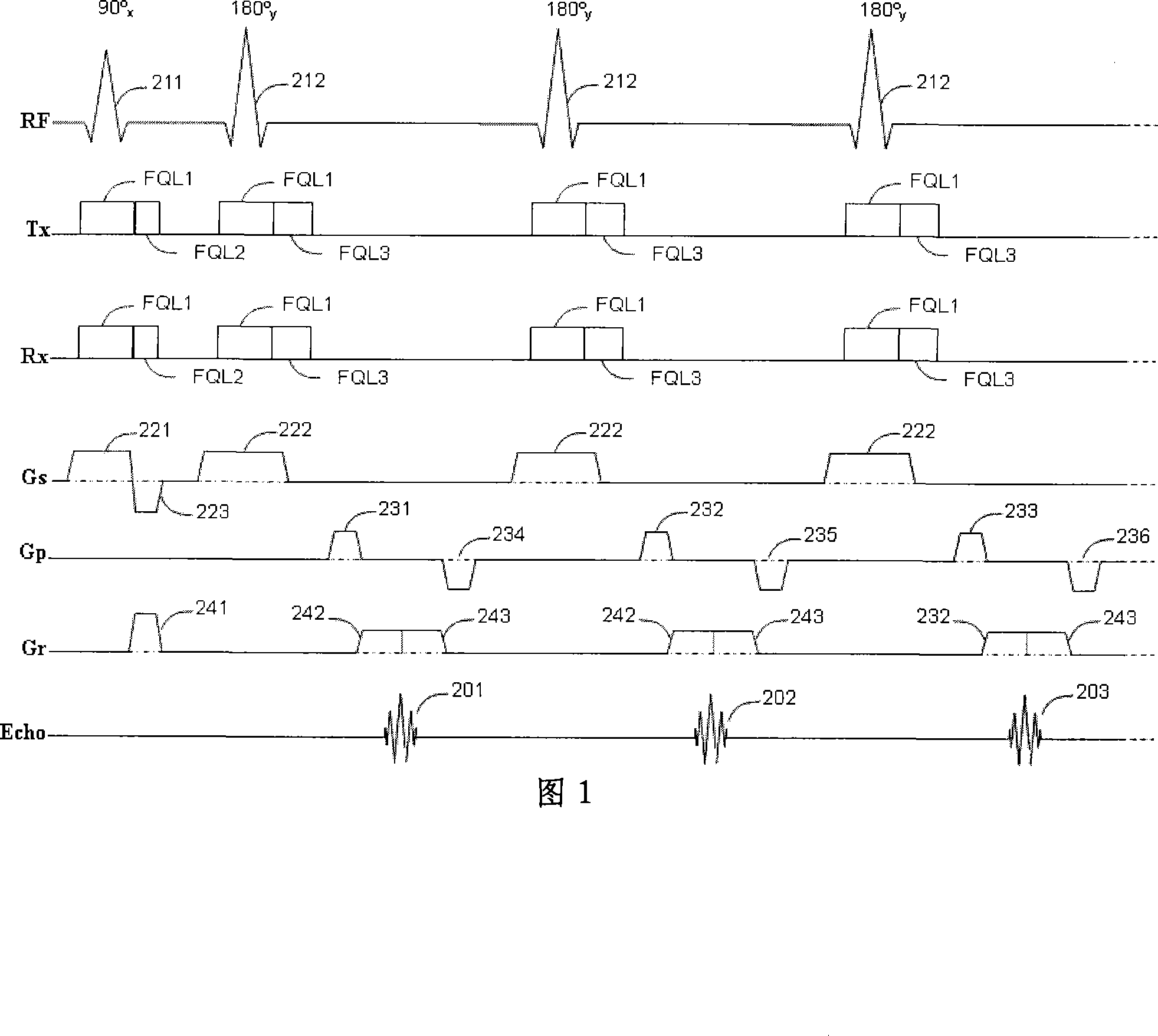
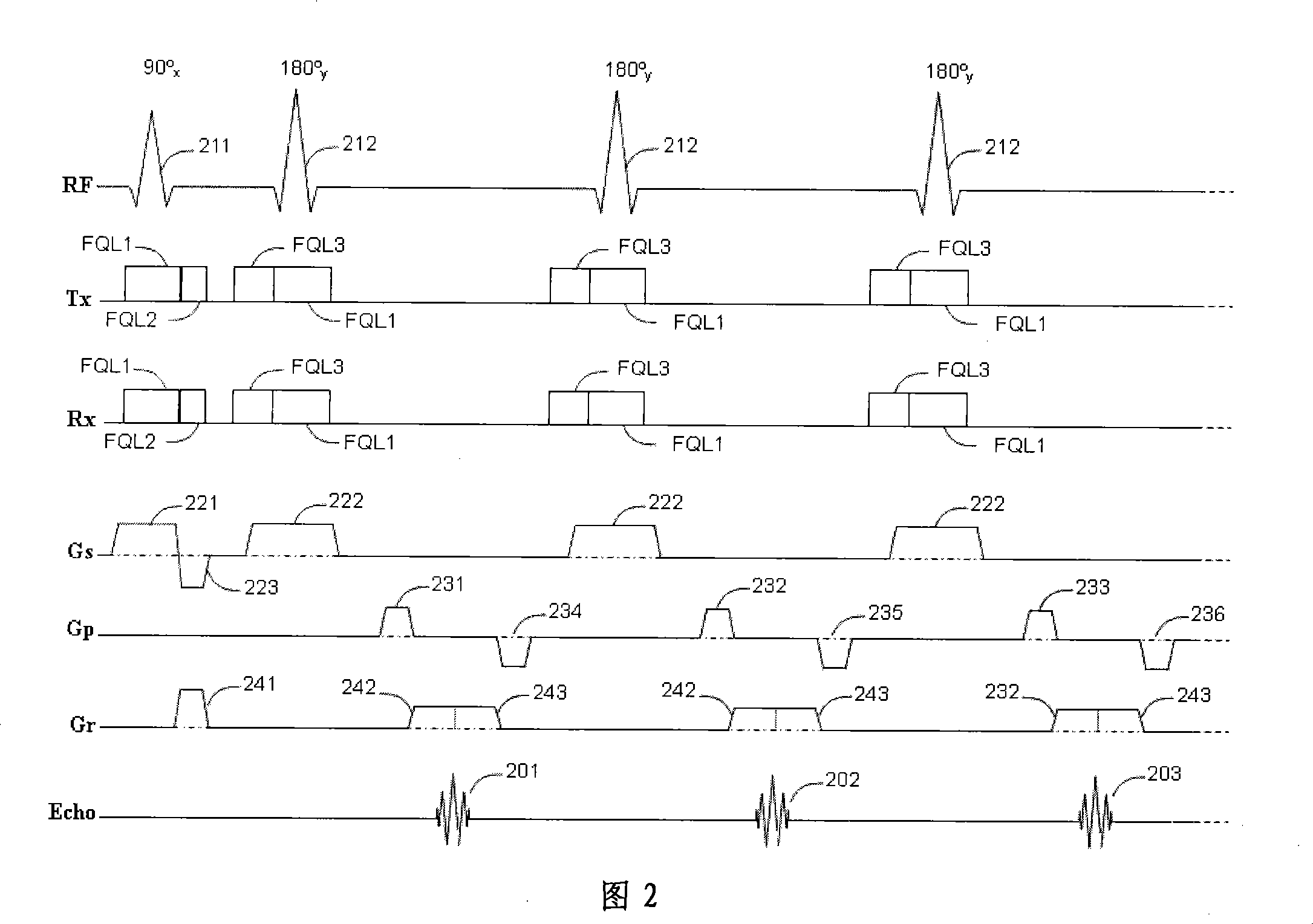
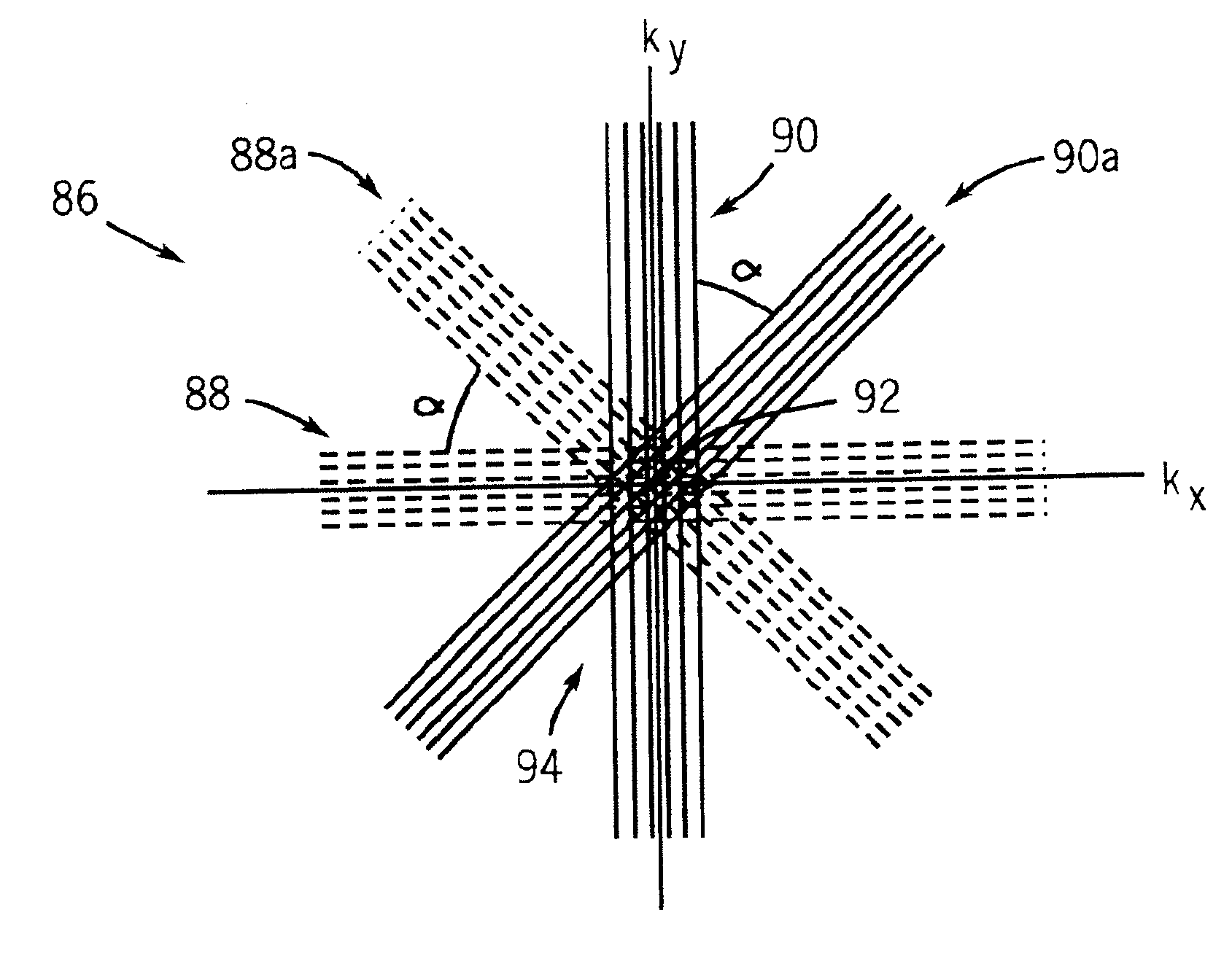
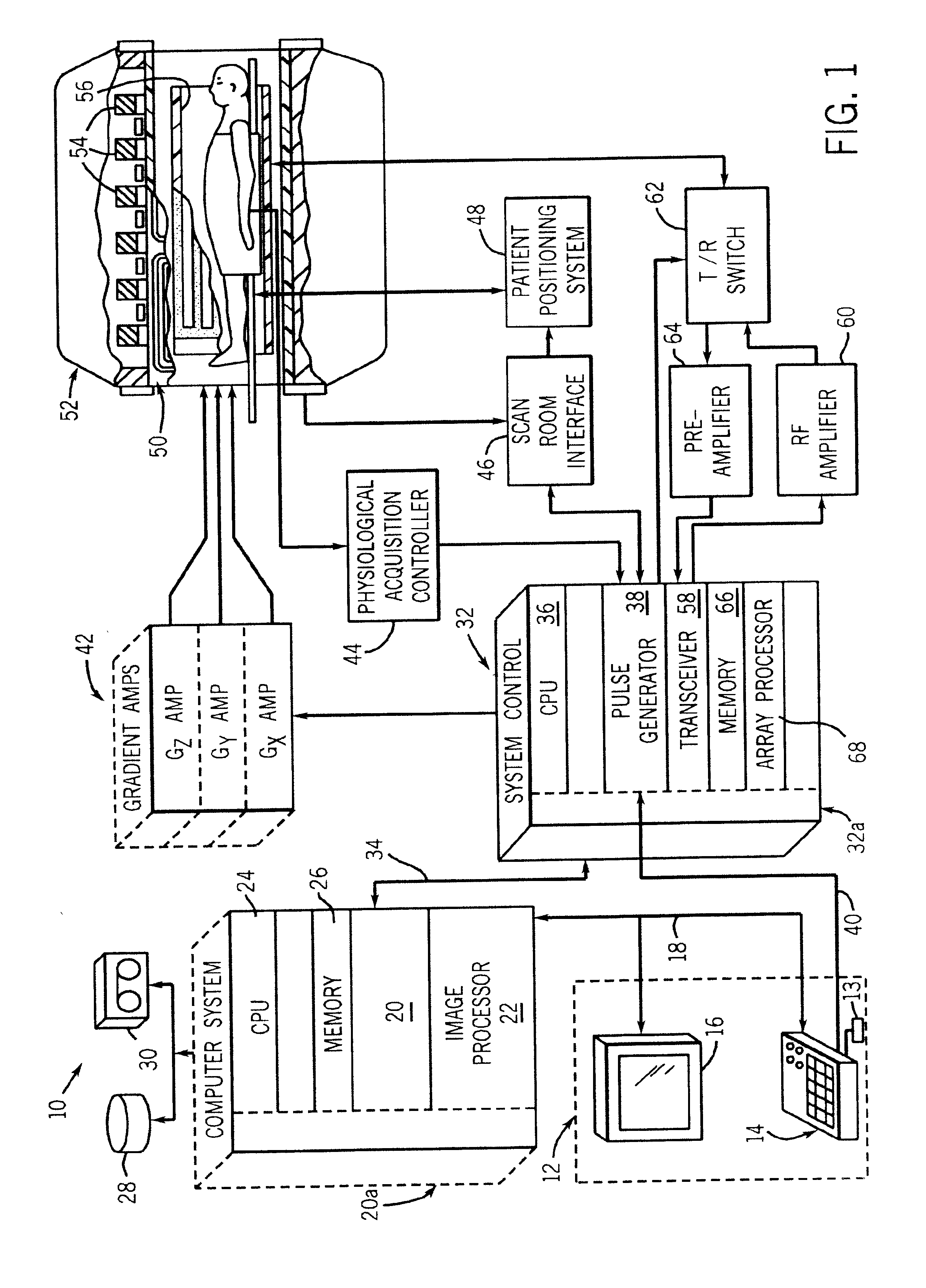
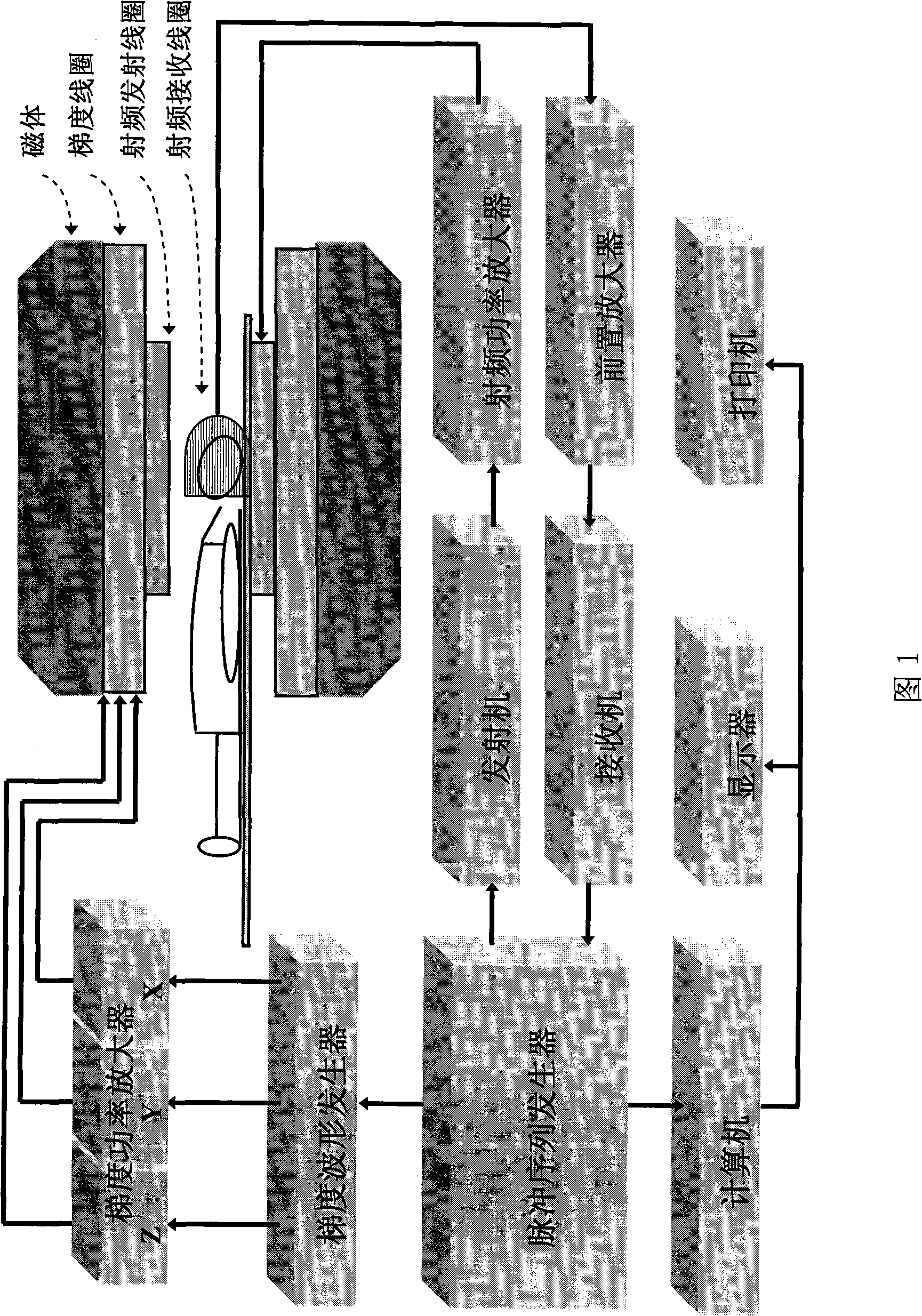
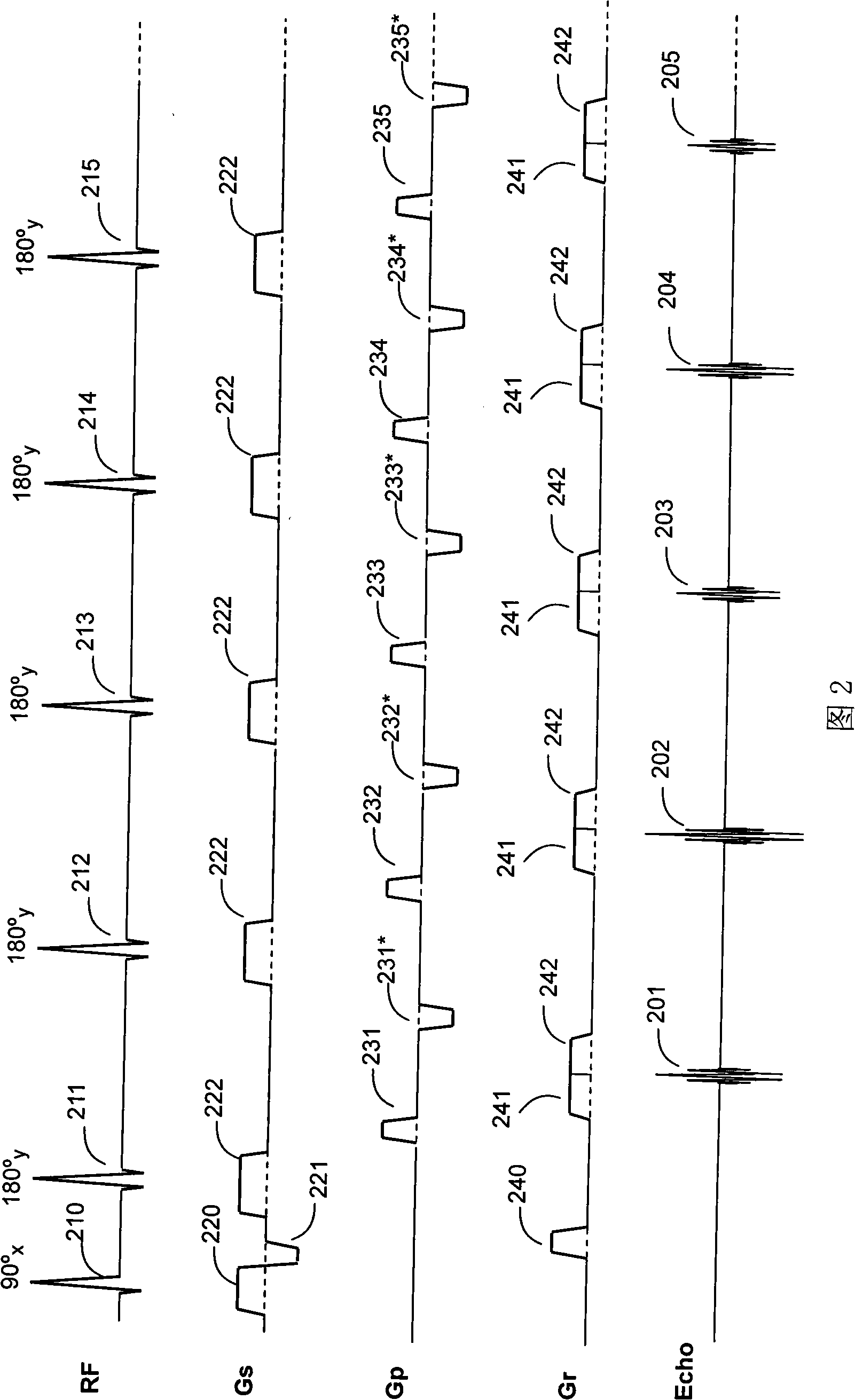
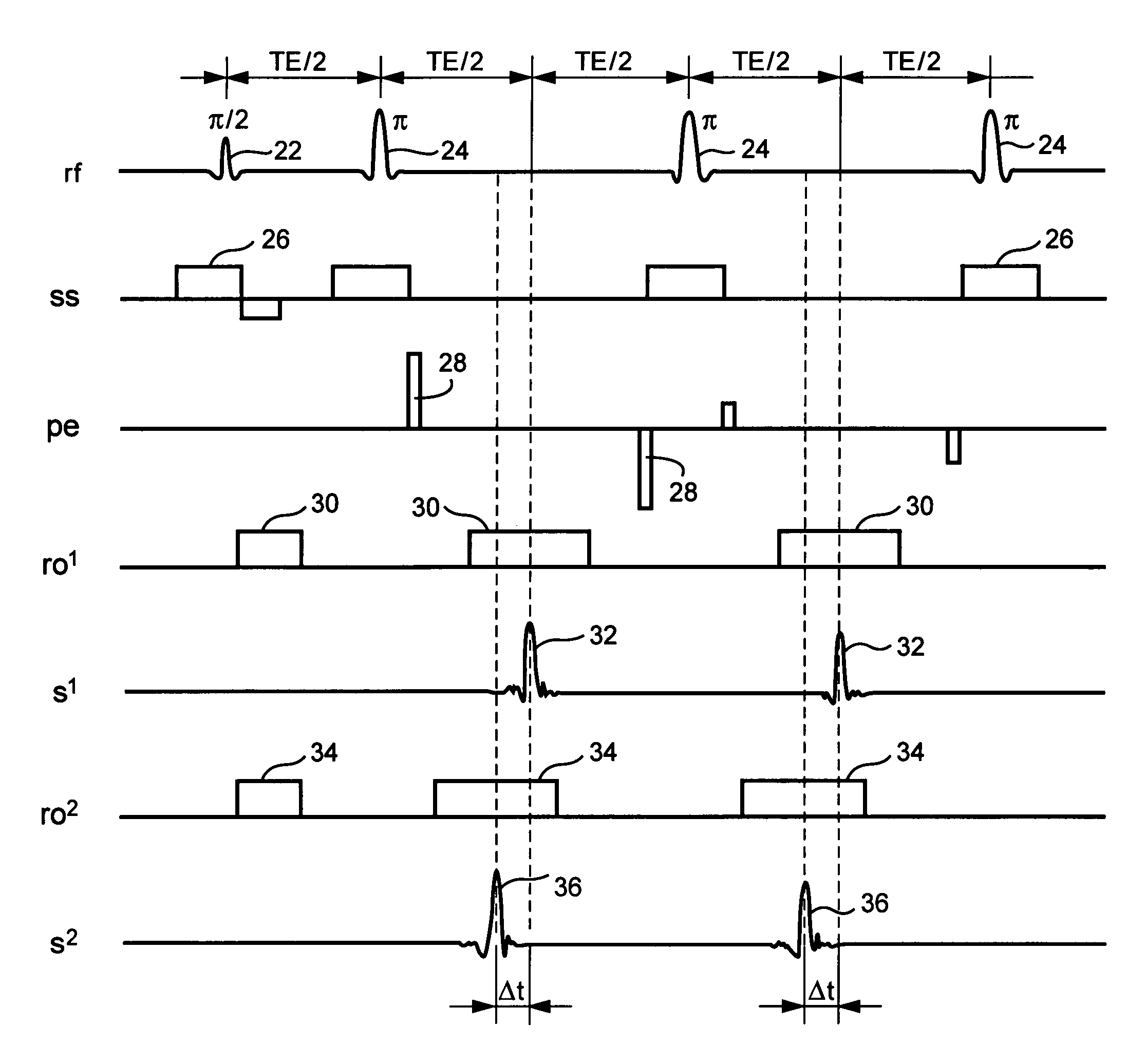
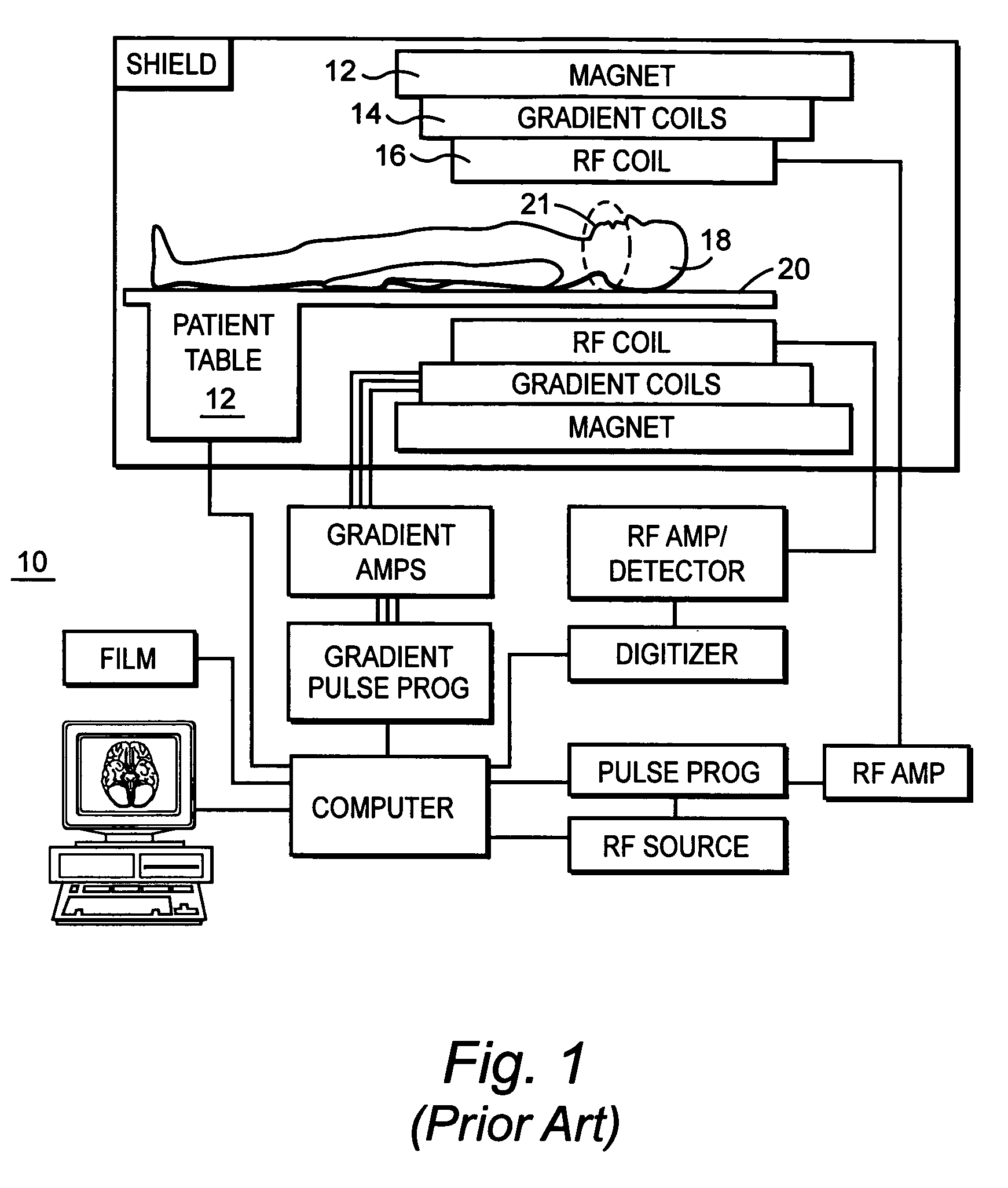
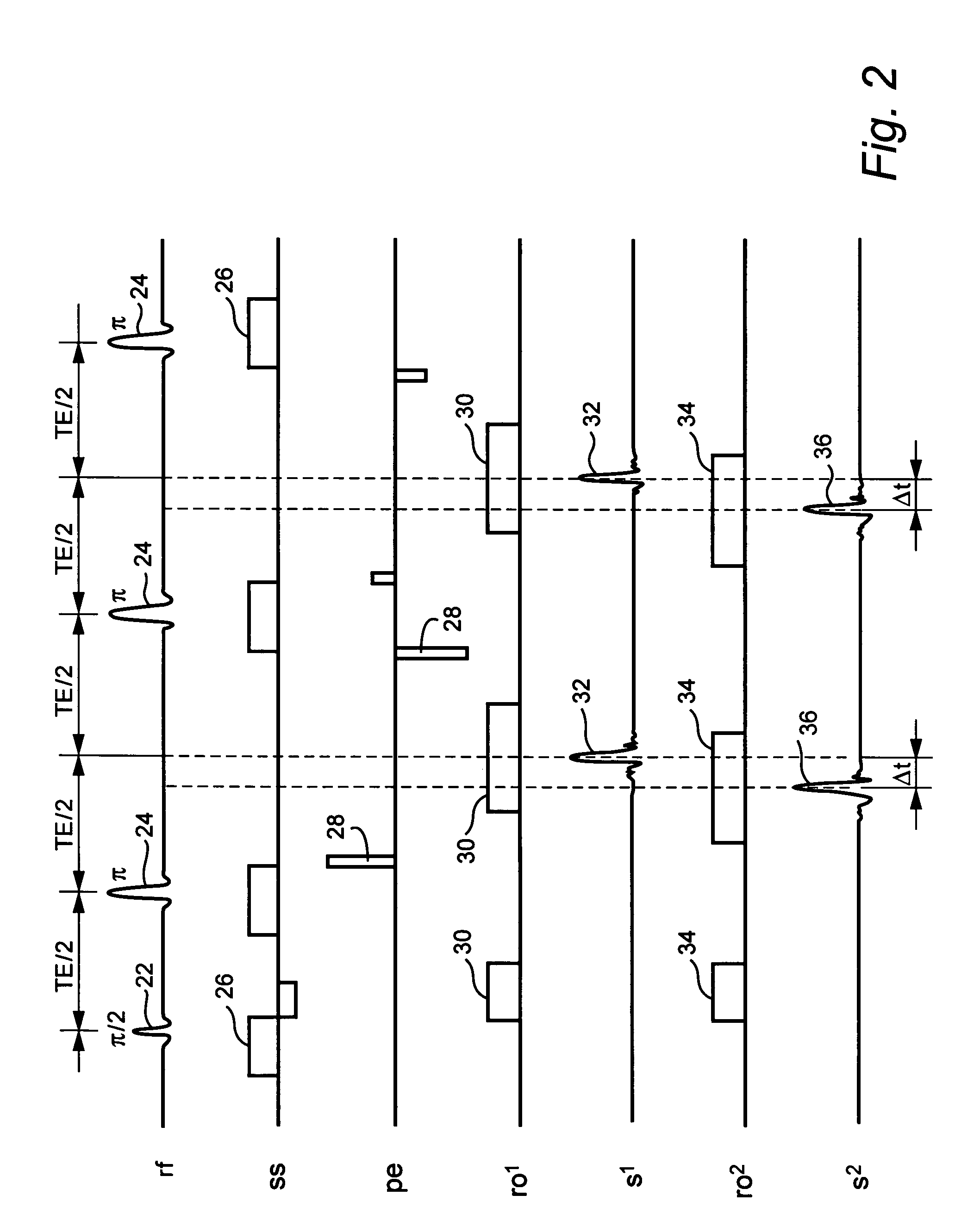
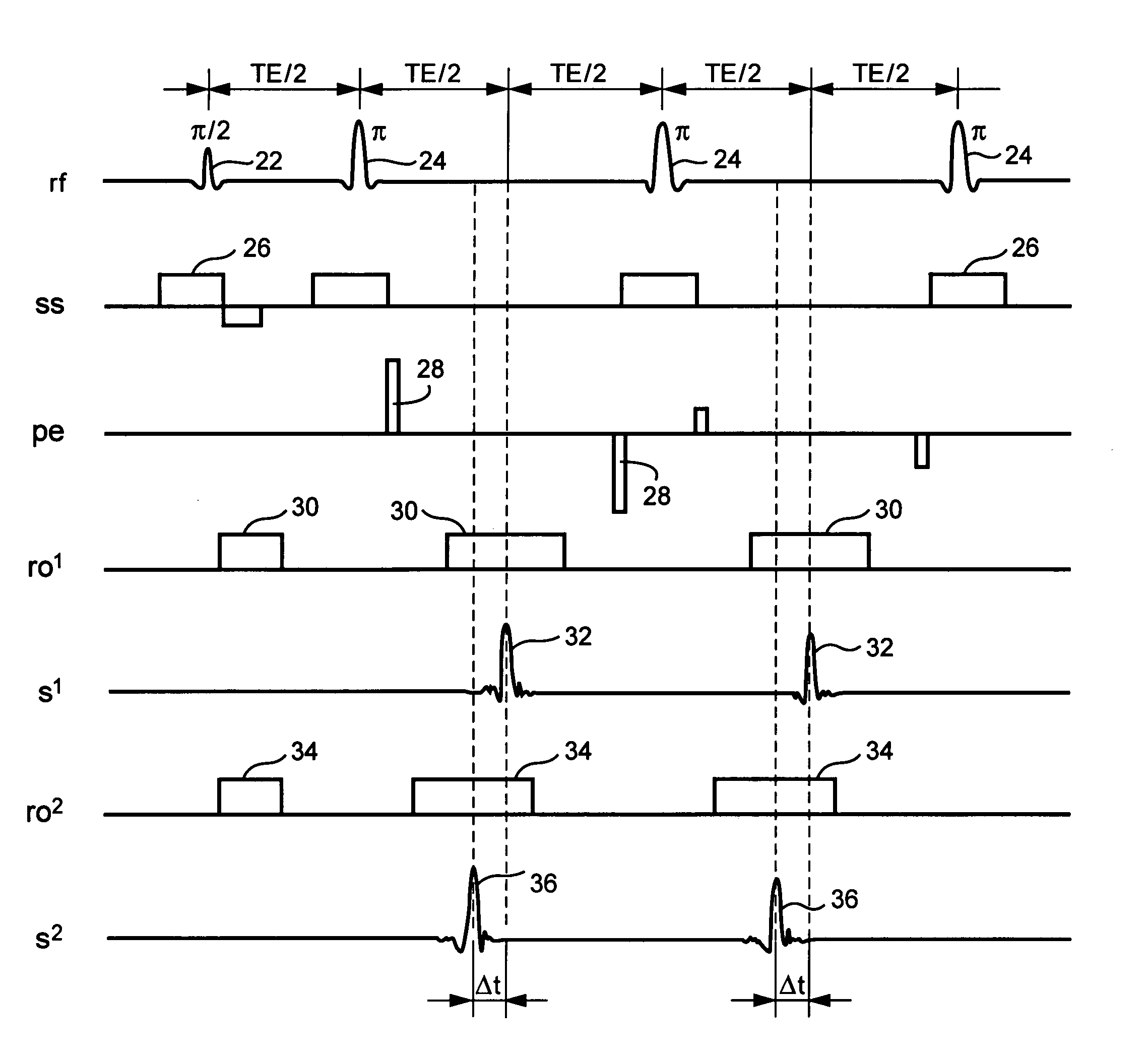
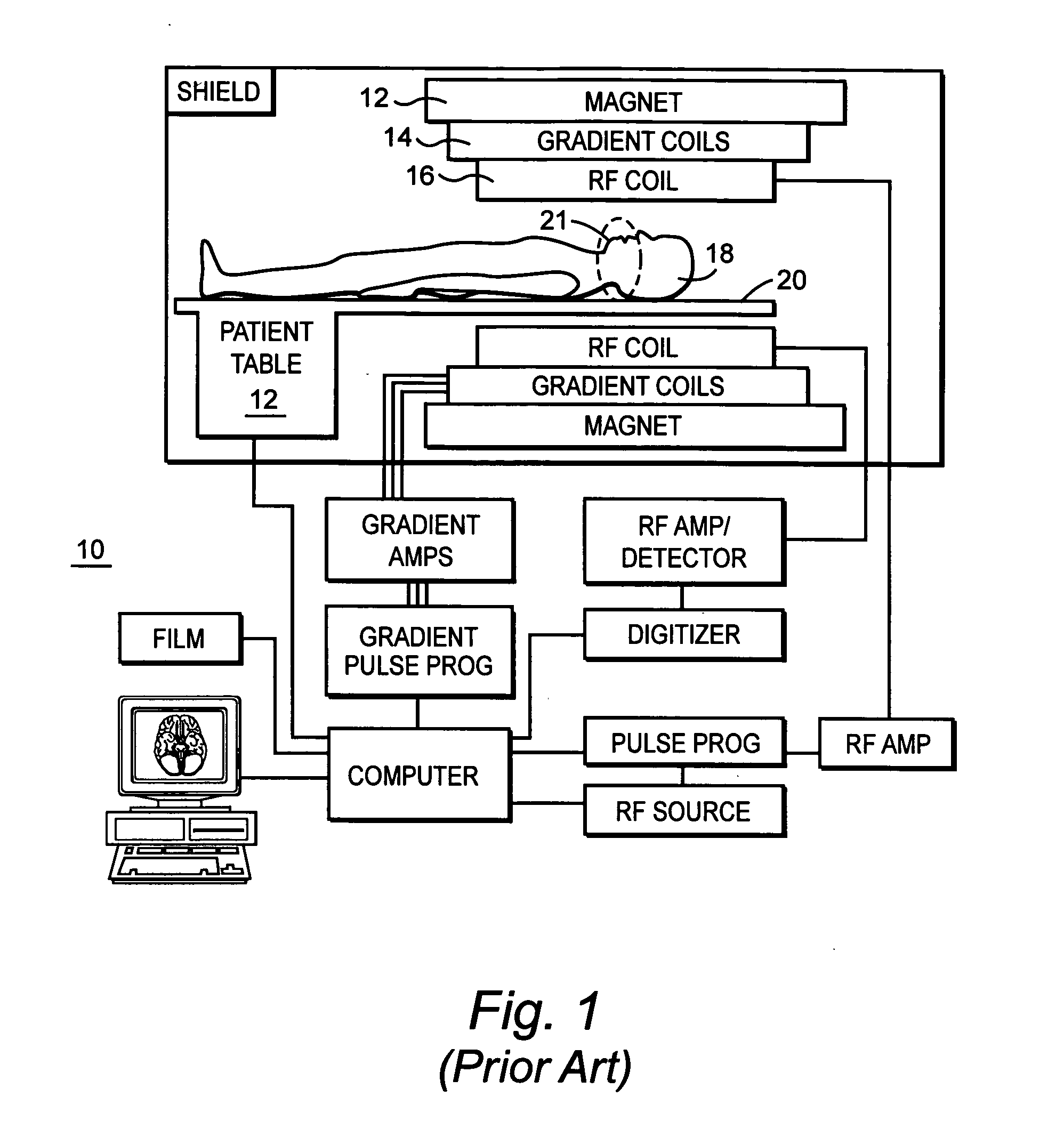
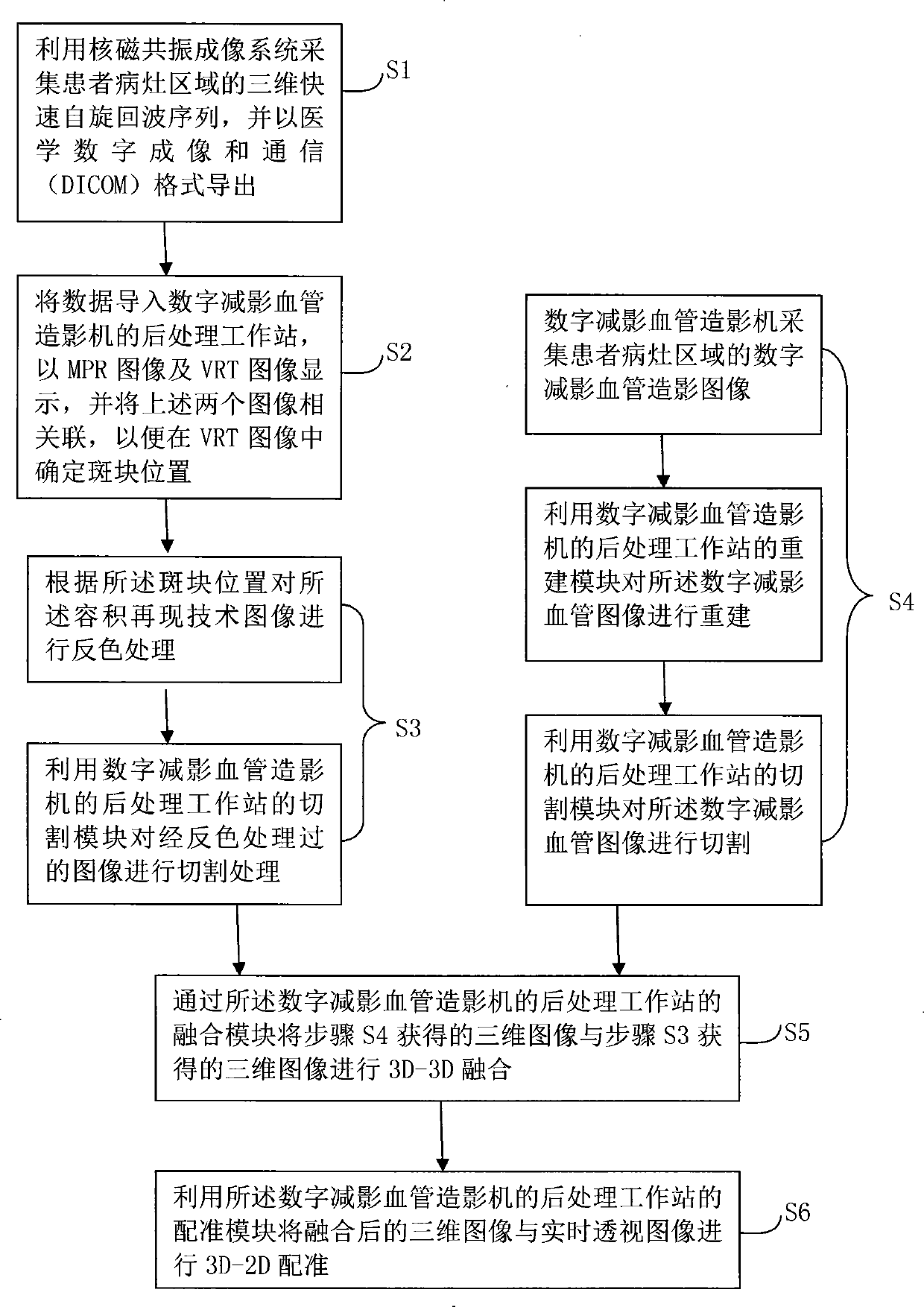
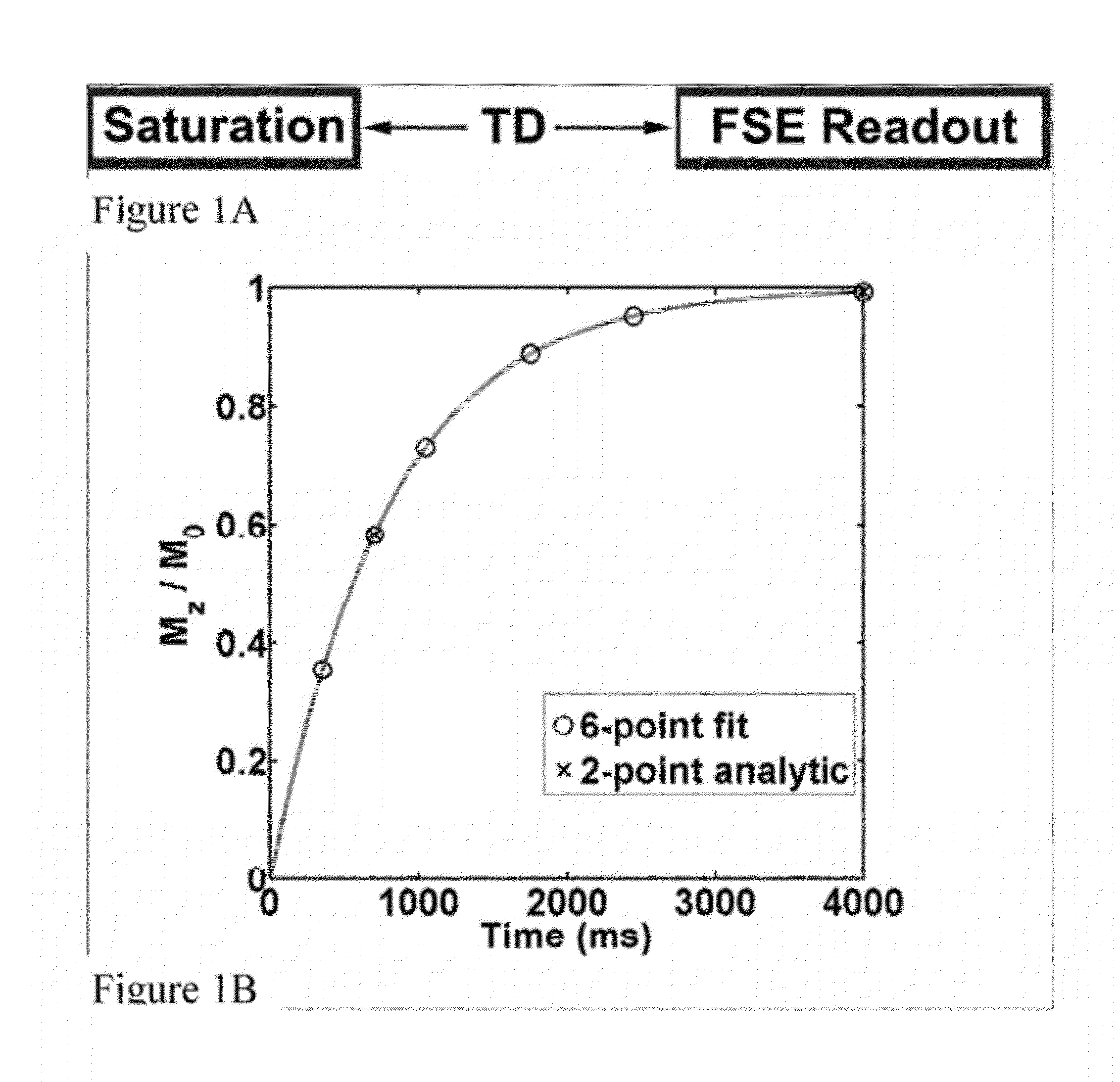
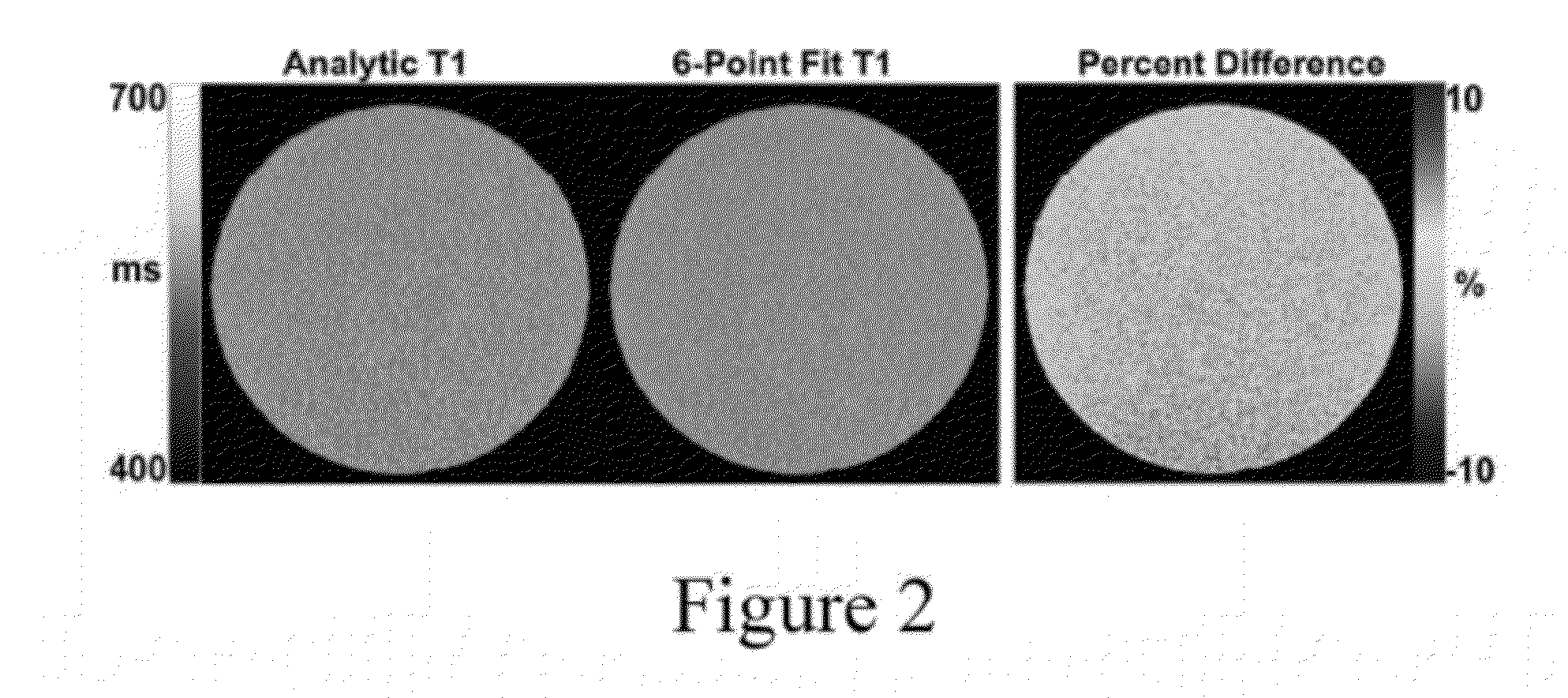
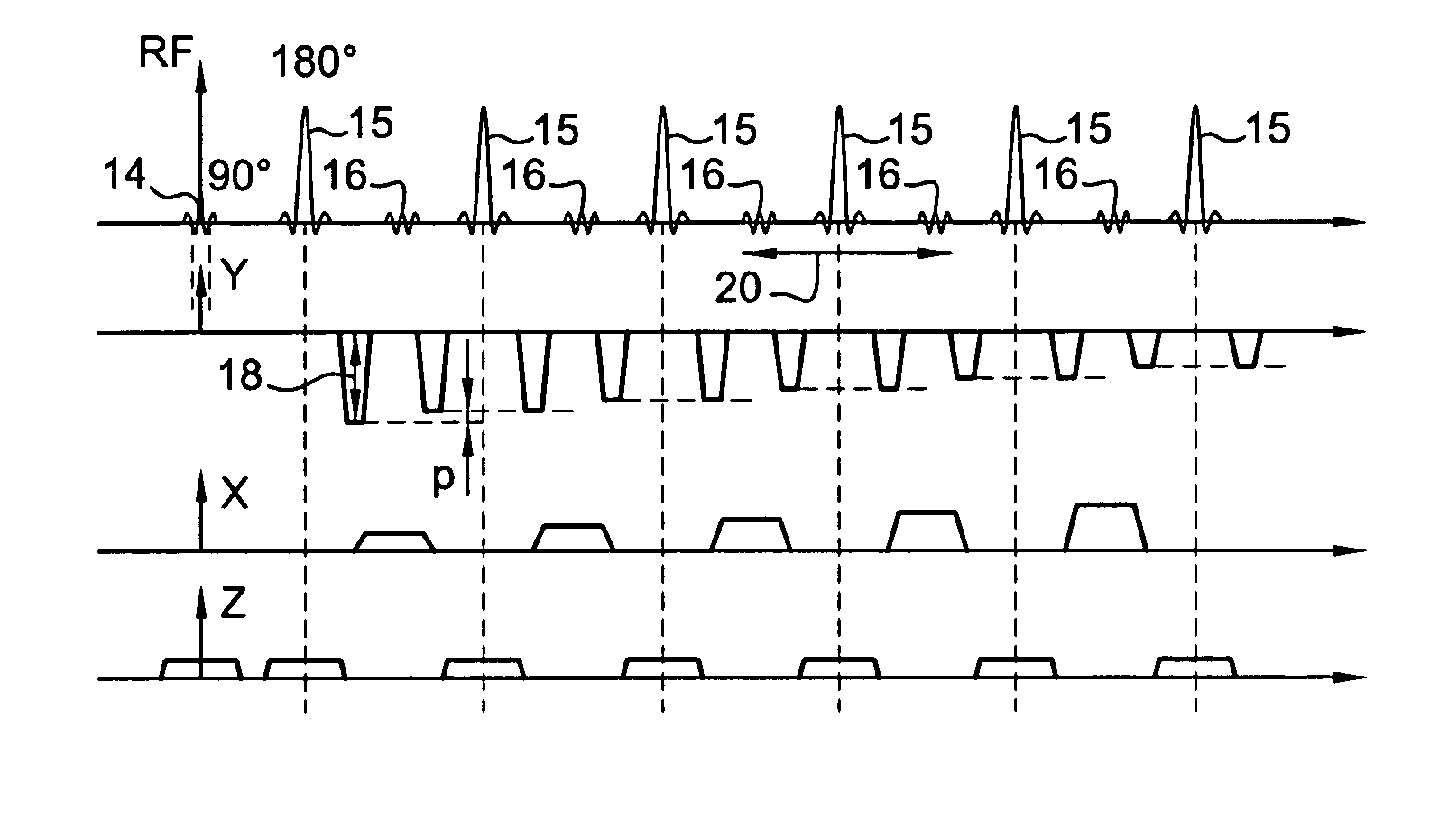
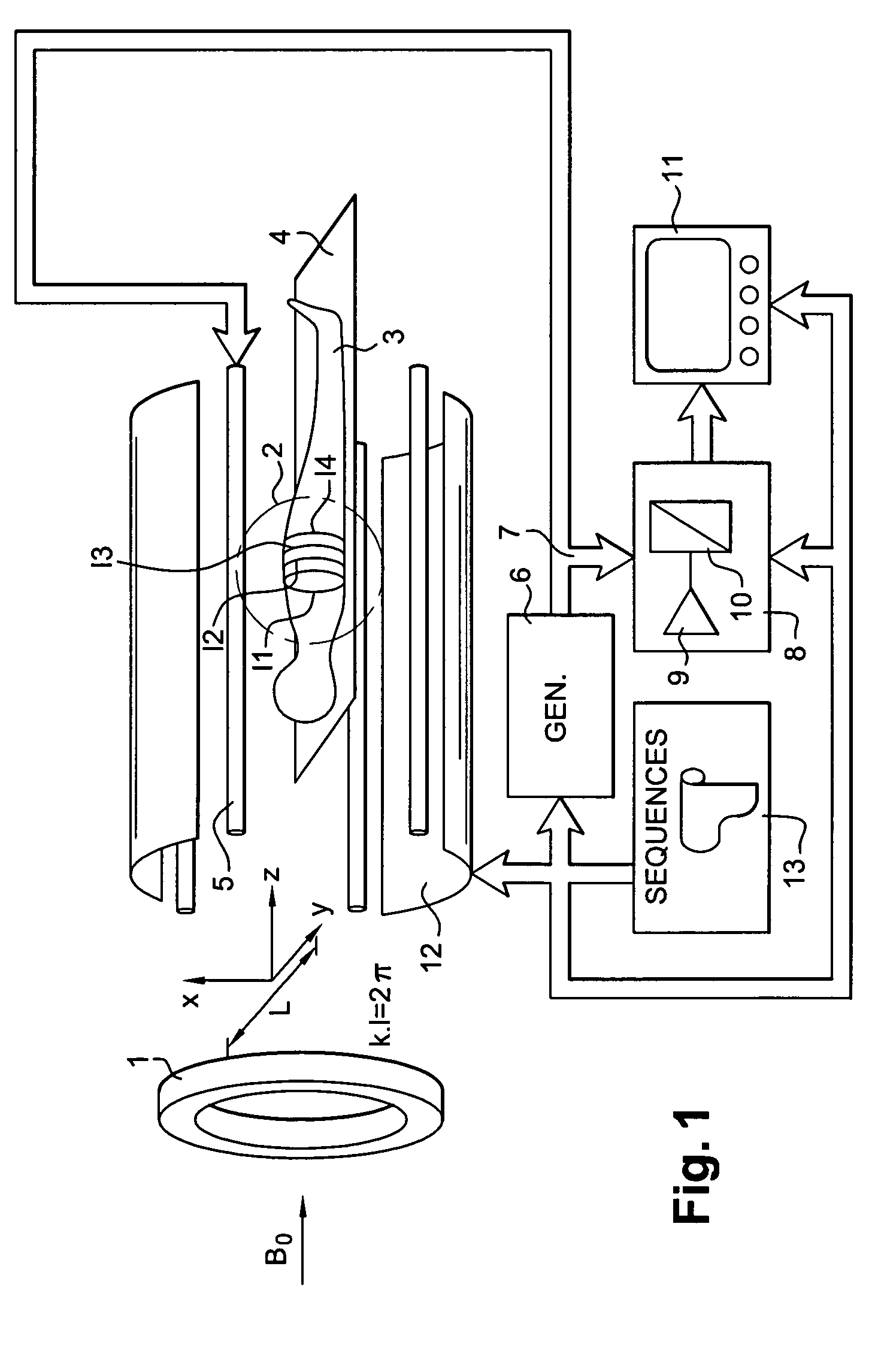
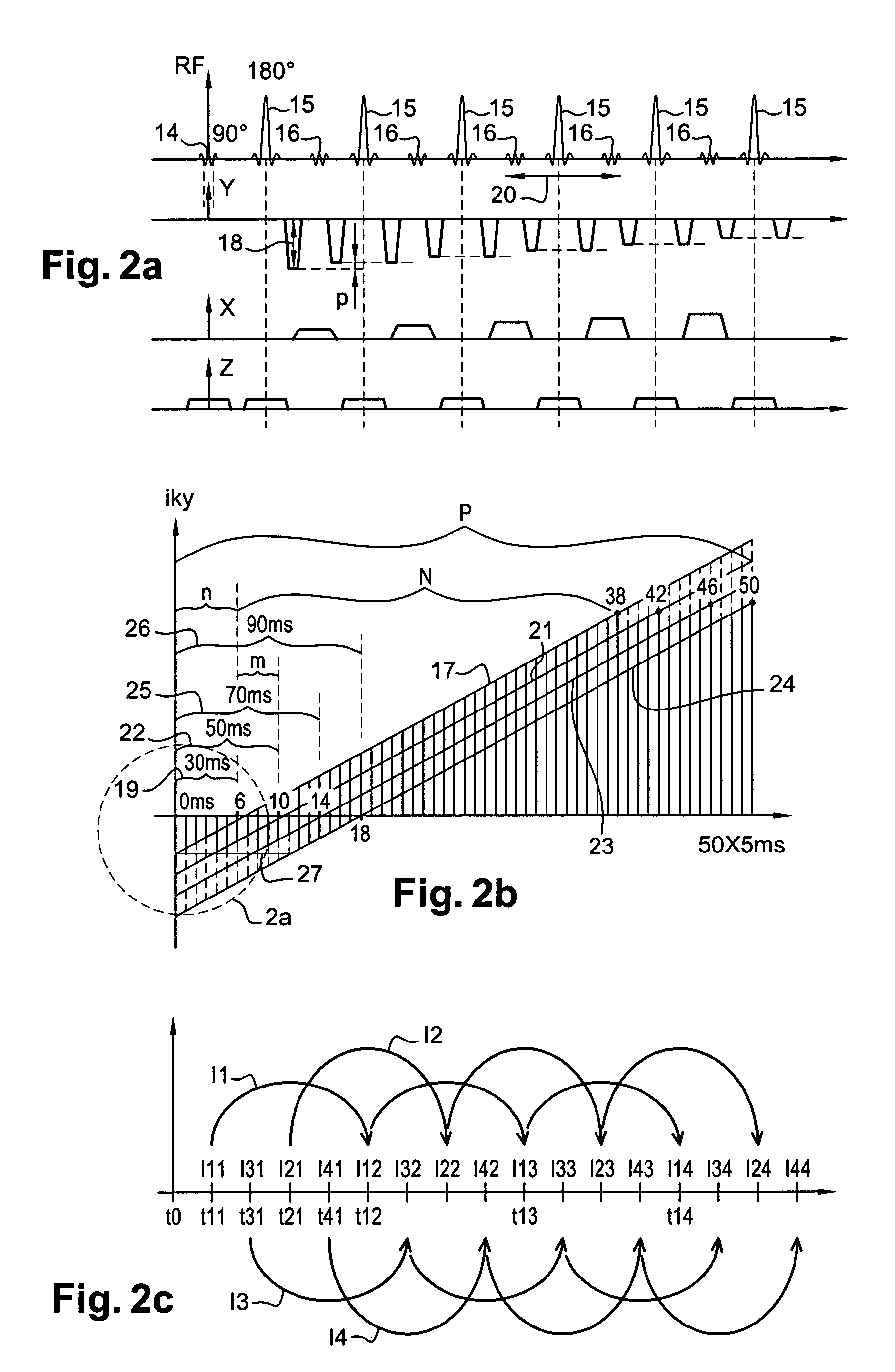
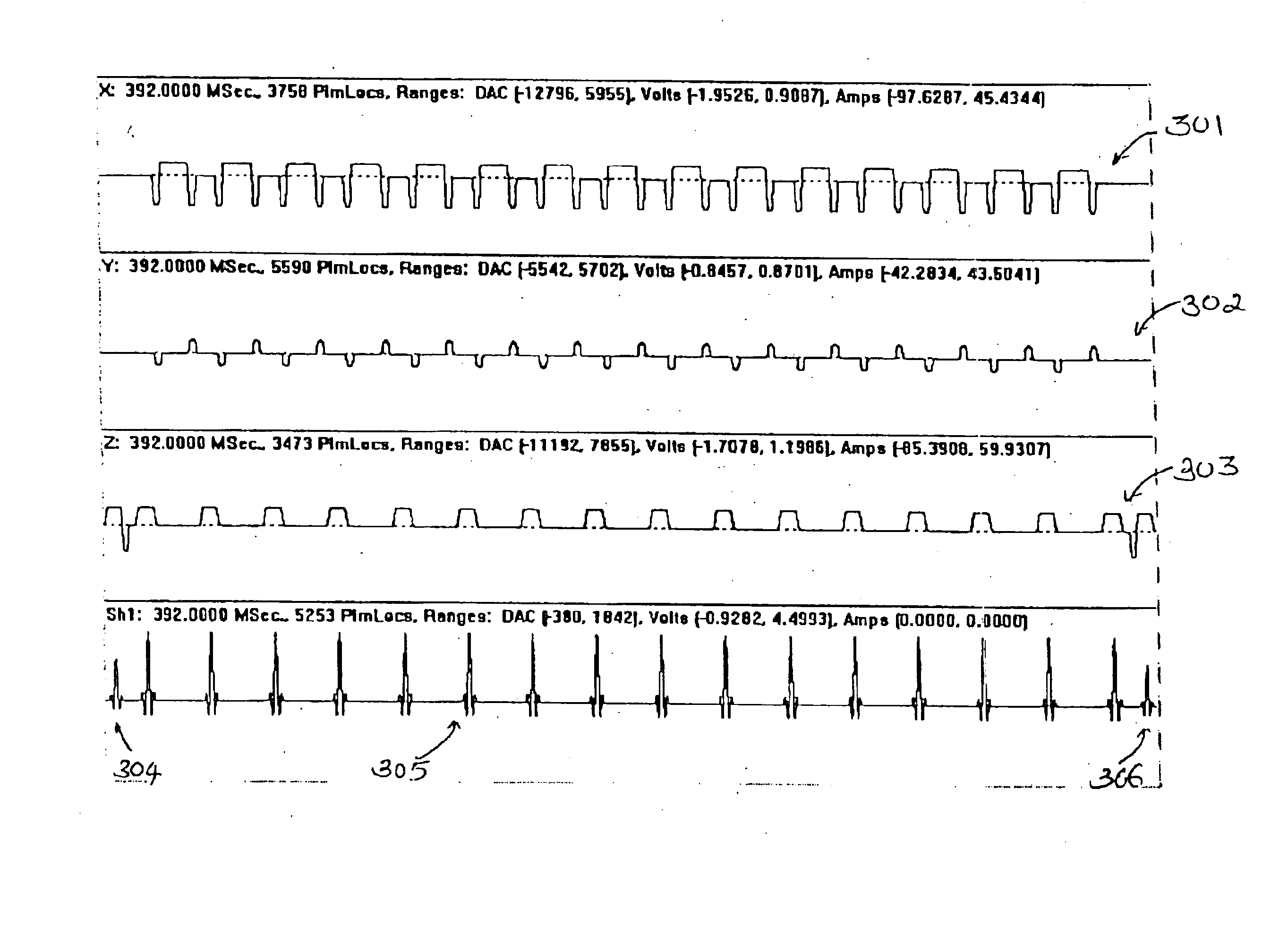
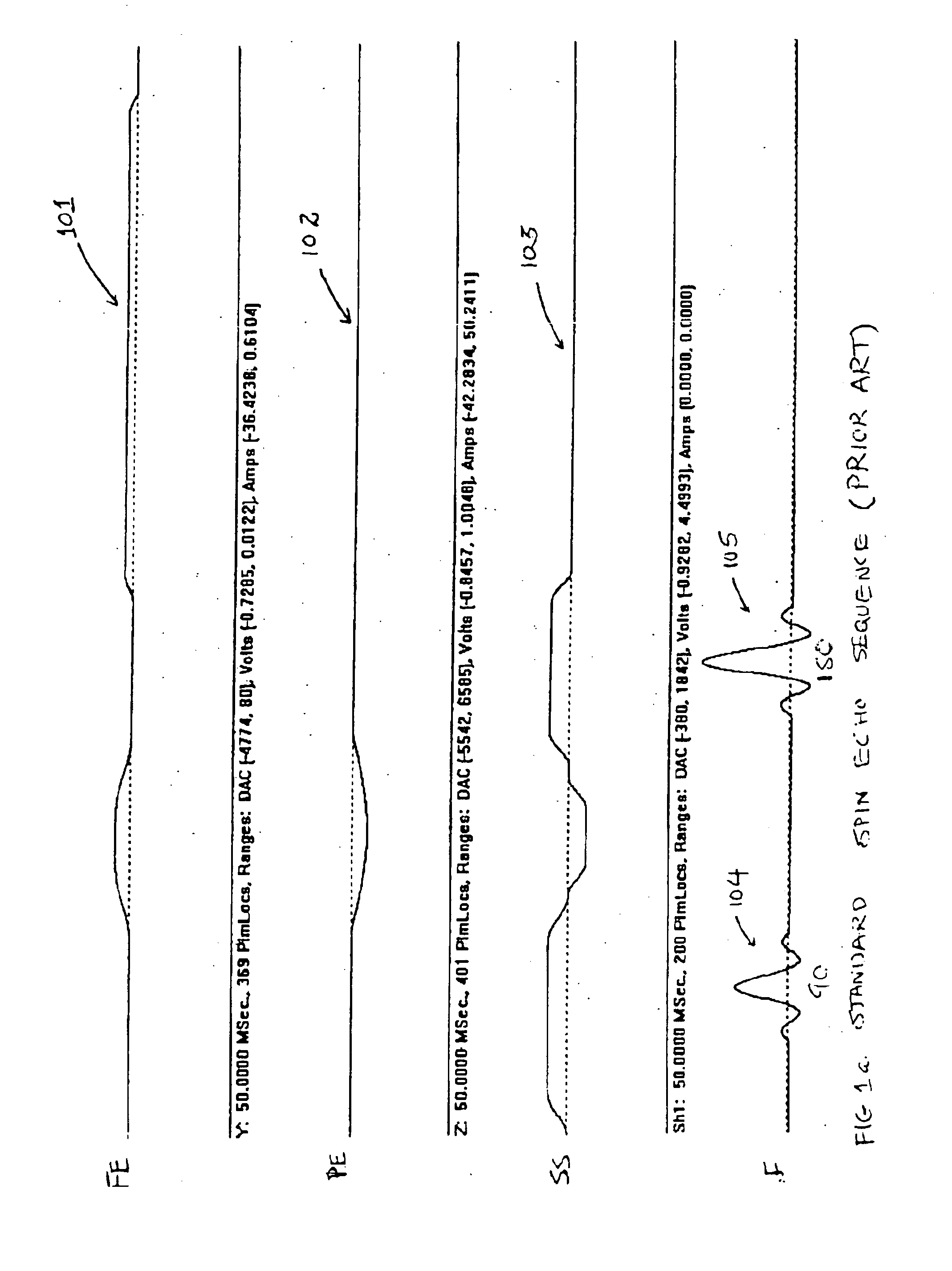
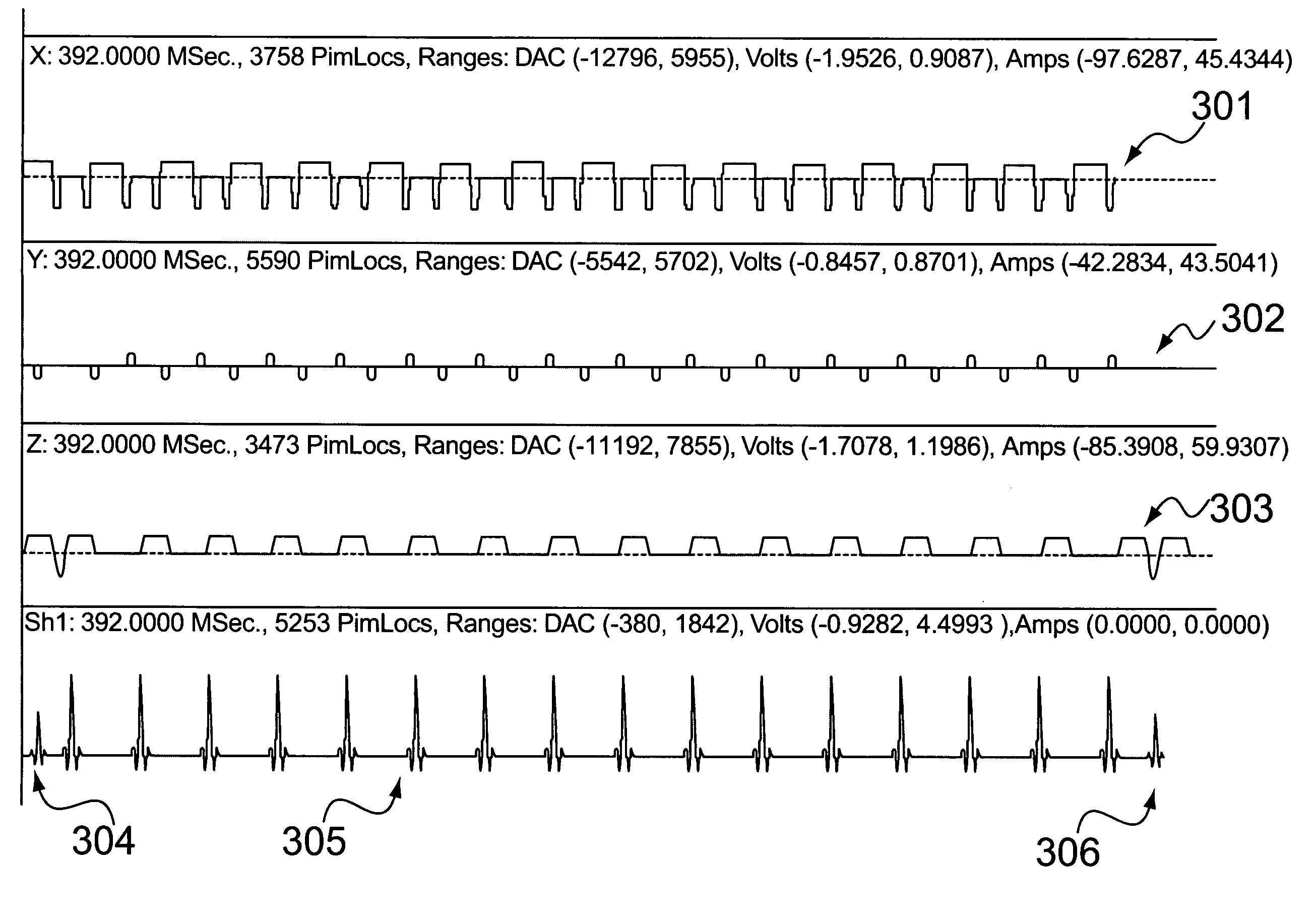
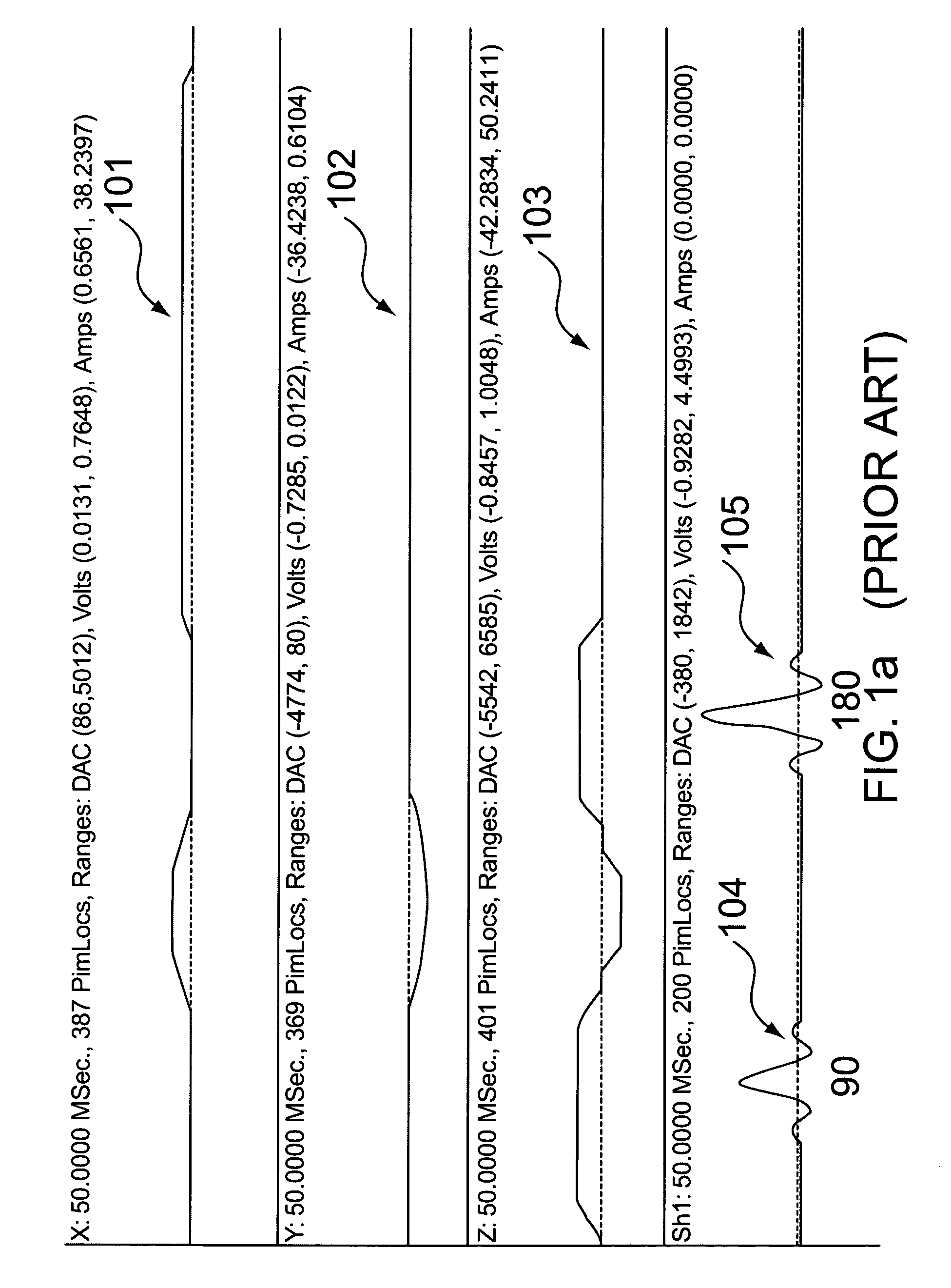
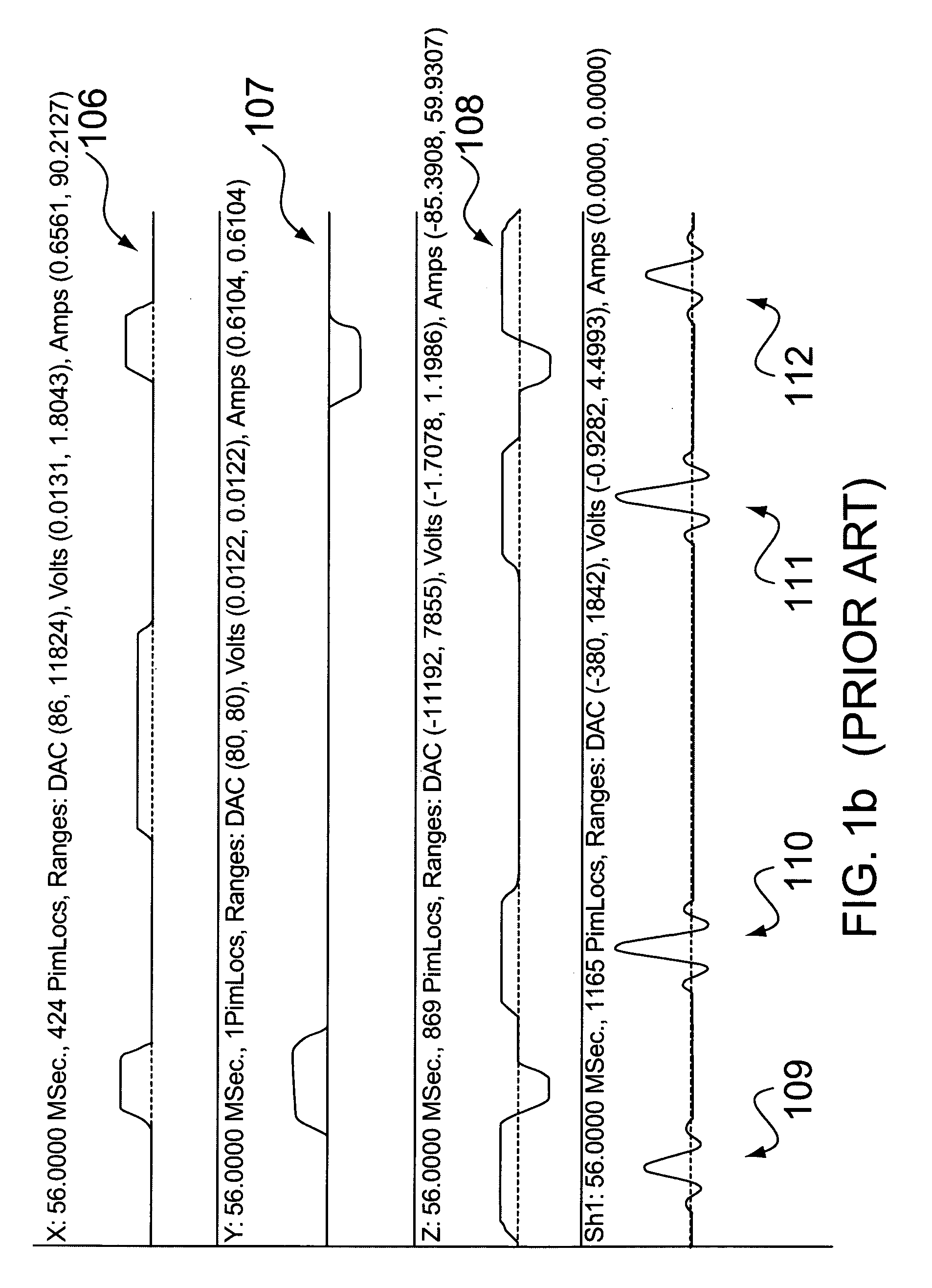
Patents
Literature
83 results about "Fast spin echo" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Fast spin echo. Dr Daniel J Bell ◉ and Dr Zach Drew et al. Fast or turbo spin echo (FSE/TSE) is an adaptation of conventional spin-echo (SE) acquisition technique designed to reduce imaging time. It has largely supplanted the original spin-echo technique due to vastly improved imaging speed.
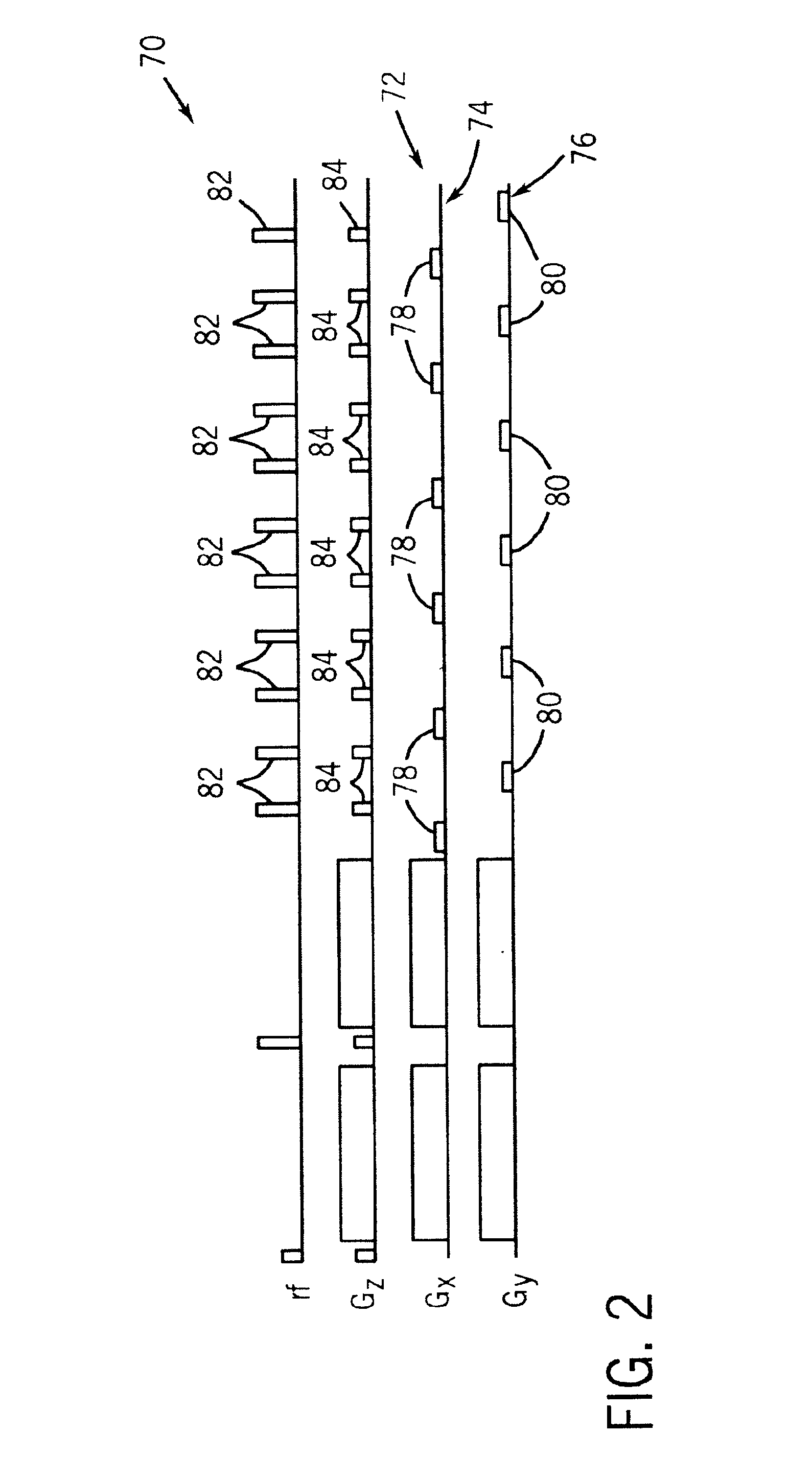
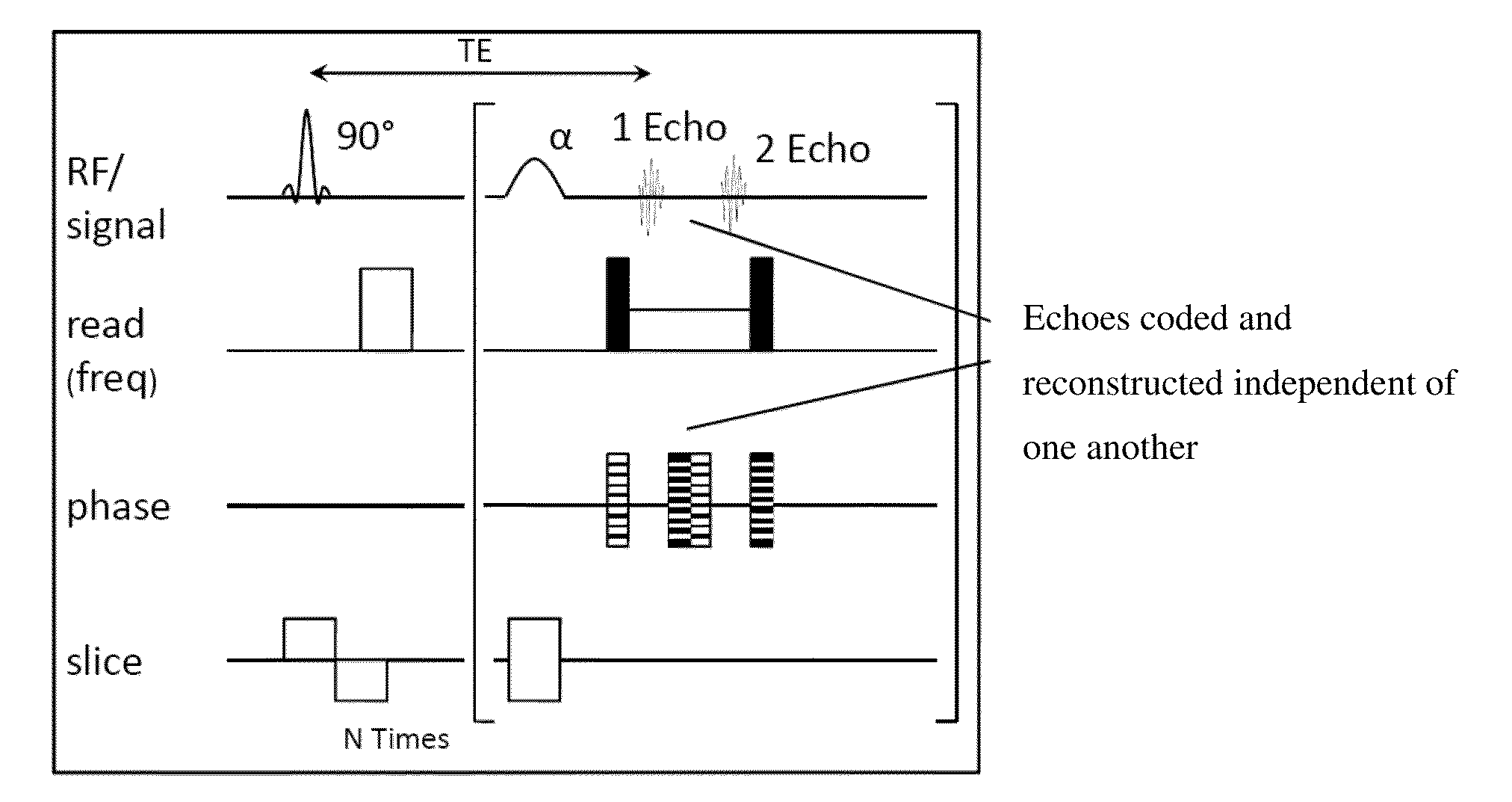
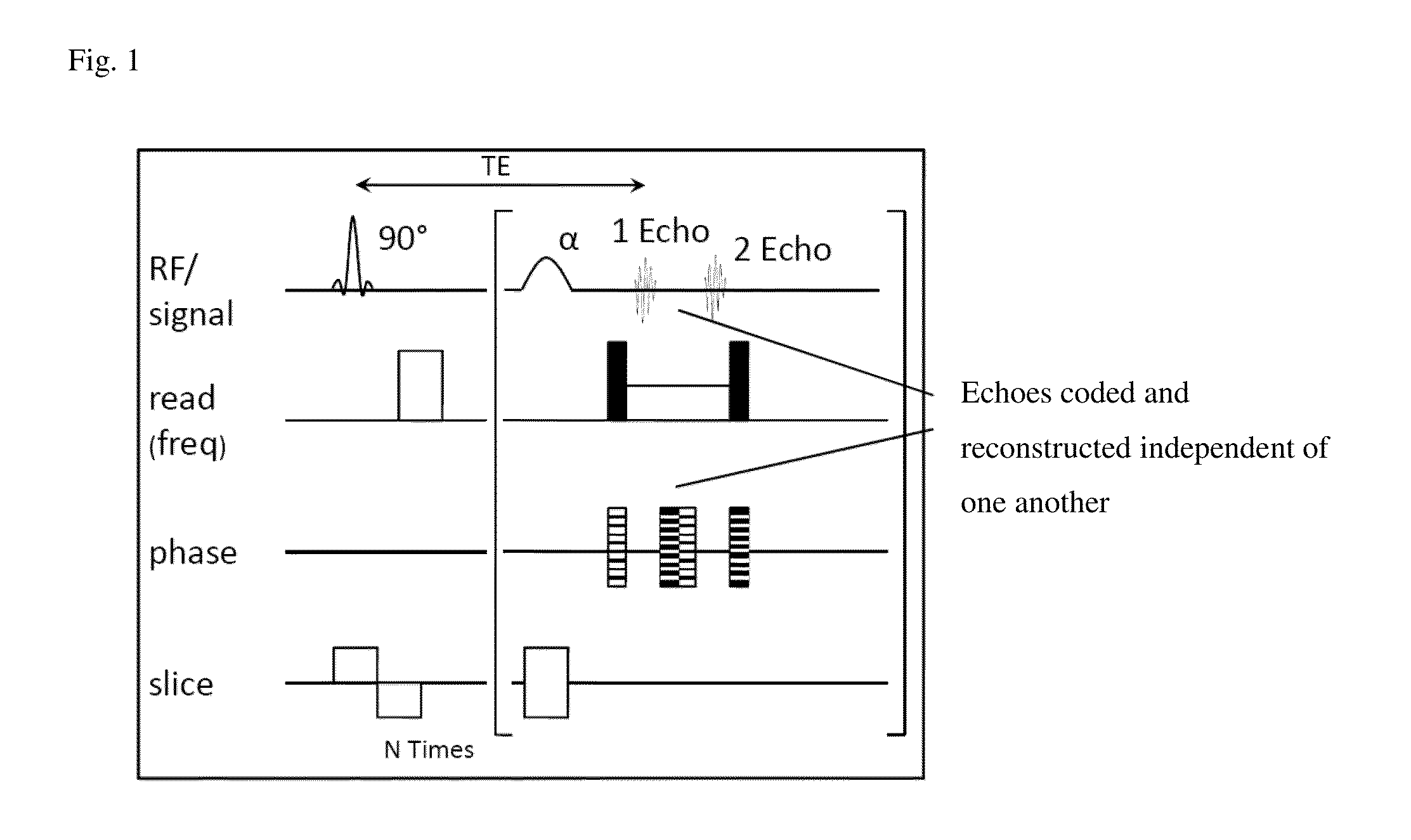
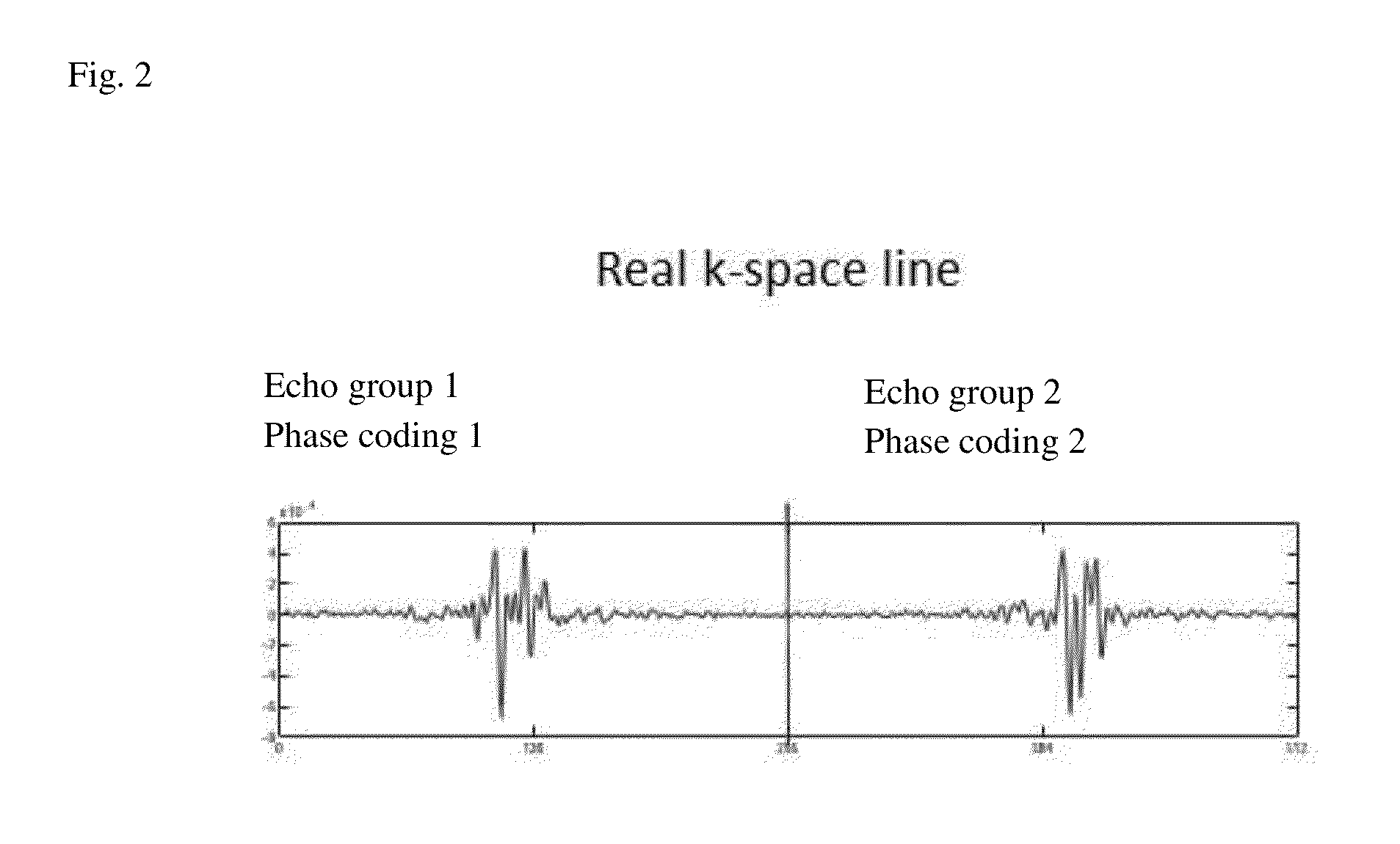
Correcting method for quick-speed spin echo pulse sequence and uses thereof
InactiveCN101162262AResolve ArtifactsEliminate image quality effectsMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringFast spin echoStimulated echo
The invention provides a method for correcting fast spin echo sequence, aiming at solving the problem that the prior FSE images have the factors of an imaging system such as artifacts, magnetic field stability, eddy current, etc. which have impact on the quality of images. The method can be used to correct the parameter of the fast spin echo (FSE) sequence of a magnetic resonance diagnostic, in particular to correct the parameter of the fast spin echo (FSE) sequence of a magnetic resonance diagnostic which can switch frequence of a transmitter and a receiver. The method for correcting fast spin echo sequence of the invention eliminates the impact of the factors of the imaging system such as artifacts, magnetic field stability, eddy current, etc. on the quality of the images; and as the parameter which is obtained by the correcting method and used in the pre-scanning is the optimal parameter, thereby solving the problem of artifacts of the prior FSE images.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Split-blade data collection for propeller MRI
InactiveUS6882148B2Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionFast spin echoPhase correction
The present invention provides a system and method of MR imaging particularly applicable with fast spin echo protocols. Odd and even echoes are used to create separate blades or strips in k-space. Preferably, each blade extends through the center of k-space. The blades are incrementally rotated about the center of k-space with each echo train until a full set of k-space data is acquired. After a phase correction, each odd and even blade is combined into a single k-space data set that is used for image reconstruction.
Owner:CATHOLIC HEALTHCARE WEST CALIFORNIA NONPROFIT PUBLIC BENEFIT D B A ST JOSEPHS HOSPITAL & MEDICAL CENT
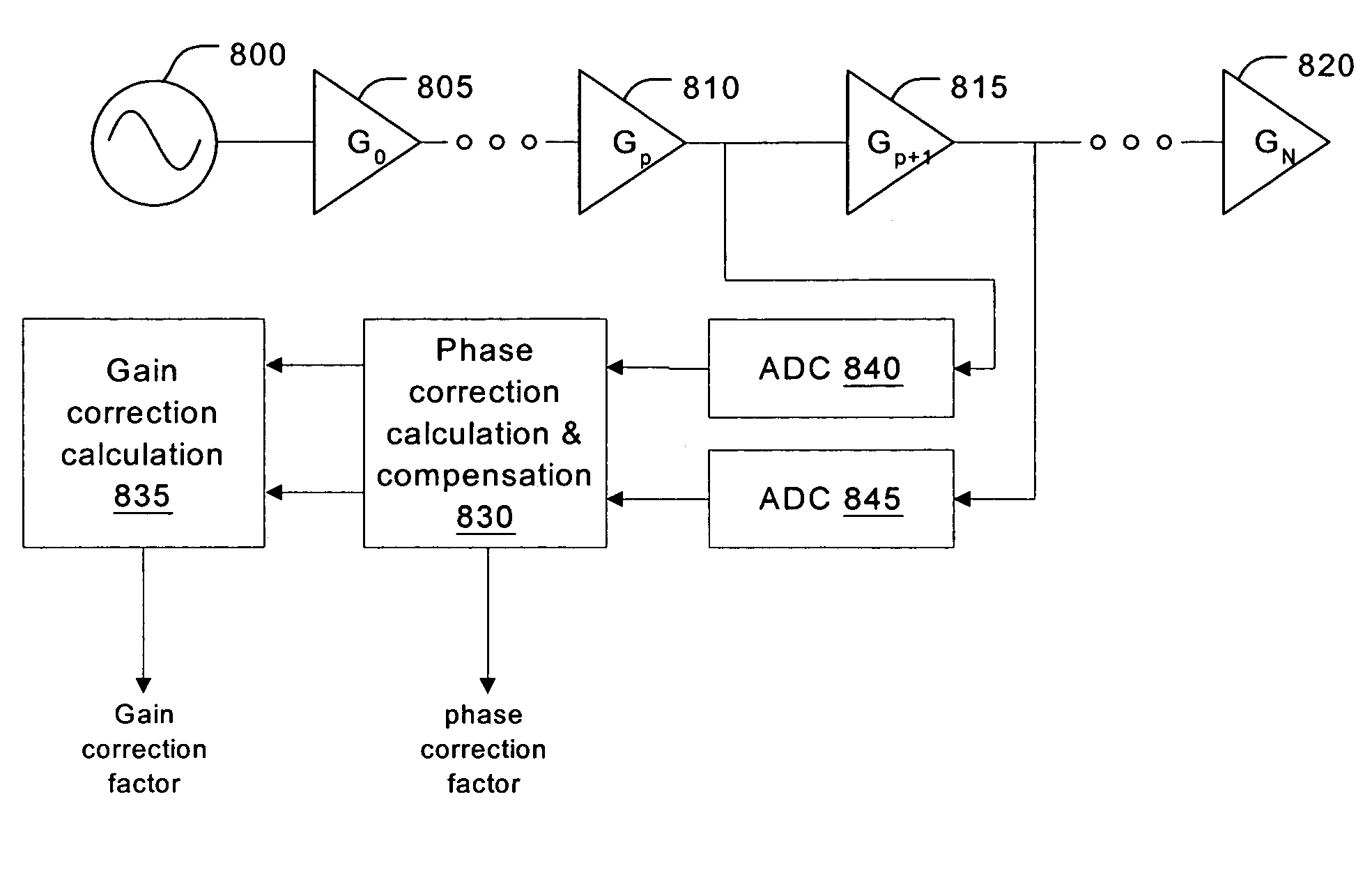
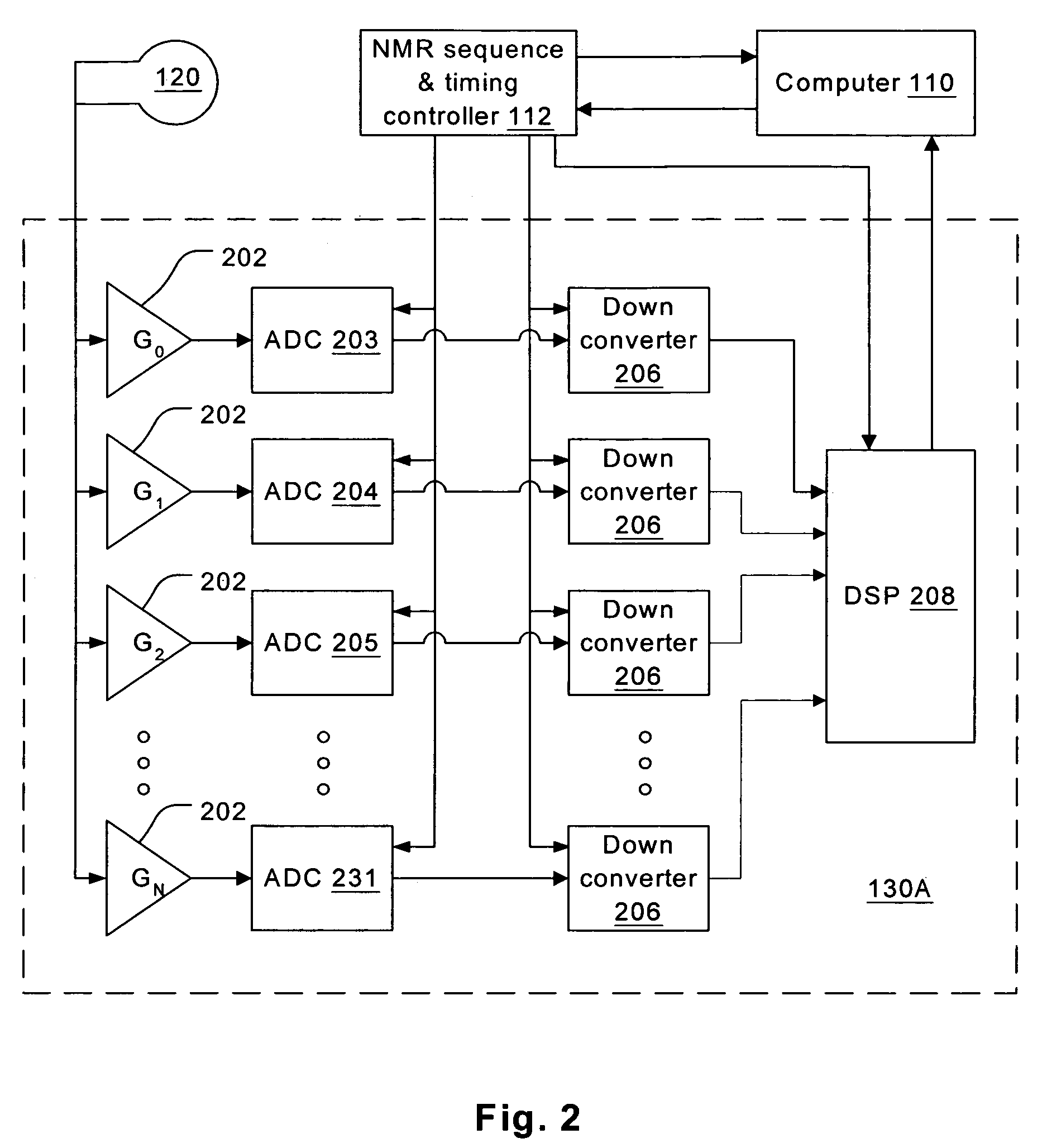
Adaptive dynamic range receiver for MRI
InactiveUS7403010B1Avoid the needLimited dynamic rangeElectric signal transmission systemsMagnetic measurementsFast spin echoRapid imaging
A receiver for a resonance signal of a magnetic resonance imaging system generates a baseband signal for image processing by dividing a raw resonance signal among multiple parallel channels, each amplified at a respective gain. A digital channel selector determines, at any given moment, a lowest-distortion channel to be further processed. Amplitude and phase error compensation are handled digitally using complex multipliers, which are derived by a calibration, based on a simple Larmor oscillator, which can be done without the need for a sample and without repeating when measurement conditions are changed. One of the important benefits of the invention is that it provides for gain selection without repeated calibration steps. This is particularly important in systems that employ fast imaging techniques such as fast spin echo, where the invention can speed imaging substantially.
Owner:FONAR
Gradient system time delay correction method for fast spin echo pulse sequence
InactiveCN102096054AReduce hardware costsReduce system complexityMagnetic measurementsFast spin echoCoronal plane
The invention provides a gradient system time delay correction method for a fast spin echo pulse sequence. In the method, a gradient system time delay is corrected by correcting a gradient pulse, and an amplitude synthetic matrix for correcting the gradient pulse is calculated by using the normalized gradient system time delay. By the method, the influence of the gradient system time delay on thefast spin echo pulse sequence is overcome, and the hardware cost and the system complexity of a magnetic resonance imaging system are not increased; and even if the gradient system time delays in x, y and z directions are unequal, the power of a gradient power amplifier is not enough to provide overshooting impulse with larger amplitude in a gradient waveform. By the method, the gradient system time delay can still be corrected so as to enhance the image quality of a sagittal plane, a coronal plane, a cross section and various diagonal planes in a fast spin echo image.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
Water and fat separation imaging method and device in magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveCN103257333ALower Momentum RequirementsReduce the amplitudeMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsFast spin echoFourier transform on finite groups
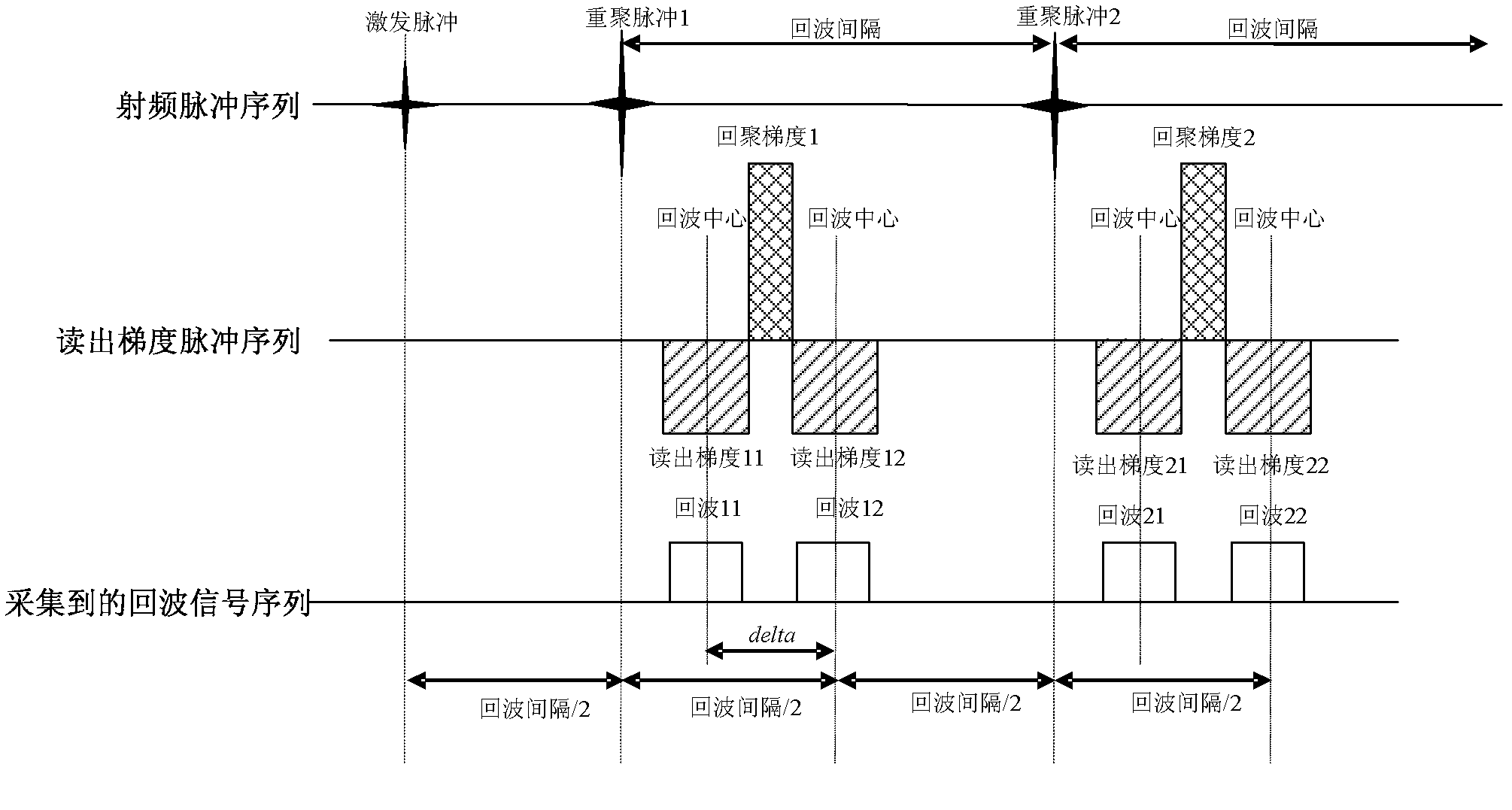
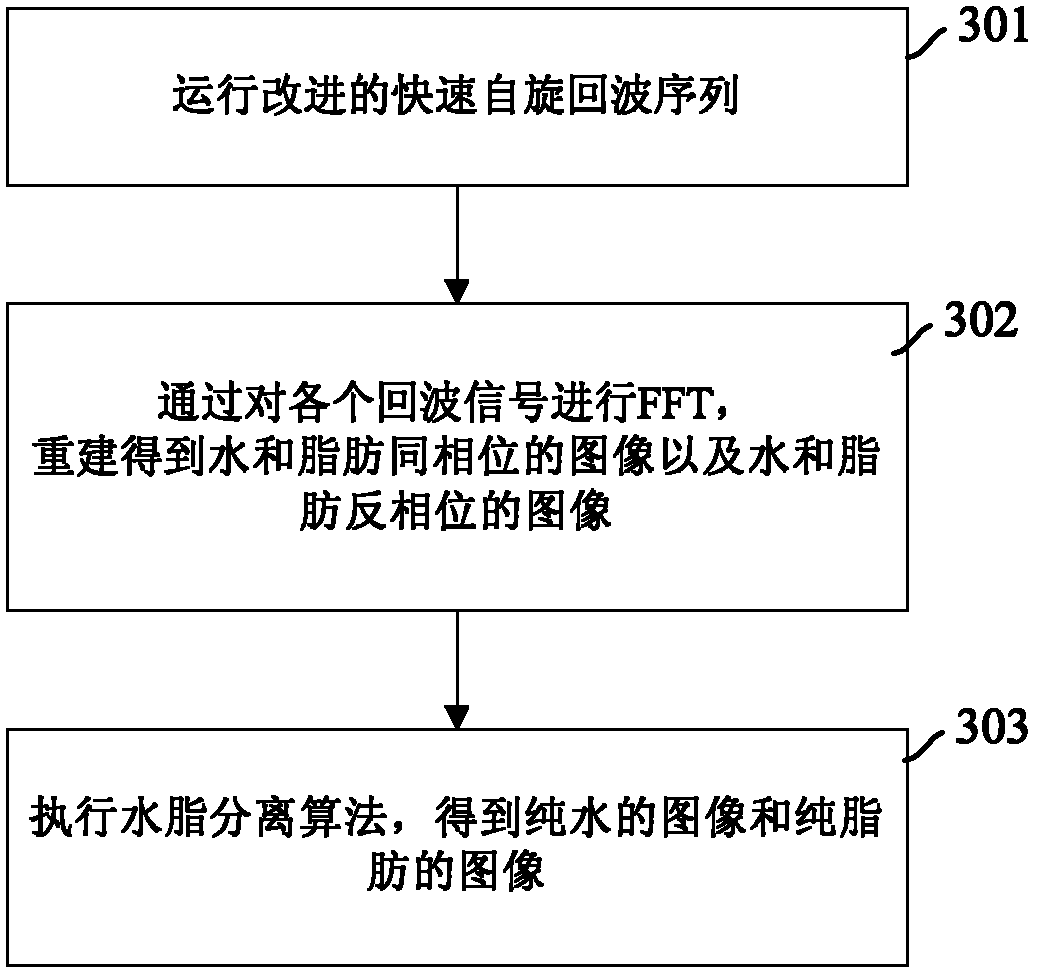
The invention discloses a water and fat separation imaging method in magnetic resonance imaging. A fast spin echo sequence based on a two-point Dixon method is adopted, wherein each refocusing radio-frequency pulse corresponds to two read-out gradients having the same polarity and a rephasing gradient having the opposite polarity, the two read-out gradients corresponding to each refocusing radio-frequency pulse are respectively divided into a front portion and a rear portion through the echo center of each of the two read gradients, the area of the rear portion of the front read gradient is less than that of the front portion of the front read gradient, and the area of the front portion of the rear read gradient is less than that of the rear portion of the rear read gradient. The method comprises operating the fast spin echo sequence; conducting fast Fourier transform (FFT) on each collected echo signal, rebuilding and obtaining water and fat in-phase images and water and fat antiphase images; conducting Fourier transform on the data executing portion of each echo signal; carrying out the water and fat separation algorithm on the water and fat in-phase images and the water and fat antiphase images to obtain pure water images and pure fat images. The invention further provides a corresponding device which can resolve the problem of image artifacts.
Owner:SIEMENS SHENZHEN MAGNETIC RESONANCE
Magnetic resonance quick spin echo imaging method
InactiveCN101357063ANo reduction in image signal-to-noise ratioNo degradation of image signal-to-noise ratioMagnetic property measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringFast spin echoTransverse relaxation
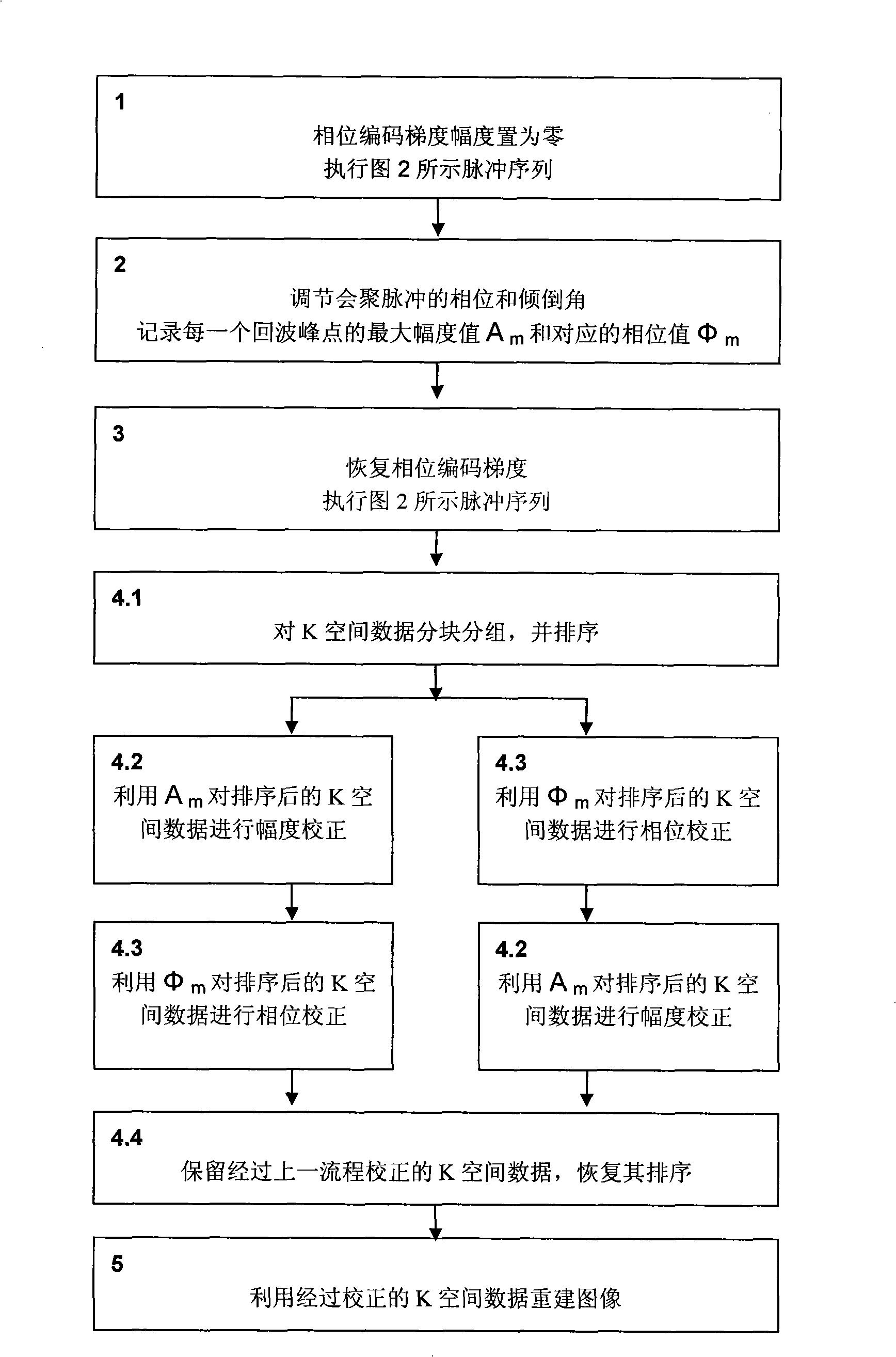
The invention relates to the field of magnetic resonance imaging technique, in particular to a magnetic resonance fast spin echo (FSE) imaging method, comprising the steps as follows: 1. phase coding gradient amplitude is reset, pre-scanning is carried out by FSE pulse sequence, the amplitude value of each etch signal peak on the echo chain is recorded; 2. the phase and inclination angle of convergence pulse is adjusted so as to lead the amplitude of each echo signal peak on the echo chain to achieve the maximum value, when the amplitude value Am and phase angle Phim of each echo signal peak are recorded; 3. the phase coding gradient is recovered, the scanning is carried out by the FSE pulse sequence, thus gaining the K space data; 4. according to the amplitude Am and Fai<m> of each echo signal peak gained in step 2, the K space data is corrected; 5. image reconstruction is carried out by the corrected K space data thus gaining the magnetic resonance images, etc. The magnetic resonance fast spin echo (FSE) imaging method solves the problems of echo amplitude phase oscillation and image blurring due to transverse relaxation of the prior art.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Water-fat separation for fast spin echo imaging in an inhomogeneous field with progressive encoding
ActiveUS7141972B2Diagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsFast spin echoInhomogeneous field
Owner:TOSHIBA AMERICA MRI
Water-fat separation for fast spin echo imaging in an inhomogeneous field with progressive encoding
ActiveUS20050122105A1Reversed fasterDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsFast spin echoInhomogeneous field
Owner:TOSHIBA AMERICA MRI
Method for generating T1-weighted magnetic resonance images and quantitative T1 maps
ActiveUS7276904B2Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionFast spin echoResonance
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Method for optimizing radio frequency impulse phases in fast spin echo impulse sequence
ActiveCN103278785AReduce dependencyImprove optimization efficiencyMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsFast spin echoStimulated echo
The invention provides a method for optimizing radio frequency impulse phases in a fast spin echo impulse sequence. According to the method, a spin echo and an excited echo are separated through the difference of effects of the spin echo and the excited echo according to spoiled gradients so as to ensure that the spin echo coincide with the excited spin echo more accurately; an optimized inversion impulse phase can be acquired through simple calculation according to the phase relation of the spin echo and an inversion impulse and the relation of the excited echo and the inversion impulse. The method for optimizing the radio frequency impulse phases in the fast spin echo impulse sequence can reduce the affect of unsatisfactory factors of instrument hardware on an FSE sequence parameter optimization process and the degree of dependence of the optimal parameter searching process on the phase step precisions, and therefore optimizing efficiency is improved.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV +1
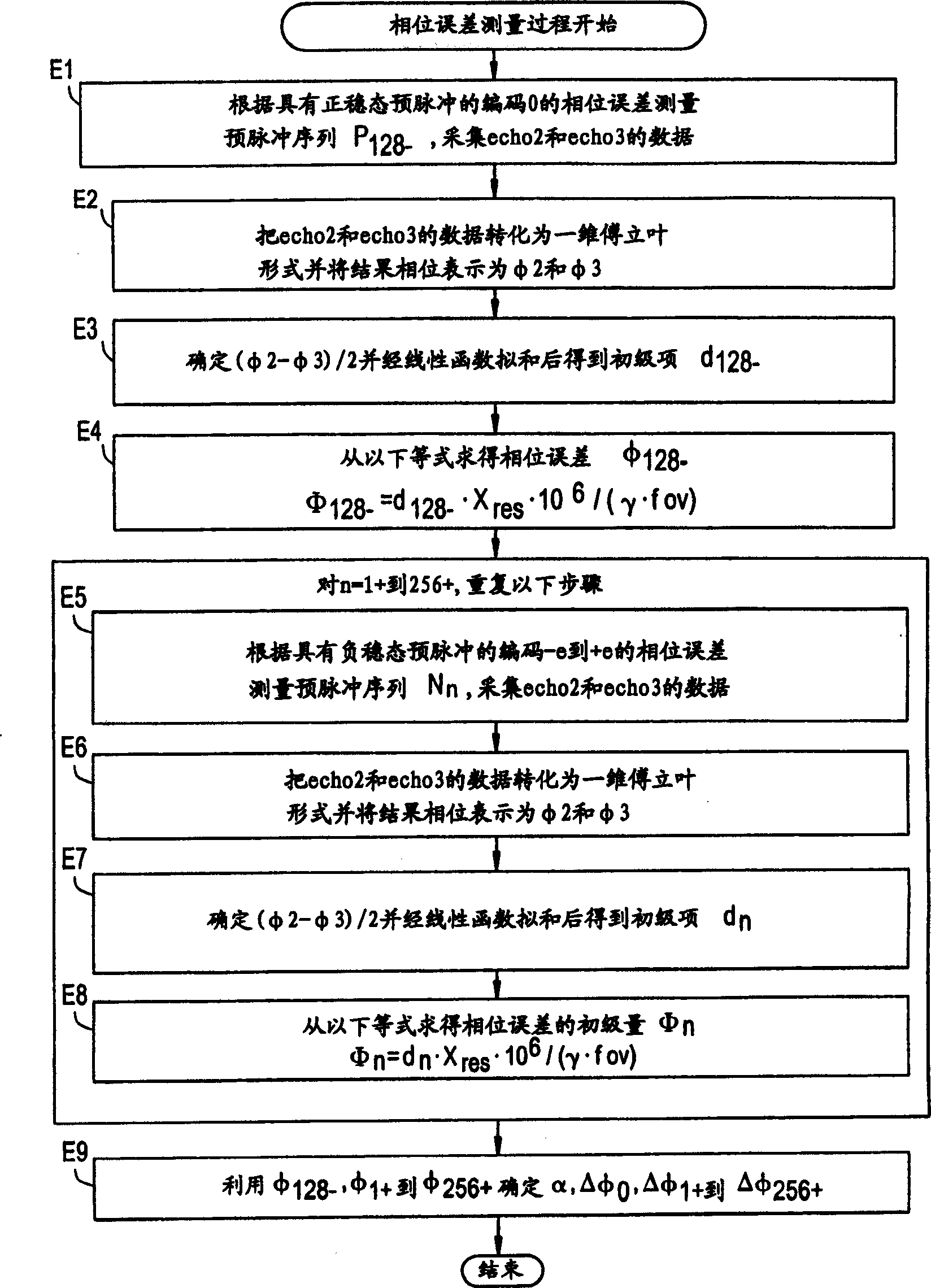
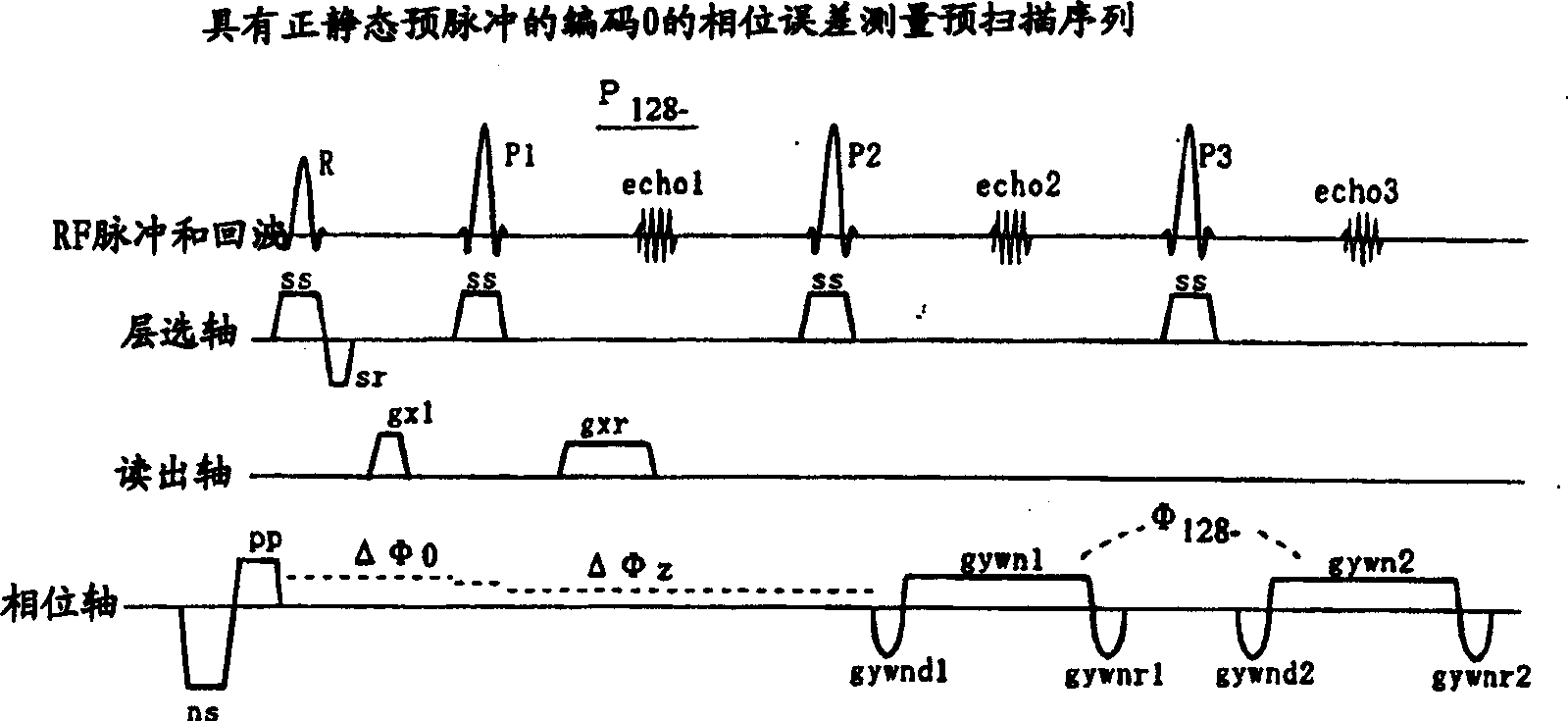
MR imaging method, phase error measuring method and MRI system
InactiveCN1363044ASuppresses the influence of residual magnetismReduce image quality degradationMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyDiagnostic recording/measuringFast spin echoImaging quality
The present invention aims to reduce degradation in image quality due to residual magnetization. In a pulse sequence of a high-speed spin echo process, a pre-pulse is applied before an excitation pulse, and a correction pulse for correcting a phase error caused by the pre-pulse is applied before an initial inversion pulse.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
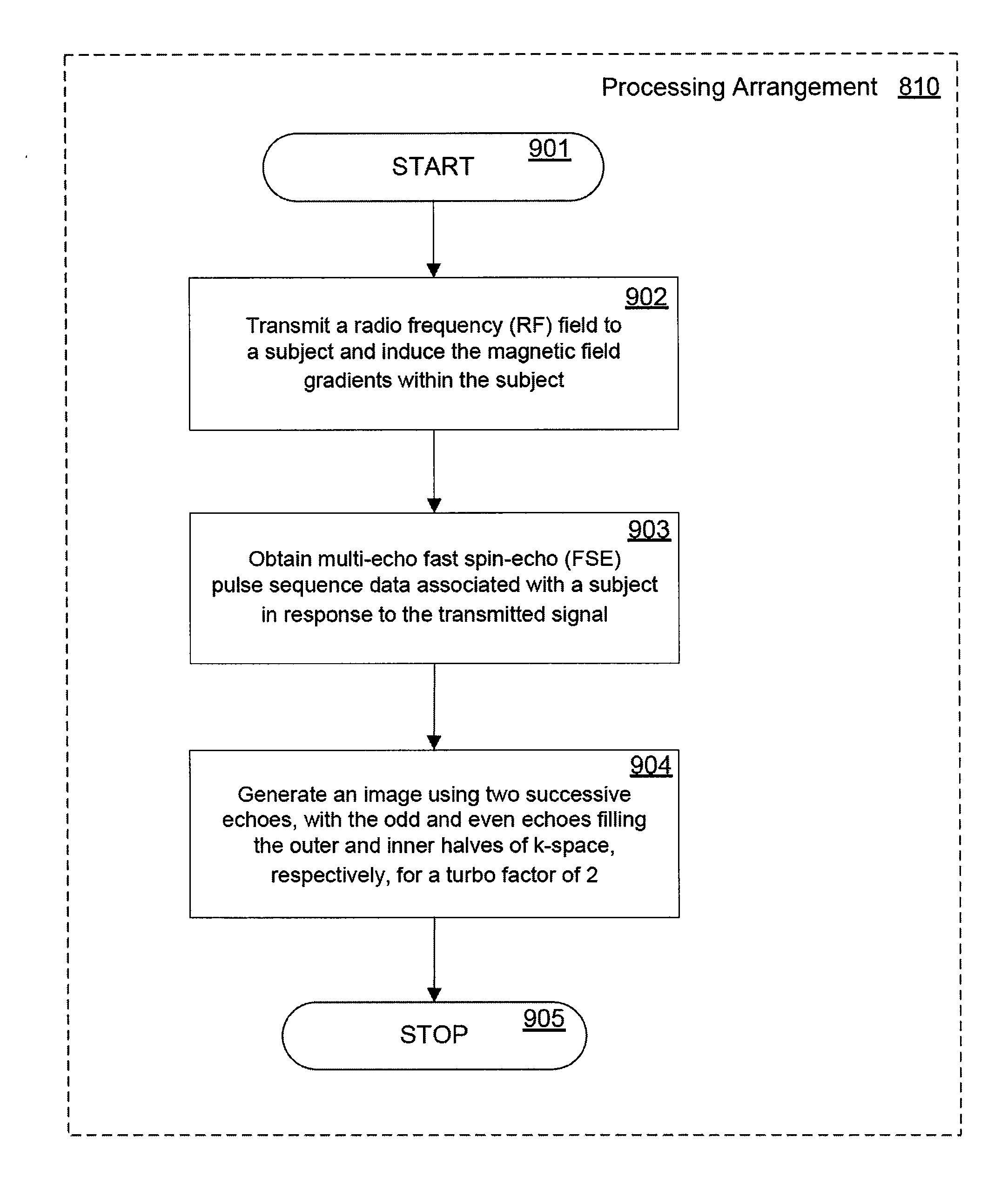
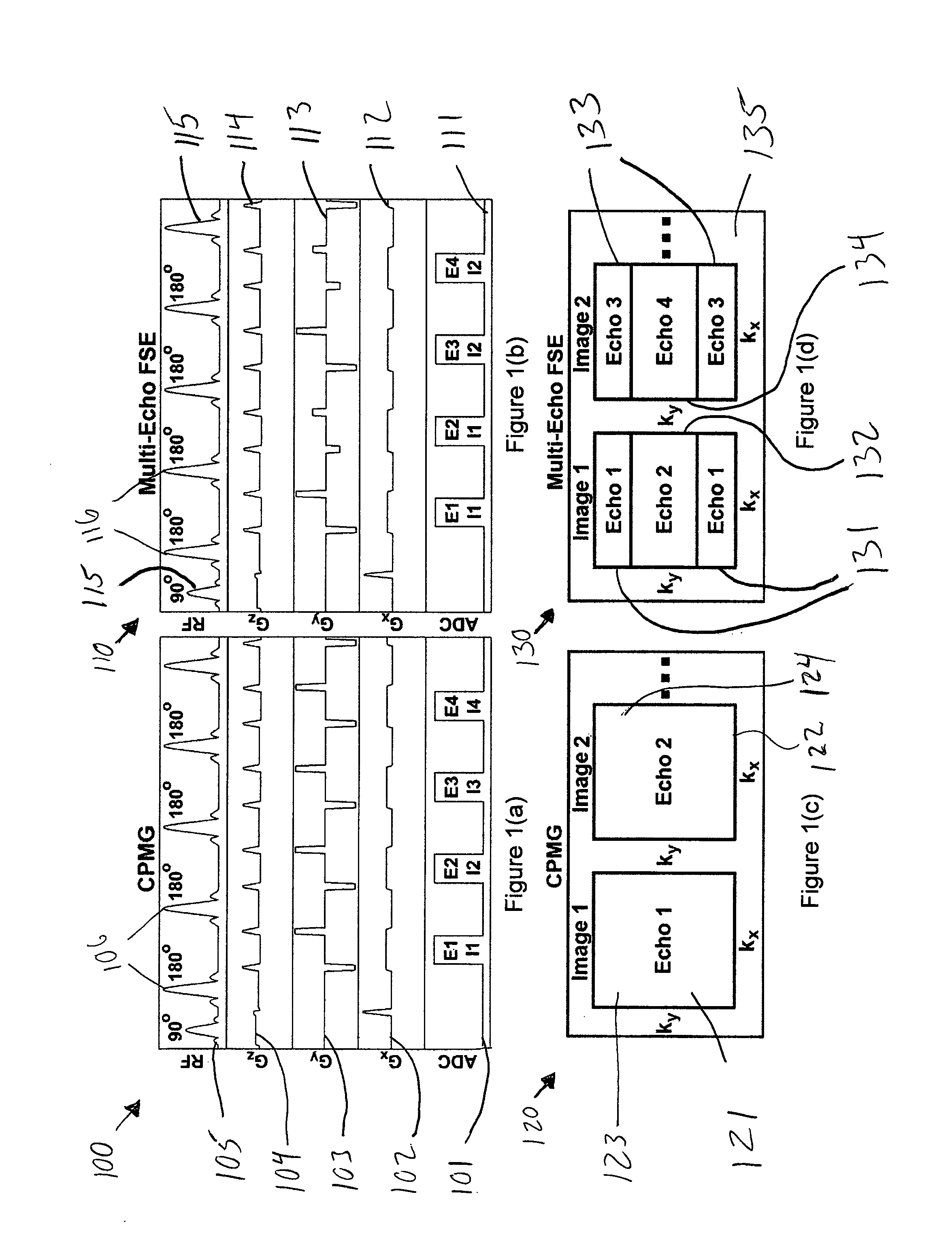
System, method and computer-accessible medium for providing breath-hold multi-echo fast spin-echo pulse sequence for accurate r2 measurement
ActiveUS20100301860A1Accurate measurementMean usedMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionAnatomical structuresFast spin echo
Exemplary embodiments of system, method and computer-accessible medium can be provided in accordance with the present disclosure can be provided for generating a plurality of images associated with at least one anatomical structure using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data. For example, using such exemplary embodiments, it is possible to obtain at least one multi-echo fast spin-echo (FSE) pulse sequence based on the MRI data, which can include, e.g., hardware specifications of the MRI system. Further, it is possible to generate each of the images based on a particular arrangement of multiple echoes produced by the multi-echo FSE pulse sequence(s).
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV +1
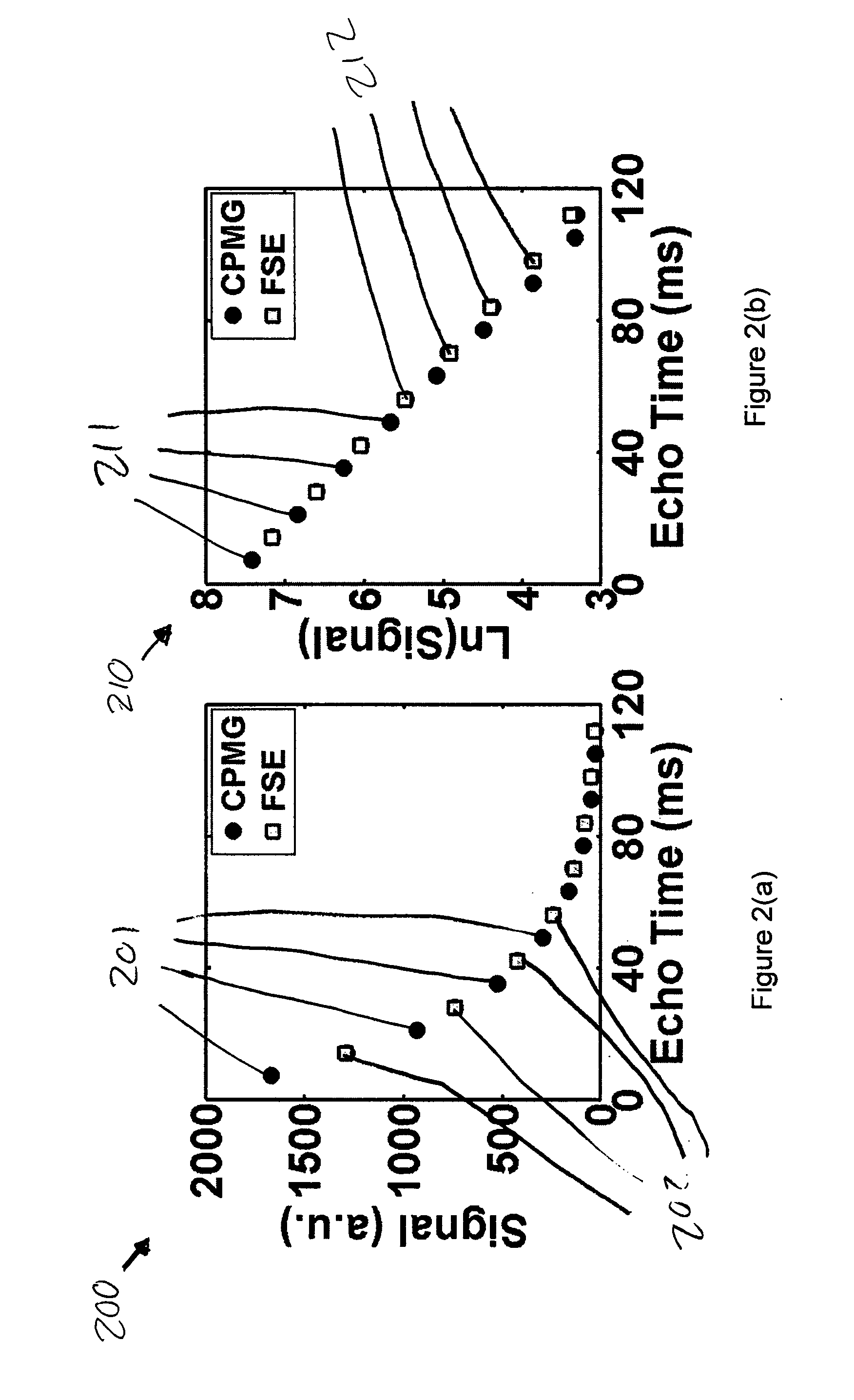
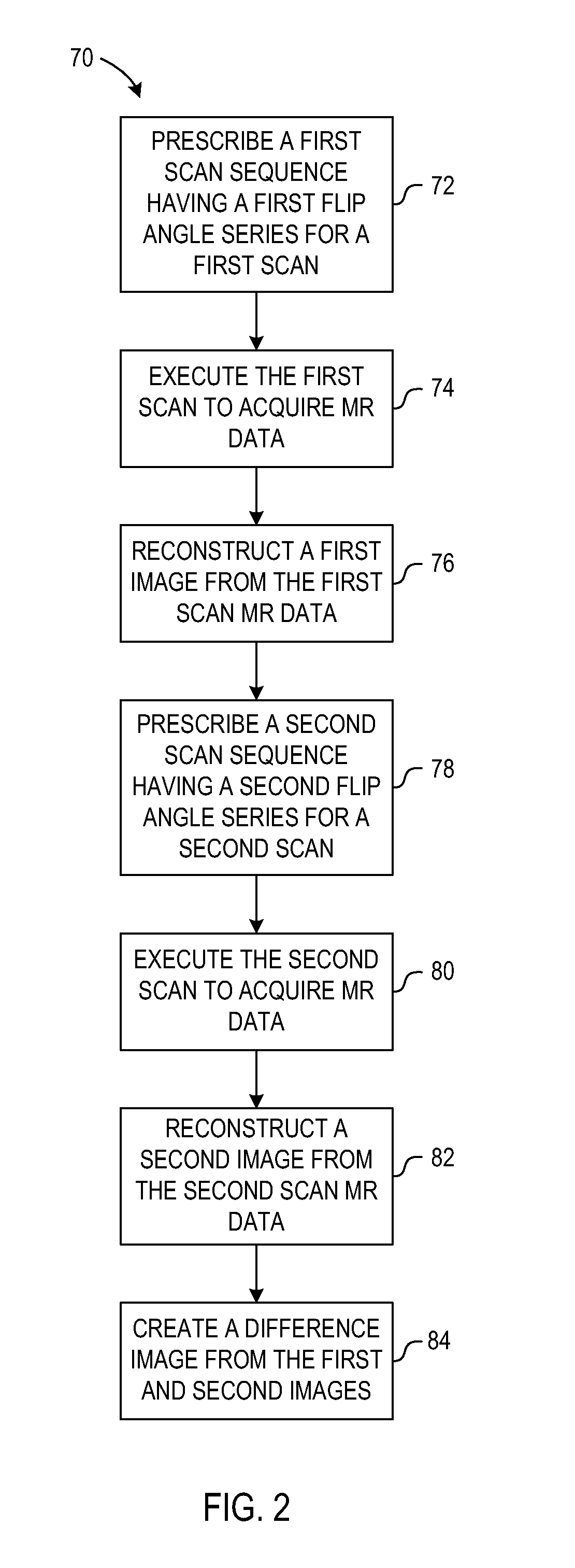
System and method for enhanced contrast mr imaging
ActiveUS20120212222A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionFast spin echoObject based
A system and method for enhanced contrast MR imaging include a computer programmed to perform a first scan of an imaging object based on a first fast spin echo (FSE) scan sequence comprising a first series of RF pulses having a first flip angle sequence to acquire a first MR data set and perform a second scan of the imaging object based on a second FSE scan sequence comprising a second series of RF pulses having a second flip angle sequence, wherein the second flip angle sequence is different from the first flip angle sequence to acquire a second MR data set. The computer is further programmed to generate a difference image based on the first and second MR data sets.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Medical image processing method
InactiveCN103810754AAccurate guideImage analysisComputerised tomographsFast spin echoFluoroscopic image
Owner:姜卫剑
Apparatus, method, and computer-accessible medium for b1-insensitive high resolution 2d t1 mapping in magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS20120271147A1Improve spatial resolutionImprove signal-to-noise ratioDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsAnatomical structuresFast spin echo
Exemplary systems, methods and computer-accessible mediums can be provided for imaging at least one anatomical structure. For example, it is possible to direct a saturation-recovery (SR) pulse sequence having fast spin echo (FSE) to or at the anatomical structure(s). At least one T1 image of the at least one anatomical structure can be generated based on the SR pulse sequence. In one example, the anatomical structure(s) can include a hip. According to another example, T1 image(s) can include a plurality of T1 images generated or provided in a plurality of rotating radial planes.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
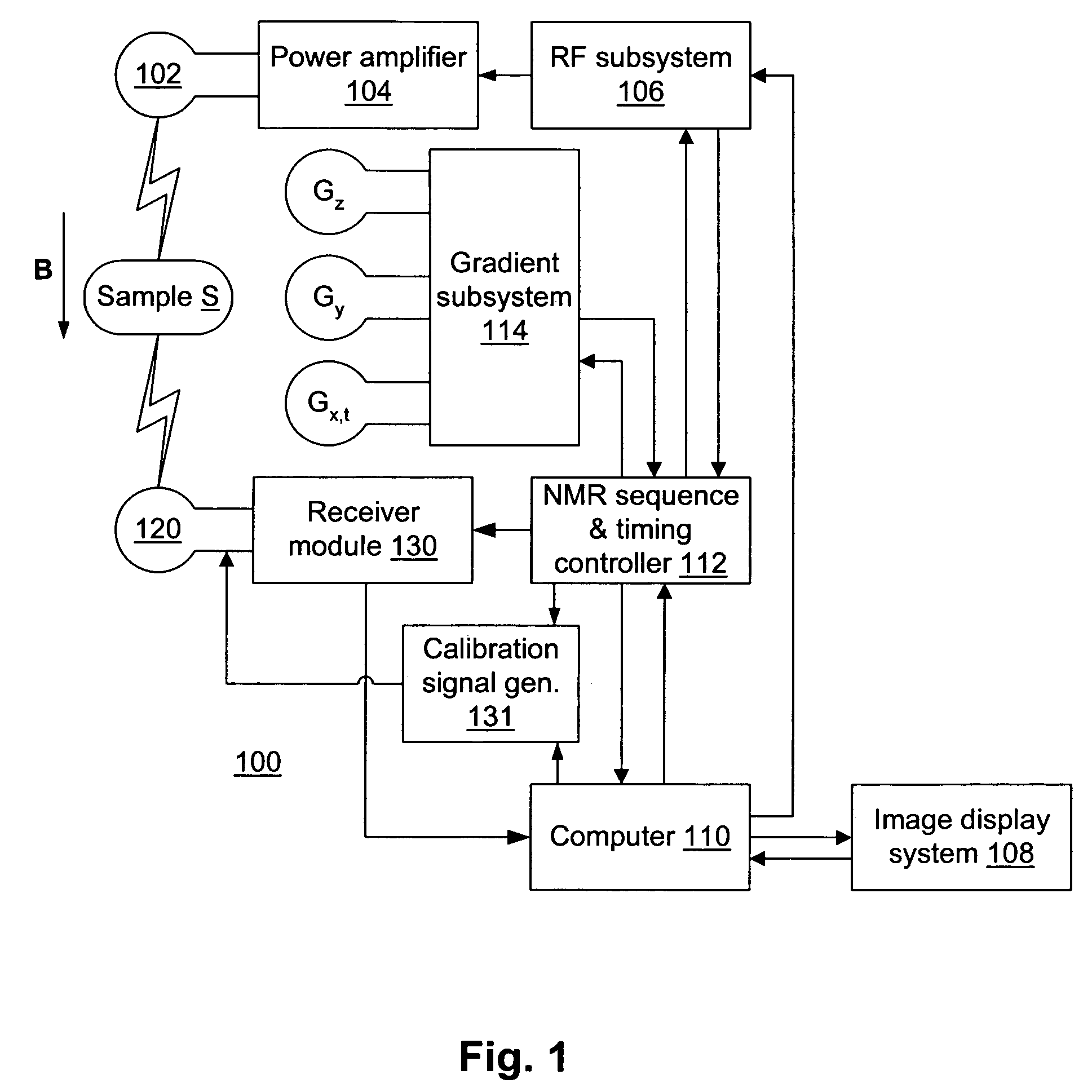
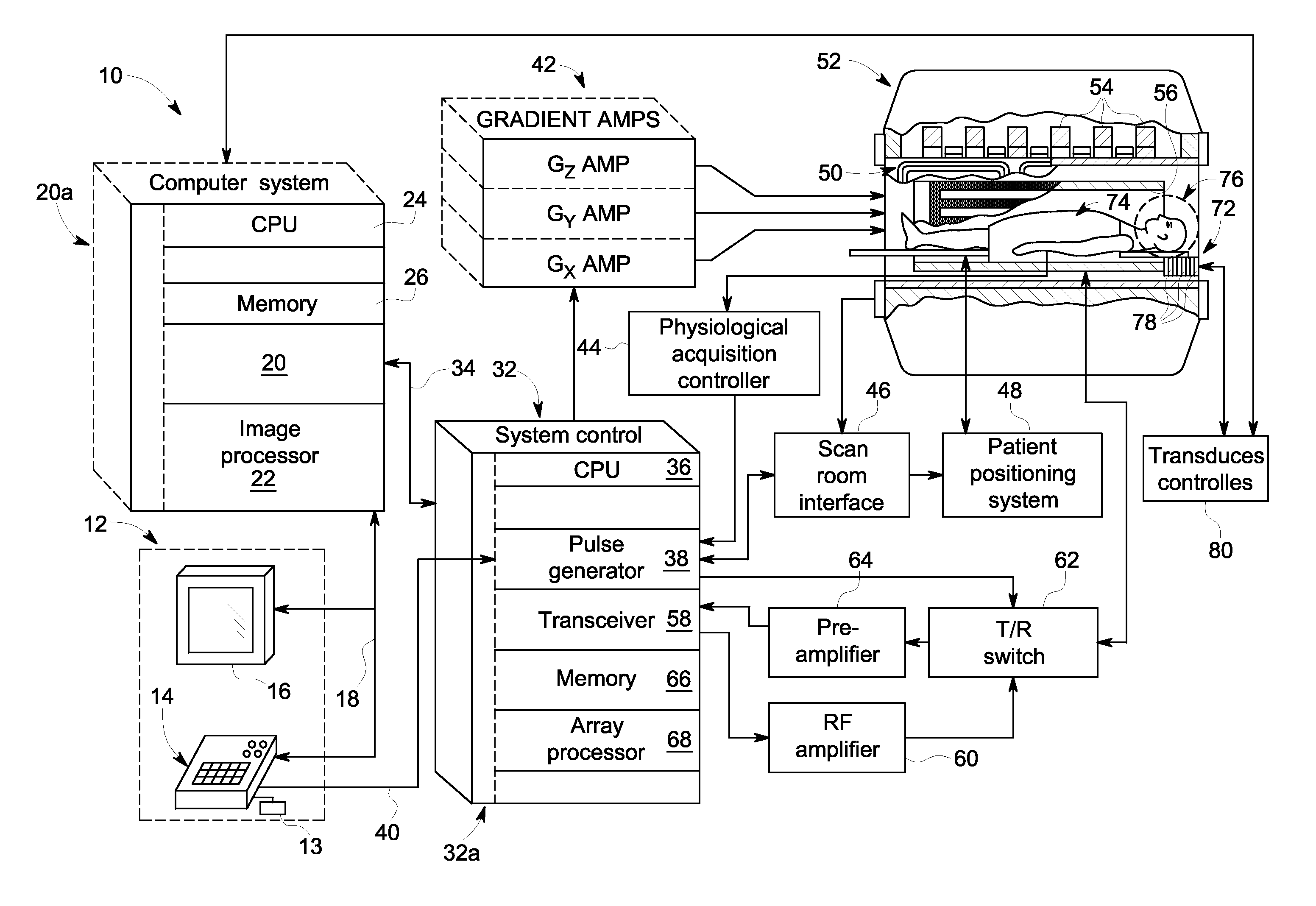
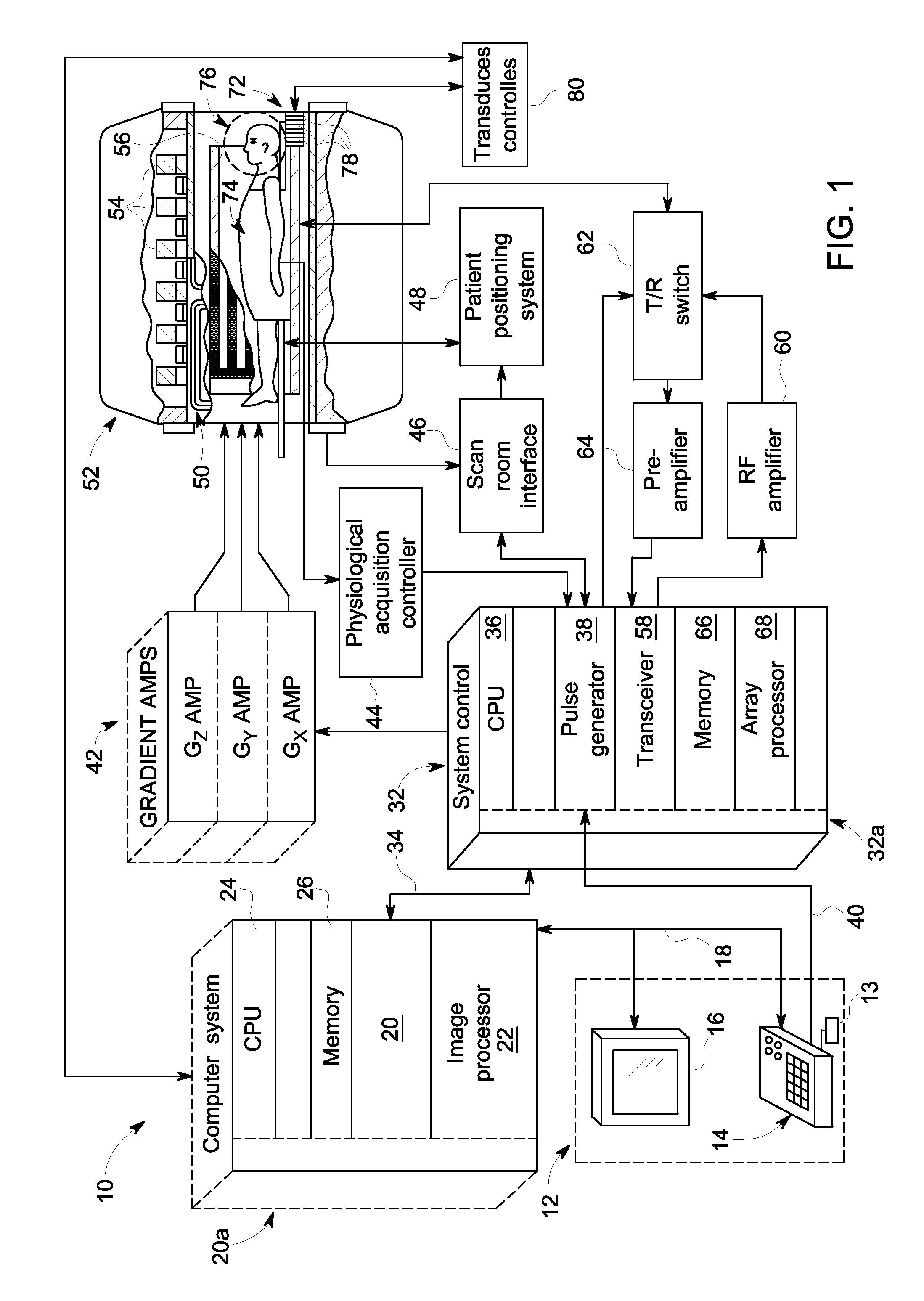
Method and apparatus for MR image acquisition
InactiveUS7061241B2Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionFast spin echoMedicine
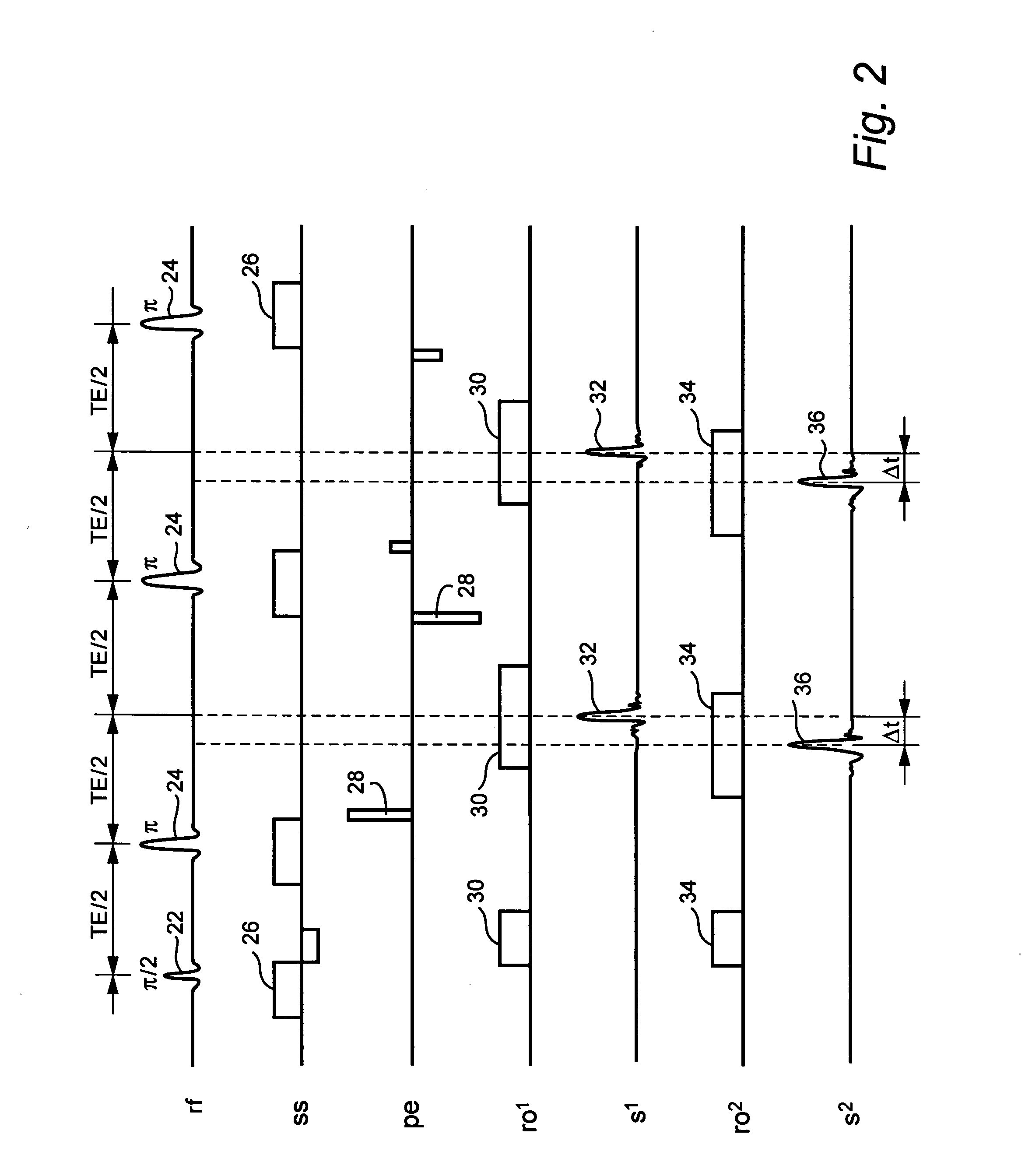
An NMR image of a patient's heart uses SSFSE (single shot fast spin echo) type pulses to condition the body by a preparation of a phase-encoding gradient pulse whose duration differs from one sequence to another so as to define, from one sequence to another, a different effective echo time. At each sequence an image is displayed representing the discrimination of the contributions of the particles of the body as a function of their time T2 compared with this effective time. For the heart, with a single respiration on the part of the patient, lesions due to infarction and transplant rejection are revealed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
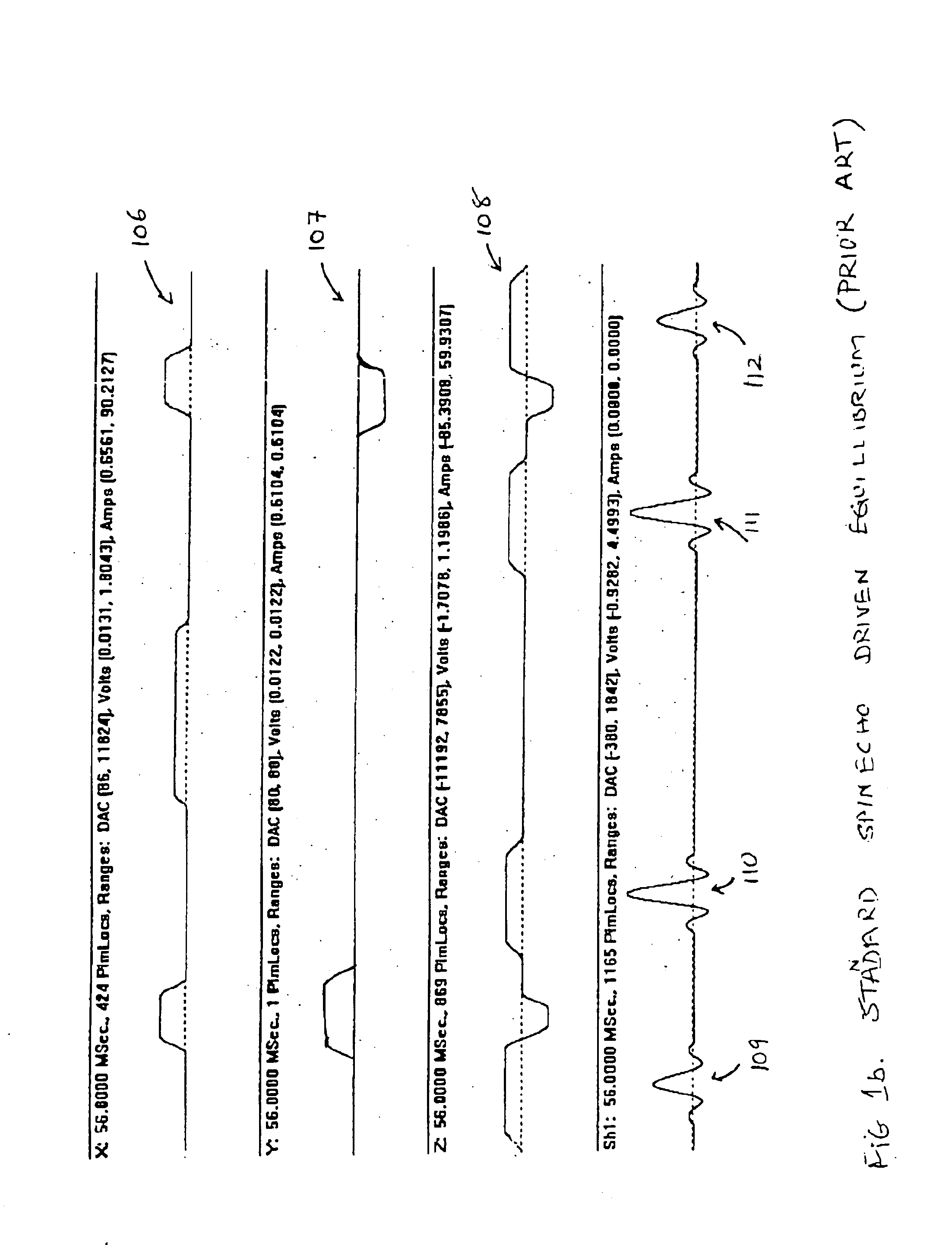
Driven equilibrium and fast-spin echo scanning
InactiveUS6847209B2Time periodShorten the time periodMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionFast spin echoSpins
An NMR imaging process utilizes both driven equilibrium and fast-spin echo techniques to acquire image data. The fast-spin echo technique is a multi-echo imaging sequence, where a 90-degree RF pulse applied at the center of any echo turns the magnetization back in the direction of the static magnetic field. Within a short waiting time after that pulse, the spins are ready to be excited again. The sequence follows a first 90-degree RF pulse by a series of n 180-degree RF pulses, followed by n echoes. A second 90-degree RF pulse applied to the nth echo returns the magnetization. A multiple single-slice mode is utilized to acquire individual slice images one at a time. A continuous single-slice mode is utilized to acquire individual slice images automatically in sequence over the region of interest. In either mode, adjacent slices can be made to overlap to a degree ranging from 0% to 100%.
Owner:FONAR
Method and apparatus for fast spin echo (FSE) prescan phase correction
ActiveUS20070063704A1Reduce phase incoherenceMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionPhase correctionFast spin echo
A method and apparatus for prescan phase correction analyzes the phase profile of the first echo sampled in a prescan and the phase profile corresponding to the lope echo of an impending FSE acquisition to determine appropriate phase correction settings of the FSE scan.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and device for accurate quantification of t2 relaxation times based on fast spin-echo nmr sequences
ActiveUS20150355298A1Accurate modelingIncrease the number ofDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsFast spin echoNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
A method and a device are provided that improve quantification of the spin-spin relaxation (“T2”) time of an image in nuclear magnetic resonance (“NMR”) applications using fast multi spin-echo sequences. The method employs time-efficient computer simulations for exact modeling of spurious stimulated echoes in multi-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging (“MRI”) runs. The method employs Bloch simulations and can use a plurality of parameters to produce echo modulation curves prior to correcting distorted experimental data based on pre-calculated simulation values.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Driven equilibrium and fast-spin echo scanning
InactiveUS7034532B1Time periodShorten the time periodMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionFast spin echoMagnetization
An NMR imaging process utilizes application of both a driven equilibrium technique and a fast-spin echo technique to acquire image. The fast-spin echo technique is a multiecho NMR imaging sequence, where different echoes are encoded differently to fill the (kx, kg) space at a speed of 1 / n of the single echo speed, where n is the number of echoes in the multiecho sequence. During this echo train, a 90-degree RF pulse applied with proper phase at the center of any echo turns the magnetization back in the direction of the static magnetic field. Within a short waiting time after the 90-degree RF pulse, the spins are ready to be excited again. The multi-echo sequence has one 90-degree RF pulse at the beginning, followed by a series of n 180-degree RF pulses, followed by n echoes. A second 90-degree RF pulse is turned on exactly at the center of the nth echo, which returns all the magnetization left at this time to the static field direction. Only one frequency is used for excitation in acquiring the NMR signal in the single slice mode. Gradients are adjusted for oblique scanning. In the multislice acquisition mode, RF phases of different slices are different from one another and the final images can be constructed either by sharing the kg space or by using a transform process to separate the slices.
Owner:FONAR
Flow compensation method for nuclear magnetic resonance imaging system
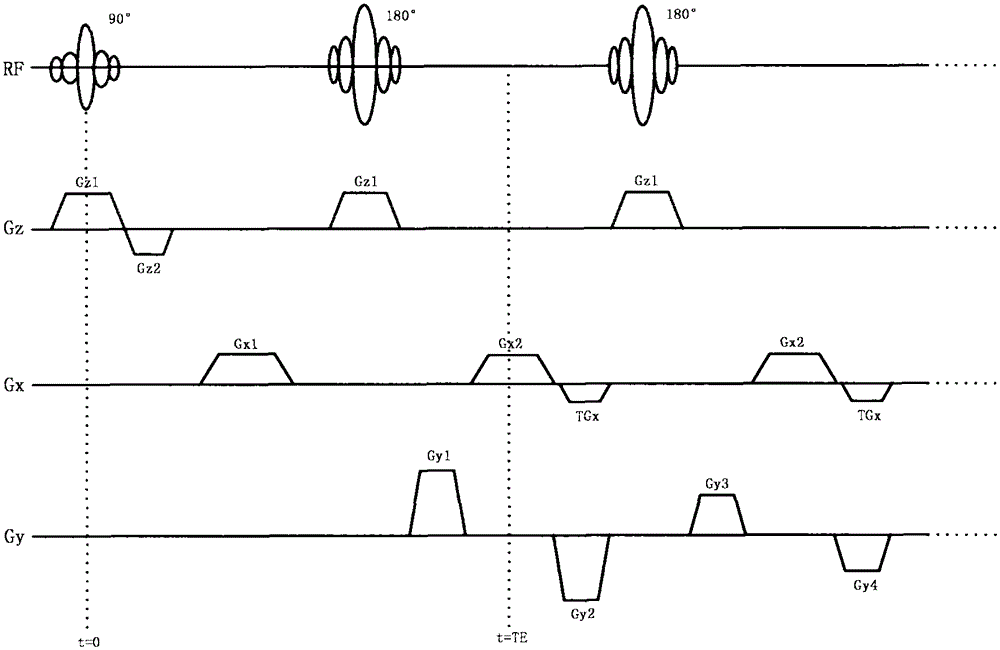
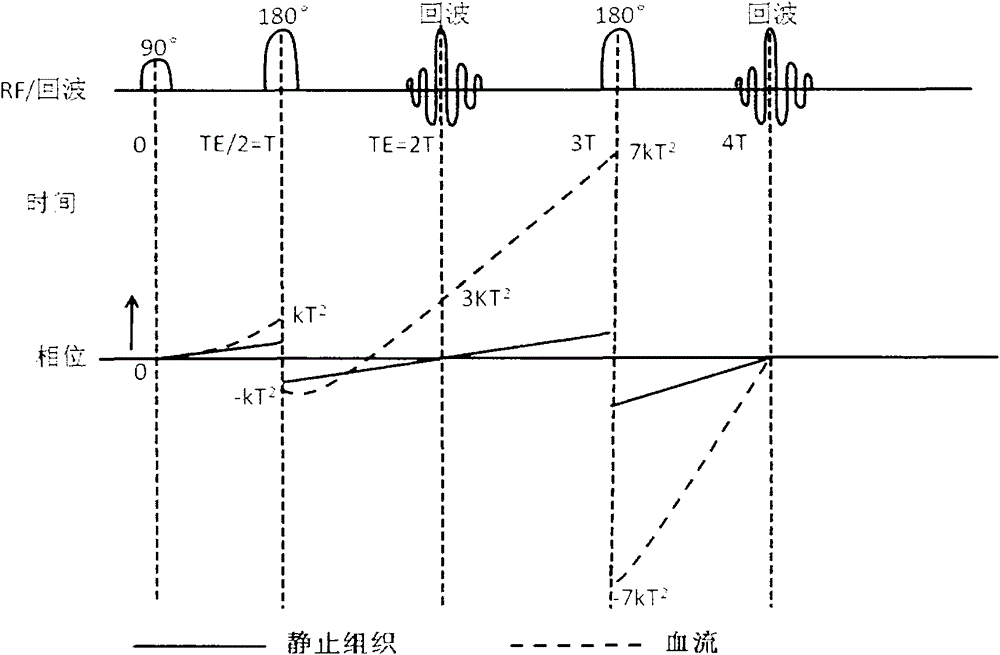
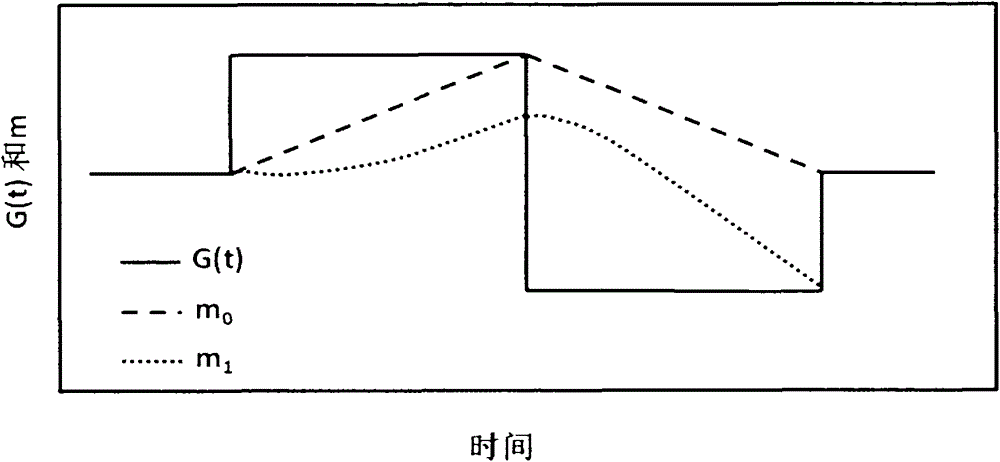
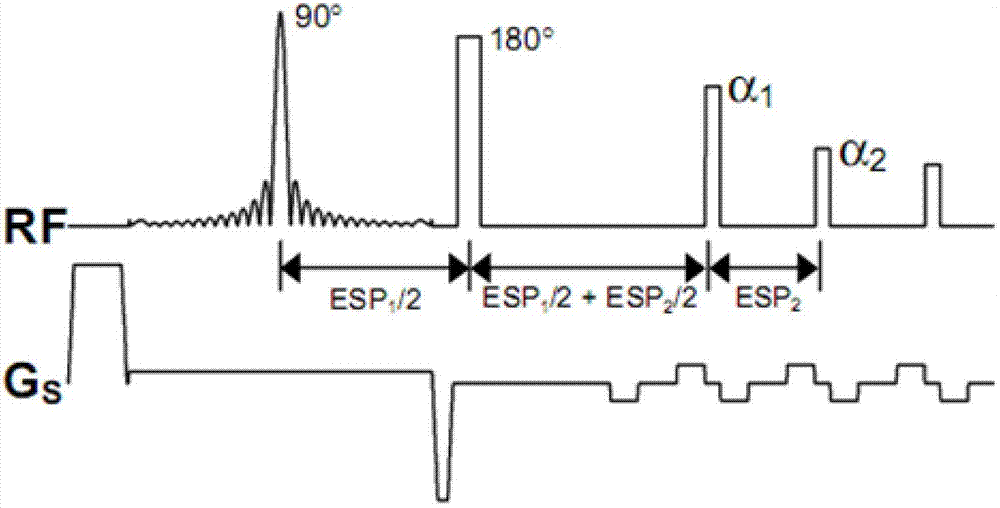
ActiveCN104459587AWeakening flow phenomenonAttenuated flow phenomenon has artifacts in existing FSE imagesMagnetic measurementsFast spin echoPhysiological movement
The invention discloses a flow compensation method for a nuclear magnetic resonance imaging system. The flow compensation method is characterized by comprising the following steps that: (1) gradient combined pulses which satisfy flow compensation are applied in a frequency encoding direction between a 90-degree radio frequency pulse time series and a 180-degree radio frequency pulse time series of a fast spin echo (FSE) sequence; (2) a scattering gradient is applied before a signal acquisition gradient and before 180-degree radio frequency pulses, and a compensation gradient is applied after the acquisition gradient, and the signal acquisition gradient, the scattering gradient and the compensation gradient jointly form a first-order gradient velocity compensation gradient; (3) phase encoding gradient amplitude is set to be zero, and the time series of the sequence is set, and the amplitudes of the gradients are adjusted, and the amplitude of echo signal peaks of an echo chain is made to reach a maximum value, and the debugging of the sequence is completed; and (4) the sequence is outputted to a spectrometer, so that flow compensation can be realized. With the flow compensation method for the nuclear magnetic resonance imaging system of the invention adopted, situations such as cerebrospinal fluid flow and spinal fluid flow artifacts and image blurring can be significantly inhibited, and therefore, the problem of image artifact generation which is caused by physiological movement such as blood flow or periodic movement can be alleviated.
Owner:BEIJING WANDONG MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
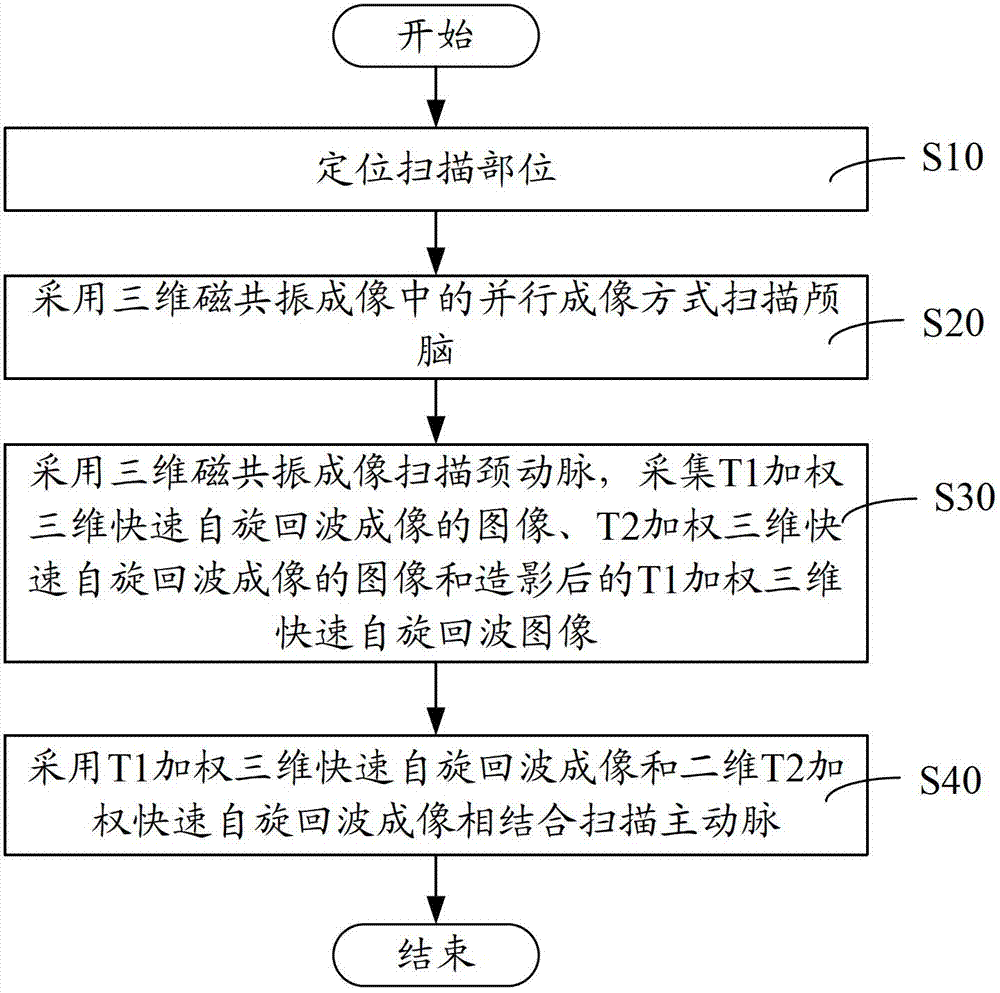
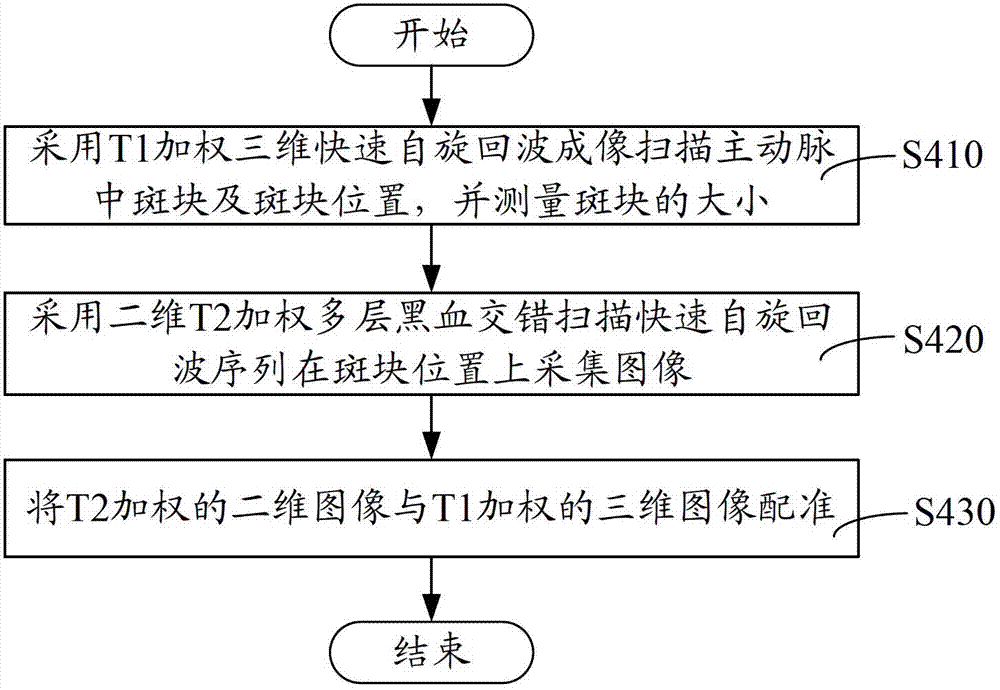
Brain, carotid artery and aorta three-in-one scanning method and scanning system
ActiveCN102727206AReduce scan timeImage analysisDiagnostic recording/measuringFast spin echoRapid imaging
The invention relates to a brain, carotid artery and aorta three-in-one scanning method, comprising the following steps of: positioning a scanning part; scanning a brain by utilizing parallel imaging of three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging; scanning a carotid artery by utilizing the three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging and collecting a T1 weighted three-dimensional rapid spin echo imaged image, a T2 weighted three-dimensional rapid spin echo imaged image and a radiographed T1 weighted three-dimensional rapid spin echo image; and scanning a carotid artery by utilizing T1 weighted three-dimensional rapid spin echo imaging and T2 weighted three-dimensional rapid spin echo imaging which are combined. The brain, carotid artery and aorta three-in-one scanning method and system disclosed by the invention firstly adopt the steps of firstly positioning the scanning part and directly scanning the brain, the carotid artery and the aorta; the positioning and the scanning do not need to be repeated so that the scanning time is shortened; the brain is scanned by using a rapid imaging method by parallel imaging so that the scanning time is reduced; and three-dimensional T1 weighted imaging and two-dimensional T2 weighted imaging are combined to scan the carotid artery so that the scanning time is further shortened.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Imaging method of nuclear magnetic resonance T2 image
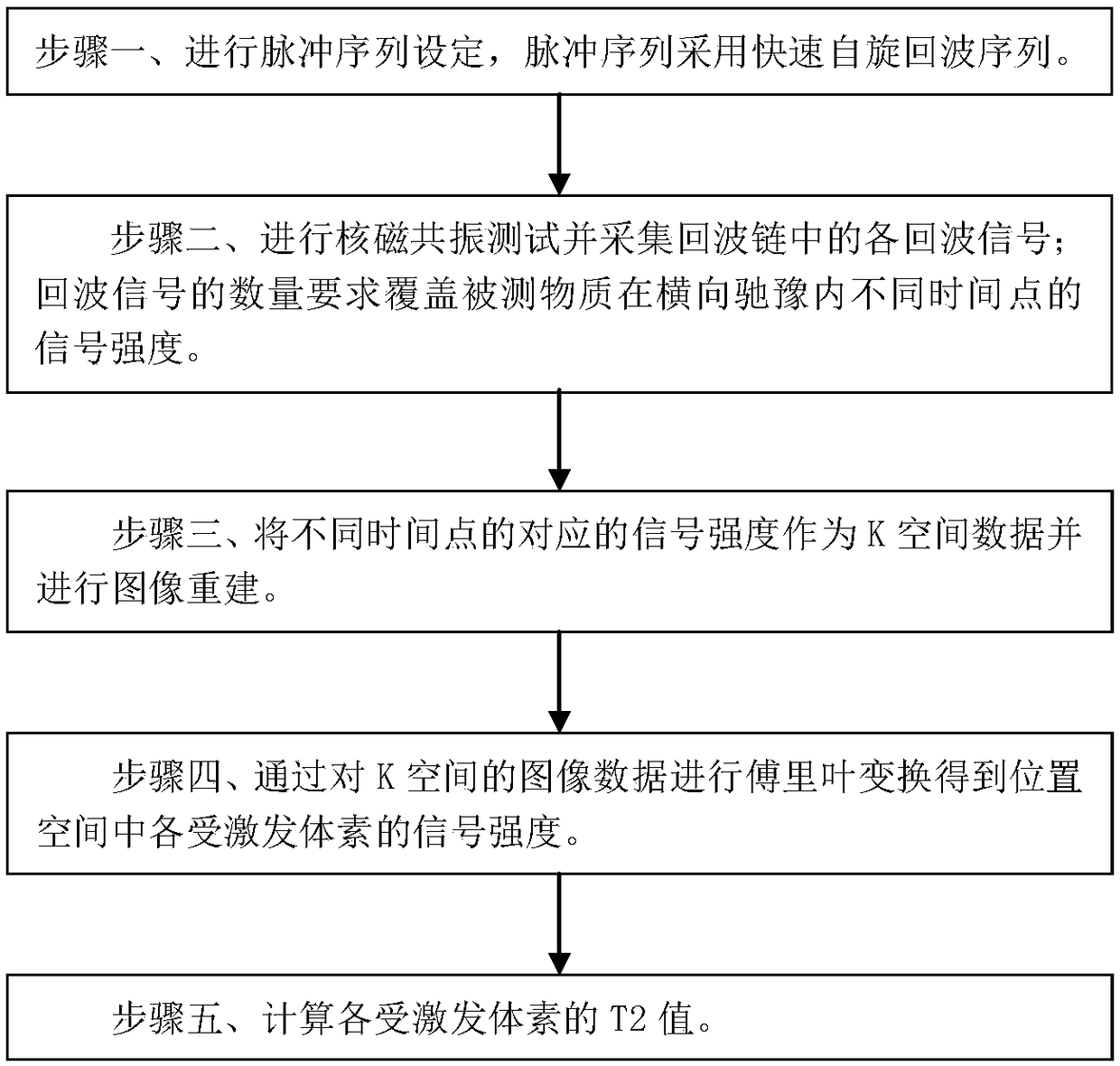
ActiveCN108872897AReduce scan timeImproving the imaging rateMeasurements using NMRFast spin echoNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
The invention discloses an imaging method of a nuclear magnetic resonance T2 image. The imaging method comprises the following steps: step one, pulse sequence setting is performed, wherein the fast spin echo sequence is used as the pulse sequence; step two, the nuclear magnetic resonance test is performed and each echo signal in the echo chain is acquired, wherein the quantity requirement of the echo signals covers the signal intensity of the measured substance at different time points in the lateral relaxation; step three, the corresponding signal intensity of different time points acts as the K space data and image reconstruction is performed; step four, Fourier transform is performed on the image data of the K space so as to obtain the MR signal intensity of each stimulated voxel in theposition space; and step five, the T2 value of each stimulated voxel is calculated. The scanning time can be reduced and the scanning speed can be improved and the method is suitable for examinationof autonomic motor organs.
Owner:SHANGHAI EAST HOSPITAL
Driven equilibrium and fast-spin echo scanning
ActiveUS7755356B1Reduce scanReduced image data collection timeMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionFast spin echoMagnetic field gradient
An NMR imaging process includes subjecting an imaging object to a uniform polarizing magnetic field. Orthogonal magnetic field gradients are applied to the imaging object. RF energy is applied to the imaging object. The RF energy includes a plurality of angular precession frequencies simultaneously applied to correspond to a respective plurality of selected slices of the imaging object. A corresponding plurality of nuclear magnetic resonance signals emitted by the imaging object are simultaneously detected. The nuclear magnetic resonance signals are processed to provide diagnostic information related to individual ones of the plurality of selected slices. In this way, multiple slices are excited and sampled simultaneously. The RF energy can be applied by applying RF energy to the imaging object according to a fast-spin echo technique and subsequently applying RF energy to the imaging object according to a driven equilibrium technique.
Owner:FONAR
Driven equilibrium and fast-spin echo scanning
InactiveUS7119540B1Reduced scanning and image data collection timeQuality improvementMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionFast spin echoMagnetization
An NMR imaging process utilizes both driven equilibrium and fast-spin echo techniques to acquire image data. The fast-spin echo technique is a multi-echo imaging sequence, where a 90-degree RF pulse applied at the center of any echo turns the magnetization back in the direction of the static magnetic field. Within a short waiting time after that pulse, the spins are ready to be excited again. The sequence follows a first 90-degree RF pulse by a series of n 180-degree RF pulses, followed by n echoes. A second 90-degree RF pulse applied to the nth echo returns the magnetization. A multiple single-slice mode is utilized to acquire individual slice images one at a time. A continuous single-slice mode is utilized to acquire individual slice images automatically in sequence over the region of interest. In either mode, adjacent slices can be made to overlap to a degree ranging from 0% to 100%.
Owner:FONAR
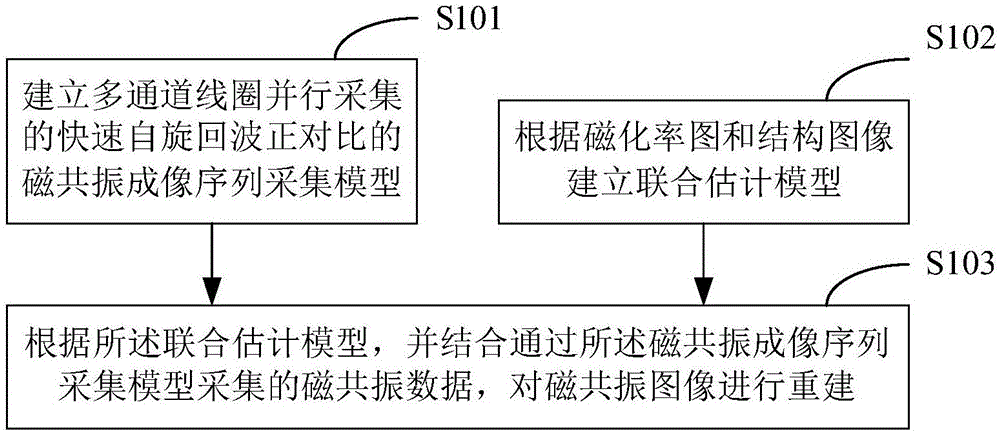
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) method and device
ActiveCN106772168APrecise positioningAccurate visualizationMagnetic measurementsFast spin echoMagnetic susceptibility
The invention applies to the technical field of magnetic resonance and provides an MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) method and device. The MRI method comprises the following steps: establishing an MRI sequence acquisition model for positive contrast of FSE (Fast spin echo) acquired parallelly by multiple-channel coils; establishing a joint estimation model according to a magnetic susceptibility map and a structure image; acquiring MRI data according to the joint estimation model in combination with the MRI sequence acquisition model so as to reconstruct an MRI image. With adoption of the method, the positional relation between an intervention device and surrounding tissue can be recognized clearly, intraductal condition of a stent device is evaluated, the imaging resolution is higher, the imaging speed is higher, and the signal-to-noise ratio is higher.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Magnetic resonance vessel wall imaging method and apparatus
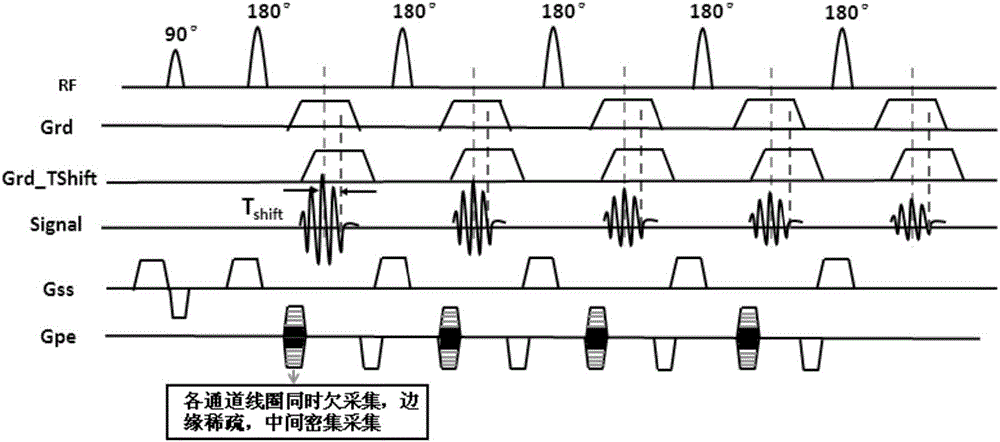
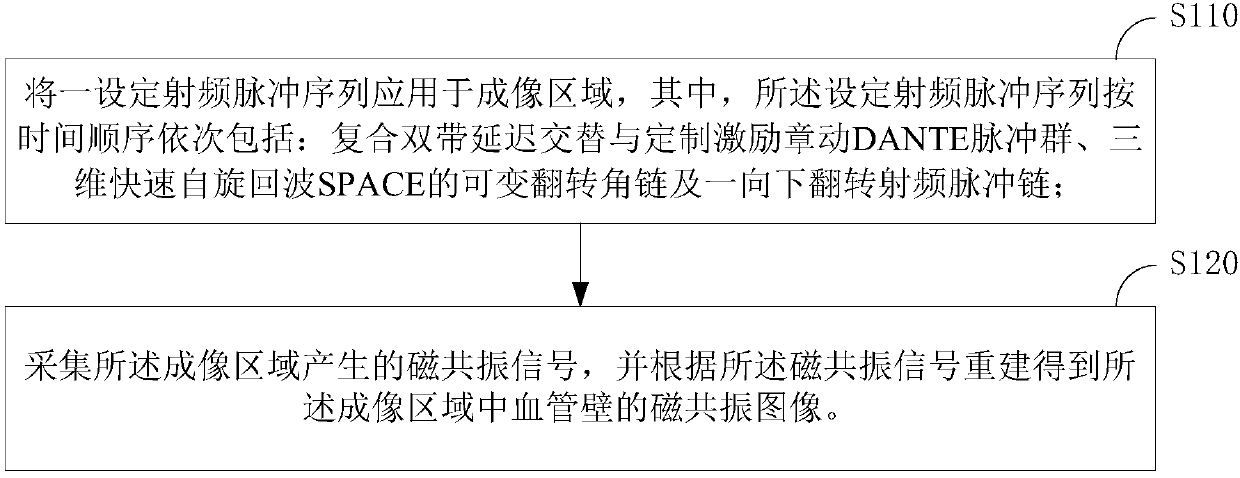
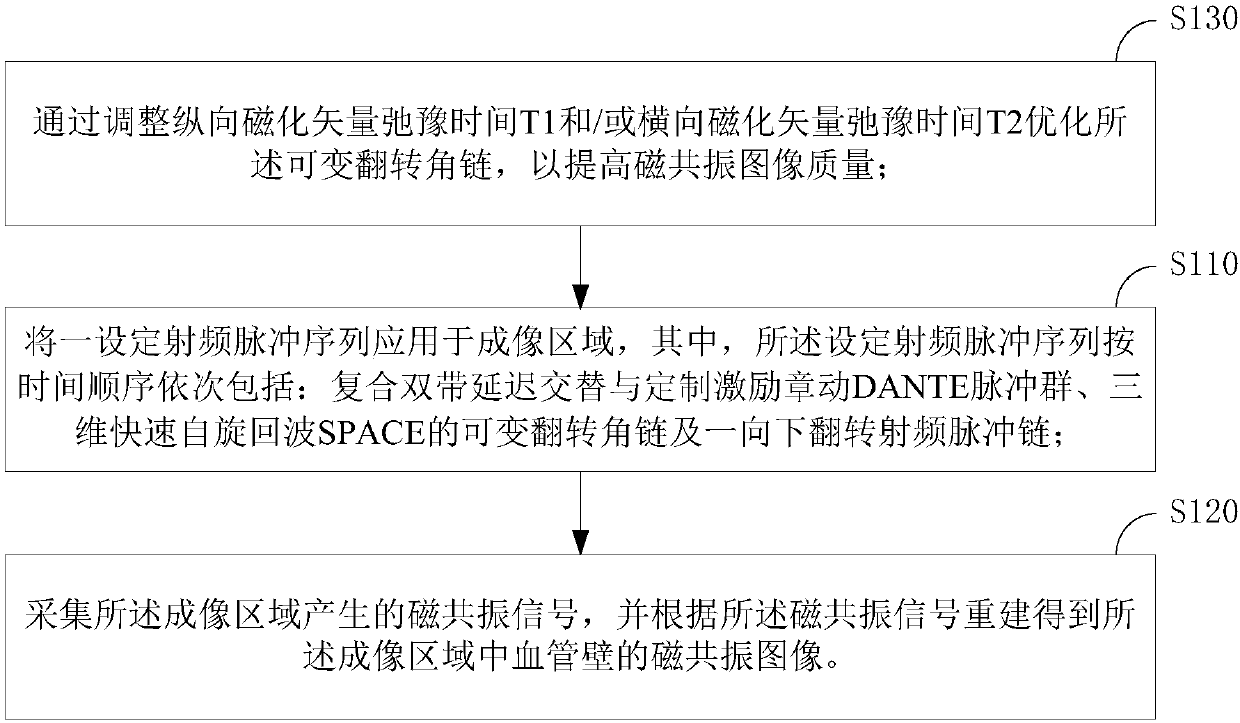
ActiveCN107690309AImprove image qualityMake up for the shortcomings of not being able to uniformly suppress the cerebrospinal fluid signalImage enhancementMedical imagingFast spin echoNutation
The invention relates to a magnetic resonance vessel wall imaging method and an apparatus. The method comprising: applying a set of radio frequency pulse sequences to an imaging area, wherein the setof radio frequency pulse sequences includes, in chronological order, a composite double-band delay alternation and a custom excitation nutation A DANTE pulse group, a variable flip angle chain of a three-dimensional fast spin echo SPACE, and a flip down radio frequency pulse chain (S110); acquiring a magnetic resonance signal generated by the imaging area and reconstructing a magnetic resonance signal to obtain the imaging area Magnetic resonance image of blood vessel wall (S120). By further inverting the cerebrospinal fluid signal of the whole brain by increasing the downward flip of the radio frequency pulse chain after the variable flip angle chain of the three-dimensional fast spin echo SPACE, the use of the DANTE pulse group can help the vascular wall at the head-neck joint Imaging.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
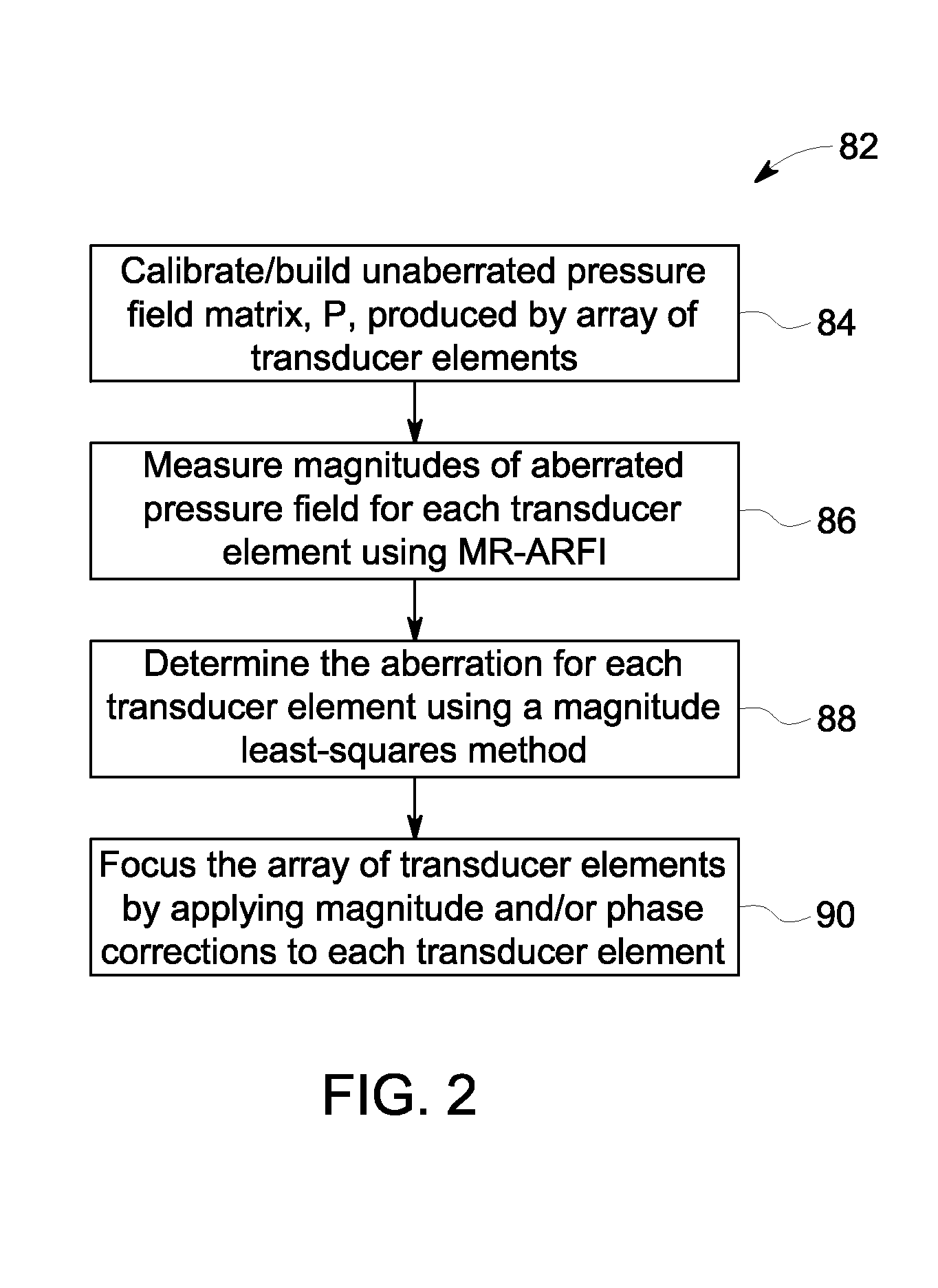
System and method for focusing of high intensity focused ultrasound based on magnetic resonance - acoustic radiation force imaging feedback
ActiveUS20150320335A1Reduce signal to noise ratioUltrasound therapySurgeryFast spin echoSonification
A system and method for MR imaging is disclosed. The method causes an RF coil assembly and plurality of gradient coils to apply a fast spin echo (FSE) pulse sequence comprising a preparation segment and a plurality of refocusing segments. The FSE pulse sequence generates a pair of echoes is generated in each of the plurality of refocusing segments that comprises a first echo generated by magnetization pathways having an even number of phase inversions and a second echo generated by magnetization pathways having an even number of phase inversions. MR signals are acquired from the first echo and the second echo and an image of at least a portion of a subject of interest is reconstructed from the acquired MR signals.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Carp brain electrode implantation method through magnetic-resonance positioning and navigation
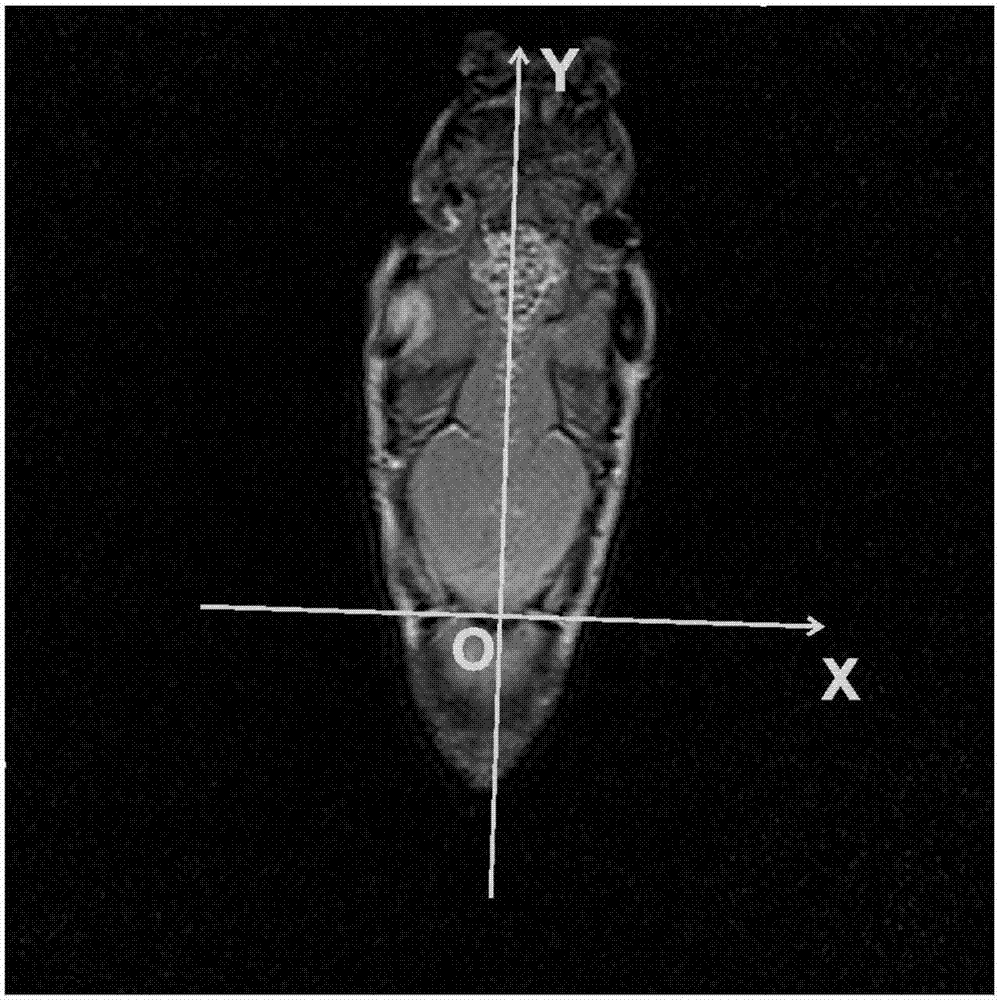
InactiveCN106974653AAccurately obtain scale parametersReduce positioning errorsHead electrodesSensorsFast spin echoImplantable Stimulation Electrodes
The invention discloses a carp brain electrode implantation method by means of magnetic resonance positioning and navigation. Taking the first fish scale (the junction of the head and the trunk) as the origin, reference scratches are made on the surface of the skull based on the characteristics of the carp skull to establish Space coordinate system; with the help of the T2WI fast spin echo scanning sequence of the magnetic resonance equipment, the brain is scanned and imaged, the two-dimensional coordinates of the electrode stimulation site are converted into three-dimensional space coordinates, and the spatial coordinates of the brain stimulation electrode implantation site are determined The coordinate value of the system; according to the coordinate value, the brain stimulation electrode is implanted for positioning and navigation. The invention can not only locate and navigate for the implantation of the carp aquatic animal robot brain stimulation electrodes, but also provide new positioning and navigation means for the implantation of various animal robot brain stimulation electrodes.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
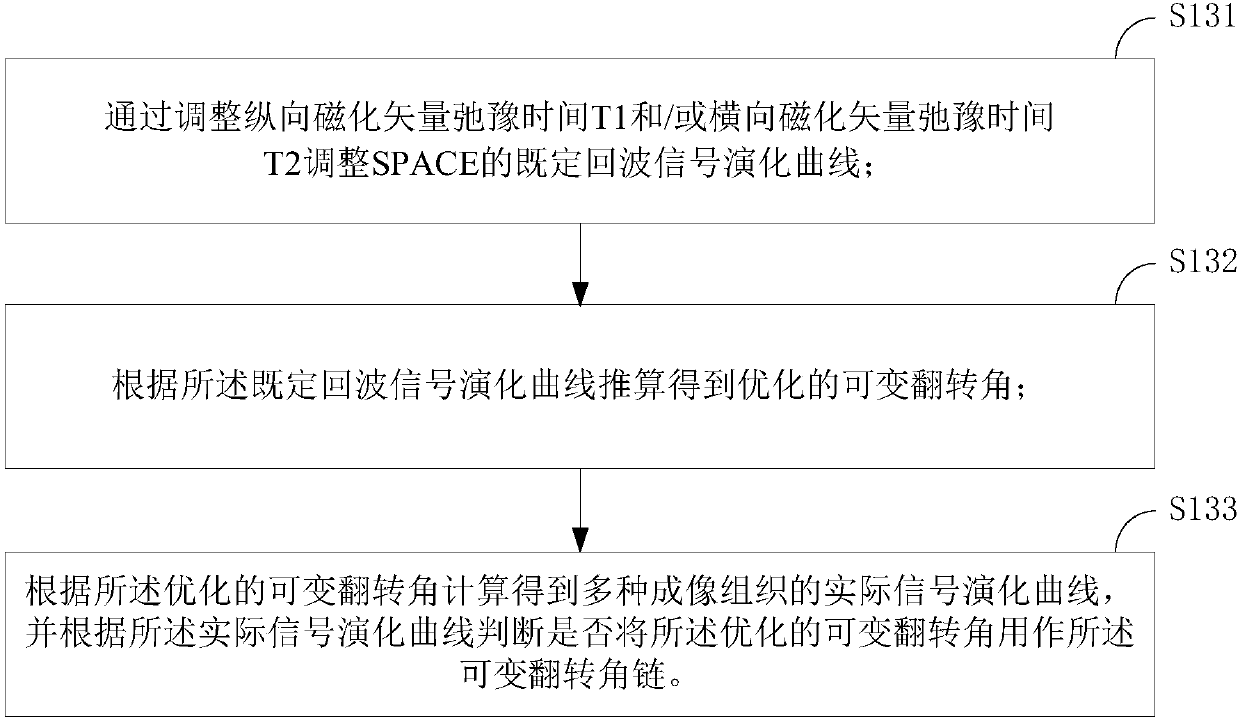
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com