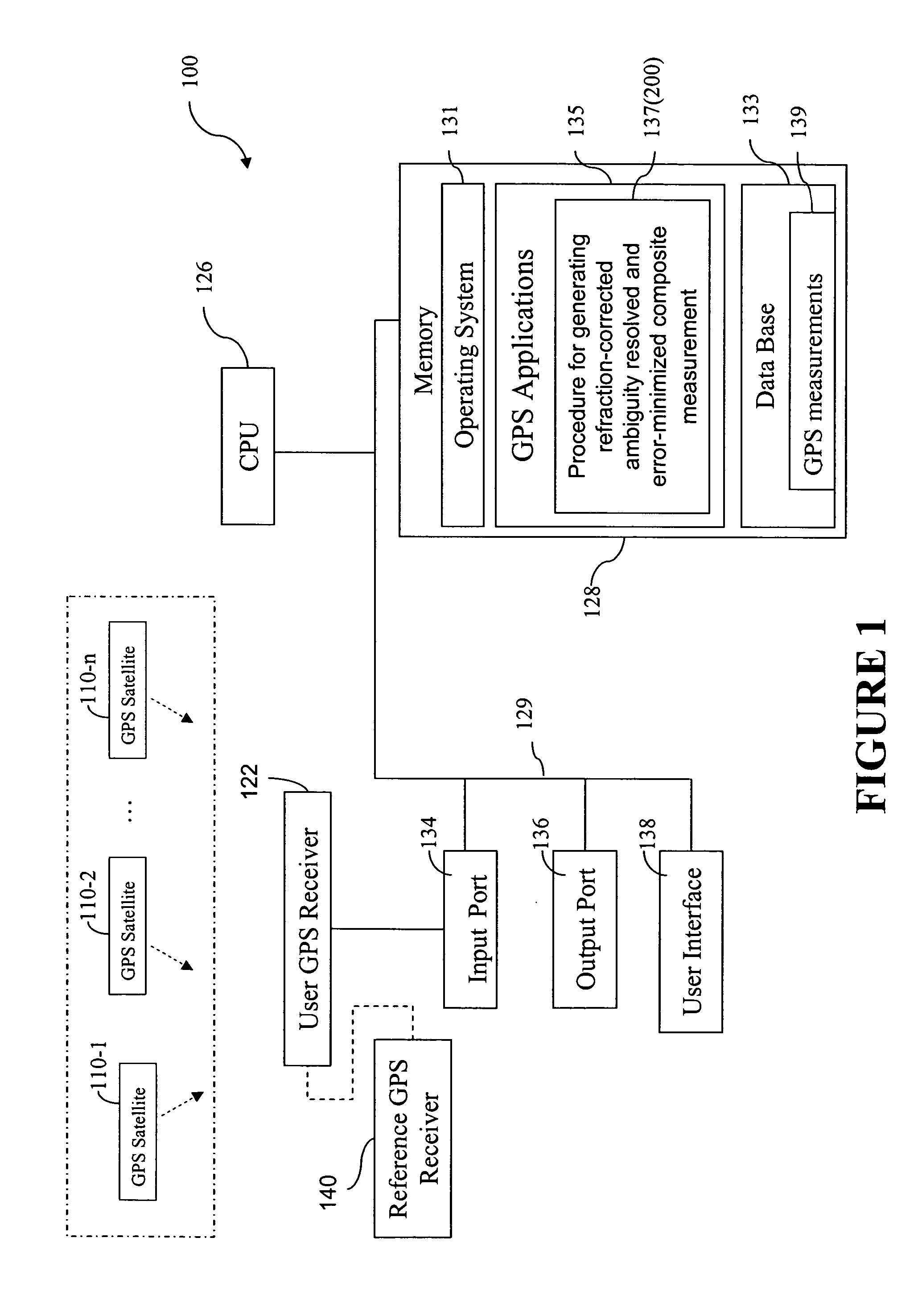
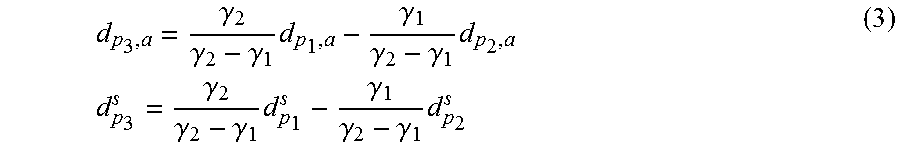Patents
Literature
269 results about "Integer ambiguity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
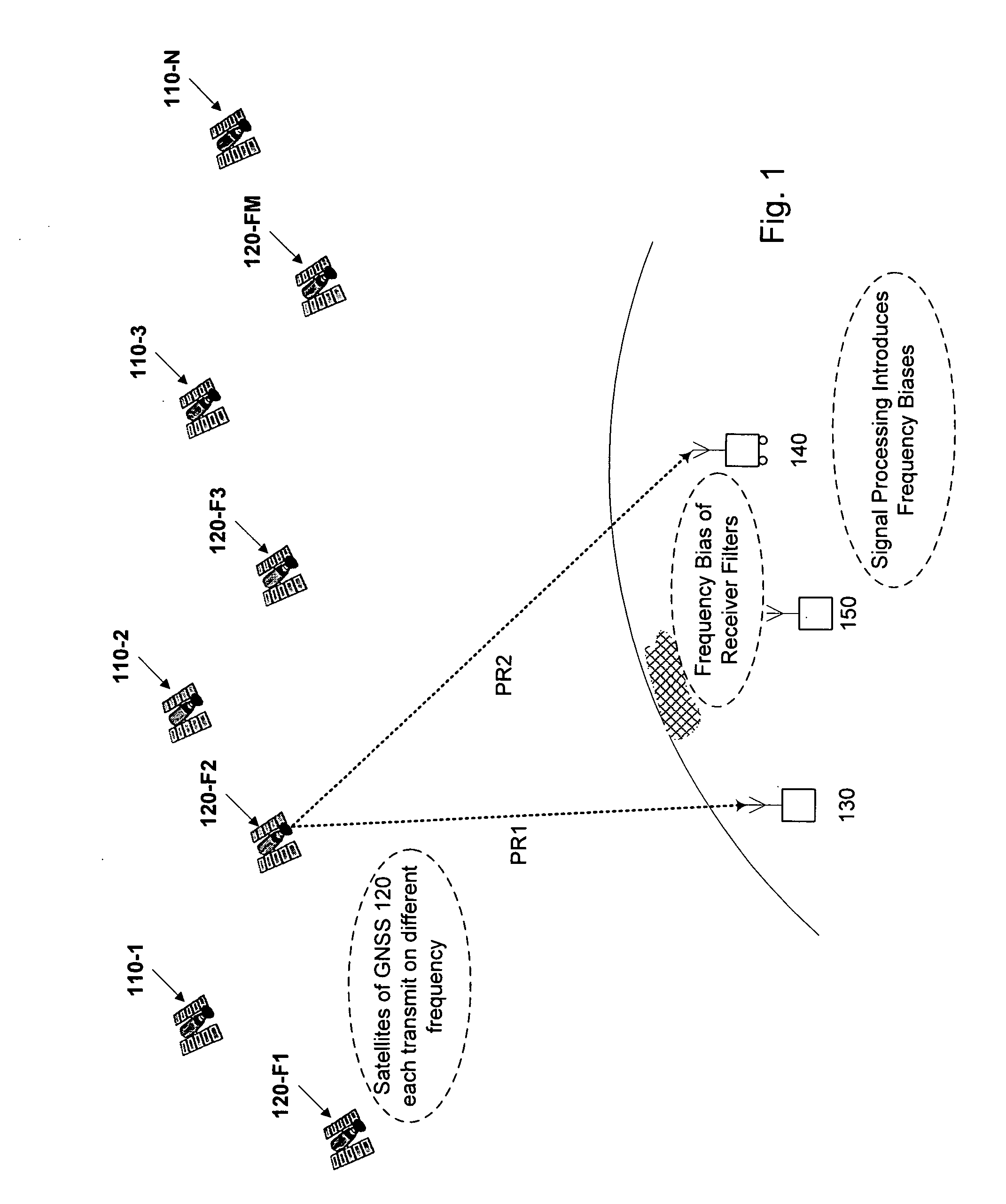
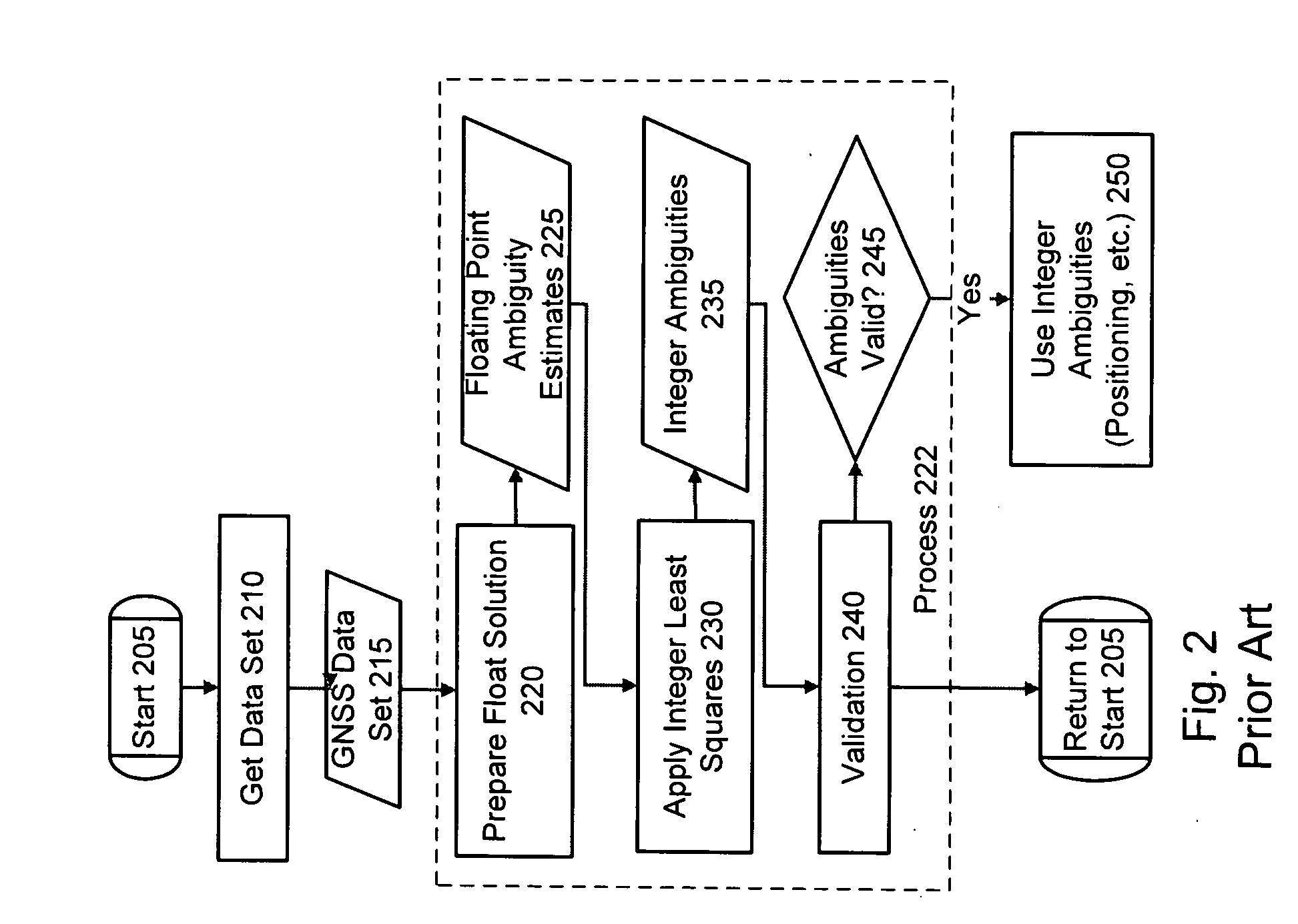
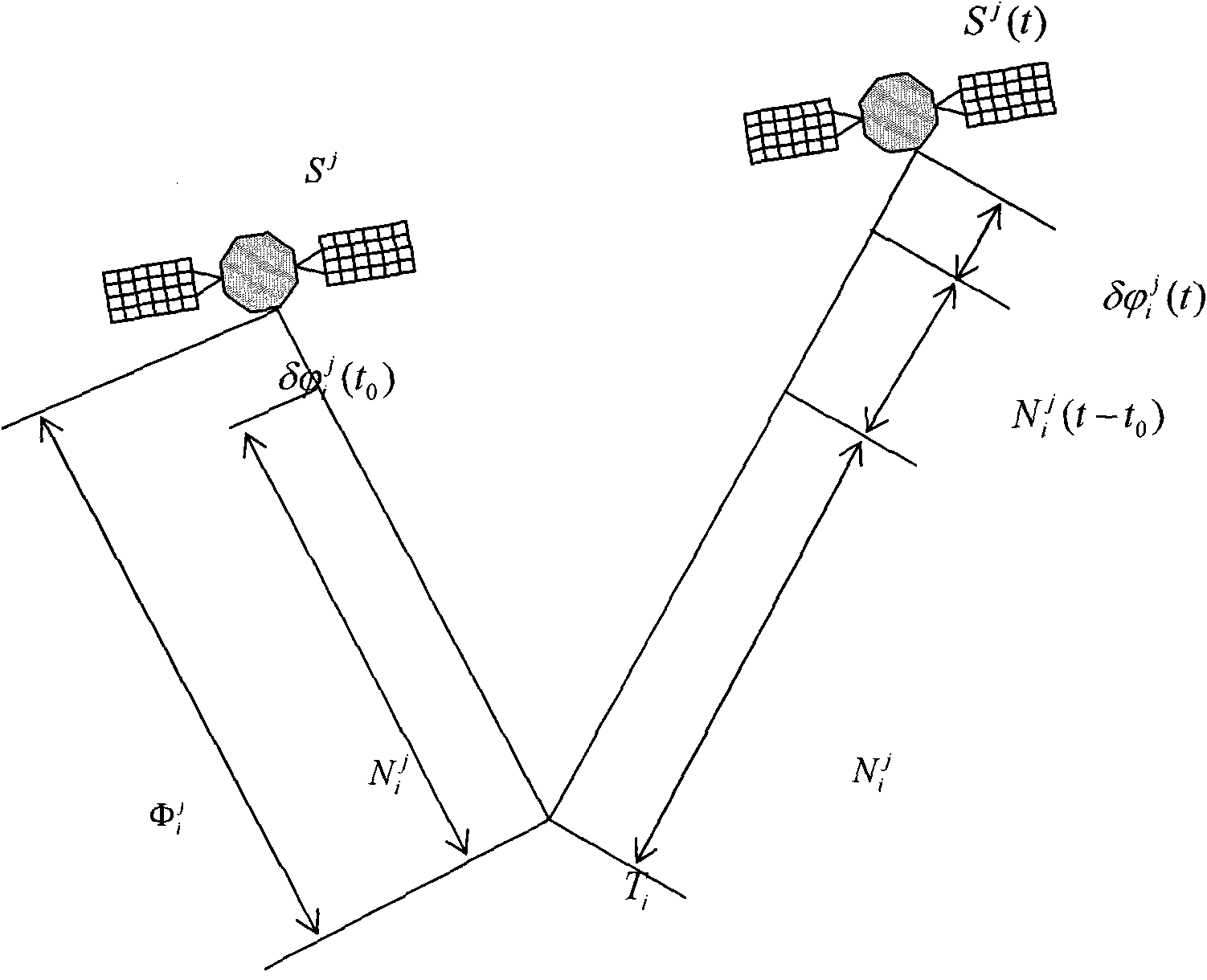
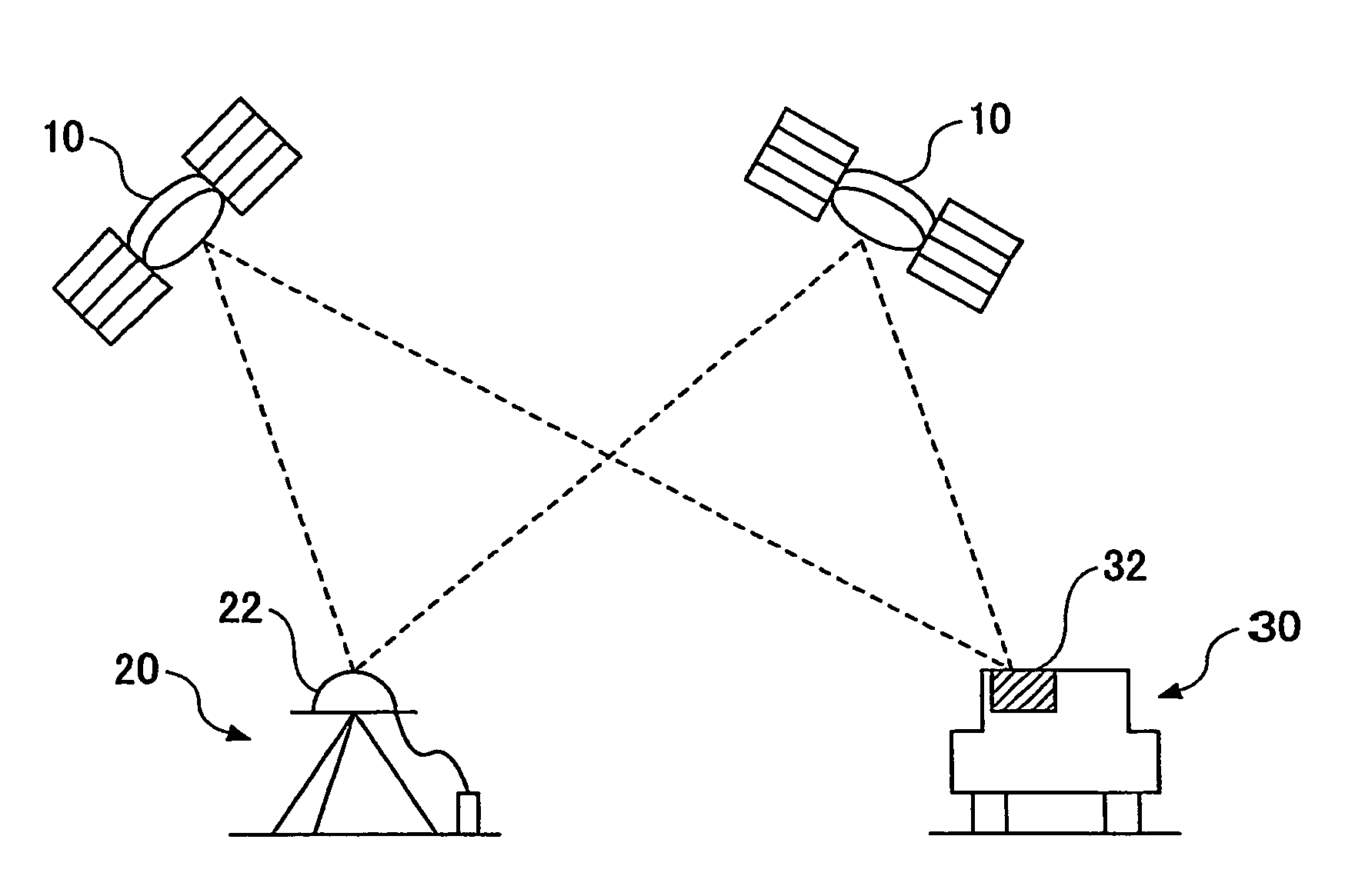
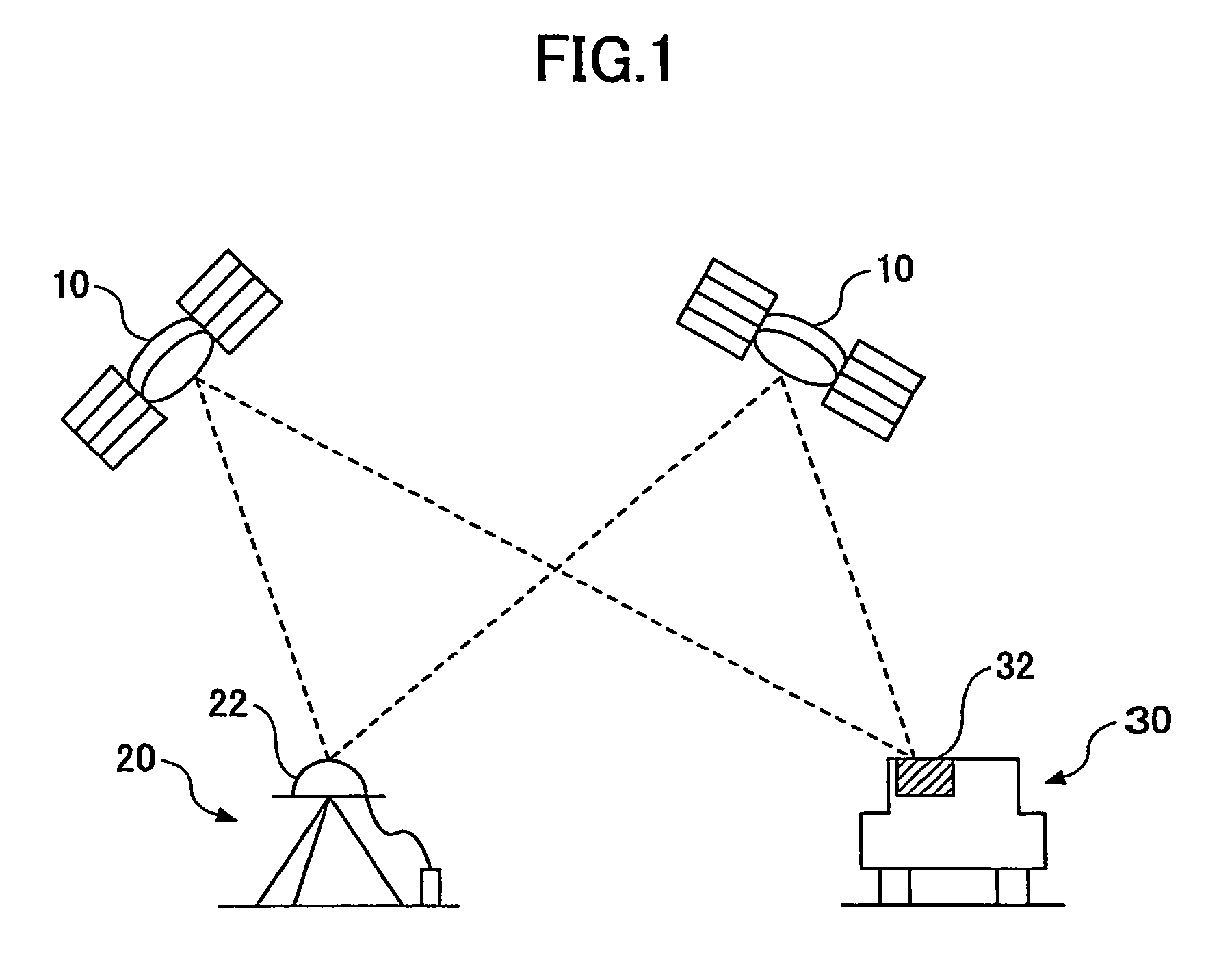
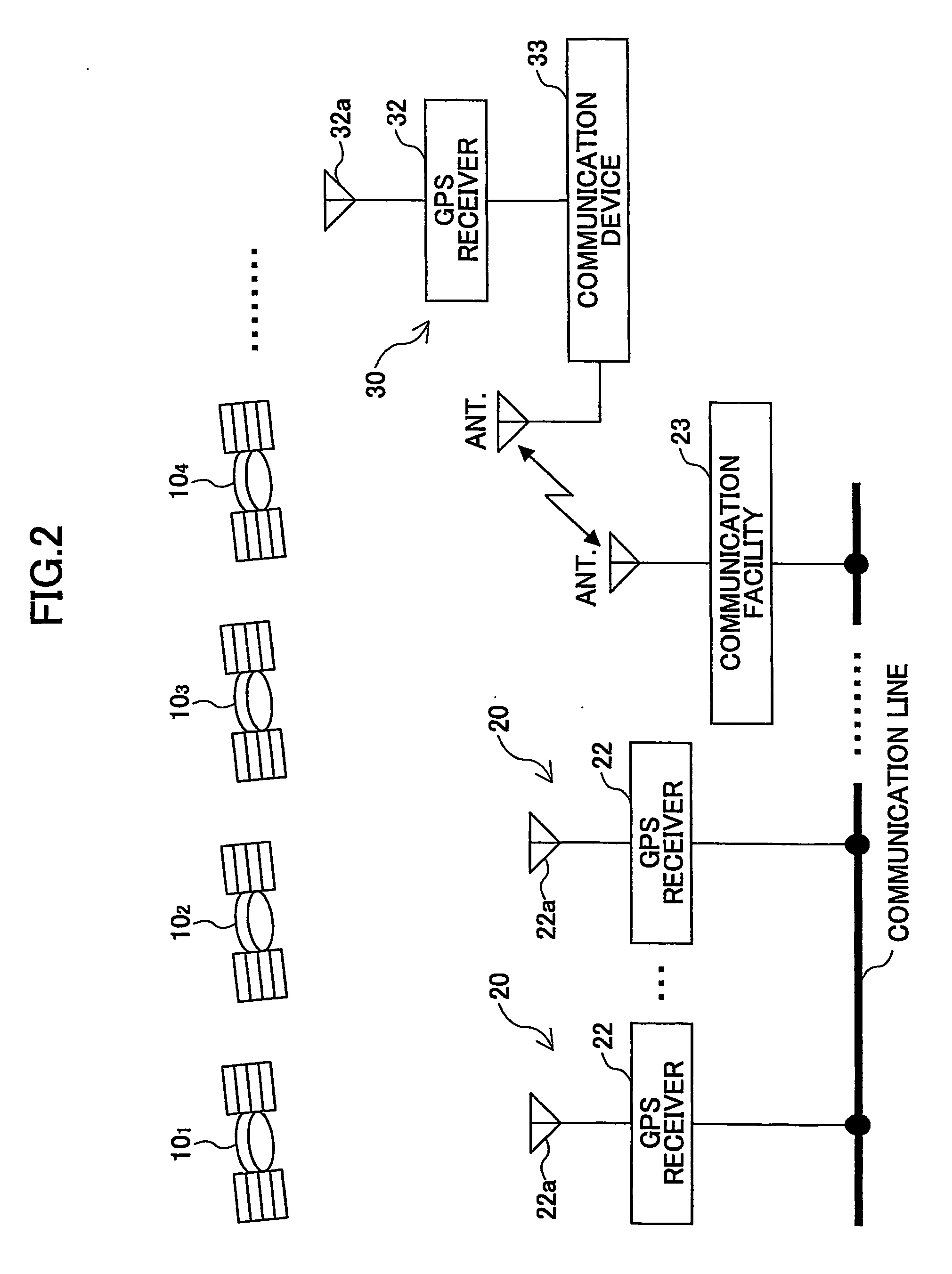
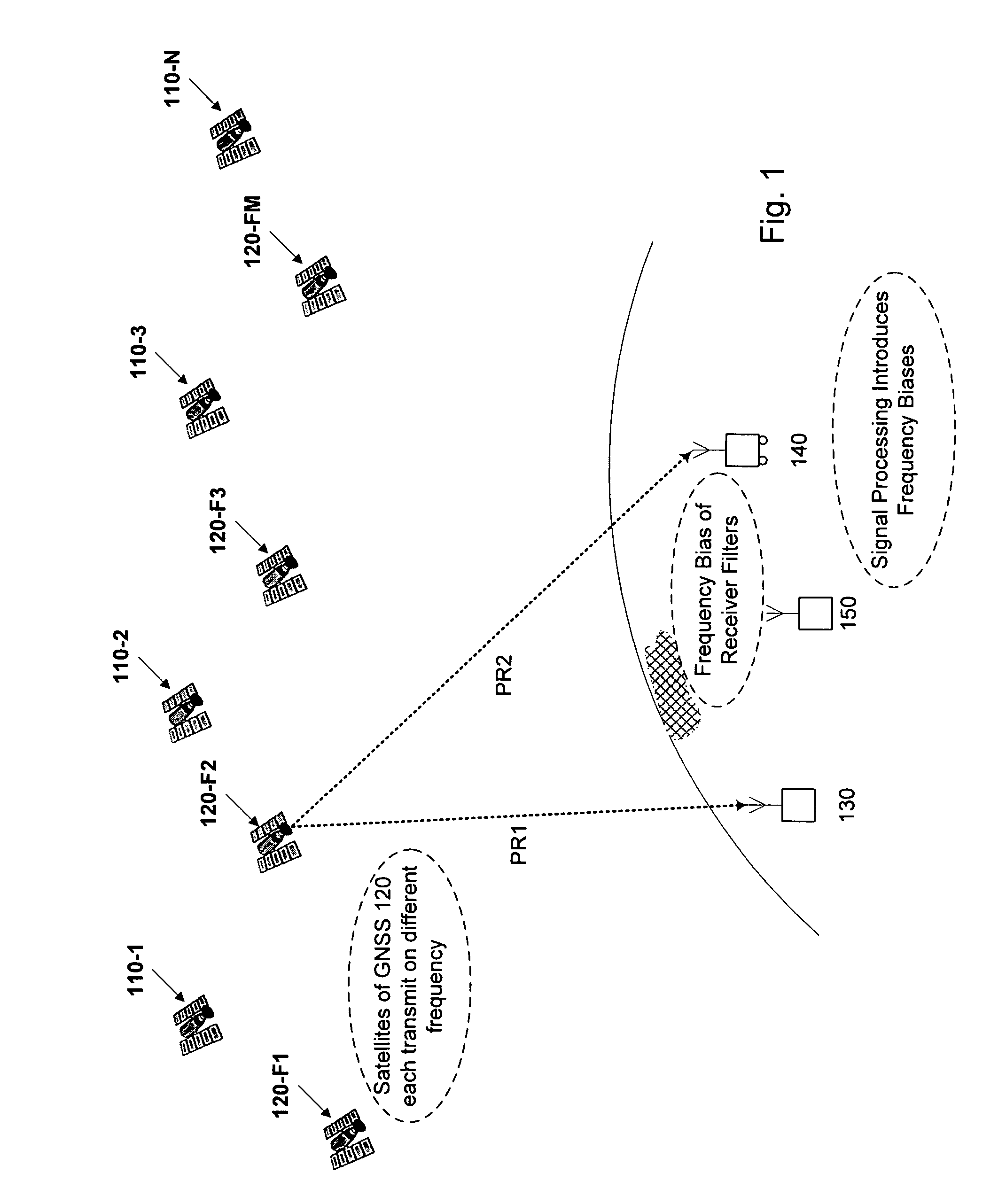
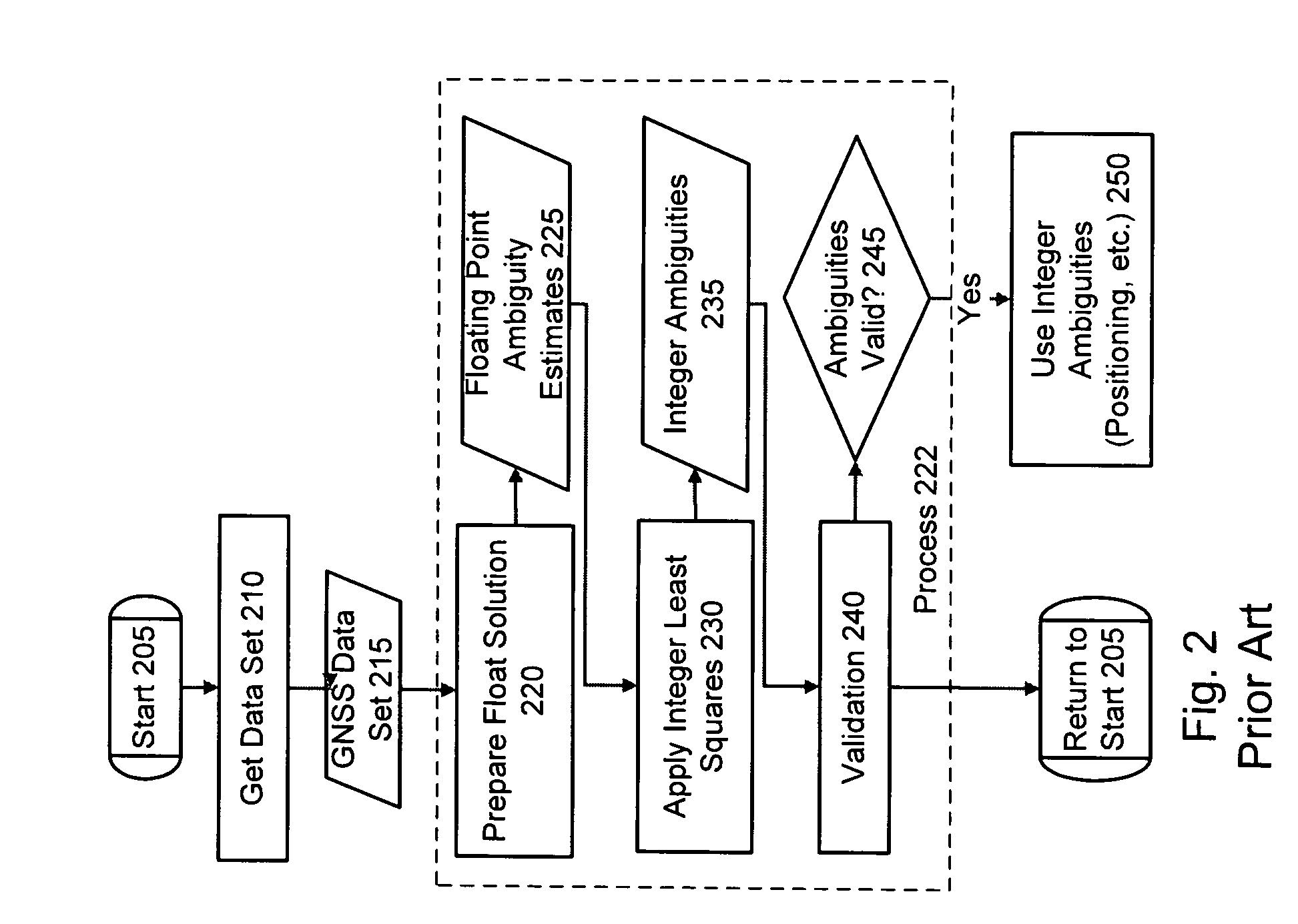
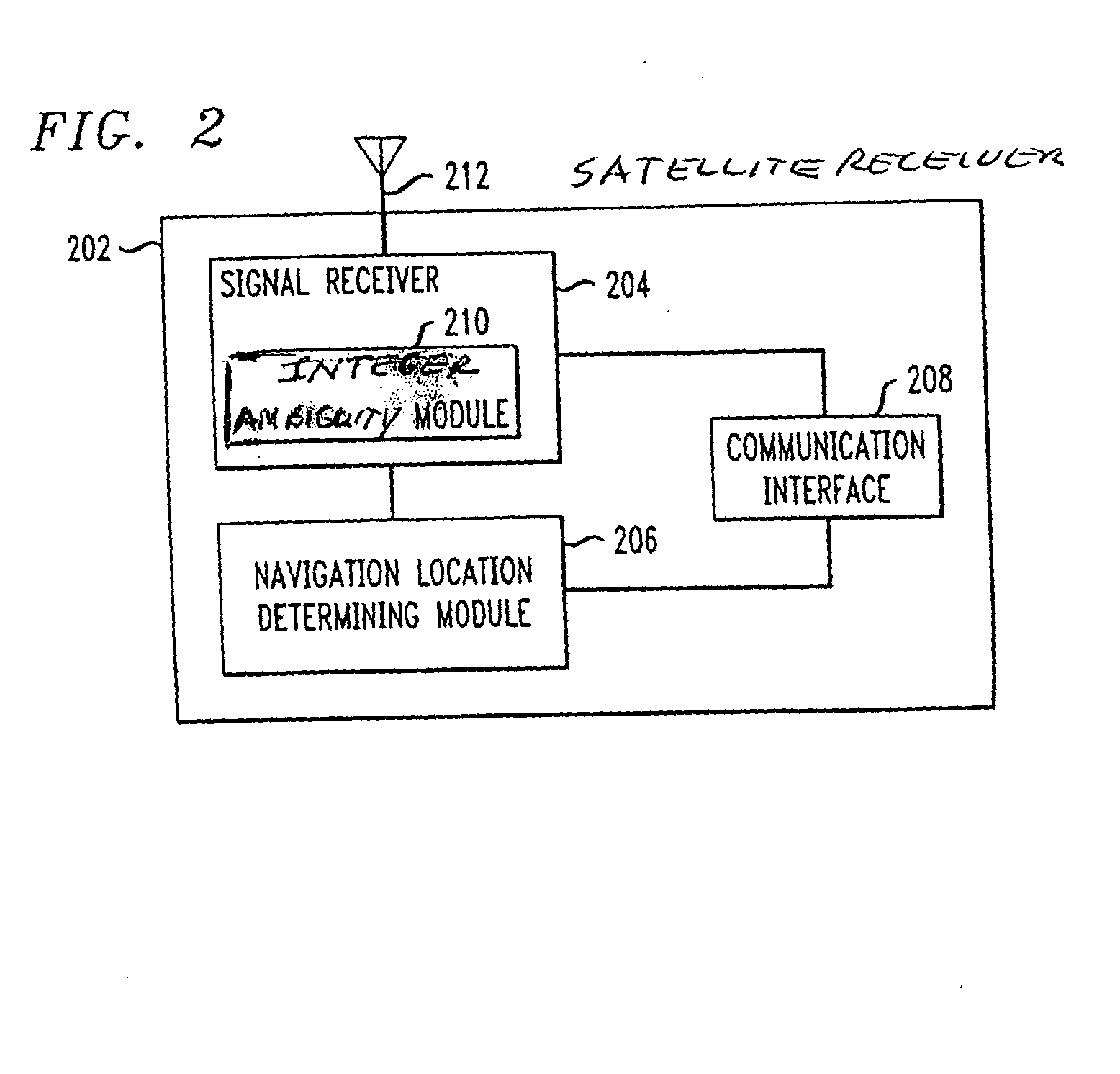
The Integer Ambiguity. The solution of the integer ambiguity, the number of whole cycles on the path from satellite to receiver, would be more difficult if it was not preceded by pseudoranges, or code phase measurements in most receivers. This allows the centering of the subsequent double-difference solution.
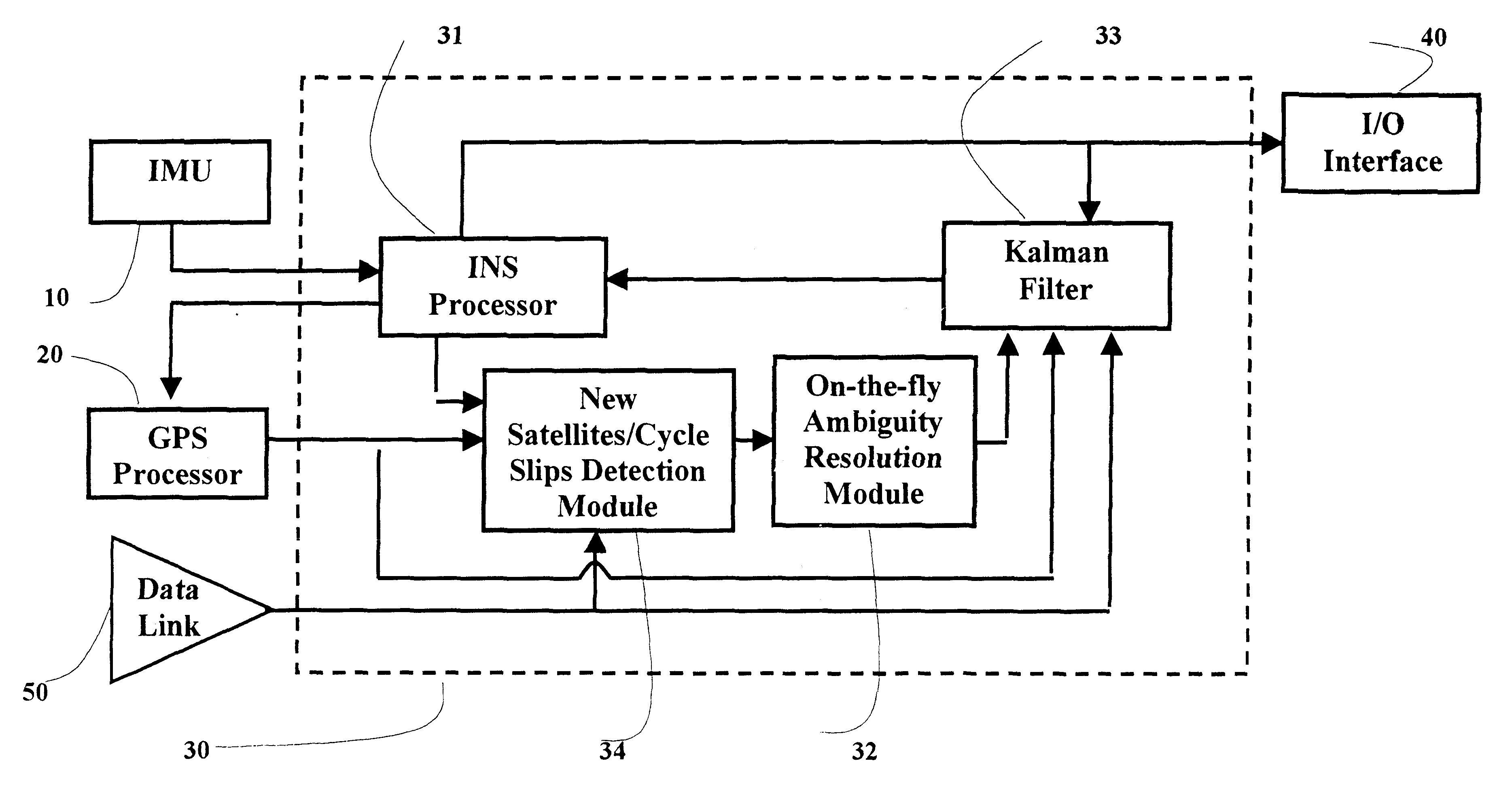
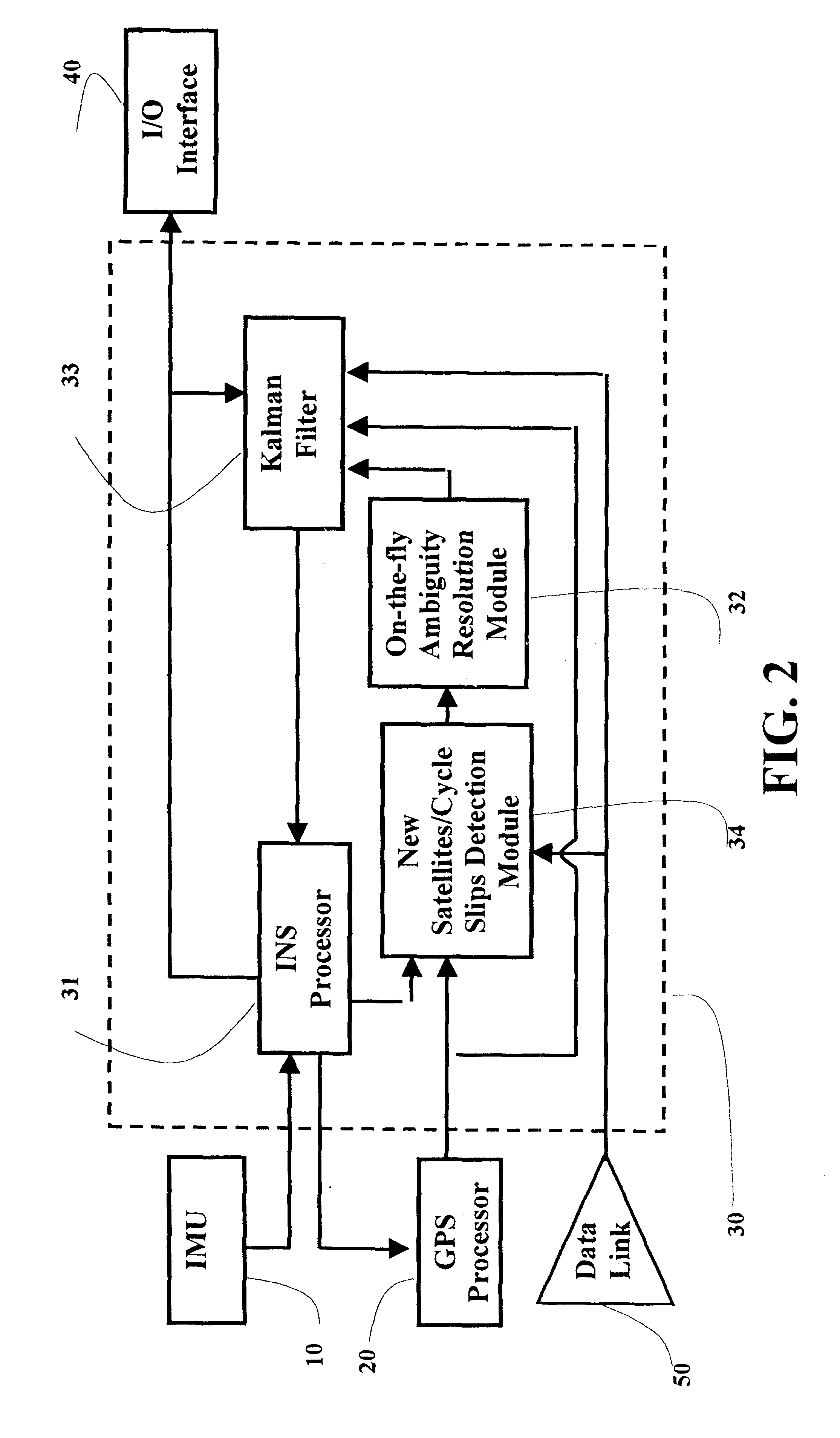
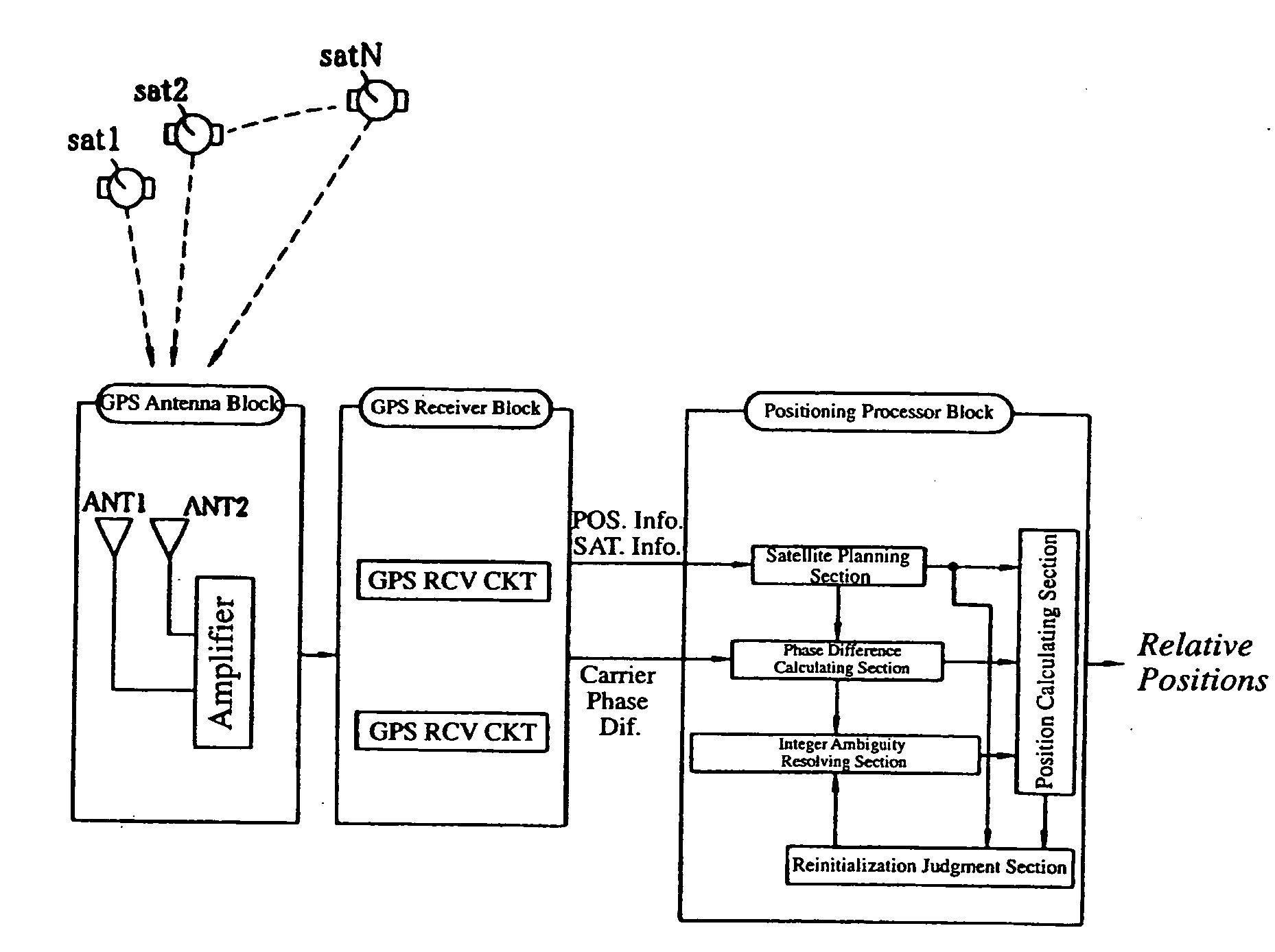
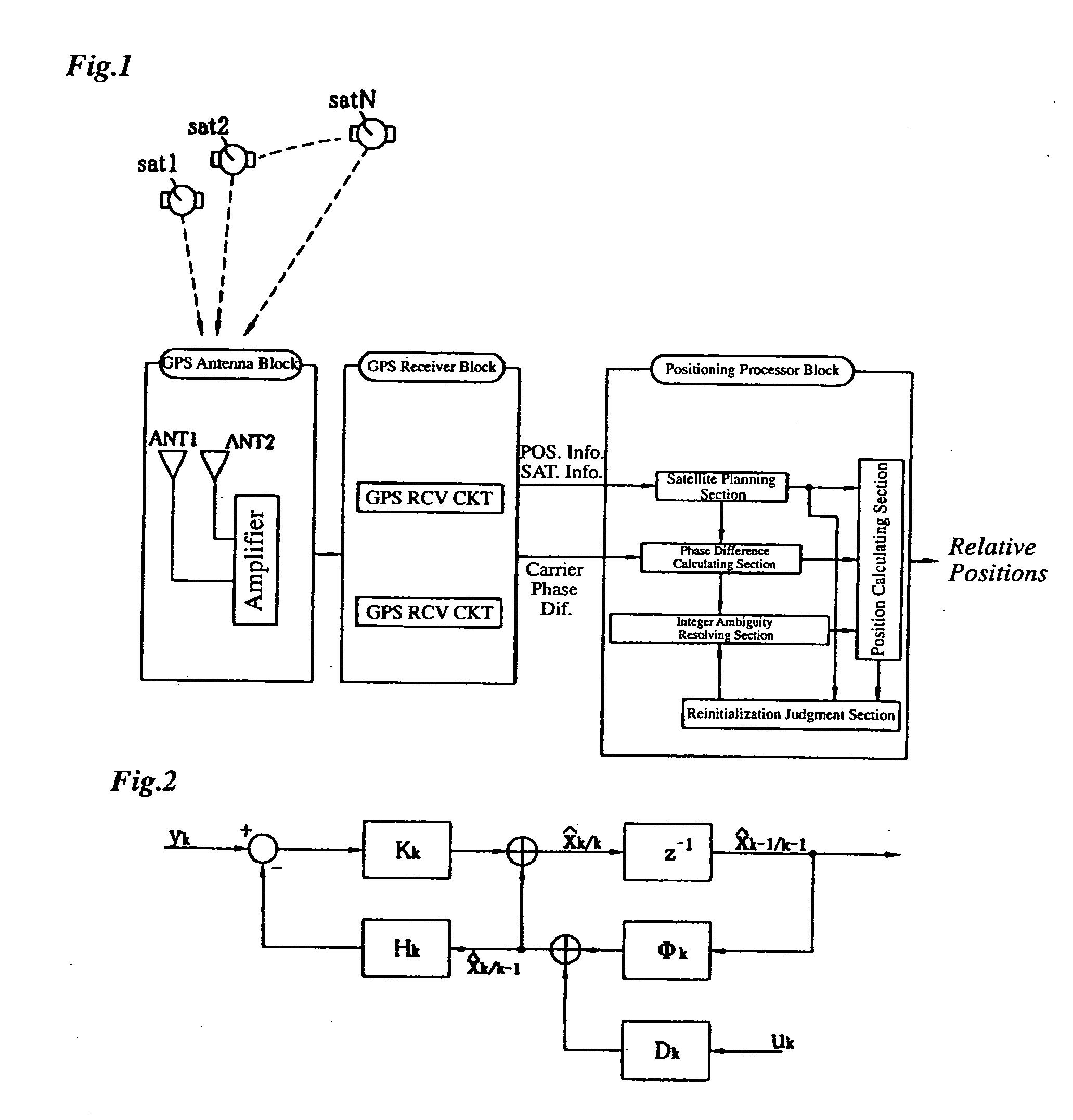
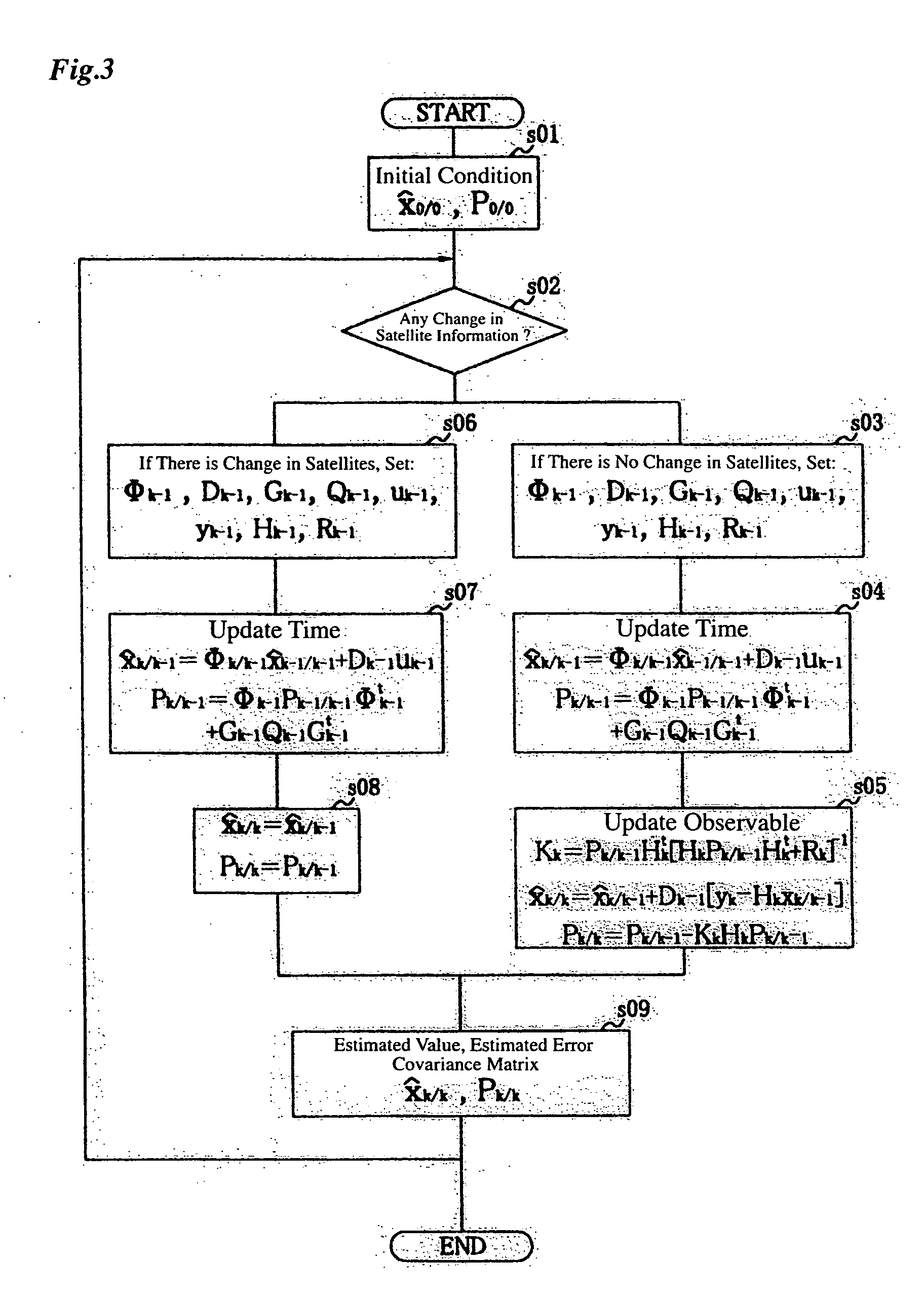
Real-time integrated vehicle positioning method and system with differential GPS
InactiveUS6496778B1Improve performanceLow costPosition fixationNavigation instrumentsDouble differenceFully coupled
A real-time integrated vehicle positioning method and system with differential GPS can substantially solve the problems encountered in either the global positioning system-only or the inertial navigation system-only, such as loss of global positioning satellite signal, sensitivity to jamming and spoofing, and an inertial solution's drift over time. In the present invention, the velocity and acceleration from an inertial navigation processor of the integrated GPS / INS system are used to aid the code and carrier phase tracking of the global positioning system satellite signals, so as to enhance the performance of the global positioning and inertial integration system, even in heavy jamming and high dynamic environments. To improve the accuracy of the integrated GPS / INS navigation system, phase measurements are used and the idea of the differential GPS is employed. However, integer ambiguities have to be resolved for high accuracy positioning. Therefore, in the present invention a new on-the-fly ambiguity resolution technique is disclosed to resolve double difference integer ambiguities. The real-time fully-coupled GPS / IMU vehicle positioning system includes an IMU (inertial measurement unit), a GPS processor, and a data link which are connected to a central navigation processor to produce a navigation solution that is output to an I / O (input / output) interface.
Owner:AMERICAN GNC
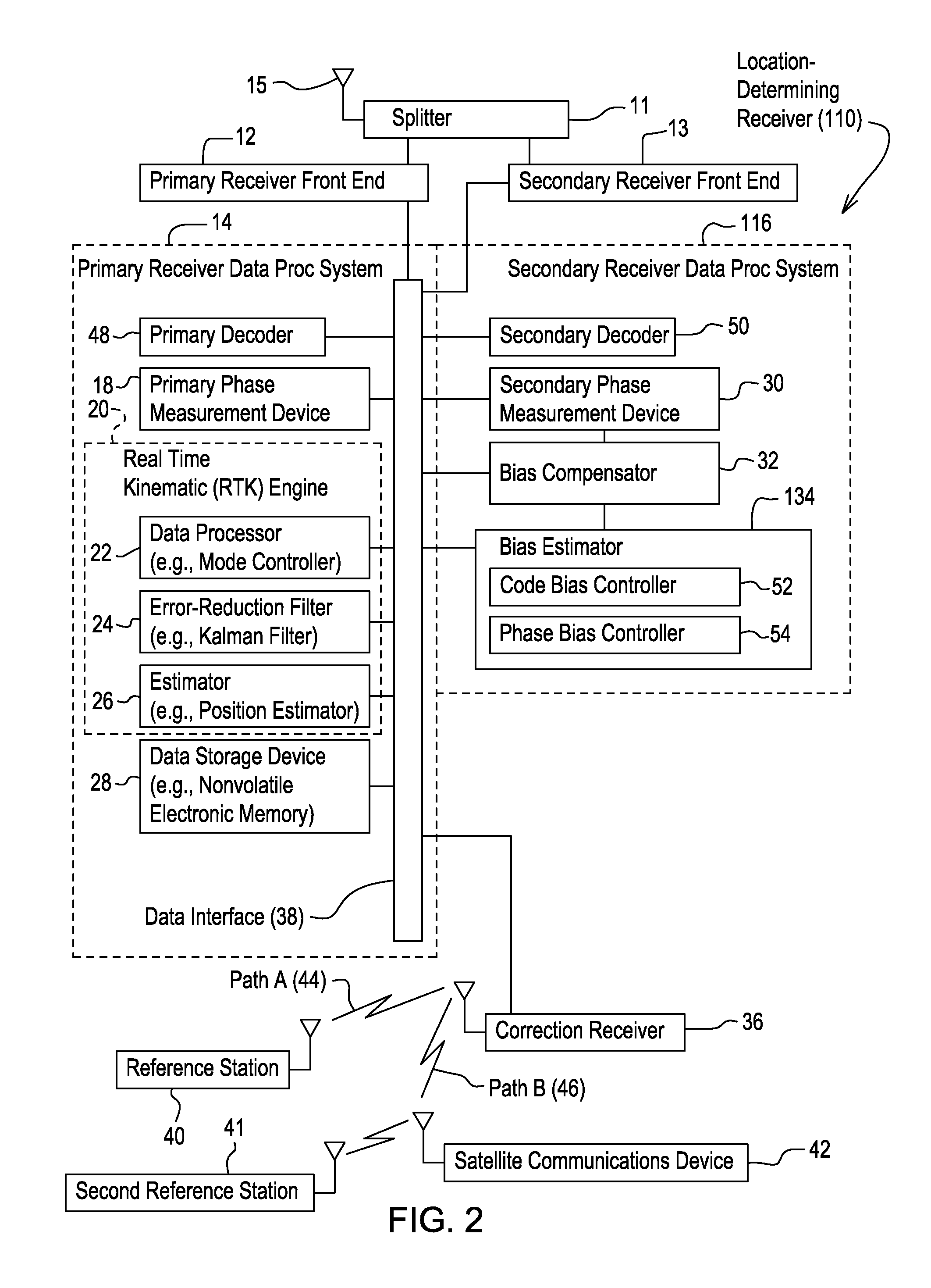
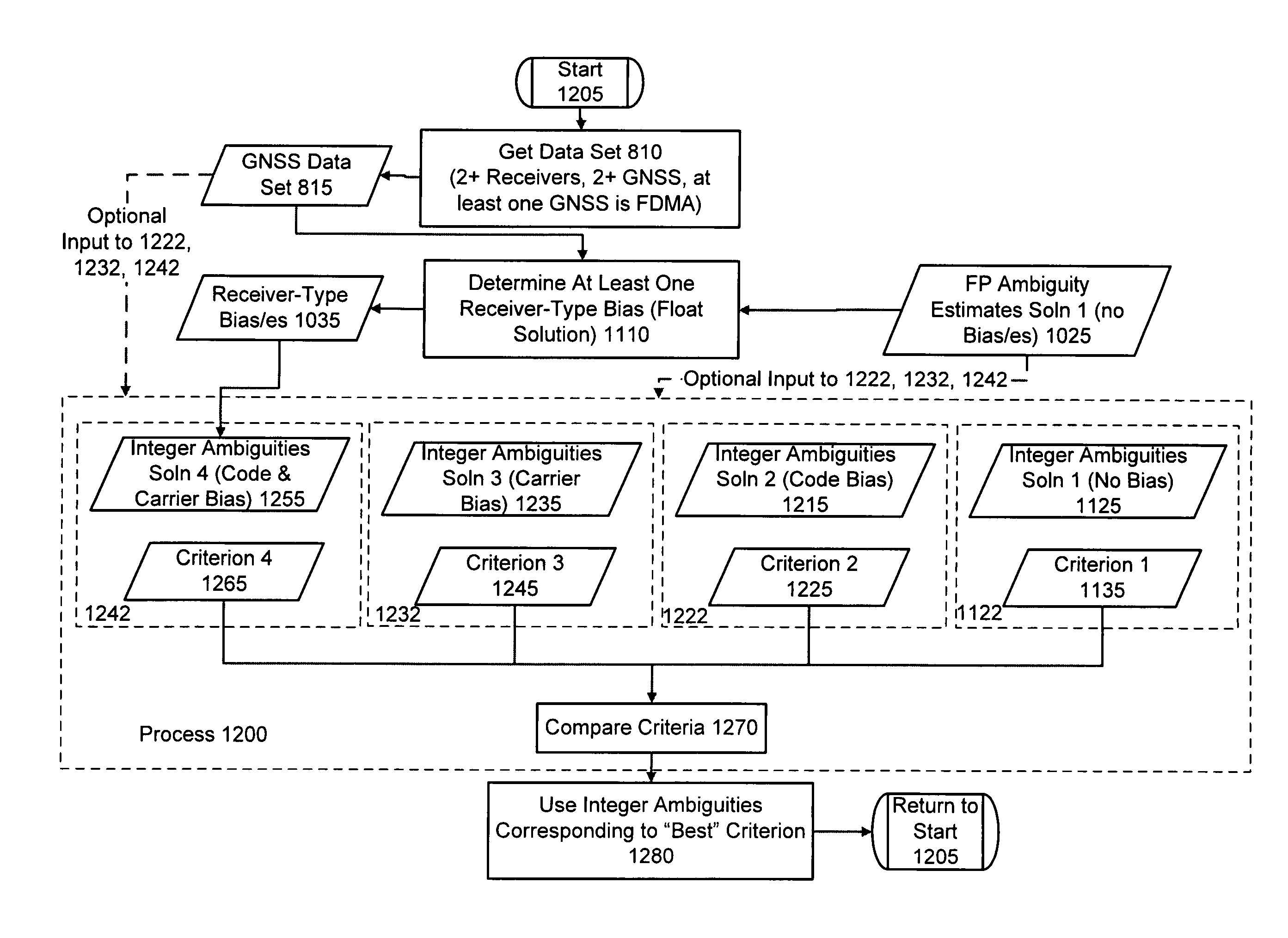
Processing Multi-GNSS data from mixed-type receivers
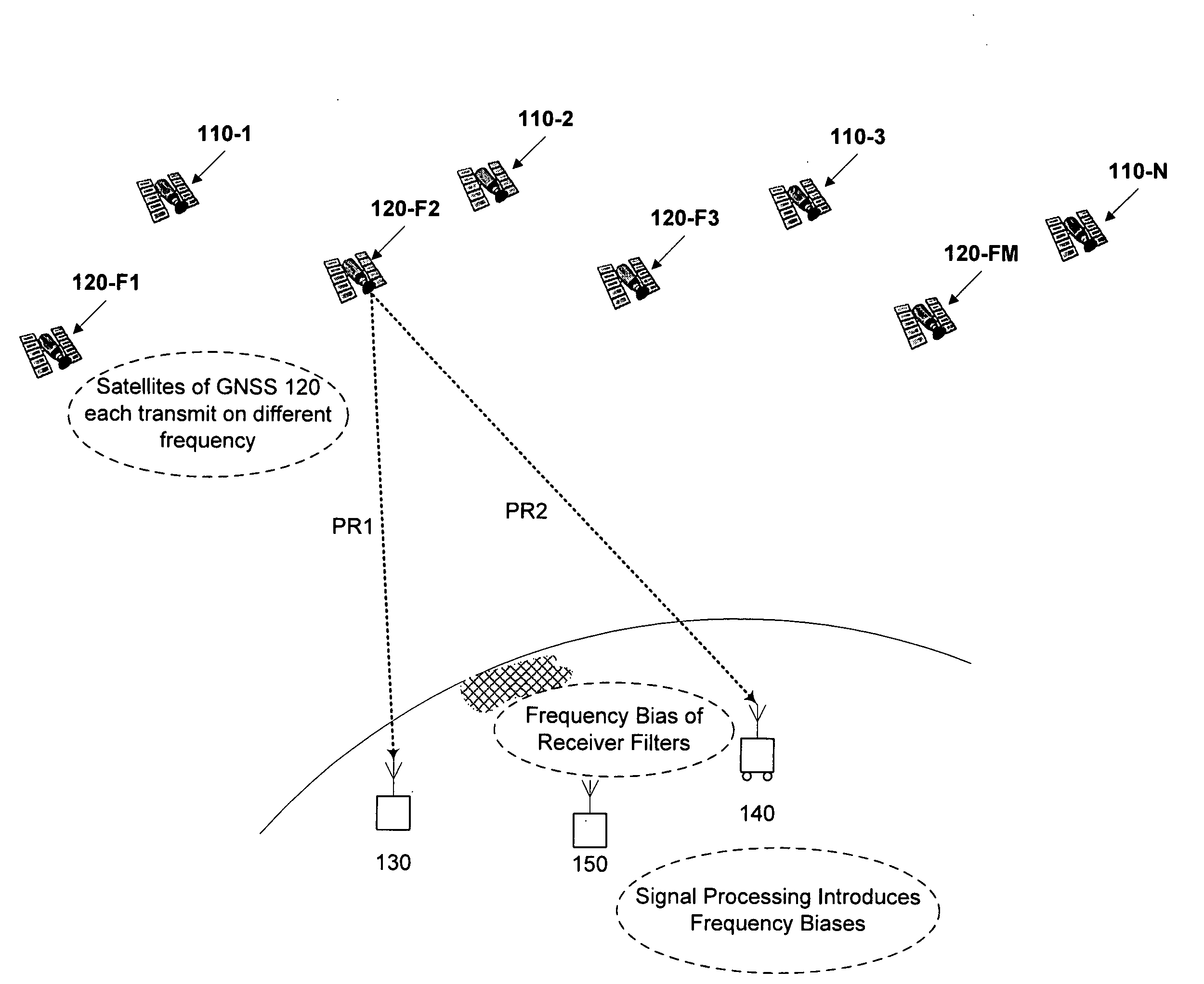
Computer-implemented methods and apparatus are presented for processing data collected by at least two receivers from multiple satellites of multiple GNSS, where at least one GNSS is FDMA. Data sets are obtained which comprise a first data set from a first receiver and a second data set from a second receiver. The first data set comprises a first FDMA data set and the second data set comprises a second FDMA data set. At least one of a code bias and a phase bias may exist between the first FDMA data set and the second FDMA data set. At least one receiver-type bias is determined, to be applied when the data sets are obtained from receivers of different types. The data sets are processed, based on the at least one receiver-type bias, to estimate carrier floating-point ambiguities. Carrier integer ambiguities are determined from the floating-point ambiguities. The scheme enables GLONASS carrier phase ambiguities to be resolved and used in a combined FDMA / CDMA (e.g., GLONASS / GPS) centimeter-level solution. It is applicable to real-time kinematic (RTK) positioning, high-precision post-processing of positions and network RTK positioning.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
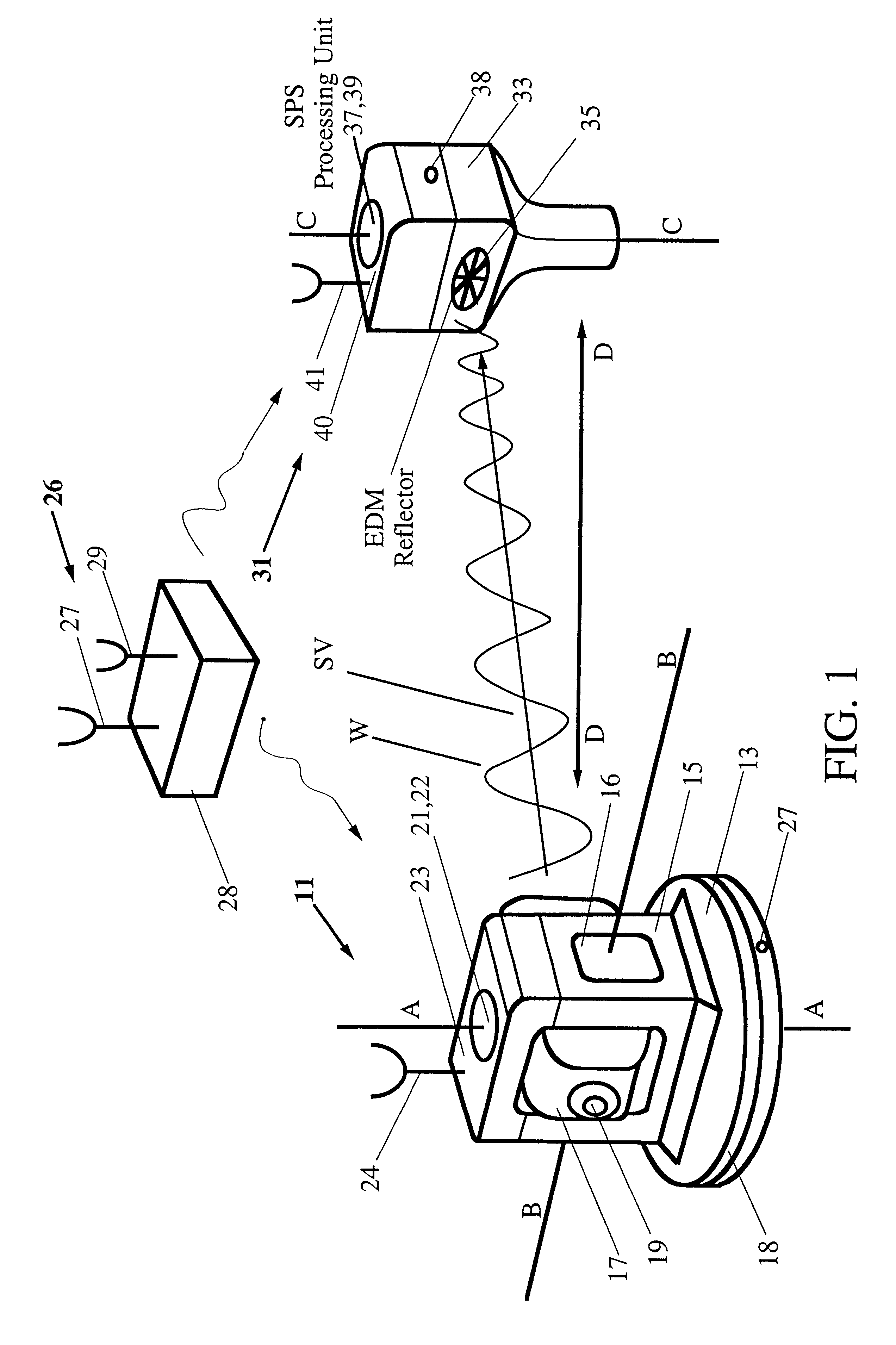
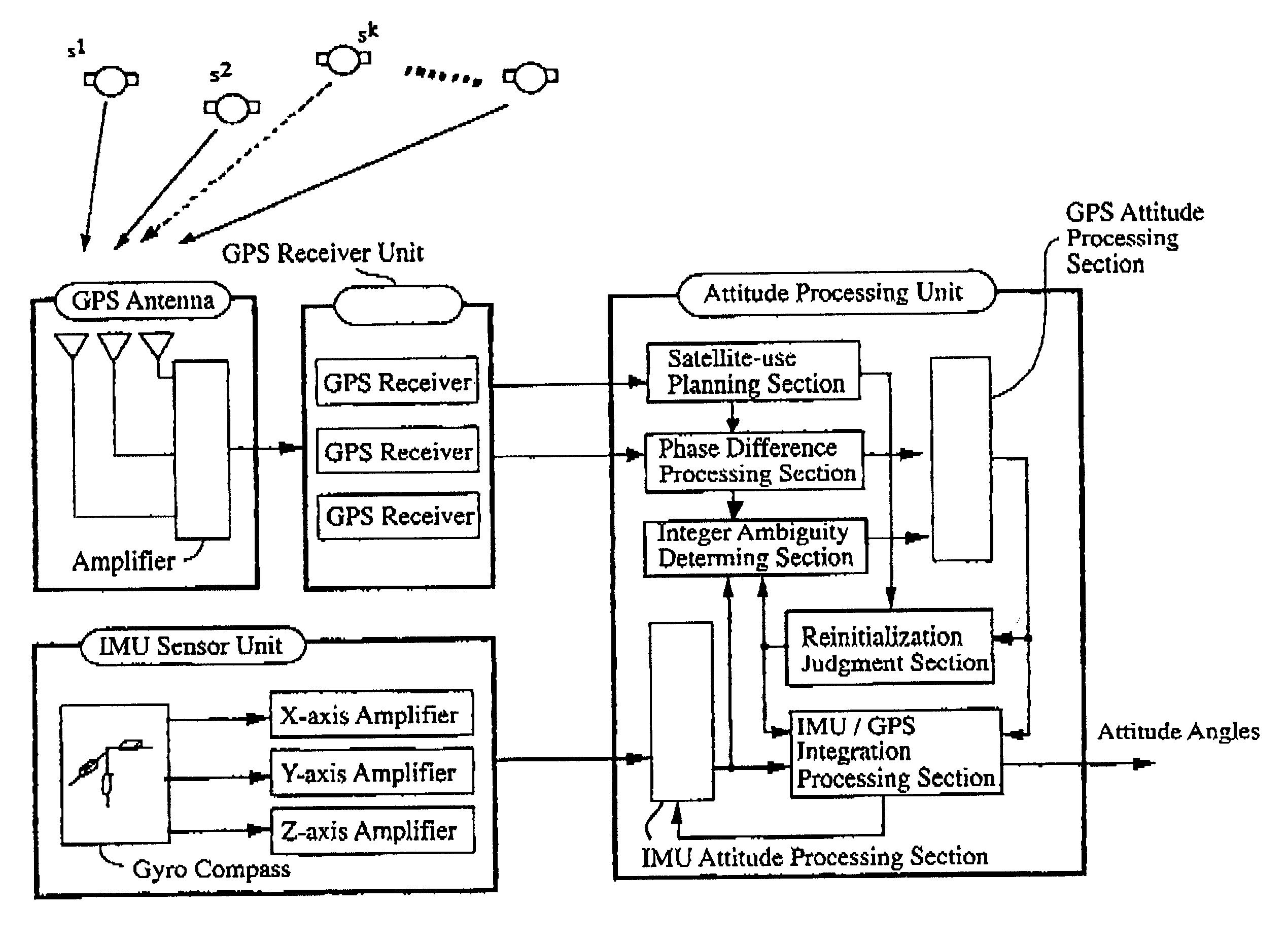
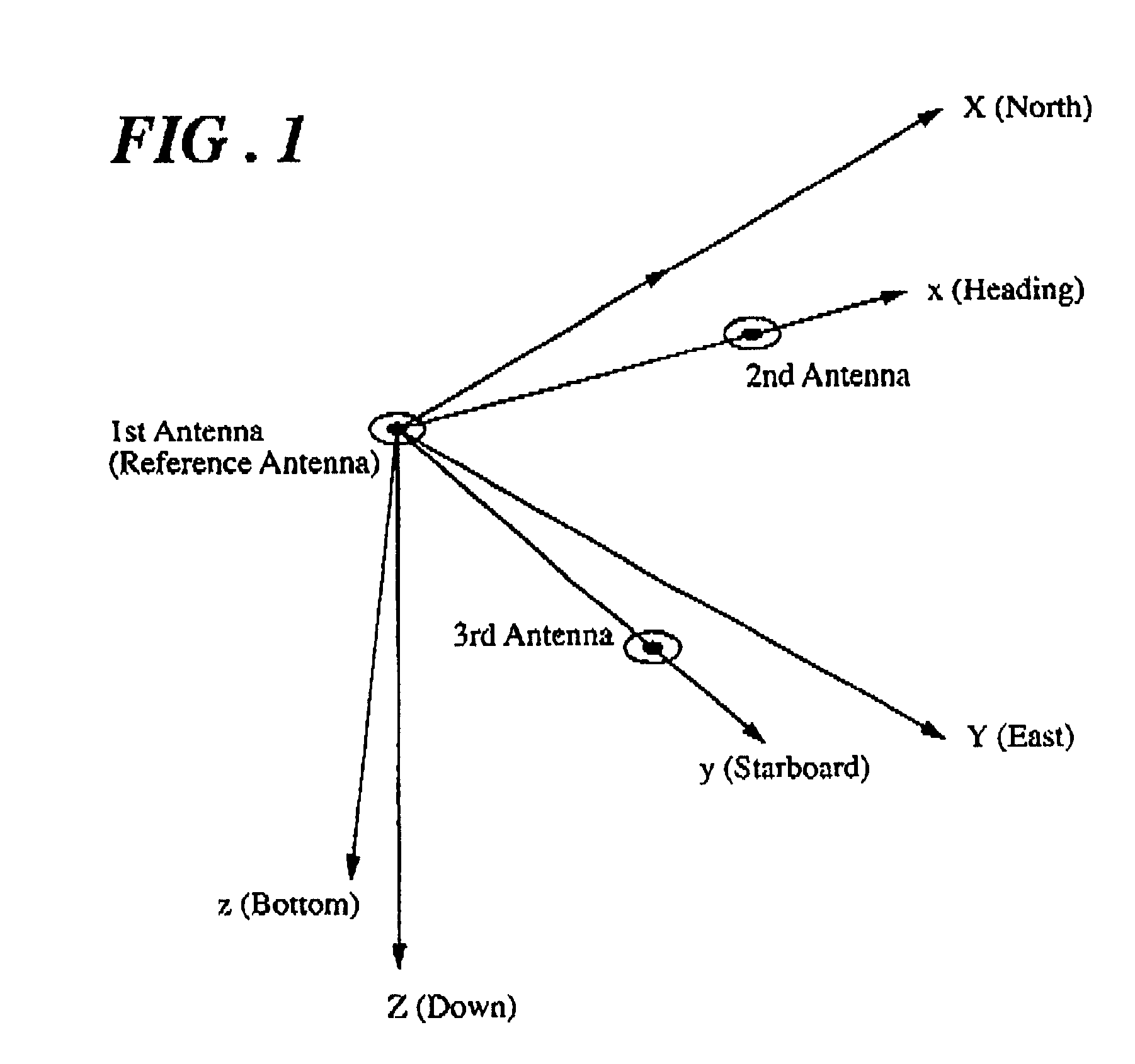
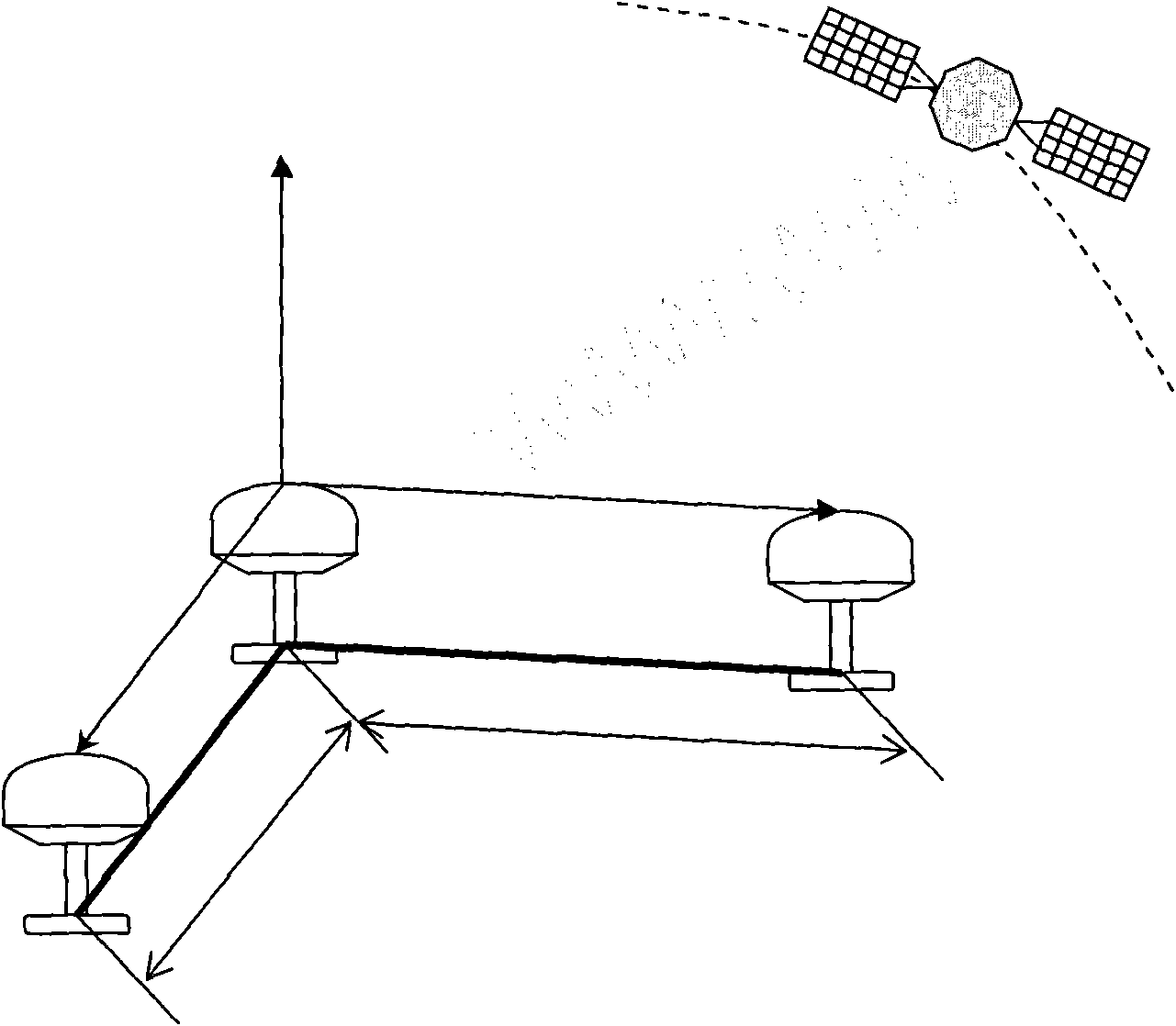
System for determining the heading and/or attitude of a body
InactiveUS6424915B1Reliably determine solutionShort timeCosmonautic vehiclesDigital data processing detailsInteger ambiguitySystem usage
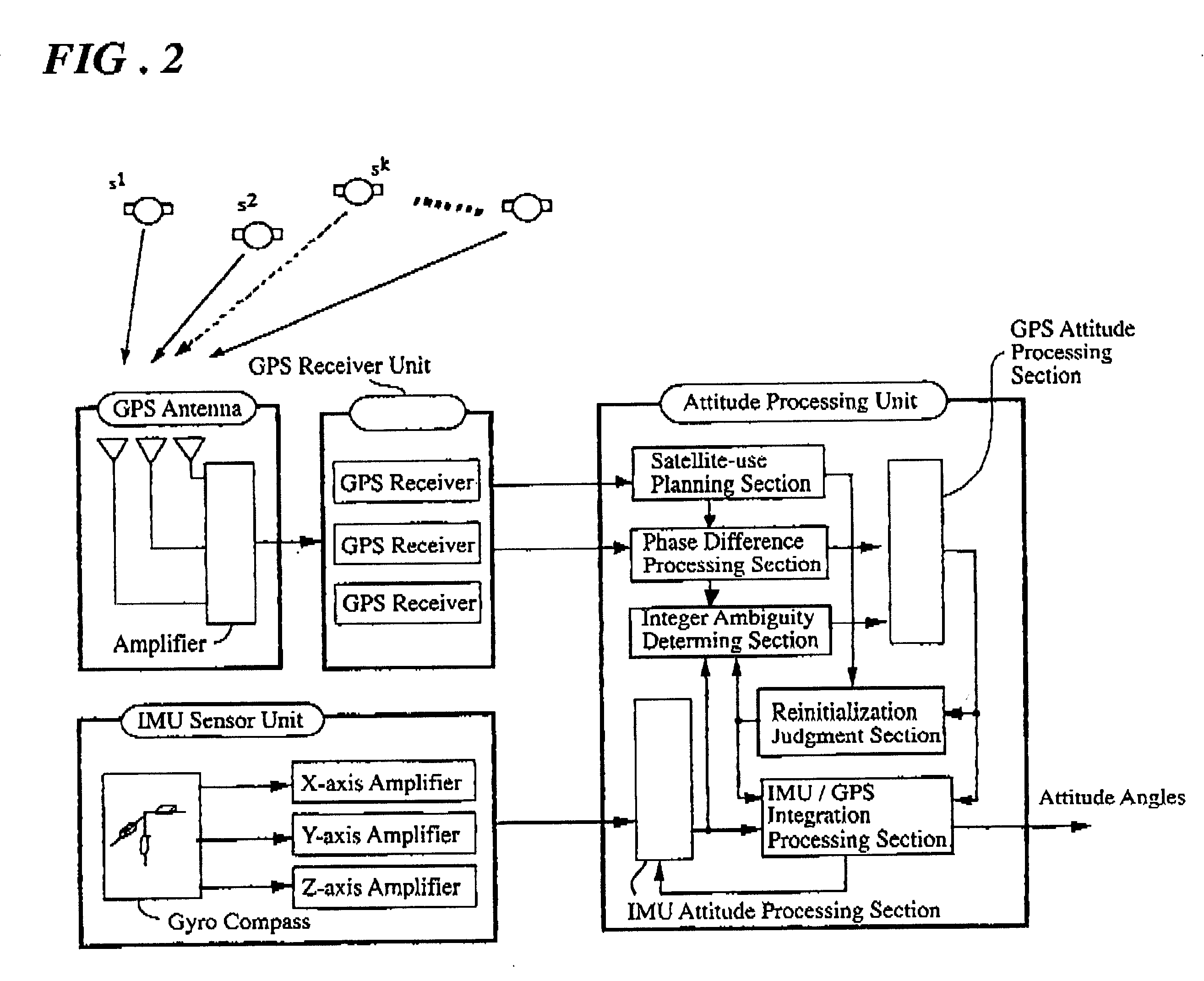
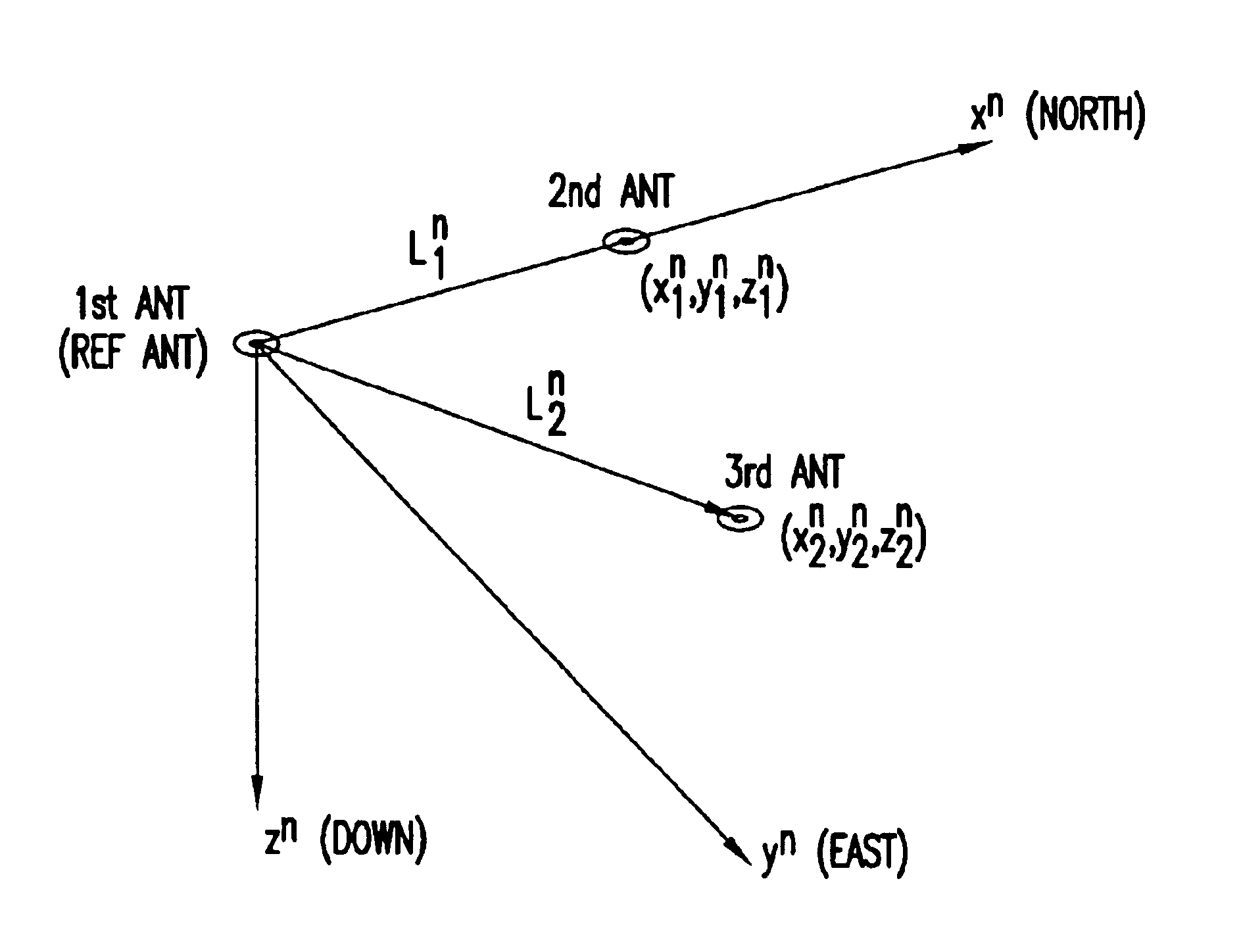
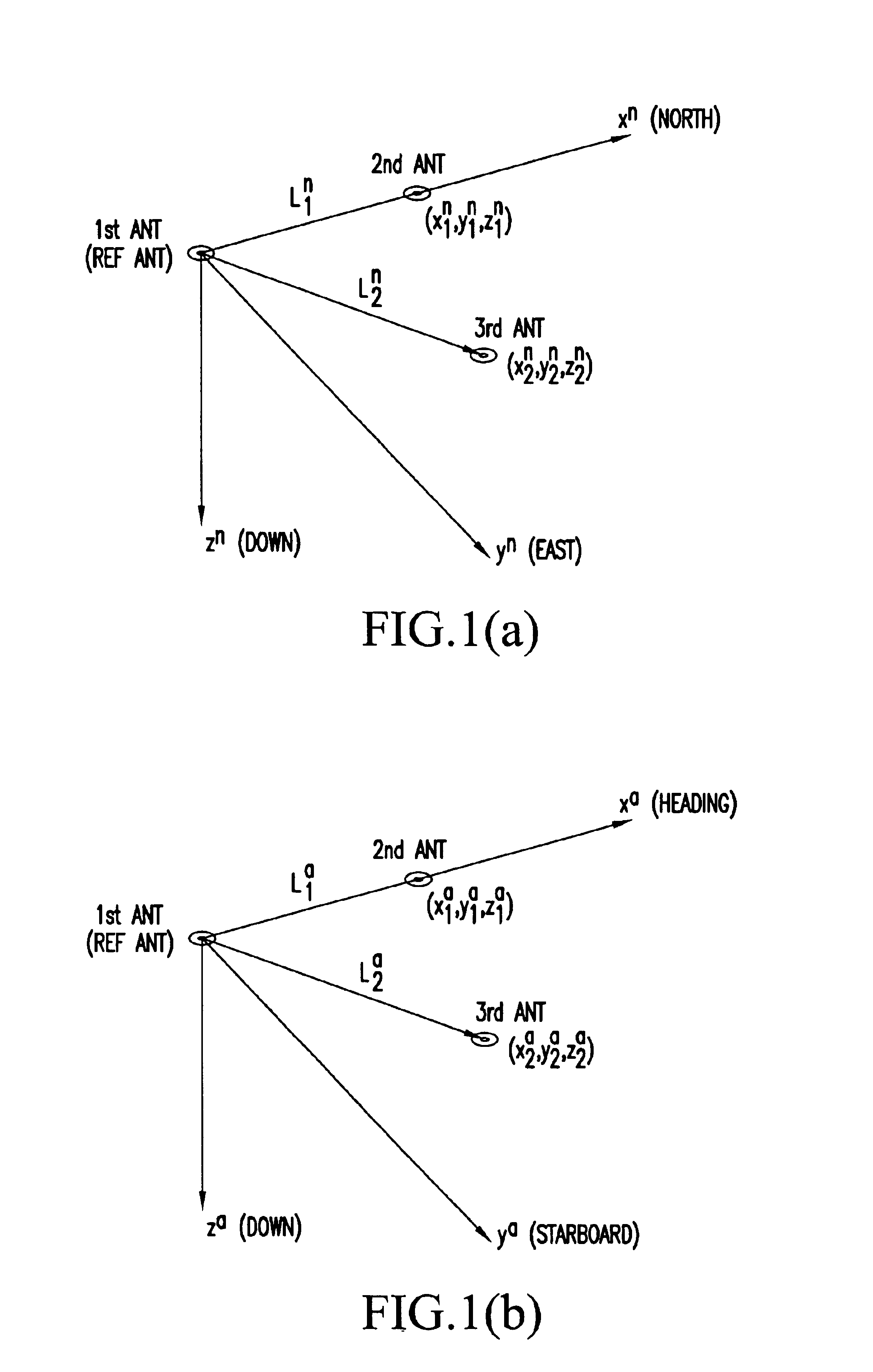
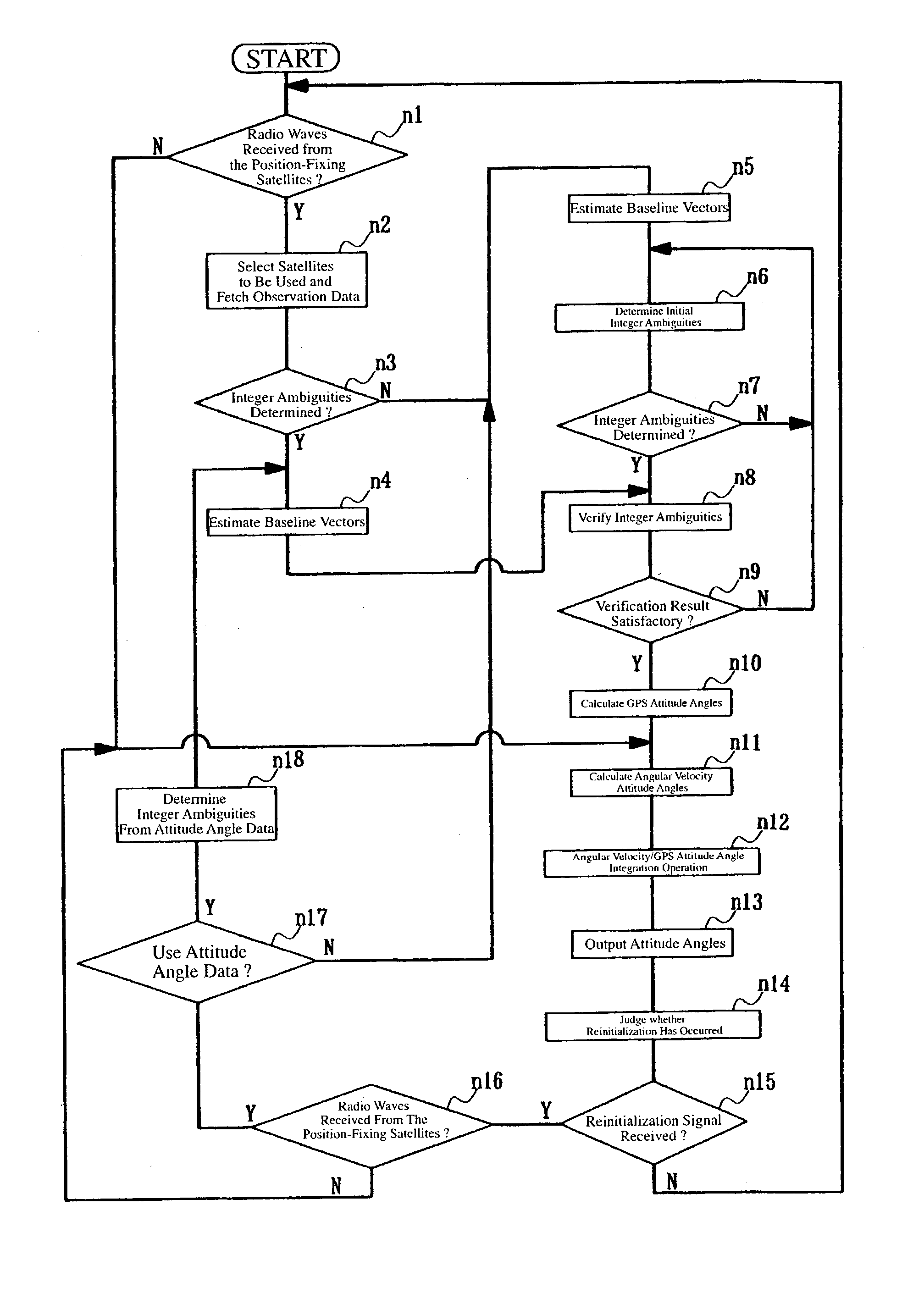
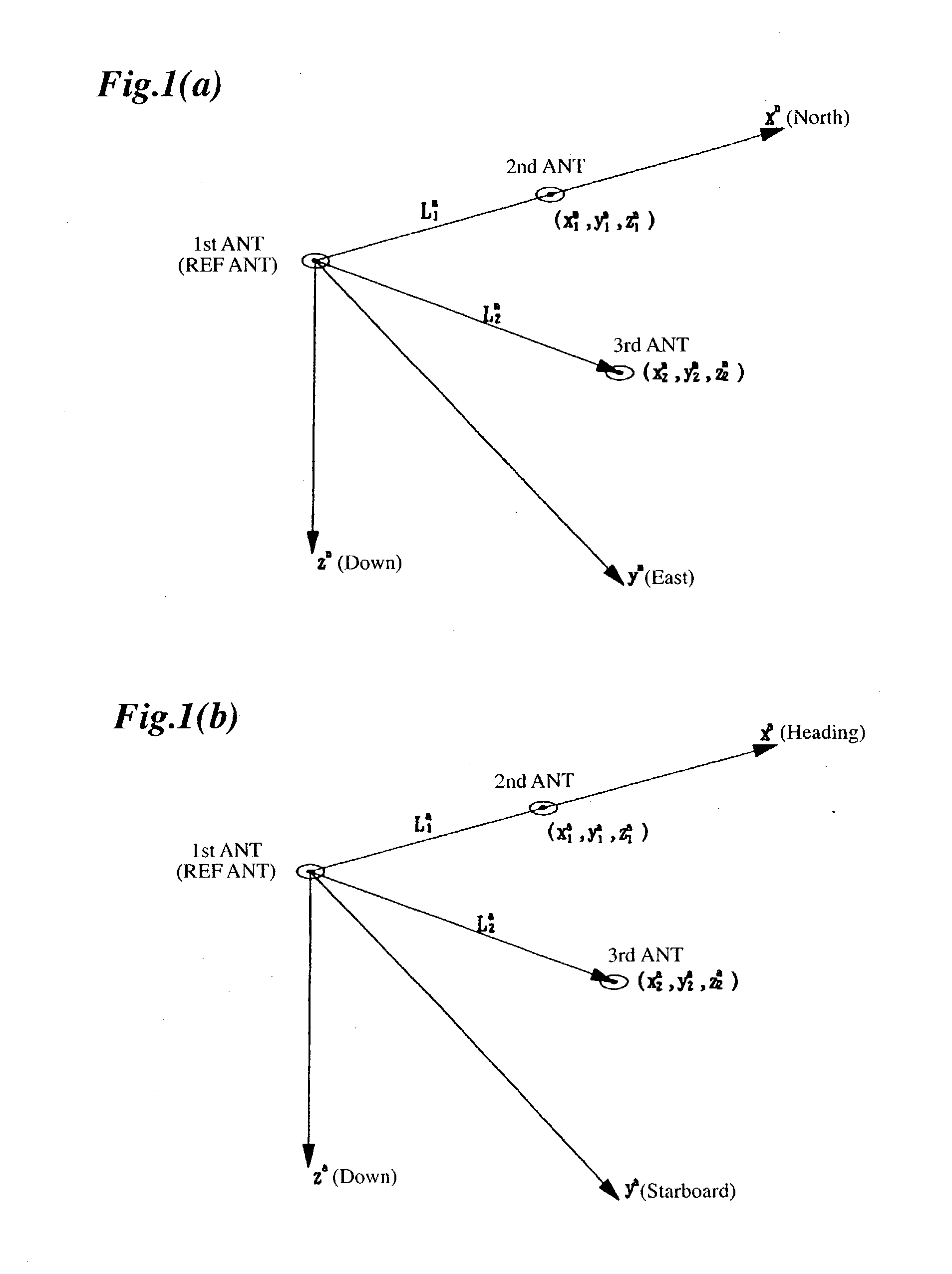
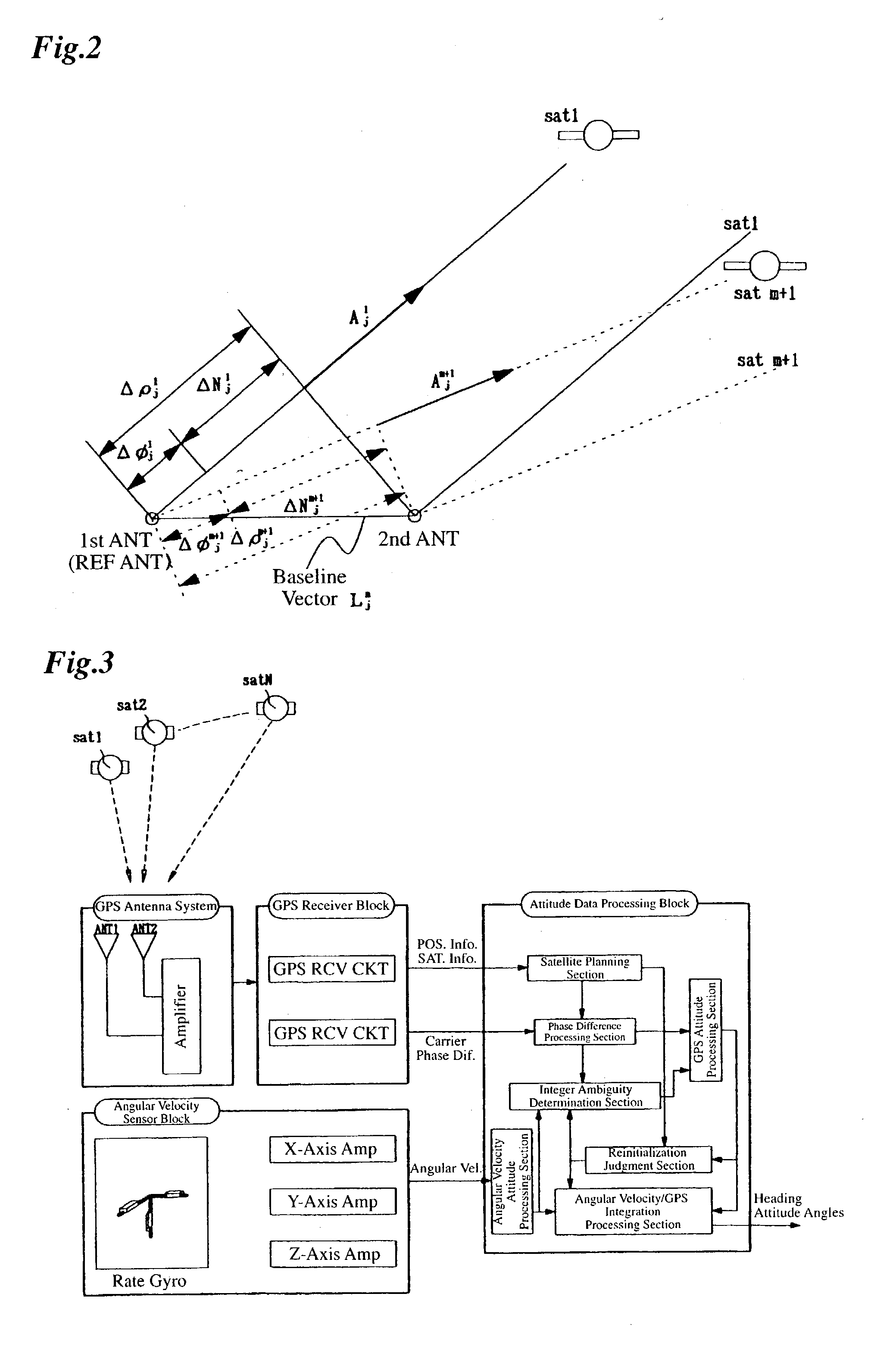
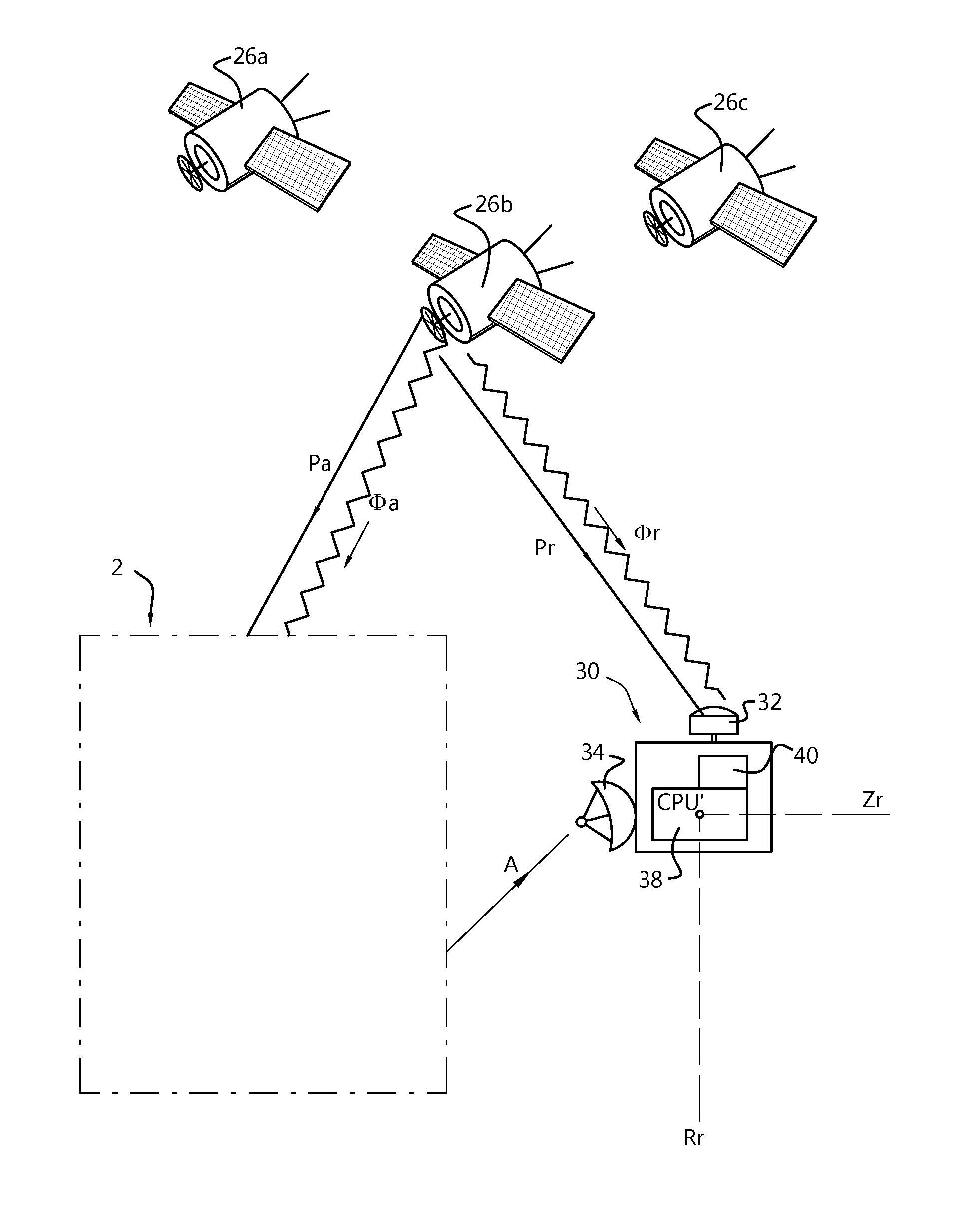
A system for determining the heading and / or attitude of a body receives radio waves from a plurality of position-fixing satellites using at least three antennas fixedly mounted at different positions of the body. To reliably obtain integer ambiguity solutions of carrier phases of the radio waves in a shorter time, the system directly determines integer ambiguities from attitude angle data obtained by an IMU attitude processing section when the integer ambiguities are to be redetermined in the event of an interruption of the received radio waves or a change in the combination of satellites to be used. This system provides a user with highly accurate uninterrupted heading and / or attitude angle information.
Owner:FURUNO ELECTRIC CO LTD
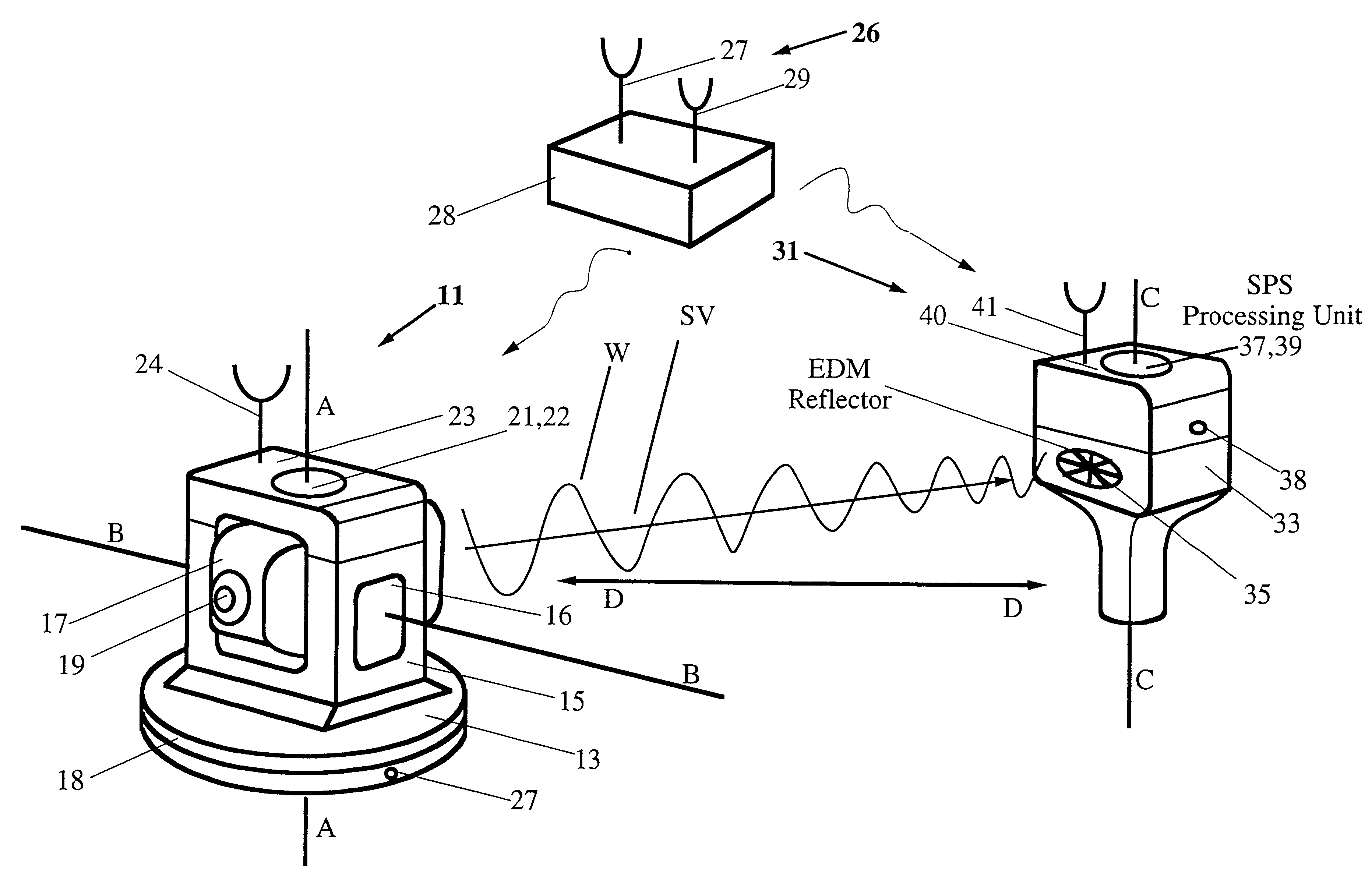
Integrated SATPS total survey station
Apparatus for measuring surveying parameters, such as distances and angular displacements between an instrument survey station and a mobile survey station, with improved accuracy. The invention combines a differential satellite positioning system (DSATPS), available with positioning systems such as GPS and GLONASS, with electromagnetic measurements of distances and optically encoded angles by a conventional electro-optical survey instrument to provide survey measurements that can be accurate to within a few millimeters in favorable situations. The DSATPS relies upon pseudorange measurements or upon carrier phase measurements, after removal of certain phase integer ambiguities associated with carrier phase SATPS signals. The SATPS may be retrofitted within the housing of the conventional electro-optical instrument. In a first approach, a remote station provides DSATPS corrections for the mobile station and / or for the instrument station. In a second approach, the mobile station provides DSATPS corrections for itself and for the instrument station. In a third approach, the instrument station provides DSATPS corrections for itself and for the mobile station.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
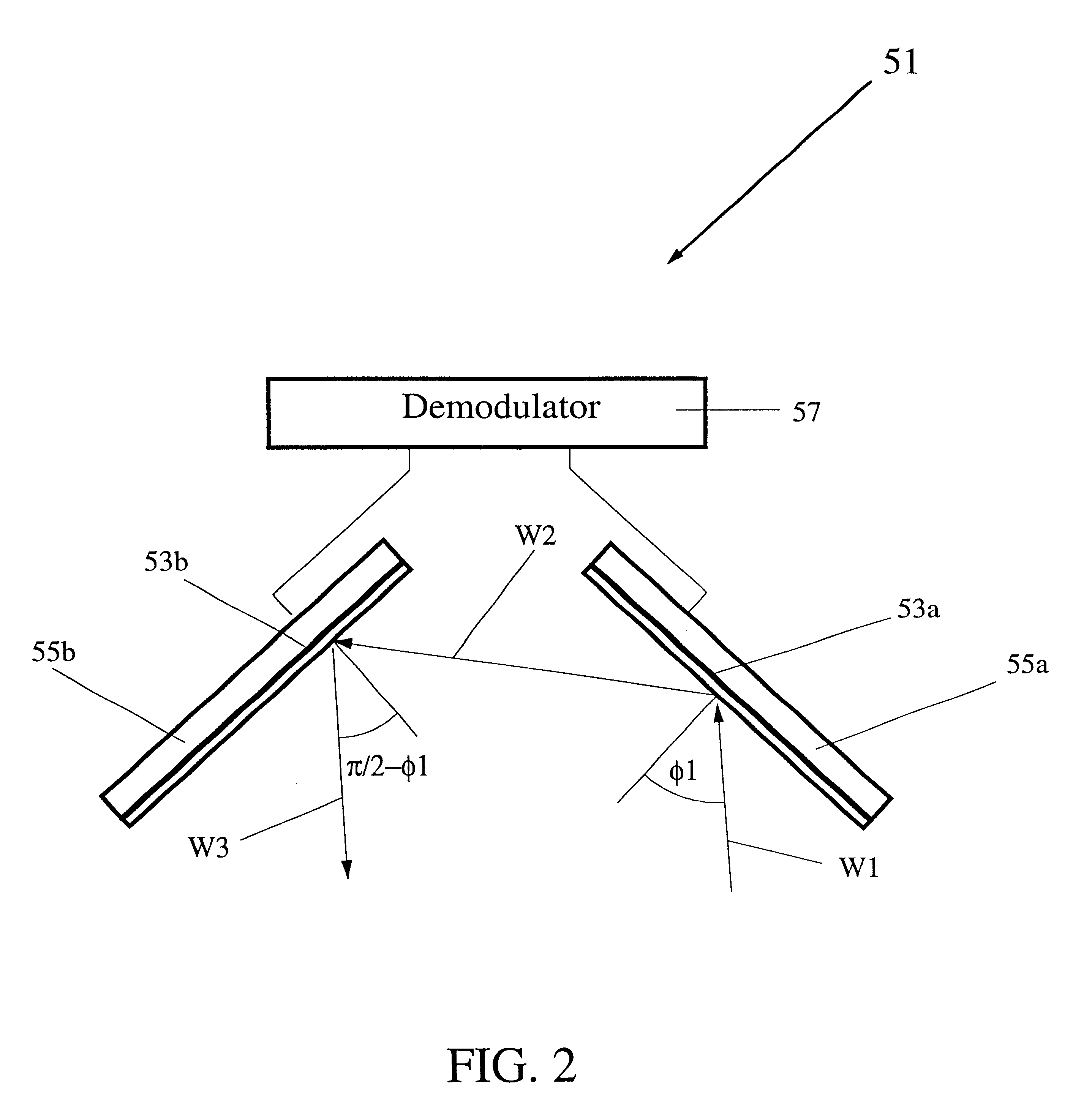
Carrier phase-based relative positioning apparatus
InactiveUS6611228B2Improve reliabilityShorten the timePosition fixationNavigation instrumentsDouble differenceReference antenna
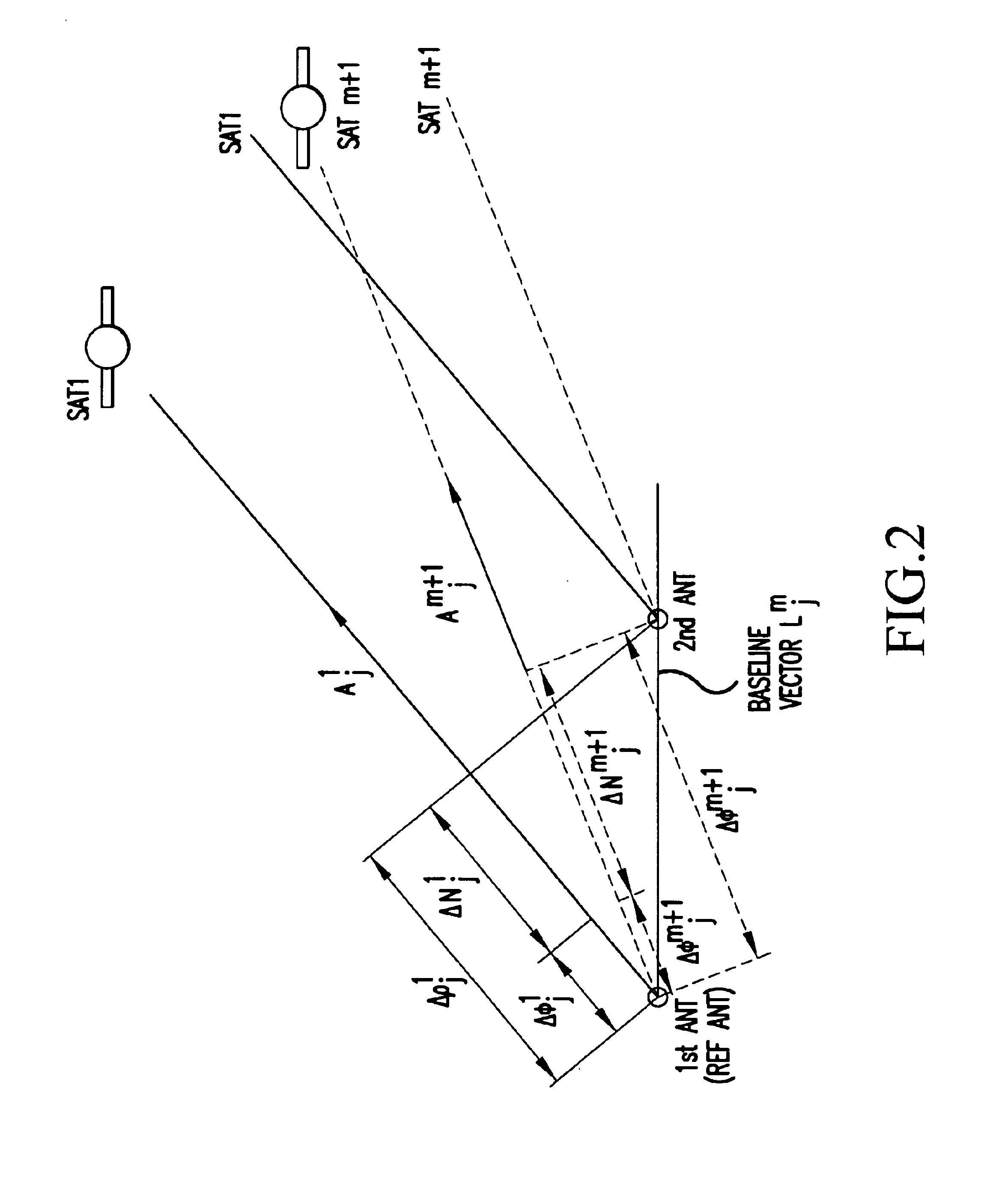
A carrier phase-based relative positioning apparatus comprises a plurality of antennas of which at least one is installed on a mobile unit. The apparatus determines the position of each antenna other than one antenna used as a reference antenna relative to the reference antenna by receiving radio signals transmitted from a plurality of position-fixing satellites with the multiple antennas, observing a single difference phase or a double difference phase, and calculating an integer ambiguity of the single difference phase or the double difference phase. The apparatus judges that the integer ambiguity has been incorrectly determined if the position of any of the antennas relative to the reference antenna (or the angle of a flat plane formed by those two antennas) falls out of a preset range in which the relative position (the angle of the flat plane) falls under normal conditions.
Owner:FURUNO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Attitude angle detecting apparatus
InactiveUS6792380B2Instantly calculateQuick checkDigital computer detailsPosition fixationAmbiguityInteger ambiguity
An attitude angle detecting apparatus receives radio waves transmitted from a plurality of position-fixing satellites with multiple antennas located at specific positions of a mobile unit, determines relative positions of the antennas and detects the heading and attitude of the mobile unit by determining carrier phase ambiguities quickly and accurately. When it is needed to redetermine integer ambiguities after recovery from an interruption of the radio waves from the position-fixing satellites or as a result of a change in combination of the position-fixing satellites, for example, the attitude angle detecting apparatus redetermines the integer ambiguities by using attitude angles and an attitude angle error covariance obtained from previous observation. This enables the attitude angle detecting apparatus to uninterruptedly obtain information on the heading and attitude of the mobile unit.
Owner:FURUNO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Attitude determination exploiting geometry constraints
A method and system for determining at least one attitude angle of a rigid body. The method comprising: receiving a plurality of Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) satellite signals with a plurality of antennas; establishing at least one pair of antennas such that each antenna of the plurality of antennas is included in at least one antenna pair; computing single- or double-difference phases corresponding to one or more GNSS satellites for each of the pairs of antennas; and constructing a single Differential Carrier Phase Attitude (DCPA) equation based on known geometry constraints of each of the pairs of antennas. The method also includes determining a solution for the DCPA equation based on a cost function, the solution yielding at least one integer ambiguity value and the at least one attitude angle.
Owner:HEMISPHERE GNSS
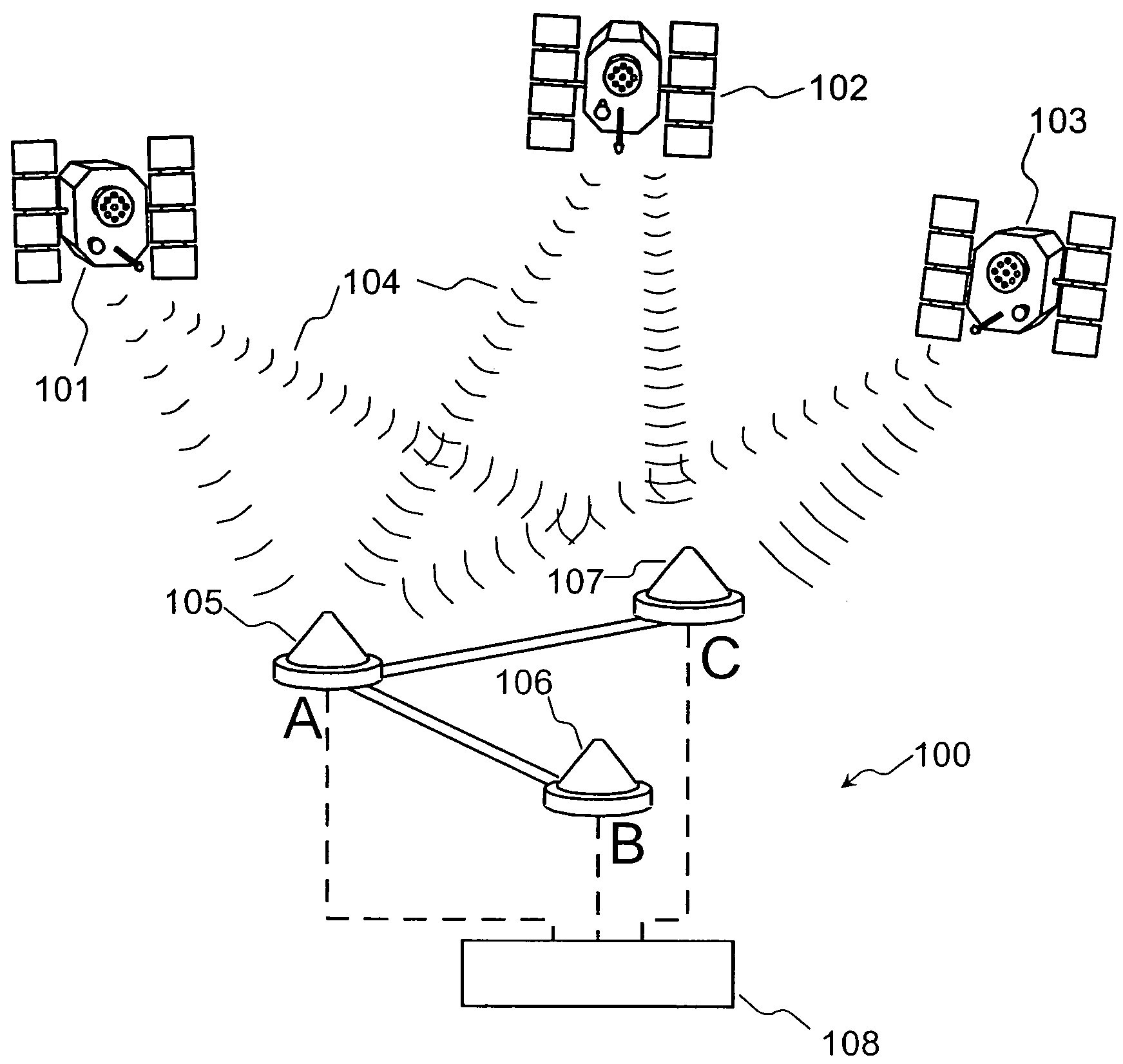
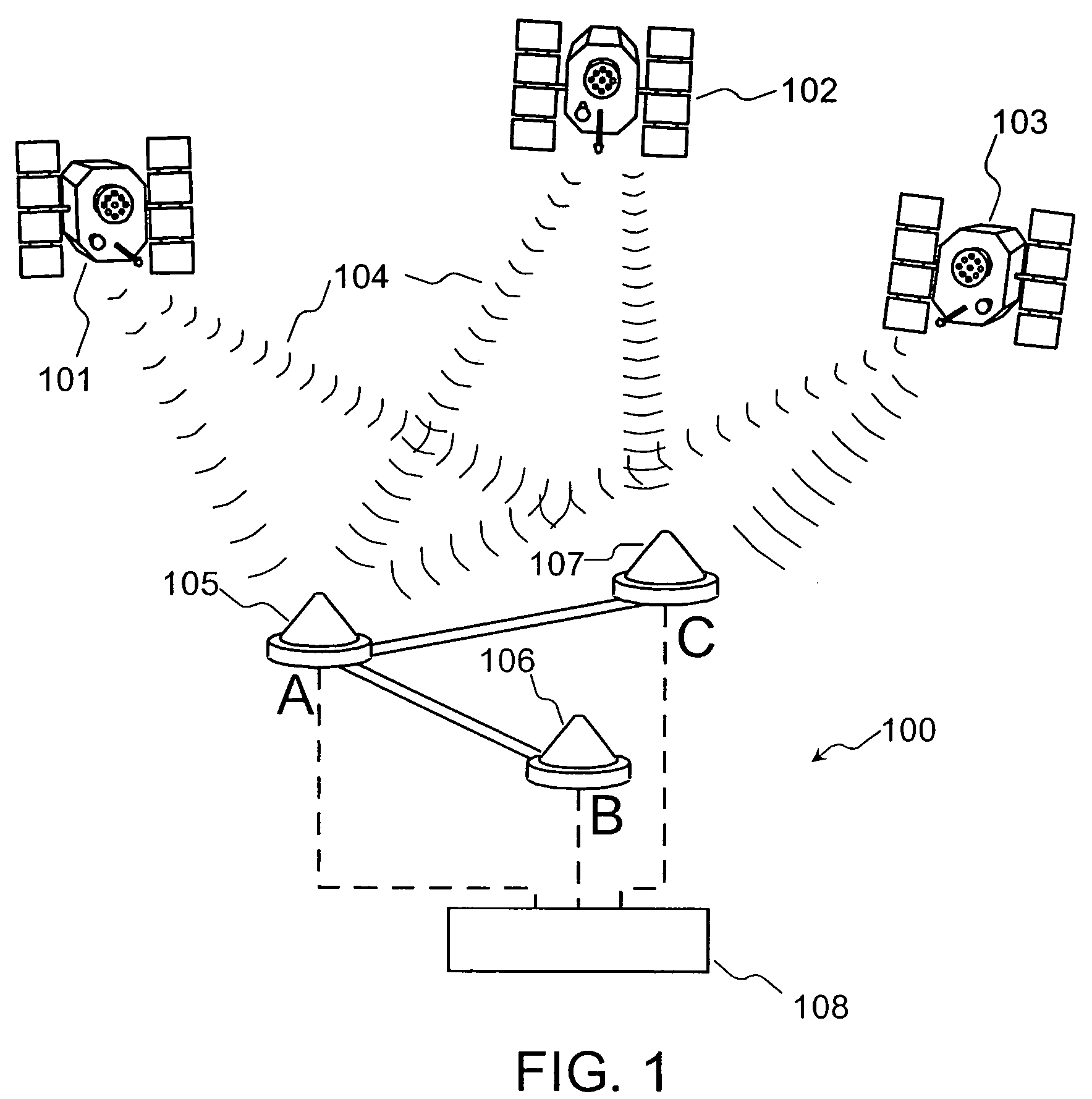
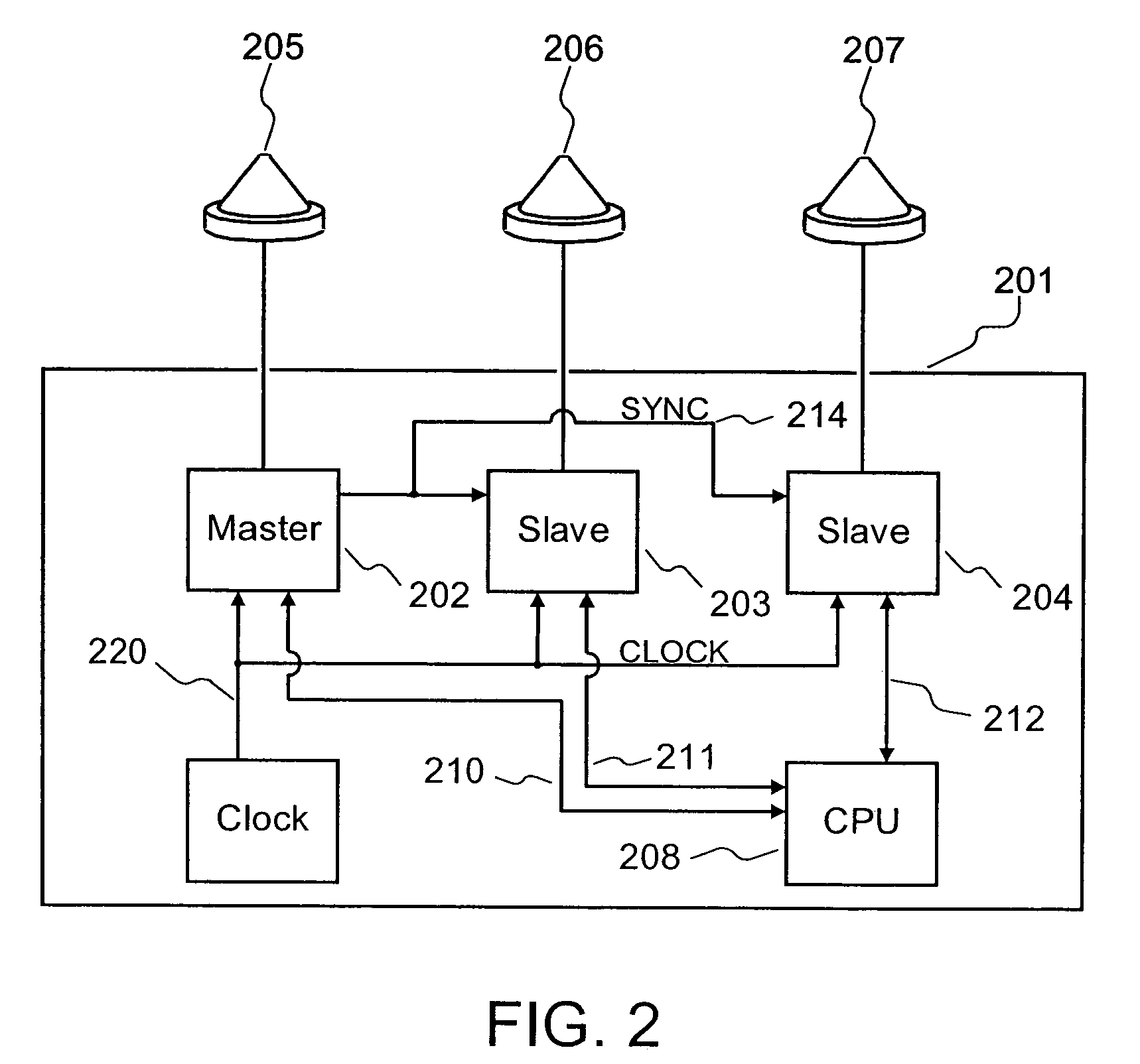
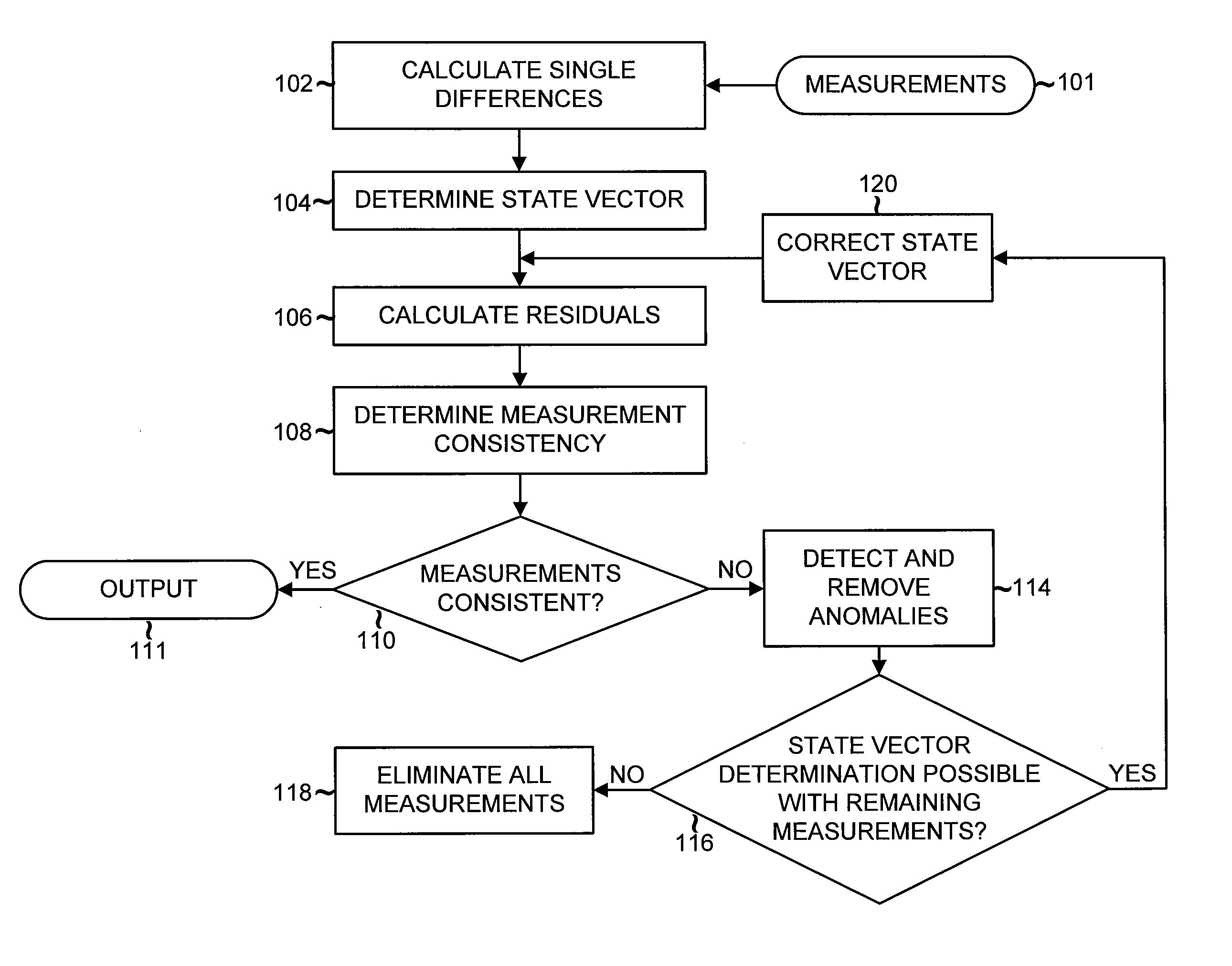
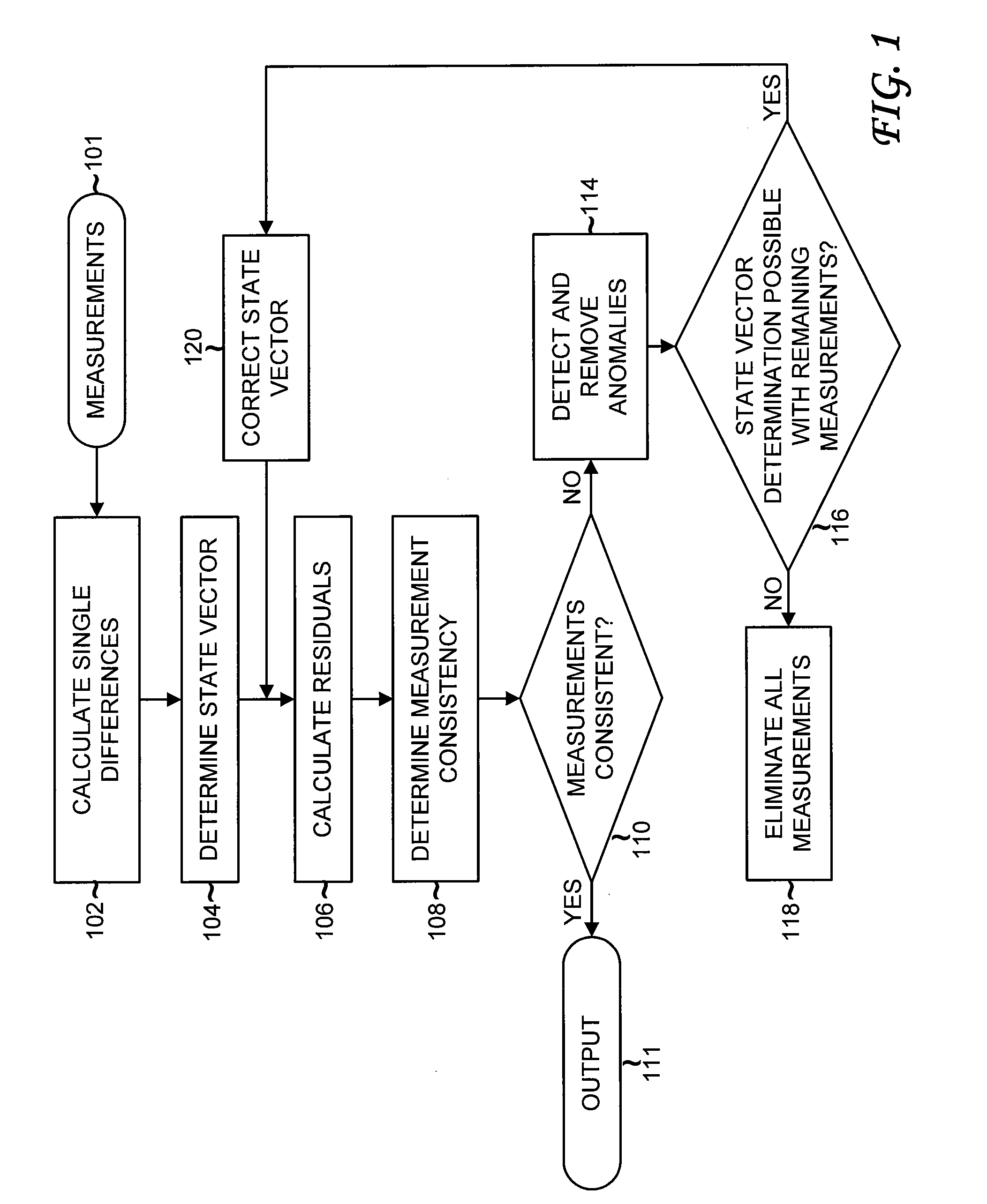
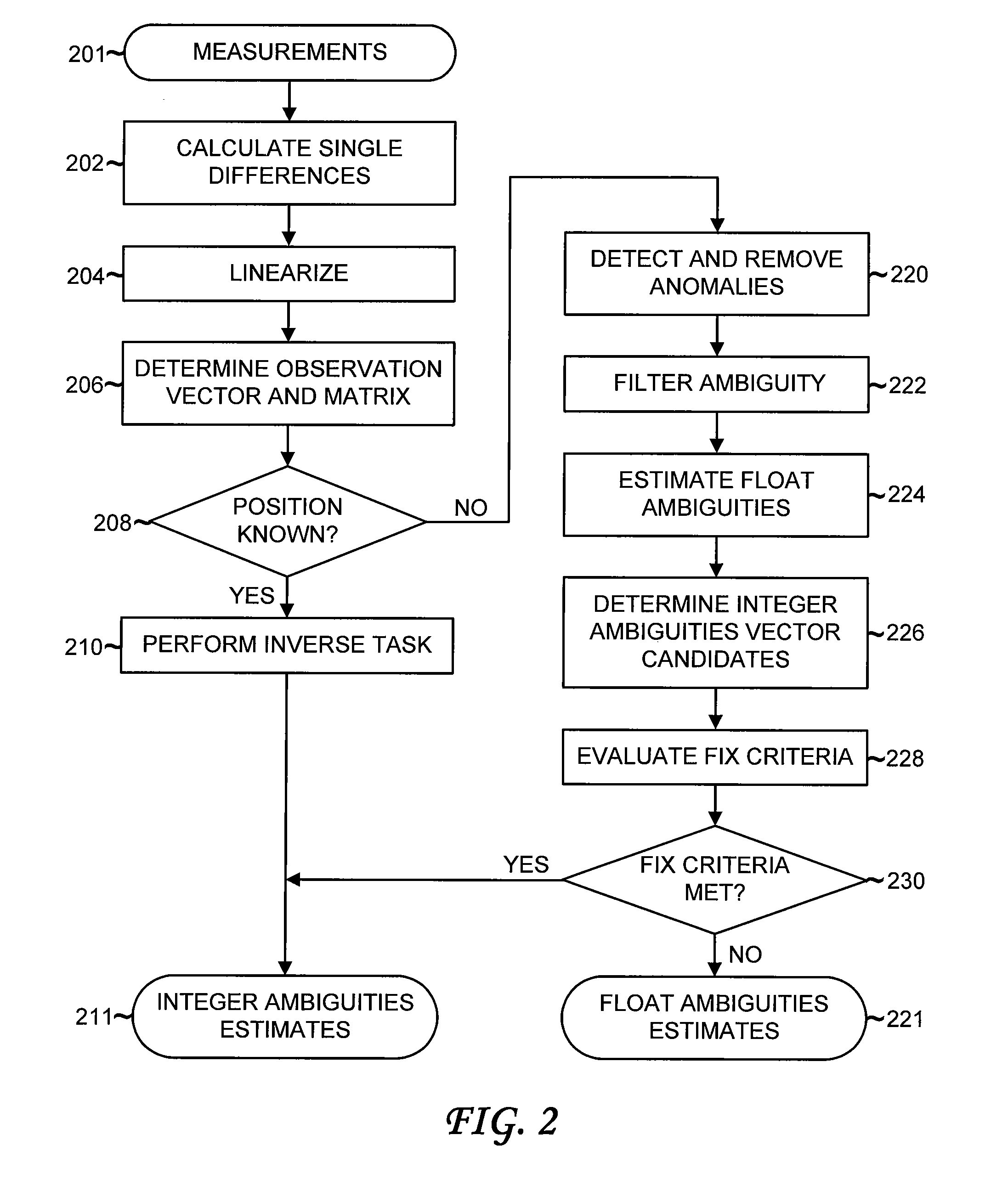
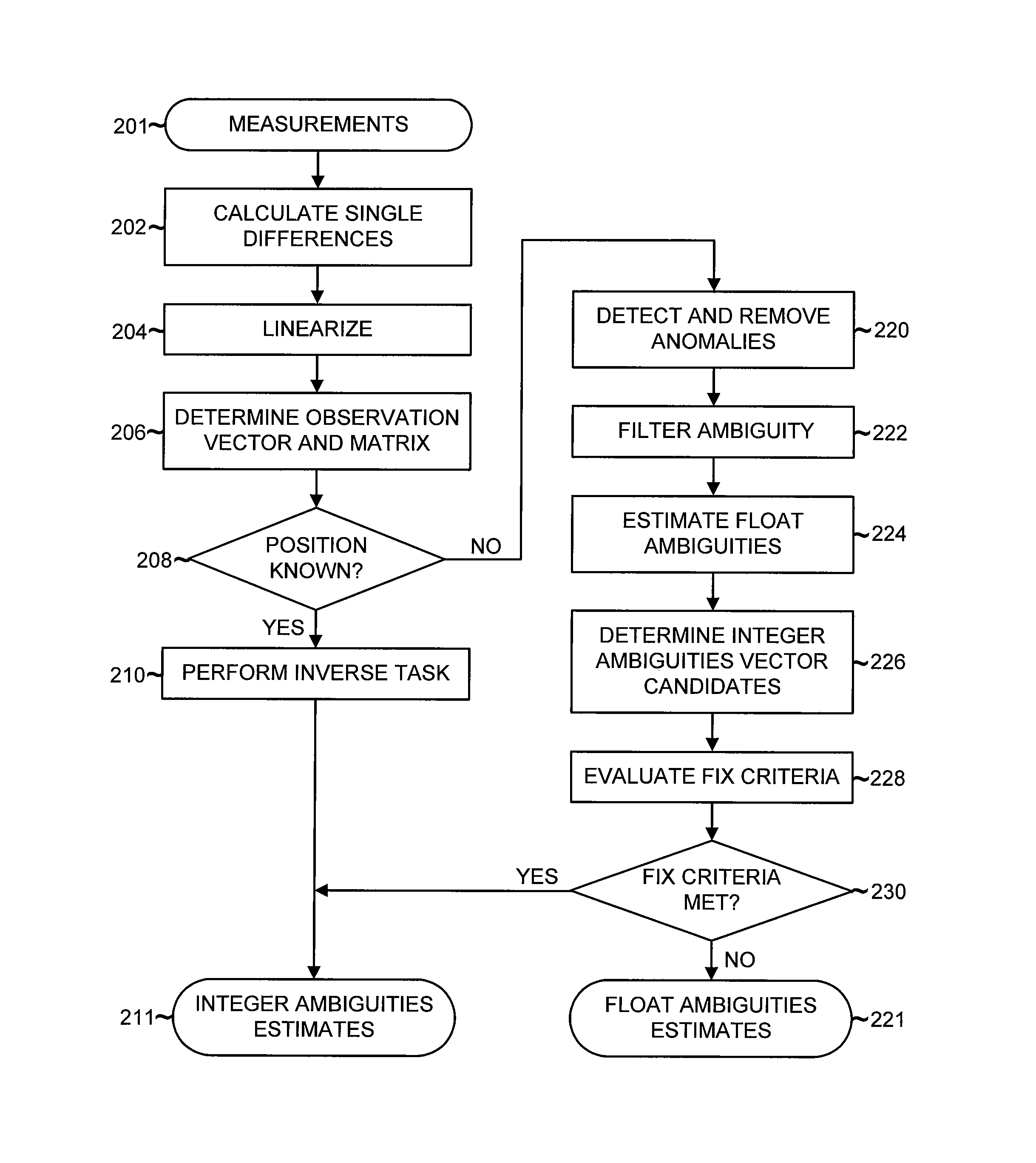
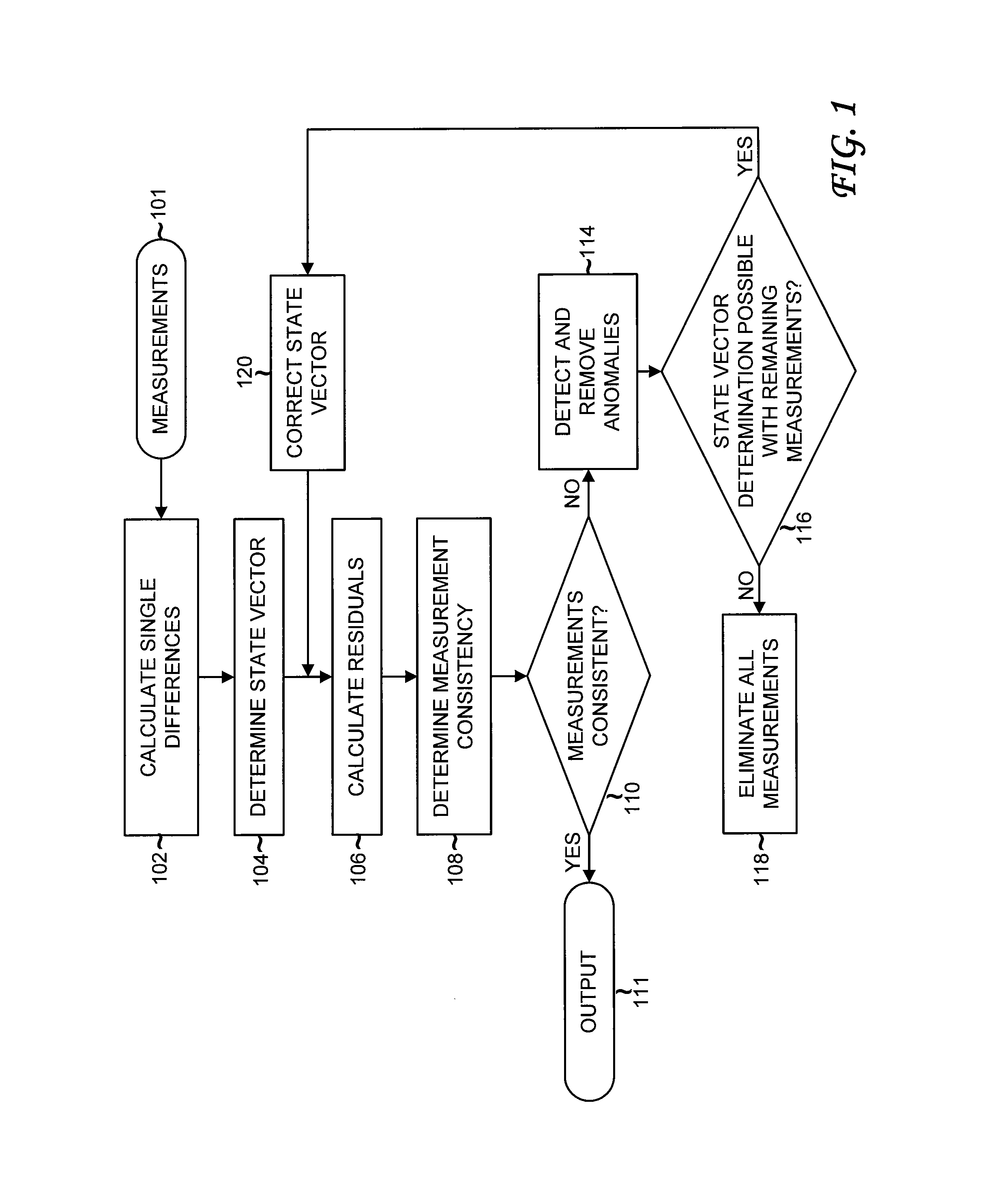
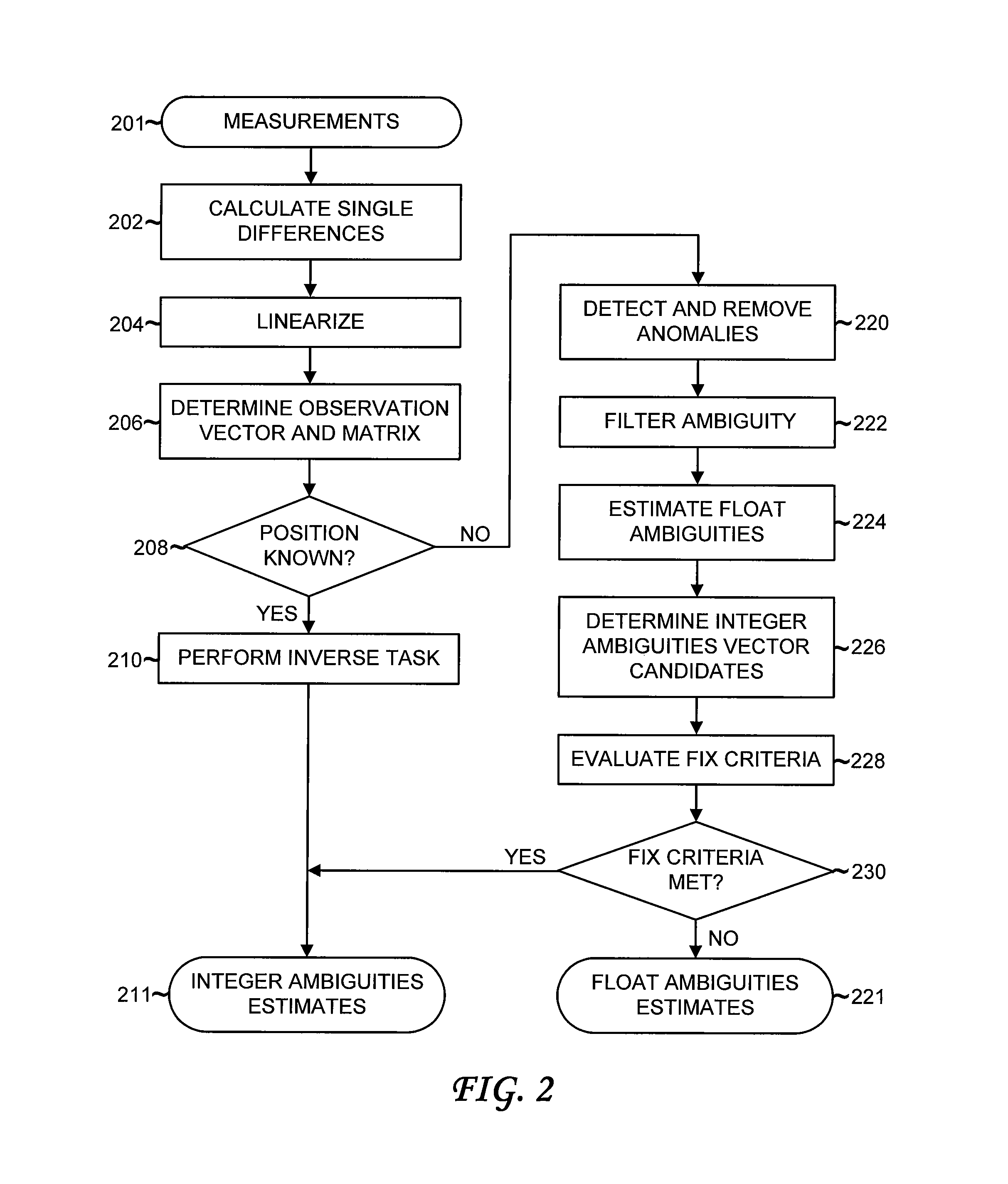
Detection and Correction of Anomalous Measurements and Ambiguity Resolution in a Global ...
A global navigation system includes a first navigation receiver located in a rover and a second navigation receiver located in a base station. Single differences of measurements of satellite signals received at the two receivers are calculated and compared to single differences derived from an observation model. Anomalous measurements are detected and removed prior to performing computations for determining the output position of the rover and resolving integer ambiguities. Detection criteria are based on the residuals between the calculated and the derived single differences. For resolving integer ambiguities, computations based on Cholessky information Kalman filters and Householder transformations are advantageously applied. Changes in the state of the satellite constellation from one epoch to another are included in the computations.
Owner:TOPCON POSITIONING SYST INC
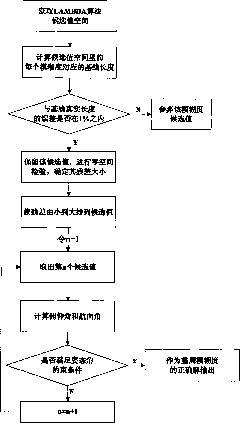
Method for measuring attitude of carrier by using additional constraint condition of GPS system
The invention relates to a method for measuring attitude of a carrier by using an additional constraint condition of a satellite, which comprises the following steps of: establishing a linearization carrier phase double-difference model for each baseline of an attitude measuring system, and determining the integer ambiguity; expanding a search space, and determining a trigonometric function constraint and a base length constraint; substituting a constraint condition containing the maximum boundary and the minimum boundary into a search process to obtain an upper bound and a lower bound of a formula ambiguity candidate value; performing a comparison according to the boundaries obtained in the search process and an original constraint, and selecting a smaller boundary as the boundary of the ambiguity; and selecting ambiguity candidate values, wherein if the ambiguity candidate values are more than one, two groups of the ambiguity candidate values with the minimum residual errors are selected to perform a verification of the next step, and the candidate values passing through a significance test are fixed solutions of the integer ambiguity. The attitude of the carrier is obtained by further using an attitude measurement algorithm through the fixed solutions. The method has the advantages of reducing the search times, reducing influences caused by noises and significantly improving the measuring accuracy and the success ratio.
Owner:周迅
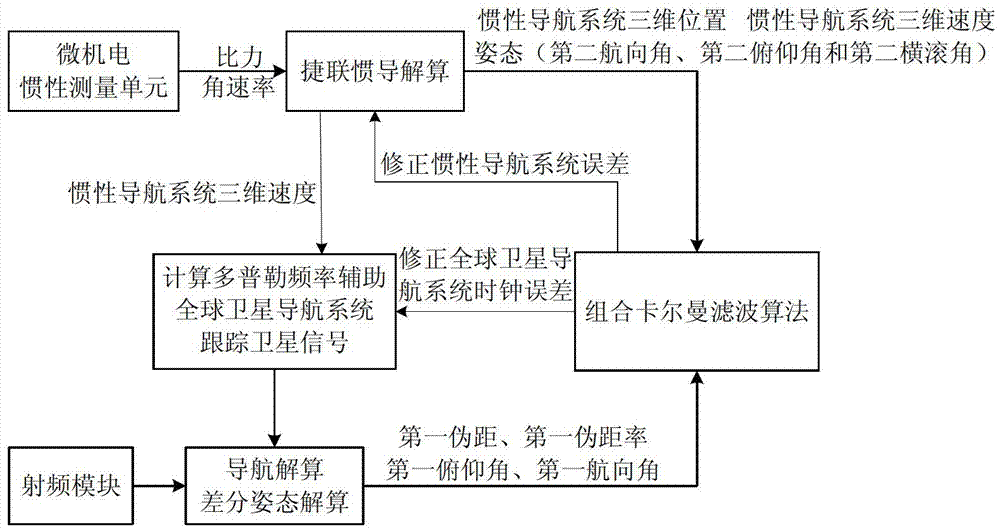
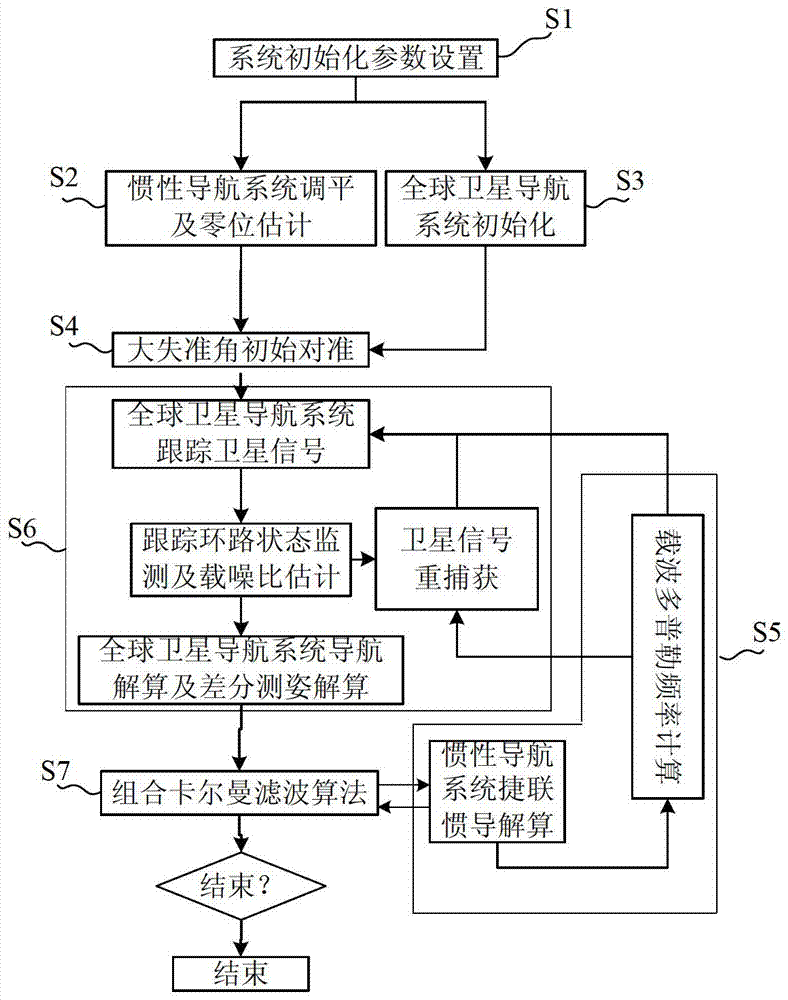
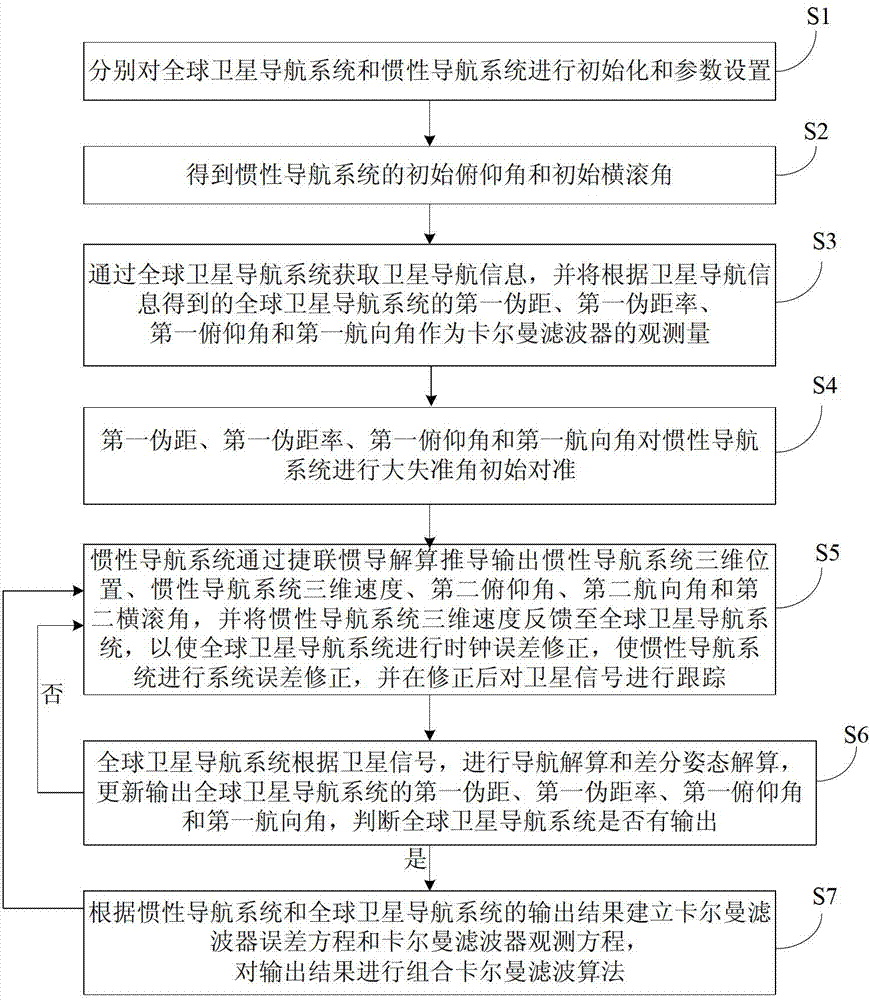
Double-antenna GNSS/INS deeply integrated navigation method and device
InactiveCN103245963AImprove robustnessCompressed ambiguity search spaceSatellite radio beaconingNavigation systemRadio frequency
The invention provides a double-antenna GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) / INS (Inertial Navigation System) deeply integrated navigation method and device. The device comprises a power supply module, an MEMS (Micro Electro Mechanical System) inertial measurement unit, a radio frequency module, an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) module, a DSP (Digital Signal Processor) module and at least two antennas. According to the device, with the assistance of an INS, the probability of cycle slip of the GNSS can be reduced effectively, the integer ambiguity searching space of the GNSS is reduced, attitude measurement information is guaranteed to be continuously outputted, and the tracking loop robustness of the GNSS is enhanced; and with the assistance of a double-antenna GNSS, quick initial alignment of the INS can be realized, the attitude observability of the INS is improved, and the attitude divergence of the INS is inhibited.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Carrier phase gps positioning device and method
ActiveUS20070057839A1Reduction of integer ambiguity estimation precision is preventableTime up to estimation of the integer ambiguity is shortenedPosition fixationNavigation instrumentsCarrier signalInteger ambiguity
A carrier phase GPS positioning device is disclosed, which acquires a carrier phase accumulation value of satellite signals at one time on the mobile station side, associates plural carrier phase accumulation values on the reference station side at plural times prior to the one time with the carrier phase accumulation value on the mobile station side, and estimates an integer ambiguity included in the carrier phase accumulation value of signals transmitted from the satellite received by the mobile station.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
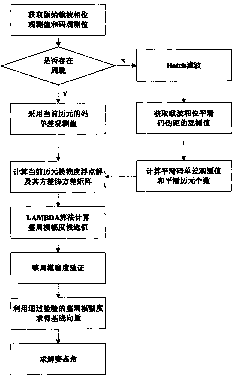
Carrier smoothing code pseudorange technology-based dynamic attitude positioning method
InactiveCN101825717AHigh precisionOvercoming the disadvantages of decreased success rateSatellite radio beaconingAlgorithmAmbiguity
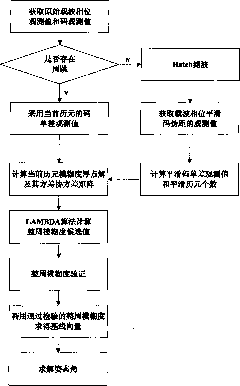
The invention discloses a carrier smoothing code pseudorange technology-based dynamic attitude positioning algorithm method, which comprises the following steps of: (1) detecting whether cycle slip occurs in the current epoch by using a three-difference method, if so, using the code observation of the current epoch, otherwise, acquiring the smoothed code observation by using Hatch filtering and recording the smoothing window length k; (2) solving the floating solution of the integer ambiguity and the variance-covariance matrix of the floating solution by utilizing the code observation and the code observation of the current epoch; (3) taking the floating solution of the integer ambiguity and the variance-covariance matrix of the floating solution as initial parameters, substituting the initial parameters into an LAMBDA algorithm for solving the fixed solution of the ambiguity, and acquiring former N ambiguity candidate values; and (4) performing the ambiguity test on the former N ambiguity candidate values in turn, until the ambiguity candidate solution meeting the constraint condition is found, and solving the obtained attitude angle. The carrier smoothing code pseudorange technology-based dynamic attitude positioning algorithm method does not have the problem of initialization time, can be effectively used for real-time dynamic attitude measurement, and can self-adaptively regulate the smoothing window length and the ambiguity candidate solution space aiming at the occurrence of the cycle slip. Therefore, the success rate and the overall efficiency of the algorithm are improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
System for determining the heading and/or attitude of a body
InactiveUS20020029110A1Shorten the timeIncrease ratingsInstruments for road network navigationDigital data processing detailsInteger ambiguitySystem usage
A system for determining the heading and / or attitude of a body receives radio waves from a plurality of position-fixing satellites using at least three antennas fixedly mounted at different positions of the body. To reliably obtain integer ambiguity solutions of carrier phases of the radio waves in a shorter time, the system directly determines integer ambiguities from attitude angle data obtained by an IMU attitude processing section when the integer ambiguities are to be redetermined in the event of an interruption of the received radio waves or a change in the combination of satellites to be used. This system provides a user with highly accurate uninterrupted heading and / or attitude angle information.
Owner:FURUNO ELECTRIC CO LTD
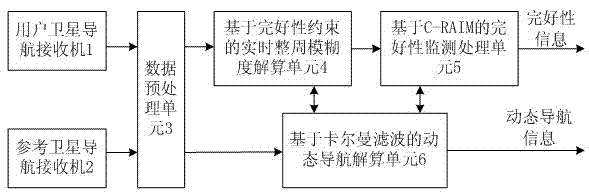
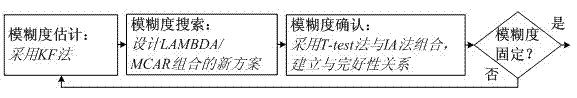
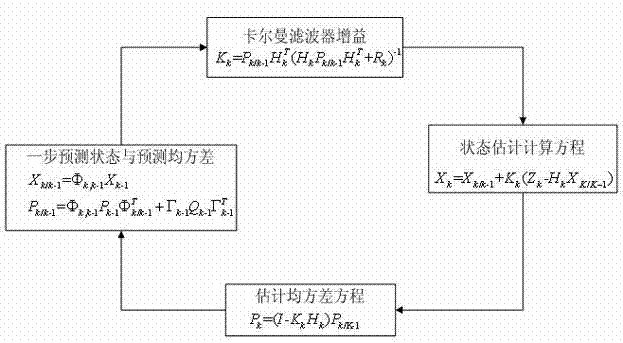
Satellite navigation integrity monitoring device based on carrier phase and application method of device
InactiveCN102819027AImprove navigation accuracyImprove integritySatellite radio beaconingCarrier signalInteger ambiguity
The invention discloses a satellite navigation integrity monitoring device based on a carrier phase and an application method of the device and belongs to the technical field of satellite navigation positioning. The device comprises a user satellite navigation receiver, a reference satellite navigation receiver, a data preprocessing unit, a real-time integer ambiguity revolving unit based on integrity constraint, an integrity monitoring processing unit based on C-RAIM (Carrier Phase-Receiver Automatic Integrity Monitoring) and a dynamic navigation resolving unit based on Kallman filtering. At present, home and abroad satellite navigation integrity monitoring technologies are mostly based on pseudo range observation, carrier phase observation is necessary in the field of high-precision satellite navigation, while the research on a satellite navigation integrity monitoring technology based on the carrier phase is rare. Compared with the prior art, the device disclosed by the invention can be used for obviously improving the navigation accuracy and integrity at the same time and has great significance in the field of high-performance navigation.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Attitude angle detecting apparatus
InactiveUS20030154049A1Measuring relative positionRedetermine the integer ambiguity quickly and accuratelyDigital computer detailsSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsAmbiguityInteger ambiguity
An attitude angle detecting apparatus receives radio waves transmitted from a plurality of position-fixing satellites with multiple antennas located at specific positions of a mobile unit, determines relative positions of the antennas and detects the heading and attitude of the mobile unit by determining carrier phase ambiguities quickly and accurately. When it is needed to redetermine integer ambiguities after recovery from an interruption of the radio waves from the position-fixing satellites or as a result of a change in combination of the position-fixing satellites, for example, the attitude angle detecting apparatus redetermines the integer ambiguities by using attitude angles and an attitude angle error covariance obtained from previous observation. This enables the attitude angle detecting apparatus to uninterruptedly obtain information on the heading and attitude of the mobile unit.
Owner:FURUNO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Precise GNSS positioning system with improved ambiguity estimation
Method for precise GNSS positioning system with improved ambiguity estimation. The method is based on the realization that, especially during convergence, the estimated float ambiguities are biased when estimated simultaneously with the ionosphere parameters. The “ionosphere-like” biases can be separated from the actual float ambiguities by using the fixed wide-lane (or extra wide-lane) integer ambiguities. The original real-valued ambiguities (e.g., one of L1, L2 and L5 in the GPS case) are corrected using the corresponding biases, resulting in reliable float ambiguities that are taken as input in the next processing step.
Owner:FUGRO
Carrier-phase-based relative positioning device
InactiveUS20040145518A1Quick fixEasily and uninterruptedly estimate integer ambiguityPosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingKaiman filterDouble phase
A carrier-phase-based relative positioning device employs a signal processing method which makes it possible to continue estimation of integer ambiguity values even when the number of positioning satellites has changed, determine an integer ambiguity value by efficiently verifying the integer ambiguities in a short time, and calculate a baseline vector. The positioning device includes an integer ambiguity resolving section which determines integer ambiguities of single or double phase differences using a Kalman filter and lambda notation. The Kalman filter is used to calculate estimated values of floating ambiguities and the lambda notation is used to calculate estimated values of the integer ambiguities based on the floating ambiguities. A candidate of a potentially true integer ambiguity that is considered most reliable is determined through various verification processes. When the number of positioning satellites has increased or decreased, or when a reference satellite has been switched, a floating ambiguity after the change in satellite information is estimated from a baseline vector estimated before the change.
Owner:FURUNO ELECTRIC CO LTD
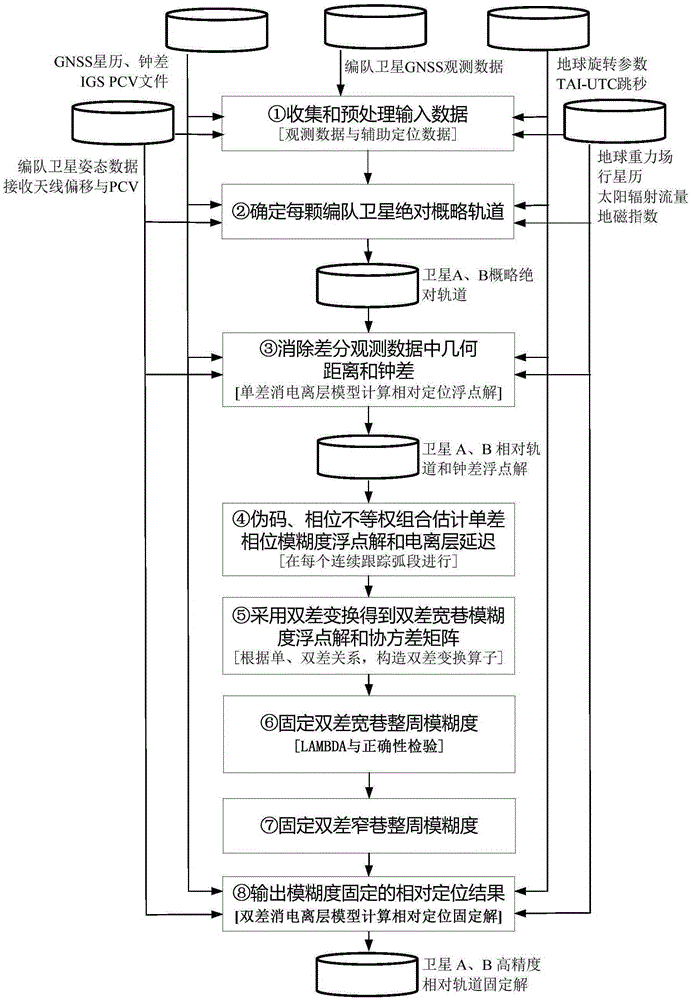
Long baseline satellite formation GNSS relative positioning method based on ambiguity fixing
ActiveCN105372691AHigh precisionOvercome the shortcoming of easy divergenceSatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceAmbiguity
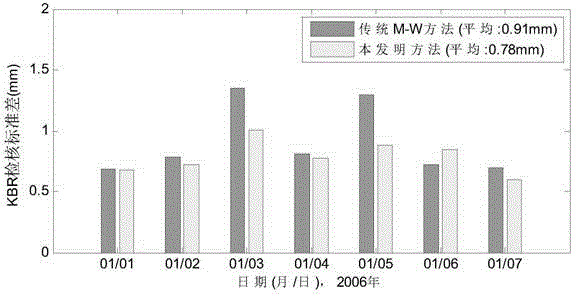
A long baseline satellite formation GNSS relative positioning method based on ambiguity fixing is provided in order to improve the success rate of ambiguity fixing and the accuracy of relative positioning results. According to the technical scheme, the method comprises the following steps: first, collecting and pre-processing input data, and determining the absolute general orbit of a formation satellite; then, eliminating the geometric distance and clock error in differential observation data, estimating a single-difference phase ambiguity float solution and a single-difference ionosphere delay parameter, carrying out double-difference transform to get a double-difference wide-lane ambiguity float solution and a covariance matrix, and fixing the double-difference wide-lane integer ambiguity and the double-difference narrow-lane integer ambiguity; and finally, outputting the relative positioning result of ambiguity fixing. By adopting the method of the invention, the problem that ambiguity fixing strongly depends on a pseudo code with low observation precision due to equally-weighted pseudo code and phase processing in M-W combination in the traditional method is avoided, the success rate of long baseline satellite formation GNSS relative positioning ambiguity fixing and the accuracy of final relative positioning results are improved, calculation is stable, and the reliability of relative positioning results is improved.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
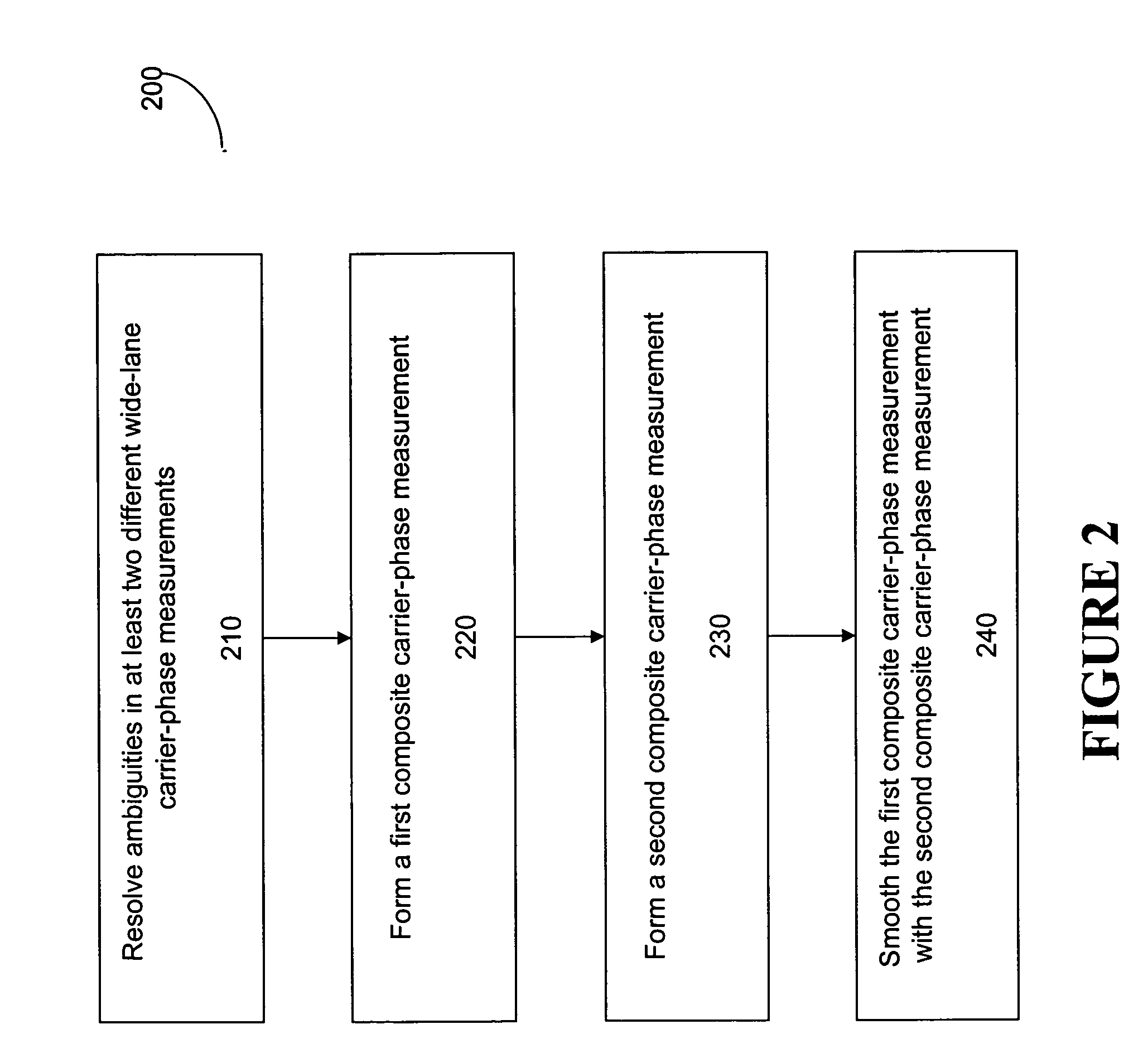
Method for using three GPS frequencies to resolve carrier-phase integer ambiguities
ActiveUS20050080560A1Remove baseline separation limitationResolve ambiguityPosition fixationNavigation instrumentsAmbiguityInteger ambiguity
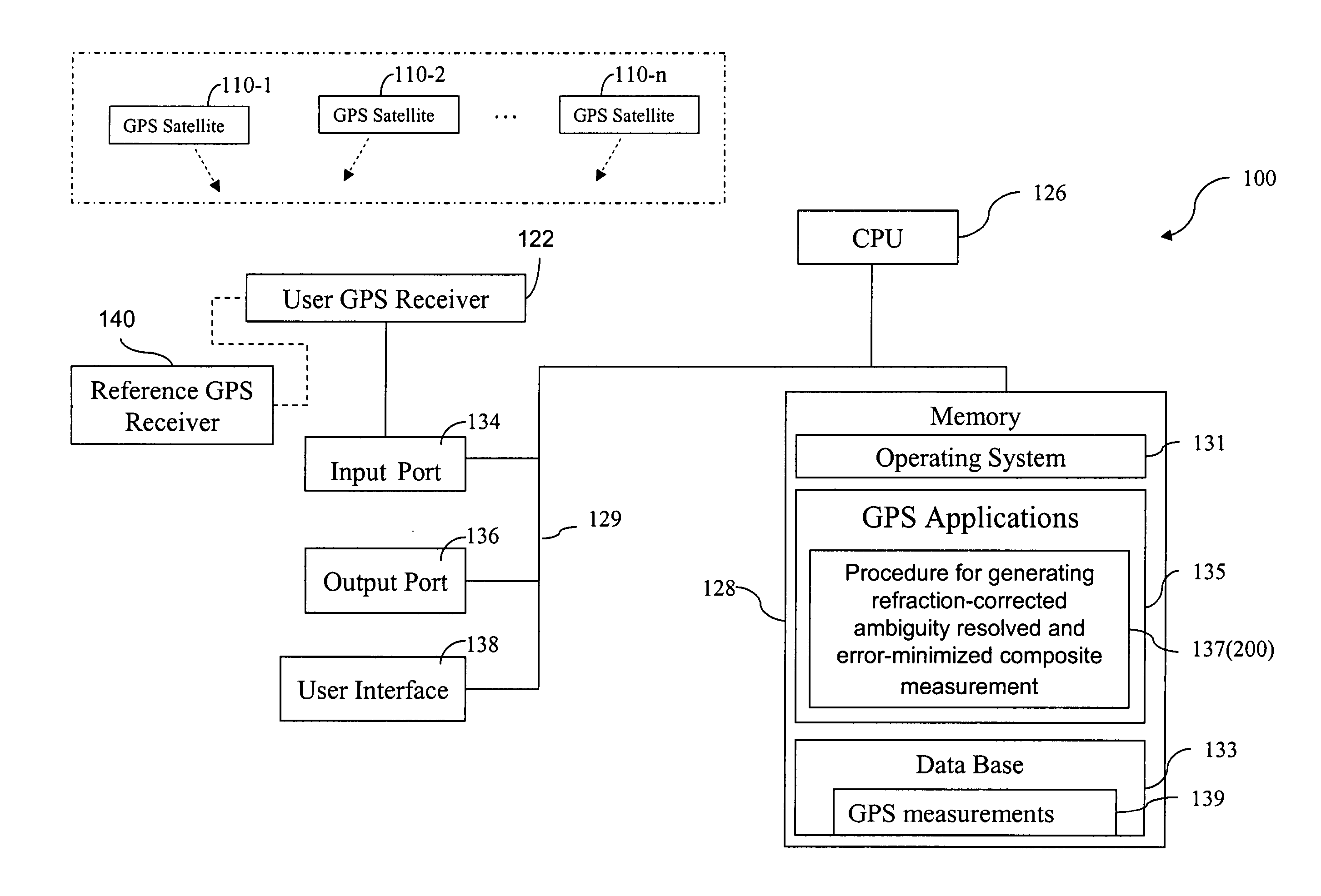
The present invention includes a method for generating an ambiguity-resolved, refraction-corrected, and noise-minimized carrier-phase measurement. The method includes forming a first composite measurement using GPS carrier-phase measurements on the L1, L2 and L5 frequencies. To reduce the noise in the first composite measurement, the method further includes forming a second composite measurement using GPS carrier-phase measurements on at least two of the three GPS carrier frequencies. The second composite measurement is formed to have a small multi-path noise therein so that it can be used to smooth the first composite measurement so that the multipath noise is minimized.
Owner:DEERE & CO
Detection and correction of anomalous measurements and ambiguity resolution in a global navigation satellite system receiver
A global navigation system includes a first navigation receiver located in a rover and a second navigation receiver located in a base station. Single differences of measurements of satellite signals received at the two receivers are calculated and compared to single differences derived from an observation model. Anomalous measurements are detected and removed prior to performing computations for determining the output position of the rover and resolving integer ambiguities. Detection criteria are based on the residuals between the calculated and the derived single differences. For resolving integer ambiguities, computations based on Cholesky information Kalman filters and Householder transformations are advantageously applied. Changes in the state of the satellite constellation from one epoch to another are included in the computations.
Owner:TOPCON POSITIONING SYST INC
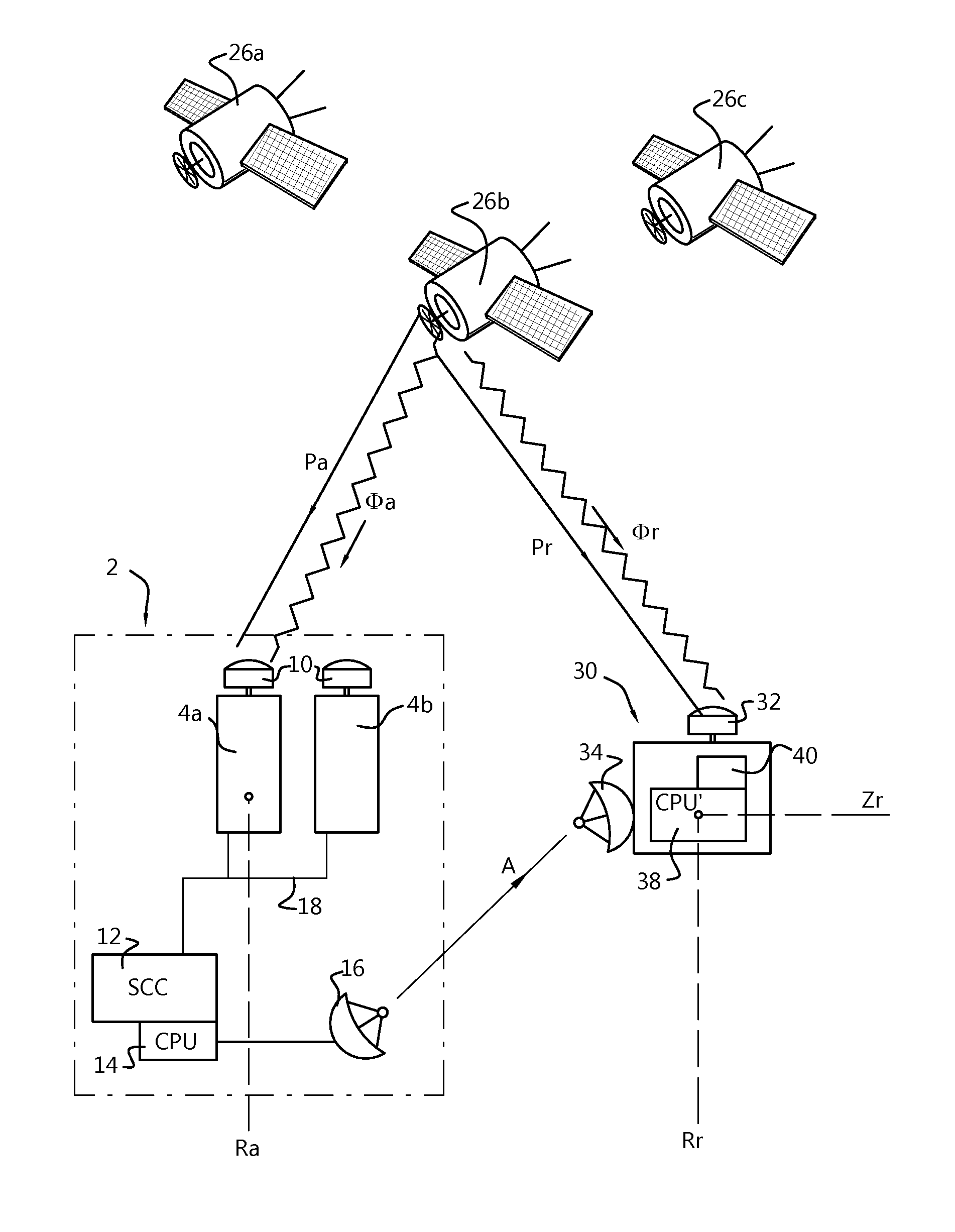
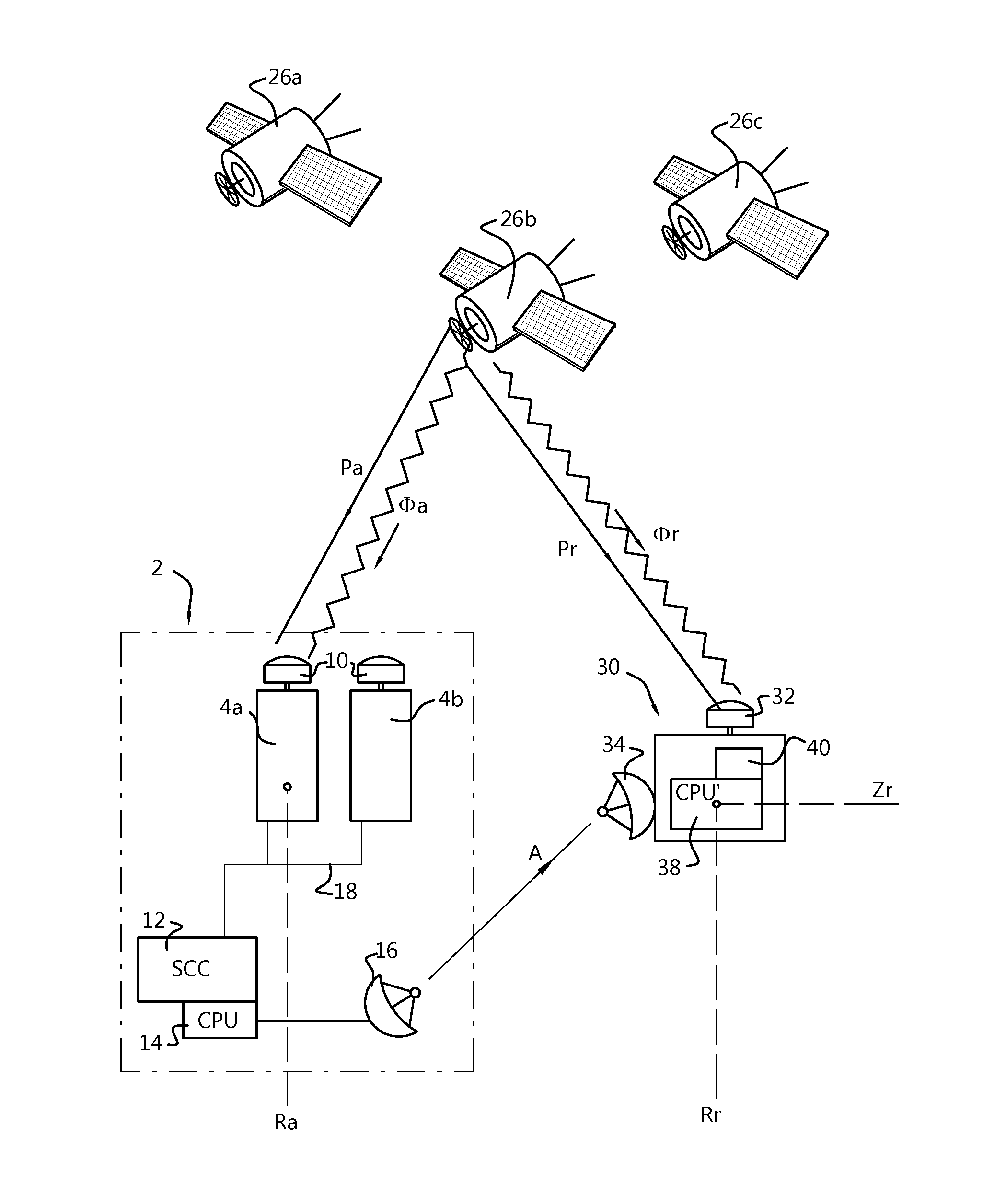
Integer ambiguity-fixed precise point positioning method and system
ActiveUS20160077213A1Efficient implementationImplemented much more efficientlySatellite radio beaconingSignal correctionObservation data
A method for providing and applying Precise Point Positioning-Integer Ambiguity Resolution (PPP-IAR) corrections for a Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS). In a GNS signal correction system, PPP-IAR corrections (ambiguities plus receiver and satellite hardware delays) are calculated based on observation data (Pi,a, Φi,a) of n satellites for individual reference stations using a functional model, and these individual PPP-IAR corrections are merged into one single and larger set of PPP-IAR corrections. In a broadcast system, the (merged) PPP-IAR corrections are encoded at a System Control Centre (SCC) and transmitted to mobiles. In a mobile system a similar functional model is used to calculate a correction Δx to an a priori position.
Owner:FUGRO
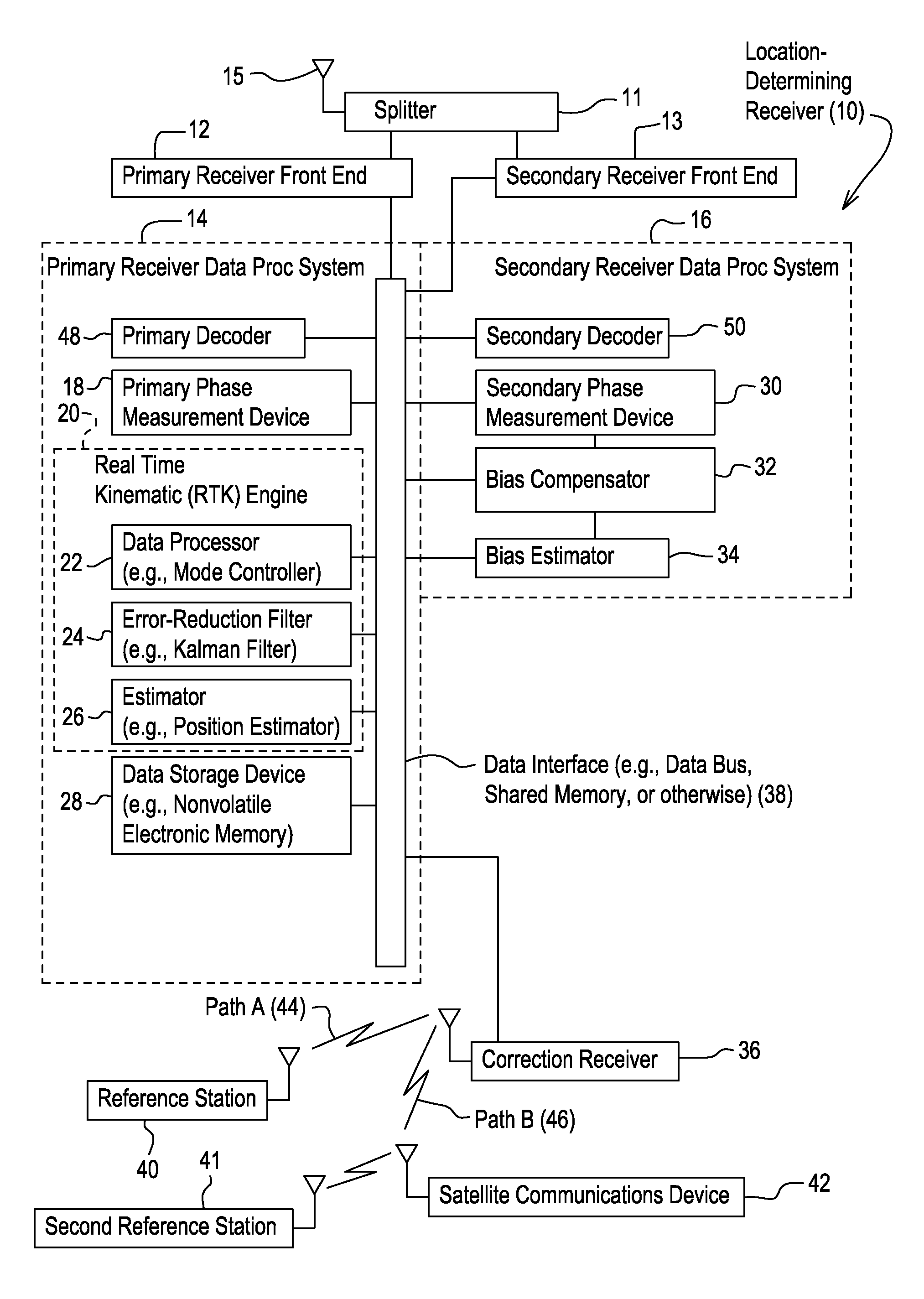
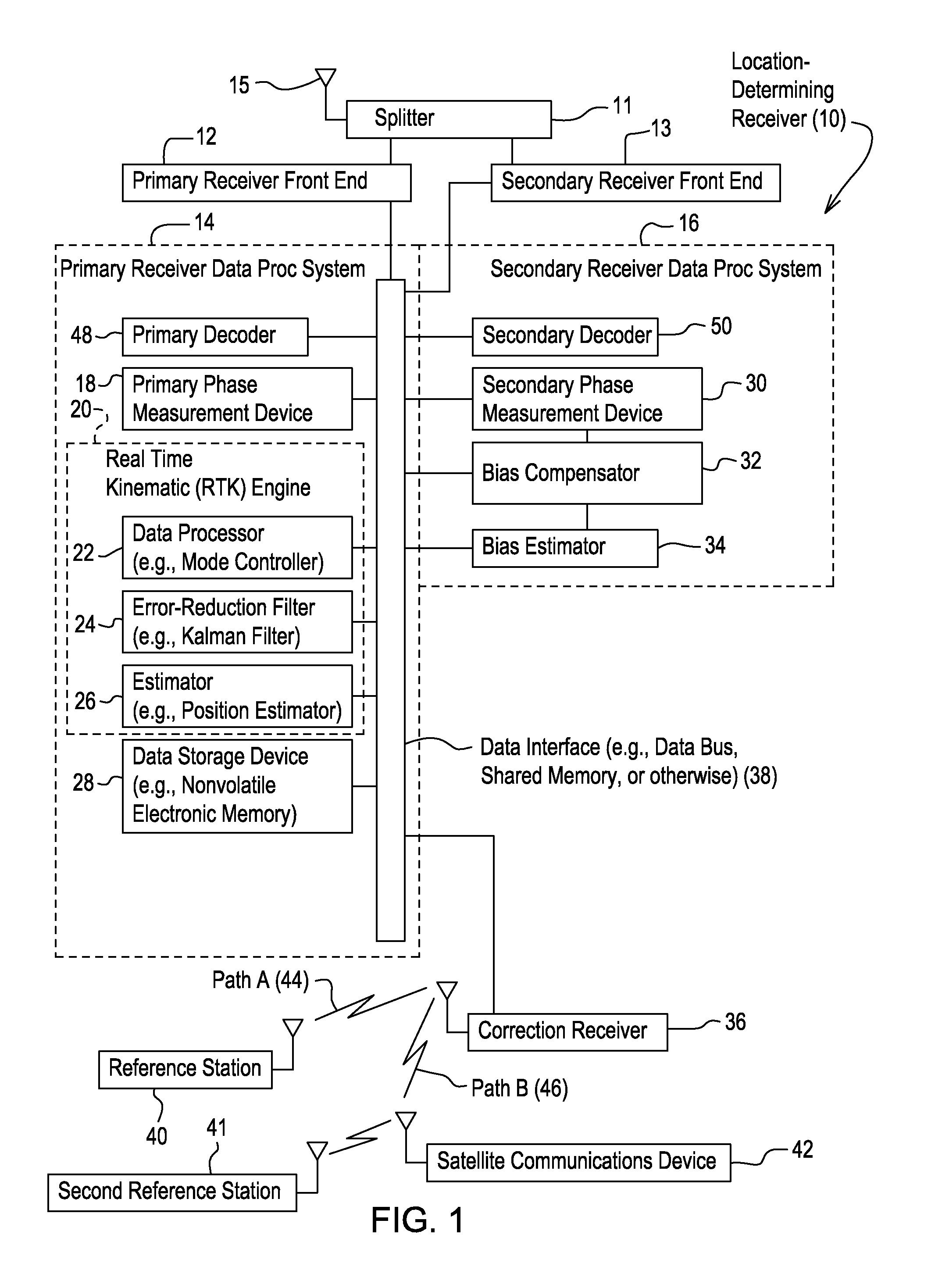
Method and system for estimating position with bias compensation
A primary phase measurement device measures a first carrier phase and a second carrier phase of carrier signals received by the location-determining receiver. A secondary phase measurement device measures the third carrier phase and the fourth carrier phase of other carrier signals. A real time kinematic engine estimates a first integer ambiguity set associated with the measured first carrier phase and a second integer ambiguity set associated with the measured second carrier phase. The real time kinematic engine estimates a third ambiguity set associated with the measured third carrier phase and a fourth ambiguity set associated with the measured fourth carrier phase. A compensator is capable of compensating for the inter-channel bias in at least one of the third ambiguity set and the fourth ambiguity set by modeling a predictive filter in accordance with various inputs or states of the filter estimated by an estimator.
Owner:DEERE & CO
Processing multi-GNSS data from mixed-type receivers
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
Adaptive genetic algorithm-based single-frequency GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) integer ambiguity acquisition method
InactiveCN102736094AReduce correlationAvoid complex calculationsSatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceInteger ambiguity
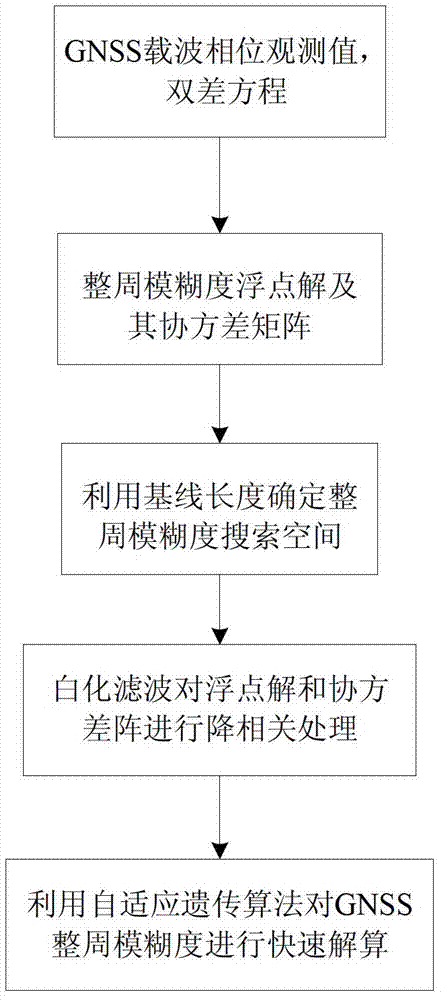
The invention discloses an adaptive genetic algorithm-based single-frequency GNSS integer ambiguity acquisition method. The method includes the following steps: step 1: acquiring the observed data of a GNSS carrier phase, and establishing a double-difference observation equation for the GNSS carrier phase; step 2: according to the double-difference observation equation obtained in step 1, utilizing the least square method to acquire the float solution and corresponding covariance matrix of GNSS integer ambiguity; step 3: utilizing known base length as a constraint condition to determine the search space of integer ambiguity; step 4: utilizing the whitening filter method to decorrelate the float solution and covariance matrix of integer ambiguity obtained in step 2; step 5: according to anobjective function, determining a fitness function, determining each operating parameter in the adaptive genetic algorithm, finally, introducing the adaptive genetic algorithm into fast solution on integer ambiguity, and searching the optimal solution of integer ambiguity.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Double-frequency multi-constellation GNSS integer ambiguity OTF solving method
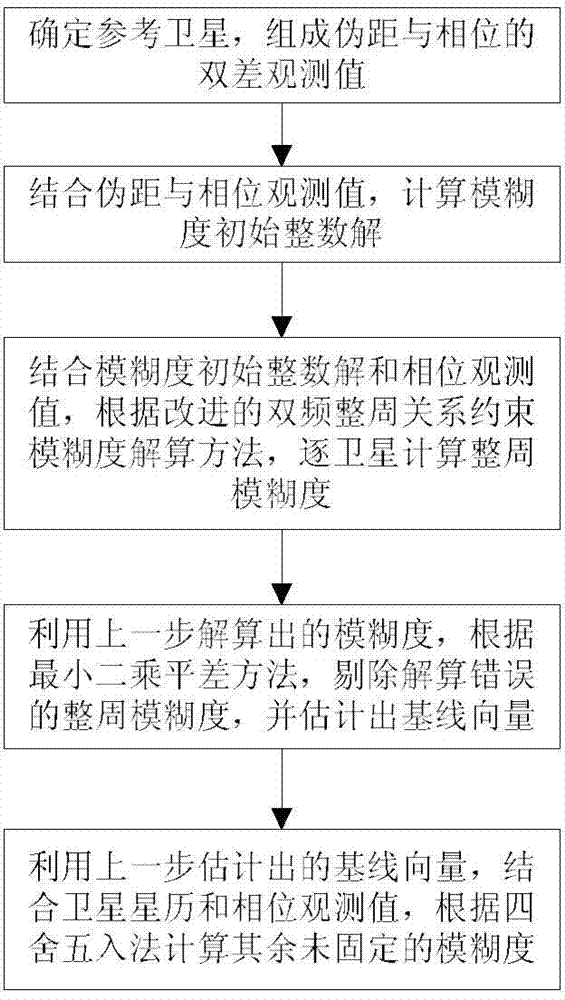
InactiveCN103576175ASimple calculationImprove work efficiencySatellite radio beaconingAmbiguityDynamic positioning
The invention discloses a double-frequency multi-constellation GNSS integer ambiguity OTF solving method. Under the condition of short base line dynamic positioning, integer ambiguity fixing of a GNSS carrier phase observed value is achieved. The method improves a traditional double-frequency integer relationship constraint ambiguity solving method, and can be suitable for integer ambiguity solving of an L1 / L2 signal pair of a GPS, a B1 / B2 signal pair and a B1 / B3 signal pair of a BDS, a G1 / G2 signal pair of a GLONASS, an E1 / E5b signal pair, an E1 / E6 signal pair and an E5a / E6 signal pair of a GALILEO. Compared with a traditional ambiguity searching method, the double-frequency multi-constellation GNSS integer ambiguity OTF solving method does not need ambiguity searching, and is simple in computing, high in working efficiency and capable of being used for integer ambiguity initialization under a dynamic environment. The double-frequency multi-constellation GNSS integer ambiguity OTF solving method can be widely applied to high precision GNSS real-time dynamic positioning, and particularly has advantages in the integer ambiguity dynamic initialization of multi-GNSS system integrated navigation positioning.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for determining biases of satellite signals
ActiveUS20110140958A1Improve accuracyReduce in quantitySatellite radio beaconingKaiman filterIonosphere
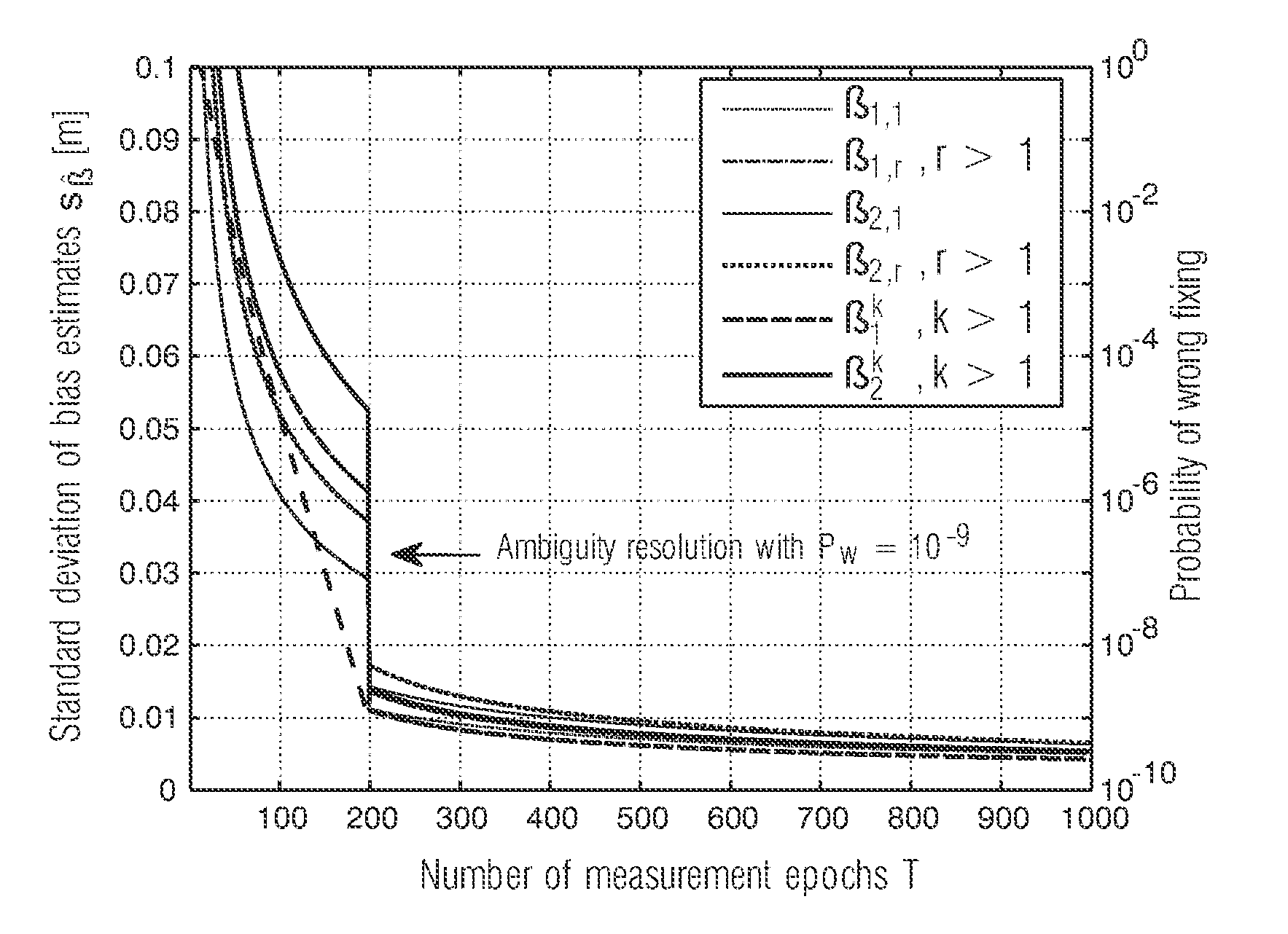
A new method for bias estimation on multiple frequencies with a Kalman filter is proposed. It consists of four steps: First, a least-squares estimation of ranges, ionospheric delays, ambiguities, receiver phase biases and satellite phase biases is performed. The code biases are absorbed in the ranges and ionospheric delays, and a subset of ambiguities is mapped to the phase biases to remove linear dependencies between the unknown parameters. In a second step, the accuracy of the bias estimates is efficiently improved by a Kalman filter. The real-valued a posteriori ambiguity estimates are decorrelated by an integer ambiguity transformation to reduce the time of ambiguity resolution. Once the float ambiguities have sufficiently converged, they are fixed sequentially in a third step. Finally, a second Kalman filter is used to separate the receiver and satellite code biases and the tropospheric delays from the ranges.
Owner:DEUTSCHES ZENTRUM FUER LUFT & RAUMFAHRT EV
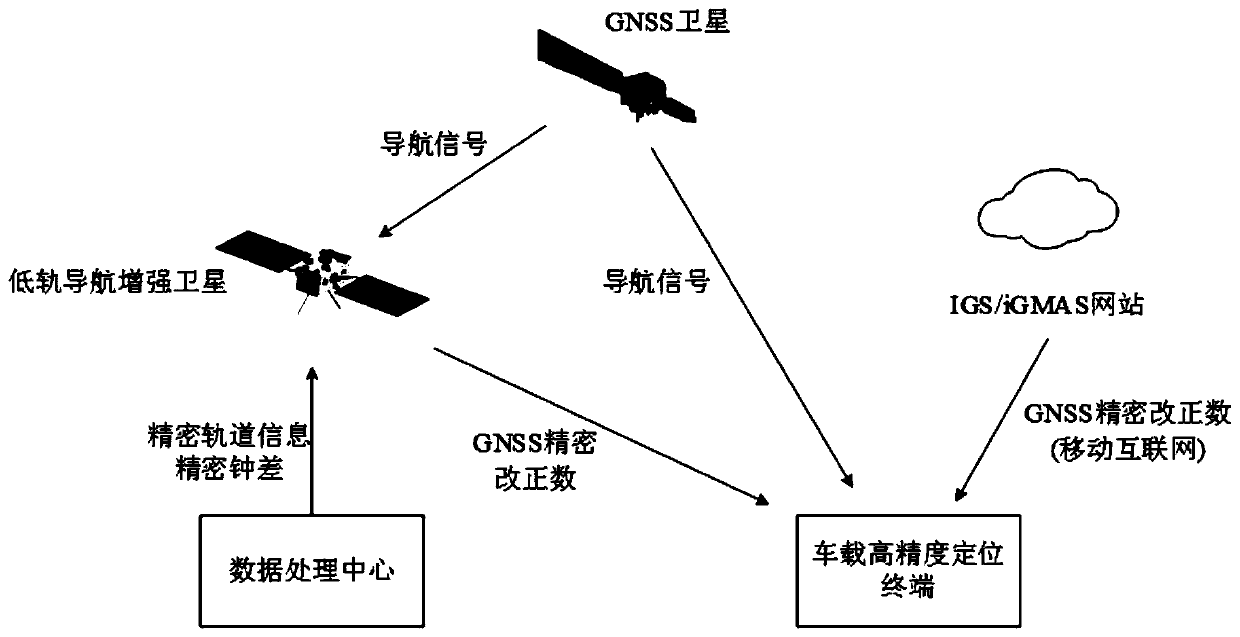
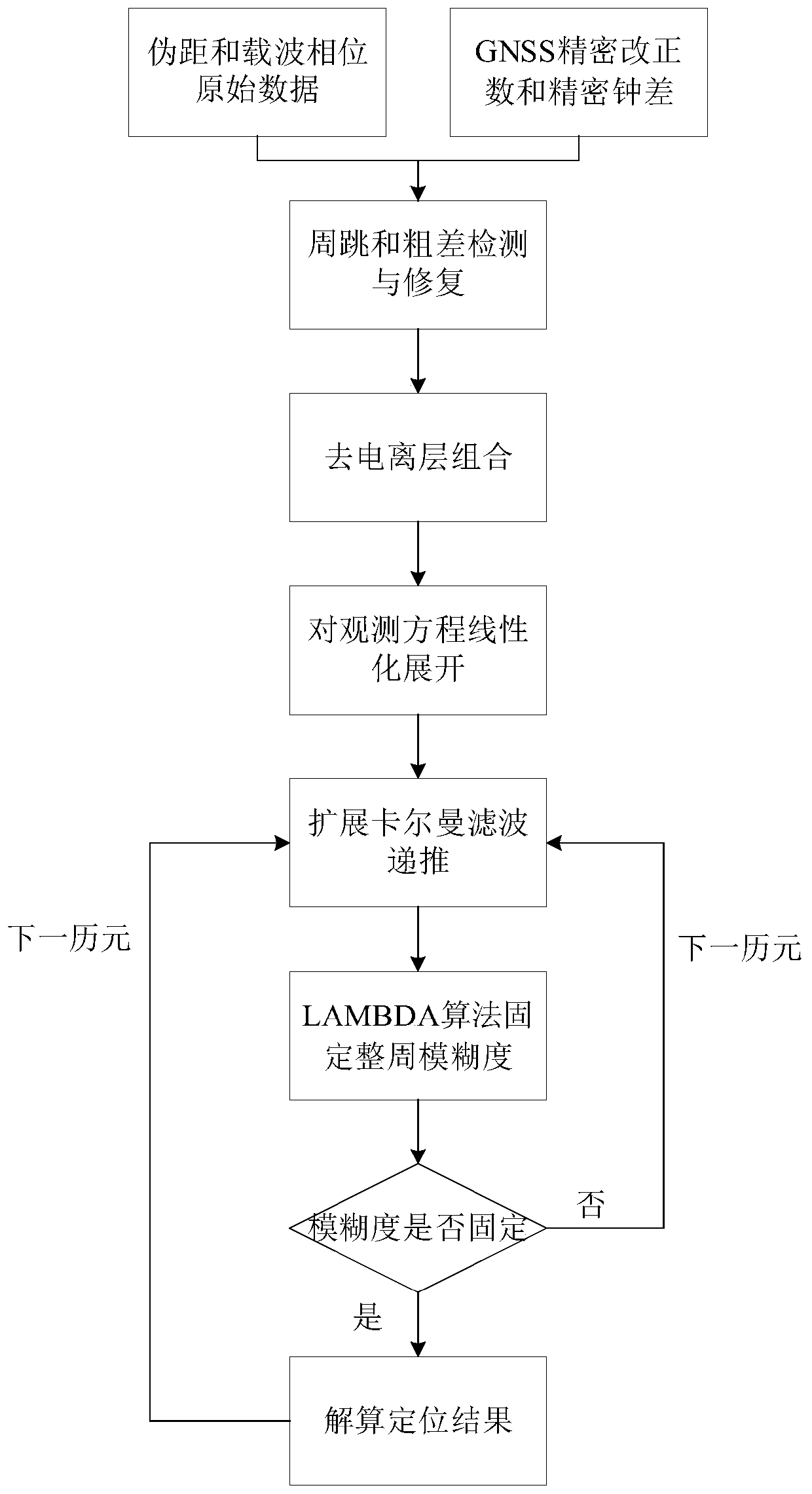
High precision positioning method based on PPP algorithm as well as system
PendingCN110531392AGet rid of distance restrictionsNear positioning accuracySatellite radio beaconingAmbiguityClock correction
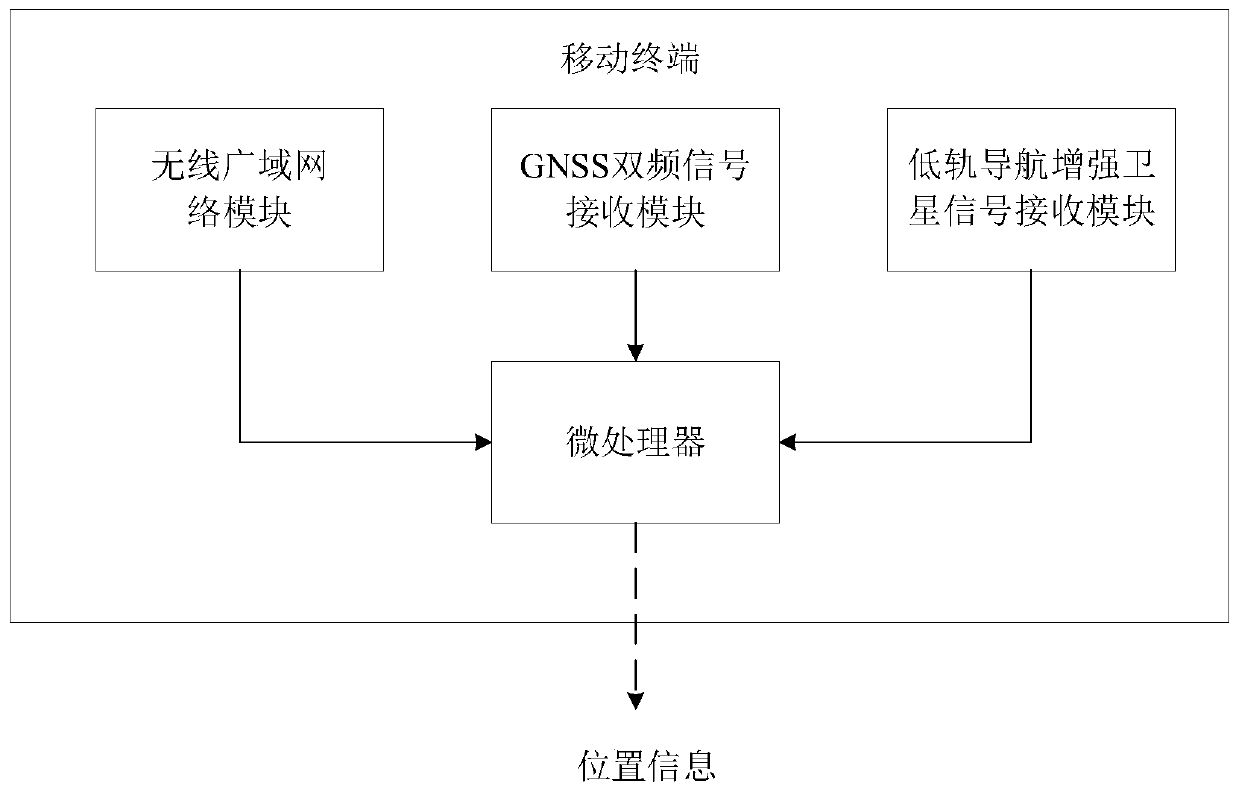
The invention discloses a high precision positioning method based on a PPP algorithm as well as a system and relates to the field of GNSS high precision positioning application. Centimeter-level highprecision positioning can be realized by being independent of a ground positioning base station, only depending on a mobile terminal, utilizing a double frequency GNSS carrier phase and an observed pseudorange value and combining a GNSS precise orbit and clock correction. The system comprises a GNSS double frequency signal receiving module, a wireless wide area network module, a low orbit navigation enhanced satellite signal receiving module and a microprocessor. The positioning method obtains the original pseudorange and carrier phase observation data by adopting GNSS double frequency observation data and GNSS precise correction, then fixes integer ambiguity by utilizing an LAMBDA algorithm and finally performs recursion and convergence on an ionized layer combined observation linear equation by adopting an expansion Kalman filtering equation, thus location information is obtained. The method and system which are disclosed by the invention have the advantages of convenience in use, high reliability and low cost.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Independent Positioning Device and Independent Positioning Method
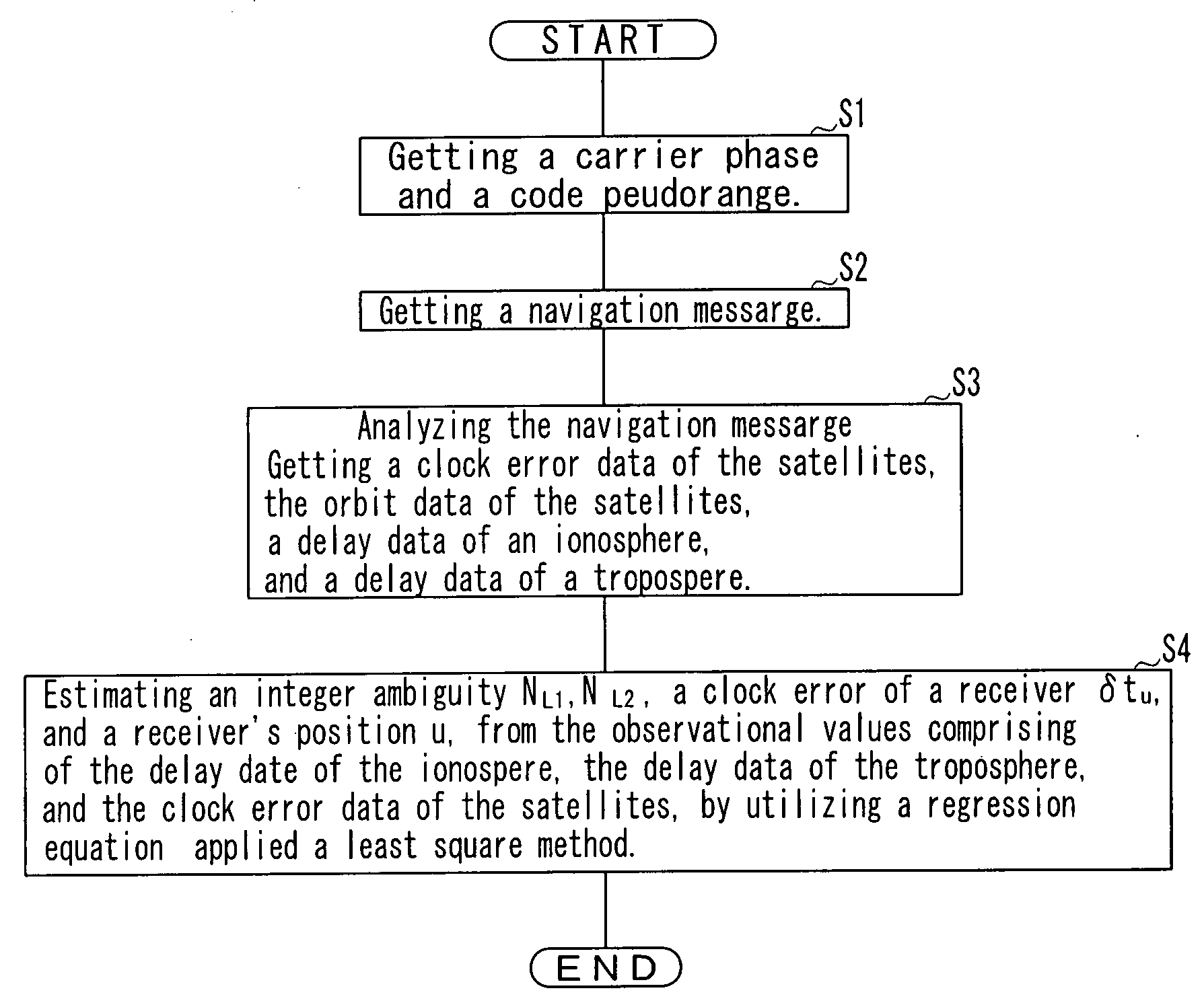
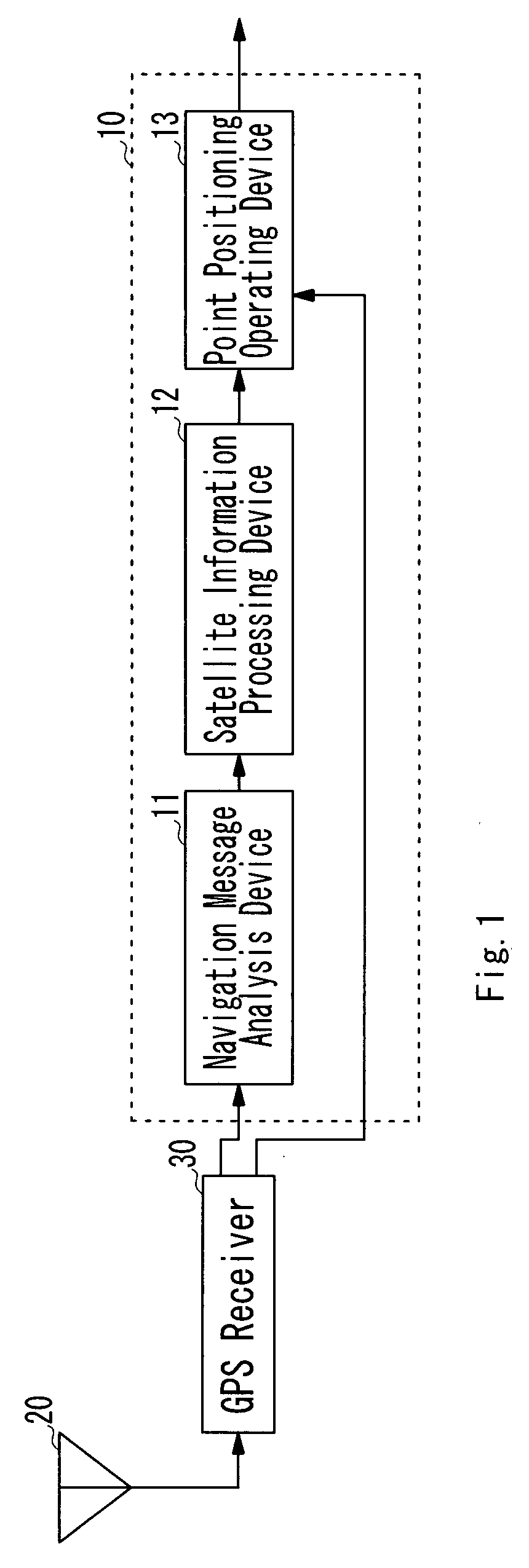
ActiveUS20080258966A1No complicationsImprove accuracyPosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingTroposphereAlgorithm
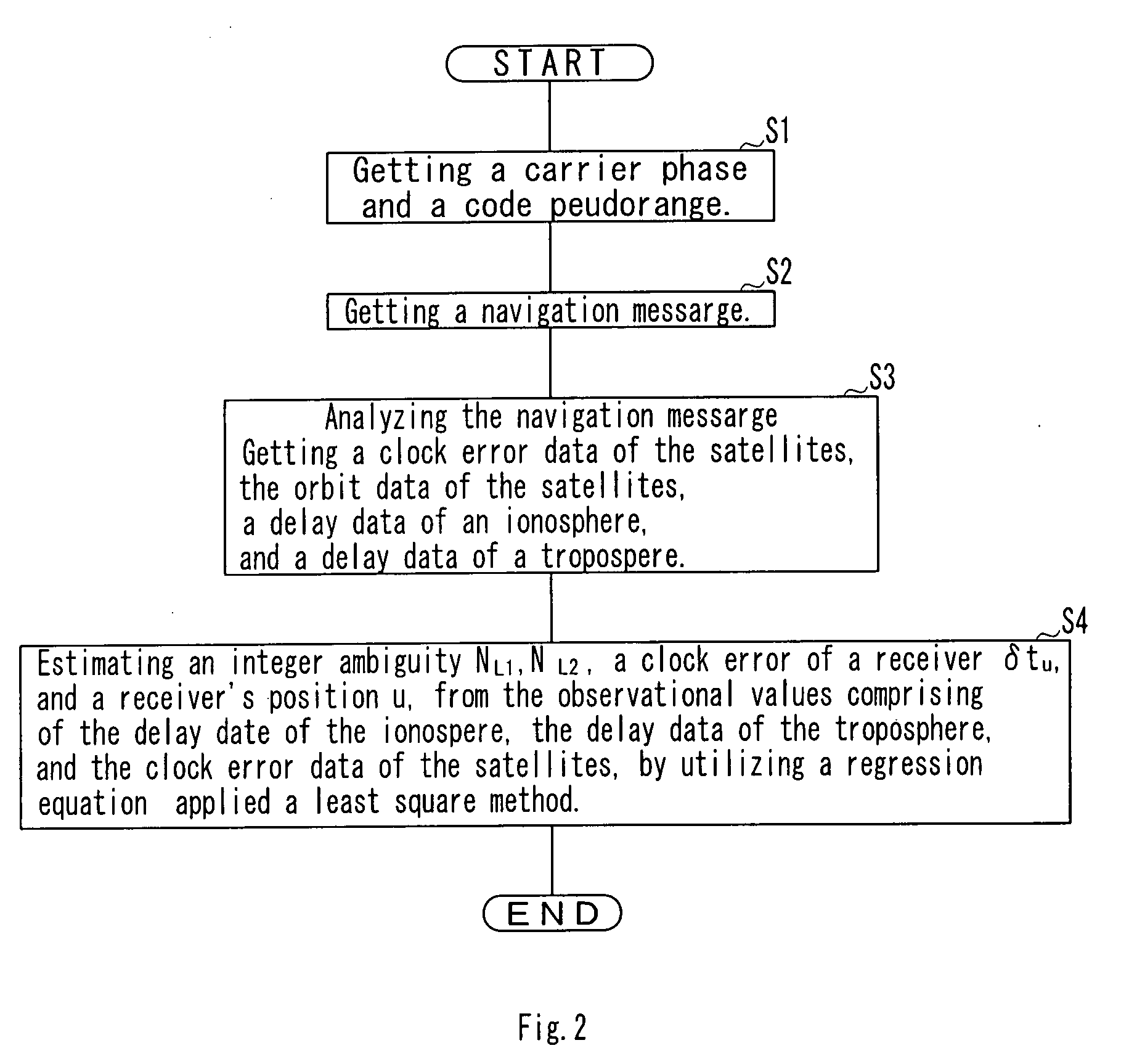
A linear regression equation is comprised of the objective variables and the explanatory variables. The objective variables are comprised of the L1 carrier phases, the L2 carrier phases, the C / A code pseudorange, the P(Y) code pseudorange, the clock error data, the delay data of the ionosphere, and the delay data of the troposphere that related with every satellite respectively. The explanatory variables are comprised of at least the integer ambiguity and a receiver's position.The receiver's position has been linear-approximated by using the estimation results of the passed receiver's positions. Applying a least square method to the regression equation, the integer ambiguity and the receiver's position is estimated.
Owner:THE RITSUMEIKAN TRUST +1
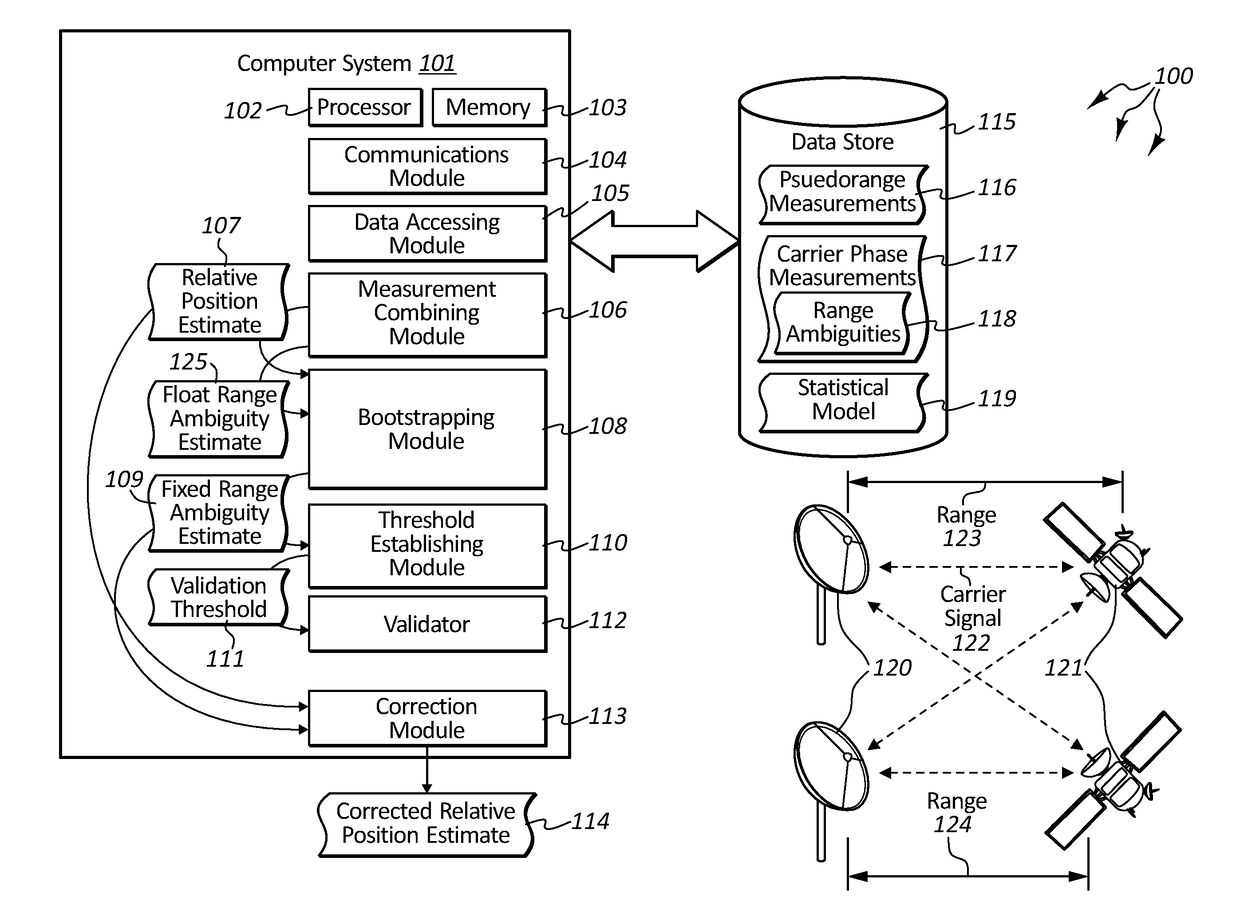
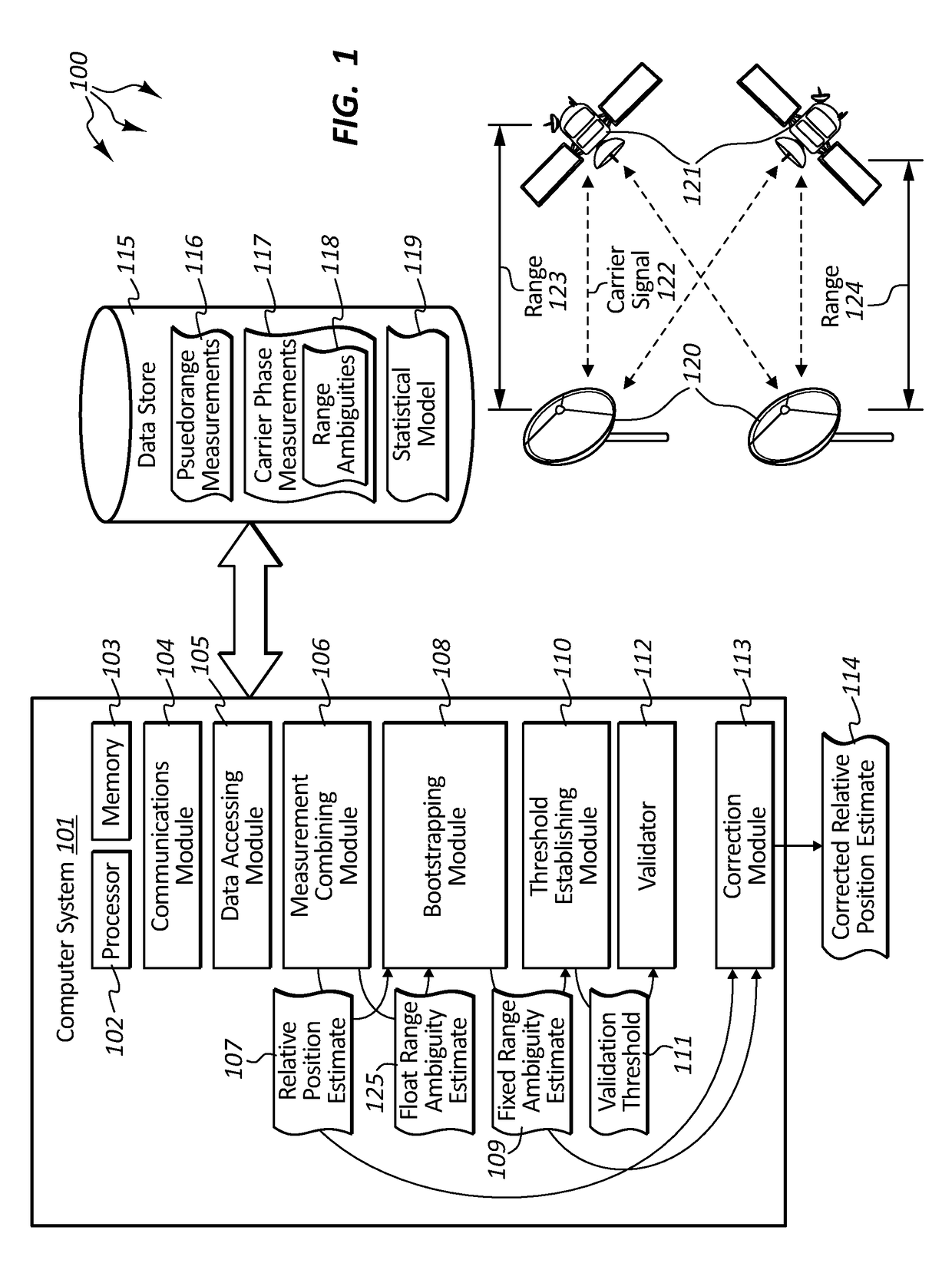
Assured validation of carrier-phase integer ambiguities for safety-of-life applications
Embodiments are directed to performing integer ambiguity validation in carrier phase differential positioning and to calculating a protection level for safety-of-life applications. In one scenario, a computer system accesses double-differenced pseudorange measurements and carrier phase measurements which are combined to produce an estimate of the relative position between receivers. Integer bootstrapping is performed to produce fixed range ambiguity estimates that are integer multiples of a carrier signal wavelength. A validation threshold is then established based on a statistical model of the pseudorange and carrier wave measurements that ensures that a specified probability of correct ambiguity resolution is met. A data-driven validation is initiated on the difference between the float range ambiguity estimates and the fixed range ambiguity estimates to validate the correctness of the fixed range ambiguity estimate. Then, upon determining that the fixed range ambiguity estimates are valid, the estimate of the relative position between the receivers is corrected.
Owner:COHERENT TECHN SERVICES
Estimation and resolution of carrier wave ambiguities in a position navigation system
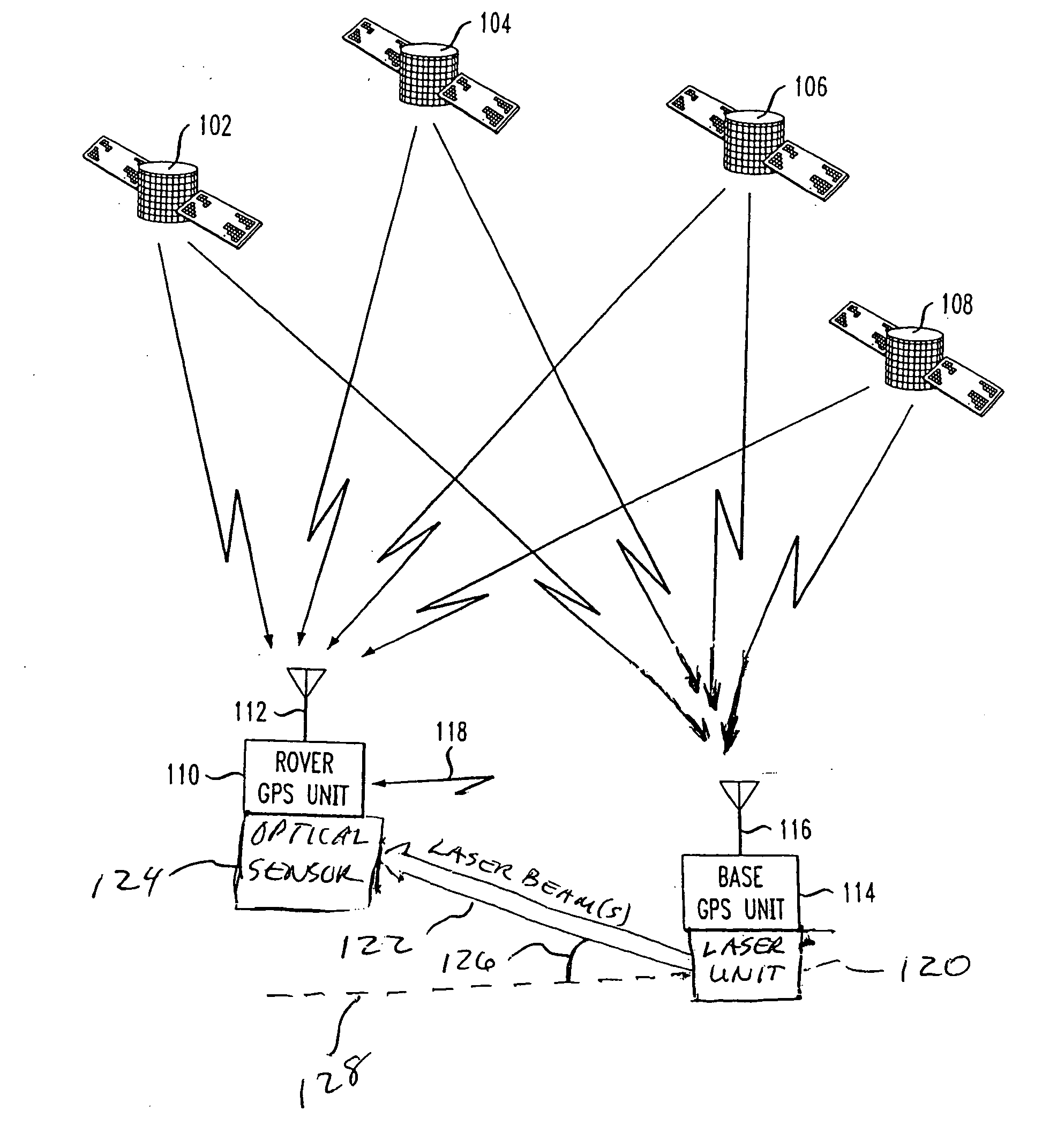
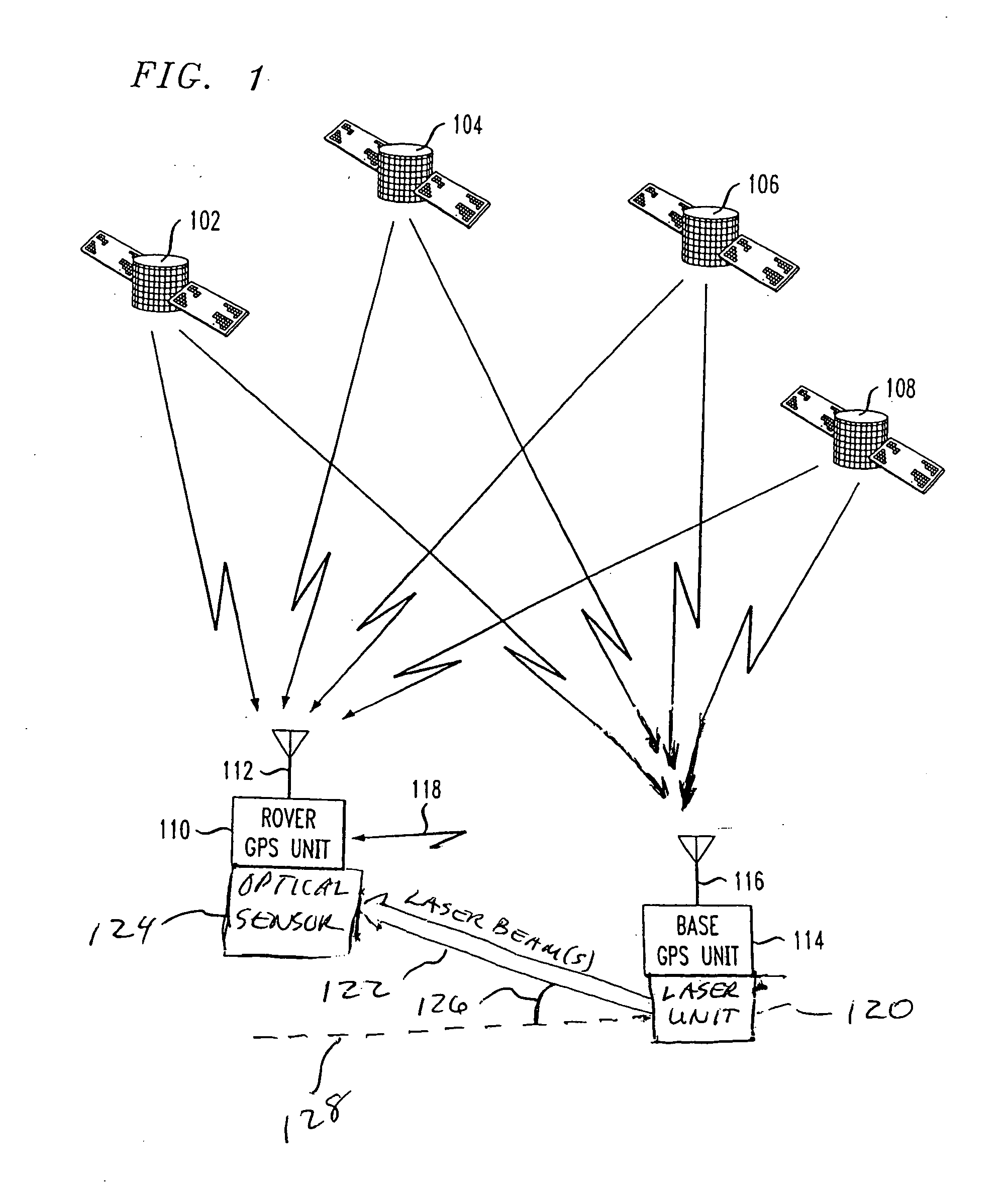
ActiveUS20050264445A1Improve accuracyError minimizationActive open surveying meansPosition fixationElevation angleImage resolution
A method and apparatus for resolving floating point and integer ambiguities in a satellite position navigation system is disclosed. A rover station is periodically positioned at unknown locations and has a satellite receiver capable of receiving the navigation signals. By calculating relative position coordinates between a base station in a known location and the rover station, and by calculating other position parameters relative to the satellite position, a geometric constraint based on a measured elevation angle between the rover and base station can be incorporated into data computations and processing to help resolve carrier phase ambiguities. The elevation angle is measured by transmitting multiple laser beams to an optical sensor on the rover station. This technique results in greater precision in determining the location of the rover.
Owner:TOPCON GPS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com