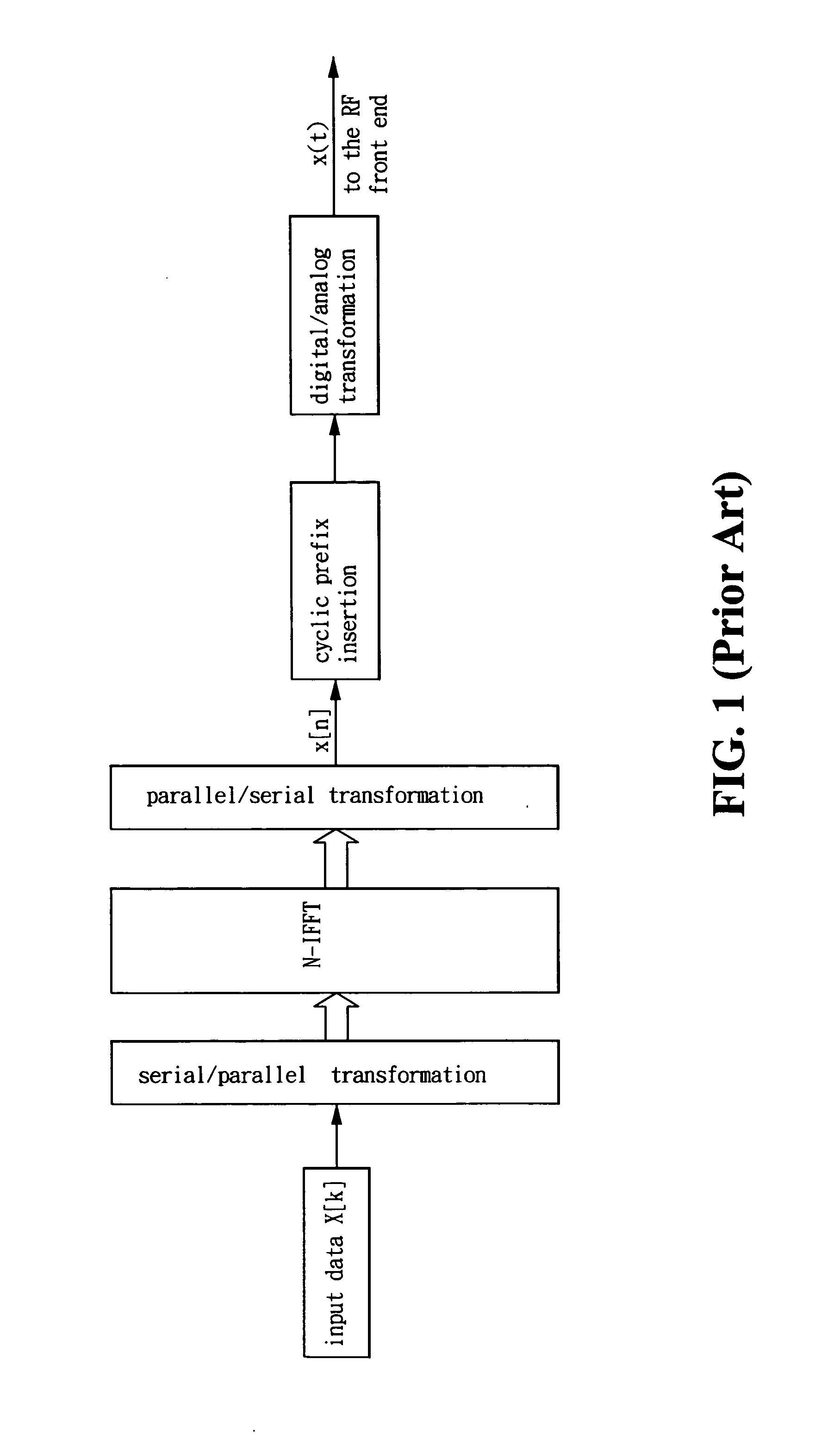
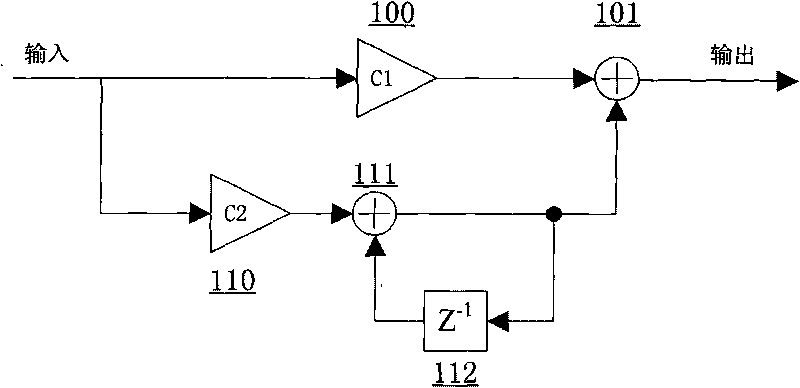
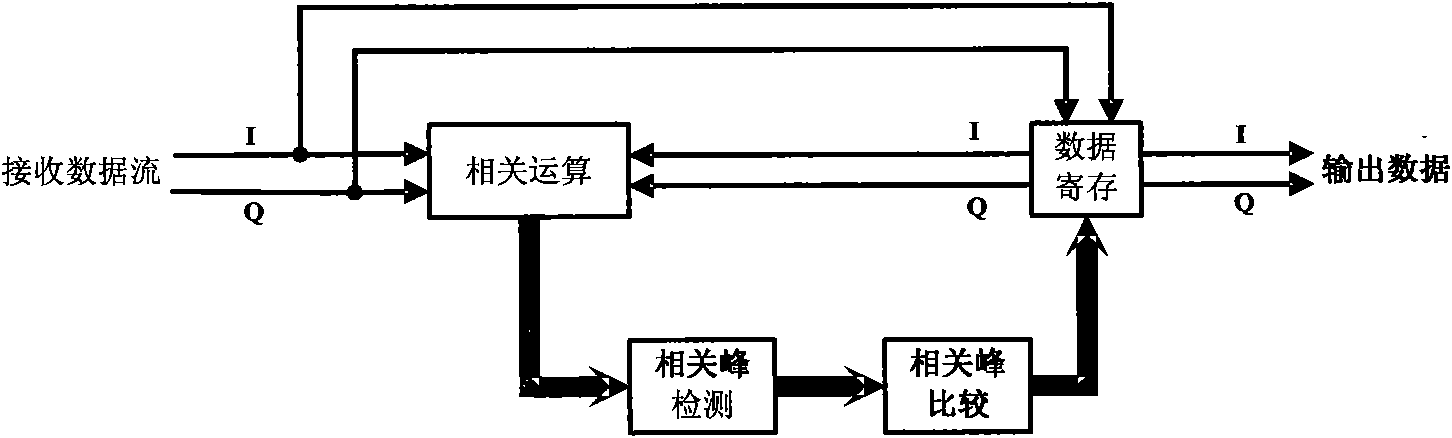
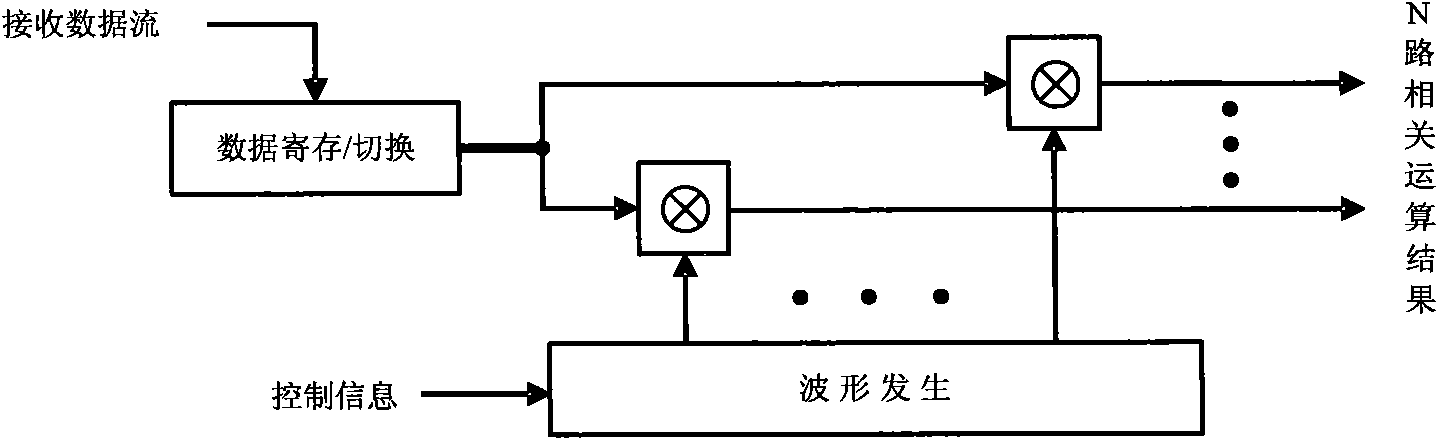
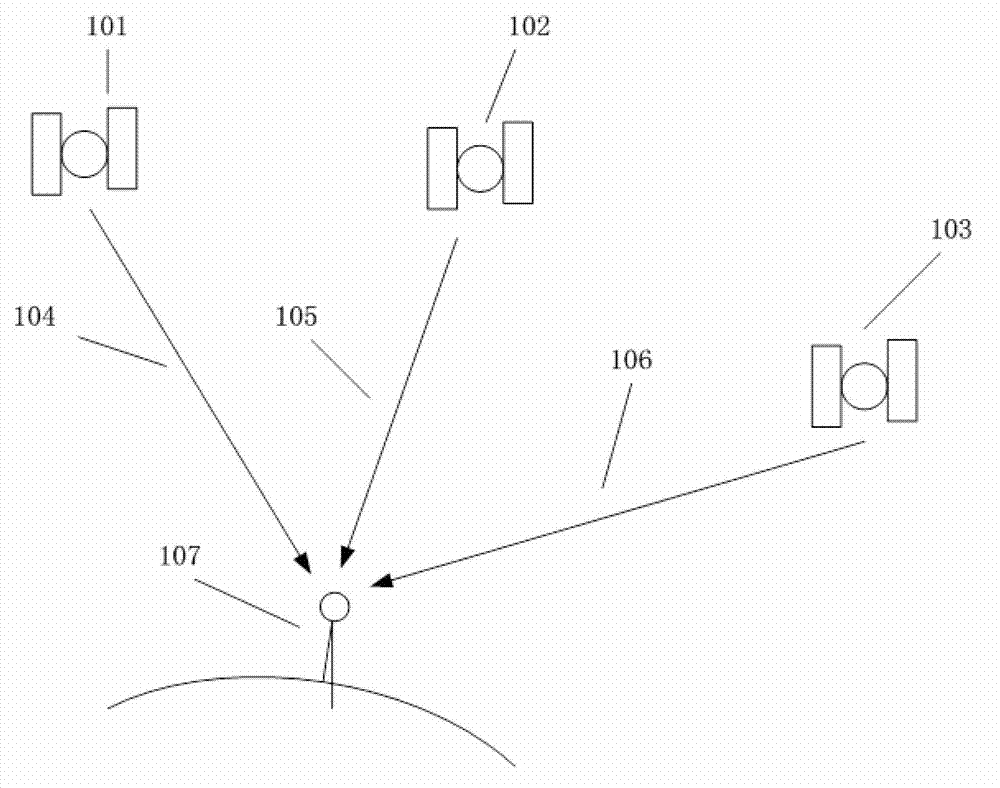
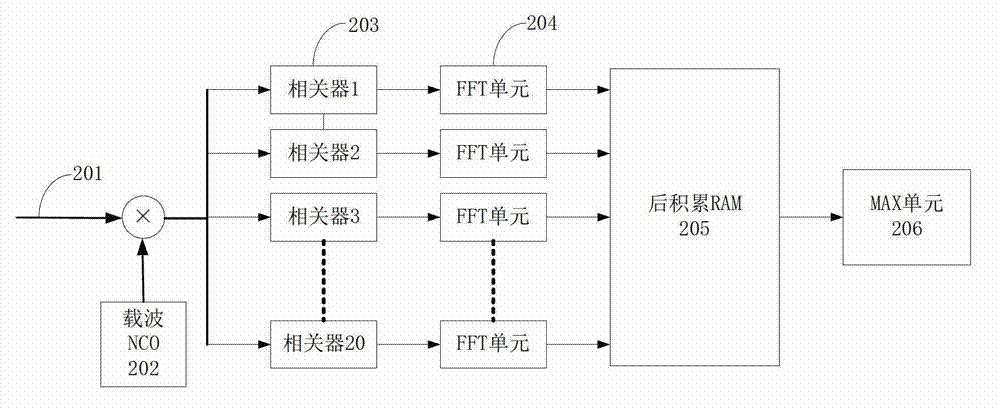
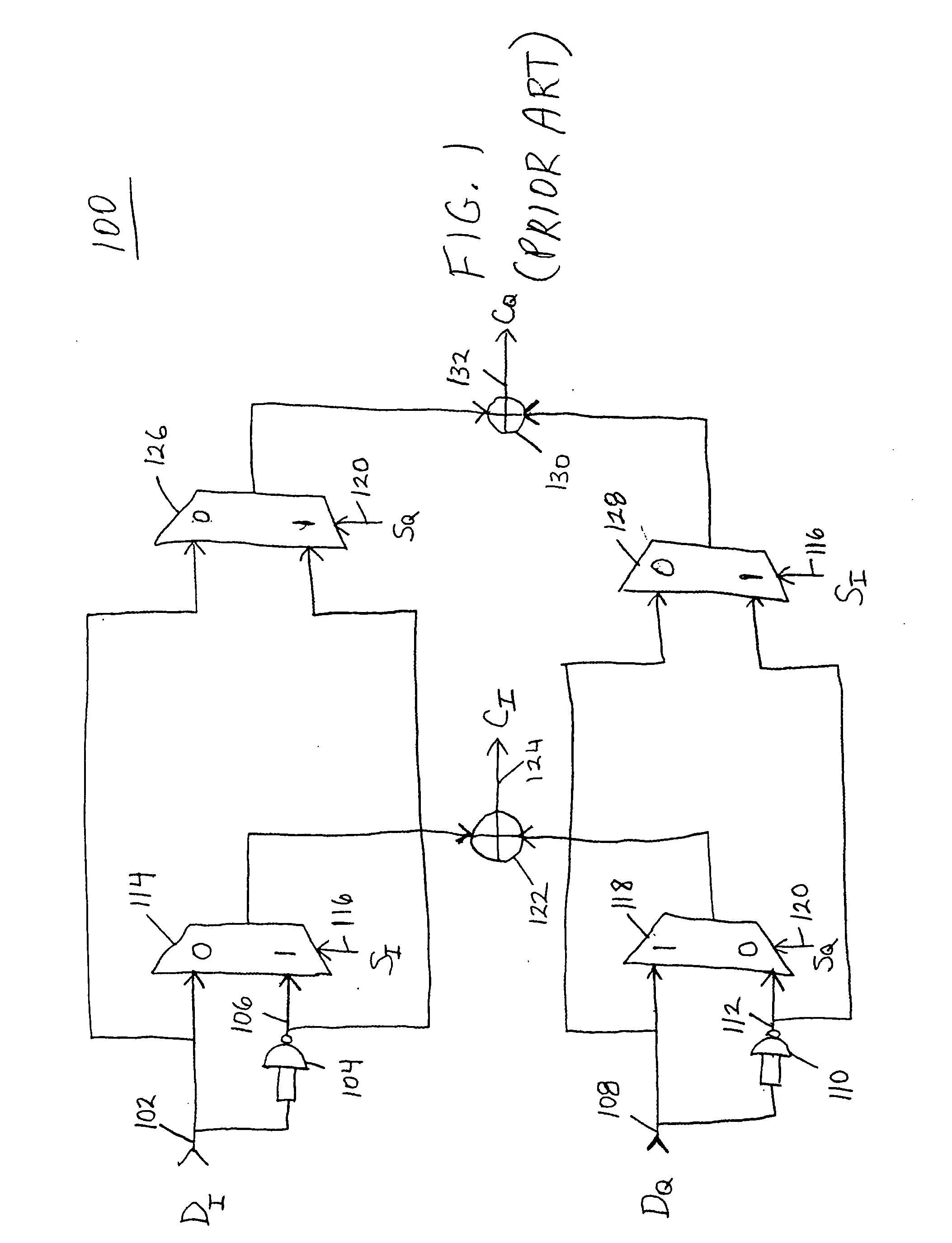
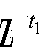Patents
Literature
133 results about "Complex multiplier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The complex multiplier is the multiplier principle in Keynesian economics (formulated by John Maynard Keynes). The simplistic multiplier that is the reciprocal of the marginal propensity to save is a special case used for illustrative purposes only. The multiplier applies to any change in autonomous expenditure, in other words, an externally induced change in consumption, investment, government expenditure or net exports.
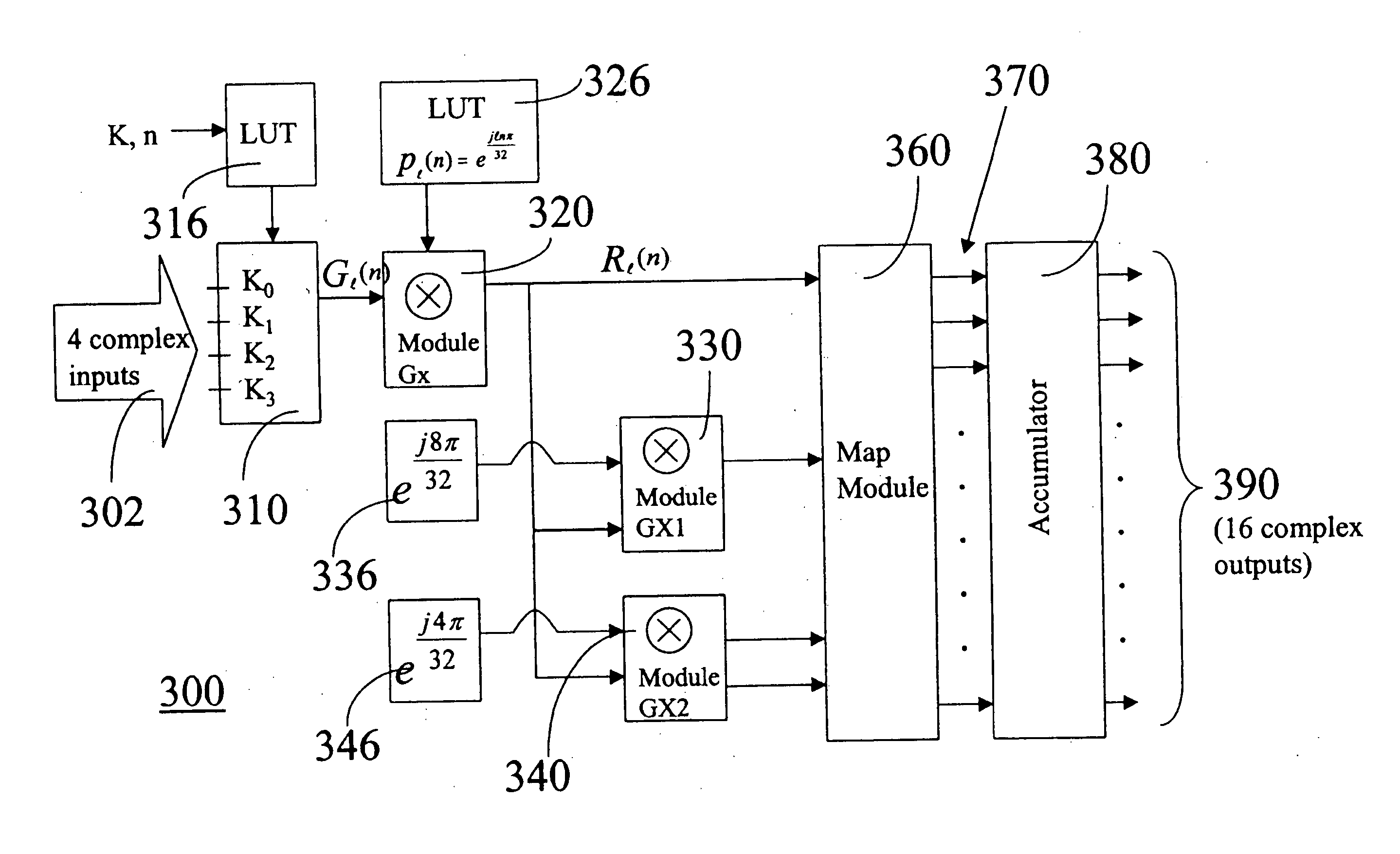
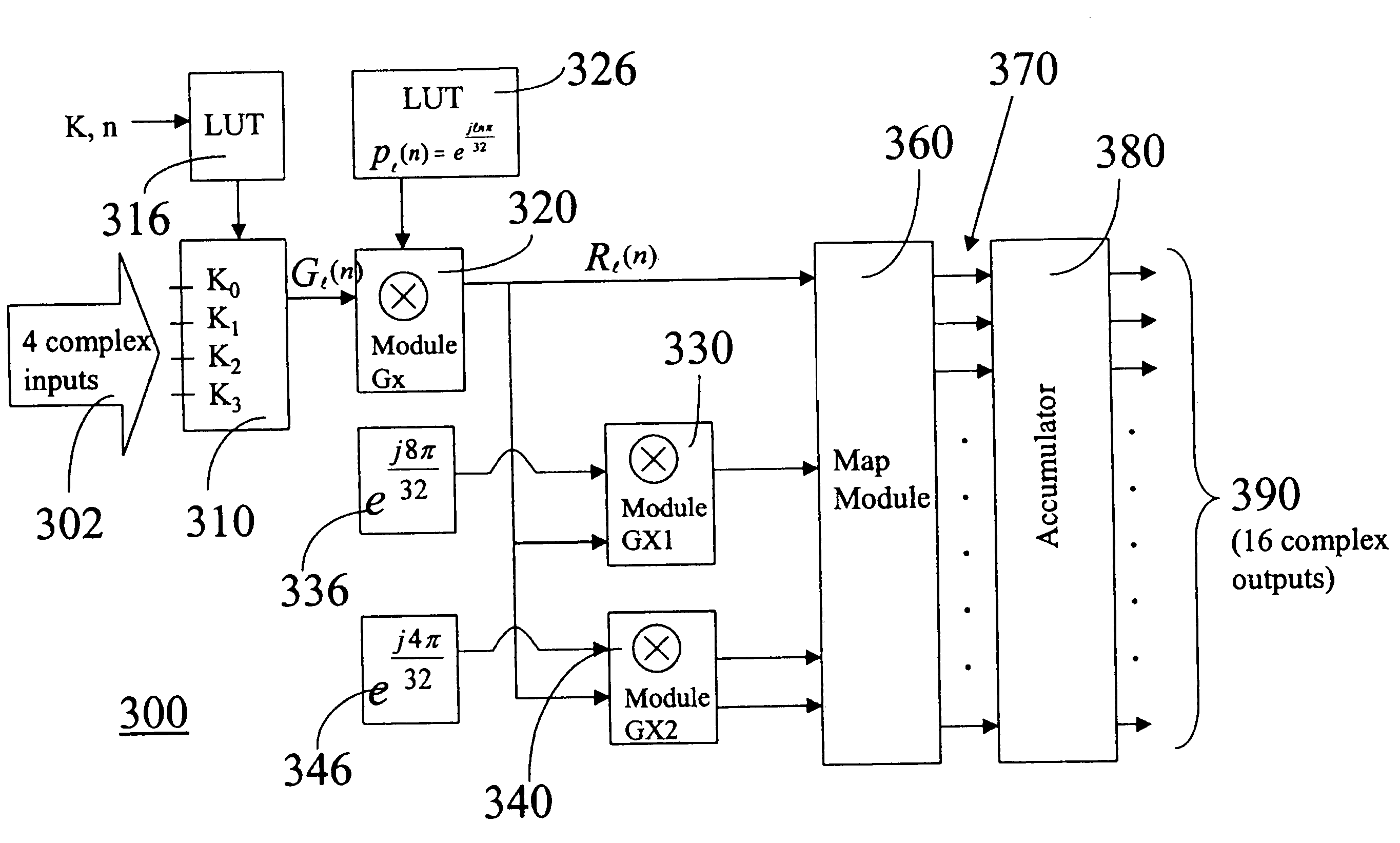
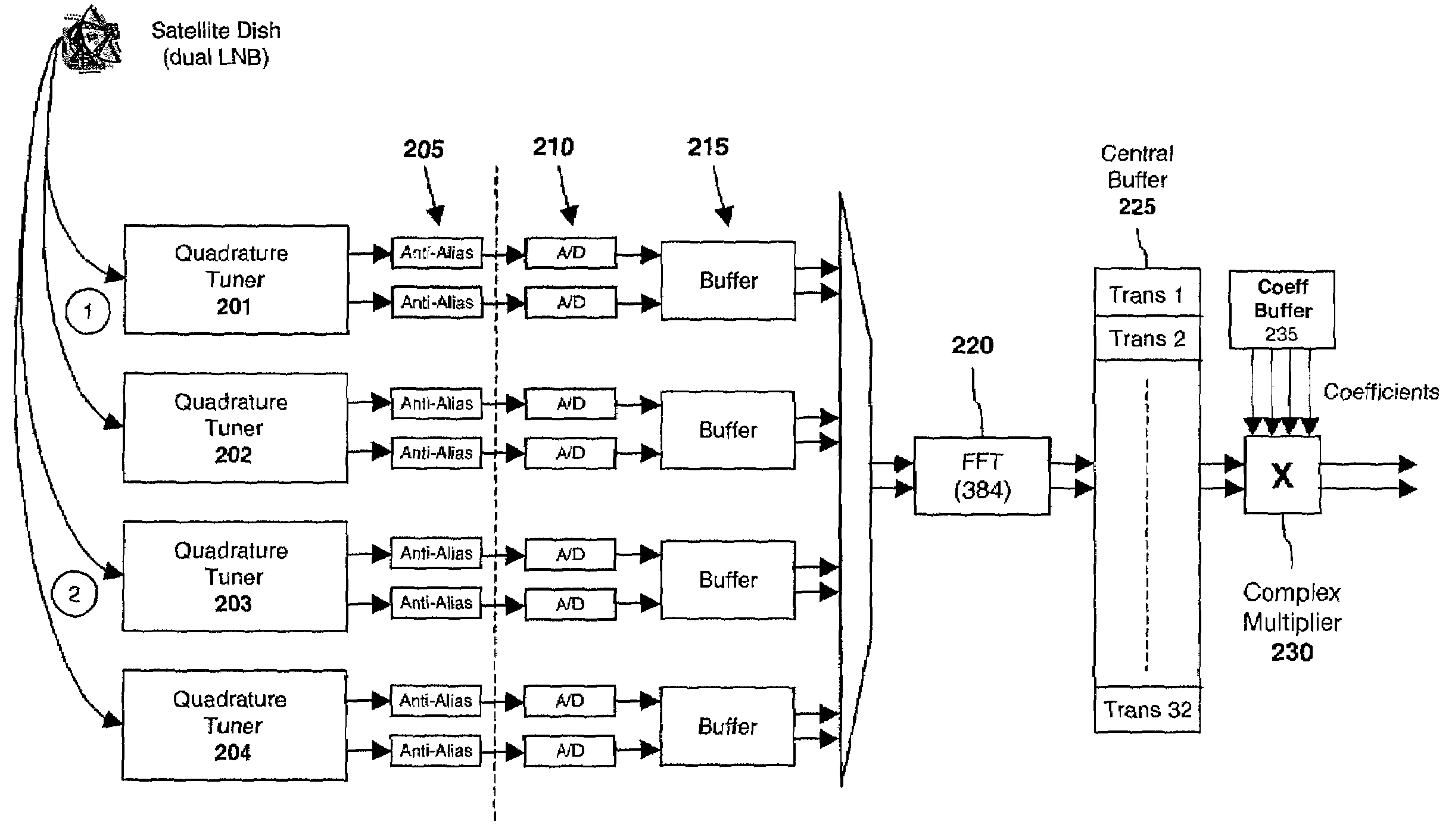
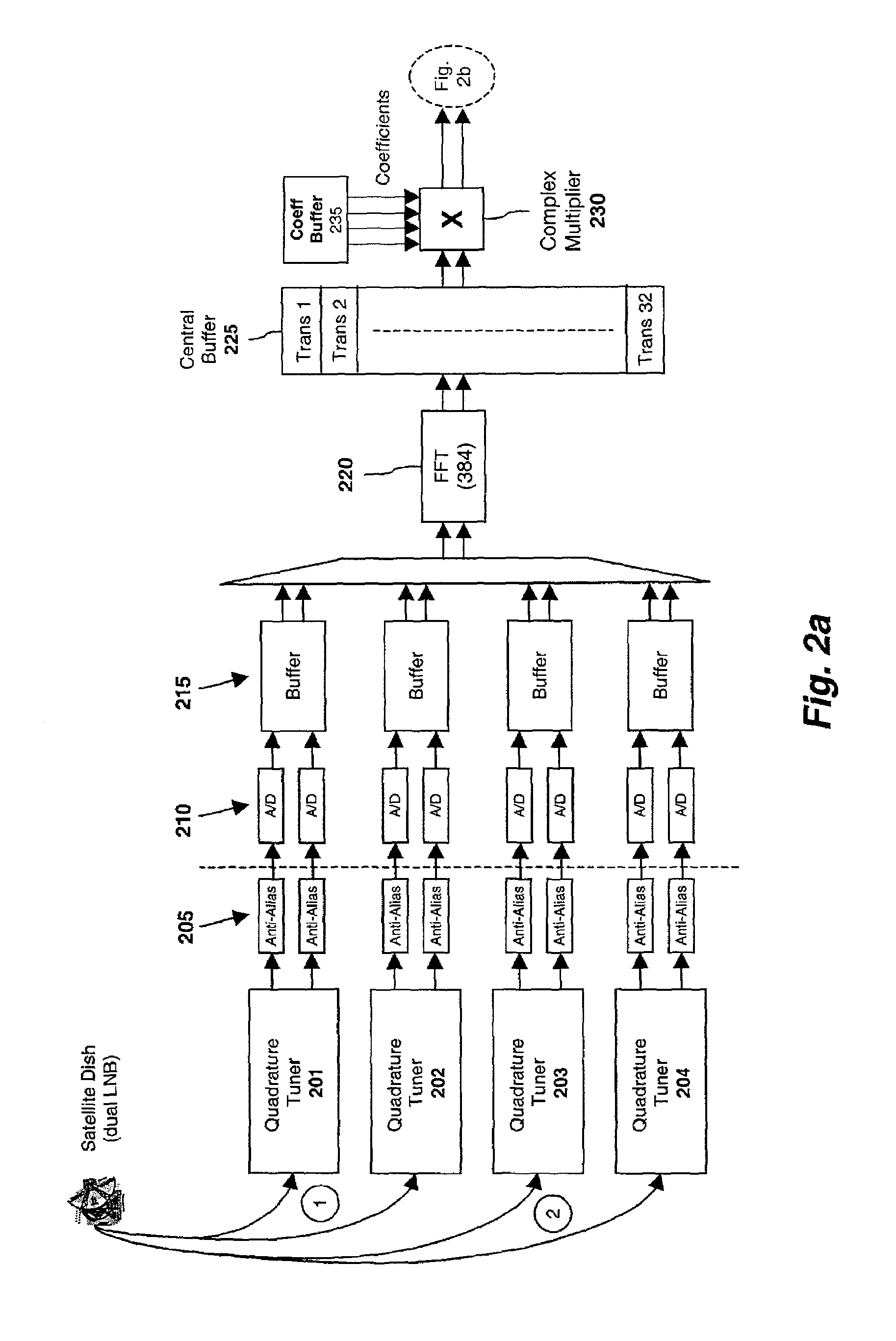
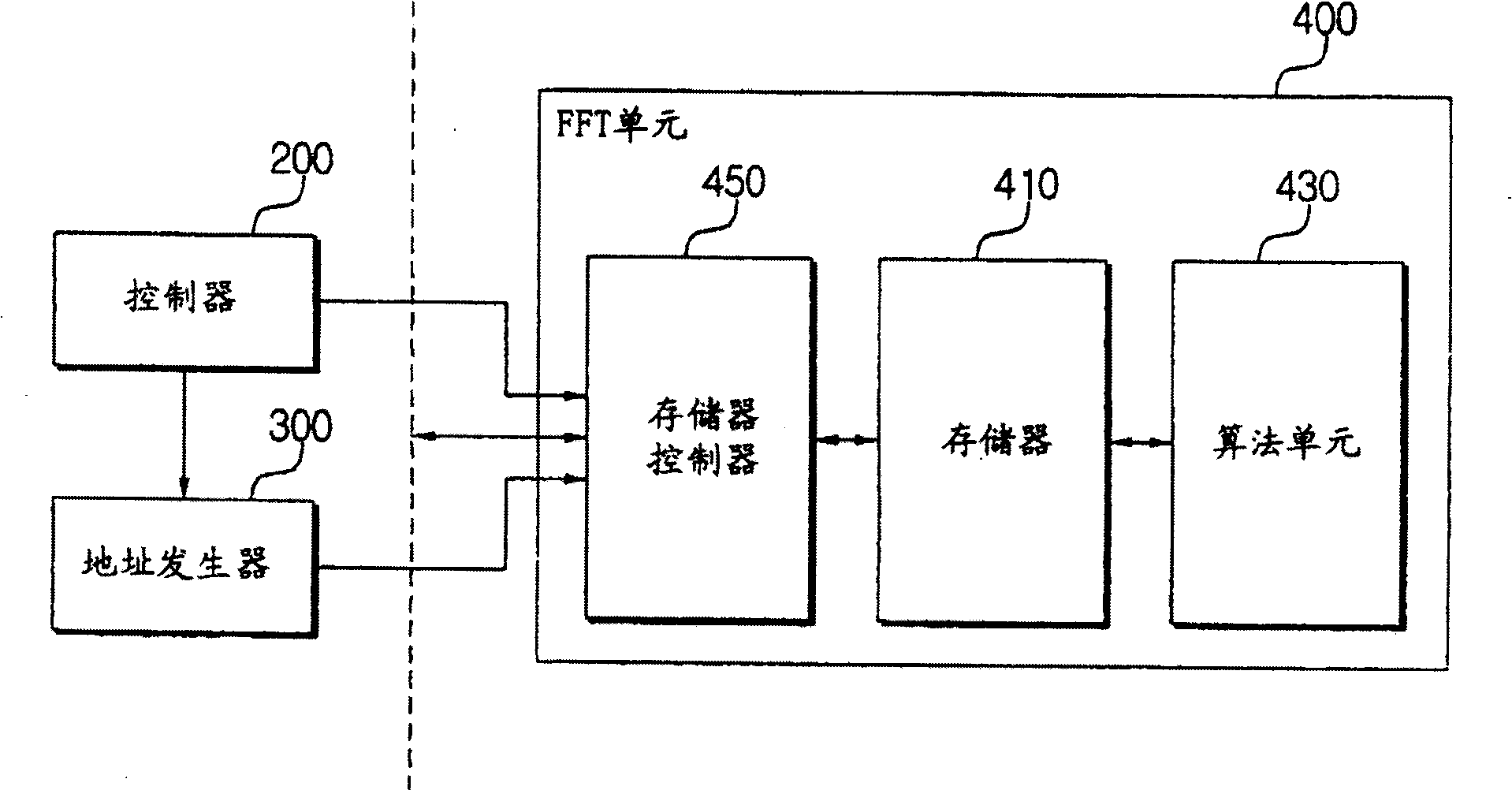
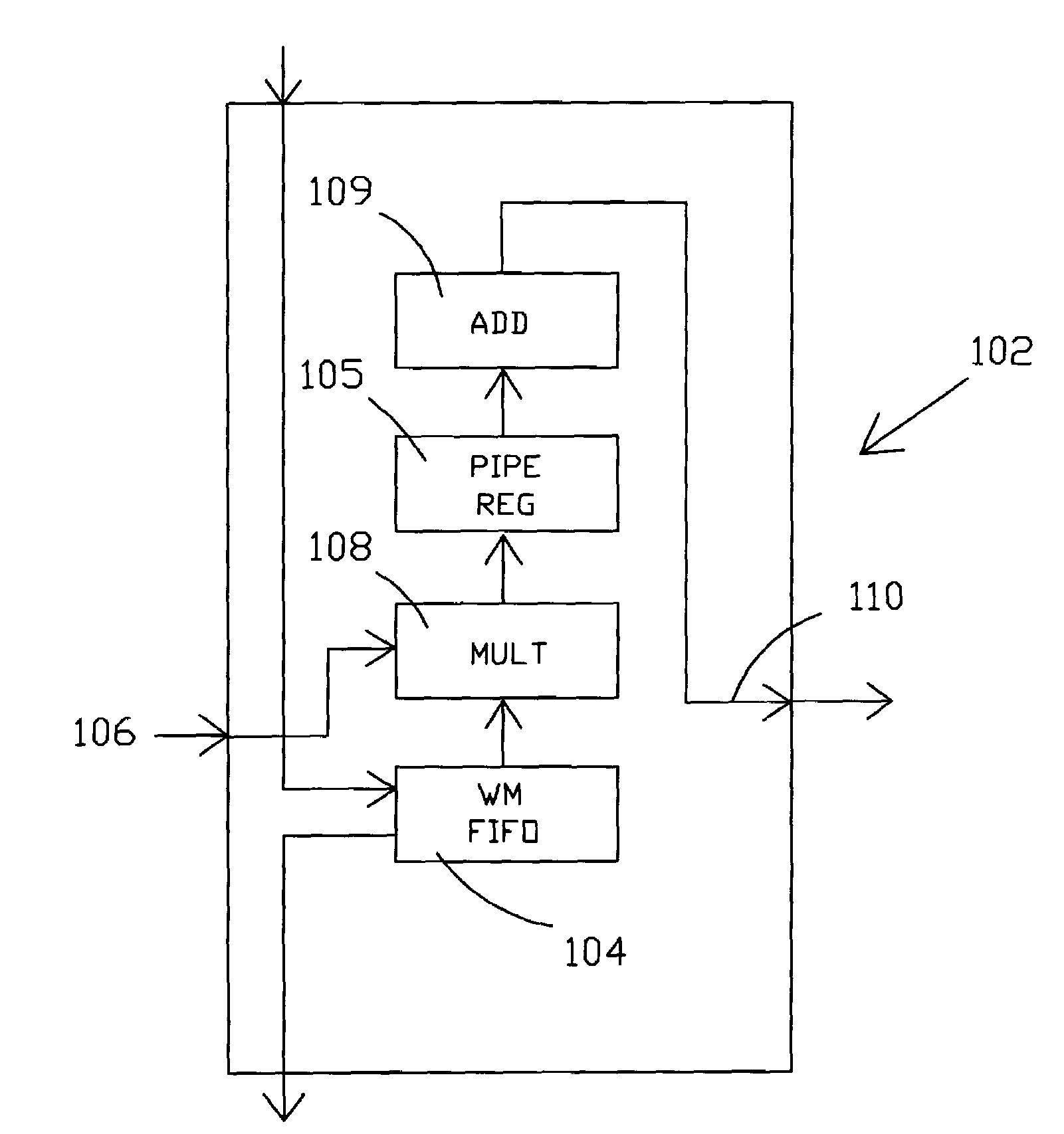
Optimized FFT/IFFT module
ActiveUS20050058059A1Ease of hardware implementationMinimize the numberAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsRadio transmissionTheoretical computer scienceComputer module
The present invention discloses an optimal hardware implementation of the FFT / IFFT operation that minimizes the number of clock cycles required to compute the FFT / IFFT while at the same time minimizing the number of complex multipliers needed. For performing an N-point FFT / IFFT operation in N clock cycles, the optimal hardware implementation consists of several modules. An input module receives a plurality of inputs in parallel and combines the inputs after applying a multiplication factor to each of the inputs. At least one multiplicand generator is used to provide multiplicands to the system. At least two complex multiplier modules for performing complex multiplications are required with at least one of the complex multiplier modules receiving an output from the input module. Each of the complex multiplier modules receives multiplicands from the at least one multiplicand generator. Furthermore, at least one of the complex multiplier modules receives an output of another complex multiplier module. A map module is provided for receiving outputs of the at least two complex multiplier modules, the map module selecting and applying a multiplication factor to each of the outputs received to generate multiple outputs. Finally, an accumulation module receives and performs an accumulation task on each of the multiple outputs of the map module thereby generating a corresponding number of multiple outputs. In a preferred embodiment, the N-point FFT / IFFT operation is performed in N clock cycles using (N32+1)complex multipliers. In a specific implementation, a system comprising 3 complex multipliers is used to compute a 64-point FFT / IFFT operation in 64 clock cycles. Advantageously, the total number of clock cycles required to complete the FFT / IFFT operation is minimized while at the same time minimizing the number of complex multipliers needed.
Owner:ZARBANA DIGITAL FUND
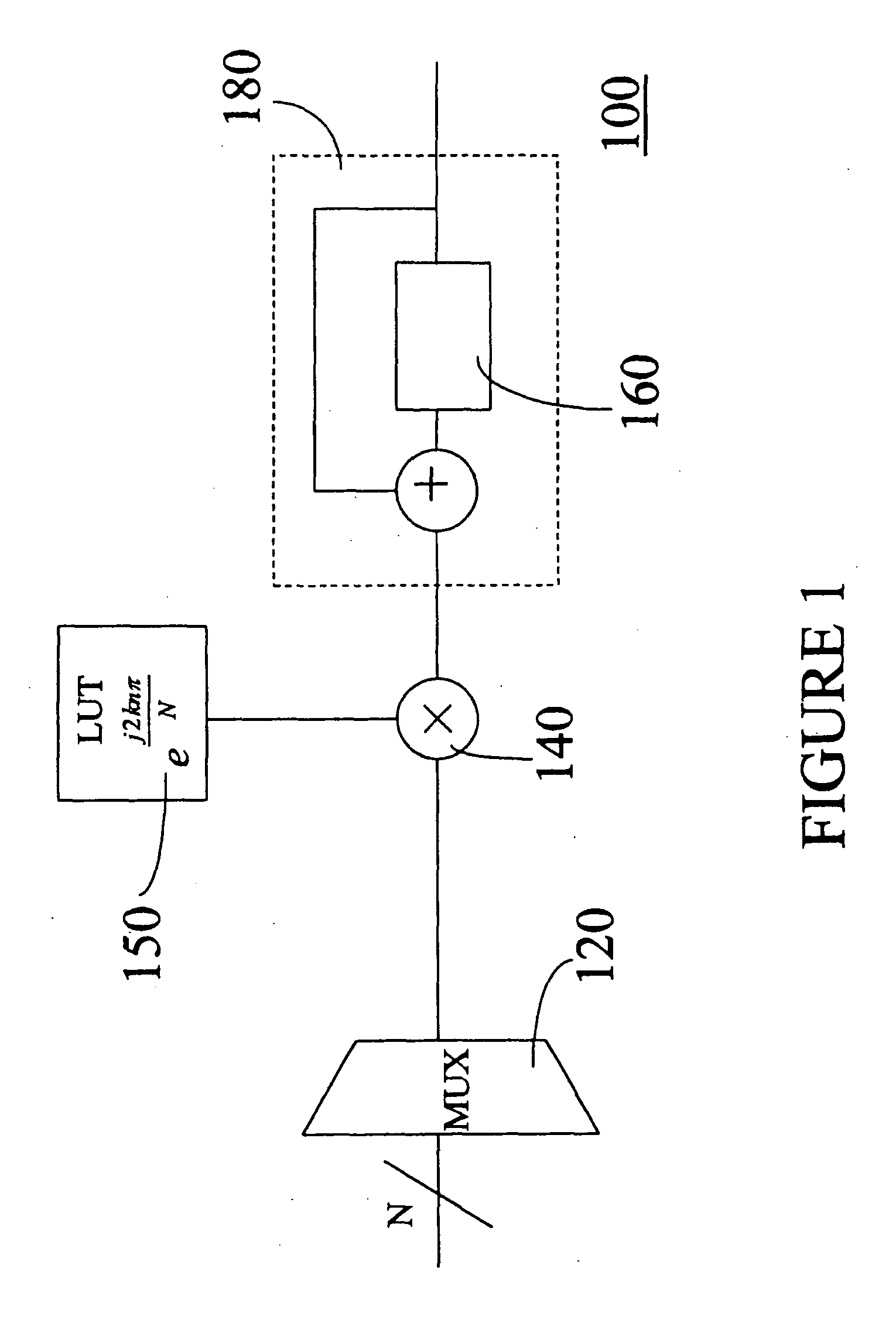
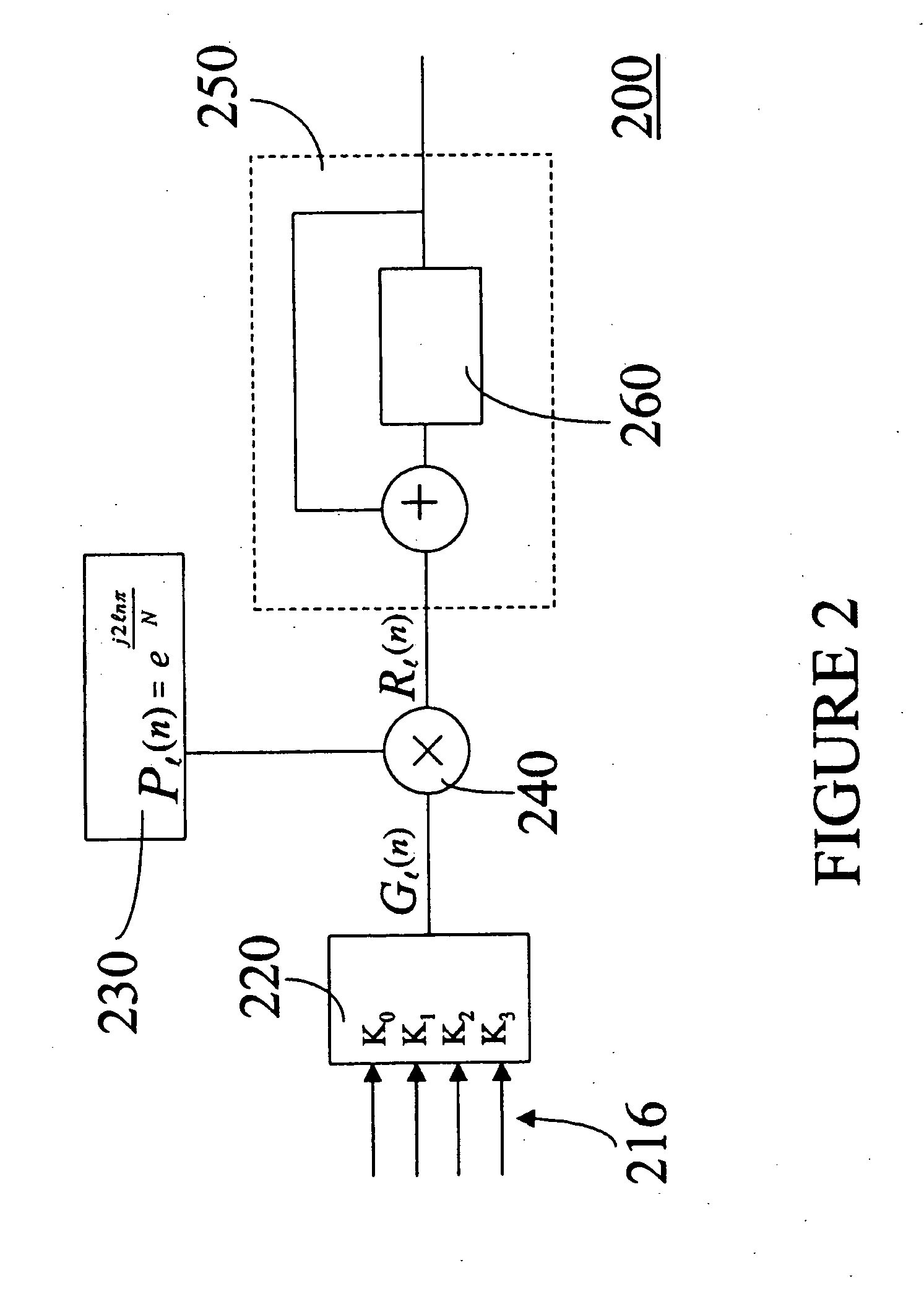
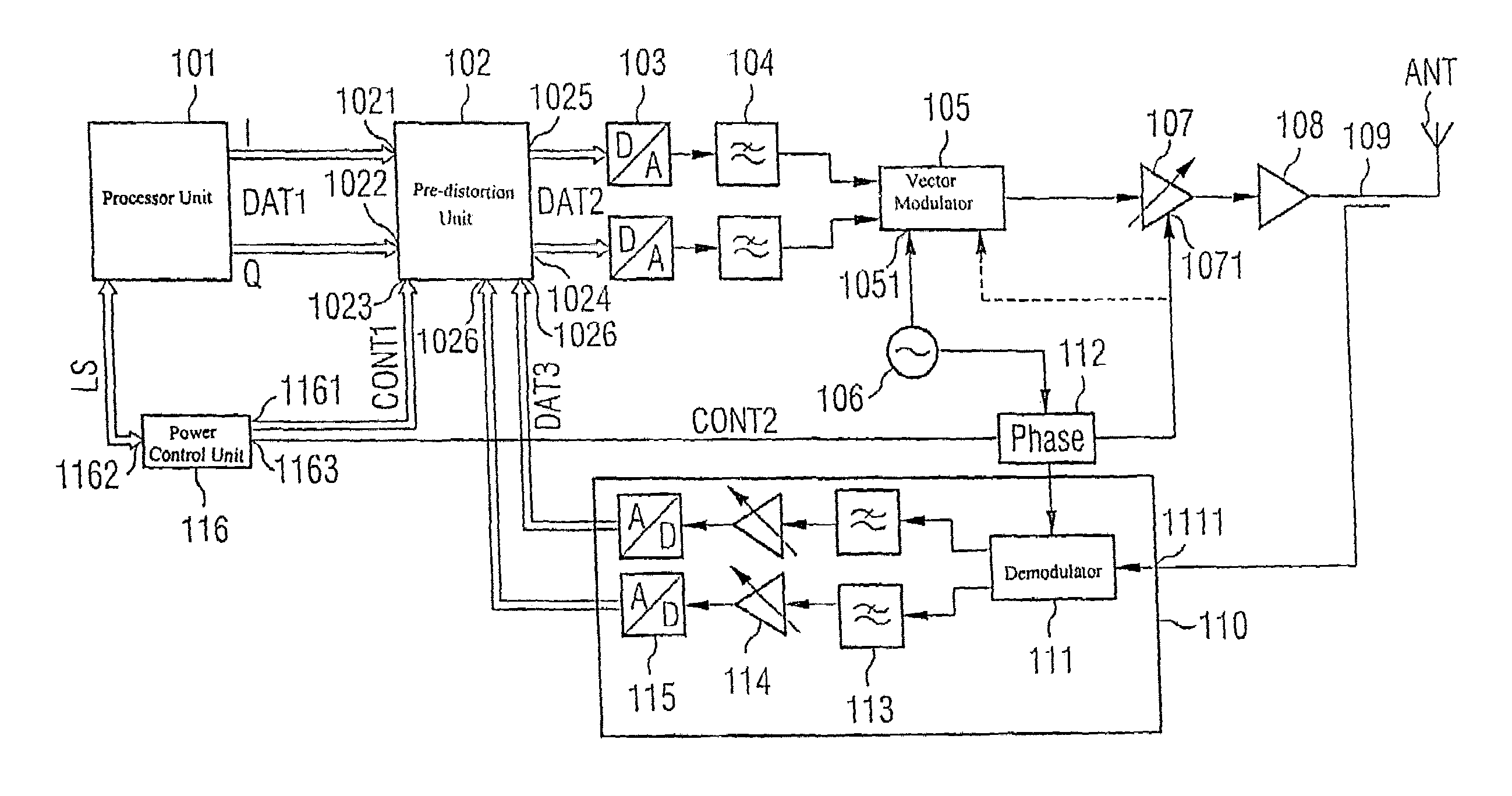
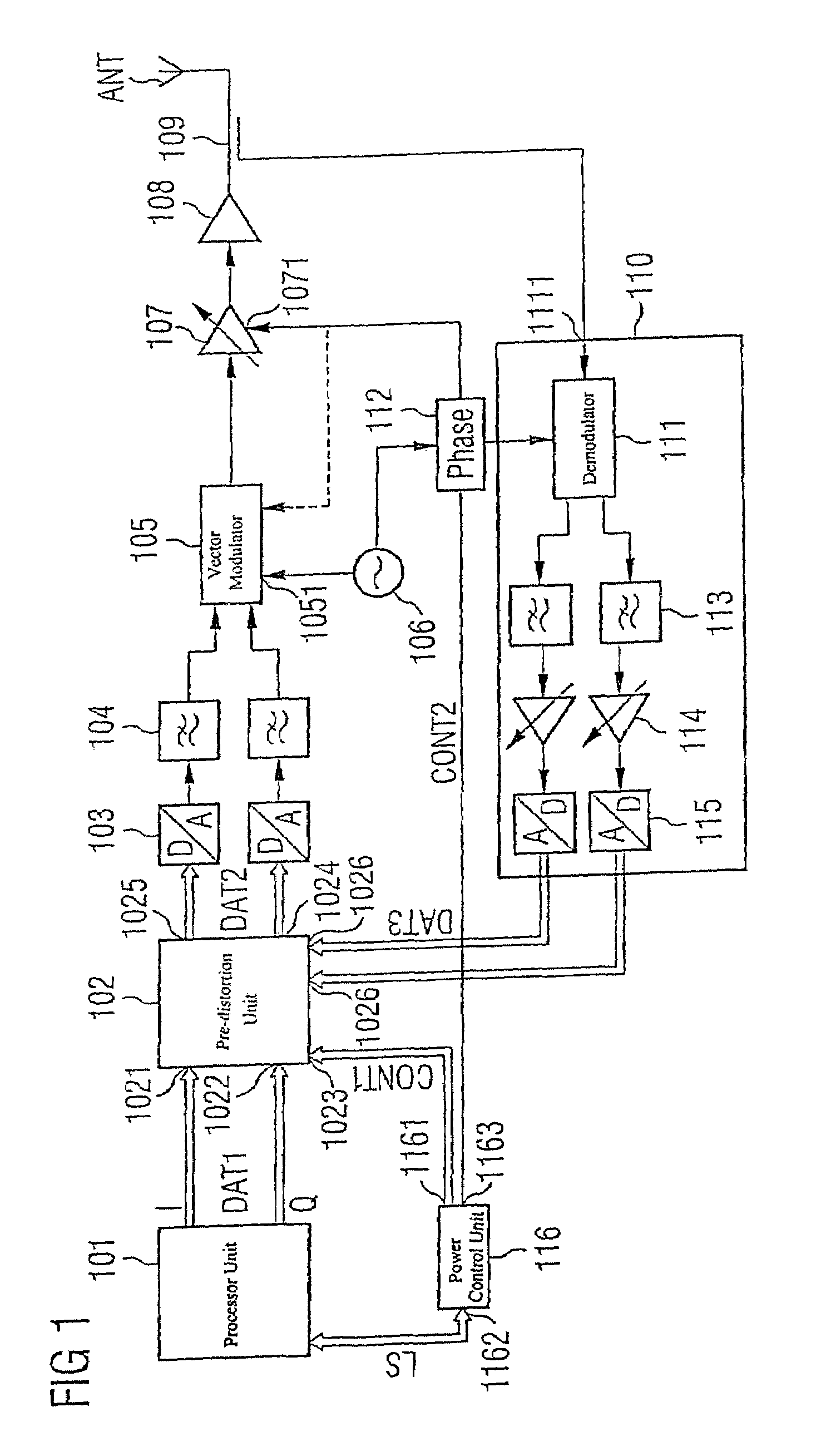
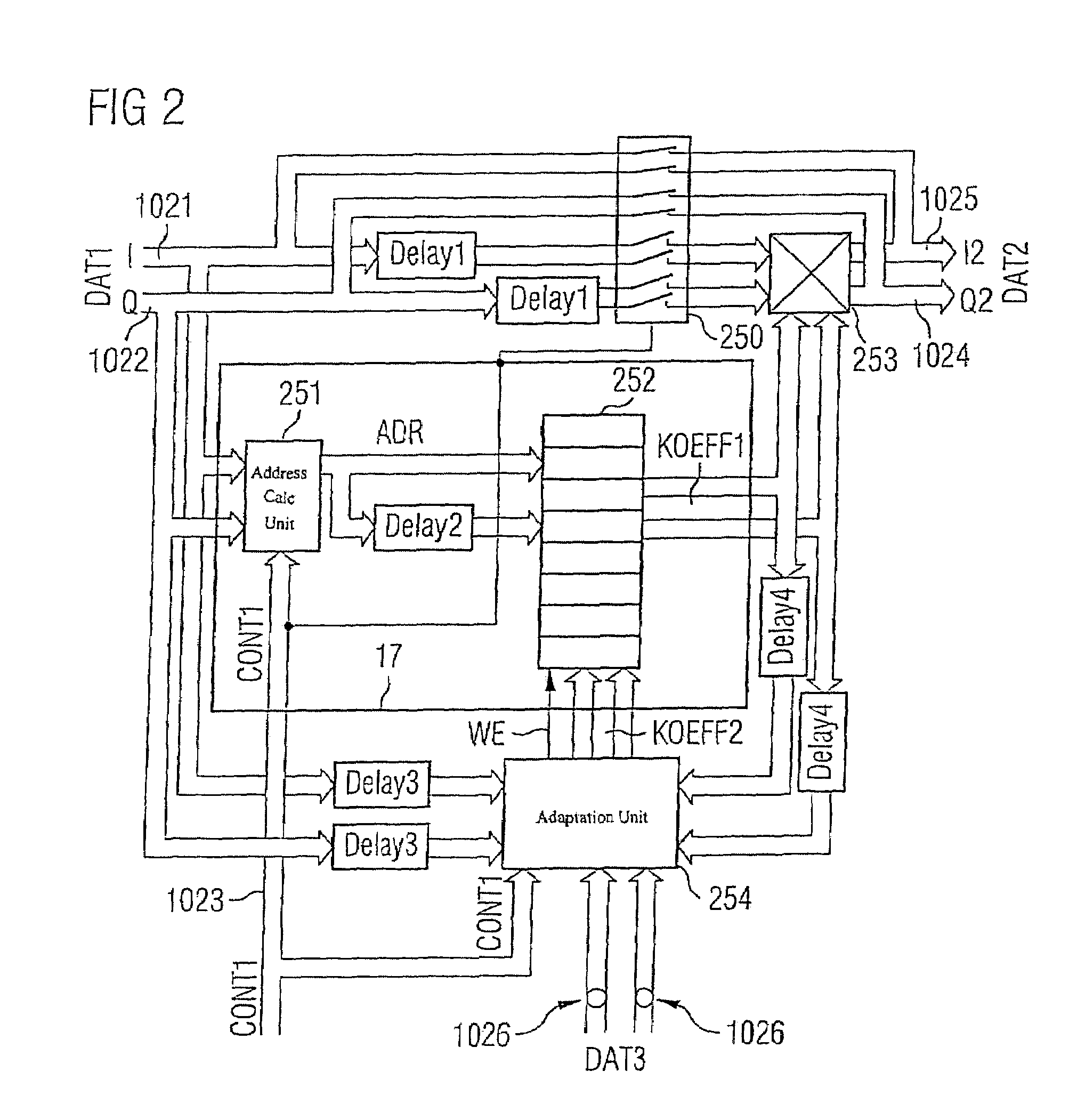
Transmission device with adaptive digital predistortion, transceiver with transmission device, and method for operating a transmission device
InactiveUS7372918B2Increase output powerGood linearityAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionGain controlBinary multiplierAudio power amplifier
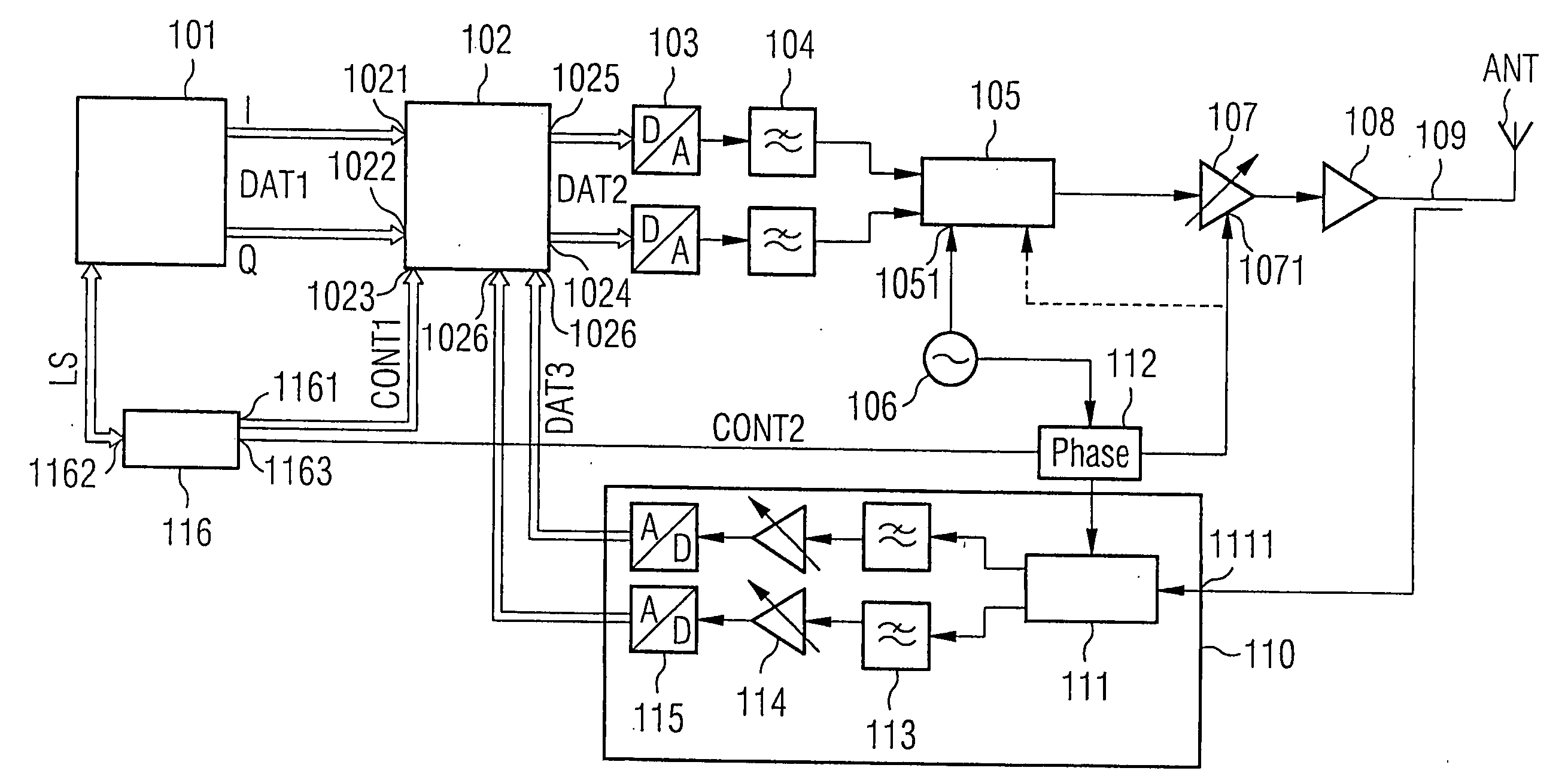
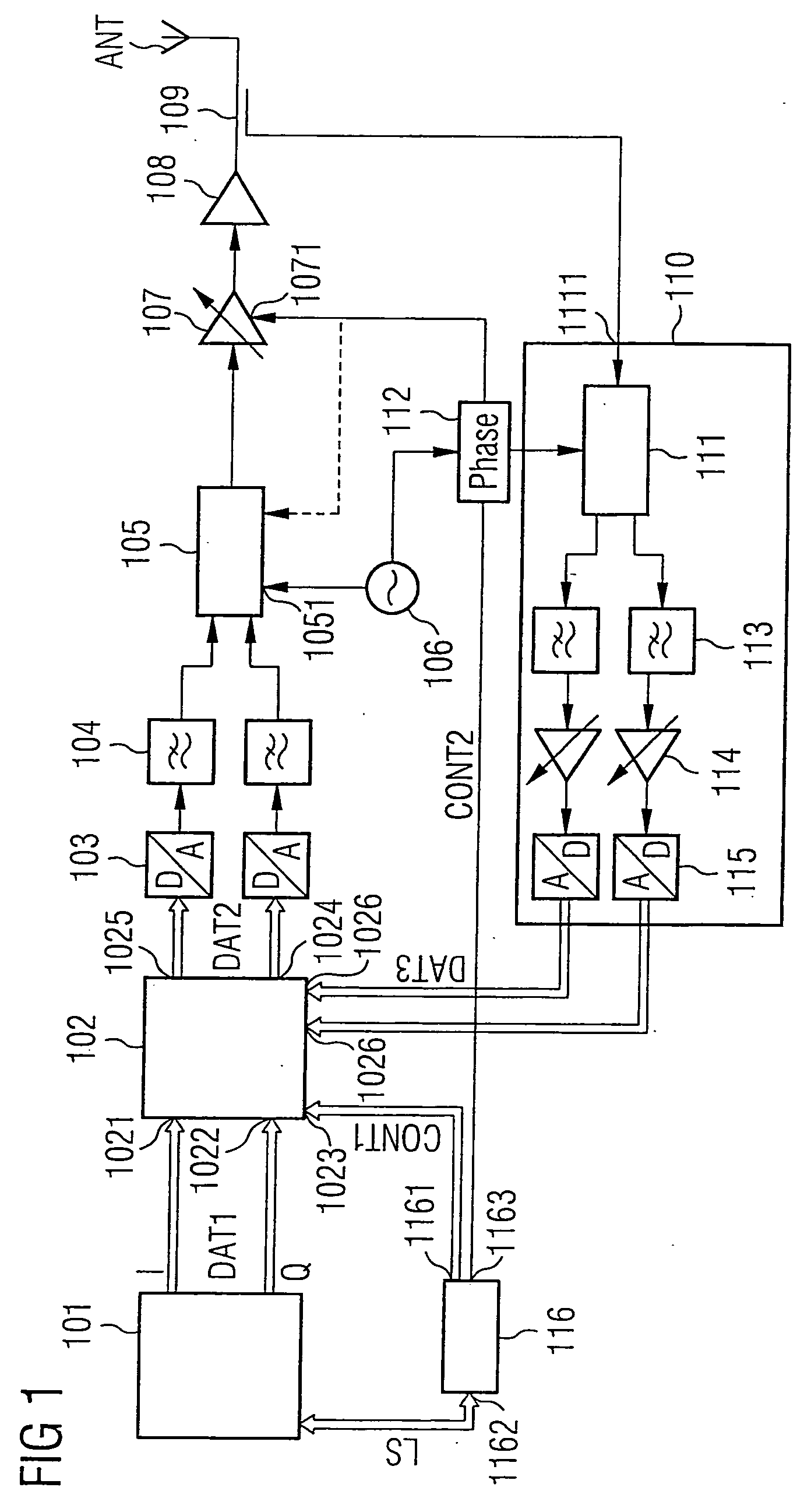
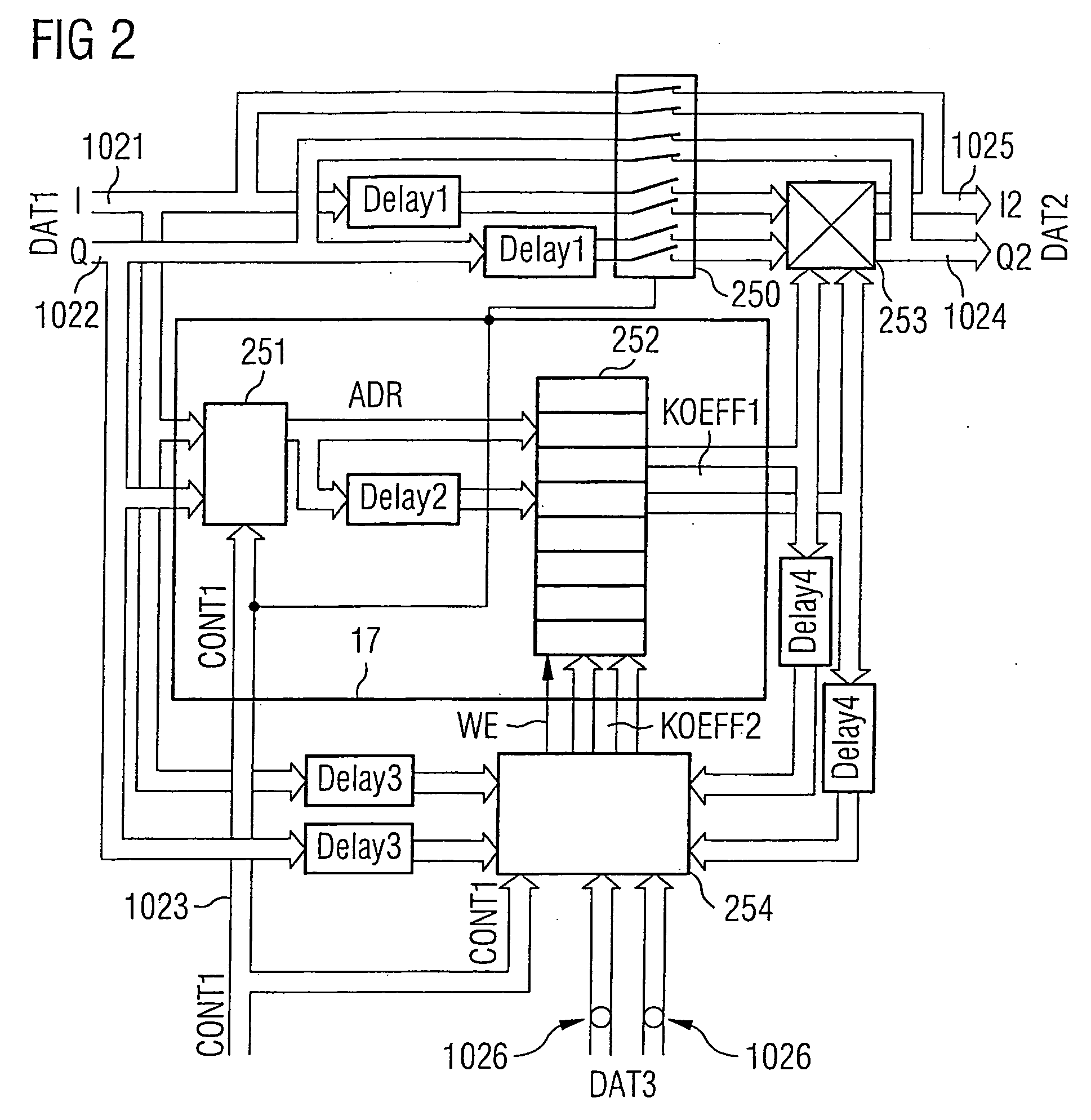
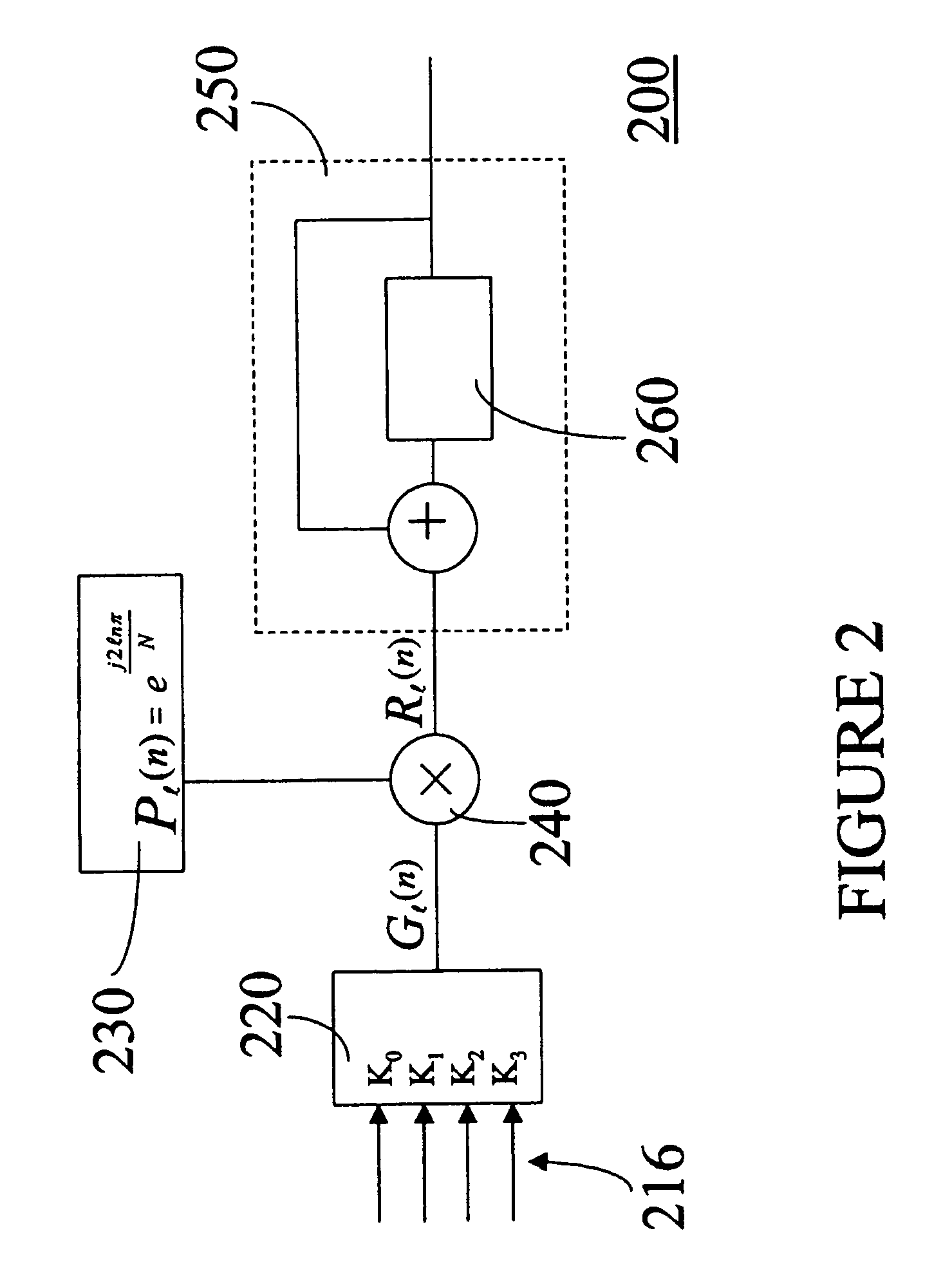
The invention provides a transmission device having adaptive digital predistortion, which has a transmission path and a feedback path. The transmission path contains a predistortion unit which takes a derived control signal (LS) and baseband signals applied to the input side as a basis for calculating the address of a predistortion coefficient (KOEFF1) stored in a memory and logically combines this predistortion coefficient with the applied baseband signals in a complex multiplication unit. The use of complex coefficients and of the complex multipliers allows compensation both for AM / AM distortion and for AM / PM distortion in an amplifier device connected downstream of the predistortion unit. Usefully, the feedback path of the transmission device with digital adaptive predistortion can also be implemented using the reception device in a transceiver.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
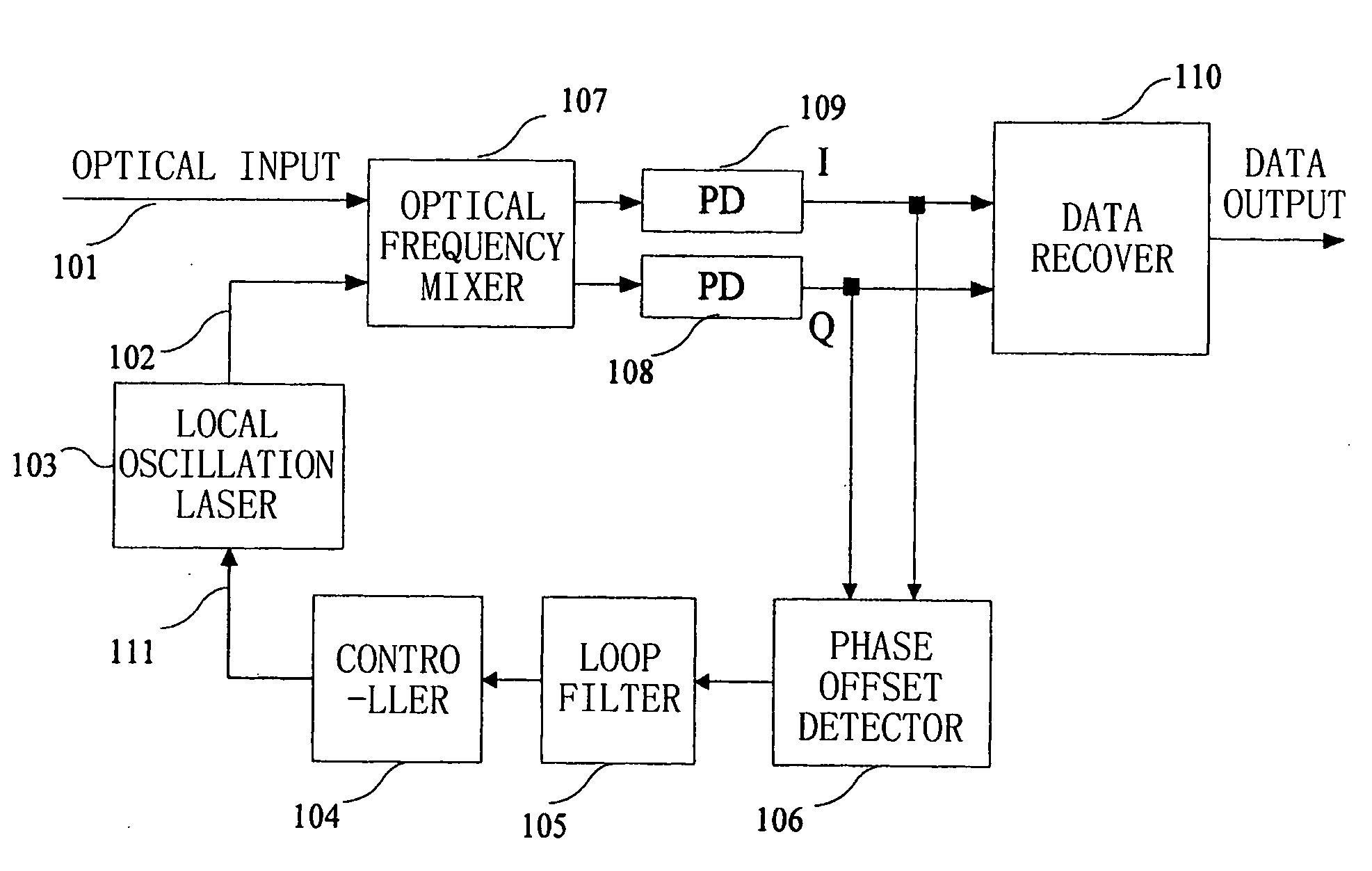
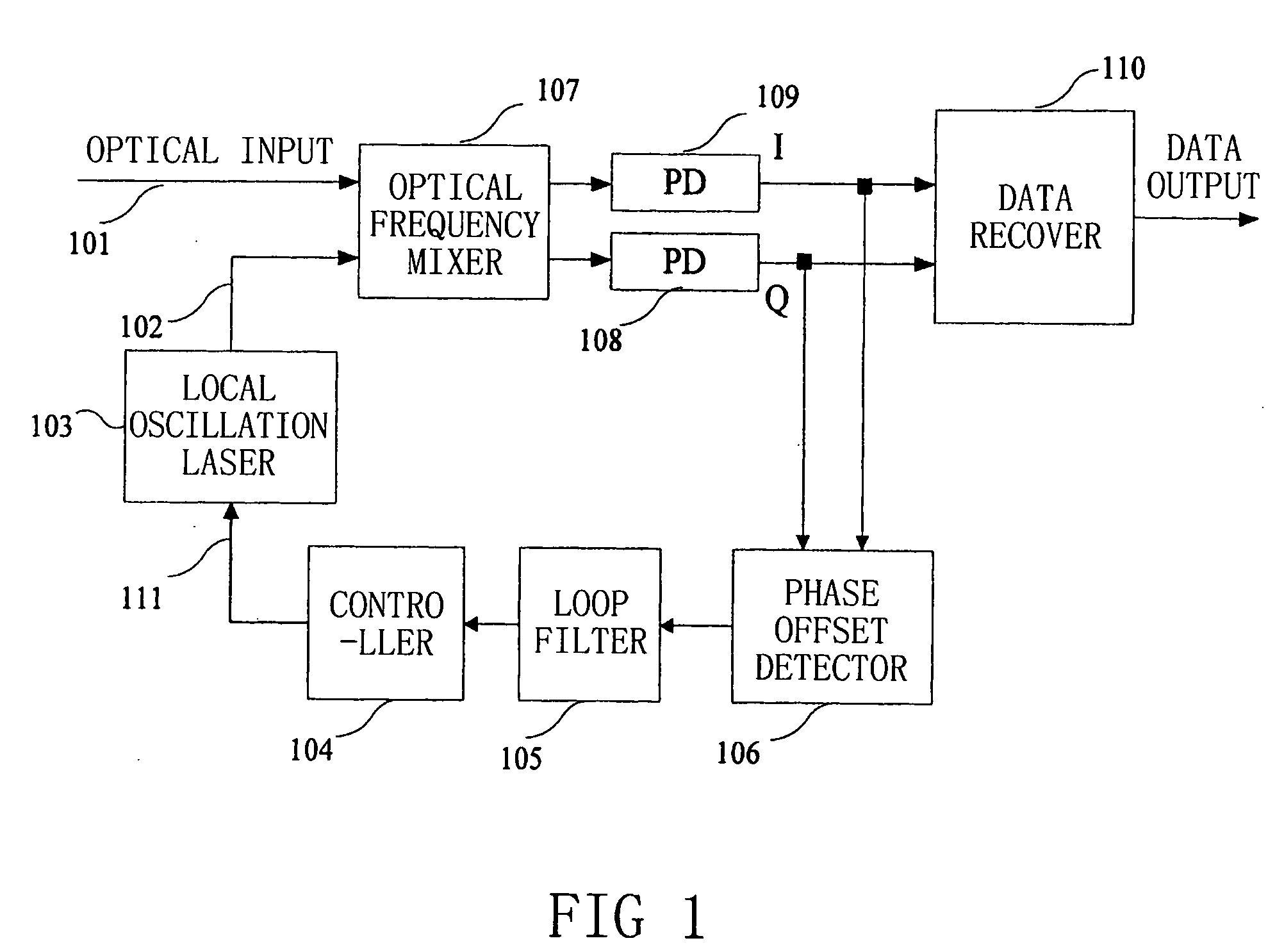
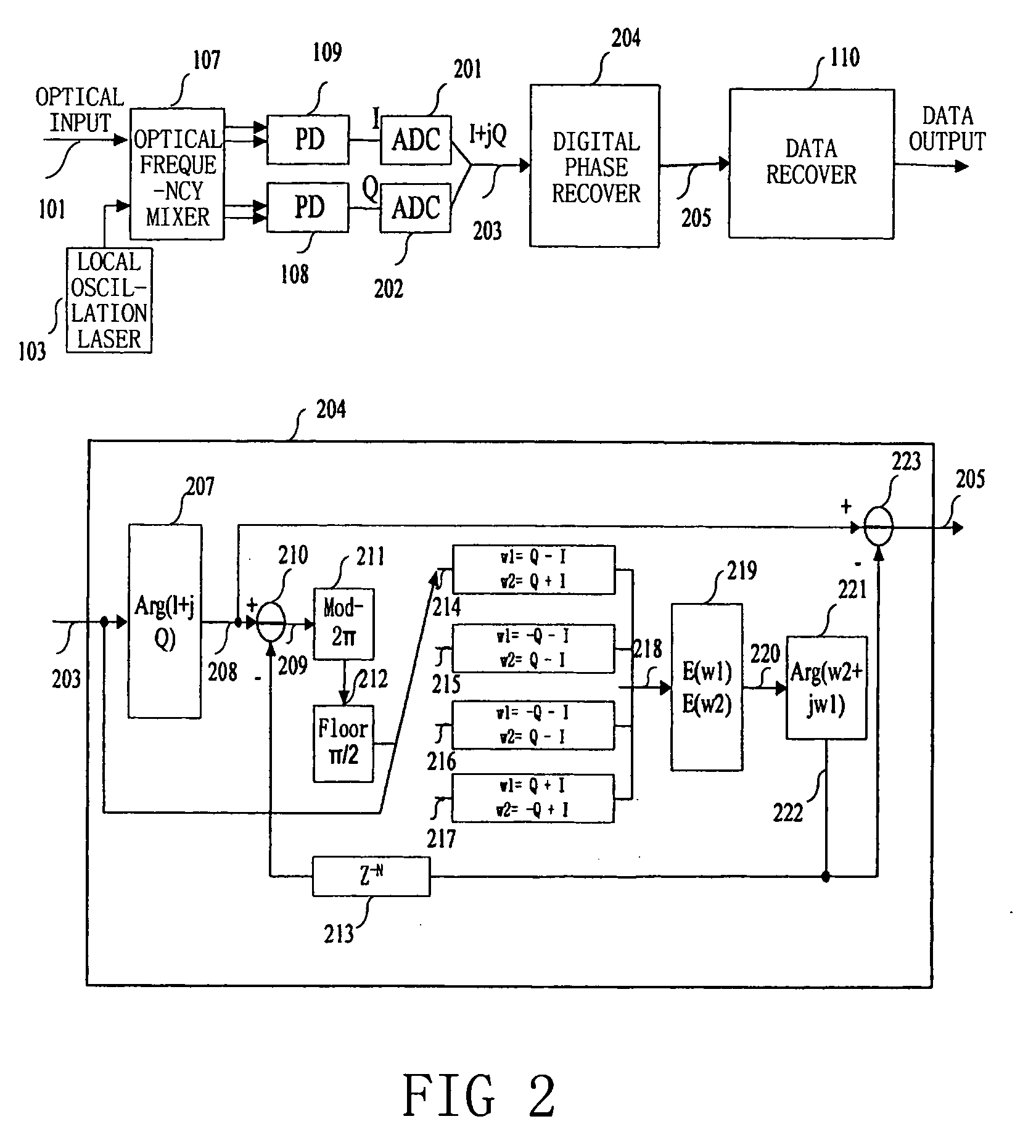
Frequency offset compensating apparatus and method, and optical coherent receiver
The present invention relates to a frequency offset compensating apparatus and method, and an optical coherent receiver. The optical coherent receiver includes a front end processor and a frequency offset estimator, of which said front end processor converts an inputted optical signal into a base band digital electric signal, and said frequency offset estimator estimates a phase offset change introduced by a frequency offset in said base band digital electric signal; said frequency offset compensating apparatus comprises an M output integrator, for integrating the phase offset change introduced by the frequency offset to acquire M inverse numbers of the phase offset introduced by the frequency offset, where M is an integer greater than 1; a series-parallel converting device, for dividing said base band digital electric signal into M sub base band digital electric signals; M complex multipliers, for constructing the corresponding inverse numbers in the M inverse numbers to be complex numbers, and multiplying them with the corresponding sub base band digital electric signals in the M sub base band digital electric signals; and a parallel-series converting device, for converting the M sub base band digital electric signals multiplied by said complex multipliers into a base band electric signal.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
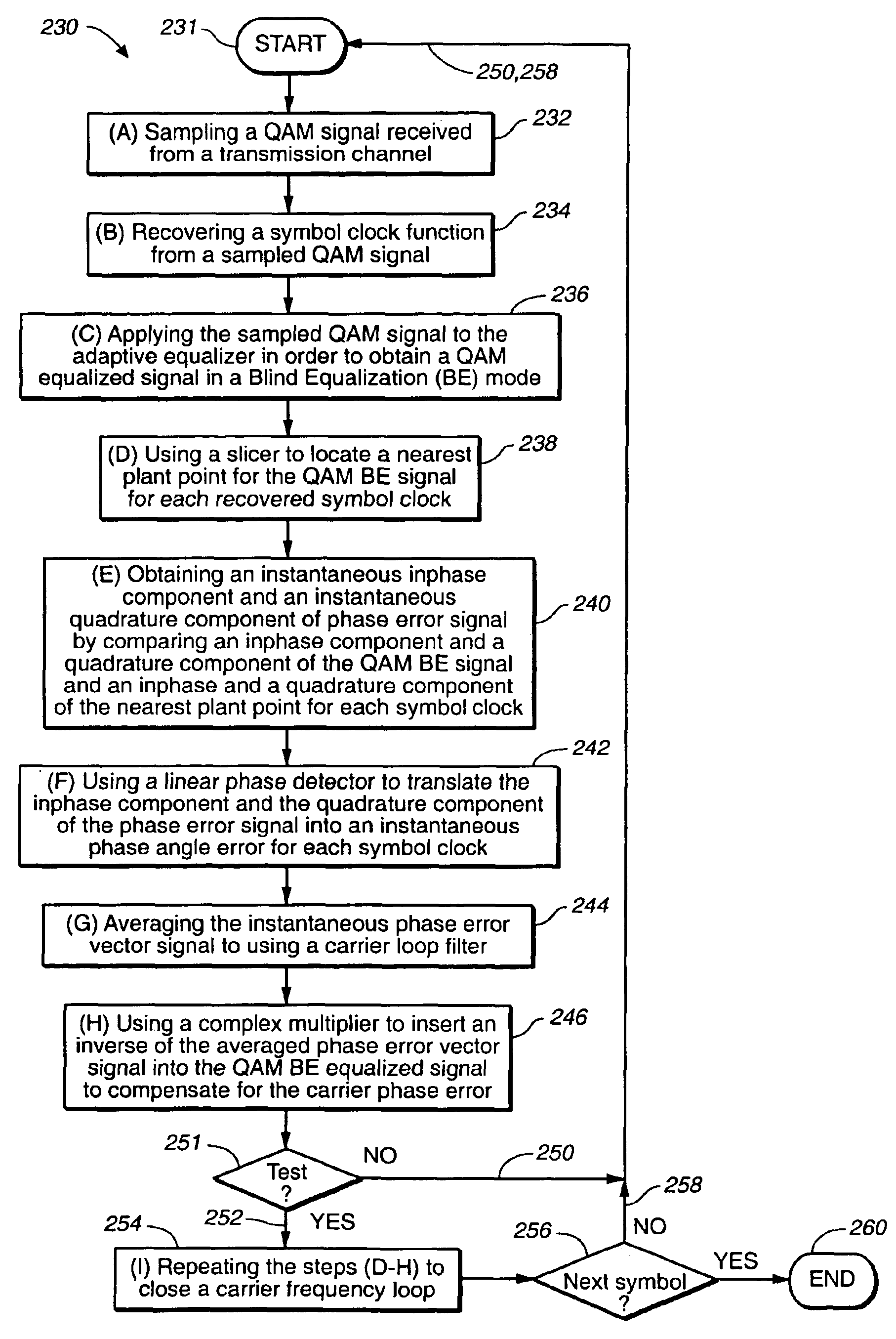
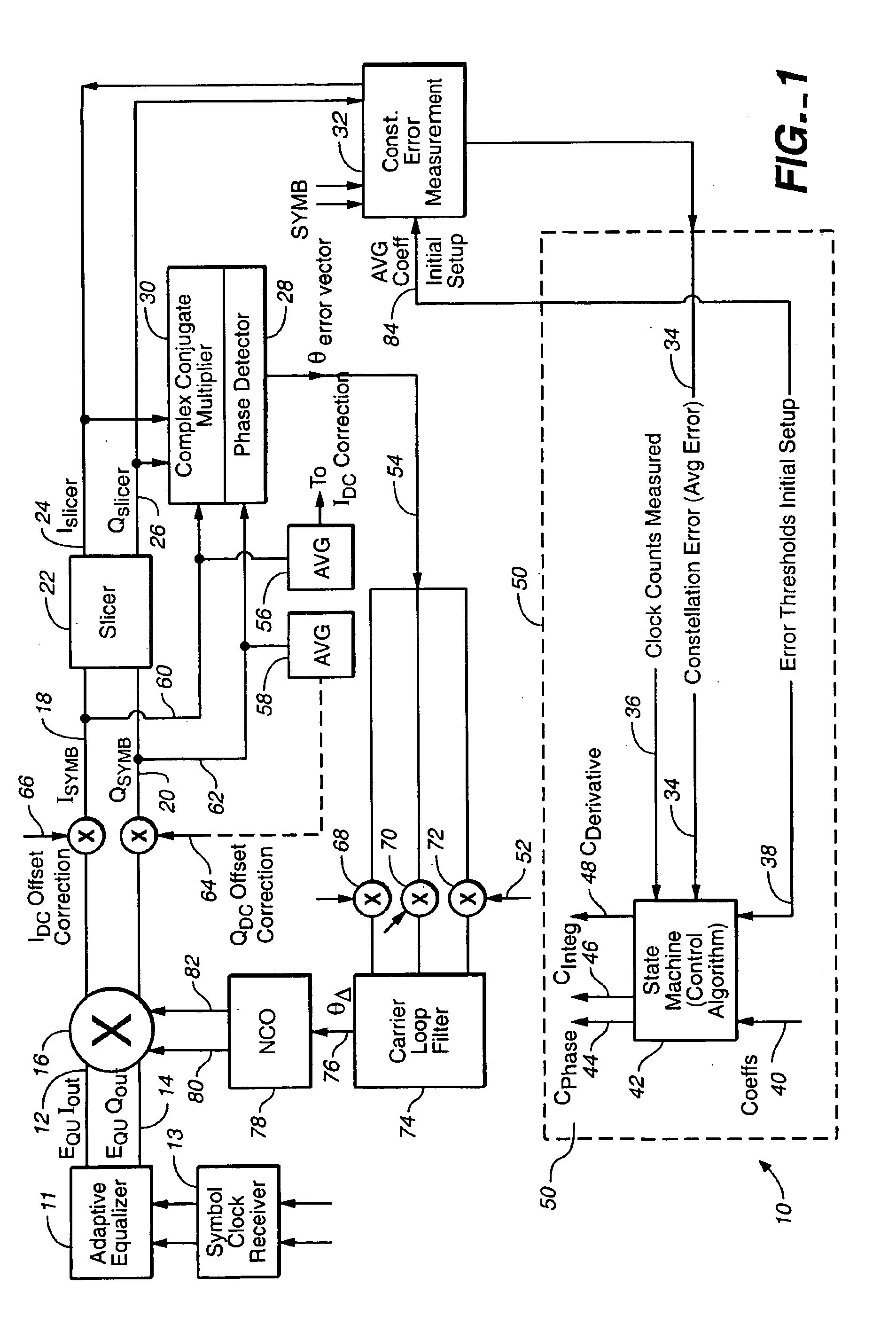
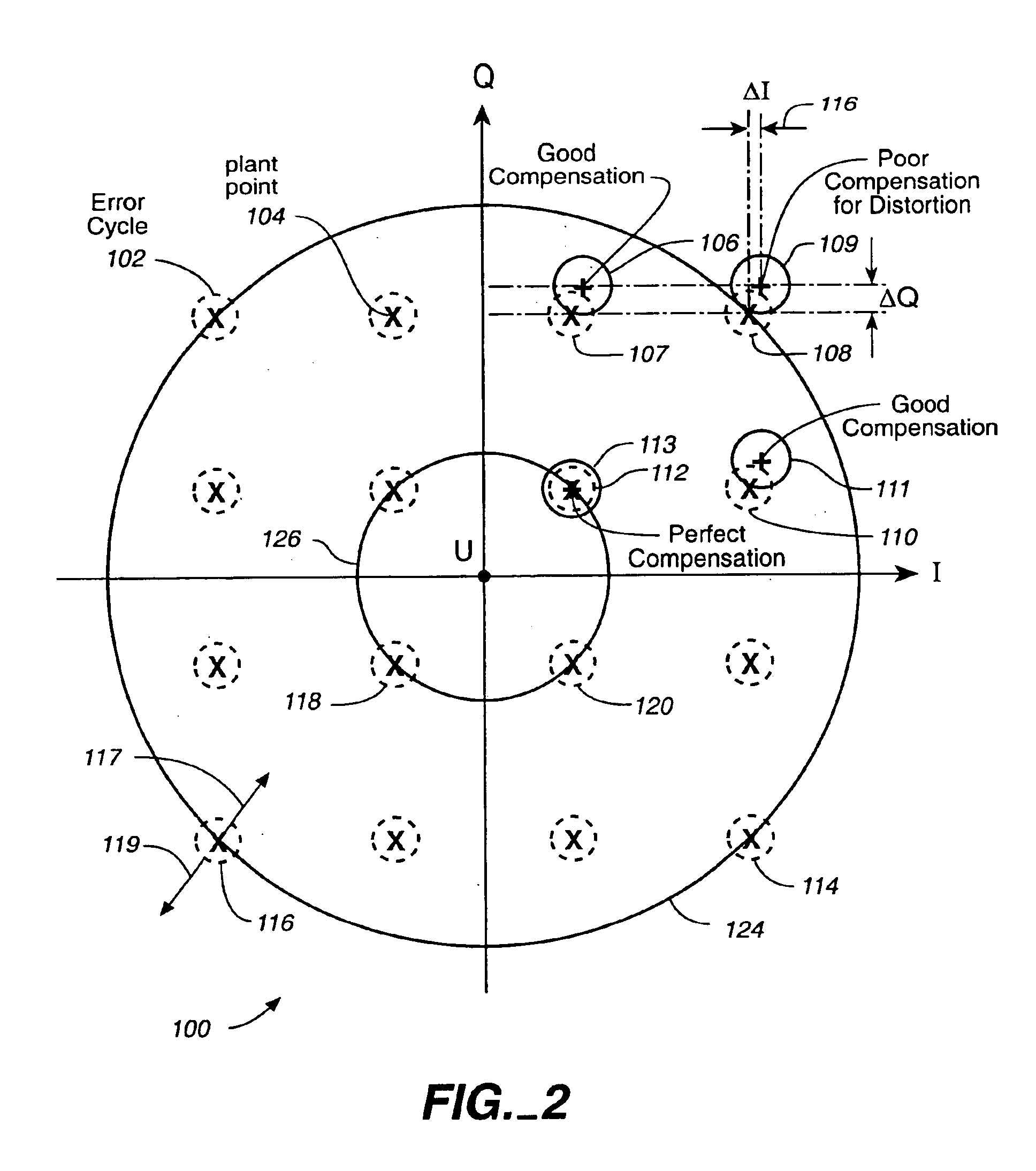
Linear phase robust carrier recovery for QAM modems
InactiveUS6904098B1Large loop bandwidthLower latencyDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionAutomatic frequency control detailsQam modulationBlind equalization
In a QAM demodulator including an adaptive equalizer, a method of carrier tracking comprising the following steps is disclosed: (A) sampling a QAM signal received from a transmission channel; (B) recovering a symbol clock function from the sampled QAM signal; (C) applying the sampled QAM signal to the adaptive equalizer in order to obtain a QAM equalized signal in a Blind Equalization (BE) mode; (D) using a slicer to locate a nearest plant point for the QAM Blind equalized signal for each recovered symbol clock; (E) using a complex conjugate multiplier to obtain an instantaneous inphase component and an instantaneous quadrature component of a phase angle error signal; (F) using a linear phase detector to obtain an instantaneous phase angle error for each symbol clock; (G) averaging the instantaneous phase angle error signal by using a carrier loop filter; (H) using a complex multiplier to insert an inverse of the averaged phase angle error signal into the QAM Blind equalized signal to compensate for the carrier phase angle error; and (I) repeating the steps (D-H) to close a carrier frequency loop.
Owner:REMEC BROADBAND WIRELESS NETWORKS LLC
Transmission device with adaptive digital predistortion, transceiver with transmission device, and method for operating a transmission device
InactiveUS20050105642A1Reduce power consumptionIncrease output powerAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceTransceiverAudio power amplifier
The invention provides a transmission device having adaptive digital predistortion, which has a transmission path and a feedback path. The transmission path contains a predistortion unit which takes a derived control signal (LS) and baseband signals applied to the input side as a basis for calculating the address of a predistortion coefficient (KOEFF1) stored in a memory and logically combines this predistortion coefficient with the applied baseband signals in a complex multiplication unit. The use of complex coefficients and of the complex multipliers allows compensation both for AM / AM distortion and for AM / PM distortion in an amplifier device connected downstream of the predistortion unit. Usefully, the feedback path of the transmission device with digital adaptive predistortion can also be implemented using the reception device in a transceiver.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Method and apparatus for high-order PAPR reduction of an OFDM signal
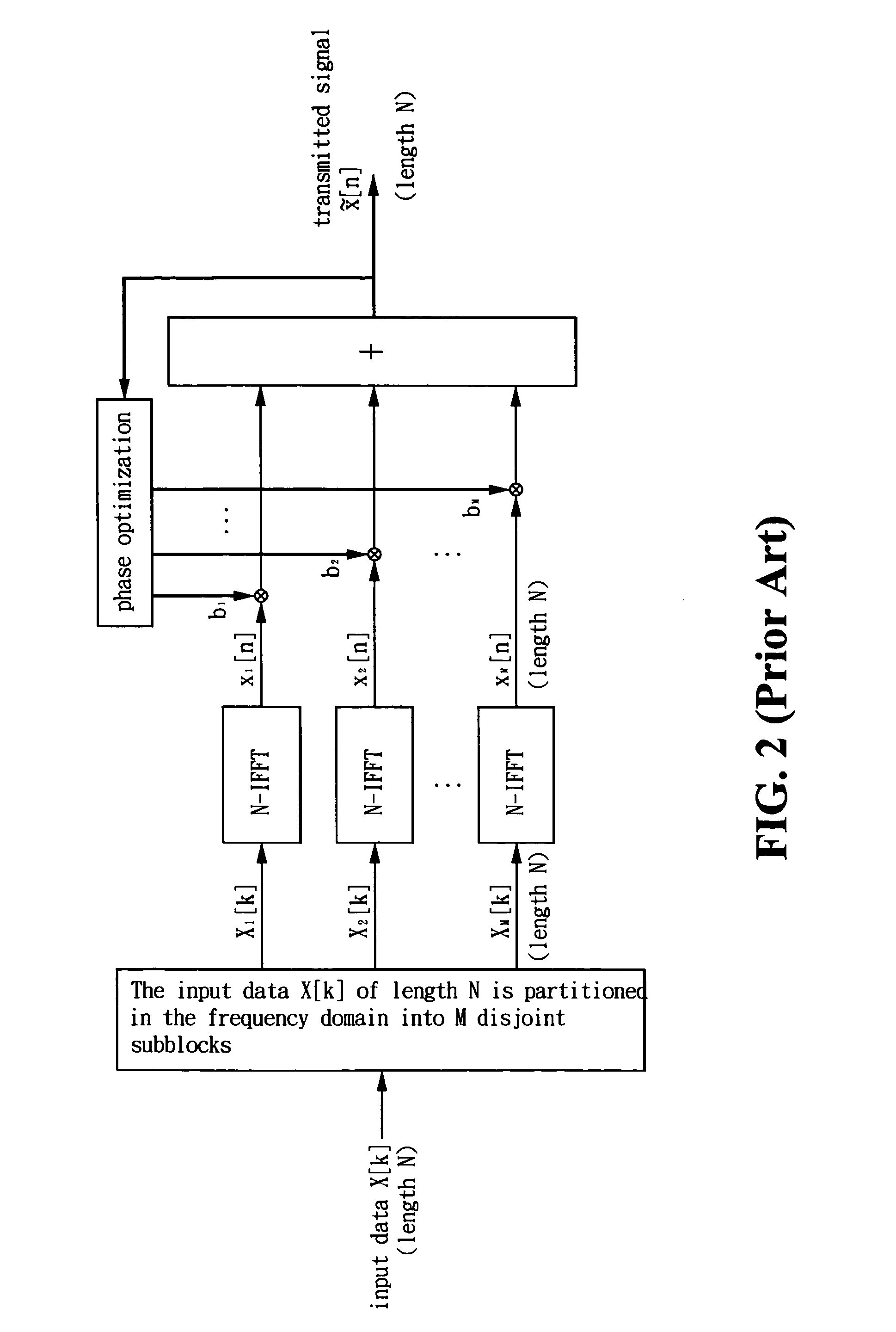
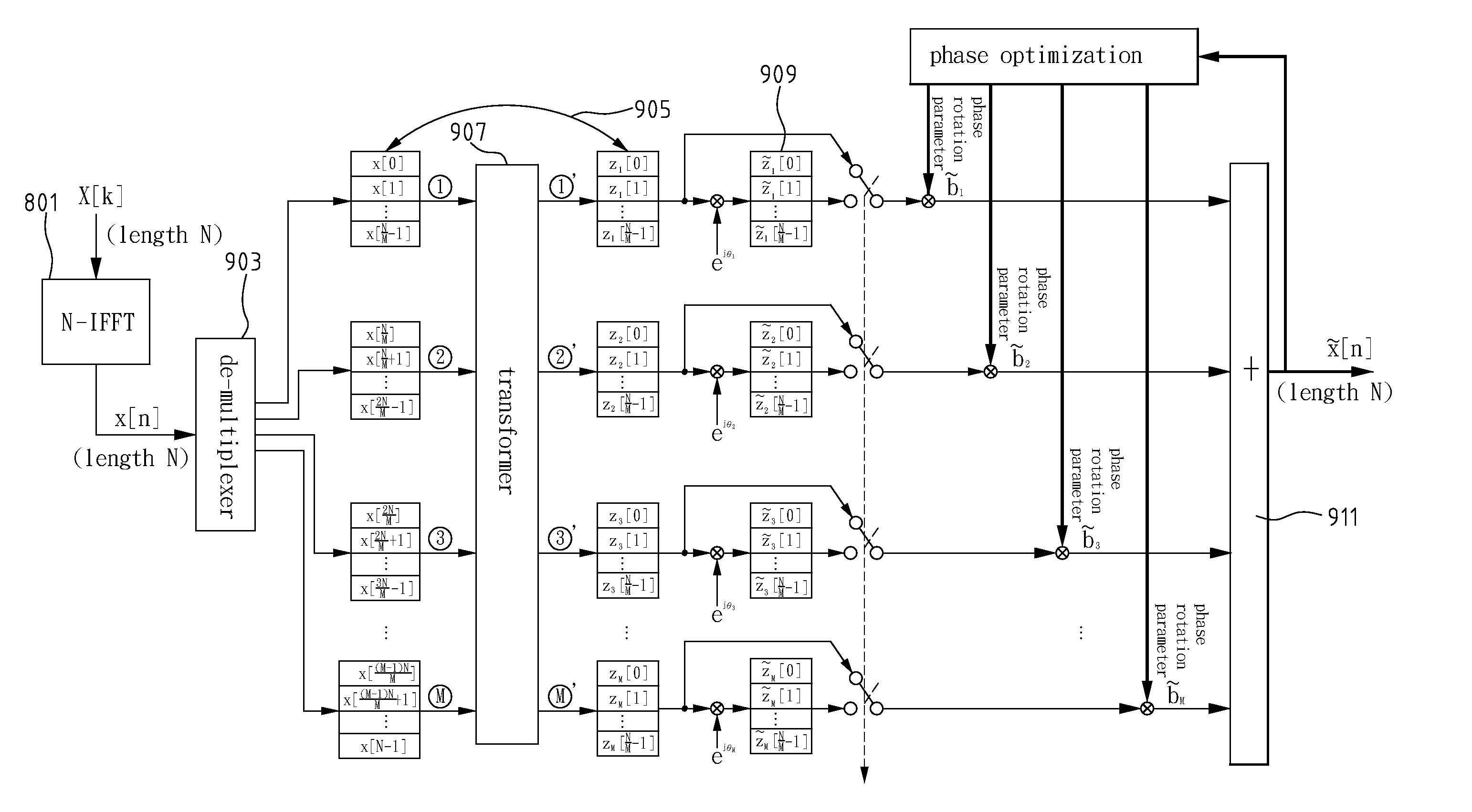
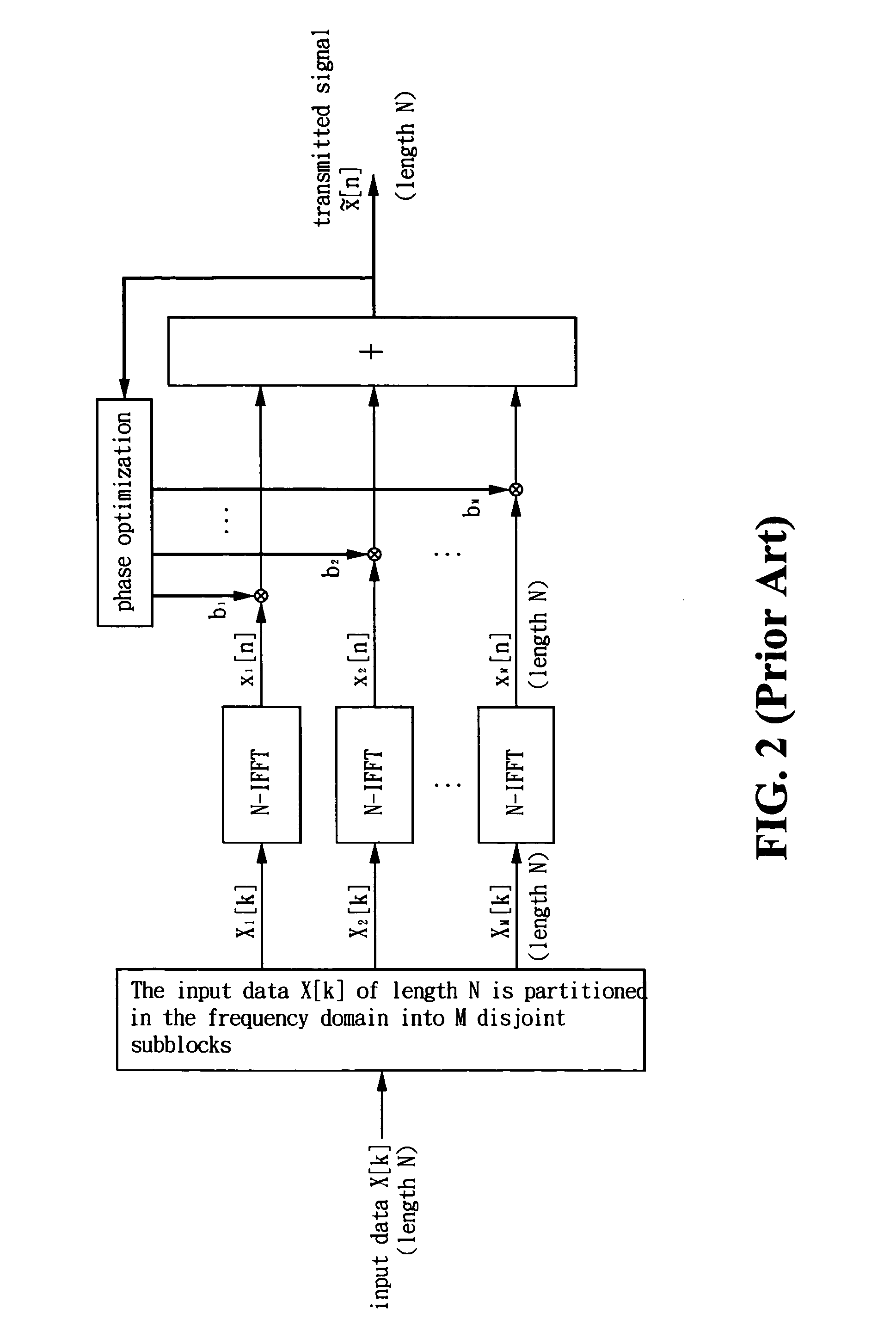
InactiveUS20050286648A1Reduce the amount of calculationReduce the amount requiredSecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainMultiplexer
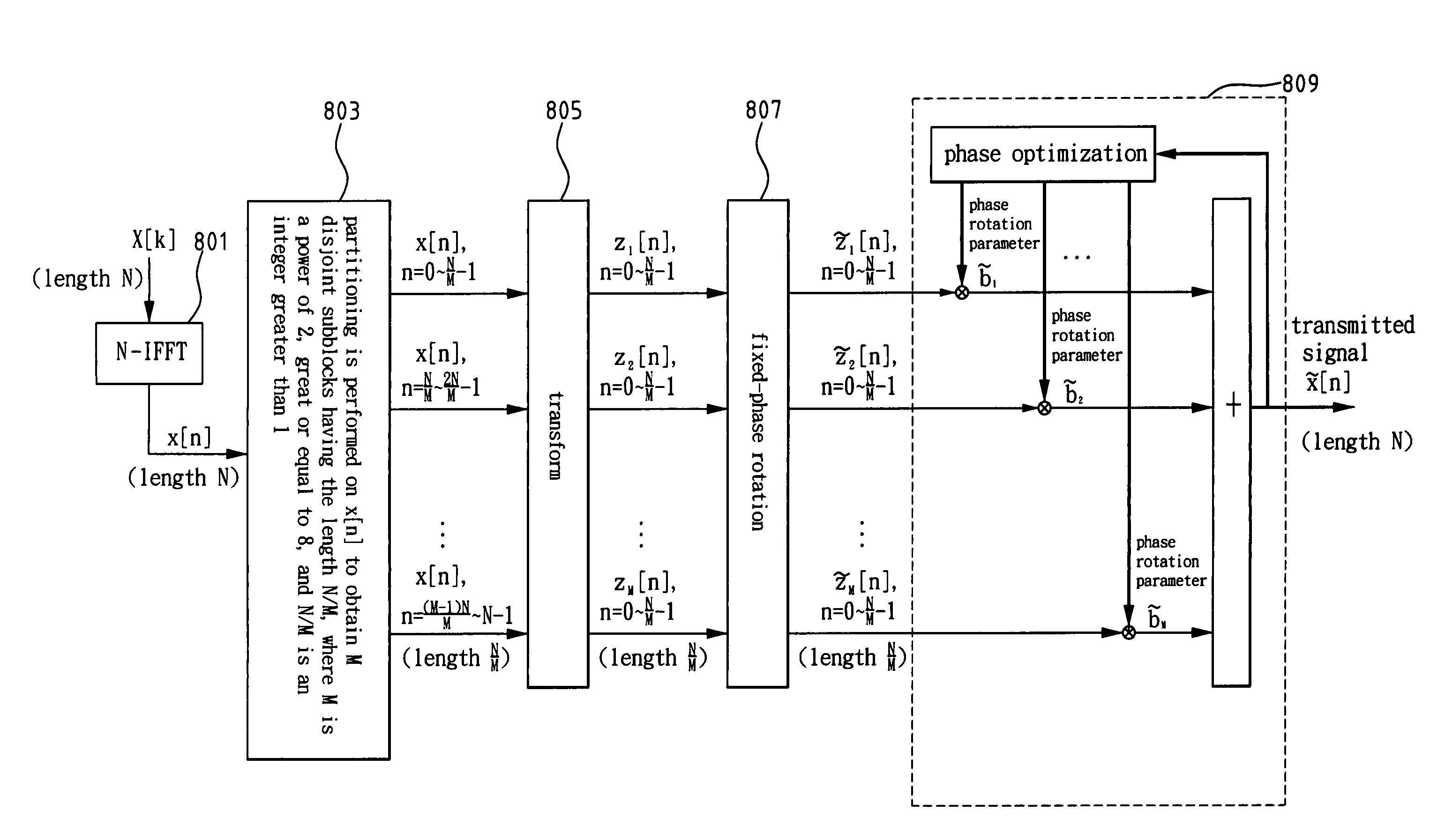
A method and apparatus for high-order peak-to-average power ratio reduction of an OFDM signal are disclosed. The method partitions time-domain input data x[n] of length N into M disjoint subblocks in time domain, and a complete N-point transmitted signal {tilde over (x)}[n], n=0, 1, . . . , N−1, is composed after transformation, complex multiplication, and phase optimization, where M is a power of 2, M≧8 and N / M>1 is an integer. Accordingly, the apparatus comprises an N-point inverse fast Fourier transform (N-IFFT), a de-multiplexer, a transformer, two sets of memories, a plurality of complex multipliers, and an adder. This invention uses only one N-IFFT, whereby it achieves significant computation reduction. As M=8, the number of complex multiplications and that of memory units required are less than or equal to (N / 2)log2N+(3N / 4) and 3N / 2, respectively. The invention also preserves the inherent property as well as advantages of an OFDM system.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
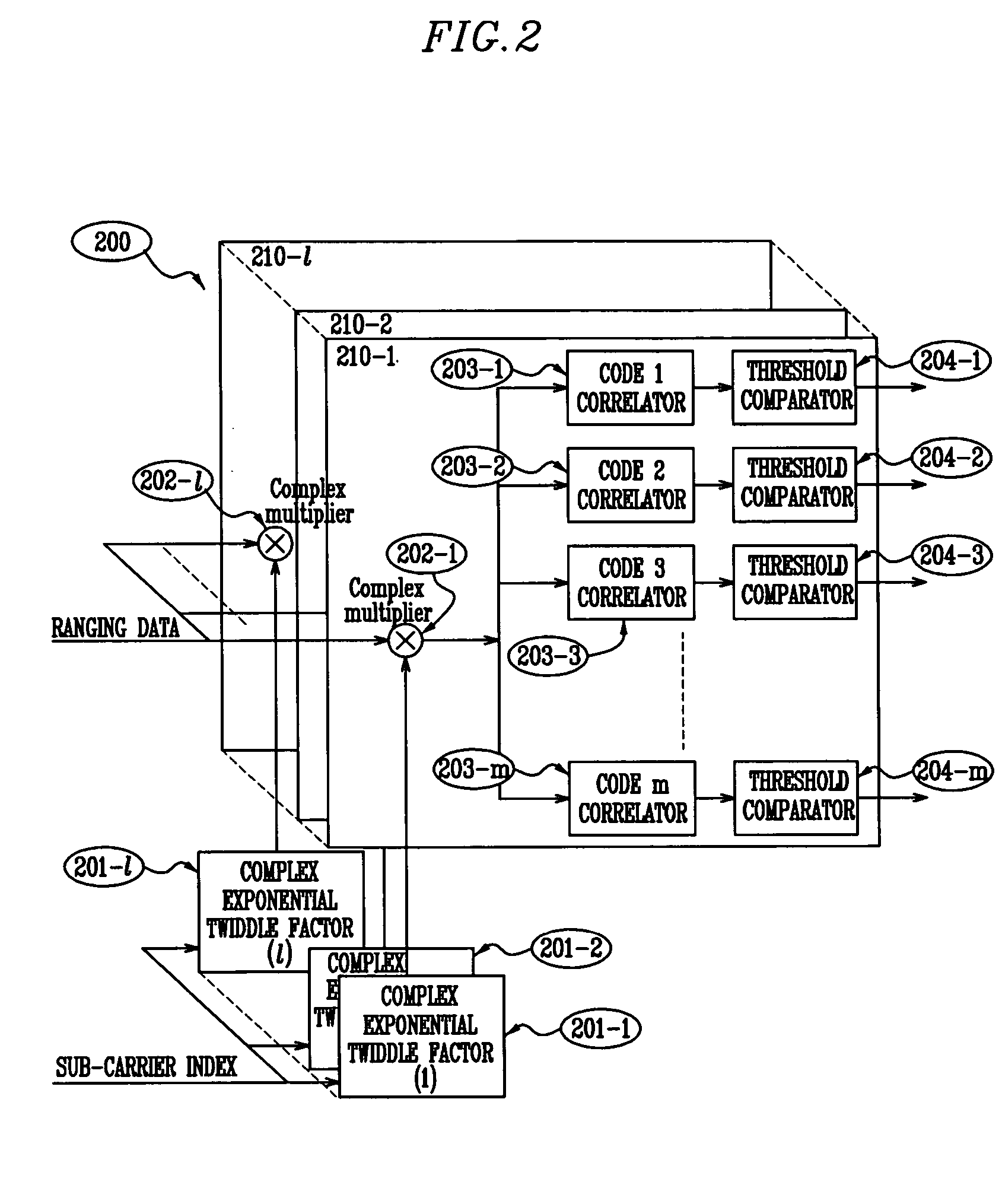
Intermediate frequency direct sequence spread spectrum receiver for satellite ranging
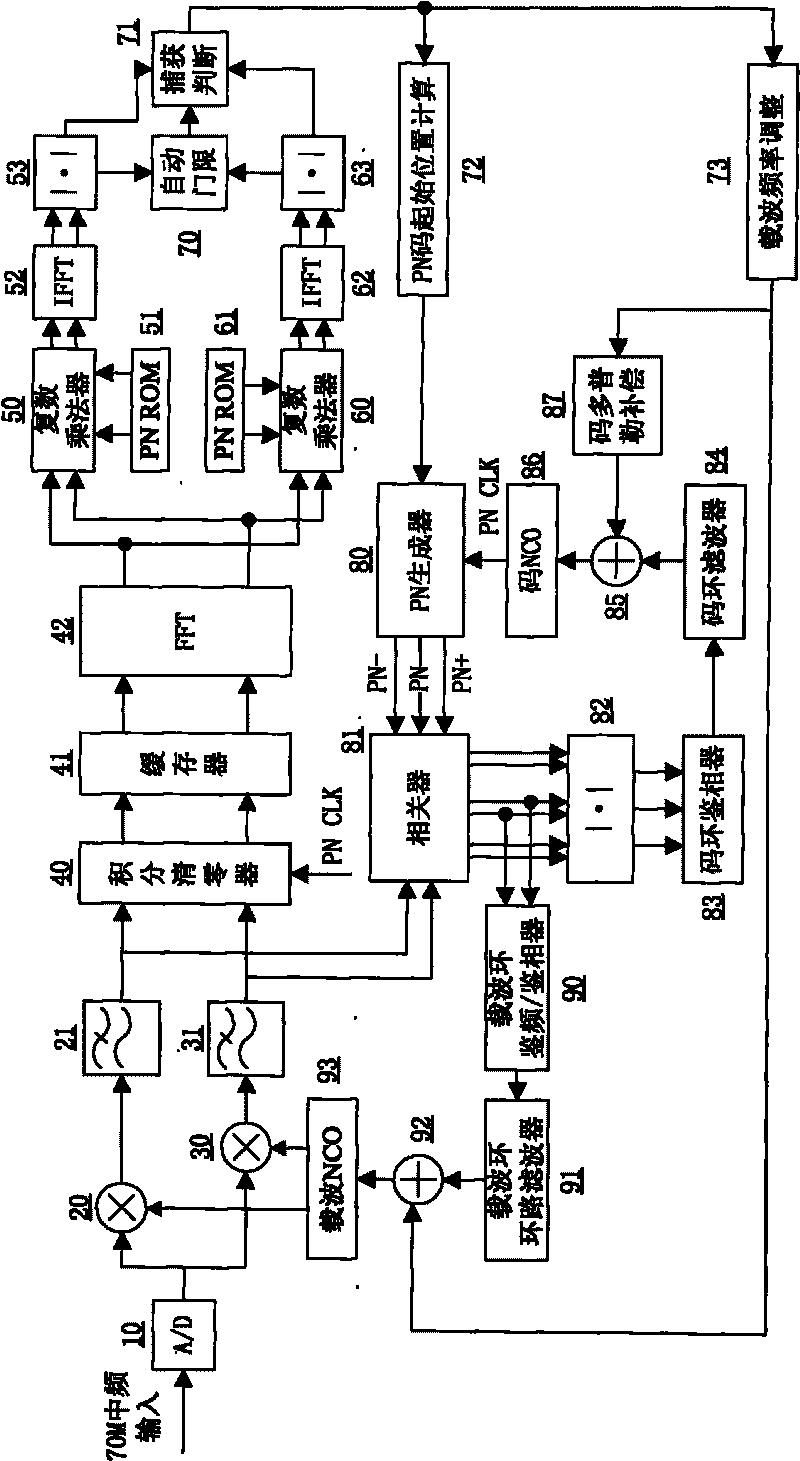
InactiveCN101726746AReduce resource consumptionFast captureSatellite radio beaconingDiscriminatorLow-pass filter
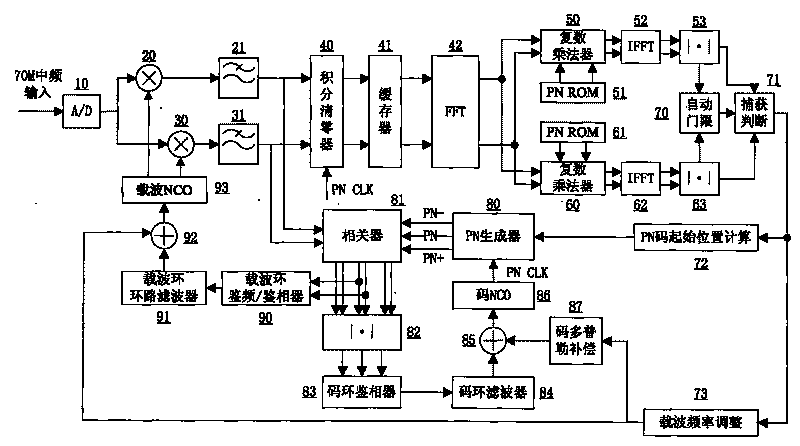
The invention relates to an intermediate frequency direct sequence spread spectrum receiver for satellite ranging, which consists of 37 parts of a front-end A / D, an FFT module, a local PN code generator, a correlator, an automatic threshold calculation module and the like. The connection relationship is as follows: the output of the front-end A / D and the output of a carrier tracking loop NCO are respectively connected to an in-phase branch multiplier and an orthogonal branch multiplier, the input of the front-end A / D and the input of the carrier tracking loop NCO enter into an in-phase branch FIR low-pass filter and an orthogonal branch FIR low-pass filter, consequently, on the one hand, the output is sent to an integral zero clearing device, then the output which is sent to the FFT module, a branch 1 local PN code memory ROM and a branch 2 local PN code memory ROM enters into a branch 1 complex multiplier and a branch 2 complex multiplier, the output is sent to a branch 1 root mean square module and a branch 2 root mean square module, the output is sent to the threshold calculation module and a capturing and judging module for carrying out code catching; and on the other hand, the output is sent to the correlator and the local PN code generator for carrying out code tracking. The output of the correlator is simultaneously sent into a frequency discriminator / phase discriminator of the carrier tracking loop and then enters into a loop filter of the carrier tracking loop, and the output of the loop filter of the carrier tracking loop enters into the carrier tracking loop NCO for carrying out carrier tracking.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
High-sensitivity satellite navigation signal capturing method and system
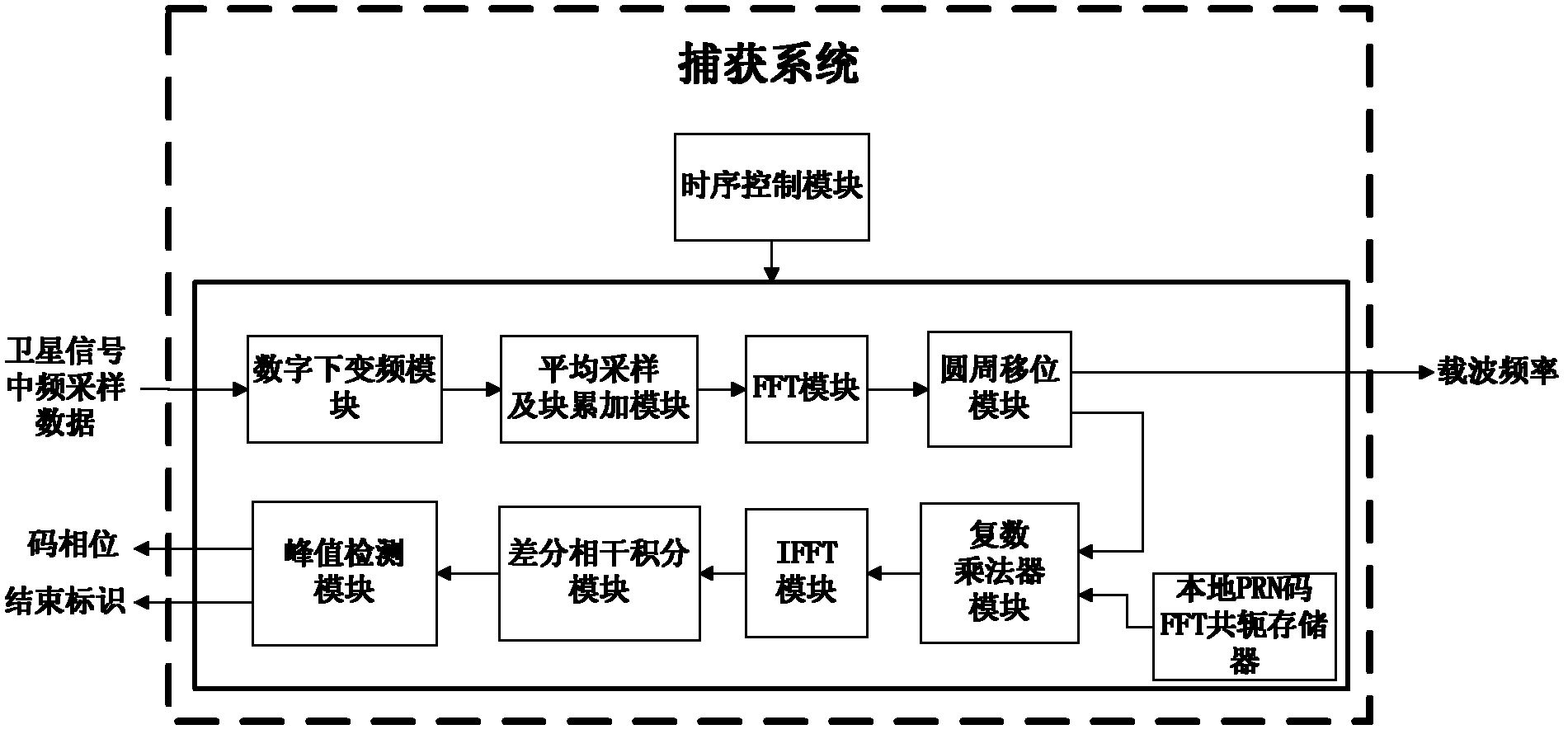
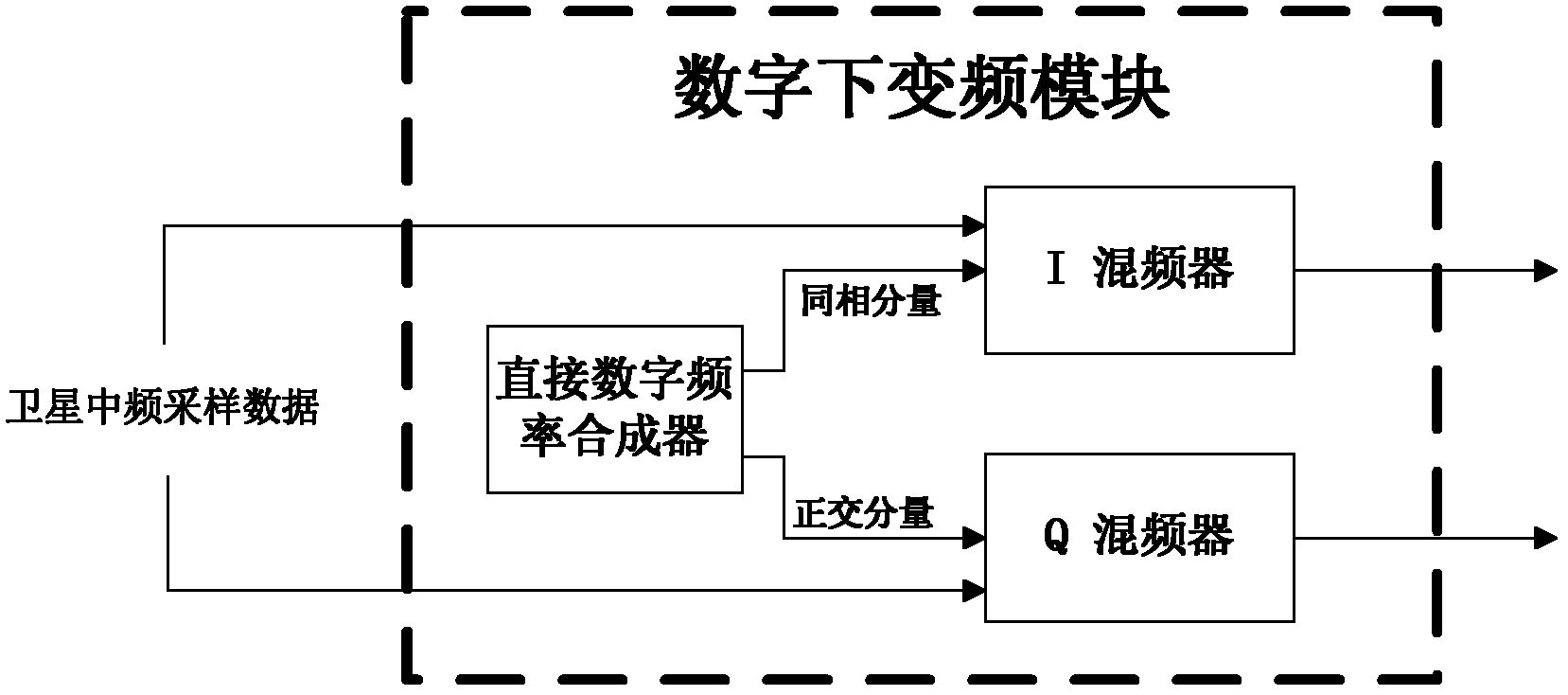
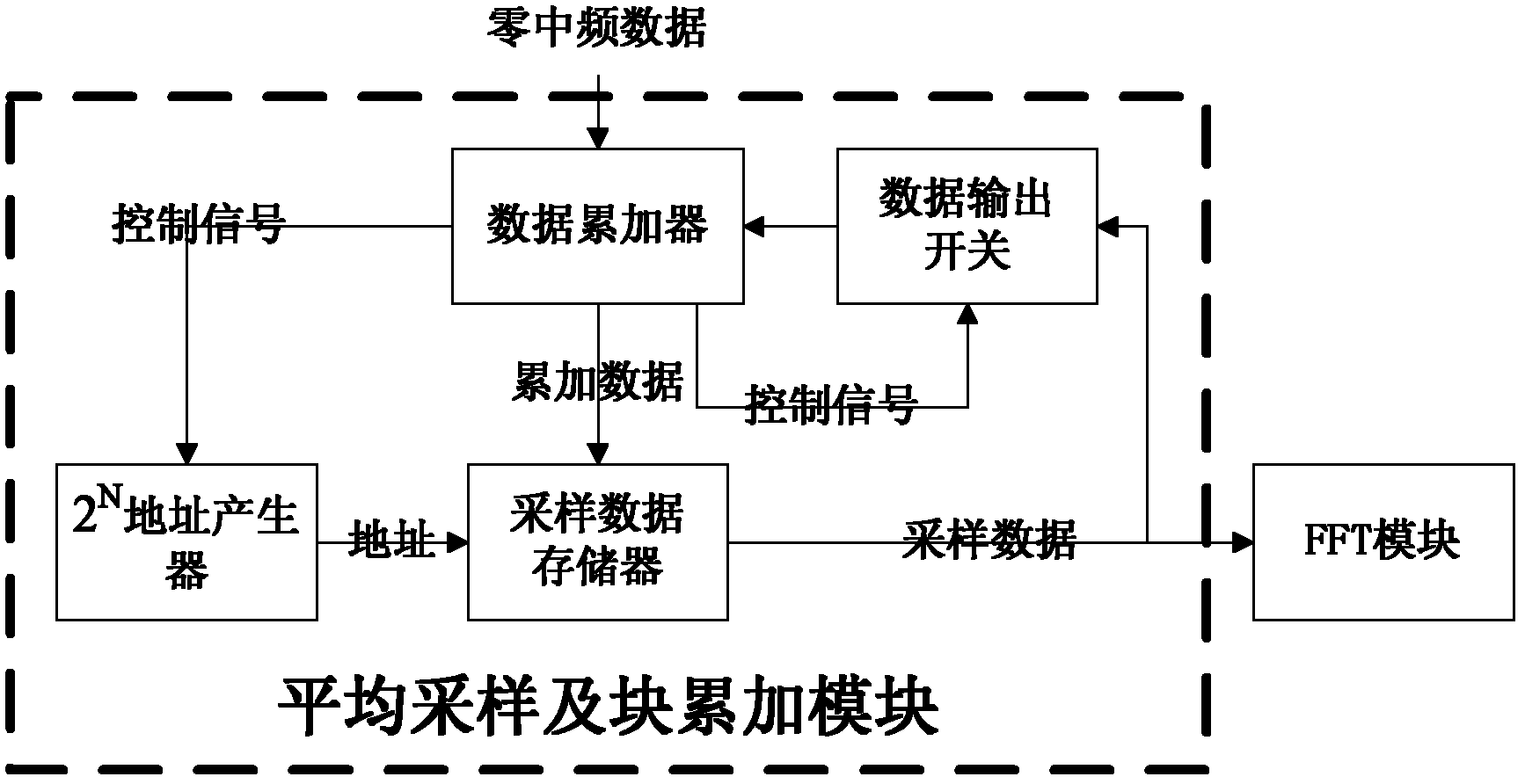
The invention discloses a high-sensitivity satellite navigation signal capturing method and a system. The system comprises a digital down-conversion module, an average sampling and block accumulation module, an FFT (fast Fourier transform) module, a circumference shifting module, a local PRN (pseudo random noise) code FFT conjugate memory, a complex multiplier module, an IFFT (inverse fast Fourier transform) module, a differential coherence integration module, a peak detection module and a sequential control module. The digital down-conversion module realizes digital down-conversion operation for satellite digital intermediate frequency signals; the average sampling and block accumulation module averagely samples satellite data and completes a block accumulation function; the FFT module searches code phase frequency domains; the circumference shifting module utilizes Doppler circumference shifting search to replace frequency compensation; the local PRN code FFT conjugate memory stores a local PRN code FFT conjugate result; the complex multiplier module realizes signal de-spreading; the IFFT module calculates different code phase coherence results; the differential coherence integration module accumulates differential coherence energy of de-spread satellite signals; the peak detection module realizes signal capturing output; and the sequential control module controls timing sequence of the various modules of the system. Weak signal capturing speed and sensitivity of a satellite navigation receiver are improved, and parameters can be configured flexibly.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Adaptive dynamic range receiver for MRI
InactiveUS7403010B1Avoid the needLimited dynamic rangeElectric signal transmission systemsMagnetic measurementsFast spin echoRapid imaging
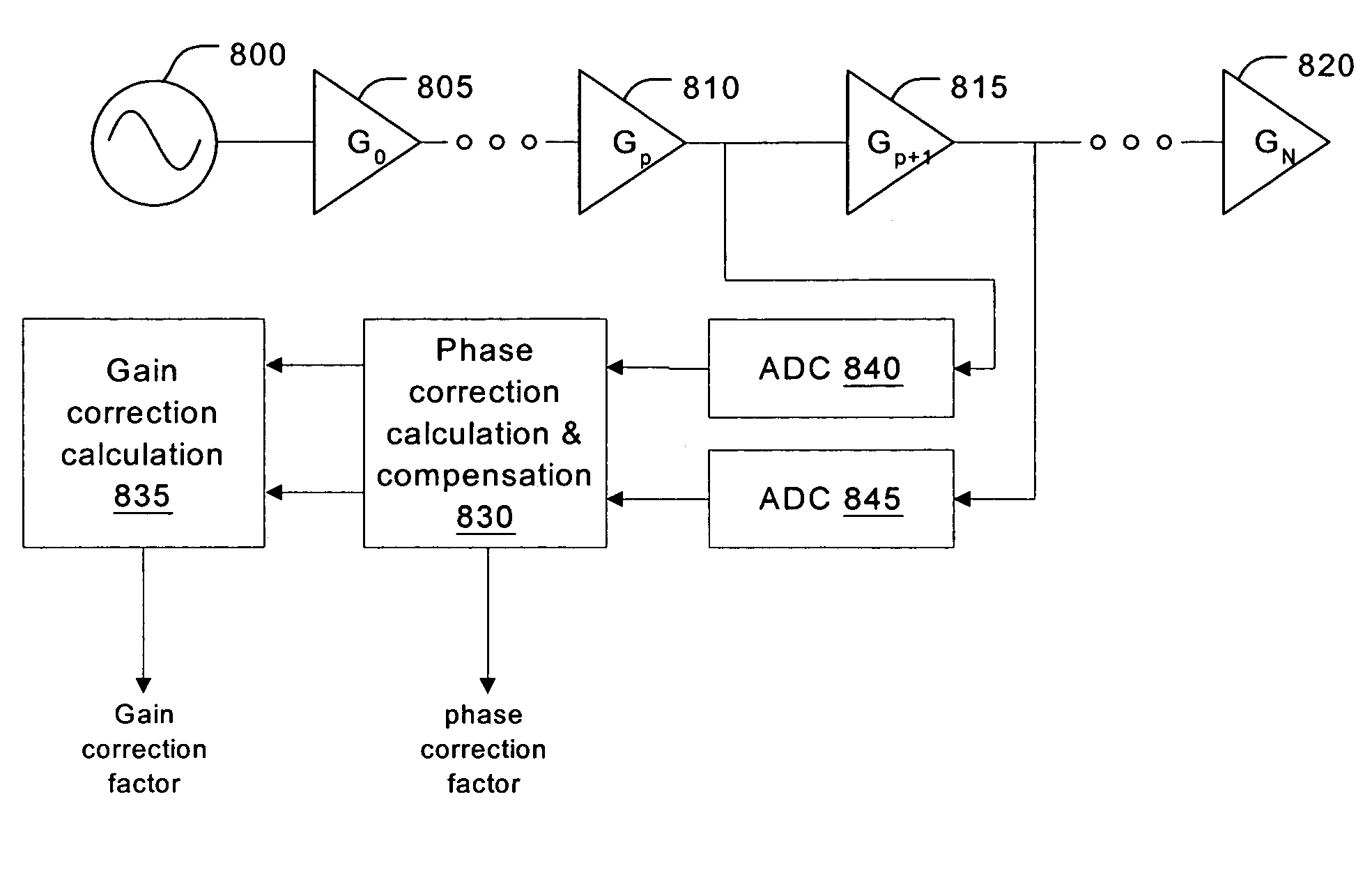
A receiver for a resonance signal of a magnetic resonance imaging system generates a baseband signal for image processing by dividing a raw resonance signal among multiple parallel channels, each amplified at a respective gain. A digital channel selector determines, at any given moment, a lowest-distortion channel to be further processed. Amplitude and phase error compensation are handled digitally using complex multipliers, which are derived by a calibration, based on a simple Larmor oscillator, which can be done without the need for a sample and without repeating when measurement conditions are changed. One of the important benefits of the invention is that it provides for gain selection without repeated calibration steps. This is particularly important in systems that employ fast imaging techniques such as fast spin echo, where the invention can speed imaging substantially.
Owner:FONAR
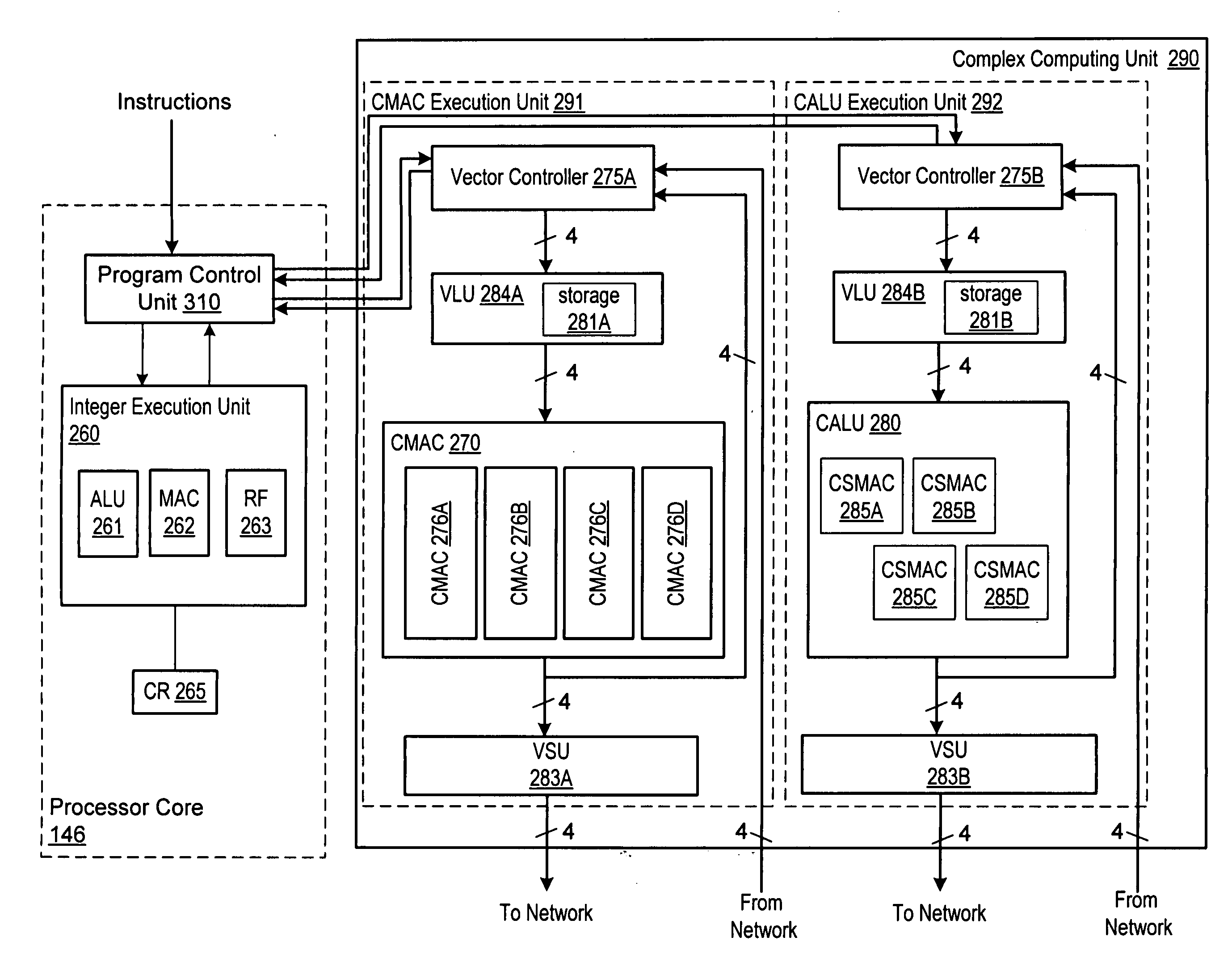
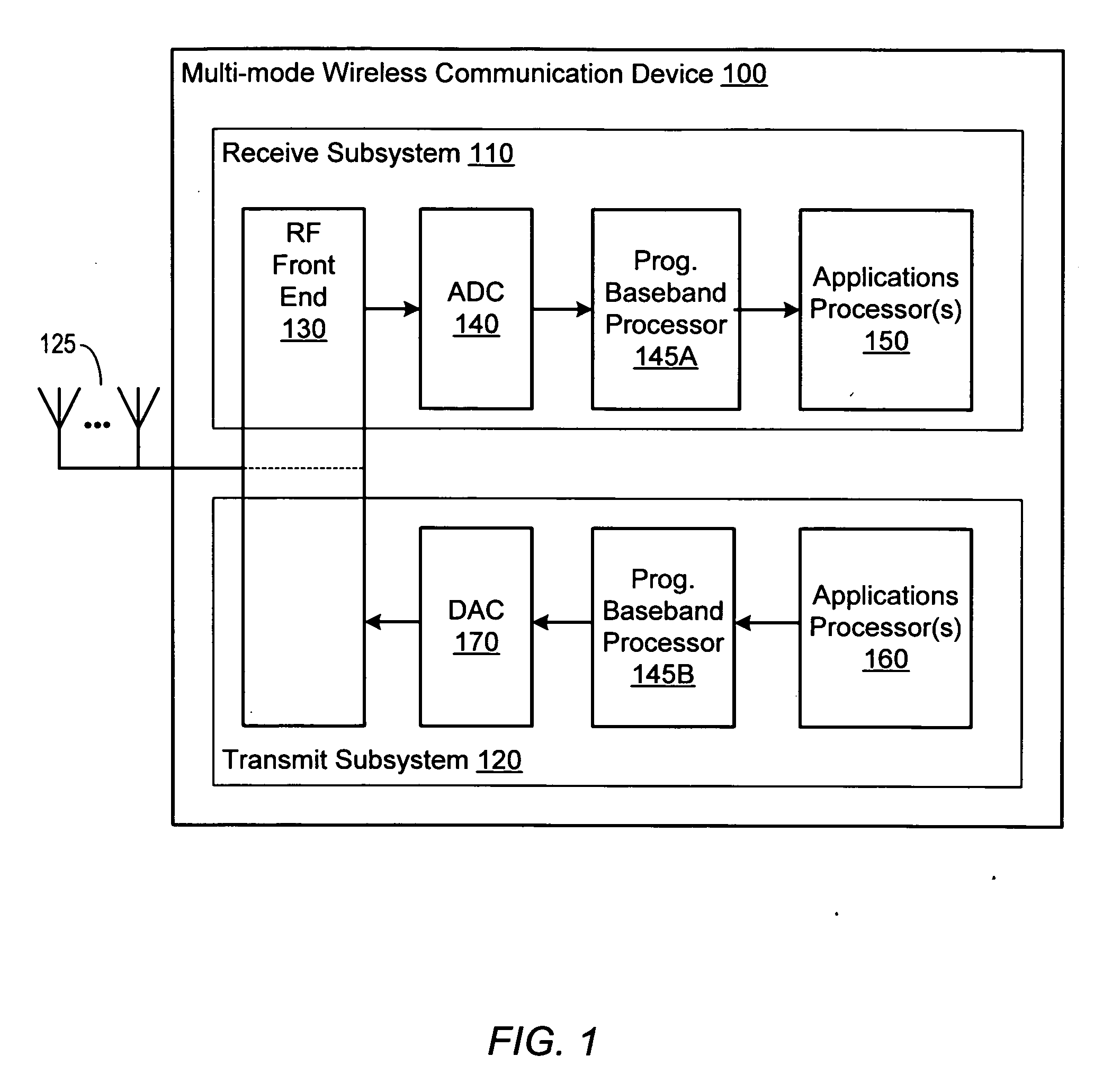
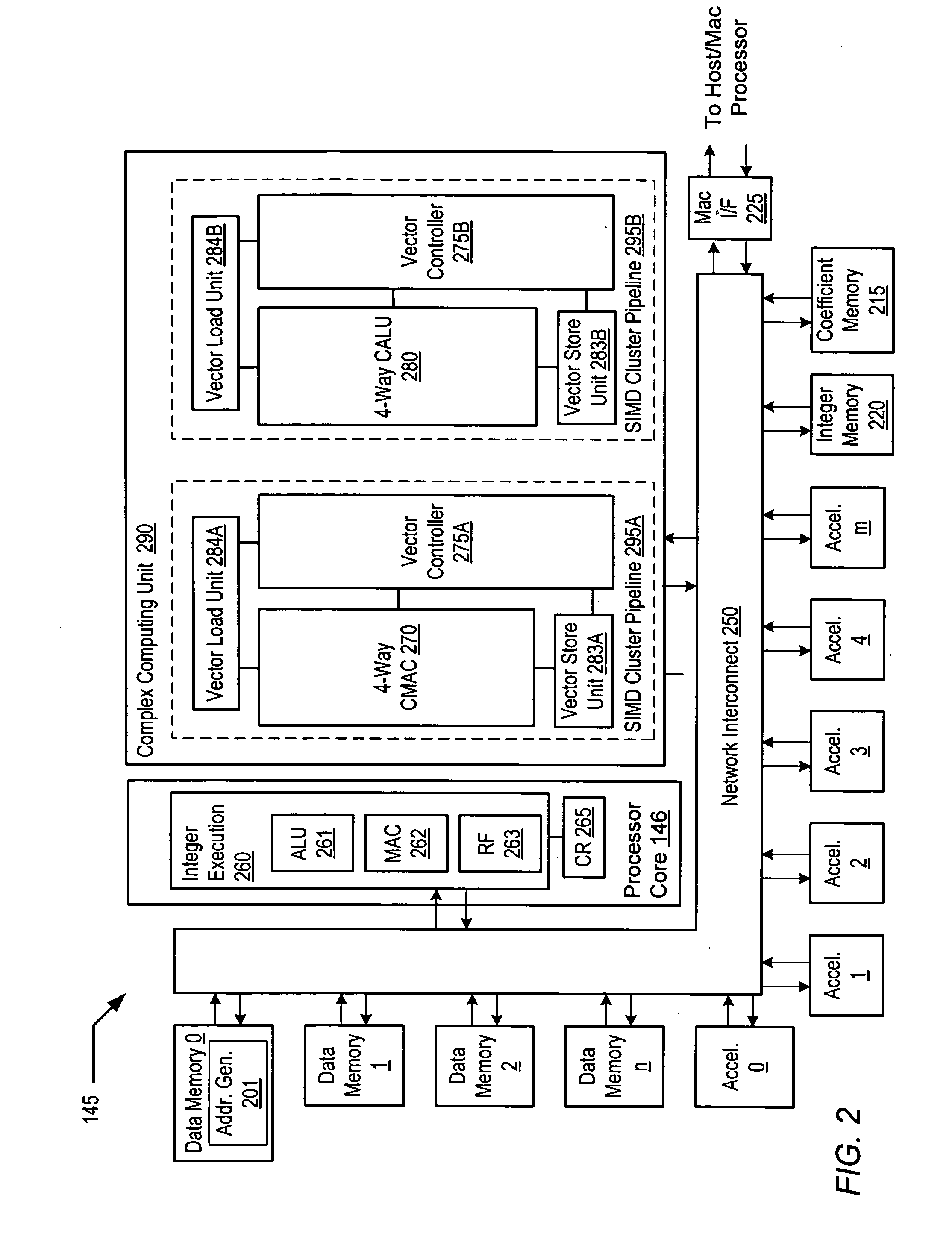
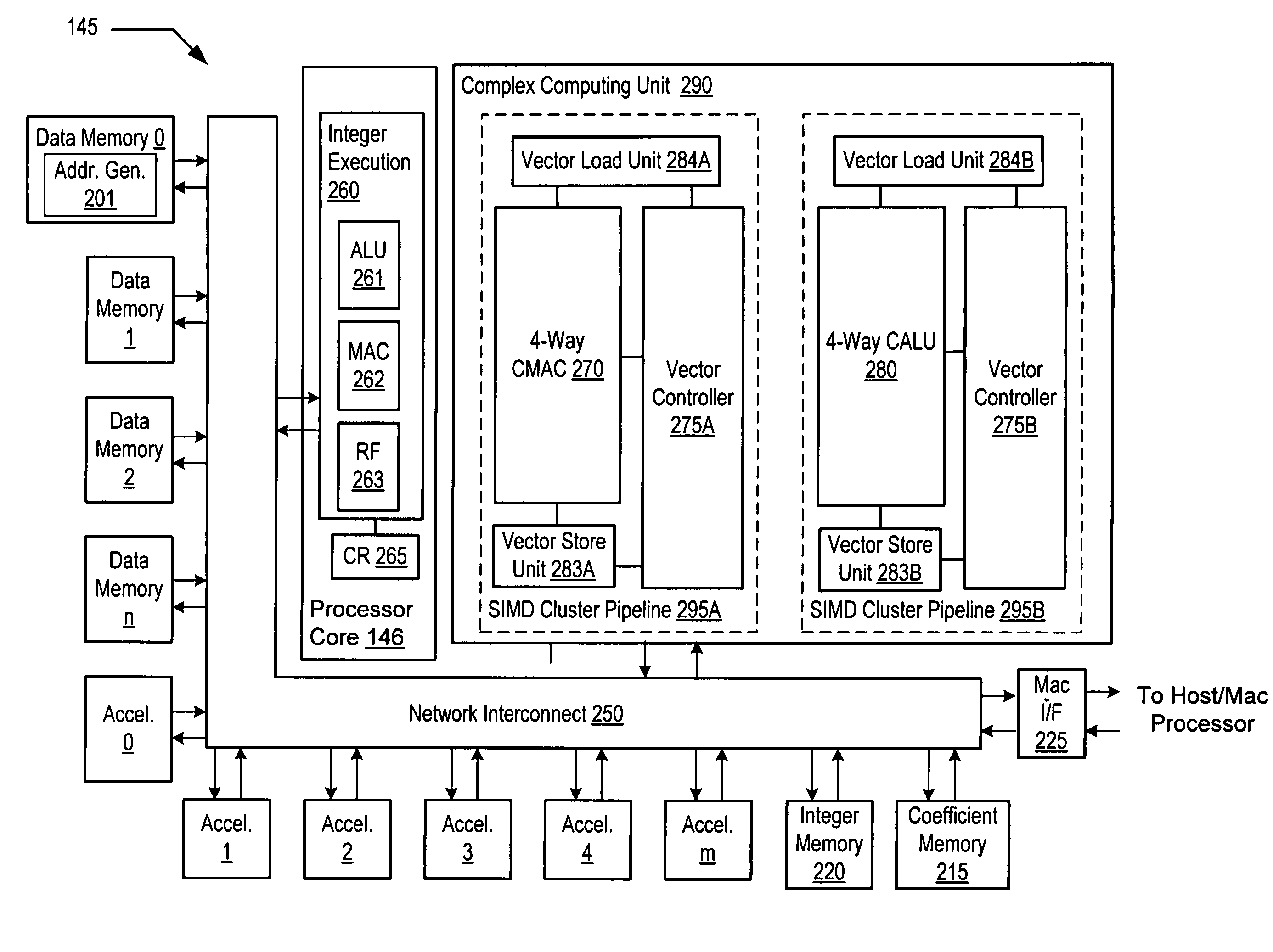
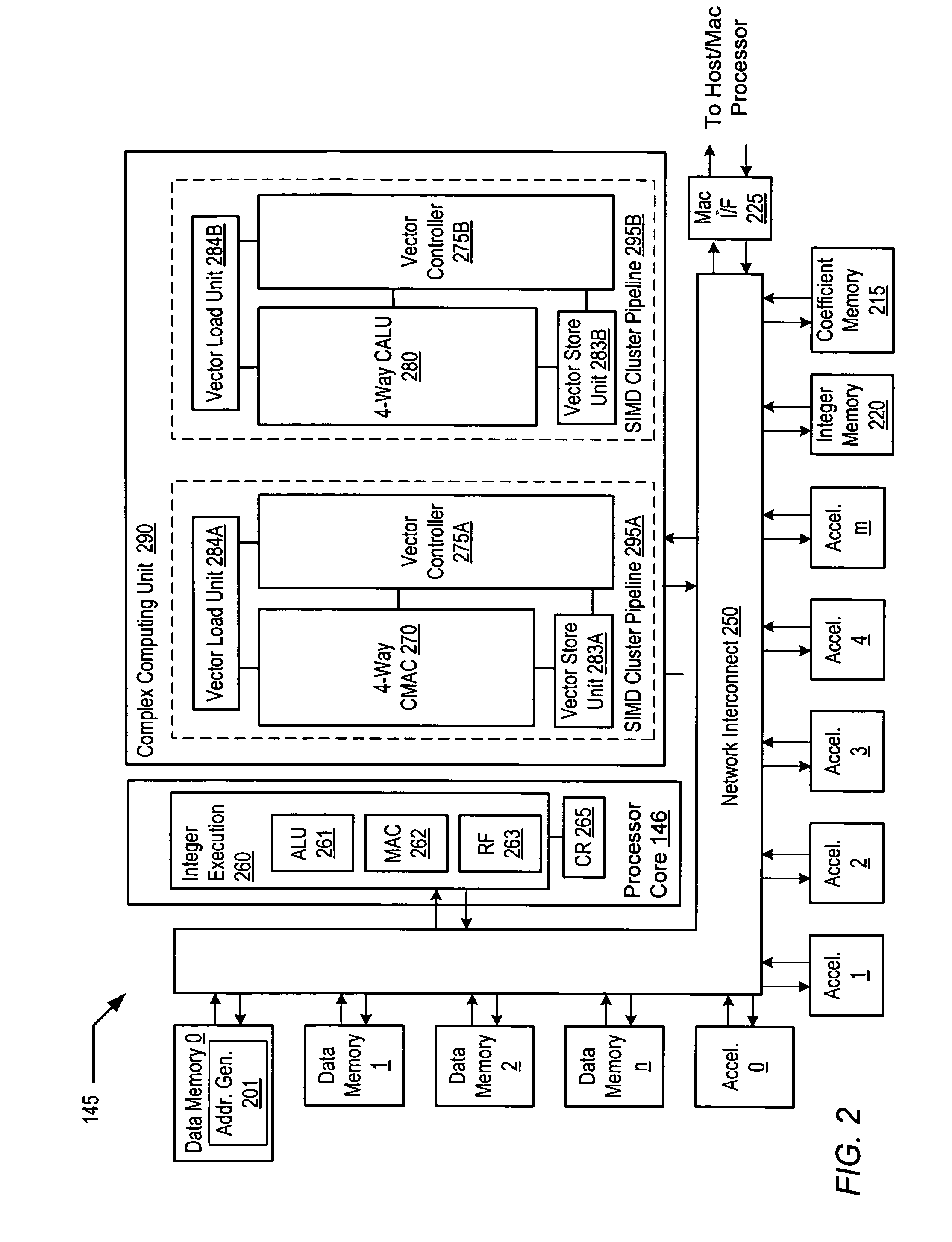
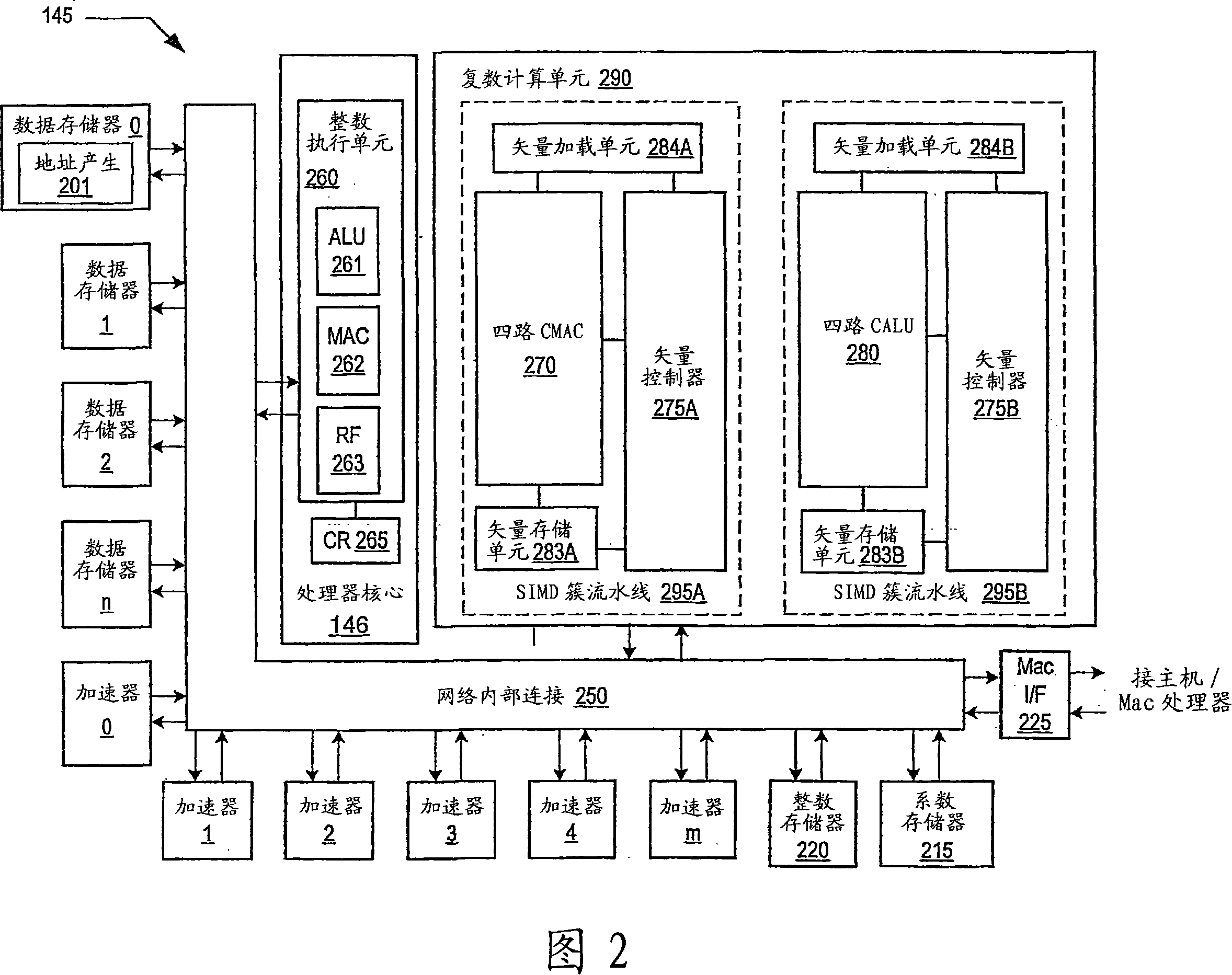
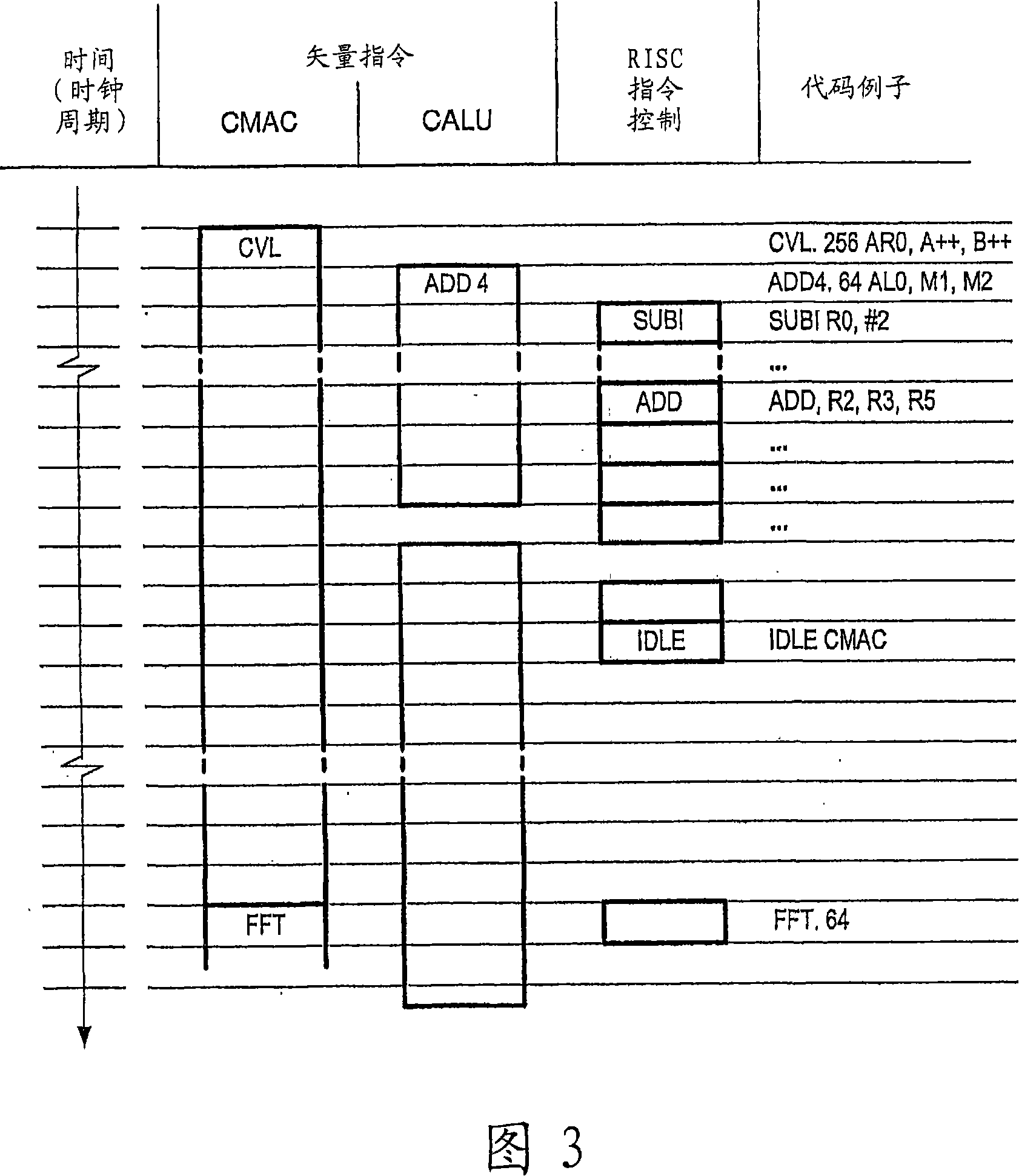
Programmable digital signal processor including a clustered SIMD microarchitecture configured to execute complex vector instructions
ActiveUS20060271764A1General purpose stored program computerSpecific program execution arrangementsArithmetic logic unitLine tubing
A programmable digital signal processor including a clustered SIMD microarchitecture includes a plurality of accelerator units, a processor core and a complex computing unit. Each of the accelerator units may be configured to perform one or more dedicated functions. The processor core includes an integer execution unit that may be configured to execute integer instructions. The complex computing unit may be configured to execute complex vector instructions. The complex computing unit may include a first and a second clustered execution pipeline. The first clustered execution pipeline may include one or more complex arithmetic logic unit datapaths configured to execute first complex vector instructions. The second clustered execution pipeline may include one or more complex multiplier accumulator datapaths configured to execute second complex vector instructions.
Owner:CORESONIC AB
Optimized FFT/IFFT module
ActiveUS7333422B2Minimize the numberDifficult challengeAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsRadio transmissionBinary multiplierTheoretical computer science
Owner:ZARBANA DIGITAL FUND
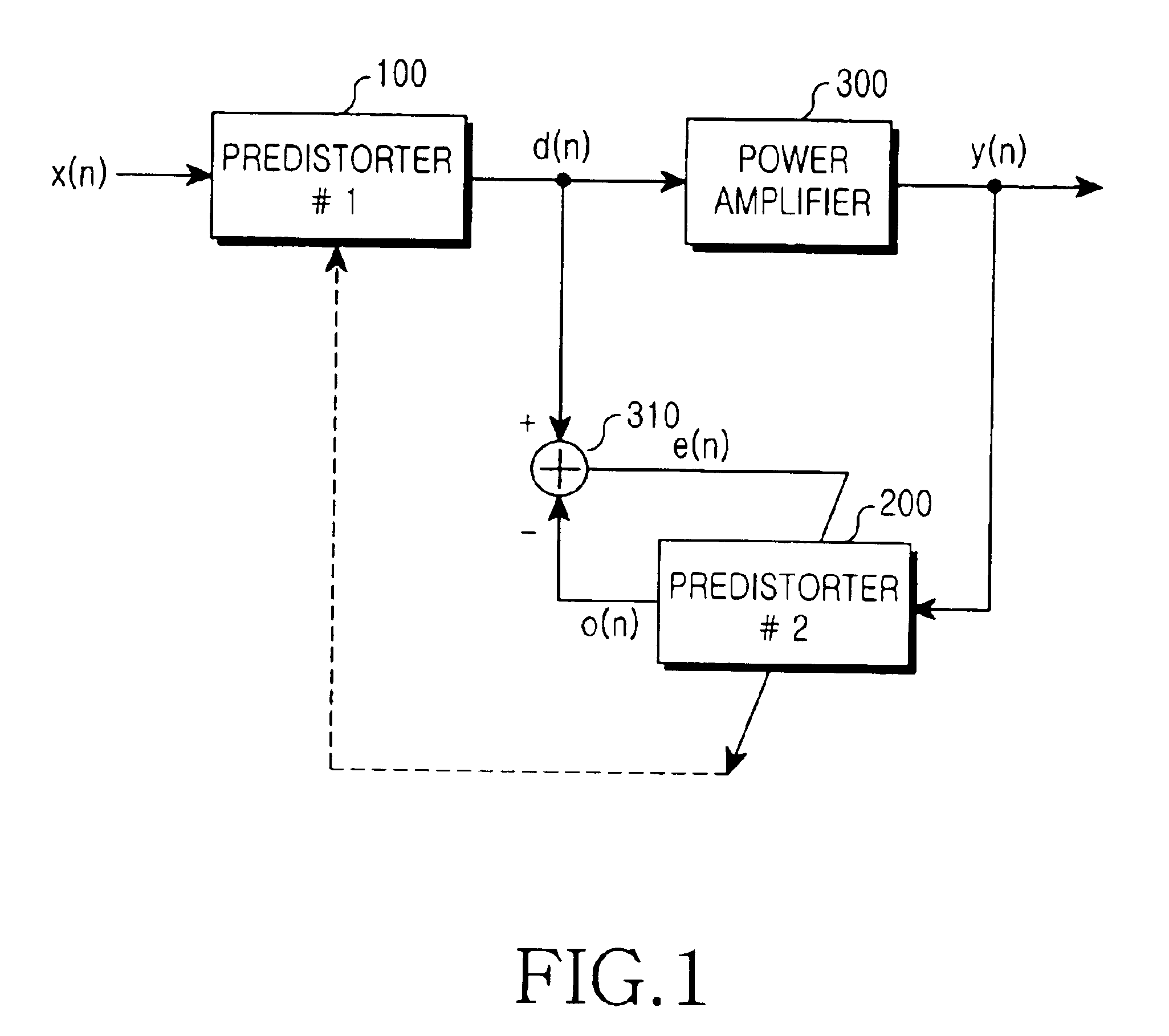
Pre-distortion model device and signal pre-distortion processing device, system and method
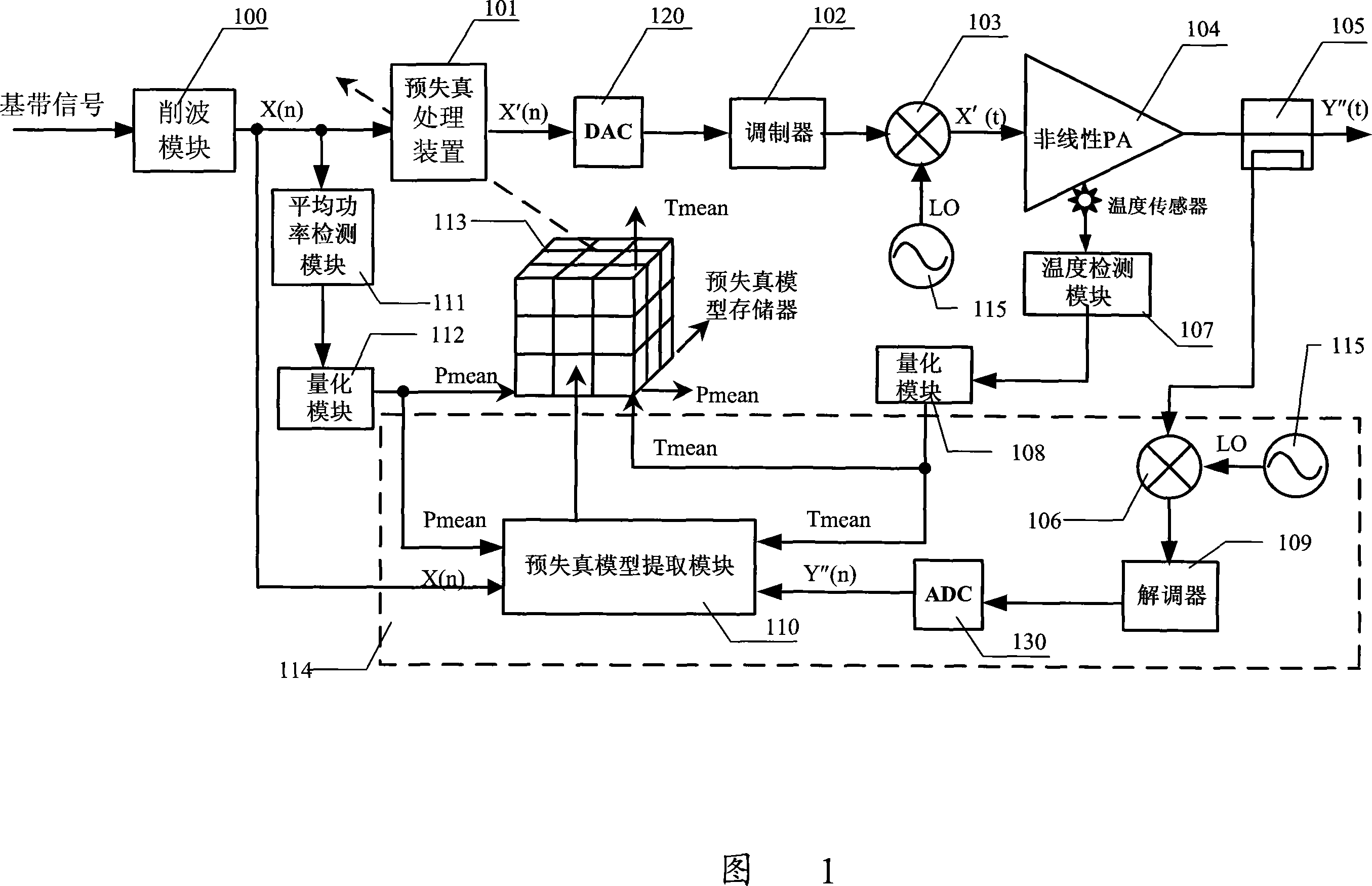
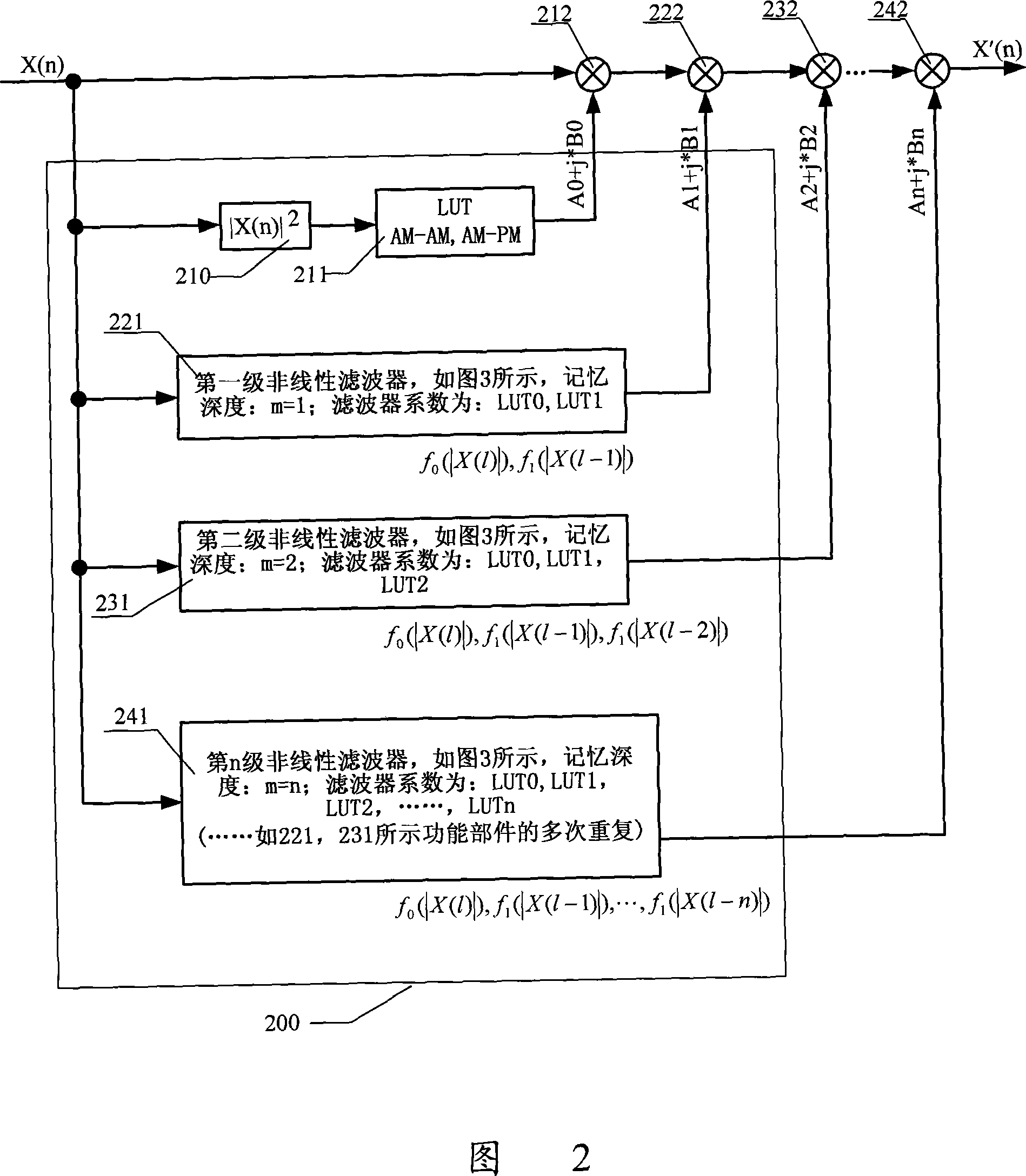
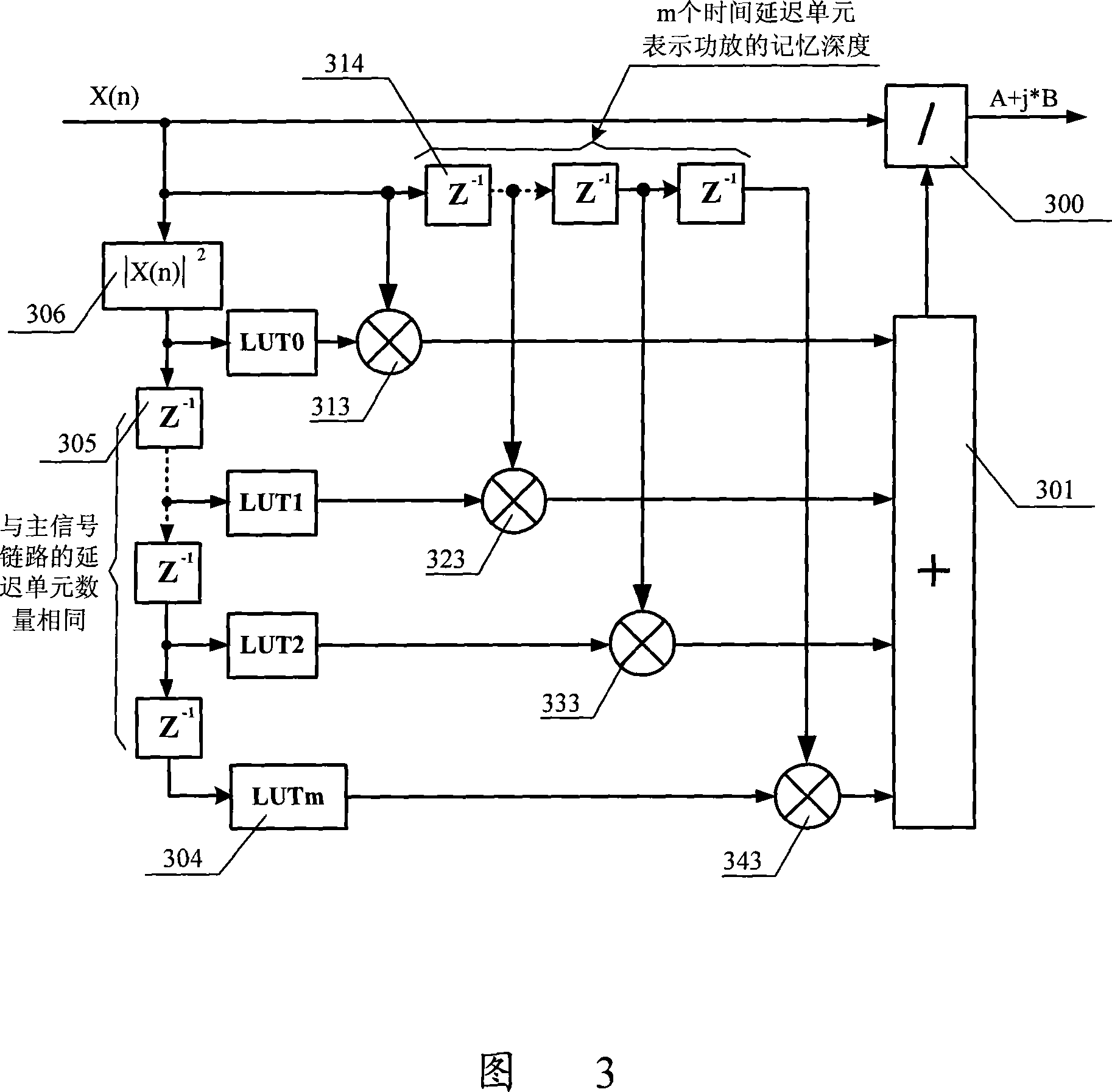
ActiveCN101056288ANo convergence errorReduce complexitySynchronous/start-stop systemsNonlinear modelEngineering
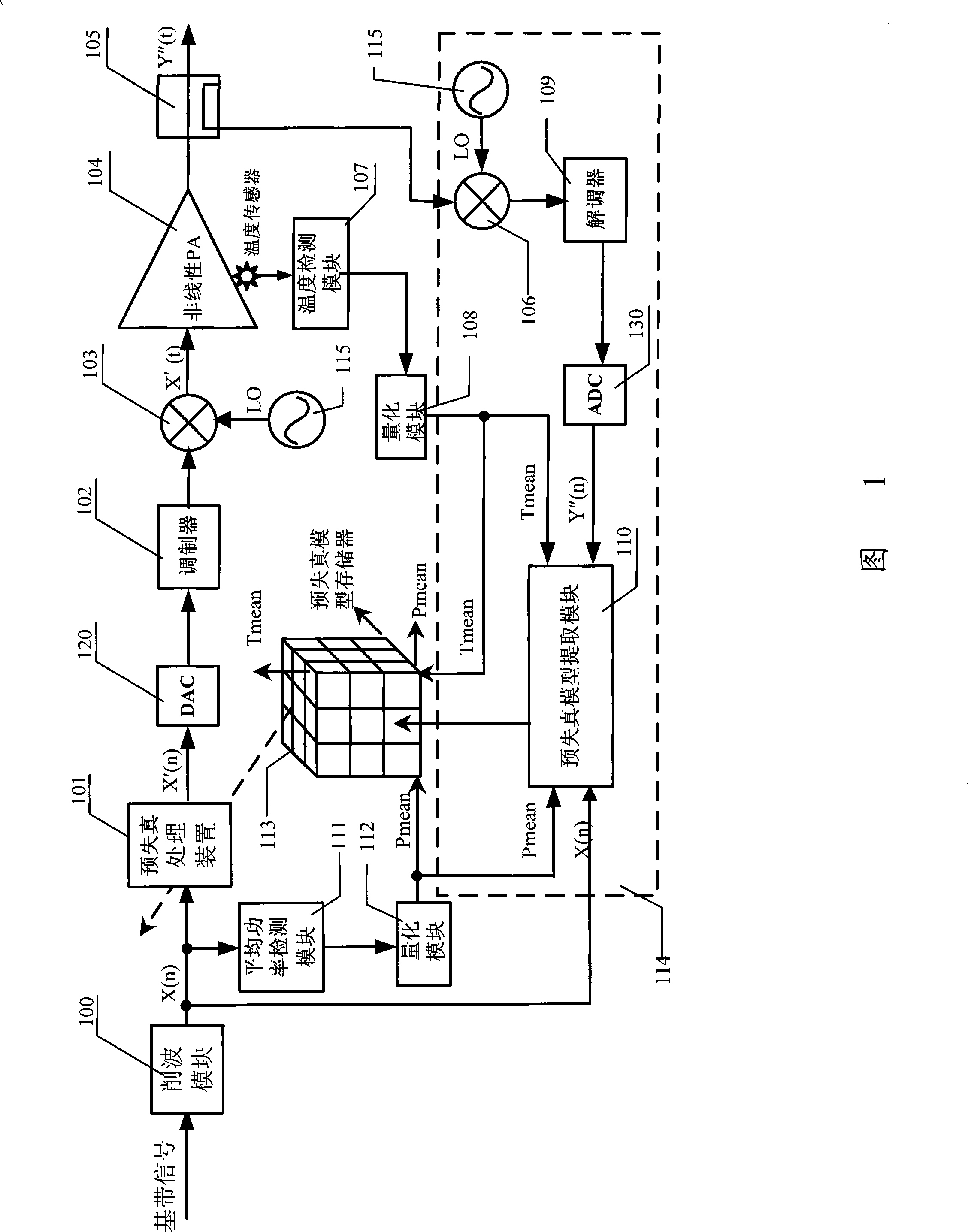
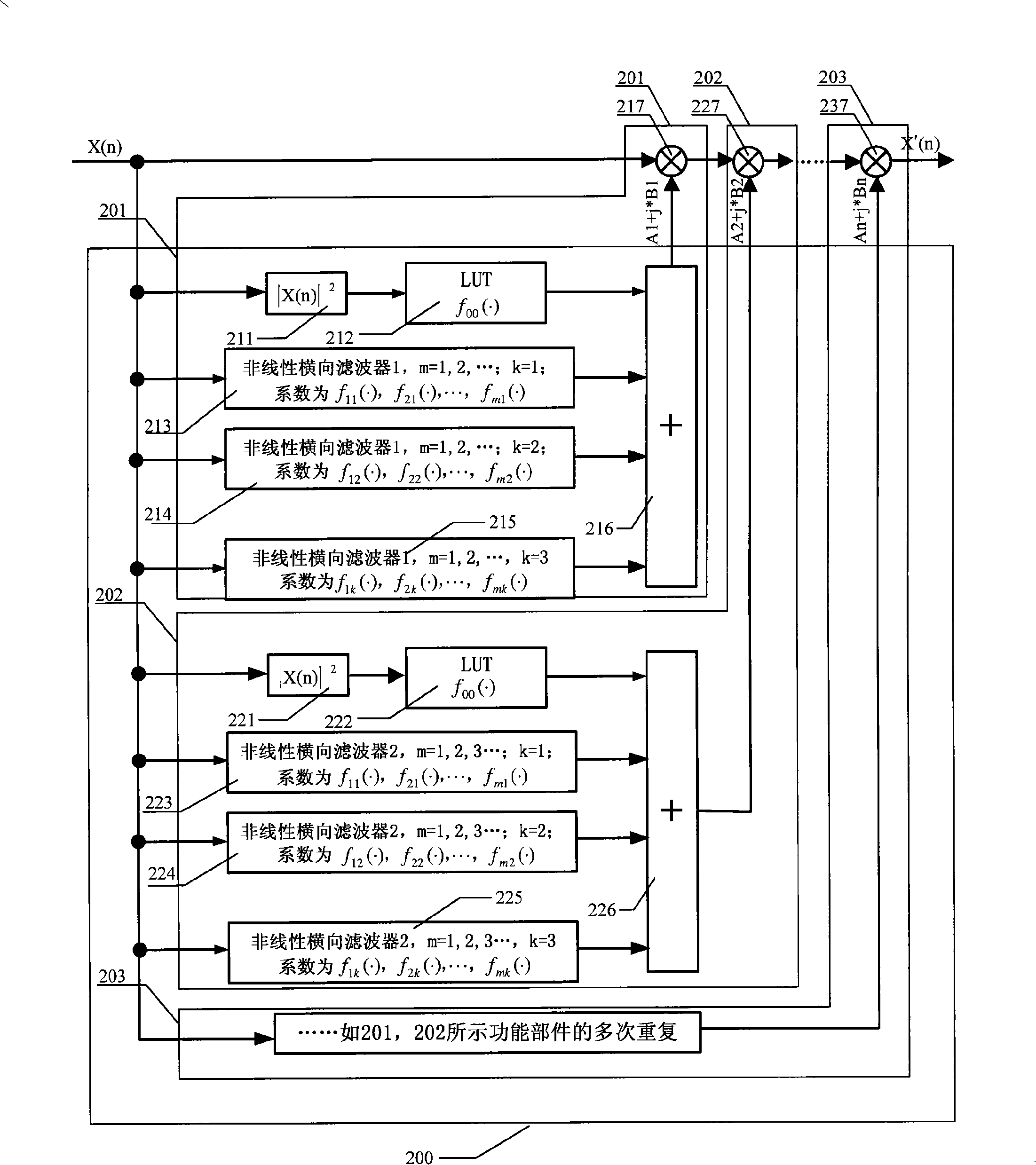
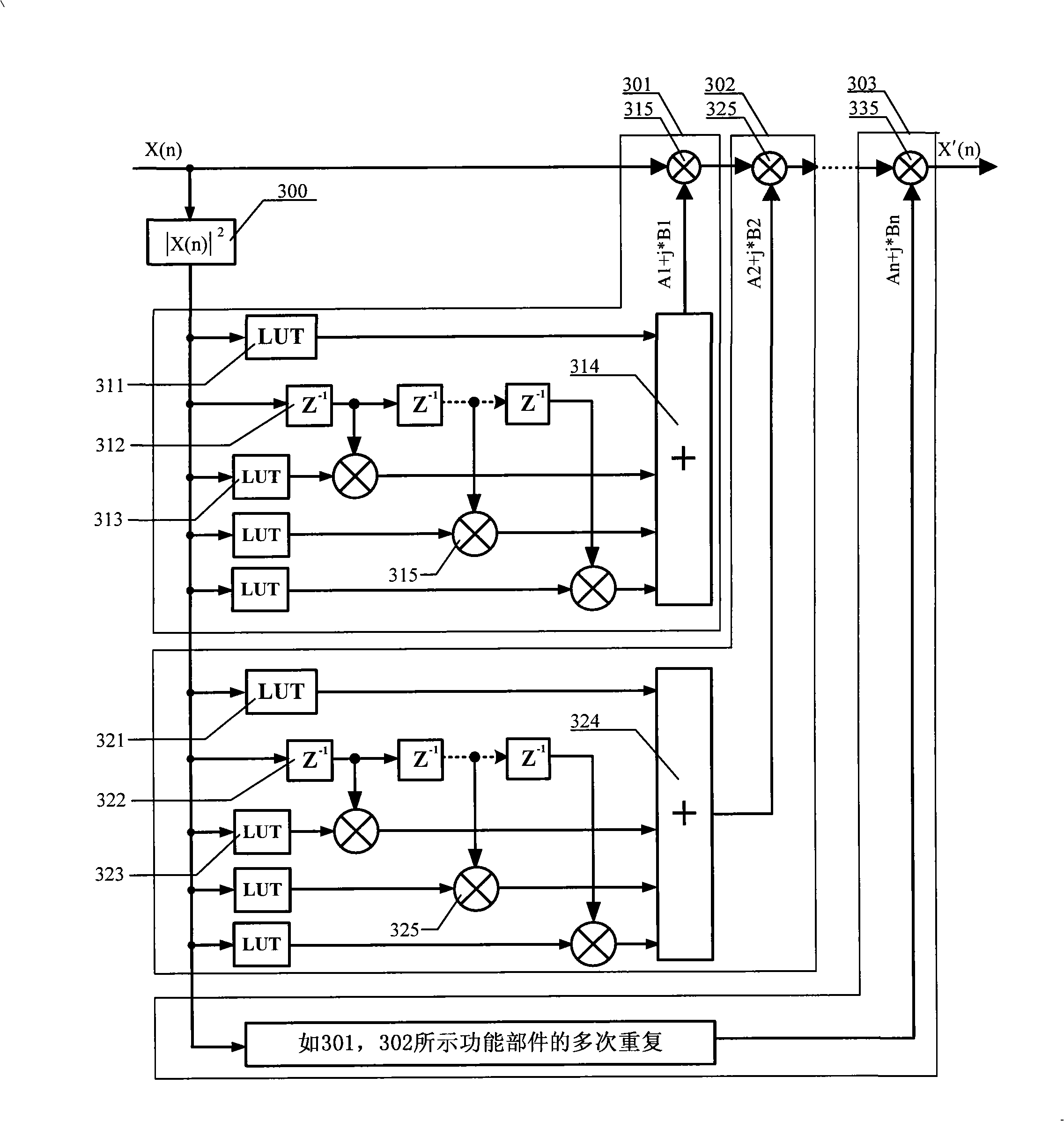
The invention discloses a pre-distortion model device, a signal pre-distortion treatment apparatus, a signal pre-distortion processing system, and a method for pre-distortion treatment of signal by utilizing the pre-distortion model device. Only one pre-distortion parameter should be exported by the pre-distortion model that the invention realized, and can cascade the complex multiplier, and can calibrate memory distortion and transient distortion of signal amplification equipment simultaneously. By using the invention, nonlinear model of the signal amplification equipment can not be extracted, which directly extract the pre-distortion model, thereby reducing the complexity of digital pre-distortion treatment, and can reduce the error.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Complex vector executing clustered SIMD micro-architecture DSP with accelerator coupled complex ALU paths each further including short multiplier/accumulator using two's complement
ActiveUS7299342B2General purpose stored program computerSpecific program execution arrangementsArithmetic logic unitExecution unit
A programmable digital signal processor including a clustered SIMD microarchitecture includes a plurality of accelerator units, a processor core and a complex computing unit. Each of the accelerator units may be configured to perform one or more dedicated functions. The processor core includes an integer execution unit that may be configured to execute integer instructions. The complex computing unit may be configured to execute complex vector instructions. The complex computing unit may include a first and a second clustered execution pipeline. The first clustered execution pipeline may include one or more complex arithmetic logic unit datapaths configured to execute first complex vector instructions. The second clustered execution pipeline may include one or more complex multiplier accumulator datapaths configured to execute second complex vector instructions.
Owner:CORESONIC AB
Programmable digital signal processor including a clustered SIMD microarchitecture configured to execute complex vector instructions
InactiveCN101238455AProgram controlArchitecture with single central processing unitArithmetic logic unitLogic cell
Owner:CORESONIC AB
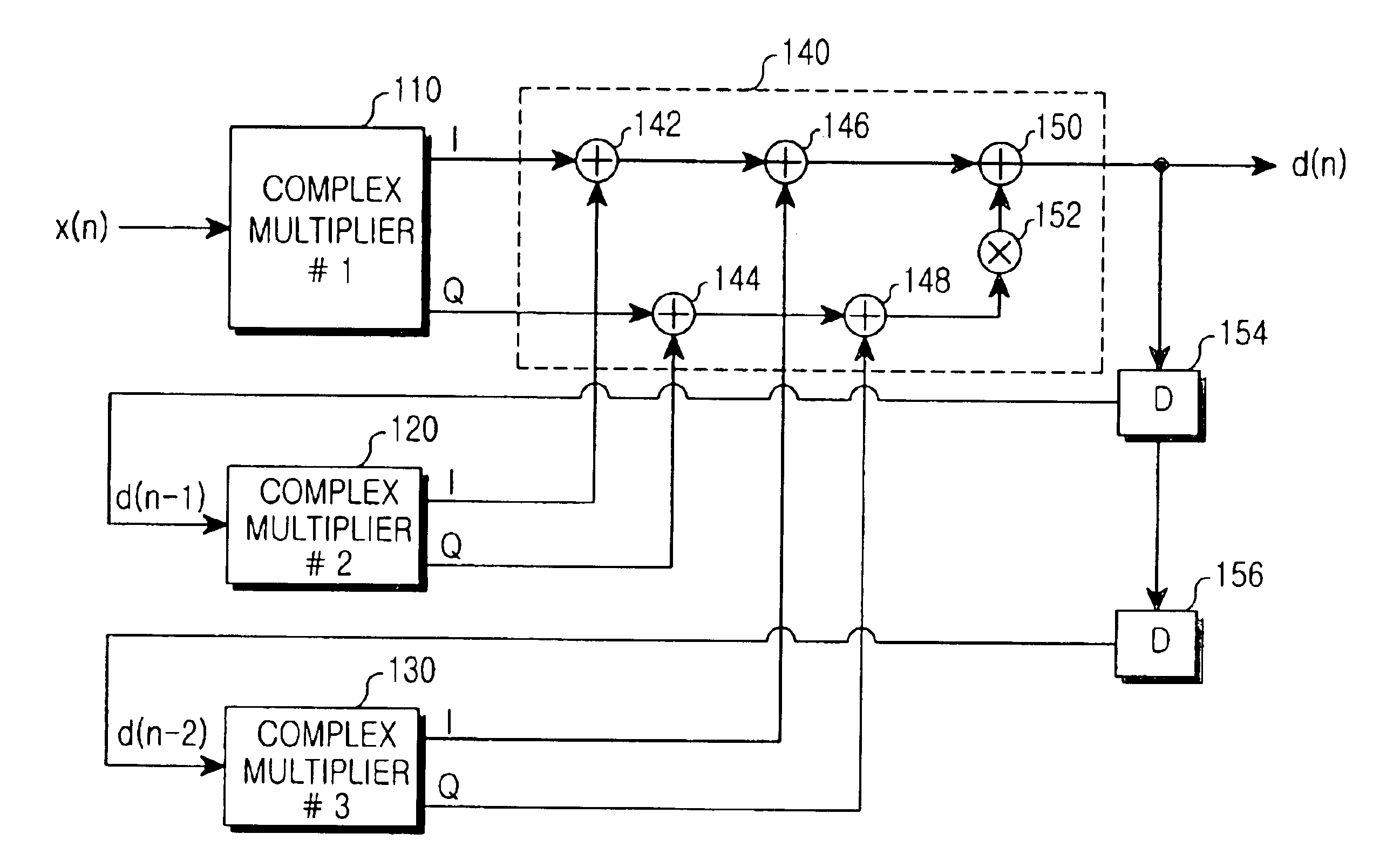
Polynomial predistorter using complex vector multiplication
ActiveUS6956433B2Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceNonlinear distortionAudio power amplifier
A polynomial predistorter and predistorting method for predistorting a complex modulated baseband signal are provided. In the polynomial predistorter, a first complex multiplier generates first complex predistortion gains, using a current input signal and complex polynomial coefficients modeled on the inverse non-linear distortion characteristic of the power amplifier, and multiplies them by I and Q signal components of the current input signal, respectively. At least one second complex multiplier generates second complex predistortion gains using the complex polynomial coefficients and previous predistorted signals and multiplies them by I and Q signal components of the previous predistorted signals, respectively. A summer sums the outputs of the first and second complex multipliers and outputs the sum as a predistorted signal to the power amplifier.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
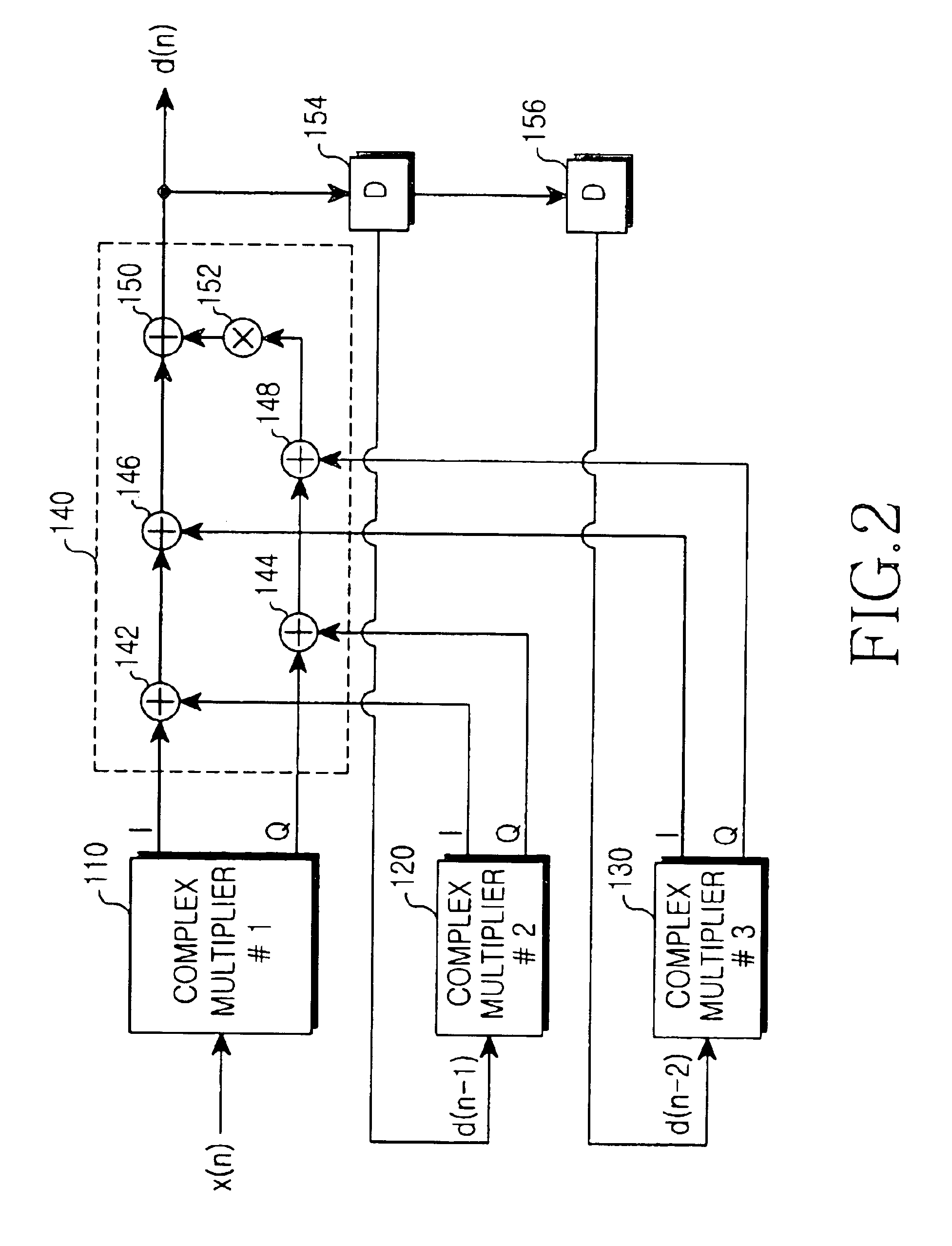
Uplink ranging system and method in OFDMA system
ActiveUS20050141474A1Effectively carrying out timing synchronizationTime-division multiplexFrequency-division multiplexBinary multiplierTwiddle factor
Disclosed is a ranging system and method in an OFDMA system. The ranging system includes complex exponential twiddle storage units for respectively storing complex exponential twiddle factors corresponding to a timing error, complex multipliers for respectively complex-multiplying the complex exponential twiddle factors by received uplink ranging data, code correlators for respectively correlating the outputs of the complex multipliers and ranging codes, and threshold comparators for respectively comparing the outputs of the code correlators with a threshold.
Owner:KT CORP +4
Method and apparatus for high-order PAPR reduction of an OFDM signal
InactiveUS7315580B2Reduce the amount of calculationReduce the amount requiredSecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainMultiplexer
A method and apparatus for high-order peak-to-average power ratio reduction of an OFDM signal are disclosed. The method partitions time-domain input data x[n] of length N into M disjoint subblocks in time domain, and a complete N-point transmitted signal {tilde over (x)}[n], n=0, 1, . . . , N−1, is composed after transformation, complex multiplication, and phase optimization, where M is a power of 2, M≧8 and N / M>1 is an integer. Accordingly, the apparatus comprises an N-point inverse fast Fourier transform (N-IFFT), a de-multiplexer, a transformer, two sets of memories, a plurality of complex multipliers, and an adder. This invention uses only one N-IFFT, whereby it achieves significant computation reduction. As M=8, the number of complex multiplications and that of memory units required are less than or equal to (N / 2)log2N+(3N / 4) and 3N / 2, respectively. The invention also preserves the inherent property as well as advantages of an OFDM system.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
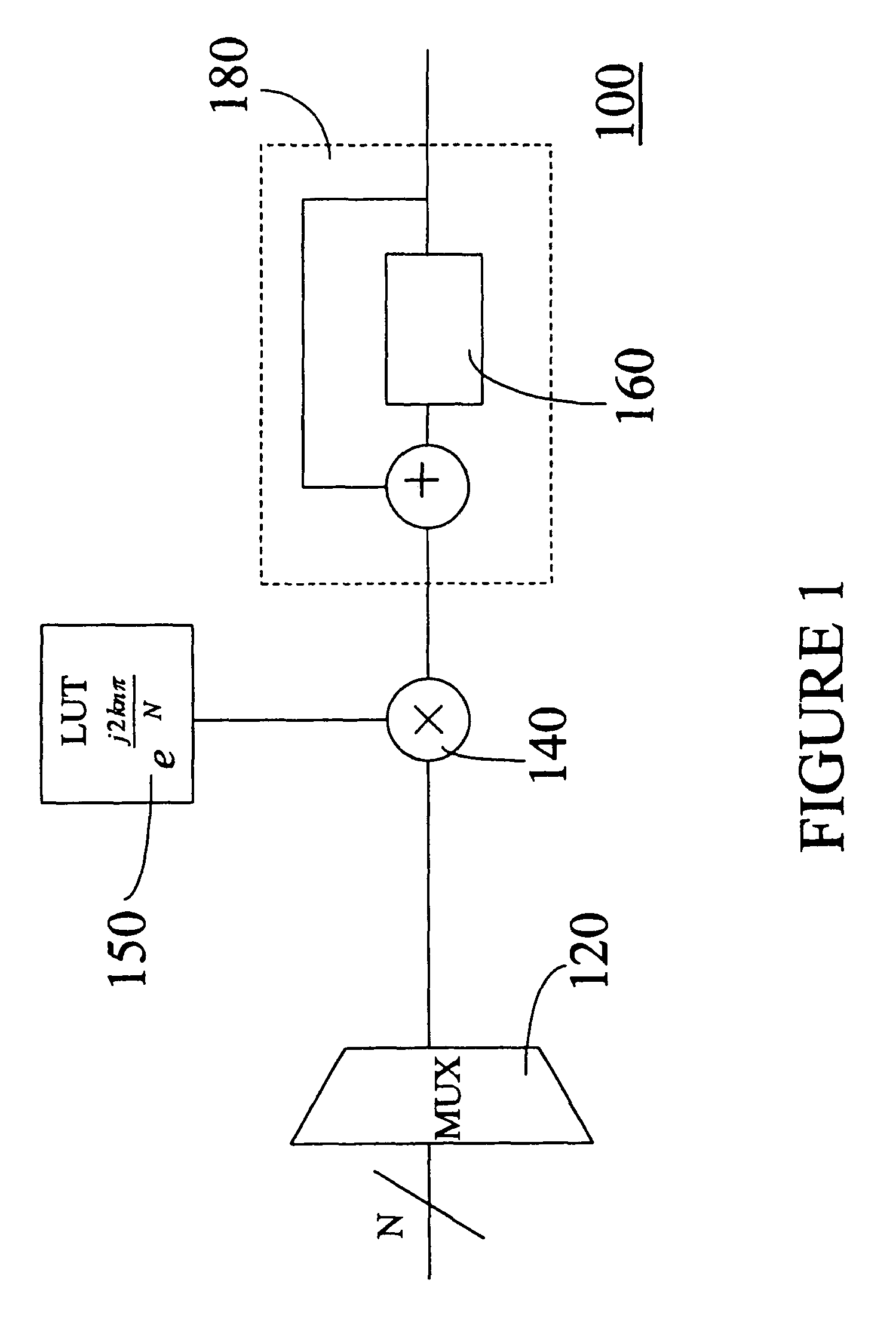
Fast fourier transform twiddle multiplication
InactiveUS20060248135A1Effectively pipelinedModulated-carrier systemsTransmission path divisionBinary multiplierTheoretical computer science
An FFT engine implementing a cycle count method of applying twiddle multiplications in multi-stages. When implementing a multistage FFT, the intermediate values need to be multiplied by various twiddle factors. The FFT engine utilizes a minimal number of multipliers to perform the twiddle multiplications in an efficient pipeline. Optimizing a number of complex multipliers based on an FFT radix and a number of values in each row of memory allows the FFT function to be performed using a reasonable amount of area and in a minimal number of cycles. Strategic ordering and grouping of the values allows the FFT operation to be performed in a fewer number of cycles.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
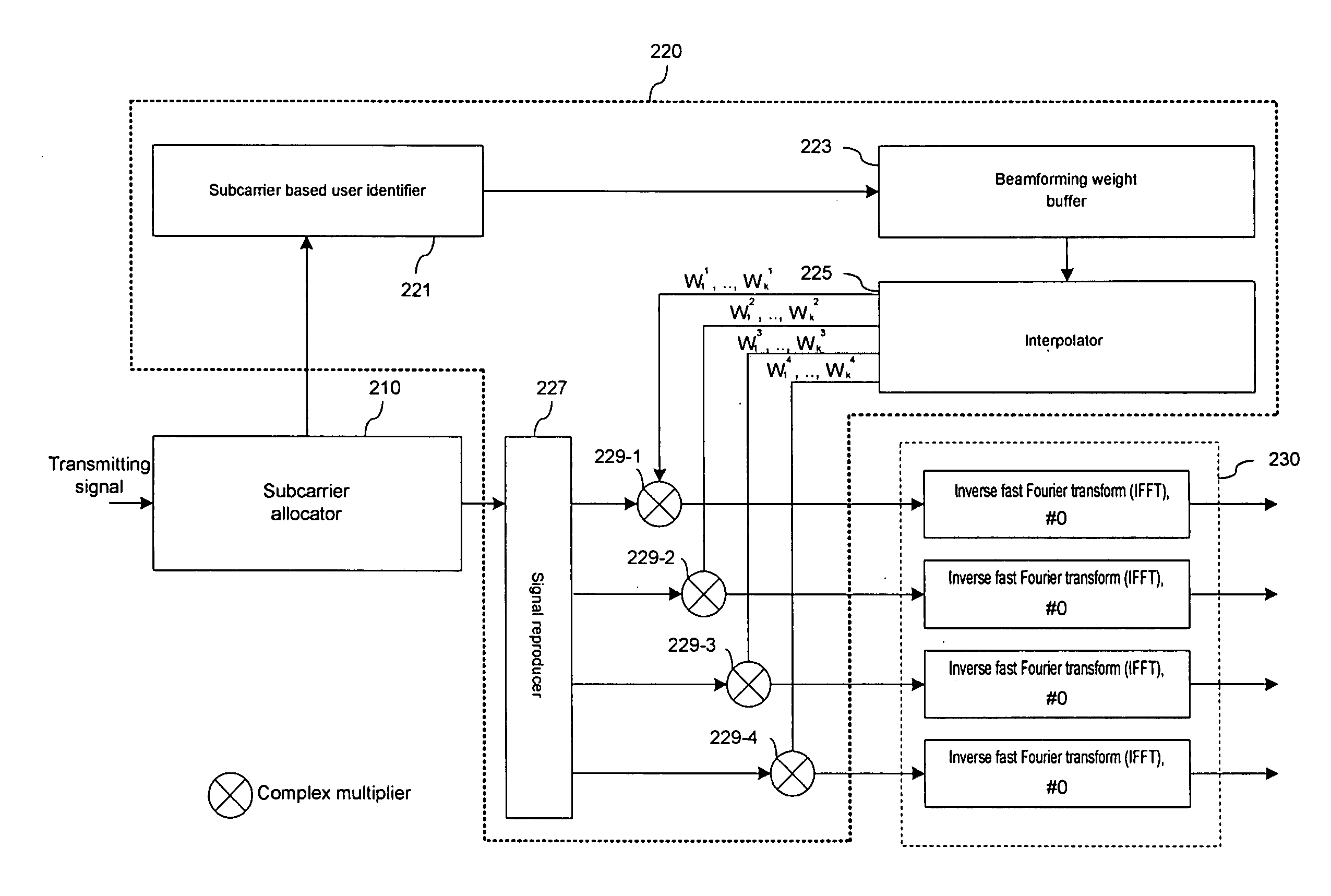
Downlink beamforming apparatus in OFDMA system and transmission apparatus including the same
InactiveUS20070135052A1Reduce power consumptionEffective structureModulated-carrier systemsLine-faulsts/interference reductionDownlink beamformingCarrier signal
A downlink beamforming apparatus and a transmission apparatus including the same includes a subcarrier based user identifier for dividing subcarriers according to users, a beamforming weight buffer for storing first beamforming weights for the subcarriers by each of transmitting antennas, an interpolator for outputting second beamforming weights for each transmitting antenna by interpolating the first beamforming weights, and a signal reproducer for reproducing the signal for each transmitting antenna. Subcarriers are allocated to the signal by each user; and a complex multiplier multiplies the signal for each transmitting antenna by the second beamforming weights.
Owner:KT CORP +4
Predistortion model apparatus as well as apparatus, system and method for processing predistortion of signal
ActiveCN101330481ANo convergence errorReduce complexityAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionPower amplifiersBinary multiplierSignal amplification
The invention discloses a predistortion model device, a predistortion processing device for signals, a predistortion processing system for signals and a method for performing predistortion processing to the signals by using the predistortion model device. The predistortion model realized through the invention can only output a predistortion parameter, can use a complex multiplier for cascade connection and also can perform calibration to the transient distortion and the memory distortion of signal amplification device at the same time. By using the invention, the non-linear model of the signal amplification device is not required to be extracted, and the predistortion model is directly extracted, therefore, the complexity of digital predistortion processing can be reduced, and the error is also reduced.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Apparatus and method for correcting signal imbalances using complex multiplication
ActiveUS7069284B2Error preventionComputation using non-contact making devicesComputer scienceFrequency domain
A complex multiplier is described for filtering a signal in the frequency domain. In one embodiment, additional, independent frequency coefficients are supplied by the complex multiplier so that gain and / or phase of the signal may be independently modified (i.e., gain may be modified without affecting phase and vice-versa).
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
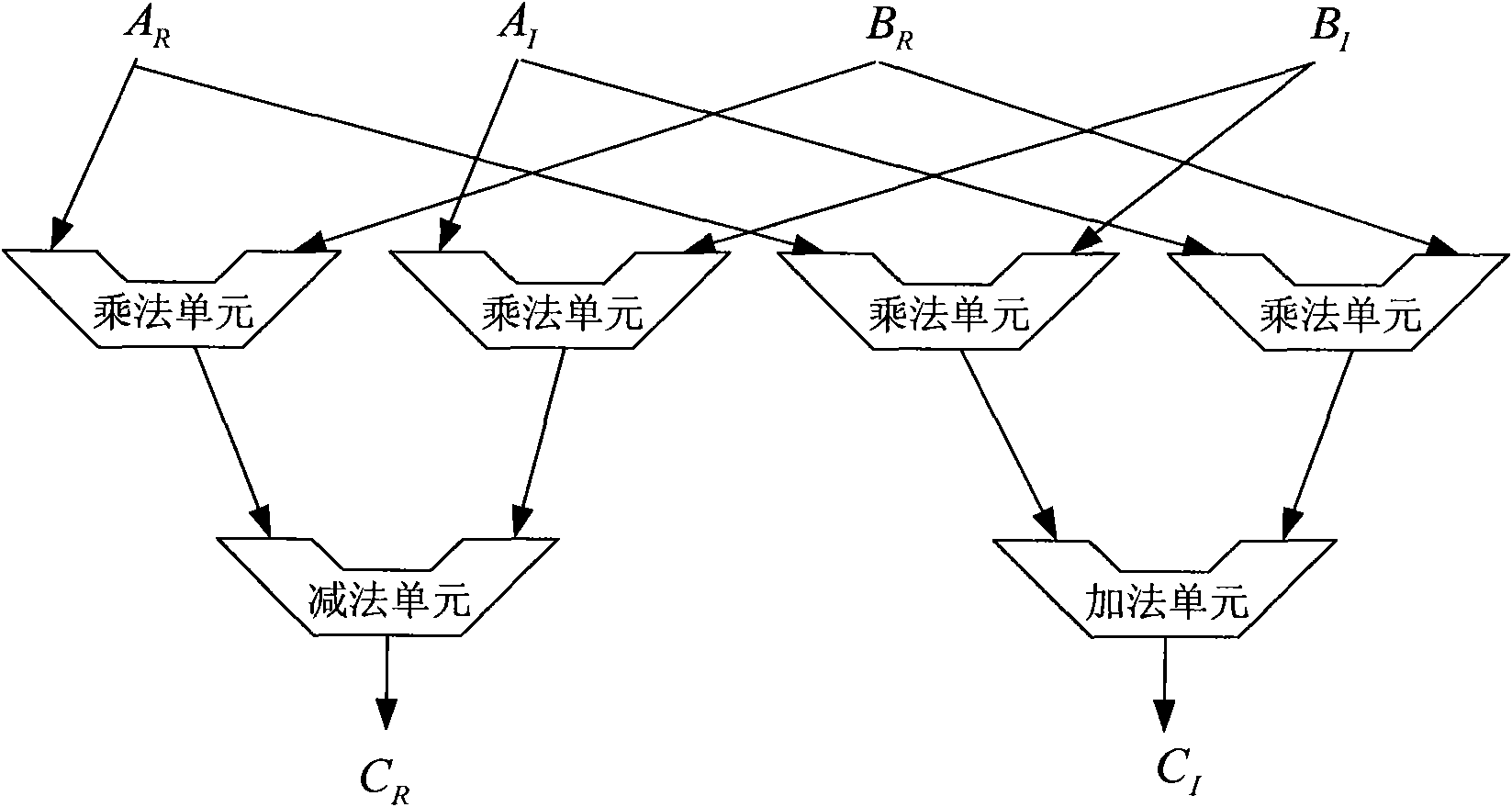
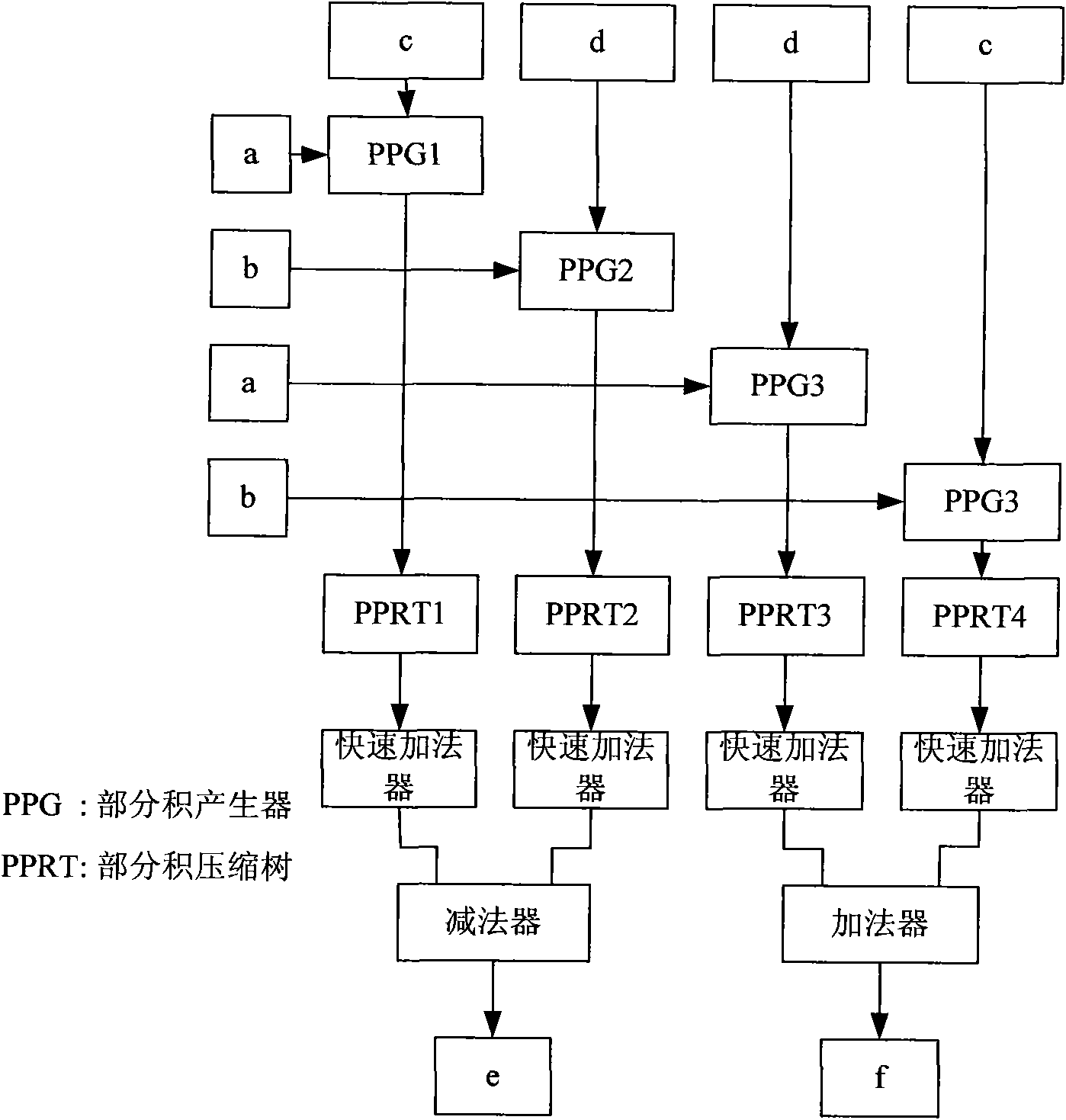
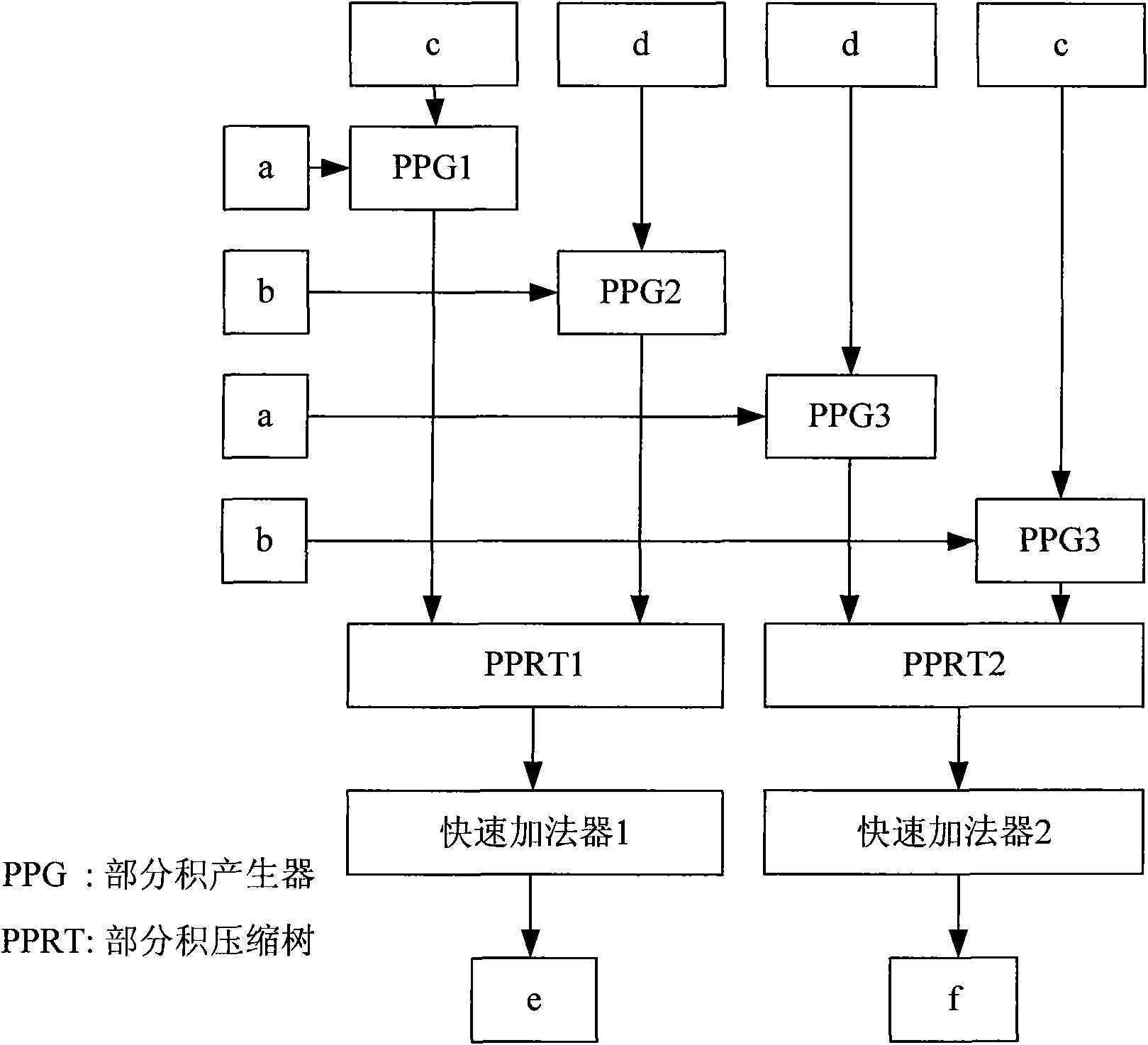
Complex multiplier
InactiveCN101685385AShorten the critical pathReduce areaComputation using non-contact making devicesCritical path methodData interface
The invention discloses a complex multiplier which comprises a data interface, a first partial product generating module, a second partial product generating module, a third partial product generatingmodule, a fourth partial product generating module, a first accumulator and a second accumulator, wherein the data interface comprises an input interface and an output interface; the first partial product generating module generates the partial product of real parts of two complex numbers; the second partial product generating module generates the negative value of the partial product of imaginary parts of the two complex numbers; the third partial product generating module generates the partial product of the real part of the first complex number and the imaginary part of the second complexnumber; and the fourth partial product generating module generates the partial product of the imaginary part of the first complex number and the real part of the second complex number. The invention reduces the area, lowers the power consumption, shortens the key path of the whole complex multiplier, and simplifies the computation, thereby improving the operating speed and the processing speed.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
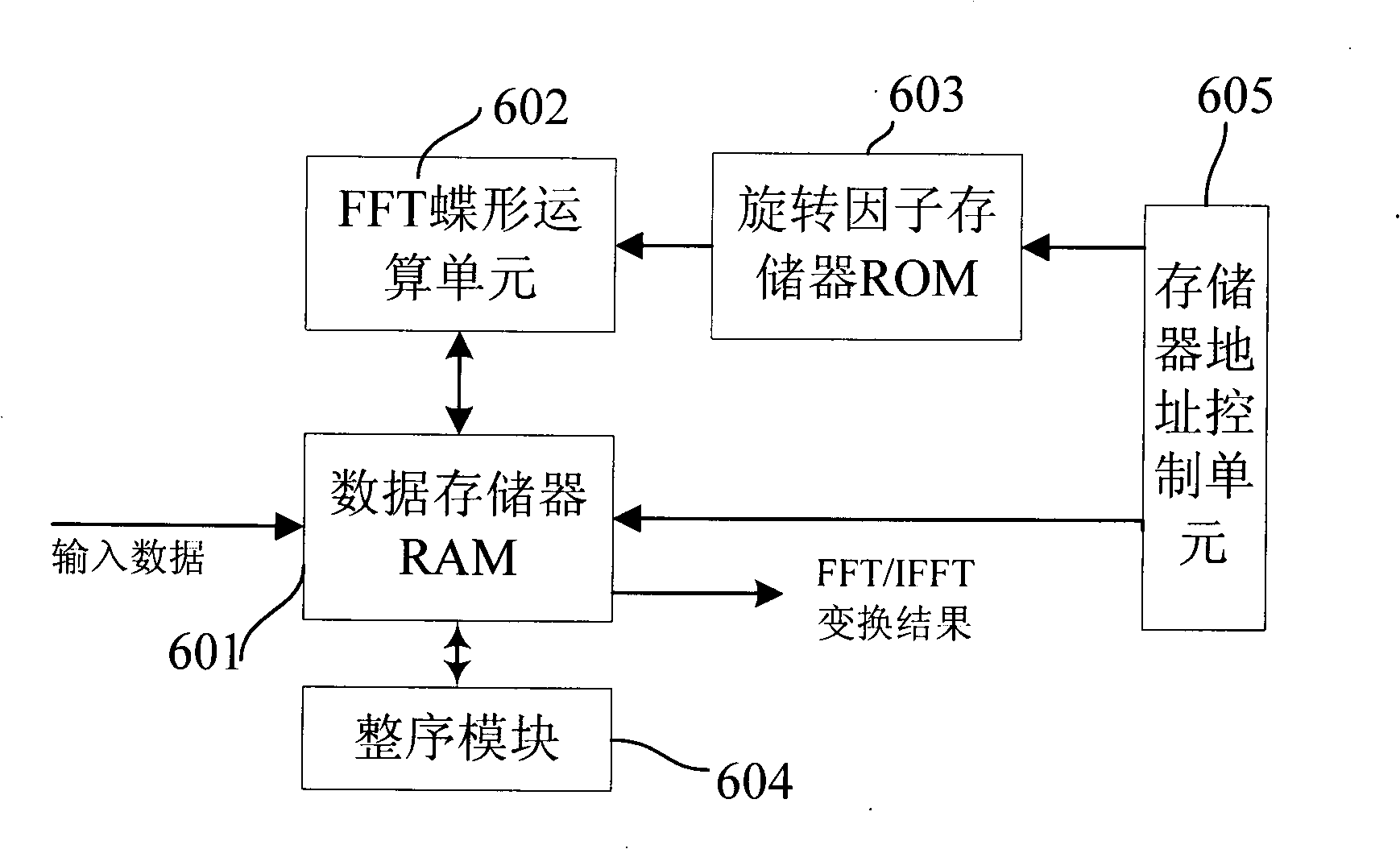
Butterfly-shaped operation FFT processor
InactiveCN101354700AReduce complexityReduce computational complexityComplex mathematical operationsBroadcast system receivingRotation factorComputation complexity
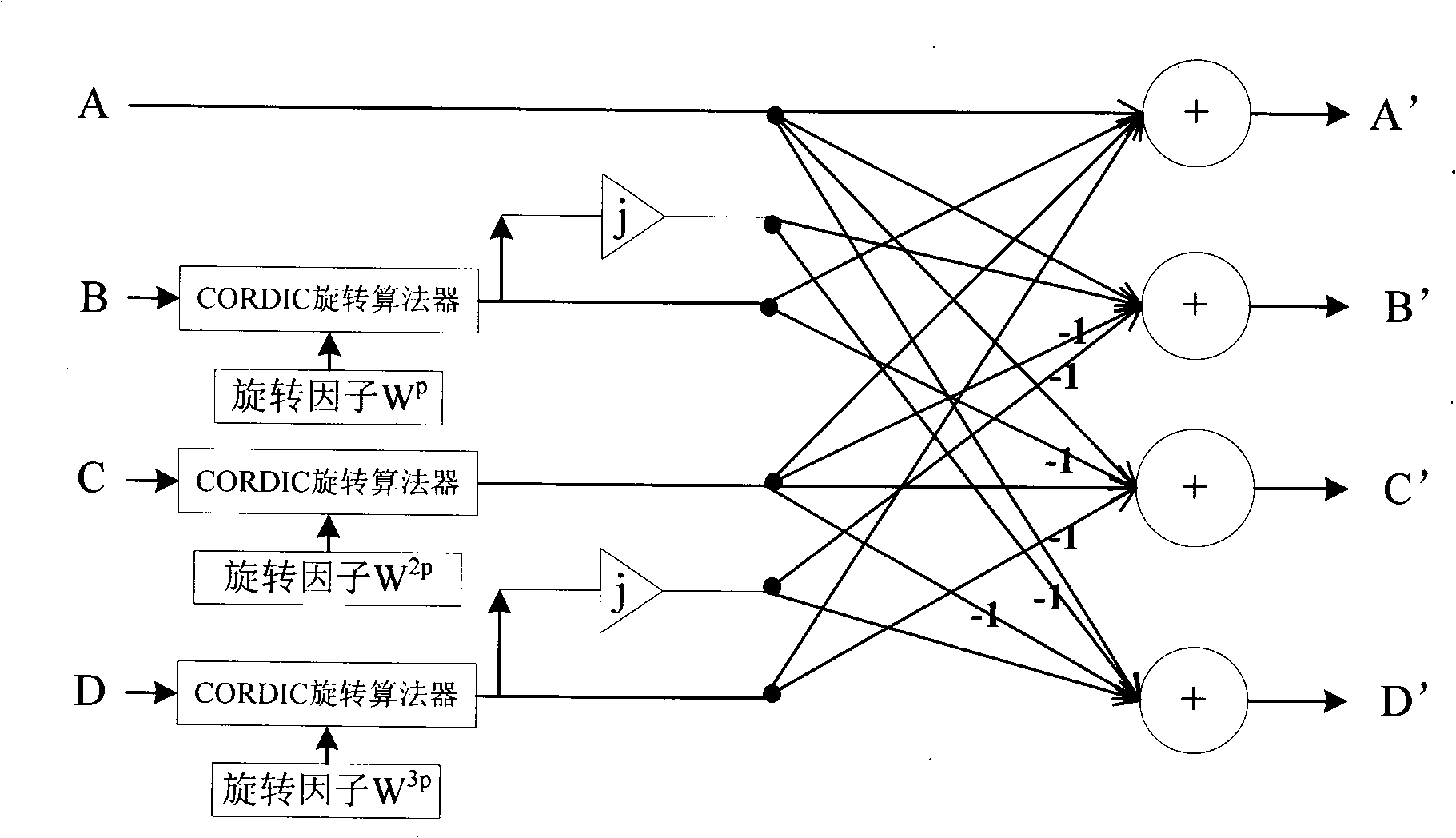
The invention discloses a butterfly computation FFT processor, wherein a complex multiplier used for realizing multiplication of data and a rotation factor is a CORDIC rotation operator, and the rotation angle corresponding to the rotation factor is stored into a rotation factor memory. The butterfly computation FFT processor adopts the CORDIC rotation algorithm to realize multiplication operation of the data and the rotation factor and then uses data shift to replace complex multiplication operation, thereby reducing the computation complexity. Simultaneously, due to adoption of the CORDIC rotation algorithm to realize complex multiplication, only the rotation angle corresponding to the rotation factor is required to be stored into the rotation factor memory without the necessity of storing the sine value and the cosine value of a corresponding angle of the rotation factor, thereby a rotation factor memory unit can be saved and the reading complexity of the rotation factor is reduced.
Owner:SICHUAN PANOVASIC TECH
High data rate CDMA wireless communication system using variable sized channel codes
InactiveUS7715461B2Reduced peak-to-average transmit powerReduce mistakesPower managementTransmission control/equalisingHigh rateCommunications system
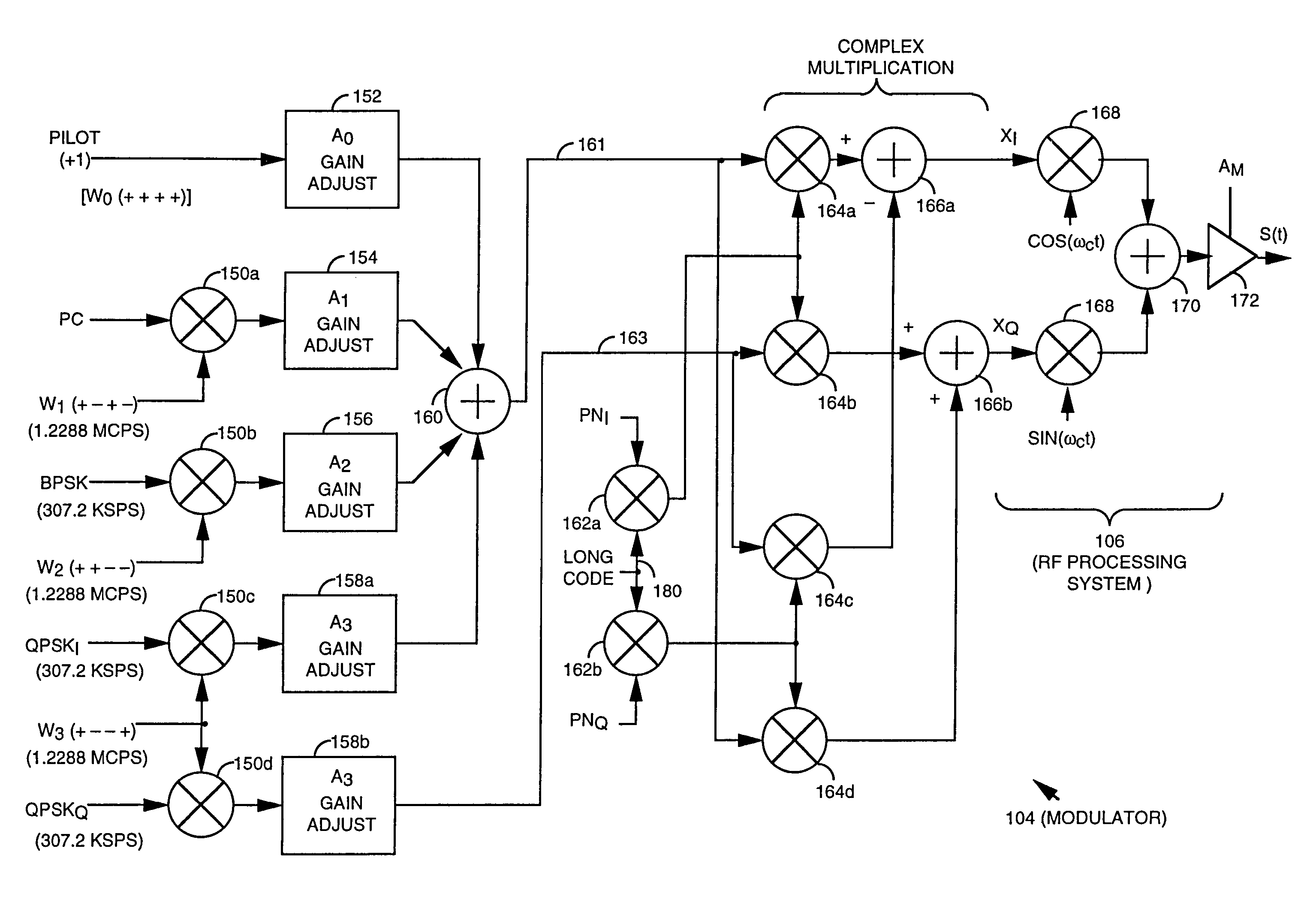
Method and apparatus for high rate code-division multiple access wireless communication is described. Each of a channel encoded data is modulated by an associated code having a small number of pseudo-noise spreading chips per orthogonal waveform period, thus producing a set of streams of modulated symbols. Each of the set of streams of modulated symbols is then gain adjusted, and combined to yield two streams of combined symbols. The combination is the set of streams is carried out to reduce a peak-to-average ratio of the transmission. The resulting two combined symbol streams are modulated by a complex multiplier using a user long code and a pseudorandom spreading code (PN code) and upconverted for transmission.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Probability calculation-based multiple input multiple output detector and detection method
ActiveCN103746731AReduce operational complexityReduce structural complexitySpatial transmit diversityError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorMarkov chainQR decomposition
The invention discloses a probability calculation-based multiple input multiple output detector, which comprises a matrix QR composer, the matrix QR composer is respectively connected with two random sequence generators, the two random sequence generators are respectively connected with a probability complex multiplier, one of the probability complex multipliers is connected with a Gibbs sampling update unit, and both the other probability complex multiplier and the Gibbs sampling update unit are connected with a log-likelihood ratio calculation unit. Because the multiple input multiple output detector uses probability calculation to carry out the MCMC (Markov chain Monte Carlo) algorithm, the complexity of operation is greatly decreased, the transition probability of the Markov chain in the MCMC algorithm is increased, and the problem of locking under a high signal-to-noise ratio is solved. A sliding window sequence generation method is utilized to carry out Gibbs sampling update, so the length of a probability sequence is reduced. When the multiple input multiple output detector is applied to construct a full-parallel detector, a high throughput rate can be achieved with the full-parallel mode.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
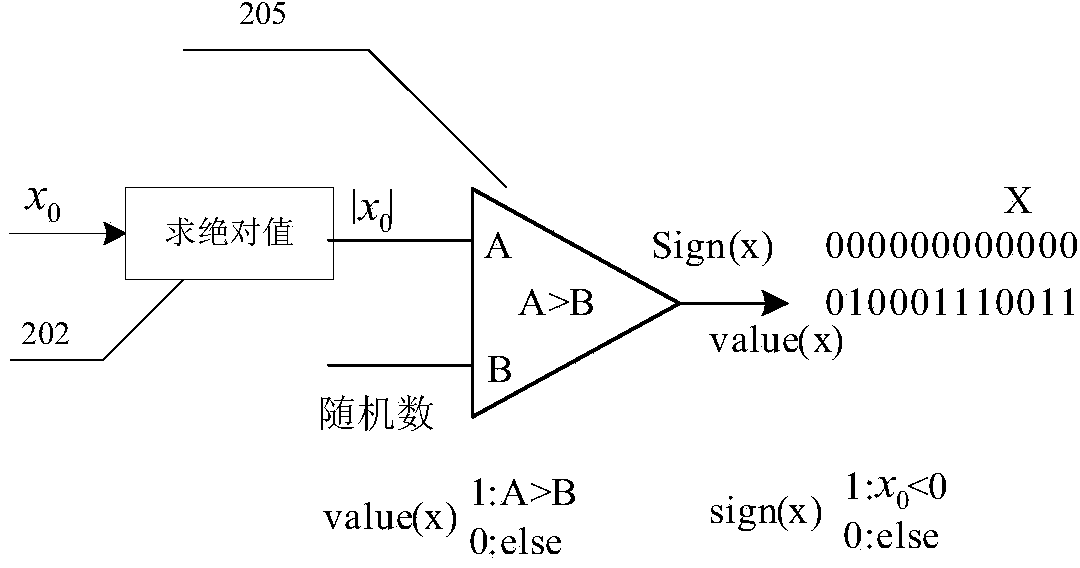
Method for measuring and compensating satellite communication link carrier frequency offset
ActiveCN101867546AImprove accuracySimple designMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksTelecommunications linkData stream
The invention relates to a method for measuring and compensating satellite communication link carrier frequency offset, which comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out matched filtering and demodulation for baseband data, carrying out correlation operation for the baseband data and multiple orthogonal carriers, and taking the frequency value corresponding to the maximum correlation peak as a rough estimate value of carrier frequency offset; subdividing frequency points near the rough estimate value, re-setting the frequency parameters of the multiple orthogonal carriers, generatingnew orthogonal carriers and carrying out the correlation operation over again, and looping until the frequency value and phase corresponding to the maximum correlation peak which meet precision requirements are found to be used as the precise estimate value of the carrier frequency offset; and finally, utilizing a sine look-up table to generate two orthogonal single-carriers according to precise frequency offset information, multiplying baseband data stream by the two orthogonal single-carriers through a complex multiplier to obtain data stream after removing frequency offset. The method can meet the real-time requirements of receiving burst data in an MF-TDMA mode, takes less hardware resources, and has small additional delay and simple and convenient realization.
Owner:SPACE STAR TECH CO LTD
GPS capture unit design method based on matched filter
InactiveCN102928854AFast captureImprove capture speedSatellite radio beaconingNumerical controlCarrier signal
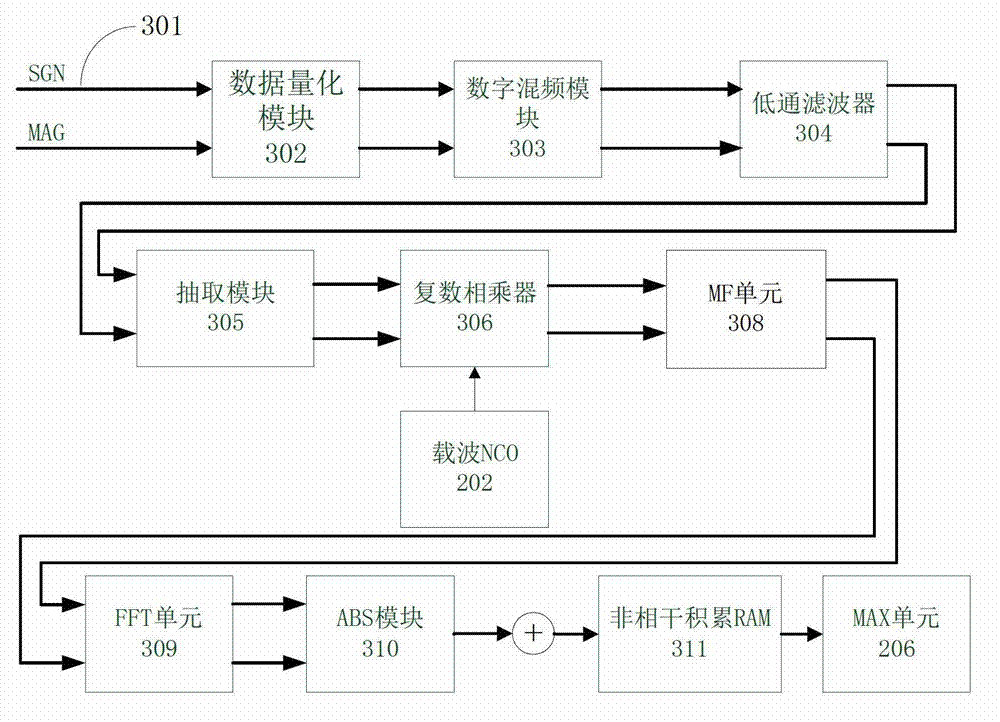
The invention discloses a GPS (Global Positioning System) capture unit design method based on a matched filter. The GPS capture unit design method comprises the following steps: a GPS signal is changed into a mid-frequency digital signal after being subject to RF (Radio Frequency) front-end processing, and then the mid-frequency digital signal is re-quantified into a digital signal by a data quantification unit; the digital signal is changed into an orthogonal signal I and an orthogonal signal Q by a data orthogonal transformation unit; the orthogonal signal I and an orthogonal signal Q are further subjected to carrier stripping through a carrier NCO (Numerical Controlled Oscillator) and a complex multiplier to be changed into baseband signals close to zero frequency; a C / A code encoder generates a local C / A code; the locally generated C / A code is utilized to strip pseudo-codes in the orthogonal signal I and the orthogonal signal Q in MF (Medium Frequency) to complete coherent integration; and an FFT (Fast Fourier Transform) module transforms the coherent integration value to the frequency domain, outputs the frequency-domain amplitude values at 32 frequency points, then conduct noncoherent integration, and after that, outputs the maximum value, as well as a frequency point and a code phase, which correspond to the maximum value. The GPS capture unit design method increases the signal capture speed of a GPS receiver.
Owner:JIANGSU SEUIC TECH CO LTD
Complex multiplication unit based on modified high-radix CORDIC algorithm
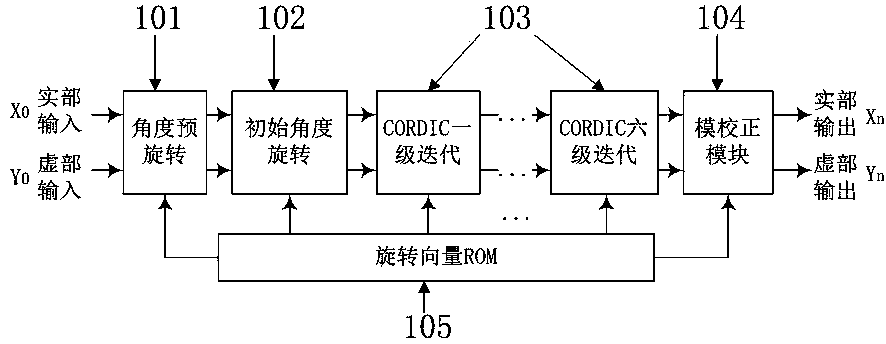
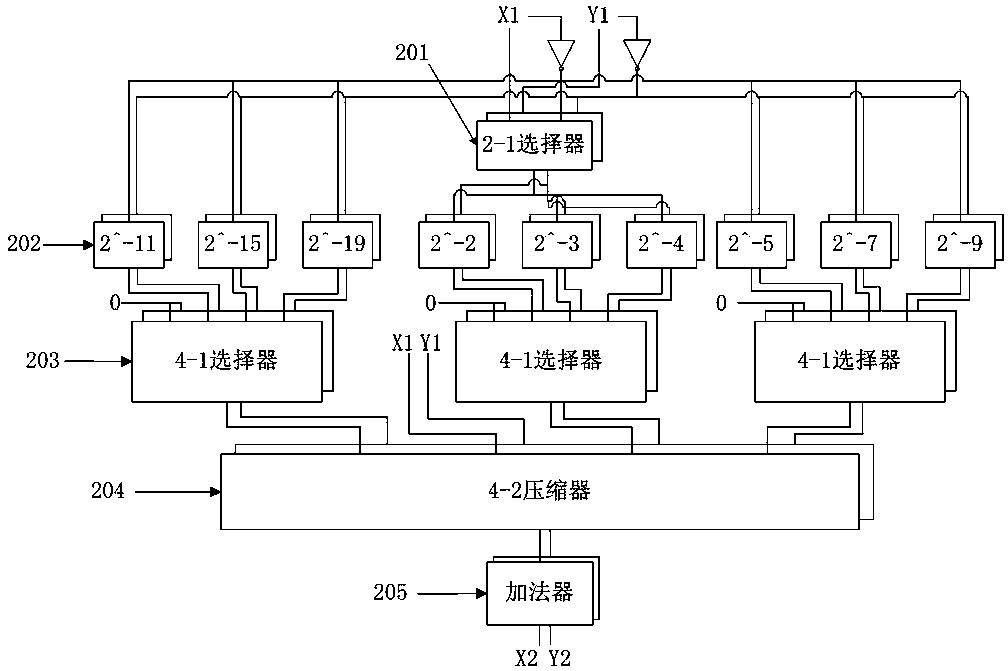
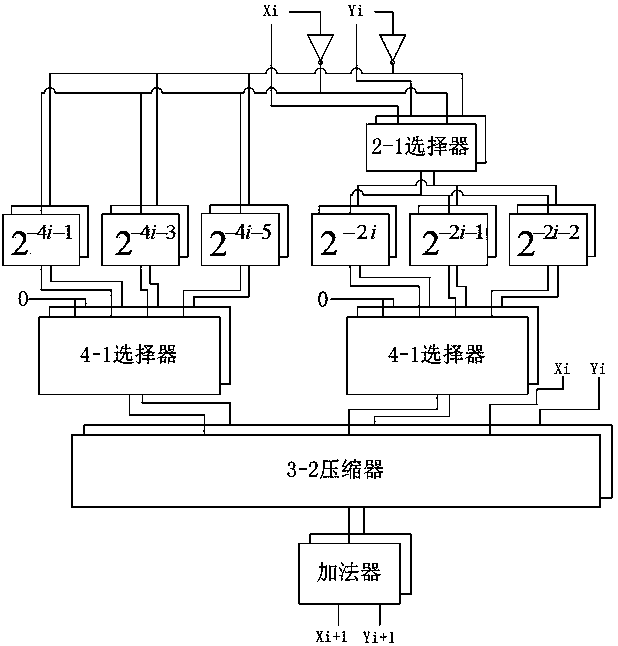
InactiveCN103488459ABroaden your optionsSimplify the multiplication operationDigital data processing detailsDigital signal processingCORDIC
The invention belongs to the technical field of design of digital signal processing and integrated circuits and particularly relates to a complex multiplication unit based on a modified high-radix CORDIC algorithm. The modified high-radix CORDIC algorithm is characterized in that selection range of iterative angle of each level in CORDIC operation is further increased, and accordingly the number of required iterations is reduced and operating speed is increased while the precision is guaranteed; a method of approximate expansion of Taylor series of a cosine function is adopted, multiplication of modulus correction factors in the high-radix CORDIC algorithm is simplified, only one constant modulus correction factor exists in the hole operating process, and hardware complexity is reduced; in an application wherein a multiplier of the multiplication is preliminarily determinable, usage of a common complex multiplier can be avoided completely, hardware area of the multiplication unit and the size of a required ROM are both advantaged, and loss of computing accuracy avoided.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Digital systolic array architecture and method for computing the discrete Fourier transform
InactiveUS7120658B2Improve throughputLower latencyDigital computer detailsComplex mathematical operationsDesign improvementFourier transform on finite groups
A more computationally efficient and scalable systolic architecture is provided for computing the discrete Fourier transform. The systolic architecture also provides a method for reducing the array area by limiting the number of complex multipliers. In one embodiment, the design improvement is achieved by taking advantage of a more efficient computation scheme based on symmetries in the Fourier transform coefficient matrix and the radix-4 butterfly. The resulting design provides an array comprised of a plurality of smaller base-4 matrices that can simply be added or removed to provide scalability of the design for applications involving different transform lengths to be calculated. In this embodiment, the systolic array size provides greater flexibility because it can be applied for use with any transform length which is an integer multiple of sixteen.
Owner:NASH JAMES G
Complex multiplication method and apparatus with phase rotation
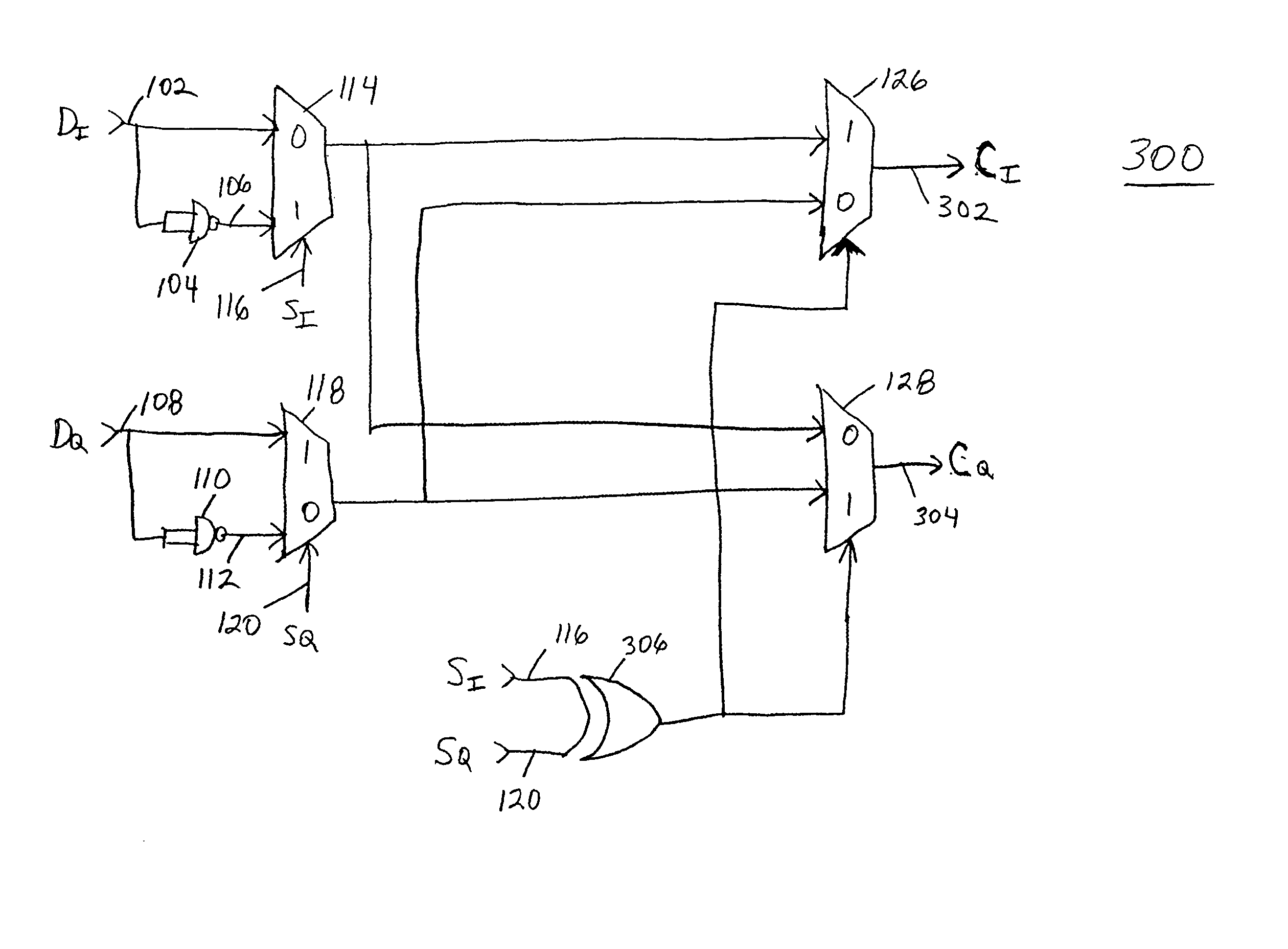
ActiveUS20040267860A1Computation using non-contact making devicesTransmissionNegationComputer science
A method and apparatus for complex multiplication includes steps of: (a) receiving a complex multiplicand having a real value and an imaginary value (704); (b) generating a negation of the real value of the complex multiplicand (706); (c) generating a negation of the imaginary value of the complex multiplicand (708); (d) receiving a complex multiplier (710); and (e) selecting a phasor constant having a value wherein a complex product of the complex multiplicand times the complex multiplier times the phasor constant has a real value equal to one of the real value of the complex multiplicand, the imaginary value of the complex multiplicand, the negation of the real value of the complex multiplicand, and the negation of the imaginary value of the complex multiplicand (712).
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com