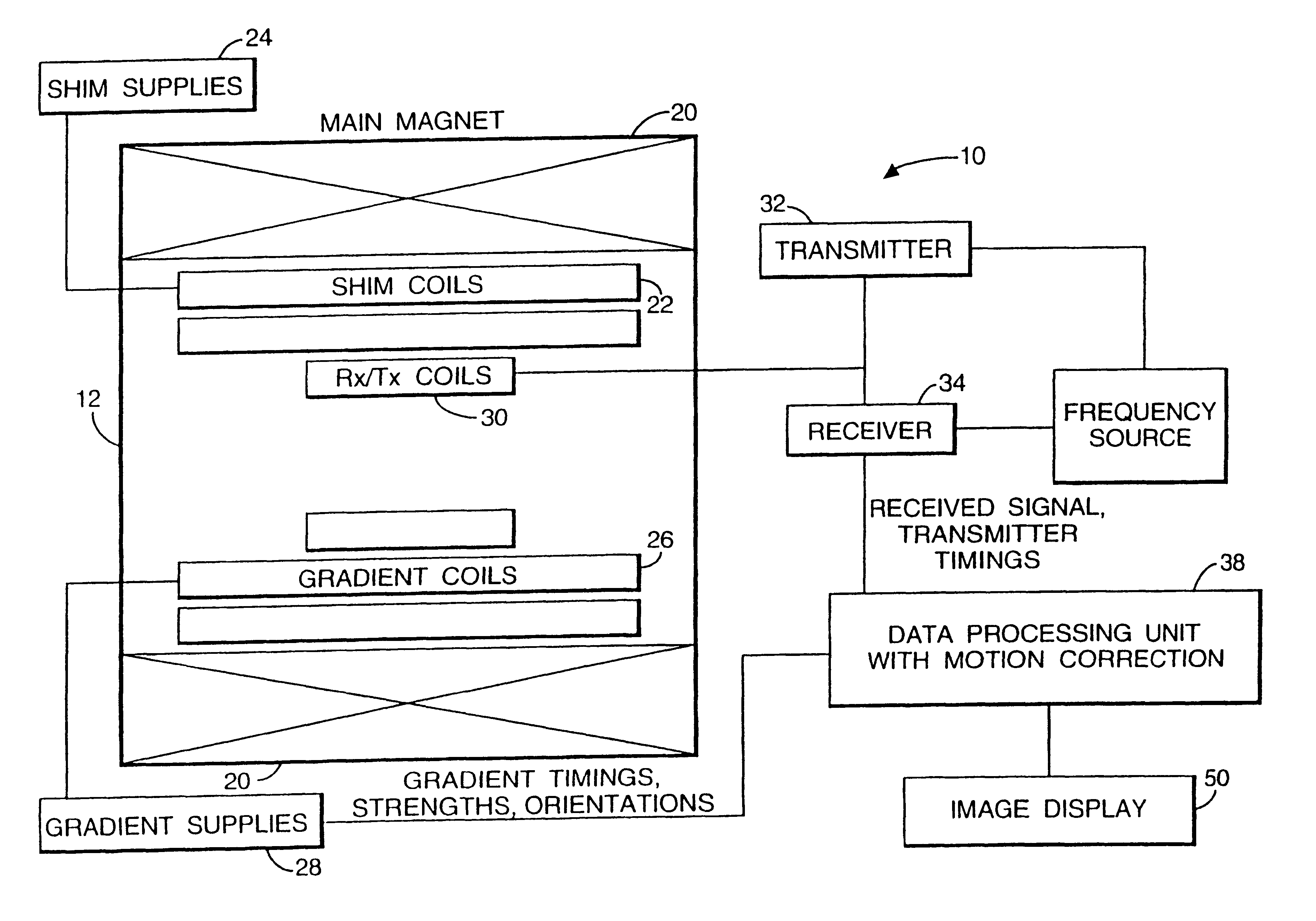
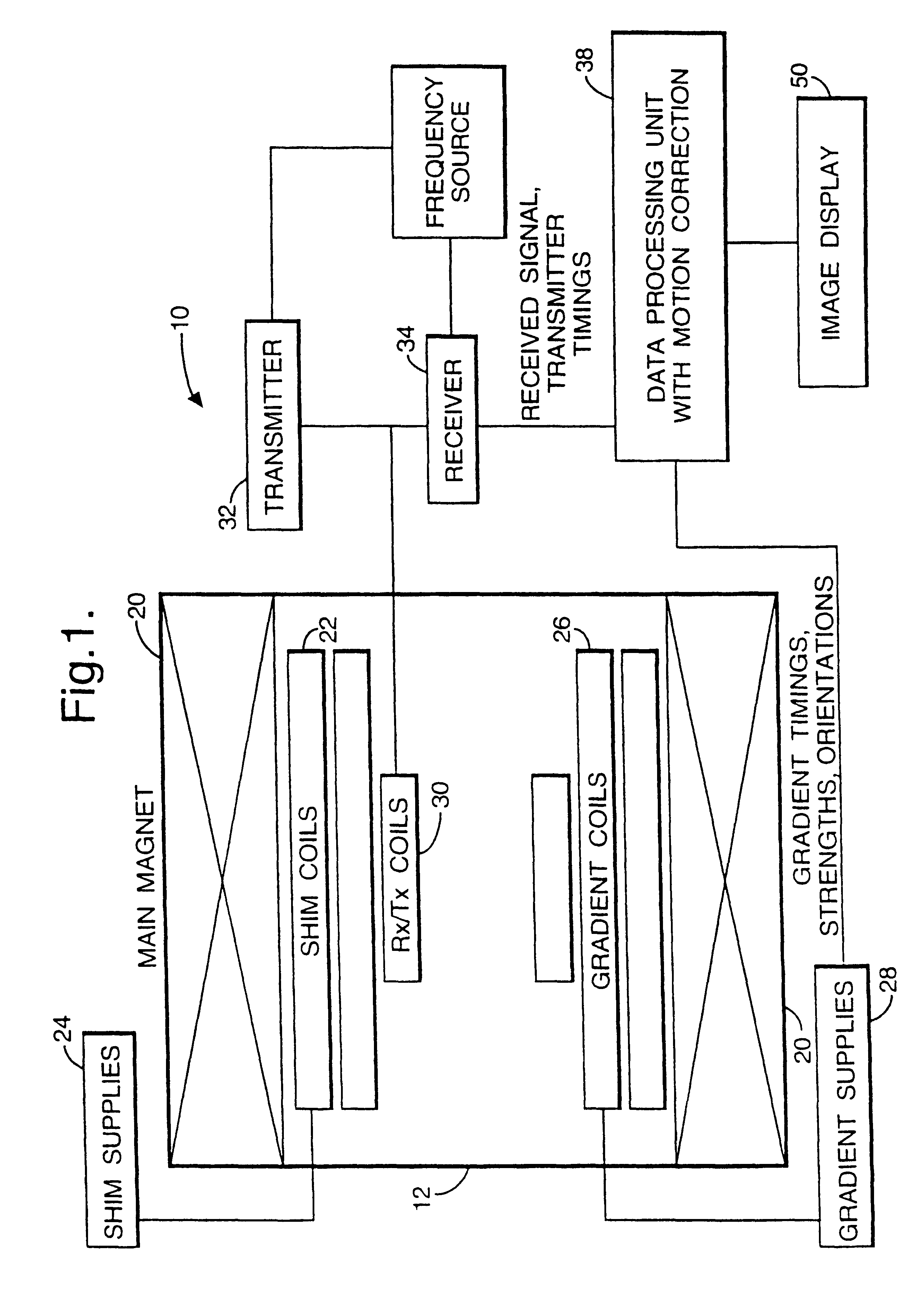
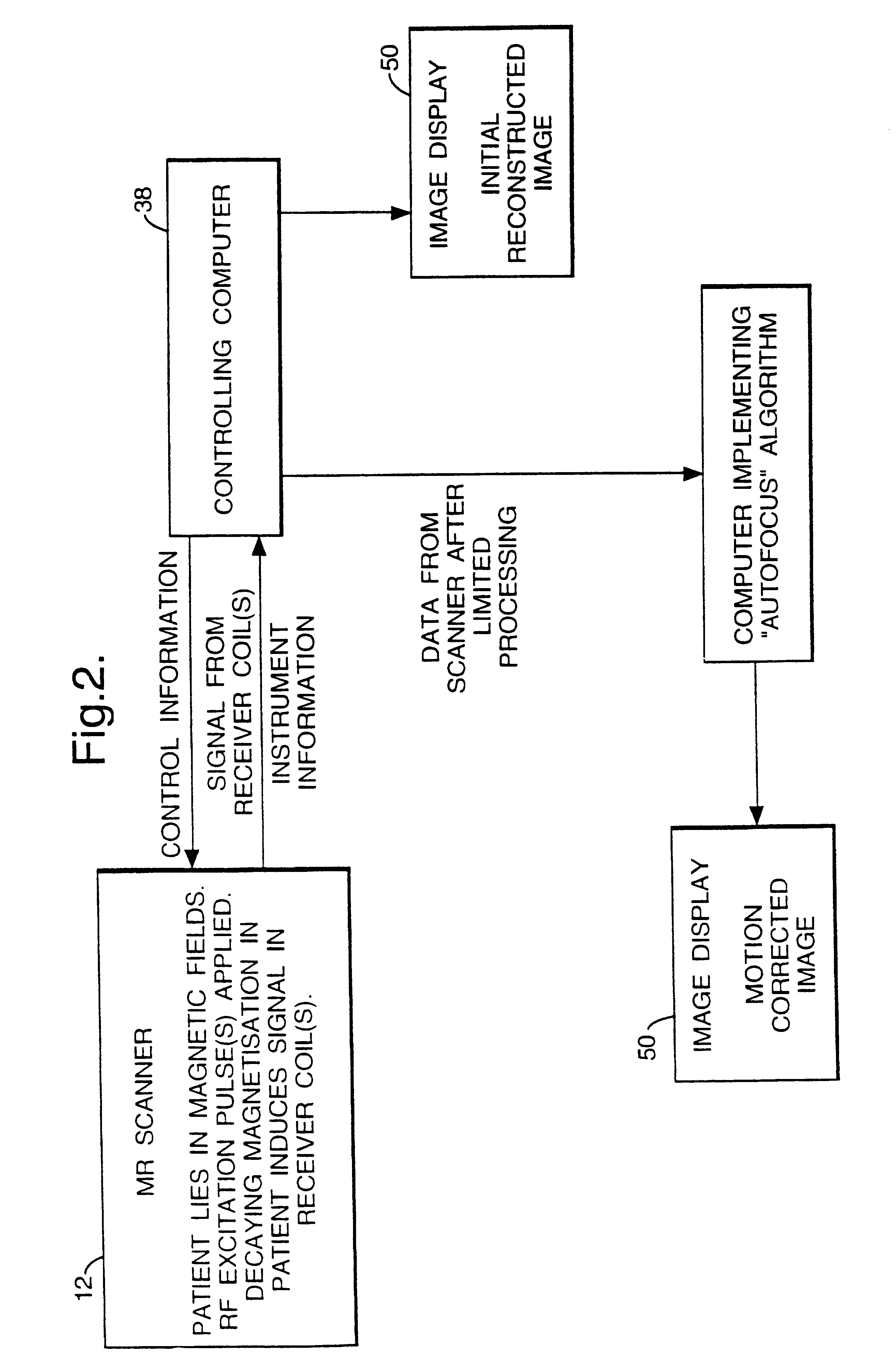
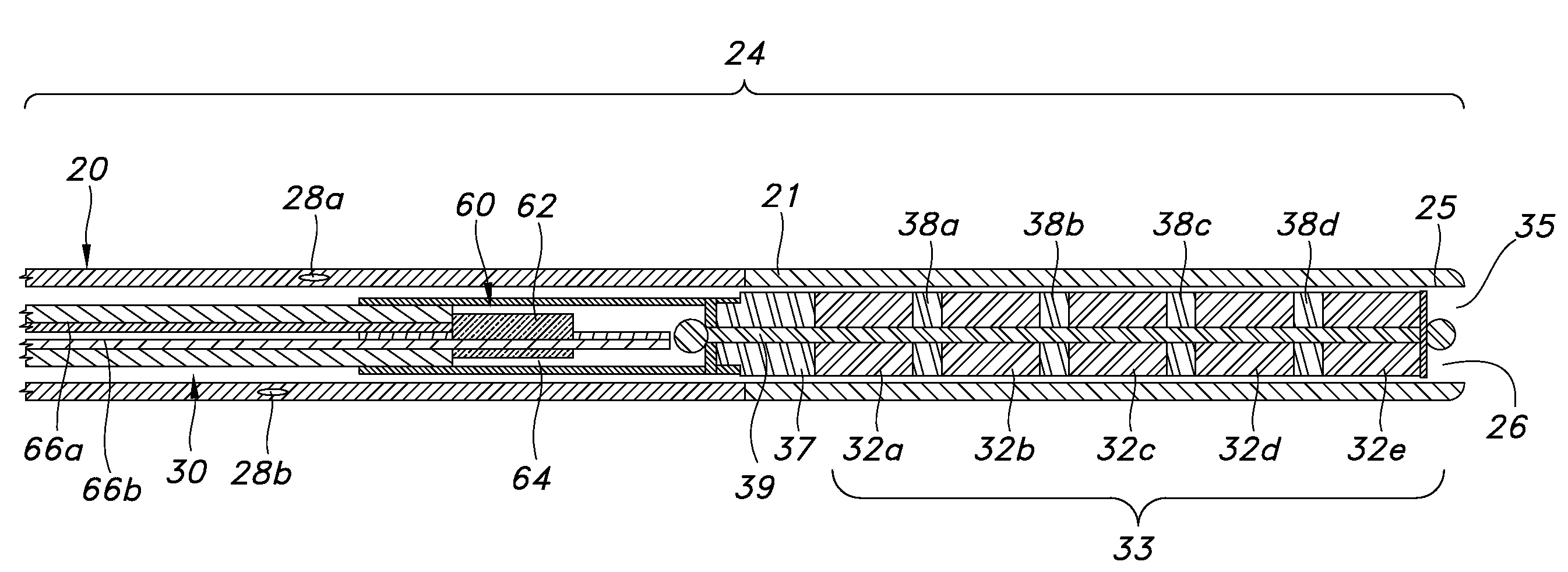
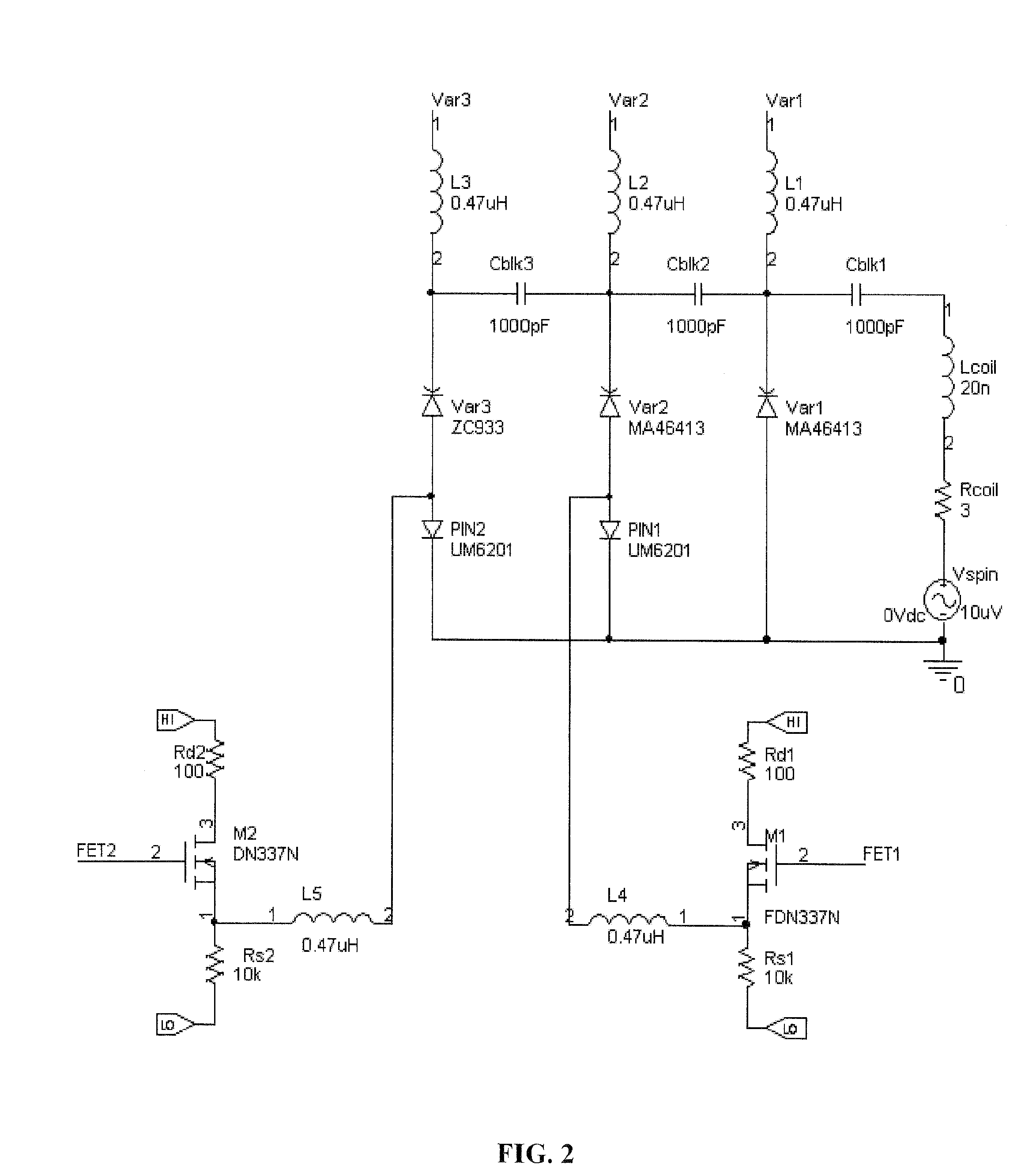Patents
Literature
3653 results about "Magnetic resonance imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
<ul><li>A radiologist interprets the results and classifies it as normal, abnormal, or potentially abnormal. An impression is provided based on the medical history and test results. In case of ambiguity, possible diagnoses (differential diagnoses) are listed.</li></ul>
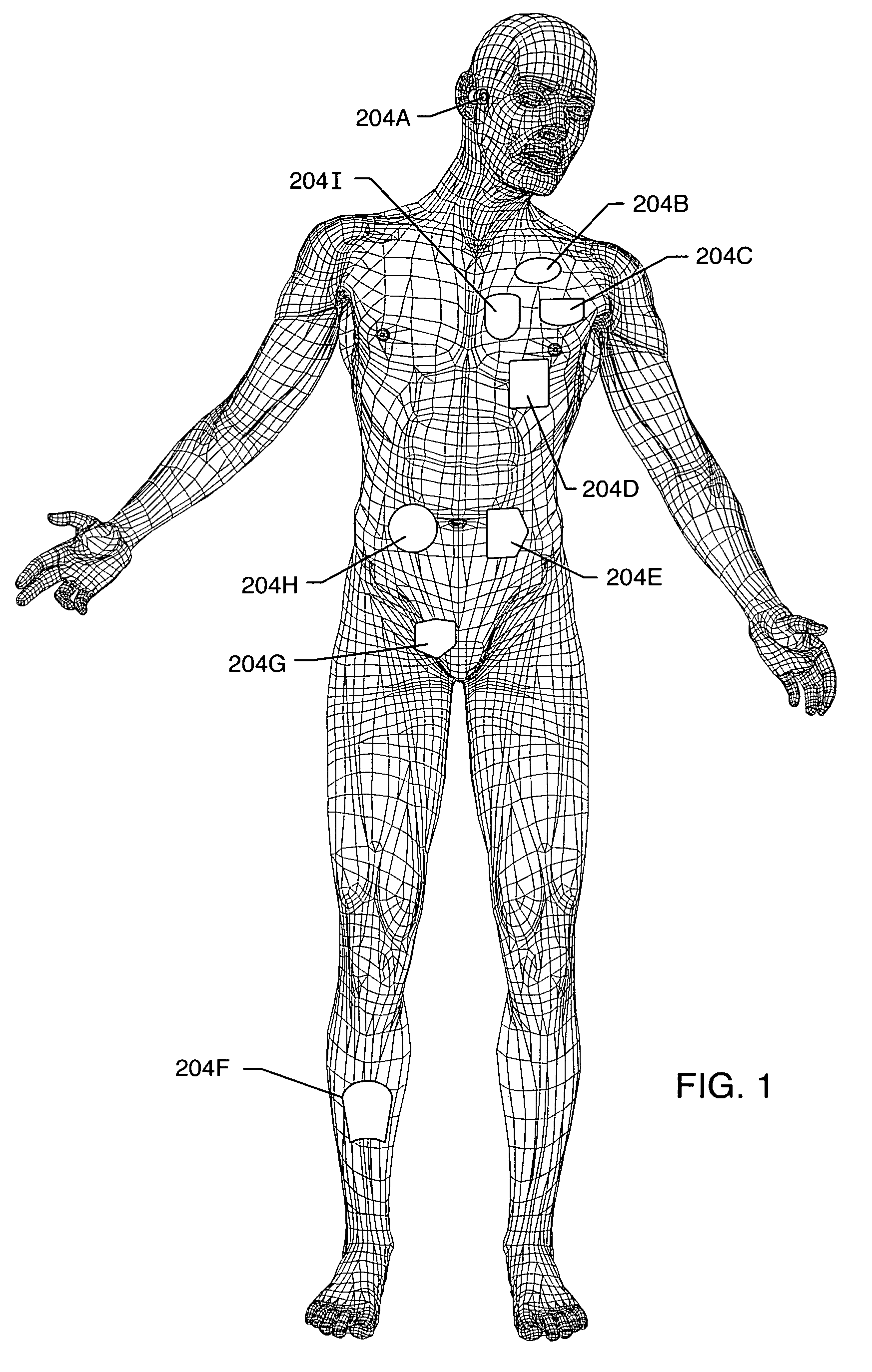
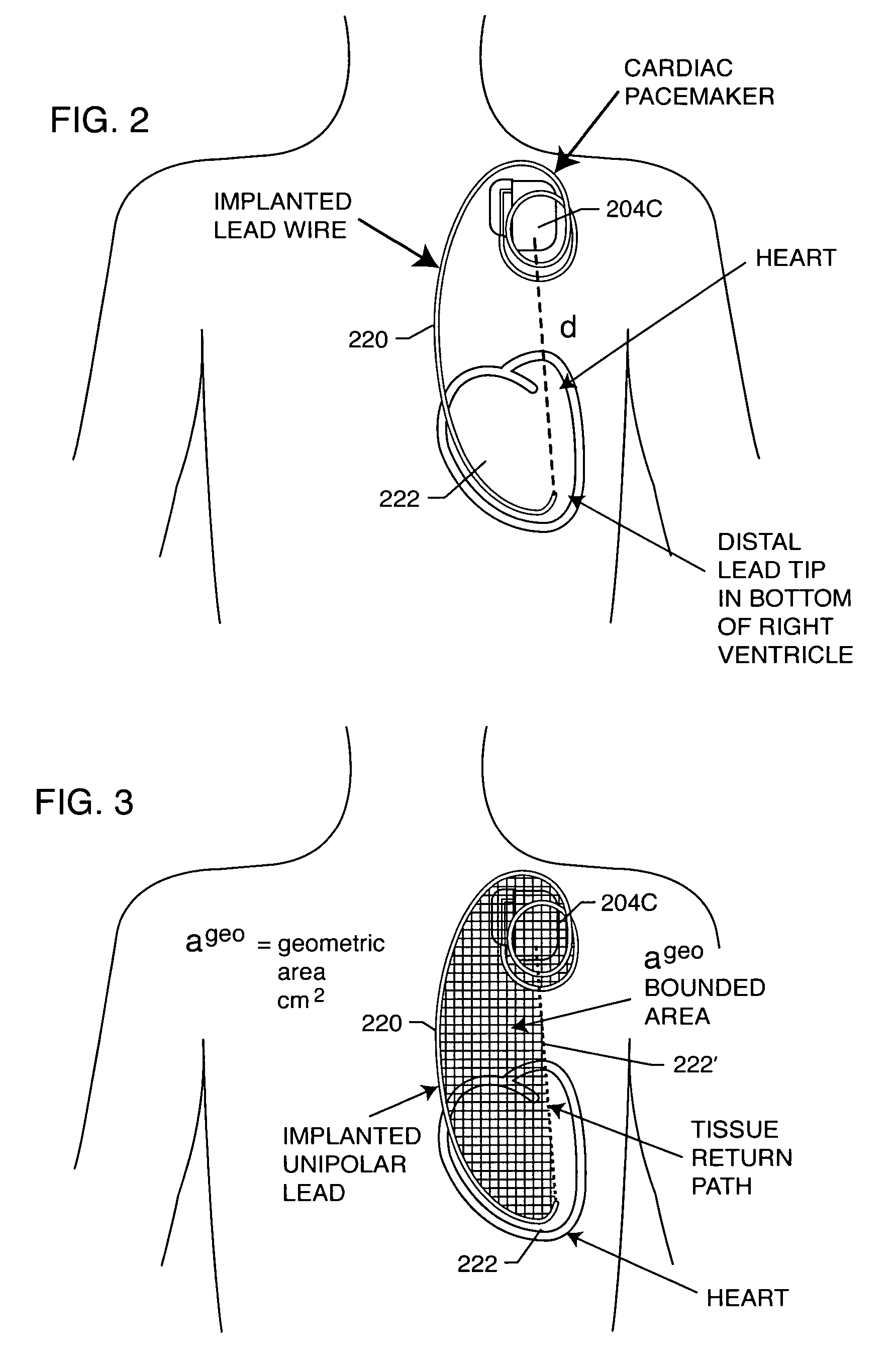
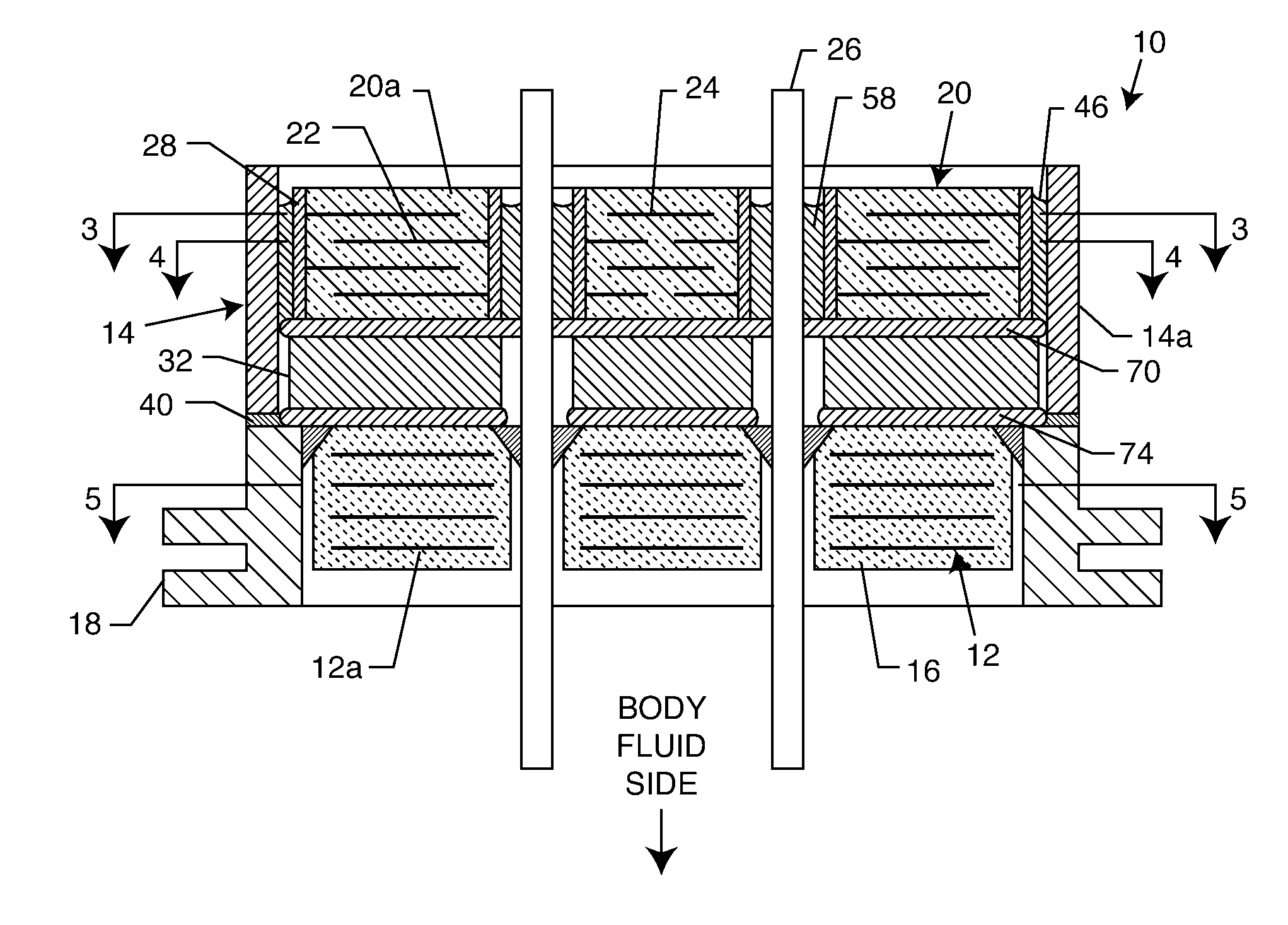
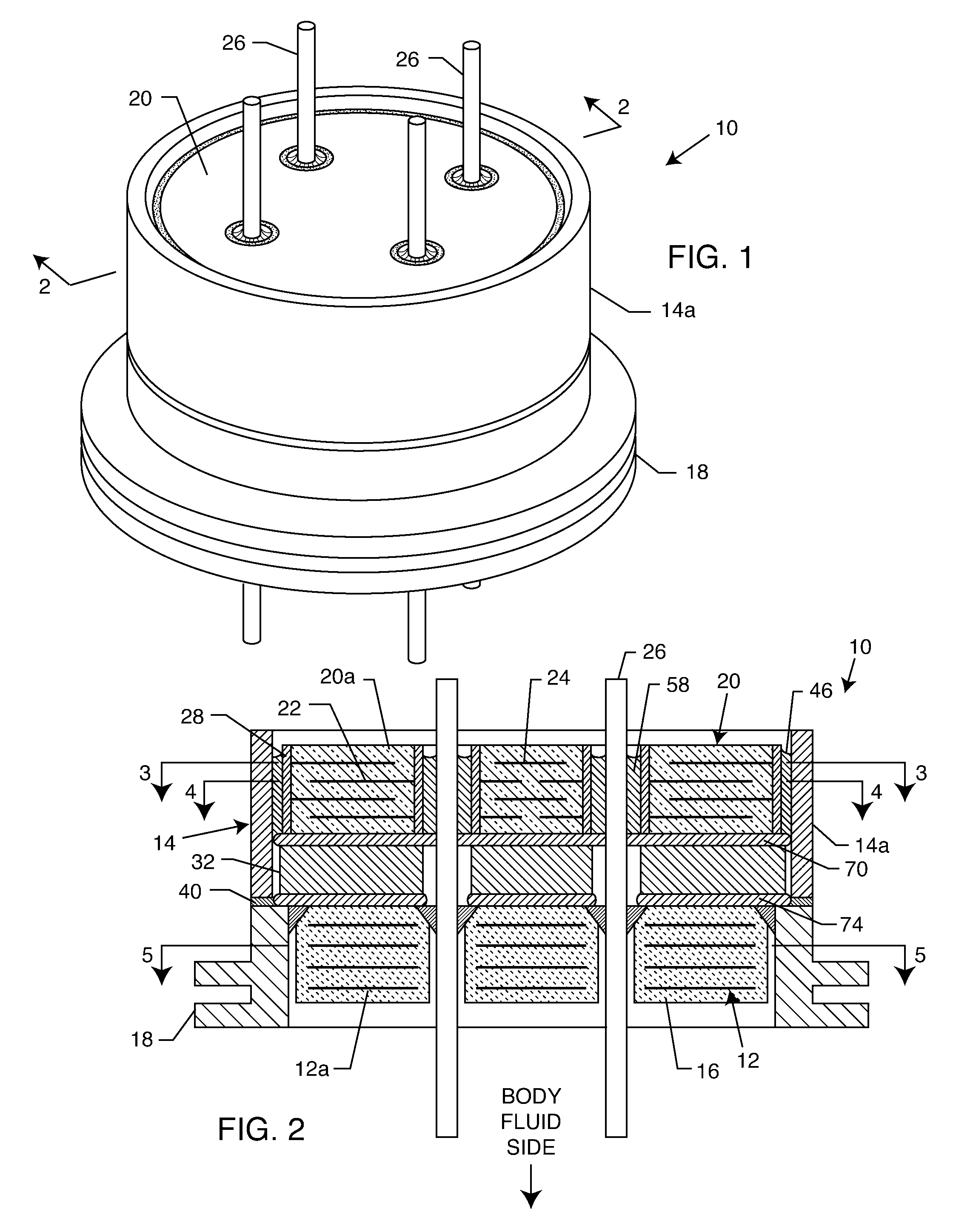
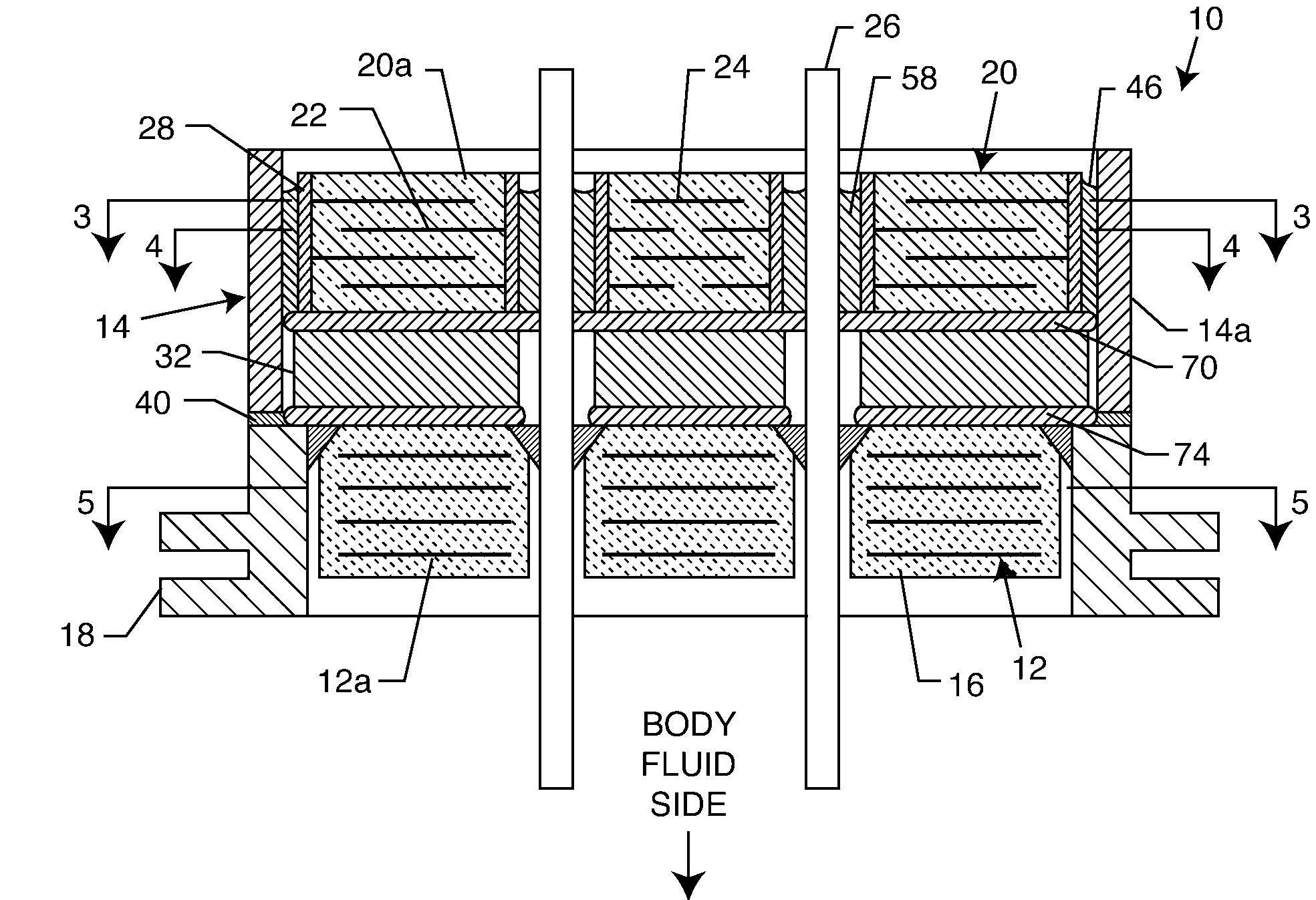
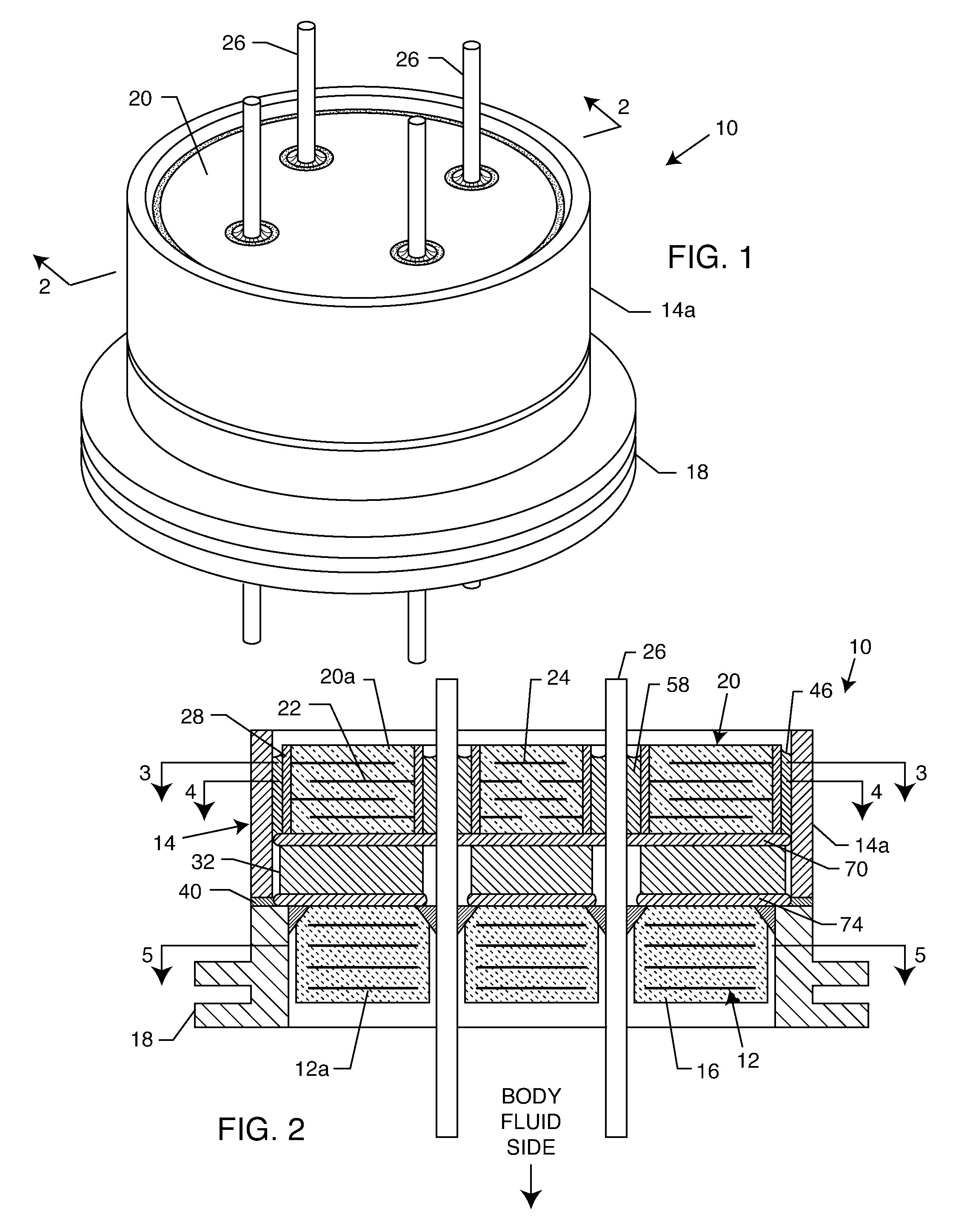
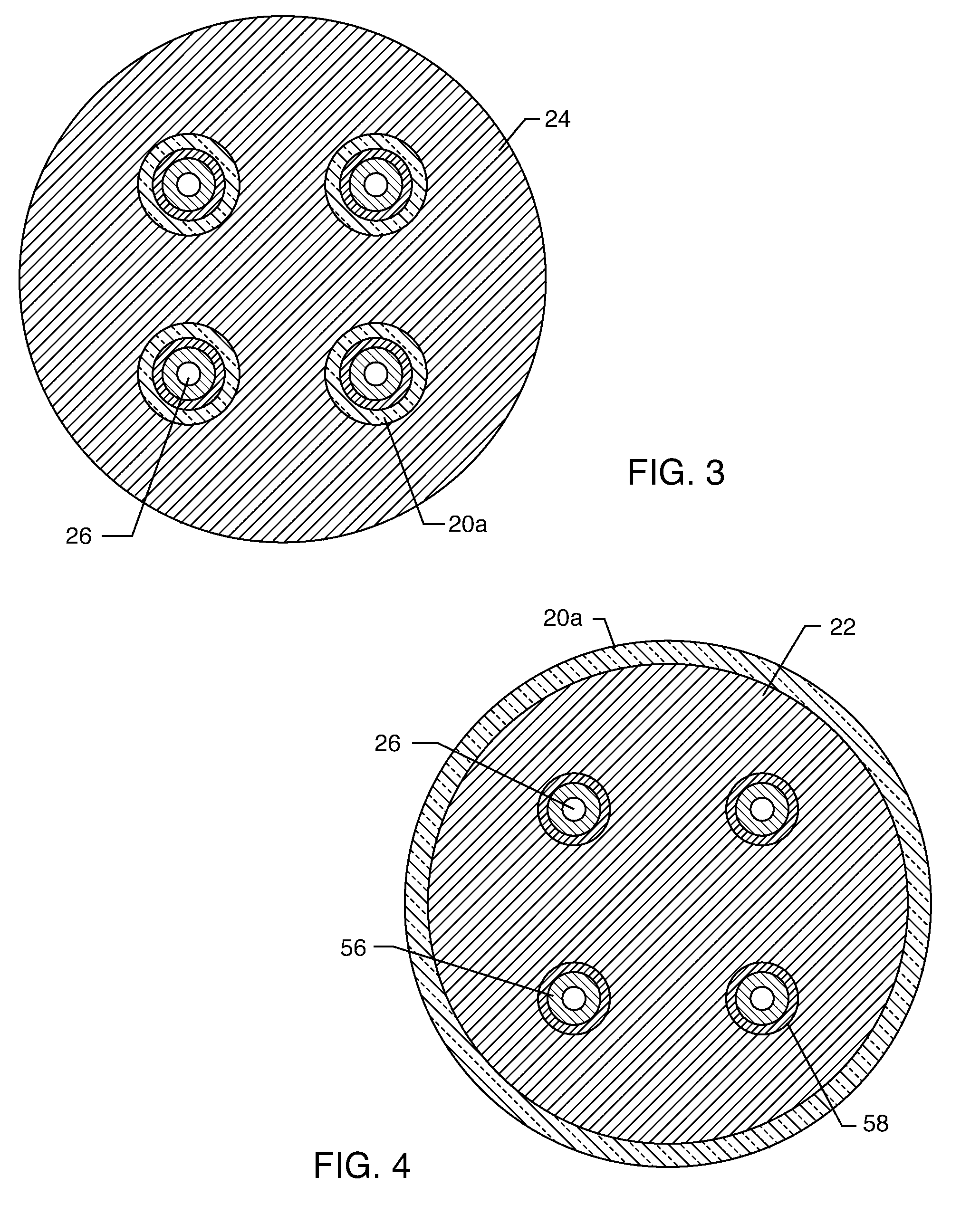
Apparatus and process for reducing the susceptability of active implantable medical devices to medical procedures such as magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS20050197677A1Improving impedanceReducing magnetic flux core saturationAnti-noise capacitorsElectrotherapyPhase cancellationElectromagnetic field
A feedthrough terminal assembly for an active implantable medical device (AIMD) includes a plurality of leadwires extending from electronic circuitry of the AIMD, and a lossy ferrite inductor through which the leadwires extend in non-conductive relation for increasing the impedance of the leadwires at selected RF frequencies and reducing magnetic flux core saturation of the lossy ferrite inductor through phase cancellation of signals carried by the leadwires. A process is also provided for filtering electromagnetic interference (EMI) in an implanted leadwire extending from an AIMD into body fluids or tissue, wherein the leadwire is subjected to occasional high-power electromagnetic fields such as those produced by medical diagnostic equipment including magnetic resonance imaging.
Owner:GREATBATCH SIERRA INC
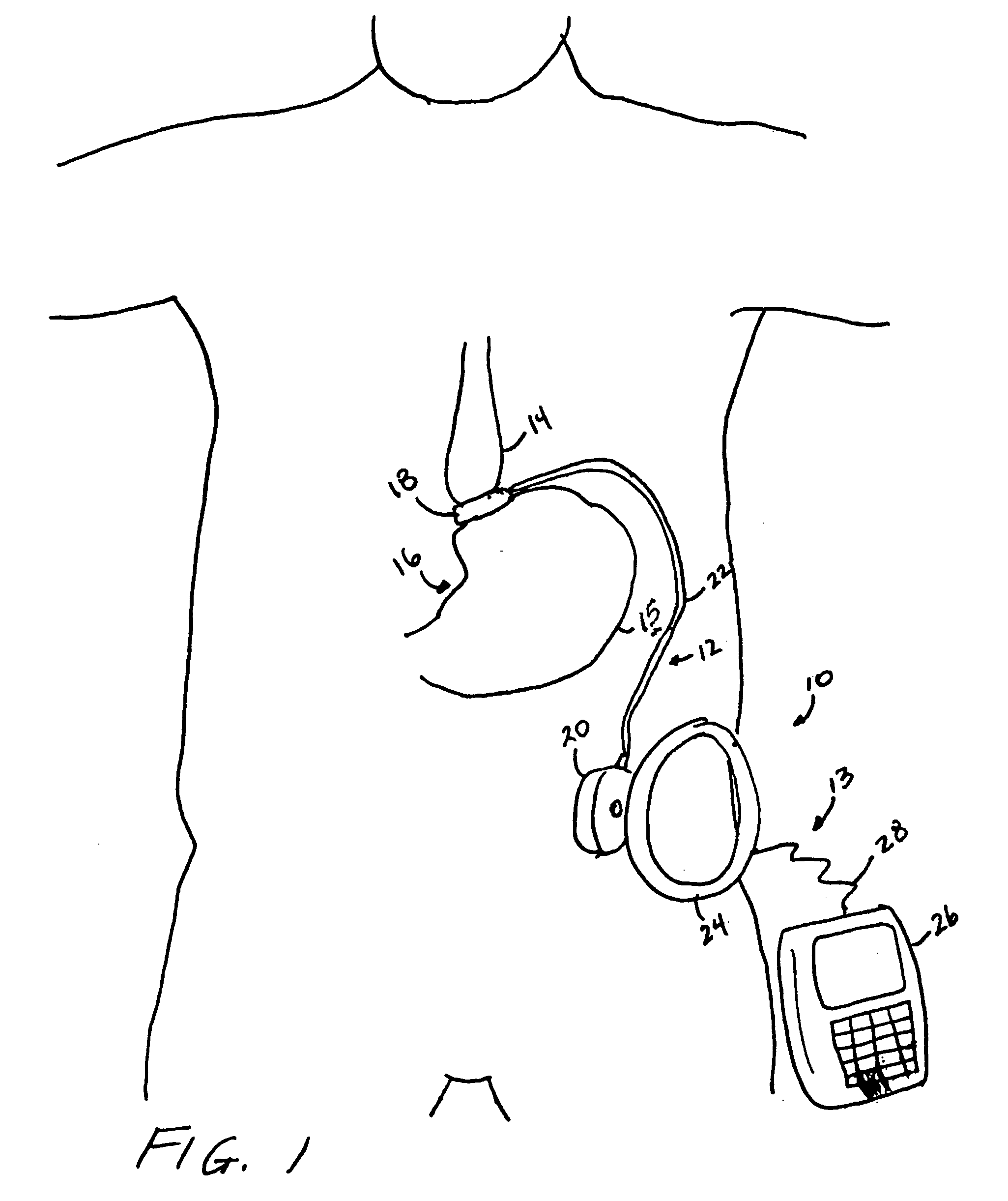
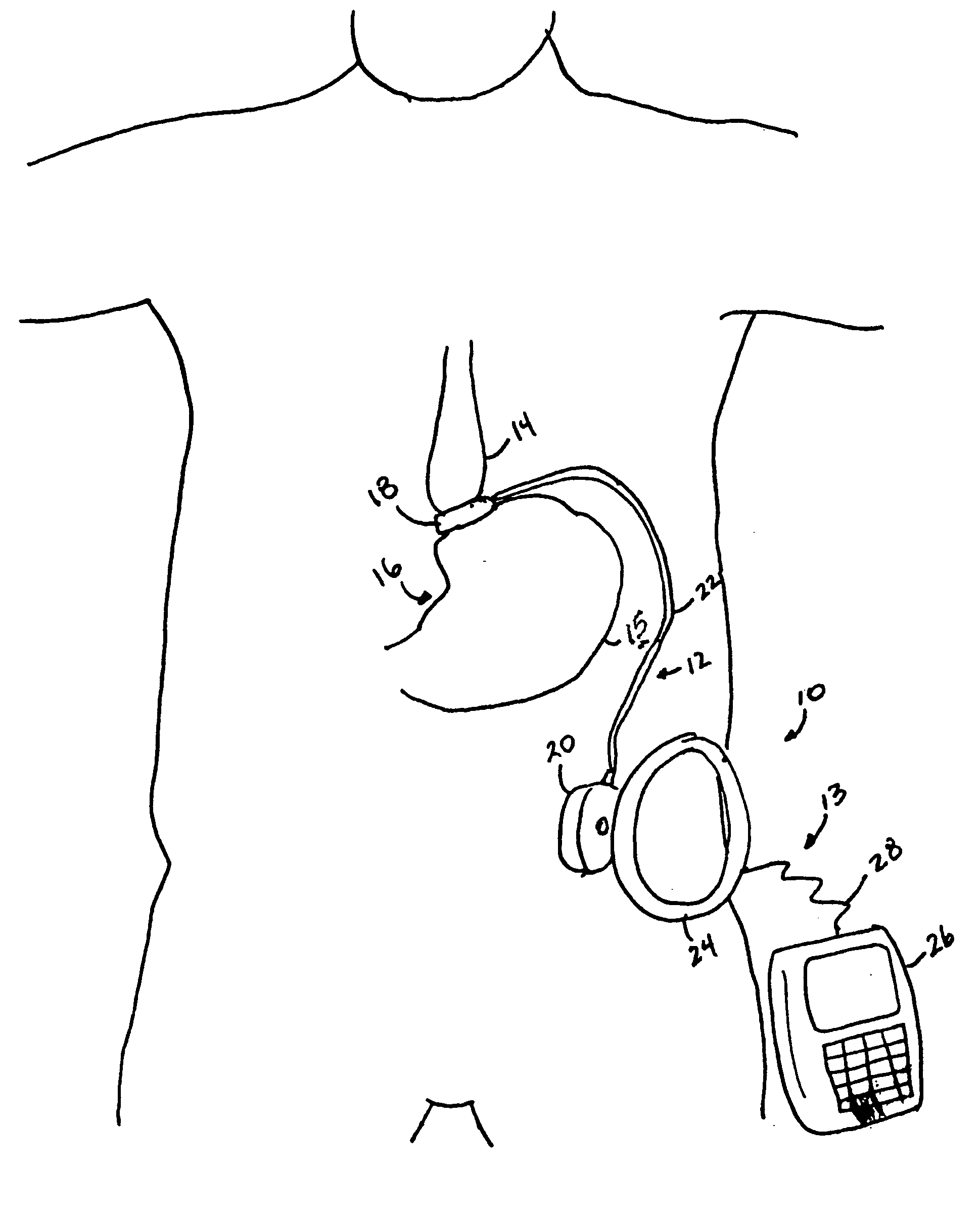
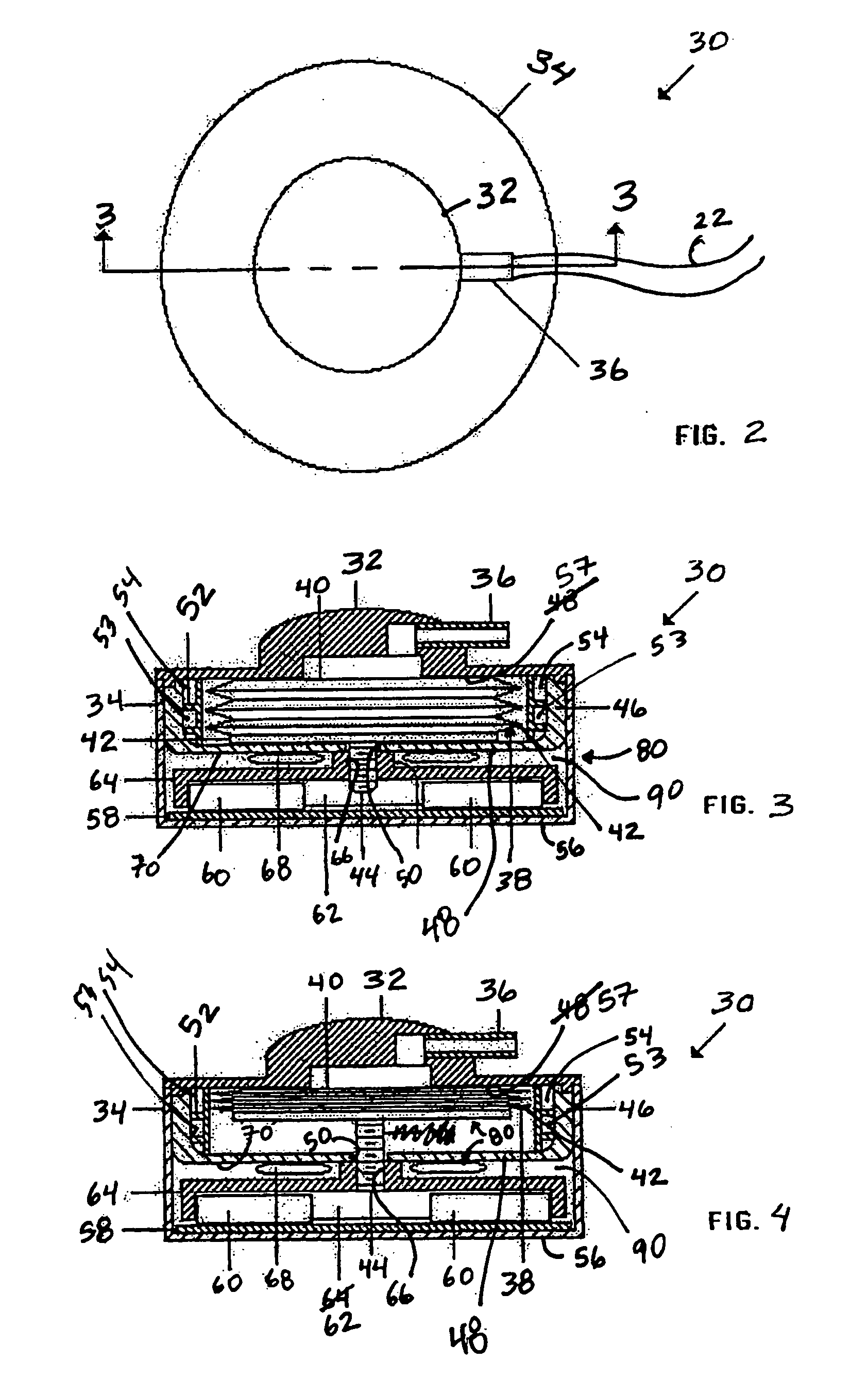
Piezo electrically driven bellows infuser for hydraulically controlling an adjustable gastric band
A remotely controlled gastric band system that is practically immune to external magnetic fields, such as from a Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) machine, incorporates a bi-directional pump and fluid reservoir to adjust fluid volume in a gastric band. A piezoelectrically driven (e.g., rotary actuator, linear actuator) selectively compresses and expands a metal bellows hermetically sealed within a biocompatible and nonferromagnetic case such as titanium.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
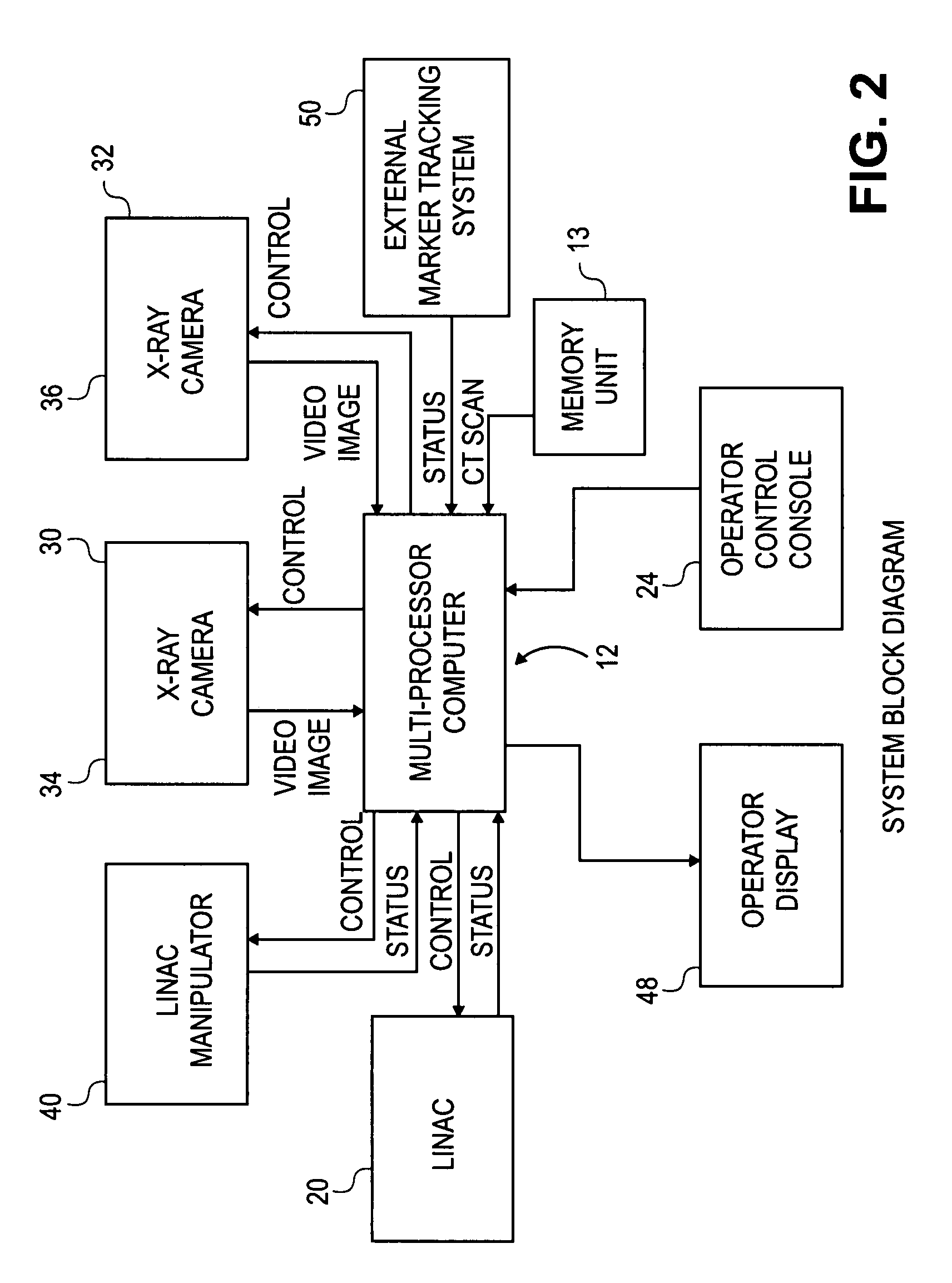
Method and apparatus for tracking an internal target region without an implanted fiducial
InactiveUS7260426B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsComputed tomographyImplanted Fiducials
A method and apparatus for locating an internal target region during treatment without implanted fiducials is presented. The method comprises producing a plurality of first images that show an internal volume including the internal target region, then producing a live image of the internal volume during treatment and matching this live image to one of the plurality of first images. Since the first images show the internal target region, matching the live image to one of the first images identifies the position of the target region regardless of whether the second image itself shows the position of the target region. The first images may be any three-dimensional images such as CT scans, magnetic resonance imaging, and ultrasound. The live image may be, for example, an x-ray image. The invention may be used in conjunction with a real-time sensor to track the position of the target region on a real-time basis.
Owner:ACCURAY
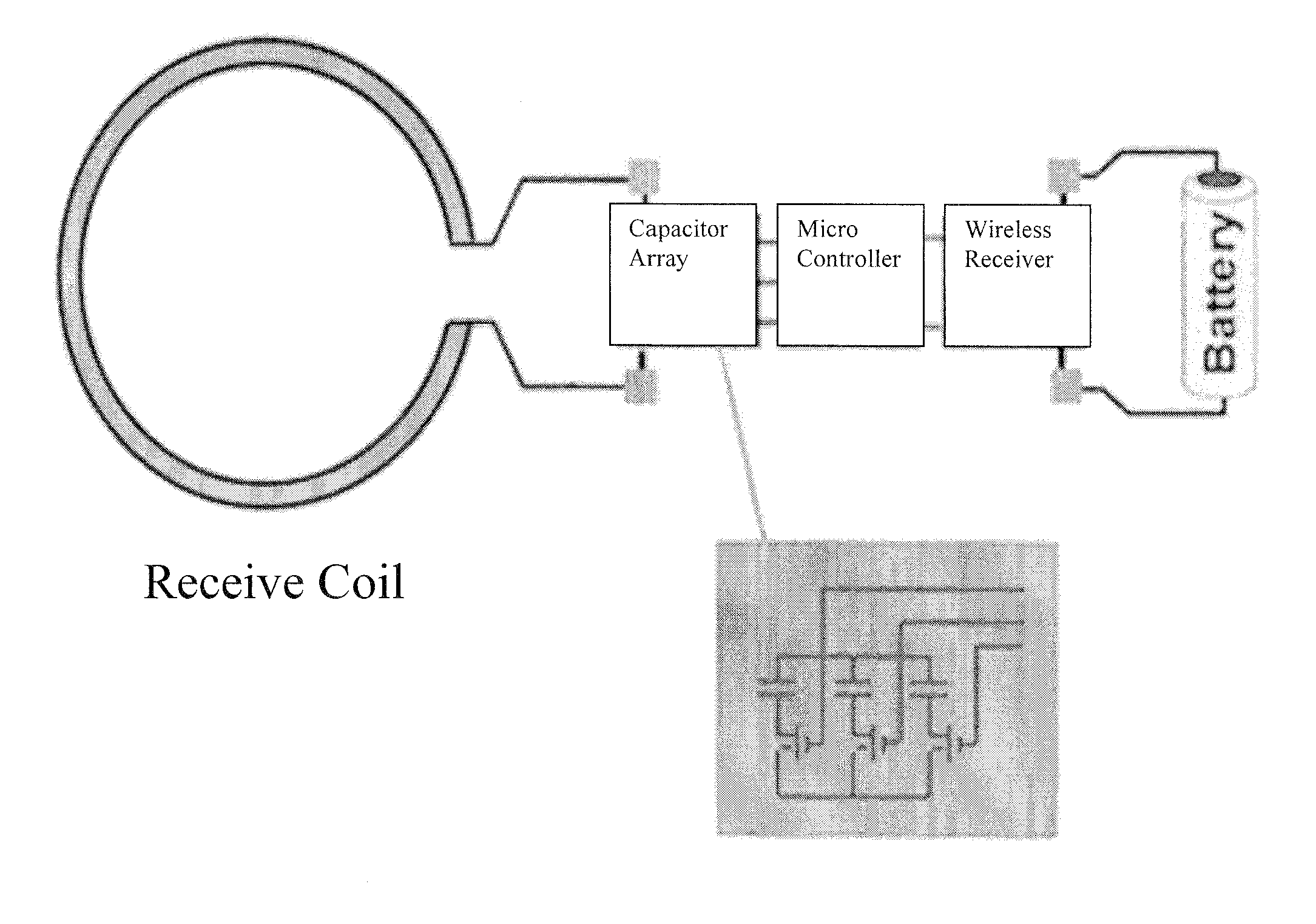
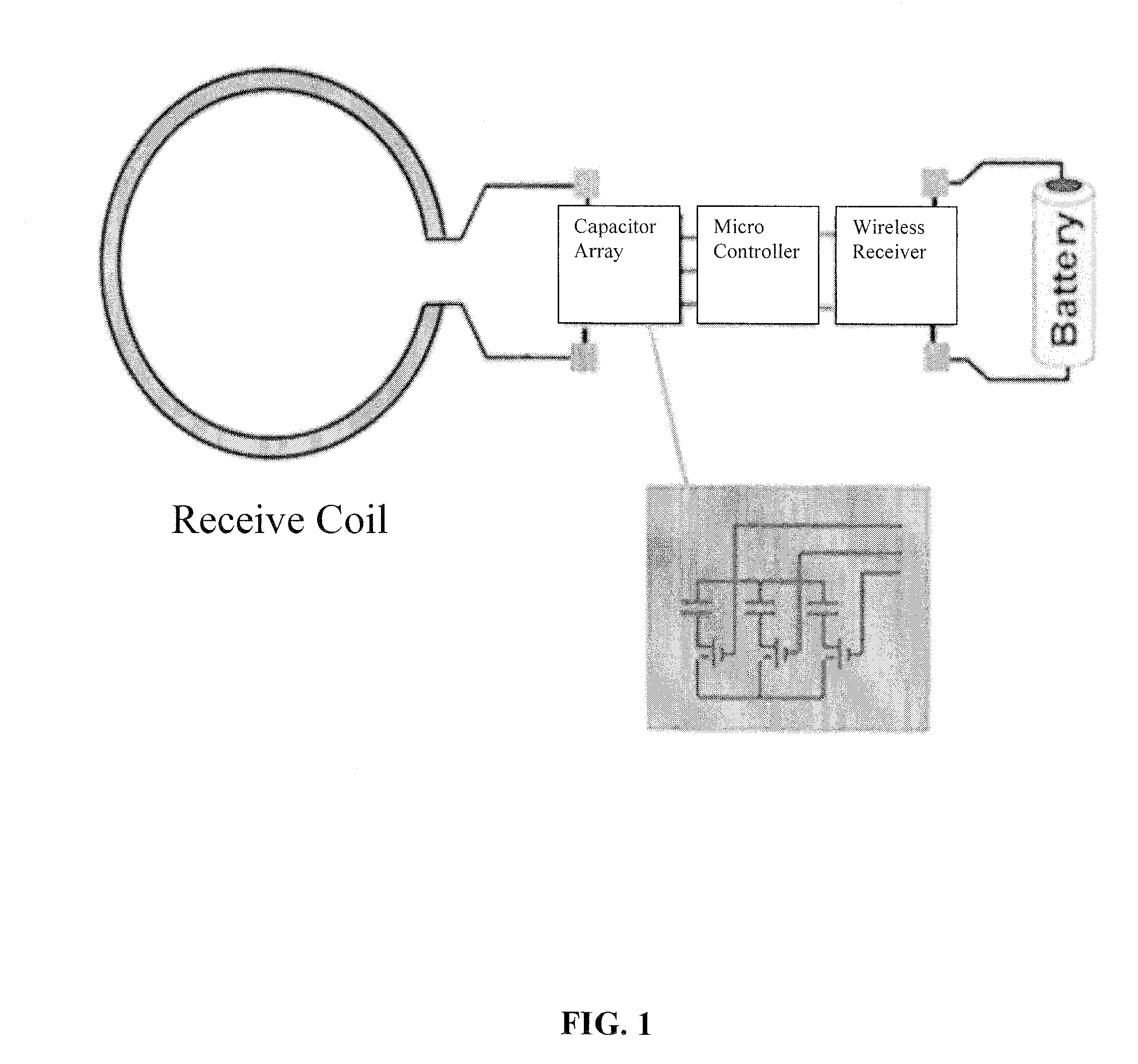
Method and Apparatus for Providing a Wireless Multiple-Frequency MR Coil
InactiveUS20100256481A1Enhanced couplingMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringResonanceSpectroscopy
Embodiments of the invention pertain to a method and apparatus for magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy (MRI / S). In a specific embodiment, the method and apparatus for MRI / S can be applied at two or more resonant frequencies utilizing a wireless RF receiving coil. In an embodiment, the wireless coil, which can be referred to as the implant coil, can be incorporated into an implantable structure. The implantable structure can then be implanted in a living body. The wireless RF receiving coil can be inductively coupled to another RF coil, which can be referred to as an external coil, for receiving the signal from the wireless implant RF coil. In an embodiment, the implantable structure can be a capsule compatible with implantation in a living body. The implantable structure can incorporate a mechanism for adjusting the impedance of the implant coil so as to alter the resonance frequency of the implant coil. In a specific embodiment, the mechanism for adjusting the impedance of the implant coil can allow the implant coil to receive at least two resonance frequencies. In an embodiment, the implant coil can receive three resonance frequencies and in a further embodiment, the implant coil can receive any number resonance frequencies. These resonance frequencies can be controlled by adjusting the impedance of the implant coil. In an embodiment, the resonance frequencies of the implant coil are selected to correlate to MRI / S signals received from living tissues.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
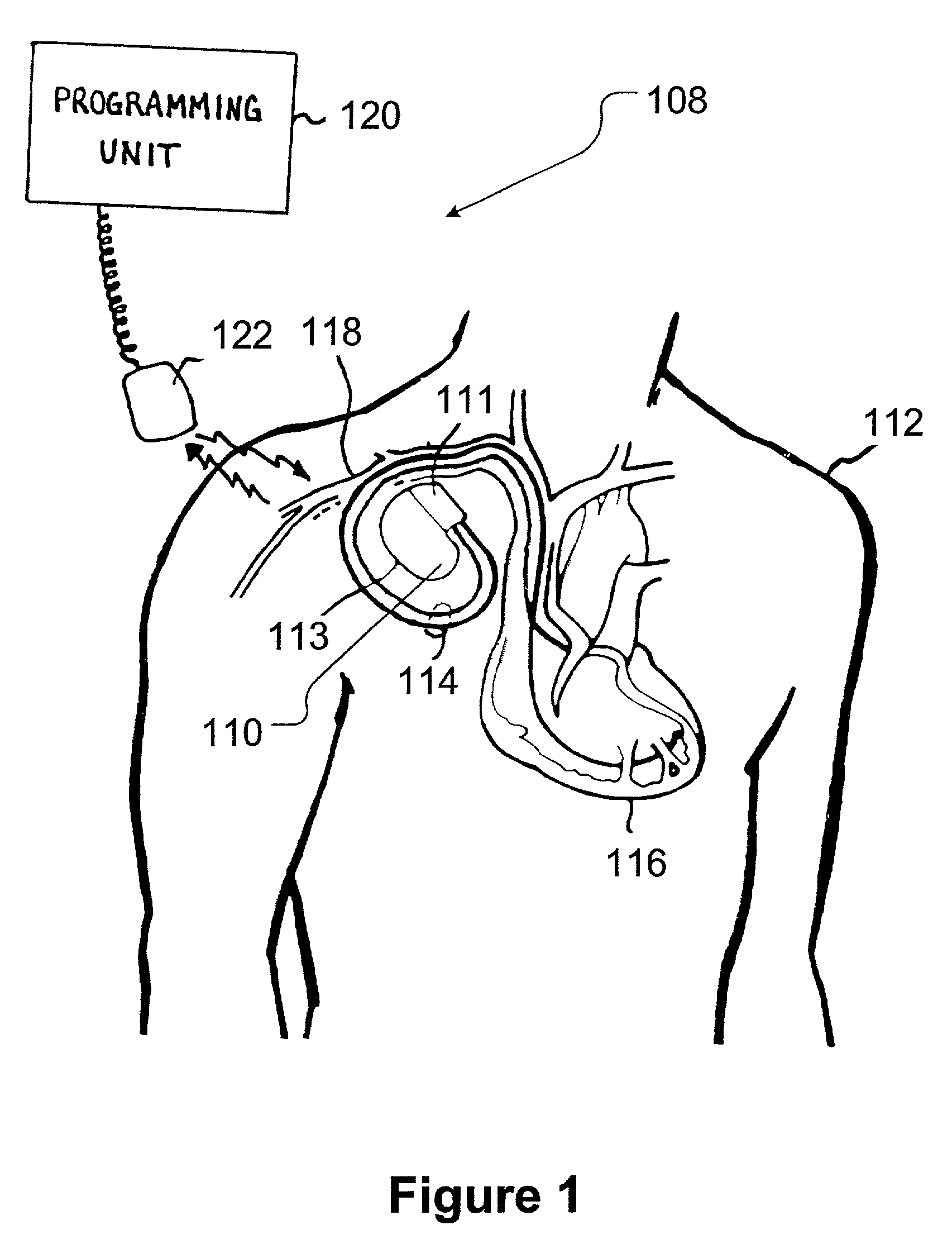
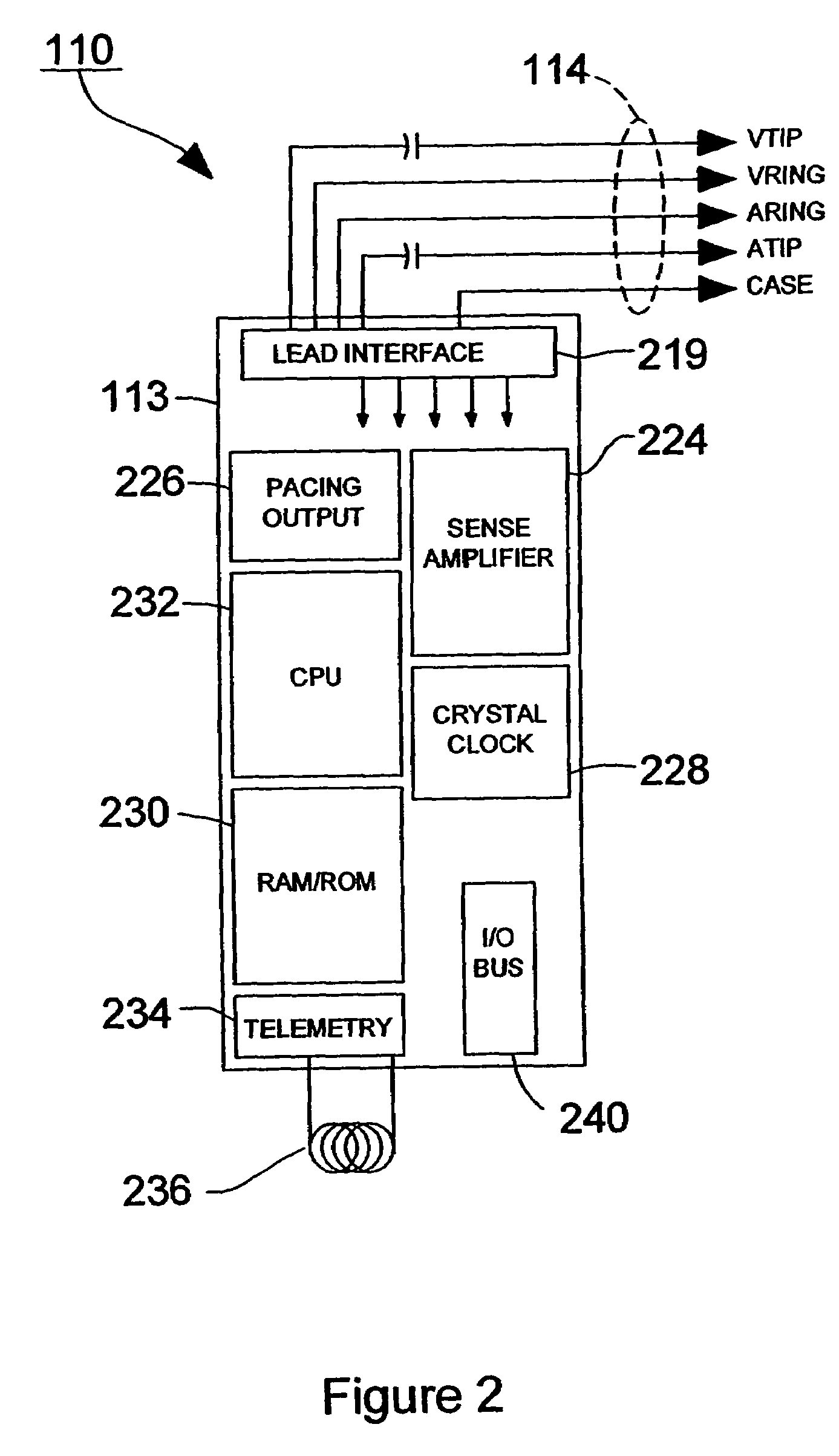
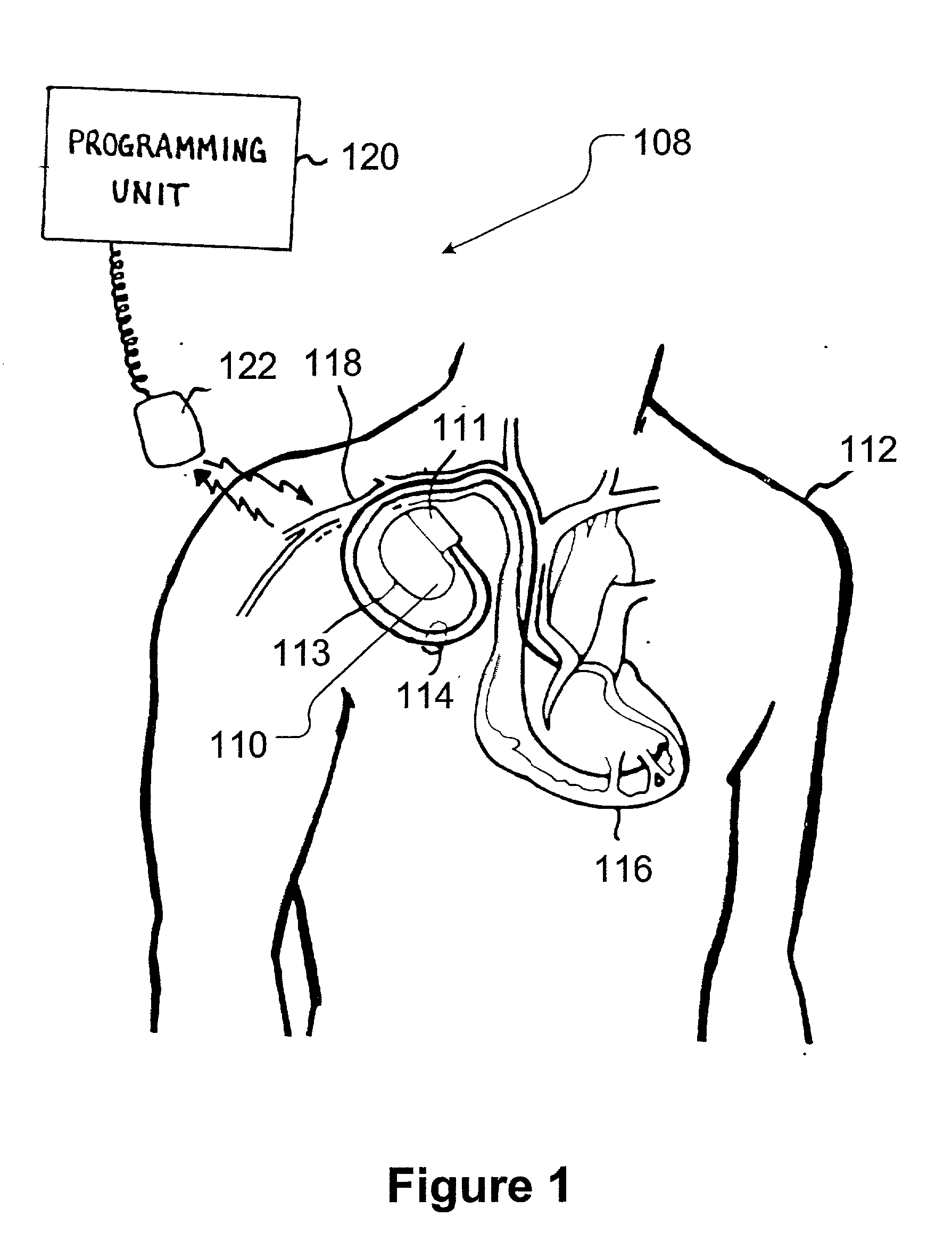
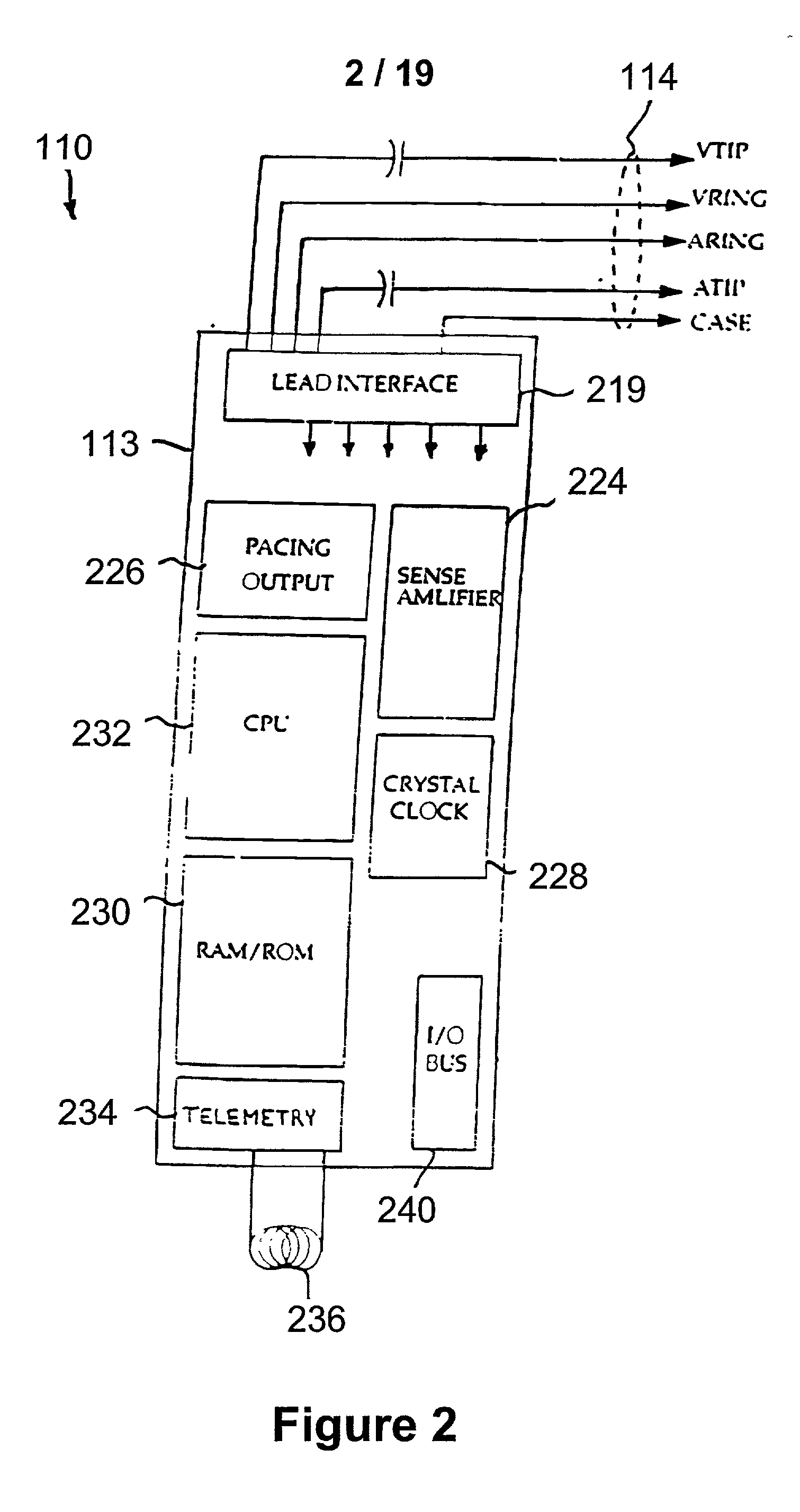
Device for sensing cardiac activity in an implantable medical device in the presence of magnetic resonance imaging interference
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Apparatus and process for reducing the susceptability of active implantable medical devices to medical procedures such as magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS7765005B2Improving impedanceReducing magnetic flux core saturationAnti-noise capacitorsElectrotherapyPhase cancellationElectromagnetic interference
A feedthrough terminal assembly for an active implantable medical device (AIMD) includes a plurality of leadwires extending from electronic circuitry of the AIMD, and a lossy ferrite inductor through which the leadwires extend in non-conductive relation for increasing the impedance of the leadwires at selected RF frequencies and reducing magnetic flux core saturation of the lossy ferrite inductor through phase cancellation of signals carried by the leadwires. A process is also provided for filtering electromagnetic interference (EMI) in an implanted leadwire extending from an AIMD into body fluids or tissue, wherein the leadwire is subjected to occasional high-power electromagnetic fields such as those produced by medical diagnostic equipment including magnetic resonance imaging.
Owner:GREATBATCH SIERRA INC
Apparatus and process for reducing the susceptibility of active implantable medical devices to medical procedures such as magentic resonance imaging
InactiveUS20060085043A1Improve immunityImprove filtering effectAnti-noise capacitorsElectrotherapyResonanceInductor
A feedthrough terminal assembly for an active implantable medical device (AIMD) includes magnetic shielding elements to block incident magnetic fields during medical procedures such as Magnetic Resonance Imaging. The assembly includes conductive or ground plate(s) embedded in an insulator surrounding elements of the assembly, a plurality of lead wires extending from electronic circuitry of the AIMD, and a lossy ferrite inductor through which the lead wires extend in non-conductive relation for increasing the impedance of the lead wires at selected RF frequencies. Alternatively, the assembly includes a conductive sleeve or cap surrounding the feedthrough capacitor and / or conductive support.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
Magnetic resonance imaging method and apparatus employing partial parallel acquisition, wherein each coil produces a complete k-space datasheet
InactiveUS6841998B1Quality improvementMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionDatasheetData set
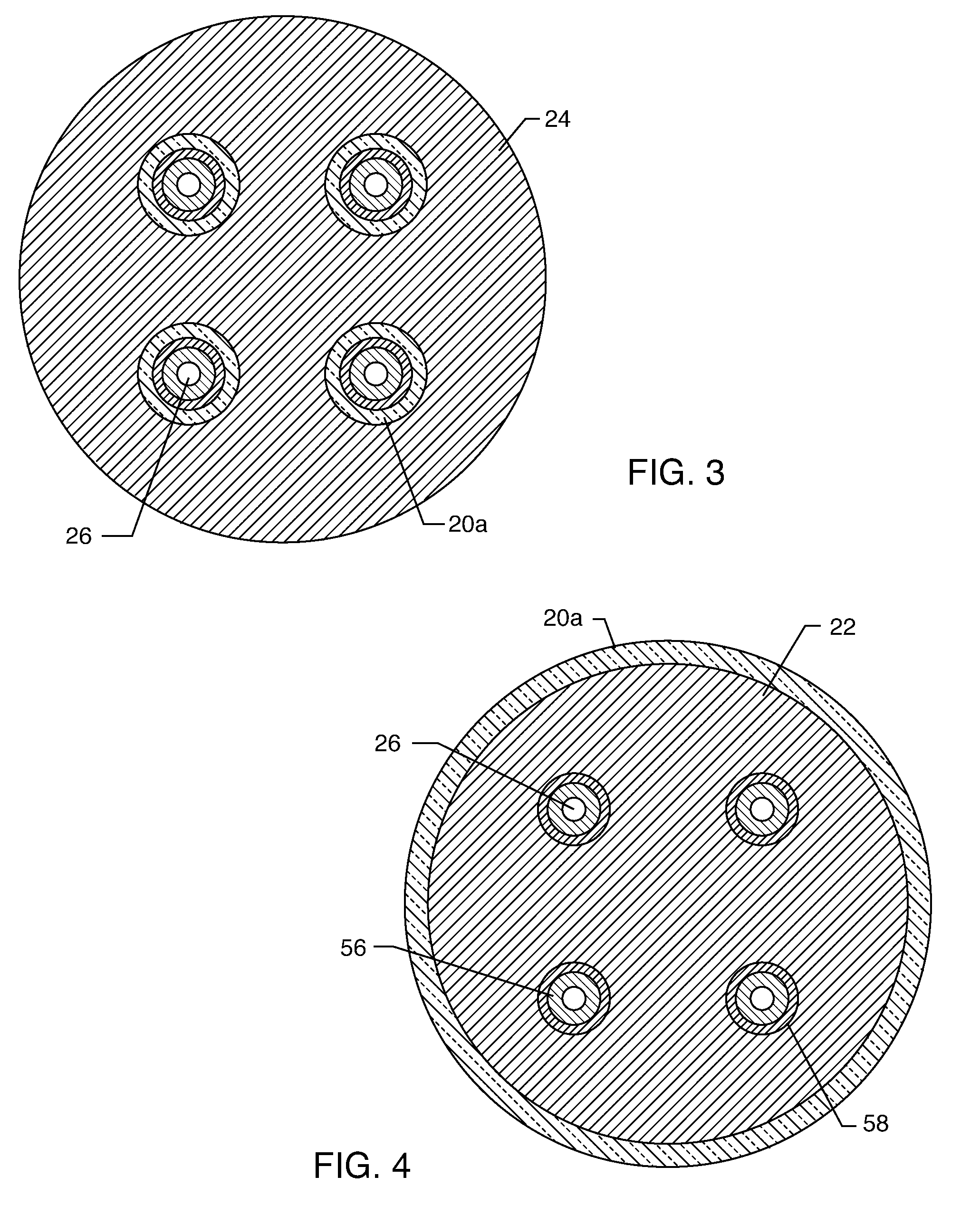
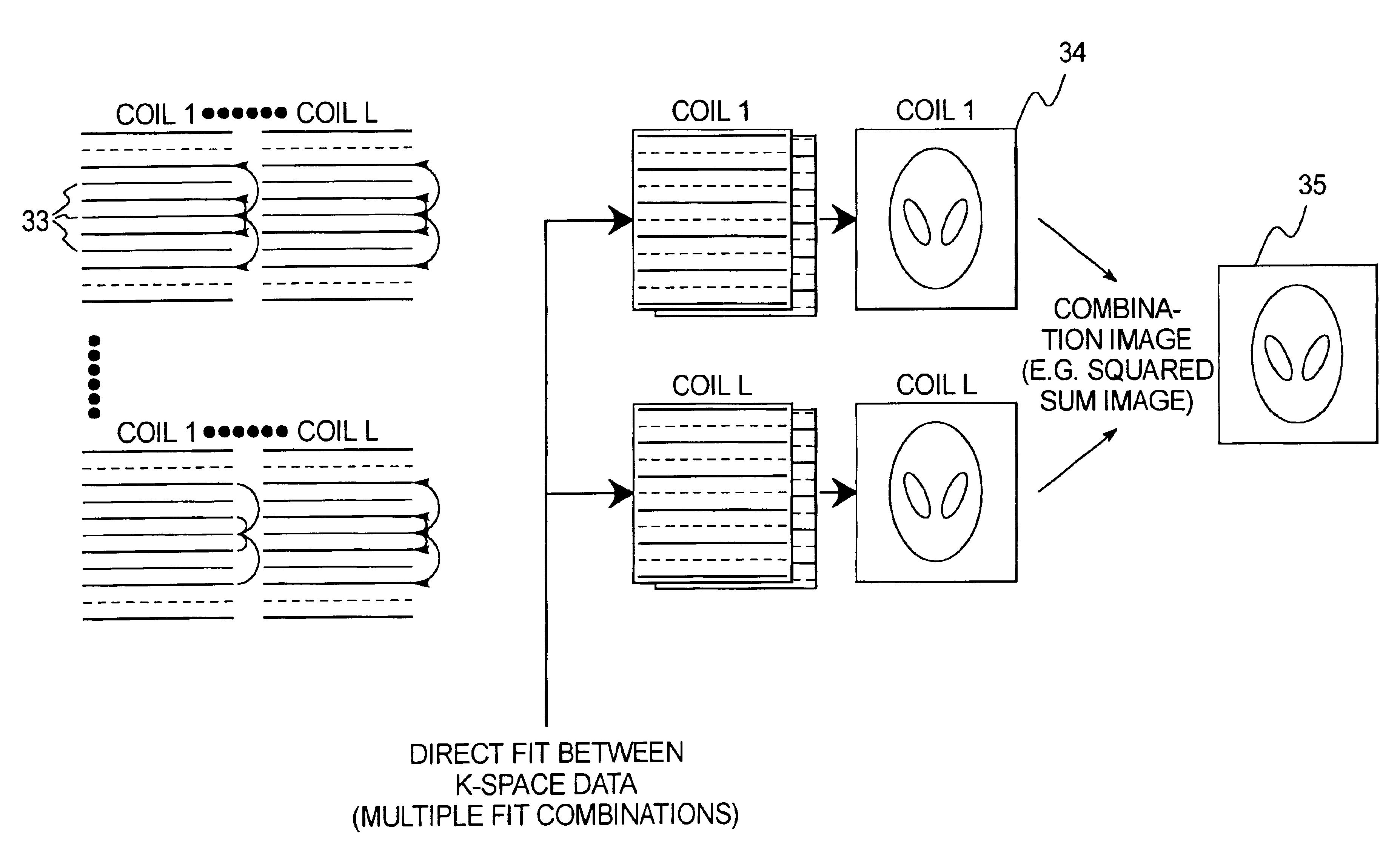
In a method and apparatus for magnetic resonance imaging of an interconnected region of a human body on the basis of a partially parallel acquisition (PPA) by excitation of nuclear spins and measurement of the radio-frequency signals produced by the excited nuclear spins, a number of spin excitations and measurements of an RF response signal are implemented simultaneously in every component coil of a number of RF reception coils. As a result a number of response signals are acquired that form a reduced dataset of received RF signals for each component coil. Additional calibration data points are acquired for each reduced dataset. A complete image dataset is formed for each component coil on the basis of the reduced dataset for that component coil and at least one further, reduced dataset of a different component coil. A spatial transformation of the image dataset of each component coil is implemented in order to form a complete image of each component coil.
Owner:GRISWOLD MARK
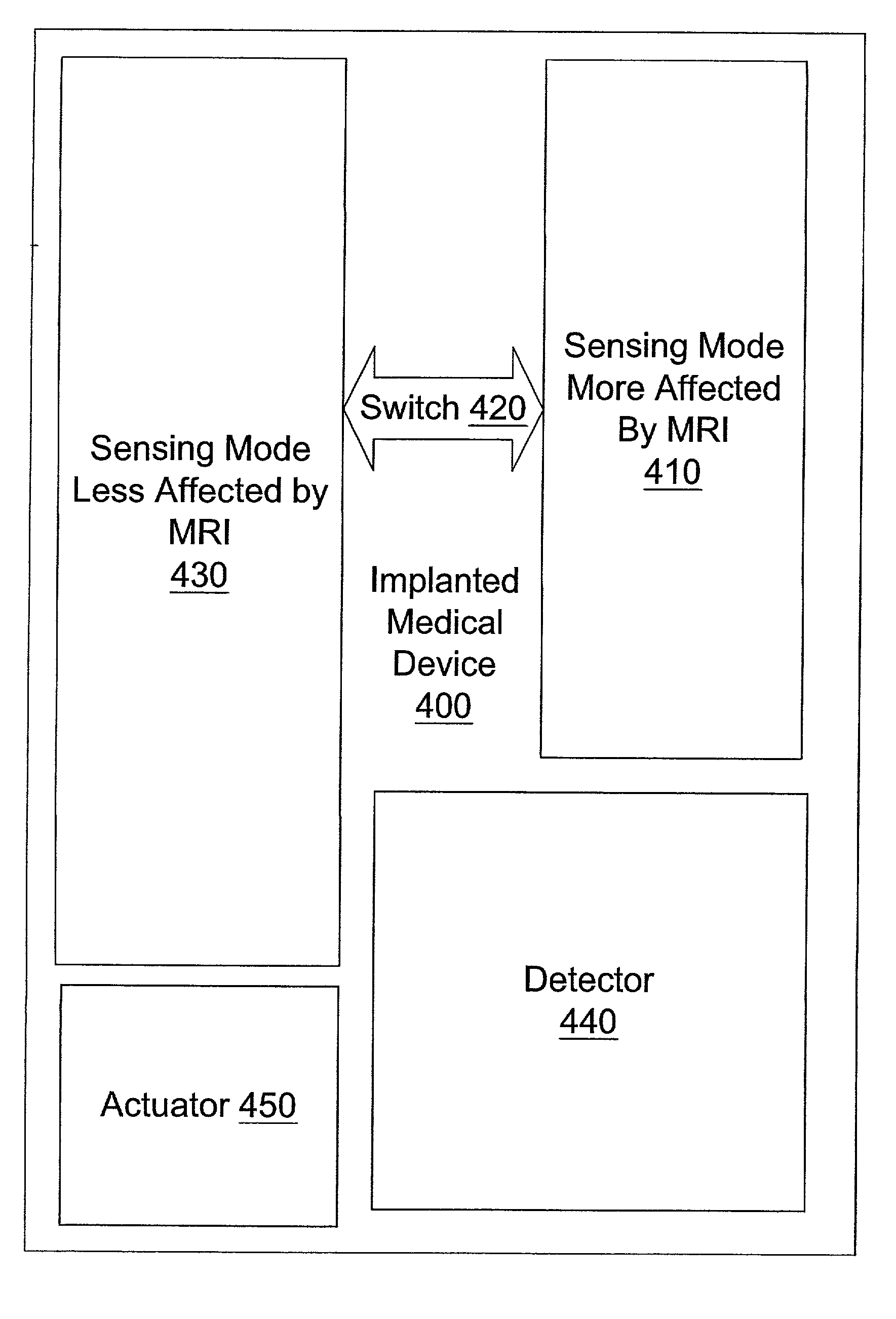
Alternative sensing method for implantable medical device in magnetic resonance imaging device
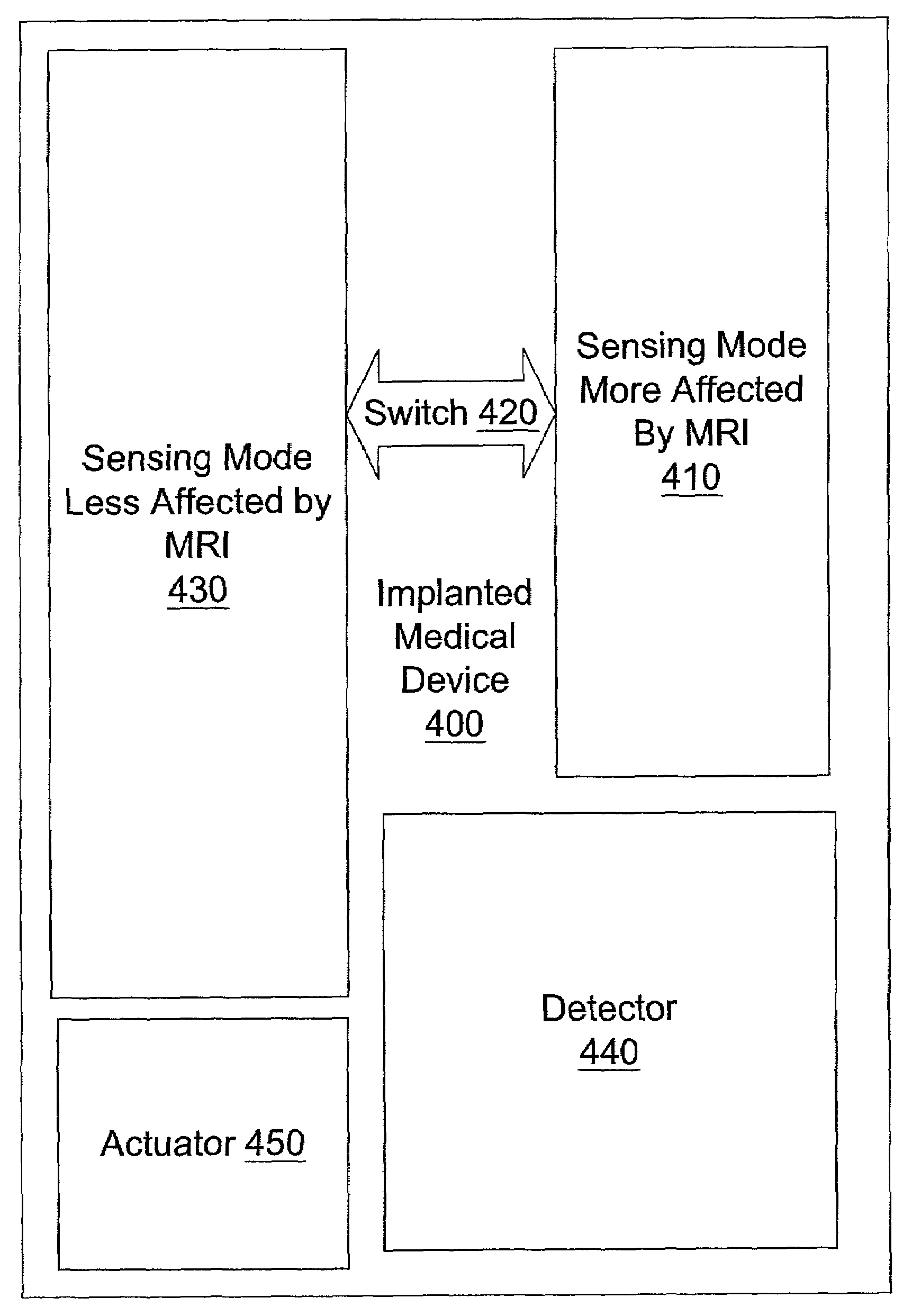
A method is provided, the method comprising detecting a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) interference signal and enabling at least one preventive measure to protect an implantable medical device from interference by the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) interference signal. The method also comprises switching from a first sensing mode more affected by the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) interference signal to a second sensing mode less affected by the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) interference signal.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Piezo electrically driven bellows infuser for hydraulically controlling an adjustable gastric band
A remotely controlled gastric band system that is practically immune to external magnetic fields, such as from a Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) machine, incorporates a bi-directional pump and fluid reservoir to adjust fluid volume in a gastric band. A piezoelectrically driven (e.g., rotary actuator, linear actuator) selectively compresses and expands a metal bellows hermetically sealed within a biocompatible and nonferromagnetic case such as titanium.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
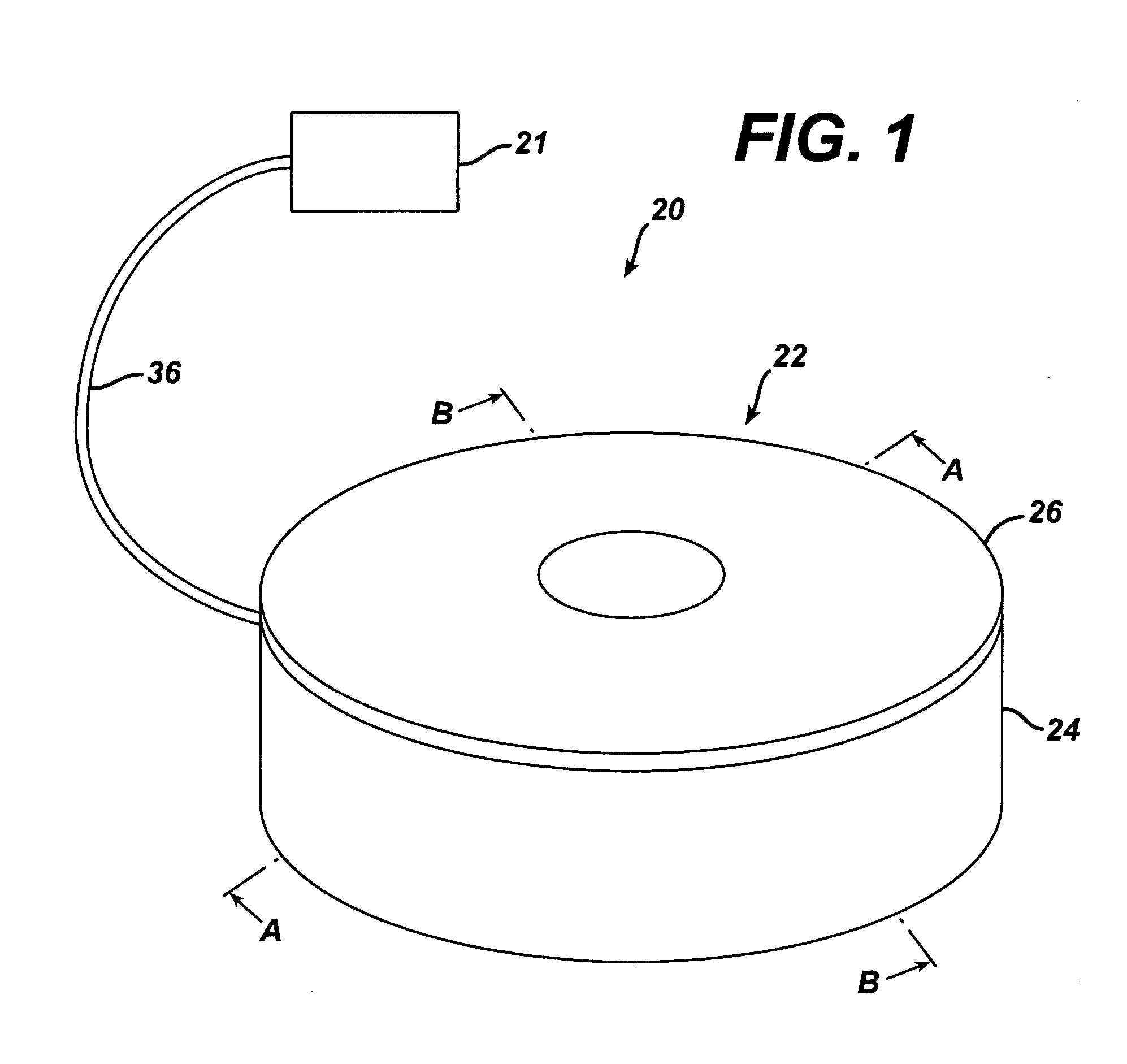
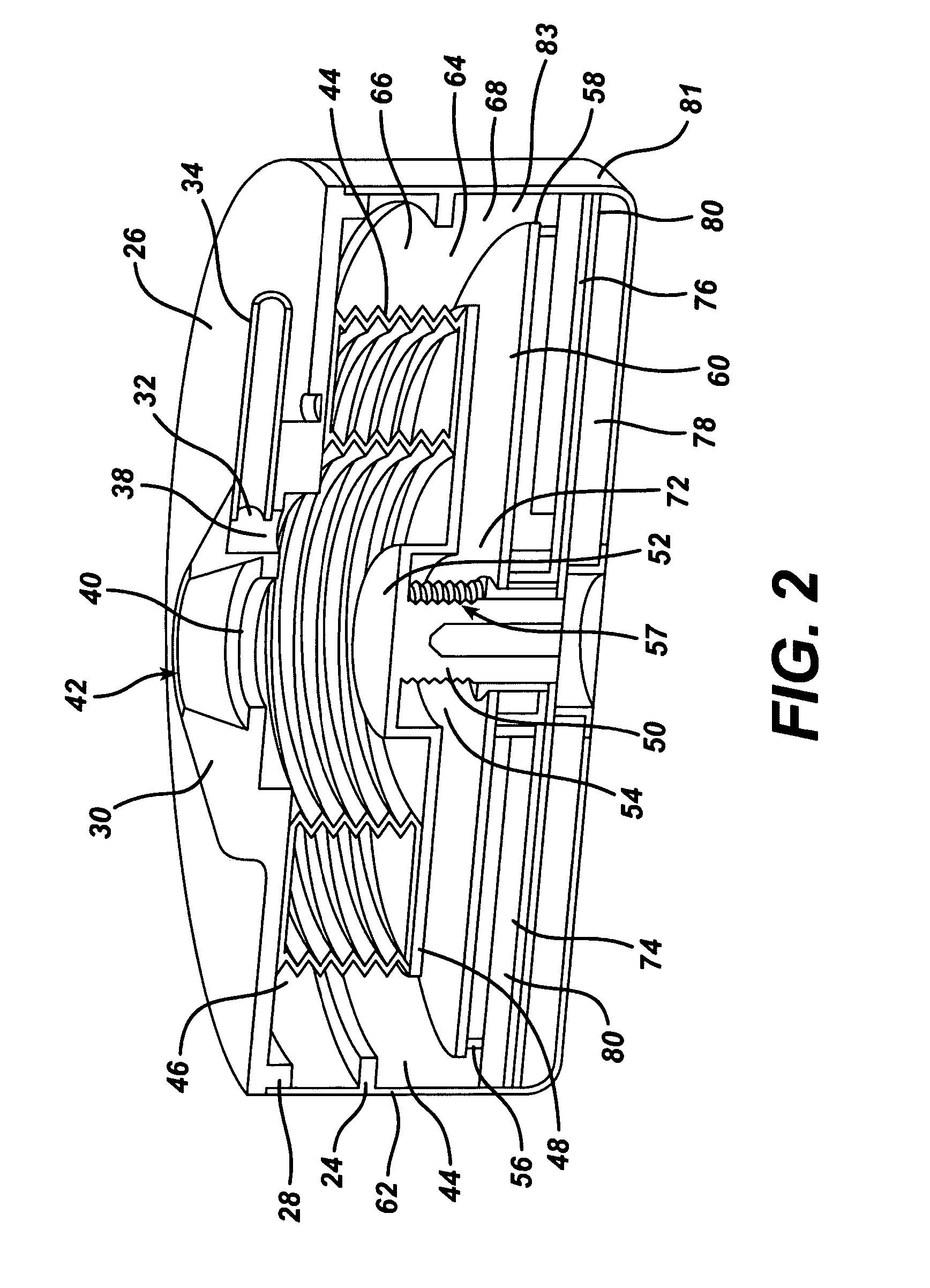
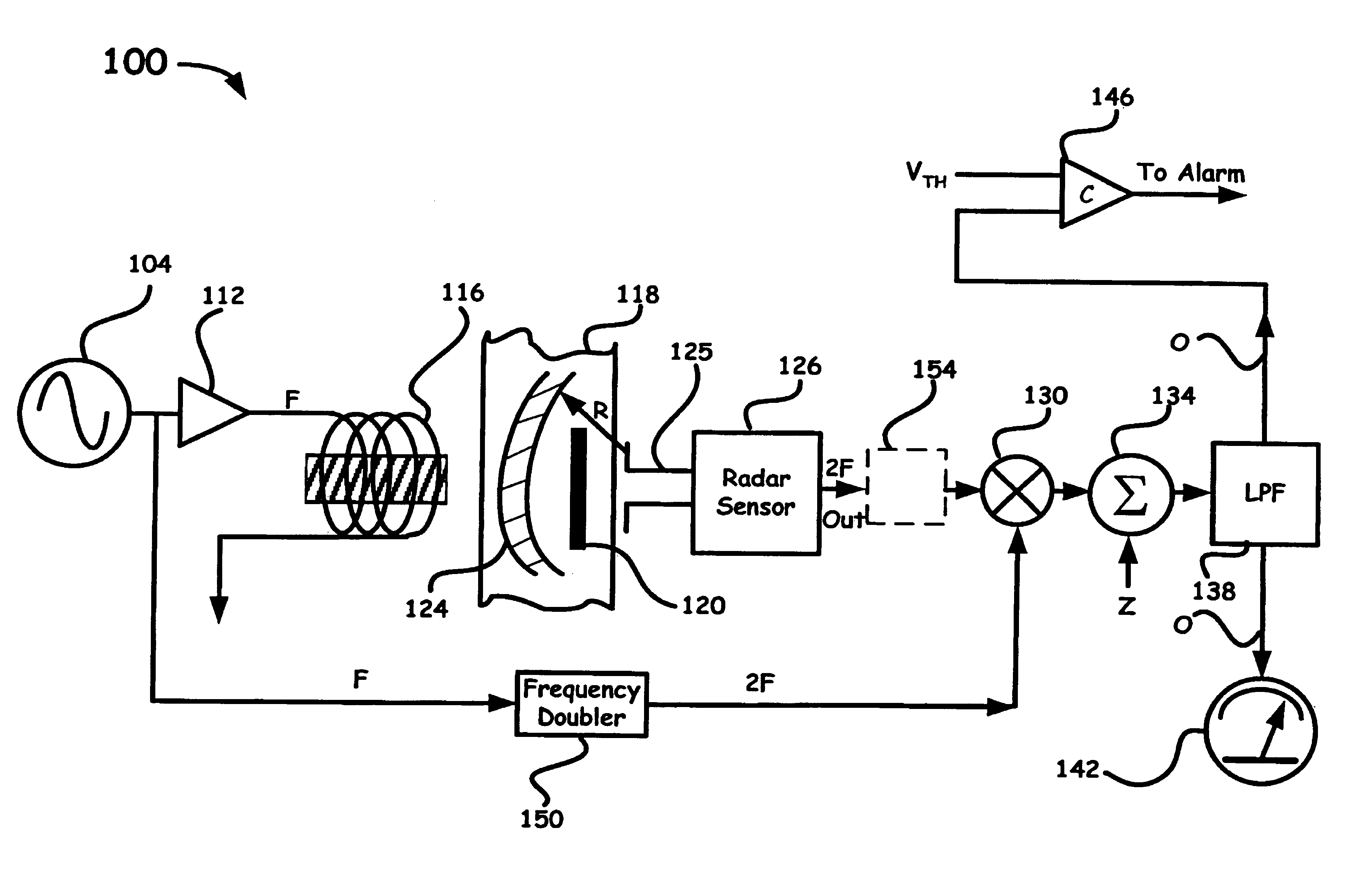
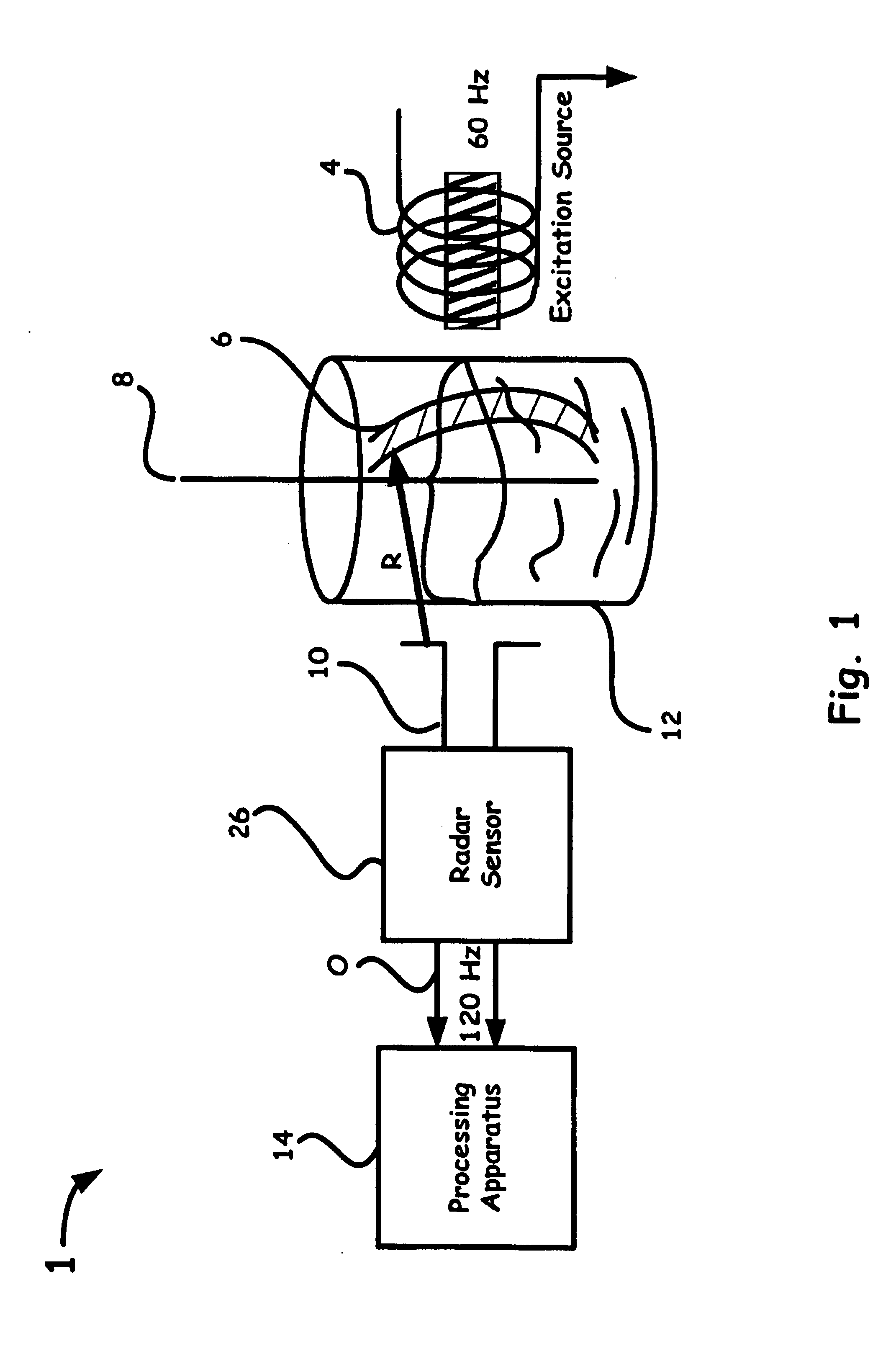
Magneto-radar detector and method
A varying magnetic field excites slight vibrations in an object and a radar sensor detects the vibrations at a harmonic of the excitation frequency. The synergy of the magnetic excitation and radar detection provides increased detection range compared to conventional magnetic metal detectors. The radar rejects background clutter by responding only to reflecting objects that are vibrating at a harmonic excitation field, thereby significantly improving detection reliability. As an exemplary arrangement, an ultra-wideband micropower impulse radar (MIR) is capable of being employed to provide superior materials penetration while providing range information. The magneto-radar may be applied to pre-screening magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) patients, landmine detection and finding hidden treasures.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Metal bellows position feedback for hydraulic control of an adjustable gastric band
InactiveUS7481763B2Avoid the needNon-surgical orthopedic devicesObesity treatmentClosed loopEngineering
A remotely controlled gastric band system that is practically immune to external magnetic fields, such as from a Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) machine, incorporates a bi-directional pump and fluid reservoir to adjust fluid volume for hydraulic control of a gastric band. A piezoelectric driver (e.g., rotary actuator, linear actuator) selectively compresses and expands a metal bellows hermetically sealed within a biocompatible and nonferromagnetic enclosure or case such as titanium. Directly sensing a position of the metal bellows yields an accurate reading of volume contained therein, allowing for closed-loop control of the gastric band.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
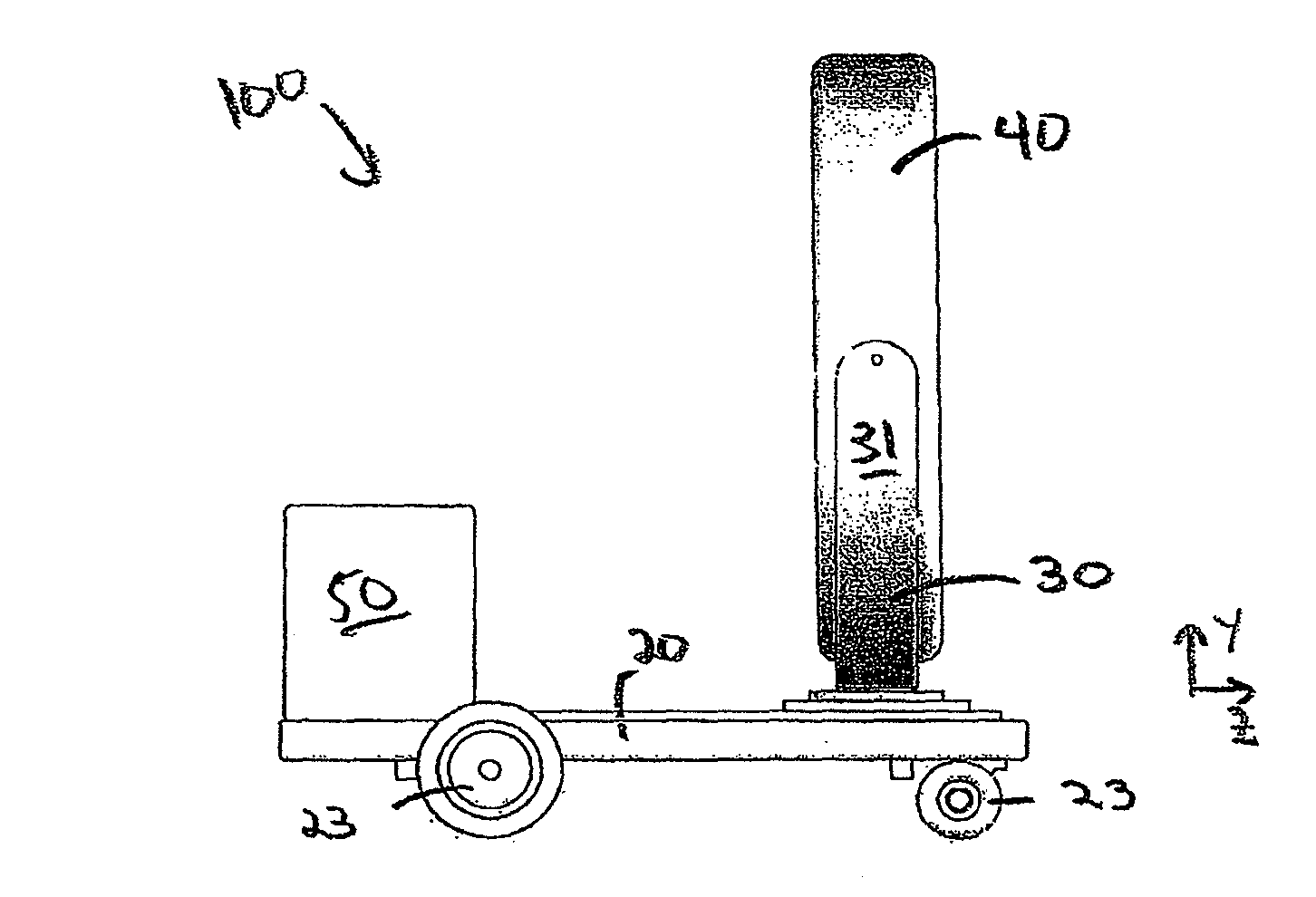
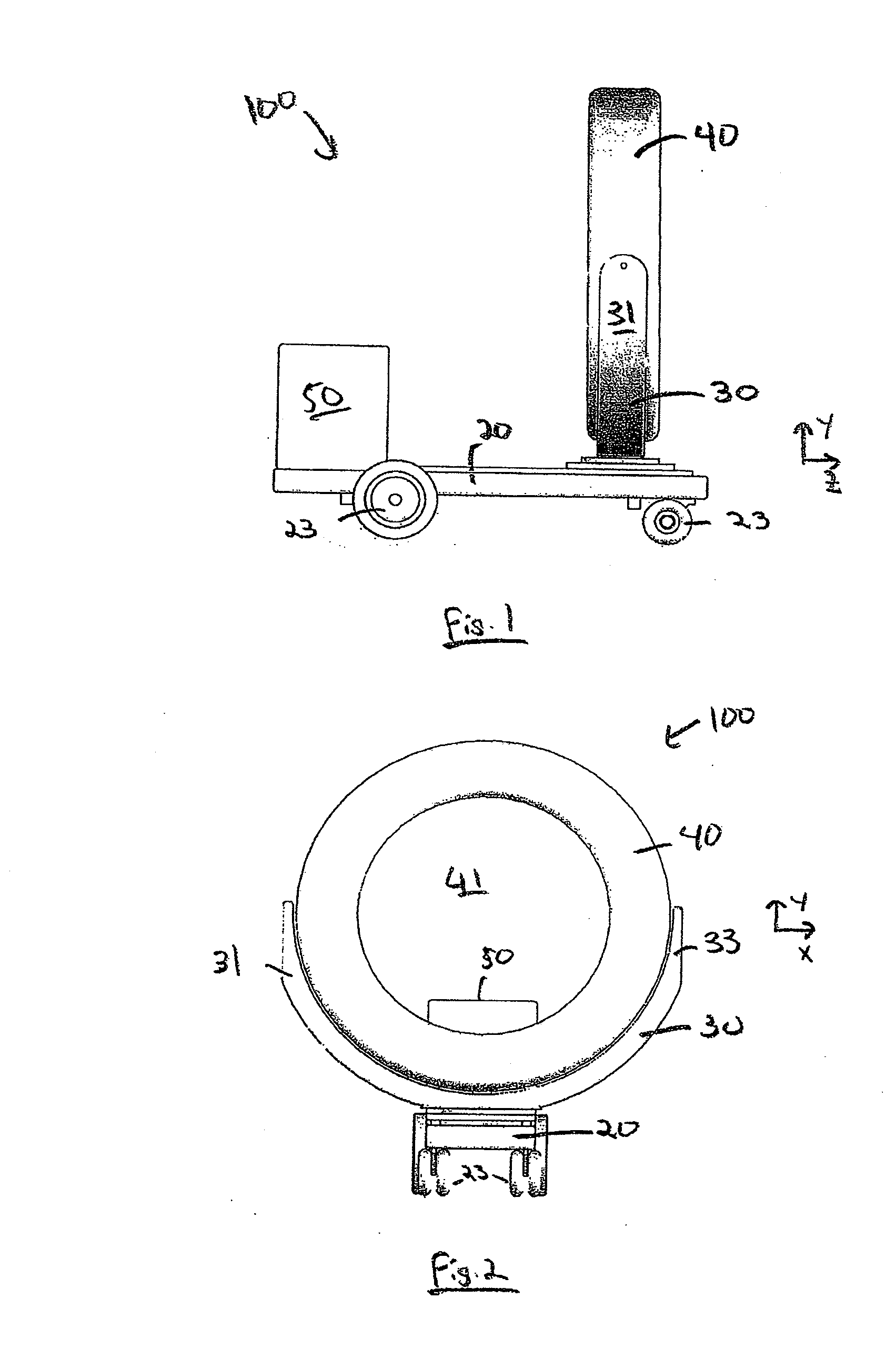
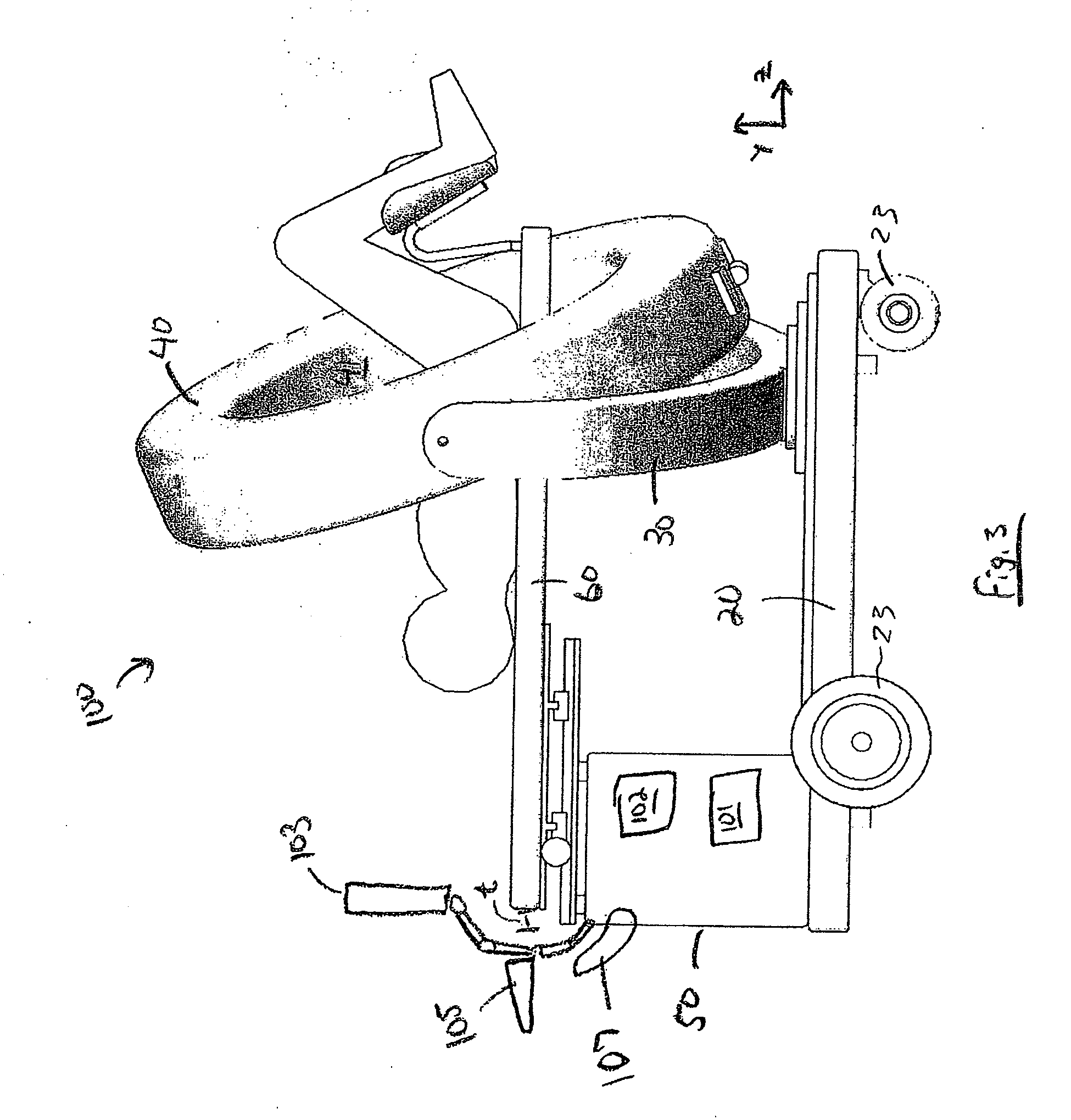
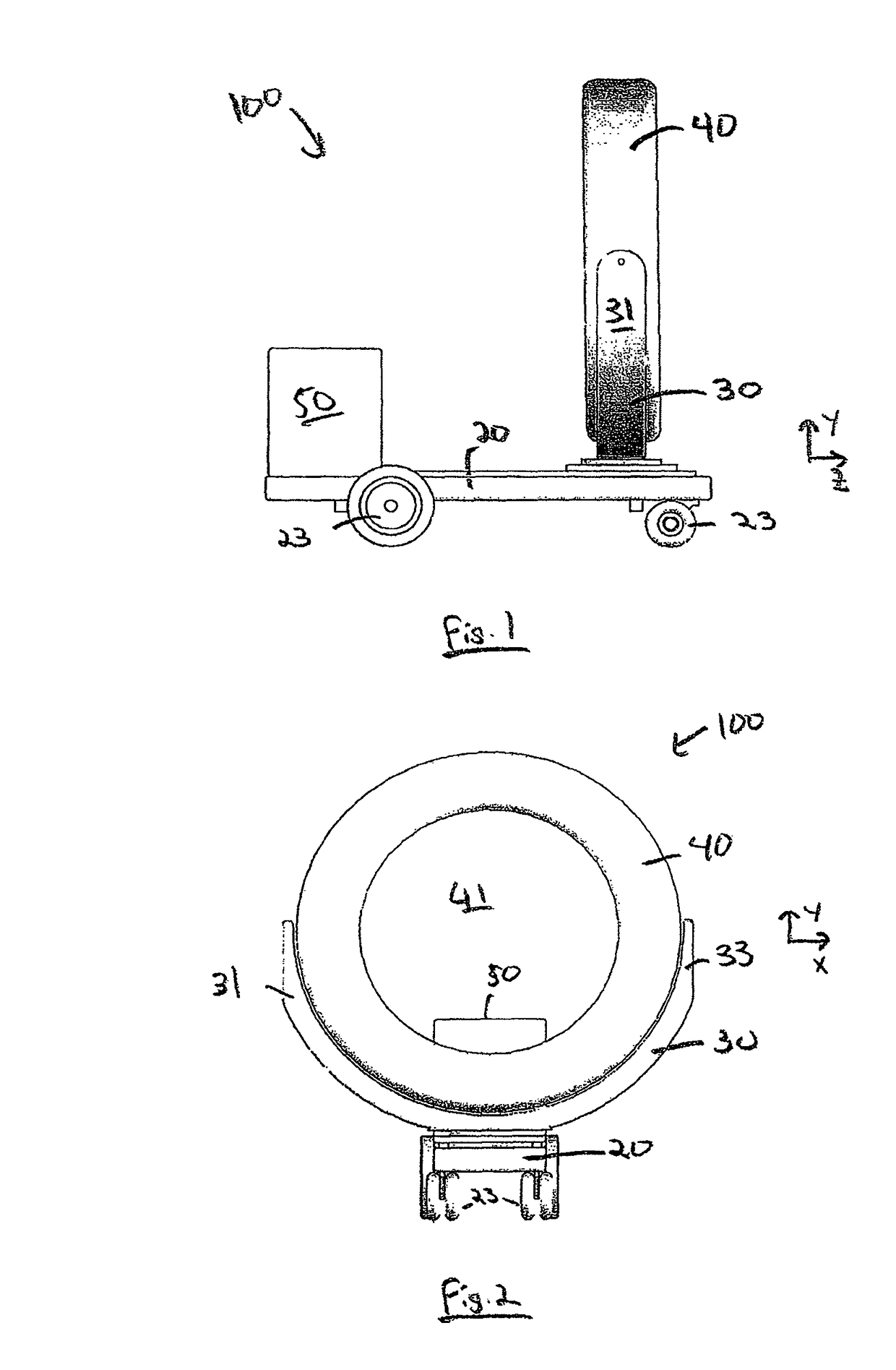
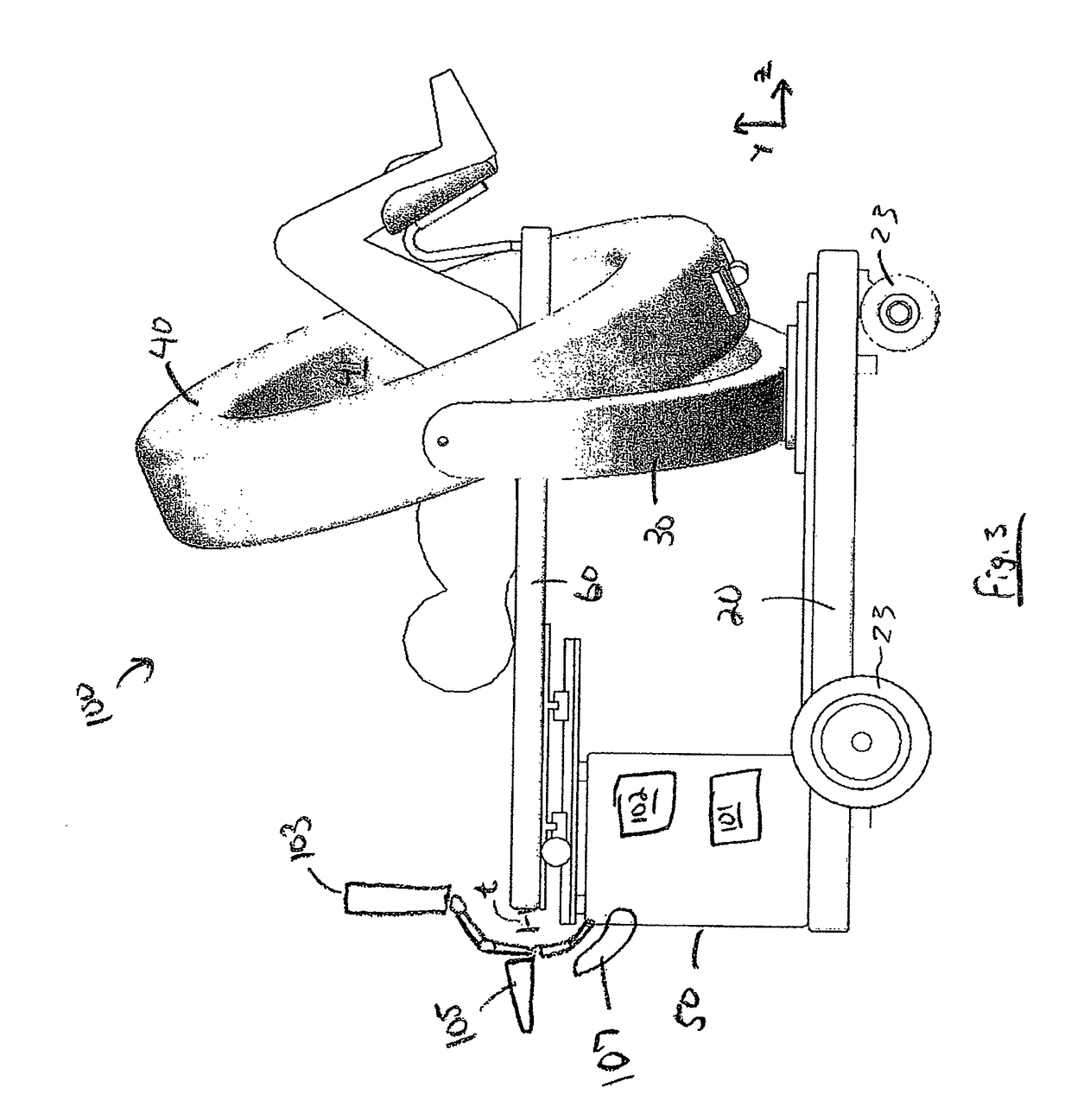
Mobile medical imaging system and methods
ActiveUS20100172468A1Easy to transportFacilitate easy transportRadiation/particle handlingPatient positioning for diagnosticsMedical imagingEngineering
A mobile medical imaging device that allows for multiple support structures, such as a tabletop or a seat, to be attached, and in which the imaging gantry is indexed to the patient by translating up and down the patient axis. In one embodiment, the imaging gantry can translate, rotate and / or tilt with respect to a support base, enabling imaging in multiple orientations, and can also rotate in-line with the support base to facilitate easy transport and / or storage of the device. The imaging device can be used in, for example, x-ray computed tomography (CT) and / or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) applications.
Owner:MOBIUS IMAGING
Apparatus and process for reducing the susceptibility of active implantable medical devices to medical procedures such as magnetic resonance imaging
A feedthrough terminal assembly for an active implantable medical device (AIMD) includes magnetic shielding elements to block incident magnetic fields during medical procedures such as Magnetic Resonance Imaging. The assembly includes conductive or ground plate(s) embedded in an insulator surrounding elements of the assembly, a plurality of lead wires extending from electronic circuitry of the AIMD, and a lossy ferrite inductor through which the lead wires extend in non-conductive relation for increasing the impedance of the lead wires at selected RF frequencies. Alternatively, the assembly includes a conductive sleeve or cap surrounding the feedthrough capacitor and / or conductive support.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
Method and apparatus for shielding a linear accelerator and a magnetic resonance imaging device from each other
InactiveUS20110012593A1Improve permeabilityReduce flux densityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSplit magnetResonance
A radiation therapy system comprises a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system combined with an irradiation system, which can include one or more linear accelerators (linacs) that can emit respective radiation beams suitable for radiation therapy. The MRI system includes a split magnet system, comprising first and second main magnets separated by gap. A gantry is positioned in the gap between the main MRI magnets and supports the linac(s) of the irradiation system. The gantry is rotatable independently of the MRI system and can angularly reposition the linac(s). Shielding can also be provided in the form of magnetic and / or RF shielding. Magnetic shielding can be provided for shielding the linac(s) from the magnetic field generated by the MRI magnets. RF shielding can be provided for shielding the MRI system from RF radiation from the linac.
Owner:VIEWRAY TECH
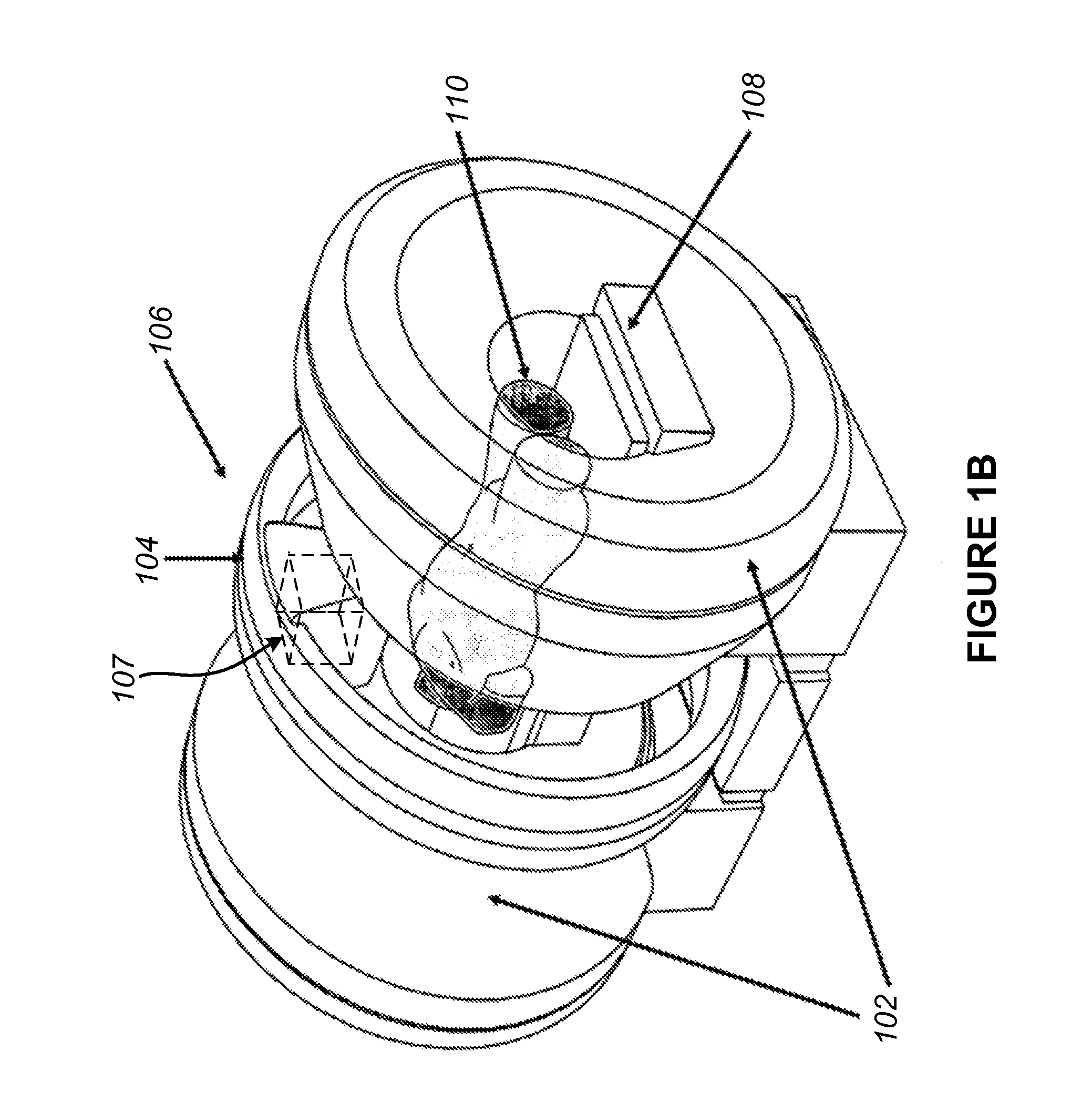
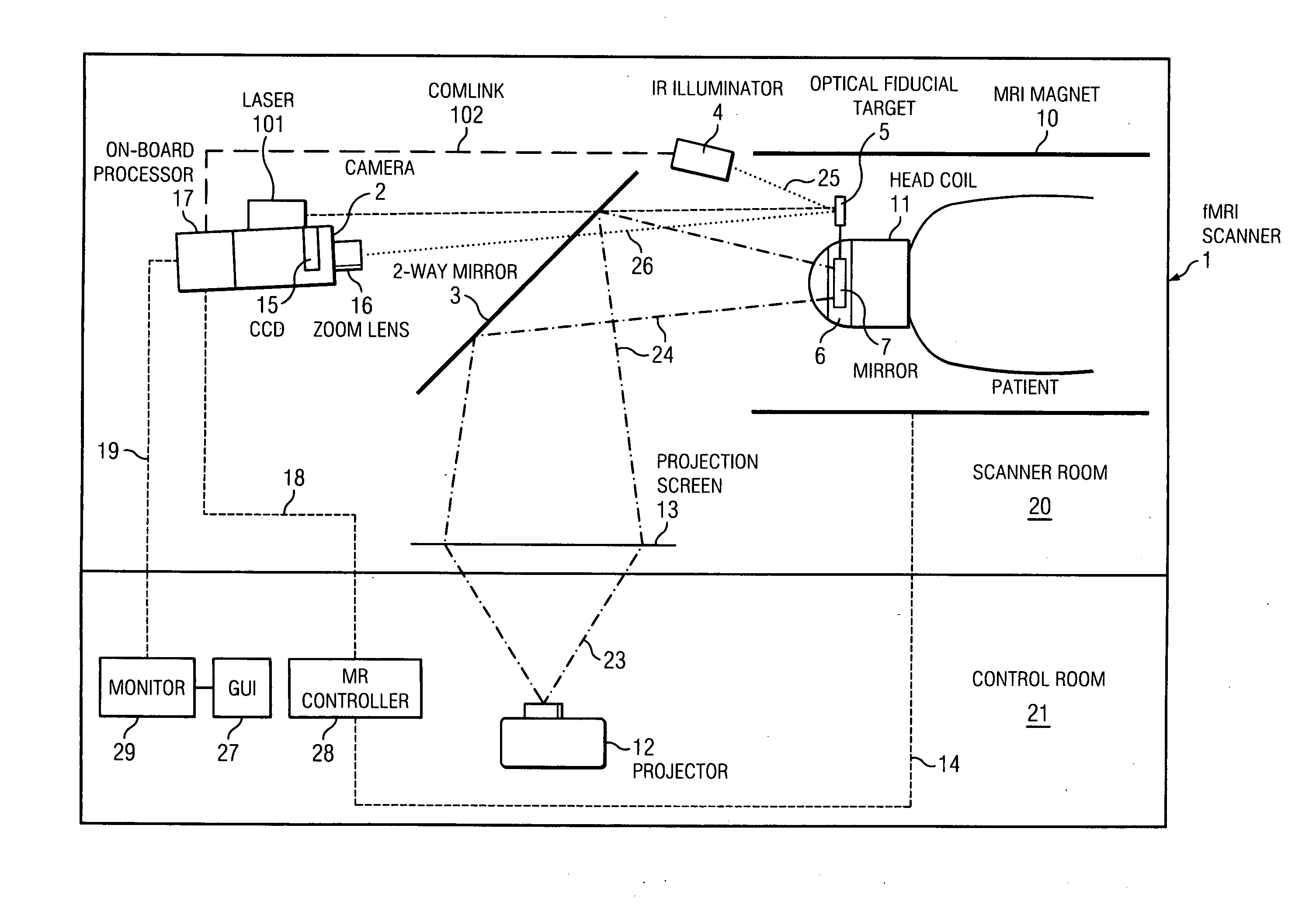
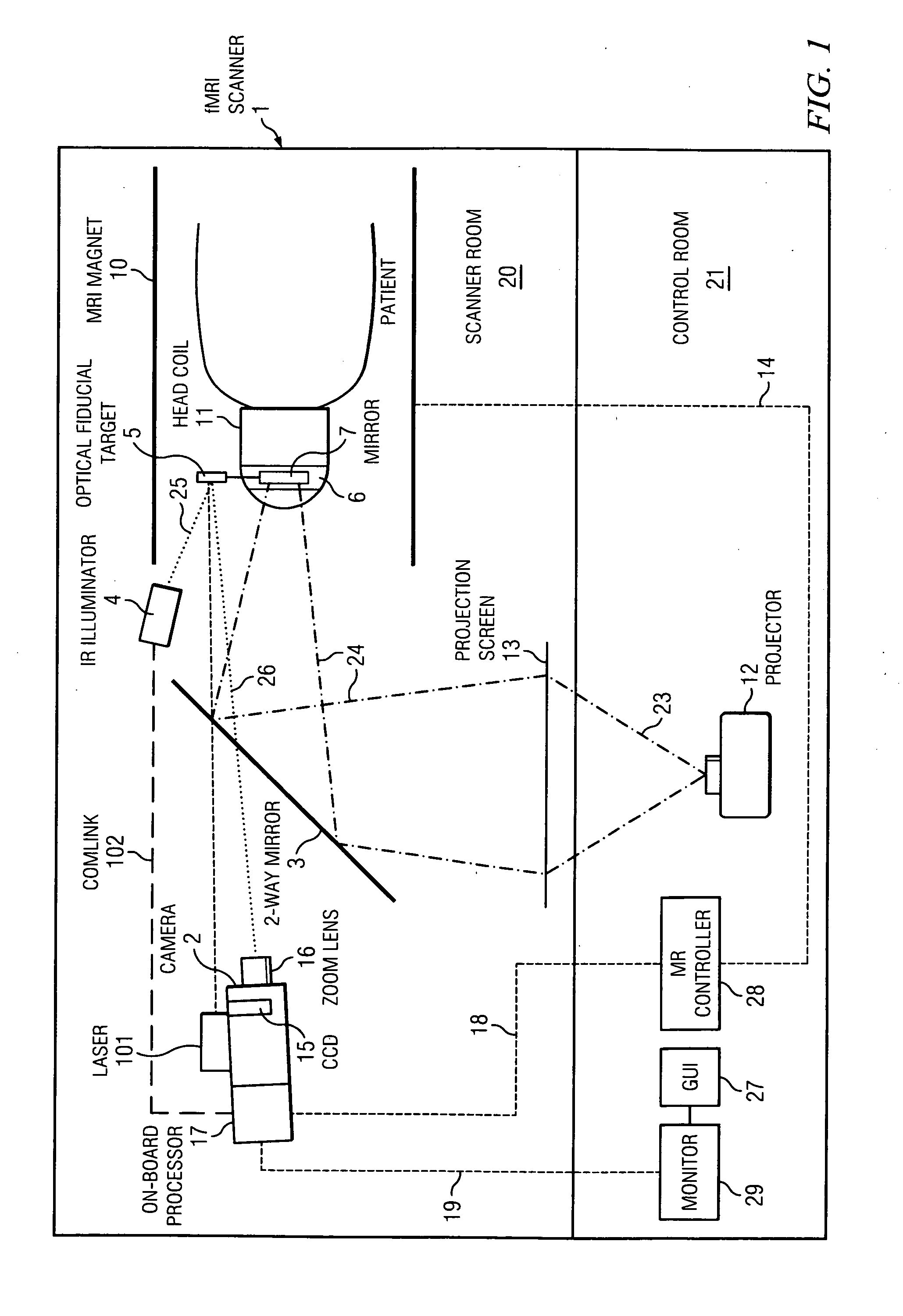
Single camera motion measurement and monitoring for magnetic resonance applications
InactiveUS20110230755A1Improves imaging timeImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisOn boardResonance
An optically-based rigid-body 6-DOF motion tracking system optimized for prospective (real-time) motion correction in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) applications using a single camera with an on-board image processor, an IR illuminator and optical fiducial targets affixed to a patient. An angle extraction algorithm operated by the on-board image processor utilizes successive approximation to solve the 3-point pose problem for angles close to the origin to achieve convergence to sub-microradian levels. A motion alarm is enabled by a monitor and GUI application in communication with the motion tracking system. A motion correction is enabled for MR scan images taken while operating the motion tracking system wherein an MRI controller is in communication with the motion tracking system.
Owner:MACFARLANE DUNCAN +1
Metal bellows position feedback for hydraulic control of an adjustable gastric band
InactiveUS20050267500A1Precise motion controlAvoid the needNon-surgical orthopedic devicesObesity treatmentClosed loopEngineering
A remotely controlled gastric band system that is practically immune to external magnetic fields, such as from a Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) machine, incorporates a bi-directional pump and fluid reservoir to adjust fluid volume for hydraulic control of a gastric band. A piezoelectric driver (e.g., rotary actuator, linear actuator) selectively compresses and expands a metal bellows hermetically sealed within a biocompatible and nonferromagnetic enclosure or case such as titanium. Directly sensing a position of the metal bellows yields an accurate reading of volume contained therein, allowing for closed-loop control of the gastric band.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Mobile medical imaging system and methods
ActiveUS8118488B2Easy to transportFacilitate easy transport and storagePatient positioning for diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringMedical imagingEngineering
A mobile medical imaging device that allows for multiple support structures, such as a tabletop or a seat, to be attached, and in which the imaging gantry is indexed to the patient by translating up and down the patient axis. In one embodiment, the imaging gantry can translate, rotate and / or tilt with respect to a support base, enabling imaging in multiple orientations, and can also rotate in-line with the support base to facilitate easy transport and / or storage of the device. The imaging device can be used in, for example, x-ray computed tomography (CT) and / or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) applications.
Owner:MOBIUS IMAGING
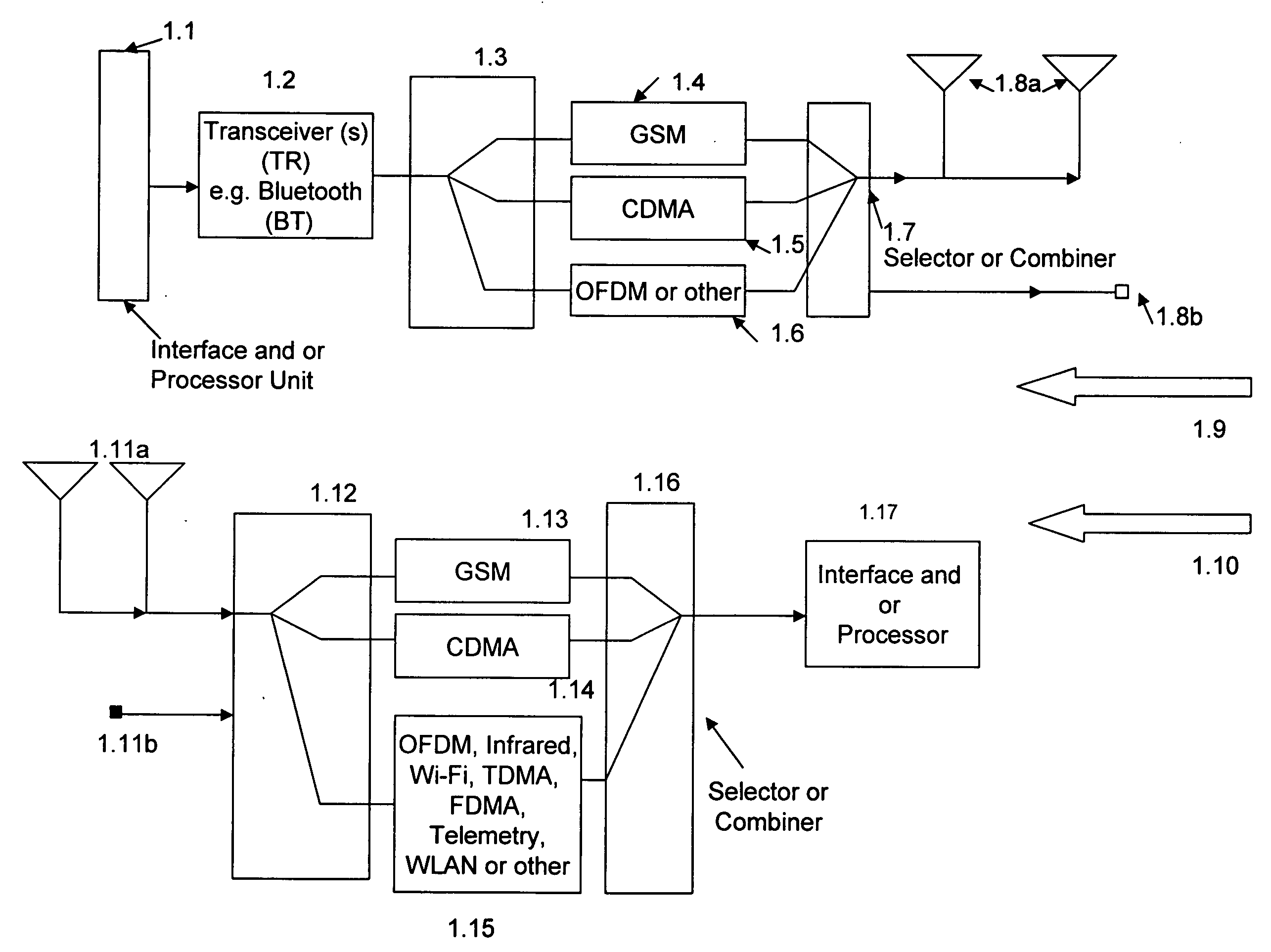
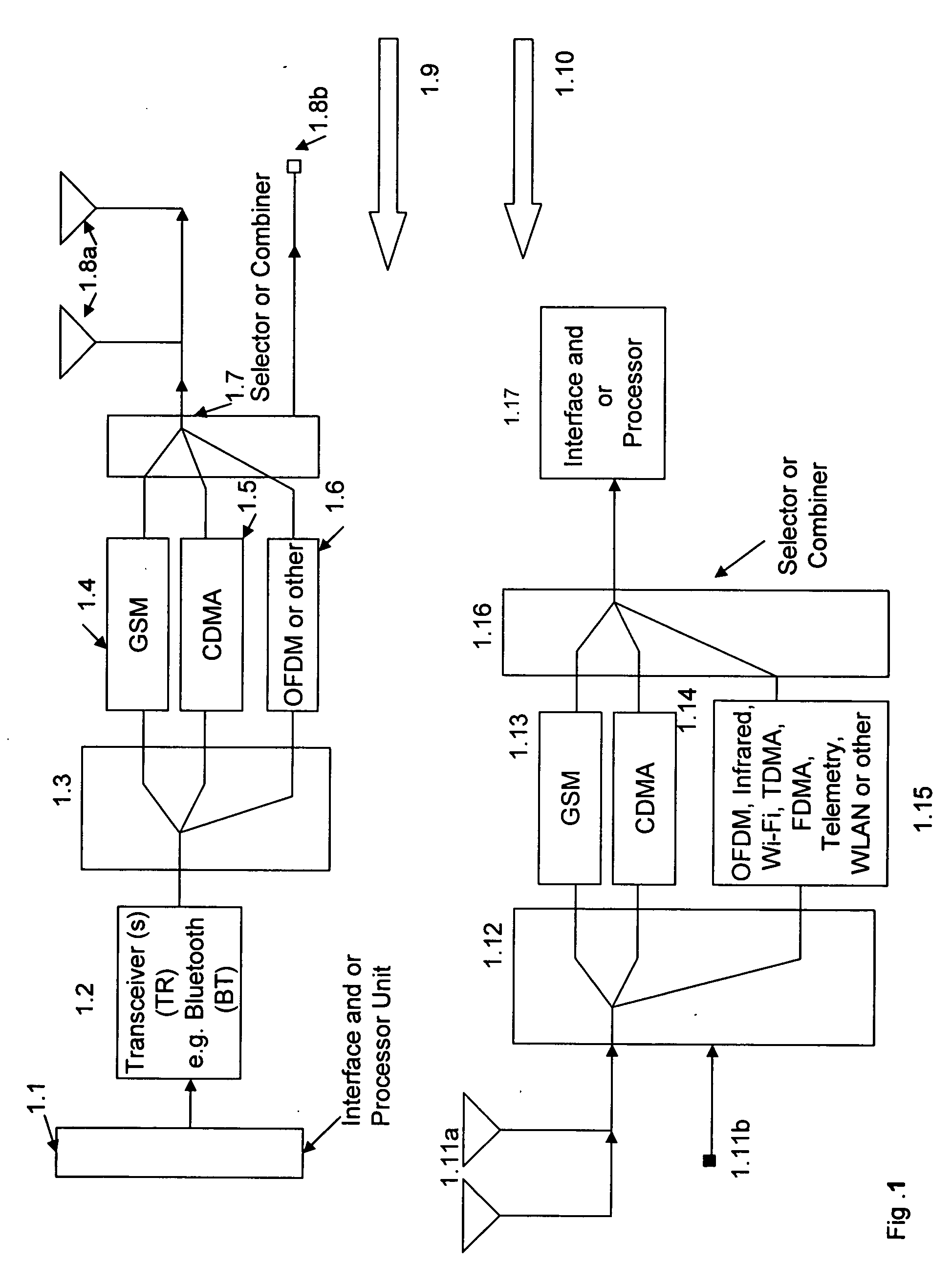
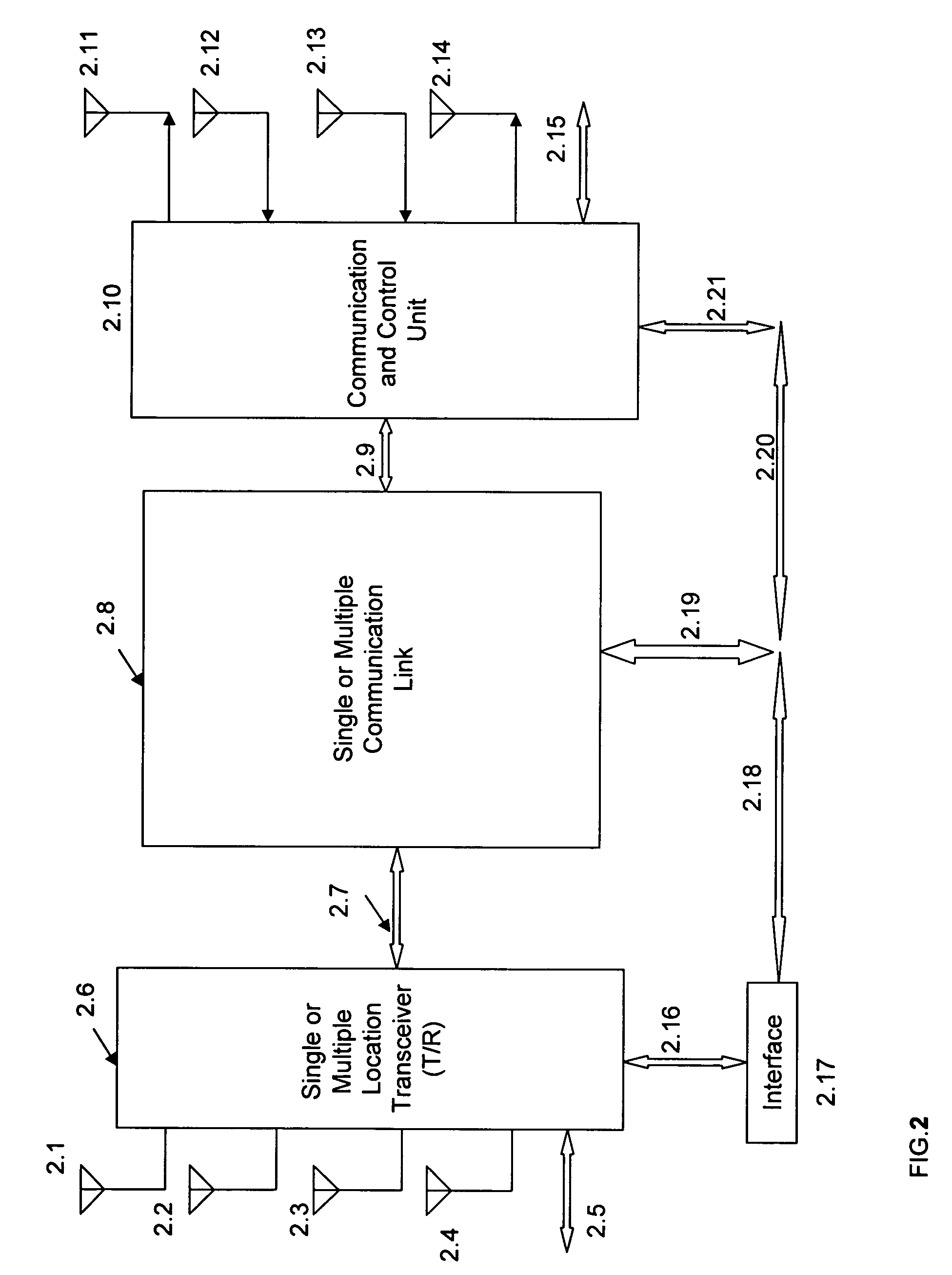
Medical diagnostic and communication system
InactiveUS20070032832A1Expand coverageImprove performanceSpatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsHeart pacemakersEmergency rooms
Cardiac stimulation device and wireless communication system, without magnetic detection or magnetic control of the heart pacemaker parameters, having leads for carrying stimulating pulses to and or from one or more electrodes located in a heart and a pulse generator configured to generate stimulation pulses. In certain embodiments and environments the heart pacemaker could operate in an emergency room, even during Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) diagnostic studies. A processor for connection of the stimulating pulses to and / or from one or more spread spectrum transmitter-receiver (T / R) circuits and / or from a signal processing network for receiving said stimulation pulses and for providing cross-correlated in-phase and quadrature-phase baseband signals. One or more modulators and demodulators for transmission and / or reception of one or more spread spectrum and / or cross-correlated signals.
Owner:FEHER KAMILO
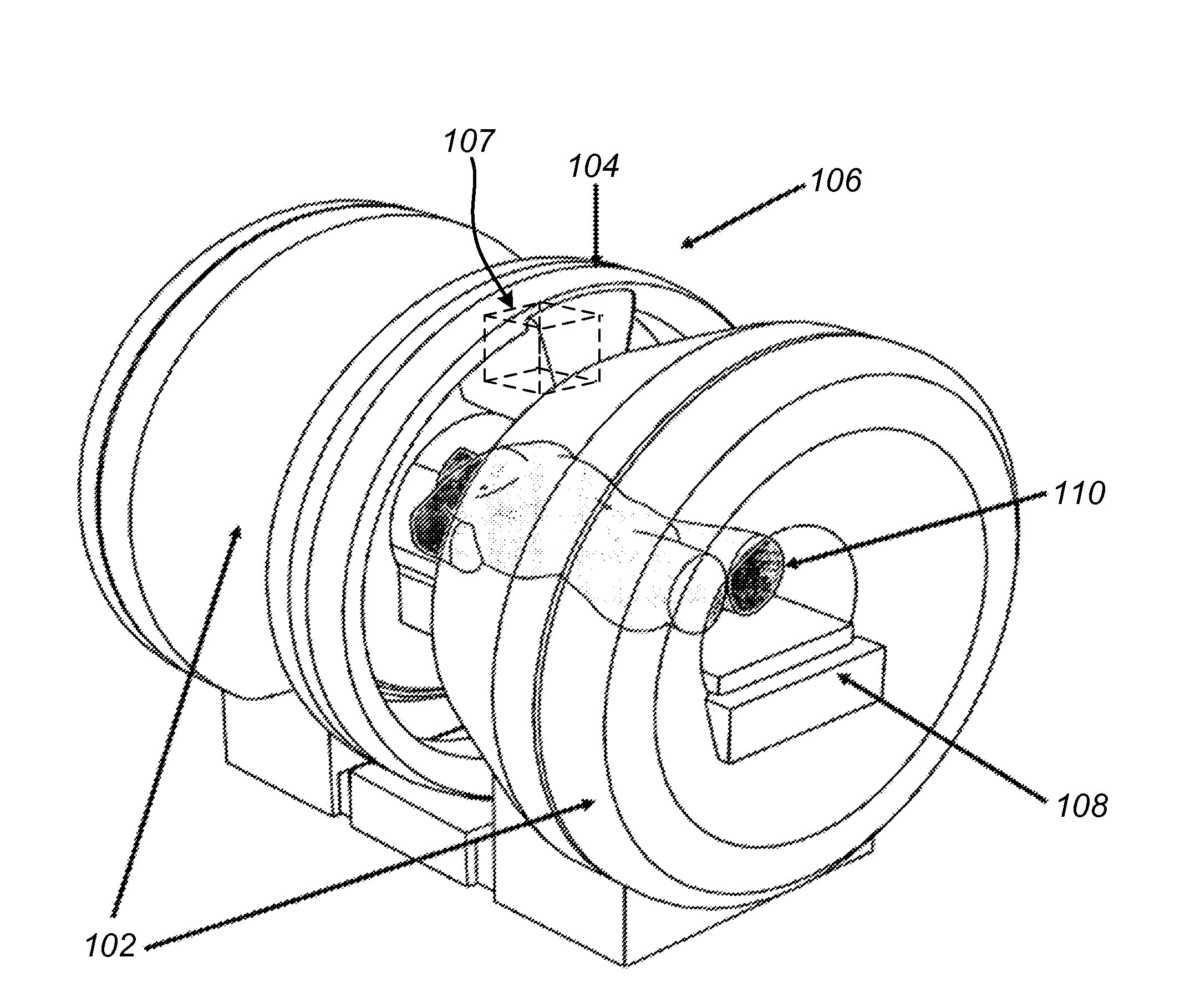
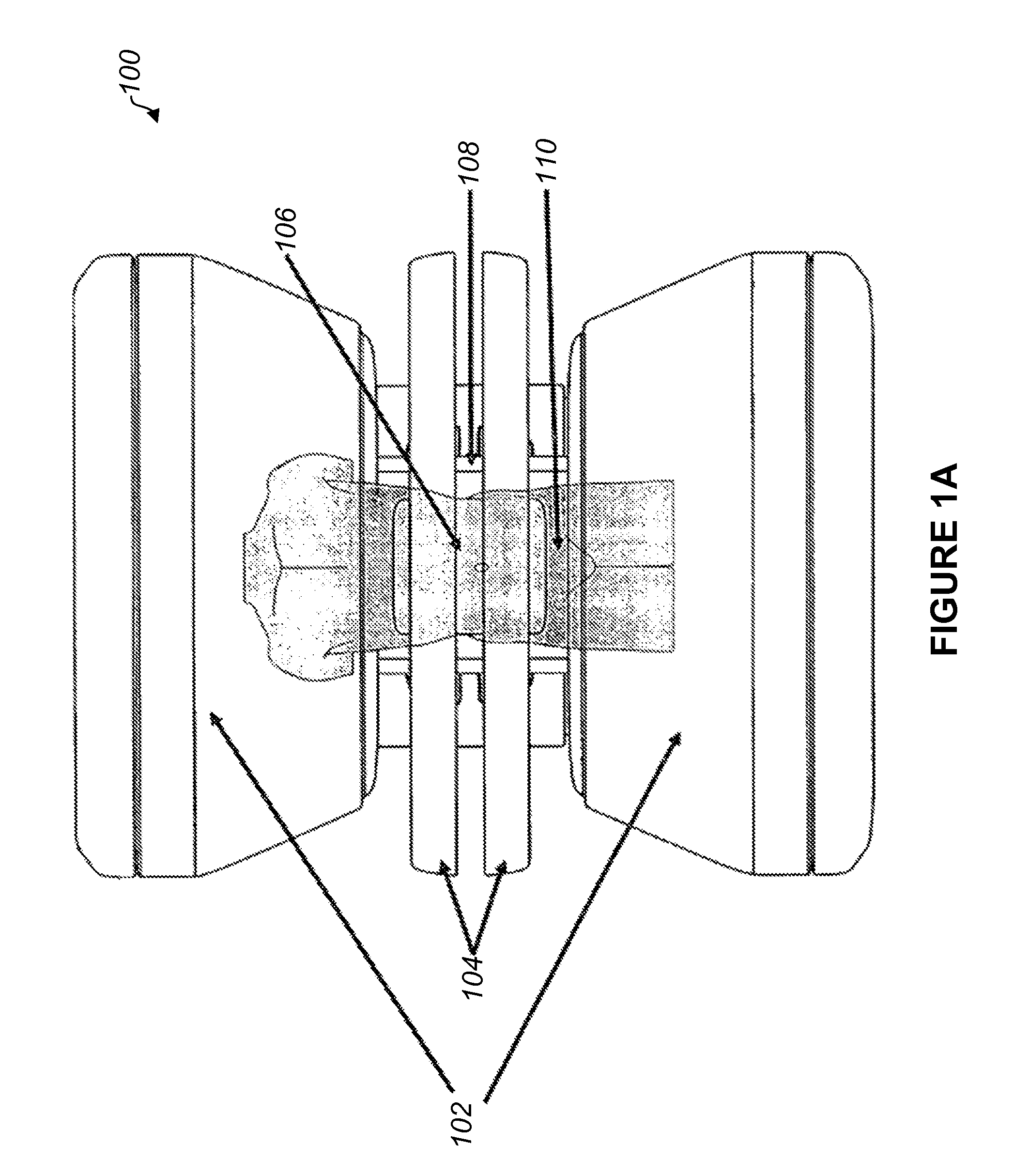
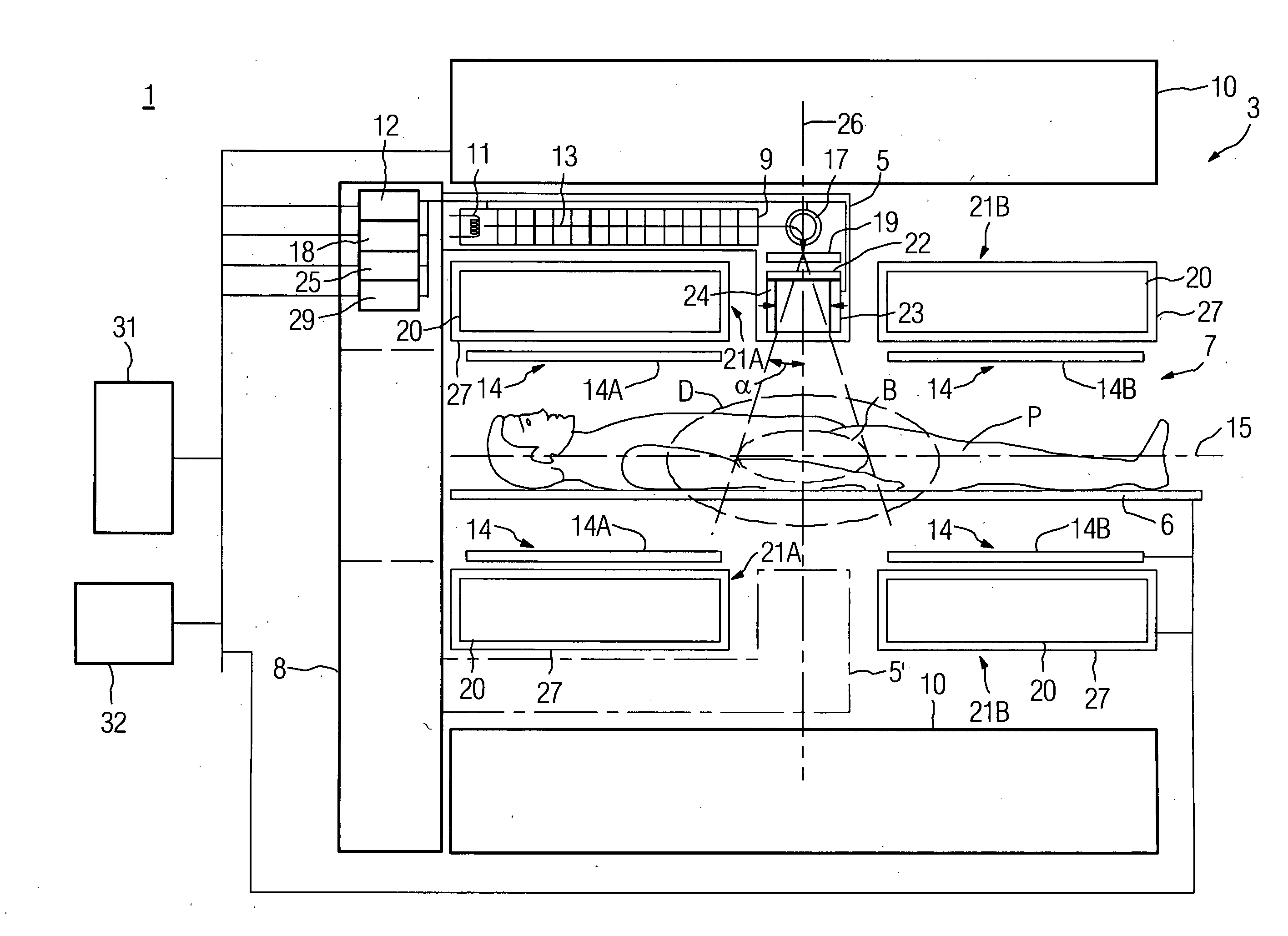
Combined radiation therapy and magnetic resonance unit
ActiveUS20080208036A1Avoid huge expensesHigh quality imagingMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringResonanceRadiation therapy
The invention relates to a combined radiation therapy and magnetic resonance unit. For this purpose, in accordance with the invention a combined radiation therapy and magnetic resonance unit is provided comprising a magnetic resonance diagnosis part with an interior, which is limited in radial direction by a main magnet, and a radiation therapy part for the irradiation of an irradiation area within the interior, wherein at least parts of the radiation therapy part, which comprise a beam deflection arrangement, are arranged within the interior.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
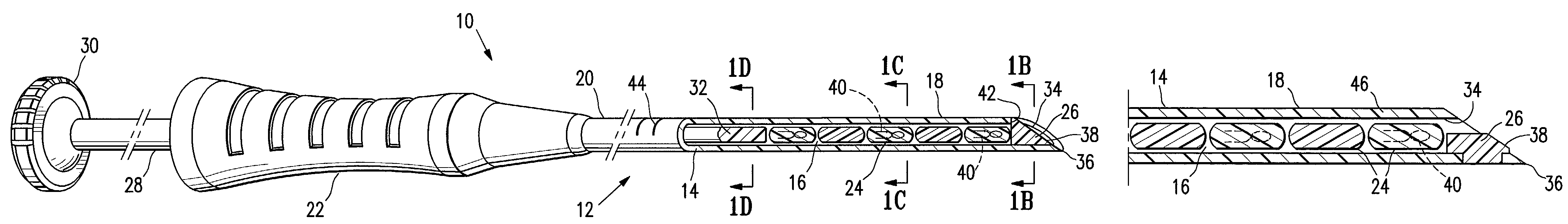
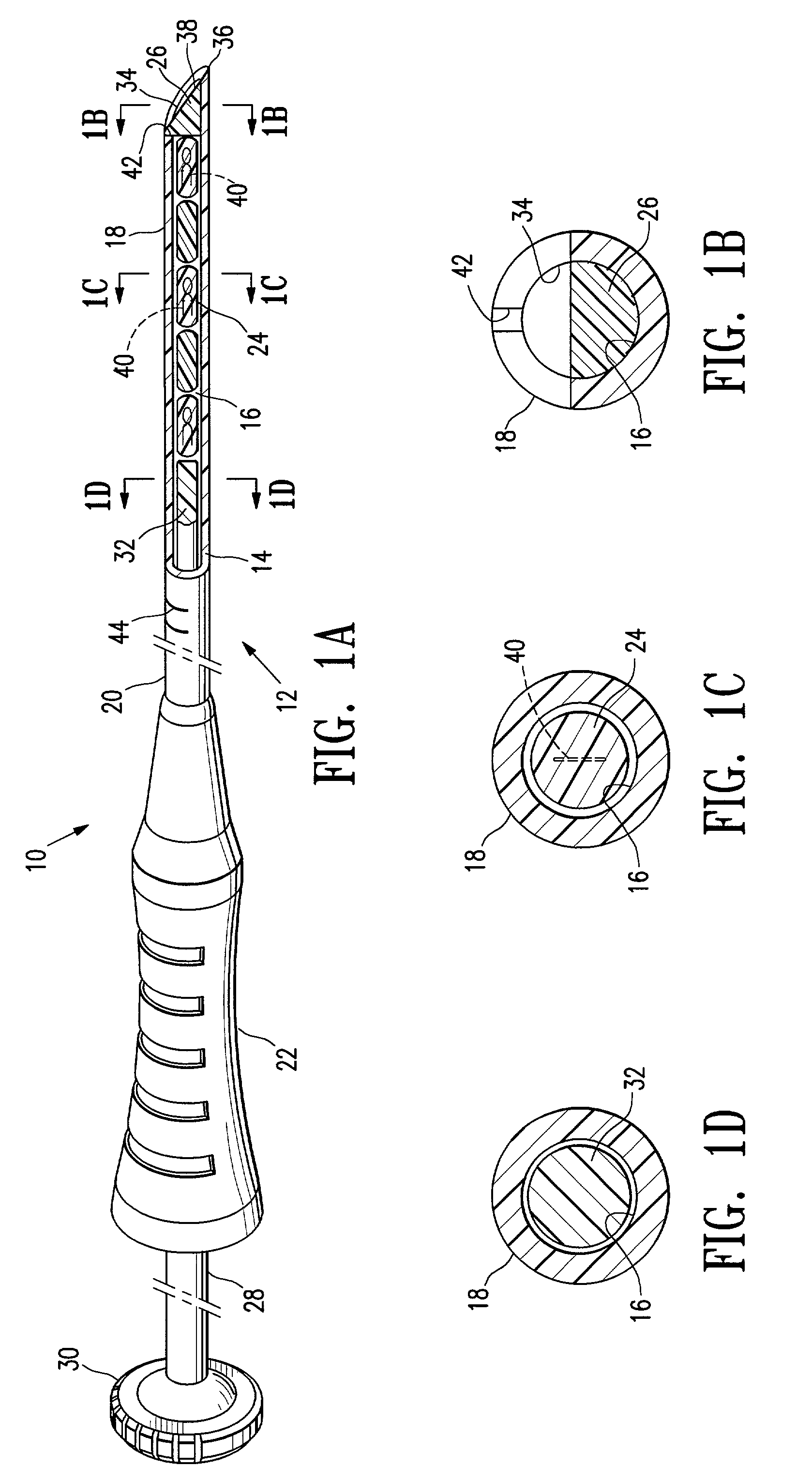
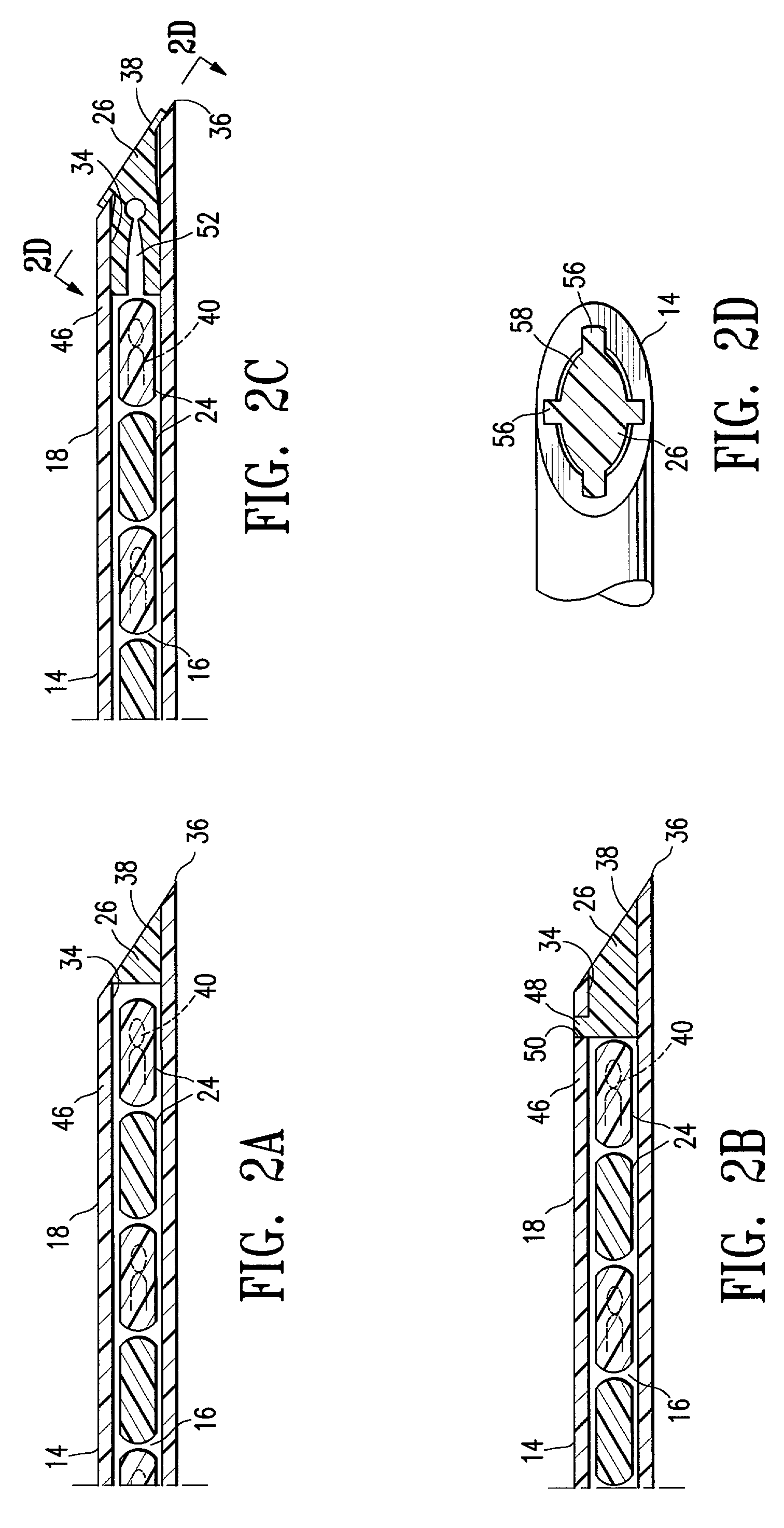
Plugged tip delivery for marker placement
InactiveUS7651505B2Improve accuracyAvoid mistakesSurgeryMedical devicesBiomedical engineeringUltrasound
The invention provides marker delivery devices, assemblies, and methods. Assemblies embodying features of the invention include marker delivery devices having a delivery tube with an orifice, markers, and a plug releasably disposed in the tube occluding the orifice. The plug prevents markers from passing through the orifice before the marker is to be placed at a desired location within a patient's body, prevents ingress of tissue into the bore of the tube, and allows markers to pass out of the orifice when marker delivery is desired. Guidance of a delivery tube to a desired location within a patient's body may include the use of an imaging device, with or without the use of a guide cannula. The plug may itself serve as a marker, and may be the sole marker. Markers may be detectable by ultrasound, X-ray, magnetic resonance imaging, and other imaging devices, and may include bioactive elements.
Owner:SENORX
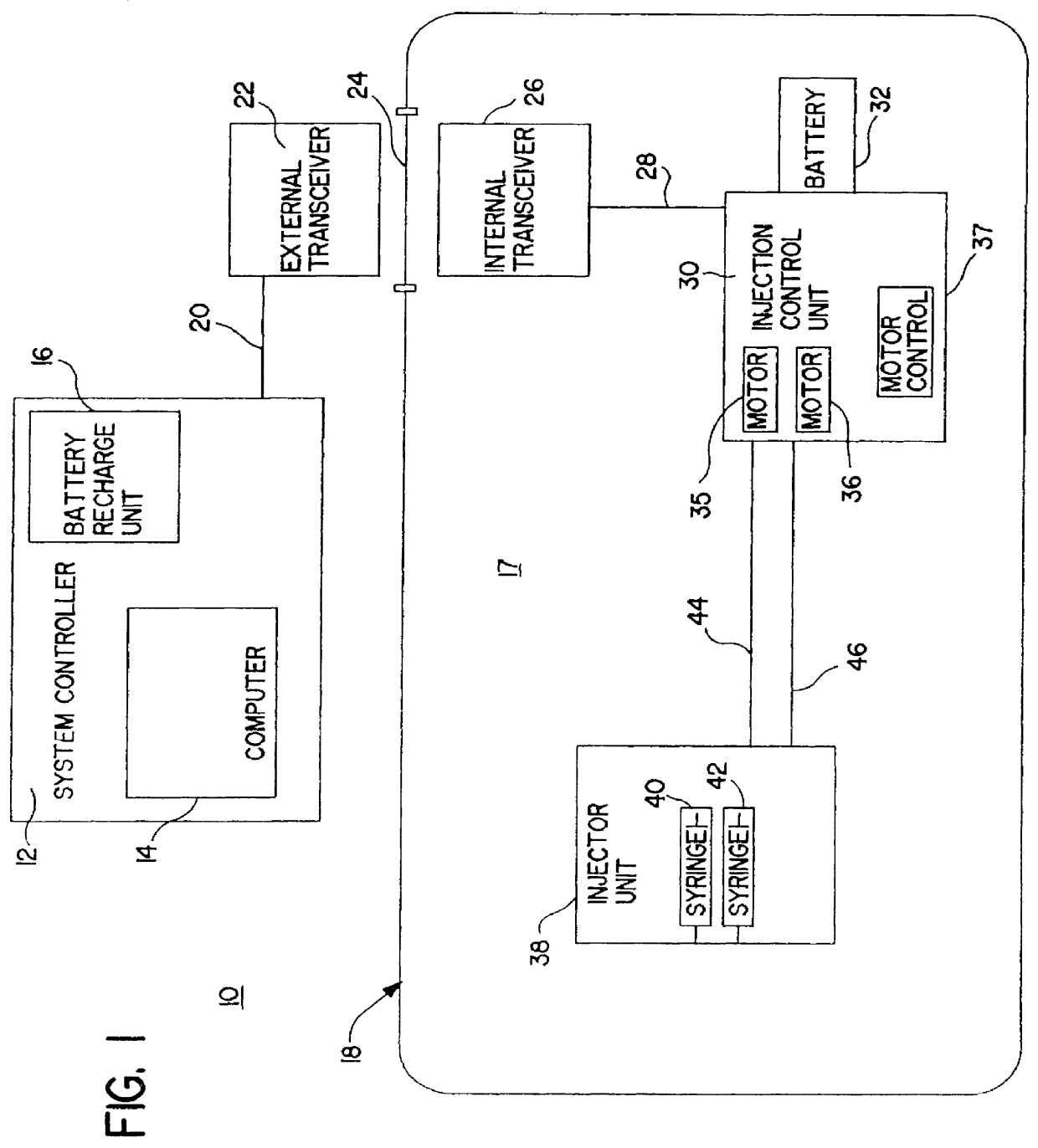
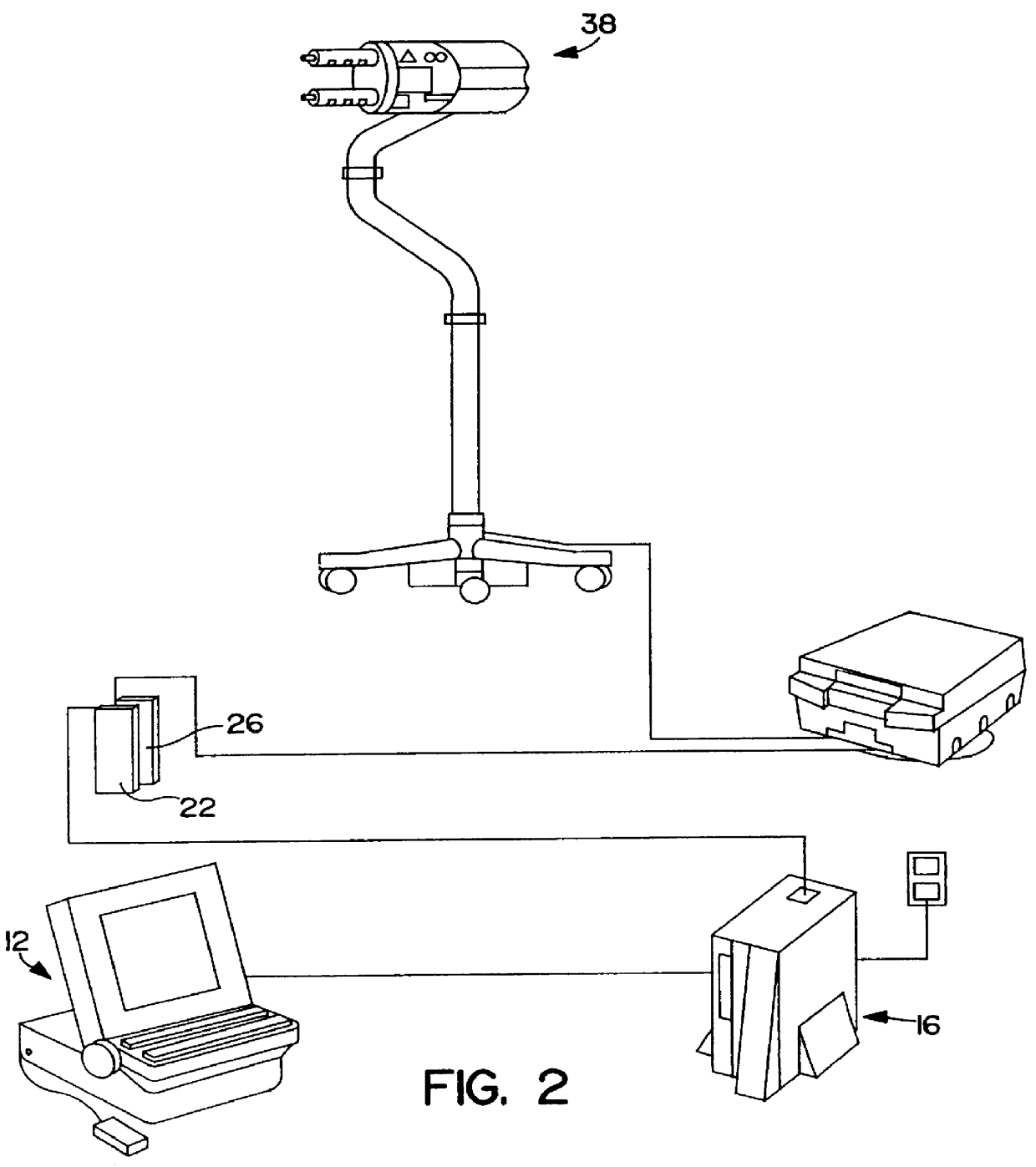
Patient infusion system for use with MRI
InactiveUSRE36648E1Maintenance characteristicMaintain integritySurgeryMedical devicesTelecommunications linkEngineering
This invention relates generally to the field of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) systems for generating diagnostic images of a patient's internal organs and more particularly, this invention relates to improved MRI systems with decreased interference between the magnetic field used for producing diagnostic images and the magnetic fields generated by the electric motors used for driving the pistons of the contrast media injectors. Additionally, the system employs an improved communication link between an externally located system controller and the injection head control unit located within the electromagnetic isolation barrier which defines the magnetic imaging room.
Owner:MEDRAD INC.
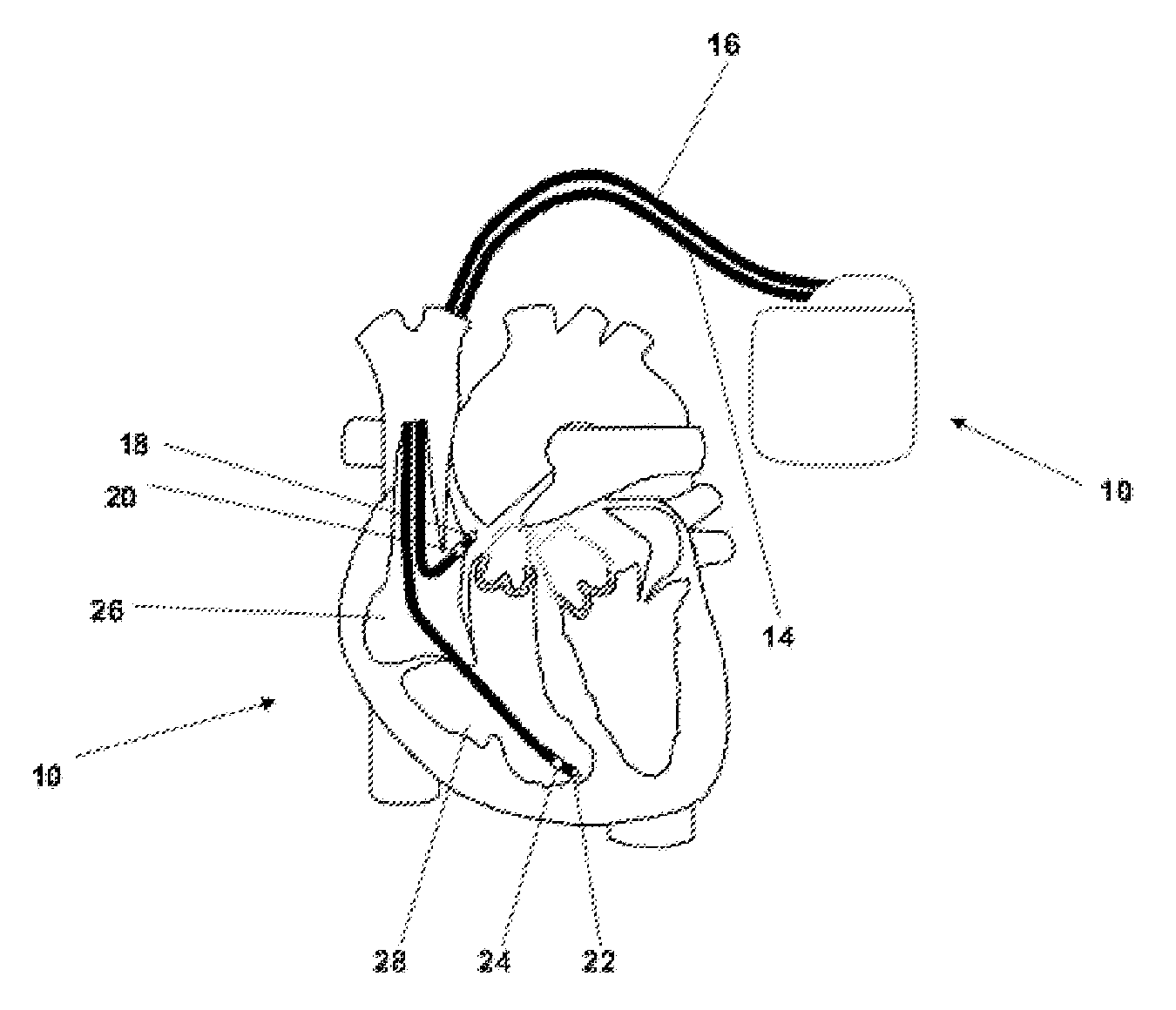
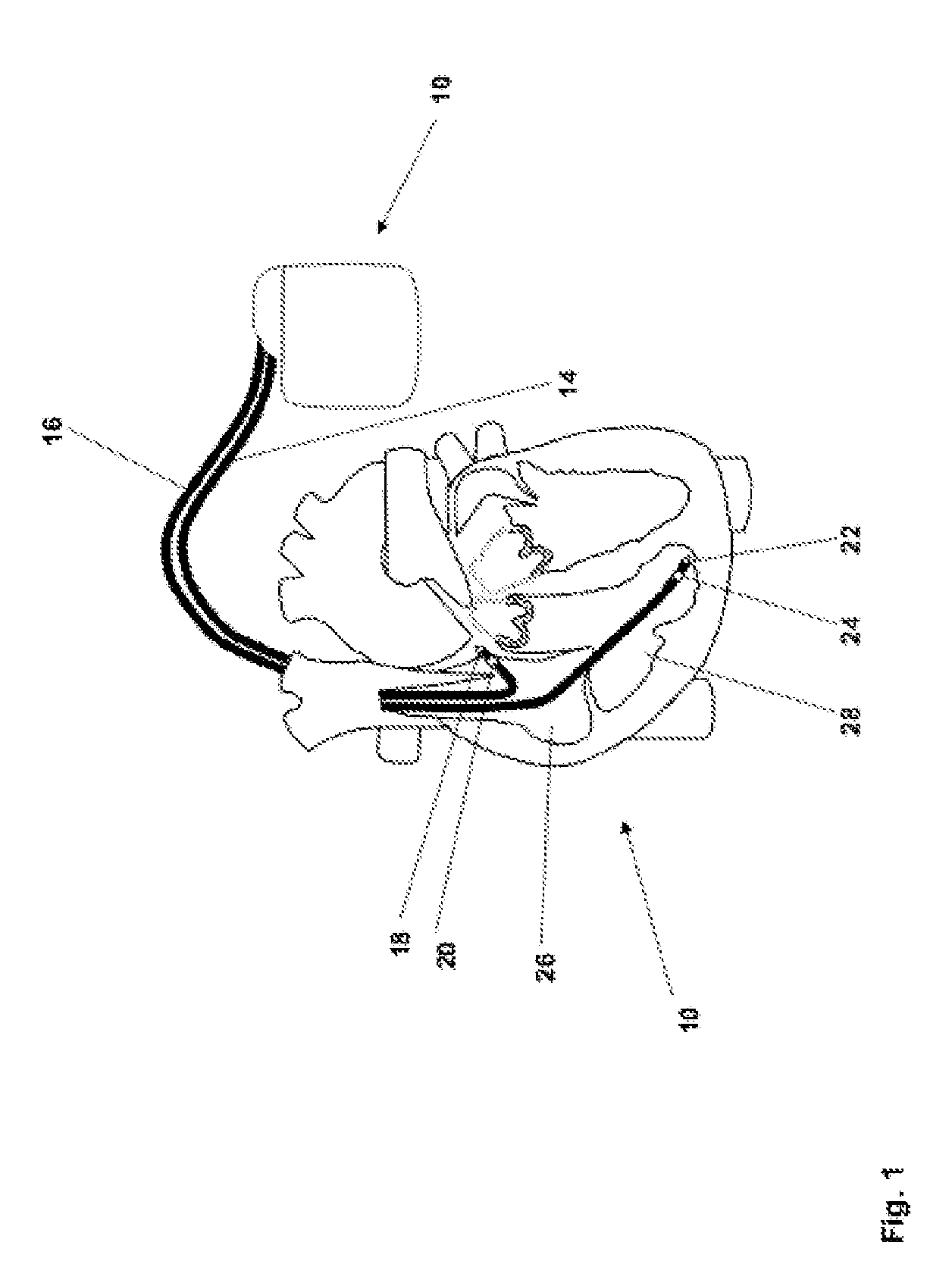
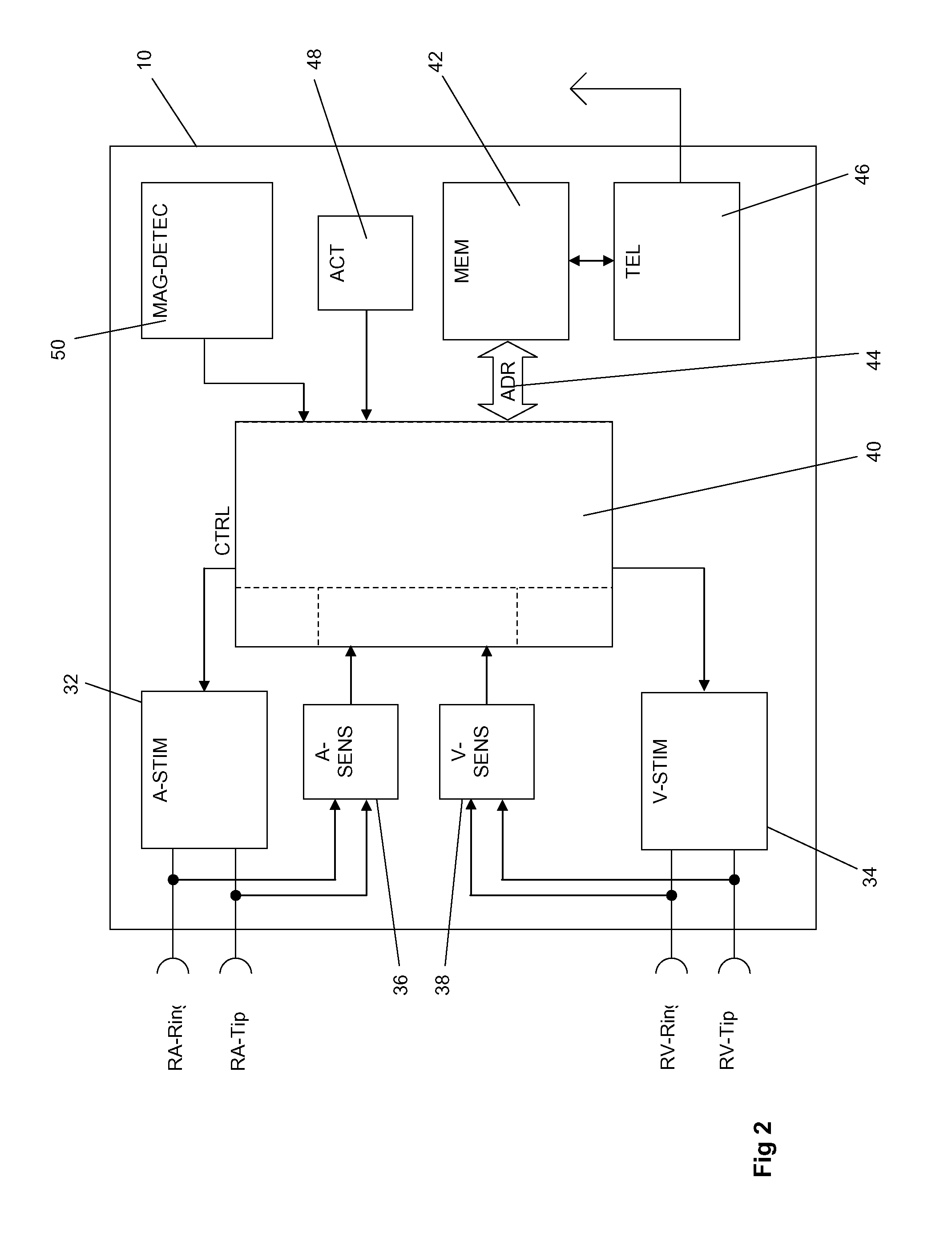
Implantable medical device comprising magnetic field detector
An implantable medical device comprises an electronic control unit and a magnetic resonance imaging magnetic field detector that is connected to the control unit. The magnetic resonance imaging magnetic field detector is adapted to generate a signal being characteristic for a magnetic field as used for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and the control unit is adapted to positively recognize a presence of a magnetic field as used for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and to cause the implantable medical device to enter an MRI-safe mode of operation.
Owner:BIOTRONIX CRM PATENT AG
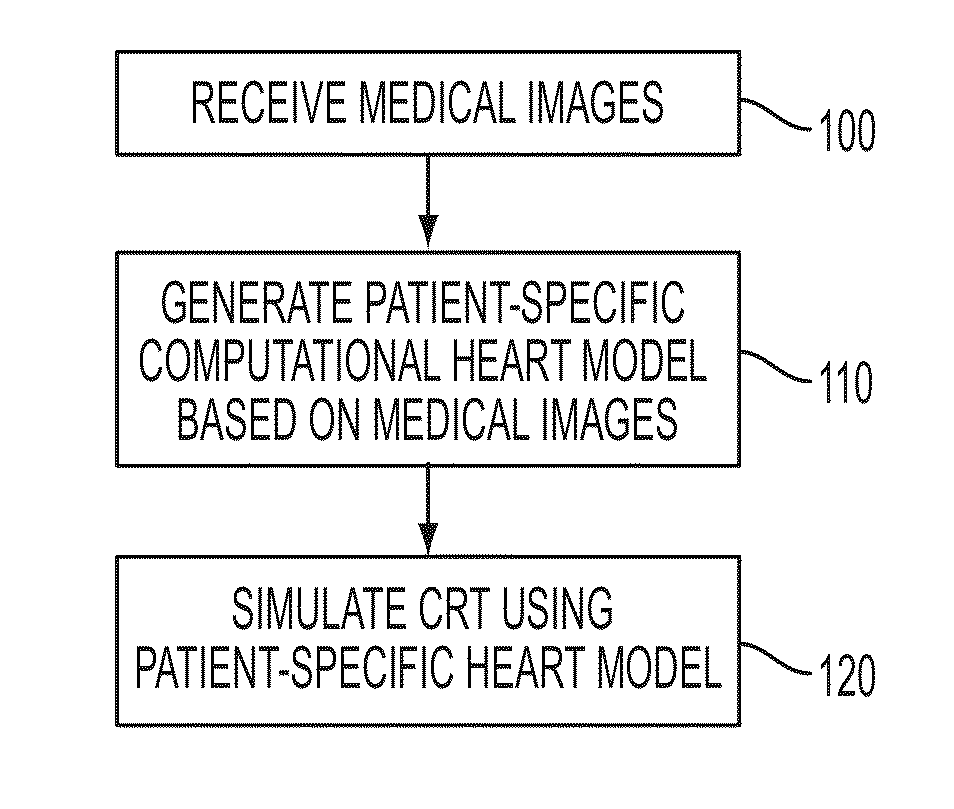
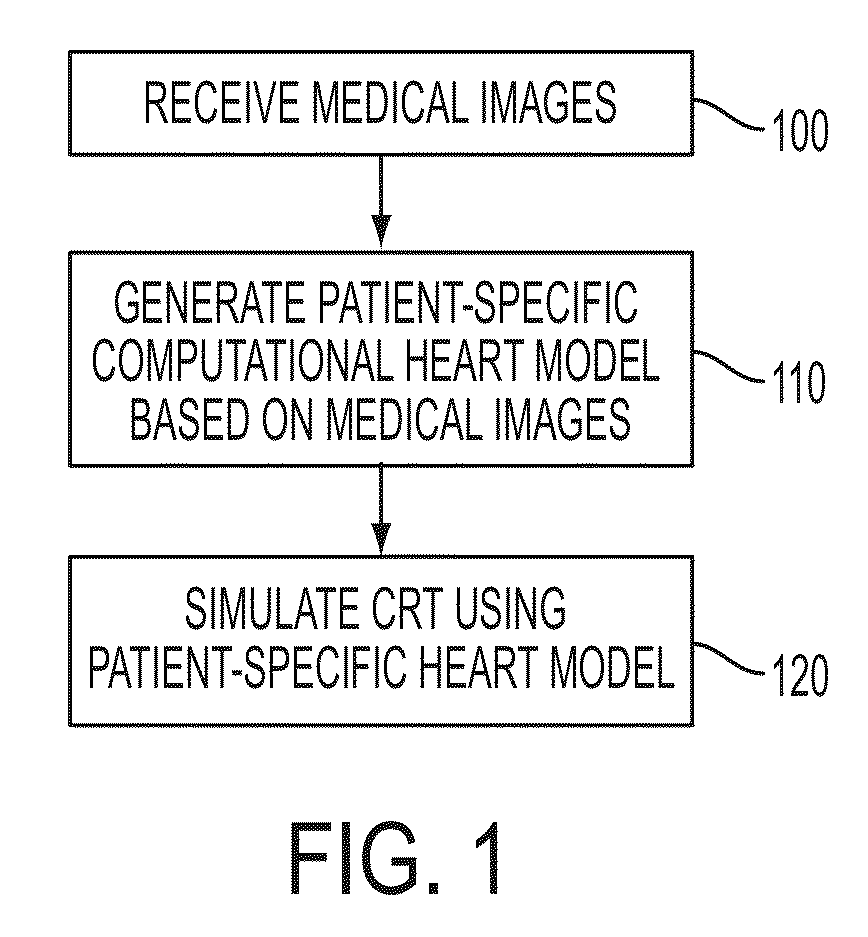
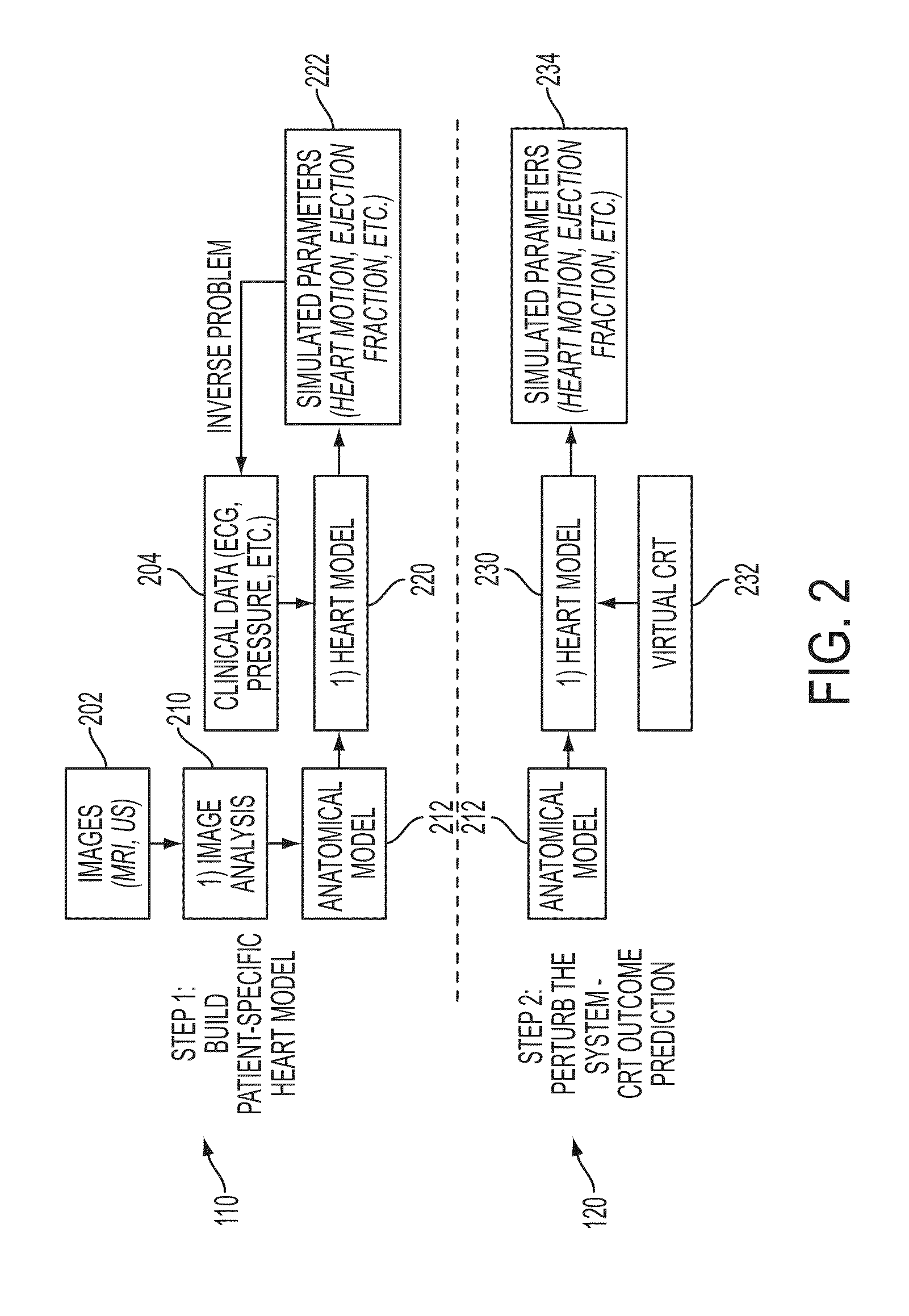
Method and System for Patient Specific Planning of Cardiac Therapies on Preoperative Clinical Data and Medical Images
ActiveUS20130197881A1Increase the number ofEasy to placeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMedical imagingSonificationBiomechanics
A method and system for patient-specific planning of cardiac therapy, such as cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT), based on preoperative clinical data and medical images, such as ECG data, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data, and ultrasound data, is disclosed. A patient-specific anatomical model of the left and right ventricles is generated from medical image data of a patient. A patient-specific computational heart model, which comprises cardiac electrophysiology, biomechanics and hemodynamics, is generated based on the patient-specific anatomical model of the left and right ventricles and clinical data. Simulations of cardiac therapies, such as CRT at one or more anatomical locations are performed using the patient-specific computational heart model. Changes in clinical cardiac parameters are then computed from the patient-specific model, constituting predictors of therapy outcome useful for therapy planning and optimization.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
In VIVO sensor and method of making same
InactiveUS20060074479A1Easy to detectUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryIn vivoRadio frequency
Implantable in vivo sensors used to monitor physical, chemical or electrical parameters within a body. The in vivo sensors are integral with an implantable medical device and are responsive to externally or internally applied energy. Upon application of energy, the sensors undergo a phase change in at least part of the material of the device which is then detected external to the body by conventional techniques such as radiography, ultrasound imaging, magnetic resonance imaging, radio frequency imaging or the like. The in vivo sensors of the present invention may be employed to provide volumetric measurements, flow rate measurements, pressure measurements, electrical measurements, biochemical measurements, temperature, measurements, or measure the degree and type of deposits within the lumen of an endoluminal implant, such as a stent or other type of endoluminal conduit. The in vivo sensors may also be used therapeutically to modulate mechanical and / or physical properties of the endoluminal implant in response to the sensed or monitored parameter.
Owner:VACTRONIX SCI LLC
Apparatus and method for noninvasive monitoring of analytes in body fluids
InactiveUS7214190B1ModificationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansIntravenous devicesMedication infusionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
Noninvasive in vivo real time analyte measurement uses a multitude of sensors binding reversibly to the analyte whereby the response of the sensors to a noninvasive stimulus is altered by their bound versus unbound state. The stimulus and responses are electromagnetic, magnetic or any other suitable forms. The sensors are bound to a blood component providing transport through the body fluids and sensor elimination. A sensor is constructed from proteins or as a nanodevice. A noninvasive device generates the stimulus, senses the responses, determines the measurement, and controls a medication infusion pump. A non-contact device is used for population screening, and one form of such a device is a nuclear magnetic resonance imager. Measurement in fluids other than blood uses a blood component flowing out of blood and into the desired fluid.
Owner:WILSON KITCHENER CLARK
Method and apparatus for imaging artefact reduction
InactiveUS6341179B1Improve image qualityReduce impactReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionImage ArtifactComputer science
The invention relates to a method and apparatus for reducing imaging artifacts in physiological images, such as magnetic resonance imaging images. A model of a physical cause for the image artifact is modelled and the effects of perturbing this model on a focus criterion of the image analyzed so as to optimize the focus criterion. For an optimized focus criterion, the model should reflect the actual physical cause of the image artifact. A focus criterion is a measure of entropy of the image, with an optimized image having reduced entropy.
Owner:NANOGEN RECOGNOMICS BMBH +1
Guided catheter with removable magnetic guide
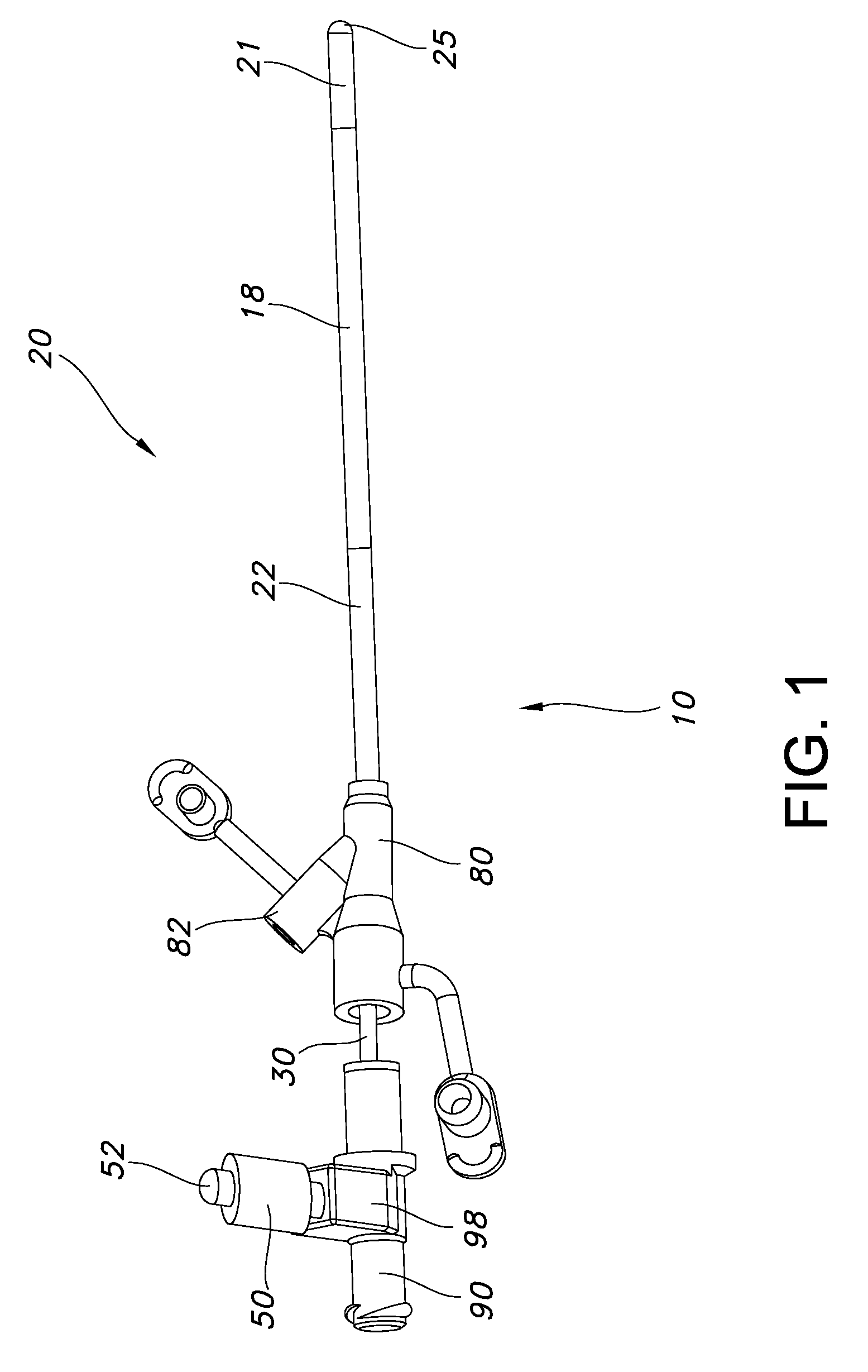
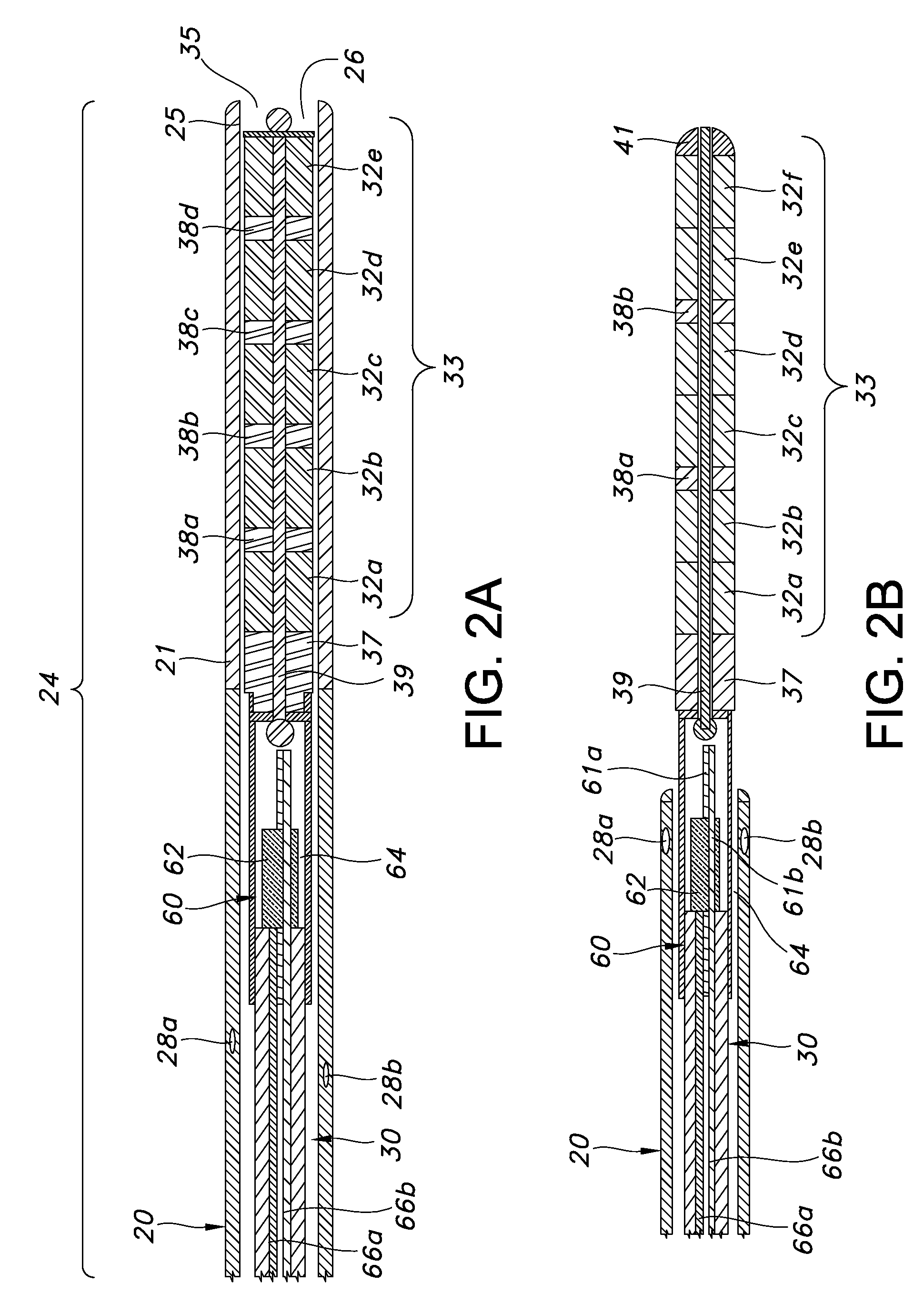
A feeding tube apparatus, a kit containing the feed tube apparatus and method for intubating a patient to deliver the feeding tube apparatus to the desired location for delivering nutrients and / or medication are described herein. The feeding tube apparatus (10) contains at least a catheter (20) and a removable stylet (30), where the removable stylet contains one or more magnetic materials (32a-j). In one embodiment, the stylet contains more than one magnetic material in the form of a magnet stack (33). The feeding tube apparatus is used in combination with a suitable external magnet (40) which a medical practitioner can use to guide the feeding tube apparatus (10) through the intestinal tract. Optionally, the feeding tube apparatus contains additional components, such as a spring wire guide. The feeding tube apparatus is inserted into the patient's body and the external magnet (40) is applied to the patient's body within the minimum distance required to create a magnetic field between the external magnet (40) and the magnetic material(s) (32) located at the distal end (34) of the stylet (30) that is sufficiently strong to allow the external magnet to guide the catheter and stylet through the intestinal tract, and into the distal duodenum (470) of the small intestine. Once the catheter is placed in the desired location, the stylet is removed, thereby removing the magnetic material(s) from the feeding tube apparatus. This allows for the catheter to remain in place while the patient undergoes diagnostic testing, such as magnetic resonance imaging.
Owner:SYNCRO MEDICAL INNOVATIONS
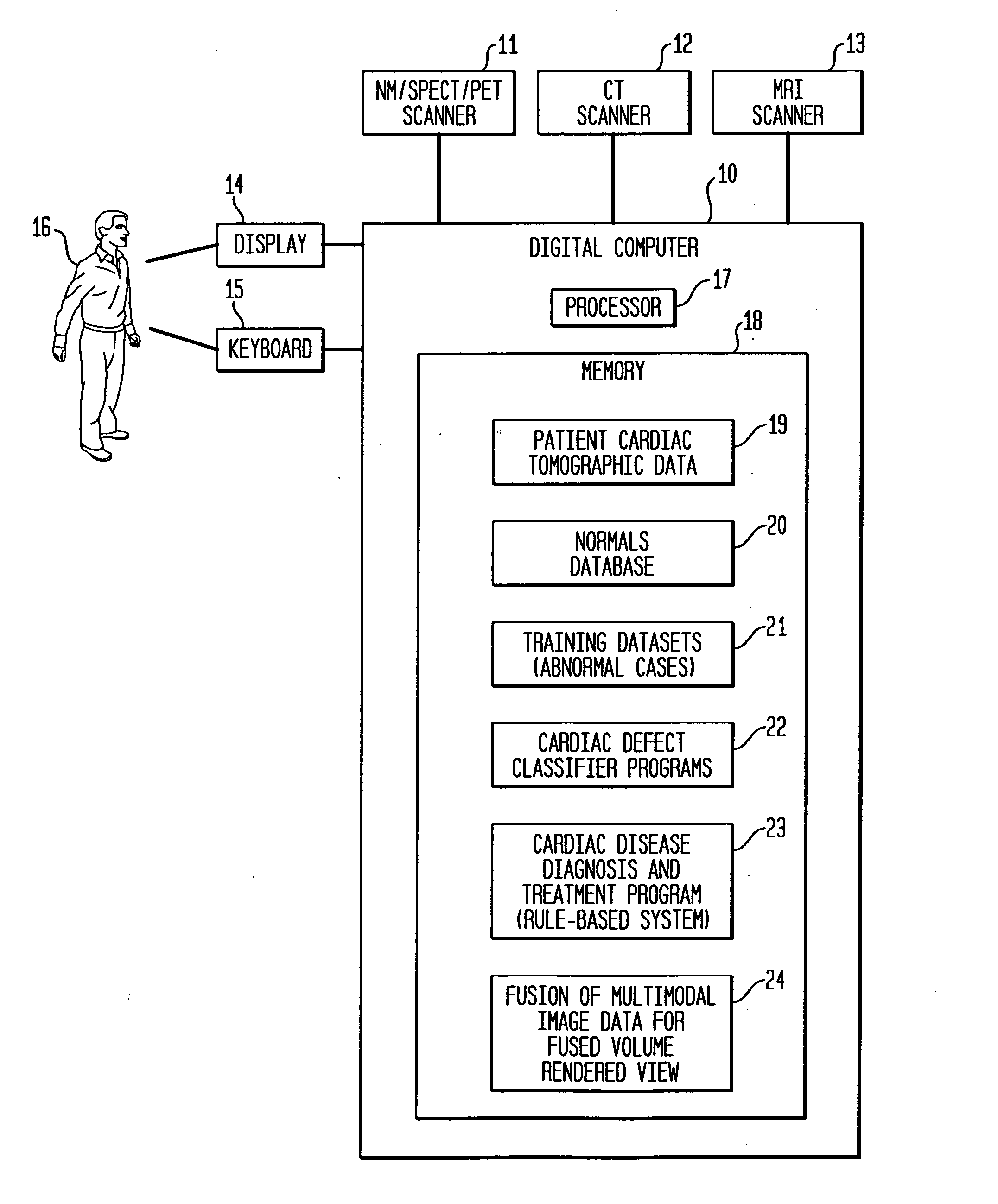
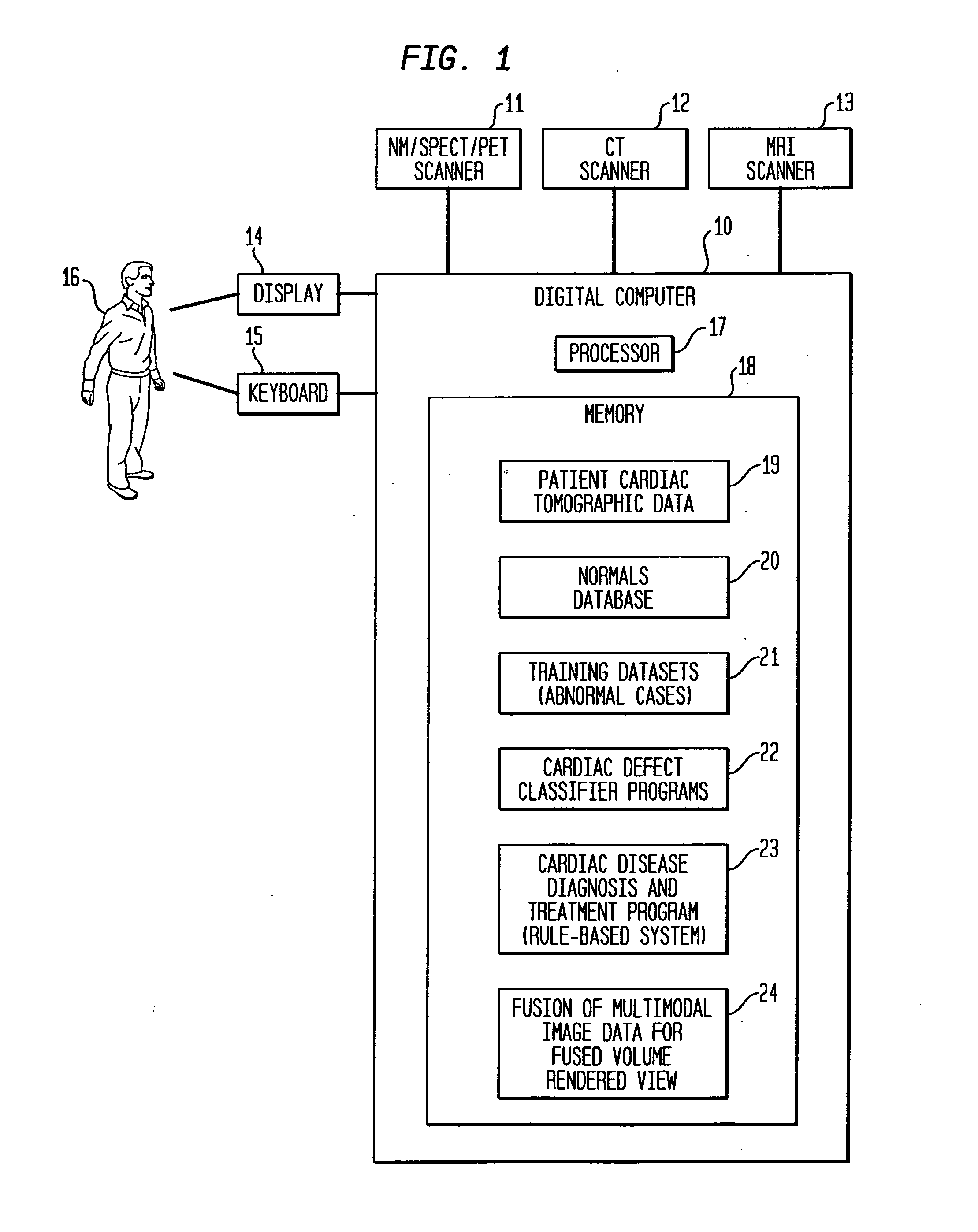
Dedicated display for processing and analyzing multi-modality cardiac data
For diagnosis and treatment of cardiac disease, images of the heart muscle and coronary vessels are captured using different medical imaging modalities; e.g., single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), positron emission tomography (PET), electron-beam X-ray computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or ultrasound (US). For visualizing the multi-modal image data, the data is presented using a technique of volume rendering, which allows users to visually analyze both functional and anatomical cardiac data simultaneously. The display is also capable of showing additional information related to the heart muscle, such as coronary vessels. Users can interactively control the viewing angle based on the spatial distribution of the quantified cardiac phenomena or atherosclerotic lesions.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
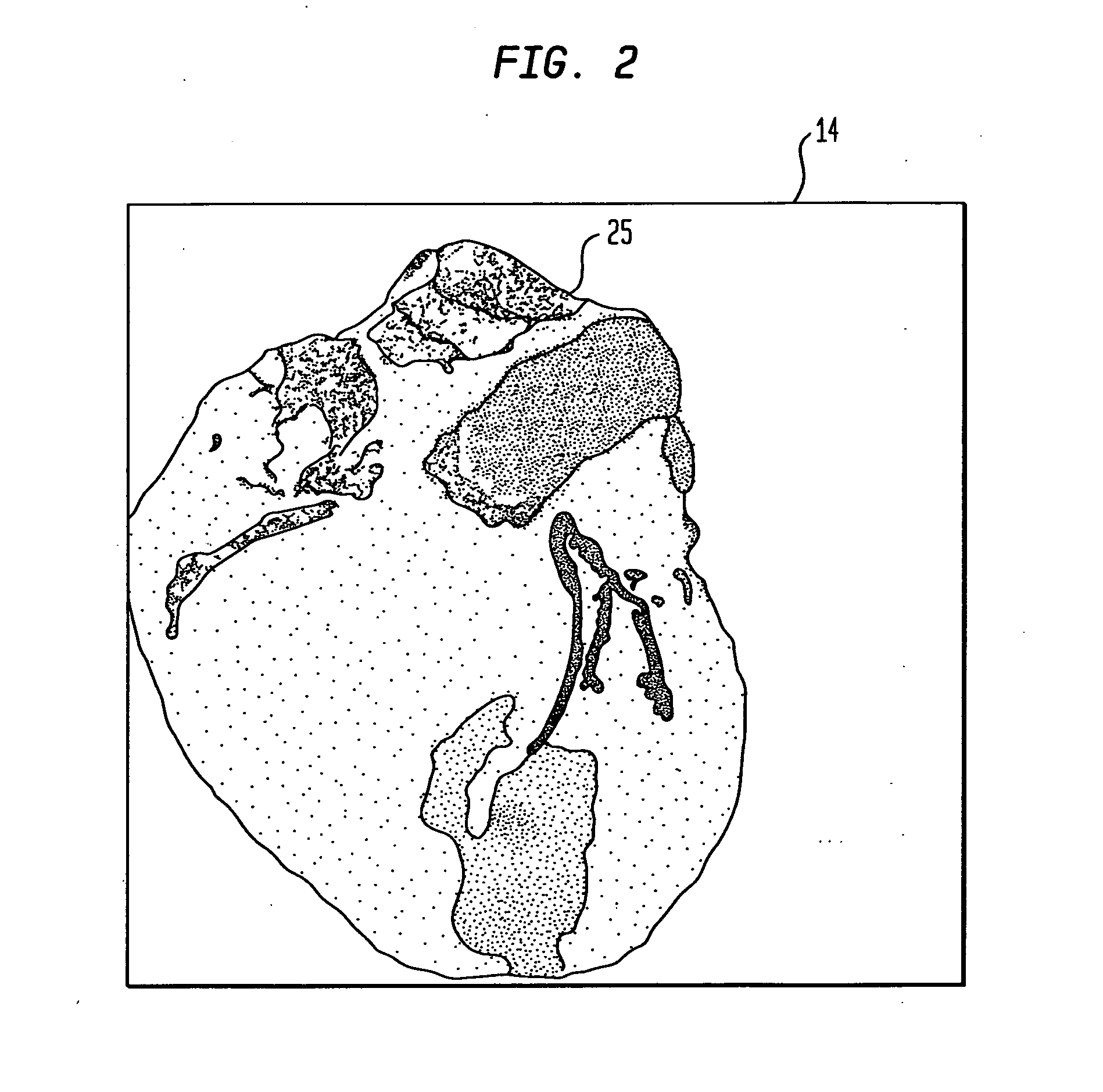
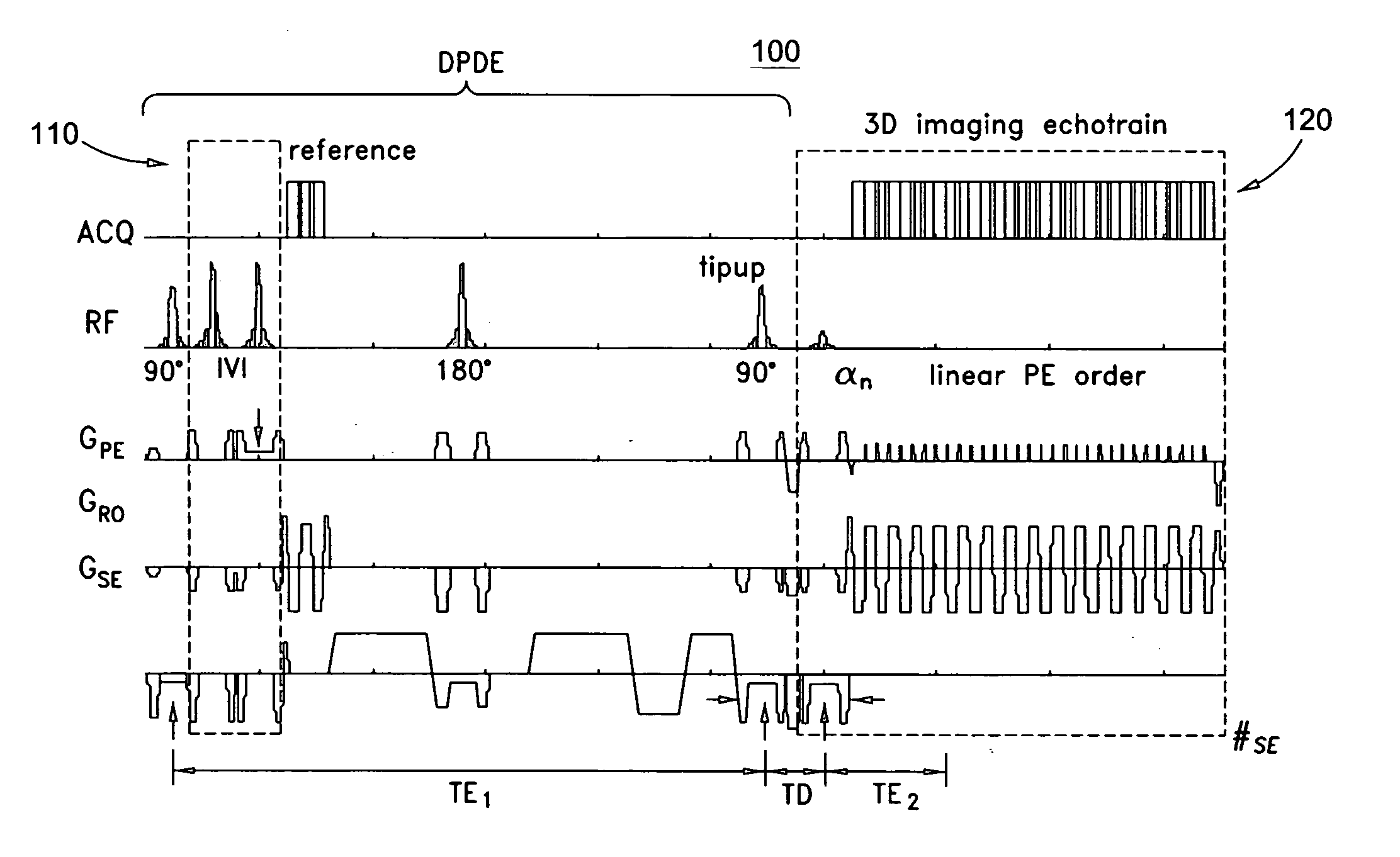
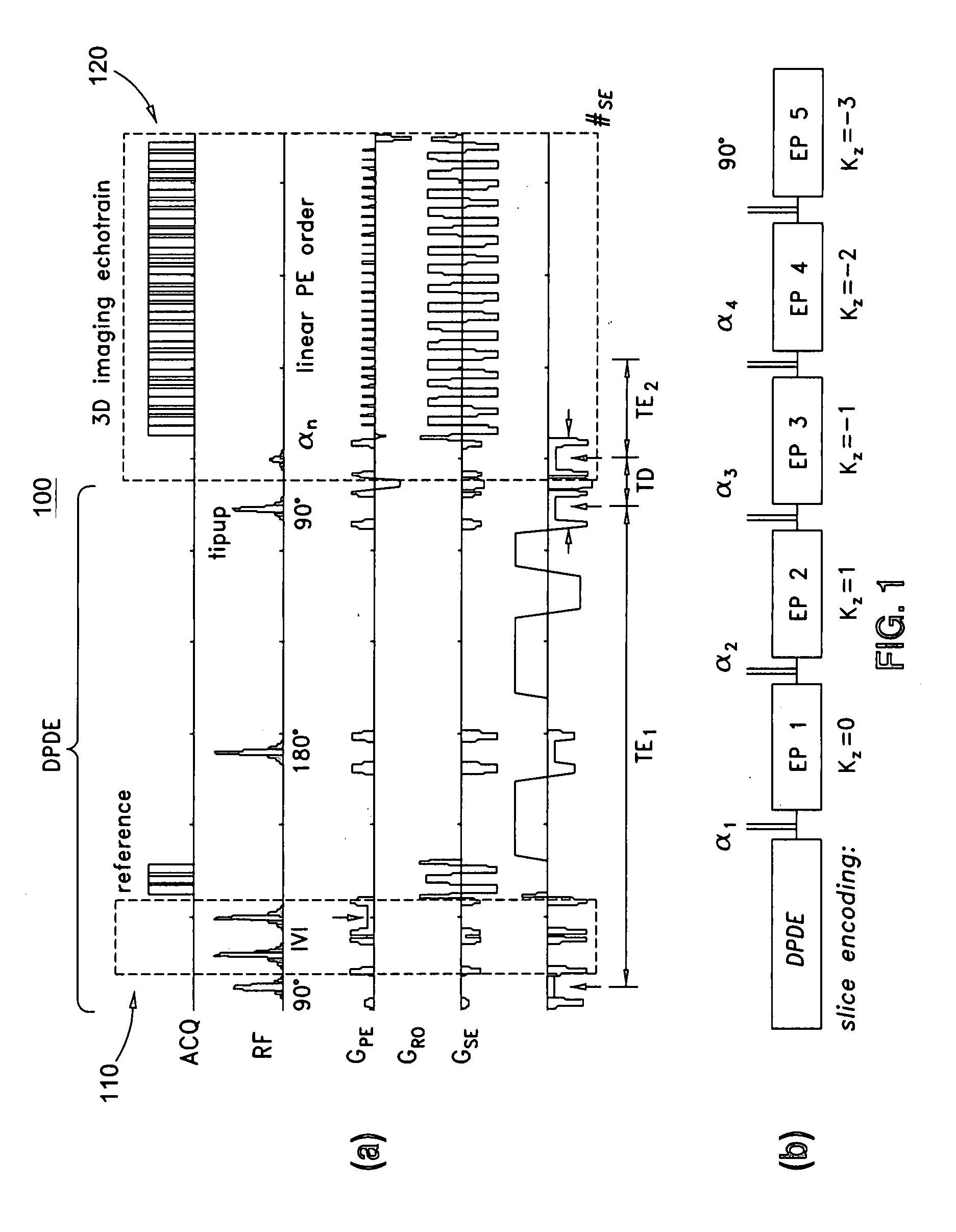
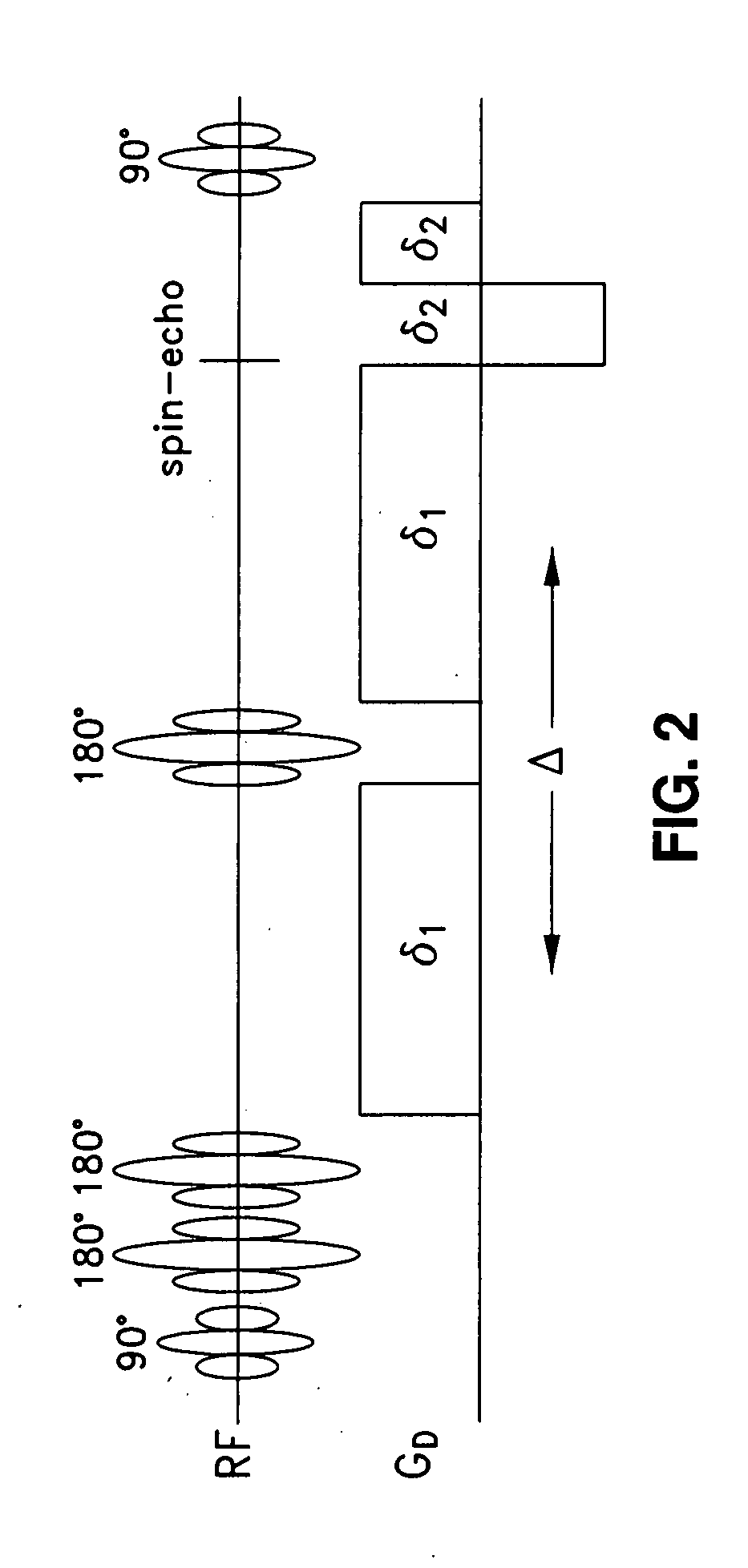
Systems and methods for magnetic resonance imaging
Methods and apparatus for operating an MRI system is provided. The disclosure provides a diffusion-prepared driven-equilibrium preparation for an imaging volume and acquiring 3-dimensional k-space data from said prepared volume by a plurality of echoplanar readouts of stimulated echoes. An excitation radio-frequency signal and first and second inversion RF signals are provided to define a field-of-view (FOV).
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com