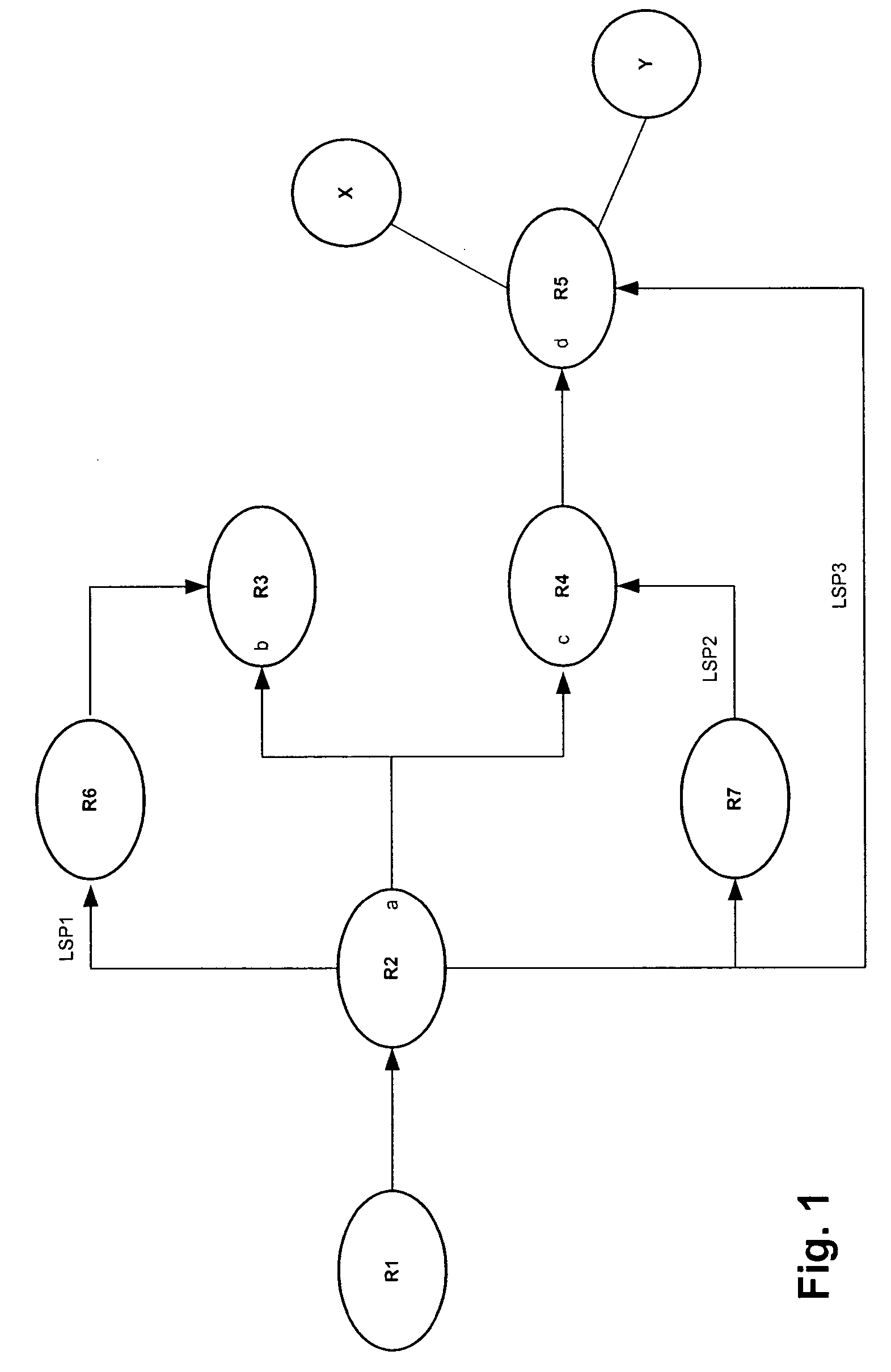
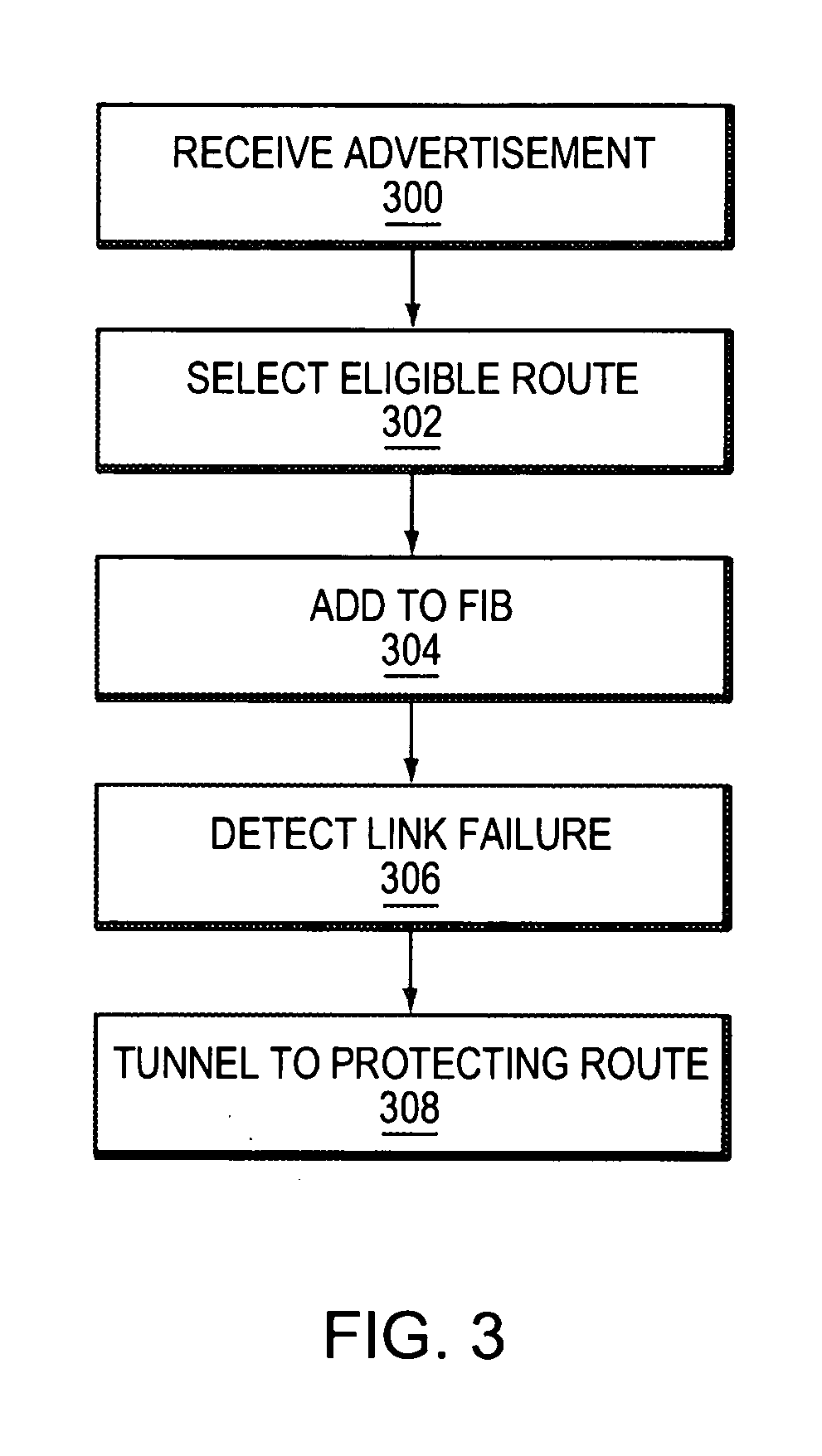
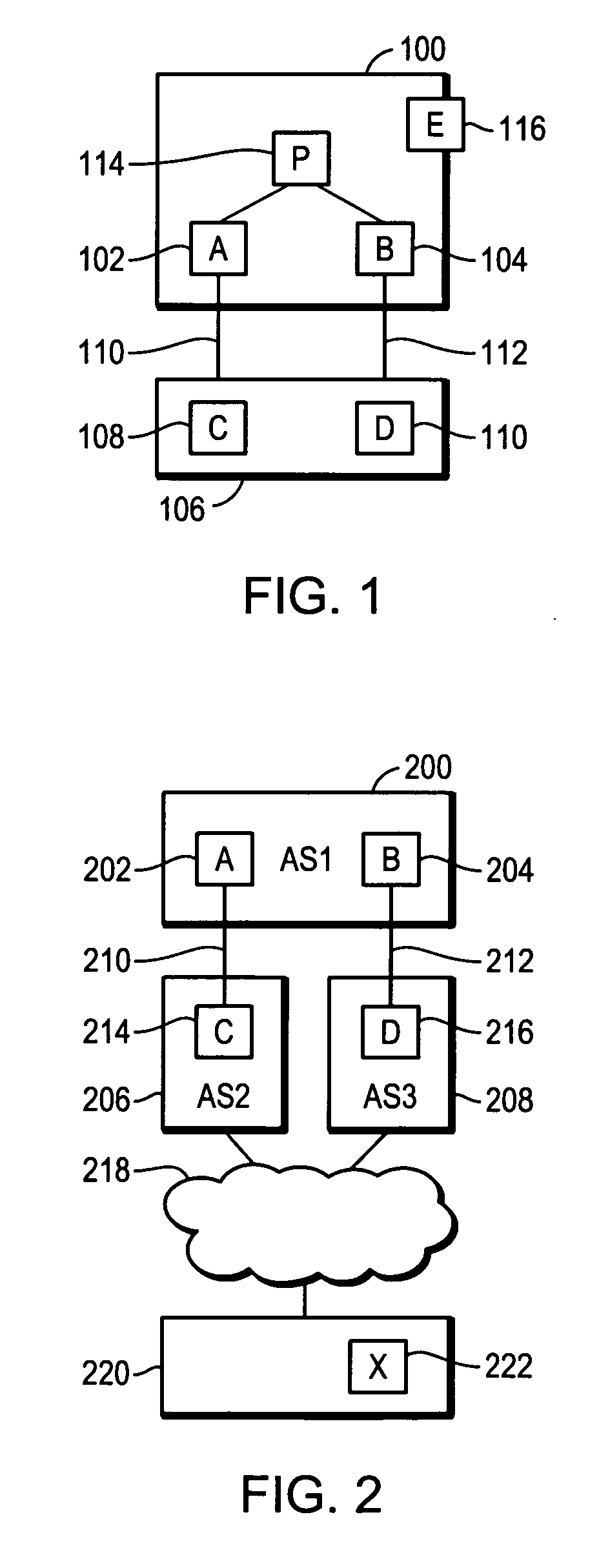
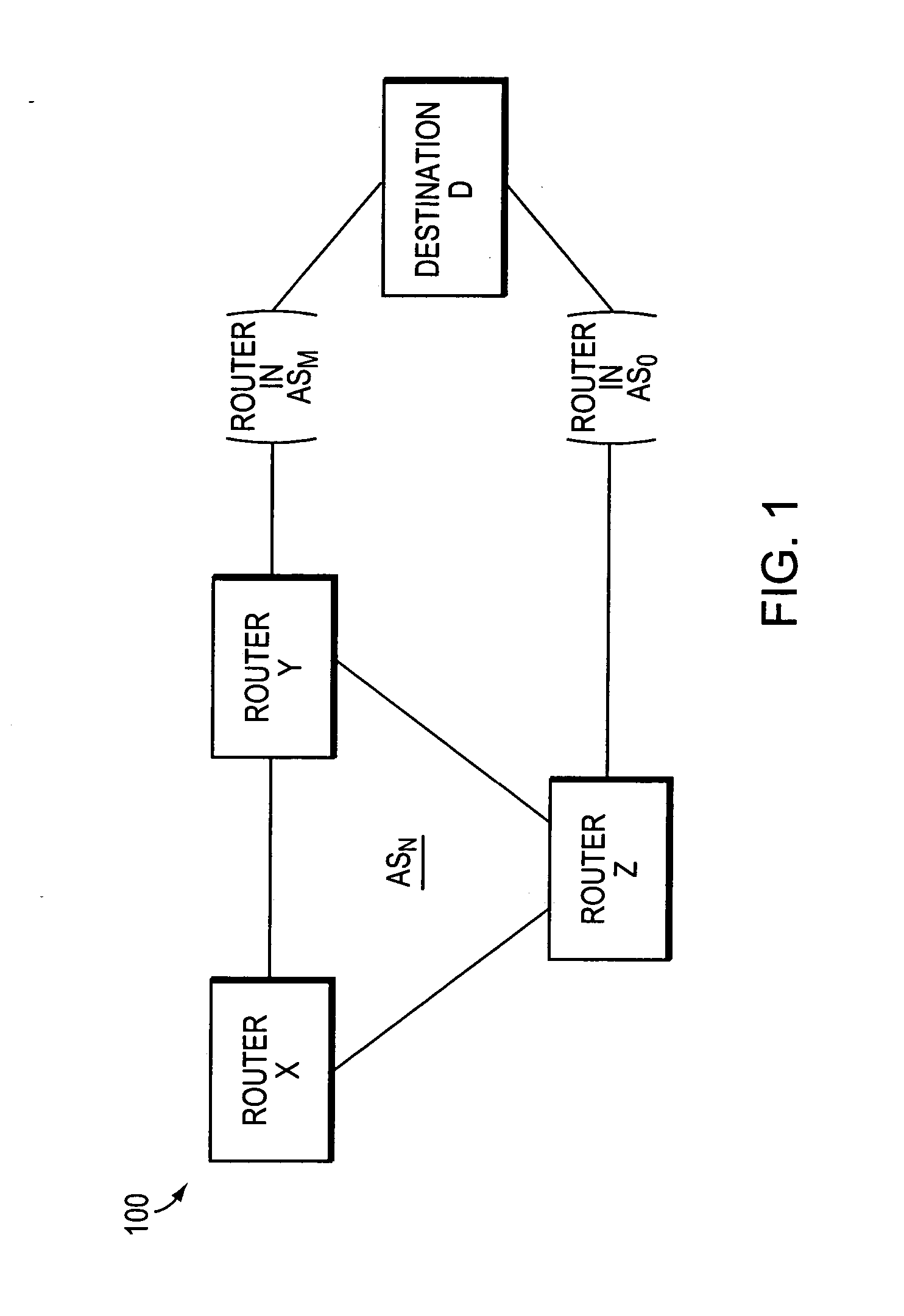
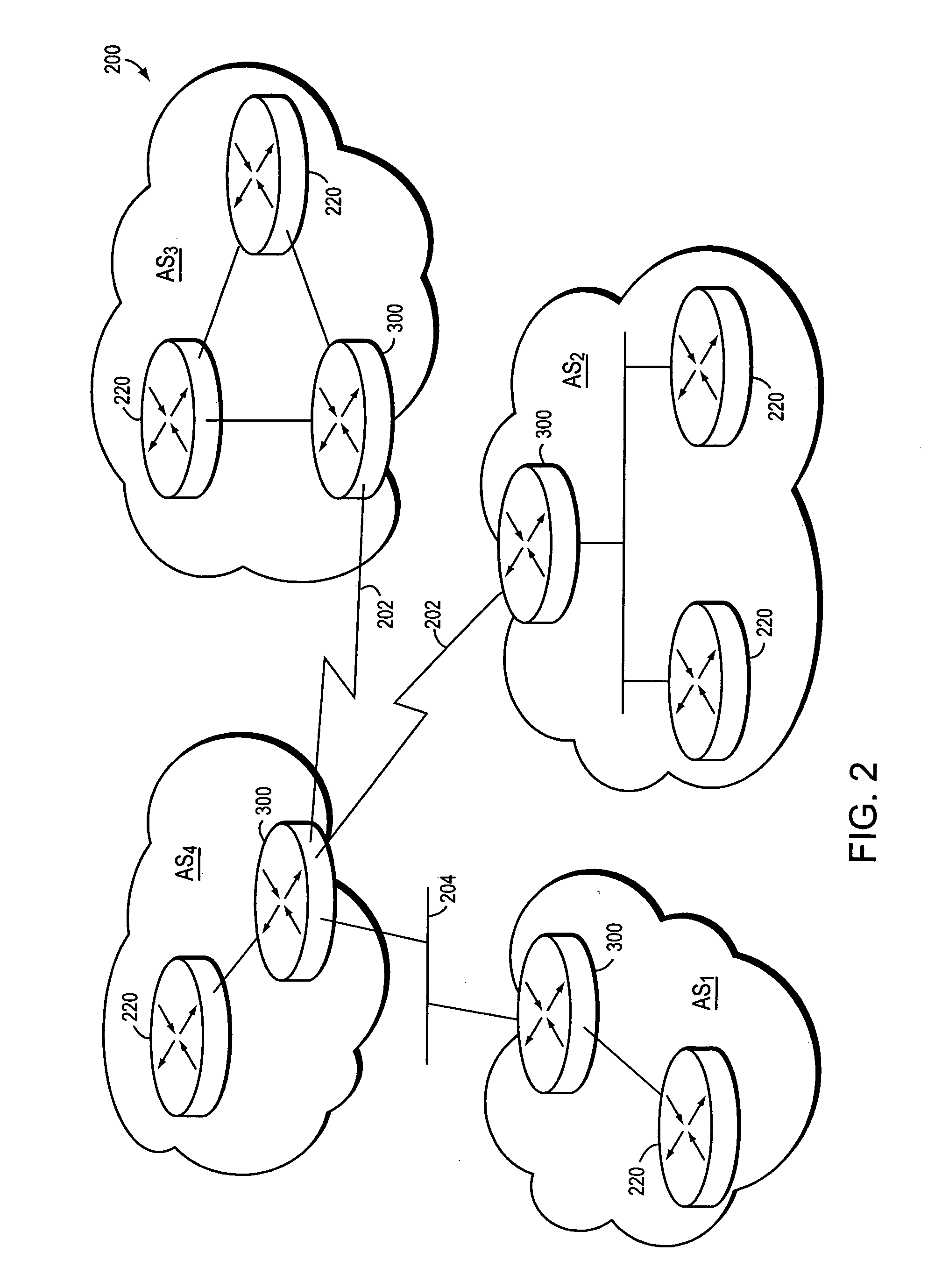
Method of constructing a backup path in an autonomous system
InactiveUS20070091794A1Minimize packet lossRapid responseError preventionTransmission systemsBackup pathComputer science
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
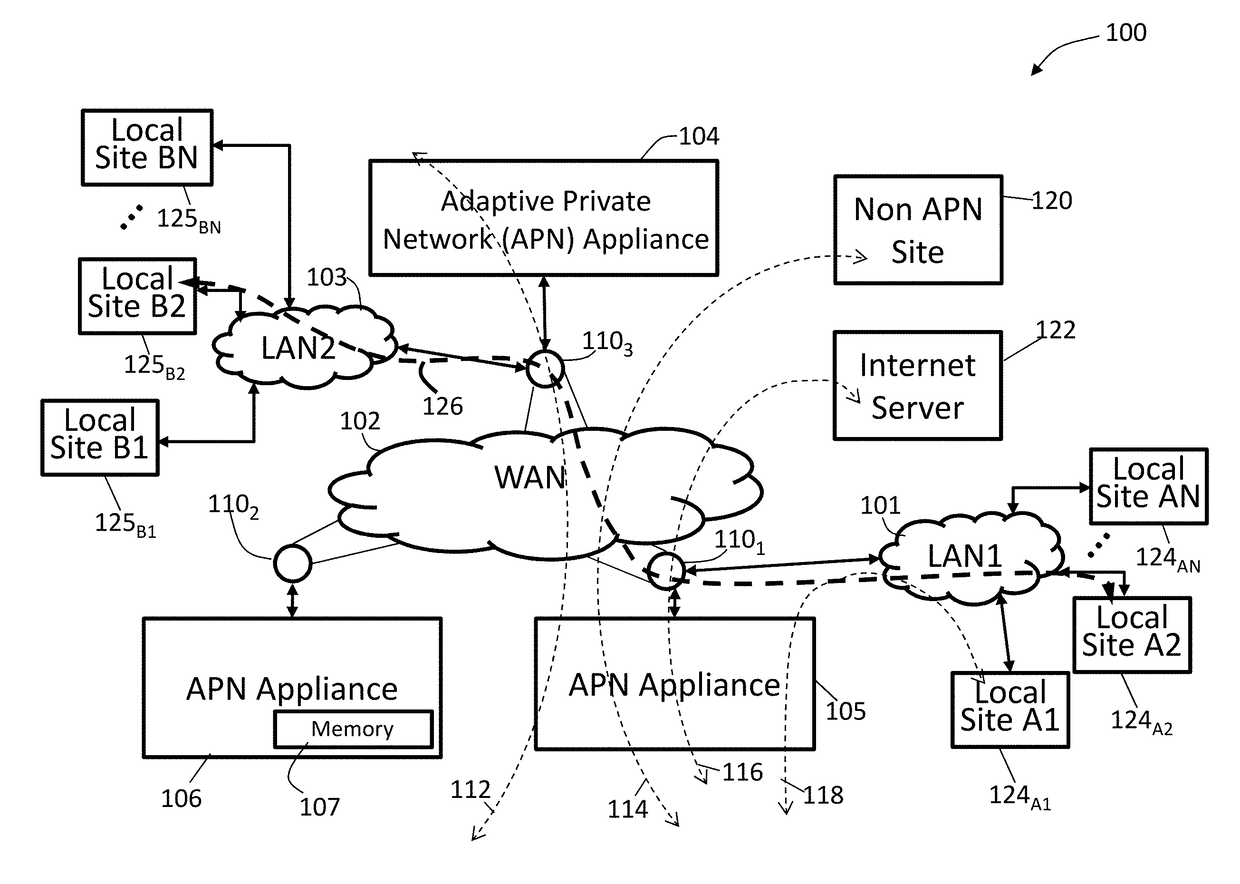
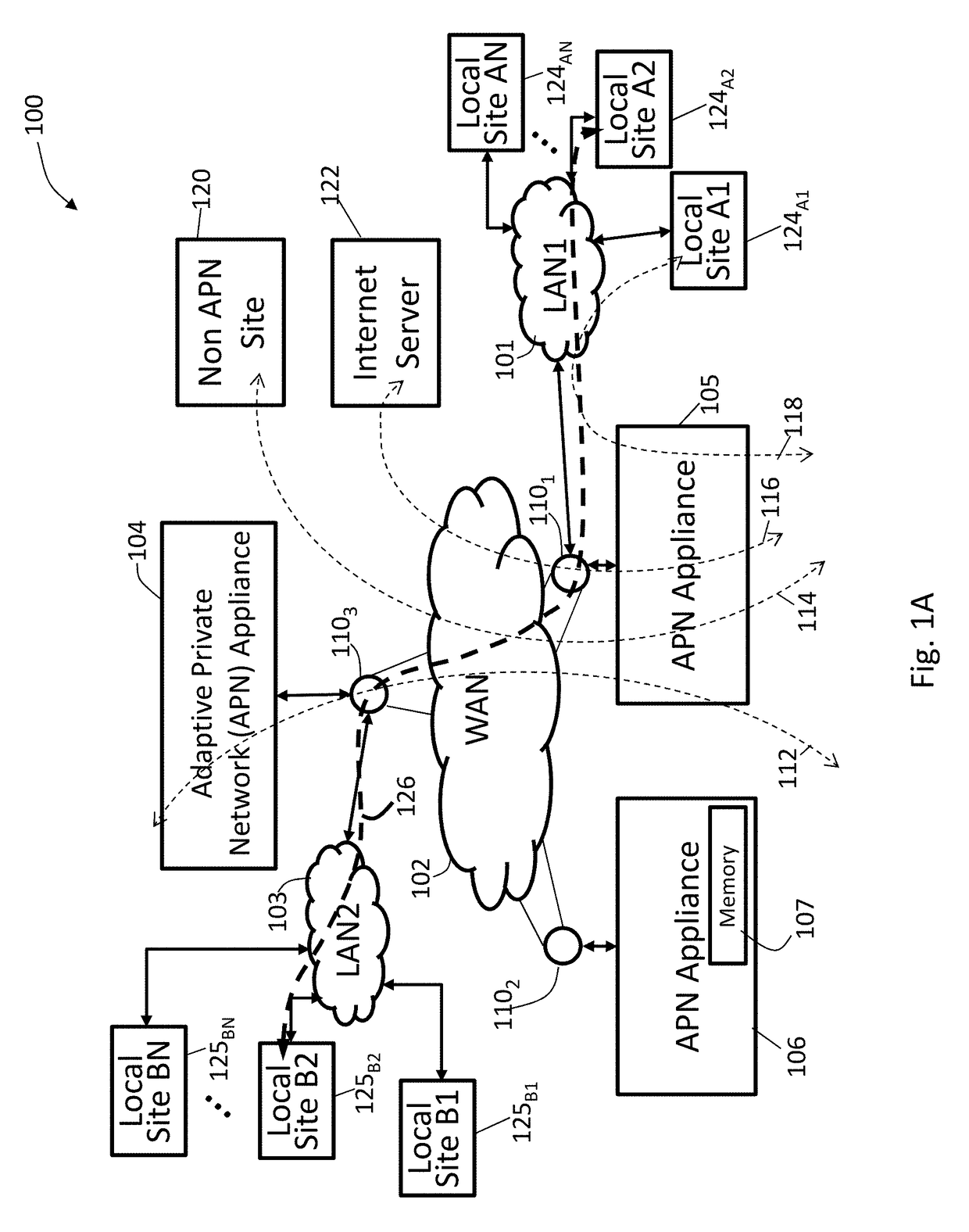
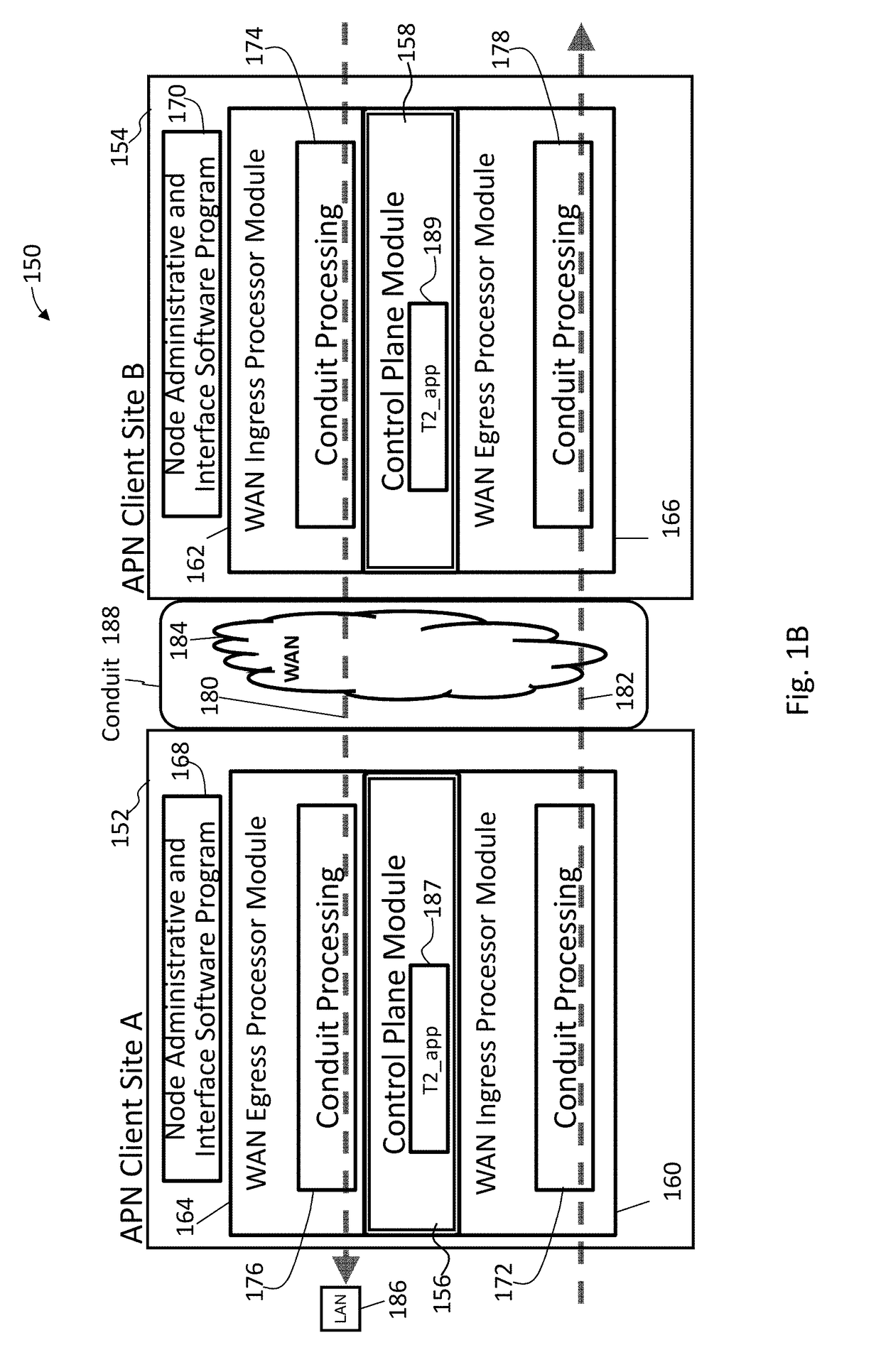
Adaptive private network (APN) bandwith enhancements
ActiveUS20170207976A1Realize automatic adjustmentSubstation equipmentData switching networksBackup pathPrivate network
Techniques are described to automatically activate and deactivate standby backup paths in response to changing bandwidth requirements in an adaptive private network (APN). The APN is configured with one or more regular active wide area network (WAN) links in an active mode and an on-demand WAN link in a standby mode. The on-demand WAN link is activated to supplement the conduit bandwidth when an available bandwidth of the conduit falls below a pre-specified trigger bandwidth threshold and the conduit bandwidth usage exceeds a usage threshold of a bandwidth of the conduit that is being supplied by the active paths (BWC). The on-demand WAN link is deactivated to standby mode when an available bandwidth of the conduit is above the pre-specified trigger bandwidth threshold and the conduit bandwidth usage drops below the usage threshold of BWC. Techniques for adaptive and active bandwidth testing of WAN links in an APN are also described.
Owner:TALARI NETWORKS
Multicast fast reroute
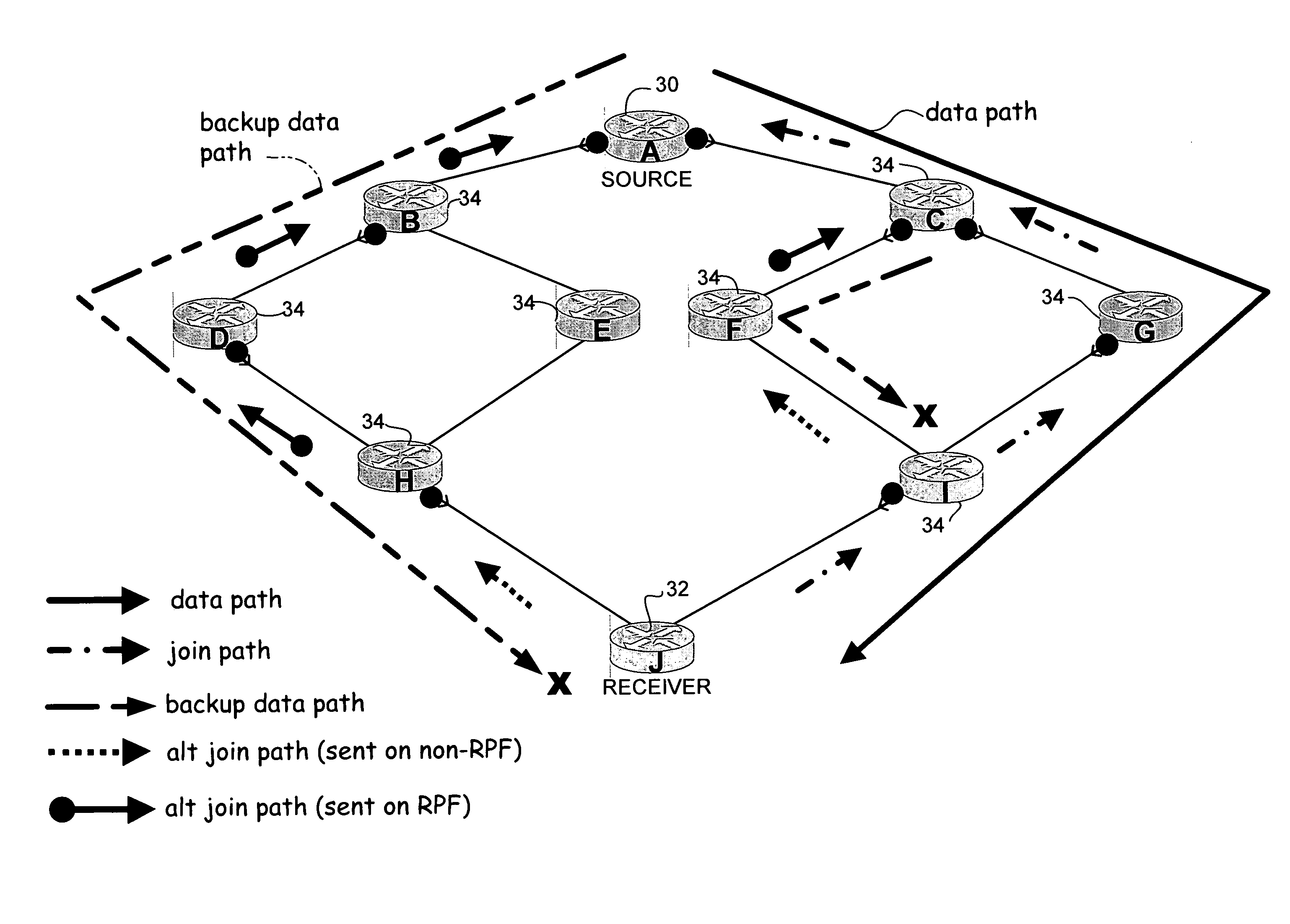
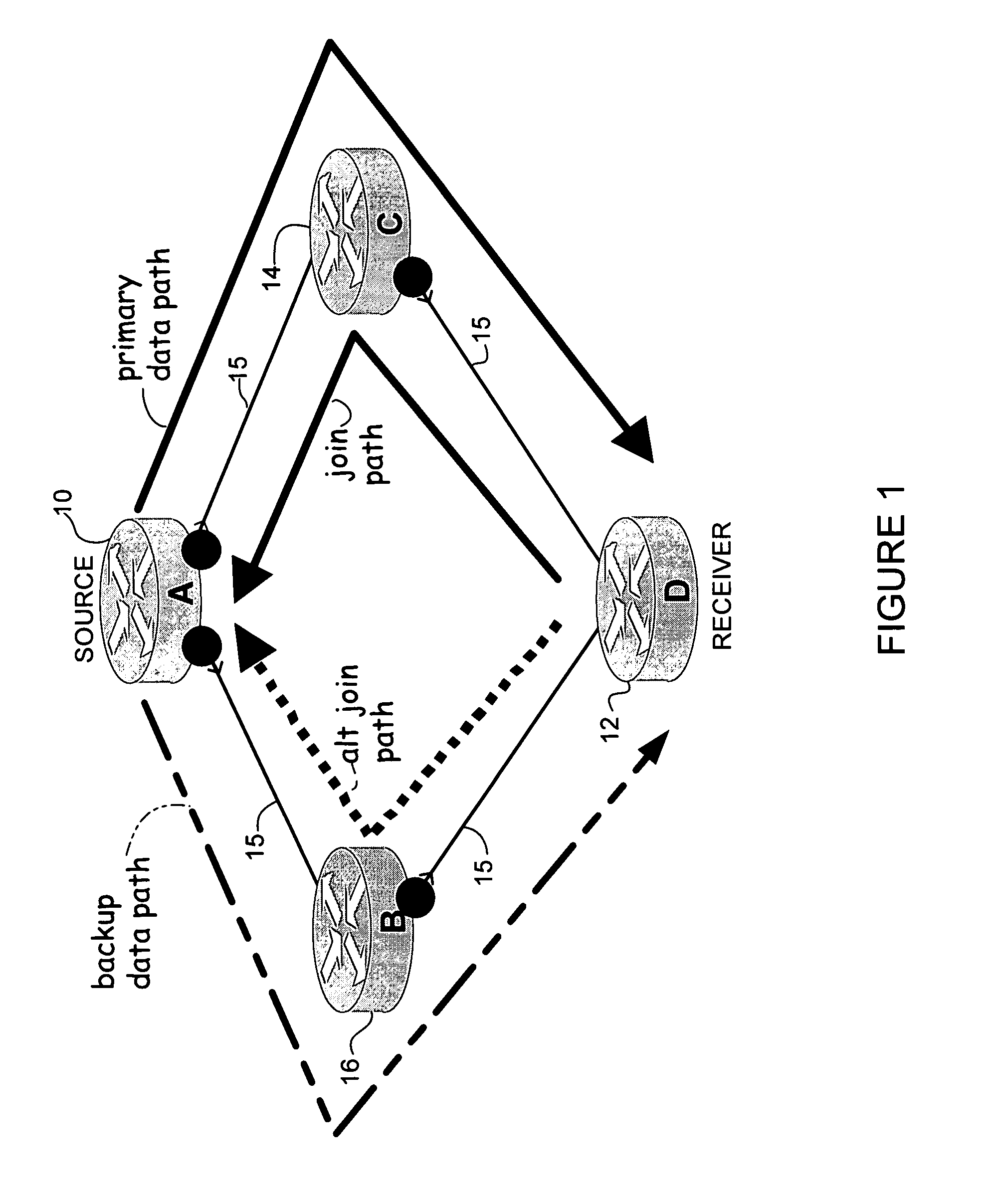
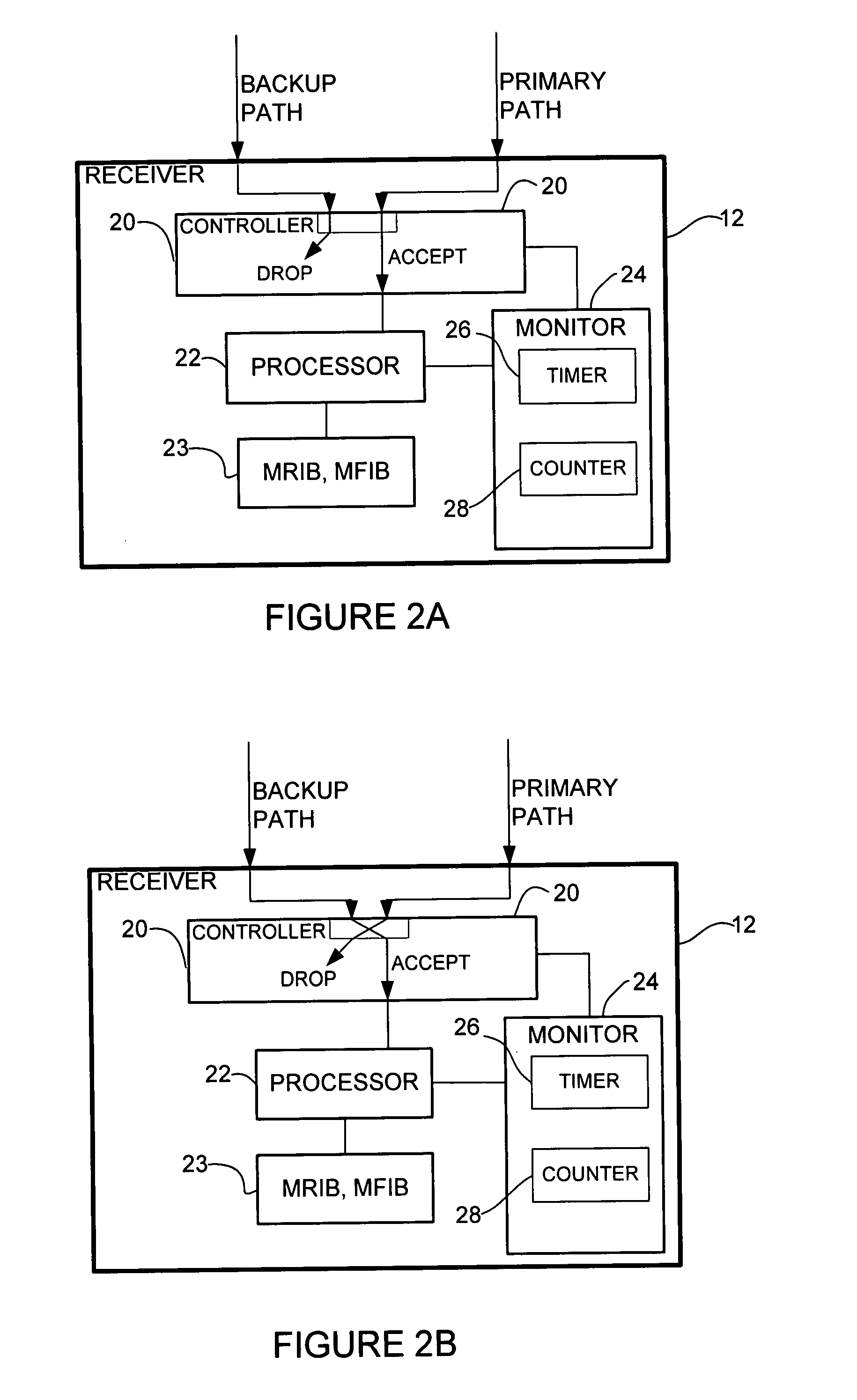
A method and apparatus for fast reroute of multicast data are disclosed. In one embodiment, a method includes transmitting a multicast join message from a receiver towards a source on a primary path and transmitting an alternate multicast join message from the receiver towards the source on a backup path. Data packets are then received from the primary and backup paths. The method further includes operating in a first mode wherein the data packets received from the primary path are accepted and the data packets received from the backup path are dropped, and switching to a second mode wherein the data packets received from the backup path are accepted, upon detecting a failure in the primary path.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method of constructing a backup path in an autonomous system
ActiveUS20070091795A1Minimize packet lossRapid responseError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPathPingBackup path
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
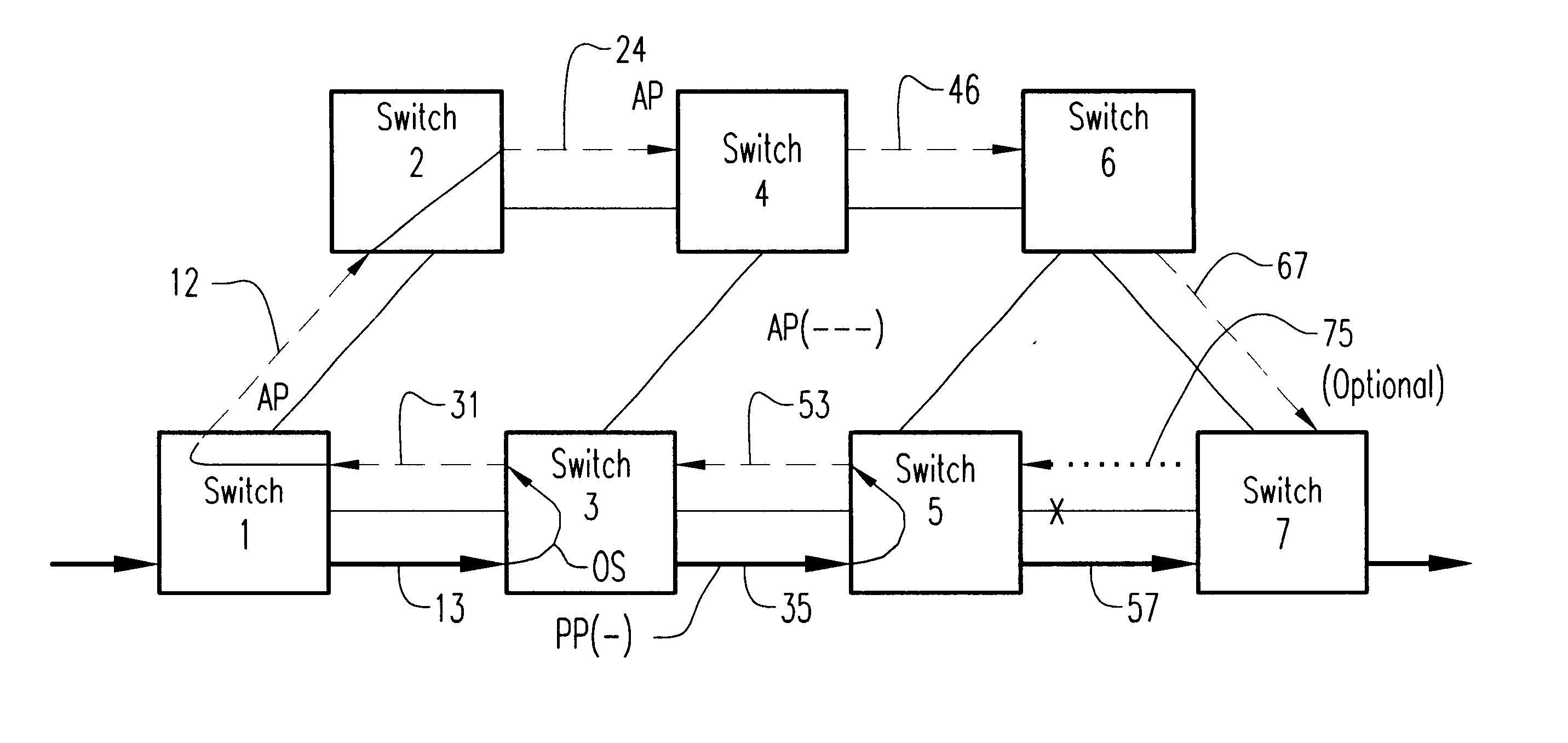
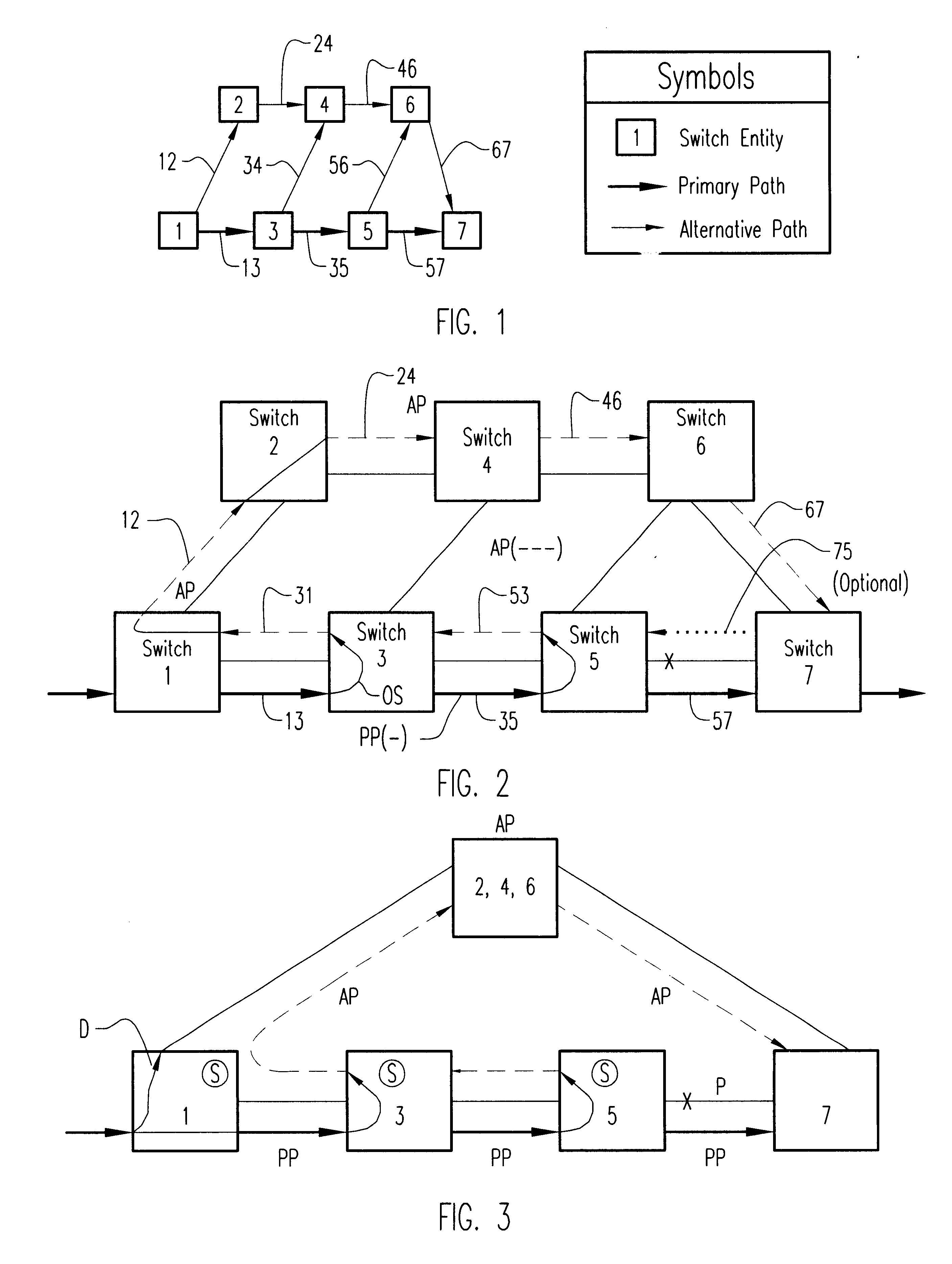
Method of and apparatus for fast alternate-path rerouting of labeled data packets normally routed over a predetermined primary label switched path upon failure or congestion in the primary path
InactiveUS6813242B1Highly efficient utilization of network resourceQuick checkInterconnection arrangementsError preventionBackup pathLabeled data
A new technique for fast alternate-path automatic rerouting of labeled data packets normally routed over a predetermined primary label switched path upon failure or congestion in the primary path.
Owner:NEXABIT NETWORKS
Avoiding micro-loop upon failure of fast reroute protected links
ActiveUS20050276216A1NetworkingSpeed andError preventionTransmission systemsBackup pathReal-time computing
A technique incorporates an efficient means for avoiding micro-loops on a backup path associated with a failed protected link. An intermediate node delays updating a forwarding database (FDB) contained in the intermediate node based on the intermediate node's distance from the failed link. Specifically, intermediate nodes near the failed protected link delay updating their FDBs for a longer period of time than nodes farther away from the failed link. By updating FDBs in this manner, micro-loops may be avoided on the failed link's backup path as nodes on the backup path that are close to the failed link do not update their FDBs ahead of nodes farther away on the backup path.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Device and method for correcting a path trouble in a communication network
InactiveUS20060256712A1Reliable failure recoveryFlexible supportMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionBackup pathDistributed computing
In a disclosed backup path bandwidth keeping method for keeping bandwidth of a backup path to which an active path is switched when the active path becomes unavailable in nodes of a communication network, each node is connected to the same destination, and the method includes a backup path bandwidth keeping phase, for M (M is a natural number equal to or less than L) channels in L (L is a natural number) channels kept as backup path bandwidth, for notifying a destination-side node existing in a destination side of the backup path of identification number information of the M channels to be kept and identification information indicating that a path for which the bandwidth is to be kept is a backup path.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Method of implementing a backup path in an autonomous system
ActiveUS20070091796A1Minimize packet lossRapid responseError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsBackup pathComputer science
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
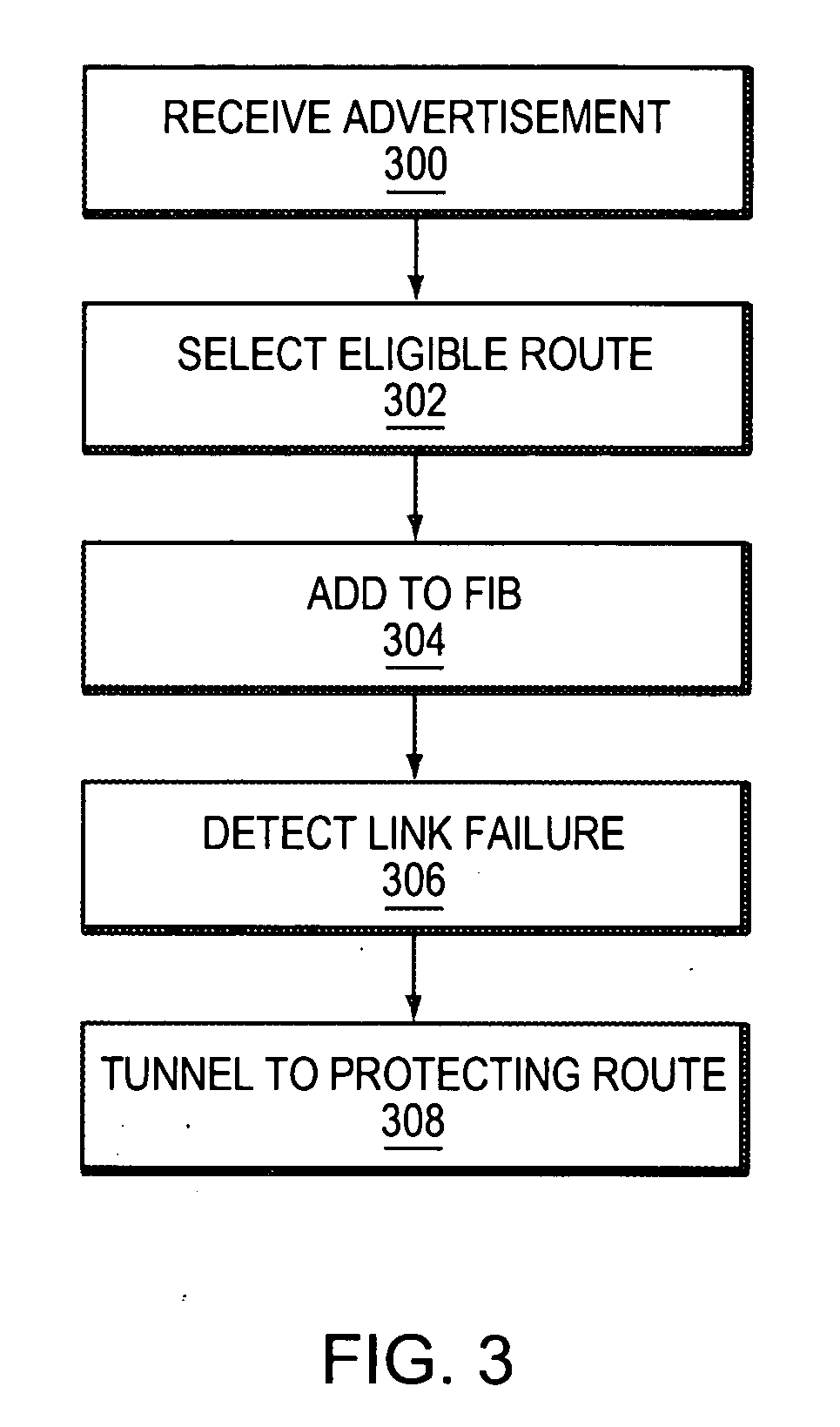
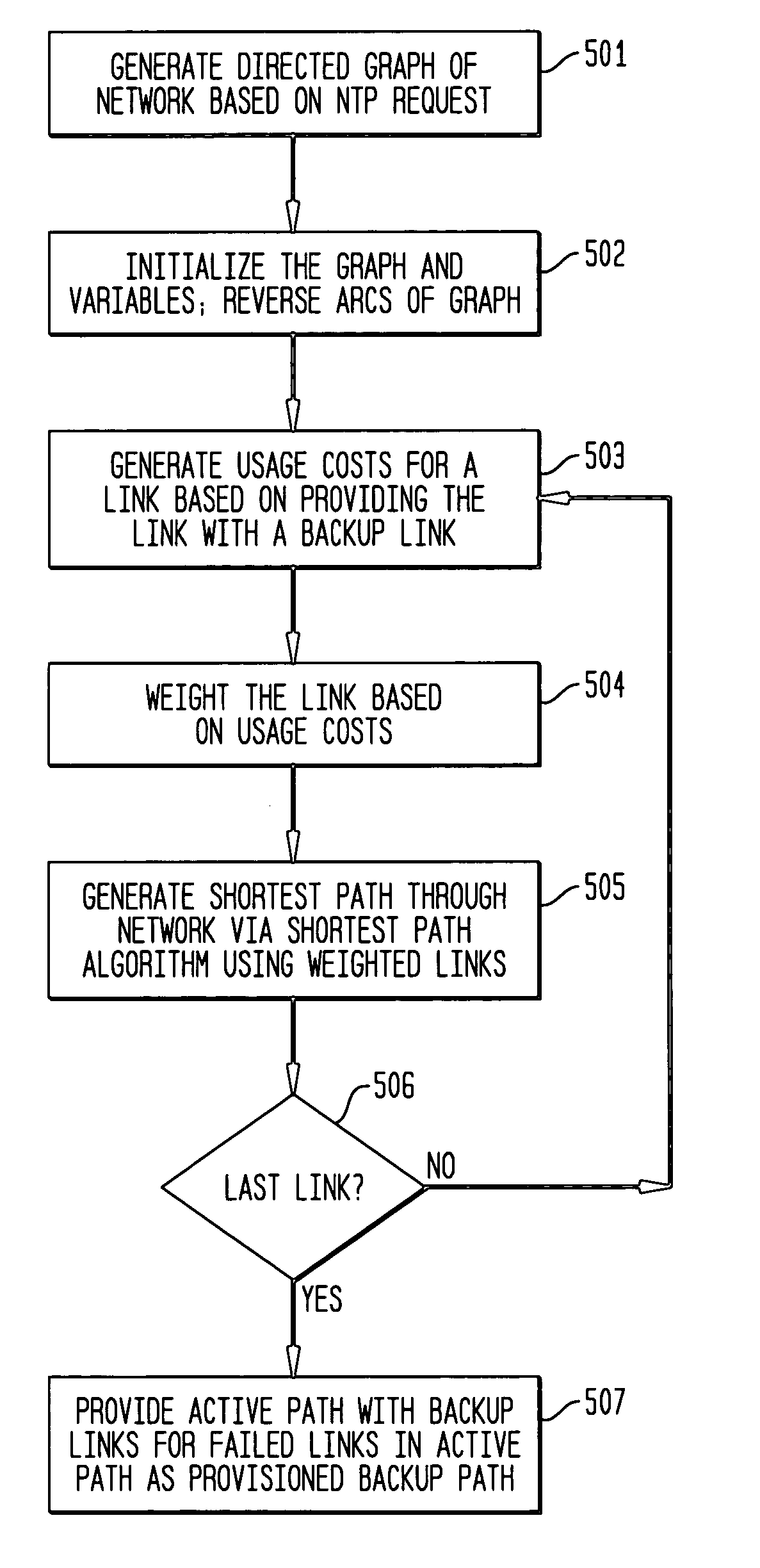
Dynamic backup routing of network tunnel paths for local restoration in a packet network
A packet network of interconnected nodes employing dynamic backup routing of a Network Tunnel Path (NTP) allocates an active and backup path to the NTP based upon detection of a network failure. Dynamic backup routing employs local restoration to determine the allocation of, and, in operation, to switch between, a primary / active path and a secondary / backup path. Switching from the active path is based on a backup path determined with iterative shortest-path computations with link weights assigned based on the cost of using a link to backup a given link. Costs may be assigned based on single-link failure or single element (node or link) failure. Link weights are derived by assigning usage costs to links for inclusion in a backup path, and minimizing the costs with respect to a predefined criterion.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Backup path convergence in the APS environment
ActiveUS20070263532A1Eliminate timeLow costError preventionTransmission systemsRouting tableBackup path
A SONET network terminated by routers includes working paths and backup paths. The routers pre-establishes in their link state data bases the links in both for both the working and backup paths. However, the links involved in the backup paths are given higher costs, then the links working paths, that the routers select only the links in the working path. If there is a failure in a link in a working path, an APS arrangement provides rapid switchover of the optical links so as to substitute one or more links in the corresponding backup path. This is accomplished by changing the relative costs of the working and backup links involved, so that the routers select the backup links for their routing tables.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
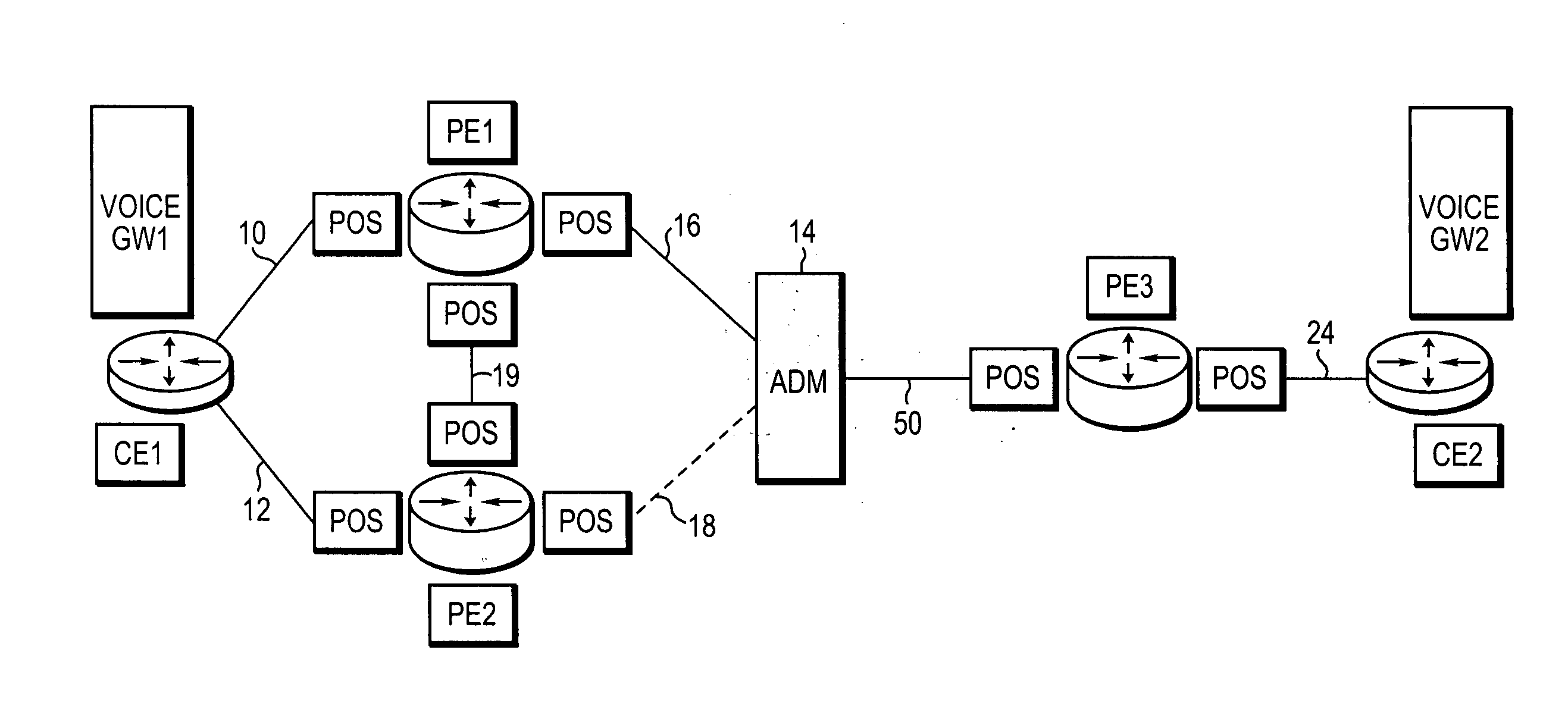
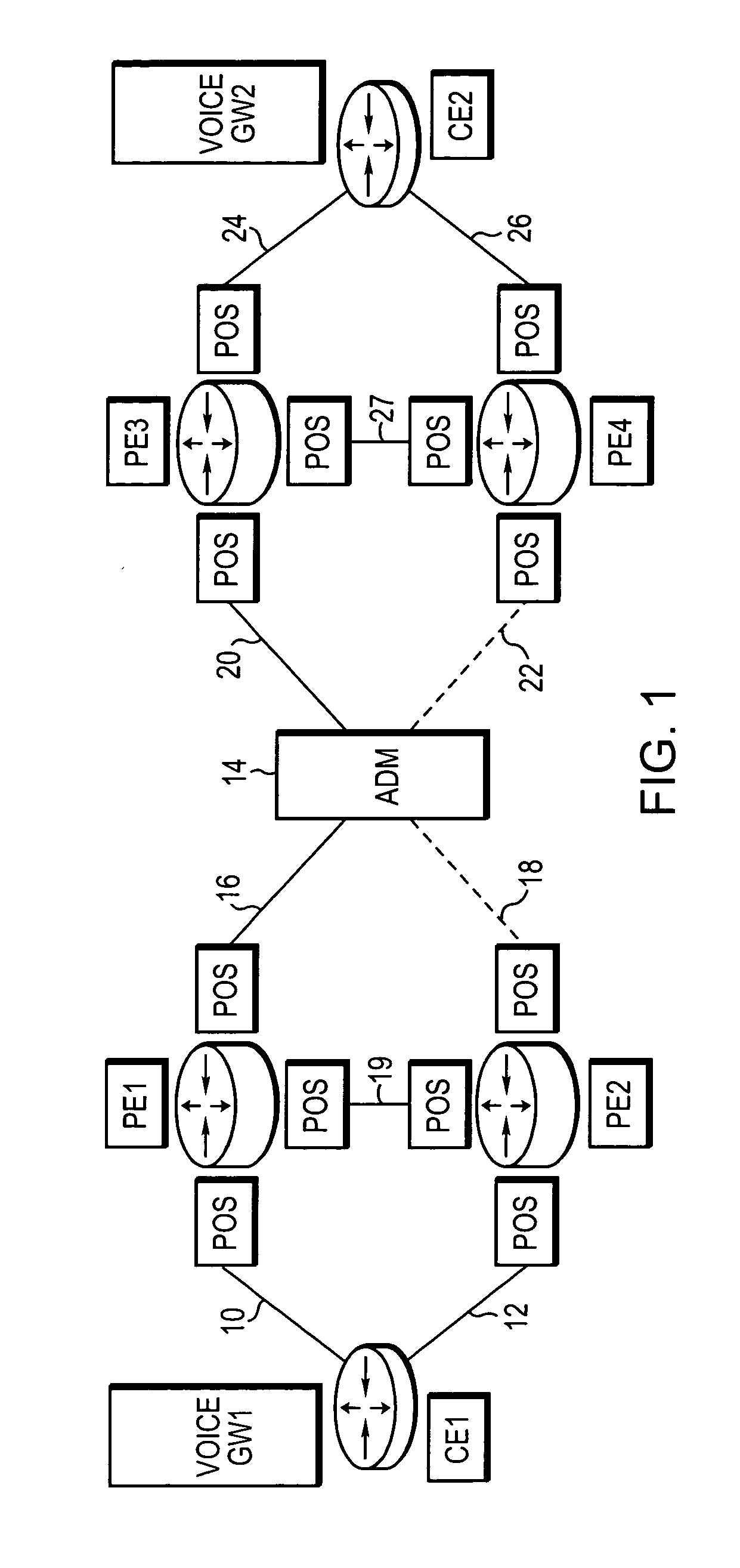
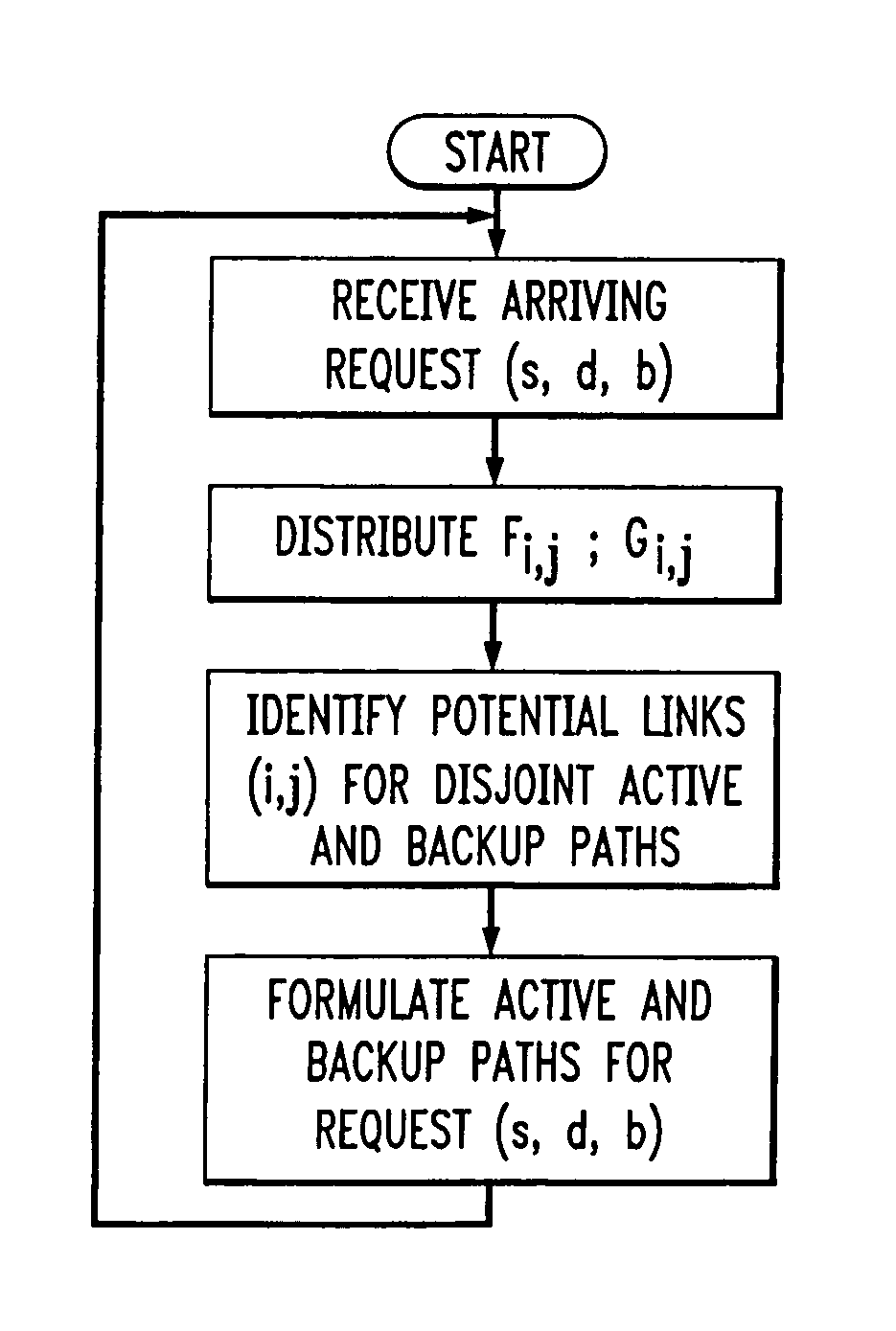
Routing of bandwidth guaranteed paths with restoration in an information network
InactiveUS7124187B1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsBackup pathInformation networks
Restorable paths in an information network are established in response to arriving traffic requests. Requests are received at a first node of the network for transmission of traffic to a second node of the network, and each request specifies a desired transmission bandwidth for an active and a backup path to be established between the nodes. Potential active links for an active path are identified in response to a given request, and potential backup links to form a backup path for restoring the active path, are also identified in response to the given request. An active and a backup path are then formulated for each given request from among the potential active links and the potential backup links that were identified in response to the given request.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
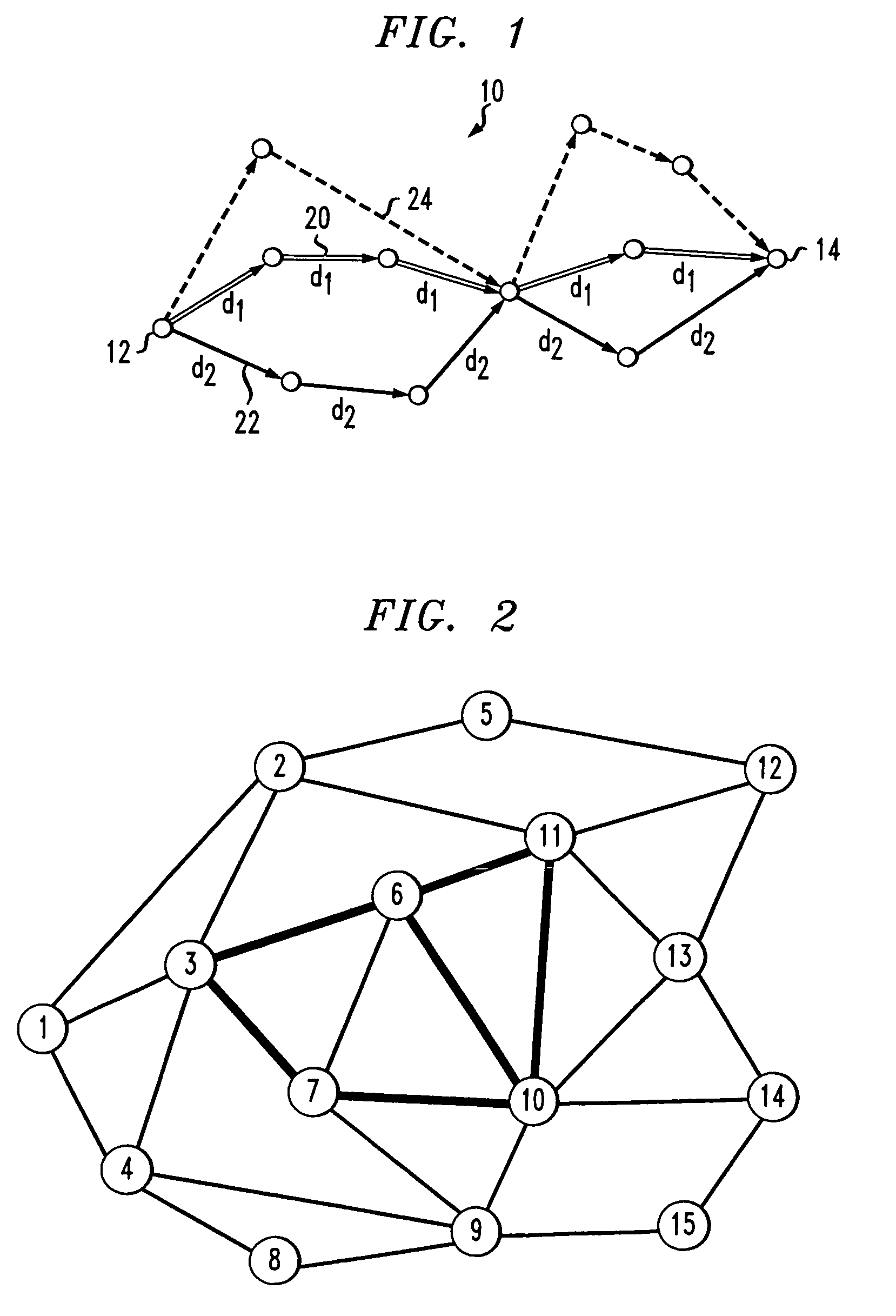
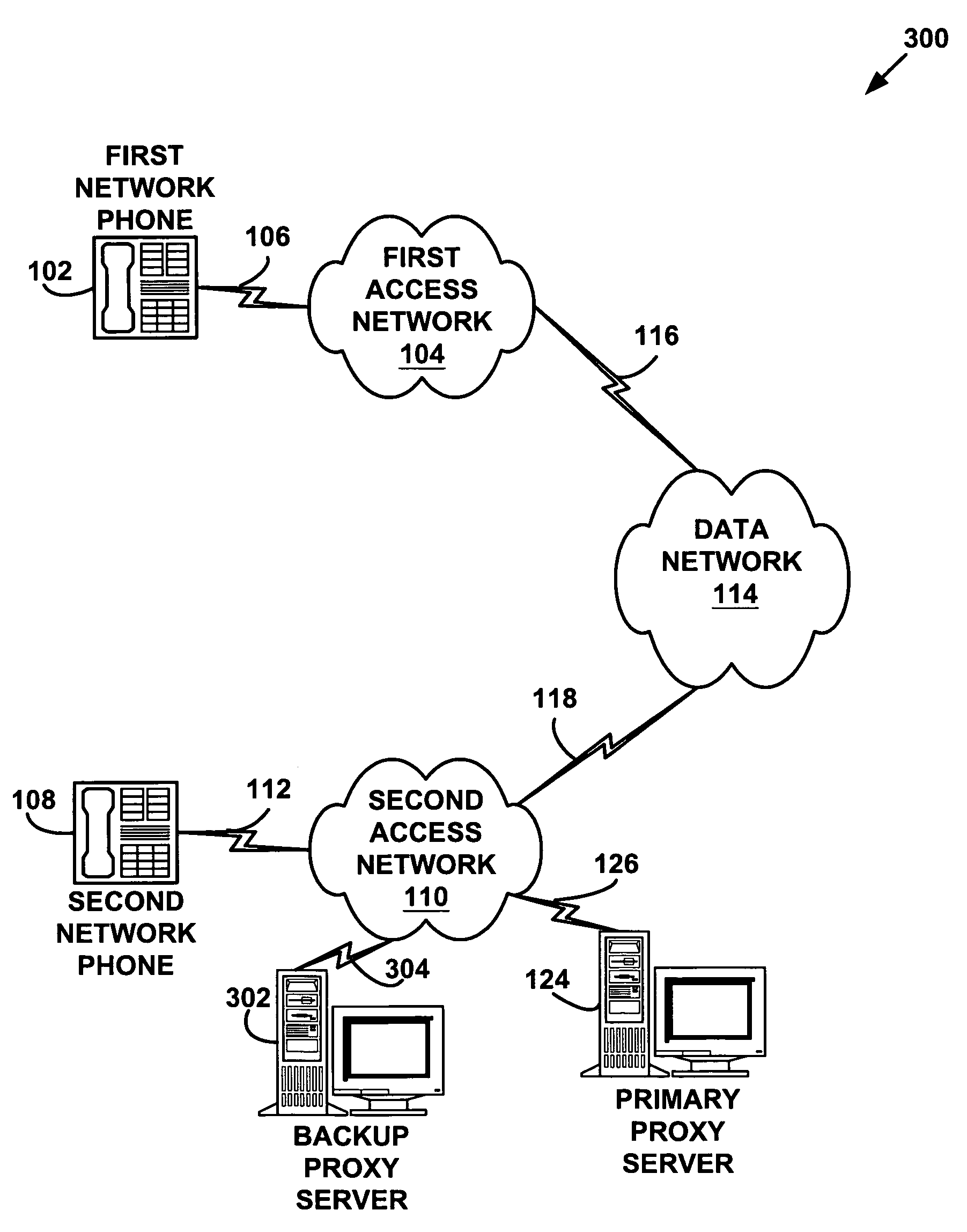
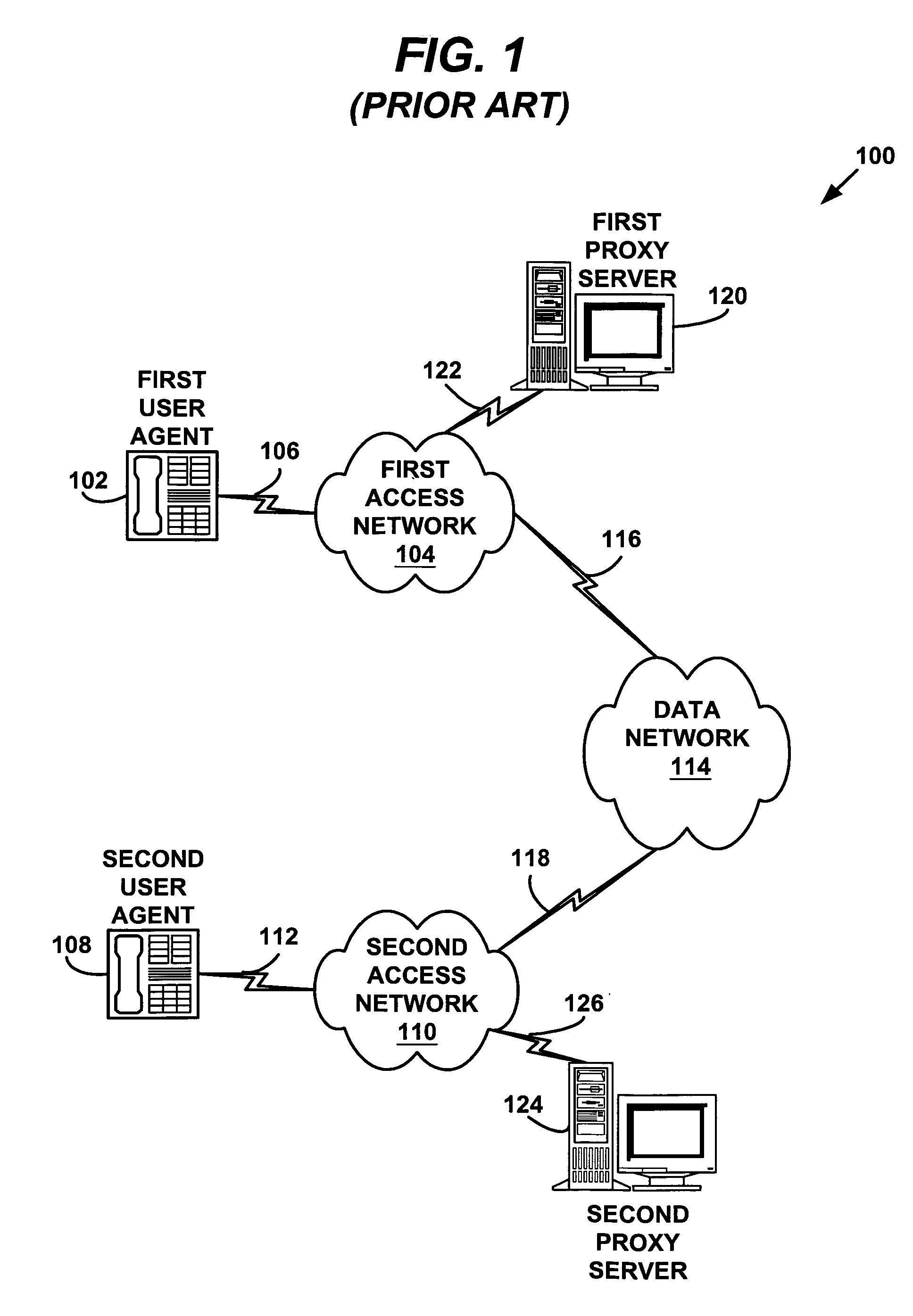
System and method for providing fault tolerance in a network telephony system
A system and method for providing fault tolerance in a network telephony system. Signaling messages according to a signaling protocol, such as the SIP protocol, are modified to include a path attribute with a network address corresponding to a backup proxy server. When a primary proxy server is supported by a backup proxy server, the primary proxy server inserts the Alternate Path tag into one or more signaling messages. When a network entity sends a message, it checks the message to identify the primary proxy server. Upon receiving a failure or timeout when attempting to send to the primary proxy server, the sending network entity should try the backup proxy server specified in the path attribute. When the backup proxy server receives the message, it may modify the message to specify the new routing path. As a result, subsequent messages get routed properly using the backup proxy server.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
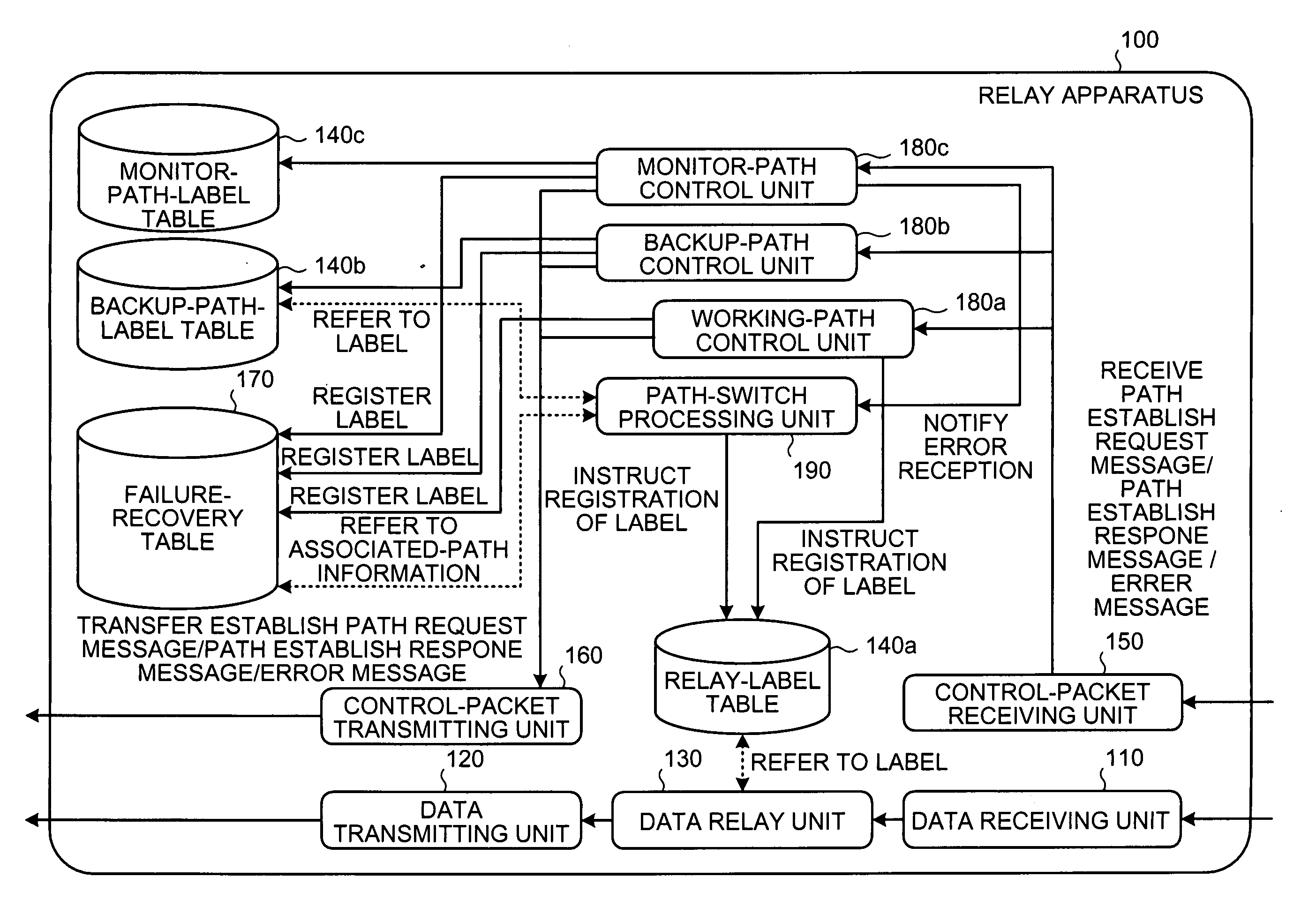
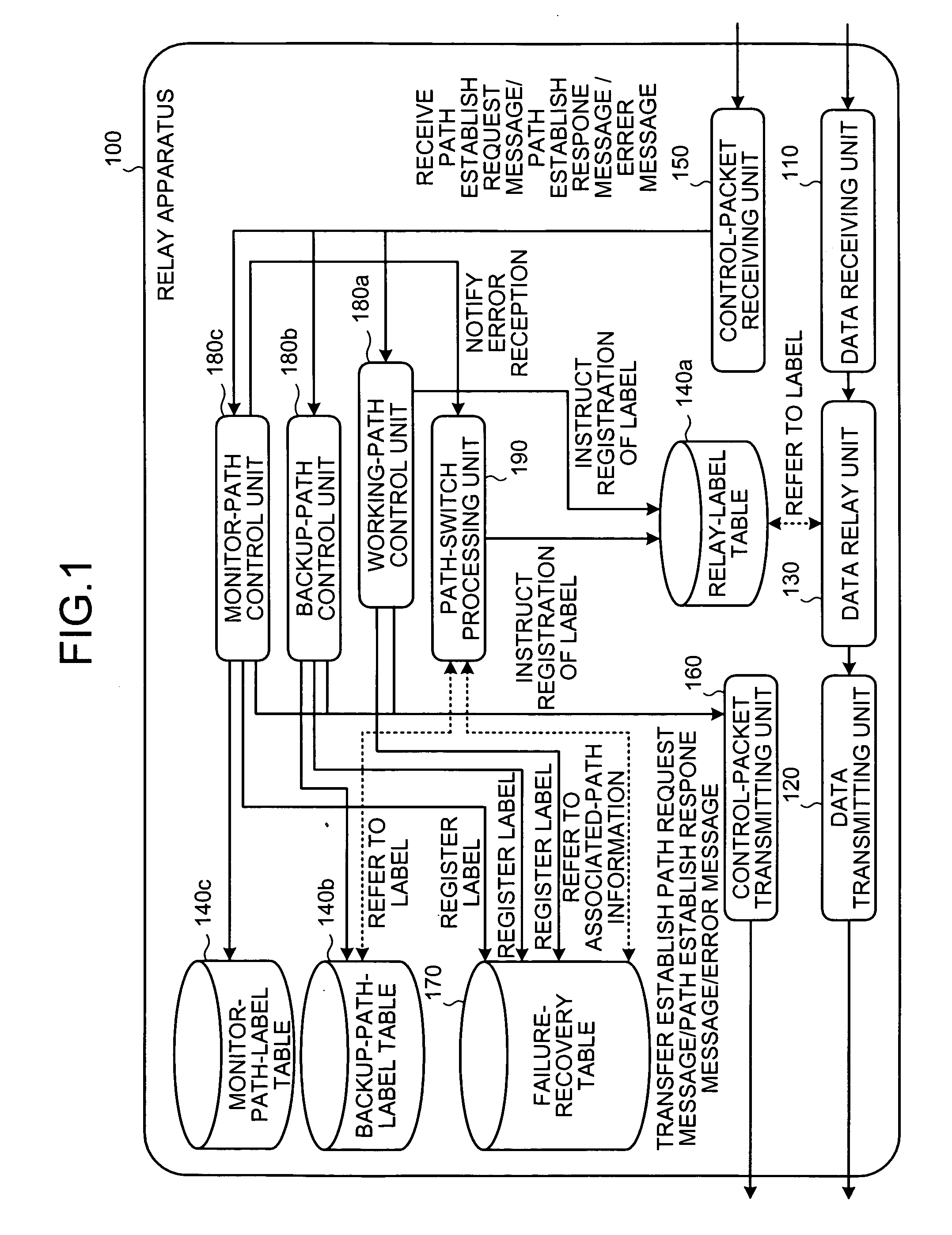
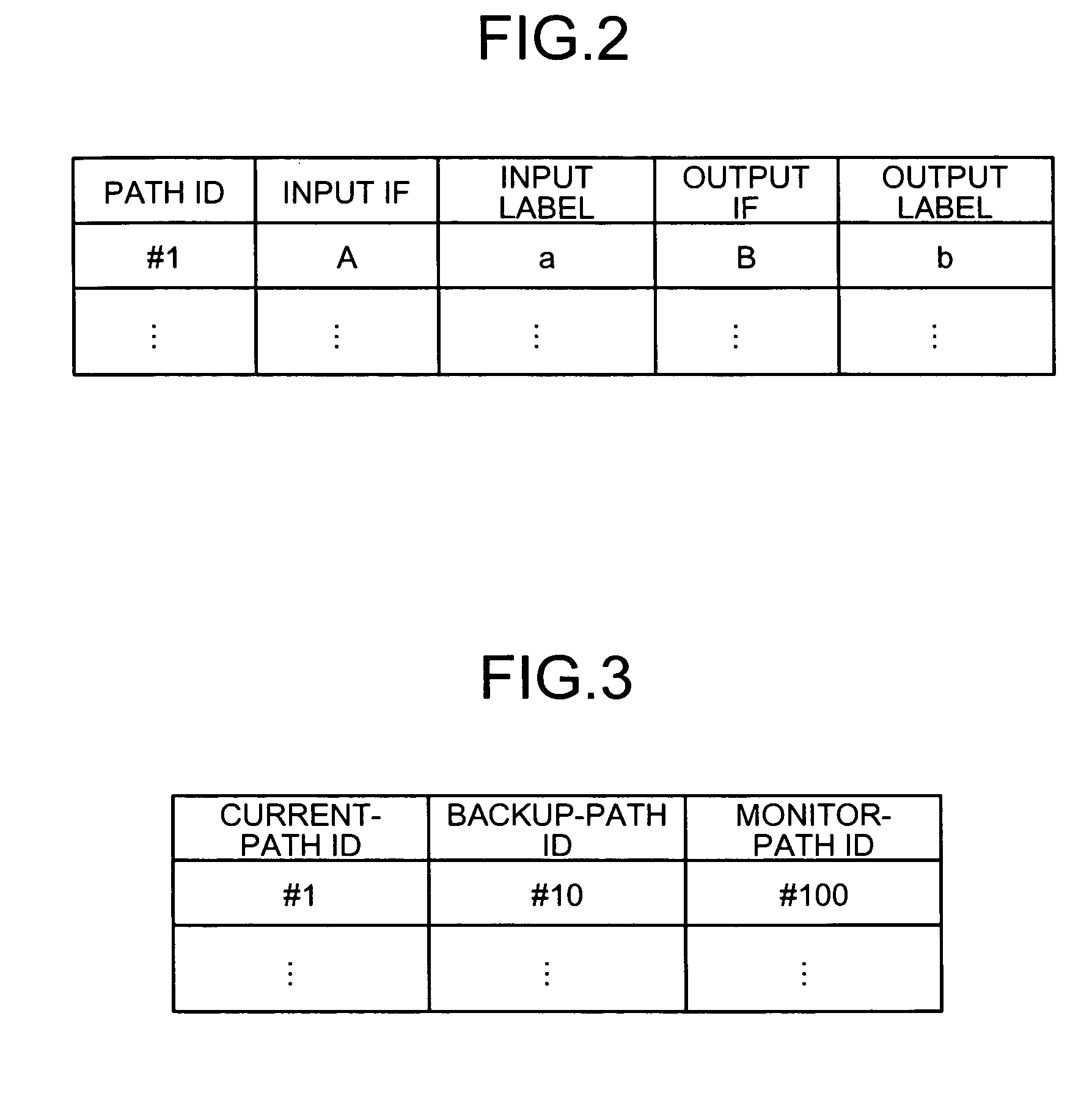
Data relay apparatus and data relay method
A failure-recovery-information storing unit stores failure-recovery information in which a working path is associated with a backup path. A failure-occurrence-notification receiving unit receives a failure-occurrence notification indicating that a failure has occurred in the working path. A backup-path searching unit searches for a backup path corresponding to the working path on which the failure has occurred, based on the failure-recovery information. A path-switch processing unit carries out a path-switch process, in such a manner that the data to be transferred using the working path in which the failure has occurred is transferred using the backup path.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
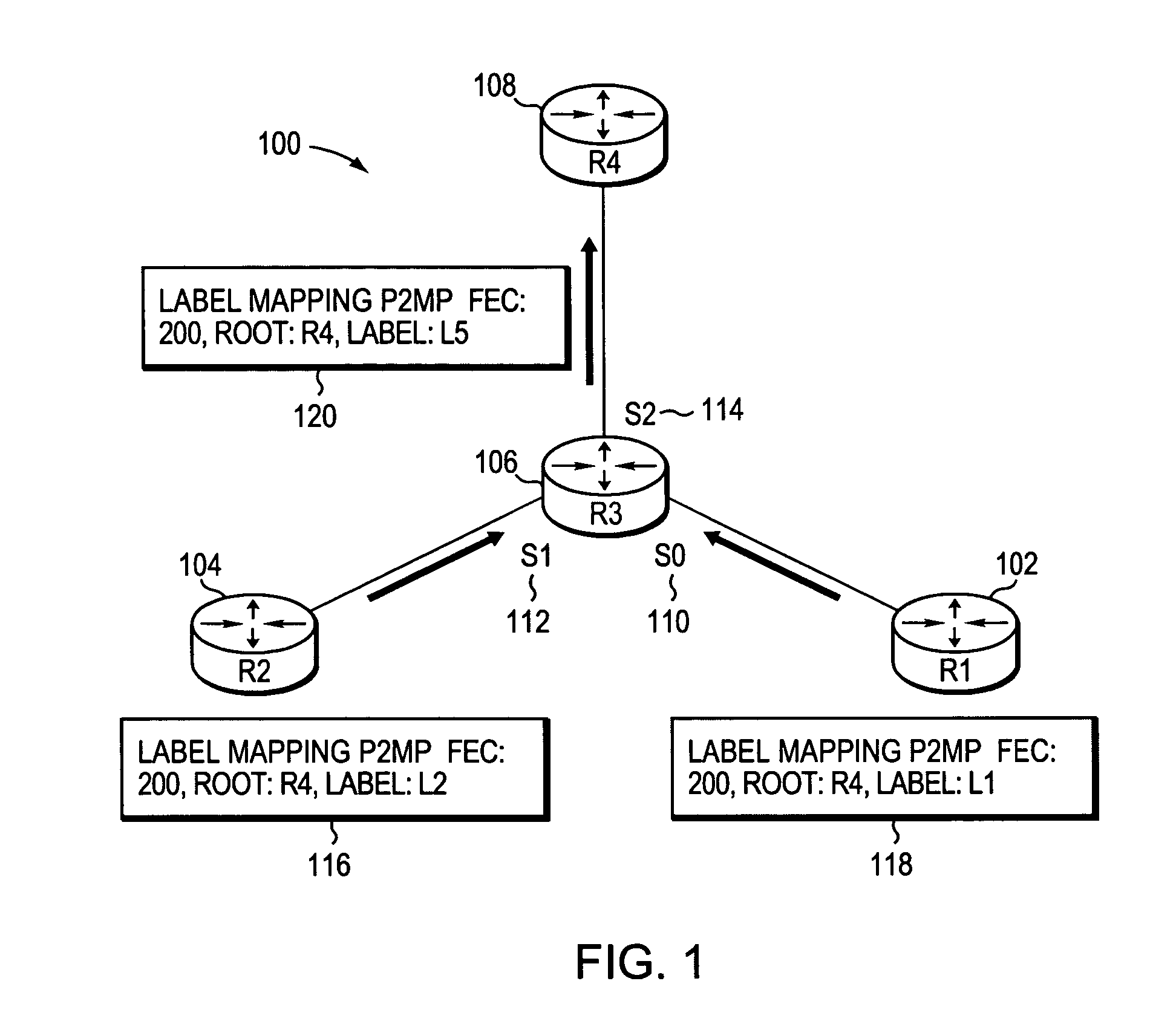
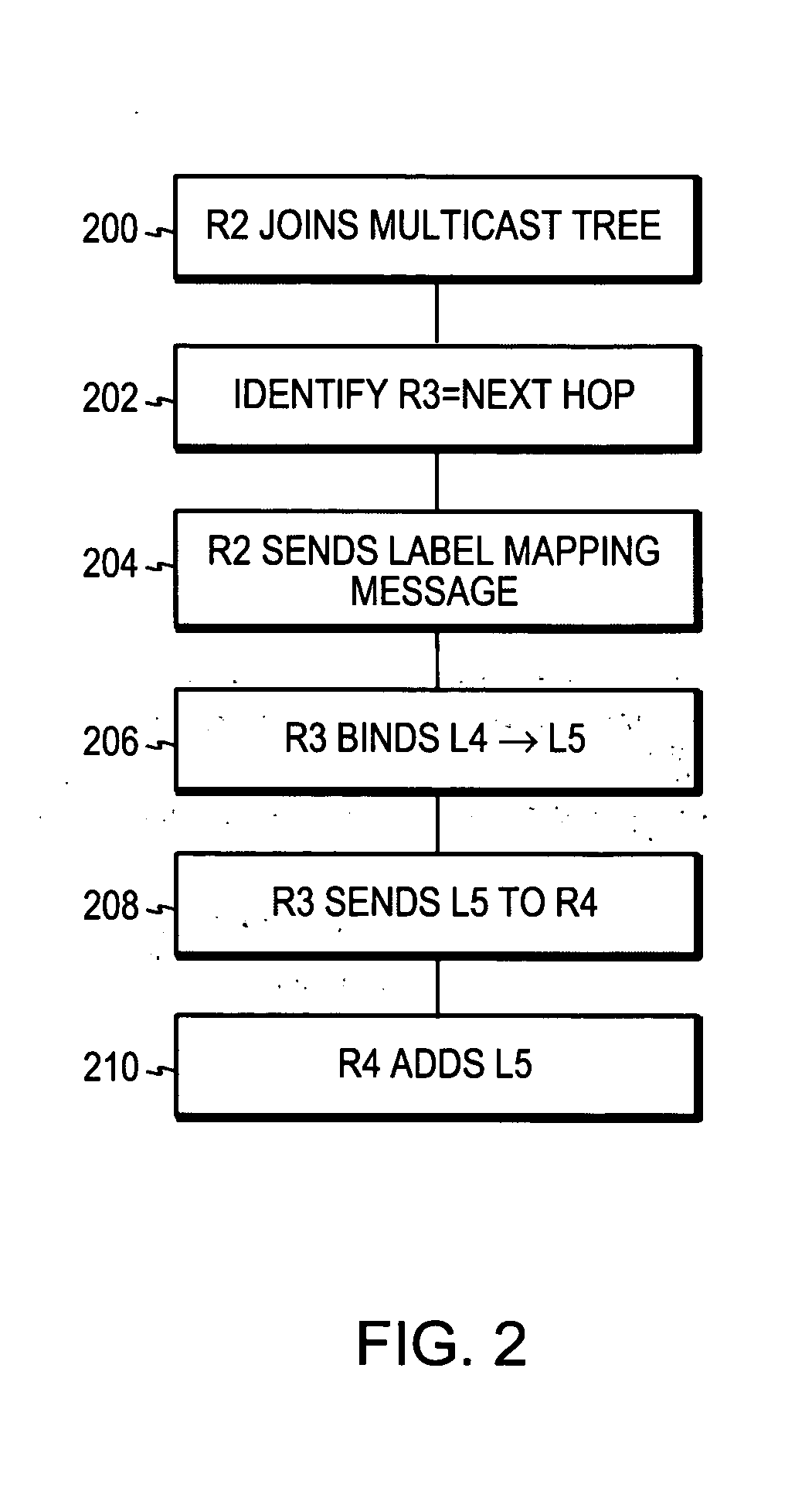
Method and apparatus for forwarding label distribution protocol multicast traffic during fast reroute
A computer apparatus comprising a processor and a forwarding engine arranged to forward LDP multicast traffic along a multicast tree having a primary and a backup path in a converged network topology, the processor being configured to cause the forwarding engine to forward traffic via the backup path upon a topology change and send a changed topology label and path vector to at least one neighbor node in the changed topology.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Automatic protection switching using link-level redundancy supporting multi-protocol label switching
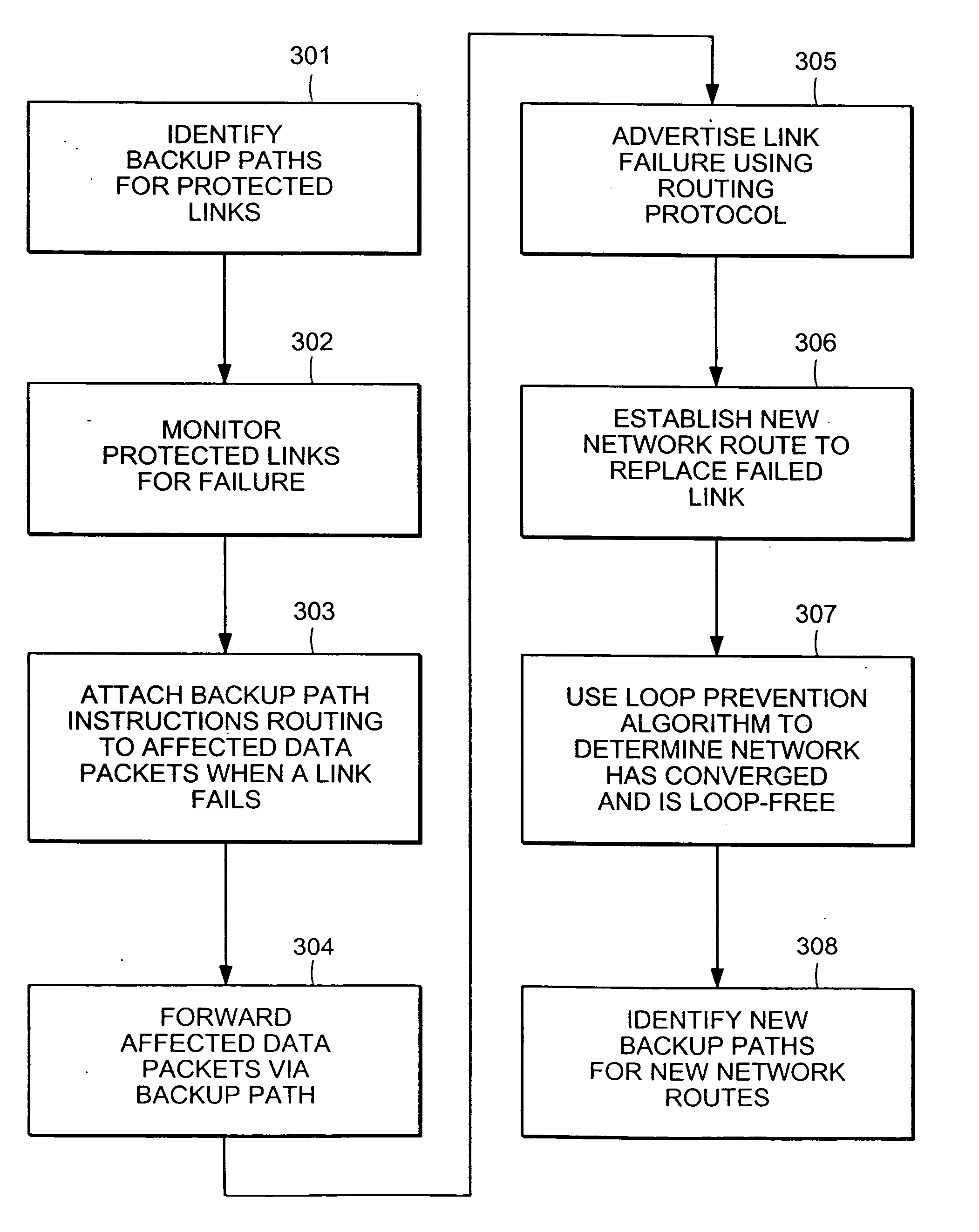
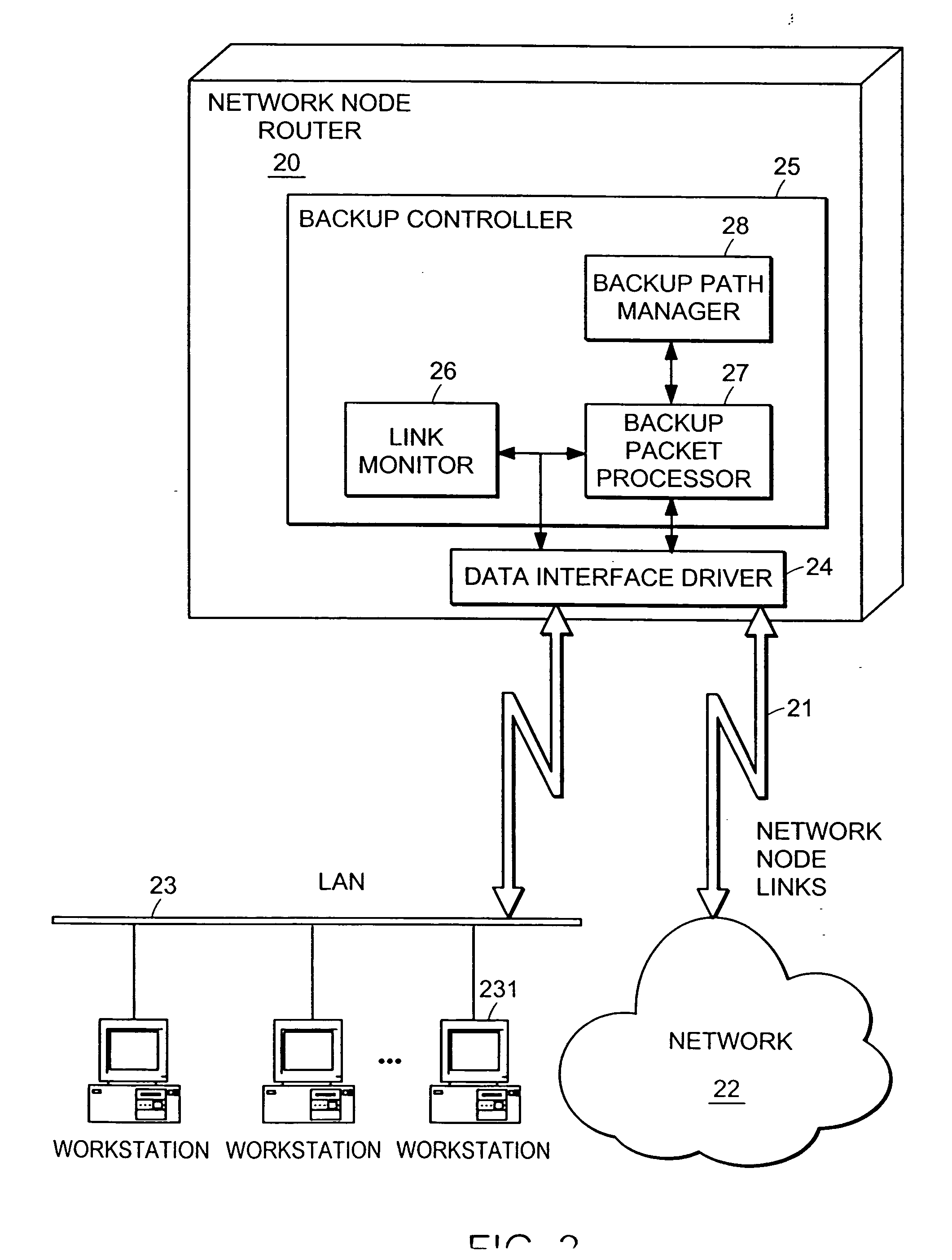
InactiveUS20050265228A1Error preventionTransmission systemsAutomatic protection switchingNetwork packet
A computer network has a plurality of routers that deliver data packets to the network via a plurality of links. At least one router provides automatic protection switching in the event of a link failure. The at least one router includes a plurality of data interfaces for streams of data packets to enter and exit the at least one router; and a backup controller. The backup controller includes a backup path manager, a link monitor, and a backup packet processor. For at least one link of the routing node, the backup path manager identifies a backup routing path for forwarding affected data packets in the event of a failure of the at least one link. The link monitor monitors the plurality of links to determine when a link fails. When a link which has a backup routing path fails, the backup packet processor attaches backup routing path instructions to affected data packets routed over the failed link, and forwards the affected data packets via the backup routing path.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
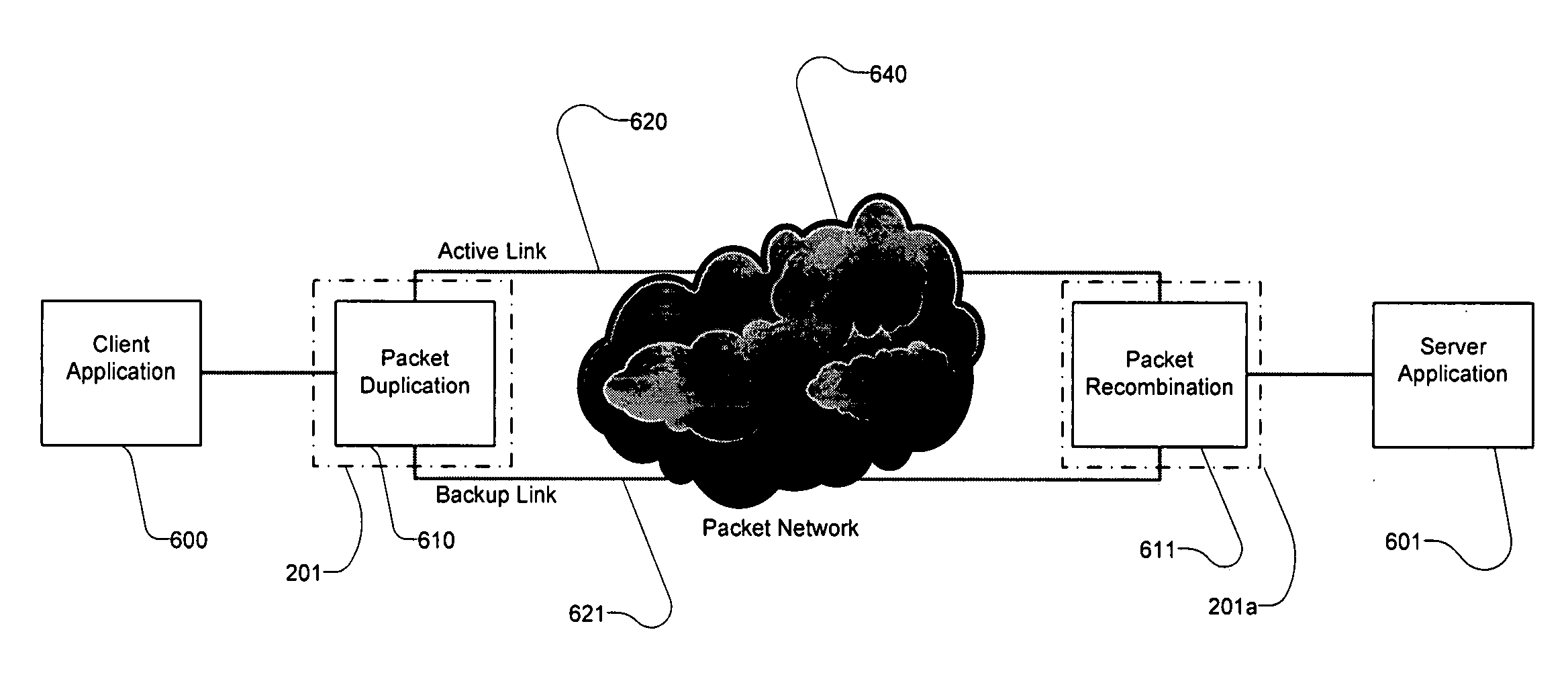
Smart Ethernet edge networking system
A telecommunications system includes a network for transporting packets on a path between selected subscriber end points. The network has multiple nodes connected by links, with each node (a) pairing the forward and backward paths of a connection and (b) allowing for the injection of messages in the backward direction of a connection from any node in the path without needing to consult a higher OSI layer. A system is also provided for protecting connection paths for transporting data packets through an Ethernet telecommunications network having a multiplicity of nodes interconnected by a multiplicity of links. Primary and backup paths are provided through the network for each of multiple connections, with each path including multiple links. Data packets arriving at a first node common to the primary and backup paths are duplicated, and one of the duplicate packets is transported over the primary path, the other duplicate packet is transported over the backup path, and the duplicate packets are recombined at a second node common to the primary and backup paths.
Owner:CIENA
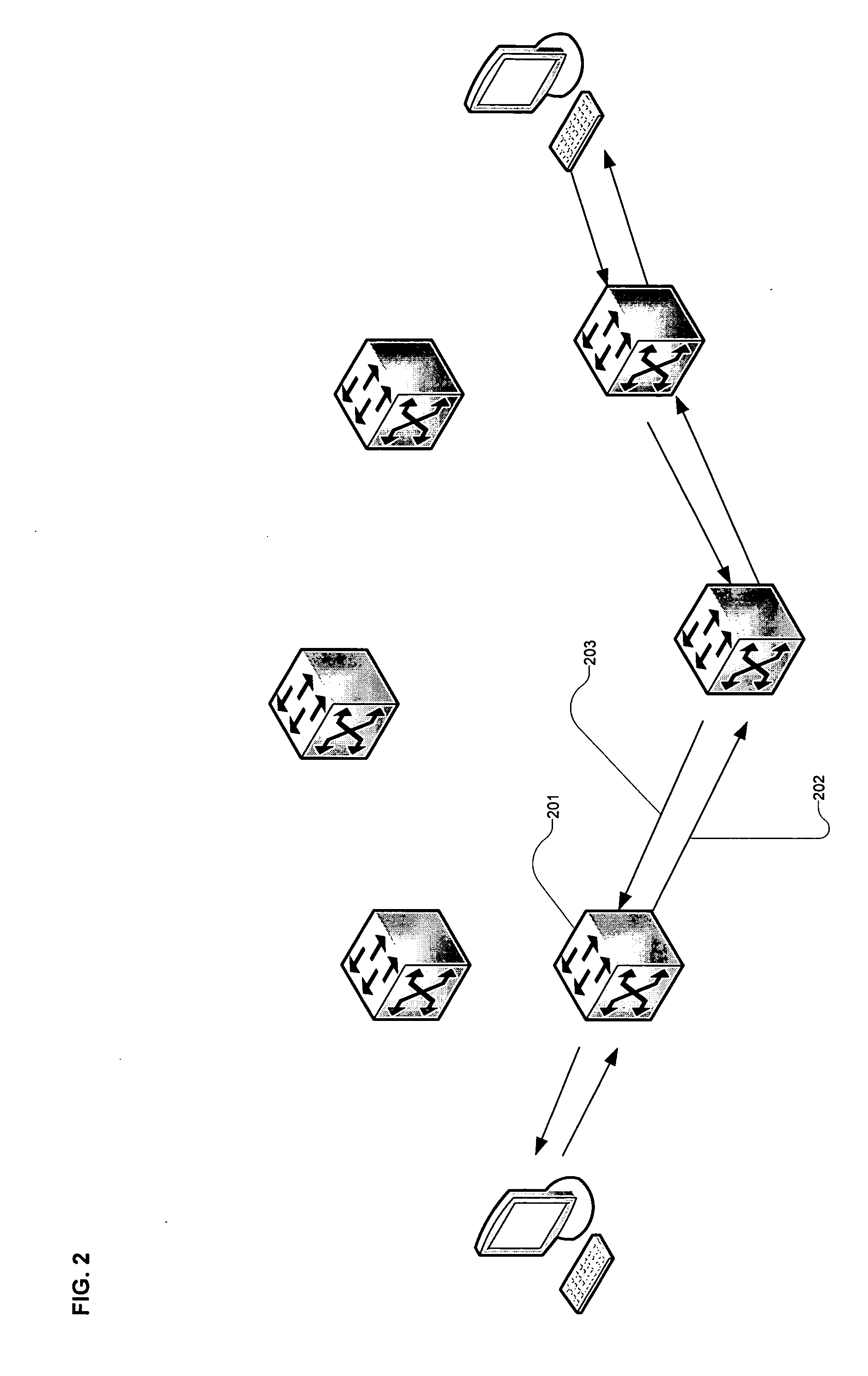
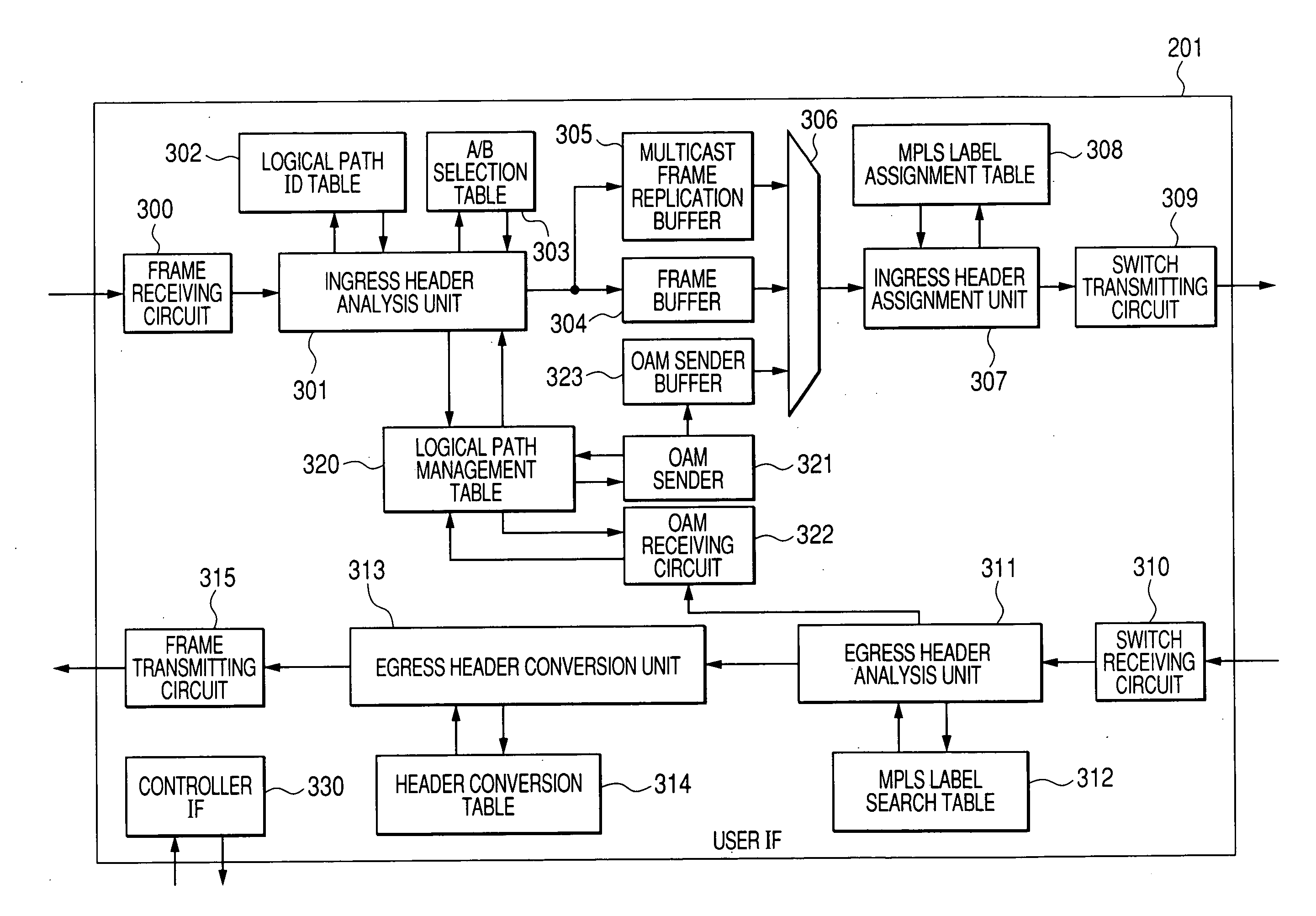
Network system and node
The invention realizes defect indication on a multipoint logical path and switching of the logical path when the multipoint logical path is configured using a transfer protocol of configuring a logical path, typified by MPLS etc., in a ring network. Two routes of the multipoint logical paths, a working path and a backup path, are set up. Each of them not only transmits a frame transmitted from a transmitting end node to multicast receiving end nodes but also forwards the frame to the transmitting end node and terminates it also at the transmitting end node after making it go around the ring. Any node that detects a defect transmits a forward defect indication frame to a multipoint logical path in which the defect occurs. The transmitting end node having received the forward defect indication frame halts the use of the notified multipoint logical path, and transmits a frame in another path in which the forward defect indication frame is not received within a fixed time period. Moreover, when the forward defect indication frame is received from the both multipoint logical paths, the transmitting end node copies the frame and forwards them to the both multipoint logical paths.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
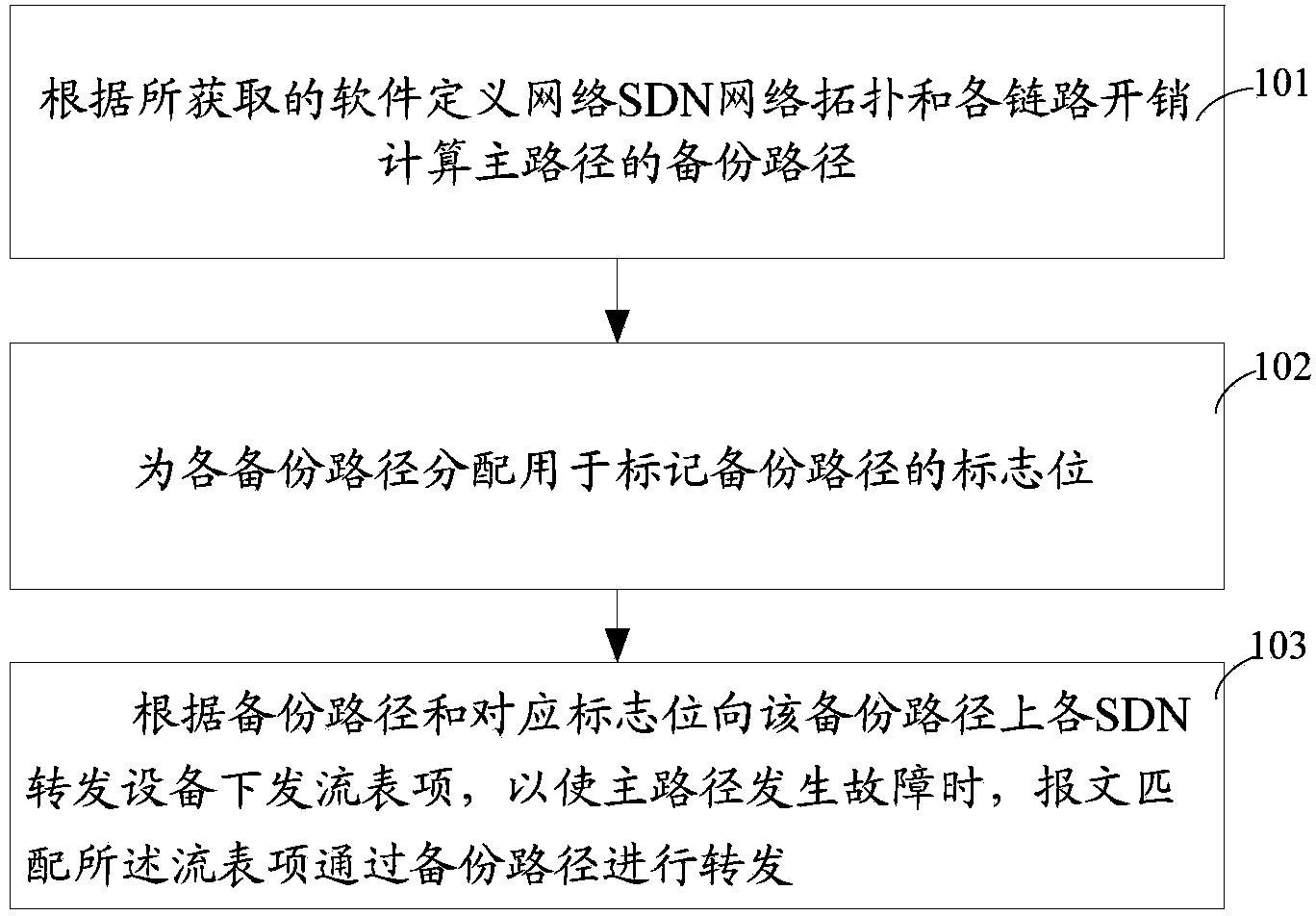
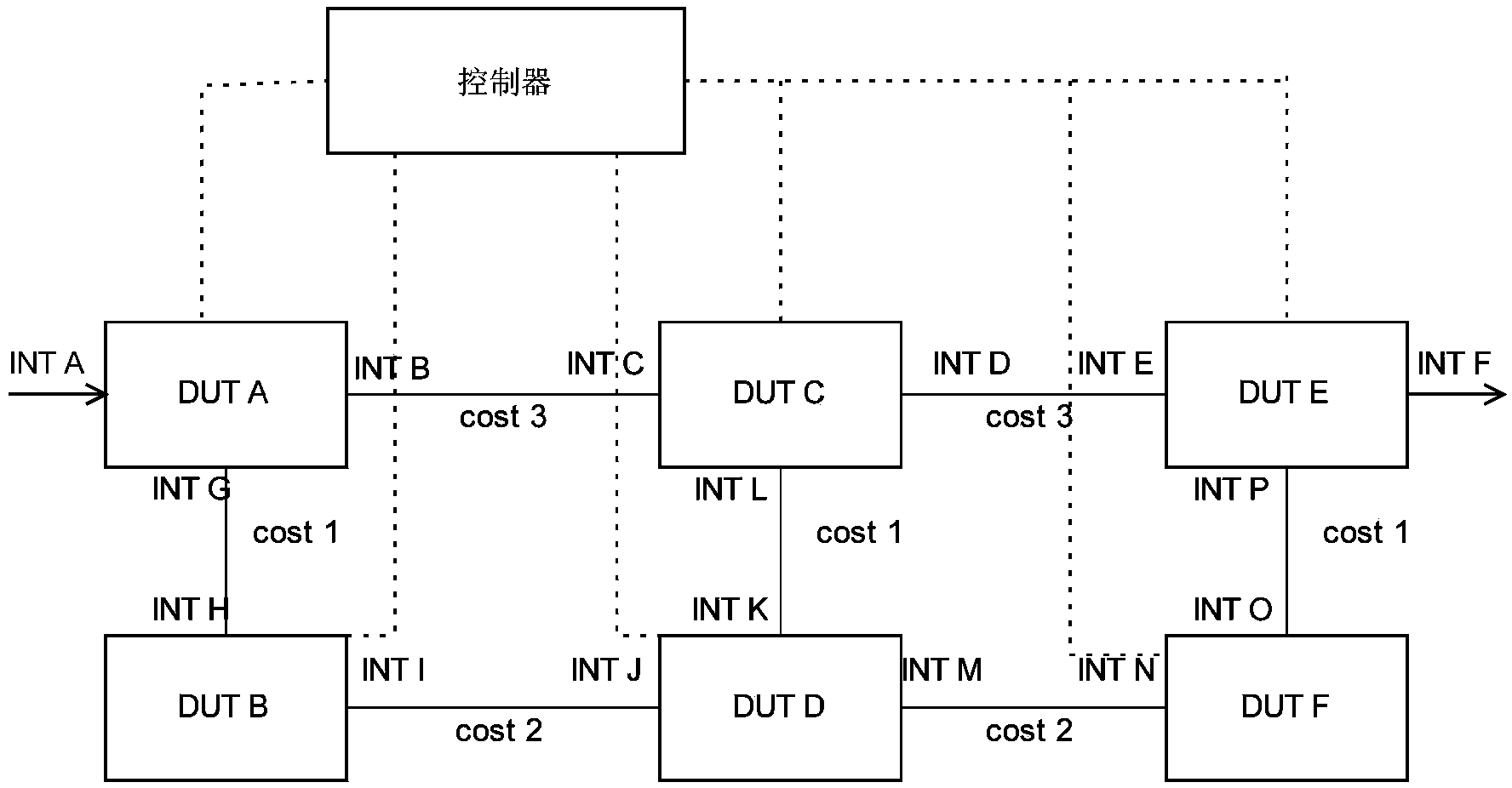
SDN controller and control method thereof
The invention discloses a control method of an SDN controller. The method comprises the steps of calculating backup paths of a main path according to an obtained software-defined network (SDN) topology and expenses of each link, distributing marker bits for marking the backup paths to the backup paths, and issuing flow table items to SDN forwarding devices on the backup paths according to the backup paths and the corresponding marker bits so that messages can be matched with the flow table items to be forwarded through the backup paths when the main path breaks down. The invention further discloses the SDN controller. By the adoption of the SDN controller and the control method of the SDN controller, it is ensured that the flow obtained before the SDN controller calculates and processes new flow is not lost when the link for forwarding the flow in a network is broken or the topology changes.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
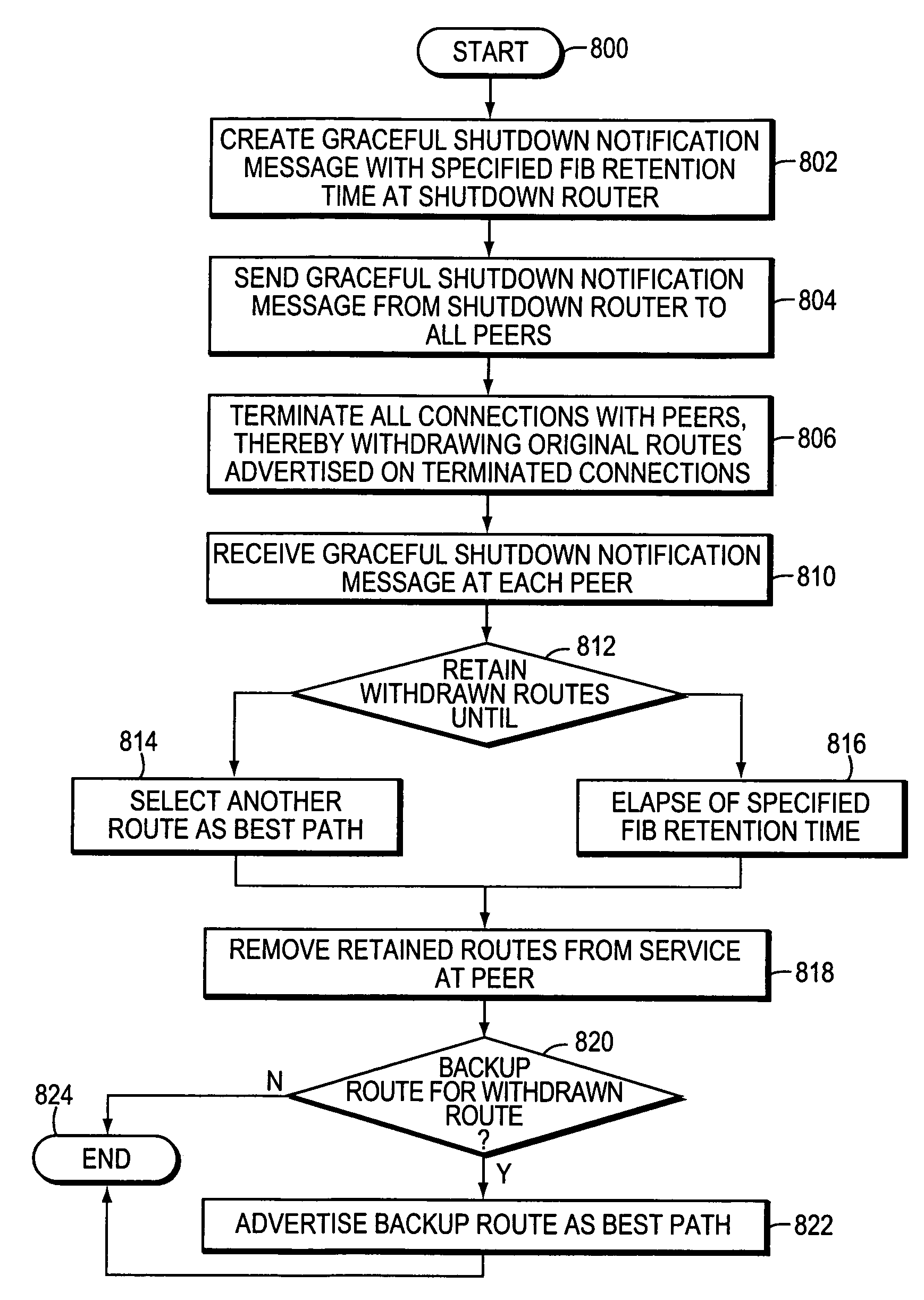
Technique for graceful shutdown of a routing protocol in a network
ActiveUS20050177634A1Reduce lossesOvercome disadvantagesMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksInformation repositoryBackup path
A graceful shutdown technique modifies a routing protocol to allow an intermediate node, such as a router, to announce to its peer routers (peers) its intention to be gracefully shutdown and removed from service in a network. By announcing its intention to be removed from service, the shutdown router closes (terminates) all connections with its peers and all original routes advertised on those connections are removed (withdrawn) from service. According to the inventive technique, the shutdown router may continue forwarding packets over the network for a “grace” period of time, i.e., the router maintains the validity of those original routes so that packets mapped to the routes are not dropped (at least during the grace period). The grace period also allows backup paths to be propagated to each peer and put into service prior to a final withdrawal of the shutdown router's paths from a forwarding information base of the peer. Thus, the grace period enables the network to continue using the shutdown router as a next hop as it re-converges to use the alternate, backup paths.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
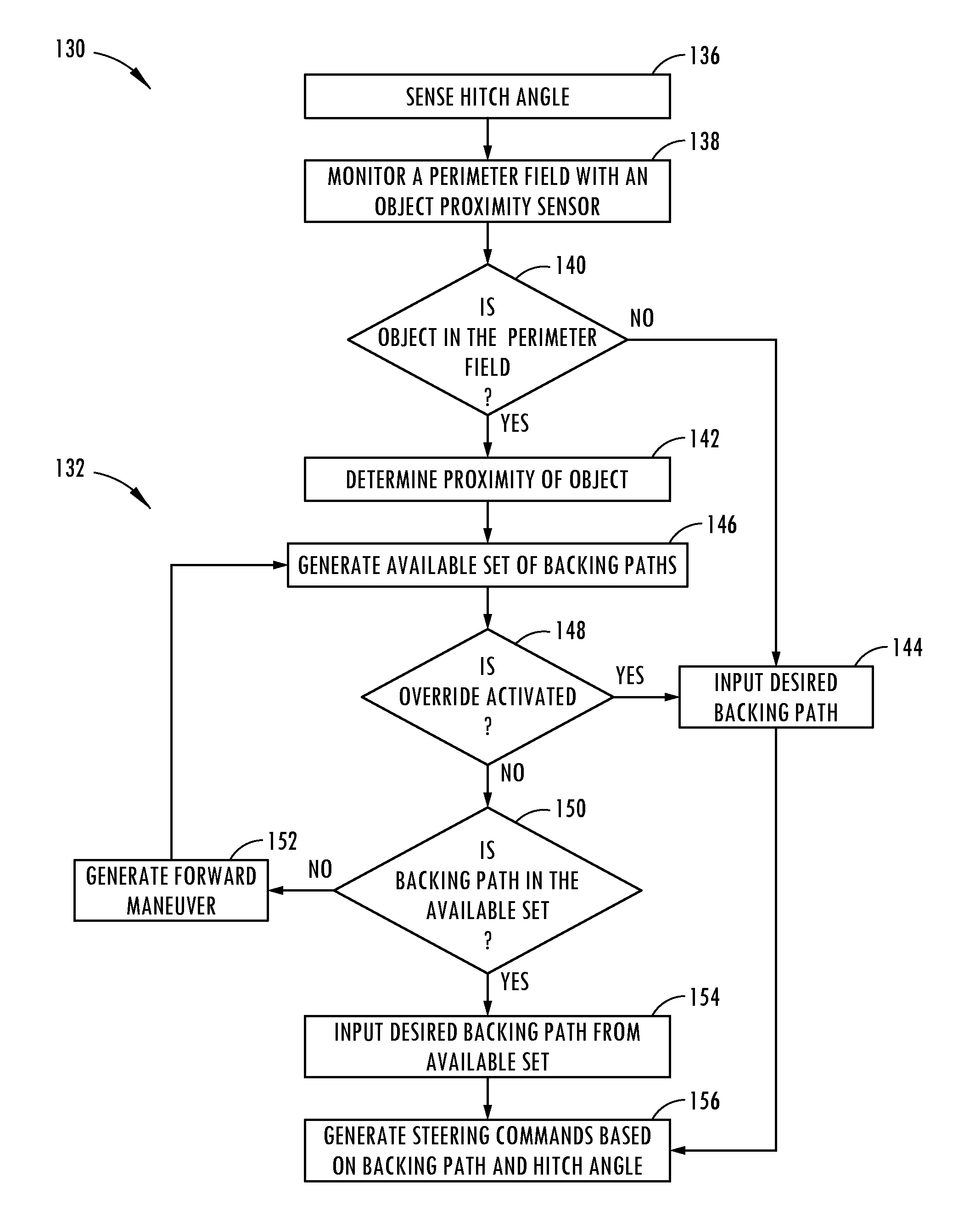
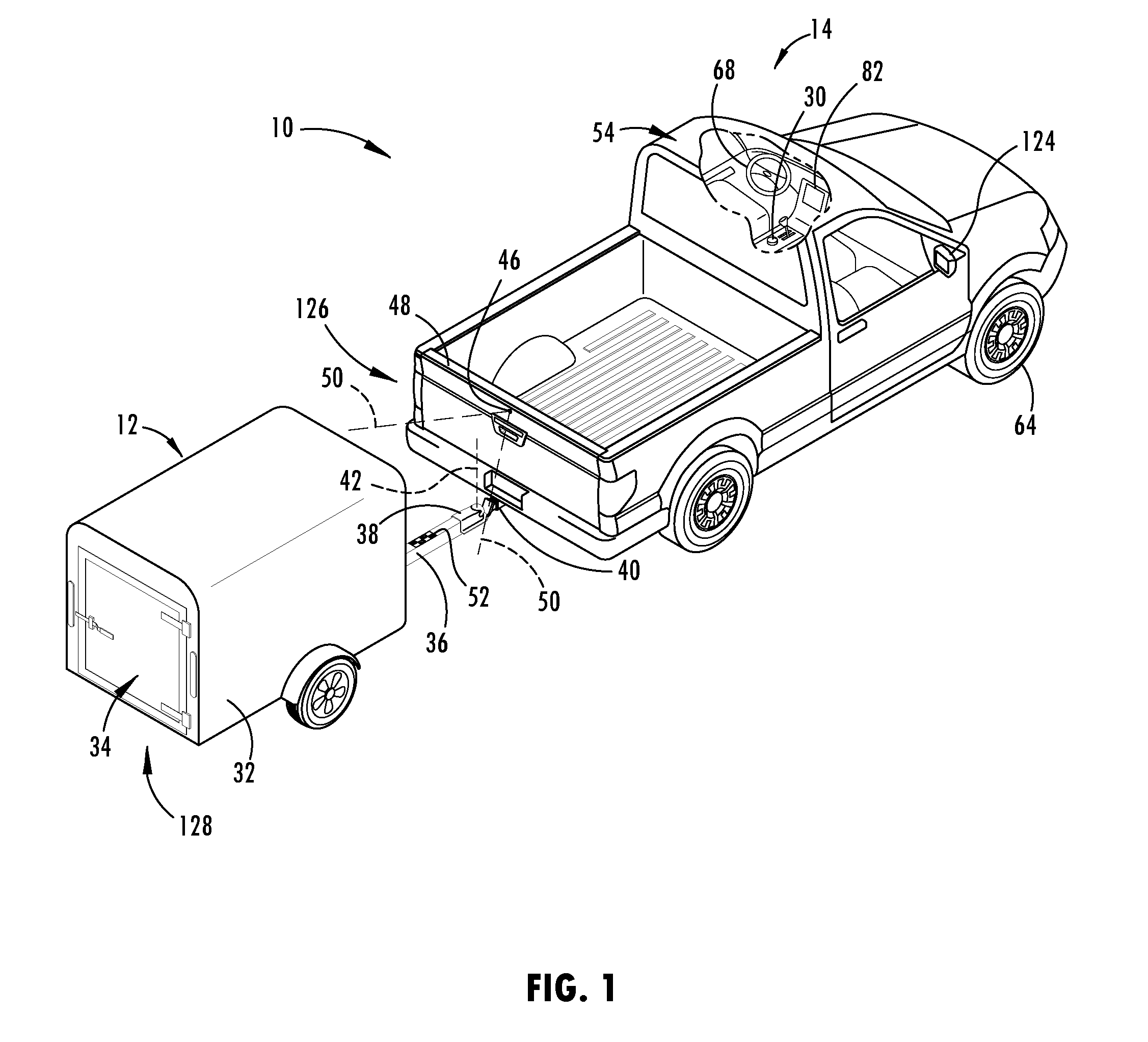
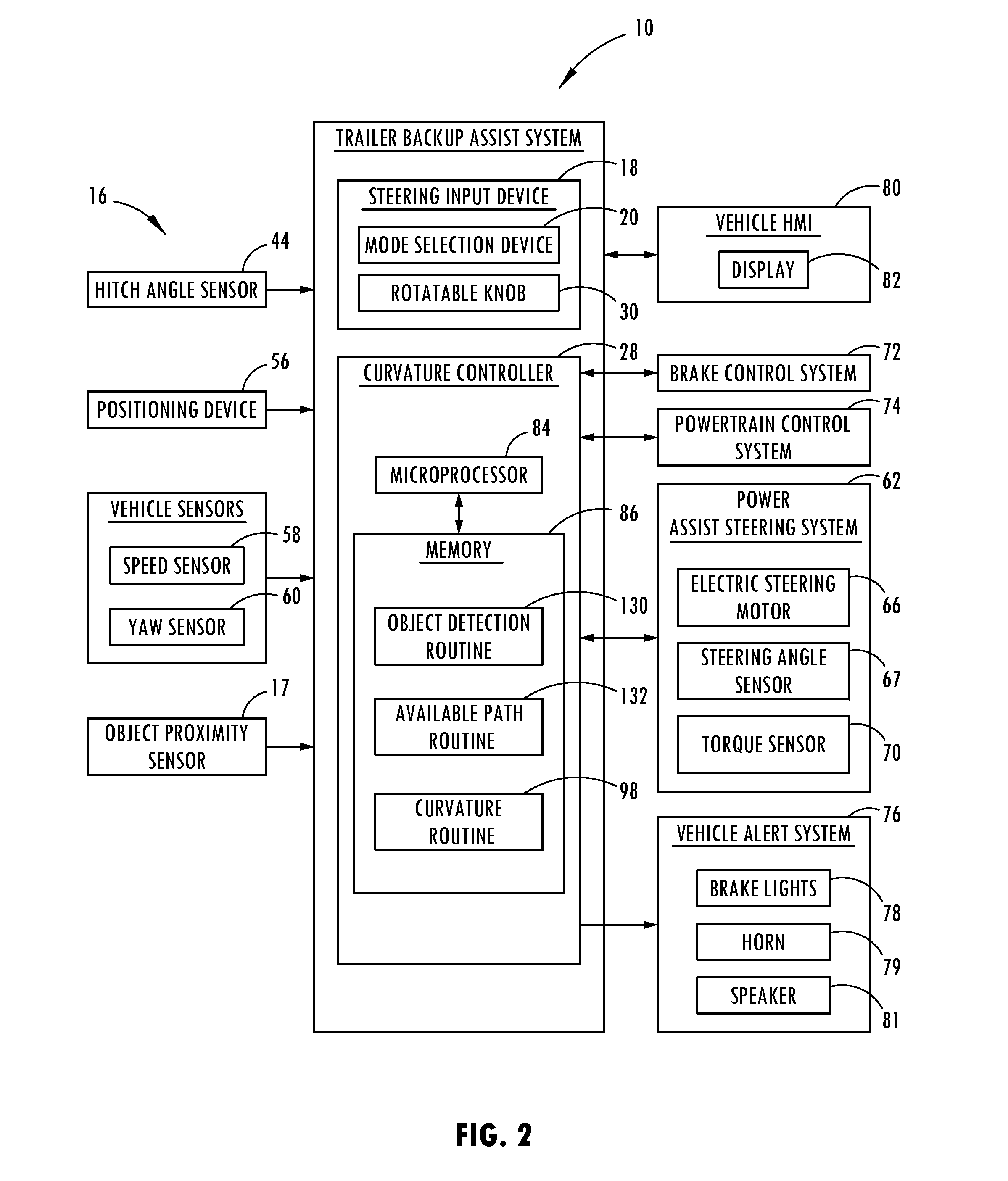
Object avoidance for a trailer backup assist system
A trailer backup assist system, according to one embodiment, includes a steering input device for inputting a desired backing path of a trailer. The trailer backup assist system also includes a first sensor that senses a hitch angle between a vehicle and the trailer. Further, the trailer backup assist system includes a second sensor that senses a proximity of an object in a perimeter field of at least one of the vehicle and the trailer. A controller of the trailer backup assist system generates an available set of backing paths for the trailer based on the proximity of the object and the hitch angle. The available set of backing paths does not include backing paths that cross a space occupied by the object or that cause a jackknife condition between the vehicle and the trailer.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Technique for graceful shutdown of a routing protocol in a network
ActiveUS7355983B2Overcome disadvantagesMaintain validityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsInformation repositoryBackup path
A graceful shutdown technique modifies a routing protocol to allow an intermediate node, such as a router, to announce to its peer routers (peers) its intention to be gracefully shutdown and removed from service in a network. By announcing its intention to be removed from service, the shutdown router closes (terminates) all connections with its peers and all original routes advertised on those connections are removed (withdrawn) from service. According to the inventive technique, the shutdown router may continue forwarding packets over the network for a “grace” period of time, i.e., the router maintains the validity of those original routes so that packets mapped to the routes are not dropped (at least during the grace period). The grace period also allows backup paths to be propagated to each peer and put into service prior to a final withdrawal of the shutdown router's paths from a forwarding information base of the peer. Thus, the grace period enables the network to continue using the shutdown router as a next hop as it re-converges to use the alternate, backup paths.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Nexthop fast rerouter for IP and MPLS
Methods and apparatus for rerouting network traffic are described herein. In one embodiment, an example of process includes maintaining as a part of a routing table of a network element information regarding one or more backup links leading to a node using label switched protocols (LSPs), the node being adjacent to the network element, and in response to a failure of a primary link coupling the network element to the node, the network element rerouting network traffic to the node via the one or more backup paths without having to notifying and waiting for a response from a headend node that originates the network traffic. Other methods and apparatuses are also described.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
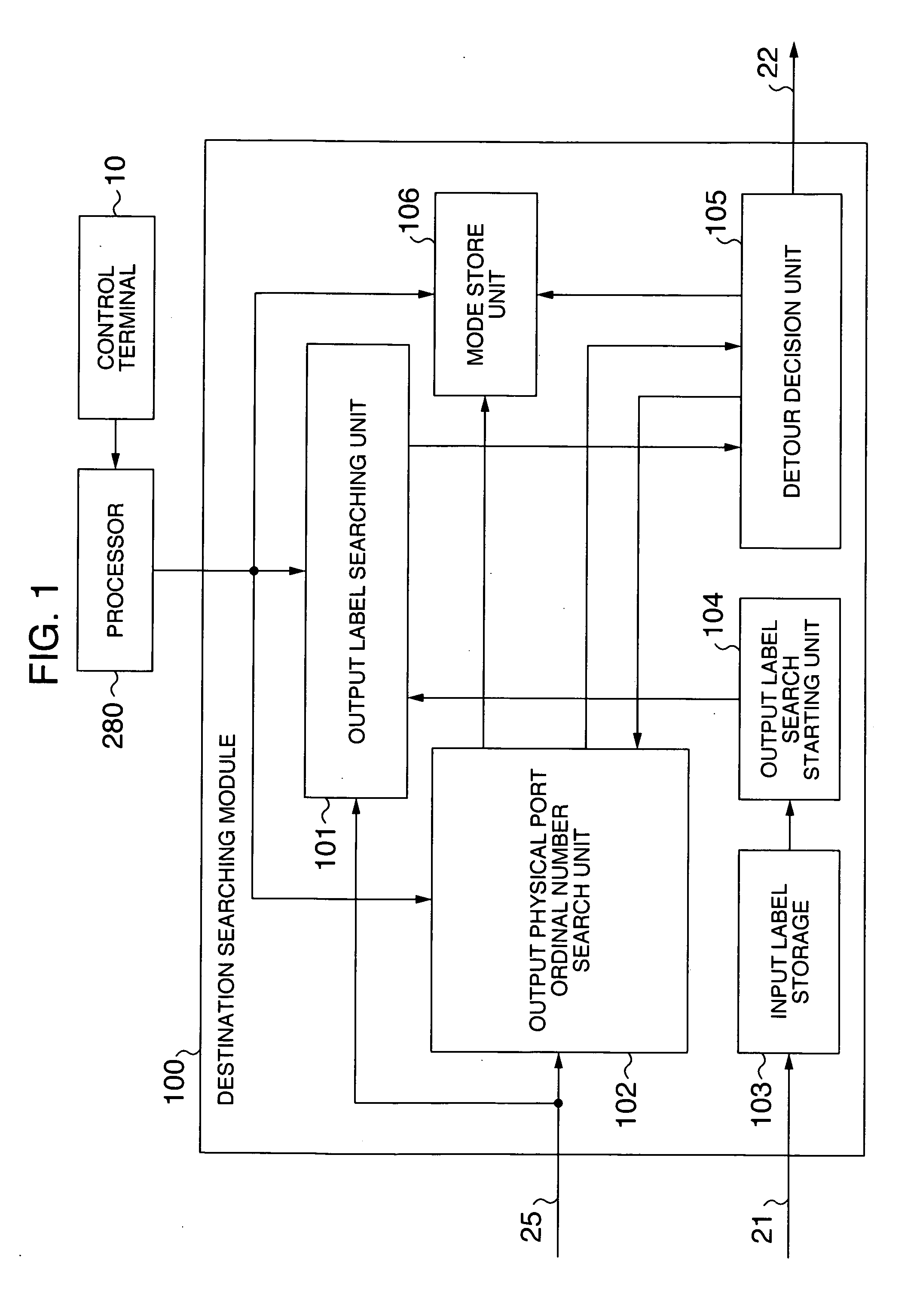
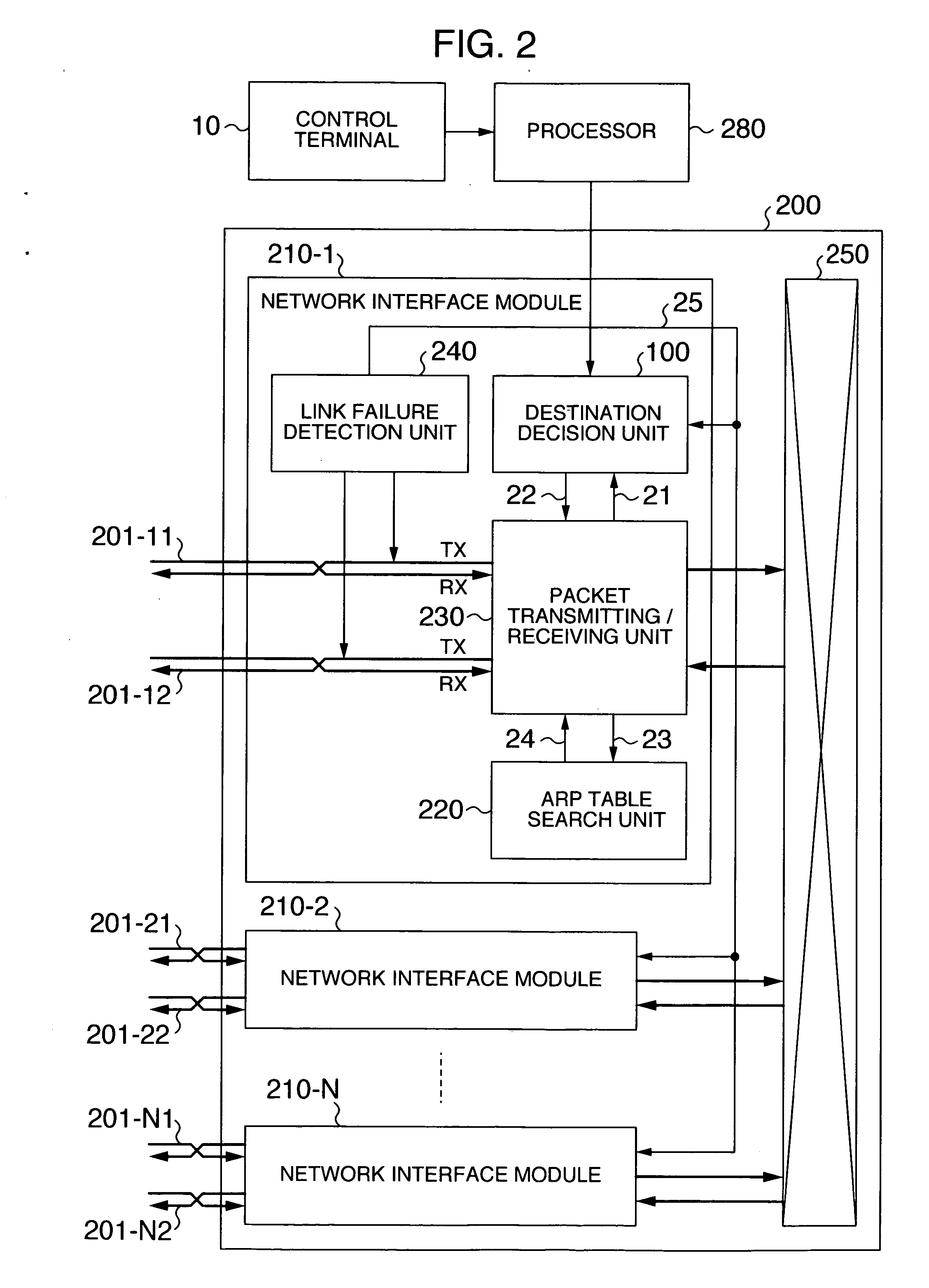
Packet forwarding apparatus with function of diverting traffic
InactiveUS20070091911A1Degraded traffic qualityReduce communication qualityEnergy efficient ICTData switching by path configurationTraffic capacityCommunication quality
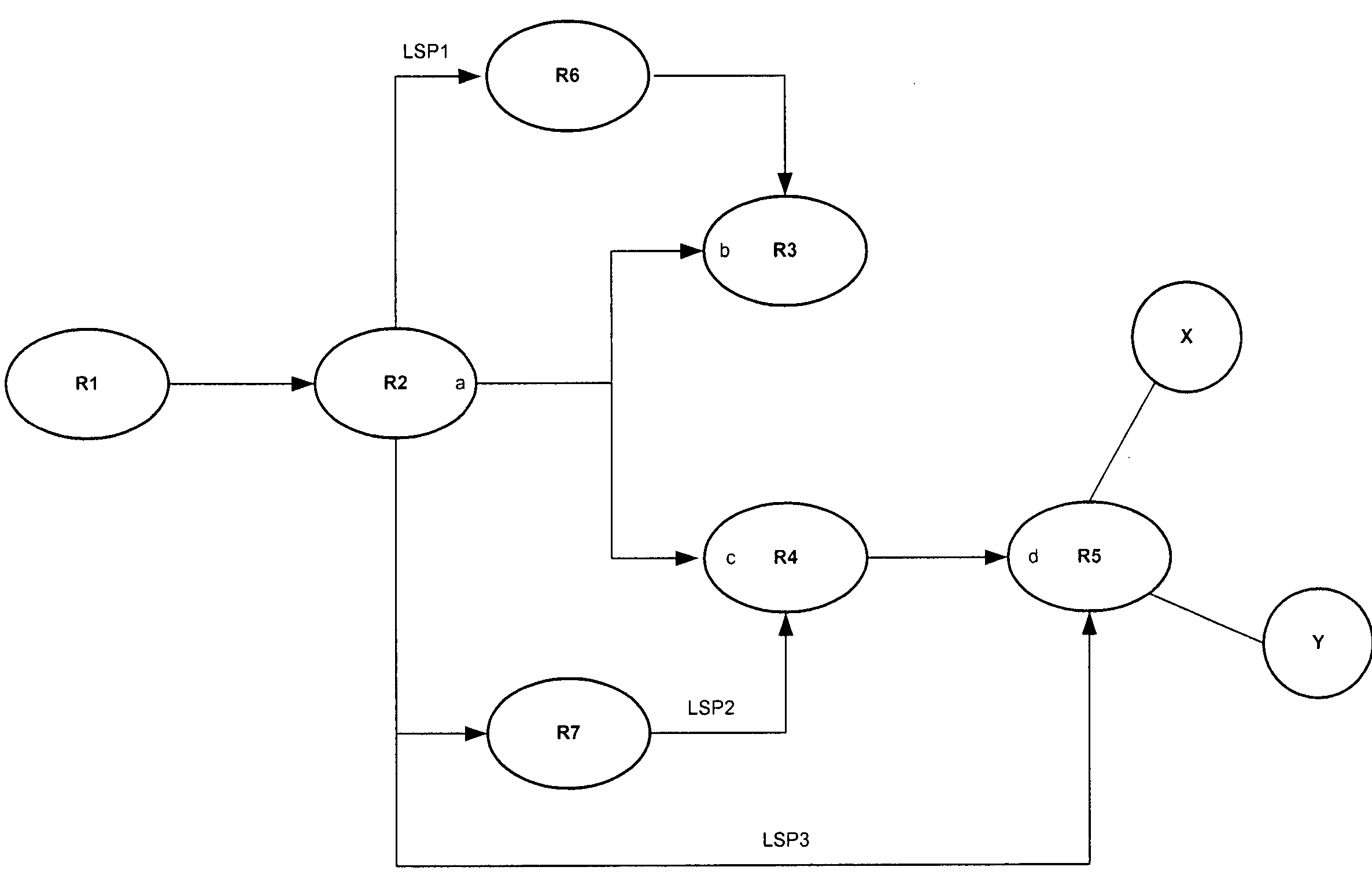
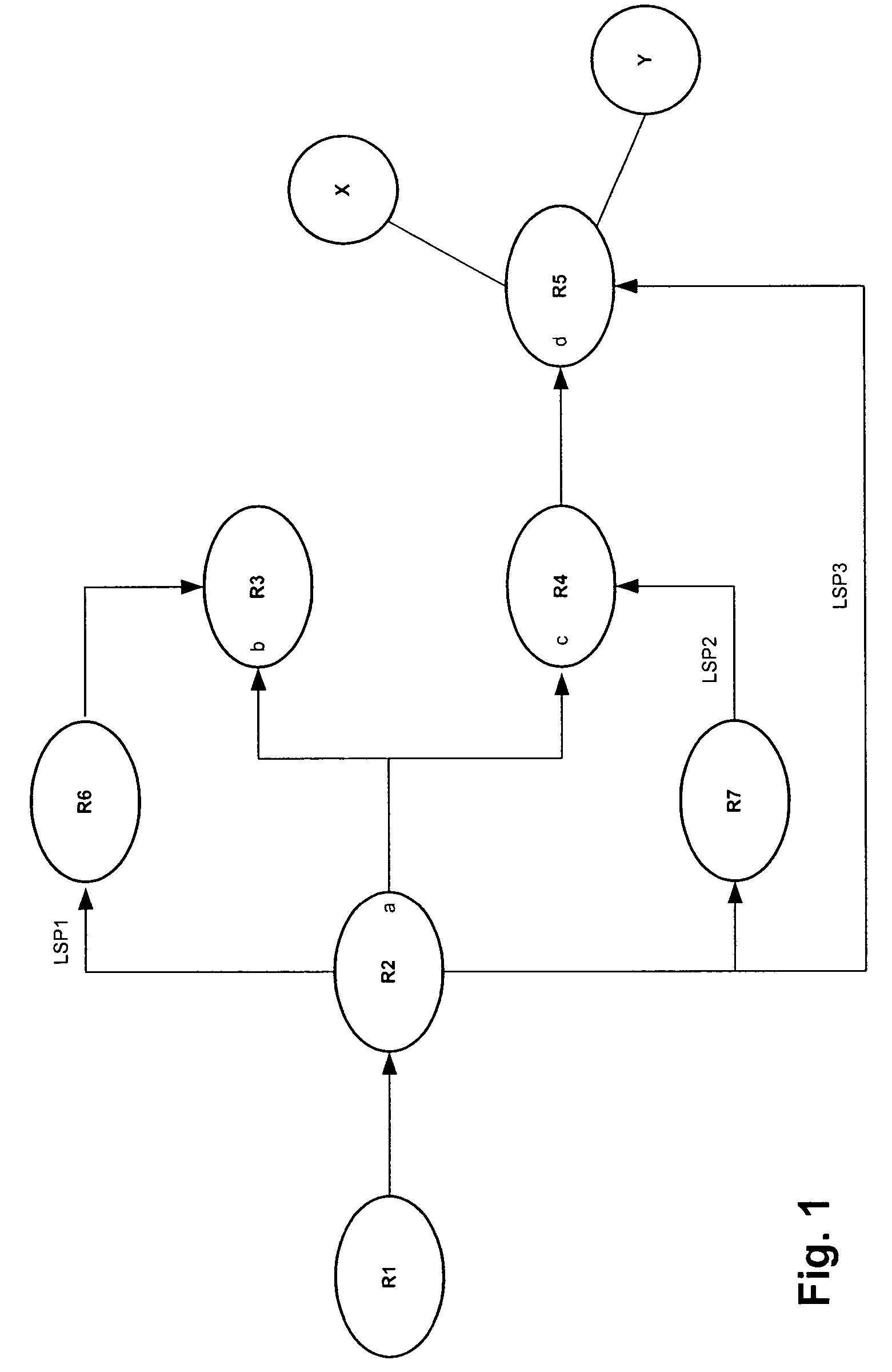
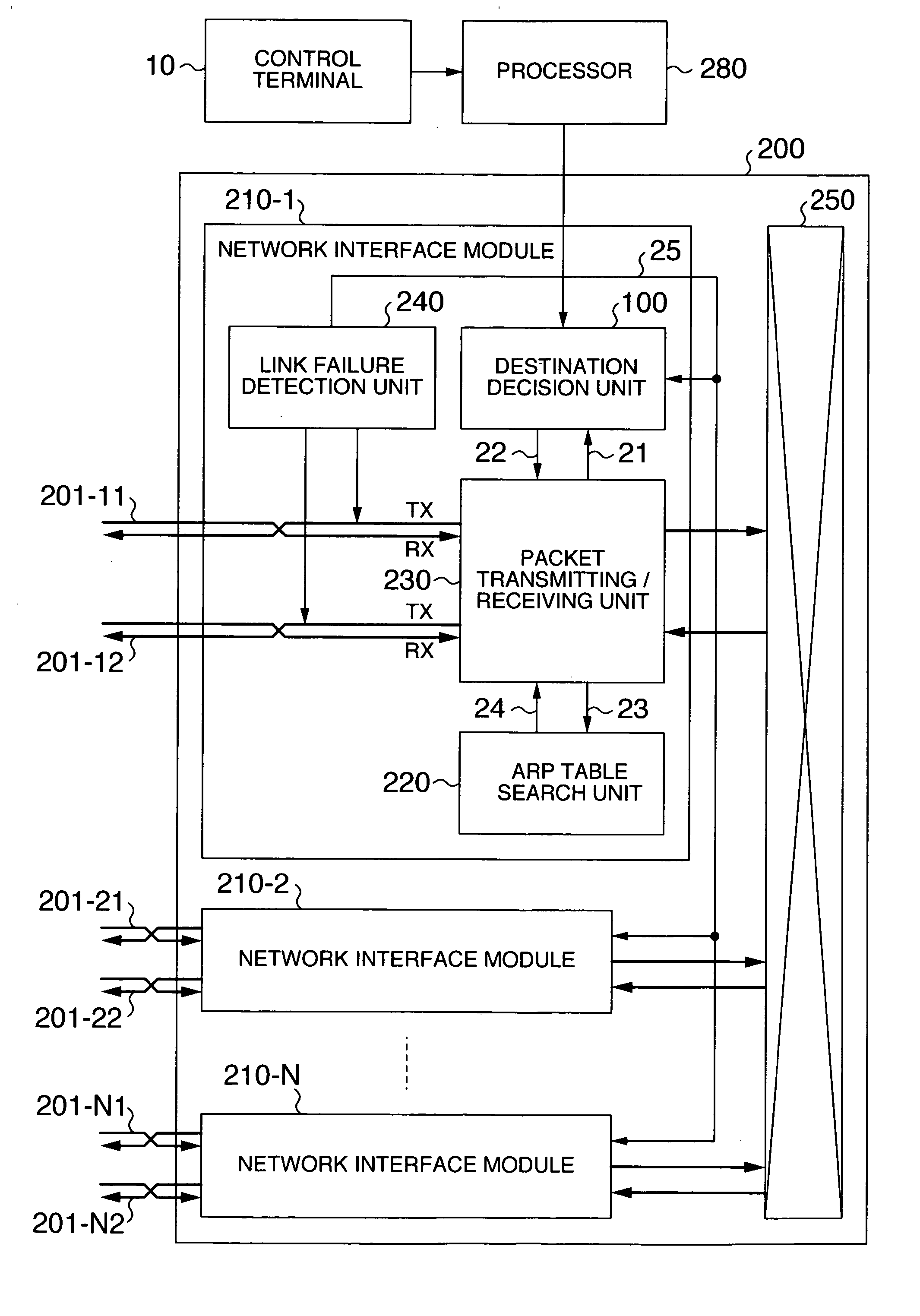
A packet forwarding apparatus is provided which can minimize traffic detoured to a backup path liable to be degraded in communication quality in the event of a link failure to thereby improve the communication quality. To this end, a technique is provided in which an output label decision unit and an output physical port ordinal number search unit which are included in a destination decision unit decide, from a header of an input packet, an output label of the packet, a first logical link to which the packet is to be outputted and a first physical link constituting the first logical link. When a failure takes place in the first physical link, the detour decision unit changes the output label to a backup label and the first physical link to a second physical link constituting a second logical link.
Owner:ALAXALA NETWORKS
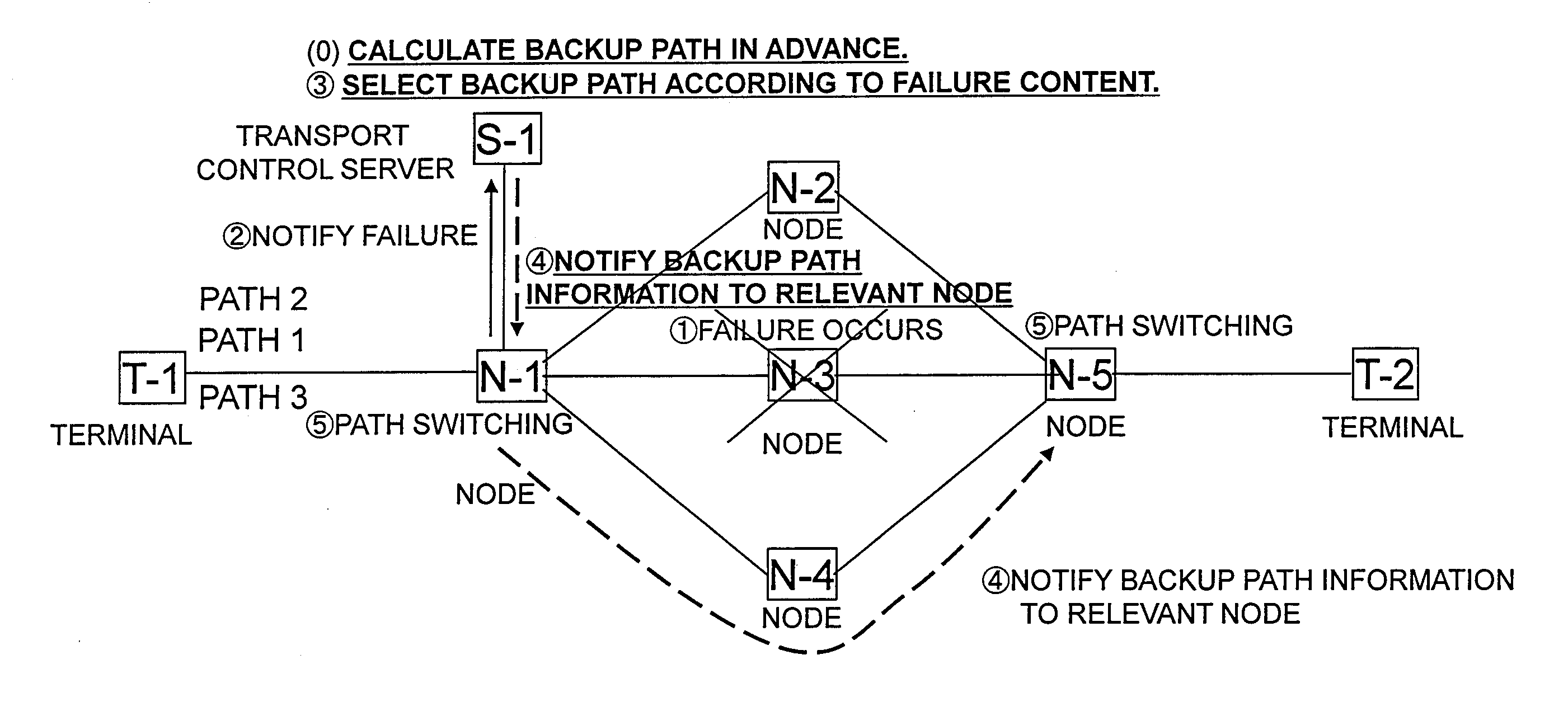
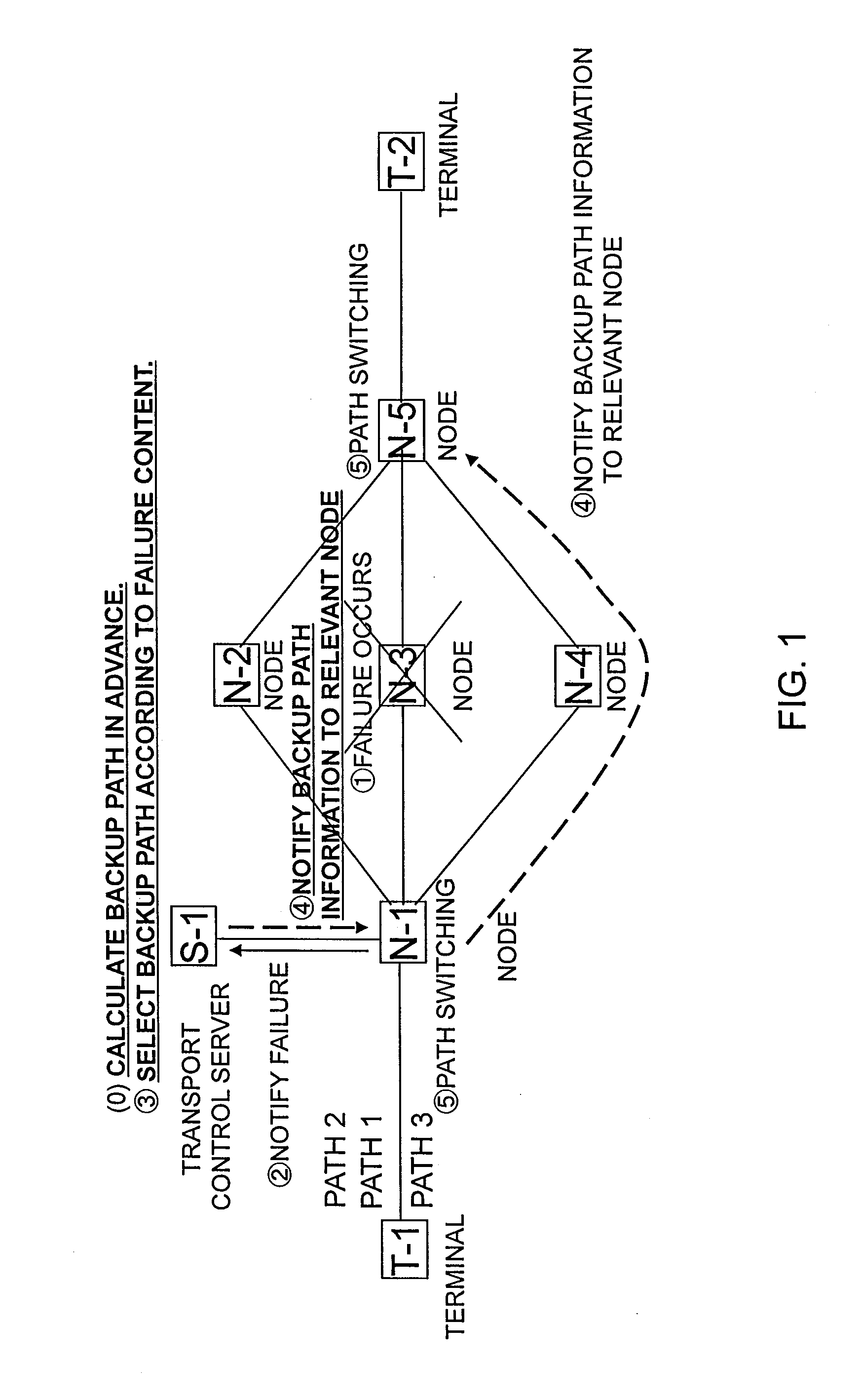
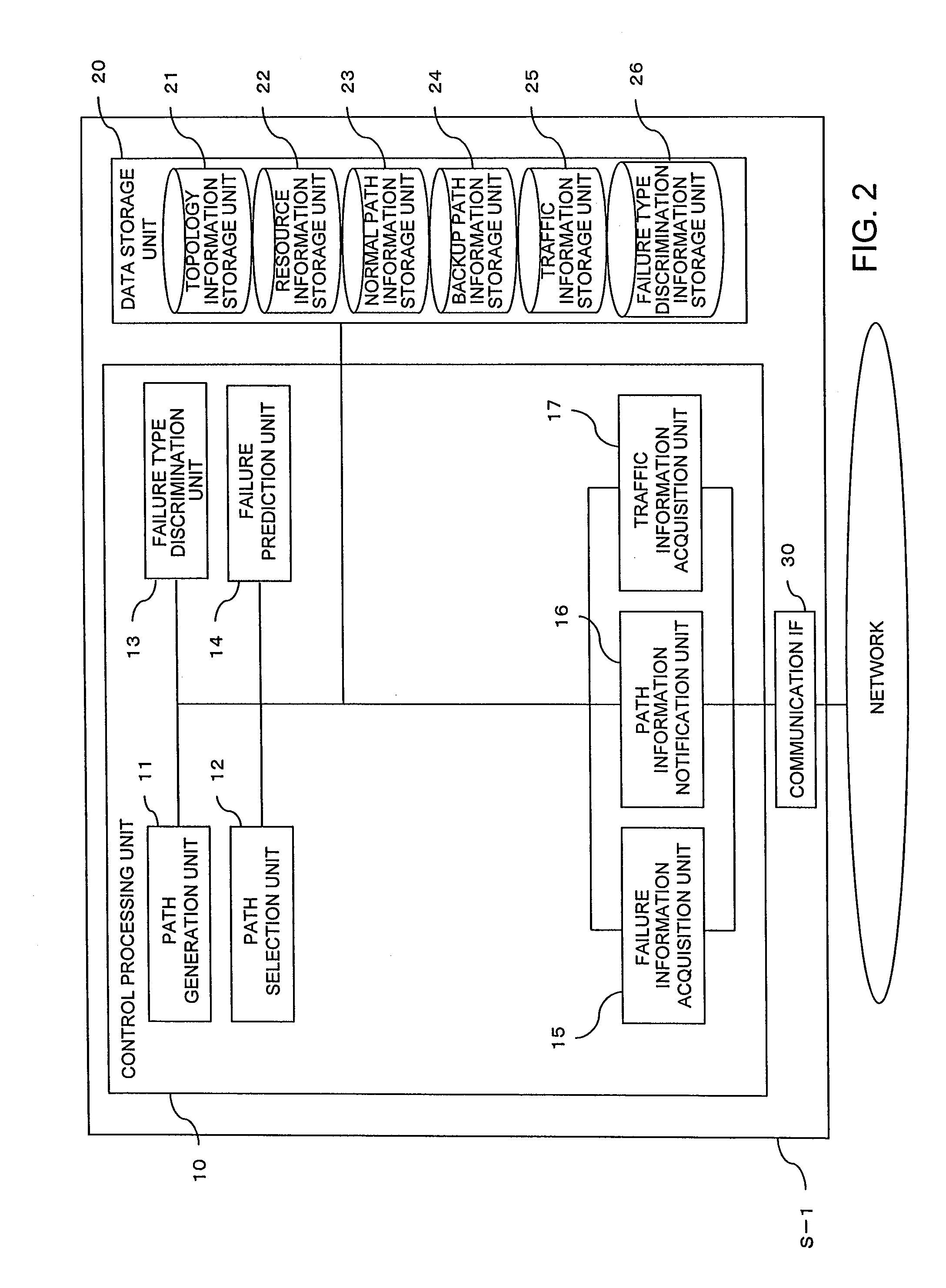
Transport control server, network system and trasnport control method
InactiveUS20110126041A1Shorten the timeTransmissionRedundant hardware error correctionTopology informationBackup path
The time required for a path recalculation and a path switching upon occurrence of a failure is shortened. A path generation unit of a transport control server (TCS) S-1 generates the normal path information in accordance with the topology information of a network and the resource information which are set. Also, the path generation unit generates in advance the backup path information for occurrence of the failure based on the prediction topology information and the prediction resource information which have been modified in accordance with a predicted failure position. A path information notification unit of the TCS (S-1) notifies nodes N of the generated normal path information. A failure information acquisition unit of the TCS (S-1) detects the occurrence of the failure. If the occurrence of the failure is detected, the path information notification unit notifies the nodes N of the backup path information that is stored.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com