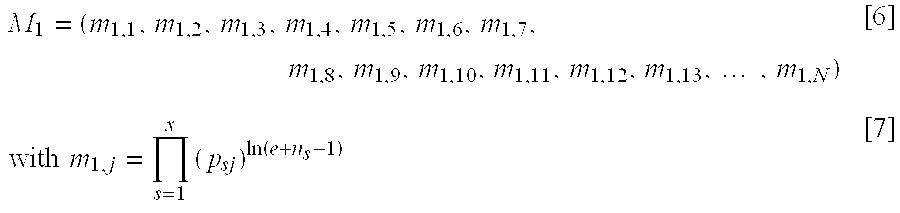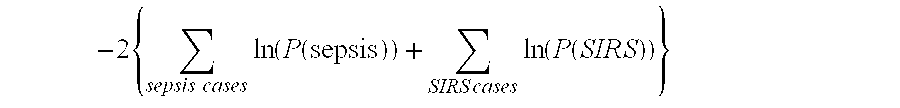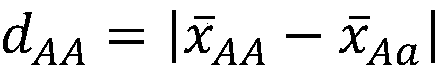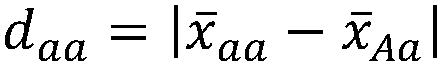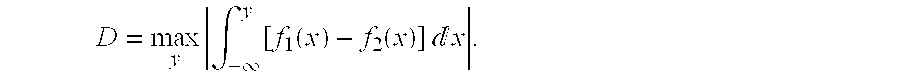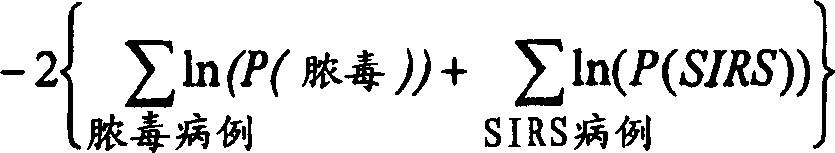Patents
Literature
65 results about "Reference population" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A study base, also called a reference population, is a defined population whose disease experience during some period of time is the source of the study data. This population gives rise to cases Defined before cases appear by a geographical area or some other identifiale entity like a health delivery system or a cohort study.
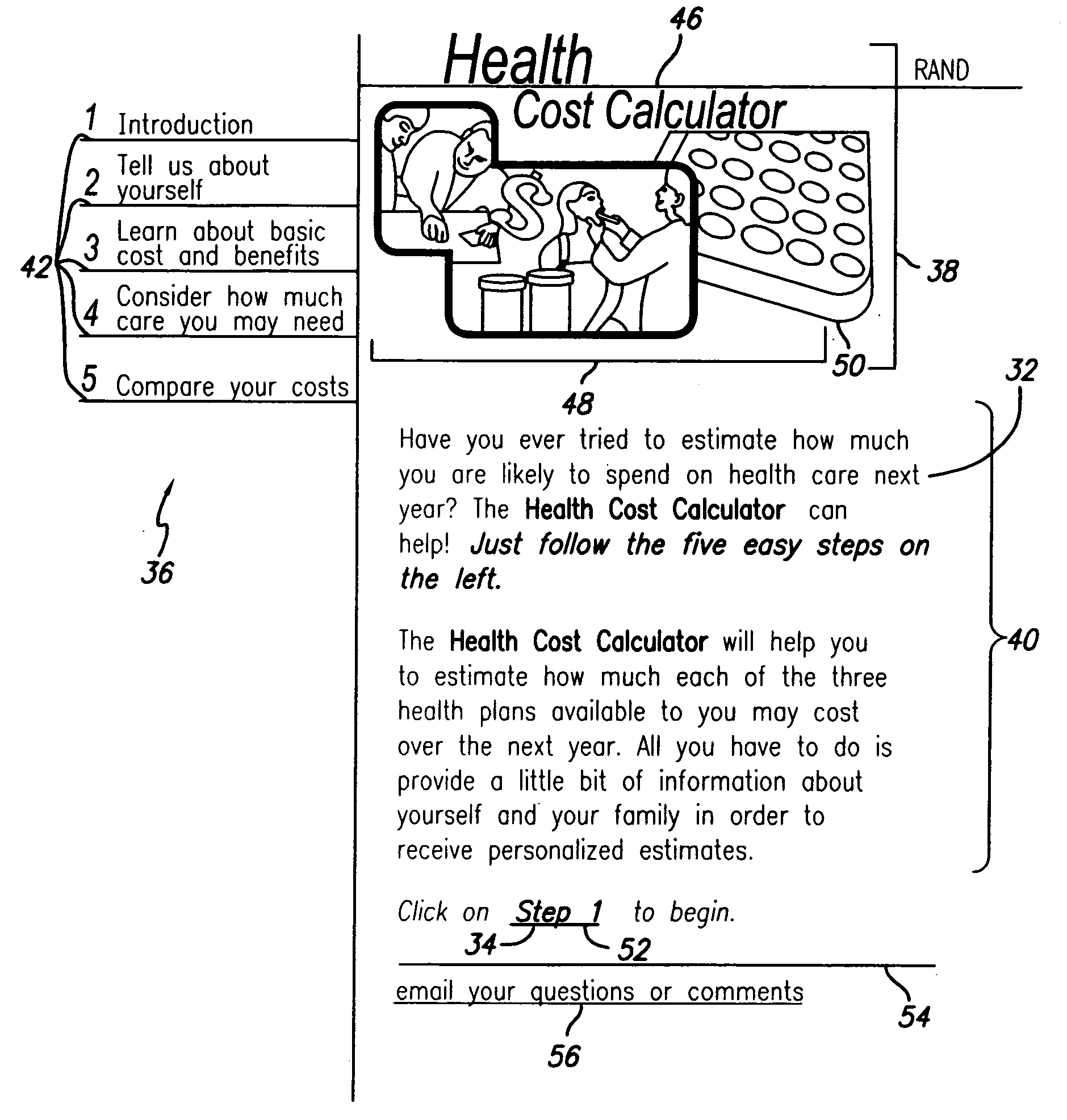
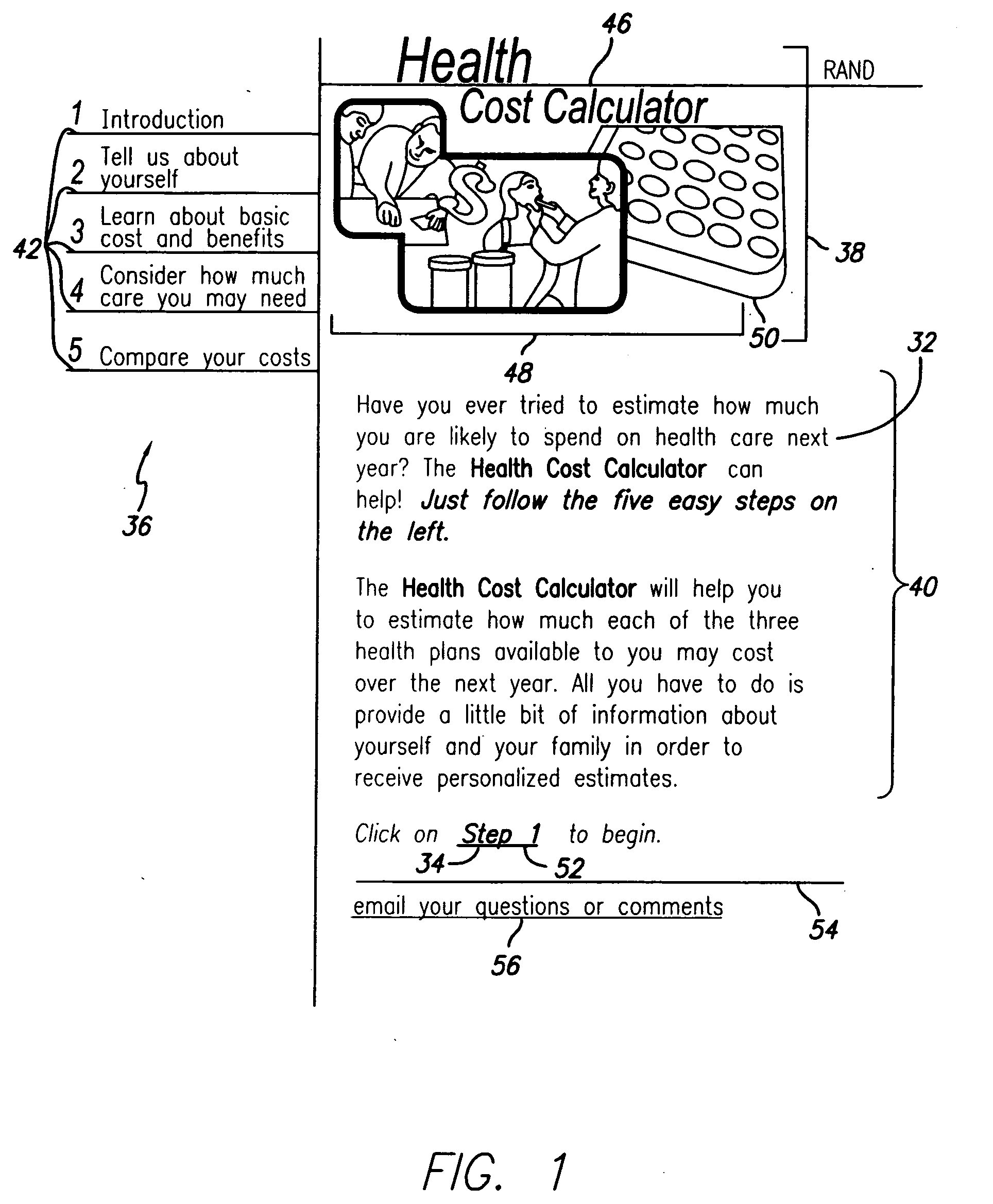
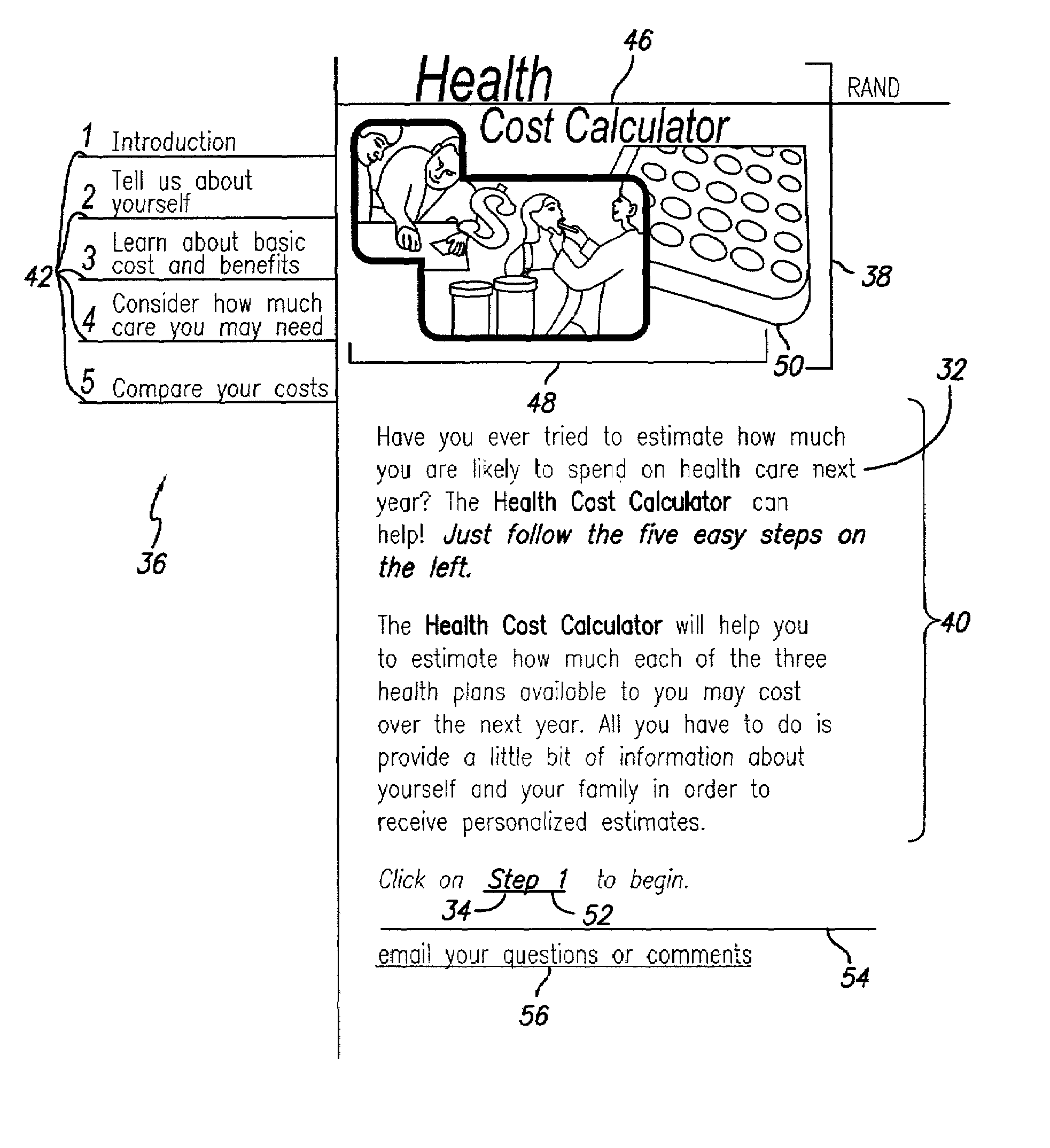
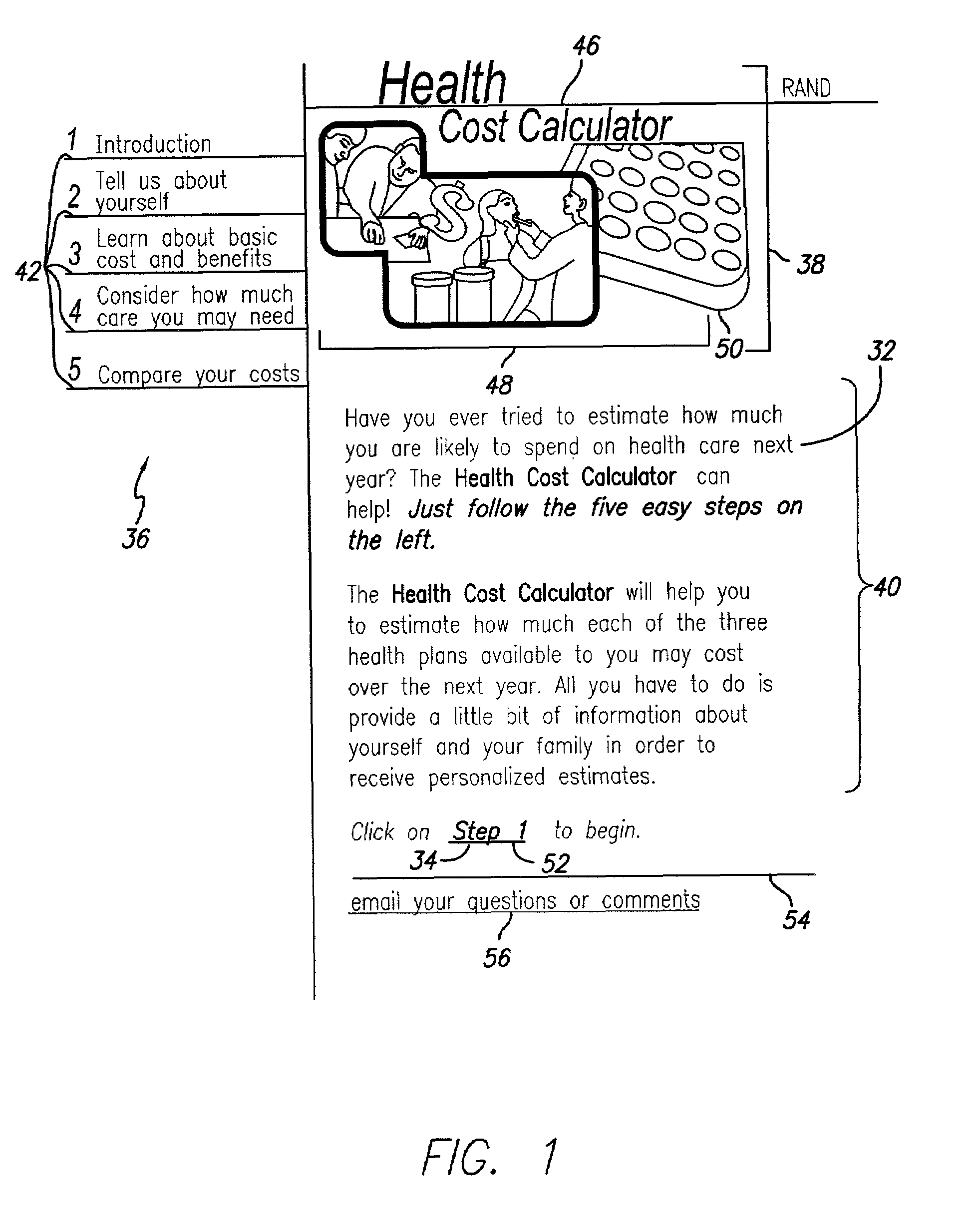
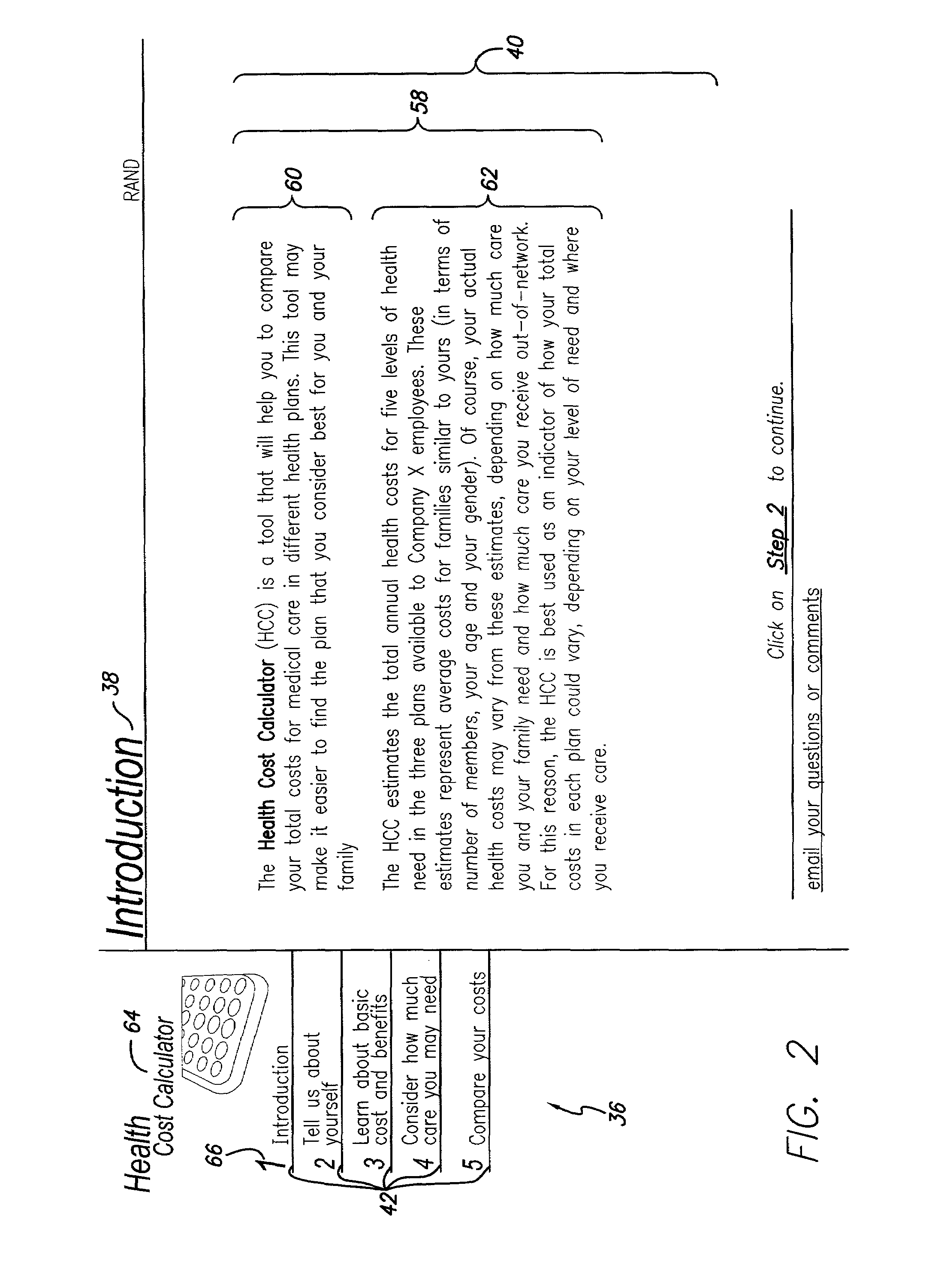
Health cost calculator/flexible spending account calculator
A method and system of providing comparative cost information for health insurance plans. Claims files are generated for the reference population of real historical patients for each the plans. Information is presented to users on the distribution of out-of-pocket costs for health care that users are likely to incur in the coming year, based on the parameters of health plans, information on the user and his / her household, and the actual health care use and costs for a reference population comparable to the users. Information is presented to users on optimal contributions to their flexible spending account for health care in the coming year and solving a dynamic numerical model based on users' objective function; solutions are based on the parameters of health plans, information on the user and his / her household, and the actual health care use and costs for a reference population comparable to the user.
Owner:SCHOENBAUM MICHAEL +1
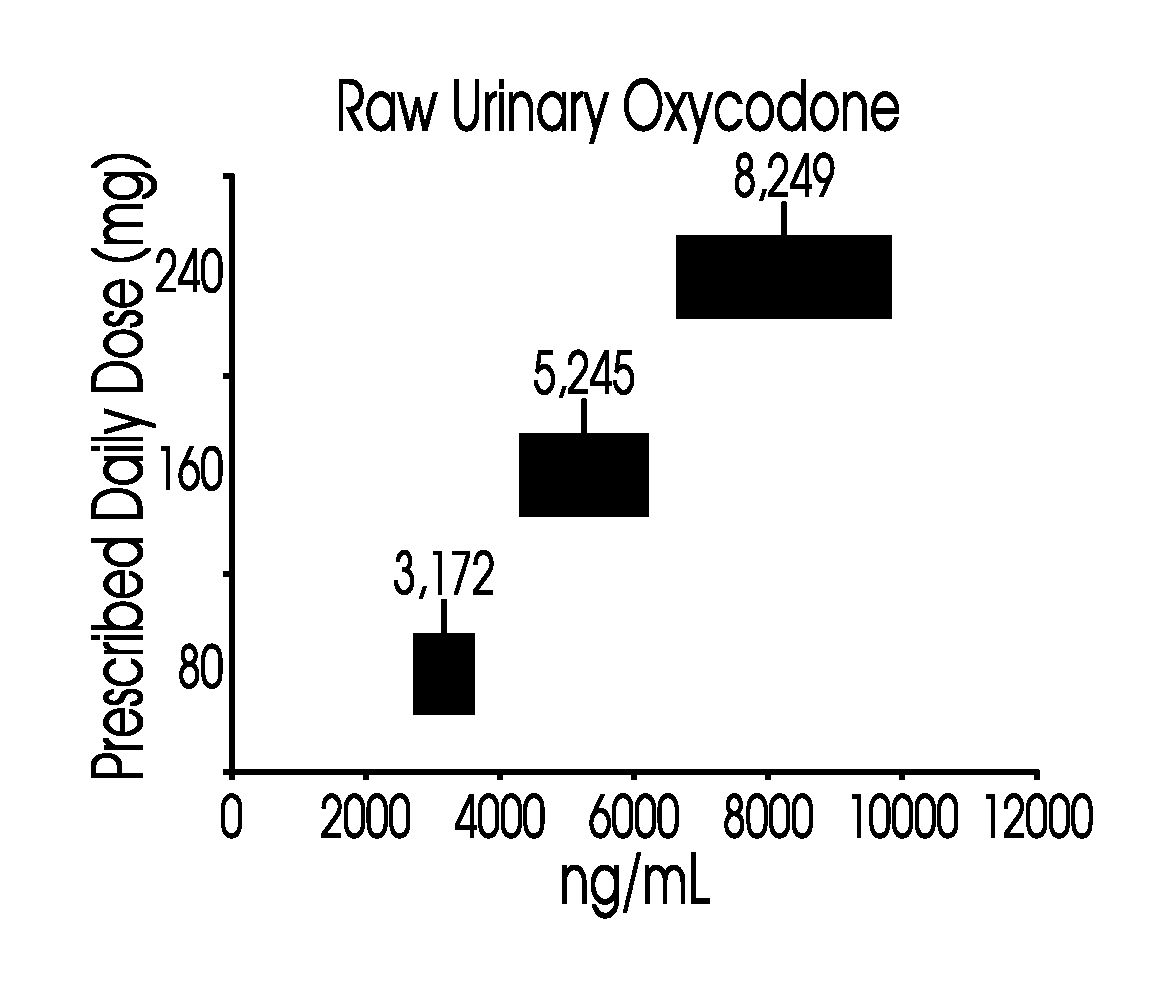
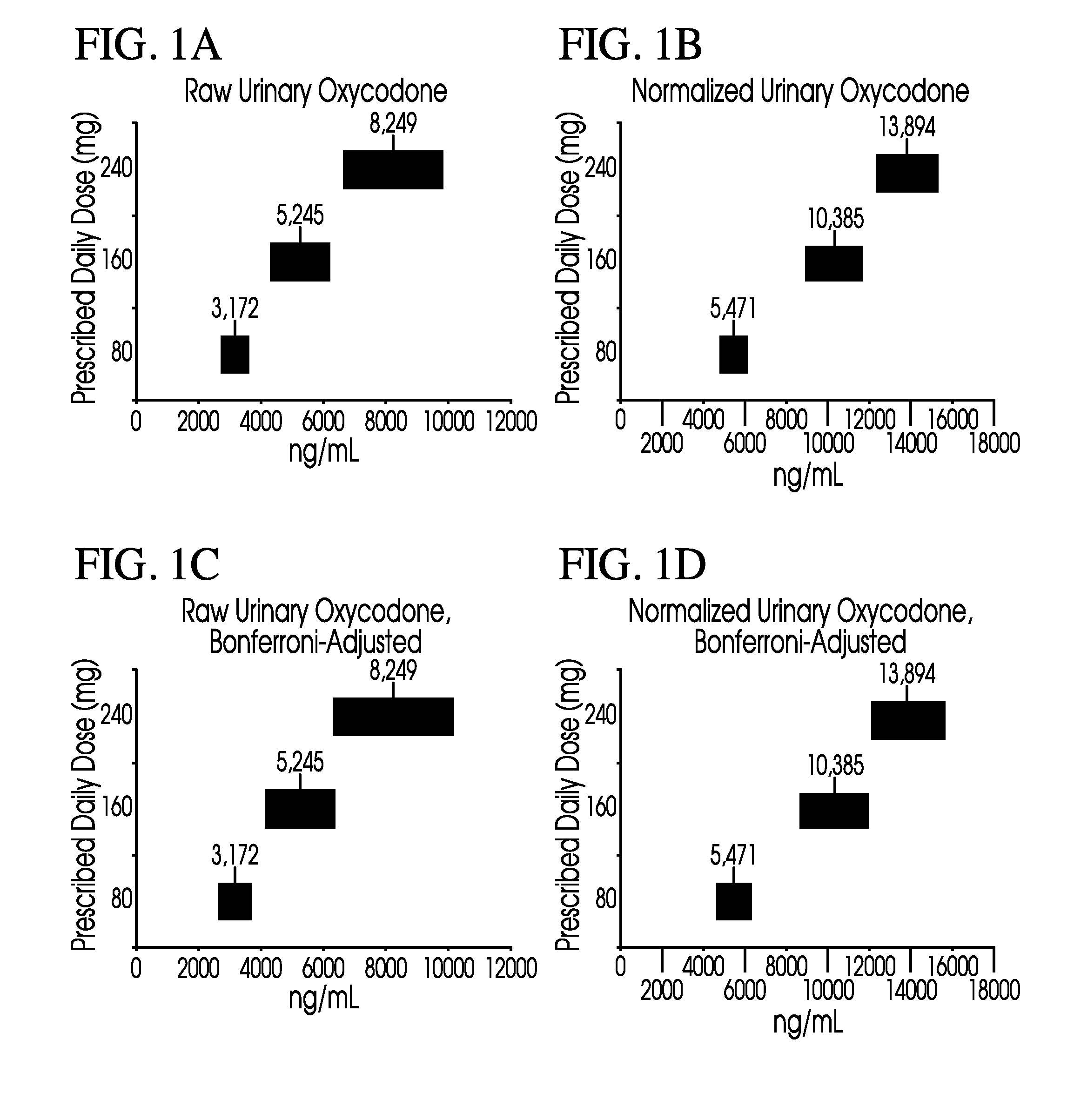
Methods of normalizing measured drug concentrations and testing for non-compliance with a drug treatment regimen
Methods for monitoring subject compliance with a prescribed treatment regimen are disclosed. In one embodiment, the method comprises measuring a drug level in fluid of a subject and normalizing said measured drug level as a function of one or more parameters associated with the subject. The normalized drug level is compared to a reference value and associated confidence intervals or to a concentration range. The reference value and associated confidence intervals and / or the concentration range may be normalized based on one or more parameters associated with subjects in a reference population.
Owner:AMERITOX LLC
Method for determining a profile of a user of a communication network
InactiveUS20070198937A1Easy to predictDigital computer detailsMarketingThe InternetReference population
The invention relates to a method and a system for determining a profile of a communications network user, the method includes: saving profile data regarding known network users in a database, these users forming a reference population, the profile data (Pi) regarding known users including a set of attributes (j) values (Pij) associated to each user (i), for each site or part of site (s) of a set of sites of interest accessible via the network, processing a set of probabilities (Psj) that represent the attribute values of users that connect to the site or part of a site (s), according to the connection history of the users of the reference population to a site or a part of a site, and processing a probability that a user to be identified has a given attribute, according to the probabilities associated to the Internet sites or parts of a site (s) of interest to which the user connects during a specific time period. The method is characterized in that the processing determines the probability (m3j) that the user to be identified has a specific attribute (j) as a combination of a decorrelated probability value (m1j) that takes into account the probabilities associated to the Internet sites or parts of a site (s) and a correlated probability value (m2j) that takes into account average profile data (gj) regarding the users that are part of the reference population.
Owner:WEBORAMA
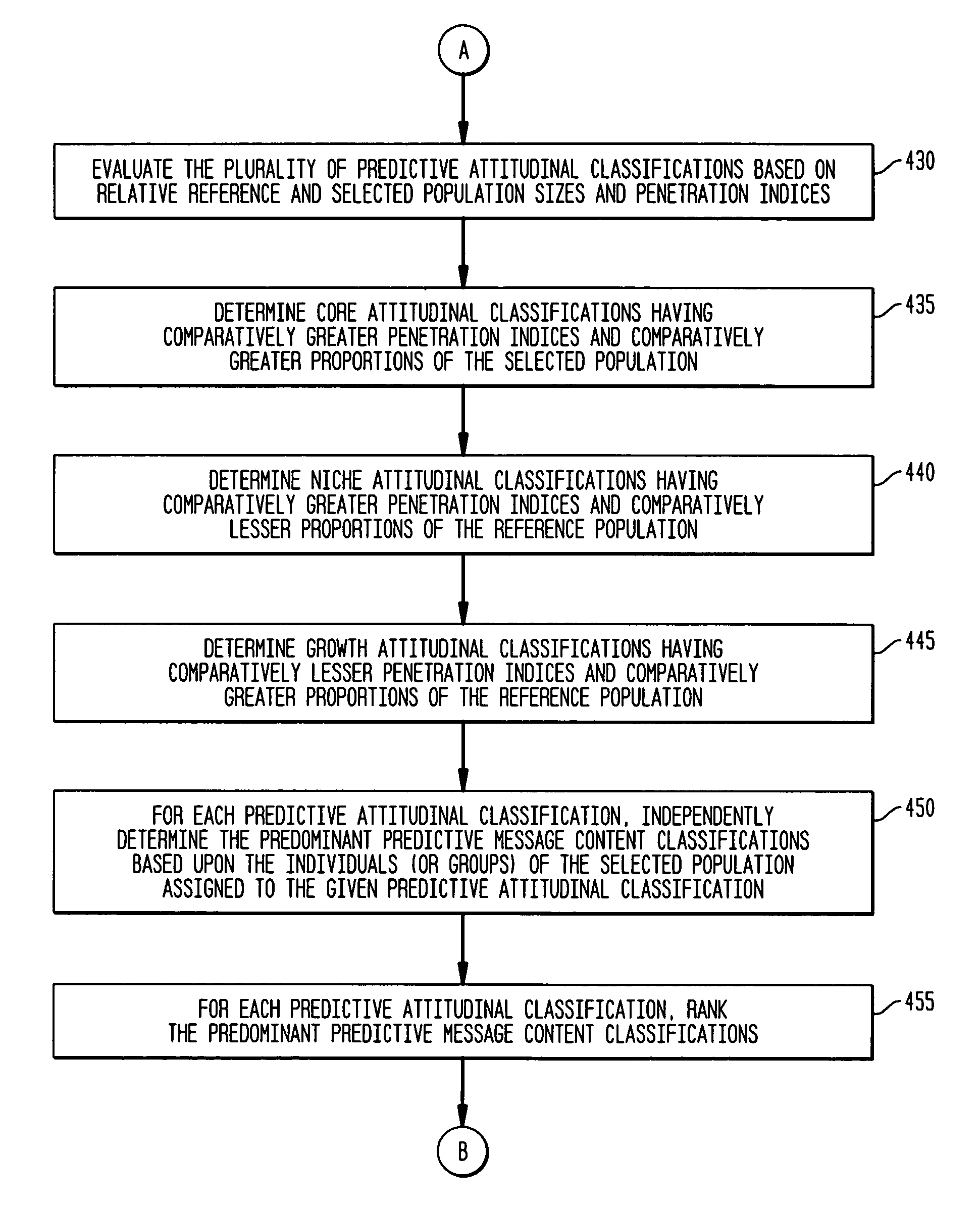
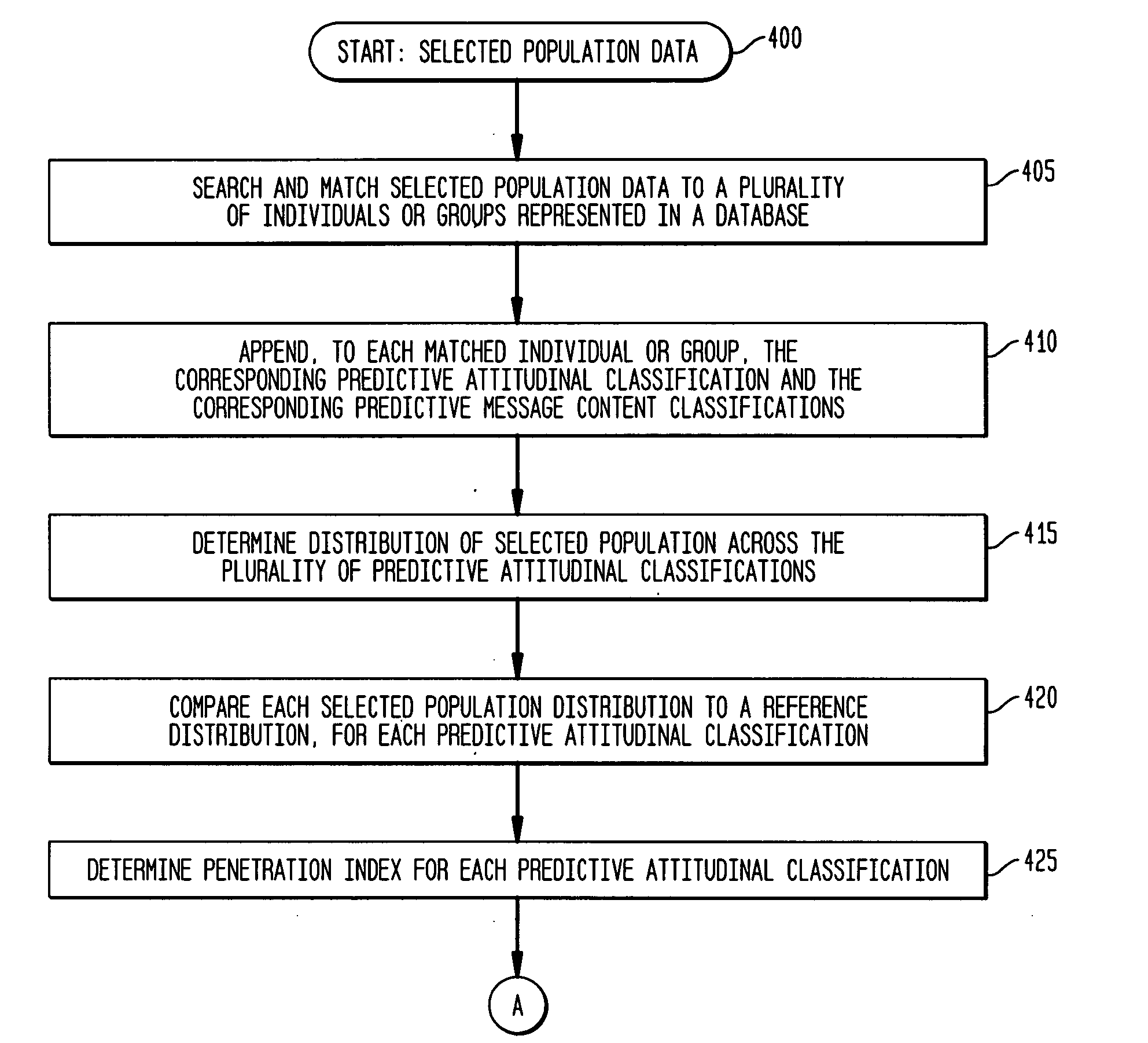
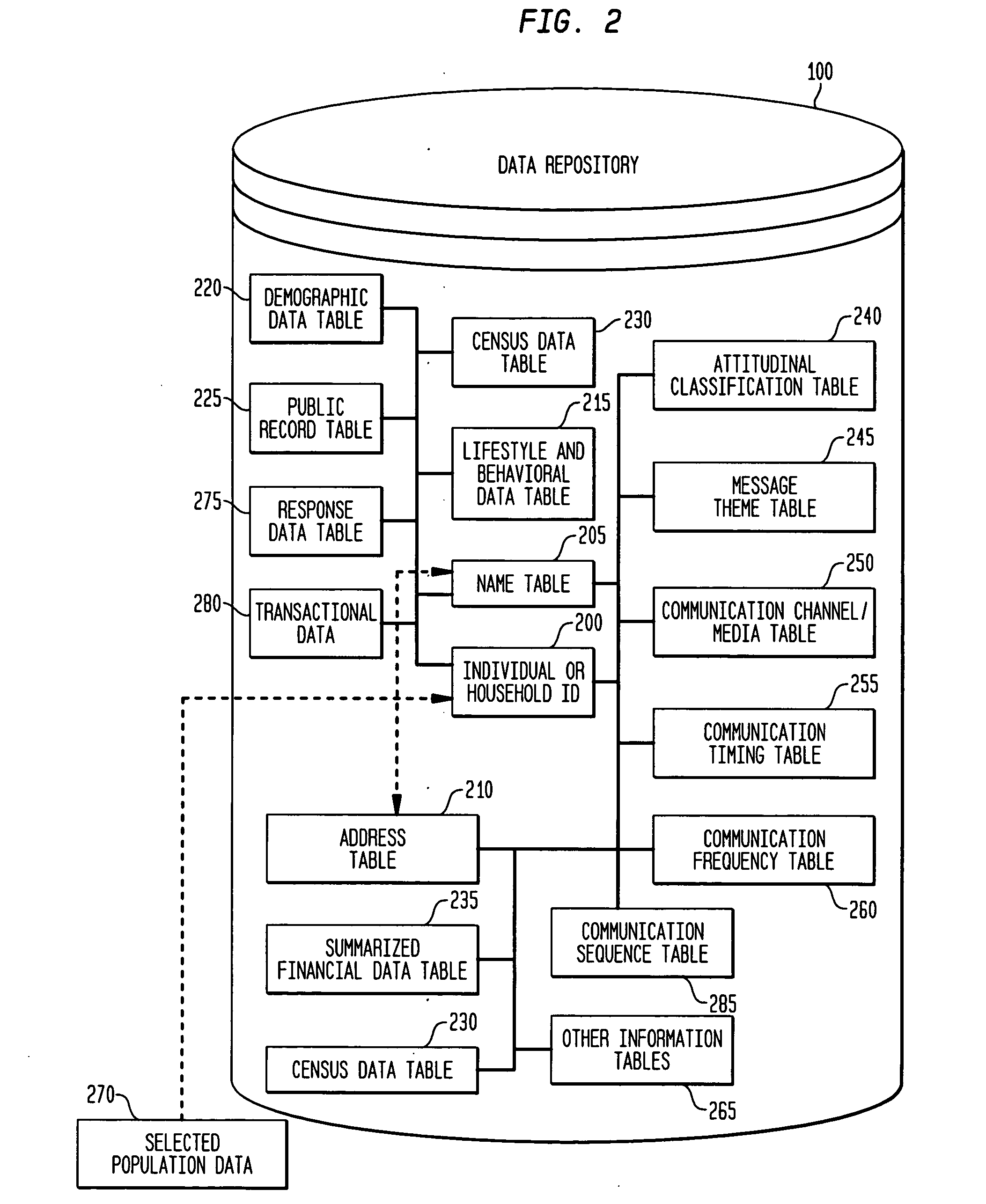
System, method, and software for prediction of attitudinal and message responsiveness
ActiveUS8346593B2Accurate of motivationsAccurate predictionMarket predictionsDemographic modelReference population
The present invention provides a system, method, software and data structure for independently predicting attitudinal and message responsiveness, using a plurality of attitudinal or other identification classifications and a plurality of message content or version classifications, for a selected population of a plurality of entities, such as individuals or households, represented in a data repository. The plurality of predictive attitudinal (or identification) classifications and plurality of predictive message content (ore version) classifications have been determined using a plurality of predictive models developed from a sample population and applied to a reference population represented in the data repository, such as attitudinal, behavioral, or demographic models. For each predictive attitudinal (or identification) classification, at least one predominant predictive message content or version classification is independently determined. The exemplary embodiments also provide, for each predictive attitudinal classification, corresponding information concerning predominant communication media (or channel) types, predominant communication timing, predominant communication frequency, and predominant communication sequencing.
Owner:EXPERIAN MARKETING SOLUTIONS
Use of igfbp-7 in the assessment of heart failure
The invention relates to a method for assessing heart failure in vitro comprising the steps of measuring in a sample the concentration of the marker IGFBP-7, of optionally measuring in the sample the concentration of one or more other marker(s) of heart failure, and of assessing heart failure by comparing the concentration determined in for IGFBP-7 and the concentration(s) determined for the optionally one or more other marker to the concentration of this marker or these markers as established in a reference population. Also disclosed are the use of IGFBP-7 as a marker protein in the assessment of heart failure, a marker combination comprising IGFBP-7 and a kit for measuring IGFBP-7.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC +1
System, method, software and data structure for independent prediction of attitudinal and message responsiveness, and preferences for communication media, channel, timing, frequency, and sequences of communications, using an integrated data repository
ActiveUS20060004622A1Accurate predictionAccurate of motivationsMarket predictionsReference populationDemographic model
The present invention provides a system, method, software and data structure for independently predicting attitudinal and message responsiveness, using a plurality of attitudinal or other identification classifications and a plurality of message content or version classifications, for a selected population of a plurality of entities, such as individuals or households, represented in a data repository. The plurality of predictive attitudinal (or identification) classifications and plurality of predictive message content (ore version) classifications have been determined using a plurality of predictive models developed from a sample population and applied to a reference population represented in the data repository, such as attitudinal, behavioral, or demographic models. For each predictive attitudinal (or identification) classification, at least one predominant predictive message content or version classification is independently determined. The exemplary embodiments also provide, for each predictive attitudinal classification, corresponding information concerning predominant communication media (or channel) types, predominant communication timing, predominant communication frequency, and predominant communication sequencing.
Method for Determining the Status of an Individual
Methods of determining status of an individual based on the use of biological specimen and analysis of reference population of cells are described.
Owner:NODALITY
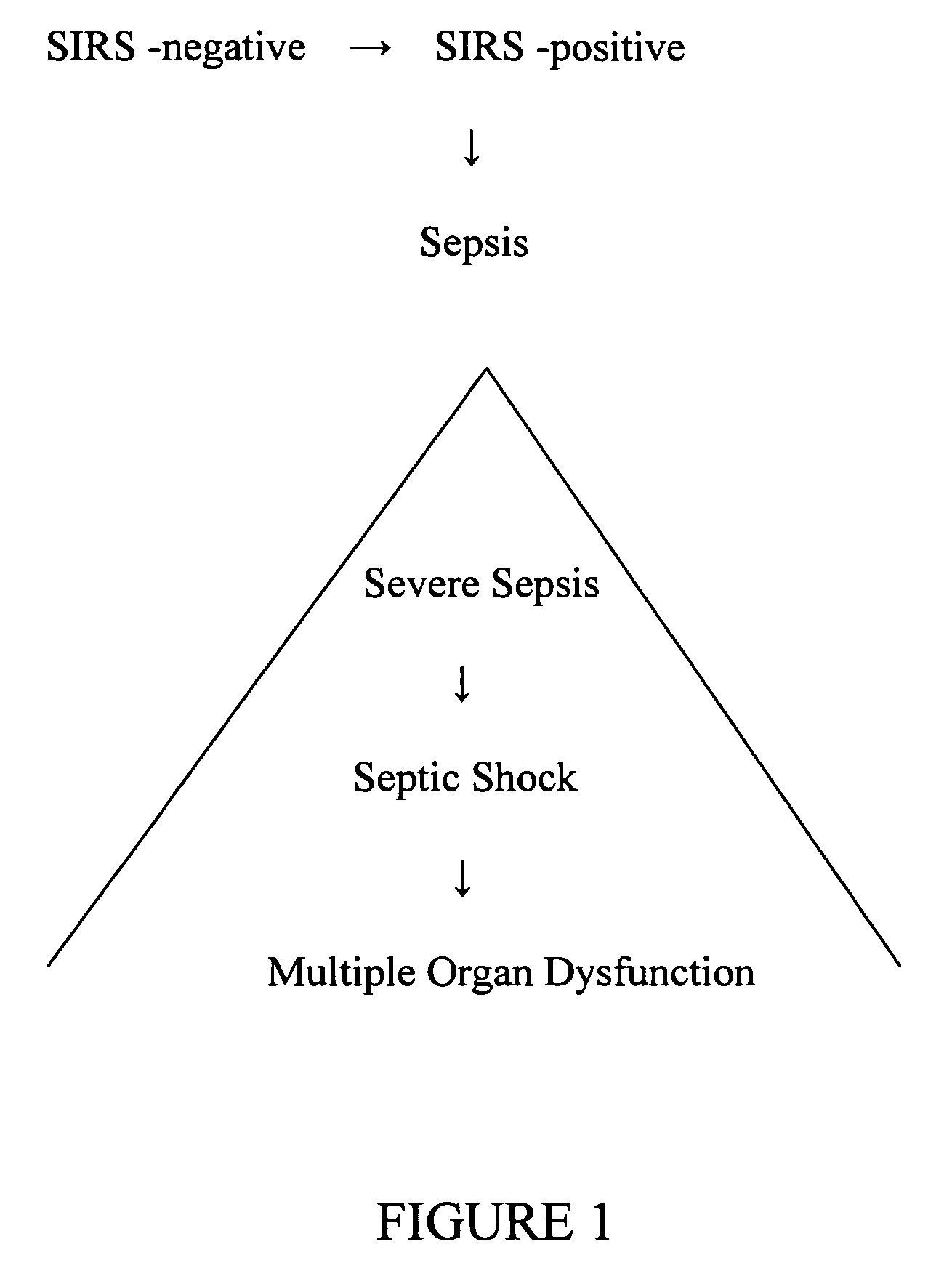
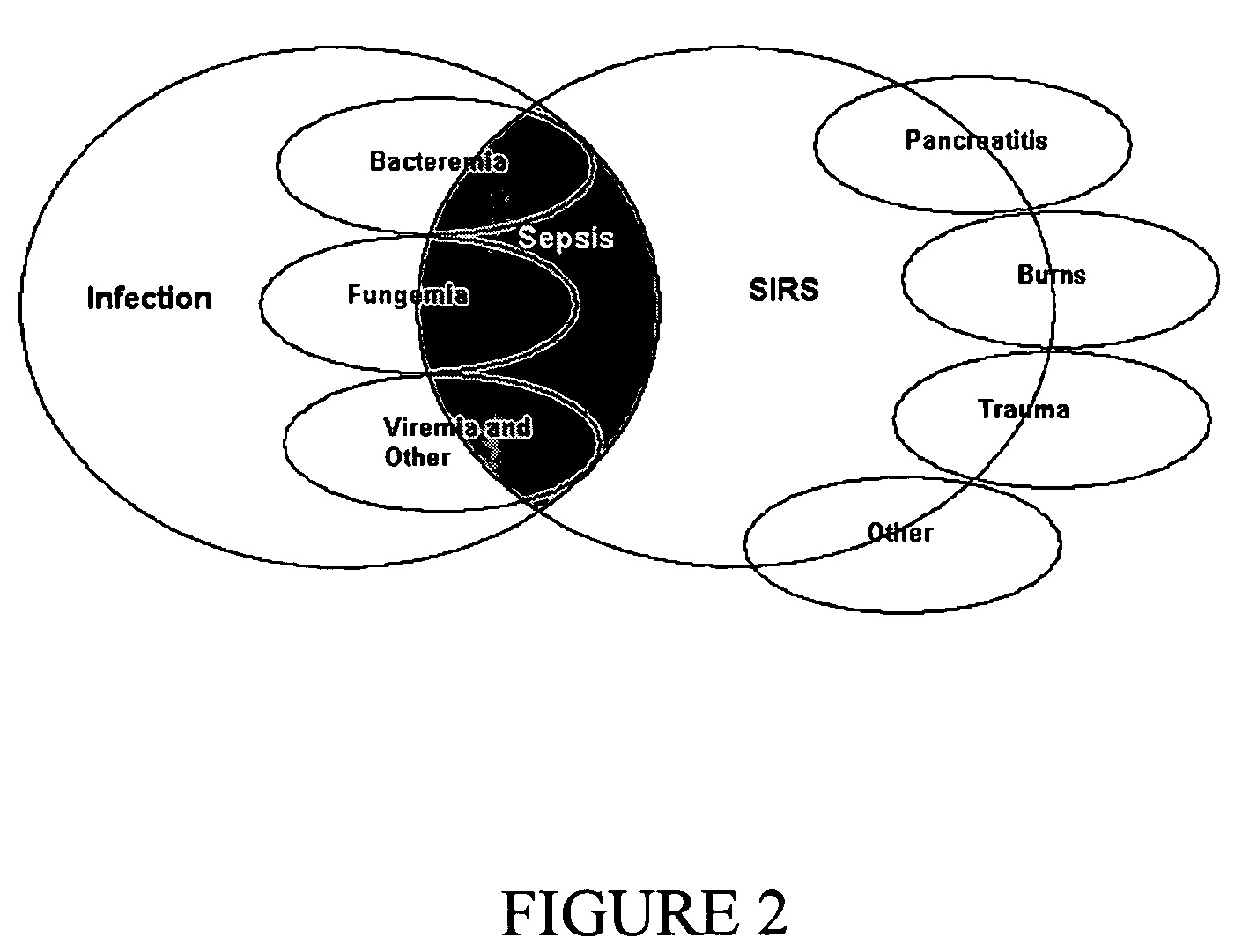
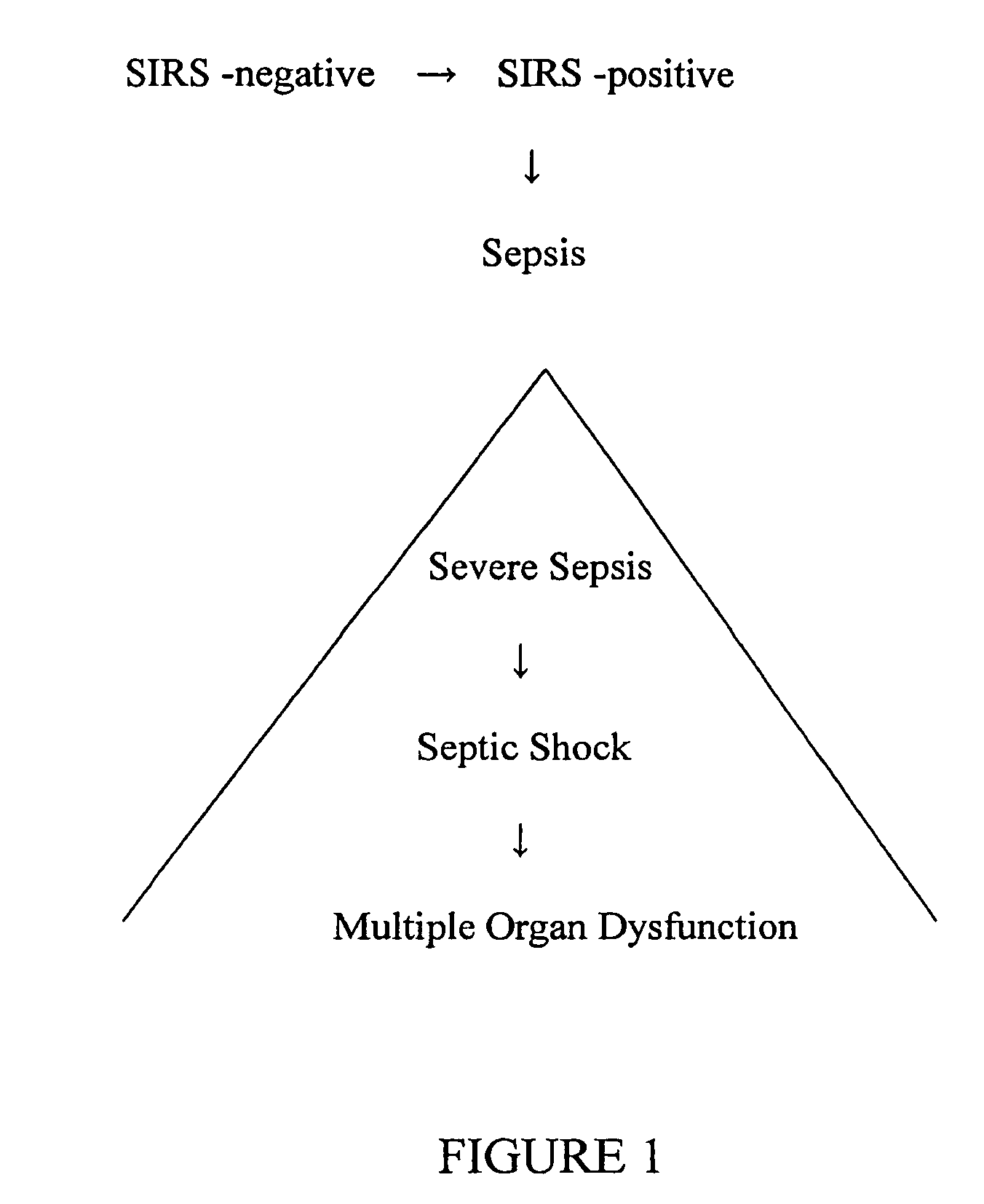
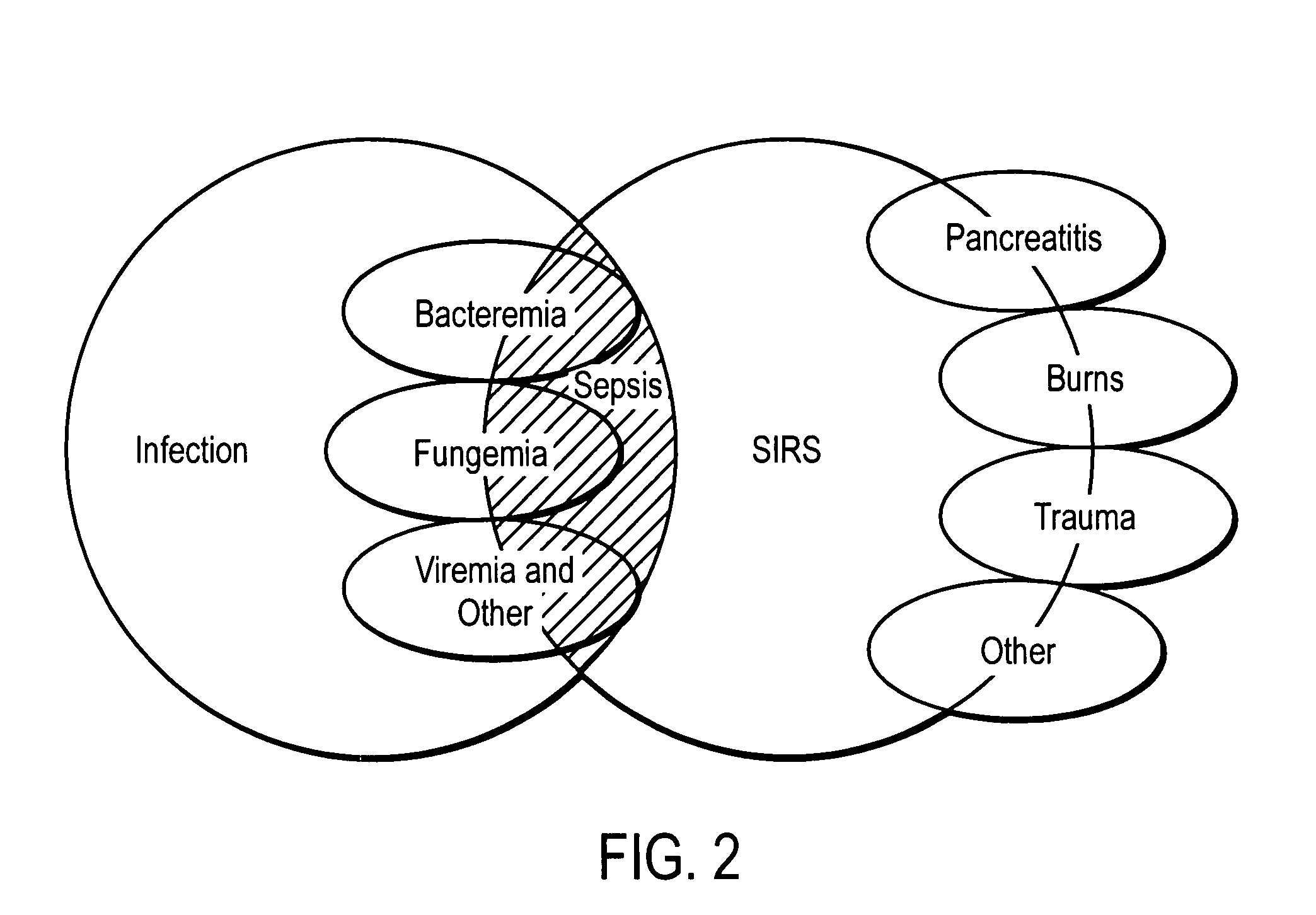
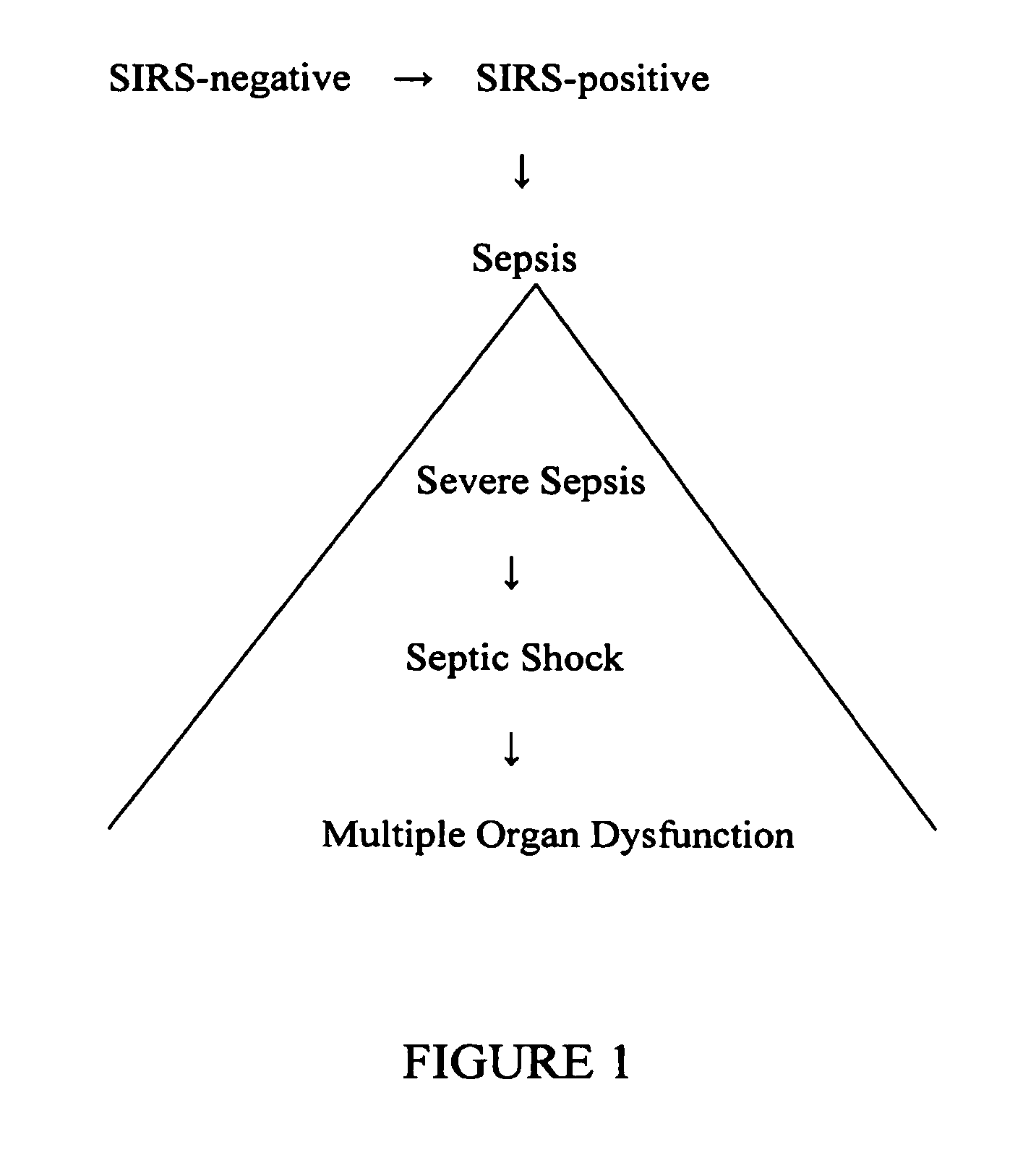
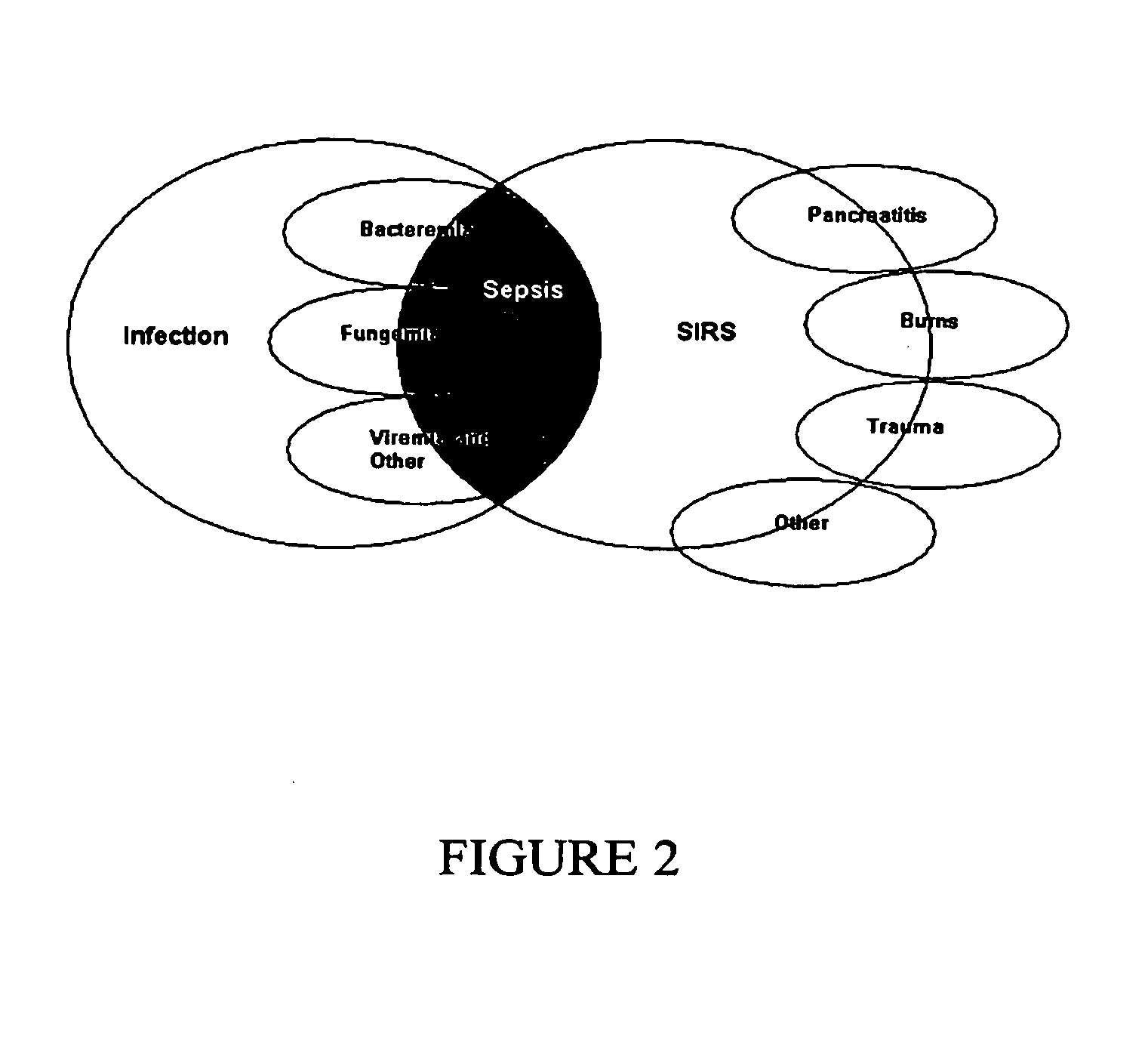
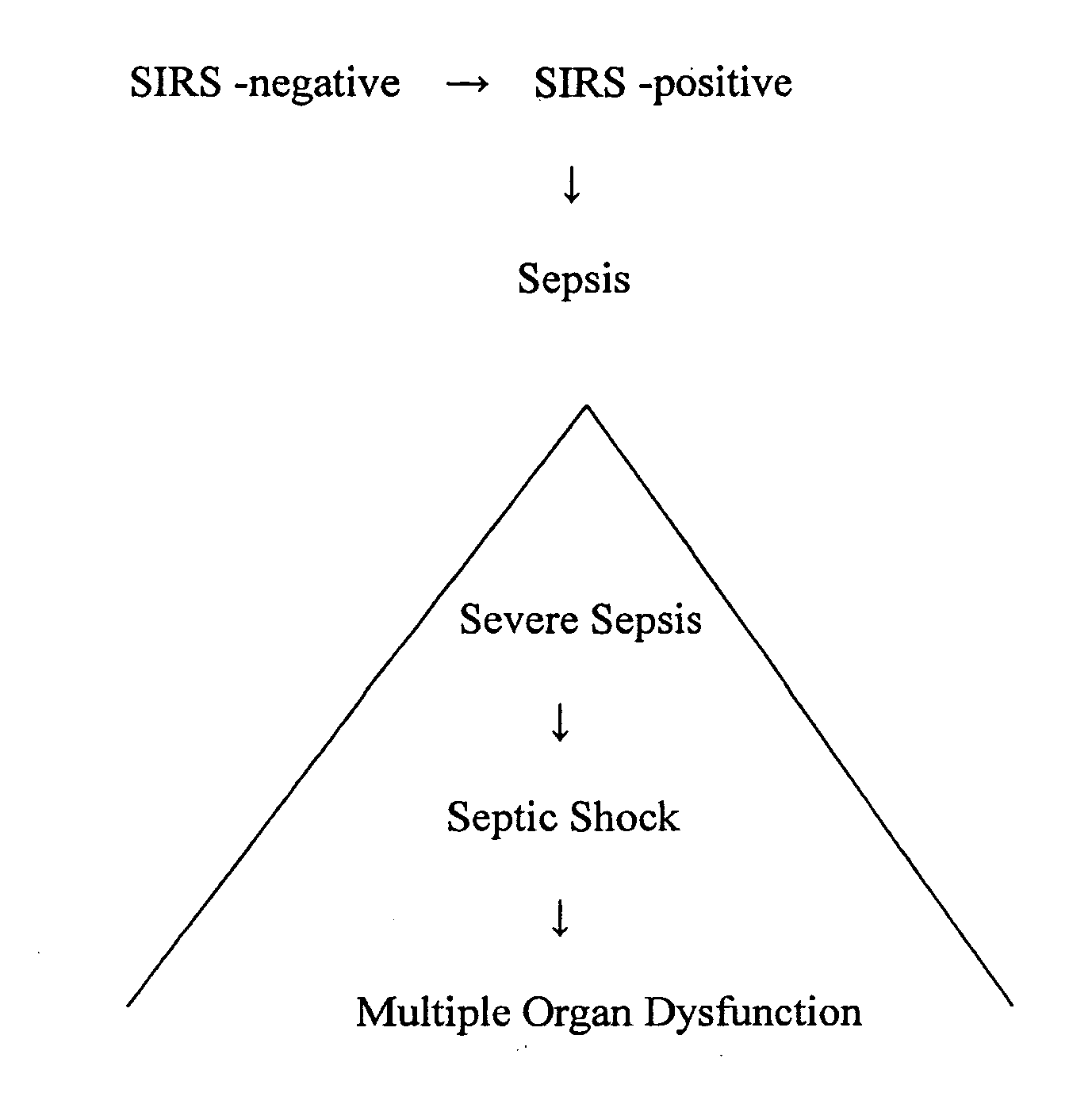
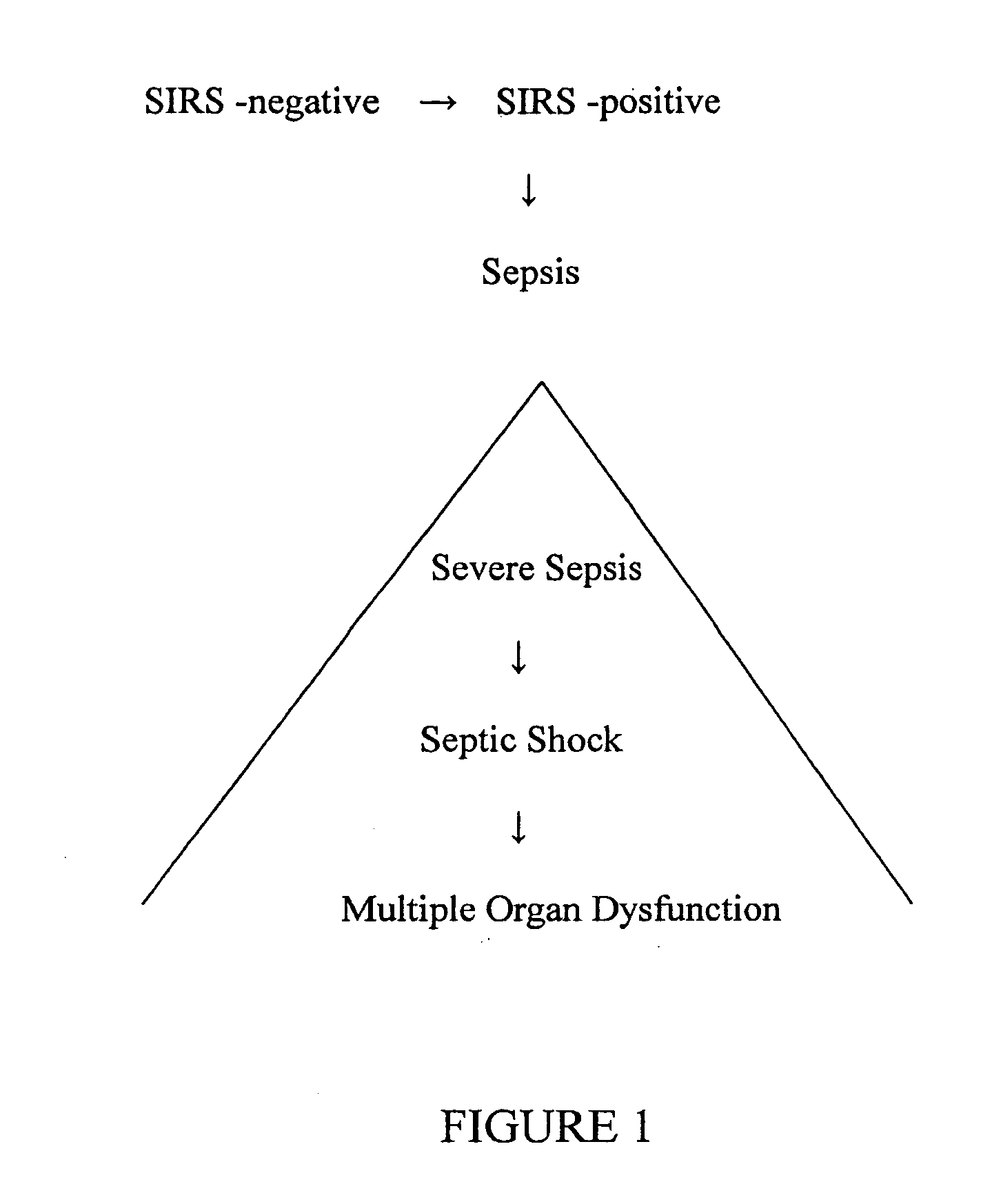
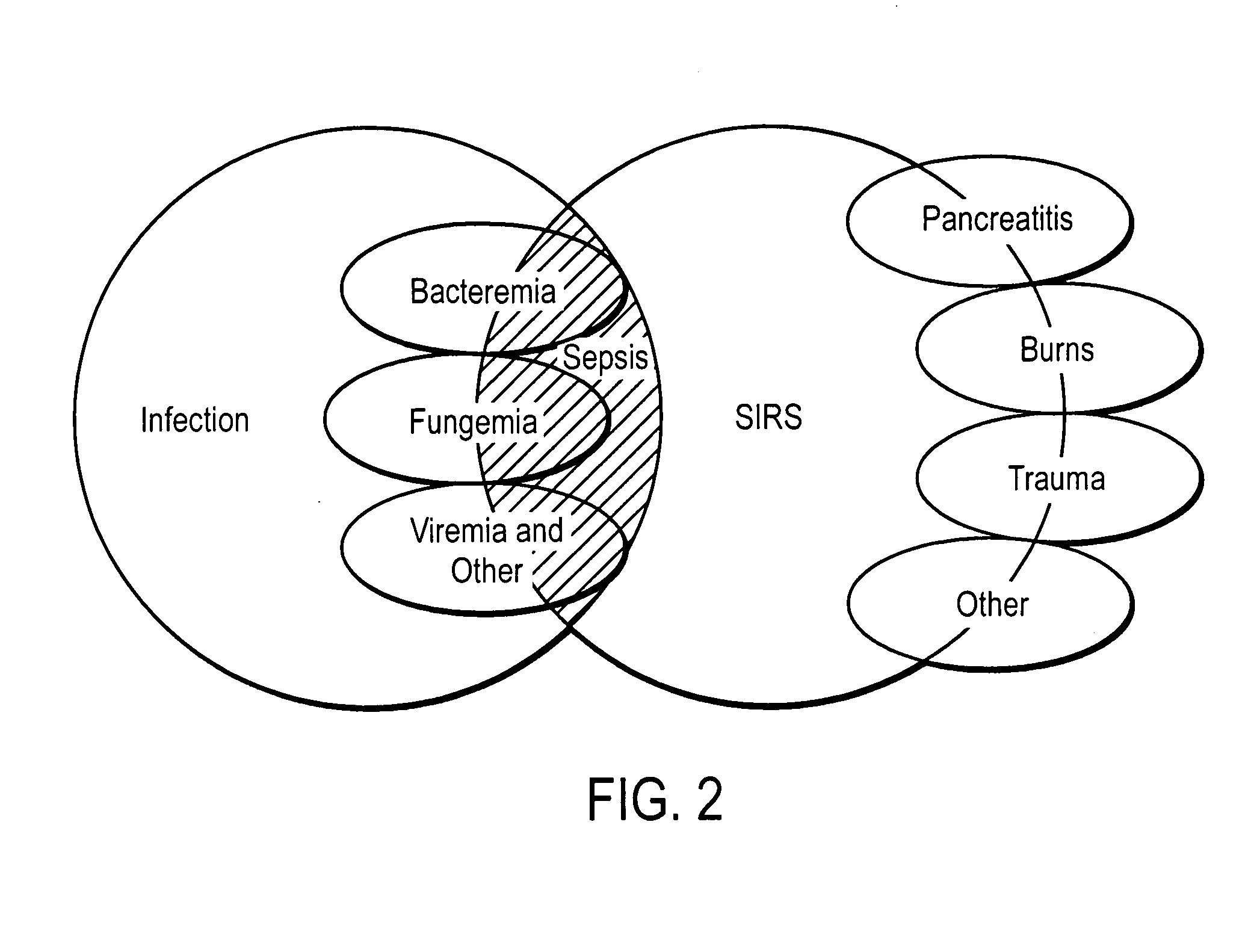
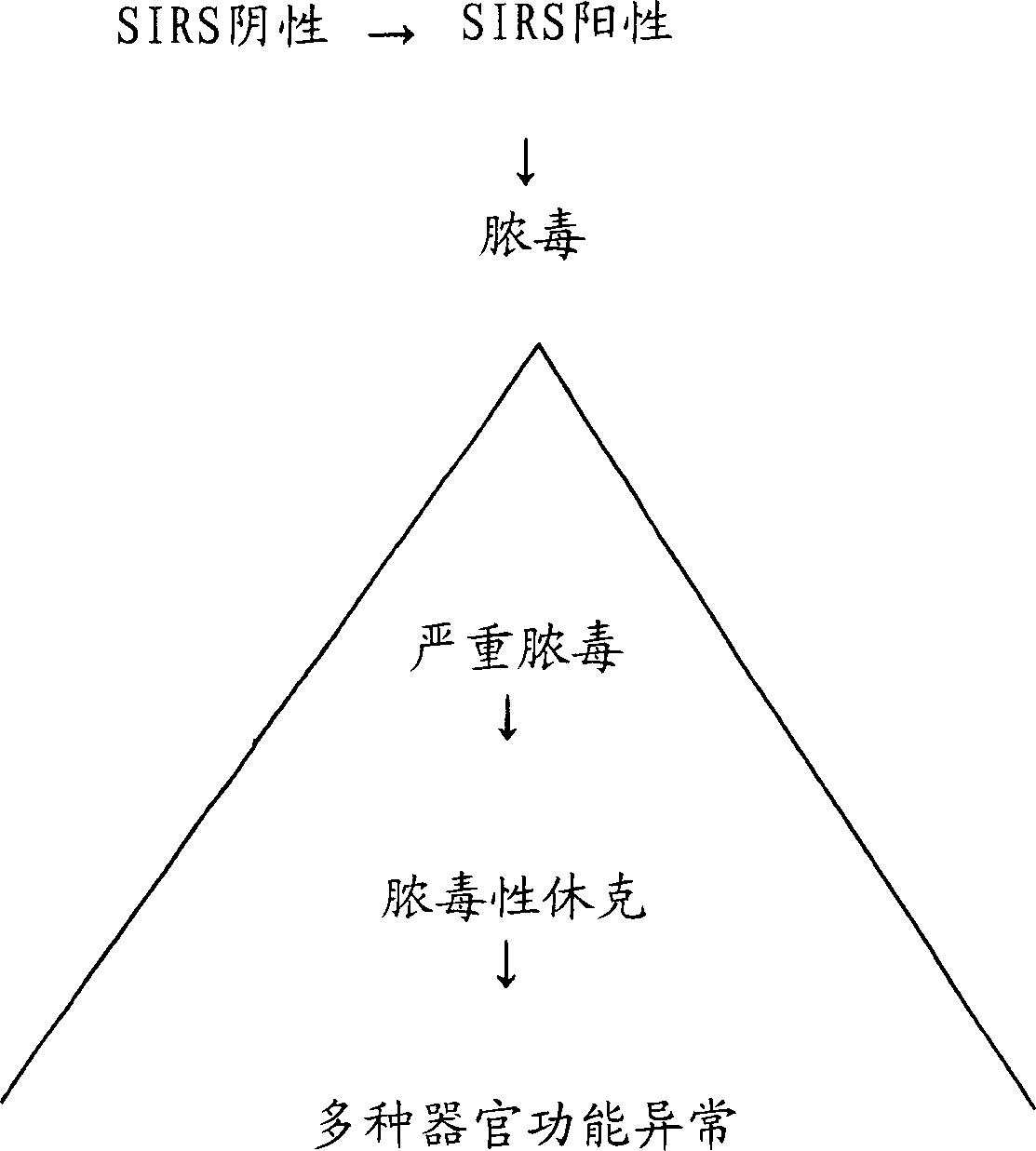
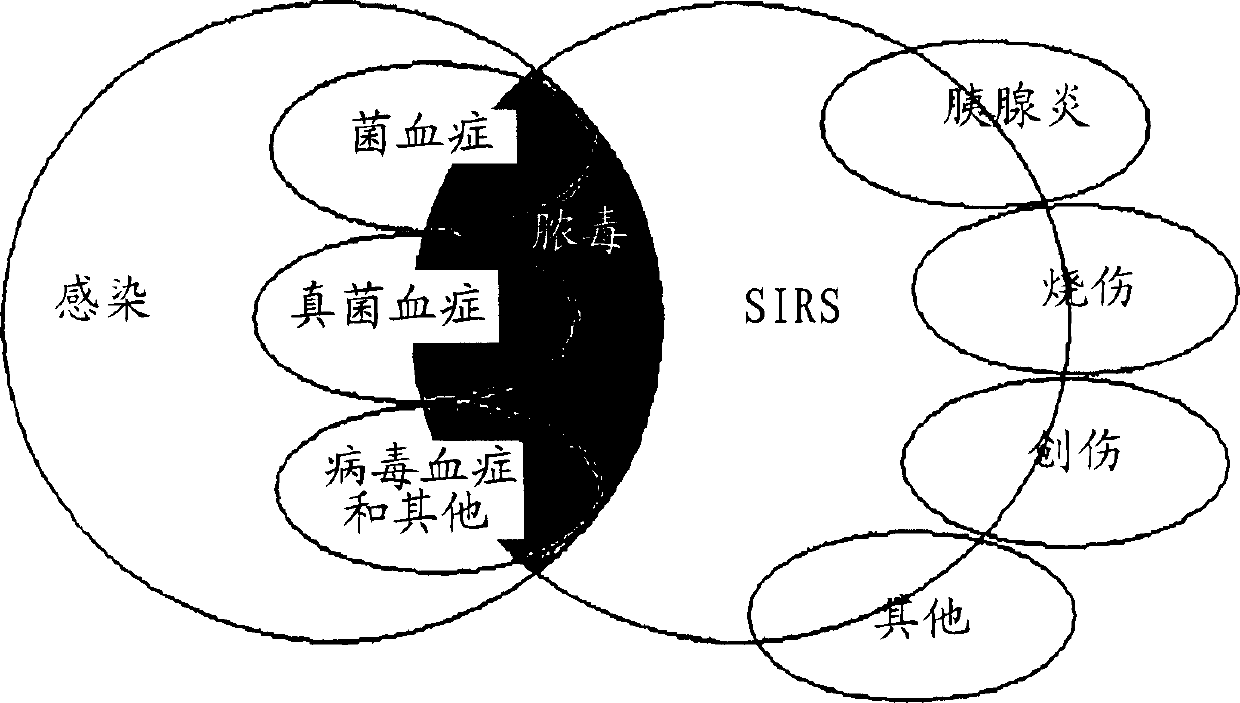
Diagnosis of sepsis or SIRS using biomarker profiles
ActiveUS7645573B2Accurate and rapid and sensitive prediction and diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisDiseaseEarly prediction
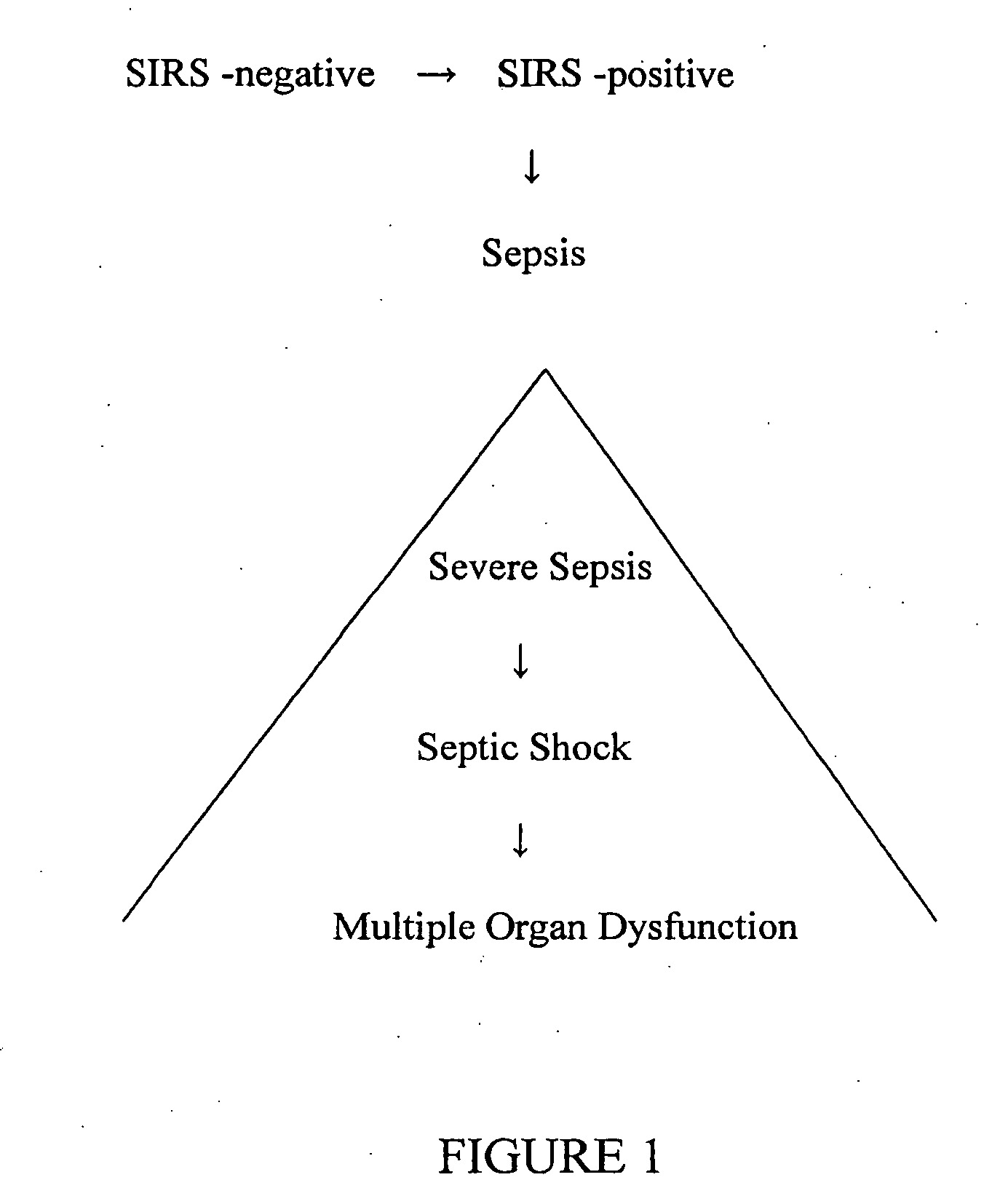
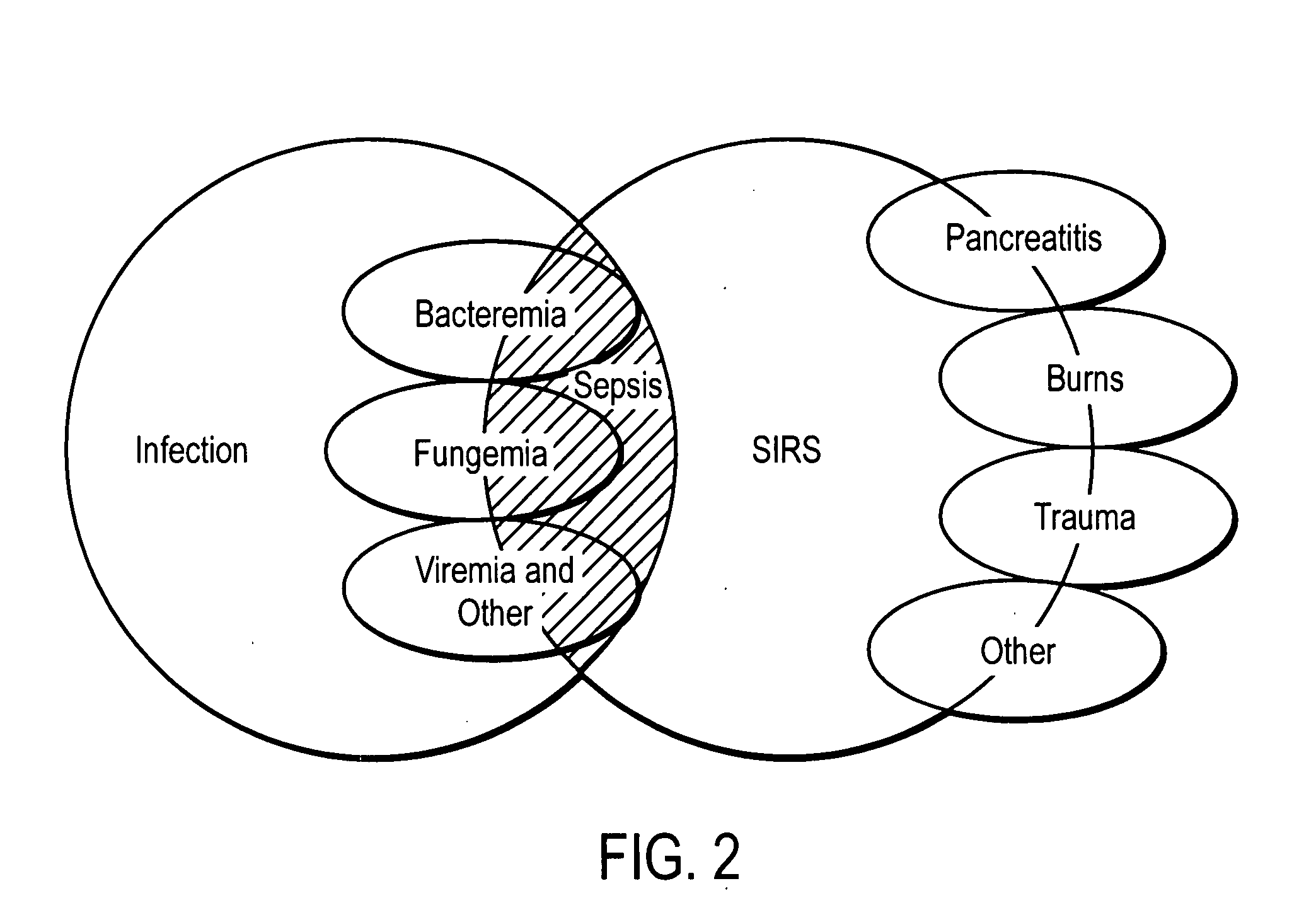
The early prediction or diagnosis of sepsis advantageously allows for clinical intervention before the disease rapidly progresses beyond initial stages to the more severe stages, such as severe sepsis or septic shock, which are associated with high mortality. Early prediction or diagnosis is accomplished using a molecular diagnostics approach, involving comparing an individual's profile of biomarker expression to profiles obtained from one or more control, or reference, populations, which may include a population who develops sepsis. Recognition of features in the individual's biomarker profile that are characteristic of the onset of sepsis allows a clinician to diagnose the onset of sepsis from a bodily fluid isolated at the individual at a single point in time. The necessity of monitoring the patient over a period of time is, therefore, avoided, advantageously allowing clinical intervention before the onset of serious symptoms. Further, because the biomarker expression is assayed for its profile, identification of the particular biomarkers is unnecessary. The comparison of an individual's biomarker profile to biomarker profiles of appropriate reference populations likewise can be used to diagnose SIRS in the individual.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Use of mass spectrometry to detect sepsis
InactiveUS20080050829A1Accurate and rapid and sensitive prediction and diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism separationESI mass spectrometryMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
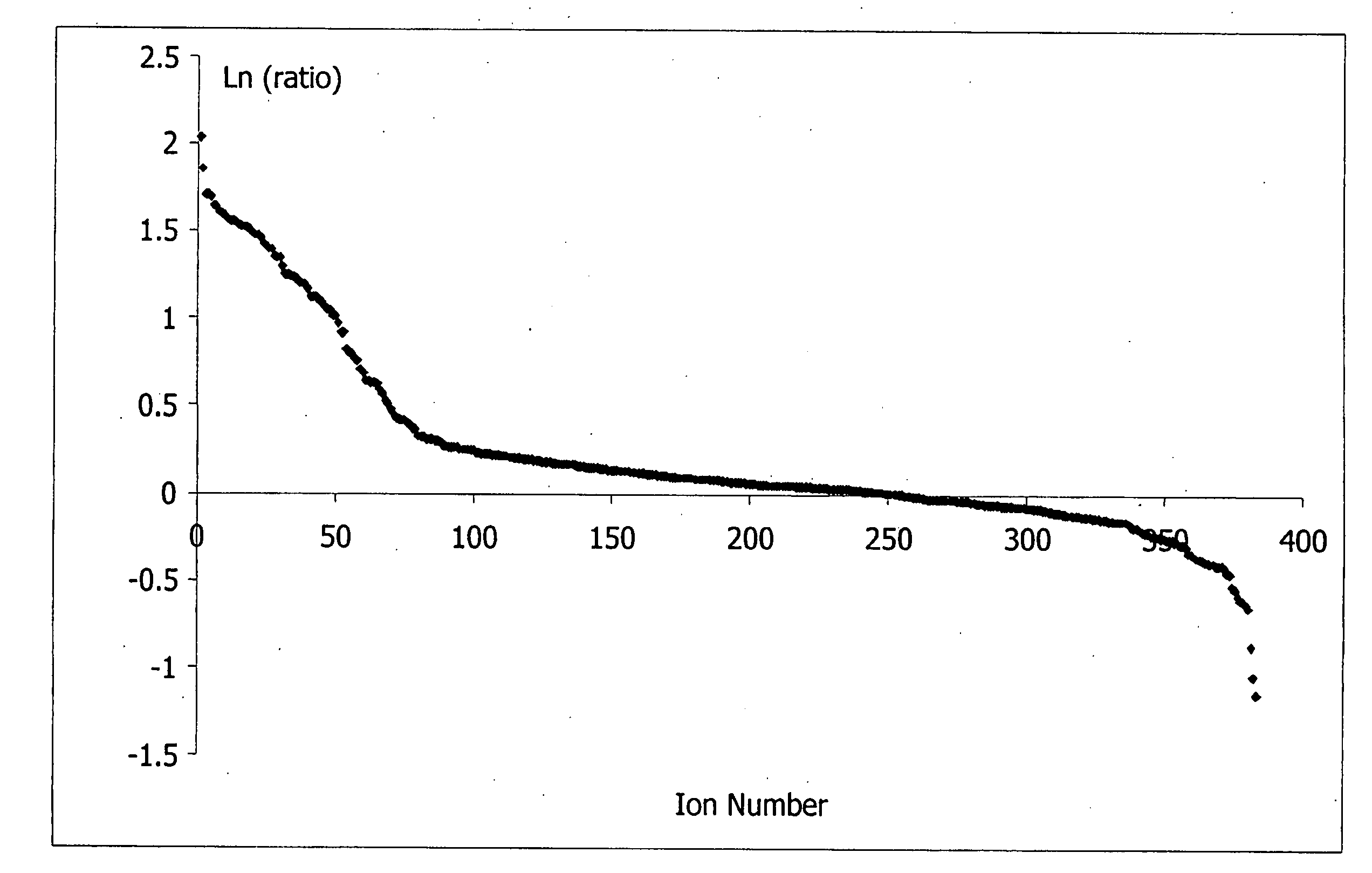
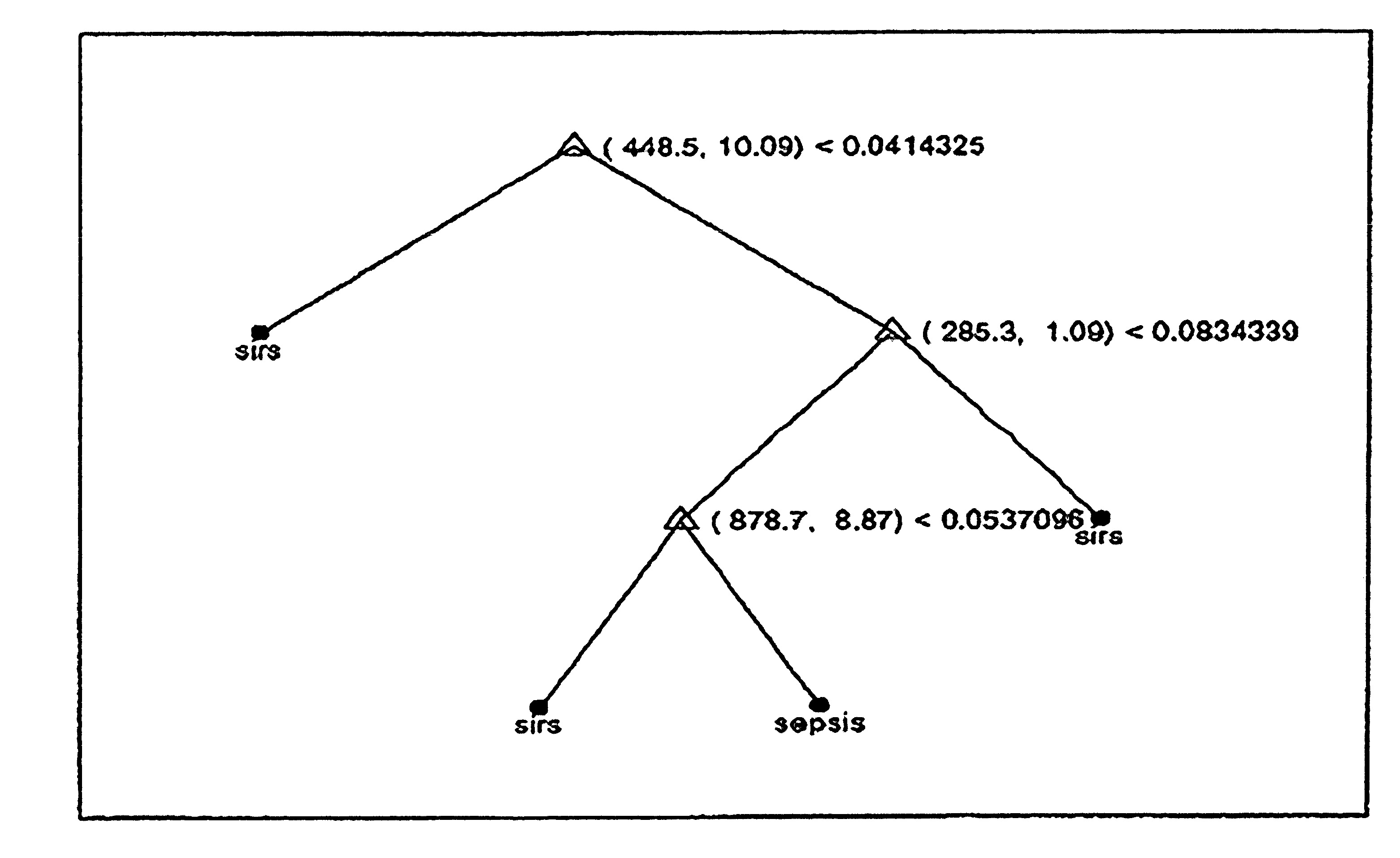
Mass spectrometry techniques for determining the status of sepsis in an individual are provided. A biomarker profile resolved from a biological sample, taken from the individual, using a mass spectrometry technique is compared to a reference biomarker profile. A single such comparison classifies the individual as belonging to or not belonging to a reference population. The individual's biomarker profile and the reference biomarker profile comprise a plurality of ions each having a mass-to-charge ratio of about 100 Daltons to about 1000 Daltons. The plurality of ions can be detected by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry in positive mode. The comparison uses a decision rule, such as a classification tree, that determines the status of sepsis in the individual without requiring knowledge of the identity of the biomarkers in the biomarker profile from the individual and without requiring knowledge of the identity of the biomarkers in the reference biomarker profile.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Method of predicting the onset of sepsis in SIRS-positive individuals using mass spectrometry
InactiveUS7632685B2Accurate and rapid and sensitive prediction and diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisESI mass spectrometryMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectrometry techniques for determining the status of sepsis in an individual are provided. A biomarker profile resolved from a biological sample, taken from the individual, using a mass spectrometry technique is compared to a reference biomarker profile. A single such comparison classifies the individual as belonging to or not belonging to a reference population. The individual's biomarker profile and the reference biomarker profile comprise a plurality of ions each having a mass-to-charge ratio of about 100 Daltons to about 1000 Daltons. The plurality of ions can be detected by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry in positive mode. The comparison uses a decision rule, such as a classification tree, that determines the status of sepsis in the individual without requiring knowledge of the identity of the biomarkers in the biomarker profile from the individual and without requiring knowledge of the identity of the biomarkers in the reference biomarker profile.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Diagnosis of sepsis or SIRS using biomarker profiles
InactiveUS20080138832A1Accurate and rapid and sensitive prediction and diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisDiseaseEarly prediction
The early prediction or diagnosis of sepsis advantageously allows for clinical intervention before the disease rapidly progresses beyond initial stages to the more severe stages, such as severe sepsis or septic shock, which are associated with high mortality. Early prediction or diagnosis is accomplished by comparing an individual's profile of biomarker expression to profiles obtained from one or more control, or reference, populations, which may include a population that develops sepsis. Recognition of features in the individual's biomarker profile that are characteristic of the onset of sepsis allows a clinician to diagnose the onset of sepsis from a bodily fluid isolated from the individual at a single point in time. The necessity of monitoring the patient over a period of time is, therefore, avoided, advantageously allowing clinical intervention before the onset of serious symptoms of sepsis. Further, because the biomarker expression is assayed for its profile, identification of the particular biomarkers is unnecessary. The comparison of an individual's biomarker profile to biomarker profiles of appropriate reference populations likewise can be used to diagnose SIRS in the individual.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
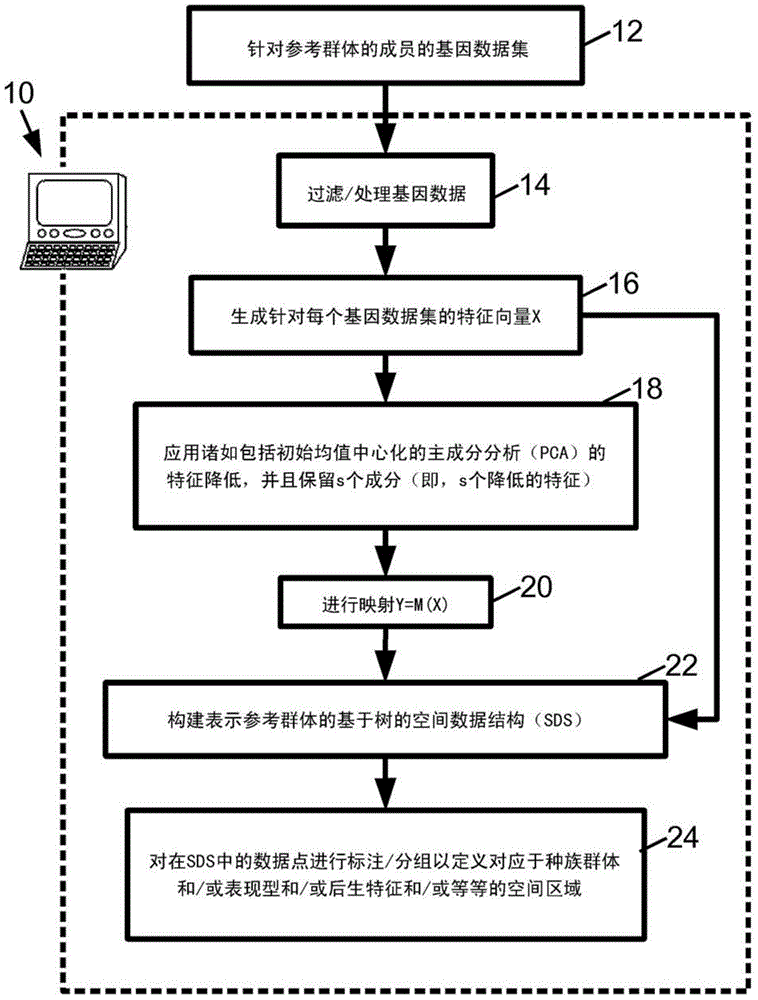
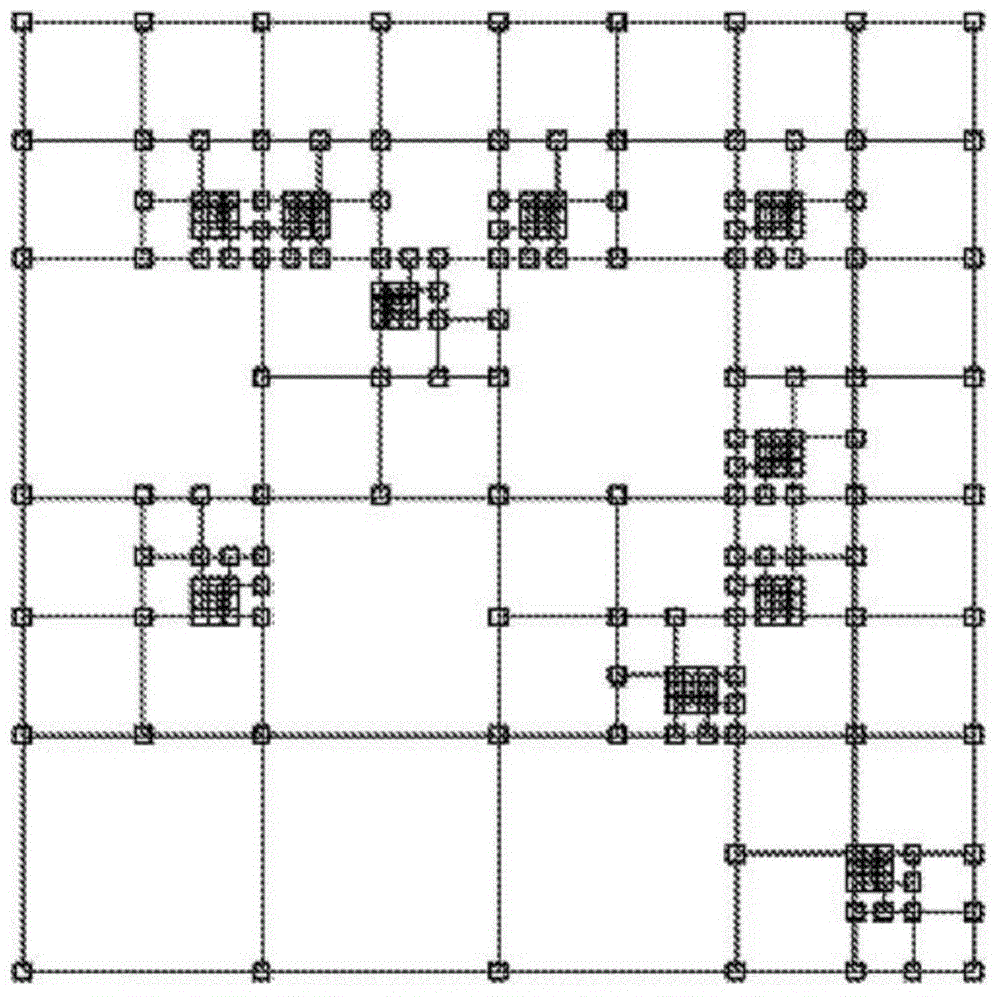
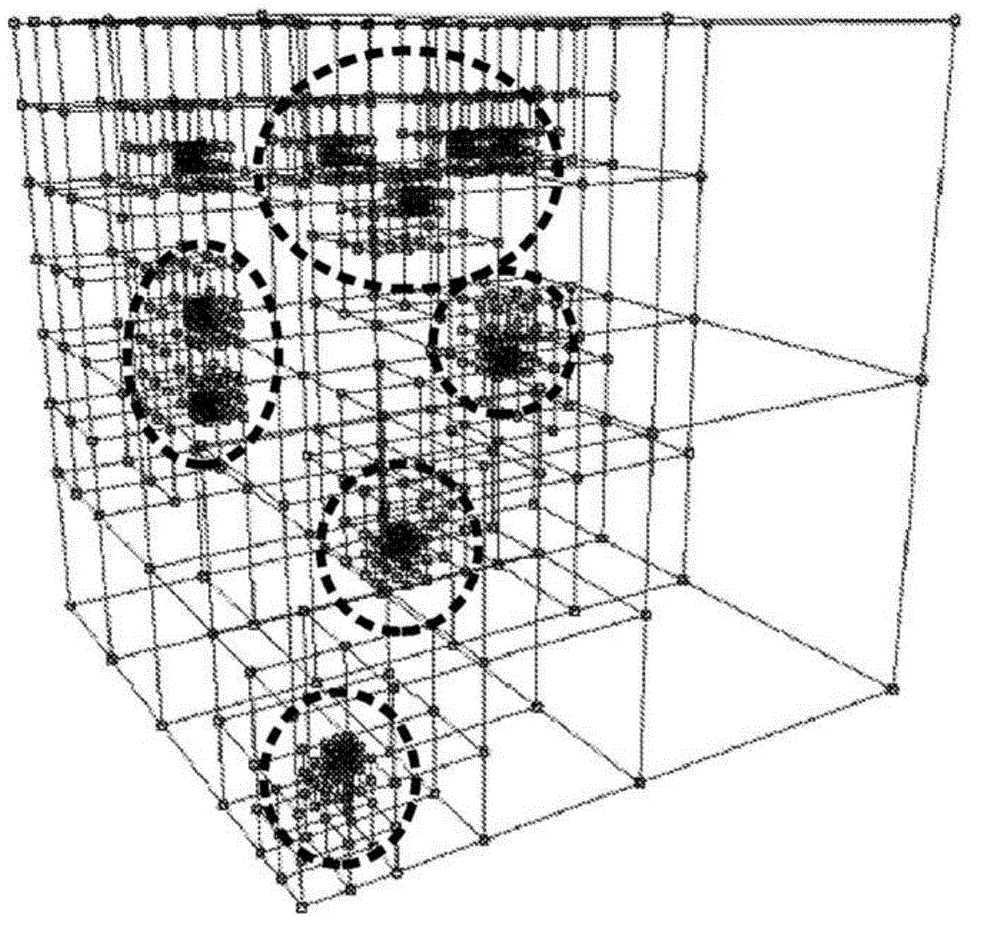
Population classification of genetic data set using tree based spatial data structure
InactiveCN104541276AAccurate classificationAccurate groupingBiostatisticsProteomicsFeature vectorData set
Reference feature vectors are constructed representing reference genetic data sets of a reference population. The reference feature vectors are transformed using a linear transformation to generate reduced dimensionality vector representations of the reference genetic data sets of the reference population. A tree-based spatial data structure is constructed to index the reference genetic data sets as data points defined by at least some dimensions of the reduced dimensionality vector representations of the reference genetic data sets of the reference population. The linear transform may be generated by performing feature reduction on the reference feature vectors. A feature vector representing a proband genetic data set is transformed using the linear transformation to generate a reduced-dimensionality vector representation that is located in the tree-based spatial data structure to perform population assignment for the proband genetic data set.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Mass spectrometry techniques for determining the status of sepsis in an individual
ActiveUS20070184512A1Accurate and rapid and sensitive prediction and diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisESI mass spectrometryMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectrometry techniques for determining the status of sepsis in an individual are provided. A biomarker profile resolved from a biological sample, taken from the individual, using a mass spectrometry technique is compared to a reference biomarker profile. A single such comparison classifies the individual as belonging to or not belonging to a reference population. The individual's biomarker profile and the reference biomarker profile comprise a plurality of ions each having a mass-to-charge ratio of about 100 Daltons to about 1000 Daltons. The plurality of ions can be detected by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry in positive mode. The comparison uses a decision rule, such as a classification tree, that determines the status of sepsis in the individual without requiring knowledge of the identity of the biomarkers in the biomarker profile from the individual and without requiring knowledge of the identity of the biomarkers in the reference biomarker profile.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
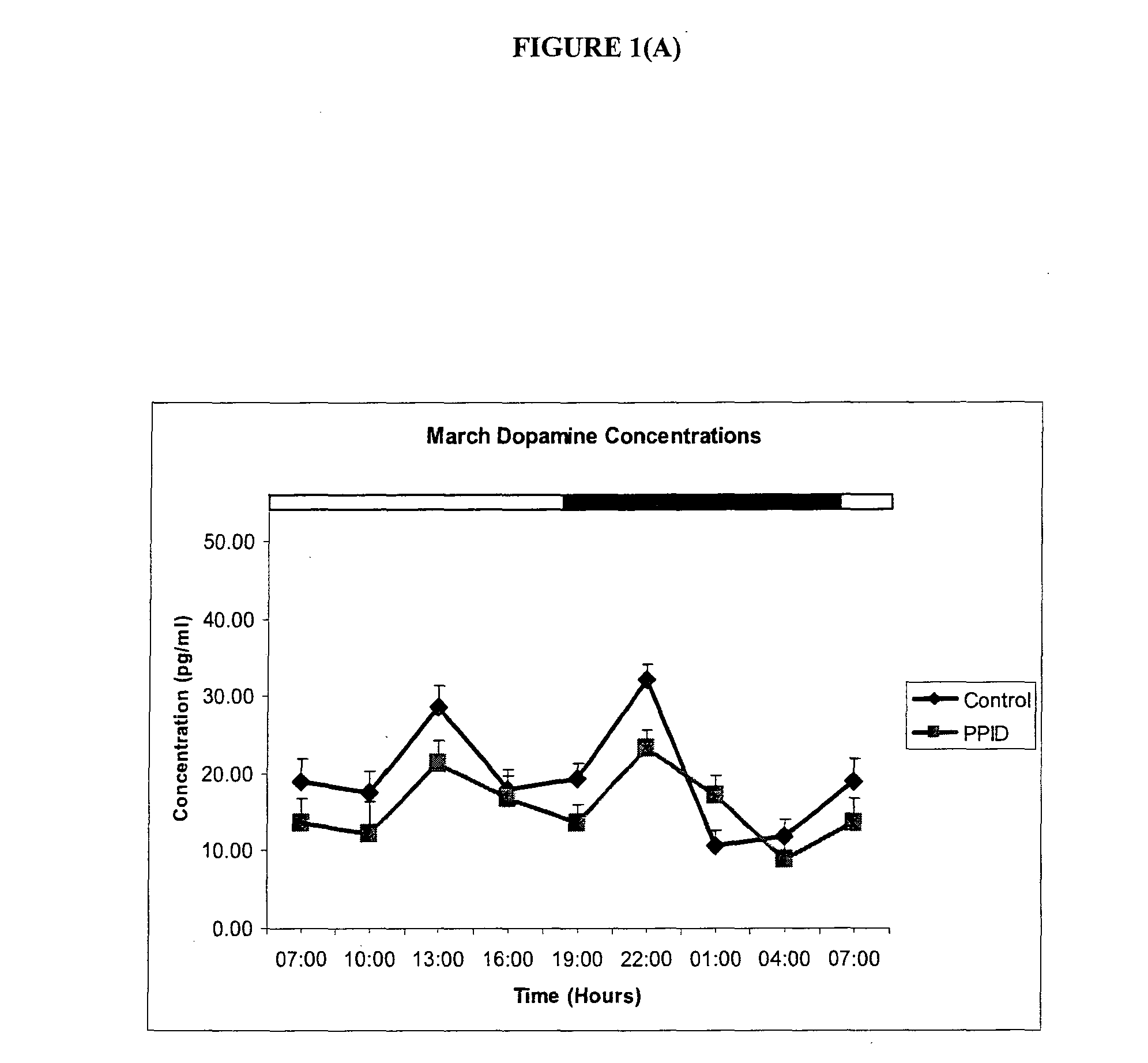
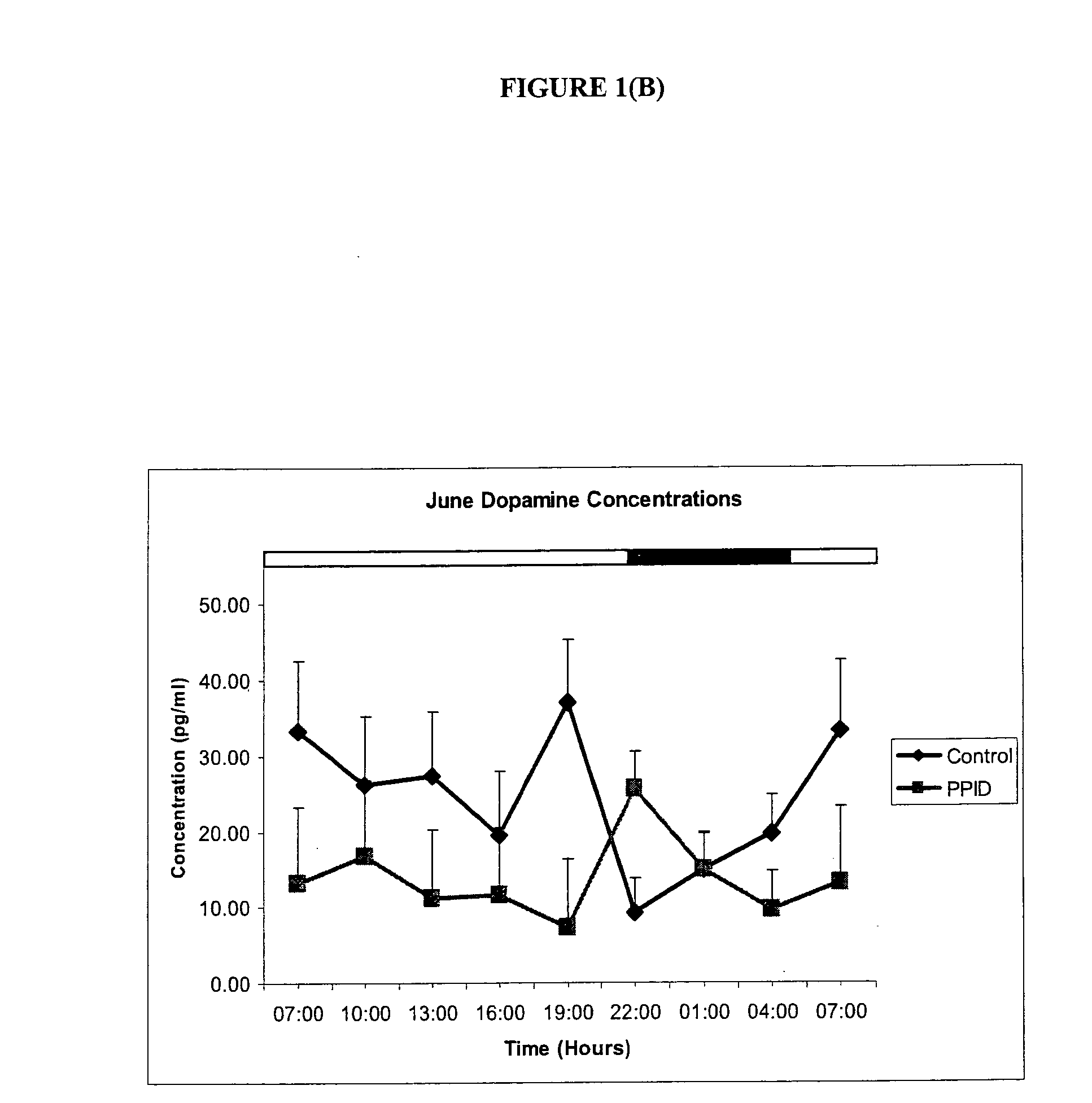
Methods of diagnosis and treatment of equine laminitis and cushing's syndrome
InactiveUS20090285916A1Increase melatonin levelIncreased susceptibilityBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementSerotoninMedicine
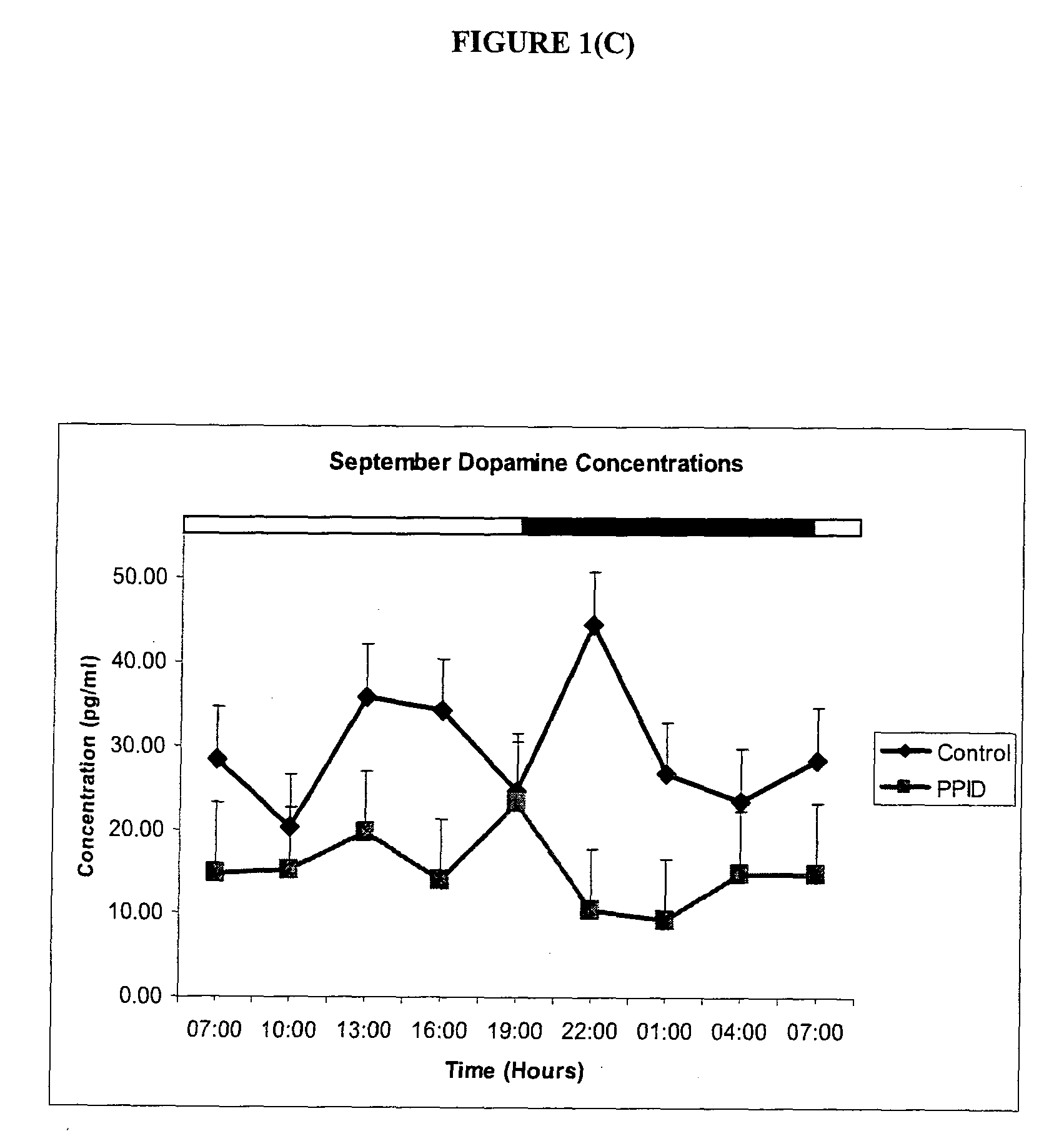
The invention provides a method for diagnosing a disorder or disease associated with an imbalance of monoamines in a subject, or of diagnosing susceptibility of the subject to the same, wherein the method comprising (a) providing a sample from a subject to be tested, (b) measuring the levels of dopamine, melatonin and / or serotonin in the sample; and (c) comparing the levels measured in step (b) with levels of dopamine, melatonin and / or serotonin associated with a reference population of subjects, wherein a difference in one or more of the levels measured in step (b) with the levels of dopamine, melatonin and serotonin associated with the reference population of subjects is indicative of a positive diagnosis. The invention further provides a method of prevention or treatment of a disorder or disease associated with an imbalance of monoamines, and kits for the same.
Owner:PEGASUS EQUINE DIAGNOSTICS
Method of, and Apparatus and Computer Software for, Performing Image Processing
ActiveUS20080219529A1Shorten the timeImprove processing efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImaging processing
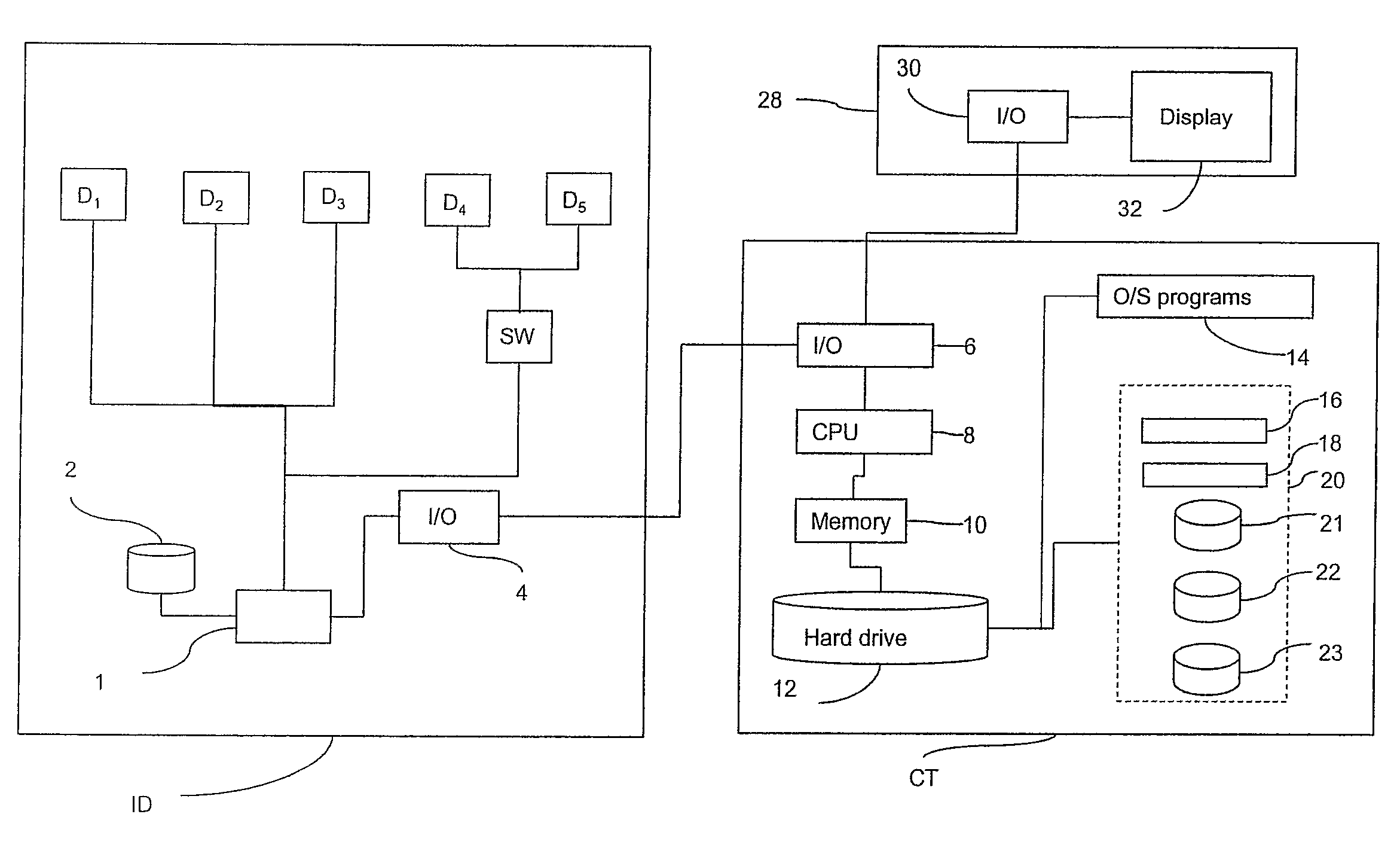
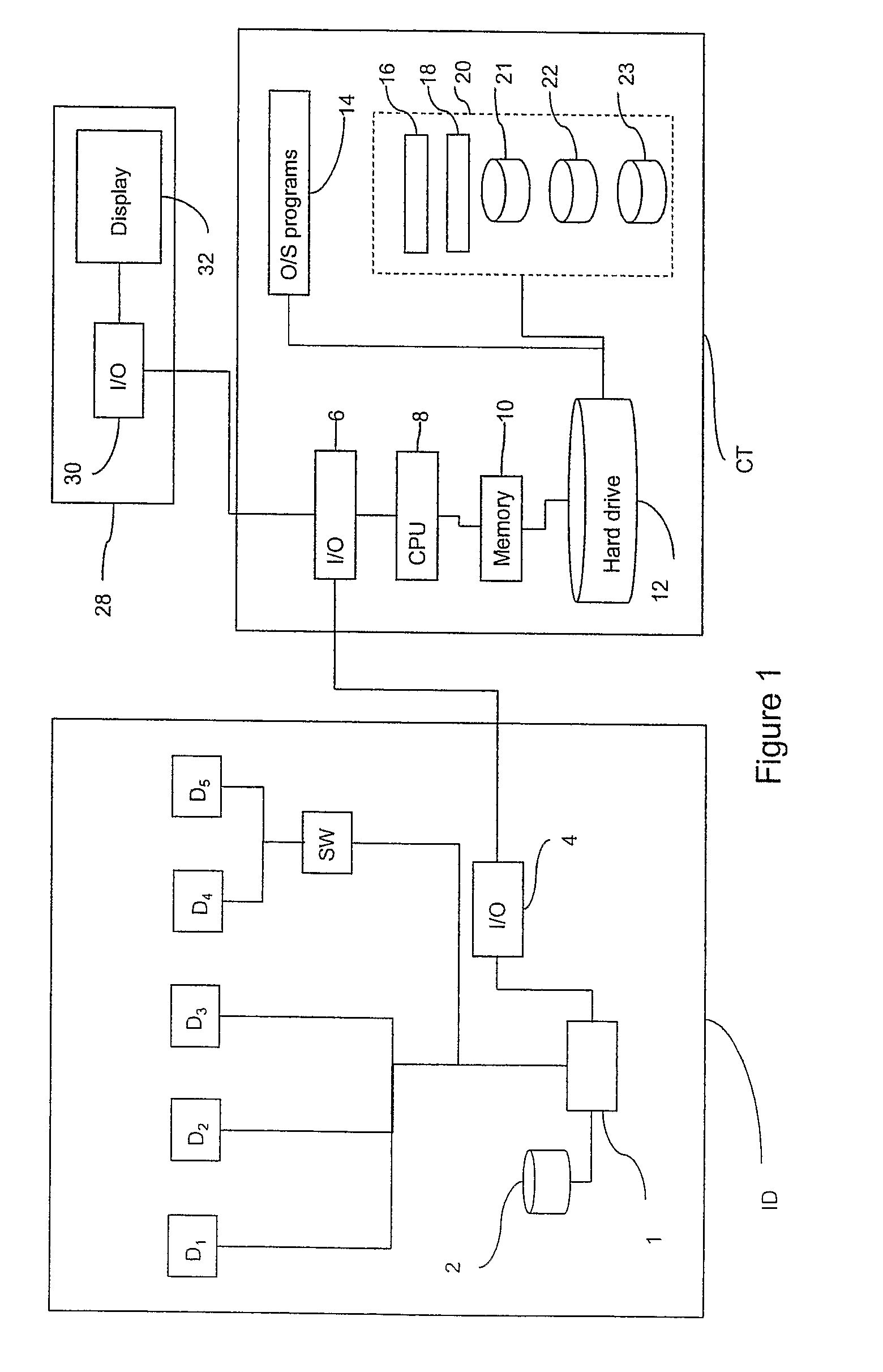
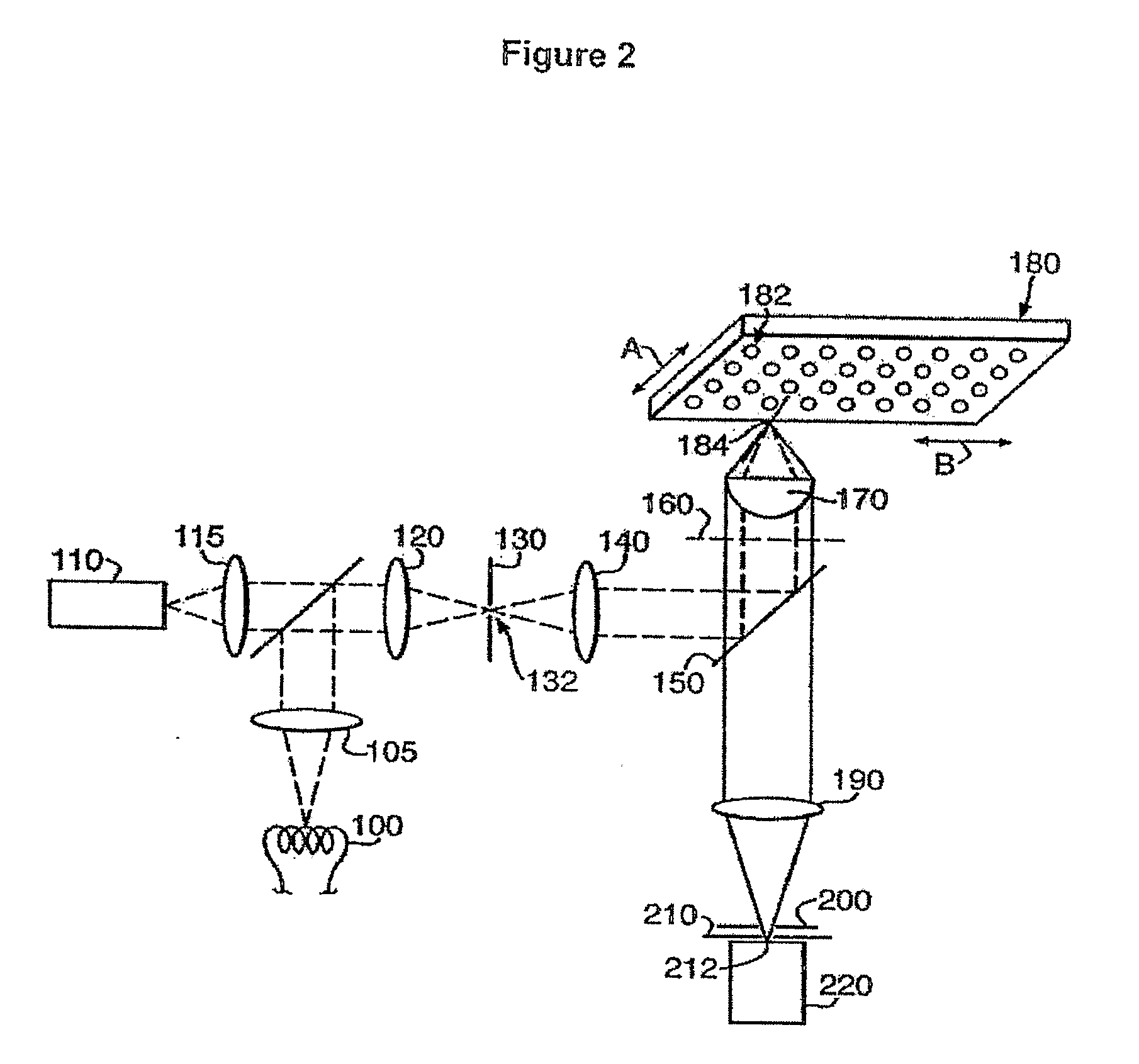
A computer-implemented method of performing image processing for images of biological objects includes: storing definitions of a plurality of descriptors; receiving image data relating to an image of a reference population of biological objects; receiving image data relating to an image of a target population of biological objects; processing the reference population image data to obtain a reference set of measurements, containing data for each of the descriptors; processing the target population image data to obtain a target set of measurements, containing data for each of the descriptors; and selecting a combination of the descriptors on the basis of comparing the reference set with the target set to define a preferred combination of the descriptors for use in identifying characteristics of a further population of biological objects which are similar to those of the target population.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS OPERATIONS UK LTD
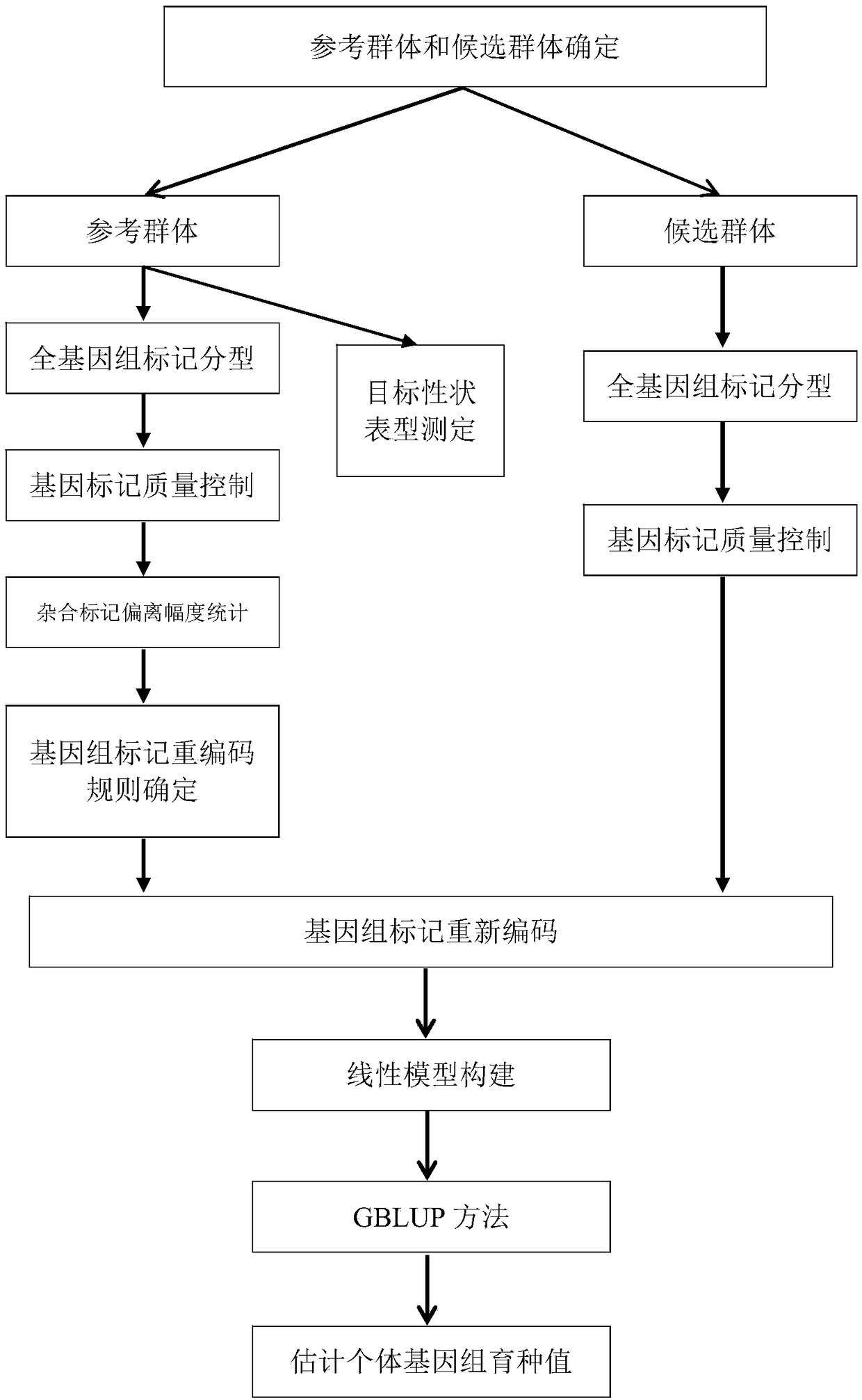
A method for estimating genomic breeding value integrating dominance effects
ActiveCN109101786AImprove accuracyIntroduce reasonableSpecial data processing applicationsHomozygous genotypeModel complexity
The invention discloses a genome breeding value estimation method for integrating dominant effect, which relates to the technical field of livestock and poultry genetic selection. The method comprisessteps identifying a reference group and a candidate group, the phenotype of the target traits of the reference population was determined, Genome-wide marker typing of reference population, quality control of gene marker of reference population, statistics of heterozygous marker deviation of reference population, formulation of genome marker re-coding rules, genome-wide marker typing of candidatepopulation, quality control of gene marker of candidate population, re-coding of genome marker and estimation of genome breeding value, etc. Based on the deviation degree between the phenotype of theheterozygous genotype and the phenotype of the homozygous genotype, the invention formulates coding rules, starts from the genomic marker end, re-codes the heterozygous genotype, causes the gene marker coding to include dominant effect, and then estimates the genomic breeding value. The invention is adapted to the needs of livestock and poultry genetic breeding, and can greatly improve the accuracy of genome estimation breeding value without increasing the complexity of the model.
Owner:ANIMAL SCI RES INST GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Interpolated image response
Systems and methods are provided for characterizing a multidimensional distribution of responses from the objects in a populations subject to a perturbation. The methods enable the creation of a “degree of response” scale interpolated from non-perturbed and perturbed reference populations. The methods enables, using the interpolated degree of response scale, the quantitation of a degree of response of a test compound subject to a given level of perturbation, and enables the generation of a dose-response curve for a test compound. The methods are useful in a wide range of applications, such cellular analysis and high-content screening of compounds, as carried out in pharmaceutical research.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Gene data processing method and gene data processing device
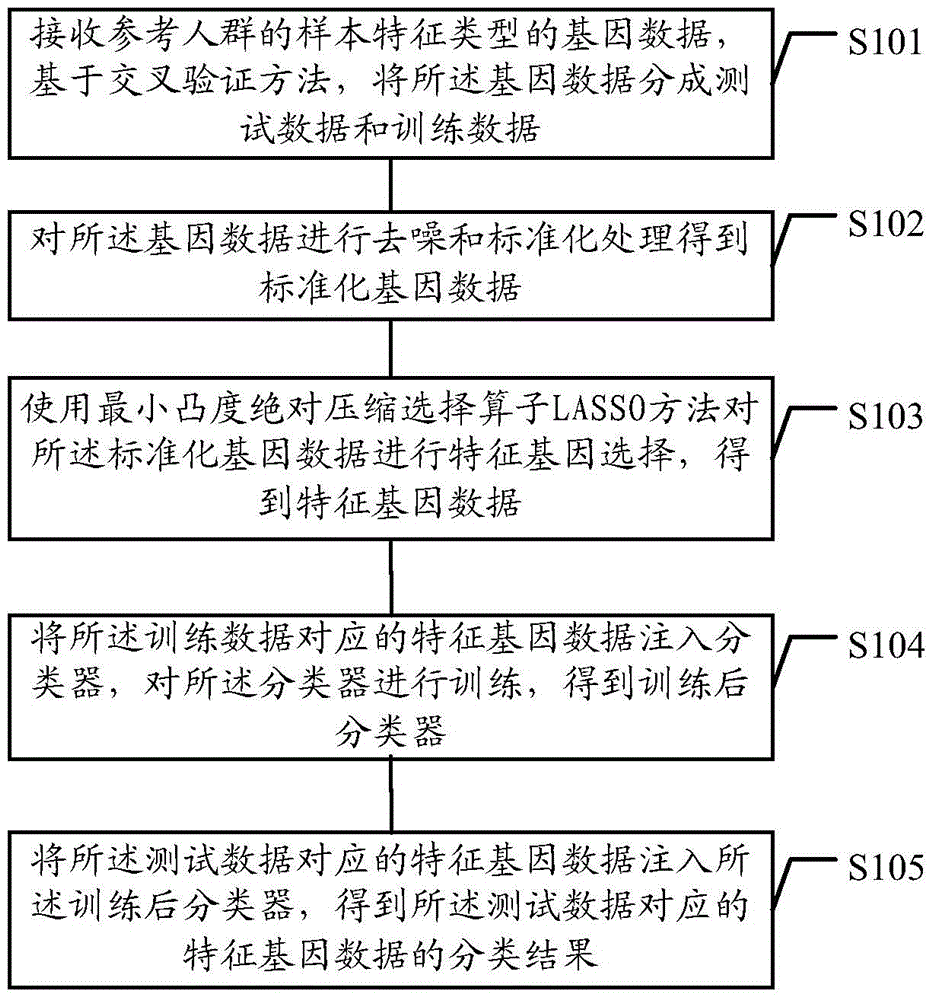
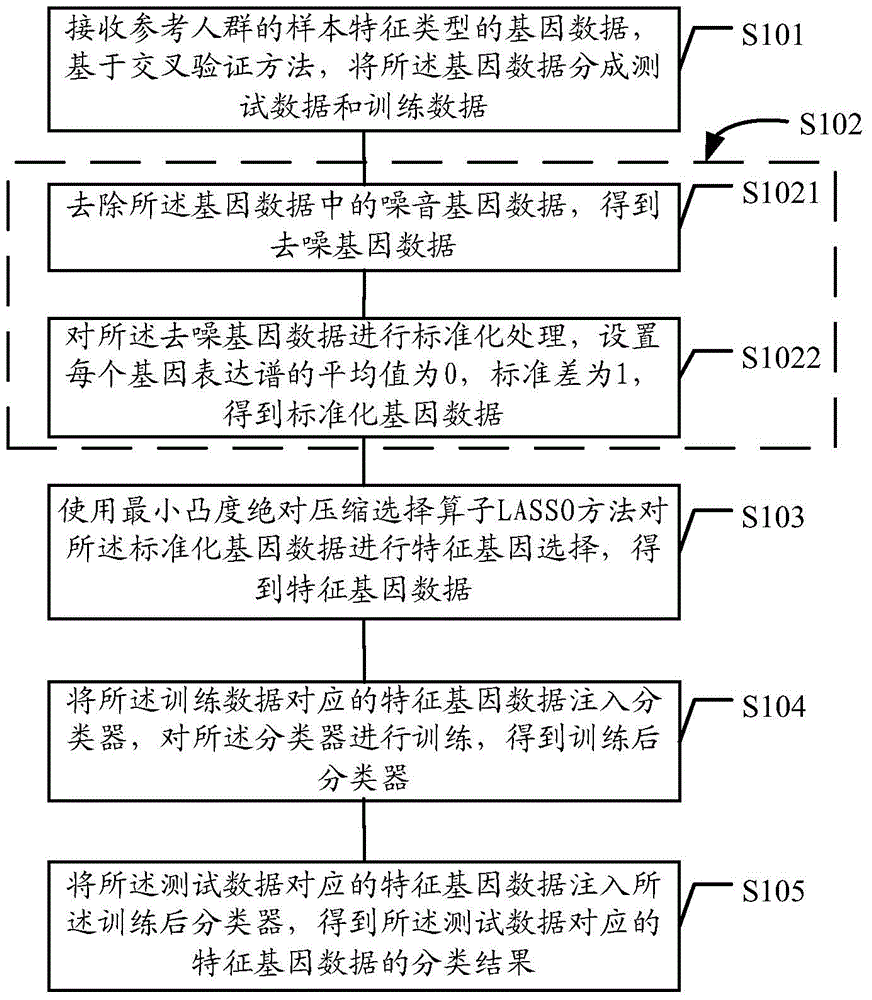
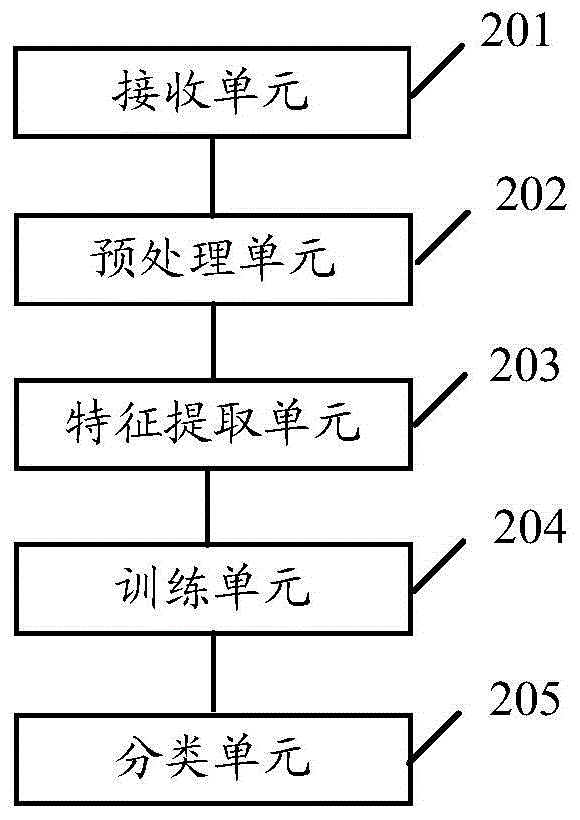
InactiveCN104408332AImprove accuracyReduce the impact of classification accuracySpecial data processing applicationsGene selectionTest sample
The embodiment of the invention discloses a gene data processing method and a gene data processing device. The method comprises the following steps: receiving gene data of a specified feature type of a reference population; preprocessing the gene data to obtain standardized gene data; performing feature gene selection on the standardized gene data by a LASSO method to obtain feature gene data; upon a cross validation method, dividing a sample set of the feature gene data into test samples and training samples; injecting the training samples into a classifier to obtain a trained classifier; injecting the test samples into the trained classifier; performing feature classification on the test samples, and performing statistics on the classification accuracy of the classifier. According to the gene data processing method and the gene data processing device provided by the embodiment of the invention, the accuracy of the feature gene selection can be improved, and the influence of the selection of the test samples and the training samples on the classification accuracy is lowered.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Method of, and apparatus and computer software for, performing image processing
ActiveUS8041090B2Shorten the timeImprove processing efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImaging processing
A computer-implemented method of performing image processing for images of biological objects includes: storing definitions of a plurality of descriptors; receiving image data relating to an image of a reference population of biological objects; receiving image data relating to an image of a target population of biological objects; processing the reference population image data to obtain a reference set of measurements, containing data for each of the descriptors; processing the target population image data to obtain a target set of measurements, containing data for each of the descriptors; and selecting a combination of the descriptors on the basis of comparing the reference set with the target set to define a preferred combination of the descriptors for use in identifying characteristics of a further population of biological objects which are similar to those of the target population.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS OPERATIONS UK LTD
Histochemical and biomarker for liver fibrosis
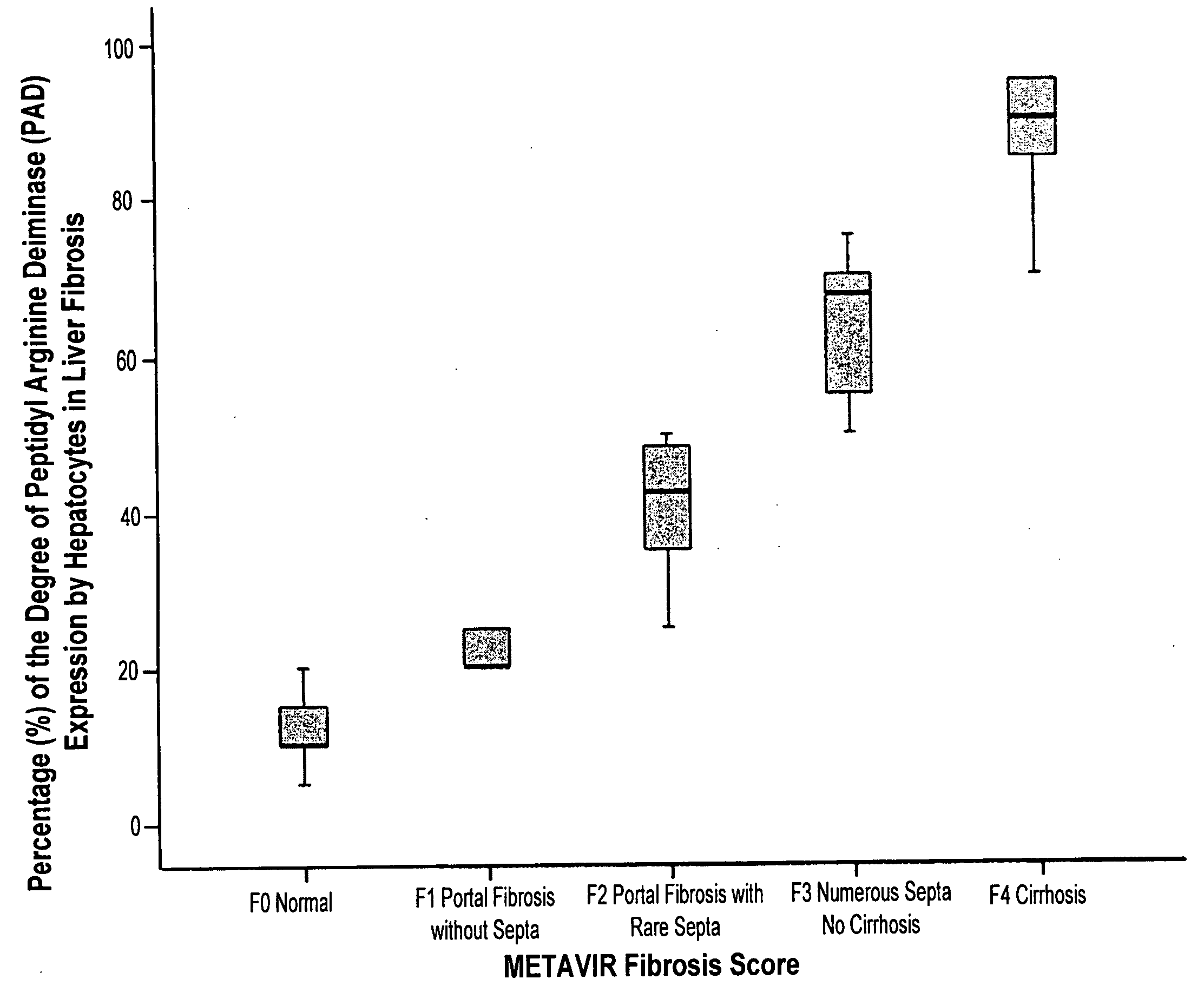
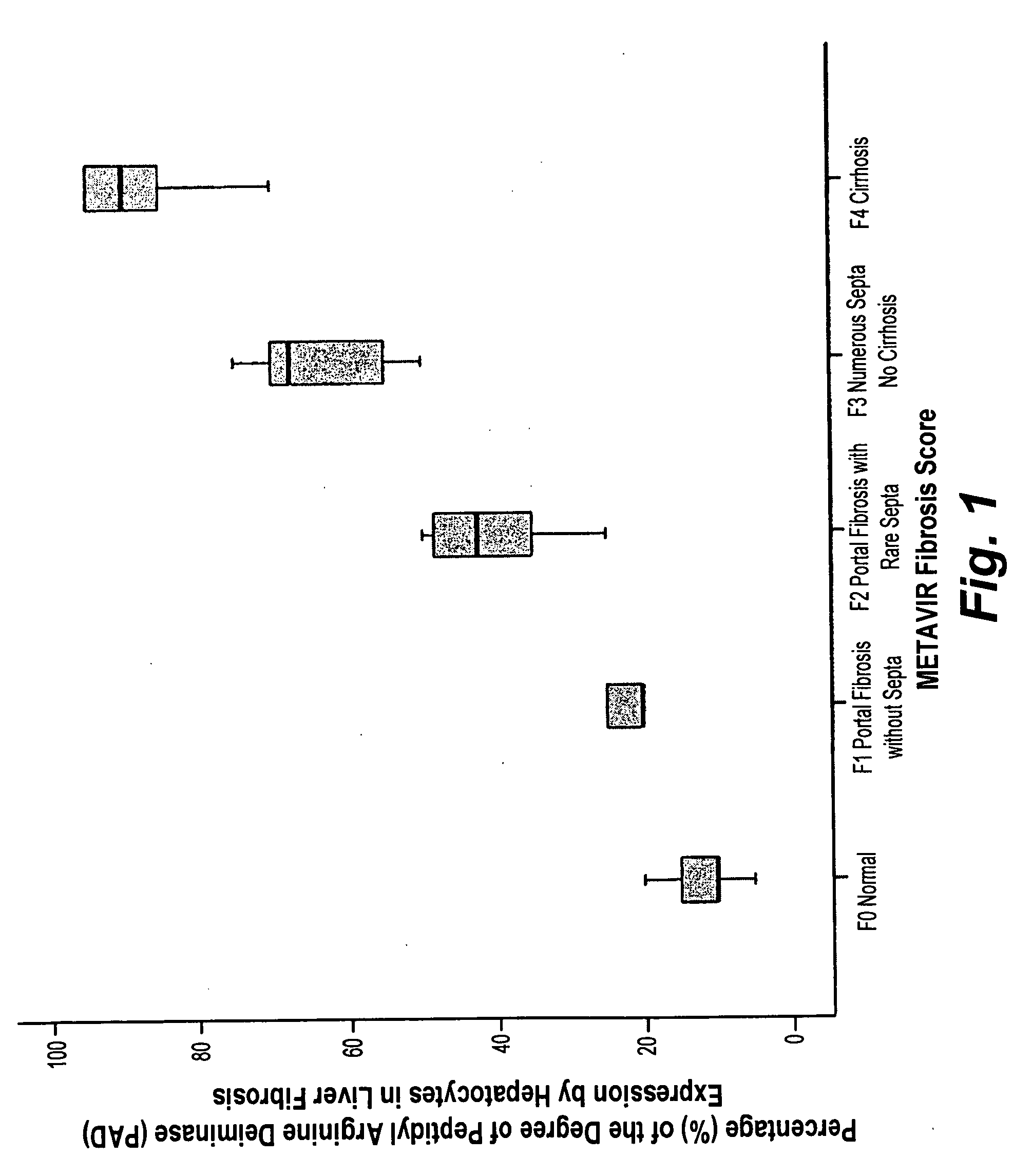
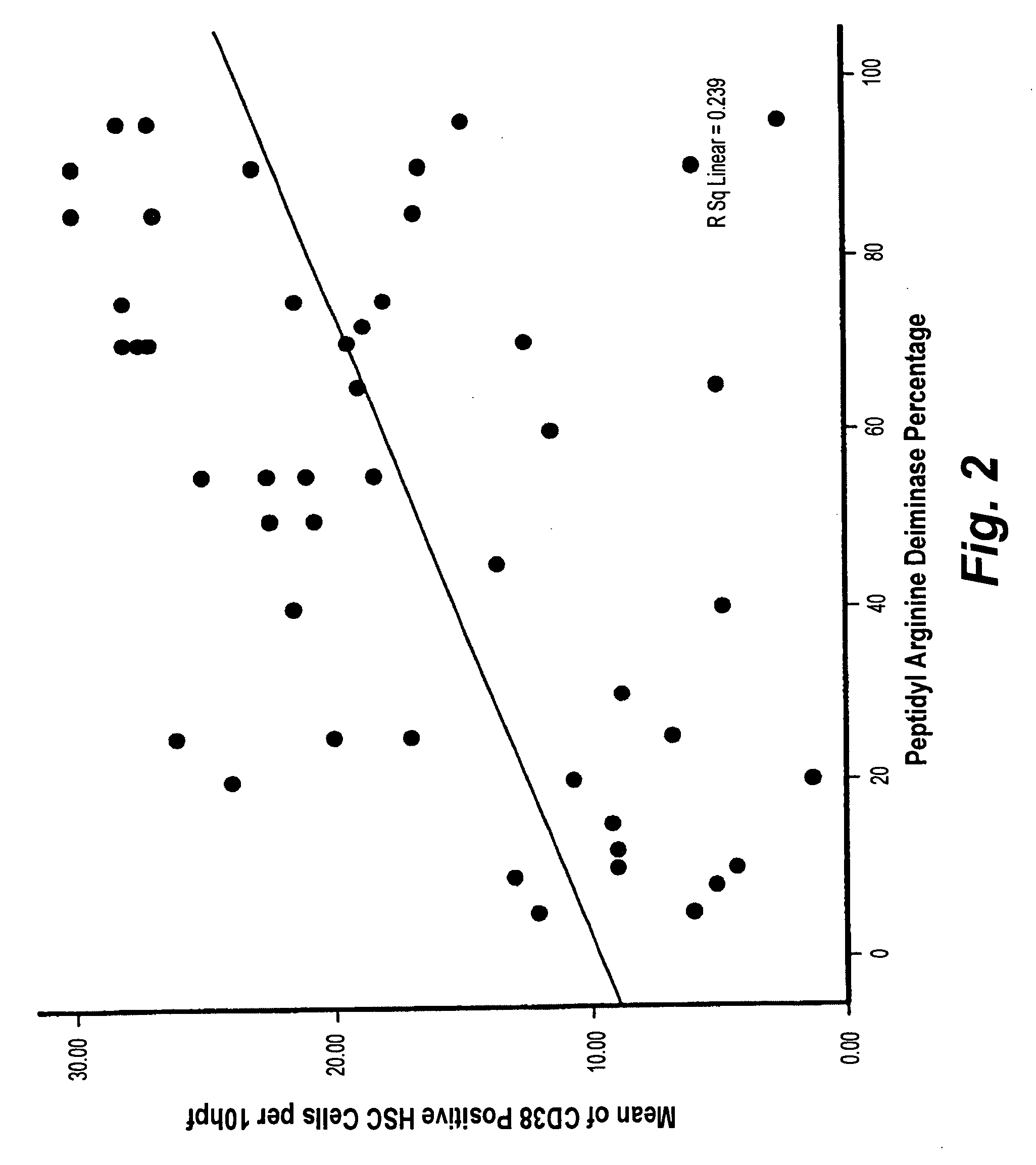
InactiveUS20100203553A1Preparing sample for investigationDisease diagnosisMETAVIR Fibrosis ScoreProper treatment
The histochemical and biomarker for liver fibrosis is a technique for determining the existence and extent of liver fibrosis by evaluating the extent of peptidylarginine deiminase (PAD) activity by immunological methods. The method is illustrated using liver biopsy. A small section of tissue from a liver biopsy is incubated overnight with a monoclonal antibody specific to PAD, stained, and examined microscopically. The number of hepatocytes that positively express PAD activity per one hundred hepatocytes is counted and expressed as a percentage. The percentage of PAD activity is then correlated with a METAVIR fibrosis score according to results from a statistically significant reference population. The degree of liver fibrosis and an appropriate treatment regimen may then be determined.
Owner:ABDEEN SUAD M +1
Diagnosis of sepsis or SIRS using biomarker profiles
InactiveCN1738908AMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisEarly predictionMortality rate
The early prediction or diagnosis of sepsis advantageously allows for clinical intervention before the disease rapidly progresses beyond initial stages to the more severe stages, such as severe sepsis or septic shock, which are associated with high mortality. Early prediction or diagnosis is accomplished using a molecular diagnostics approach, involving comparing an individual's profile of biomarker expression to profiles obtained from one or more control, or reference, populations, which may include a population that develops sepsis. Recognition of features in the individual's biomarker profile that are characteristic of the onset of sepsis allows a clinician to diagnose the onset of sepsis from a bodily fluid isolated at the individual at a single point in time. The necessity of monitoring the patient over a period of time is, therefore, avoided, advantageously allowing clinical intervention before the onset of serious symptoms of sepsis. Further, because the biomarker expression is assayed for its profile, identification of the particular biomarkers is unnecessary. The comparison of an individual's biomarker profile to biomarker profiles of appropriate reference populations likewise can be used to diagnose SIRS in the individual.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Genetic and environmental correlation-based colorectal cancer data model analysis method
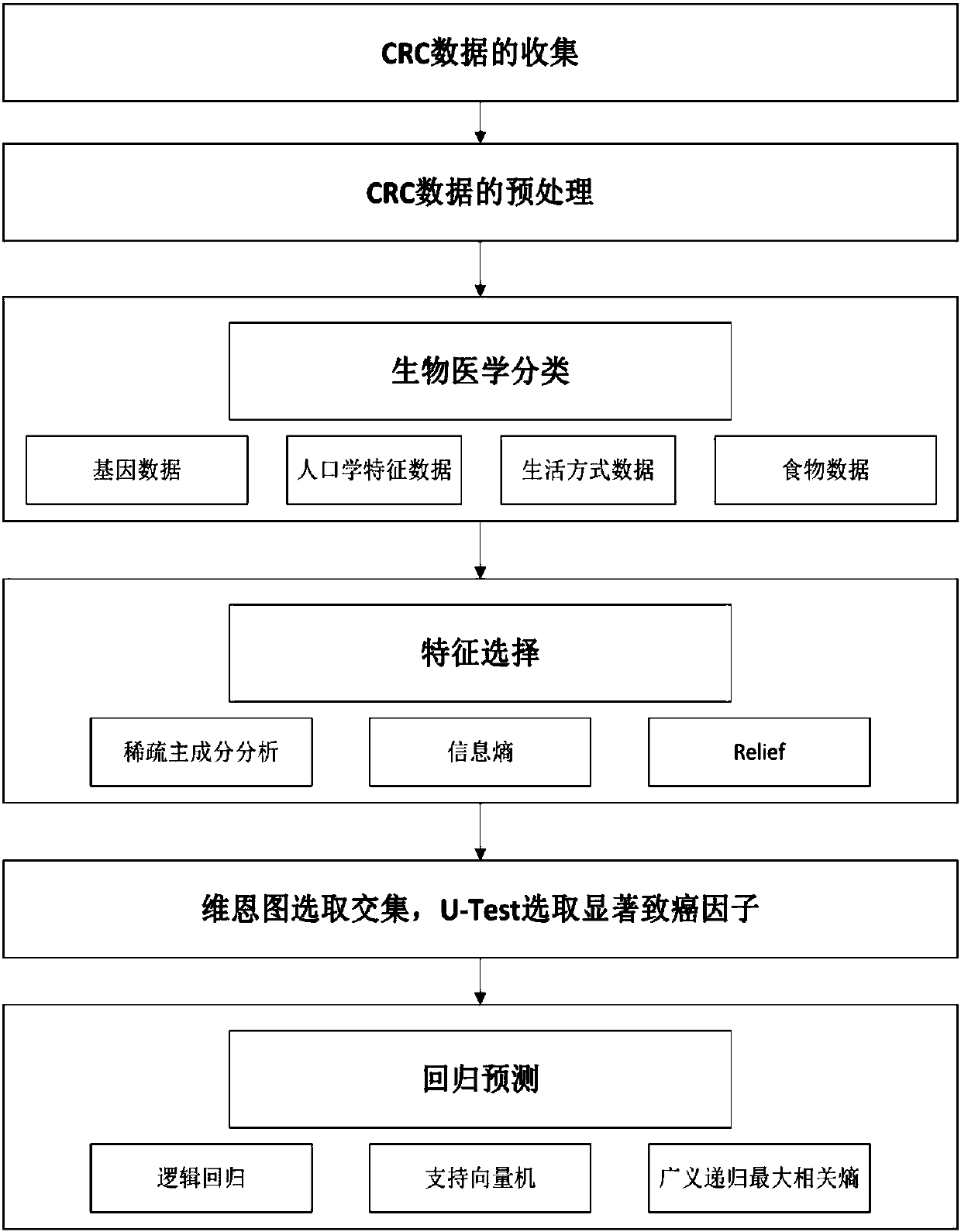
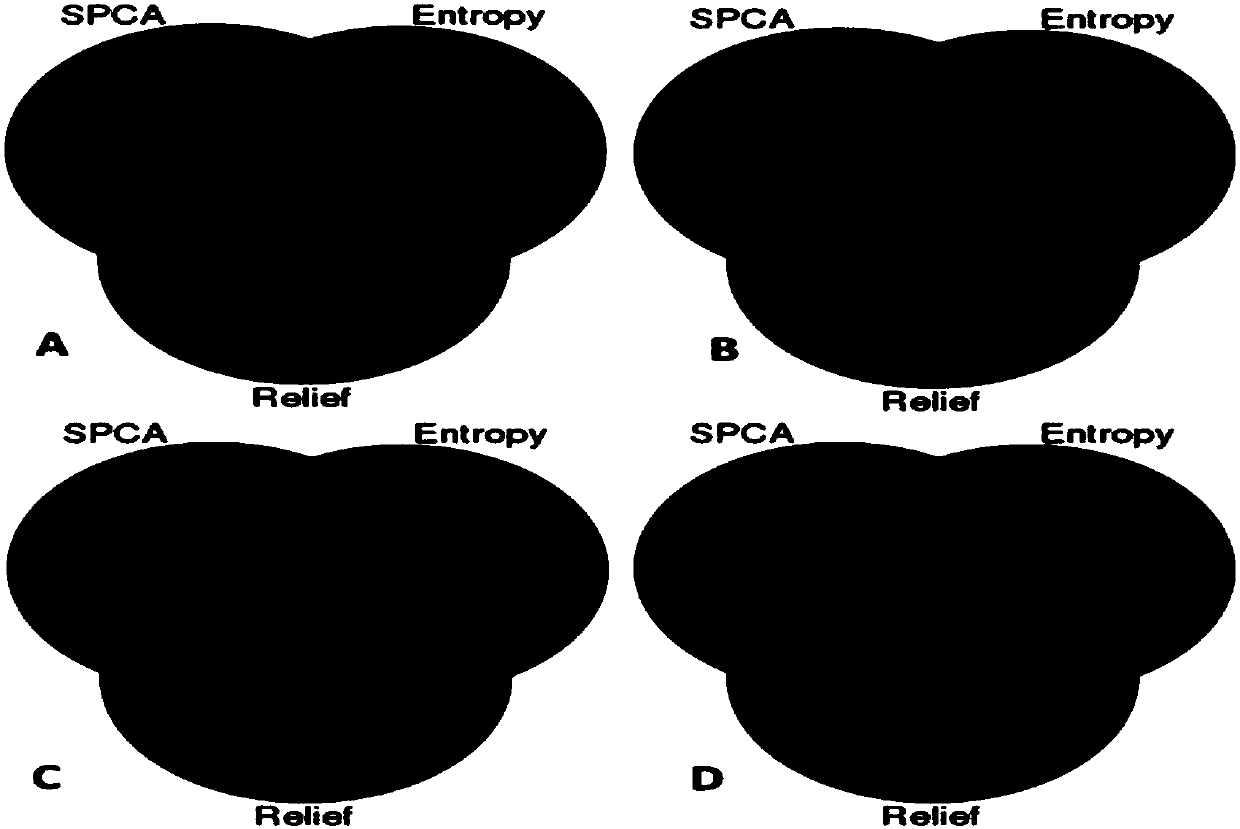
ActiveCN107066781AImprove robustnessImprove reliabilityMedical data miningSpecial data processing applicationsCarcinogenPrincipal component analysis
The invention provides a genetic and environmental correlation-based colorectal cancer data model analysis method. The method comprises the steps of receiving colorectal cancer (CRC) data of a specified feature type of a reference population; preprocessing the data to obtain standardized data; based on the standardized data, classifying the data; performing feature selection on each subclass by using a sparse principal component analysis method, an information entropy method and / or a Relief method; obtaining an intersection of three methods by using a Venn diagram, and obtaining features with remarkable difference by using a U test; and dividing a feature gene data sample set into test samples and training samples, obtaining a trained classifier according to the training samples, injecting the test samples into the trained classifier, performing feature classification on the test samples, and performing statistics on classification accuracy of the classifier. According to the method, the accuracy of extracting carcinogens can be improved and the classification accuracy can be improved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Use of multiple risk predictors for diagnosis of cardiovascular disease
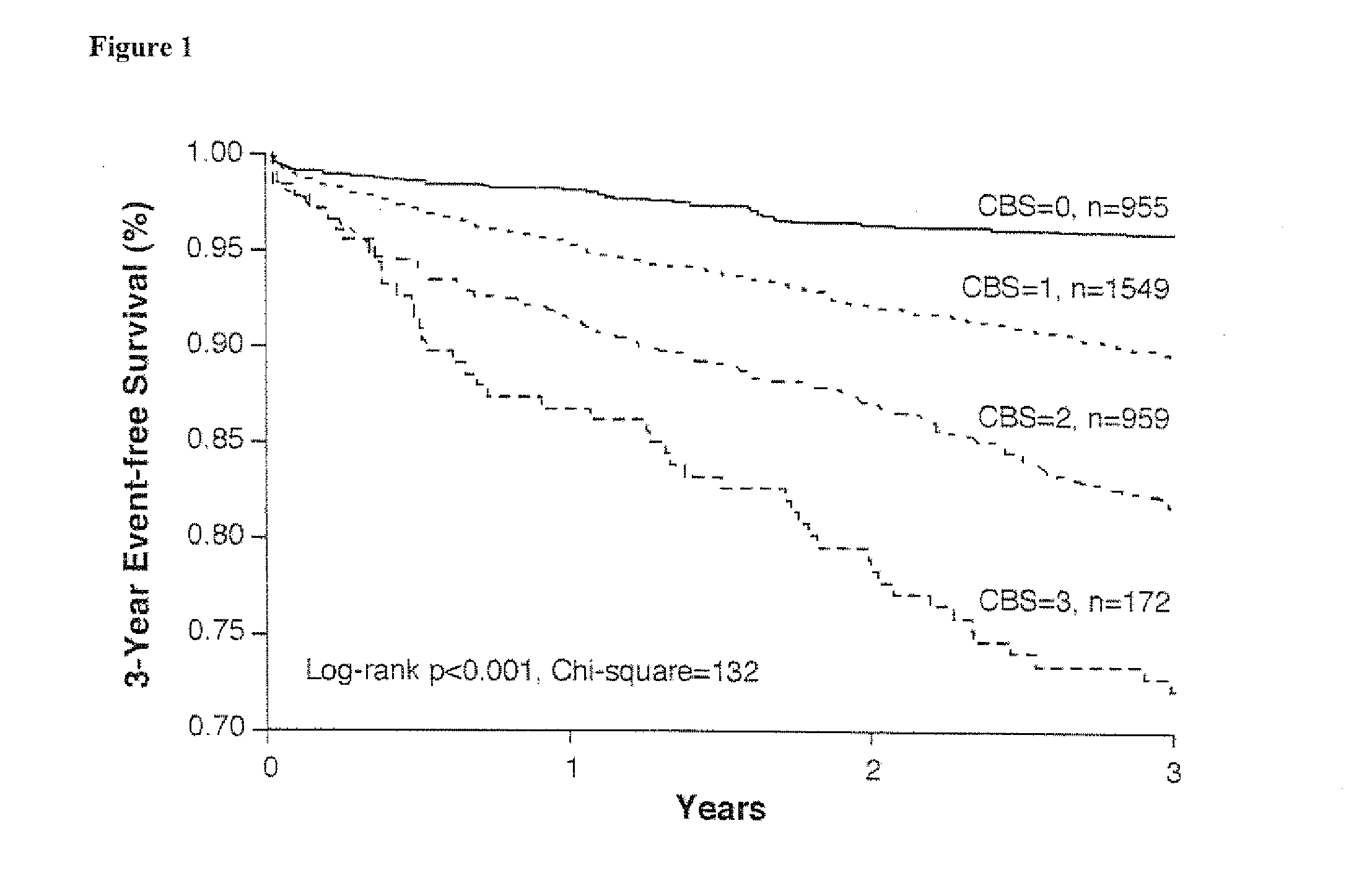
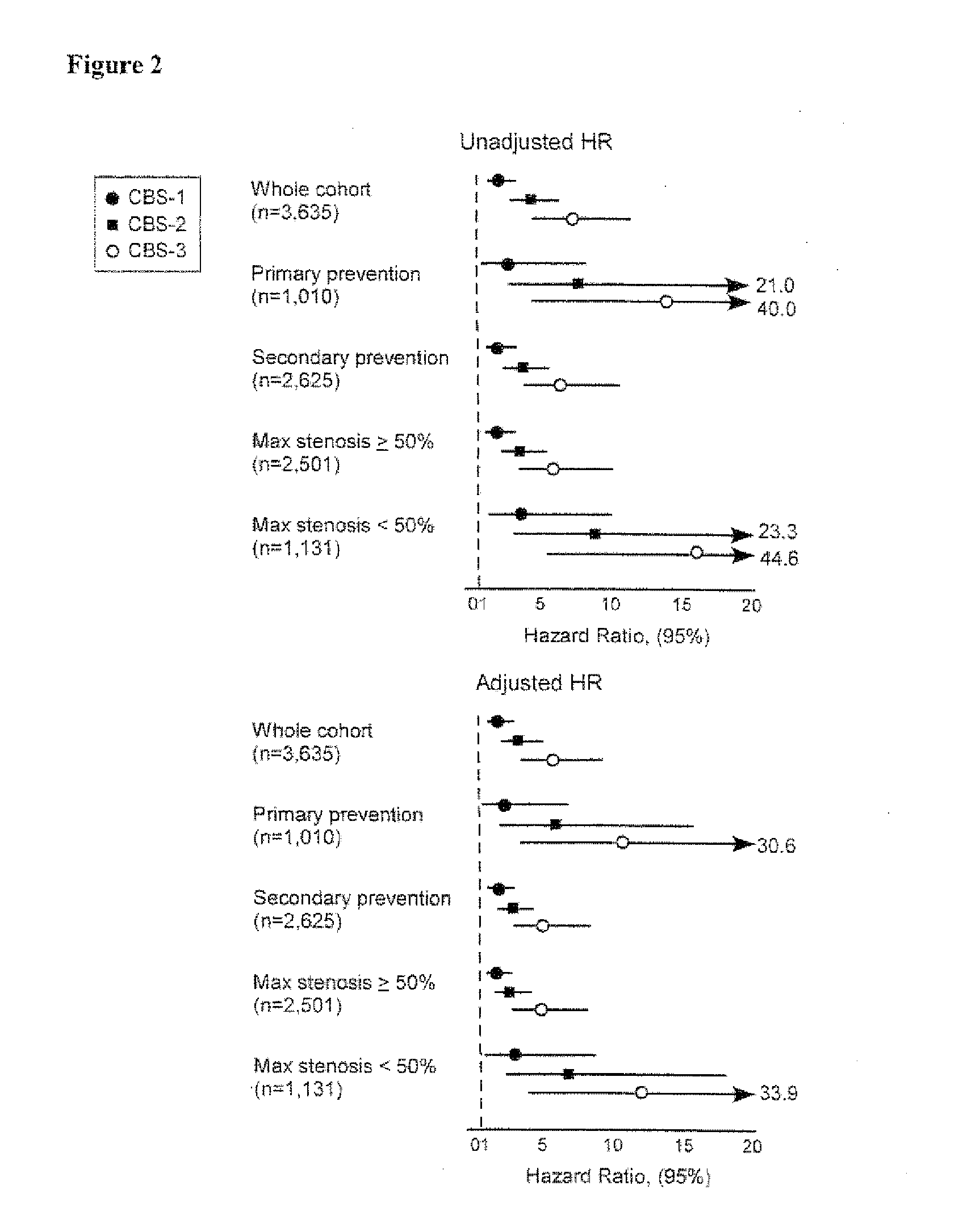
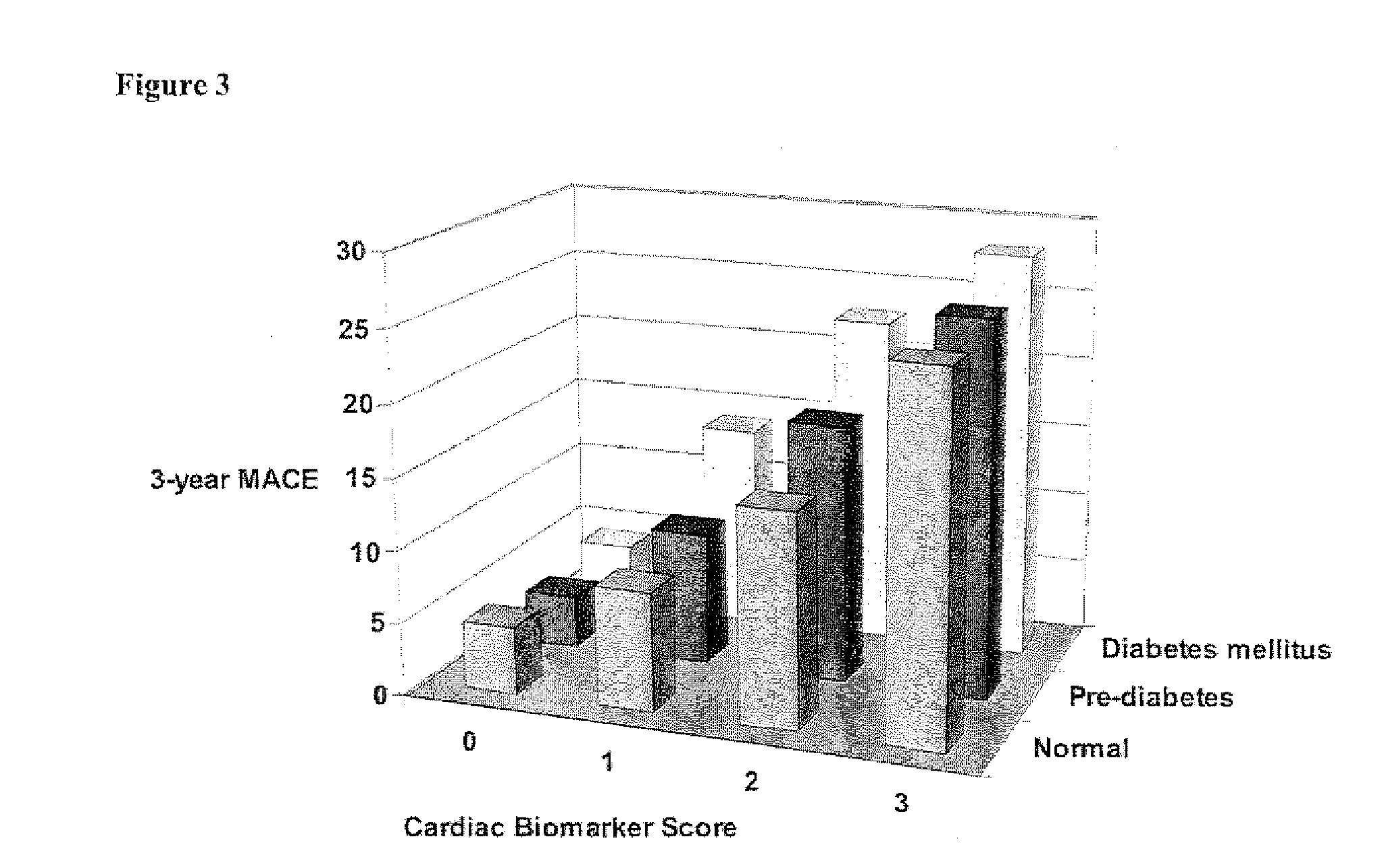
Methods and kits for characterizing the risk of developing cardiovascular disease are described. The methods include determining the levels of a plurality of risk predictors selected from the group consisting of B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP), myeloperoxidase (MPO), and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) predictors in a biological sample from a subject. The levels of the plurality of risk predictors are then compared to corresponding control values to obtain a risk predictor differential for each risk predictor. The plurality of risk predictor differentials are then added to provide a cardiac biomarker score, and the cardiac biomarker score is compared to a reference biomarker score. A positive difference between the cardiac biomarker score and the reference biomarker score indicates the subject has an increased risk of developing cardiovascular disease compared to the risk of a reference population. The methods can be used for risk stratification.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
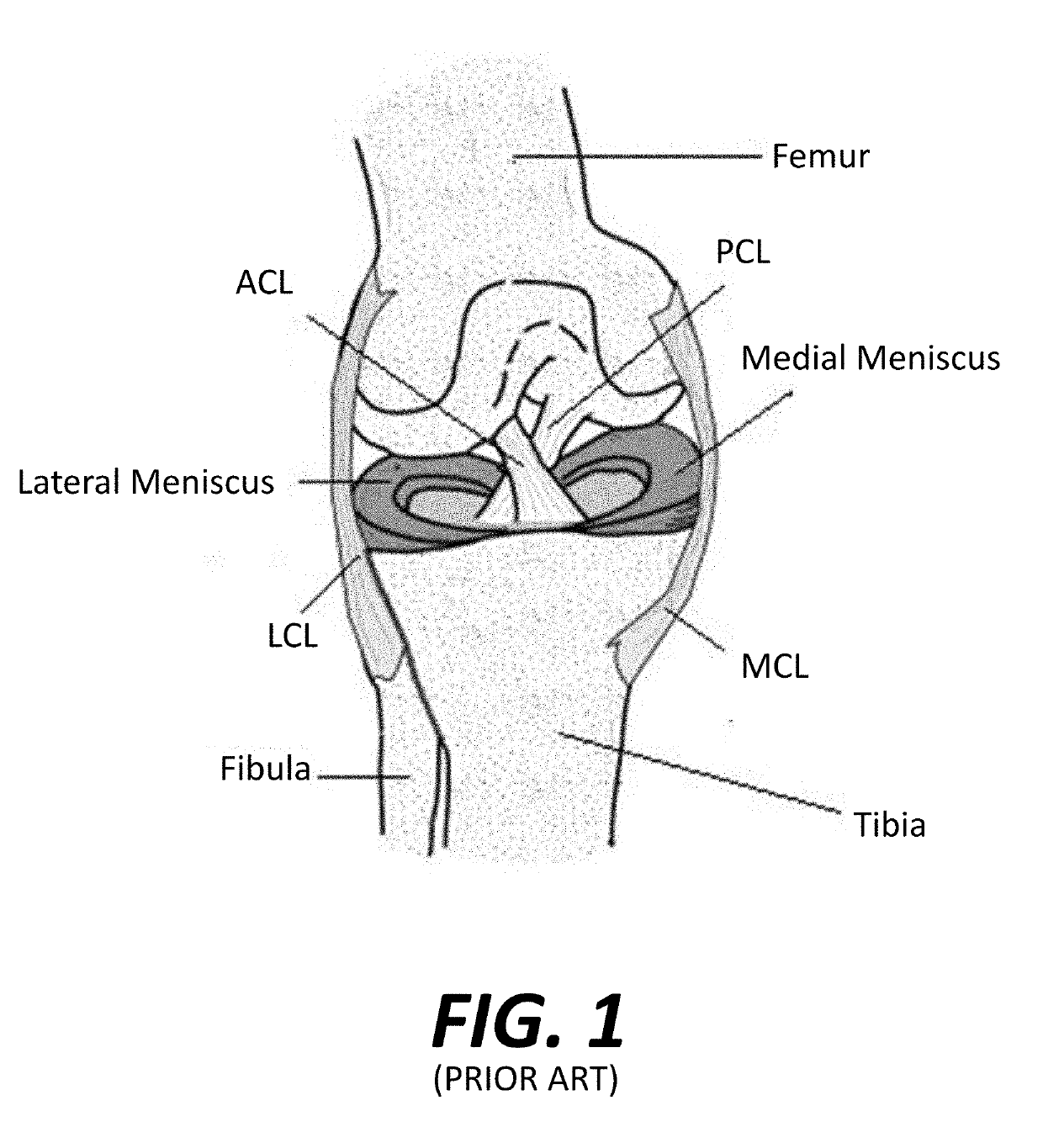
Virtual Ligament Balancing
A method of generating a correction plan for a knee of a patient includes obtaining a ratio of reference bone density to reference ligament tension in a reference population. A bone of the knee of the patient may be imaged. From the image of the bone, a first dataset may be determined including at least one site of ligament attachment and existing dwell points of a medial femoral condyle and lateral femoral condyle of the patient on a tibia of the patient. Desired positions of contact in three dimensions of the femoral condyles of the patient with the tibia of the patient may be obtained by determining a relationship in which a ratio of bone density to ligament tension of the patient is substantially equal to the ratio of reference bone density to reference ligament tension.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
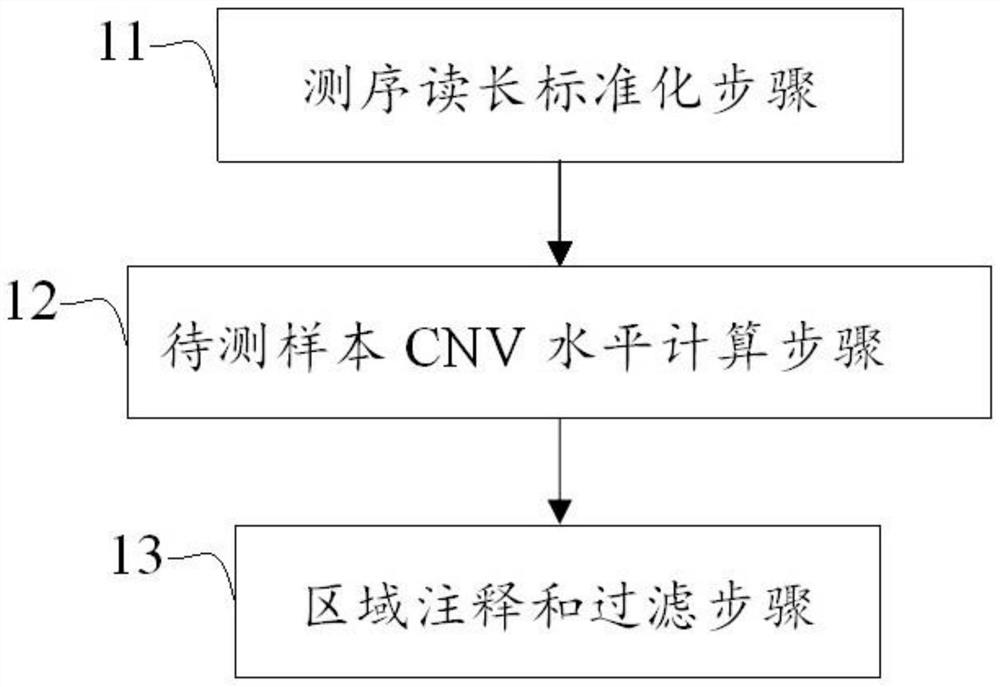
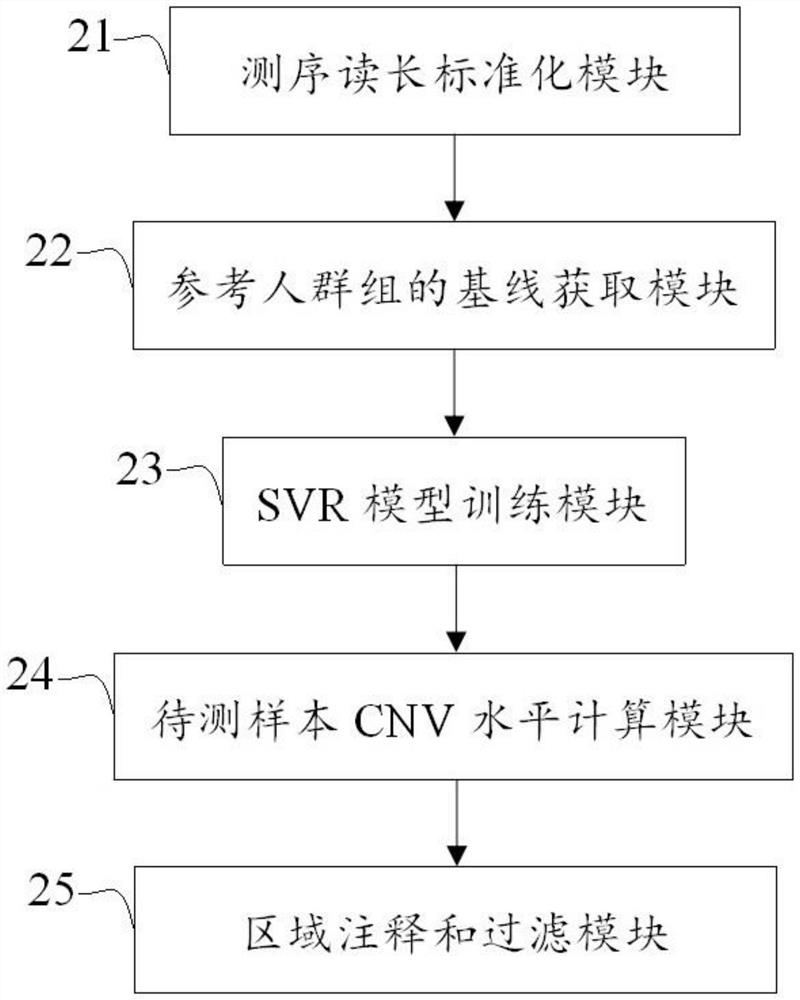
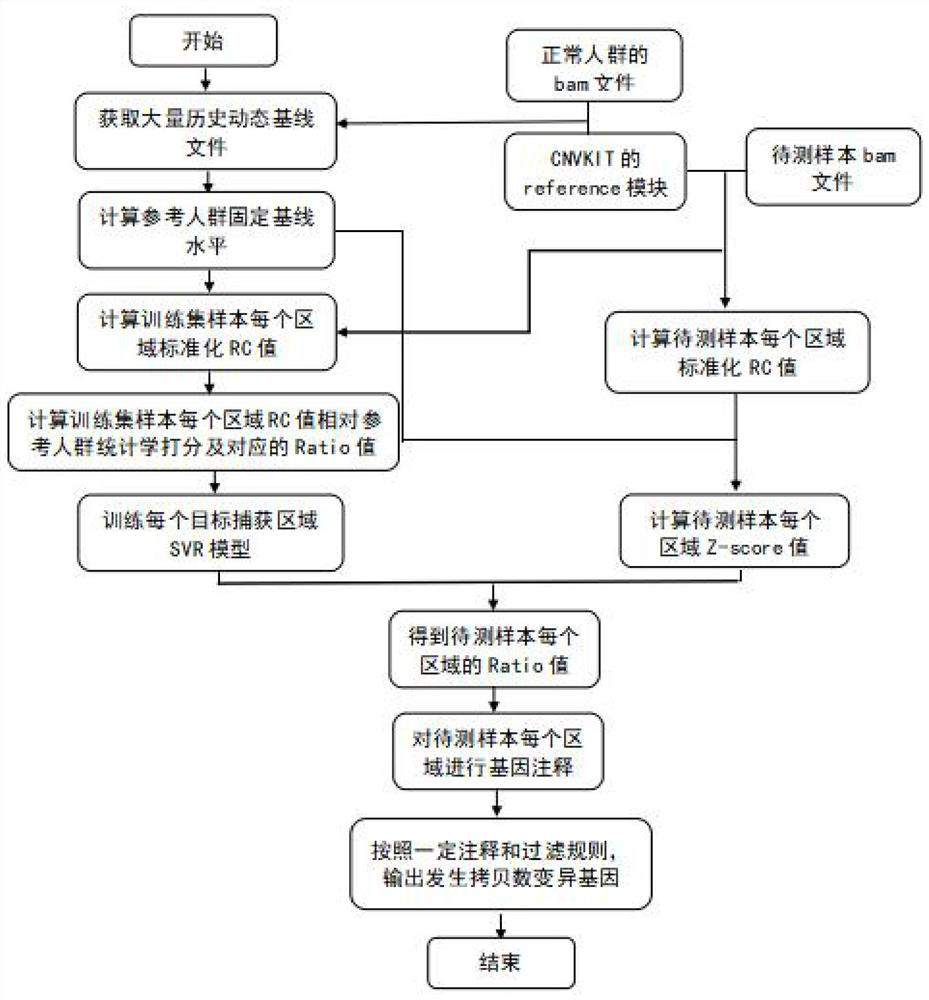
Method and device for detecting DNA copy number variation of single sample tumor
ActiveCN112634987ASolve the dilemma of not being able to detect copy number variationHigh sensitivityBiostatisticsProteomicsSingle sampleTarget capture
The invention discloses a single-sample tumor DNA copy number variation detection method and device. According to the method and the device, the reference population benchmark level is simulated by utilizing the dynamic baseline fluctuation level, and the Z-score value of the RC value of the training set sample constructed by the clinical tissue sample relative to the reference population in each capture region is calculated based on the reference population benchmark level fluctuation of each capture region; an SVR model of each target capture area is trained by using the statistical score; when single-sample tumor DNA copy number variation detection is carried out, the SVR model of each region is used to calculate the ratio value of the region, and finally, the region with copy number variation is output according to annotation and filtering rules. According to the invention, the problem that the existing copy number variation detection method and software cannot perform copy number variation detection under the condition of a single sample is solved, and the defects of low sensitivity, low accuracy and the like caused by factors in the aspect of sequencing environment are overcome.
Owner:北京吉因加医学检验实验室有限公司
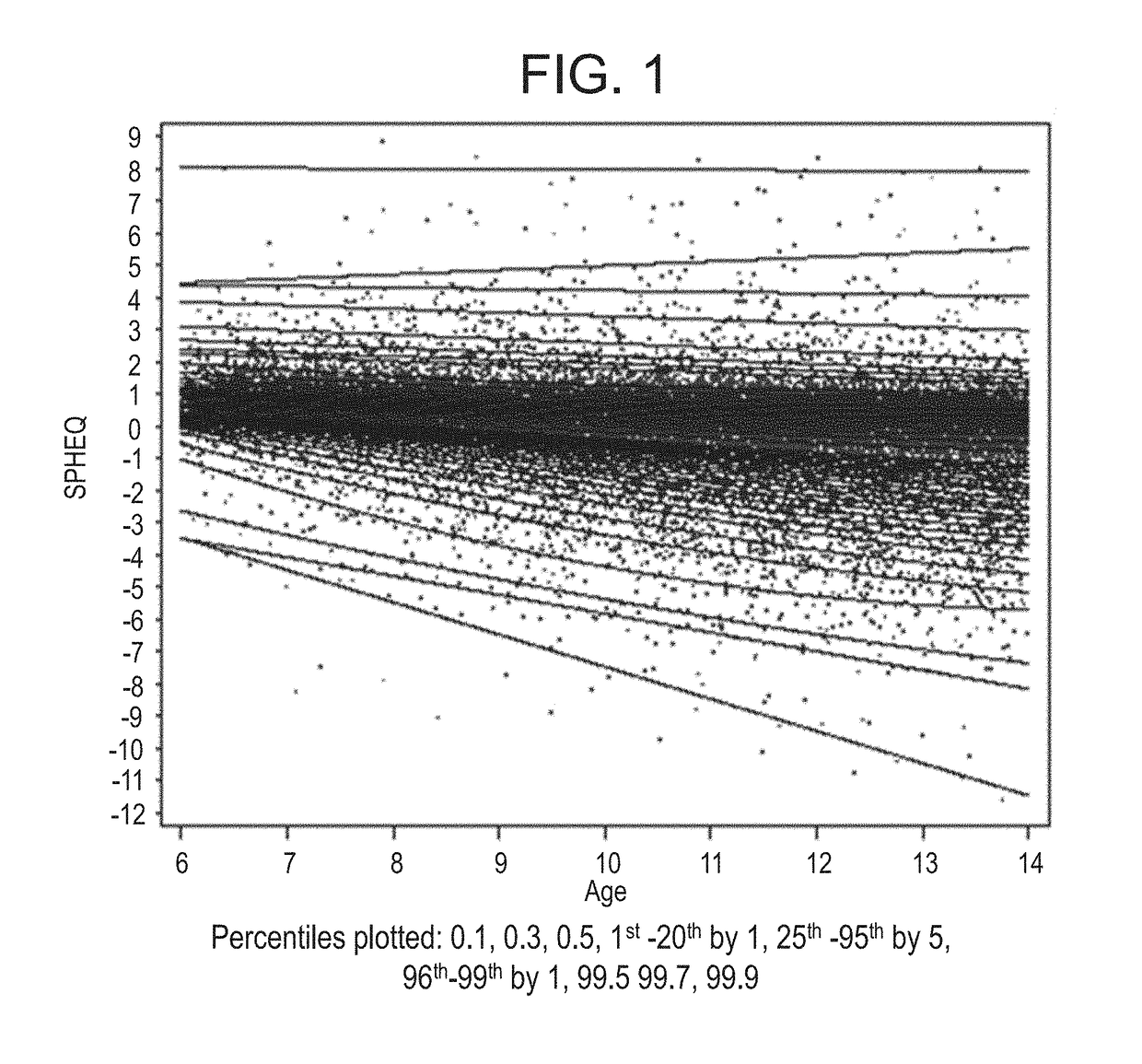
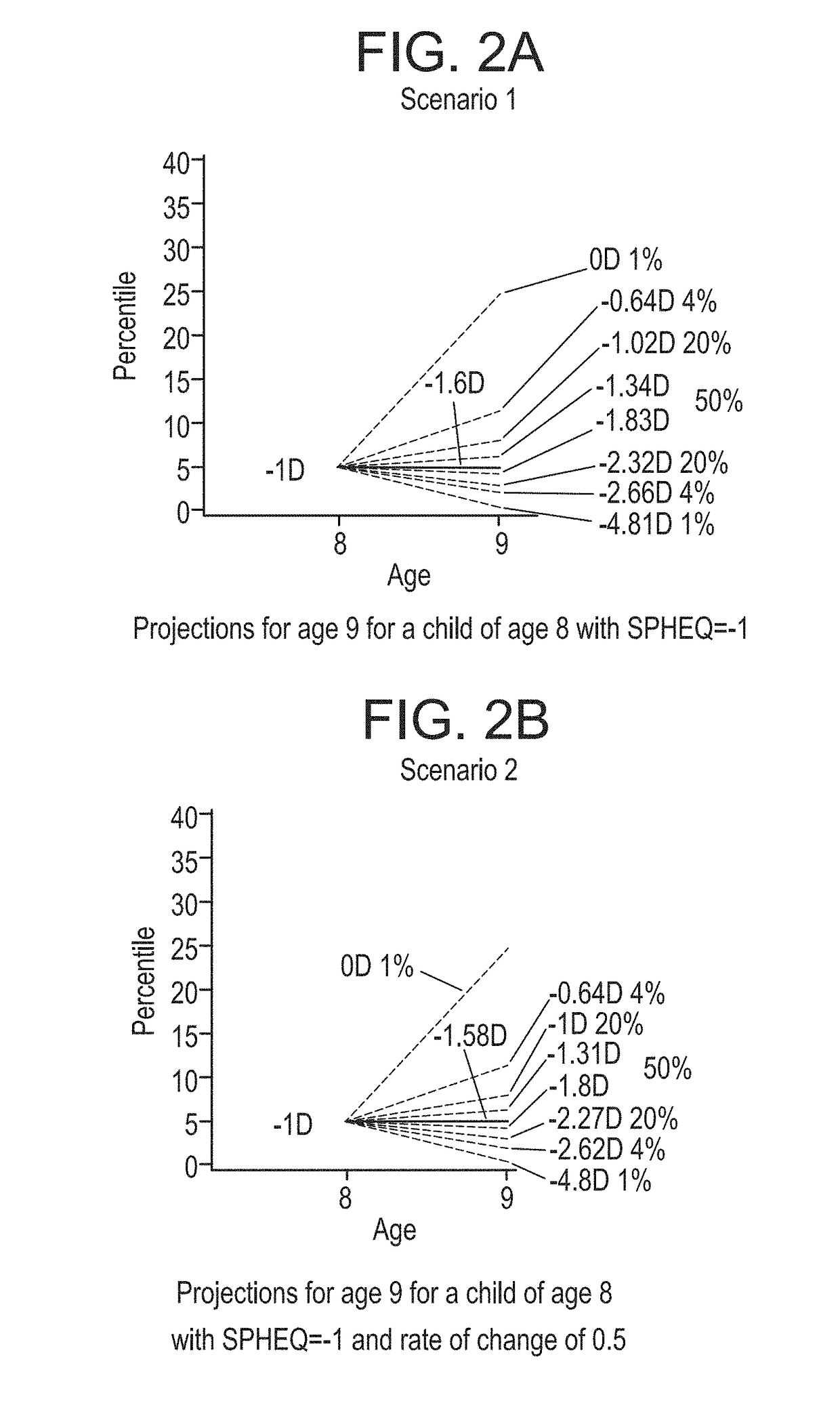
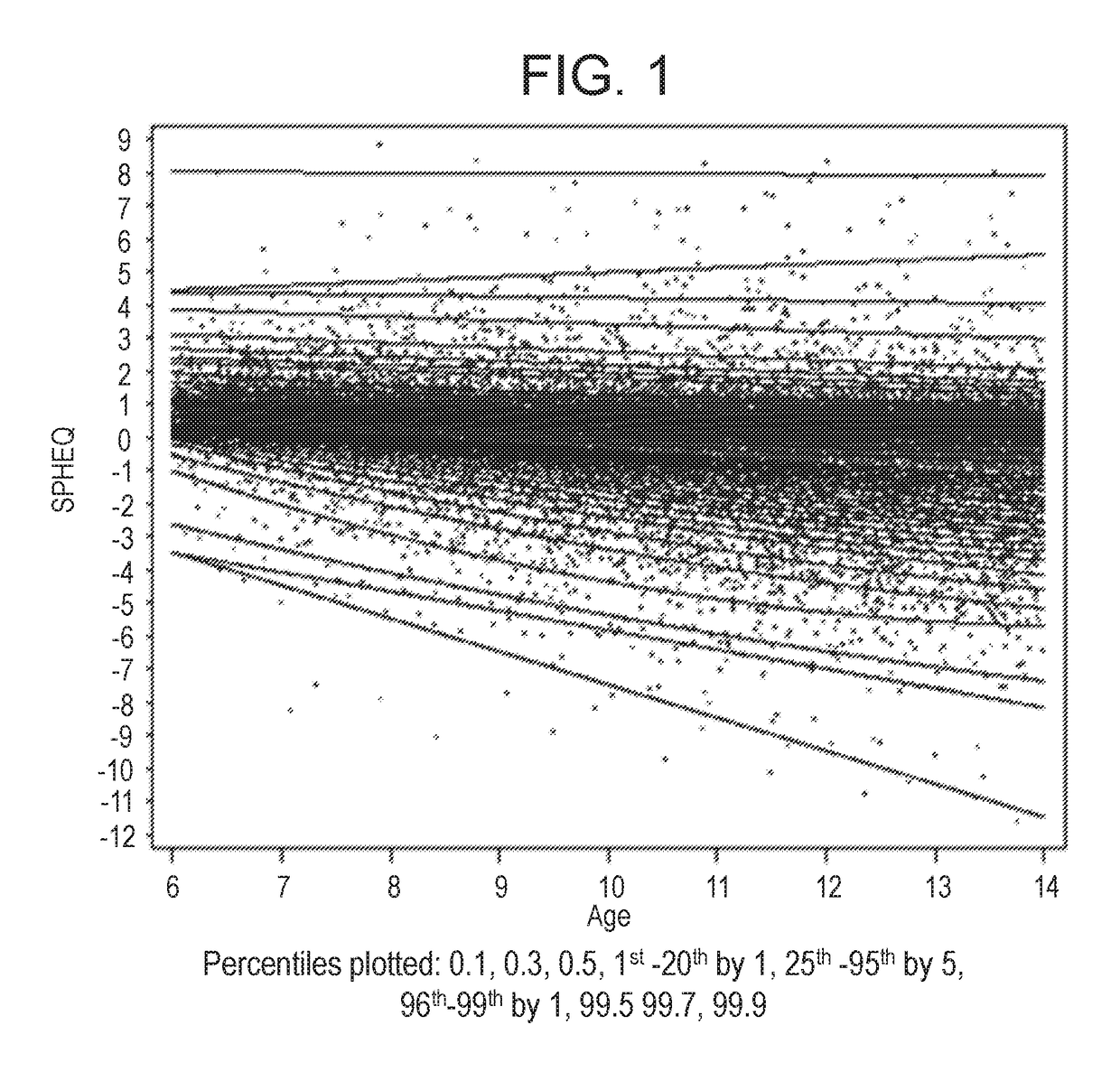
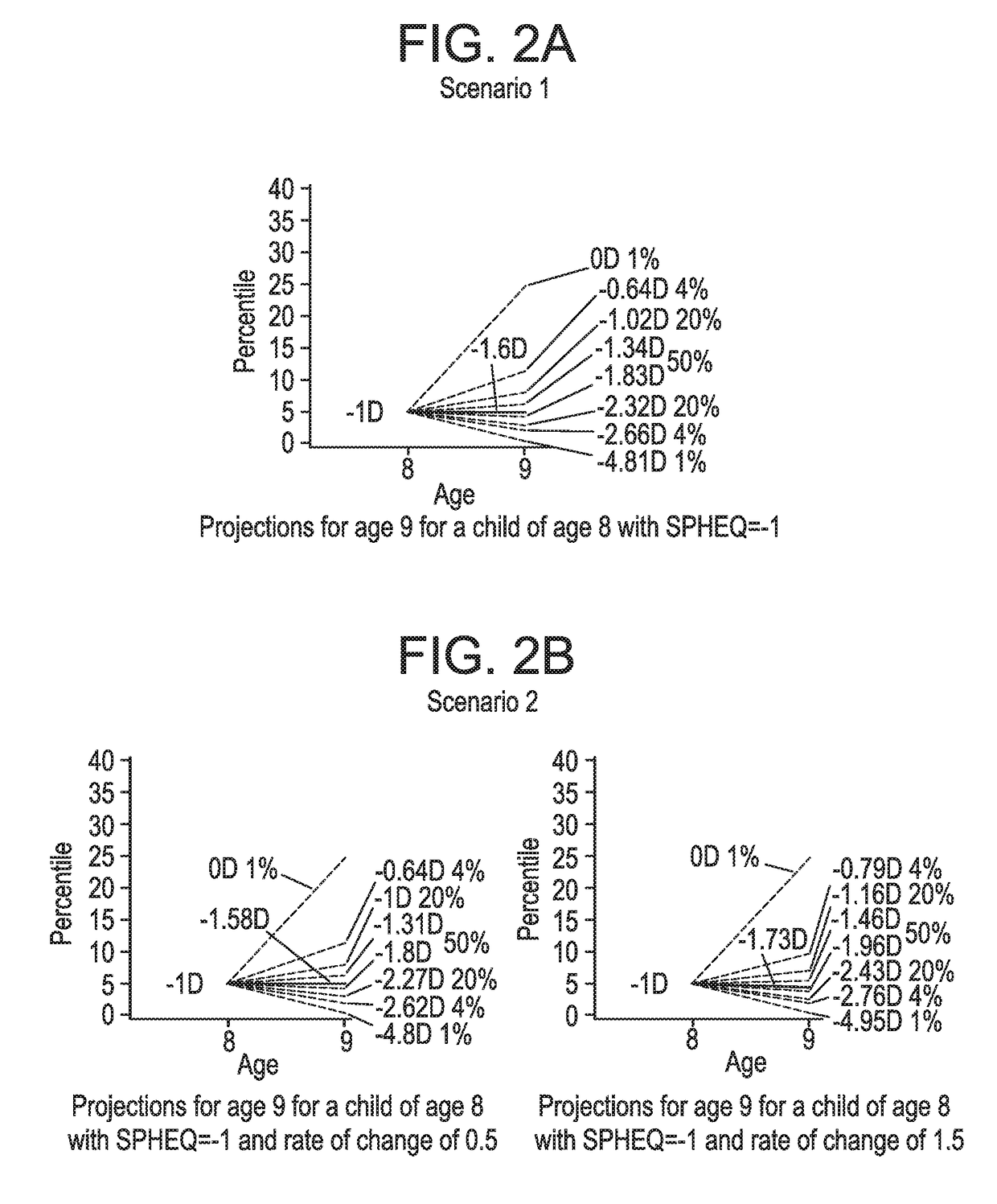
Ametropia treatment tracking methods and system
ActiveUS20170209036A1Shorten the progressMedical simulationSpectales/gogglesRefractive errorMedicine
A method for estimating and tracking refractive error progression of an individual includes estimating a percentile of Spherical Equivalent Refraction (SPHEQ) as a function of at least the individual's age by comparison to a reference population; estimating an expected SPHEQ trajectory over a future predetermined period of time; comparing the expected SPHEQ trajectory with the reference population; and comparing the expected SPHEQ trajectory with an expected SPHEQ trajectory using an ametropia control treatment, thereby showing a possible treatment benefit over the predetermined period of time.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Ametropia treatment tracking methods and system
ActiveUS20180140181A1Shorten the progressSpectales/gogglesMedical simulationRefractive errorMedicine
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
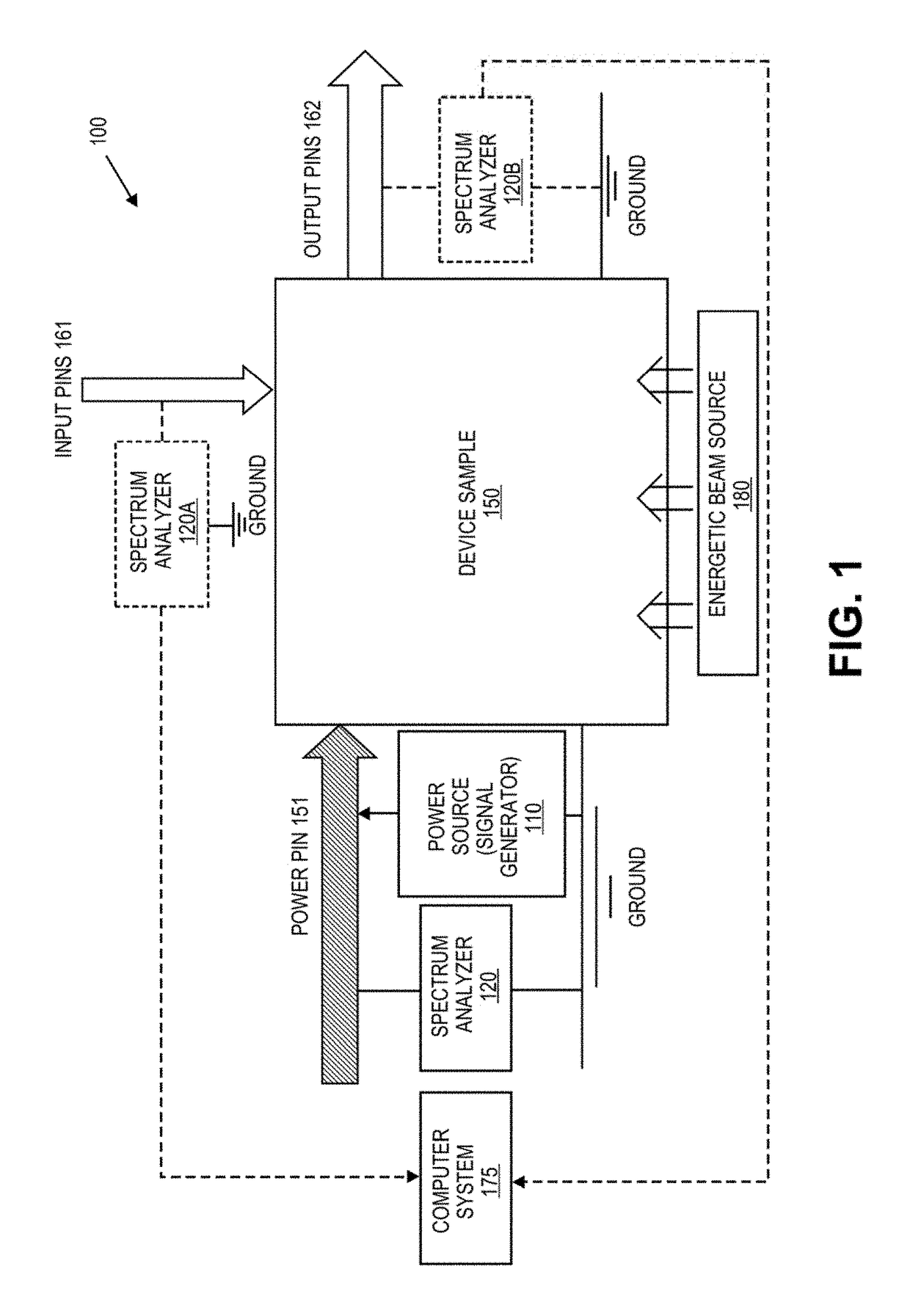
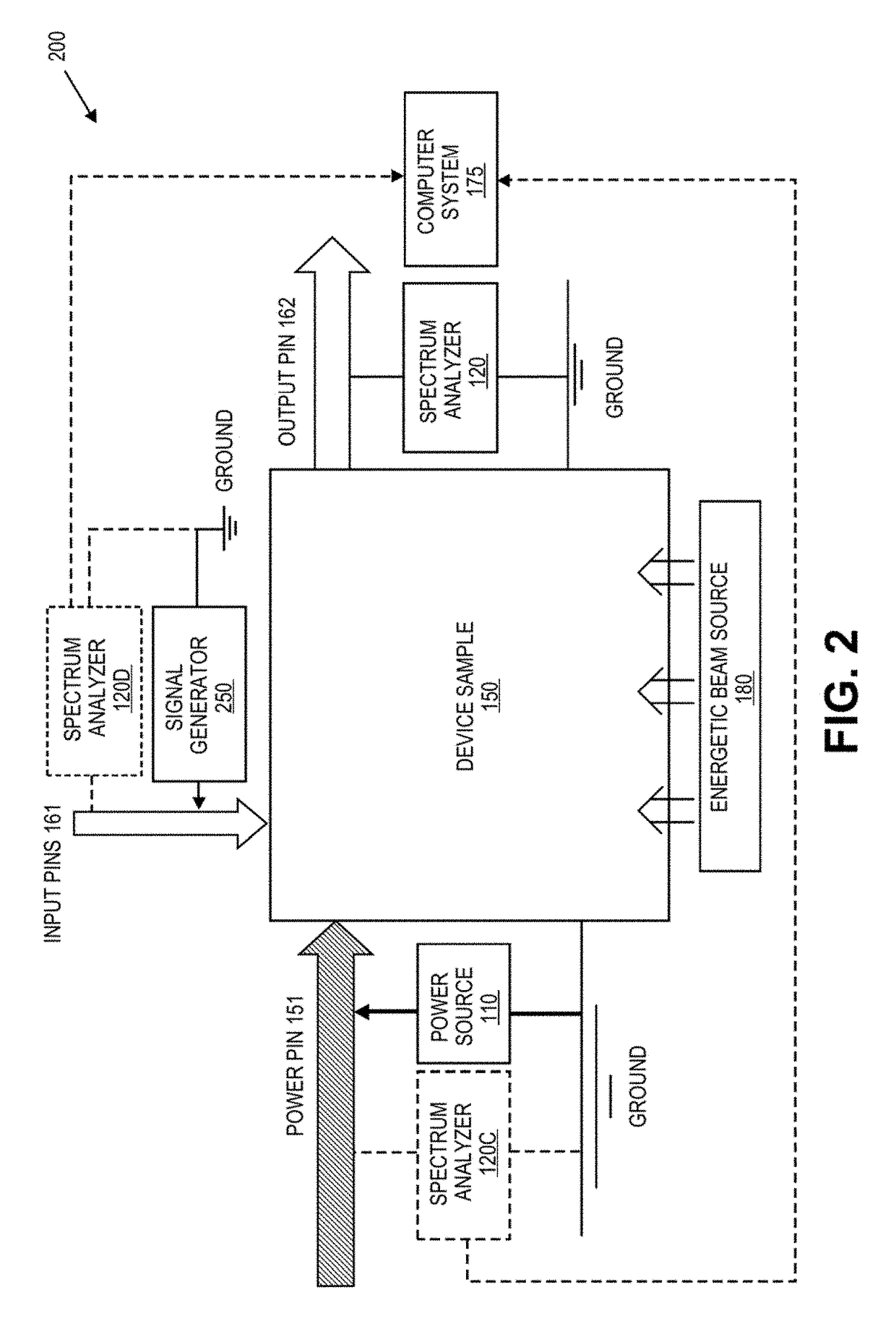
Defect screening method for electronic circuits and circuit components using power spectrum anaylysis
ActiveUS10145894B1Spectral/fourier analysisElectronic circuit testingNon destructivePrincipal component analysis
A method involving the non-destructive testing of a sample electrical or electronic device is provided. The method includes measuring a power spectrum of the device and performing a Principal Component Analysis on the power spectrum, thereby to obtain a set of principal components of the power spectrum. The method further includes selecting a subset consisting of some of the principal components, and comparing the subset to stored reference data that include representations in terms of principal components of one or more reference populations of devices. Based at least partly on the comparison, the sample device is classified relative to the reference populations.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Use of slim-1 in the assessment of heart failure
The invention relates to a method for assessing heart failure in vitro comprising the steps of measuring in a sample the concentration of the marker SLIM-1, of optionally measuring in the sample the concentration of one or more other marker(s) of heart failure, and of assessing heart failure by comparing the concentration determined in for SLIM-1 and the concentration(s) determined for the optionally one or more other marker to the concentration of this marker or these markers as established in a reference population. Also disclosed are the use of SLIM-1 as a marker protein in the assessment of heart failure, a marker combination comprising SLIM-1 and a kit for measuring SLIM-1.
Owner:THE GOVERNING COUNCIL OF THE UNIV OF TORONTO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com