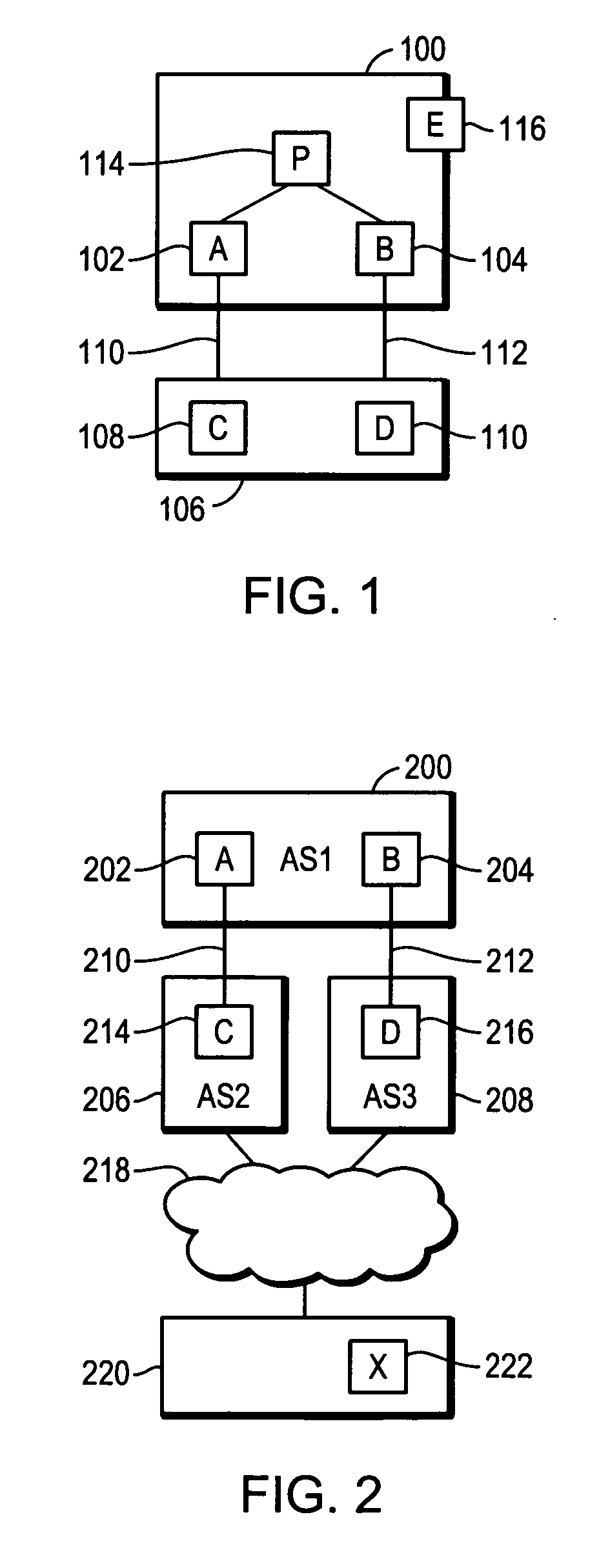
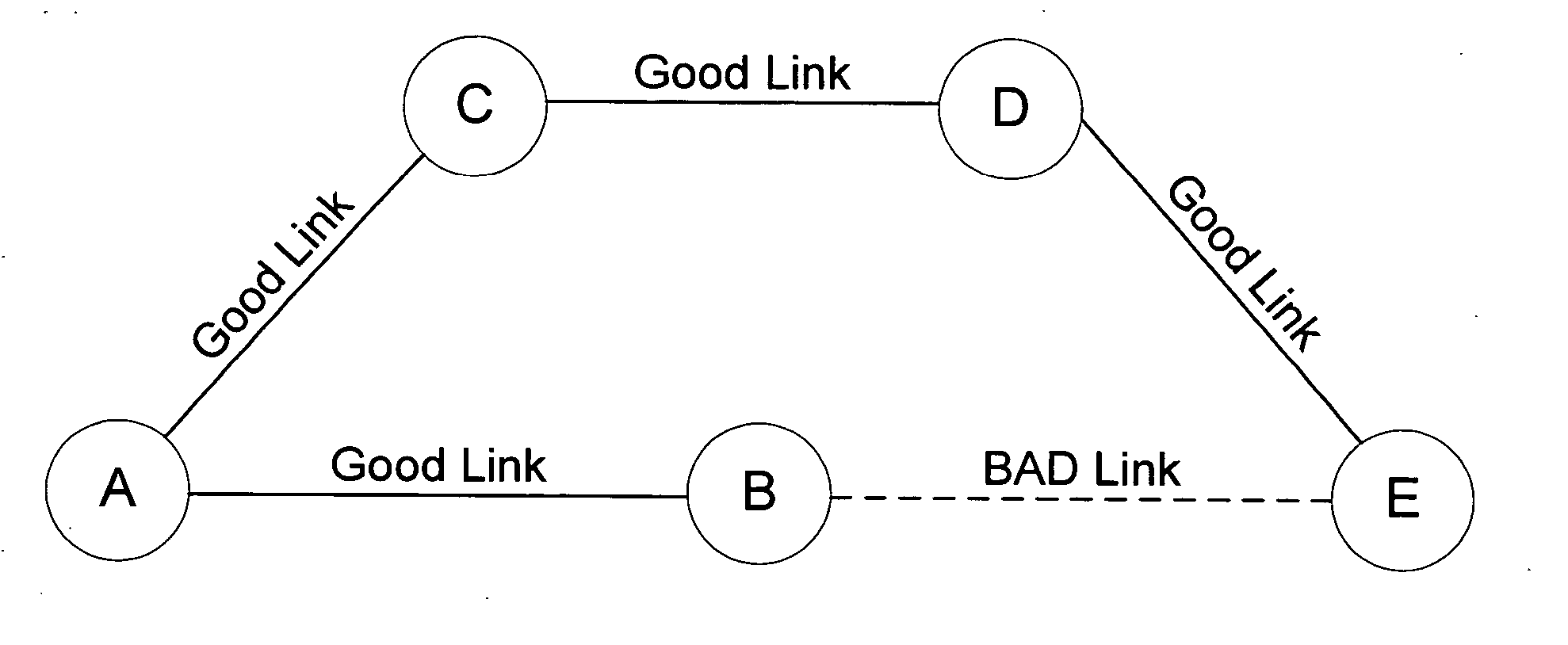
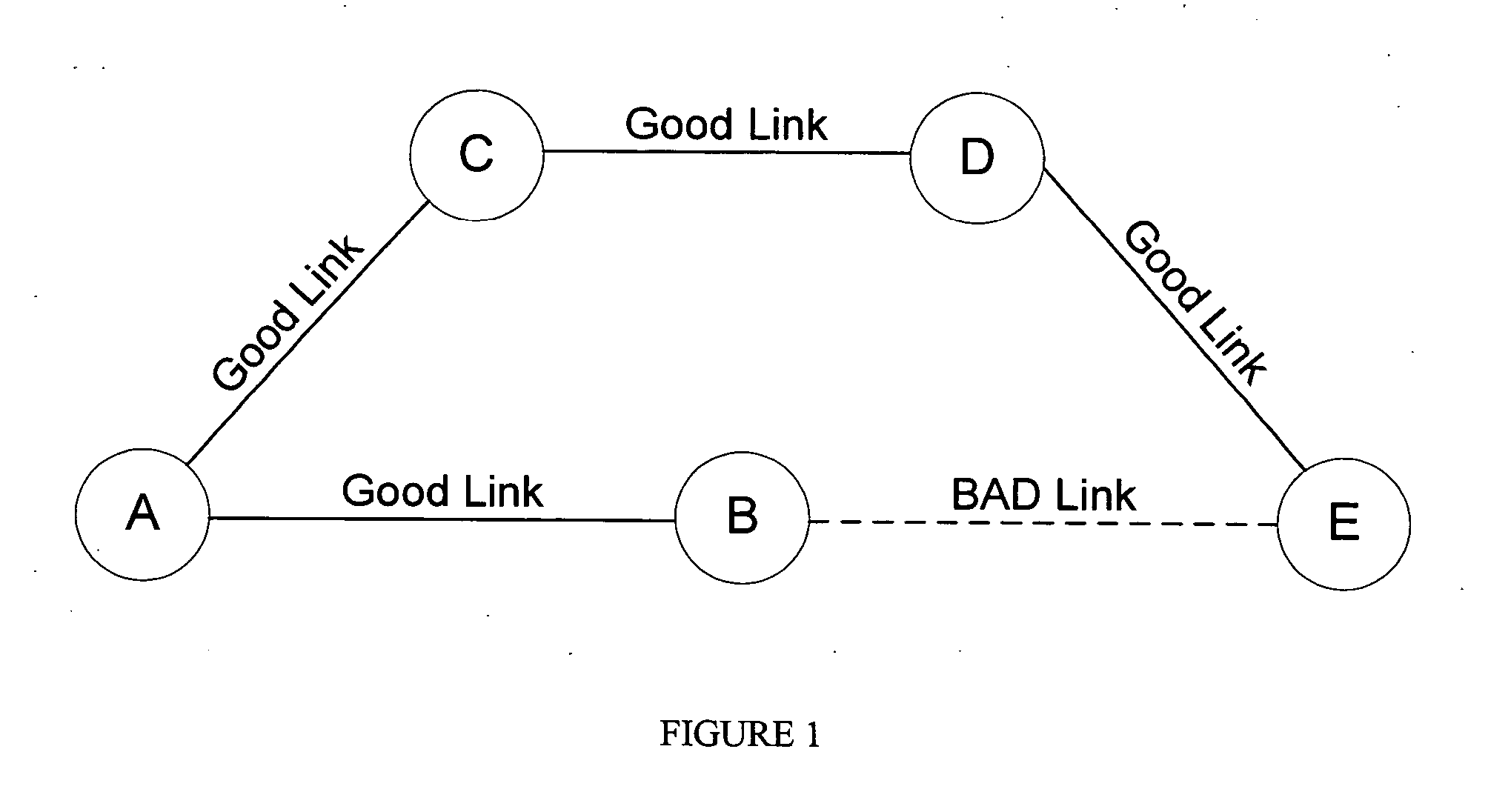
Patents
Literature
375results about How to "Shorten convergence time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
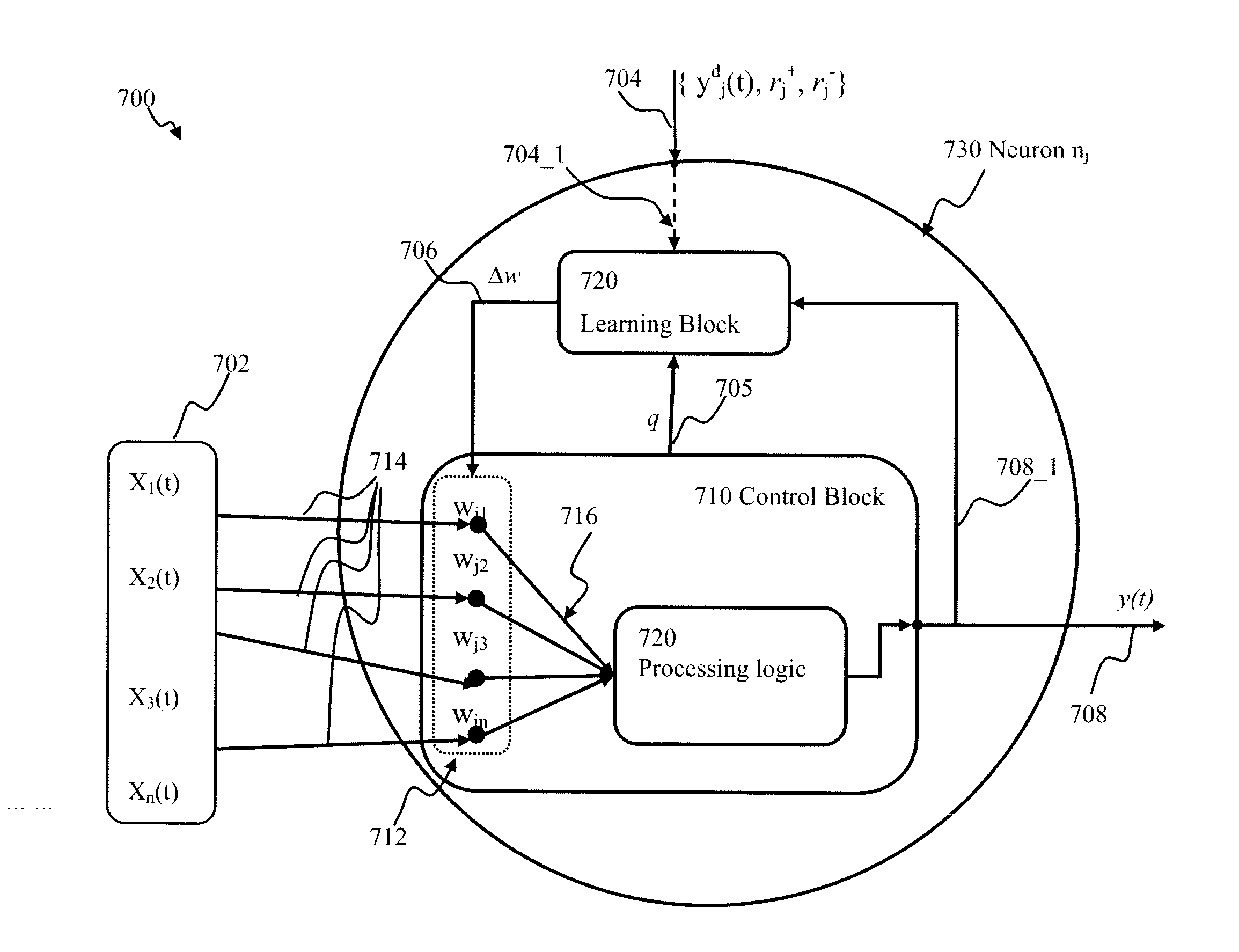
Learning stochastic apparatus and methods
InactiveUS20130325774A1Shorten the timeNot alleviating taskDigital computer detailsDigital dataModularitySelf adaptive
Generalized learning rules may be implemented. A framework may be used to enable adaptive signal processing system to flexibly combine different learning rules (supervised, unsupervised, reinforcement learning) with different methods (online or batch learning). The generalized learning framework may employ non-associative transform of time-averaged performance function as the learning measure, thereby enabling modular architecture where learning tasks are separated from control tasks, so that changes in one of the modules do not necessitate changes within the other. The use of non-associative transformations, when employed in conjunction with gradient optimization methods, does not bias the performance function gradient, on a long-term averaging scale and may advantageously enable stochastic drift thereby facilitating exploration leading to faster convergence of learning process. When applied to spiking learning networks, transforming the performance function using a constant term, may lead to non-associative increase of synaptic connection efficacy thereby providing additional exploration mechanisms.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
Method of constructing a backup path in an autonomous system
ActiveUS20070091795A1Minimize packet lossRapid responseError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPathPingBackup path
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
System and method to decrease the route convergence time and find optimal routes in a wireless communication network
ActiveUS20060098608A1Decrease route convergence timeEffective and efficient wayError preventionTransmission systemsCompletion rateReal-time computing
A system and method for decreasing the route convergence time in a wireless communication network, such as a wireless ad-hoc peer-to-peer network, by finding an alternate route if the nodes anticipate weakening or breakage of a route currently in use. The system and method which enables reactive routing protocols to find optimal routes between nodes in these types of networks when those routes cannot otherwise be found in certain conditions. The system and method thus decrease the route convergence time, provide an effective and efficient way to find optimal routes, and improve overall performance of the network with regard to throughput, delay, packet completion rate and other factors.
Owner:STRONG FORCE IOT
Discrete time amplifier circuit and analog-digital converter
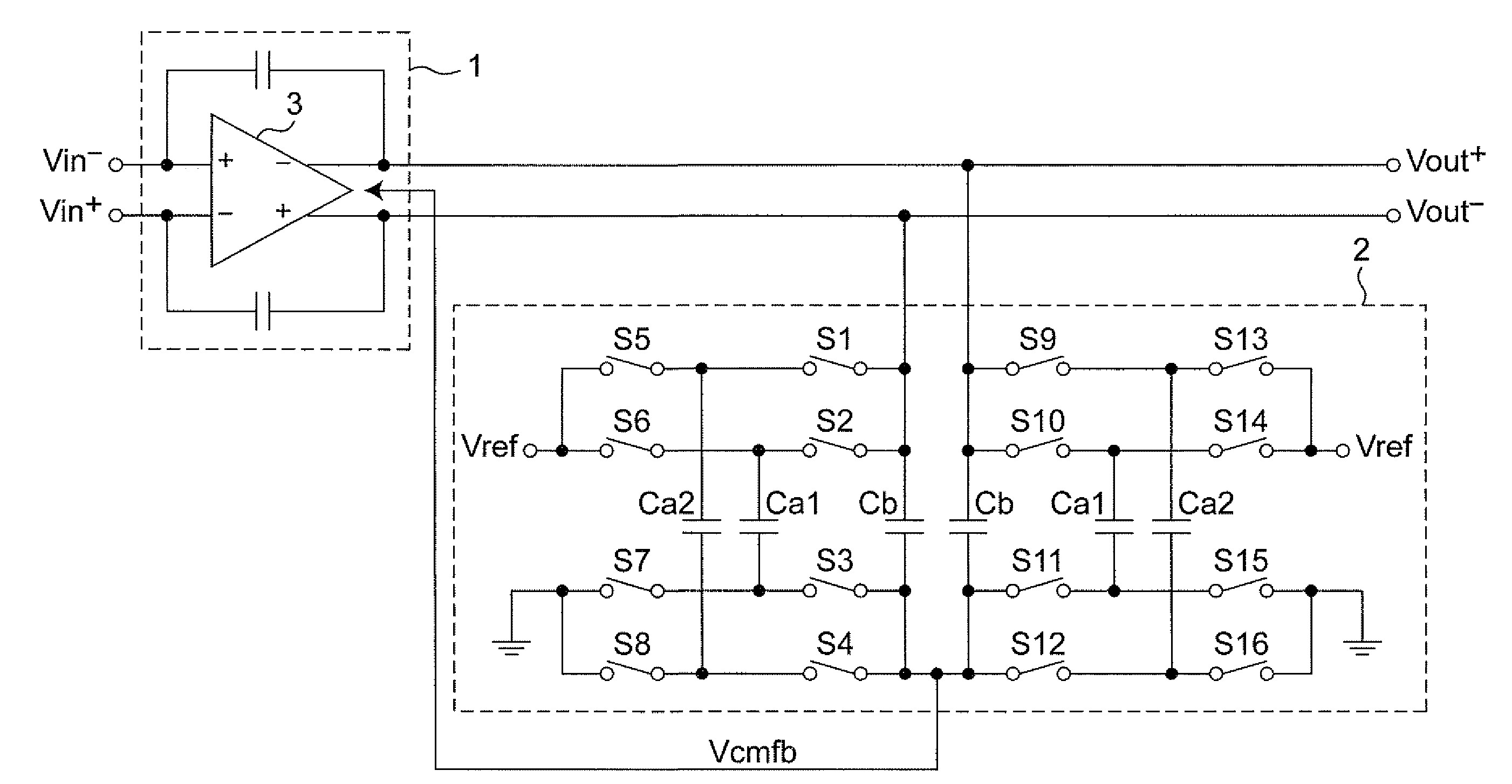
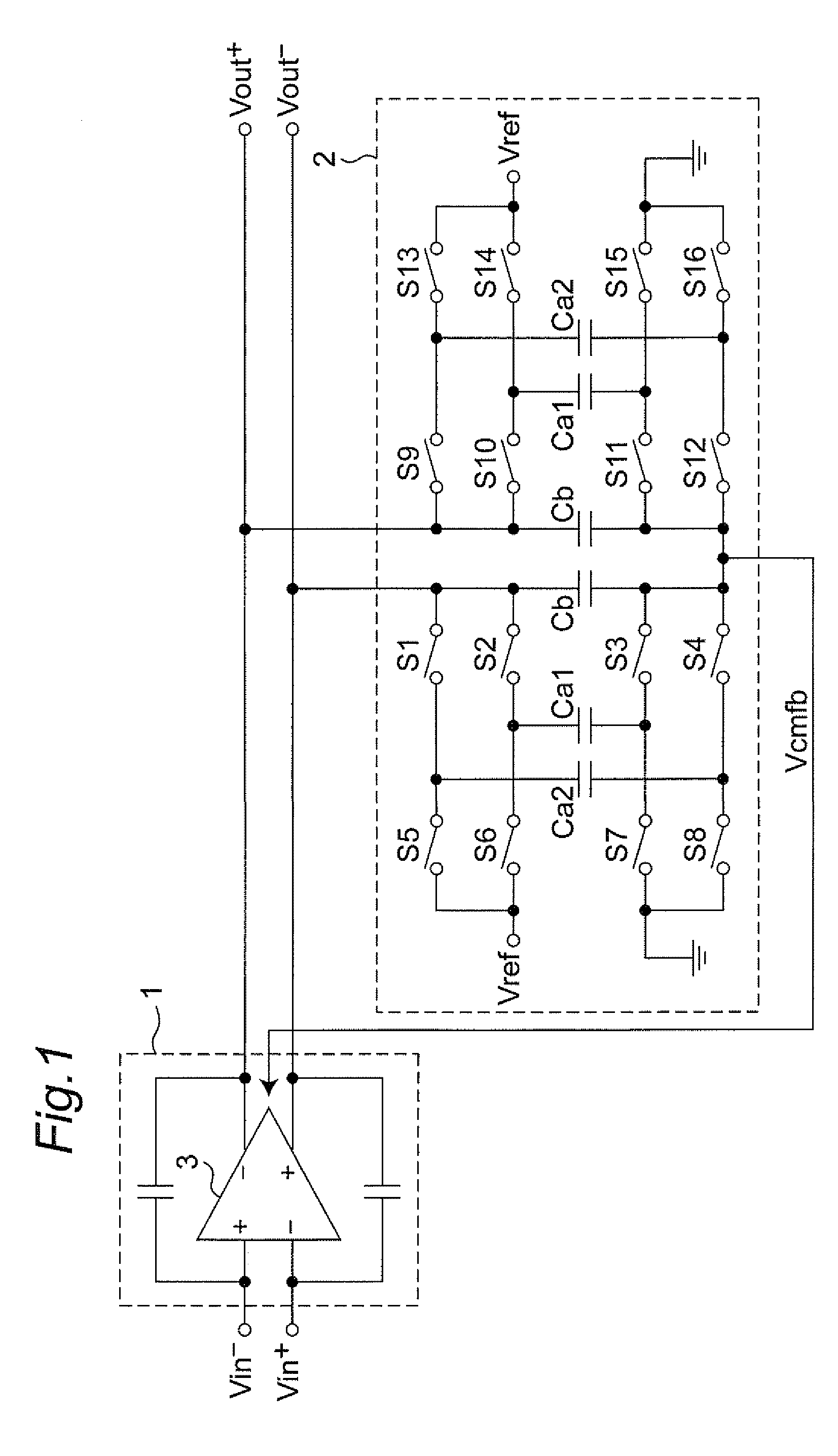
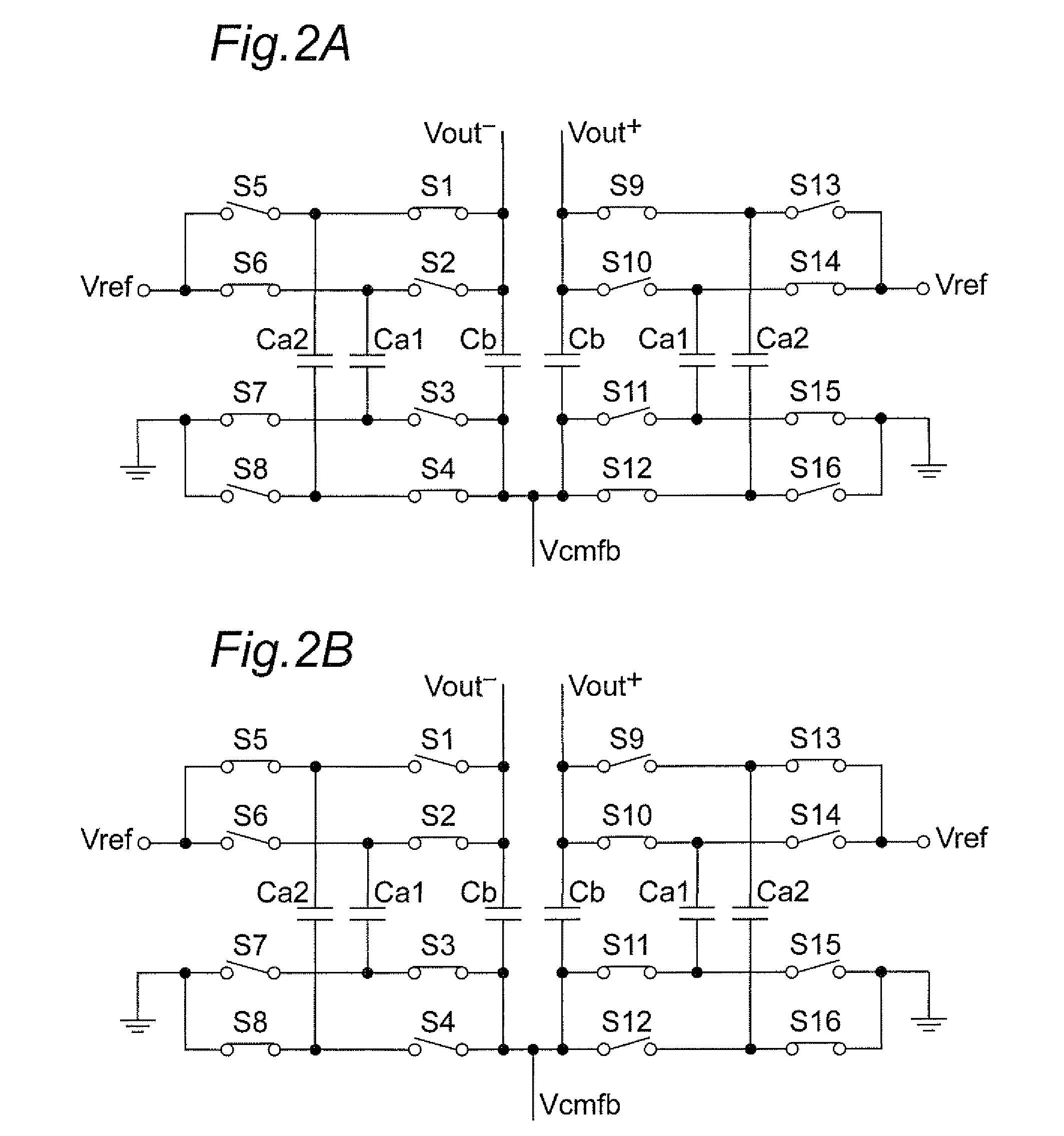
ActiveUS20090115523A1Simple circuit configurationShorten convergence timeElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersAudio power amplifierA d converter
The present invention is intended to attain simplified circuit configuration and low current consumption in a discrete time amplifier circuit and an AD converter, to improve the convergence from the transient response state to the steady state of the amplifier circuit and to reduce noise and distortion owing to the variation in the output common-mode voltage. The discrete time amplifier circuit and the AD converter are provided with a switched-capacitor common-mode feedback (CMFB) circuit capable of detecting and feeding back the output common-mode voltage at every sampling timing in the case that the circuit operates at double sampling timing (every ½ cycle).
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
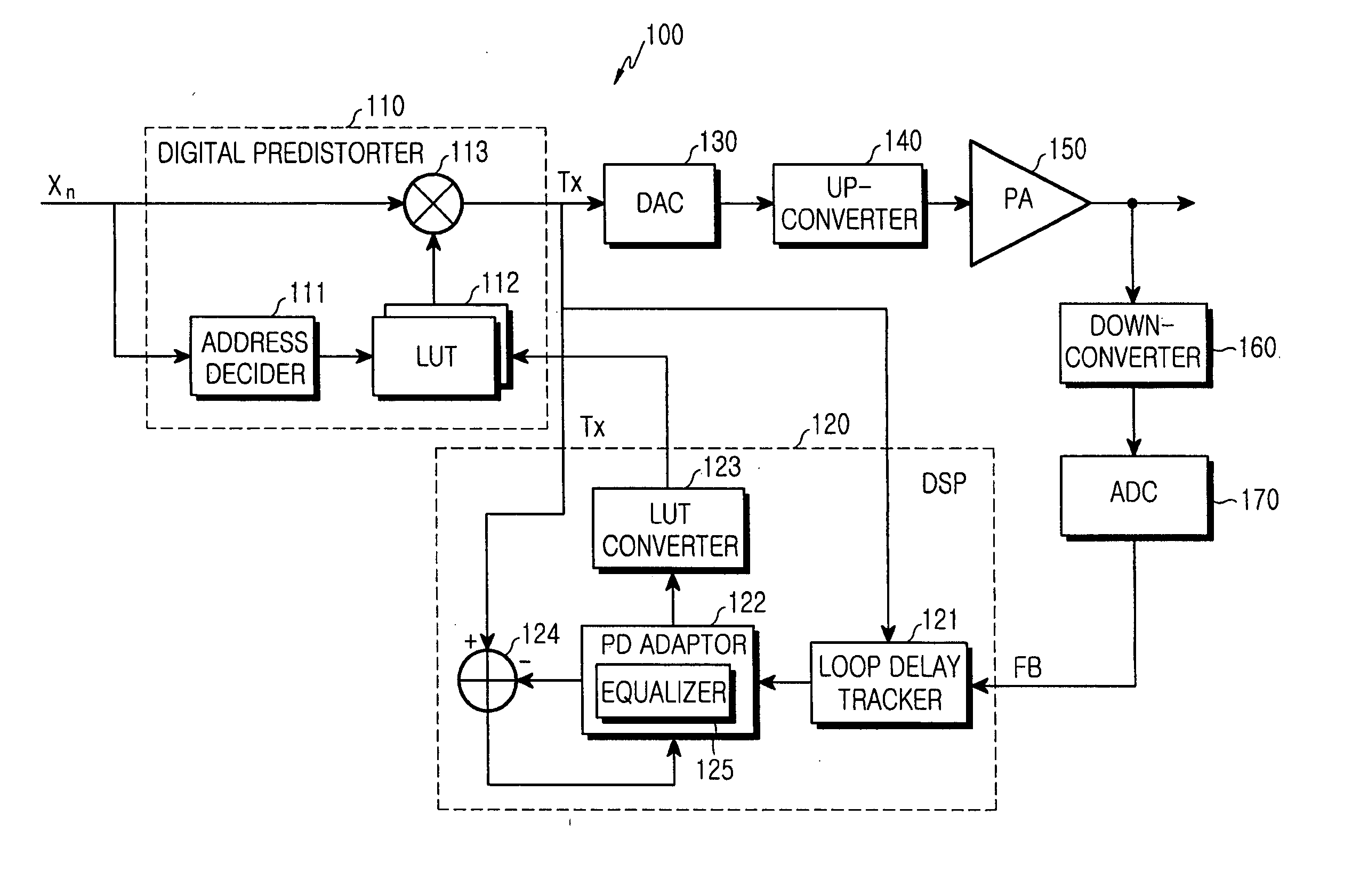
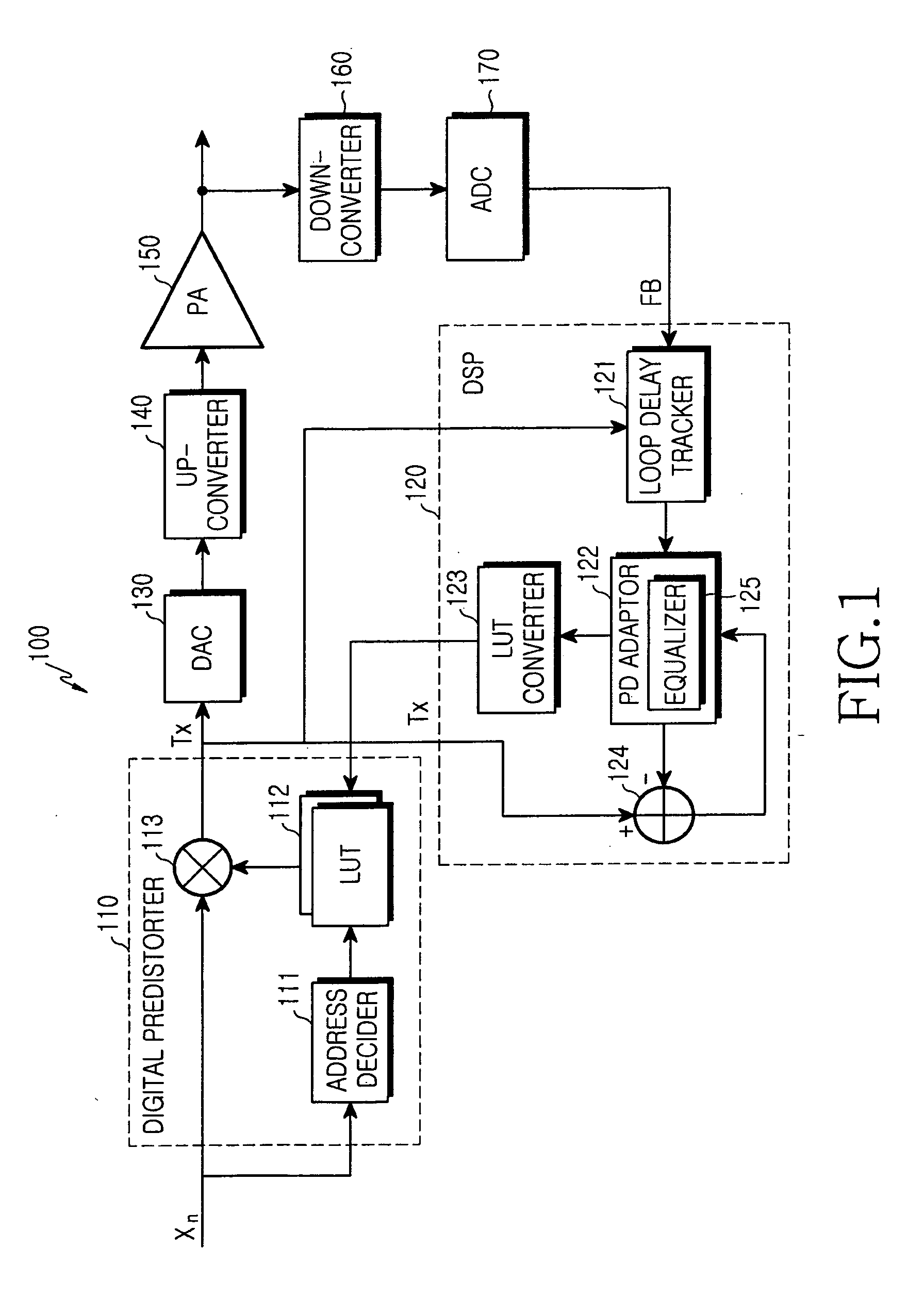
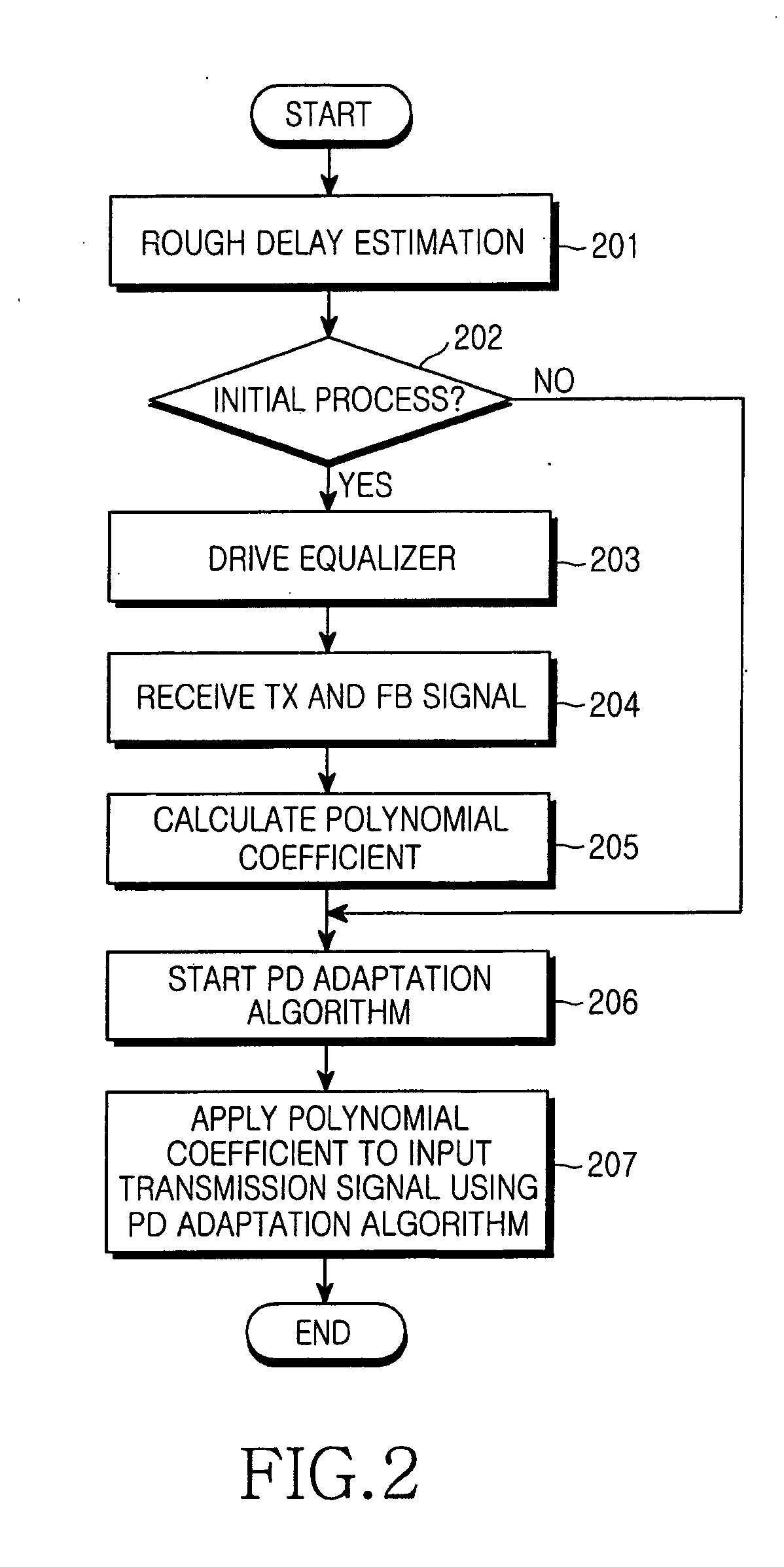
Digital predistortion apparatus and method for a wideband power amplifier
InactiveUS20050253745A1Performance maximizationShorten convergence timeAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionElectric signal transmission systemsCommunications systemAudio power amplifier
A method and apparatus compensate for a non-linear characteristic of a wideband power amplifier in a transmitter for a communication system, which has the wideband power amplifier for amplifying a digital input signal. The method involves the steps of (a) generating an address based on the digital input signal, reading a distortion control value corresponding to the address from a look-up table, and applying the read distortion control value to the digital input signal to predistort the digital input signal; (b) frequency up-converting the predistorted signal and amplifying the frequency up-converted signal; (c) frequency down-converting the amplified signal and compensating for a delay of the frequency down-converted signal; and (d) updating a predetermined distortion control value in the look-up table to compensate for an error value generated in the power amplifier and an analog path occurring in steps (b) and (c) based on the compensated signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
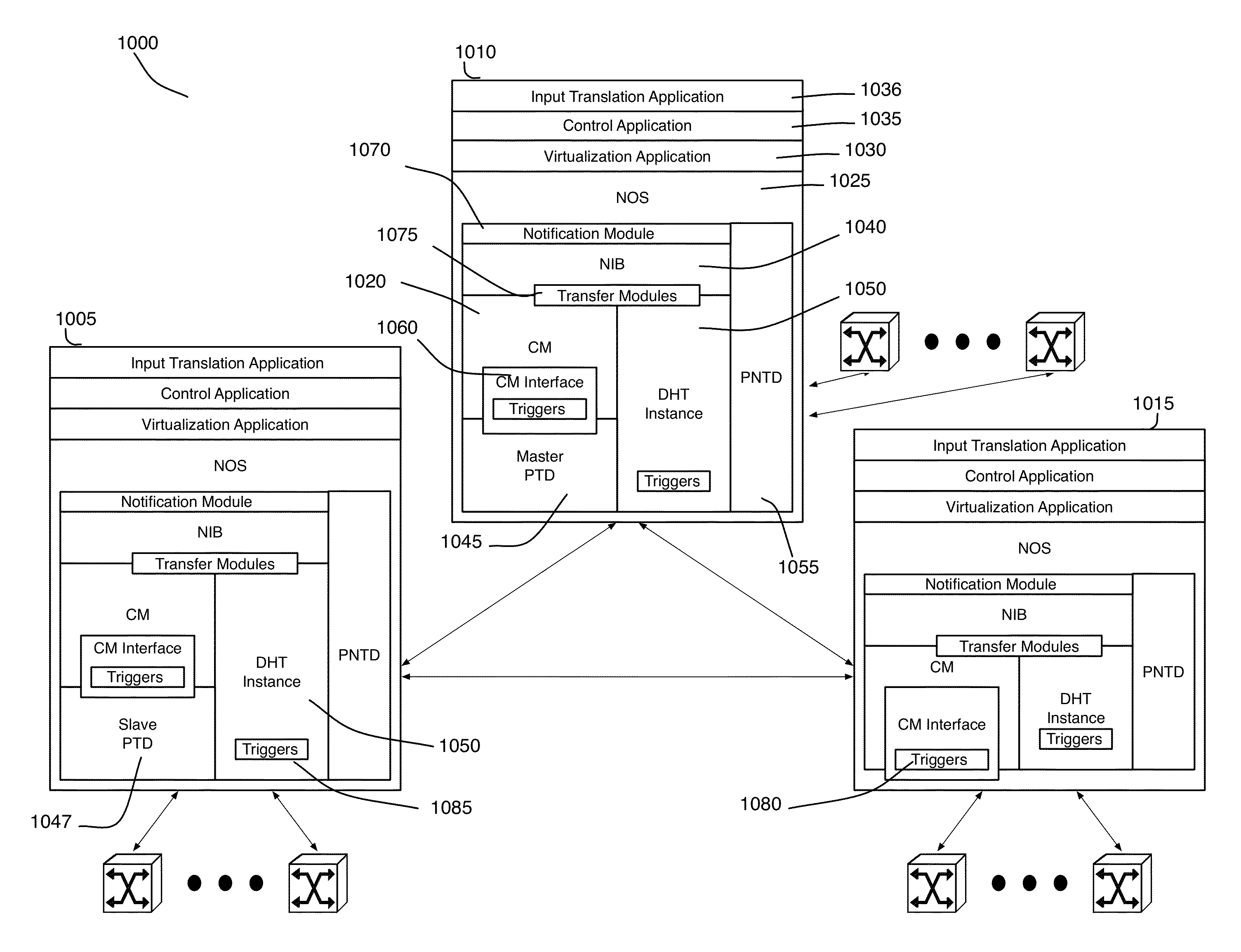
Network virtualization apparatus and method with scheduling capabilities
ActiveUS20130114466A1Reduces overall network convergence timeReduce computing timeData switching by path configurationInformation repositoryData transformation
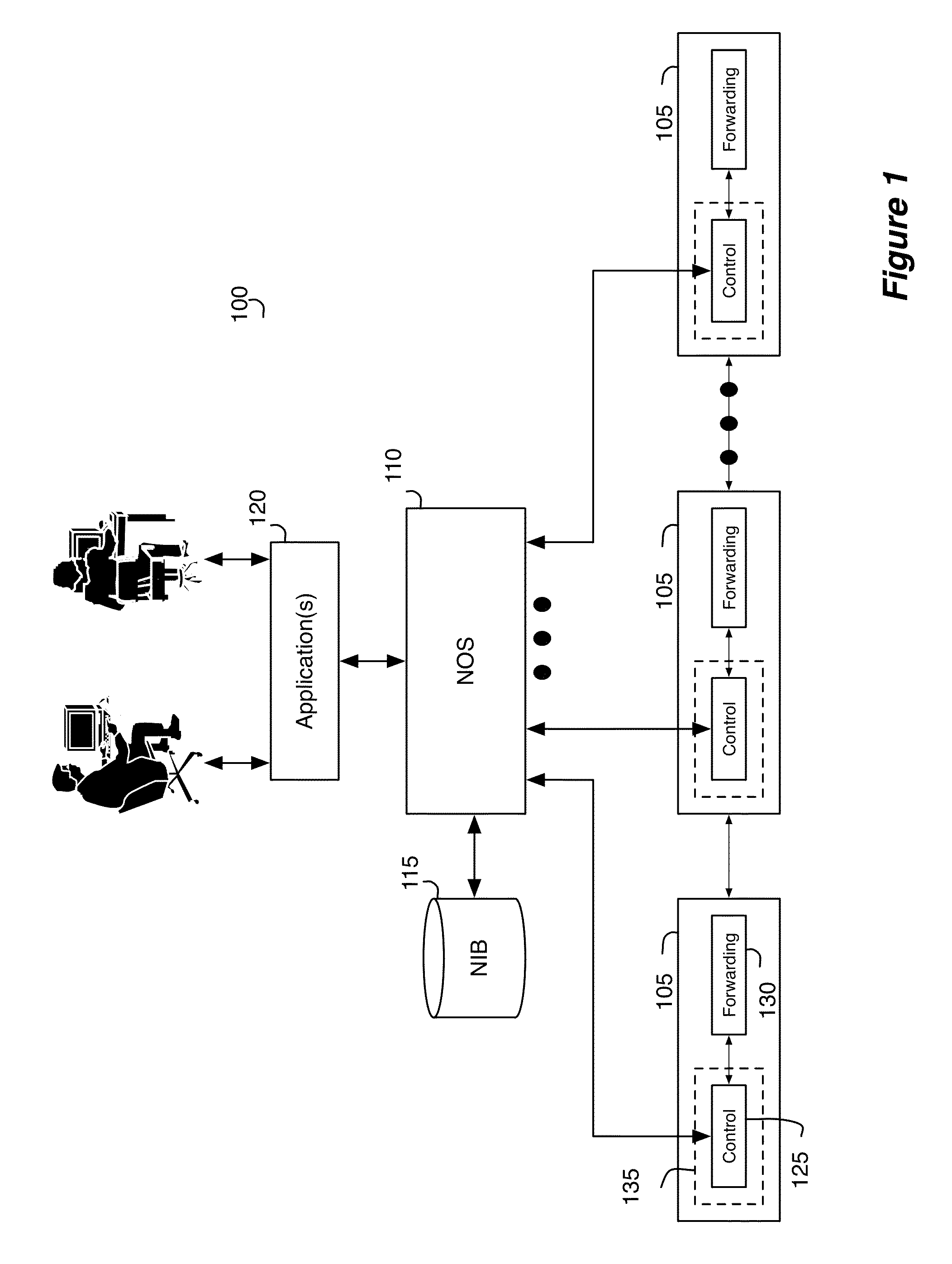
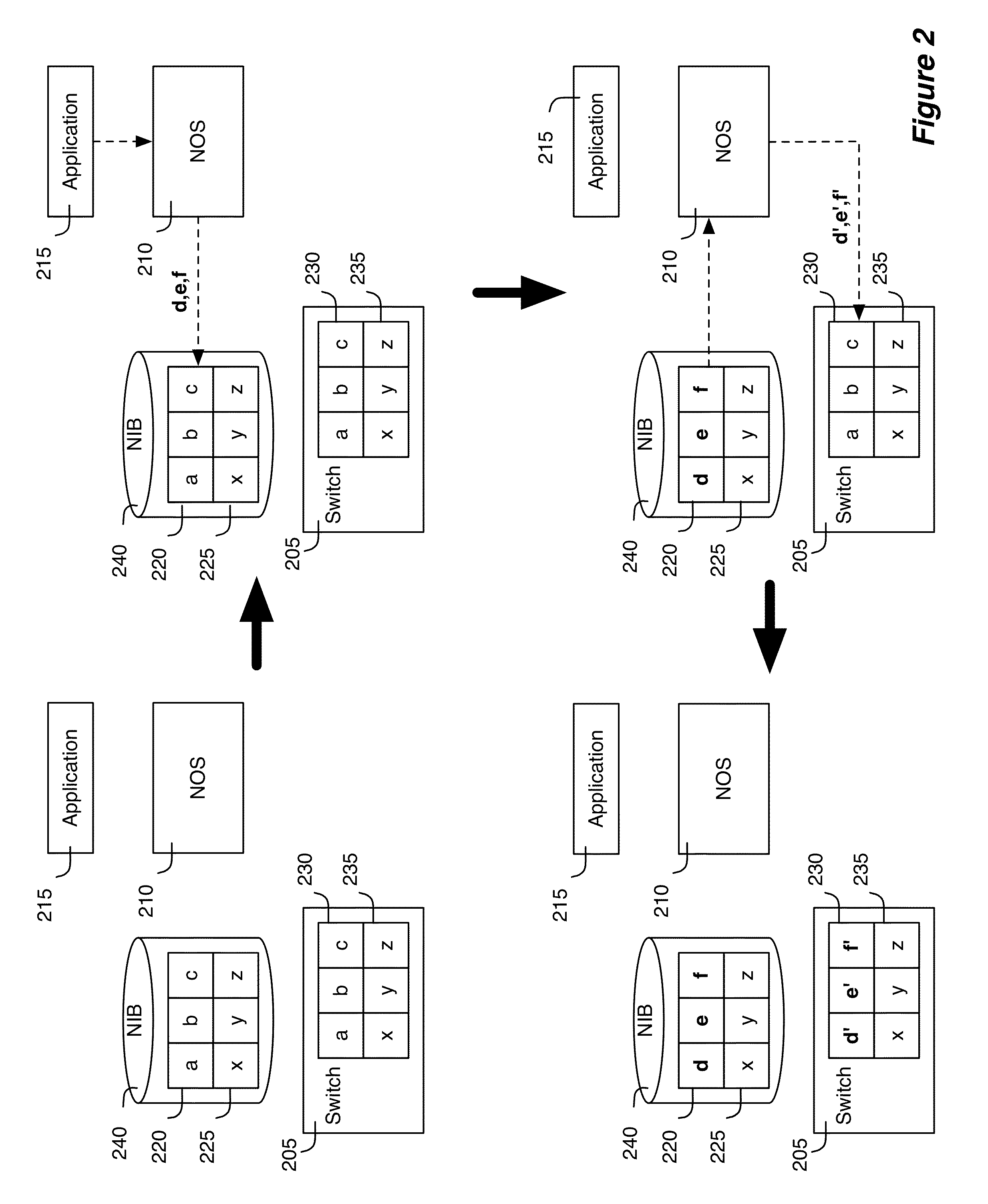
Some embodiments provide a controller for managing several managed switching elements that forward data in a network. The controller includes an interface for receiving input logical control plane data in terms of input events data. The controller includes an input scheduler for (1) categorizing the input events data into different groups based on certain criteria and (2) scheduling supplying of the input event data into a converter based on the groups so that the converter processes a group of input events data together. The controller includes the converter for converting the input logical control plane data to output logical forwarding plane data. The controller includes a network information base (NIB) data structure module for storing the output logical forwarding plane data. The logical forwarding plane data is for subsequent translation into physical control plane data.
Owner:NICIRA
Route exchange method suitable for GEO/LEO double layered constellation network
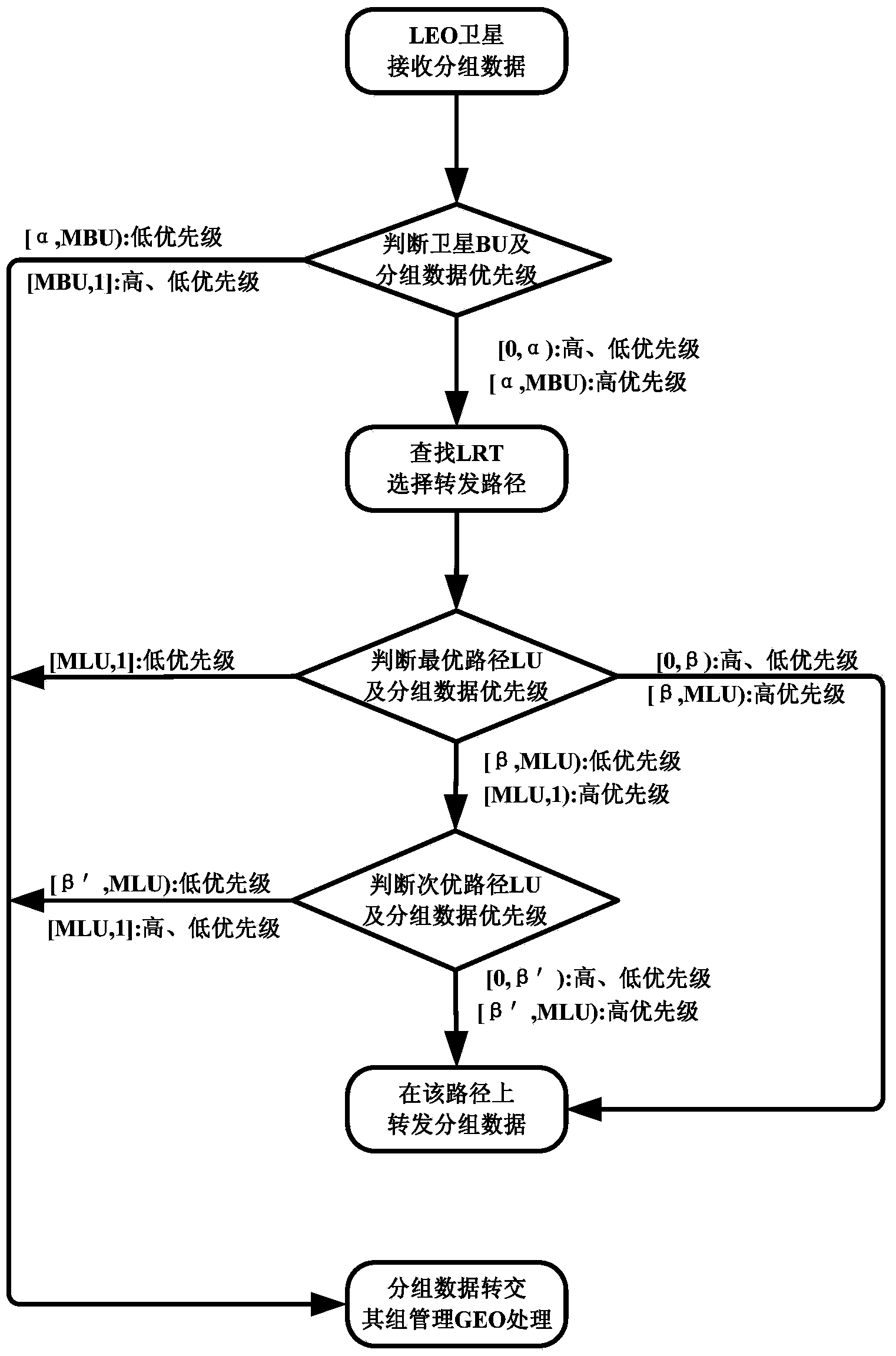
InactiveCN103905306AReduce overheadShorten convergence timeData switching networksOn boardBoundary values
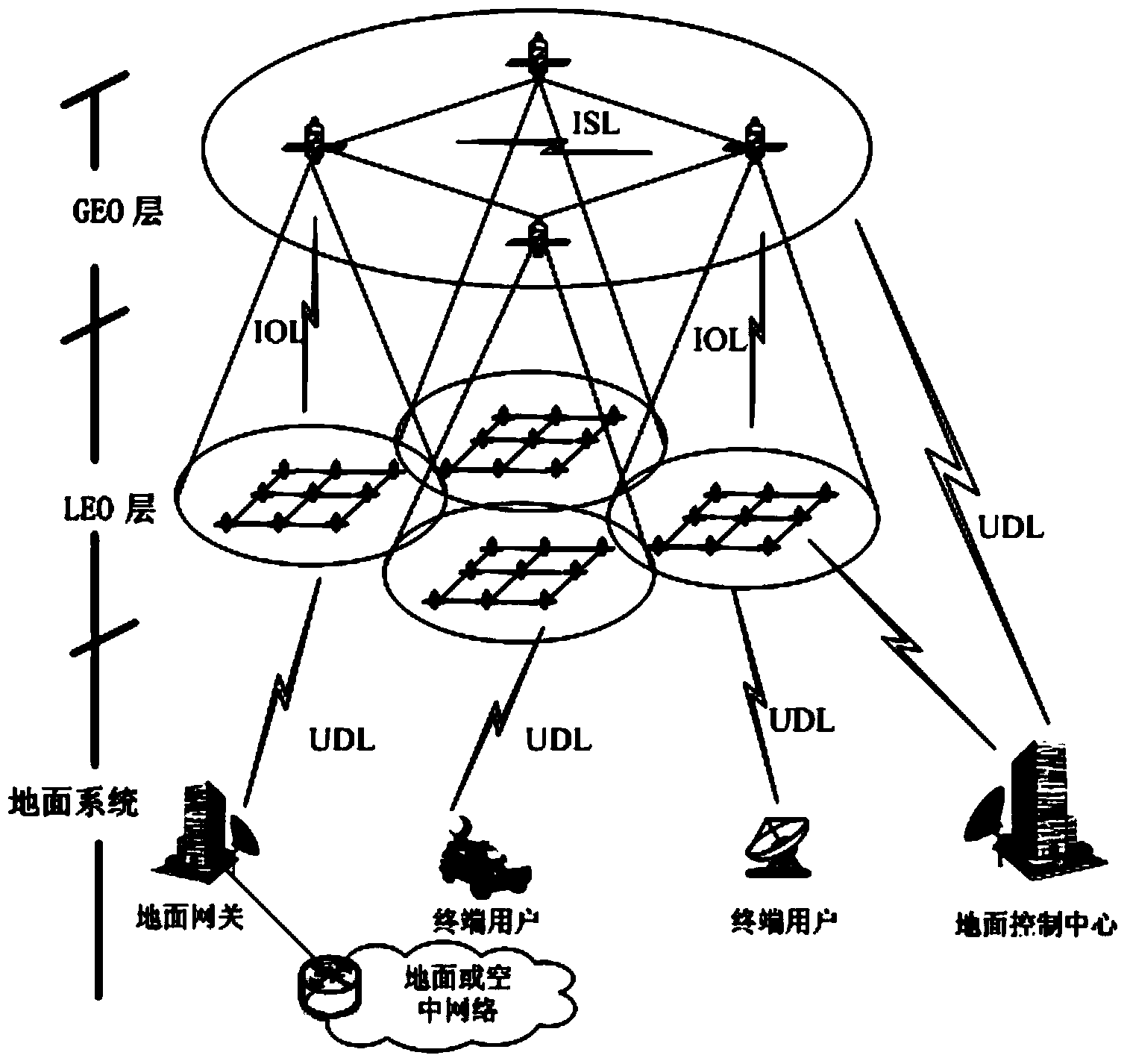
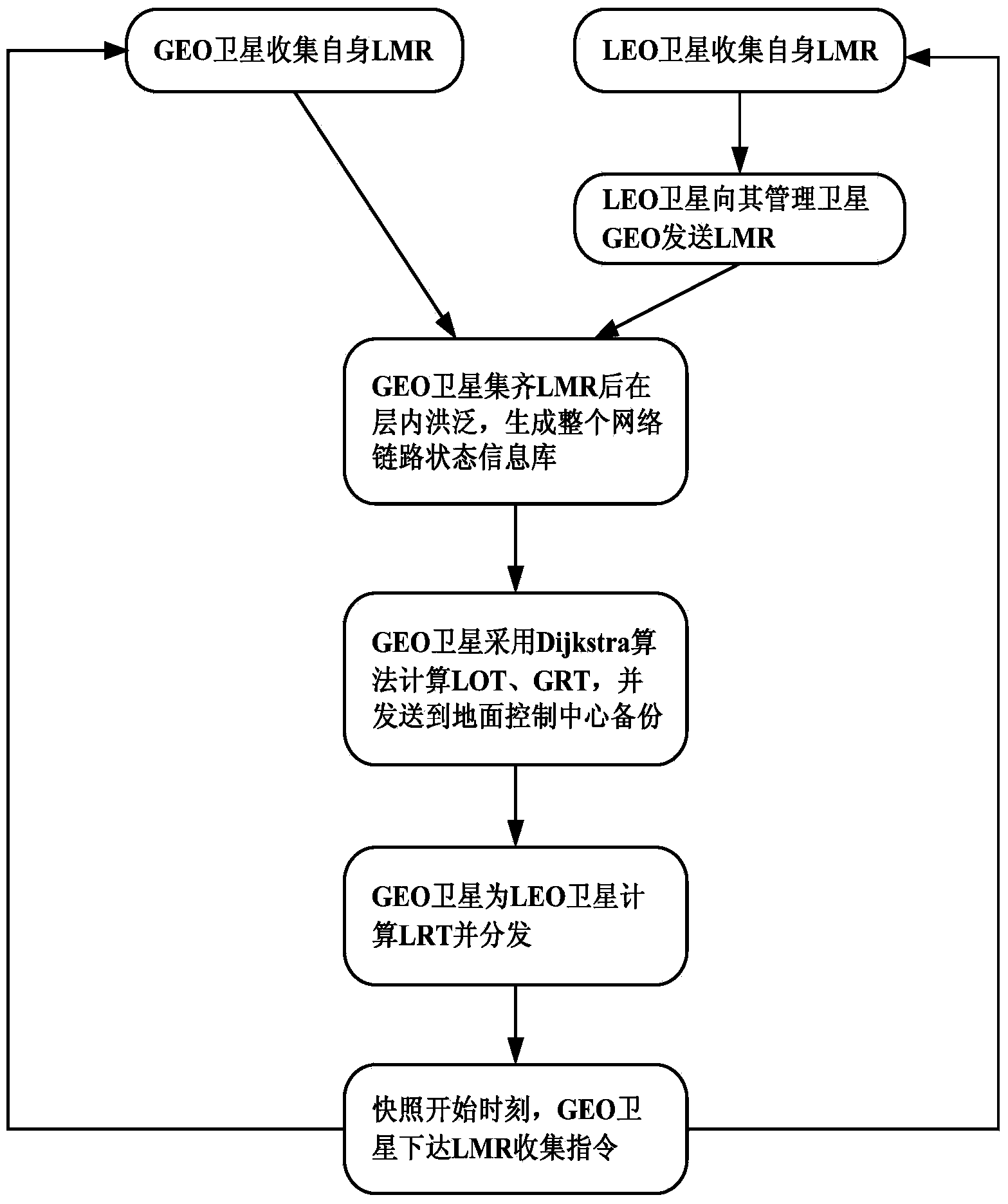
The invention discloses a route exchange method suitable for a GEO / LEO double layered constellation network. According to the method, a system period is divided into equal-duration time sections based on a dynamic boundary value; a GEO layer satellite high in on-board processing capacity is used for calculating the best route and the second best route for each LEO satellite; in the processes of information transmission and exchange, when loads of the LED satellites are large, the GEO satellite shares part of low priority services in time for the LED satellites, and it is guaranteed that important information is reliably transmitted in real time; when link congestion, node ineffectiveness and other emergency conditions happen in the satellite network, in order to avoid rerouting of the whole network, and the GEO satellite only calculates rerouting for affected routes; after link congestion is eliminated, the LED satellites recover route information in time before congestion in order to avoid link resource waste in the network. In the network that topology time varying happens, links are prone to congestion, on-board resources are limited, continuous high-load flows are prone to being generated, and nodes are prone to being ineffective at the special period, the method can reduce constellation system cost, shorten convergence time, save the on-board resources, increase the utilization rate of the link resources, guarantee that important information is reliably transmitted in real time and improve invulnerability and robustness of the satellite network.
Owner:中国人民解放军西安通信学院
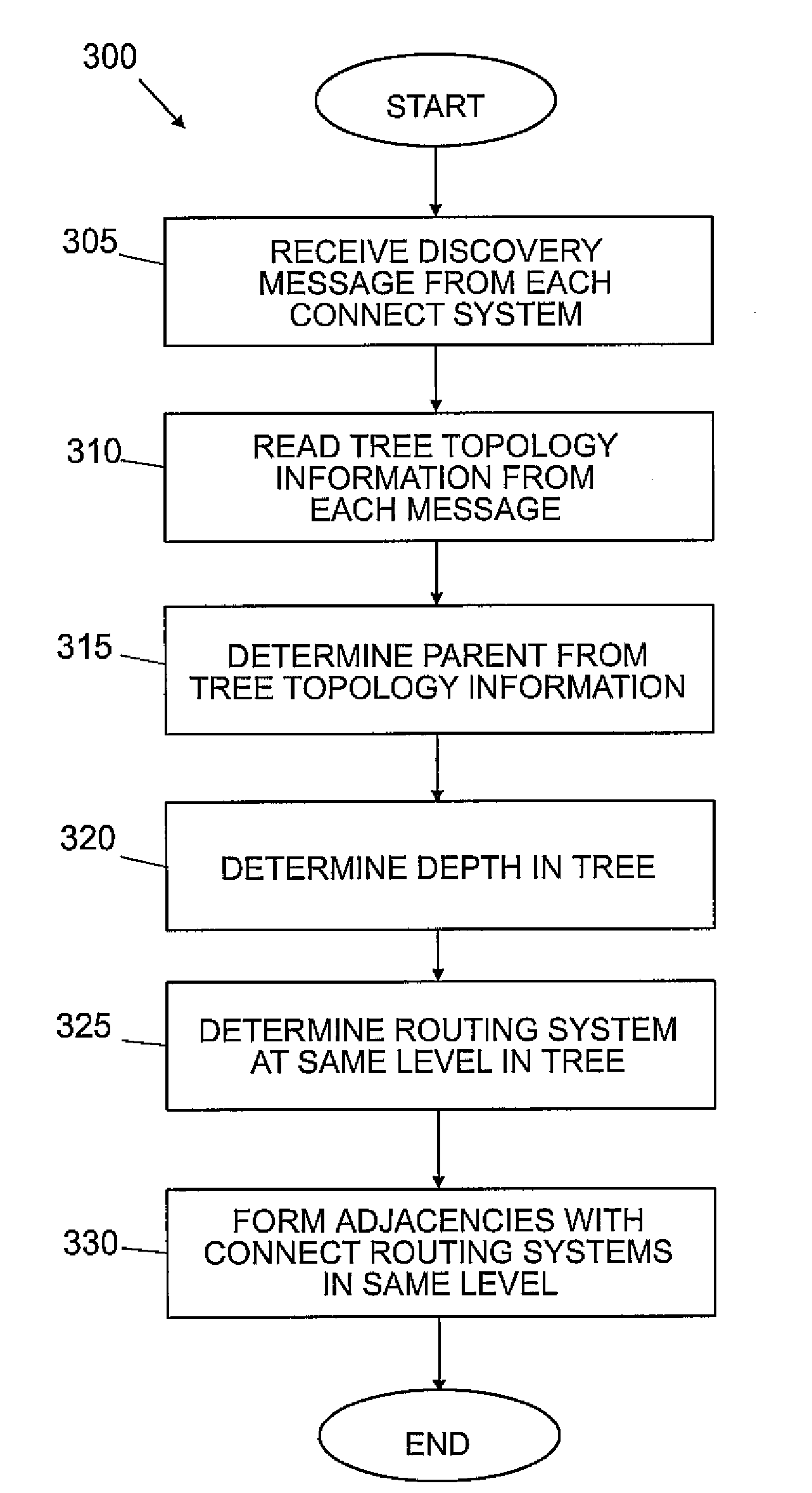
Tree based wireless mesh for an ospf network with intra-tree communication optimization
ActiveUS20080080401A1Shorten convergence timeReduce floodingAssess restrictionConnection managementTopology informationDevice Grid
A system for providing a tree topology for a network having an interior gateway protocol. A first router receives a hello message from all connected routers in the network. The hello messages include tree topology information. The first router then uses the tree topology information to determine a parent of the router. The first router then establishes connections with directly connected routers at the same level in the tree topology. The first router also generates link messages that include all of the prefixes for children of the first router and broadcasts the link messages.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
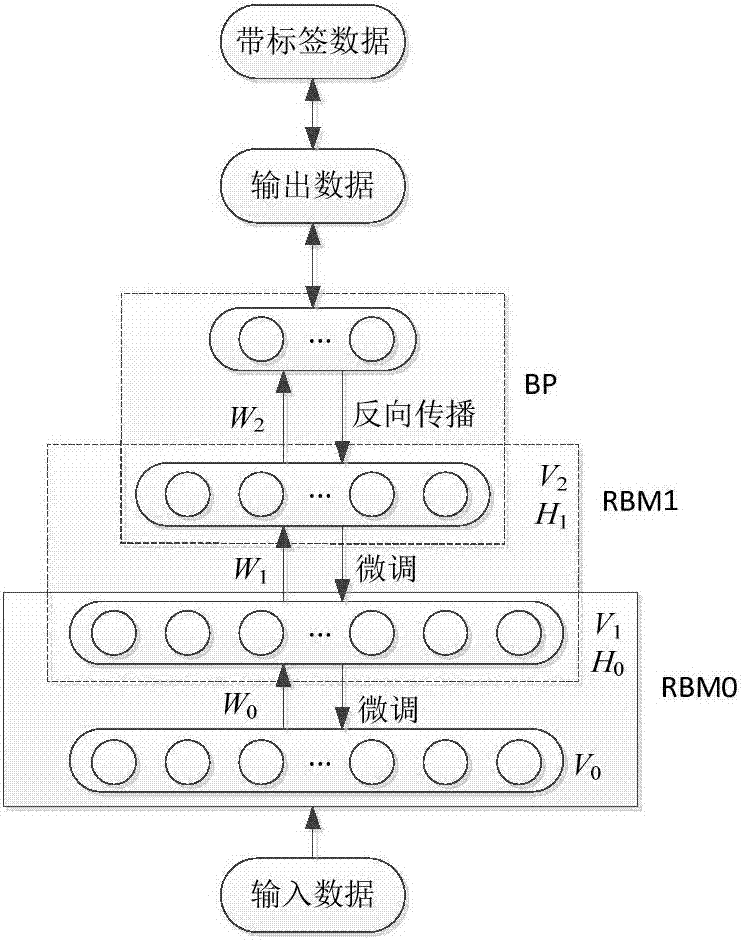
Feature extraction and state recognition of one-dimensional physiological signal based on depth learning
ActiveCN107256393ATo solve the classification accuracy is not highOptimize network structureCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesSignal classificationAnalysis models
The present invention discloses a feature extraction and state recognition method for one-dimensional physiological signal based on depth learning. The method comprises: establishing a feature extraction and state recognition analysis model DBN of a on-dimensional physiological signal based on depth learning, wherein the DBN model adopts a "pre-training+fine-tuning" training process, and in a pre-training stage, a first RBM is trained firstly and then a well-trained node is used as an input of a second RBM, and then the second RBM is trained, and so forth; and after training of all RBMs is finished, using a BP algorithm to fin-tune a network, and finally inputting an eigenvector output by the DBN into a Softmax classifier, and determining a state of an individual that is incorporated into the one-dimensional physiological signal. The method provided by the present invention effectively solves the problem that in the conventional one-dimensional physiological signal classification process, feature inputs need to be selected manually so that classification precision is low; and through non-linear mapping of the deep confidence network, highly-separable features / feature combinations are automatically obtained for classification, and a better classification effect can be obtained by keeping optimizing the structure of the network.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
System and method to decrease the route convergence time and find optimal routes in a wireless communication network
ActiveUS7408911B2Effective and efficient wayImprove performanceError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsComputer scienceReactive routing protocol
A system and method for decreasing the route convergence time in a wireless communication network, such as a wireless ad-hoc peer-to-peer network, by finding an alternate route if the nodes anticipate weakening or breakage of a route currently in use. The system and method which enables reactive routing protocols to find optimal routes between nodes in these types of networks when those routes cannot otherwise be found in certain conditions. The system and method thus decrease the route convergence time, provide an effective and efficient way to find optimal routes, and improve overall performance of the network with regard to throughput, delay, packet completion rate and other factors.
Owner:STRONG FORCE IOT
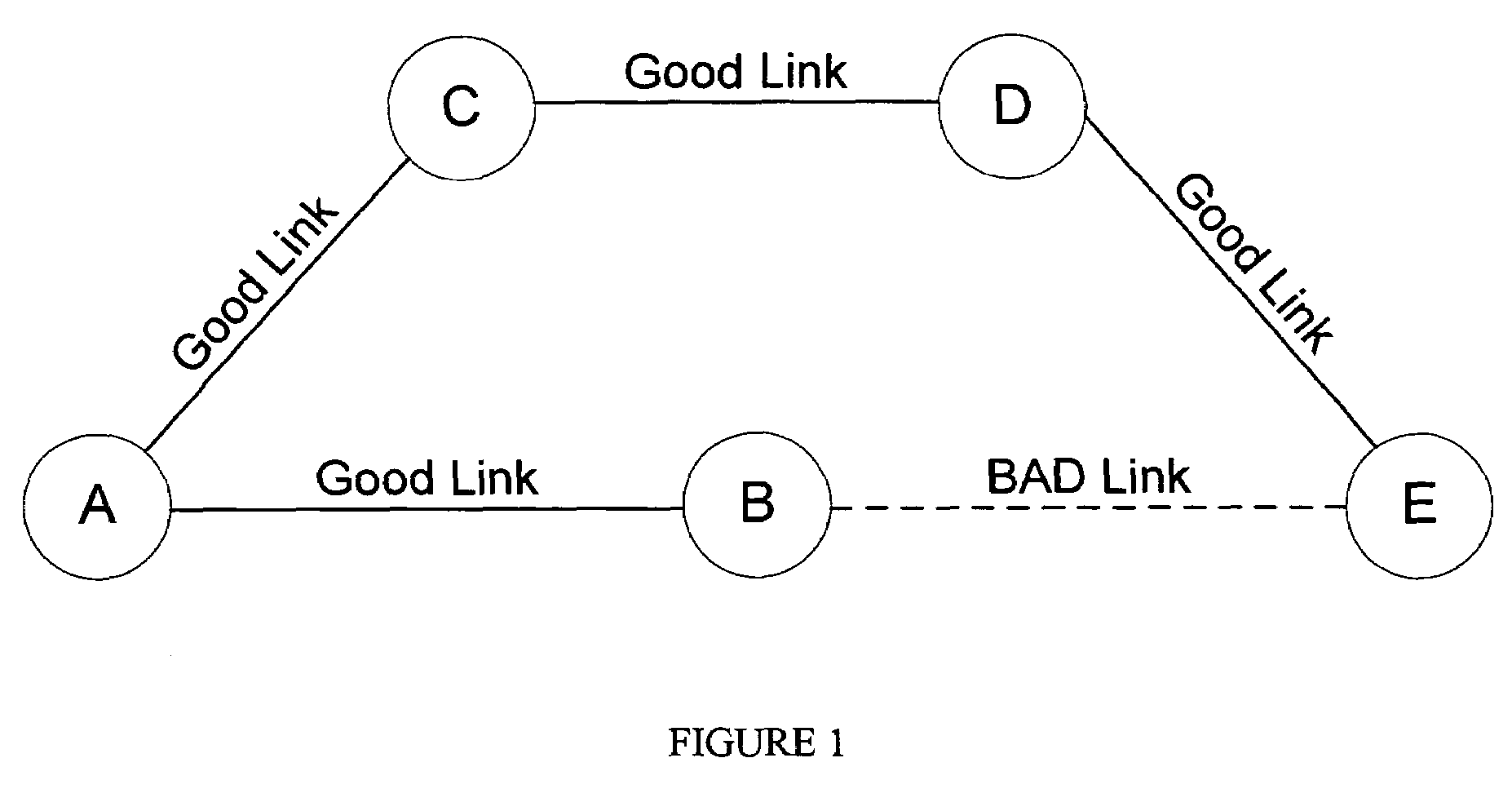
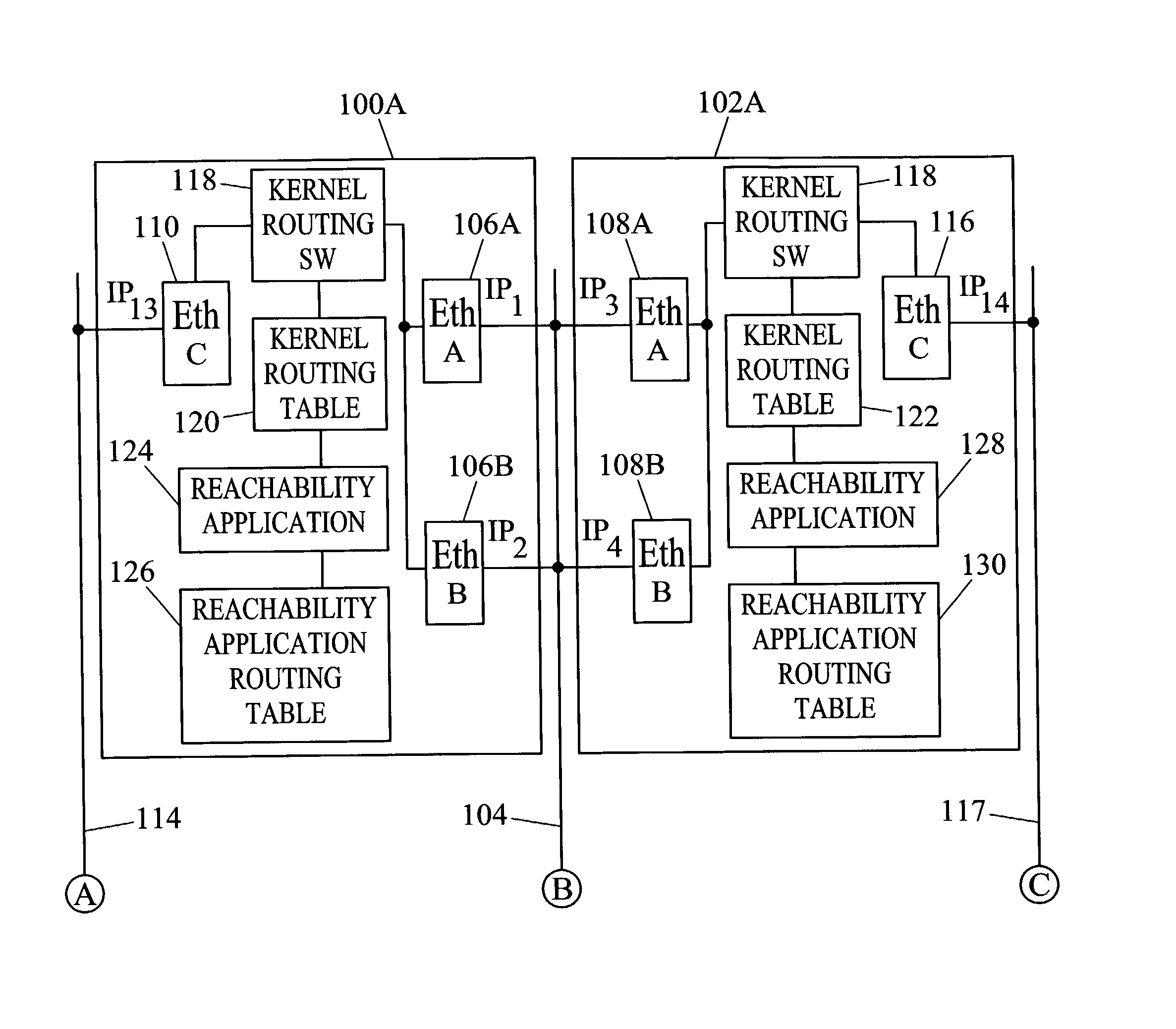
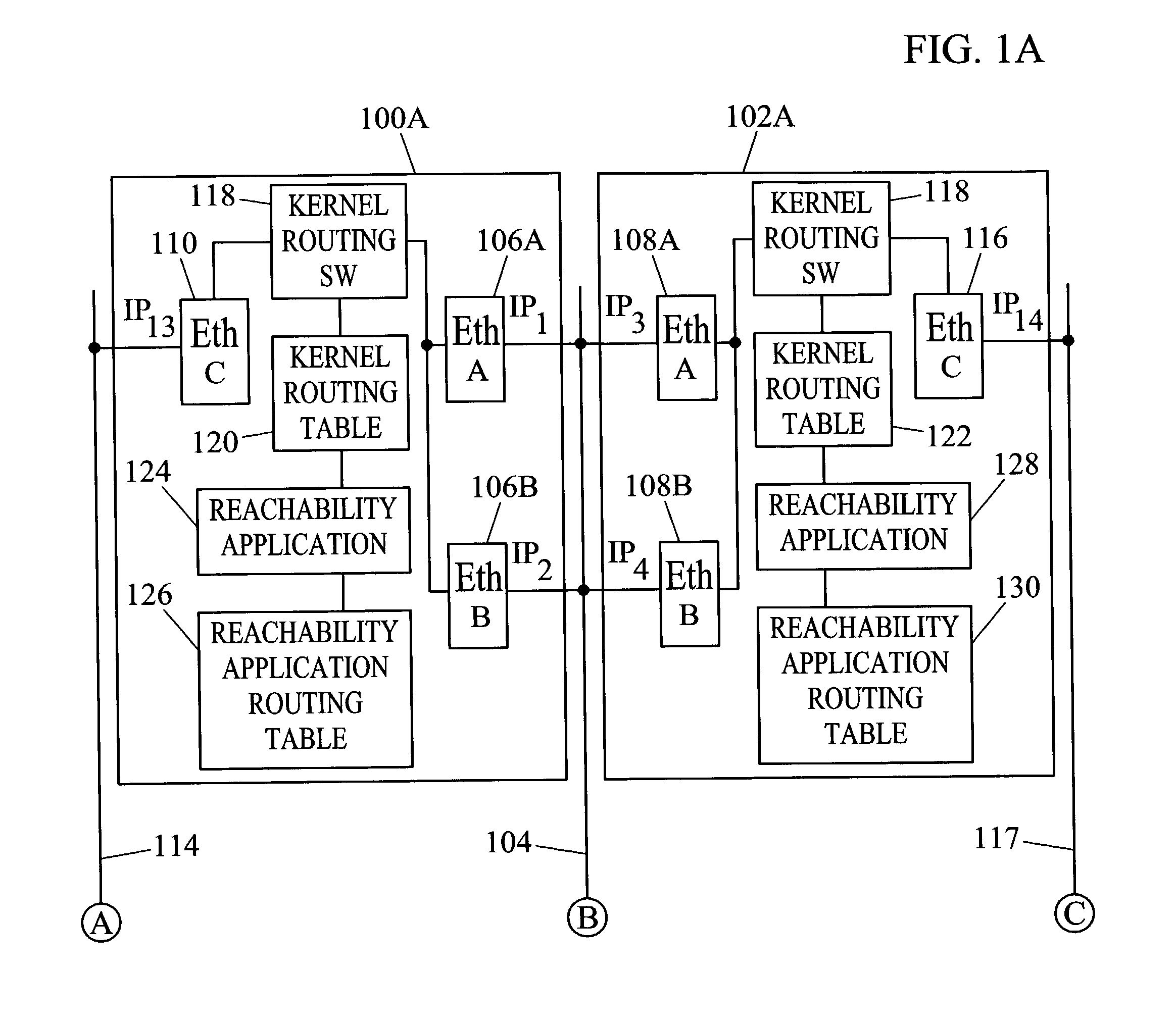
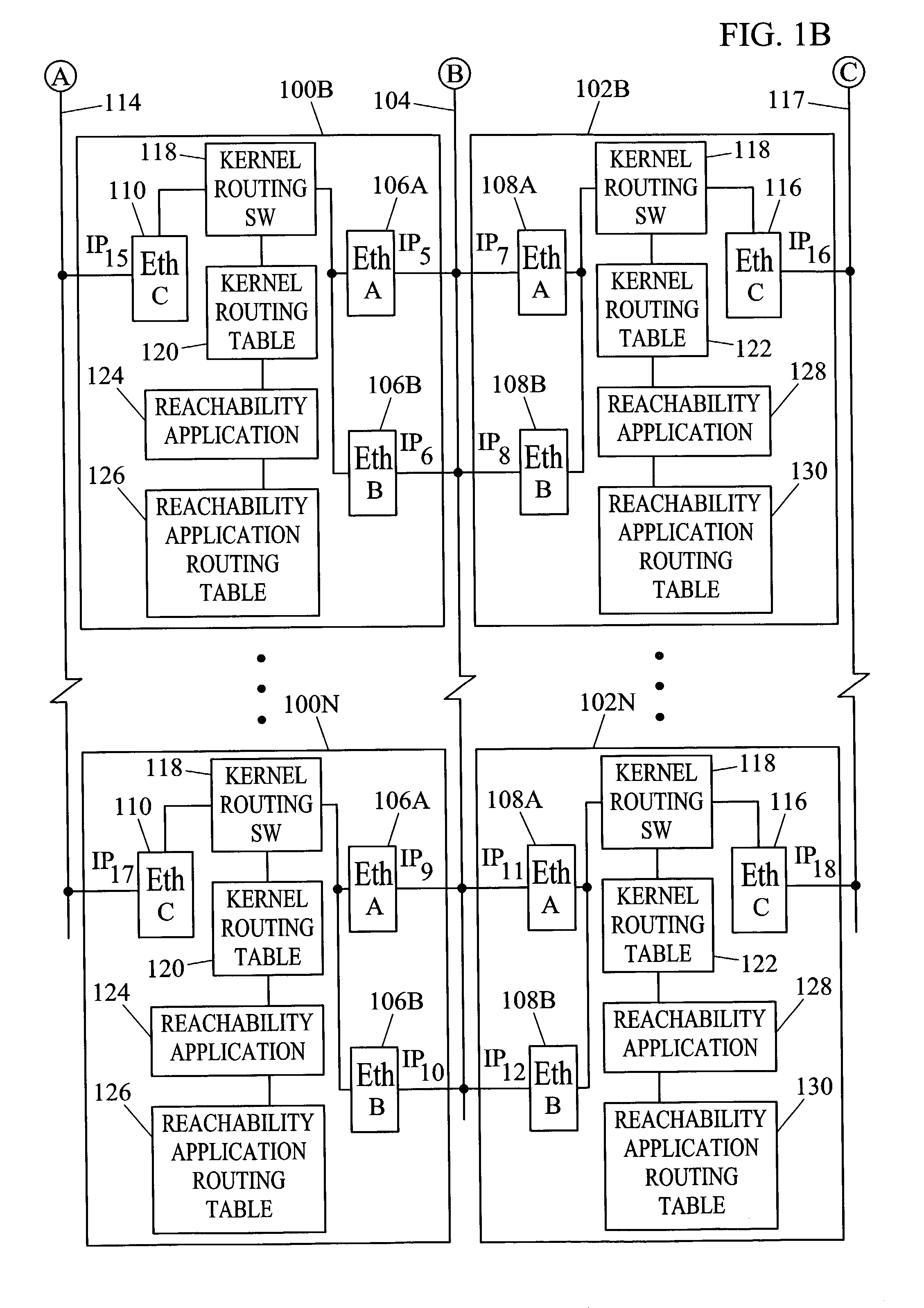
Methods and systems for exchanging reachability information and for switching traffic between redundant interfaces in a network cluster
InactiveUS20040078481A1Quick switchShorten the timeDigital computer detailsData switching networksComputer networkRouting table
Methods and systems for exchanging reachability information and for switching between redundant interfaces in a network cluster are disclosed. Nodes in the network cluster are connected via redundant links and exchange reachability messages at periodic intervals. Each node includes a kernel routing table used to route messages and a reachability application routing table for storing reachability information used to update entries in the kernel routing table. Each node executes a predetermined algorithm for selecting entries in the reachability application routing table to be written to the kernel routing table.
Owner:TEKELEC GLOBAL INC
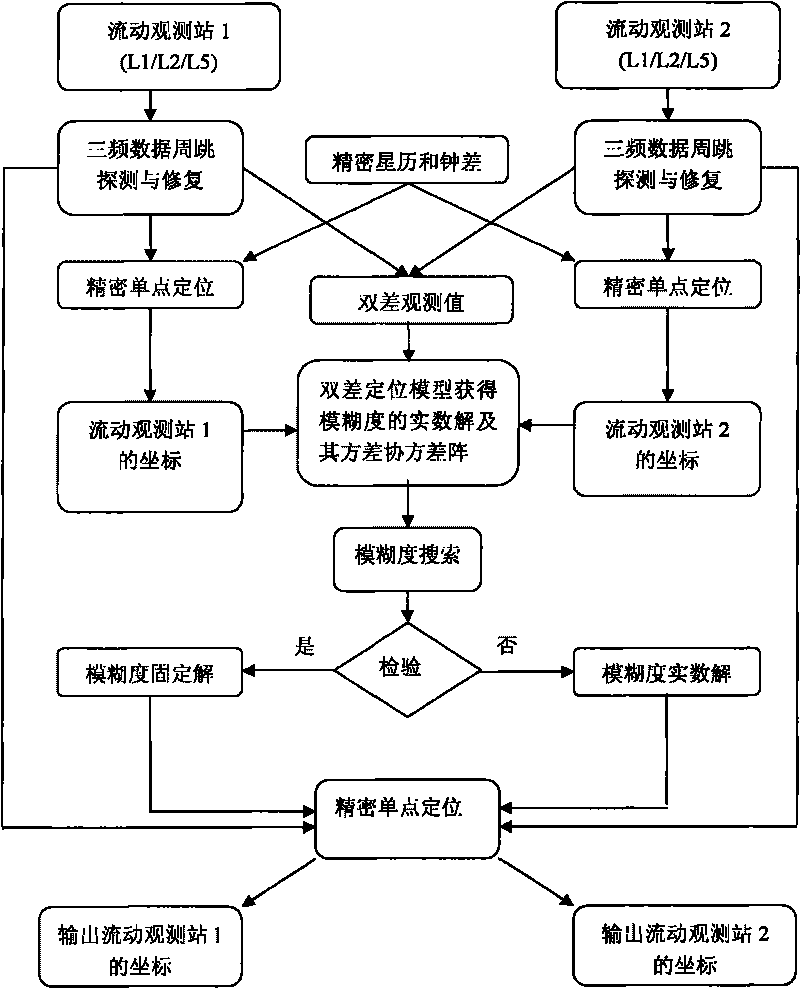
Global navigation satellite system (GNSS) triple-frequency motion-to-motion positioning method
ActiveCN101710179AImprove calculation accuracyHigh precisionSatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceLow noise
The invention relates to a global navigation satellite system (GNSS) triple-frequency motion-to-motion positioning method. In the original epoch, the triple-frequency precision single-point positioning technology is adopted to obtain the coordinates of two movable carriers, one of the two movable carries is selected as the reference station for the triple-frequency double-difference position, the triple-frequency double-difference positioning technology is adopted to calculate the baseline component of the two movable carriers and the integer ambiguity resolution of the double-difference carrier phase, and the baseline component of the two movable carriers and the integer ambiguity resolution of the double-difference carrier phase are used as the constraint conditions for the triple-frequency precision single-point positioning in the subsequent epochs to improve the single-point position precision and the convergence speed thereof. The geometry-Base TCAR ambiguity resolution fixation method is adopted to calculate the triple-frequency integer ambiguity resolution. The three irrelevant combination observation values of the triple-frequency non-ionizing layer and the long wave-length and low noise carrier are adopted to detect and repair the cycle slip of the original observation data.
Owner:威海五洲卫星导航科技股份有限公司
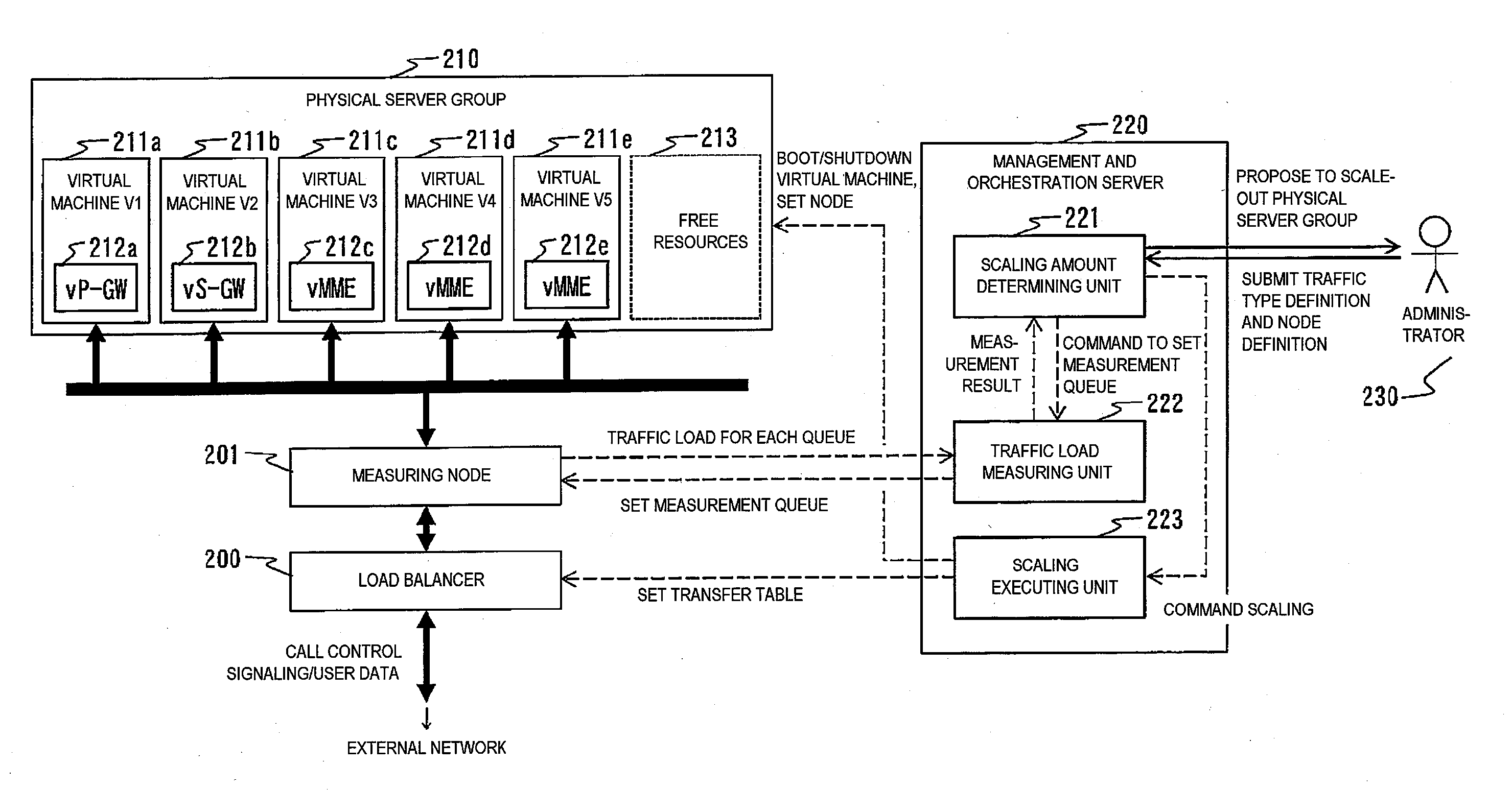
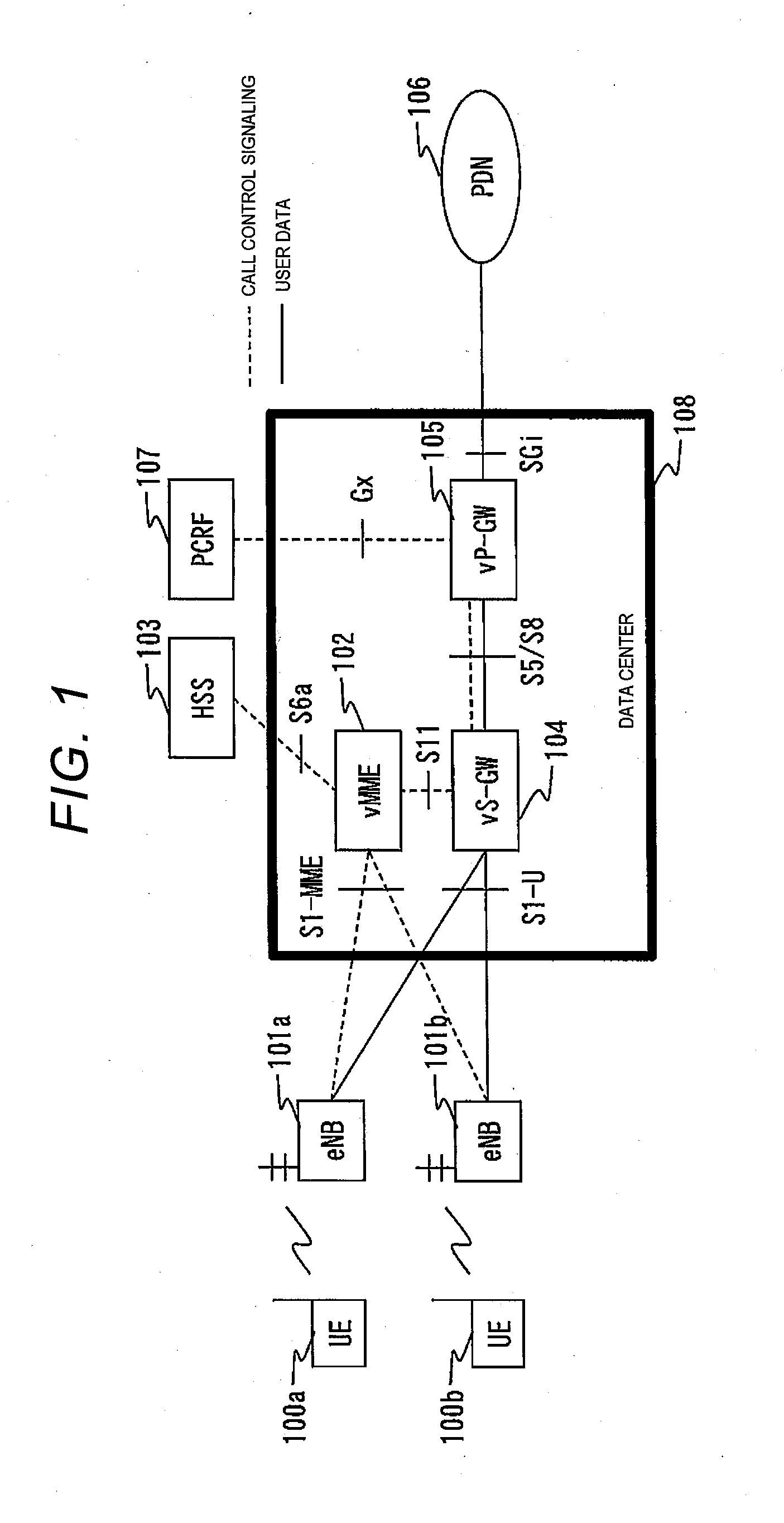
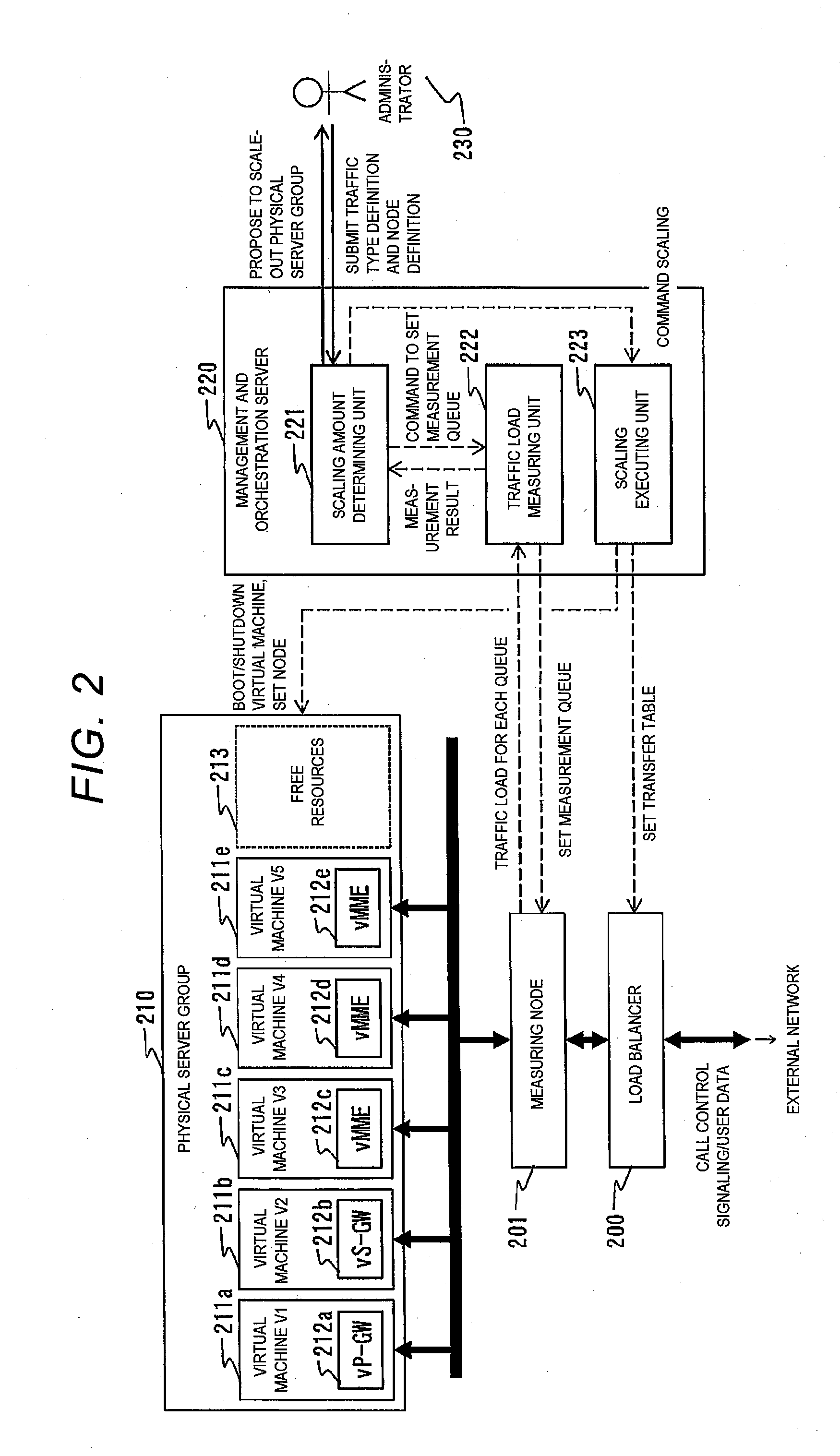
Management and orchestration server
InactiveUS20150222515A1Shorten convergence timeDigital computer detailsData switching networksVirtualizationTraffic volume
A management and orchestration server which manages a plurality of types of virtualized nodes included in server group includes a scaling executing unit configured to command the server group to scale virtual machines included in each of the plurality of types of virtualized nodes, a traffic load measuring unit configured to manage a traffic load of each of the virtual machines, and a scaling amount determining unit configured to determine a number of the virtual machines to be scaled. In this case, the traffic load measuring unit acquires a traffic load for each of the traffic types to be processed by each of the plurality of types of virtualized nodes, and the scaling amount determining unit determines the type of virtualized node for which virtual machines are to be scaled and a number of machines to be scaled based on the traffic loads of the traffic types.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
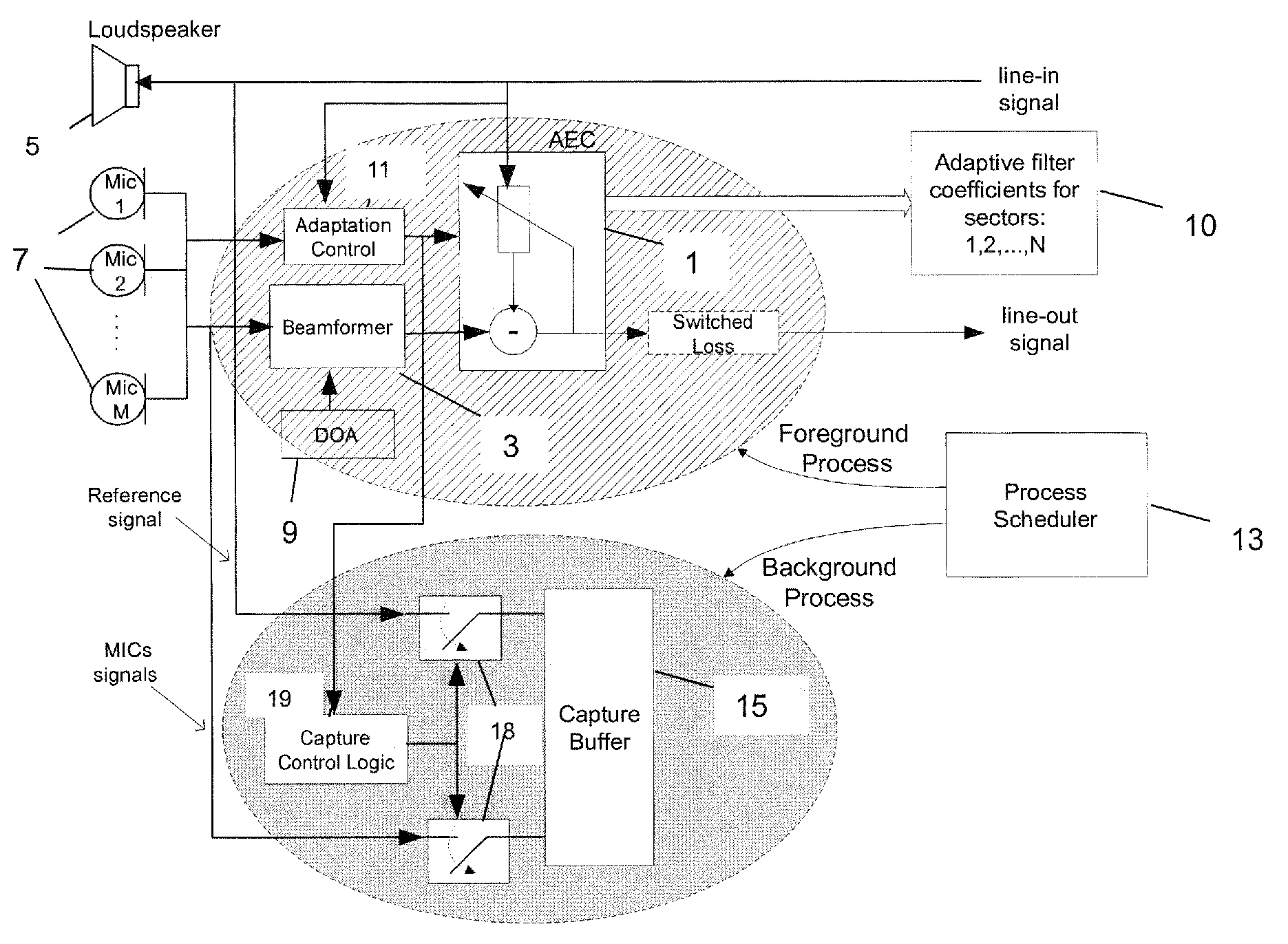
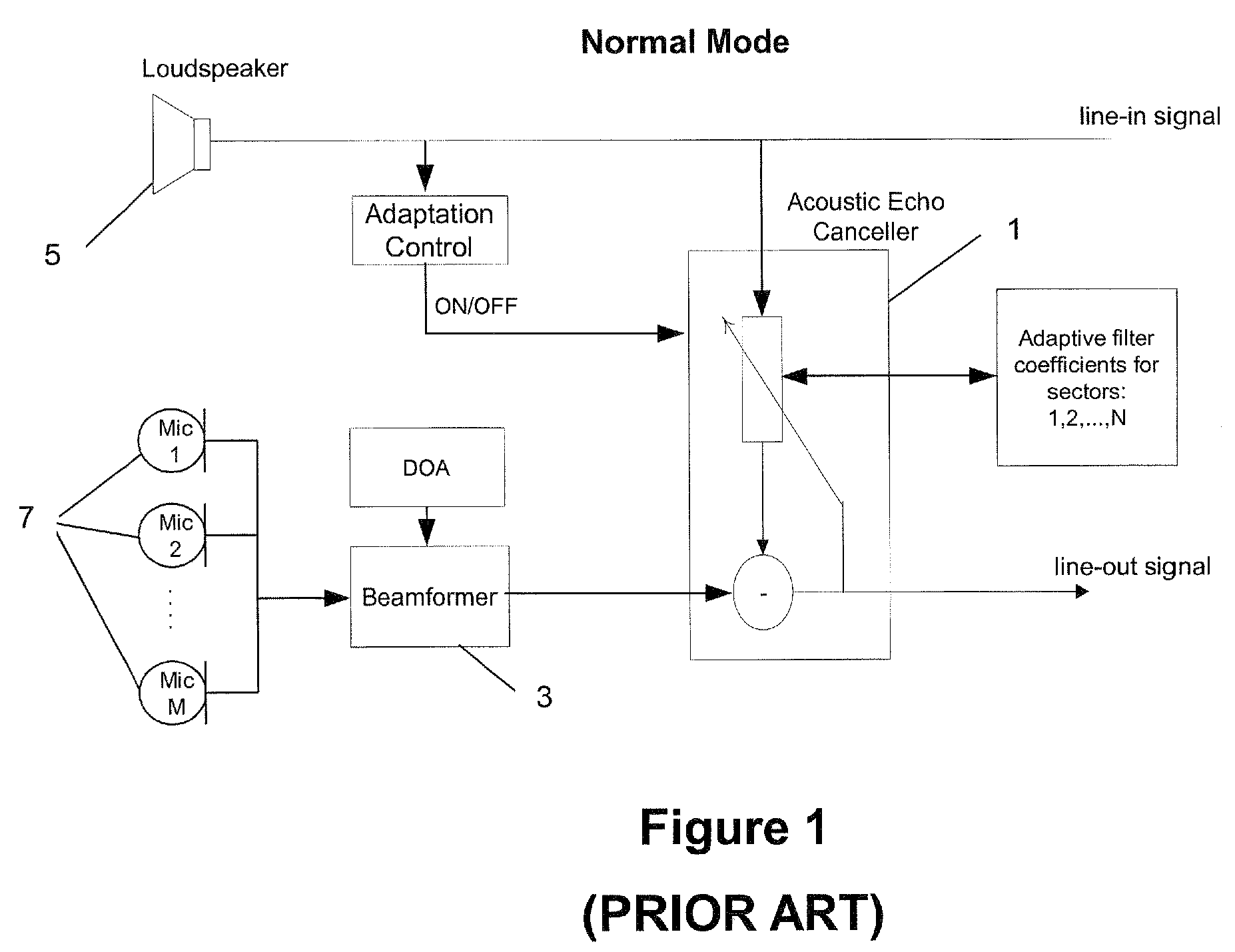
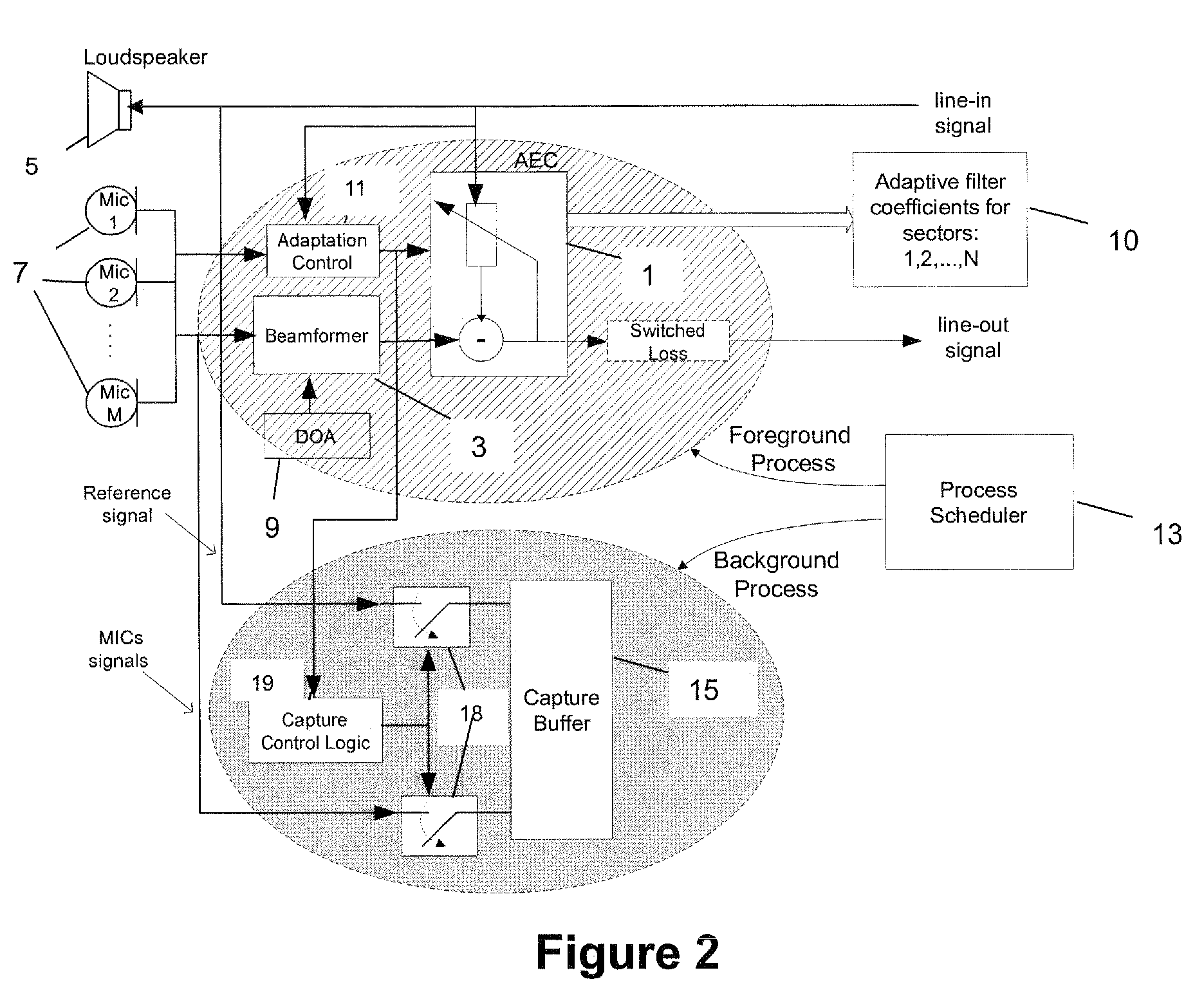
Method to reduce training time of an acoustic echo canceller in a full-duplex beamforming-based audio conferencing system
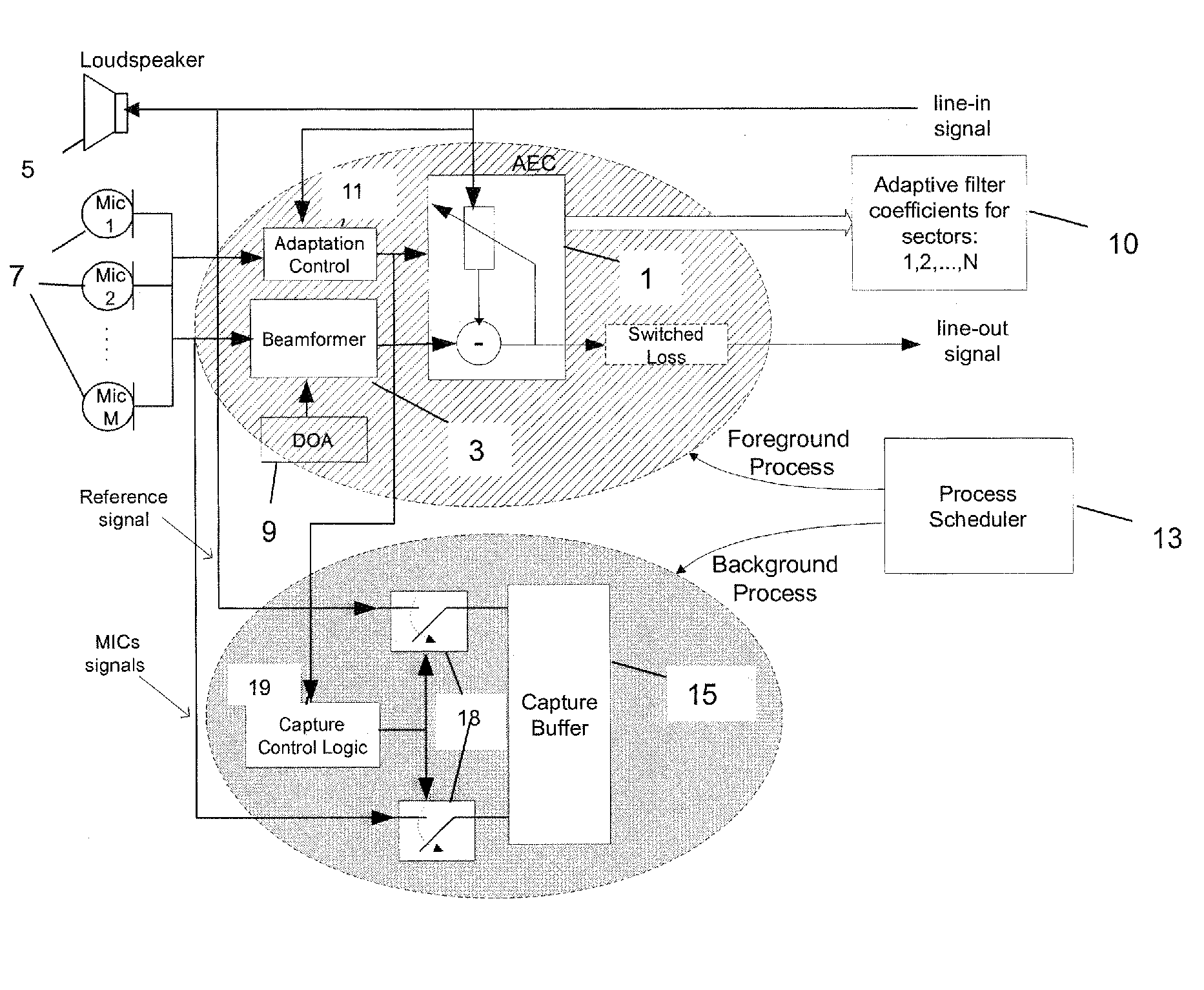
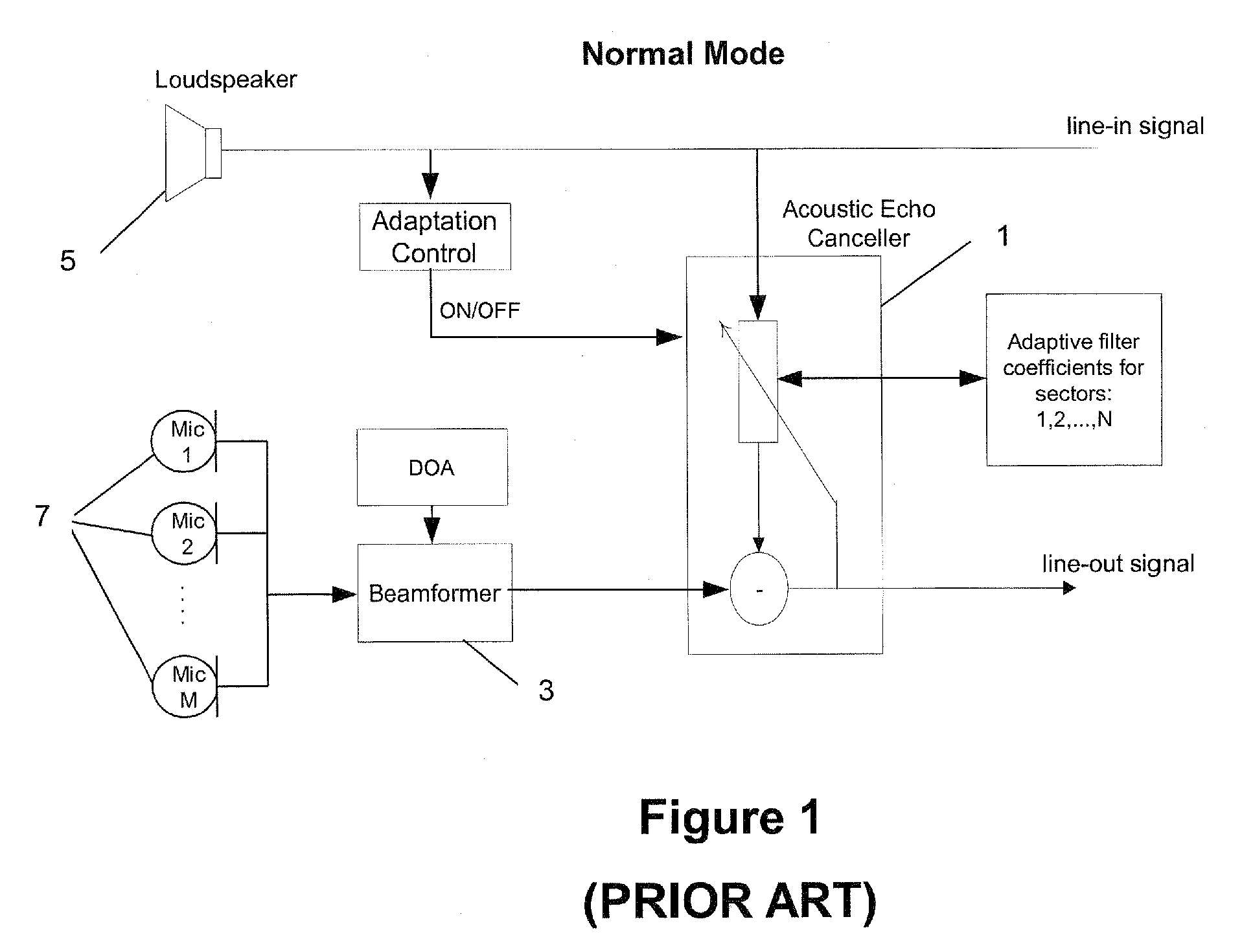
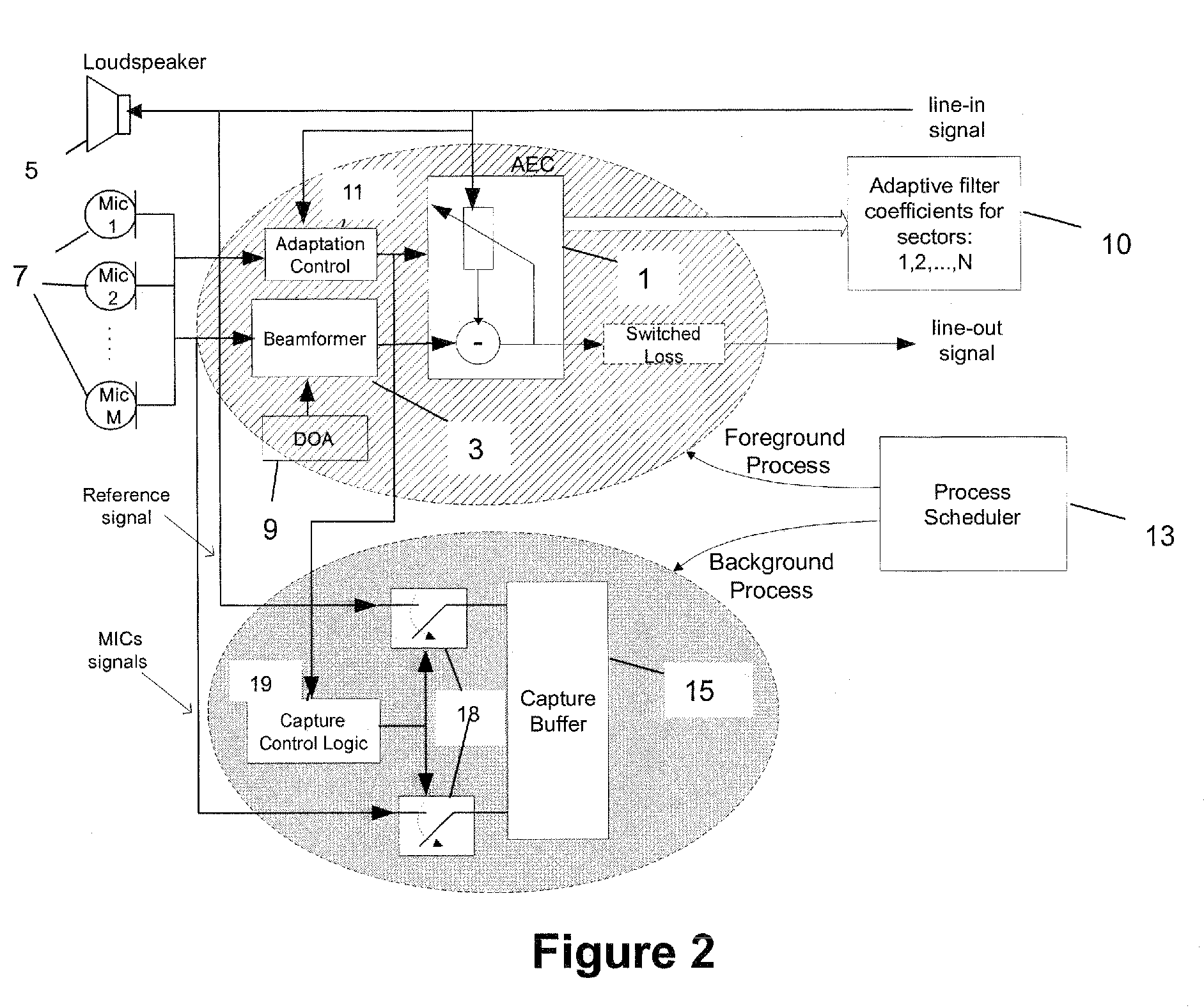
ActiveUS7831036B2Shorten convergence timeTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsLoudspeakerBackground process
A method is set forth for reducing the total acoustic echo cancellation convergence time for all look directions in a microphone array based full-duplex system. The method is based on capturing the loudspeaker signal due to the first far-end speech bursts when the conferencing system is first used, as well as the corresponding loudspeaker feedback signals in the individual microphones. The captured signals are then used for consecutive adaptation of the acoustic echo canceller on all echo paths corresponding to all look directions of the beamformer, thereby training the AEC. This training process can be executed concurrently with normal phone operation, for example, as a background process that utilizes available processing cycles.
Owner:MITEL
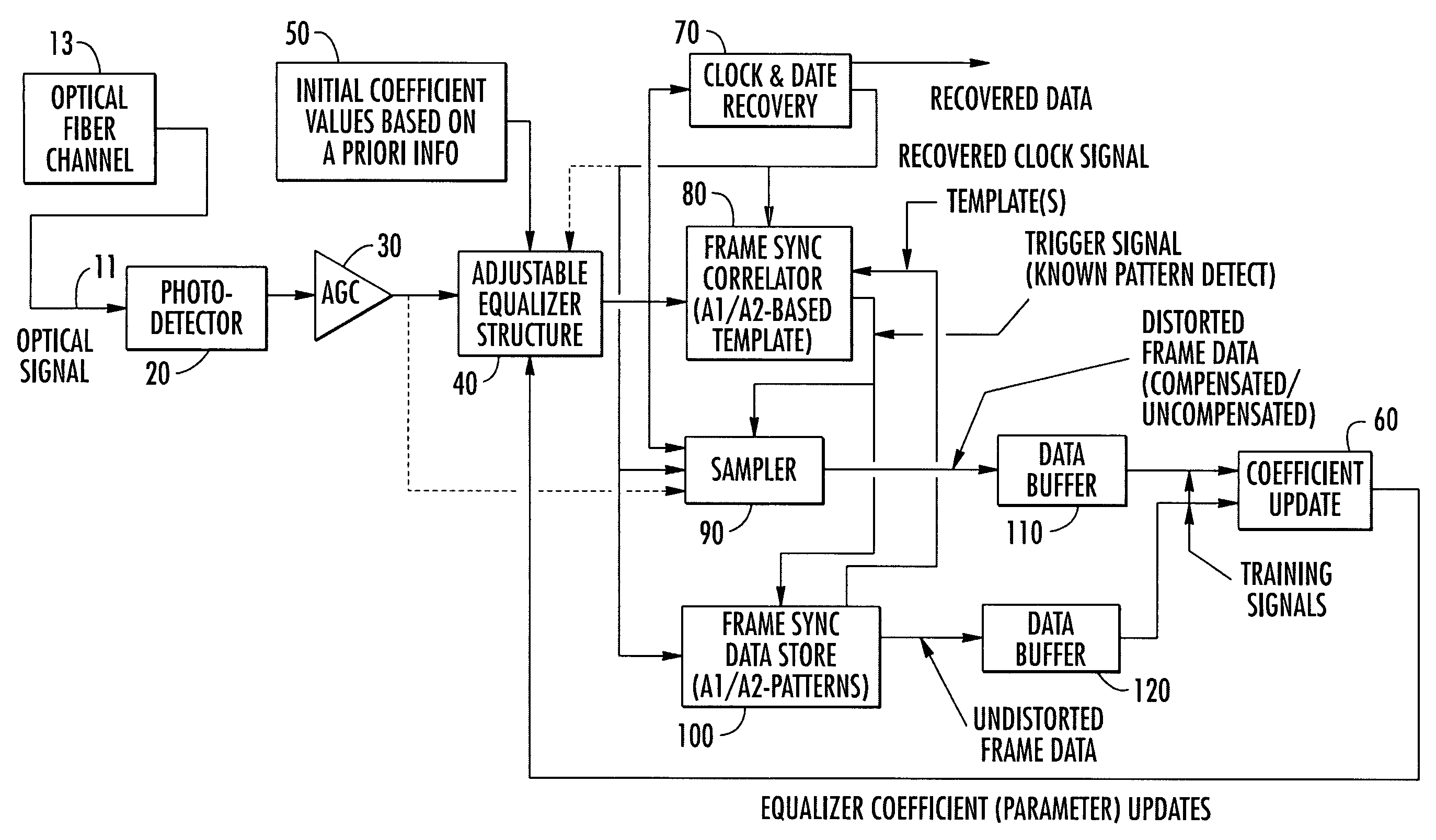
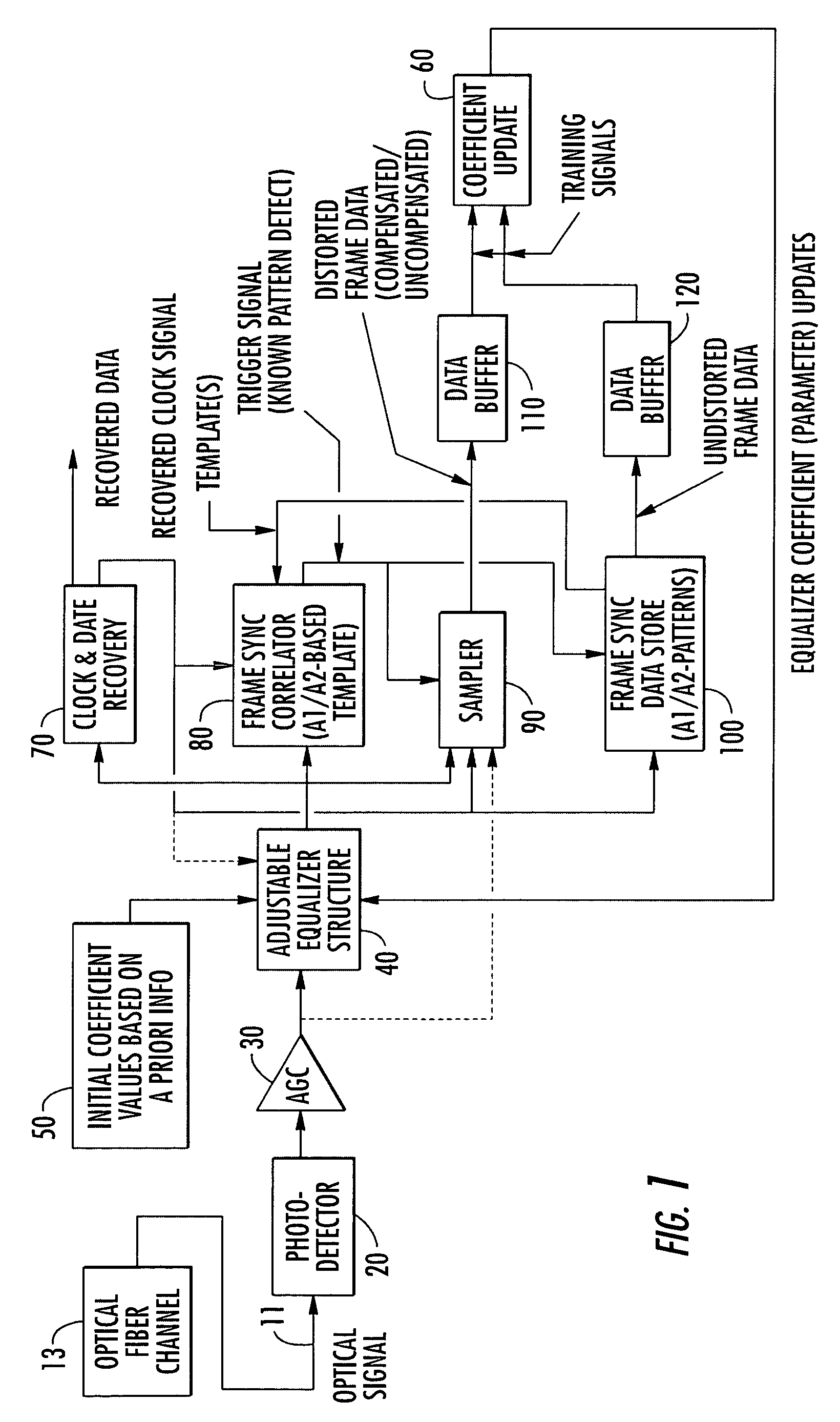
Updating adaptive equalizer coefficients using known or predictable bit patterns distributed among unknown data
InactiveUS7194025B2Shortens initial coefficient convergence timeIncrease probabilityMultiple-port networksAdaptive networkWeight coefficientSelf adaptive
An embedded pattern-based adaptive equalizer coefficient updating mechanism updates weighting coefficients of an adaptive equalizer in accordance with an error or differential signal obtained by processing the distorted version of a known signal pattern, that is repetitively distributed among information signals contained within the electrical communication signal output from the equalizer, with a copy of the known signal pattern. No dedicated ‘training sequence’ communication with the transmitter is required, so that the coefficient update mechanism does not impact the operation or bandwidth availability of the channel.
Owner:NORTH SOUTH HLDG
Time domain bidirectional iteration-based turbine vane flutter stress forecasting method
InactiveCN101908088AFast convergenceRealize all-in-one computingSpecial data processing applicationsTime domainPredictive methods
The invention discloses a time domain bidirectional iteration-based turbine vane flutter stress forecasting method. The method is characterized in that: a set of bidirectional iteration method for a time domain is designed by taking a vane and a surrounding flow field thereof as a three-dimensional fluid solid coupling system, and the flutter stress of the vane is obtained by alternately solving vane deformation and unsteady flow field. The method comprises the following steps of: setting a structural calculation module, a fluid calculation module, a data conversion module, a flutter stress output module, an initial value calculation module and a bidirectional iteration module in a computer; acquiring static vane deformation and steady flow field serving as an initial value by nonlinear iteration; alternately calling the structural calculation module and the fluid calculation module to propel the whole system on time; transmitting fluid solid boundary information through the data conversion module; and outputting the flutter stress on time history. The method realizes integrated calculation of the vane and the flow field, takes the nonlinearity of the coupling system into consideration, and can allow the observation of the whole flutter development process and forecast the flutter stress of the vane.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Internet of Things service low-delay load distribution method and device based on edge computing
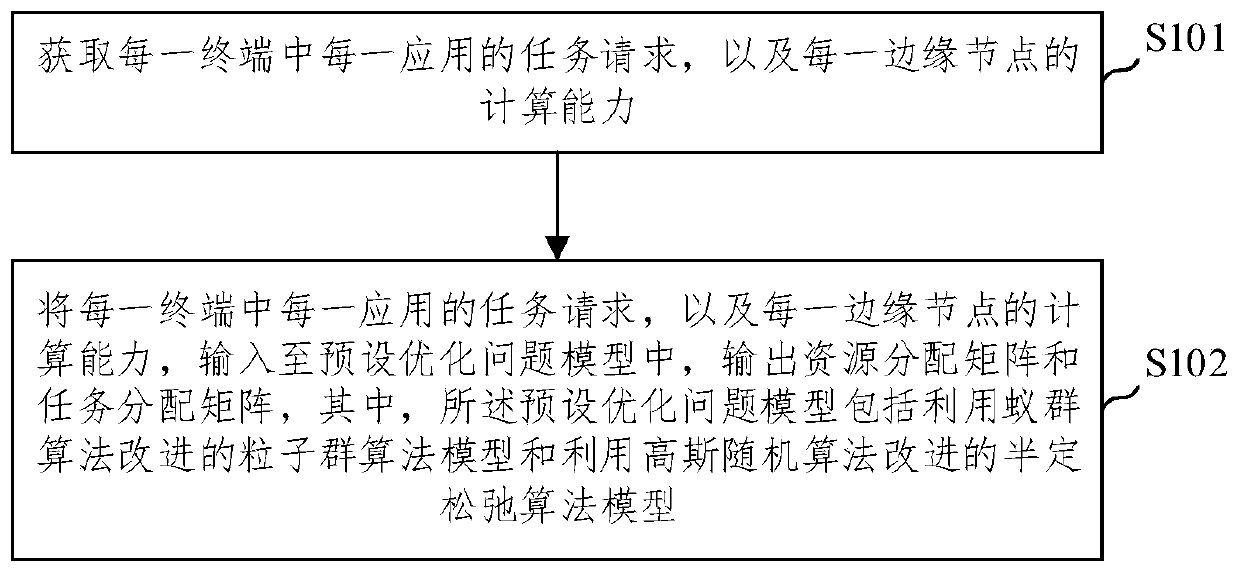
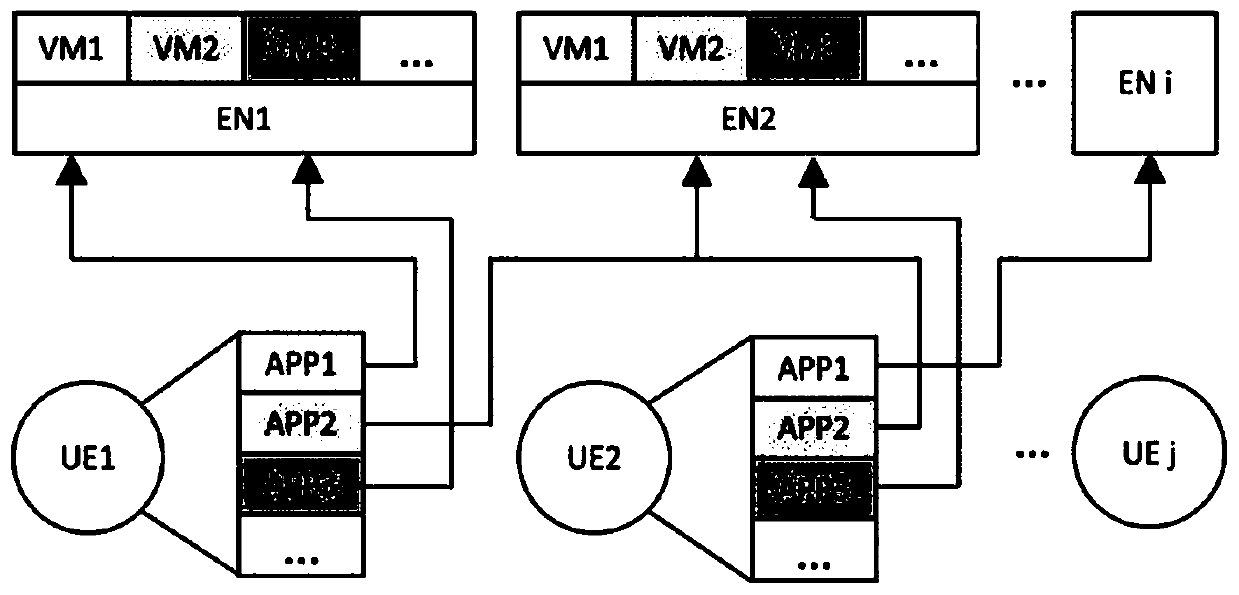
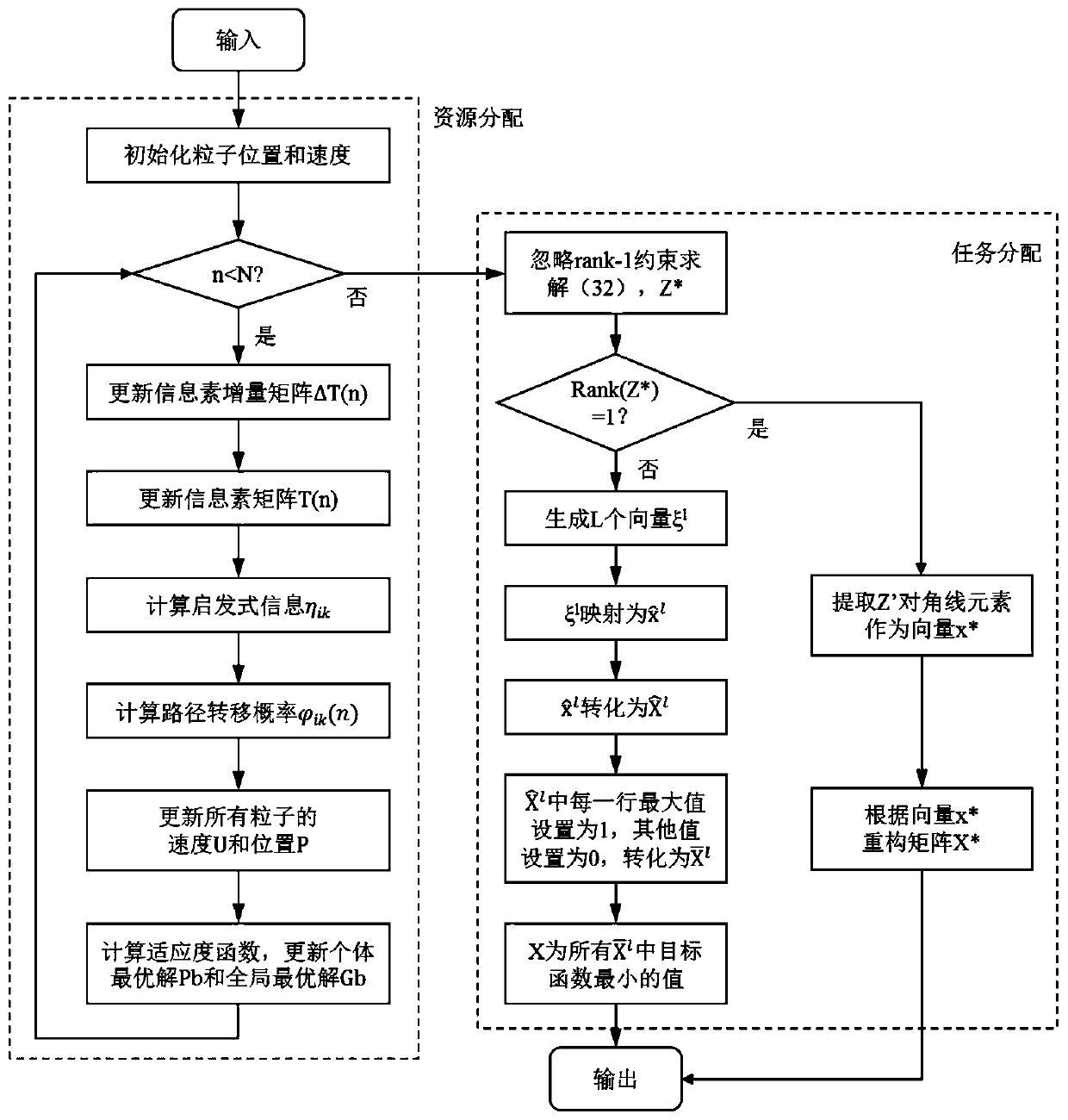
ActiveCN110365753AShorten convergence timeImprove performanceResource allocationArtificial lifeEdge computingStochastic algorithms
The embodiment of the invention provides an Internet of Things service low-delay load distribution method and device based on edge computing. The Internet of Things service low-delay load distributionmethod comprises the steps: acquiring a task request of each application in each terminal and the computing capacity of each edge node; and inputting the task request of each application in each terminal and the computing capacity of each edge node into a preset optimization problem model, and outputting a resource allocation matrix and a task allocation matrix, wherein the preset optimization problem model comprises a particle swarm algorithm model improved through an ant colony algorithm and a semi-definite relaxation algorithm model improved through a Gaussian random algorithm. The Internet of Things service low-delay load distribution method and device based on edge computing improve particle swarm optimization by applying the ant colony algorithm, reduce the convergence time of the algorithm, improve the performance of the resource allocation result, solve the rank 1 constraint in the semi-definite relaxation problem by applying the Gaussian random variable, improve the performance of the task allocation result, and finally reduce the service delay.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM +2
Method and device for multicast traffic redundancy protection
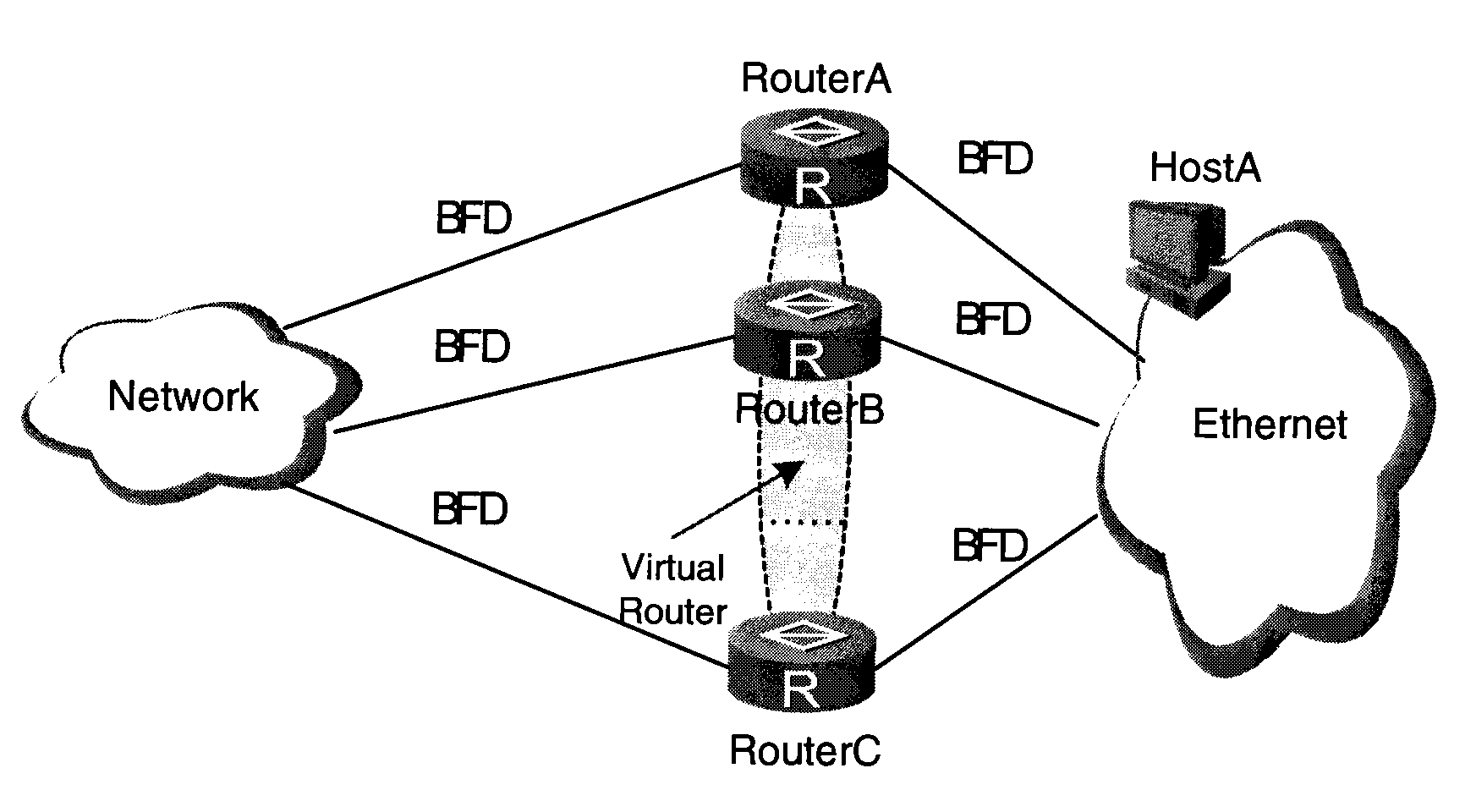
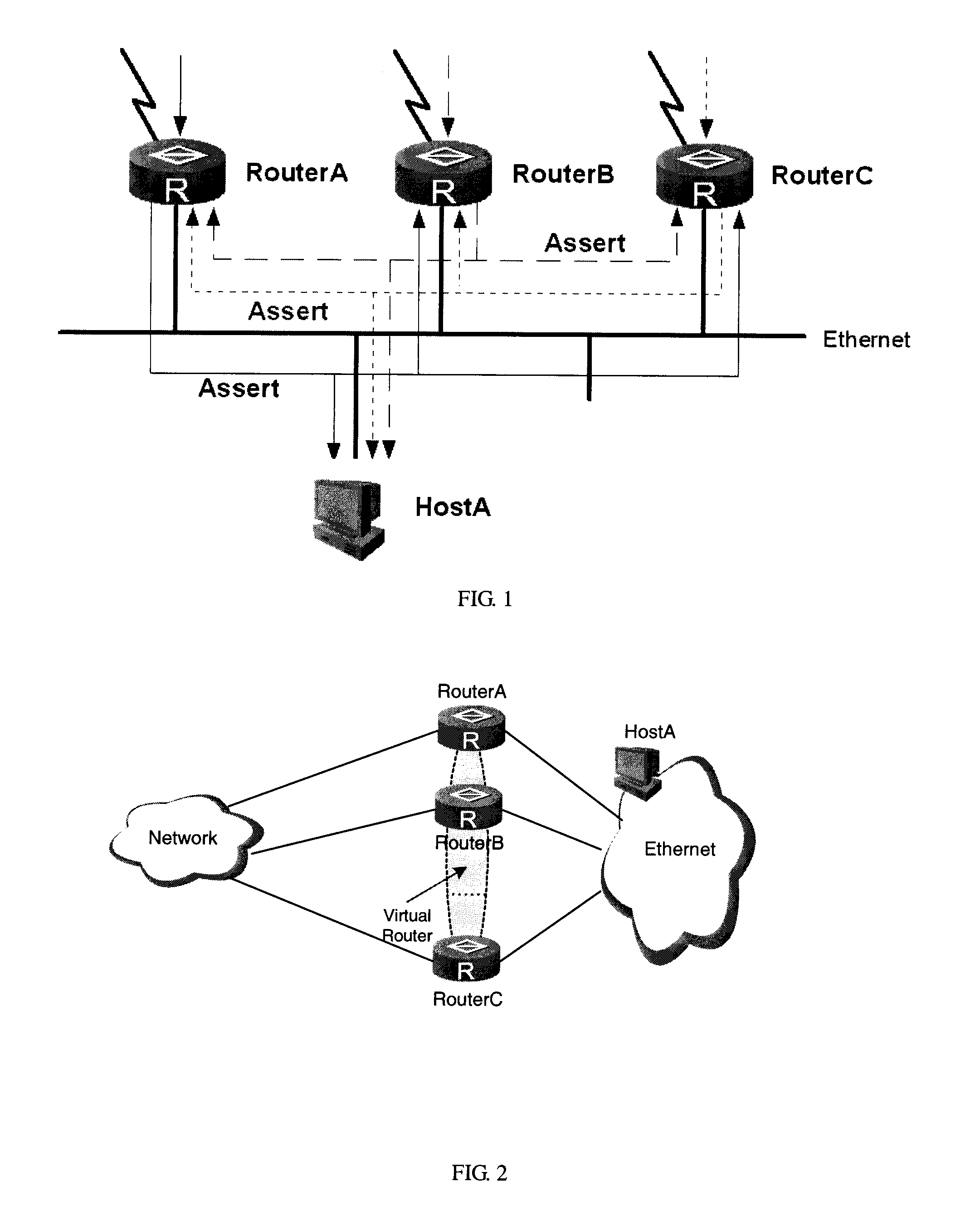
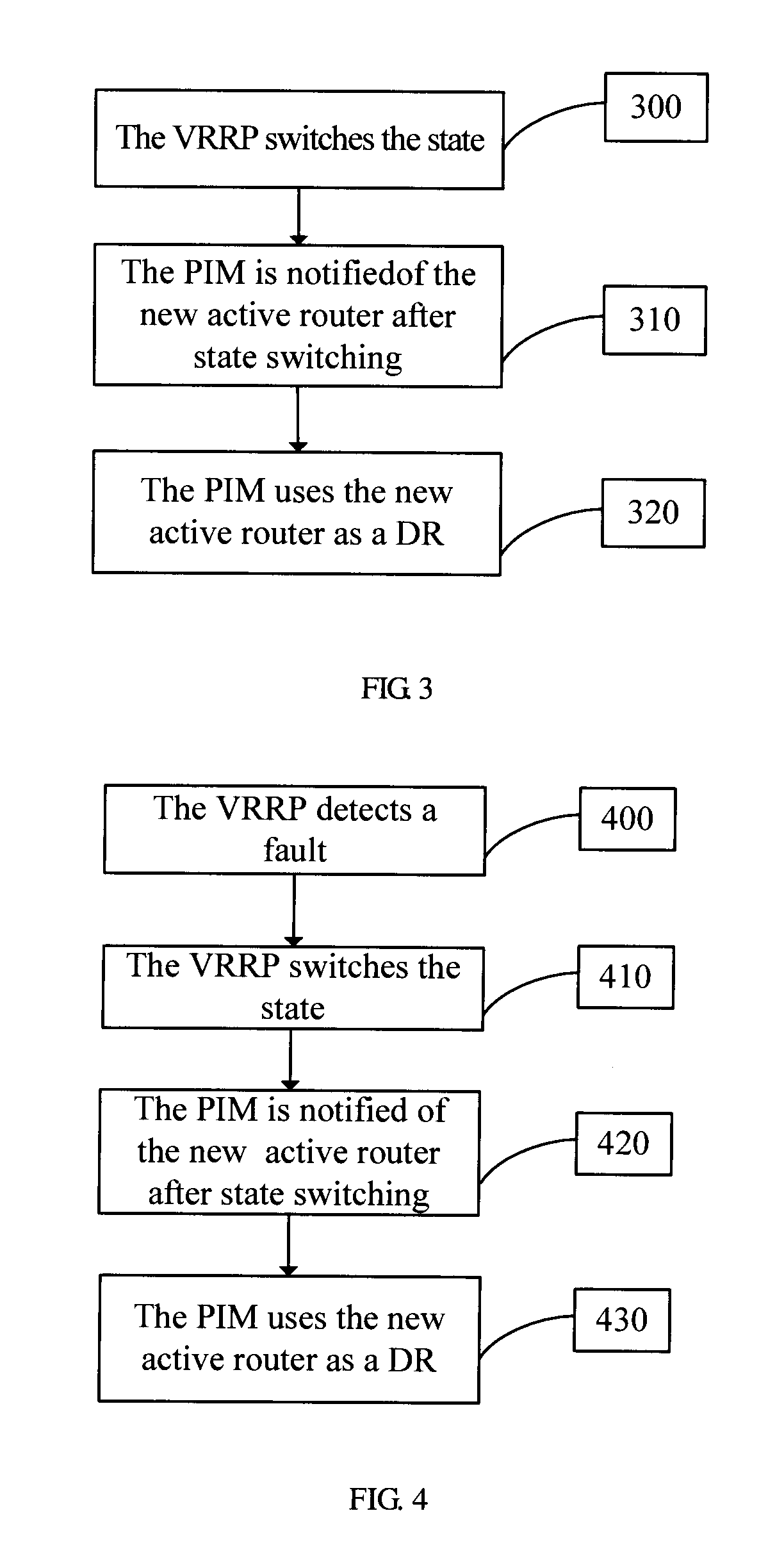
ActiveUS20090268607A1Avoid transient interruptionReduce switching delayError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic volumeTraffic capacity
A method and apparatus of multicast traffic redundancy protection is provided. After a fault occurs, the VRRP selects a new active router and notifies the PIM routing protocol, and the PIM uses the new active router as its DR.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method for controlling steering stability of distributed-drive electric vehicle
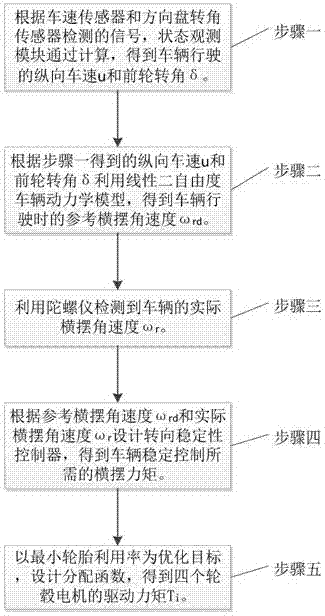
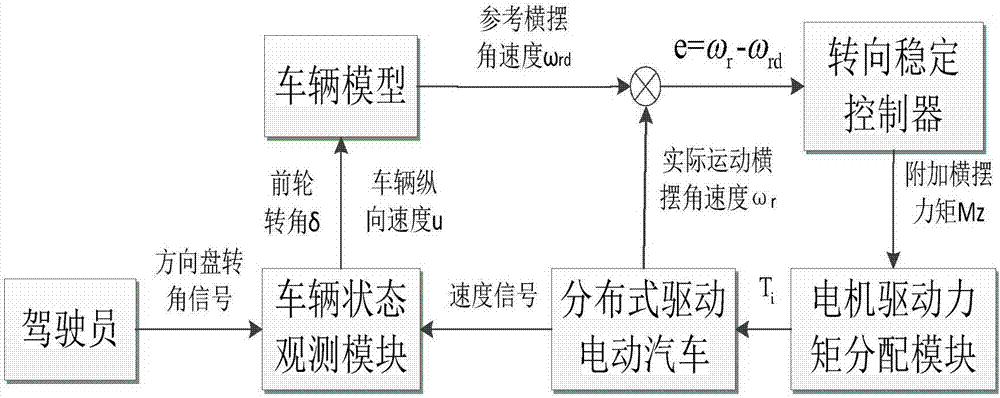
InactiveCN107415939AReduce buffetingShorten convergence timeSpeed controllerElectric devicesVehicle dynamicsGyroscope
The invention discloses a method for controlling steering stability of a distributed-drive electric vehicle. The method comprises the following steps of: step 1: according to signals detected by a vehicle speed sensor and a steering wheel angle sensor, obtaining a longitudinal vehicle speed u and a forewheel steering angle delta of a running vehicle through calculation of a state observation module; step 2: according to the longitudinal vehicle speed u and the forewheel steering angle delta obtained in the step 1, and obtaining a reference yaw rate omega rd of the running vehicle by a linear two-degree-of-freedom vehicle dynamic model; step 3: detecting an actual yaw rate omega r of the vehicle by using a gyroscope; step 4: according to the reference yaw rate omega rd and the actual yaw rate omega r, designing a steering stability controller and obtaining a yaw moment required by the steering stability control of the vehicle; and step 5: using the minimum tire utilization rate as an optimization objective, designing a distribution function and obtaining a driving torque Ti of four wheel hub motors. The phenomenon of ''chattering'' of a system is effectively suppressed, robustness is improved, and the steering stability of the distributed-drive electric vehicle is well controlled.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Automatic gain control method and control circuit suitable for orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFM) system
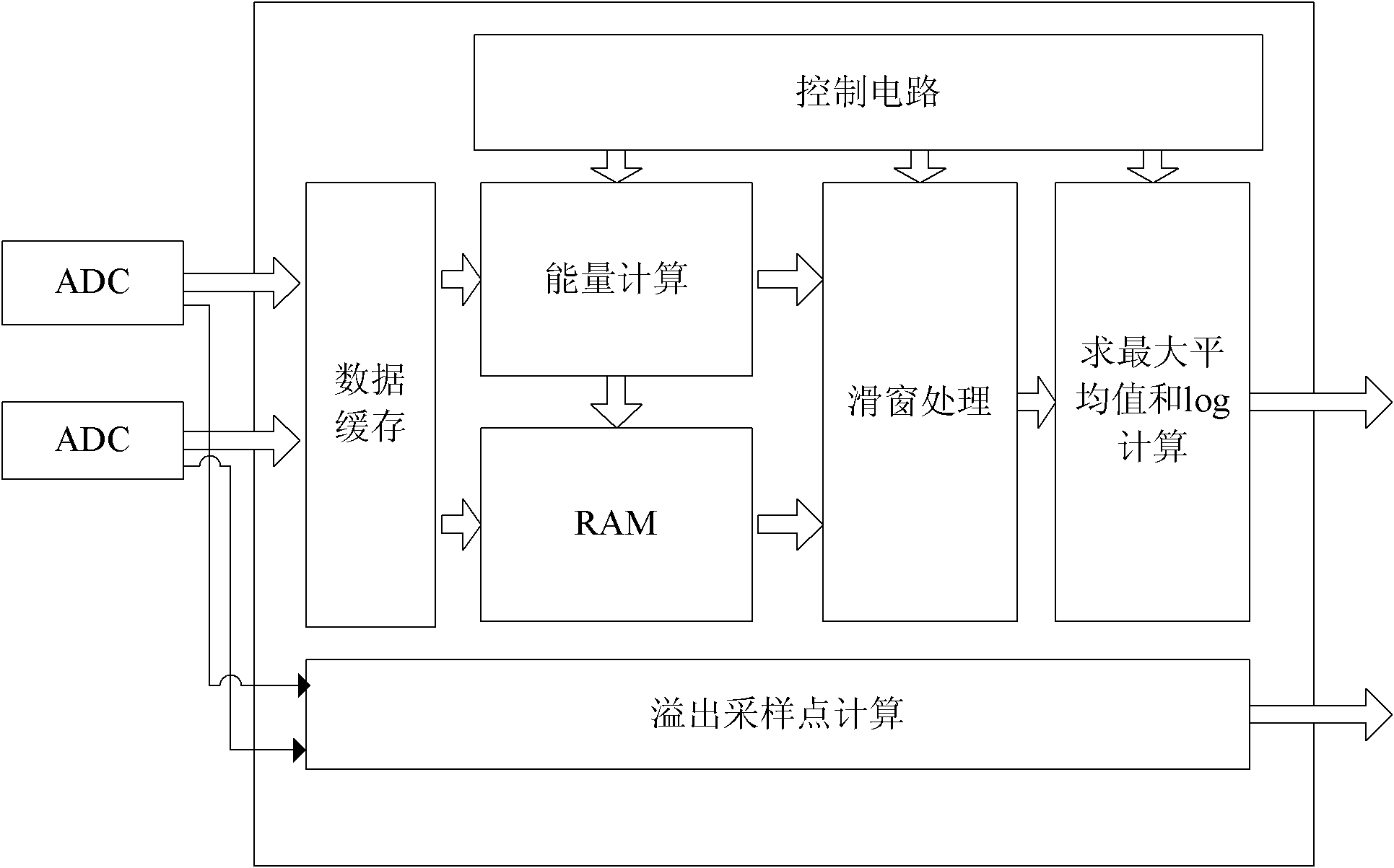
InactiveCN101964774ASimplified Computational ComplexityStrong lockPower managementMulti-frequency code systemsSlide windowReceived signal strength indication
The invention discloses an automatic gain control method and an automatic gain control circuit which are suitable for an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFM) system. The method comprises the following steps of: measuring a baseband signal; and adjusting gain. Slide window processing is performed during signal measuring so as to average signal energy in a window. A gain adjustment algorithm determines reasonable gain of the next adjustment period through conditions such as the gain of an upper frame, a measured value of the upper frame, the number of overflow sampling points, the receiving signal intensity indication on the current antenna and the like. Simultaneously, the gain of a radio frequency receiving chip is changed by circulating prefix time so as to track an OFDM symbol level.
Owner:江西开昂教育股份有限公司
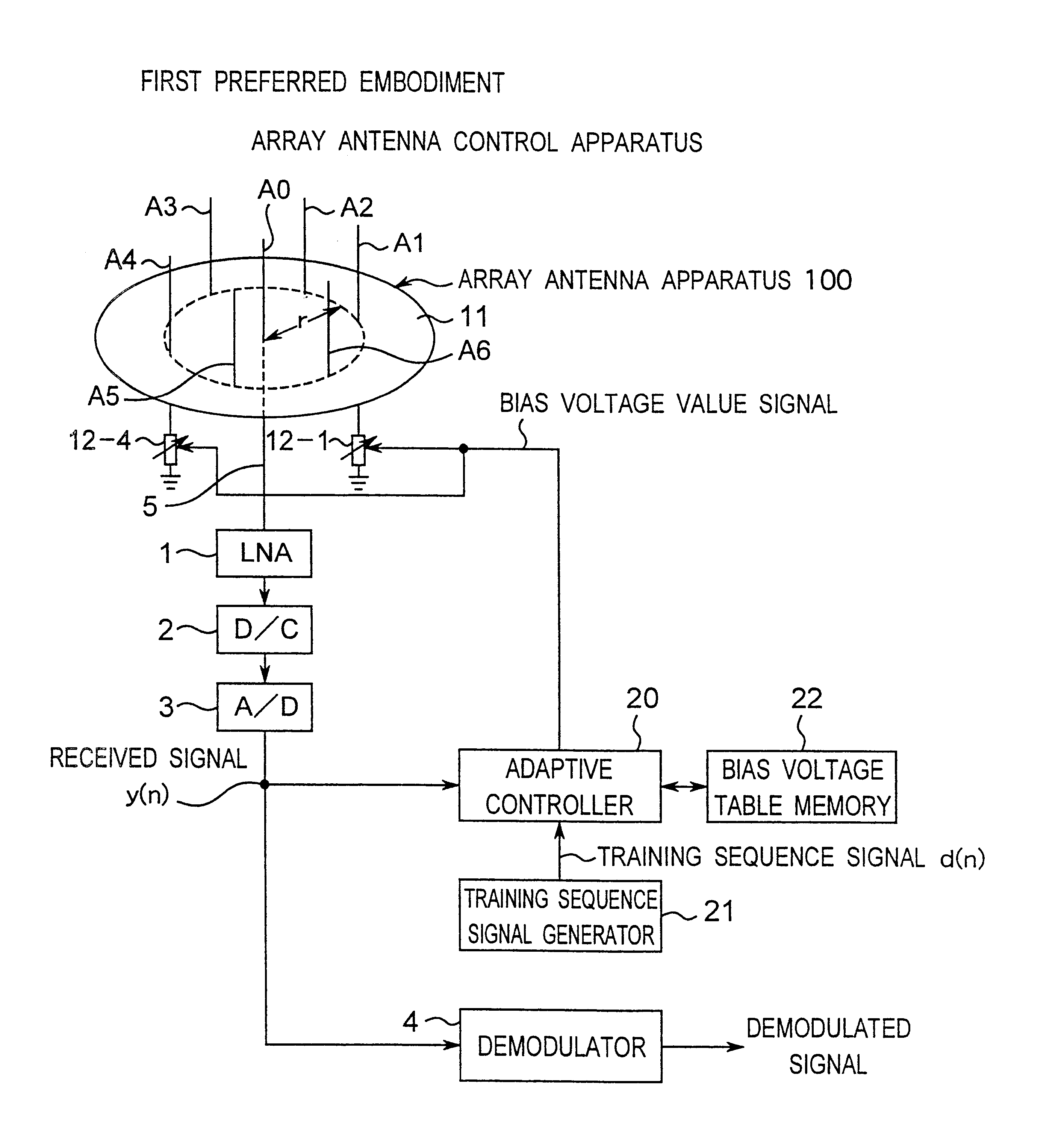
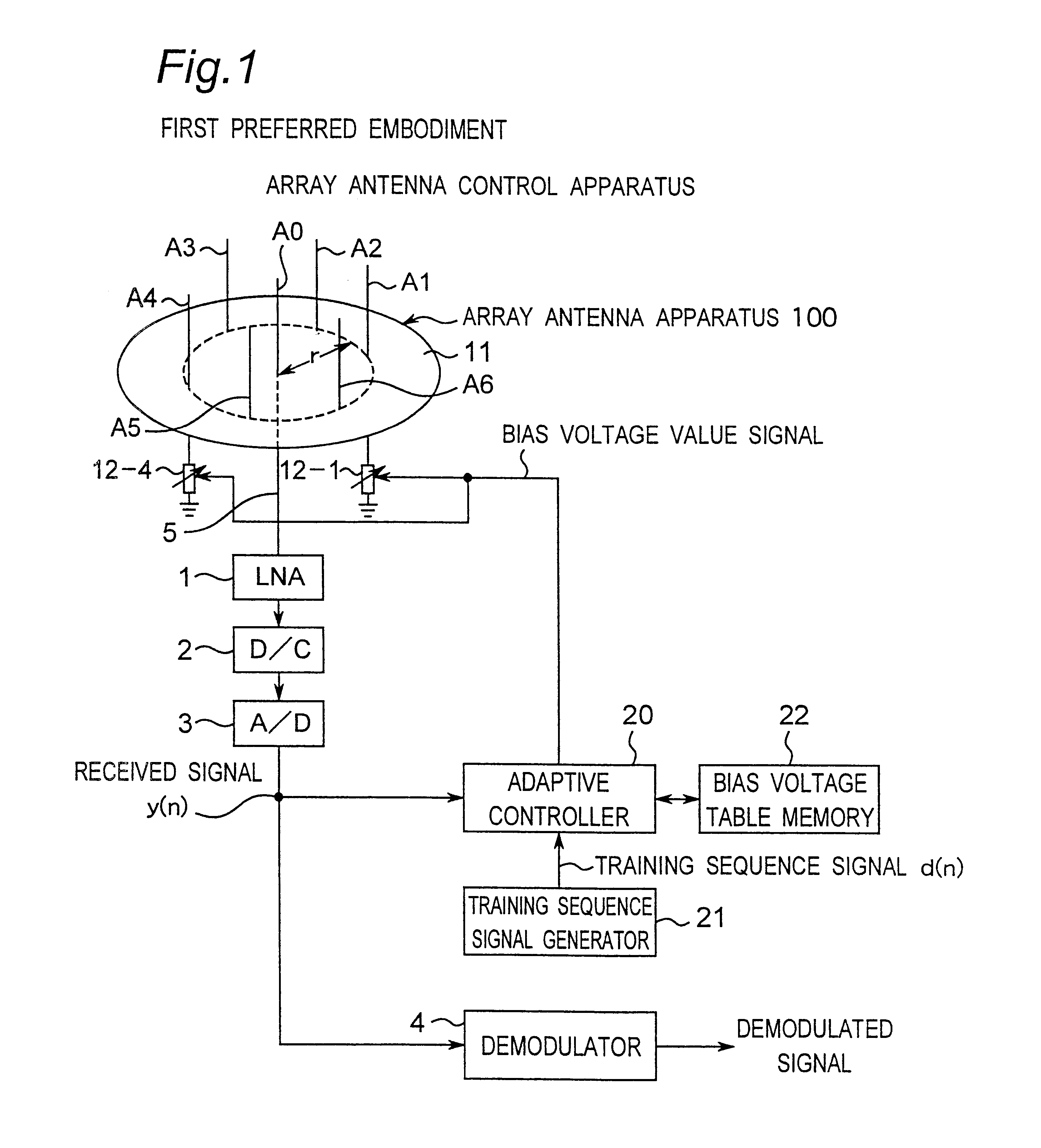
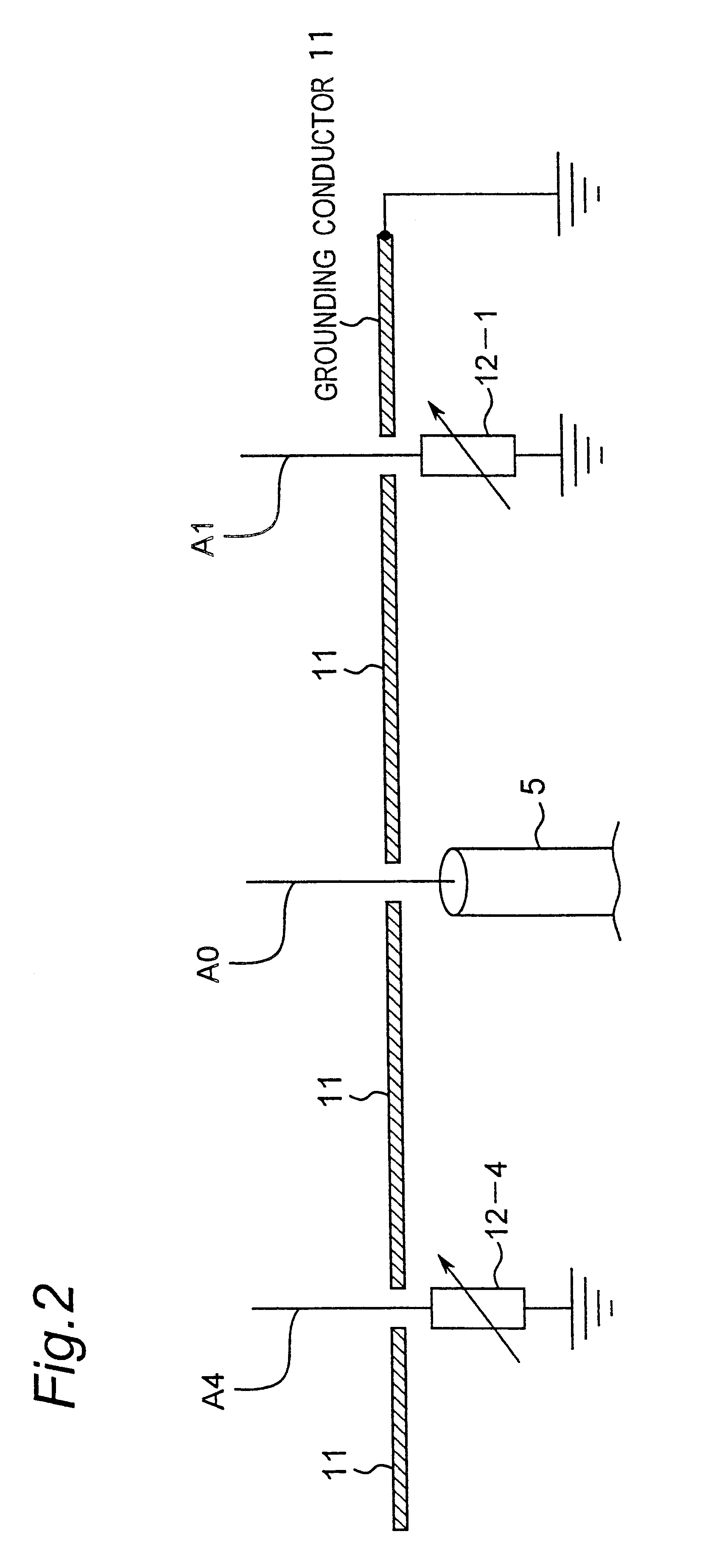
Method for controlling array antenna equipped with single radiating element and a plurality of parasitic elements
InactiveUS6677898B2Shorten convergence timeReduce the amount of calculationAntenna arraysSequence signalVoltage vector
An adaptive controller for an ESPAR antenna randomly perturbs a bias voltage vector V(n) composed of elements of bias voltage values Vm by a random vector R(n) generated by a random number generator, compares an objective function value J(n) of a cross correlation coefficient for a bias voltage vector V(n) before the perturbation with an objective function value J(n+1) of a cross correlation coefficient for a bias voltage vector V(n+1) after the perturbation, and selects and sets the bias voltage Vm corresponding to that when the cross correlation coefficient increases before and after the perturbation. Then the adaptive controller repeats the random perturbation and setting from the bias voltage of respective varactor diodes. This leads to that it is not necessary to provide a long training sequence signal, and the control process can be executed with learning so that a performance can be improved every iteration for search.
Owner:ATR ADVANCED TELECOMM RES INST INT
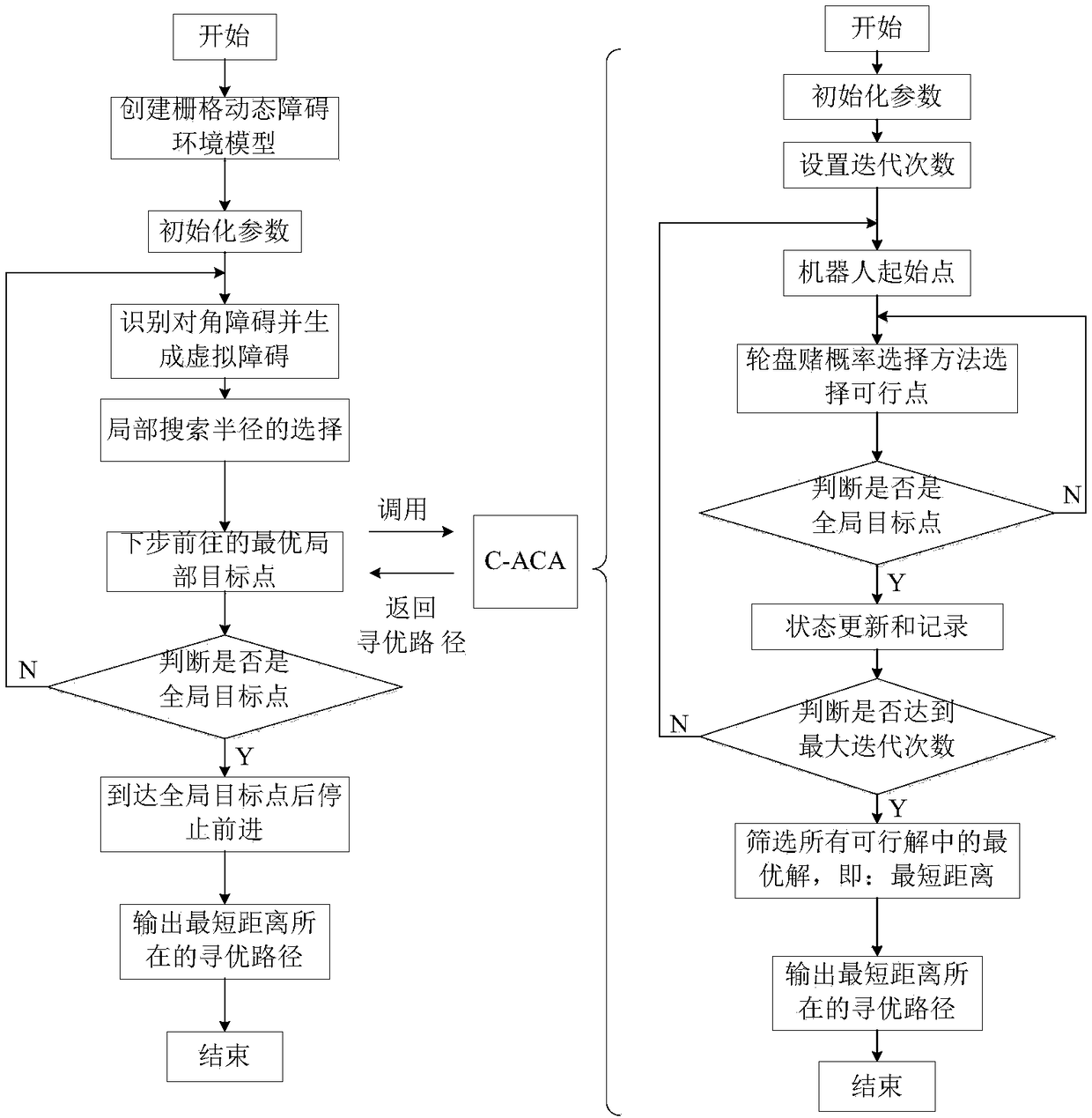
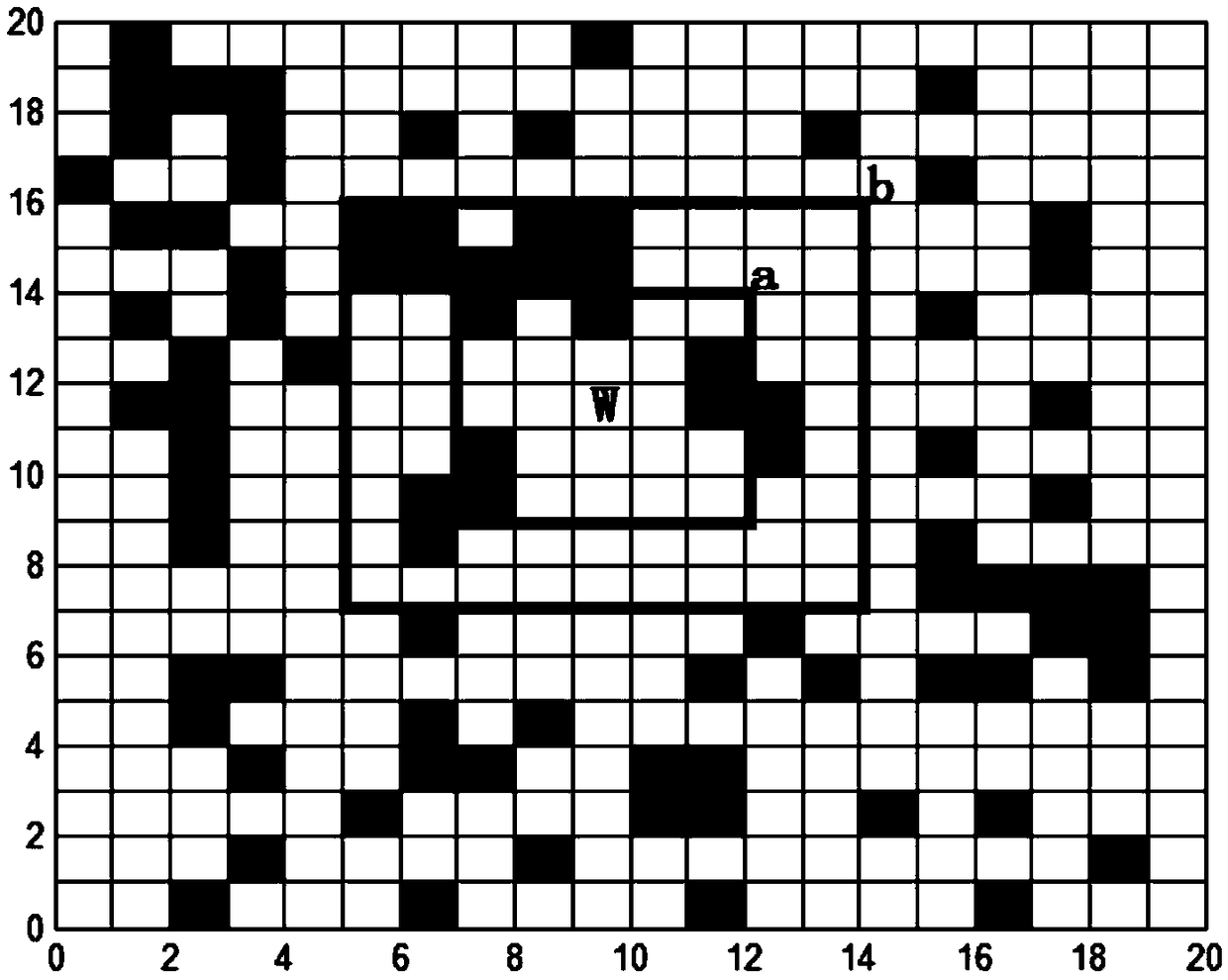
Ant colony-clustering algorithm-based self-adaptive dynamic path planning method of robot
ActiveCN109164810ATake advantage ofEfficient Dynamic Path PlanningPosition/course control in two dimensionsCluster algorithmDynamic planning
The invention relates to an ant colony-clustering algorithm-based self-adaptive dynamic path planning method of a robot, and belongs to the technical field of an intelligent algorithm of the robot. The ant colony-clustering algorithm-based self-adaptive dynamic path planning method comprises the steps of performing environment modeling by a grid method; determining a searching radius upper bound of local dynamic path planning according to planning real-time requirement; determining a searching radius value of local dynamic path planning by employing a selection rule of radius searching and bytaking a current position of a mobile robot as a current position; calling a random roulette method to determine an optimal local target point of local dynamic path planning; calling an ant colony algorithm to plan the local optimization path; calculating two norm of the optimal local target point and a preset terminal, and taking the optimal local target point as a global target point if the twonorm is zero; and repeating if the two norm is not zero. By the ant colony-clustering algorithm-based self-adaptive dynamic path planning method, the appropriate searching radius can be automaticallyselected according to the obstacle distribution condition, the path dynamic planning is completed, and favorable environment adaptability and relatively good comprehensive path optimization performance are achieved.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
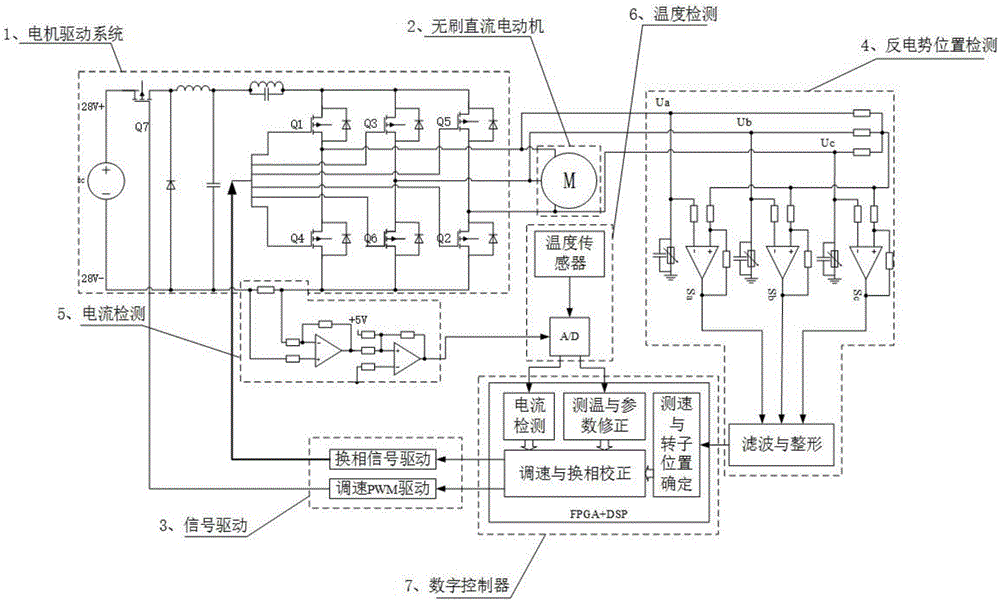
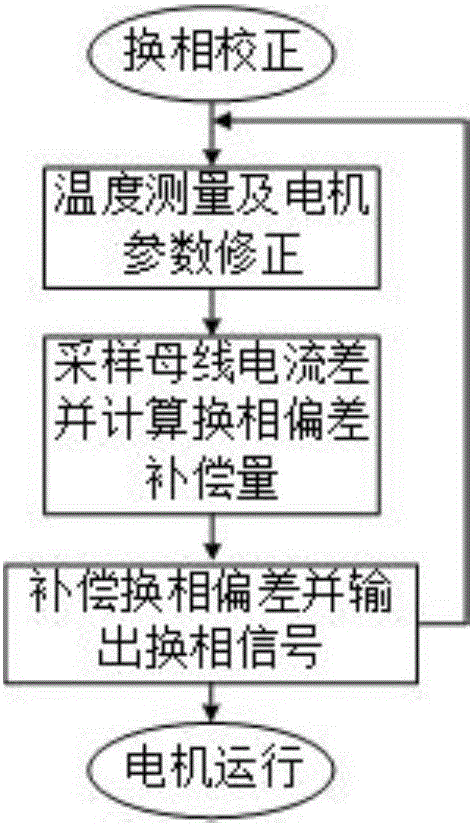
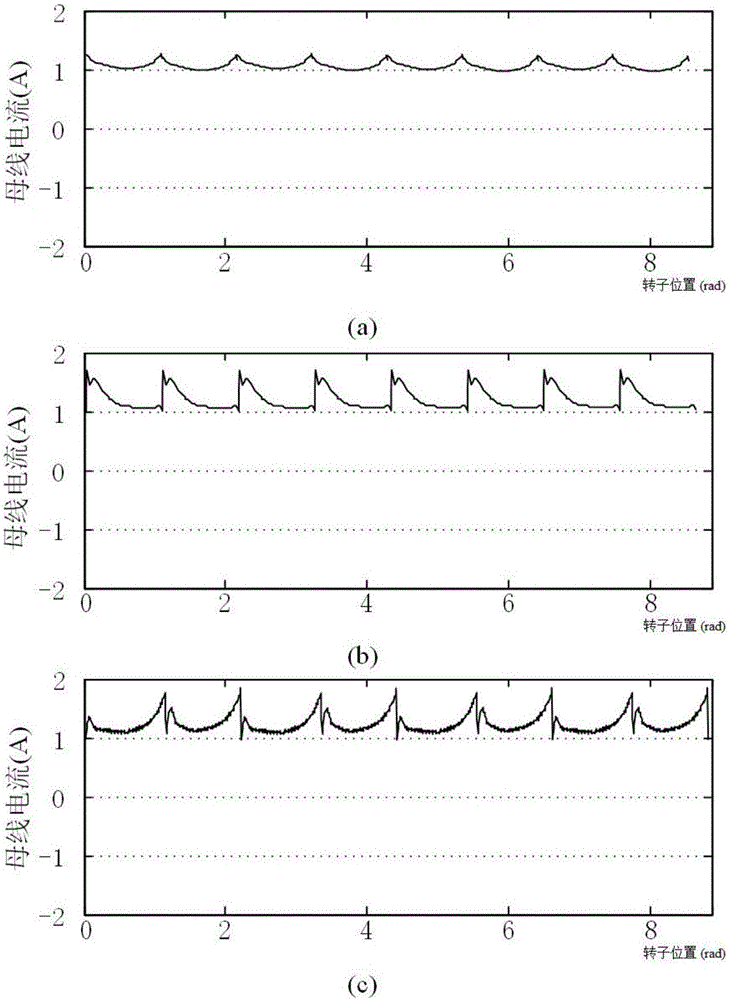
Sensorless brushless DC motor commutation deviation fast correction control system
ActiveCN106655918AShorten convergence timeAccurate calculationElectronic commutation motor controlElectric motor controlPower flowControl system
The invention relates to a sensorless brushless DC motor commutation deviation fast correction control system and a method. An analytical equation between the bus current difference before and after commutation and commutation deviation is derived according to the bus current fluctuation value before and after commutation. In view of the influence of commutation ripple and motor three-phase winding asymmetry on the accuracy of sampled current during actual bus current sampling, a method for current offset sampling in the same conduction zone is designed. The bus current difference is obtained according to the designed current sampling method, the commutation deviation is calculated based on the analytical equation, and the commutation signal is compensated and corrected in real time. By designing the sensorless motor commutation deviation fast correction control system, the commutation deviation convergence time is reduced greatly, and the commutation precision is improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
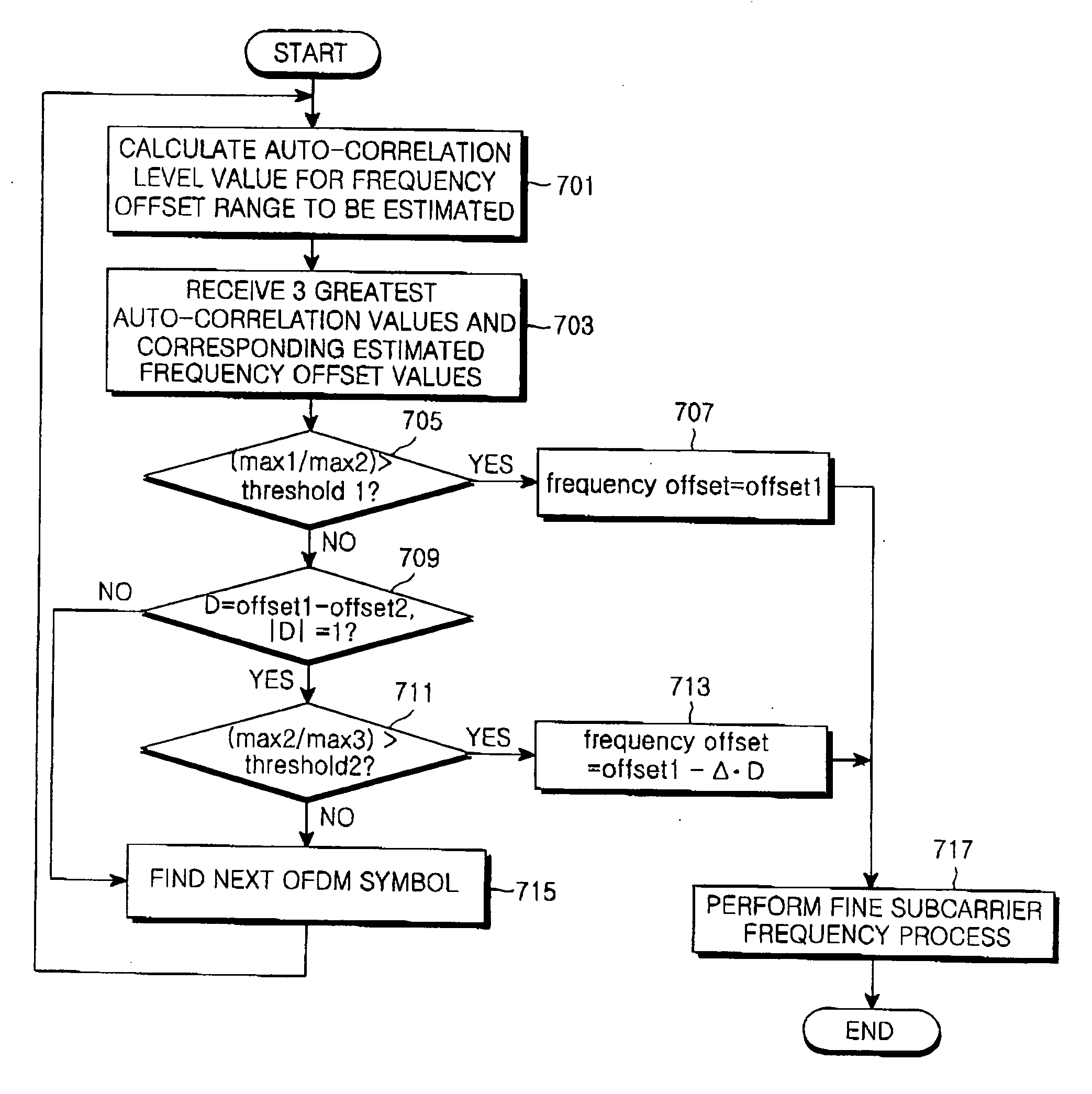
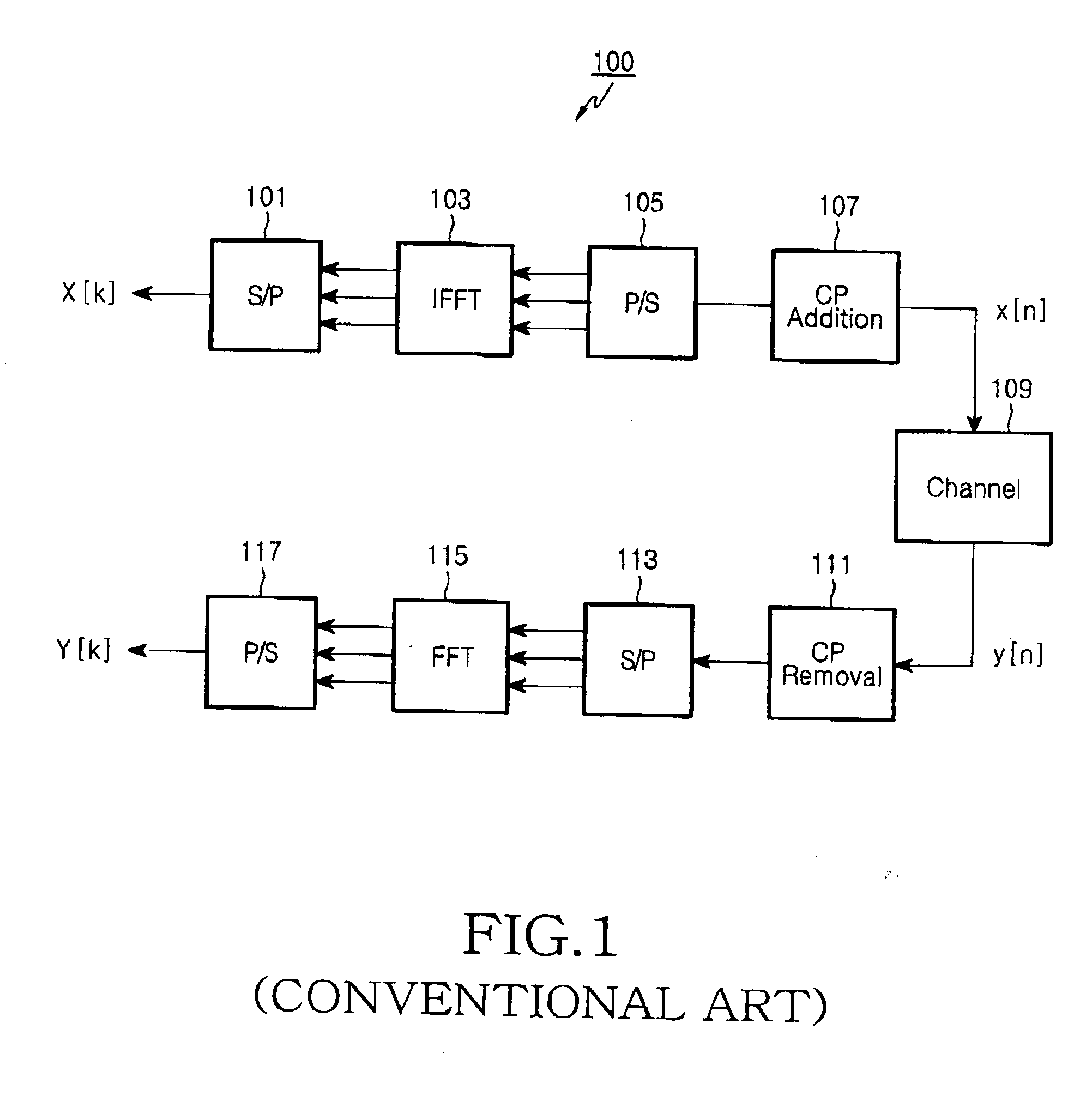
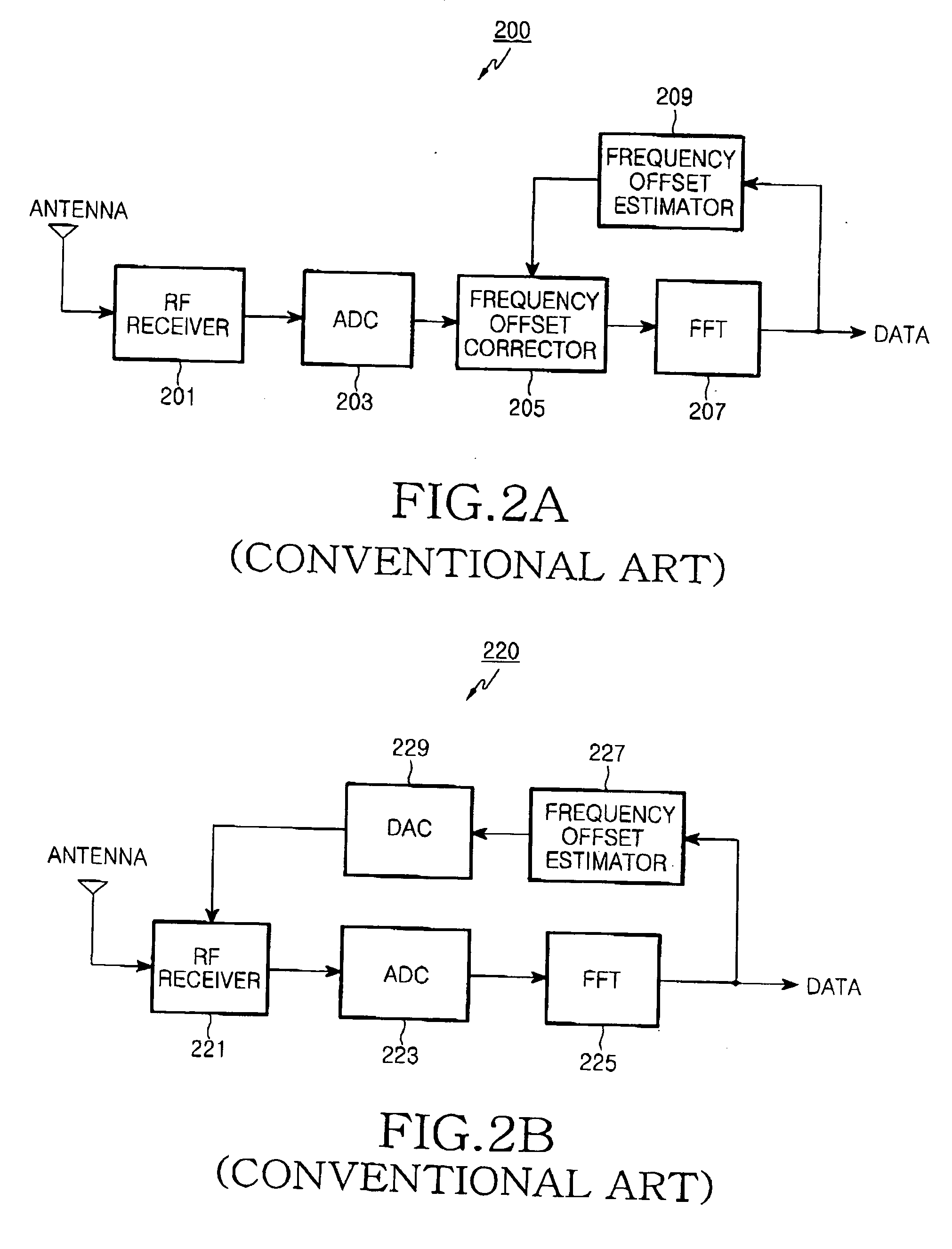
Apparatus and method for recovering frequency in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing system
ActiveUS20070133699A1Improving carrier frequency estimation performanceShorten convergence timeTime-division multiplexSecret communicationSelf correlationCarrier frequency offset
An apparatus and method for recovering a carrier frequency of a received signal using a predefined symbol in an OFDM system is provided. A maximum value detector detects at least three values and their corresponding offsets in descending order among auto-correlation values calculated within a specific frequency offset range between a received signal and a predefined symbol. A frequency offset corrector compares a ratio of a first auto-correlation value to a second auto-correlation value with a predetermined first threshold, determines whether first and second frequency offsets corresponding to the first and second auto-correlation values are adjacent to each other if the ratio of the auto-correlation values is less than the first threshold, and determines an initial carrier frequency offset using a difference between the first frequency offset and a frequency offset correction value determined according to system, if the first and second frequency offsets are adjacent to each other and a ratio of the second auto-correlation value and a third auto-correlation value is greater than a predetermined second threshold.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
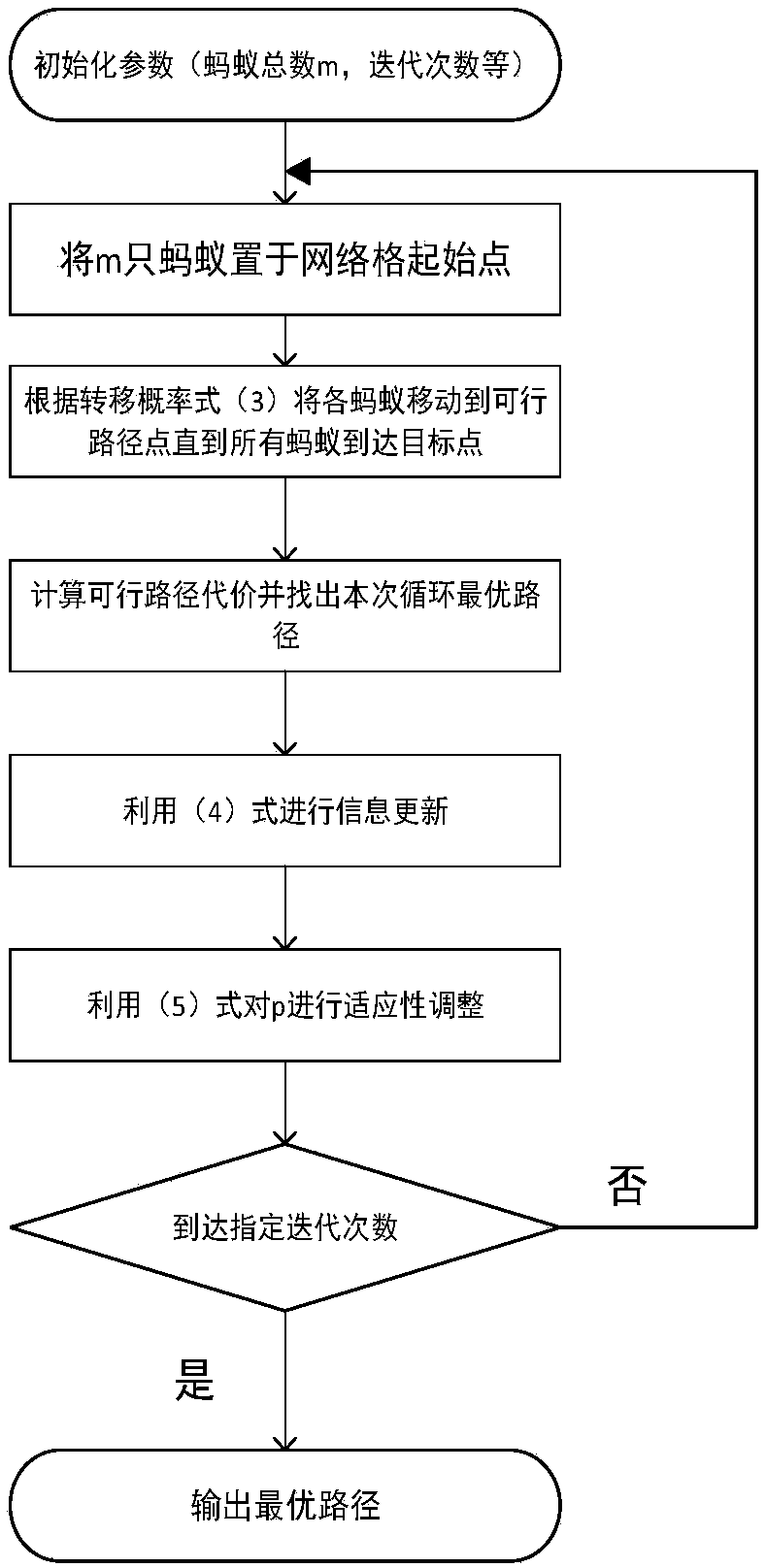
Unmanned aerial vehicle optimal path planning method based on adaptive ant colony algorithm
InactiveCN107562072AIncrease success rateShorten convergence timeAdaptive controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsSimulationPlanning approach
The present invention discloses an unmanned aerial vehicle optimal path planning method based on an adaptive ant colony algorithm. The method comprises: performing meshing of a flight area, performingparameter initialization, and putting ants at a starting point of grids; moving each ant to a feasible path point until all ants reach target points, and calculating a feasible path cost and findingout a cycle optimal path; performing information updating, and performing adaptive regulation for [Rho]; and finally, outputting the optimal path. The unmanned aerial vehicle optimal path planning method based on an adaptive ant colony algorithm can effectively improve a success rate when an unmanned aerial vehicle executes a defense penetration reconnaissance mission, and an efficient unmanned aerial vehicle flight path must be planned and designed prior to execution of the reconnaissance mission in an enemy defense area, so that it is ensured that the unmanned aerial vehicle can reach a target point with the minimum detected probability and the optimal path. Sizes of pheromone volatilization factors are regulated according to the enemy defense area, and an adaptive ant colony algorithm suitable for path planning is used. The adaptive ant colony algorithm is employed to obtain an optimal path length, and an algorithm convergence time is obviously shortened compared to other methods.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
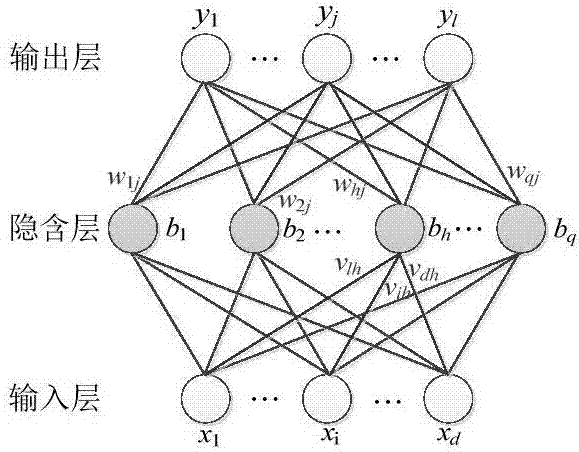
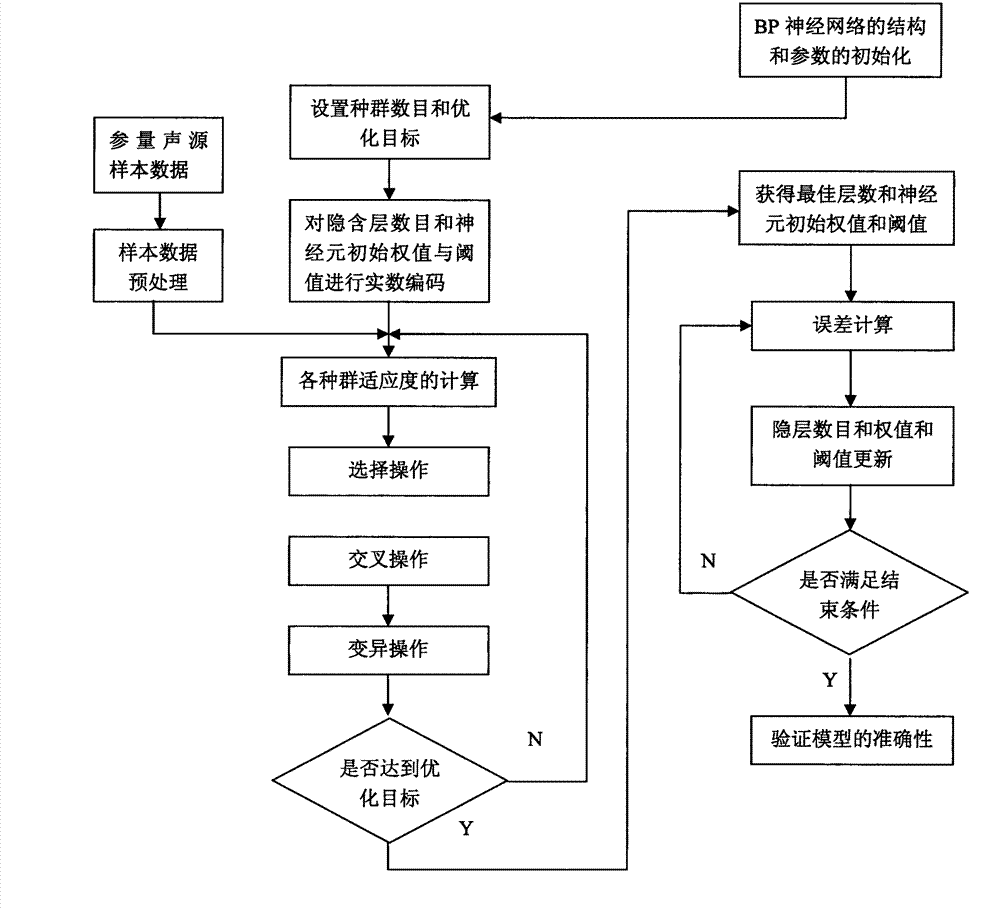
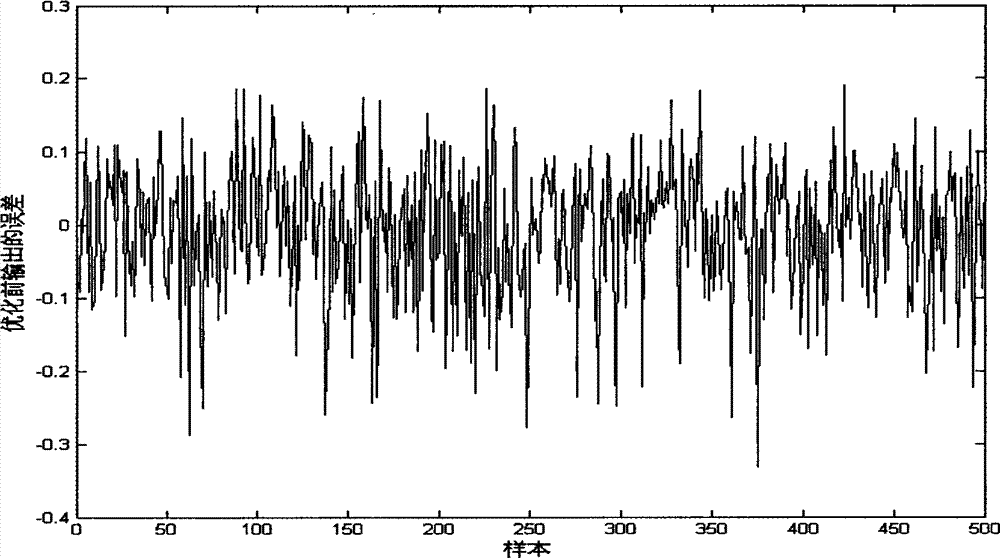
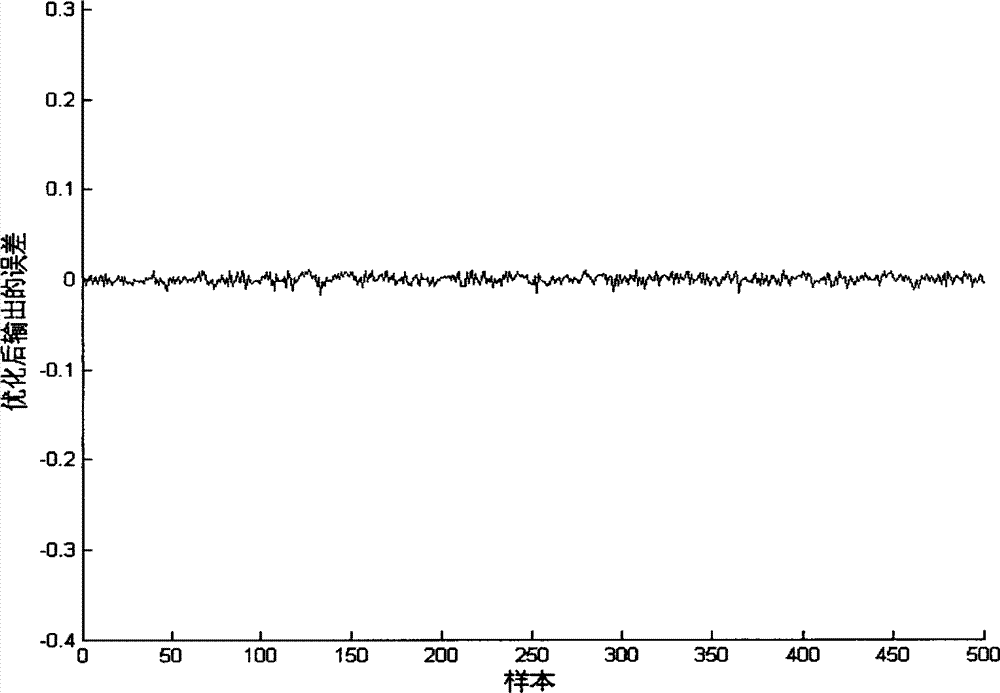
Parameter sound source modeling method based on improved BP (Back Propagation) neural network
ActiveCN103077267ASimplify the build processHigh precisionGenetic modelsBiological neural network modelsNerve networkSound sources
The invention provides a parameter sound source modeling method based on an improved BP (Back Propagation) neural network, in order to solve the problem of difficulty in modeling a parameter sound source system at present. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, collecting sufficient training and testing sample data and preprocessing the data; establishing a neural network model; adopting a genetic algorithm for performing optimizing process on the structure and parameter of the neural network model; searching for an initial weight value and a threshold value between the number of better neural network hidden layers and neural cells; and lastly, training and testing an established parameter sound source model based on the improved BP neural network by using the sample data. The model has the advantages of reliability and higher assessing precision.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
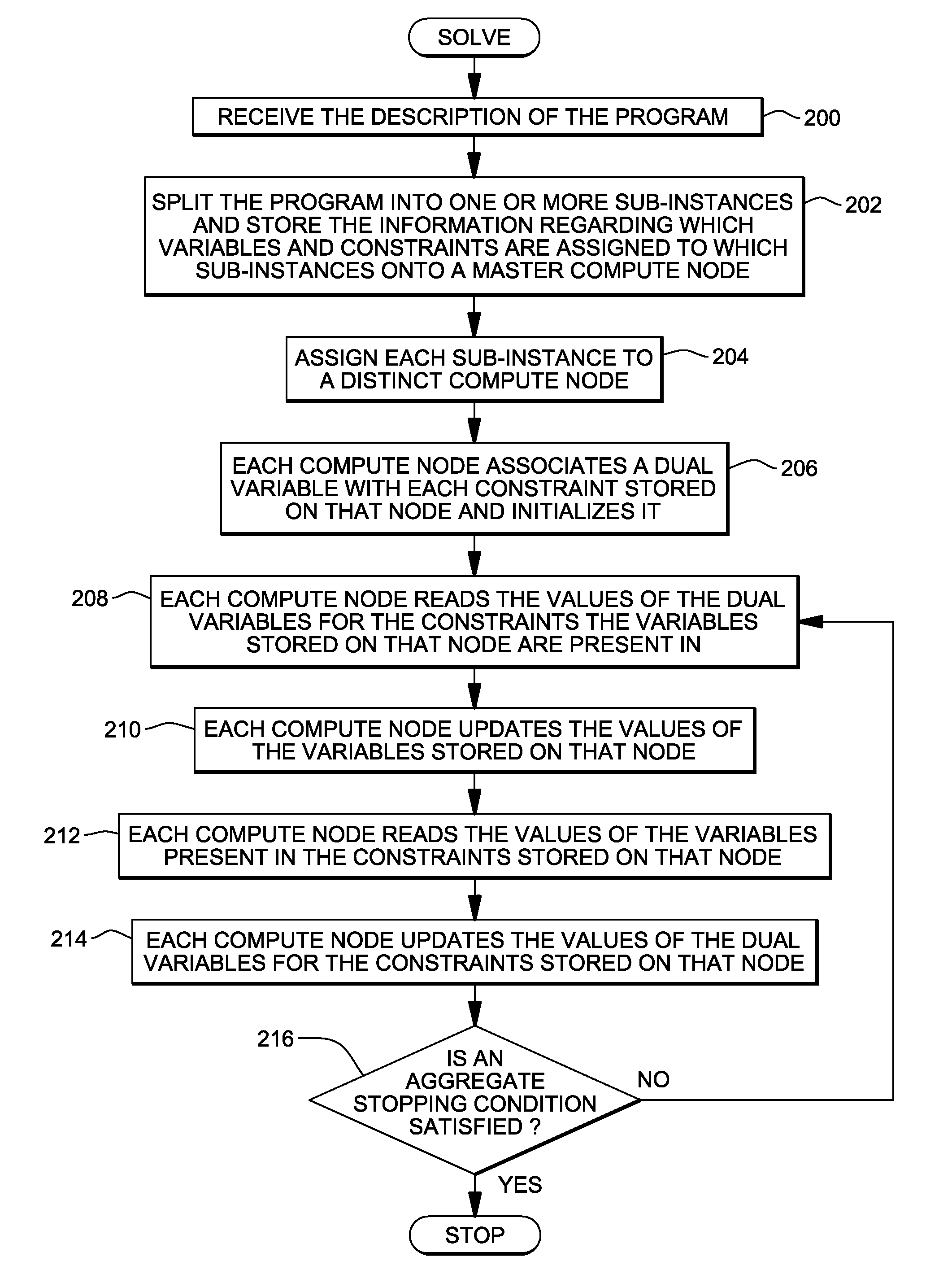
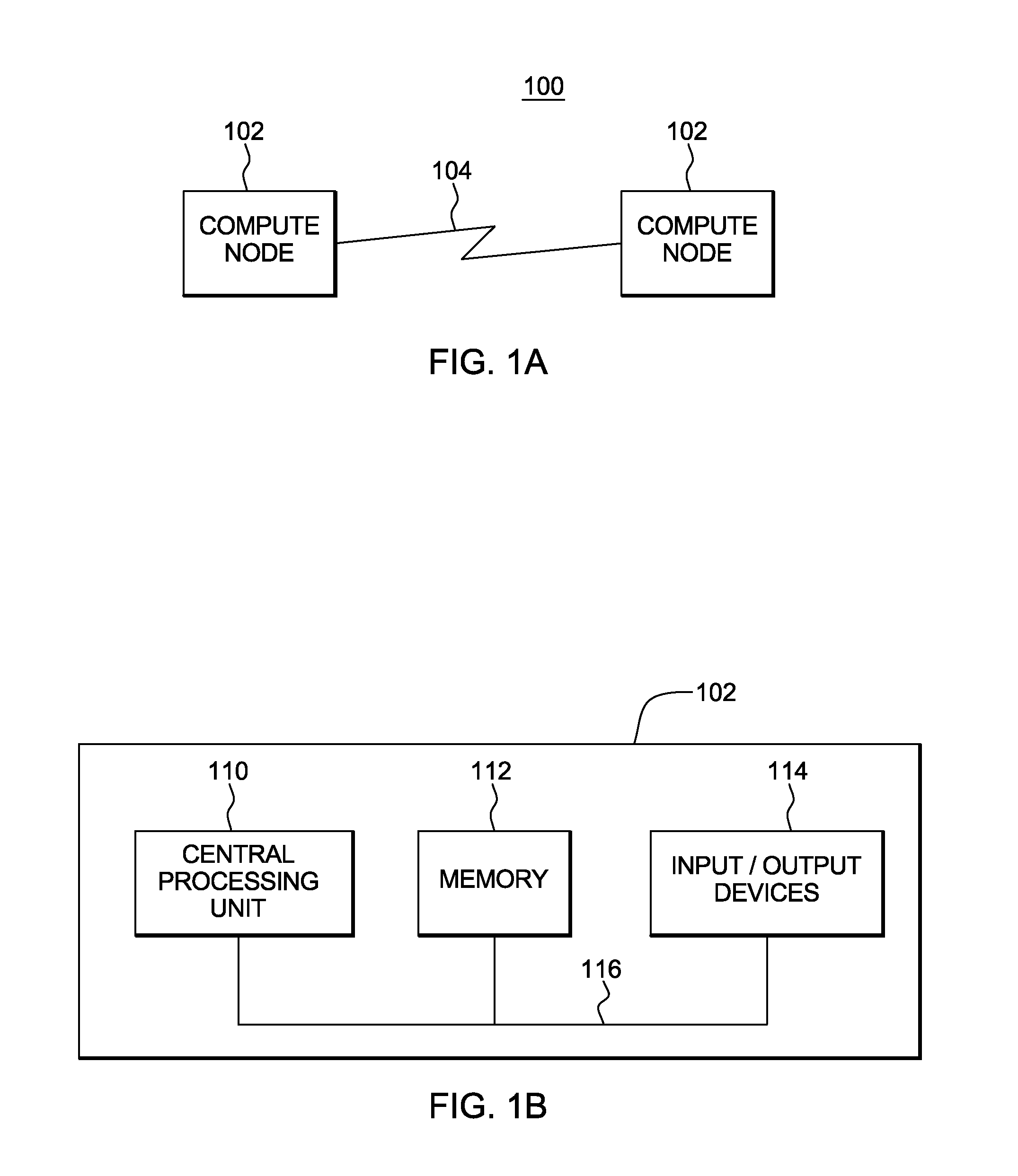
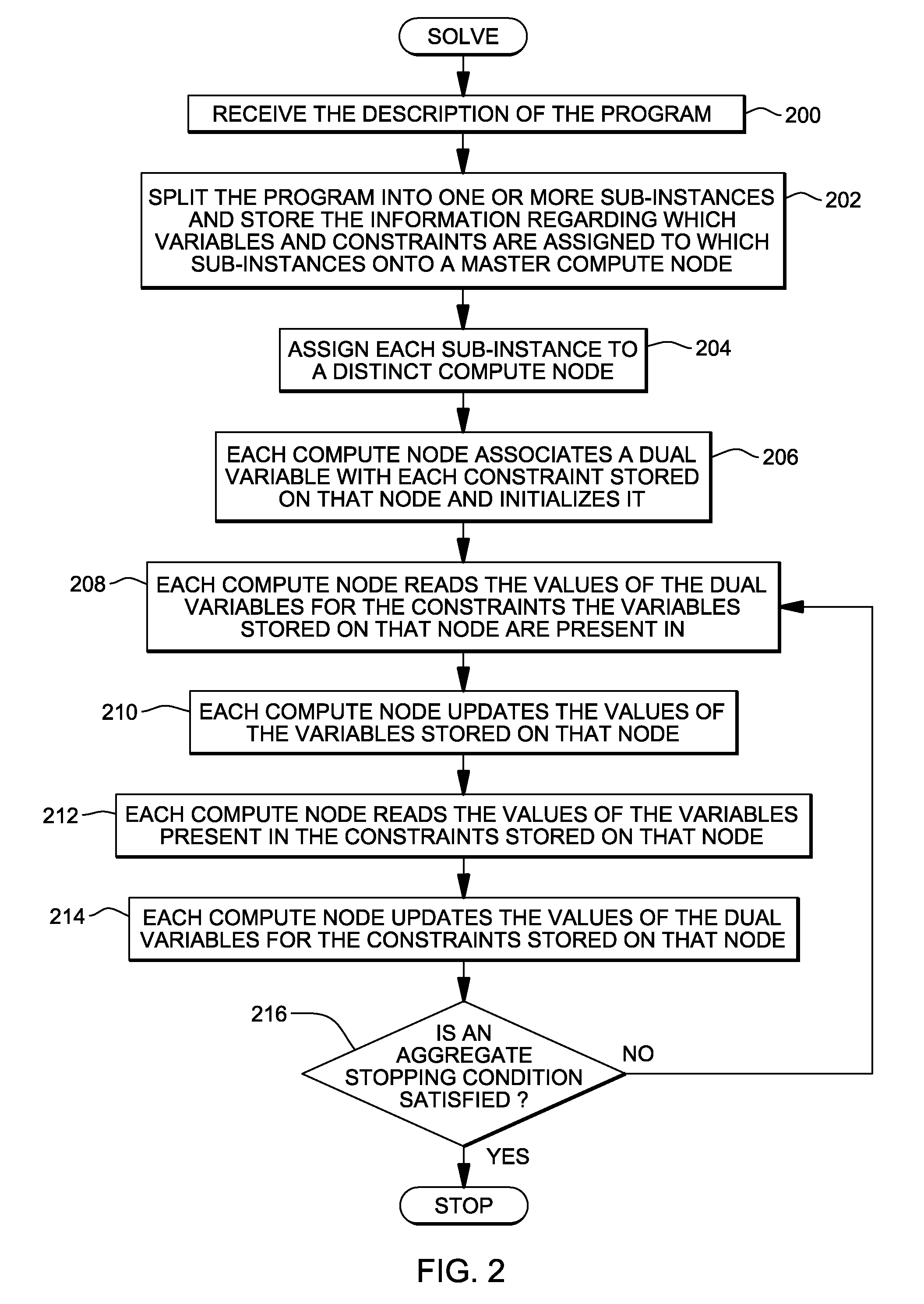
Distributed solutions for large-scale resource assignment tasks
InactiveUS20110258246A1Reduce communication costsOptimize data processingResource allocationDigital computer detailsDistributed Computing EnvironmentResource allocation
Distributed data processing of problems representing resource assignment tasks. The problems are modeled as programs, and the programs are partitioned into sub-instances. Those sub-instances are executed in a distributed computing environment. The partitioning reduces communication costs between sub-instances and convergence time for the optimization program.
Owner:IBM CORP
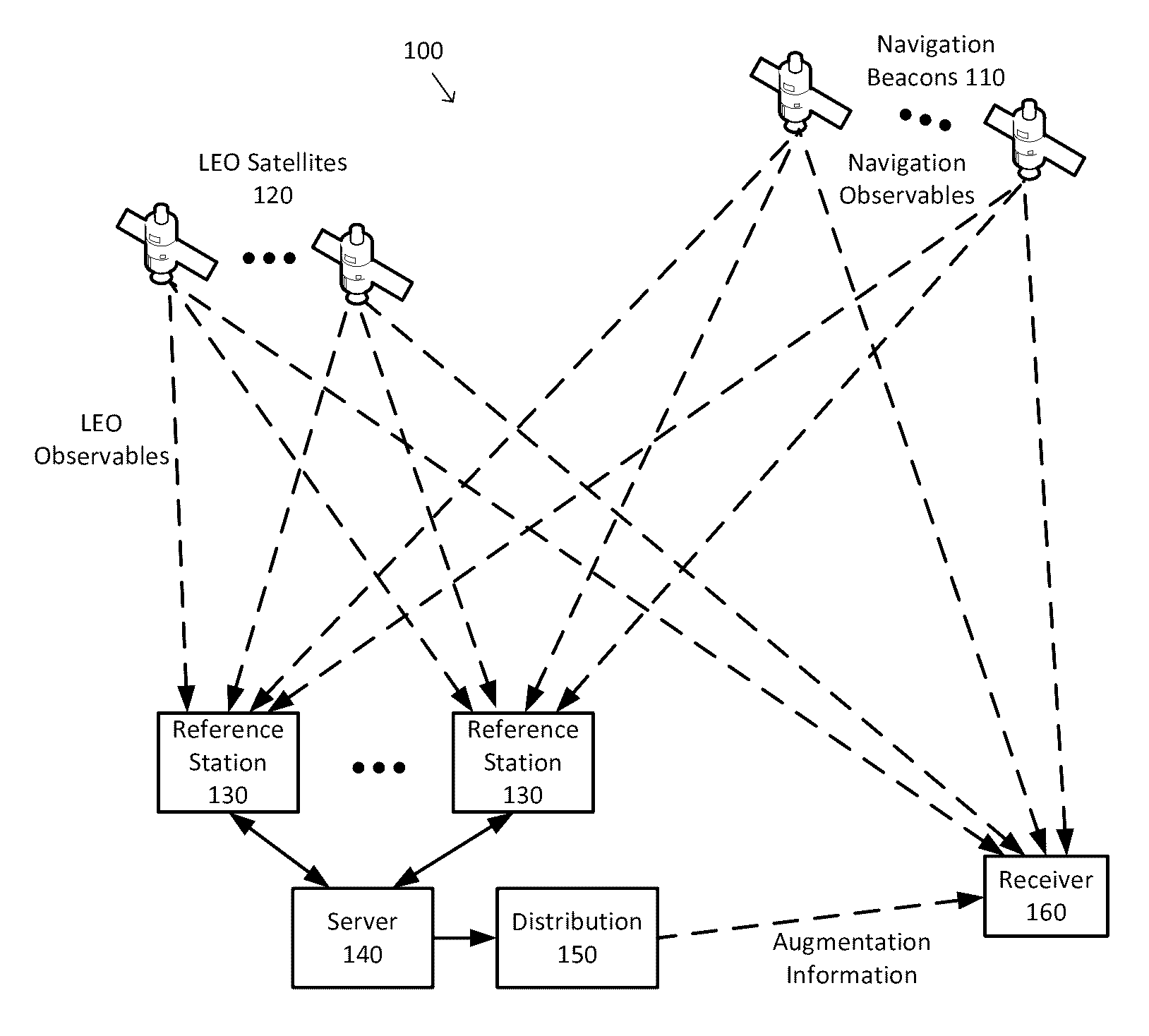
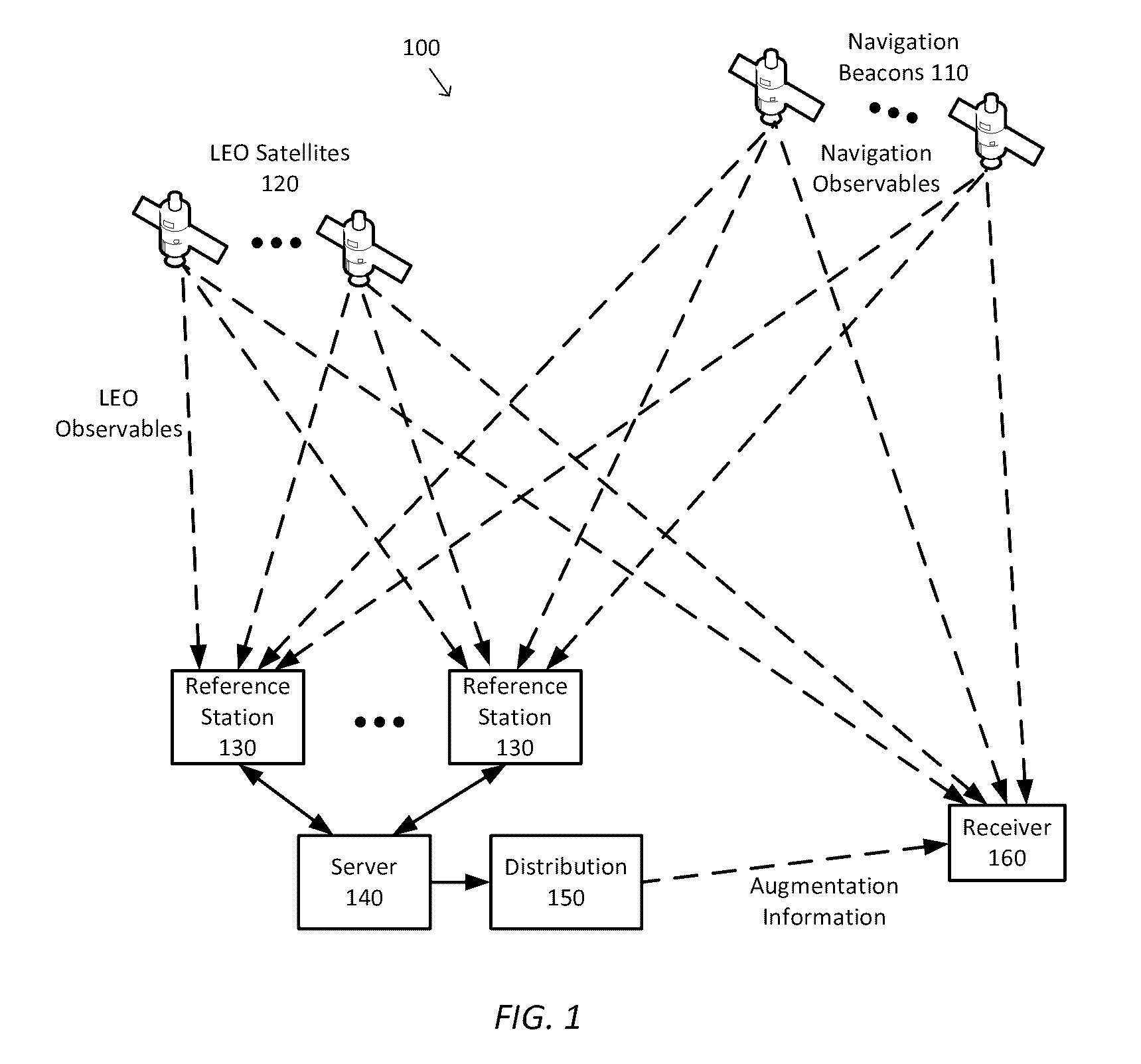
Systems, methods, devices and subassemblies for creating and delivering a GNSS augmentation service
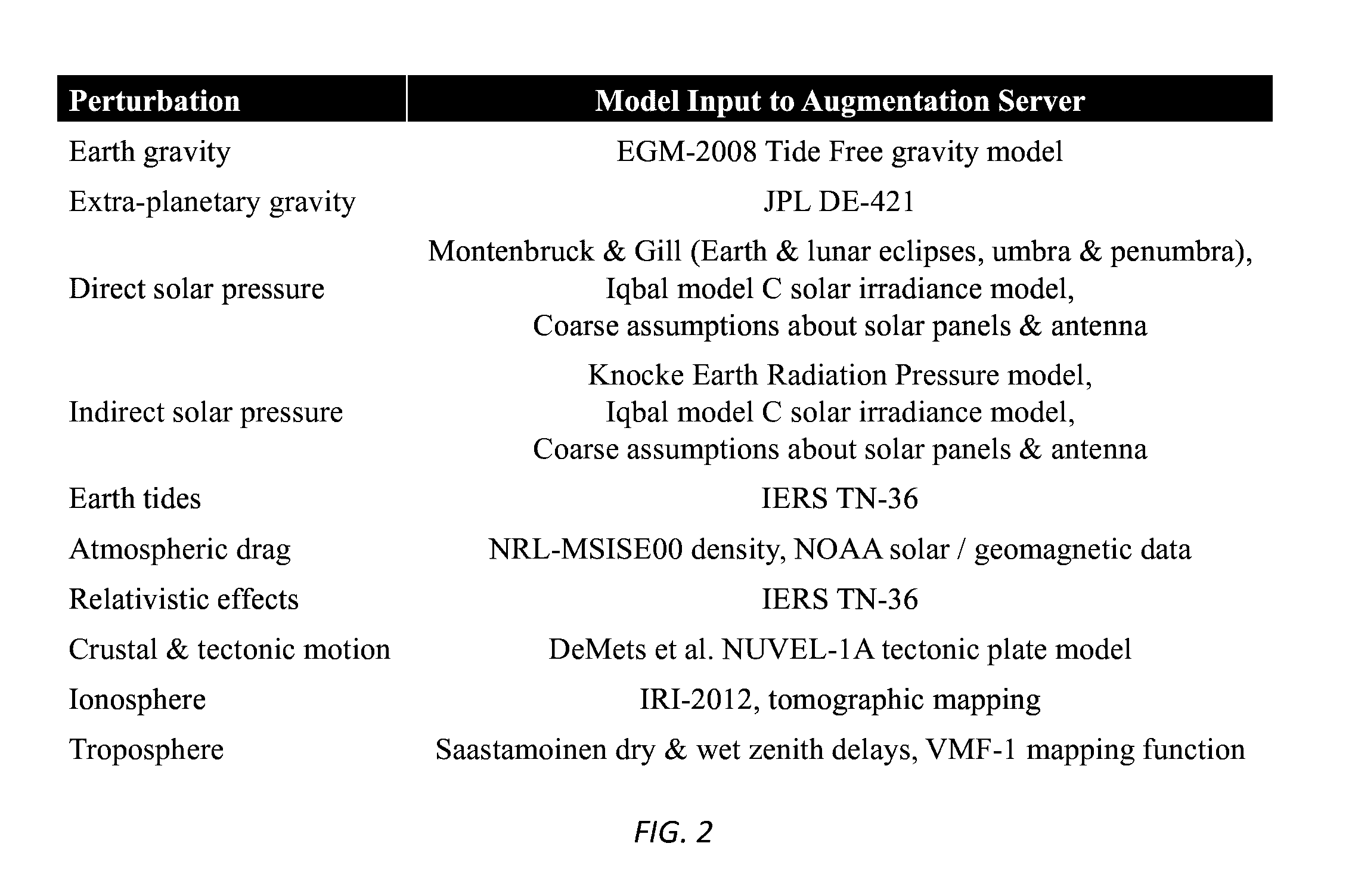
InactiveUS9557422B1Extension of timeShorten convergence timeSatellite radio beaconingGPS enhancementComputational model
Systems, methods, devices and subassemblies for creating and delivering a GNSS augmentation service include one or more reference stations for receiving signals transmitted by navigation beacons and an augmentation server coupled to the reference stations. At least one of the reference stations is able to receive at least one of the signals from a low earth orbit satellite. Each of the reference stations determines first navigation observables based on the received signals and transmit information associated with the first navigation observables to the augmentation server. The augmentation server is configured to determine and distribute augmentation information to a receiver. The augmentation information is based on the received information associated with the first navigation observables, locations of the reference stations, and computational models. The distributed augmentation information is usable by the receiver to determine a high-precision position, velocity, and time solution for the receiver based on second navigation observables associated with the receiver.
Owner:APPLE INC
A method to reduce training time of an acoustic echo canceller in a full-duplex beamforming-based audio conferencing system
ActiveUS20060250998A1Reducing total acoustic echo cancellation convergence timeShorten convergence timeTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsLoudspeakerBackground process
A method is set forth for reducing the total acoustic echo cancellation convergence time for all look directions in a microphone array based full-duplex system. The method is based on capturing the loudspeaker signal due to the first far-end speech bursts when the conferencing system is first used, as well as the corresponding loudspeaker feedback signals in the individual microphones. The captured signals are then used for consecutive adaptation of the acoustic echo canceller on all echo paths corresponding to all look directions of the beamformer, thereby training the AEC. This training process can be executed concurrently with normal phone operation, for example, as a background process that utilizes available processing cycles.
Owner:MITEL
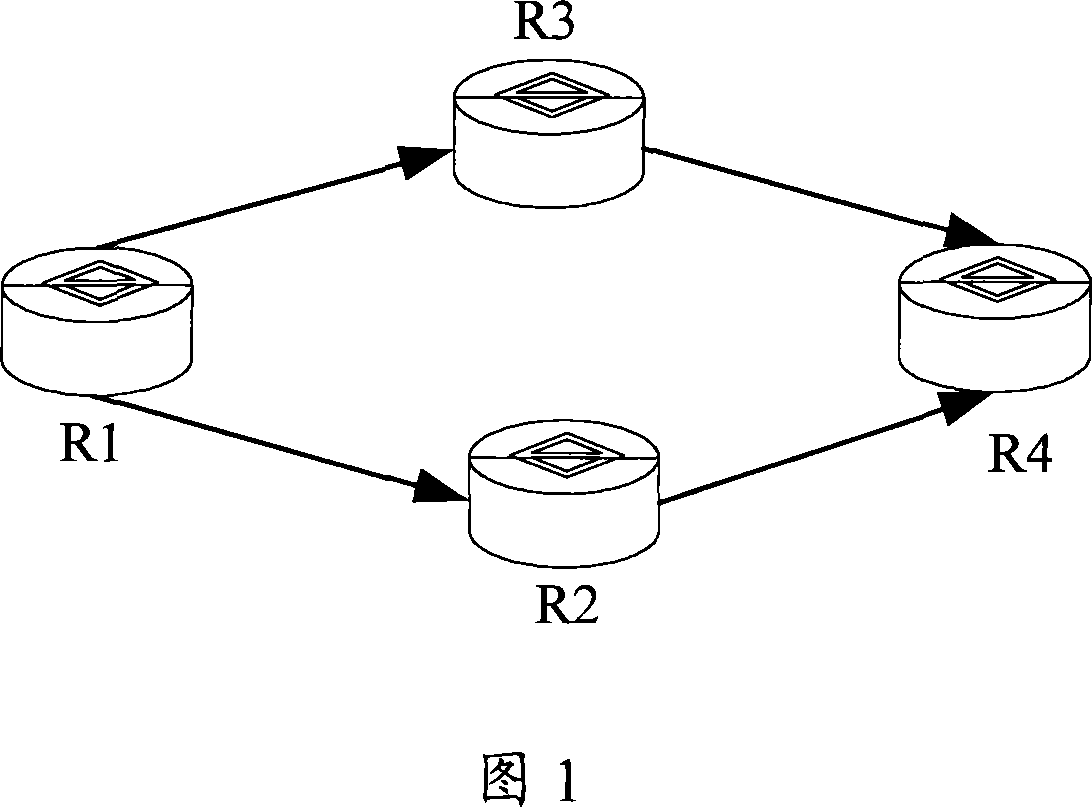
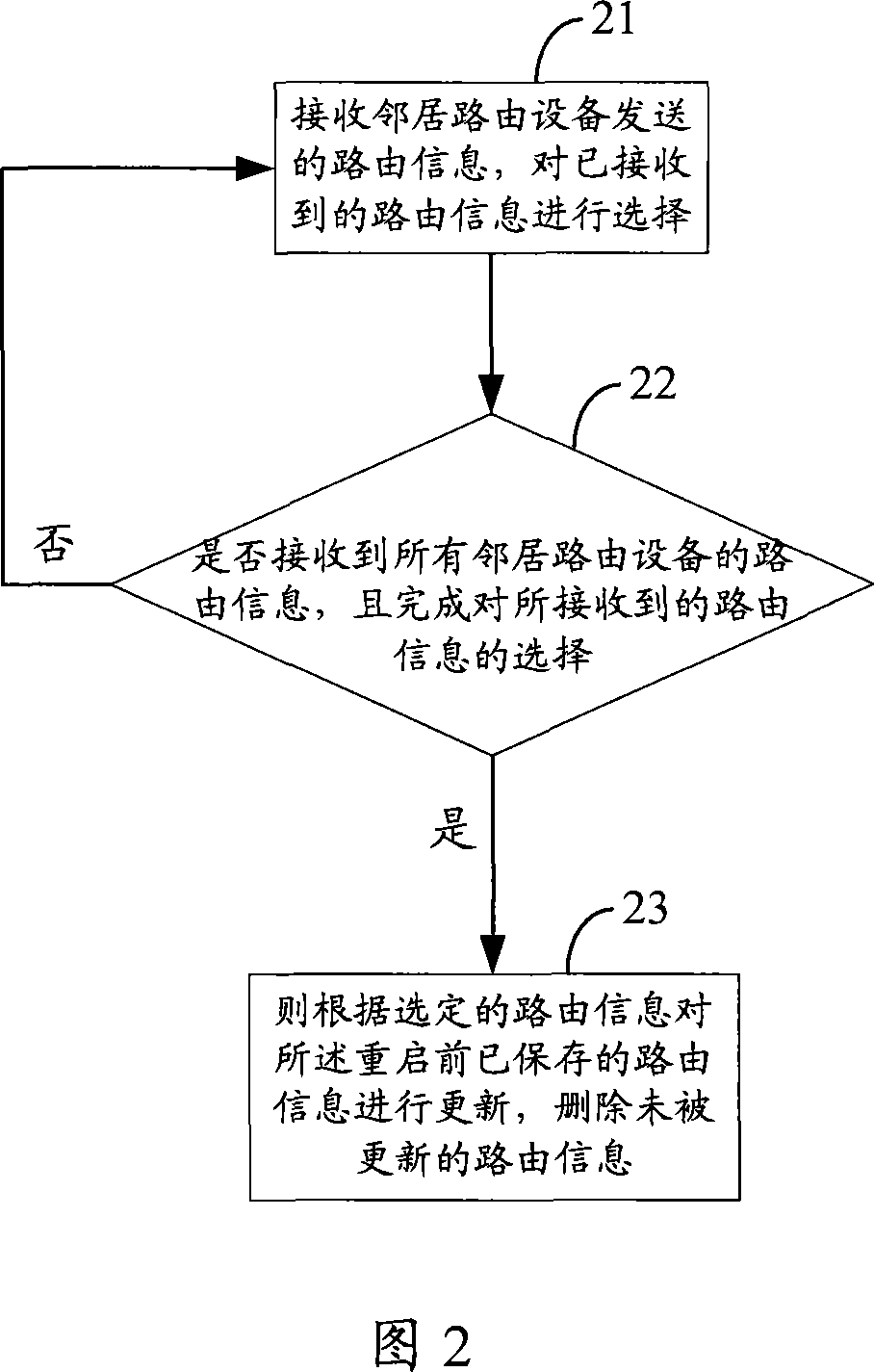
A route convergence method and routing device
ActiveCN101056270AAvoid oscillationShorten convergence timeNetwork connectionsInformation repositoryTime effect
The invention provides a method for route convergence and routing device. The described method includes: receive the route information of multiple adjacent routing devices, select the route from the received route message, and save the route selection results into the first route information library; identify that all route messages of multiple adjacent routing devices are received and the route selection is completed; update the second route information library according to the information of the first route information library and the second route information library is sued to guide the forwarding of the data packets. The implementation of the invention reduces the convergence time of the route and improves the convergence speed of the route. Especially when the route volume is higher, it will spend much time in selecting the route, so the implementation of the invention will reduce the convergence time effect of this route more effectively.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com