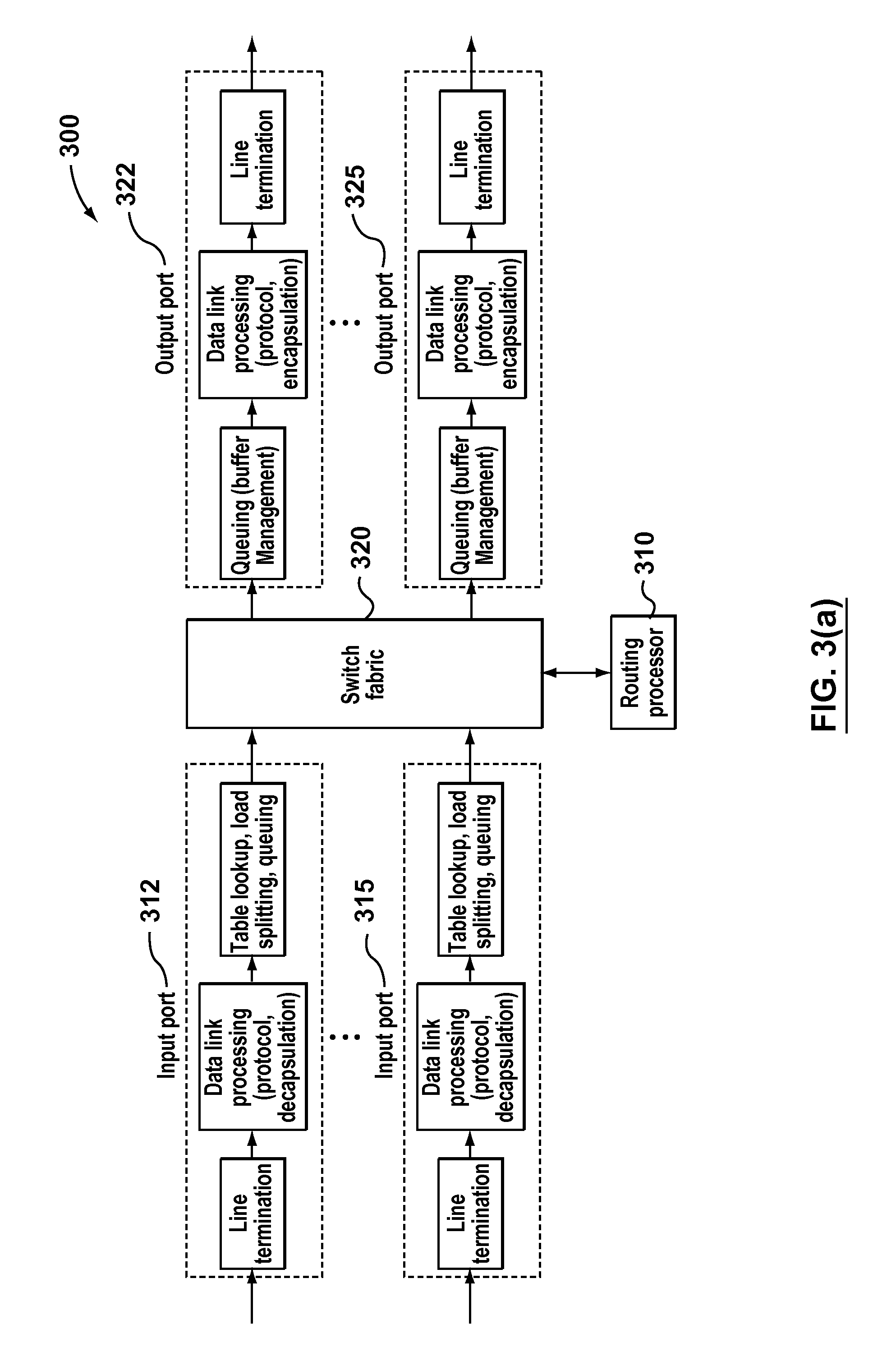
Patents
Literature
170 results about "Link weight" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
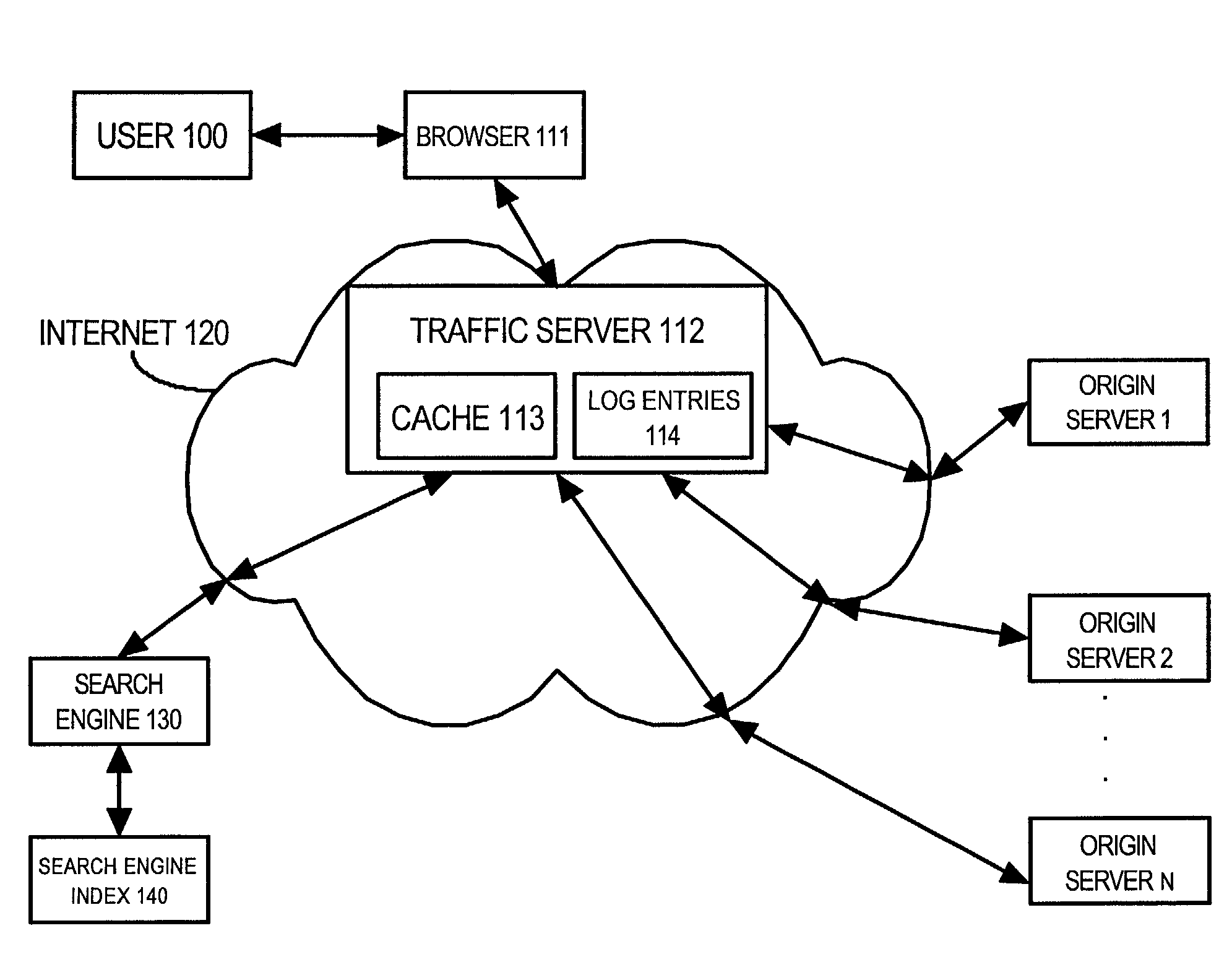
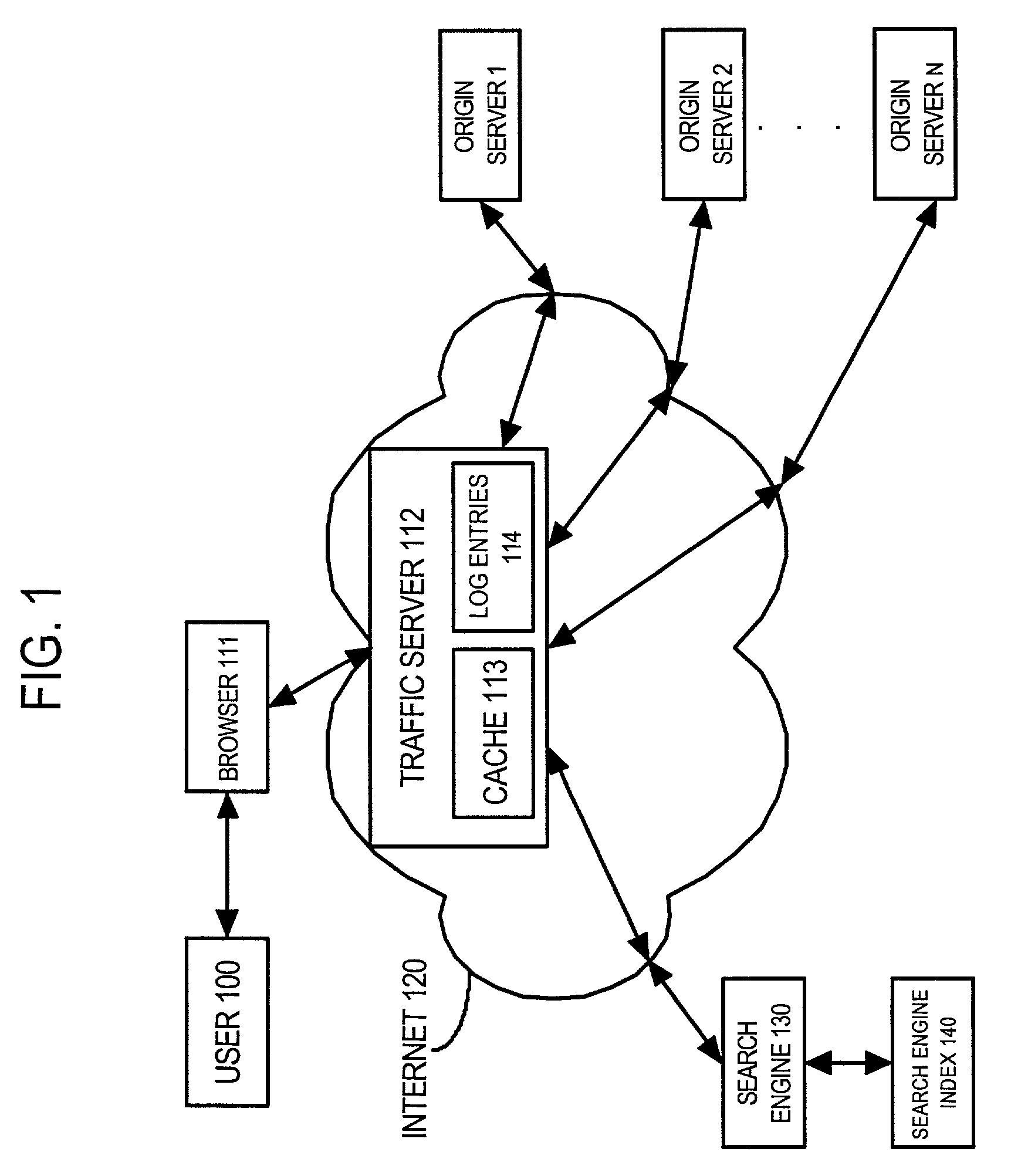
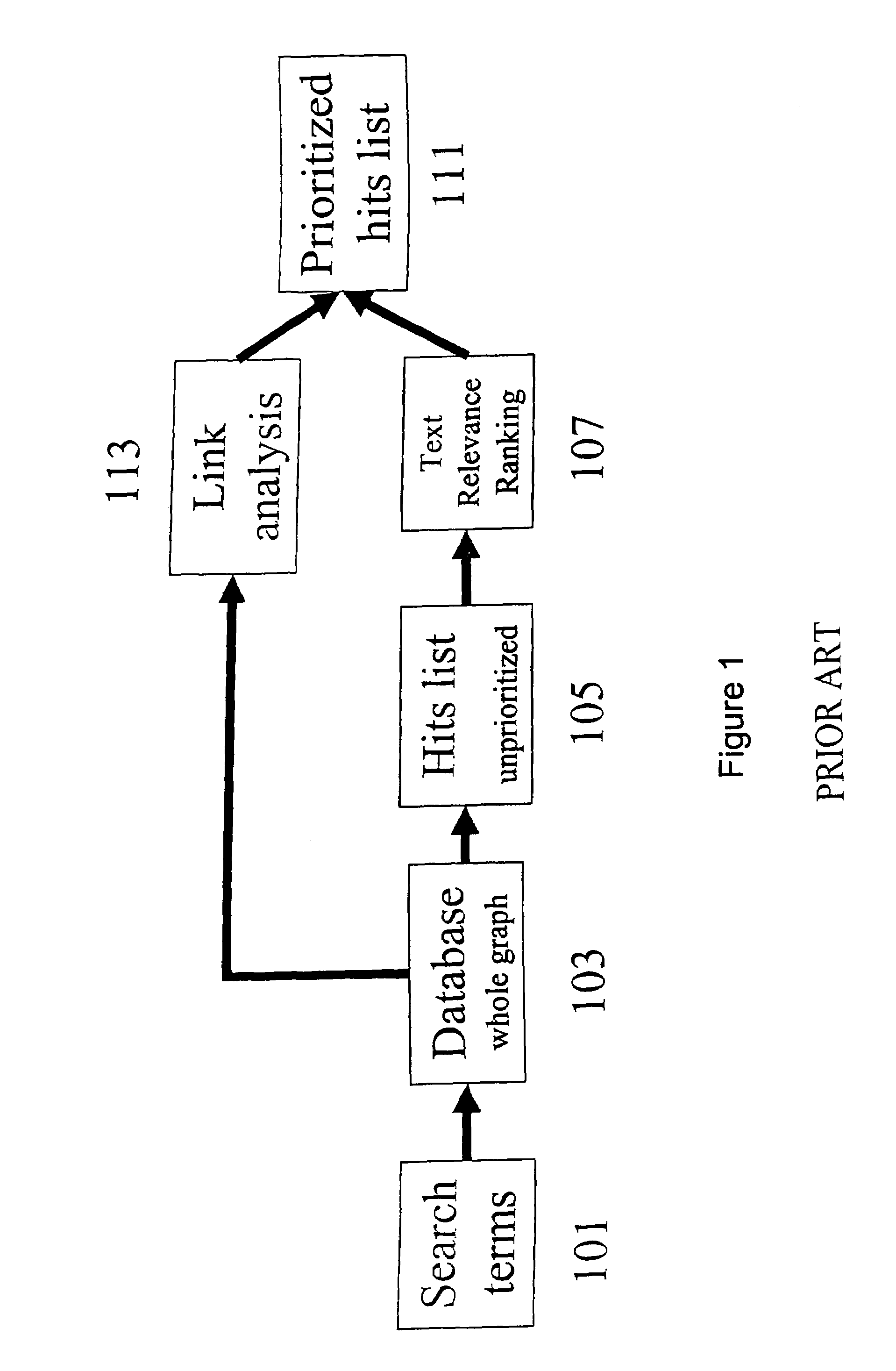
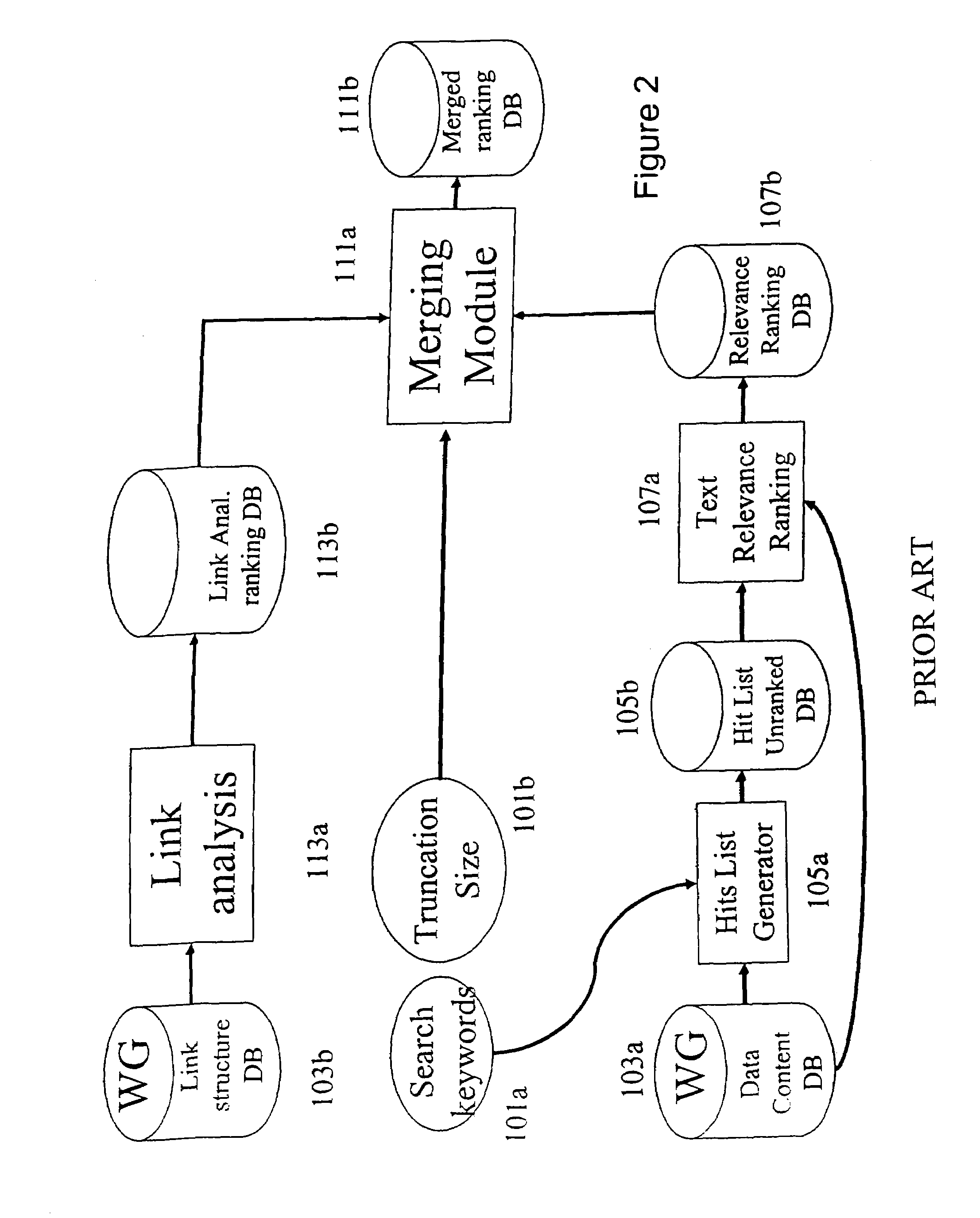
Using network traffic logs for search enhancement
ActiveUS7398271B1Handy search resultsImprove the level ofData processing applicationsWeb data indexingTraffic capacityLink weight
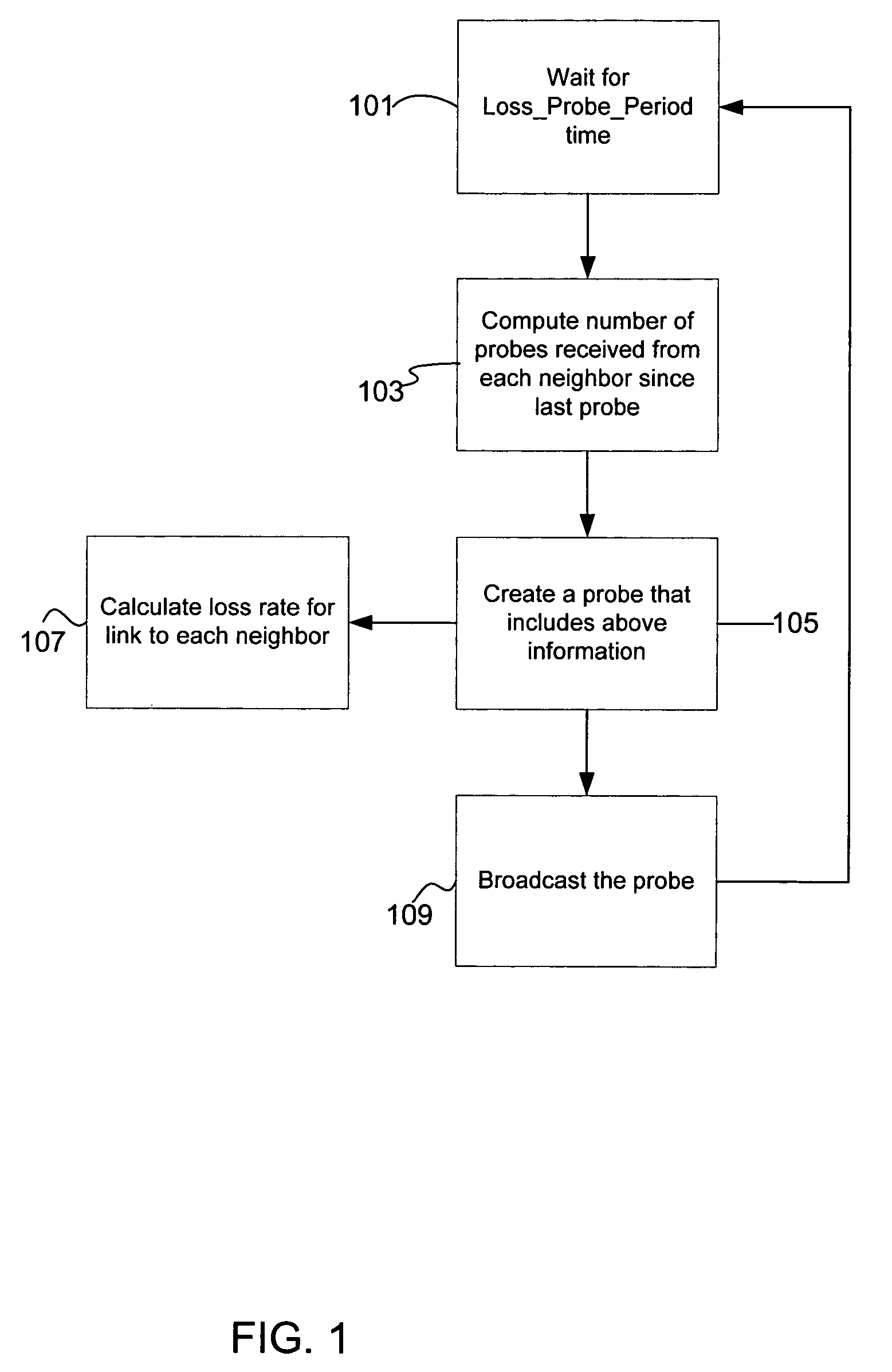
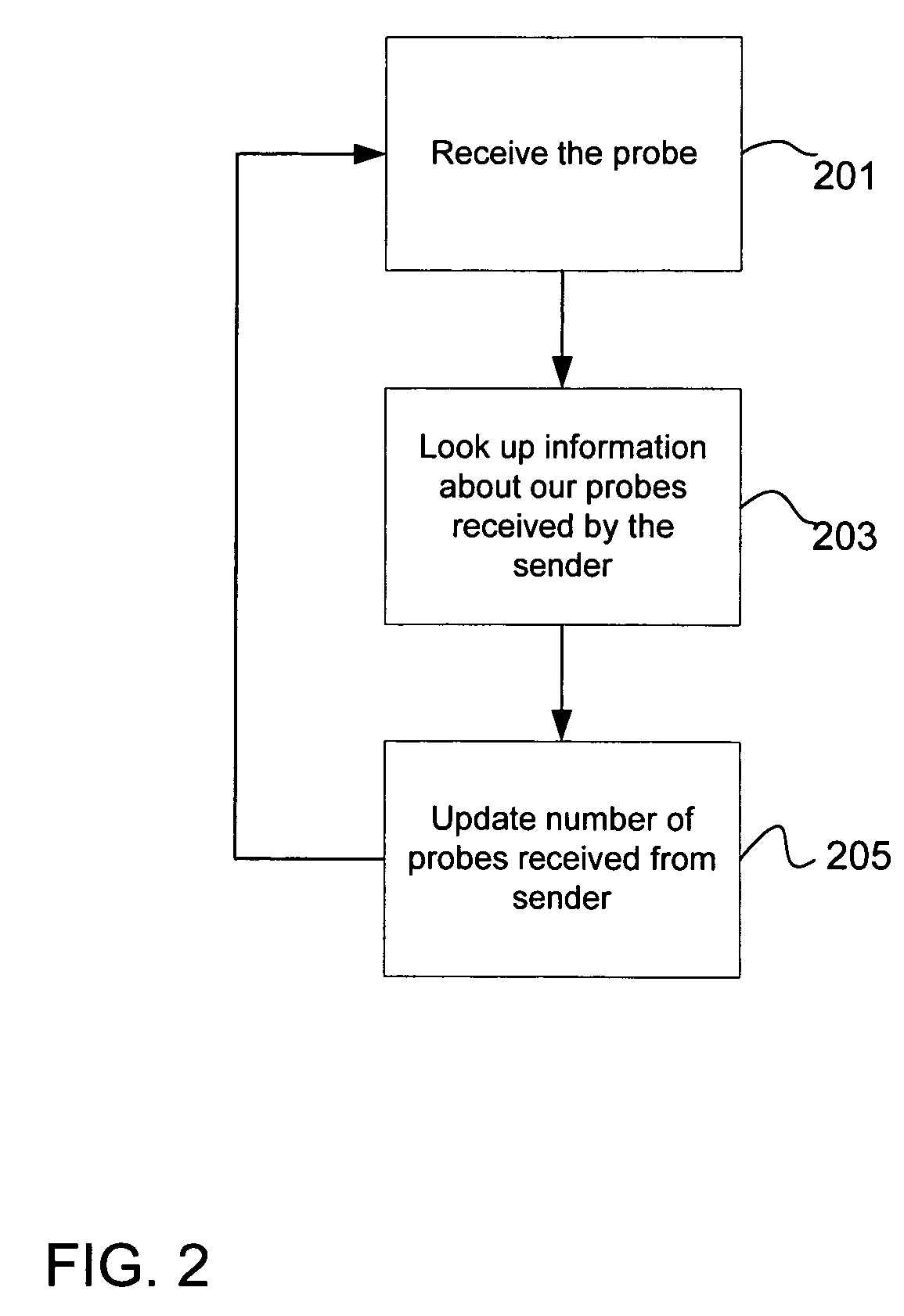
A method and apparatus for using network traffic logs for search enhancement is disclosed. According to one embodiment, network usage is tracked by generating log files. These log files among other things indicate the frequency web pages are referenced and modified. These log files or information from these log files can then be used to improve document ranking, improve web crawling, determine tiers in a multi-tiered index, determine where to insert a document in a multi-tiered index, determine link weights, and update a search engine index.
Owner:R2 SOLUTIONS
System and method for link quality routing using a weighted cumulative expected transmission time metric
A system and method for link quality routing uses a weighted cumulative expected transmission time path metric. A system for routing in a multi-hop ad hoc network, and a method for measuring the link quality of a route in the network, include assignment of a weight to a link in accordance with an expected transmission time of a packet over the link, and a combining of individual link weights for a route into a path metric. The path metric accounts for interference among links that use a shared channel. In the calculation of the path metric, the expected transmission times of links that interfere with one another are added, while the expected transmission times for non-interfering links are considered separately.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
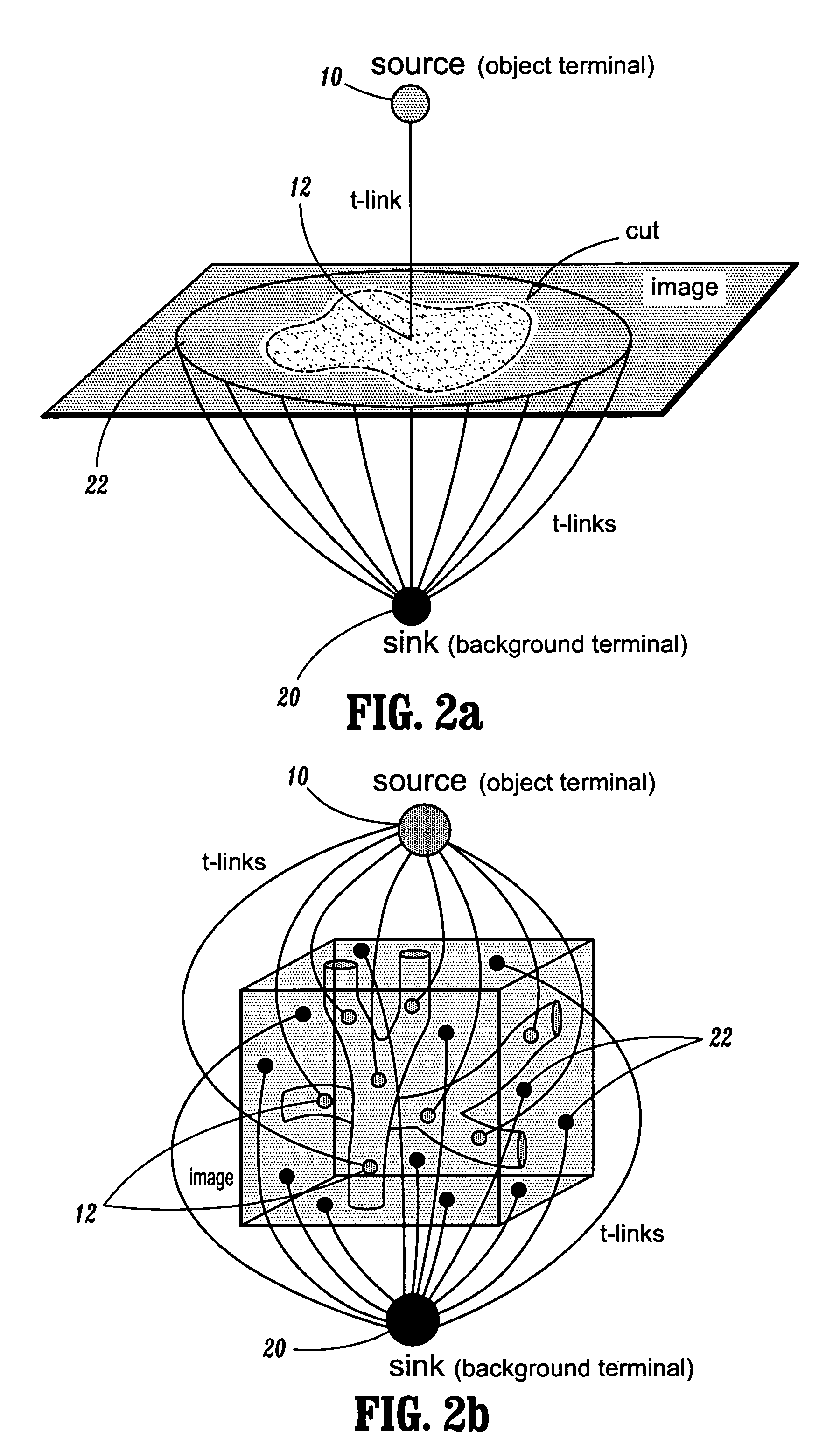
Graph cuts for binary segmentation of n-dimensional images from object and background seeds
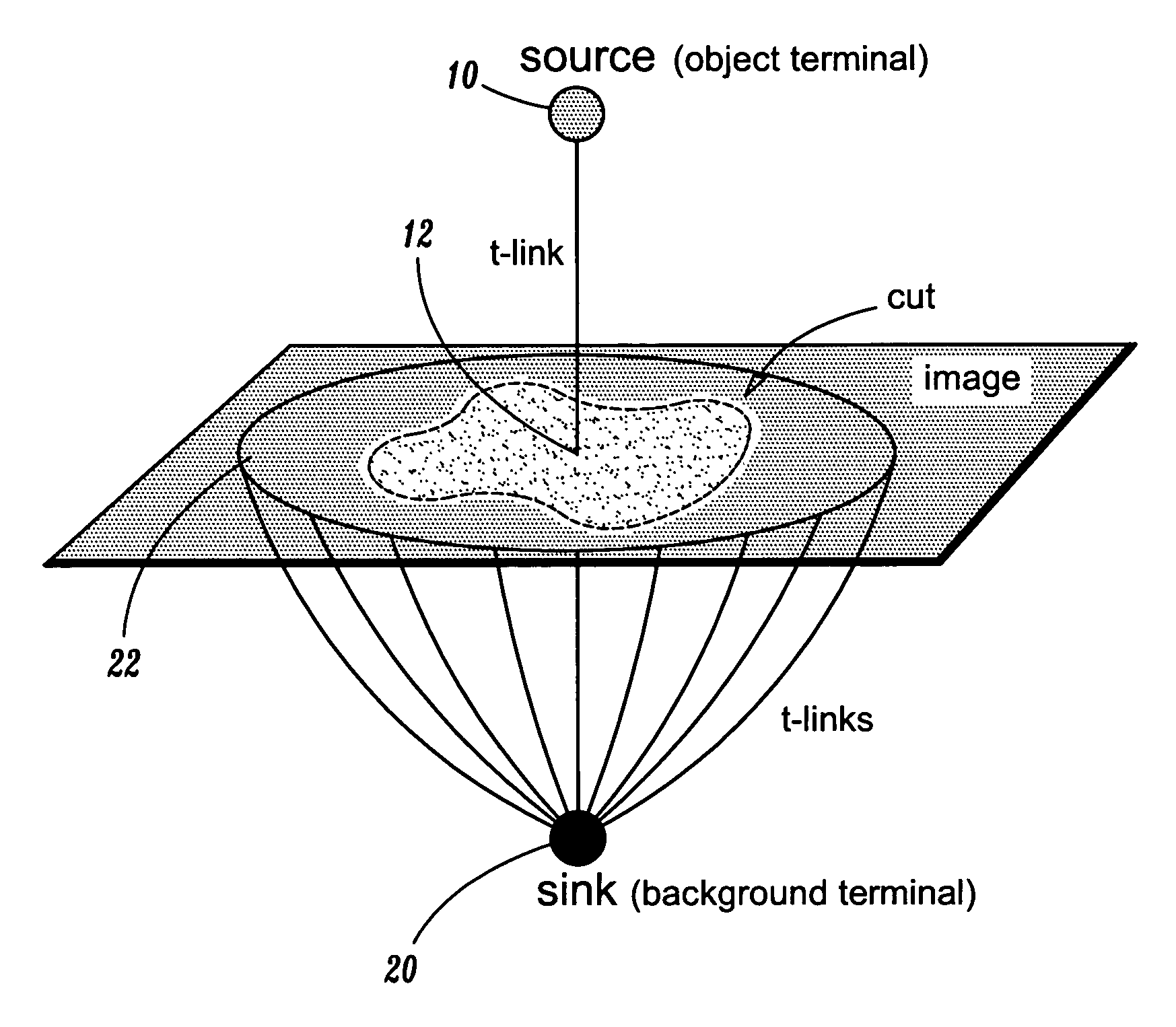
Disclosed is a method of segmenting one or more objects from one or more backgrounds in an image, the method comprising defining a plurality of image nodes, each said image node corresponding to one or more pixels of said image, connecting pairs of adjacent nodes with n-links, each said n-link weighted with an n-link cost, defining a source node, defining a sink node, defining one or more object seeds, said object seeds corresponding to image nodes within said objects, defining one or more background seeds, said background seeds corresponding to image nodes within said backgrounds, connecting said source node with each said object seed with a plurality of t-links, connecting said sink node with each said background seed with a plurality of t-links, wherein each said t-links is weighted with a t-link cost, and calculating a segmentation cut having the smallest total cost of all cuts separating said source from said sink, wherein said total cost of each said cut is defined as the sum of the costs of all said n-links and t-links that each said cut severs.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
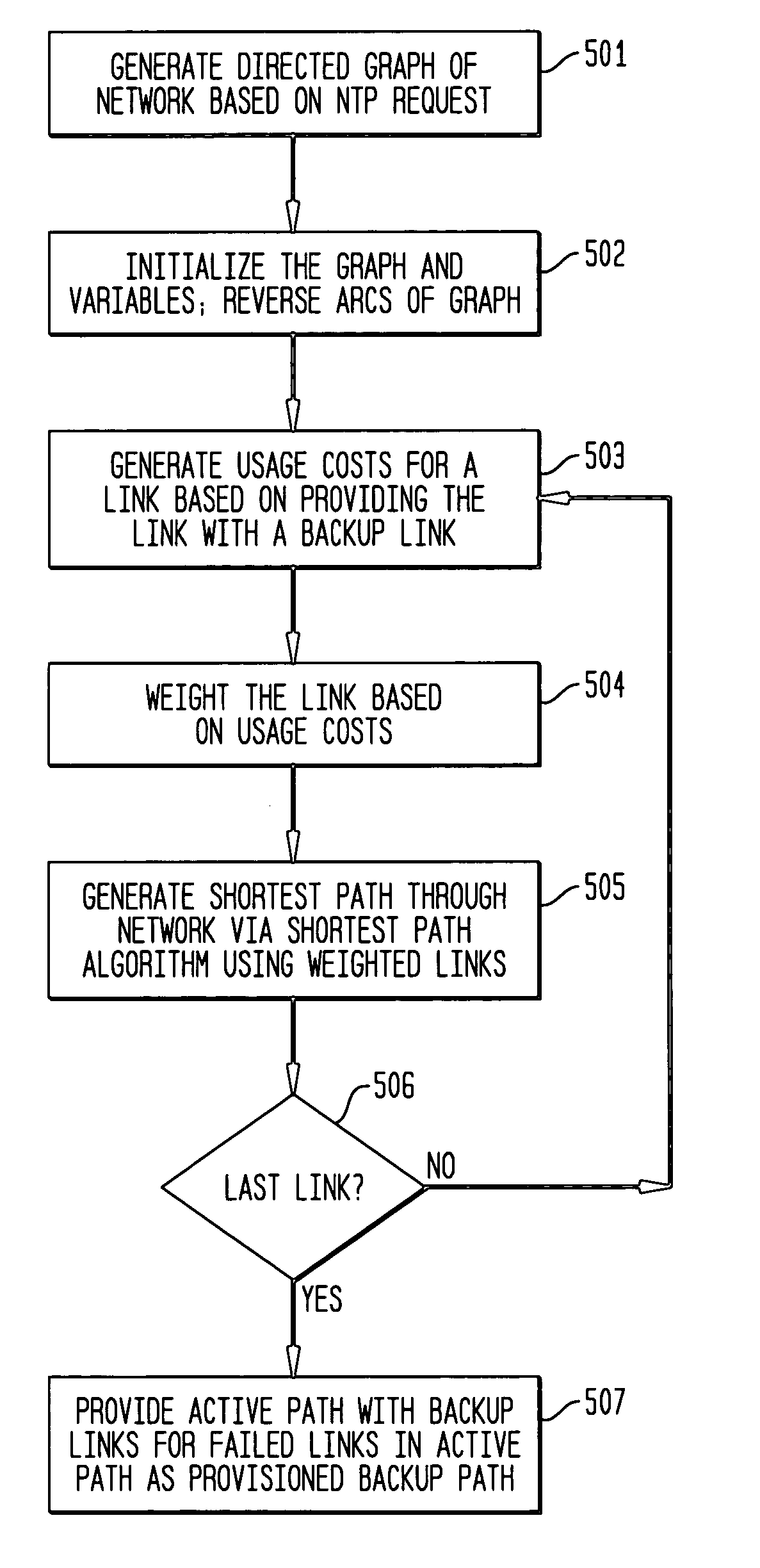
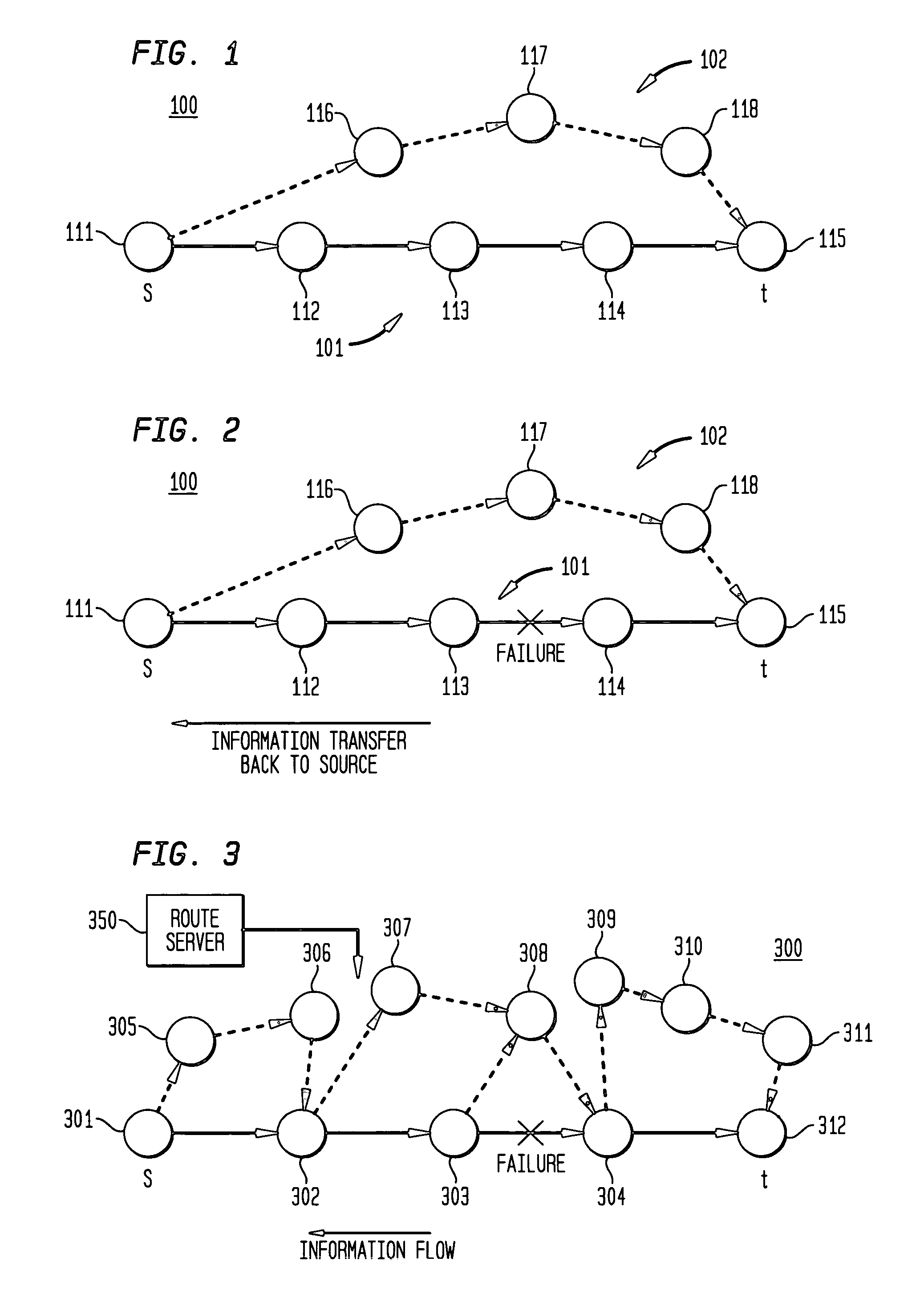
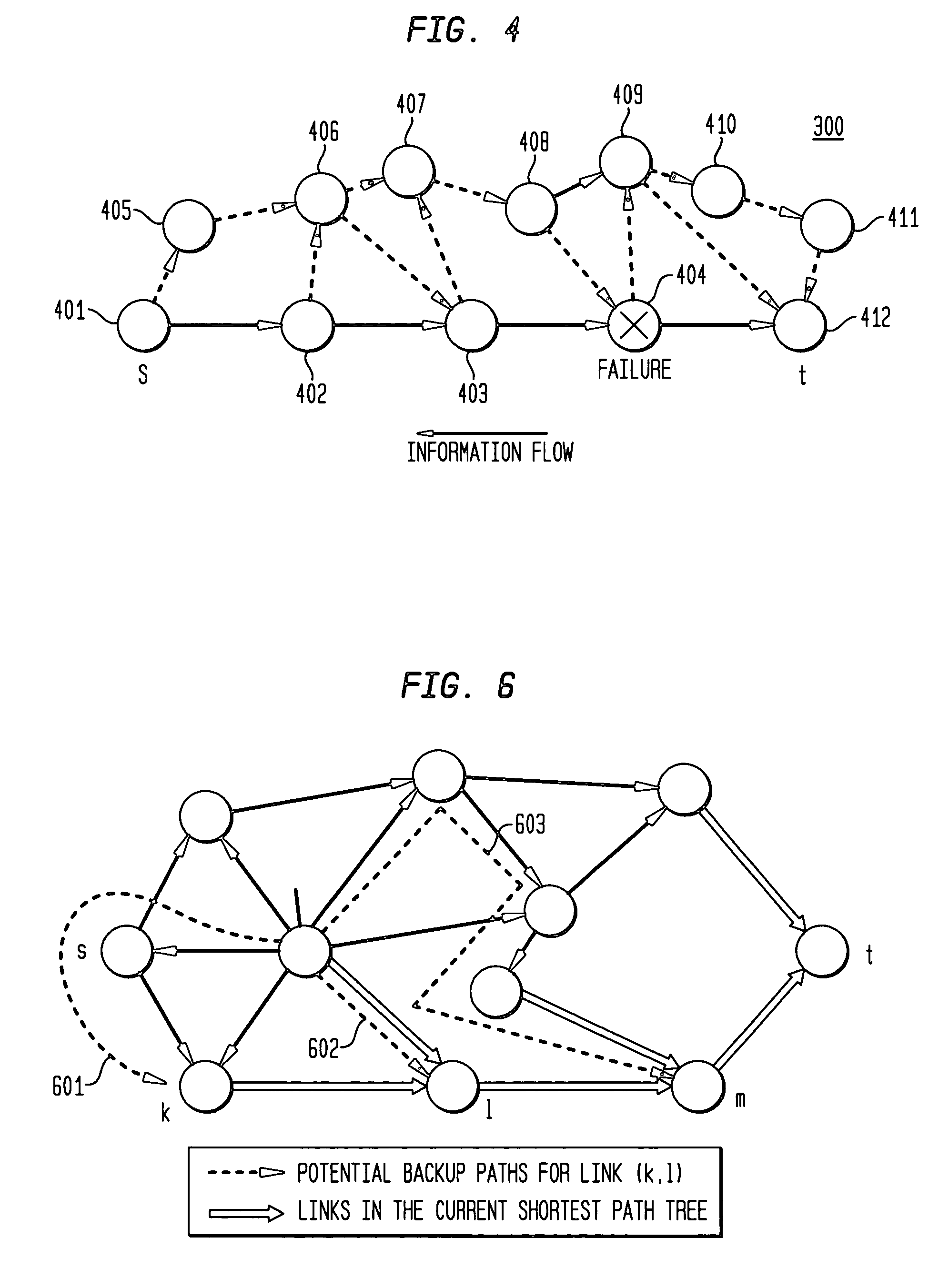
Dynamic backup routing of network tunnel paths for local restoration in a packet network
A packet network of interconnected nodes employing dynamic backup routing of a Network Tunnel Path (NTP) allocates an active and backup path to the NTP based upon detection of a network failure. Dynamic backup routing employs local restoration to determine the allocation of, and, in operation, to switch between, a primary / active path and a secondary / backup path. Switching from the active path is based on a backup path determined with iterative shortest-path computations with link weights assigned based on the cost of using a link to backup a given link. Costs may be assigned based on single-link failure or single element (node or link) failure. Link weights are derived by assigning usage costs to links for inclusion in a backup path, and minimizing the costs with respect to a predefined criterion.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Optical and packet path computation and selection systems and methods
ActiveUS20160112327A1Low costSolve insufficient capacityMultiplex system selection arrangementsOptical multiplexLink weightSelection system
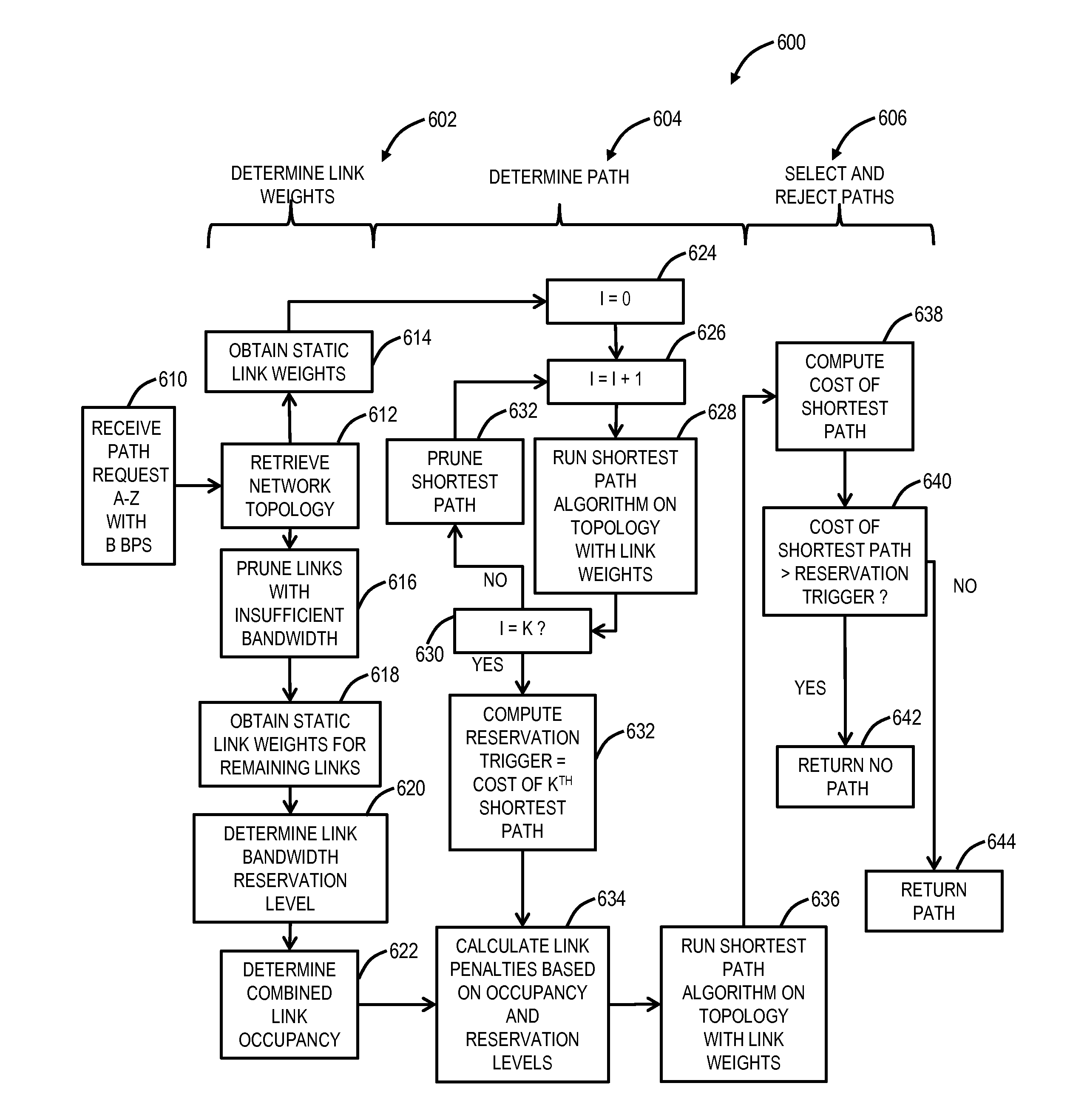
A method for path computation in a network includes determining dynamic link weights for links in the network, responsive to a request for a path, for a connection, between a source node and a destination node in the network with a requested bandwidth amount, wherein the dynamic link weights, for each link, are based on a current status of the link and a future status of the link; determining one or more paths for the request based on the dynamic link weights; and selecting a path of the one or more paths to minimize cost in the network. The method can be implemented through a Software Defined Networking (SDN) controller.
Owner:CIENA
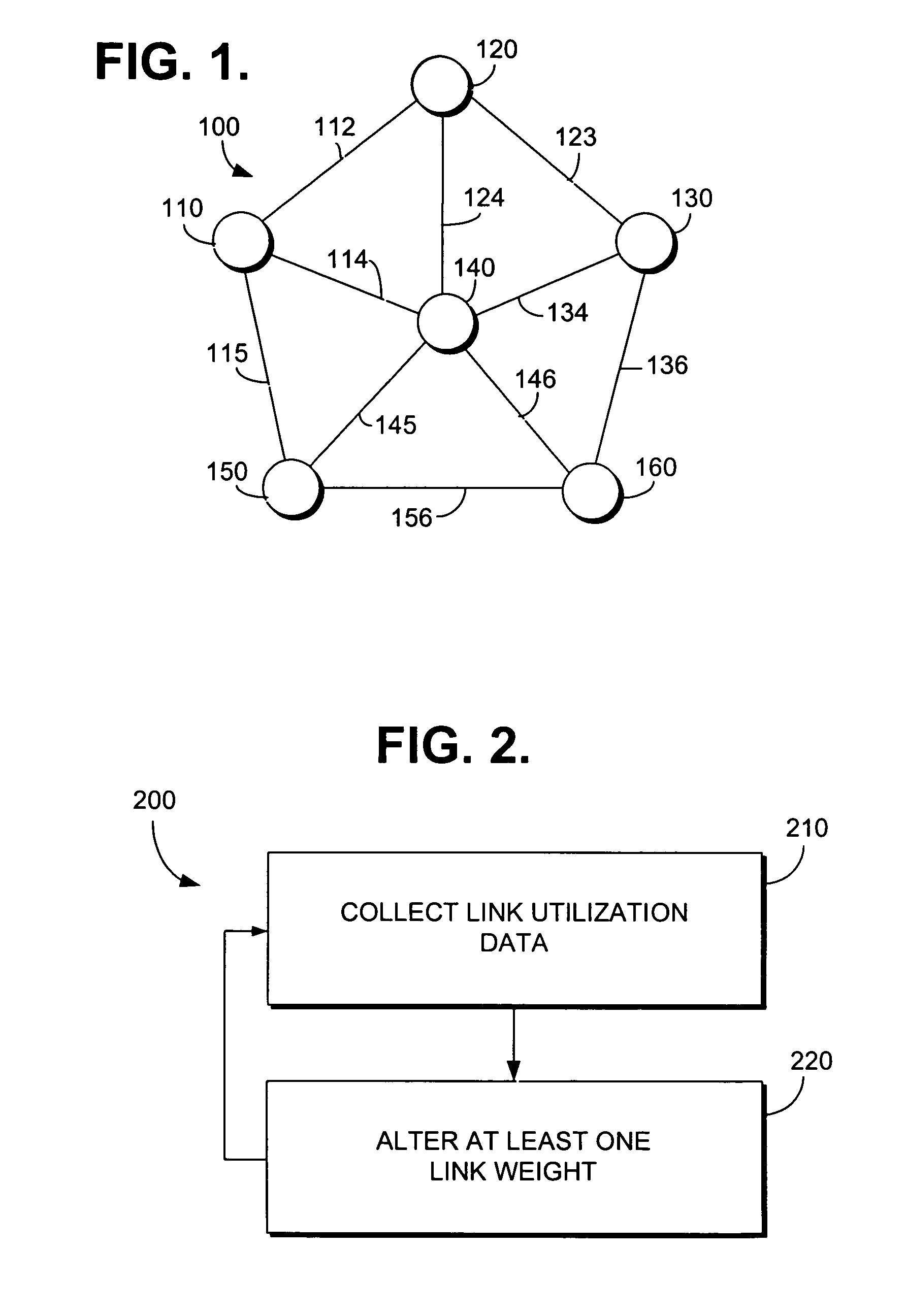
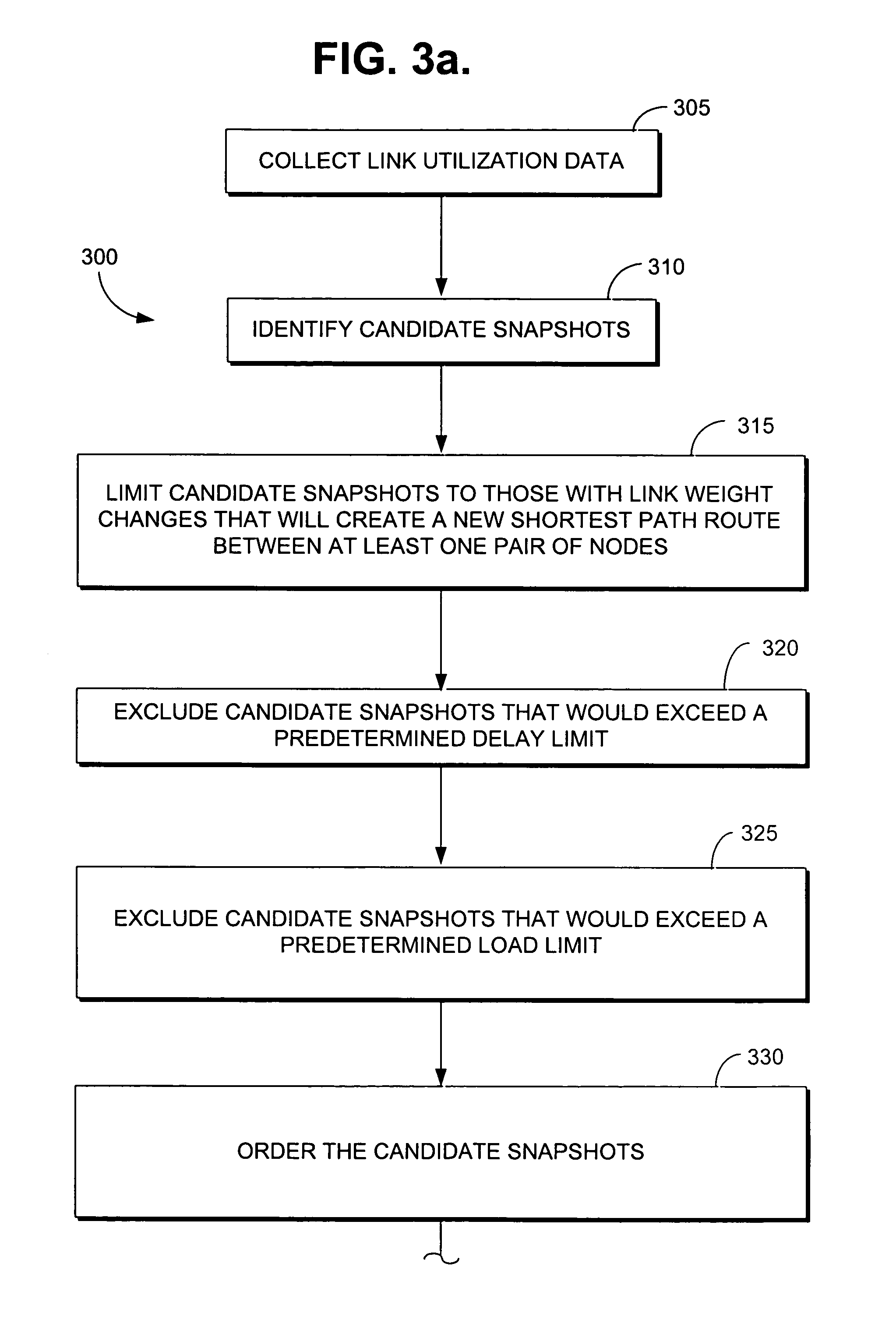
Method for altering link weights in a communication network within network parameters to provide traffic information for improved forecasting
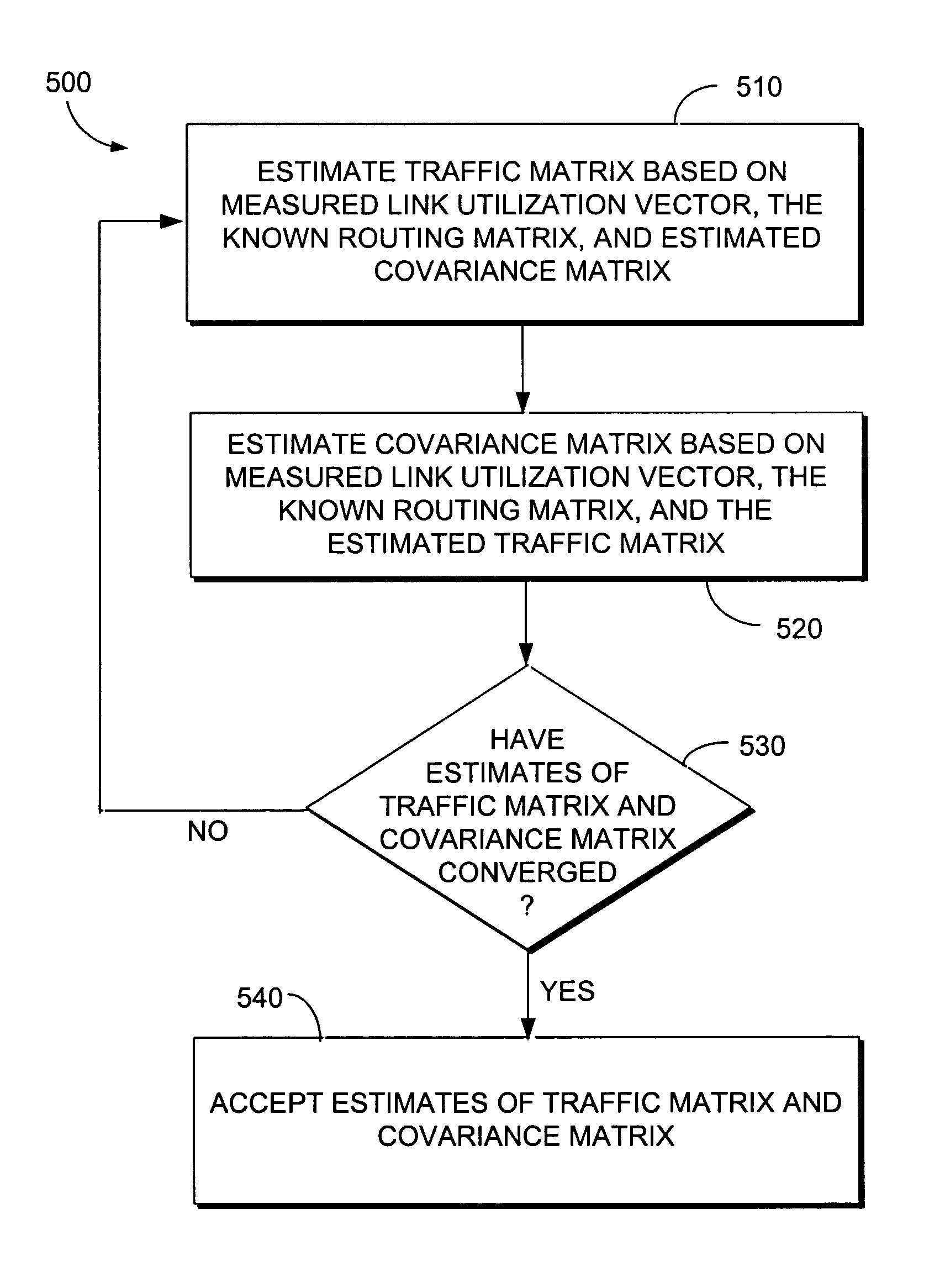
InactiveUS7313629B1Improve forecastAdd modelDigital computer detailsTransmissionTraffic capacityLink weight
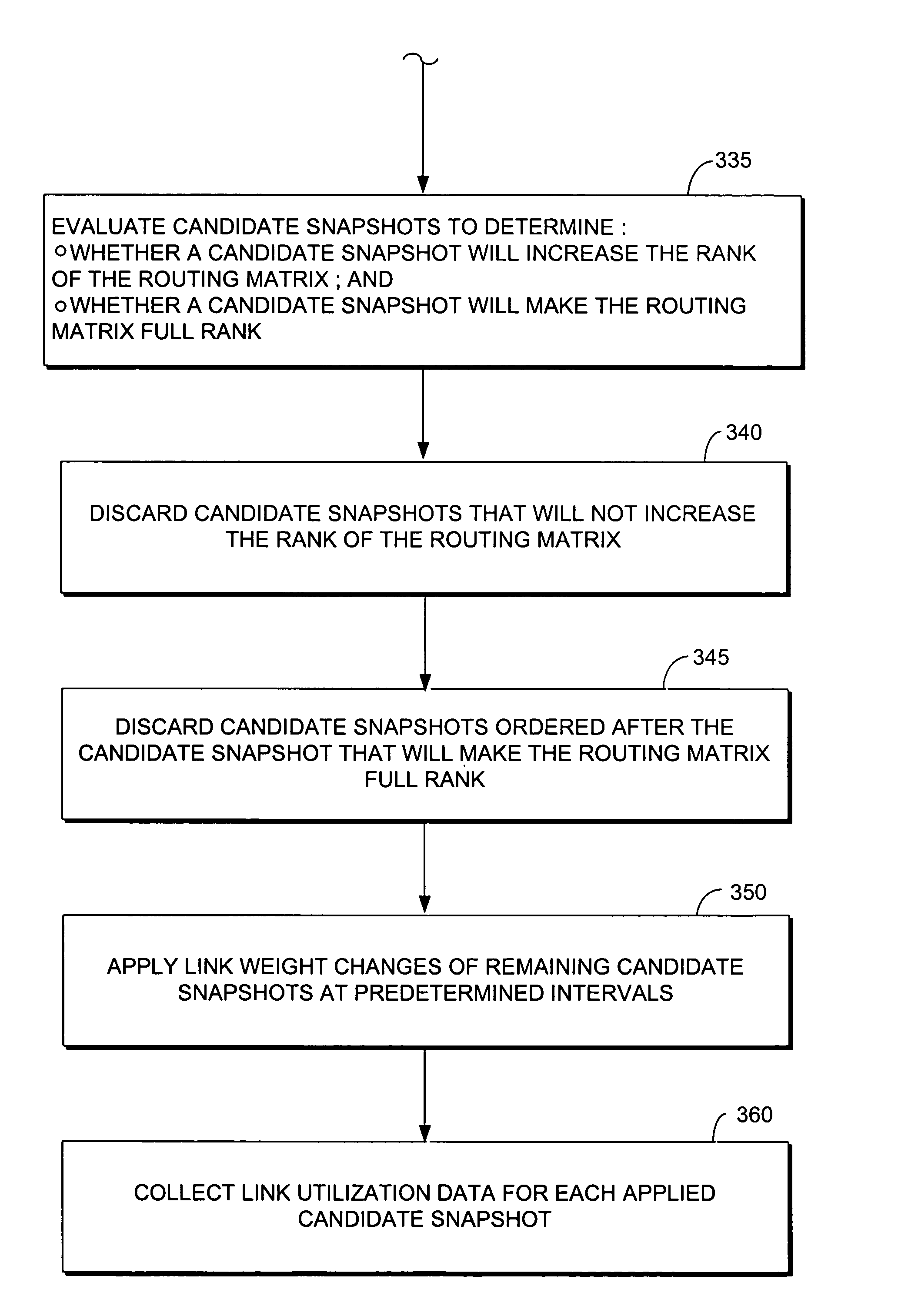
The present invention comprises methods for increasing the rank of the routing matrix of an IP network by systematically altering link weights in the IP network. A full rank routing matrix may be used with further methods in accordance with the present invention to estimate the mean traffic of the IP network based upon the full rank routing matrix and measured link utilization values. The mean traffic and the covariance of the traffic may be iteratively estimated until the estimates coverage. Example methods in accordance with the present invention for estimating mean traffic and covariance of traffic are described for both stationary and non-stationary link utilization data.
Owner:SPRINT CORPORATION
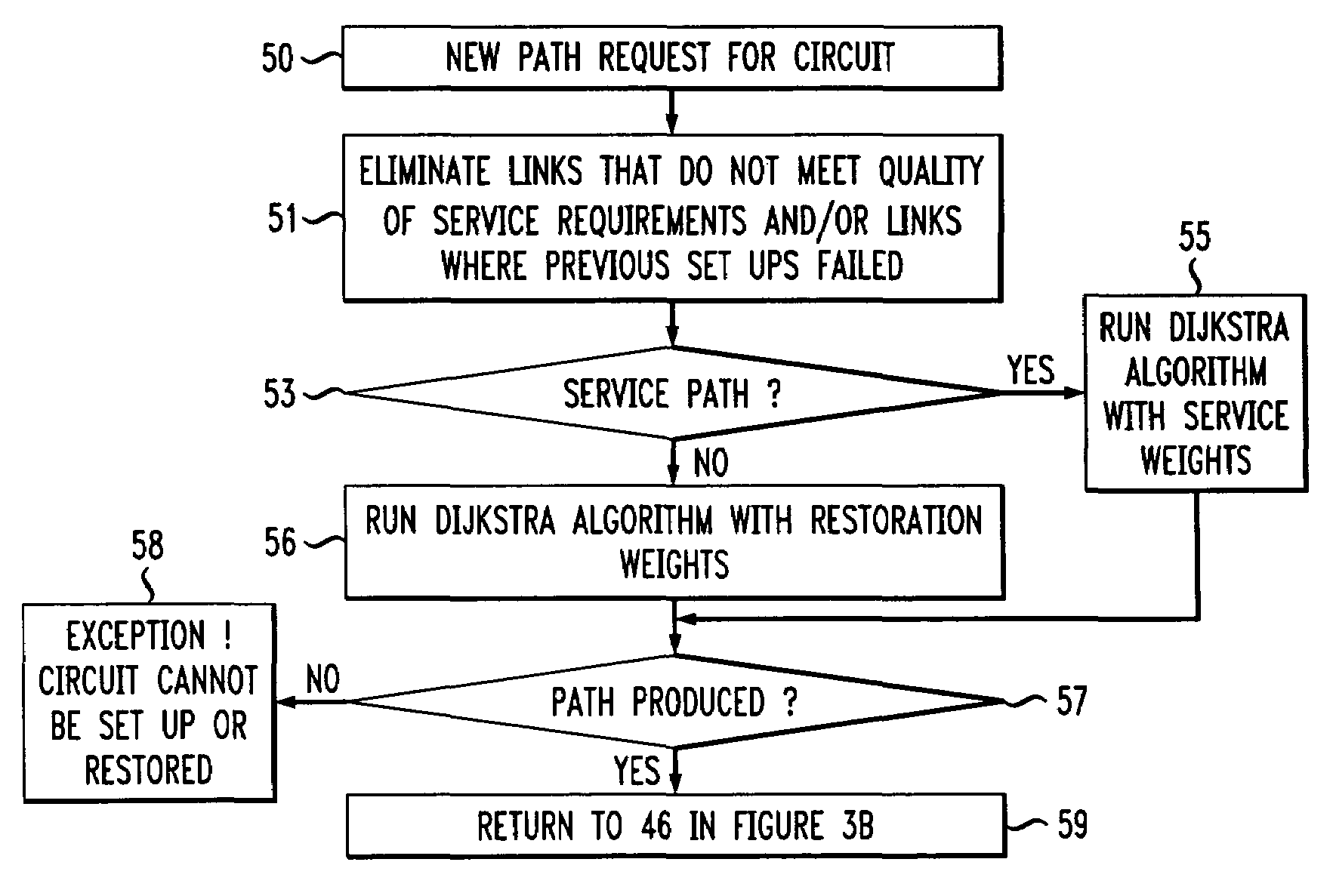
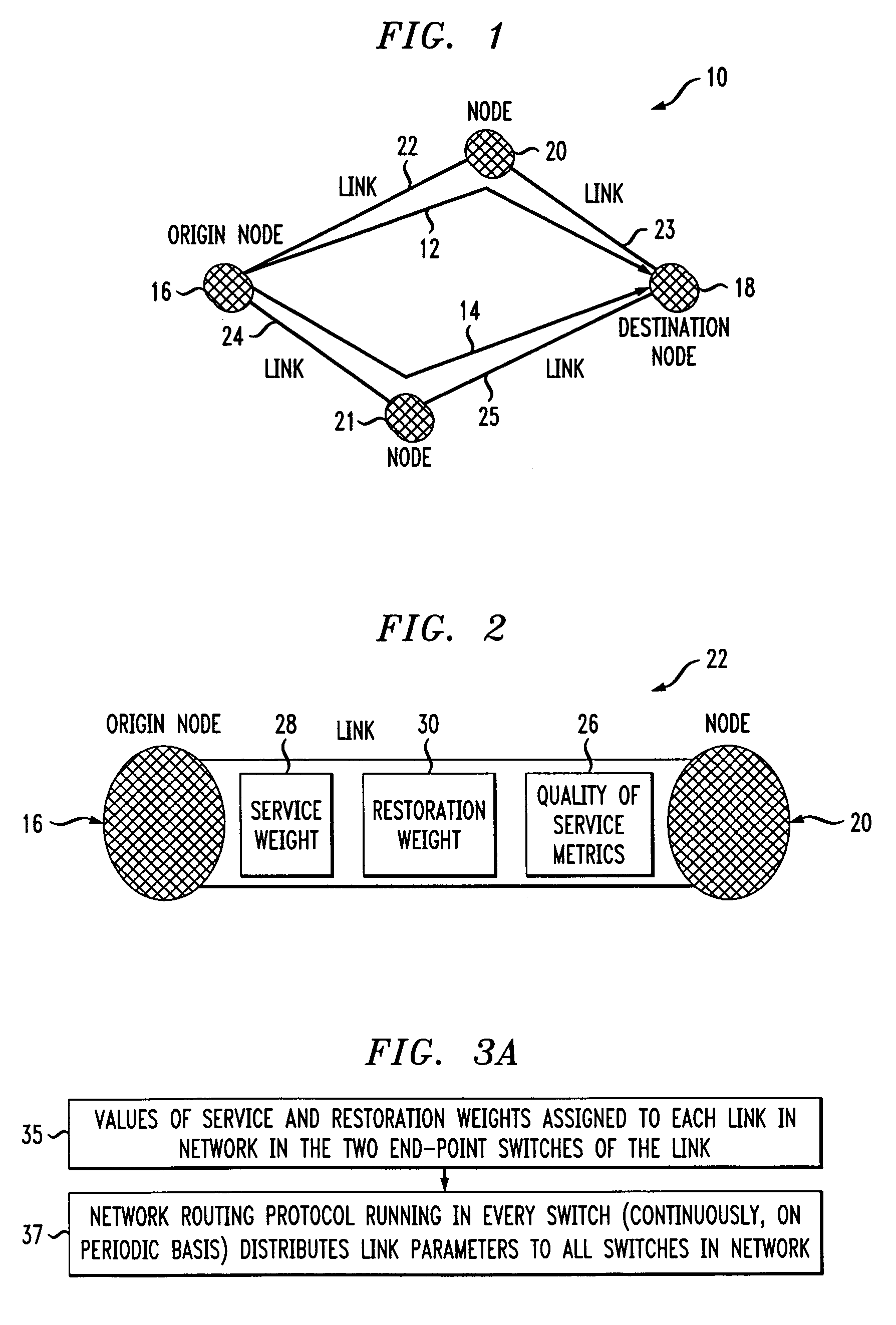
Method and apparatus for providing alternative link weights for failed network paths
InactiveUS7130262B1Improve network efficiencyIncrease internet speedError preventionTransmission systemsLink weightNetwork link
A data network wherein network links have an assigned service weight and a restoration weight that are used as factors for respectively determining an optimum primary data path and a back-up data path through the network. The restoration path is used in the event of a failure of the primary service path and a Dijkstra or similar algorithm may be used for determining these paths. Service weights may be assigned to the links to prioritize finding the shortest possible path, whereas restoration weights may be assigned to the links to find a path with the maximum available capacity.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Weight factor based allocation of time slot to use link in connection path in network on chip IC
ActiveUS7564865B2Reduce chanceMore freedomGeneral purpose stored program computerLoop networksLink weightCoupling
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV +1
Two-phase fast reroute with optimized traffic engineering
ActiveUS7859993B1Maximize sharingMinimizing capacityLaser detailsError preventionTraffic capacityCost Measures
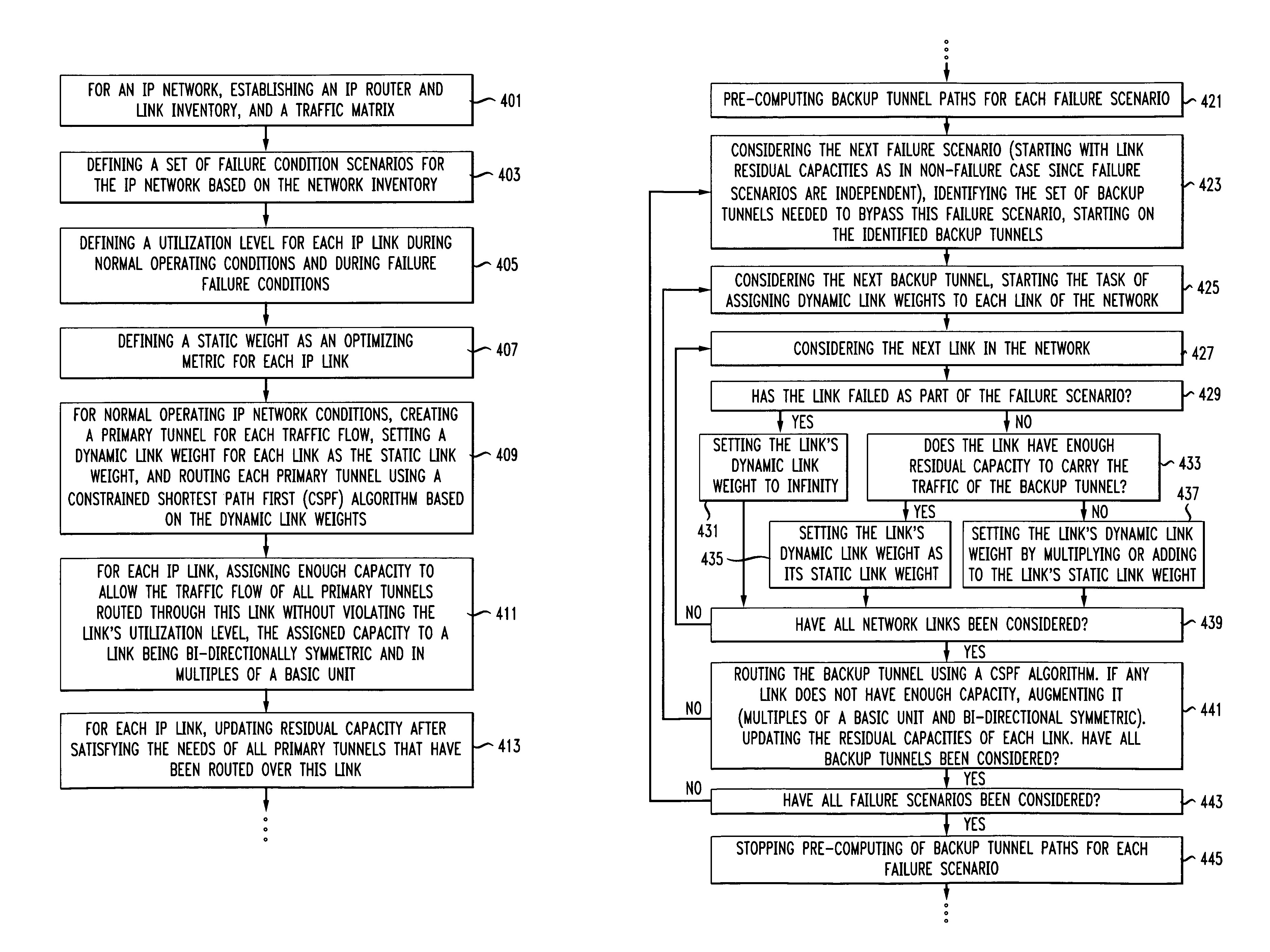
Systems and methods are described for restoring IP traffic flows routed in an IP network in less than 100 ms after the IP network sustains a network failure. The systems and methods are a two-phase fast reroute that uses distributed optimized traffic engineering during backup tunnel restoration and end-to-end tunnel restoration that maximizes sharing among all independent failure scenarios and minimizes the total capacity, total cost, or a linear combination of the two. For defined failure condition scenarios, restoration traffic is routed using pre-computed backup tunnels using a constrained shortest path first method where link weights along the path are chosen dynamically and depend on available and total capacity of the link, latency, and other cost measures such as IP port costs. During the capacity allocation phase, the method reuses capacity already allocated for other independent failure scenarios as much as possible but also adds capacity, if necessary. When an actual IP network failure occurs, the backup tunnels are used to immediately restore service to affected IP network traffic flows. In parallel, end-to-end tunnels corresponding to each affected traffic flow are rerouted and once the rerouting process is complete, traffic is switched over from the old end-to-end tunnel routes (using backup tunnels) to new end-to-end tunnel routes without using backup tunnels.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
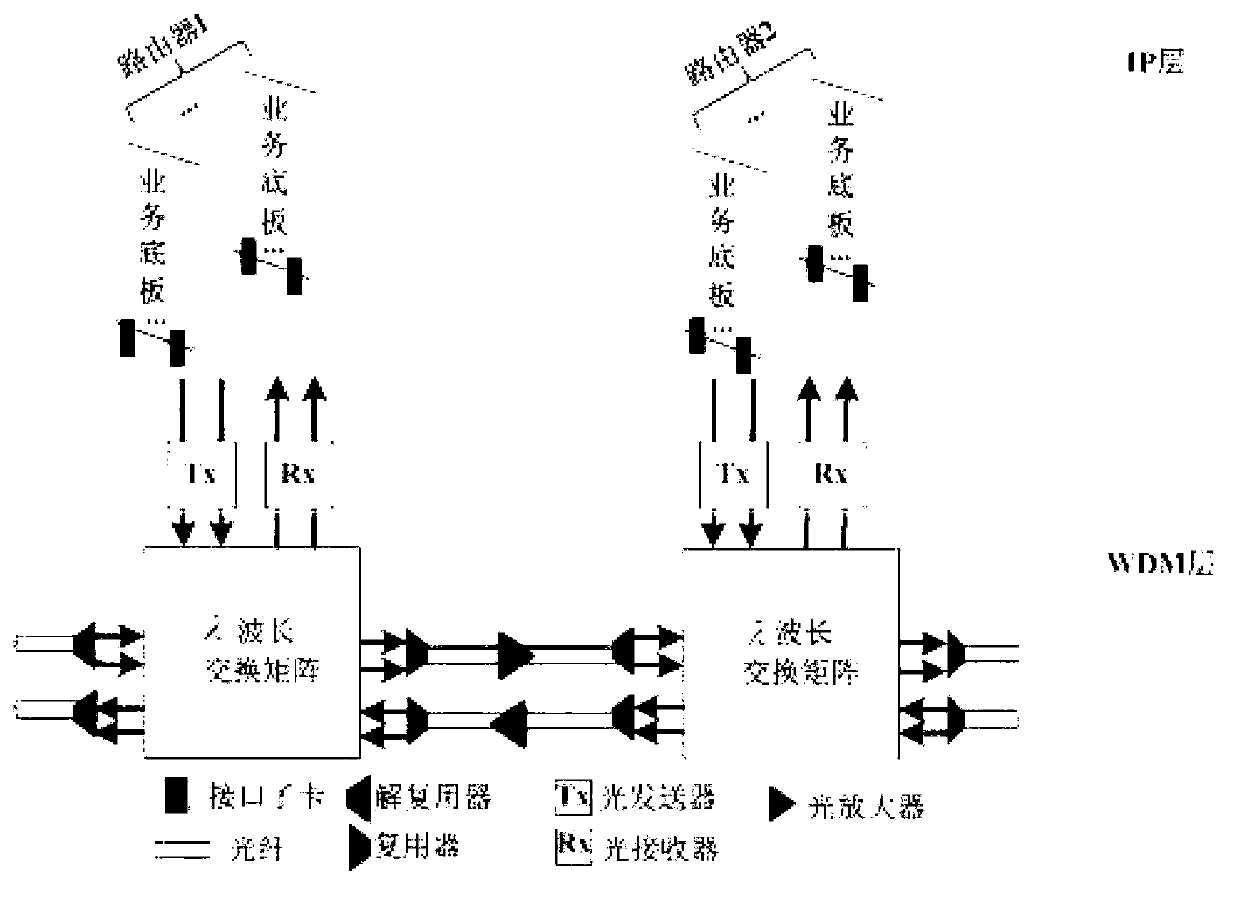
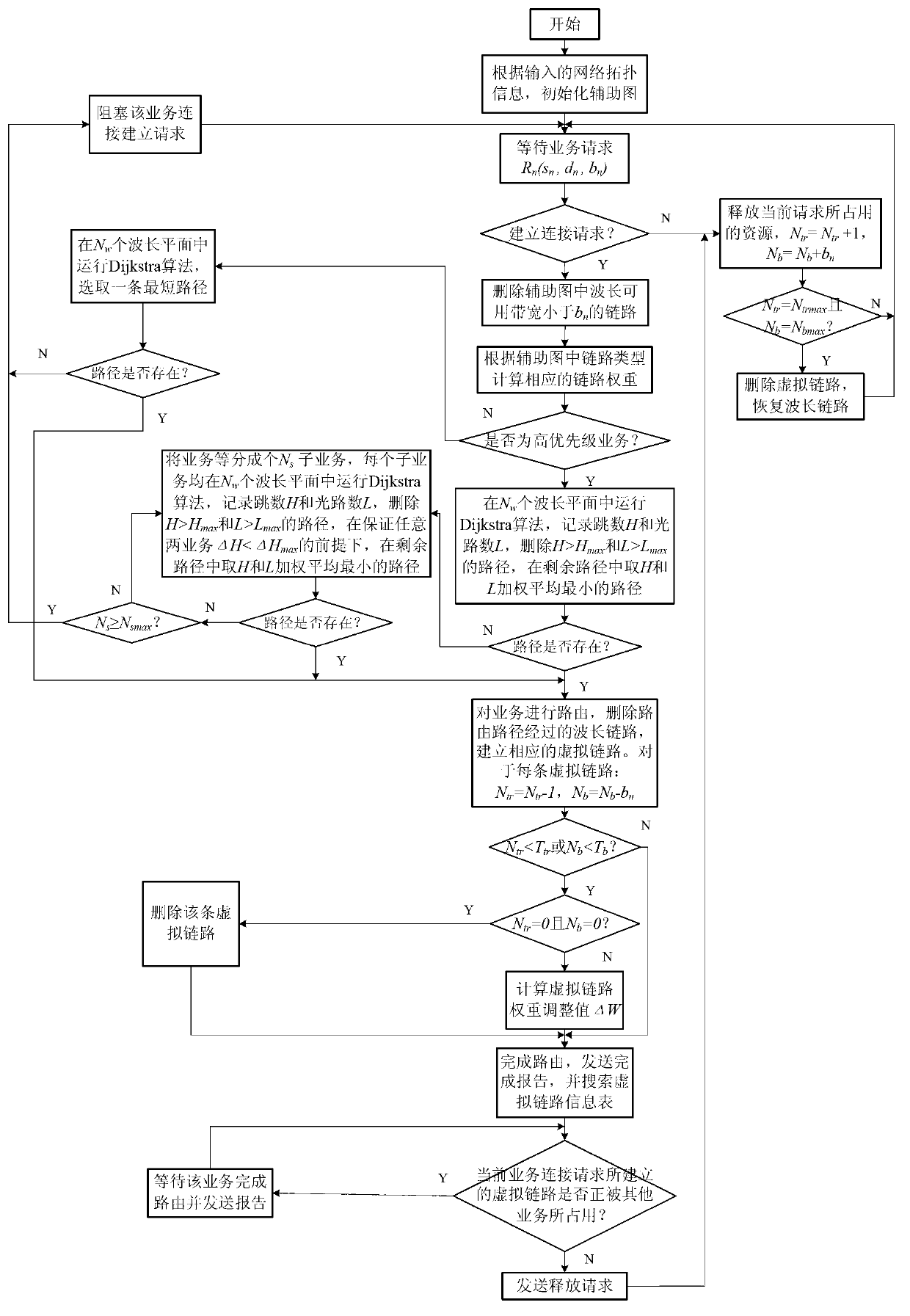
Internet protocol (IP) over wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) network energy-aware routing method based on multipriority business
InactiveCN102970225AReduce energy consumptionPacket Loss GuaranteeEnergy efficient ICTData switching networksQuality of serviceLink weight
The invention relates to an internet protocol (IP) over wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) network energy-aware routing method based on multipriority business. The IP over WDM network energy-aware routing method is used for achieving energy saving of an optical network under different QoS constraint conditions of dynamic business. According to the method, the business is divided into different grades. For low-priority business, a Dijkstra algorithm is improved to achieve energy saving by combining an optical bypass and a business volume guidance technology and enabling energy consumption to serve as link weight; and for high-priority business, routing is performed with an optimal path forecasting function serving as a routing standard, a flow partition mechanism and a link weight dynamic adjustment mechanism are integrated while network energy consumption is reduced so as to guarantee the requirements of the business for time delay, packet loss rate and blocking rate. Compared with the prior art, different routing methods can be designed according to priority level of the business, energy-saving efficiency of the network is improved on the premises that a certain service quality is guaranteed, and energy saving of the multipriority business in the IP over WDM network is achieved comprehensively.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
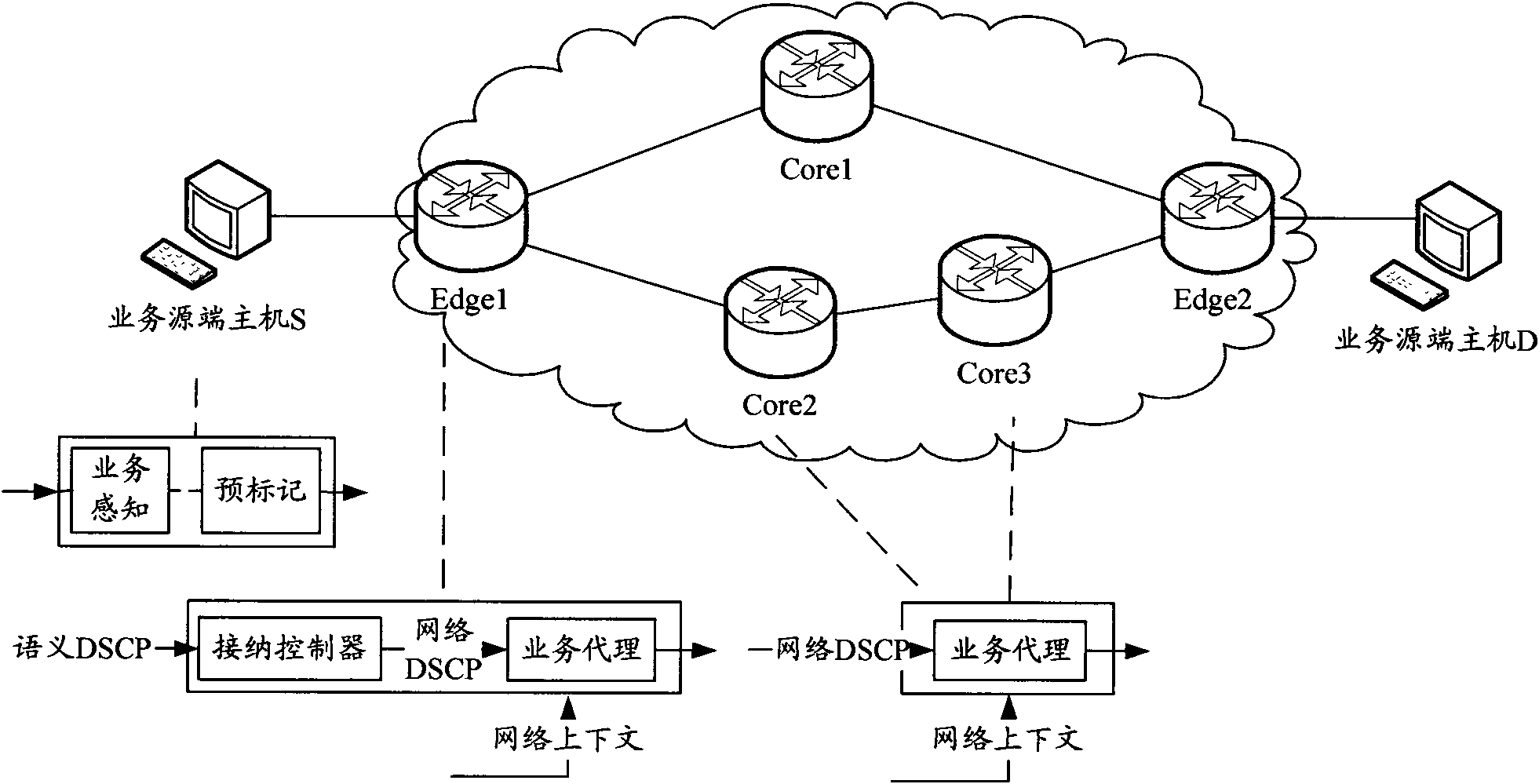
Network system and method for guaranteeing multi-type service quality
InactiveCN102075444AEasy to manageGuaranteed service qualityNetworks interconnectionQuality of serviceTraffic capacity
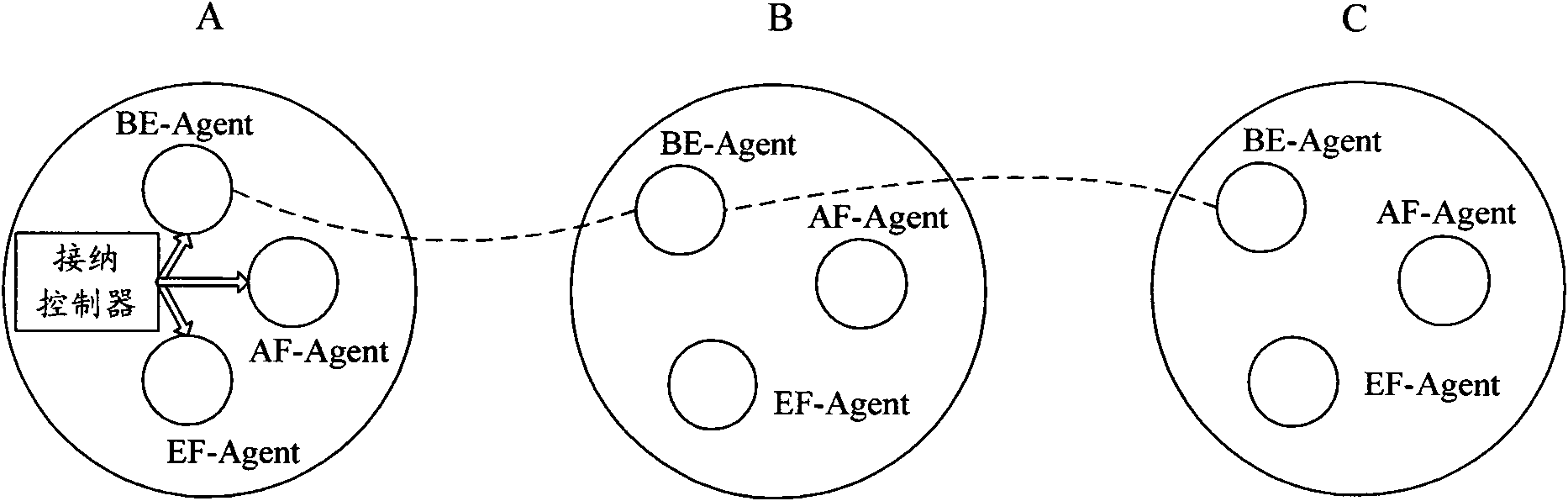
The invention discloses a network system and a method for guaranteeing multi-type service quality. A service perception module and a pre-labeling module are arranged in a source host and used for perceiving sent service data packets and pre-labeling the grouped data packets with different semantic priorities for sending according to the perception information when a network layer is encapsulated.An edge router and a core router are provided with a multi-service agent respectively. The edge router is also provided with an acceptance controller for mapping the semantic priorities of the service data packets into network priorities and distributing the service data packets to the corresponding service agents. The homogeneous service agents in all the routers are interconnected to form virtual topologies, and each virtual topology is provided with an independent routing table for routing selection of the service data packets of different priorities on the corresponding virtual topologiesrespectively. Service routing of high priority is guaranteed, and influence on low priority services is reduced as much as possible; and the invention also provides a method for setting link weights,which distributes the network traffic to each link more uniformly and improves the throughput rate.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
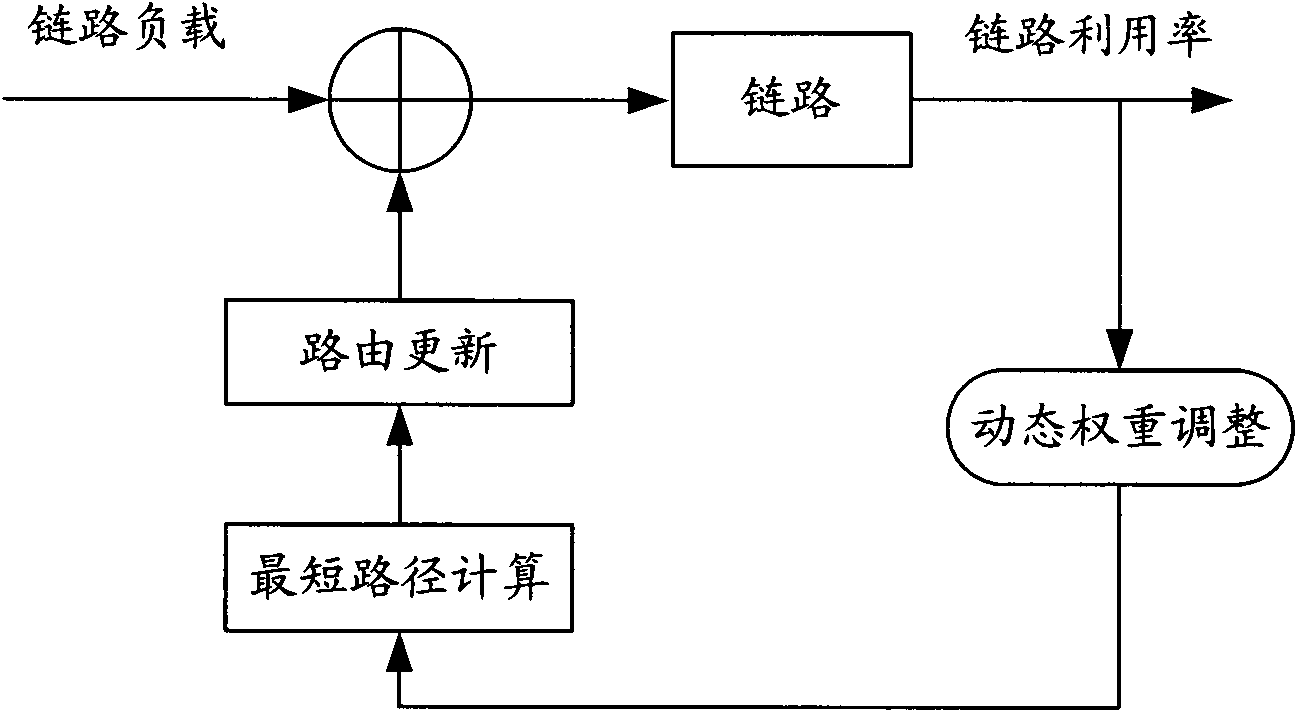
Integrated service leading method for WDM optical network
InactiveCN1791000ASave resourcesLow costWavelength-division multiplex systemsData switching networksLink weightTransceiver
The invention provides a synthesis persuasion business method WDM OTN. Wherein, building a persuasion chart model combined with virtual topological design, rout and wavelength allocation problem, calculating on the chart to find out proper persuasion path. For business request, using built optical link for persuasion. This invention uses dynamic regulation link weight to regulate dynamically whole network link weight at any moment to balance load, and saves optical transceiver resources to reduce cost.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
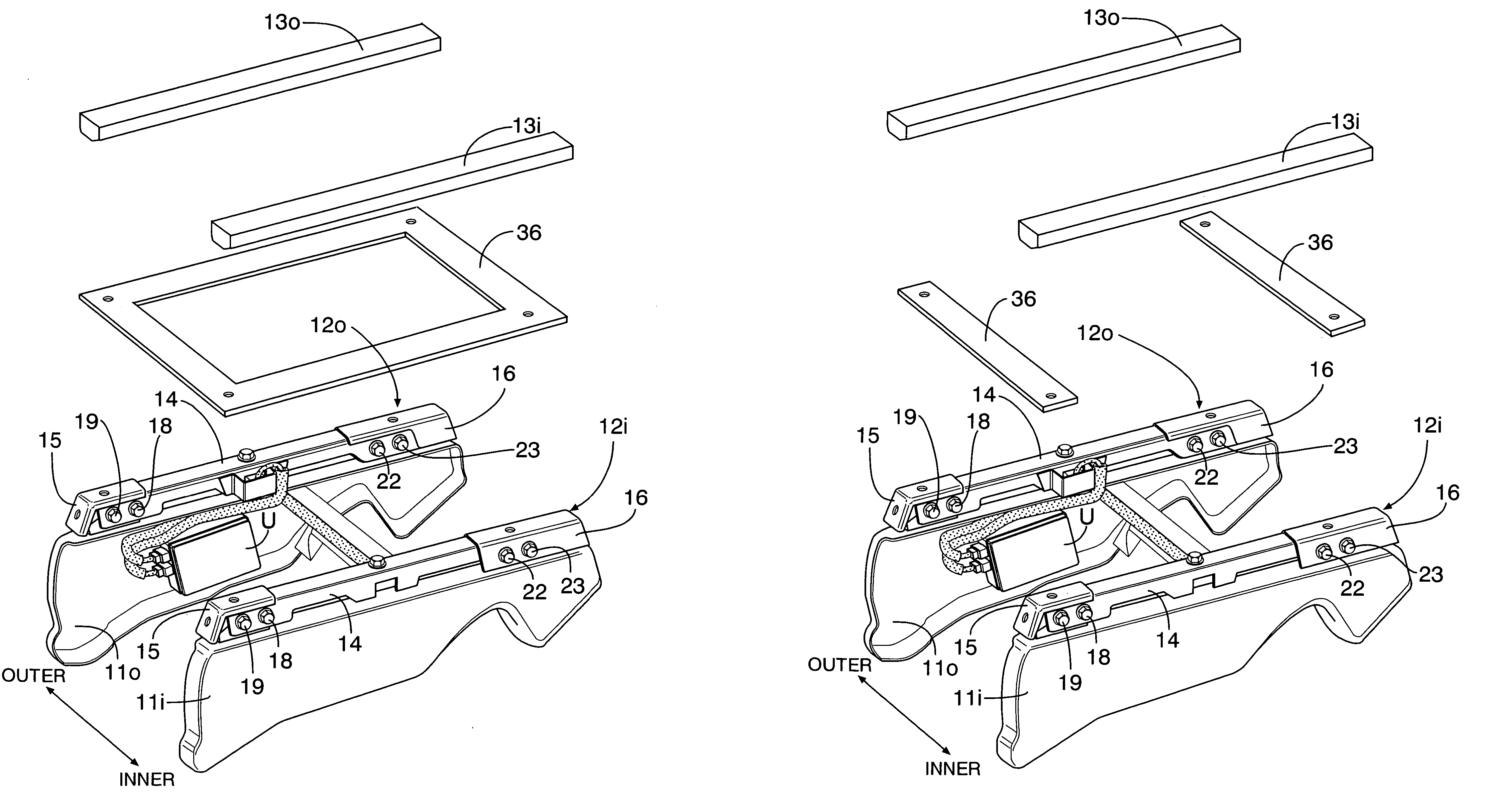
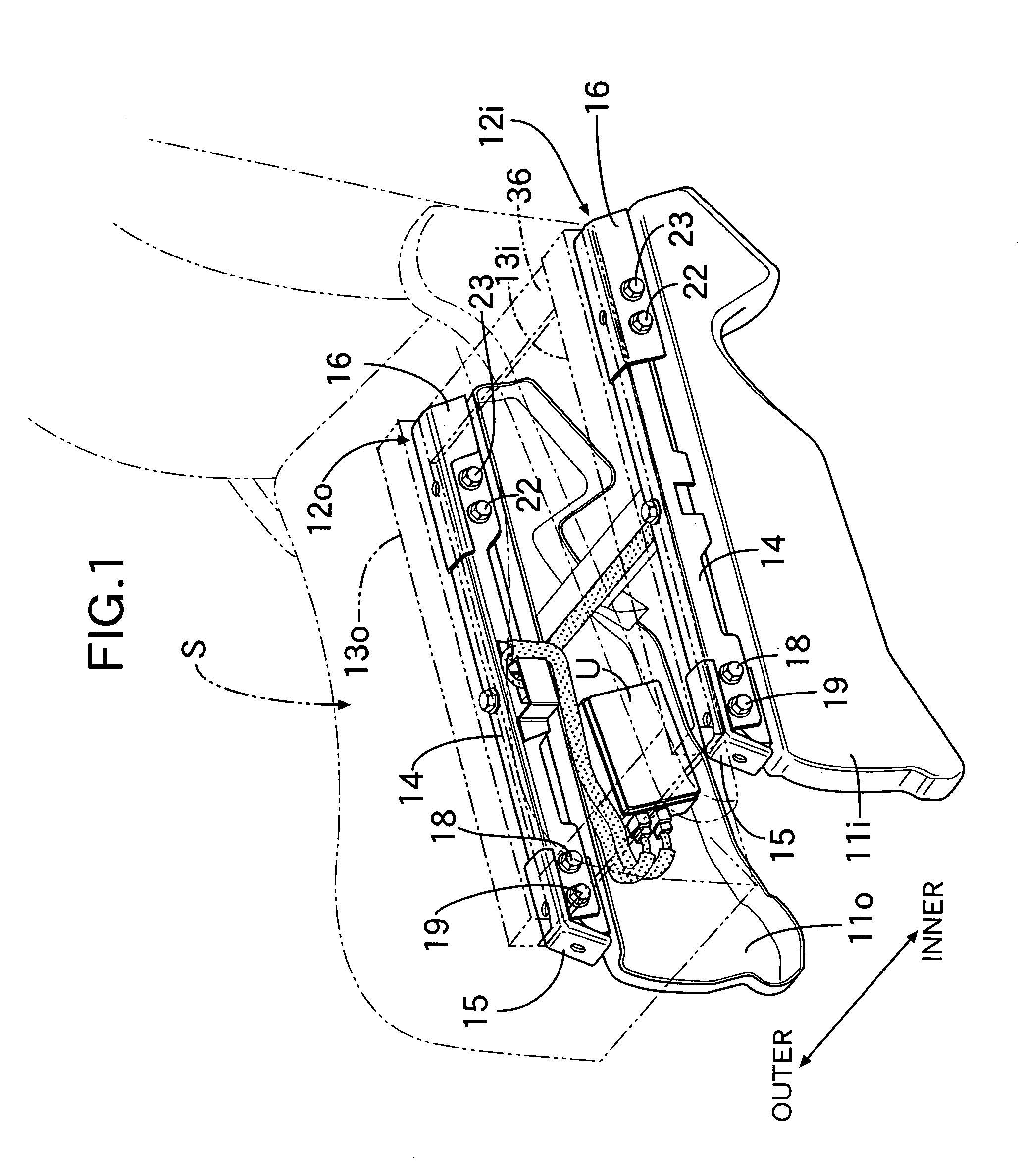
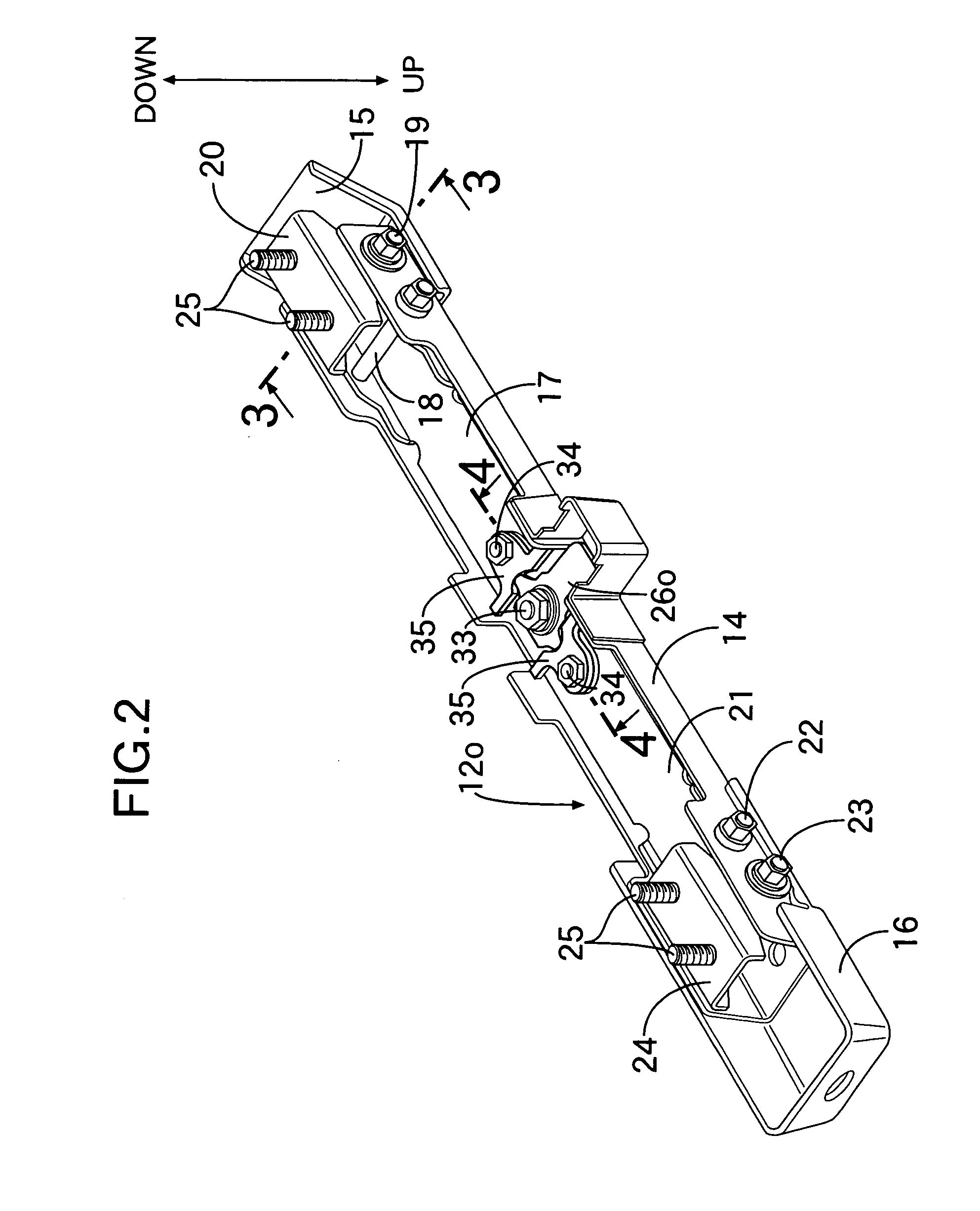
Occupant weight detection system having linked weight detection means with maintained positional relationships
InactiveUS7091426B2Improve detection accuracyMaintain detection accuracyVehicle seatsElectric devicesEngineeringLink weight
In an occupant weight detection system, a pair of weight detection units are mounted along upper faces of base members fixed to a floor of an automobile. A square-frame-shaped linking member made of an iron sheet is interposed between the pair of weight detection units and a pair of seat rails. The pair of weight detection units are integrally linked by the linking member to maintain a positional relationship to each other at a predetermined relationship. Therefore, it is possible to prevent these weight detection means from being mounted in a state in which they are twisted or displaced relative to each other, thereby maintaining the detection accuracy.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
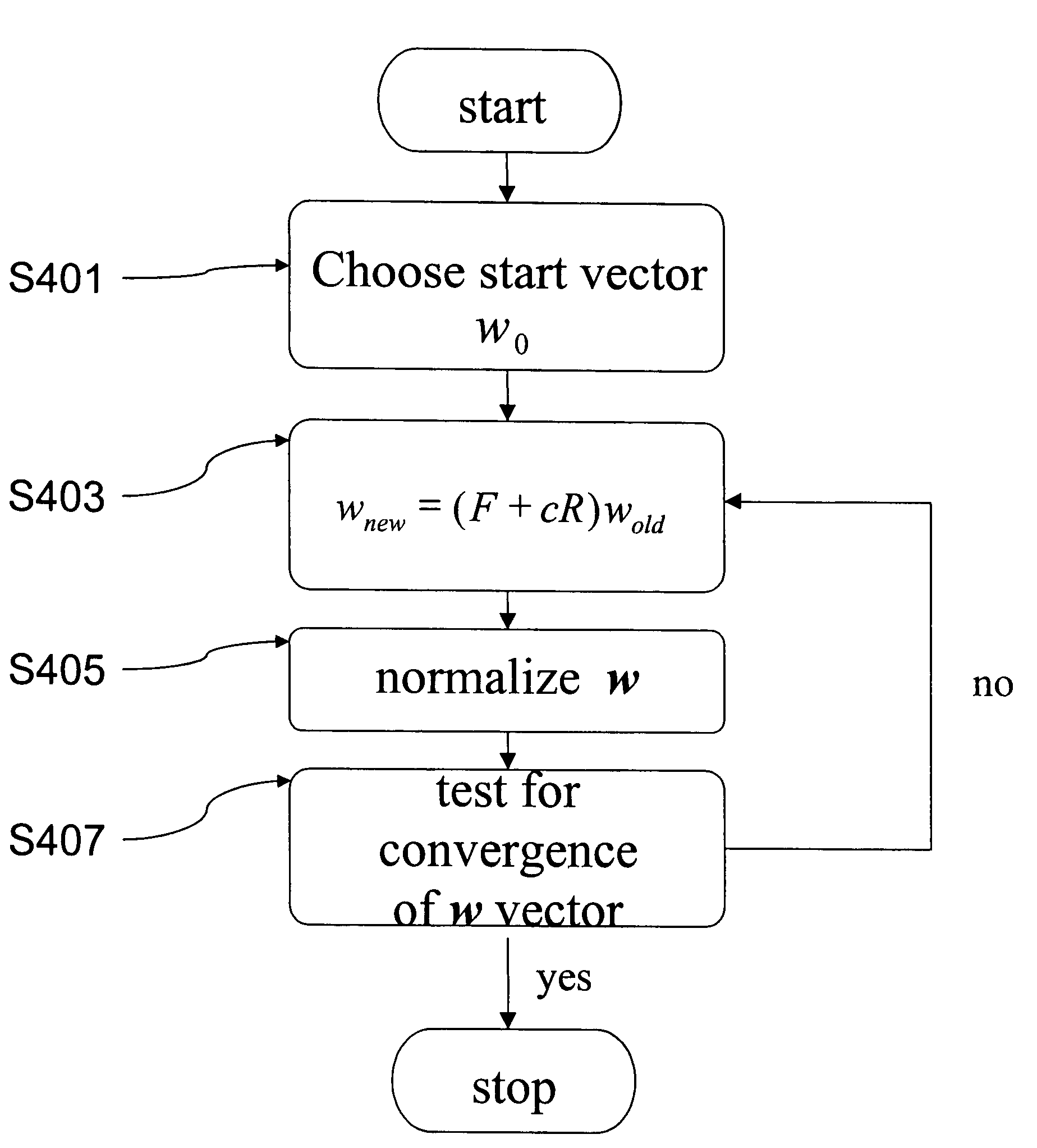
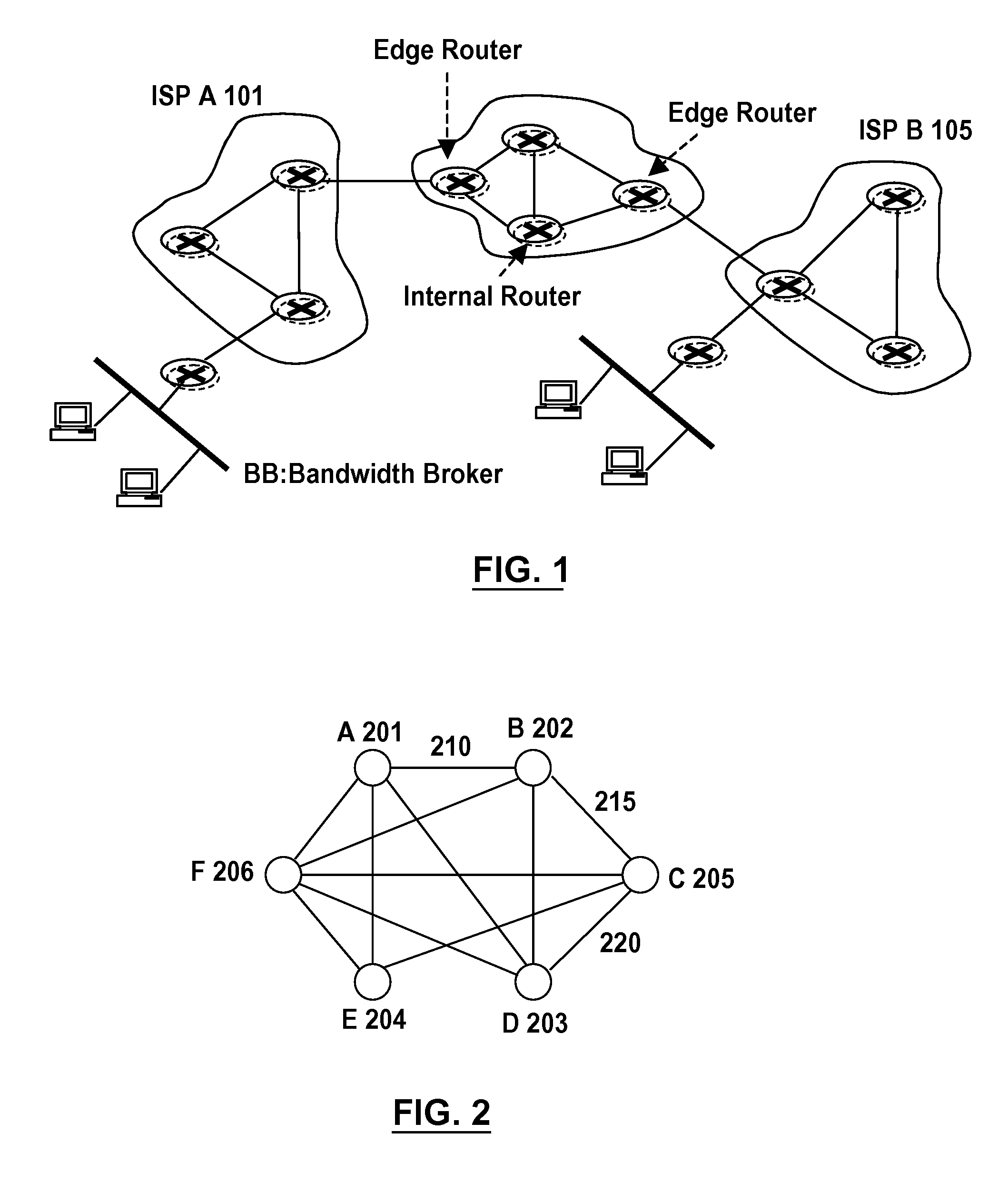
Backward and forward non-normalized link weight analysis method, system, and computer program product
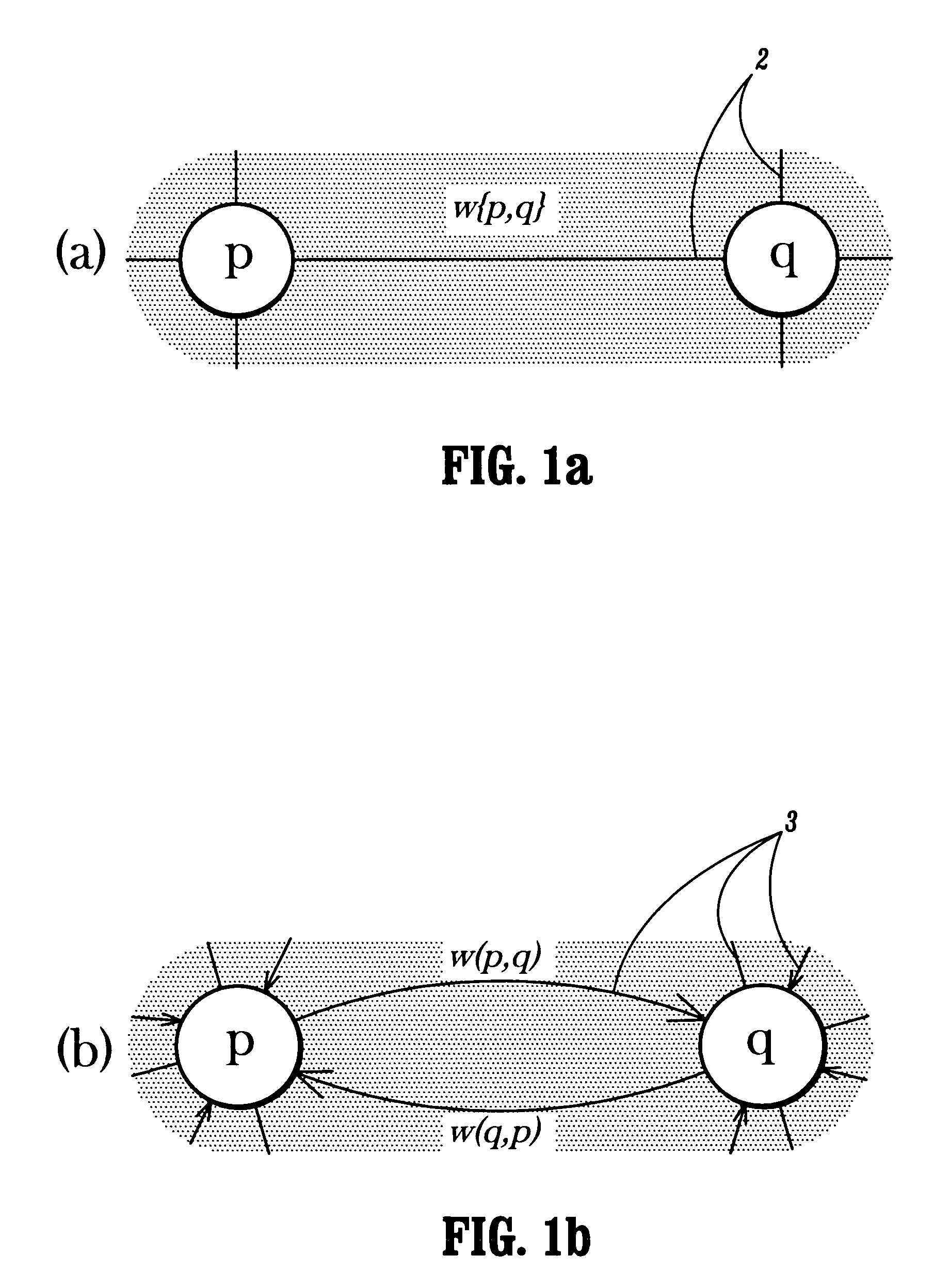
A method, system, and computer program product for hypertext link analysis that includes independently employing non-normalized backward and forward operators to obtain two independent weights for each document in a hypertext-linked graph, for subsequent ranking and analysis.
Owner:TELENOR AS
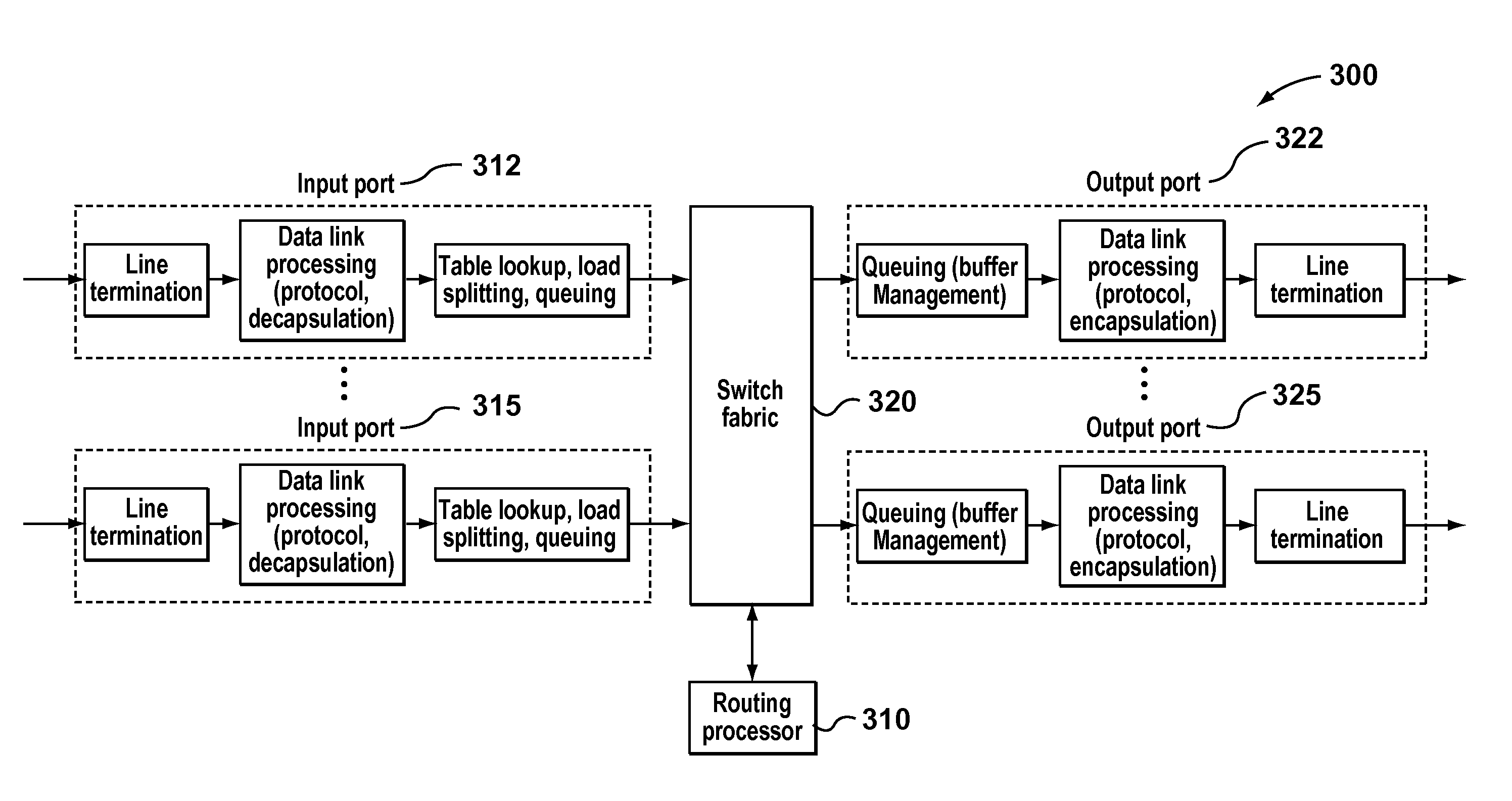
Non-blocking destination-based routing networks
InactiveUS7898957B2Simple designFAC will be greatly simplifiedError preventionTransmission systemsLink weightThe Internet
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
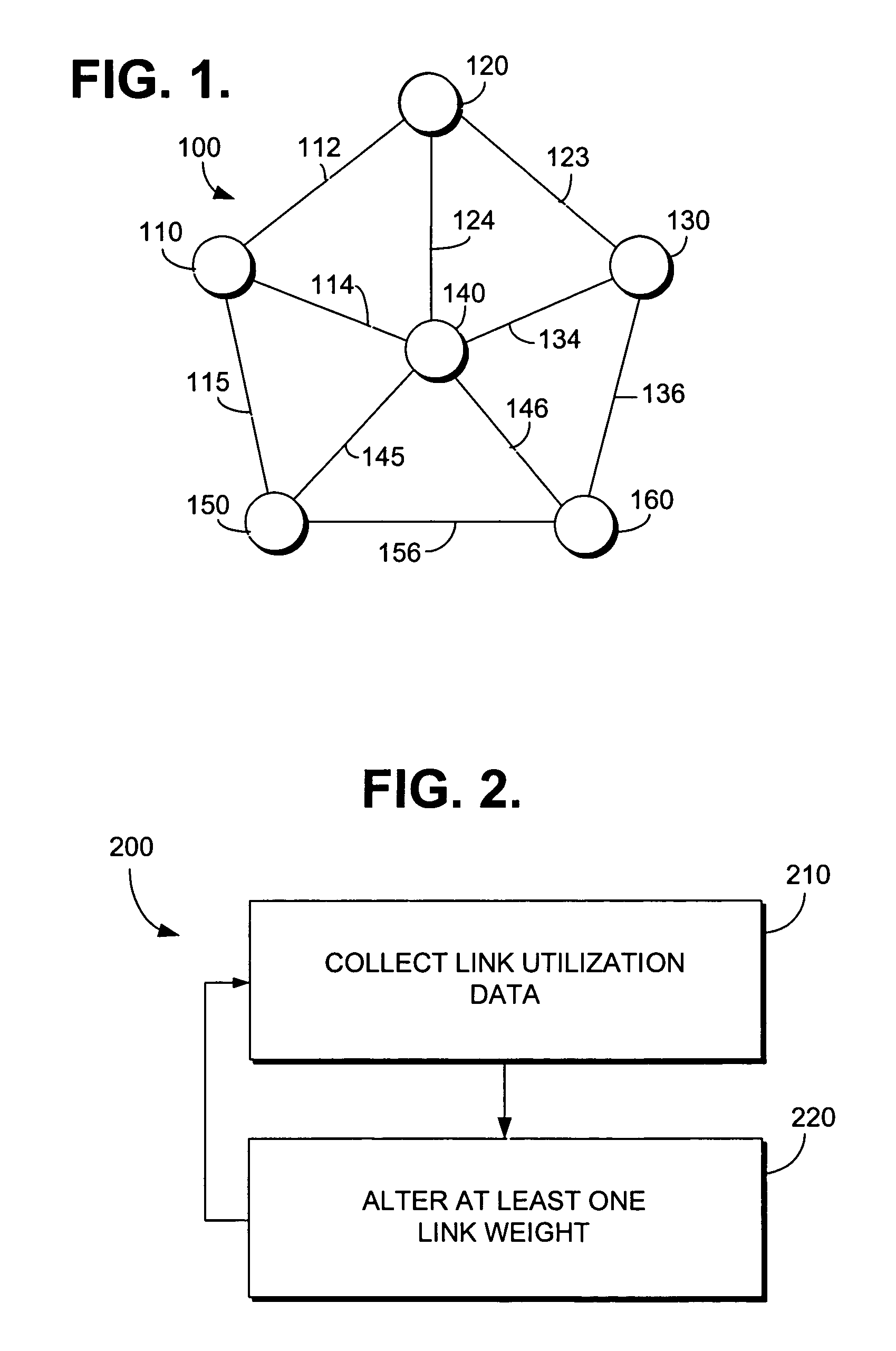
Method for assigning link weights in a communications network
InactiveUS7395351B1Improve performanceEfficient workError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsLink weightRandom choice
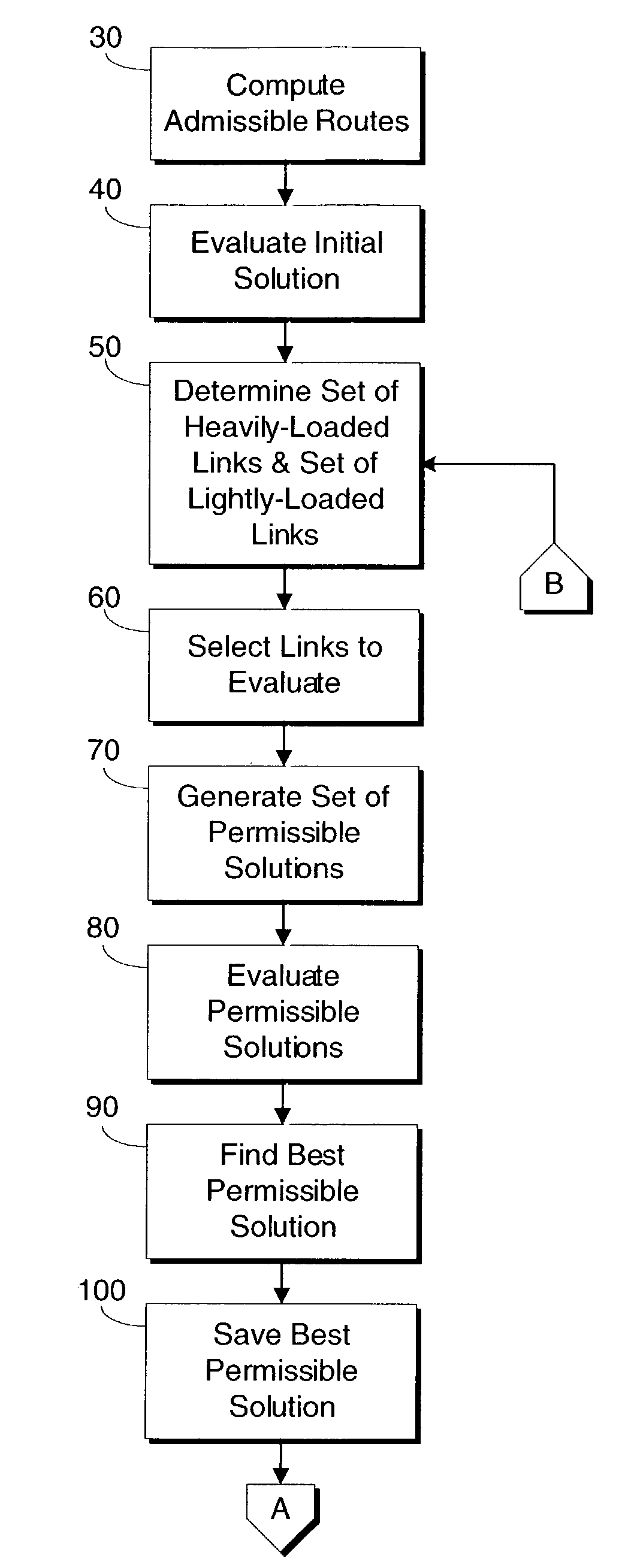
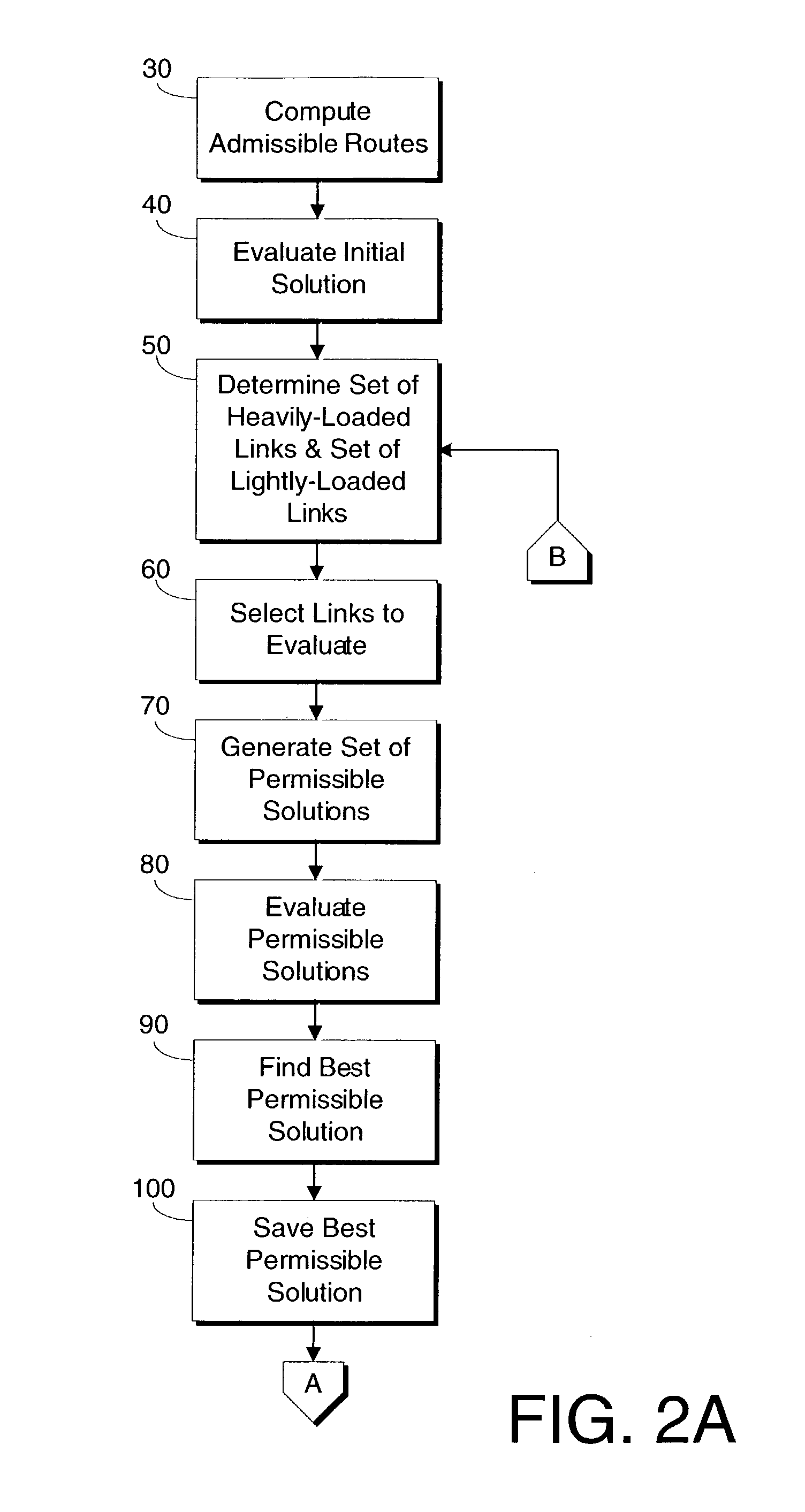
The present invention includes a method and system for determining link weights that when utilized will optimize the performance of a network in the event of a link failure without the need to alter the link weights. The method includes determining two sets of links, one that includes links with a significant amount of loading and one that includes links with a modest amount of loading. A set of permissible solutions is generated utilizing one randomly chosen link from each set. After omitting recent best permissible solutions, the remaining permissible solutions are evaluated by analyzing for the complete network topology and for the topologies corresponding to all single-link failure states and the best permissible solution is found. If the best permissible solution is better than the current optimal solution, then the best permissible solution is made the optimal solution. These steps are repeated until a predetermined number of iterations have been evaluated without a change in the optimal solution. When that occurs, the number of links used to generate the set of potential solutions is randomly changed and the above-described steps are repeated. The method is complete after a second predetermined number of iterations have been evaluated no matter how many changes to the optimal solution.
Owner:SPRINT CORPORATION
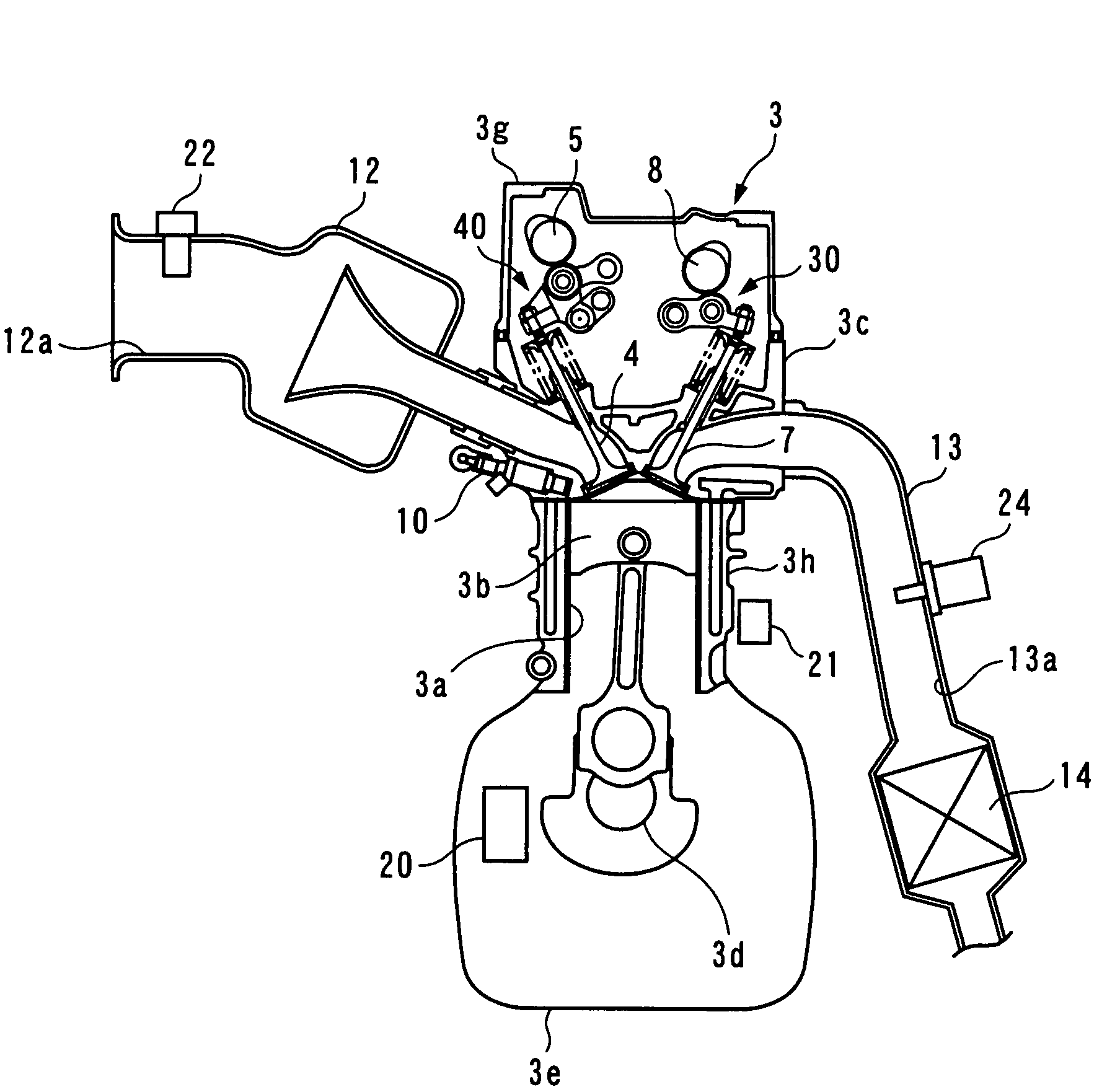
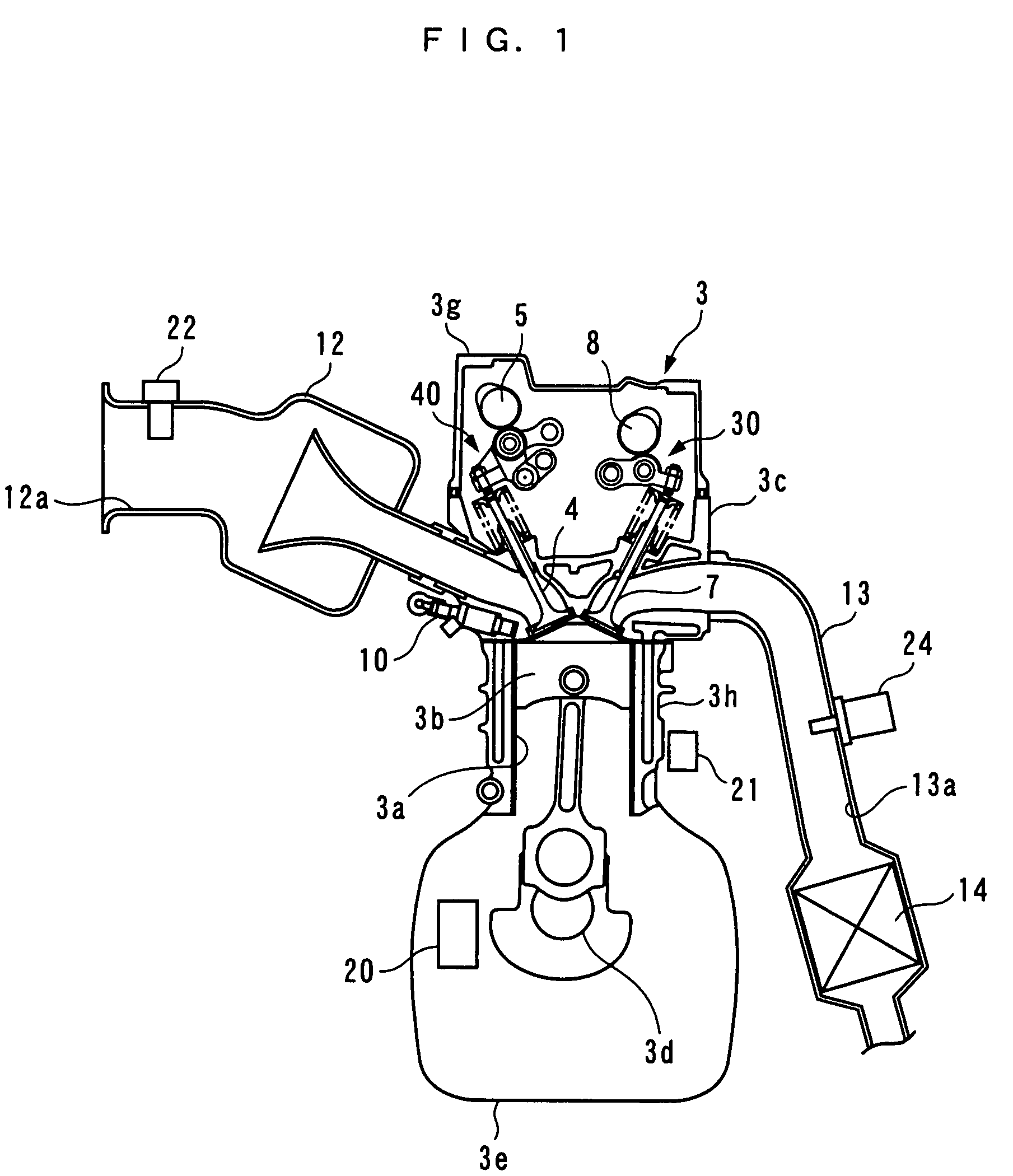
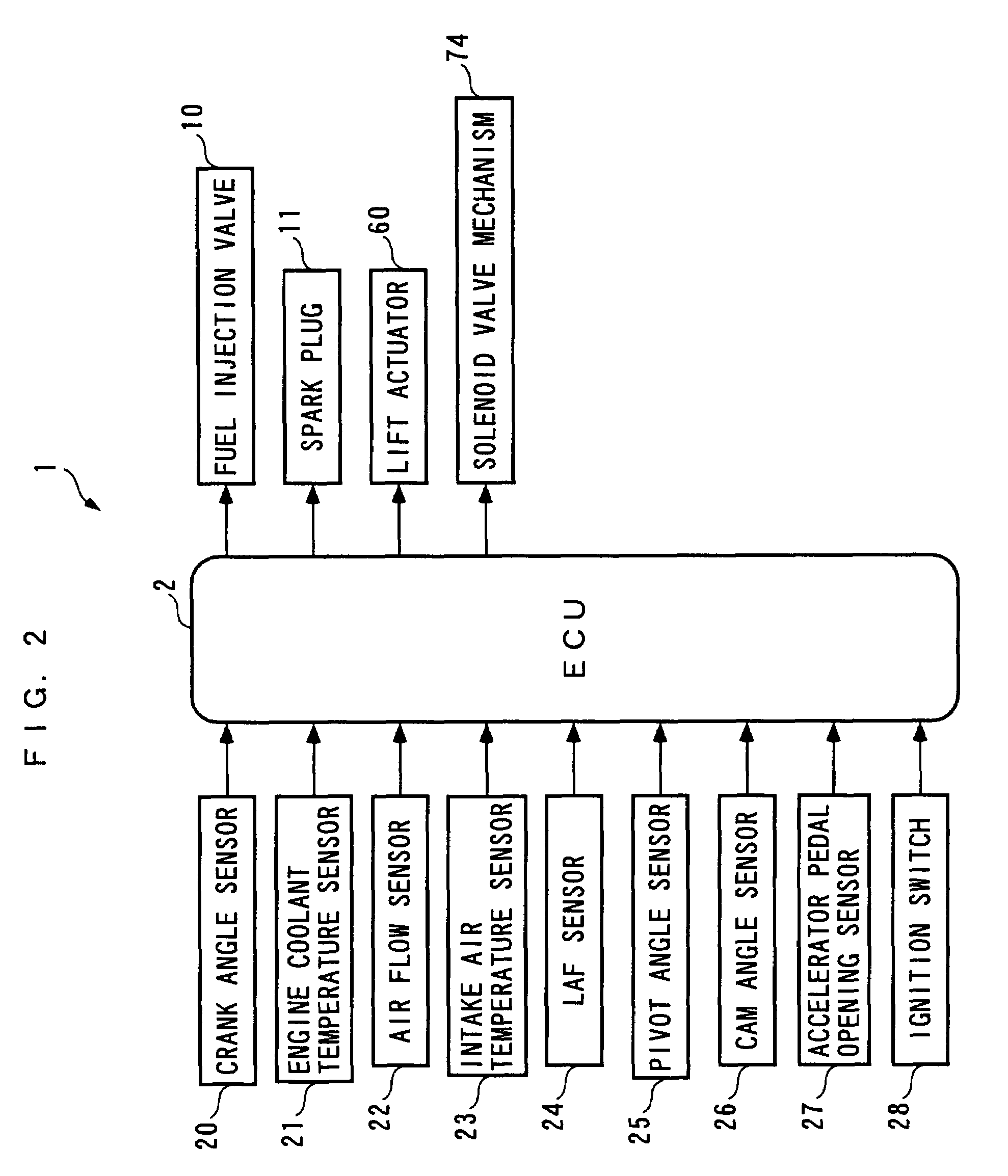
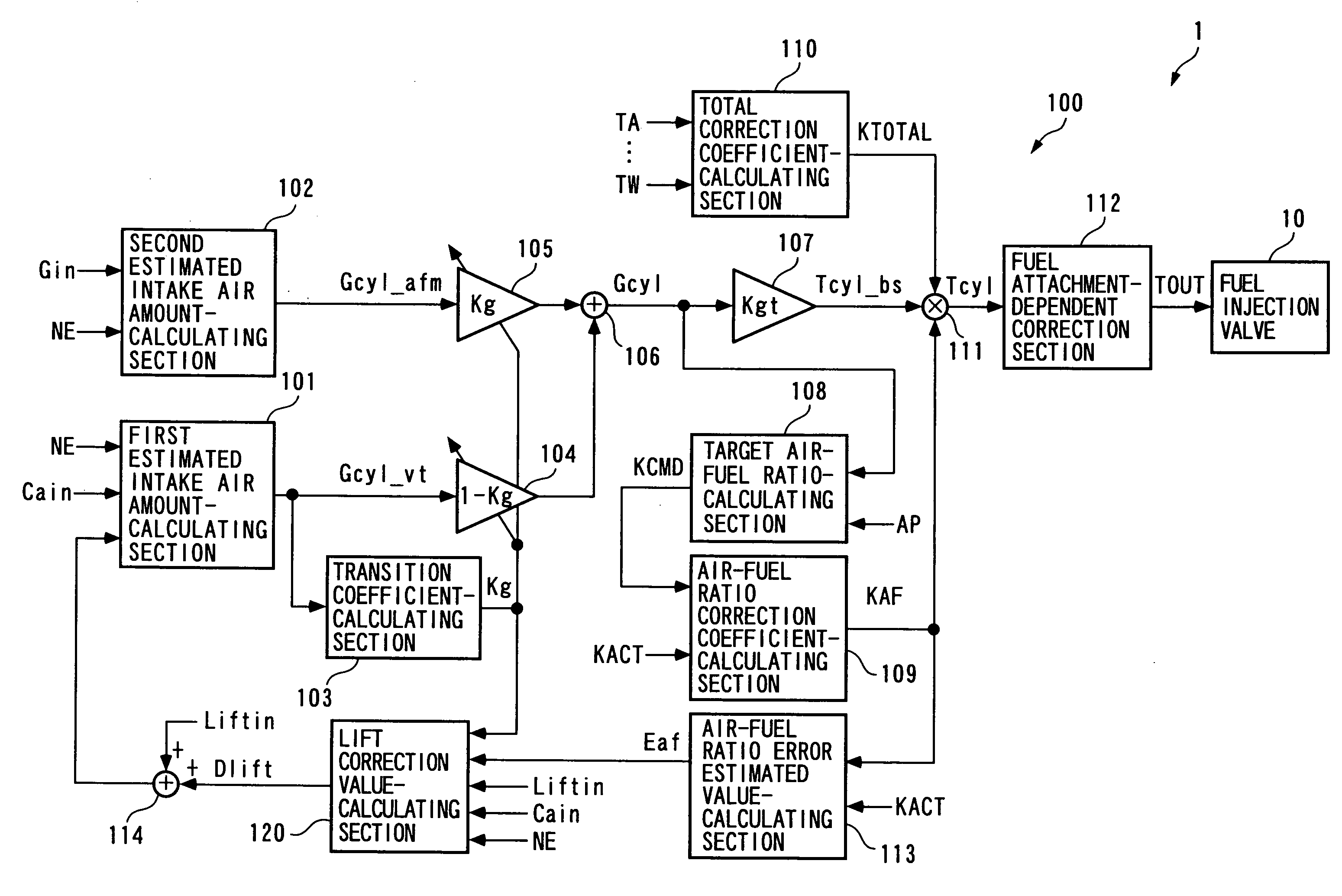
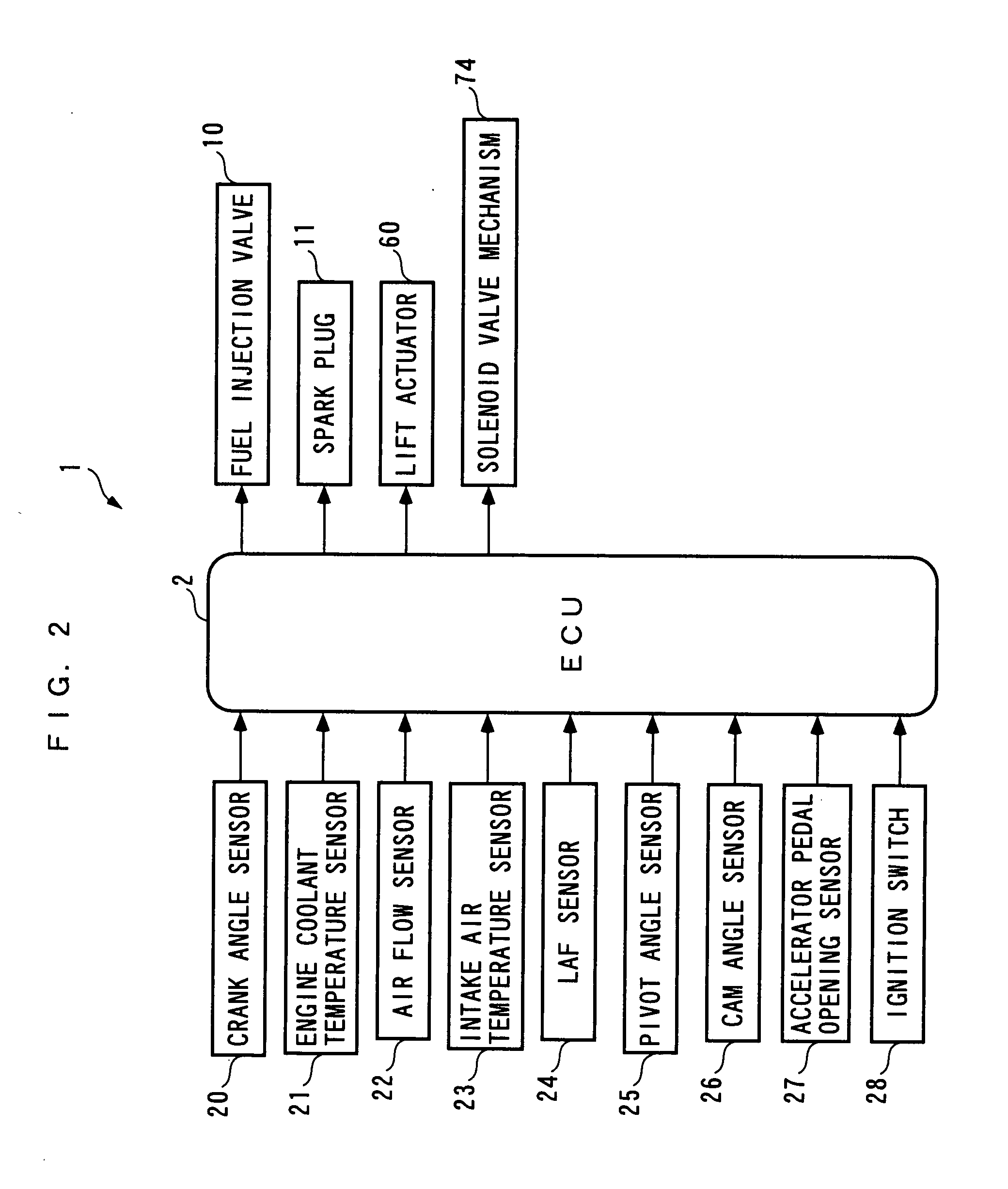
Control apparatus, control method, and engine control unit
A control apparatus which is capable of compensating for a control error properly and quickly even under a condition where the control error is temporarily increased e.g. by degradation of reliability of the detection results of reference parameters other than controlled variables, thereby making it possible to ensure a high accuracy of control. An air-fuel ratio controller of the control apparatus calculates modified errors by multiplying e.g. an air-fuel ratio error estimated value by link weight functions, calculates basic local correction values such that the modified errors become equal to 0; calculates local correction values by multiplying the basic local correction values and the like by the link weight functions; calculates corrected valve lift by adding a lift correction value, which is the total sum of the local correction values, to a value of valve lift; calculates a first estimated intake air amount for feedforward control of an air-fuel ratio, based on the corrected valve lift; calculates an air-fuel ratio correction coefficient for feedback control of the air-fuel ratio; and calculates a fuel injection amount based on these.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
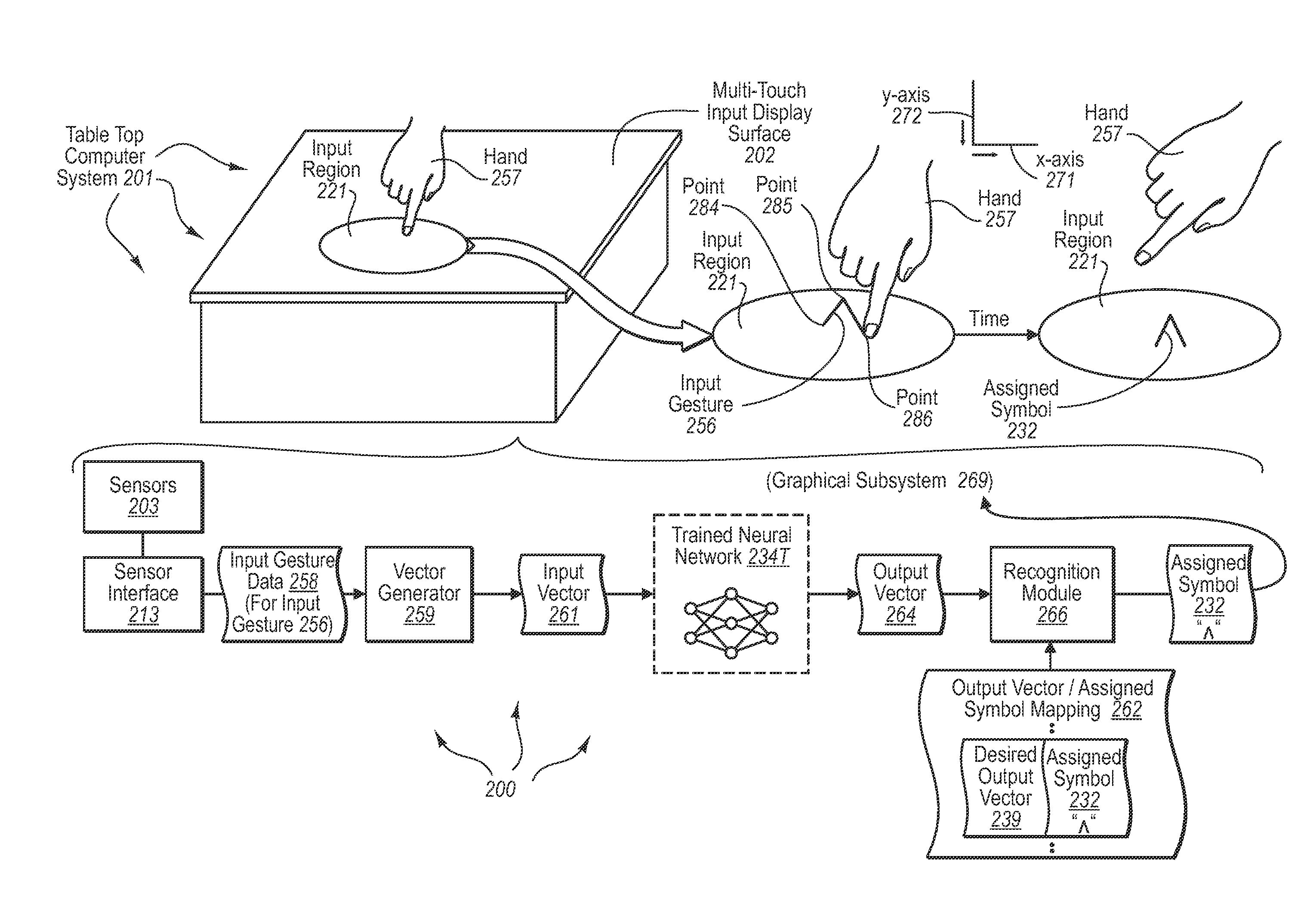
Recognizing input gestures using a multi-touch input device, calculated graphs, and a neural network with link weights
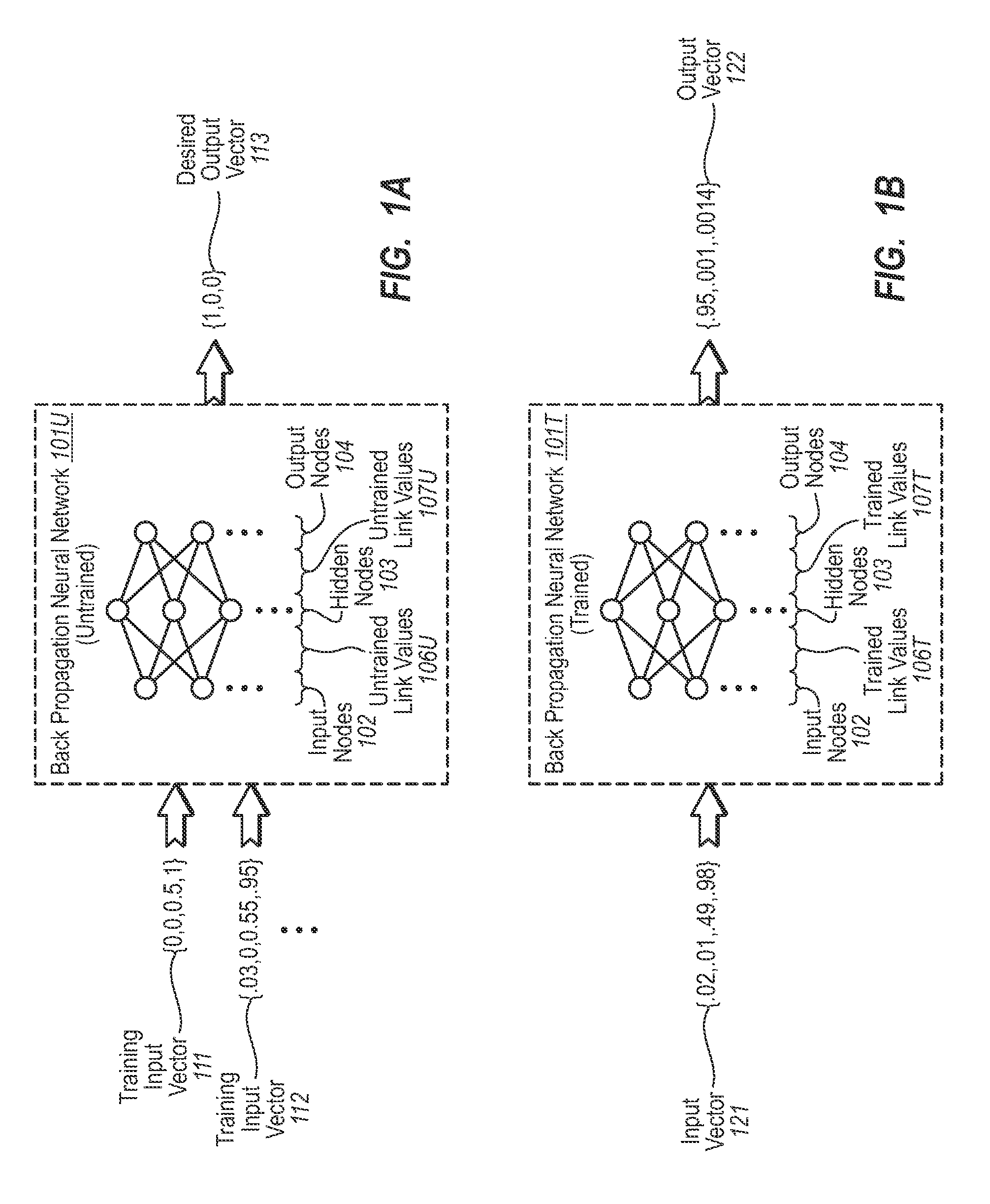
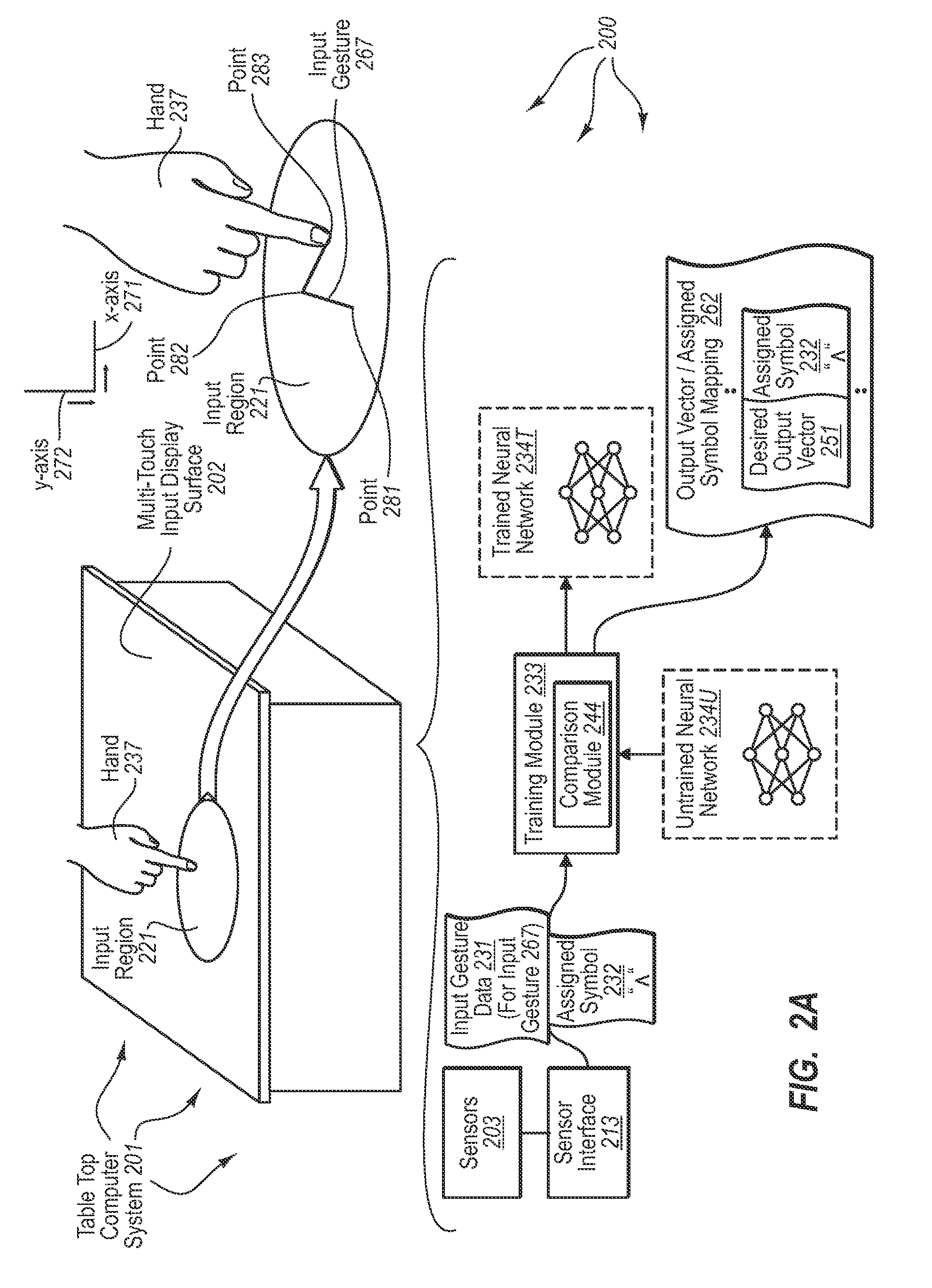
The present invention extends to methods, systems, and computer program products for recognizing input gestures. A neural network is trained using example inputs and backpropagation to recognize specified input patterns. Input gesture data is representative of movements in contact on a multi-touch input display surface relative to one or more axes over time. Example inputs used for training the neural network to recognize a specified input pattern can be created from sampling input gesture data for example input gestures known to represent the specified input pattern. Trained neural networks can subsequently be used to recognize input gestures that are similar to known input gestures as the specified input pattern corresponding to the known input gestures.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Routing selection method for software defined network
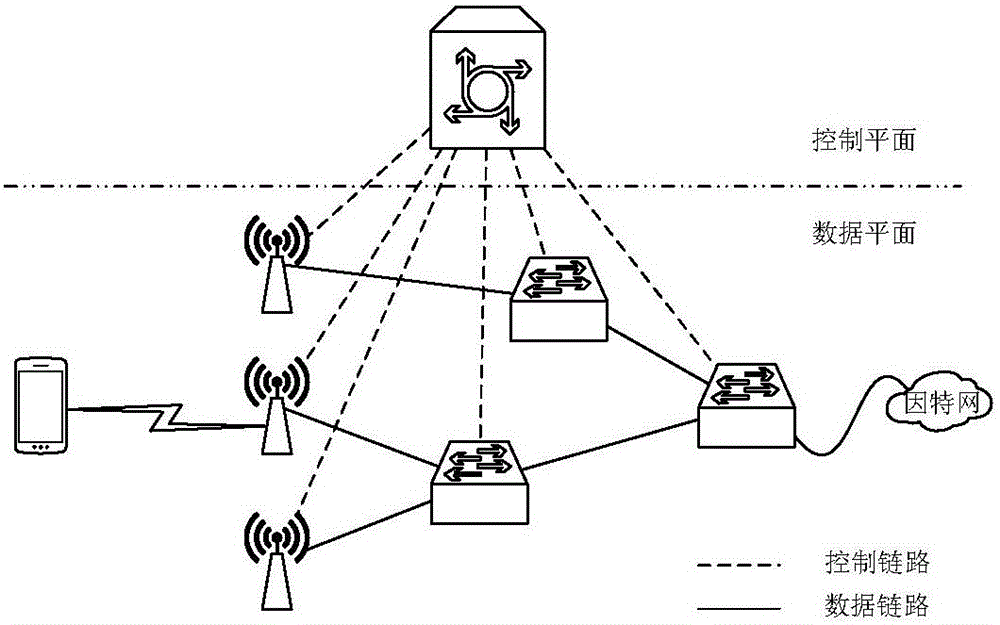
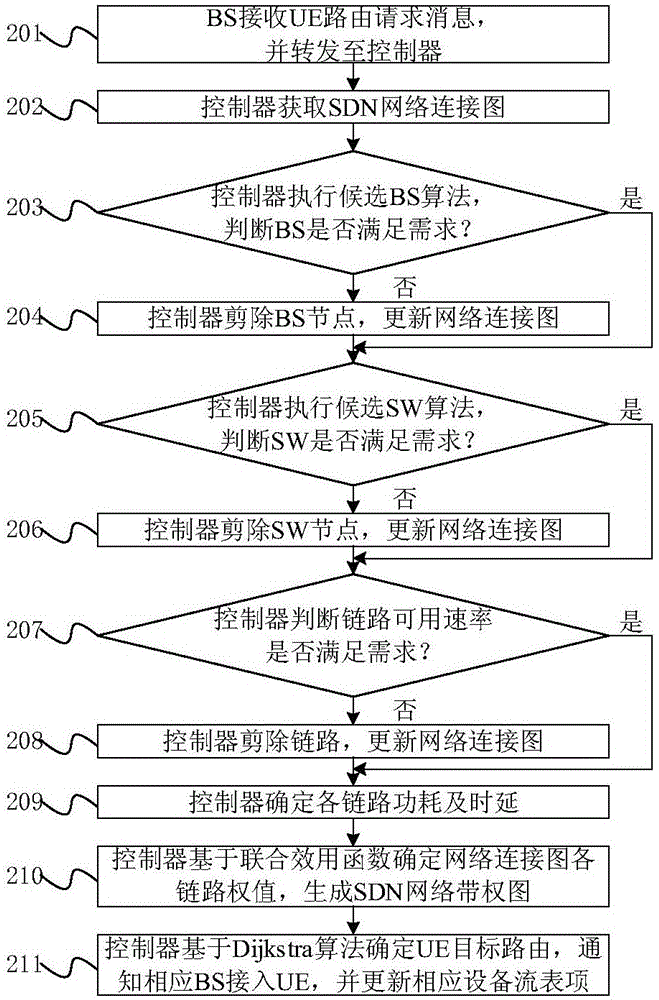
ActiveCN105721302AReduce power consumptionImprove stabilityData switching networksLink weightUser equipment
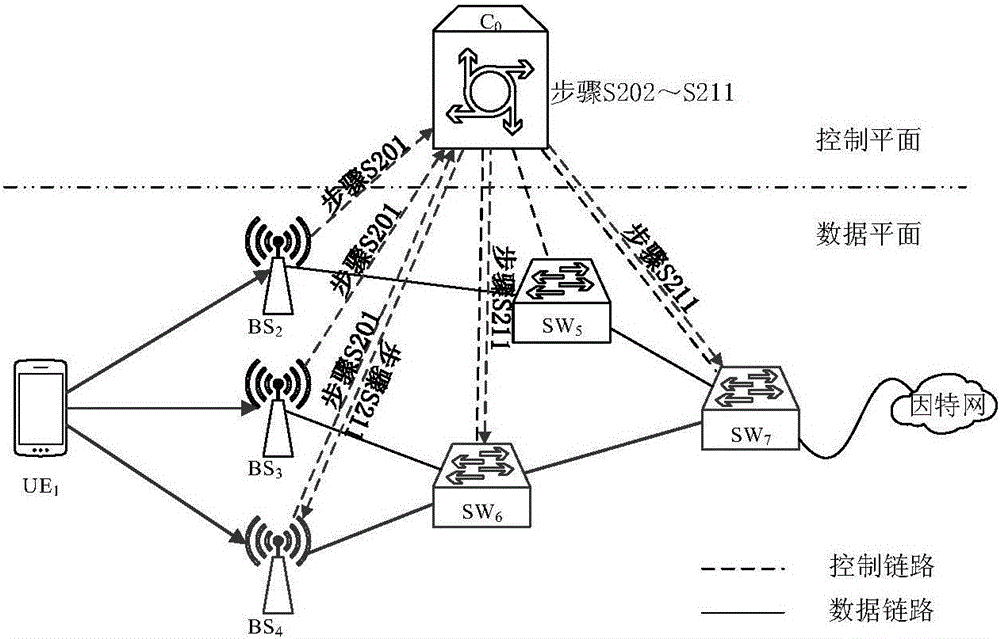
The invention relates to a routing selection method for a software defined network, and belongs to the field of mobile communication technology. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining an SDN (Software Defined Network) connection diagram by a controller according to a user equipment (UE) routing request message; determining a candidate base station (BS), a candidate switch (SW) and a candidate link according to the business demand of the UE; and determining each link weight based on power consumption and a delay joint utility function, generating a network weighted graph, and determining a target routing based on a Dijkstra algorithm. According to the routing selection method provided by the invention, the business demand of the UE, the transmission rates of the BS and the SW,a power message and delay and other information are comprehensively considered, the optimized routing selection of the UE under SDN architecture is realized for jointly optimizing the routing power consumption and the delay, the network power consumption can be effectively saved, the delay is shortened and the network stability is improved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
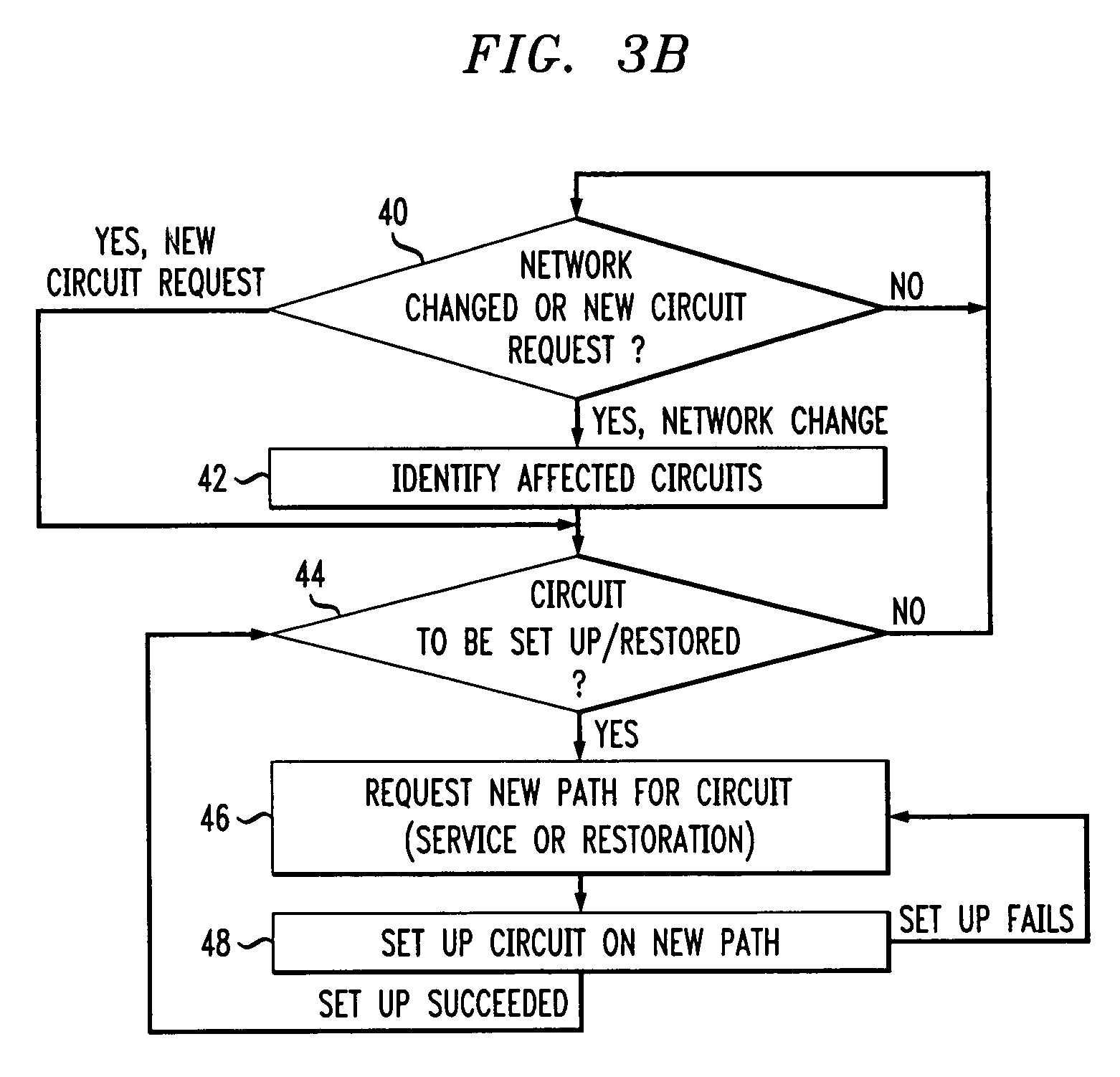
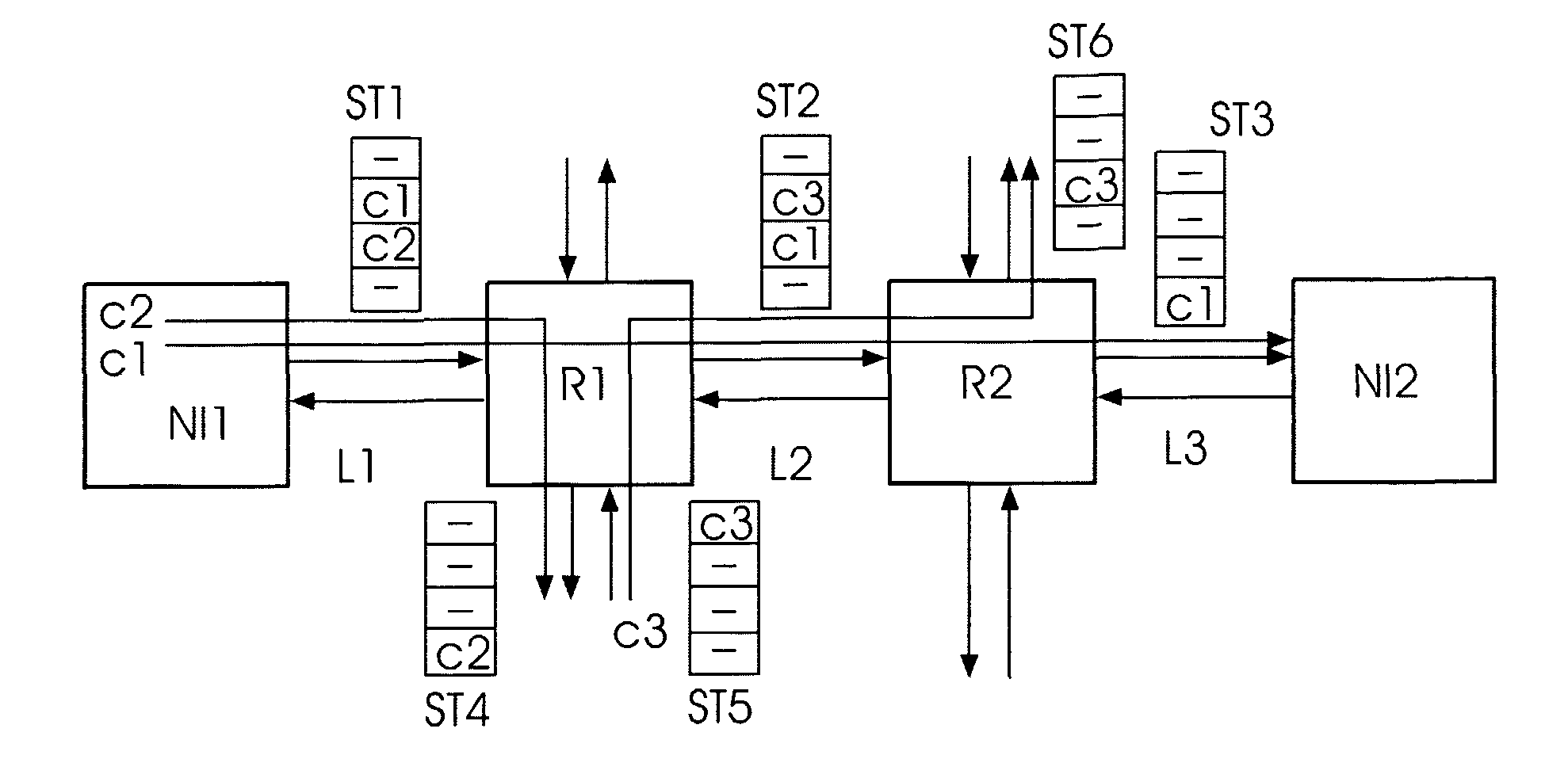
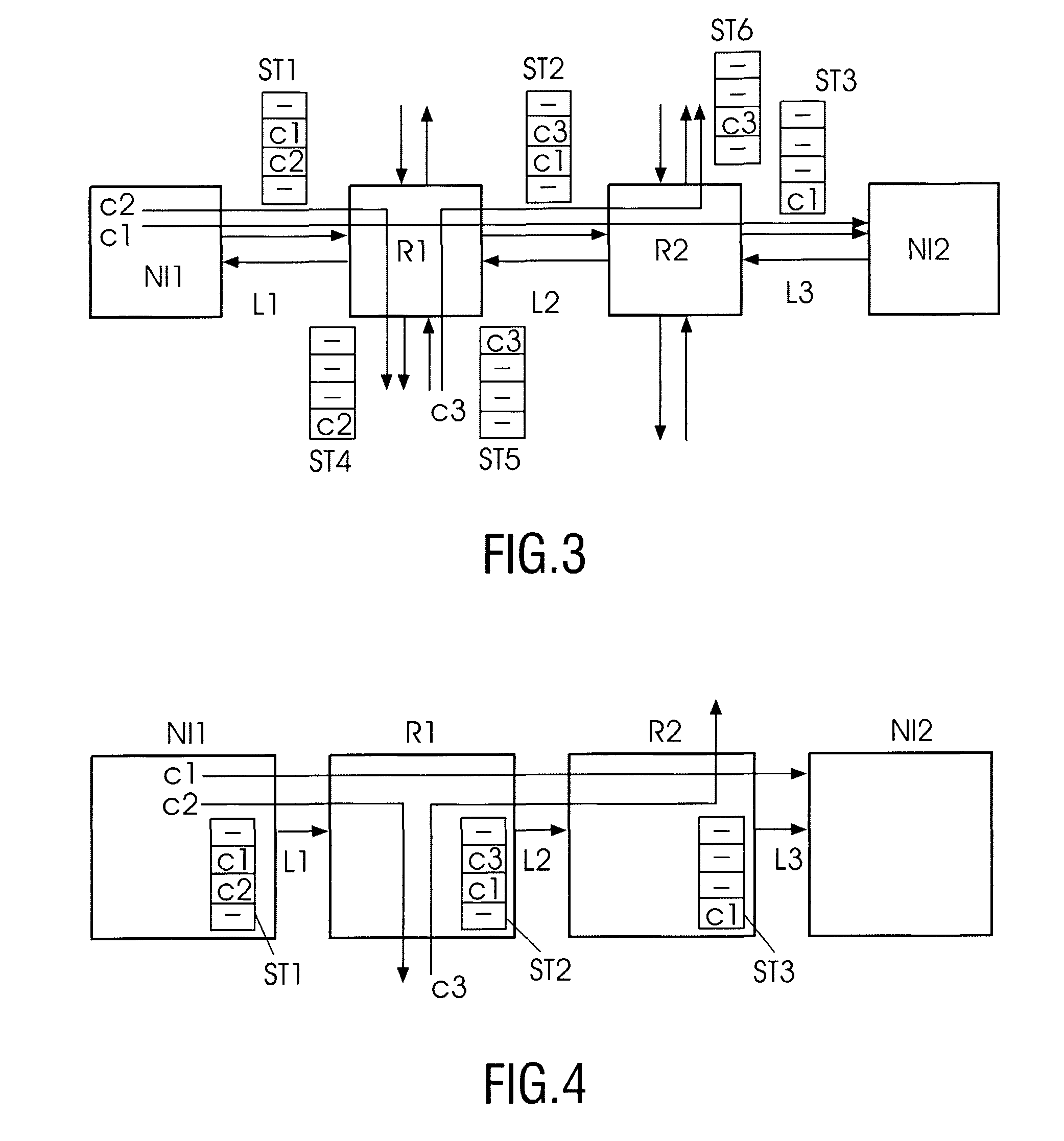
Scheme for routing circuits with dynamic self-adjusting link weights in a network
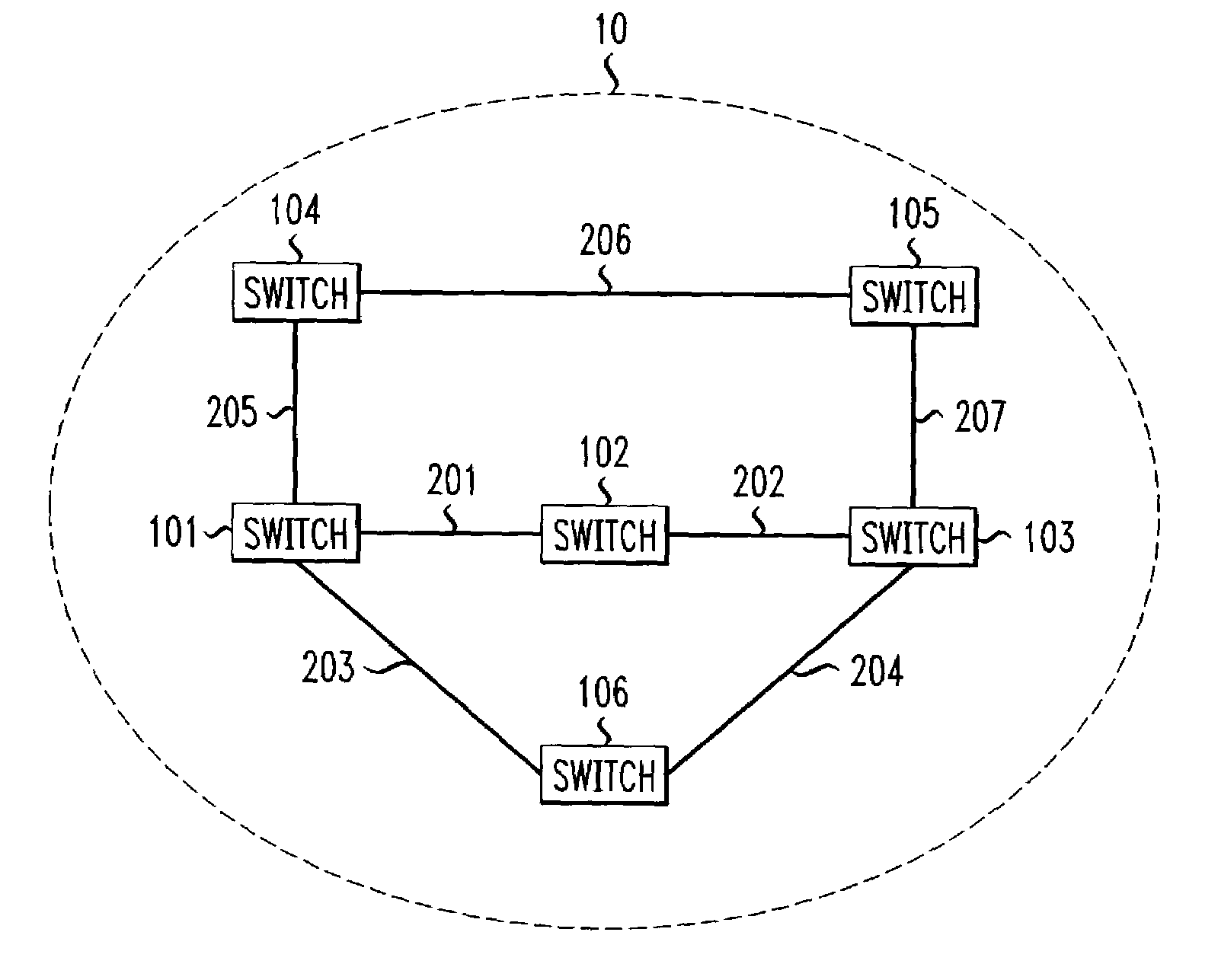
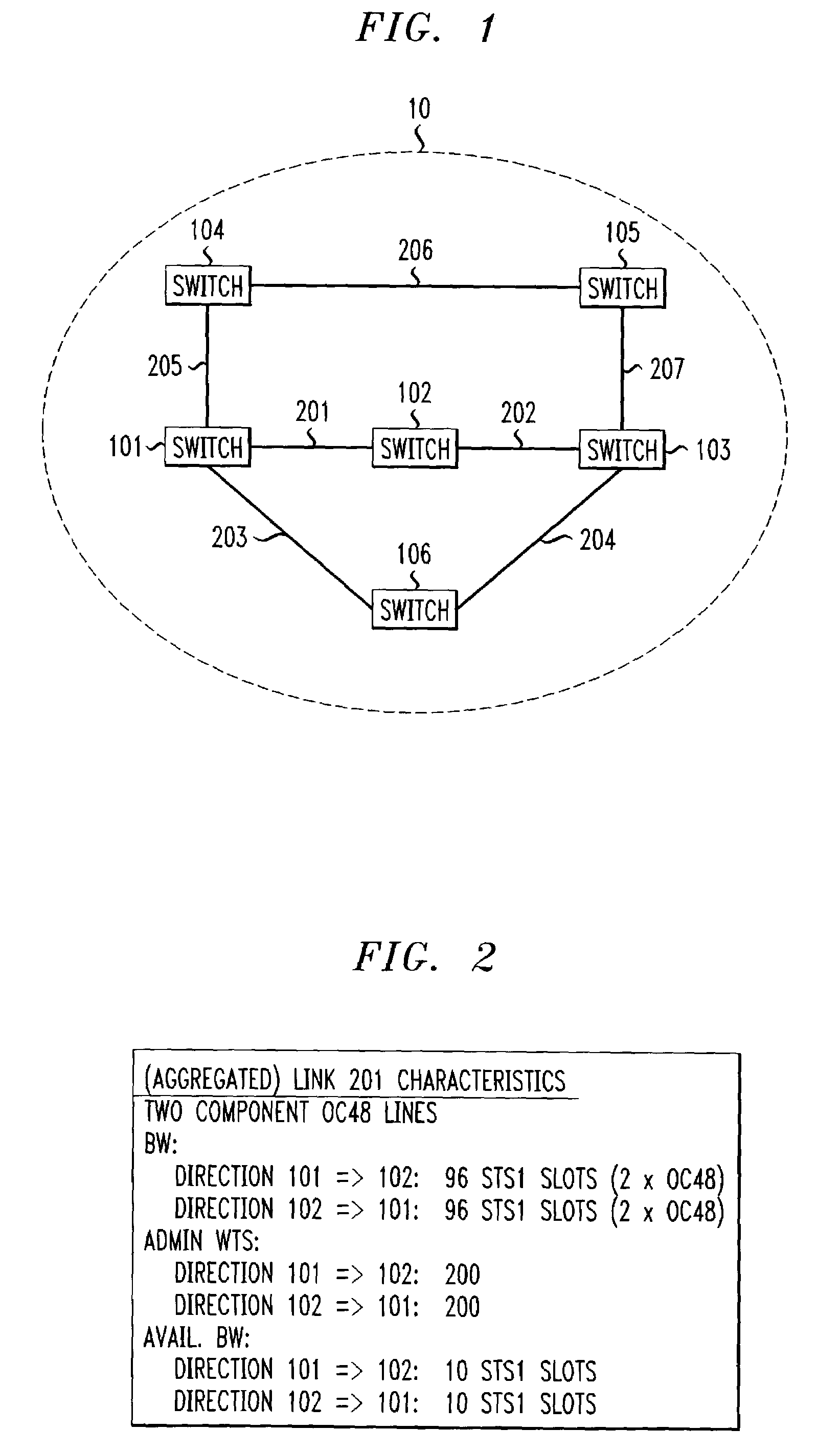
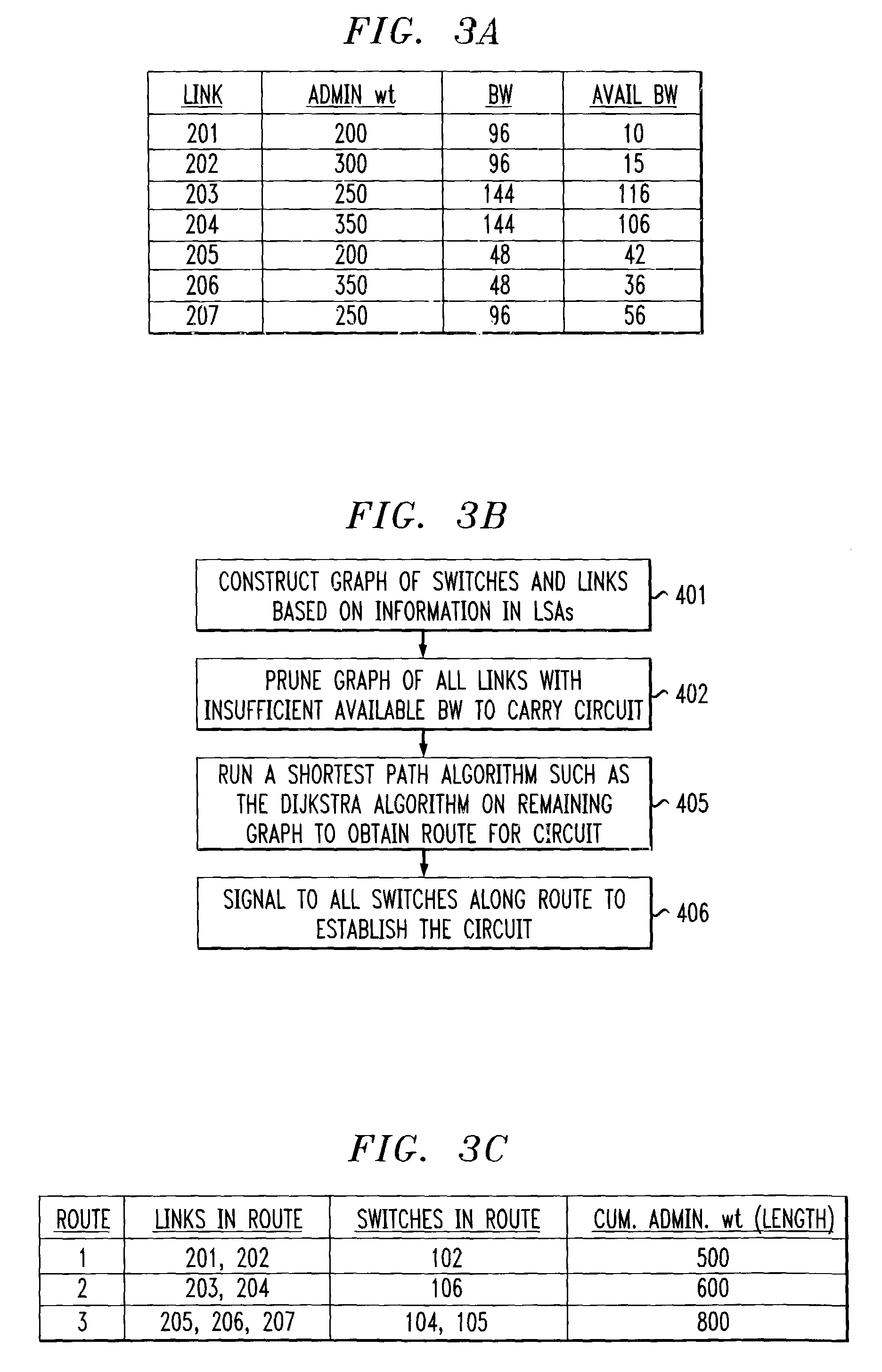
InactiveUS7242679B1Efficient and economical mannerImprove balanceData switching by path configurationLink weightCross connection
The present invention relates generally to routing of circuits in a network. More particularly, the invention encompasses a method and an apparatus for routing circuits using dynamic self-adjusting link weights within a network. The invention further includes multiple schemes for routing circuits with dynamic self-adjusting link weights in a SCN (Switched Communication Network). The network could consist of optical, ATM, FR, or IP / MPLS switches and cross-connects.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Method and apparatus for learning a probabilistic generative model for text
ActiveUS20070208772A1Digital data information retrievalNatural language analysisProbit modelProbabilistic relevance model
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that learns a generative model for textual documents. During operation, the system receives a current model, which contains terminal nodes representing random variables for words and cluster nodes representing clusters of conceptually related words. Within the current model, nodes are coupled together by weighted links, so that if a cluster node in the probabilistic model fires, a weighted link from the cluster node to another node causes the other node to fire with a probability proportionate to the link weight. The system also receives a set of training documents, wherein each training document contains a set of words. Next, the system applies the set of training documents to the current model to produce a new model.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Method and apparatus for learning a probabilistic generative model for text
ActiveUS8024372B2Digital data information retrievalNatural language analysisProbit modelProbabilistic relevance model
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that learns a generative model for textual documents. During operation, the system receives a current model, which contains terminal nodes representing random variables for words and cluster nodes representing clusters of conceptually related words. Within the current model, nodes are coupled together by weighted links, so that if a cluster node in the probabilistic model fires, a weighted link from the cluster node to another node causes the other node to fire with a probability proportionate to the link weight. The system also receives a set of training documents, wherein each training document contains a set of words. Next, the system applies the set of training documents to the current model to produce a new model.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
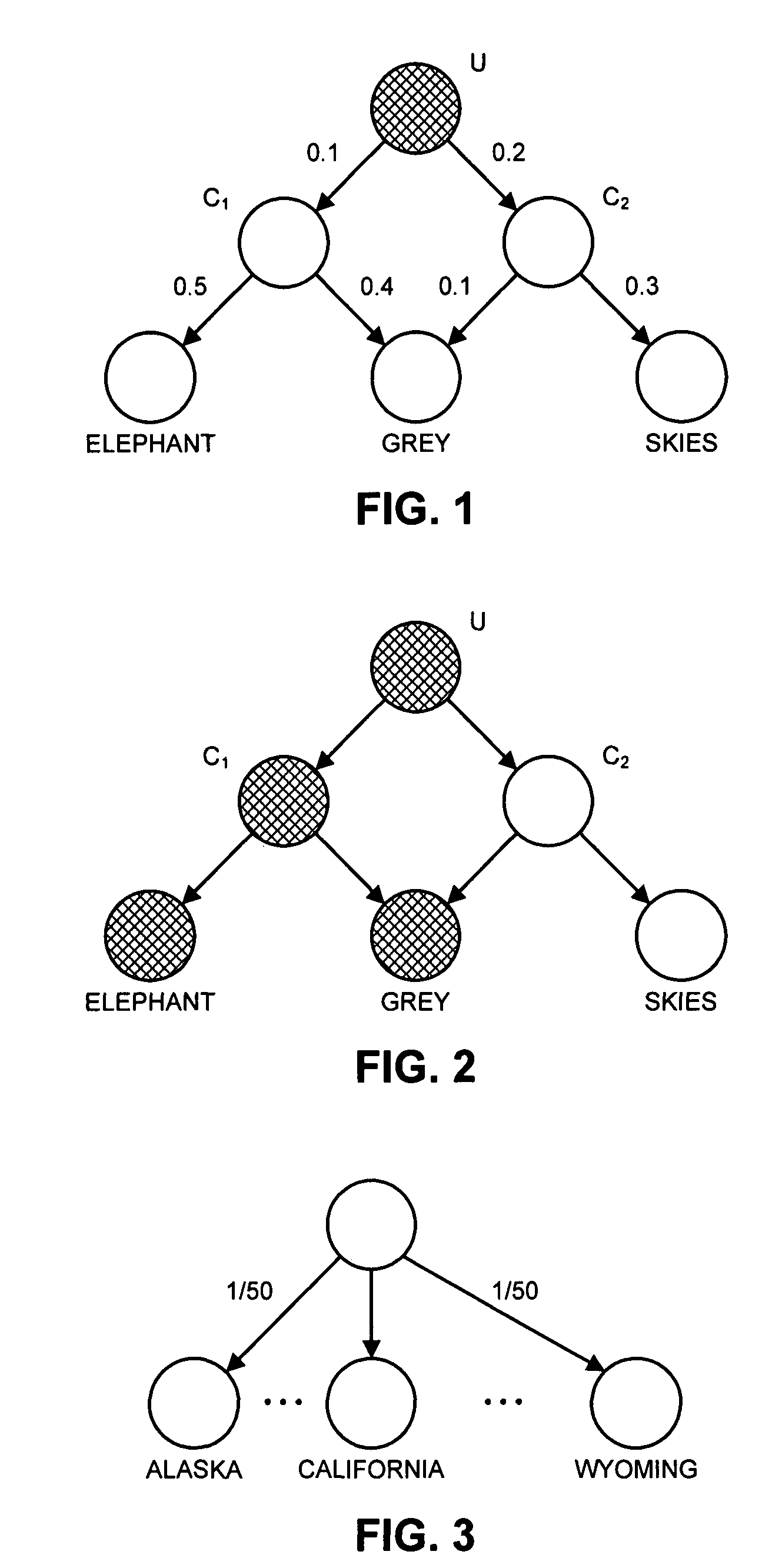
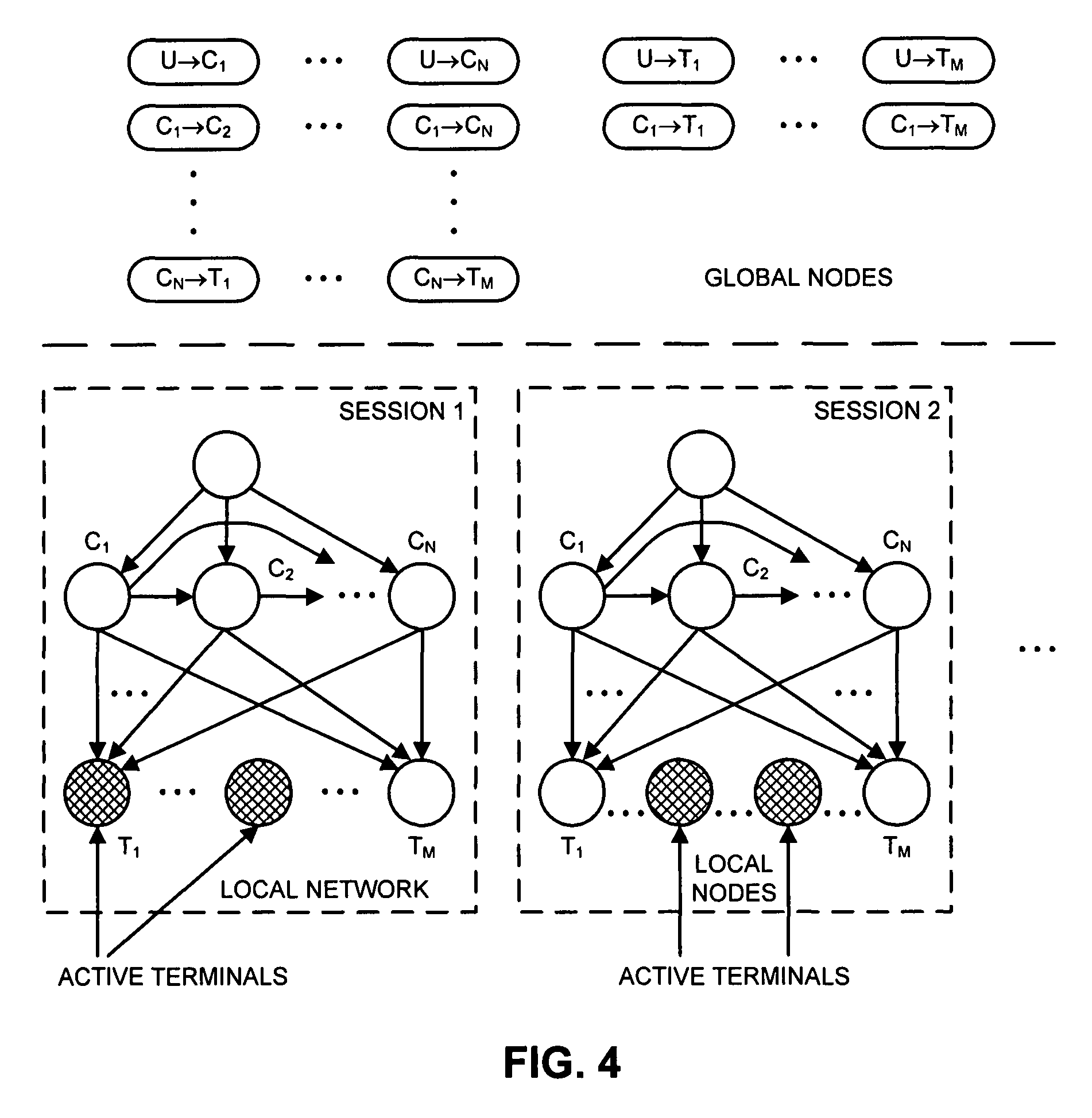
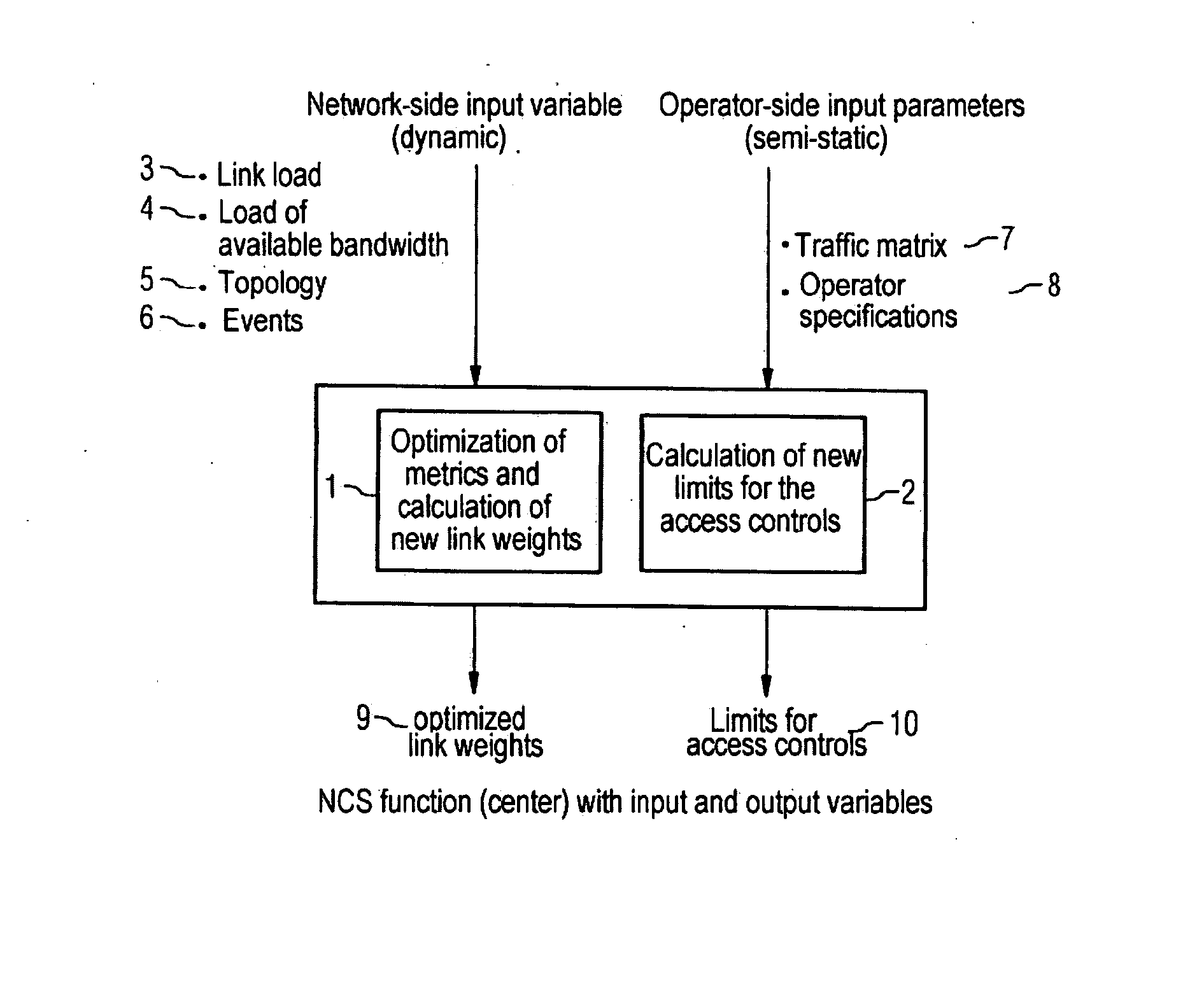
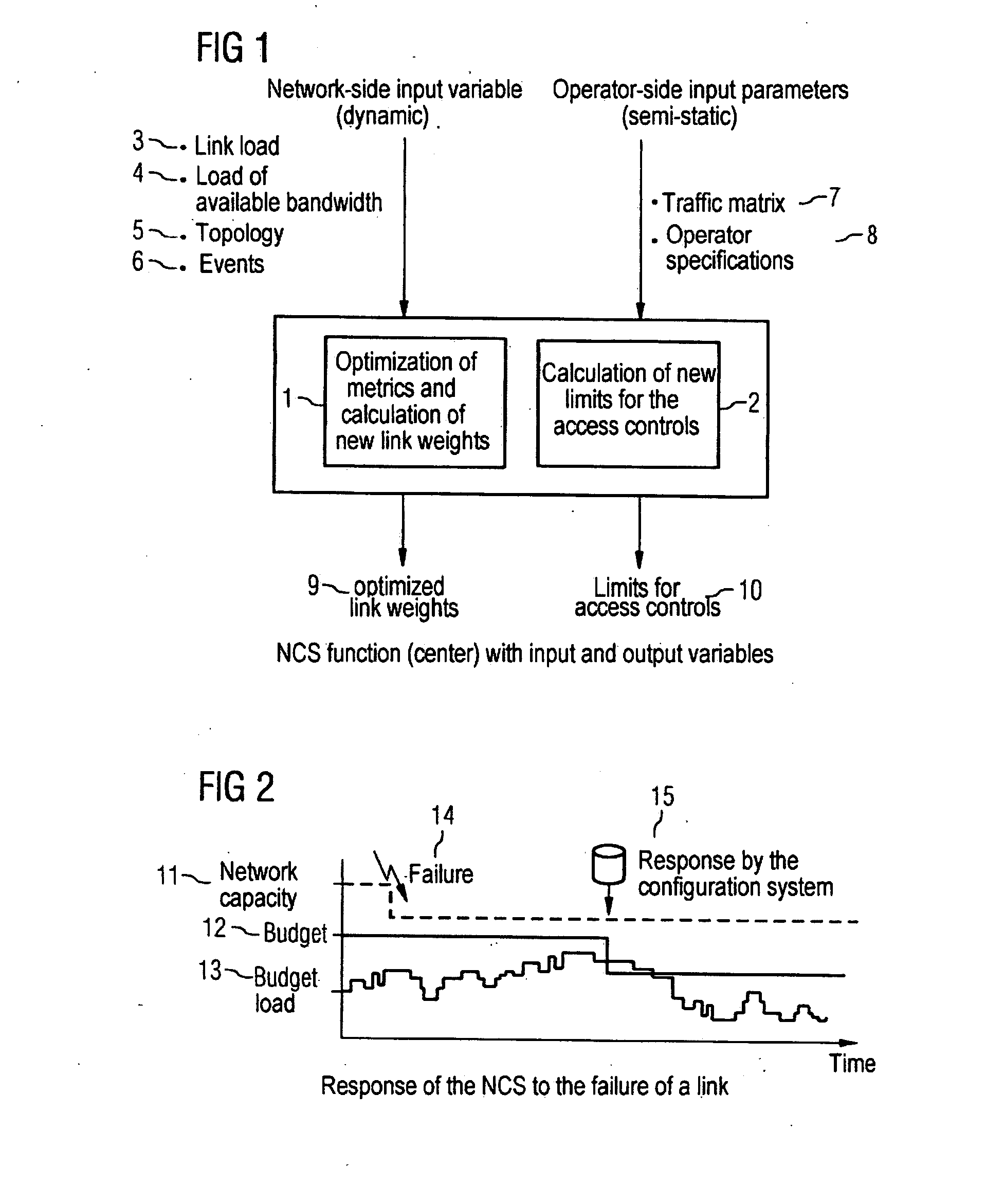
Method and Device for the Automatic Readjustment of Limits for Access Controls Used to Restrict Traffic in a Communication Network
InactiveUS20070263540A1Low costEasy to useError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityLink weight
There is described a method and a configuration system for the automatic readjustment of limits for access controls used to restrict the traffic in a communication network formed by links, said communication network comprising control bodies for performing the access controls. The readjustment of limits for access controls is triggered by an event. A traffic matrix of the network is recorded in the configuration system of the communication network, and a recalculation of link weights is carried out by the configuration system by means of a traffic matrix. New limits are determined limits are respectively transmitted to associated control bodies for performing the access restriction and are activated for access controls. The method enables the limits for the access controls to be automatically monitored.
Owner:NOKIA SIEMENS NETWORKS GMBH & CO KG
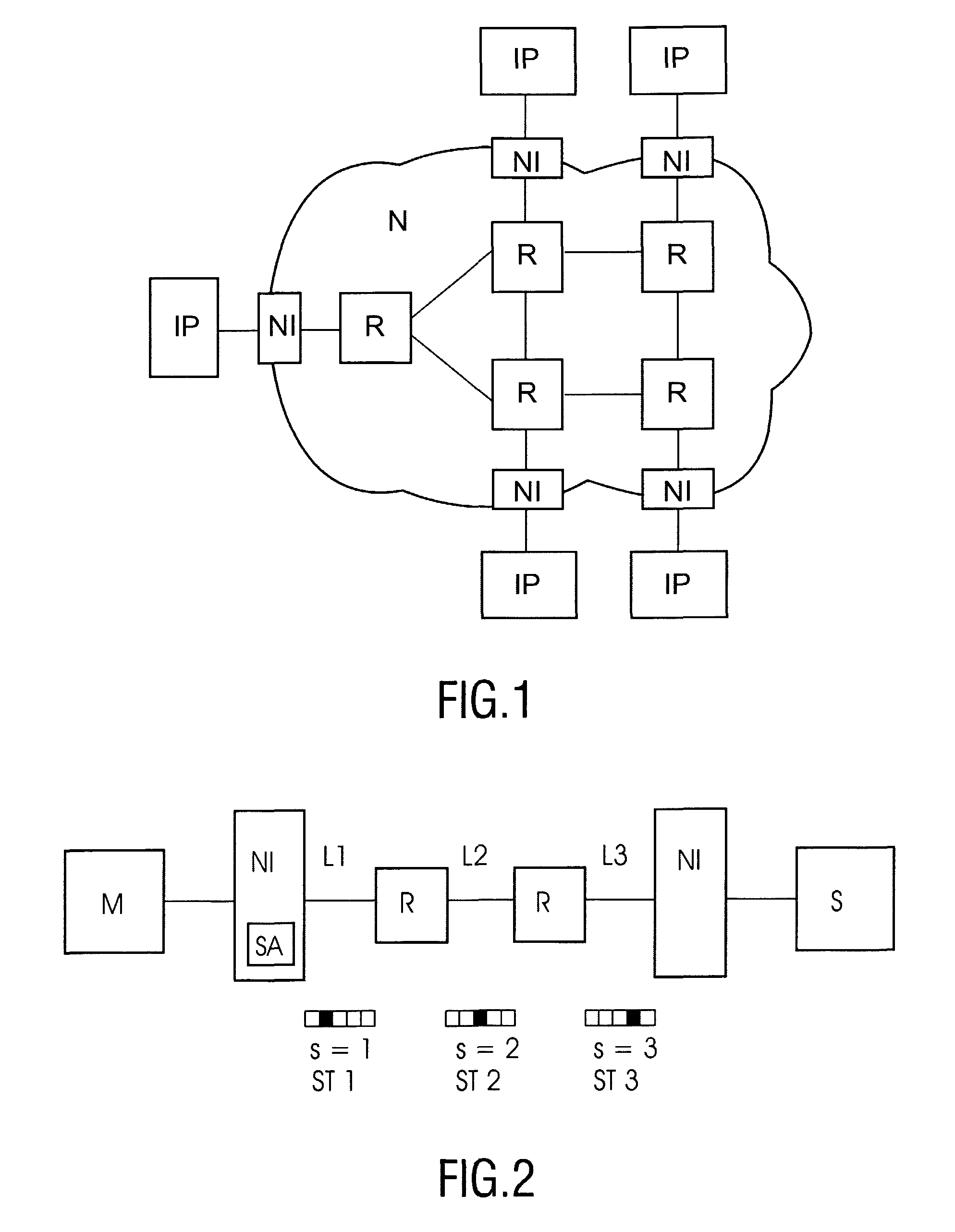
Integrated circuit and method for time slot allocation
ActiveUS20070195748A1Reduce chanceMore freedomData switching by path configurationLink weightCoupling
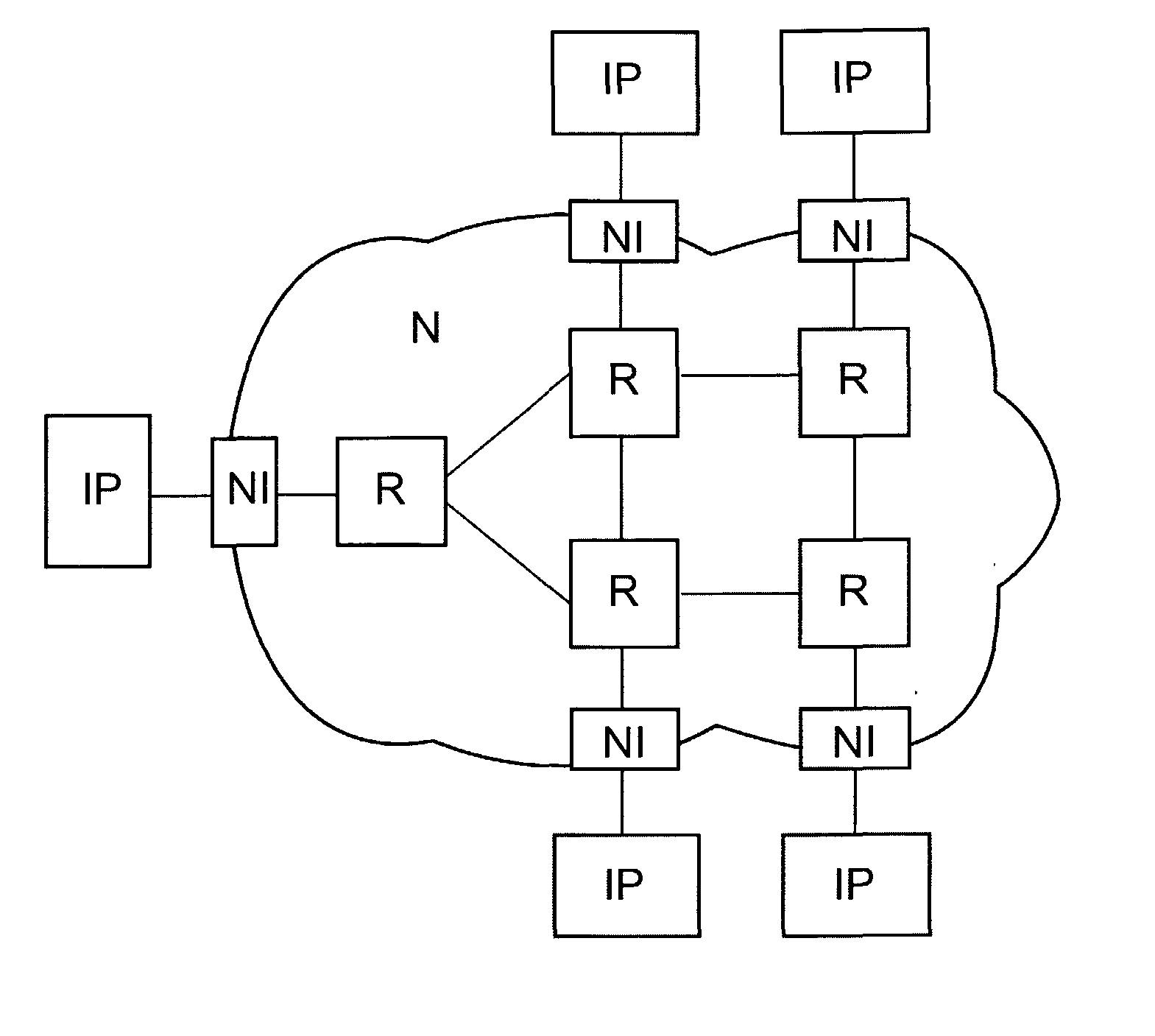
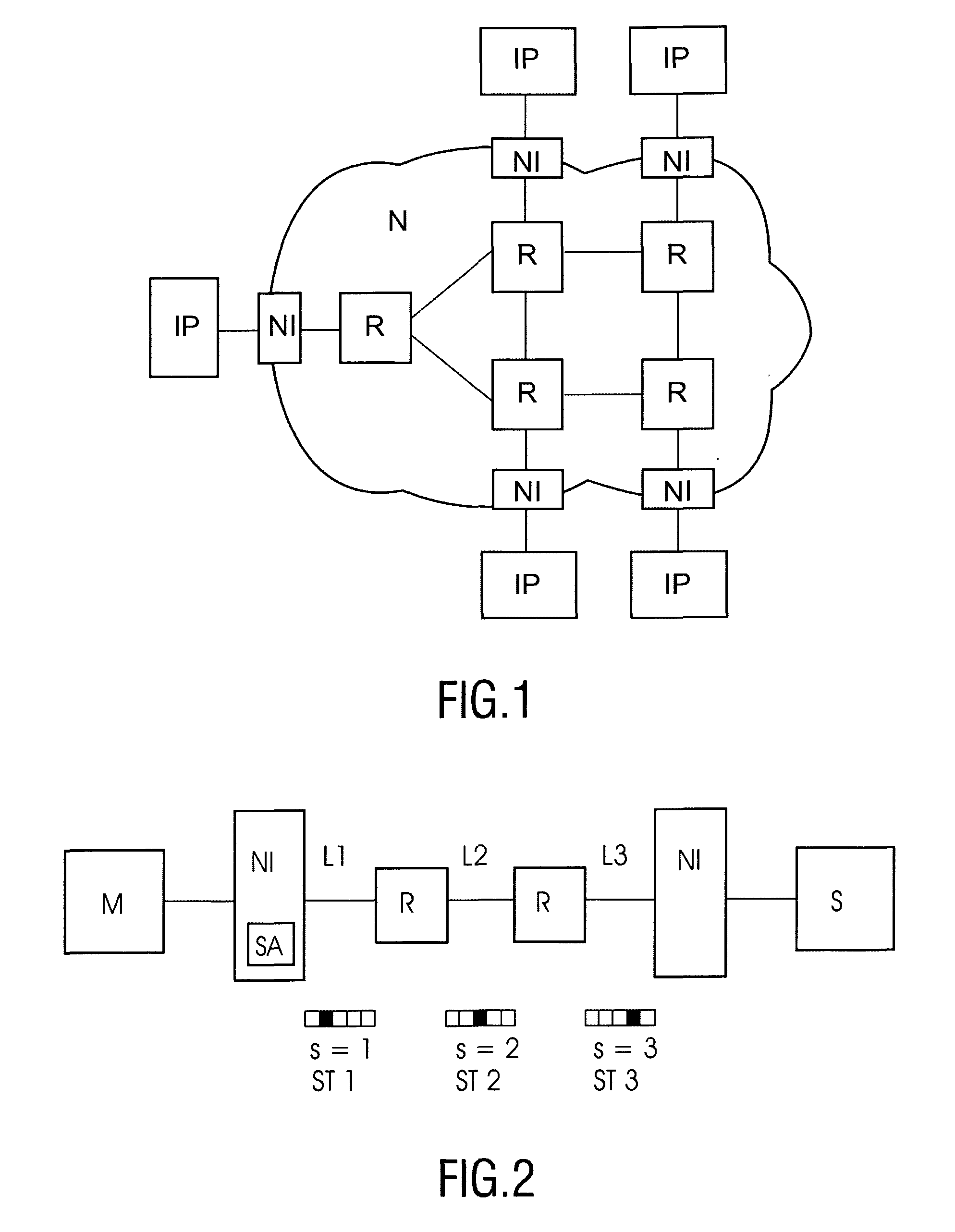
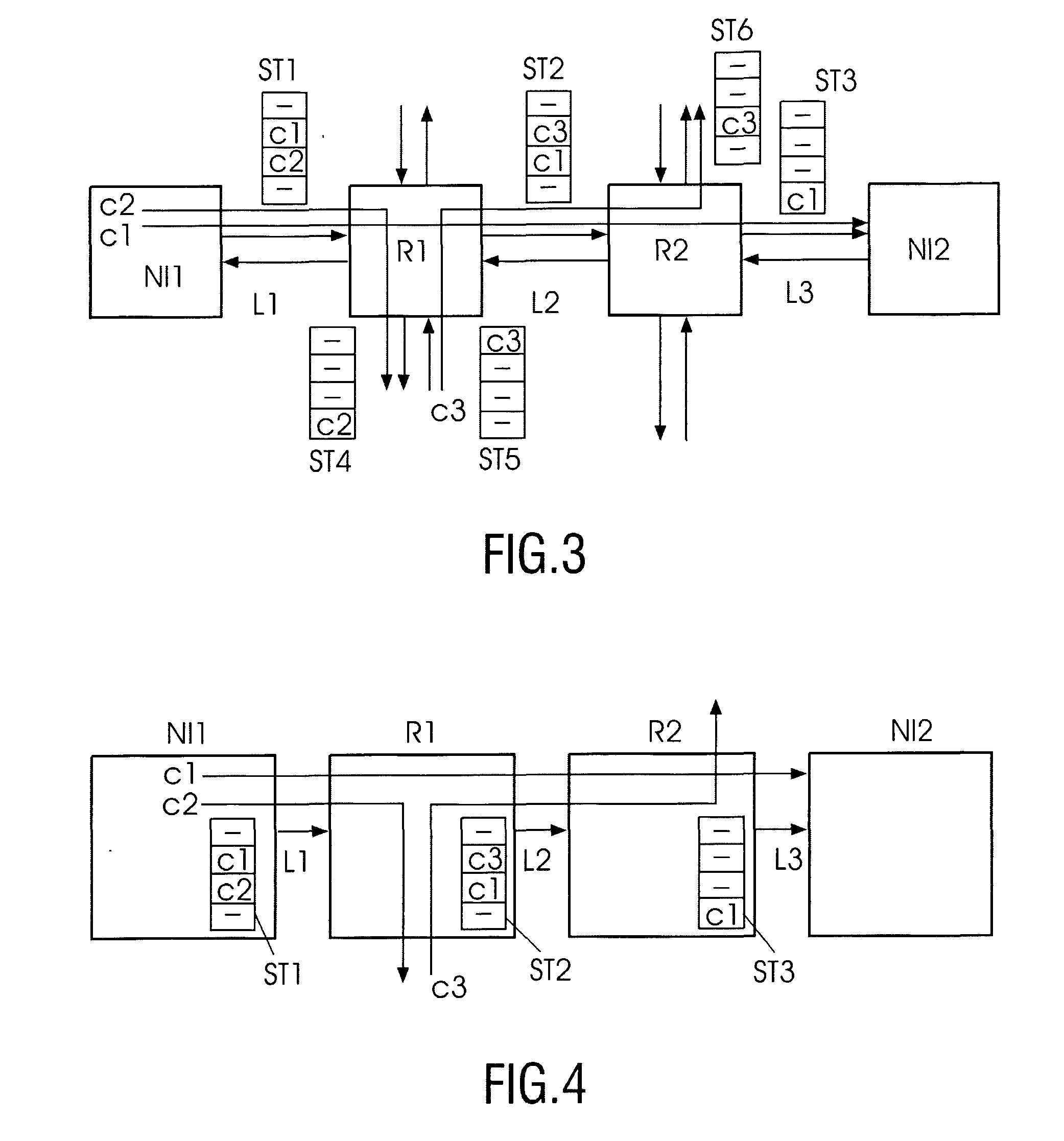
An integrated circuit comprising a plurality of processing modules (M, S; IP) and a network (N) arranged for coupling said modules (M, S; IP) is provided. Said integrated circuit further comprises a plurality of network interfaces (NI) each being coupled between one of said processing modules (M, S; IP) and said network (N). Said network (N) comprises a plurality of routers (R) coupled via network links (L) to adjacent routers (R). Said processing modules (M, S; IP) communicate between each other over connections using connection paths (C1-C12) through the network (N), wherein each of said connection paths (C1-C12) employ at least one network link (L) for a required number of time slots. At least one time slot allocating unit (SA) is provided for computing a link weight factor for at least one network link (L) in said connection path (C1-C12) as a function of at least one connection requirement for said at least one network link (L), for computing a connection path weight factor for at least one connection path (C1-C12) as a function of the computed link weight factor of at least one network link (L) in said connection path (C1-C12), and for allocating time slots to said network links (L) according to the computed connection path weight factors.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV +1
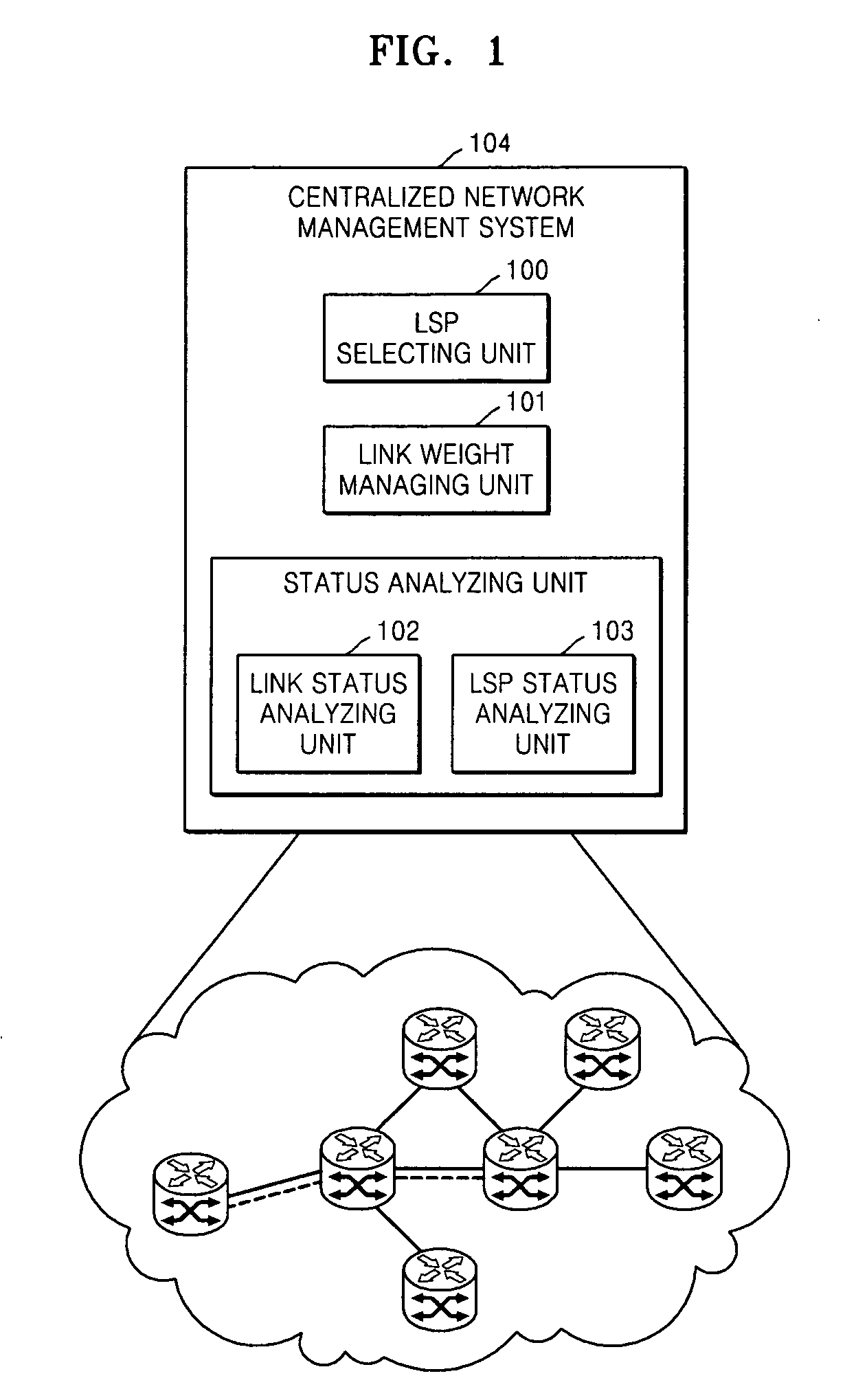
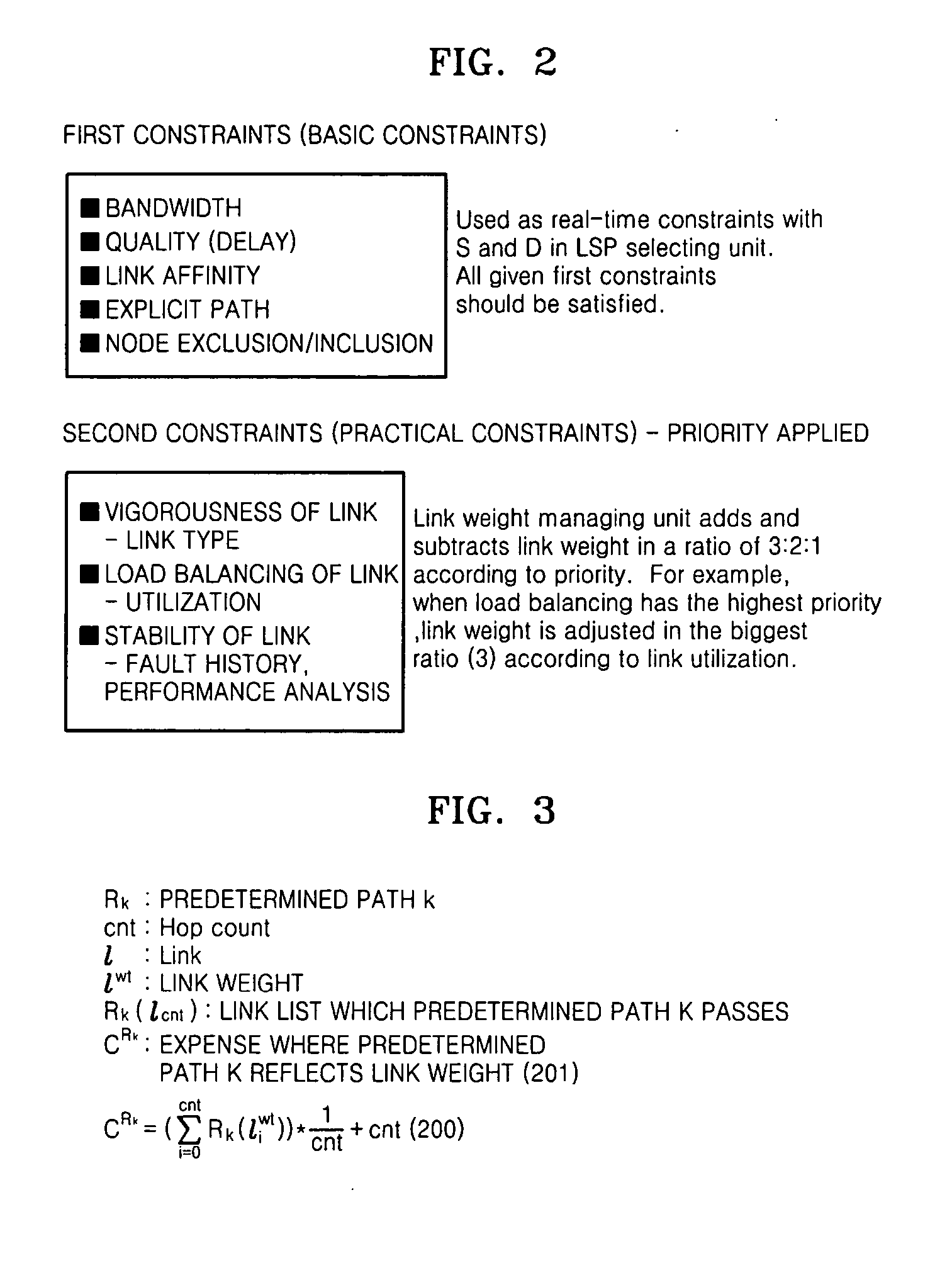
Apparatus and method of selecting label switched path in network management system
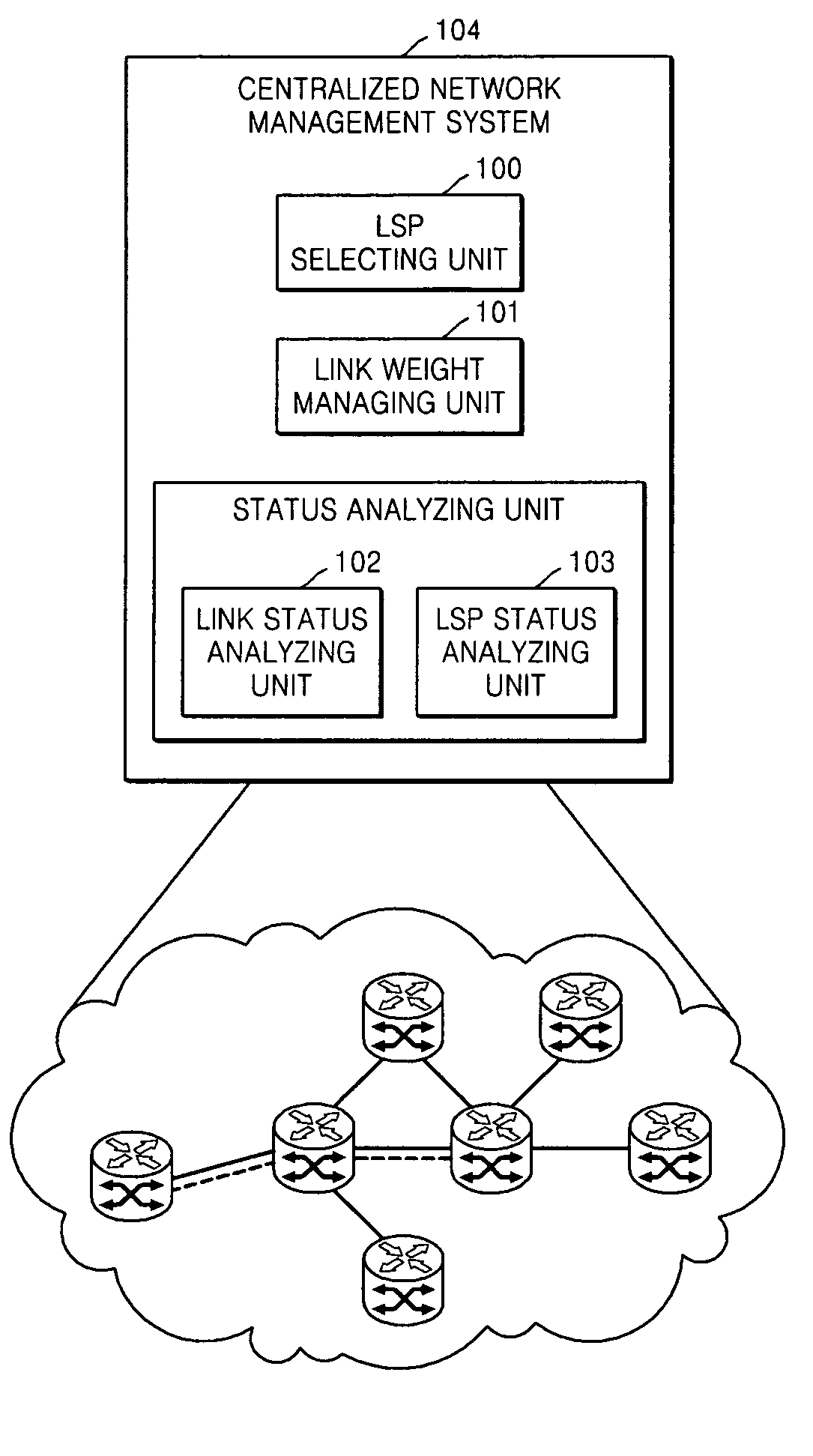
ActiveUS20070133433A1Improve reliabilityImprove adaptabilityData switching by path configurationManagement unitLink weight
Provided are an apparatus and method of selecting a label switched path (LSP) in a network management system. The apparatus comprises a status analyzing unit which analyzes and digitizes performance information, fault occurrence, and fault history of a link in order to convert the performance information, fault occurrence, and fault history into standardized values, a link weight managing unit which determines link weight values using values obtained by adding and subtracting reference values, calculated using a predetermined weight calculation algorithm on second constraints that corresponds to qualitative information related to performance analysis of a path required by an administrative network policy, to and from the standardized values of the status analyzing unit, and an LSP selecting unit which prepares a path list by using a method of executing a predetermined background task by appointing a source and a destination from among all nodes in the administrative network, selects a path, from among paths on the path list, that satisfies first constraints which corresponds to objective information related to a path selection required by the administrative network policy, and, when there are several selected paths, selects a path that minimizes expense using the link weight values. Using the apparatus, the optimum path according to the administrative network policy can be selected.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Method for estimating a traffic matrix in a communication network using stationary data
InactiveUS7353294B1Improve forecastAdd modelError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityLink weight
The present invention comprises methods for increasing the rank of the routing matrix of an IP network by systematically altering link weights in the IP network. A full rank routing matrix may be used with further methods in accordance with the present invention to estimate the mean traffic of the IP network based upon the full rank routing matrix and measured link utilization values. The mean traffic and the covariance of the traffic may be iteratively estimated until the estimates coverage. Example methods in accordance with the present invention for estimating mean traffic and covariance of traffic are described for both stationary and non-stationary link utilization data.
Owner:SPRINT CORPORATION
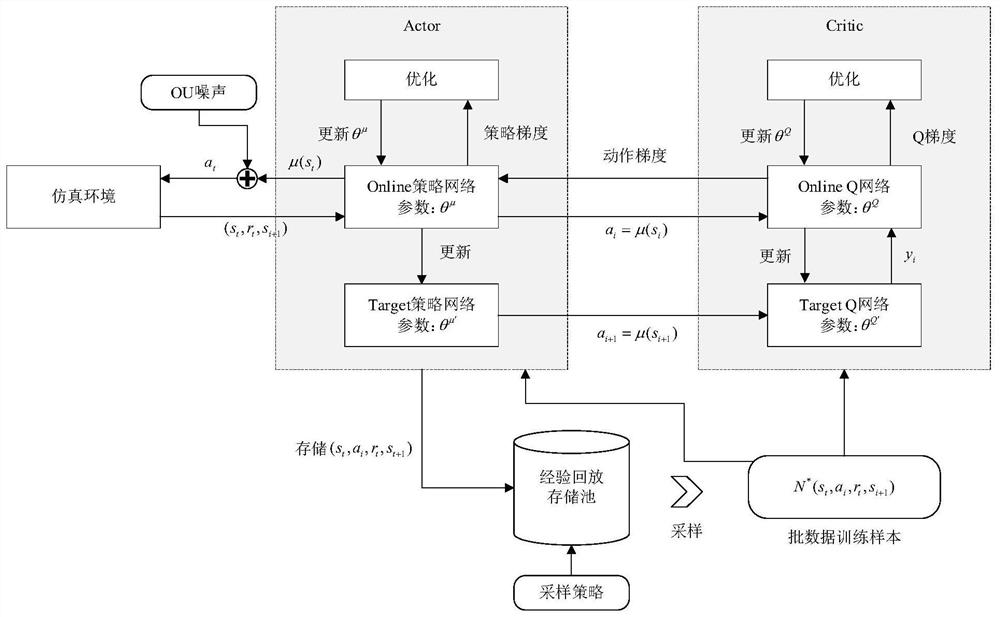
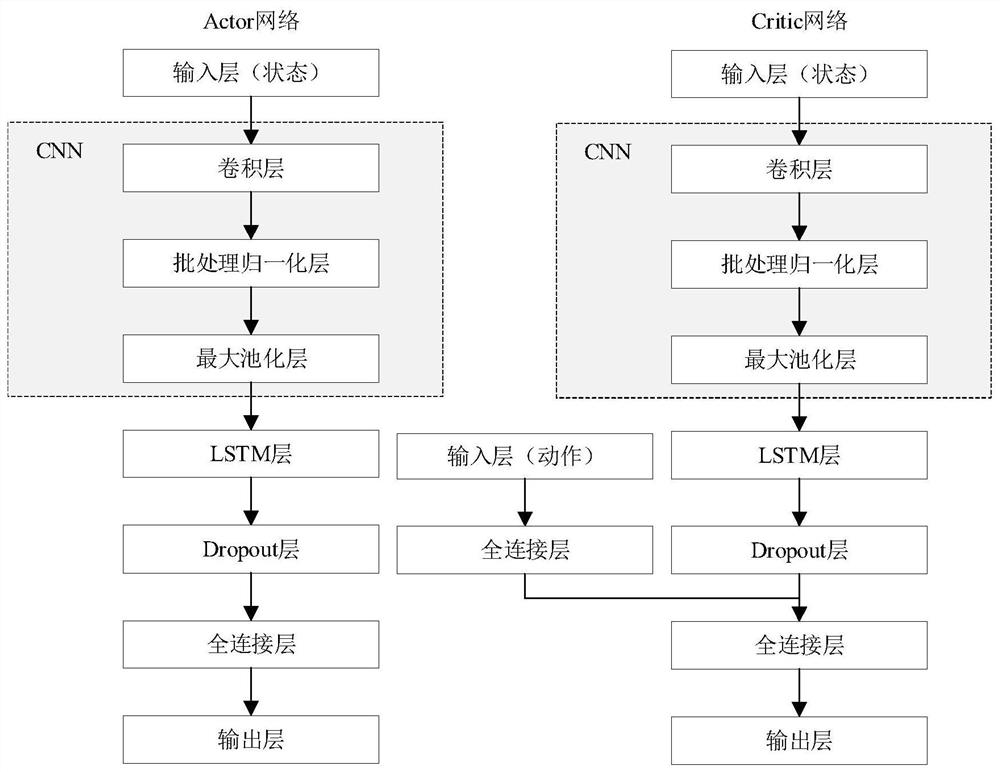
Network autonomous intelligent management and control method based on deep reinforcement learning
ActiveCN113328938ARealize autonomous intelligent management and controlRealize self-optimizationMachine learningNeural architecturesPathPingEngineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of artificial intelligence, and particularly relates to a network autonomous intelligent management and control method based on deep reinforcement learning. The method comprises the steps of firstly constructing a network topology, then introducing a CNN, an LSTM layer and a delay updating strategy to construct a routing decision-making model based on a DDPG reinforcement learning algorithm, and finally performing iterative training on the routing decision-making model based on deep reinforcement learning. In each iterative training, an intelligent agent obtains an output action, namely a group of link weights, according to a measured network state and a neural network, and calculates a service route by using a shortest path algorithm according to the link weights. According to a routing calculation result, the intelligent agent issues a flow table, and acquires end-to-end time delay and a packet loss probability of the service to calculate a reward value of the iteration. The algorithm has good convergence, and can effectively reduce the end-to-end delay and packet loss rate of the service.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
System and method for determining initial relevance of a document with respect to a given category
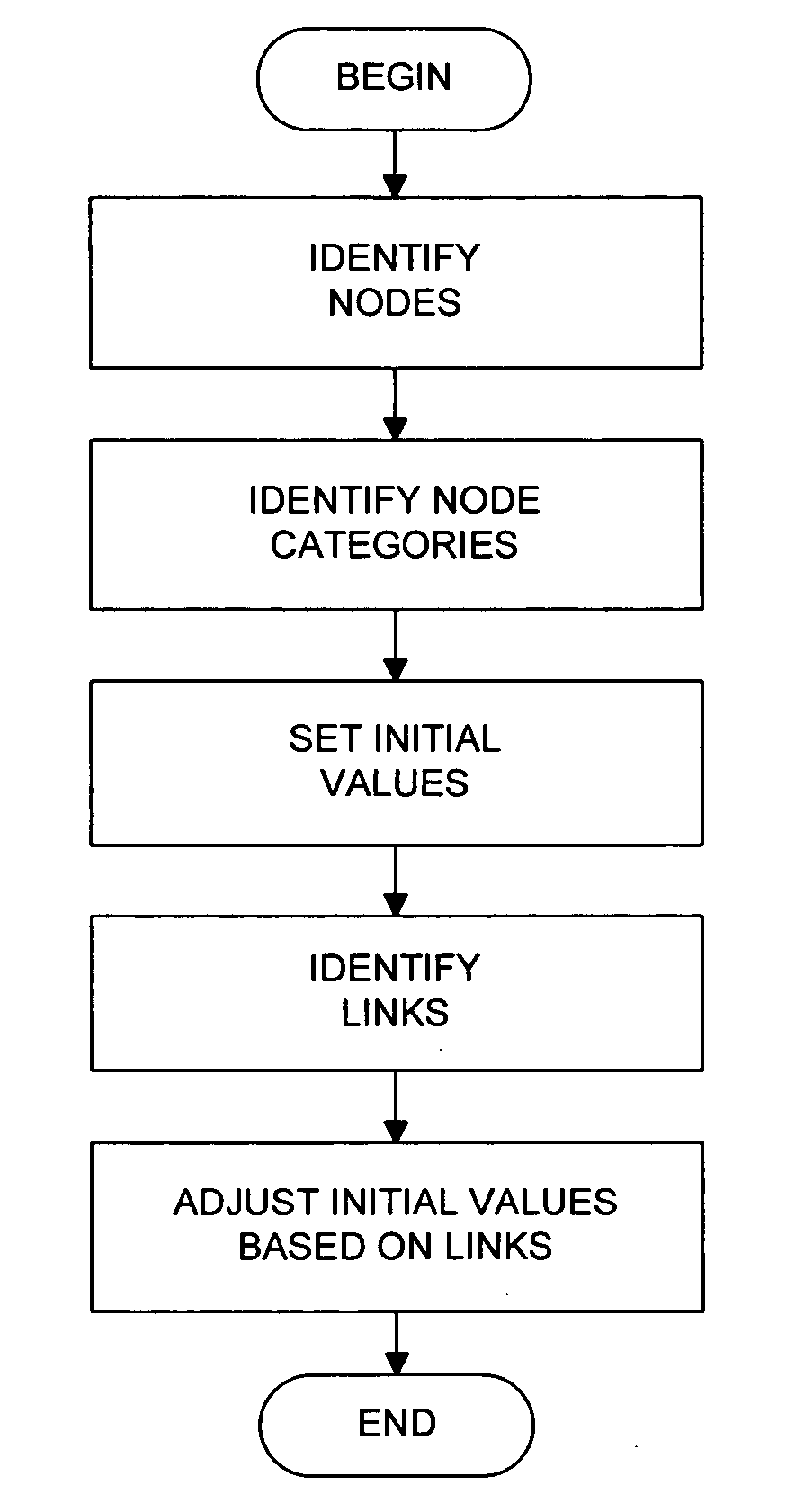
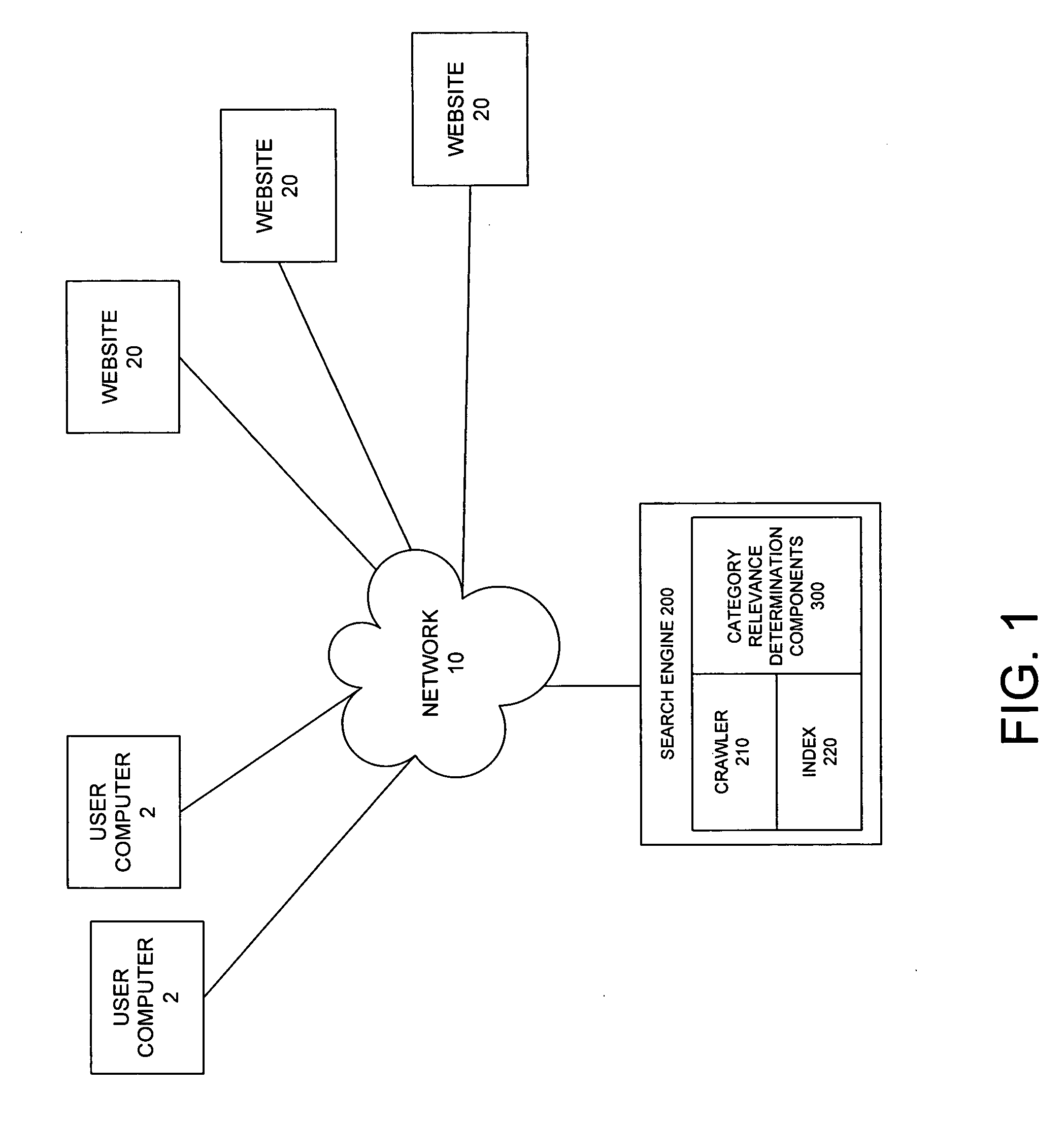
InactiveUS20060195439A1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalLink weightPaper document
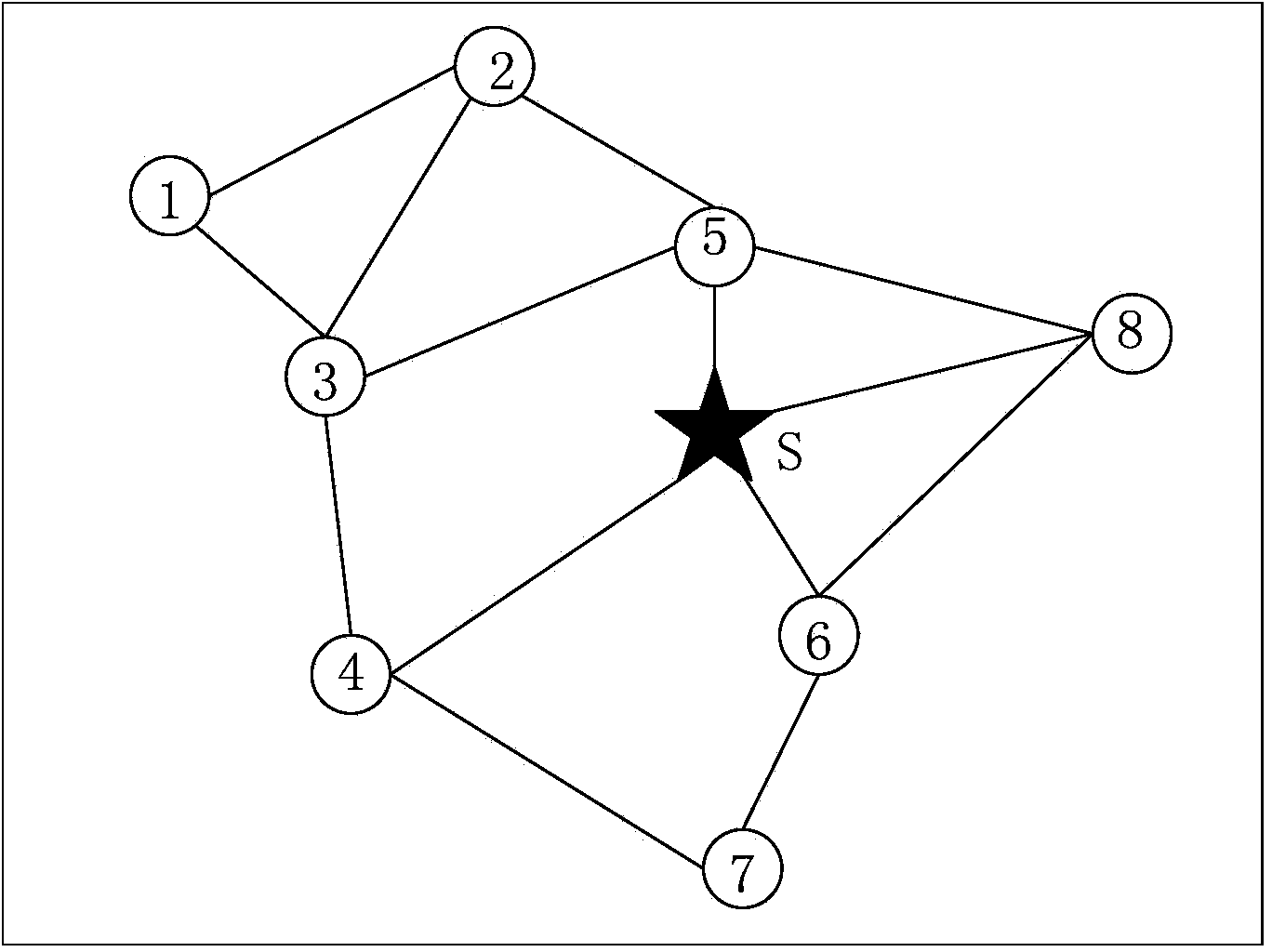
A system and method are provided for determining document relevance determination to a selected category for a document contained within a linked network of documents. The network may be represented by a network map including nodes representing documents and edges representing links between the documents. The method may include identifying each node in the network map known to belong to the selected category, identifying each node known to be outside of the selected category, and identifying nodes having an unknown category. The method may also include assigning a category rank based on the node category identification, identifying each link from each node and each link to each node, and assigning link weights based on the identified links. The method may additionally include determining node relevance to the selected category based on the assigned category rank and the assigned link weights. An origination domain and a destination domain for each link may be determined such that link weights are assigned for both incoming and outgoing links for each node.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
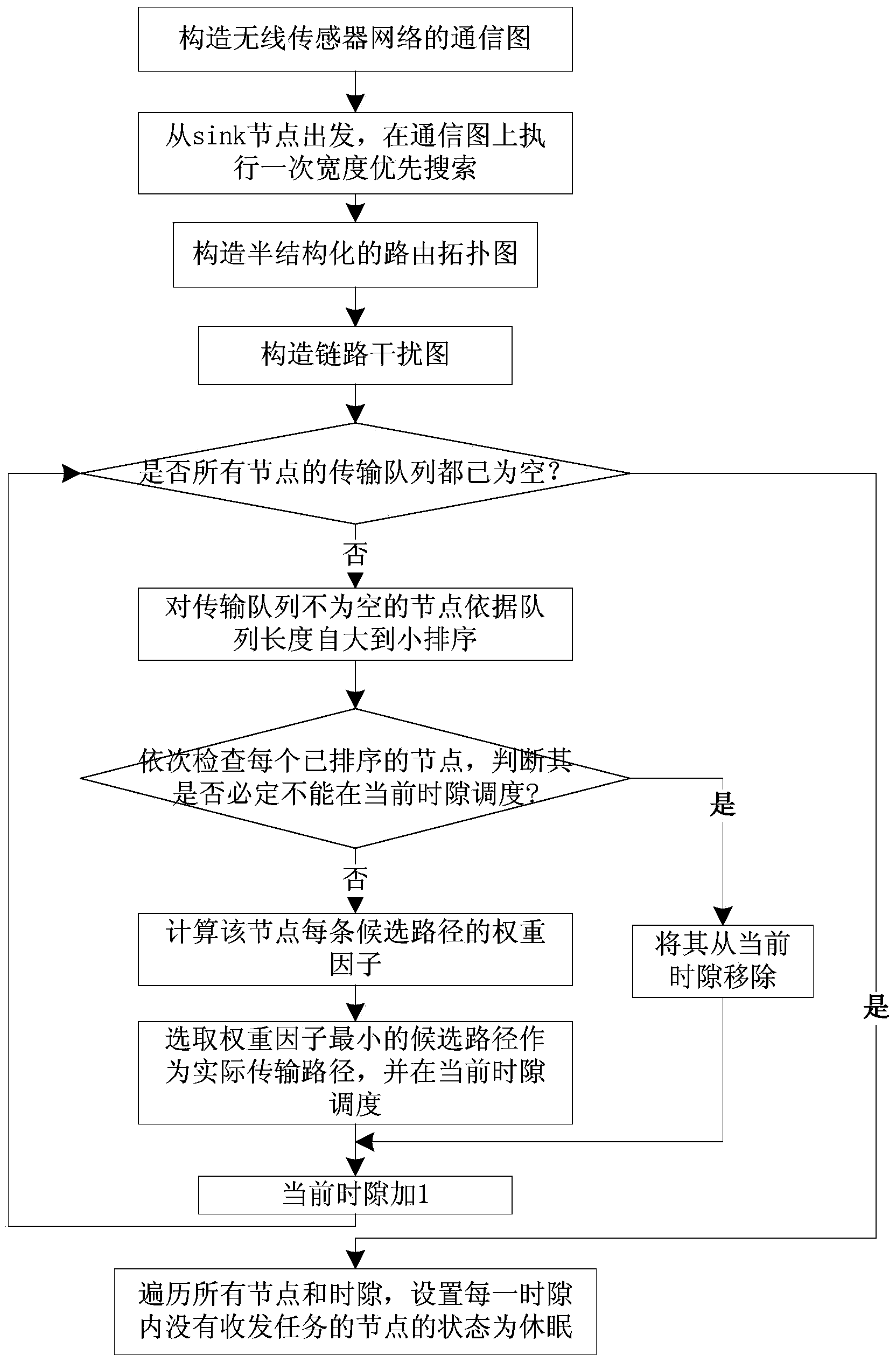
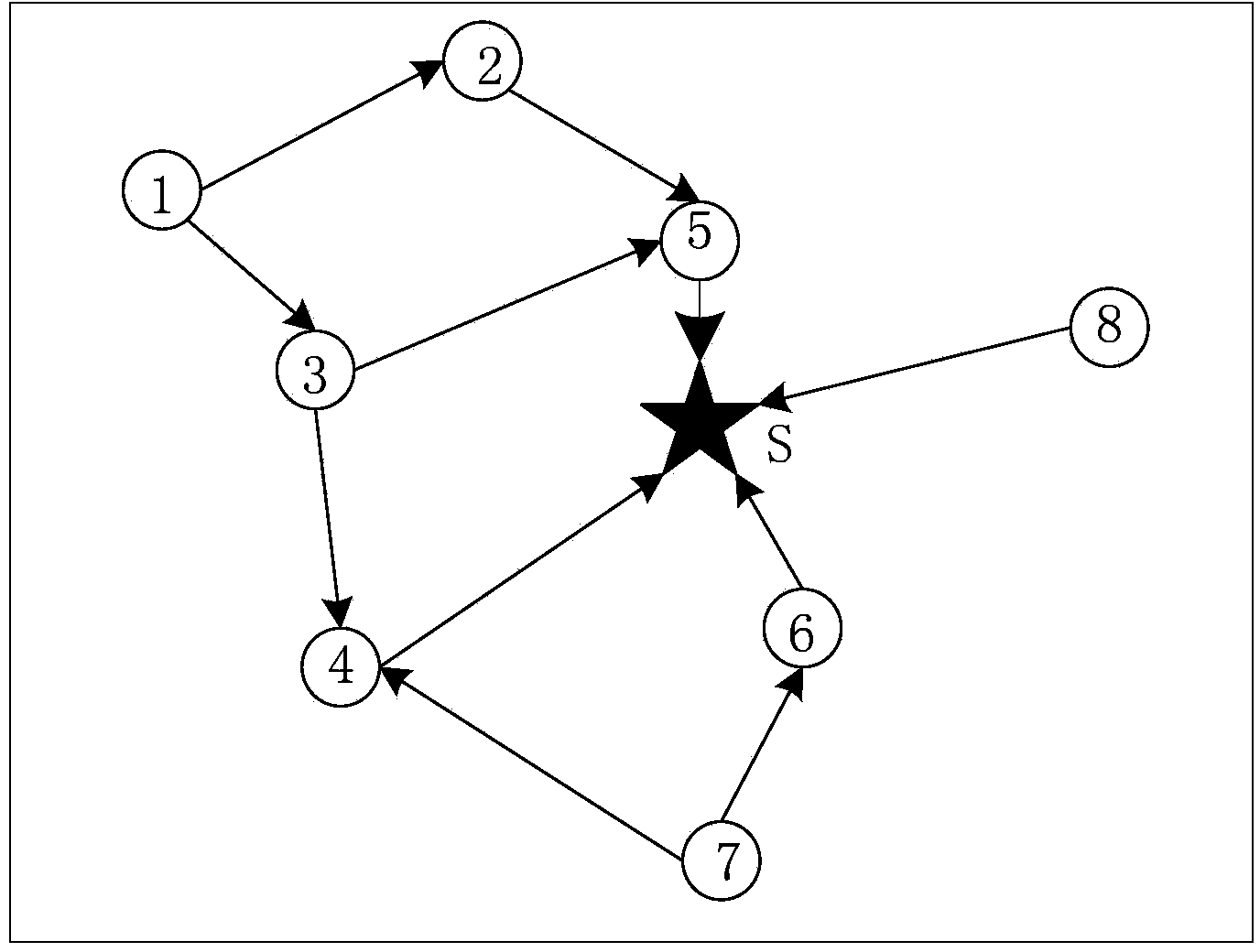
Semi-structured transmission dispatching method orienting wireless sensor network data collection
ActiveCN104301966AReduce energy consumptionExtend the life cyclePower managementHigh level techniquesSemi-structured dataInterference factor
The invention discloses a semi-structured transmission dispatching method orienting wireless sensor network data collection. The method is characterized by comprising the steps that 1, breadth-first search is carried out on a network communication graph, so that a slack semi-structured data collection route topological graph is constructed; 2, a link interference graph is constructed according to the main interference and subsidiary interference relation between transmission links in a network; 3, link weight interference factors are defined, so that the interference intensity caused to other links of the network from transmission loads of sending nodes and sending links is comprehensively weighed; 4, the dynamic link selection and time slot allocation strategy based on preference of the minimum weight is carried out; 5, a node dormant state is controlled in an explicit mode, and a data collection period is adjusted in a self-adaptive mode. According to the method, routing and dispatching are designed in a unified mode on the basis of a cross-layer design idea, the time slot utilization rate of dispatching is increased by fully utilizing the redundancy of a path, time delay of data collection is shortened, and the handling capacity of the network is improved. The method is applied to the wireless sensor network with the high requirement for the real-time property.
Owner:中科水研(江西)科技股份有限公司
Control apparatus, control method, and engine control unit
A control apparatus which is capable of compensating for a control error properly and quickly even under a condition where the control error is temporarily increased e.g. by degradation of reliability of the detection results of reference parameters other than controlled variables, thereby making it possible to ensure a high accuracy of control. An air-fuel ratio controller of the control apparatus calculates modified errors by multiplying e.g. an air-fuel ratio error estimated value by link weight functions, calculates basic local correction values such that the modified errors become equal to 0; calculates local correction values by multiplying the basic local correction values and the like by the link weight functions; calculates corrected valve lift by adding a lift correction value, which is the total sum of the local correction values, to a value of valve lift; calculates a first estimated intake air amount for feedforward control of an air-fuel ratio, based on the corrected valve lift; calculates an air-fuel ratio correction coefficient for feedback control of the air-fuel ratio; and calculates a fuel injection amount based on these.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com