Patents
Literature
917 results about "Magnetic field gradient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
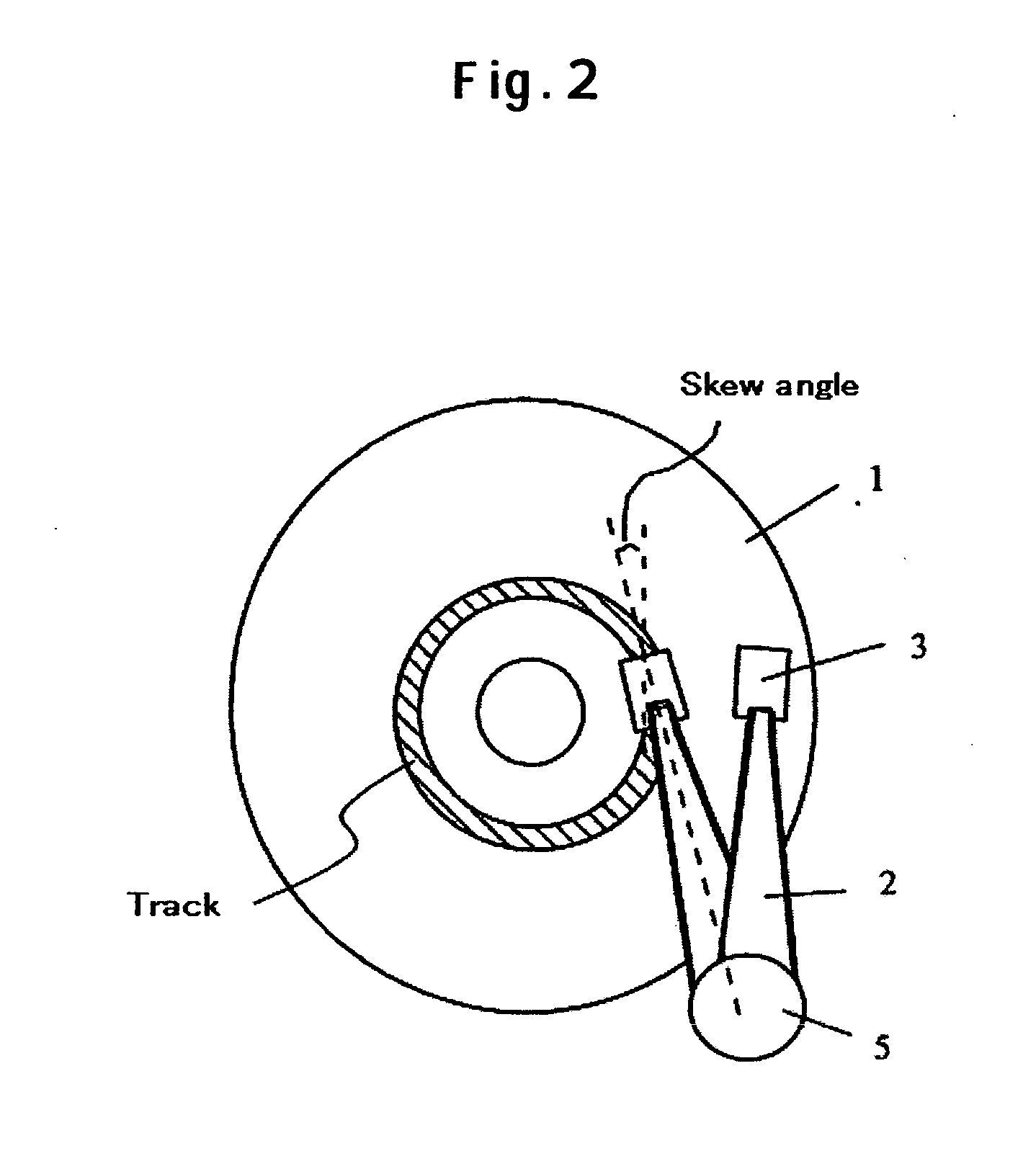
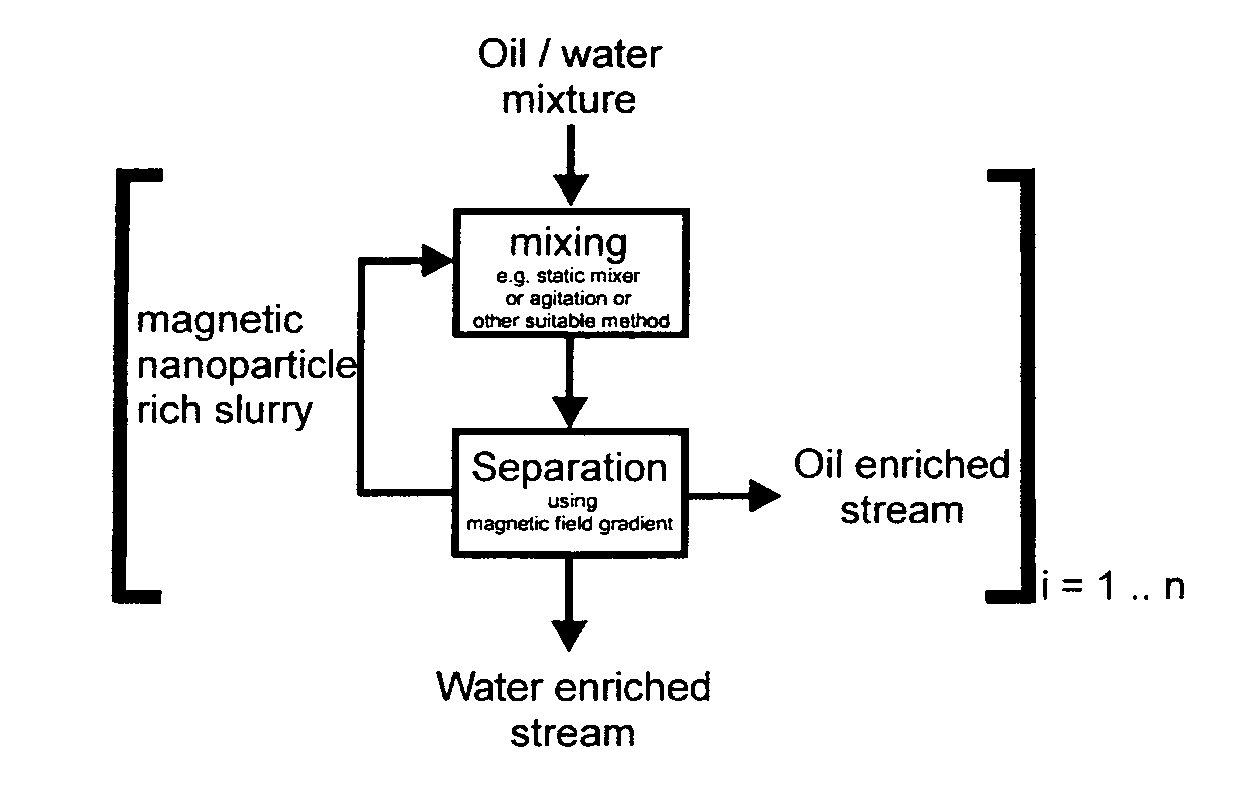
Magnetic field gradients are the forces used in quantum physics that exert a translationalforce on both a stationary and moving charged particles such as a Sodium ion (Na+). This is in contrast to a uniform magnetic field such as from a bipolar magnet which exerts zero force on charged particles.
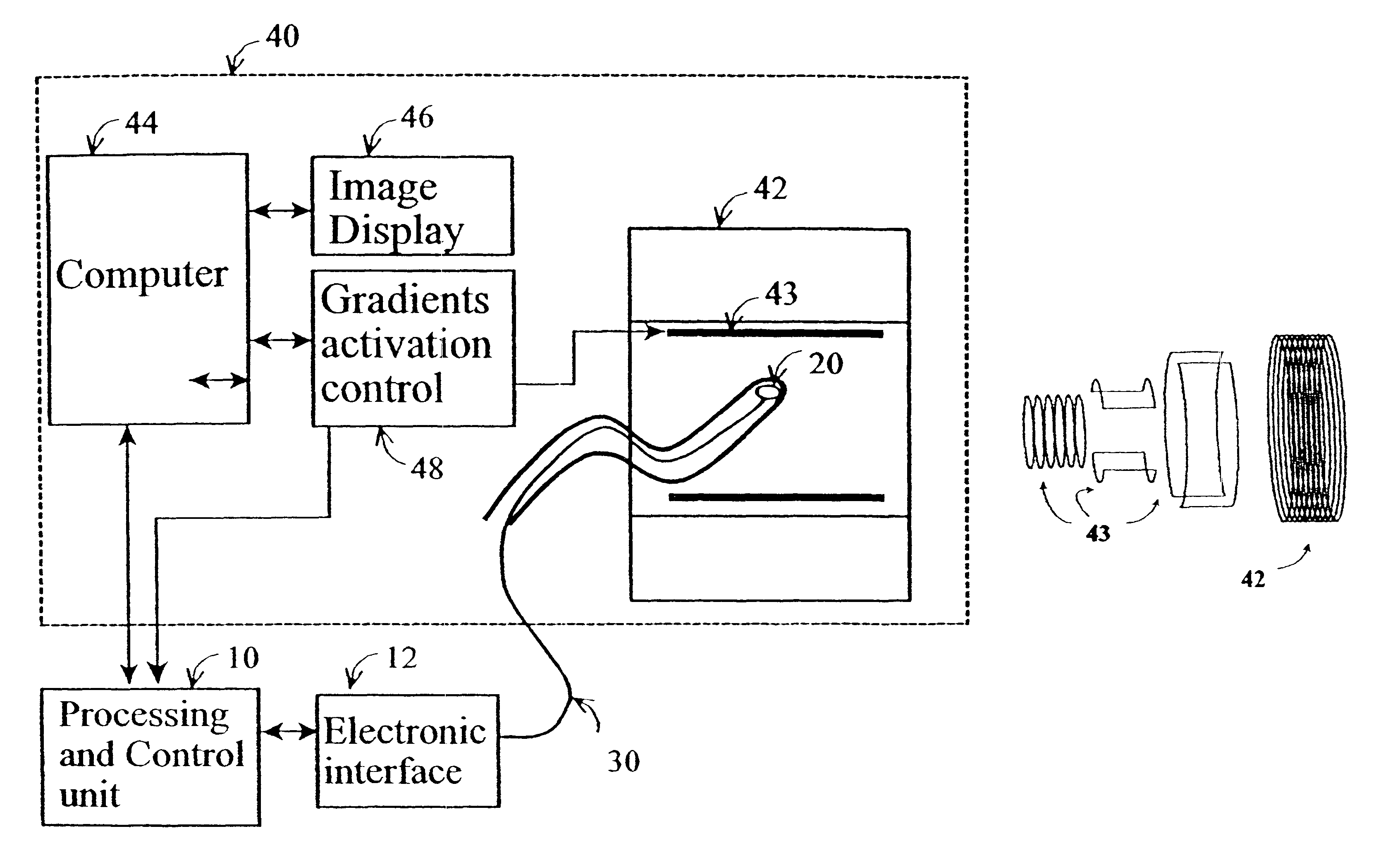
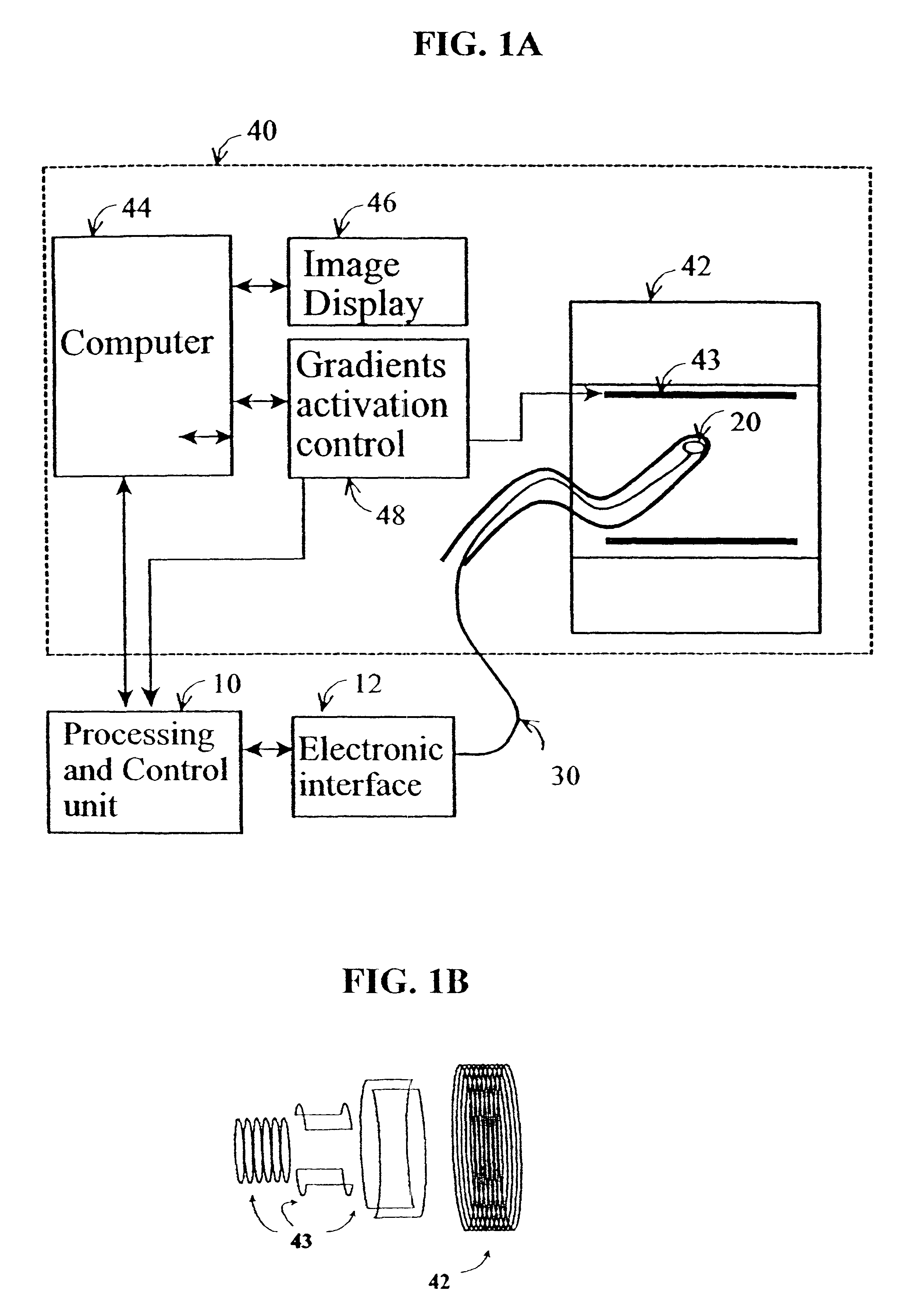
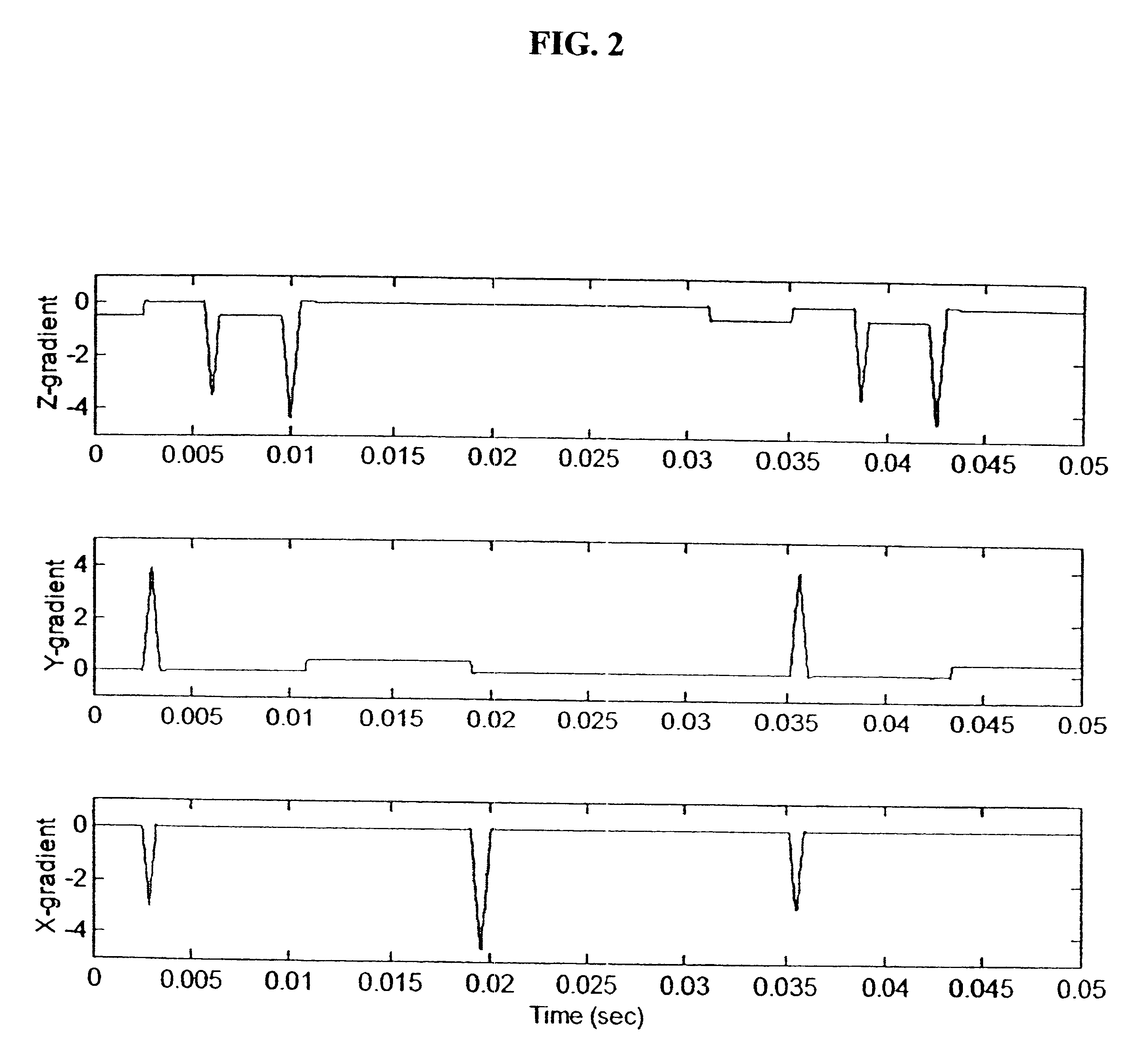
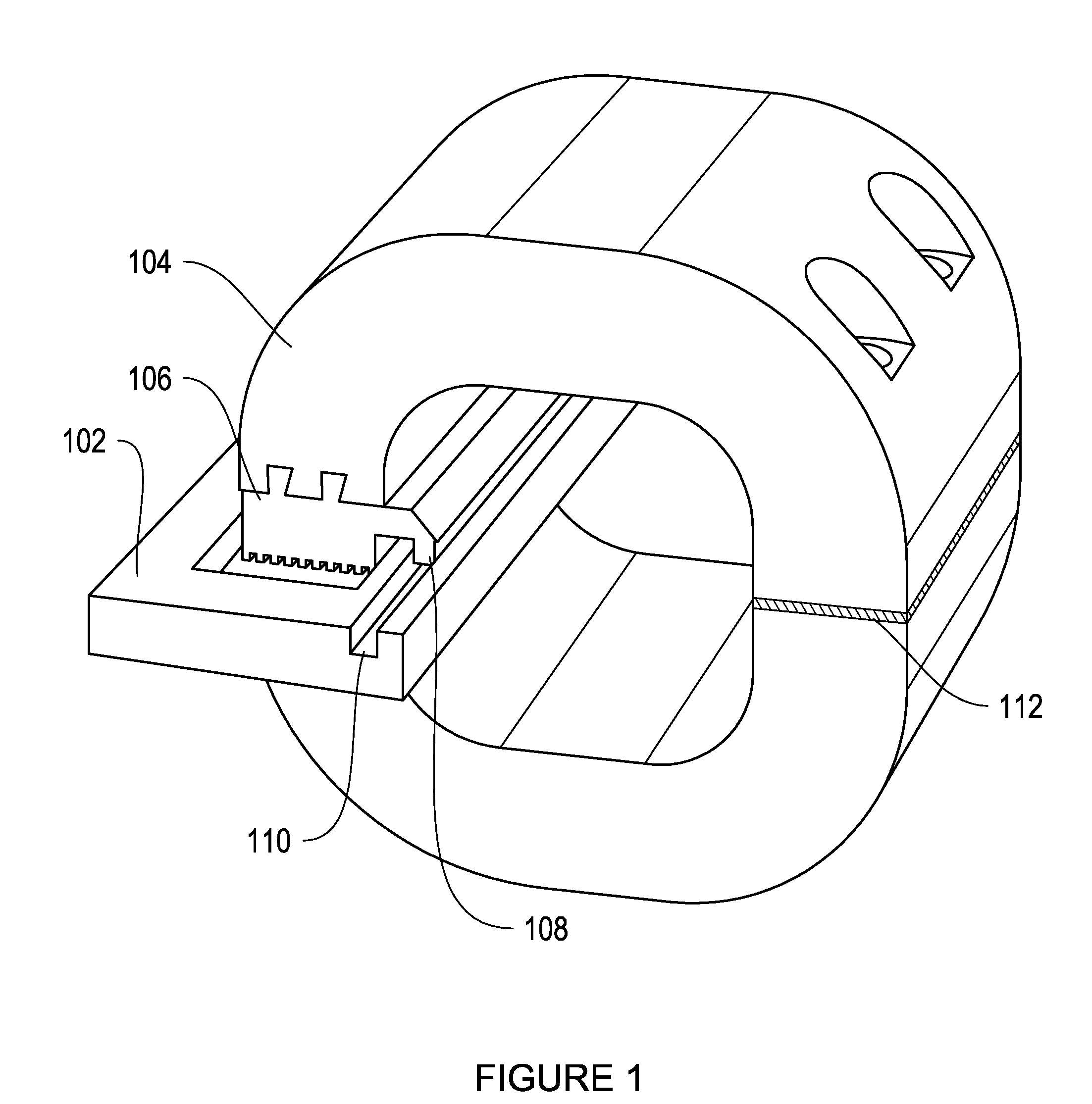
Method and apparatus to estimate location and orientation of objects during magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS6516213B1Limited accuracy of orientationSatisfies requirementDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMagnetic field gradientThree-dimensional space
Method and apparatus for determining the instantaneous location, the orientation of an object moving through a three-dimensional space by applying to the object a coil assembly including a plurality of sensor coils (20) having axes of known orientation with respect to each other including components in the three orthogonal planes; generating a time-varying, three-dimensional magnetic field gradient having known instantaneous values of magnitude and direction; applying the magnetic field gradient to the space, and object moving therethrough to induce electrical potentials in the sensor coils; measuring the instantaneous values of the induced electrical potentials generated in the sensor coils; processing the measured instantaneous values generated in the sensor coils together with the known magnitude, direction of the generated magnetic field gradient, the known relative orientation of the sensor coils in the coil assembly to compute the instantaneous location, orientation of the object within the space.
Owner:ROBIN MEDICAL
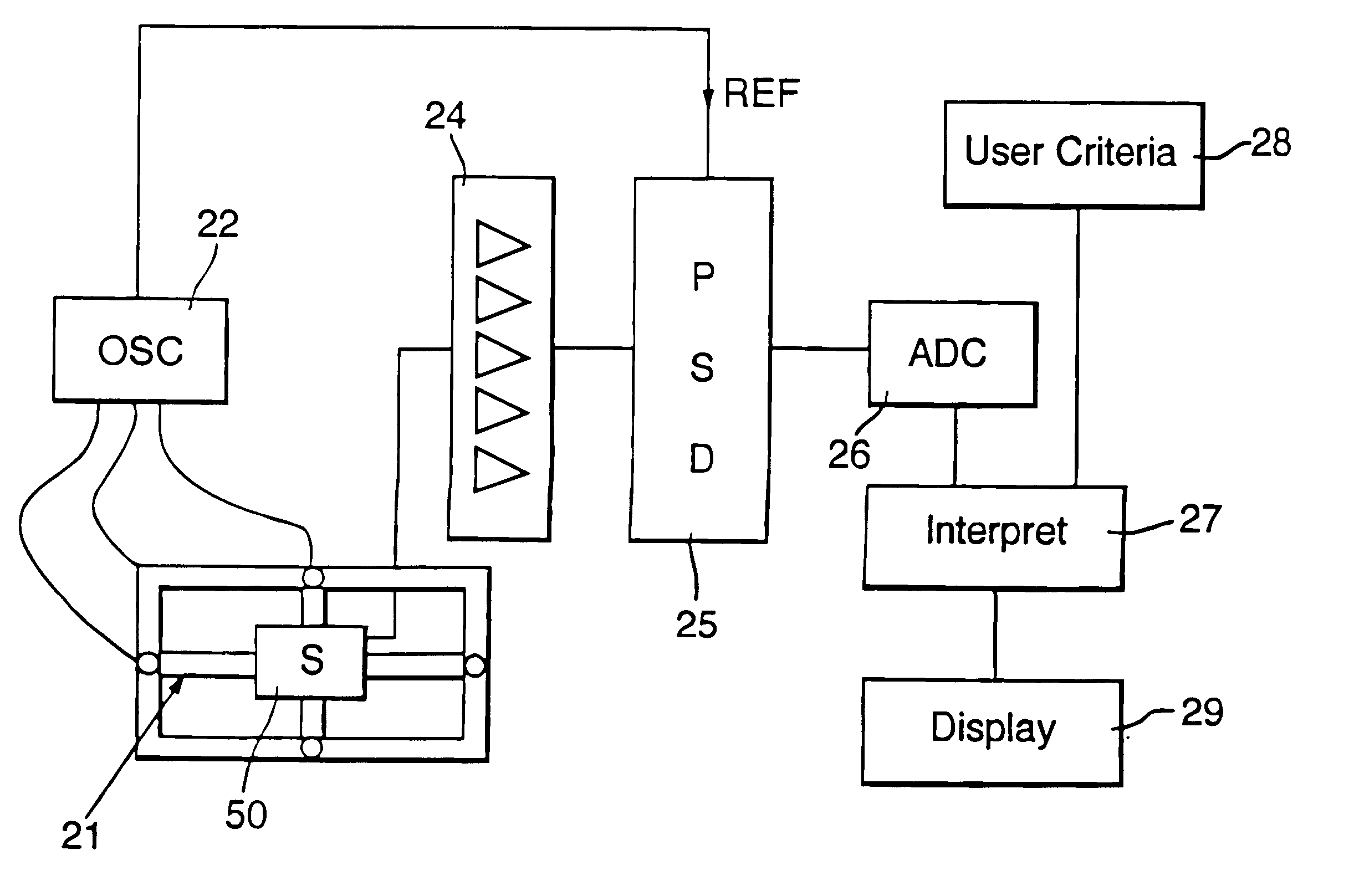
Precision metal locating apparatus
InactiveUS6541966B1Magnetic property measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringMagnetic field gradientMetallic Object
Apparatus for detecting a metal object comprises a transmitter for generating a pulsed or an alternating magnetic field in the vicinity of the metal object to be detected and a detector for detecting the secondary magnetic field induced in the metal object by the transmitted magnetic field. The detector measures at least three magnetic field gradient components of at least first order of the secondary magnetic field. The apparatus also comprises a processor for determining at least one of the position or the electro-magnetic cross-section or an estimate of the shape of the metal object from the measured magnetic field spatial gradient components. The processor fits the measured components to dipole, multiple dipole, multipole, or extended source models. In a preferred embodiment, the invention may comprise three or more pairs of gradiometric coils, or other sensing means. The detector measures at least five magnetic field gradient components of at least first order, and one or more components of the secondary magnetic field. The detector may be coils, or any other magnetic sensors. The processor enters pre-determined criteria to discriminate against detection of metal objects of no interest or to selectively detect metal objects of interest.
Owner:QINETIQ LTD
Magnetic recording head for perpendicular recording, fabrication process, and magnetic disk storage apparatus mounting the magnetic head
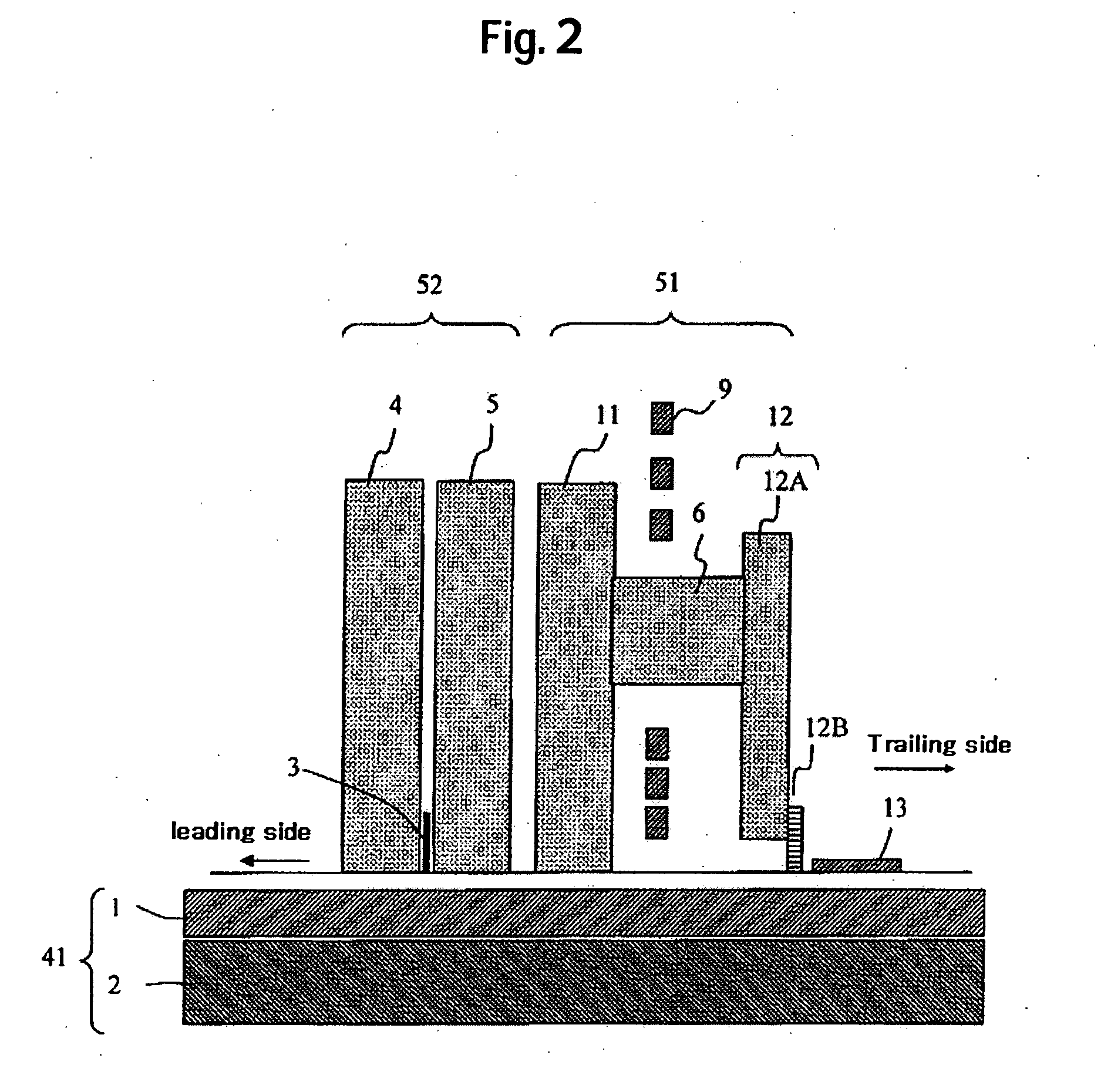
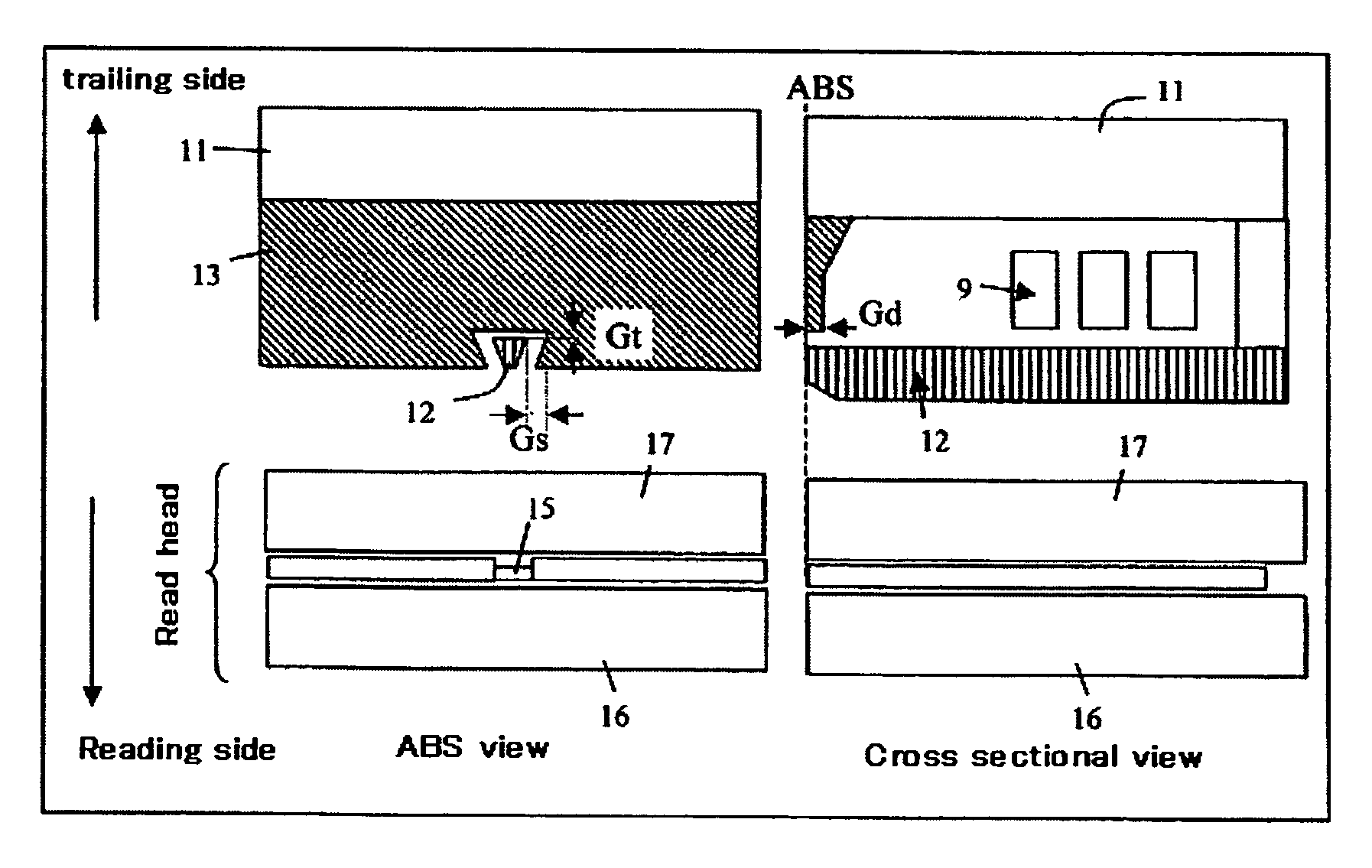
InactiveUS20050141137A1Improving recording magnetic field gradientIncreasing the thicknessManufacture head surfaceHeads using thin filmsMagnetic field gradientMagnetic media
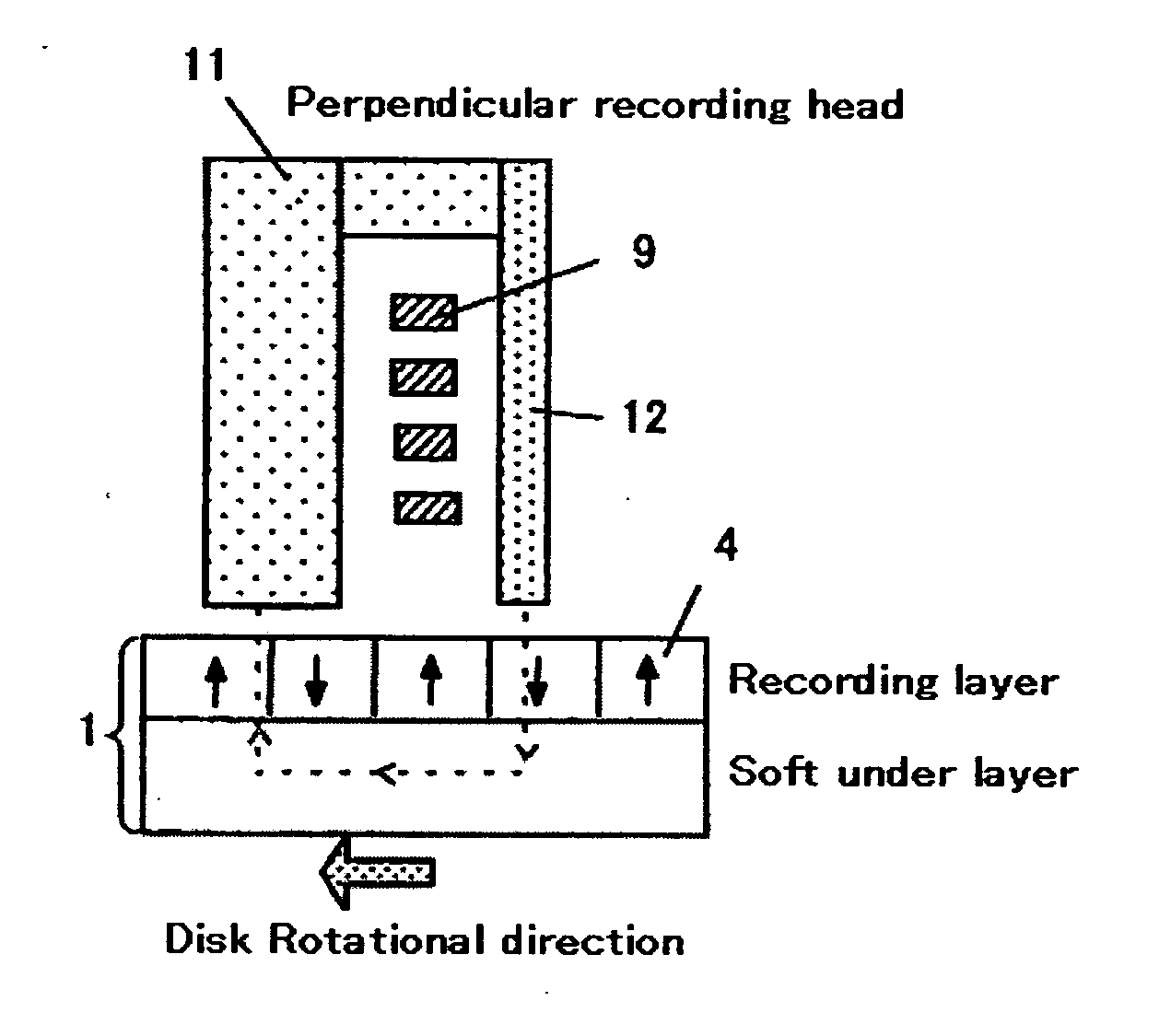
Embodiments of the invention provide a perpendicular magnetic writing head with a suppressed effective track width to be written on a magnetic medium while increasing writing magnetic field gradient. In one embodiment a trailing side shield is disposed by way of a gap film to a main pole of a perpendicular writing magnetic head. A gap distance (Gt) on a trailing side of the main pole and a gap distance (Gs) on a lateral side of the main pole is defined as Gt<Gt, and a thickness (Gd) from an air bearing surface of the shield is made equal to or less than a throat height. Alternatively, the thickness of Gd on the side of the main pole is reduced to less than that on the trailing side of the main pole. Further, for preventing defoliation of the shield upon fabrication of the air bearing surface, a thickness for a portion away from the main pole is increased.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
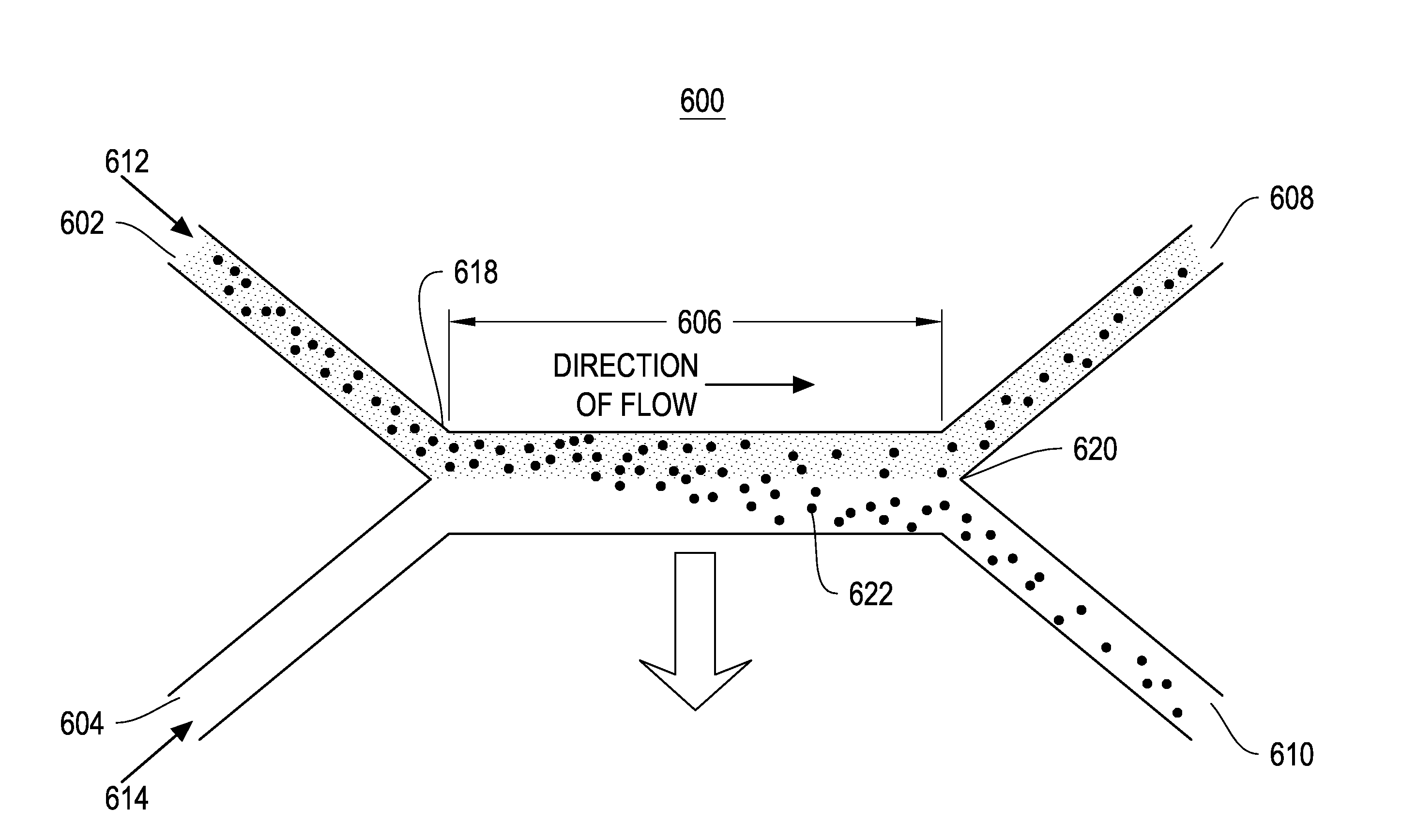
Device for Filtration of Fluids Therethrough and Accompanying Method
ActiveUS20120149021A1Easy to separateEasy to removeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMagnetic field gradientFluid filtration
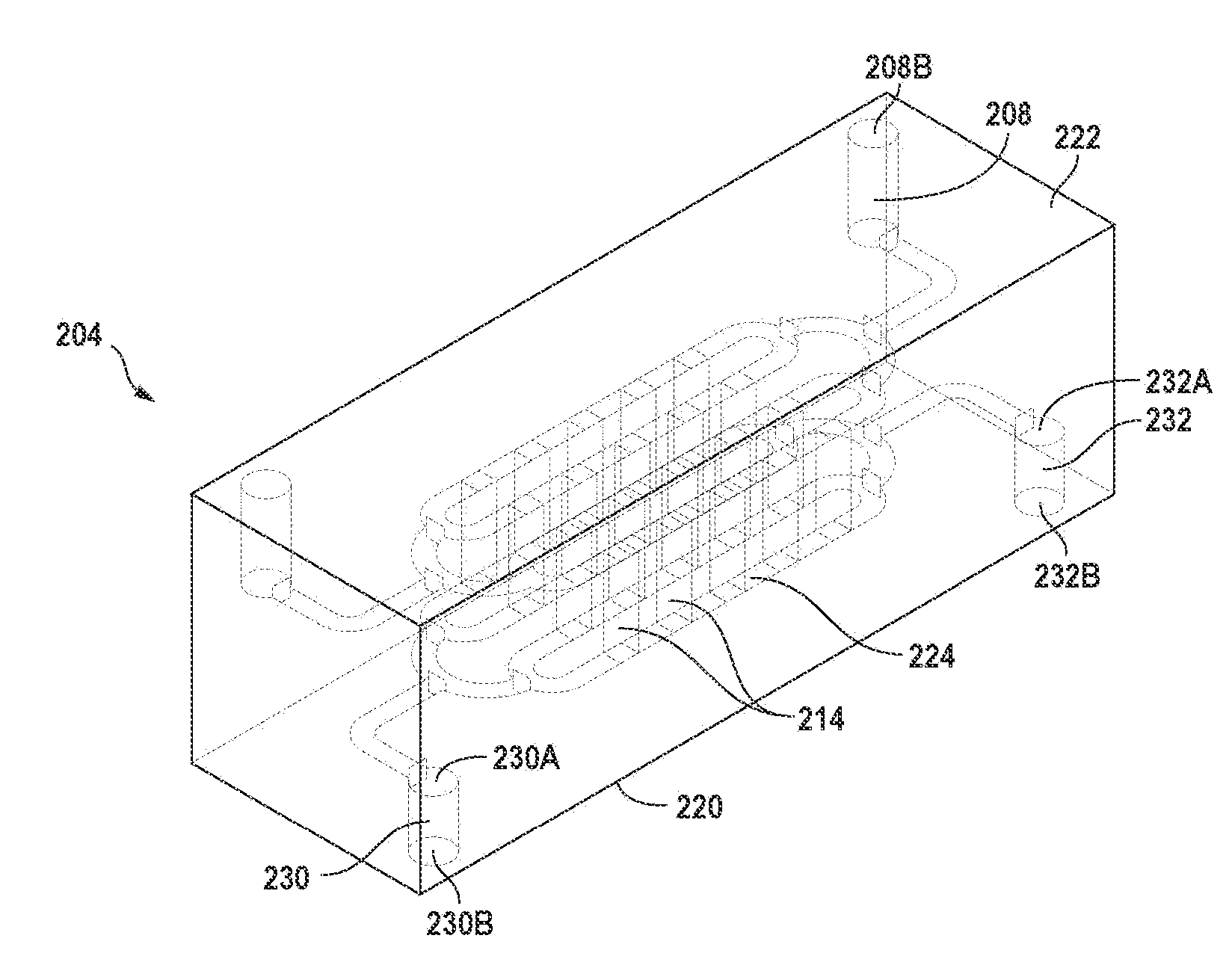
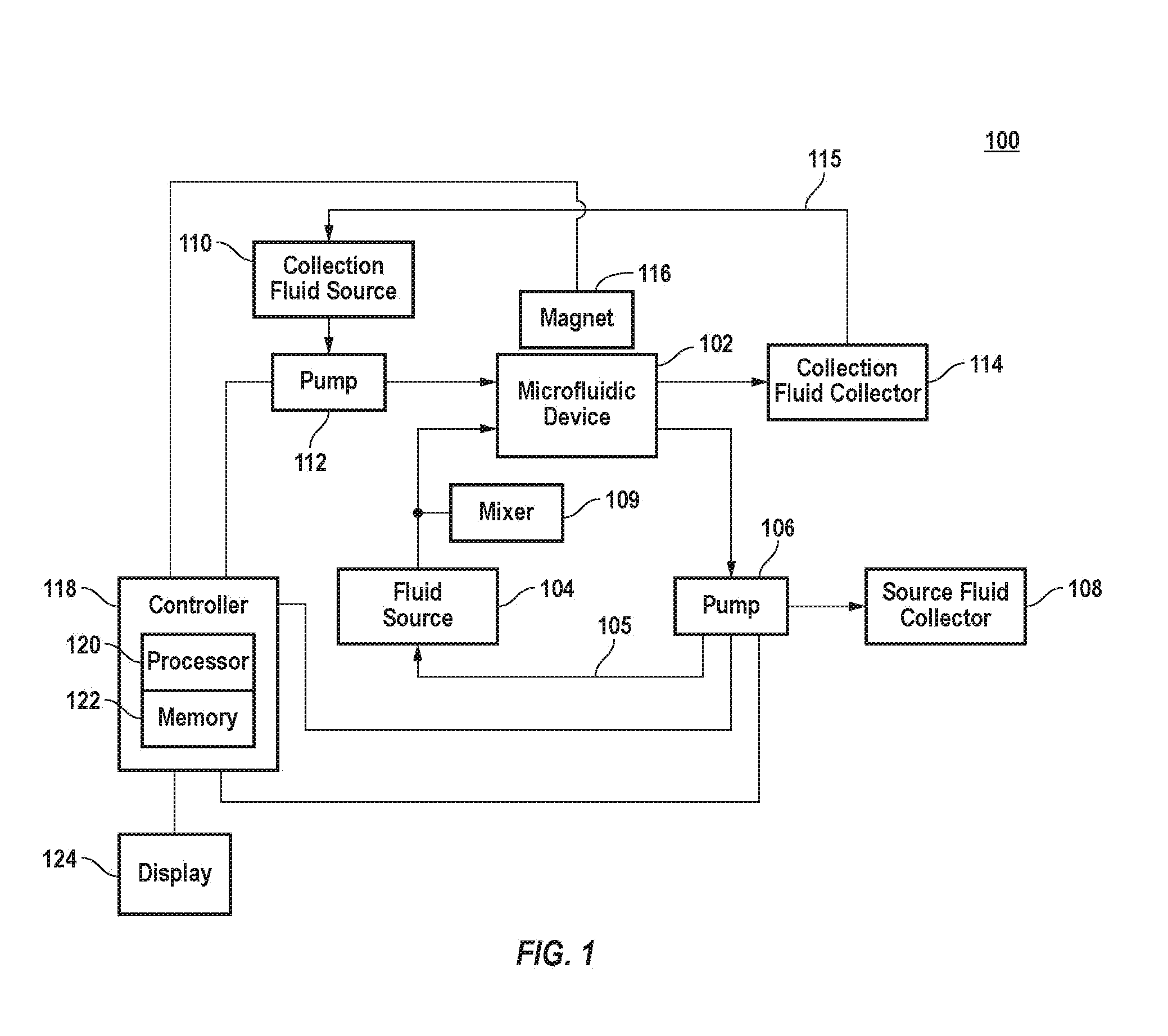
A microfluidic device for separating target components from a source fluid includes one or more source channels connected to one or more collection channels by one or more transfer channels. The target components of the source fluid can be magnetic or bound to magnetic particles using a know binding agent. A source fluid containing magnetically bound target components can be pumped through the source channel of the microfluidic device. A magnetic field gradient can be applied to the source fluid in the source channel causing the magnetically bound target components to migrate through the transfer channel into the collection channel. The collection channel can include a collection fluid that is stagnant until a predefined volume of source fluid is processed or a predefined volume of target components accumulate in the collection channel, at which point collection fluid can be pumped into the collection channel to flush the target components out of the collection channel. The target components can be subsequently analyzed for detection and diagnosis.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY +1
Device and method for combined microfluidic-micromagnetic separation of material in continuous flow
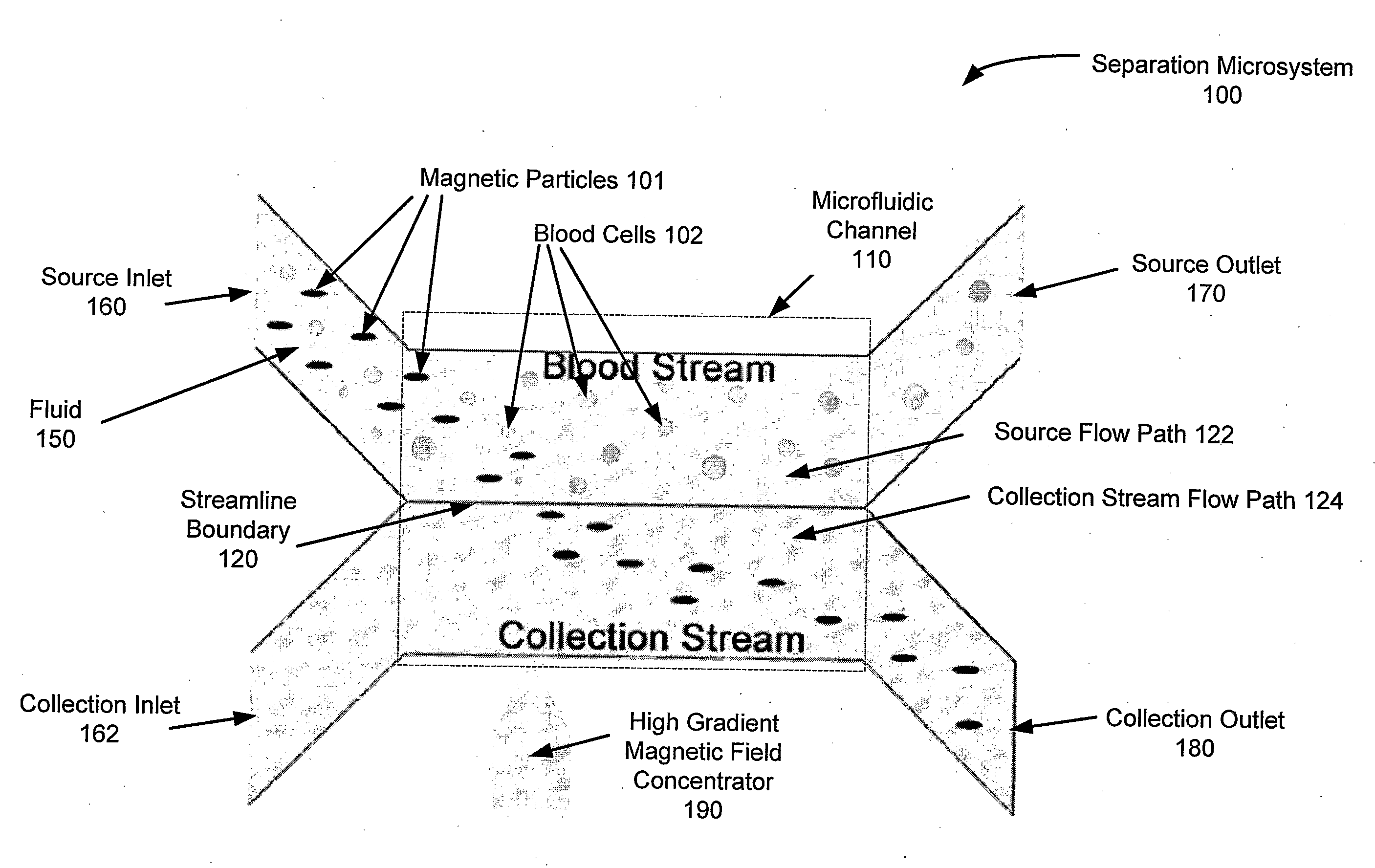
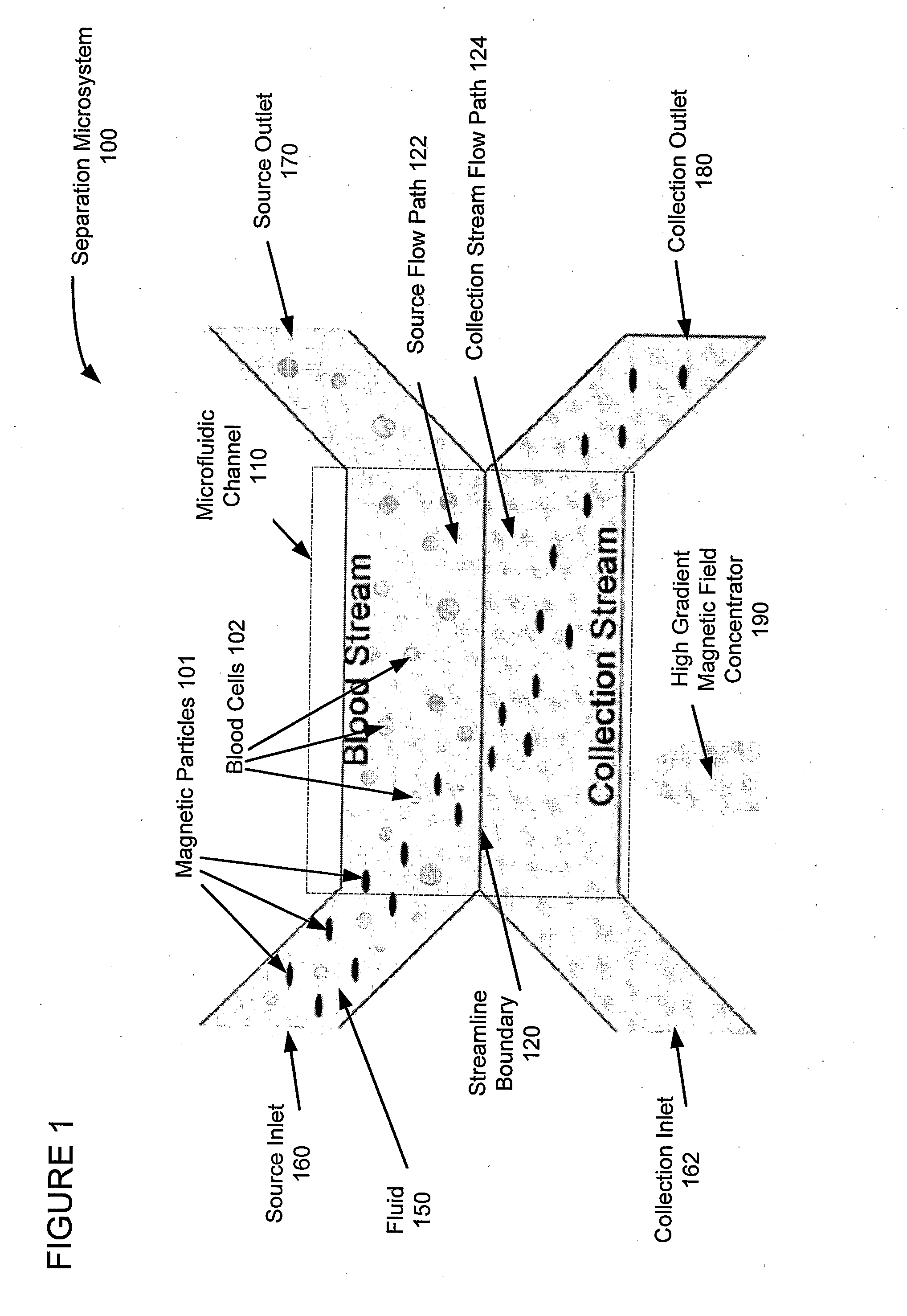
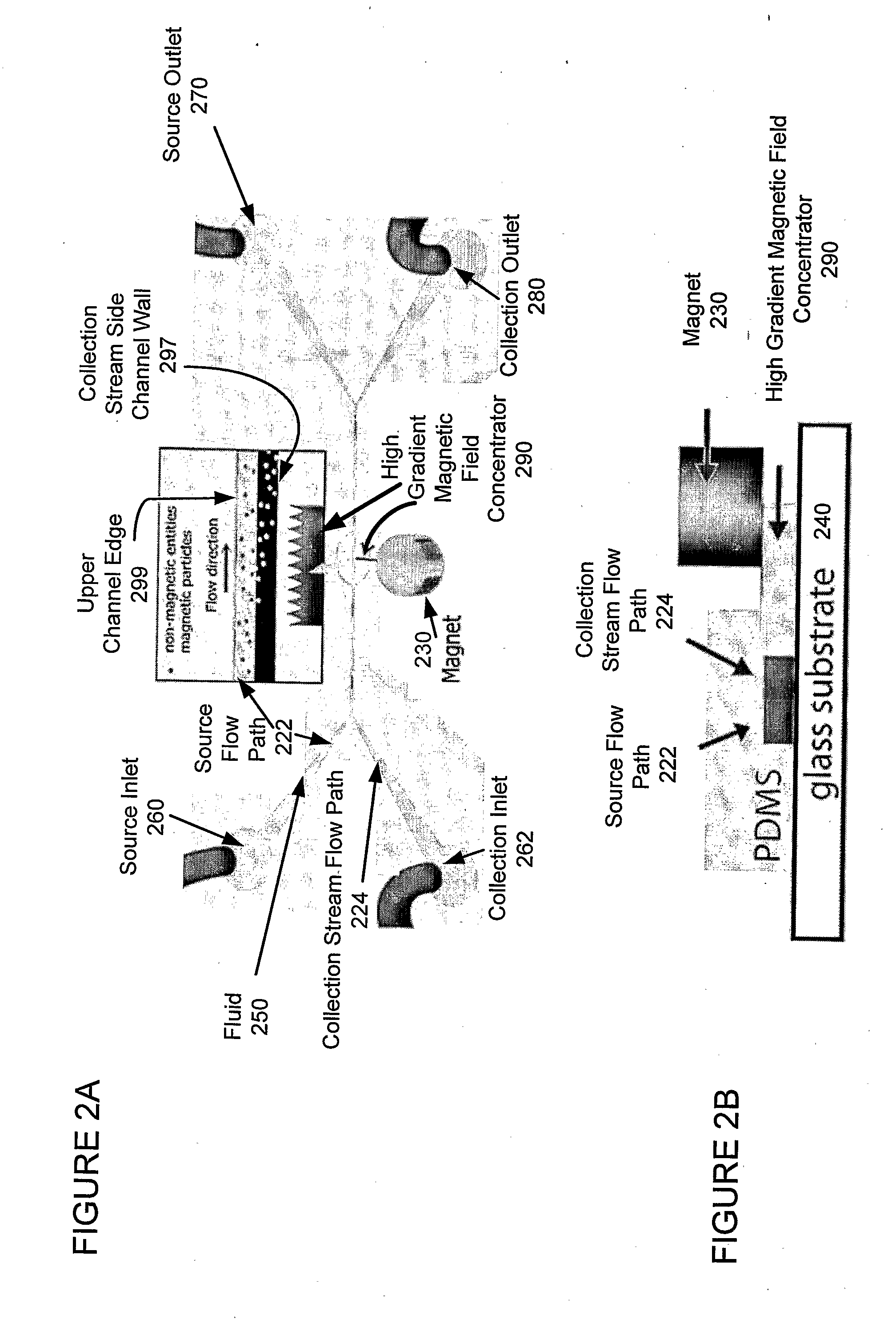
ActiveUS20090220932A1Minimize disturbanceEfficient separationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMagnetic field gradientChemical physics
A miniaturized, integrated, microfluidic device pulls materials bound to magnetic particles from one laminar flow path to another by applying a local magnetic field gradient. The device removes microbial and mammalian cells from flowing biological fluids without any wash steps. A microfabricated high-gradient magnetic field concentrator (HGMC) is integrated at one side of a microfluidic channel. When magnetic particles are introduced into one flow path, they remain limited to that flow path. When the HGMC is magnetized, the magnetic beads are pulled from the initial flow path into the collection stream, thereby cleansing the fluid. The microdevice allows large numbers of beads and materials to be sorted simultaneously, has no capacity limit, does not lose separation efficiency as particles are removed, and is useful for cell separations from blood and other biological fluids. This on-chip separator allows cell separations to be performed in the field outside of hospitals and laboratories.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
Magnetic particle based electrochemiluminescent detection apparatus and method
InactiveUS6133043AHigh sensitivityFaster assay timeMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceMagnetic field gradientElectrochemiluminescence
A method and apparatus for measuring electrochemiluminescence from a sample composition are described wherein magnetically responsive electrochemiluminescent active species are captured on the electrode with the aid of a capture magnet having a configuration such that the magnetic flux lines (or the magnetic field gradient) of at least one magnetic field source therein are compressed and / or dispersed. This capture magnet improves the distribution of the magnetically responsive electrochemiluminescent active species on the electrode surface and reduces interference with the photomultiplier tube, thereby enhancing the ECL signal and improving sensitivity. The improved capture and distribution also allows for shorter assay times.
Owner:BIOVERIS CORP
Method and morphologically adaptable apparatus for altering the charge distribution upon living membranes with functional stabilization of the membrane physical electrical integrity
ActiveUS7608035B2Relieve painShorten wound healing timeElectrotherapySurgeryEnergy balancingMagnetic field gradient
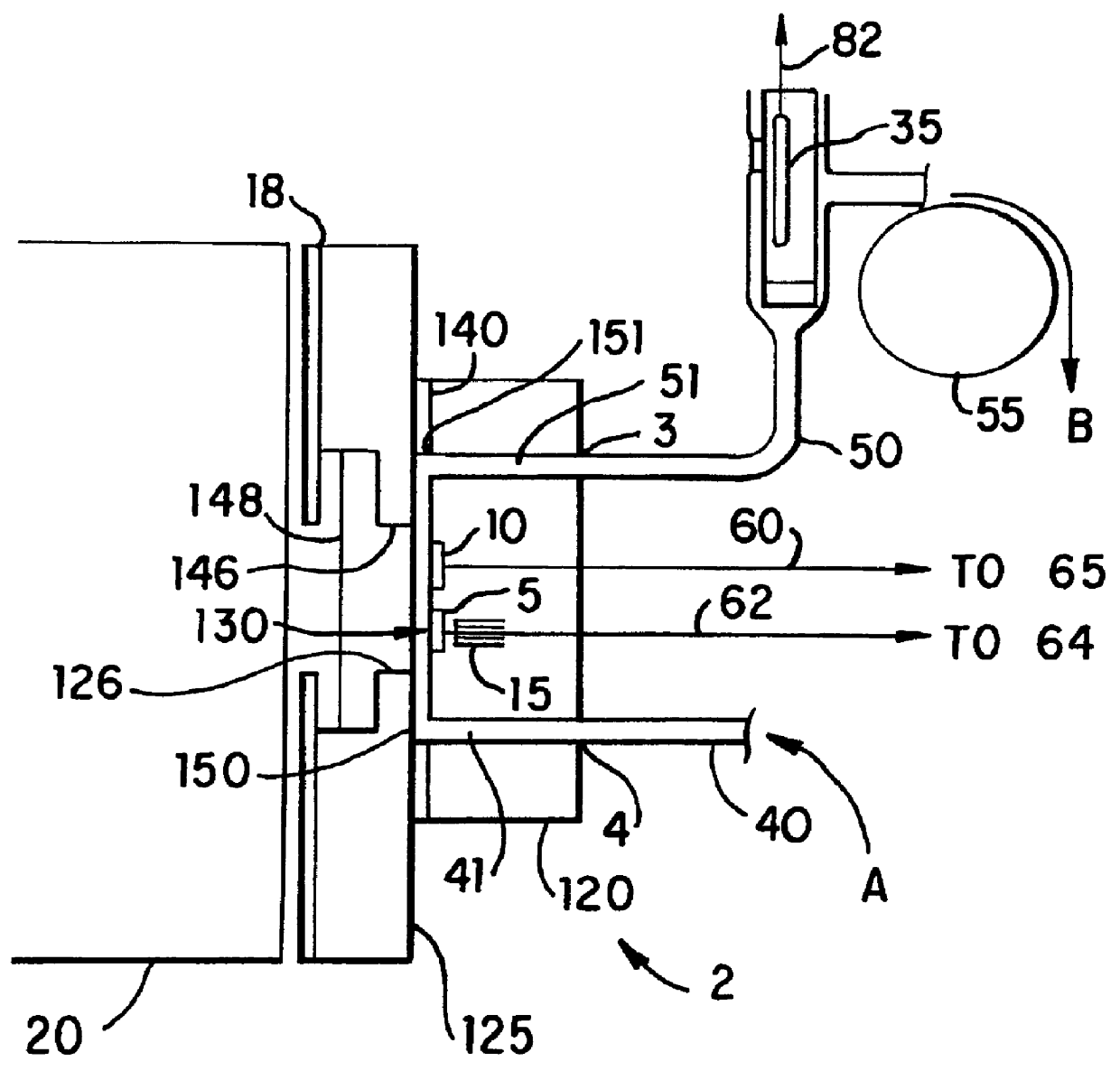
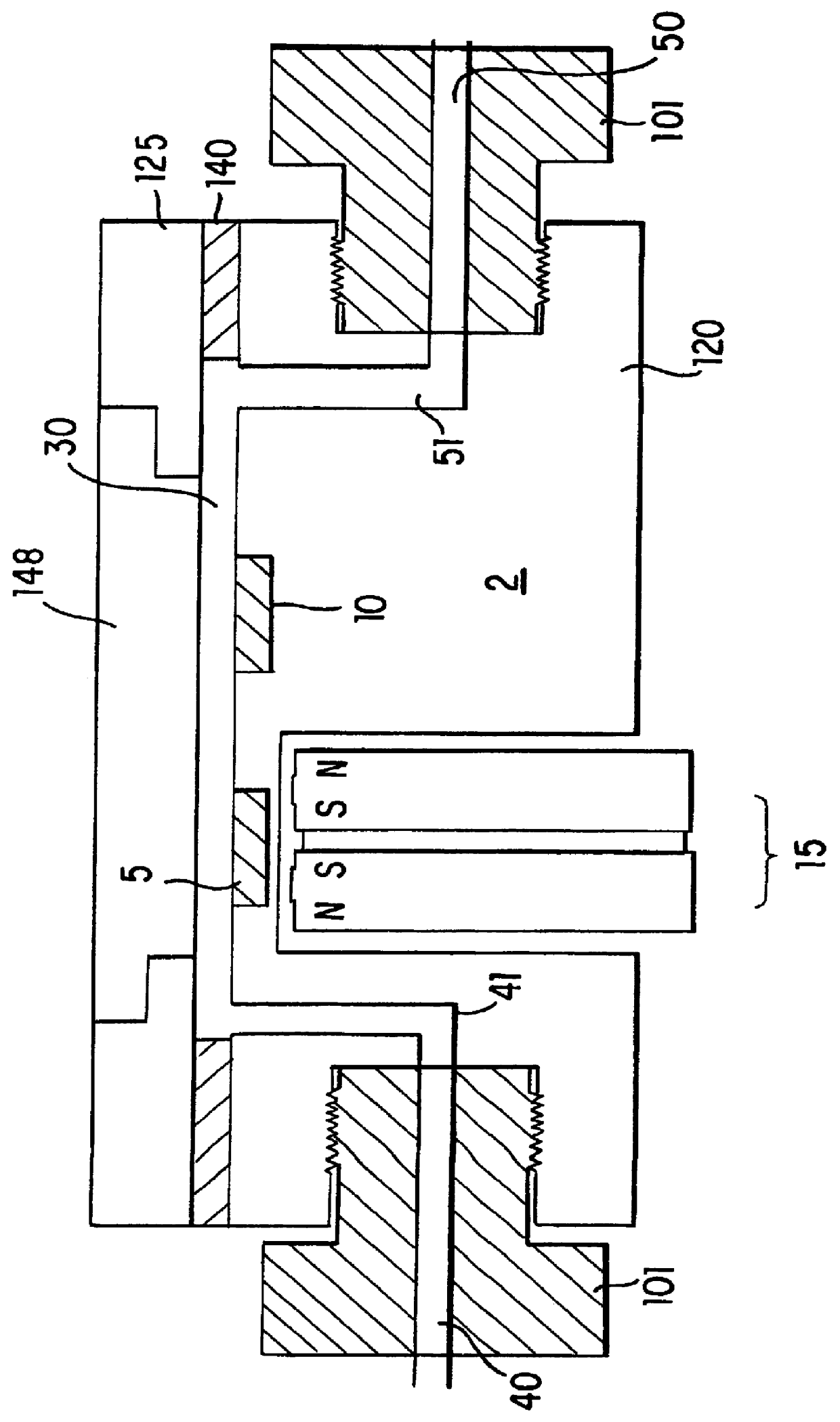
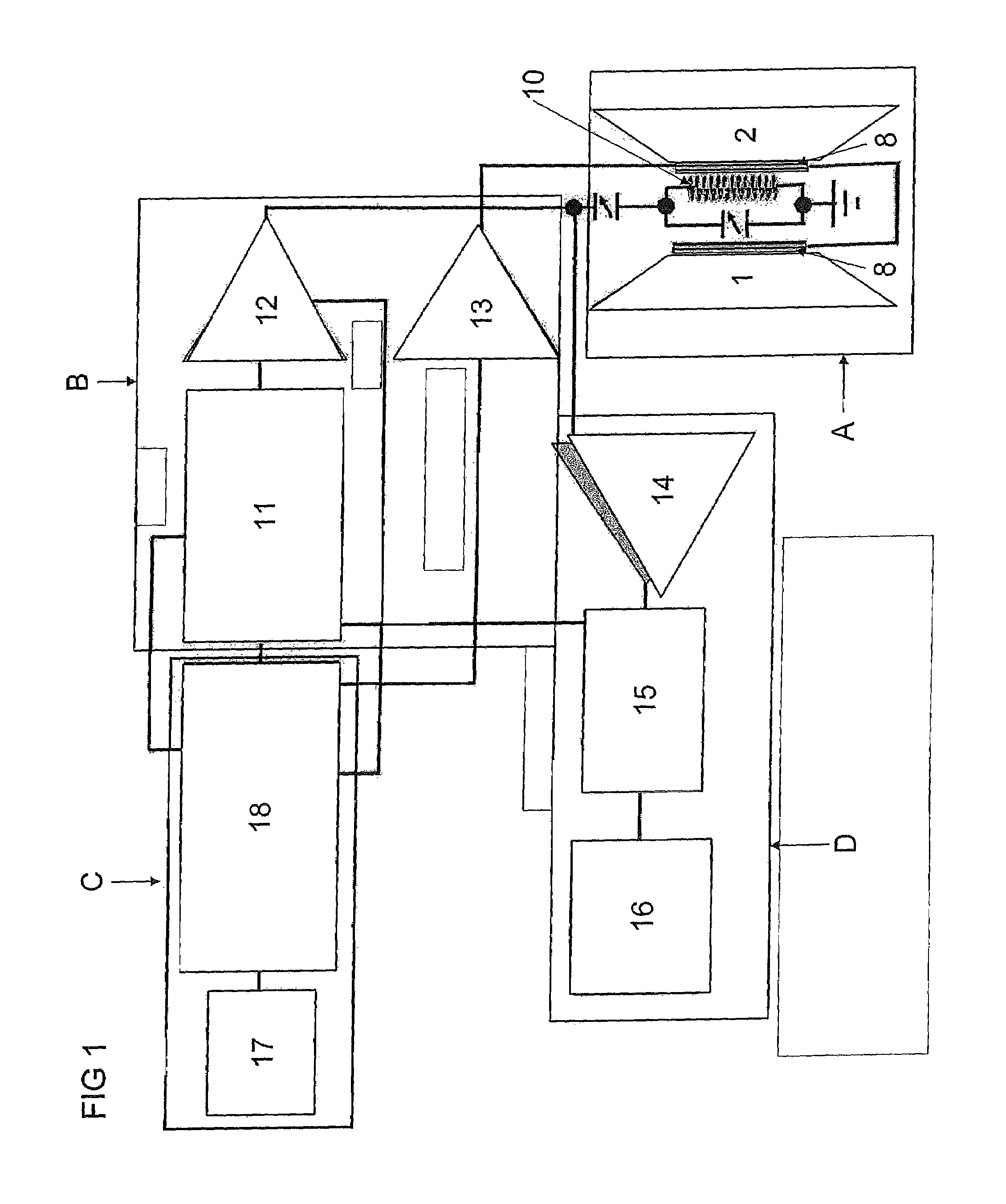
A method and morphologically adaptable apparatus for altering the charge distribution upon living membranes with functional stabilization of the membrane physical electrical integrity further comprising a method for using quadripolar, circular, center charged, energy balanced magnetic device in a four (4) magnet array of alternating polarity in which the magnetic poles are in multiple planes and are separated by a predetermined distance which provide an effective magnetic sphere of influence on all adjacent poles to suppress the firing of action potentials of mammalian sensory neurons. The method and apparatus further provides a static magnetic device for production of a magnetic field for treatment of various disorders that can be focused at the site of pain or edema to deliver a gradient in the magnetic field to prevent or reduce charge flow. Further there is provided a static magnetic device for production of a magnetic field for treatment of disorders wherein the device provides a static magnetic field such that the focused magnetic field gradient is oriented To be perpendicular to the neuron or membrane charge flow providing maximum deflection of the ion or charge flow.
Owner:GRADIENT TECH
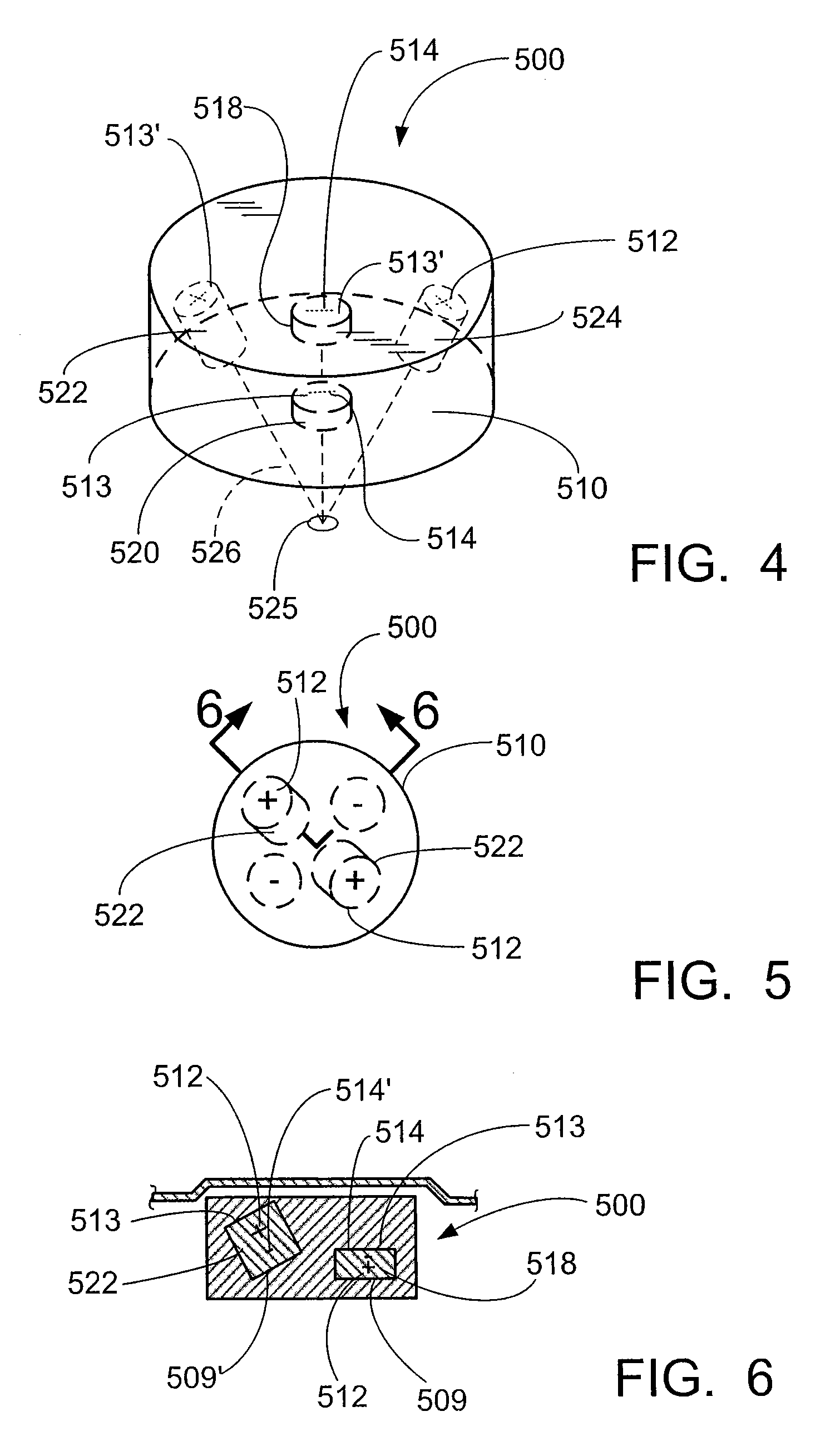
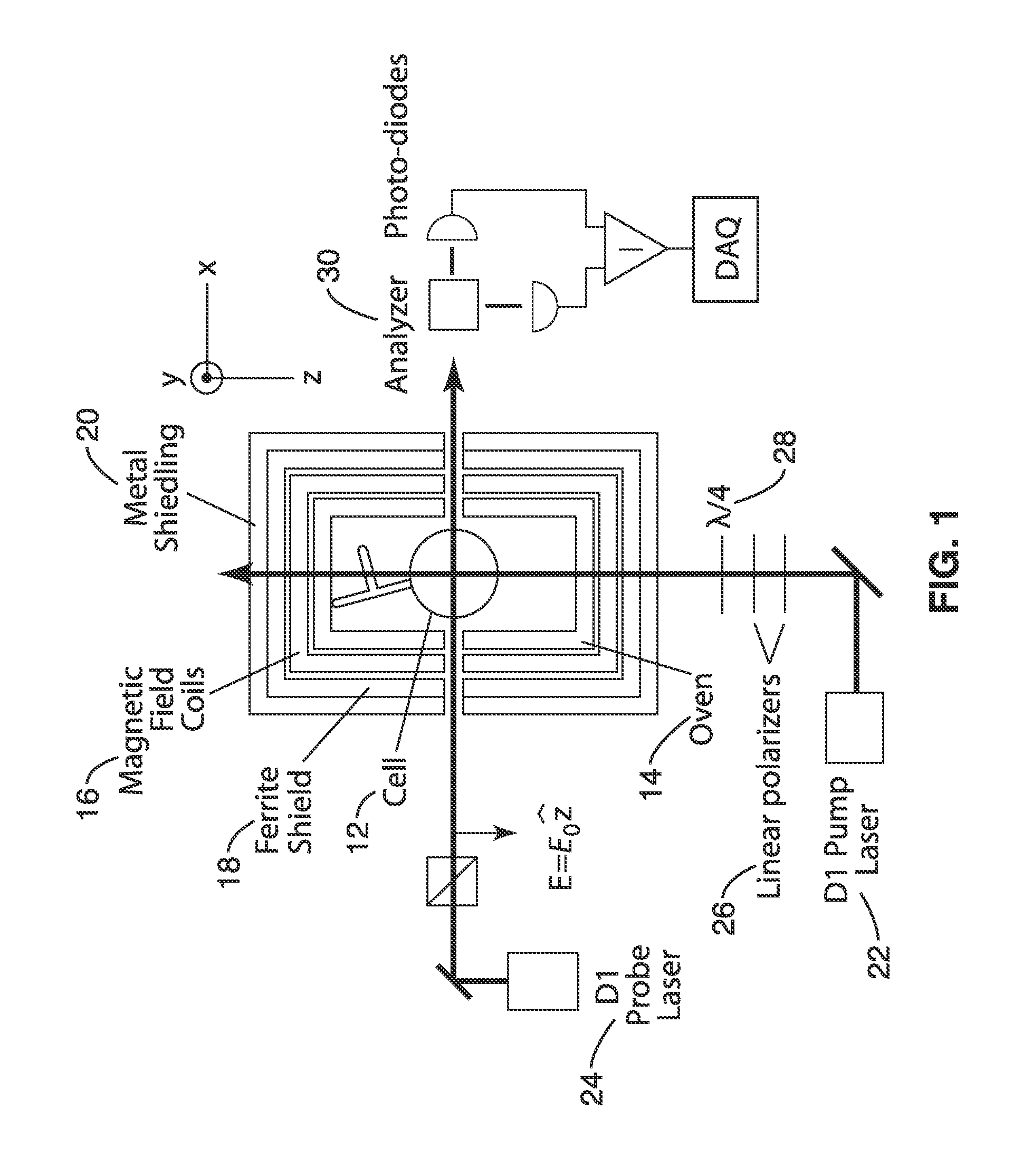
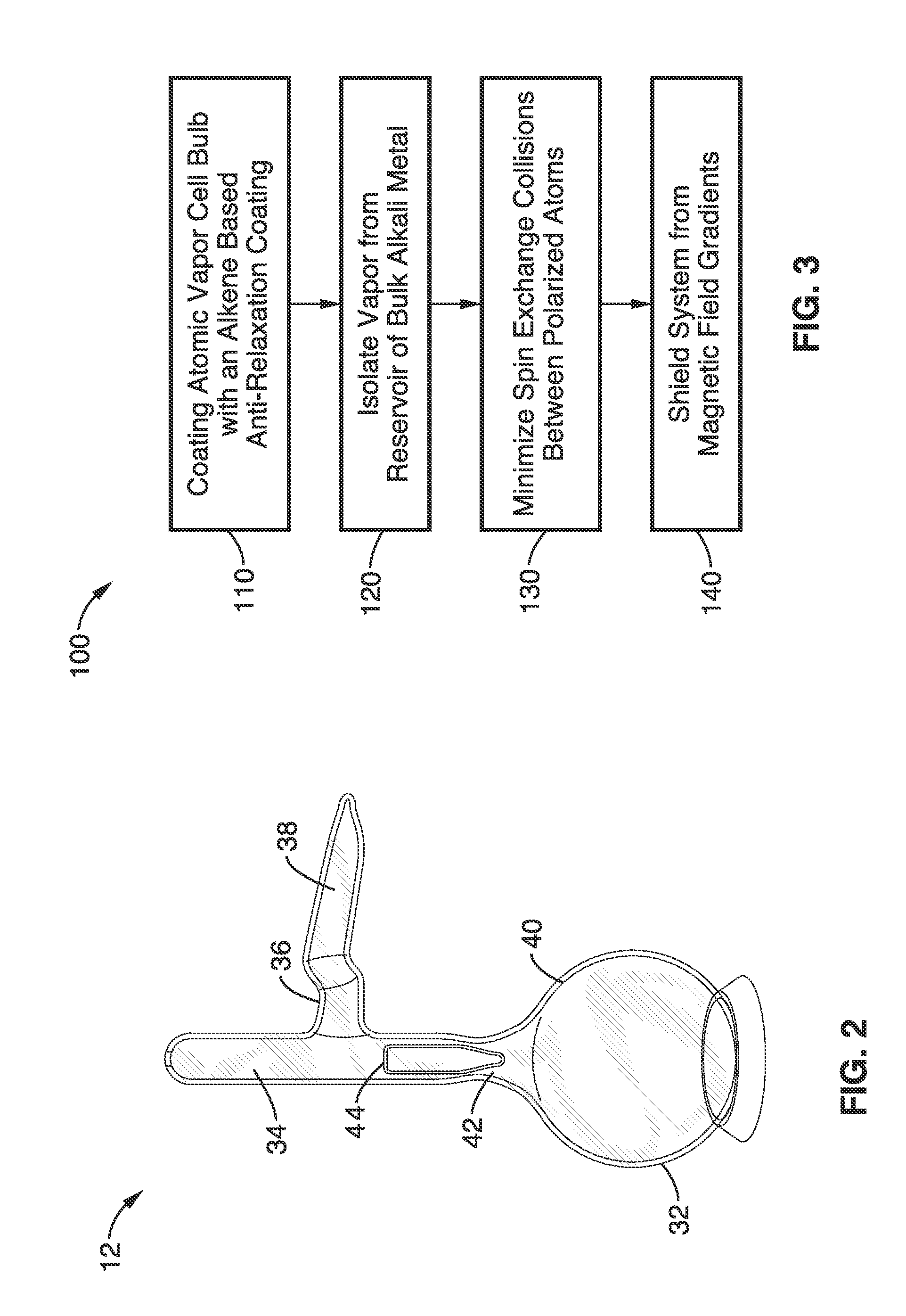
Apparatus and method for increasing spin relaxation times for alkali atoms in alkali vapor cells
InactiveUS20120112749A1Slow downReducing relaxation rateElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceMagnetic field gradientSpins
An atomic vapor cell apparatus and method for obtaining spin polarized vapor of alkali atoms with relaxation times in excess of one minute is provided. The interior wall of the vapor cell is coated with an alkene-based material. The preferred coatings are alkenes ranging from C18 to C30 and C20-C24 are particularly preferred. These alkene coating materials, can support approximately 1,000,000 alkali-wall collisions before depolarizing an alkali atom, an improvement by roughly a factor of 100 over traditional alkane-based coatings. Further, the method involves a combination of one or more of the following: the use of a locking device to isolate the atoms in the volume of the vapor cell from the sidearm used as a reservoir for the alkali metal vapor source, careful management of magnetic-field gradients, and the use of the spin-exchange-relaxation-free (SERF) technique for suppressing spin-exchange relaxation.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
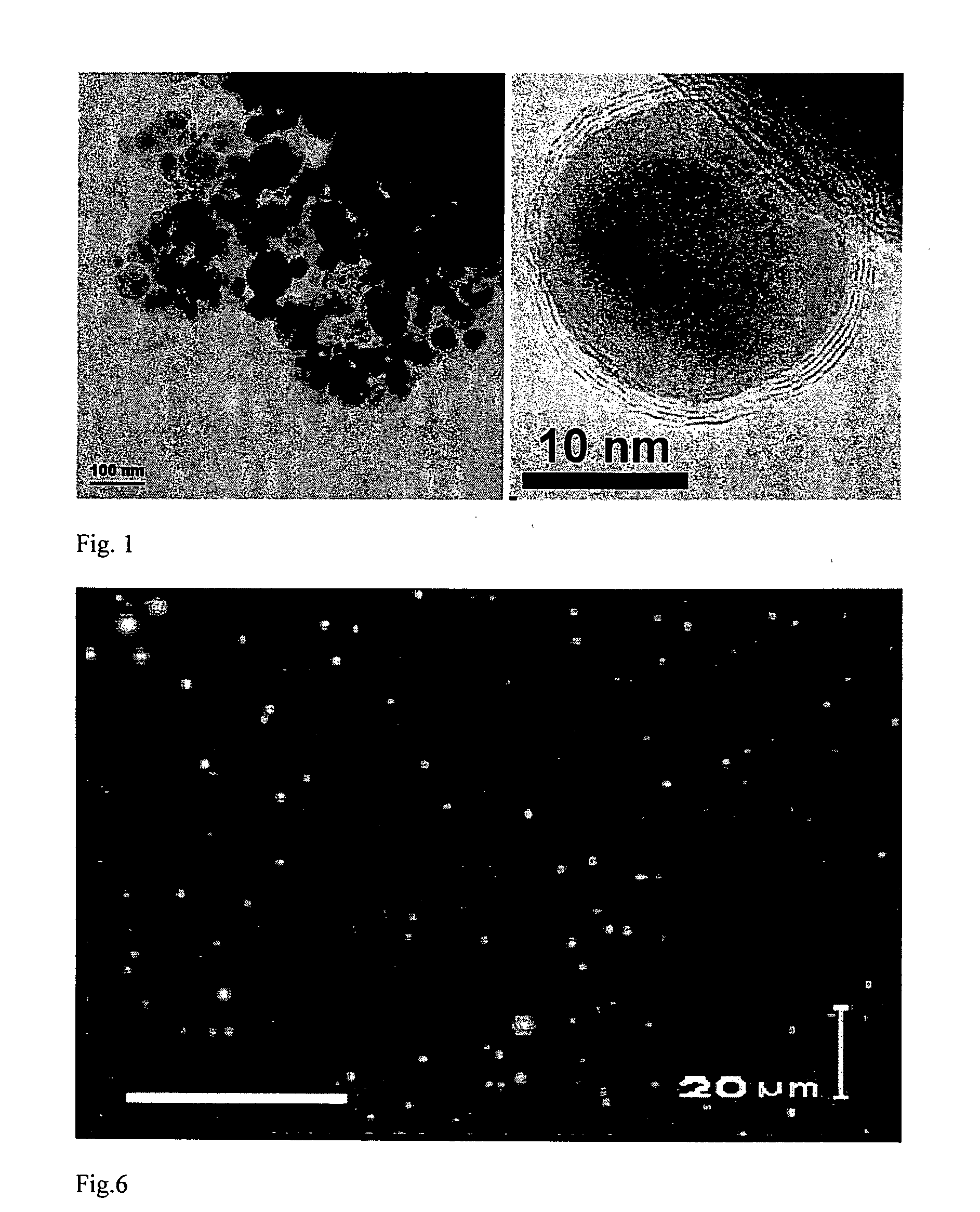
Carbon Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles and Their Use in Separation Processes
ActiveUS20100059449A1Improve mobilityRapidity and efficiencyNanomagnetismLiquid separation by electricityMagnetic field gradientMagnetite Nanoparticles
The invention relates to a process for separating a dispersed phase from a continuous phase comprising the steps of i) contacting said phases with an effective amount of nanoparticles; ii) applying a magnetic field gradient to the obtained system; iii) separating the obtained phases wherein said nanoparticles are of the core shell type, said core consists of a metal or alloy having soft magnetic properties and said shell contains a graphene layers which are optionally functionalized; to new nanoparticles and method of manufacturing such nanoparticles.
Owner:ETH ZZURICH
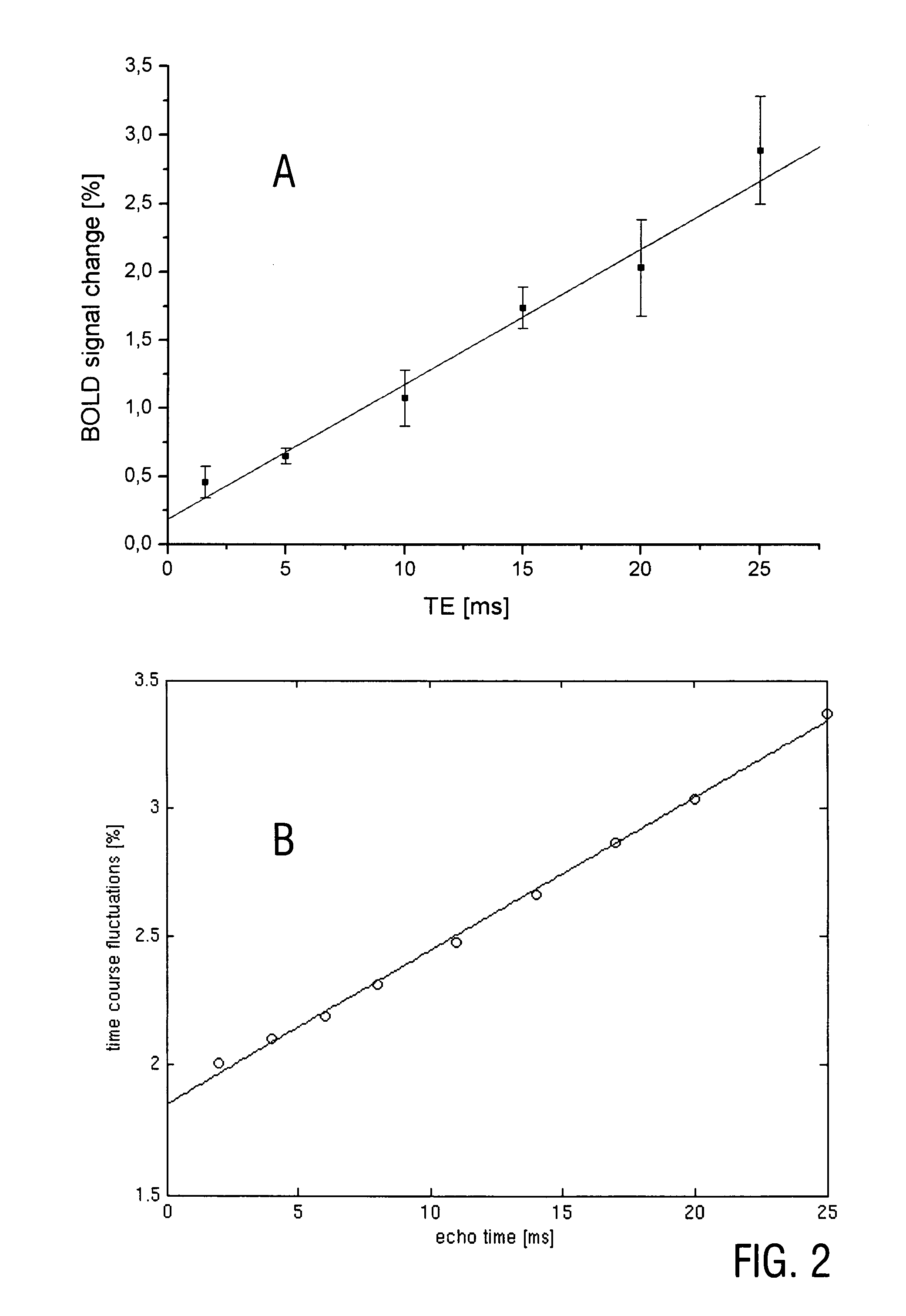
Magnetic resonance imaging with improved imaging contrast
InactiveUS20120013336A1Minimize timeMinimal echo timeMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic field gradientObject based
A method of magnetic resonance imaging of an object comprises the steps of arranging the object in a stationary magnetic field, subjecting the object to an excitation and encoding sequence of magnetic field gradients resulting in k-space sampling in two segments along the phase encoding direction, wherein the encoding sequence of the magnetic field gradients is selected such that the two segments in k-space are sampled along trajectories beginning with a central k-space line through the k-space center and continuing to opposite k-space borders of the two segments, collecting magnetic resonance signals created in the object, and reconstructing an image of the object based on the magnetic resonance signals, wherein one central k-space line is sampled in both of the two k-space segments, and intersegment phase and / or intensity deviations are corrected in both k-space segments using the magnetic resonance signals collected along the central k-space line. Furthermore, an imaging device for magnetic resonance imaging of an object is described.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
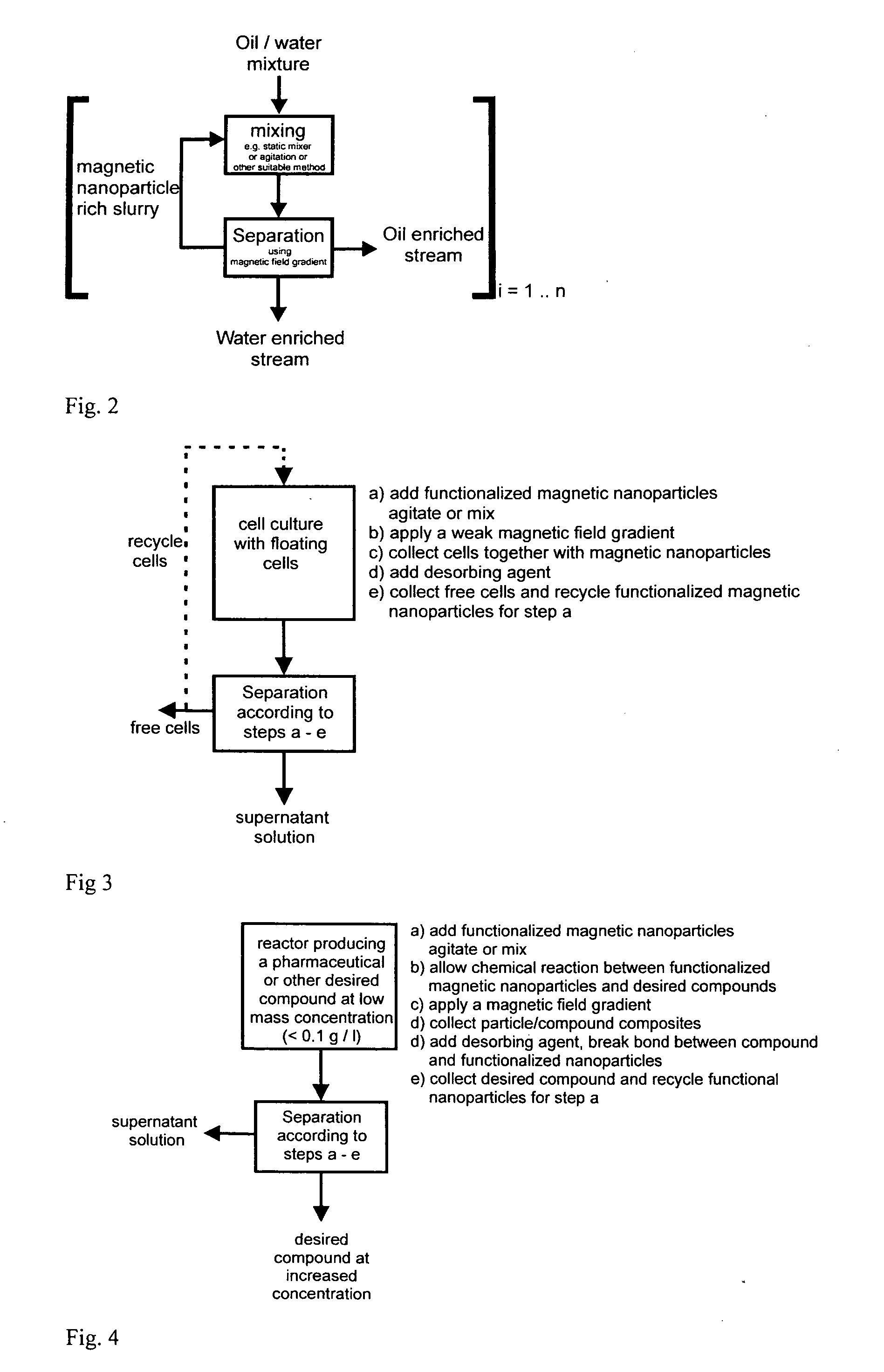
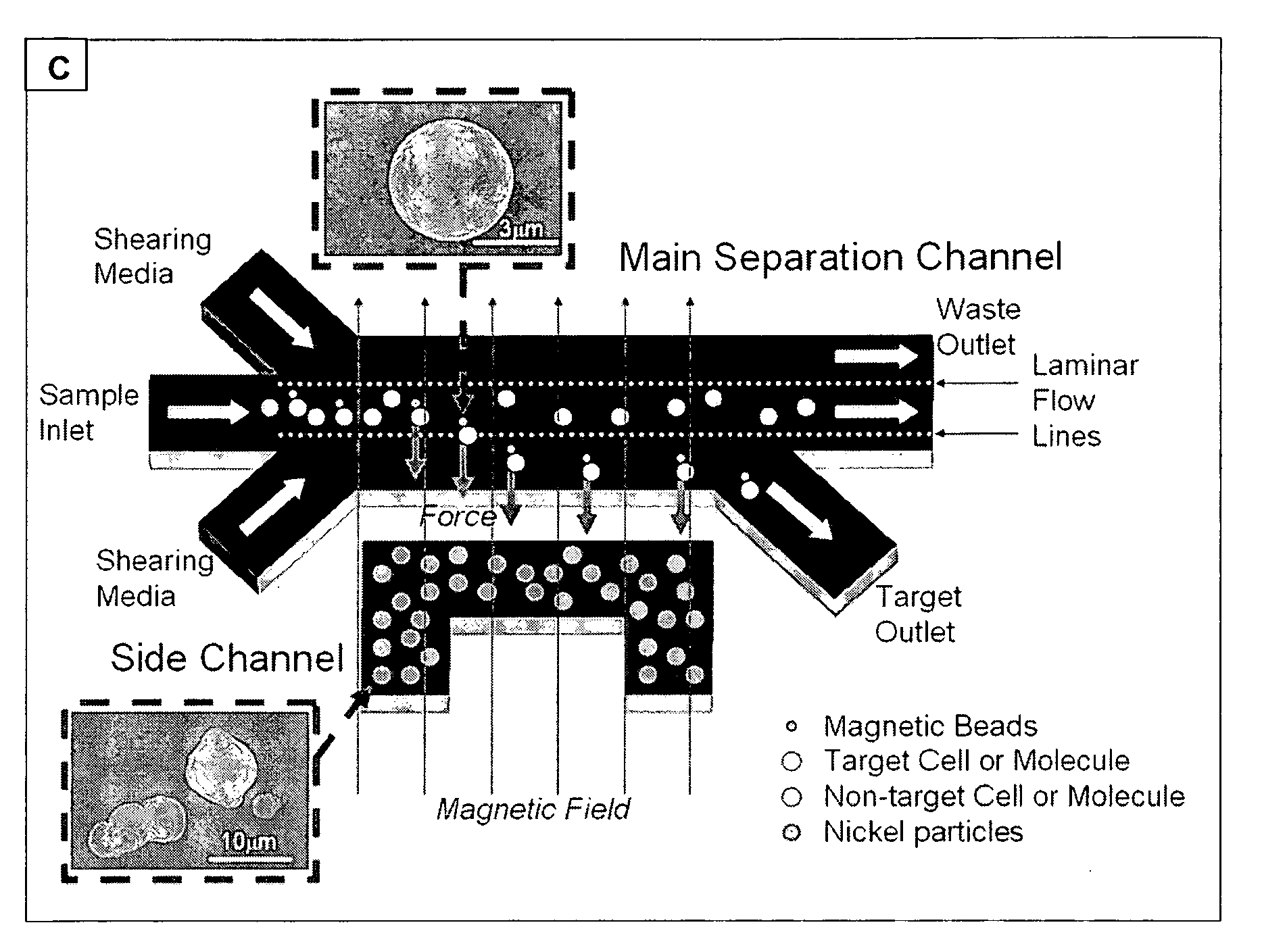
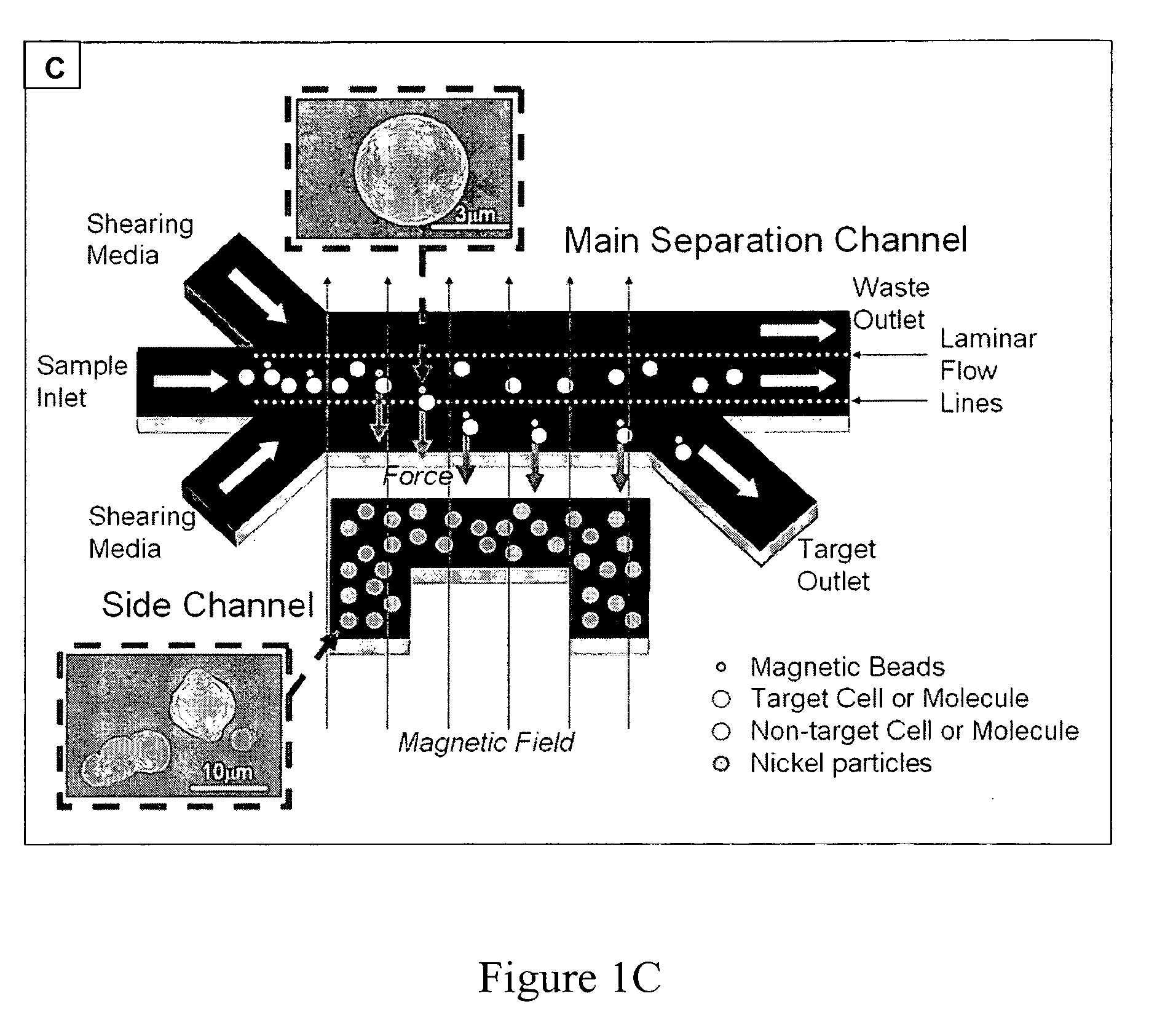
Method and apparatus for separating particles, cells, molecules and particulates
InactiveUS20090078614A1Easy to makeLow costElectrostatic separationMicrobiological testing/measurementMagnetic field gradientParticulates
A method and apparatus for continuously separating or concentrating particles that includes flowing two fluids in laminar flow through a magnetic field gradient which causes target particles to migrate to a waste fluid stream, and collecting each fluid stream after being flowed through the magnetic field gradient.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY +1
Magnetic gradiometer incorporating global feedback
InactiveUS6339328B1Minimizing energySufficient dynamic rangeMagnetic field measurement using flux-gate principleMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesMagnetic field gradientGradiometer
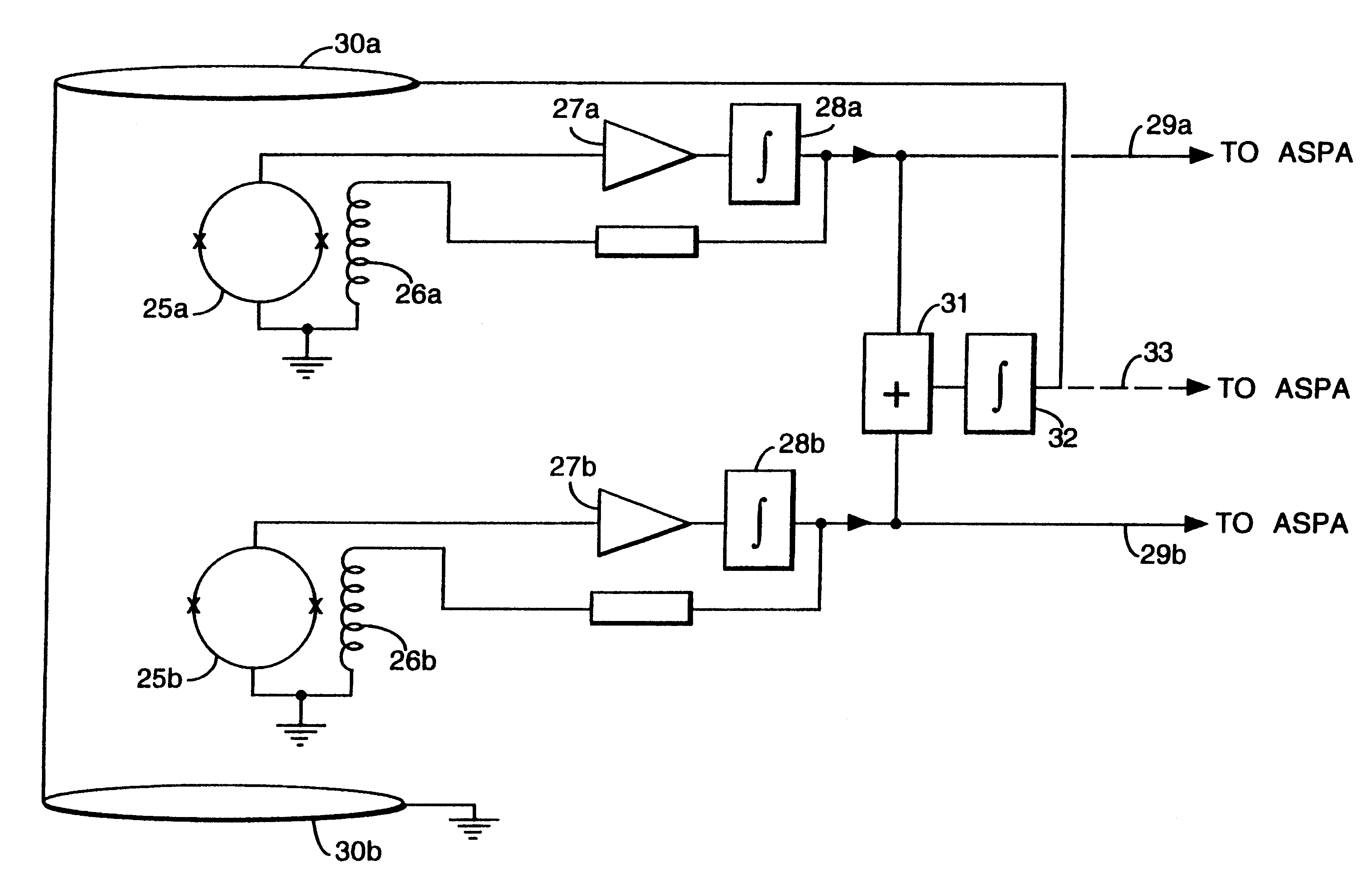
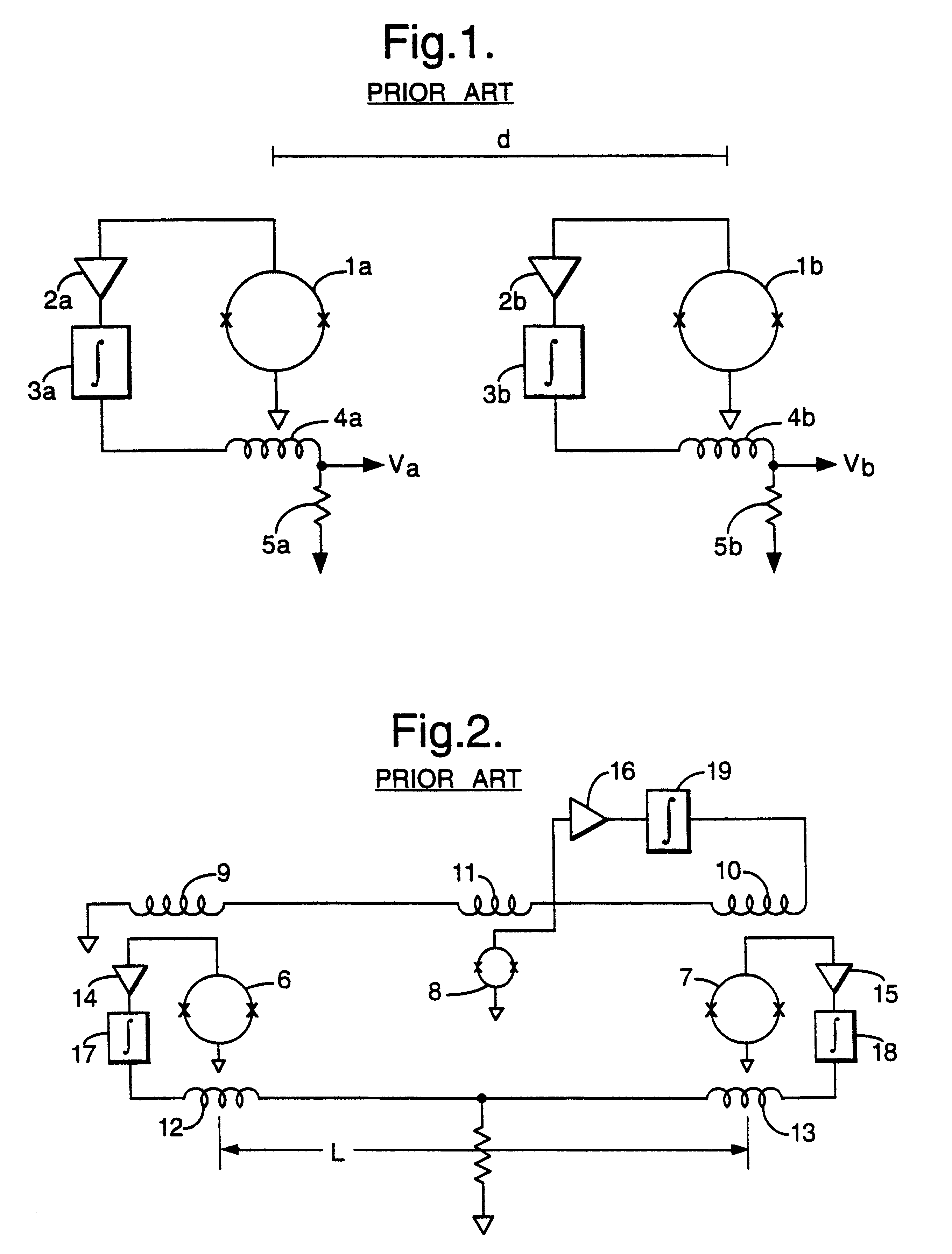
A gradiometer for measuring properties of a magnetic field and in particular, for measuring magnetic field gradient components, comprising at least two magnetic sensors wherein at least two of the magnetic sensors are arranged to sense the magnetic field component in substantially the same direction. The magnetic sensors may be super conducting quantum interference device (SQUID) magnetometers, Hall probes, flux gates or magneto-resistive magnetometers. The gradiometer also includes a computer processor loaded with an adaptive signal-processing algorithm, for performing adaptive signal balancing of the magnetometer outputs. In a preferred embodiment the gradiometer may comprise at least eight magnetometers in a three-dimensional arrangement, and a set of three orthogonal global feedback coils, one for each direction x, y, z, such that the five independent magnetic field gradient components may be measured. The gradiometer may also be used to measure second or higher order magnetic field gradient components.
Owner:QINETIQ LTD
Magnetic decoupler
An improved magnetic decoupler with a magnetic field shape, strength and gradient optimized for releasing security tags, such as an antitheft device of the type described above. Due to the structure of the magnetic decoupler, it contains less ferrous material than prior art decouplers heretofore employed. Reduction in size of the magnetic decoupler, along with improved magnetic strength, derive from the magnet assembly including magnets arranged with orientations that increase axial magnetic field gradient by superposition of the magnetic fields of each magnet.
Owner:DEXTER MAGNETIC TECH
Device for magnetic immobilization of cells
InactiveUS7285412B2Strong yet uniform external magnetic fieldForce is smallBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMagnetic field gradientElectrical battery
The present invention relates to an apparatus and methods that immobilize one or more cells associated with magnetic material on a substrate on which are located one or more magnetic receptacle(s). Alternatively, in another aspect the present invention, the device arrays cells associated with magnetic material on a substrate having a pattern of magnetic receptacles disposed thereon. The size of the magnetic receptacle(s) determines the number of target cells that it is capable of immobilizing. The size of the magnetic receptacle is defined by the strength of a localized magnetic field gradient. The localized magnetic field gradient may be derived from 1) permanent magnets embedded in the substrate or alternatively, the localized magnetic field gradient may be derived from an 2) external magnet whose strength is focused by objects of highly-permeable-magnetic material which create localized magnetic field gradients. The invention apparatus comprises a removable cell delivery device and a substrate, which has one or more magnetic receptacles disposed thereon.
Owner:SURFACE LOGIX INC
Apparatus and method for processing magnetic particles
InactiveUS20030127396A1Simple construction operationMaximizes mixing efficiencyElectrostatic separationWater/sewage treatment by magnetic/electric fieldsMagnetic gradientMagnetic source
An apparatus and method for carrying out the affinity separation of a target substance from a liquid test medium by mixing magnetic particles having surface immobilized ligand or receptor within the test medium to promote an affinity binding reaction between the ligand and the target substance. The test medium with the magnetic particles in a suitable container is removably mounted in an apparatus that creates a magnetic field gradient in the test medium. This magnetic gradient is used to induce the magnetic particles to move, thereby effecting mixing. The mixing is achieved either by movement of a magnet relative to a stationary container or movement of the container relative to a stationary magnet. In either case, the magnetic particles experience a continuous angular position change with the magnet. Concurrently with the relative angular movement between the magnet and the magnetic particles, the magnet is also moved along the length of the container causing the magnetic field gradient to sweep the entire length of the container. After the desired time, sufficient for the affinity reaction to occur, movement of the magnetic gradient is ended, whereby the magnetic particles are immobilized on the inside wall of the container nearest to the magnetic source. The remaining test medium is removed while the magnetic particles are retained on the wall of the container. The test medium or the particles may then be subjected to further processing.
Owner:SIGRIS RES
Particle-Based Microfluidic Device for Providing High Magnetic Field Gradients
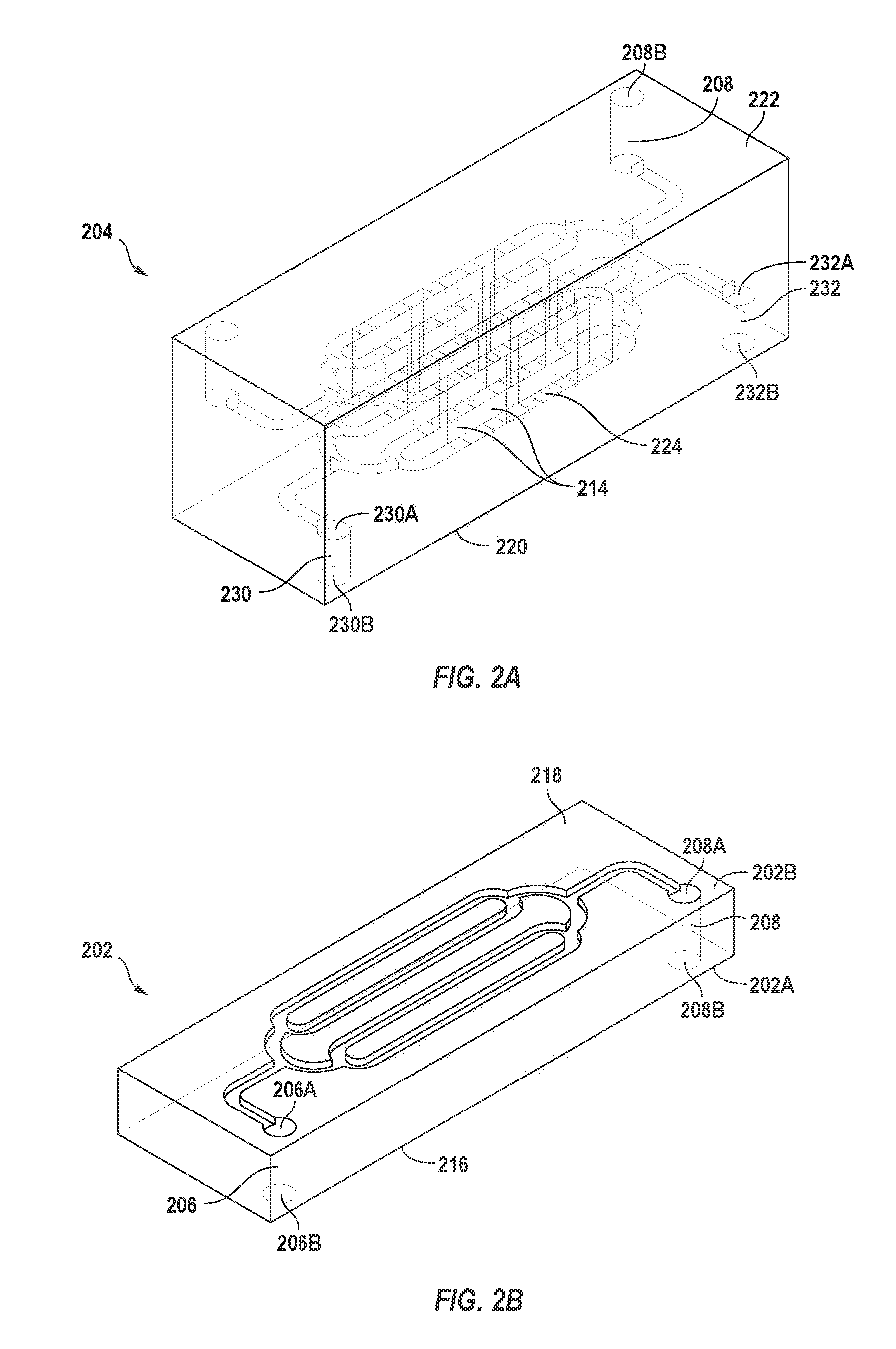
InactiveUS20100044232A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrostatic separatorsParticulatesMagnetic field gradient
A microfluidic device for manipulating particles in a fluid has a device body that defines a main channel therein, in which the main channel has an inlet and an outlet. The device body further defines a particulate diverting channel therein, the particulate diverting channel being in fluid connection with the main channel between the inlet and the outlet of the main channel and having a particulate outlet. The microfluidic device also has a plurality of microparticles arranged proximate or in the main channel between the inlet of the main channel and the fluid connection of the particulate diverting channel to the main channel. The plurality of microparticles each comprises a material in a composition thereof having a magnetic susceptibility suitable to cause concentration of magnetic field lines of an applied magnetic field while in operation. A microfluidic particle-manipulation system has a microfluidic particle-manipulation device and a magnet disposed proximate the microfluidic particle-manipulation device.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
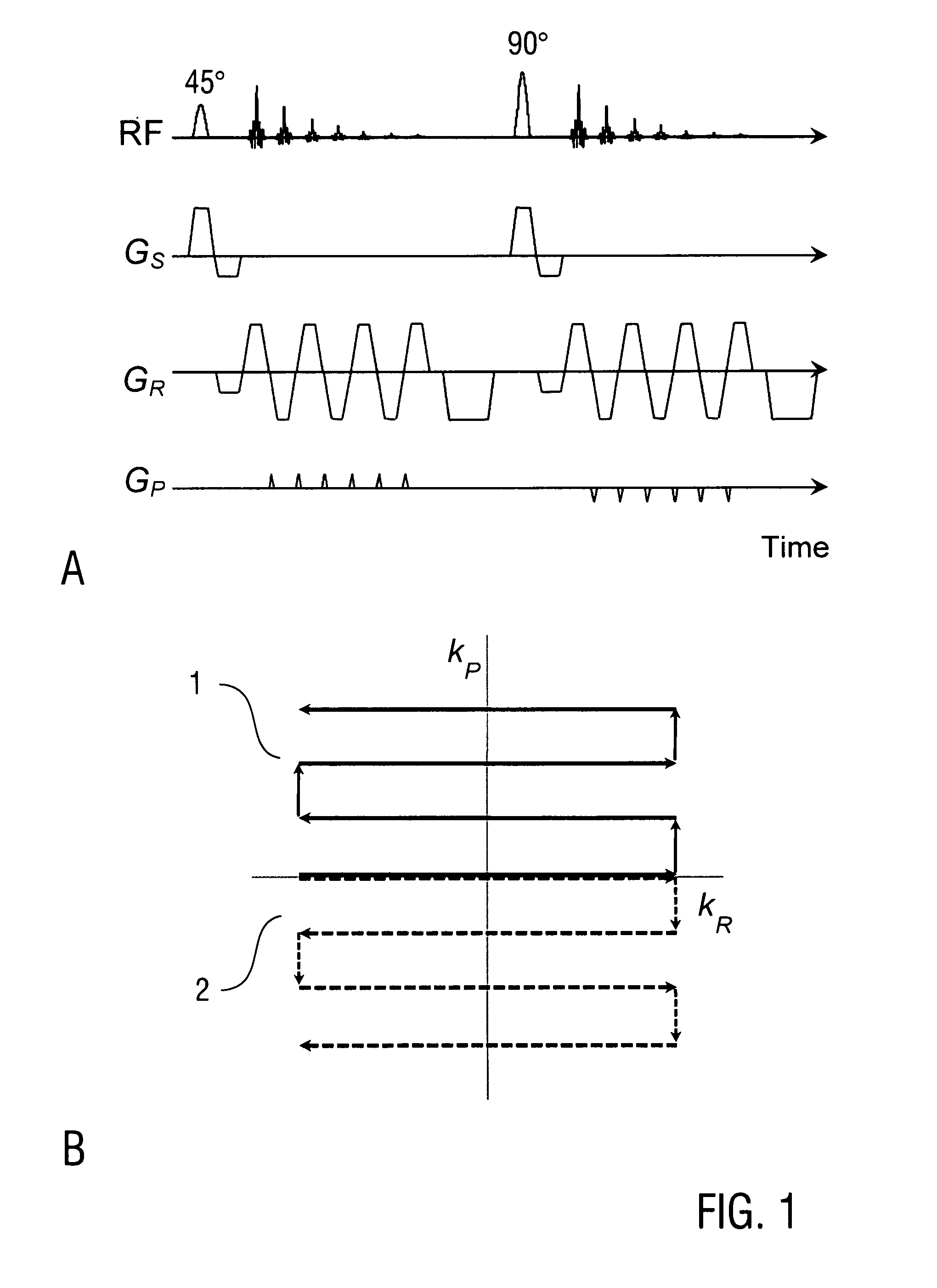
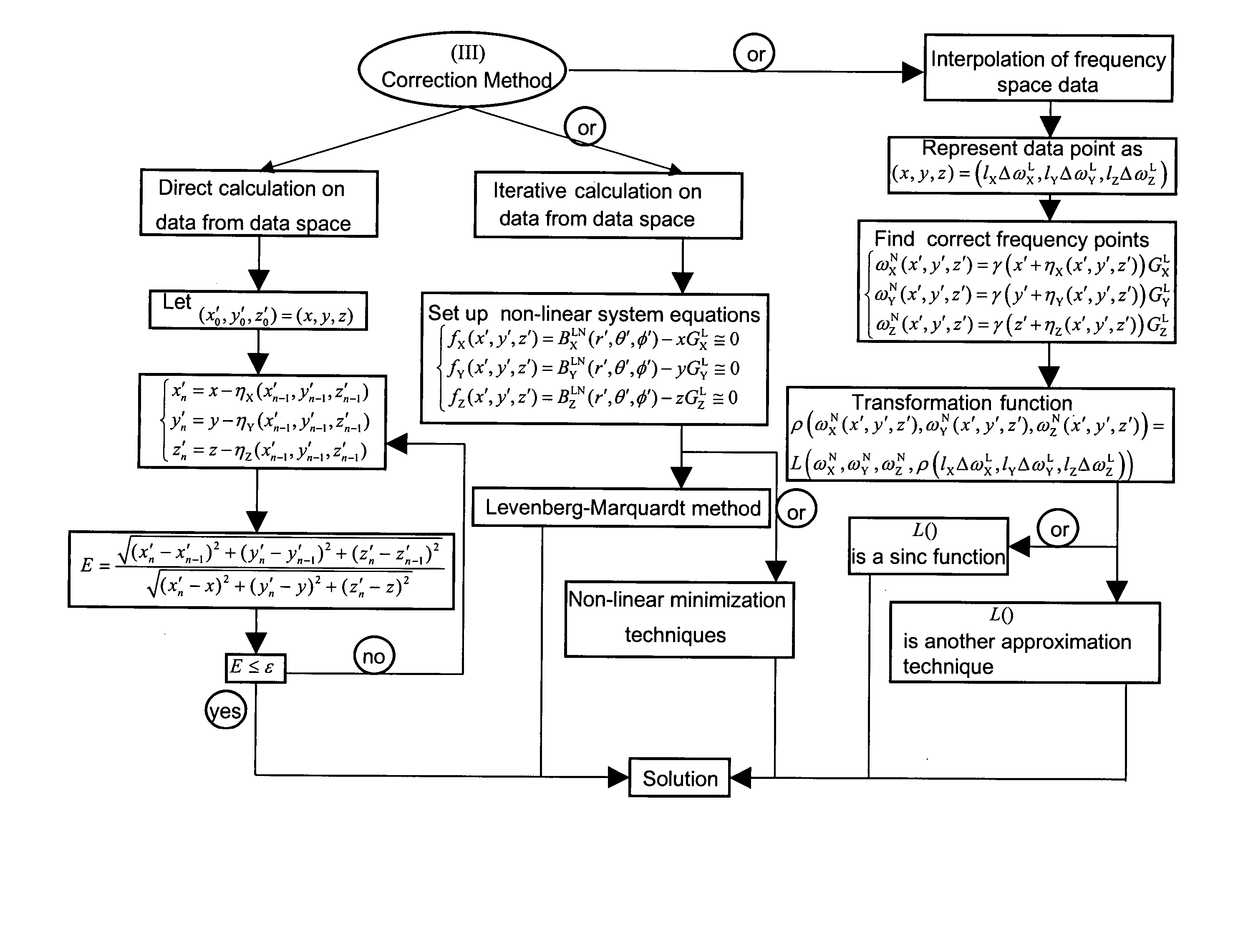
Correction of magnetic resonance images
InactiveUS20050024051A1Avoid artifactsAccurate imagingMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringMagnetic field gradientFourier transform on finite groups
Spatial encoding in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) techniques is achieved by sampling the signal as a function of time in the presence of magnetic field gradients, e.g., X, Y, and Z gradients. The gradient magnets have in the past been assumed to generate a linear gradient, and typical image reconstruction techniques have relied upon this assumption. However, to achieve high speed performance, gradient magnets often sacrifice linearity for speed. This non-linearity, in turn, results in distorted images, the distortion often being sufficiently large to compromise the usefulness of MRI images for stereotaxy or longitudinal studies, where precise volumetric information is required. The disclosure provides practical methods for correcting distorted images resulting from such non-linearity in the gradient fields, as well as distortions resulting from translational, rotational, and / or winding / design errors in the field generating devices. The methods employ spherical harmonic expansions of the gradient fields and fast Fourier transform techniques to provide well-corrected images without undue computational burdens.
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND
Ferrographic method
InactiveUS6156208AAccelerated dissipationReduce adventitious depositionWithdrawing sample devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansMagnetic field gradientFree interface
A ferrographic apparatus and method incorporate a priming operation that moves a priming fluid, in a direction opposite to the flow direction subsequently followed by the sample fluid, through a fluid pathway including the flow chamber. The fluid pathway is configured to facilitate dissipation of any gas bubble introduced into it during the priming operation and to reduce adventitious deposition of specimen material at locations other than the substrate. Sample fluid to be analyzed is added to the reservoir so as to form a bubble-free interface with the priming fluid, and the direction of movement through the flow chamber is reversed. The resulting continuous fluid column is advanced through the fluid pathway so that the sample fluid enters the flow chamber through the inlet port and passes through the magnetic field gradient, exiting through an orifice at the opposite end of the flow chamber serving as the outlet port. The flow chamber of the ferrograph is preferably contained in a deposition cassette comprising the substrate, a gasket and a platen which incorporates an integral fluid reservoir in communication with the inlet port. A pump is preferably configured to move each liquid through the fluid pathway at a distinct flow rate and in a direction according to the function performed by the respective liquid.
Owner:INST GUILFOYLE
Diagnostic and therapeutic magnetic propulsion capsule and method for using the same
InactiveUS20110301497A1Reduced field generator powerImprove art of robotic guidanceVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsEndoscopesMagnetic field gradientMagnetic gradient
A guided medical propulsion capsule driven by strong electro-magnetic interaction between an external AC / DC magnetic gradient-lobe generator and a set of uniquely magnetized ferrous-conductive elements contained within the capsule. The capsule is navigated through the lumens and cavities of the human body wirelessly and without any physical contact for medical diagnostic, drug delivery, or other procedures with the magnetically guiding field generator external to the human body. The capsule is equipped with at least two sets of magnetic rings, disks and / or plates each possessing anisotropic magnetic properties. The external magnetic gradient fields provide the gradient forces and rotational torques on the internal conductive and magnetic elements needed to make the capsule move, tilt, and rotate in the body lumens and cavities according to the commands of an operator.
Owner:NEURO KINESIS CORP +1
Multi-component marine electromagnetic signal acquisition cable and system
InactiveUS20080265895A1Detection using electromagnetic wavesAcoustic wave reradiationMagnetic field gradientEngineering
A marine electromagnetic sensor cable includes a plurality of sensor modules disposed at spaced apart locations along a cable. Each module includes at least one pair of electrodes associated with the module. The electrodes are arranged to measure electric field in a direction along the direction of the cable. The cable is arranged to form a closed pattern. Another marine electromagnetic sensor cable includes a plurality of sensor modules disposed at spaced apart locations along a cable. Each module includes at least one pair of electrodes associated therewith. The electrodes are arranged to measure electric field in a direction along the direction of the cable. A plurality of spaced apart magnetic field sensors is associated with each module and arranged to enable determining an electric field amplitude in a direction transverse to the direction of the cable from magnetic field gradient.
Owner:KJT ENTPR
Perpendicular magnetic recording head and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20070217069A1High gradientImprove accuracyManufacture head surfaceElectrical transducersMagnetic field gradientEngineering
Embodiments in accordance with the present invention provide a trailing side shield around a main pole and control the gap length on its trailing side to high accuracy so as to increase a recording magnetic field gradient. An etching signal layer is provided on a main pole, and the gap length on the trailing side of the main pole is controlled to high accuracy by stopping ion milling when a signal from this layer is detected.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Compact and portable low-field pulsed NMR dispersion analyzer
ActiveUS7417426B2Small and portableLow costAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMagnetic field gradientLiquid ratio
A compact and integrated portable device is provided for the analysis of dispersions by low-field pulsed NMR including: an NMR probe module, a means for generating radio frequency and magnetic field gradient pulses, a signal processor, and a master controller. Also provided are methods for using the device to measure one or more characteristics of phases or particles comprising a dispersion such as surface area, solid / liquid ratio, particle size, and elemental analysis.
Owner:XIGO NANOTOOLS
Nuclear magnetic resonance module
ActiveUS20080150524A1Low cost designSufficient signal to noise ratioElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceMagnetic field gradientNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
A nuclear magnetic resonance apparatus that may be used in connection with a variety of different tools, including a down-hole side-wall coring tool as well as with manufacturing process controllers. In one embodiment, the nuclear magnetic resonance apparatus may include a magnet assembly constructed around a sample chamber. The magnet assembly is constructed and arranged to provide a non-uniform magnetic field having a known magnetic field gradient inside the sample chamber. The use of gradient fields may allow for a more flexible and robust magnet assembly design that may be suitable for a variety of different applications.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
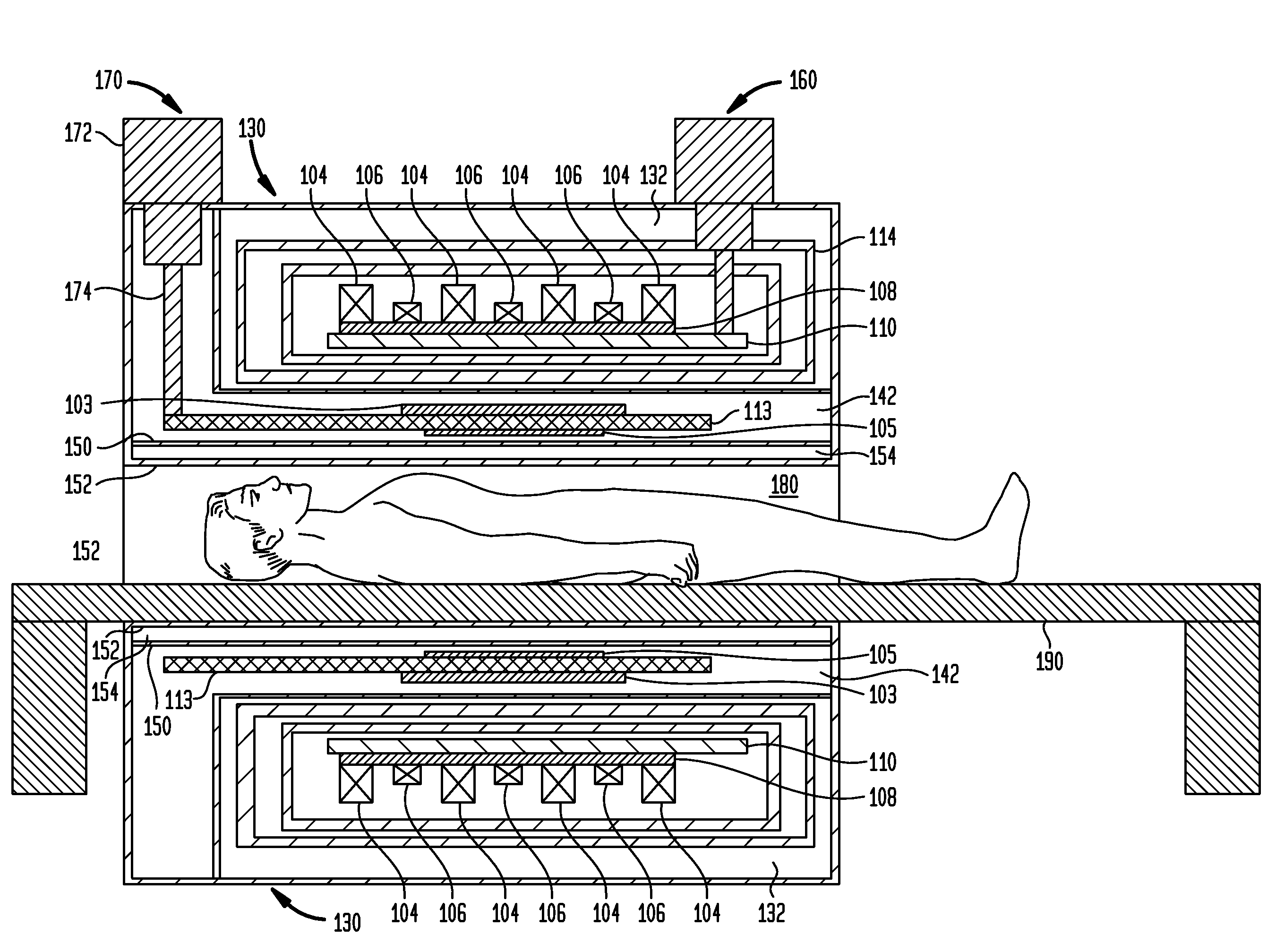
Superconductor Magnetic Resonance Imaging System and Method (SUPER-MRI)
ActiveUS20100231215A1Improve conductivityMachines/enginesSuperconductor devicesMagnetic field gradientMagnetic resonance spectrometry
Methods and apparatuses for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and / or magnetic resonance spectroscopy comprising a superconducting main magnet operable to generate a uniform magnetic field in an examination region, at least one superconducting gradient field coil operable to apply a respective at least one magnetic field gradient within the examination region, and at least one RF coil that is operable to transmit and receive radio frequency signals to and from the examination region, and that is configured for cooling and comprises at least one of (i) a non-superconducting material that when cooled to a temperature below room temperature has a conductivity higher than that of copper at that temperature and (ii) a superconducting material. The main magnet, the gradient coils, and each of the at least one RF coil of a given system may each be implemented as high temperature superconductor materials.
Owner:TIME MEDICAL HLDG
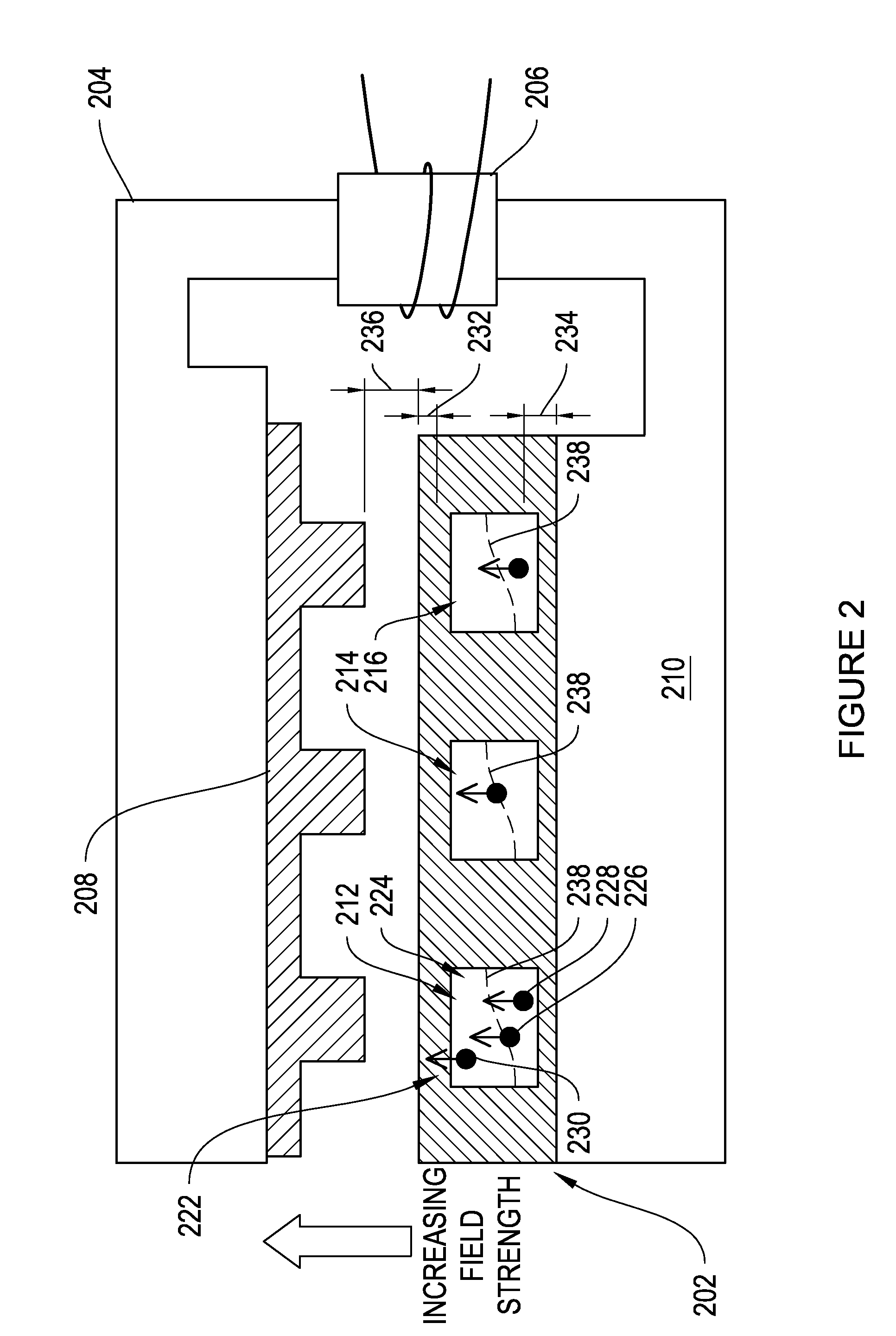
Magnet coil system for contactless movement of a magnetic body in a working space
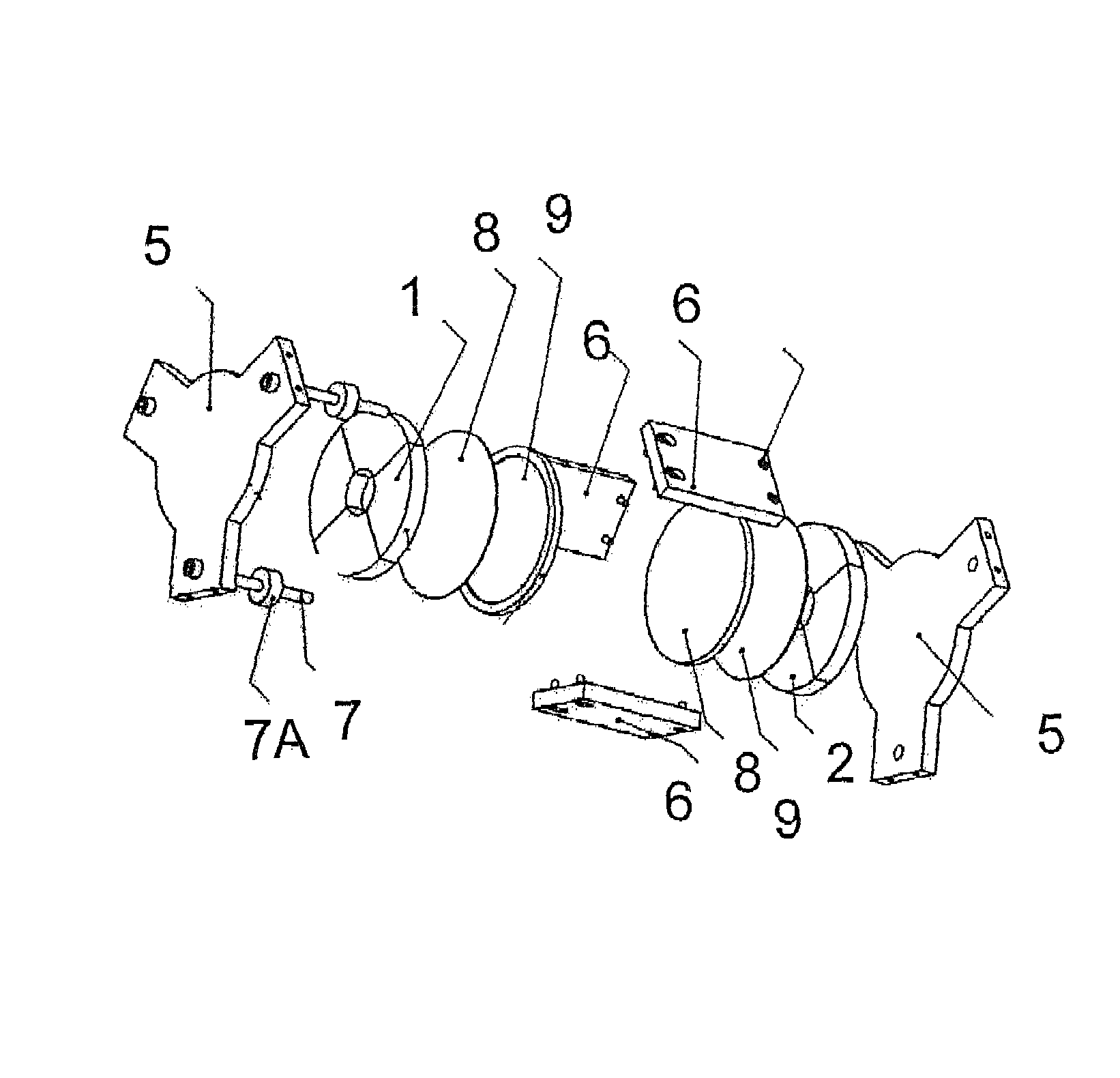
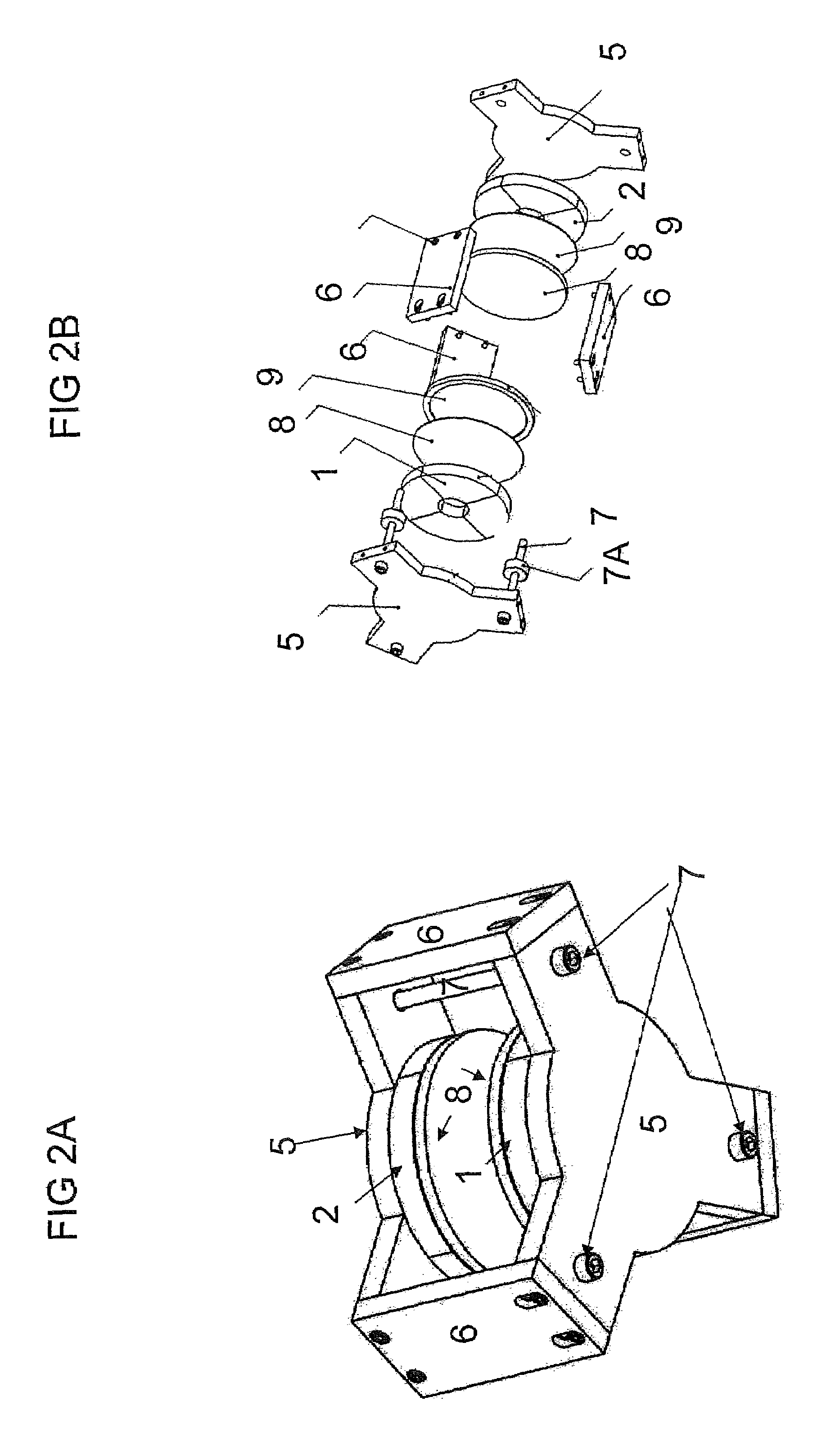
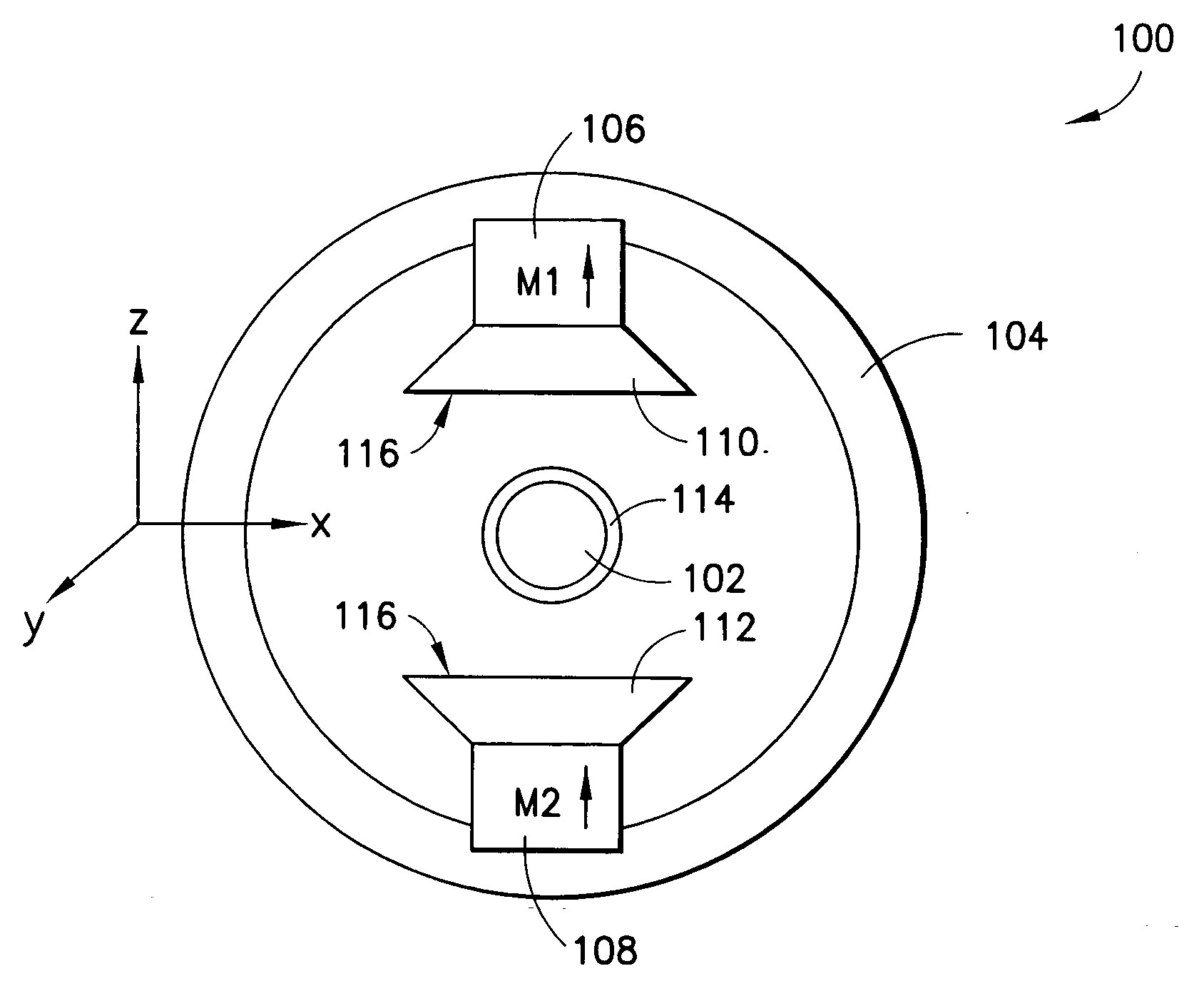
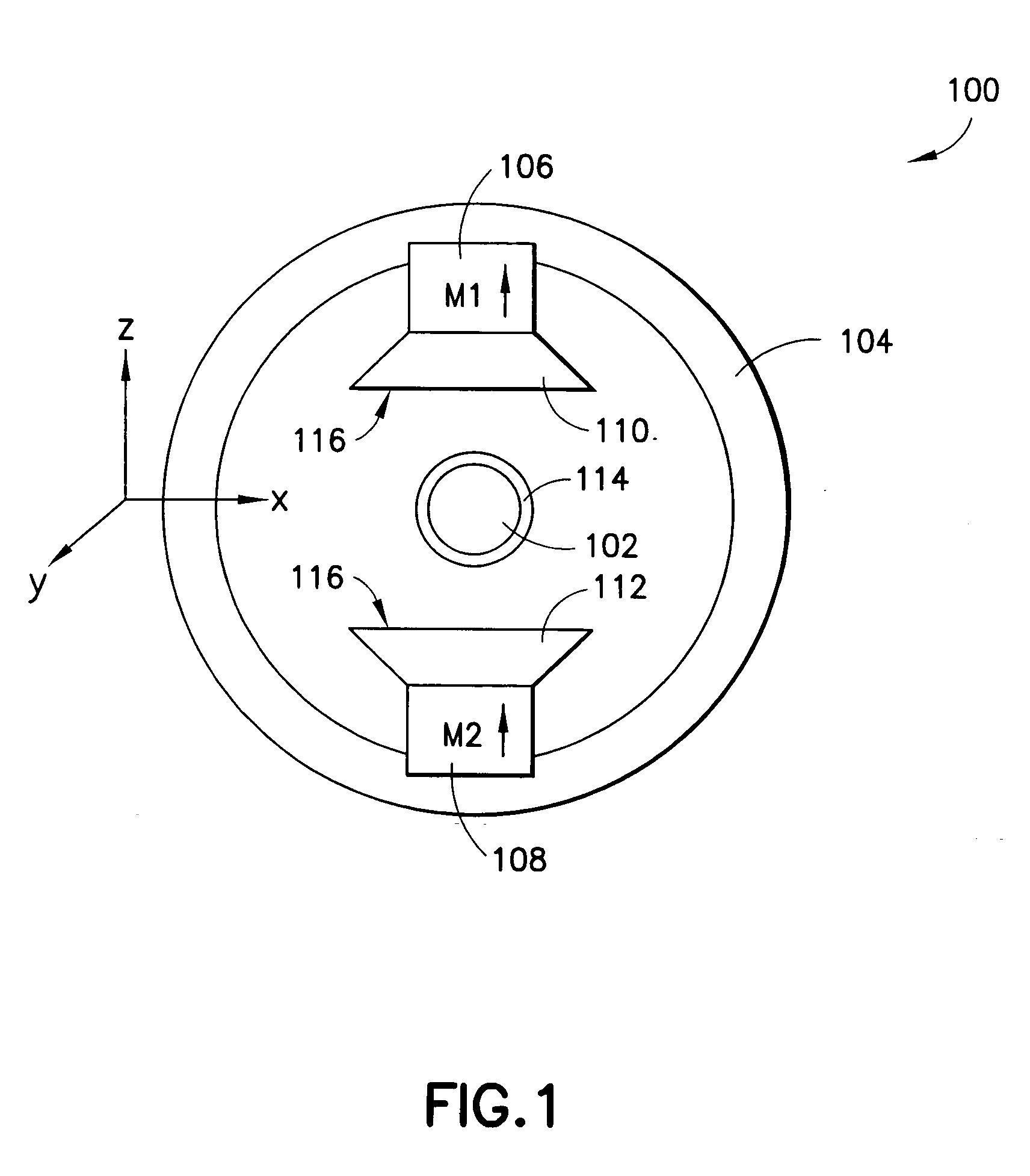
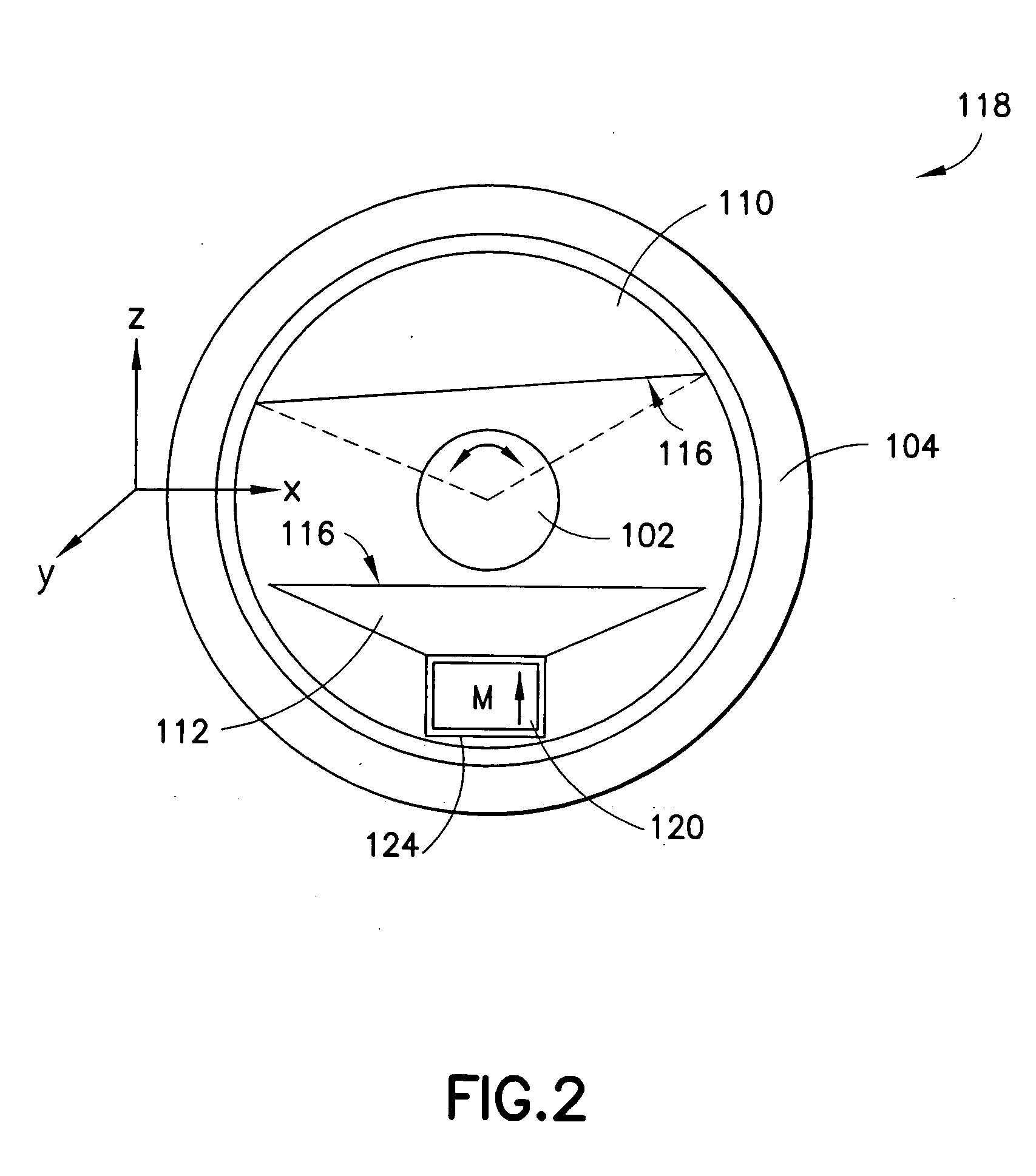
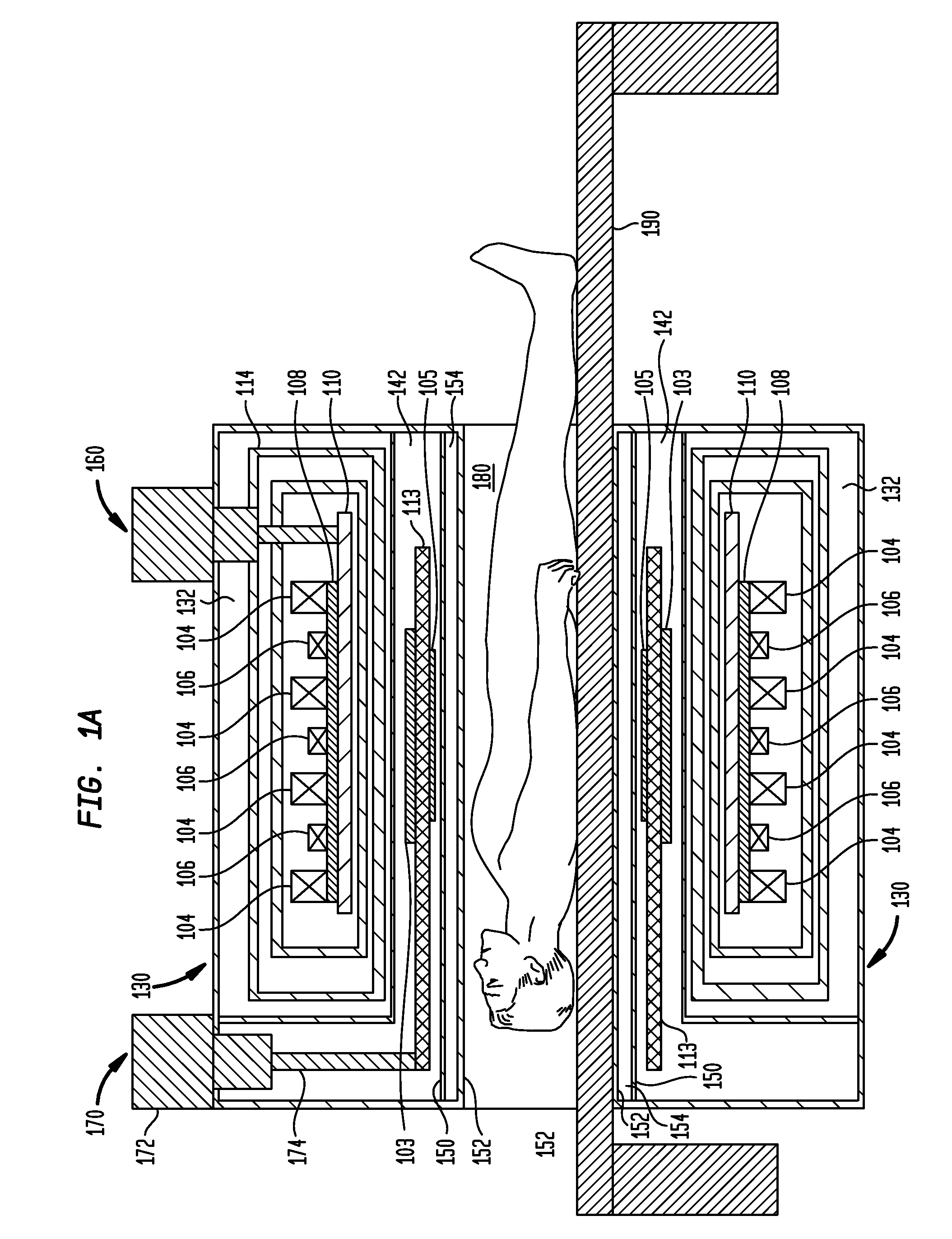
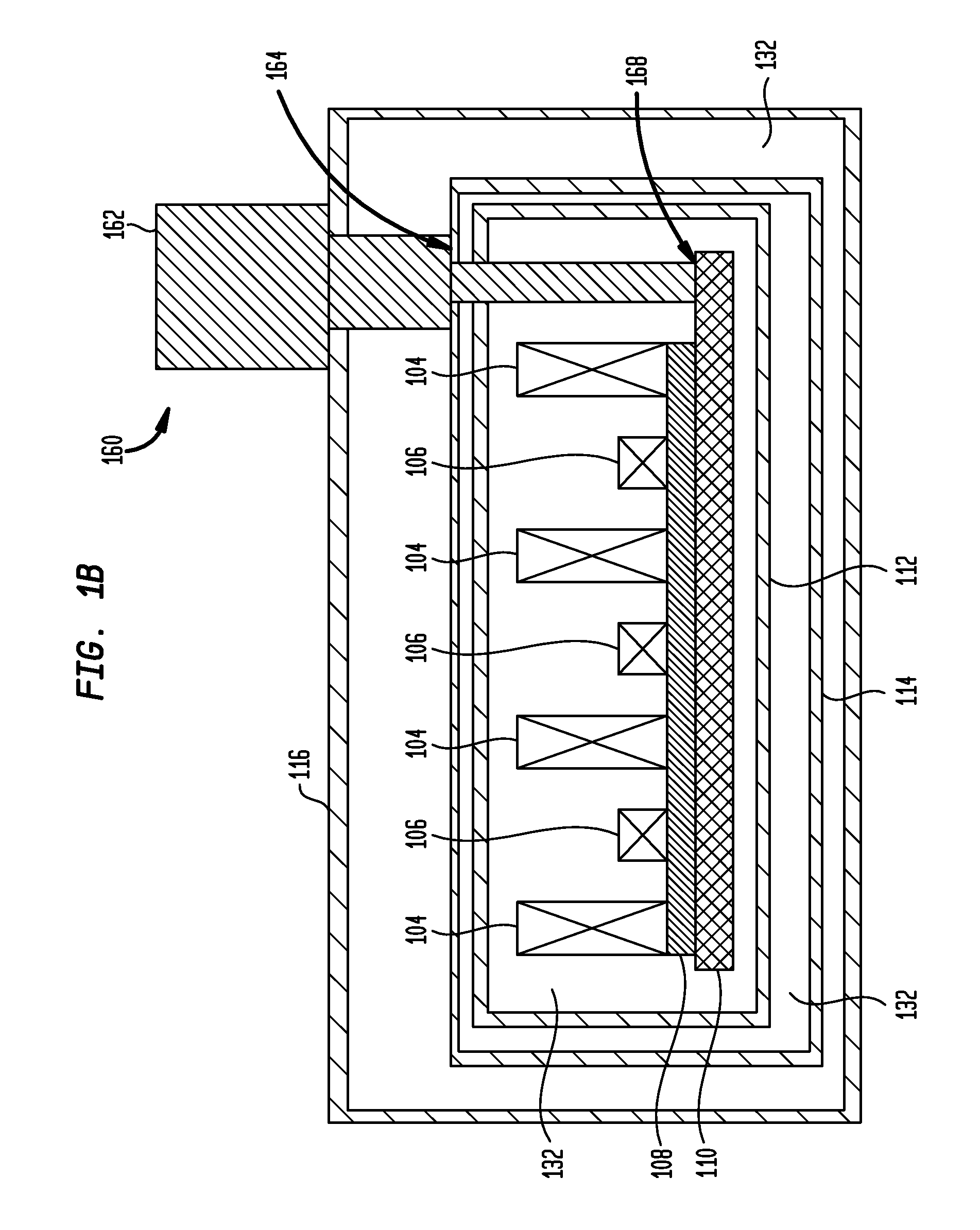
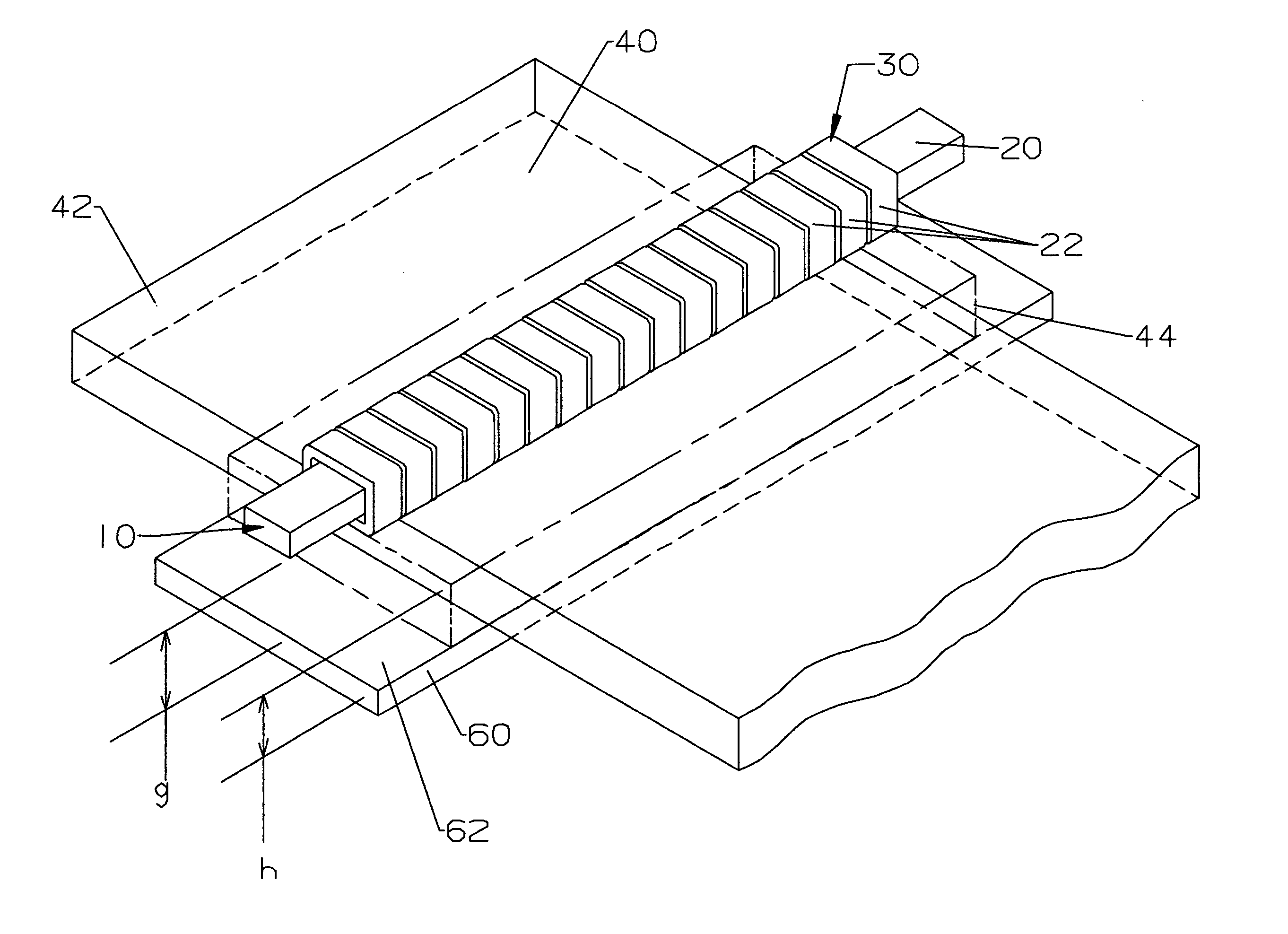
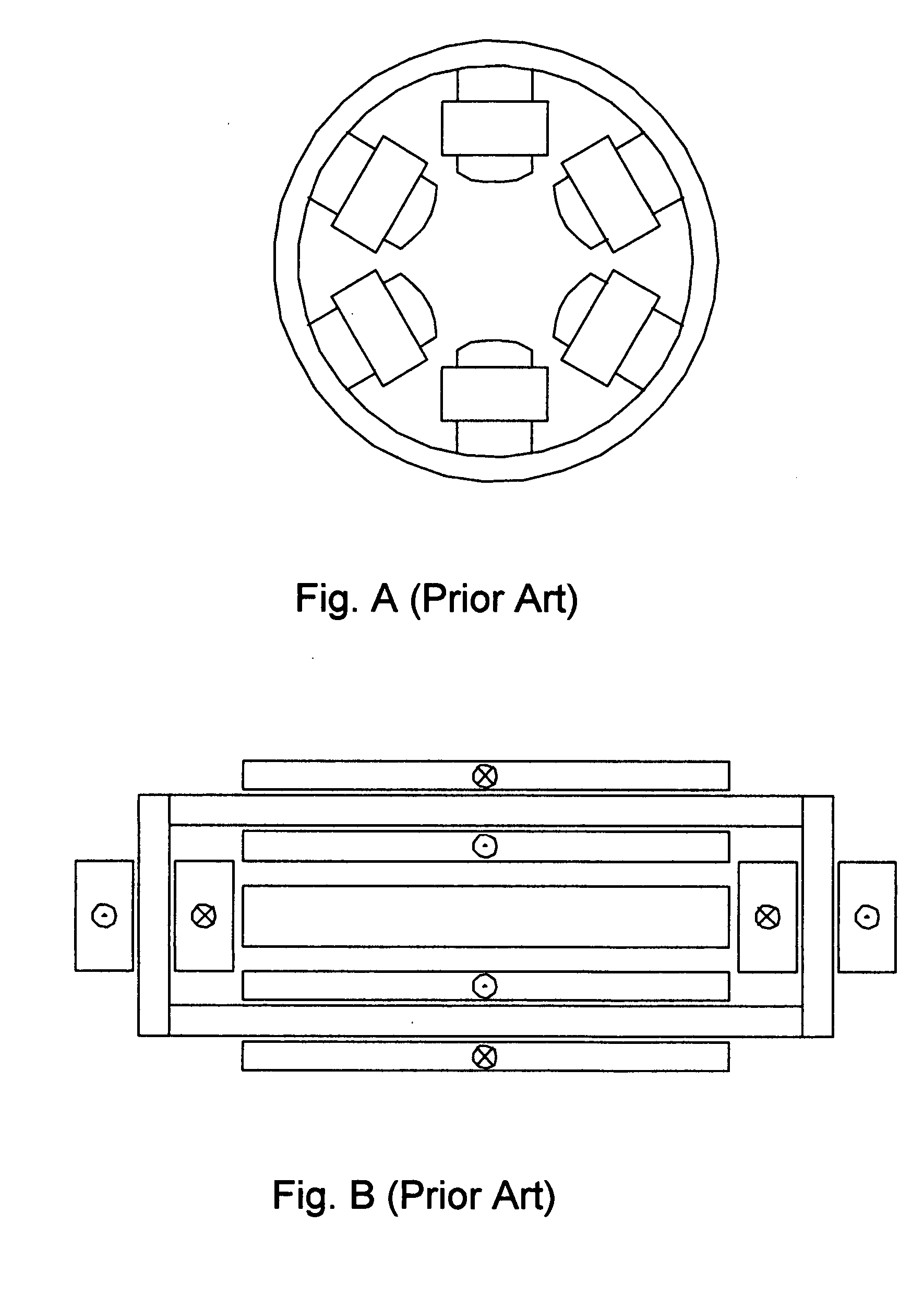
ActiveUS7173507B2Improve accessibilityClear designElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsMagnetic field gradientMagnet coil
A magnetic body is to be moved in a contactless fashion in a working space with the aid of the magnet coil system composed of fourteen individually drivable individual coils. The coil system is to be used for this purpose to produce three magnetic field components and five magnetic field gradients. The individual coils are preferably arranged on end-face or lateral surfaces situated oppositely in pairs, and on a tubular peripheral surface surrounding the working space.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Multicoil NMR data acquisition and processing methods
ActiveUS20060186882A1Reduce noiseMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonanceMagnetic field gradientAcquisition apparatus
A multicoil NMR data acquisition apparatus and processing method for performing three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging in a static magnetic field without the application of controlled static magnetic field gradients. A preferred application relates specifically to the detection and localization of groundwater using the Earth's magnetic field. Multicoil arrays are used in both transmit and receive modes, and coherent data processing algorithms applied to the data to generate three-dimensional NMR spin density estimates. Disclosed are methods for acquiring NMR data using an array of at least two transmit and receive coils, and for processing such multicoil data to estimate the three-dimensional NMR spin density distributions.
Owner:VISTA CLARA
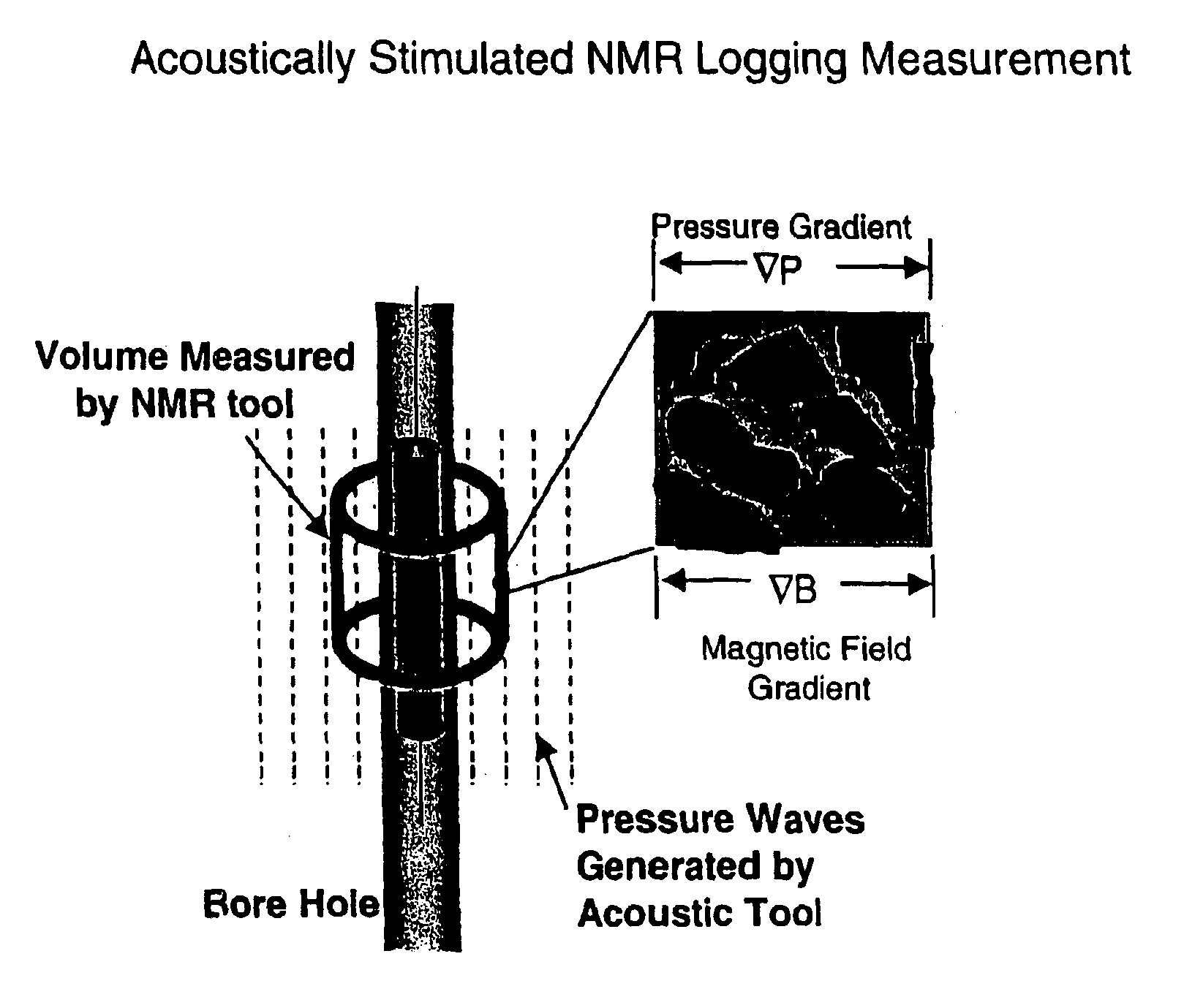
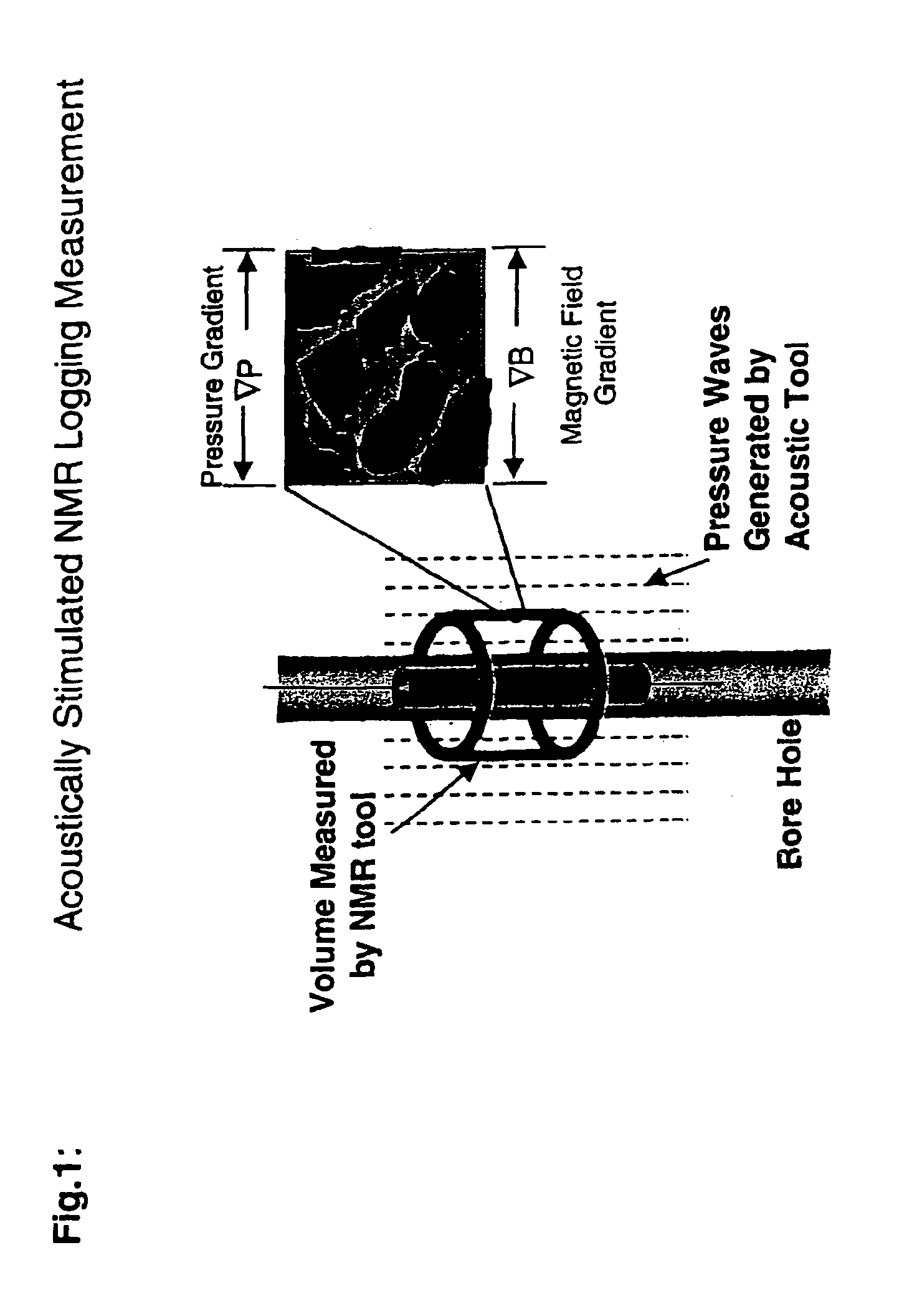
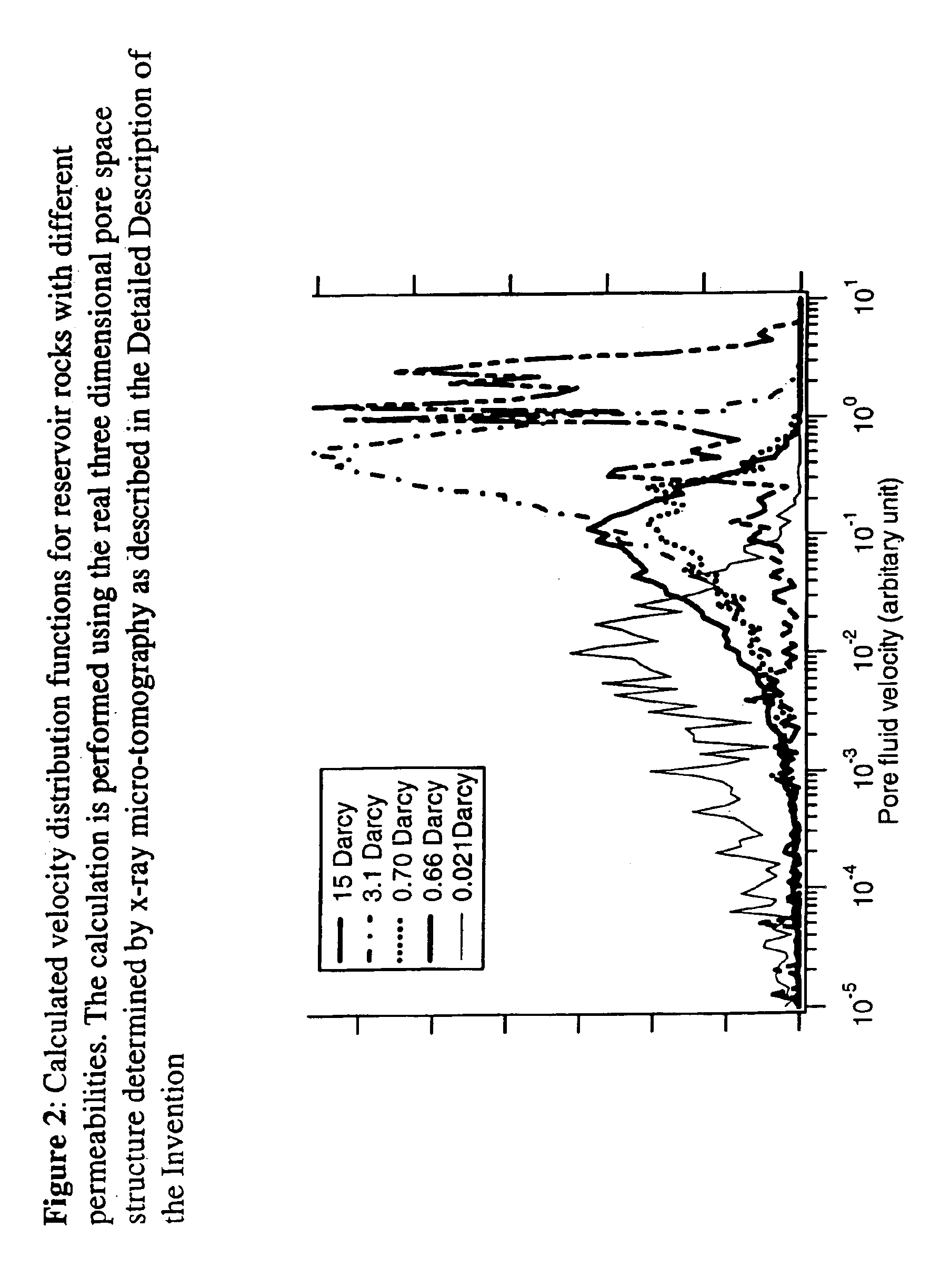
Fluid flow properties from acoustically stimulated NMR
ActiveUS6933719B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial analysis by using resonanceMagnetic field gradientNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Electromagnetic regulator assembly for adjusting and controlling the current uniformity of continuous ion beams
An electromagnetic regulator assembly for the production of contiguous magnetic fields which are applied to a continuous ion beam is described. The assembly is structured for controlling the uniformity of traveling continuous ribbon-shaped beams; and allows for direct adjustment of the magnetic field gradient of the magnetic field as the parameter for increasing the current uniformity.
Owner:WHITE NICHOLAS R
Magnetic recording head for perpendicular recording, fabrication process, and magnetic disk storage apparatus mounting the magnetic head
InactiveUS7715152B2Growth inhibitionHigh gradientManufacture head surfaceHeads using thin filmsMagnetic field gradientMagnetic media
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Method and apparatus for acquiring high resolution spectral data or high definition images in inhomogeneous environments
InactiveUS20100001727A1High definitionReduce complicationsMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic field gradientData treatment
A method and apparatus for treating a sample for acquiring high-definition magnetic resonance images (MRI images) or high resolution nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra even in the presence of magnetic field distortions within one or multiple scans. The spatial nature and temporal dependence of the field inhomogeneities are determined a priori using any of several literature procedures. A static or oscillating magnetic field gradient is applied on the sample so as to endow spins at different positions within the sample with different resonance frequencies. A phase- and amplitude-modulated radiofrequency (RF) pulse is applied in unison with the magnetic field gradient so as to endow spins at different positions within the sample with a homogeneous excitation / inversion profile. The nature of the spatially-selective RF irradiation is tailored in such a way that, when added on top of the effects of the inhomogeneities, the spins' evolution phases and their signal amplitudes at the time of the acquisition become independent of the inhomogeneities. The spin signals thus created are captured and decoded, so as to obtain the spins' response as if the inhomogeneity was not present. The collected data is processed to a suitable rearrangement and Fourier analysis procedure to retrieve a final undistorted image or spectrum. The magnetic field gradient can be oscillated to impose this kind of inhomogeneity corrections on multiple spatial dimensions sequentially, or simultaneously.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com