Patents
Literature
44 results about "High-content screening" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
High-content screening (HCS), also known as high-content analysis (HCA) or cellomics, is a method that is used in biological research and drug discovery to identify substances such as small molecules, peptides, or RNAi that alter the phenotype of a cell in a desired manner. Hence high content screening is a type of phenotypic screen conducted in cells involving the analysis of whole cells or components of cells with simultaneous readout of several parameters. HCS is related to high-throughput screening (HTS), in which thousands of compounds are tested in parallel for their activity in one or more biological assays, but involves assays of more complex cellular phenotypes as outputs. Phenotypic changes may include increases or decreases in the production of cellular products such as proteins and/or changes in the morphology (visual appearance) of the cell. Hence HCA typically involves automated microscopy and image analysis. Unlike high-content analysis, high-content screening implies a level of throughput which is why the term "screening" differentiates HCS from HCA, which may be high in content but low in throughput.
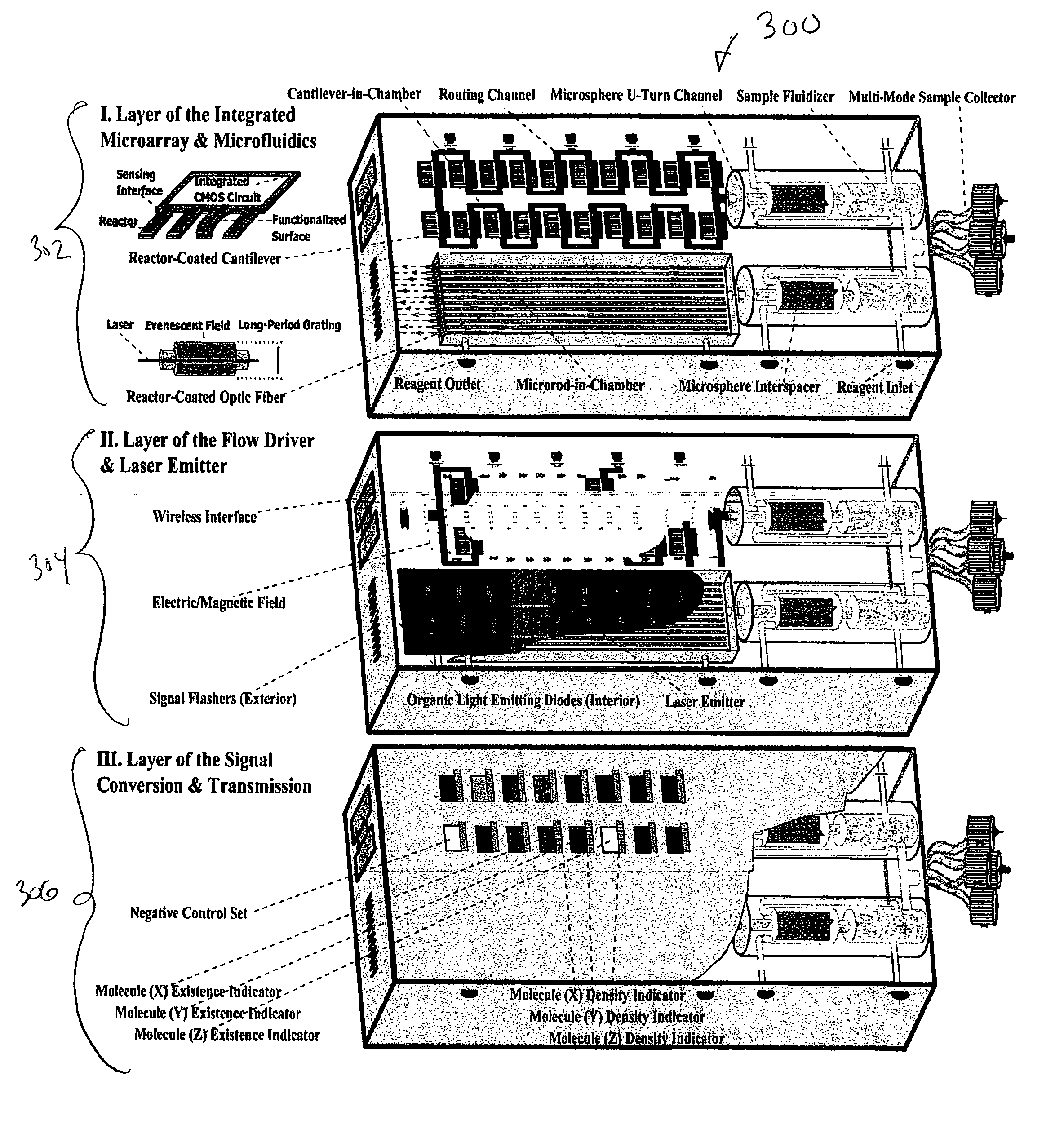
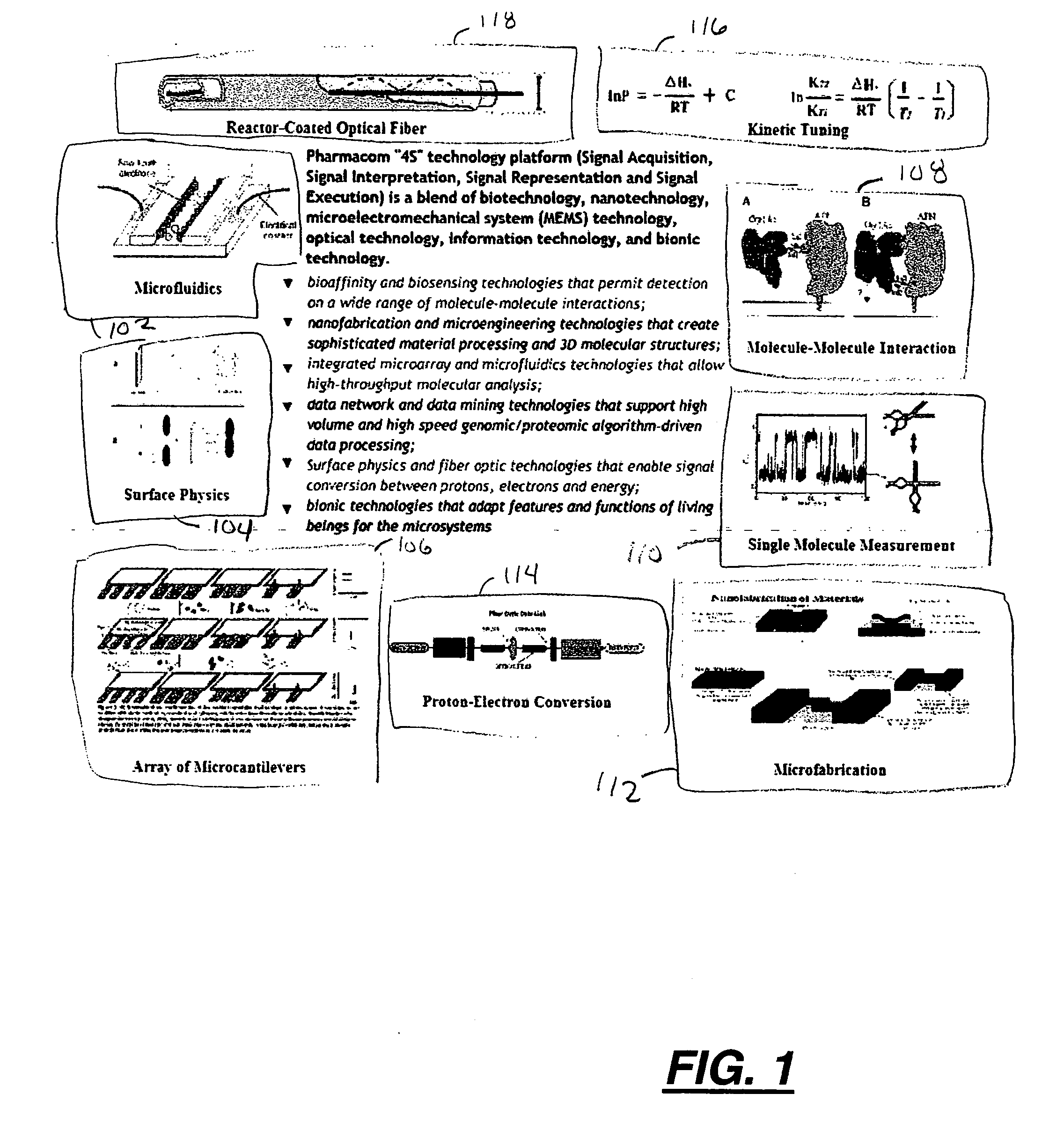
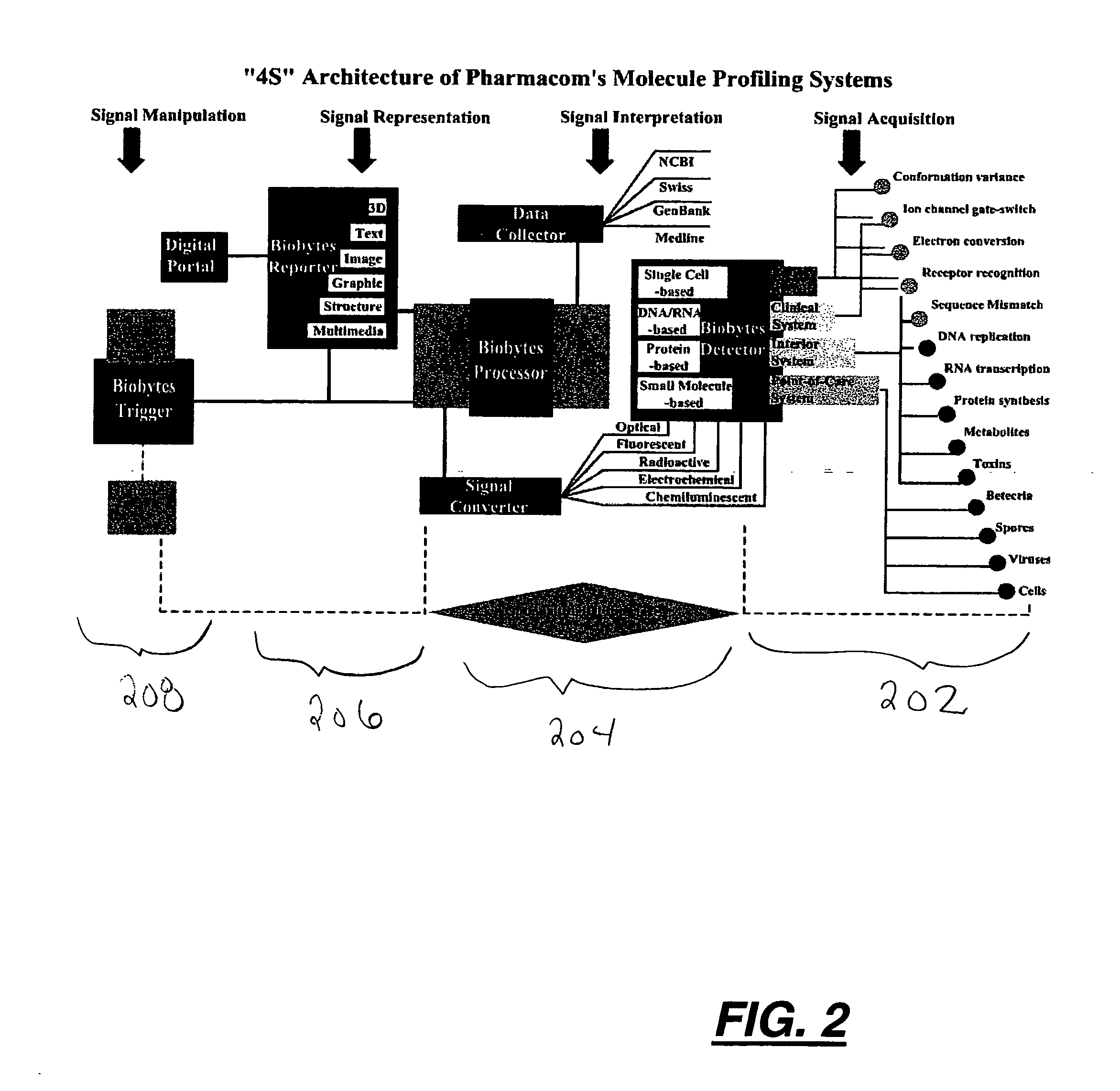
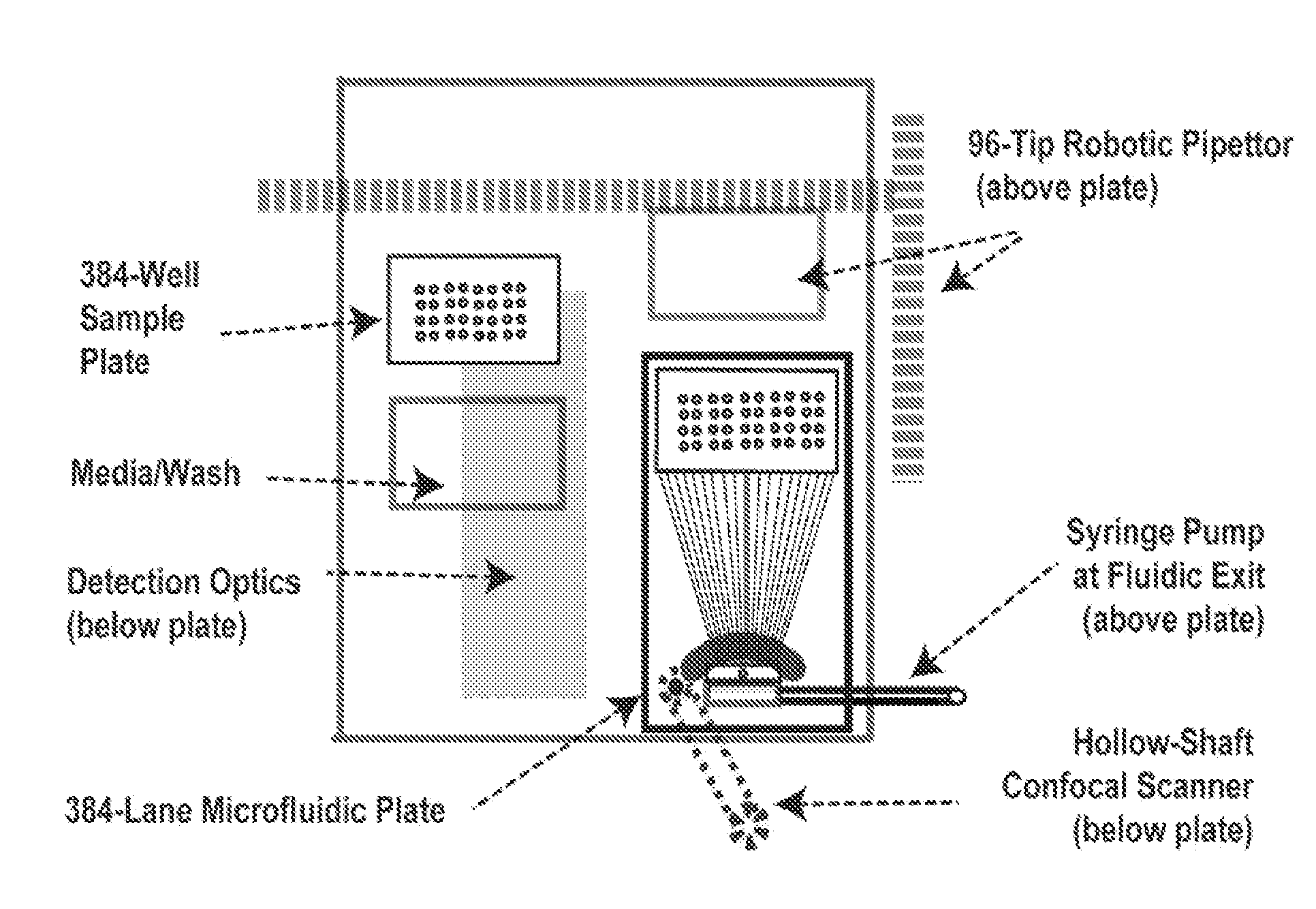
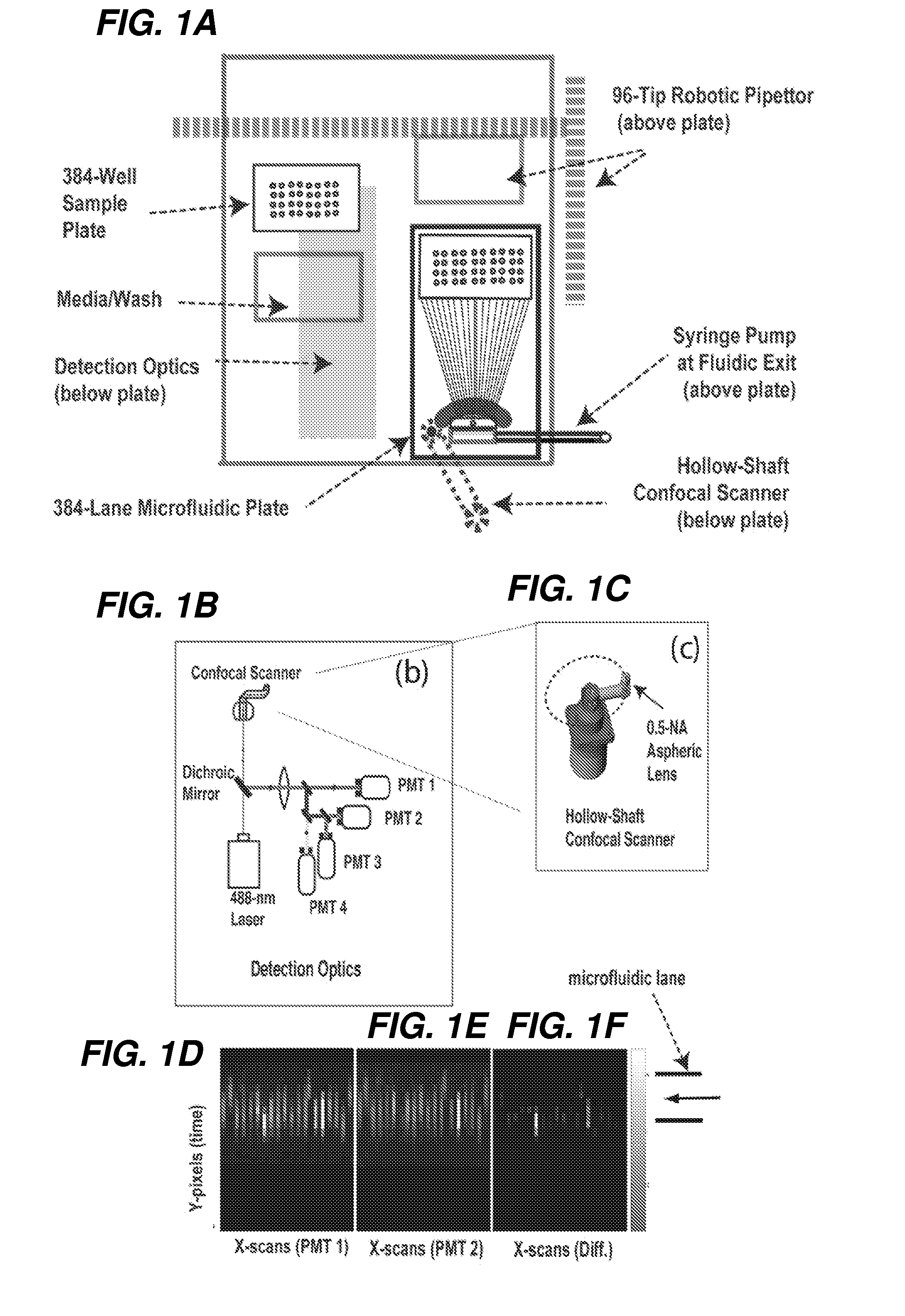
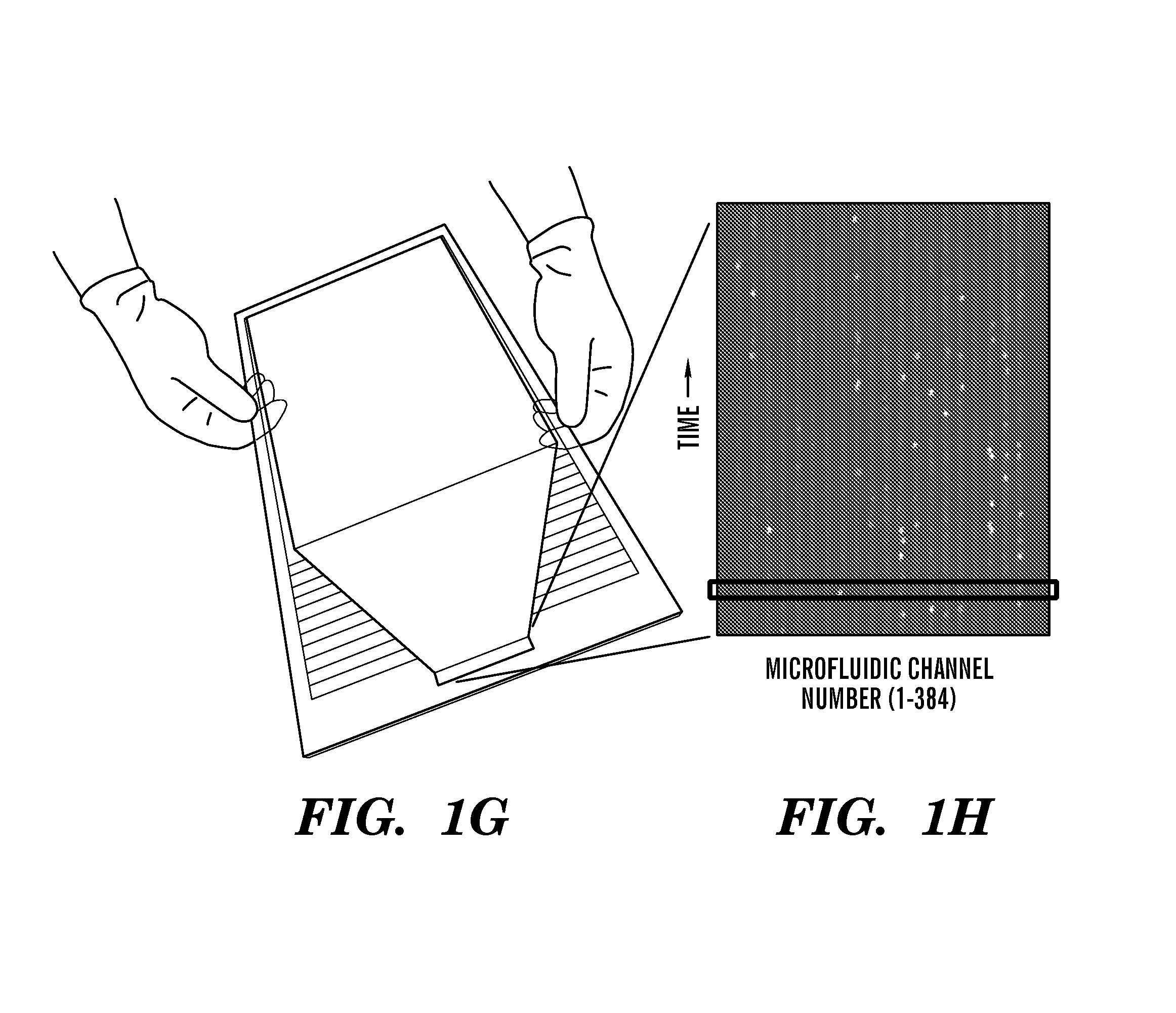
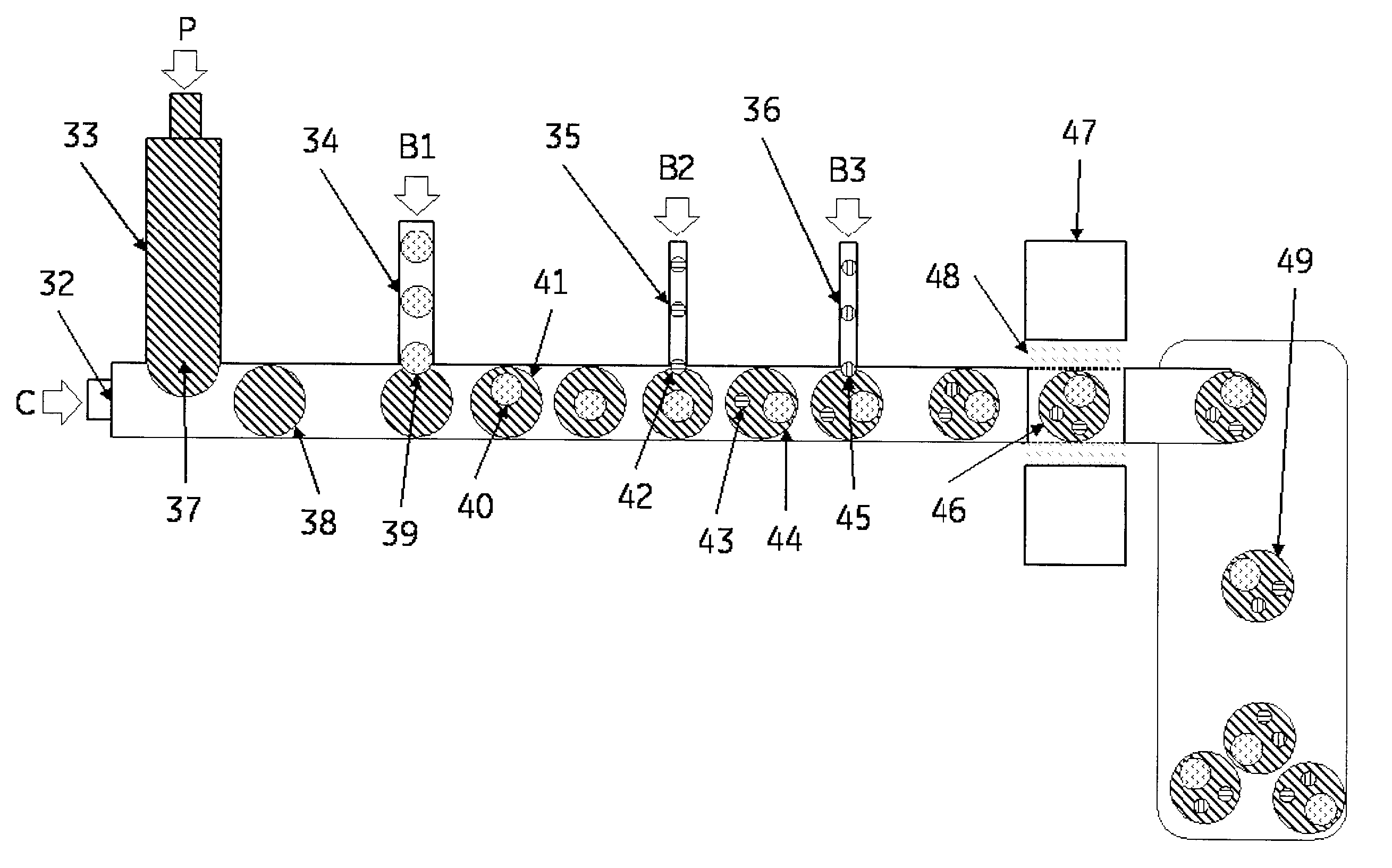
Microsystems that integrate three-dimensional microarray and multi-layer microfluidics for combinatorial detection of bioagent at single molecule level
InactiveUS20070116607A1Reduce resultHigh detection sensitivityAnalysis using chemical indicatorsWithdrawing sample devicesBiological bodyHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
Stand-alone microsystems adapted for performing combinatorial detection of bioagents at single molecule level wherein the microsystems are featured with three-dimensional microarray and multi-layer microfluidics to thereby provide high throughput screening and high content screening sufficient to allow for substantially real-time performance of the microsystem. Methods for detection of bioagents at a single molecule level or single organism level include providing a reconfigurable microsystem adapted for performing combinatorial detection of bioagents at a single molecule level and reconfiguring the reconfigurable microsystem for various environments.
Owner:PHARMACOM MICROELECTRONICS
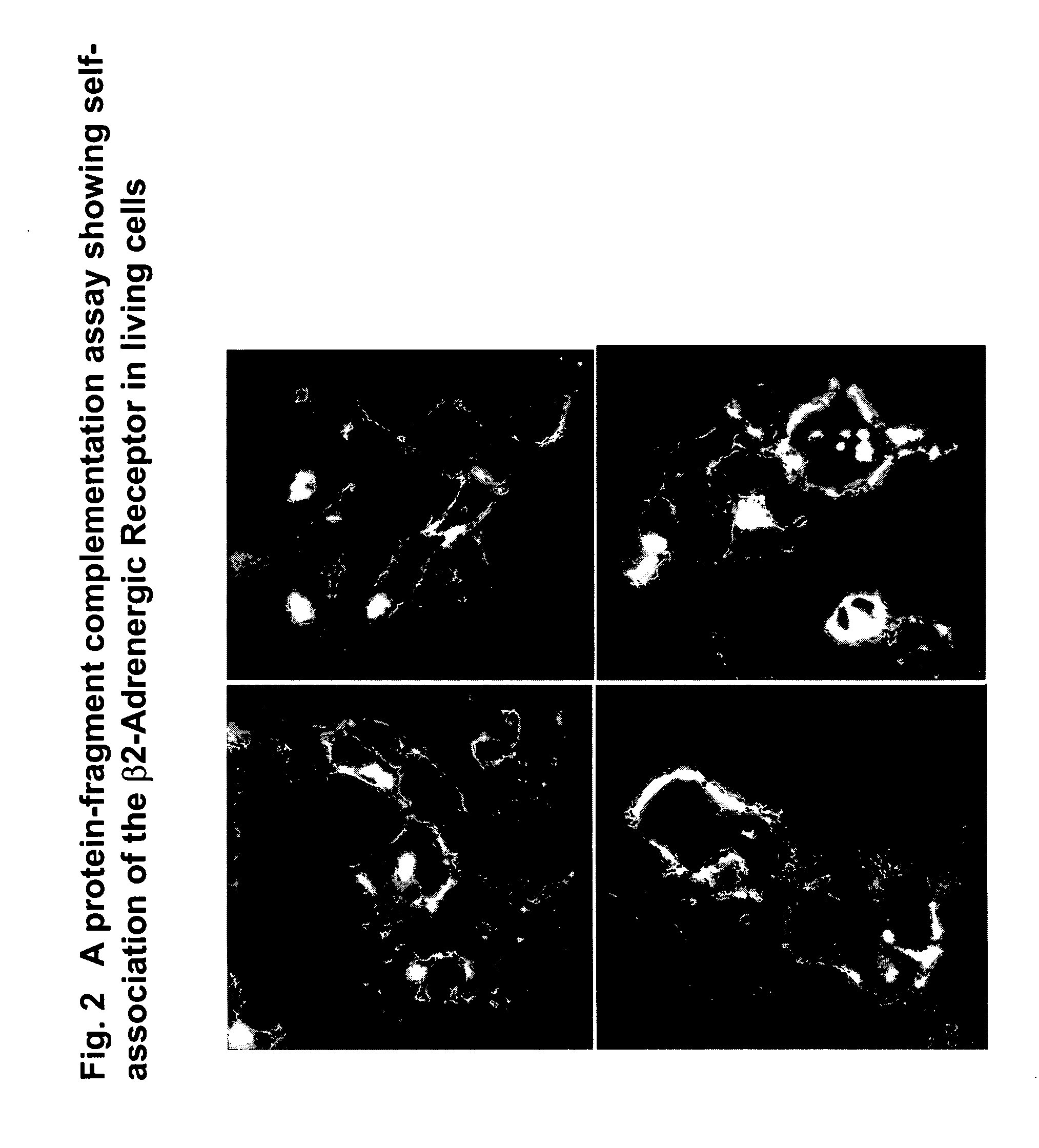
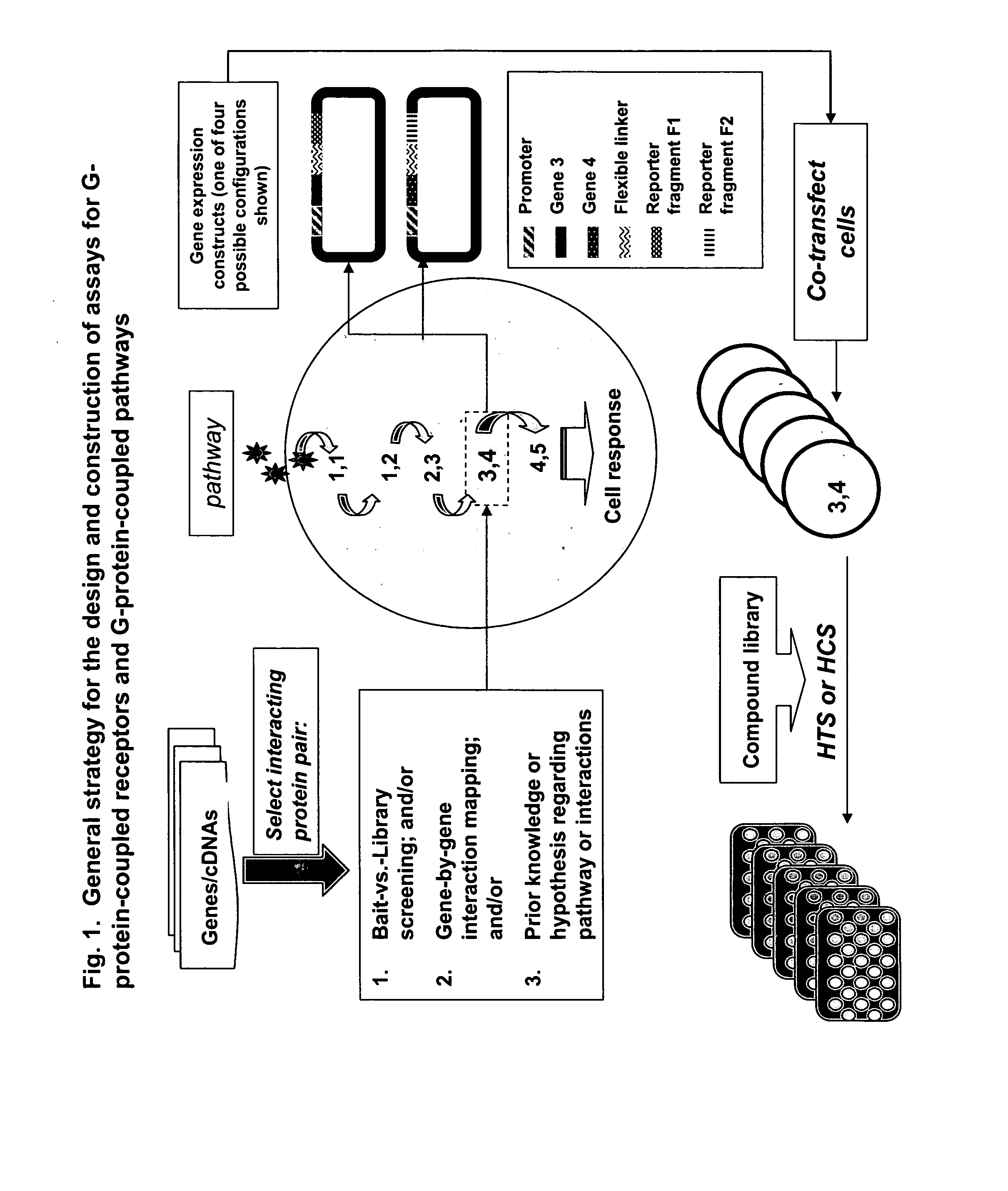
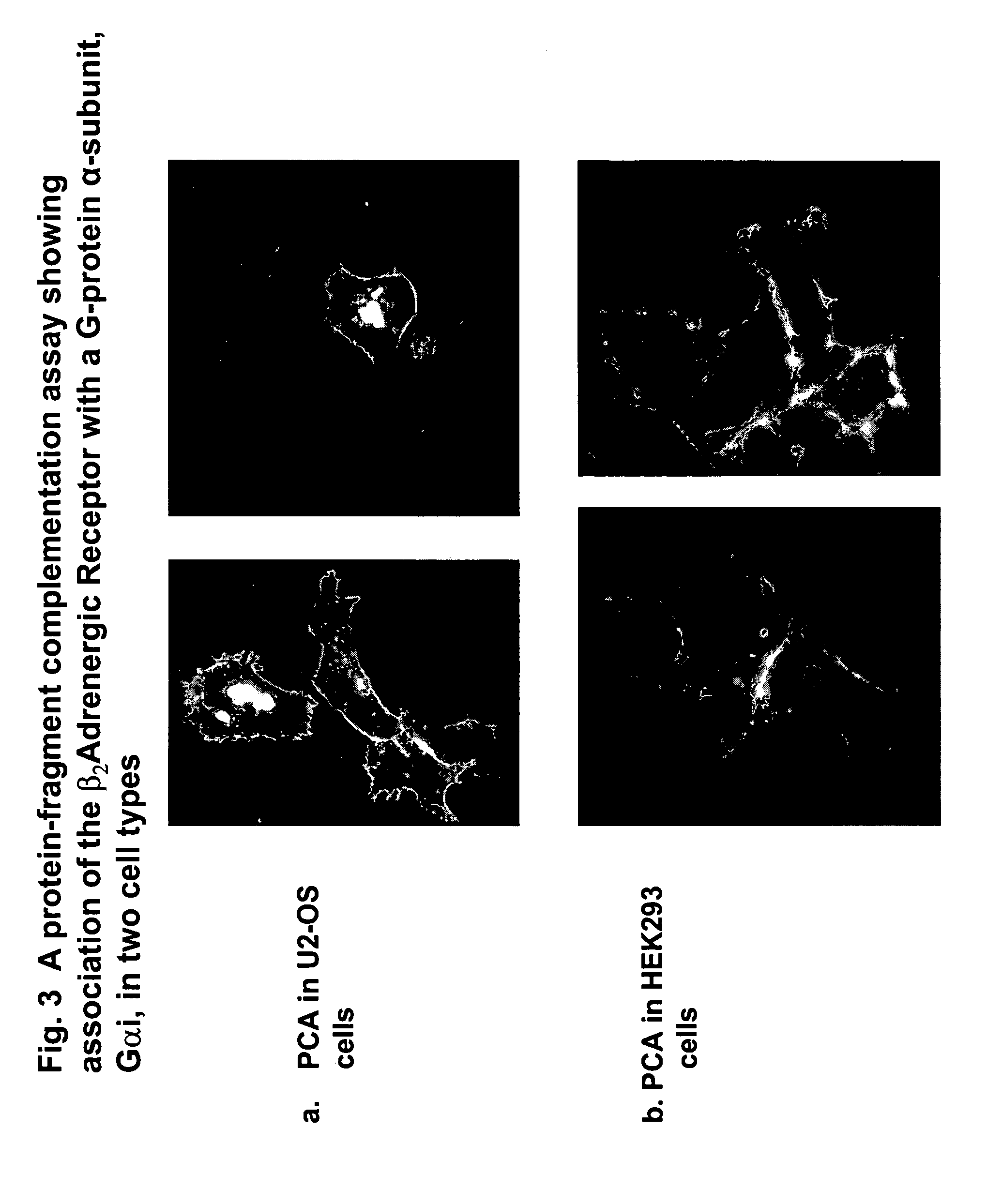
Fragment complementation assays for G-protein-coupled receptors and their signaling pathways
InactiveUS20050181452A1Fast constructionHigh sensitivityCompound screeningPeptide librariesHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsG protein-coupled receptor
This invention relates generally to the fields of biology, molecular biology, chemistry and biochemistry. The invention is directed to a large number of novel assays for G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) and their signaling pathways. Methods are described for constructing such assays for one or more steps in a GPCR pathway. The invention can be used for functional characterization of GPCRs, target validation, de-orphanization of receptors, high-throughput screening, high-content screening, pharmacological profiling, and other drug discovery applications. The assays can be used directly to assess whether a compound library or a biological extract contains an agonist or antagonist of a receptor. Assay compositions are also provided. The development of such assays is shown to be straightforward, providing for a broad, flexible and biologically relevant platform for the discovery of novel drugs and natural ligands that act on GPCRs or their cognate pathways.
Owner:ODYSSEY THERA INC
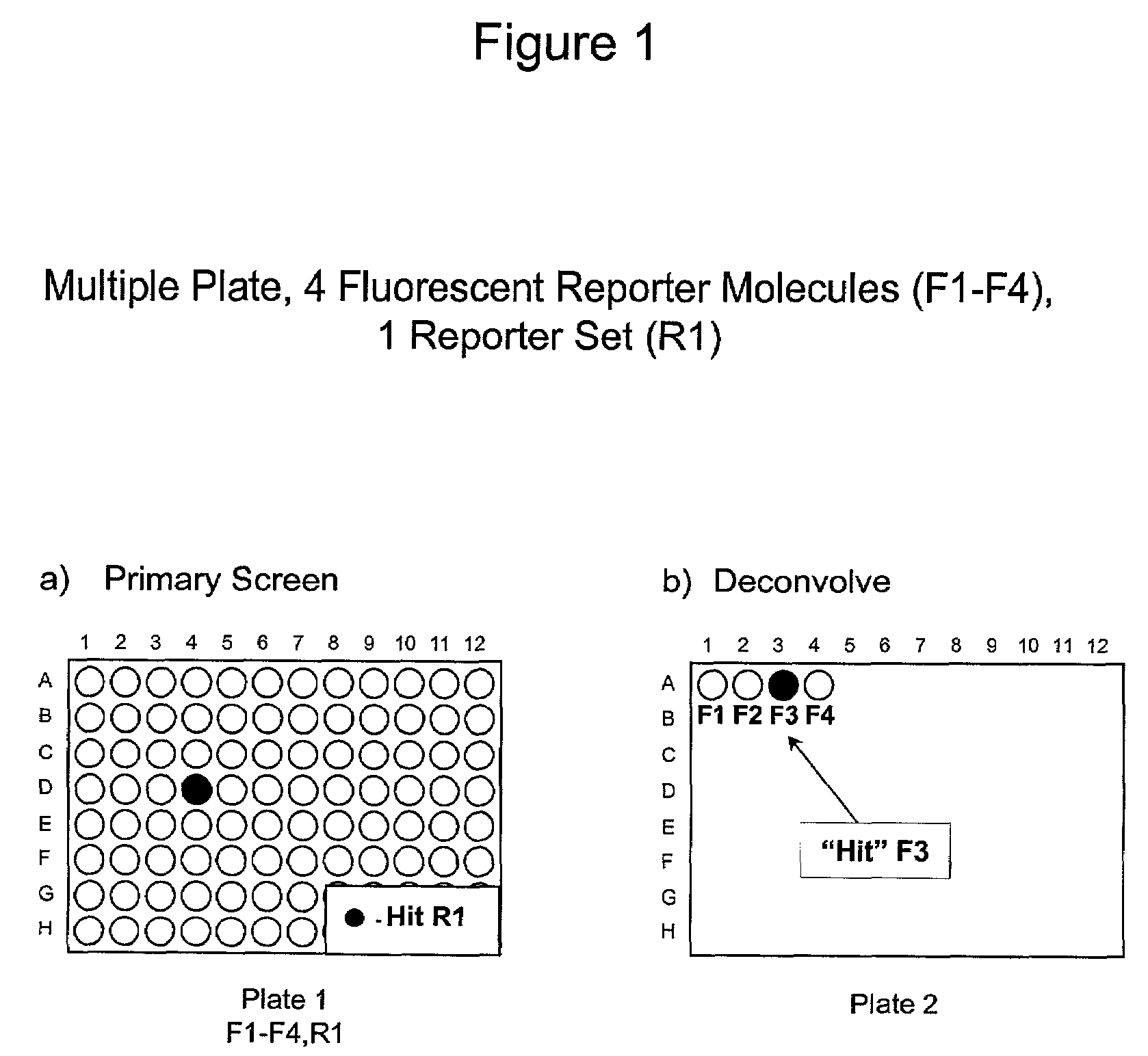
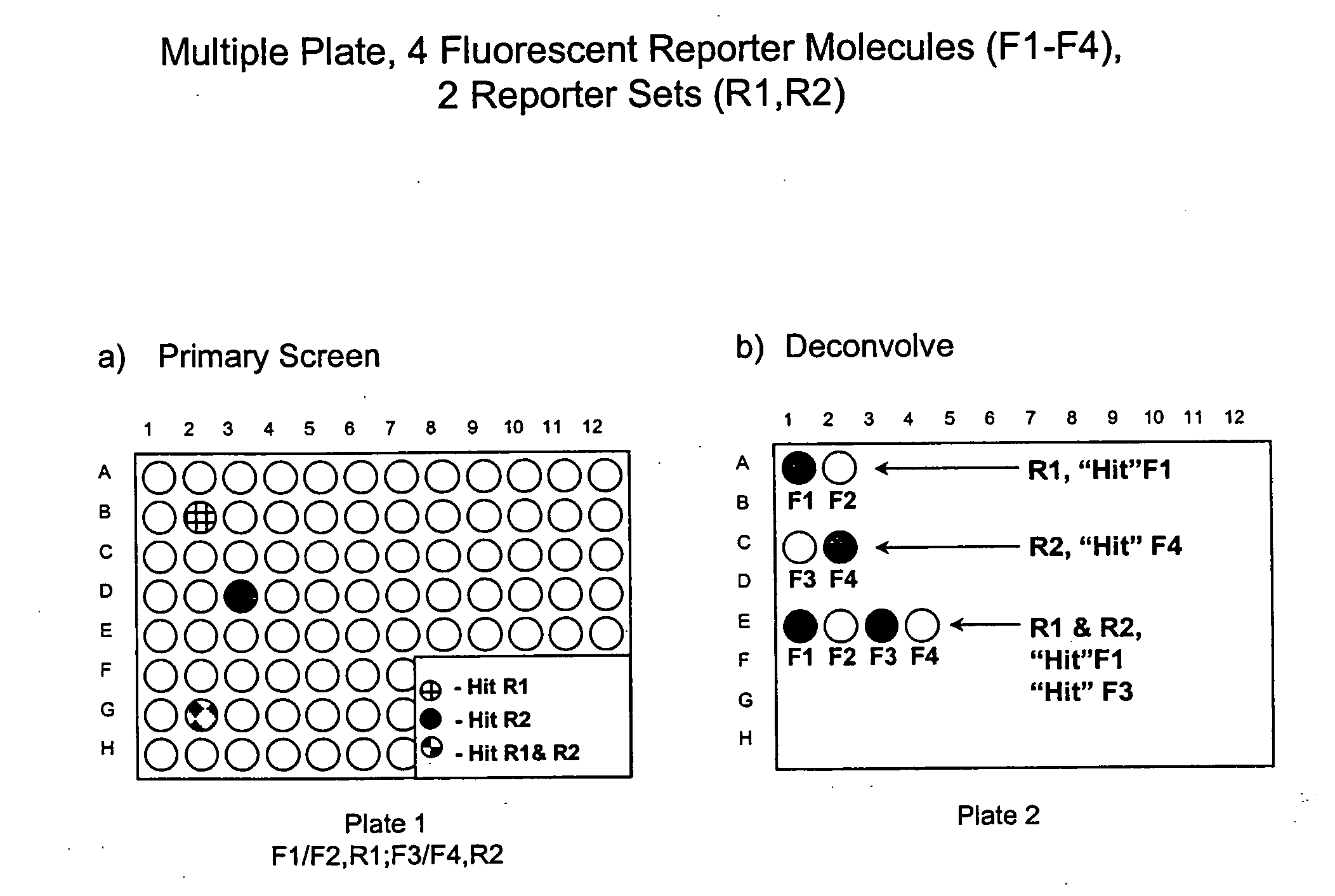
Methods to increase the capacity of high content cell-based screening assays
InactiveUS7085765B2Increase capacityMaintaining “ hit ” rateCompound screeningApoptosis detectionCell basedBiology
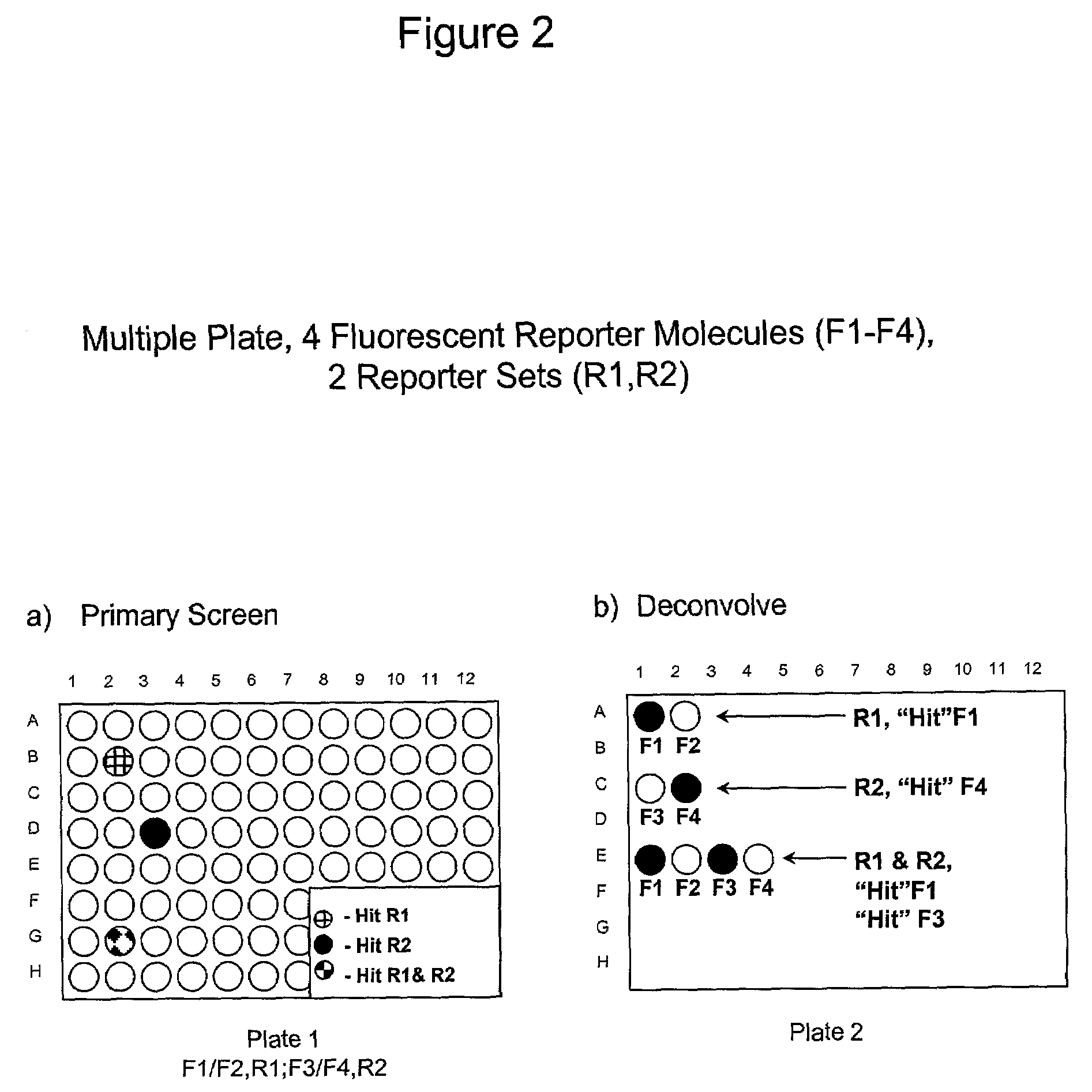
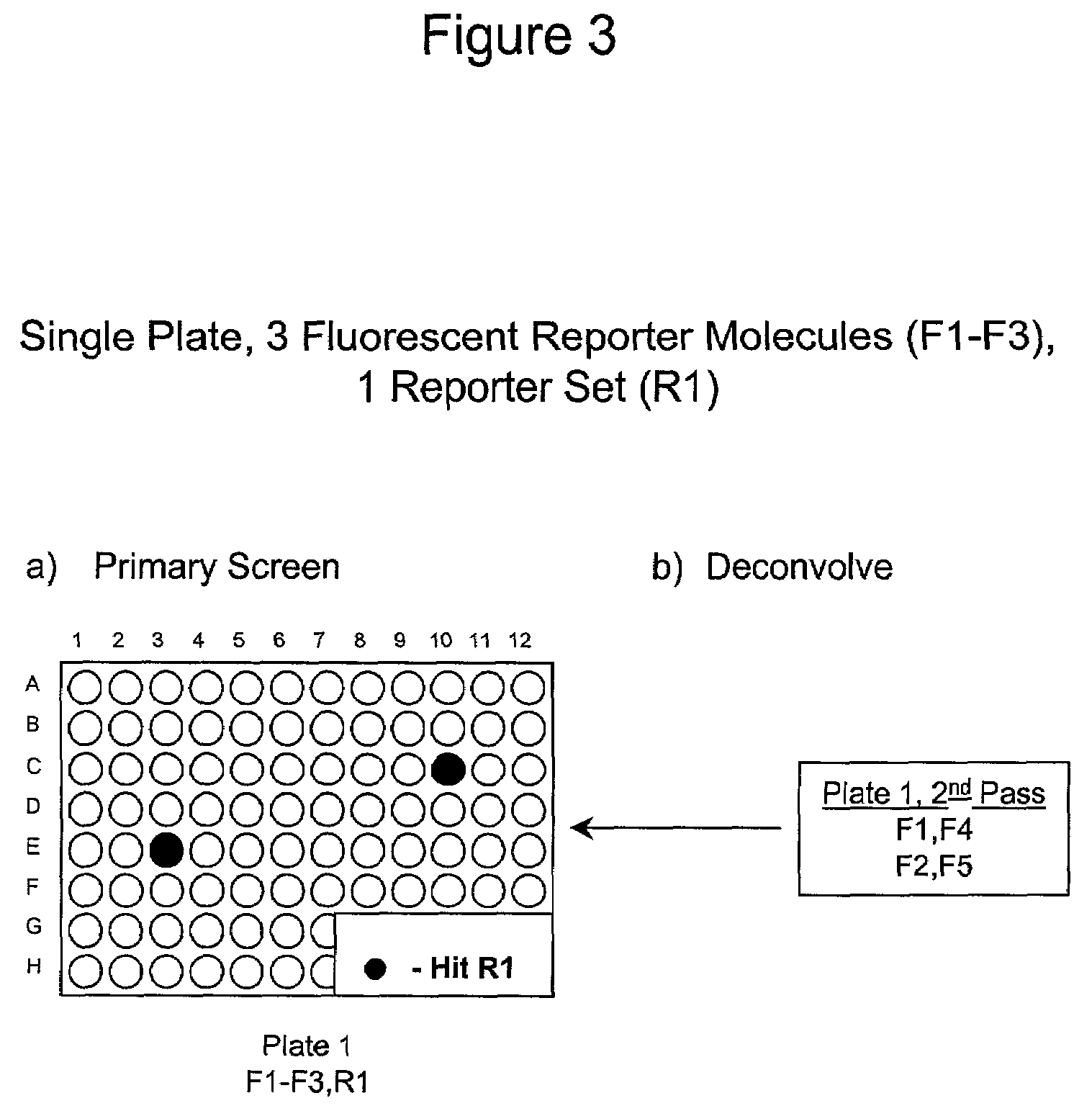
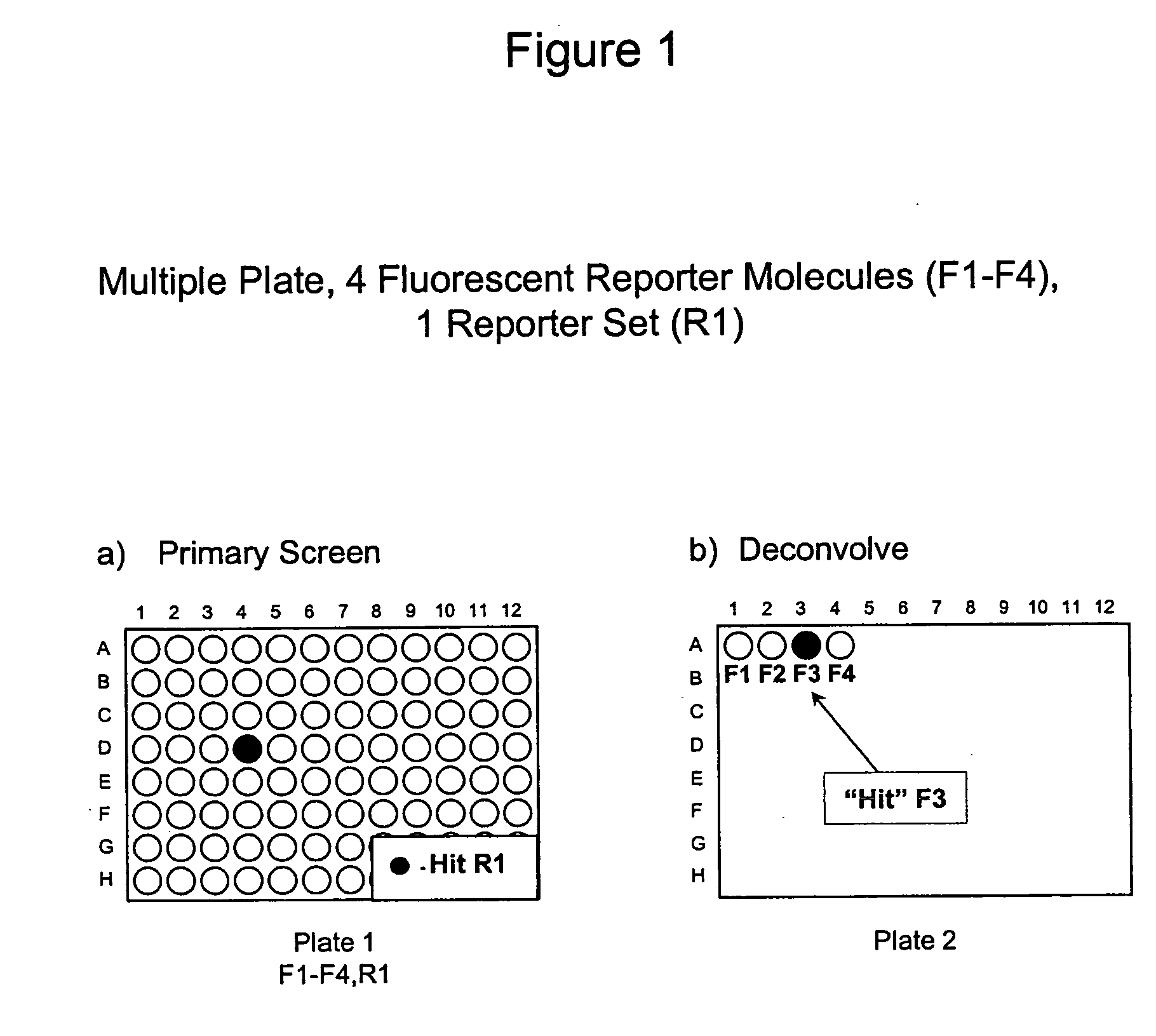
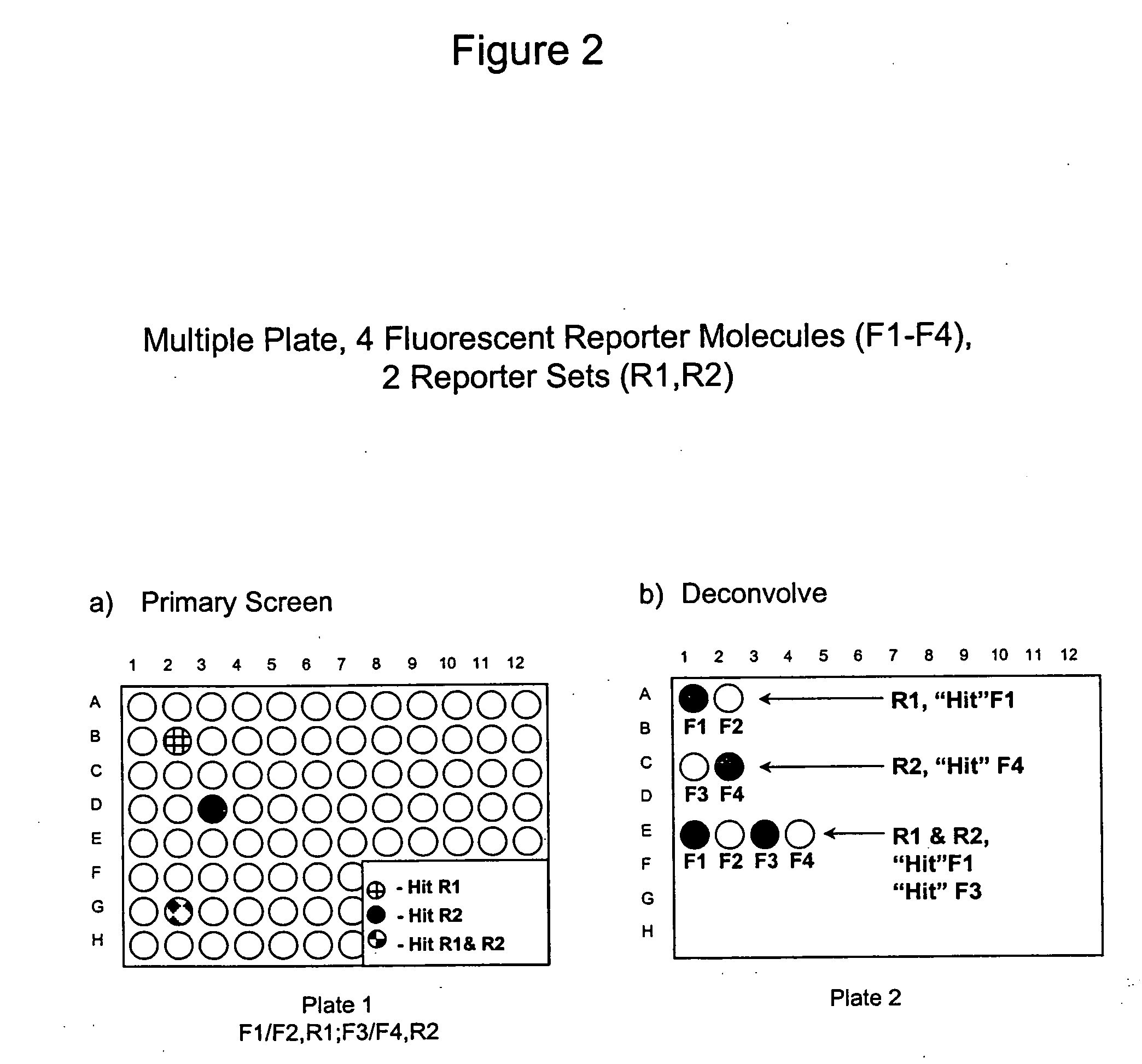
The present invention involves the pooling of multiple high content cell-based screening assays, and carrying out a primary screen in a one or more channels of a fluorescence detection device, which drastically increases the number of simultaneous high content cell-based screening events that can be carried out. Subsequent deconvolution of primary screen “hits” (ie: those wells or locations on an array of locations in which the one or more test compounds caused a change in the fluorescence signal(s) from the fluorescent reporter molecules in the cells) enables much more rapid generation of high content cell screening data than was previously possible, and at significantly reduced costs.
Owner:CELLOMICS
Protein fragment complementation assays for high-throughput and high-content screening
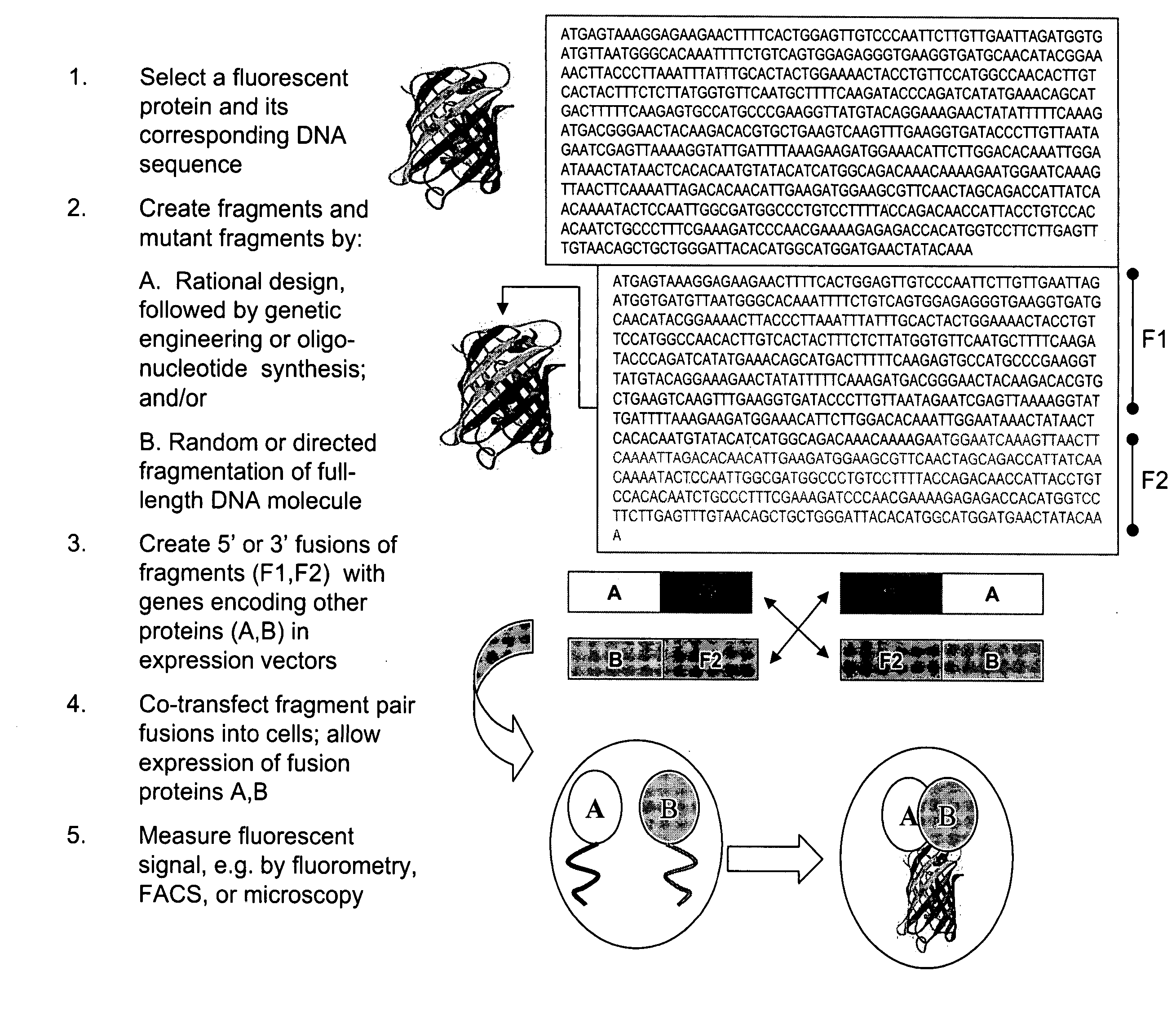
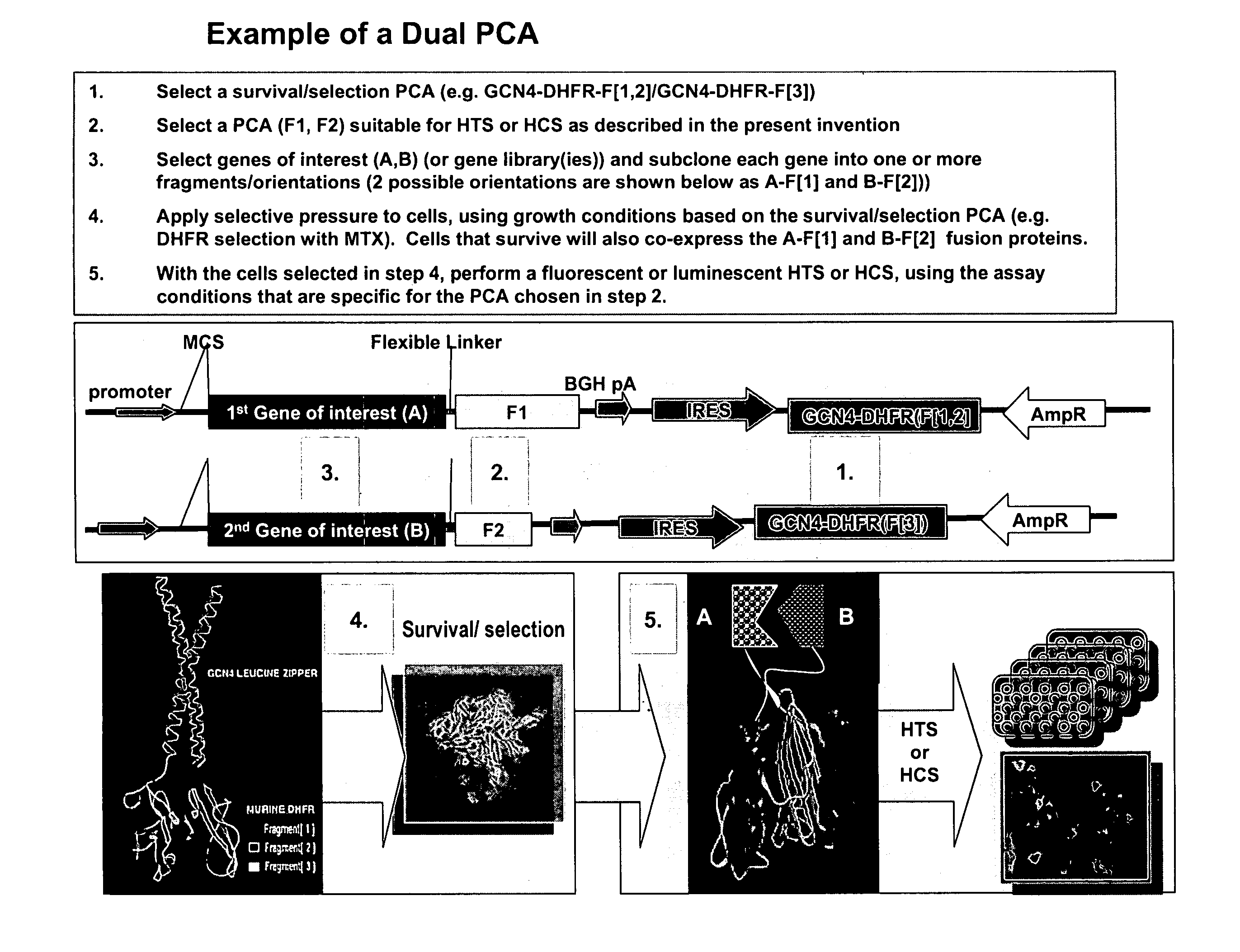
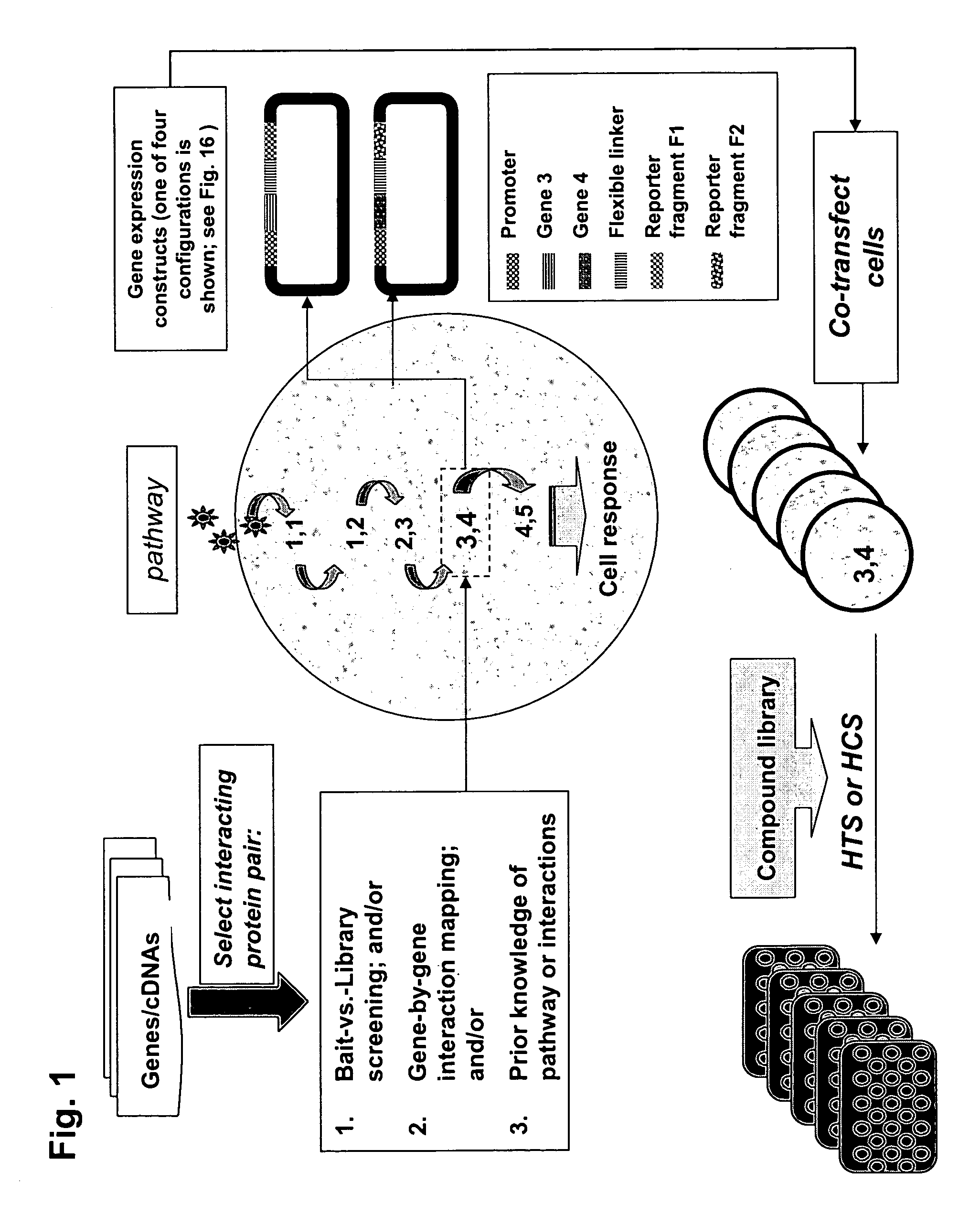
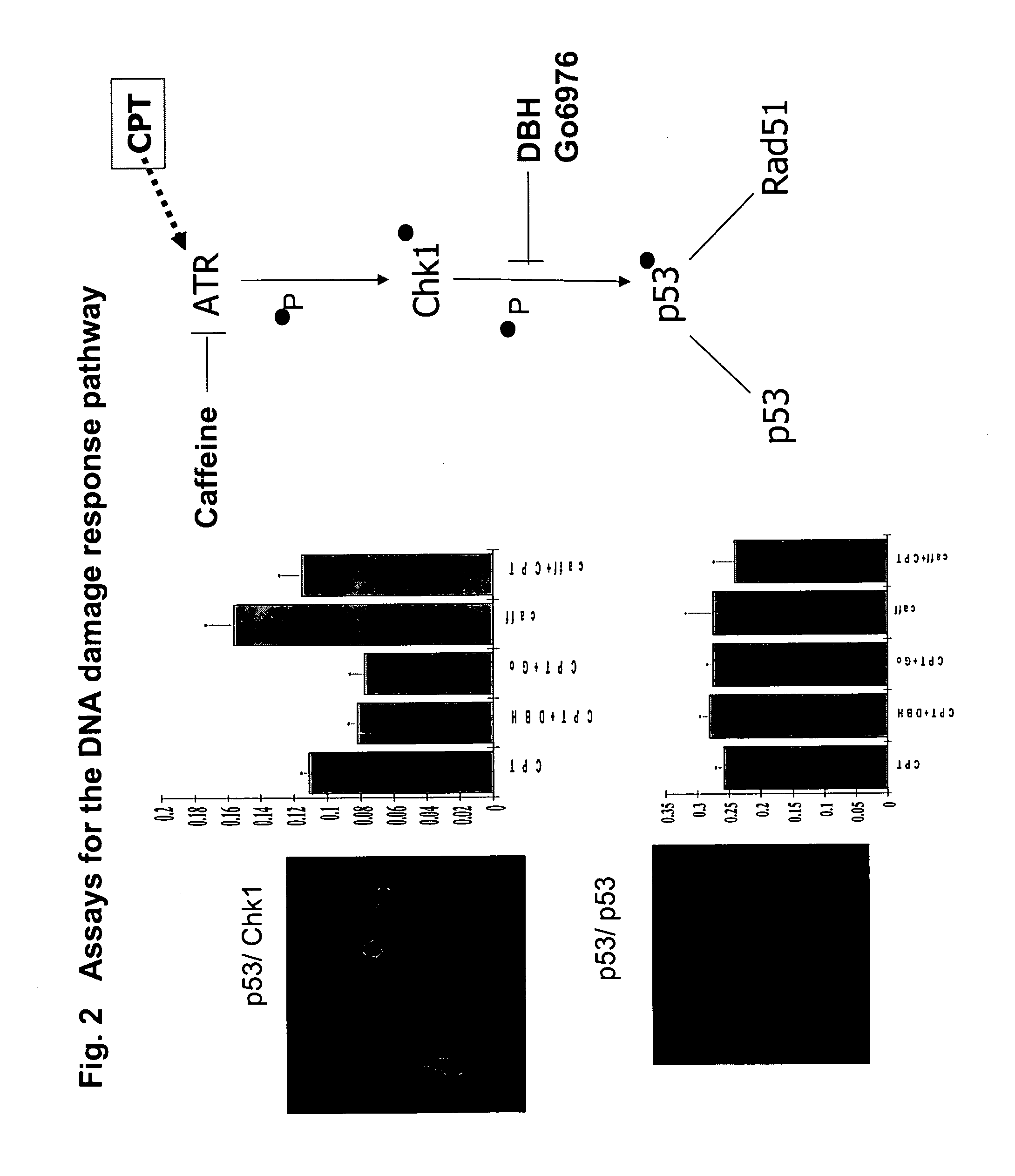
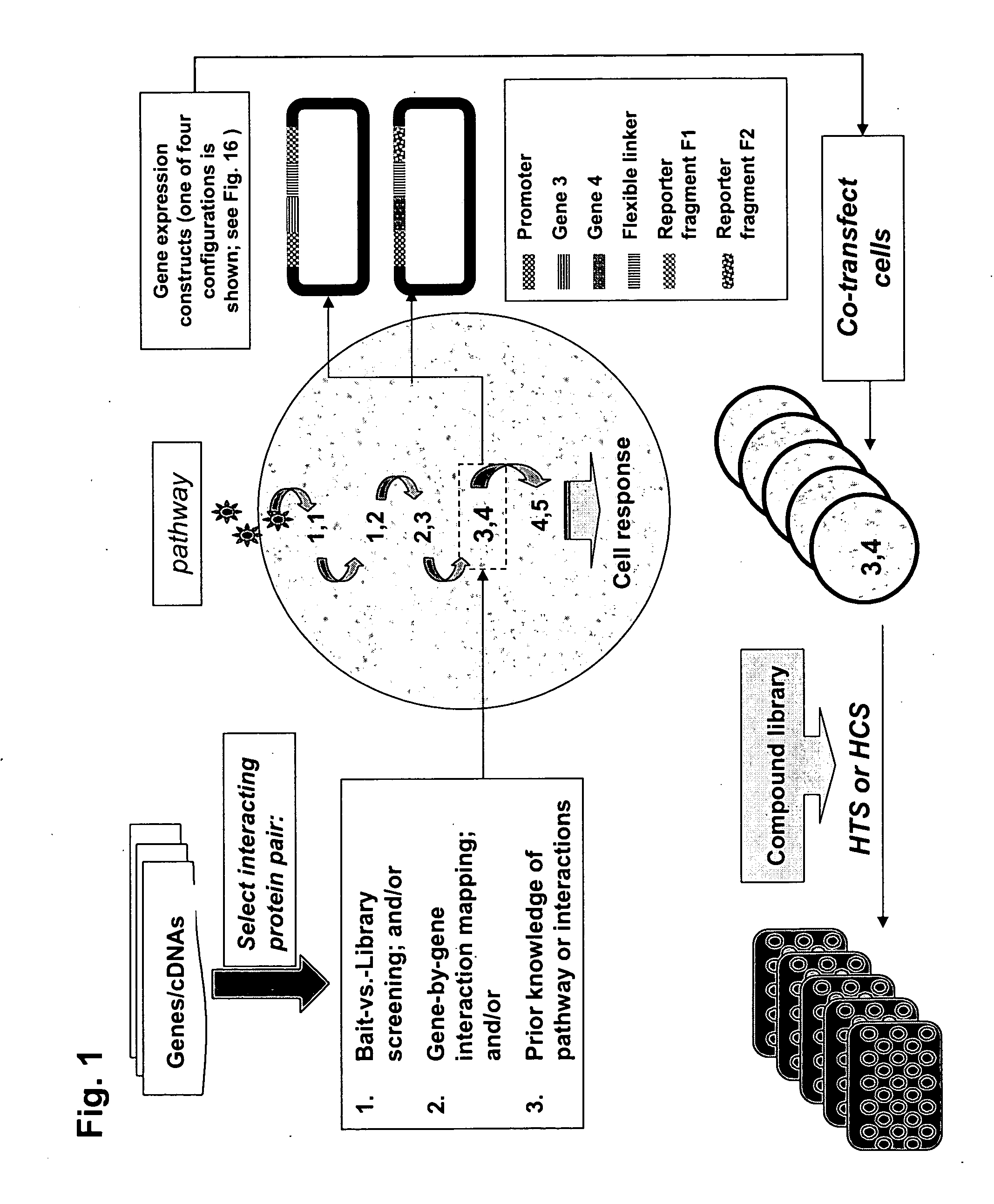
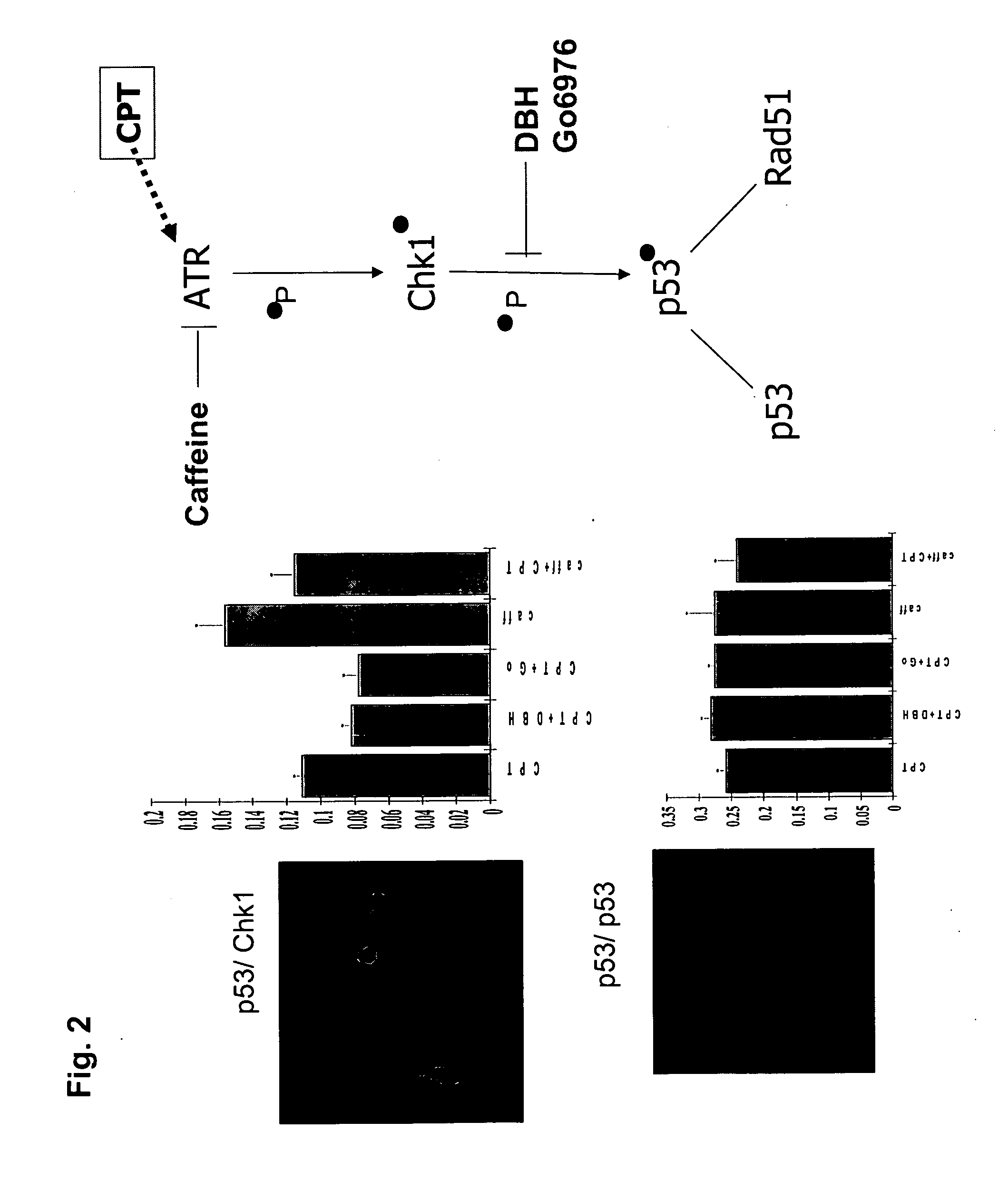
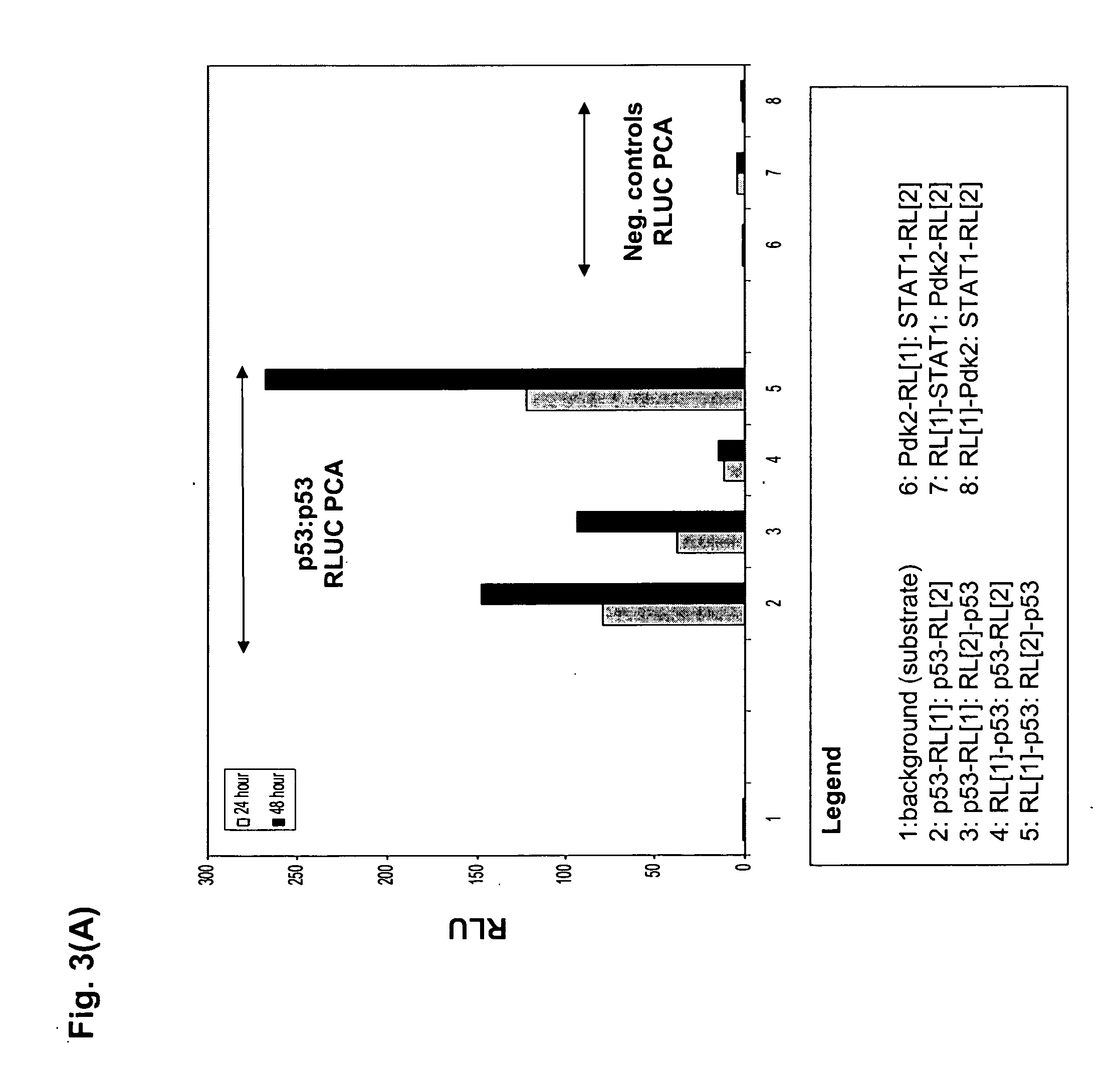
The present invention provides protein fragment complementation assays for drug discovery, in particular to identify compounds that activate or inhibit cellular pathways. Based on the selection of an interacting protein pair combined with an appropriate PCA reporter, the assays may be run in high-throughput or high-content mode and may be used in automated screening of libraries of compounds. The interacting pair may be selected by cDNA library screening; by gene-by-gene interaction mapping; or by prior knowledge of a pathway. Fluorescent and luminescent assays can be constructed using the methods provided herein. The selection of suitable PCA reporters for high-throughput or high-content (high-context) assay formats is described for a diversity of reporters, with particular detail provided for examples of monomeric enzymes and fluorescent proteins. Methods are described for constructing such assays for one or more steps in a biochemical pathway; testing the effects of compounds from combinatorial, natural product, peptide, antibody, nucleic acid or other diverse libraries on the protein or pathway(s) of interest; and using the results of the screening to identify specific compounds that activate or inhibit the protein or pathway(s) of interest. Single-color and multi-color assays are disclosed. Further disclosed are universal expression vectors with cassettes that allow the rapid construction of assays for a large and diverse number of gene / reporter combinations. The development of such assays is shown to be straightforward, providing for a broad, flexible and biologically relevant platform for drug discovery.
Owner:ODYSSEY THERA INC
Protein fragment complementation assays for high-throughput and high-content screening
Owner:ODYSSEY THERA INC
High throughput multichannel reader and uses thereof
InactiveUS8936762B2Increase contentImprove throughputBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsImage detectionLarge particle
The present invention relates generally to the field of high content screening of particles, e.g., cells in a flow cytometric system. In particular, the present invention relates to devices, methods and systems to obtain line-scan images of particles, e.g., cells, of a plurality of different samples simultaneously, where the line-scan images can be used to identify cells based on at least one of a variety of phenotypic characteristics such as shape, asymmetry, and intracellular information for cell sorting and selection. In some embodiments, the line-scan images are obtained as the particles, e.g., cells, in a plurality of different samples flow through a plurality of microchannels, reducing the need and time for focusing of the image detection system. In some embodiments, the laser spot size has a small spatial resolution for rapid capturing of images of cells. In some embodiments, the laser spot size has a larger spatial resolution for imaging of larger particles or cells, e.g., rare cells in a sample. In some embodiments, the devices, methods and systems are automated for a high-throughput, high content screening of particles such as cells in a plurality of samples.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Intra-Culture Perfusion Methods and Applications Thereof
ActiveUS20140106452A1Limit lossResistive lossBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsHigh-throughput screening
Disclosed are intra-culture perfusion methods applied to standard cell culture disposables using three-dimensional cell culture scaffold and synthetic vasculature compositions in high-throughput screening and high-content screening applications, and assay development.
Owner:LENA BIOSCI INC
Interpolated image response
Systems and methods are provided for characterizing a multidimensional distribution of responses from the objects in a populations subject to a perturbation. The methods enable the creation of a “degree of response” scale interpolated from non-perturbed and perturbed reference populations. The methods enables, using the interpolated degree of response scale, the quantitation of a degree of response of a test compound subject to a given level of perturbation, and enables the generation of a dose-response curve for a test compound. The methods are useful in a wide range of applications, such cellular analysis and high-content screening of compounds, as carried out in pharmaceutical research.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Microscopy imaging phantoms
InactiveUS20100261811A1Quality improvementLimit full visualisationMaterial analysis by optical meansNuclear monitoringRadiographic PhantomsInstrumentation
The invention relates to imaging phantoms for validation, optimisation and calibration of microscopy instrumentation and software used for analysis of microscope images. The materials and methods of the invention find particular use in high content screening and high content analysis.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE LTD
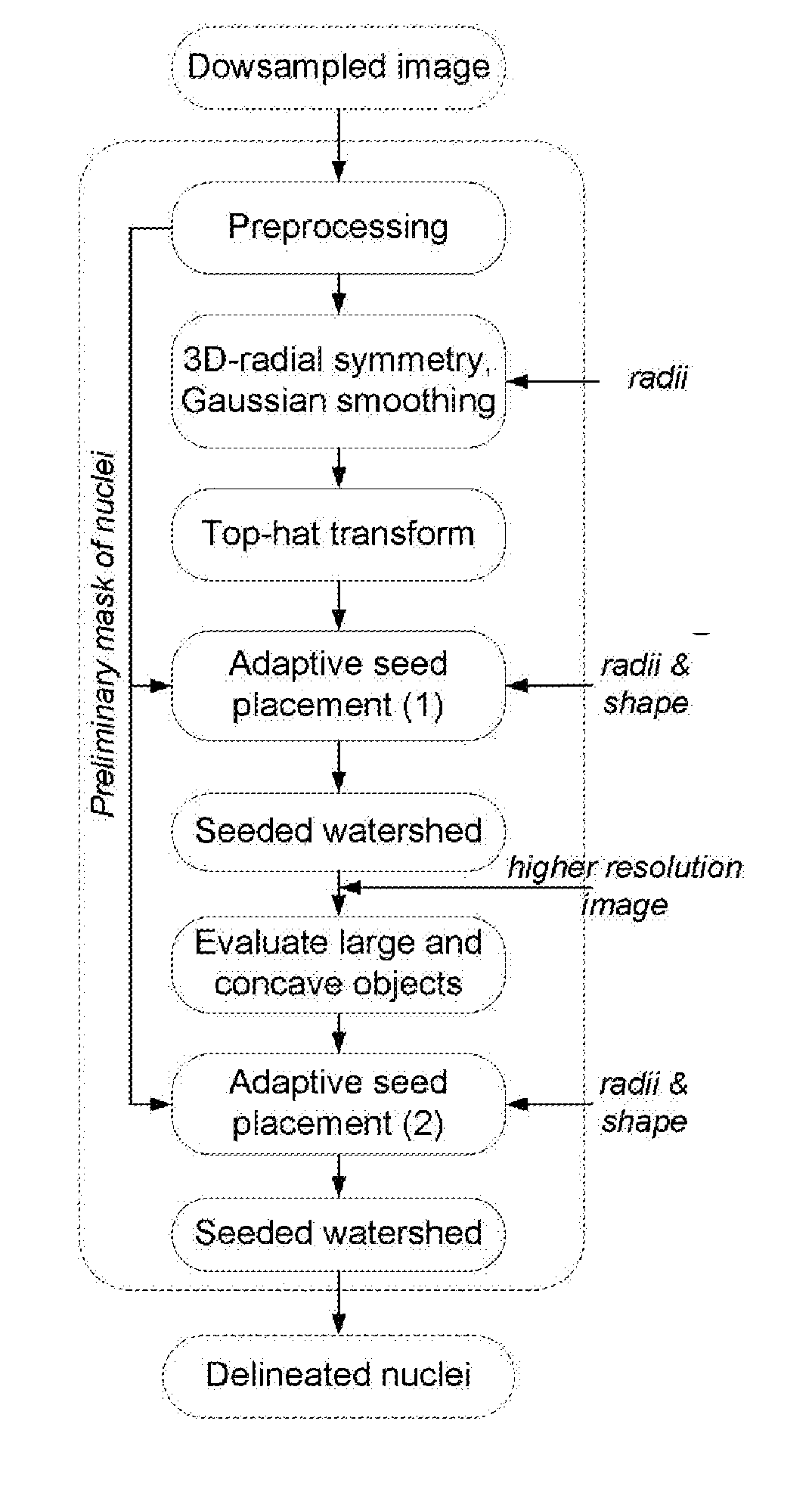
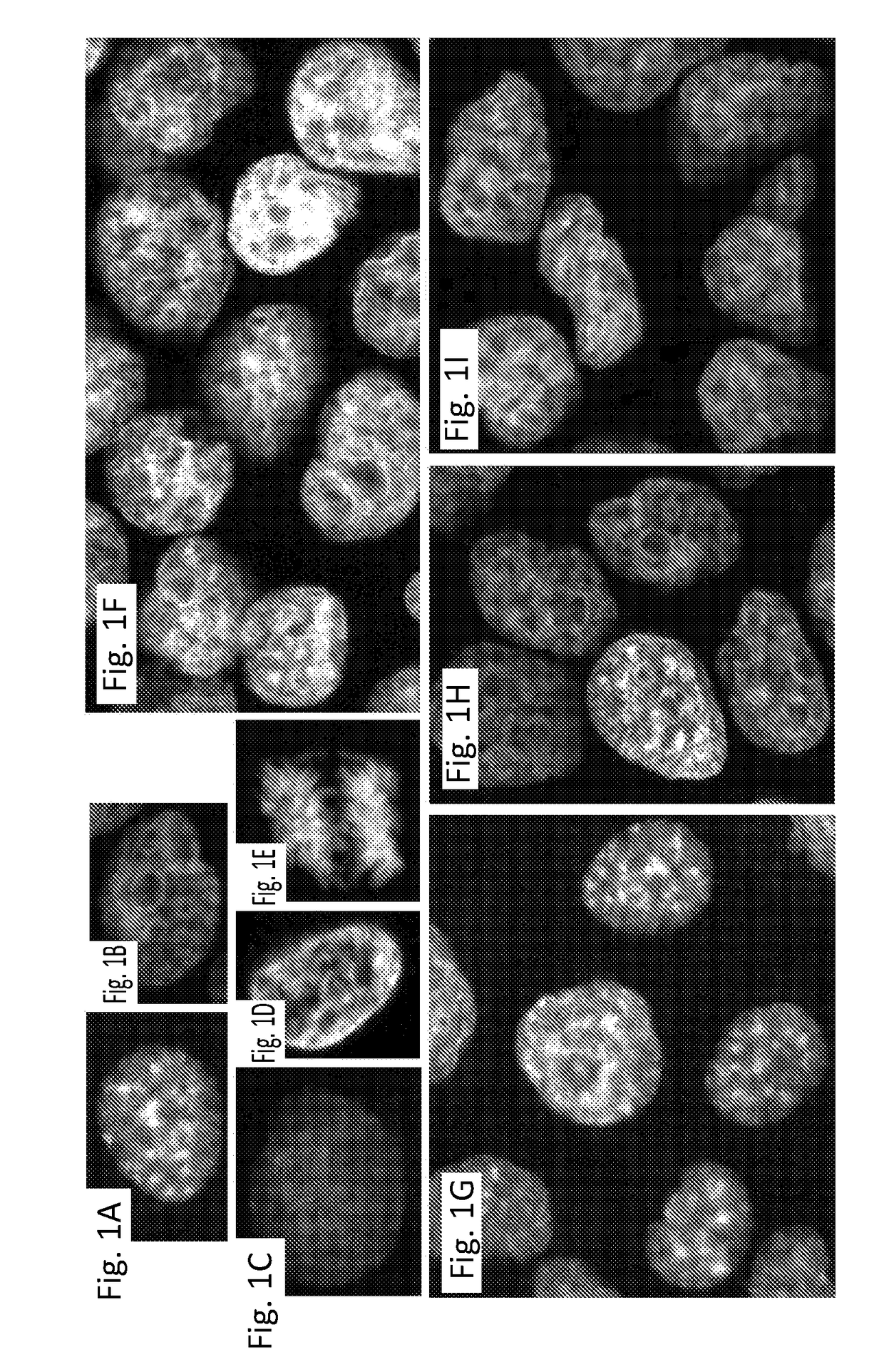
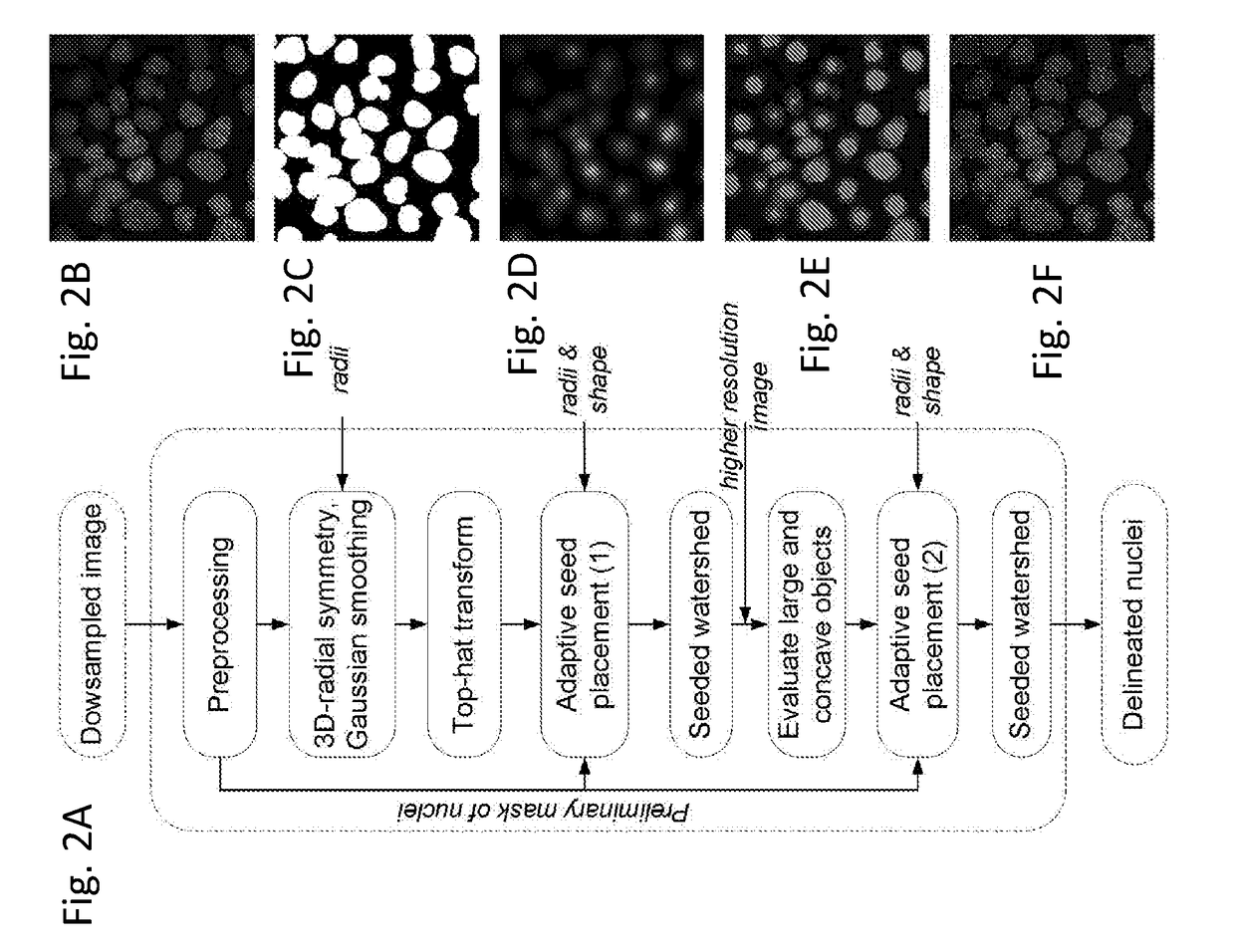
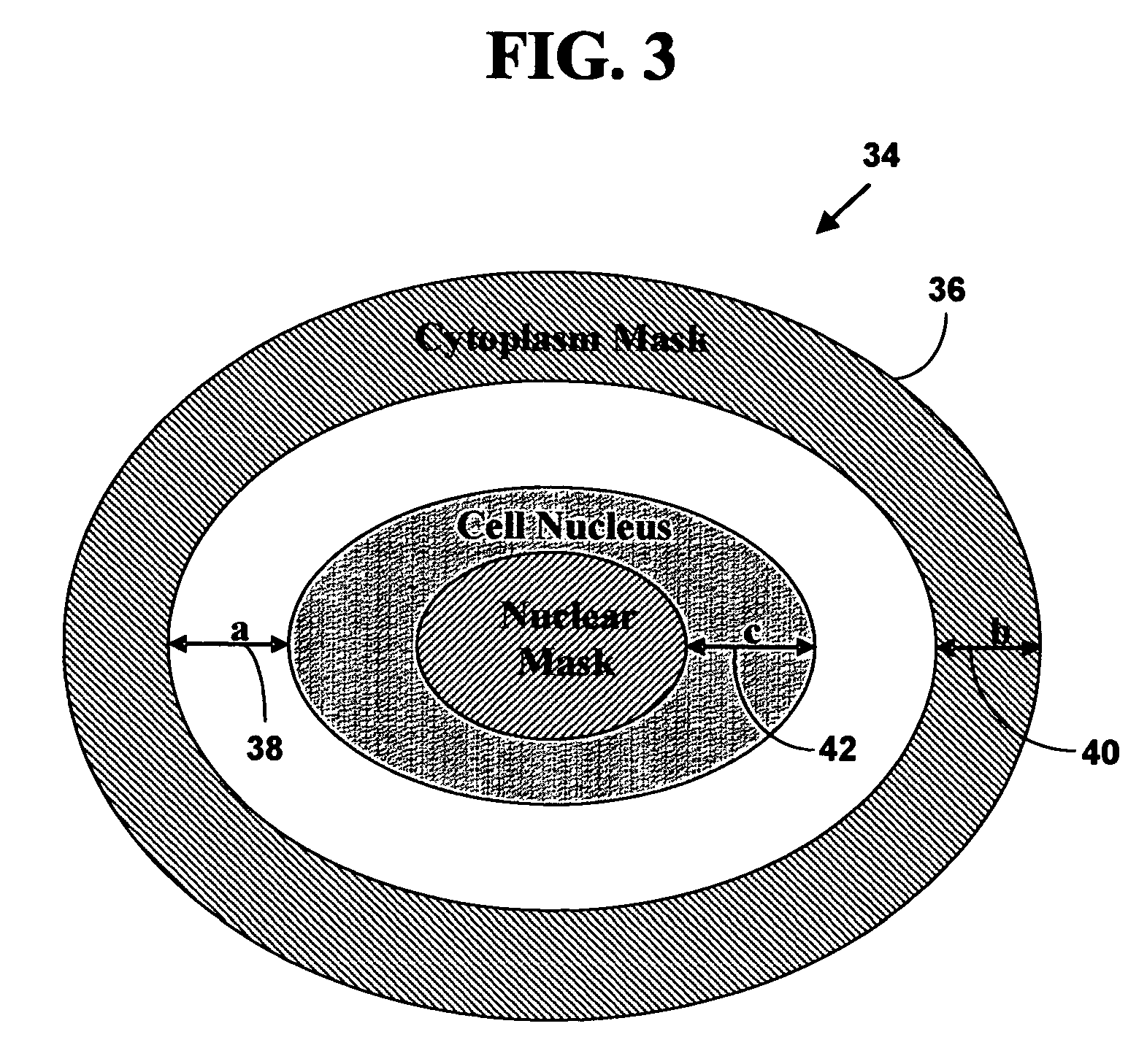
Automated delineation of nuclei for three dimensional (3-d) high content screening
ActiveUS20180075279A1Preparing sample for investigationCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer visionConfocal microscopy
In various embodiments, the invention teaches systems and methods for analyzing an image of cells, including an image obtained by confocal microscopy, and delineating cell nuclei in the image. In some embodiments, the systems and methods apply a three-dimensional (3-D) radial symmetry transform followed by adaptive post processing of symmetry images to arrive at a mask of seeds that can guide watershed-based segmentation.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
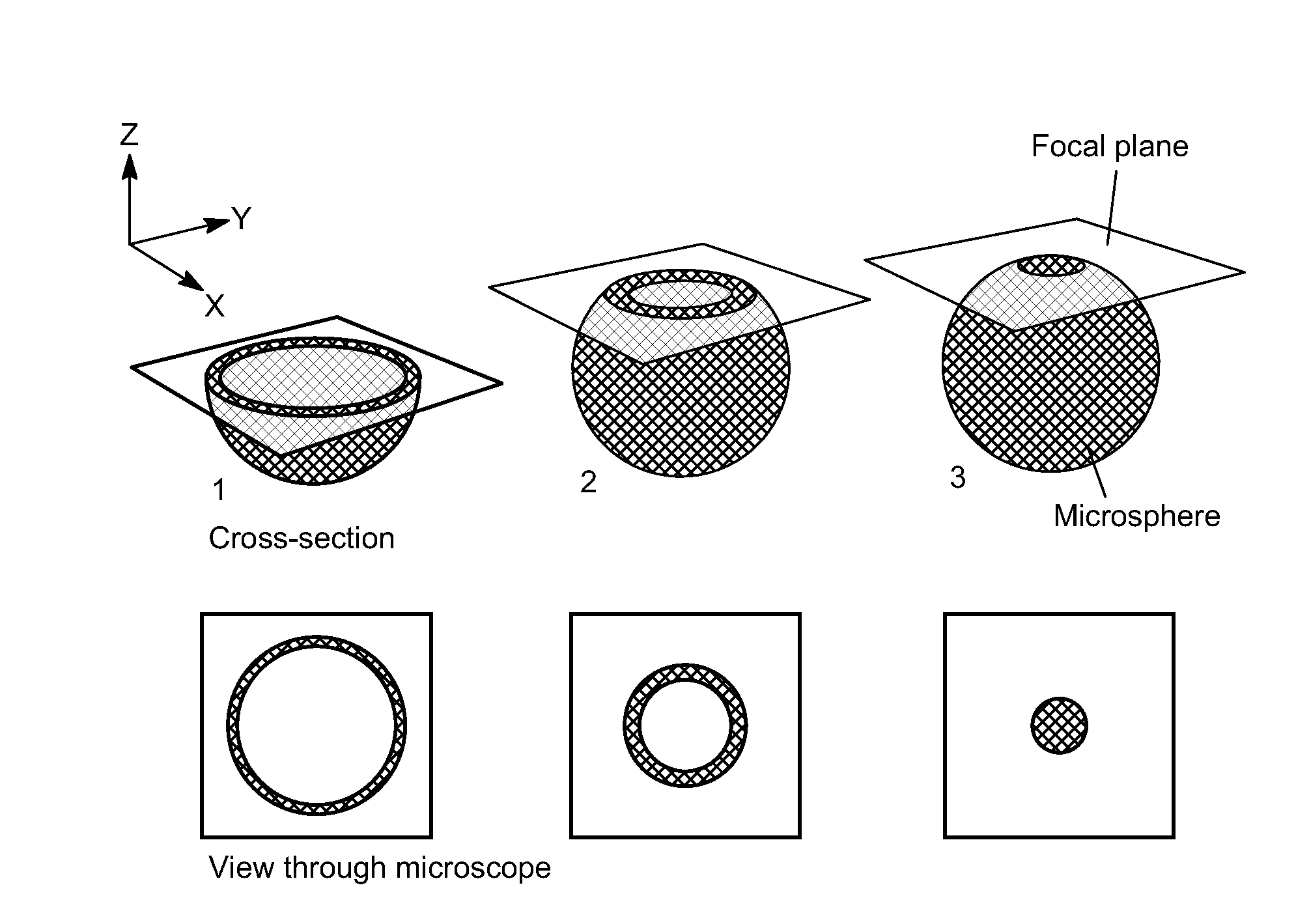
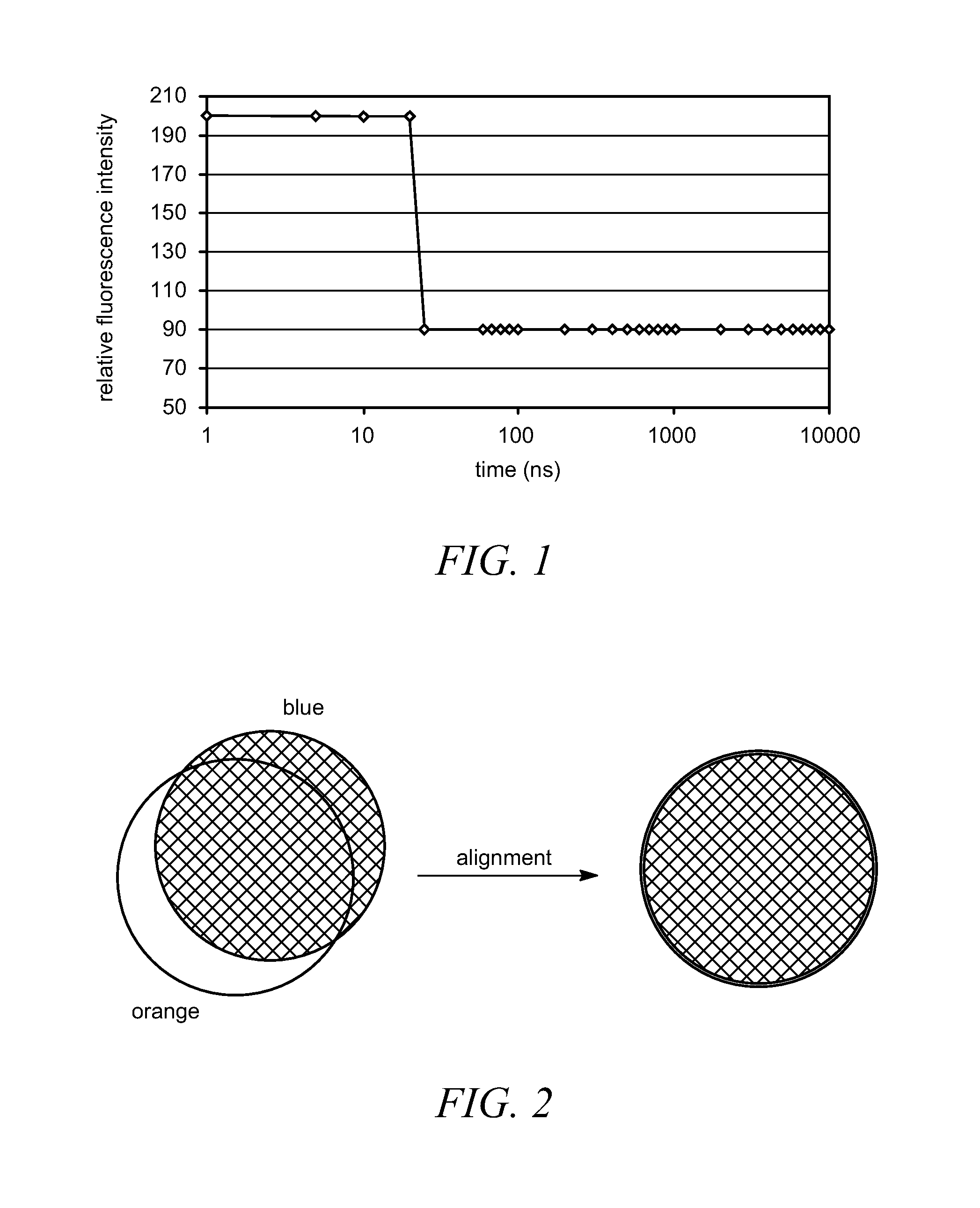
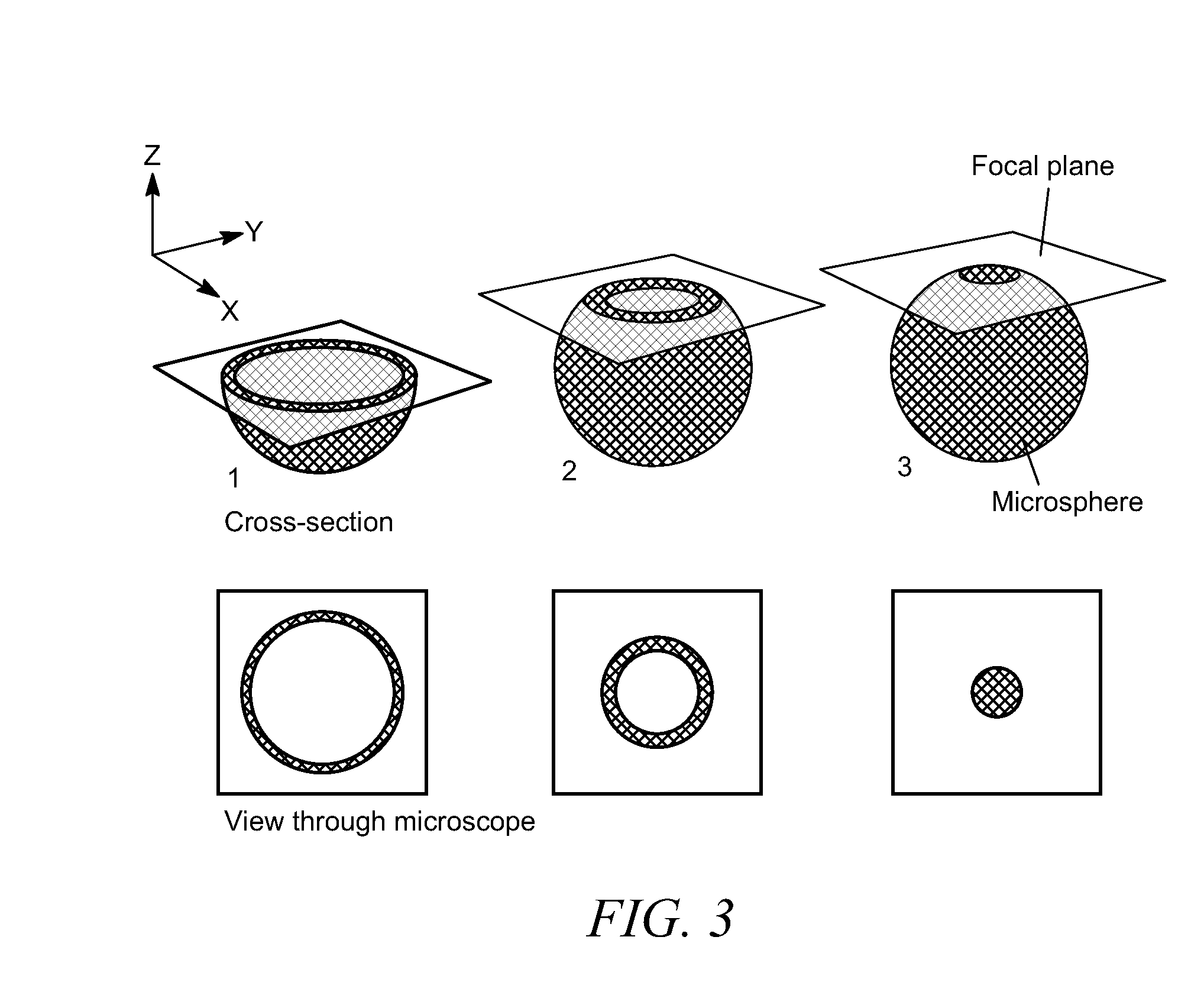
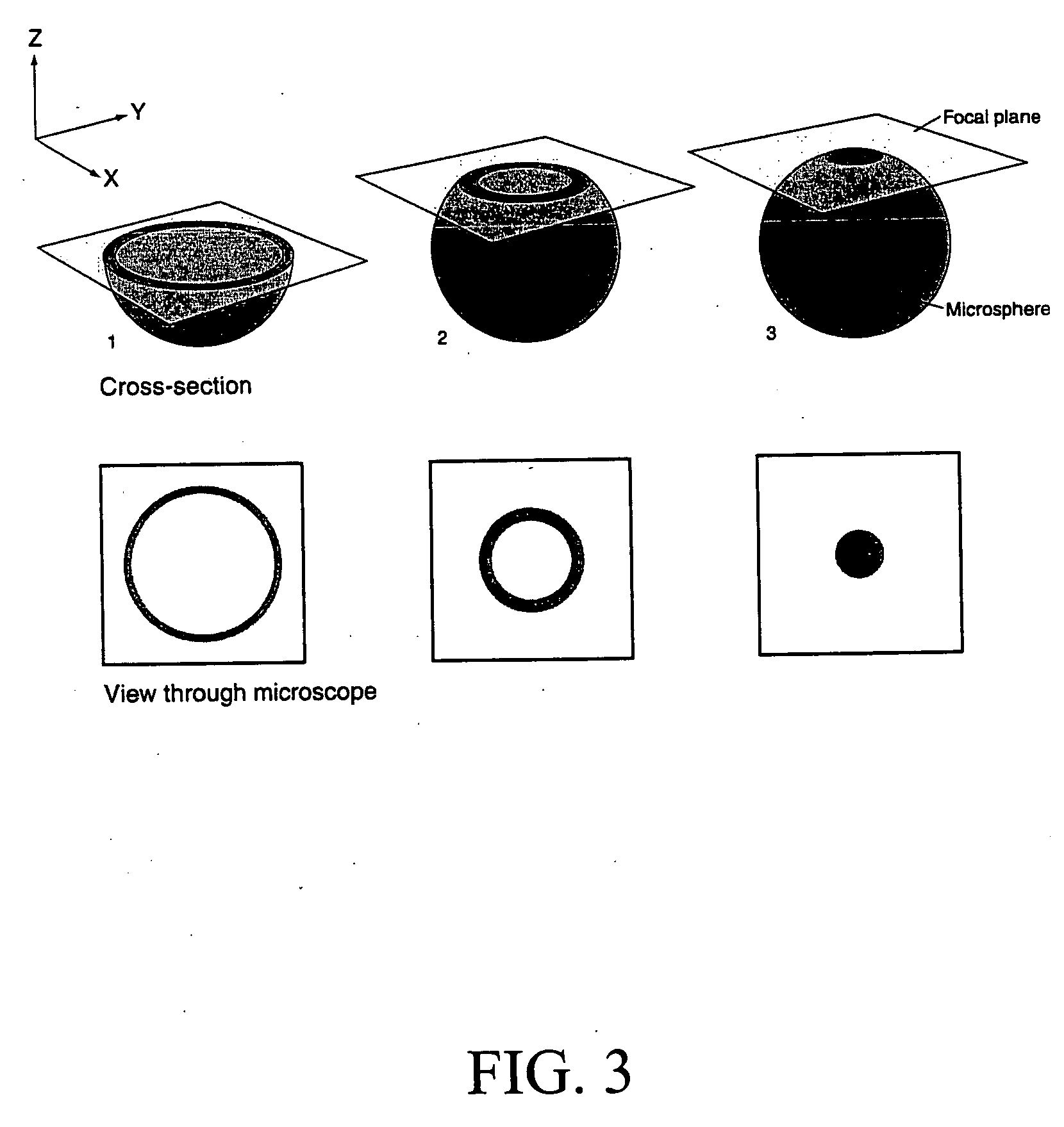
Microplates containing microsphere fluorescence standards, microsphere standards, and methods for their use
InactiveUS20100178712A1Analysis using chemical indicatorsChemical analysis using titrationFluorescenceMicrosphere
Microplates containing spherical “microsphere” fluorescence standards are disclosed. The microplates can be prepared using several methods including airbrushing, application with an inkjet printer, or controlled evaporation. Spherical bead standards containing two or more regions stained with dyes of different fluorescence lifetimes, and methods for their preparation are also disclosed. The microplates can be used as calibration standards for fluorescence and confocal microscopes, and as calibration tools for microscope-based high content screening (“HCS”) instruments.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
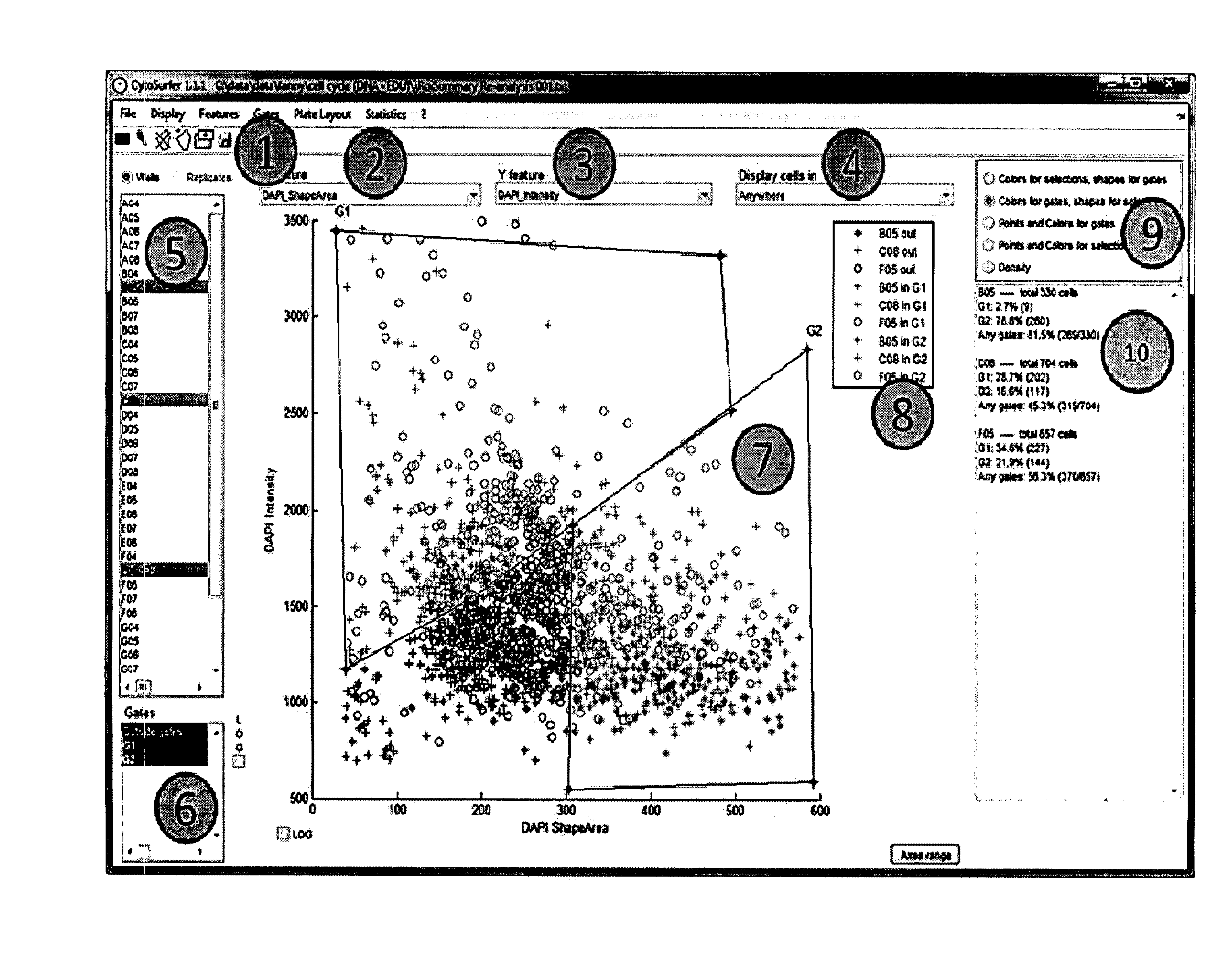
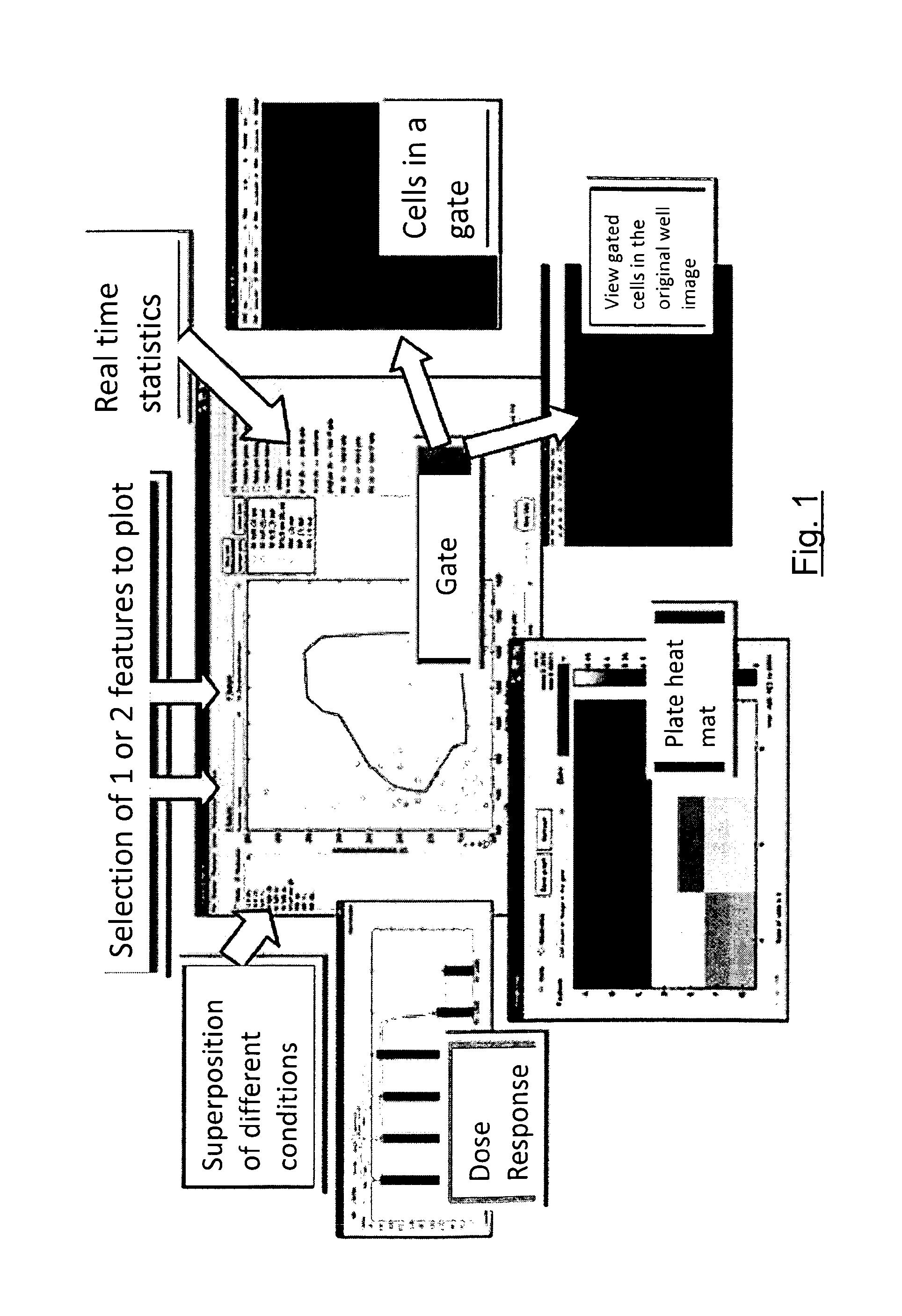
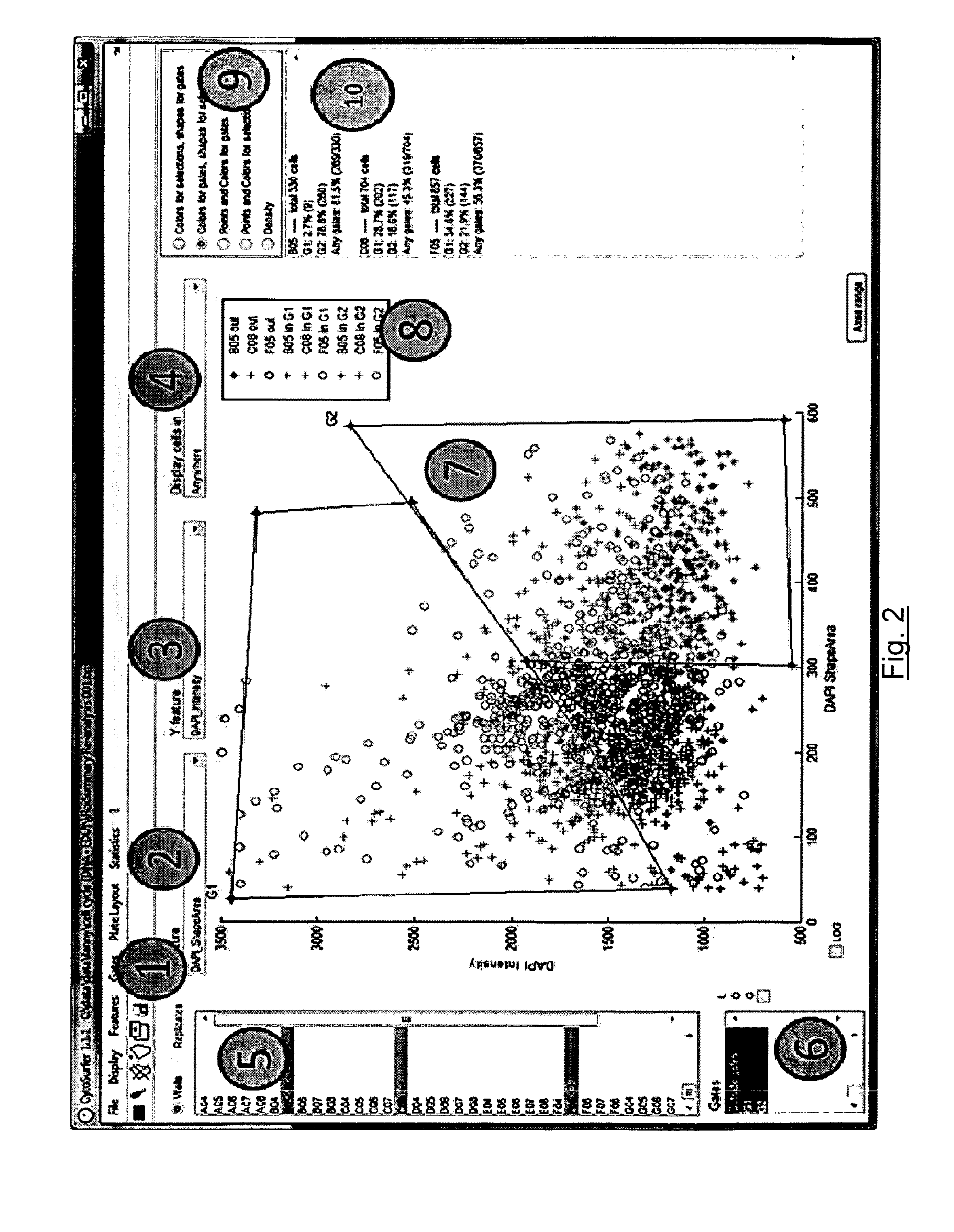
System and method to visualize and analyze data from image-based cellular assays or high content screening
InactiveUS20150131887A1Accurate placementSimplified navigationDigital data information retrievalImage analysisBiological conditionData processing system
Data processing system for generating representations and analyses of cytometric information for:—loading one set of data including:—one image of two wells on a plate each having one cell in a predetermined biological condition, each image being acquired with a microscope;—features of each cell from each image;—processing loaded data for obtaining representations and analyses of the data, from:—Histogram in one dimension;—Scattergram in two-dimensions;—Density in two-dimensions;—Plate layout management;—Cell montage;—Field;—Plate heatmap;—Dose response with regrouping of replicates;—Statistics information percentage of cell in different gates;—zFactor calculation with regrouping of replicates;—List of well for selection and list of biological condition for selection;—Statistics export capability;—Ready to print layout capability on the selected well or biological condition or all wells and biological conditions.
Owner:FLUOFARMA
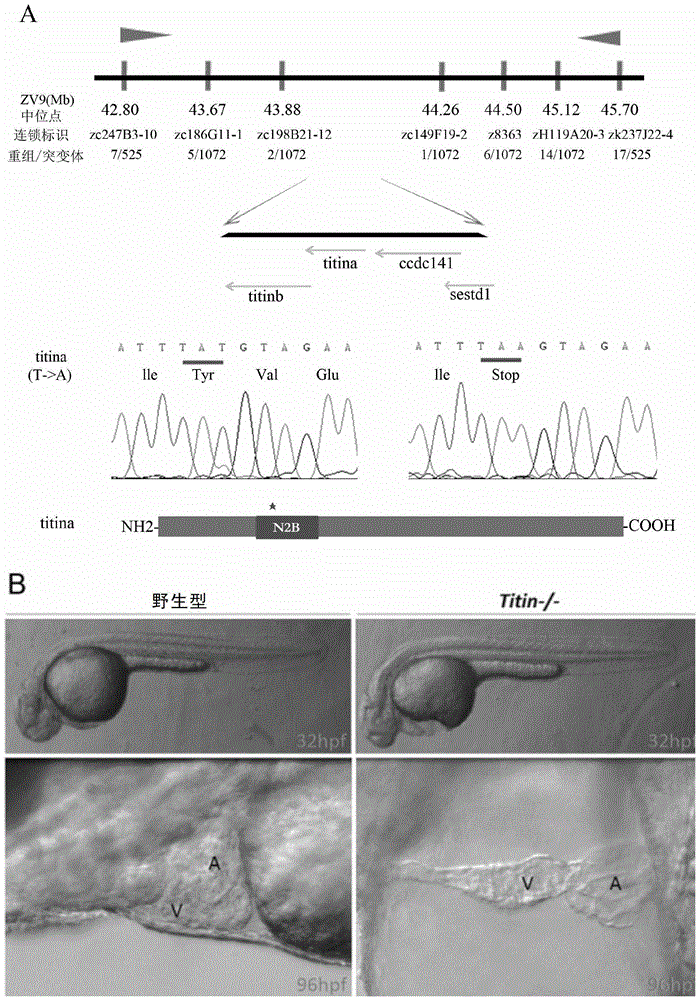
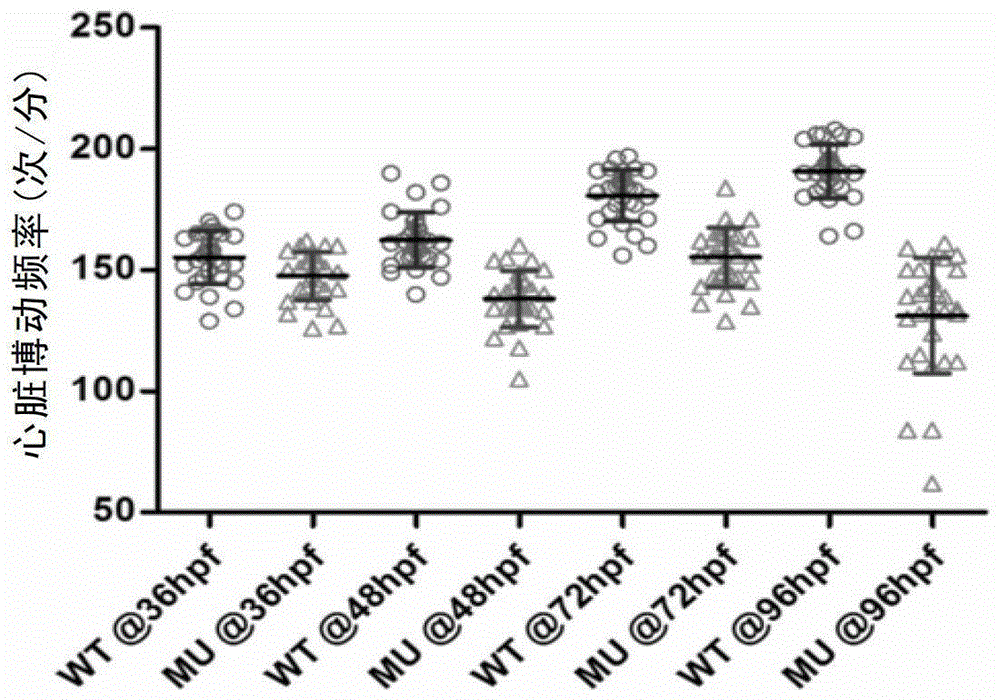
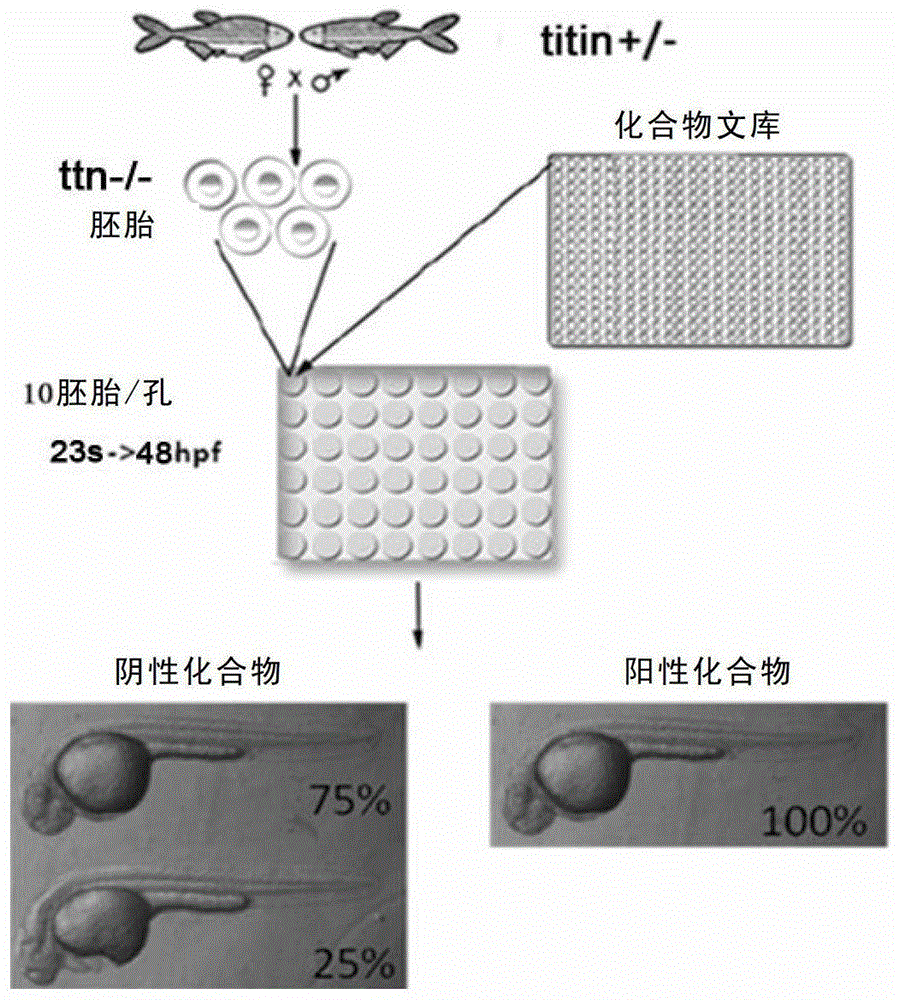
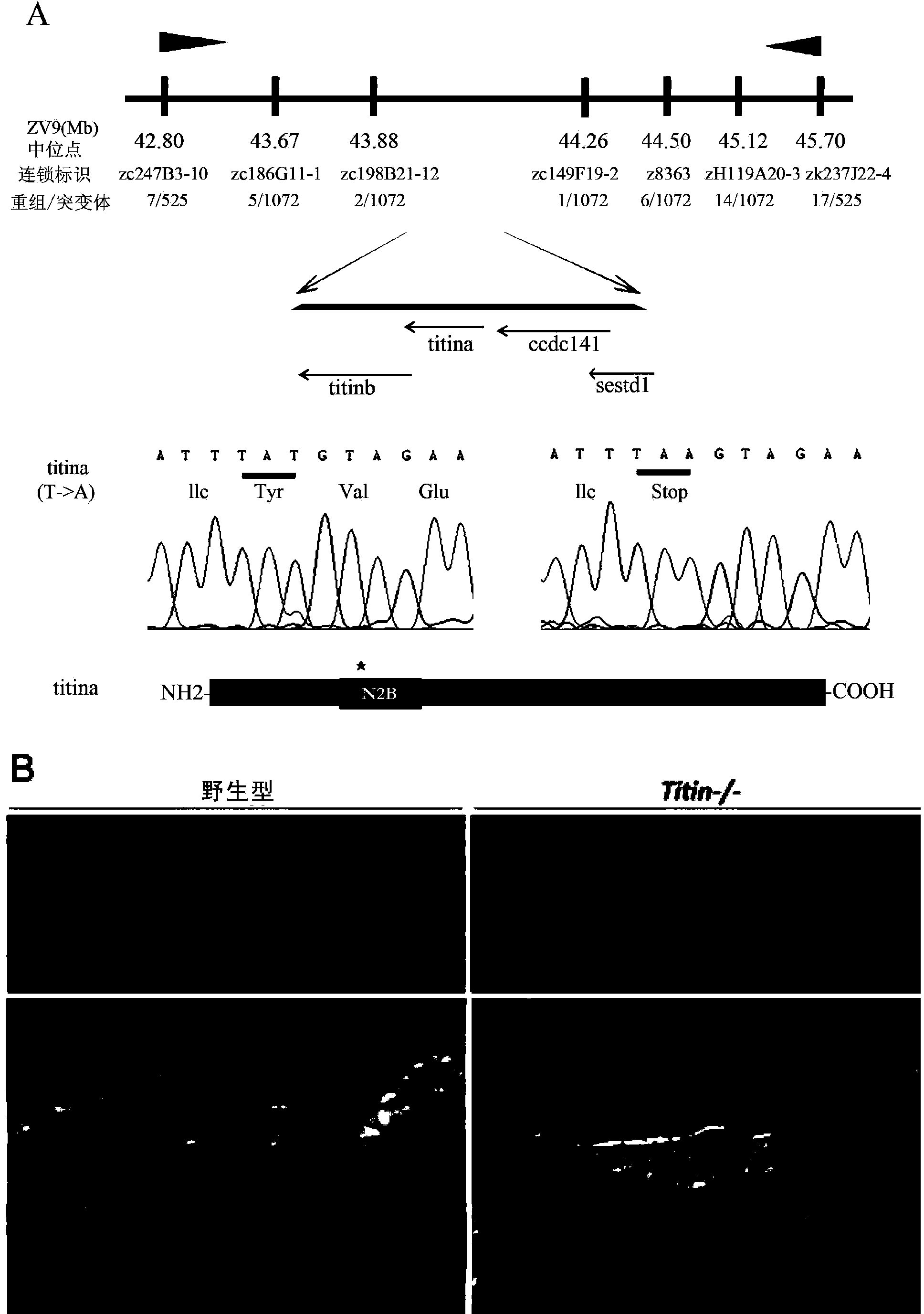
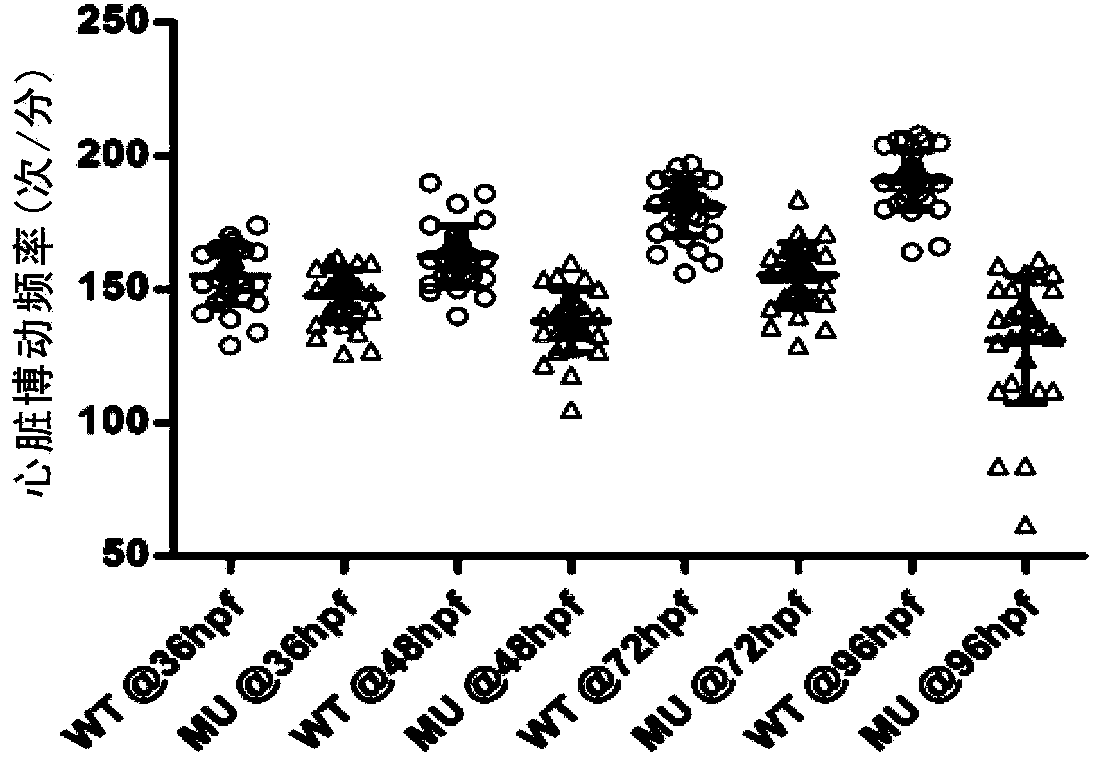
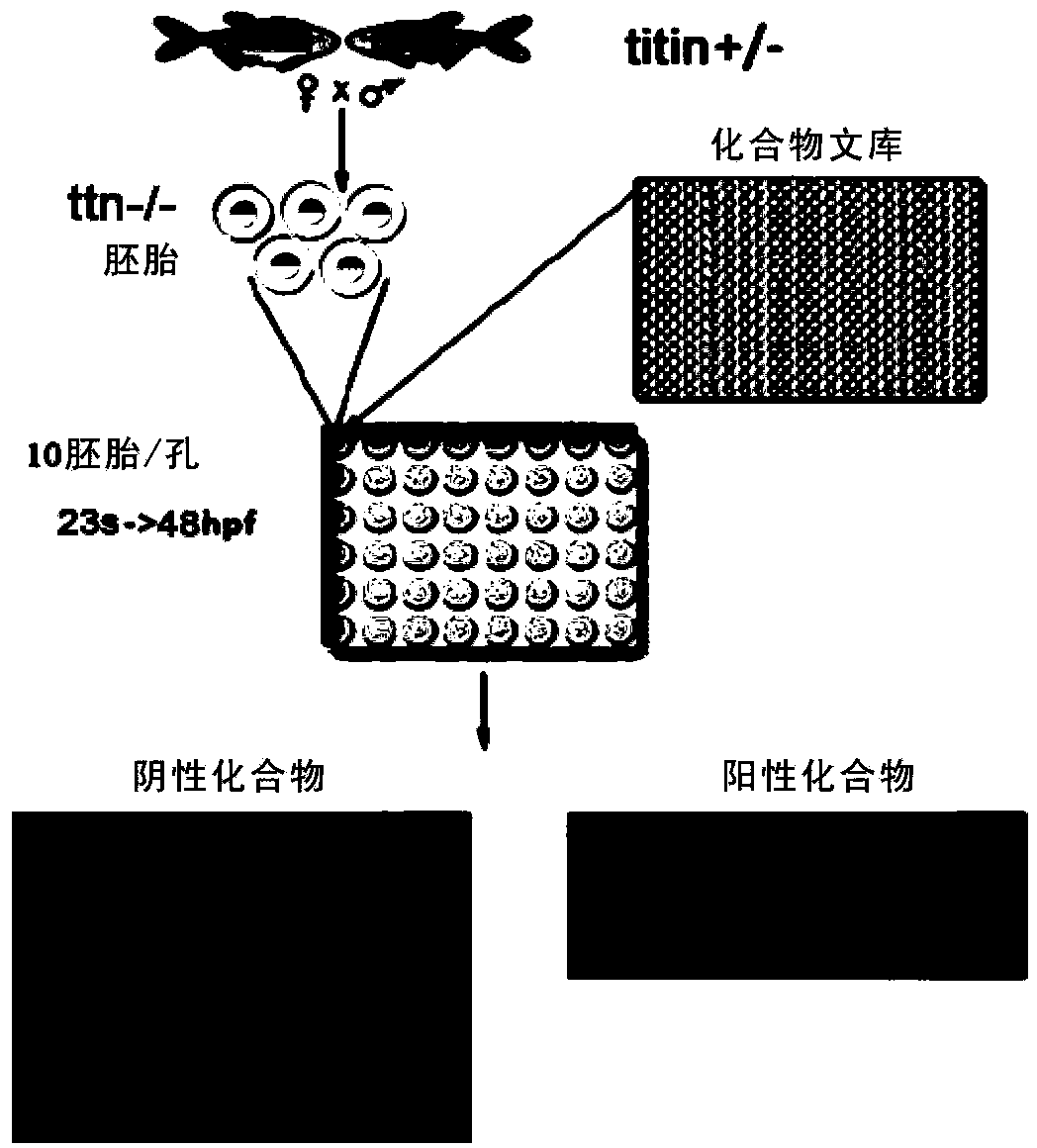
Establishing method and application of dilated cardiomyopathy and zebrafish disease model
ActiveCN104274464AOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseHigh-content screening
The invention relates to an establishing method and application of a dilated cardiomyopathy and zebrafish disease model. A disease model simulating human congenital dilated cardiomyopathy (CDCM) is firstly established; and the disease model can be used as a drug screening model to be applied to screening of drugs capable of relieving symptoms of heart failure caused by CDCM. The method provided by the invention is an economic and rapid high-content screening method; and the obtained compound has relatively high specificity and druggability.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
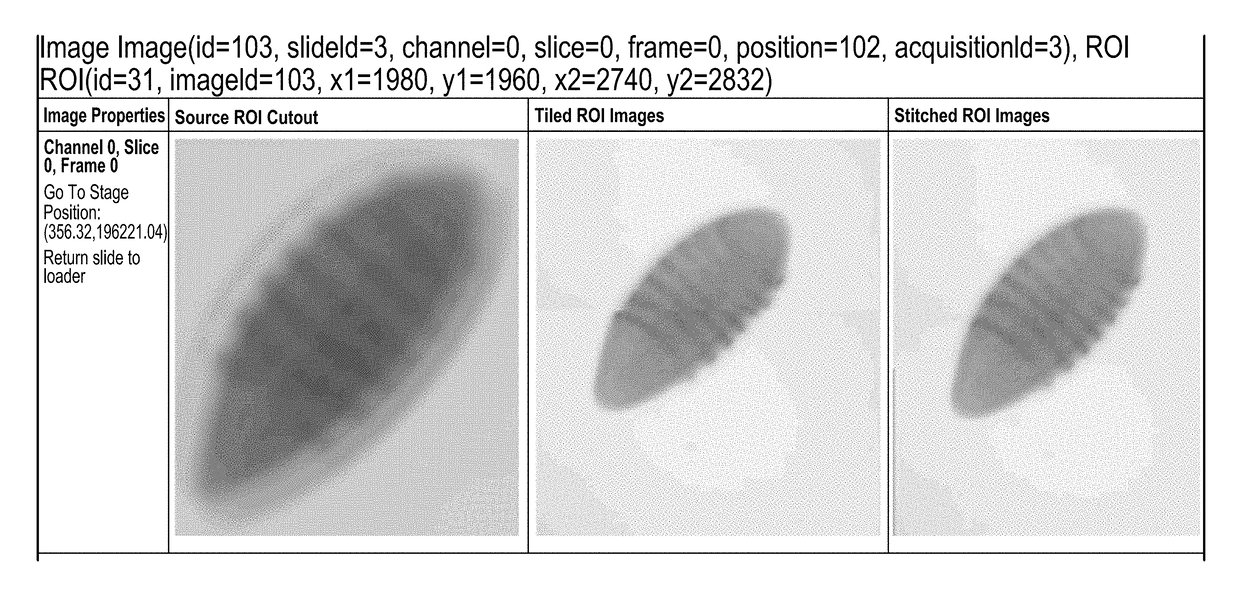
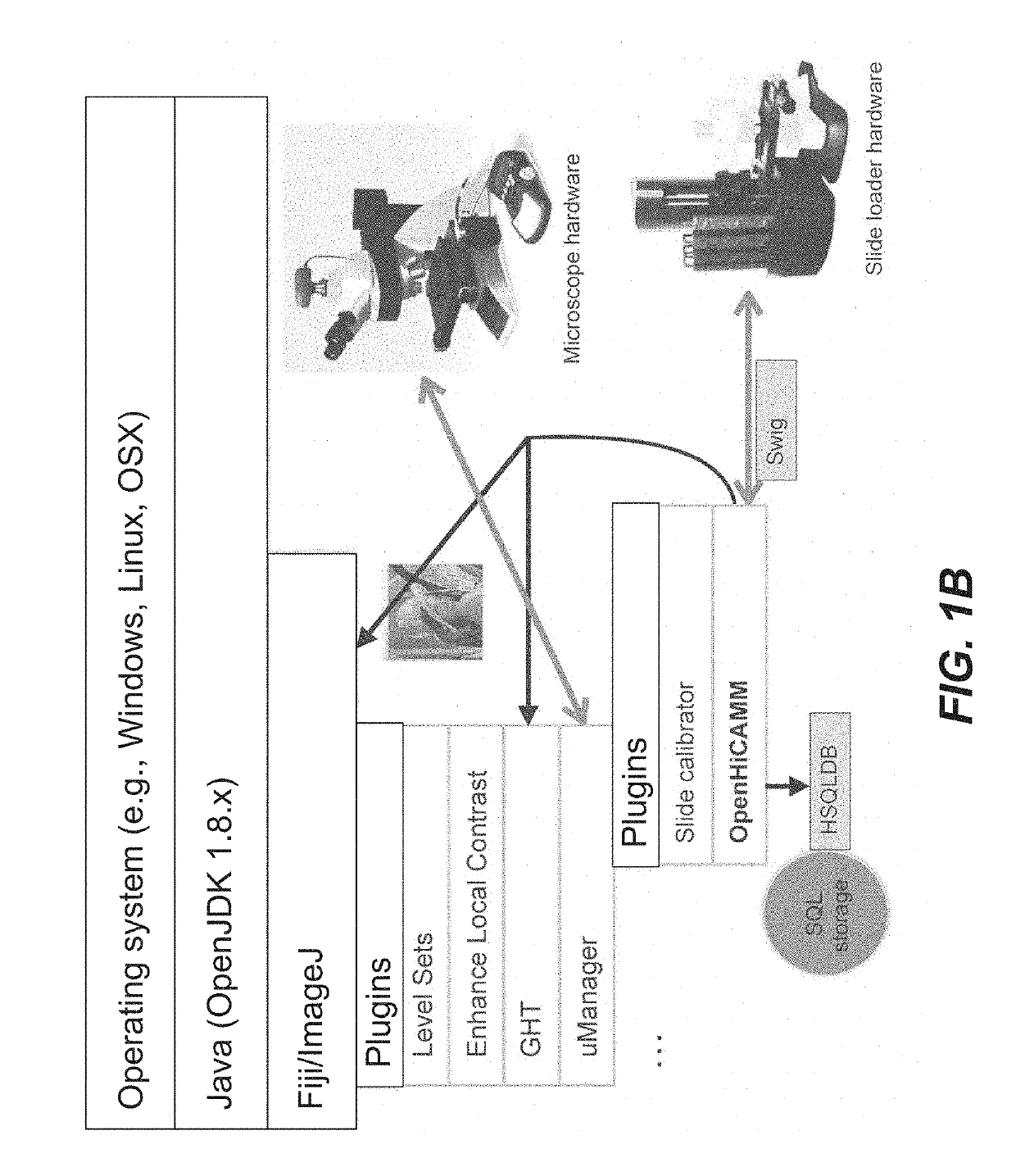
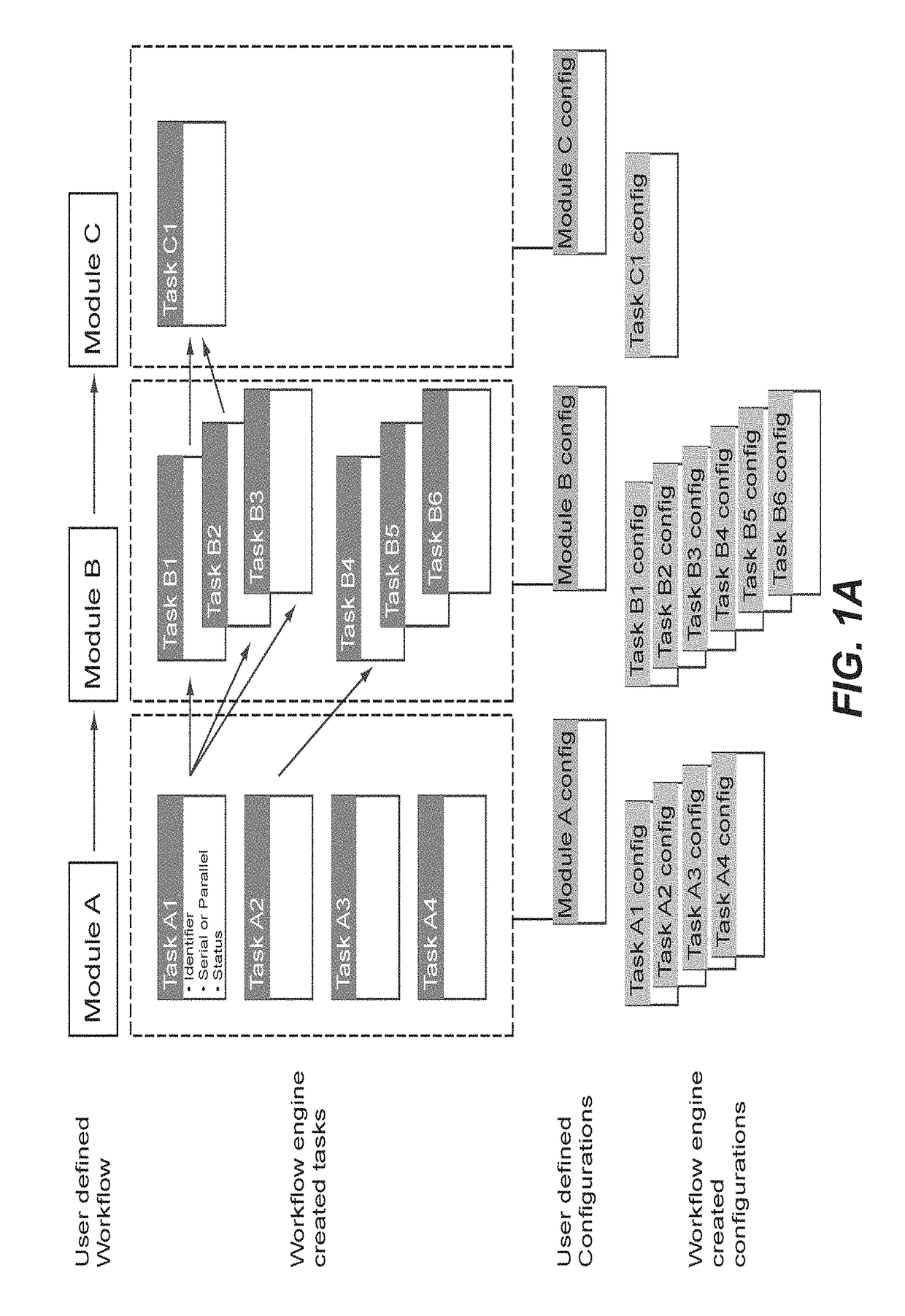
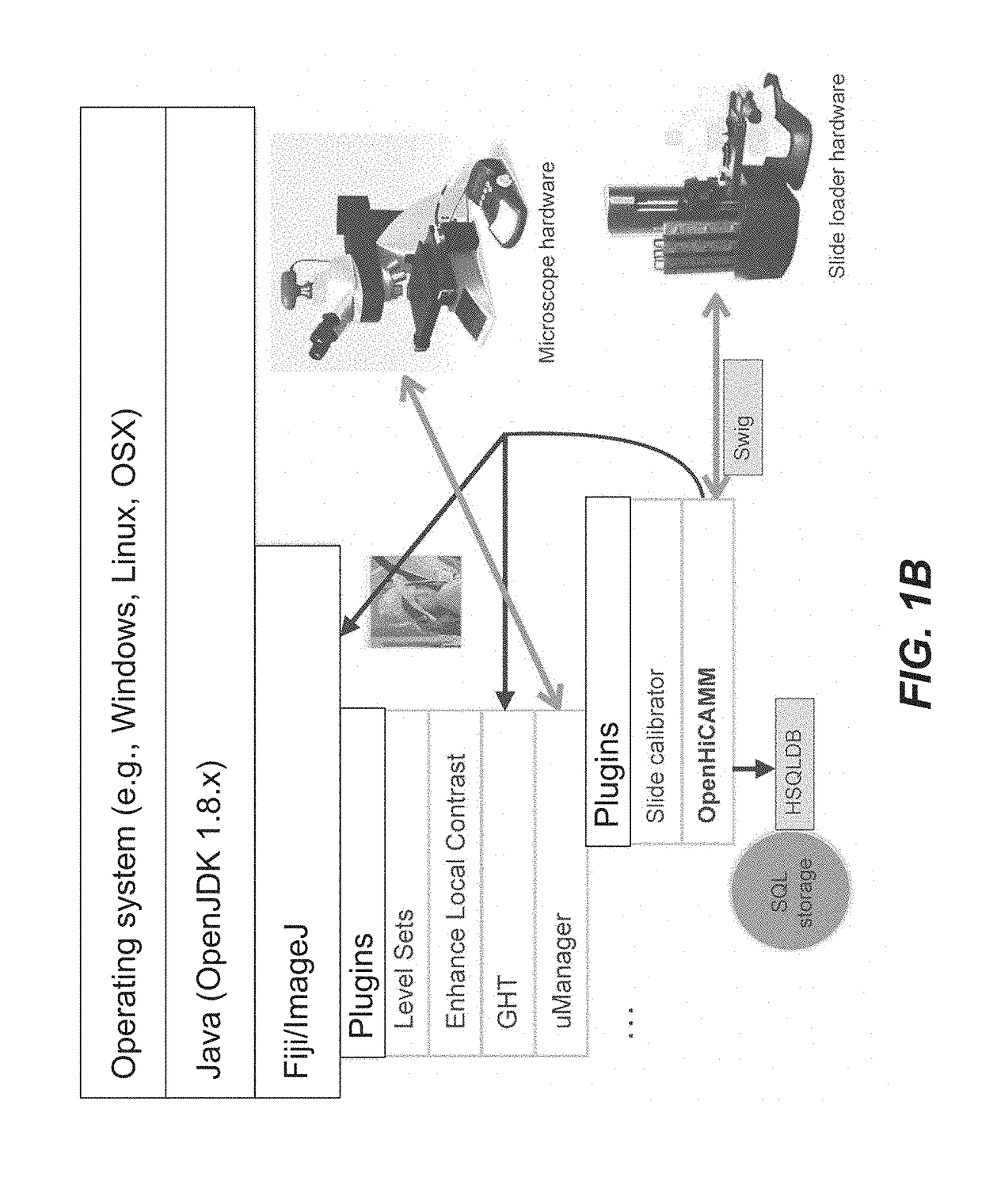
High content screening workflows for microscope imaging
Disclosed herein are systems methods for high content screening for microscope imaging. In some embodiments, the system comprises: a microscope; and a processor configured to implement: a slide loader module; a reference imager module; a slide imager module; a region of interest (ROI) finder module; a compare imager module; a calibrator module; and an image stitcher module.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
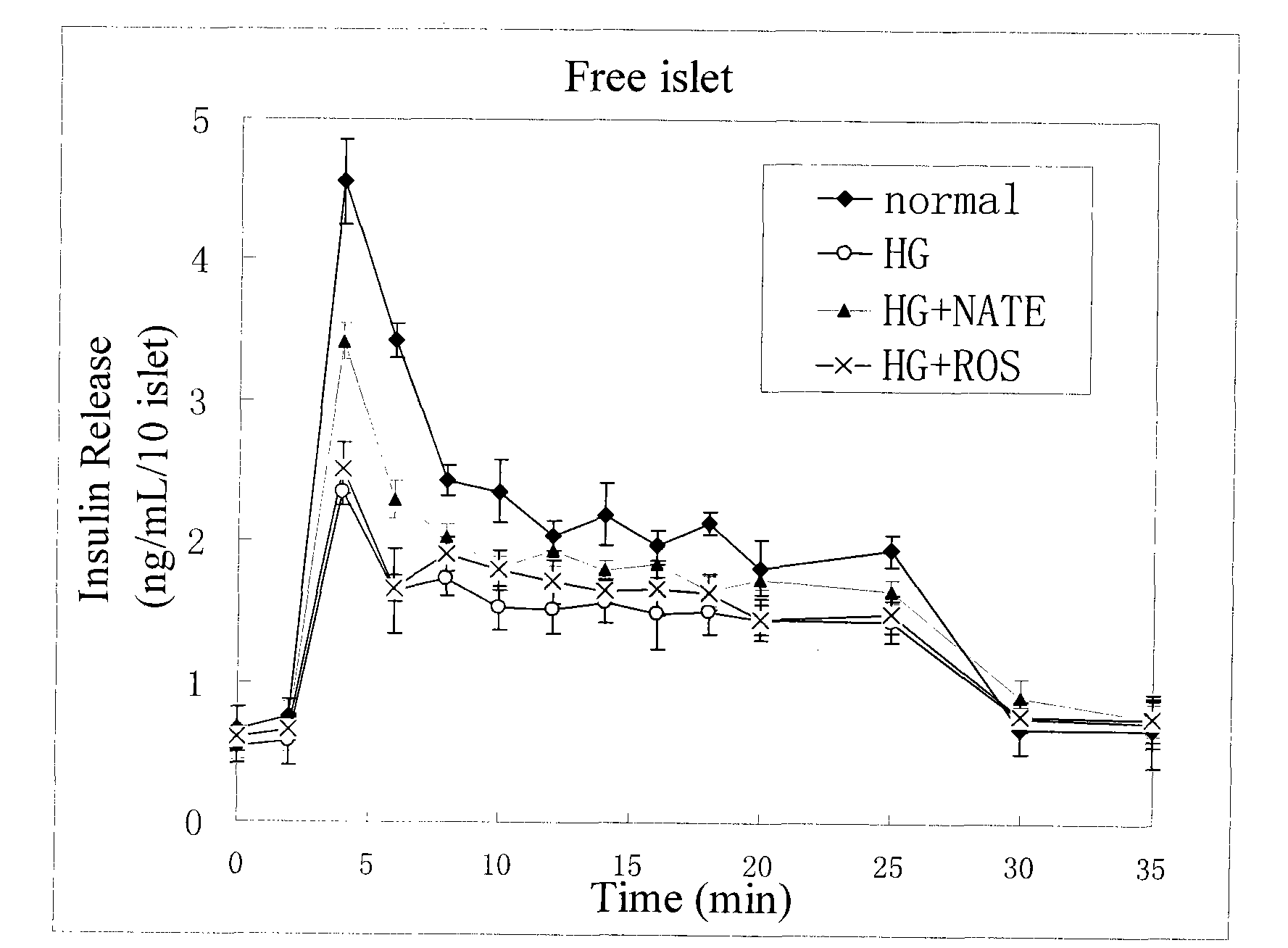
Method for high content screening of therapeutic drugs for diabetes
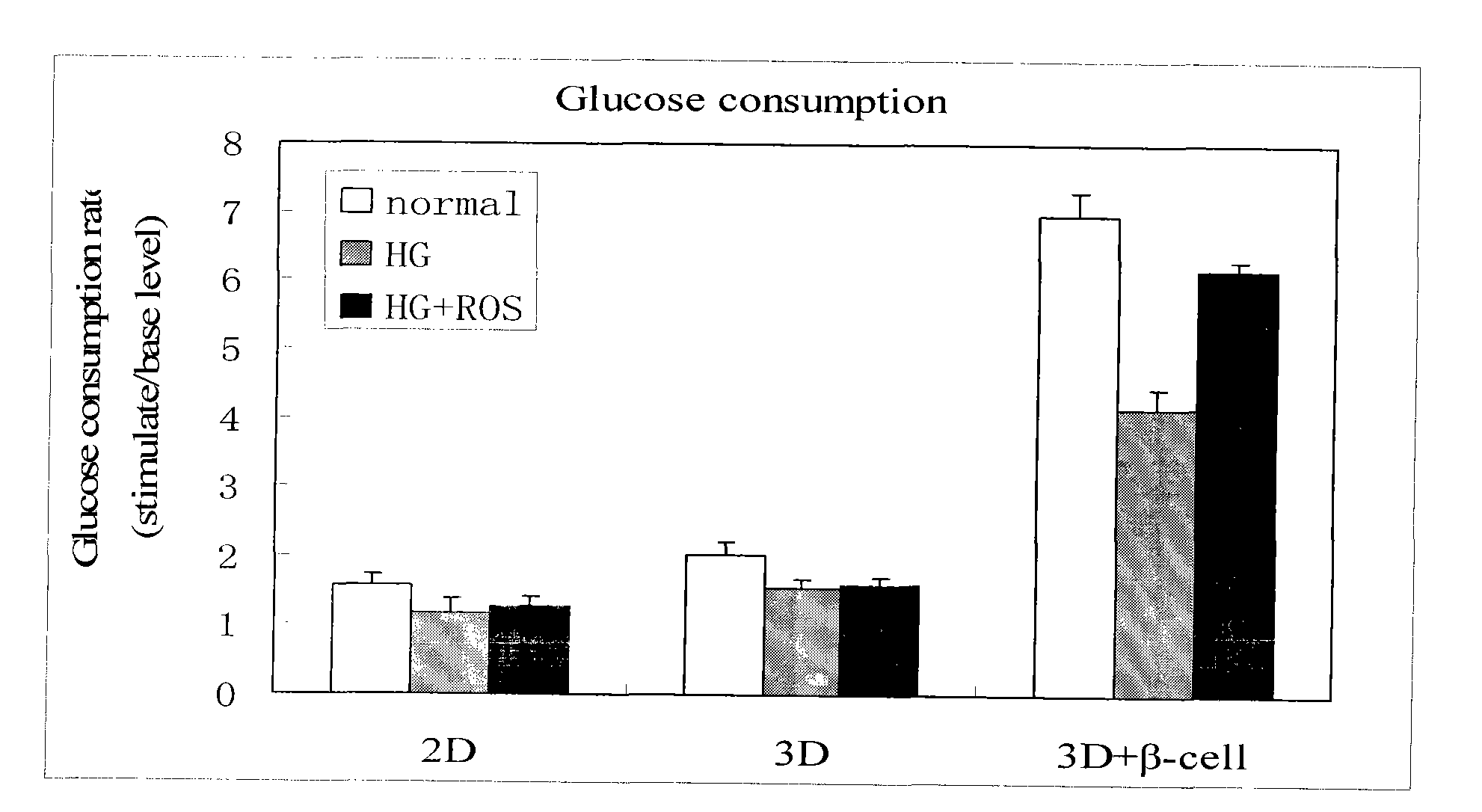
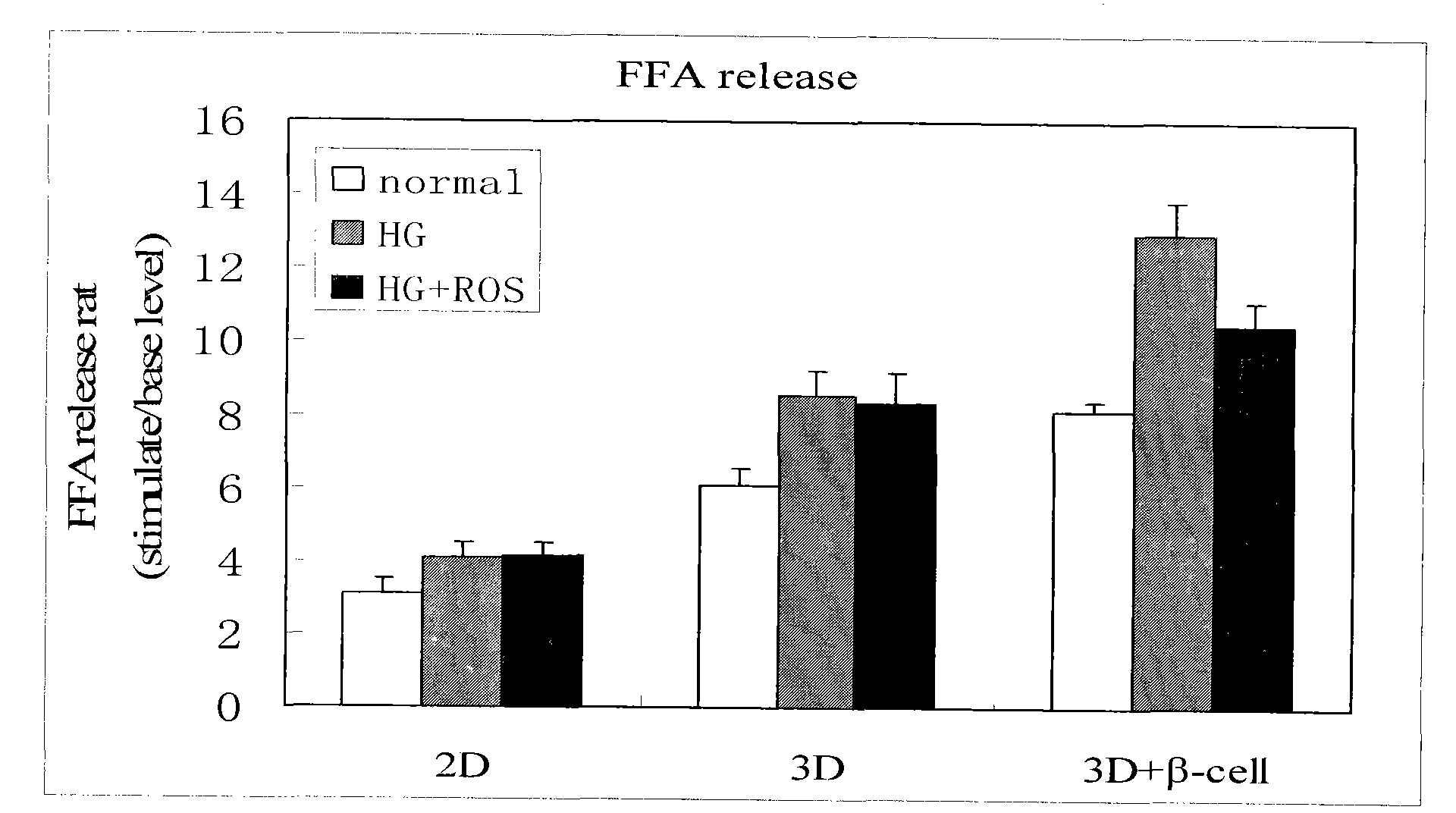
ActiveCN101775431AStable and reliable biological cross-linking technologyControl curingMicrobiological testing/measurementPorosityHigh concentration
The invention relates to a diabetes pathological model based on cell assembly technology and application thereof in high content drug screening. Adipose-derived stem cells and simulated extracellular matrix material are assembled to form a cell-containing three-dimensional structure with certain porosity; the inducing differentiation condition is controlled to enable the adipose-derived stem cells on the surface of the inner passage of the three-dimensional structure to differentiate into endothelial cells and to enable the adipose-derived stem cells inside the matrix material to differentiate into fat cells; and pancreas islet separated out from the body of an animal is directly assembled in the gaps of the three-dimensional structure. The system model is excited for a long time by high-concentration dextrose, fatty acid insulin, TNF or cytokine secretion of fat cells and the like so as to induce the system model to produce pathology and symptom of diabetes. The drug to be tested is put into a culture system, and by detecting the level of the relevant markers of the model under normal condition and pathological condition, the pharmacological activity of the drug to be tested can be analyzed and thereby high content screening can be carried out to the drug.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Microplates containing microsphere fluorescence standards, microsphere standards, and methods for their use
InactiveUS20060045814A1Analysis using chemical indicatorsLaboratory glasswaresFluorescenceMicrosphere
Microplates containing spherical “microsphere” fluorescence standards are disclosed. The microplates can be prepared using several methods including airbrushing, application with an inkjet printer, or controlled evaporation. Spherical bead standards containing two or more regions stained with dyes of different fluorescence lifetimes, and methods for their preparation are also disclosed. The microplates can be used as calibration standards for fluorescence and confocal microscopes, and as calibration tools for microscope-based high content screening (“HCS”) instruments.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
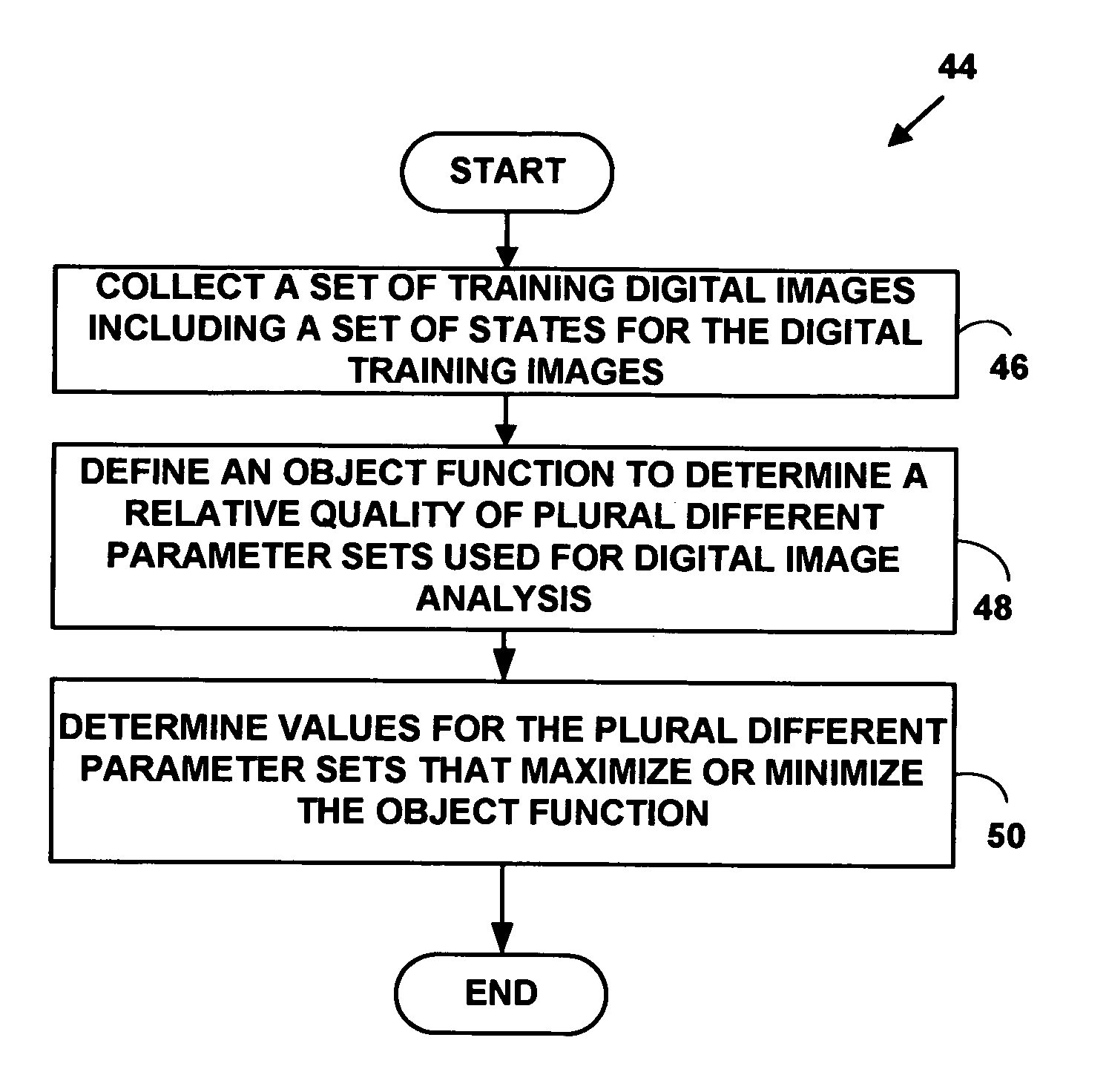
Automated method and system for setting image analysis parameters to control image analysis operations
A method and system for setting image analysis parameters to control image analysis operations. The method and system include collecting set of digital training images including a set of states for the set of digital training images. An objective function is defined to determine a relative quality of plural different parameter sets used for digital image analysis. Values for the plural different parameter sets that maximize (or minimize) the objective function are determined. The method and system increases a usability of high content screening technologies by reducing a required level of expertise required to configure digital image processing.
Owner:CELLOMICS
Methods to increase the capacity of high content cell-based screening assays
InactiveUS20060265137A1Increase capacityLow costCompound screeningApoptosis detectionCell basedBiology
The present invention involves the pooling of multiple high content cell-based screening assays, and carrying out a primary screen in a one or more channels of a fluorescence detection device, which drastically increases the number of simultaneous high content cell-based screening events that can be carried out. Subsequent deconvolution of primary screen “hits” (ie: those wells or locations on an array of locations in which the one or more test compounds caused a change in the fluorescence signal(s) from the fluorescent reporter molecules in the cells) enables much more rapid generation of high content cell screening data than was previously possible, and at significantly reduced costs.
Owner:CELLOMICS
High content screening workflows for microscope imaging
Disclosed herein are systems methods for high content screening for microscope imaging. In some embodiments, the system comprises: a microscope; and a processor configured to implement: a slide loader module; a reference imager module; a slide imager module; a region of interest (ROI) finder module; a compare imager module; a calibrator module; and an image stitcher module.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method and apparatus for multi-parameter data analysis
ActiveUS20120035859A1Reduce processing timeAccurate measurementBiological testingSpecial data processing applicationsData setMulti parameter
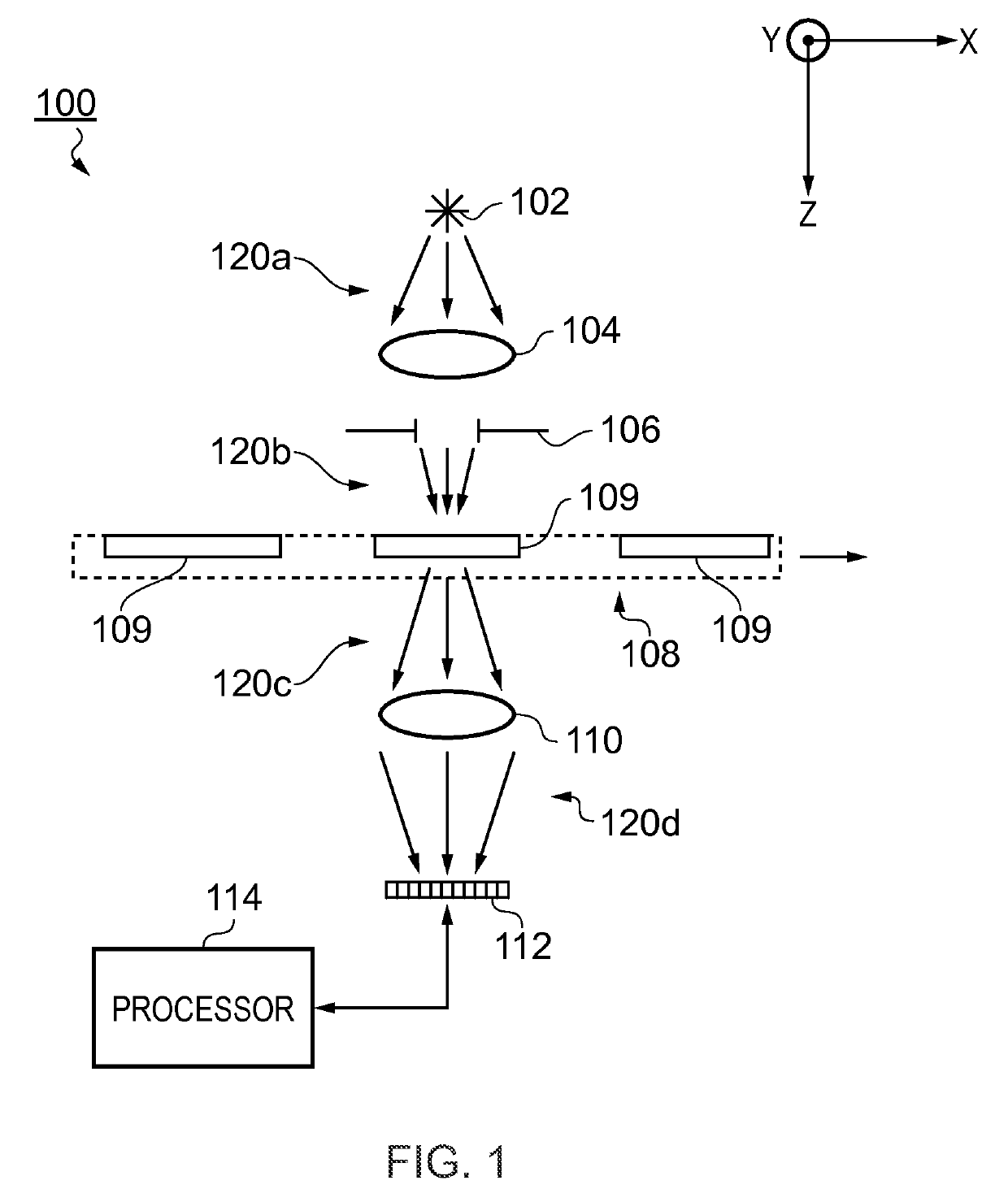
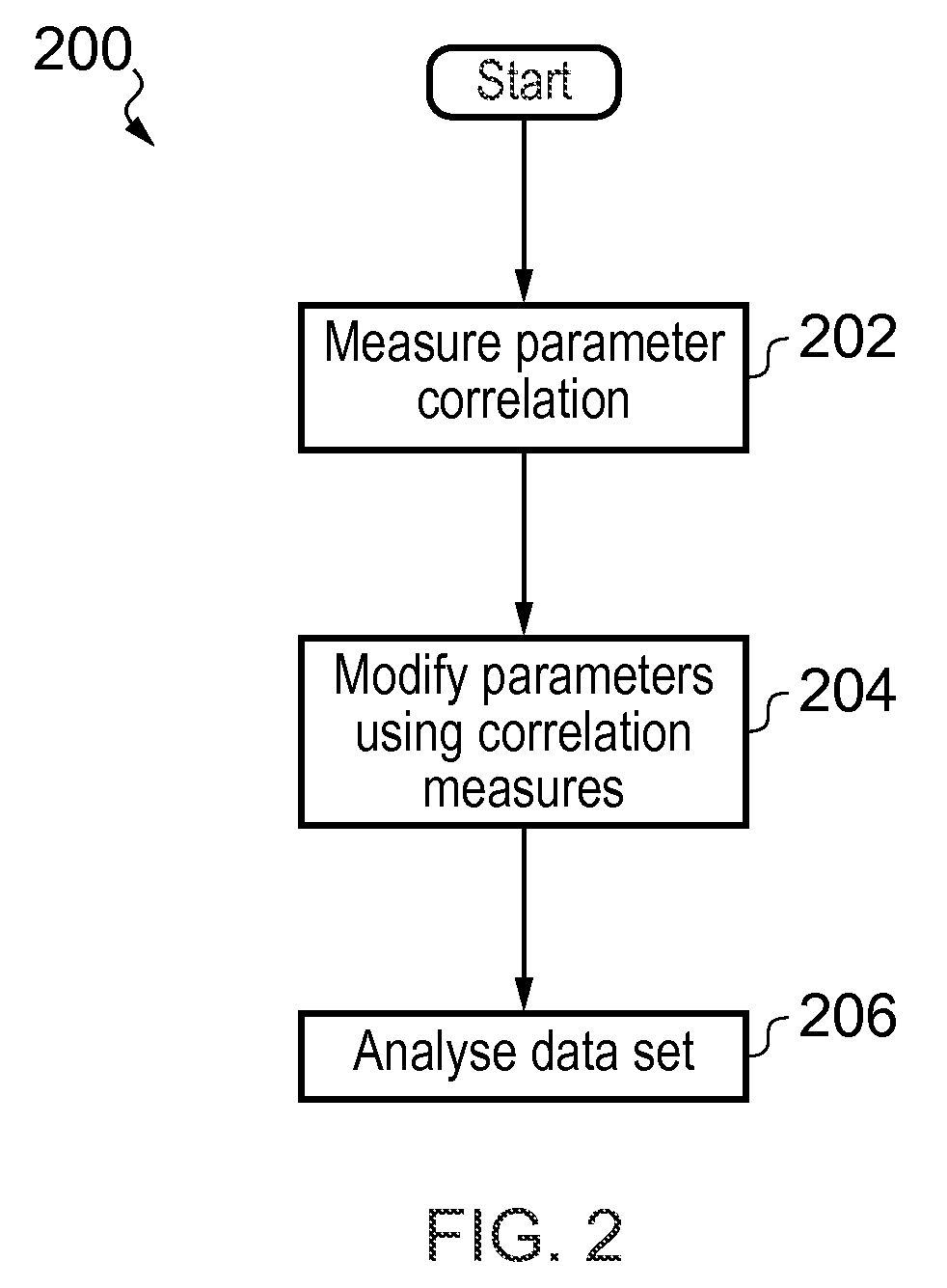
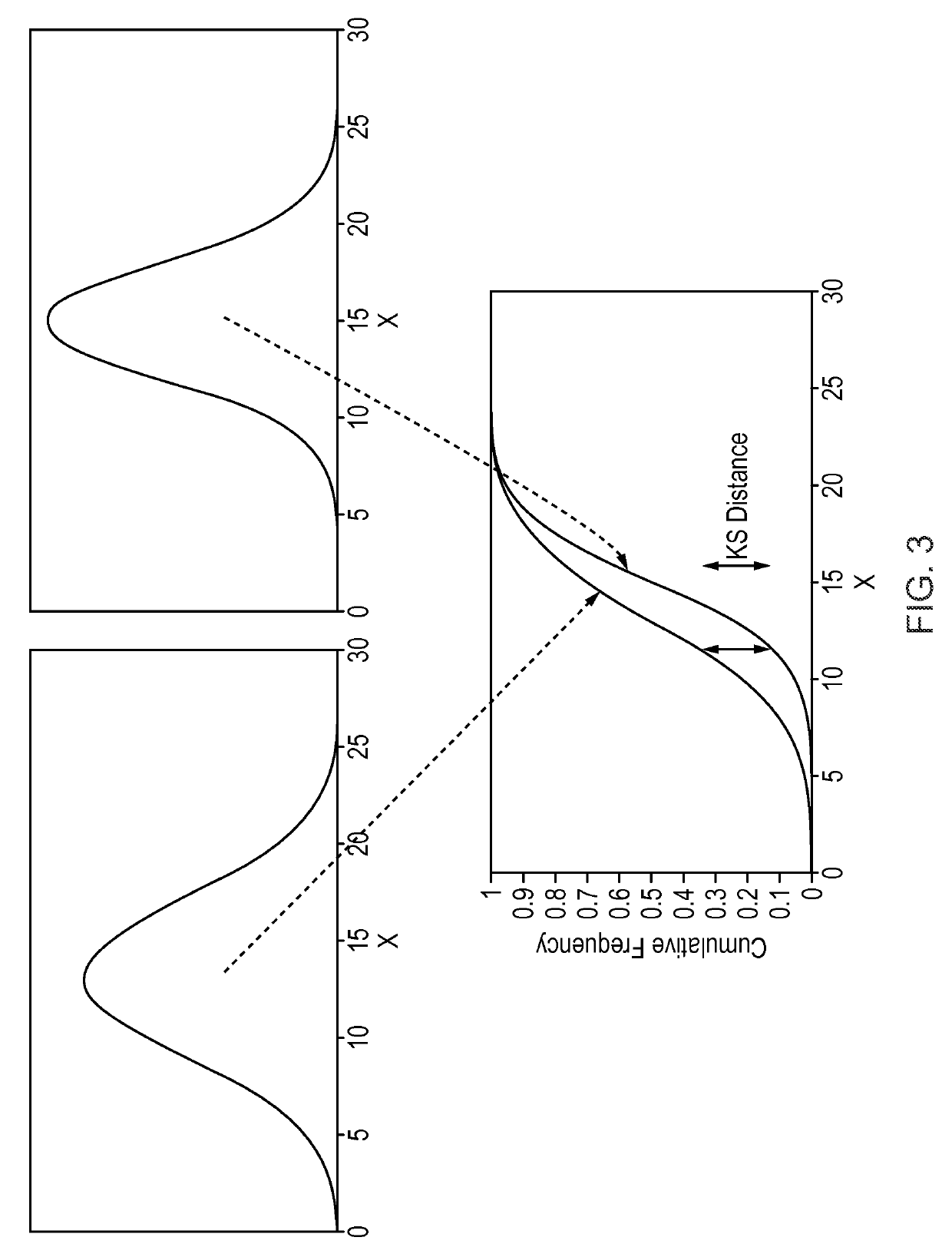
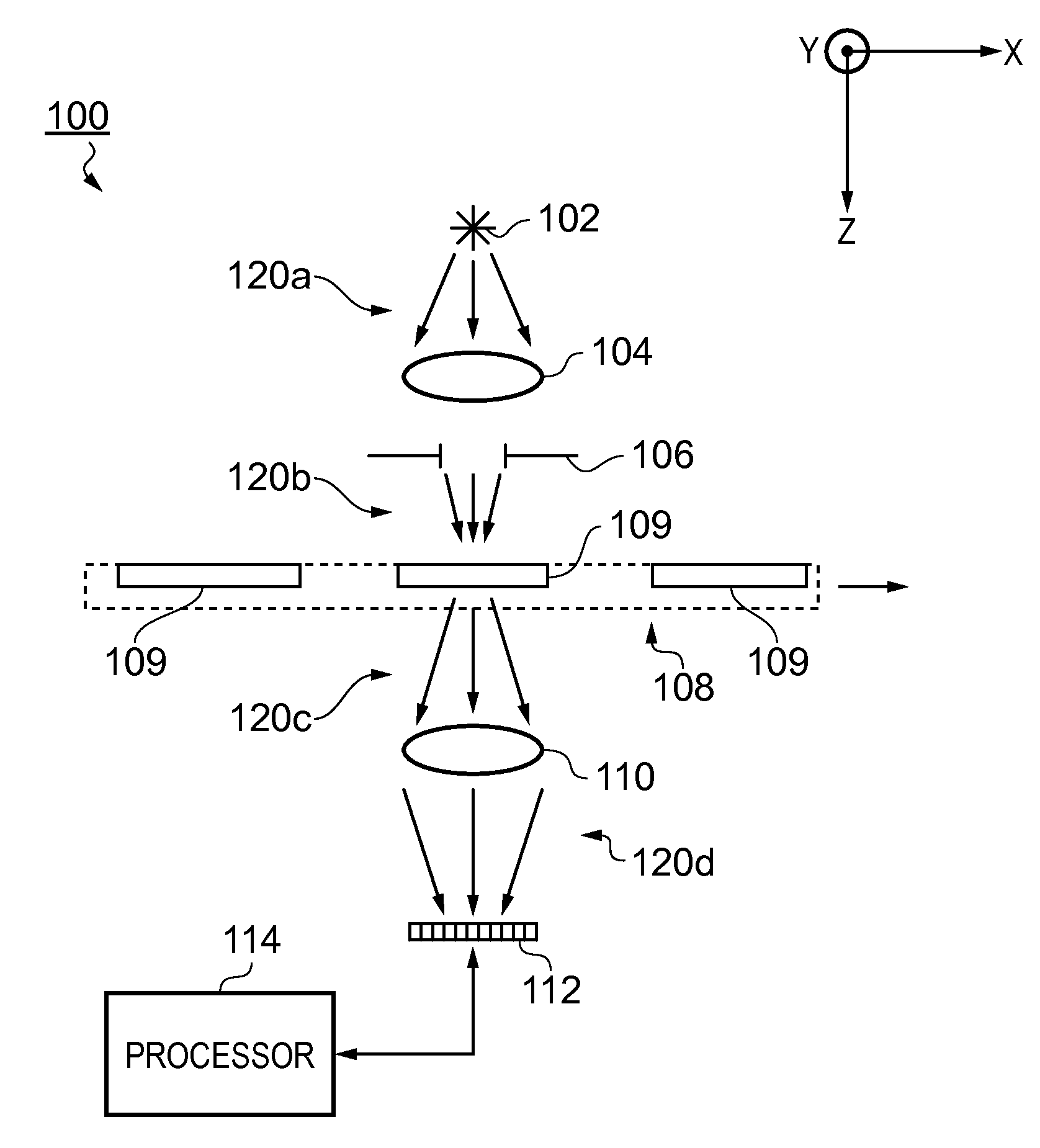
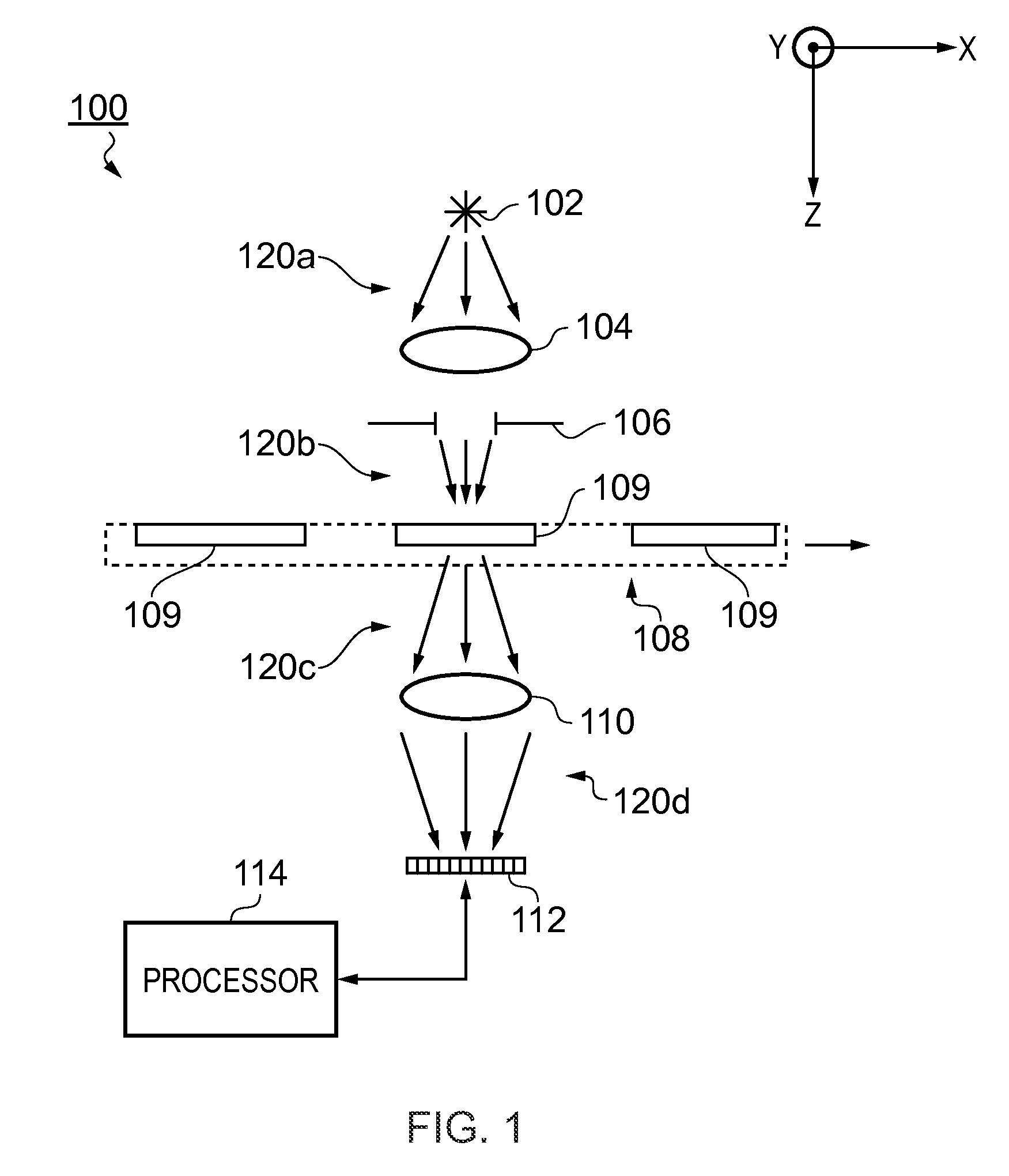
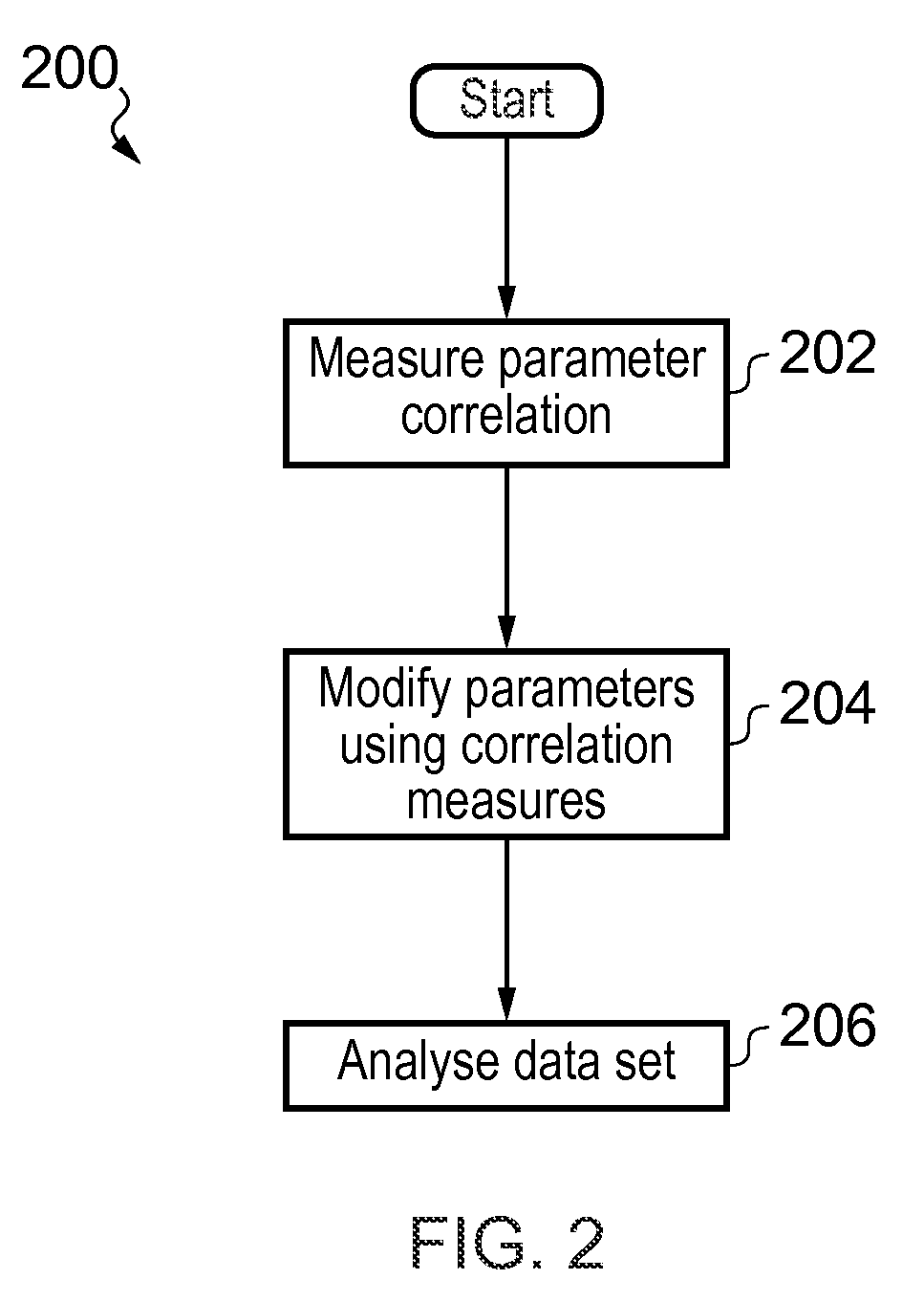
In one aspect, the present invention relates to a method 200 for identifying one or more phenotypes from a multi-parameter data set. The method 200 comprises measuring 202 correlation between pairs of parameters within the multi-parameter data set, modifying 204 correlated parameter values within a predetermined multi-parameter data analysis set to form an analysis parameter set, and analysing 206 the multi-parameter data set using the analysis parameter set to identify one or more phenotypes from the multi-parameter data set. Various embodiments of the present invention may, for example, be used in an automated high-content screening (HCS) apparatus 100 for biological cellular analysis.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS OPERATIONS UK LTD
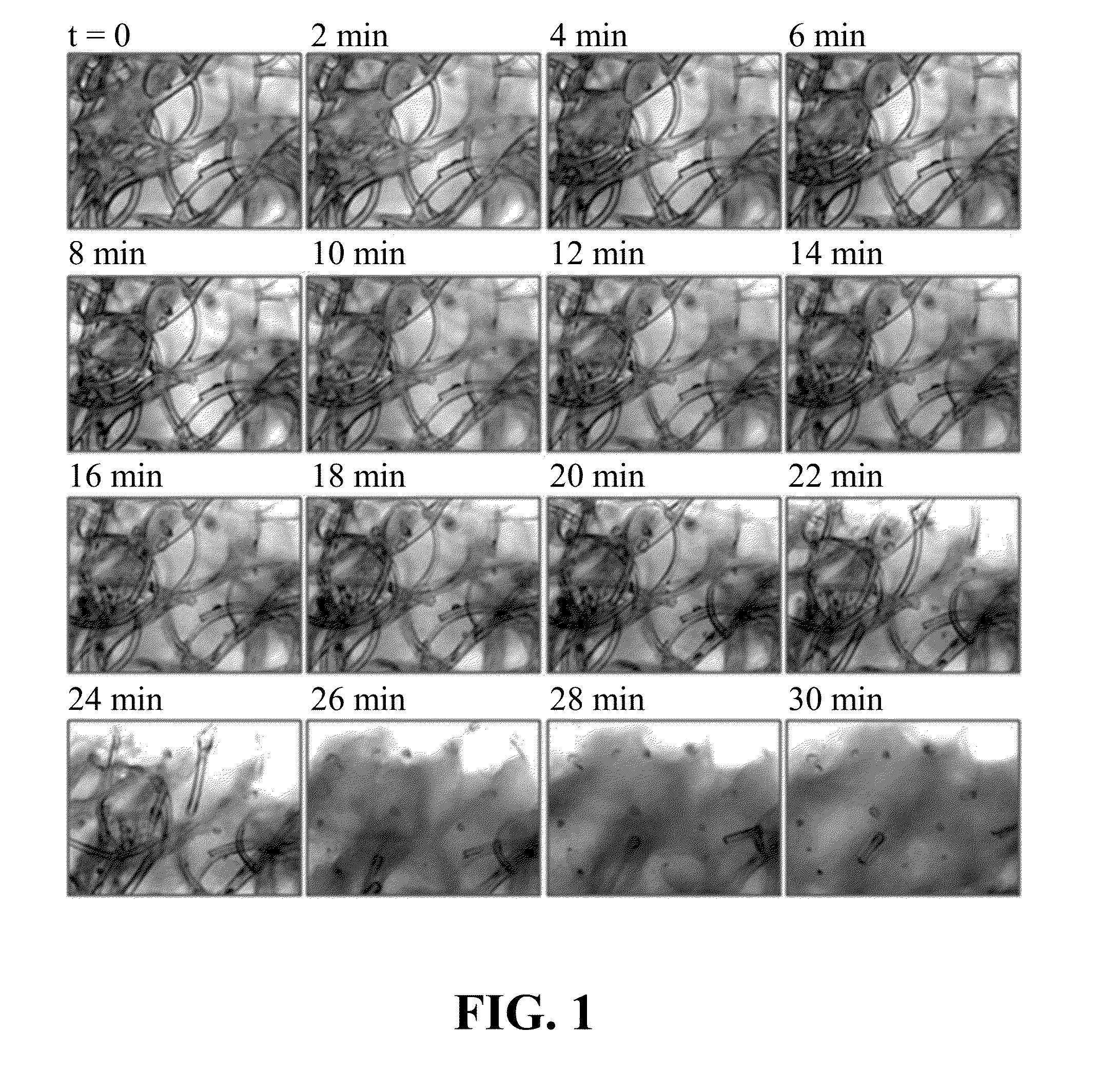
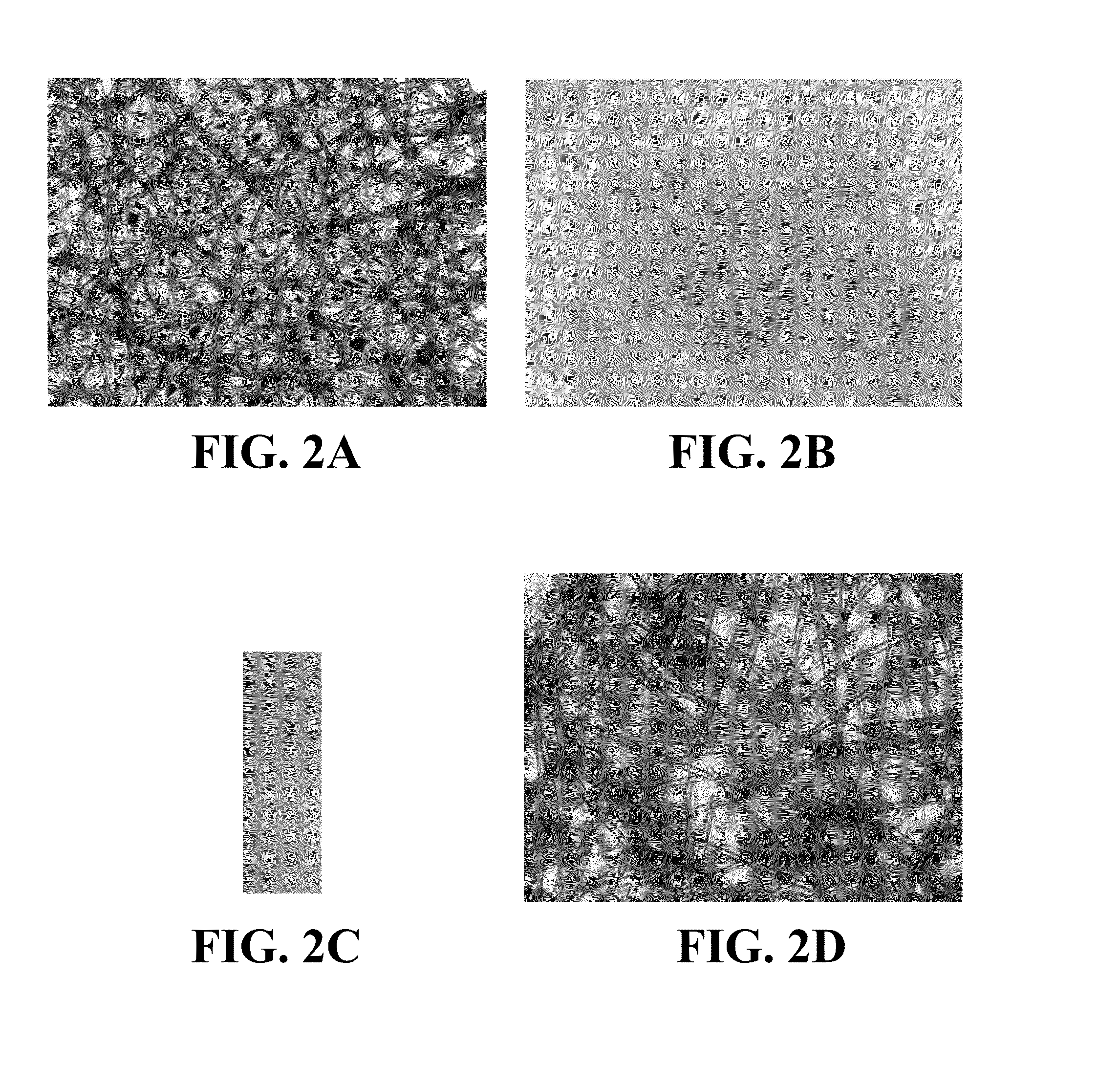
Cell model for screening [kappa] opioid receptor agonist, and screening method thereof
ActiveCN105462930AHigh sensitivityReduce stepsMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesOpioid AgonistHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
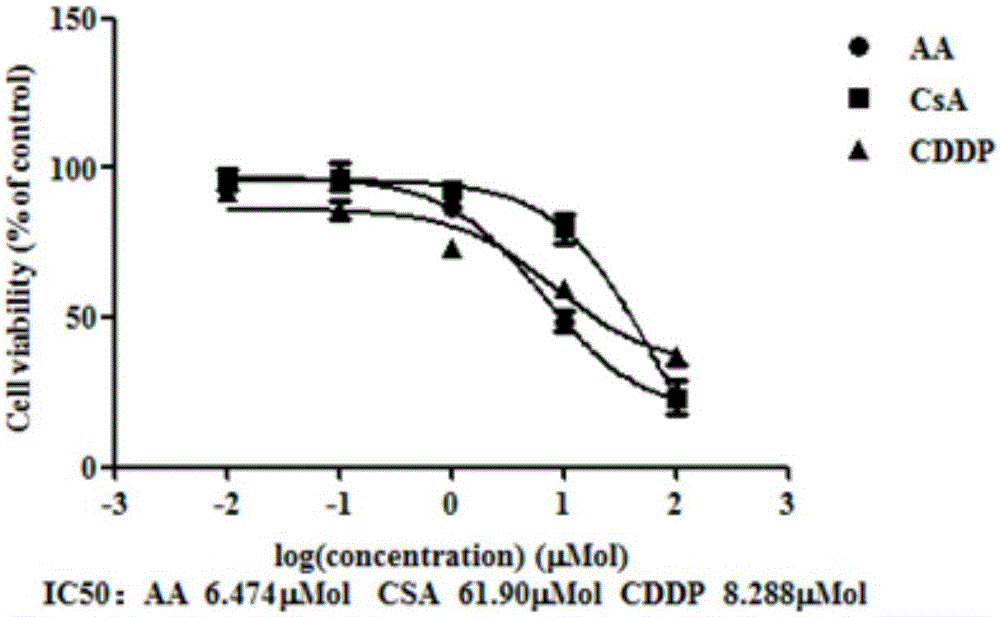
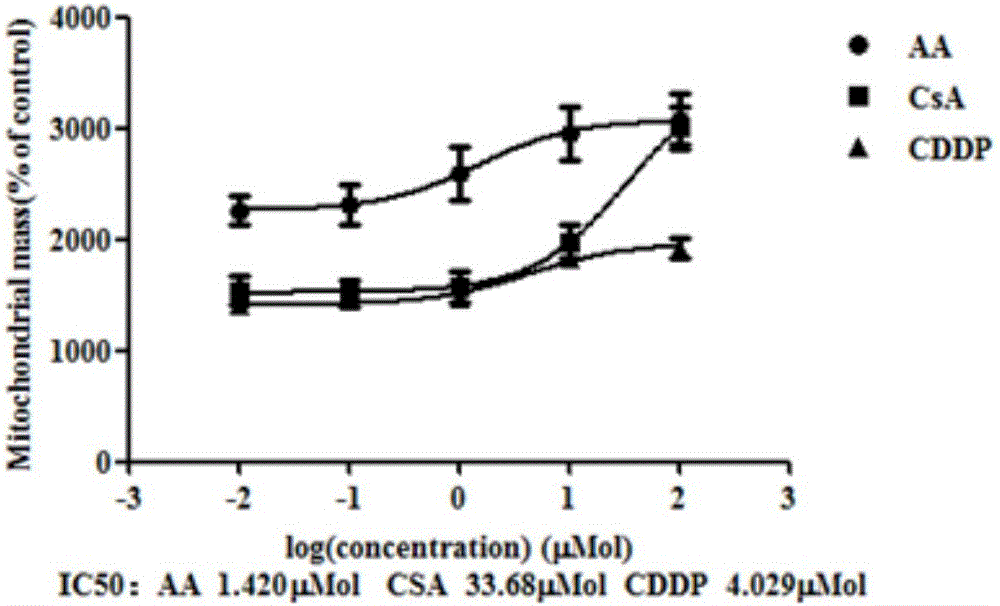
The present invention belongs to the field of cell biology and pharmacy, and relates to a cell model for screening an OPRK opioid receptor agonist, and a screening method thereof. Particularly the present invention relates to a cell, which expresses an opioid receptor and PKA. The present invention further relates to a method for screening the opioid receptor agonist, a method for evaluating excitation activity or cytotoxicity of a compound or composition on the opioid receptor, and uses of the cell in opioid receptor agonist screening. According to the present invention, the established cell model is sensitive, efficient and reliable, and can be used for high-throughput screening and / or high content screening of the opioid receptor, especially the OPRK opioid agonist.
Owner:INST OF PHARMACOLOGY & TOXICOLOGY ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI P L A
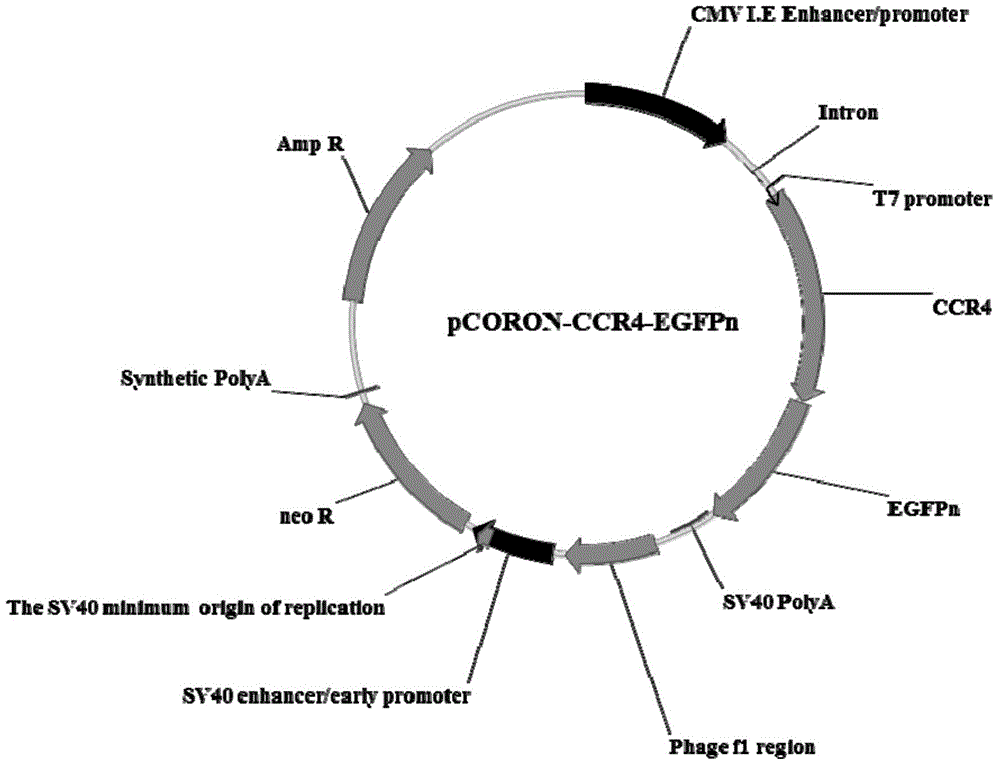
Cell model for screening CCR4 antagonist, and screening method thereof
ActiveCN105462929AEasy to operateStable growthMicrobiological testing/measurementForeign genetic material cellsScreening methodBiological activation
The present invention belongs to the field of pharmacy and cell biology, and relates to an efficient and reliable high content CCR4 antagonist screening cell model using human chemokine receptor 4 as a target, and a screening method thereof. According to the present invention, a cell line being subjected to human CCR4-enhanced green fluorescent protein fusion expression introducing is established, excitation is performed through human thymus activation regulated chemokine and human macrophage chemotatic factor, the CCR4 with green fluorescent protein is induced to produce re-distribution so as to form green fluorescent particles, and the CCR4 antagonist screening cell model for high-content screening is established; the bioactivity of the compound is evaluated by determining the CCR4 green fluorescent particle formation excited or inhibited by the screened compound through the model; and the established drug screening model is the sensitive, efficient and reliable CCR4 antagonist screening cell model suitable for high-throughput and high-content screening, and the method is the sensitive, efficient and reliable method suitable for high-throughput and high-content screening.
Owner:INST OF PHARMACOLOGY & TOXICOLOGY ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI P L A
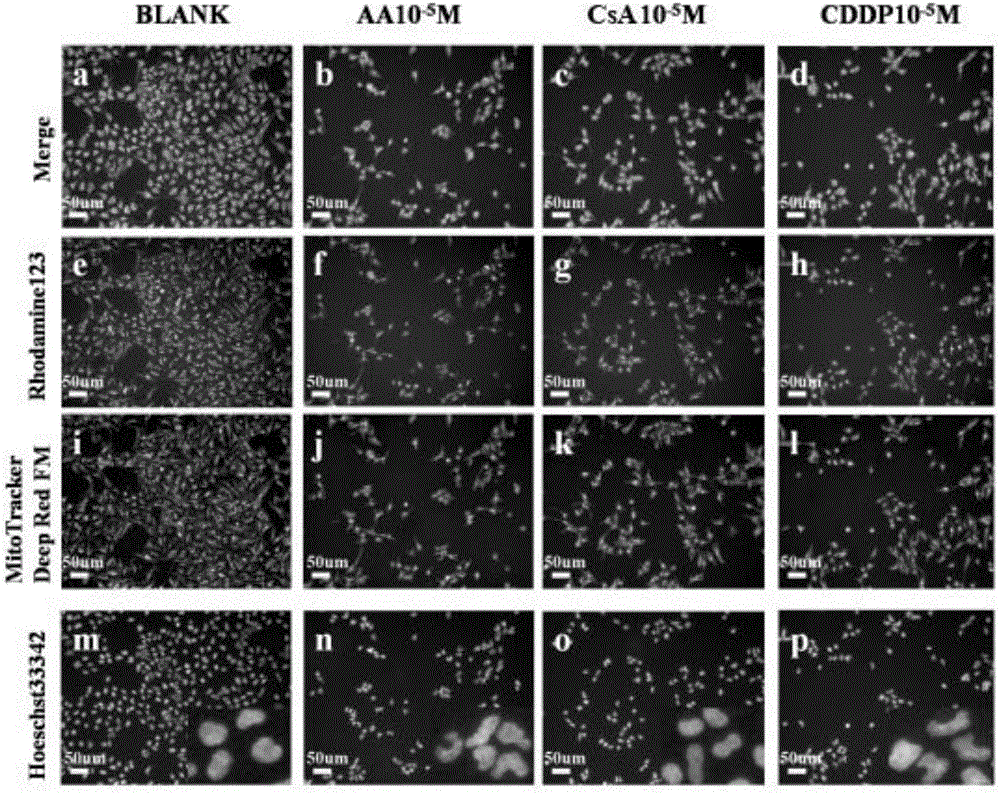
Cell phenotype based high-content multi-index renal toxicity detection method and applications thereof
InactiveCN105928913AMaintain structureMaintain integrityFluorescence/phosphorescenceCell phenotypeFluorescence
The invention discloses a cell phenotype based high-content multi-index renal toxicity detection method and applications thereof. According to the detection method, A fluorescent molecular probe that can change the functions of nucleus or mitochondrial and carry out specific detection is adopted to label cells; a high content screening system is taken as the detection means, based on the high content screening system, live cells, which are injected with drugs to be detected, are subjected to imaging analysis so as to determine at least one influence of the drugs on cell number, nucleus and mitochondrial, and thus the influence of the drugs on the cells can be determined. The invention also discloses applications of the detection method. The provided detection method has the advantages that multiple indexes can be detected, while the cell structure and functional integrity are maintained, and the detection method has the characteristics of rapidness, high flux, low cost, and high accuracy.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
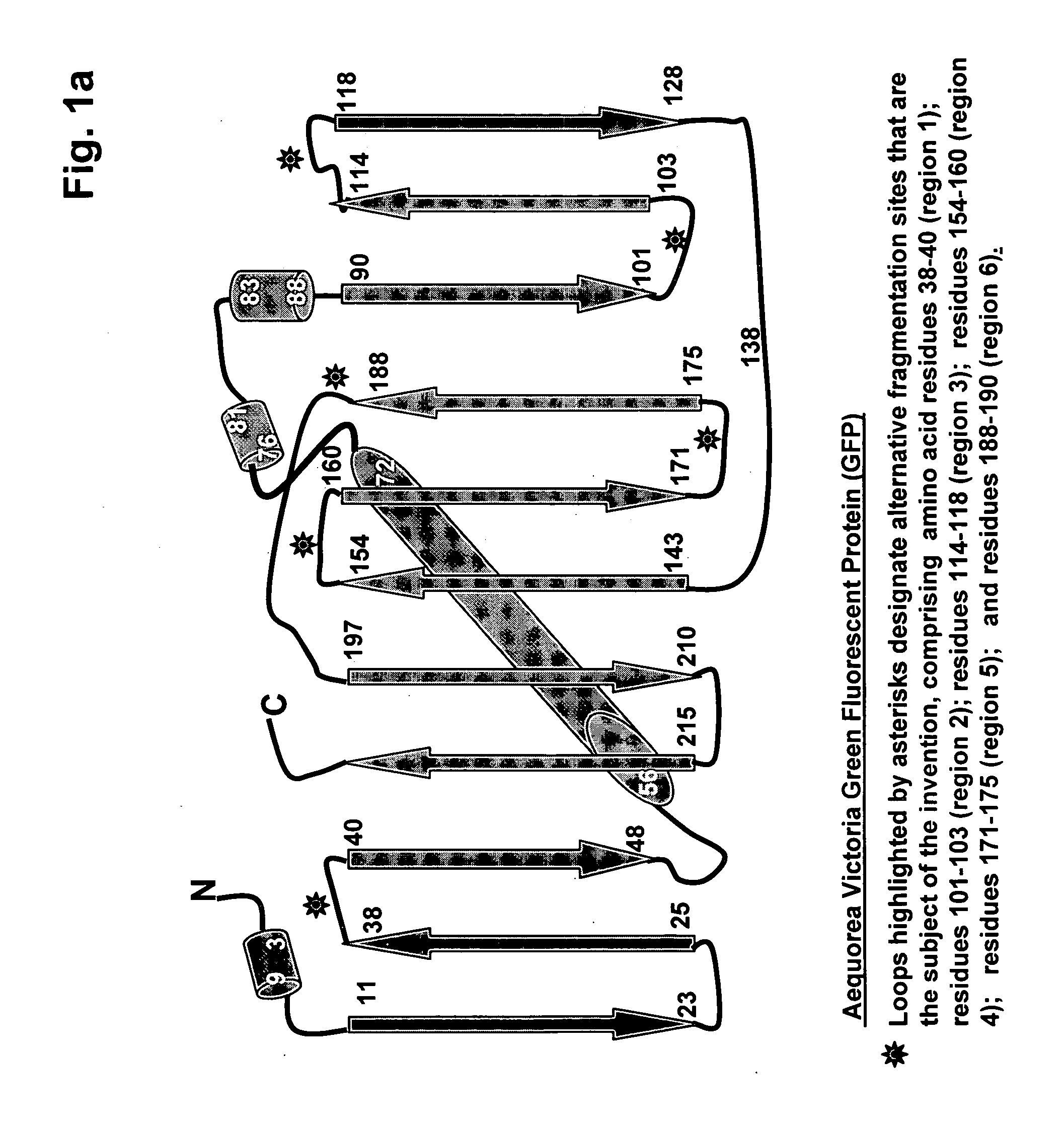
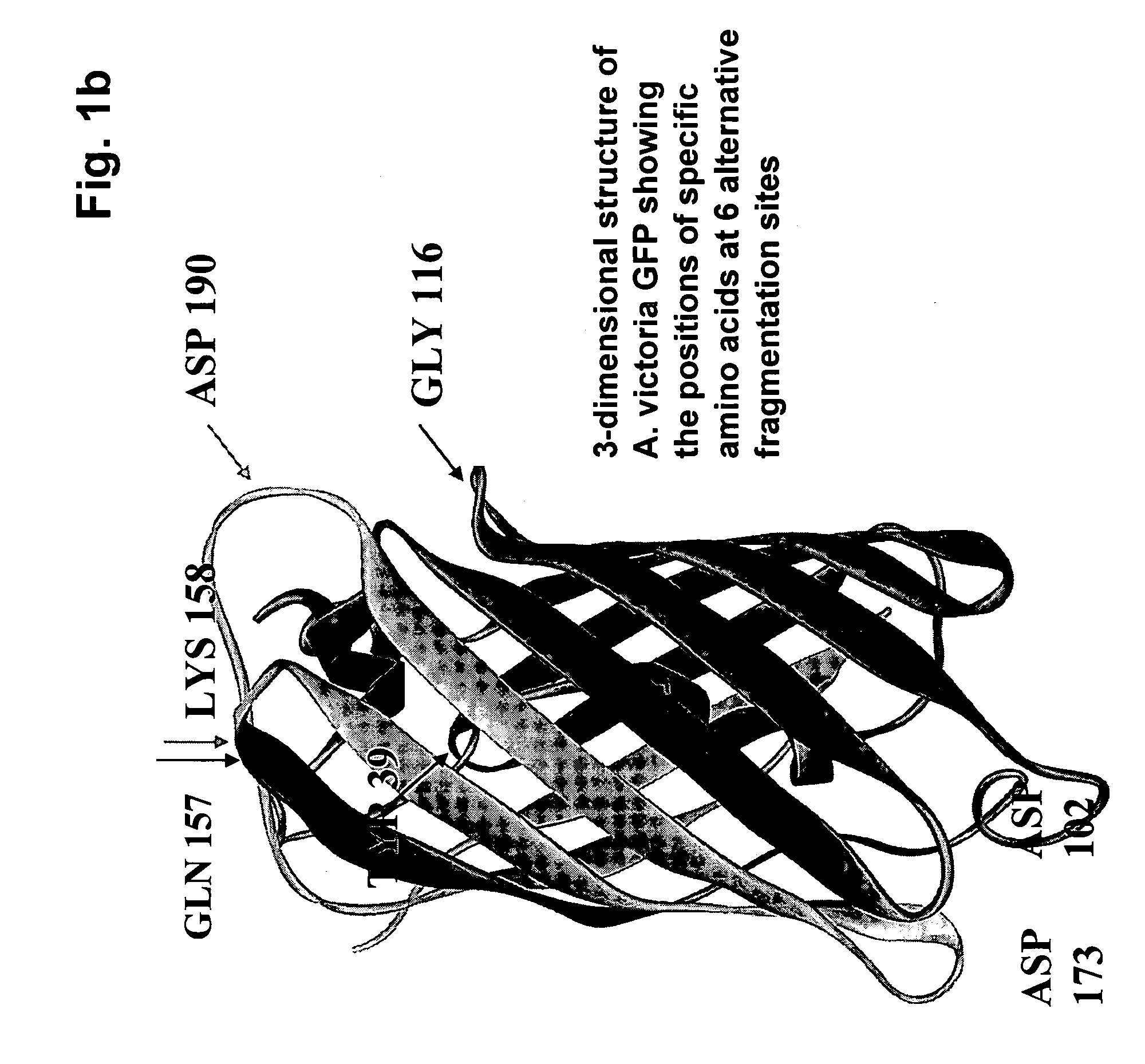
Fragments of fluorescent proteins for protein fragment complementation assays
InactiveUS20070254373A1Biological material analysisPeptide preparation methodsDiscosomaFluorescent protein
The present invention is directed to Protein-fragment Complementation Assays (PCAs) and assay compositions based on fluorescent proteins. The invention provides methods for fragmenting fluorescent proteins and generating mutant fragments with desired spectral characteristics for PCA. The invention encompasses assays and compositions based on fluorescent proteins from the species Aequorea, Anemonia and Anthozoa. In particular, the invention is directed to fragments of mutant fluorescent proteins having improved spectral properties over the wild-type proteins. The invention encompasses fragments of mutant versions of A. Victoria green fluorescent protein (GFP), in particular yellow fluorescent proteins (EYFP and super-EYFP), ‘Venus’, cyan, ‘citrine’, blue, cyan-green, and photoactivatable variants of GFP The invention also encompasses red fluorescent PCAs based on Discosoma red fluorescent protein (RFP PCA)and a kindling fluorescent protein PCA (KFP1 PCA) derived from Anemonia sulcata. Any useful mutation of a fluorescent protein can be engineered into a fragment, generating a wide range of assays useful for drug discovery, target validation, high-throughput screening, high-content screening, pathway mapping, drug mechanism-of-action studies, biosensors, and diagnostics.
Owner:ODYSSEY THERA INC
Automated method and system for setting image analysis parameters to control image analysis operations
A method and system for setting image analysis parameters to control image analysis operations. The method and system include collecting set of digital training images including a set of states for the set of digital training images. An objective function is defined to determine a relative quality of plural different parameter sets used for digital image analysis. Values for the plural different parameter sets that maximize (or minimize) the objective function are determined. The method and system increases a usability of high content screening technologies by reducing a required level of expertise required to configure digital image processing.
Owner:CELLOMICS
Method and apparatus for multi-parameter data analysis
ActiveUS10451536B2Reduce processing timeAccurate measurementIndividual particle analysisBiological testingBiological cellData set
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS OPERATIONS UK LTD
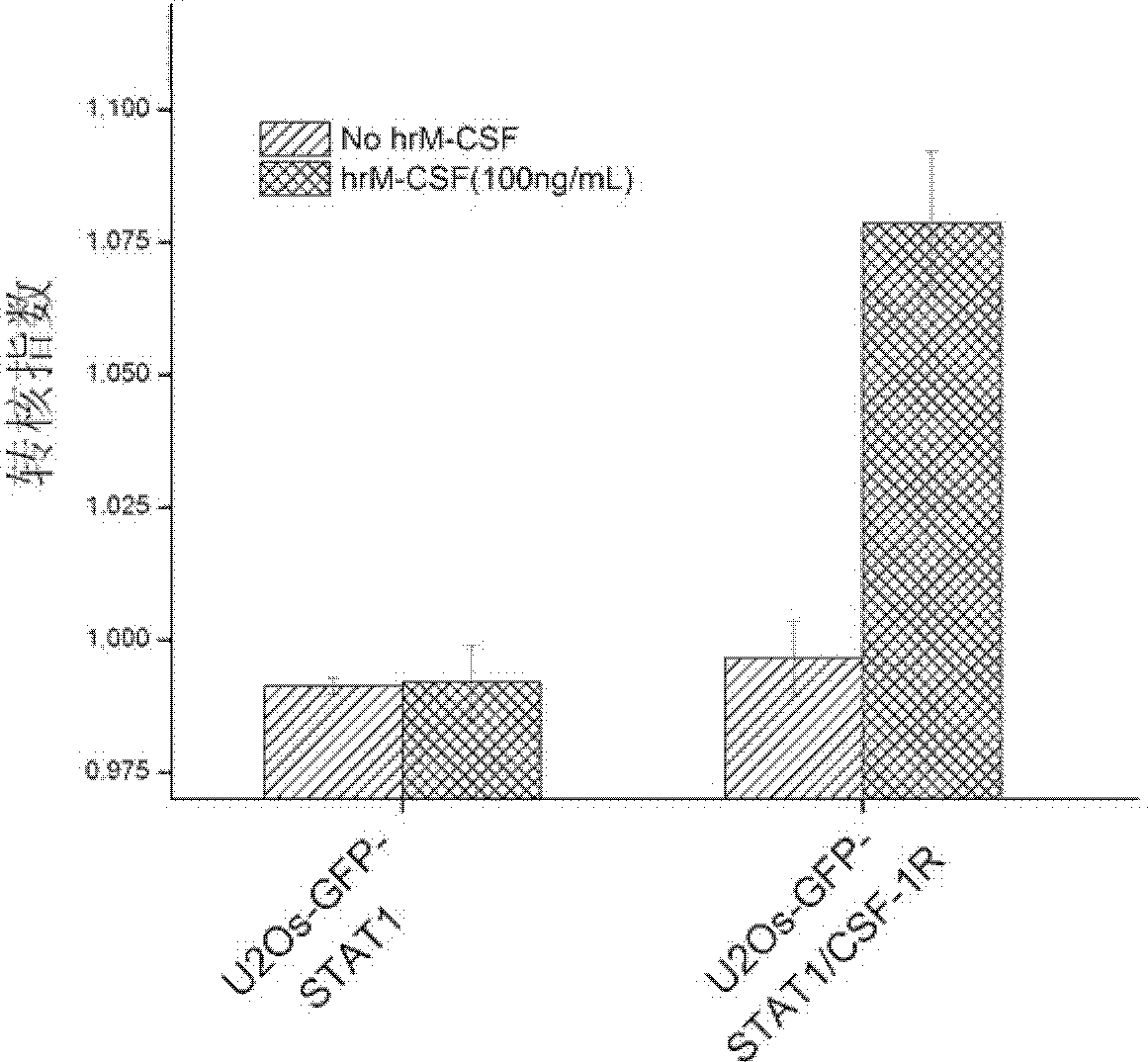
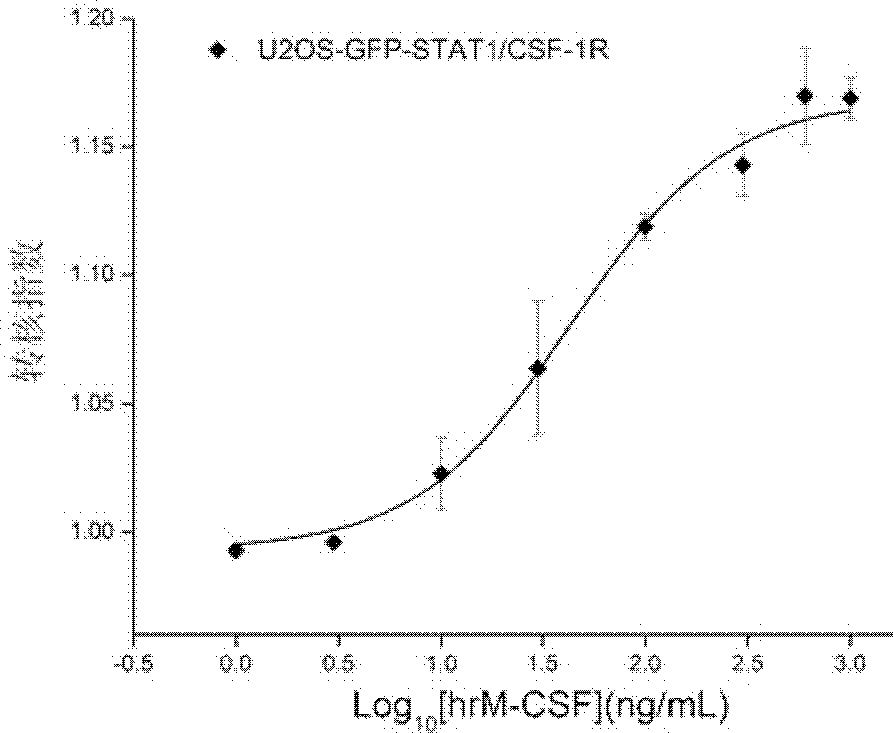
Cell model and method for screening c-Fms kinase inhibitor
InactiveCN102719404AHigh sensitivityEasy to operateCompound screeningApoptosis detectionHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsTyrosine-kinase inhibitor
The invention belongs to the fields of cell biology and pharmacy and relates to a cell model and a method for screening a c-Fms kinase inhibitor, concretely to a cell which simultaneously expresses a macrophage colony stimulating factor receptor and an STAT1protein. The invention also relates to a method for screening a c-Fms tyrosine kinase inhibitor, a method for accessing inhibitory activity of a compound or a combination to the c-Fms tyrosine kinase and a purpose of the cell in screening the c-Fms tyrosine kinase inhibitor. The cell model established in the invention is sensitive, efficient, reliable and capable of being used in a high throughput screening and / or a high content screening of the c-Fms tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Owner:INST OF PHARMACOLOGY & TOXICOLOGY ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI P L A
Three dimensional cell culture compositions and methods of use
ActiveUS9334473B2Cell culture supports/coating3D cultureHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsCell-Extracellular Matrix
Owner:LENA BIOSCI INC
Establishment and application of dilated cardiomyopathy zebrafish disease model
The invention relates to an establishing method and application of a dilated cardiomyopathy and zebrafish disease model. A disease model simulating human congenital dilated cardiomyopathy (CDCM) is firstly established; and the disease model can be used as a drug screening model to be applied to screening of drugs capable of relieving symptoms of heart failure caused by CDCM. The method provided by the invention is an economic and rapid high-content screening method; and the obtained compound has relatively high specificity and druggability.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
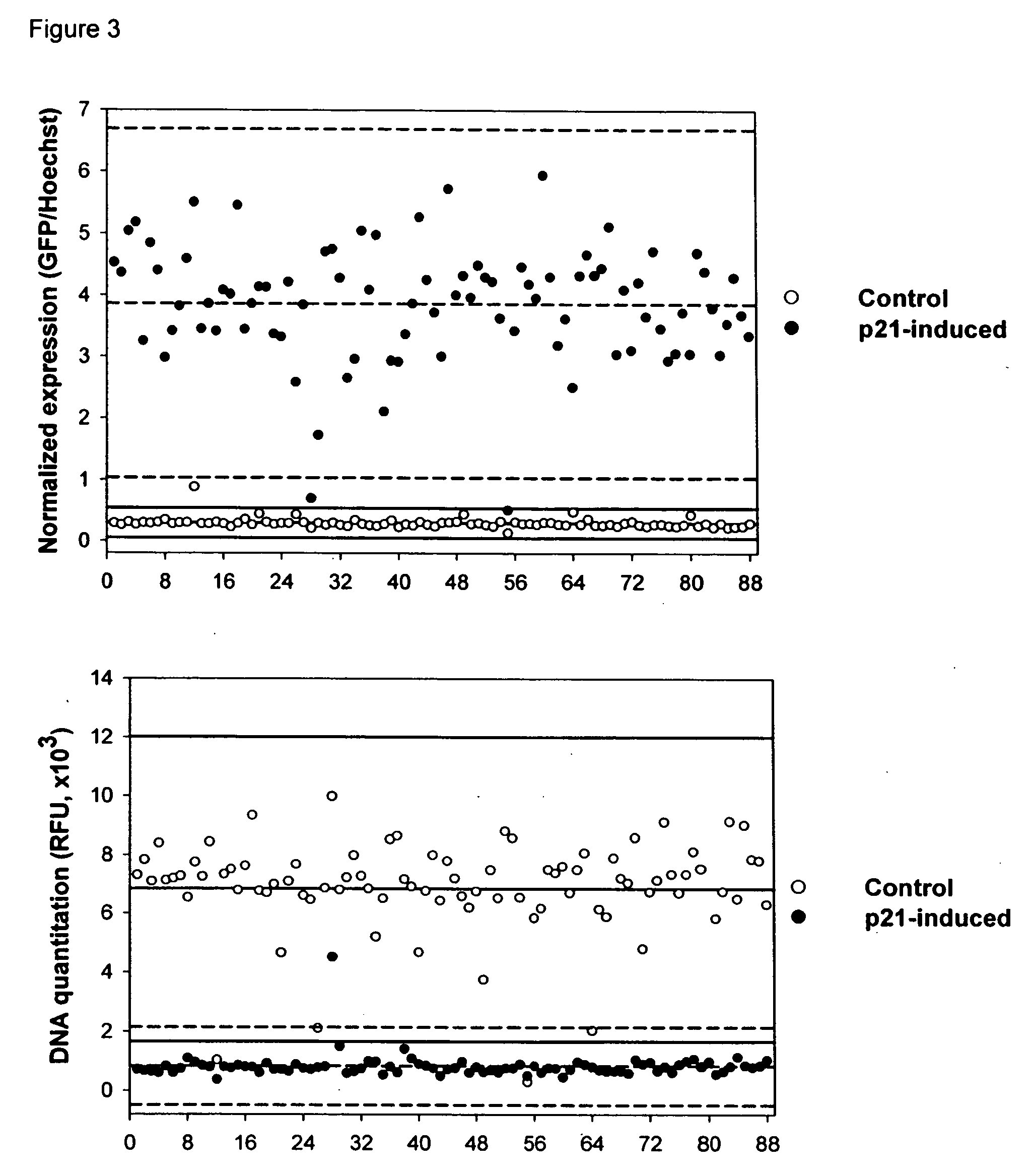
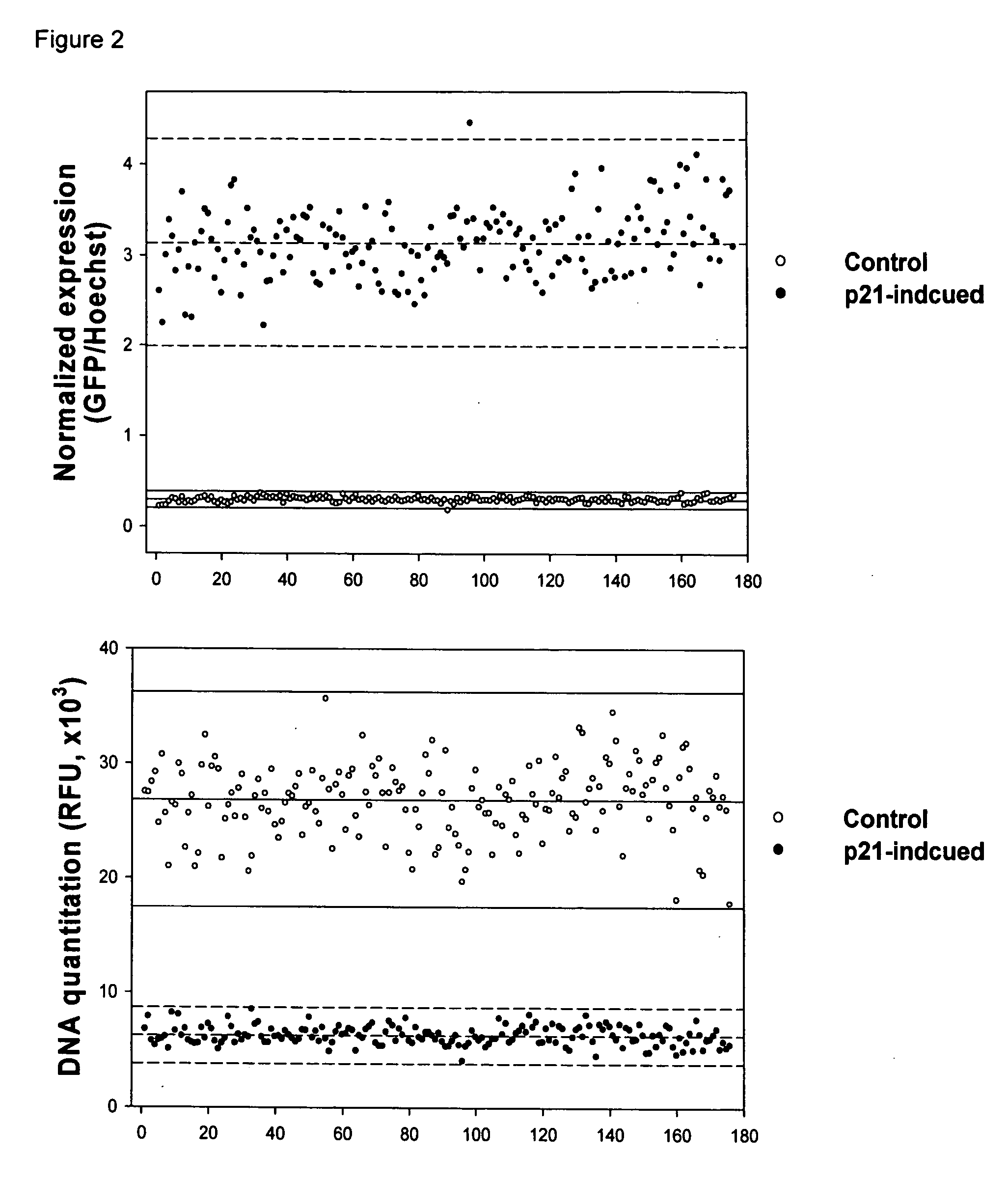
High-content screening for drugs against cancer and age-related diseases
InactiveUS20060154287A1Rapid and efficient identificationModulate effectMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisPromoter activityAge related disease
The invention relates to methods for high-throughput screening for compounds that modulate cell growth or promoter activity. The invention provides the use of cell lines with properly regulated promoter-reporter expression, suitable for high-throughput screening. More particularly, the invention relates to such screening to identify compounds that affect cell growth and / or that modulate the effect of cell cycle arrest on the function of a promoter that is responsive to cell cycle inhibition.
Owner:SENEX BIOTECHNOLOGY INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com



![Cell model for screening [kappa] opioid receptor agonist, and screening method thereof Cell model for screening [kappa] opioid receptor agonist, and screening method thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/81a8e5a5-0512-46c7-9086-f299a5c6f665/HDA0000525856930000011.PNG)
![Cell model for screening [kappa] opioid receptor agonist, and screening method thereof Cell model for screening [kappa] opioid receptor agonist, and screening method thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/81a8e5a5-0512-46c7-9086-f299a5c6f665/HDA0000525856930000012.PNG)
![Cell model for screening [kappa] opioid receptor agonist, and screening method thereof Cell model for screening [kappa] opioid receptor agonist, and screening method thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/81a8e5a5-0512-46c7-9086-f299a5c6f665/HDA0000525856930000021.PNG)