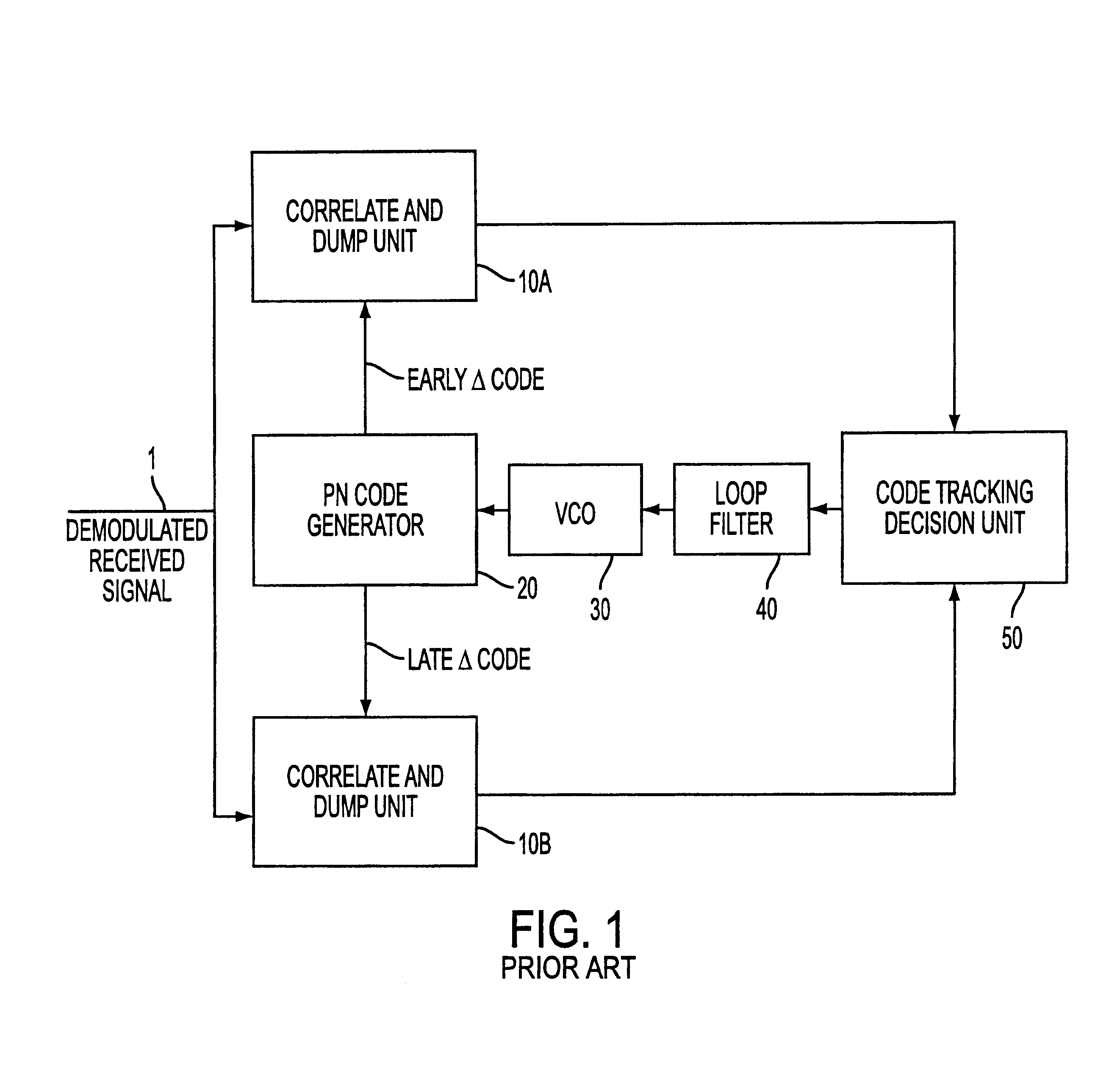
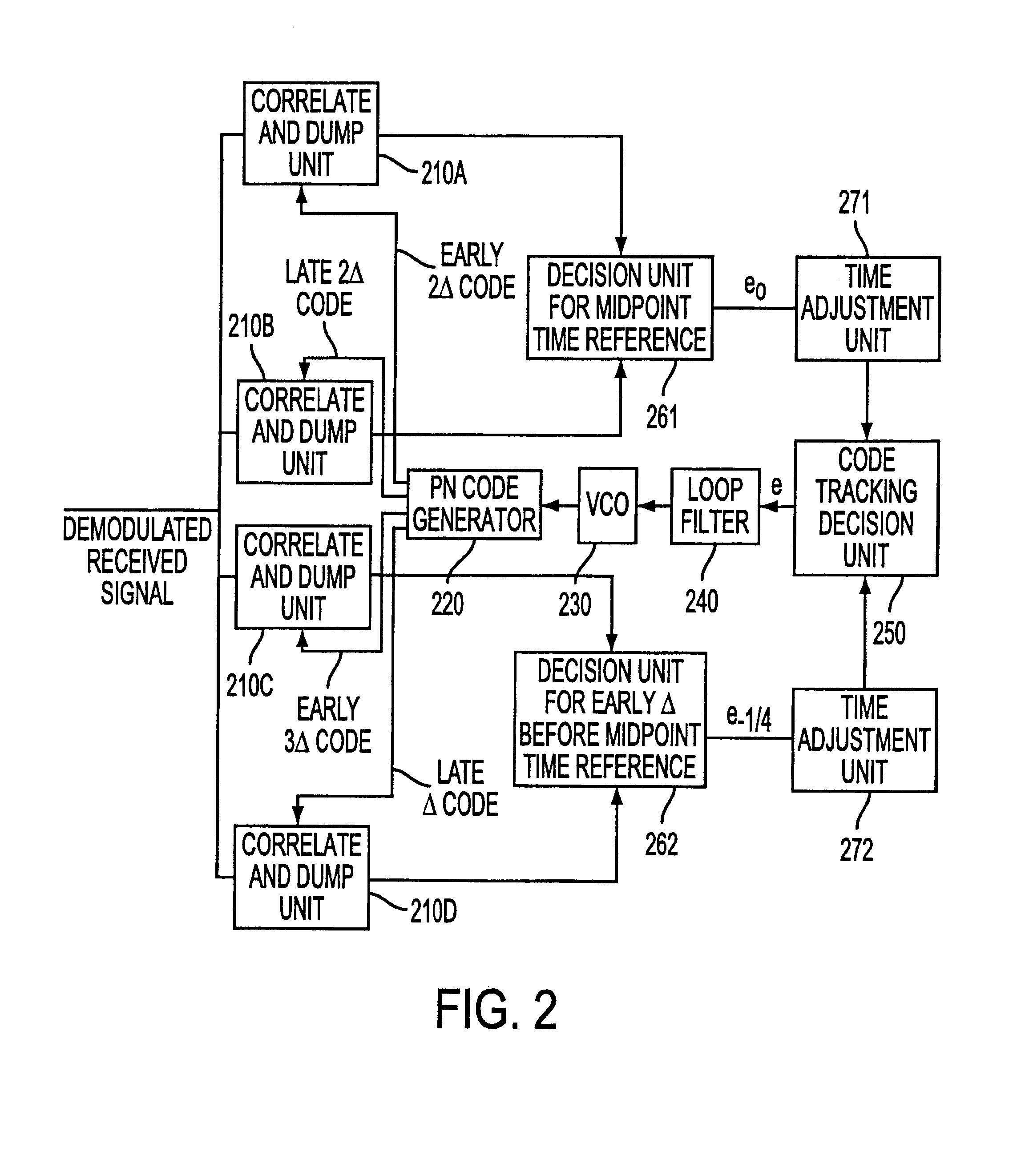
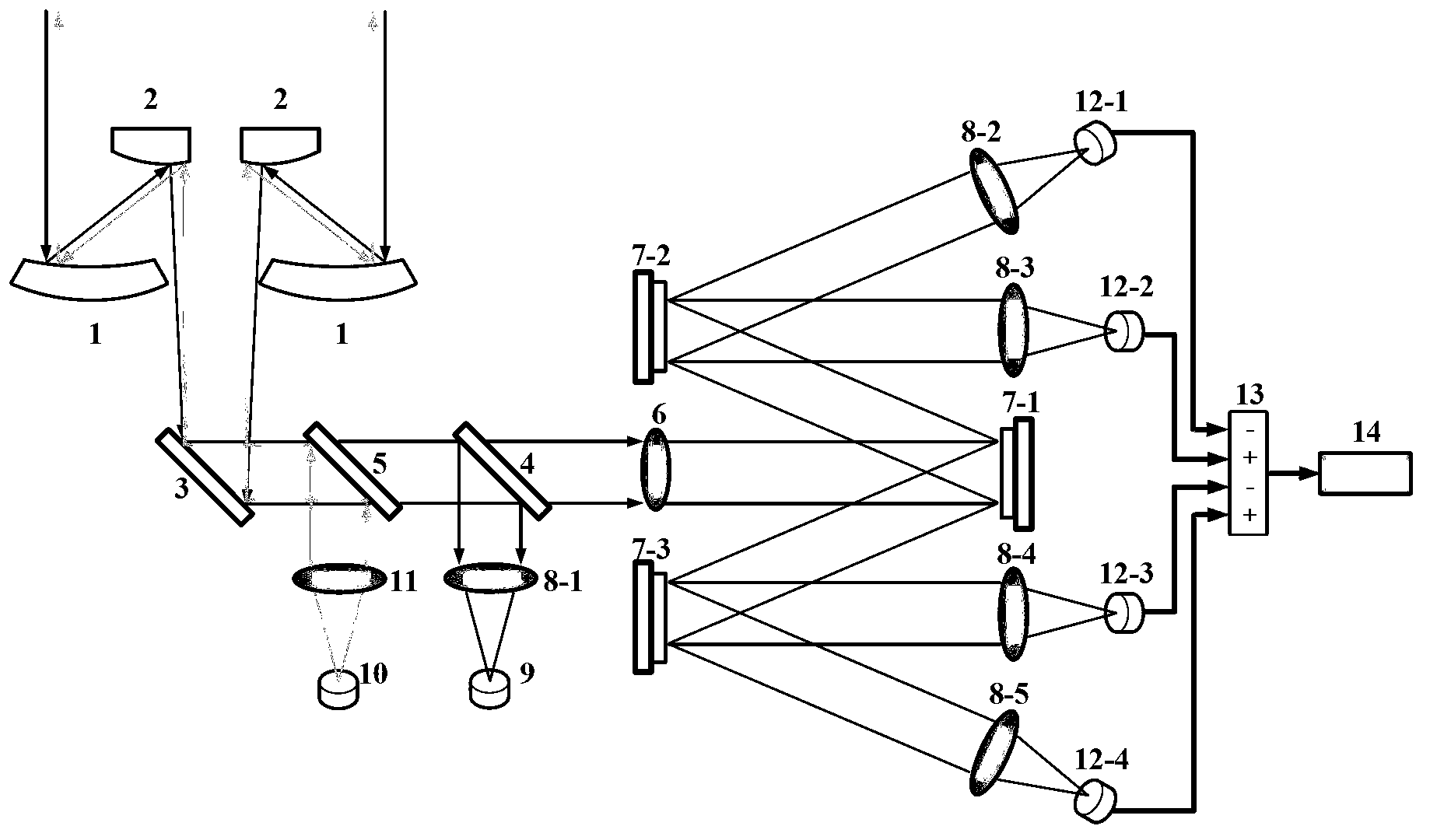
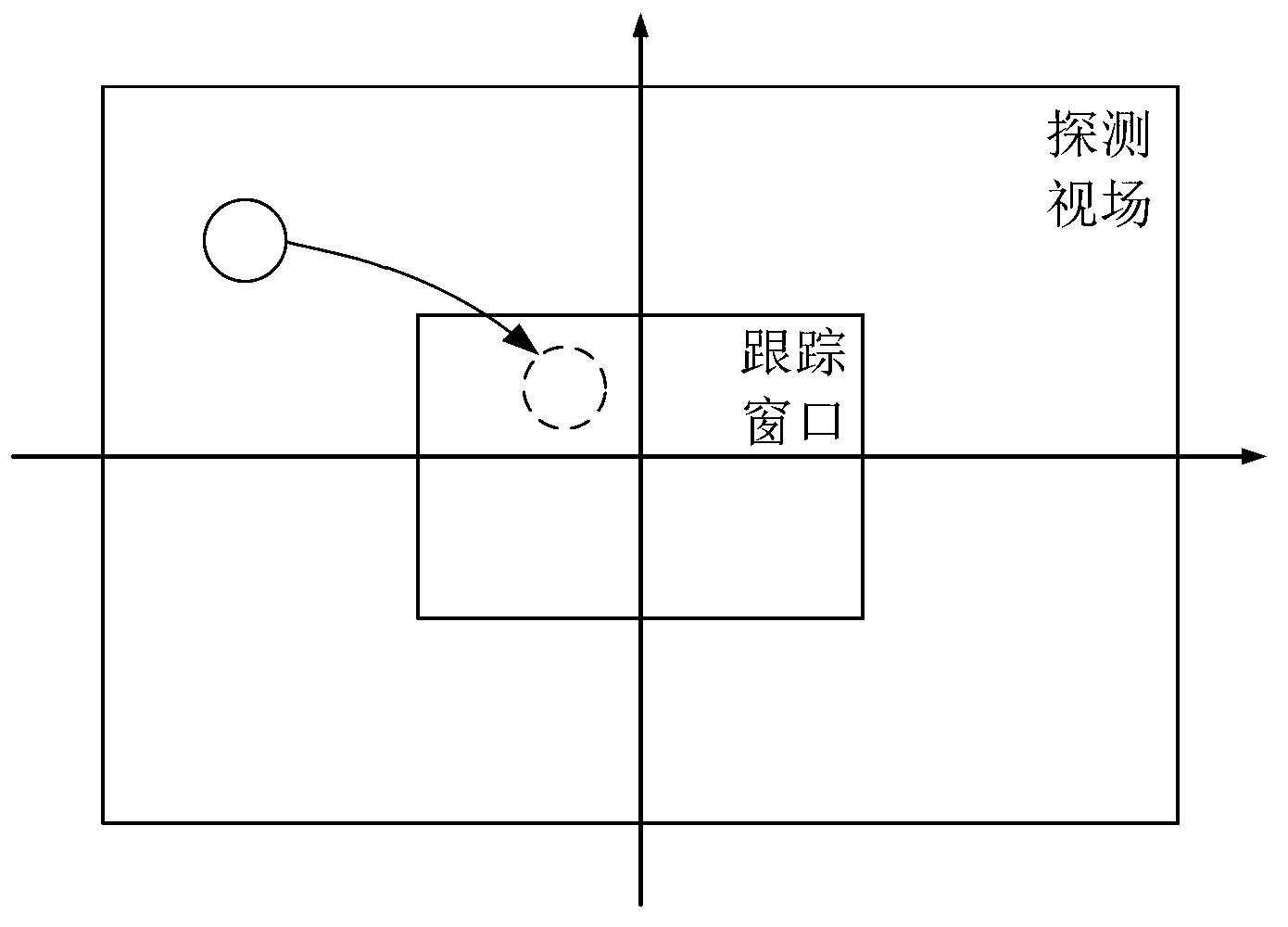
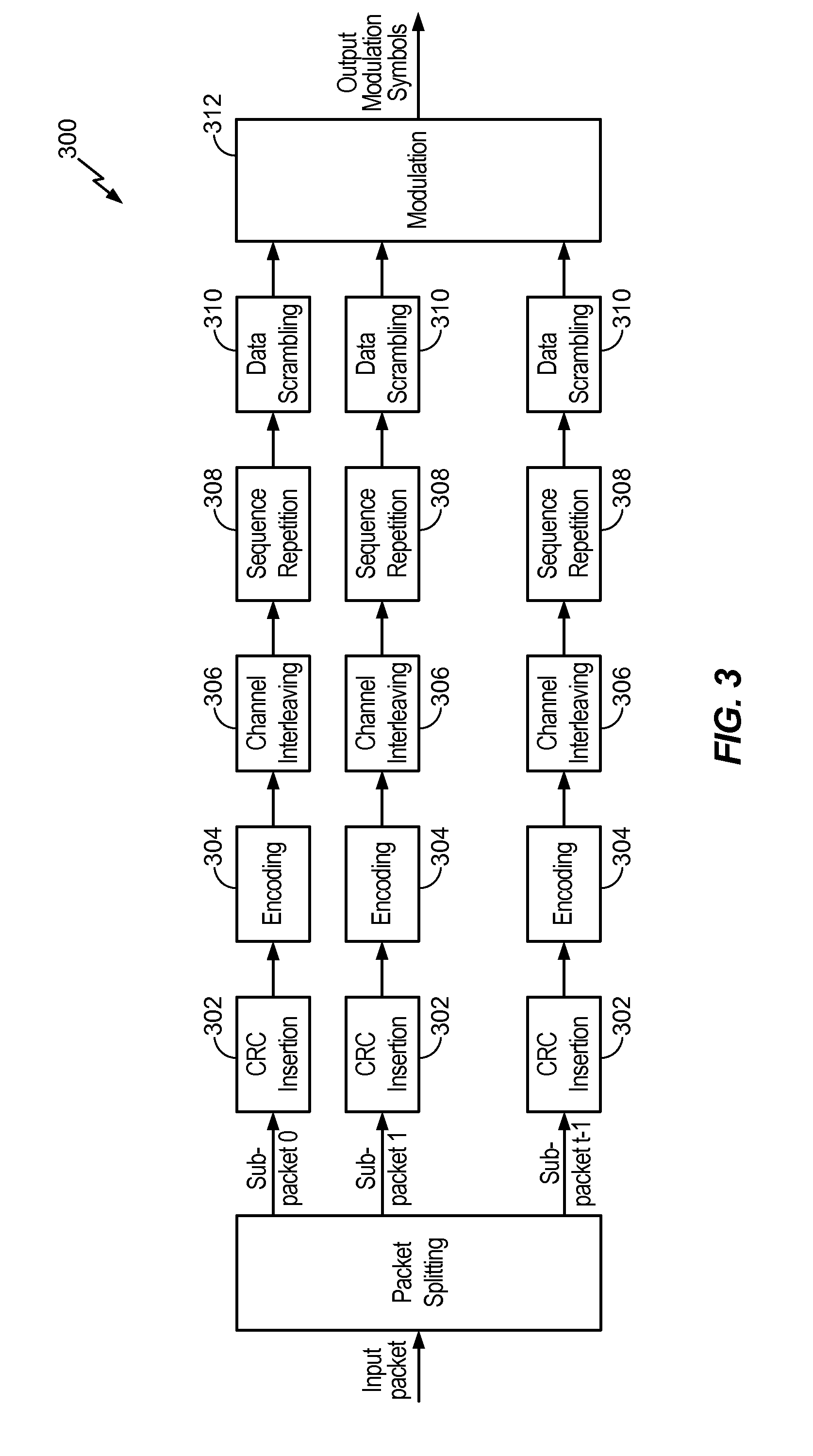
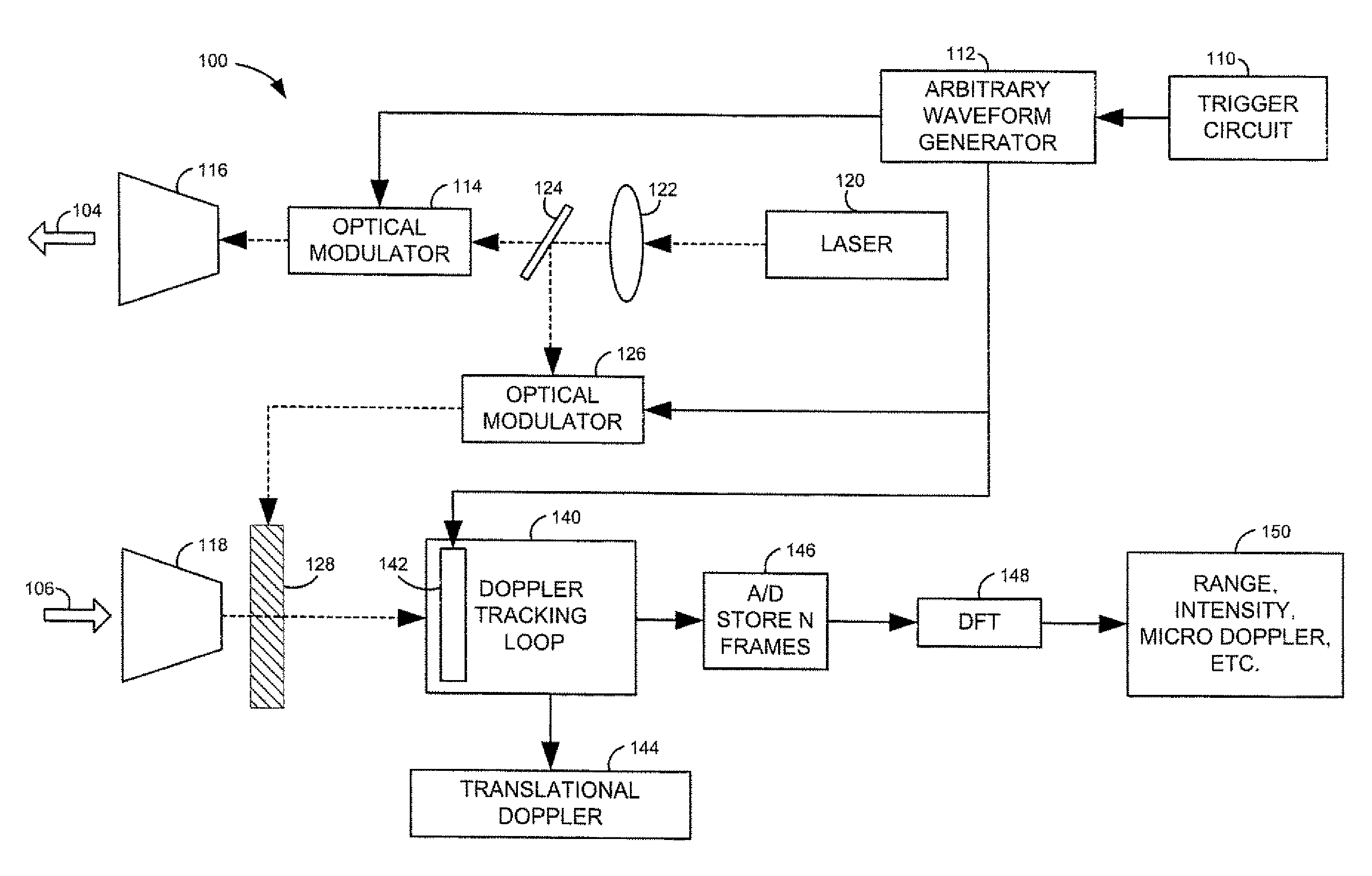
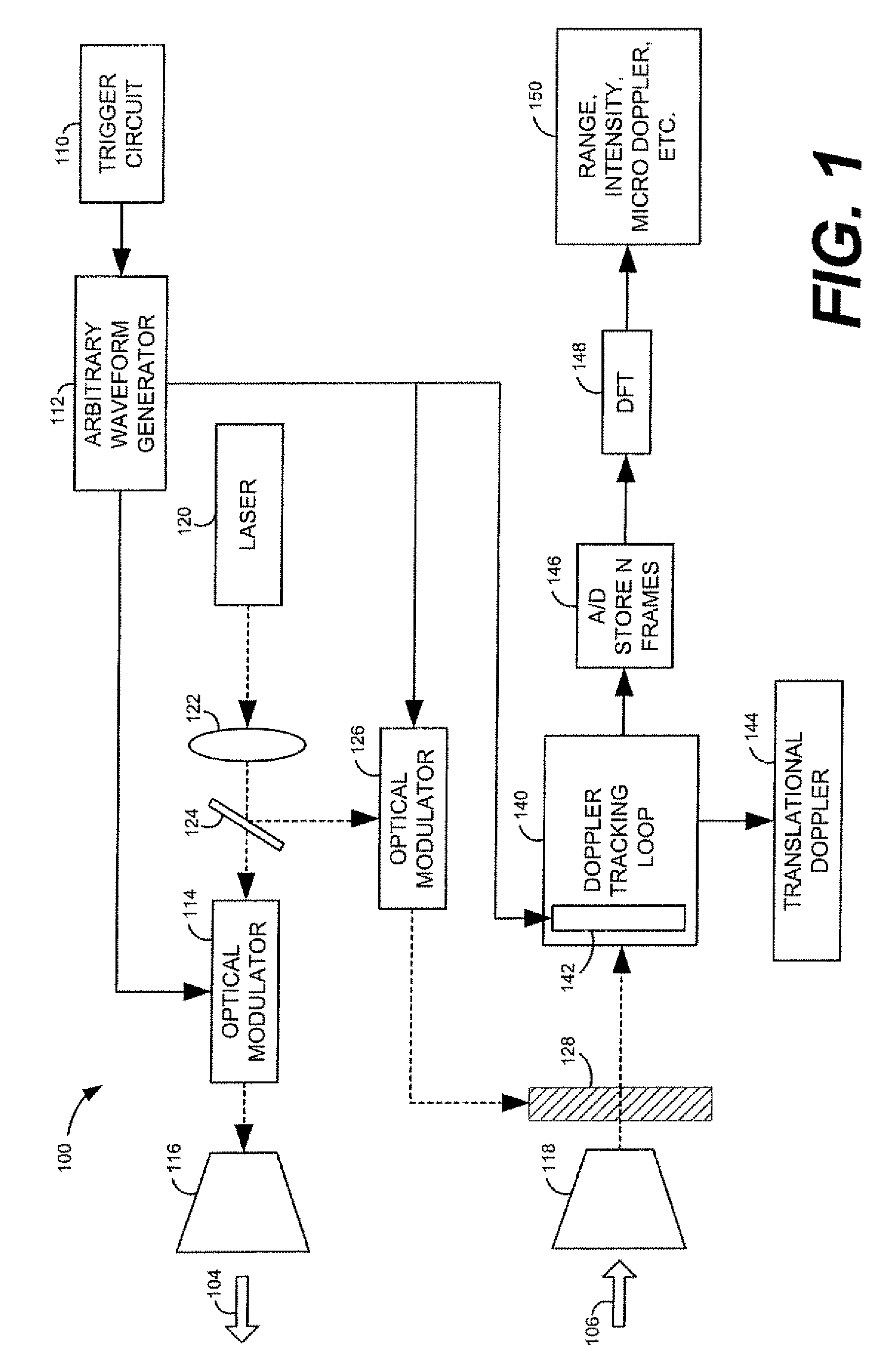
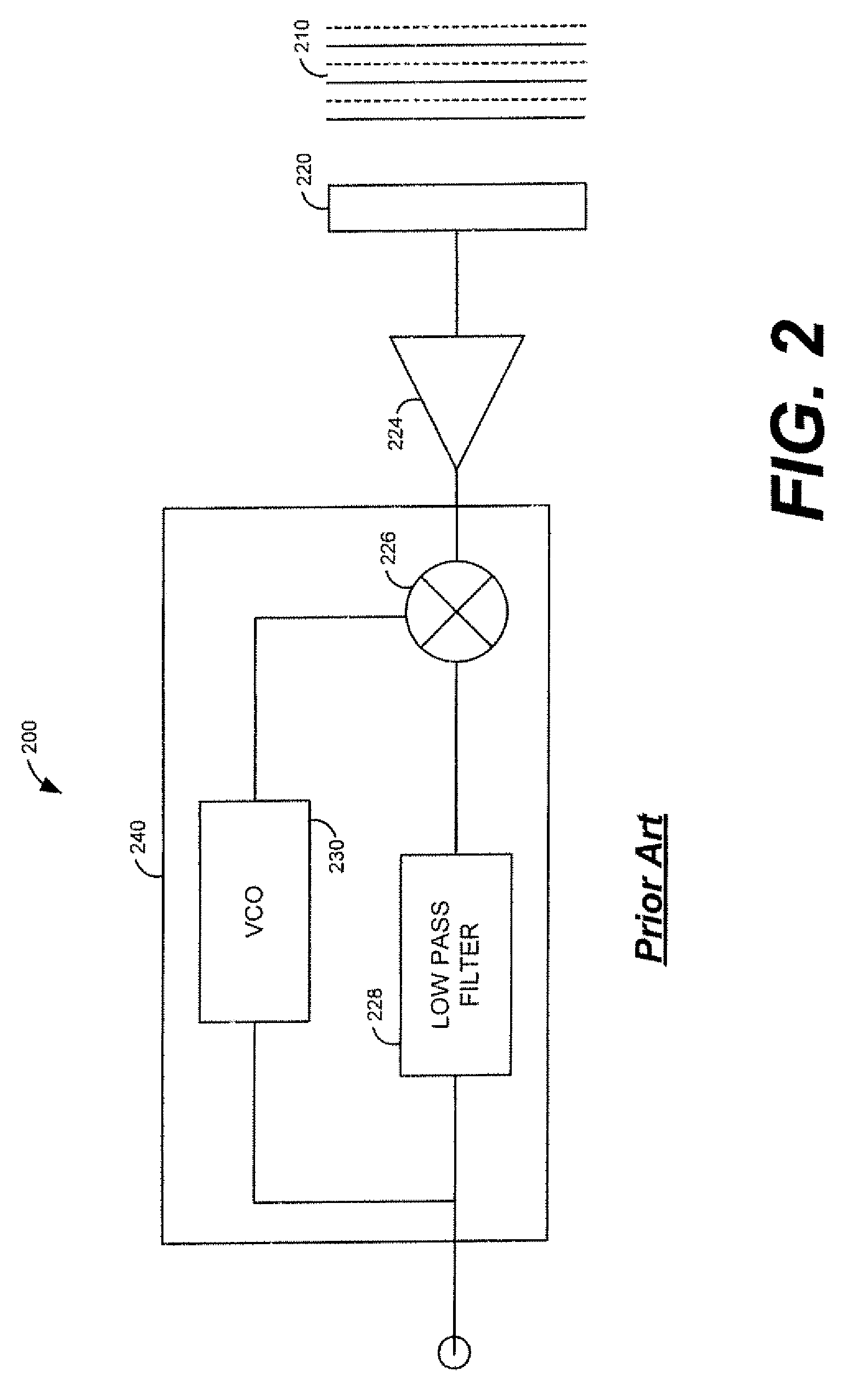
Patents
Literature
623 results about "Tracking loop" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
RF transmitter with variably biased RF power amplifier and method therefor
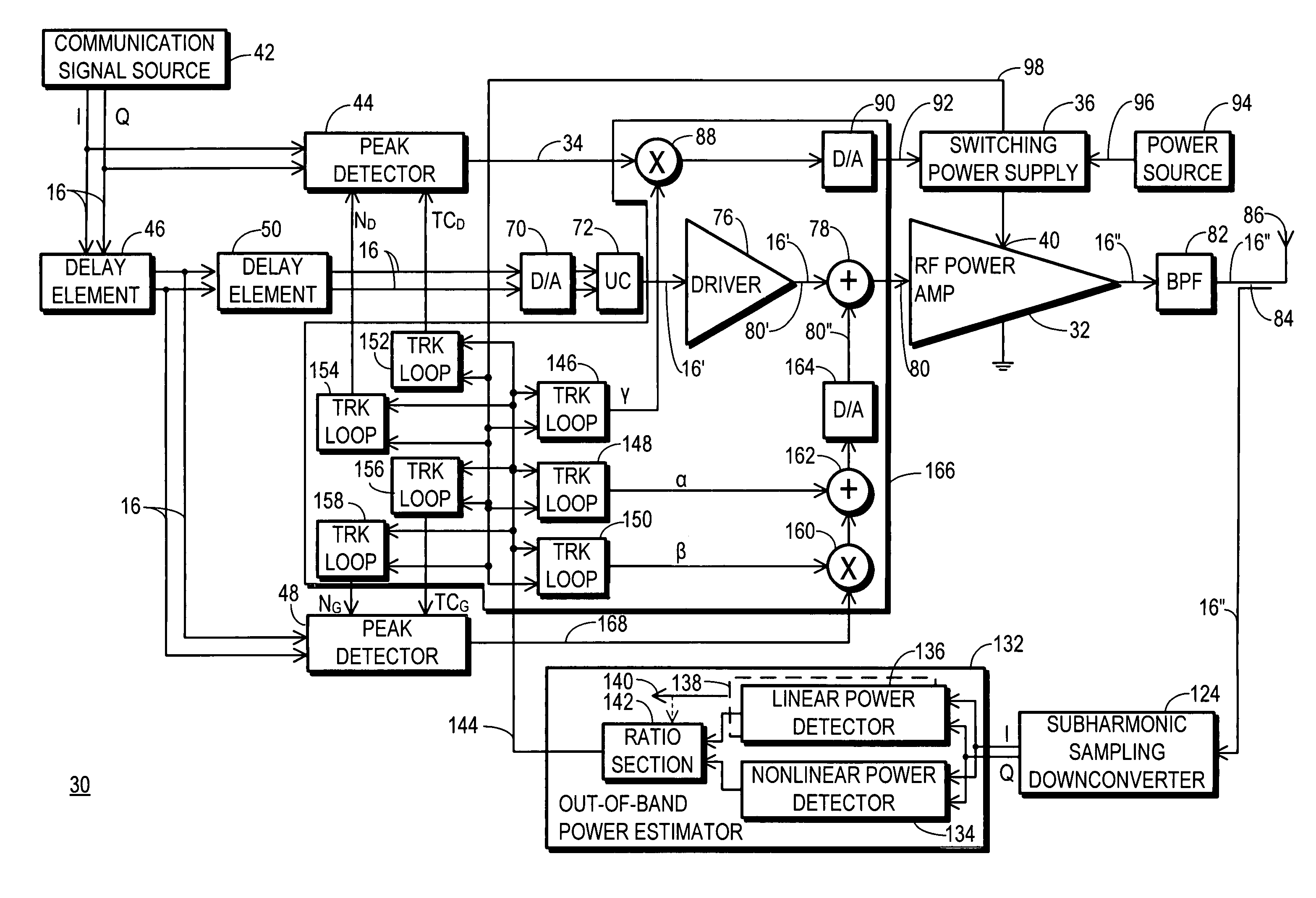
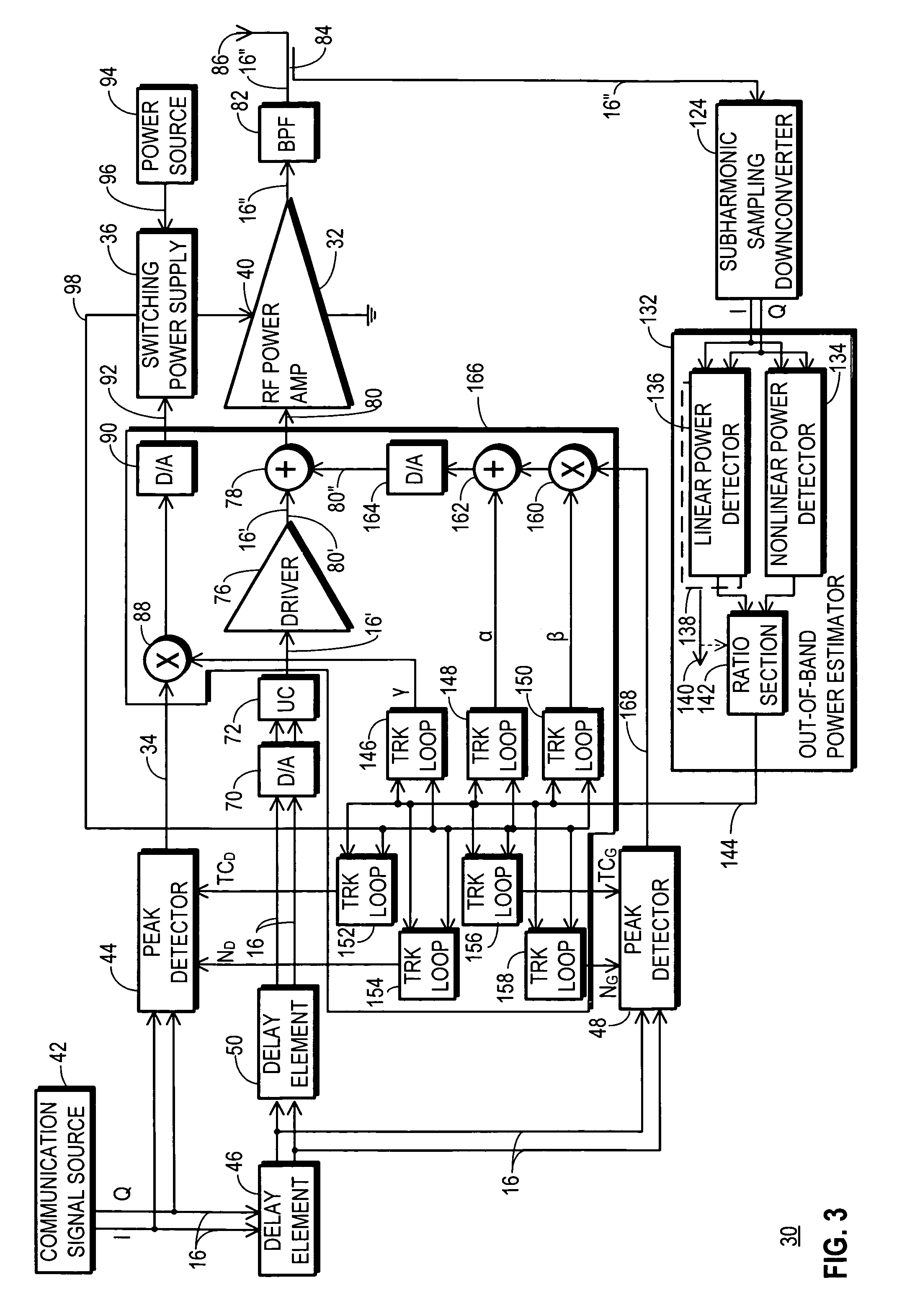
InactiveUS20070281635A1More powerSimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationResonant long antennasPeak valueWide band
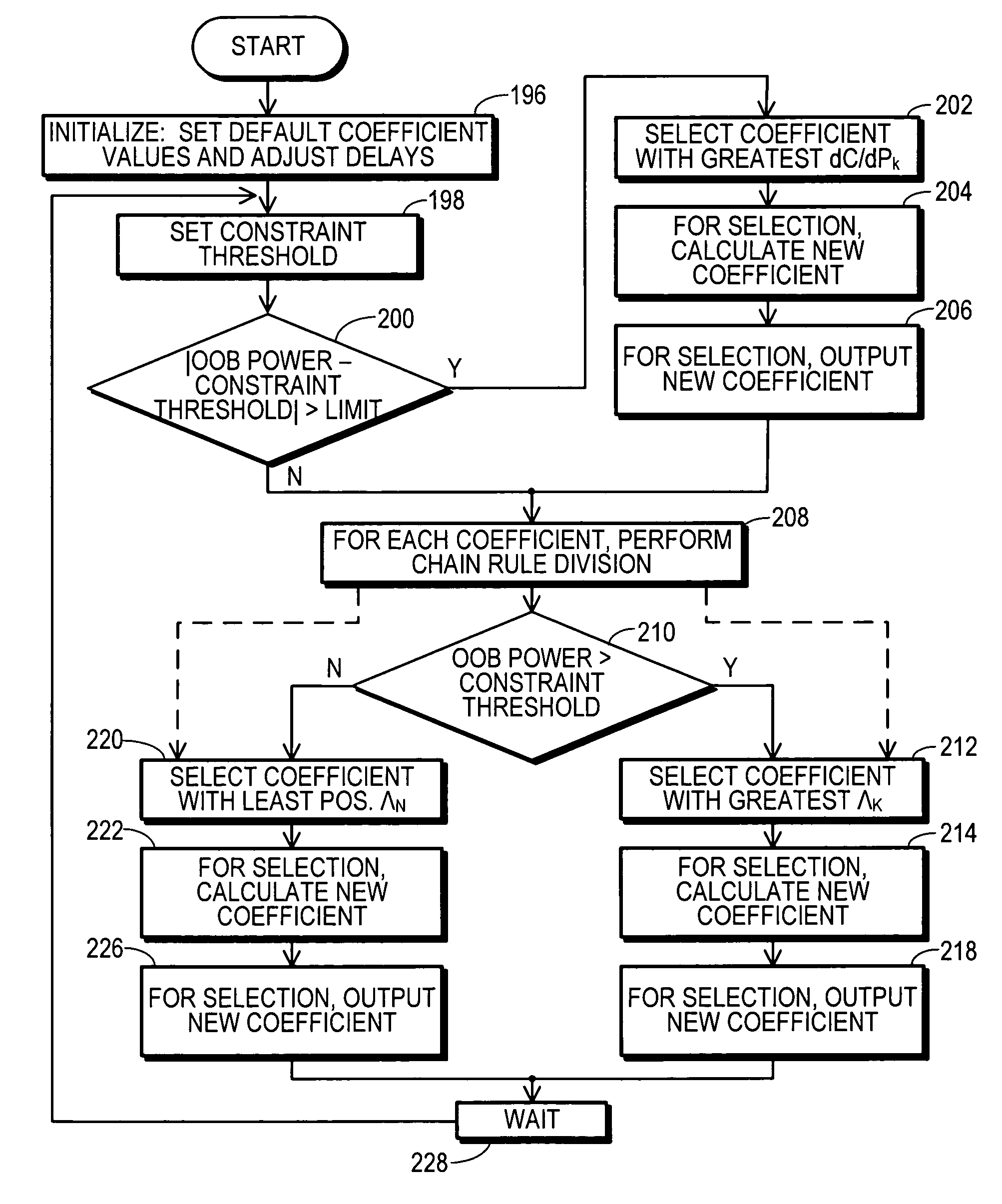
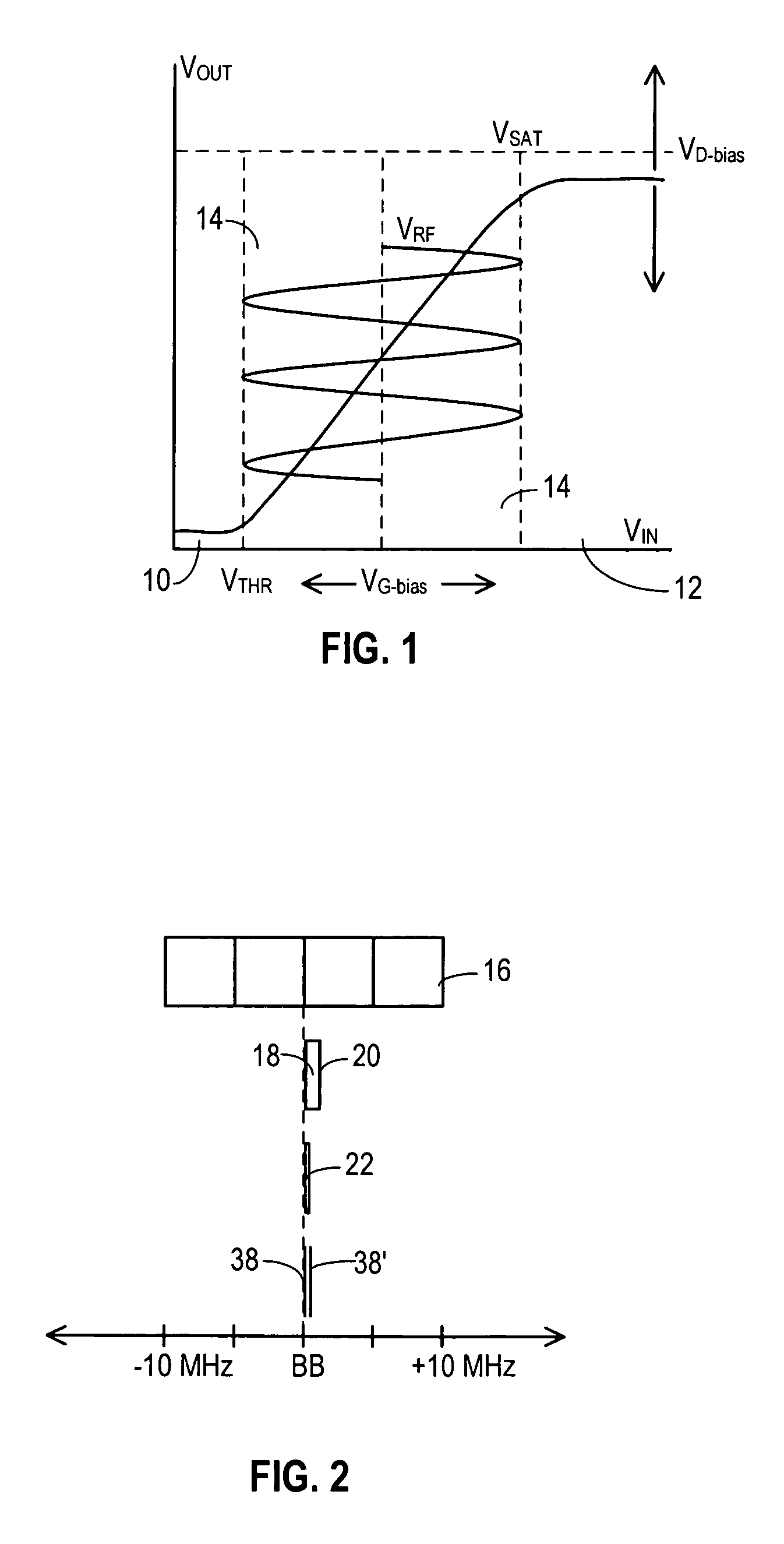
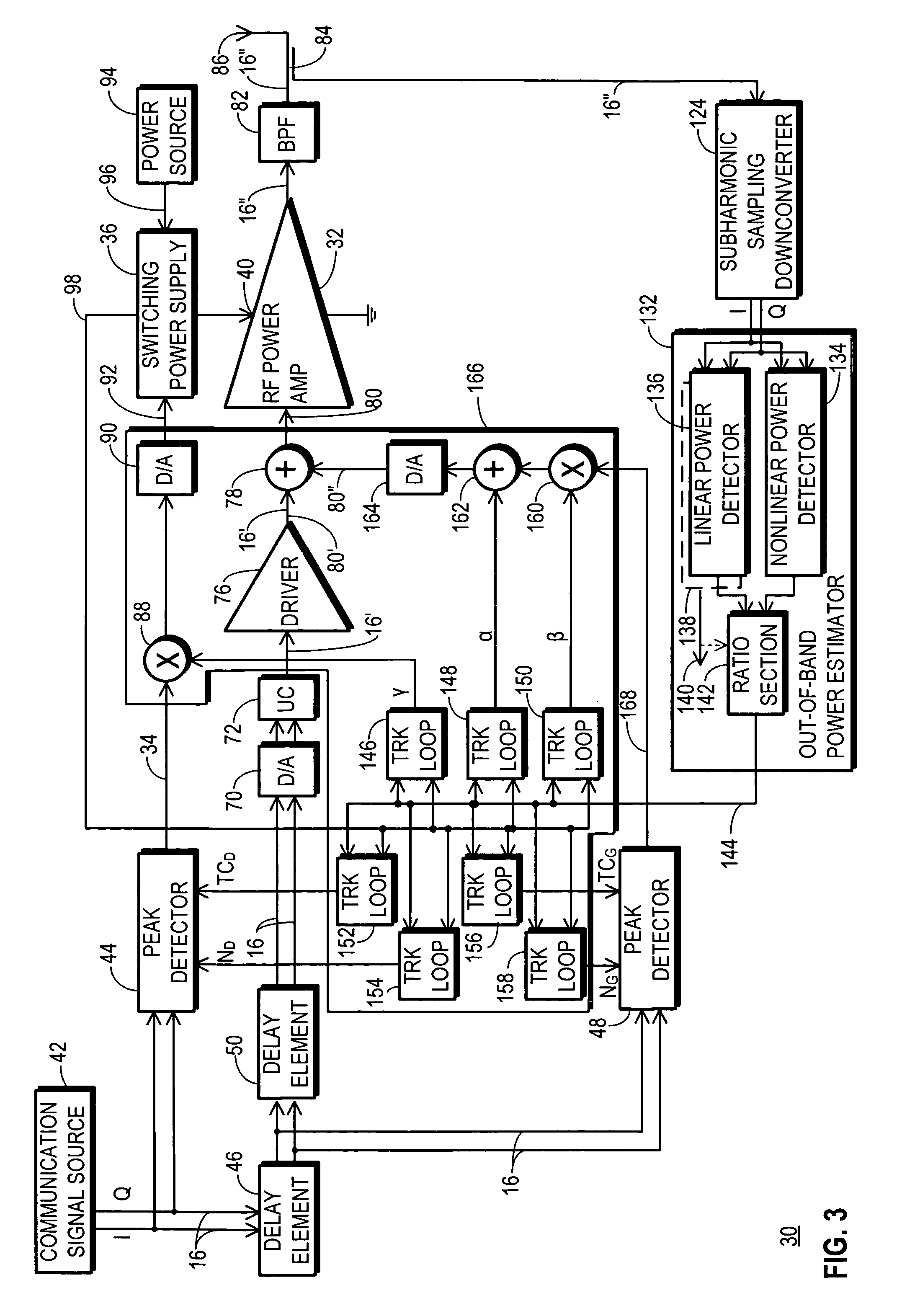
An RF transmitter (30) includes an RF power amplifier (32) for which the power input bias voltage (40) and signal input bias voltage (80) are controlled within feedback loops. A peak detector (44) generates a lowered-spectrum, peak-tracking signal (34) that follows the largest amplitude peaks of a wide bandwidth communication signal (16) but exhibits a lower bandwidth. This signal (34) is scaled in response to the operation of a drain bias tracking loop (146) then used to control a switching power supply (36) that generates the power input bias voltage. The tracking loop (146) is responsive to out-of-band power detected in a portion of the amplified RF communication signal (16″). A ratio of out-of-band power (128) to in-band power (126) is manipulated in the tracking loop (146) so that the power input bias voltage is modulated in a way that holds the out-of-band power at a desired predetermined level.
Owner:CRESTCOM INC
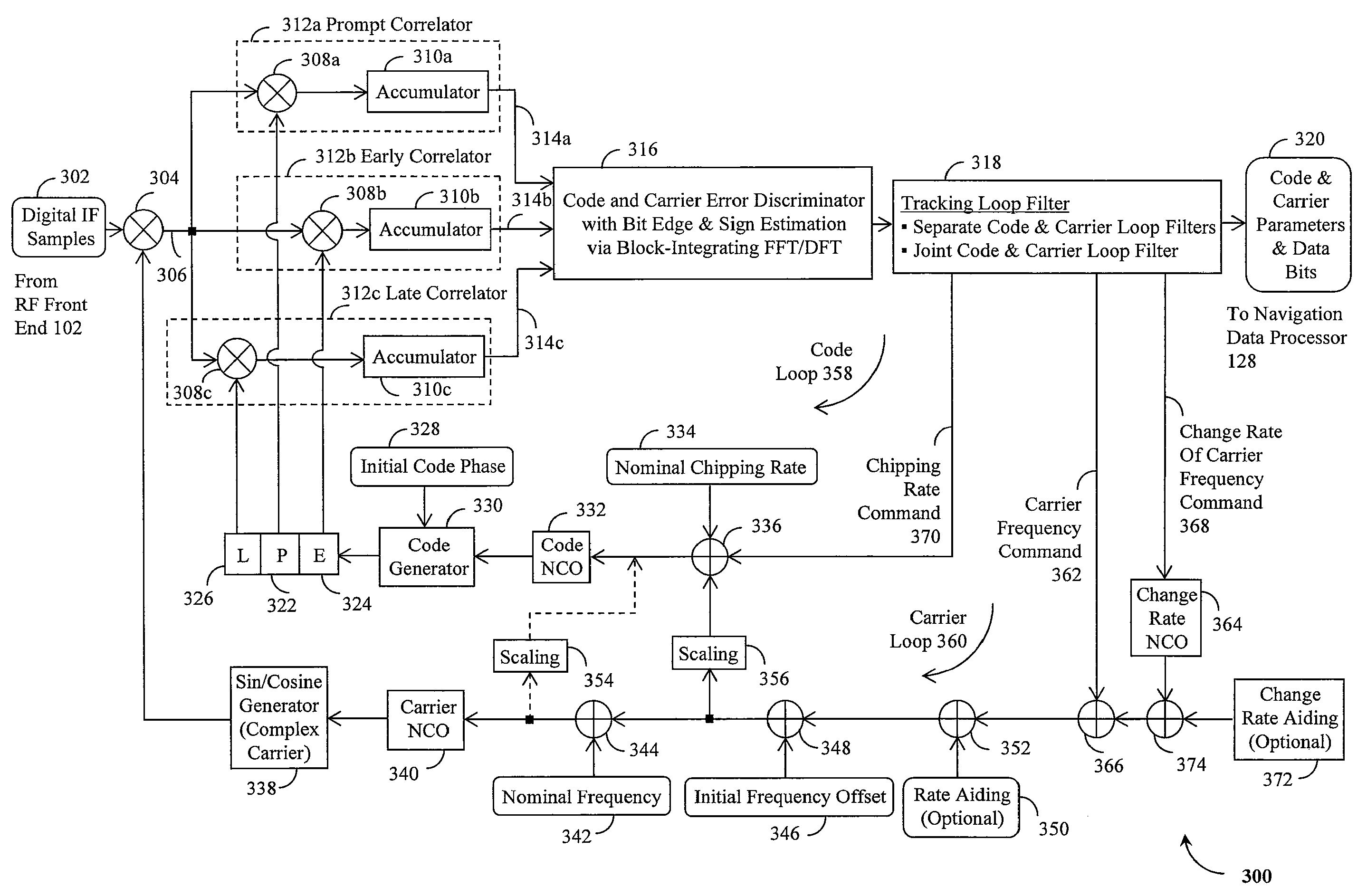
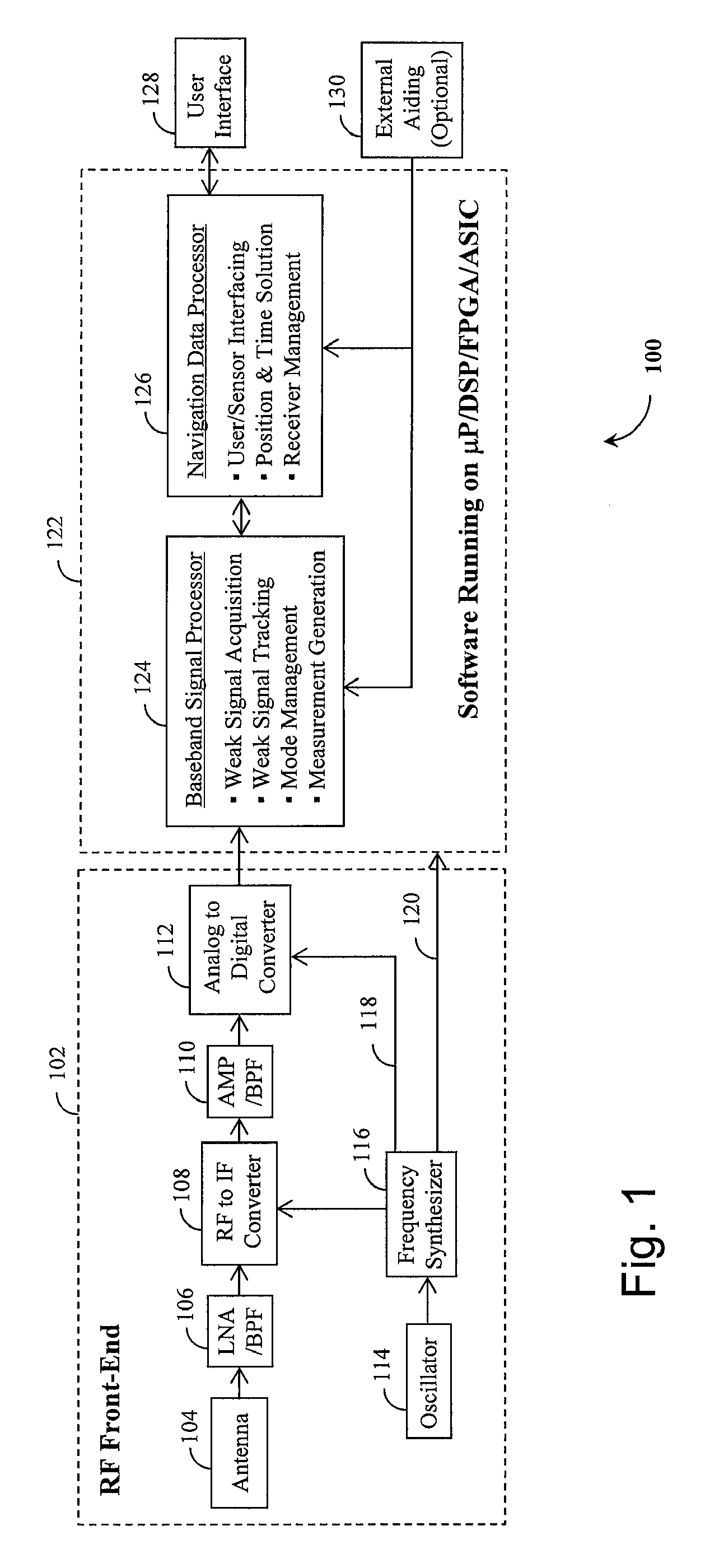
Method and device for tracking weak global navigation satellite system (GNSS) signals
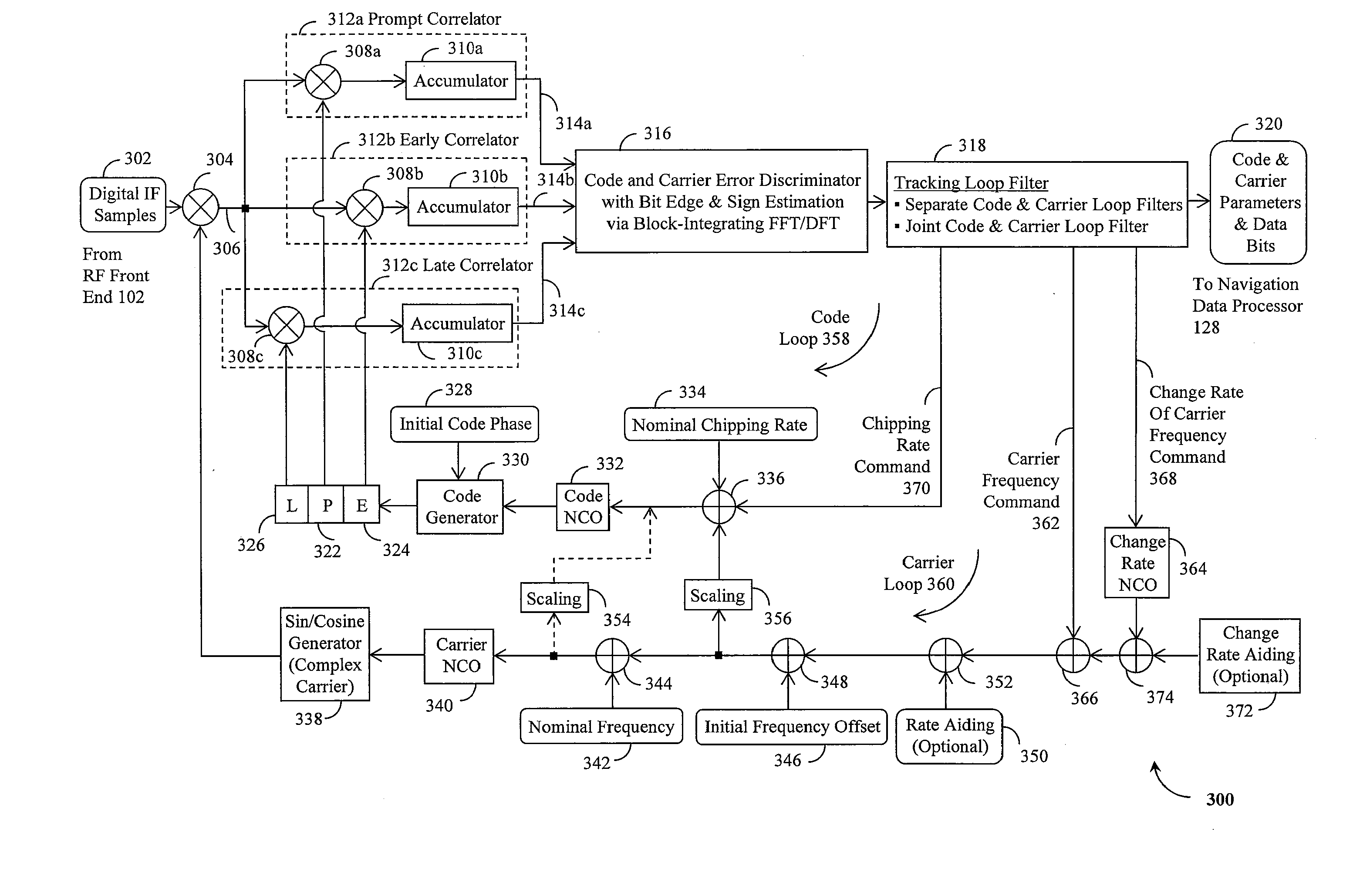
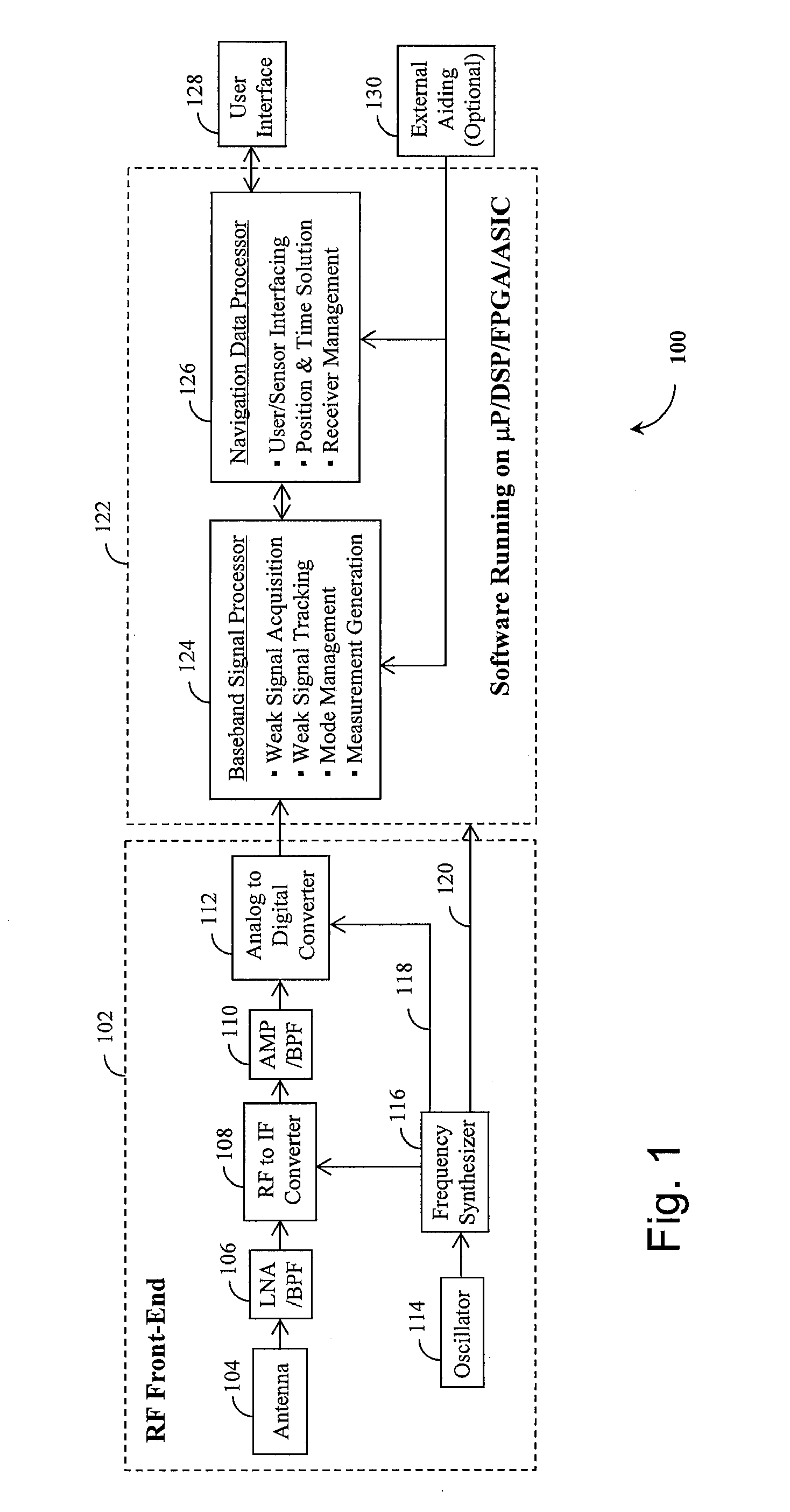
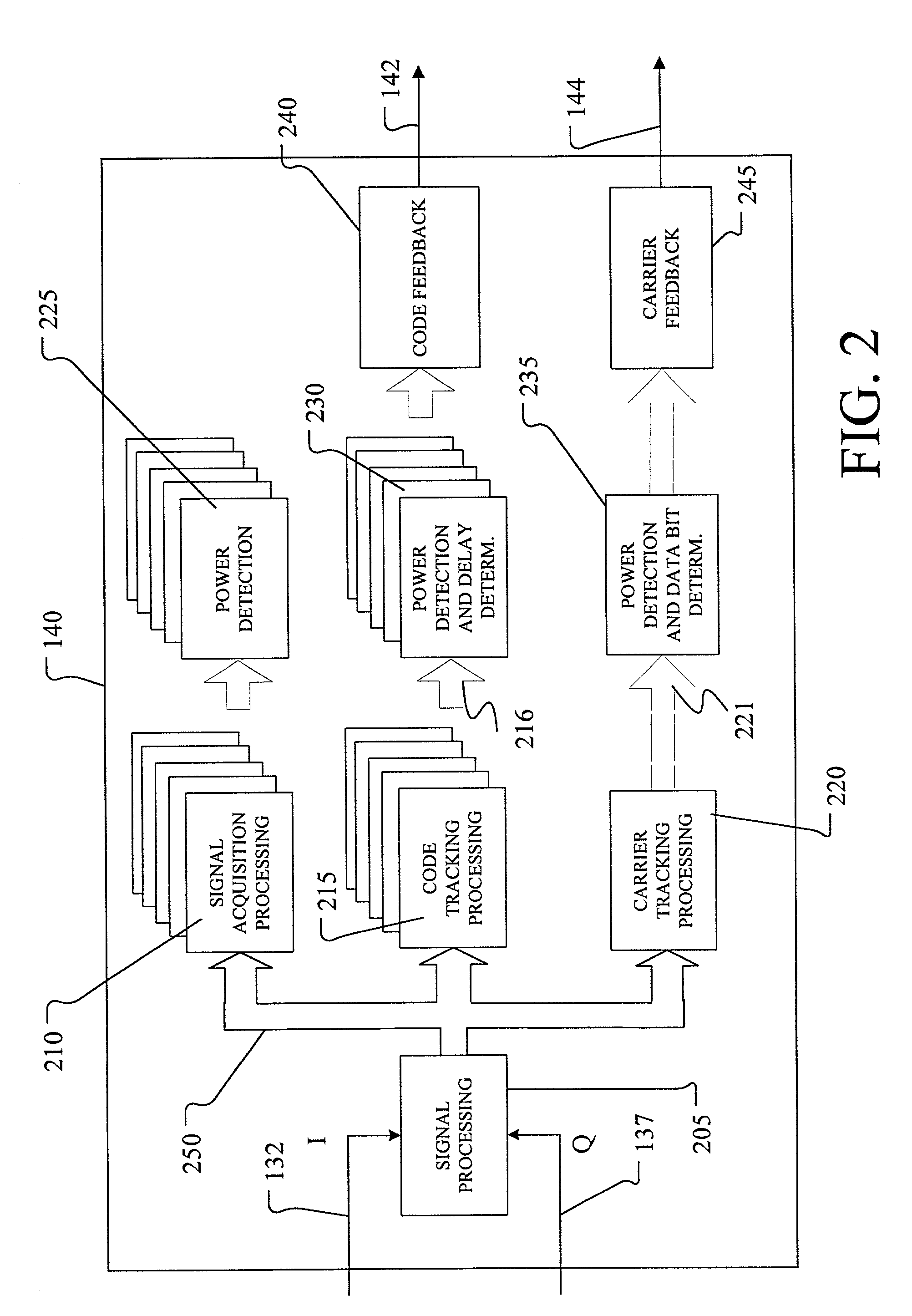
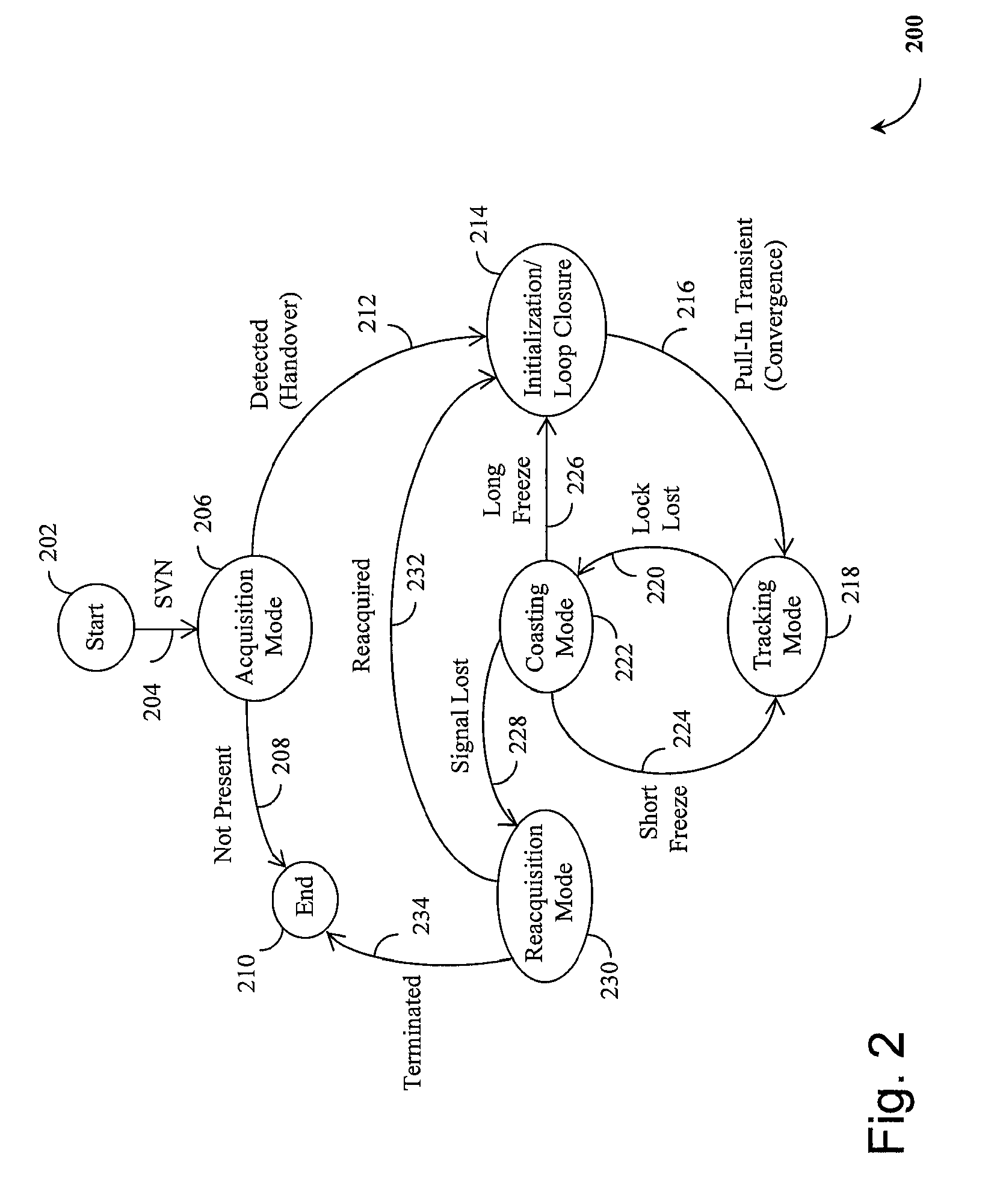
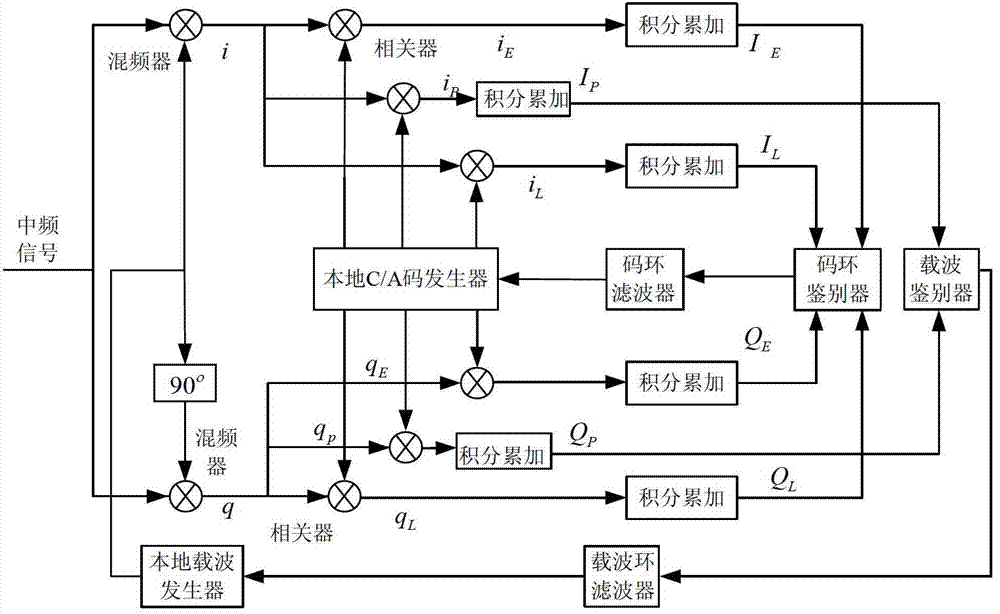
A Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) receiver and associated method capable of tracking weak GNSS signals from a plurality of GNSS satellites. In a preferred embodiment, code and carrier tracking loops are initially closed around the code phase, carrier frequency, and data bit edge estimates handed over from an acquisition mode. In subsequent tracking, early, prompt, and late copies of the code replica are correlated with the incoming signal. The prompt correlations are coherently integrated over an extended updating interval for data bit edge and sign estimation as well as for carrier phase and frequency error discrimination whereas the early and late correlations are used for code error discrimination. Code delay and carrier phase and frequency errors are used to update the code and carrier tracking loop filters. Together with data bits, they form observables of a GNSS signal's time and frequency parameters for timing and position fixing.
Owner:CSR TECH HLDG
RF transmitter with variably biased RF power amplifier and method therefor
InactiveUS7570931B2More powerSimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationResonant long antennasPeak valueEngineering
An RF transmitter (30) includes an RF power amplifier (32) for which the power input bias voltage (40) and signal input bias voltage (80) are controlled within feedback loops. A peak detector (44) generates a lowered-spectrum, peak-tracking signal (34) that follows the largest amplitude peaks of a wide bandwidth communication signal (16) but exhibits a lower bandwidth. This signal (34) is scaled in response to the operation of a drain bias tracking loop (146) then used to control a switching power supply (36) that generates the power input bias voltage. The tracking loop (146) is responsive to out-of-band power detected in a portion of the amplified RF communication signal (16″). A ratio of out-of-band power (128) to in-band power (126) is manipulated in the tracking loop (146) so that the power input bias voltage is modulated in a way that holds the out-of-band power at a desired predetermined level.
Owner:CRESTCOM INC
Precise tracking and measuring method of high dynamic signal of air fleet link
InactiveCN101776752ASolve the defect of poor precisionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDigital signal processingAviation
The invention relates to a precise tracking and measuring method of a high dynamic signal of an air fleet link, belonging to the technical field of aeronautical data links and radio navigation, and aiming at providing a precise tracking and measuring method of the high dynamic signal the an air fleet link and an implementation structure to solve the problems in the prior art. The invention provides a system framework of the precise tracking and measuring method of the high dynamic signal of the air fleet link, which can be implemented on a digital signal processor (DSP) and a FPGA (field programmable gate array) of a circuit board, and overcomes the defects of the unfavorable precision of a traditional high dynamic receiver by utilizing a double-loop structure of a frequency tracking loop of carrier tracking and a phase locking loop as well as a code phase locking loop to realize the high precise tracking under a high dynamic condition. The method can be widely applied to satellite navigation receivers, range measurement systems and communication systems based on a quiescent carrier modulation direct sequence spread spectrum system.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
Efficient And Accurate 3D Object Tracking
ActiveUS20090324018A1Well formedError minimizationImage enhancementImage analysisTracking loopObject model
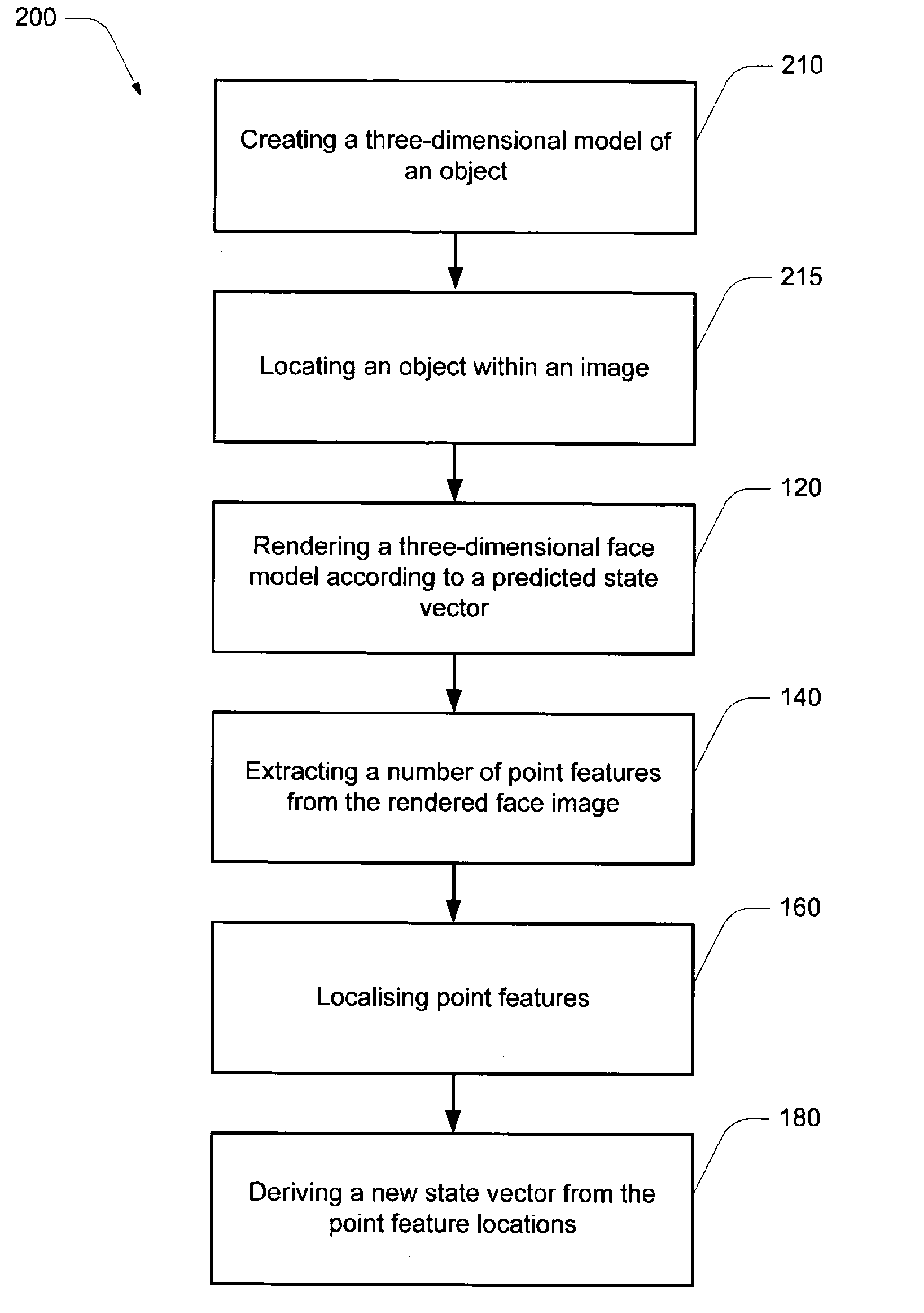
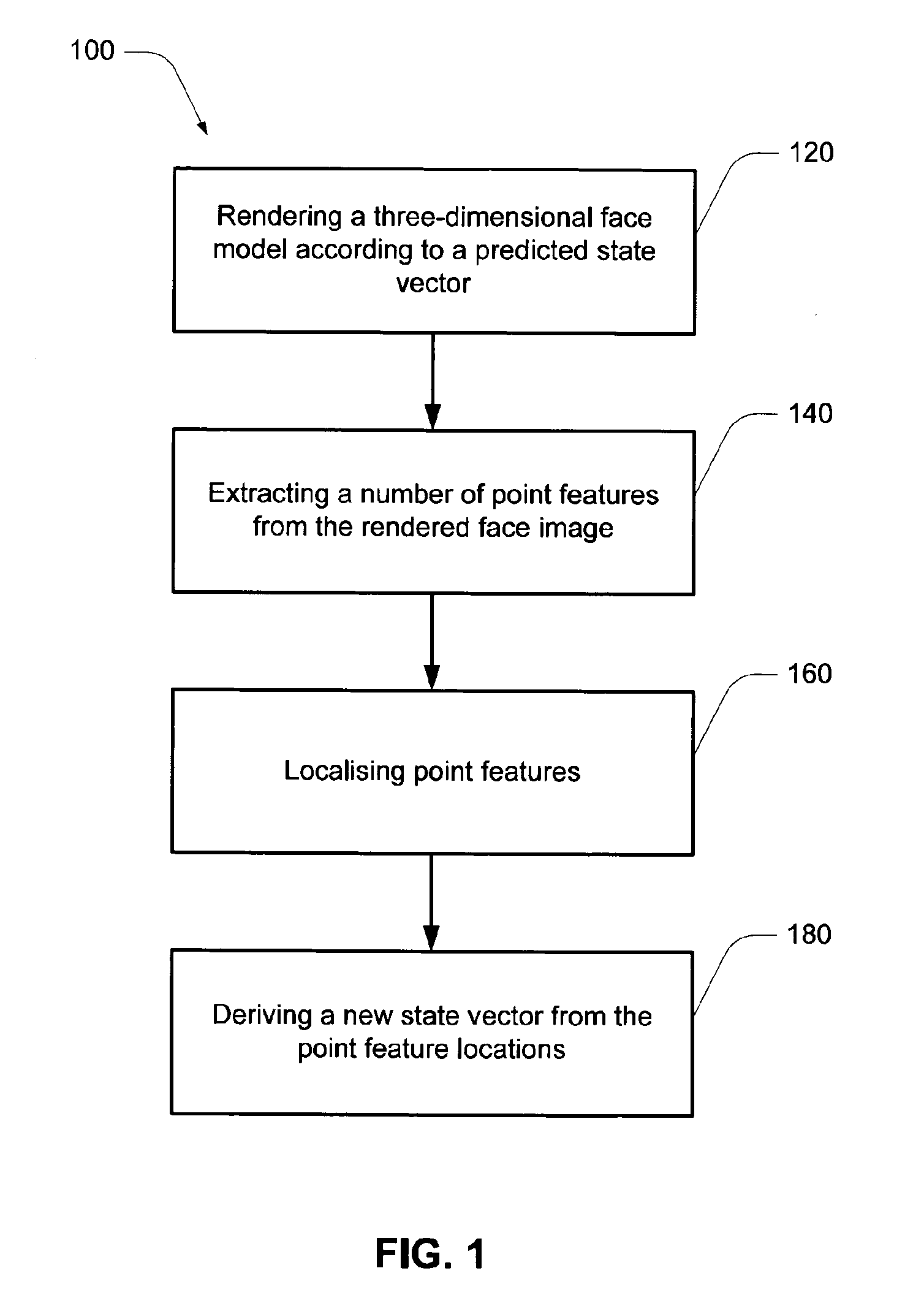
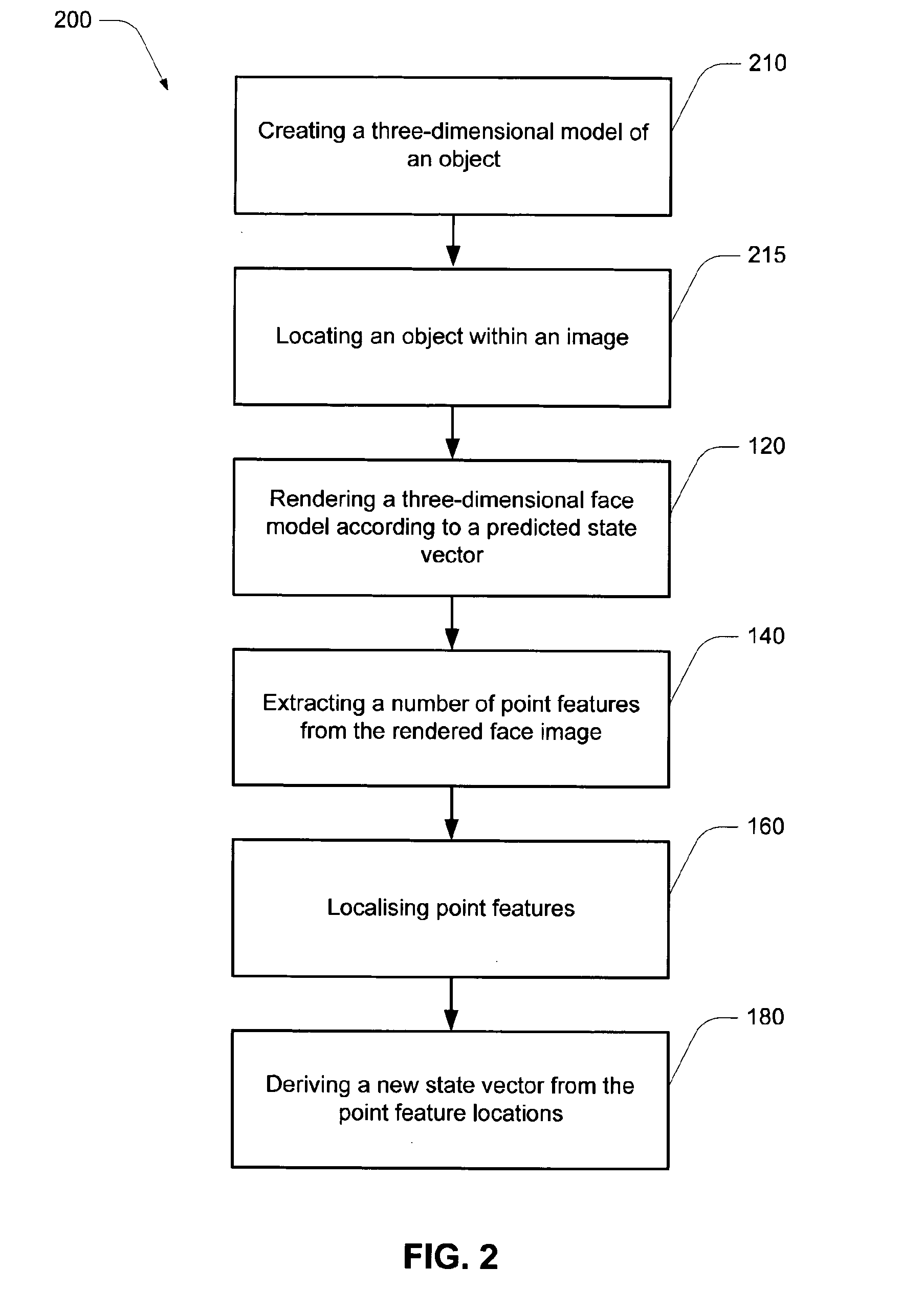
A method of tracking an object in an input image stream, the method comprising iteratively applying the steps of: (a) rendering a three-dimensional object model according to a previously predicted state vector from a previous tracking loop or the state vector from an initialisation step; (b) extracting a series of point features from the rendered object; (c) localising corresponding point features in the input image stream; (d) deriving a new state vector from the point feature locations in the input image stream.
Owner:SEEING MACHINES
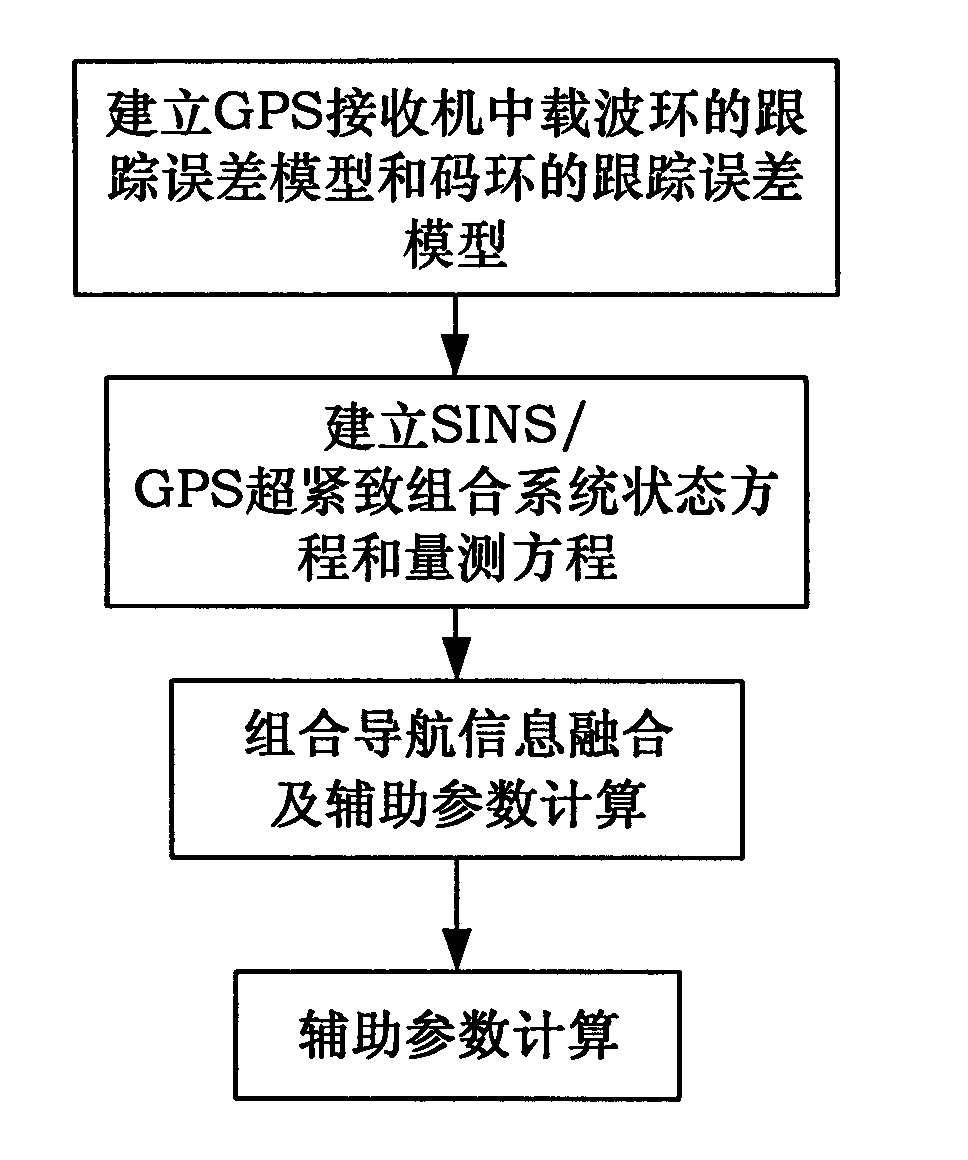
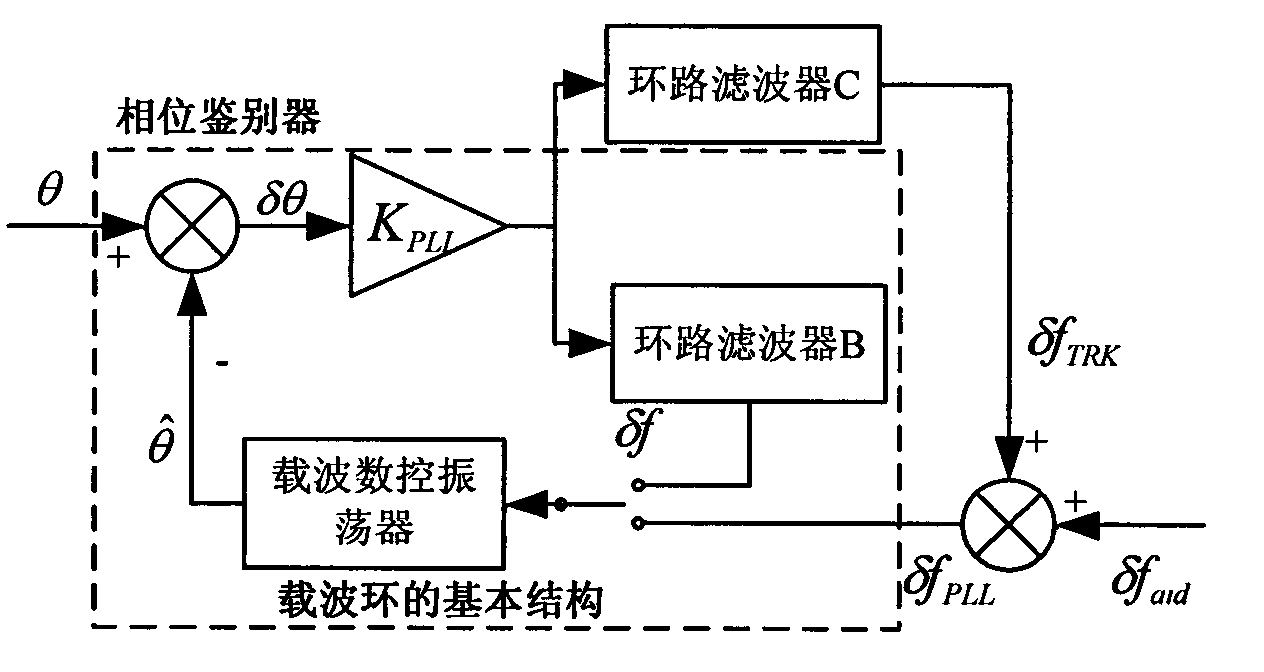
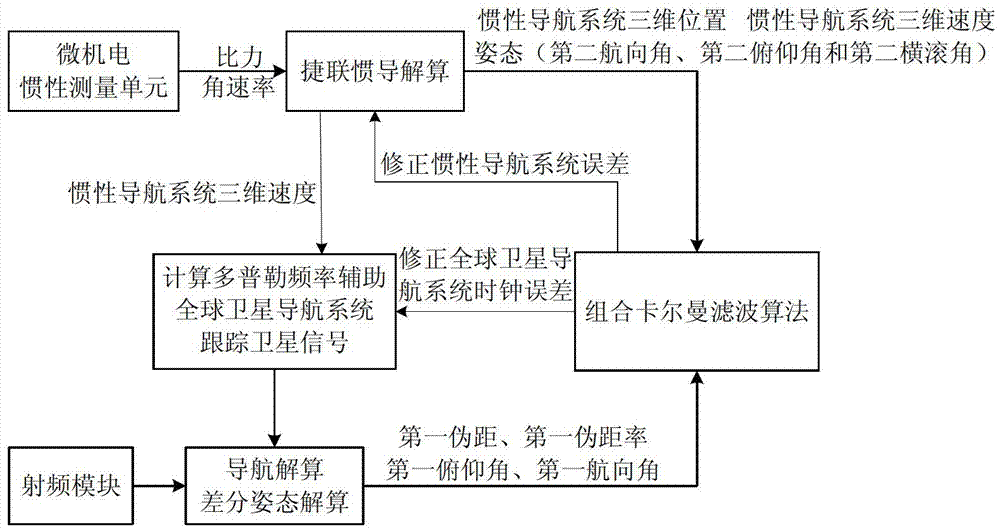
SINS/GPS super-compact integrated navigation system and implementing method thereof
InactiveCN101666650AIncrease equivalent bandwidthReduce dynamic tracking rangeBeacon systems using radio wavesPosition fixationCarrier signalGps receiver
The invention discloses an SINS / GPS super-compact integrated navigation system and an implementing method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: the doppler frequency assistance is provided for a GPS carrier loop by using the velocity information of a strapdown inertial navigation system, therefore, the loop equivalent bandwidth is increased, the influence of the carrier dynamic stateon the carrier loop is lowered, and the noise suppression capability is improved by reducing the bandwidth of a filter; meanwhile, in order to eliminate the correlation between the pseudo-range rate error and the inertial navigation error, a carrier loop tracking error model is obtained by establishing the relationship between the carrier tracking error and the inertial navigation speed error, andthe influence of the carrier tracking error is subduced in the measurement equation; and in addition, the carrier frequency is adjusted according to the output error estimation information, and the tracking accuracy of the carrier loop is enhanced. The invention can effectively enhance the noise suppression capability and the dynamic tracking performance of the tracking loop and enhance the tracking accuracy of a GPS receiver and the navigation accuracy of the integrated navigation system under strong interference and high dynamic circumstance.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
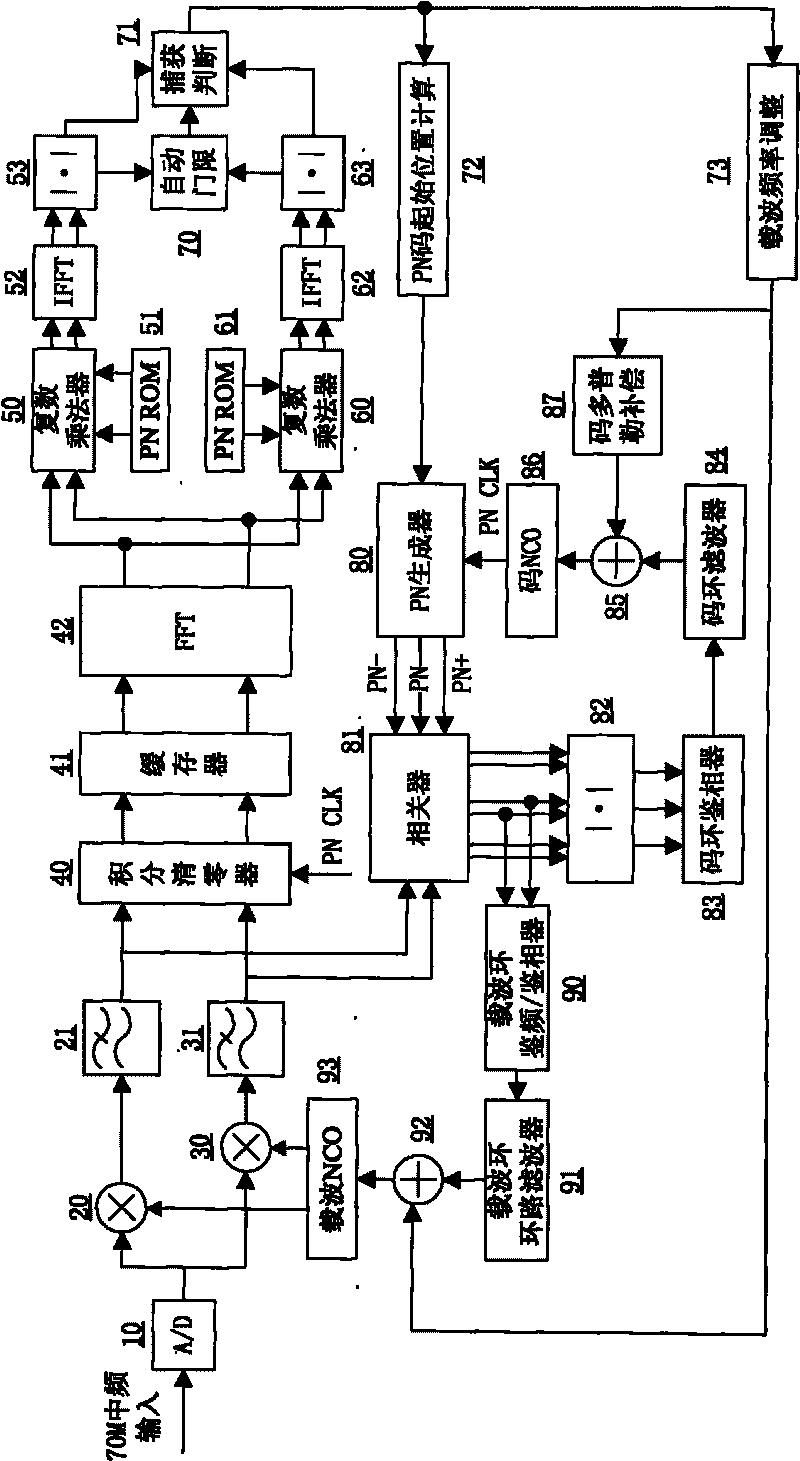
Intermediate frequency direct sequence spread spectrum receiver for satellite ranging
InactiveCN101726746AReduce resource consumptionFast captureSatellite radio beaconingDiscriminatorLow-pass filter
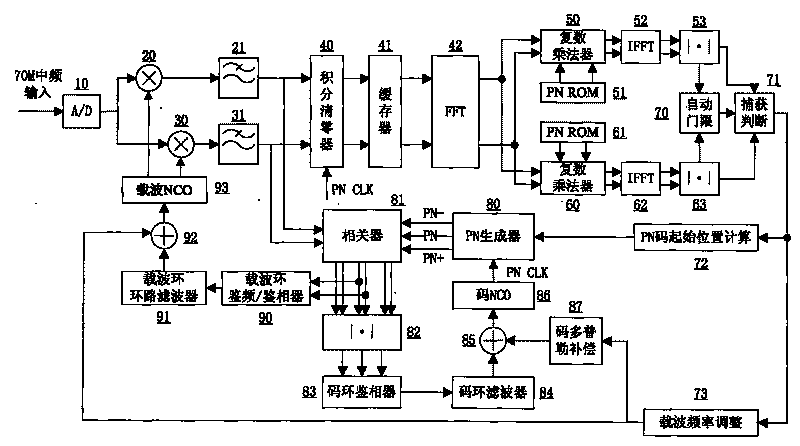
The invention relates to an intermediate frequency direct sequence spread spectrum receiver for satellite ranging, which consists of 37 parts of a front-end A / D, an FFT module, a local PN code generator, a correlator, an automatic threshold calculation module and the like. The connection relationship is as follows: the output of the front-end A / D and the output of a carrier tracking loop NCO are respectively connected to an in-phase branch multiplier and an orthogonal branch multiplier, the input of the front-end A / D and the input of the carrier tracking loop NCO enter into an in-phase branch FIR low-pass filter and an orthogonal branch FIR low-pass filter, consequently, on the one hand, the output is sent to an integral zero clearing device, then the output which is sent to the FFT module, a branch 1 local PN code memory ROM and a branch 2 local PN code memory ROM enters into a branch 1 complex multiplier and a branch 2 complex multiplier, the output is sent to a branch 1 root mean square module and a branch 2 root mean square module, the output is sent to the threshold calculation module and a capturing and judging module for carrying out code catching; and on the other hand, the output is sent to the correlator and the local PN code generator for carrying out code tracking. The output of the correlator is simultaneously sent into a frequency discriminator / phase discriminator of the carrier tracking loop and then enters into a loop filter of the carrier tracking loop, and the output of the loop filter of the carrier tracking loop enters into the carrier tracking loop NCO for carrying out carrier tracking.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Carrier track loop for GNSS derived attitude
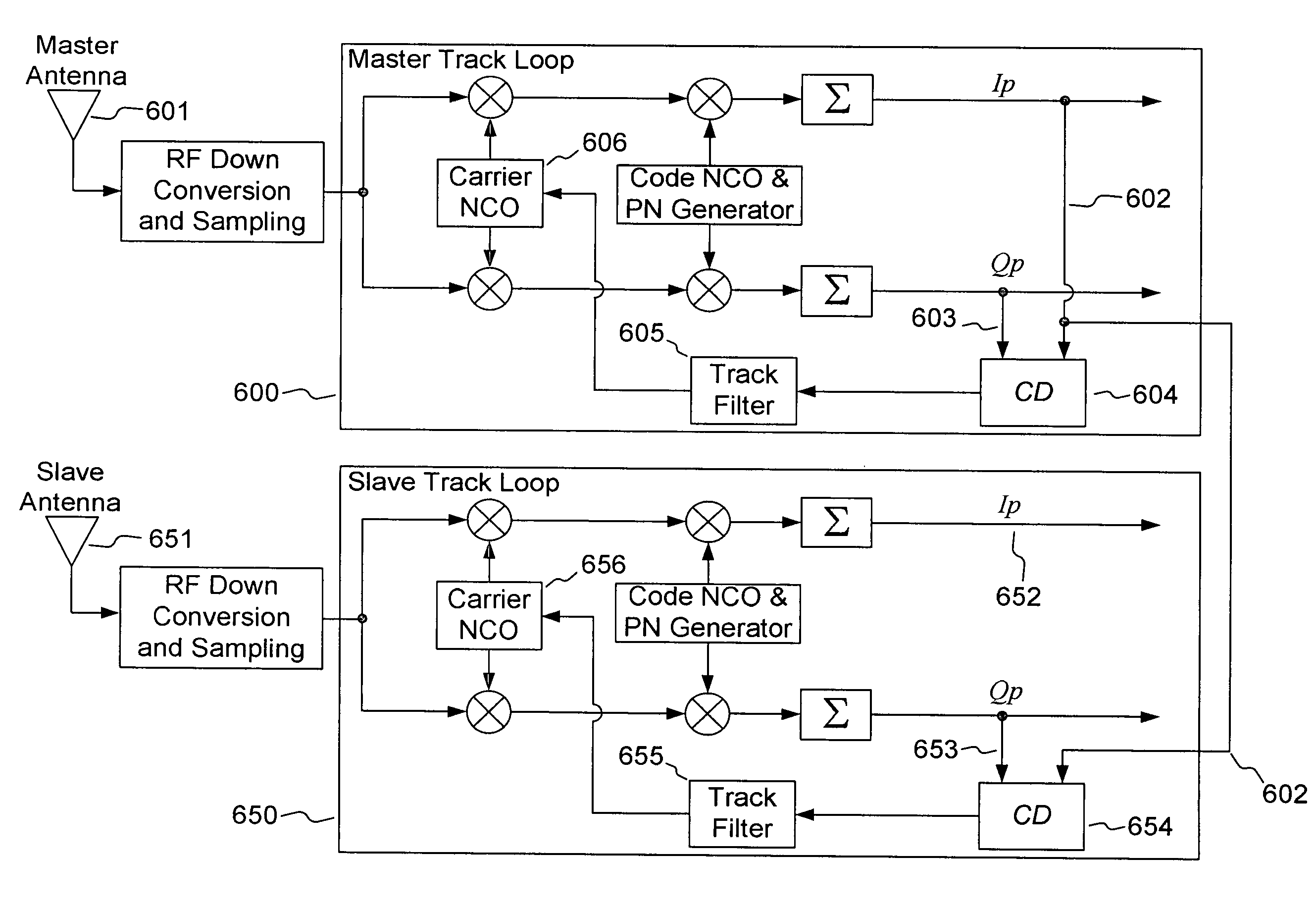
ActiveUS7388539B2Strong commonalityReduce ambiguityPosition fixationBeacon systemsAmbiguityCarrier signal
A method and system for reducing Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) carrier tracking loop ambiguities comprising: receiving a plurality of GNSS satellite signals with a first antenna in operable communication with a first tracking device and a second antenna in communication with a second tracking device in at least one GNSS receiver; and sharing of data between the first tracking device and the second tracking device. The sharing is configured to facilitate a commonality in a carrier phase derived in the first and second tracking devices. The sharing also results in a cancellation of the commonality when a difference phase is formed between a carrier phase from the first tracking device and a carrier phase from the second tracking device.
Owner:HEMISPHERE GNSS
Self-adaptive tracking loop and implementation method
InactiveCN102540216AAccurate trackingSolve the noiseSatellite radio beaconingNumerical controlDiscriminator
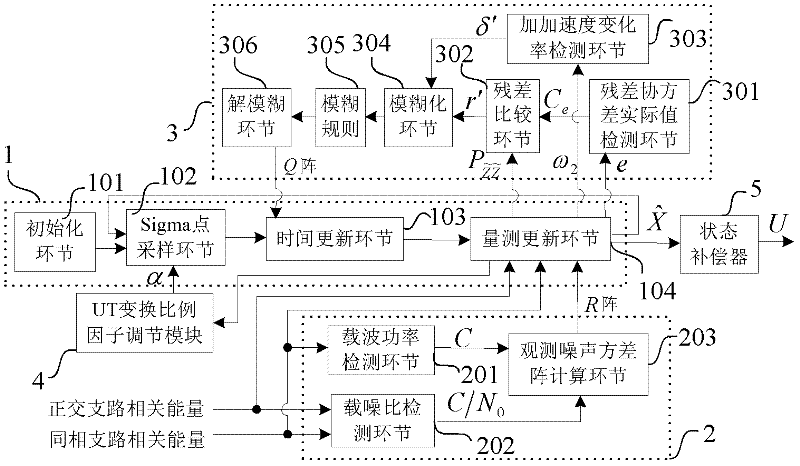
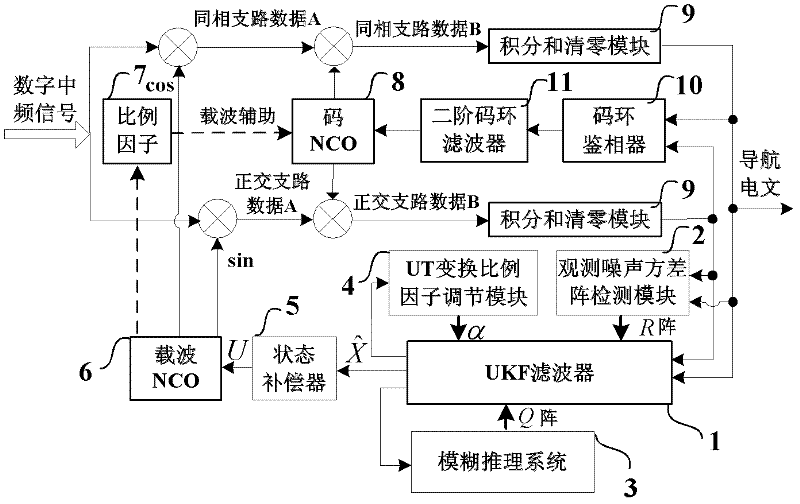
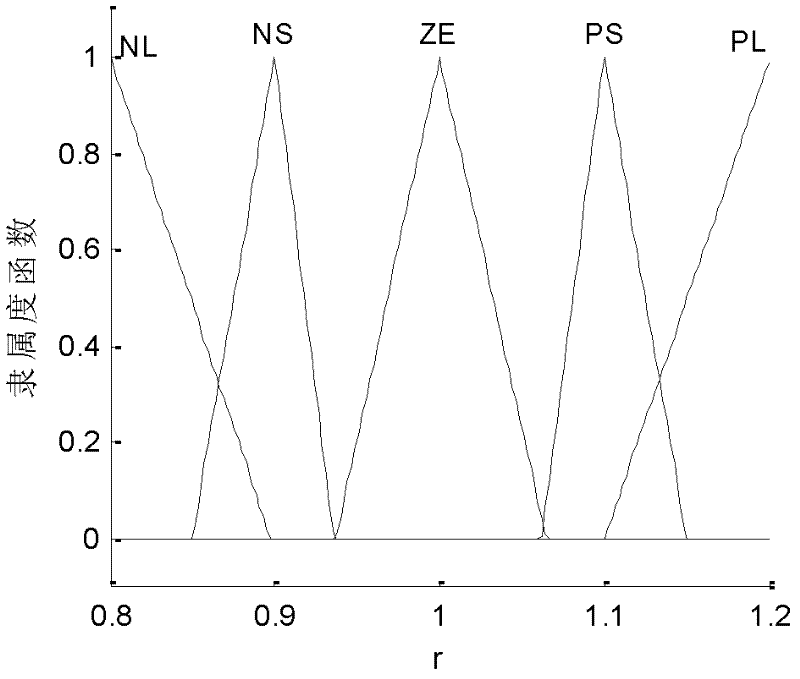
The invention discloses a self-adaptive tracking loop, which comprises an unscented Kalman filter (UKF), an observation noise variance matrix detection module, a fuzzy inference system, an unscented transformation (UT) scale factor regulation module, a state compensator, a carrier wave numerical controlled oscillator (NCO), scale factors, a code NCO, an integration and zero-clearing module, a code loop phase discriminator and a second order code loop filter, and additionally discloses an implementation method for the self-adaptive tracking loop. The implementation method comprises a step 1 ofsignal correlation, integration and zero clearing; a step 2 of code phase tracking; a step 3 of UKF modeling; a step 4 of observation noise variance matrix estimation; a step 5 of process noise variance matrix estimation; a step 6 of UT scale factor regulation; a step 7 of state estimation deviation compensation; and a step 8 of assistance of the carrier wave NCO in the code NCO. According to theself-adaptive tracking loop, the UKF, the observation noise variance matrix detection module and the fuzzy inference system are designed in the carrier tracking loop, so not only can a contradiction between thermal noise vibration in the tracking loop and a dynamic stress error be solved, but a process noise variance matrix and an observation noise variance matrix can be regulated in a self-adaptive manner according to changes of the external environment, and thereby the self-adaptive ability of the tracking loop under complex changeable environments of high dynamic, strong interference, and the like is effectively improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Binary offset carrier signal tracking loop
InactiveCN101826889AImplement separate trackingEliminate Tracking AmbiguitySatellite radio beaconingPhase-modulated carrier systemsDiscriminatorIntermediate frequency
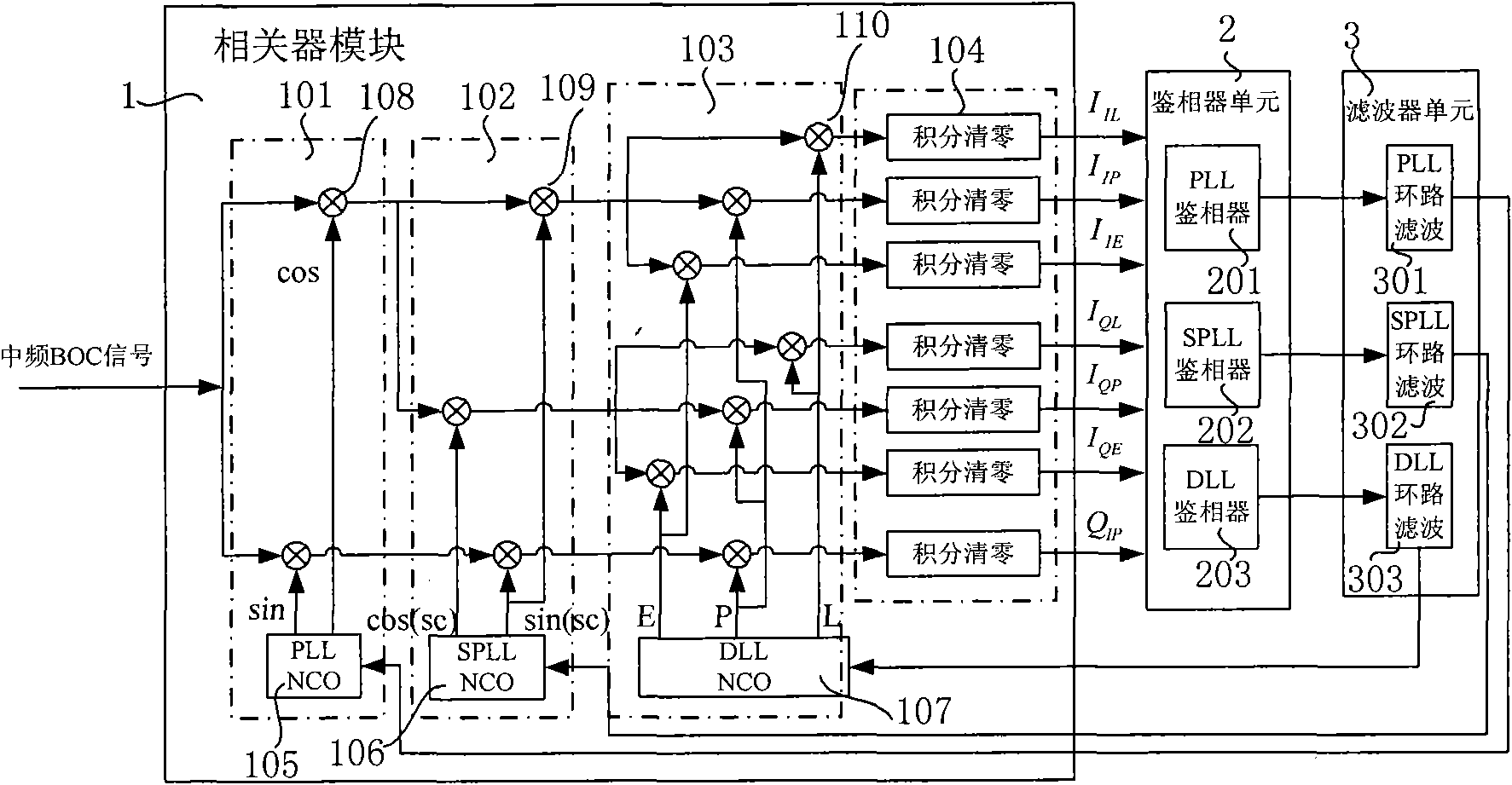
The invention discloses a binary offset carrier signal tracking loop, which comprises a correlator module, a phase discriminator unit and a filter unit. The correlator module is used for performing demodulation and despread processing on the input intermediate frequency BOC signals, and acquiring multi-path correlation values IIP, IIE, IIL, IQP, IQE, IQL and QIP between local signals and the intermediate frequency BOC signals; the phase discriminator unit is used for detecting the tracking error theta of the carrier phase and the subcarrier phase and measuring the tracking error tau of the spreading codes; and the filter unit is used for performing noise reduction and smoothing on the phase demodulation result, converting the output tracking error into corresponding frequency control words, correspondingly feeding the frequency control words back to the correlator module, tracking the input intermediate frequency BOC signals, and closing the tracking loop. The binary offset carrier signal tracking loop realizes the split tracking of the subcarrier and spreading codes, eliminates the tracking fuzziness of the BOC signals, reduces the requirement on the acquisition precision, improves the tracking performance of weak signals, widens the dynamic range of the loop, and improves the tracking stability of the BOC signals by using the periodicity of the subcarrier.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Automatic gain control configuration
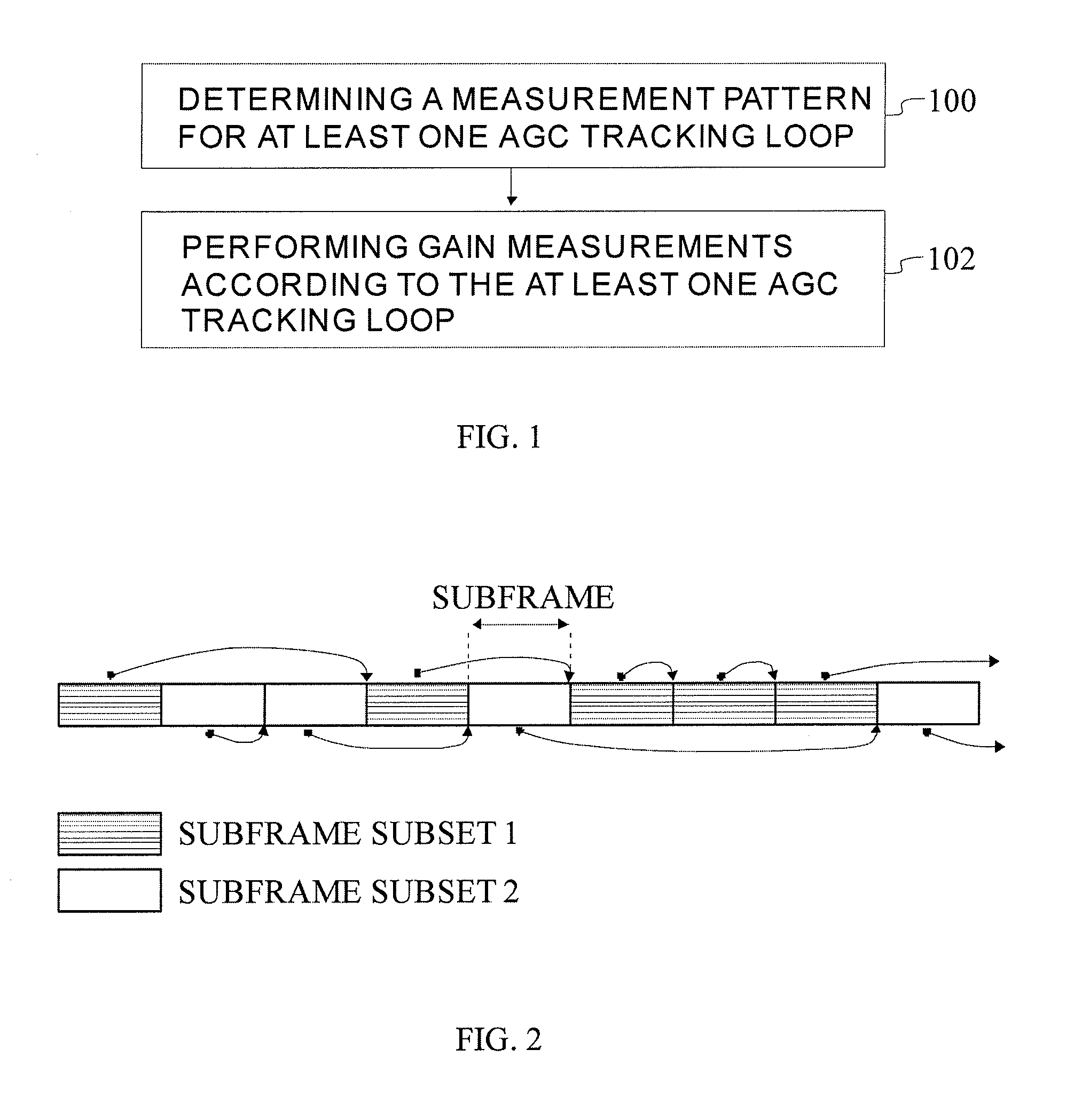
ActiveUS20130017793A1Efficient AGC operationAccurate measurementPower managementAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsUser equipmentComputer science
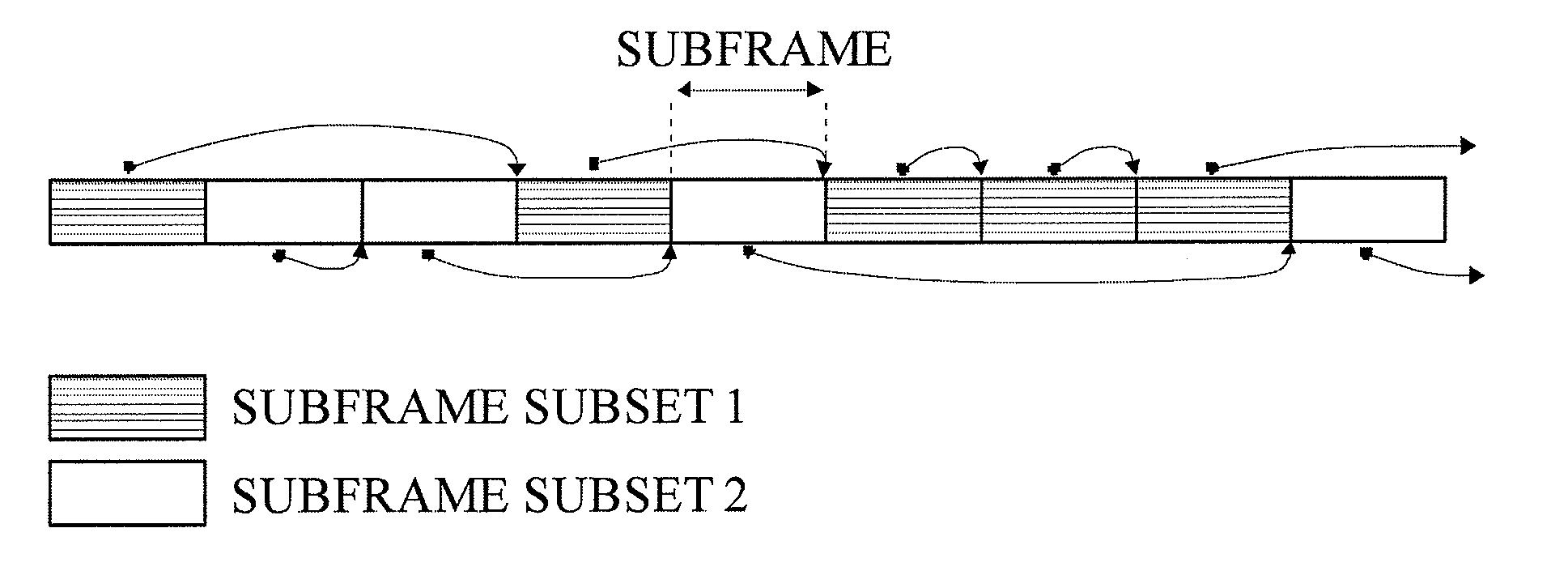
The invention teaches a solution, for example, for Long Term Evolution (LTE) networks. The solution comprises determining a measurement pattern for at least one automatic gain control tracking loop when resource restrictions have been configured for a user equipment, the resource restrictions comprising at least one measurement restriction pattern, wherein each automatic gain control tracking loop is associated with at least one measurement restriction pattern; and performing automatic gain control measurements according to the measurement patterns of the at least one automatic gain control tracking loop.
Owner:BROADCOM INT +1
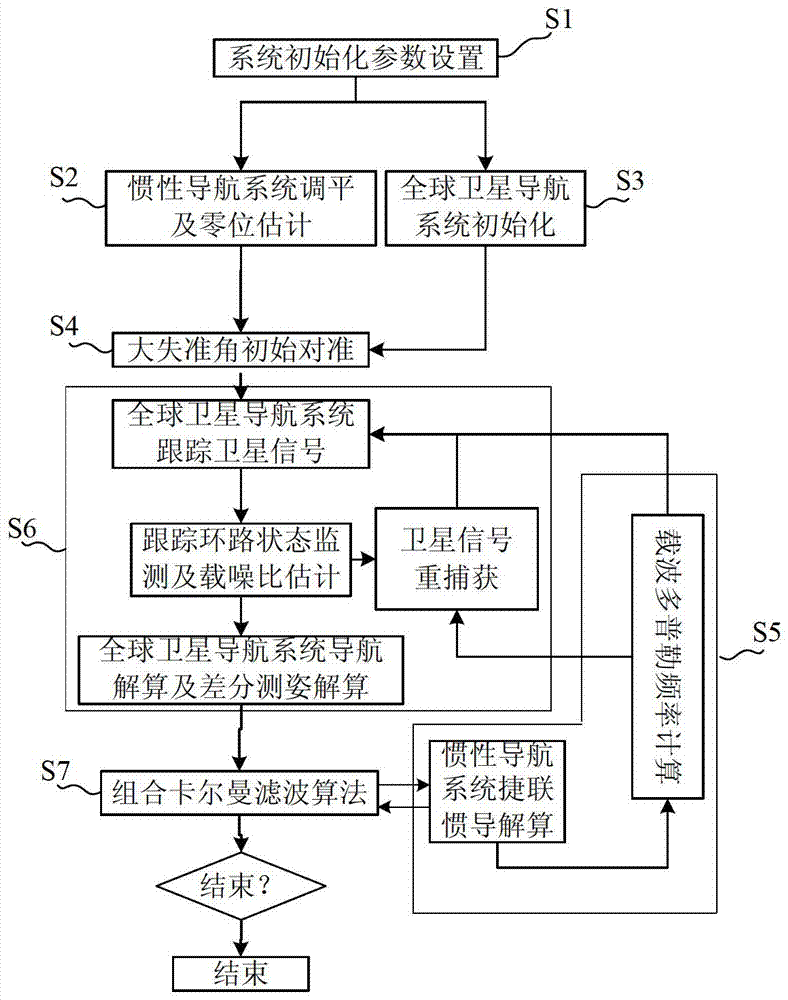
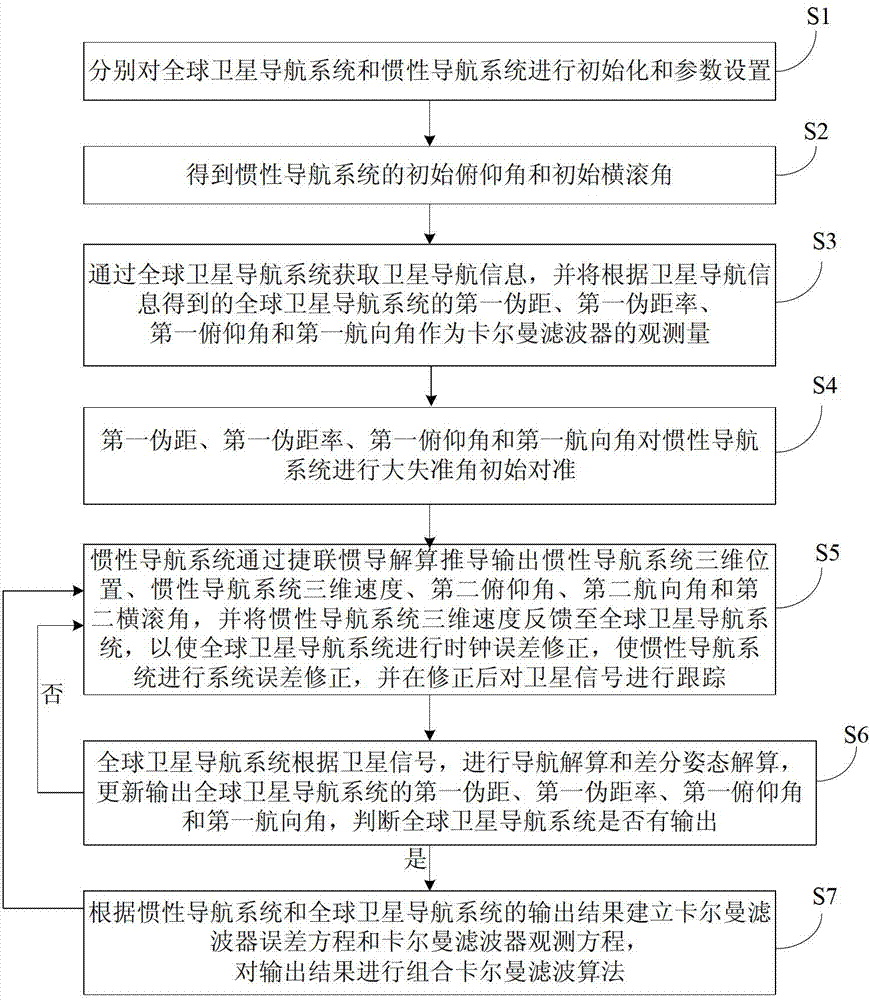
Double-antenna GNSS/INS deeply integrated navigation method and device
InactiveCN103245963AImprove robustnessCompressed ambiguity search spaceSatellite radio beaconingNavigation systemRadio frequency
The invention provides a double-antenna GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) / INS (Inertial Navigation System) deeply integrated navigation method and device. The device comprises a power supply module, an MEMS (Micro Electro Mechanical System) inertial measurement unit, a radio frequency module, an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) module, a DSP (Digital Signal Processor) module and at least two antennas. According to the device, with the assistance of an INS, the probability of cycle slip of the GNSS can be reduced effectively, the integer ambiguity searching space of the GNSS is reduced, attitude measurement information is guaranteed to be continuously outputted, and the tracking loop robustness of the GNSS is enhanced; and with the assistance of a double-antenna GNSS, quick initial alignment of the INS can be realized, the attitude observability of the INS is improved, and the attitude divergence of the INS is inhibited.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
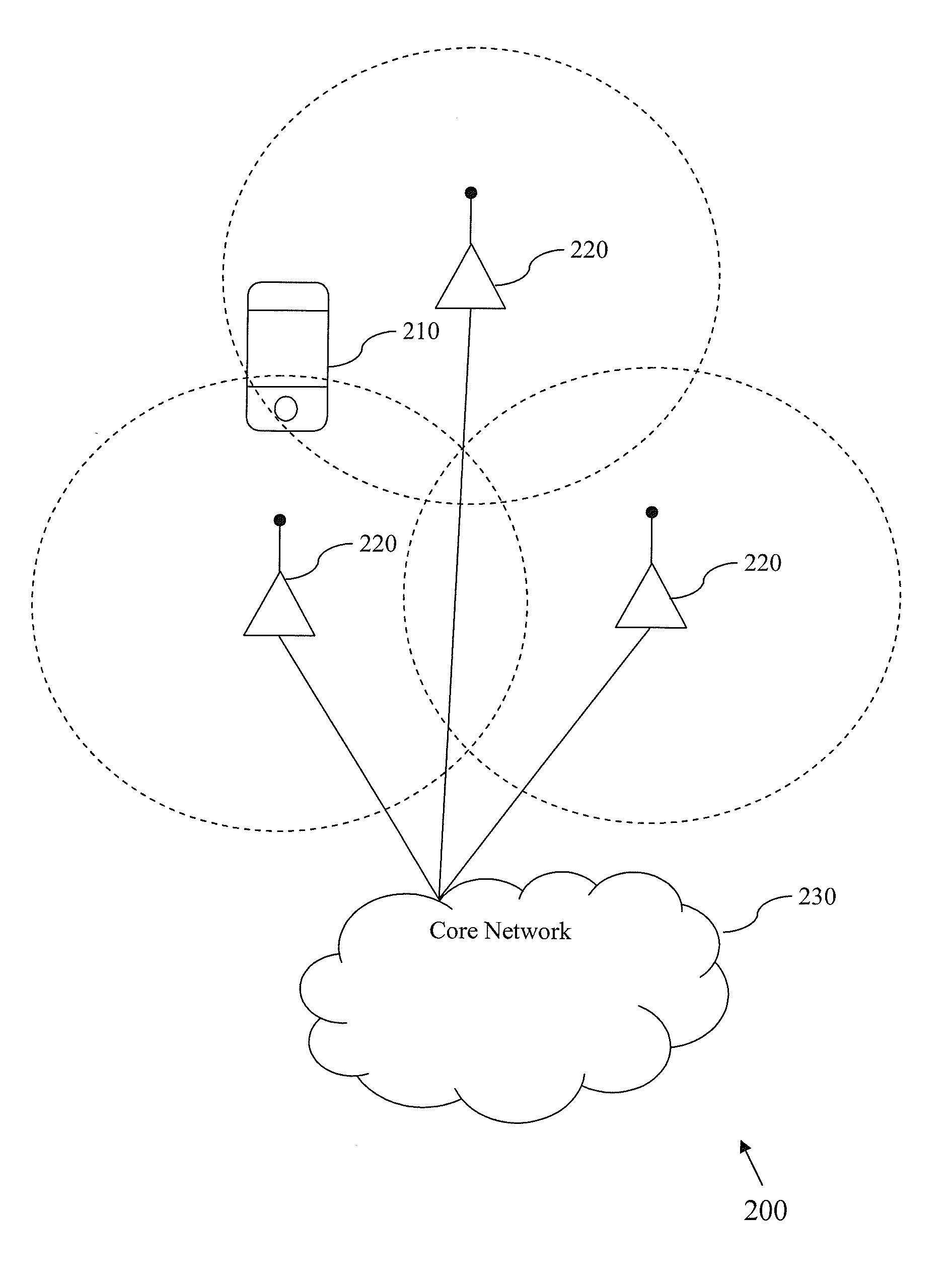
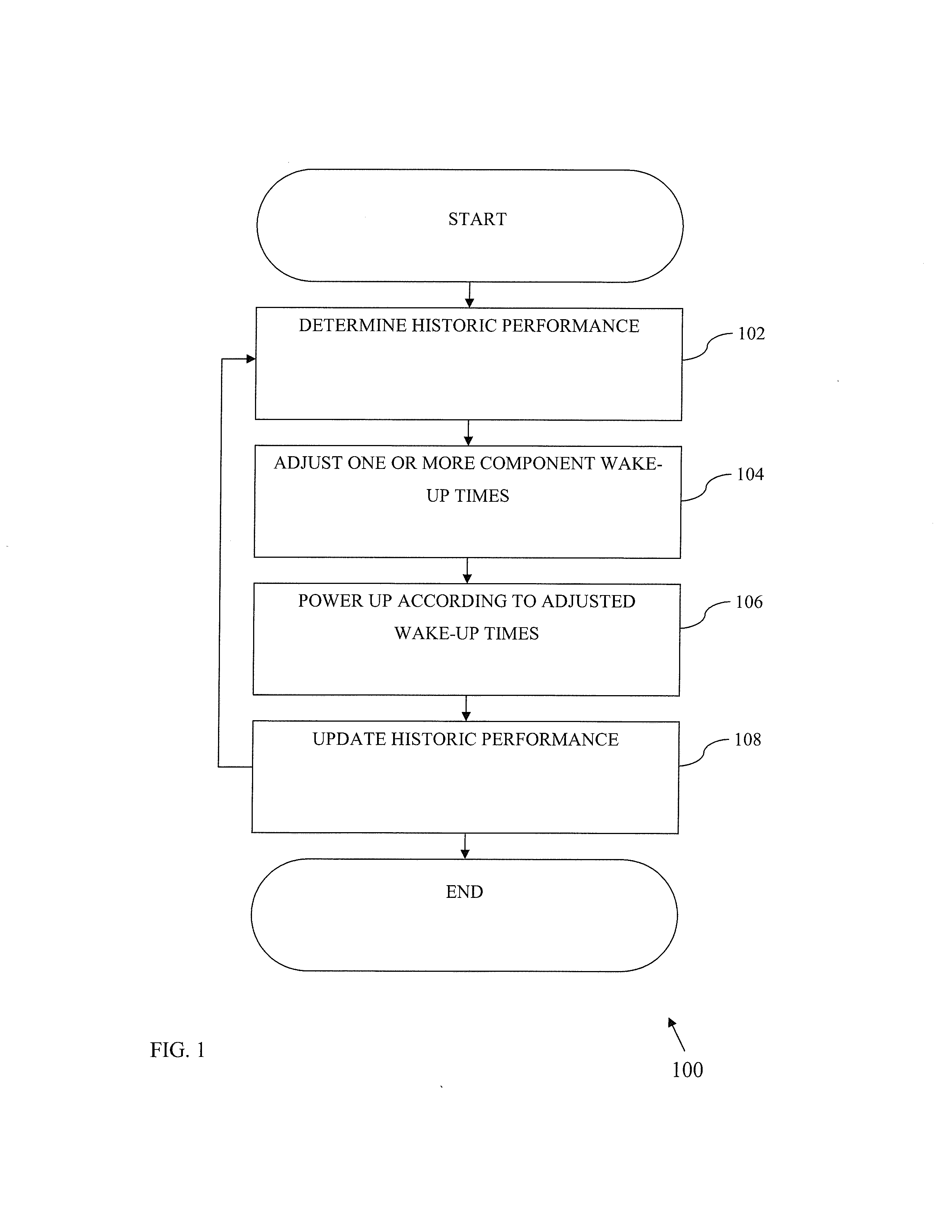
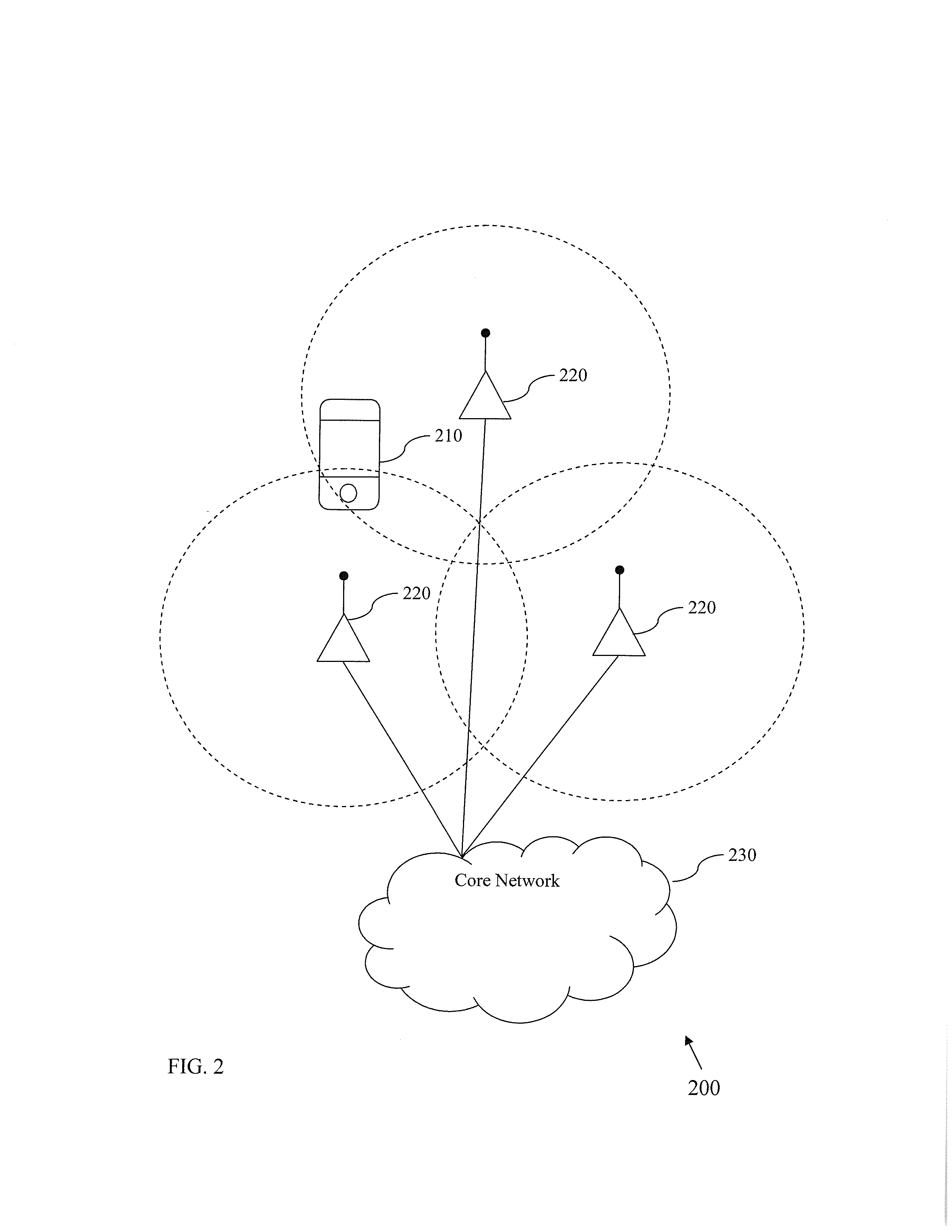
Methods and apparatus for power consumption management during discontinuous reception
ActiveUS20130176873A1Reduce wake up timeReduce energy usePower managementError preventionTrack algorithmSelf adaptive
Methods and apparatus for adaptively adjusting temporal parameters such as e.g., wake-up times of digital tracking algorithms (such as timing, frequency and power control). In one exemplary embodiment, wake-up times for tracking loops are based on success / error metrics (e.g., Block Error Rate (BLER), Bit Error Rate (BER), Packet Error Rate (PER), Cyclic Redundancy Checks (CRC), etc.) of one or more previous discontinuous reception (DRX) cycles. In a second embodiment, wake-up times for tracking loops are based on residual frequency and timing errors, etc.
Owner:APPLE INC
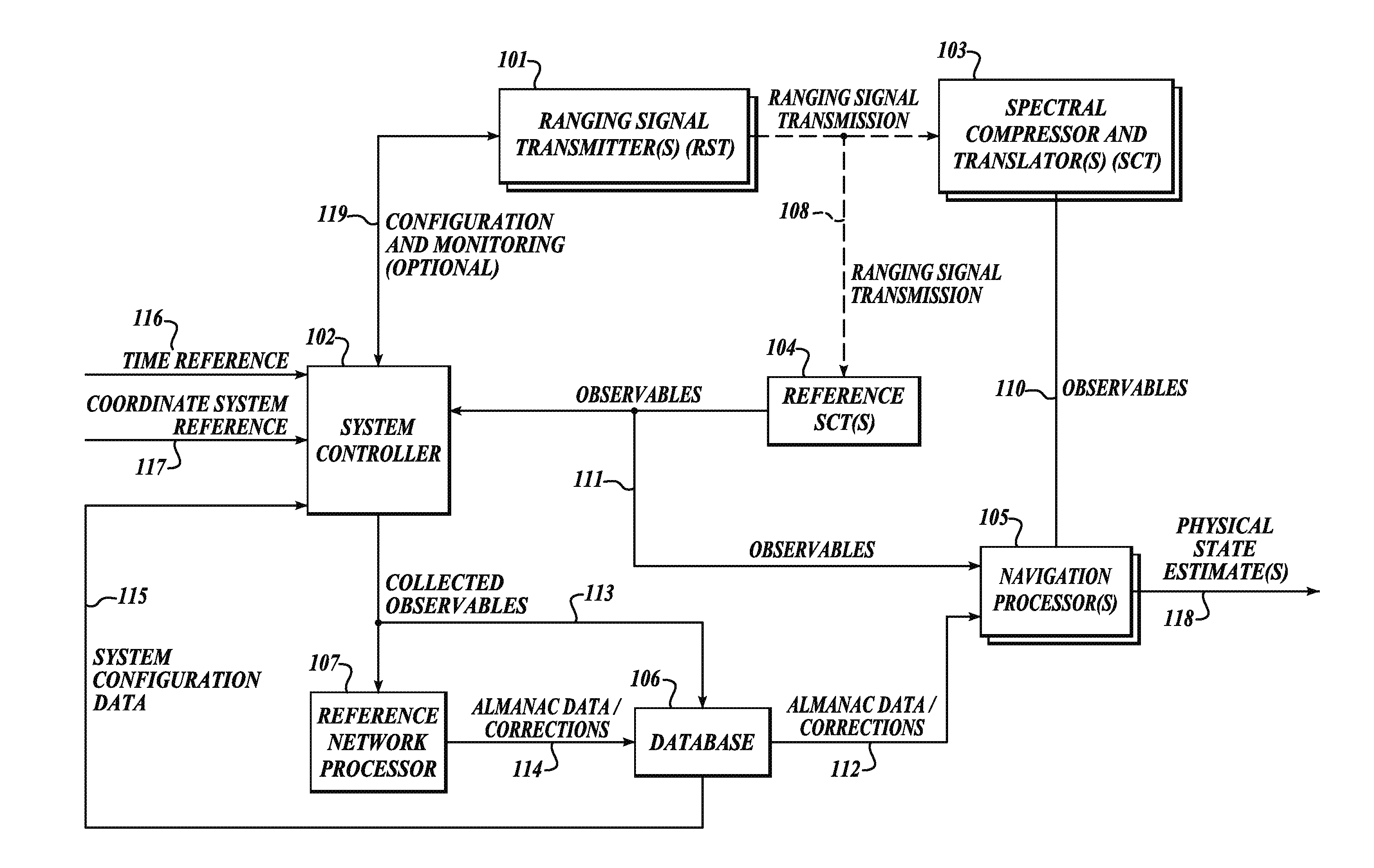
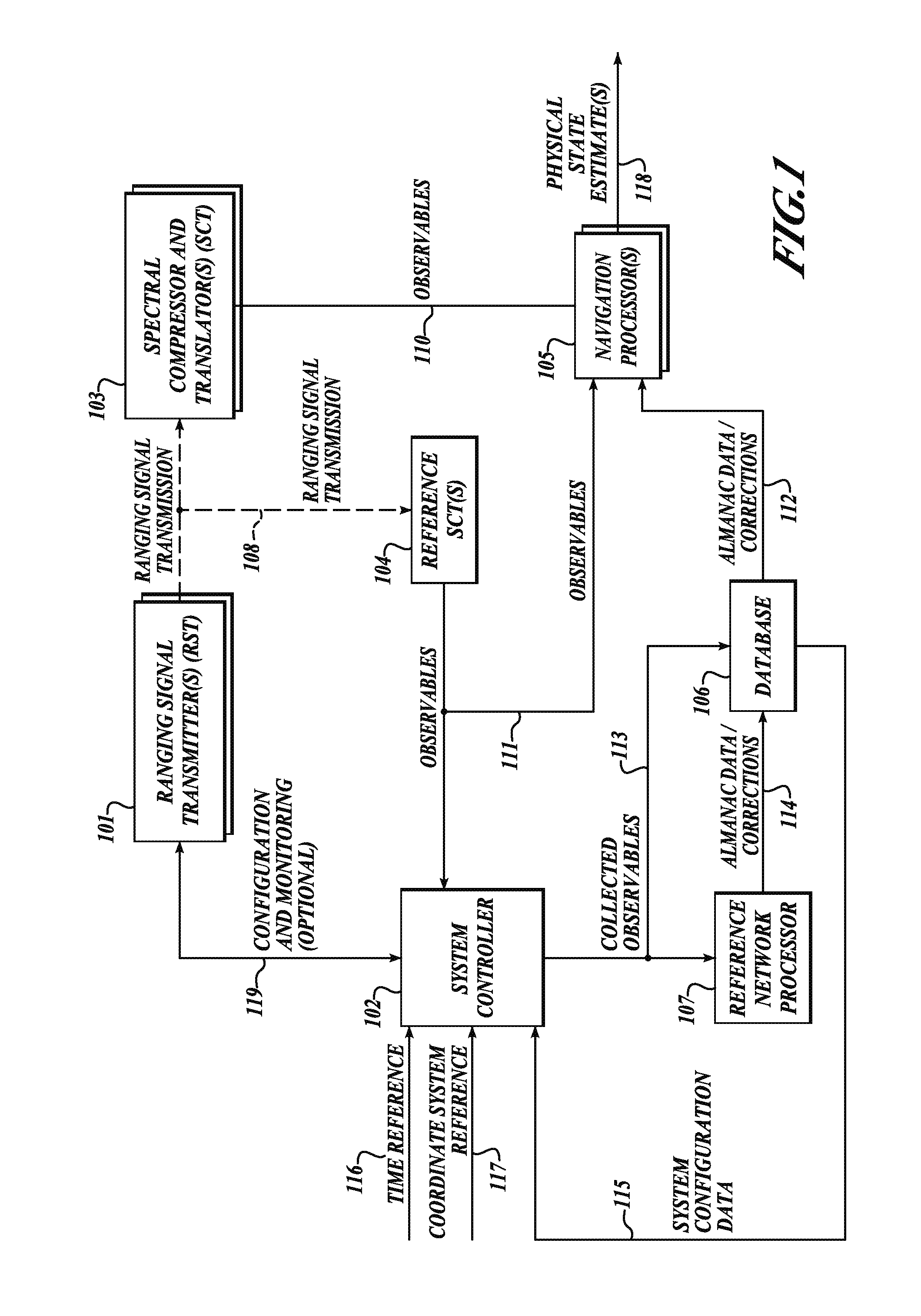
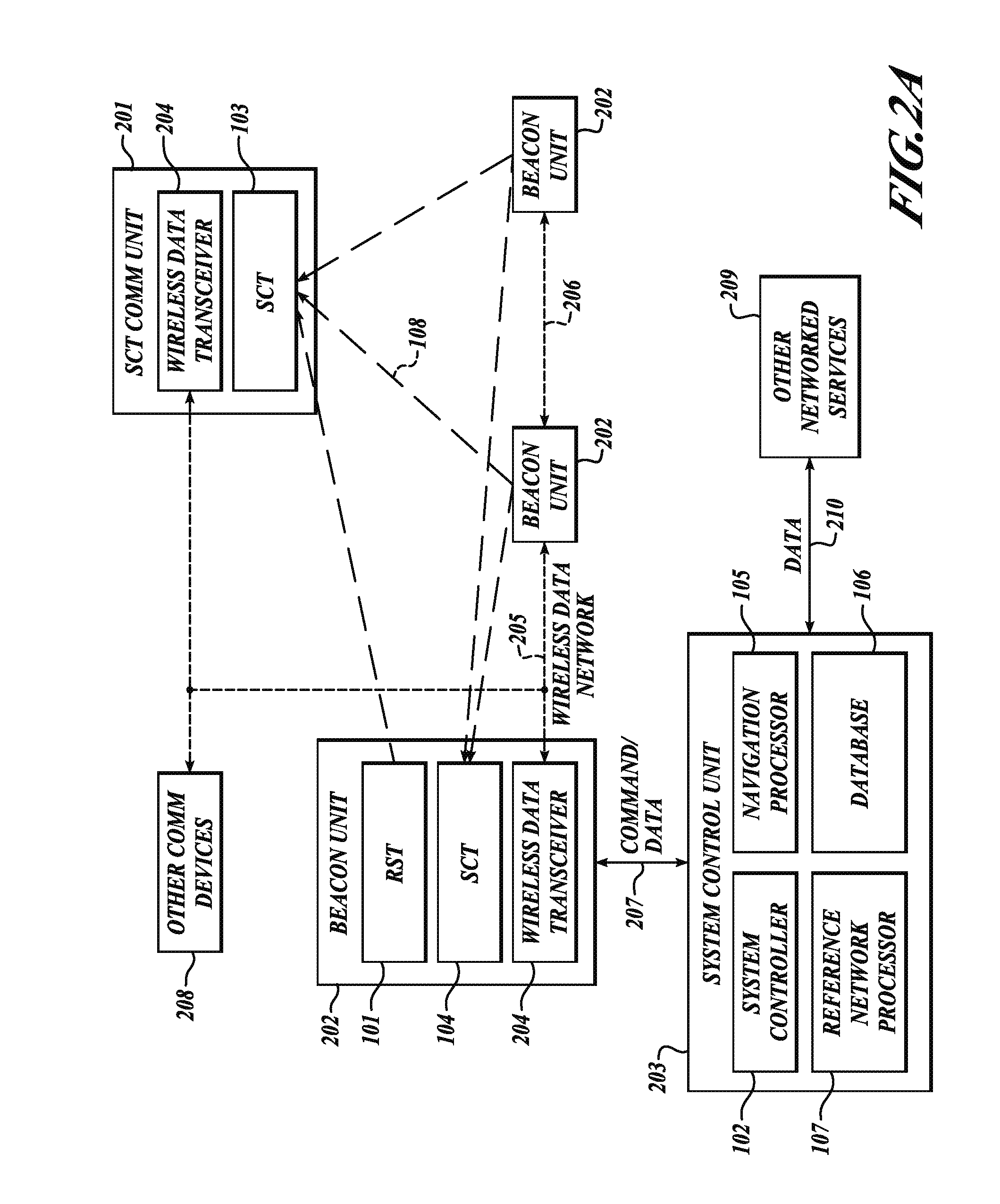
System and method for positioning using hybrid spectral compression and cross correlation signal processing
InactiveUS20120169542A1Easy to implementRapidly deployableDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationFrequency spectrumCode division multiple access
The present invention relates to a system and method for positioning and navigation using hybrid spectral compression and cross correlation signal processing of signals of opportunity, which may include Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) as well as other wideband energy emissions in GNSS obstructed environments. Examples of these signals of opportunity include but are not limited to GPS, GLONASS, cellular Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) communications signals, and 802.11 Wi-Fi. Combining spectral compression with spread spectrum cross correlation enables extraction of code and carrier observables without the need to implement the tracking loops (e.g. Costas tracking loop) commonly used in conventional GNSS receivers. For applications where dynamics and transmission medium may make it difficult to continuously track carrier phase, the hybrid approach of the present invention has significant utility.
Owner:TELECOMM SYST INC
Method of enhancing signal tracking in global positioning system receivers
ActiveUS6959057B1Enhancing signal trackingPosition fixationAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsCarrier signalDiscrete-time signal
A method of enhancing signal tracking in a global positioning system receiver utilizing a frequency banked filter in providing code and carrier tracking loops includes acquiring a continuous time global positioning signal and separating the continuous time global positioning signal into in-phase and quadrature signals I and Q. The signals I and Q are sampled over a predetection interval (PDI) to provide discrete time signals, and the discrete time signals are used to generate a component in-phase measurement and a component quadrature measurement for each of multiple PDI segments of one PDI. For each of multiple different frequency bins, composite in-phase and quadrature measurements are generated by combining component in-phase measurements and component quadrature measurements from the PDI. Power is detected in each of the multiple different frequency bins for the PDI using the corresponding composite in-phase measurement and the corresponding composite quadrature measurement generated for the frequency bin.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Apparatus and method for SCDMA digital data transmission using orthogonal codes and a head end modem with no tracking loops
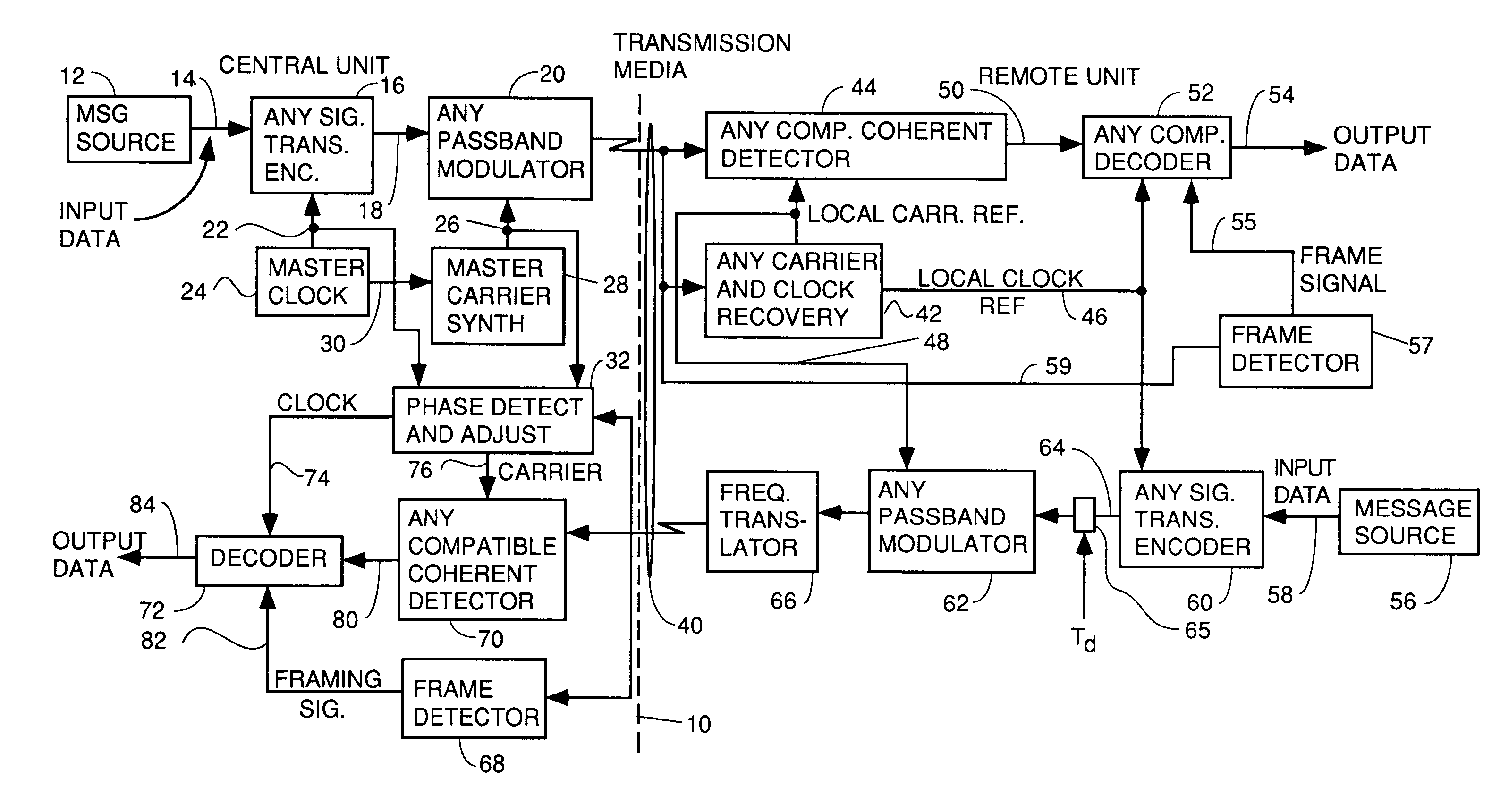
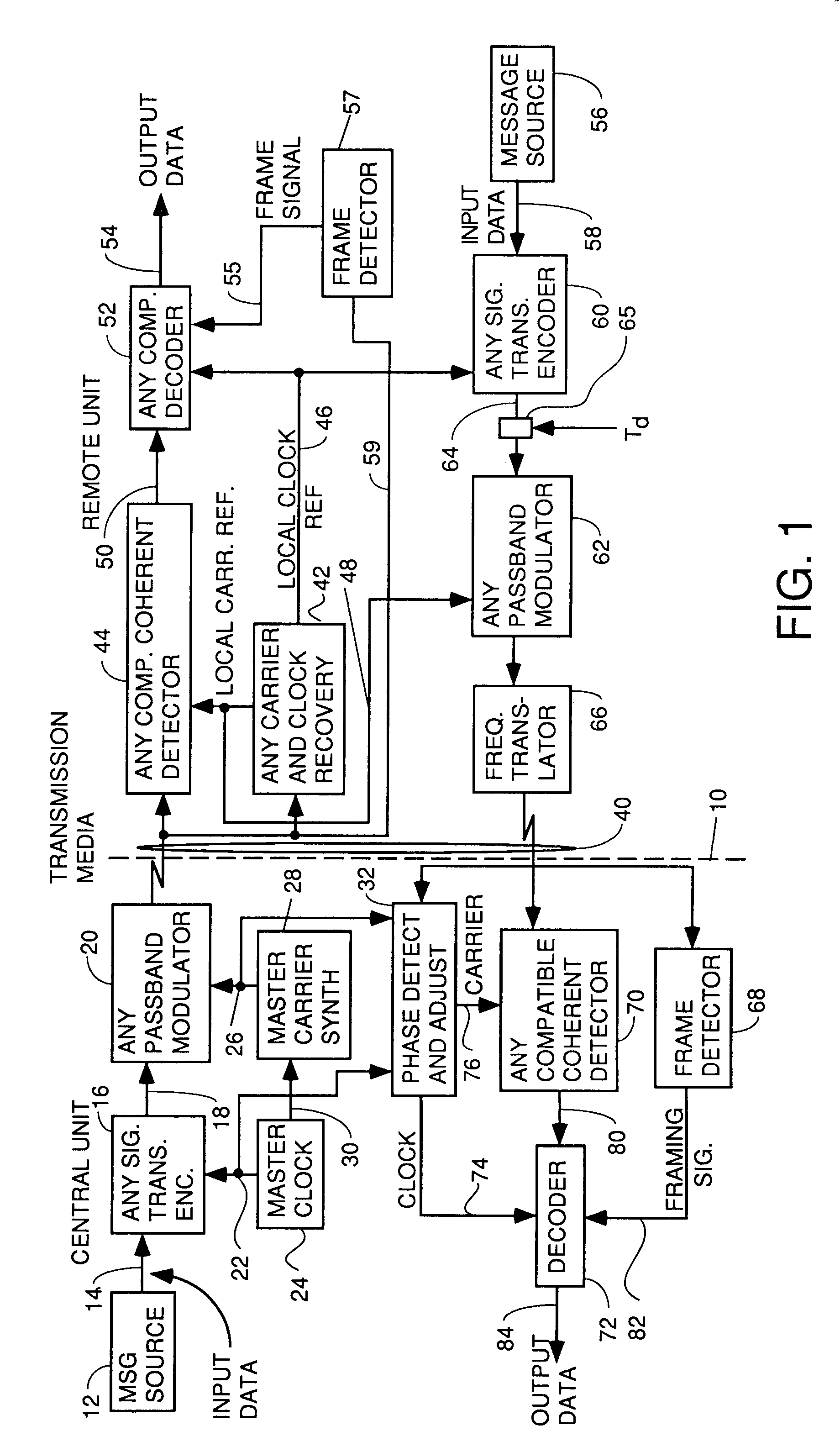
InactiveUS7031344B2Improve throughputReduce error ratePulse modulation television signal transmissionError preventionDigital dataModem device
A system for bidirectional communication of digital data between a central unit and a remote unit wherein the need for tracking loops in the central unit has been eliminated. The central unit transmitter generates a master carrier and a master clock signal which are used to transmit downstream data to the remote units. The remote units recover the master carrier and master clock and synchronize local oscillators in each remote unit to these master carrier and master clock signals to generate reference carrier and clock signals for use by the remote unit receiver. These reference carrier and clock signals are also used by the remote unit transmitters to transmit upstream data to the central unit. The central unit receiver detects the phase difference between the reference carrier and clock signals from the remote units periodically and adjusts the phase of the master carrier and master clock signals for use by the central unit receiver to receive the upstream data.
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
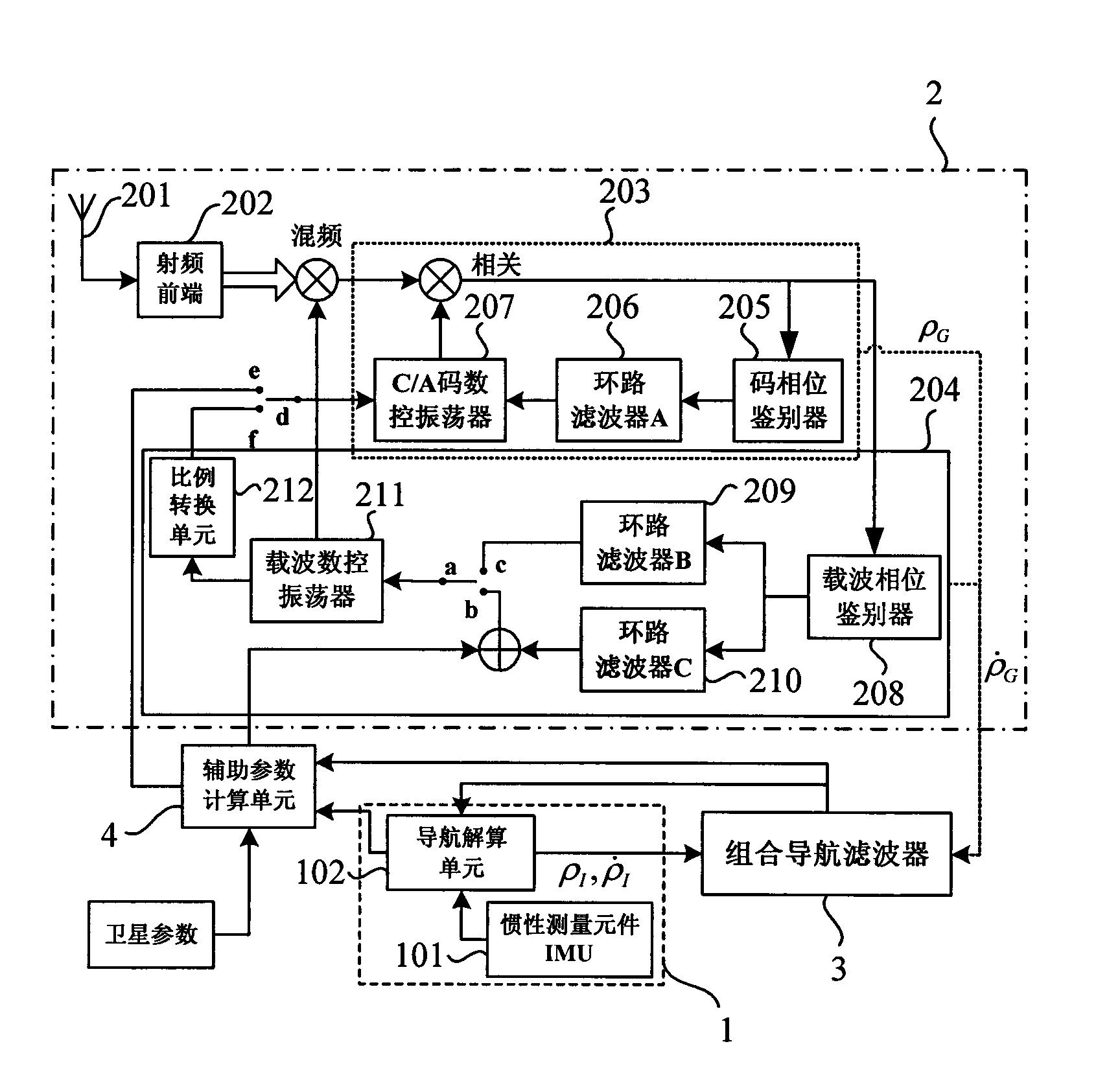
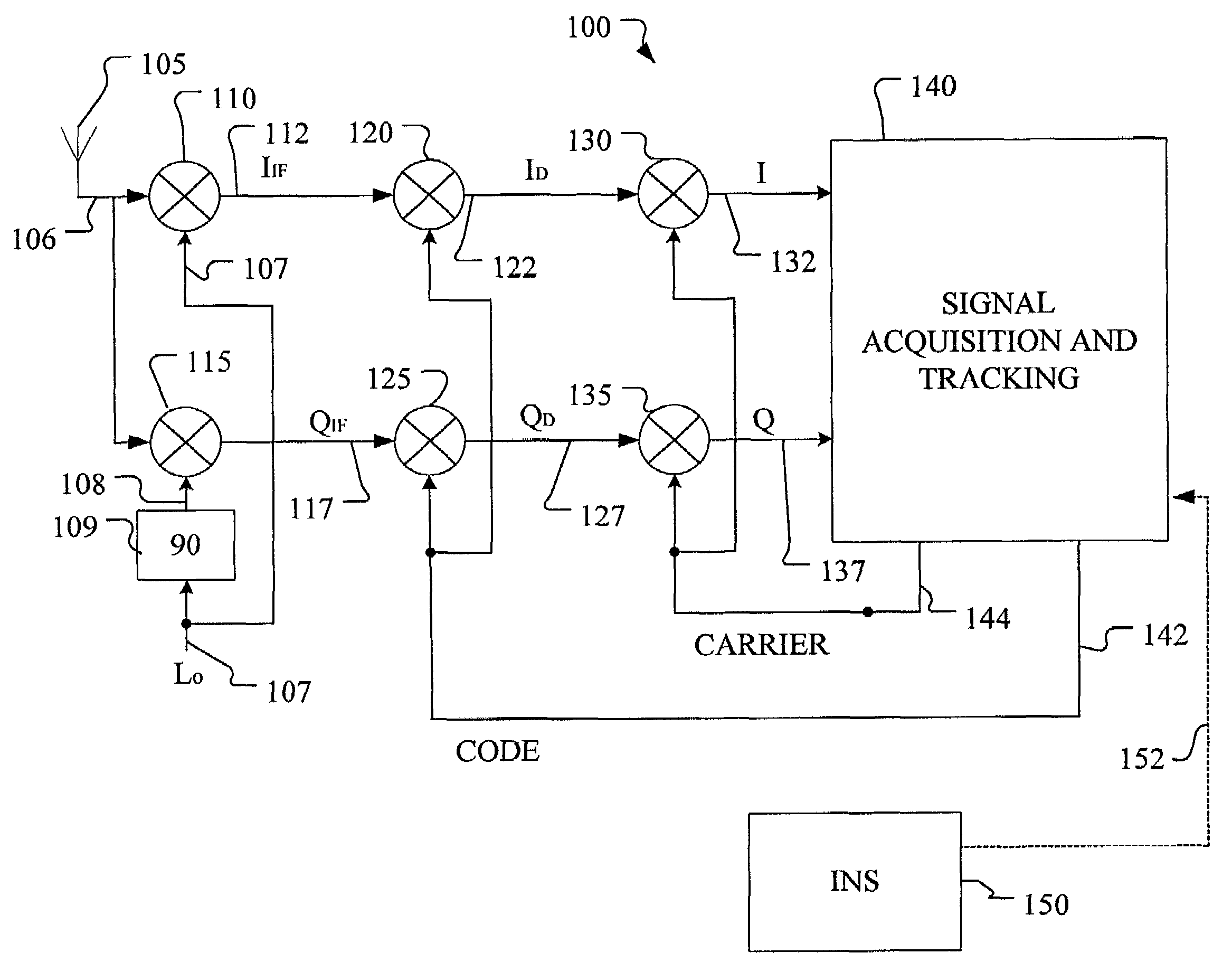
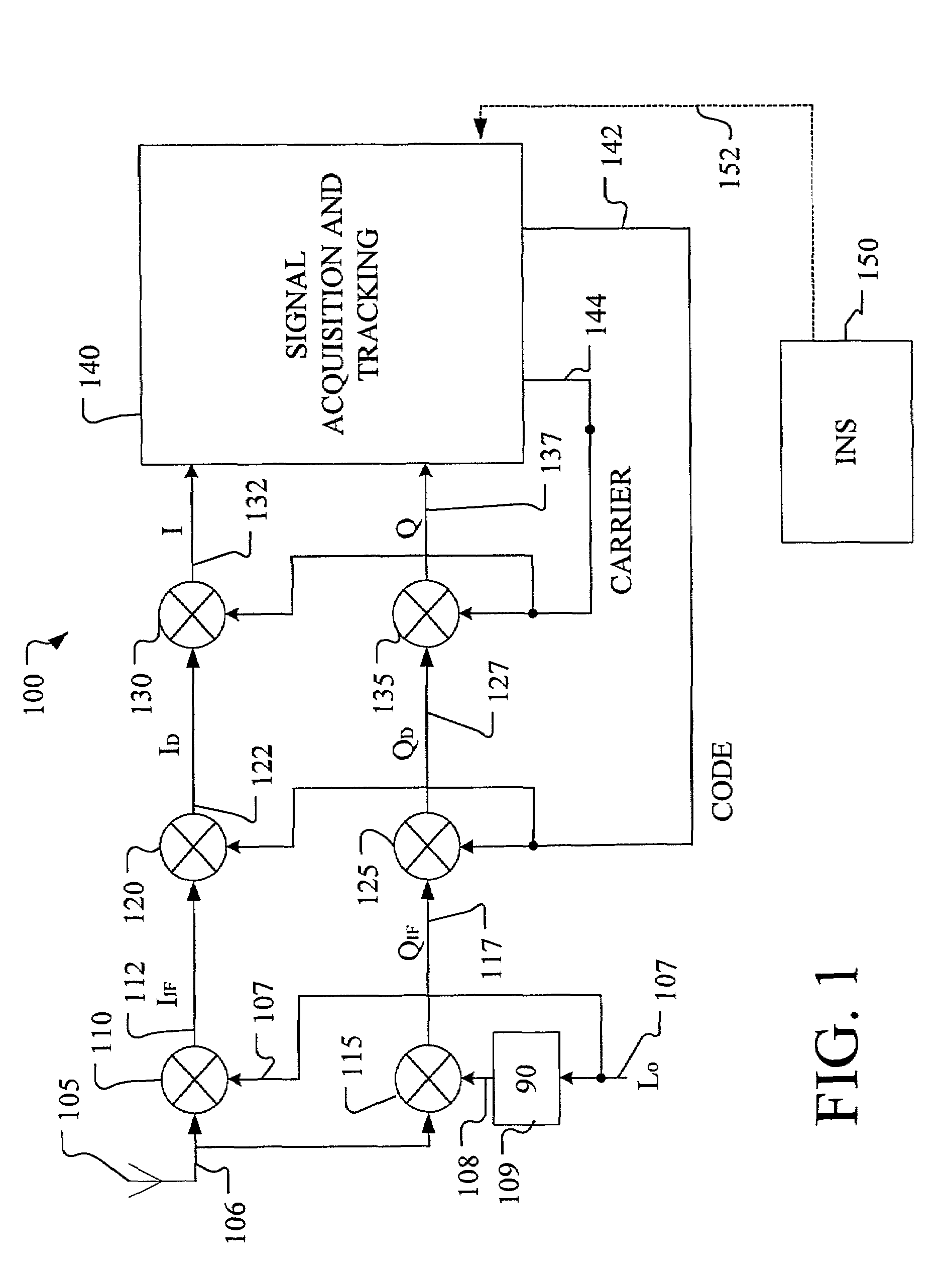
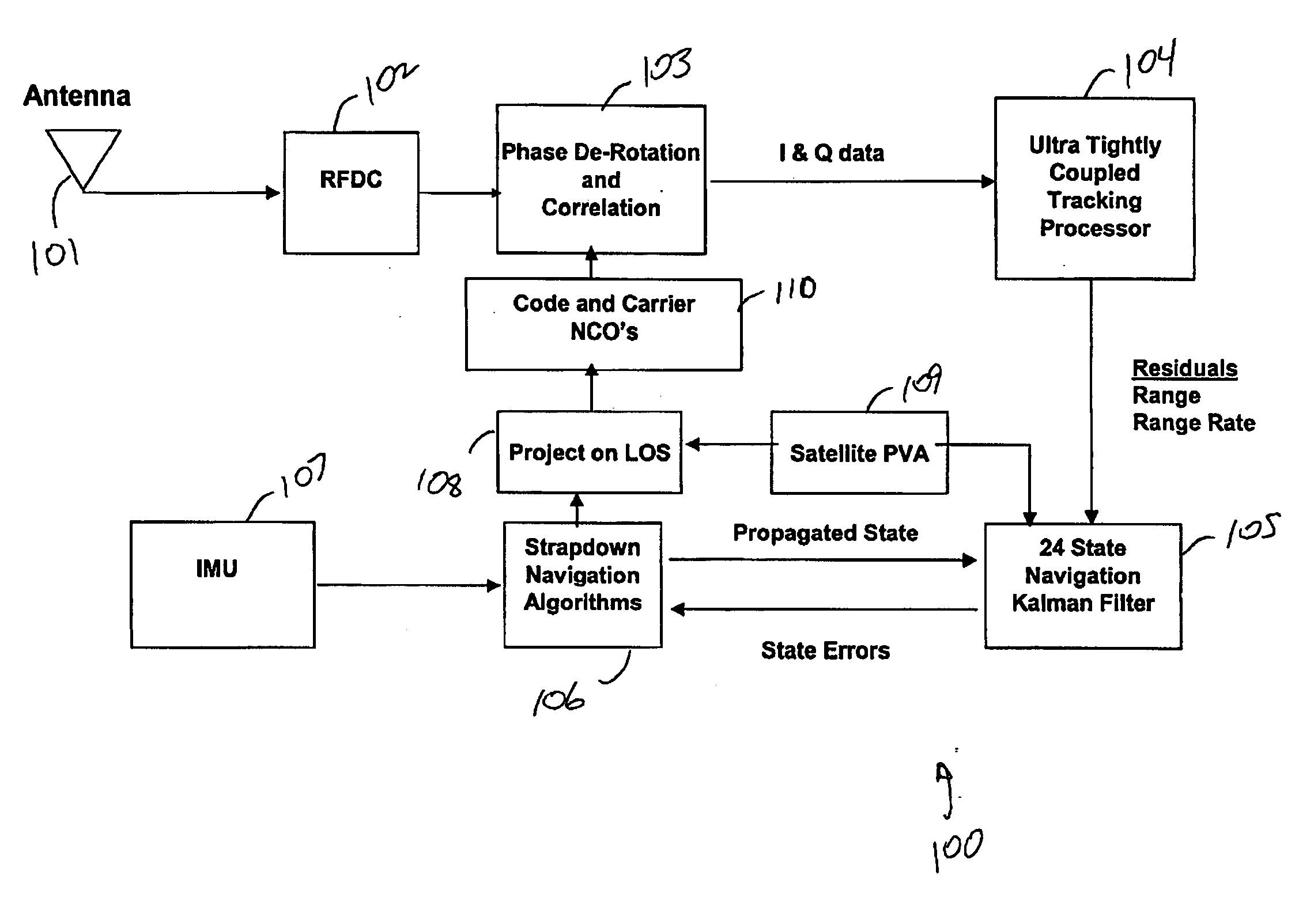
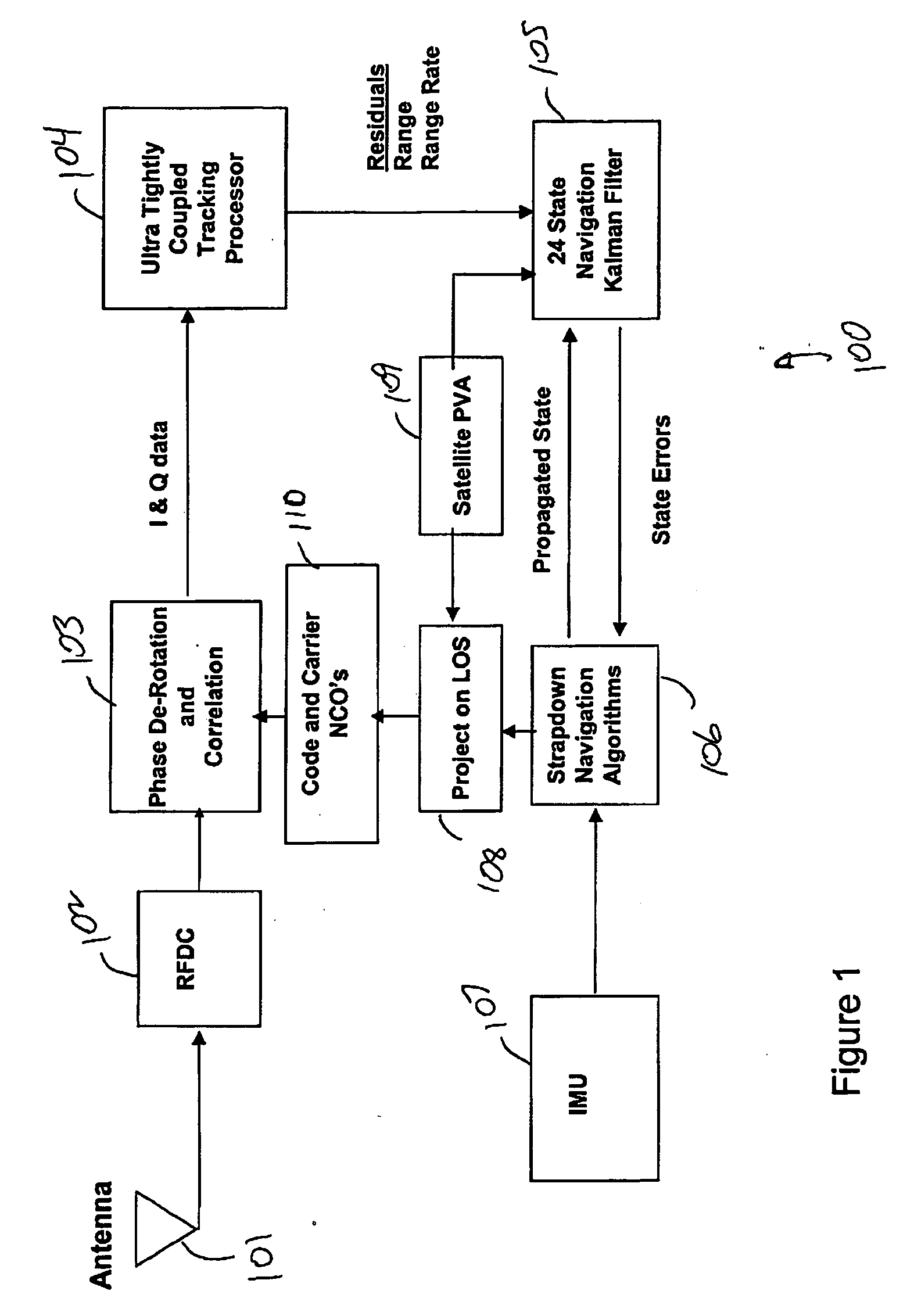
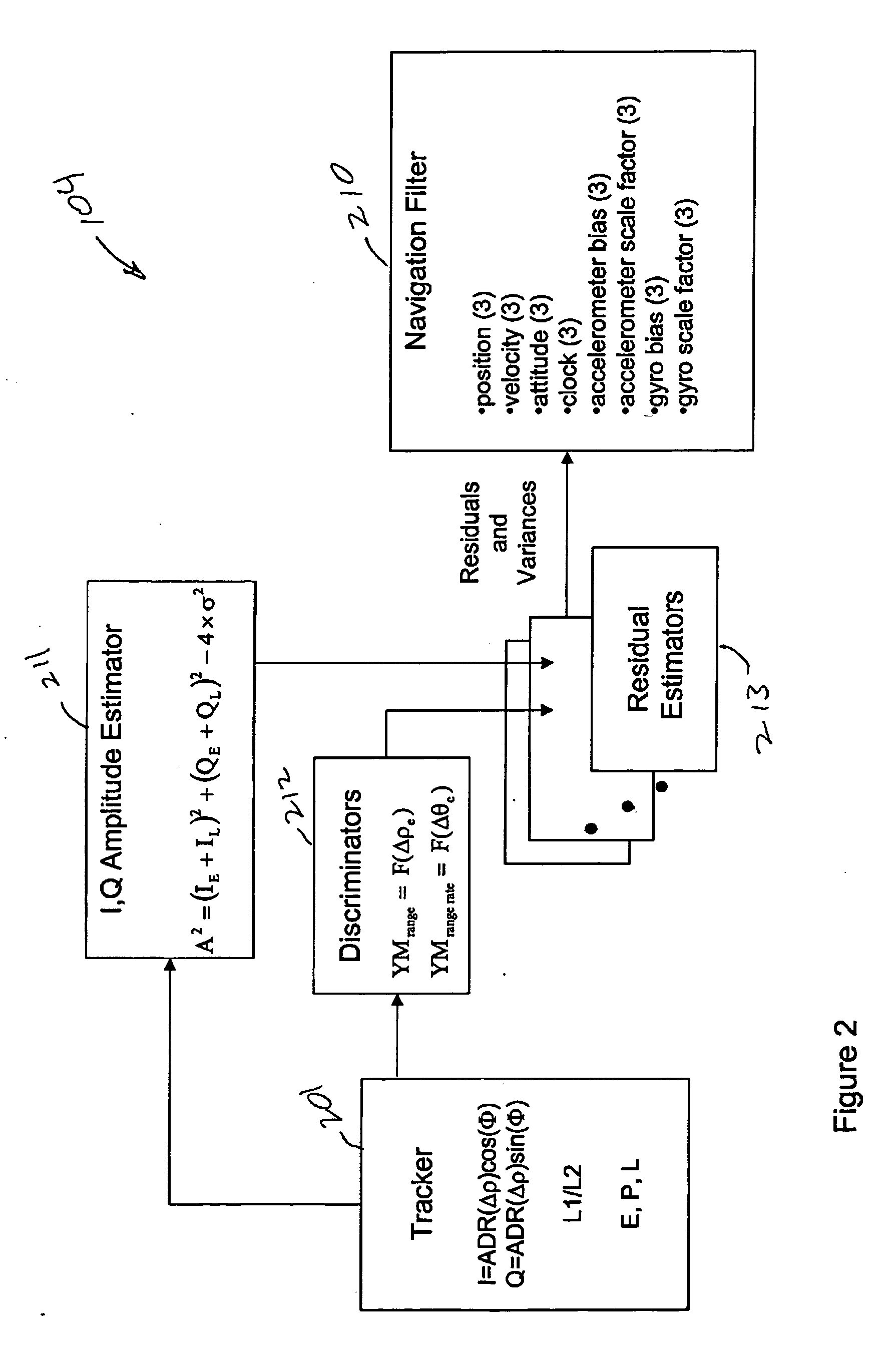
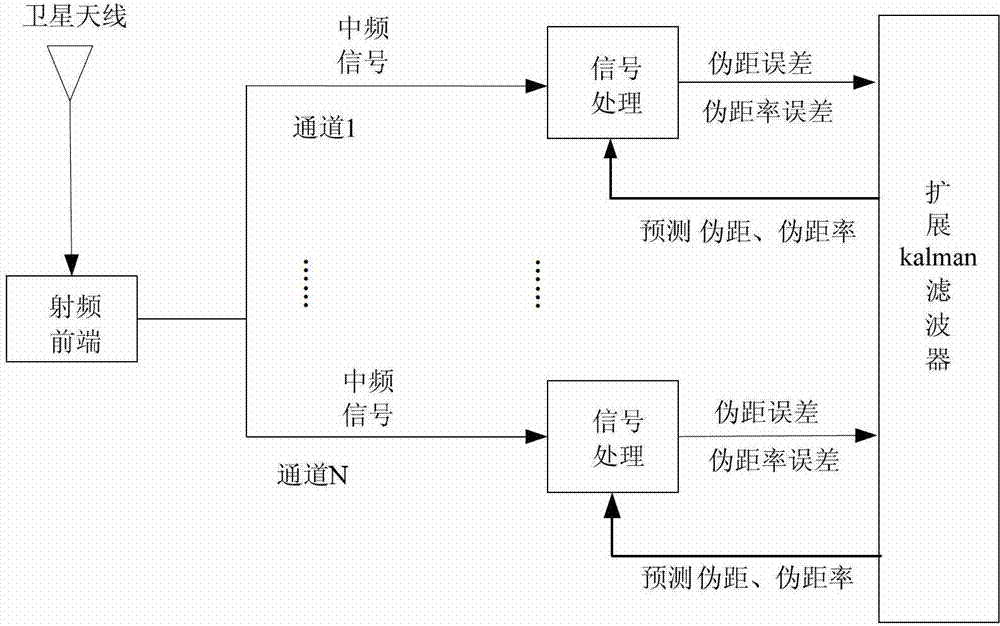
System and method for advanced tight coupling of GPS and inertial navigation sensors
ActiveUS20060161329A1Easily integrated into existing navigation filter designImprove the environmentDigital data processing detailsPosition fixationDiscriminatorSystem configuration
A system and method for generating a navigation solution in high interference and dynamic environments using Global Positioning System (GPS) and inertial measurement unit (IMU) data is described. The system configuration is a multi-satellite tracking loop structure obtained by closing each satellite's tracking loop through a single, multi-state navigation filter. This generates a robust navigation solution that can track GPS signals in a lower signal to noise ratio than can the standard GPS tightly coupled tracking loops. The system contains an Advanced Tightly Coupled (ATC) tracking processor which accepts early, late, and on-time I and Q data from the GPS signal tracker and outputs vehicle to satellite range, range rate and range acceleration residual measurements to a navigation Kalman filter. The ATC includes nonlinear discriminators which transform I and Q data into linear residual measurements corrupted by unbiased, additive, and white noise. It also includes an amplitude estimator configured to operate in rapidly changing, high power noise; a measurement noise variance estimator; and a linear residual smoothing filter for input to the navigation filter.
Owner:L3 TECH INC
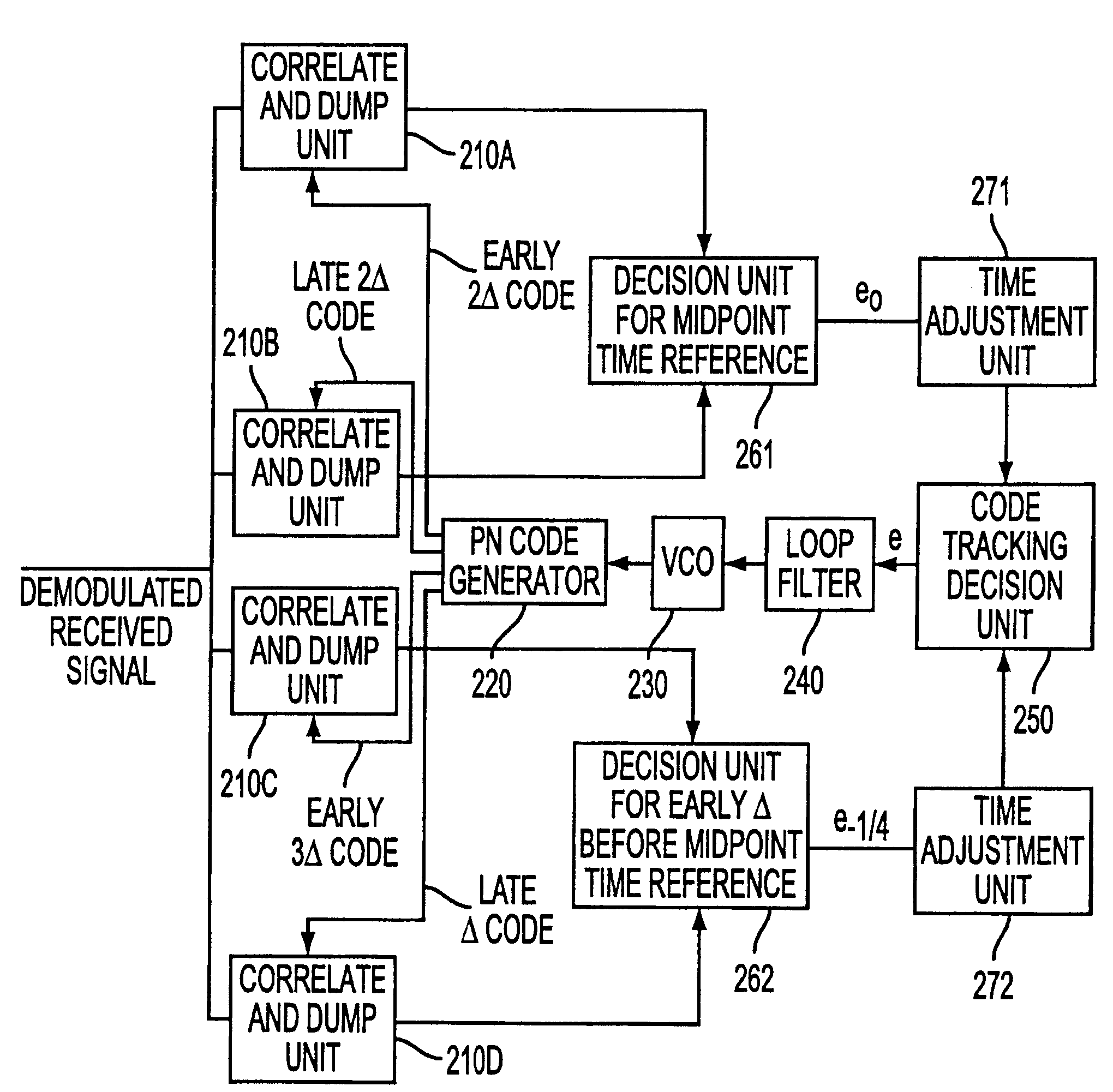
Delay lock code tracking loop employing multiple timing references
InactiveUS6901106B1Effective trackingOccurrence is very lowCode division multiplexMulti-frequency code systemsCommunications systemCode division multiple access
A code tracking system and method especially for use in direct sequence code division multiple access (DS-CDMA) communication systems employs multiple timing references within a chip by tracking the multiple timing references relative to the exact midpoint of the chip, then adjusting the timing references to the exact midpoint of the chip, and outputting an error tracking signal in accordance with the minimum error associated with the multiple timing references. The system performs effective code tracking with low lock-loss rate even when the noise of a receiving path interferes with detection of some of the timing references. The system uses multiple delay-locked loops for the different timing references.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Free space optical-communication APT system and method based on compressive sensing receiver
ActiveCN103326780AGuaranteed stabilityImplementing a Coarse Tracking LoopFree-space transmissionBeam splitterSpatial light modulator
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
Signal tracing algorithm of GNSS receiver
InactiveCN103809191AQuickly restore locked stateReliable Signal TrackingSatellite radio beaconingVector trackingUsability
The invention discloses a signal tracing algorithm of a GNSS receiver. The signal tracing algorithm is capable of overcoming the phase-locked loop lock loosing problem by means of a frequency locking / phase locking cascade tracking loop, after the phase-locked loop is unlocked, a frequency locking loop helps the phase-locked loop to restore quickly, and moreover, a loop filter reset scheme is designed to control the error between the output value of the loop filter and the Doppler observed value at the last time, so that the phase-locked loop is fastened to restore from the lock loos state. The signal tracing algorithm automatically switches between a vector tracking loop and a scalar tracking loop according to the signal environment so as to improve the usability and dynamic property of the receiver. Whether the signal to noise ratio is low or the signal is momently interrupted due to shield, the performance of the receiver is not lower than the ordinary GNSS receiver, the influence of the accumulative error caused by the signal failure or interference of a satellite on the other satellite signal processing channels is avoided, and the system stability and the location output reliability are improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
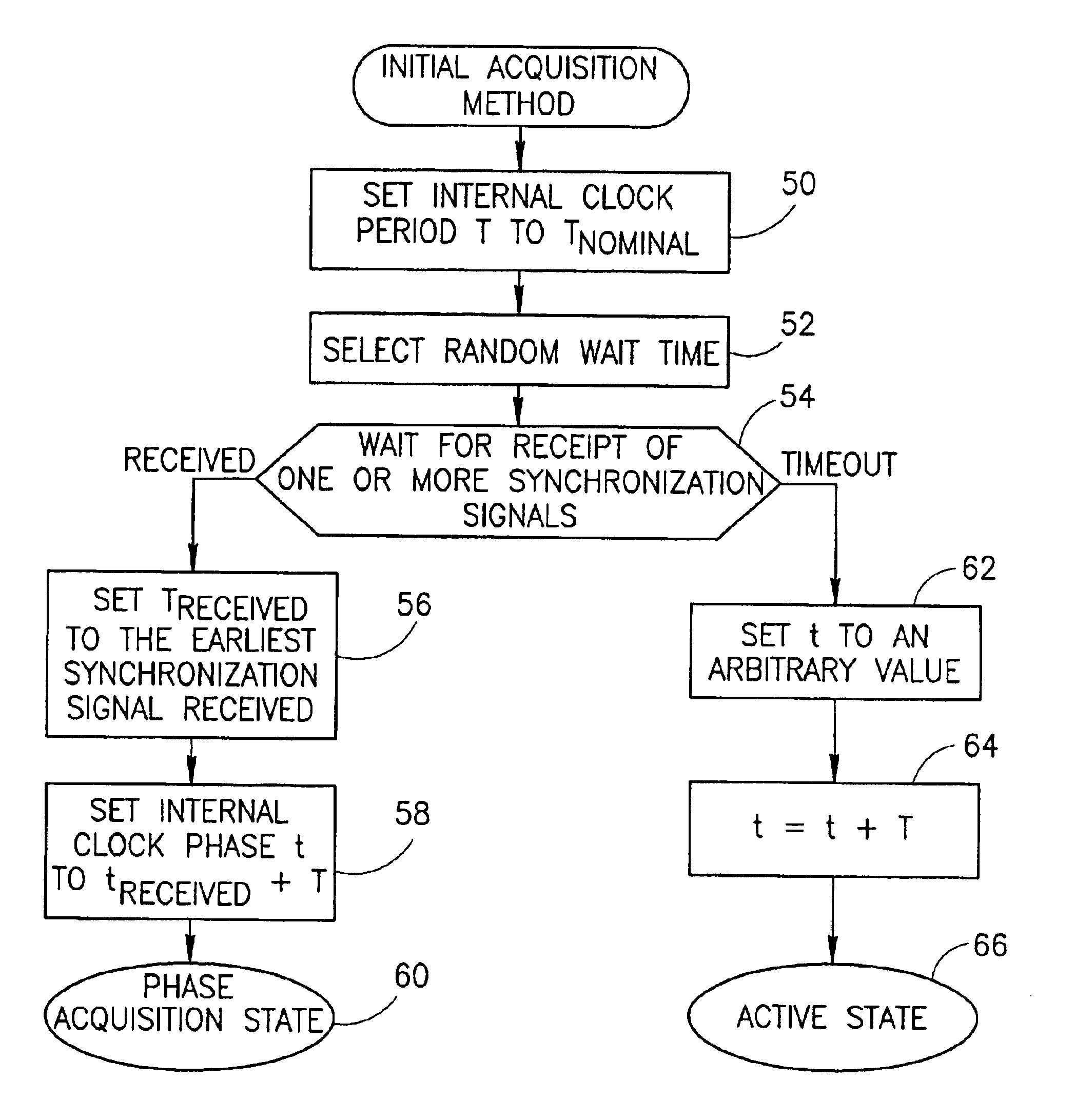
Distributed synchronization mechanism for shared communications media based networks
InactiveUS6907472B2Optimization mechanismEfficient workReceiver initialisationTransmission/receiving by adding signal to waveComputer scienceCommunications media
A novel and useful distributed synchronization mechanism. The synchronization loop of each station on the shared media based network considers only synchronization signals received having a time phase earlier than the time phase of its internal clock. From among the plurality of synchronization signals received by a given station having a time phase earlier than that of its internal clock, only the earliest of the received synchronization signals is considered. This allows the use of a second order synchronization tracking loop wherein both the phase and rate of the internal clock are tracked and adjusted. The station with the fastest internal clock effectively functions as an ad-hoc synchronization master for all stations in a given maximum connected group.
Owner:ITRAN COMM
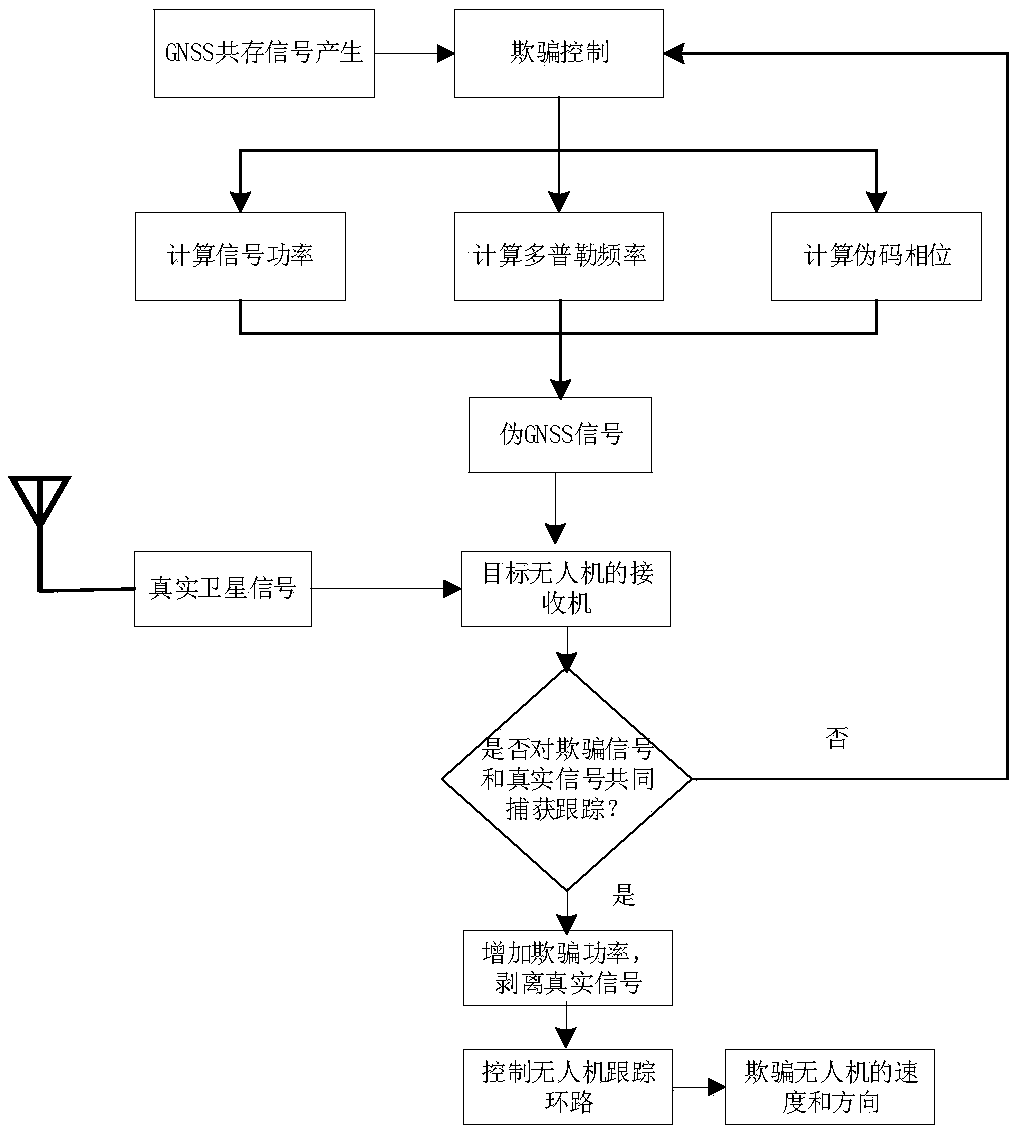
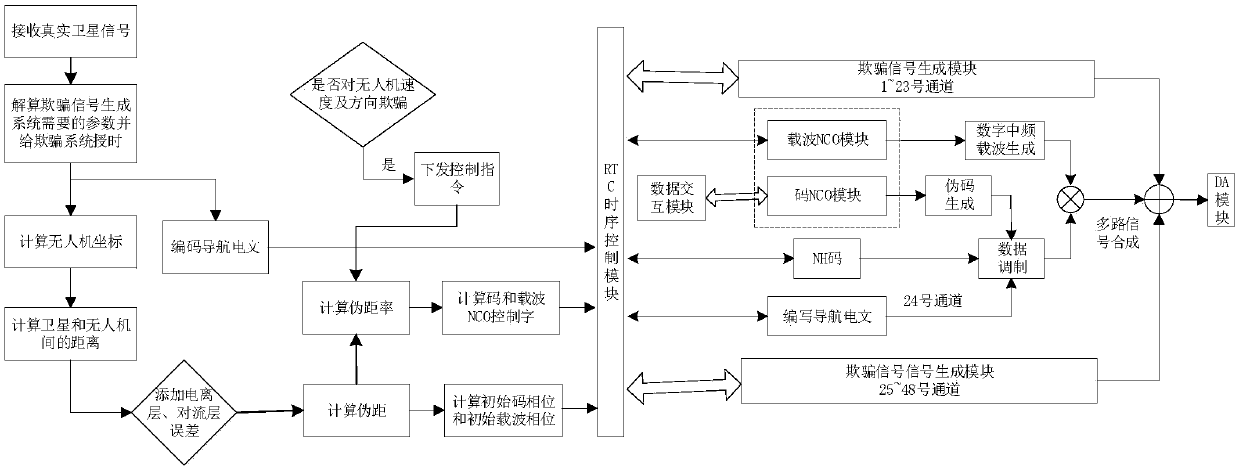
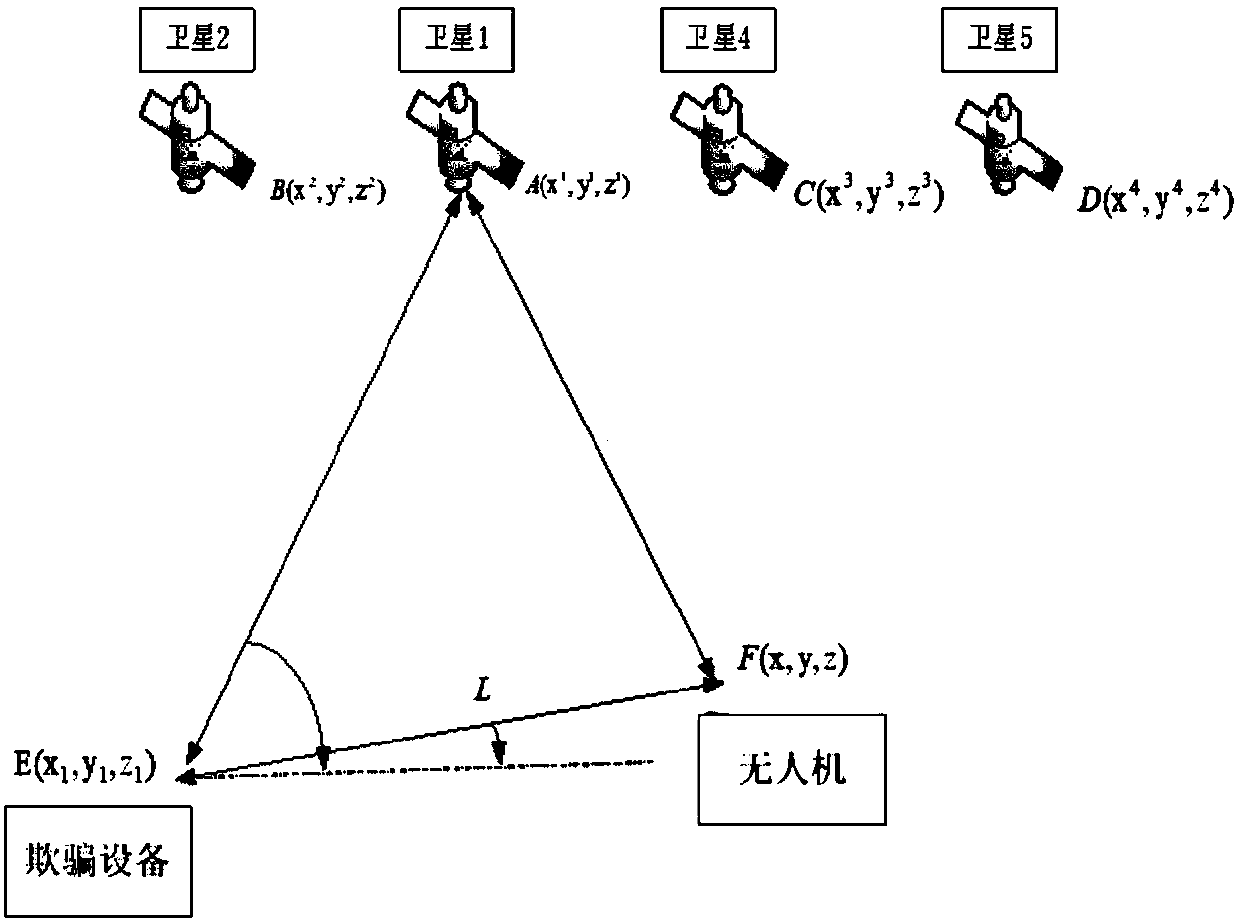
Navigation decoy system and method for coexistence unmanned aerial vehicle
ActiveCN108333600AReduce signal to noise ratioCheating achievedSatellite radio beaconingFlight directionDecoy
The invention provides a navigation decoy system and method for a coexistence unmanned aerial vehicle. The decoy system comprises a satellite search system, a cheat signal generation control system and a signal transmission system. The satellite search system is used for receiving and parsing a true satellite signal, and parsed result data is transmitted to the cheat signal generation control system; the cheat signal generation control system is used for calculating related parameters and generating a cheat signal; the signal transmission system sends the cheat signal generated by the cheat signal generation control system to a target unmanned aerial vehicle, and a receiver of the target unmanned aerial vehicle captures and tracks the cheat signal and the true satellite signal at the sametime; the cheat signal generation control system increases the power of the cheat signal to remove the true signal and controls a tracking loop of the target unmanned aerial vehicle. According to thenavigation decoy system and method, a synchronous false satellite is generated and coexists in the target receiver with a sky satellite, the power of the cheat signal is gradually increased after coexistence, the processed noise basis of the receiver is increased, and the output signal-to-noise ratio of the true signal in a correlator of the receiver is lowered; by relying on the power advantage of the cheat signal, the true signal is gradually removed out of the tracking loop, then the tracking loop is controlled, and cheat for the flight direction and speed of the black-flight unmanned aerial vehicle is achieved.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Method and device for tracking weak global navigation satellite system (GNSS) signals
A Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) receiver and associated method capable of tracking weak GNSS signals from a plurality of GNSS satellites. In a preferred embodiment, code and carrier tracking loops are initially closed around the code phase, carrier frequency, and data bit edge estimates handed over from an acquisition mode. In subsequent tracking, early, prompt, and late copies of the code replica are correlated with the incoming signal. The prompt correlations are coherently integrated over an extended updating interval for data bit edge and sign estimation as well as for carrier phase and frequency error discrimination whereas the early and late correlations are used for code error discrimination. Code delay and carrier phase and frequency errors are used to update the code and carrier tracking loop filters. Together with data bits, they form observables of a GNSS signal's time and frequency parameters for timing and position fixing.
Owner:CSR TECH HLDG
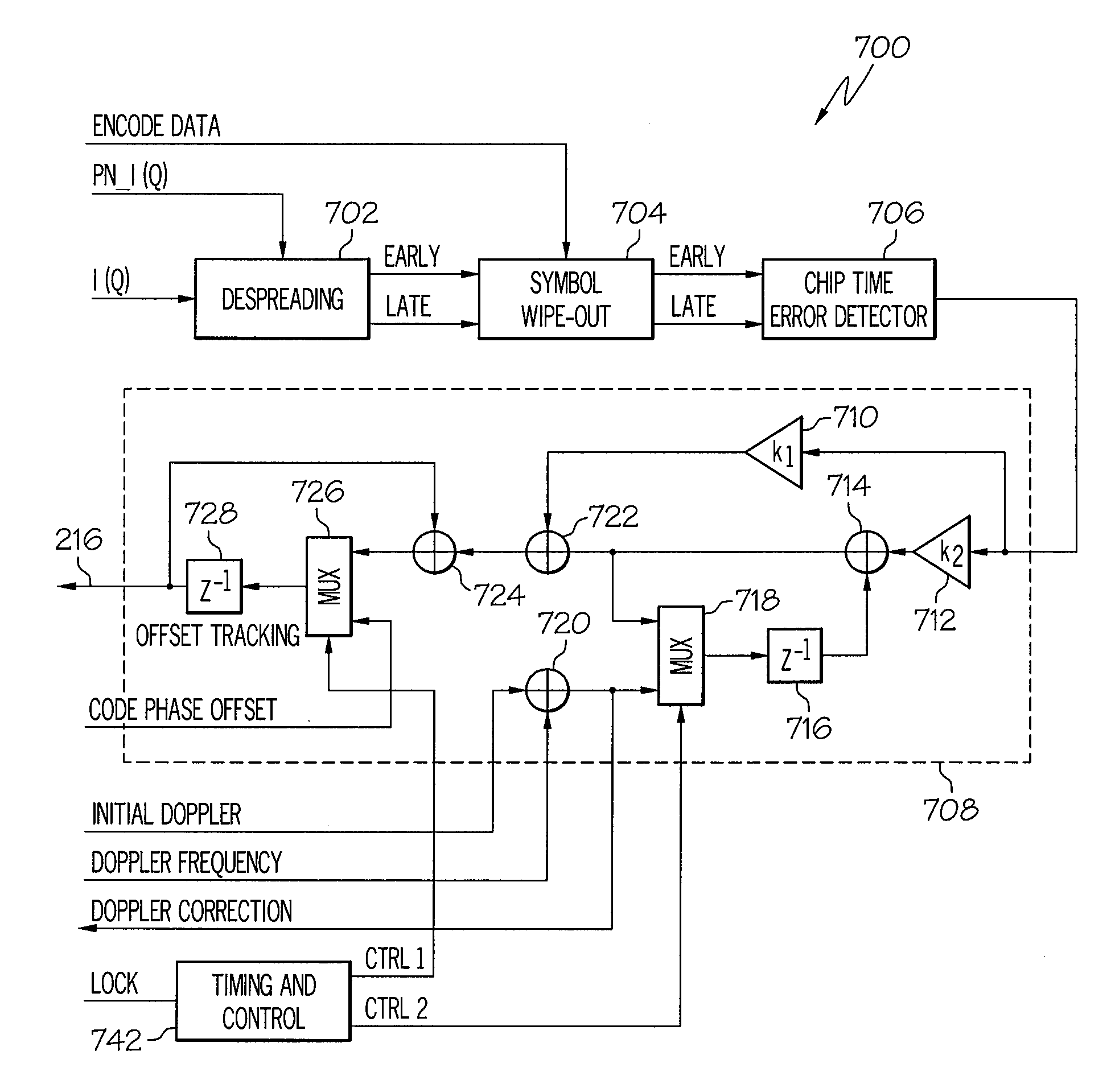
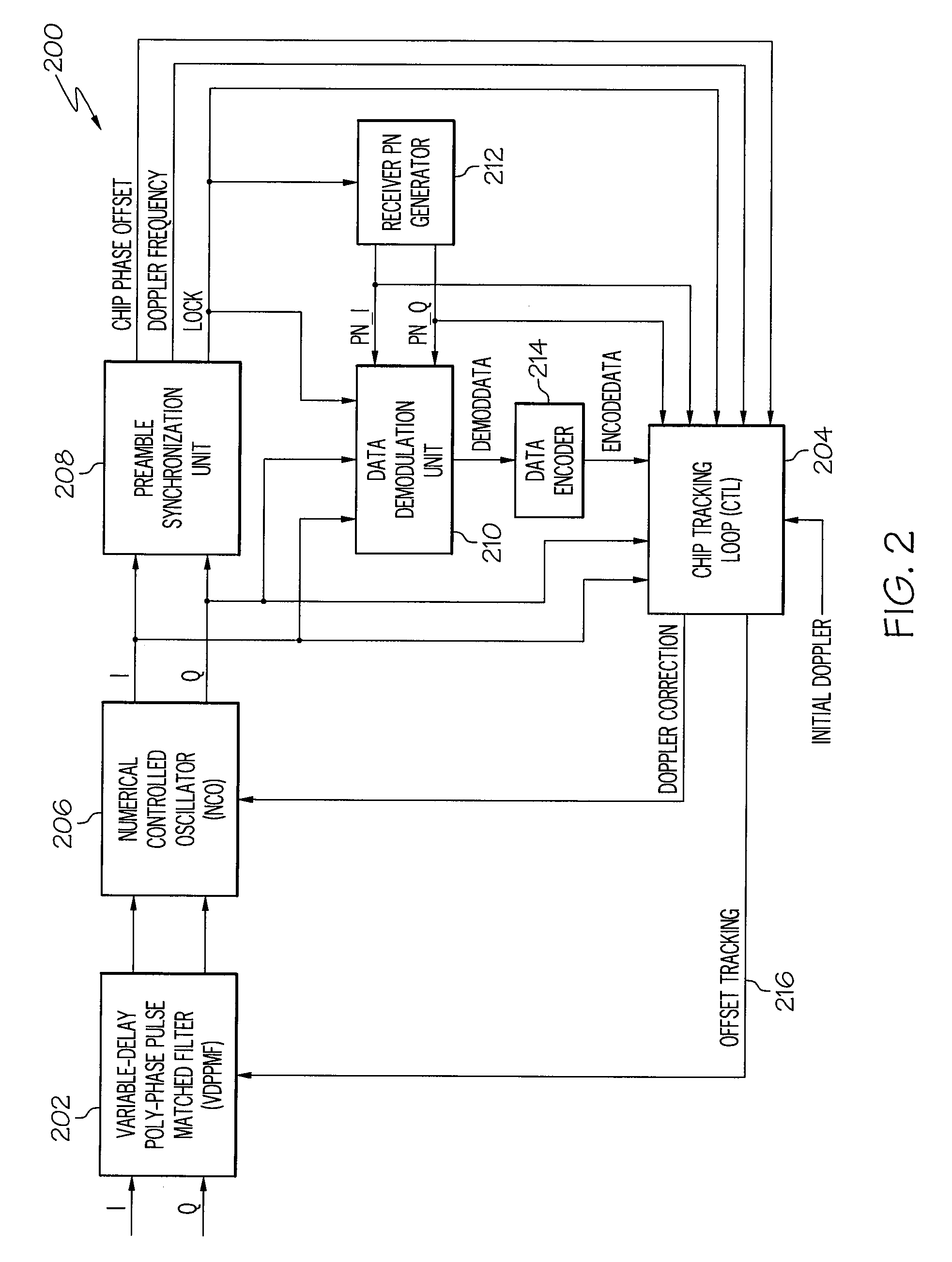
Device and method for fast transition from preamble synchronization to data demodulation in direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) communications
ActiveUS20090180524A1Quick transitionOffset errorTransmissionNumerical controlNumerically controlled oscillator
A device for fast transition from preamble synchronization of a received baseband signal to demodulation of the received baseband signal may include a baseband chip tracking loop to generate an offset tracking value to track any initial chip phase offset and Doppler-caused baseband chip frequency drift associated with the received baseband signal. The device may also include a numerical controlled oscillator to correct any Doppler-caused phase rotation associated with the received signal. The device may additionally include a preamble synchronization unit to detect a preamble of the received baseband signal, and to measure a chip phase offset and a baseband Doppler frequency shift associated with the received baseband signal. The chip phase offset may be used to set an initial chip phase offset value of the chip tracking loop so that the chip tracking loop starts with approximately a zero pull-in error. The baseband Doppler frequency shift may be used to set initial frequency offset values in the chip tracking loop and the numerical controlled oscillator so that both start with substantially near-zero offset errors for substantially immediate demodulation of the received signal. The device may further include an output device to output the data demodulated from the received baseband signal.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Ntsc signal detector
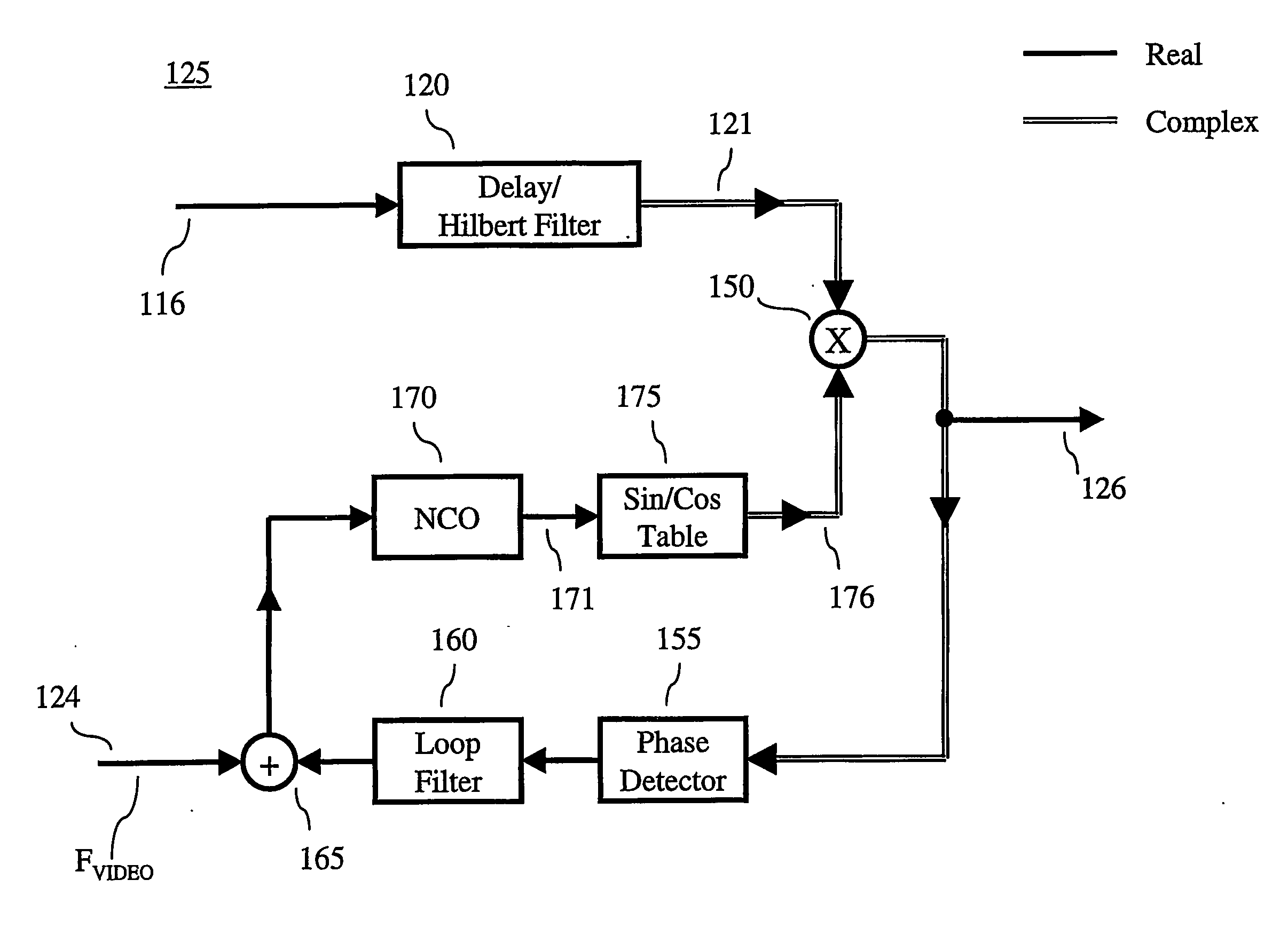
InactiveUS20060146200A1Improve noise immunityReduce presenceTelevision system detailsCarrier regulationTelevision systemCarrier signal
An NTSC (National Television Systems Committee) co-channel interference detector includes at least a carrier tracking loop, peak detector and a D / U (Desired-to-Undesired) signal power ratio estimator. The carrier tracking loop provides a tracking signal representative of the possible presence of a video carrier of an interfering NTSC video signal while the peak detector provides peak data derived from the tracking signal to the D / U signal power ratio estimator. The latter provides, as a function of the peak data, an estimate of a D / U signal power ratio with respect to a desired ATSC (Advanced Television Systems Committee) co-channel signal.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
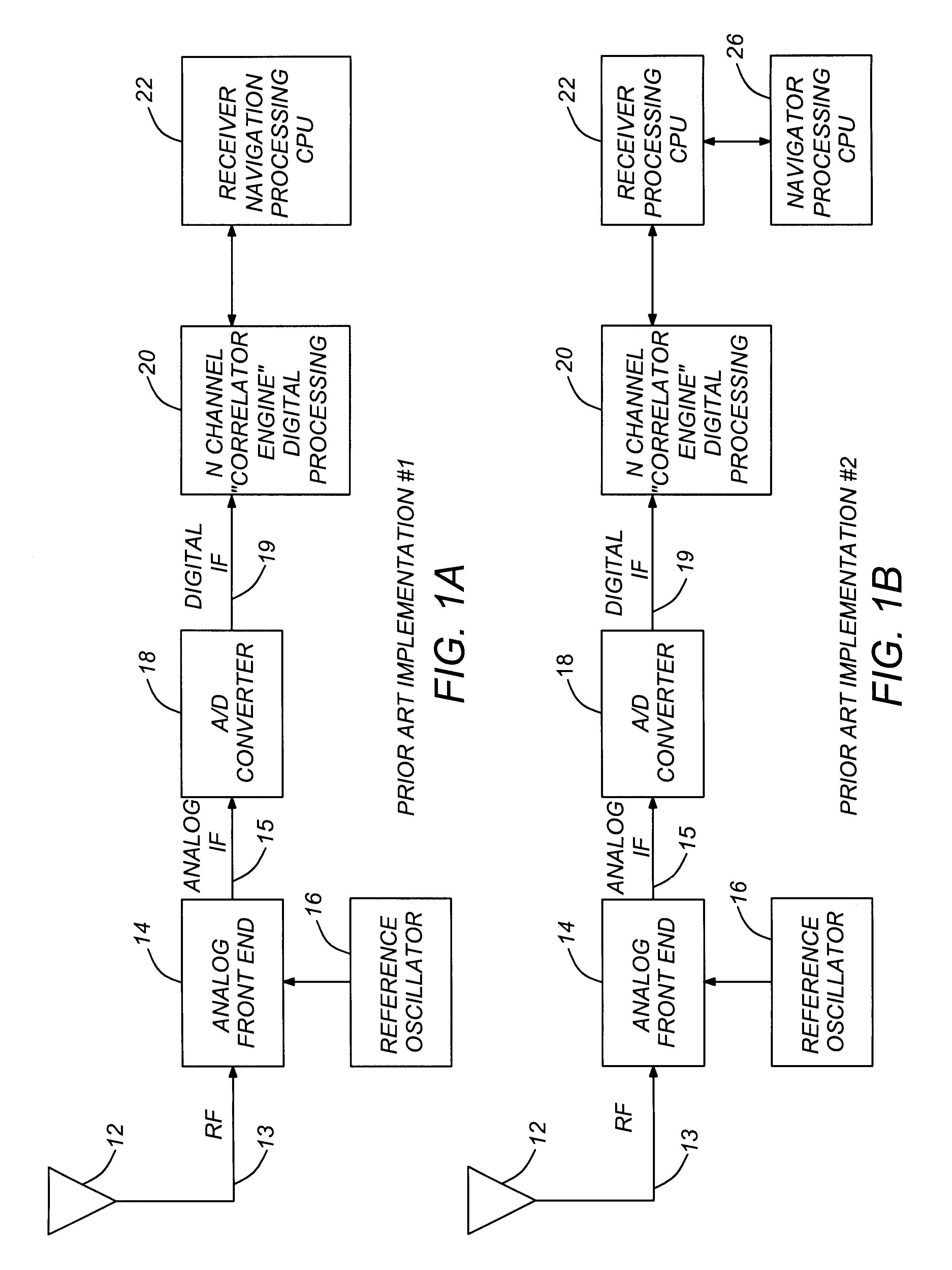
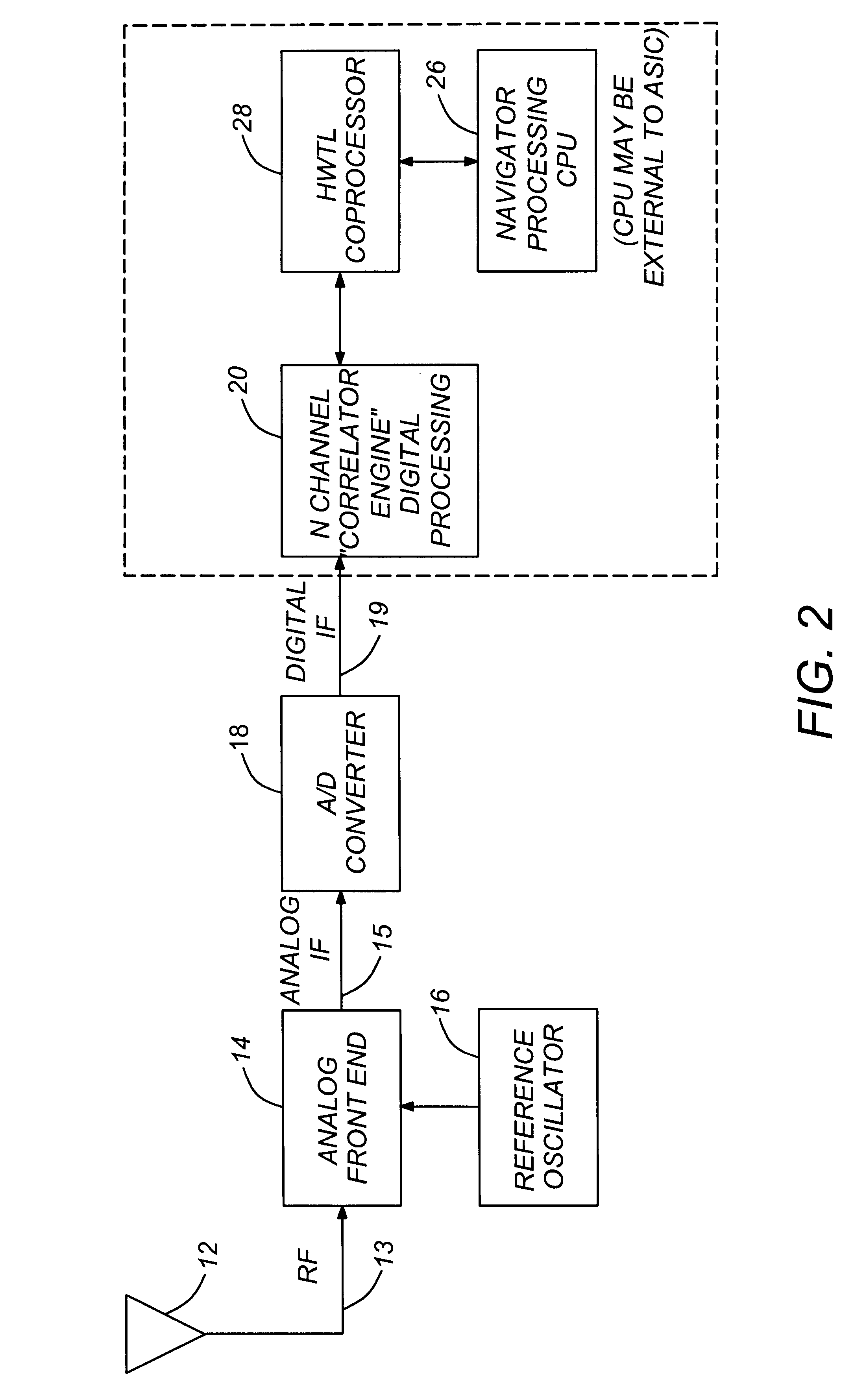
Autonomous hardwired tracking loop coprocessor for GPS and WAAS receiver
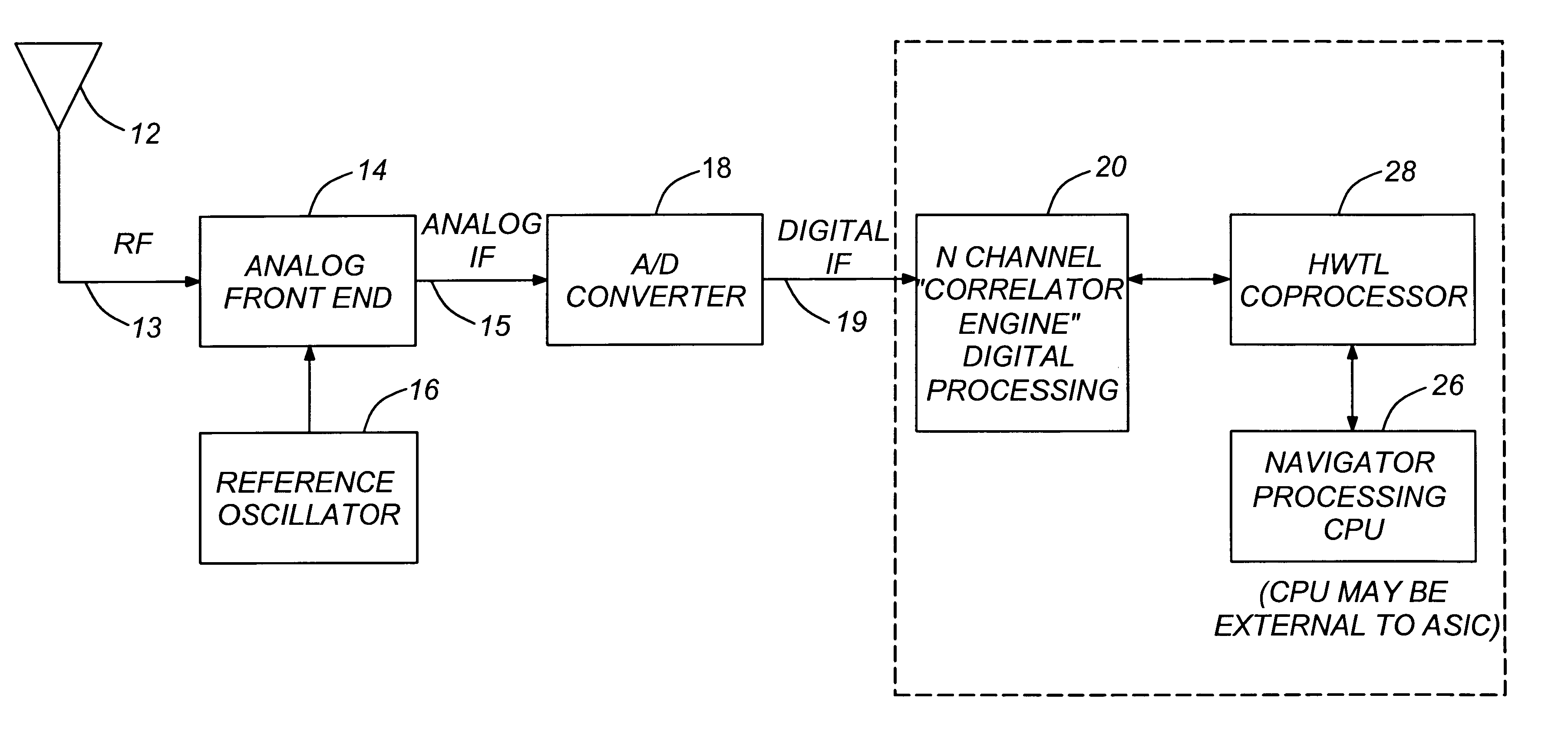
InactiveUS6278403B1Low costMinimize power consumptionPosition fixationAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsHigh rateIntermediate frequency
An autonomous Hardwired Tracking Loop (HWTL) ASIC comprising a HWTL coprocessor provided for implementing most of the receiver processing function for data acquisition and tracking functions of a radio receiver system in dedicated hardware. With the expanded functionality provided by an HWTL coprocessor in the autonomous HWTL ASIC, the interruption of CPU performing the navigation processing is significantly reduced to thereby maximize throughput and minimize power burden on the microprocessor. In the preferred embodiment, the HWTL ASIC also comprises the CPU and a correlator, wherein the correlator provides the high rate greater than approximately 1 KHz signal processing operations, the HWTL coprocessor providing the data acquisition and tracking (medium frequency signal processing) operations, and the CPU thereby freed to provide more bandwidth for lower frequency processing, i.e., navigation and non-radio receiver operations, such as user applications, processing requiring CPU intervention at approximately 10 Hz or less CPU processing rate.
Owner:CSR PLC
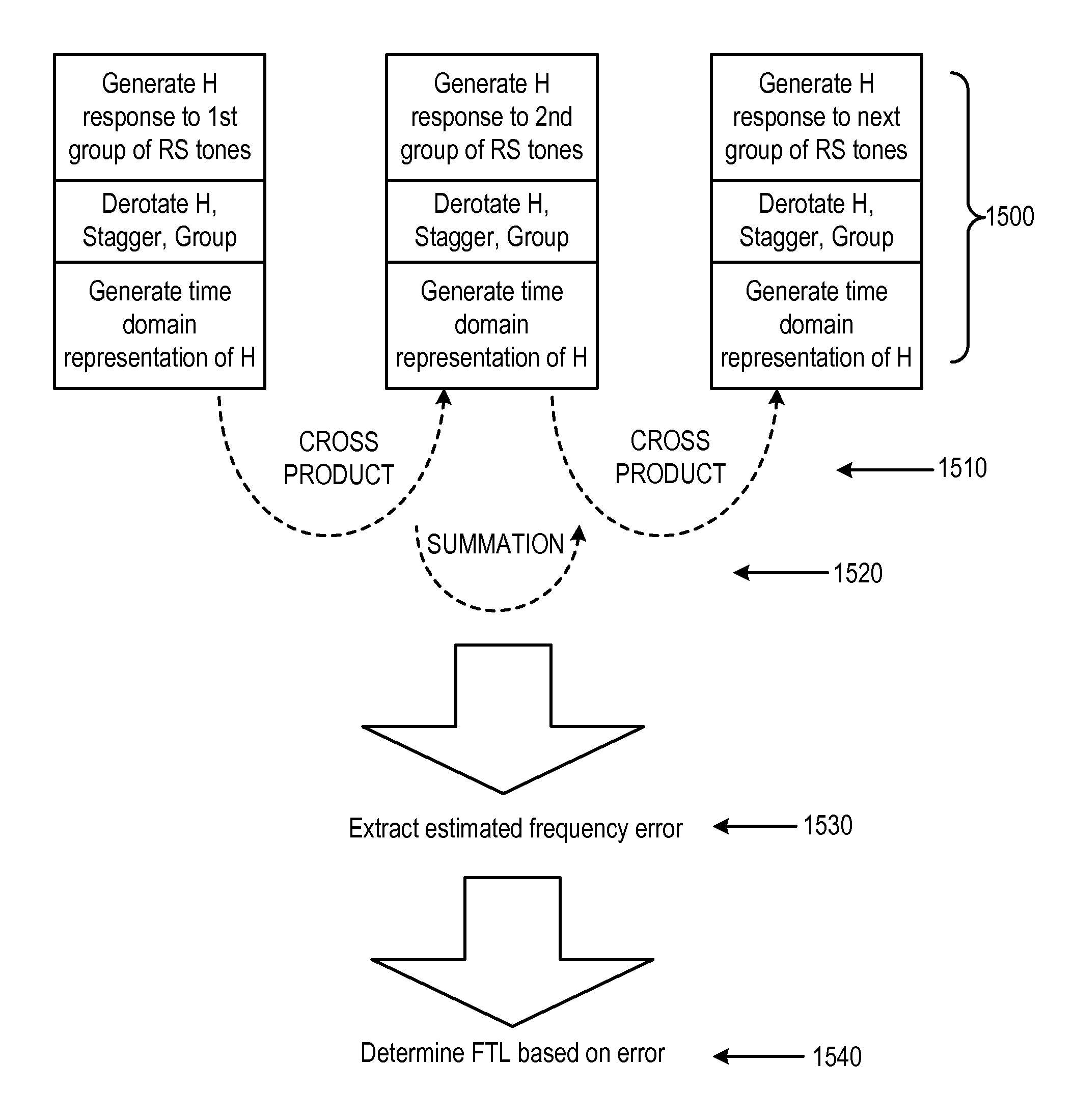
Channel impulse response (CIR)-based and secondary synchronization channel (SSC)-based (frequency tracking loop (FTL)/time tracking loop (TTL)/channel estimation
InactiveUS8494070B2Easy to trackTransmission monitoringChannel estimationTime domainChannel impulse response
Methods and systems are disclosed for channel estimation and frequency tracking in mobile communication systems. Particularly, various ways of using the time domain impulse channel response based on the staggered frequency domain pilot tones are presented that enable rapid frequency error estimation and frequency tracking control. A mathematical model is developed that provides a convenient metric for evaluating tolerable frequency error, as well as modes for switching between channel impulse response (CIR)-based and secondary synchronization channel (SSC)-based frequency tracking.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Systems for doppler tracking using photonic mixing detectors
Owner:US SEC THE ARMY THE
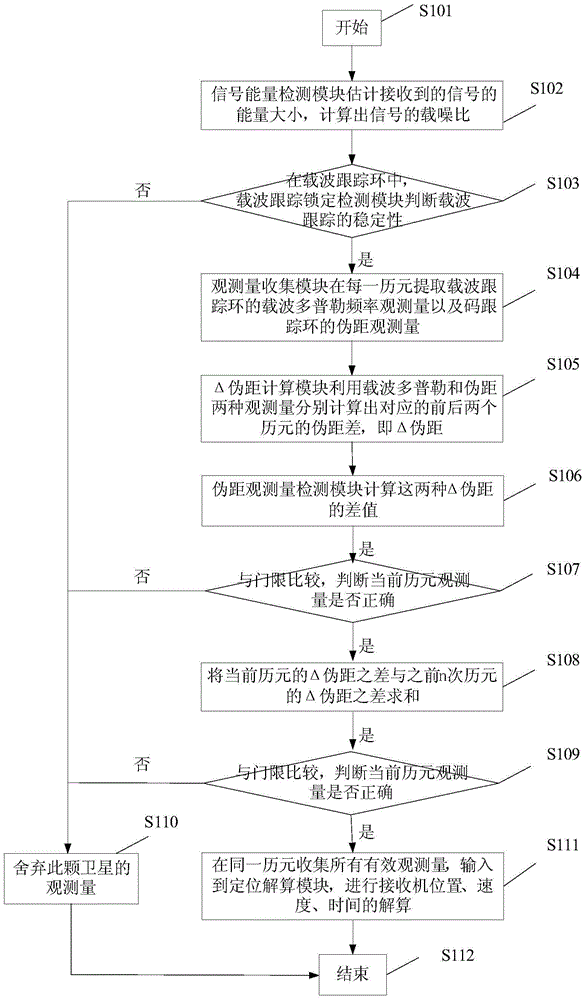
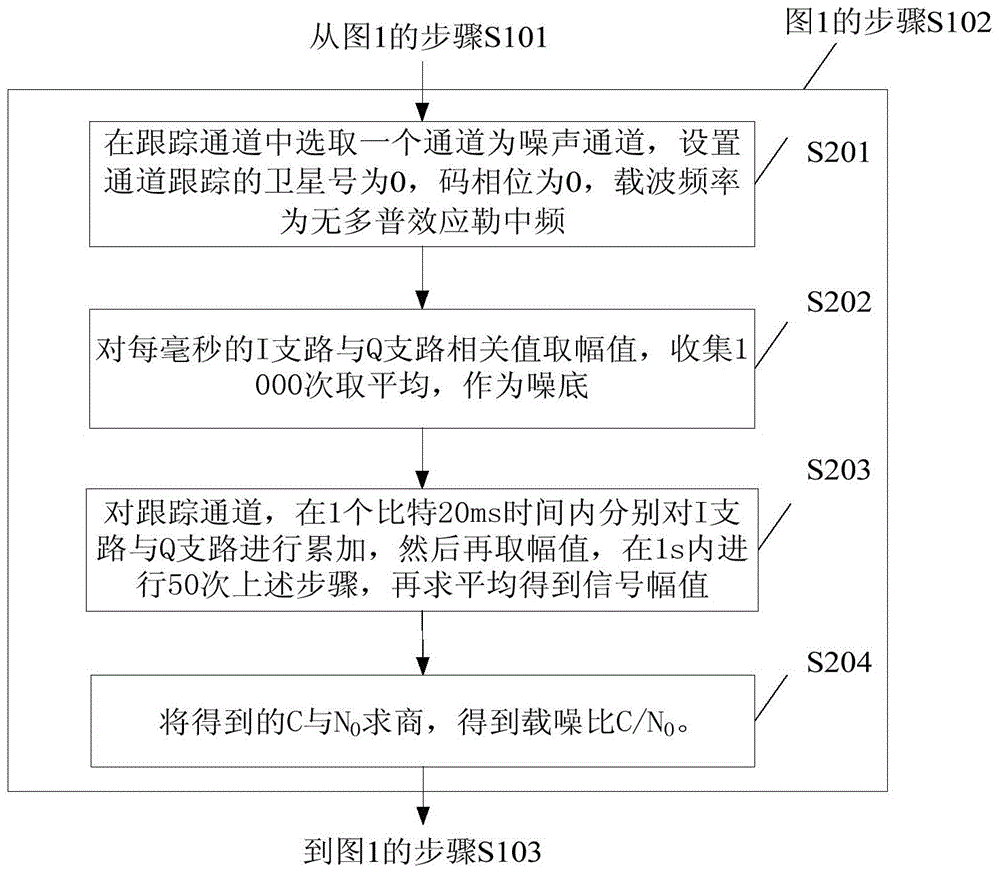
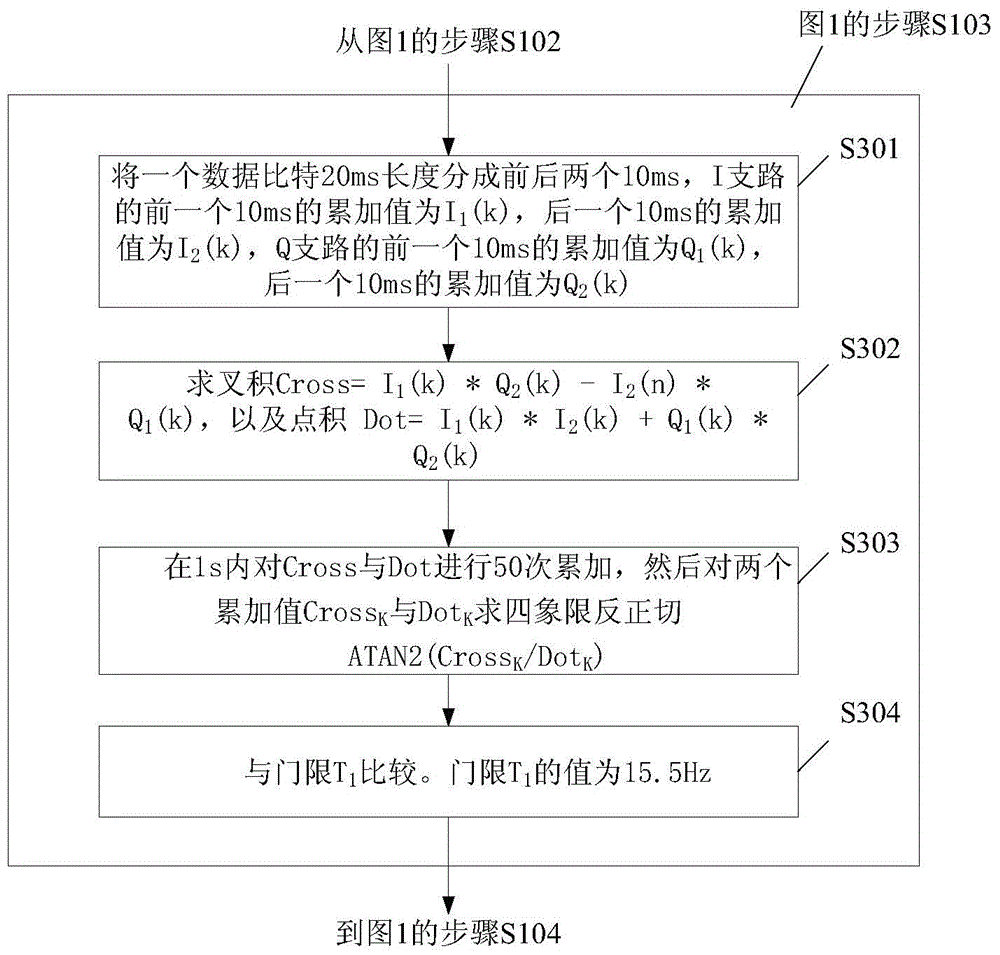
Method for detecting observed quantity validity in navigation receiver
ActiveCN105044737ASolve the problem of positioning stabilitySatellite radio beaconingCarrier signalEngineering
A method for detecting observed quantity validity in a navigation receiver mainly includes: S1. calculating a carrier-to-noise ratio of a signal; S2. judging stability of carrier tracking; S3. Extracting carrier Doppler frequency observed quantity of a carrier tracking loop and pseudo-range observed quantity of a code tracking loop in each epoch; S4. utilizing the two kinds of observed quantity to calculate a pseudo-range difference of corresponding two successive epoch respectively; S5. calculating a difference value of the pseudo-range differences and comparing with a threshold, thereby judging whether pseudo-range observed quantity of the current epoch is correct; S6. summing a difference of delta pseudo ranges of the current epoch and differences of delta pseudo ranges of n previous epochs, comparing with a threshold, and judging whether pseudo range observed quantity is correct; and S7. performing the abovementioned steps on each satellite which keeps tracking, collecting all signals of satellites whose observed quantity is judged to be correct, and inputting the signals to a positioning resolving module. The method provided by the invention does not need redundant information, and solves the problem of positioning stability of a receiver in complex environment with a relatively small calculated amount.
Owner:BEIJING MXTRONICS CORP +1
Anti-inference method based on vector tracking loop
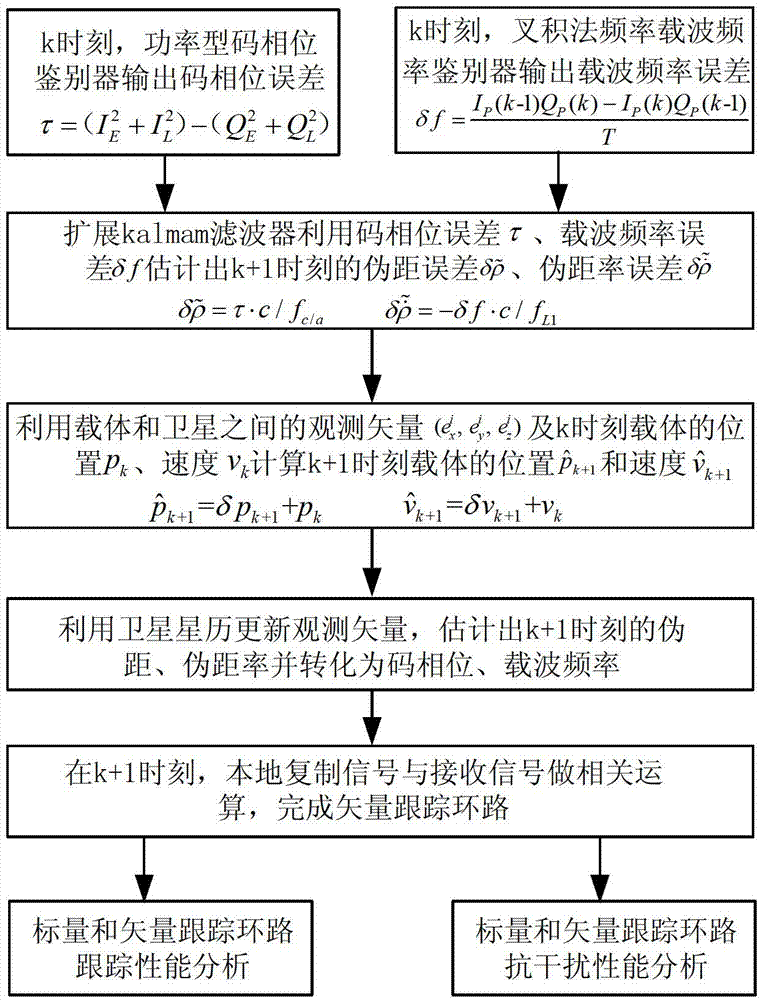
InactiveCN103116169AImprove tracking performanceInhibition effectSatellite radio beaconingDiscriminatorWeight coefficient
The invention relates to the field of satellite navigation, in particular to a global position system (GPS) receiver anti-interference method based on a vector tracking loop. The anti-inference method based on the vector tracking loop includes inputting signals into a C / A code phrase discriminator and a carrier wave frequency discriminator at a k moment, obtaining a pseudo-range error which is tested by a receiver and a pseudo-range rate error which is tested by the receiver, estimating a real pseudo-range error and a real pseudo-range rate error between a carrier and a satellite at a k+1 moment; calculating a position error and a speed error of the receiver at the k+1 moment, obtaining position and speed of the carrier at the k+1 moment and updating a unit observation vector. The anti-inference method based on the vector tracking loop utilizes a method that various track channels distribute various weight coefficients, enables channel information with a high signal to noise radio to assist channel information with a low signal to noise radio, improves the whole tracking ability of the tracking loop and inhibits influence of interference signals on the tracking loop.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com