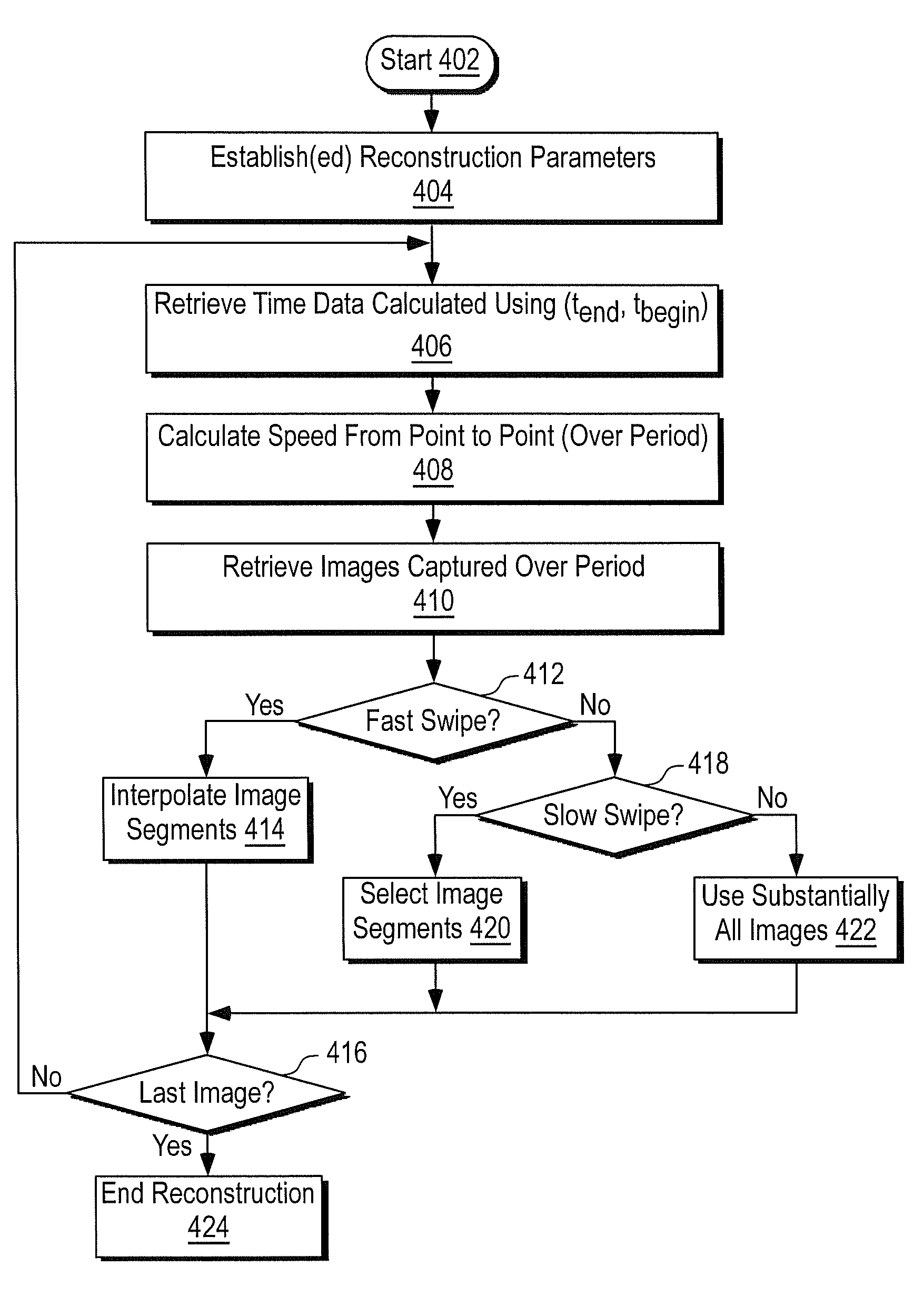
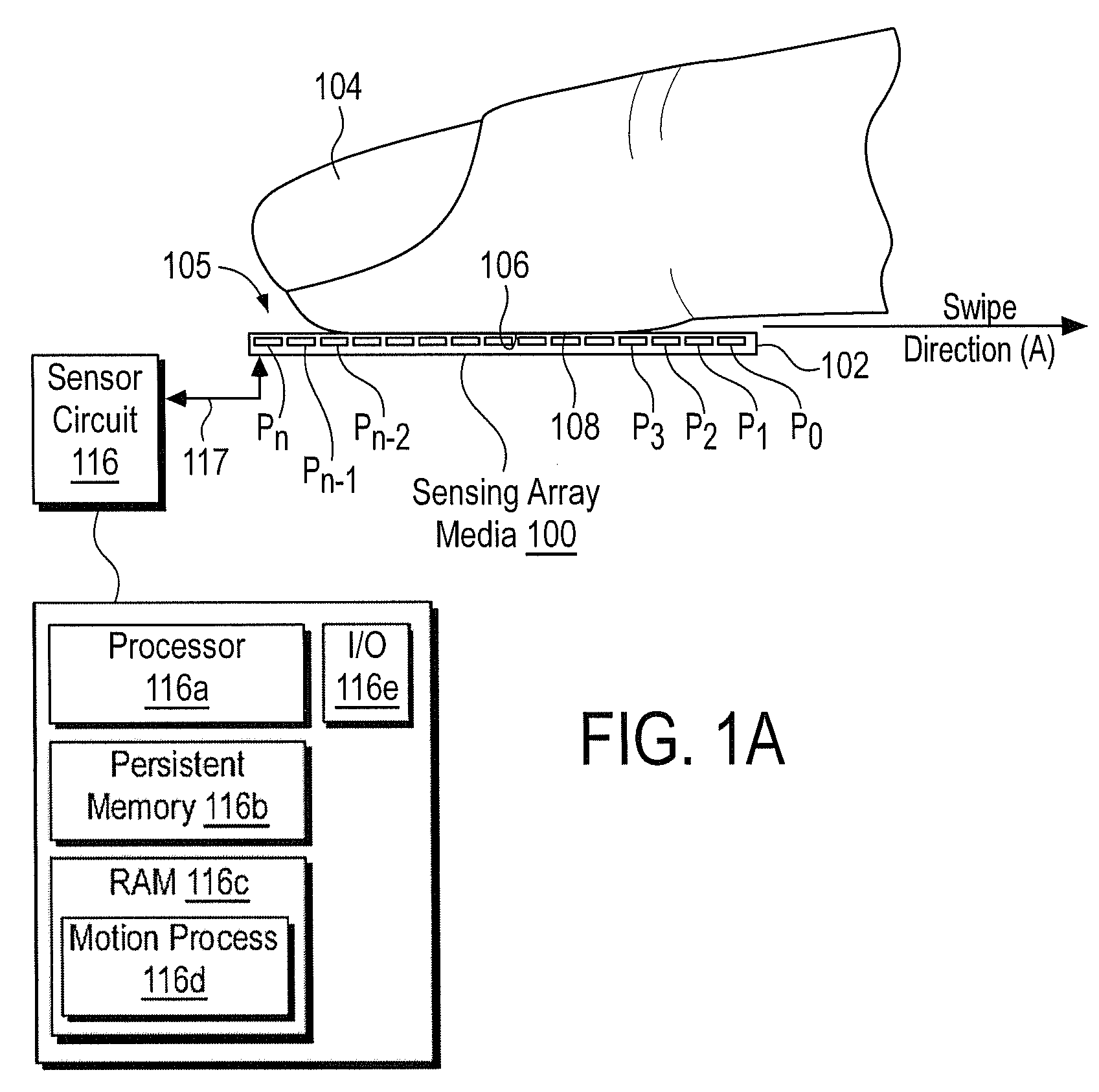
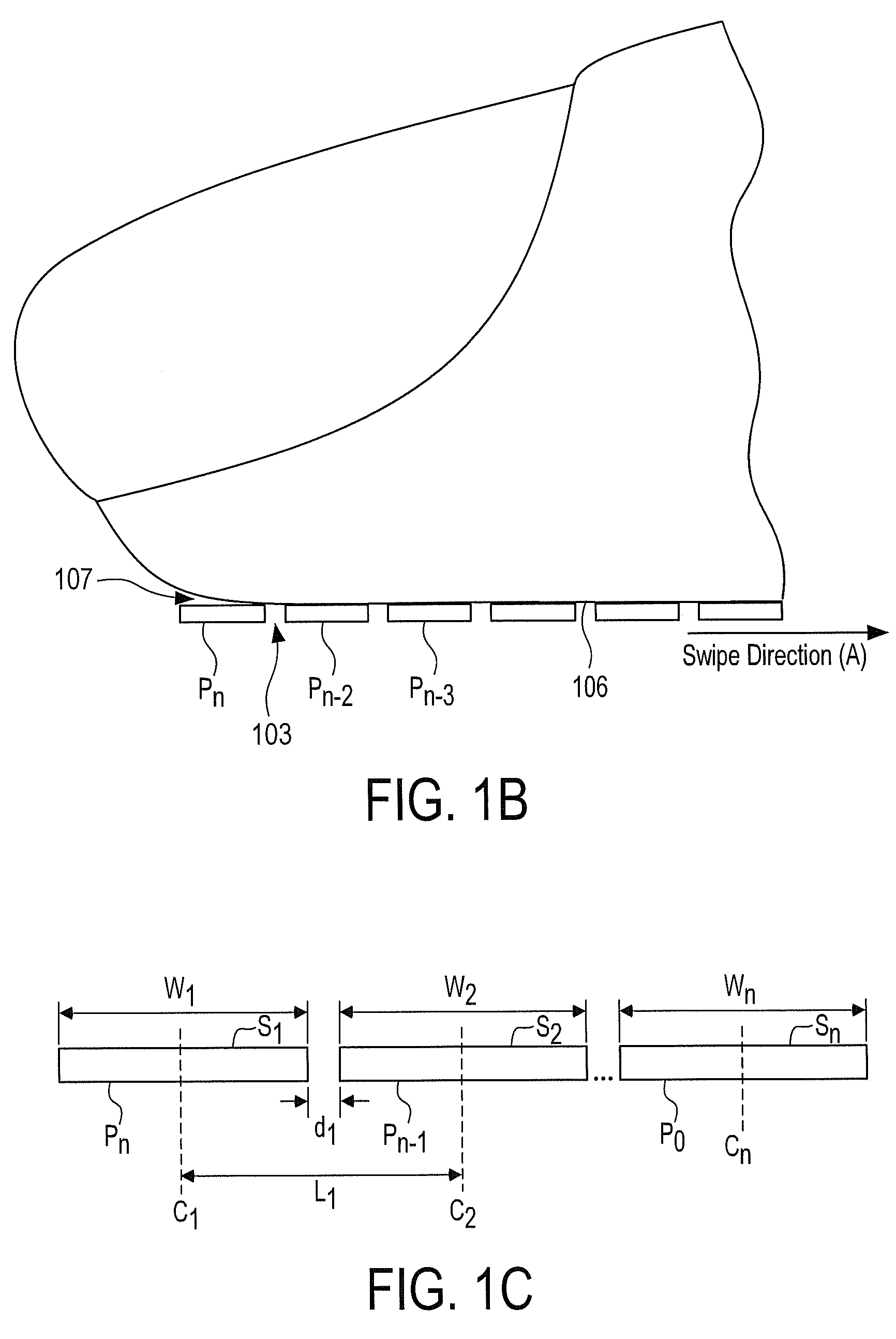
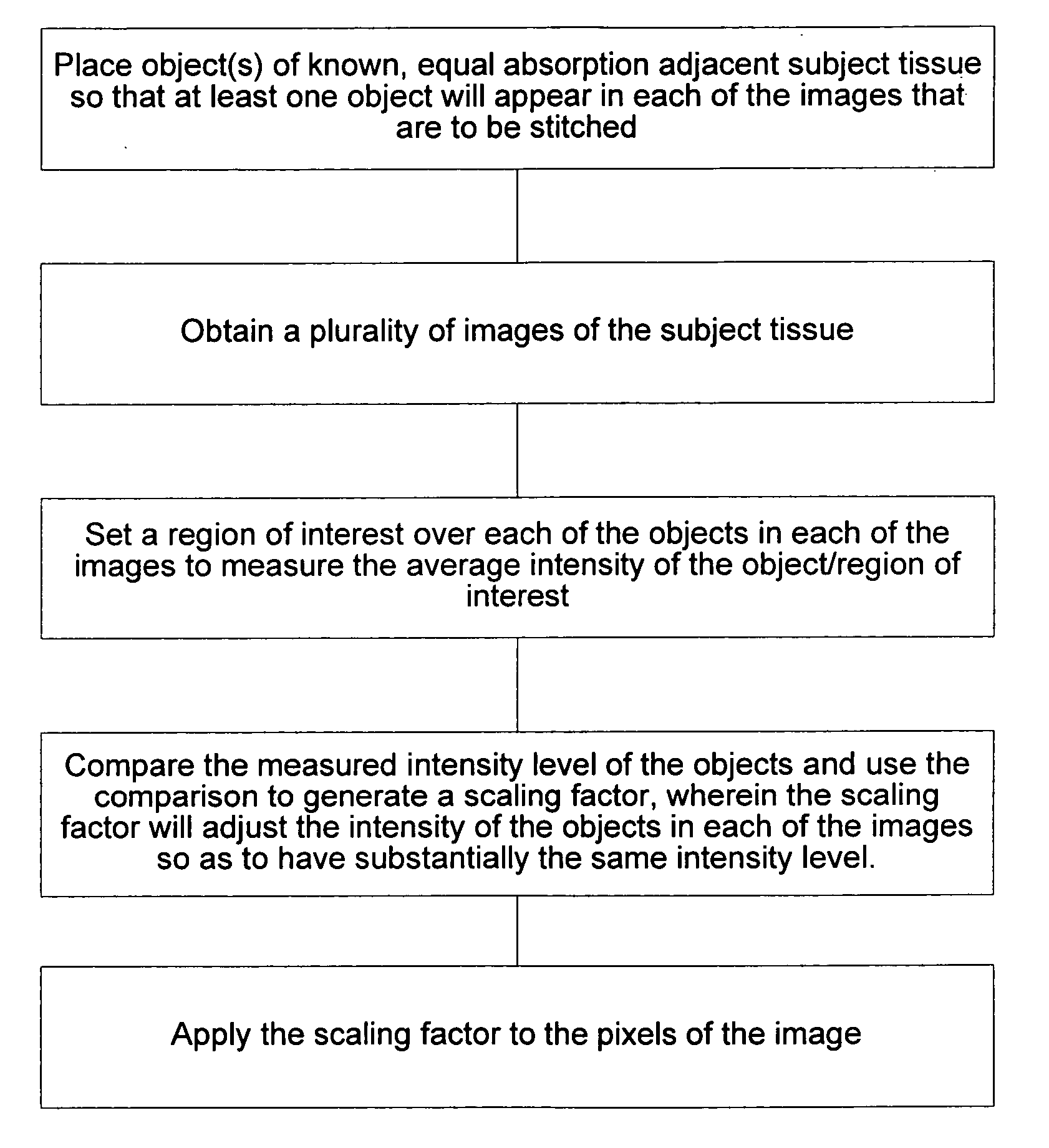
Patents
Literature
1145results about How to "Accurate imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
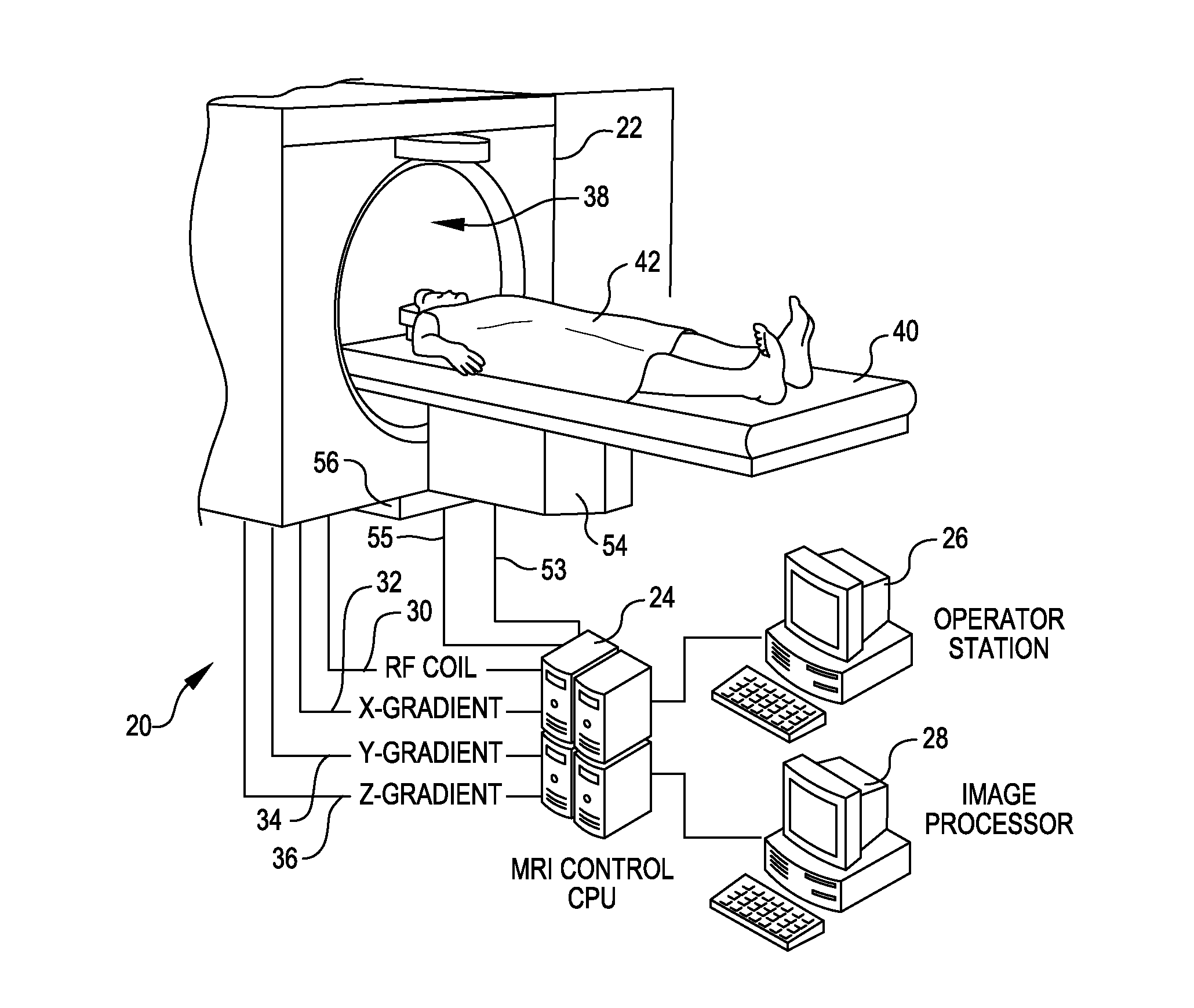
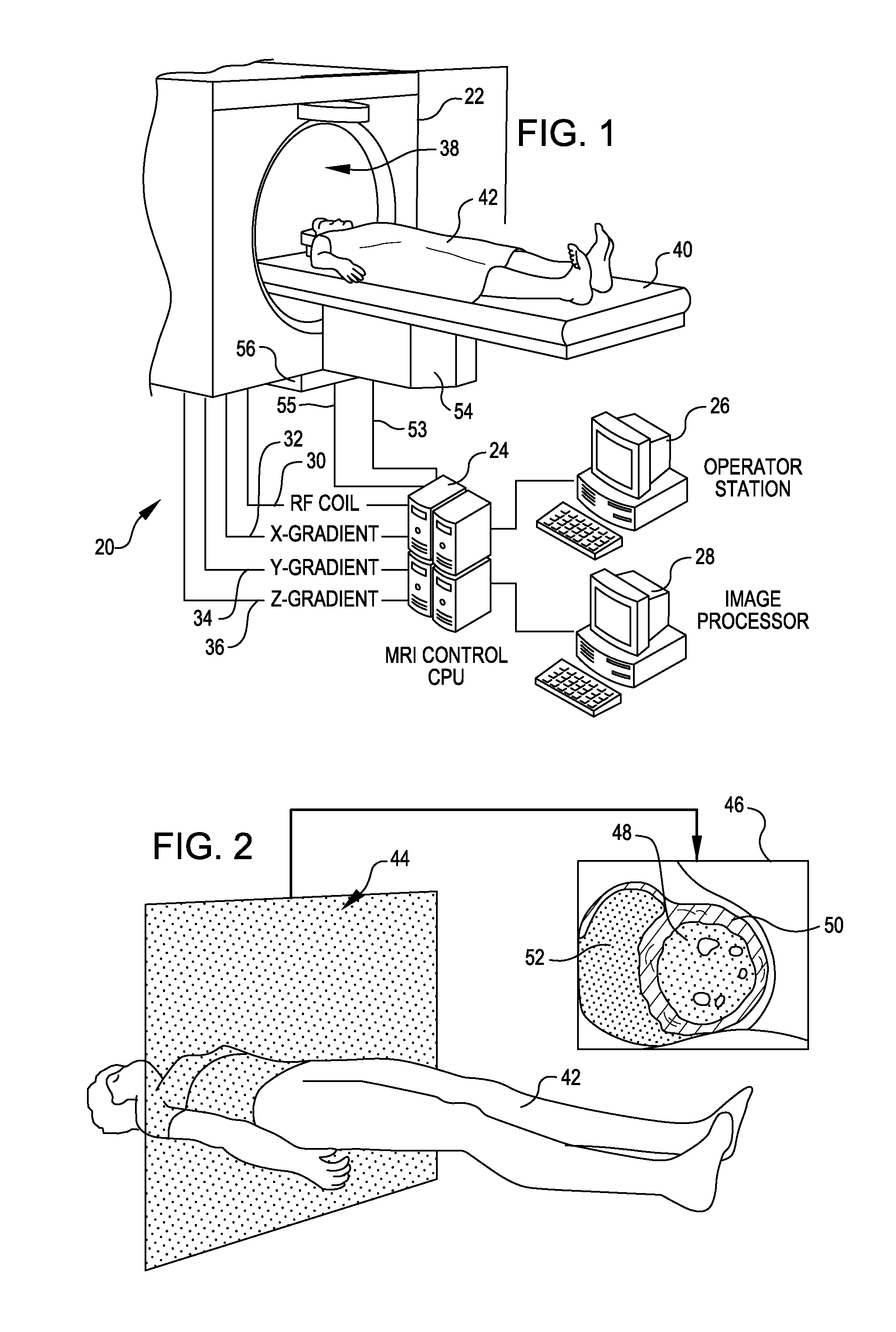
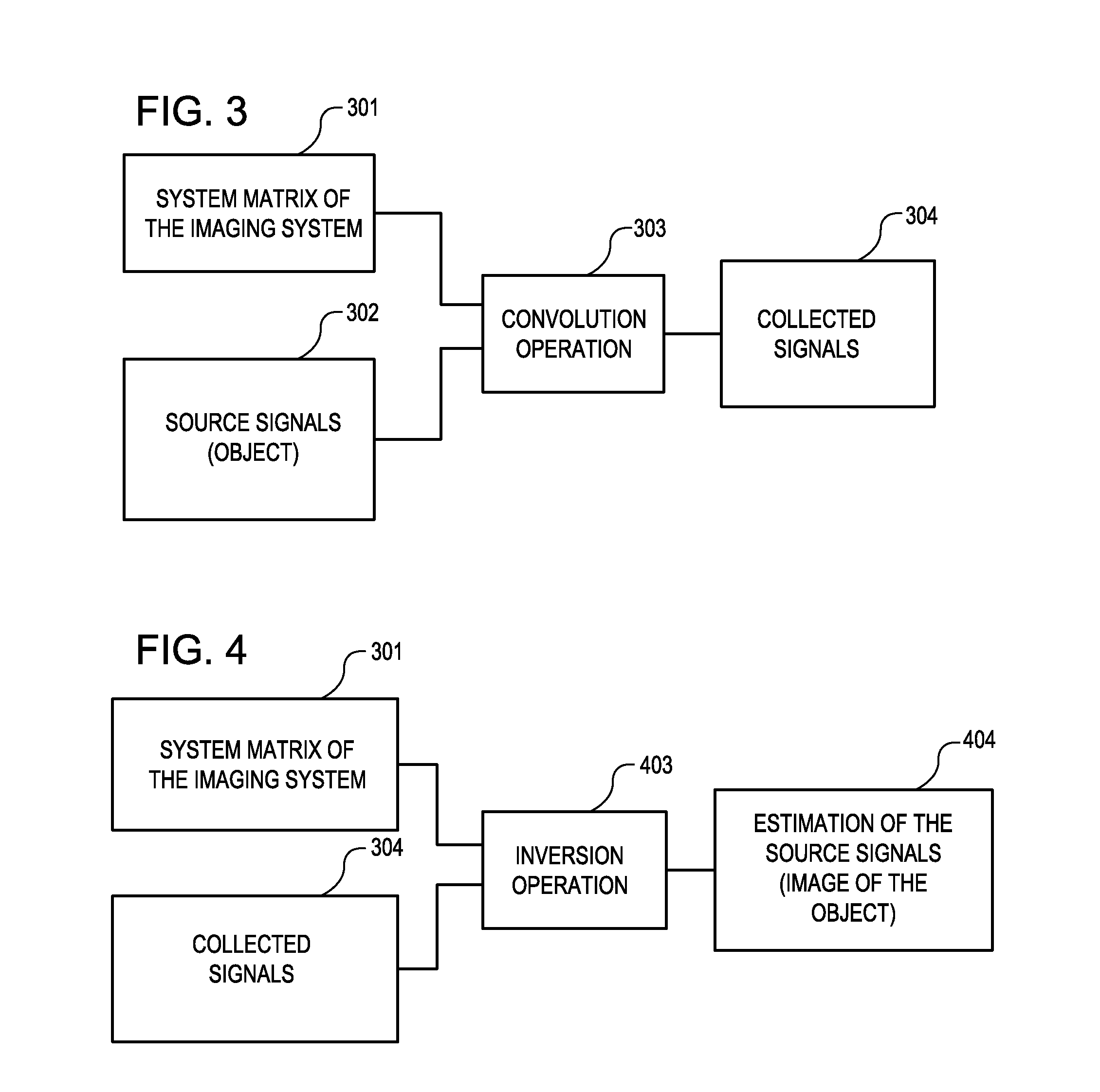
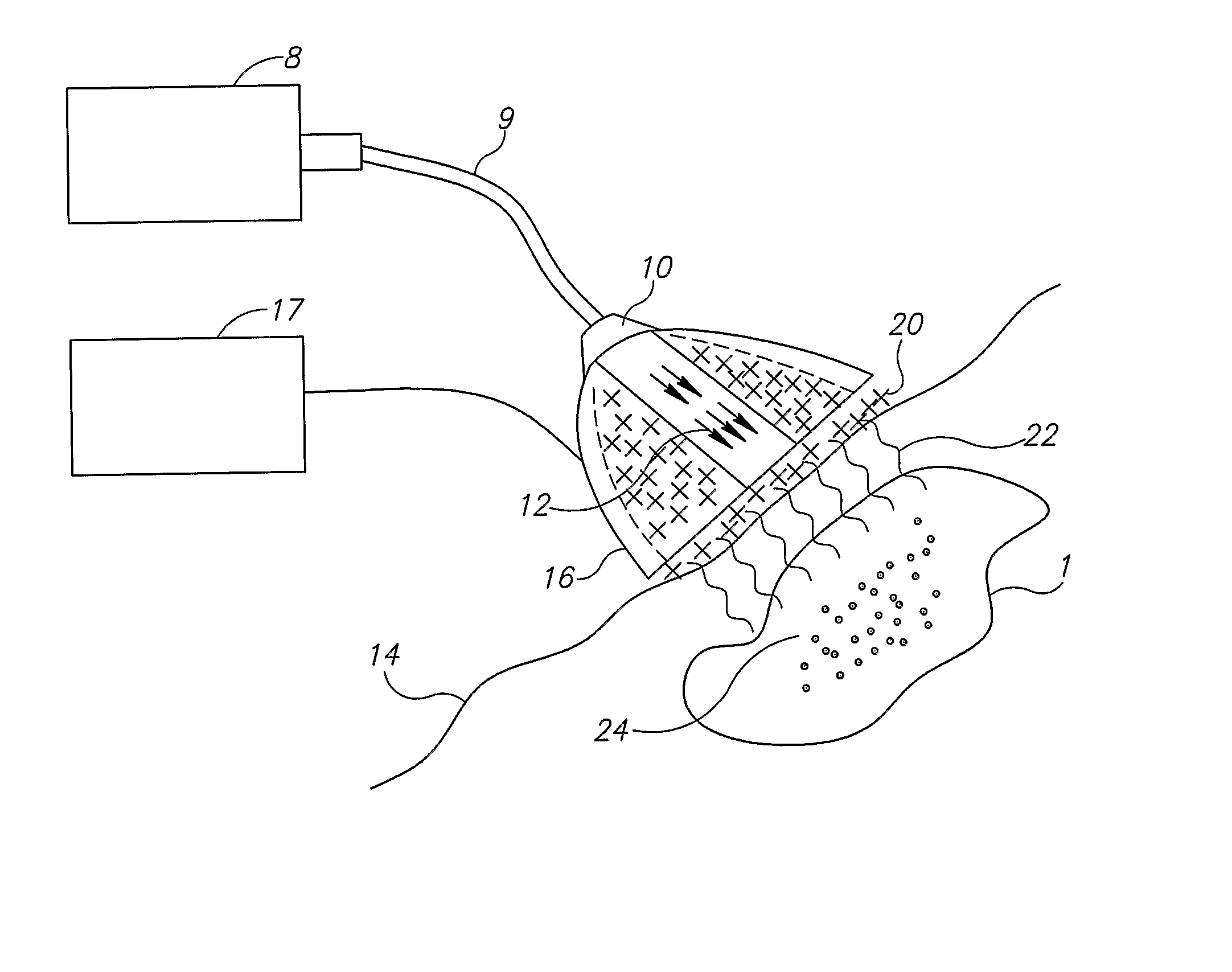
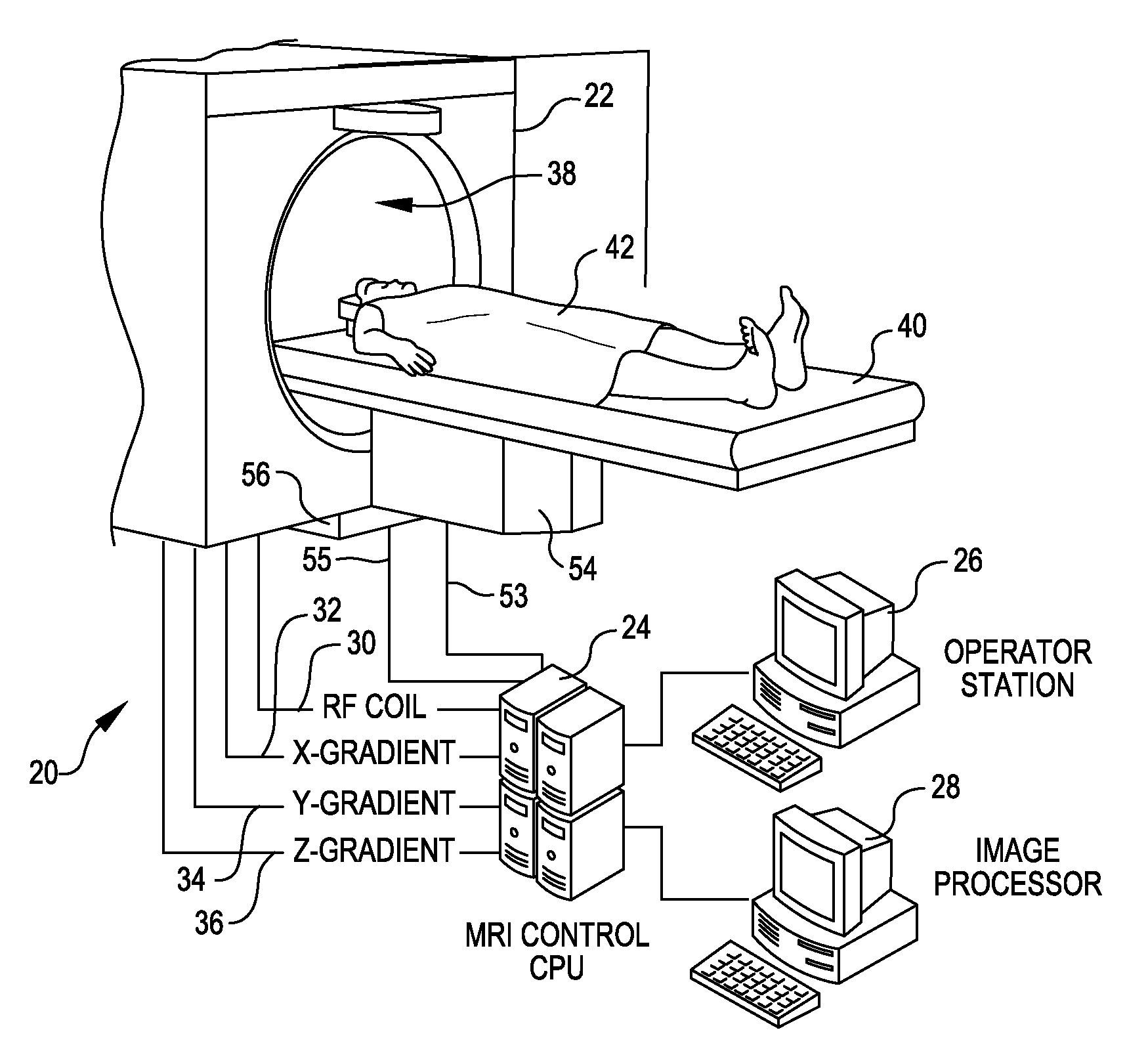
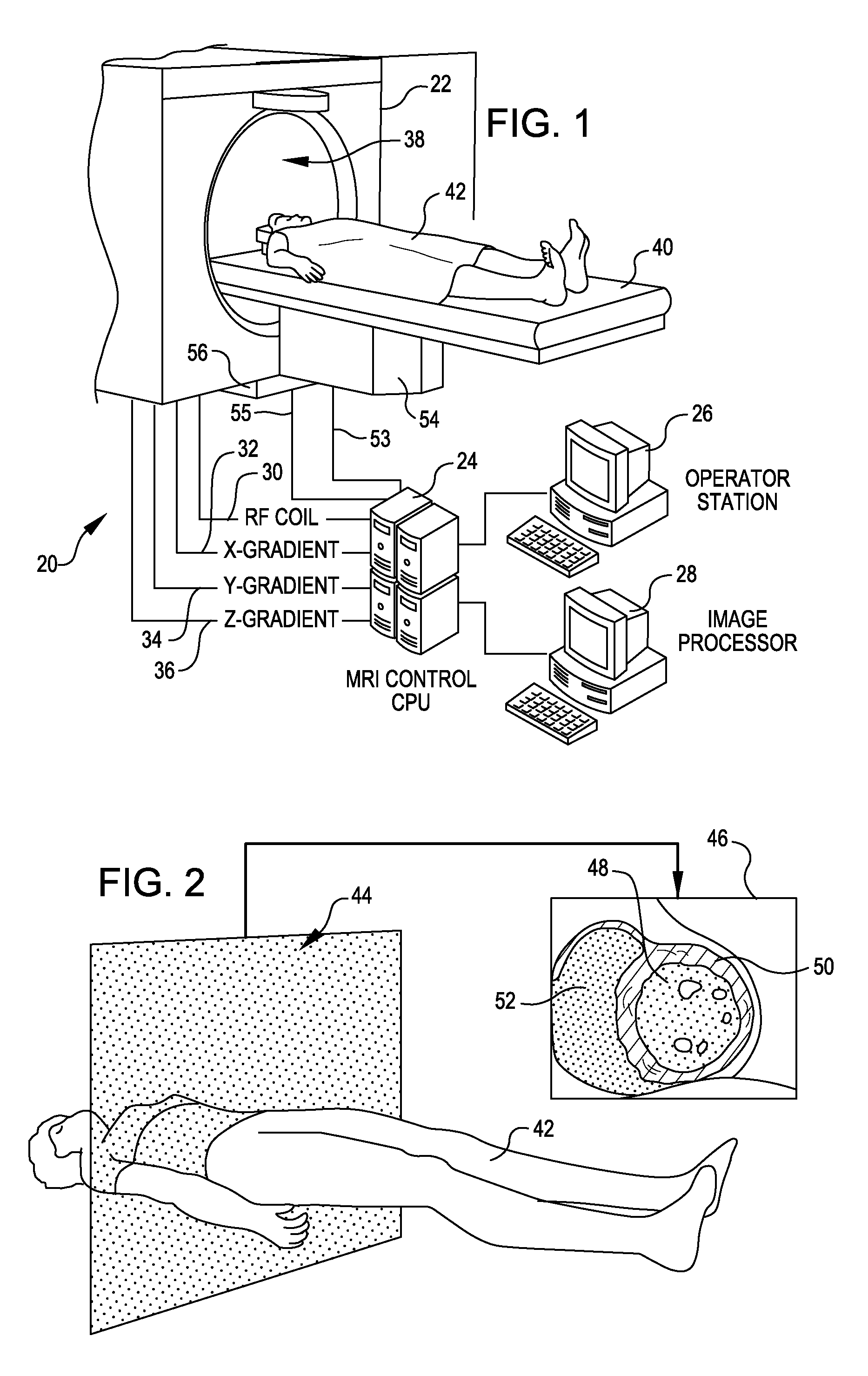
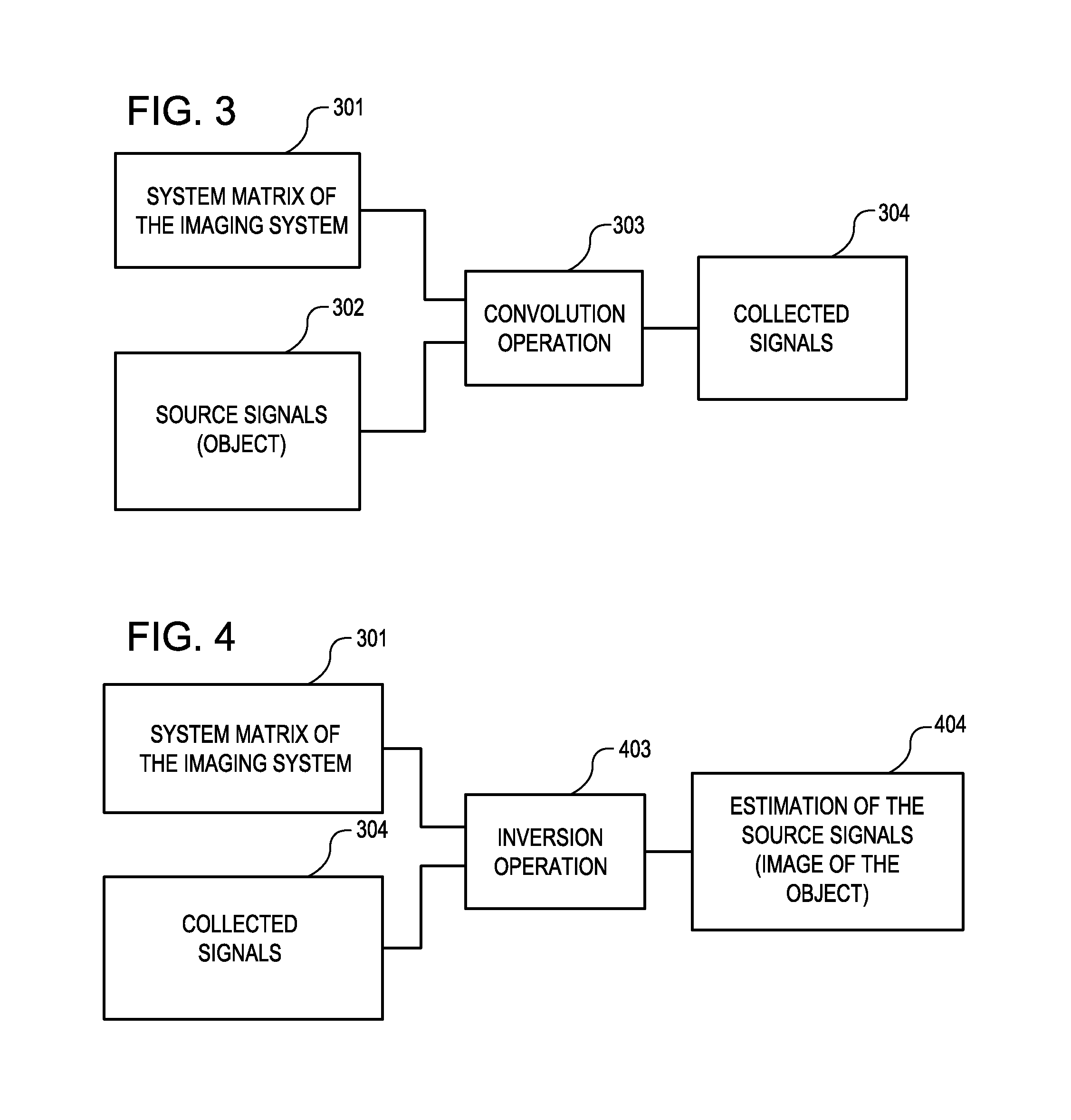
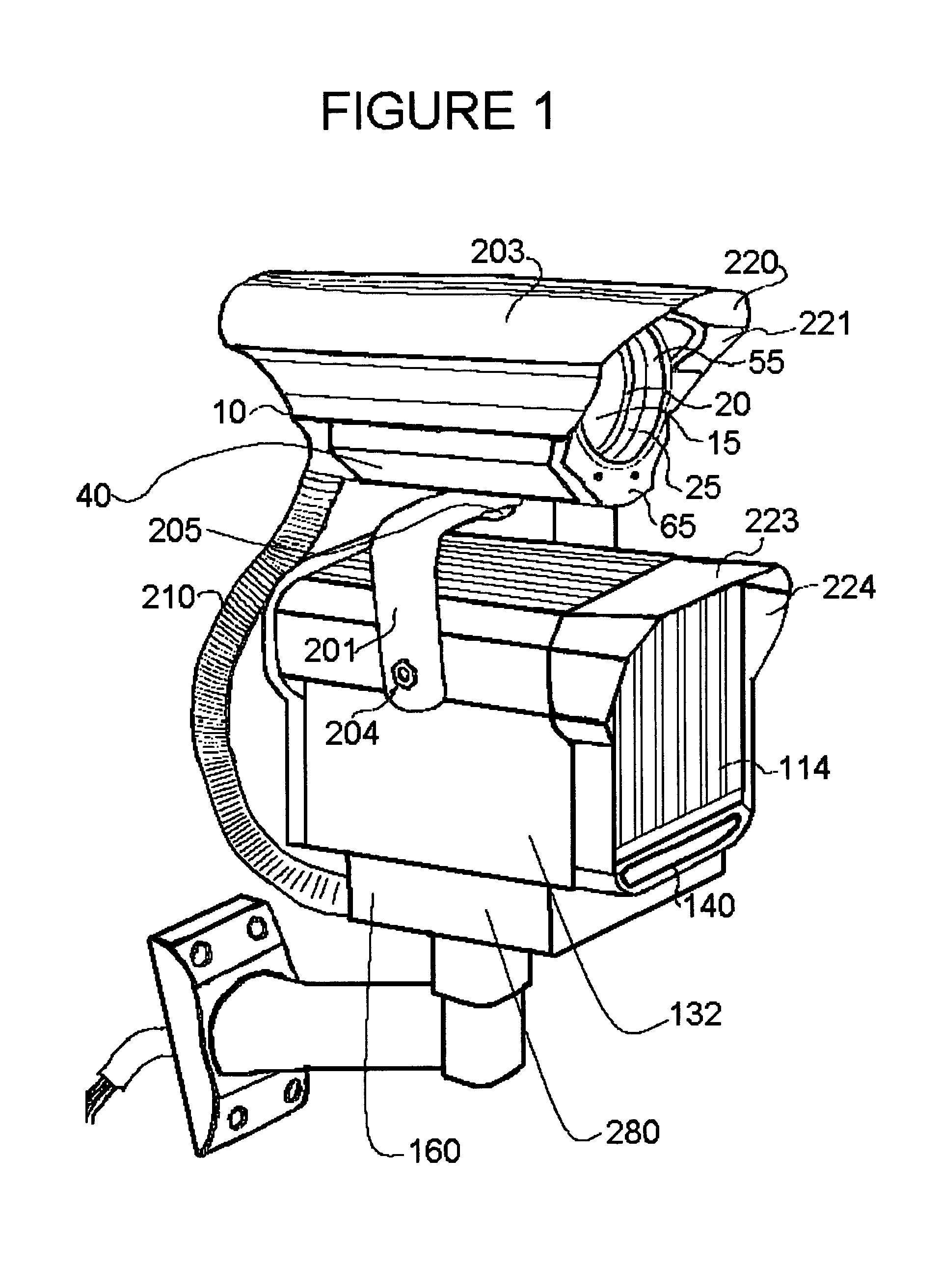
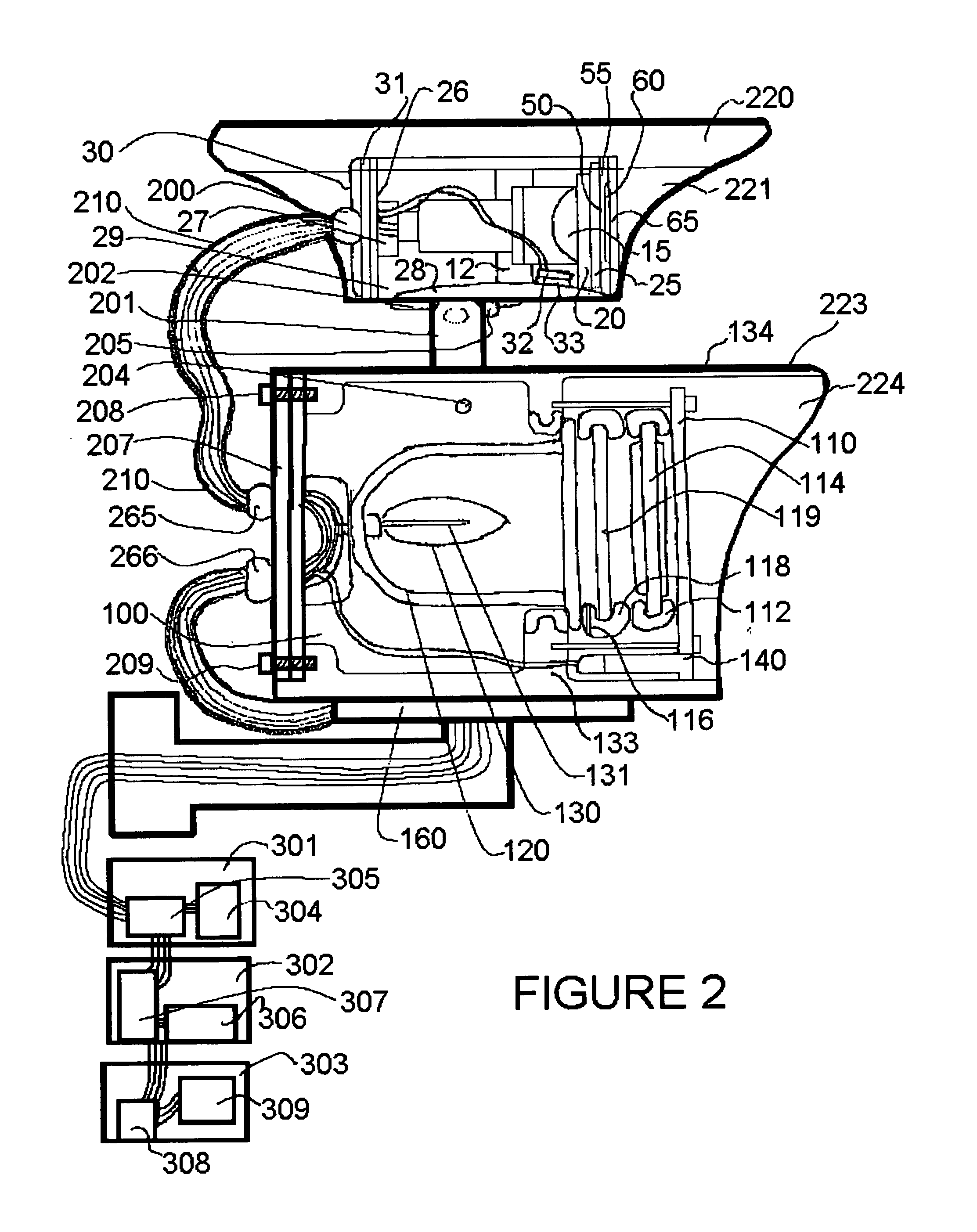
Tool for accurate quantification in molecular MRI
ActiveUS20110044524A1Minimize cost functionAccurate imagingCharacter and pattern recognitionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMagnetic sourceMagnetic susceptibility
A method and apparatus is provided for magnetic source magnetic resonance imaging. The method includes collecting energy signals from an object, providing additional information of characteristics of the object, and generating the image of the object from the energy signals and from the additional information such that the image includes a representation of a quantitative estimation of the characteristics, e.g a quantitative estimation of magnetic susceptibility. The additional information may comprise predetermined characteristics of the object, a magnitude image generated from the object, or magnetic signals collected from different relative orientations between the object and the imaging system. The image is generated by an inversion operation based on the collected signals and the additional information. The inversion operation minimizes a cost function obtained by combining the data extracted from the collected signals and the additional information of the object. Additionally, the image is used to detect a number of diagnostic features including microbleeds, contract agents and the like.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Miniature bone-mounted surgical robot
InactiveUS6837892B2Highly accurateImprove efficiencyMechanical apparatusJointsSurgical robotSurgical site
A miniature surgical robot and a method for using it are disclosed. The miniature surgical robot attaches directly with the bone of a patient. Two-dimensional X-ray images of the robot on the bone are registered with three-dimensional images of the bone. This locates the robot precisely on the bone of the patient. The robot is then directed to pre-operative determined positions based on a pre-operative plan by the surgeon. The robot then moves to the requested surgical site and aligns a sleeve through which the surgeon can insert a surgical tool.
Owner:MAZOR ROBOTICS
Imaging optical lens assembly
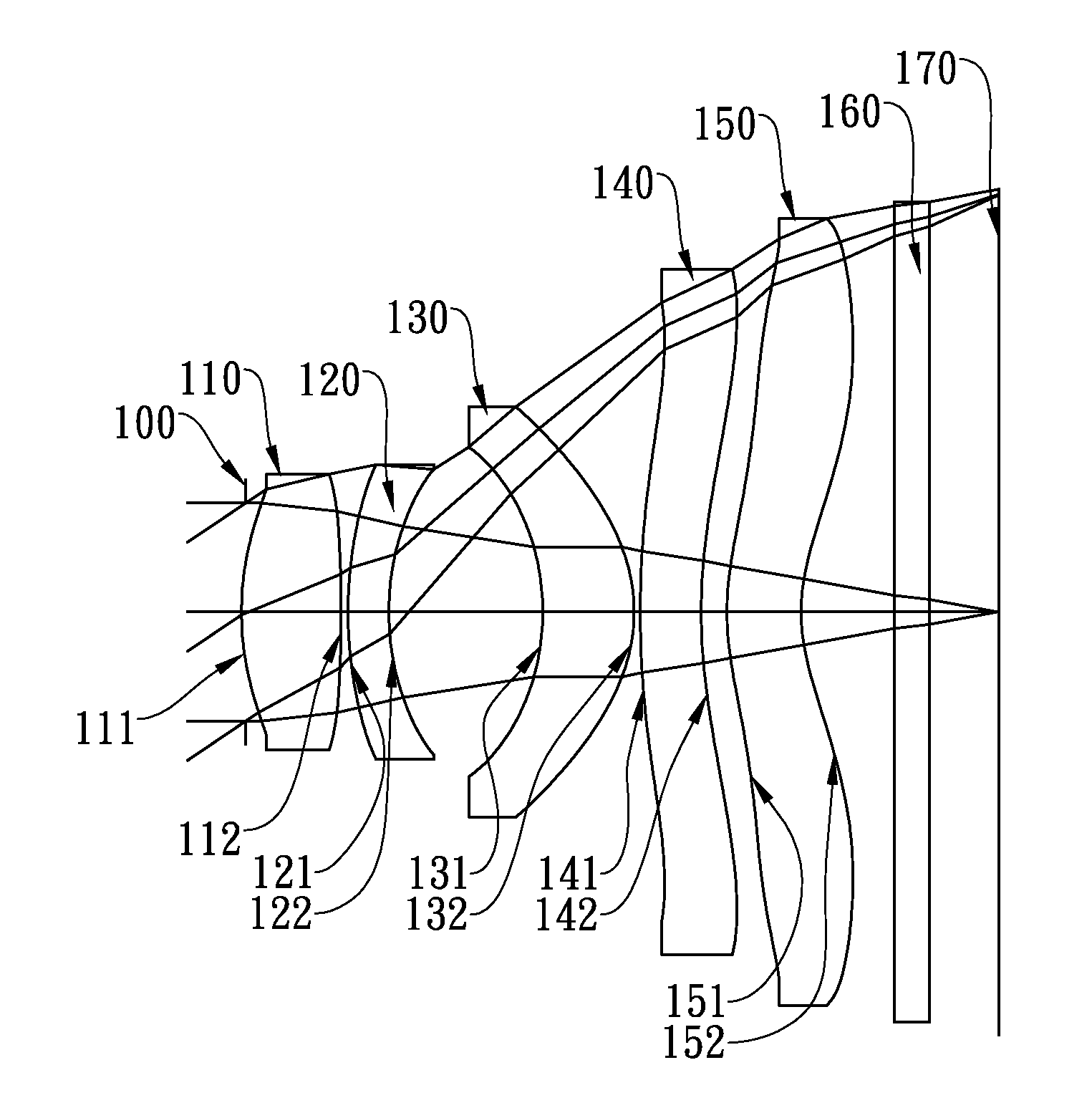
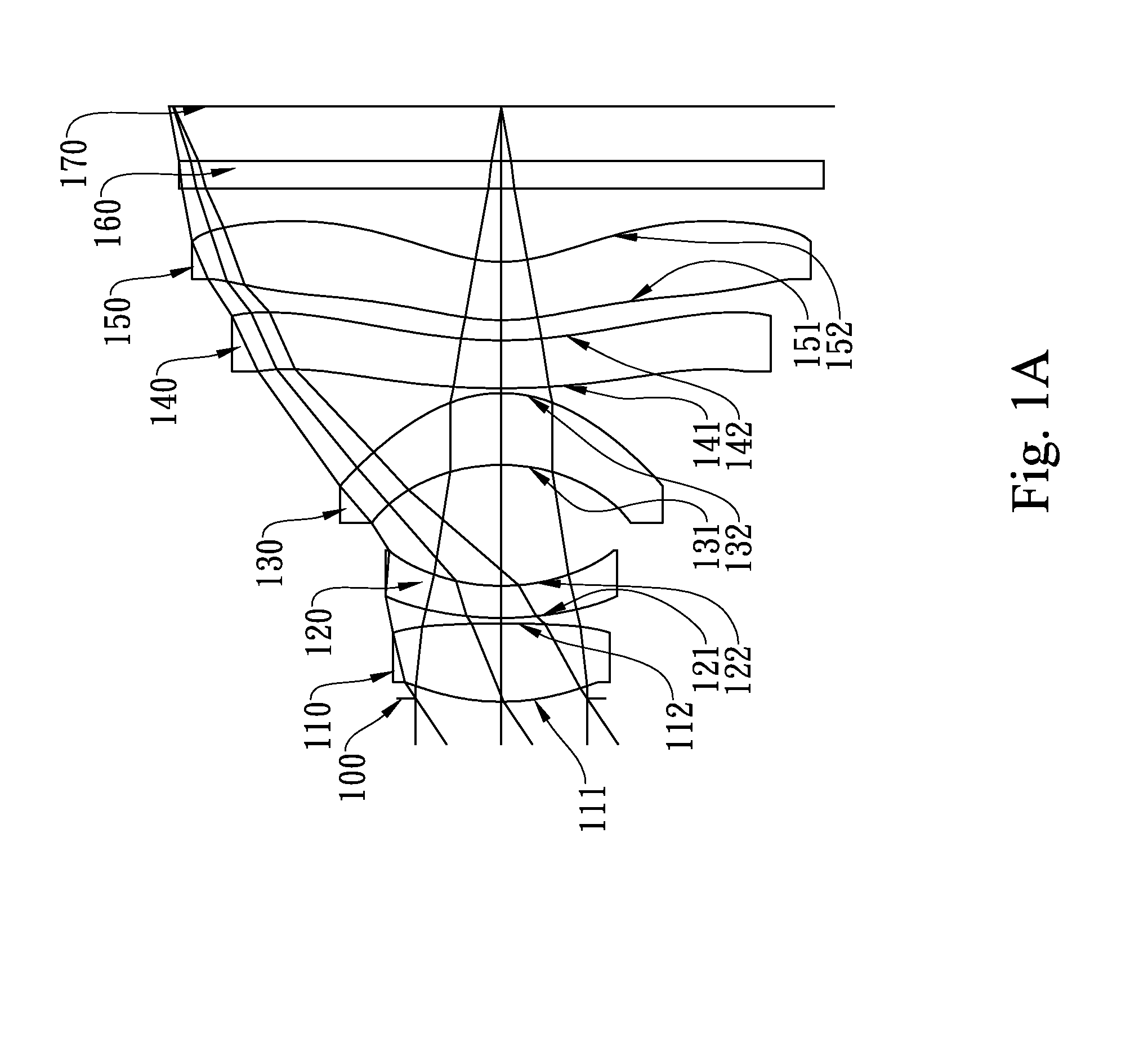
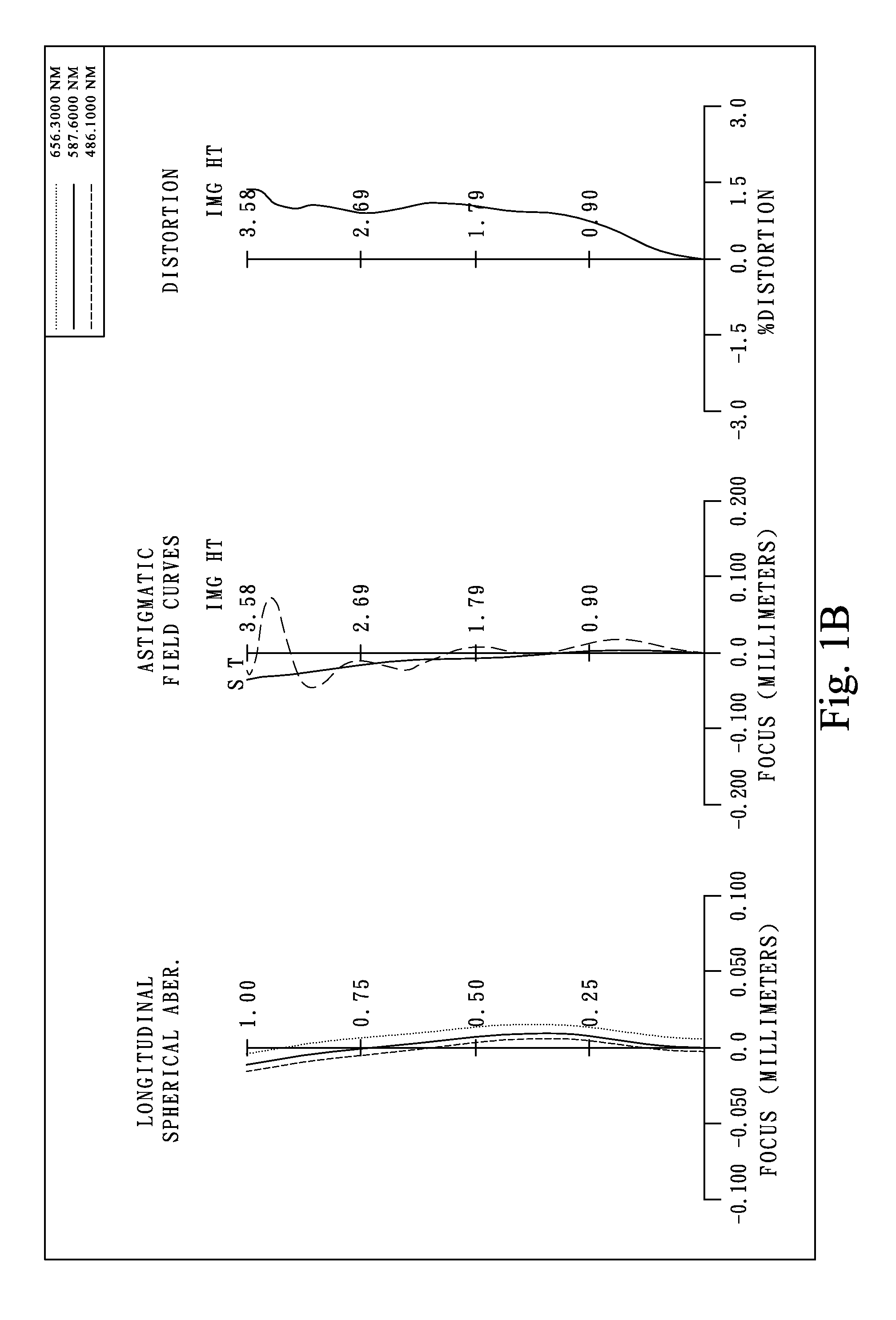
This invention provides an imaging optical lens assembly including: in order from an object side toward an image side: a first lens with positive refractive power and having a convex object-side surface, a second lens with negative refractive power and having a convex object-side surface and a concave image-side surface, a third lens with positive refractive power and having a concave object-side surface and a convex image-side surface, a fourth lens with negative refractive power and having a concave image-side surface, the object-side and image-side surfaces being aspheric, and a fifth lens having a concave image-side surface, the object-side and image-side surfaces being aspheric. The imaging optical lens assembly further comprises an aperture stop, disposed between an imaged object and the second lens, and an electronic sensor, disposed at the image plane for image formation.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
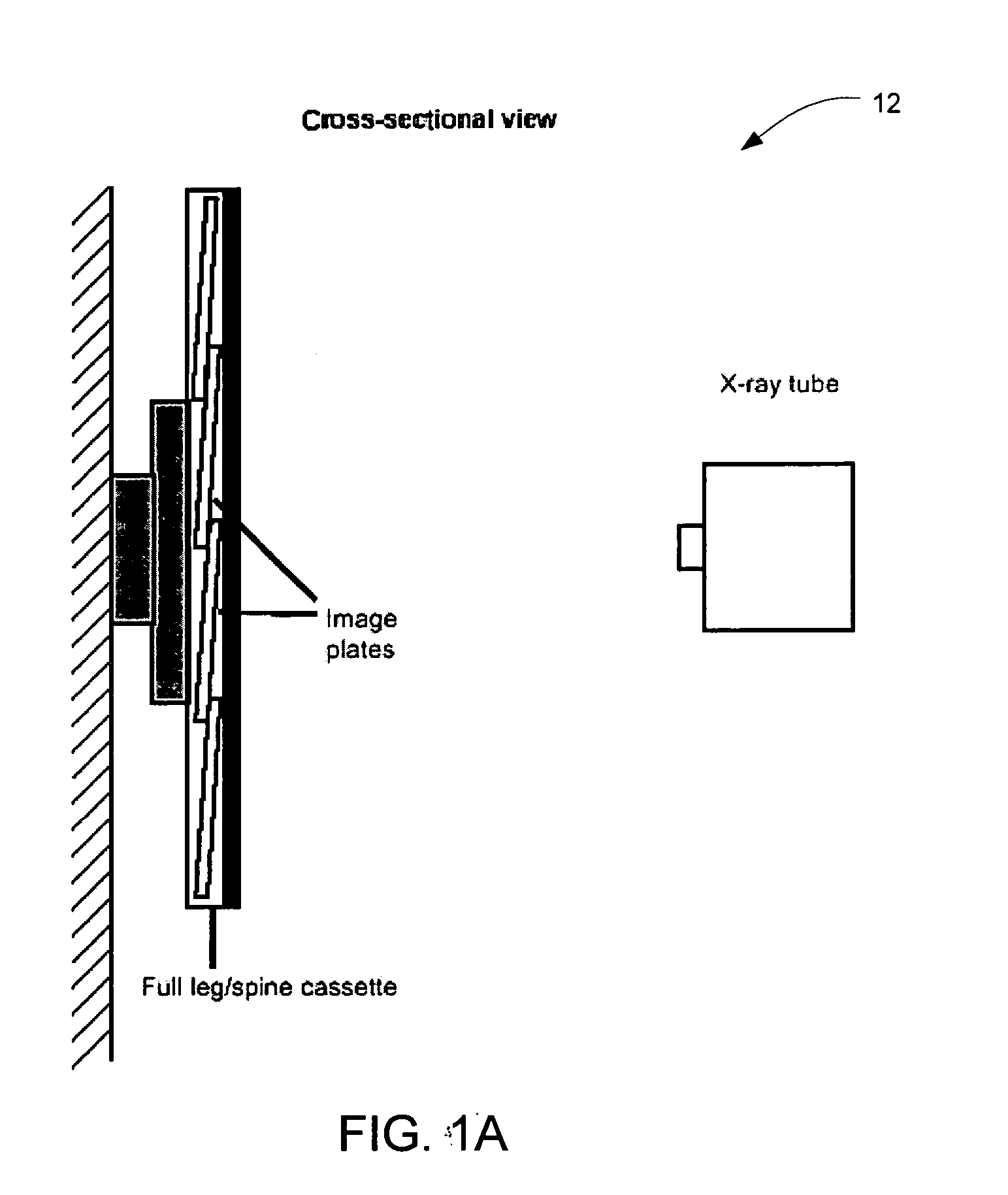
System and method for x-ray fluoroscopic imaging
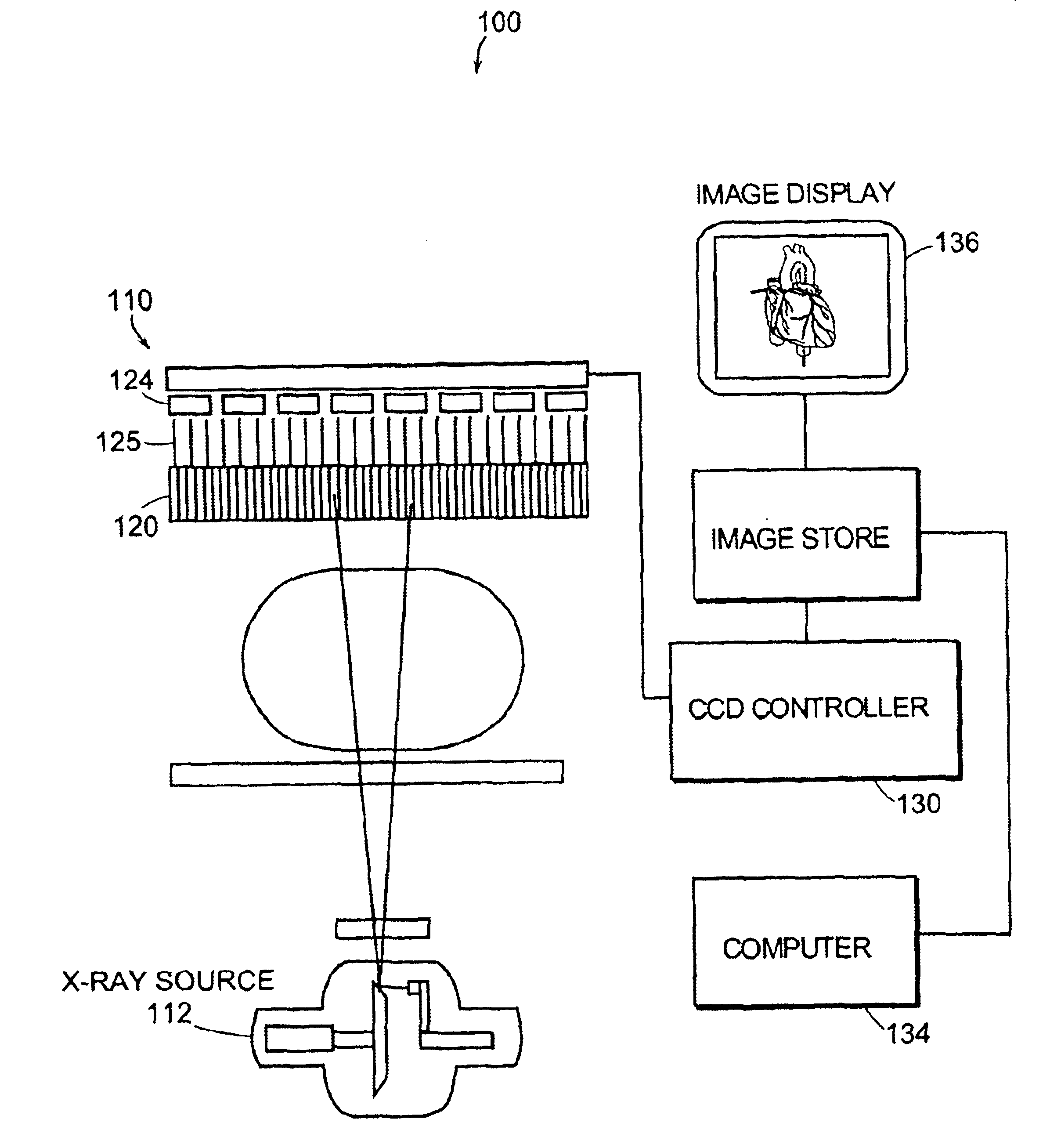
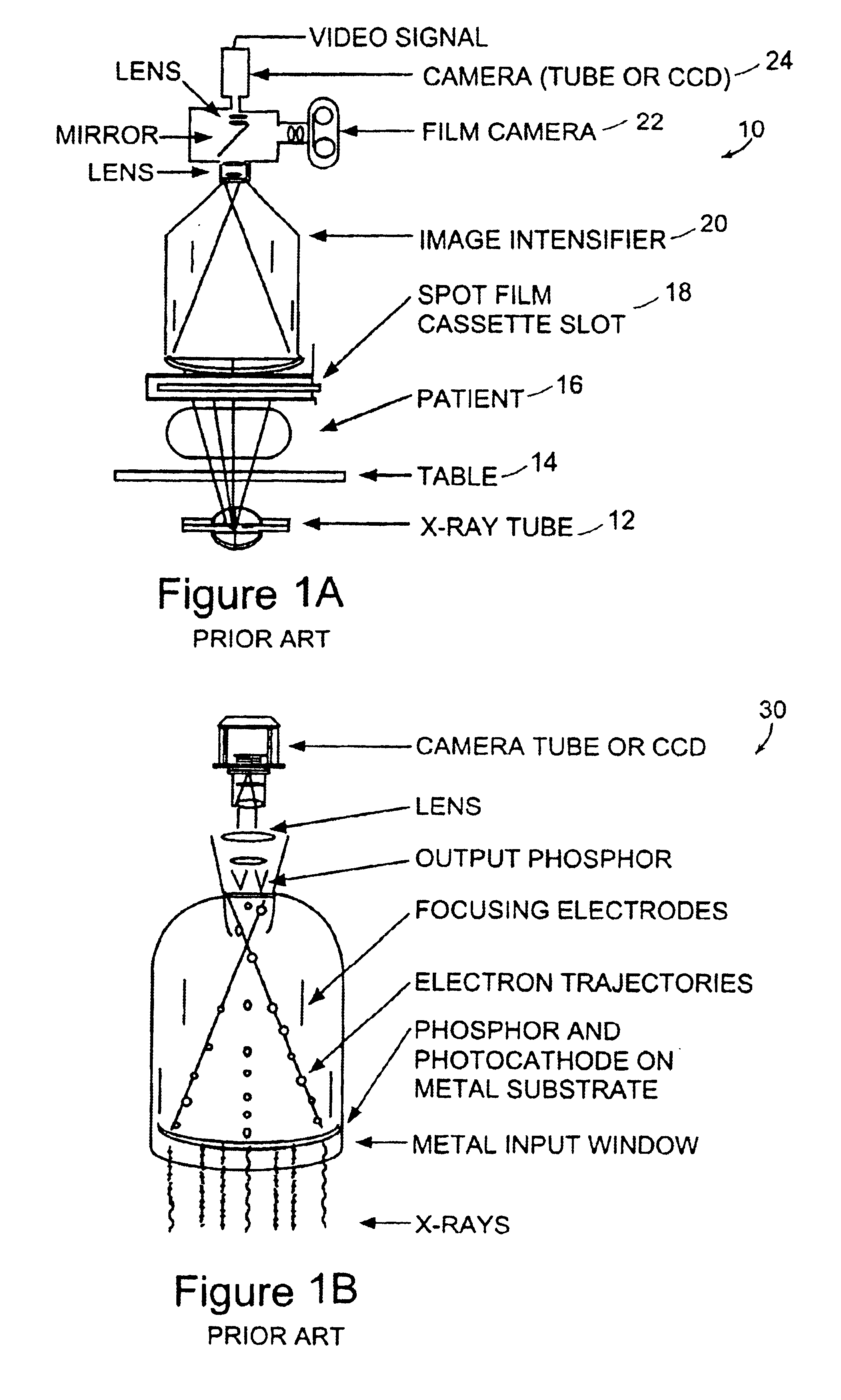
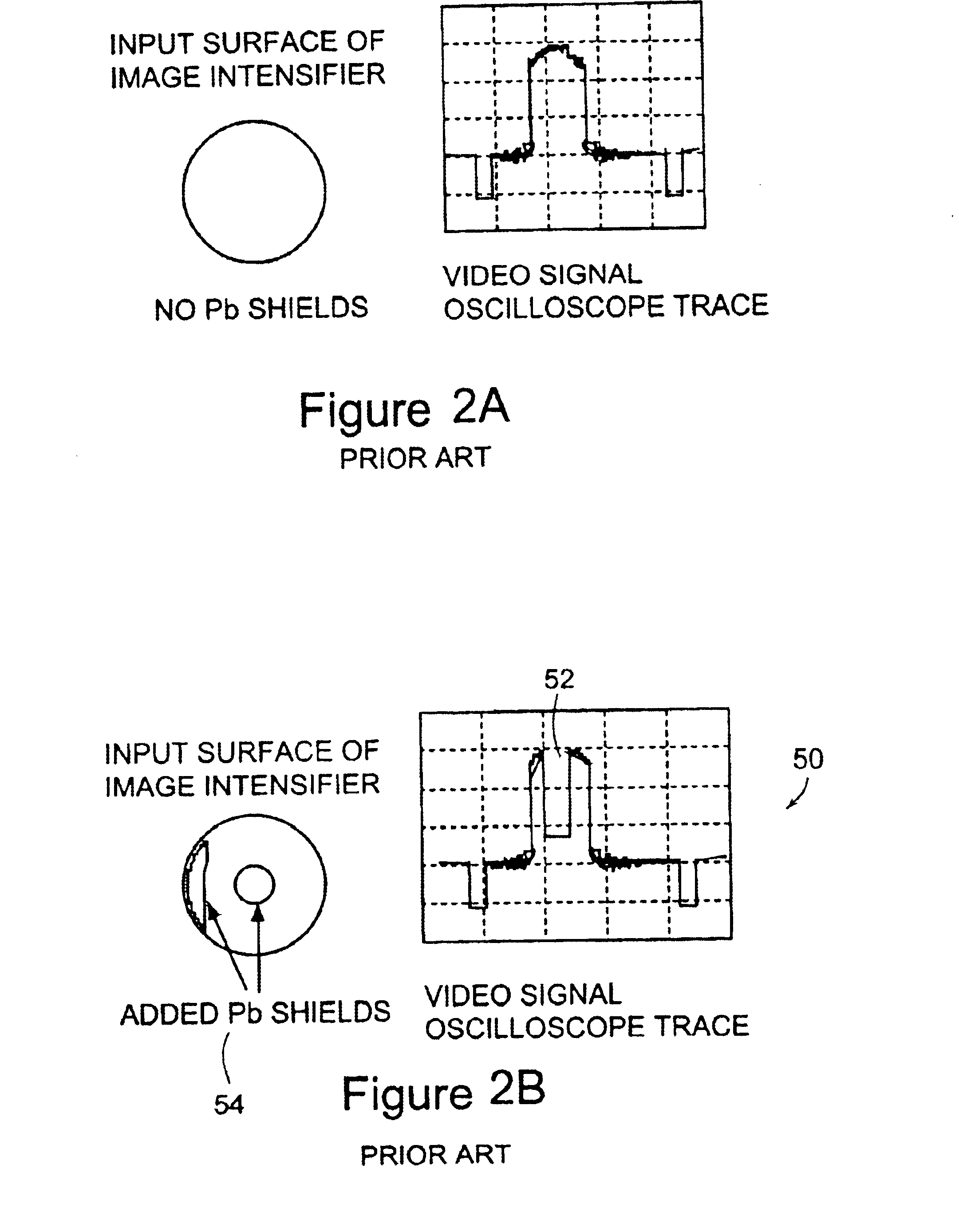
InactiveUS6895077B2Increase frame rateAccurate imagingTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesFluorescenceX-ray
A system for x-ray fluoroscopic imaging of bodily tissue in which a scintillation screen and a charge coupled device (CCD) is used to accurately image selected tissue. An x-ray source generates x-rays which pass through a region of a subject's body, forming an x-ray image which reaches the scintillation screen. The scintillation screen re-radiates a spatial intensity pattern corresponding to the image, the pattern being detected by the CCD sensor. In a preferred embodiment the imager uses four 8×8-cm three-side buttable CCDs coupled to a CsI:T1 scintillator by straight (non-tapering) fiberoptics and tiled to achieve a field of view (FOV) of 16×16-cm at the image plane. Larger FOVs can be achieved by tiling more CCDs in a similar manner. The imaging system can be operated in a plurality of pixel pitch modes such as 78, 156 or 234-μm pixel pitch modes. The CCD sensor may also provide multi-resolution imaging. The image is digitized by the sensor and processed by a controller before being stored as an electronic image. Other preferred embodiments may include each image being directed on flat panel imagers made from but not limited to, amorphous silicon and / or amorphous selenium to generate individual electronic representations of the separate images used for diagnostic or therapeutic applications.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS MEDICAL CENT
Method Of Manufacture And The Use Of A Functional Proppant For Determination Of Subterranean Fracture Geometries
ActiveUS20090288820A1Accurate imagingPromote recoveryMaterial nanotechnologyElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingElectricityGeophone
Proppants having added functional properties are provided, as are methods that use the proppants to track and trace the characteristics of a fracture in a geologic formation. Information obtained by the methods can be used to design a fracturing job, to increase conductivity in the fracture, and to enhance oil and gas recovery from the geologic formation. The functionalized proppants can be detected by a variety of methods utilizing, for example, an airborne magnetometer survey, ground penetrating radar, a high resolution accelerometer, a geophone, nuclear magnetic resonance, ultra-sound, impedance measurements, piezoelectric activity, radioactivity, and the like. Methods of mapping a subterranean formation are also provided and use the functionalized proppants to detect characteristics of the formation.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Nanoparticle Mediated Ultrasound Therapy and Diagnostic Imaging
InactiveUS20080045865A1Enhanced and localized and targeted hyperthermiaMinimizing collateral damageUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyDiseaseTissue repair
The present invention relates to systems and methods for localized delivery of heat, useful for localized imaging and treatment of a biological material. The systems and methods of the invention can be utilized for localized treatment of cancer, inflammation or other disorders involving over proliferation of tissue, and for tissue repair. The method comprises exposing nanoparticles to electromagnetic radiation under conditions wherein the nanoparticles generate microbubbles which emit heat when exposed to ultrasonic radiation.
Owner:KISLEV HANOCH
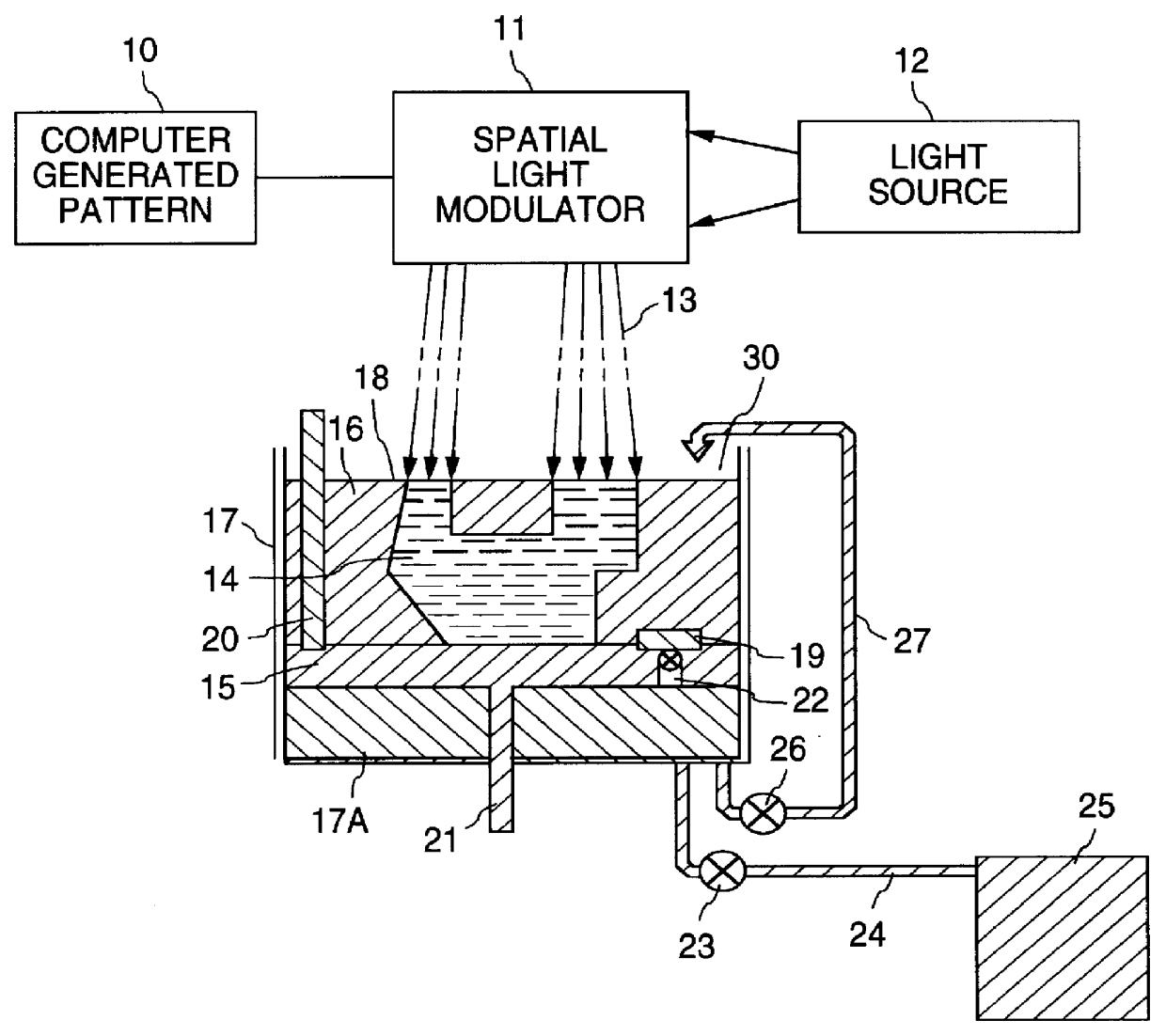
Apparatus and method for production of three-dimensional models by spatial light modulator
InactiveUS6051179AFacilitate cross-linkingHigh mechanical strengthAdditive manufacturing apparatusAnalogue computers for control systemsSpatial light modulatorWide beam
An apparatus and the method of its operation for rapid prototyping of a three-dimensional object which includes a radiant energy source of a wide beam of radiant energy of suitable intensity and wavelength for curing a layer of photo-curable resin contained in an open vat, a spatial light modulator (SLM) having an array of pixel elements which are individually digitally controllable by a computer, for modulating the radiant energy beam projected from the radiant energy source on a pixel by pixel basis, to form a series of time sequential images of the cross-sectional laminae of the object, an optical system for focusing each image formed by the SLM, one at a time, onto successive layers of photo-curable resin for predetermined exposure times to thereby form stacked laminae of cured resin, each lamina of cured resin being in the shape of a different one of the cross-sectional laminae, and a piston support for lowering each lamina of cured resin after it is formed by the SLM and for depositing a layer of resin corresponding to the thickness of one cross sectional lamina of the three-dimensional object before the step of projecting a new image by the SLM. The SLM, the piston support for lowering, and the optical system operate repeatedly and sequentially until a complete copy of the object is thereby produced.
Owner:GLOBAL FILTRATION SYST
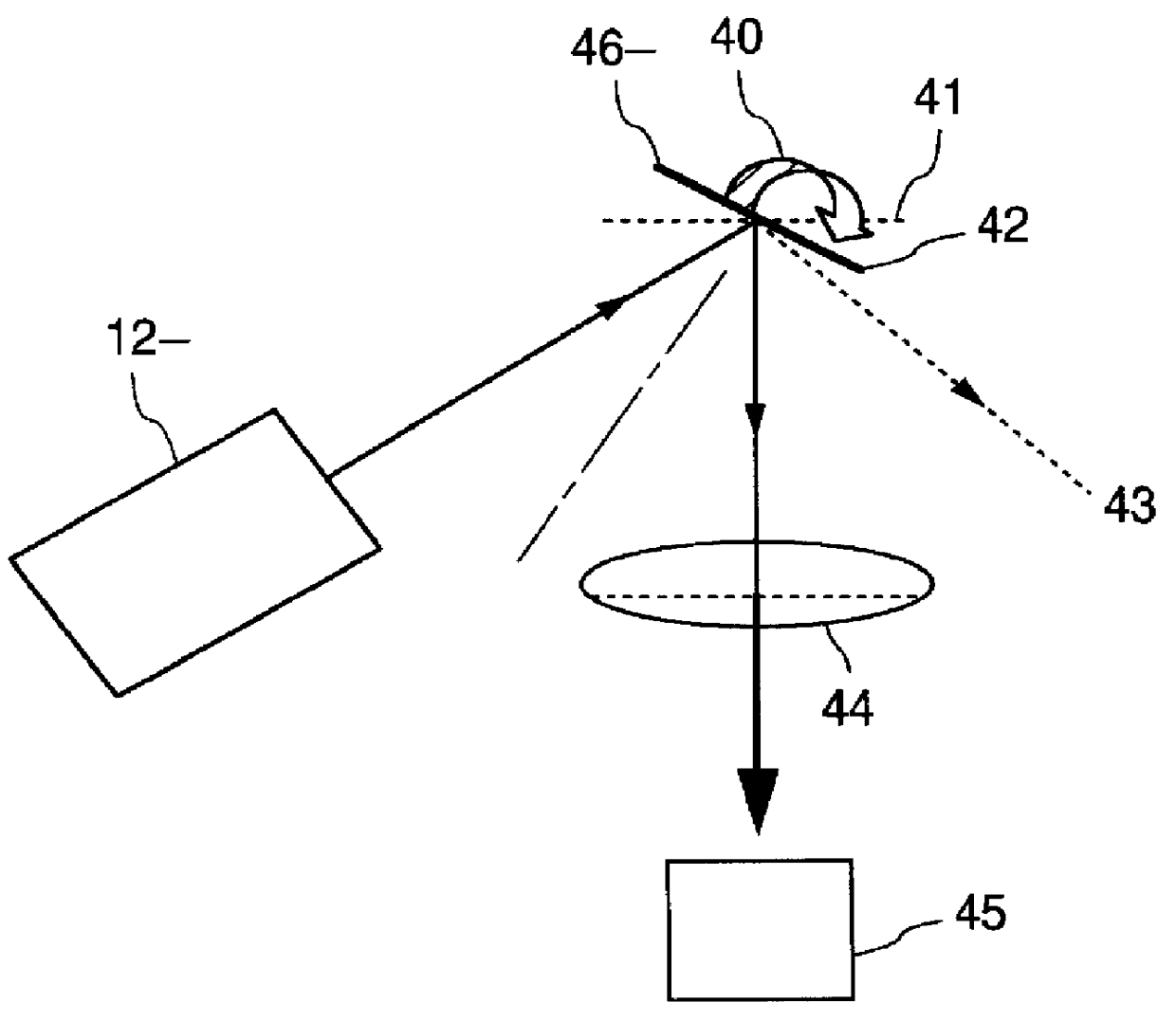
Wave front sensing method and apparatus
ActiveUS7649160B2Reduce fieldHigh resolutionImage enhancementOptical measurementsWavefront sensorMetrology
Owner:LYNCEE TEC
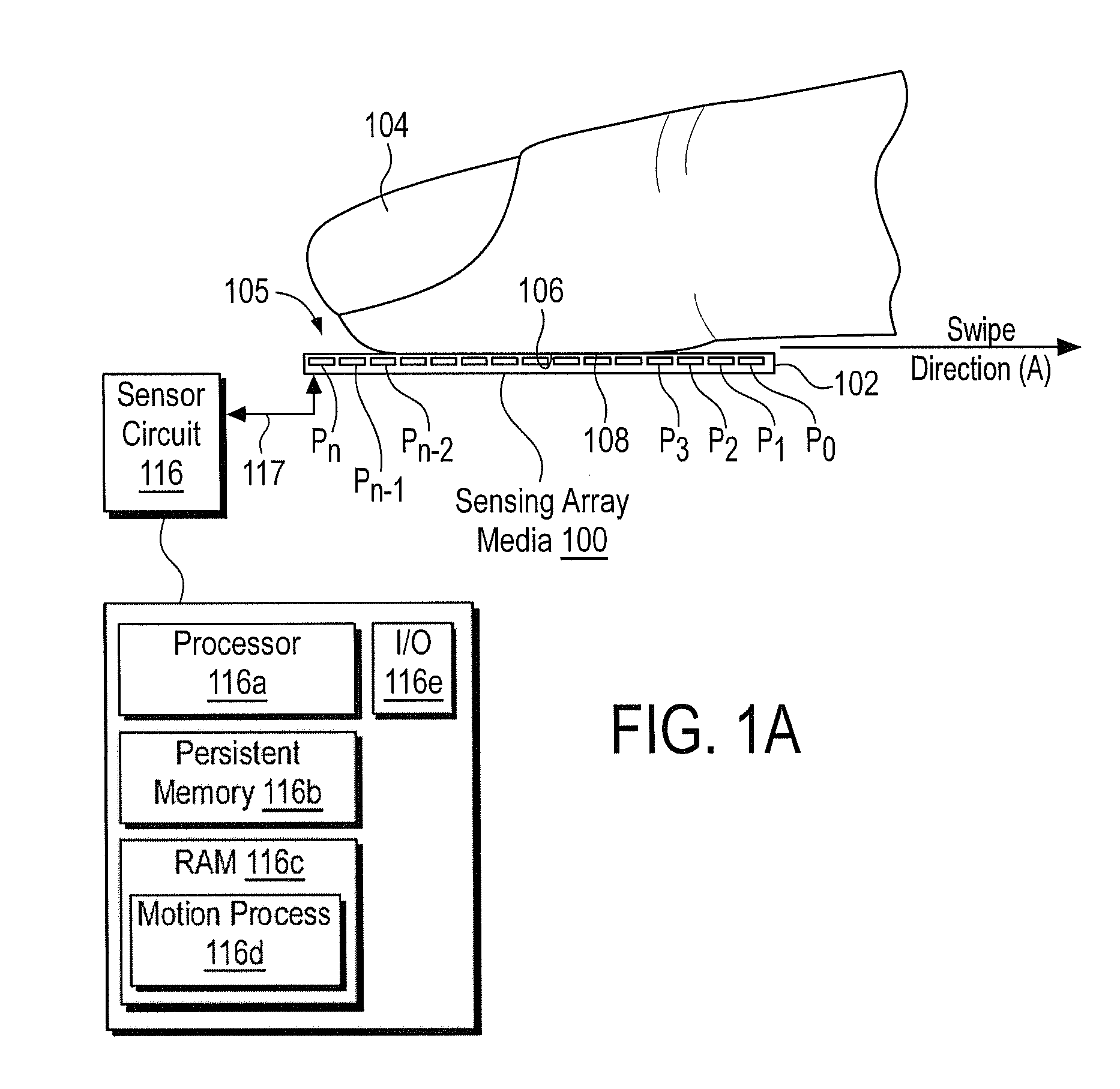
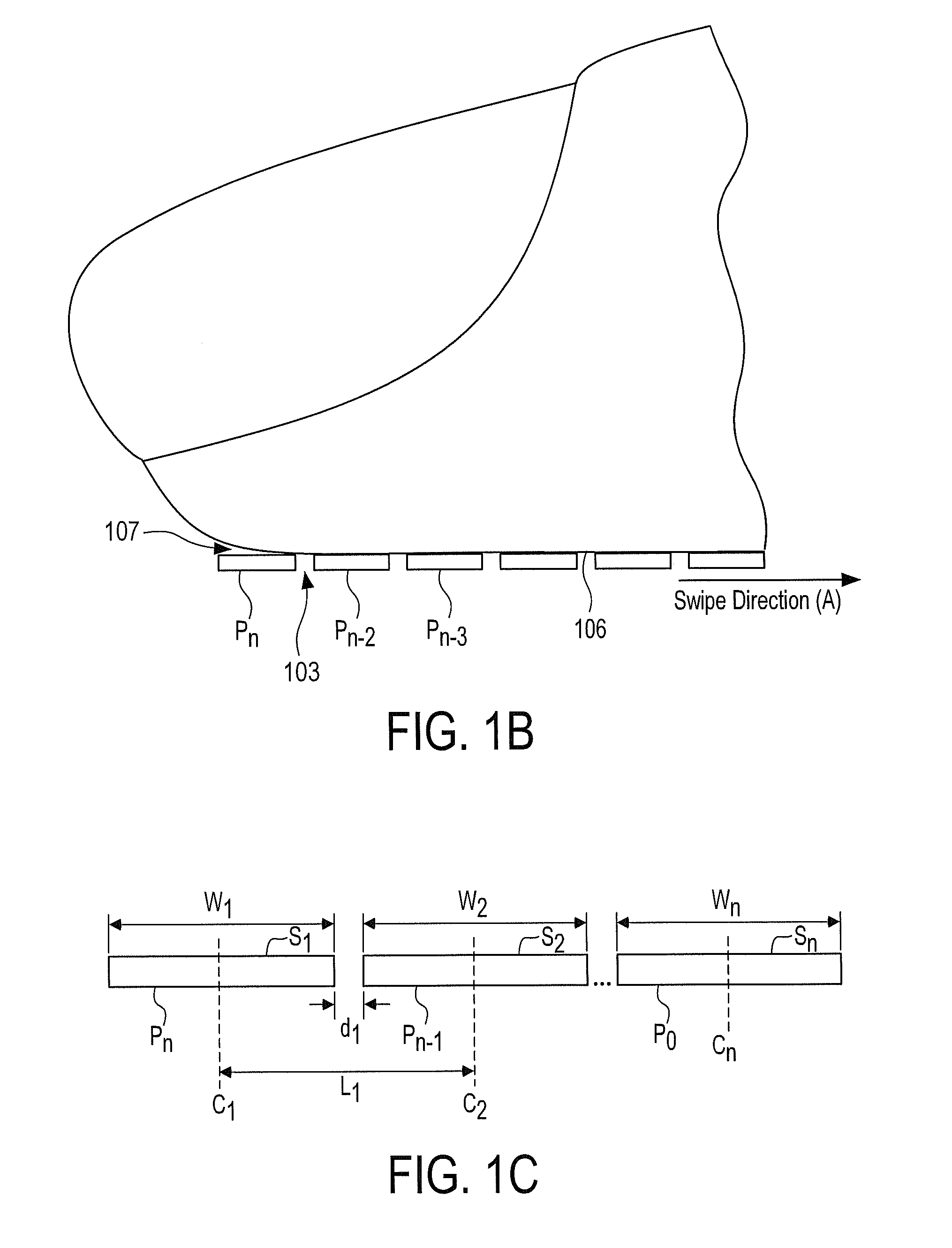
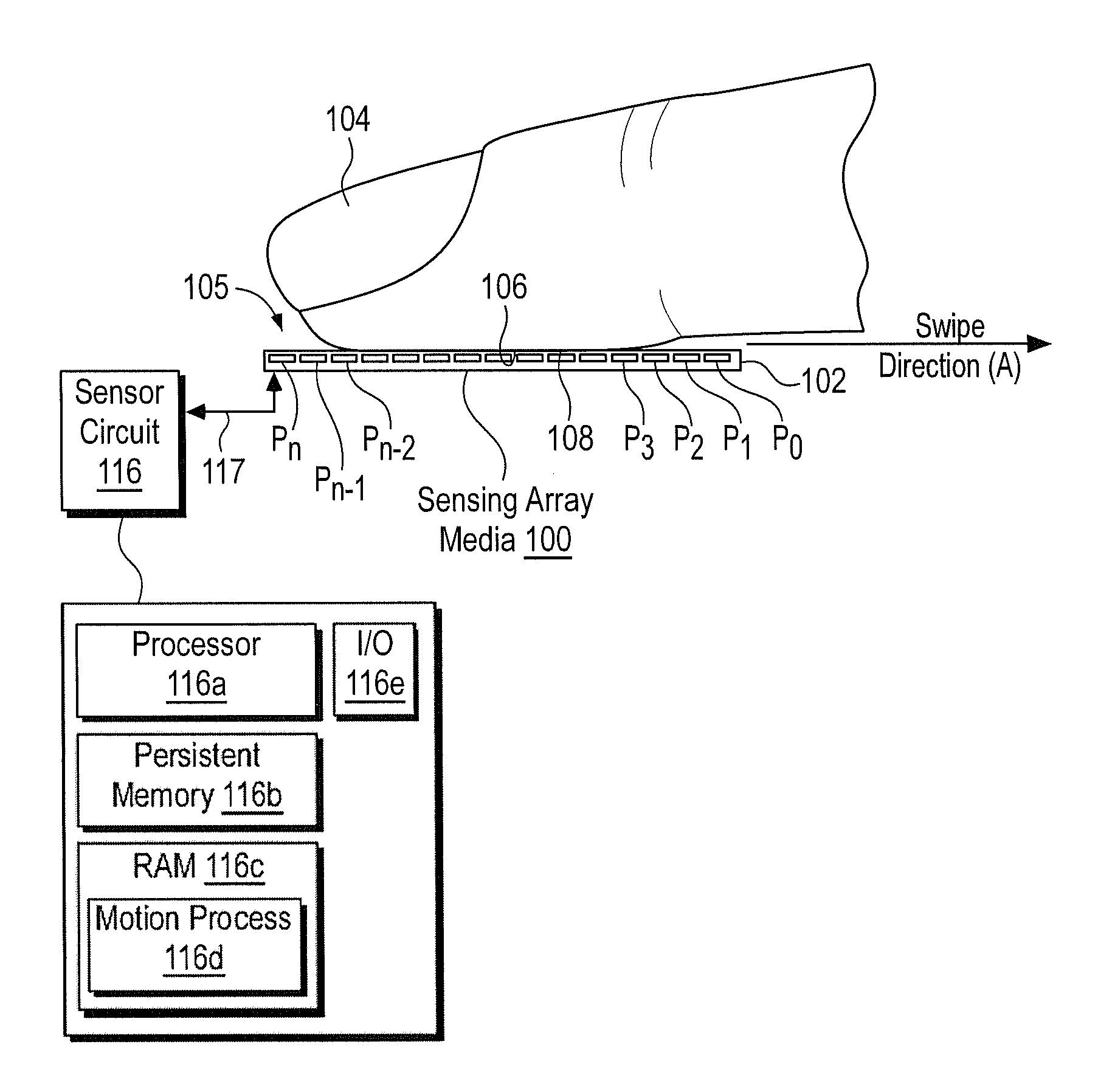
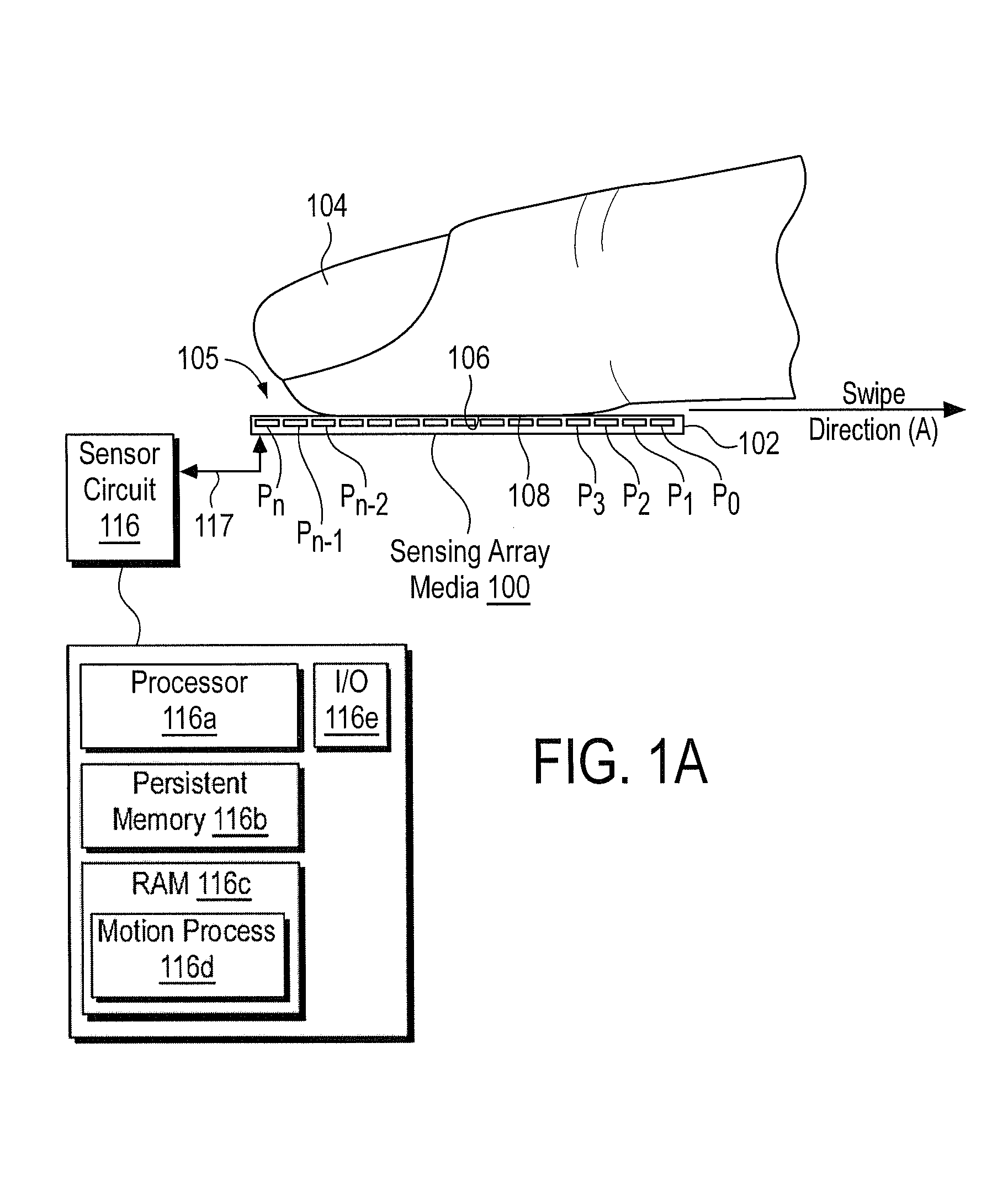
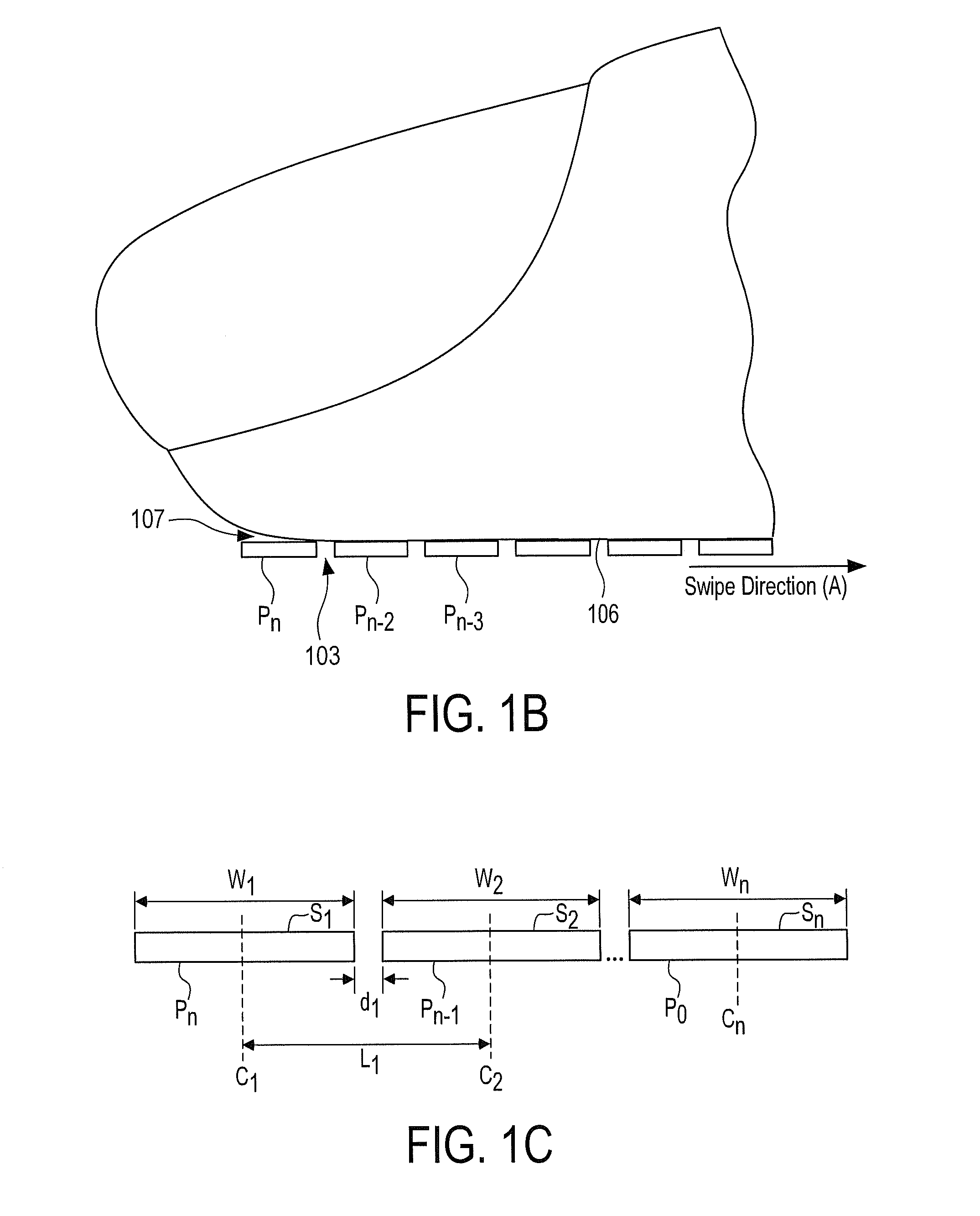
Method and Apparatus for Two-Dimensional Finger Motion Tracking and Control
ActiveUS20080240523A1Improve accuracyImprove robustnessCharacter and pattern recognitionElectric digital data processingCombined useEngineering
Enhanced accuracy finger position and motion sensors devices, algorithms, and methods are disclosed that can be used in a variety of different applications. The sensors can be used in conjunction with partial fingerprint imagers to produce improved fingerprint scanners. The finger motion sensors may also be used (either with or without a partial fingerprint imager) to control electronic devices. When several of these finger motion and position sensors are aligned in different directions, finger motion over a two dimensional surface may be detected. This creates a finger controlled “mouse” computer input device. Motion of a finger along the surface of such sensors may allow a user to control the movement of an indicator on a display screen, and control a microprocessor device. Such techniques are particularly useful for small space constrained devices, such as cell phones, smart cards, music players, portable computers, personal digital accessories, and the like.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
Method and arrangement for high-resolution microscope imaging or cutting in laser endoscopy
ActiveUS20080081950A1Accurate imagingPrecise microcuttingEndoscopesCatheterMicroscopic imageFlexible endoscope
The invention is directed to a method and an arrangement for high-resolution microscopic imaging in laser endoscopy based on laser-induced object reaction radiation and for performing microscopic cuts in biological tissue. In using multiphoton processes for endoscopic applications in biological materials with an accuracy of under one millimeter, radiation of a pulsed femtosecond laser is focused into an object by means of a transmission focusing optics unit comprising a transmission system and miniature focusing optics having a high numerical aperture greater than 0.55 to trigger a local object reaction radiation in the micrometer to nanometer range, and the distal end of the transmission focusing optics unit is moved in at least two dimensions for highly spatially resolved scanning of the object and for transmitting object reaction radiation which is scanned in a locally progressive manner to an image-generating system with a photon detector. In an other embodiment the femtosecond laser radiation is energy enhanced is applied to the same transmission focusing optics unit to perform microendoscopic surgery in biological tissue.
Owner:JENLAB
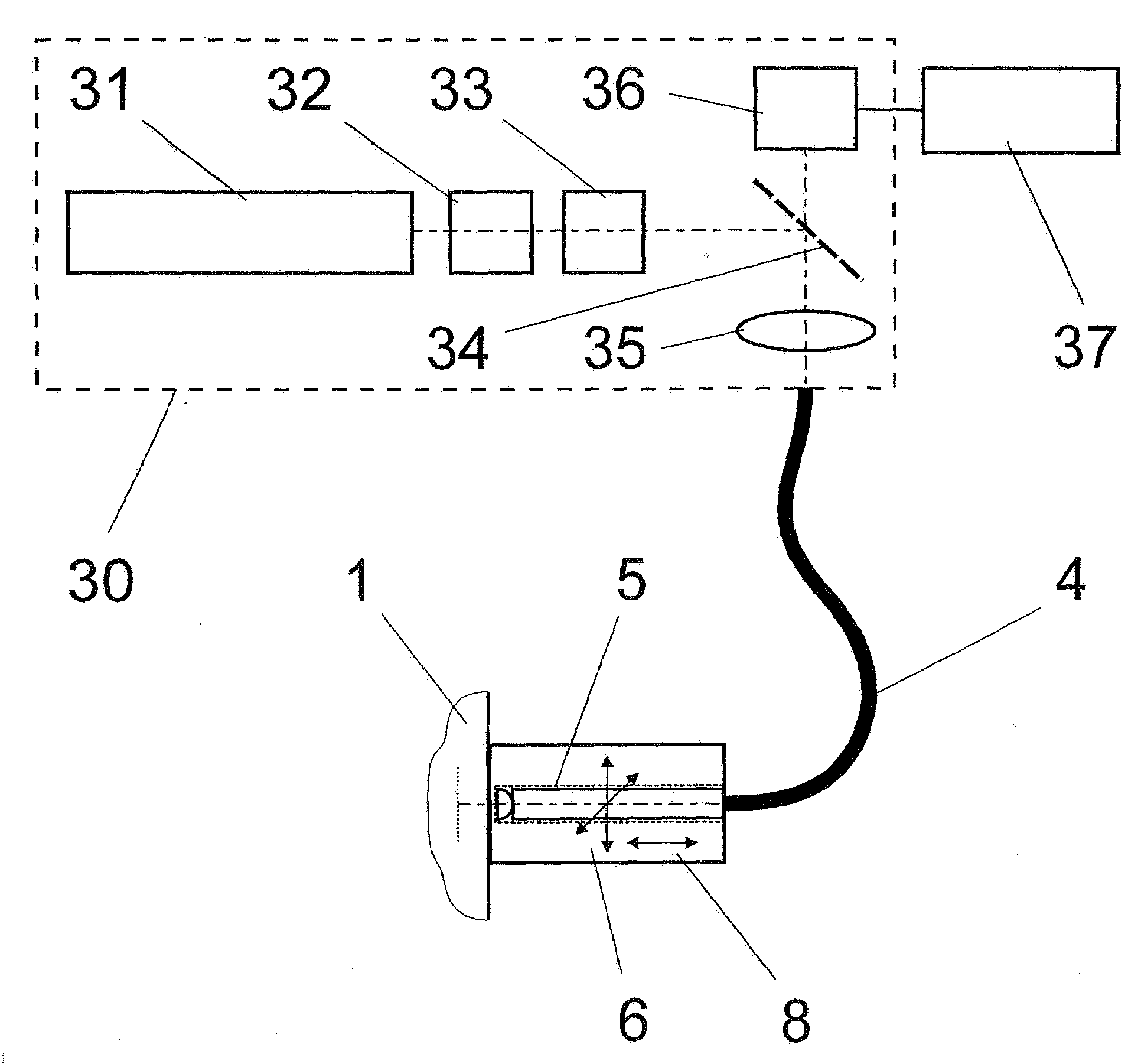
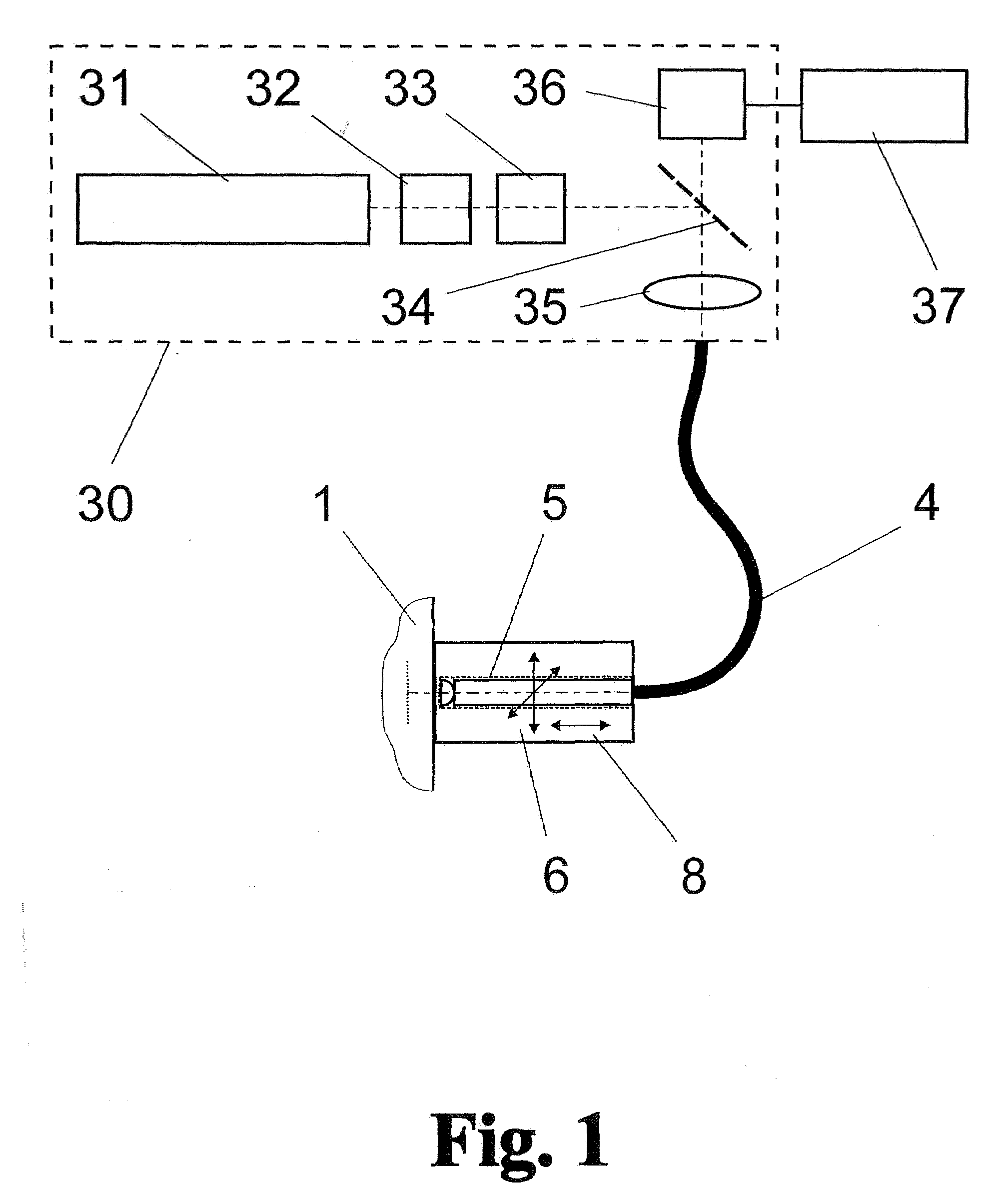
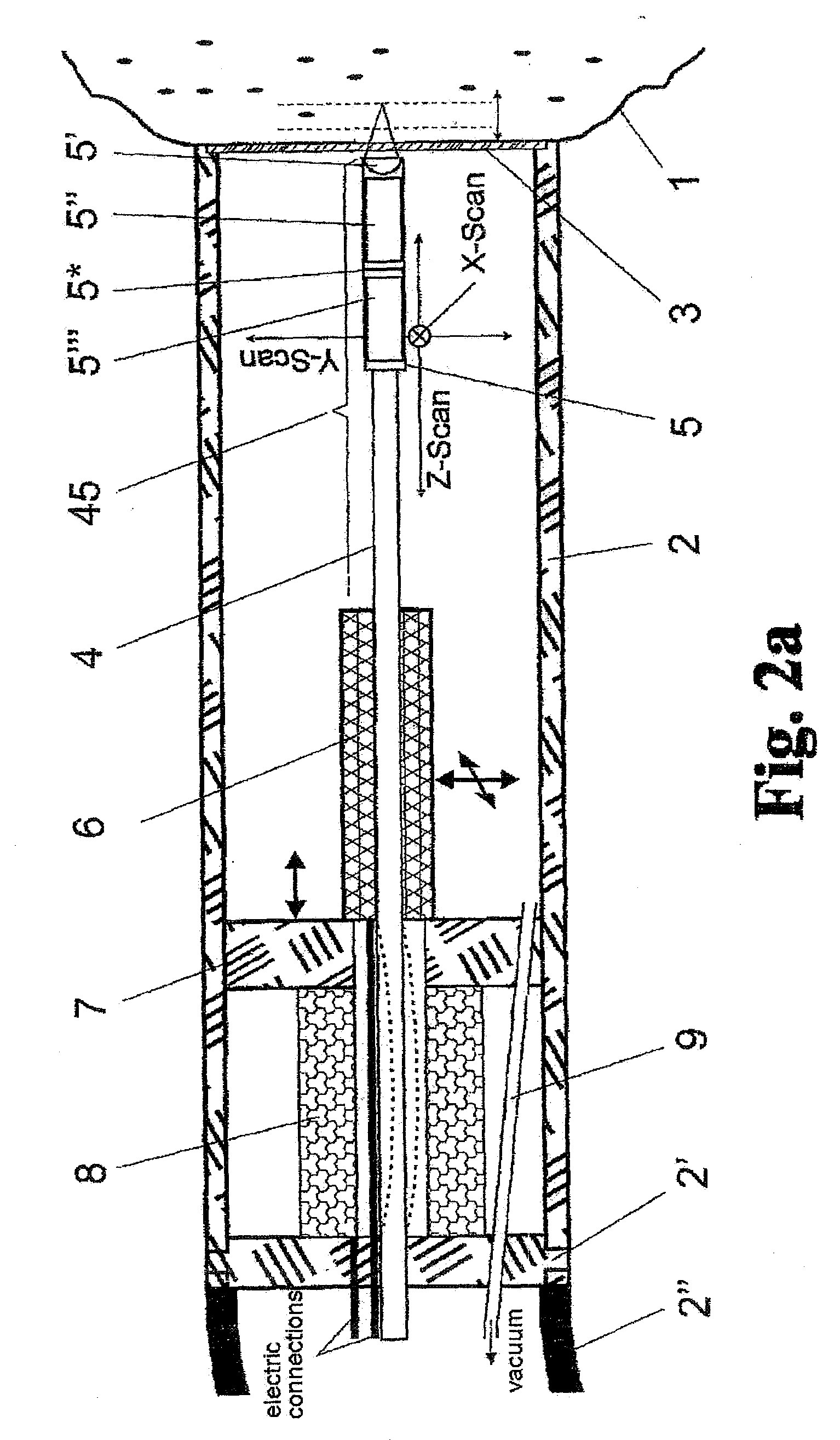
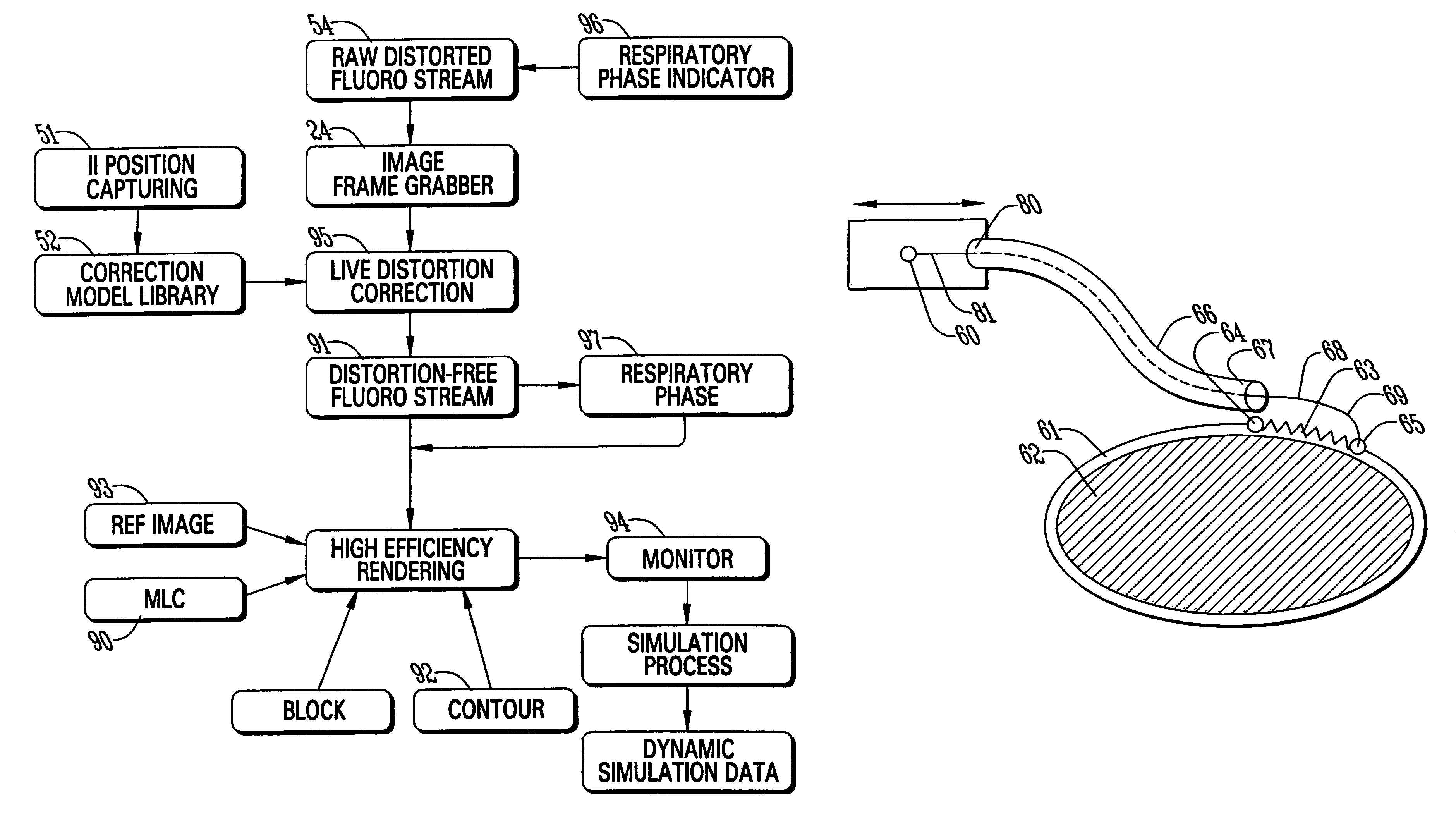
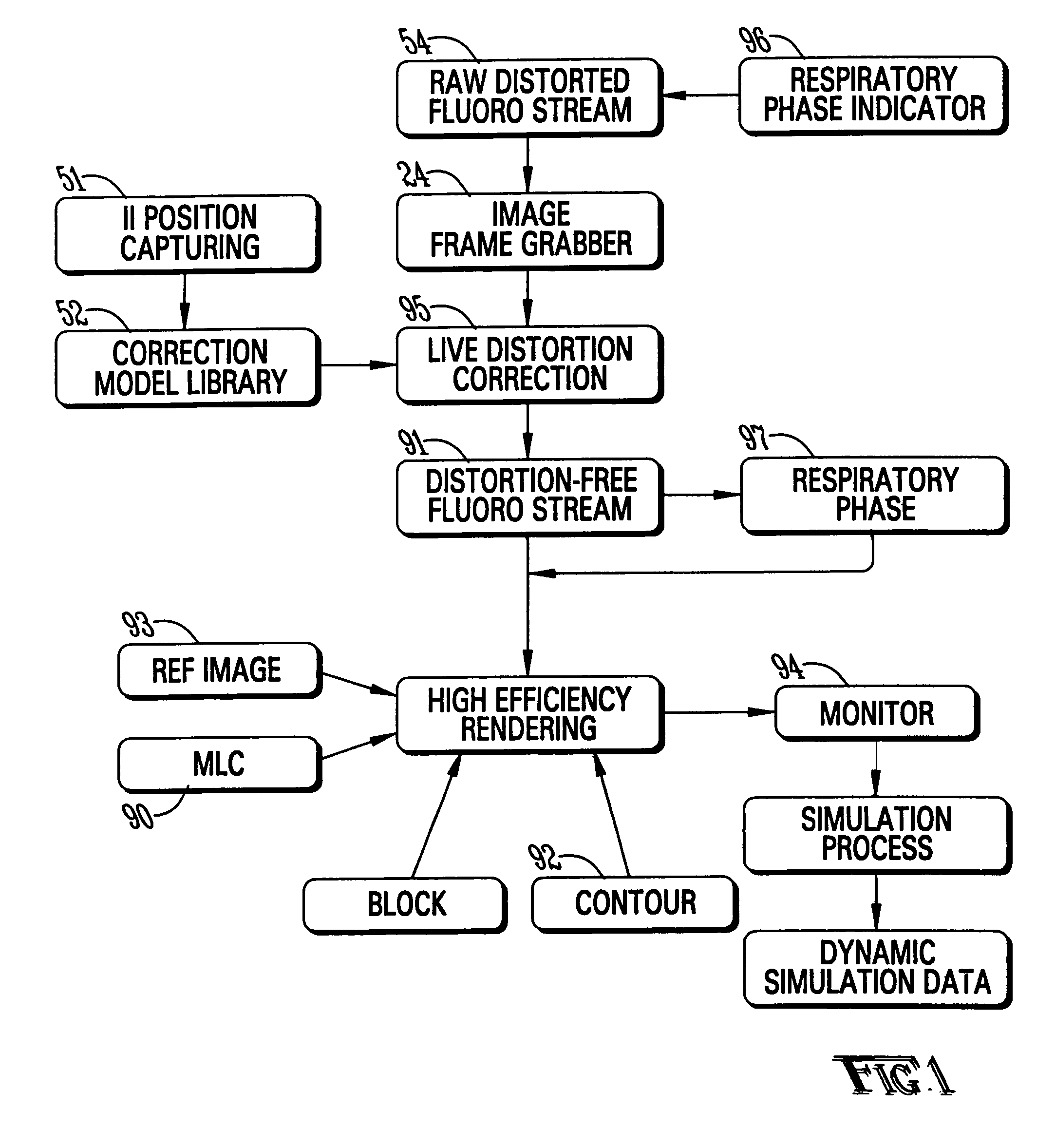
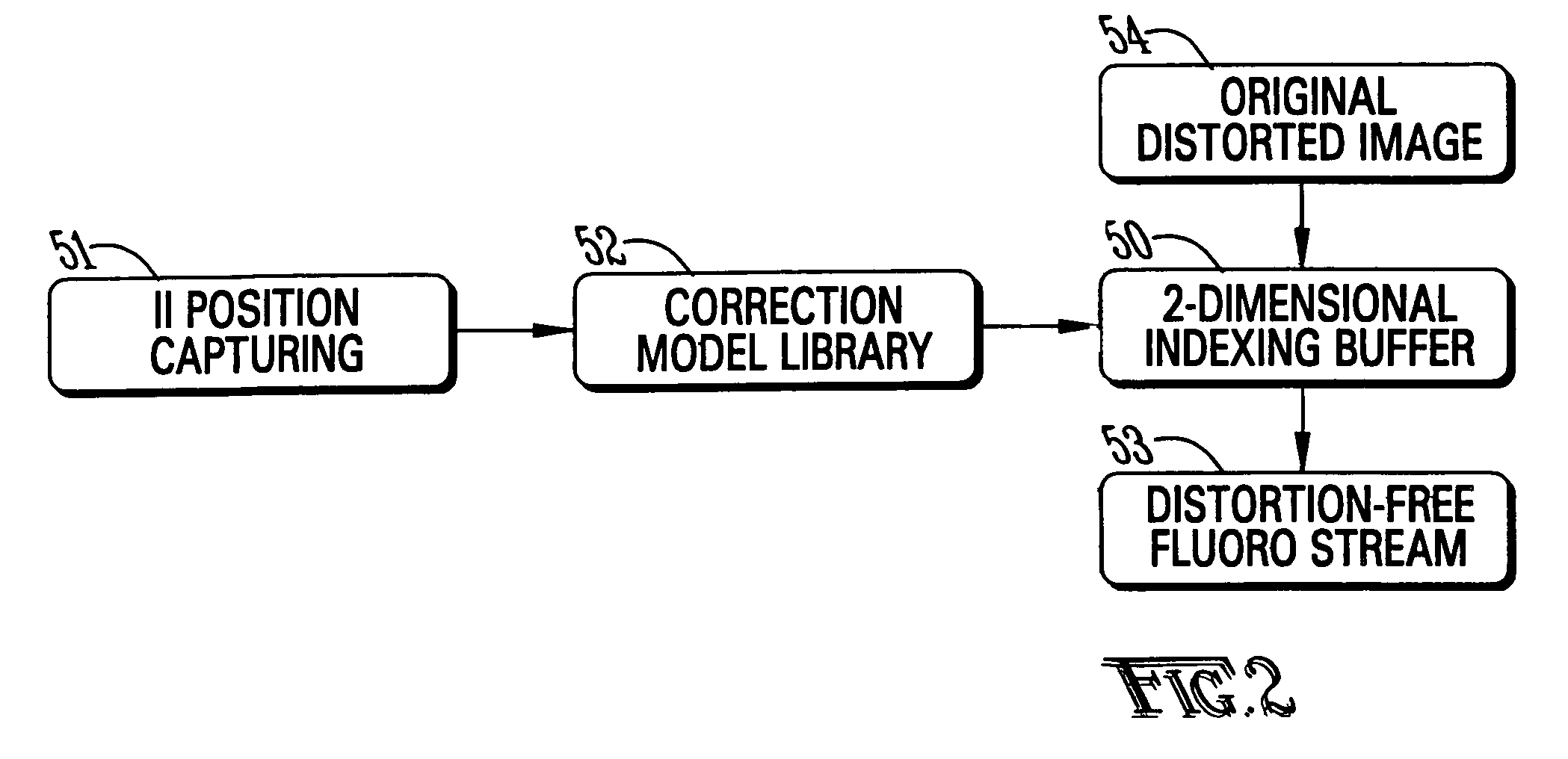
Dynamic radiation therapy simulation system
InactiveUS7349522B2Accurate treatment of tumorAccurate imagingMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingFluoroscopic imageComputerized system
A system for dynamic treatment simulation for radiotherapy. Software is implemented on a computer system to perform dynamic simulation by displaying every segment of dynamic treatment beams on top of real-time fluoroscopic image sequences. Automated distortion correction of the fluoroscopic image due to the image intensifier is performed in real-time. A respiration phase indicator measures changes in circumference of the patient's chest through the movement of a radio-opaque marker that appears directly in the fluoroscopic images of the patient.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
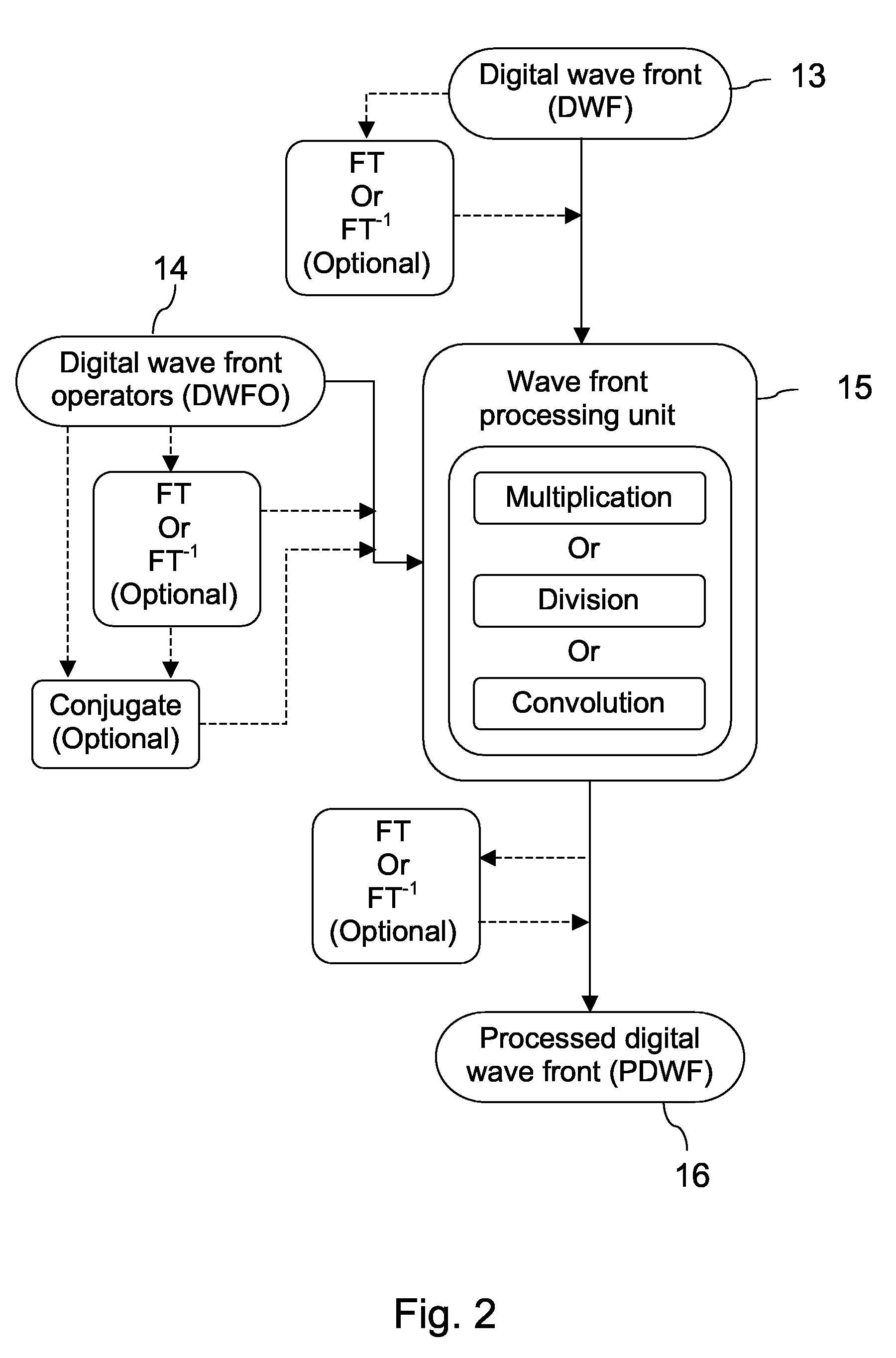
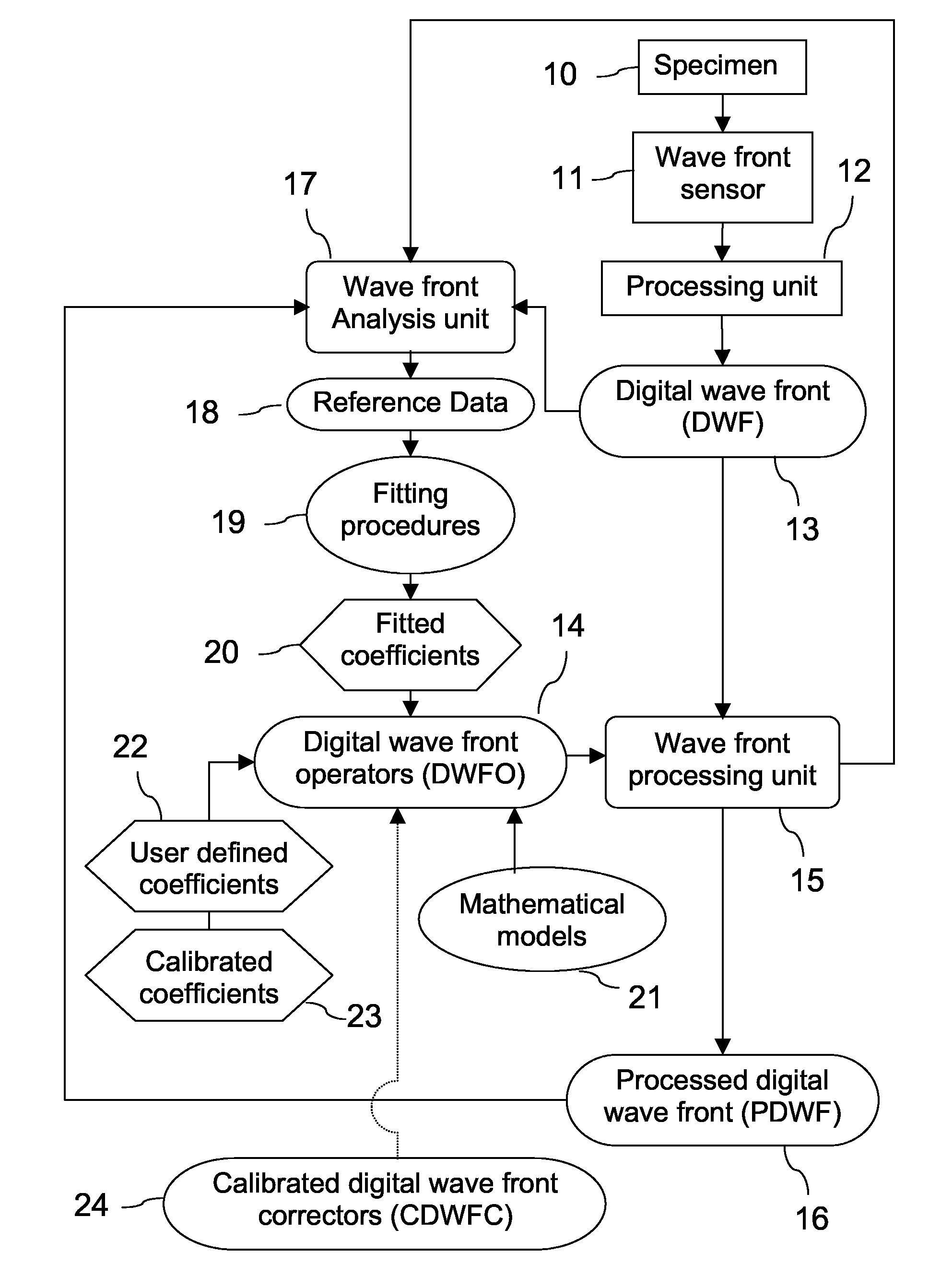
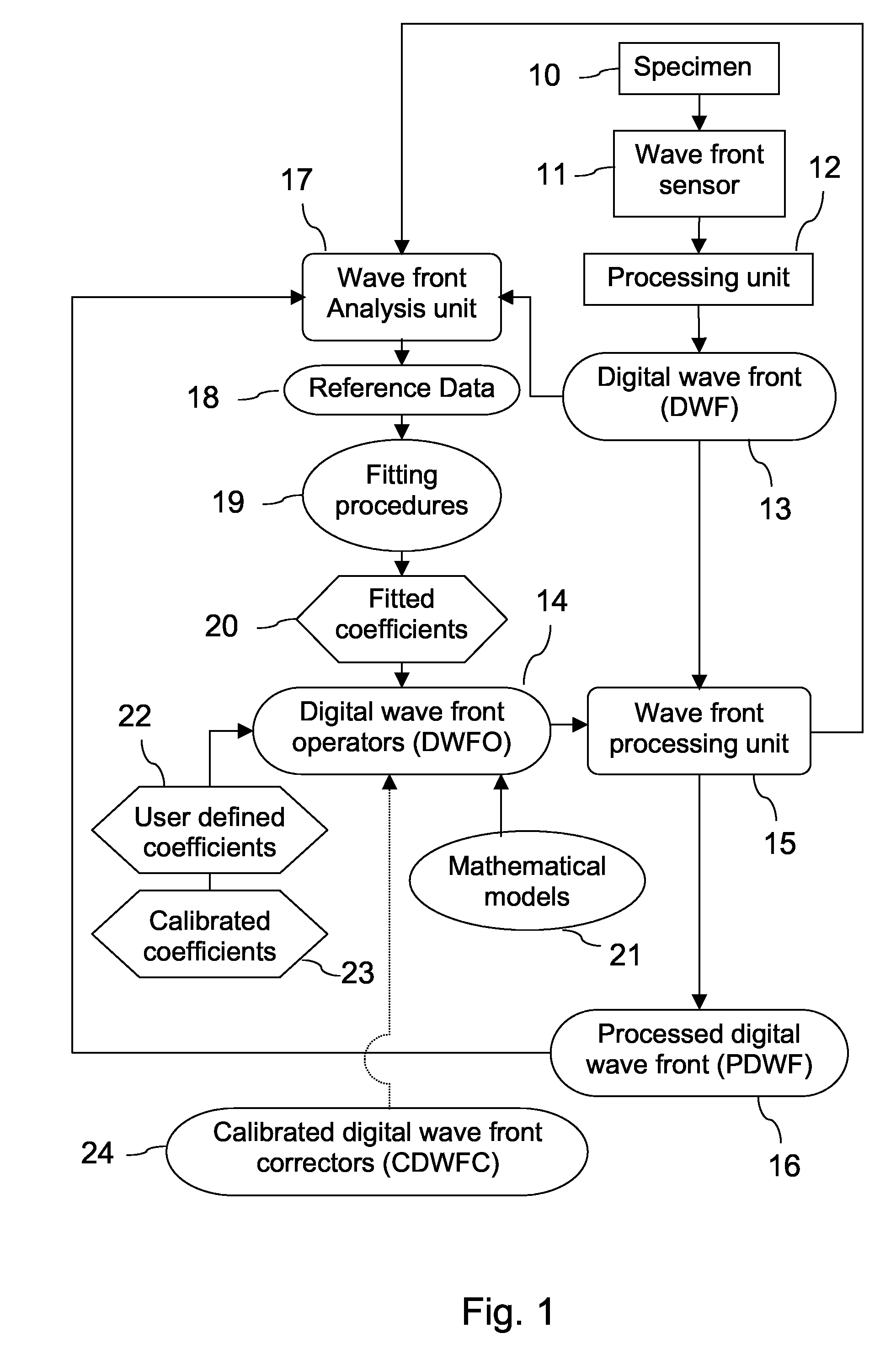
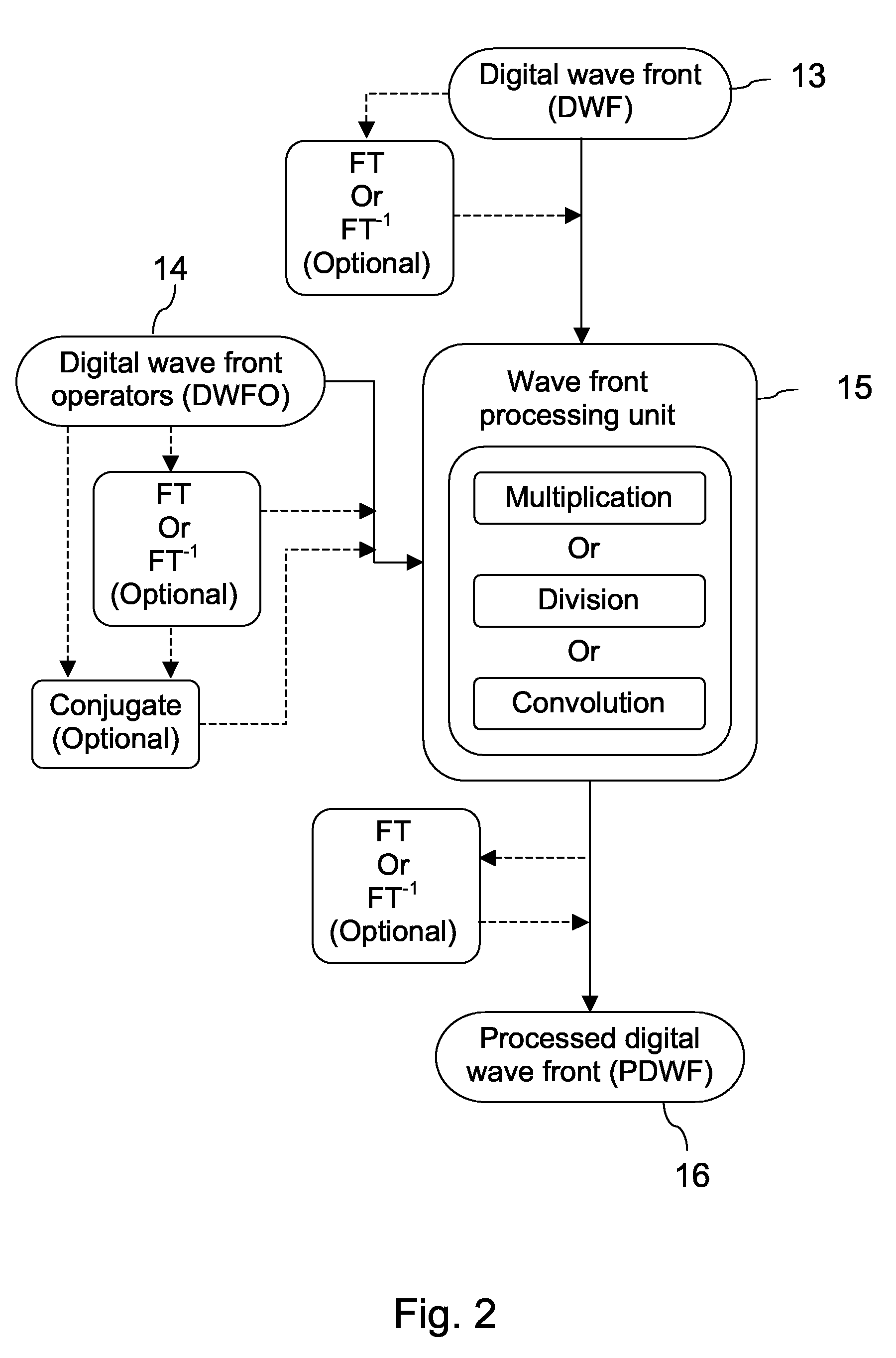
Wave Front Sensing Method and Apparatus
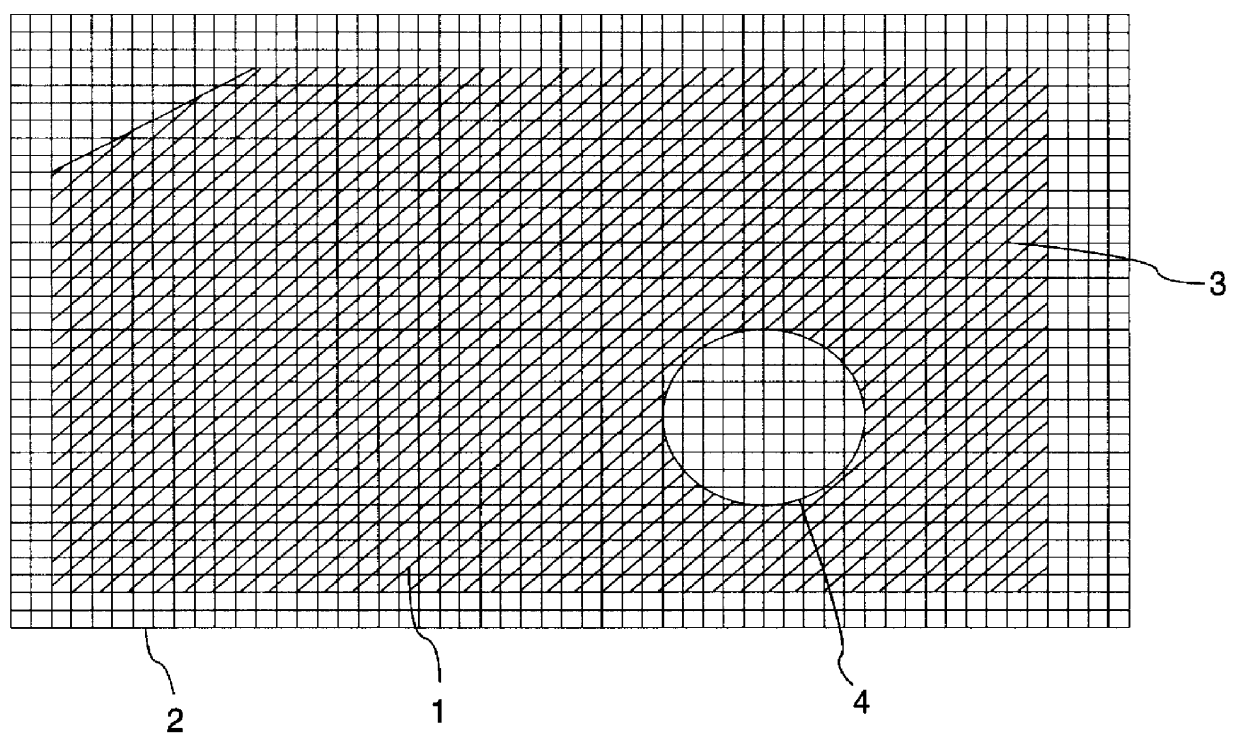
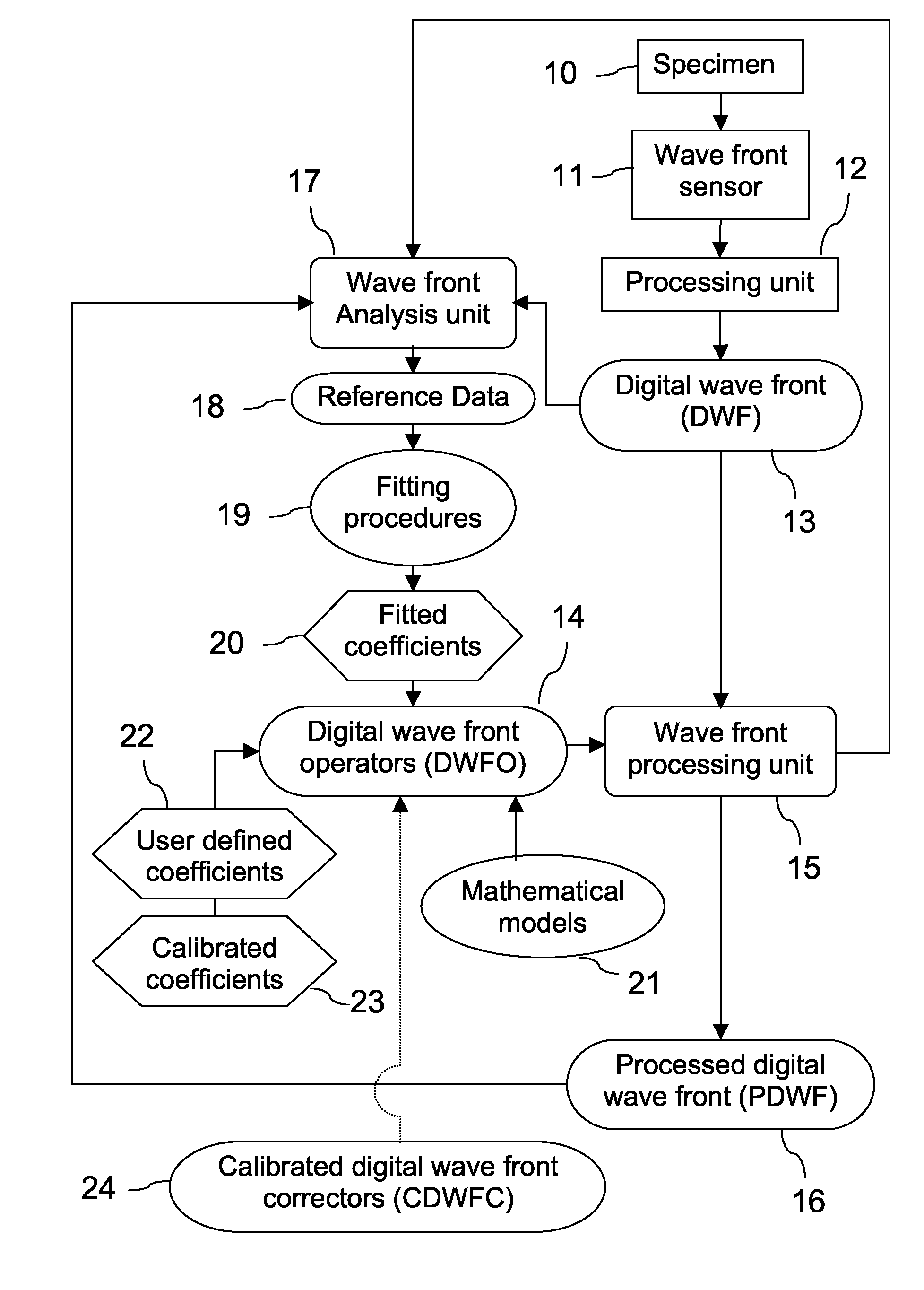
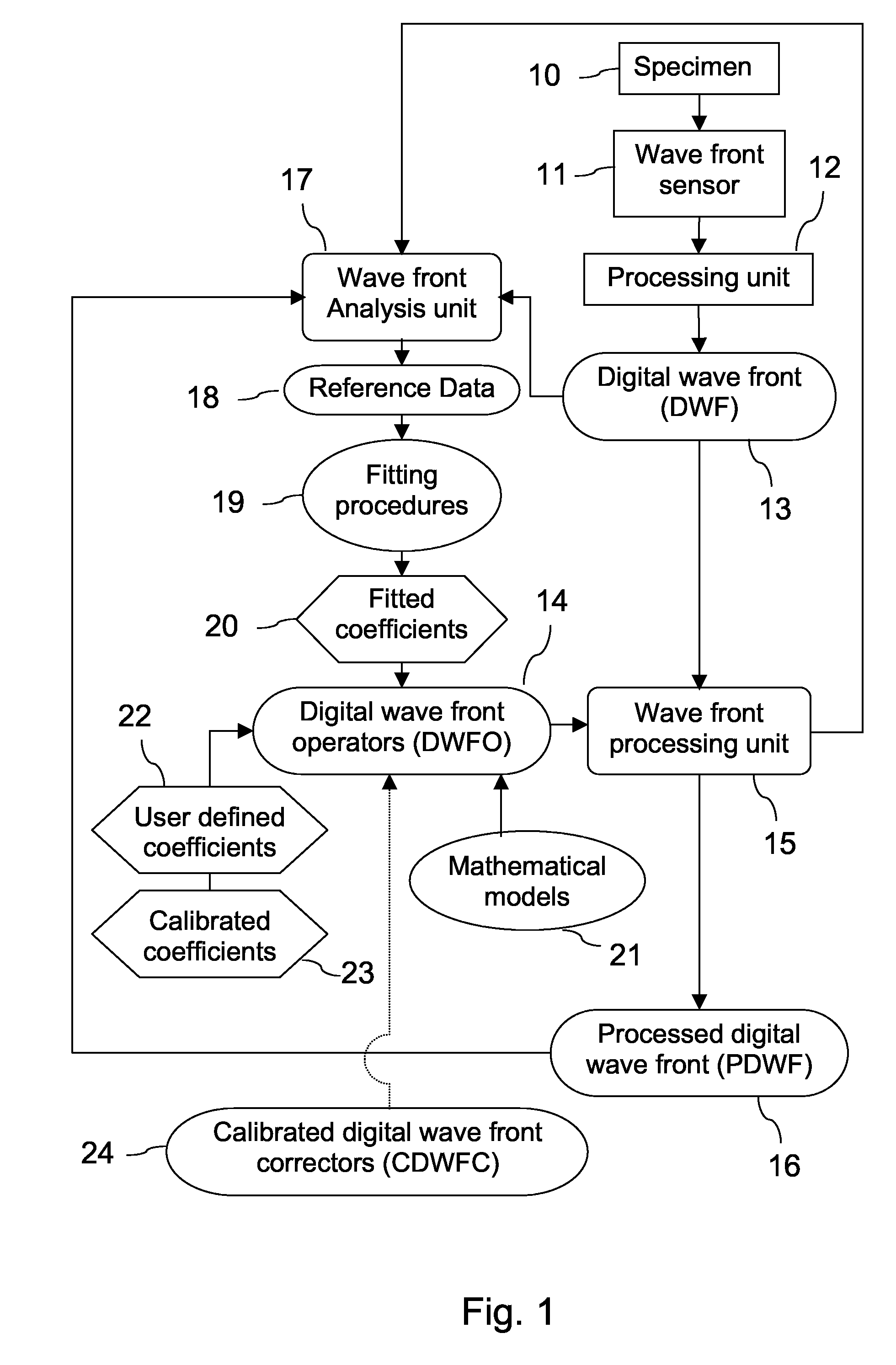
ActiveUS20080265130A1Improve performanceHigh imaging performanceImage enhancementPhotometry using reference valueWavefront sensorMetrology
A new way of mixing instrumental and digital means is described for the general field of wave front sensing. The present invention describes the use, the definition and the utility of digital operators, called digital wave front operators (DWFO) or digital lenses (DL), specifically designed for the digital processing of wave fronts defined in amplitude and phase. DWFO are of particular interest for correcting undesired wave front deformations induced by instrumental defects or experimental errors. DWFO may be defined using a mathematical model, e.g. a polynomial function, which involves coefficients. The present invention describes automated and semi-automated procedures for calibrating or adjusting the values of these coefficients. These procedures are based on the fitting of mathematical models on reference data extracted from specific regions of a wave front called reference areas, which are characterized by the fact that specimen contributions are a priori known in reference areas. For example, reference areas can be defined in regions where flat surfaces of a specimen produce a constant phase function. The present invention describes also how DWFO can be defined by extracting reference data along one-dimensional (1D) profiles. DWFO can also be defined in order to obtain a flattened representation of non-flat area of a specimen. Several DWFO or DL can be combined, possibly in addition with procedures for calculating numerically the propagation of wave fronts. A DWFO may also be defined experimentally, e.g. by calibration procedures using reference specimens. A method for generating a DWFO by filtering in the Fourier plane is also described. All wave front sensing techniques may benefit from the present invention. The case of a wave front sensor based on digital holography, e.g. a digital holographic microscope (DHM), is described in more details. The use of DWFO improves the performance, in particular speed and precision, and the ease of use of instruments for wave front sensing. The use of DWFO results in instrumental simplifications, costs reductions, and enlarged the field of applications. The present invention defines a new technique for imaging and metrology with a large field of applications in material and life sciences, for research and industrial applications.
Owner:LYNCEE TEC
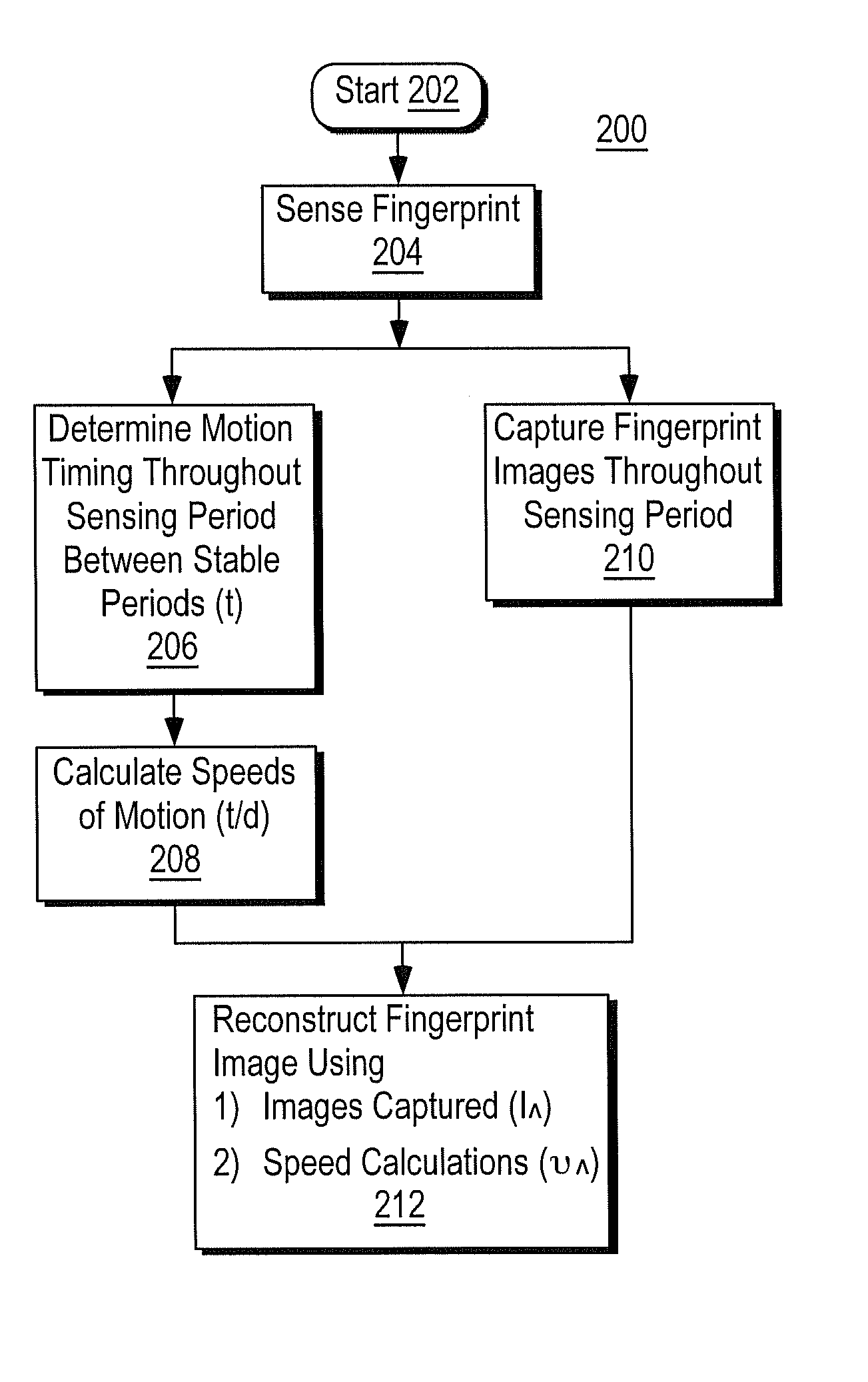
Method and Algorithm for Accurate Finger Motion Tracking
InactiveUS20080219521A1Improve noise immunityAccurate image of fingerprint imageCharacter and pattern recognitionControl electronicsCombined use
Enhanced accuracy finger position and motion sensors devices, algorithms, and methods are disclosed that can be used in a variety of different applications. The sensors can be used in conjunction with partial fingerprint imagers to produce improved fingerprint scanners. The finger motion sensors may also be used (either with or without a partial fingerprint imager) to produce highly accurate fingerprint images as well as to control electronic devices. Here improved signal analysis algorithms and methods are disclosed that enable finger position to be determined with higher levels of accuracy as the finger is swiped over finger position sensing arrays. These algorithms are particularly useful for deep finger penetrating radio frequency (RF) based sensing arrays.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
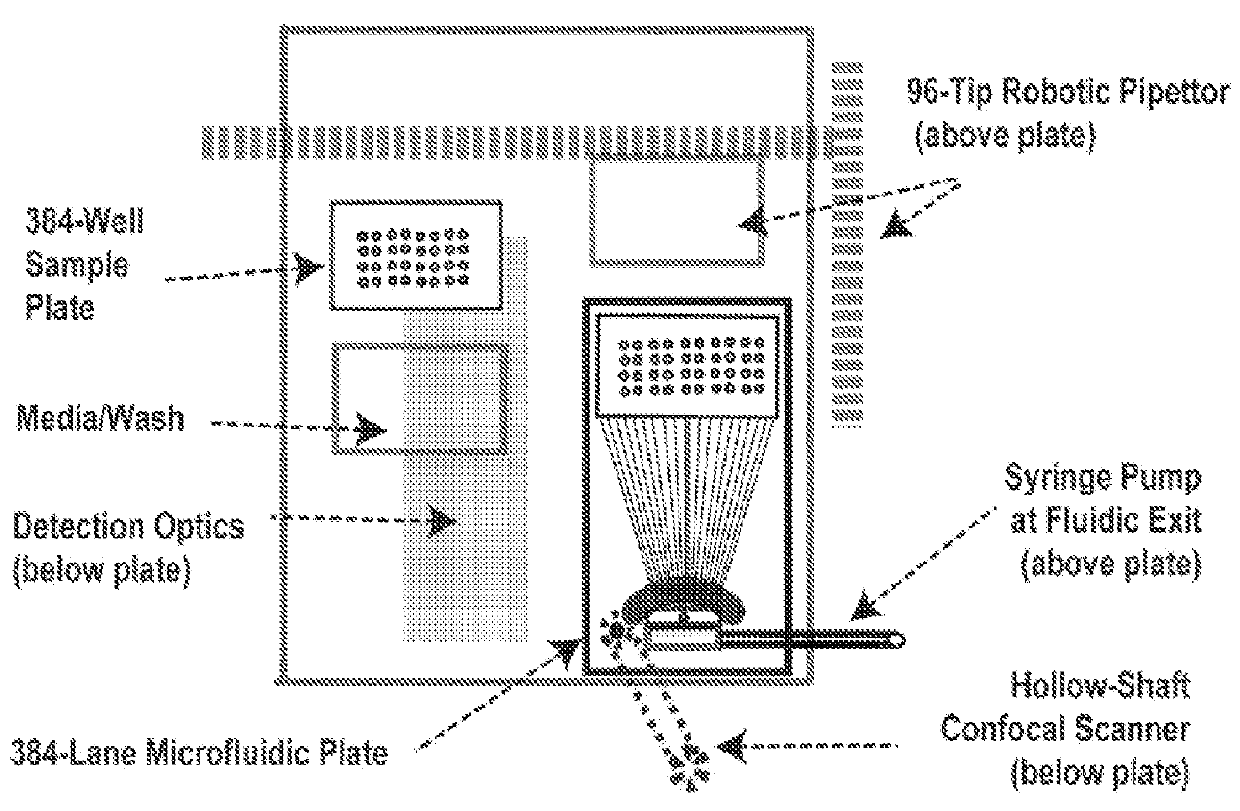
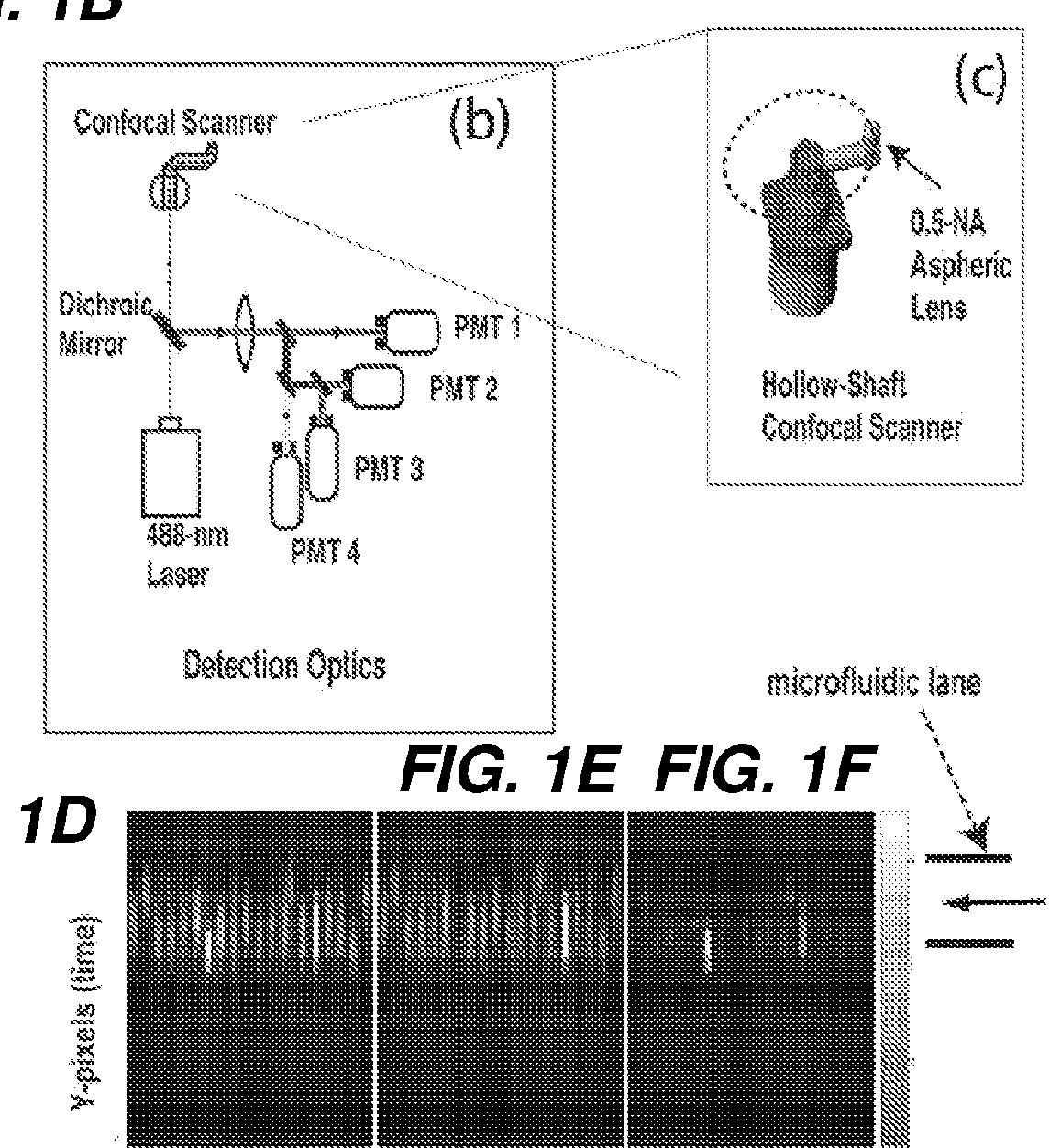
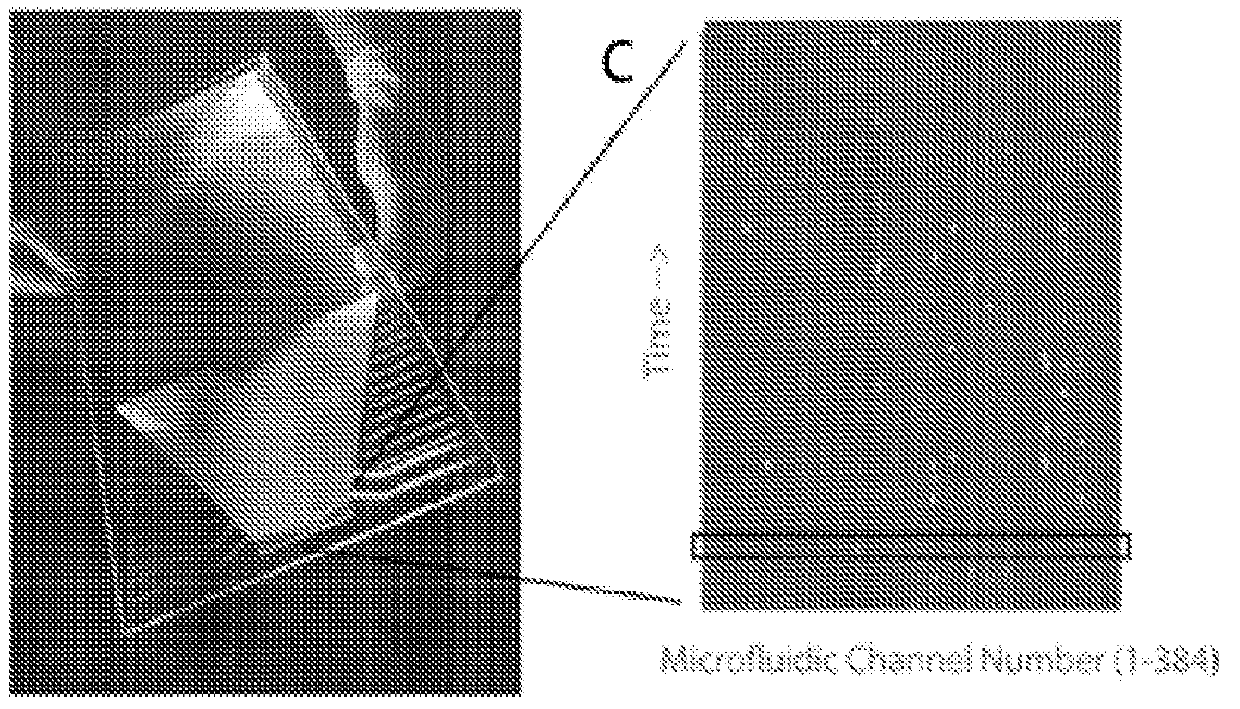
High throughput multichannel reader and uses thereof
InactiveUS20120220022A1Fast image captureAccurate and clear imageBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell basedImage resolution
The present invention relates generally to the field of high content screening of particles, e.g., cells in a flow cytometric system. In particular, the present invention relates to devices, methods and systems to obtain line-scan images of particles, e.g., cells, of a plurality of different samples simultaneously, where the line-scan images can be used to identify cells based on at least one of a variety of phenotypic characteristics such as shape, asymmetry, and intracellular information for cell sorting and selection. In some embodiments, the line-scan images are obtained as the particles, e.g., cells, in a plurality of different samples flow through a plurality of microchannels, reducing the need and time for focusing of the image detection system. In some embodiments, the laser spot size has a small spatial resolution for rapid capturing of images of cells. In some embodiments, the laser spot size has a larger spatial resolution for imaging of larger particles or cells, e.g., rare cells in a sample. In some embodiments, the devices, methods and systems are automated for a high-throughput, high content screening of particles such as cells in a plurality of samples.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
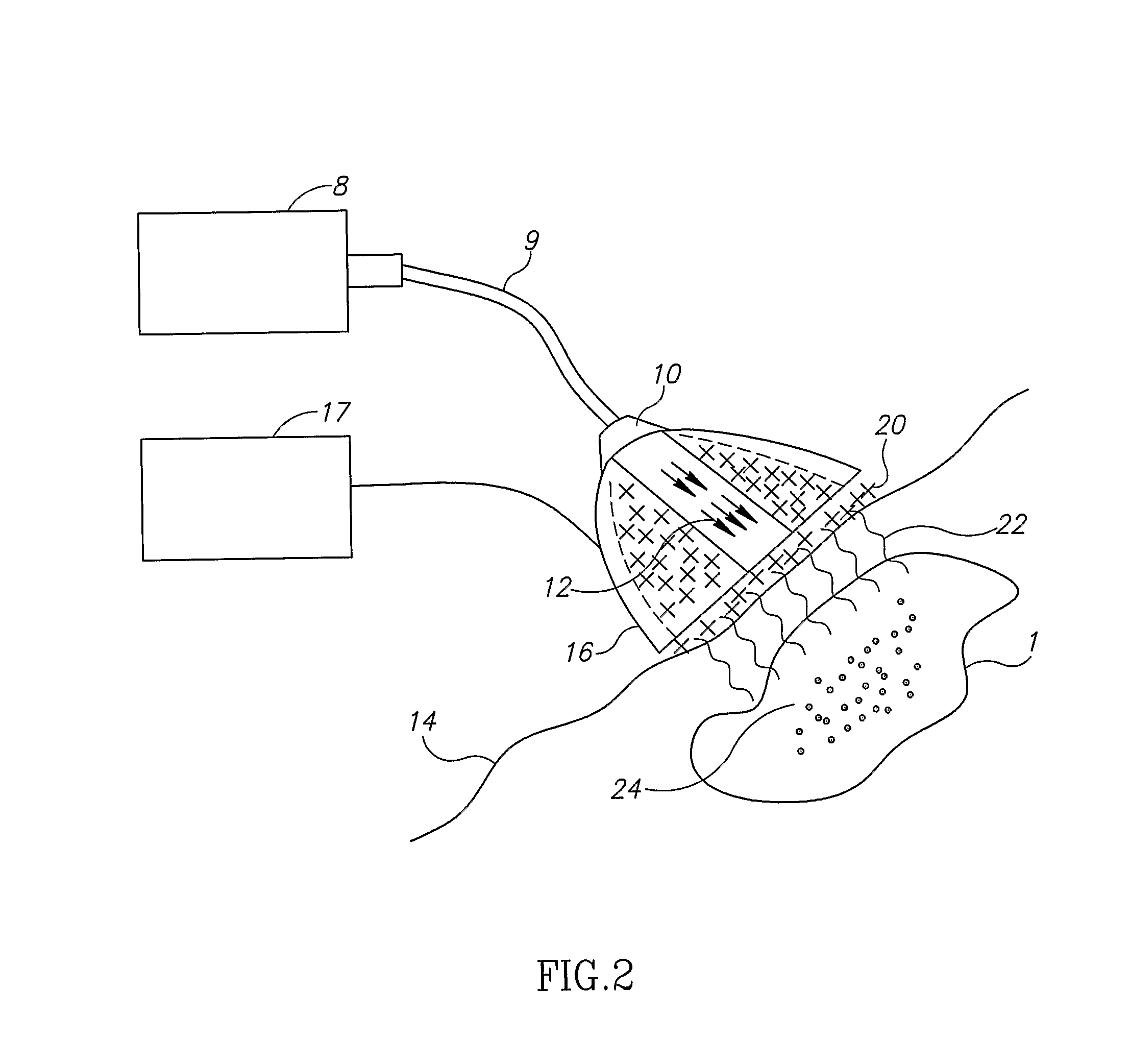
Tool for accurate quantification in molecular MRI
ActiveUS8781197B2Minimize cost functionAccurate imagingCharacter and pattern recognitionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMagnetic sourceMagnetic susceptibility
A method and apparatus is provided for magnetic source magnetic resonance imaging. The method includes collecting energy signals from an object, providing additional information of characteristics of the object, and generating the image of the object from the energy signals and from the additional information such that the image includes a representation of a quantitative estimation of the characteristics, e.g a quantitative estimation of magnetic susceptibility. The additional information may comprise predetermined characteristics of the object, a magnitude image generated from the object, or magnetic signals collected from different relative orientations between the object and the imaging system. The image is generated by an inversion operation based on the collected signals and the additional information. The inversion operation minimizes a cost function obtained by combining the data extracted from the collected signals and the additional information of the object. Additionally, the image is used to detect a number of diagnostic features including microbleeds, contract agents and the like.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Method of generating range images and apparatus therefor
InactiveUS20080106620A1Highly accurate range imageIncrease in size of apparatusTelevision system detailsImage analysisImage generationImage sensor
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Laser scanning digital camera with pupil periphery illumination and potential for multiply scattered light imaging
ActiveUS20100128221A1Imaging is performedIncrease illuminationCharacter and pattern recognitionColor television detailsScattered lightLaser scanning
A portable, lightweight digital imaging device uses a slit scanning arrangement to obtain an image of the eye, in particular the retina. In at least one embodiment, a digital retinal imaging device includes an illumination source operable to produce a source beam, wherein the source beam defines an illumination pathway, a scanning mechanism operable to cause a scanning motion of the illumination pathway in one dimension with respect to a target, an optical element situated within the illumination pathway, the optical element operable to focus the illumination pathway into an illumination slit at a plane conjugate to the target, wherein the illumination slit is slit shaped, a first two dimensional detector array operable to detect illumination returning from the target and acquire one or more data sets from the detected illumination, wherein the returning illumination defines a detection pathway, and a shaping mechanism positioned within the illumination pathway, wherein the shaping mechanism shapes the source beam into at least one arc at a plane conjugate to the pupil. In at least one exemplary embodiment, the digital retinal imaging device is operable to minimize at least one aberration from the optical element or an unwanted reflection from the target or a reflection from a device.
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
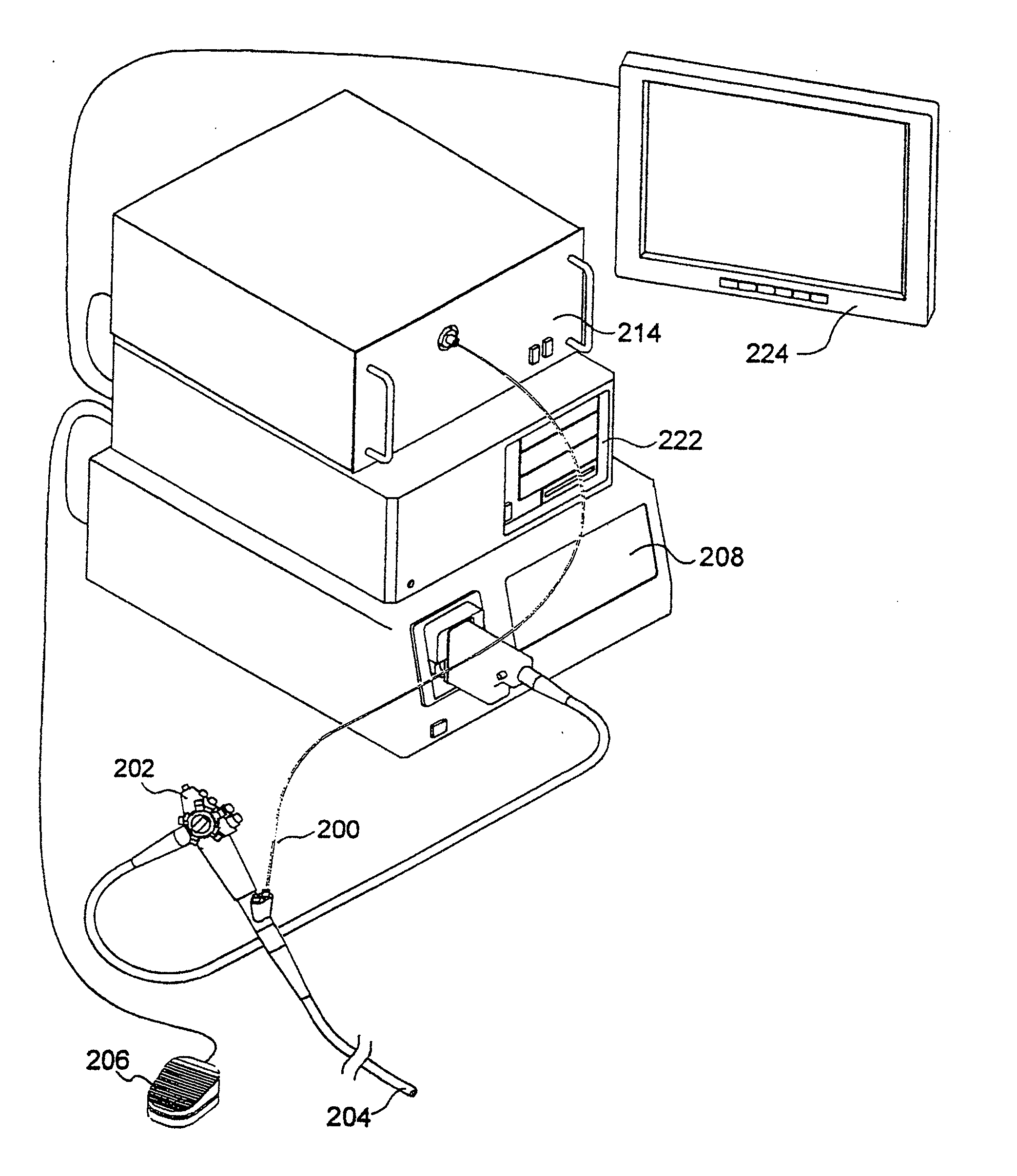
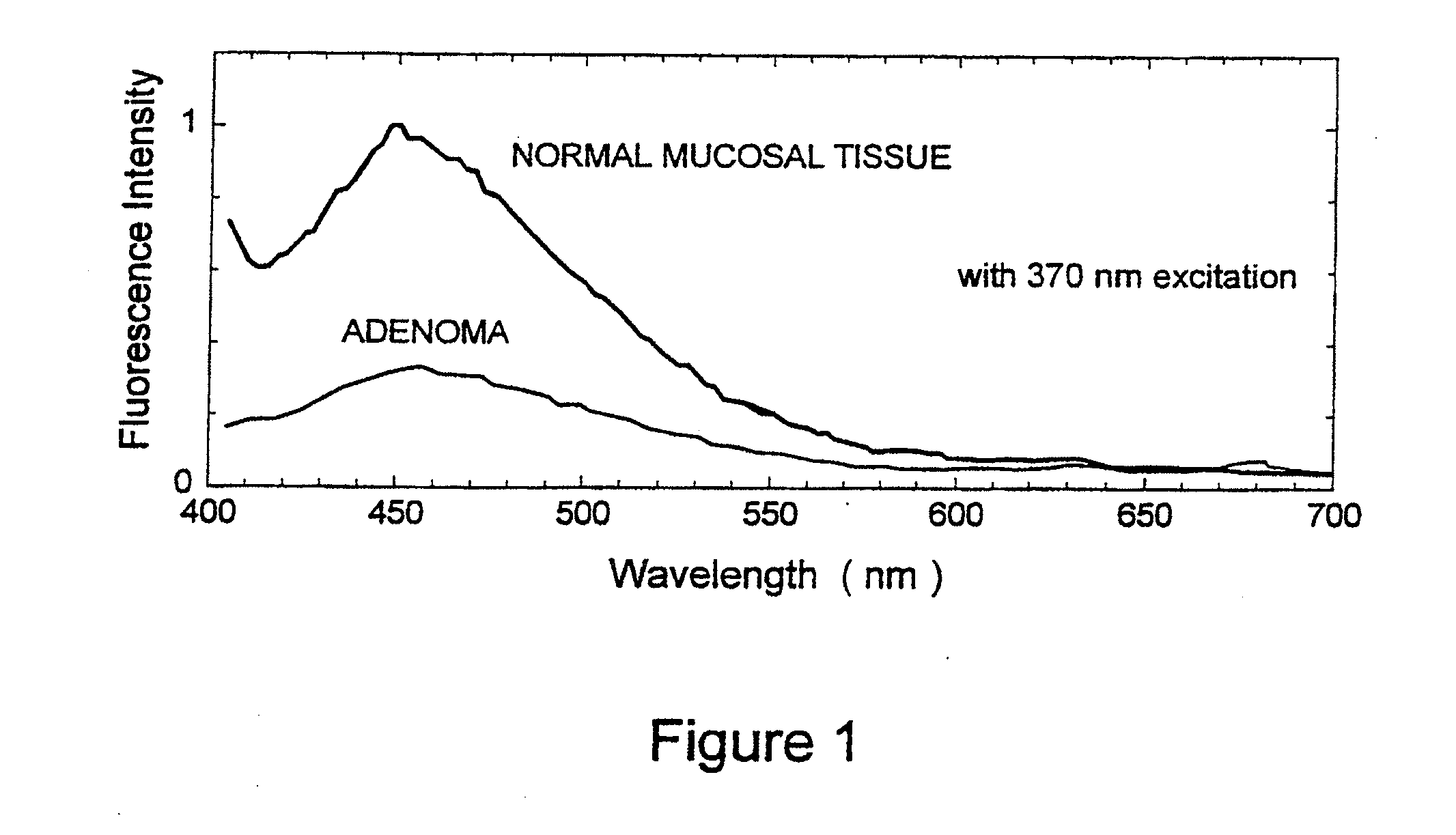
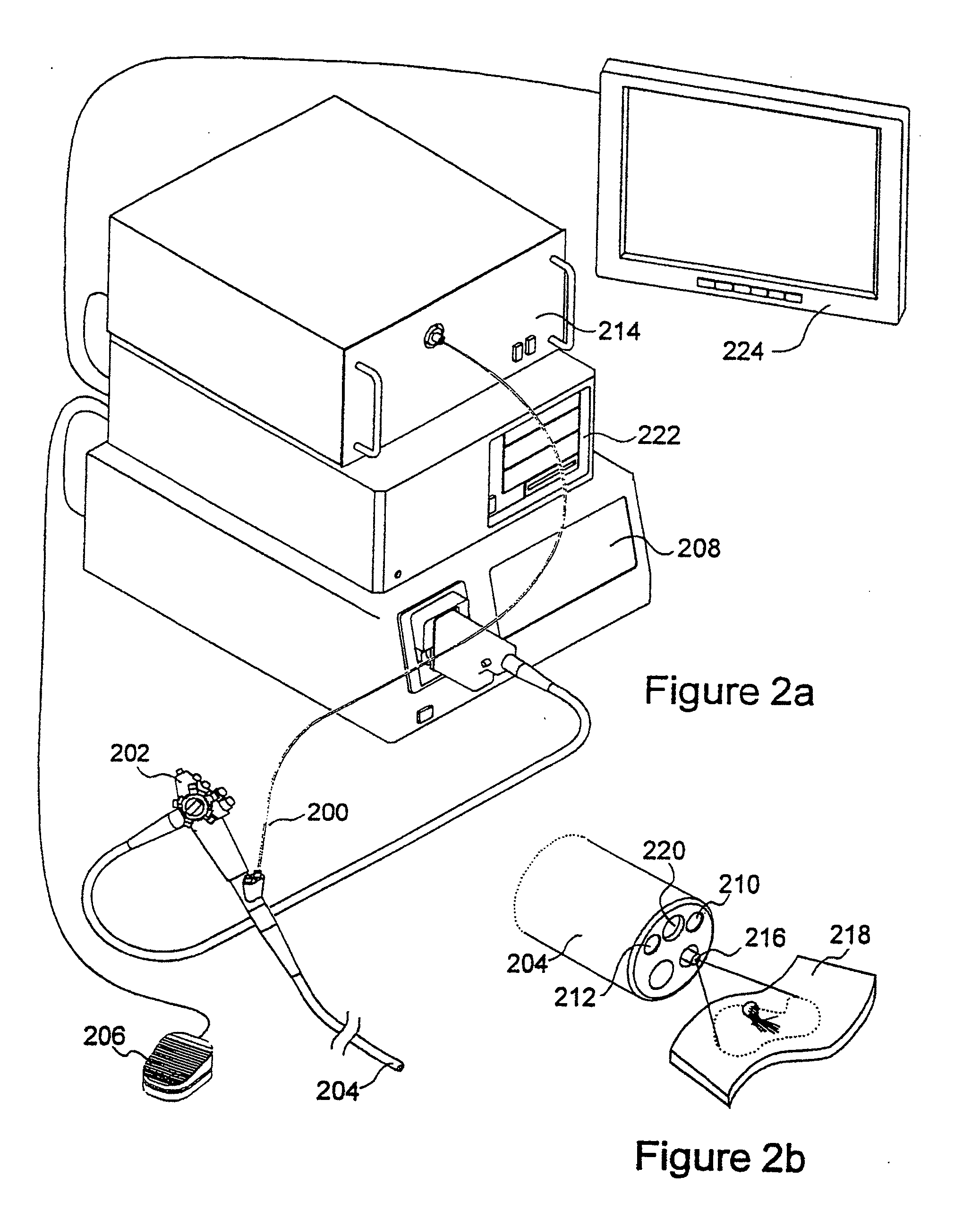
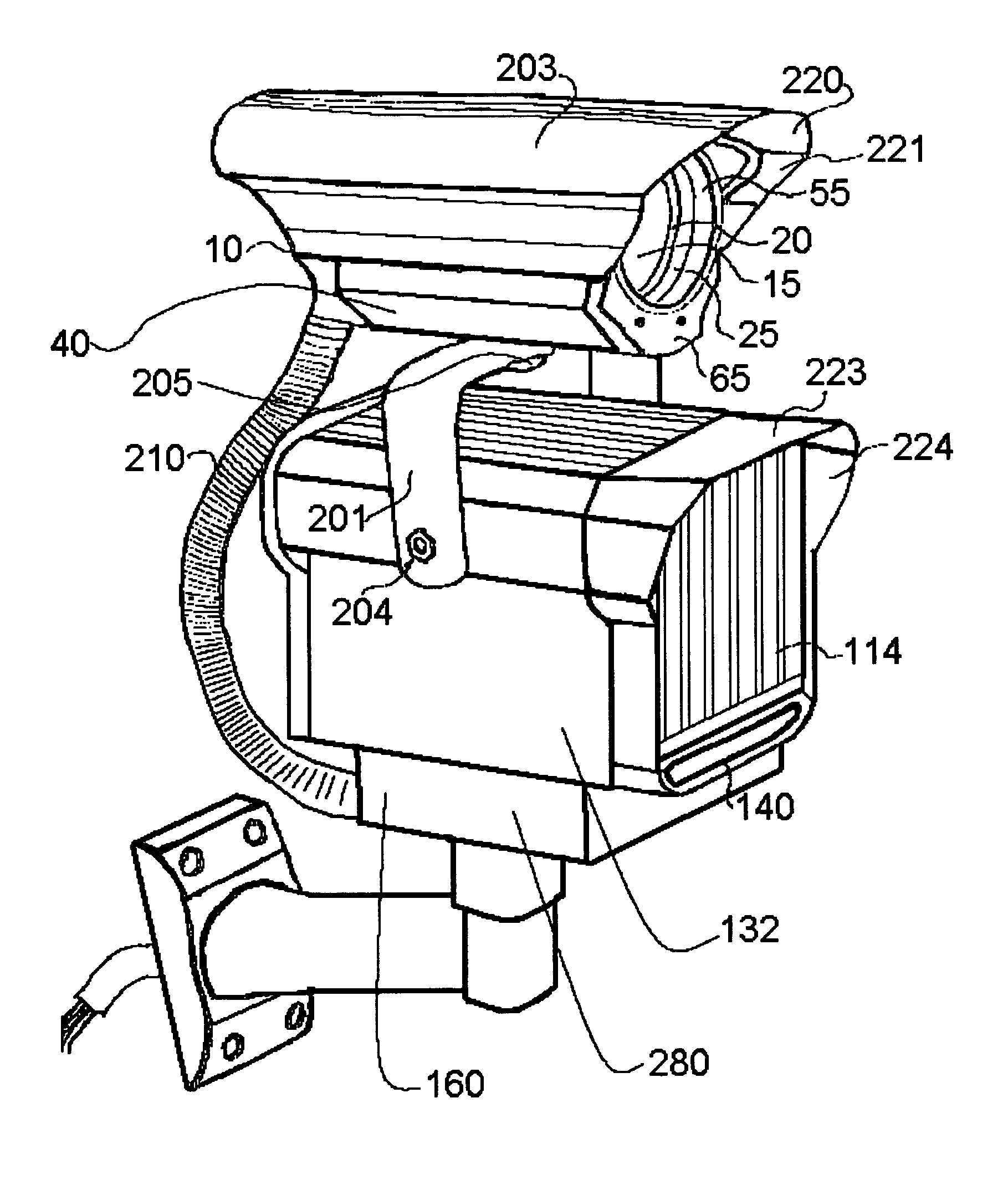
Autofluorescence imaging system for endoscopy
InactiveUS20110213252A1Improve featuresQuantitative precisionSurgeryEndoscopesColor imageUltraviolet lights
A system and method for imaging tissue autofluorescence through a video endoscope is described, comprising a light source capable of providing both ultraviolet light capable of inducing tissue autofluorescence and visible light which induces little or no autofluorescence, an optical system to deliver both wavelength bands to the tissue with the same apparent spatial and angular intensity distribution, a means for digitally acquiring the resulting, visible fluorescence and visible reflectance images using a single imaging detector at the distal tip of the endoscope and a means for digitally processing said images to generate a final, false-color image for display which indicates regions of tissue dysplasia. This system can either be added on to an existing video endoscope or integrated into its structure. The combined system can be electronically switched between normal white light imaging and fluorescence imaging.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Vehicle license plate imaging and reading system for day and night
ActiveUS7016518B2Avoid sensor overload headlightAvoid reflected glareOptical rangefindersRoad vehicles traffic controlLicense numberInfrared
This invention provides an infrared illuminator and camera system for imaging of auto vehicle license plates. The system works in ambient light conditions, ranging from bright sunlight, to dim light, to dark, to zero ambient light. It yields high-contrast imaging of the letters and numbers on retro-reflective license plates. The images of the license letter and number combinations can be read manually by a remote operator. They can be converted to text format with optical character recognition computer hardware and software. The text data can then be compared to data files listing license numbers to provide further data about the owner of a licensed vehicle. A decision can be made quickly about whether to allow a vehicle to proceed through a gate, or whether to take other action. The system uses a mono camera that is enhanced for infrared sensitivity and combined with a high power infrared illuminator to maximize range at night, and with shutter speeds set up to capture clear license plate pictures even with fast moving vehicles and even with their headlights on and interfering with human observation of the license plates. Optical filtering to pass infrared in the range of the illuminator and to reduce light outside this range, combines with a lens set up, to avoid vertical smear and sensor overload caused by headlights at night and by highlight reflected glare from the sun in daytime.
Owner:EXTREME CCTV
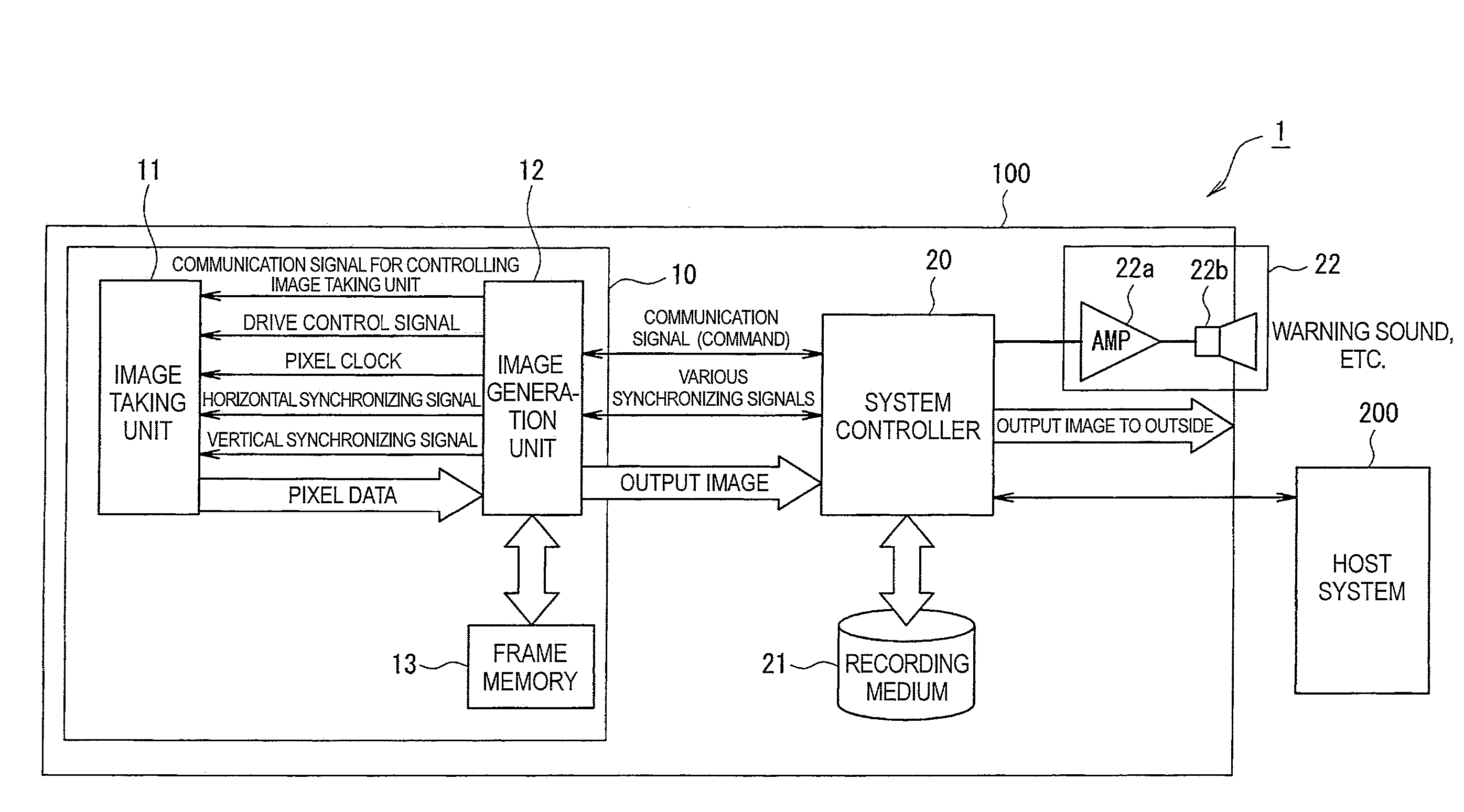
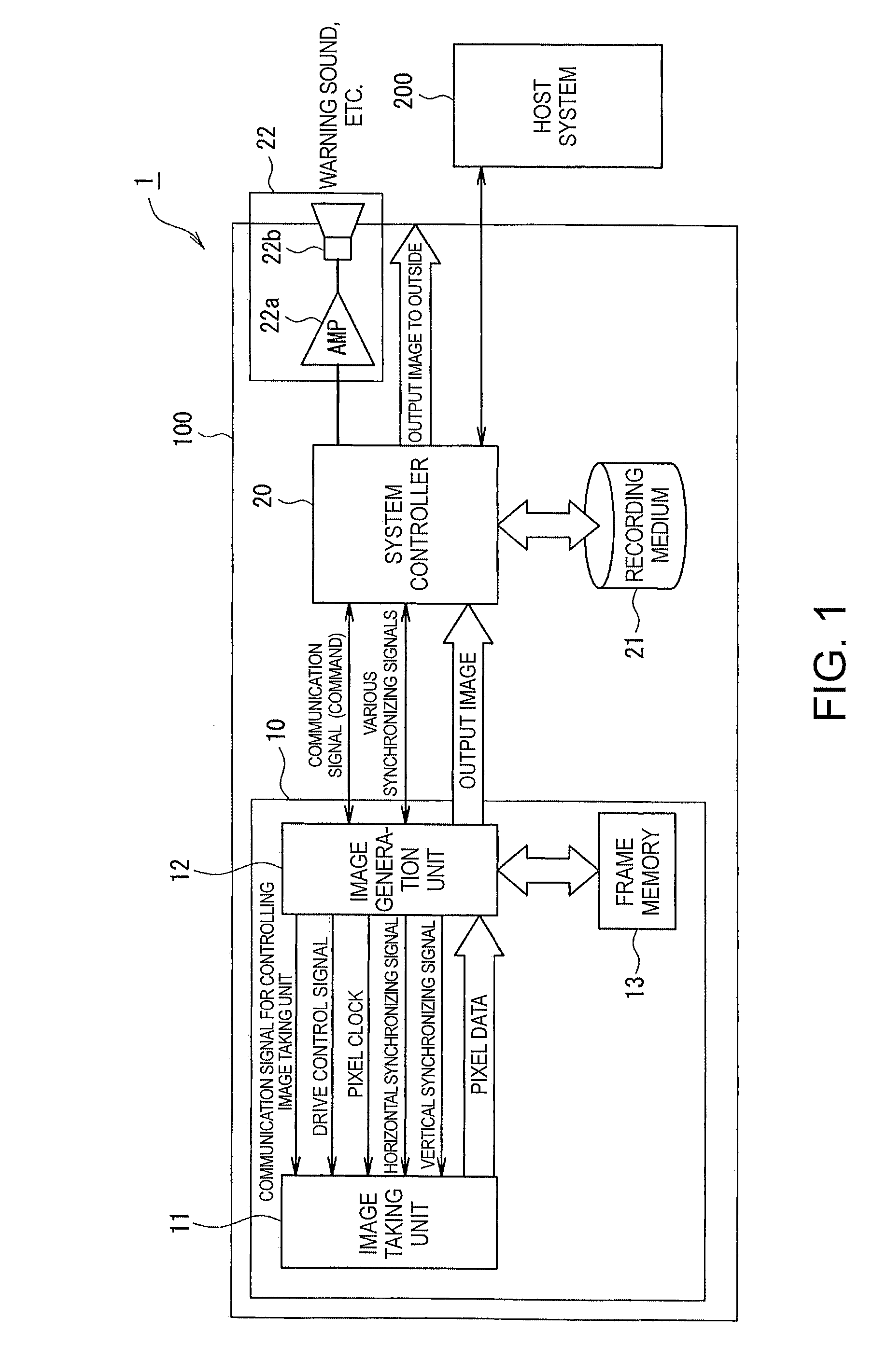
Image taking apparatus and image recorder
InactiveUS20090135271A1Accurately taking imageIncrease probabilityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsEngineeringPhotoelectric conversion
An image taking apparatus includes: a photoelectric conversion unit including a plurality of photoelectric conversion elements, the photoelectric conversion elements disposed in a two-dimensional matrix, the photoelectric conversion elements converting received light into electric charge and accumulating the electric charge; an image sensor having a function of controlling an exposure time of each of the photoelectric conversion elements of the photoelectric conversion unit on a line-by-line basis; an area division unit for logically dividing the photoelectric conversion unit into an N number of uniform areas on the basis of information related to a taken image of a subject, each of the uniform areas including a line having some of the photoelectric conversion elements, N being a natural number of two or more; an interlaced scanning unit for scanning the photoelectric conversion elements in the first to N-th areas by M lines starting with a predetermined line in a predetermined area of the first to N-th areas while changing an area to be scanned to another area in a predetermined order each time the M lines are scanned, M being a natural number of one or more; and a pixel signal reading unit for reading, from each of the photoelectric conversion elements scanned by the interlaced scanning unit, a pixel signal including an electric signal corresponding to an amount of electric charge accumulated in each photoelectric conversion element.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Video endoscope with a rotatable video camera
A video endoscope includes a tube fitted at its distal end with an affixed objective lens, a video camera mounted behind the objective lens in the tube, the camera together with an elongated rotation element constituting a swivel unit that is supported both at the distal and proximal end zones in each case by swivel bearing at the tube. The swivel element being rotationally adjustable relative the tube by a swivel drive system. The distal swivel bearing is axially and radially bearing and the proximal swivel bearing is only radially bearing.
Owner:OLYMPUS WINTER & IBE
Method and apparatus for fingerprint image reconstruction
ActiveUS8131026B2Improve accuracyImprove precisionElectric signal transmission systemsImage analysisMissing dataImaging analysis
Enhanced accuracy finger position and motion sensors devices, algorithms, and methods are disclosed that can be used in a variety of different applications. The sensors can be used in conjunction with partial fingerprint imagers to produce improved fingerprint scanners. Such improved scanners can use image analysis techniques, such as interpolation between partial fingerprint images to correct for missing data, or discarding redundant partial fingerprint image data, to produce adequate fingerprint images even when the finger has not been applied to the sensor using an optimum technique.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
Method of manufacture and the use of a functional proppant for determination of subterranean fracture geometries
ActiveUS8168570B2Accurate imagingPromote recoveryElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial nanotechnologyGeophoneElectricity
Proppants having added functional properties are provided, as are methods that use the proppants to track and trace the characteristics of a fracture in a geologic formation. Information obtained by the methods can be used to design a fracturing job, to increase conductivity in the fracture, and to enhance oil and gas recovery from the geologic formation. The functionalized proppants can be detected by a variety of methods utilizing, for example, an airborne magnetometer survey, ground penetrating radar, a high resolution accelerometer, a geophone, nuclear magnetic resonance, ultra-sound, impedance measurements, piezoelectric activity, radioactivity, and the like. Methods of mapping a subterranean formation are also provided and use the functionalized proppants to detect characteristics of the formation.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Methods and systems for intensity matching of a plurality of radiographic images
ActiveUS20050213849A1Smooth transitionImprove visualizationImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersComputer scienceBrightness perception
Methods and systems for intensity / brightness matching of a plurality of radiographic images. Software can be used to provide various stitching and blending methods to join first and second images into a composite, larger image before or after the intensity / brightness of the radiographic images are modified.
Owner:MERATIVE US LP
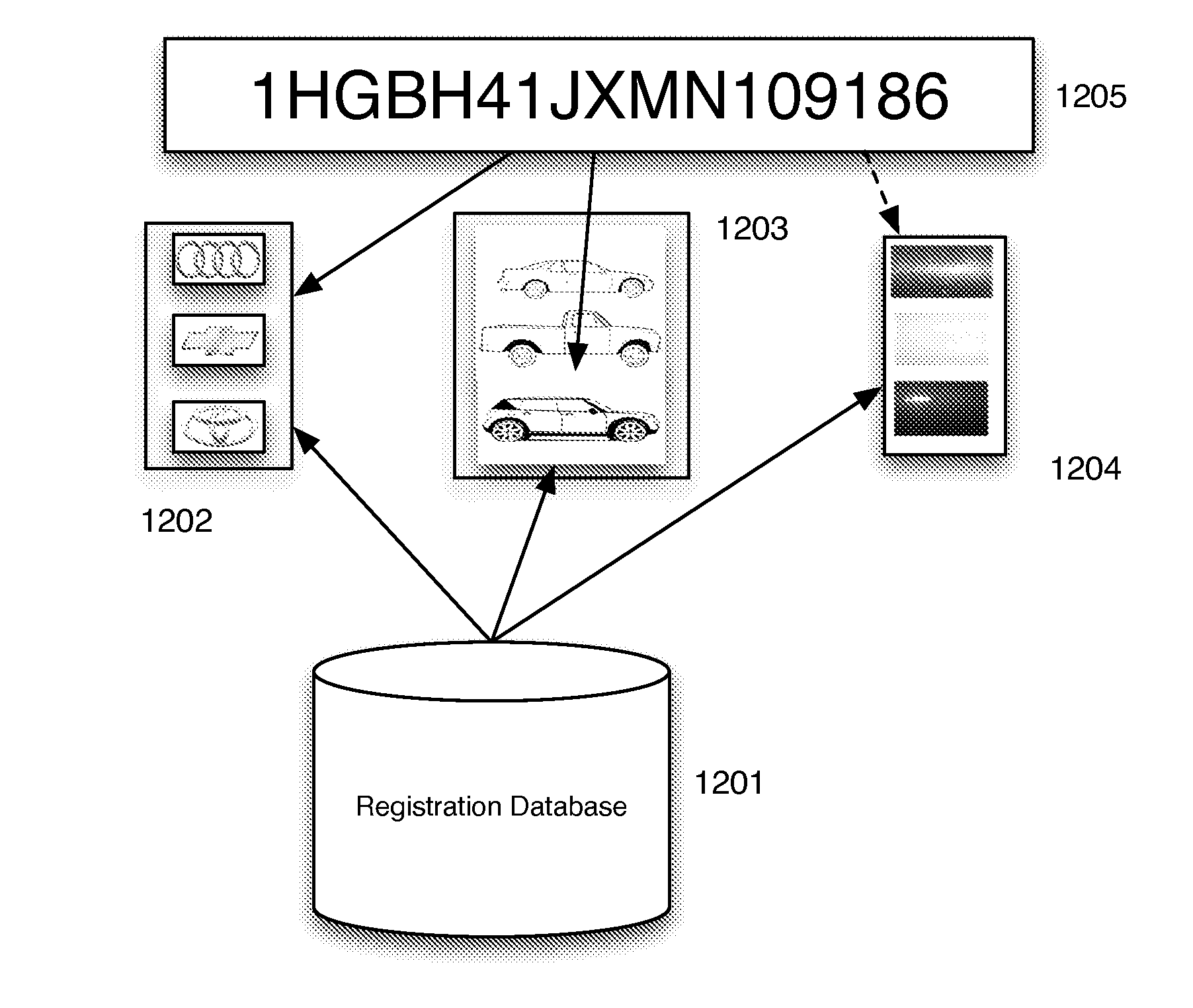
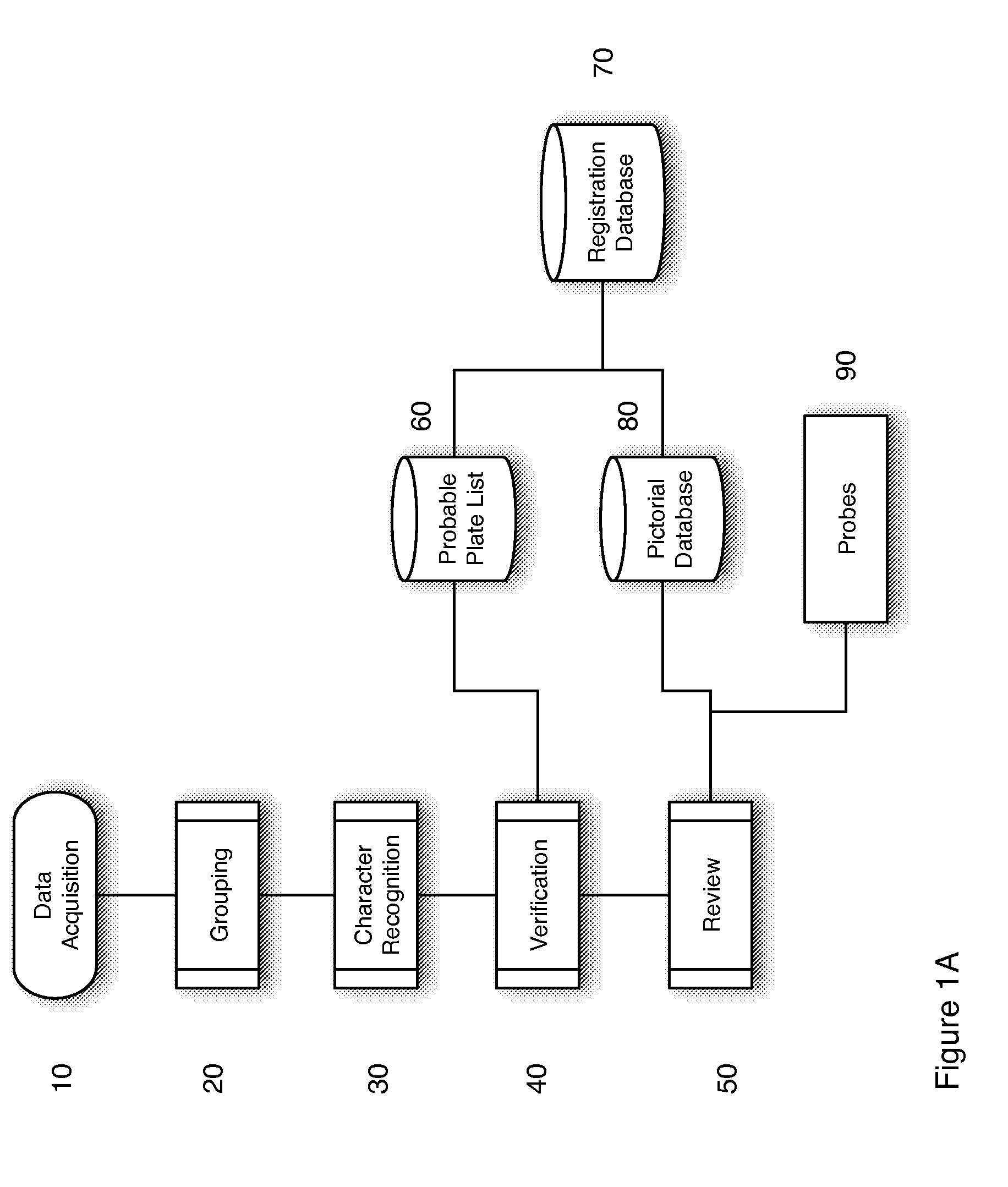
License Plate Recognition
ActiveUS20150049914A1Improve recognition resultsMake up for deficienciesCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionComputer science
A license plate recognition and image review system and processes are described. The system includes grouping of images that are determined to be of the same vehicle, using an image encoded database such that verification of a license plate read is done through comparison of images of the actual vehicle to images from the encoded database and testing of the accuracy of a manual review process by interspersing previously identified images with real images being reviewed in a batch process.
Owner:ALVES JAMES
Echogenic devices and methods of making and using such devices
InactiveUS7014610B2Improve propertiesHigh practical echogenicityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPreparing sample for investigationPorous particleMedical device
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Context aware user interface for image editing
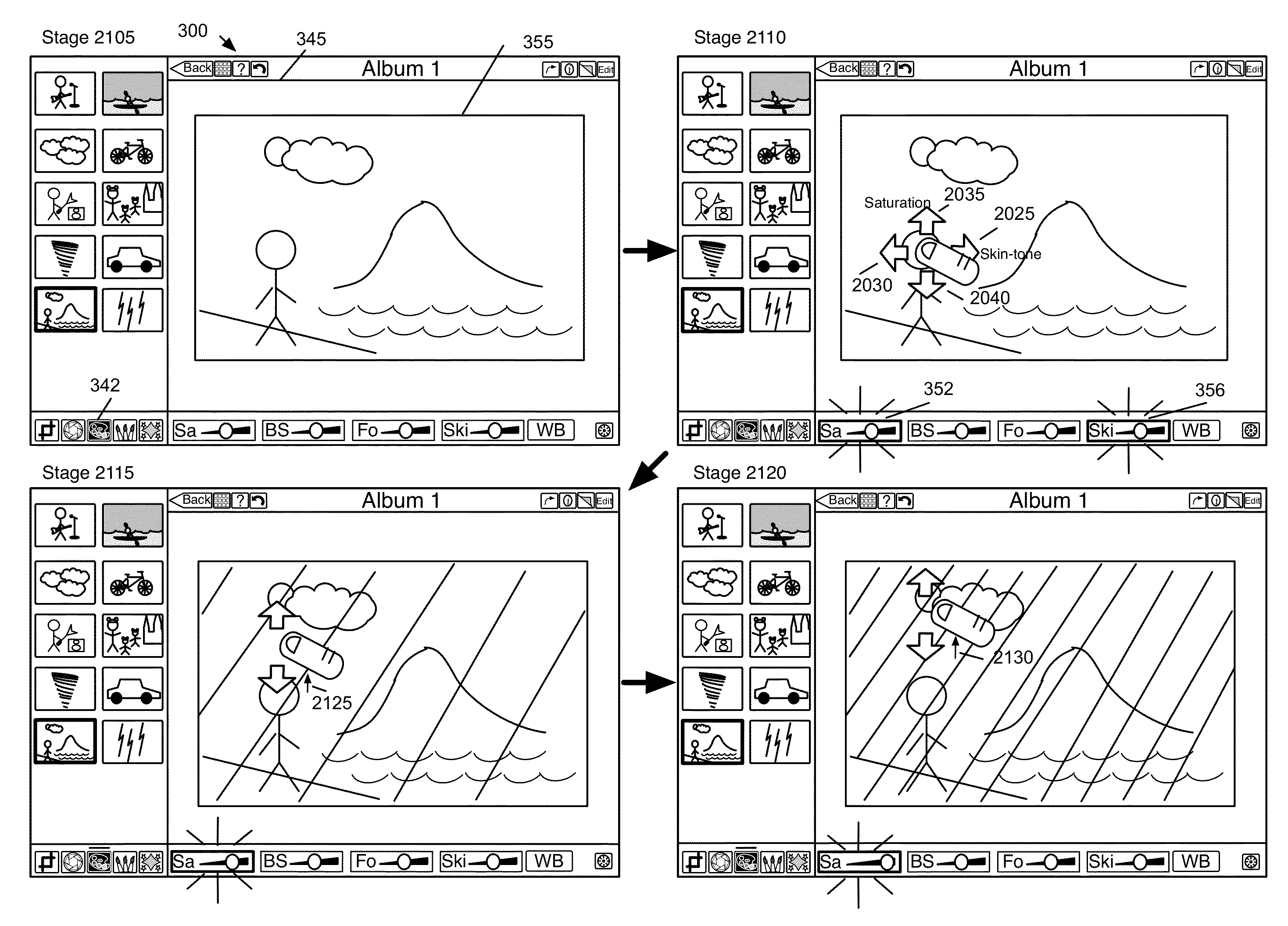
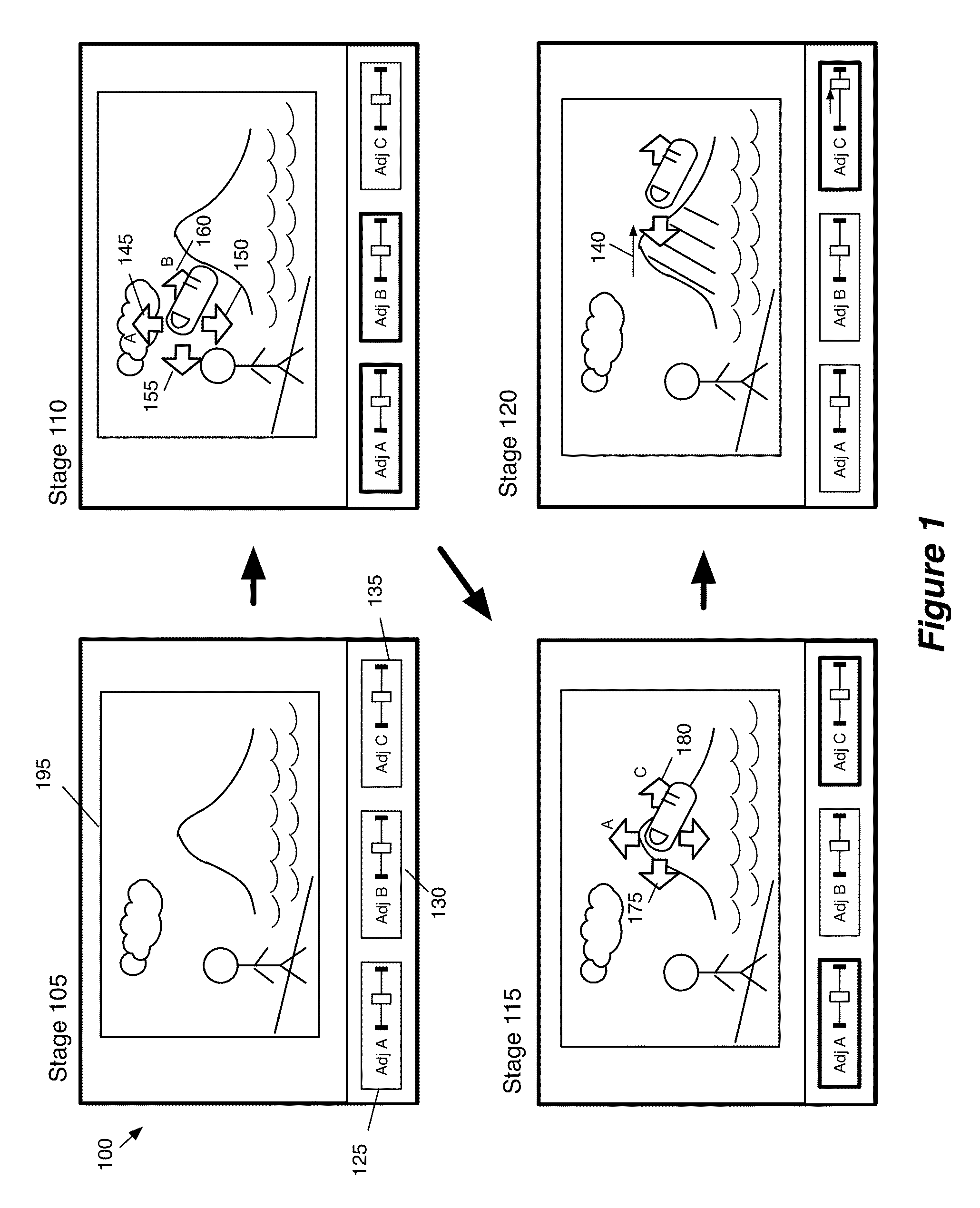
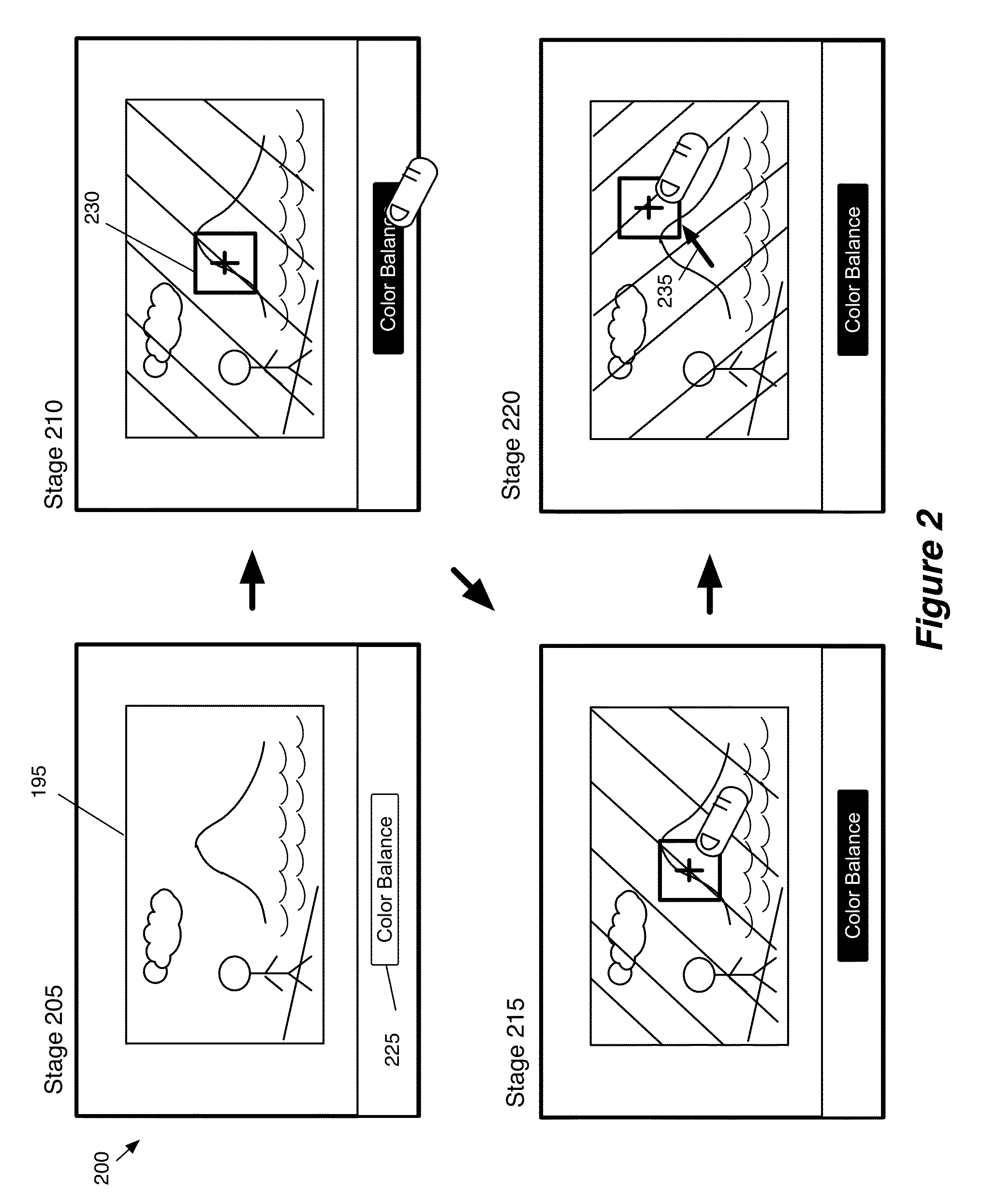
ActiveUS20130235069A1Adjust color balanceAccurate imagingTexturing/coloringCathode-ray tube indicatorsUser interfaceComputer program
A non-transitory machine readable medium that a computer program for performing a color balance operation on color values of an image represented in a color space is described. The computer program receives a selection of a location on the image that includes several pixels. Each of the several pixels of the image includes a set of color values. Based on a set of color values of a set of pixels that corresponds to the selected location of the image, the computer program identifies a set of parameters for generating a color space transform that modifies the color space. The computer program then uses the color space transform to perform a color balance operation on the image.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method and apparatus to correct distortion of document copies
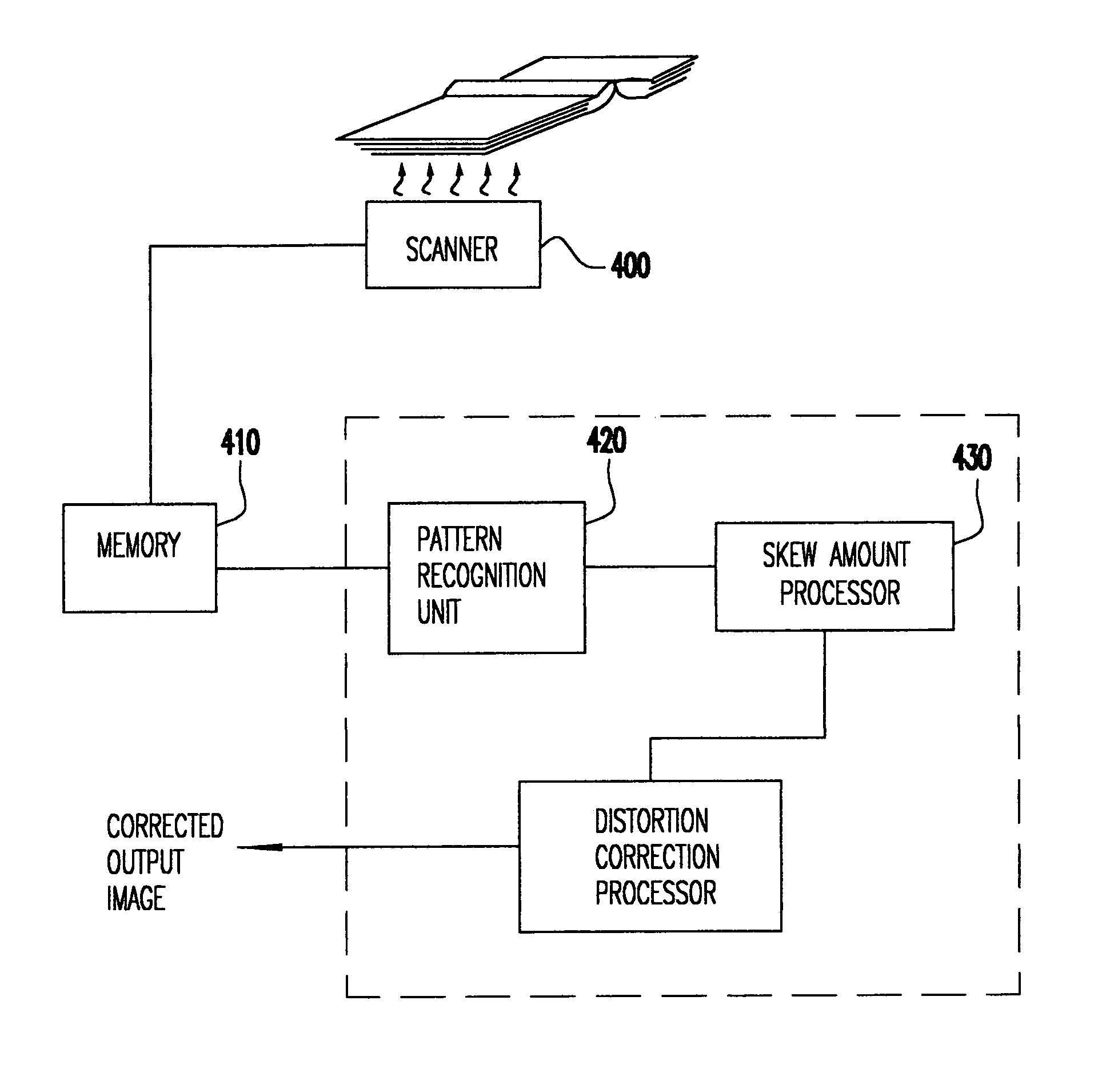
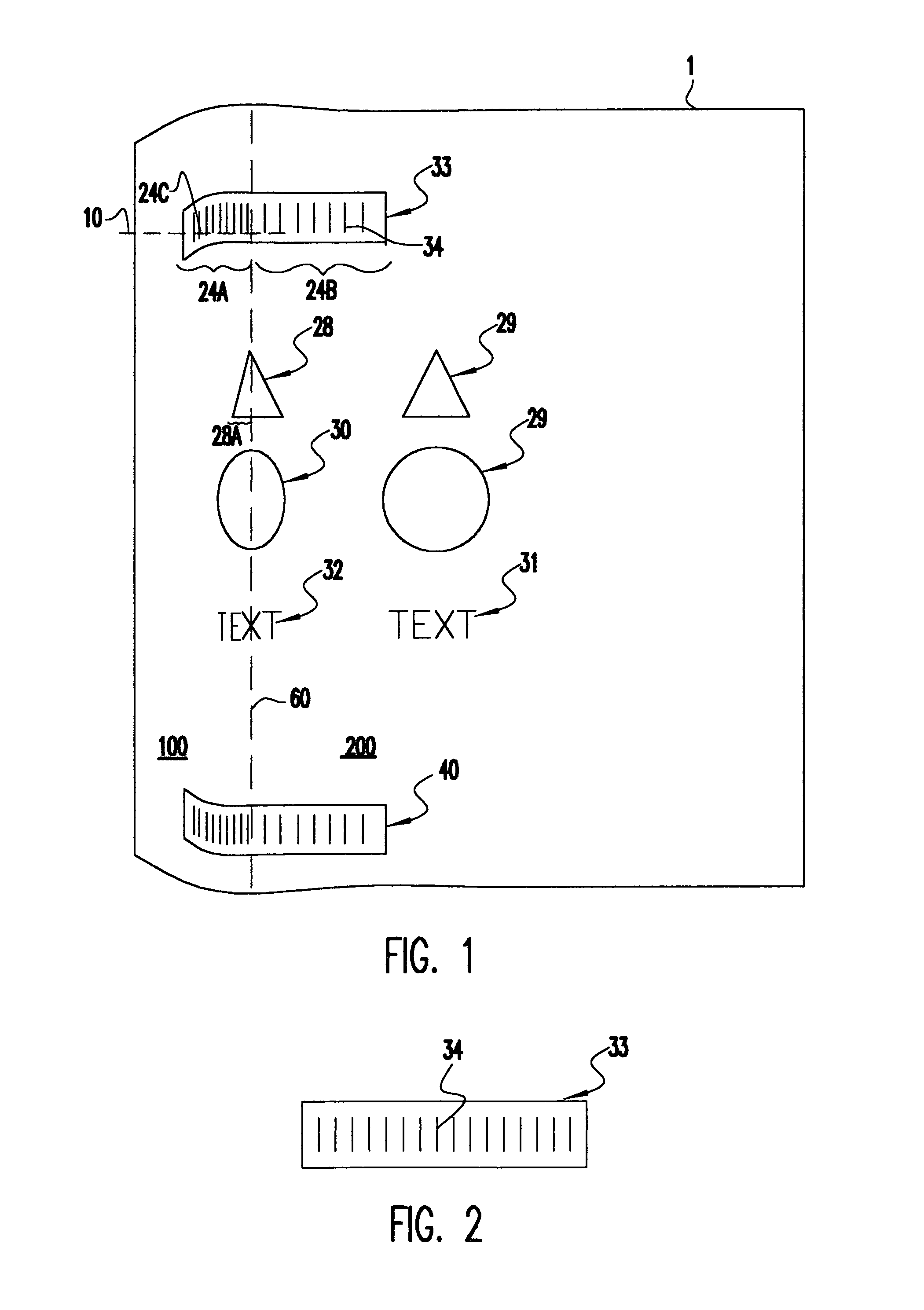
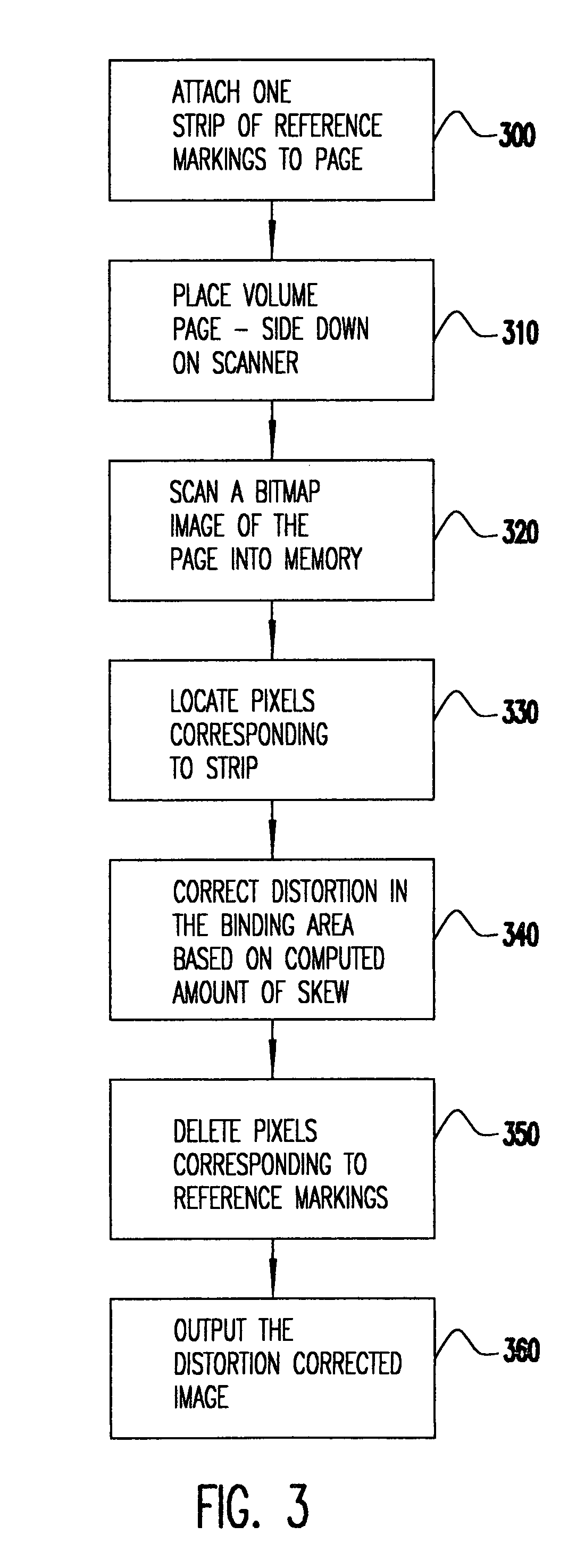
InactiveUS6954290B1Easy to separateGood adhesionImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionDocumentationComputer science
Pages of books are copied without distortion due to curvature of the page near the book binding or the distortion in a copied page is corrected using the spacing of equidistant bars on tape strips applied to the top and bottom edges of a page before copying. The tape is preferably transparent and rather narrow and easily attached to a page to be copied. The first step in the distortion correction procedure is to locate the bars at the top and bottom of the page. The distortion of the spacing between the imaged bars is computed based on the known distance between the equidistant bars. The computed distortion of the spacing is then input to a distortion correction algorithm. The output of the distortion correction algorithm generates a corrected image. This image may also optionally delete the bars so that they are not printed in the copy. The corrected image is then copied.
Owner:IBM CORP
Real image forming eye examination lens utilizing two reflecting surfaces providing upright image
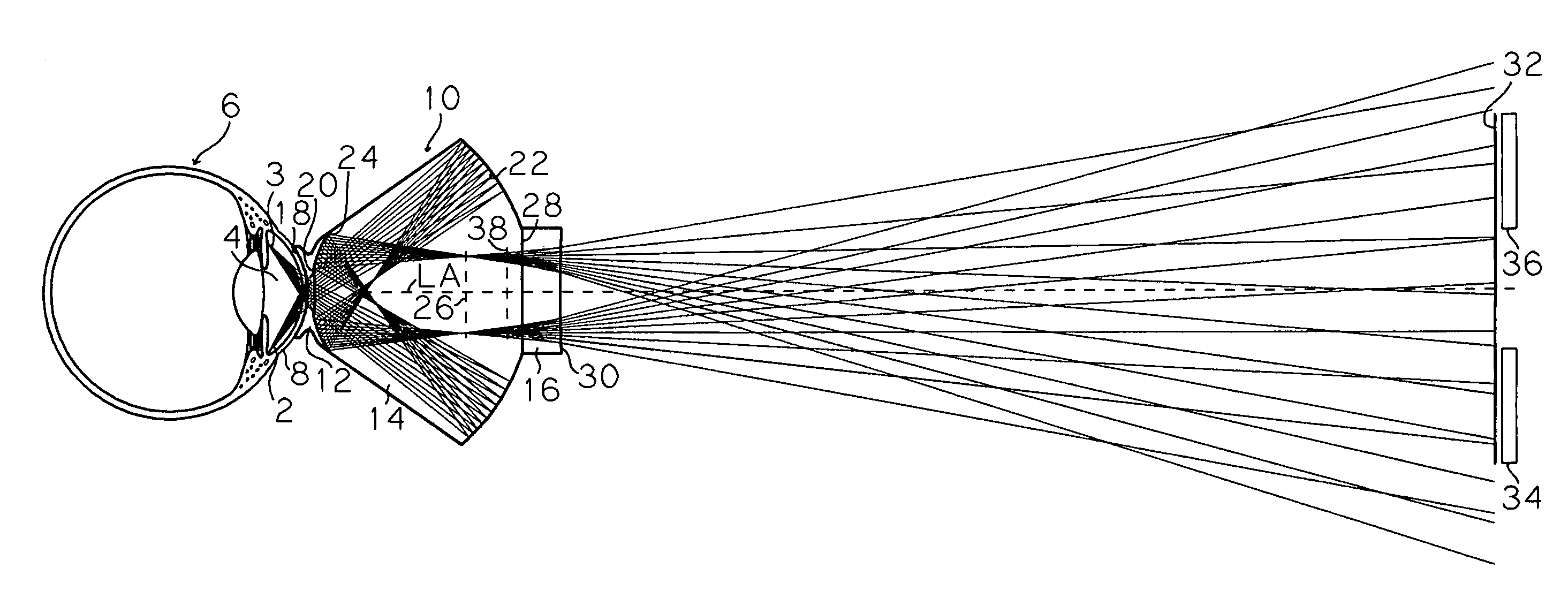
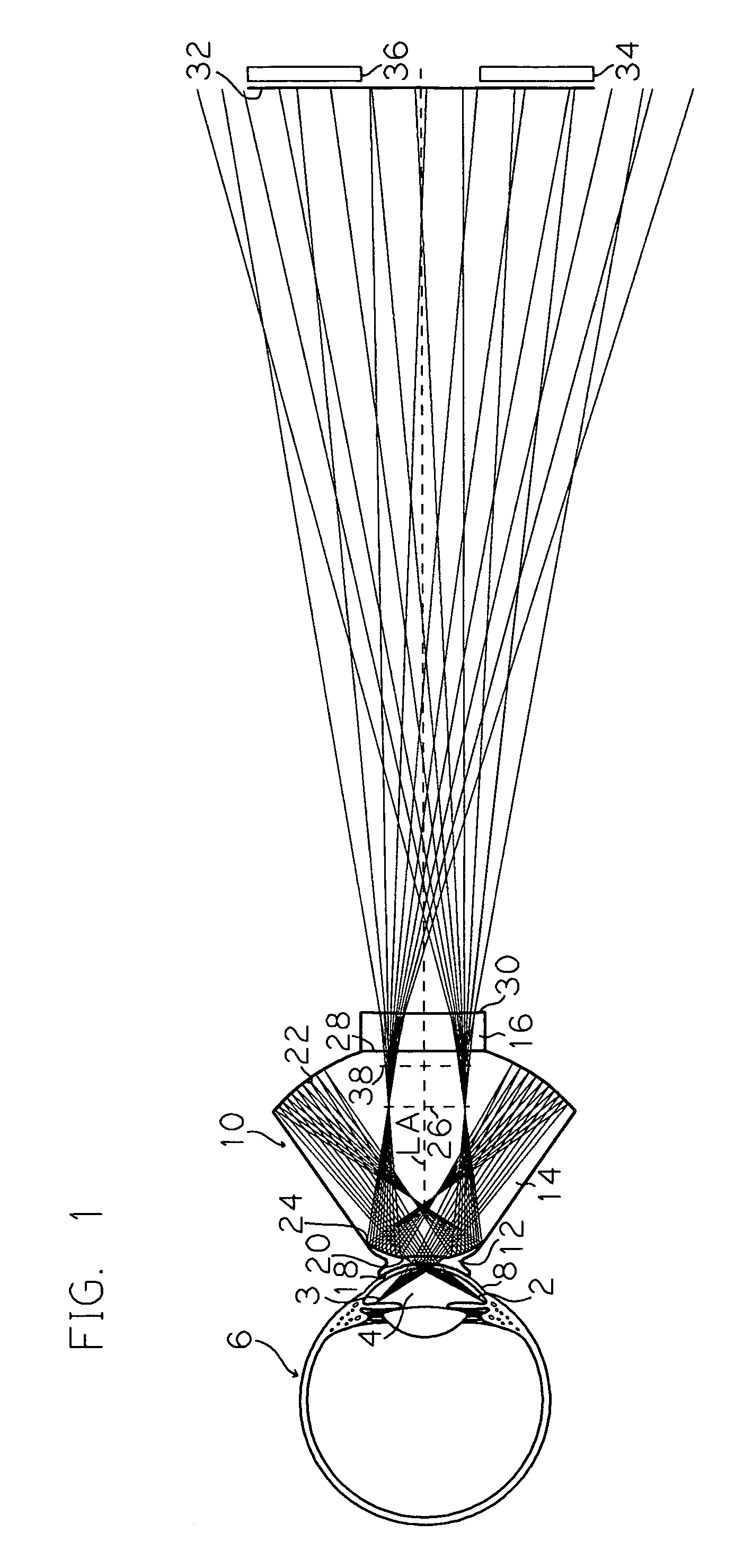
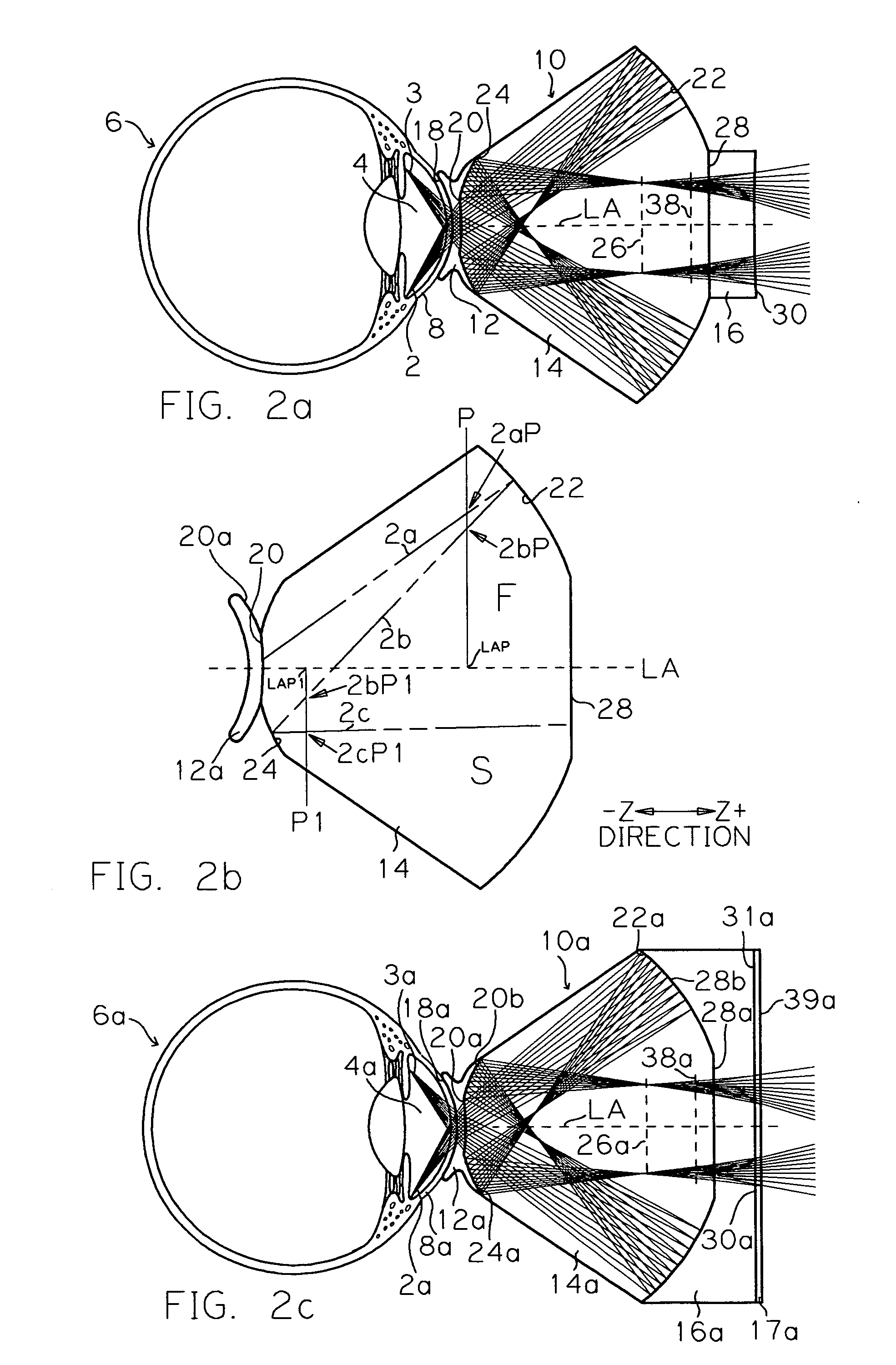
InactiveUS20090185135A1Excellent optical propertiesPrecise positioningOptical articlesEye treatmentEye examinationEye structure
A diagnostic and therapeutic contact lens is provided for use with biomicroscopes for the examination and treatment of structures of the eye. The lens comprises a contacting surface adapted for placement on the cornea of an eye, two reflecting surfaces, and a refracting surface. A light ray emanating from the structure of the eye enters the lens and contributes to the formation of a correctly oriented real image. The light ray is reflected in an ordered sequence of reflections, first as a negative reflection in a posterior direction from an anterior reflecting surface and next as a positive reflection in an anterior direction from a posterior reflecting surface. The light ray contributes to forming the image of the structure of the eye either anterior to the lens or within the lens and proceeds along a pathway to the objective lens of the biomicroscope used for stereoscopic viewing and image scanning.
Owner:VOLK DONALD A
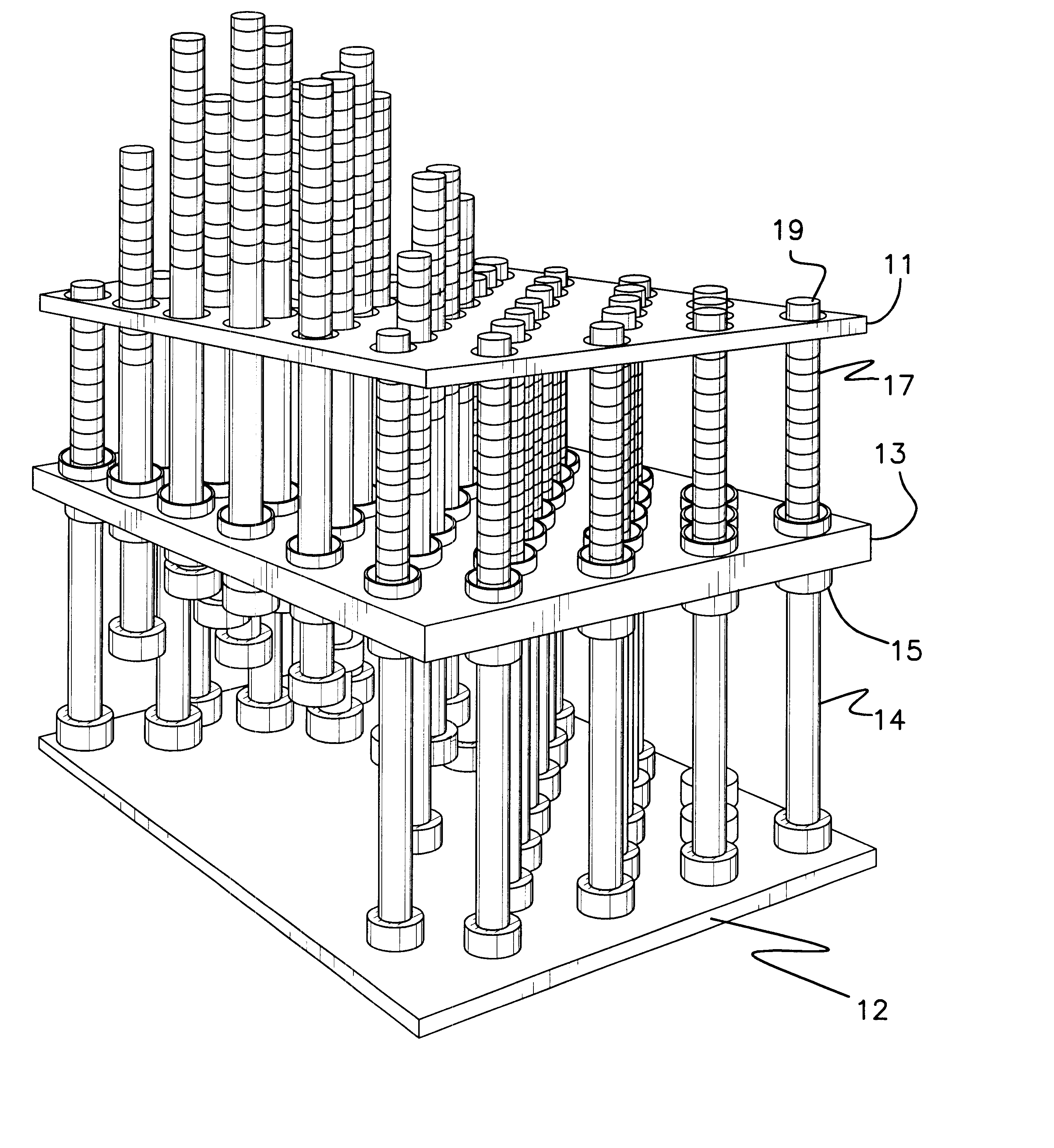
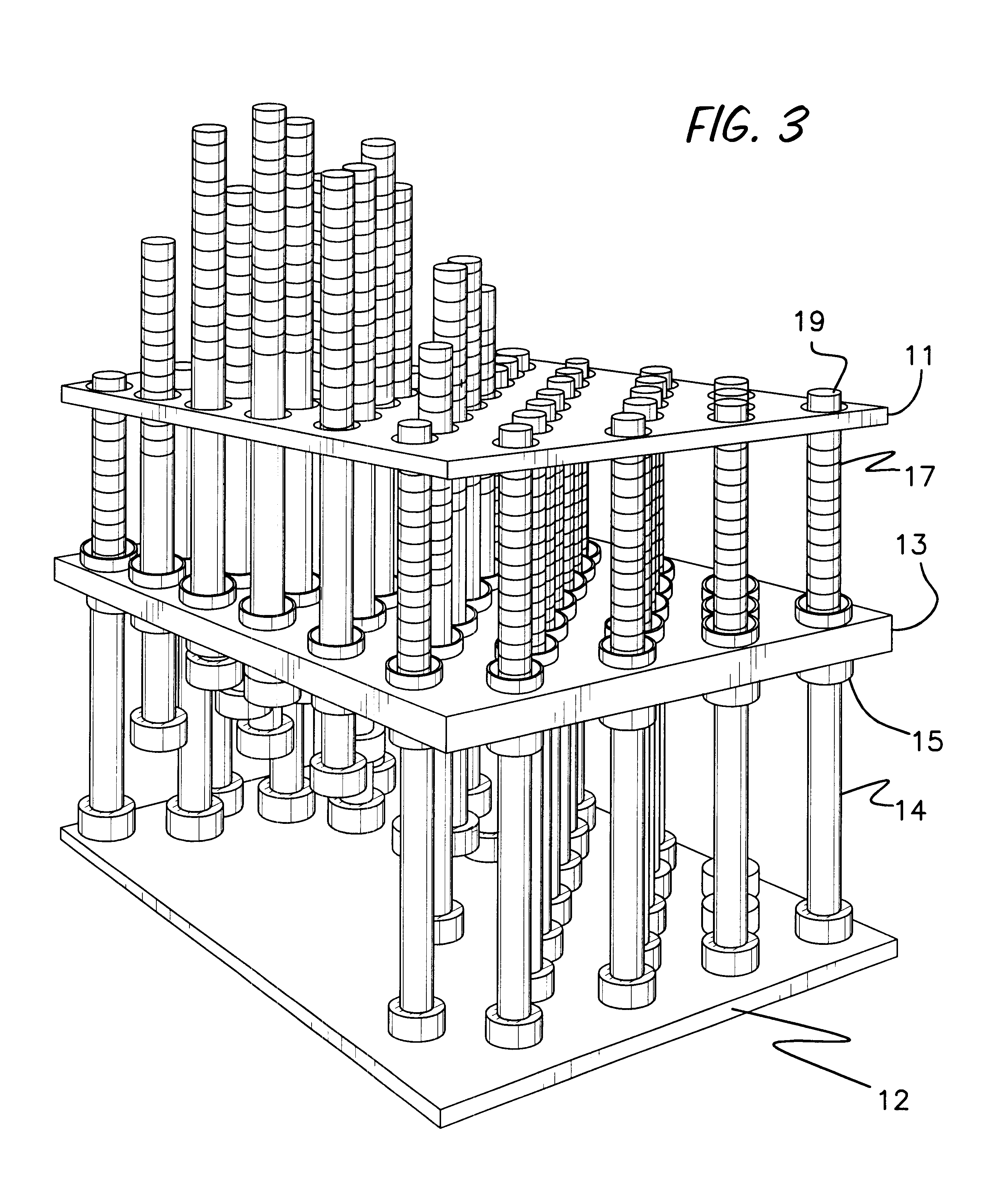
Three dimensional monitor and tactile scanner
InactiveUS6462840B1Accurate imagingImprove responseCharacter and pattern recognitionSteroscopic systemsComputer graphics (images)Effect light
A three-dimensional display system including a method of operating the display as a tactile scanner. A three dimensional display is formed from a number of moveable rods arranged in a matrix. Each rod has selectively illuminated pixels made from LEDs or similar devices. The rods can be moved independent to position the pixels into position to model a pre-defined object to present a three-dimensional model and overlaying image. The pixels can also be illuminated by an external lighting source such as a laser. Stationary embodiments of the monitor are also disclosed which are formed of a three dimensional grid of LEDs or other light sources which can be selectively illuminated to provide a true three dimensional display.
Owner:KRAVTSOV GRIGORY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com