Patents
Literature
5039 results about "Principal component analysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Principal component analysis (PCA) is a statistical procedure that uses an orthogonal transformation to convert a set of observations of possibly correlated variables (entities each of which takes on various numerical values) into a set of values of linearly uncorrelated variables called principal components. This transformation is defined in such a way that the first principal component has the largest possible variance (that is, accounts for as much of the variability in the data as possible), and each succeeding component in turn has the highest variance possible under the constraint that it is orthogonal to the preceding components. The resulting vectors (each being a linear combination of the variables and containing n observations) are an uncorrelated orthogonal basis set. PCA is sensitive to the relative scaling of the original variables.
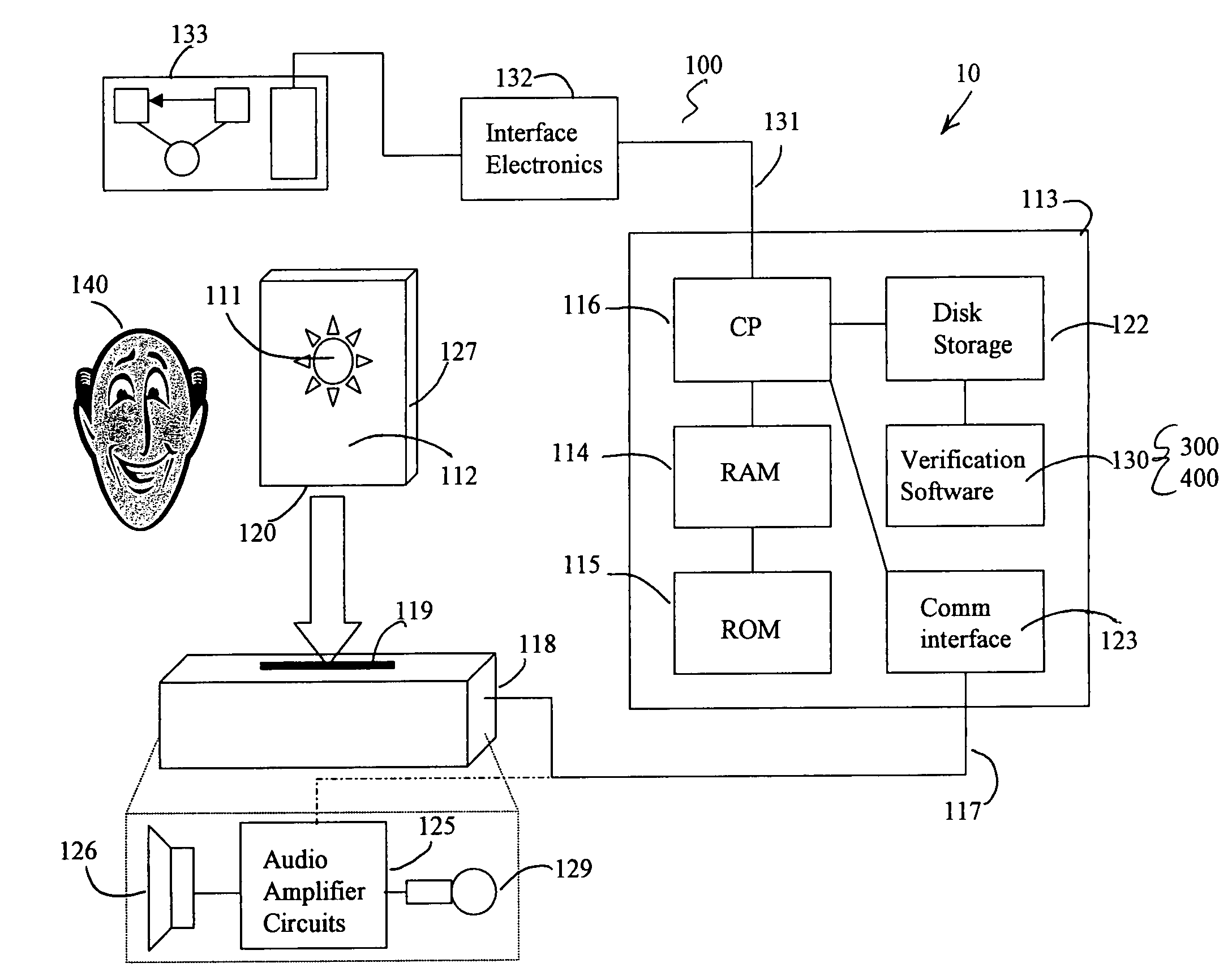
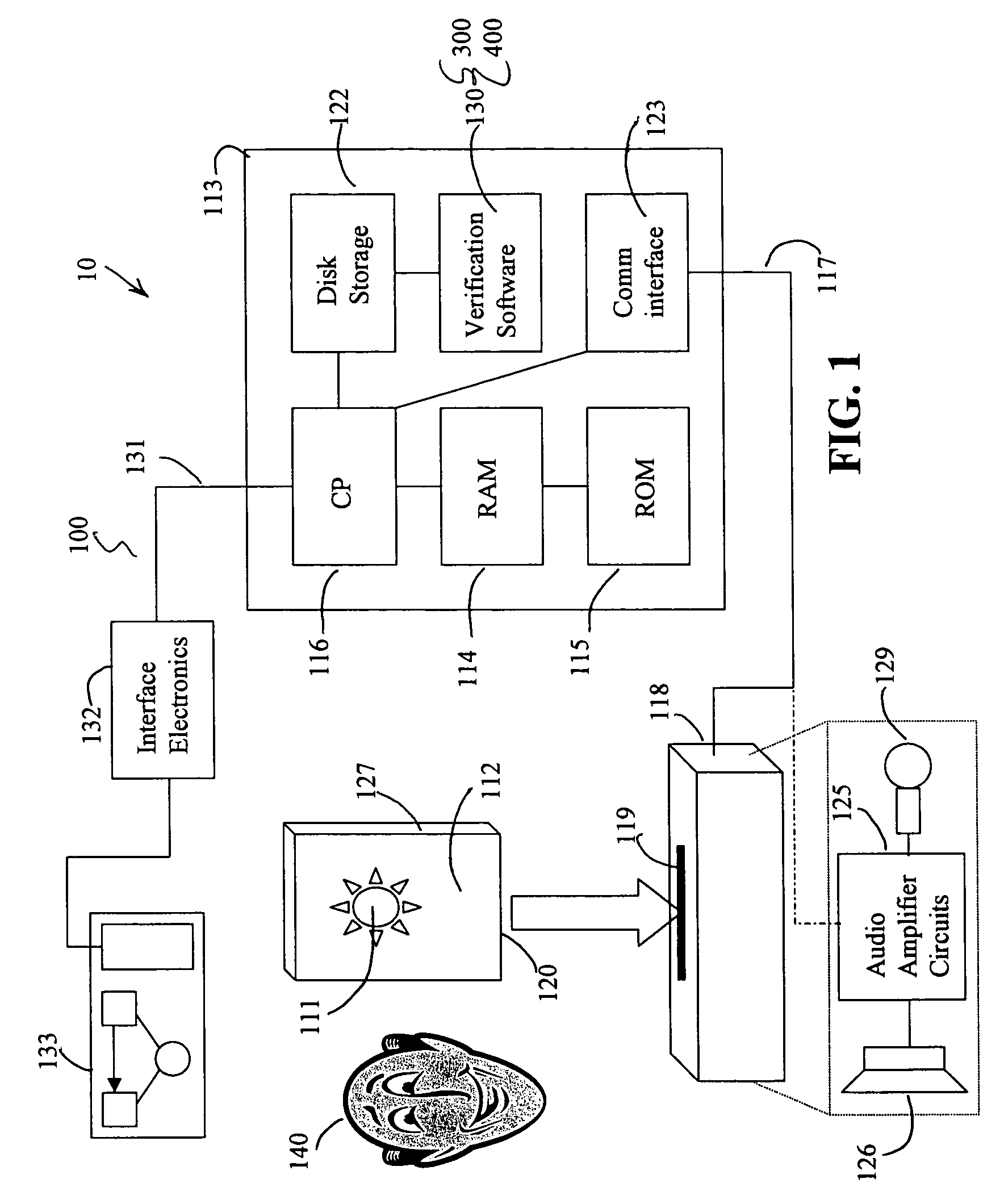
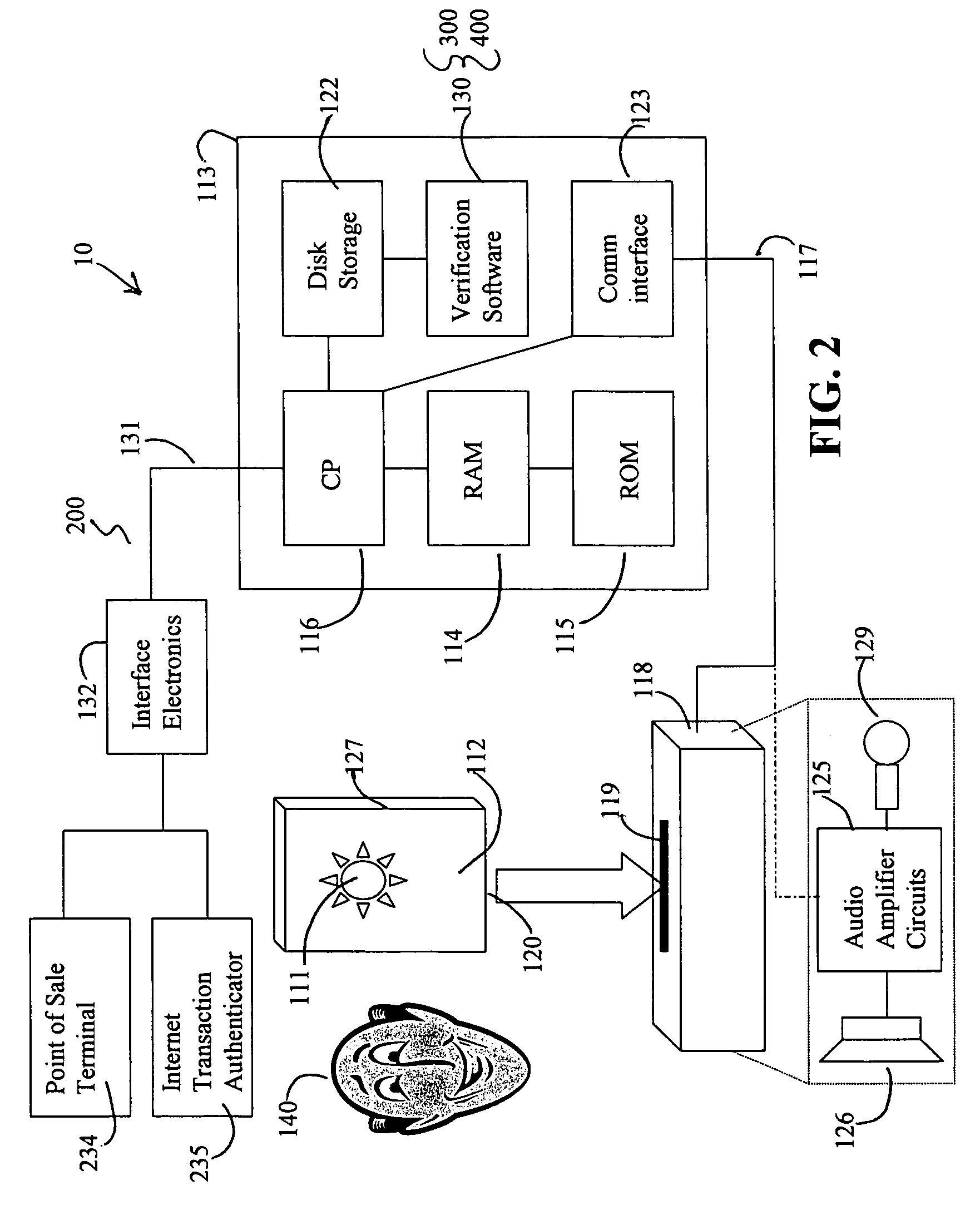
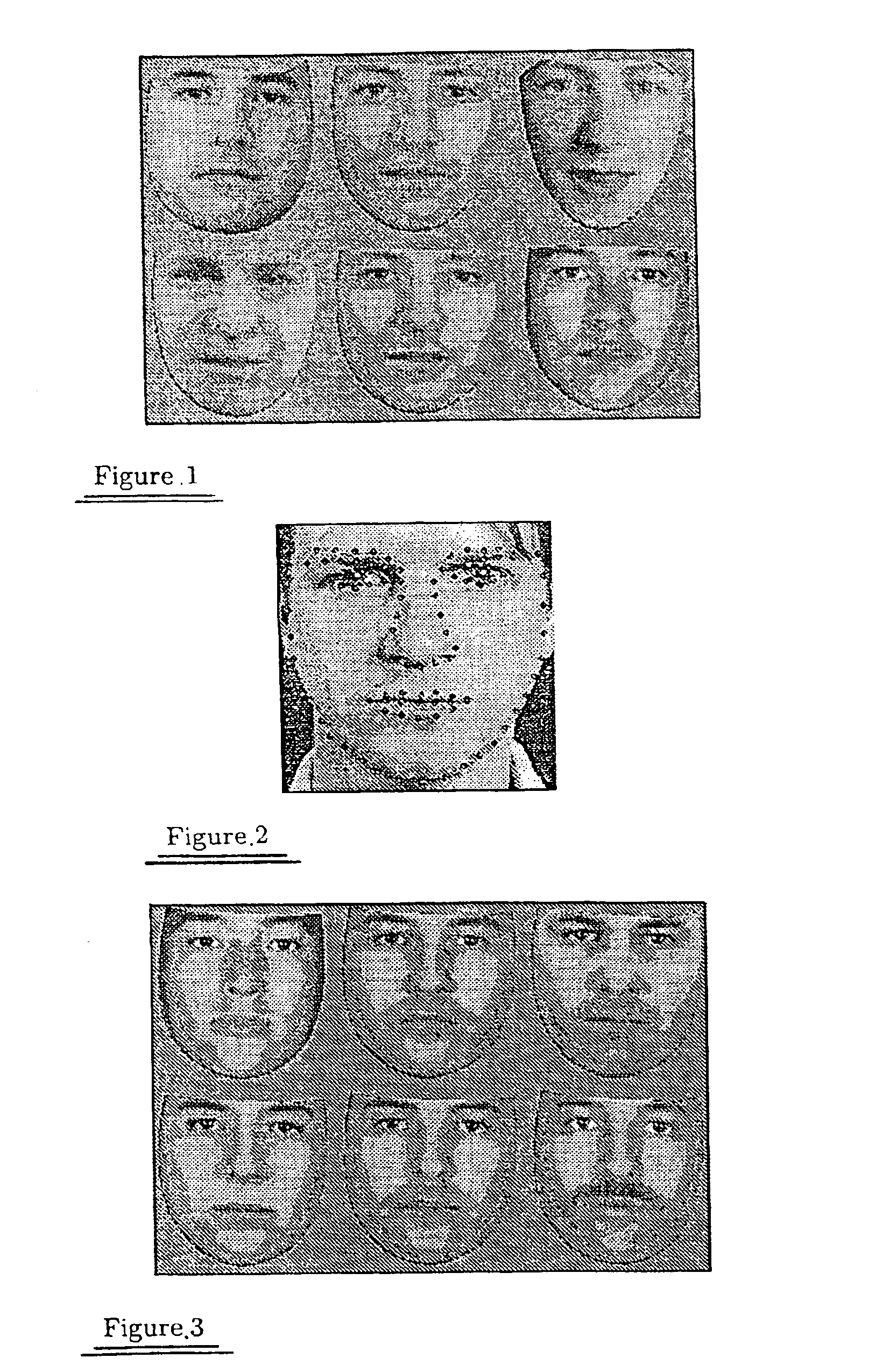
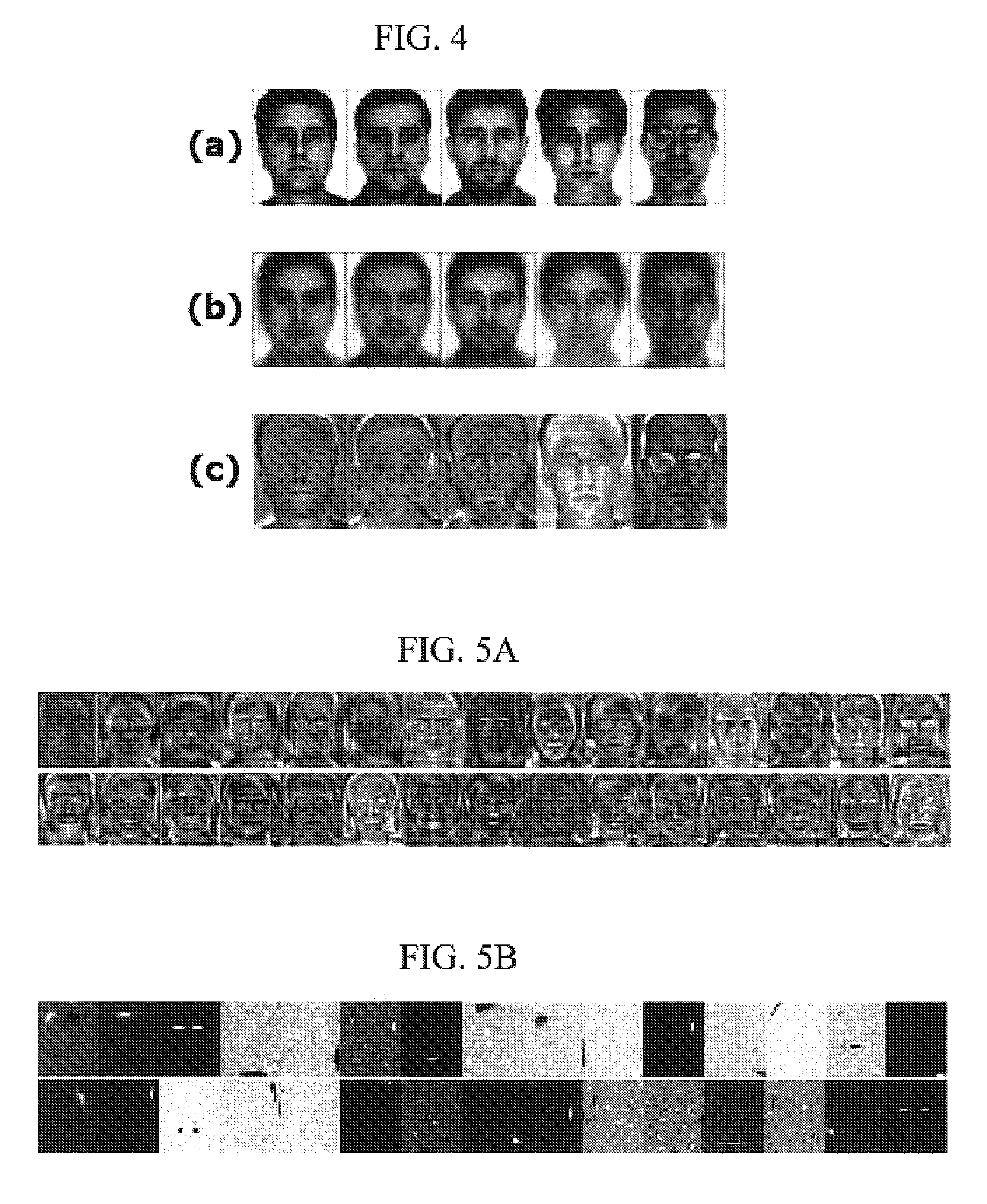
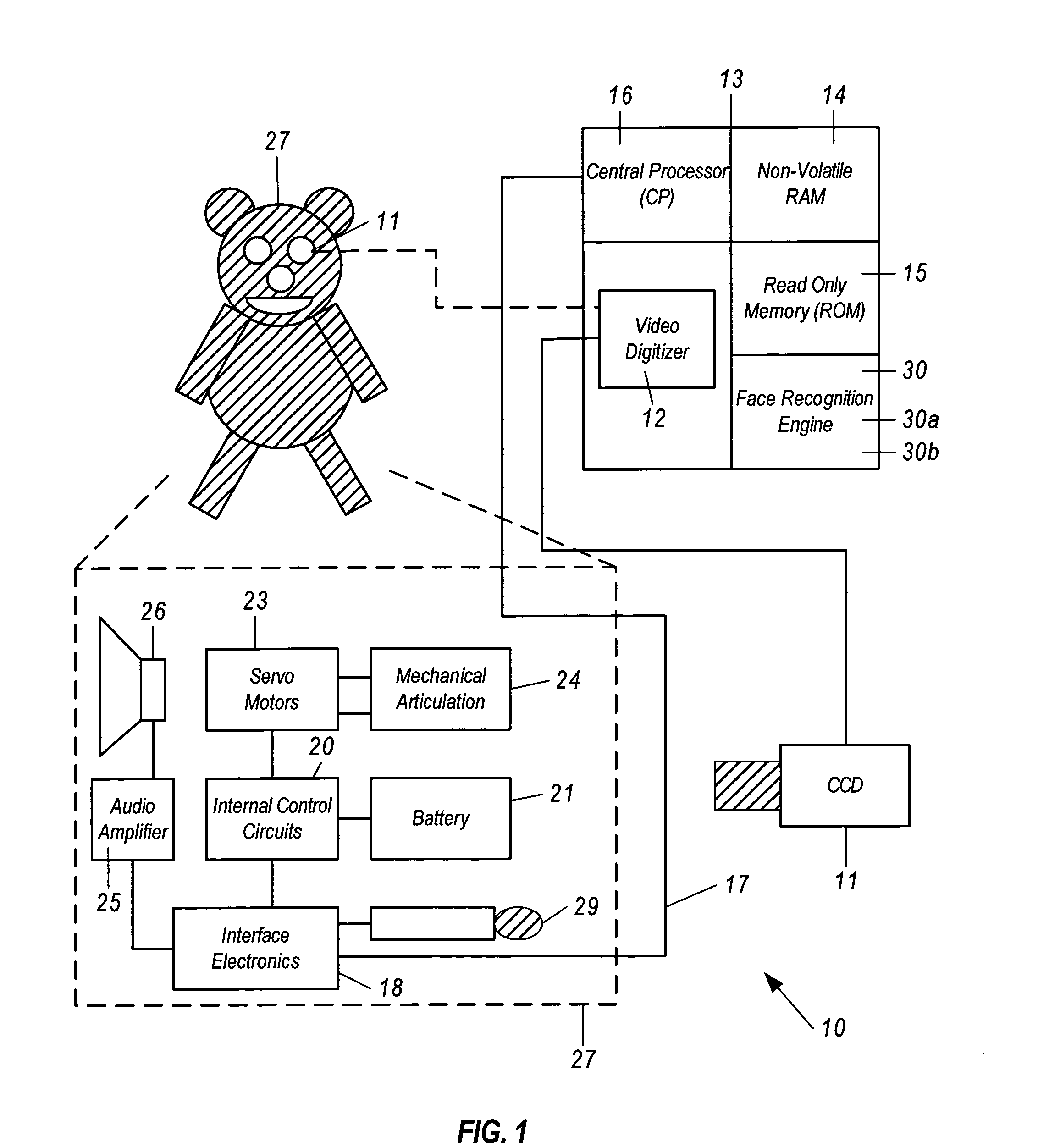
Facial image verification utilizing smart-card with integrated video camera
InactiveUS7039221B1Prevent fraudProvide securityAcutation objectsCharacter and pattern recognitionDocking stationPrincipal component analysis
A biometric facial image verification system capable of recognizing human users which includes a smart-card having stored thereon encoded first human facial images, a video camera and video digitizer embedded within said smart-card for acquiring data representative of a second human facial image. A computer-based device with a docking station capable of receiving said smart-card and software resident within said computer-based device for facial recognition, which includes Principal Component Analysis, Neural Networks, or another equivalent algorithm for comparing said first human facial images with said second human facial image and producing an output signal therefrom for use in verifying the identity of said human users. The apparatus can further include software for fingerprint and speech recognition. In addition, said smart-card is capable of acquiring and storing information pertaining to each of said human users such as would be required for use in a high-security environment or preventing fraud in point of sale and Internet-based financial transactions.
Owner:DONALD R STARKWEATHER
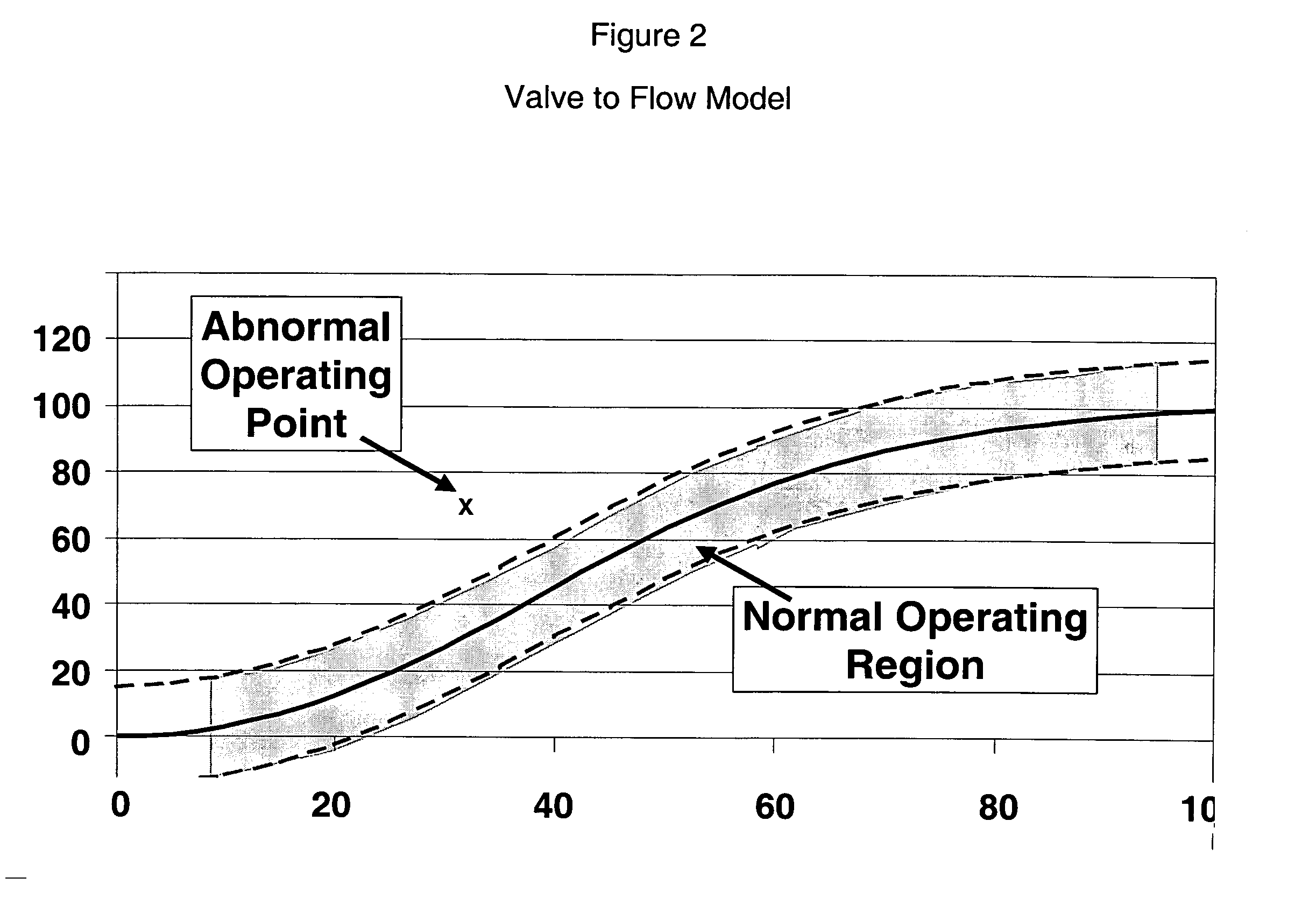
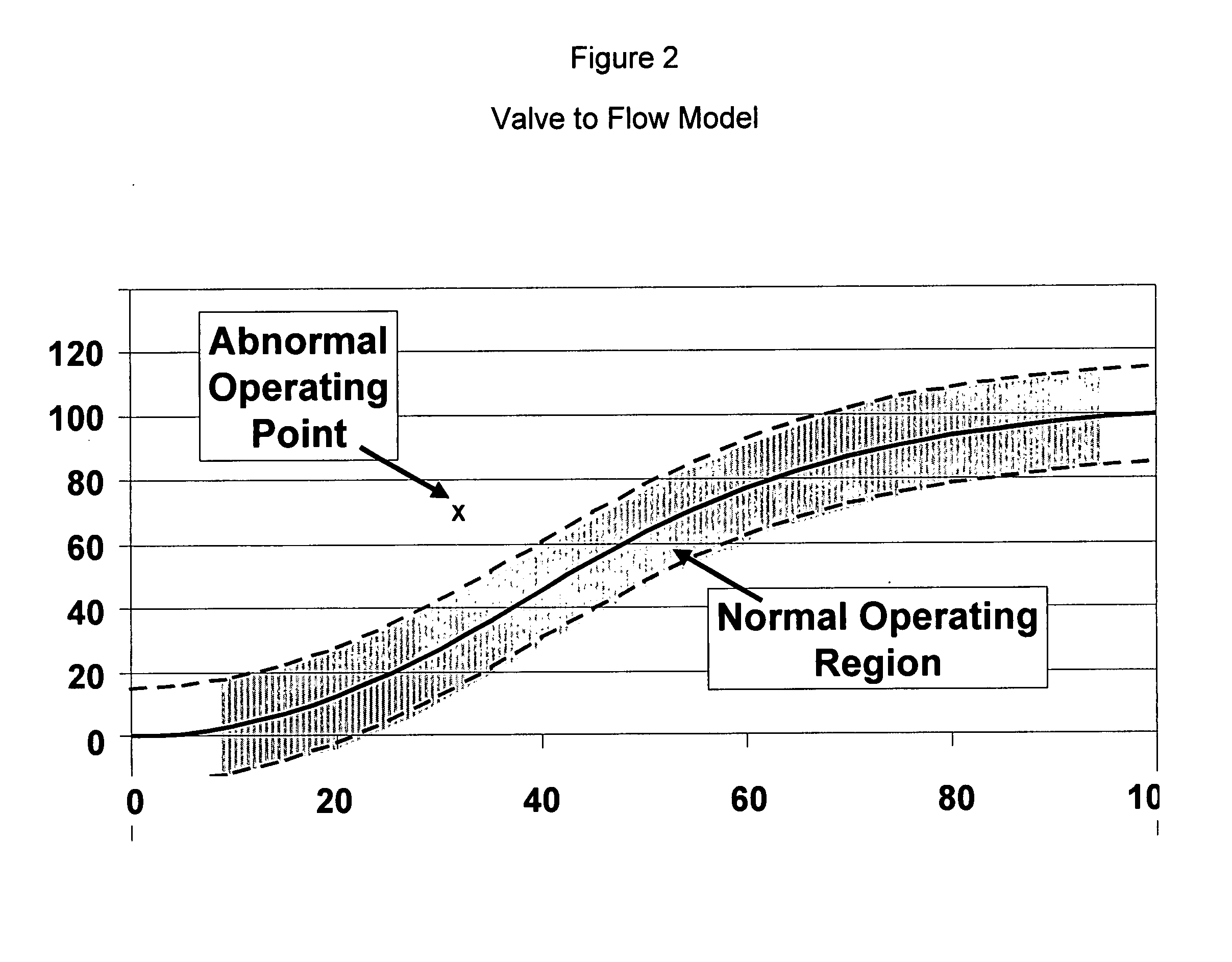
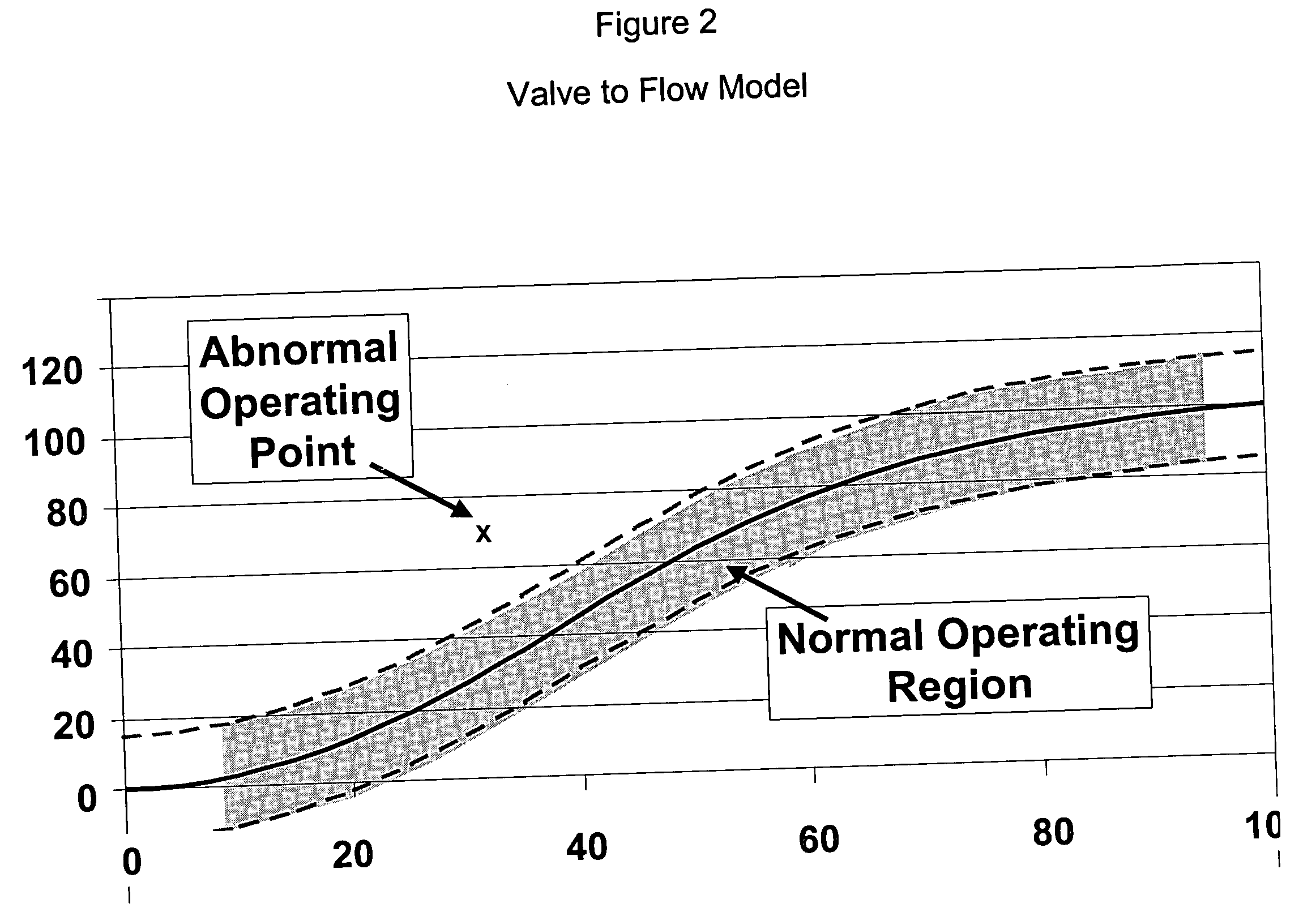
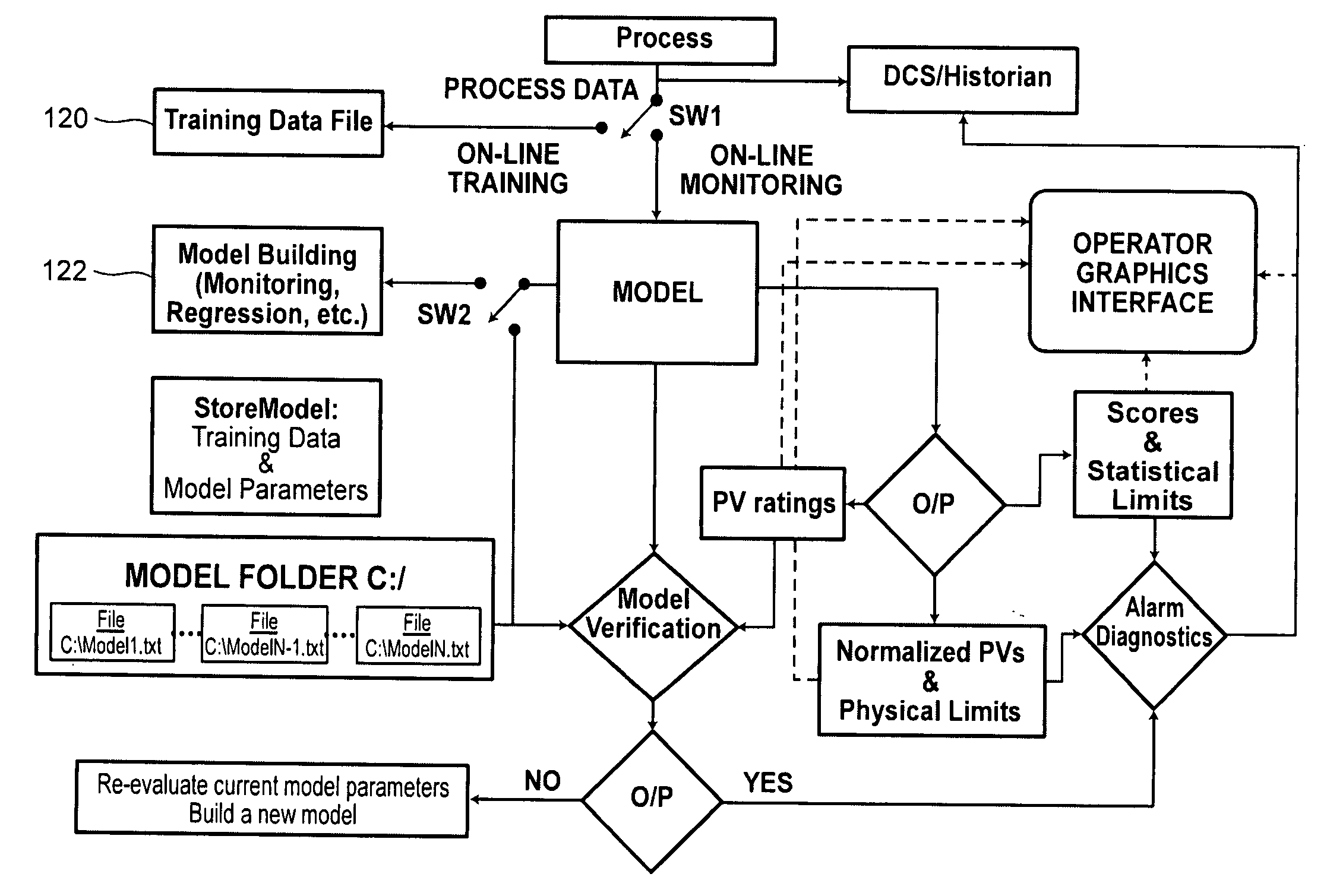
Application of abnormal event detection technology to fluidized catalytic cracking unit
ActiveUS20060073013A1PropellersSpecial data processing applicationsPrincipal component analysisCorrelation analysis
The present invention is a method for detecting an abnormal event for process units of a Fluidized Catalytic Cracking Unit. The method compares the operation of the process units to a statistical and engineering models. The statistical models are developed by principle components analysis of the normal operation for these units. In addition, the engineering models are based on partial least squares analysis and correlation analysis between variables. If the difference between the operation of a process unit and the normal model result indicates an abnormal condition, then the cause of the abnormal condition is determined and corrected.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
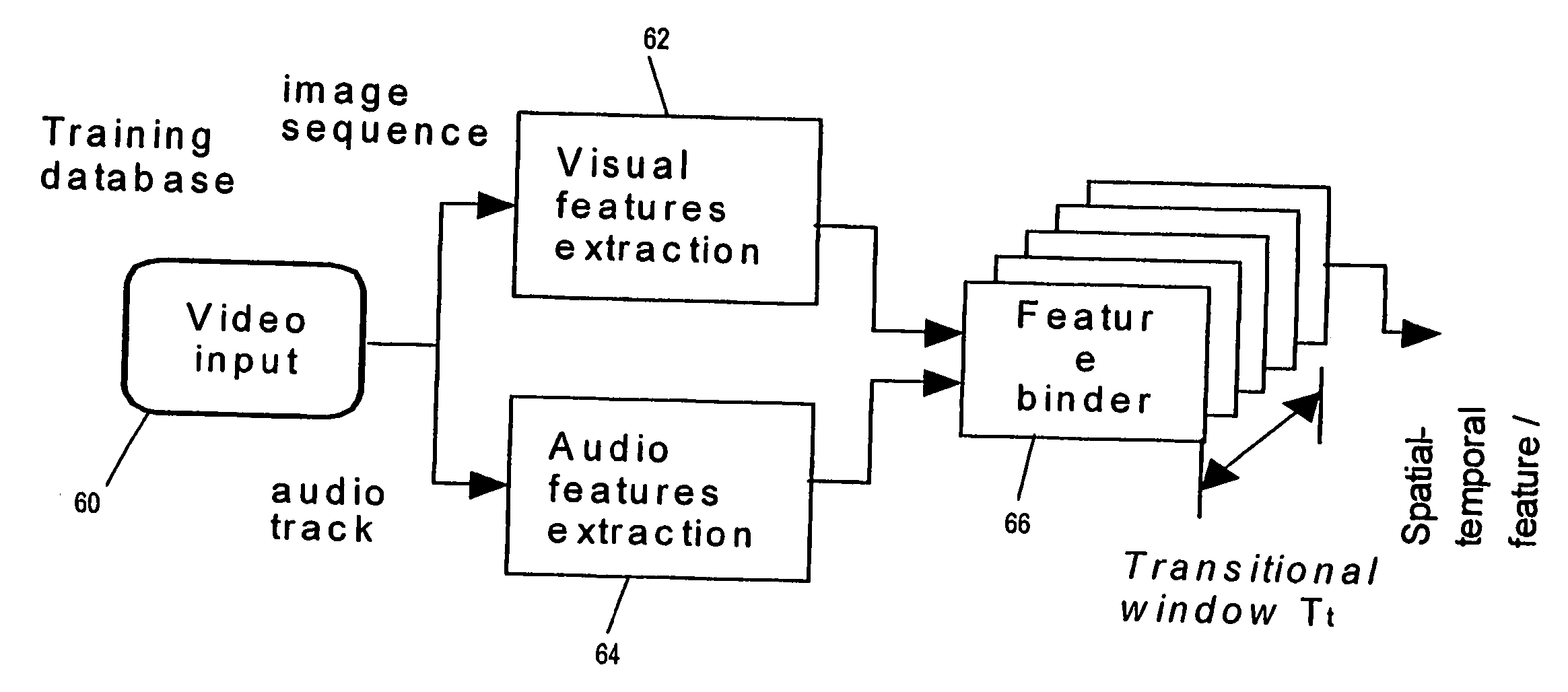
Method and system for classification of semantic content of audio/video data
InactiveUS20050238238A1Minimising within-class varianceMaximising between-class varianceDigital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorFeature extraction
Audio / Visual data is classified into semantic classes such as News, Sports, Music video or the like by providing class models for each class and comparing input audio visual data to the models. The class models are generated by extracting feature vectors from training samples, and then subjecting the feature vectors to kernel discriminant analysis or principal component analysis to give discriminatory basis vectors. These vectors are then used to obtain further feature vector of much lower dimension than the original feature vectors, which may then be used directly as a class model, or used to train a Gaussian Mixture Model or the like. During classification of unknown input data, the same feature extraction and analysis steps are performed to obtain the low-dimensional feature vectors, which are then fed into the previously created class models to identify the data genre.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
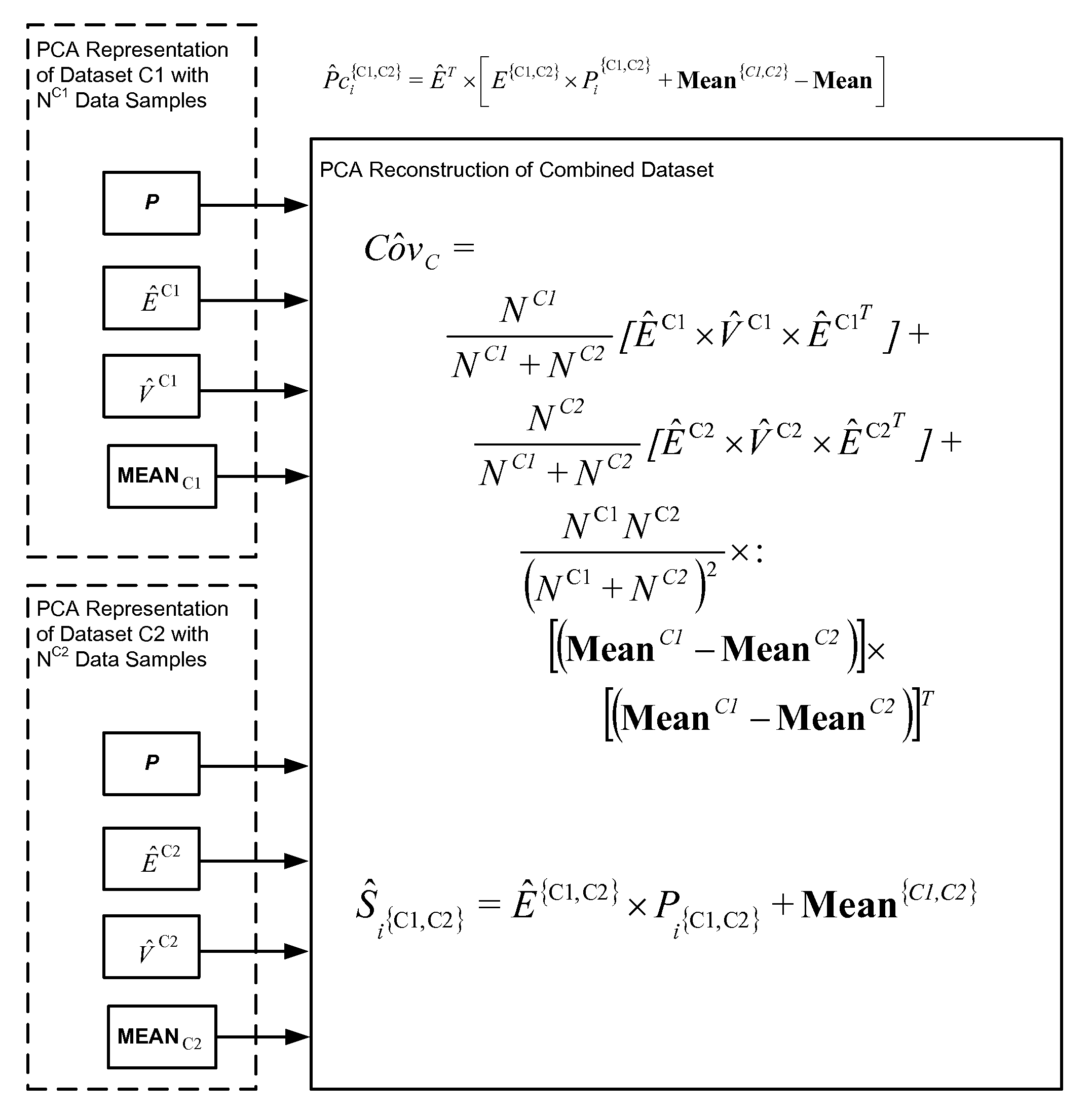
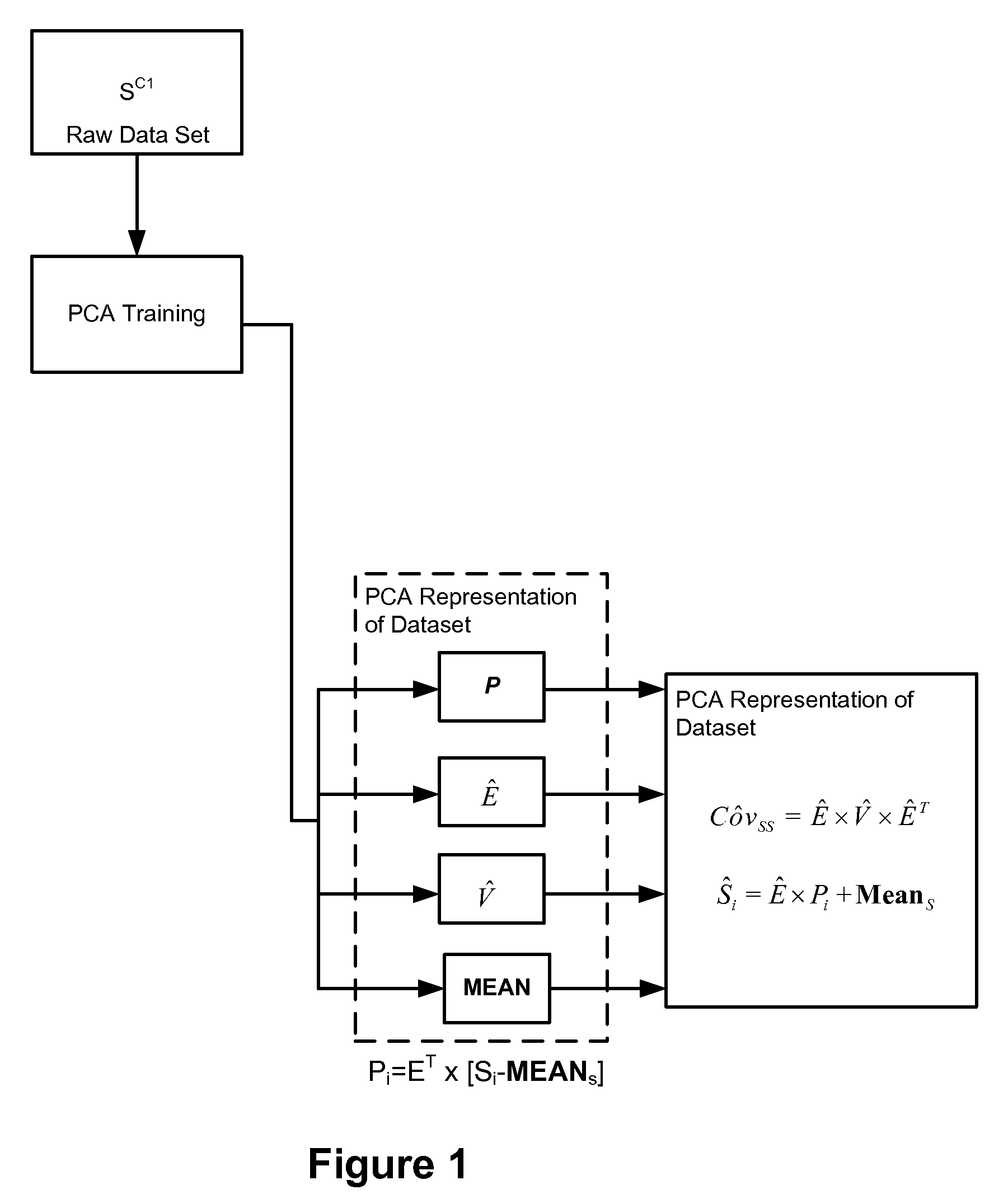
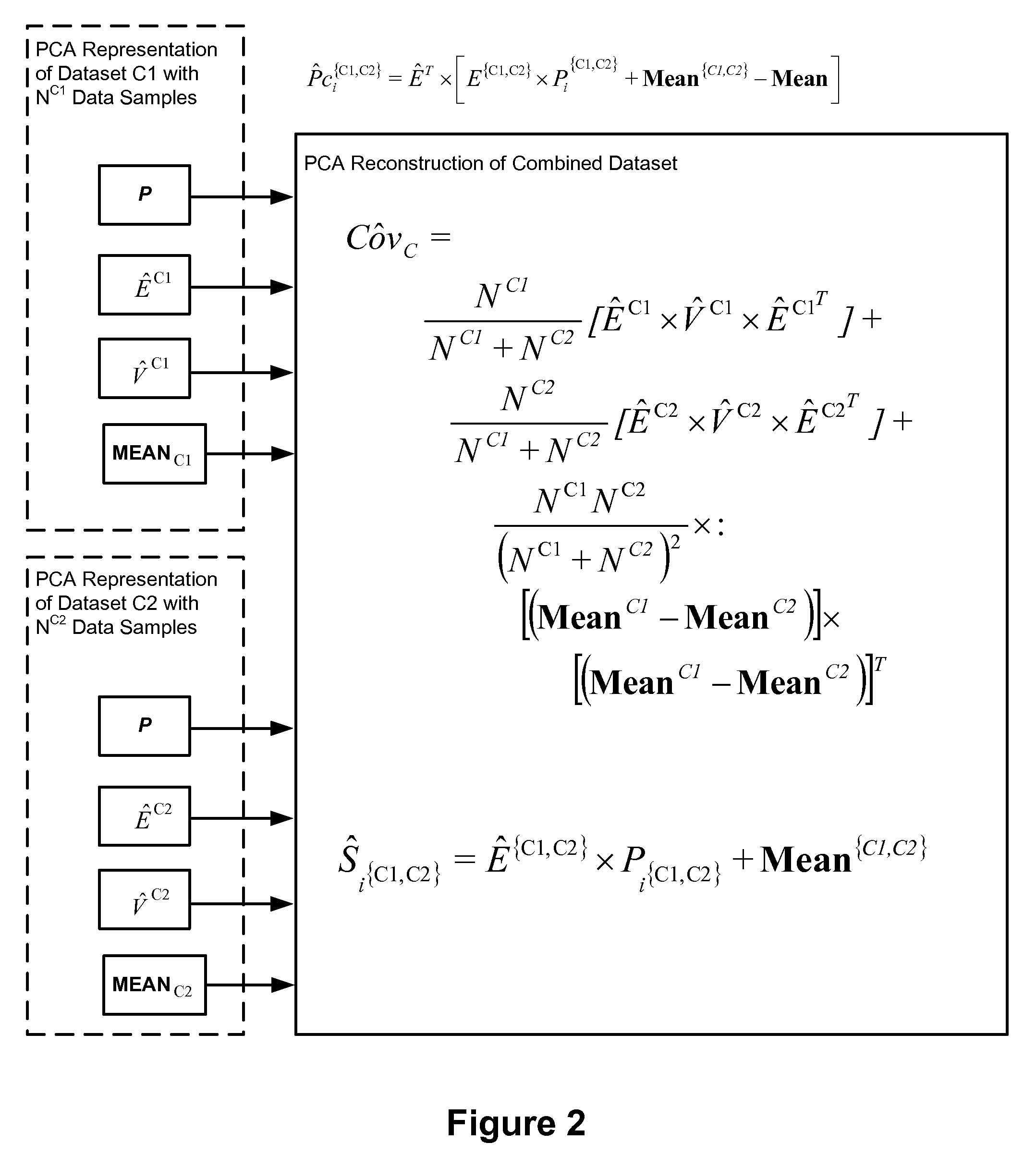
Face recognition with combined PCA-based datasets
A face recognition method for working with two or more collections of facial images is provided. A representation framework is determined for a first collection of facial images including at least principle component analysis (PCA) features. A representation of said first collection is stored using the representation framework. A modified representation framework is determined based on statistical properties of original facial image samples of a second collection of facial images and the stored representation of the first collection. The first and second collections are combined without using original facial image samples. A representation of the combined image collection (super-collection) is stored using the modified representation framework. A representation of a current facial image, determined in terms of the modified representation framework, is compared with one or more representations of facial images of the combined collection. Based on the comparing, it is determined which, if any, of the facial images within the combined collection matches the current facial image.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
Face sub-space determination
InactiveUS6876755B1Improve identityElectric signal transmission systemsImage analysisPrincipal component analysisComputer vision
A method of determining face sub-spaces includes making initial estimates of the sub-spaces, for example lighting, pose, identity and expression, using Principle Component Analysis on appropriate groups of faces. An iterative algorithm is applied to image codings to maximize the probability of coding across these non-orthogonal sub-spaces, obtaining the projection on each sub-space, and recalculating the spaces.
Owner:UNIV OF MANCHESTER
Method and apparatus for coordination of motion determination over multiple frames
InactiveUS6157677AEasy to compressEasy to controlTelevision system detailsImage analysisMotion fieldMultiple frame
PCT No. PCT / EP96 / 01272 Sec. 371 Date Nov. 21, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Nov. 21, 1997 PCT Filed Mar. 22, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 29679 PCT Pub. Date Sep. 26, 1996The present invention concerns improved motion estimation in signal records. A method for estimating motion between one reference image and each frame in a sequence of frames, each frame consisting of a plurality of samples of an input signal comprises the steps of: transforming the estimated motion fields into a motion matrix, wherein each row corresponds to one frame, and each row contains each component of motion vector for each element of the reference image; performing a Principal Component Analysis of the motion matrix, thereby obtaining a motion score matrix consisting of a plurality of column vectors called motion score vectors and a motion loading matrix consisting of a plurality of row vectors called motion loading vectors, such that each motion score vector corresponds to one element for each frame, such that each element of each motion loading vector corresponds to one element of the reference image, such that one column of said motion score matrix and one motion loading vector together constitute a factor, and such that the number of factors is lower than or equal to the number of said frames; wherein the results from the Principal Component Analysis on the motion matrix are used to influence further estimation of motion from the reference image to one or more of the frames.
Owner:IDT INT DIGITAL TECH DEUTLAND
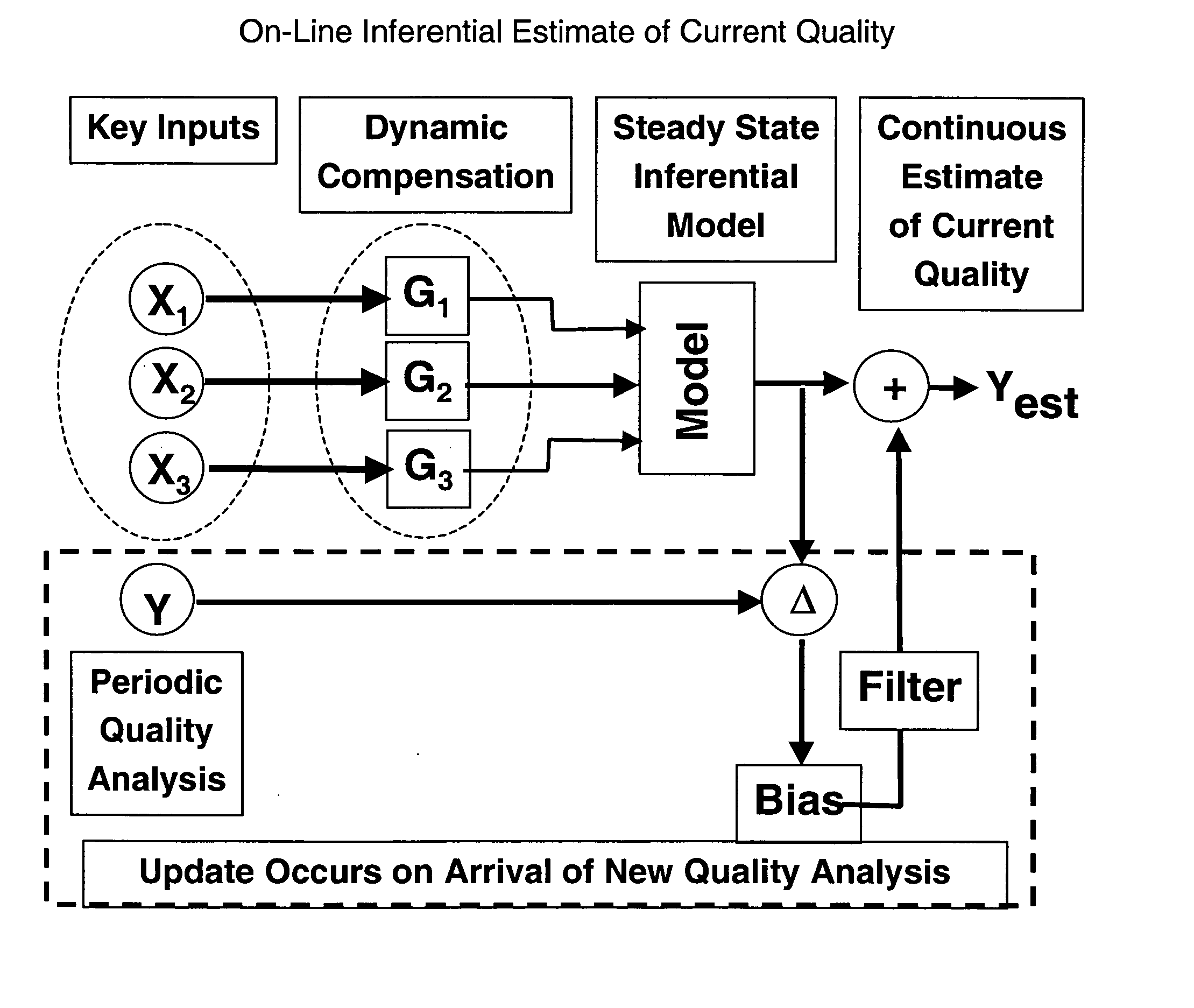
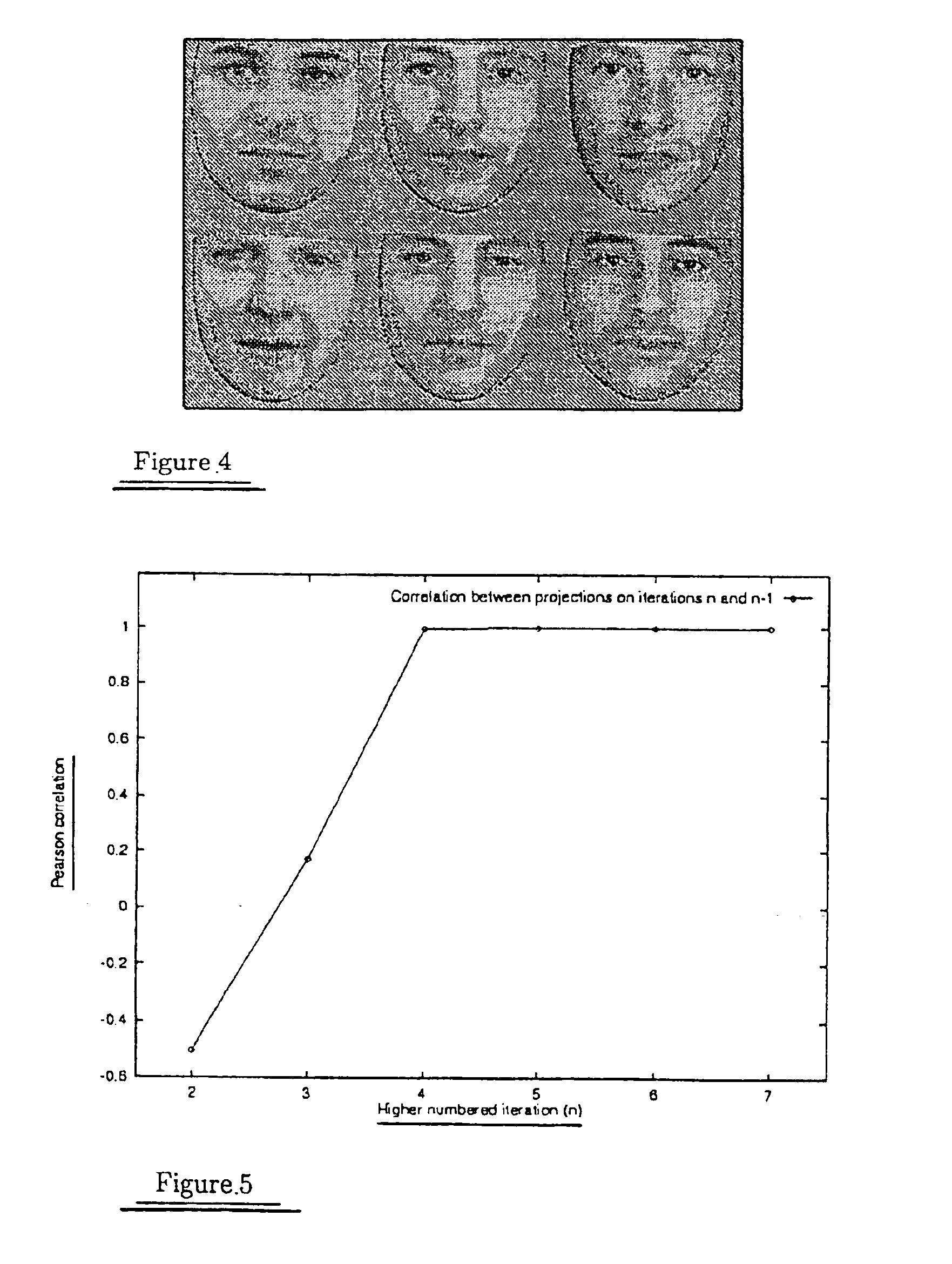
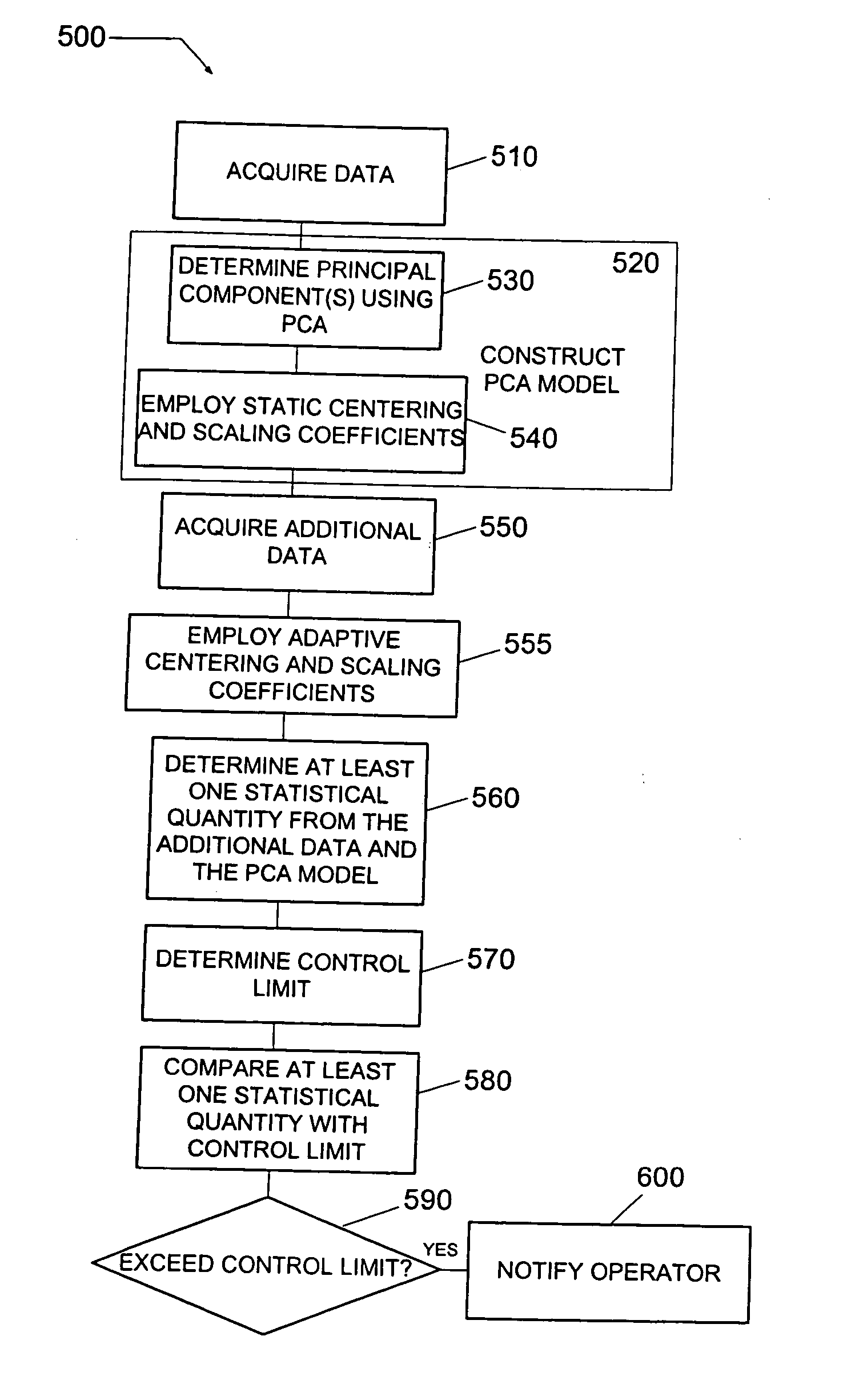
Method and system of diagnosing a processing system using adaptive multivariate analysis
ActiveUS20050060103A1Useful applicationAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsPrincipal component analysisControl limits
A method and system of monitoring a processing system and for processing a substrate during the course of semiconductor manufacturing. As such, data is acquired from the processing system for a plurality of observations, the data including a plurality of data parameters. A principal components analysis (PCA) model is constructed from the data and includes centering coefficients. Additional data is acquired from the processing system, the additional data including an additional observation of the plurality of data parameters. The centering coefficients are adjusted to produce updated adaptive centering coefficients for each of the data parameters in the PCA model. The updated adaptive centering coefficients are applied to each of the data parameters in the PCA model. At least one statistical quantity is determined from the additional data using the PCA model. A control limit is set for the statistical quantity and compared to the statistical quantity.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
System and method for detecting face
InactiveUS7321670B2Quickly and correctly decidingImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionFace detectionFeature vector
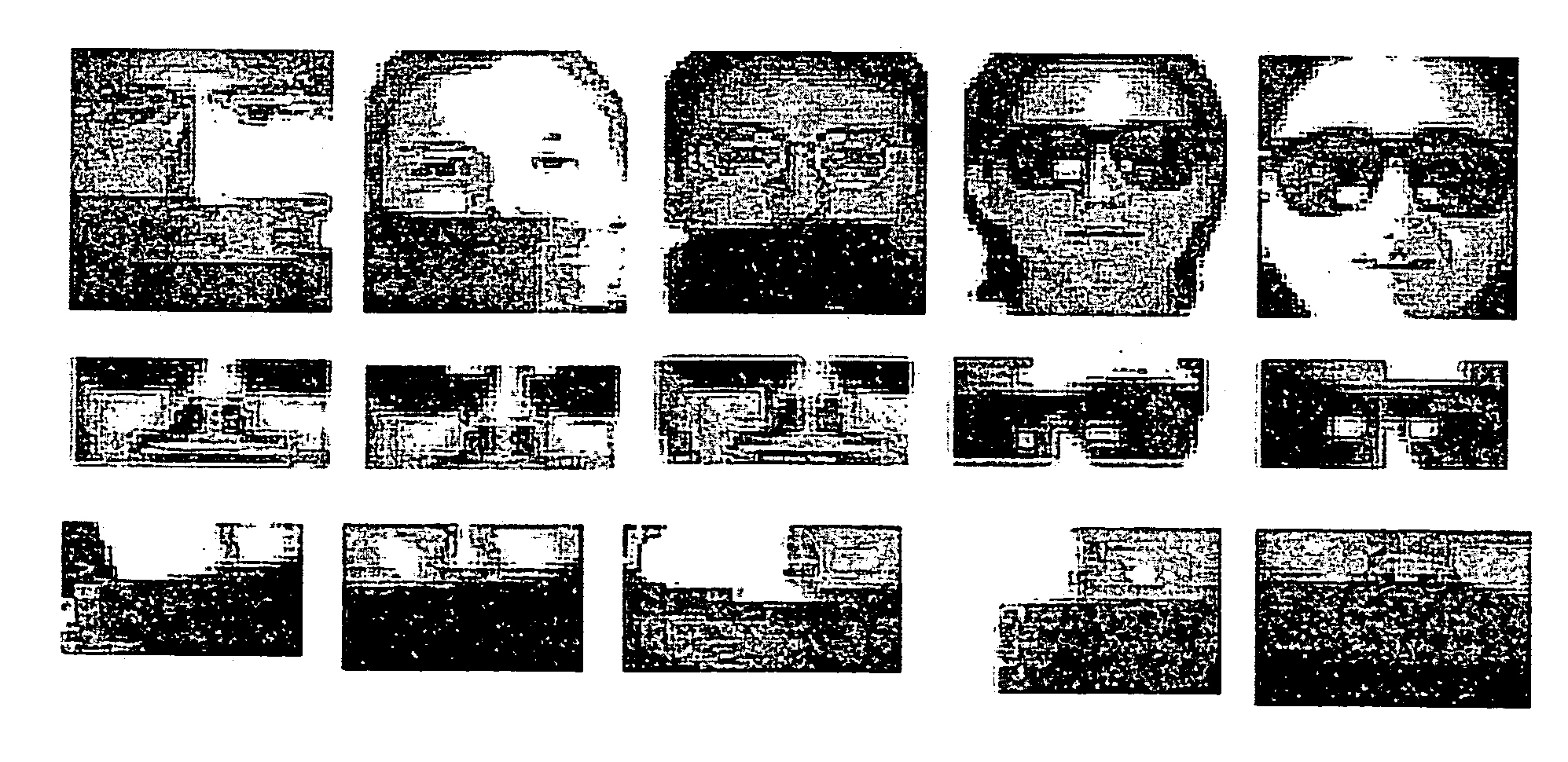
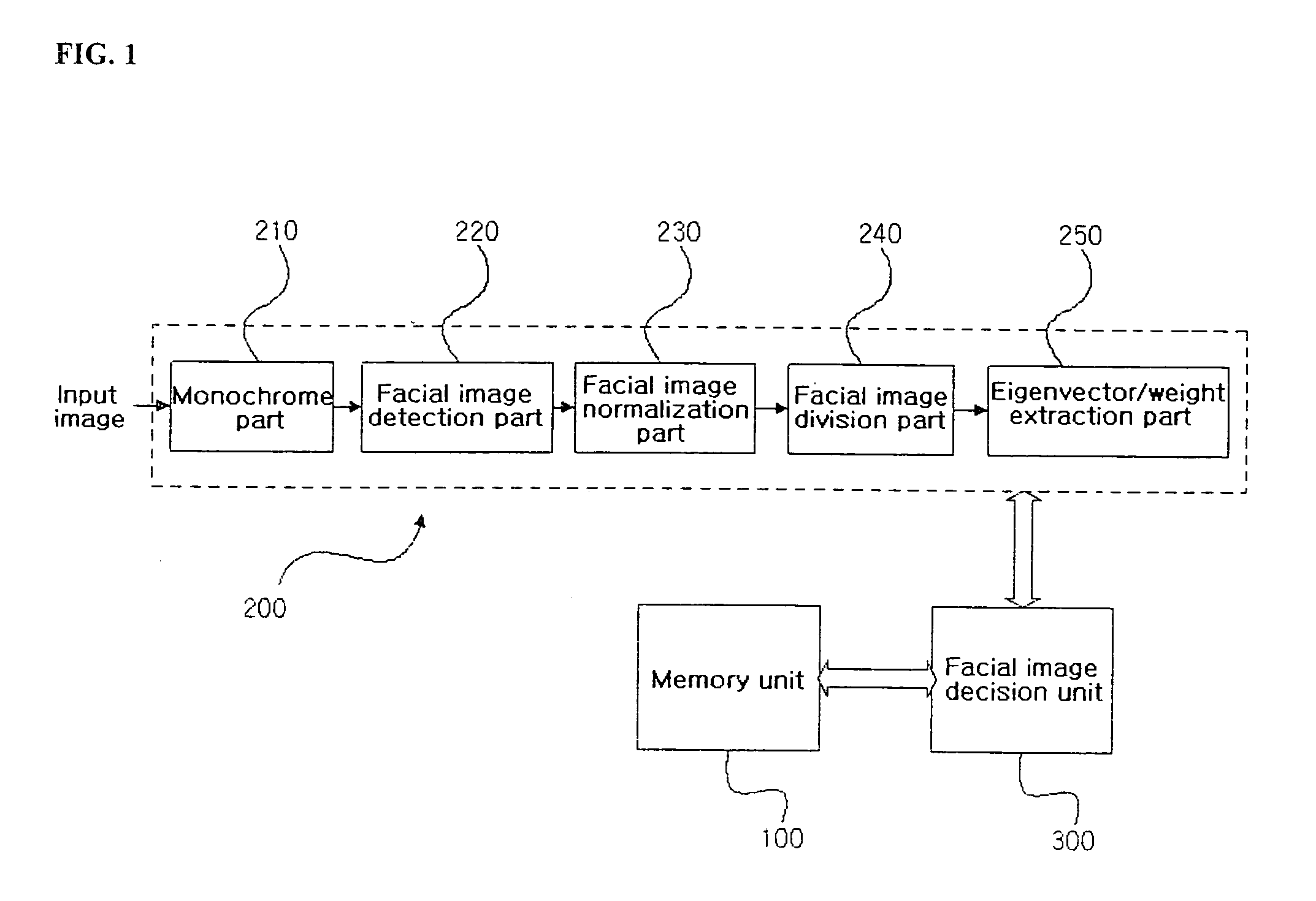
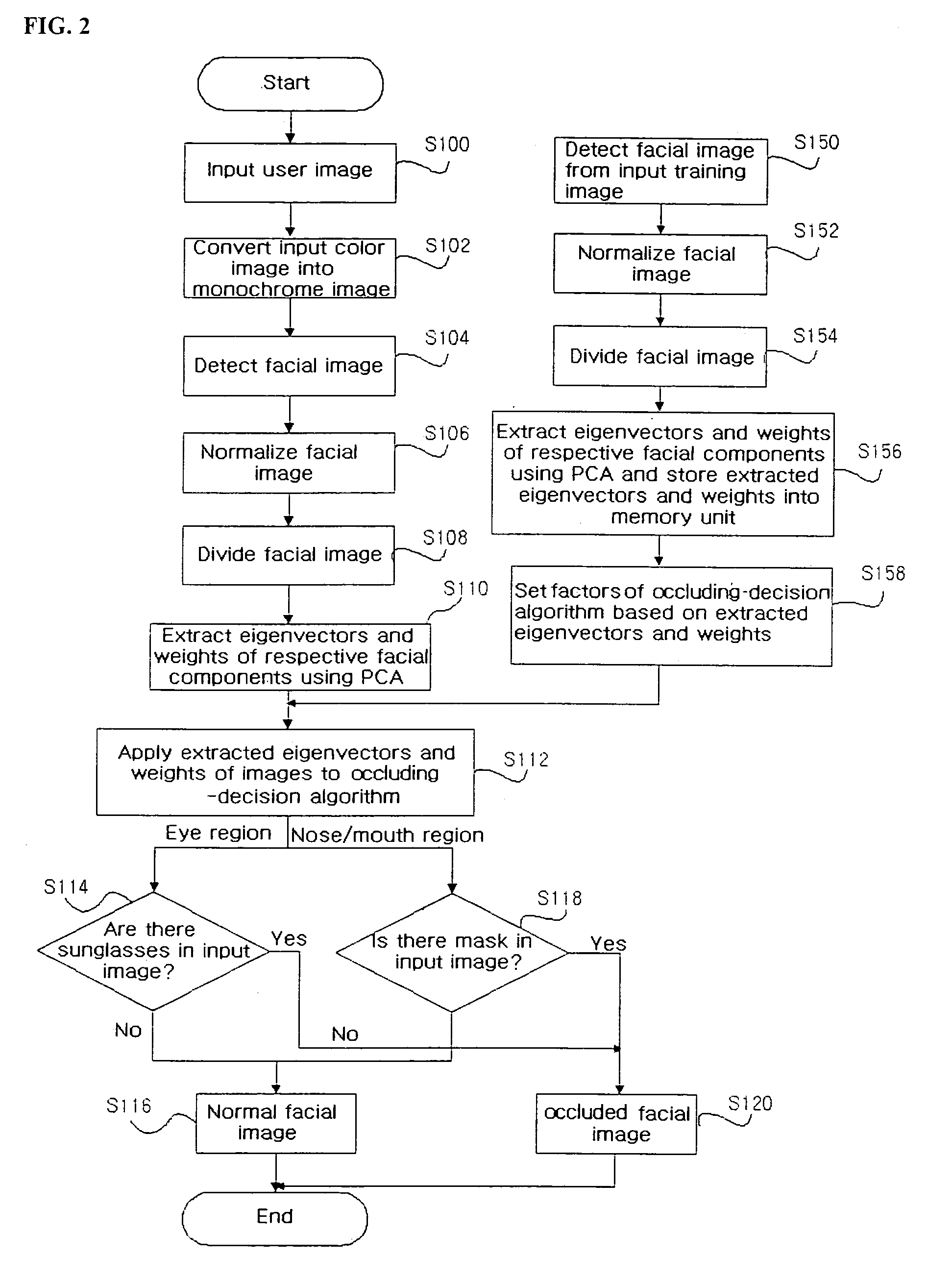
The present invention relates to a system and method for detecting a face that is capable of quickly and correctly deciding whether an input facial image is occluded, regardless of any type of facial image to be inputted. The present invention is characterized in that eigenvectors and weights are extracted from the input facial image using principal component analysis (PCA) and the extracted eigenvectors and weights of the user image are substituted into a occluding-decision algorithm, whereby it can be determined whether the facial image is occluded.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
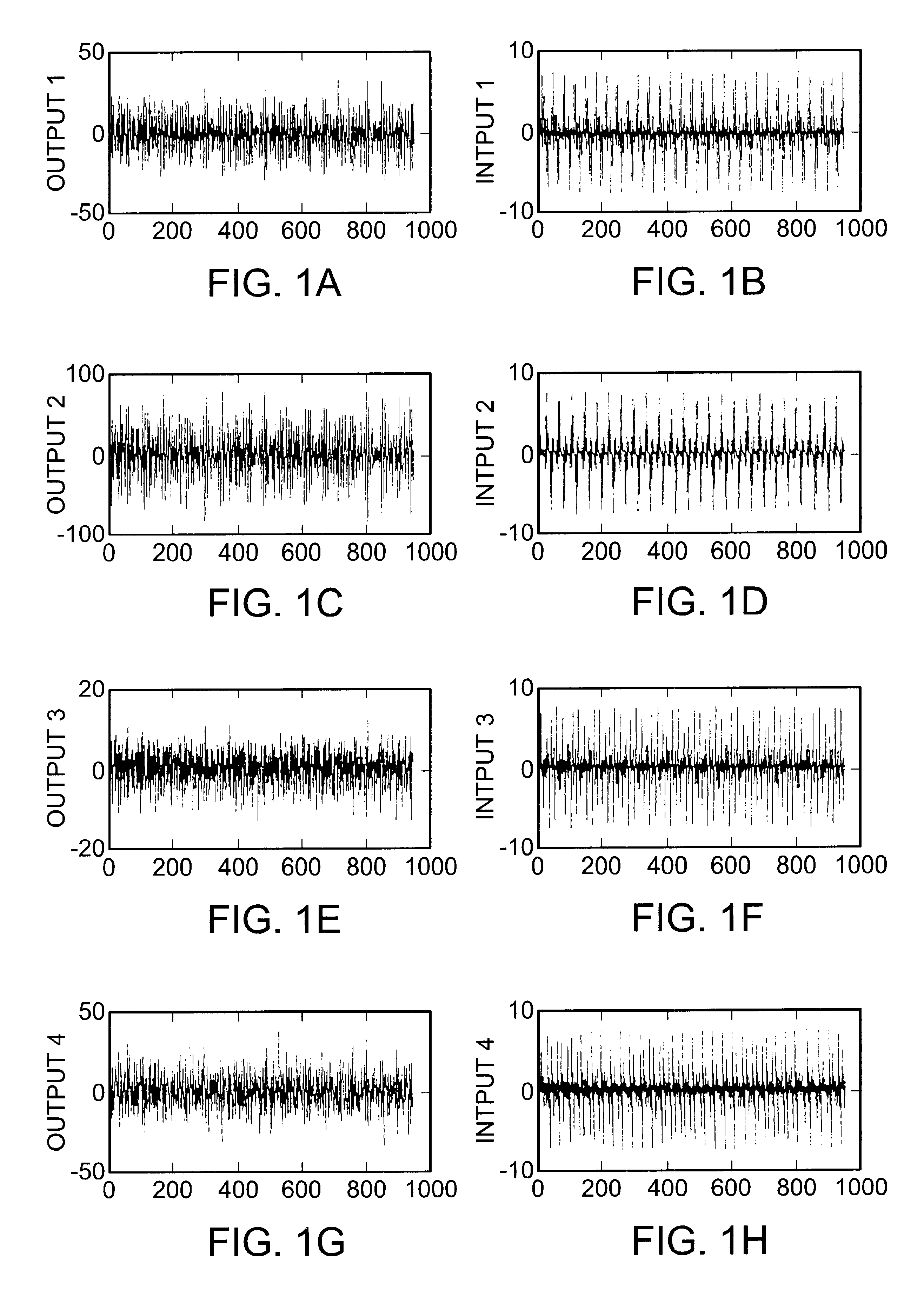
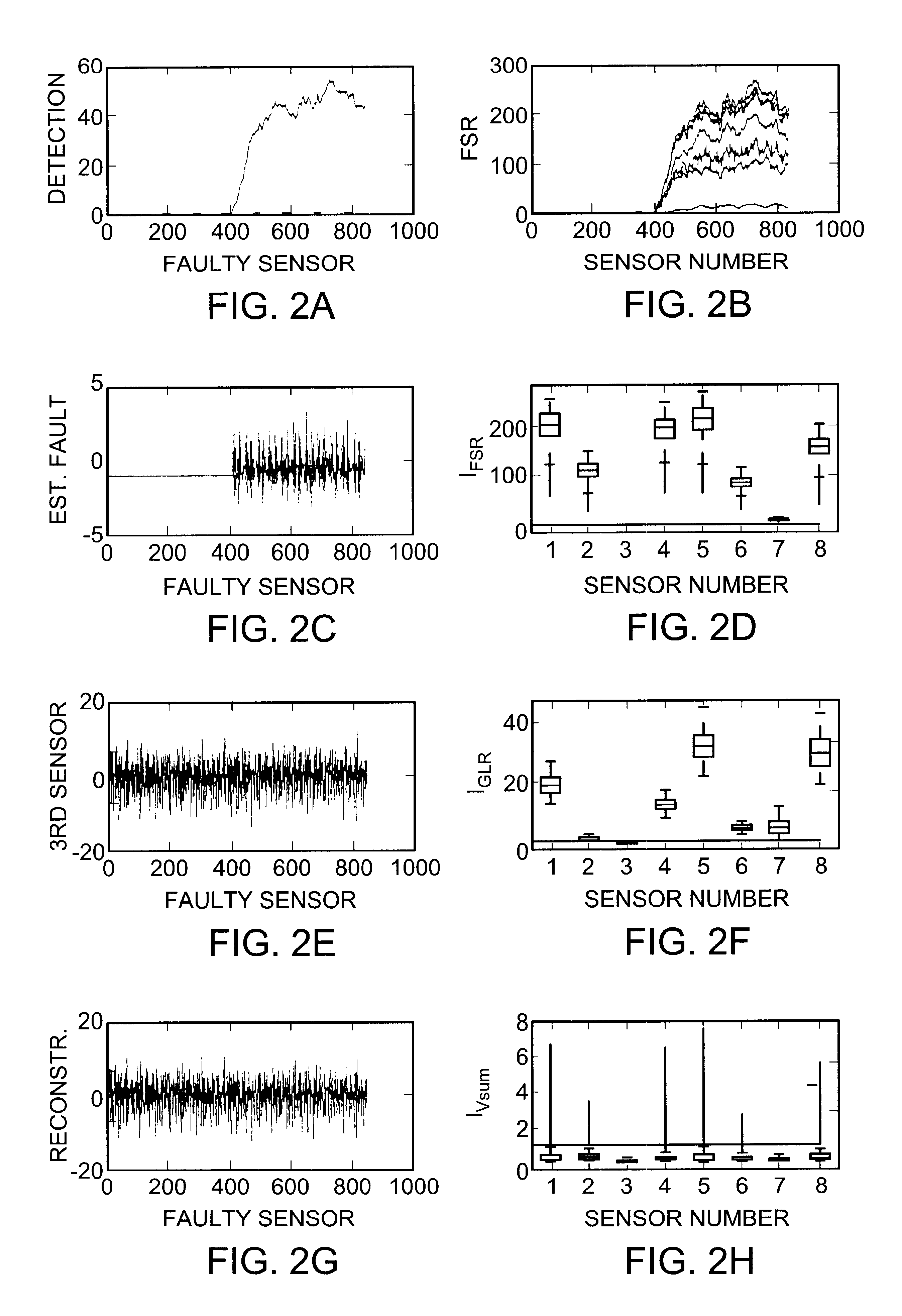
Sensor validation apparatus and method
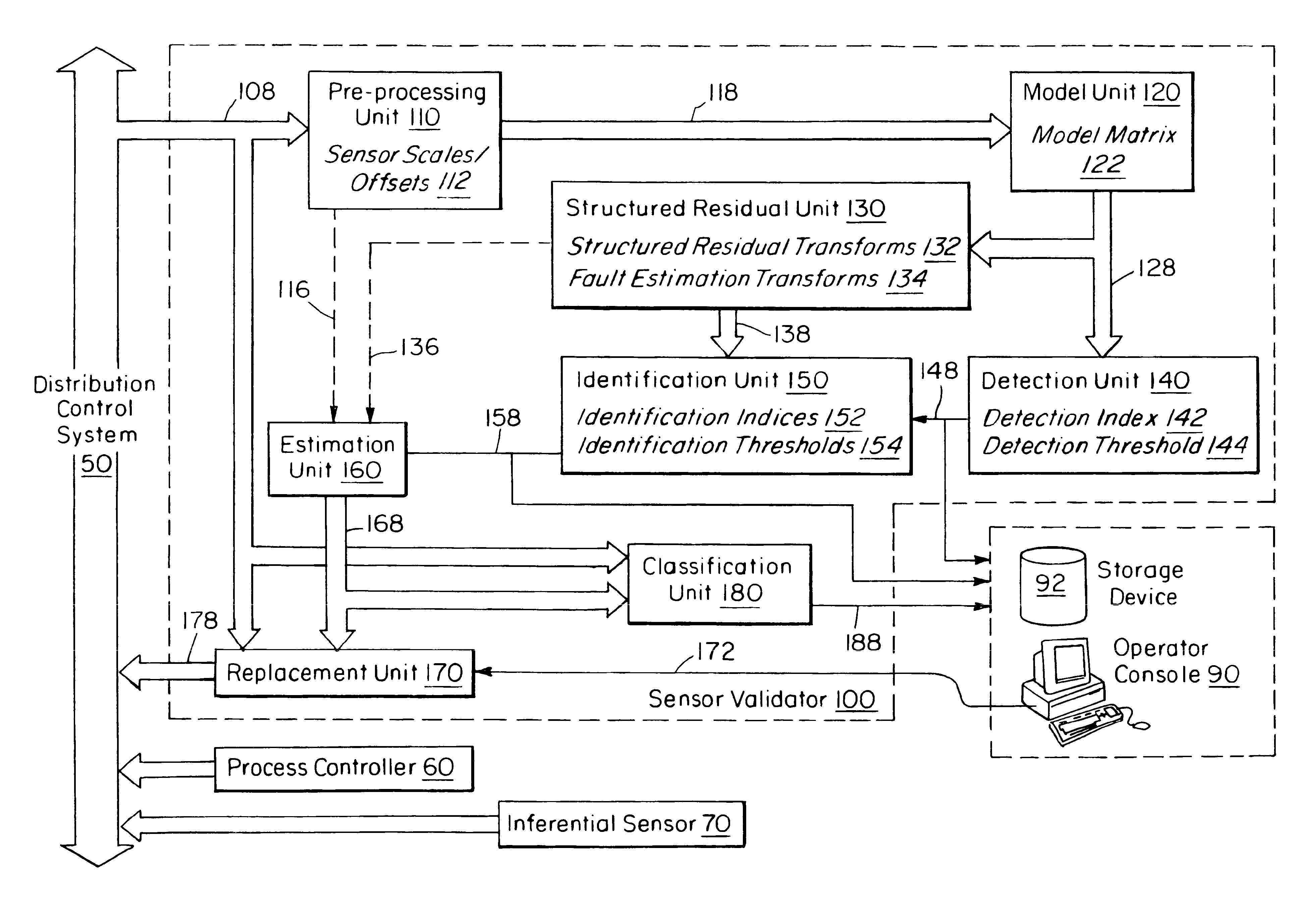
An apparatus and method is disclosed for detecting, identifying, and classifying faults occurring in sensors measuring a process. A variety of process models can be used such as first principles models, dynamic multivariable predictive control models, from data using statistical methods such as partial least squares (PLS) or principal component analysis. If faults are identified in one or more sensors, the apparatus and method provide replacement values for the faulty sensors so that any process controllers and process monitoring systems that use these sensors can remain in operation during the fault period. The identification of faulty sensors is achieved through the use of a set of structured residual transforms that are uniquely designed to be insensitive to specific subsets of sensors, while being maximally sensitive to sensors not in the subset. Identified faults are classified into one of the types Complete Failure, Bias, Drift, Precision Loss, or Unknown.
Owner:ASPENTECH CORP
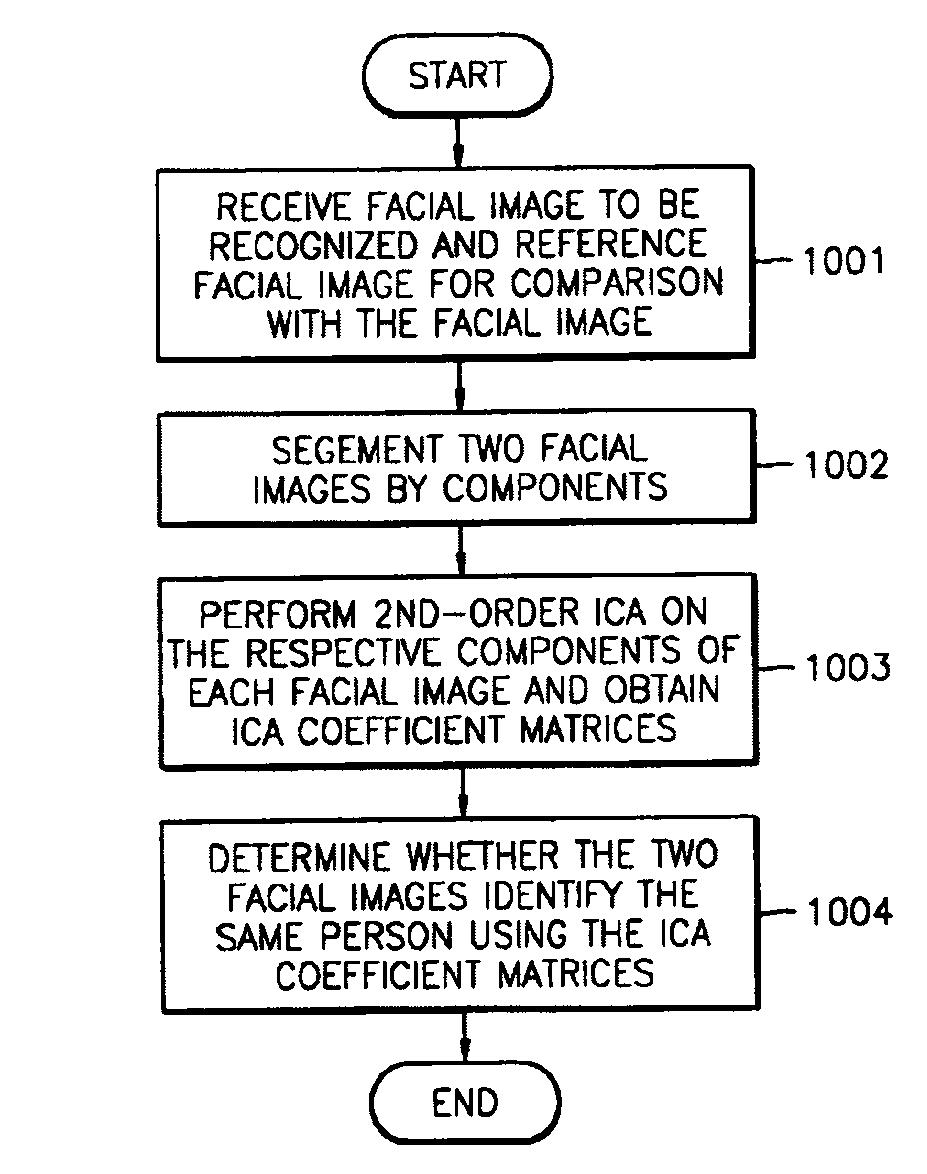
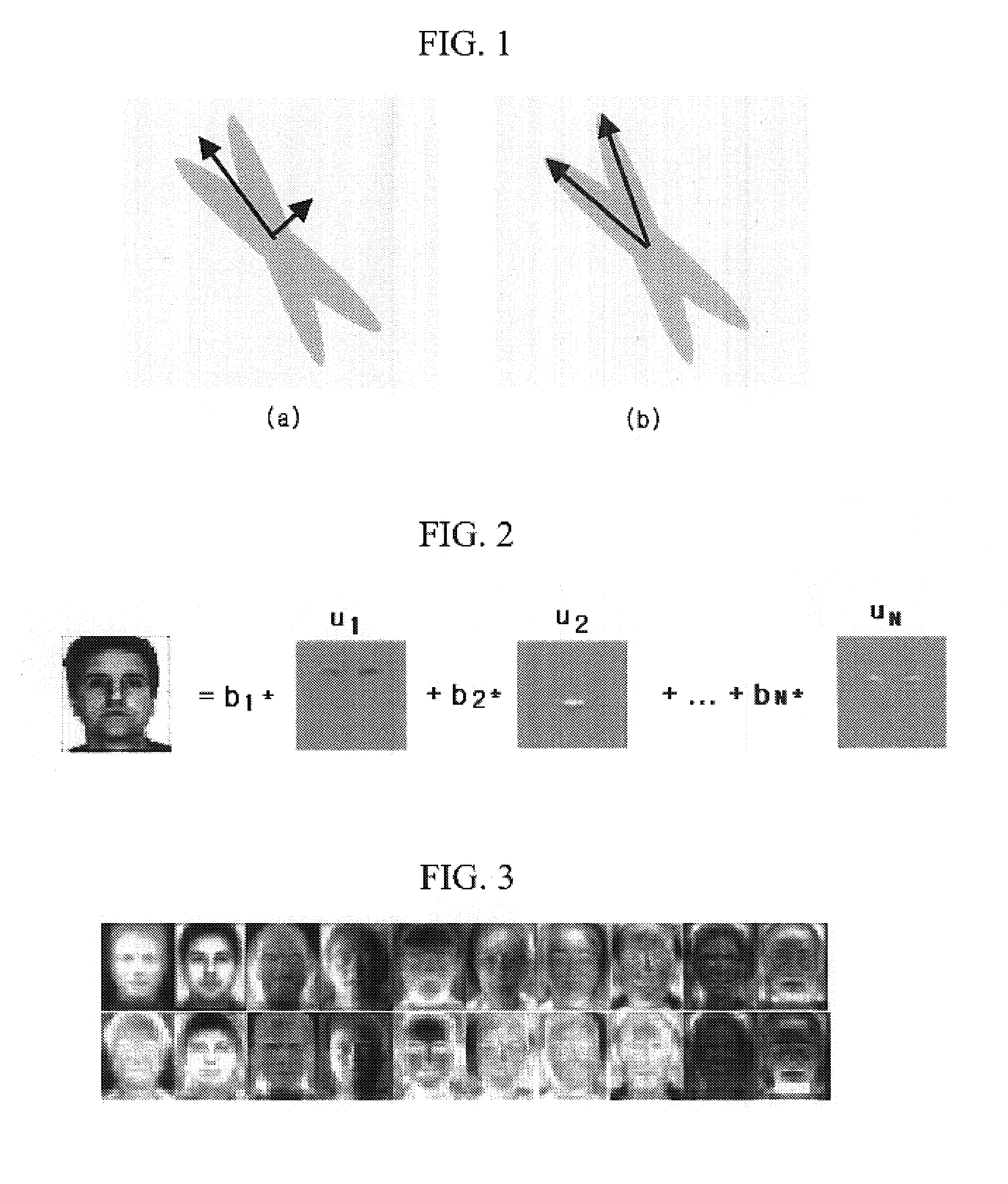
Method and apparatus of recognizing face using component-based 2nd-order principal component analysis (PCA)/independent component analysis (ICA)
ActiveUS7254257B2Image analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPrincipal component analysisIndependent component analysis
A method and apparatus for recognizing and searching for a face using 2nd-order independent component analysis (ICA) are provided. The method for describing feature points uses 2nd-order ICA d to describe a facial image space and improve recognition performance in various illumination conditions. According to the method and apparatus, use of pose or illumination invariant face descriptor enables retrieval of human faces and authentication of a specific individual.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Application of abnormal event detection technology to delayed coking unit
ActiveUS20070250292A1Efficiently presentedPlug gaugesMeasurement arrangements for variablePrincipal component analysisCorrelation analysis
The present invention is a method for detecting an abnormal event for process units of a Delayed Coking Unit. The method compares the operation of the process units to statistical and engineering models. The statistical models are developed by principal components analysis of the normal operation for these units. The engineering models are based statistical and correlation analysis between variables. If the difference between the operation of a process unit and the normal model result indicates an abnormal condition, then the cause of the abnormal condition is determined and corrected.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
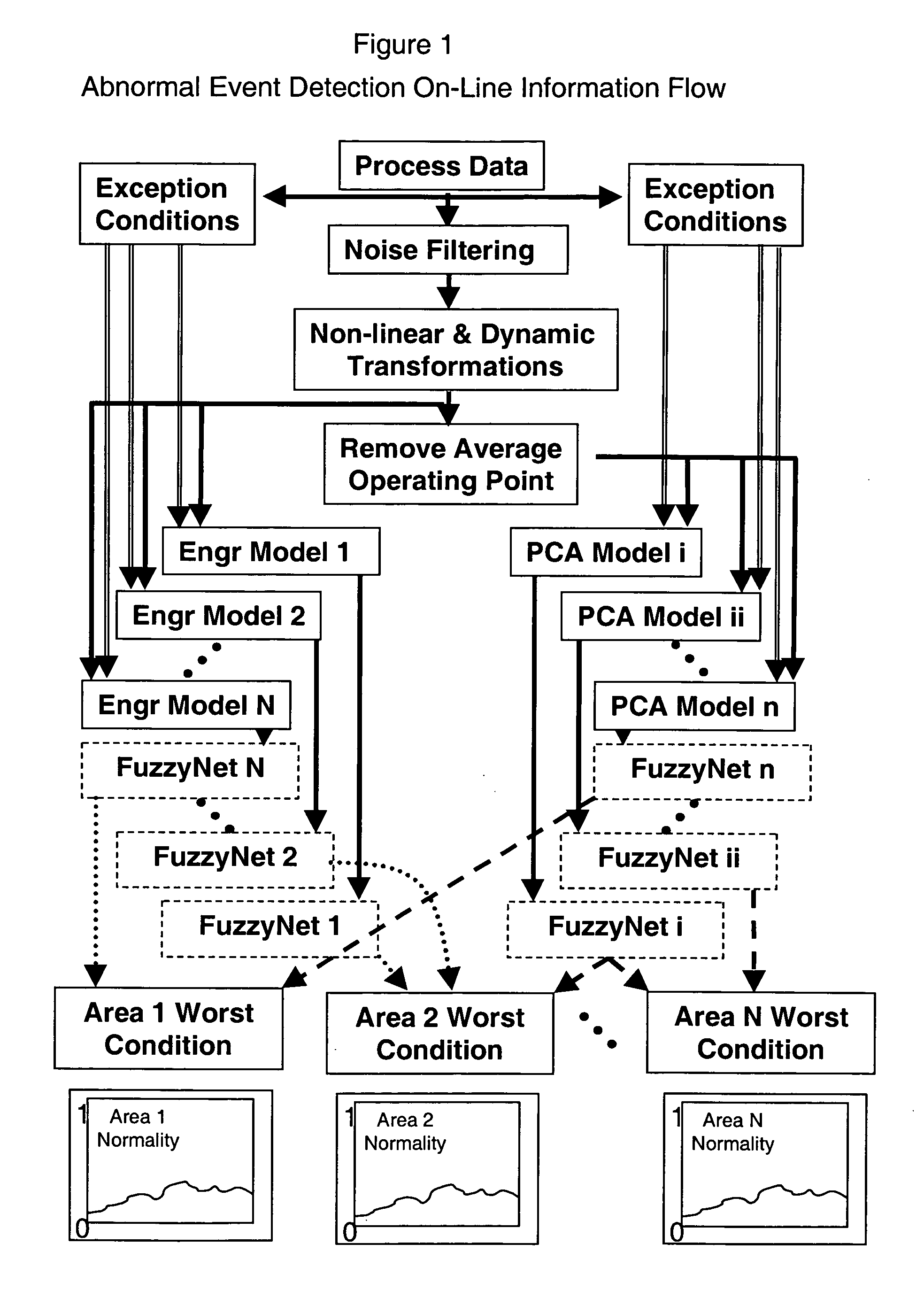
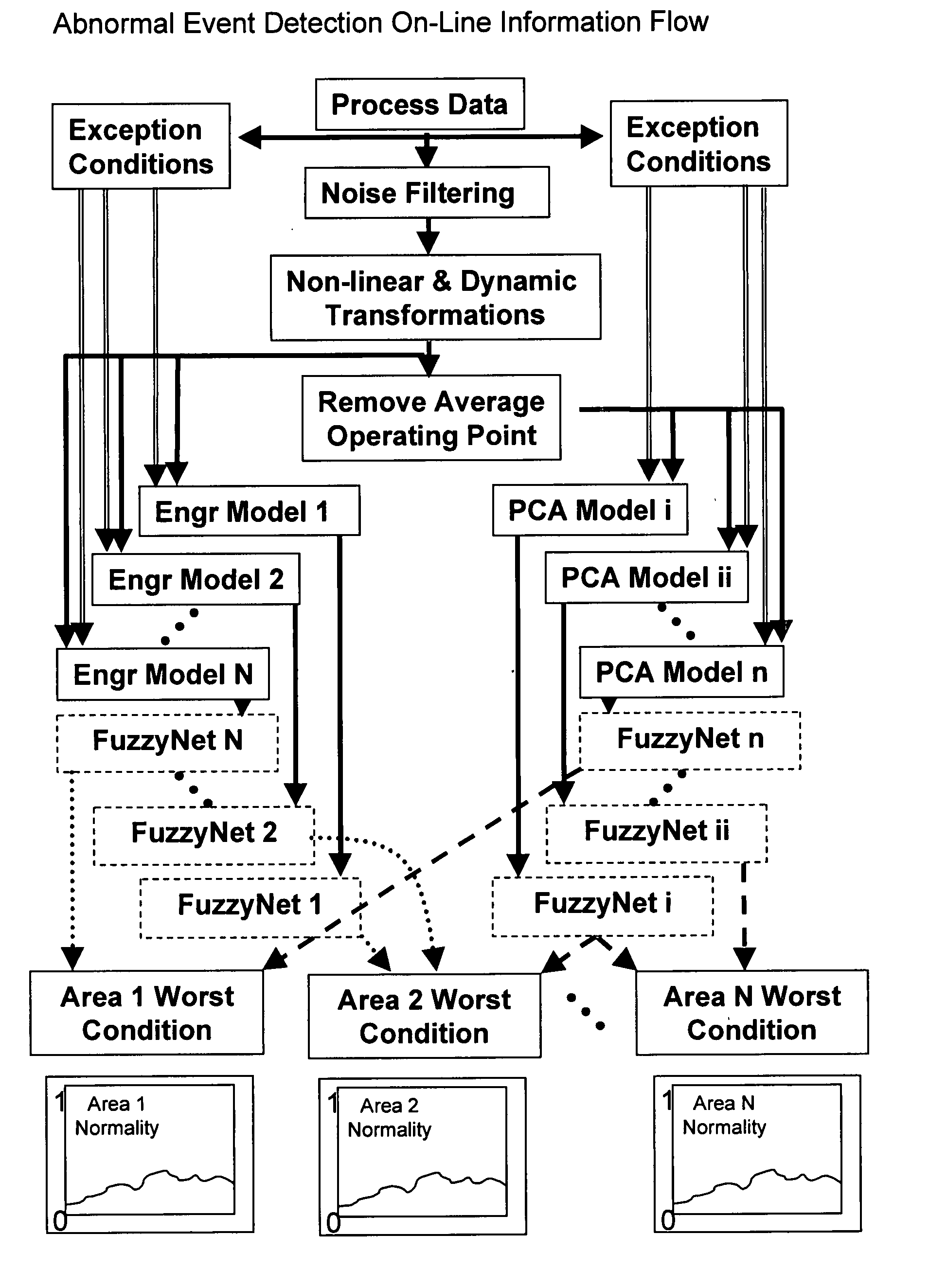
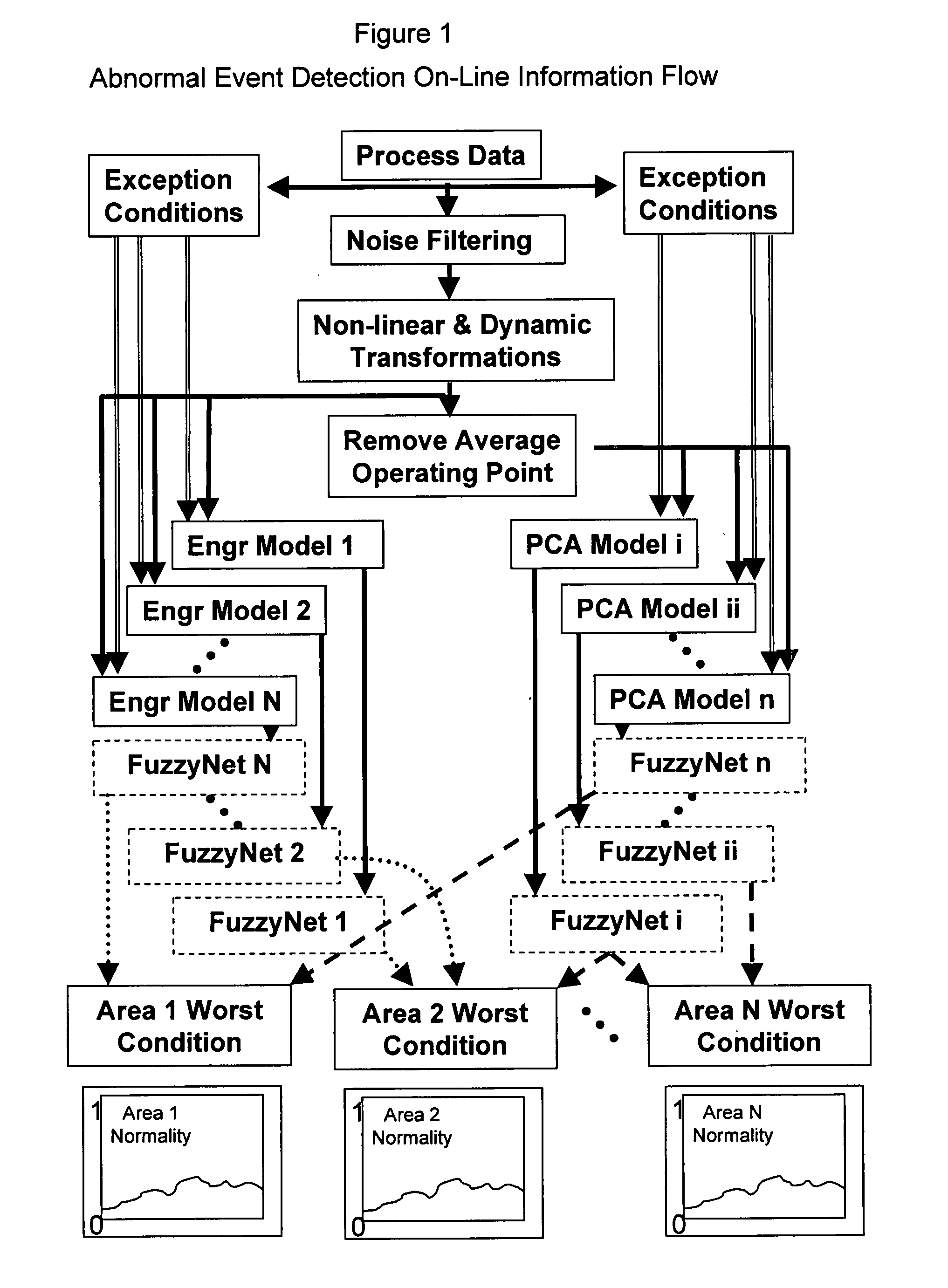
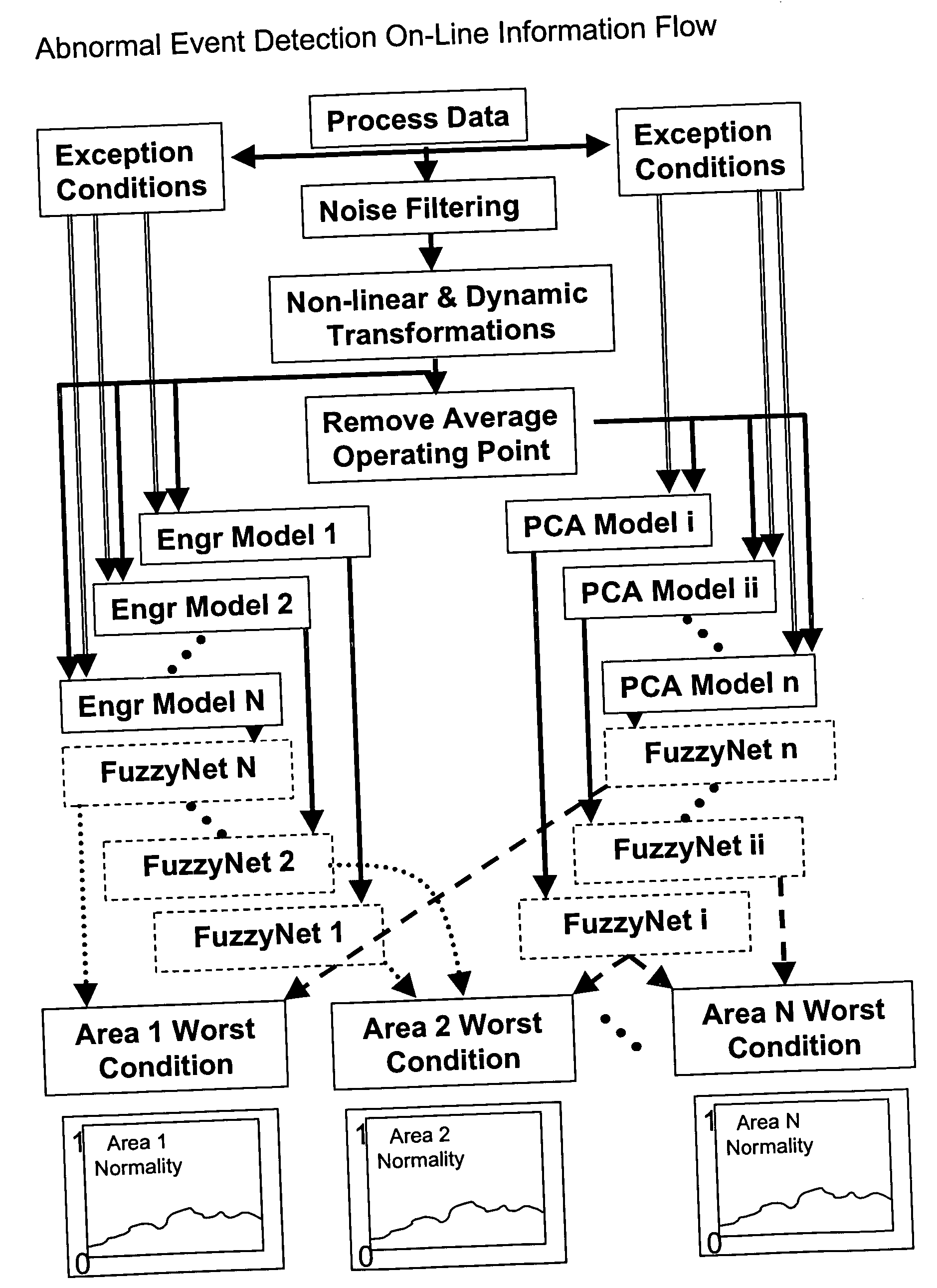
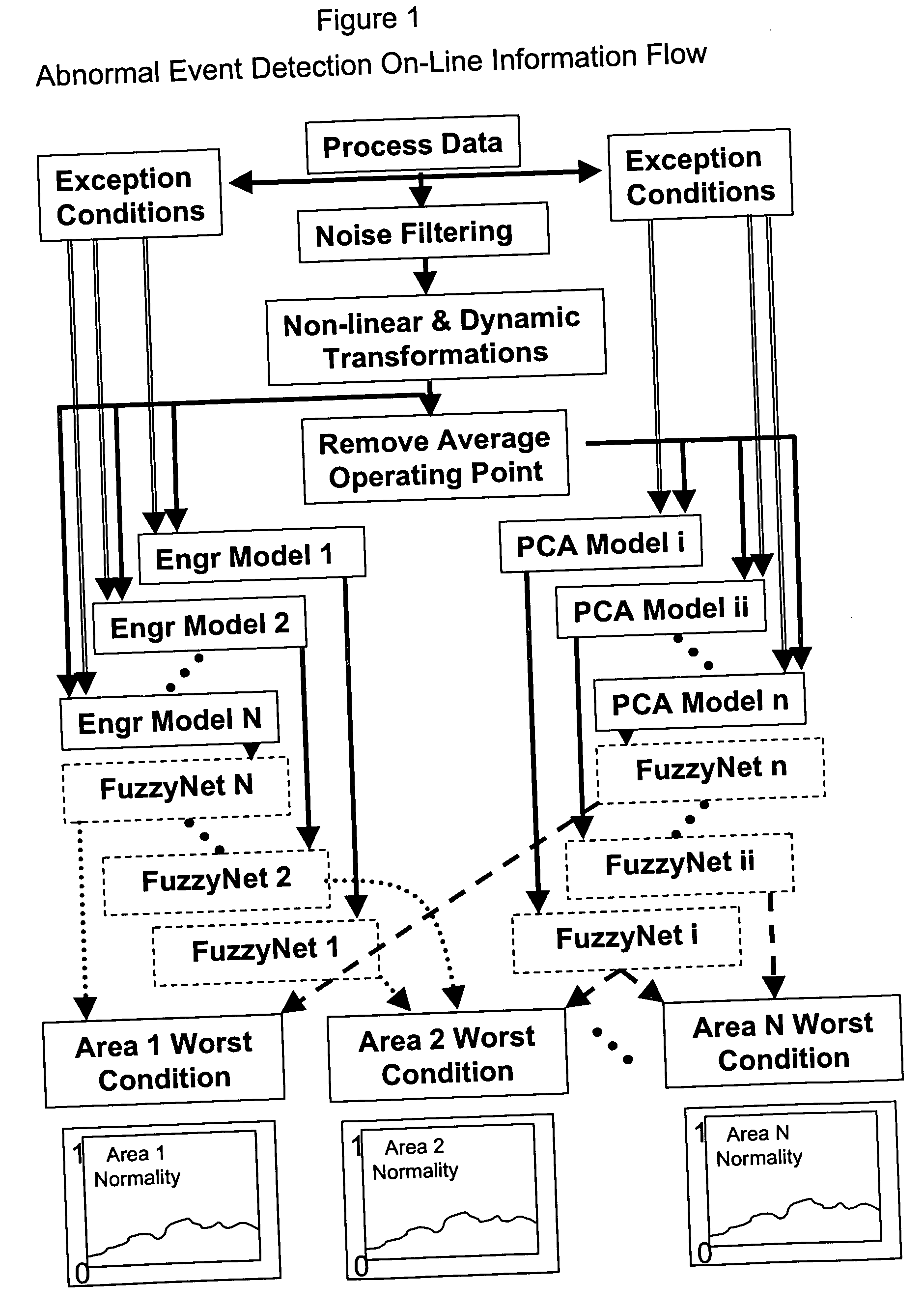
System and method for abnormal event detection in the operation of continuous industrial processes
ActiveUS20060058898A1Eliminate the effects ofEasy to monitorCatalytic crackingTesting/monitoring control systemsMultivariate statisticsPrincipal component analysis
Thousands of process and equipment measurements are gathered by the modern digital process control systems that are deployed in refineries and chemical plants. Several years of these data are historized in databases for analysis and reporting. These databases can be mined for the data patterns that occur during normal operation and those patterns used to determine when the process is behaving abnormally. These normal operating patterns are represented by sets of models. These models include simple engineering equations, which express known relationships that should be true during normal operations and multivariate statistical models based on a variation of principle component analysis. Equipment and process problems can be detected by comparing the data gathered on a minute by minute basis to predictions from these models of normal operation. The deviation between the expected pattern in the process operating data and the actual data pattern are interpreted by fuzzy Petri nets to determine the normality of the process operations. This is then used to help the operator localize and diagnose the root cause of the problem.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
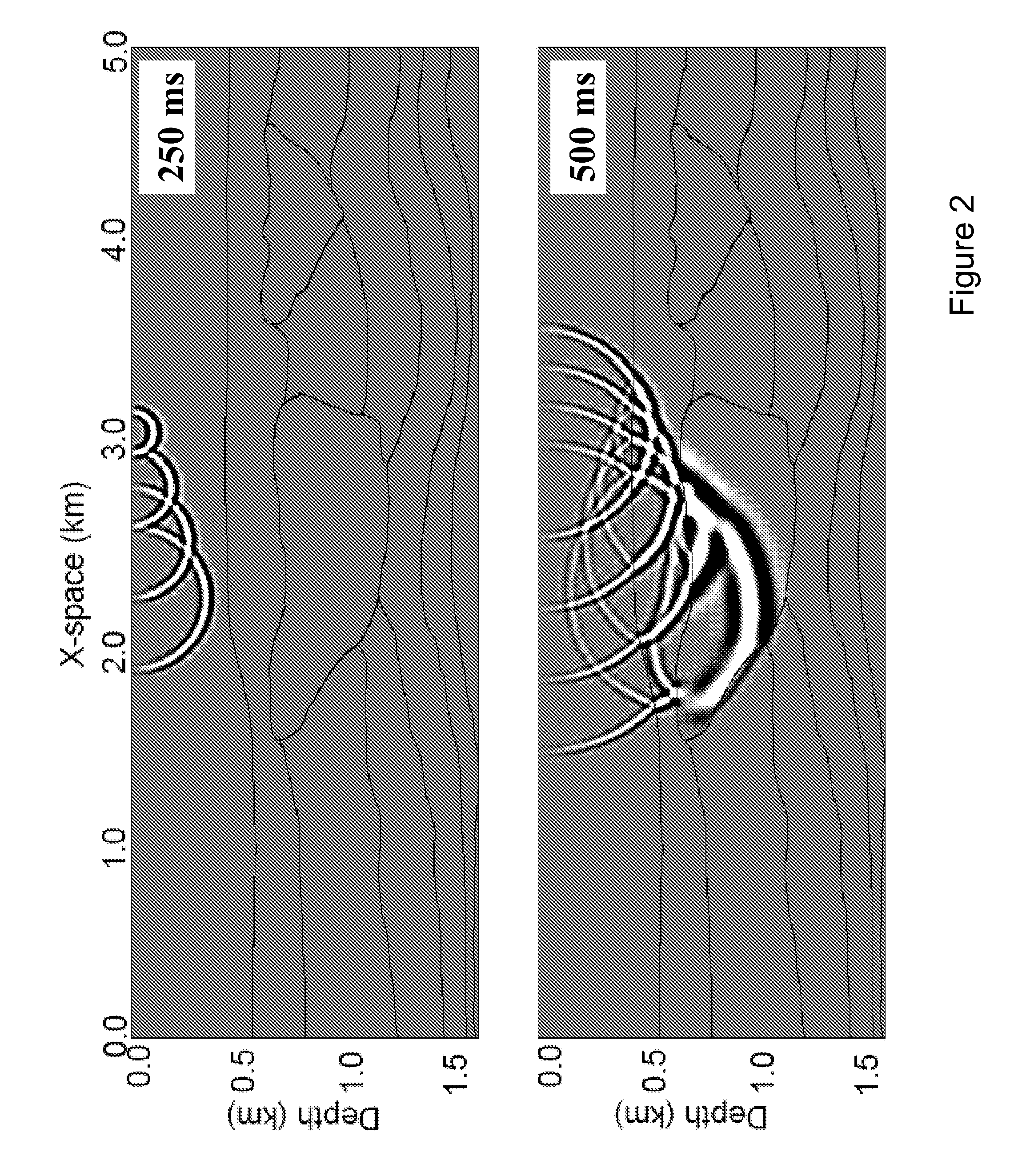
Coding and Decoding: Seismic Data Modeling, Acquisition and Processing
InactiveUS20070274155A1Seismic data acquisitionSeismic signal processingSource encodingData modeling
A method for coding and decoding seismic data acquired, based on the concept of multishooting, is disclosed. In this concept, waves generated simultaneously from several locations at the surface of the earth, near the sea surface, at the sea floor, or inside a borehole propagate in the subsurface before being recorded at sensor locations as mixtures of various signals. The coding and decoding method for seismic data described here works with both instantaneous mixtures and convolutive mixtures. Furthermore, the mixtures can be underdetemined [i.e., the number of mixtures (K) is smaller than the number of seismic sources (I) associated with a multishot] or determined [i.e., the number of mixtures is equal to or greater than the number of sources). When mixtures are determined, we can reorganize our seismic data as zero-mean random variables and use the independent component analysis (ICA) or, alternatively, the principal component analysis (PCA) to decode. We can also alternatively take advantage of the sparsity of seismic data in our decoding process. When mixtures are underdetermined and the number of mixtures is at least two, we utilize higher-order statistics to overcome the underdeterminacy. Alternatively, we can use the constraint that seismic data are sparse to overcome the underdeterminacy. When mixtures are underdetermined and limited to single mixtures, we use a priori knowledge about seismic acquisition to computationally generate additional mixtures from the actual recorded mixtures. Then we organize our data as zero-mean random variables and use ICA or PCA to decode the data. The a priori knowledge includes source encoding, seismic acquisition geometries, and reference data collected for the purpose of aiding the decoding processing.The coding and decoding processes described can be used to acquire and process real seismic data in the field or in laboratories, and to model and process synthetic data.
Owner:IKELLE LUC T
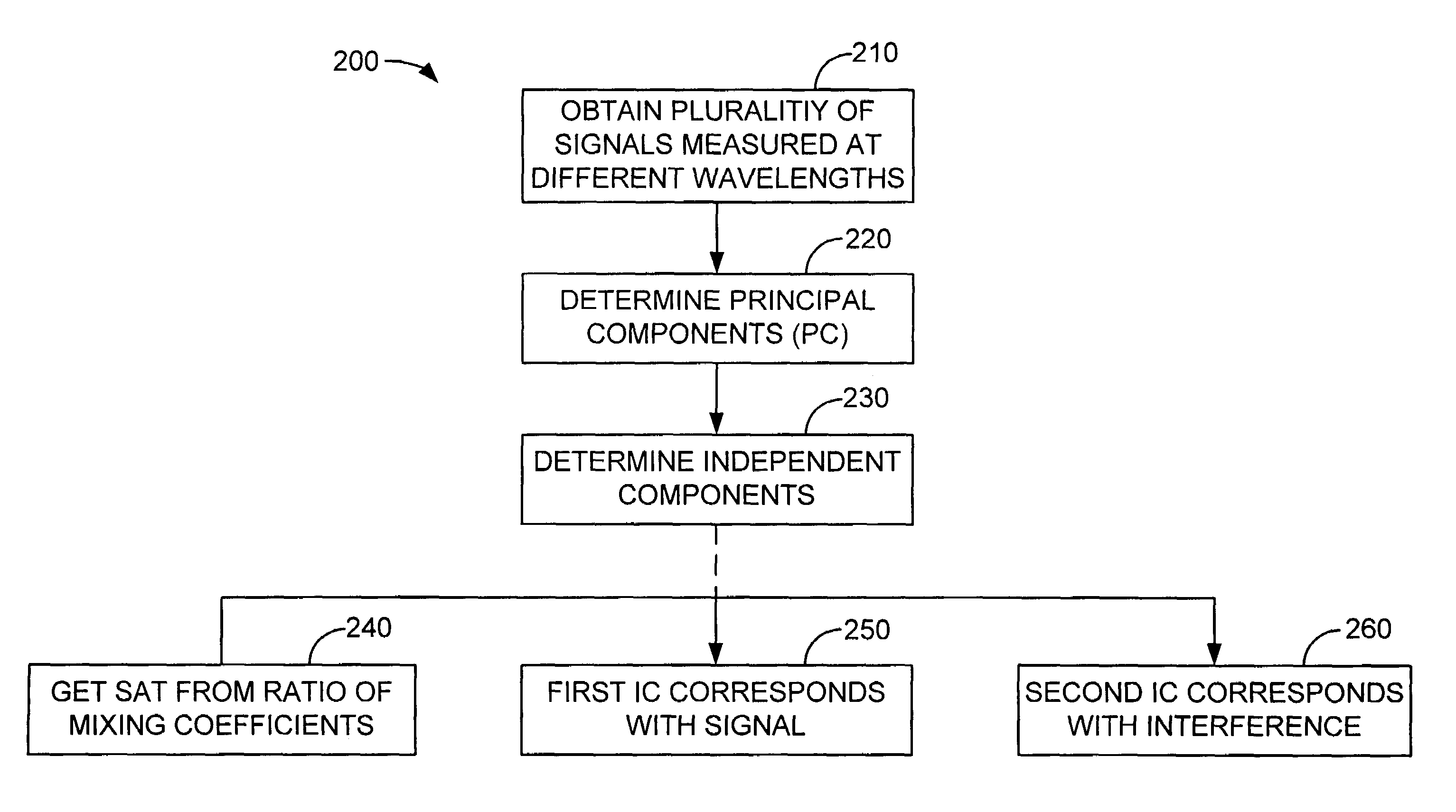
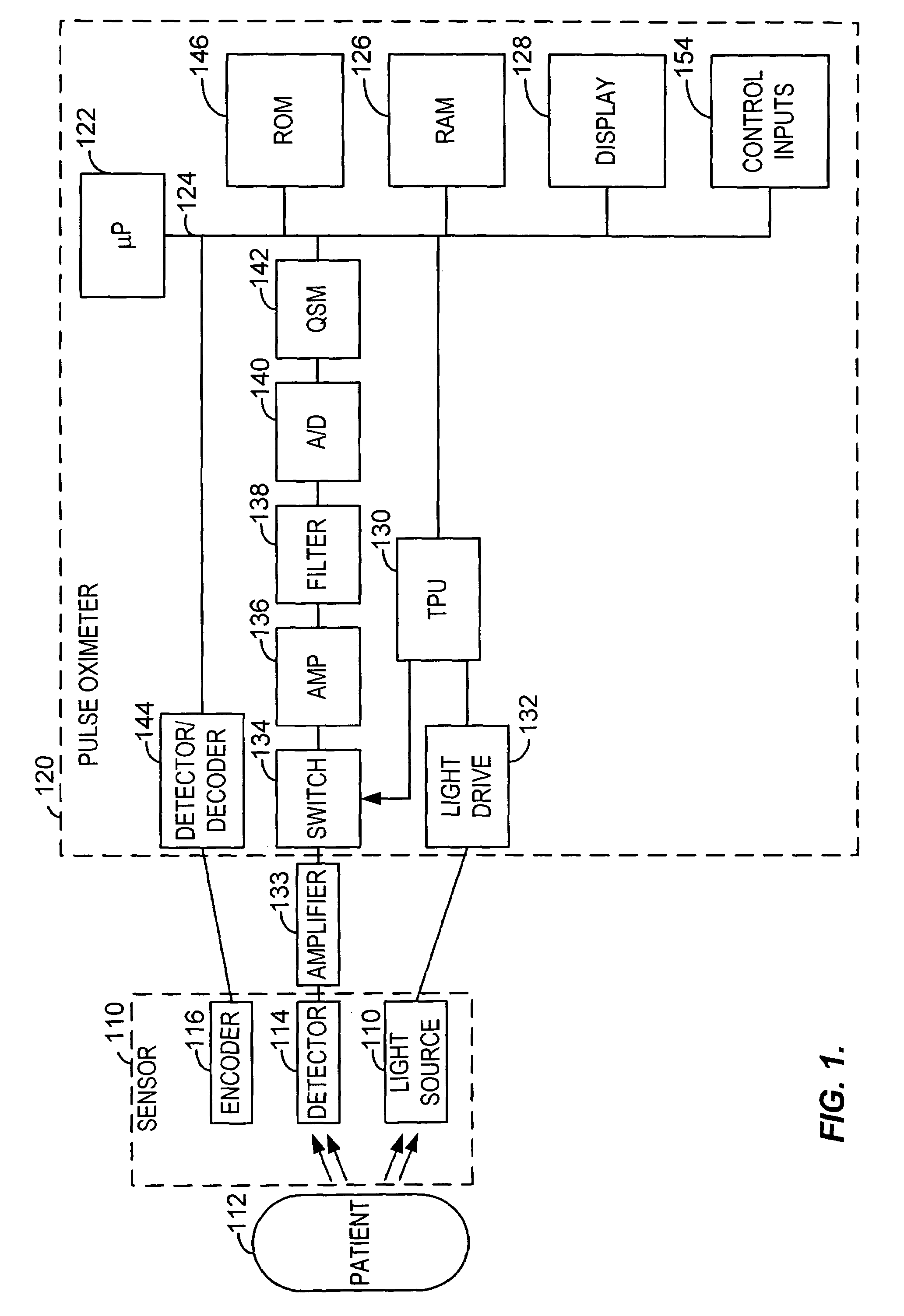
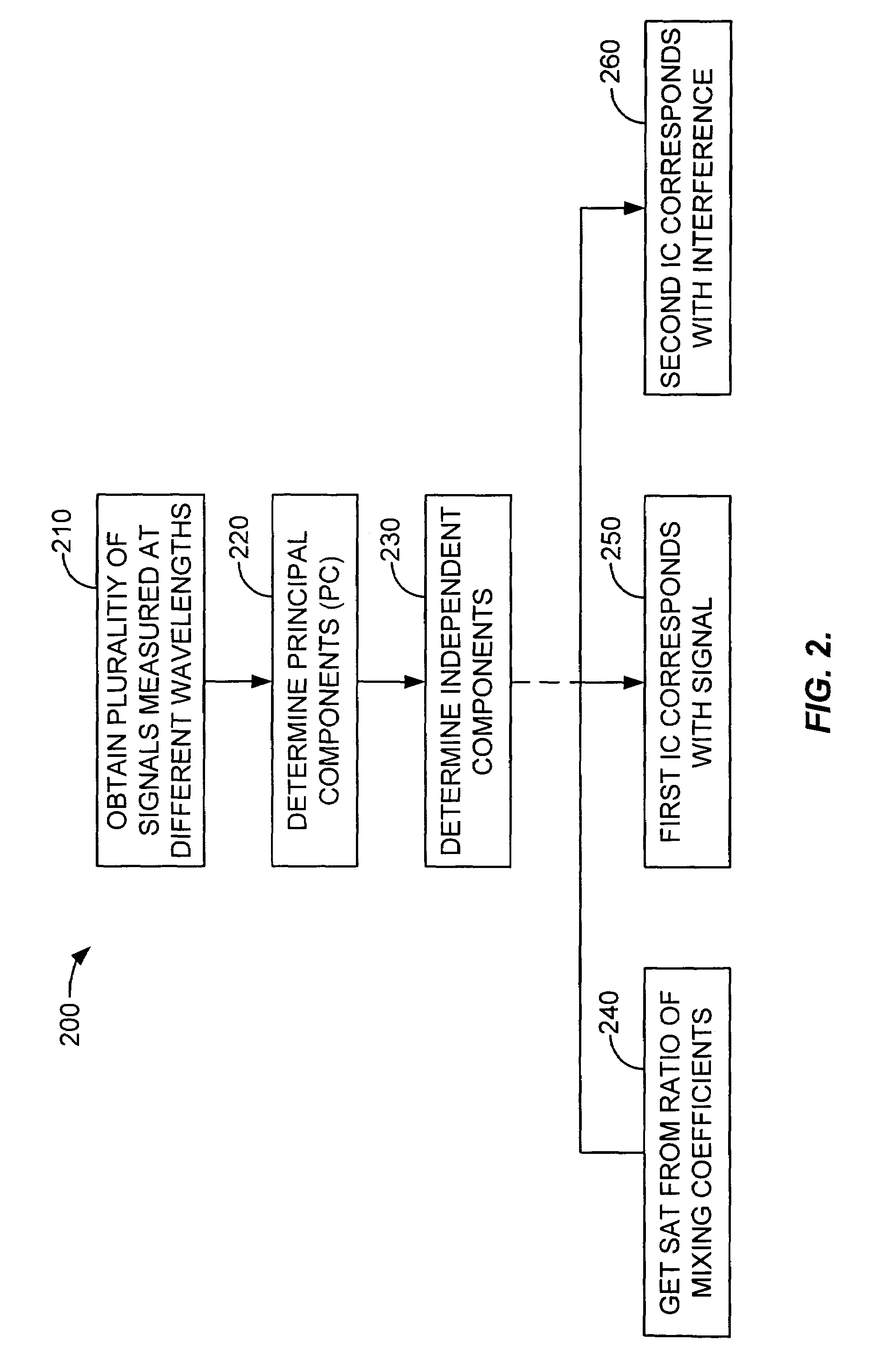
Blind source separation of pulse oximetry signals
InactiveUS7079880B2Minimize cross-correlationImprove performanceSensorsMeasuring/recording heart/pulse ratePrincipal component analysisPulse oximetry
A method and apparatus for the application of Blind Source Separation (BSS), specifically independent Component Analysis (ICA) to mixture signals obtained by a pulse oximeter sensor. In pulse oximetry, the signals measured at different wavelengths represent the mixture signals, while the plethysmographic signal, motion artifact, respiratory artifact and instrumental noise represent the source components. The BSS is carried out by a two-step method including an ICA. In the first step, the method uses Principal Component Analysis (PCA) as a preprocessing step, and the Principal Components are then used to derive sat and the Independent Components, where the Independent Components are determined in a second step. In one embodiment, the independent components are obtained by high-order decorrelation of the principal components, achieved by maximizing the sum of the squares of the higher-order cumulants of the plurality of mixture signals.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
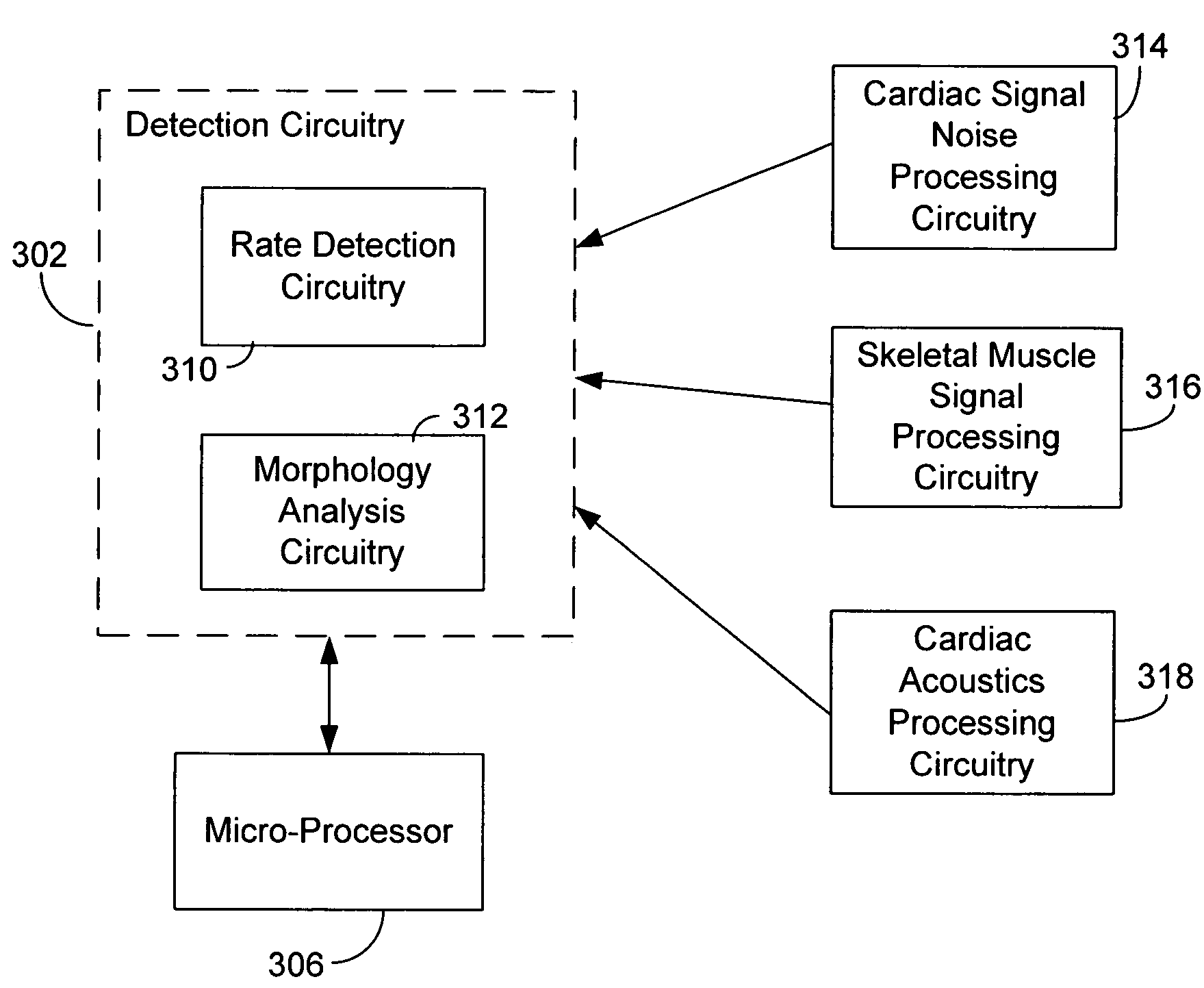
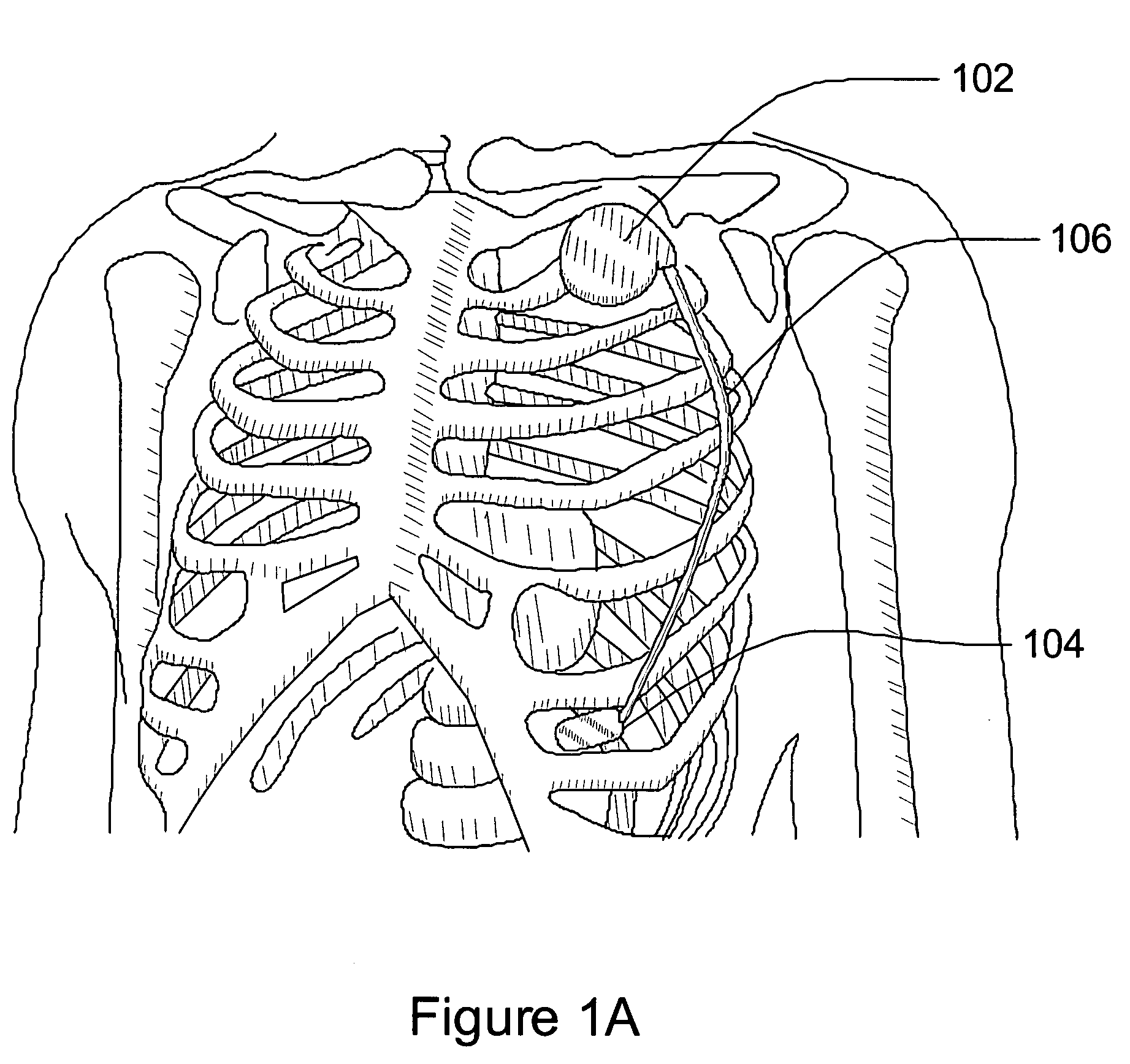
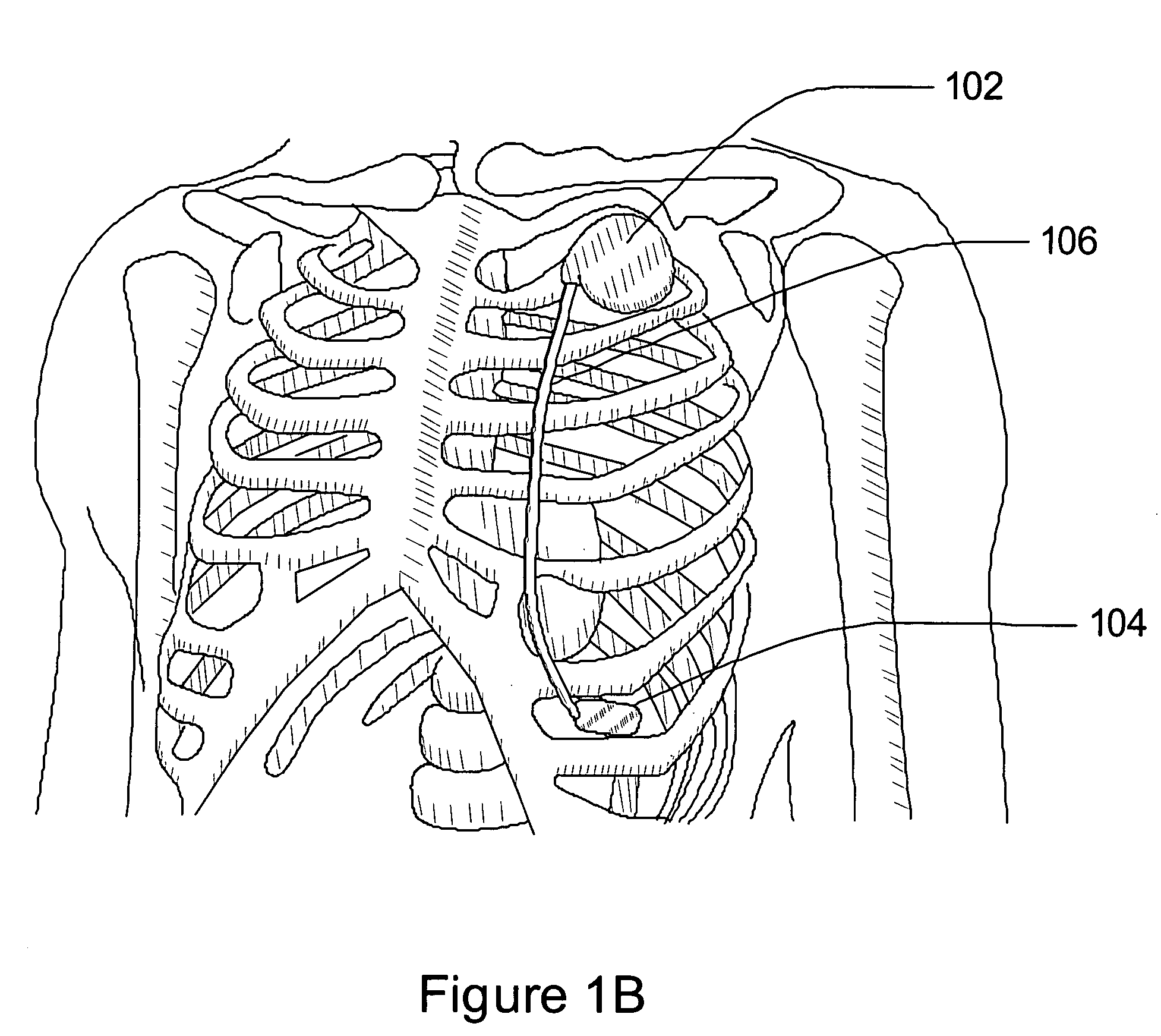
Separation of a subcutaneous cardiac signal from a plurality of composite signals
A cardiac monitoring and / or stimulation method and systems provide monitoring, defibrillation and / or pacing therapies, including systems detecting and / or treating cardiac arrhythmia. A system includes a housing coupled to a plurality of electrodes configured for subcutaneous non-intrathoracic sensing. A signal processor receives a plurality of composite signals associated with a plurality of sources, separates a signal from the plurality of composite signals using blind source separation, and identifies a cardiac signal. The signal processor may iteratively separate signals from the plurality of composite signals until the cardiac signal is identified. A method of signal separation includes detecting a plurality of composite signals at a plurality of locations, separating a signal using blind source separation, and identifying a cardiac signal. The separation may include a principal component analysis and / or an independent component analysis. The composite signals may be filtered before separation using band-pass filtering, adaptive, or other filters.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Weather prediction method for forecasting selected events
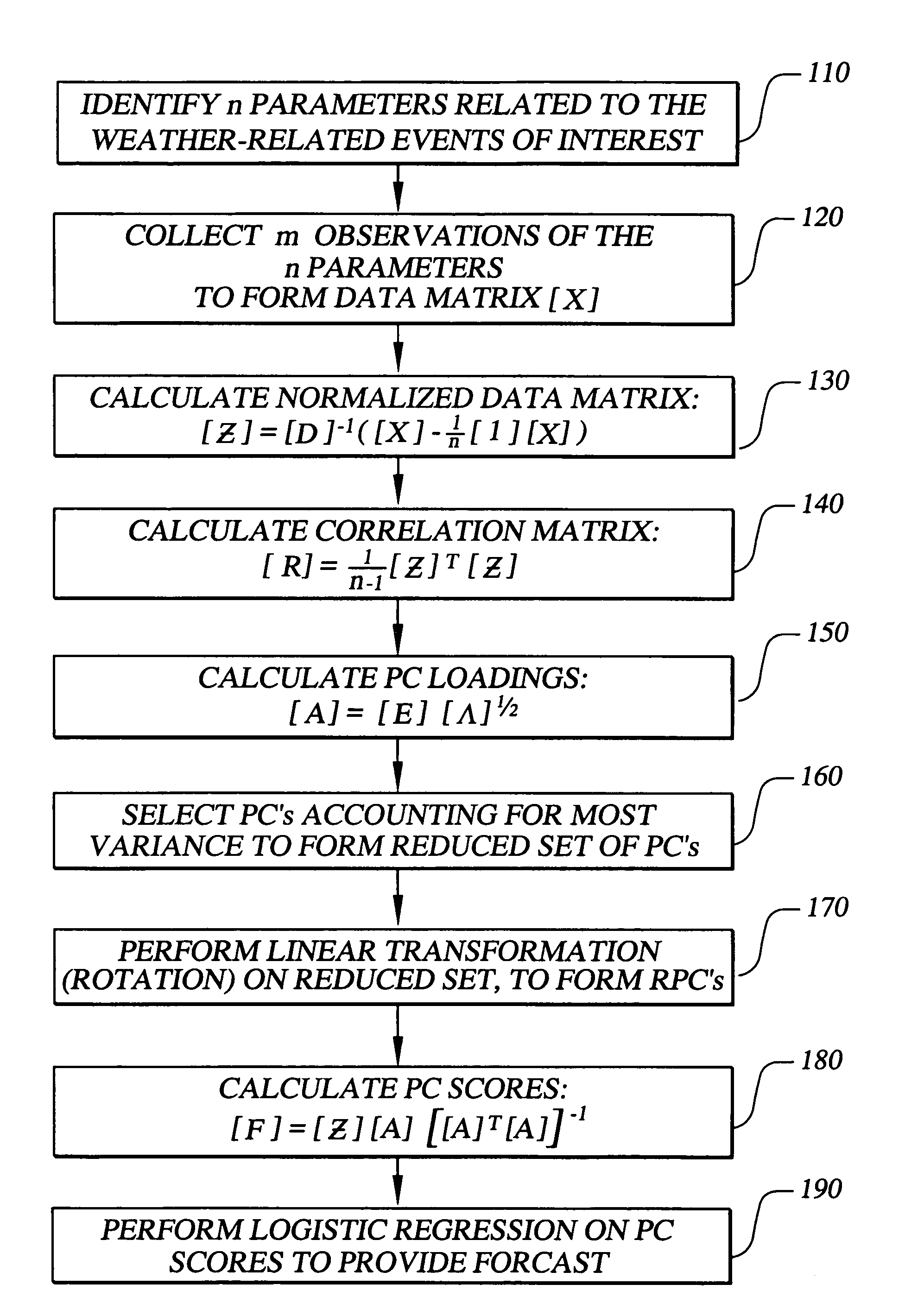
InactiveUS7069258B1Accurate predictionWeather condition predictionDigital computer detailsData setPrincipal component analysis
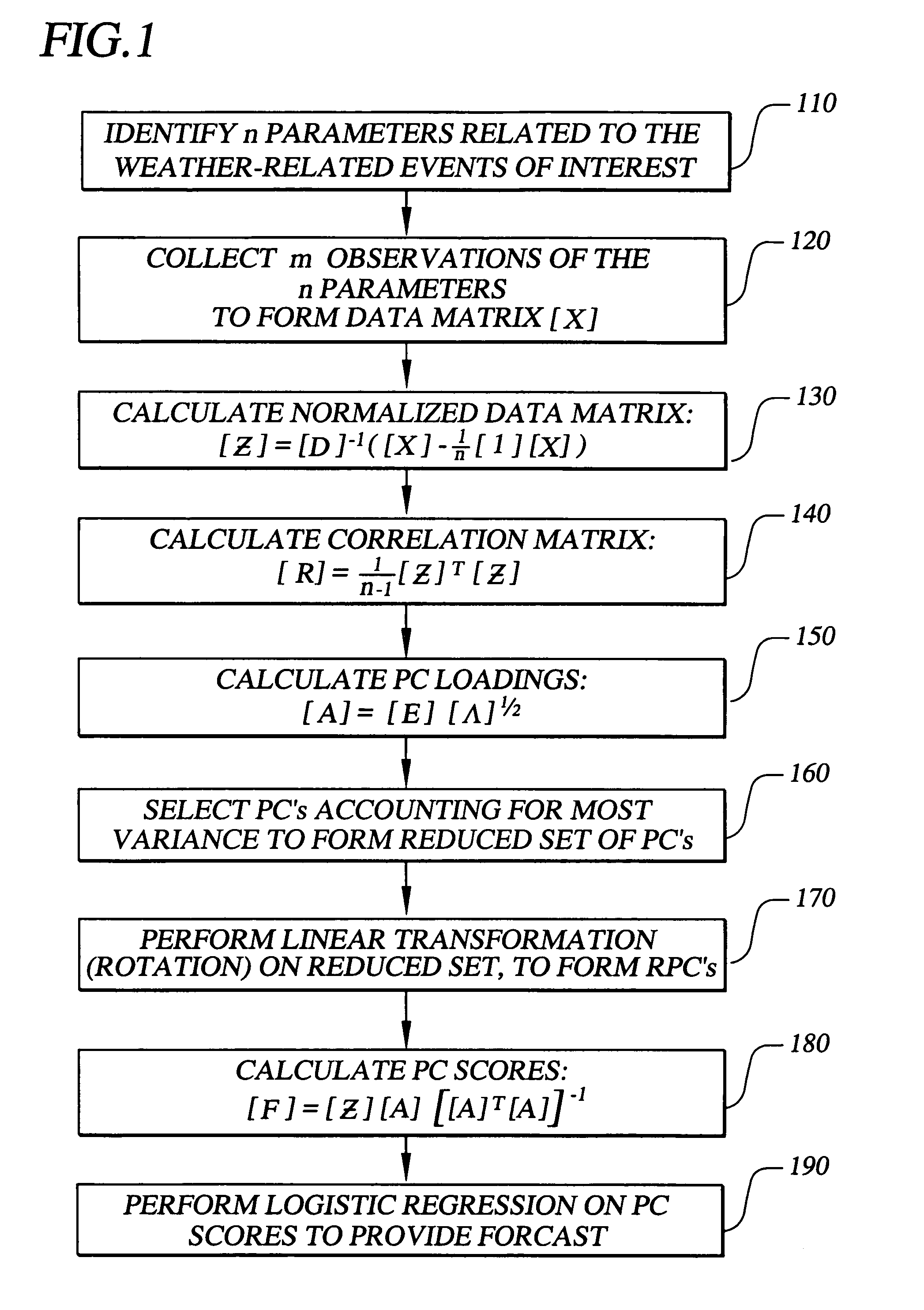
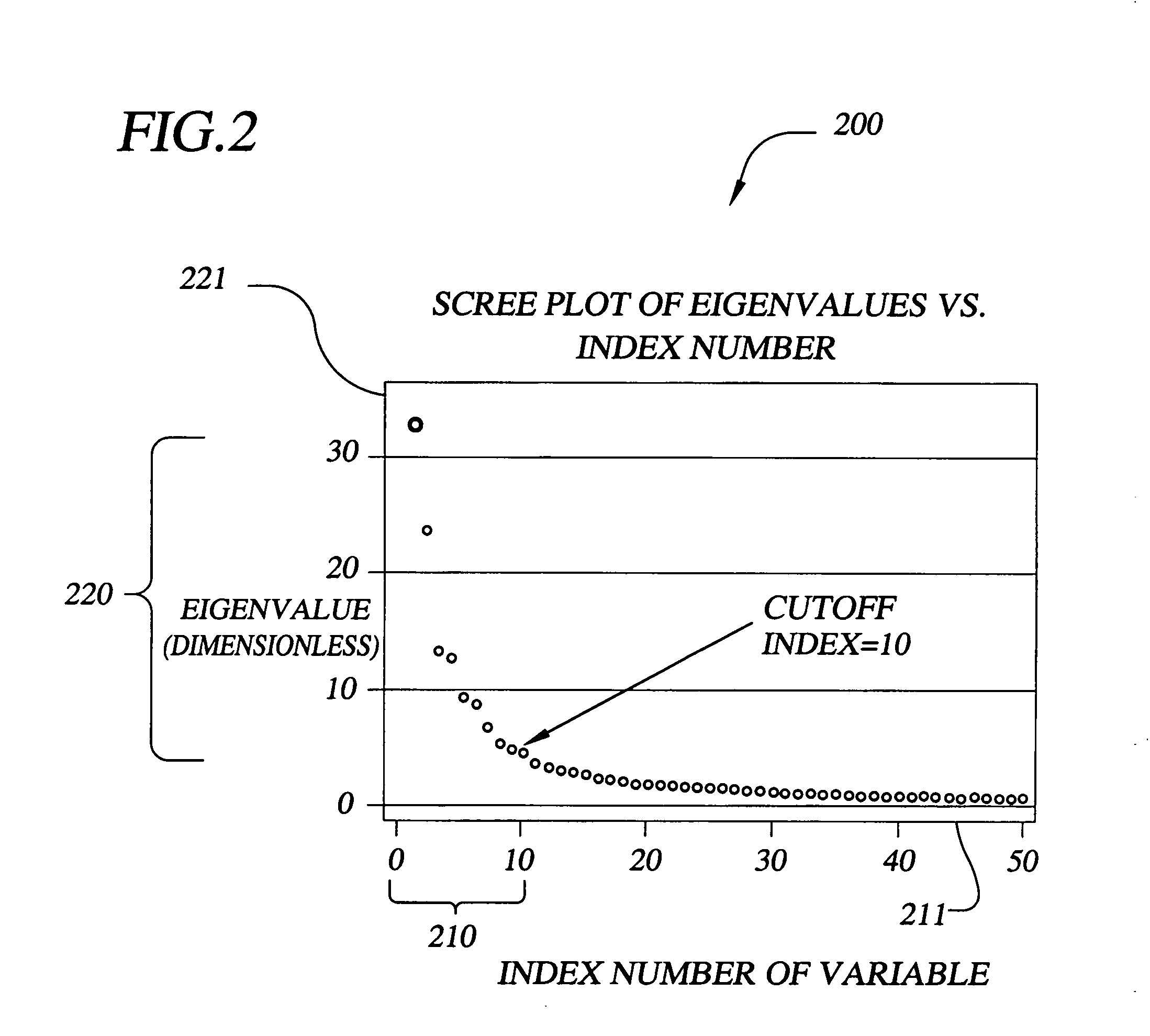
The invention provides methods, systems, and computer program products for short term probability forecasting of selected weather-related events. These embodiments are adaptable for any geographical region that can be identified and for which a reasonable number of data points exist. The inventive method uses a data set of n observations of m parameters, where the parameters may be statistically correlated. A Principal Component Analysis may be performed, with the data set as input, to provide a reduced set of principal components that are uncorrelated and account for most of the variance in the input data set. An orthogonal transformation may be performed on the reduced set of principal components to provide a rotated set of principal components that are aligned with the corresponding parameters in the input data set. Finally a logistic regression may be performed on the rotated set of principal components to derive an S-shaped predictive equation for the probability of a binary weather-related event of interest. An illustrative embodiment of the invention is given for forecasting the probability for the number of lightning flashes exceeding a selected value, for the western United States climatological area.
Owner:BOTHWELL PHILLIP D
Brain wave analysis method
InactiveCN101690659AReal-time evaluationTargetedSurgeryDiagnostic recording/measuringSupport vector machineFeature extraction
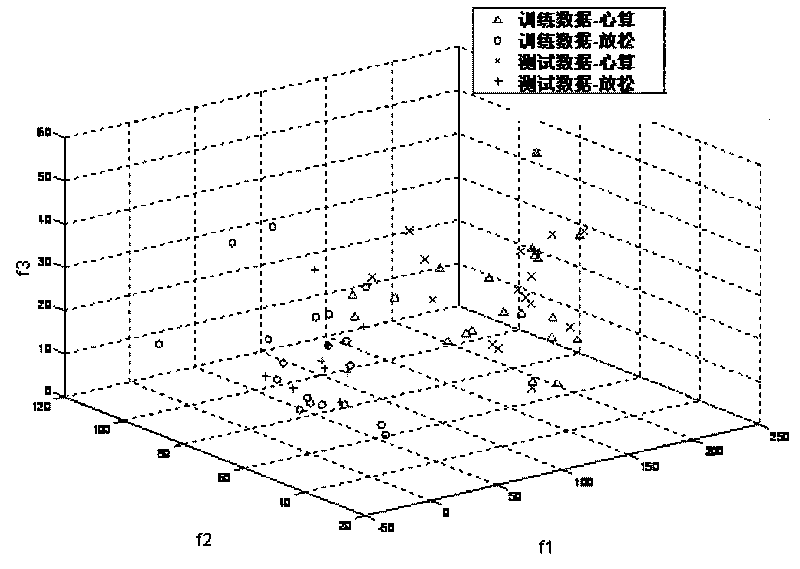
The invention provides a brain wave analysis method. The method uses classical time-frequency domain analysis and principal component analysis methods to solve the problem of electroencephalographic feature extraction, successfully extracts time-frequency domain parameters closely related to the tension, fatigue and relaxation of human bodies, maps the time-frequency domain parameters into principal component space, and uses a support vector machine to efficiently analyze non-linear relation in the principal component space so as to improve the accuracy and validity of interpretation.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Buried object locating and tracing method and system employing principal components analysis for blind signal detection
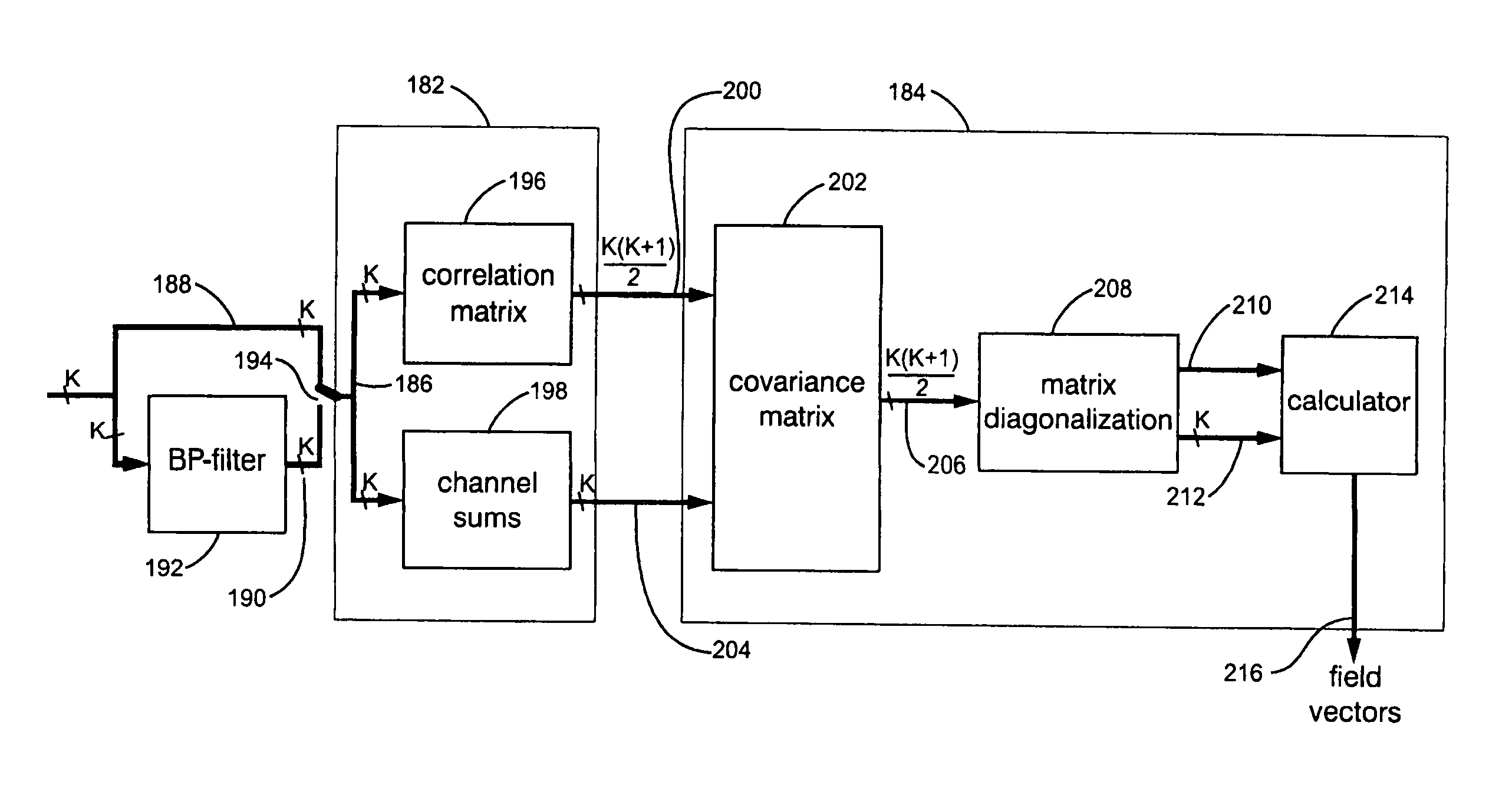
ActiveUS7136765B2Eliminates usual ambiguityResistance/reactance/impedenceVoltage-current phase angleSensor arrayMaximum eigenvalue
A blind locating system for finding and tracing buried objects such as utility lines, conductive pipes and sondes. A sensor array is coupled to a signal processor, which determines a field vector for one or more buried objects by producing a data signal representing a covariance matrix corresponding to the covariances of the time-varying sensor array signals over a selected frequency band and accumulation interval. The covariance matrix is characterized by eigenvalues and associated eigenvectors and a user interface (UI) indicates the field vector associated with the eigenvector having the largest eigenvalue. Using several different frequency bands, a plurality of underground objects may be simultaneously detected and indicated in the UI without foreknowledge of their existence or characteristics.
Owner:SEESCAN
Statistical signatures used with multivariate analysis for steady-state detection in a process
ActiveUS20080082181A1Easy to detectReduce dimensionalityData processing applicationsTesting/monitoring control systemsSteady state detectionPrincipal component analysis
Methods and systems to detect steady-state operations in a process of a process plant include collecting process data. The collected process data is generated from a plurality of process variables of the process. A multivariate statistical model of the operation of the process is generated using the process data. The multivariate statistical model may be generated from a principal component analysis. The model is executed to generate outputs corresponding to the most significant variations in the process. Statistical measures of the outputs are generated and used to determine whether a steady-state or unsteady-state is related to the process.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
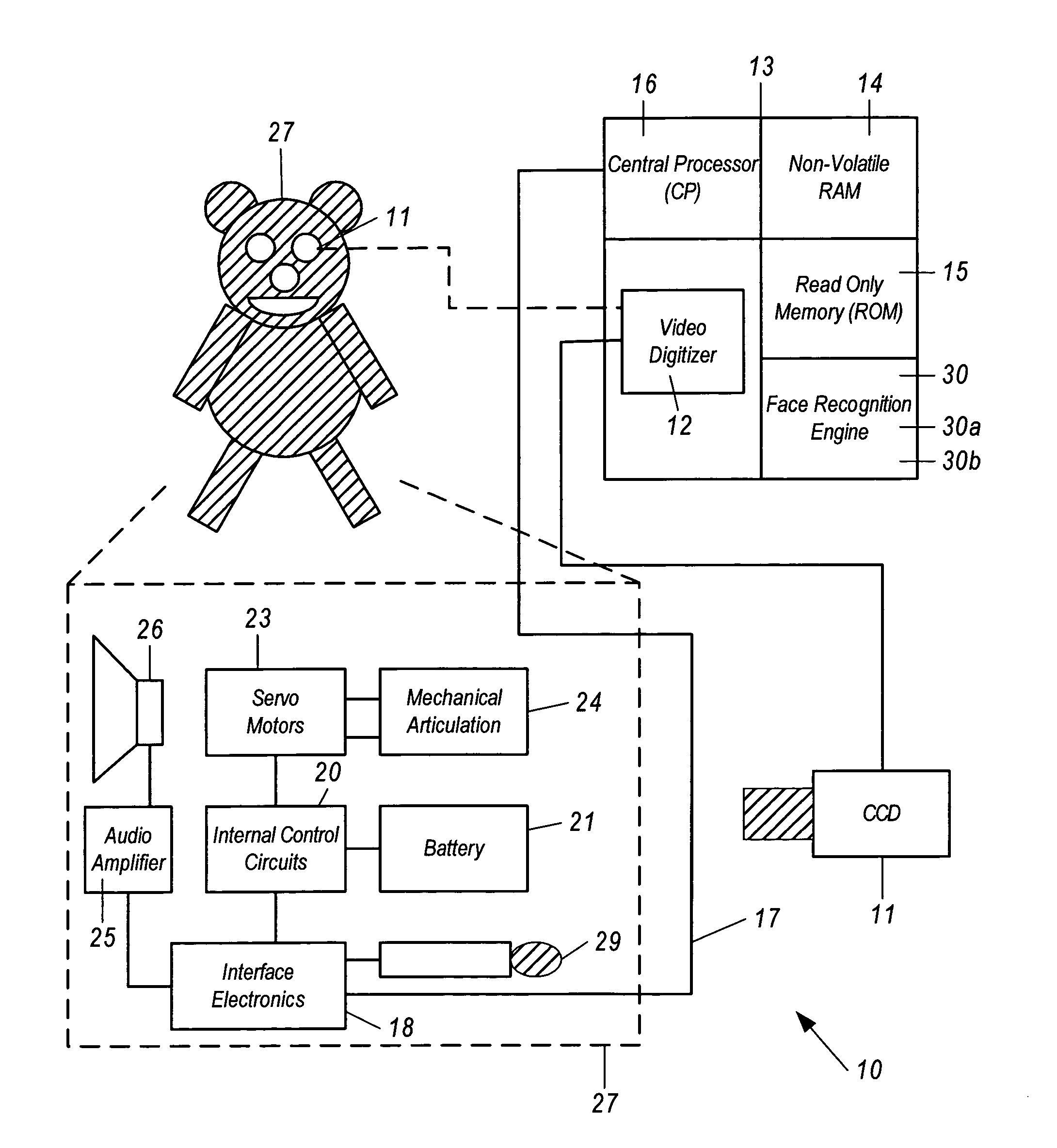
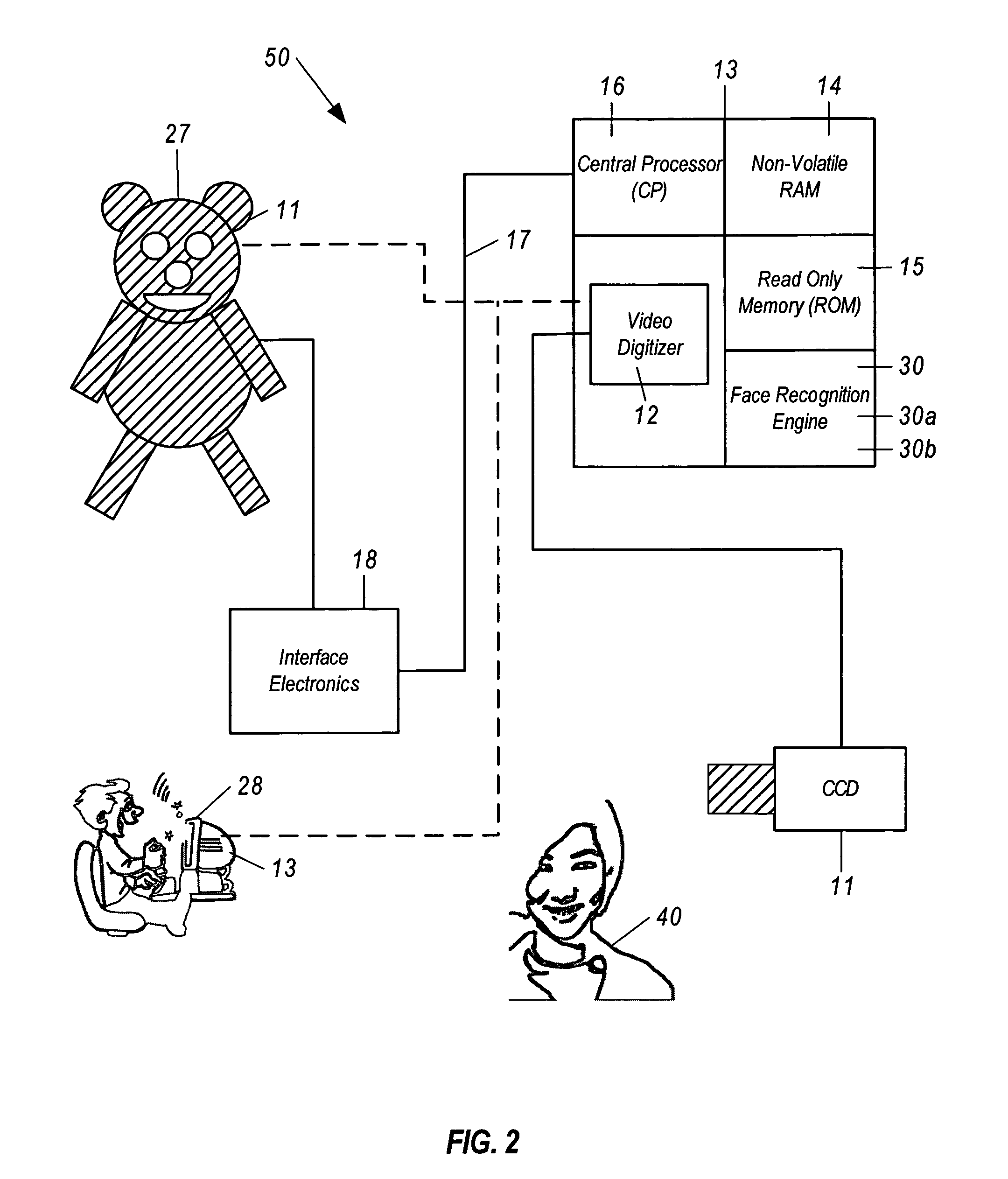
Animated toy utilizing artificial intelligence and facial image recognition
InactiveUS7062073B1Run fastOvercome limitationsDollsComputerized toysPrincipal component analysisAnimation
An articulated and animated toy capable of recognizing human users and selected inanimate objects and interacting therewith which includes a computer-based device having stored thereon encoded first human or human-like facial images, a video camera and video digitizer for acquiring data representative of a second human or human-like facial image, and software resident within said computer-based device for facial recognition, which includes Principal Component Analysis, Neural Networks, or another equivalent algorithm for comparing said first human or human-like facial images with said second human or human-like facial image and producing an output signal therefrom for use in identifying said human users. The apparatus can further include software for recognizing speech, generating speech and controlling animation of the articulated toy. In addition, said computer-based device is capable of learning and storing information pertaining to each of said human users such as name, age, sex, favorite color, etc., and to interact with each of said human users on an individual basis, providing entertainment tailored specifically to each of said human users.
Owner:INTELLIGENT VERIFICATION SYST
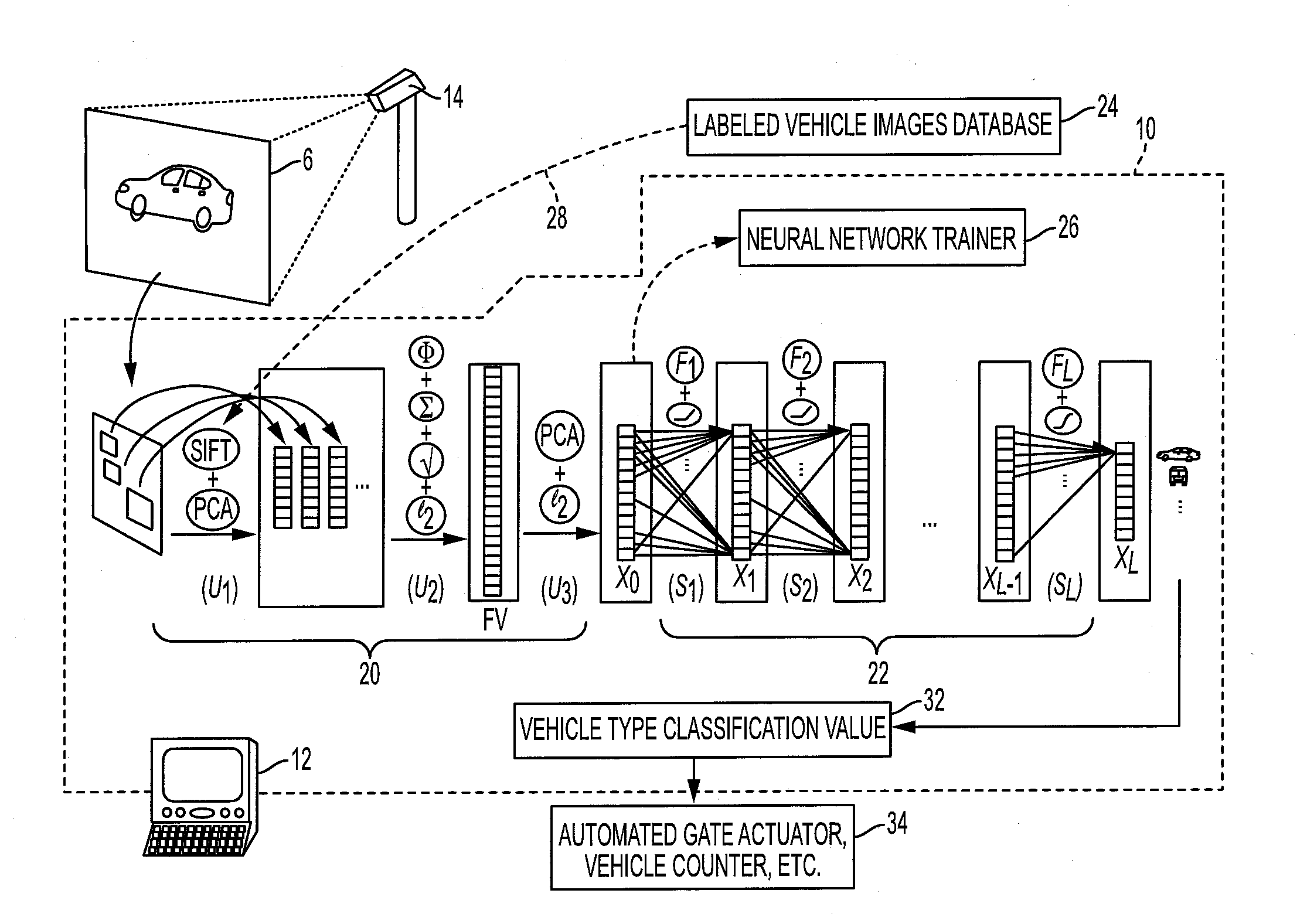
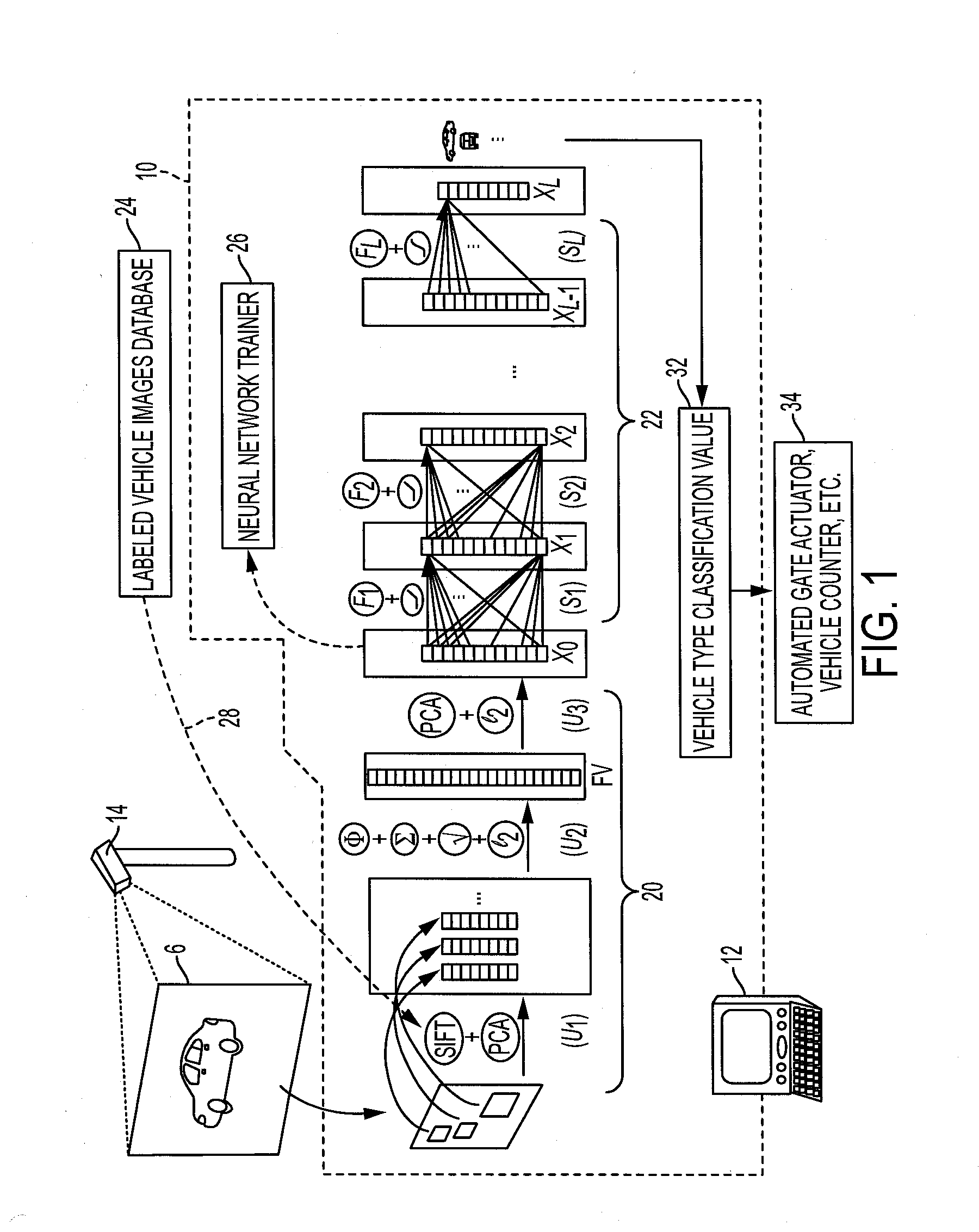
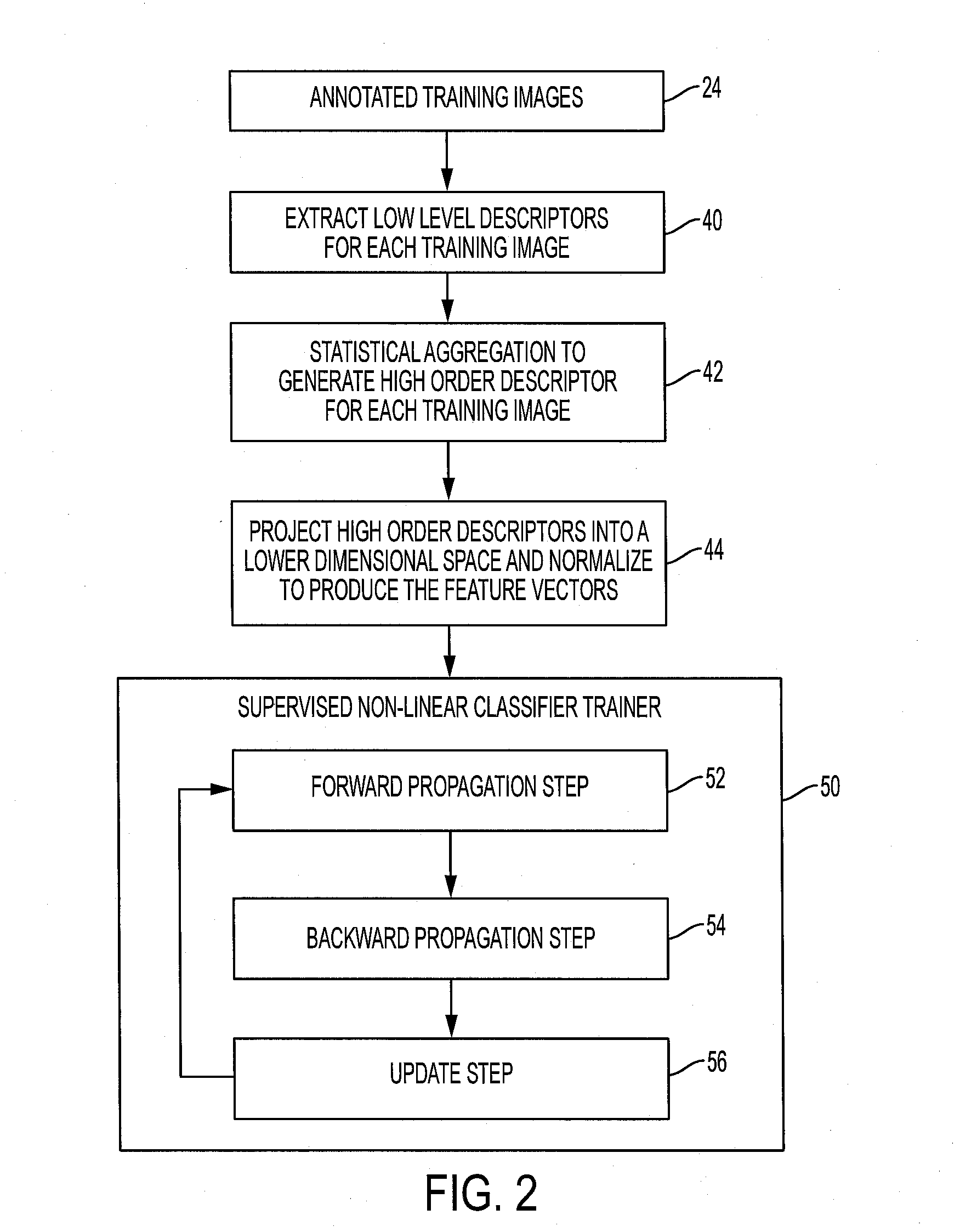
Fisher vectors meet neural networks: a hybrid visual classification architecture
ActiveUS20160307071A1Character and pattern recognitionNeural learning methodsFeature vectorPrincipal component analysis
In an image classification method, a feature vector representing an input image is generated by unsupervised operations including extracting local descriptors from patches distributed over the input image, and a classification value for the input image is generated by applying a neural network (NN) to the feature vector. Extracting the feature vector may include encoding the local descriptors extracted from each patch using a generative model, such as Fisher vector encoding, aggregating the encoded local descriptors to form a vector, projecting the vector into a space of lower dimensionality, for example using Principal Component Analysis (PCA), and normalizing the feature vector of lower dimensionality to produce the feature vector representing the input image. A set of mid-level features representing the input image may be generated as the output of an intermediate layer of the NN.
Owner:XEROX CORP
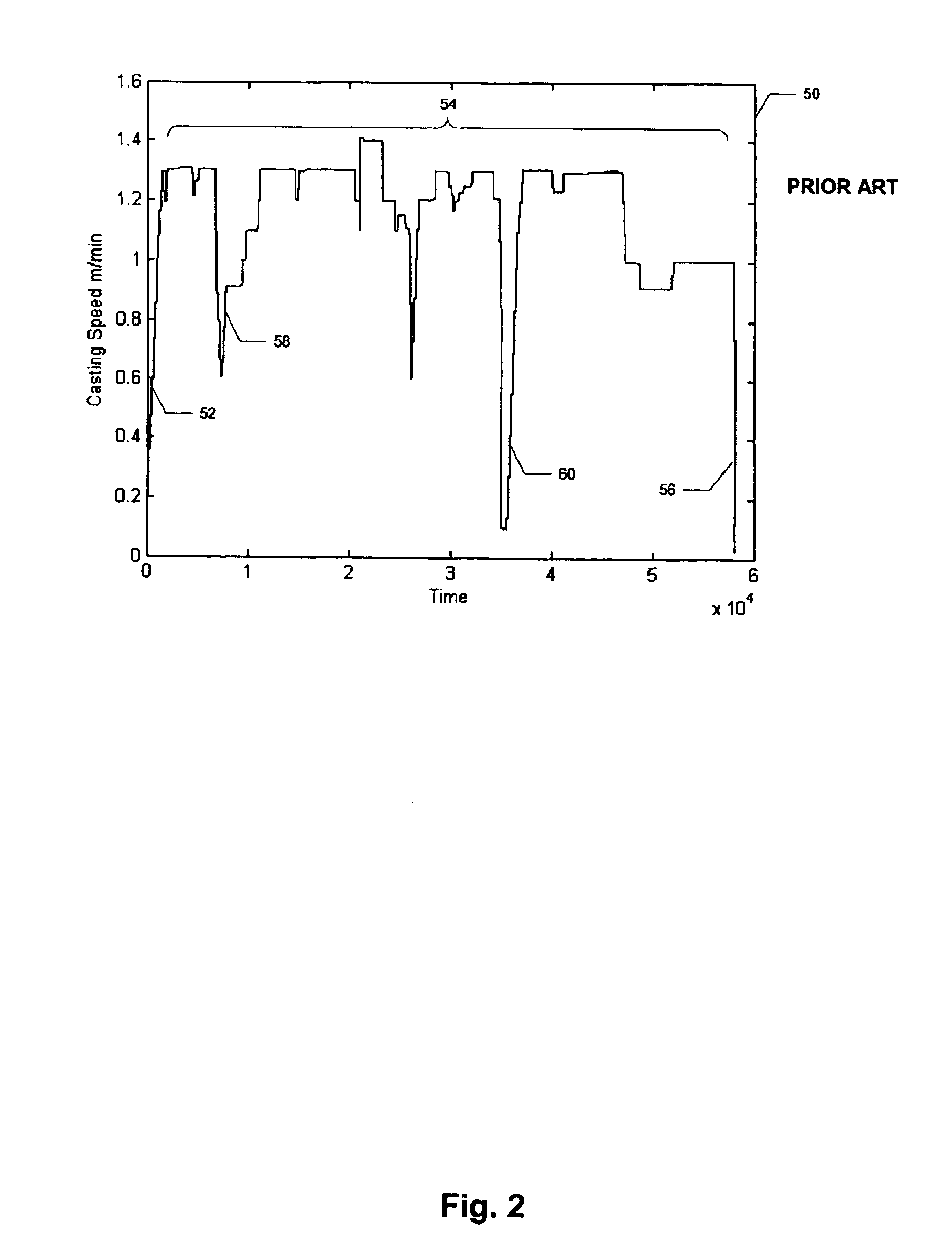
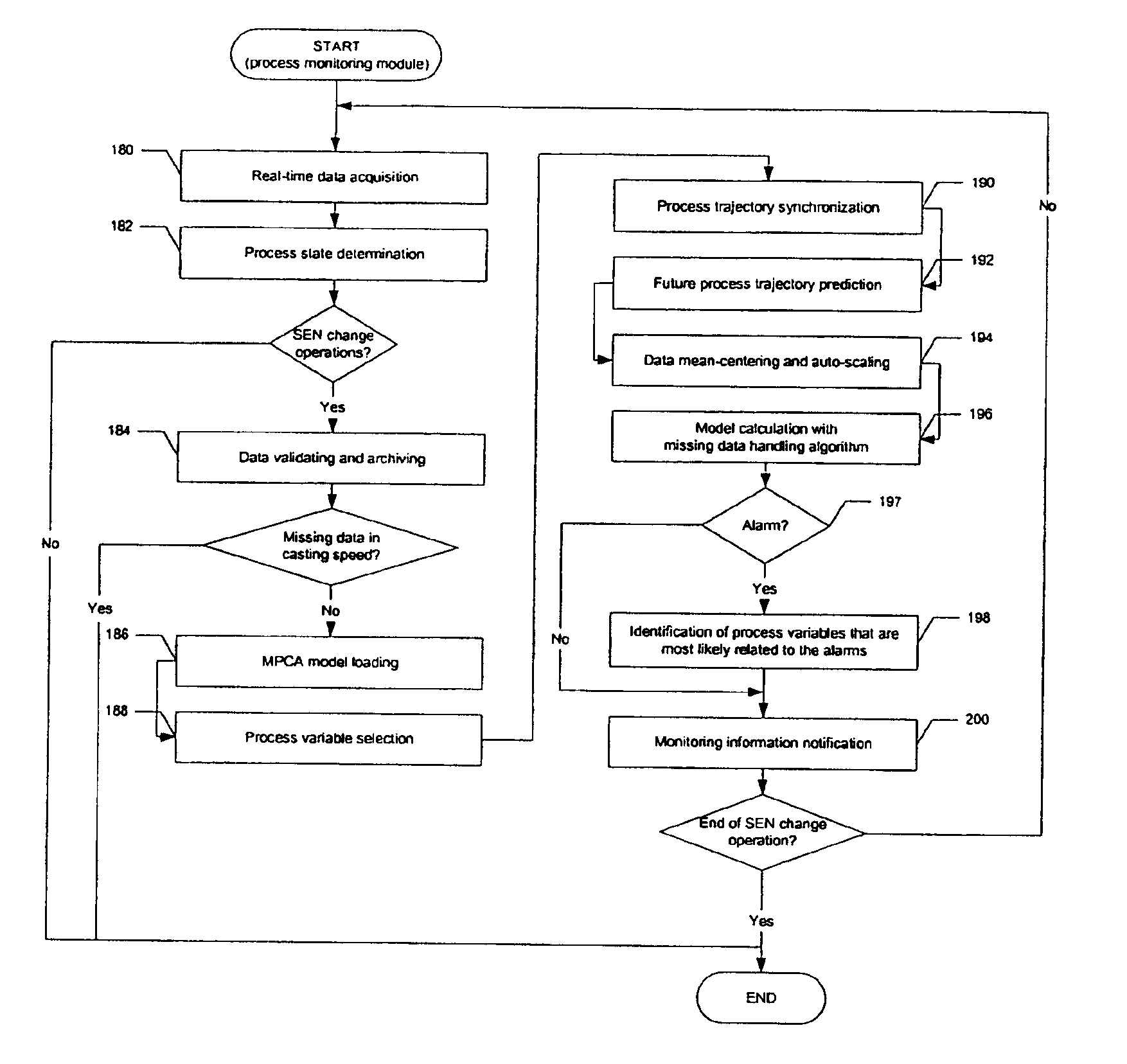
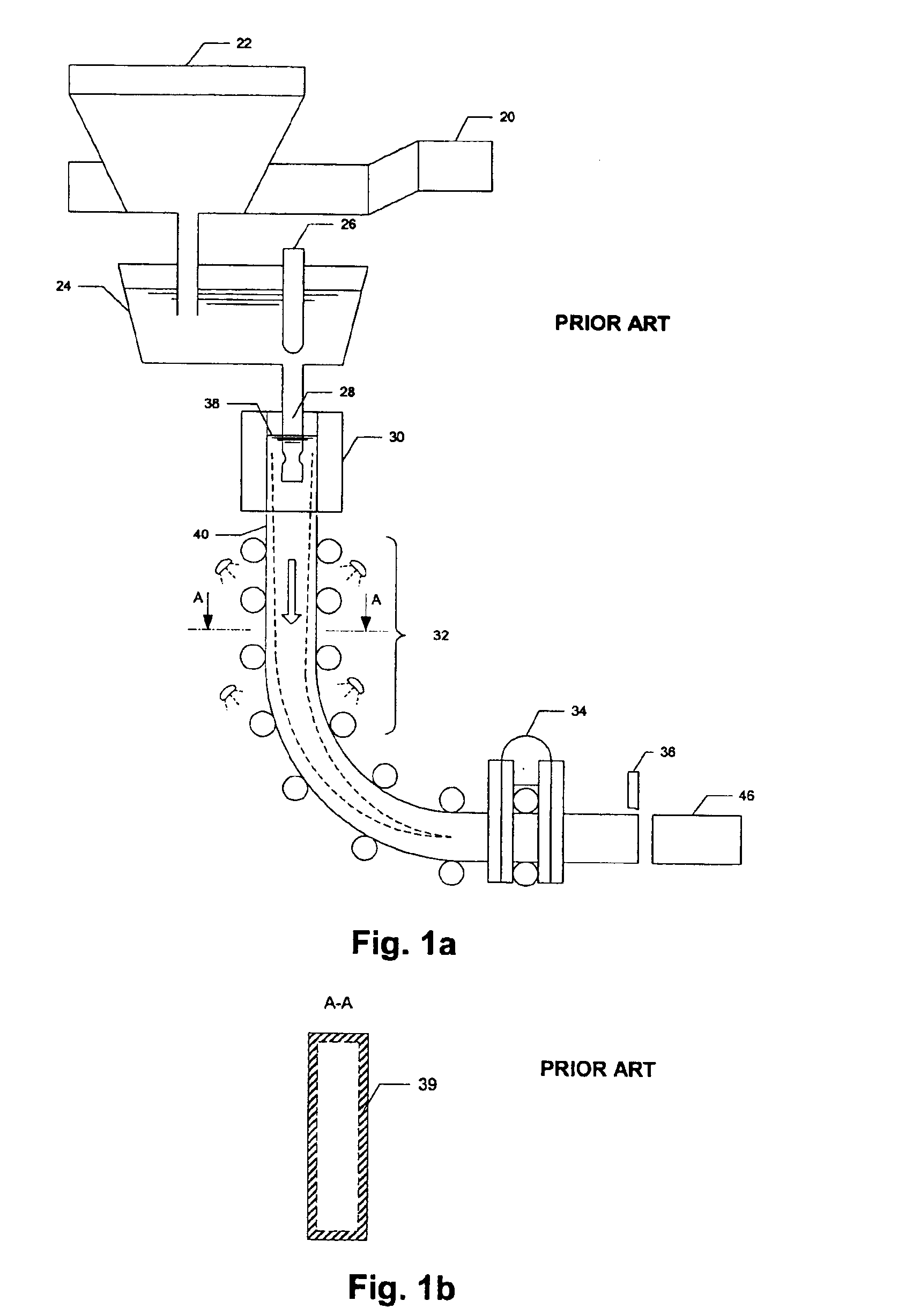
Real-time system and method of monitoring transient operations in continuous casting process for breakout prevention
ActiveUS6885907B1Testing/monitoring control systemsMoulding machine componentsPrincipal component analysisMultivariate statistical
A real-time system and method for online monitoring a transient operation in a continuous casting process. The transient operation refers to, but is not limited to, submerged entry nozzle changes, flying tundish changes, product grade changes, etc. This invention treats the aforementioned transient operations as batch processes and utilizes multiway principal component analysis to develop a multivariate statistical model to characterize normal process transitions based on carefully selected historical process data. Such a model is used by an online monitoring system to determine if a continuous caster transient operation is normal. This monitoring system can further be used to predict an impending breakout, one type of catastrophic process failures which may occur in a continuous casting process, during the transient operation. Process variables that are most likely related to the predicted breakout are identified by the system such that appropriate control actions can be taken to prevent an actual breakout occurrence.
Owner:DOFASCO INC
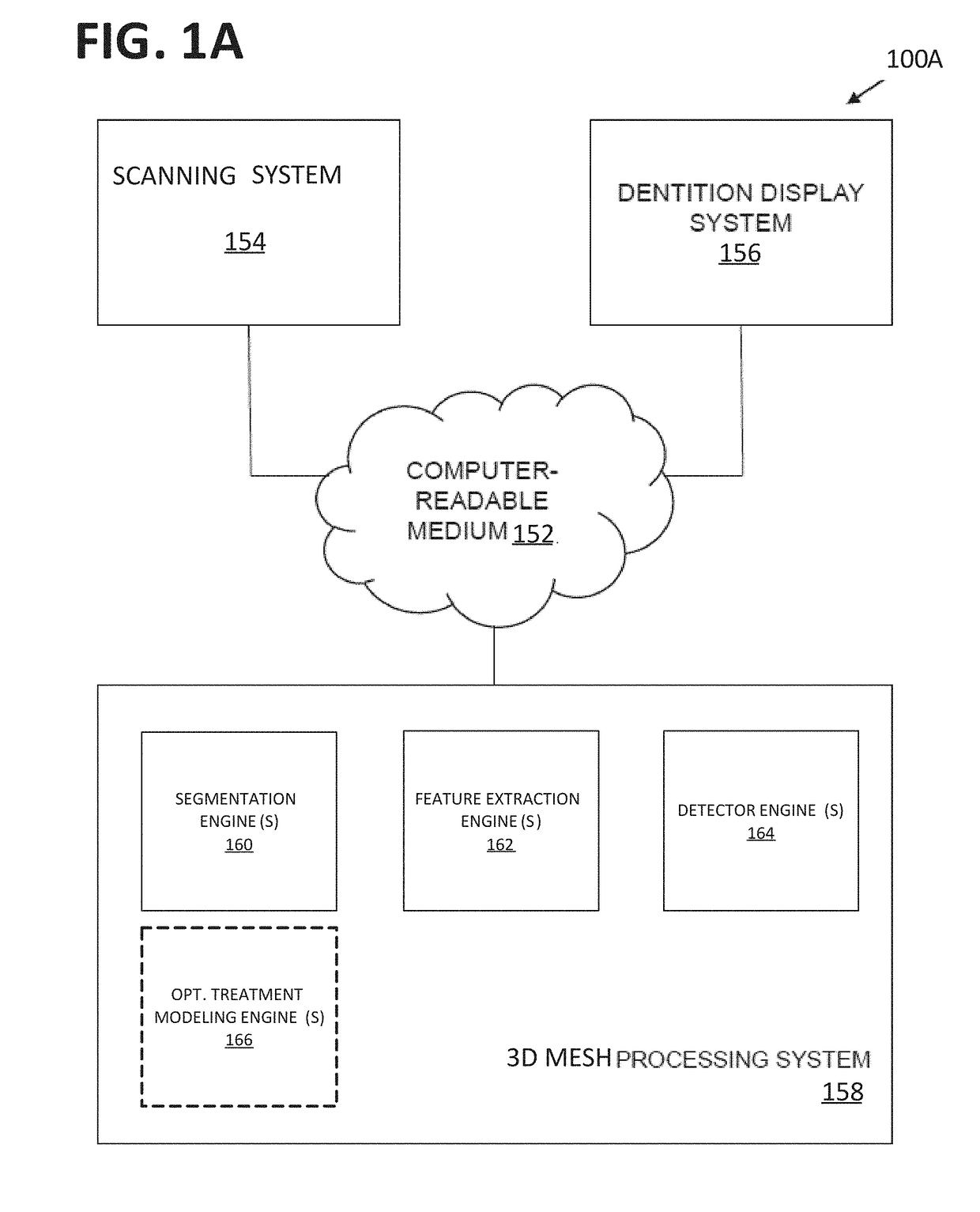
Automatic detection of tooth type and eruption status
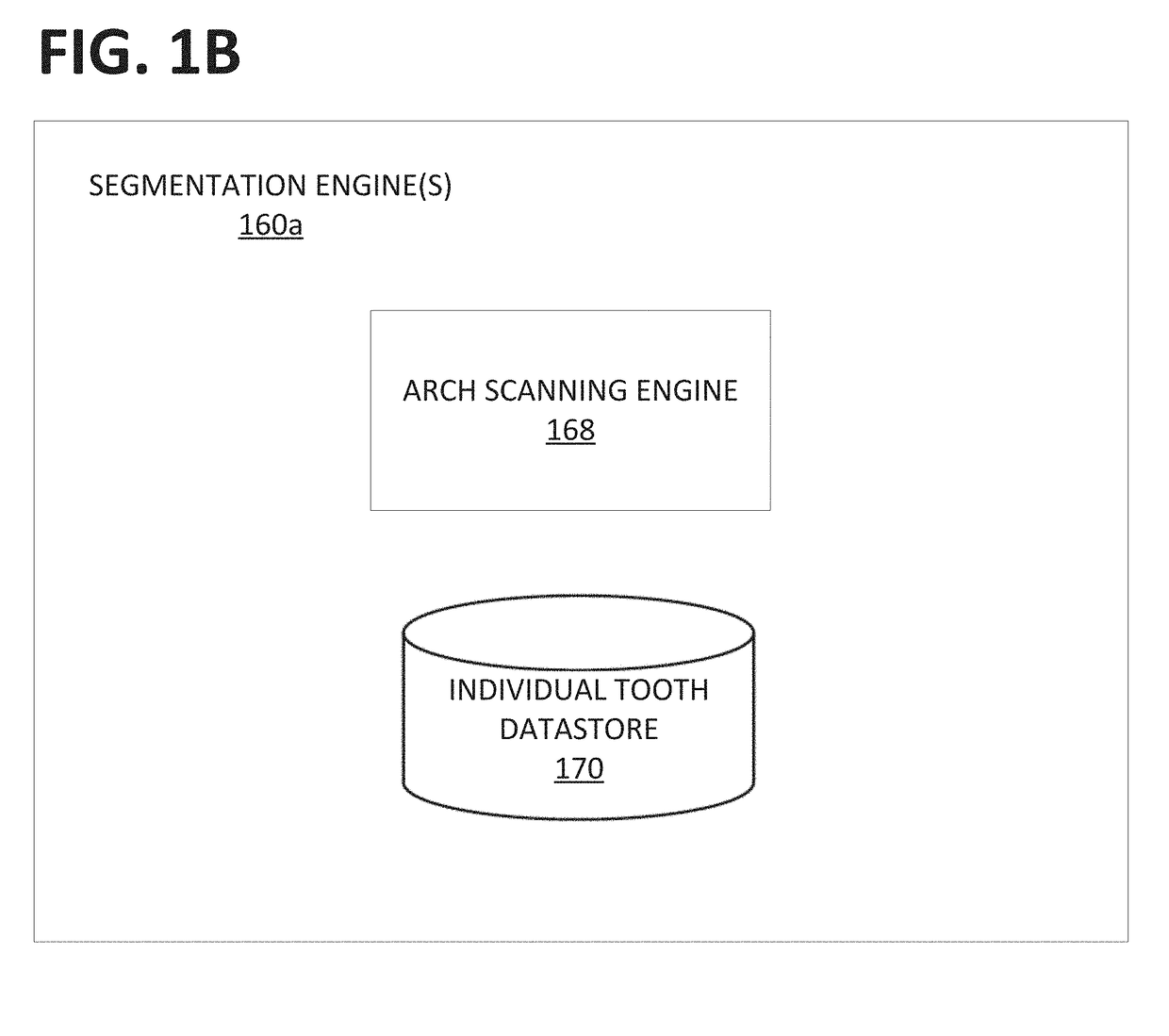
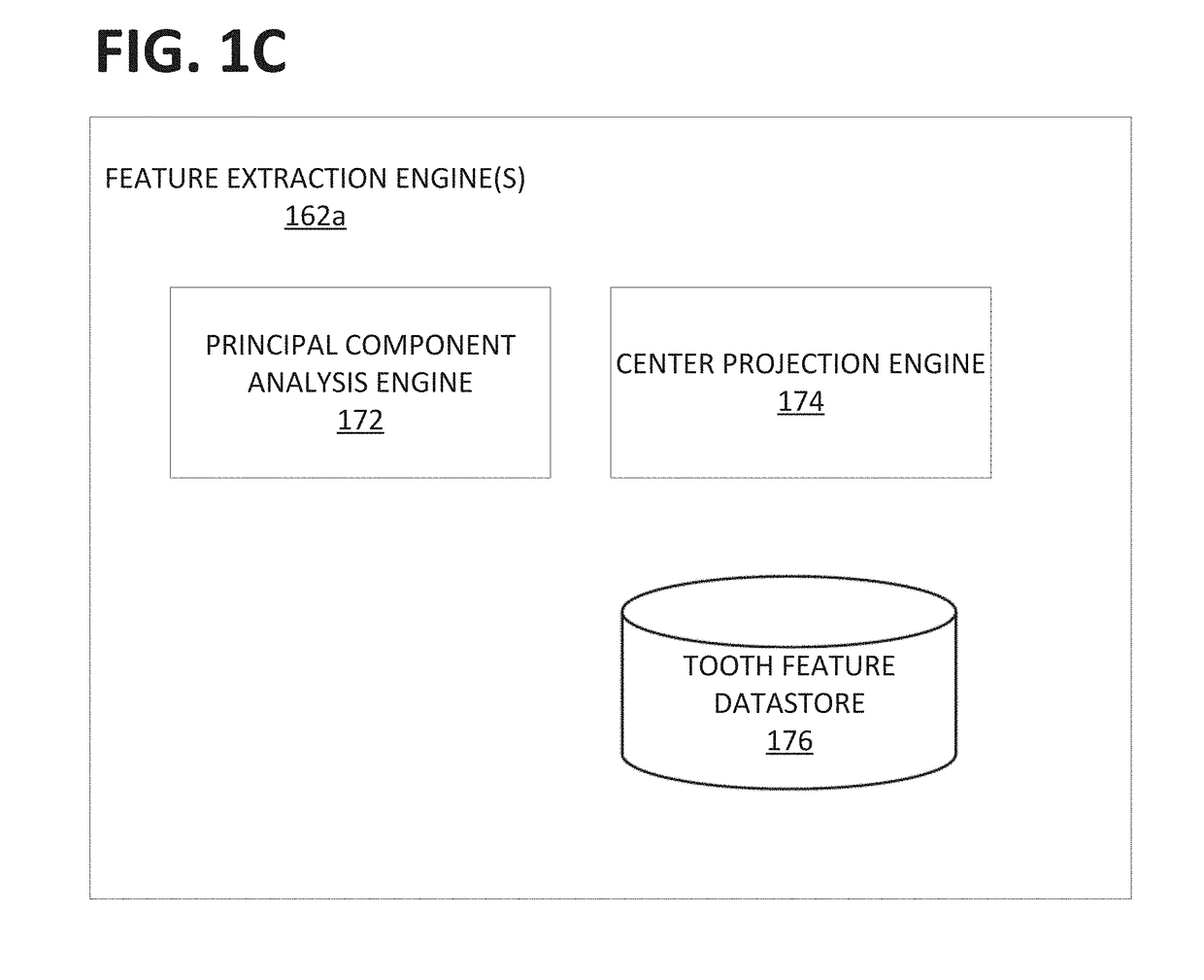
Provided herein are systems and methods for detecting the eruption state (e.g., tooth type and / or eruption status) of a target tooth. A patient's dentition may be scanned and / or segmented. A target tooth may be identified. Dental features, principal component analysis (PCA) features, and / or other features may be extracted and compared to those of other teeth, such as those obtained through automated machine learning systems. A detector can identify and / or output the eruption state of the target tooth, such as whether the target tooth is a fully erupted primary tooth, a permanent partially erupted / un-erupted tooth, or a fully erupted permanent tooth.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
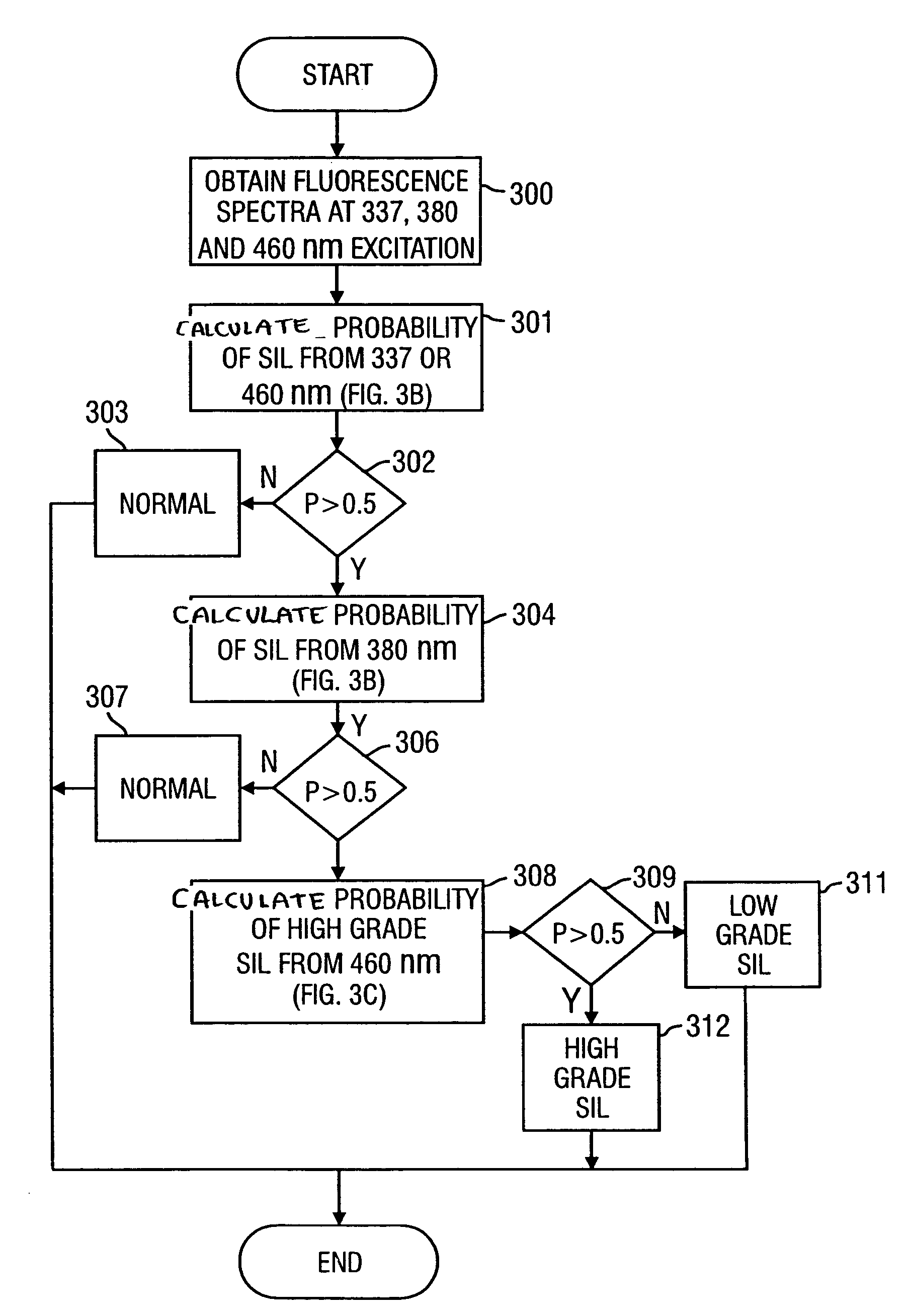
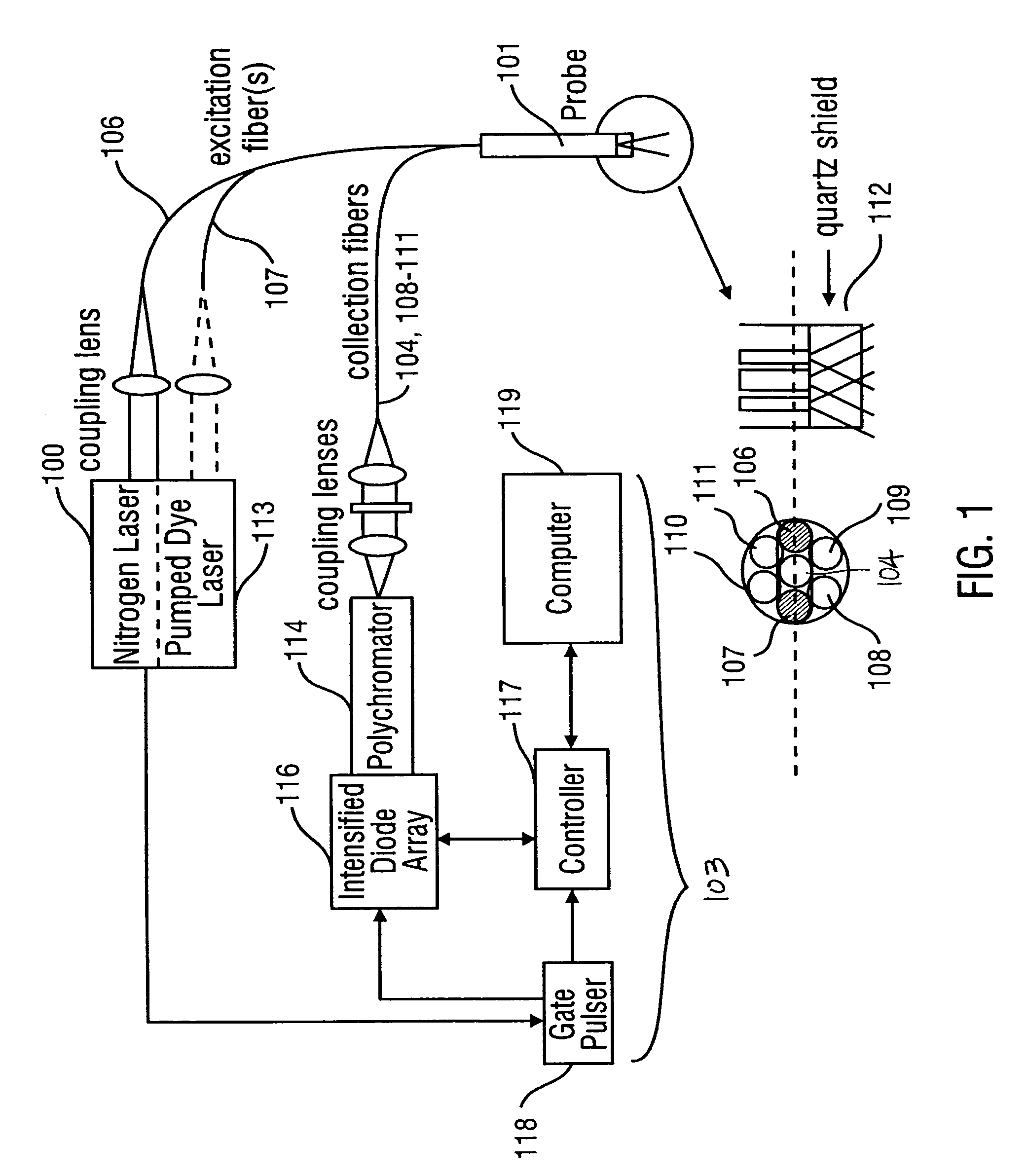
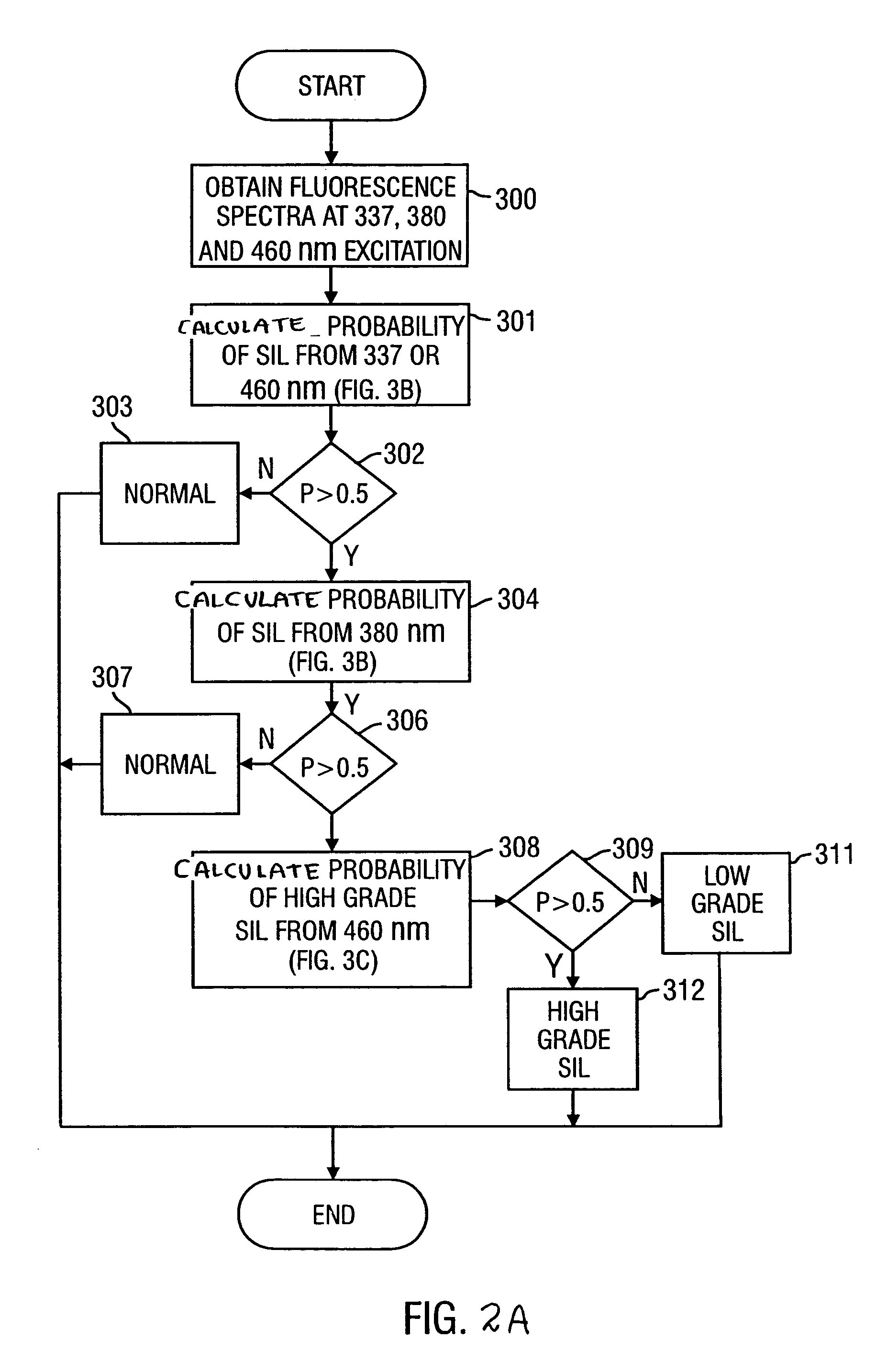
Method for probabilistically classifying tissue in vitro and in vivo using fluorescence spectroscopy
InactiveUS7236815B2Faster and effective managementReduce mortalityDiagnostics using spectroscopyDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionMultivariate statisticalPrincipal component analysis
Fluorescence spectral data acquired from tissues in vivo or in vitro is processed in accordance with a multivariate statistical method to achieve the ability to probabilistically classify tissue in a diagnostically useful manner, such as by histopathological classification. The apparatus includes a controllable illumination device for emitting electromagnetic radiation selected to cause tissue to produce a fluorescence intensity spectrum. Also included are an optical system for applying the plurality of radiation wavelengths to a tissue sample, and a fluorescence intensity spectrum detecting device for detecting an intensity of fluorescence spectra emitted by the sample as a result of illumination by the controllable illumination device. The system also include a data processor, connected to the detecting device, for analyzing detected fluorescence spectra to calculate a probability that the sample belongs in a particular classification. The data processor analyzes the detected fluorescence spectra using a multivariate statistical method. The five primary steps involved in the multivariate statistical method are (i) preprocessing of spectral data from each patient to account for inter-patient variation, (ii) partitioning of the preprocessed spectral data from all patients into calibration and prediction sets, (iii) dimension reduction of the preprocessed spectra in the calibration set using principal component analysis, (iv) selection of the diagnostically most useful principal components using a two-sided unpaired student's t-test and (v) development of an optimal classification scheme based on logistic discrimination using the diagnostically useful principal component scores of the calibration set as inputs.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
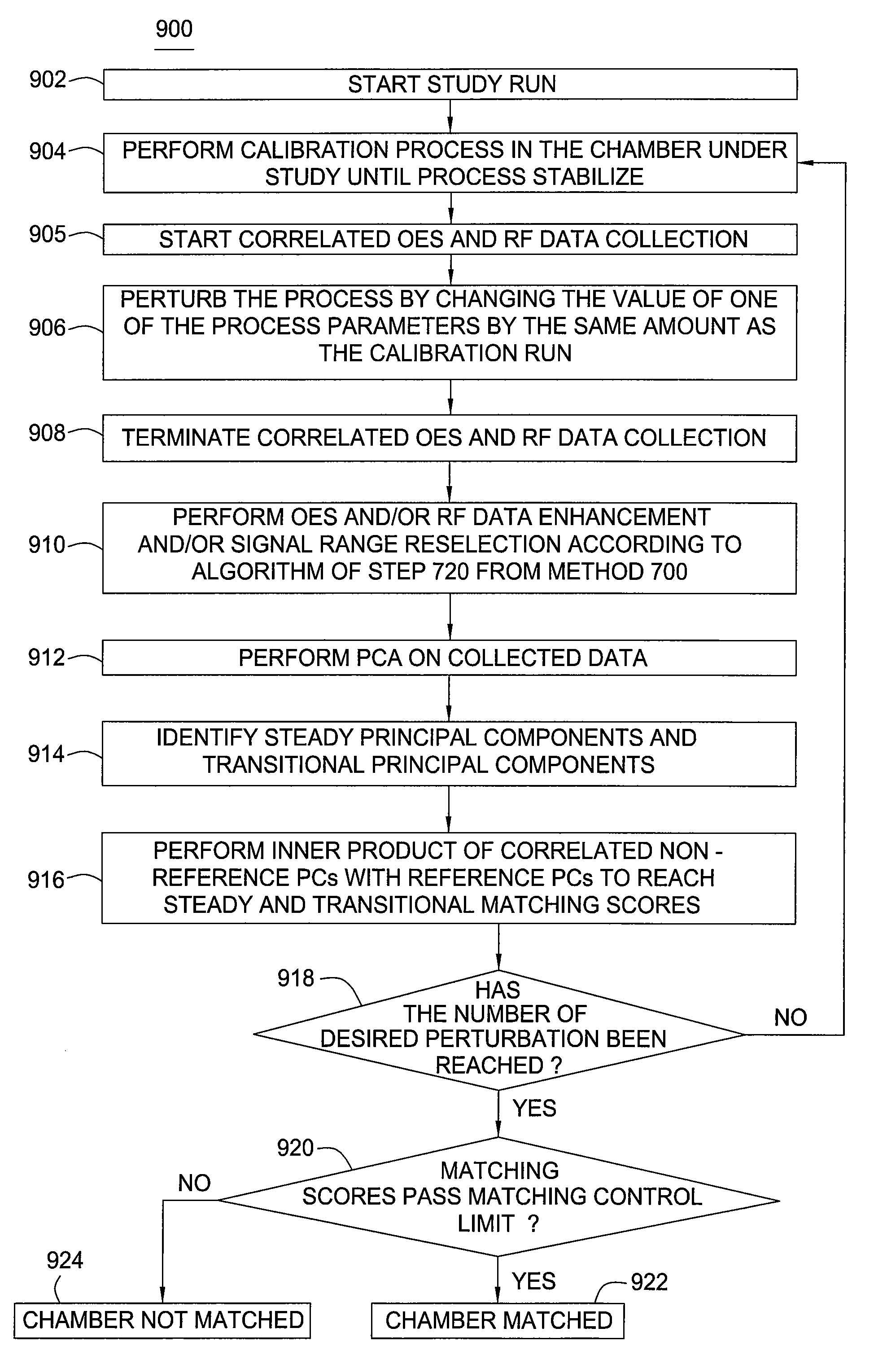
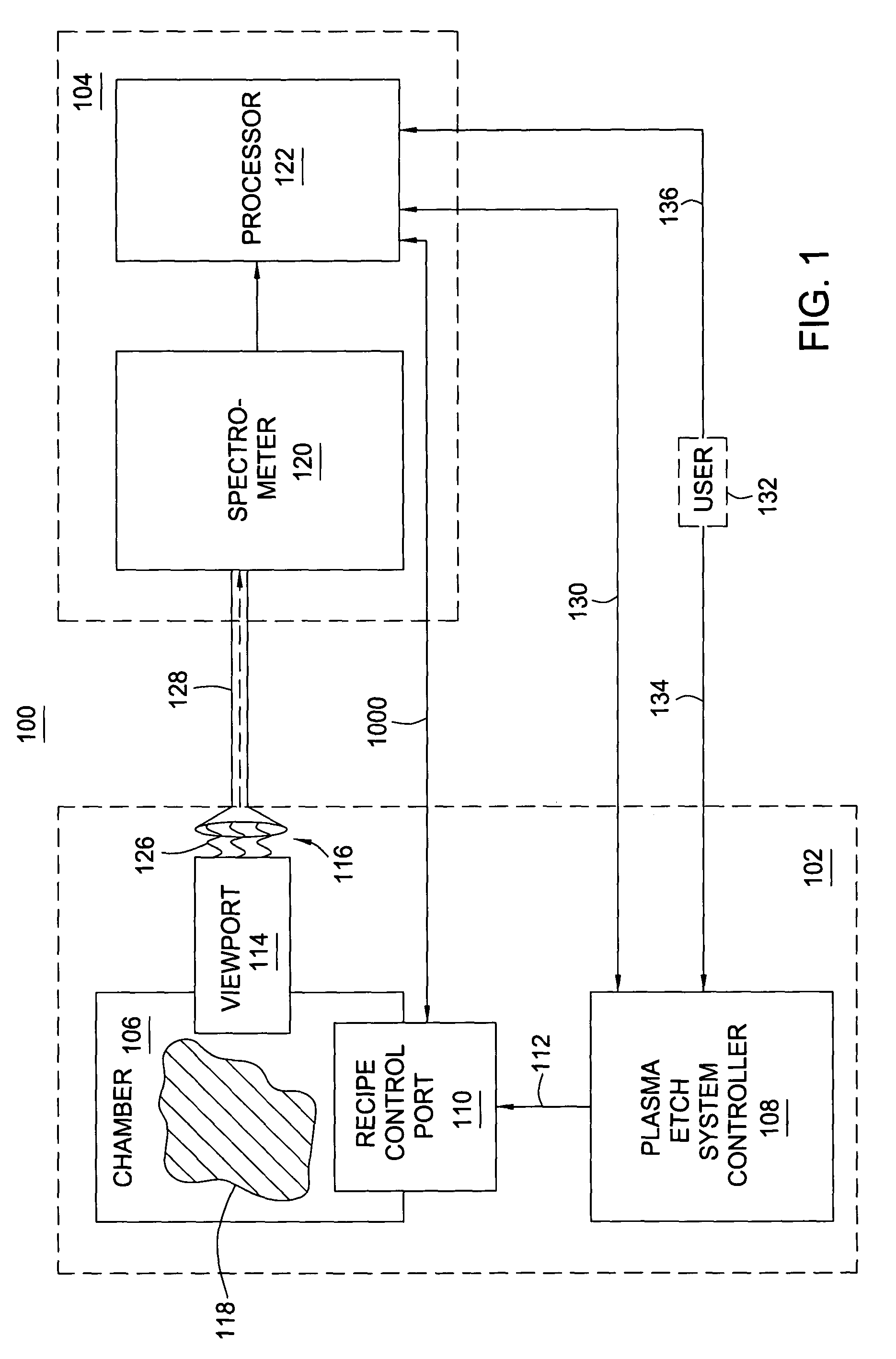
Method for automatic determination of semiconductor plasma chamber matching and source of fault by comprehensive plasma monitoring
InactiveUS7169625B2Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor plasmaProcedural parameter
A method and apparatus for automatic determination of semiconductor plasma chamber matching a source of fault are provided. Correlated plasma attributes are measured for process used for calibration both in a chamber under study and in a reference chamber. Principal component analysis then is performed on the measured correlated attributes so as to generate steady principal components and transitional principal components; and these principal components are compared to reference principal components associated with a reference chamber. The process used for calibration includes a regular plasma process followed by a process perturbation of one process parameter. Similar process perturbation runs are conducted several times to include different perturbation parameters. By performing inner products of the principal components of chamber under study and the reference chamber, matching scores can be reached. Automatic chamber matching can be determined by comparing these scores with preset control limits. The potential source(s) of chamber fault can also be identified by the lowest matching score(s).
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Frequency domain projection algorithm
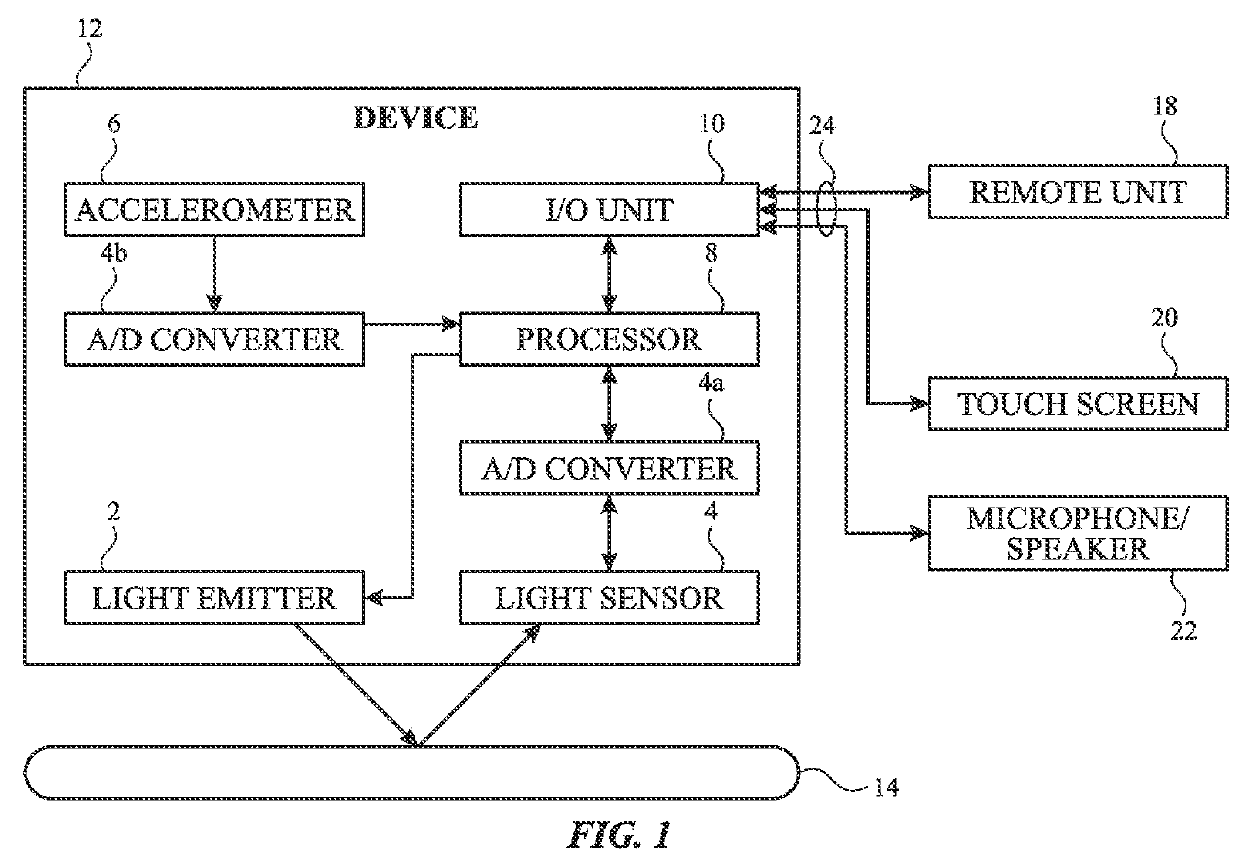
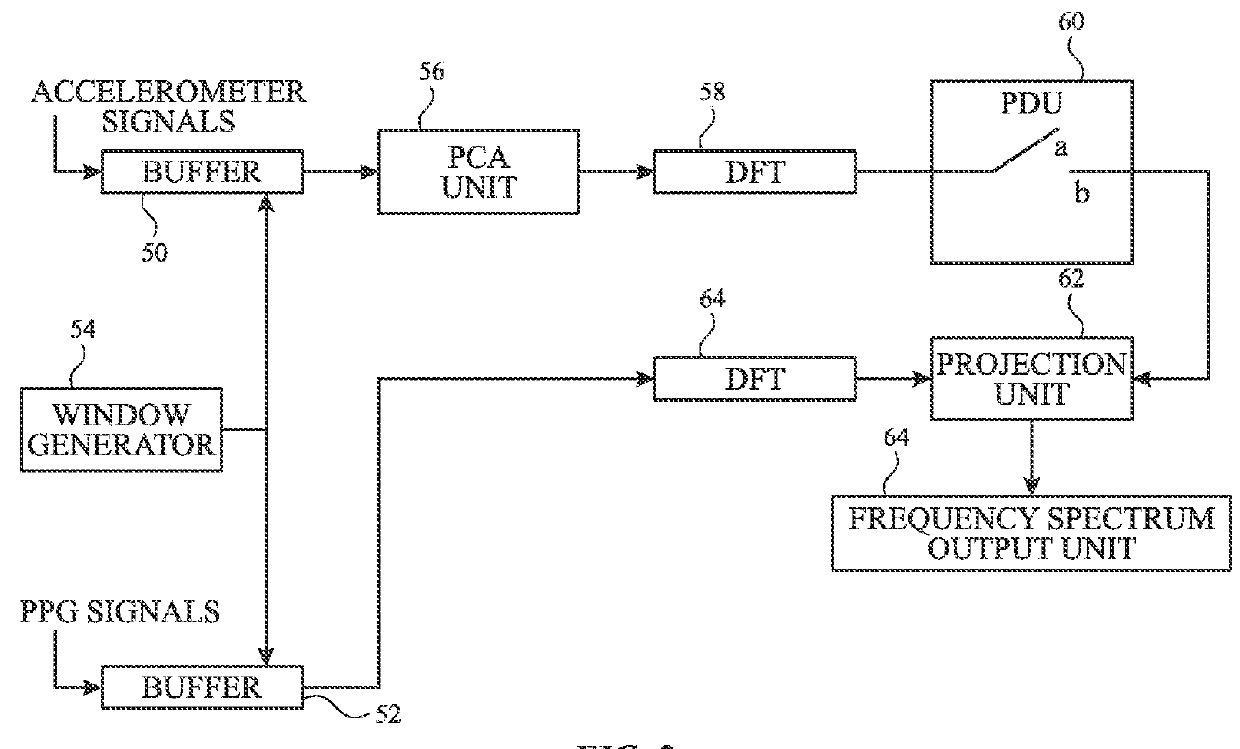
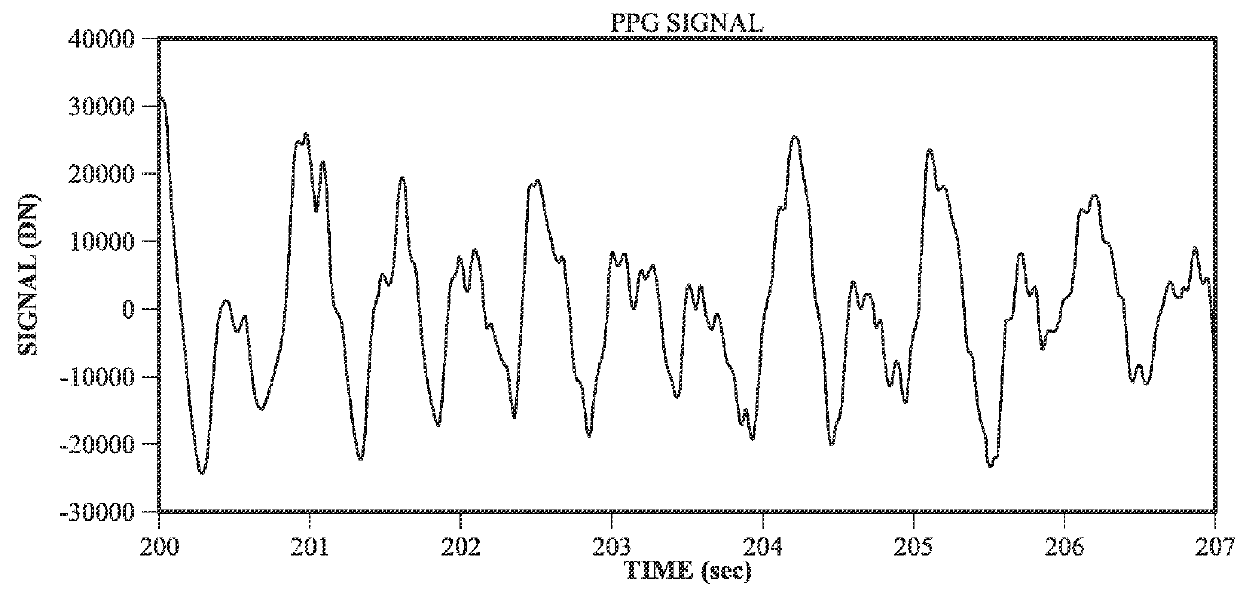
ActiveUS20160051157A1Improve accuracyDelay minimizationCatheterSensorsAccelerometerPrincipal component analysis
An algorithm for determining heart rate by removing motion artifacts from a PPG signal in the frequency domain utilizes a principal component analysis. Some examples of the present disclosure process PPG signals in combination with accelerometer signals to remove unwanted artifacts in the frequency domain. For example, principal components of the accelerometer signal can be generated and combined with the PPG signal to filter out acceleration contributions represented in the PPG signal to reveal heart rate peaks. Additionally, in some examples, templates may be stored for correlation with candidate heart rate peaks to select those peaks with the highest correlations with the stored templates.
Owner:APPLE INC
Gesture identification method and gesture identification system
InactiveCN104680127AAvoid interferenceHigh precisionCharacter and pattern recognitionPoint sequencePrincipal component analysis
The invention discloses a gesture identification method and a gesture identification system, wherein the method comprises the following steps: step S1, a gesture detecting step: detecting a gesture in video stream in real time, marking a region in which the gesture is detected as an interested region; step S2, a gesture segmenting step: processing the interested region by utilizing skin color segmentation, and then performing edge detecting and outline extracting to obtain a point sequence of a hand-shaped outline; step S3, a gesture identifying step: firstly extracting a Fourier descriptor of the hand-shaped outline and then mapping the Fourier descriptor to a new vector of a characteristic space by utilizing PCA (principal components analysis), comparing the distance between the new vector and a gesture clustering center obtained by training, and judging a gesture type represented by the vector. The gesture identification method and the gesture identification system disclosed by the invention can improve the gesture identification accuracy and the gesture identification efficiency, and can effectively avoid background color interference.
Owner:WINGTECH COMM
Multi-behavior process monitoring method based on pivot analysis and vectorial data description support
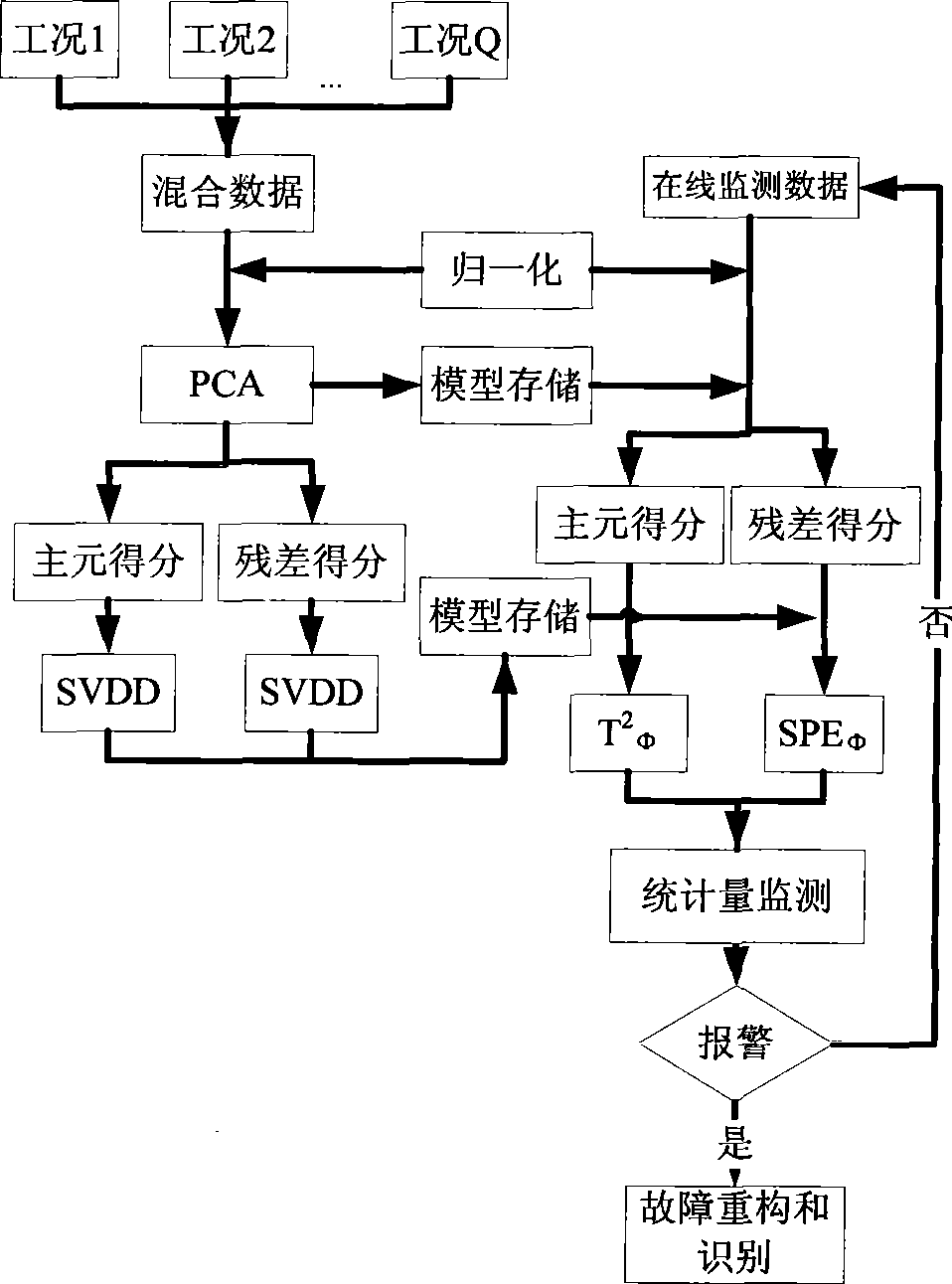
InactiveCN101458522ATighten statistical limitsHigh sensitivityTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlData descriptionPrincipal component analysis
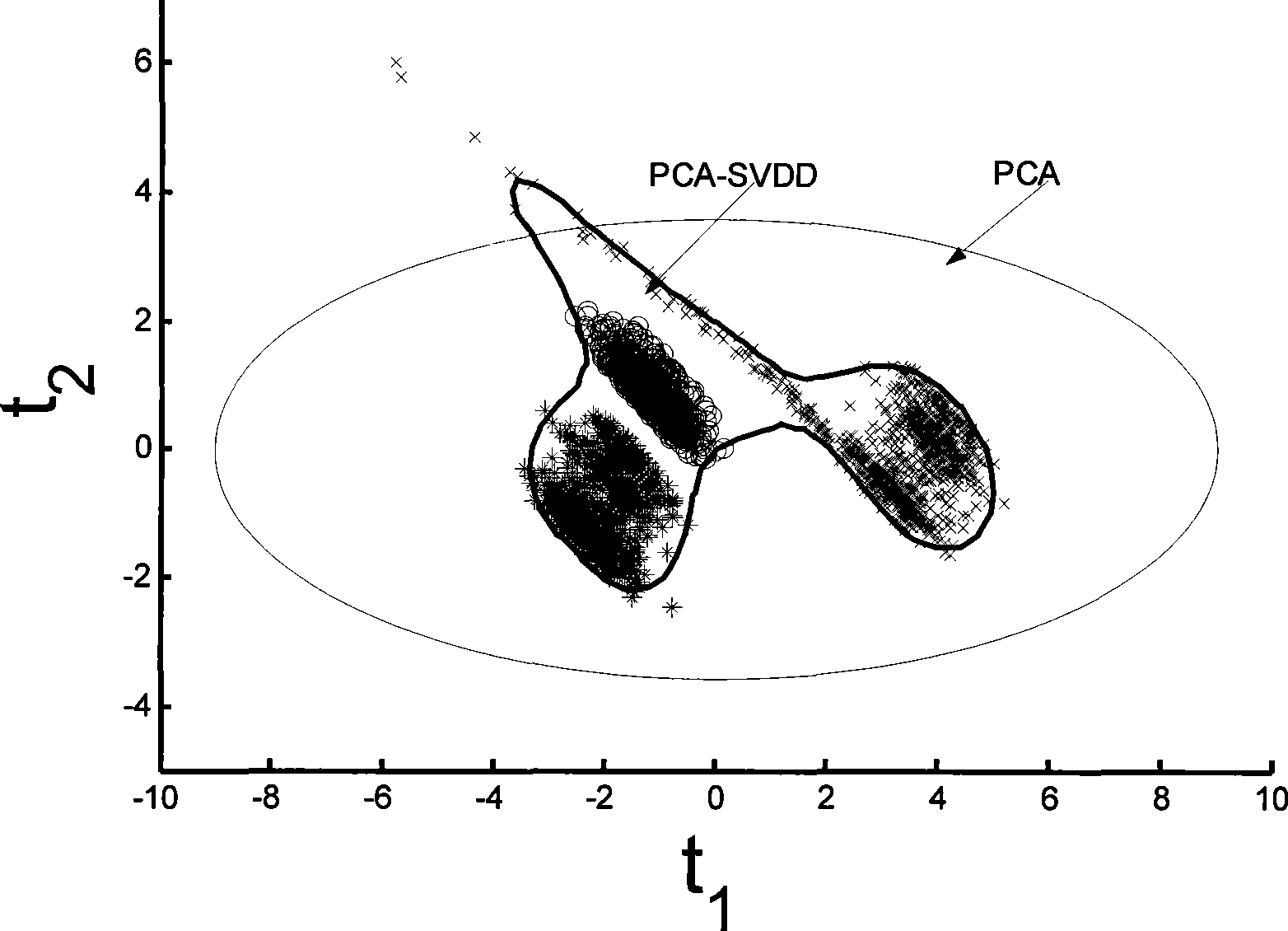
The invention discloses a multi-operating process monitor method based on principal component analysis and support vectors data. The method establishes a uniform PCA model to various operating mixed data firstly, puts score vectors of principal component space and residual space to high dimension characteristic space. Two new statistics are established in the characteristic space for monitoring the principal component space and residual space. When the process goes wrong, a fault reconstruction method based on SVDD identifies fault. The method establishes two SVDD statistics monitor model to various operating based that the principal analysis method is used for reducing process variable dimension, reduces statistics limit of processing monitor, increases sensitivity of processing monitoring. In addition, the invention provides a fault reconstruction and identifying method aiming at detected process fault which can locate source of fault commendably, is benefit to removing fault as soon as possible, returns process to normal operation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
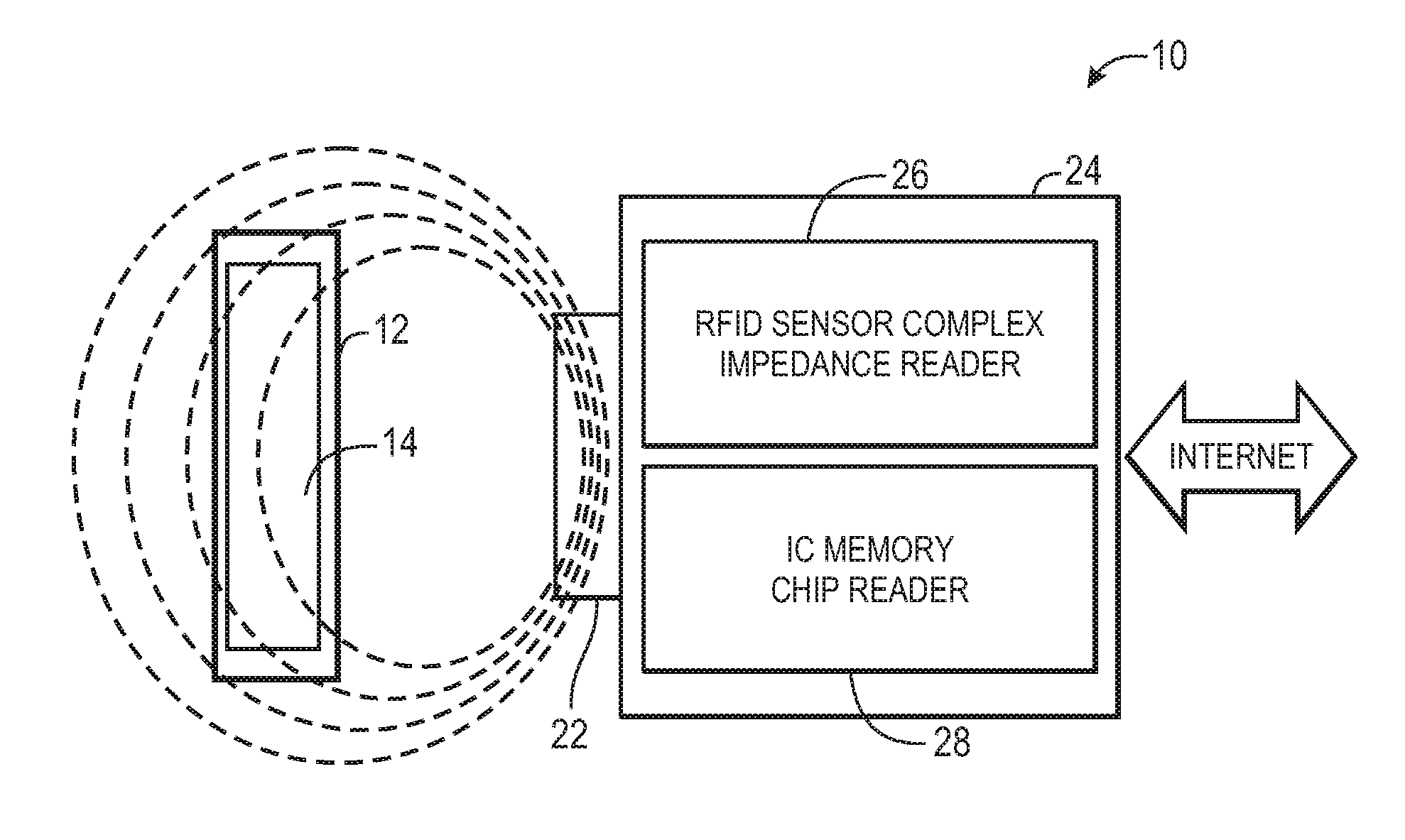
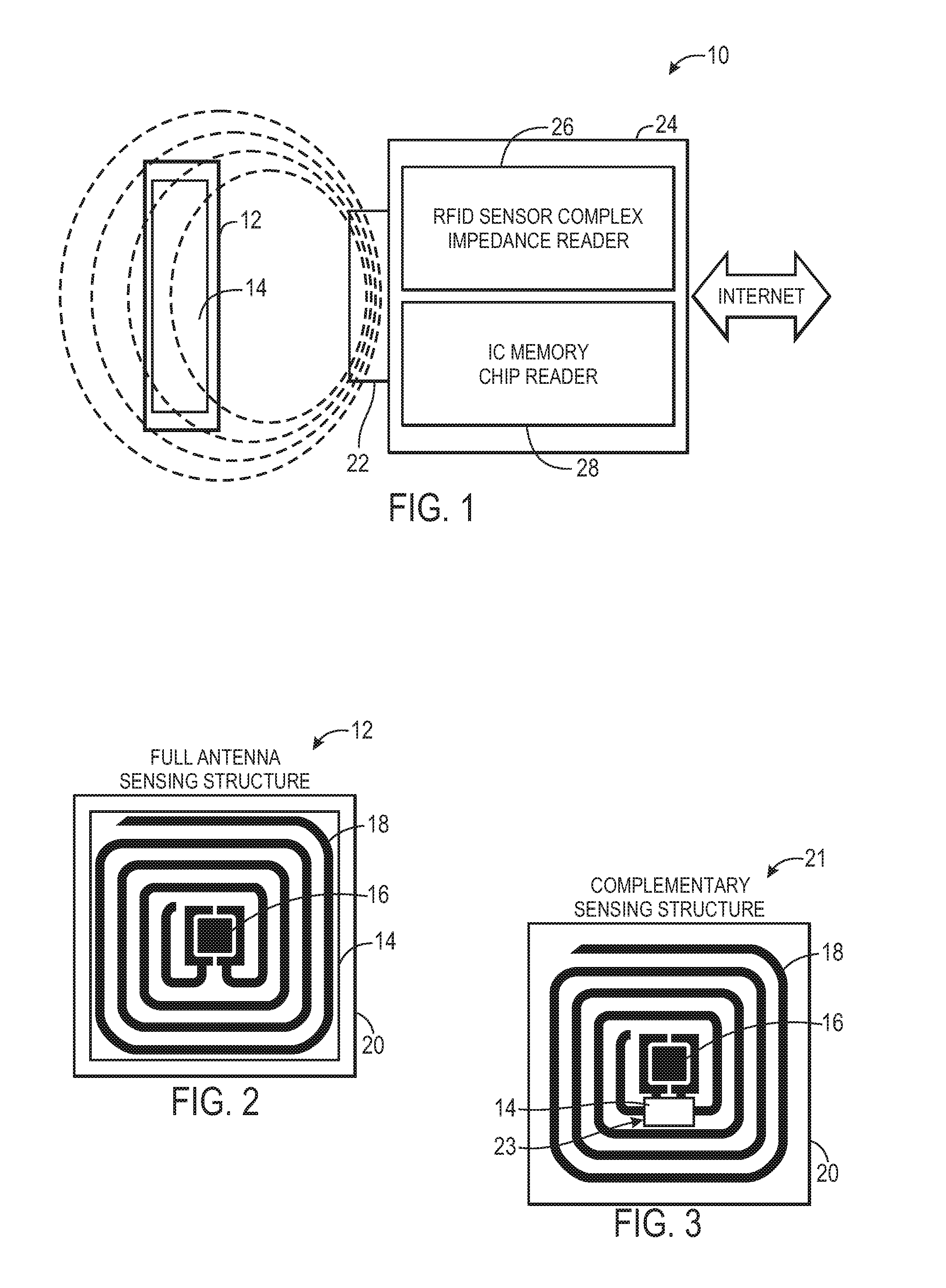
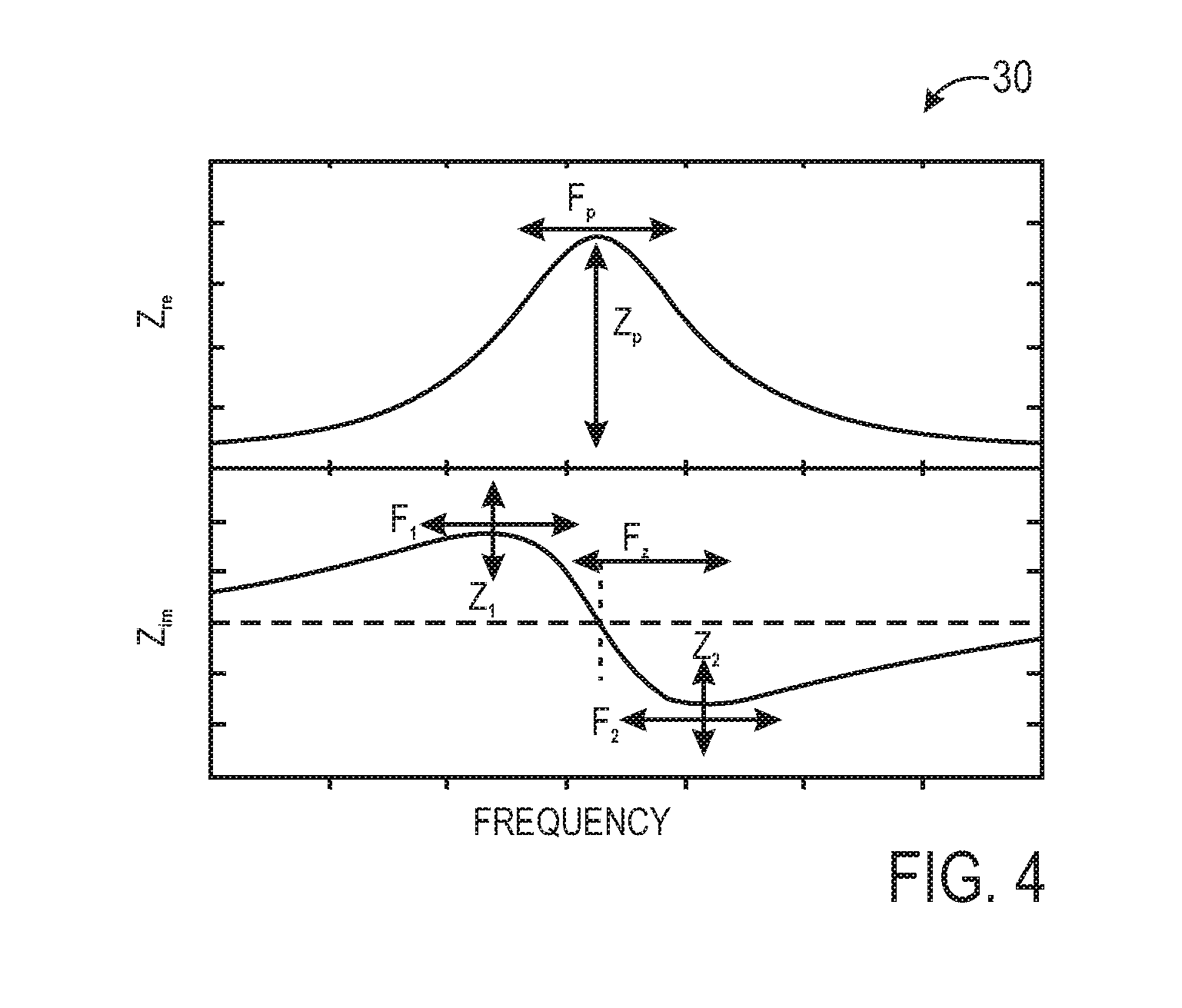
Highly selective chemical and biological sensors
ActiveUS20120116683A1Resistance/reactance/impedenceBiological testingHigh concentrationPrincipal component analysis
Methods and sensors for selective fluid sensing are provided. Each sensor includes a resonant inductor-capacitor-resistor (LCR) sensor that is coated with a sensing material. In order to collect data, an impedance spectrum is acquired over a relatively narrow frequency range, such as the resonant frequency range of the LCR circuit. A multivariate signature may be calculated from the acquired spectrum to discern the presence of certain fluids and / or fluid mixtures. The presence of fluids is detected by measuring the changes in dielectric, dimensional, resistance, charge transfer, and other changes in the properties of the materials employed by observing the changes in the resonant electronic properties of the circuit. By using a mathematical procedure, such as principal components analysis (PCA) and others, multiple fluids and mixtures can be detected in the presence of one another, even in a high humidity environment or an environment wherein one or more fluids has a substantially higher concentration (e.g. 10×, 1,000,000×) compared to other components in the mixture.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Ordered data compression system and methods
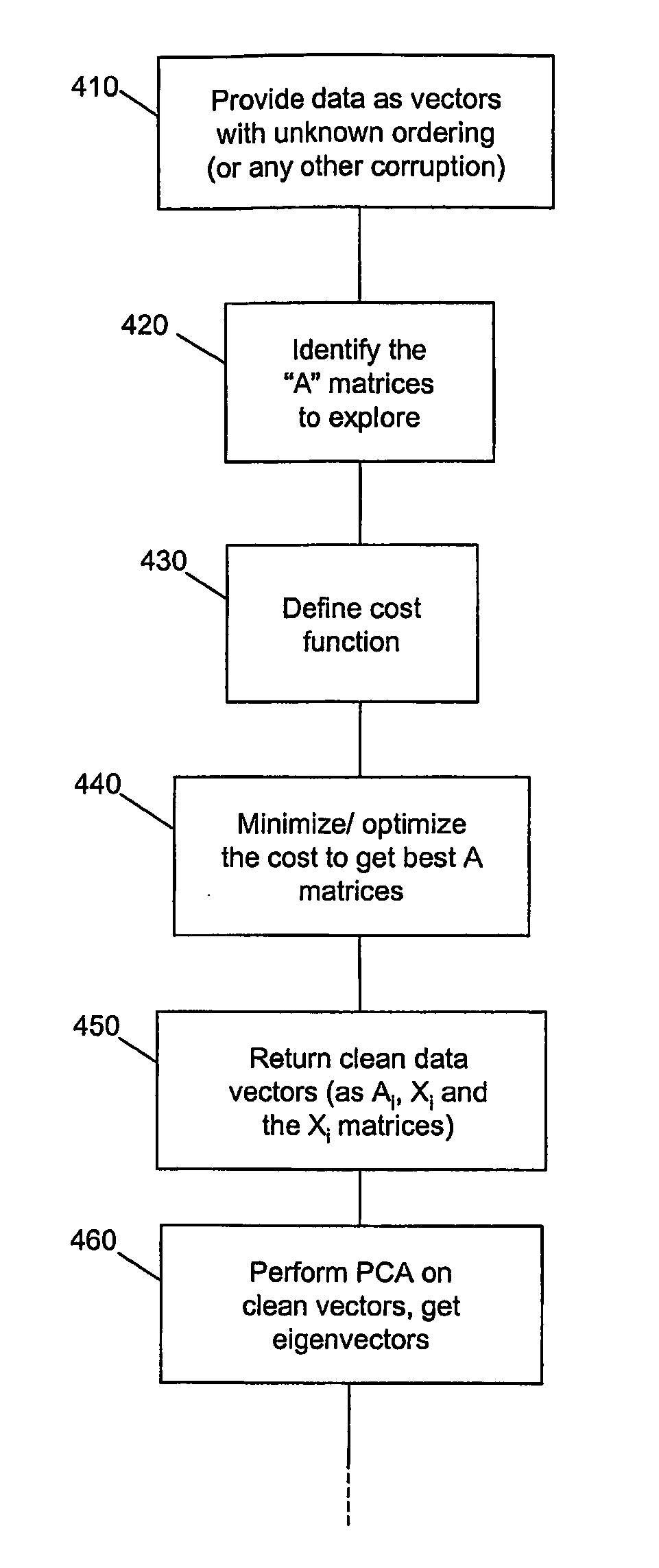
Methods and systems are provided for encoding, transmission and decoding of vectorized input data, for example, video or audio data. A convex invariance learning framework is established for processing input data or a given data type. Each input vector is associated with a variable transformation matrix that acts on the vector to invariantly permute the vector elements. Joint invariance and model learning is performed on a training set of invariantly transformed vectors over a constrained space of transformation matrices using maximum likelihood analysis. The maximum likelihood analysis reduces the data volume to a linear subspace volume in which the training data can be modeled by a reduced number of variables. Principal component analysis is used to identify a set of N eigen vectors that span the linear subspace. The set of N eigenvectors is used a basis set to encode input data and to decode compressed data.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com