Patents
Literature
260 results about "Core router" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
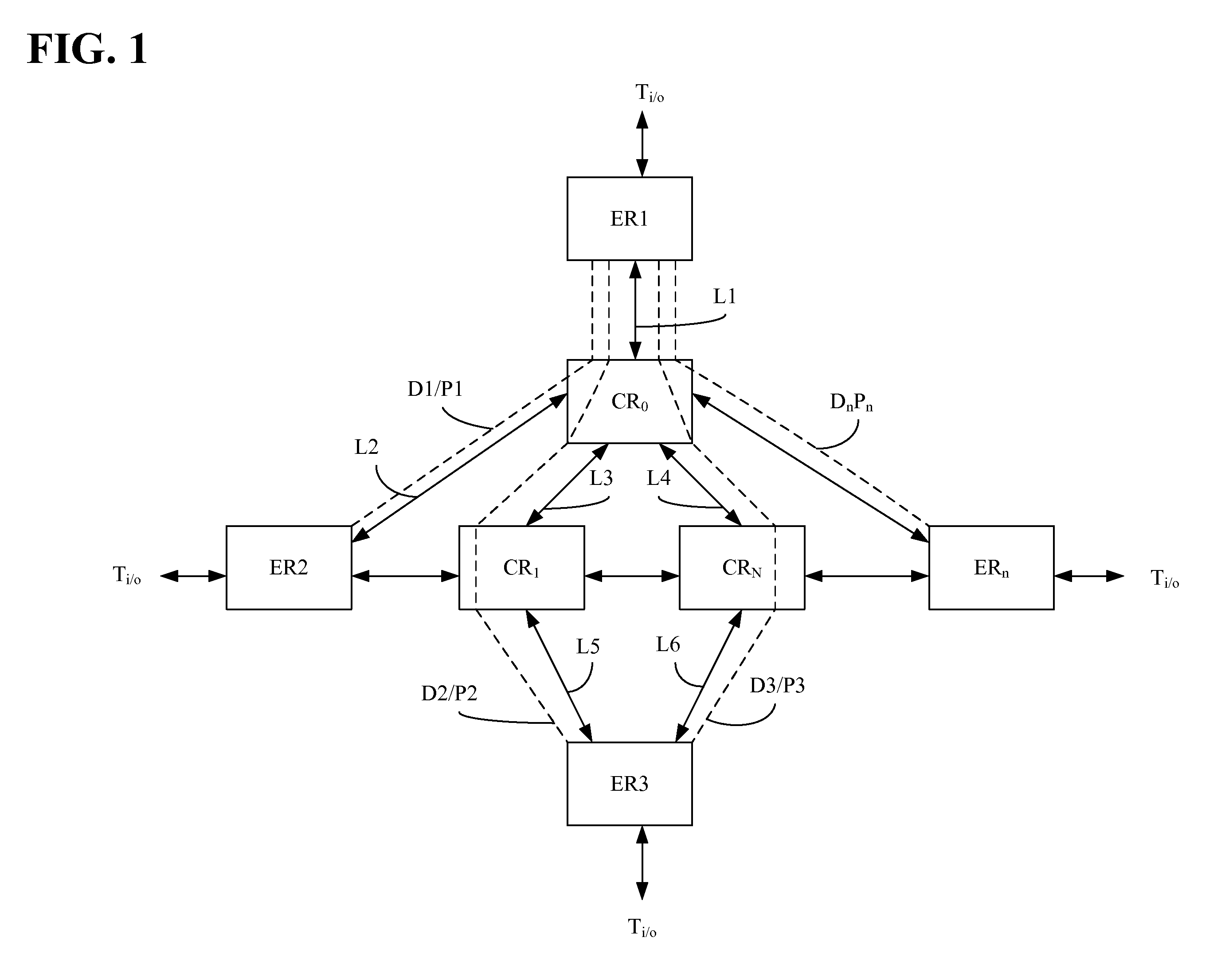
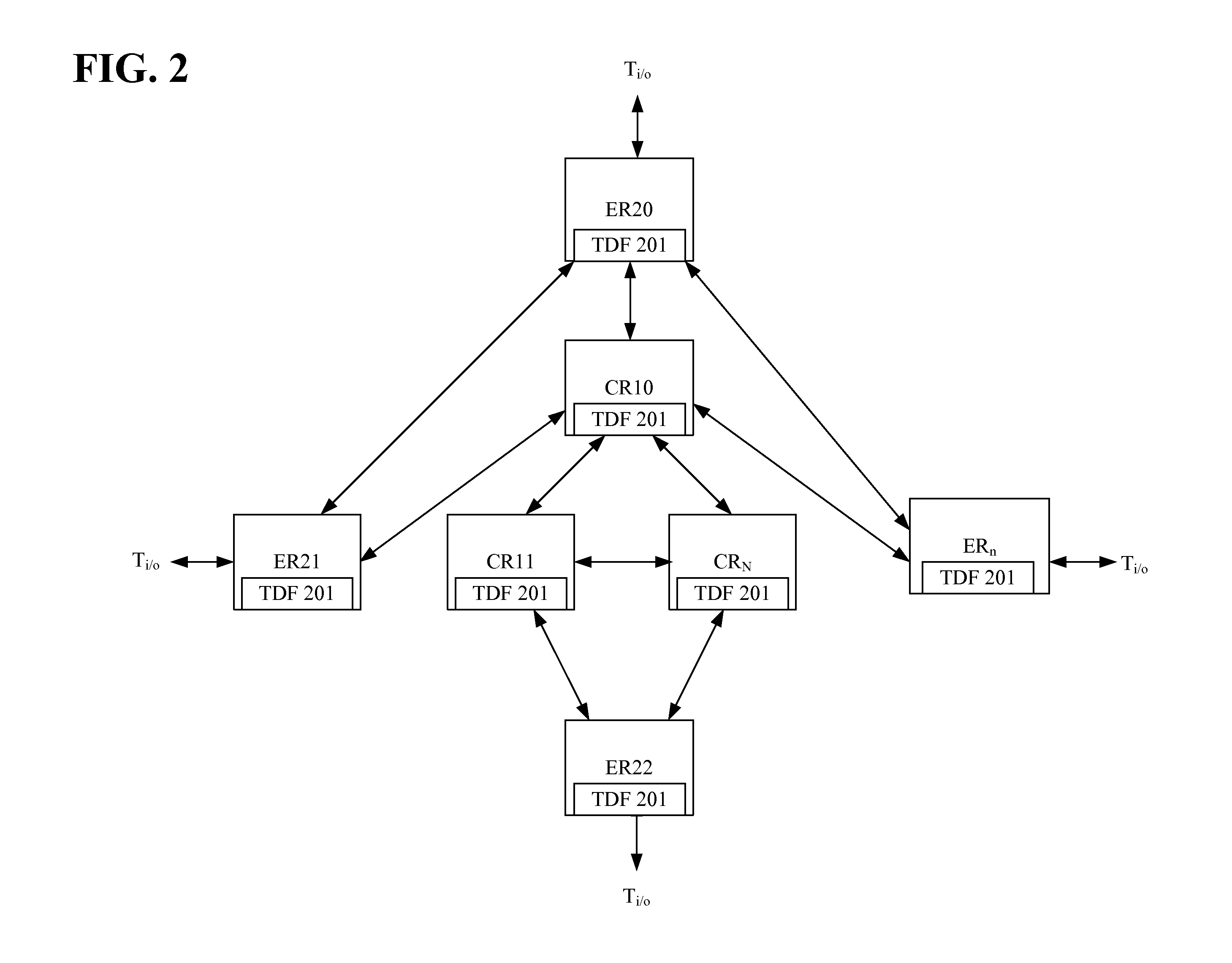
A core router is a router designed to operate in the Internet backbone, or core. To fulfill this role, a router must be able to support multiple telecommunications interfaces of the highest speed in use in the core Internet and must be able to forward IP packets at full speed on all of them. It must also support the routing protocols being used in the core. A core router is distinct from an edge router: edge routers sit at the edge of a backbone network and connect to core routers.
System for pricing-based quality of service (PQoS) control in networks
InactiveUS6910024B2Avoid congestionMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsTelephonic communicationQuality of serviceData stream
Owner:HRL LAB
Method and apparatus for worm detection and containment in the internet core
ActiveUS7712134B1Simple relationshipBridging the gapMemory loss protectionUser identity/authority verificationThe InternetCore router
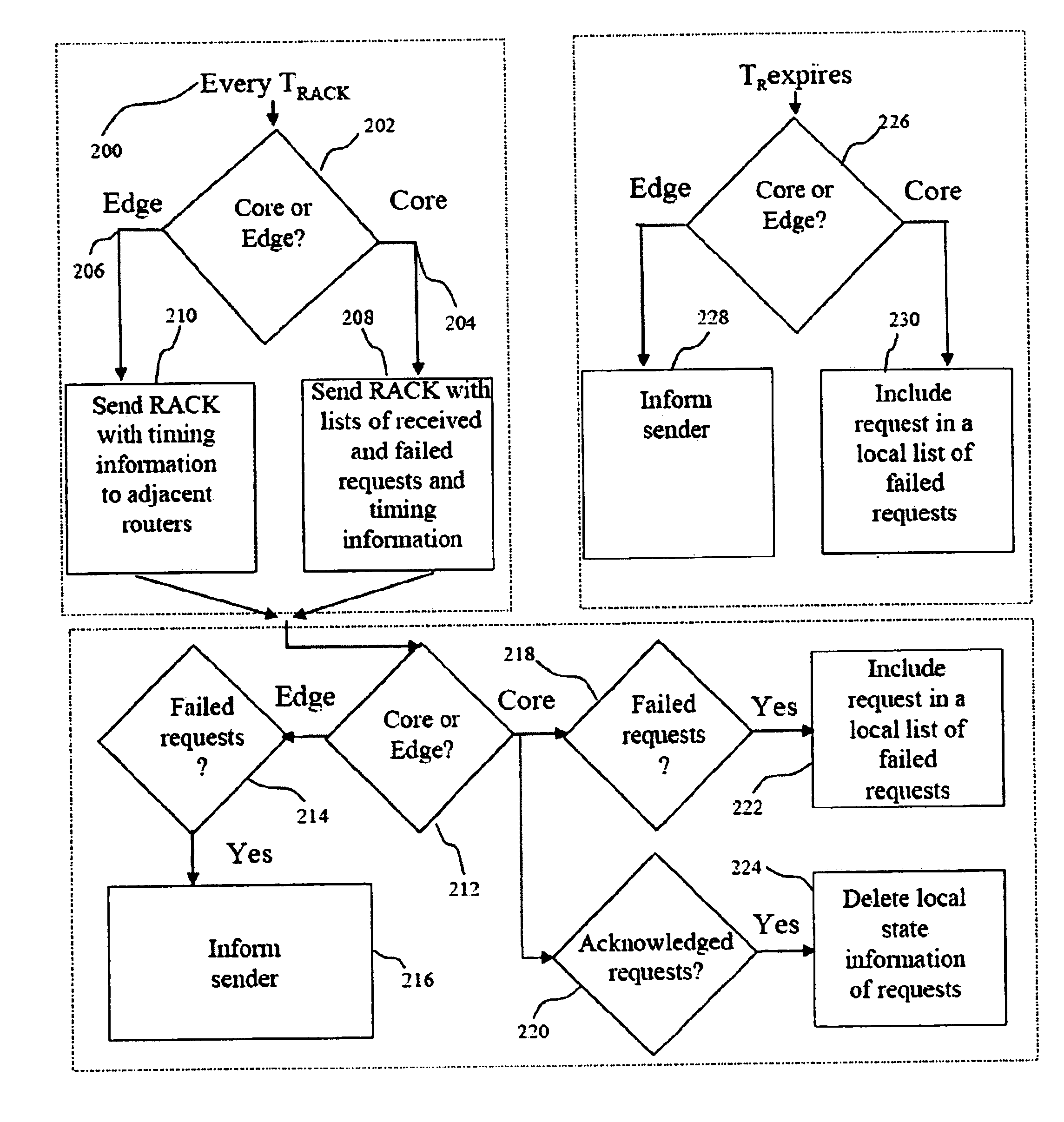
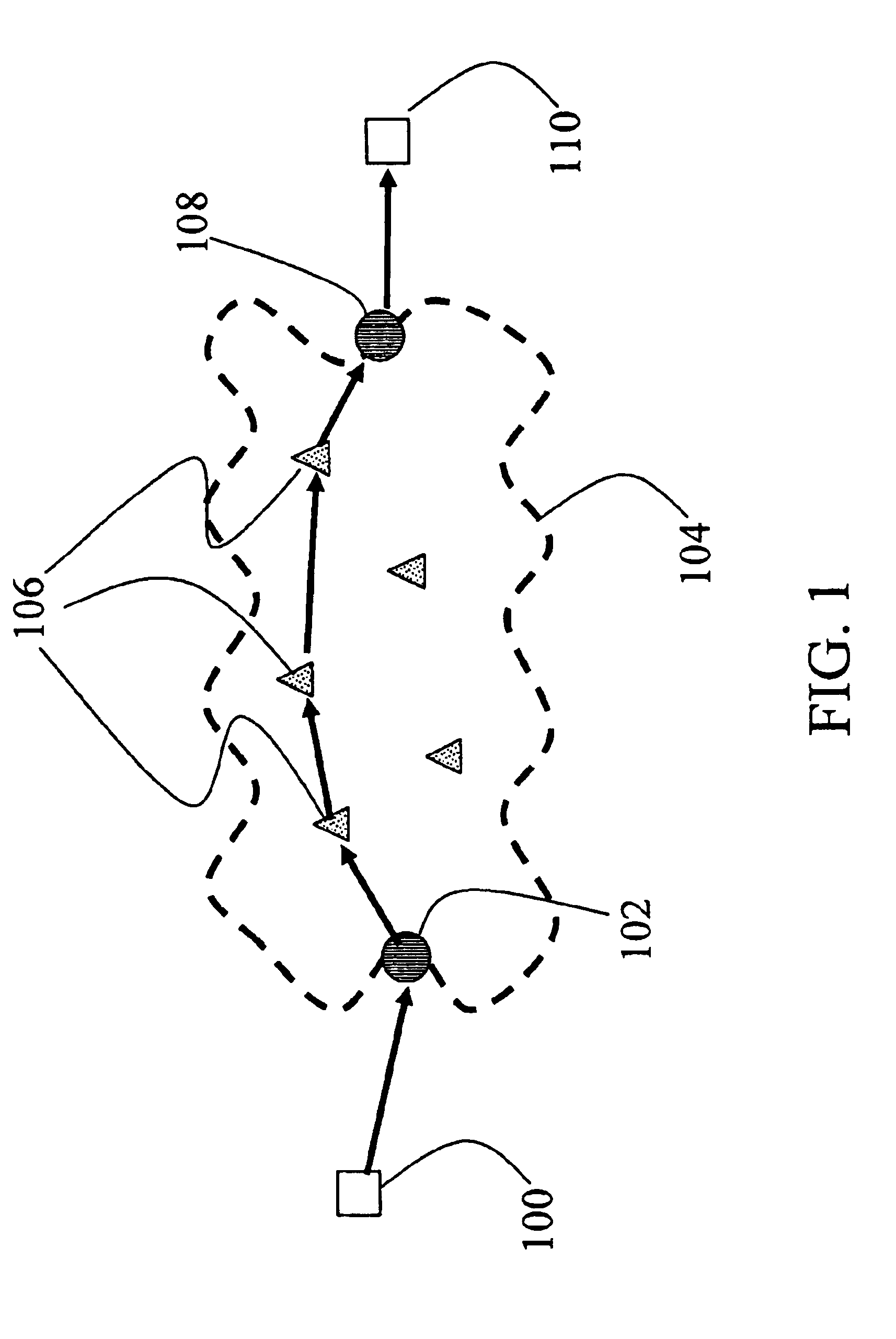
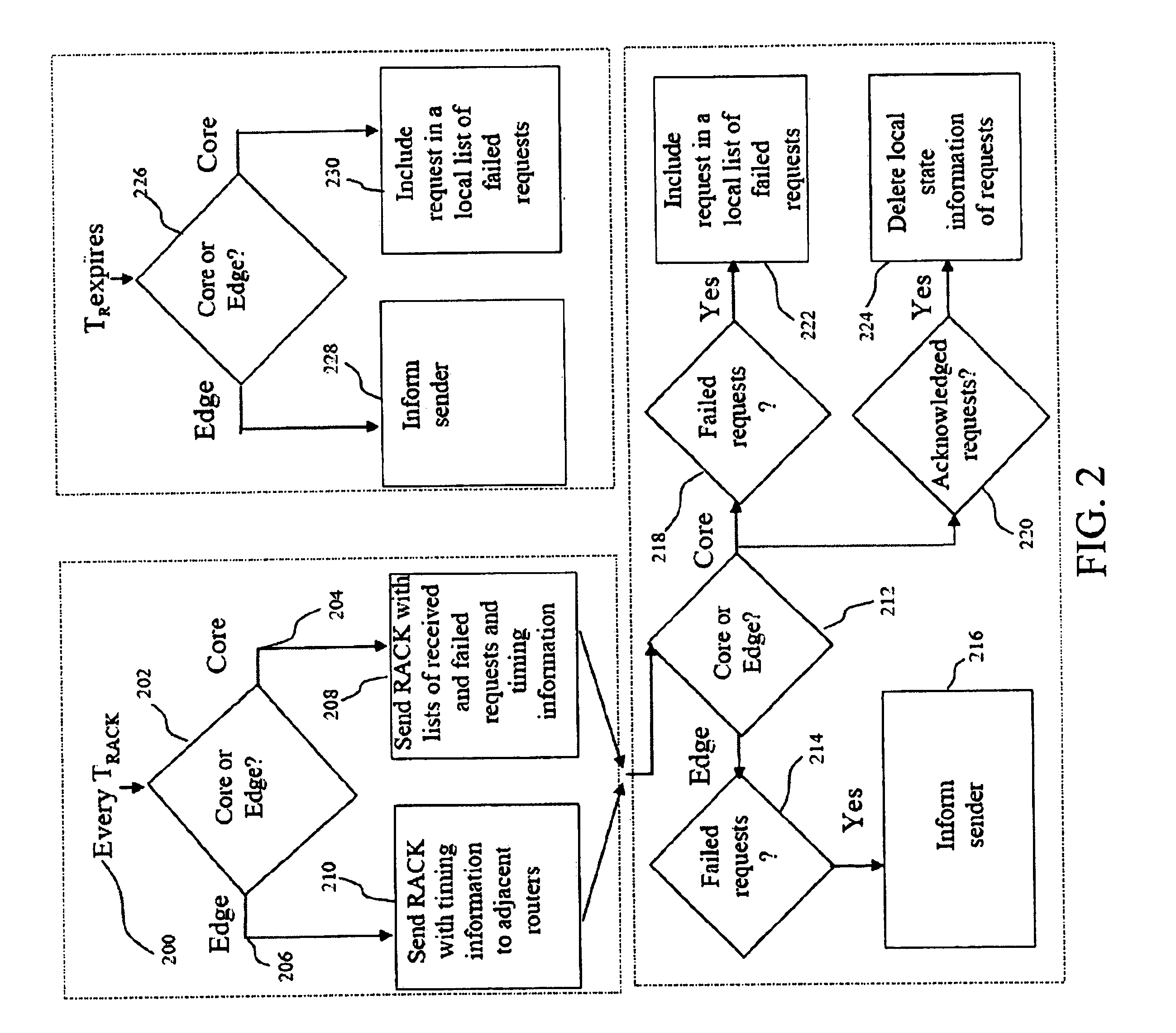
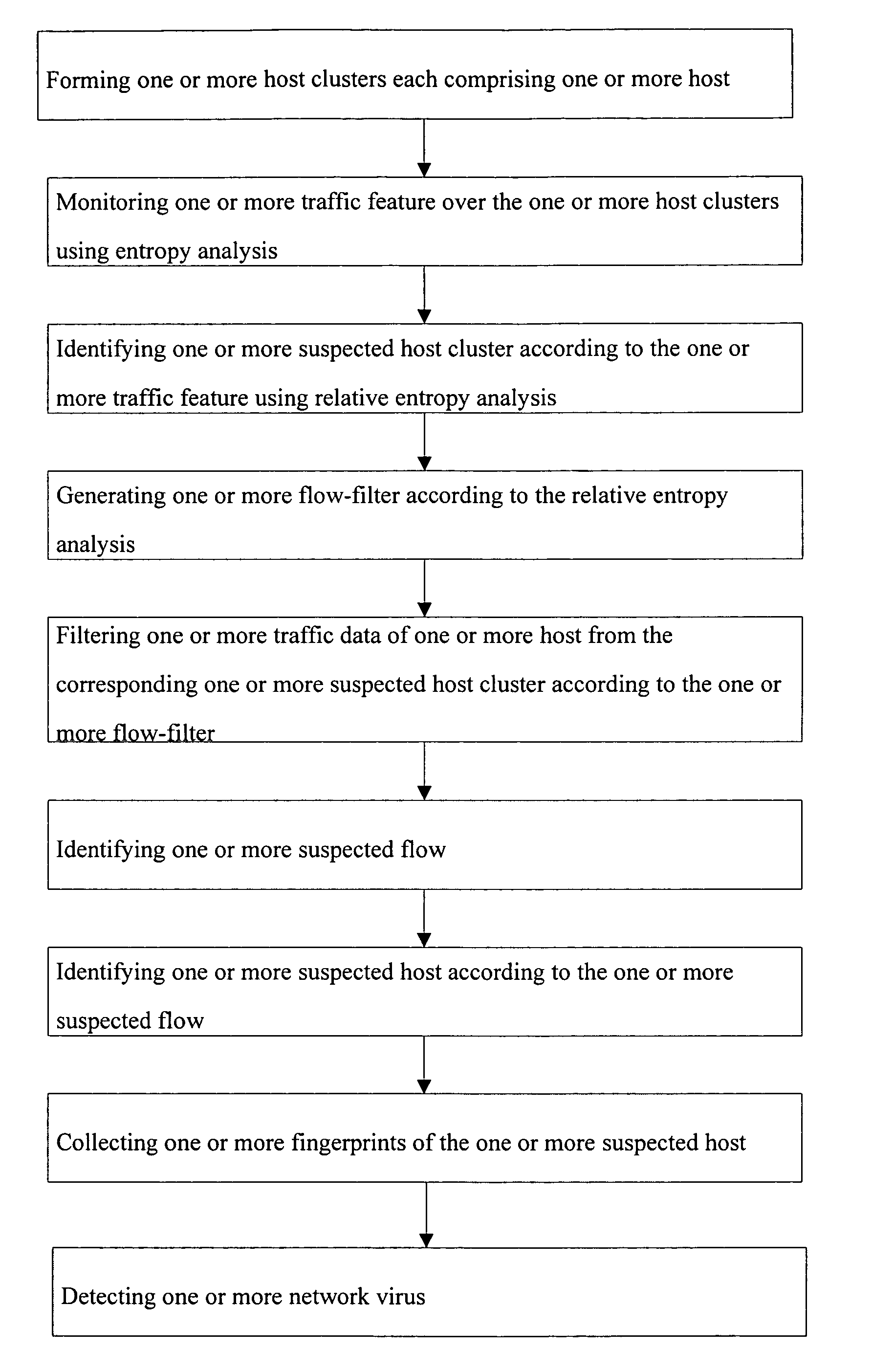
A method and an apparatus is provided that is efficient in detecting network virus and worms while using only the layer-4 information that is easily extracted from core routers and also be scalable when layer-7 information is available. Entropy analysis is used to identify anomalous activity at the flow level. Thereafter, only the contents of suspicious flows are analyzed with fingerprinting extraction. By doing so, the present invention brings together the characteristics of being deployable for real-time high data to rate links and the efficiency and reliability of content fingerprinting techniques.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
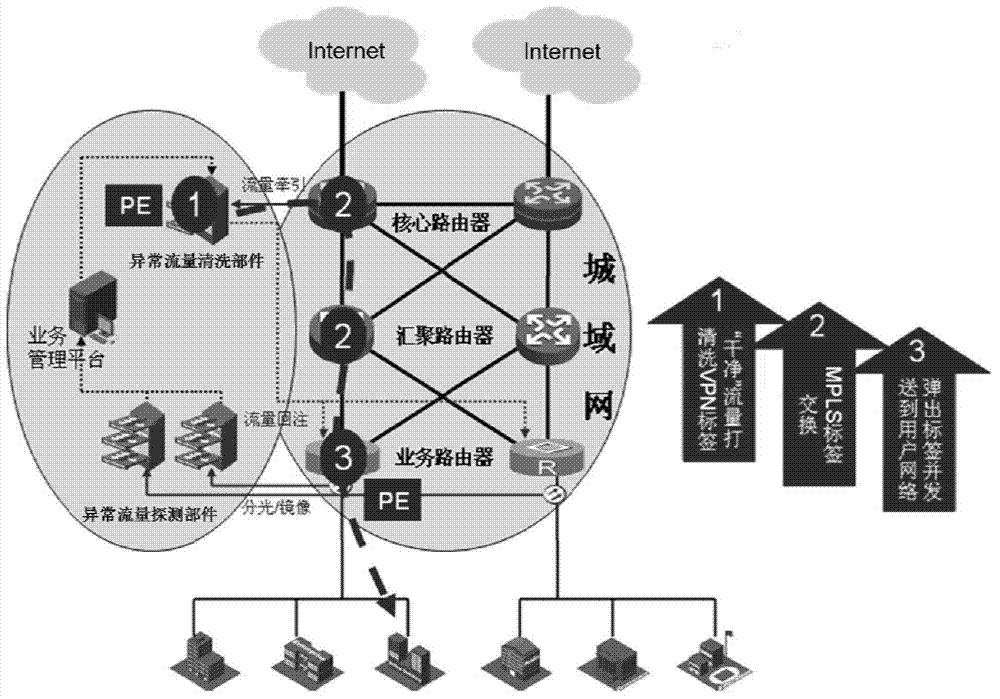
Flow cleaning framework and device and flow lead and reinjection method
The invention discloses a flow cleaning framework and device and a flow lead and reinjection method. The flow lead and reinjection method comprises the steps that a flow cleaning flow table and a flow reinjection flow table are generated by an OpenFlow controller and are issued to an OpenFlow cleaning switcher; a flow lead flow table is generated and is issued to an OpenFlow core router. When a server is attacked, flow of the attacked server led according to the flow lead flow table is matched by the OpenFlow cleaning switcher according to the flow cleaning flow table to carry out flow cleaning; the cleaned clean flow is forwarded according to the flow reinjection flow table to achieve flow reinjection. According to the flow cleaning framework based on OpenFlow, flow lead and flow reinjection are achieved uniformly; an abnormal flow cleaning component is composed of the OpenFlow controller and the OpenFlow cleaning switcher to achieve separation of control over a flow cleaning system and forwarding of the flow cleaning system; when service requirements are changed, all kinds of flow tables can be updated just through the OpenFlow controller, and accordingly reconfiguration and redeploy of a network are easily and flexibly achieved.
Owner:CHINA UNITED NETWORK COMM GRP CO LTD
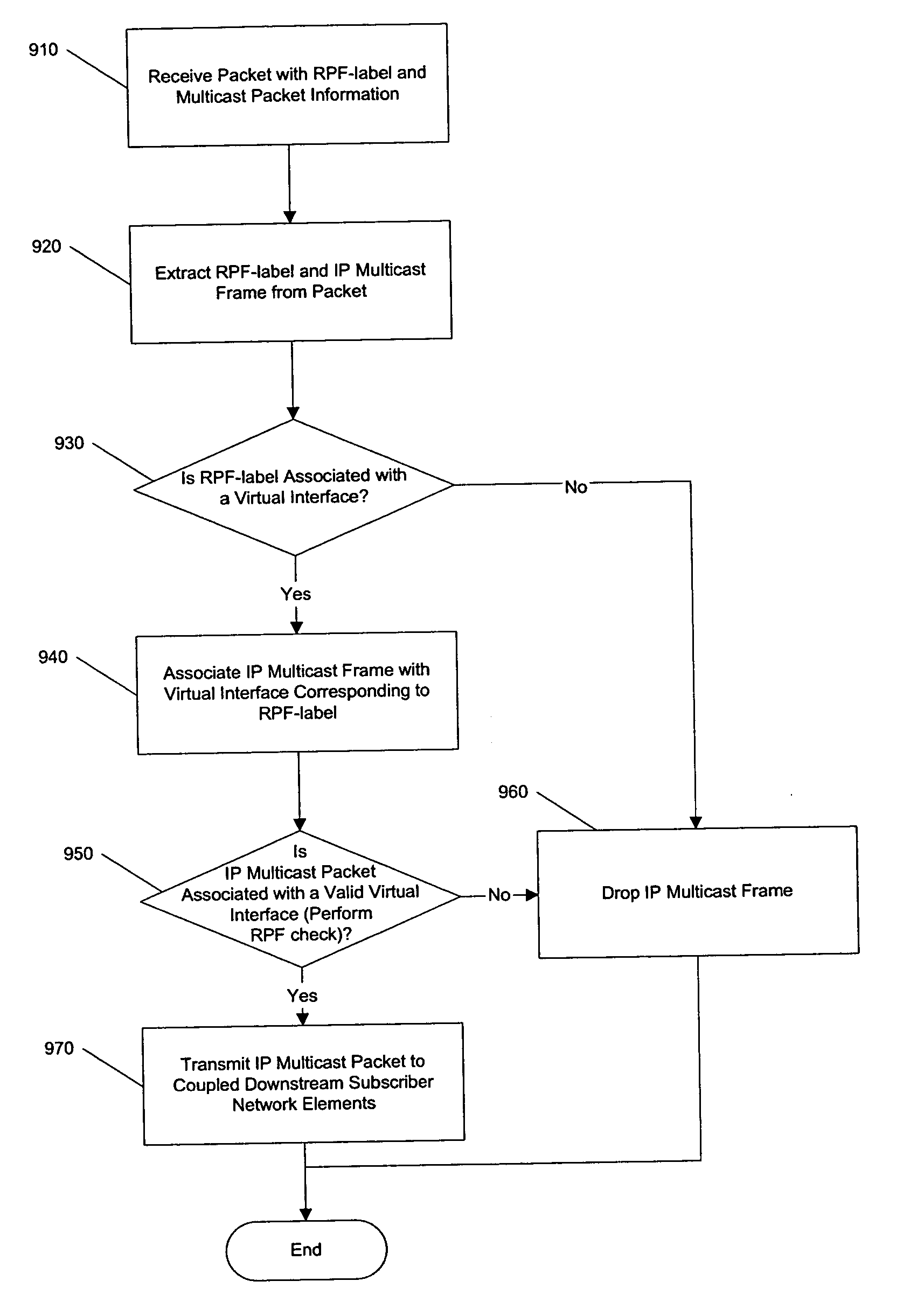
Transporting multicast over MPLS backbone using virtual interfaces to perform reverse-path forwarding checks
ActiveUS20060221975A1Special service provision for substationTime-division multiplexReverse path forwardingData set
A mechanism is provided in which multicast reverse path forwarding can be performed at a provider network egress edge router wherein core routers of the provider network are not configured to support multicast protocols or point-to-multipoint LSPs. An embodiment of the present invention provides for the creation of virtual interfaces in the egress edge router element during configuration of a multicast connection in response to a subscriber request. A virtual interface will be associated with an upstream ingress edge router element and that ingress edge router element is provided a label associated with the virtual interface. Such a label can then be included in datastream packets transmitted through the provider network. The label can then be used by reverse path forward checking at the egress edge router element to ascertain whether the multicast datastream is being received by the correct upstream interface (e.g., the virtual interface associated with the ingress edge router element). In such a manner, core network router elements of the provider's network need not be configured to process multicast transmissions as such, nor need the core router elements be configured to use the same network protocols as those used by the customer networks (e.g., customer networks can use IPv6 while the core network routers can use IPv4).
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Customer behavior analysis and service system based on web contents
InactiveCN101556609AImprove favorabilityIncrease dependenceData switching networksSpecial data processing applicationsPersonalizationData center
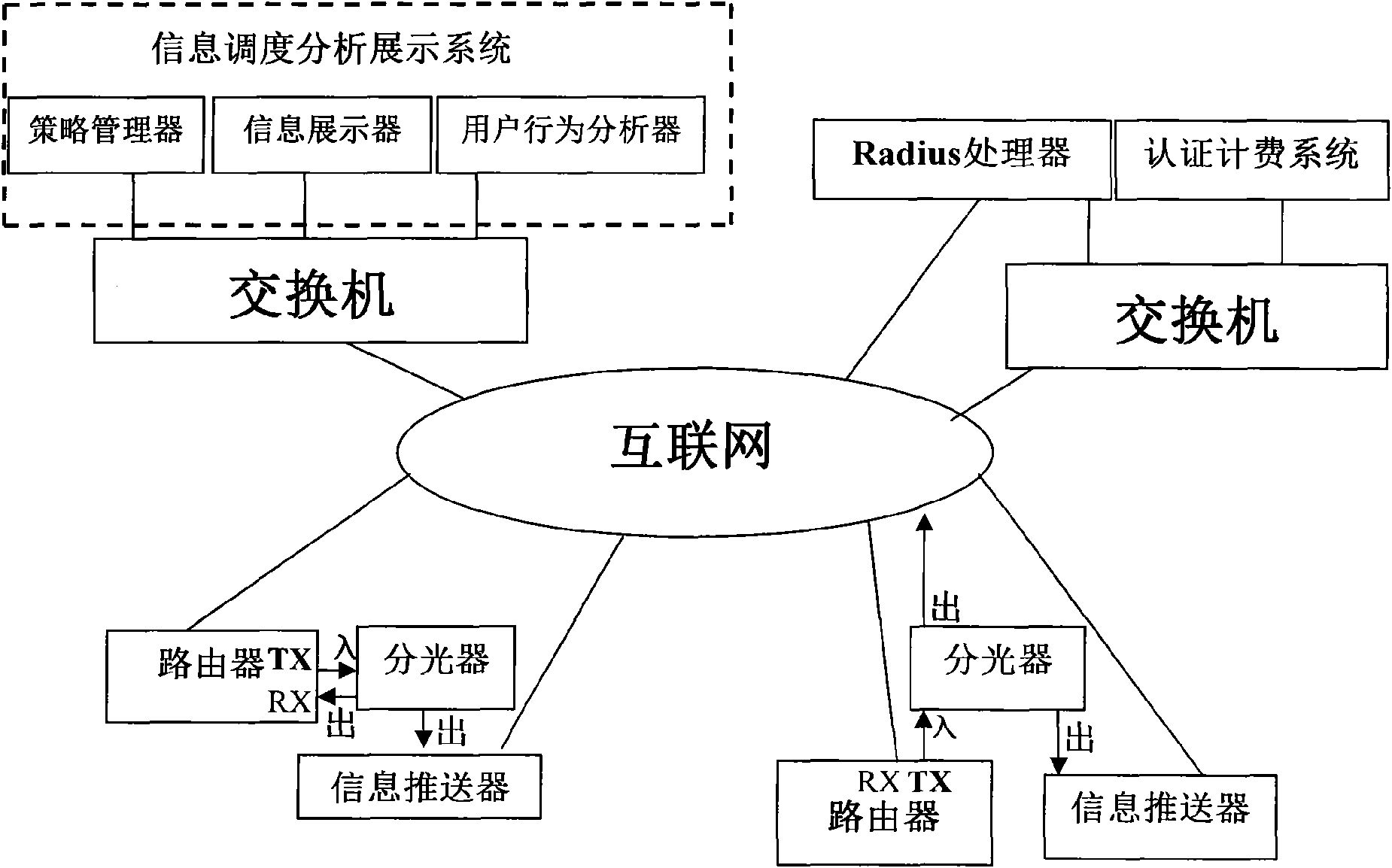
The invention discloses a customer behavior analysis and service system based on web contents, which comprises an information scheduling, analysis and display system arranged at an operator data center, an information pusher connected with a core router and a Radius processor connected with an operator accounting system, wherein the information scheduling, analysis and display system comprises a policy manager, an information display device and a user behavior analyzer. The invention does not need to install software on the client, as long as the user browses web pages during surfing on the Internet, according to a web site database, the system can do in-deep analysis, match and classify based on the analysis of visited web sites when the user uses mobile phones or broadband Internet to get online and then summarize user preference, therefore the system can individually display valuable contents on the web site for the user according to the user preference.
Owner:深圳市易信成科技股份有限公司
Transporting multicast over MPLS backbone using virtual interfaces to perform reverse-path forwarding checks
ActiveUS8089964B2Special service provision for substationError preventionReverse path forwardingCore router
A mechanism is provided in which multicast reverse path forwarding can be performed at a provider network egress edge router wherein core routers of the provider network are not configured to support multicast protocols or point-to-multipoint LSPs. An embodiment of the present invention provides for the creation of virtual interfaces in the egress edge router element during configuration of a multicast connection in response to a subscriber request. A virtual interface will be associated with an upstream ingress edge router element and that ingress edge router element is provided a label associated with the virtual interface. Such a label can then be included in datastream packets transmitted through the provider network and be used by reverse path forward checking at the egress edge router element to ascertain whether the multicast datastream is being received by the correct upstream interface.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
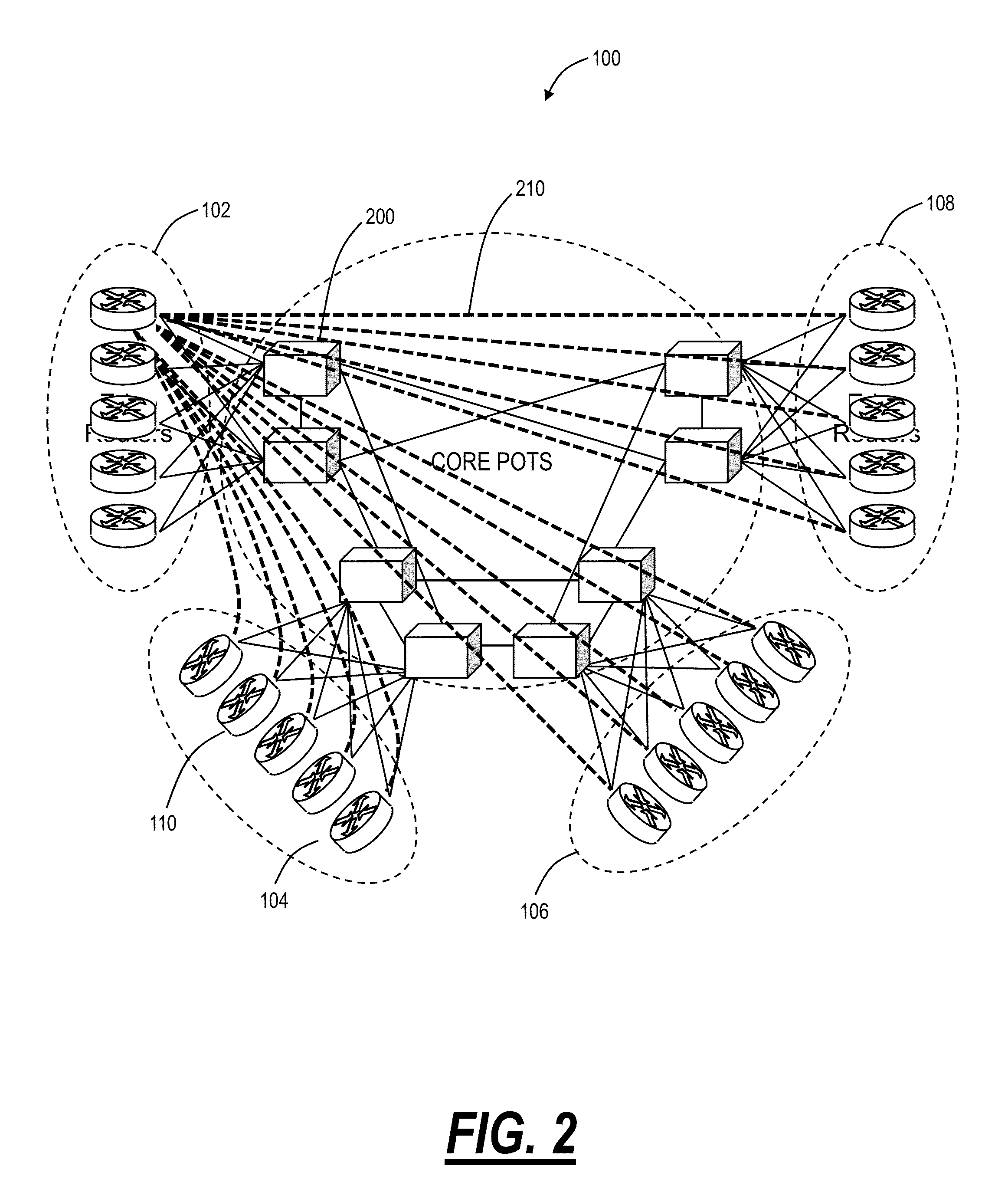
Virtual core router and switch systems and methods with a hybrid control architecture
The present disclosure provides virtual router / switch systems and methods with a domain of optical switches operating as a single, virtualized router using a control plane design combining centralized control of higher layer packet switching functions with distributed control over transport switching functions. The virtual router systems and methods simplify and reduce cost of Internet Protocol (IP) networks by removing the core routers, replacing them with lower cost, high capacity optical switches which are Packet Optical Transport Systems (POTS). The virtual router systems and methods avoids full mesh connectivity of the edge routers and the associated need to maintain routing adjacencies to each of the other edge routers. The virtual router systems and methods include a centralized IP layer management. Further, the virtual router systems and methods include distributed control of the optical layers.
Owner:CIENA
Network system and method for guaranteeing multi-type service quality
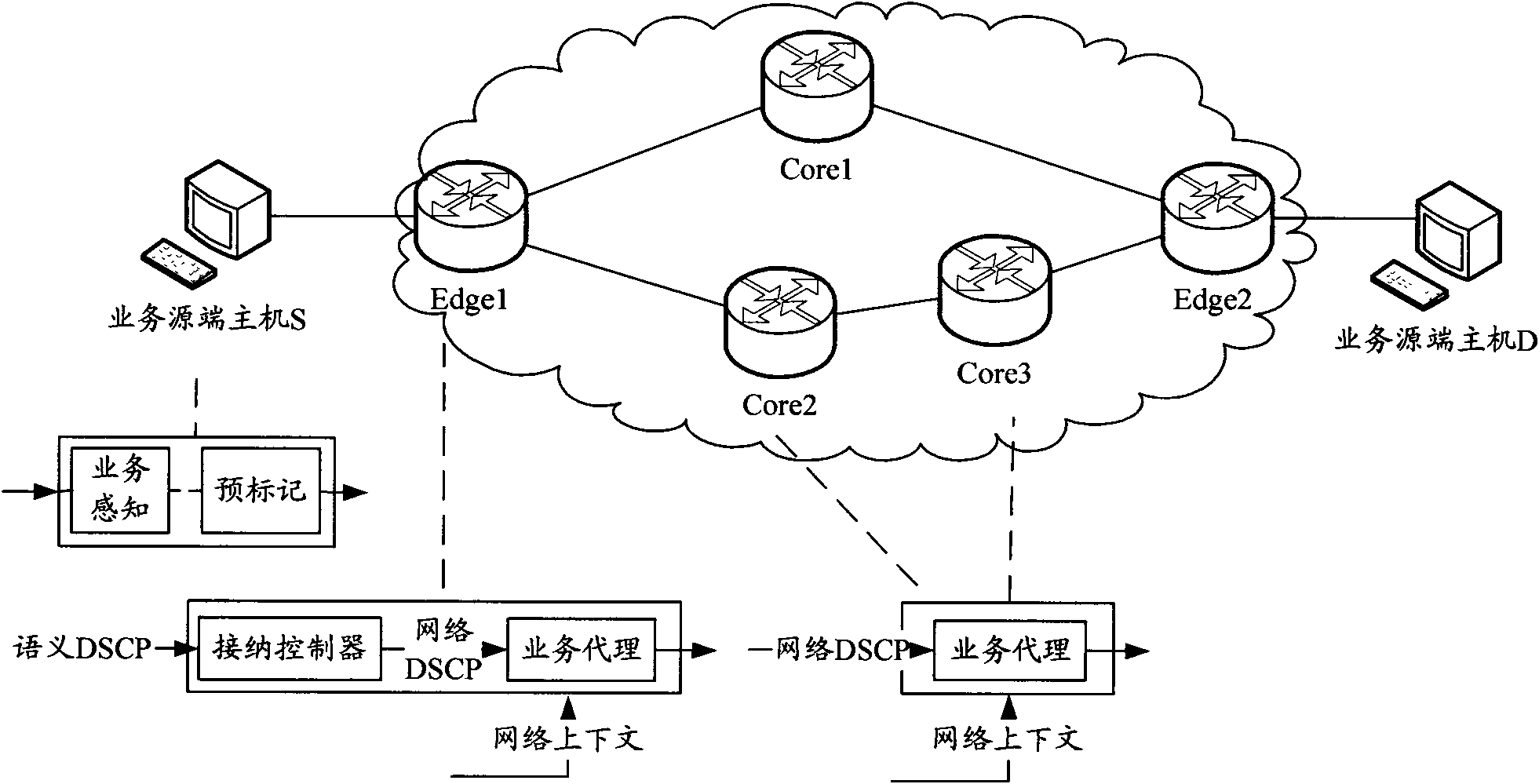
InactiveCN102075444AEasy to manageGuaranteed service qualityNetworks interconnectionQuality of serviceTraffic capacity
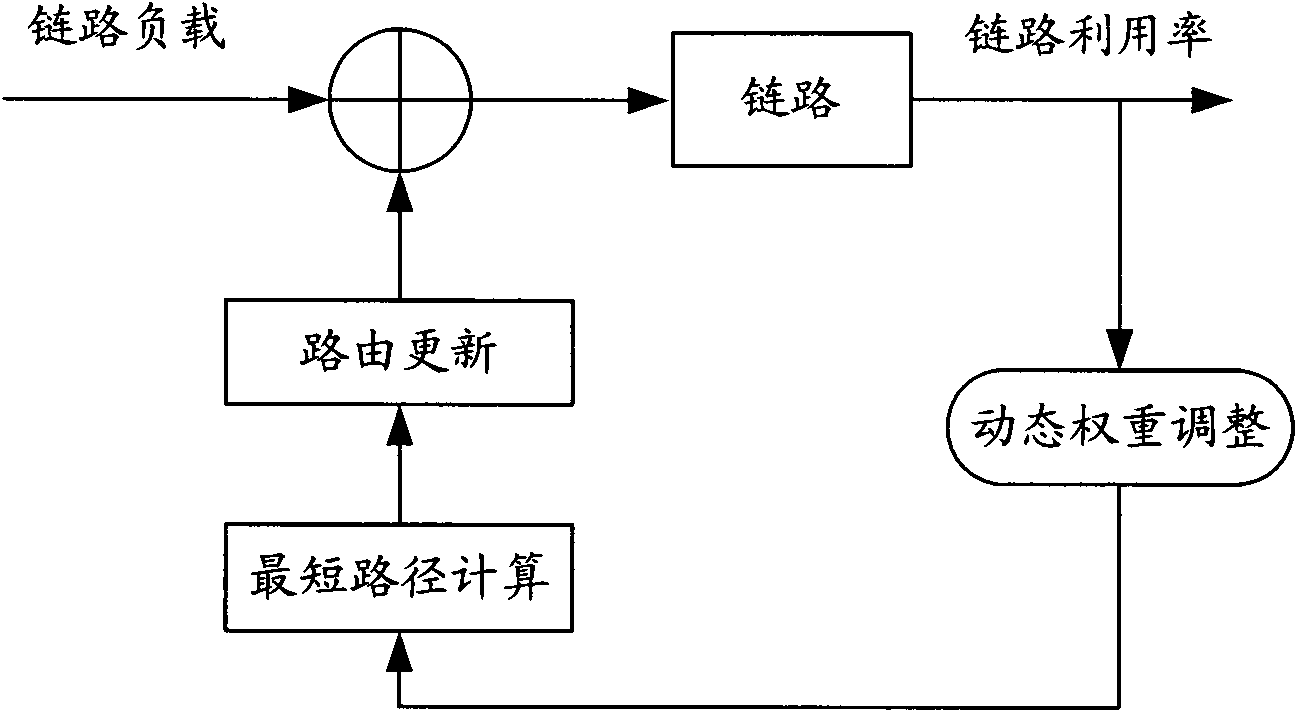
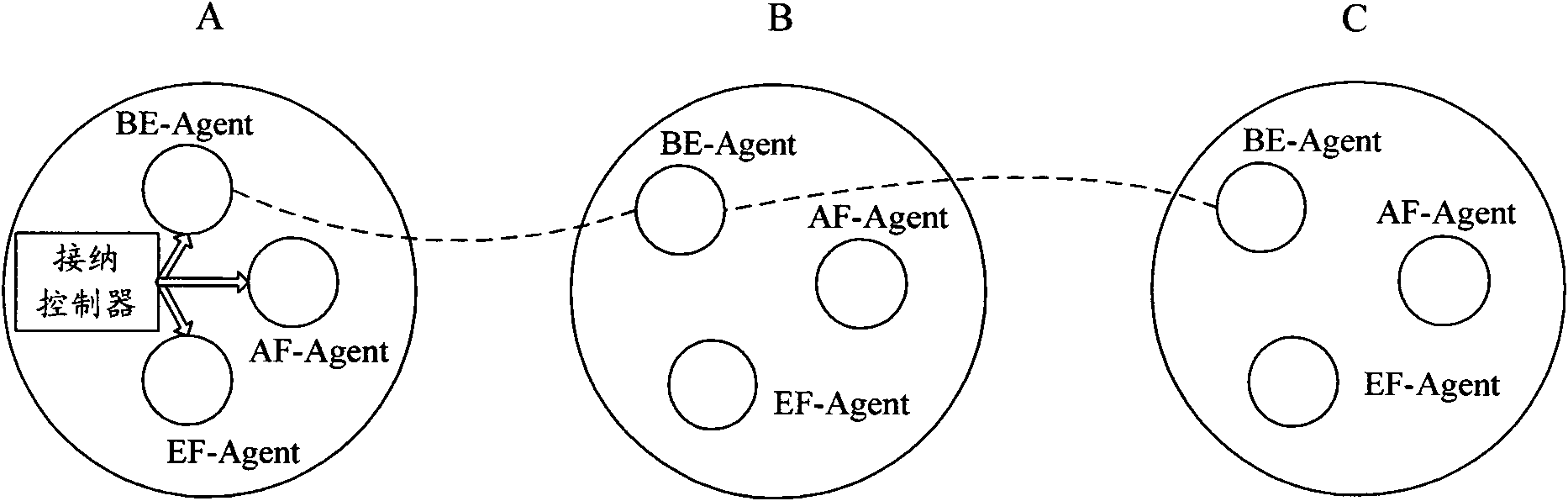
The invention discloses a network system and a method for guaranteeing multi-type service quality. A service perception module and a pre-labeling module are arranged in a source host and used for perceiving sent service data packets and pre-labeling the grouped data packets with different semantic priorities for sending according to the perception information when a network layer is encapsulated.An edge router and a core router are provided with a multi-service agent respectively. The edge router is also provided with an acceptance controller for mapping the semantic priorities of the service data packets into network priorities and distributing the service data packets to the corresponding service agents. The homogeneous service agents in all the routers are interconnected to form virtual topologies, and each virtual topology is provided with an independent routing table for routing selection of the service data packets of different priorities on the corresponding virtual topologiesrespectively. Service routing of high priority is guaranteed, and influence on low priority services is reduced as much as possible; and the invention also provides a method for setting link weights,which distributes the network traffic to each link more uniformly and improves the throughput rate.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
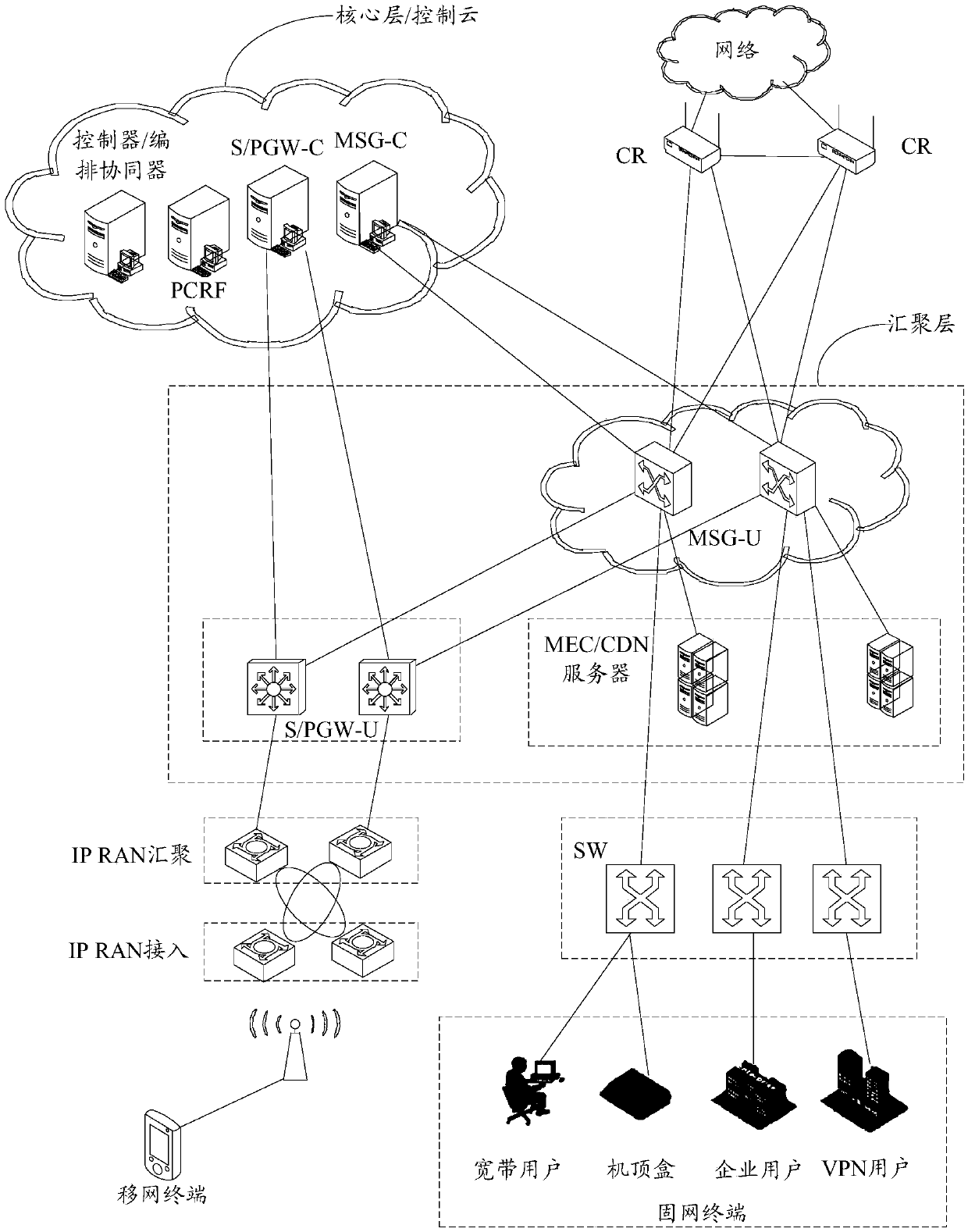
Multi-service MEC network architecture, multi-service data stream processing method and device
ActiveCN109640348ARealize differentiated servicesLower performance requirementsWireless communicationData informationData stream processing
The application discloses a multi-service MEC network architecture, and a multi-service data stream processing method and device, relates to the technical field of communications, and is used for a low-latency network to improve user experience. The multi-service MEC network architecture comprises a core layer, an aggregation layer, and a plurality of terminals, wherein the core layer comprises anS / PGW-C, an MSG-C, an orchestration synergy, and a PCRF; the aggregation layer comprises at least one multi-service MEC server, at least one MSG-U, at least one S / PGW-U, and at least one CDN server;the plurality of terminals comprise at least one mobile terminal and at least one fixed network terminal; and the multi-service MEC network further comprises at least one pair of core routers CRs forsending the data information corresponding to the service request received by the MSG-U to the network to obtain a data stream corresponding to the data information. The embodiment of the applicationis applied to terminals to acquire data resources from the network.
Owner:CHINA UNITED NETWORK COMM GRP CO LTD
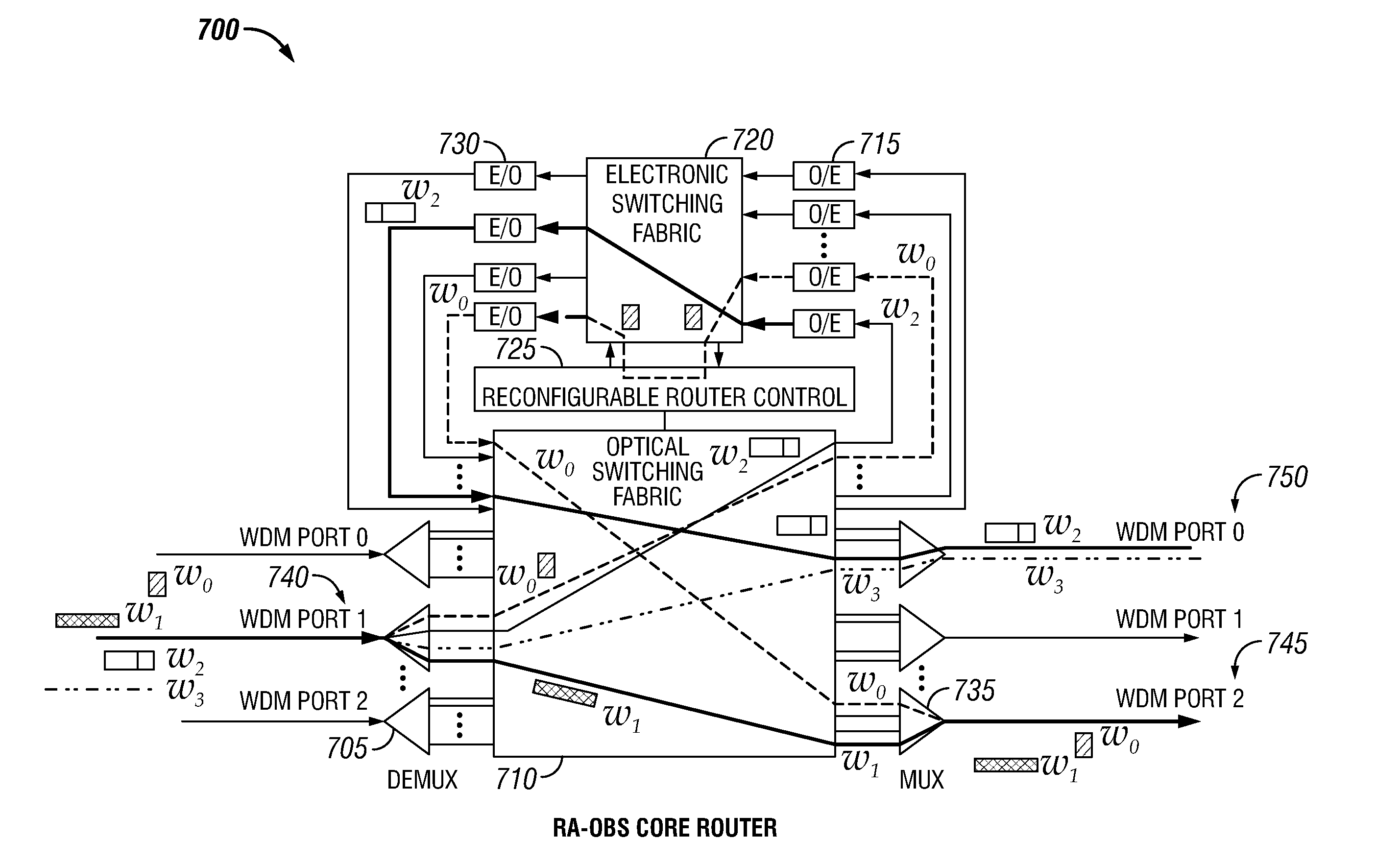
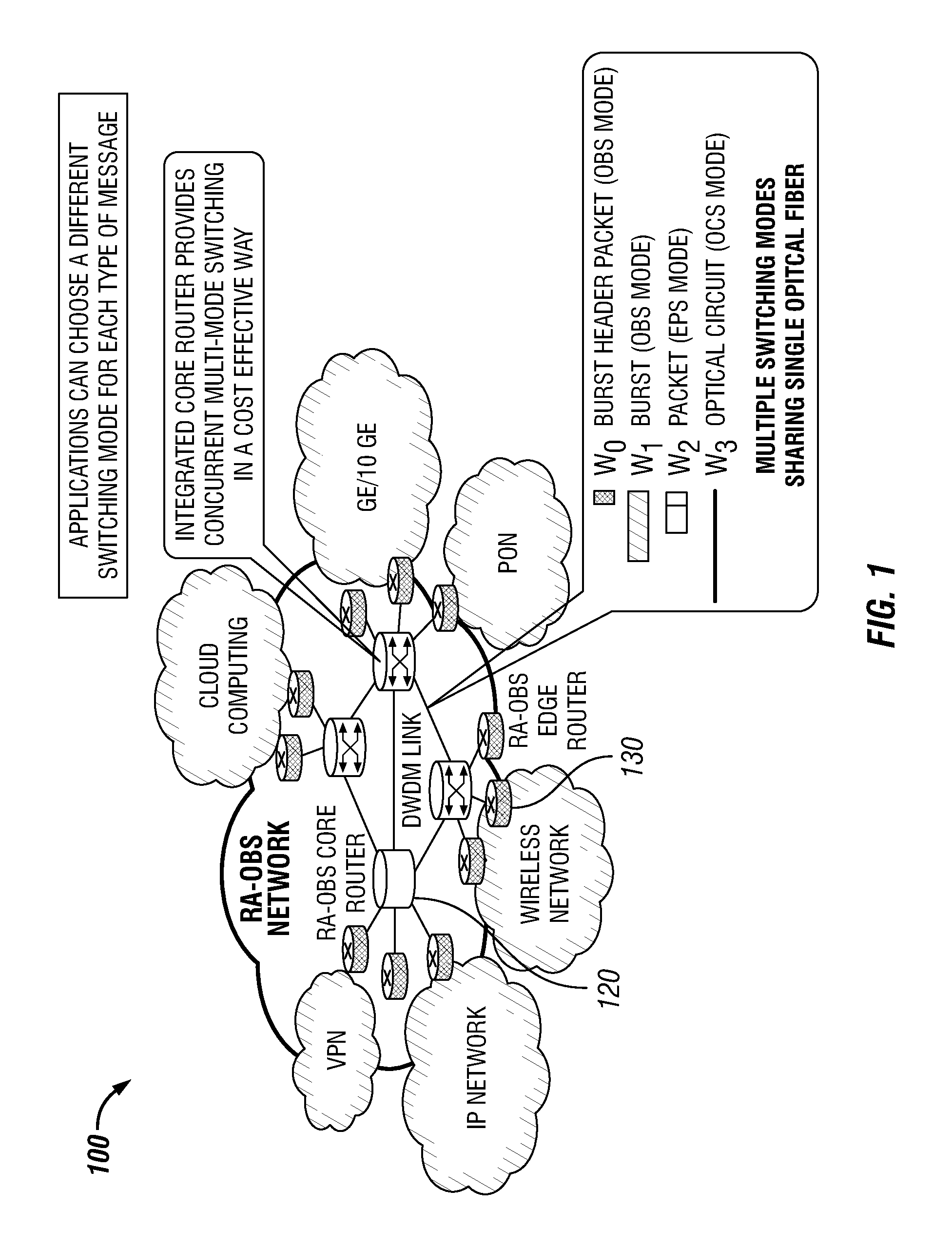
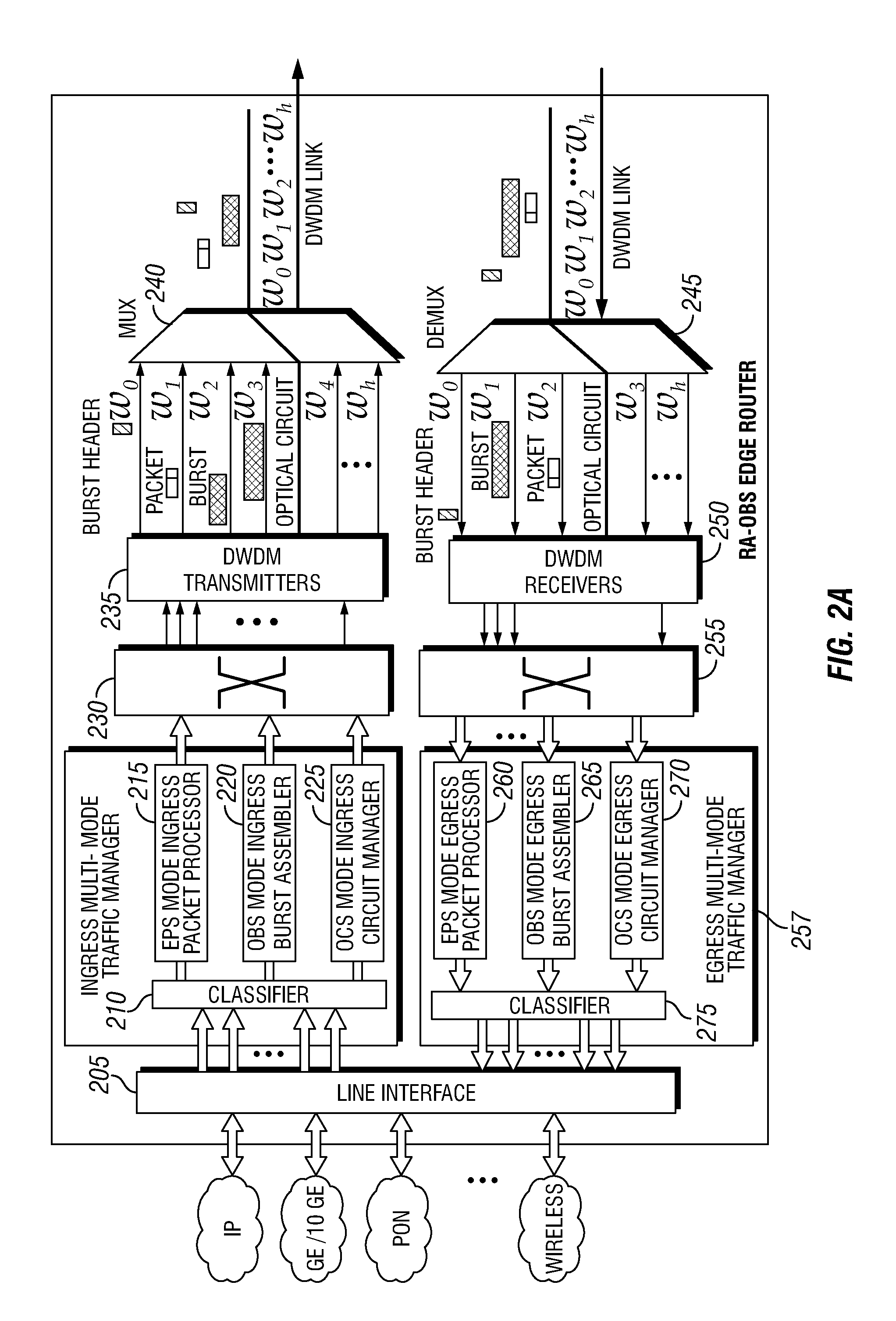
Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing Multi-Mode Switching Systems and Methods for Concurrent and Dynamic Reconfiguration with Different Switching Modes
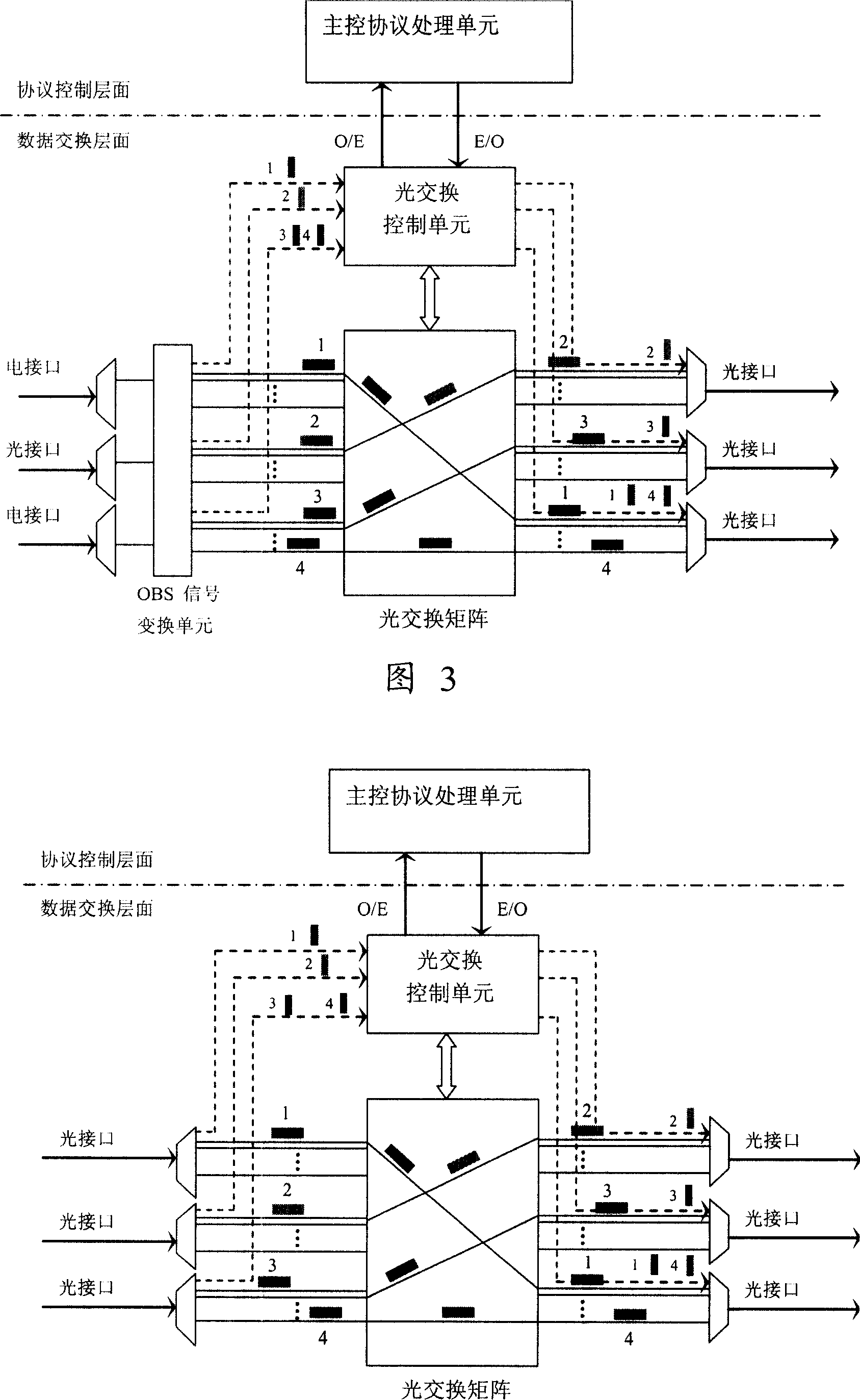
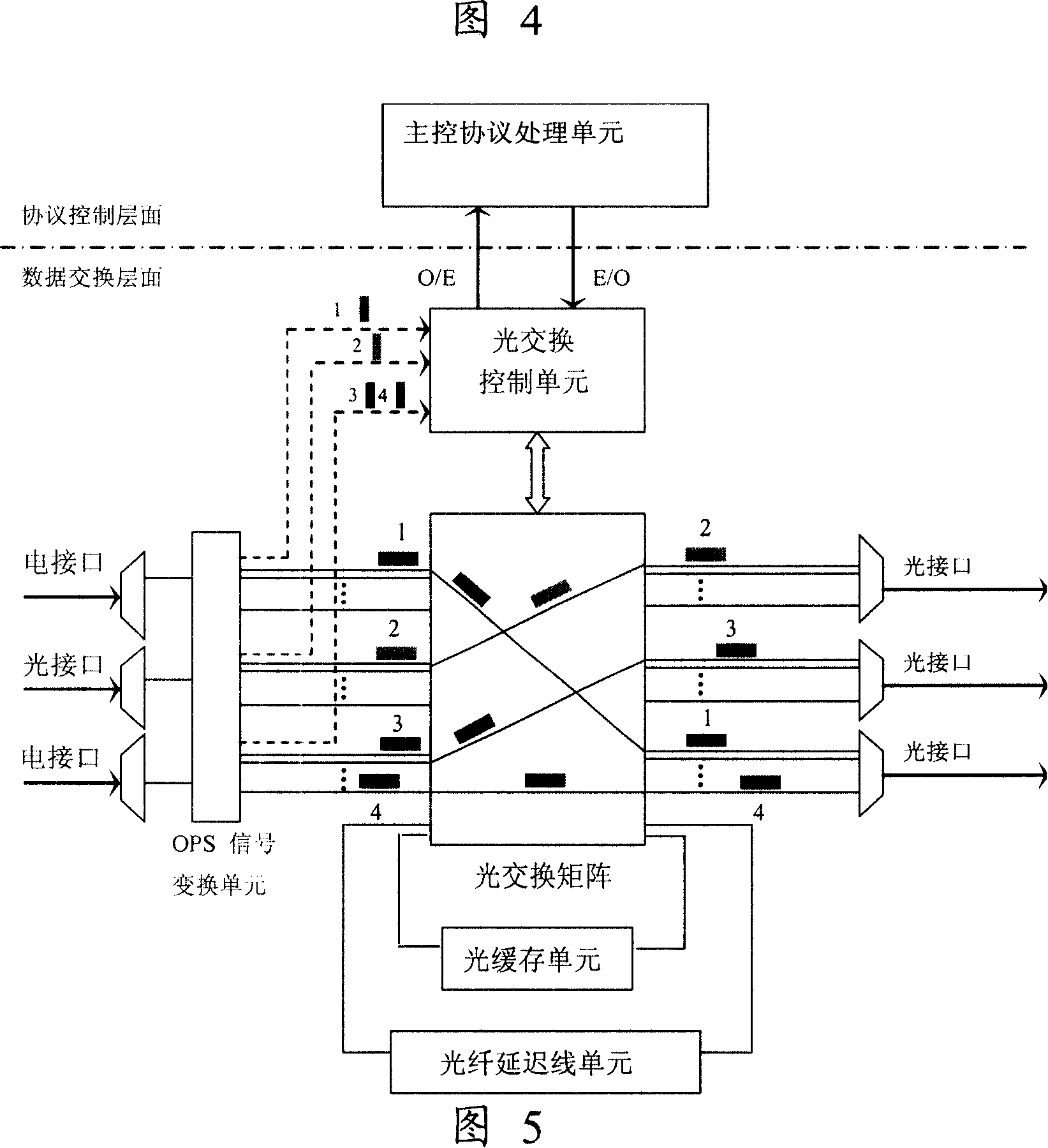
ActiveUS20120148242A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmissionOptical burst switchingCore router
A Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) multi-mode switching system and method and method provides concurrent switching in various switching modes. For example, WDM links may communicate data in various switching modes including, but not limited to, an electronic packet switching (EPS) mode, optical circuit switching (OCS) mode, and optical burst switching (OBS) mode. Edge routers and core routers in the WDM multi-mode switching systems and methods provide switching and processing necessary to handle data provided in the various switching modes. Further, the WDM multi-mode switching systems and methods can also provide dynamic reconfiguration between the various switching modes.
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST
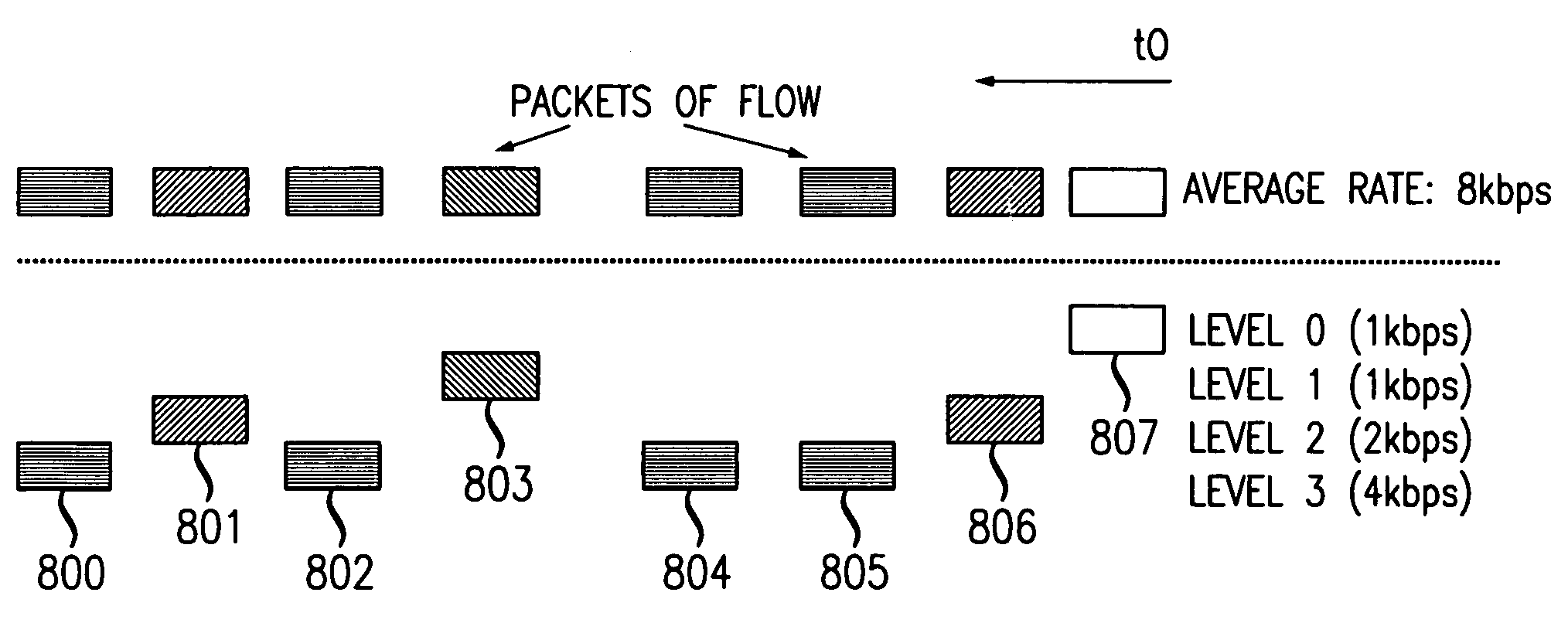
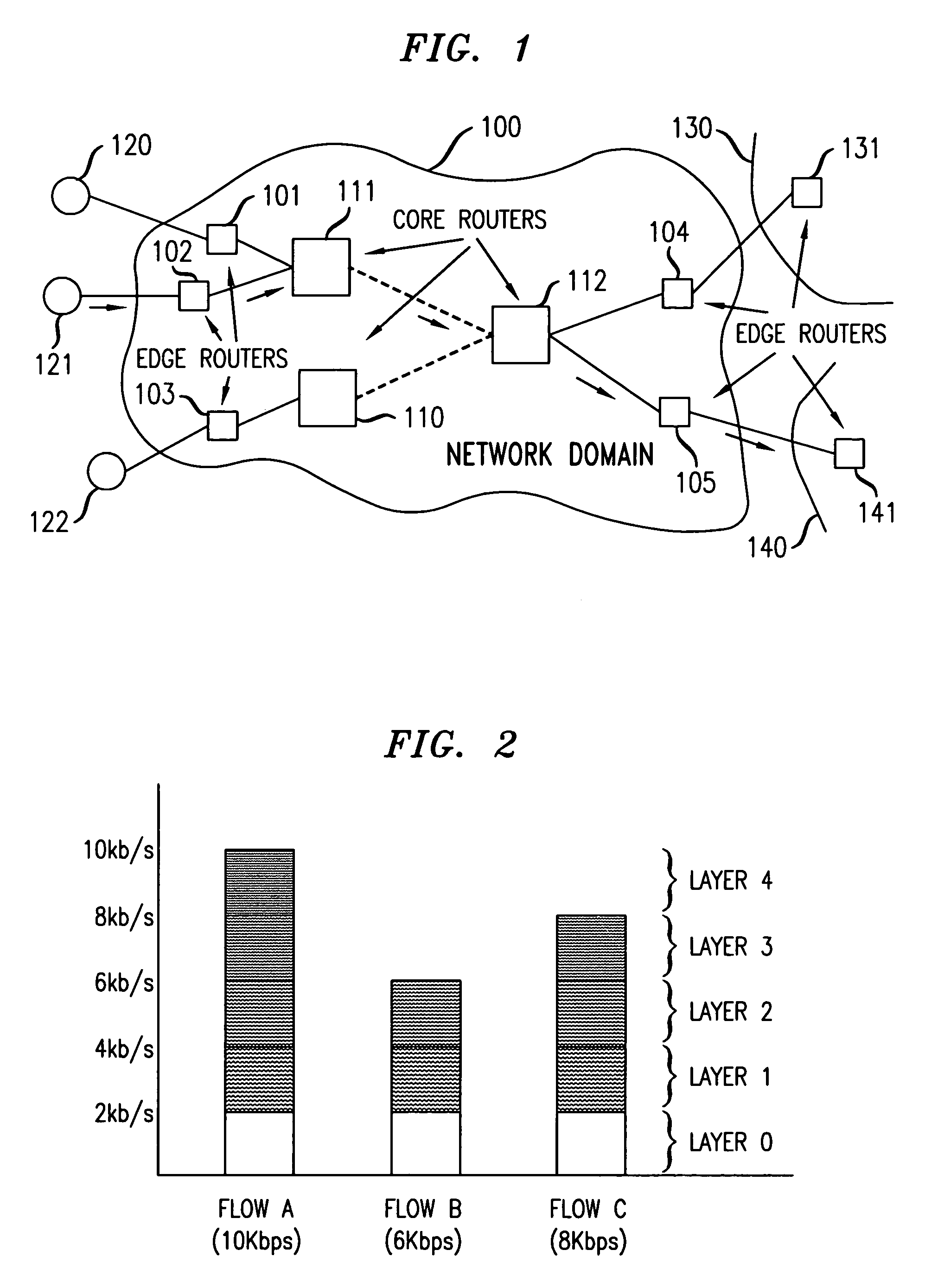
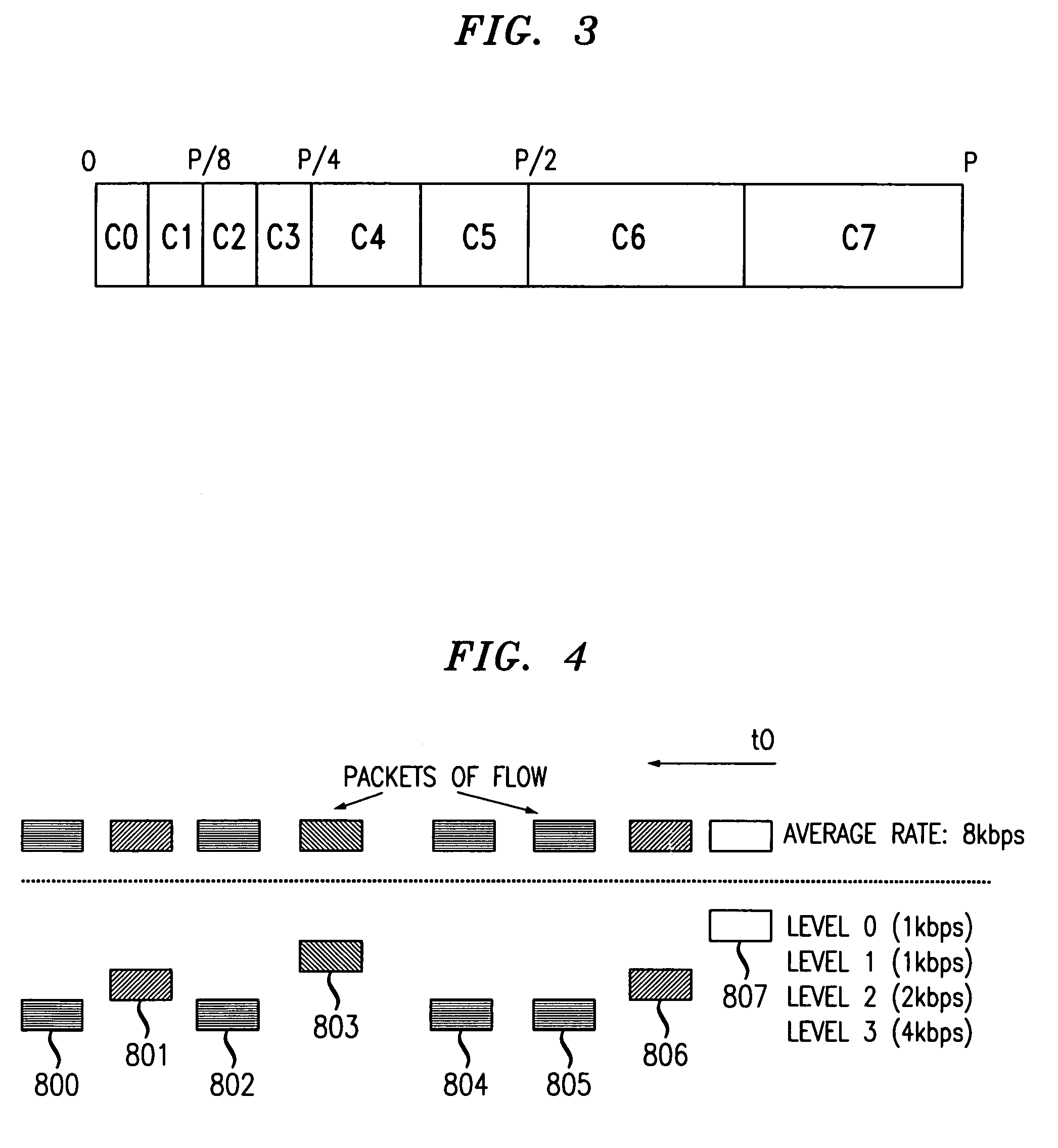
Technique for bandwidth sharing in internet and other router networks without per flow state record keeping
InactiveUS6985442B1Easy to operateSimple hardware implementationError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsData streamThe Internet
In a network of interconnected edge and core routers, where packet data flows are received at edge routers and then transmitted toward intended destinations via a path through one or more core routers, fair bandwidth sharing is achieved without per-flow state monitoring in the interior routers. Each edge router is arranged to divide each input data flow into a set of layers each having an associated level, based on rate. The division process is done without reference to the content of the flow, and can use layers of equal or unequal size. The packets in a flow are marked at an edge router with their layer level, in a globally consistent manner. Each core router maintains a layer level threshold, based upon buffer management conditions, and drops layers whose level exceeds the threshold. During congestion, the level threshold is decreased; when congestion clears, the level threshold is increased.
Owner:SOUND VIEW INNOVATIONS
Attack traffic protection system, method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium
The invention relates to the technical field of network security, in particular to an attack traffic protection system, method and device, electronic equipment and a storage medium, which are used forproviding an automatic hierarchical protection method and improving the protection efficiency, and the system comprises: a core router cluster used for forwarding received mirror image traffic of traffic to be processed to an attack detection module; an attack detection module which is used for detecting the mirror image flow, generating alarm information after the attack traffic is detected, andreporting the alarm information to the central centralized control module; and a central centralized control module which is used for determining the attack type of the attack traffic according to the traffic feature information in the alarm information, wherein if the attack type comprises a bandwidth consumption type attack, the core router cluster is enabled to protect the to-be-processed flow, and if the attack type comprises the resource consumption type attack, the cleaning module is enabled to protect the to-be-processed flow. Since automatic layered protection is performed according to the flow characteristic information of the attack flow, the protection efficiency is improved.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Method and apparatus for scalable virtual private network multicasting
ActiveUS20060133375A1Quantity minimizationBroadcast with distributionTime-division multiplexDistribution treeData stream
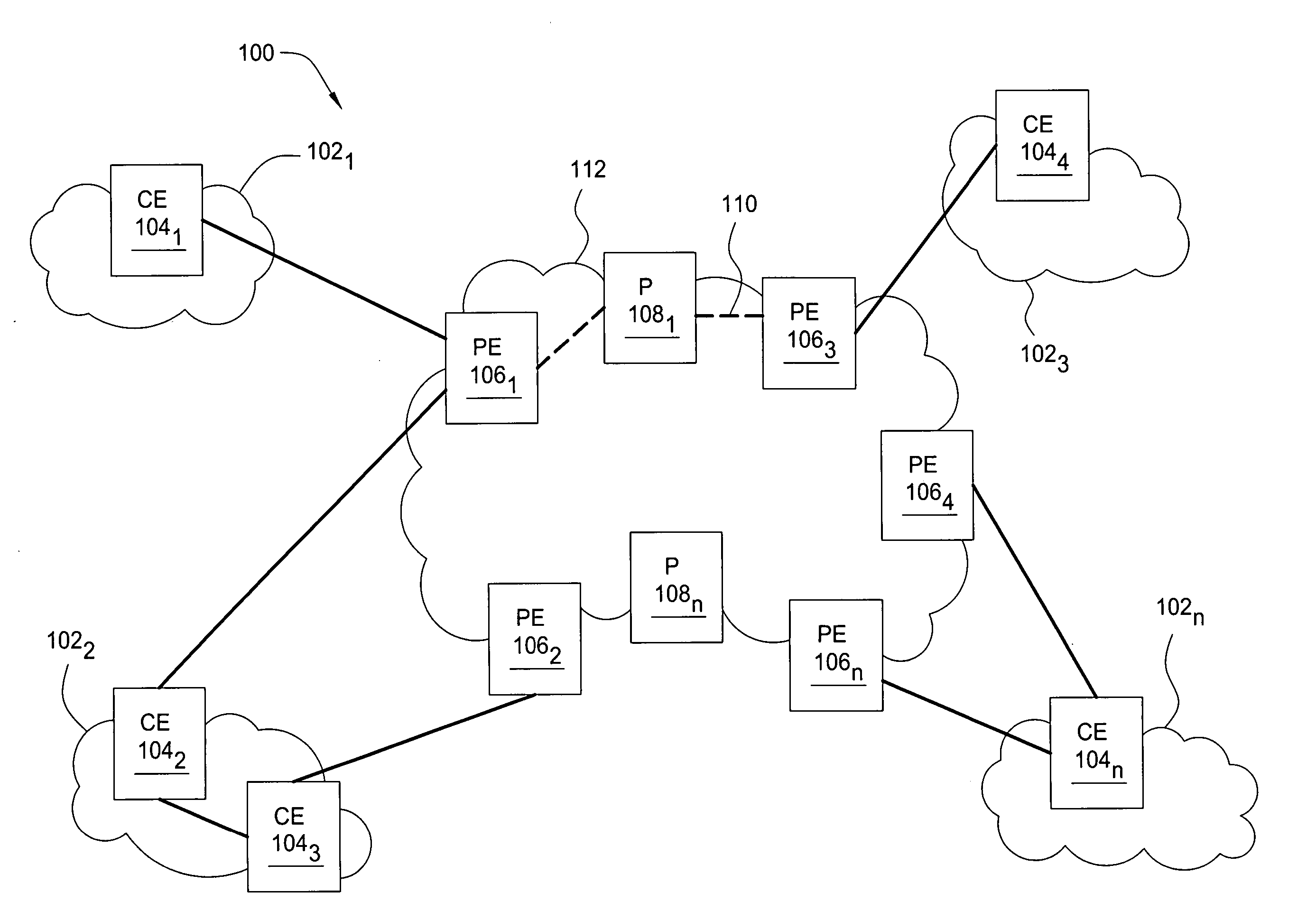
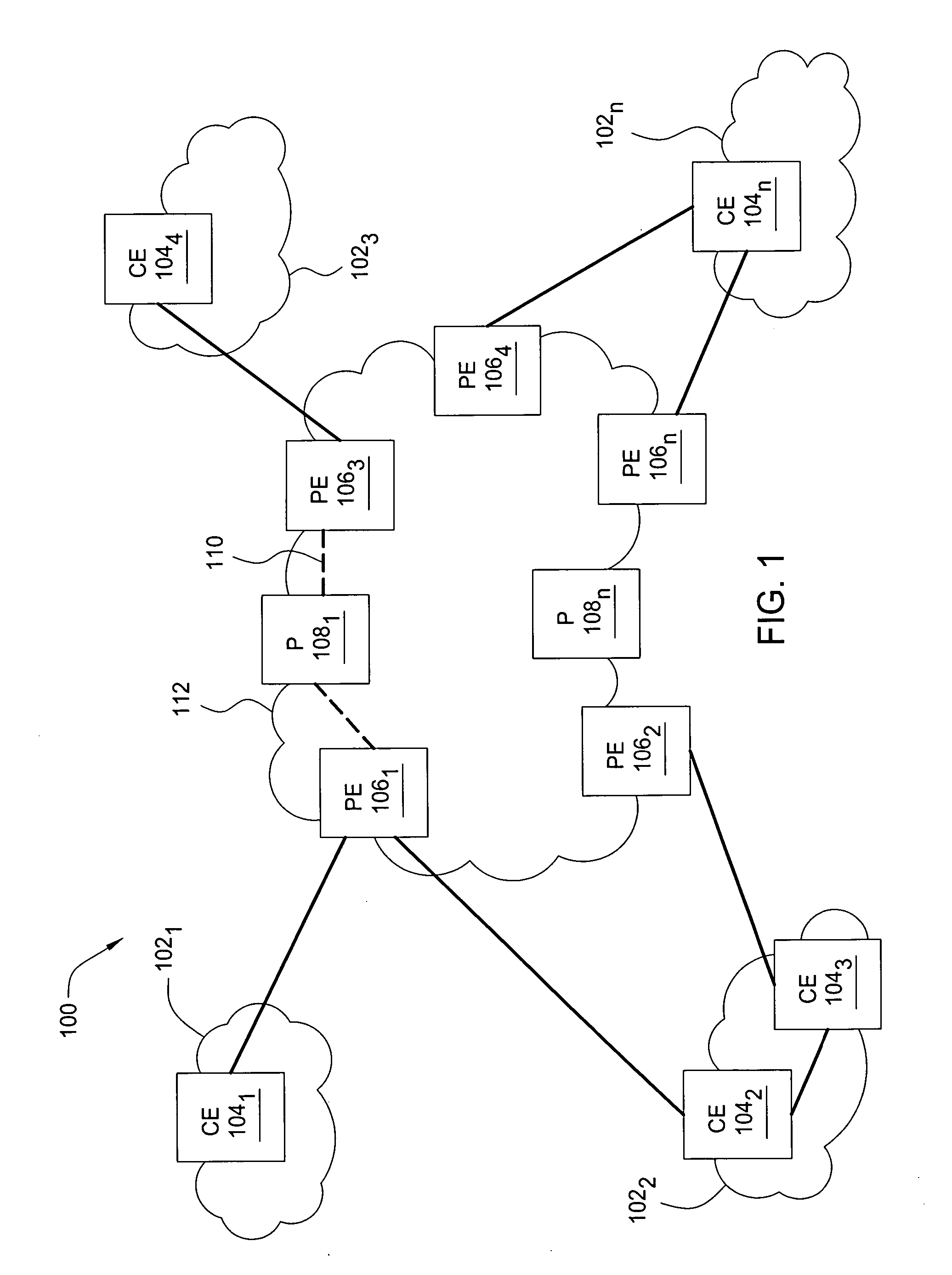
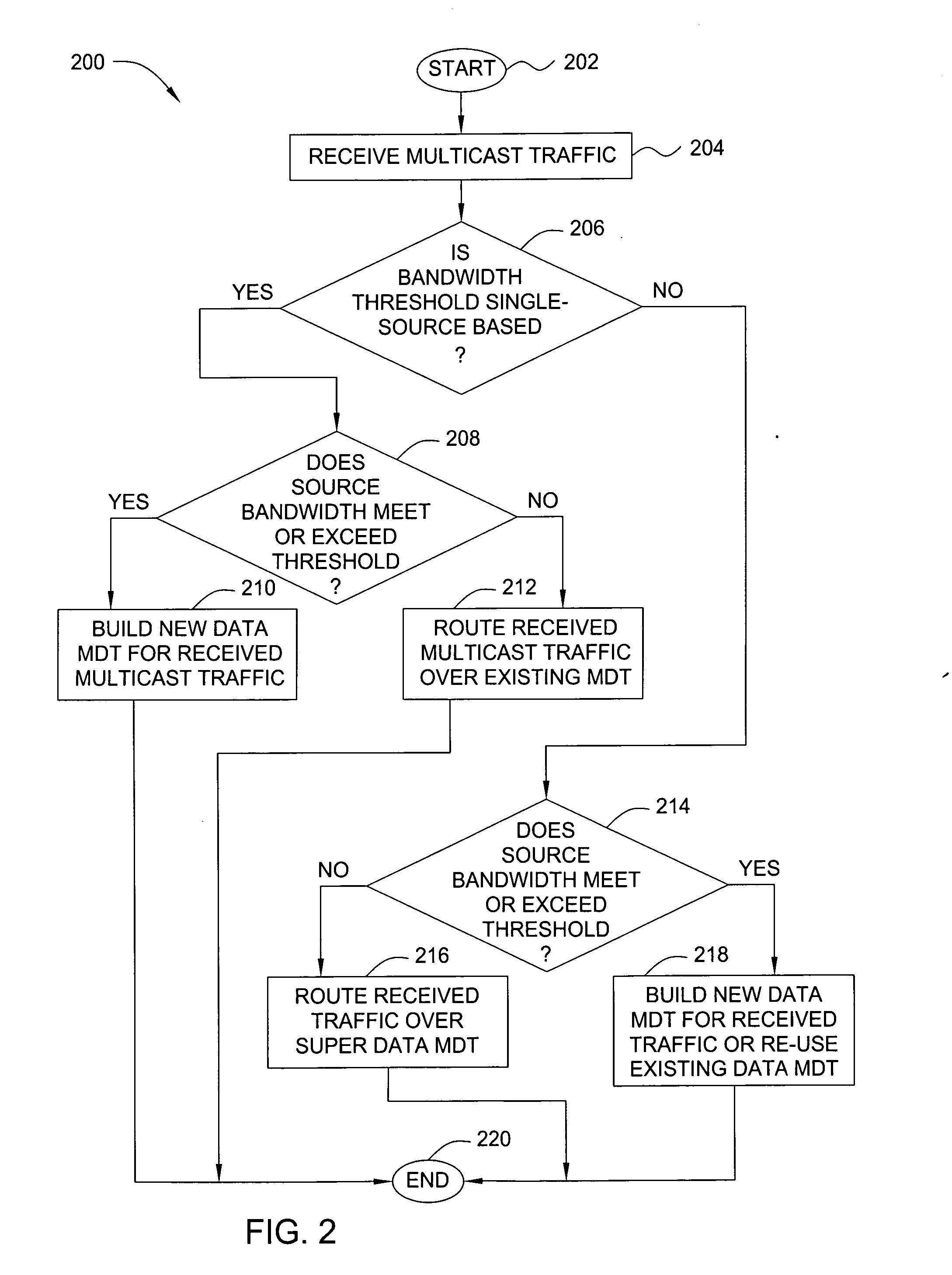
In one embodiment, the present invention is a method and apparatus for scalable virtual private network multicasting. In one embodiment a service network builds a new data multicast distribution tree for each high-bandwidth multicast data flow (e.g., multicast data flows that require an amount bandwidth meeting or exceeding a predefined threshold). However, if the multicast data flow is a low-bandwidth flow (e.g., if the required amount of bandwidth falls below the predefined threshold), the multicast data flow is routed over an existing multicast distribution tree in order to minimize an amount of state information that must be maintained by service provider core routers in the backbone network.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Routing device, routing method and transmission switching network
InactiveCN101155120AEasy to handleImprove performanceMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching networksElectricityTransmission switching
The invention discloses a route device using optical switching as core, in order to increase the capability and performance of route. A route method comprises: a receiving signal step of receiving light signal in the formula defined by the router; a sending signal step of sending the light signal in the formula defined by the router; a route analyzing step of obtaining the routing information of light signal in the formula defined by the router; a control exchanging step of controlling the route of light signal in the formula defined by the router based on the result of the route analyzing step. The optical switching mechanism is used inside the router to break through the limit of electrical exchange capacity of the existing Internet core router, so that the capability and performance of router is increased. Because the treatment capacity and ability is increased, in the new networking, the light transmission network is replaced therefore the networking and maintaining is simplified.
Owner:GLOBAL INNOVATION AGGREGATORS LLC
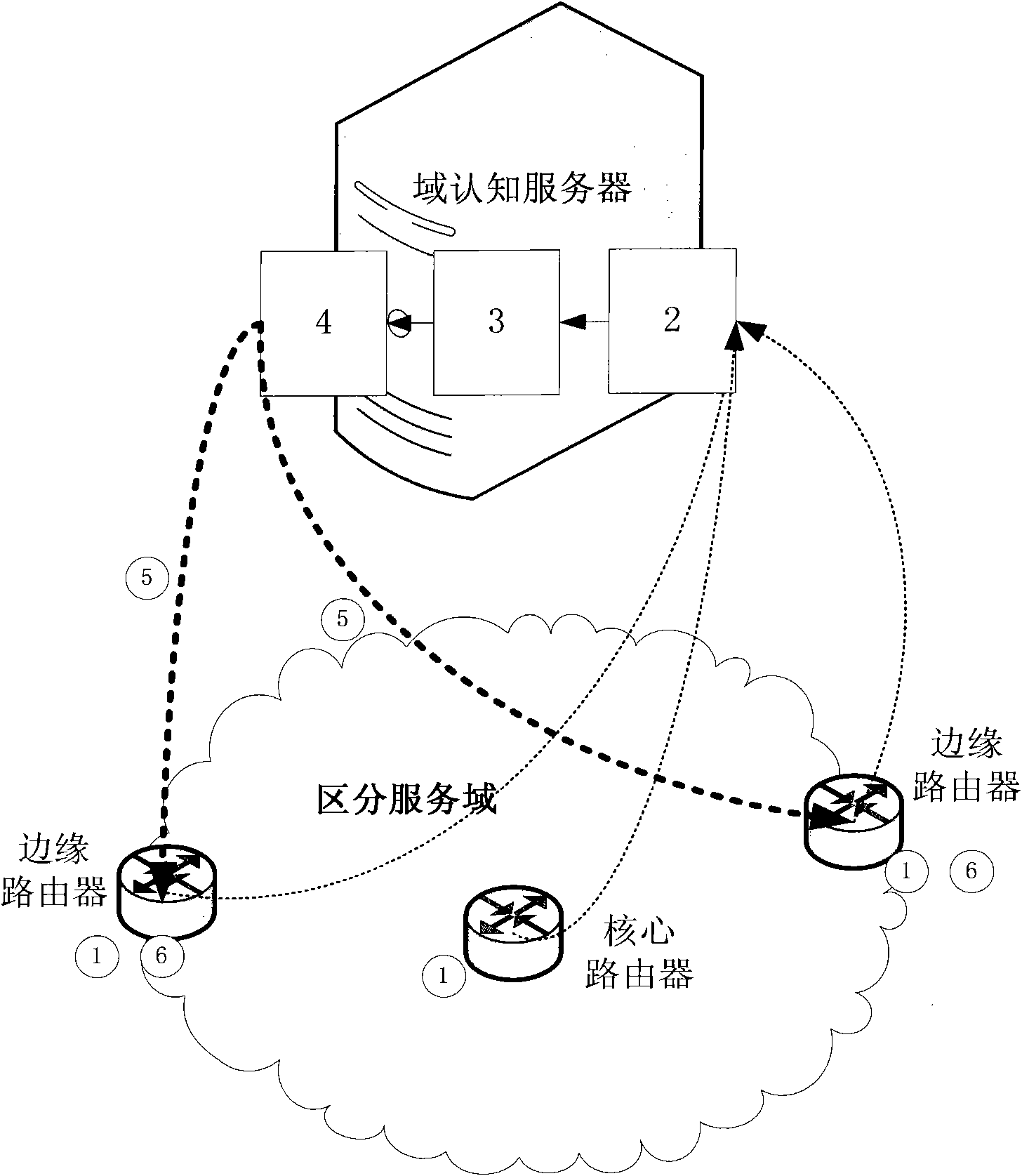
Cognitive network QoS (quality of service) guarantee method on basis of service differentiation
ActiveCN102025620AAchieve distinctionAvoid congestionData switching networksDifferentiated servicesInformation processing
The invention discloses a cognitive network QoS (quality of service) guarantee method on the basis of service differentiation. The method takes services as the center, the information is gathered to a domain cognitive server for the purpose of being processed by collecting network QoS parameters, service information and network state information, and a processing result serves as a training sample to train a support vector machine (SVM) to obtain a classifier; the classifier predicts possible problems in a network in real time according to an information processing result collected by an edgerouter and a core router; the server issues a new strategy to the edge router according to the problems possibly happening; and the edge router distributes different priority levels to different services according to the new strategy so as to provide guarantee for network QoS. The method is combined with the existing differentiated service frame and has expandability; meanwhile, an artificial intelligence method is introduced in, so that the method can effectively make a decision before problems occur so as to realize network cognition.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Sharing IP network resources
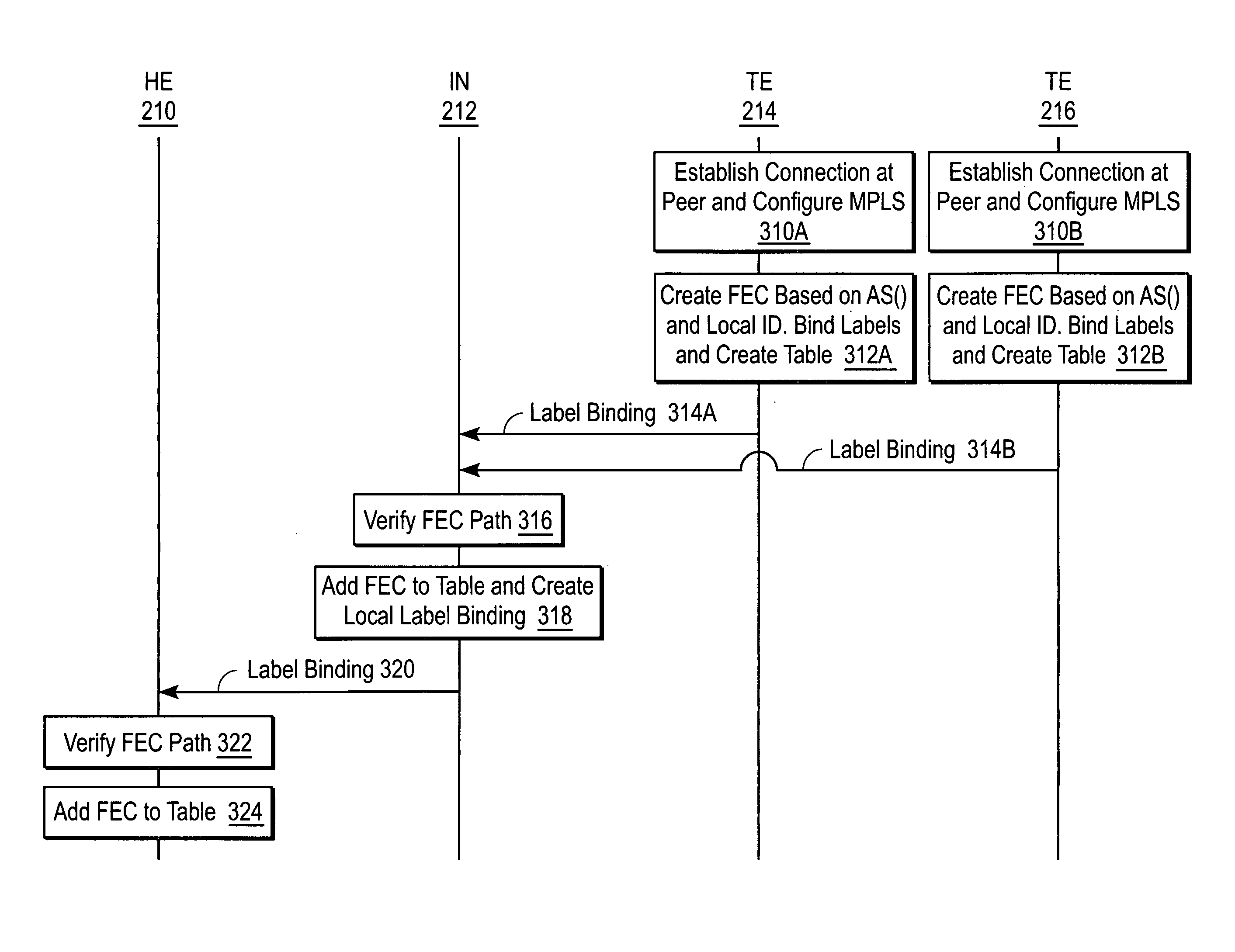
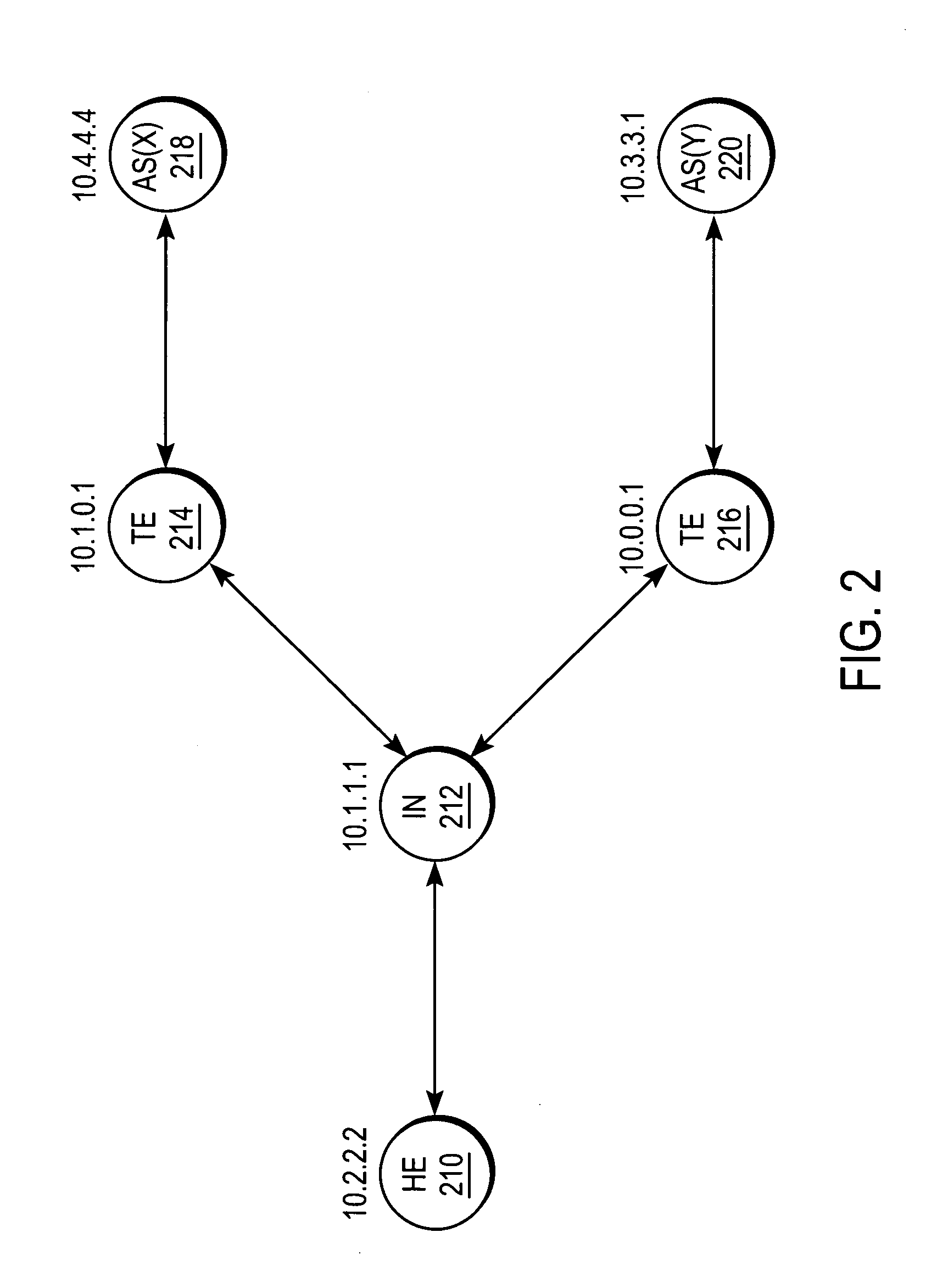
InactiveUS6985963B1Efficient sharingEnergy efficient ICTDigital computer detailsAccess networkMultiprotocol Label Switching
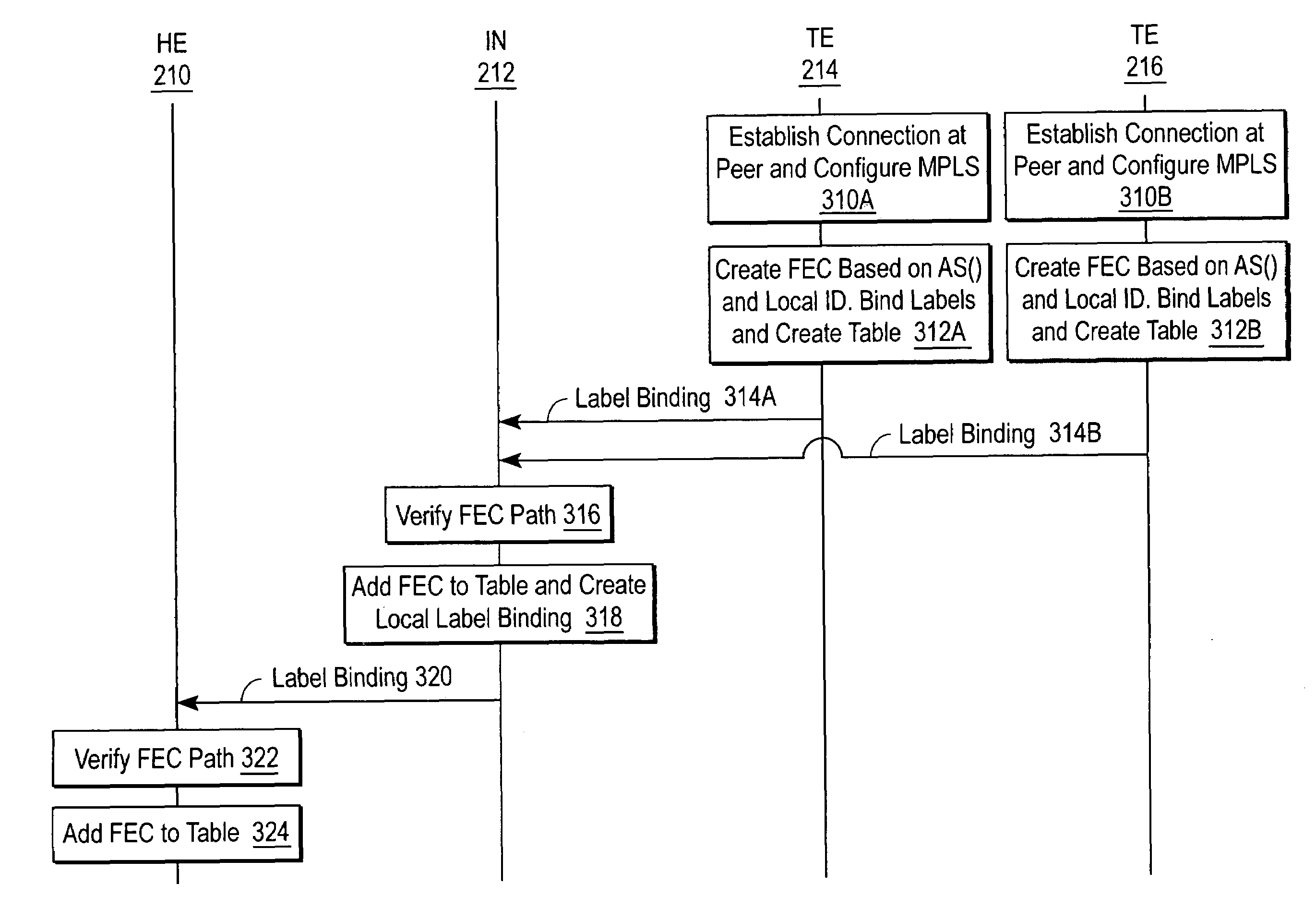
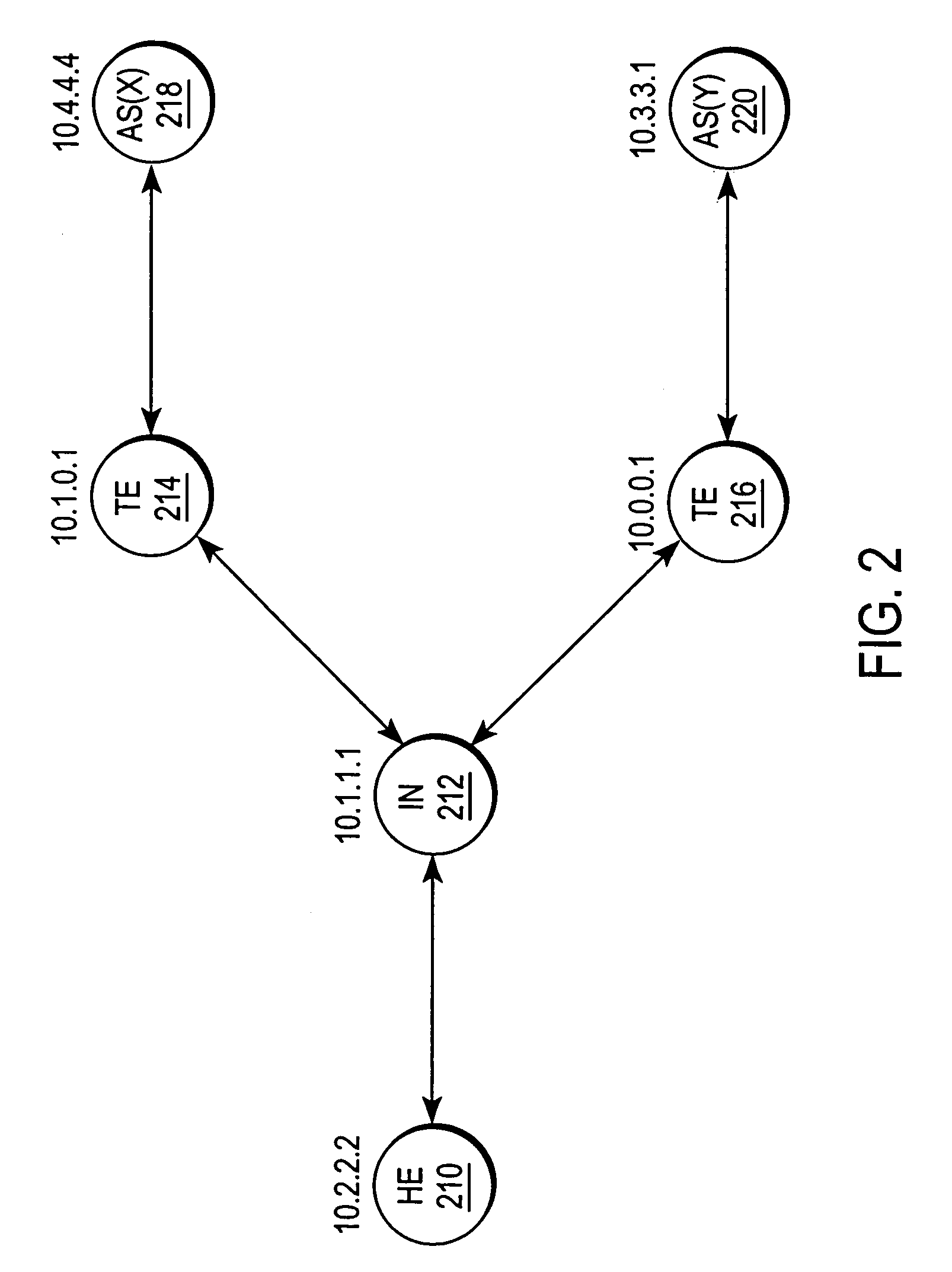
A system and method for sharing access to an internet protocol (IP) network among multiple internet service providers (ISPs) uses multiprotocol label switching (MPLS). End-users are coupled to a broadband customer access network. Each end-user is also associated with at least one of the ISPs. An aggregation router interfaces the customer access network with a network backbone. The network backbone includes a border router for interfacing between the network backbone and the network of an ISP. When the border router is activated, it creates a forwarding equivalency class (FEC) corresponding to the ISP. The border router stores a label for the FEC and the interface for reaching the ISP in an FEC table. The border router advertises the label binding for the FEC to all upstream nodes. An intermediate node receiving the label binding creates its own FEC table, associates a new label with the FEC, and advertises the new label binding to its upstream nodes. The aggregation router receives and builds a FEC table containing the label bindings for all ISPs reachable over the network backbone. When the aggregation router receives a data packet from an end-user, the aggregation router determines the ISP associated with the end-user, labels the data packet with the label corresponding to the FEC for that ISP, and routes the packet on the network backbone. The packet eventually reaches the border router, which pops off the label and passes the packet to the ISP.
Owner:AT HOME BONDHOLDERS LIQUIDATING TRUST +1
Sharing IP network resources
InactiveUS20060041682A1Efficient sharingEnergy efficient ICTMultiprogramming arrangementsAccess networkMultiprotocol Label Switching
A system and method for sharing access to an internet protocol (IP) network among multiple internet service providers (ISPs) uses multiprotocol label switching (MPLS). End-users are coupled to a broadband customer access network. Each end-user is also associated with at least one of the ISPs. An aggregation router interfaces the customer access network with a network backbone. The network backbone includes a border router for interfacing between the network backbone and the network of an ISP. When the border router is activated, it creates a forwarding equivalency class (FEC) corresponding to the ISP. The border router stores a label for the FEC and the interface for reaching the ISP in an FEC table. The border router advertises the label binding for the FEC to all upstream nodes. An intermediate node receiving the label binding creates its own FEC table, associates a new label with the FEC, and advertises the new label binding to its upstream nodes. The aggregation router receives and builds a FEC table containing the label bindings for all ISPs reachable over the network backbone. When the aggregation router receives a data packet from an end-user, the aggregation router determines the ISP associated with the end-user, labels the data packet with the label corresponding to the FEC for that ISP, and routes the packet on the network backbone. The packet eventually reaches the border router, which pops off the label and passes the packet to the ISP.
Owner:AT HOME BONDHOLDERS LIQUIDATING TRUST
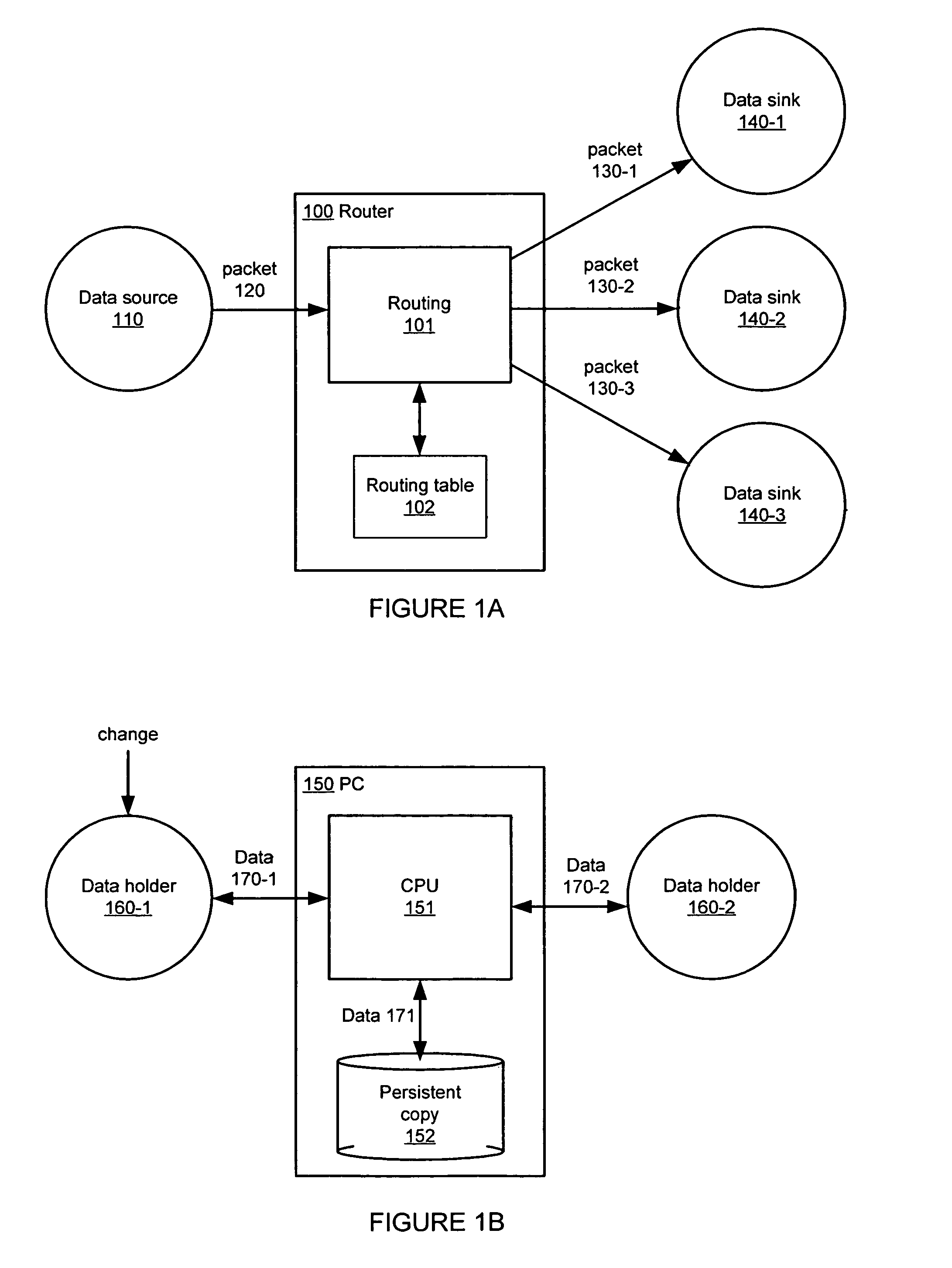
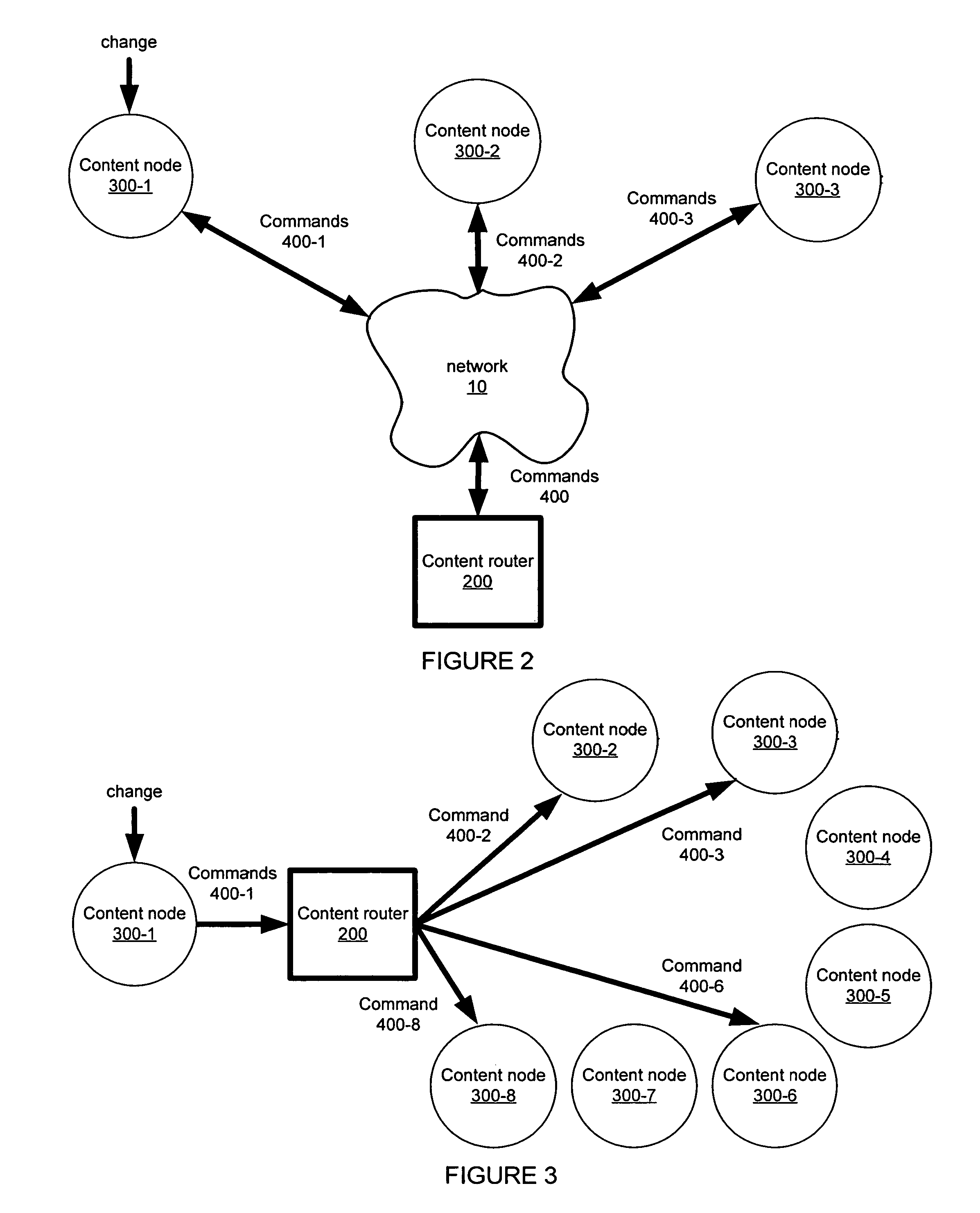
Content router
ActiveUS7849199B2Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsUser deviceError processing
A method, apparatus and system for routing changes to information between a plurality of content nodes and a command memory of a content router. Content nodes may be user devices (such as mobile phones) and user accounts (such as email accounts). Content nodes may hold one or more content types such as email, contacts, tasks, events and library items. A command memory centralizes conflict detection, resolution and error handling within a content routing system.
Owner:YAHOO ASSETS LLC
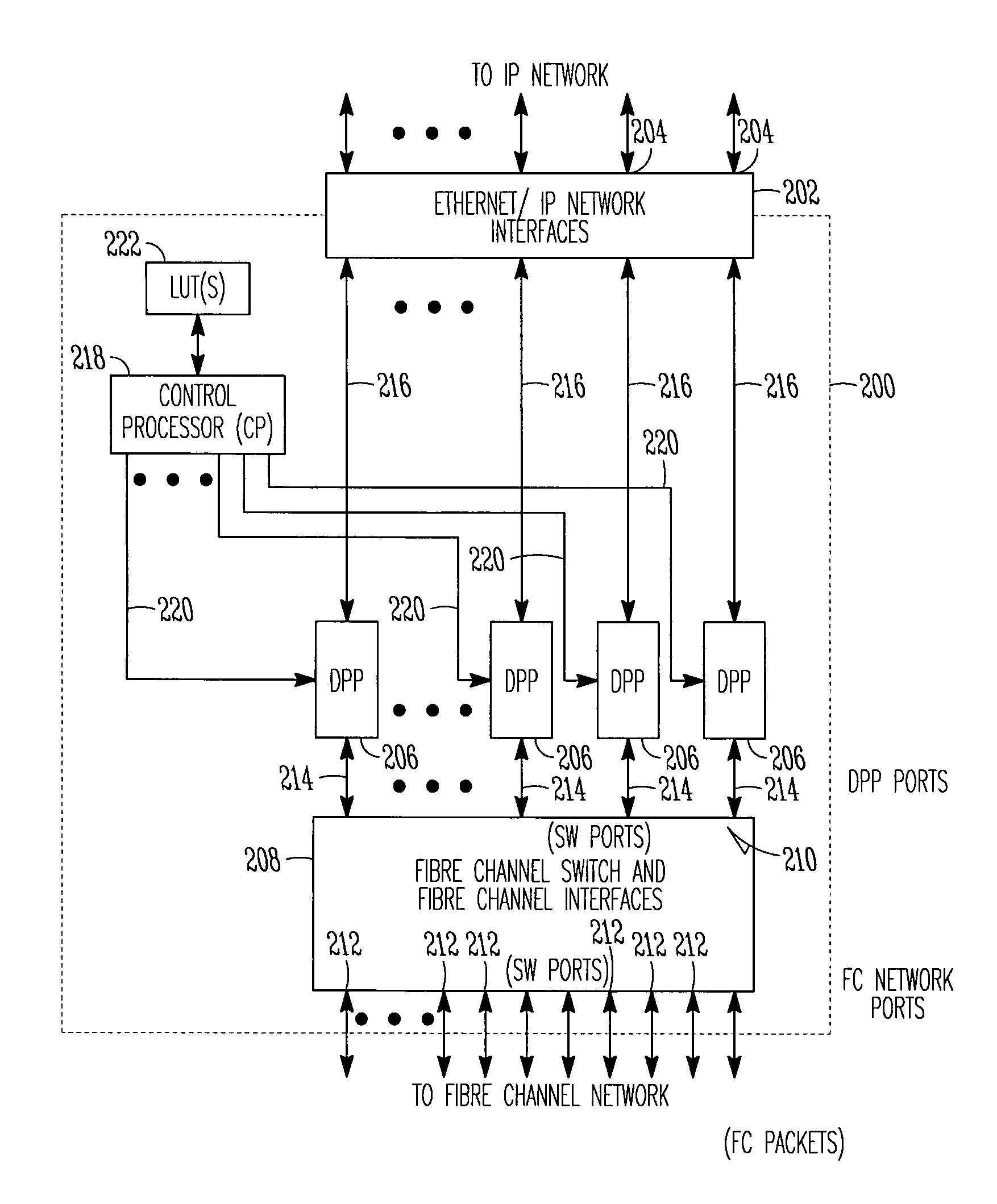
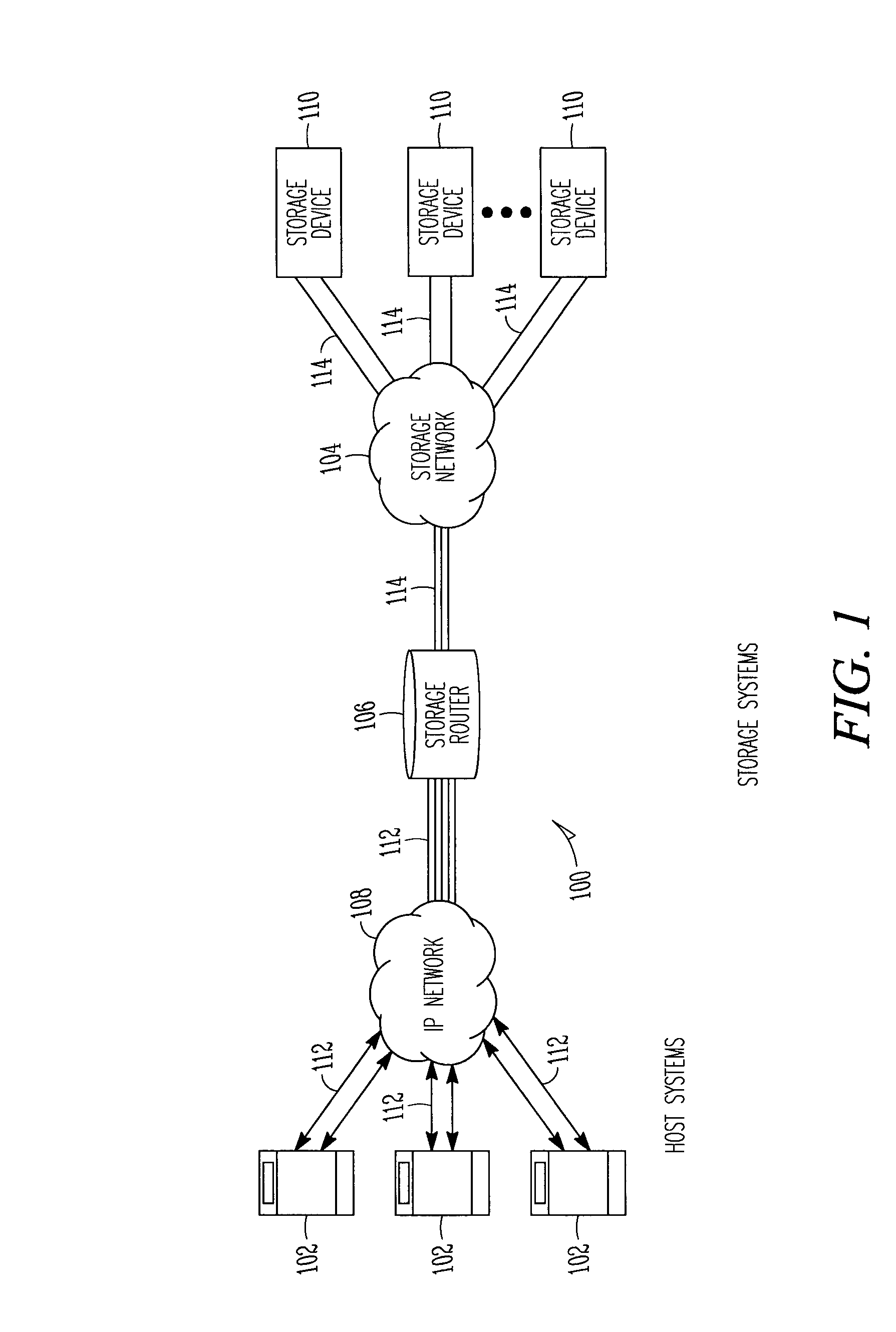
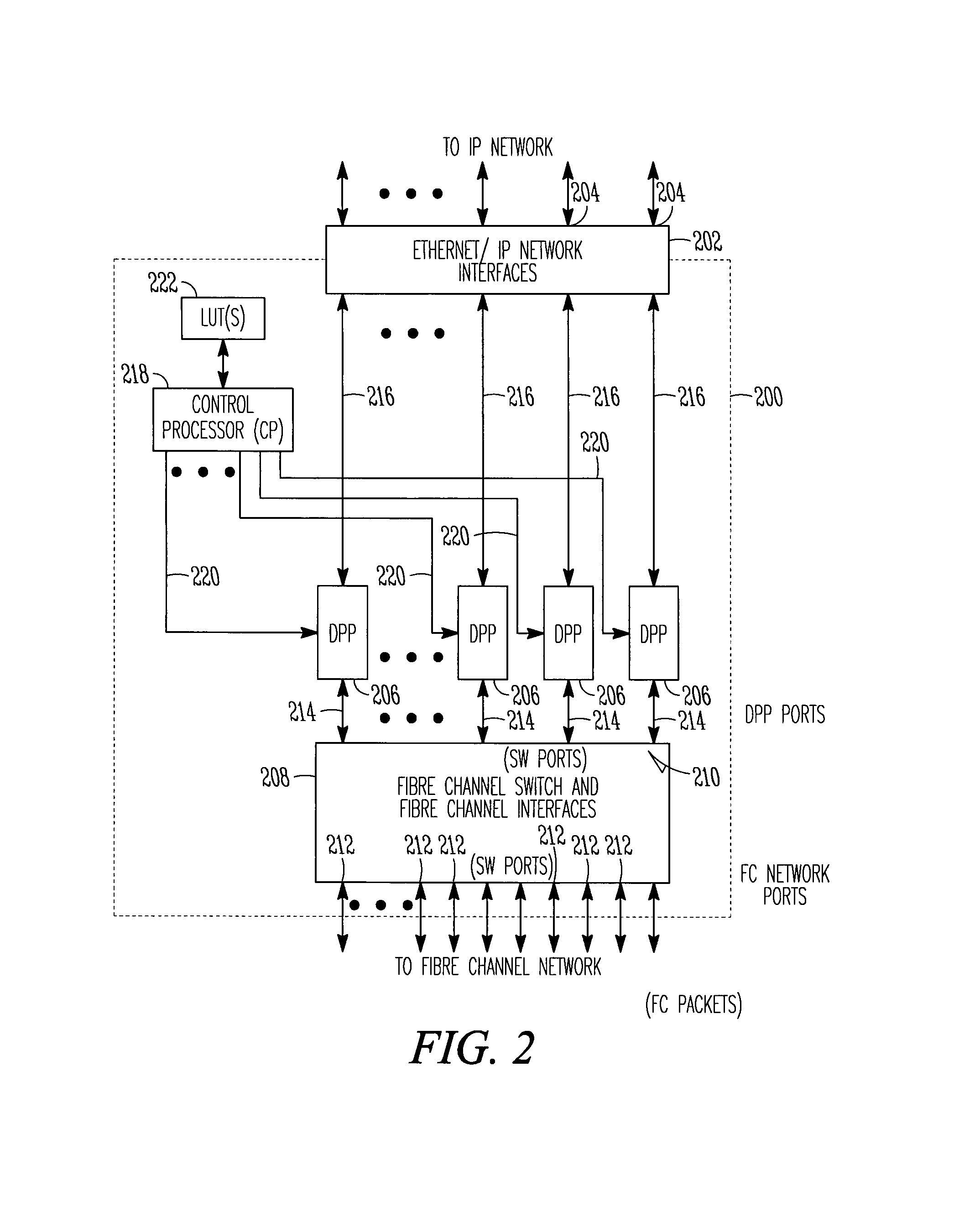
Storage router and method for routing IP datagrams between data path processors using a fibre channel switch
A storage router includes an IP network interface with IP network ports and data path processors. Each of the data path processors may control one of the IP network ports. High speed communication links couple the data path processors with a fiber channel switch. The storage router may route IP datagrams between the data path processors using the fiber channel switch. The fiber channel switch switches fiber channel packets between the data path processors and a plurality of fiber channel switch ports. The fiber channel packets may be encapsulated IP datagrams. Fiber channel packets received at a data path processor may be re-encapsulated and sent back through the fiber channel switch to another data path processor when the packets are destined for IP addresses associated with IP network ports controlled by other data path processors. Among other things, asymmetric data paths, and multiple and redundant communication paths with host systems are supported.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
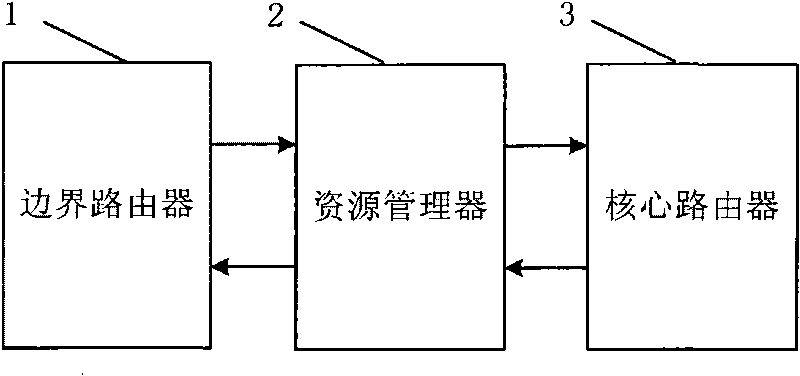
Dynamic resource allocation system and allocation method used for supporting end-to-end time delay warranty
InactiveCN101729430ALoad balancingSmall granularityData switching networksBalancing networkDifferentiated services
The invention discloses a dynamic resource allocation system used for supporting end-to-end time delay warranty, mainly solving the problems that the existing differentiated service network QoS warranty capacity is low and network resource is not fully utilized. The system thereof comprises a boundary router, a resource manager and a core router; wherein the resource manager calculates time delay allocation value on each link of end-to-end transmission path according to time delay upper limit requirement in a service request message transmitted by the boundary router and combining link load degree in network load information and time delay estimated value of each PHB at each link port; on related core router, optimal PHB is dynamically selected for resource allocation and packet retransmission by matching of time delay allocation value and bandwidth requirement according to local available resource state. The invention can effectively balance network load, reduce QoS warranty granularity and improve network resource utilization ratio while ensuring service end-to-end time delay requirement and can be applied to IP network and packet switching network.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Congestion Control in Stateless Domains
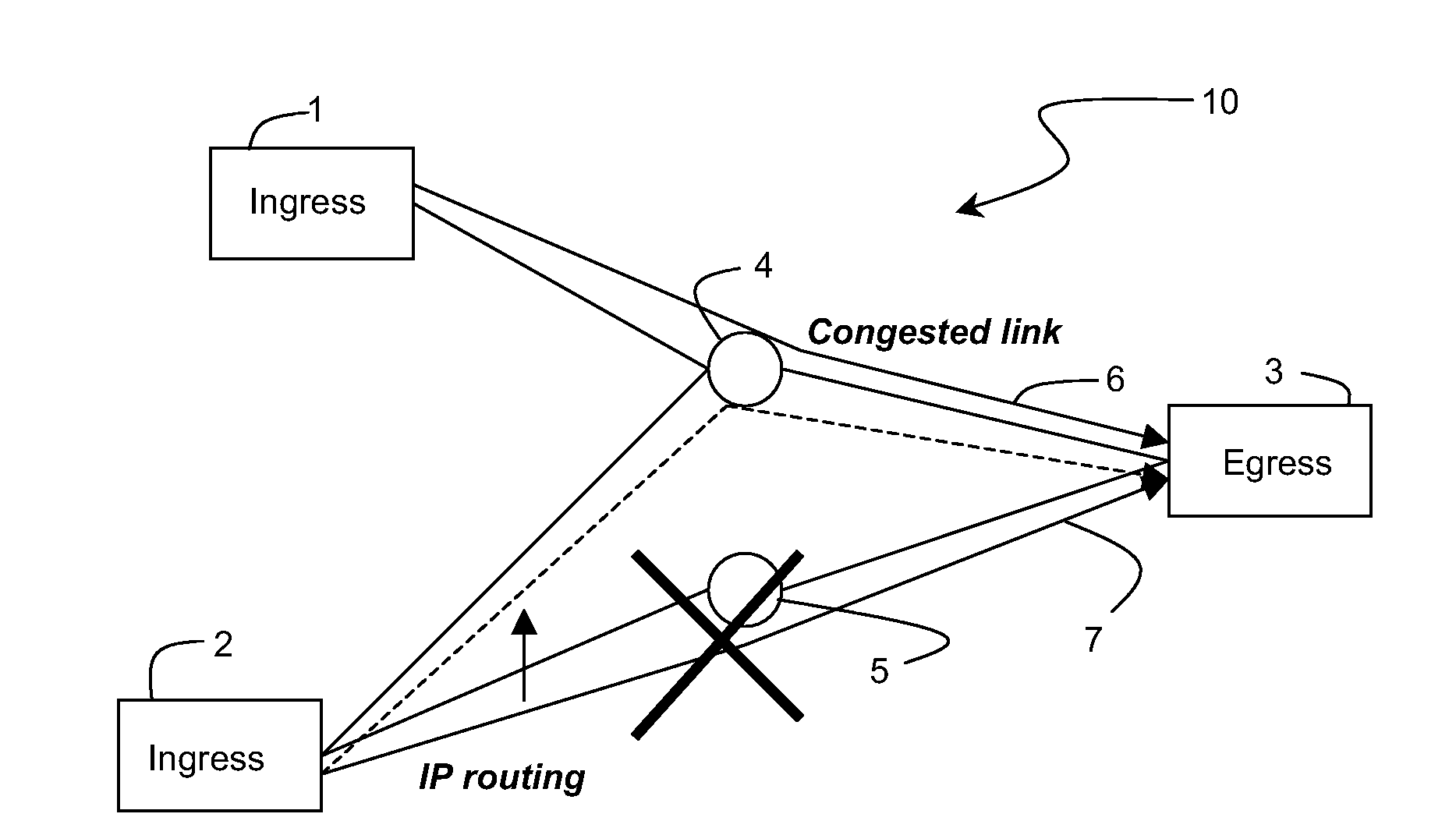
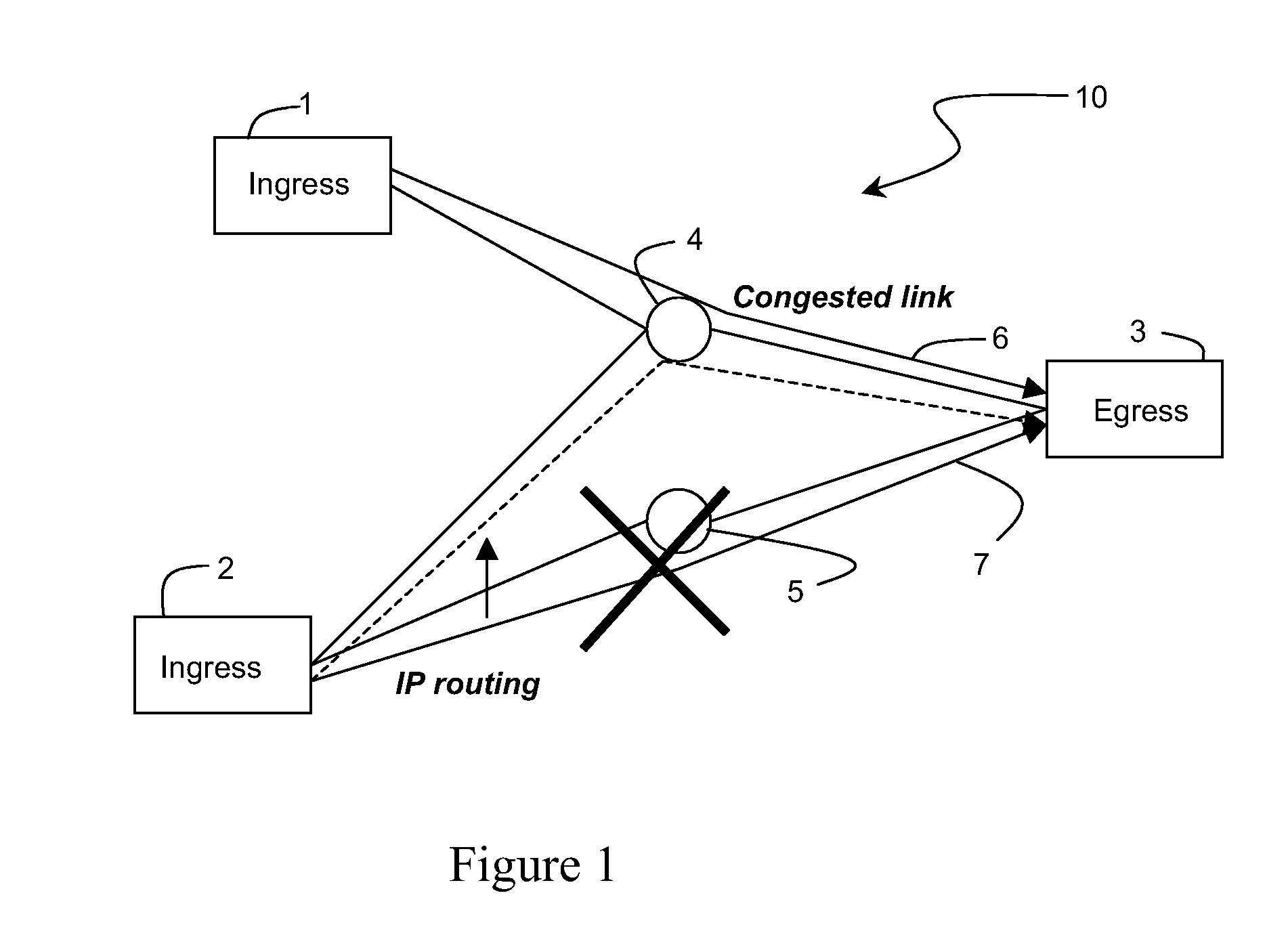
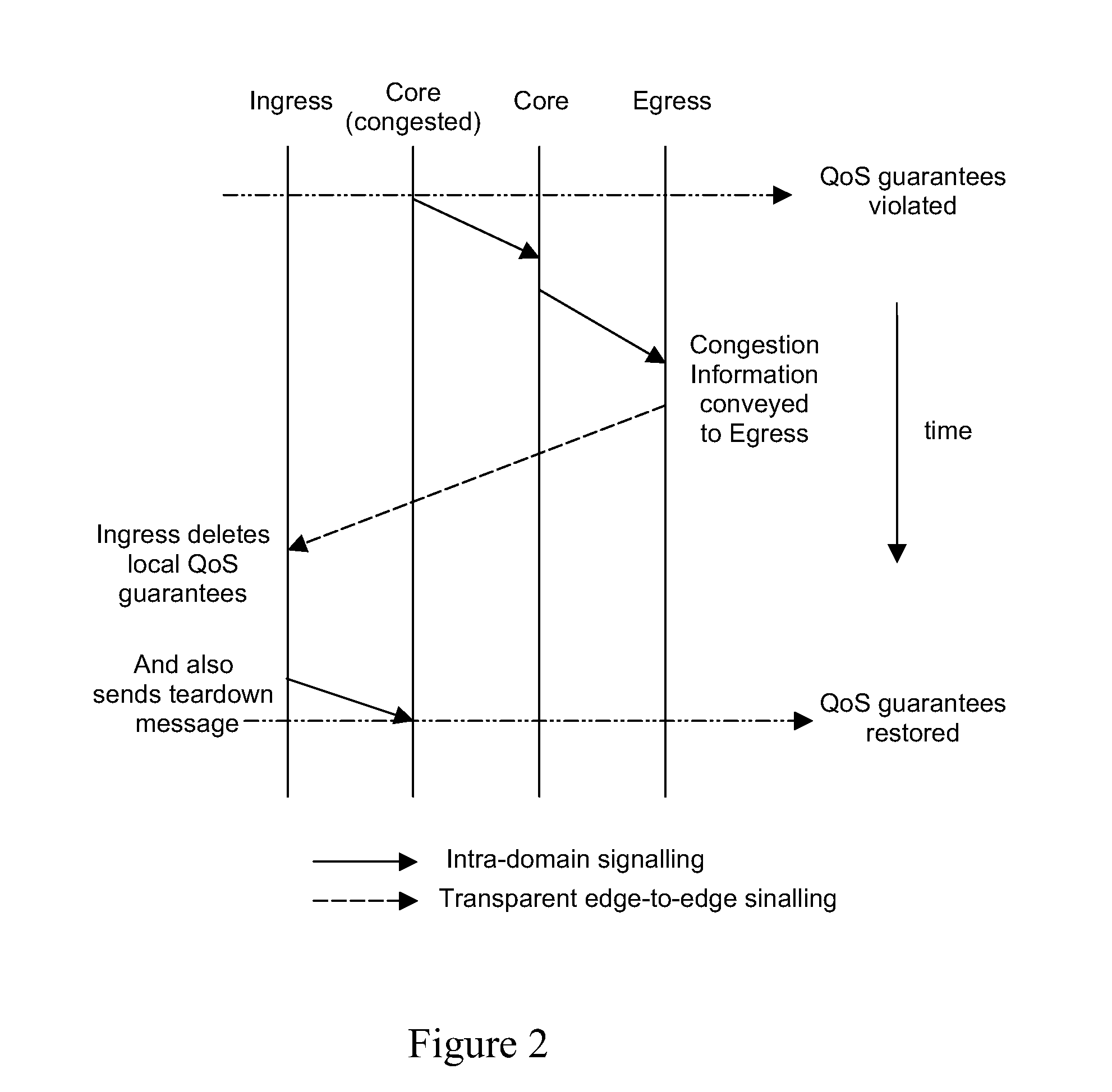
InactiveUS20100182907A1Shorten the timeProvide informationError preventionTransmission systemsEdge nodeCore router
Reducing congestion in an IP domain wherein congested data flows arriving at an egress edge node of the network are identified. Total congestion represented by the congested flows is determined, and a congestion extent notification is sent from the egress edge node to its ingress edge node peer. The congestion extent notification includes information regarding the total congestion and is sent on a per-class basis. Congested core routers in the network insert DSCPs into data packets passing through them to enable the egress edge nodes to identify the affected flows. The core routers may also send congestion metric messages, designed to follow the same path as the marked packets, to inform the egress edge nodes of the extent of congestion. In an alternative method, the egress edge nodes inform their ingress peers that congestion is present, without initially identifying the extent. The ingress edge node sends a query downstream with a congestion metric.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Content router with multiple forwarding elements instantiated on hardware entities
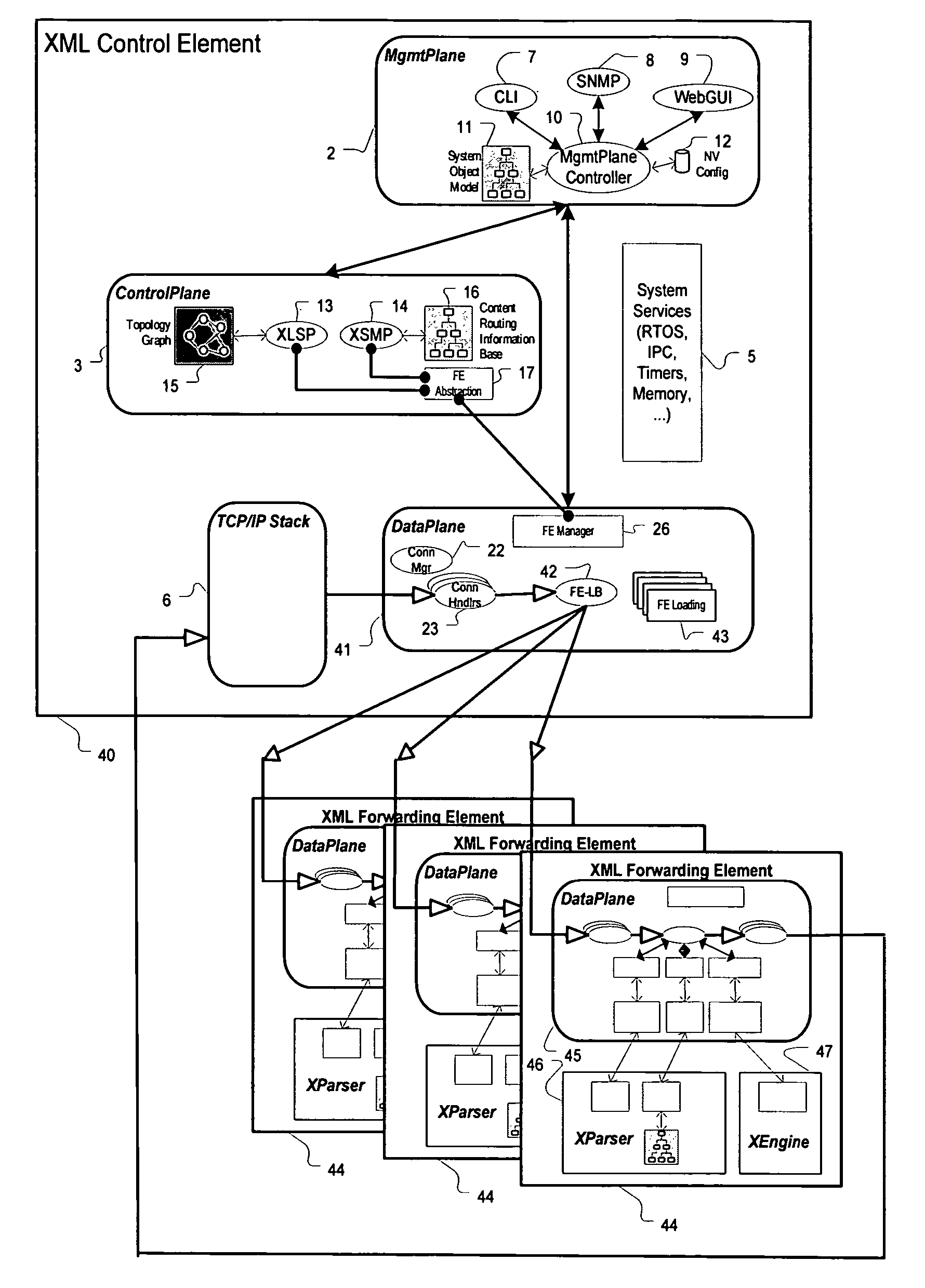
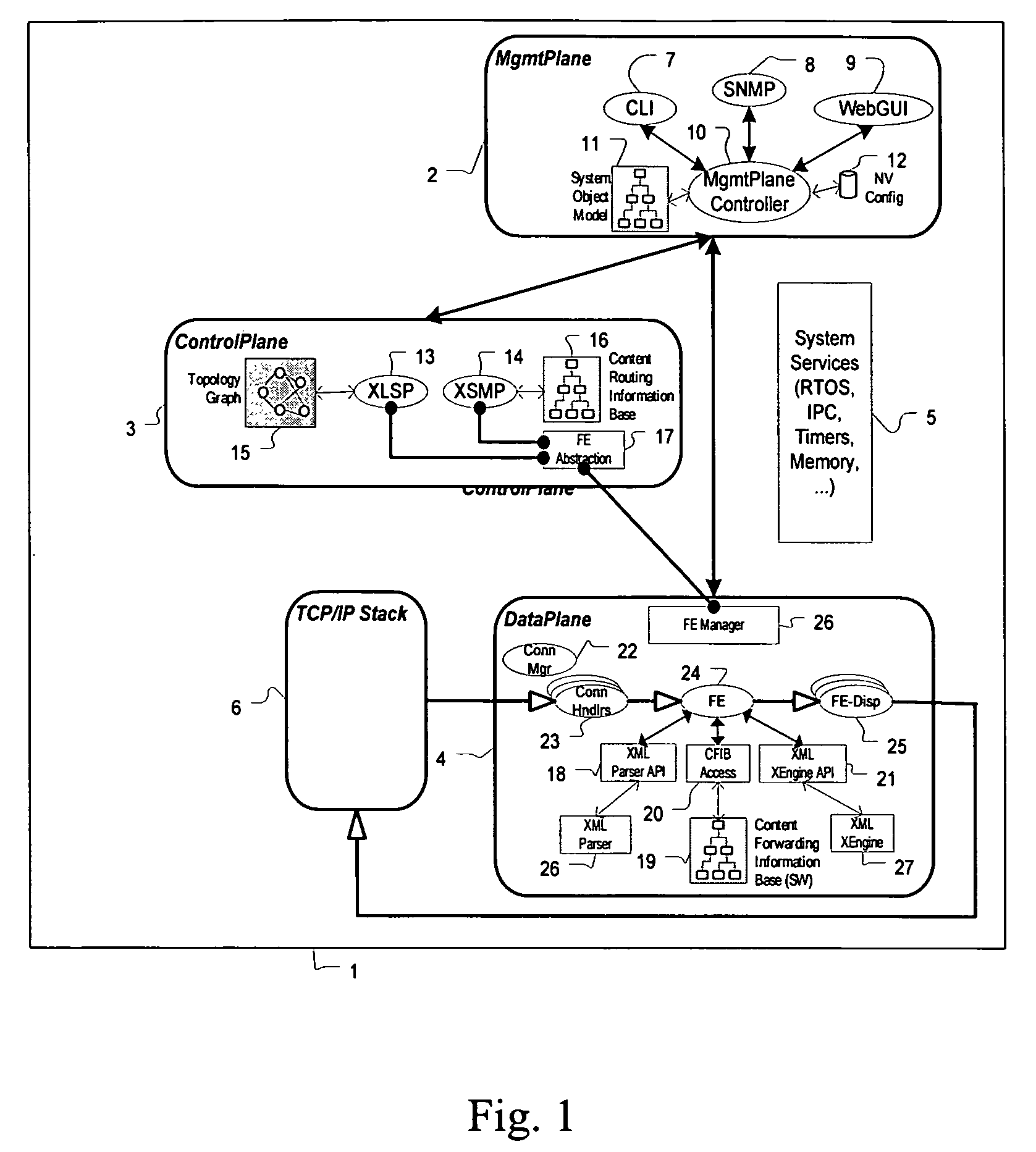
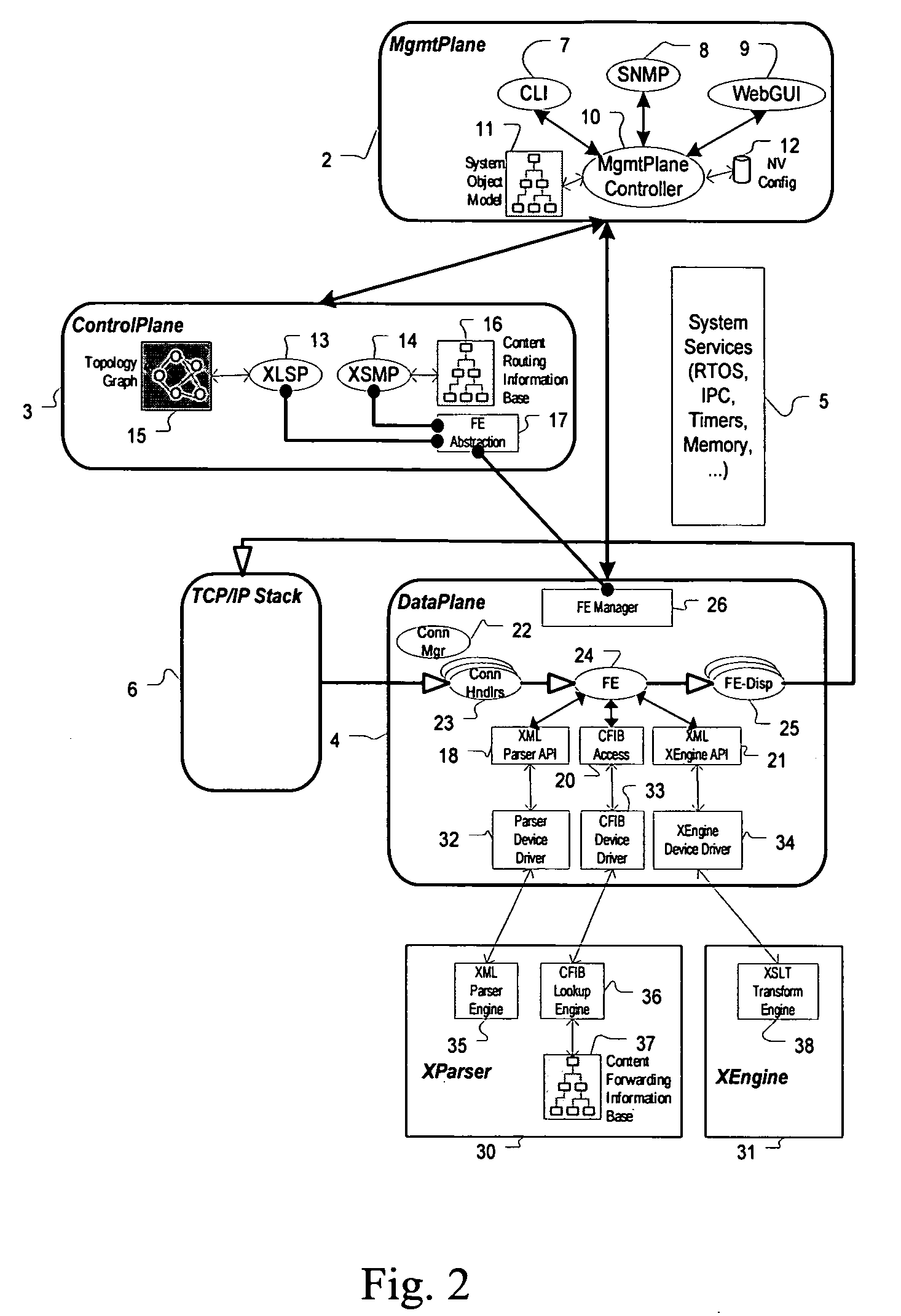
ActiveUS7844733B2Digital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsCarrier gradeNetwork management application
A carrier grade content router, includes a distinct management plane for housing externally visible management applications, and coordinating and relaying external management requests to appropriate underlying application code in the router; a distinct control plane for running control protocols required within an XML routed network; and a distinct data plane for receiving and forwarding customer data. Some functions can be implemented in software or via a hardware accelerator.
Owner:SOLACE CORP
Packet transmission method based on network dual exit and exit router
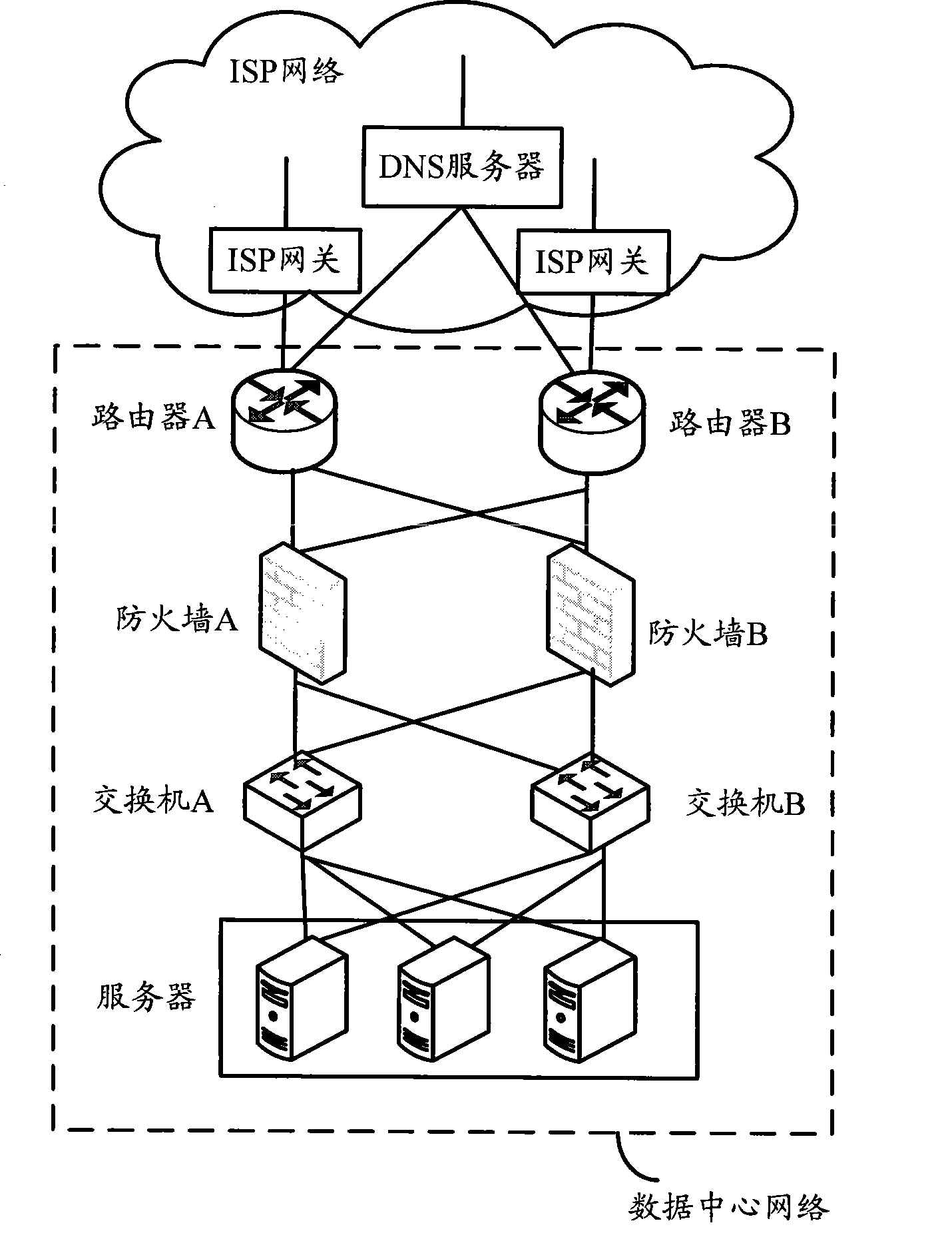
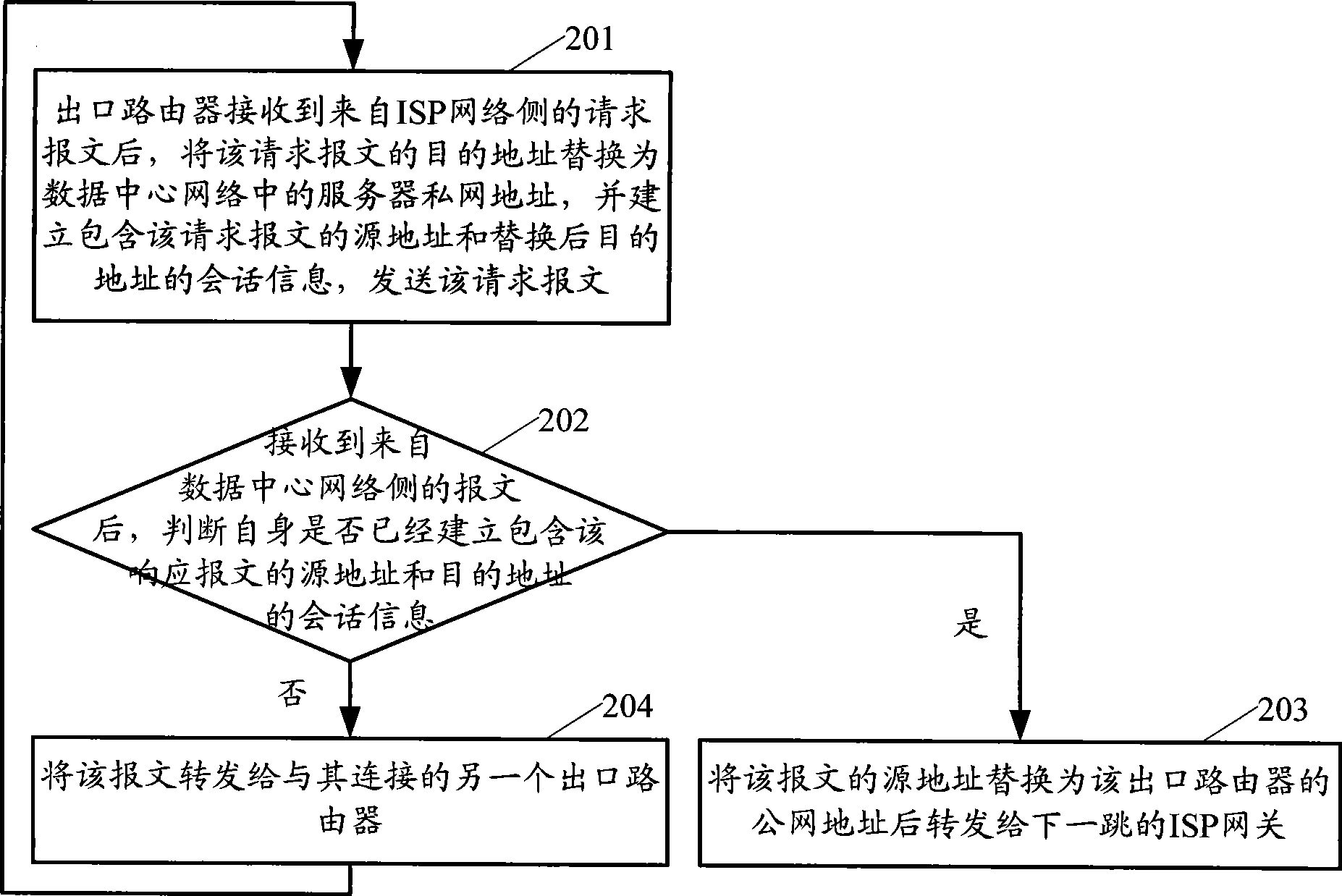
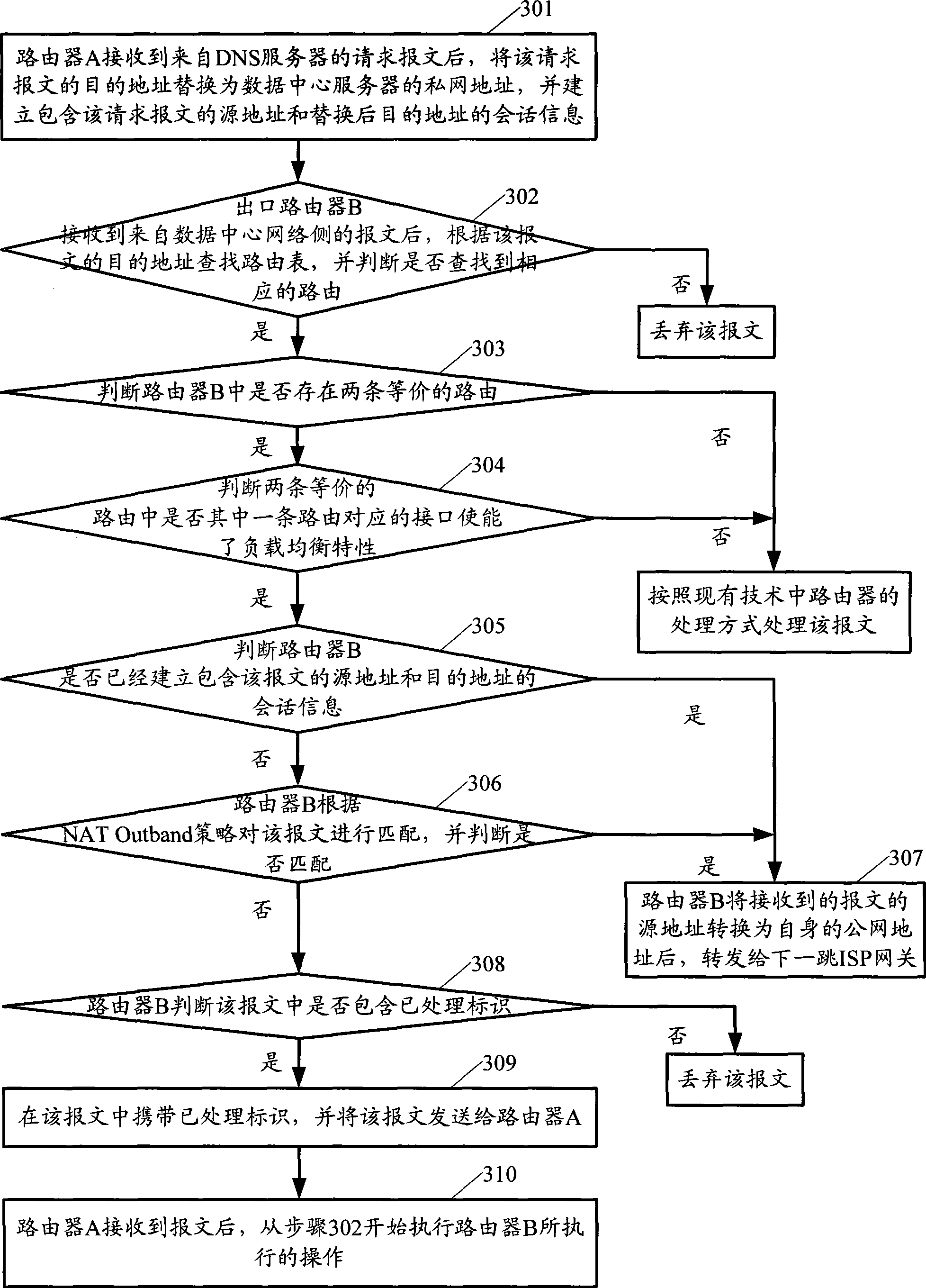
InactiveCN101383778AImprove securityGuaranteed balanceData switching networksData centerEgress router
The invention provides a message transmission method based on double output-ports of the network and output-port routers, which are applied in a data centre network containing two output-port routers, and a connection is established between the two outlet-port routers; after receiving a request message from the (ISP) network side of a service supplier, each output-port router merely conducts the displacement of destination address, and creates a conversation information containing the source address of the request message and the destination address after the displacement, and then sends the request message; after receiving the message from the network side of the data center, by judging whether the self creates the conversation information containing the source address of the message and the destination address, if yes, the output-port router replaces the source address of the message by a public network address of the output-port routers and then transmits the public network address to the ISP gateway of the next hop; otherwise, the output-port router transmits the message to the other output-port router connected with the output-port router. The invention is favorable for realizing safety precautions of the servers in the data center network and improving the security of the data center network.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
Packet transfer method, packet transfer device, and packet transfer system
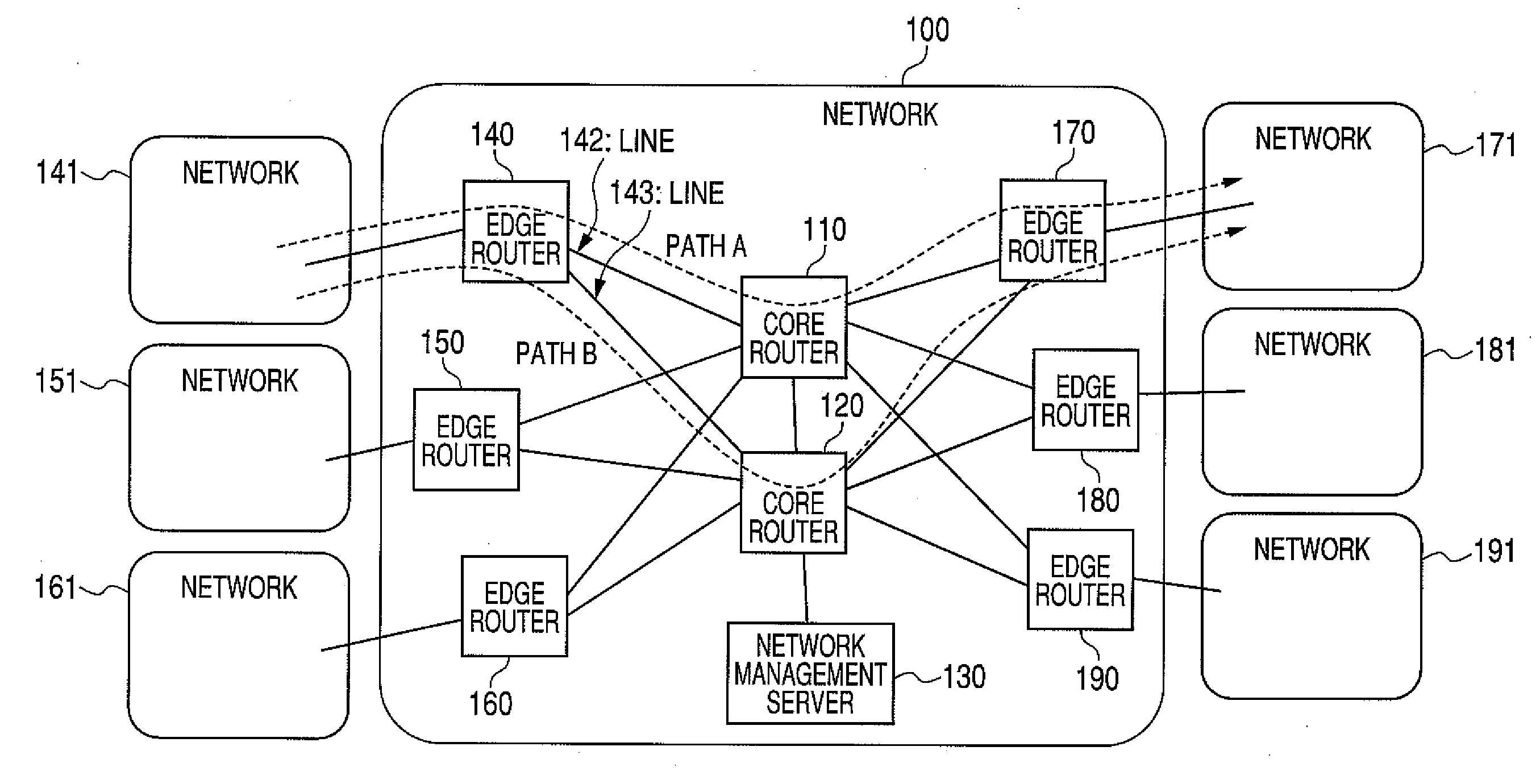
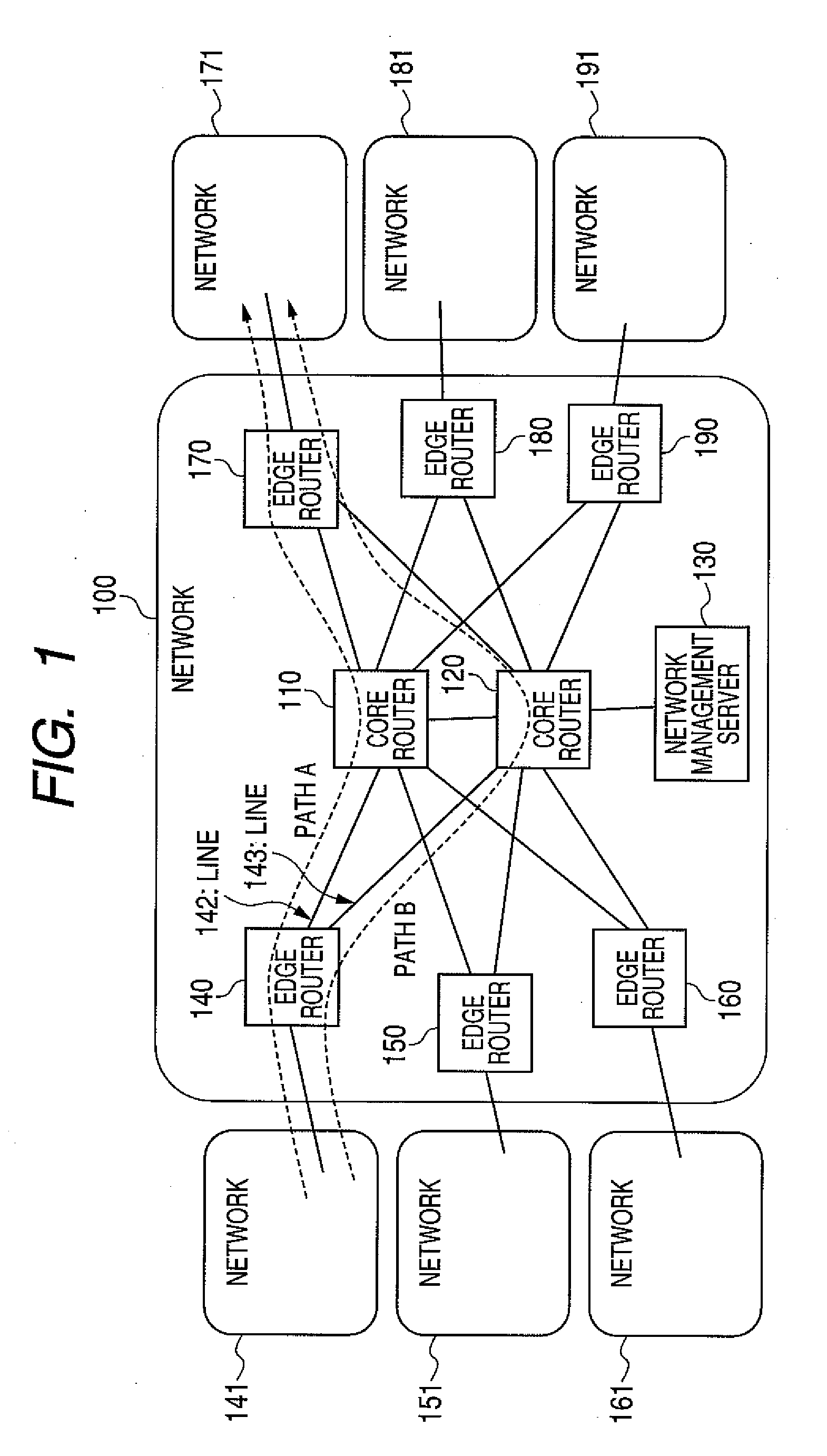
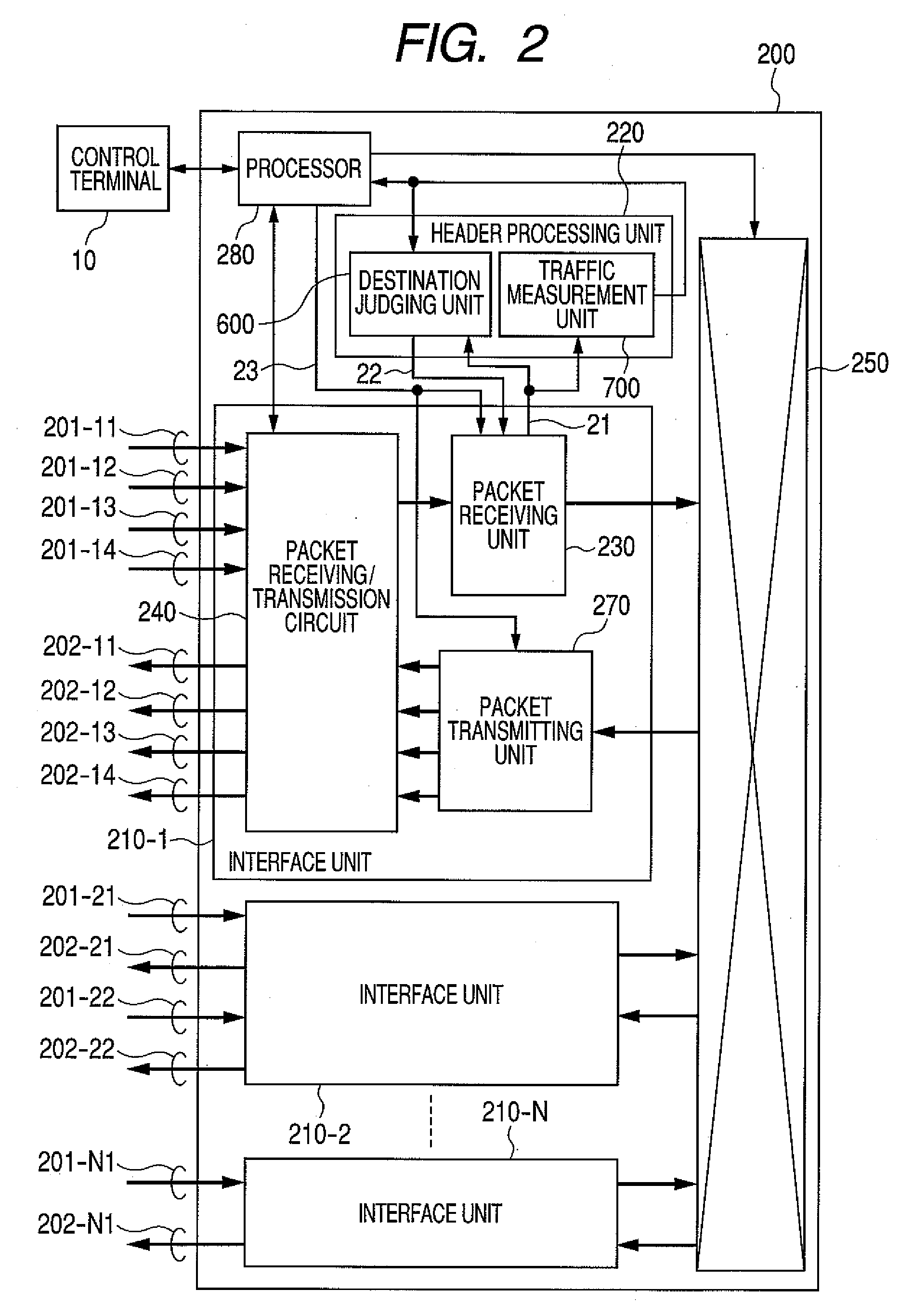
InactiveUS20100157830A1Reduce power consumptionReduce loadEnergy efficient ICTError preventionRouting tableTransfer system
An edge router measures a traffic volume inputted into a network, and the measurement result is notified to a network management server. If the network management server judges that the notified traffic volume is “smaller” than a capacity of a second core router, it will direct a first core router to shift to a power saving mode. The first core router notifies the edge router of the shift to the power saving mode, and the edge router updates a routing table so that the packet to the first core router may be bypassed to the second core router. The first core router shifts to the power saving mode that does not perform packet transfer, and reduction in electric power is realized.
Owner:ALAXALA NETWORKS
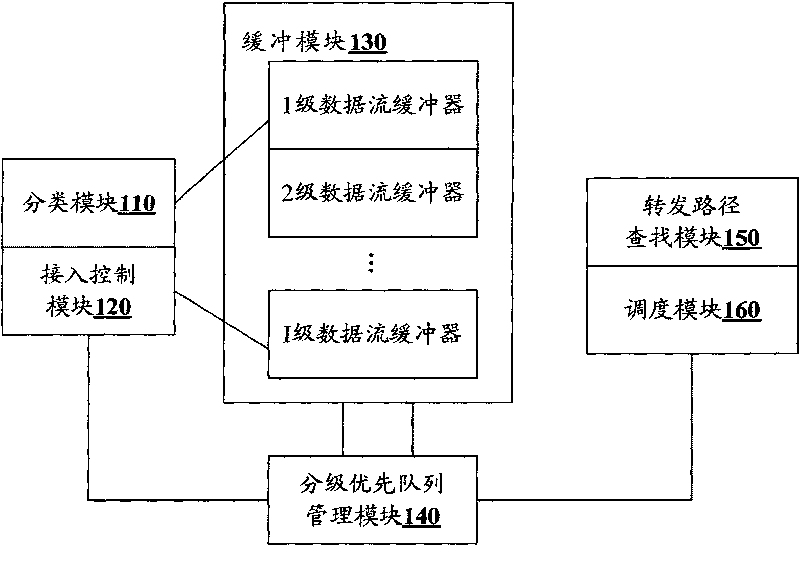
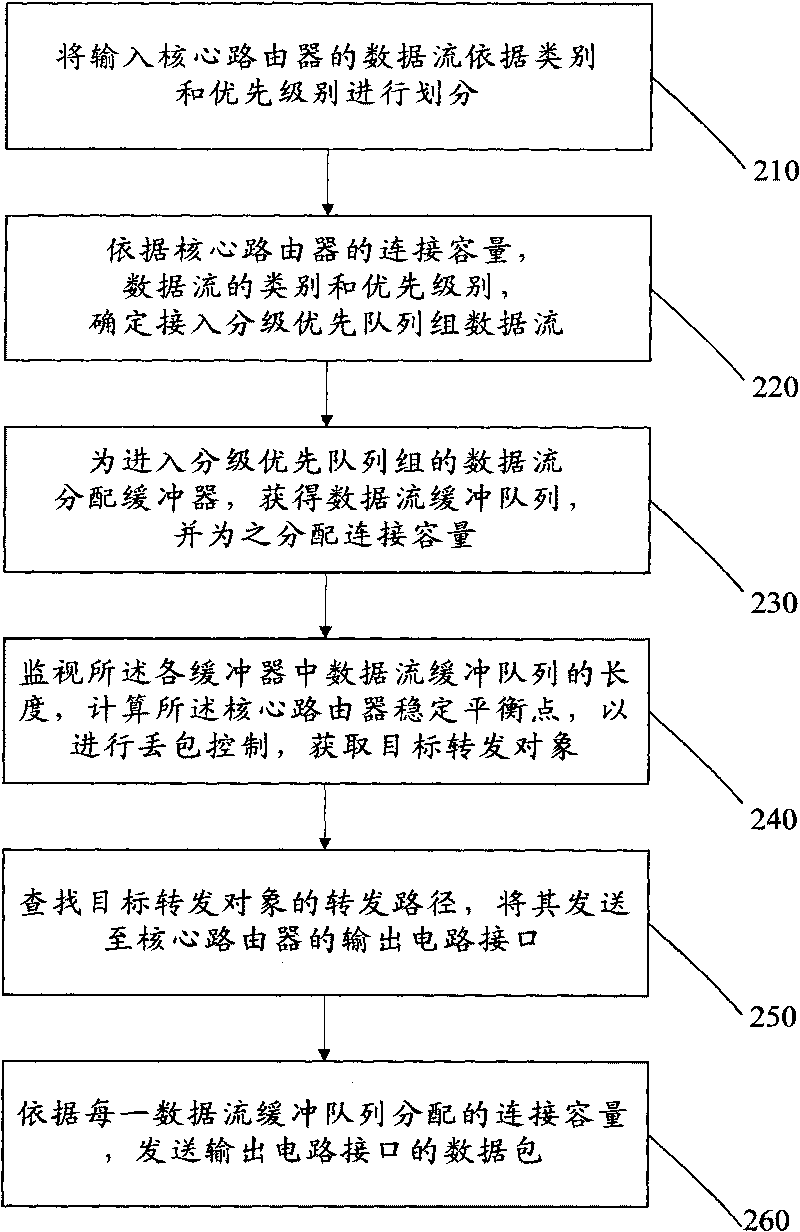
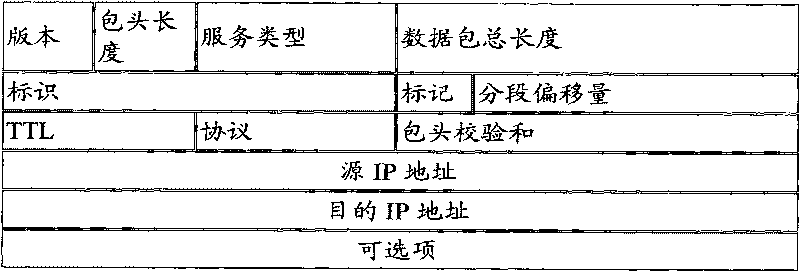
Differentiated service core router and data forwarding method thereof
InactiveCN101692657AGuaranteed rateMinimum delayData switching networksDifferentiated servicesData stream
The invention discloses a differentiated service core router and a data forwarding method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: differentiating data stream input to the core router according to the class and priority rating; determining the access data stream according to the output connection capacity of the core router; acquiring a data buffer queue; performing packet loss control for each data stream of low priority; searching a forwarding path of the data stream of high priority in the differentiated priority queue according to a routing table; and preferentially forwarding the data stream of high priority. Through the technical means of input data stream differentiation, access control, differentiated priority queue packet loss control and the like, the exit bandwidth of the router is fully utilized, and the rate, minimum delay and packet loss rate of the data stream of voice service and multimedia service of high priority users are ensured.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Method and apparatus for distributing label
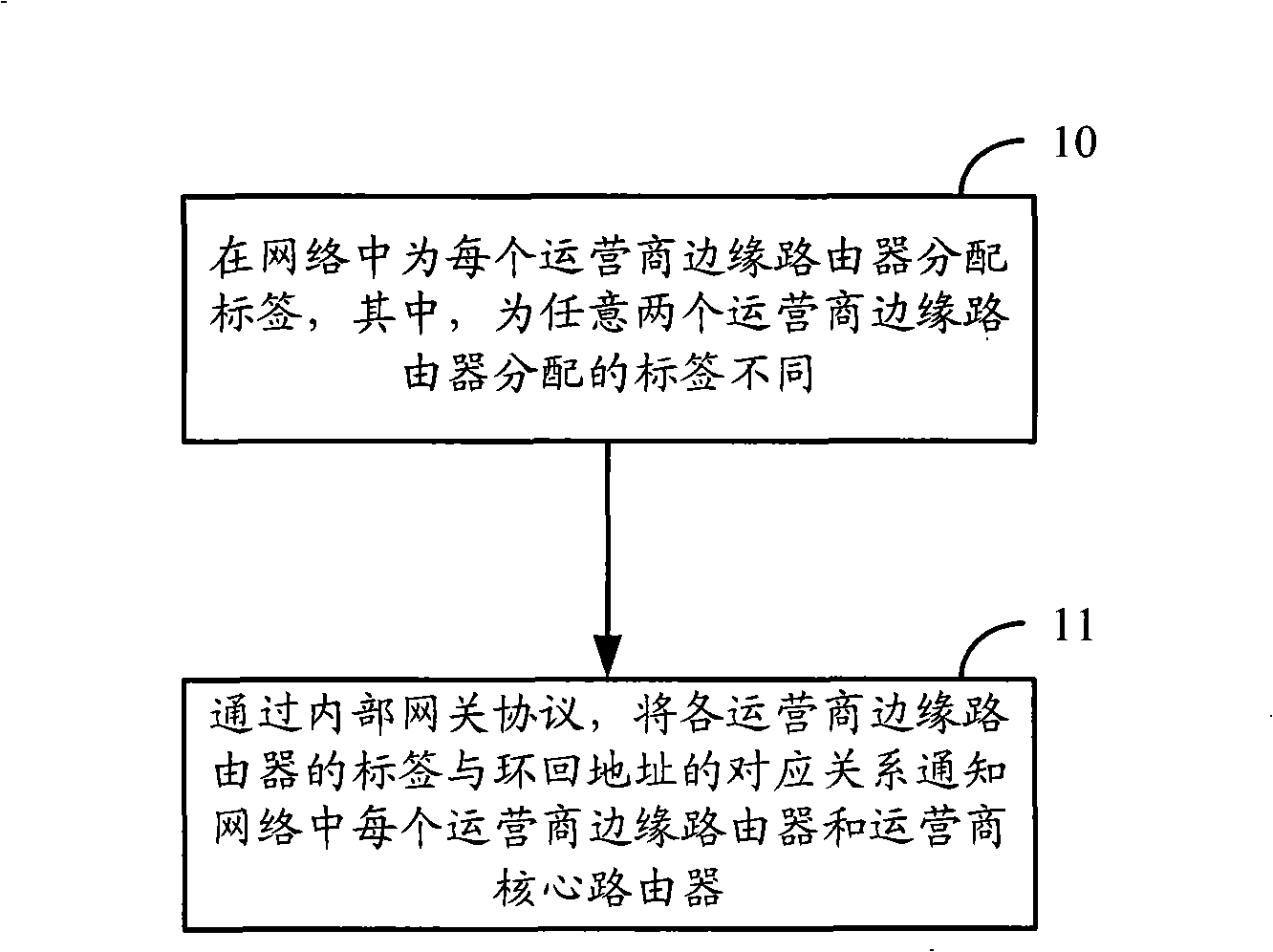
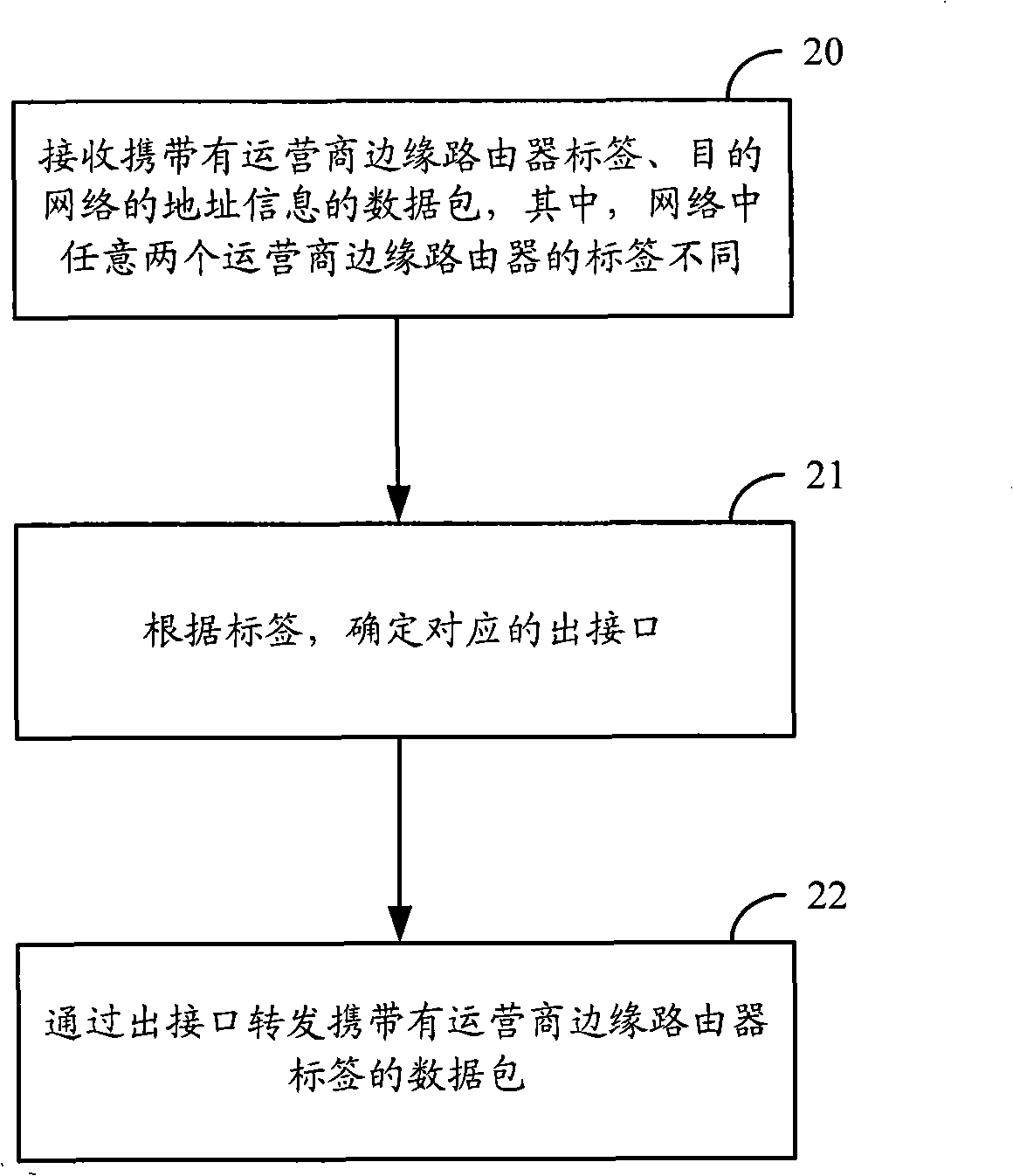
ActiveCN101355487AShorten convergence timeReduce overheadNetworks interconnectionCore routerData mining
The invention discloses a method for label distribution, comprising the following steps: a label is allocated for each operator edge router in a network, wherein labels allocated for any two operator edge routers are different; and through an inner gateway protocol, the corresponding relation of the label of each operator edge router and a loopback address is notified to each operator edge router and an operator core router. Meanwhile, the invention discloses a label processing method, a label distribution device and a label processing device. The method can realize label distribution without adopting dynamic label distribution protocols such as LDP.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE COMM GRP CO LTD
Method and apparatus for the distribution of network traffic
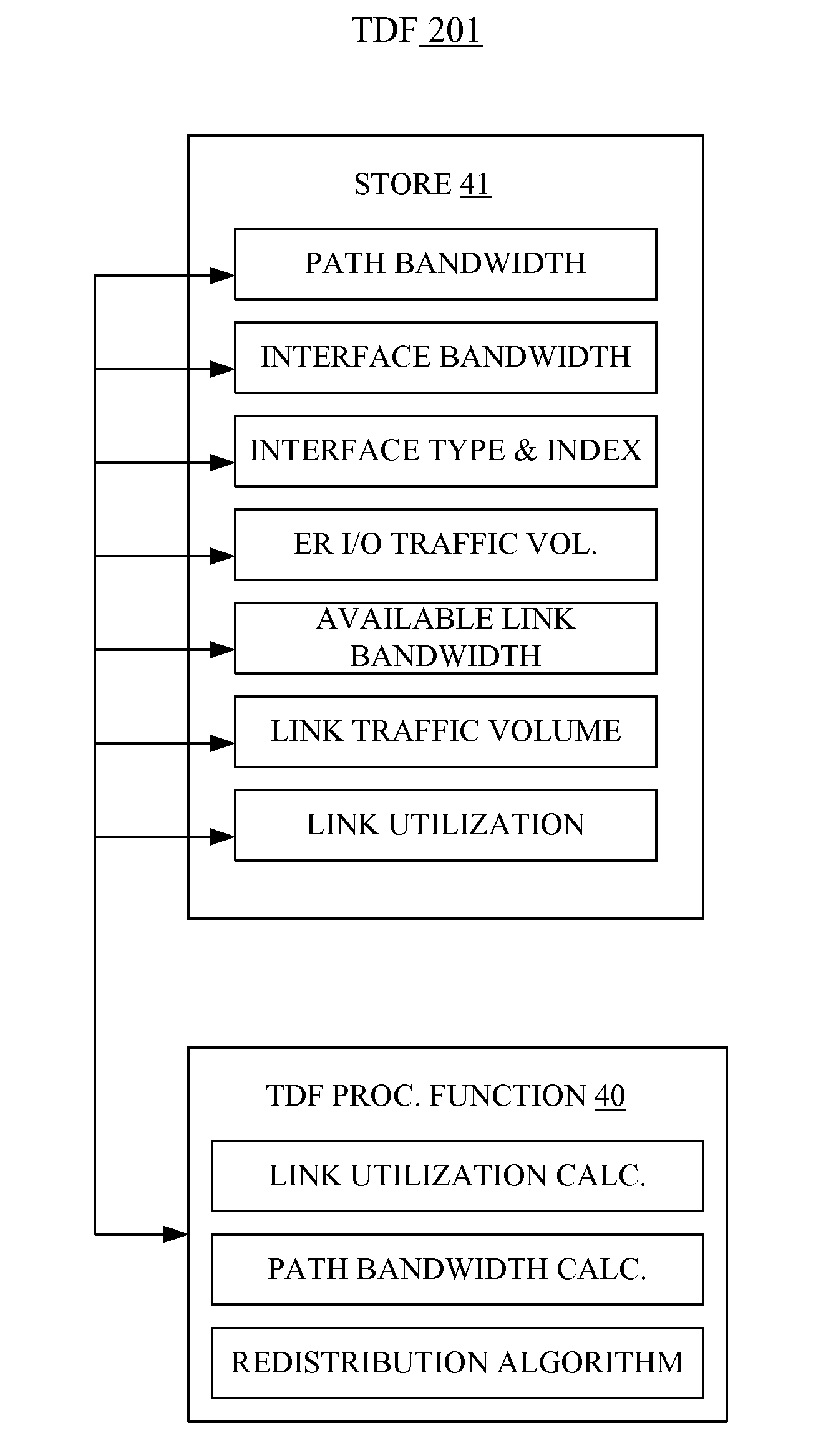
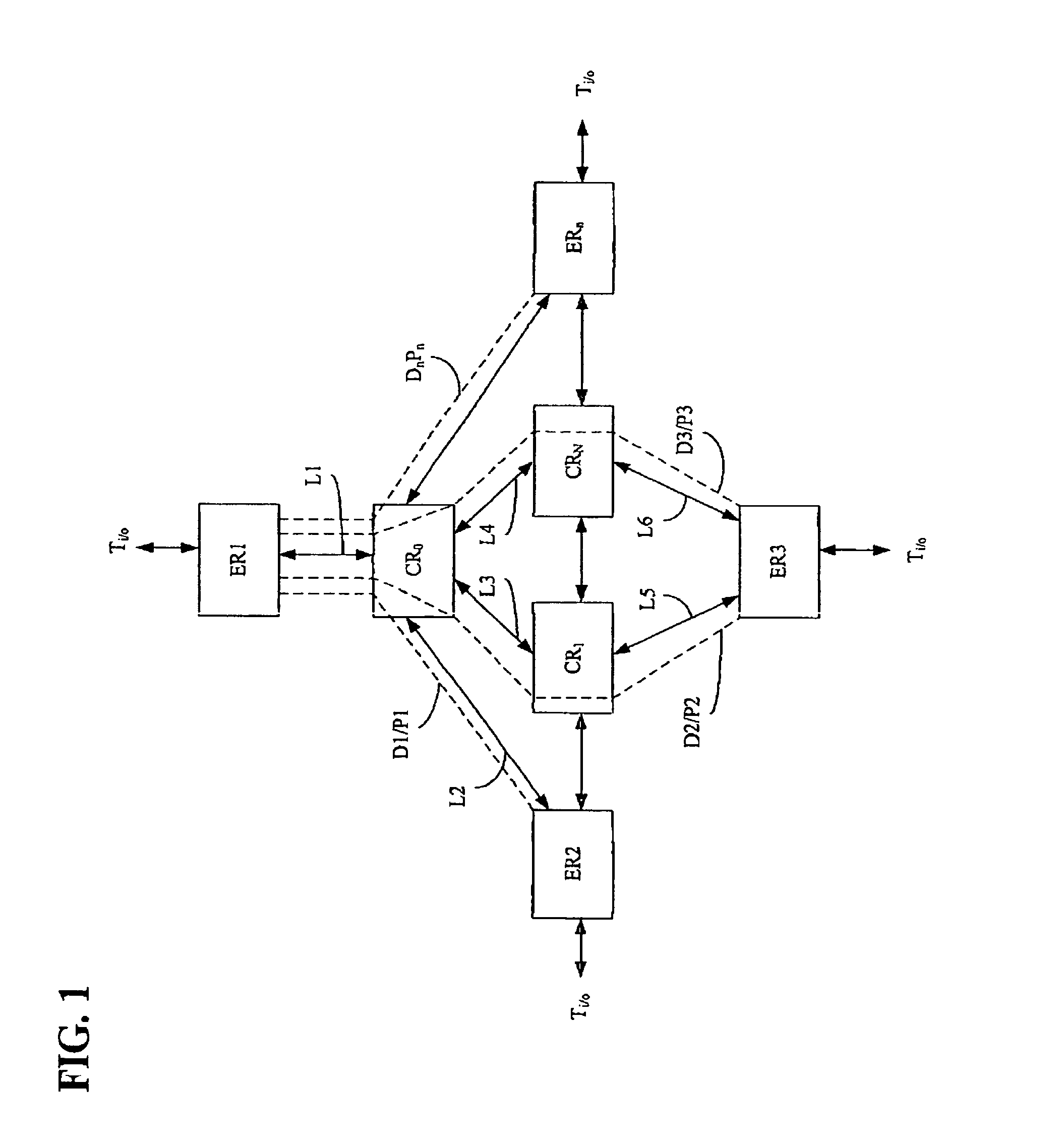
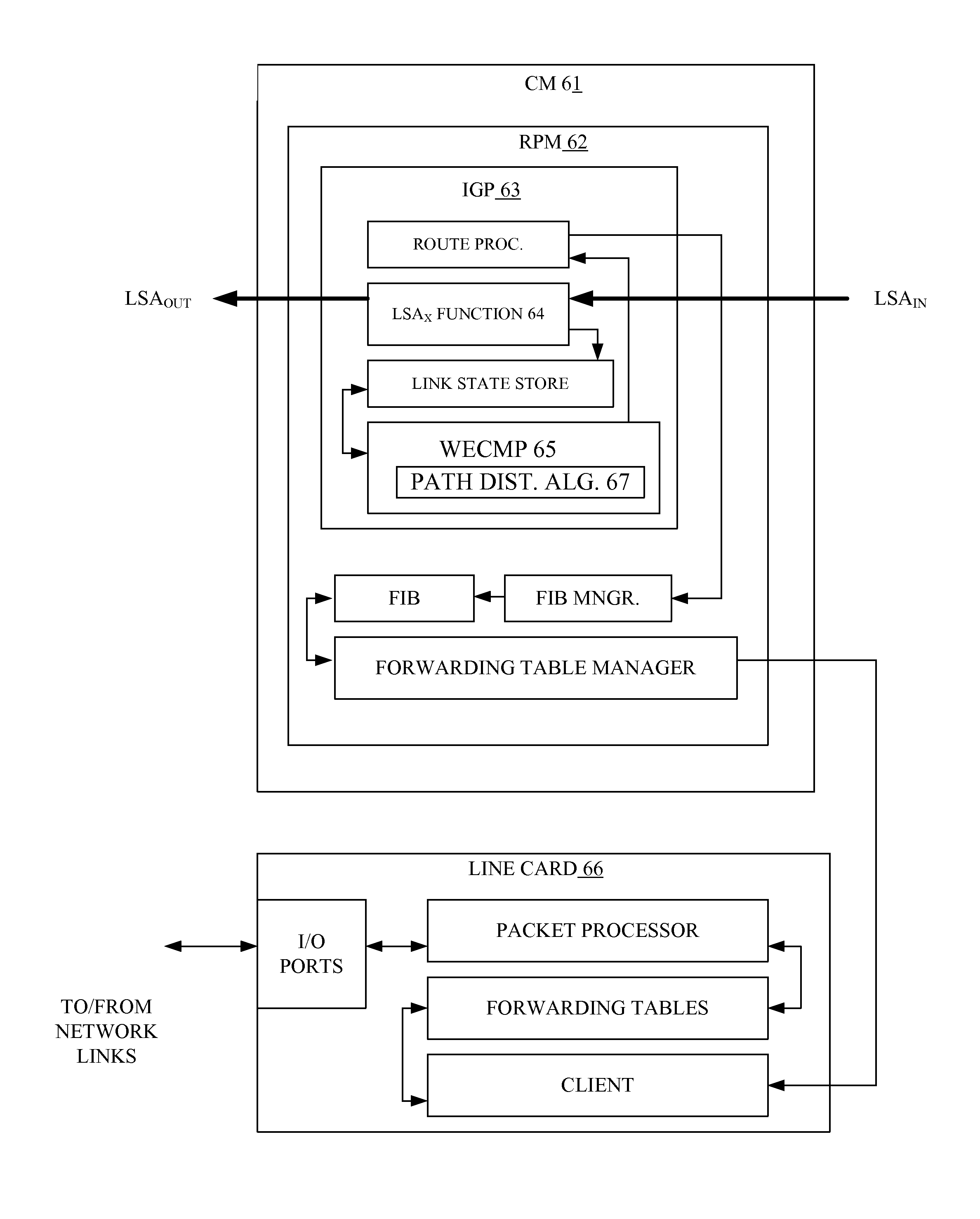
ActiveUS8630297B2Optimize networkReduce traffic lossError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityCore router
A packet network system, such as an autonomous system, includes a plurality of packet network devices some of which are edge routers and some of which are core routers. Each of the edge and core routers include functionality that operates to receive network traffic, process the traffic as needed and to forward the traffic to its destination. Additionally, each router includes a traffic distribution function that operates to calculate path bandwidths for all of the paths over which the traffic can be forwarding through the system and to use the volume of traffic ingressing to the system, link utilization information and the calculated path bandwidth to redistribute the traffic in the system such that traffic loss in the system in minimized.
Owner:DELL MARKETING CORP
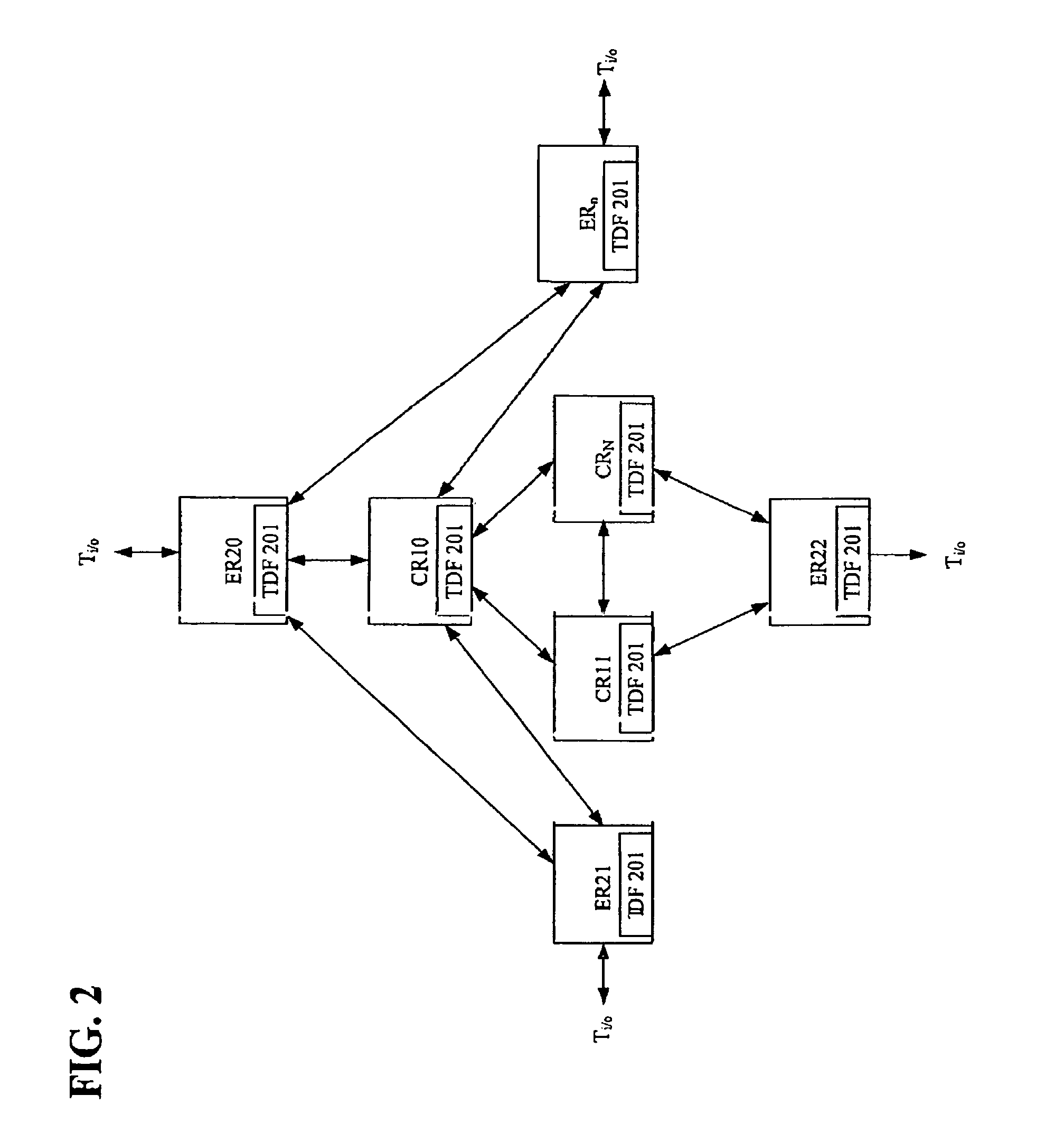
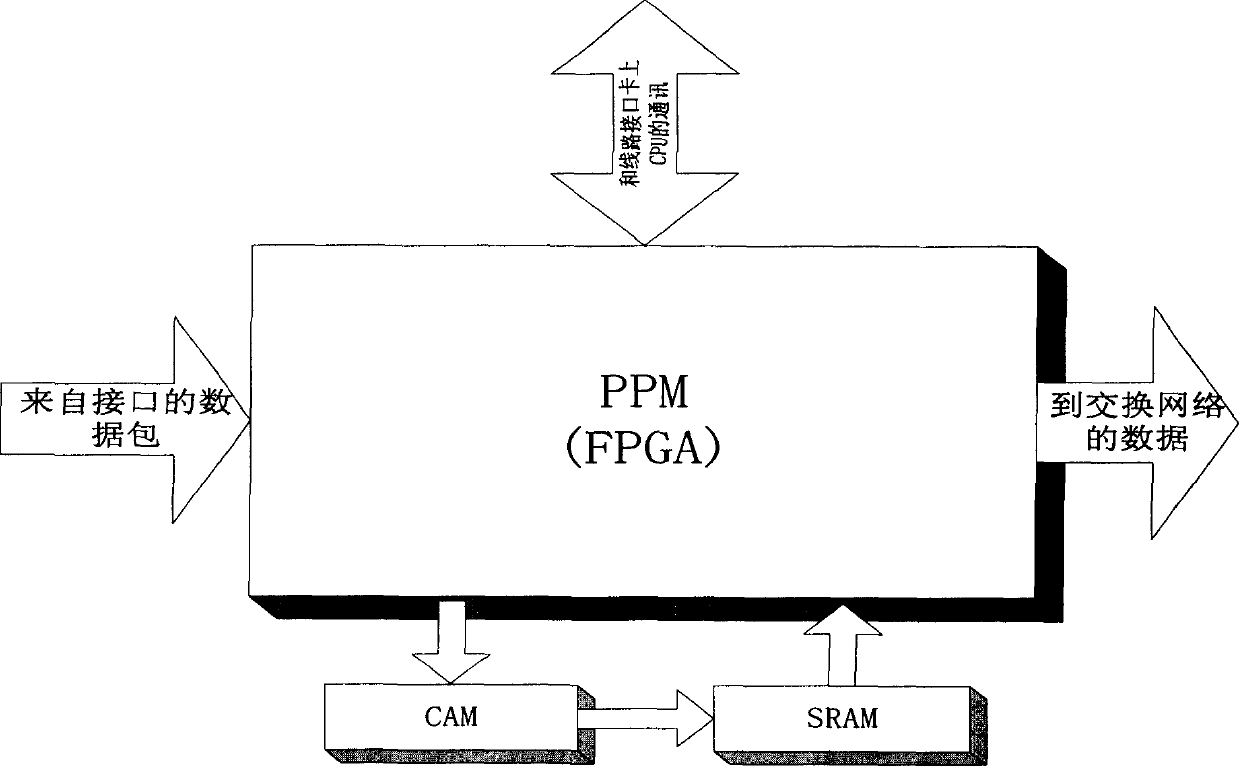
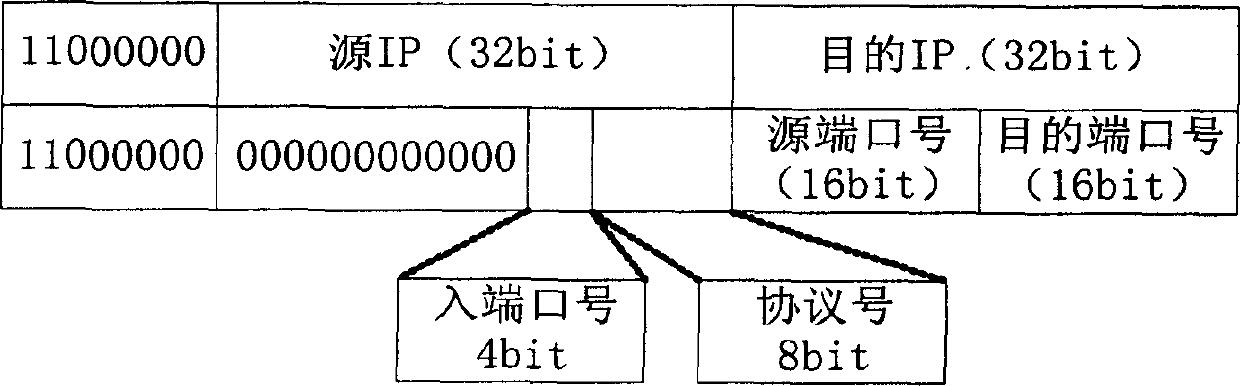
Double stack compatible router searching device supporting access control listing function on core routers
InactiveCN1655534AGuaranteed Speed ProcessingDoes not affect forwarding performanceData switching networksExchange networkSoftware engineering
This invention relates to core router supportive visit and control sequence double shed compatible router finding device, which belongs to Internet core router hardware technique field. The invention is characterized by comprising package pre-process circuit element and parallel CAM and SRAM and forms one router and ACL list through TCAM system and supports the list items dynamic alignment. The package pre-process circuit elements receive the data package and process them and extract needed information and ACL filtered information and send to the TCAM system and decide package process means according to the requirement results.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method & apparatus for the distribution of network traffic
ActiveUS20120201252A1Optimize networkReduce traffic lossData switching by path configurationNetwork connectionsInternet trafficNetworked system
A packet network system, such as an autonomous system, includes a plurality of packet network devices some of which are edge routers and some of which are core routers. Each of the edge and core routers include functionality that operates to receive network traffic, process the traffic as needed and to forward the traffic to its destination. Additionally, each router includes a traffic distribution function that operates to calculate path bandwidths for all of the paths over which the traffic can be forwarding through the system and to use the volume of traffic ingressing to the system, link utilization information and the calculated path bandwidth to redistribute the traffic in the system such that traffic loss in the system in minimized.
Owner:DELL MARKETING CORP
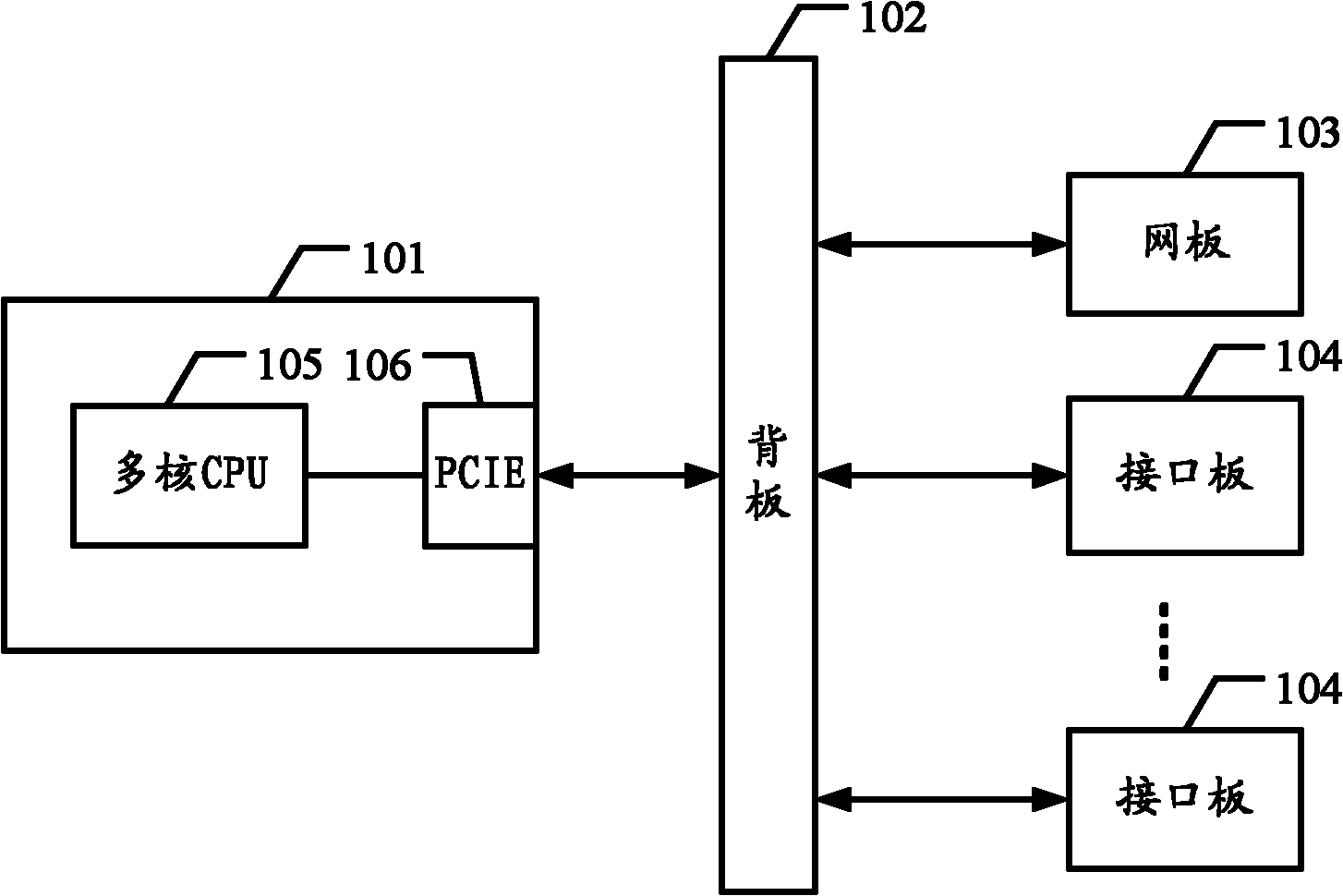
Multi-core router
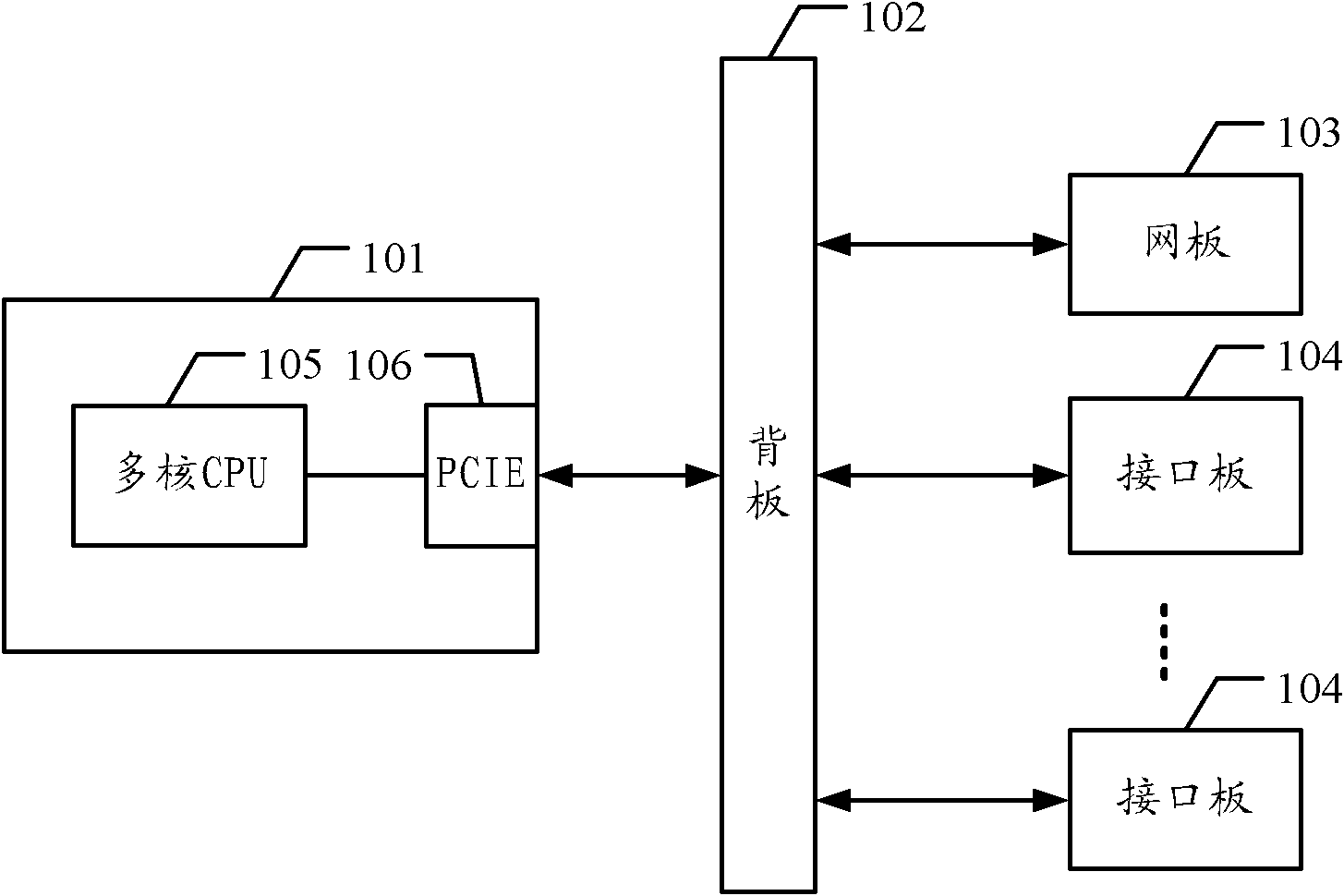
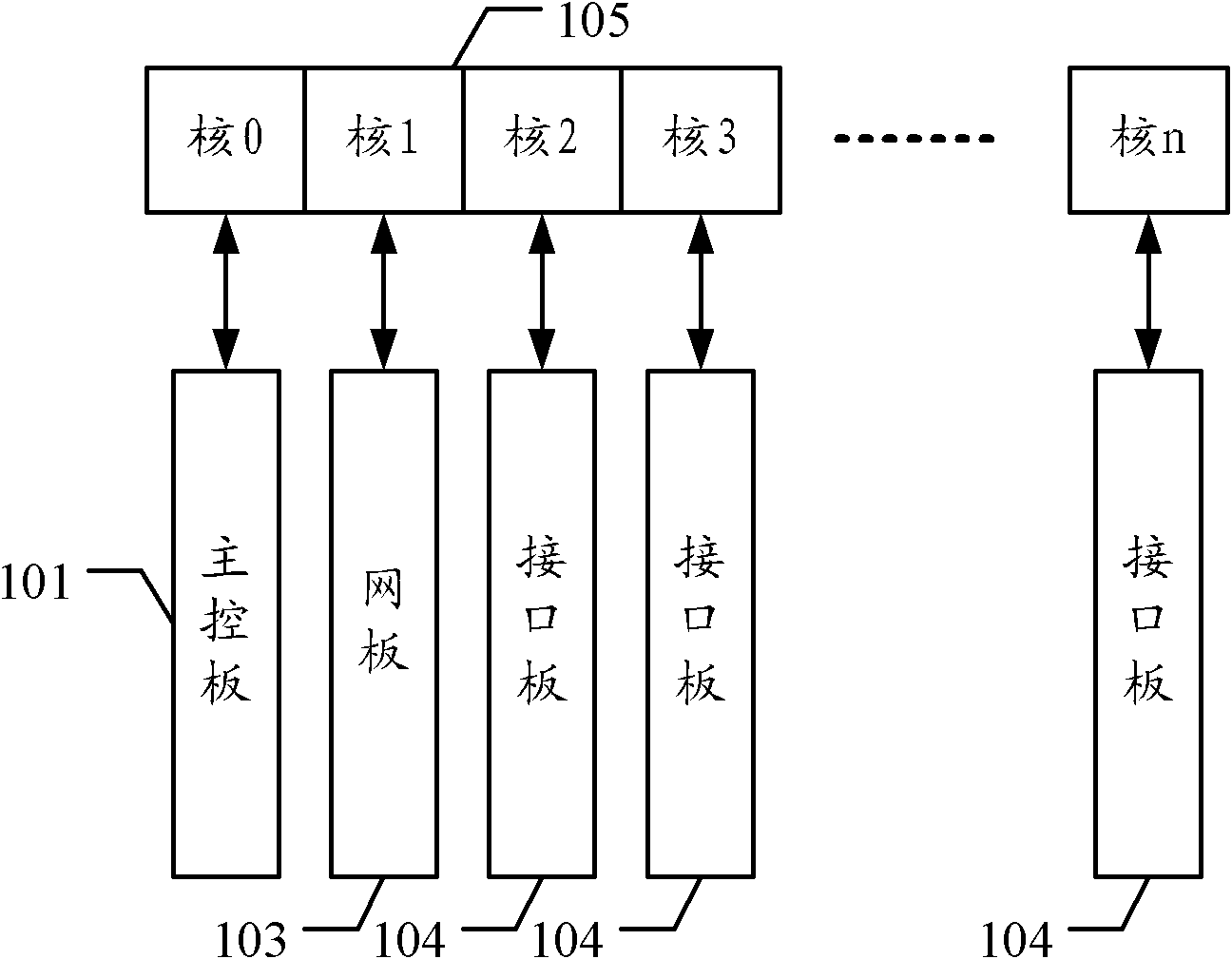
ActiveCN102204185ASave resourcesReduce power consumptionData switching networksCore routerData transmission
The invention embodiment discloses a multi-core router. The internal bus of the multi-core router is based on PCIE which connects the master control board of the multi-core router to the backboard of the multi-core router; the multi-core router further internally includes a network board and at least an interface board, wherein the network board and the interface board are respectively connected with the backboard via PCIE, thus to realize data transmission; and the master control board includes a multi-core CPU which respectively controls the network board and the interface board. The invention embodiment can effectively save hardware resources and reduce power consumption.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com