Patents
Literature
331 results about "Motion field" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In computer vision the motion field is an ideal representation of 3D motion as it is projected onto a camera image. Given a simplified camera model, each point (y₁,y₂) in the image is the projection of some point in the 3D scene but the position of the projection of a fixed point in space can vary with time. The motion field can formally be defined as the time derivative of the image position of all image points given that they correspond to fixed 3D points.
Method and apparatus for coordination of motion determination over multiple frames
InactiveUS6157677AEasy to compressEasy to controlTelevision system detailsImage analysisMotion fieldMultiple frame
PCT No. PCT / EP96 / 01272 Sec. 371 Date Nov. 21, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Nov. 21, 1997 PCT Filed Mar. 22, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 29679 PCT Pub. Date Sep. 26, 1996The present invention concerns improved motion estimation in signal records. A method for estimating motion between one reference image and each frame in a sequence of frames, each frame consisting of a plurality of samples of an input signal comprises the steps of: transforming the estimated motion fields into a motion matrix, wherein each row corresponds to one frame, and each row contains each component of motion vector for each element of the reference image; performing a Principal Component Analysis of the motion matrix, thereby obtaining a motion score matrix consisting of a plurality of column vectors called motion score vectors and a motion loading matrix consisting of a plurality of row vectors called motion loading vectors, such that each motion score vector corresponds to one element for each frame, such that each element of each motion loading vector corresponds to one element of the reference image, such that one column of said motion score matrix and one motion loading vector together constitute a factor, and such that the number of factors is lower than or equal to the number of said frames; wherein the results from the Principal Component Analysis on the motion matrix are used to influence further estimation of motion from the reference image to one or more of the frames.
Owner:IDT INT DIGITAL TECH DEUTLAND
Method for Scalable Video Coding
ActiveUS20090304090A1Improve device performanceColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMotion fieldImage resolution
A method for estimating motion for the scalable video coding, includes the step of estimating the motion field of a sequence of photograms which can be represented with a plurality of space resolution levels including computing the motion field for the minimum resolution level and, until the maximum resolution level is reached, repeating the steps of: rising by one resolution level; extracting the photograms for such resolution level; and computing the motion field for such resolution level. The motion field is computed through an optical flow equation which contains, for every higher level than the minimum resolution level, a regularization factor between levels which points out the difference between the solution for the considered level and the solution for the immediately lower resolution level. A more or less high value of the regularization factor implies more or less relevant changes of the component at the considered resolution during the following process iterations.
Owner:TELECOM ITALIA SPA
Rapid movement estimating method
InactiveCN1925614AImprove smoothnessFast convergenceDigital video signal modificationStandards conversionMotion fieldEstimation methods
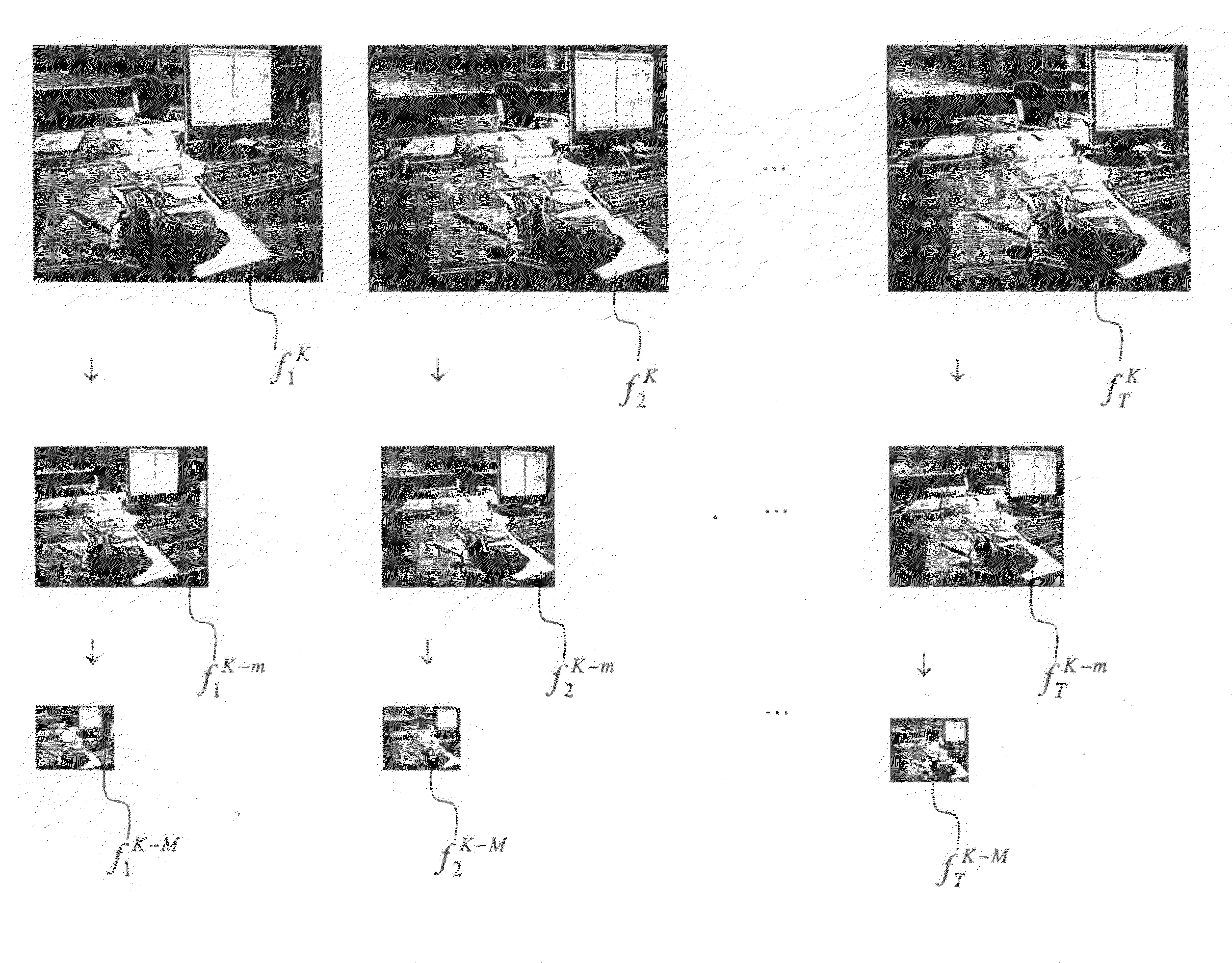
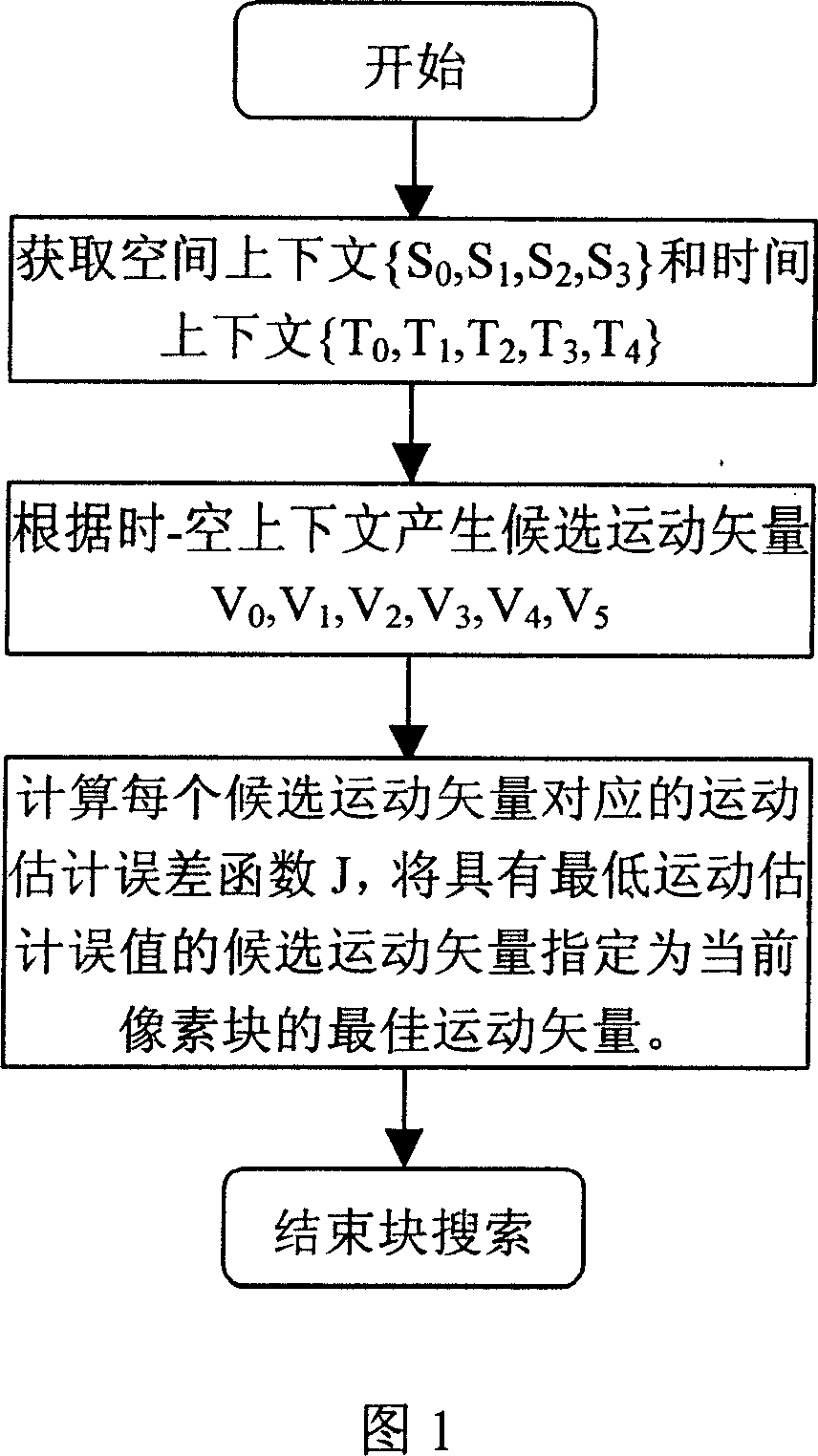
This invention relates to one rapid movement estimation method, which comprises the following steps: a, dividing each frame of images into several blocks and determining vector space upper and down message on each current image composed of upper and down messages to determine several prepare motion vector; computing each prepare motion vector matching error values with low motion matching error values with current pixel module designed as motion vector step.
Owner:深圳清研创业投资有限公司
Exception action detecting method based on athletic ground partial statistics characteristic analysis
The invention relates to an anomaly detection method based on a motion field local statistical character analysis. The system mainly comprises the motion field analysis of video images, a local statistical character extraction and a statistical study and a mode identification technology based on samples. Firstly, the characteristics of objects in an image are extracted through a basic motion analyzing technology, the motion status is calculated, and a motion field is formed. On the basis, the statistical character extraction is implemented on the local motion information to obtain the local motion characteristics of the motion field. Finally, the space distribution relationship of the motion characteristics is expressed by global structured information. A method based on the statistical study is adopted for recognizing behavior styles. The algorithm implements the behavior recognition directly through the analysis based on the motion information to improve the efficiency and the robustness of the algorithm.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Realtime stereo and motion analysis on passive video images using an efficient image-to-image comparison algorithm requiring minimal buffering
InactiveUS20050100207A1Less storageFew operationImage enhancementImage analysisMotion processingMotion field
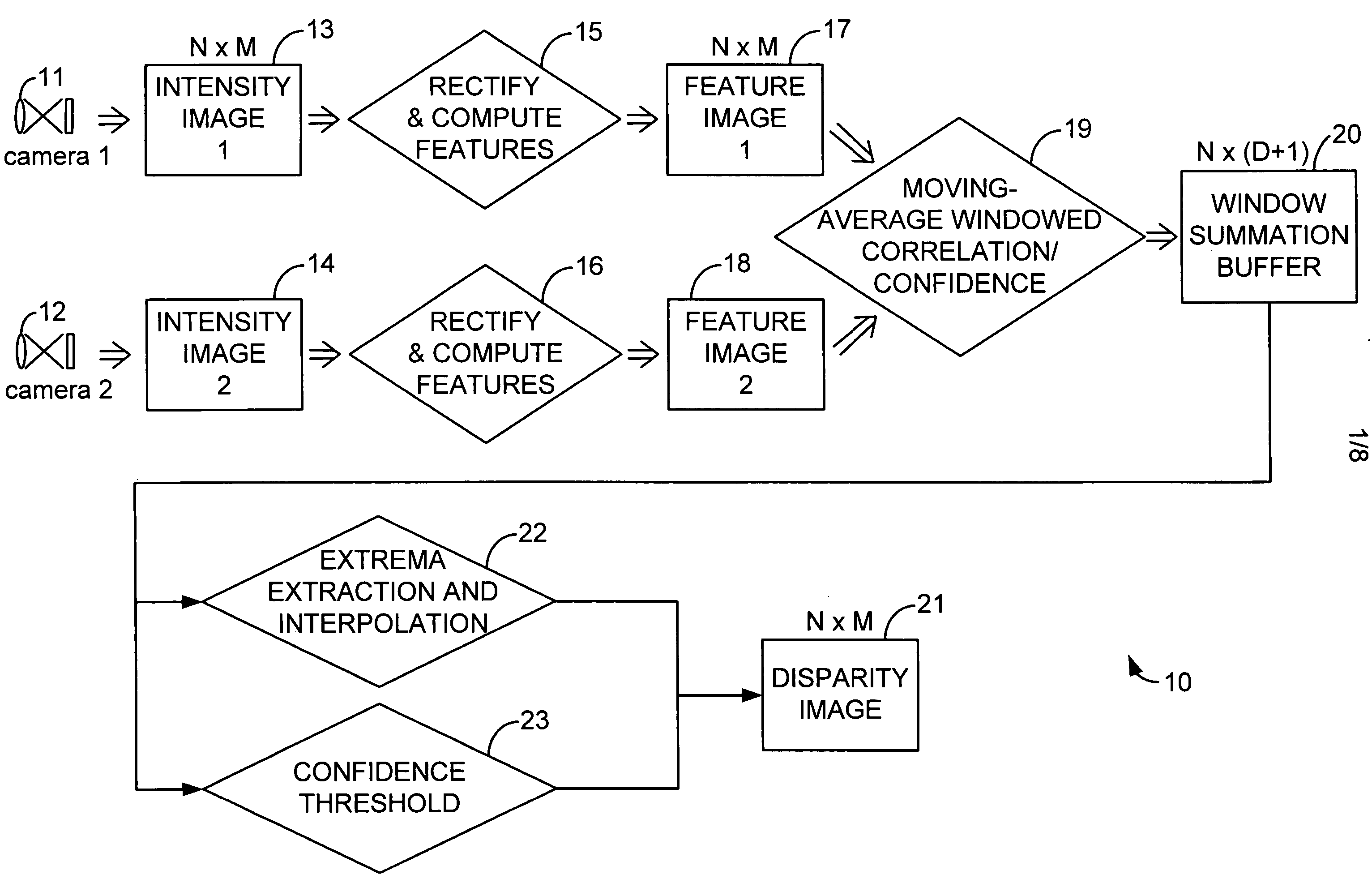
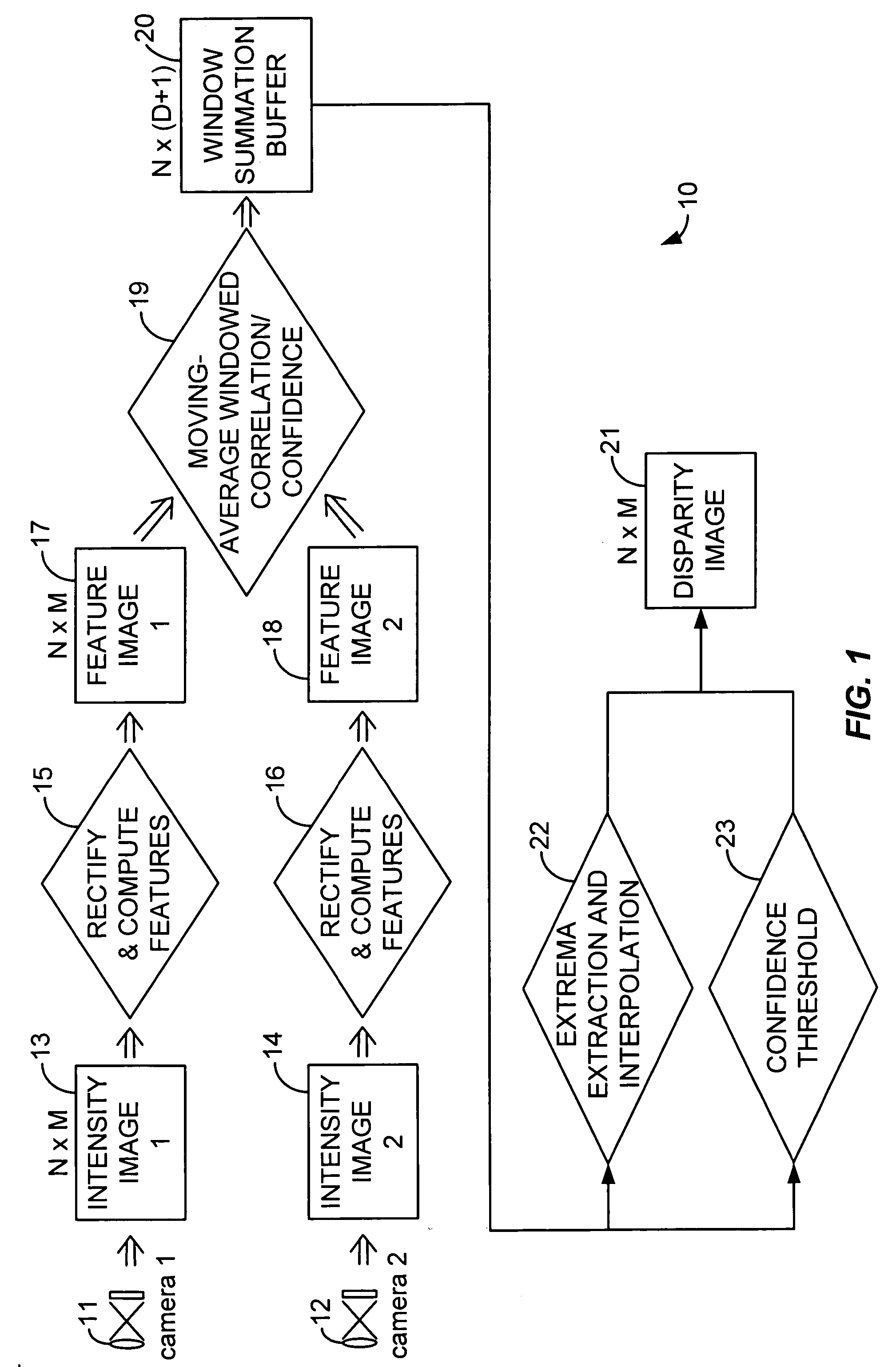
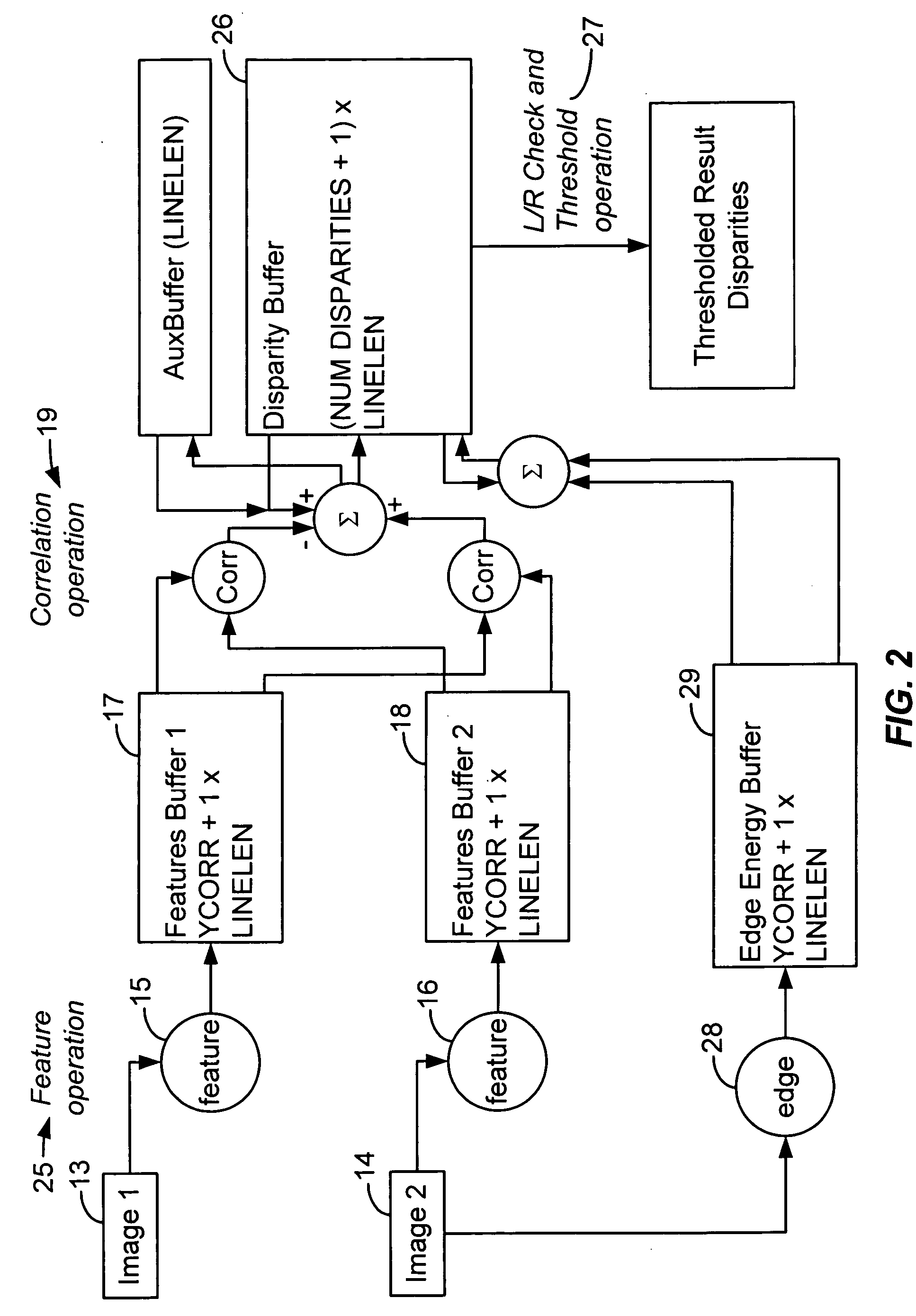
A compact, inexpensive, real-time device for computing dense stereo range and motion field images, which are fundamental measurements supporting a wide range of computer vision systems that interact with the real world, where objects move through three-dimensional space includes a novel algorithm for image-to-image comparison that requires less storage and fewer operations than other algorithms. A combination of standard, low-cost and low-power components are programmed to perform algorithm and performs realtime stereo and motion analysis on passive video images, including image capture, digitization, stereo and / or motion processing, and transmission of results.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
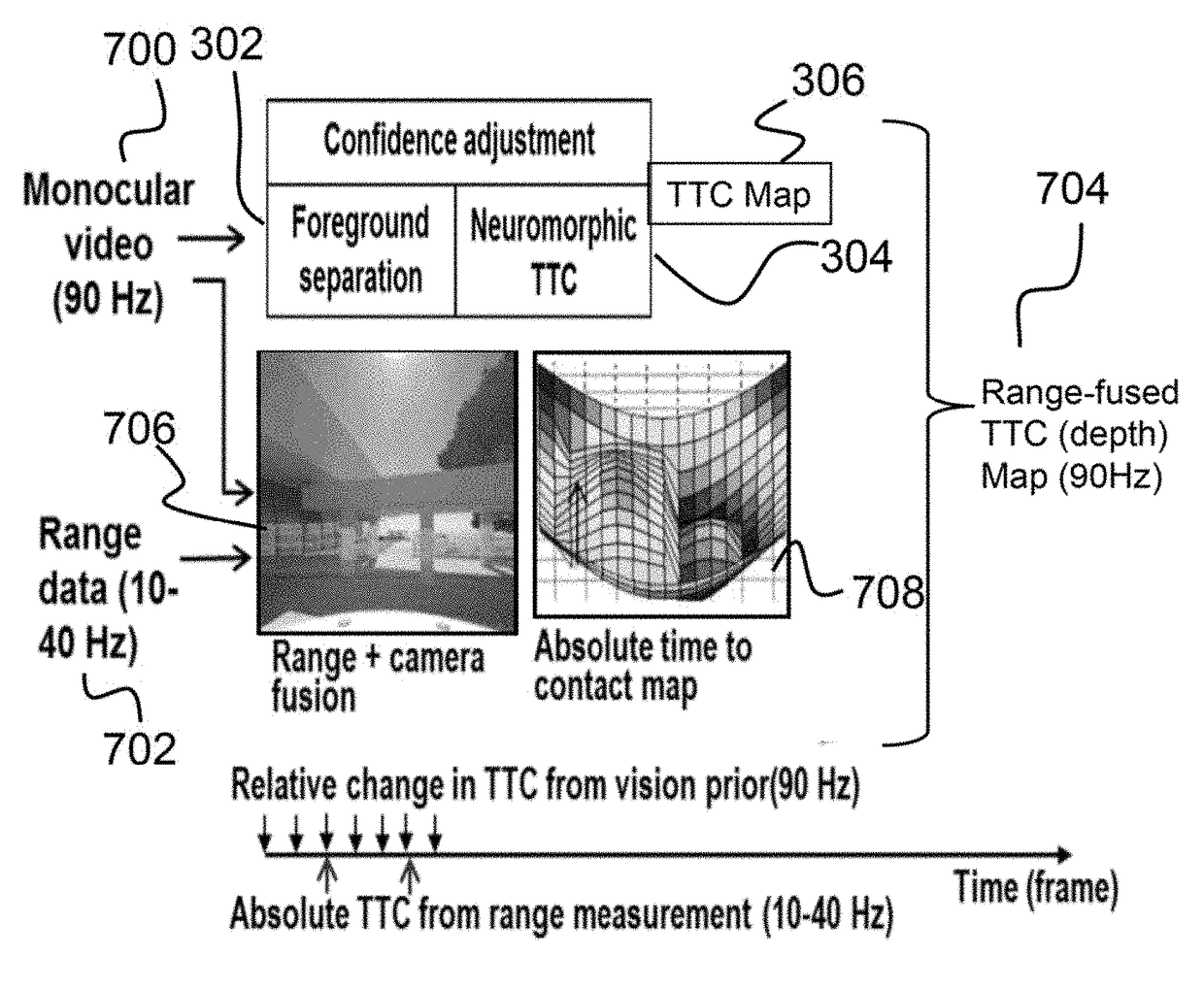
System and method for achieving fast and reliable time-to-contact estimation using vision and range sensor data for autonomous navigation
Described is a robotic system for detecting obstacles reliably with their ranges by a combination of two-dimensional and three-dimensional sensing. In operation, the system receives an image from a monocular video and range depth data from a range sensor of a scene proximate a mobile platform. The image is segmented into multiple object regions of interest and time-to-contact (TTC) value are calculated by estimating motion field and operating on image intensities. A two-dimensional (2D) TTC map is then generated by estimating average TTC values over the multiple object regions of interest. A three-dimensional TTC map is then generated by fusing the range depth data with image. Finally, a range-fused TTC map is generated by averaging the 2D TTC map and the 3D TTC map.
Owner:HRL LAB
Foreground object detection in a video surveillance system
ActiveUS20110052003A1Improve tracking performanceImage enhancementImage analysisVideo monitoringMotion field
Techniques are disclosed for detecting foreground objects in a scene captured by a surveillance system and tracking the detected foreground objects from frame to frame in real time. A motion flow field is used to validate foreground objects(s) that are extracted from the background model of a scene. Spurious foreground objects are filtered before the detected foreground objects are provided to the tracking stage. The motion flow field is also used by the tracking stage to improve the performance of the tracking as needed for real time surveillance applications.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
Method of signalling motion information for efficient scalable video compression
InactiveUS20060239345A1Reduce relative motionEfficient methodColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMotion fieldMotion parameter
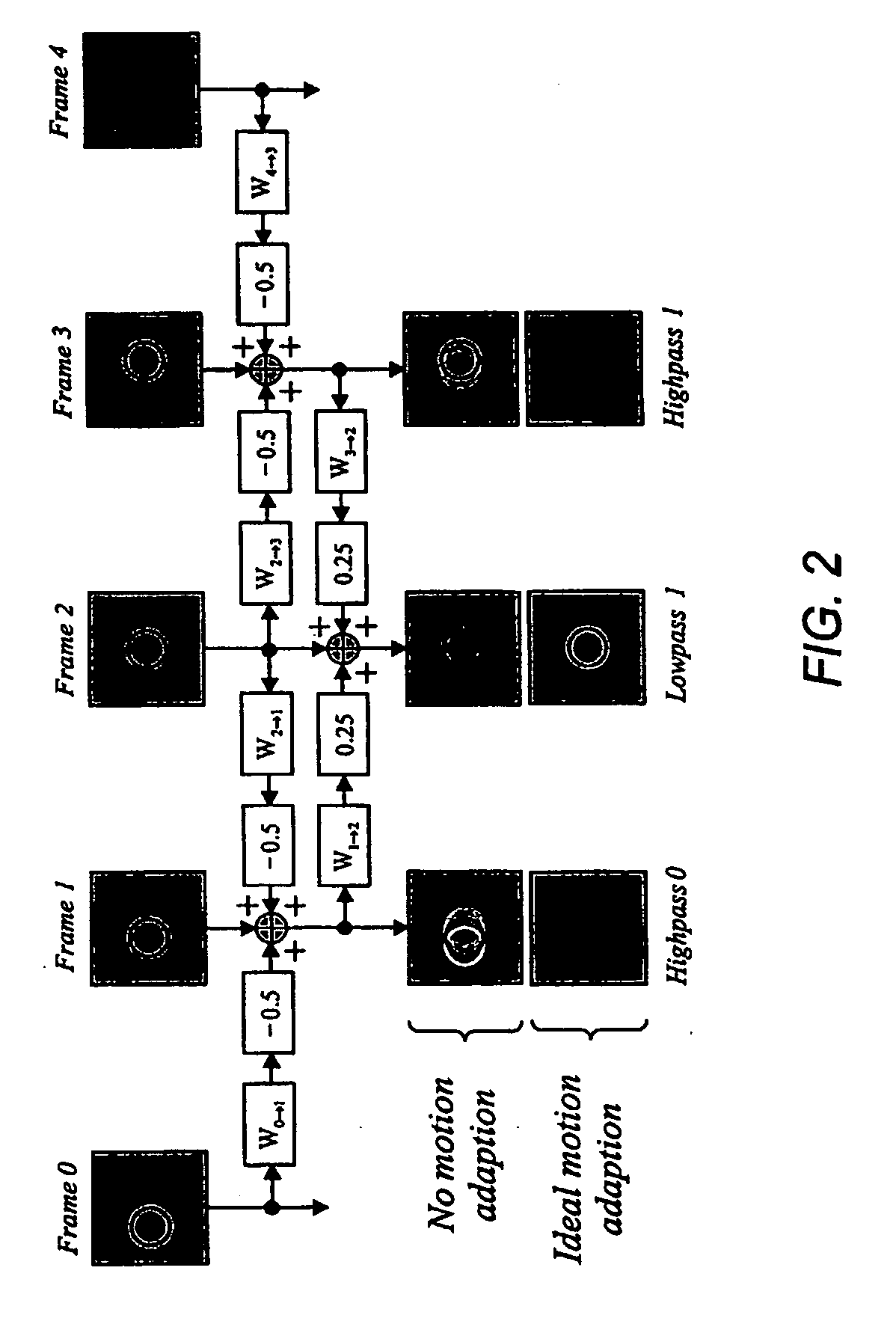
A method for incrementally coding and signalling motion information for a video compression system involving a motion adaptive transform and embedded coding of transformed video samples comprises the steps of: (a) producing an embedded bit-stream, representing each motion field in coarse to fine fashion; and (b) interleaving incremental contributions from said embedded motion fields with incremental contributions from said transformed video samples. A further embodiment of a method for estimating and signalling motion information for a motion adaptive transform based on temporal lifting steps comprises the steps of: (a) estimating and signalling motion parameters describing a first mapping from a source frame onto a target frame within one of the lifting steps; and (b) inferring a second mapping between either said source frame or said target frame, and another frame, based on the estimated and signalled motion parameters associated with said first mapping.
Owner:UNISEARCH LTD
Dynamic 2D imposters of 3D graphic objects
InactiveUS20050110789A1Minimizing processor timeMinimizing memoryVideo games3D-image renderingGraphicsMotion field
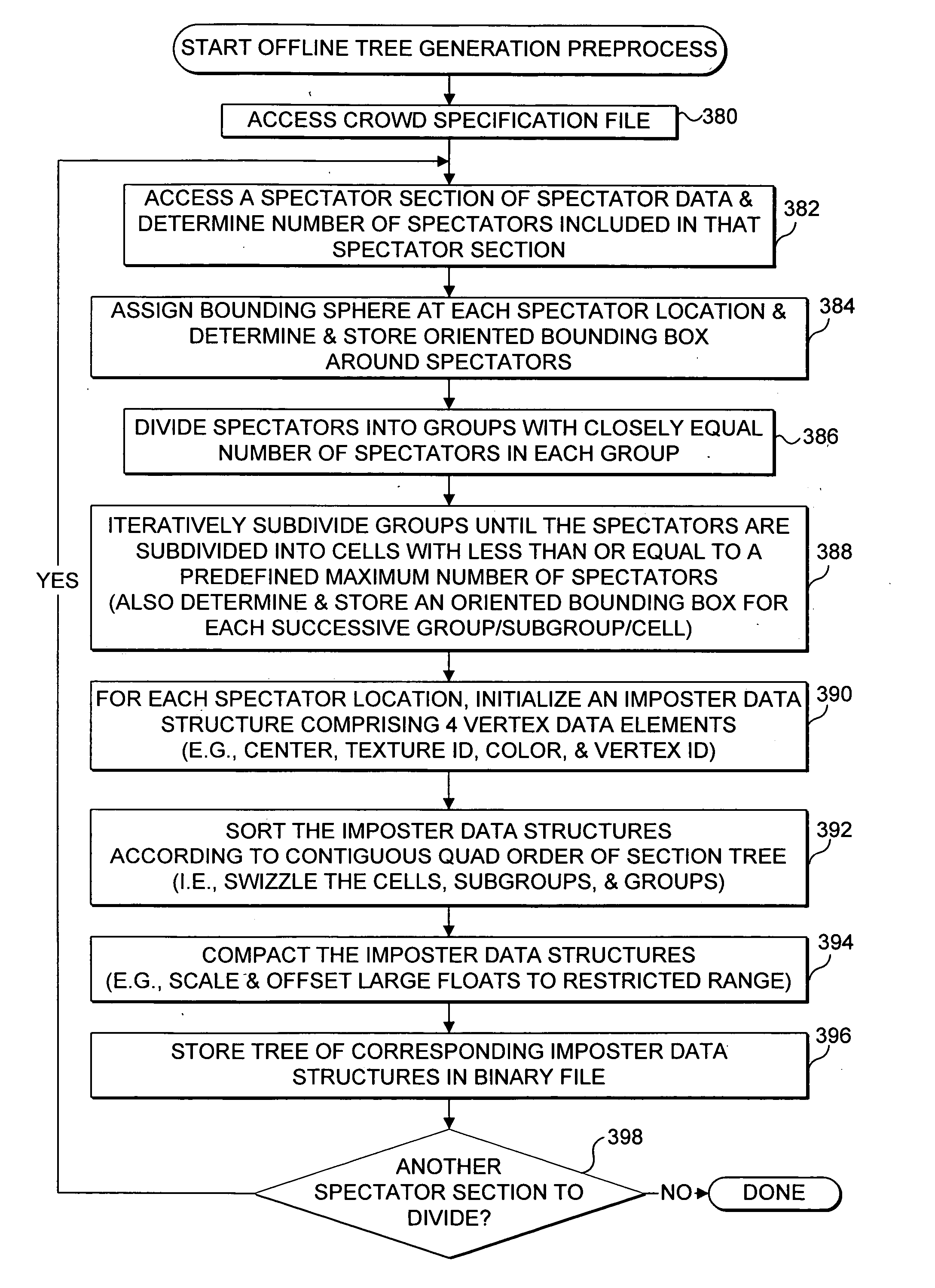
2D imposters representing 3D graphical objects, such as virtual spectators in a simulated sports arena, are dynamically displayed at predefined locations relative to an arbitrarily movable camera position in a virtual space. A hierarchical data structure is created with branches corresponding to iteratively subdivided groups of imposter data structures and is used to store polygon vertices, texture data, and other 2D imposter data generated during run-time. Center locations of the hierarchically divided groupings are used to determine a common projection location within a current view volume at which each 2D imposter is projected as an oriented image from each corresponding animated 3D graphical object. Sets of contiguous 2D imposter data are determined based on currently visible groupings of predefined locations that do not require rendering as 3D graphical objects due to their distance from the camera position. Each set of contiguous 2D imposters is rendered with a single draw primitive.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
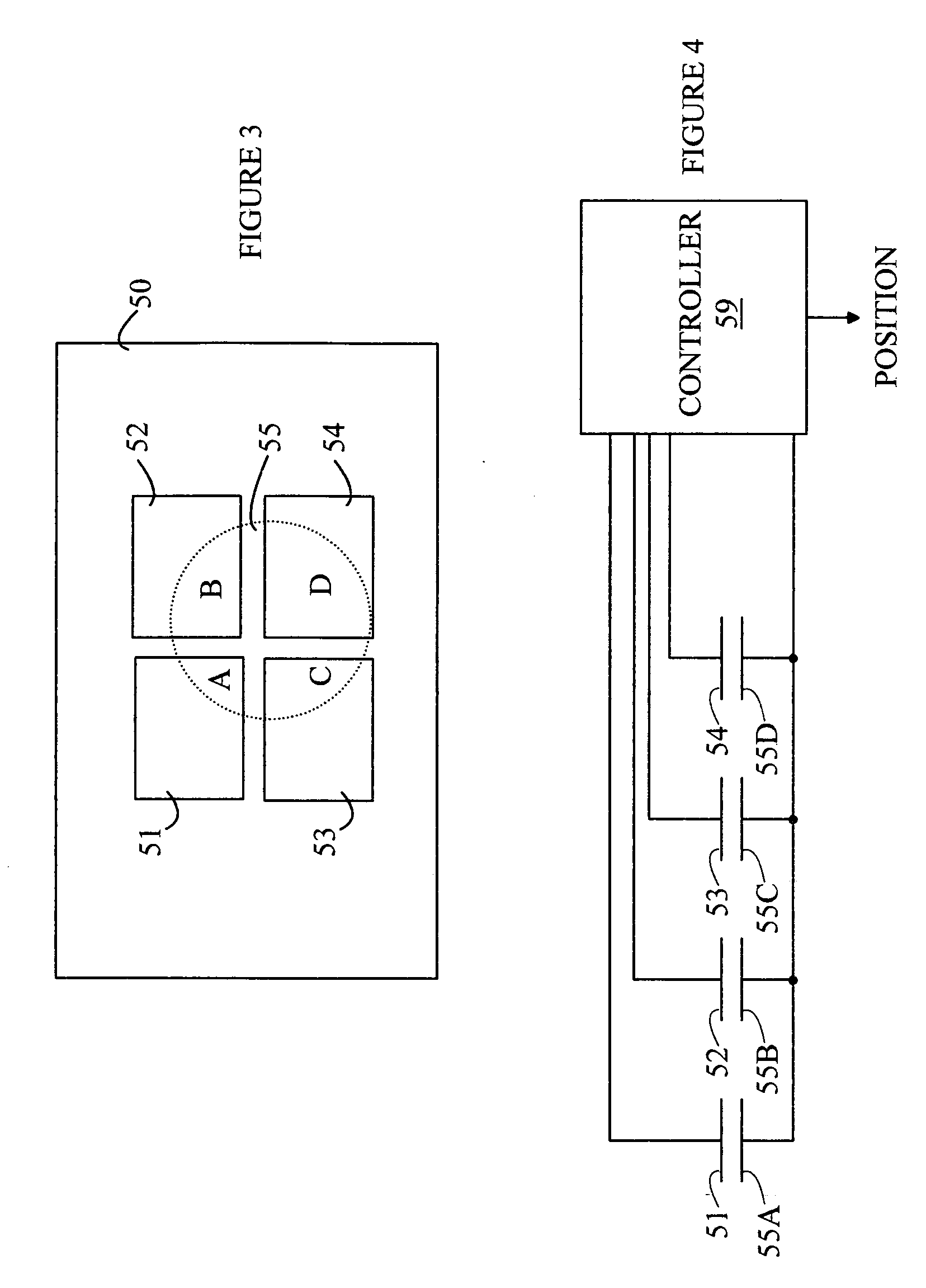
Pointing device adapted for small handheld devices
ActiveUS20070139374A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsDetails for portable computersCircular discMotion field
A display device having a puck, a display screen, and a controller is disclosed. The puck moves in a puck field of motion on a surface, the field of motion being divided into a pointing region and a function region. The controller determines a position of the puck within the field of motion. The display screen has first and second display modes, the display screen displaying a two-dimensional scene in the first display mode and a sub-scene of the two-dimensional scene in the second display mode. A cursor that moves within the sub-scene in a manner controlled by the puck position in the pointing region is displayed in the second mode. The controller causes the display scene to change between modes when the puck moves between regions. The sub-scene position moves in response to the position of the puck in the function region in the first display mode.
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
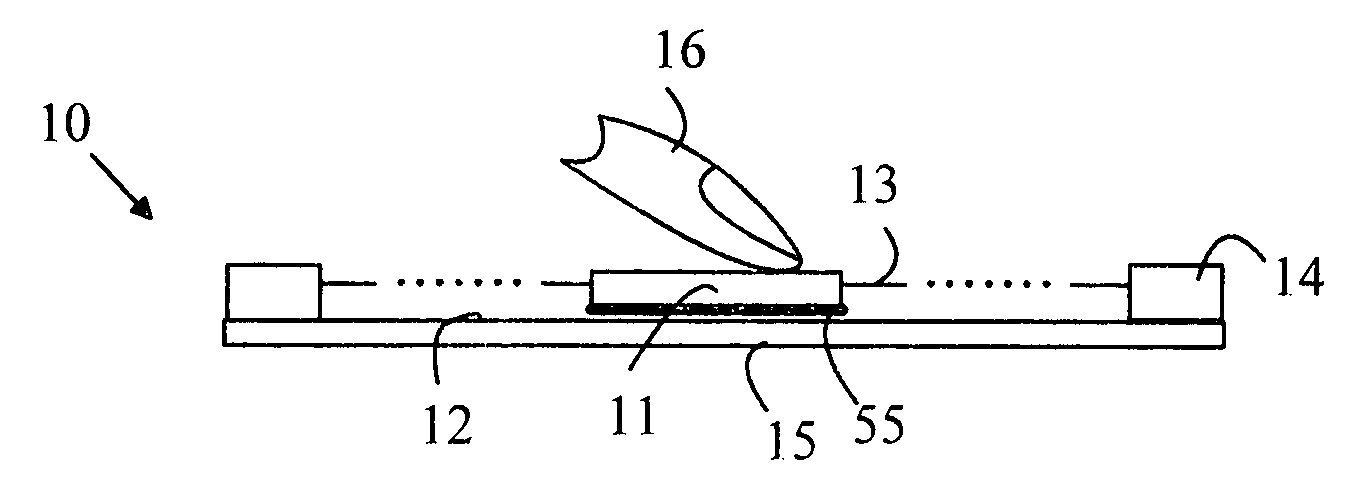
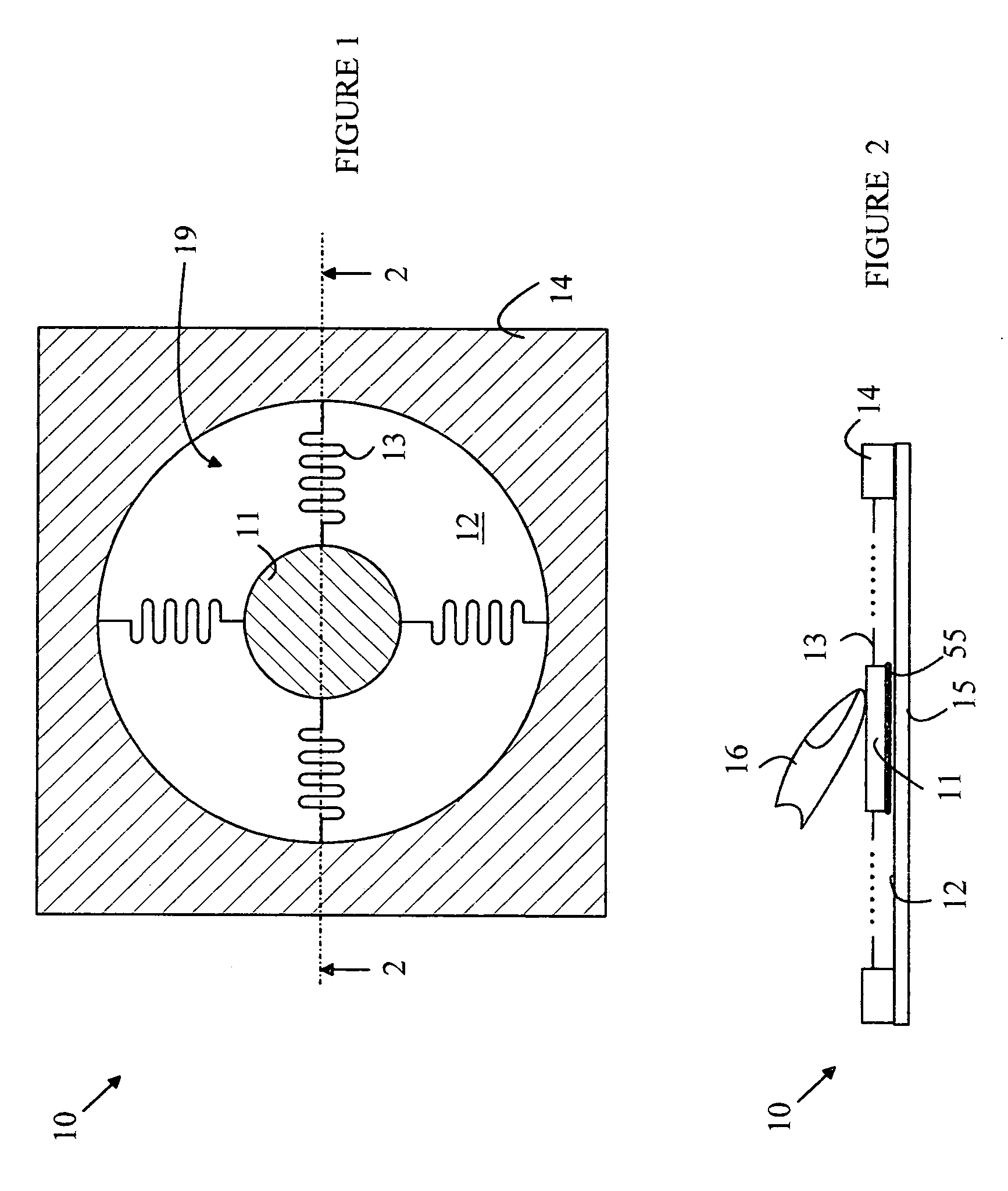
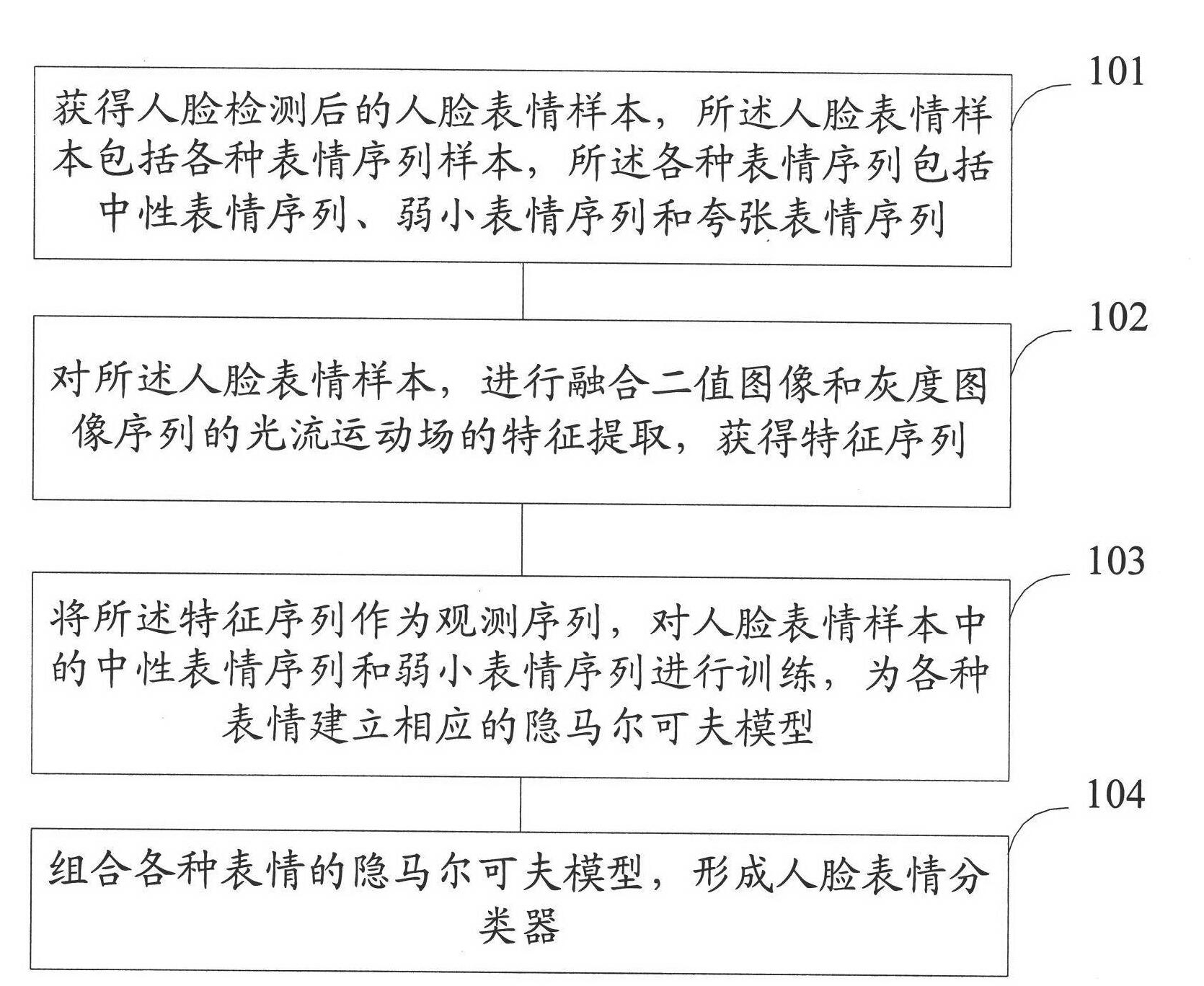
Facial expression recognition method and system, and training method and system of expression classifier
InactiveCN101877056ARealize identificationComplete sequence of continuous expressionsCharacter and pattern recognitionMotion fieldHide markov model
The invention provides a facial expression recognition method and a system, and a training method and a system of a facial expression classifier. The facial expression recognition method specifically comprises the following steps: carrying out feature extraction on an optical flow motion field fusing the sequences of a binary image and a gray scale image and obtaining a feature sequence; and taking the inputted feature sequence as an observation sequence and judging the expression category of the observation sequence according to the facial expression classifier, wherein the facial expression classifier is obtained by combining hidden markov models of a variety of expressions, and the hidden markov models are obtained by training neutral expression sequences and weak expression sequences in facial expression samples. The invention is used for overcoming the shortcomings of discrete results, jumping and unnatural property of the existing expression recognition.
Owner:VIMICRO CORP
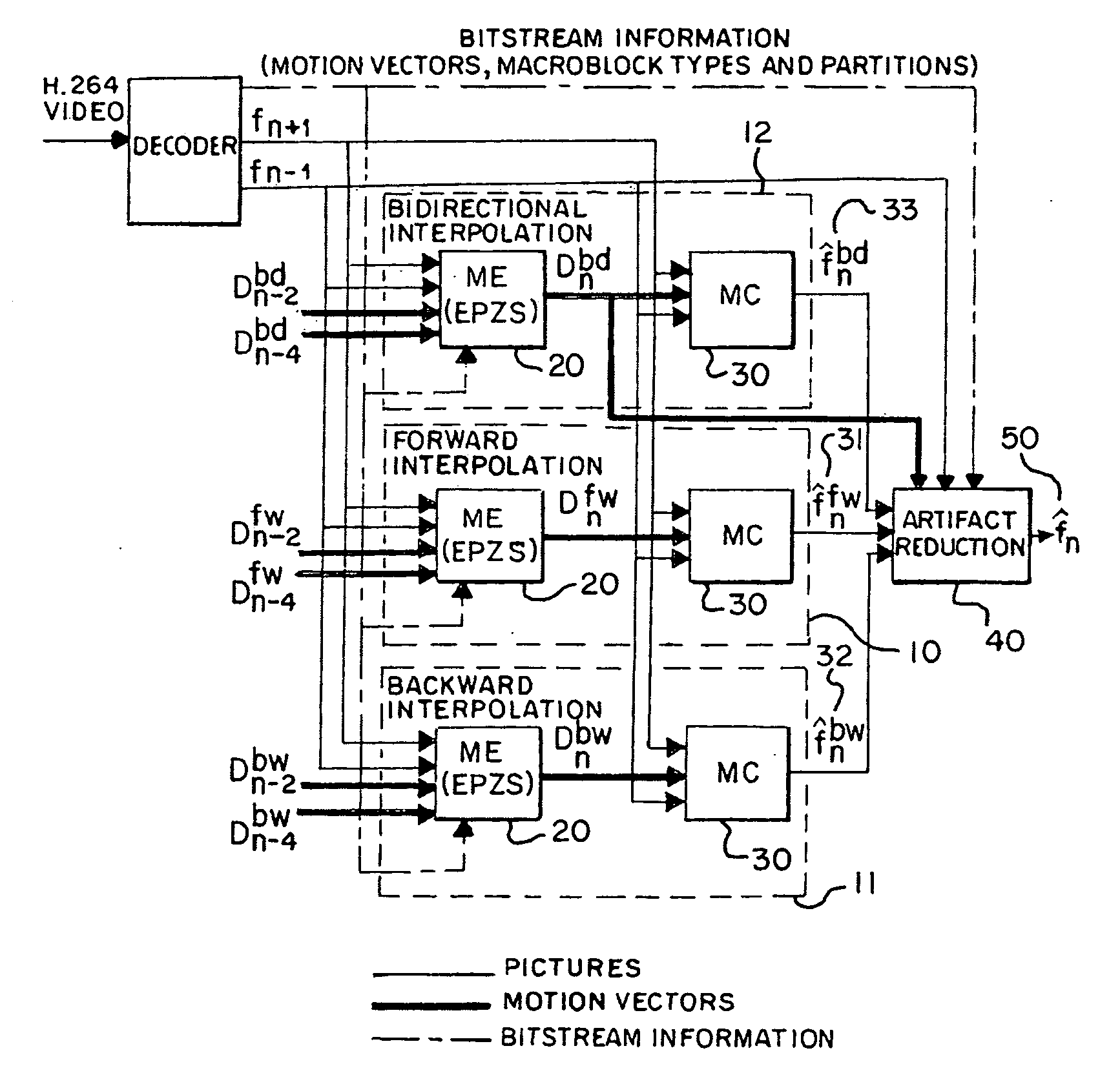
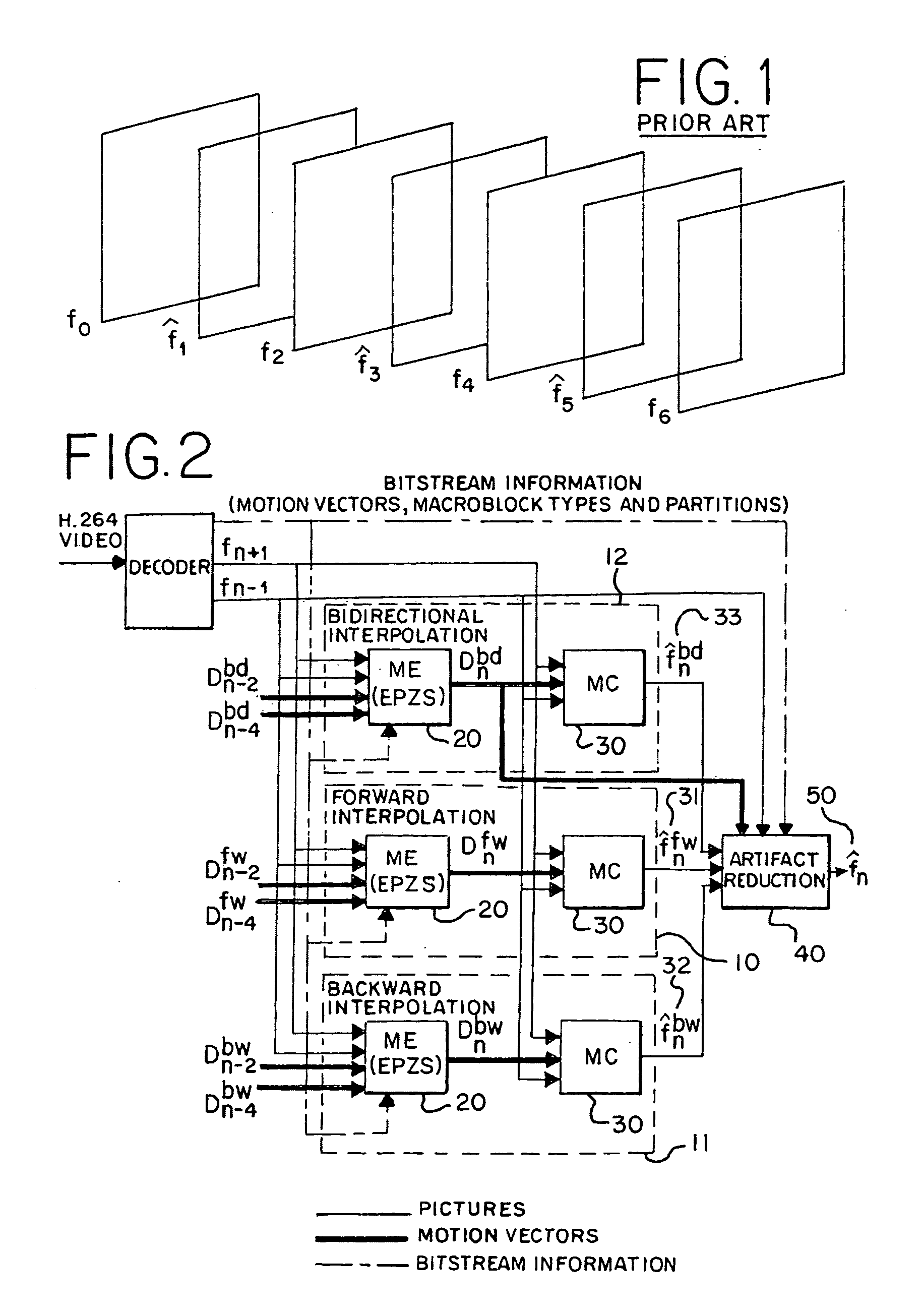
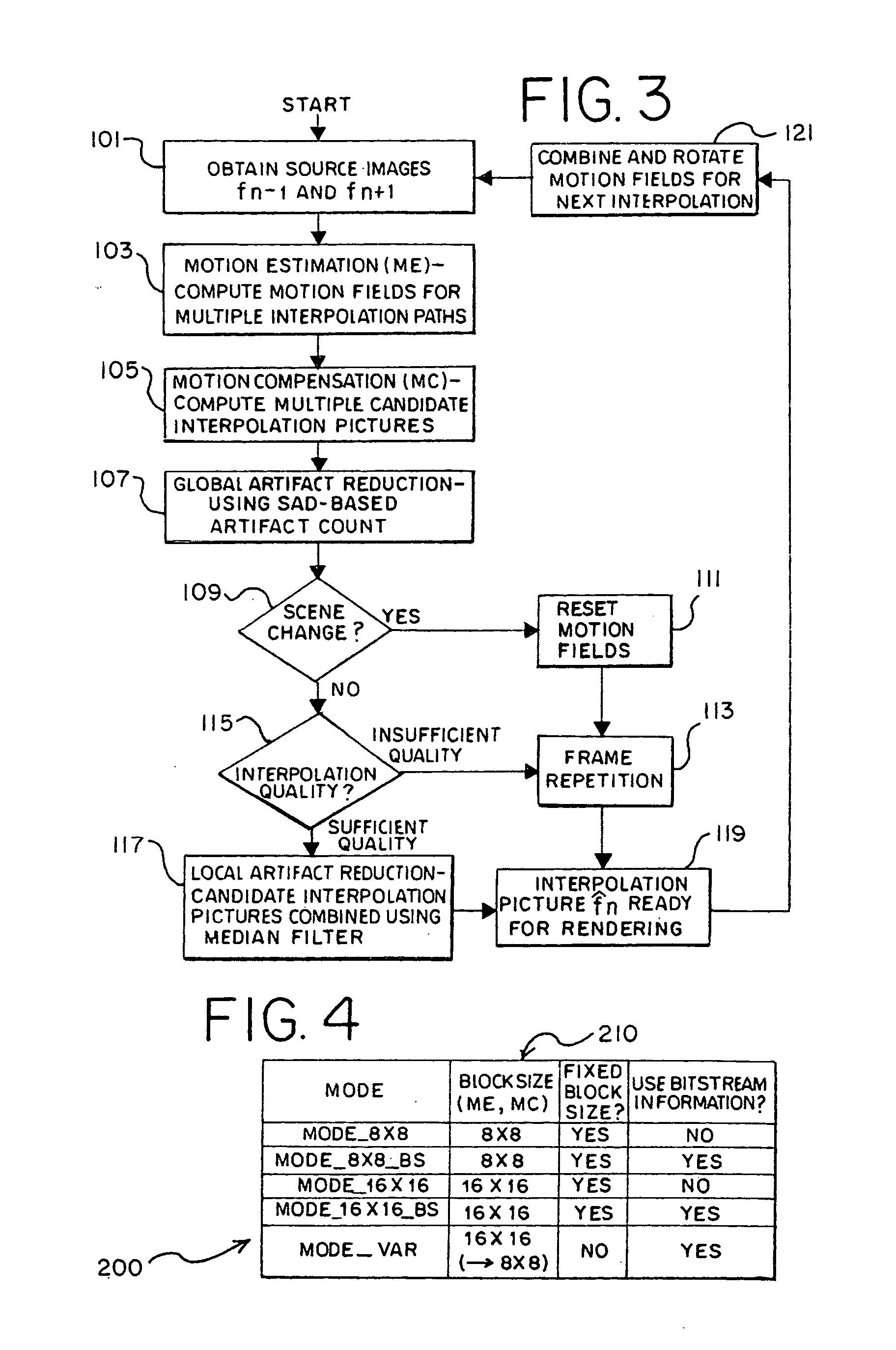
System and method for frame interpolation for a compressed video bitstream
InactiveUS20100201870A1Without usingImprove interpolation qualityPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningVideo bitstreamMotion field
A system and a method perform frame interpolation for a compressed video bitstream. The system and the method may combine candidate pictures to generate an interpolated video picture inserted between two original video pictures. The system and the method may generate the candidate pictures from different motion fields. The candidate pictures may be generated partially or wholly from motion vectors extracted from the compressed video bitstream. The system and the method may reduce computation required for interpolation of video frames without a negative impact on visual quality of a video sequence.
Owner:LUESSI MARTIN +4
Foreground object detection in a video surveillance system
ActiveUS8218819B2Improve tracking performanceImage enhancementImage analysisVideo monitoringMotion field
Techniques are disclosed for detecting foreground objects in a scene captured by a surveillance system and tracking the detected foreground objects from frame to frame in real time. A motion flow field is used to validate foreground objects(s) that are extracted from the background model of a scene. Spurious foreground objects are filtered before the detected foreground objects are provided to the tracking stage. The motion flow field is also used by the tracking stage to improve the performance of the tracking as needed for real time surveillance applications.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
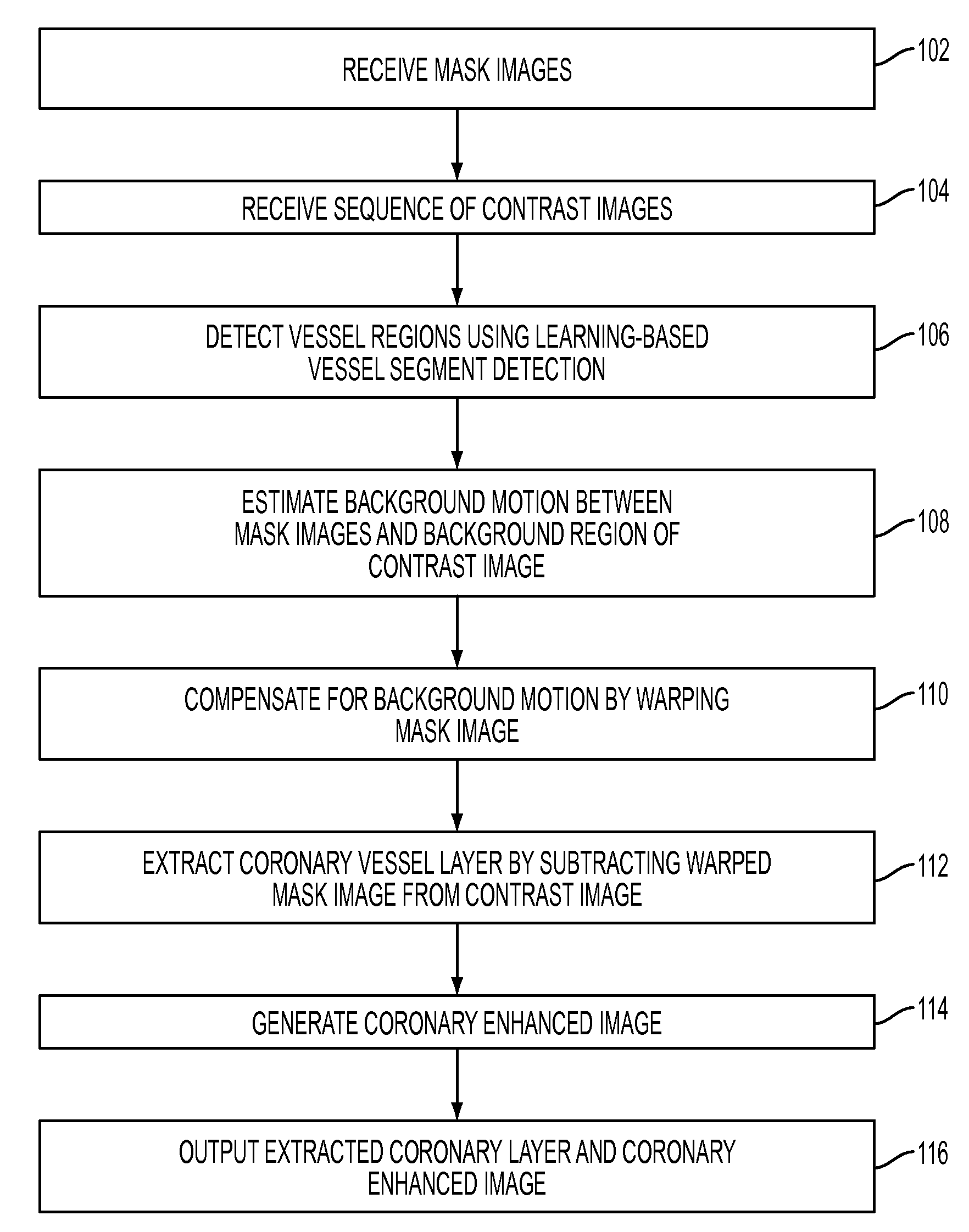
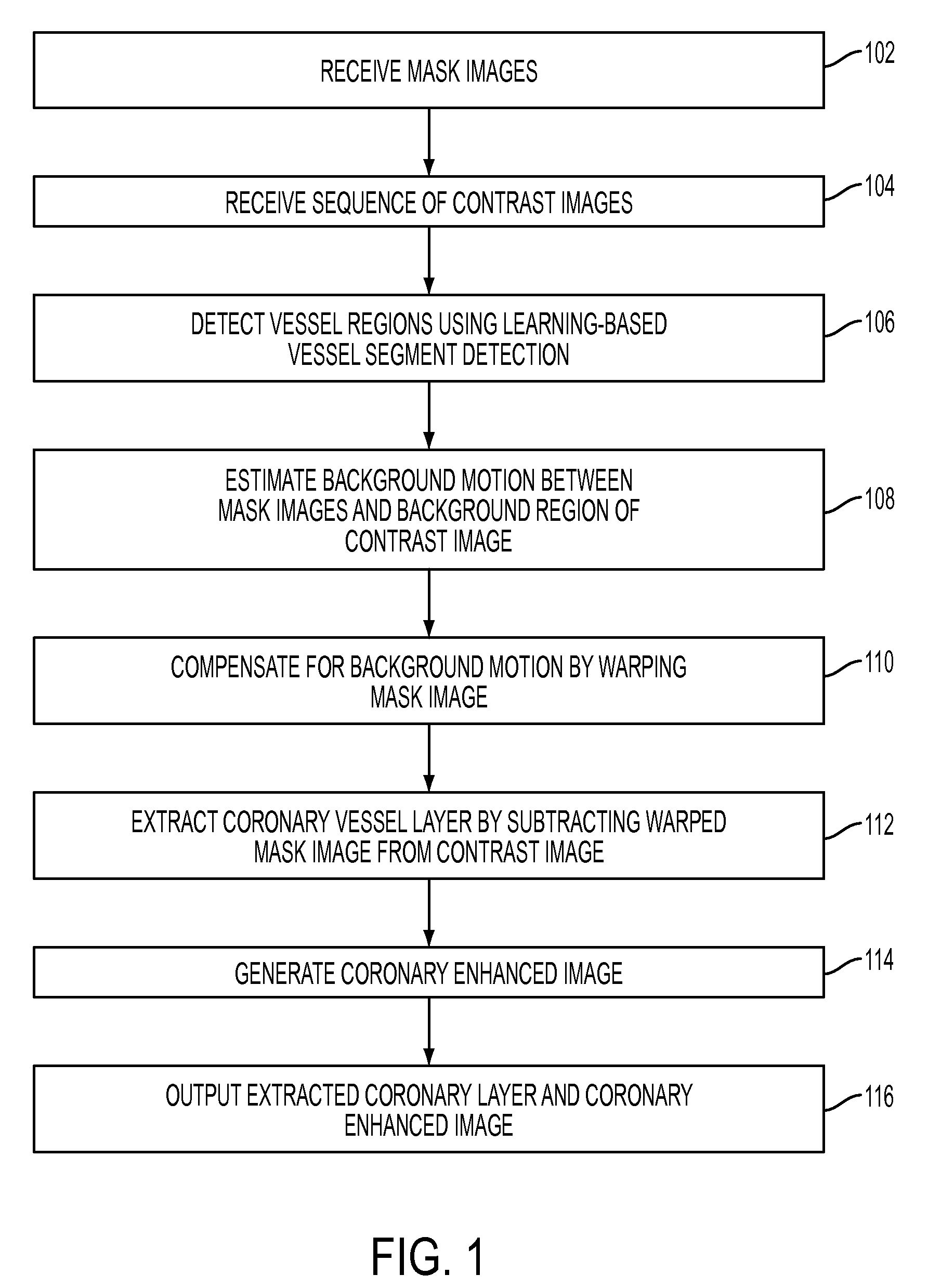
System and Method for Coronary Digital Subtraction Angiography
A method and system for extracting coronary vessels fluoroscopic image sequences using coronary digital subtraction angiography (DSA) are disclosed. A set of mask images of a coronary region is received, and a sequence of contrast images for the coronary region is received. For each contrast image, vessel regions are detected in the contrast image using learning-based vessel segment detection and a background region of the contrast image is determined based on the detected vessel regions. Background motion is estimated between one of the mask images and the background region of the contrast image by estimating a motion field between the mask image and the background image and performing covariance-based filtering over the estimated motion field. The mask image is then warped based on the estimated background motion to generate an estimated background layer. The estimated background layer is subtracted from the contrast image to extract a coronary vessel layer for the contrast image.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Foreground object tracking
Techniques are disclosed for detecting foreground objects in a scene captured by a surveillance system and tracking the detected foreground objects from frame to frame in real time. A motion flow field is used to validate foreground objects(s) that are extracted from the background model of a scene. Spurious foreground objects are filtered before the foreground objects are provided to the tracking stage. The motion flow field is also used by the tracking stage to improve the performance of the tracking as needed for real time surveillance applications.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
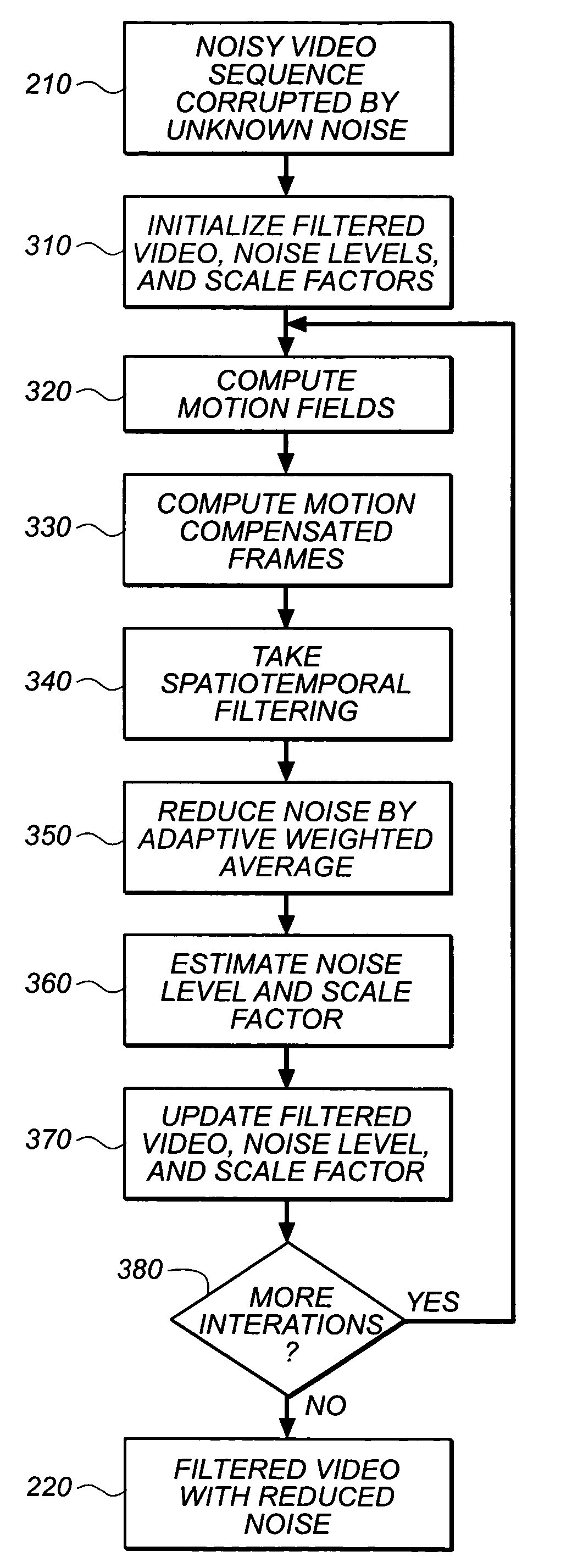
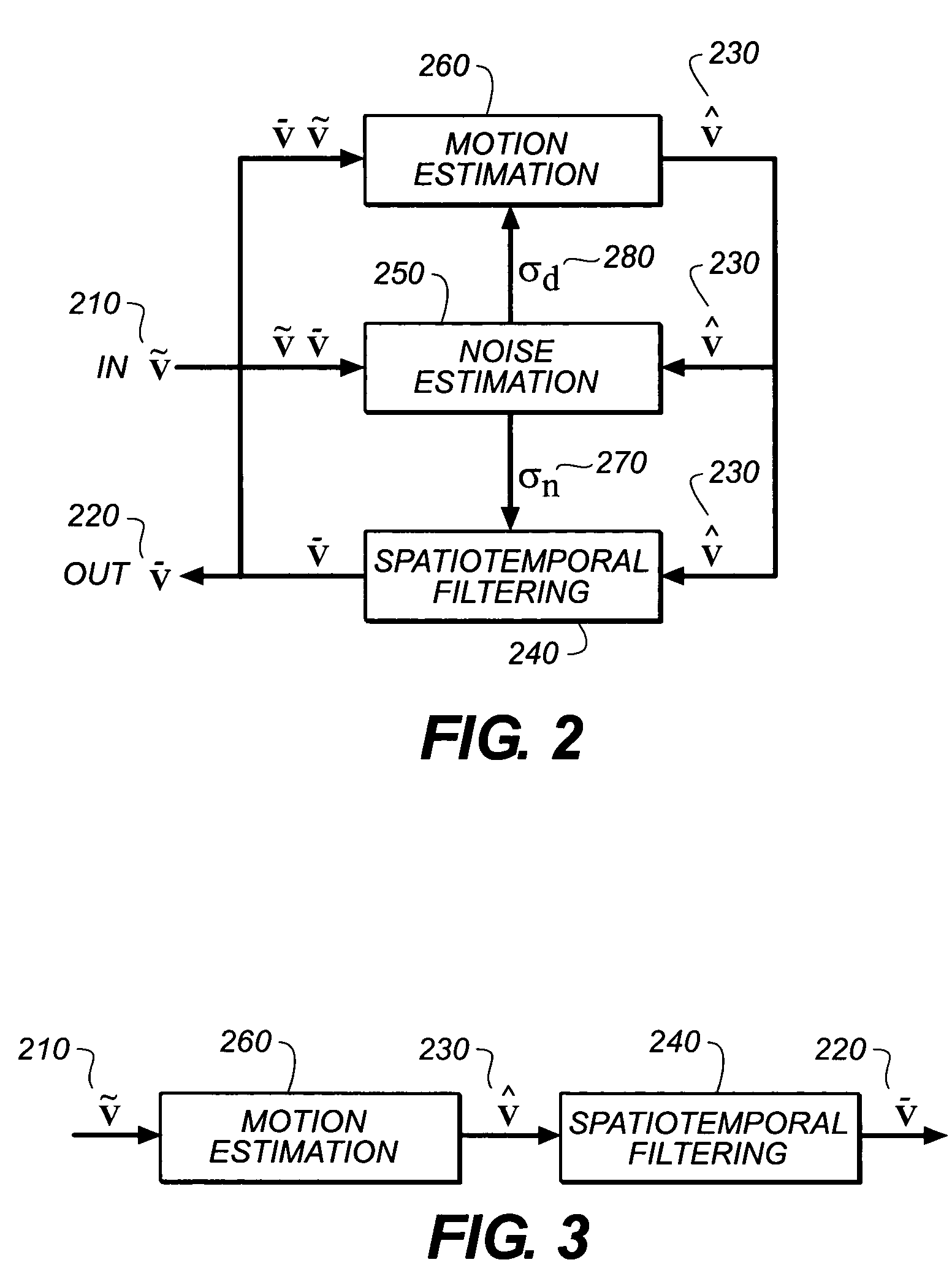
Method and system for video filtering with joint motion and noise estimation
ActiveUS7295616B2Reduce random noiseImprove performanceTelevision system detailsImage enhancementMotion fieldNoise level
A method for video filtering of an input video sequence by utilizing joint motion and noise estimation includes the steps of: (a) generating a motion-compensated video sequence from the input video sequence and a plurality of estimated motion fields; (b) spatiotemporally filtering the motion compensated video sequence, thereby producing a filtered, motion-compensated video sequence; (c) estimating a standard deviation from the difference between the input video sequence and the filtered, motion-compensated video sequence, thereby producing an estimated standard deviation; (d) estimating a scale factor from the difference between the input video sequence and the motion compensated video sequence; and (e) iterating through steps (a) to (d) using the scale factor previously obtained from step (d) to generate the motion-compensated video sequence in step (a) and using the estimated standard deviation previously obtained from step (c) to perform the filtering in step (b) until the value of the noise level approaches the unknown noise of the input video sequence, whereby the noise level is then characterized by a finally determined scale factor and standard deviation.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
Foreground object tracking
Techniques are disclosed for detecting foreground objects in a scene captured by a surveillance system and tracking the detected foreground objects from frame to frame in real time. A motion flow field is used to validate foreground objects(s) that are extracted from the background model of a scene. Spurious foreground objects are filtered before the foreground objects are provided to the tracking stage. The motion flow field is also used by the tracking stage to improve the performance of the tracking as needed for real time surveillance applications.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
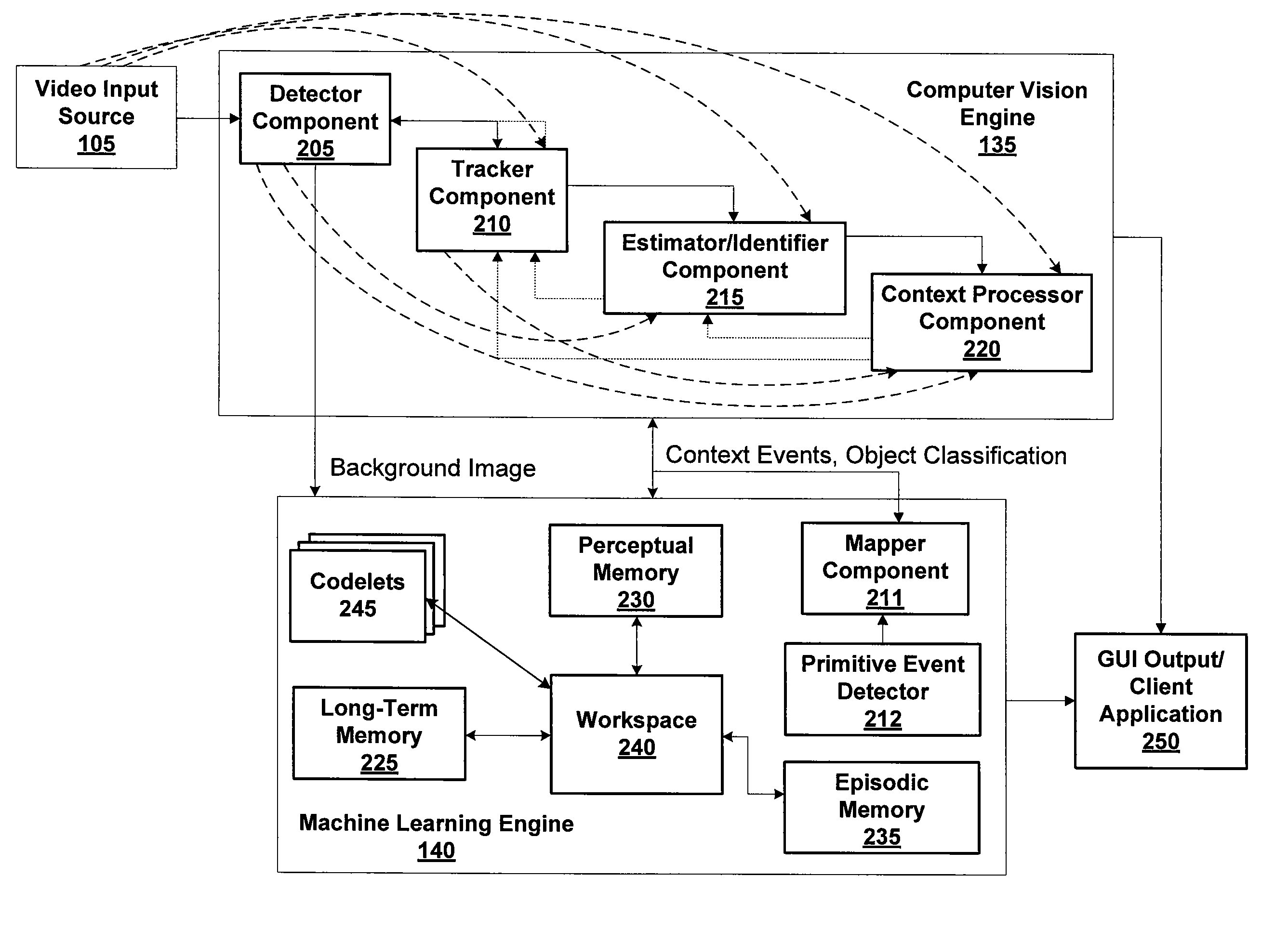
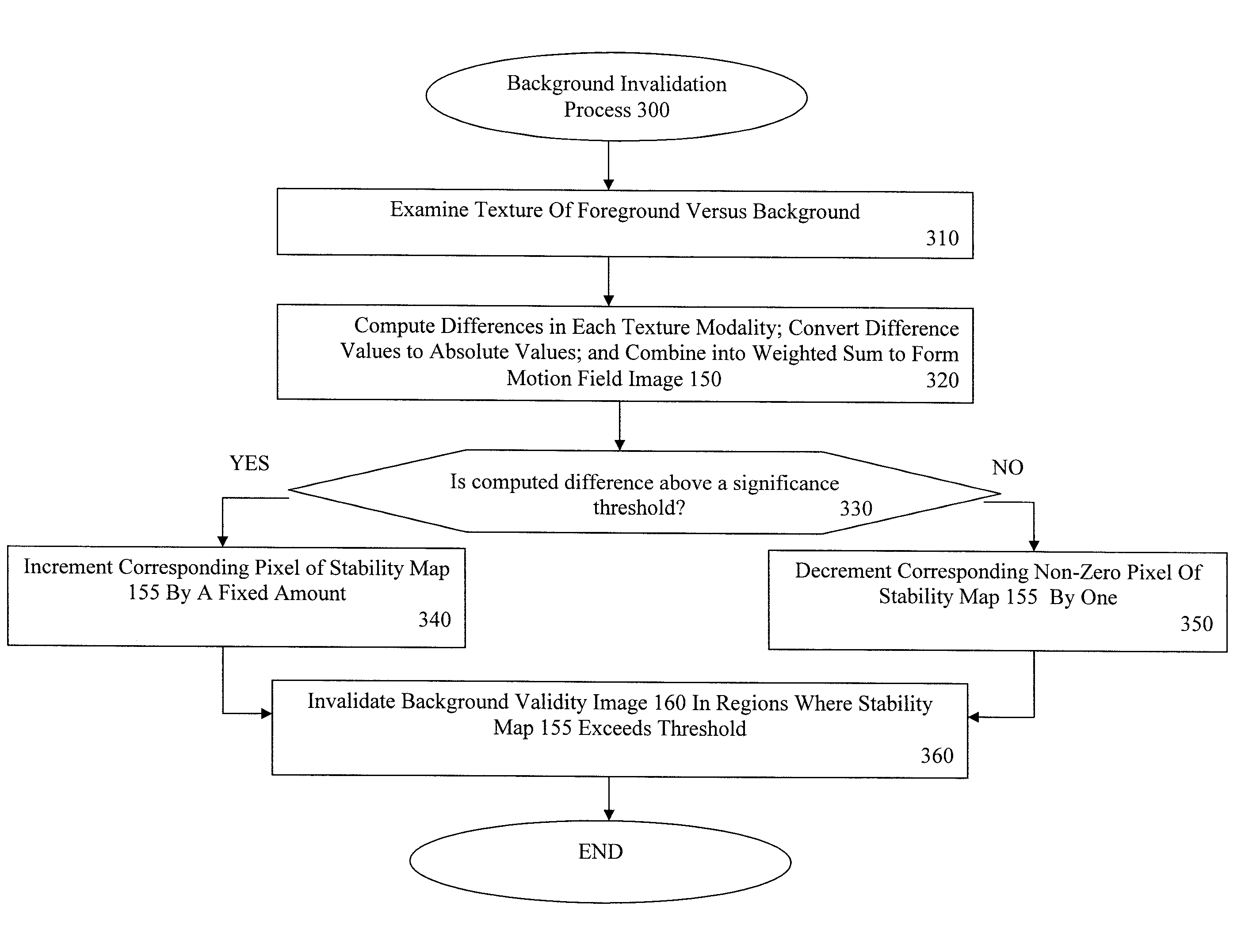
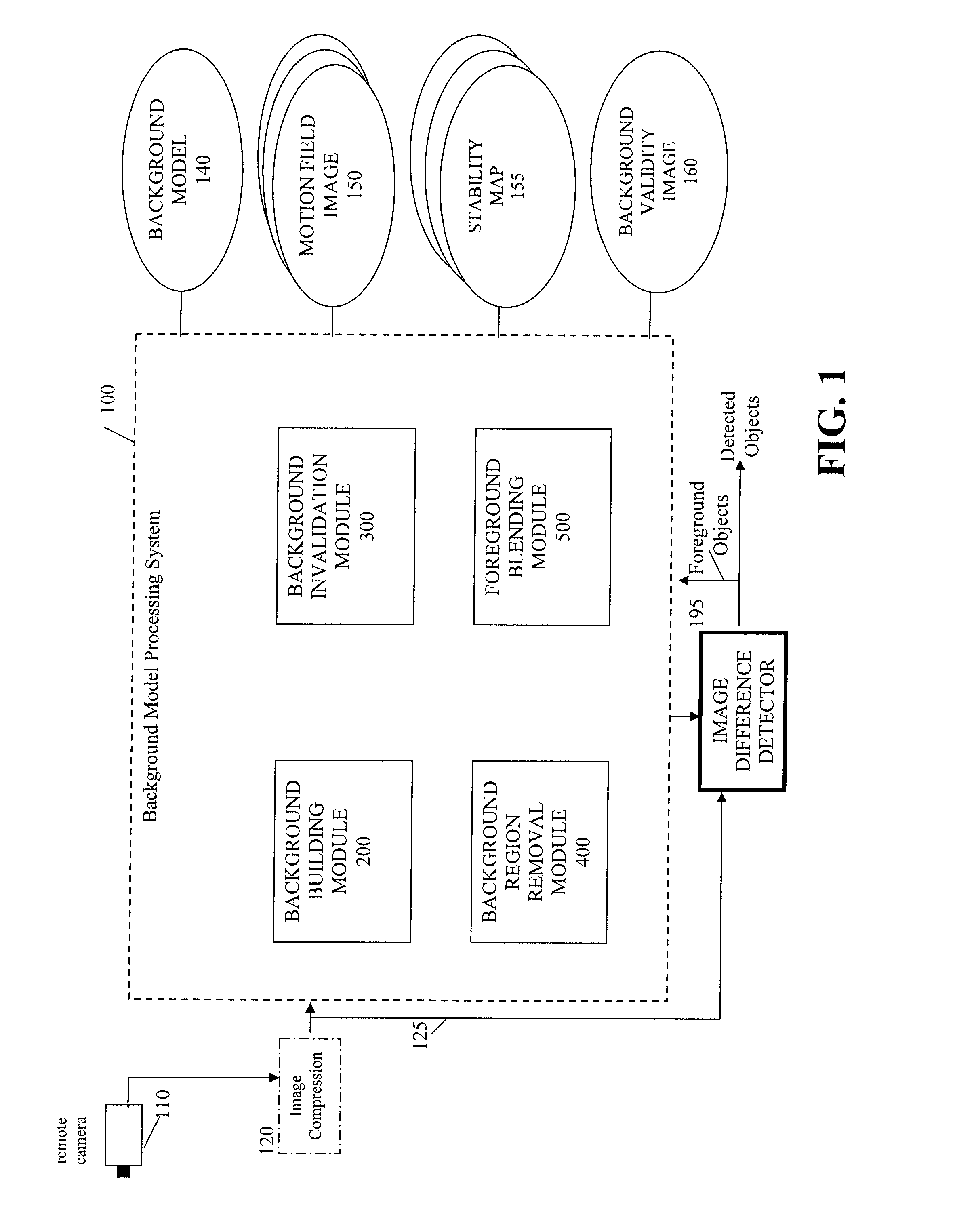
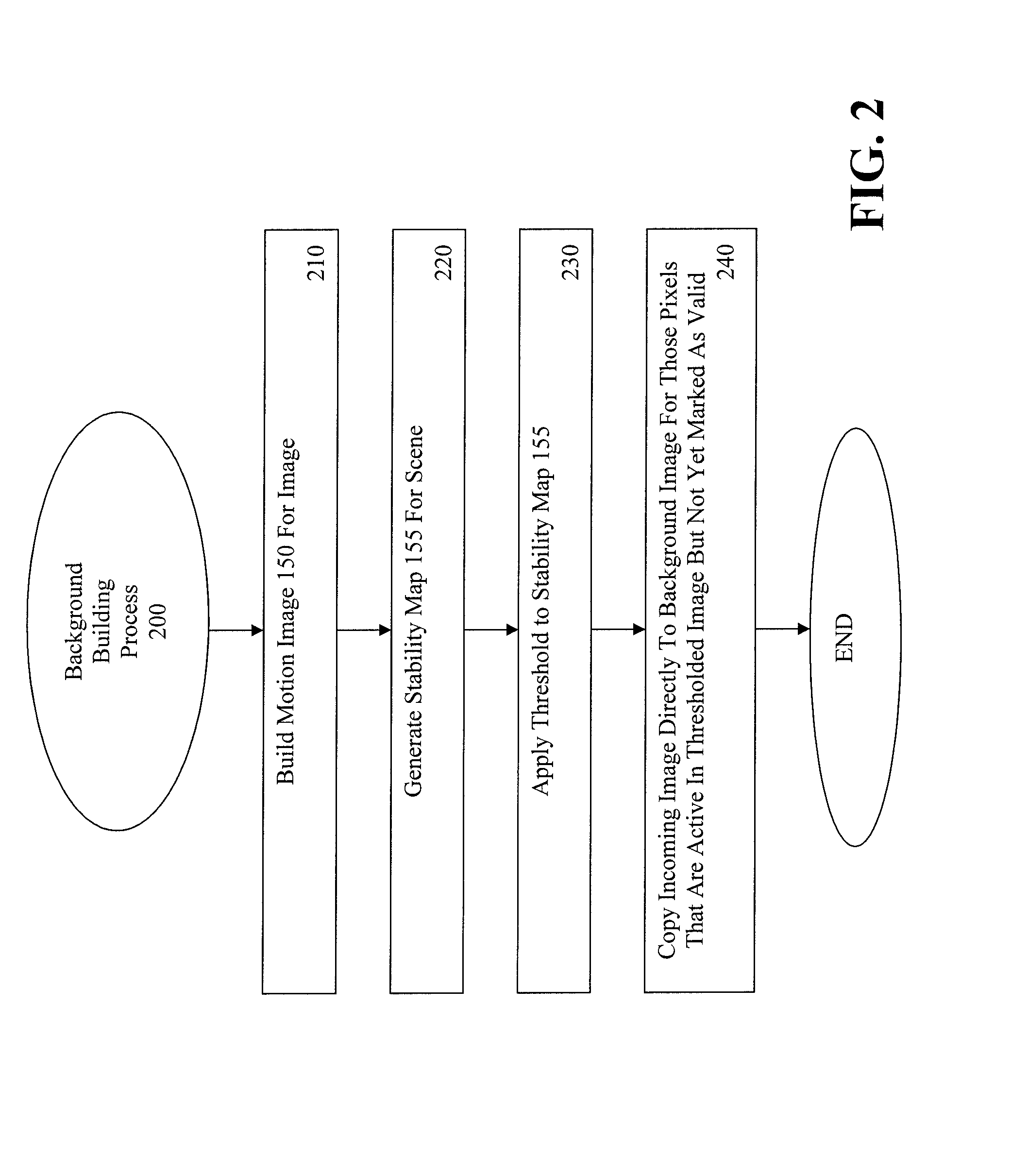
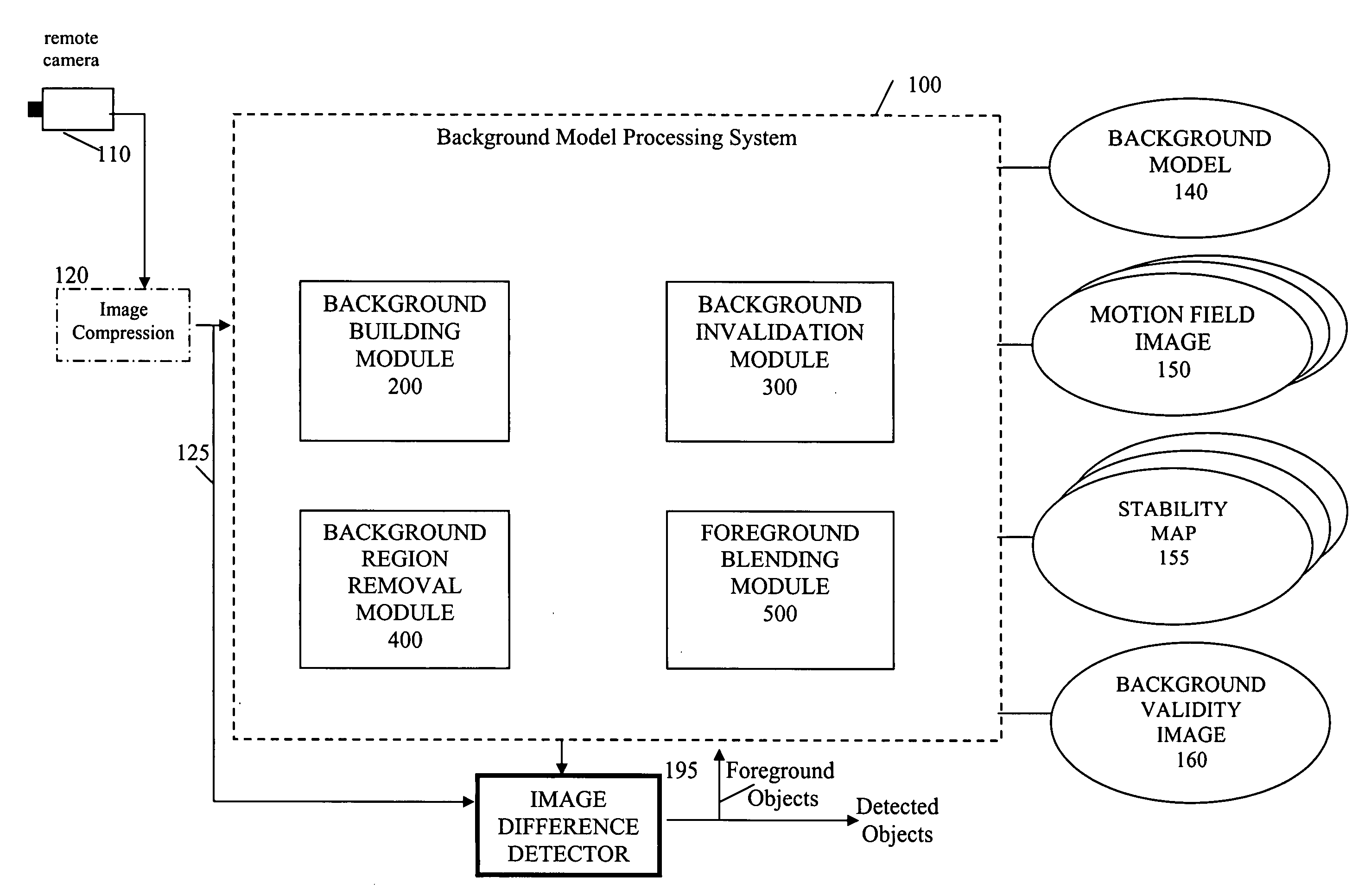
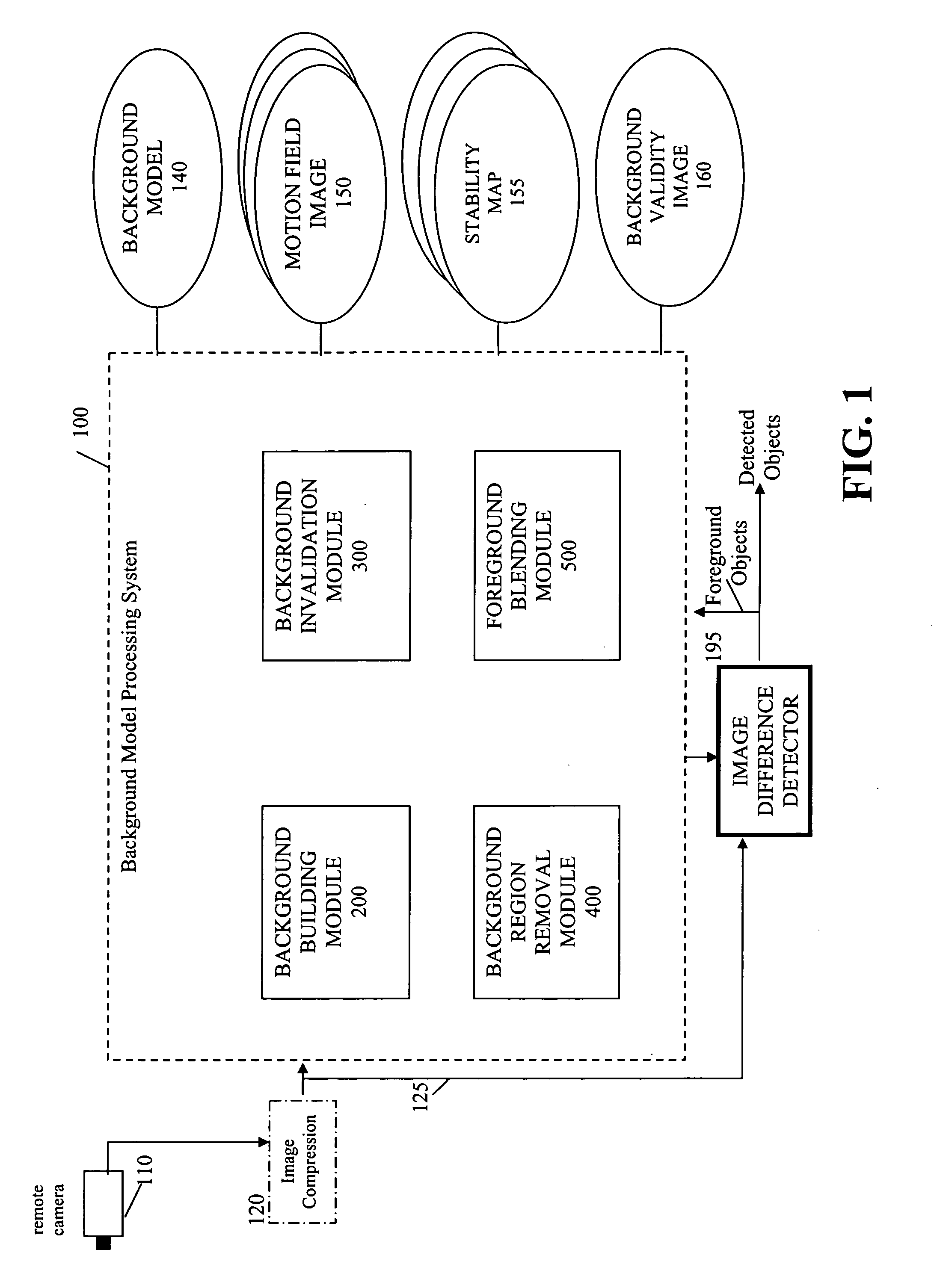
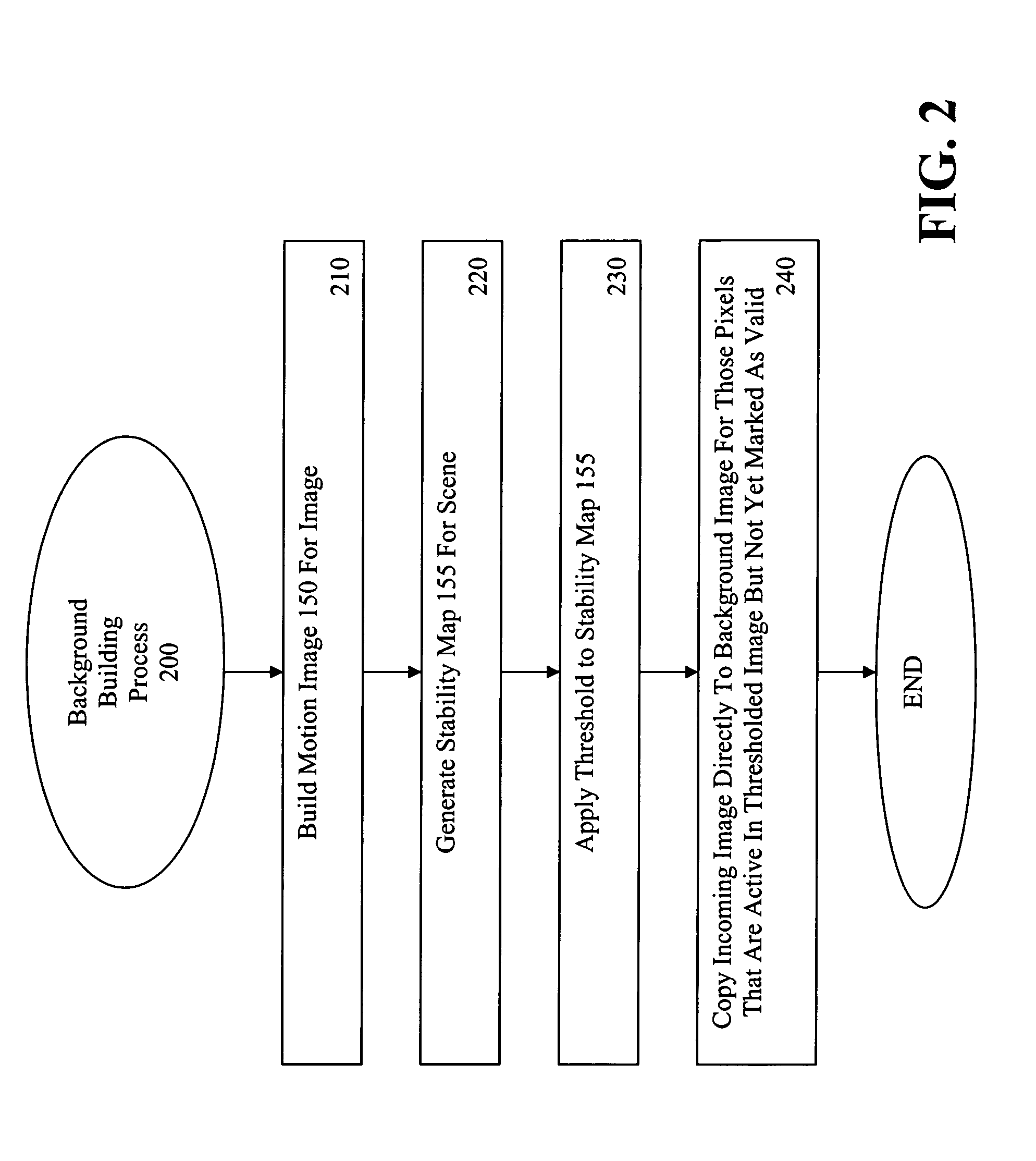
Method and Apparatus for Maintaining a Background Image Model in a Background Subtraction System Using Accumulated Motion
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
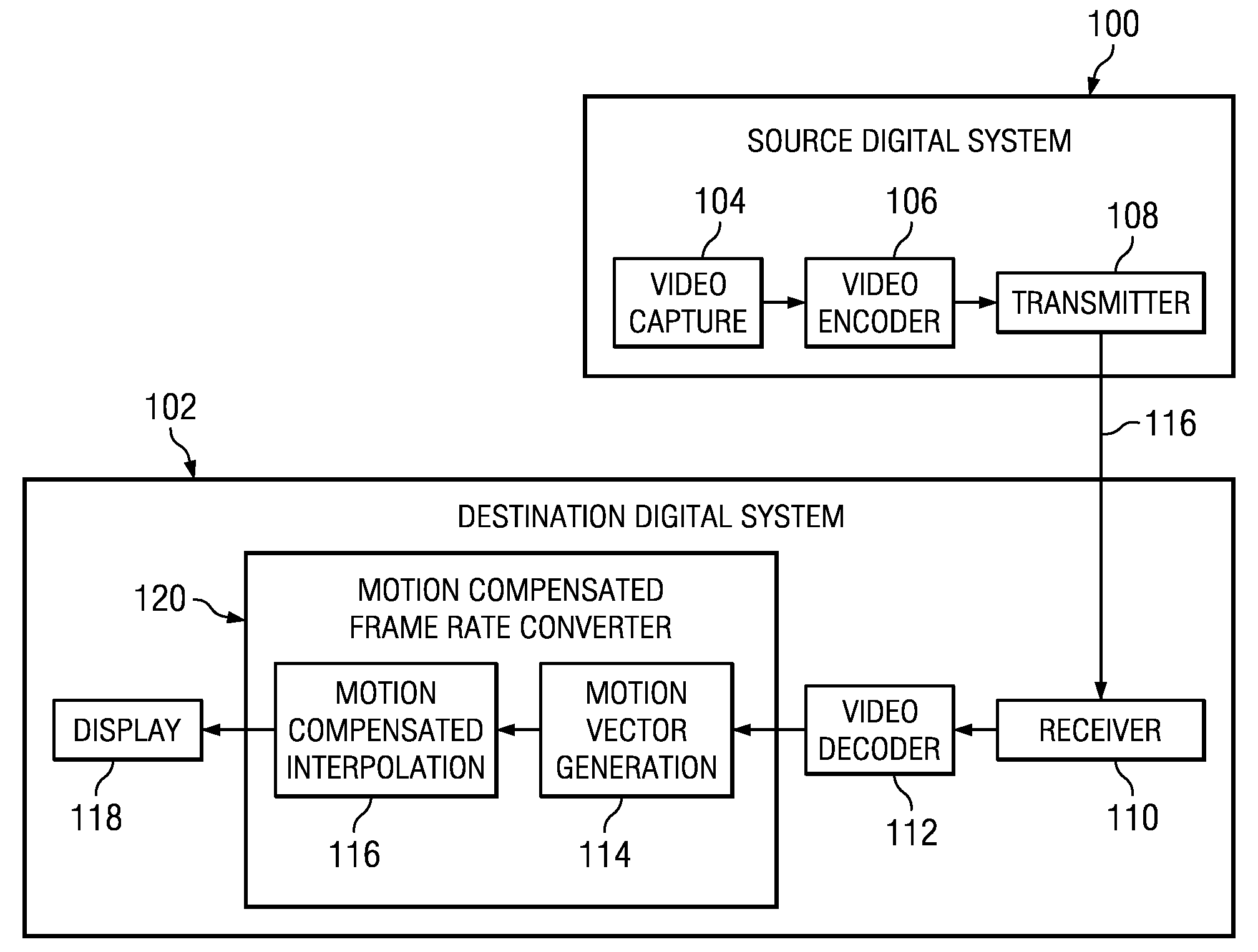
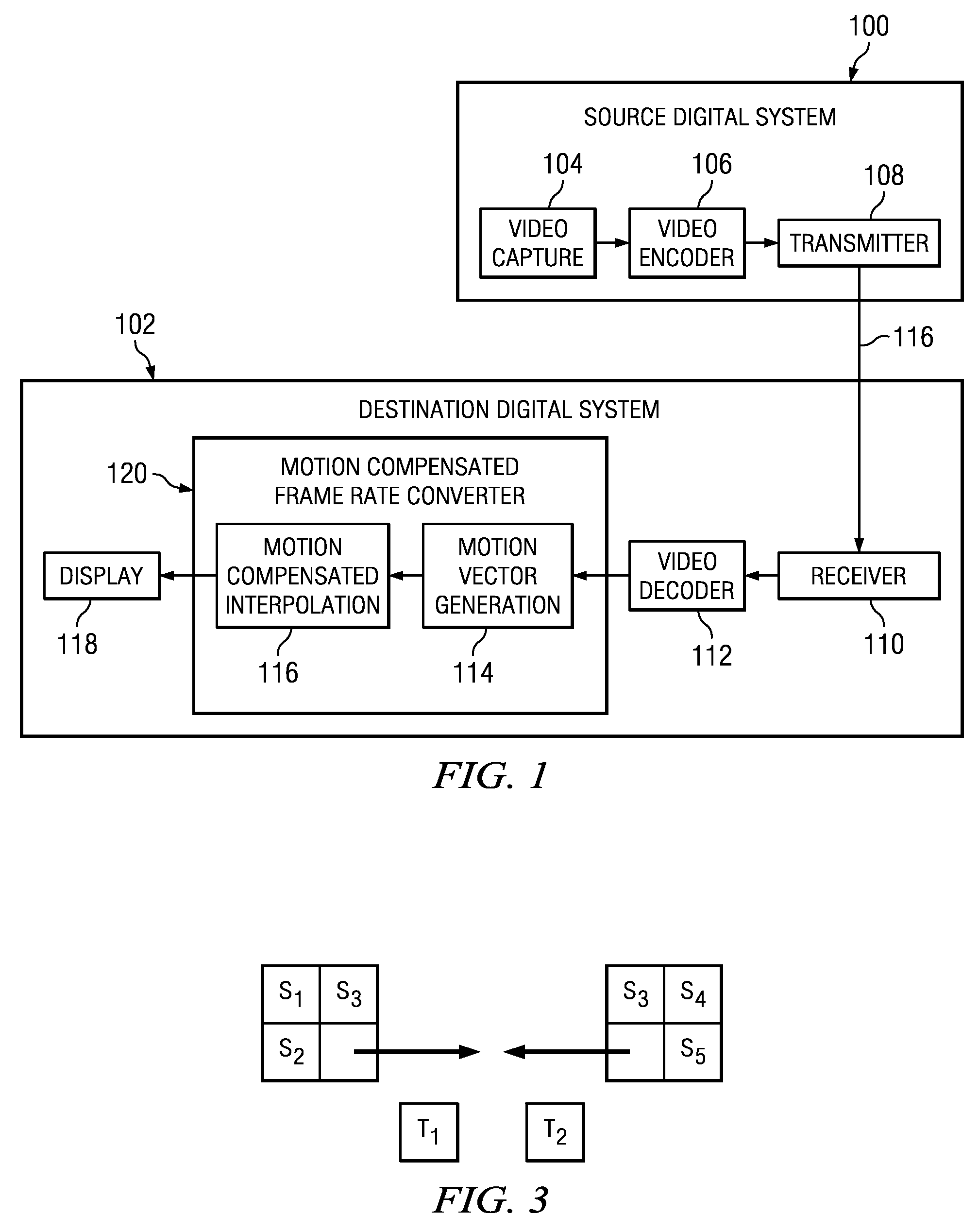
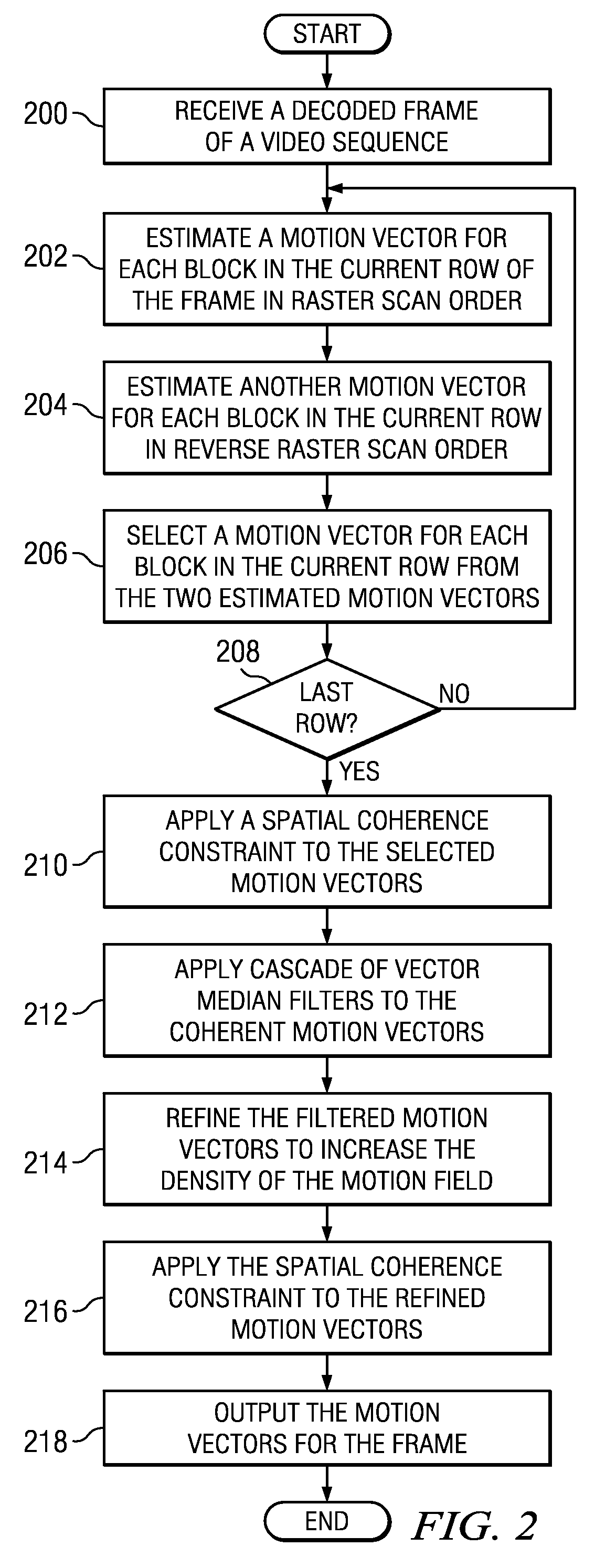
Method and System for Block-Based Motion Estimation for Motion-Compensated Frame Rate Conversion
InactiveUS20110026596A1Television system detailsColor television with pulse code modulationGratingMotion field
Methods for coherent block-based motion estimation for motion-compensated frame rate conversion of decoded video sequences are provided. In some of the disclosed methods, motion vectors are estimated for each block in a decoded frame in both raster scan order and reverse raster scan order using prediction vectors from selected spatially and temporally neighboring blocks. Further, in some of the disclosed methods, a spatial coherence constraint that detects and removes motion vector crossings is applied to the motion vectors estimated for each block in a frame to reduce halo artifacts in the up-converted video sequence. In addition, in some of the disclosed methods, post processing is performed on estimated motion vectors to improve the coherence of the motion vectors. This post-processing includes application of vector median filters to the estimated motion vectors for a frame and / or application of a sub-block motion refinement to increase the density of the motion field.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
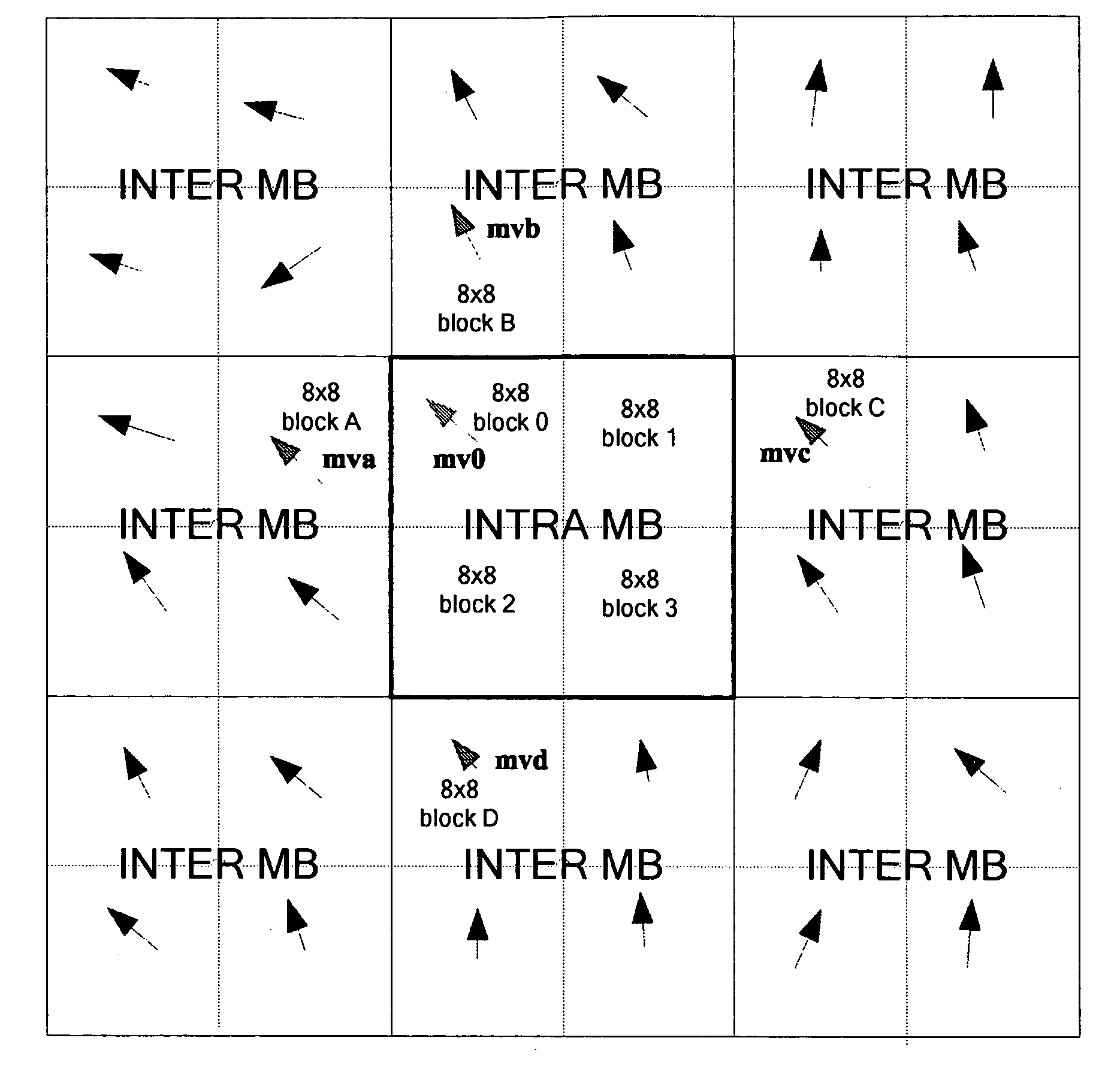
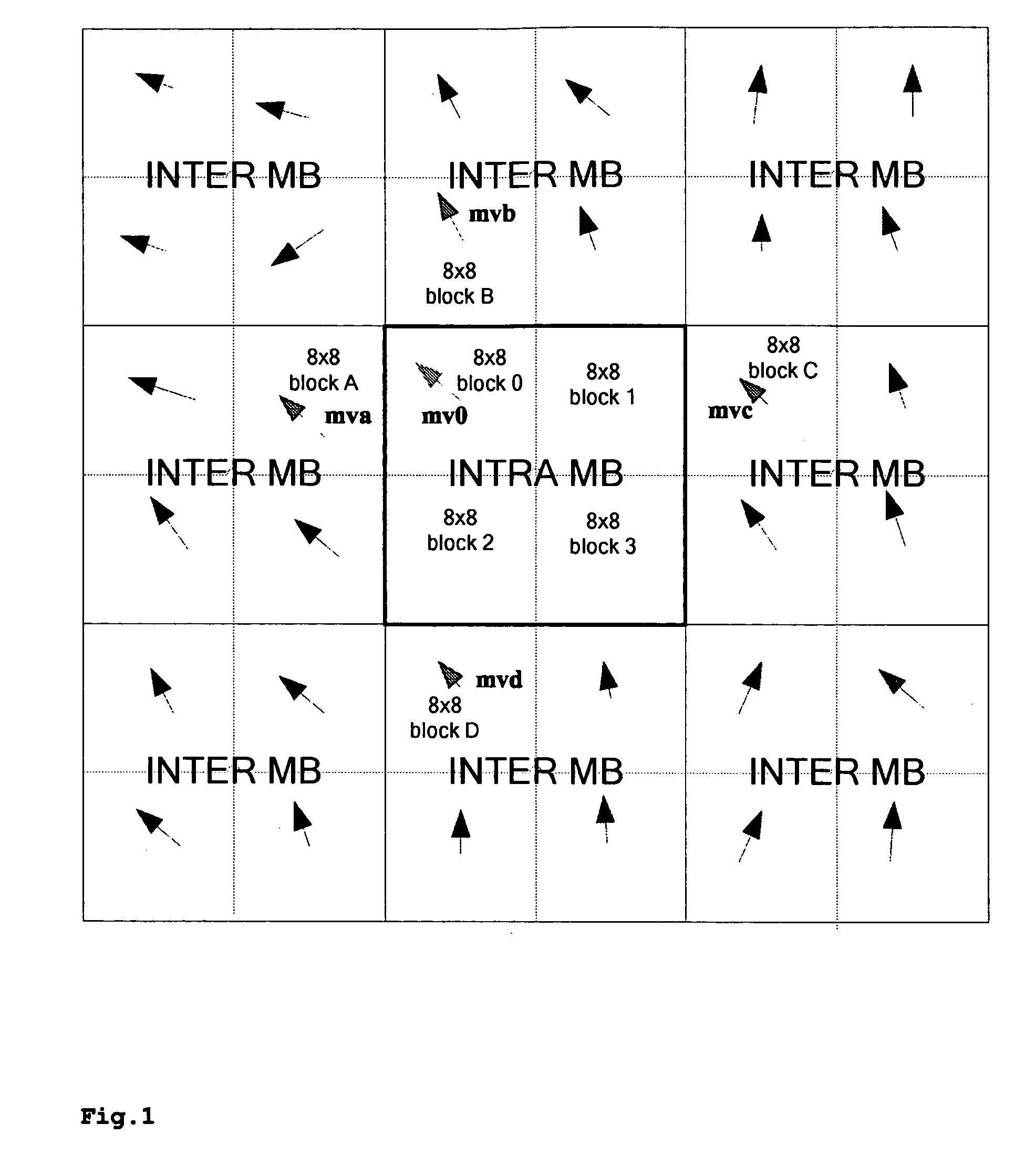
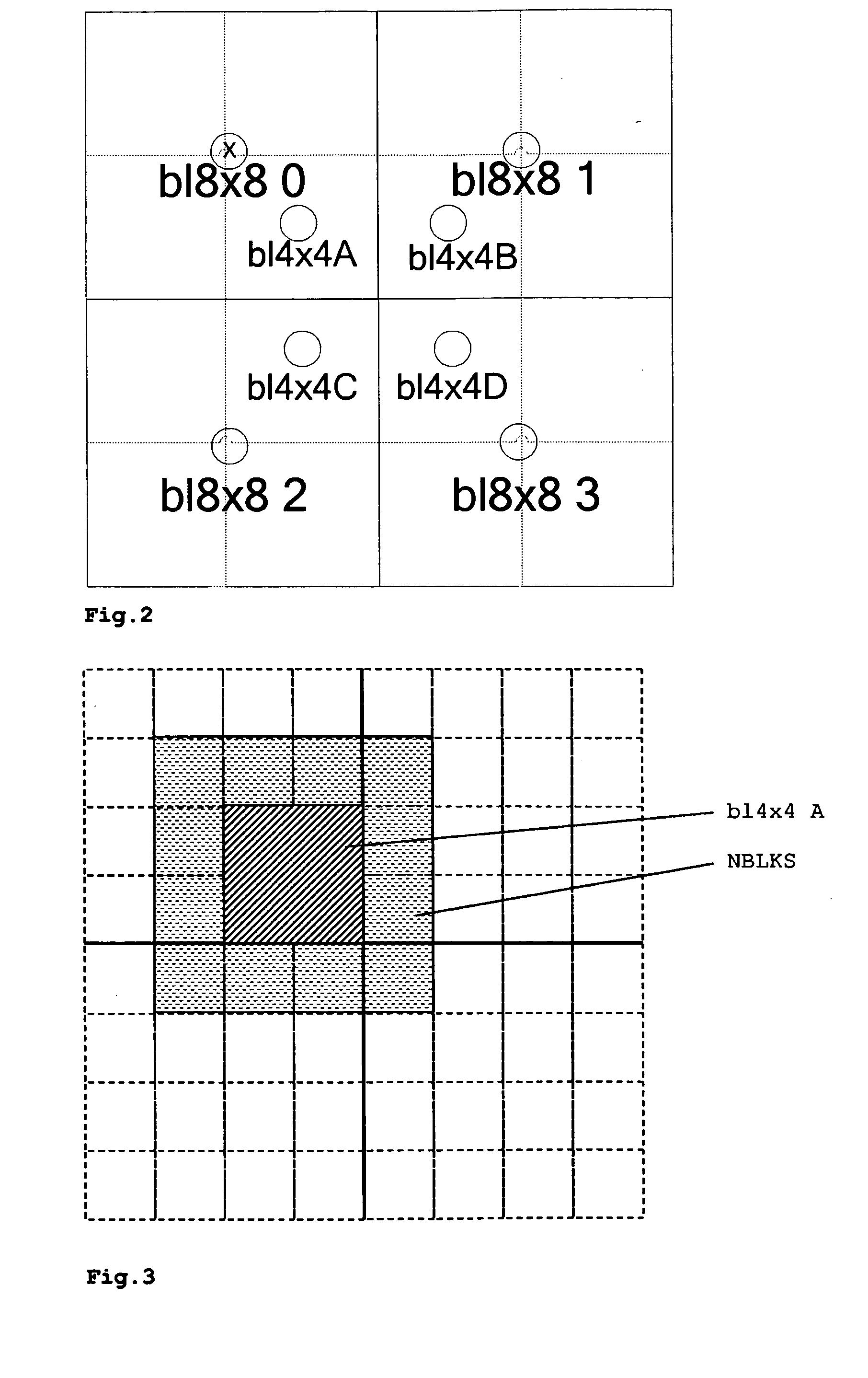
Method and Apparatus for Encoding Enhancement Layer Video Data
ActiveUS20090285299A1Improve accuracyImprove coding efficiencyPulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesMotion fieldMotion vector
A method for improving the performance of the BLSkip mode in SVC includes the steps of upsampling the motion field of the base layer, interpolating the motion vectors for the intra MBs, interpolating the 8×8 block motion field to a 4×4 block motion field, and generating a MV predictor for a 4×4 block in BLSkip mode using neighbor candidates.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
System and method for controlling movement of a plurality of game objects along a playfield
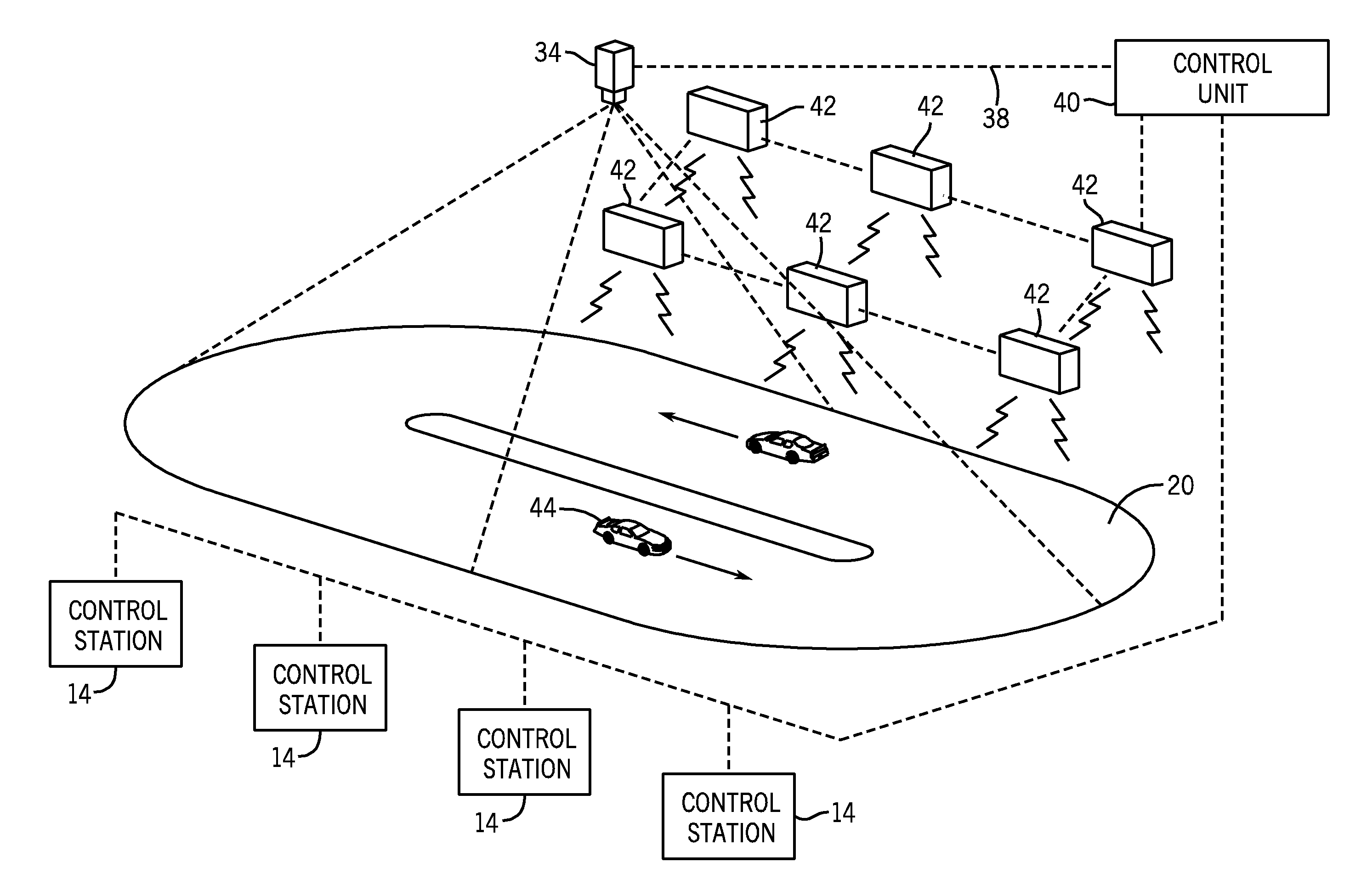
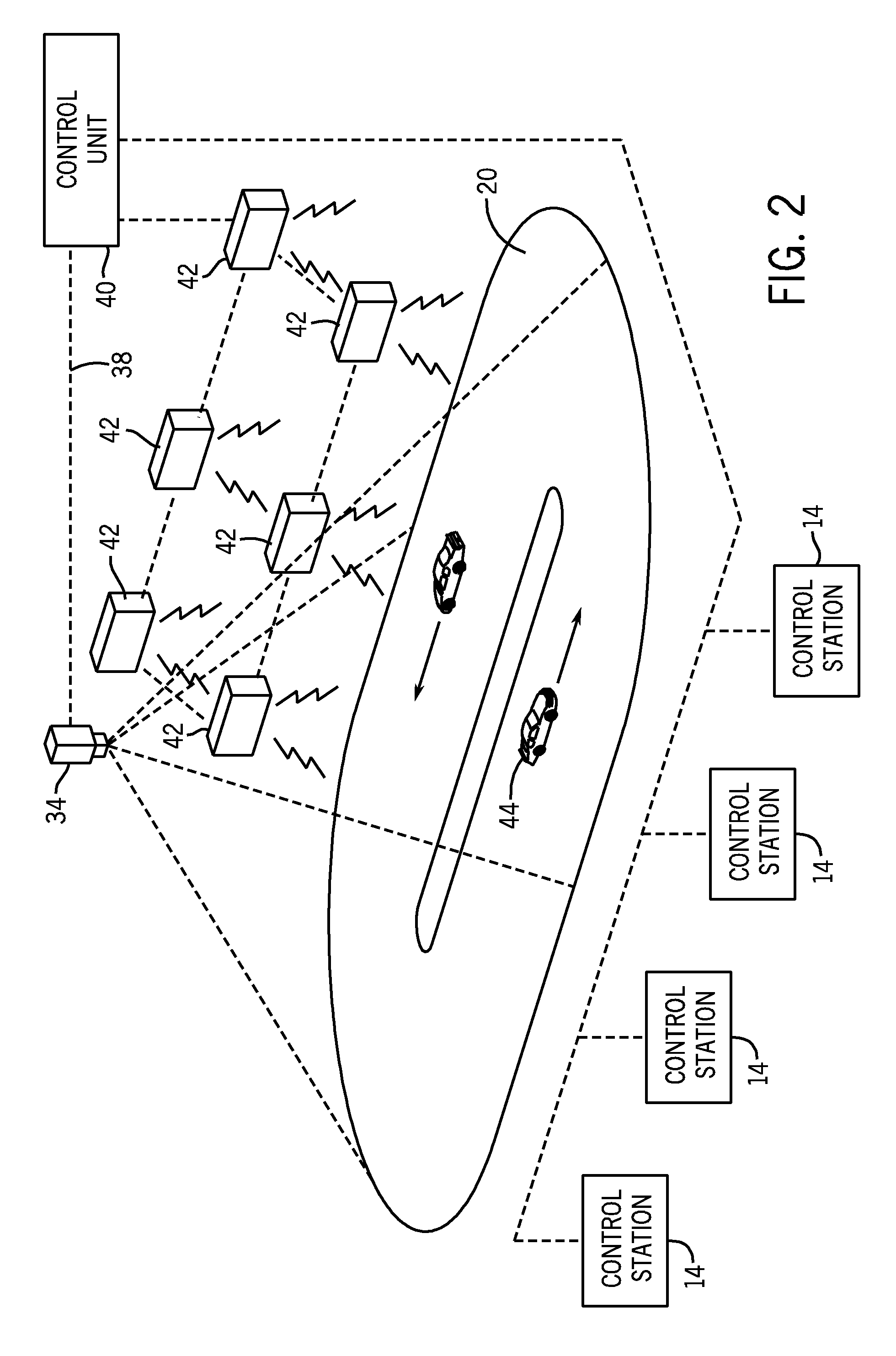
An amusement game and method that utilize an image sensing device to track and determine the position of a plurality of game objects on a playfield. The amusement game includes an image sensing device, such as a CCD or CMOS camera, that is positioned to view the playfield of the amusement game and track the movement of a plurality of game objects along the playfield. During game play, the control unit may control the movement of one or more of the game objects along the playfield. The control unit receives a series of sequential image scans from the image sensing device and determines the position and movement of the game objects along the playfield. Based upon the detected position of the game objects under computer control, the control unit modifies the control parameters of the game object during game play.
Owner:BAY TEK GAMES
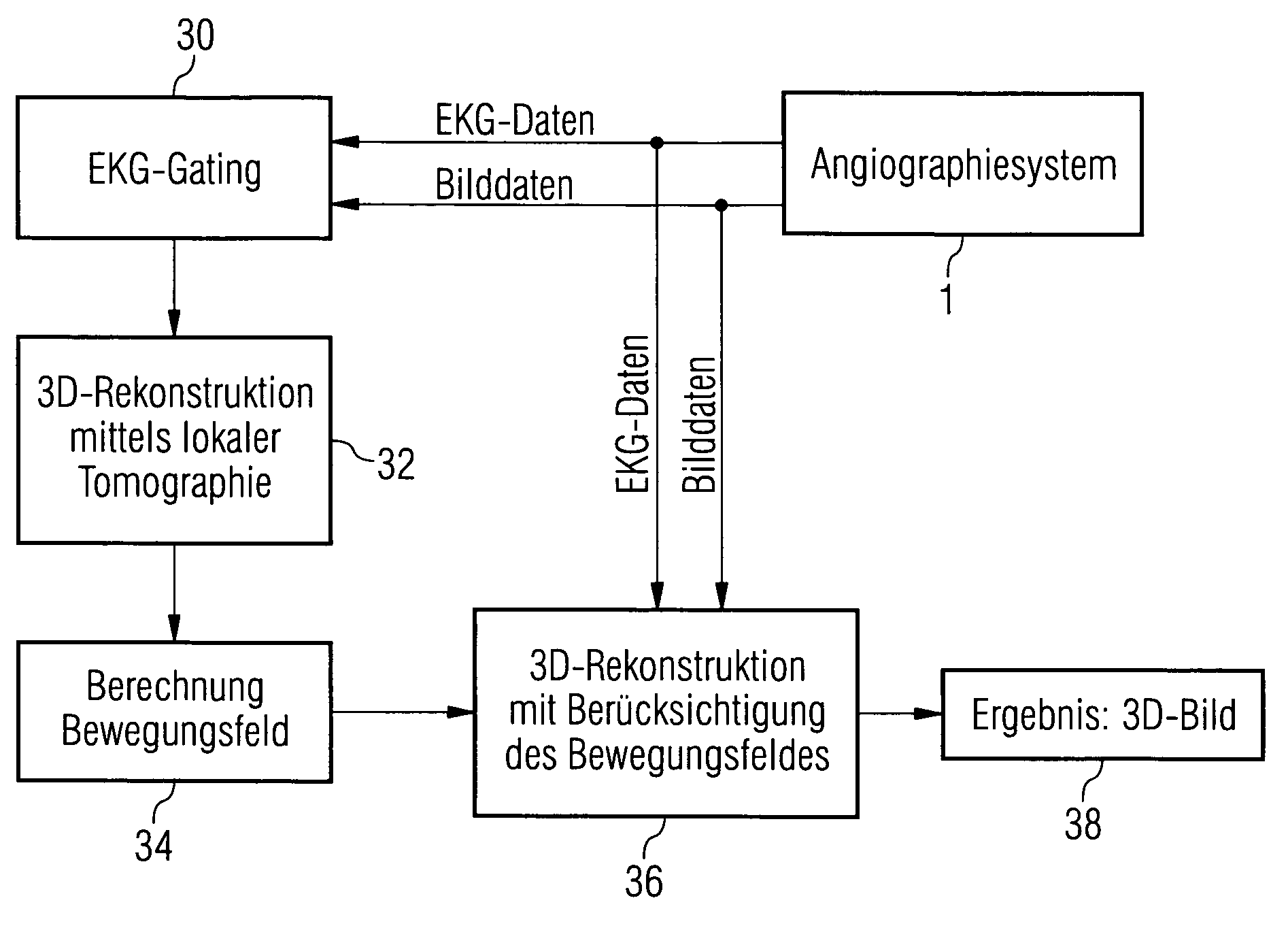
Method and device for reconstructing a 3D image data set of a moving object
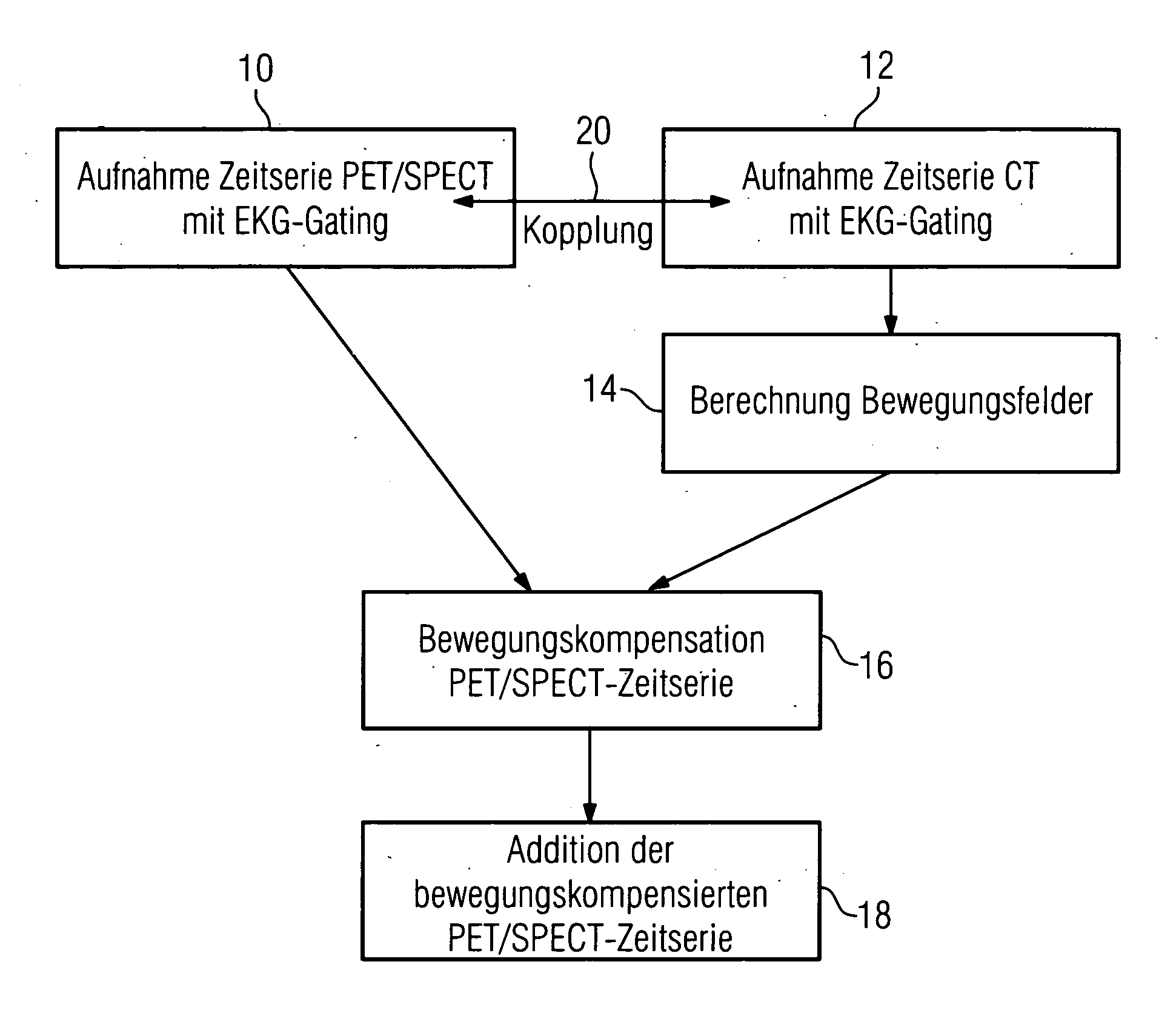
InactiveUS20060285632A1High quality imagingReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationEcg gatingMotion field
The invention relates to a method and device for reconstructing a 3D image data set of a moving object from a set of projection images, which were recorded at least partially one after the other from different projection directions. The projection images are hereby assigned by ECG gating to a motion phase of the object in each instance and an incomplete 3D image of the object is computed in this motion phase from these few projection images using local tomography. Motion fields are determined from these 3D images and are used during the final 3D image reconstruction for motion corrections.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Image-based object detection apparatus and method
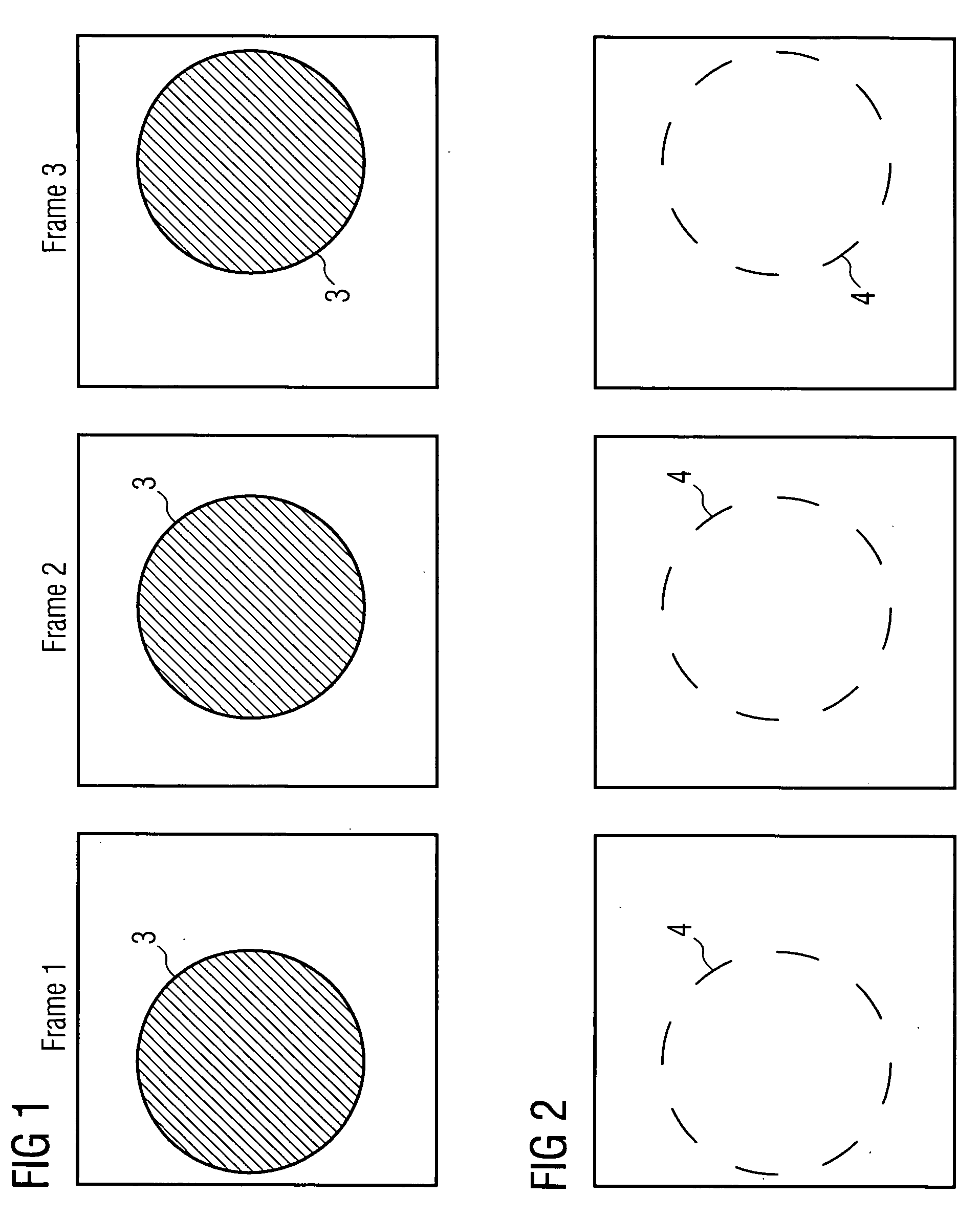
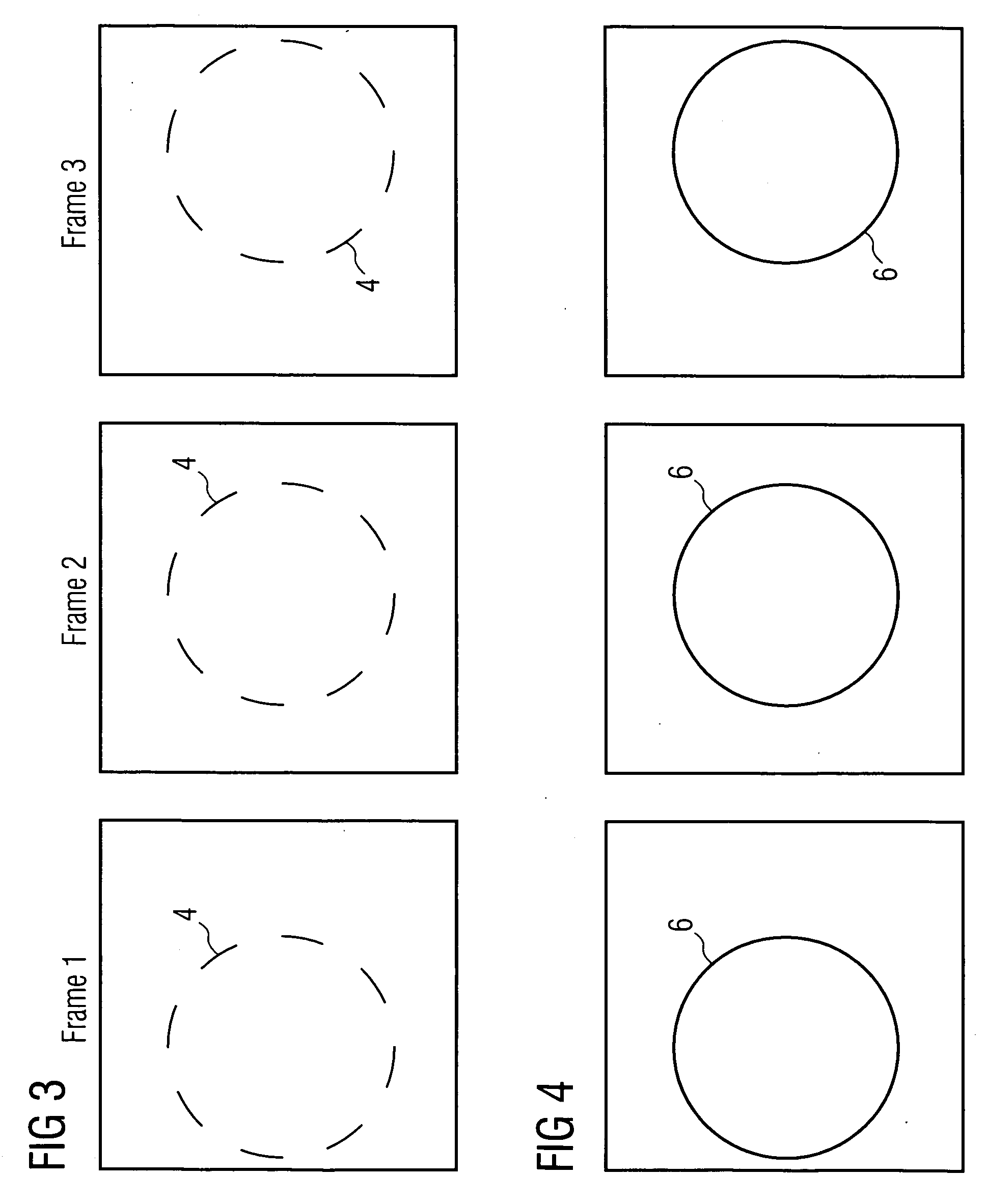
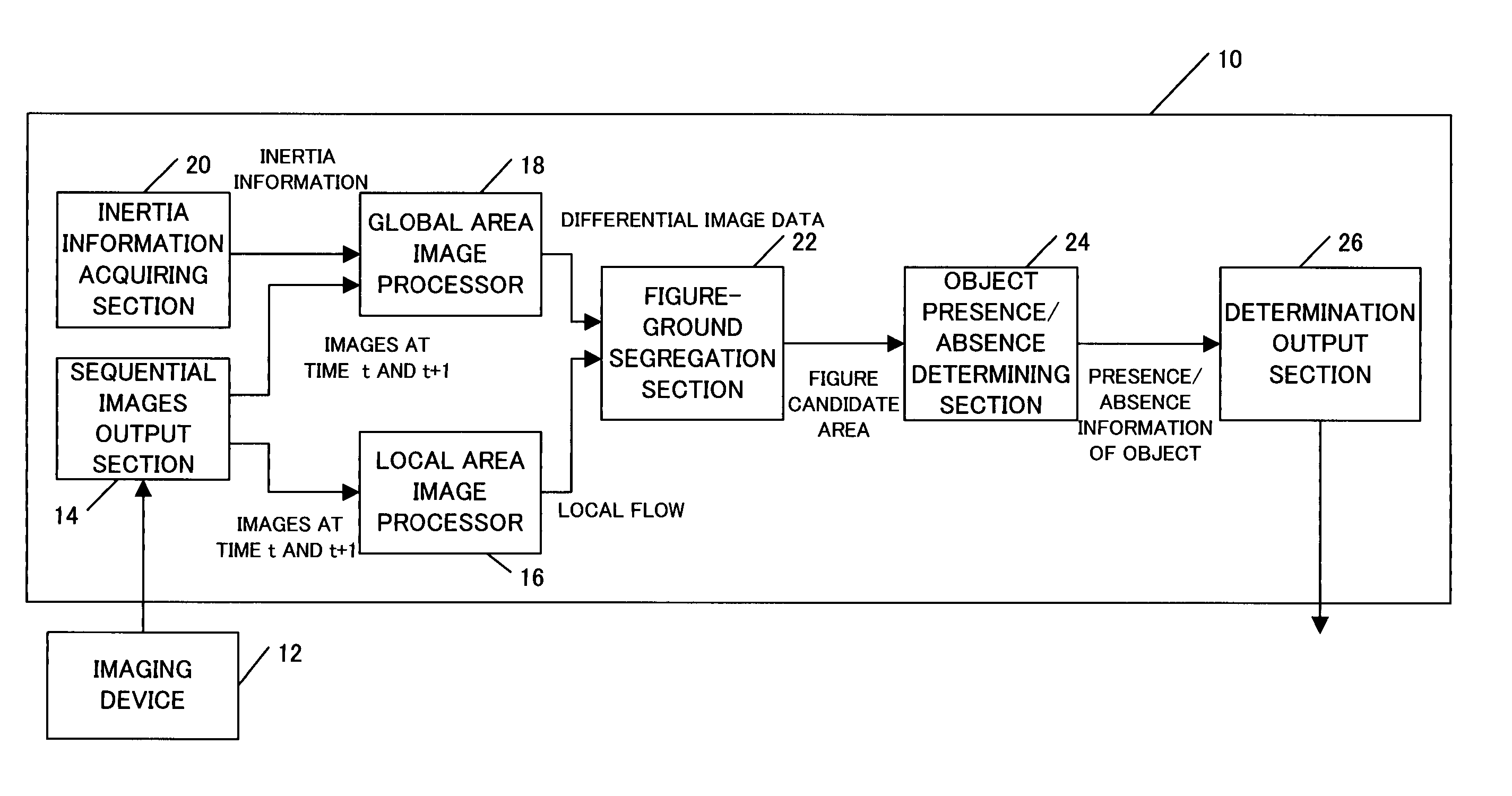
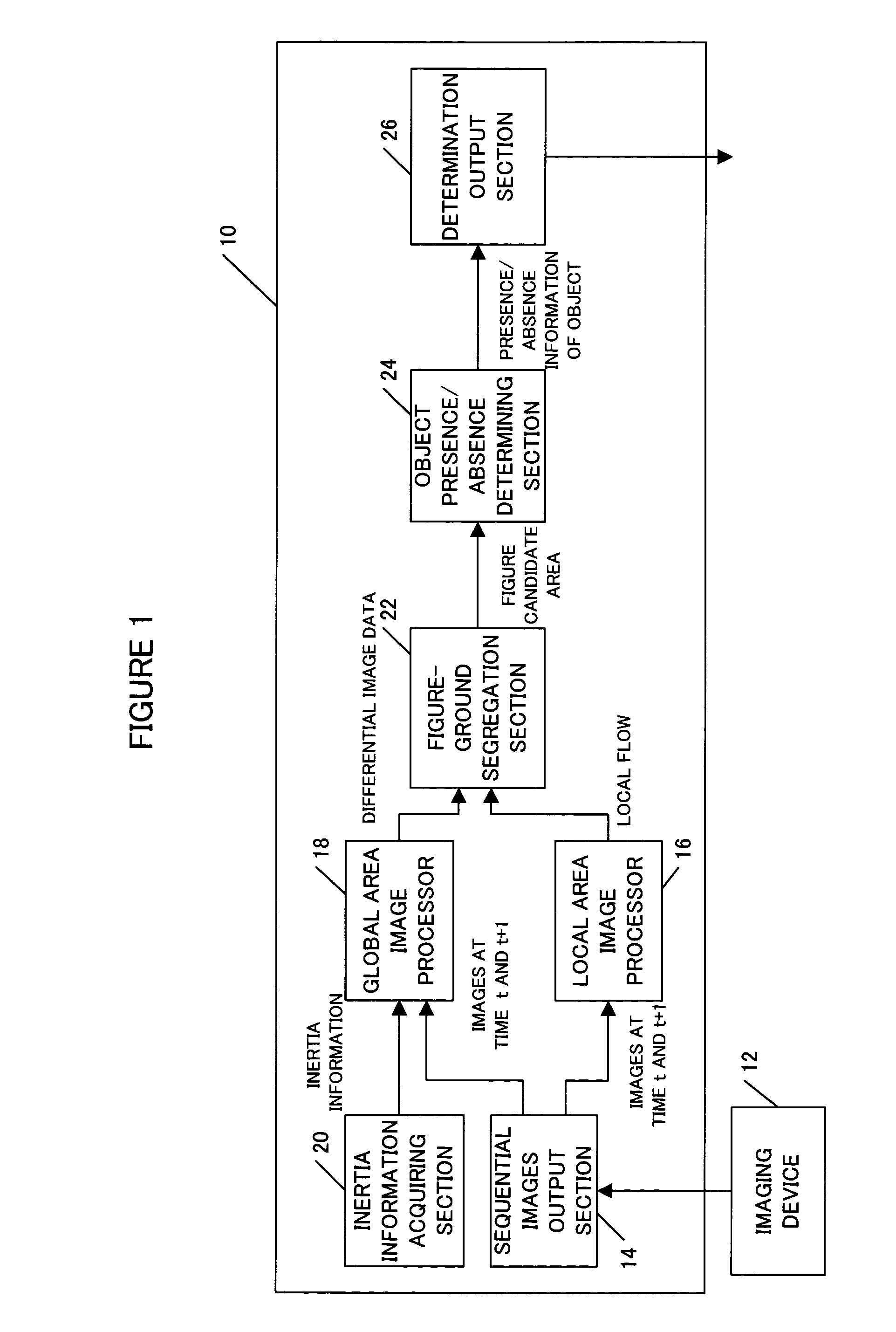
InactiveUS20050248654A1Improve accuracyAccurate detectionTelevision system detailsImage analysisObject basedVisual perception
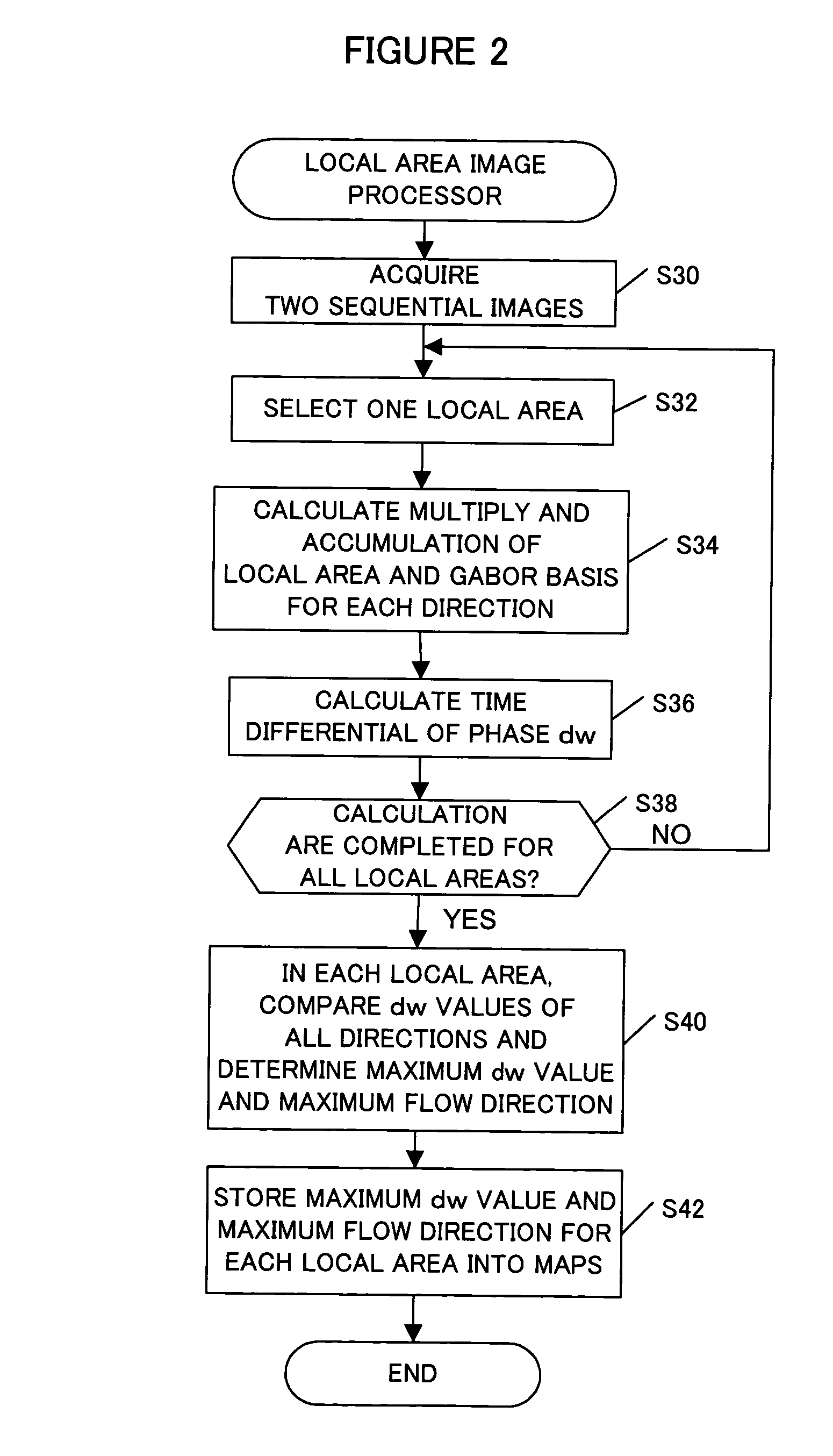
An object detection apparatus and method capable of detecting objects based on visual images captured by a self-moving unit. A sequential images output section makes a train of a first input image and a second input image sequential to the first input image and outputs said train. A local area image processor calculates local flows based on said first input image and said second input image. An inertia information acquiring section measures self-motion of the unit to calculate inertia information thereof. A global area image processor uses said inertia information to estimate global flow, which is a motion field of the entire view associated to the self-motion, using said global flow and said first input image and creates a predictive image of said second input image. The global area image processor then calculates differential image data, which is a difference between said predictive image and said second input image. A figure-ground segregation section uses said differential image data to refine said local flows and compares the refined local flows with a predetermined threshold value to extract a figure candidate area, which is the area having a high probability of an object existing in the input image. An object presence / absence determination section determines presence / absence of objects in said figure candidate area.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
PET image acquiring method and system
InactiveCN105147312AReduce radiation timeImprove clinical experienceComputerised tomographsTomographyUltrasound attenuationMotion field
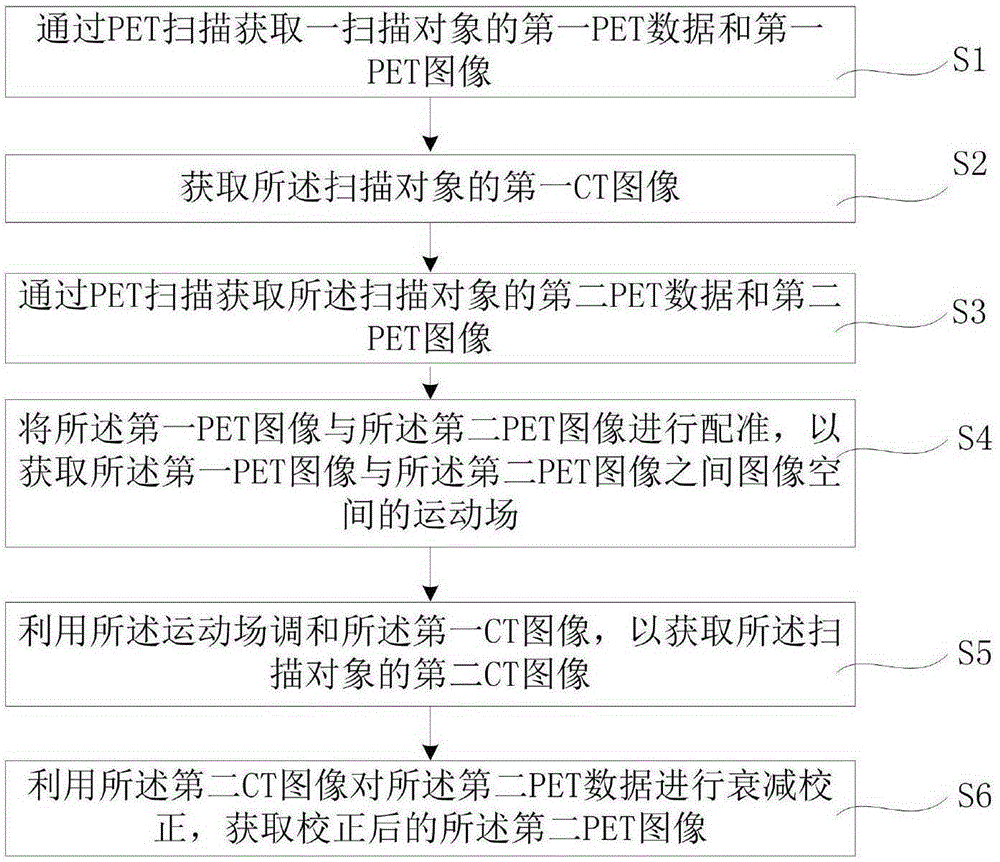
The invention provides a PET image acquiring method and system. The method comprises registering a first PET image and a corrected second PET image to acquire a motion field of an image space between the corrected first PET image and a second PET image; harmonizing a first CT image using the motion field to acquire a second CT image of a scanned object; carrying out attenuation correction on second PET data using the second CT image to acquire the corrected second PET iamge. According to the PET image acquiring method and system, the corrected second PET image can be acquired through carrying out attenuation correction on second PET data using the second CT image, a process for acquiring the second CT image through secondary CT scanning can be omitted, time of X-ray radiation during CT scanning can be shortened, and a better clinic experience can be achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
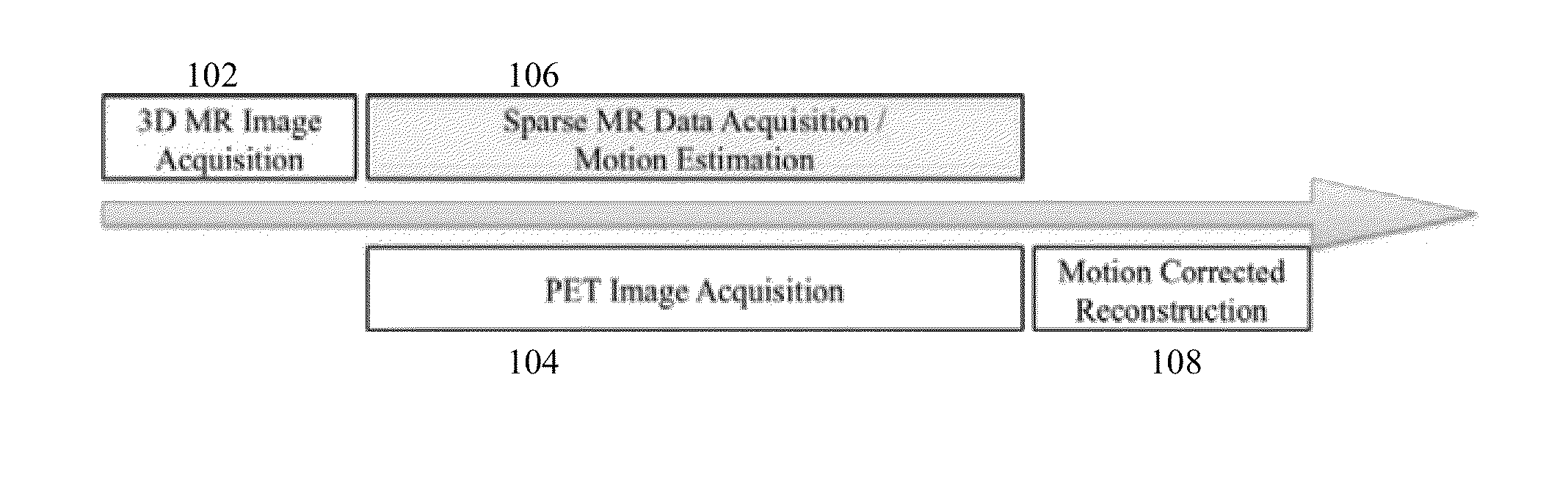
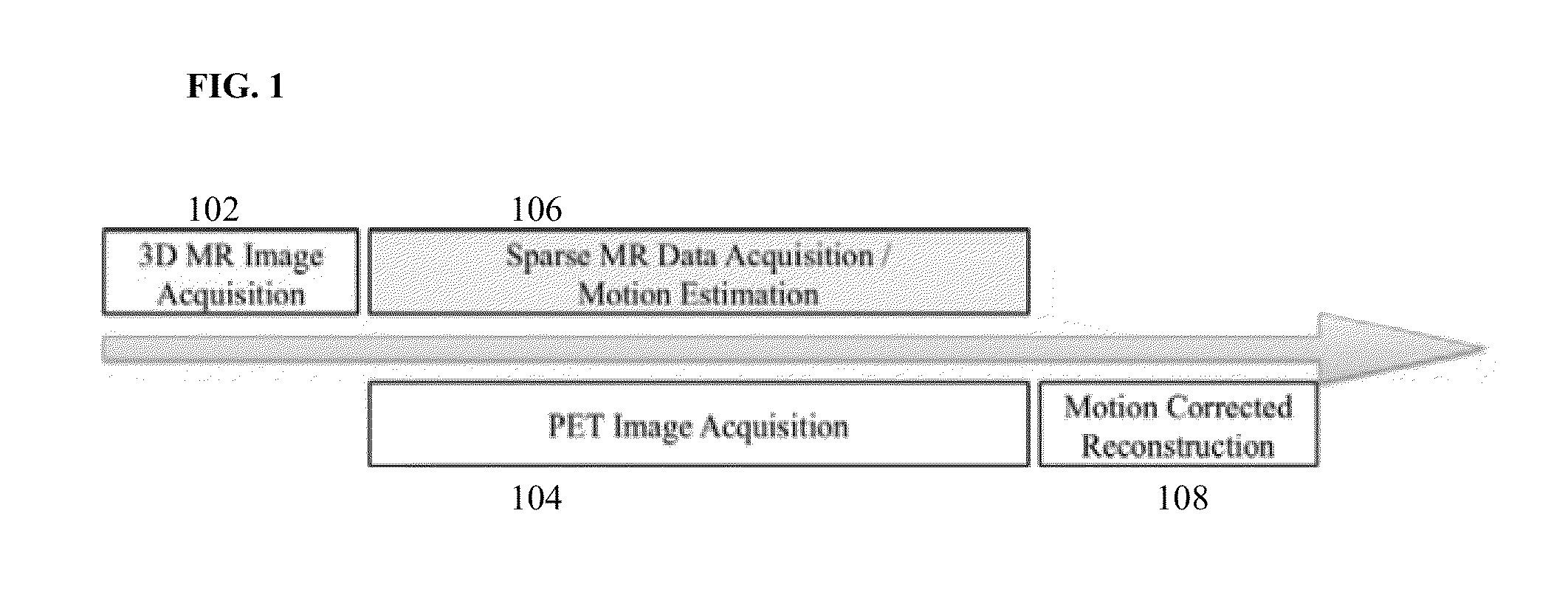
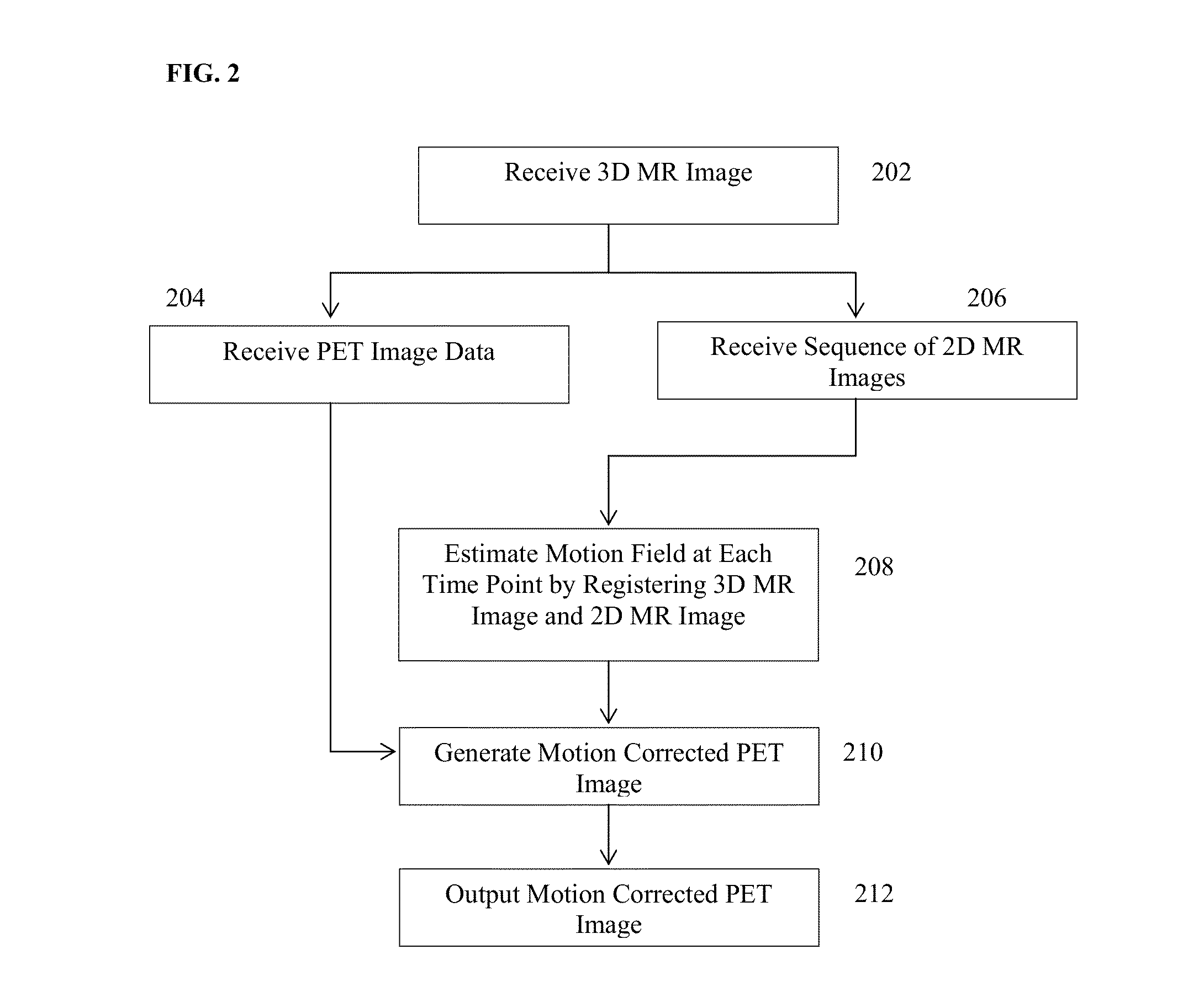
System and Method for Magnetic Resonance Imaging Based Respiratory Motion Correction for PET/MRI
A method and system for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) based motion correction in position emission tomography (PET) images is disclosed. A static 3D magnetic resonance (MR) image of a patient is received. PET image data of the patient and a series of 2D MR images of the patient acquired simultaneous to the acquisition of the PET image data are received. A 3D+t motion field is estimated by registering the series of 2D MR images acquired at the plurality of time points to the static 3D MR image. A motion corrected PET image is generated based on the estimated 3D+t motion field using motion corrected PET reconstruction.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
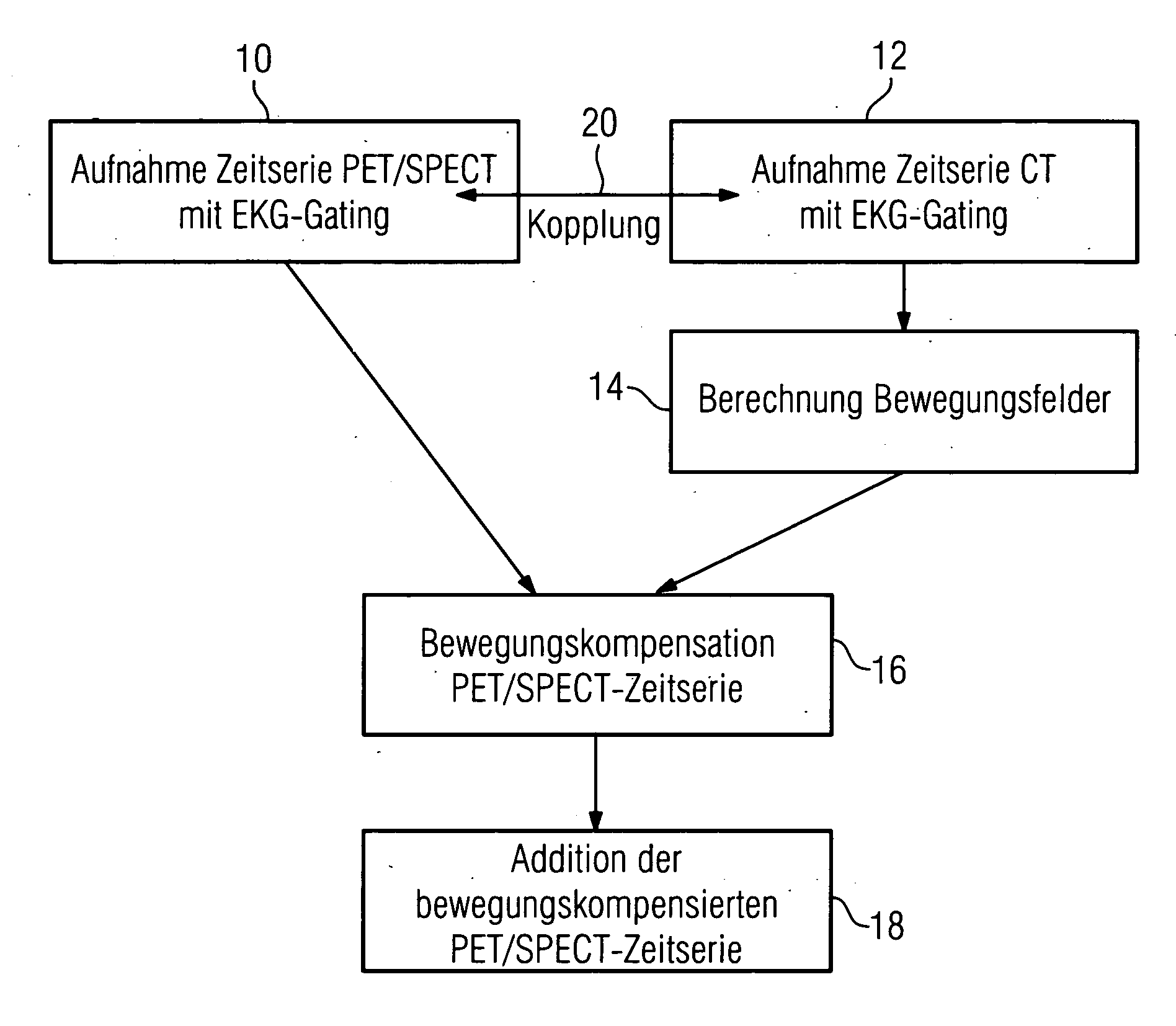
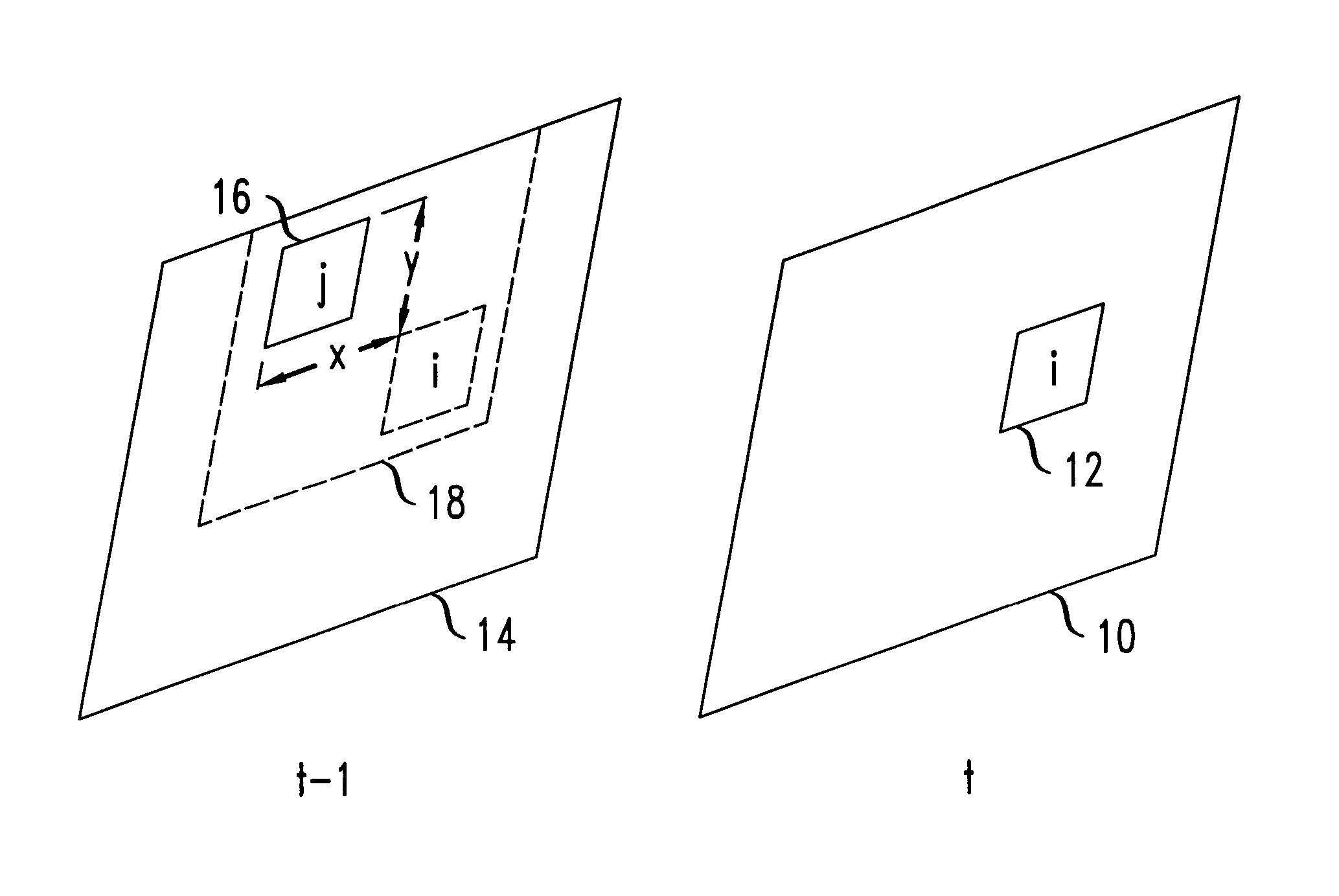
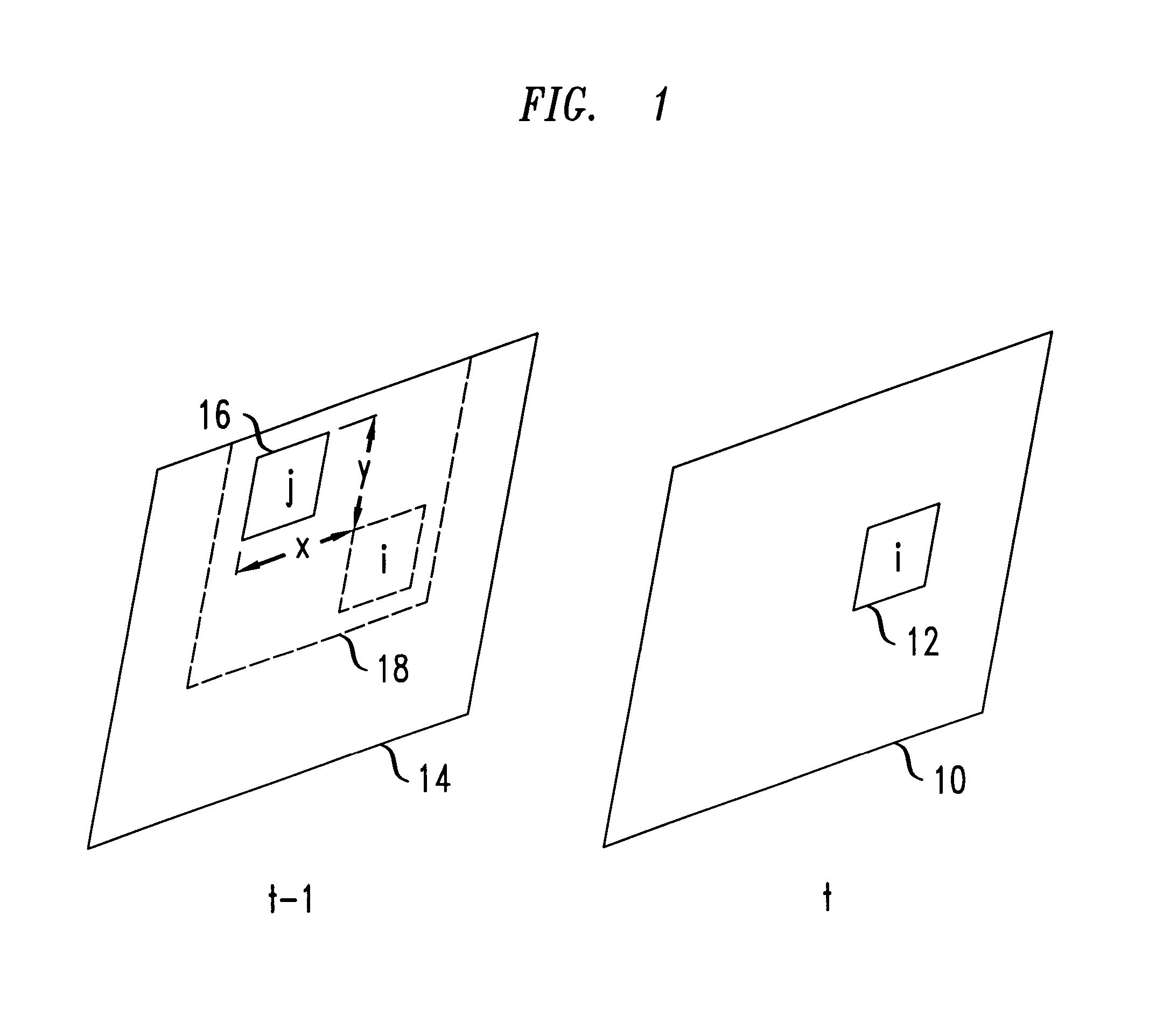
Method for movement-compensation in imaging
ActiveUS20060235295A1Reduce in quantityLimited diagnostic valueUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage analysisMotion field3d image
In a method for mathematical compensation of a periodic movement of an organ in a first image-generation method used to image said organ, two time series of three-dimensional image data are acquired using gating, one by the first image-generation method and one by the second image-generation method, the image data that have been acquired by the second image-generation method being used to calculate motion fields which are applied for the compensation of the data from the time series which was acquired by the first image-generation method. The compensation encompasses the mathematical inclusion of motion fields and the mapping of the image data to a reference time. All the image data mapped back to the reference time are added together.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Motion estimation and compensation for video compression
InactiveUS6845130B1Reduce image resolutionColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMotion fieldGroup of pictures
An encoding method for reducing motion video data sizes using a multitude of variable-sized data blocks that are derived from spatial translation vectors and the motion field of an image. Using variable-block sizes to characterize the groups of picture elements (pixels) in an image frame allows for the inter-mixing of coarse (for static areas) and fine (for areas of complex motion) resolution data descriptions in the same descriptive data block.A comparison of motion event areas is made between successive video frames, and a motion displacement vector is calculated for each pixel location in the frame. A data tree is constructed from these pixel motion vectors and is pruned to eliminate static areas. The remaining leaves of the pruned tree are encoded differentially and applied to a lossless arithmetic encoder to provide a significantly reduced data block that still retains the highest resolution of the image.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Imaging method and imaging system of dynamic optical fields of multichannel space-time coding apertures
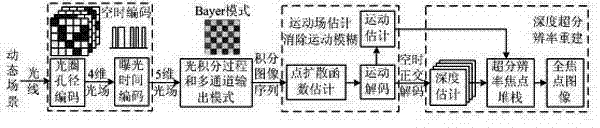
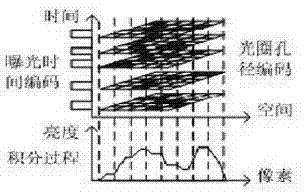
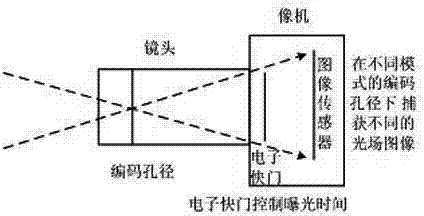
ActiveCN102595171AAchieve decouplingAchieve recoverySteroscopic systemsOptical elementsImaging qualitySignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
The invention discloses an imaging method and an imaging system of dynamic optical fields of multichannel space-time coding apertures, which comprise the steps of establishing a five-dimensional dynamic optical field module of space-time coding, introducing exposure time regarded as a time dimension into coding apertures based on a four-dimensional optical filed, and achieving space-time joint coding of a aperture mode and orthogonal space-time coding apertures based on multiplexing; estimating motion fields, eliminating motion blur, and achieving recovery of motion blur images based on exposure time coding; reestablishing multichannel depth super resolution; and achieving decoupling of motion fields and depth fields and recovering full focus images. Through multiplexing, signal to noise ratio of images and influence of shutter noise are reduced, and optical filed imaging quality is improved. Frequency response characteristics of the exposure time decoding and recovery of the motion blur images can improve definition of images after being recovered, and reestablishment of the depth super resolution improves depth resolution and modifies estimation errors of depth images with low resolution.
Owner:浙江欧托电气有限公司
Method and apparatus for image processing
InactiveUS7120276B1Easy to detectImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionMotion fieldComputer graphics (images)
An example system and method for processing image data of a plurality of time-separated images of a non-rigid body to detect movement of the body involves calculating and storing, for each of a plurality of sampling points in each image, a plurality of candidate movements together with the estimated probability of each candidate. For each sampling point, the probability of each of the candidate movements is recalculated based on the stored probability of that candidate movement and the probabilities of the candidate movements at neighboring sampling points. A motion field indicative of the non-rigid body movement is generated from the recalculated probabilities.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Method and apparatus for maintaining a background image model in a background subtraction system using accumulated motion
Methods and apparatus are provided for maintaining a background image model in a background subtraction system using accumulated motion. A background image model is maintained by obtaining a map of accumulated motion; and adjusting the background image model based on the map of accumulated motion. The map of accumulated motion may be obtained, for example, based on one or more of motion field images; stability maps; frame differences; or information from a background subtraction system. Objects can be added to or removed from the background model or the background model can be otherwise updated. One or more pixels from an image are added to the background image model if a stability measure for the one or more pixels satisfies a predefined criteria. A portion of the background image model can be invalidated in regions where the map of accumulated motion exceeds a predefined threshold.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com