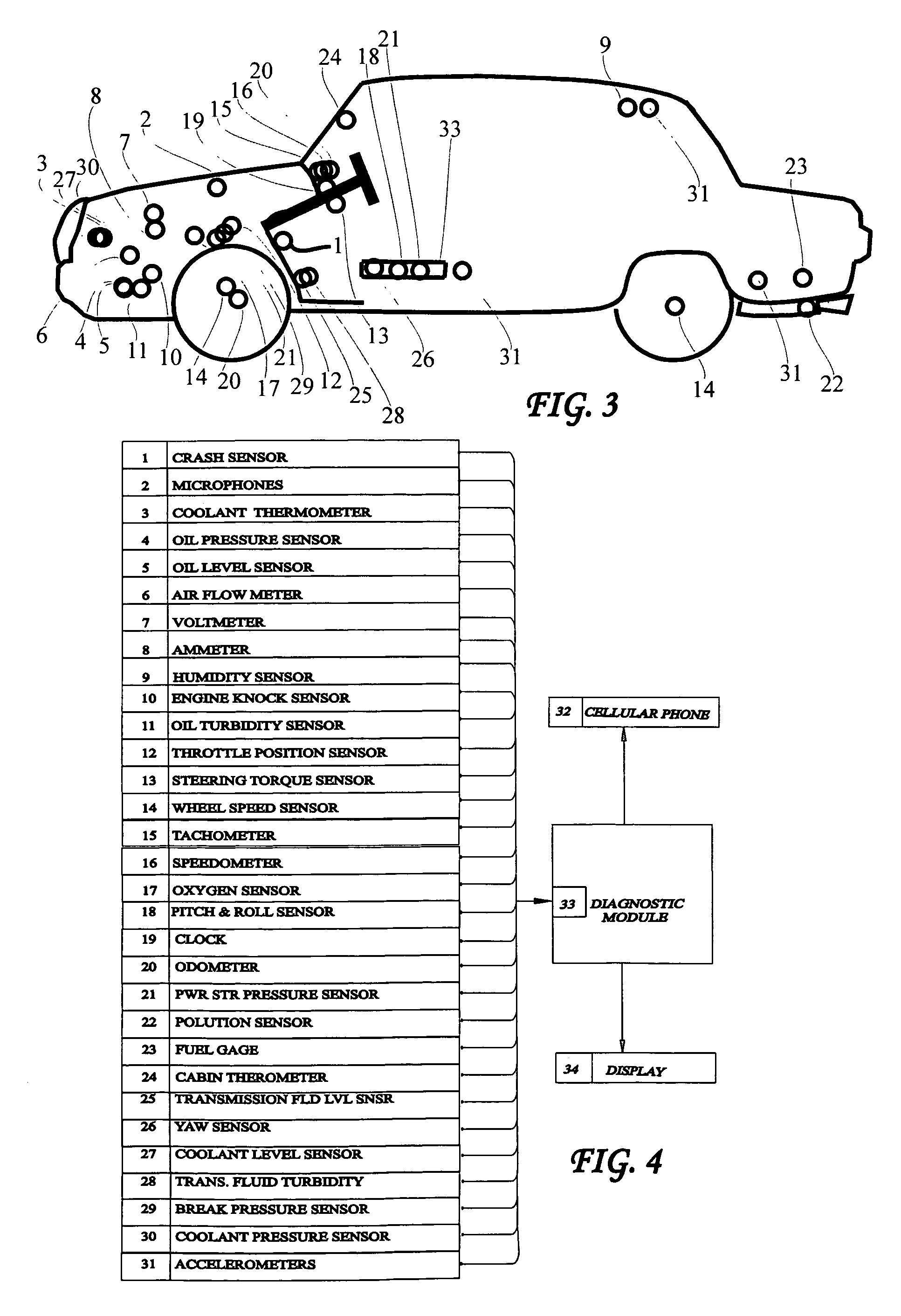
Patents
Literature
40247results about "Radio wave reradiation/reflection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
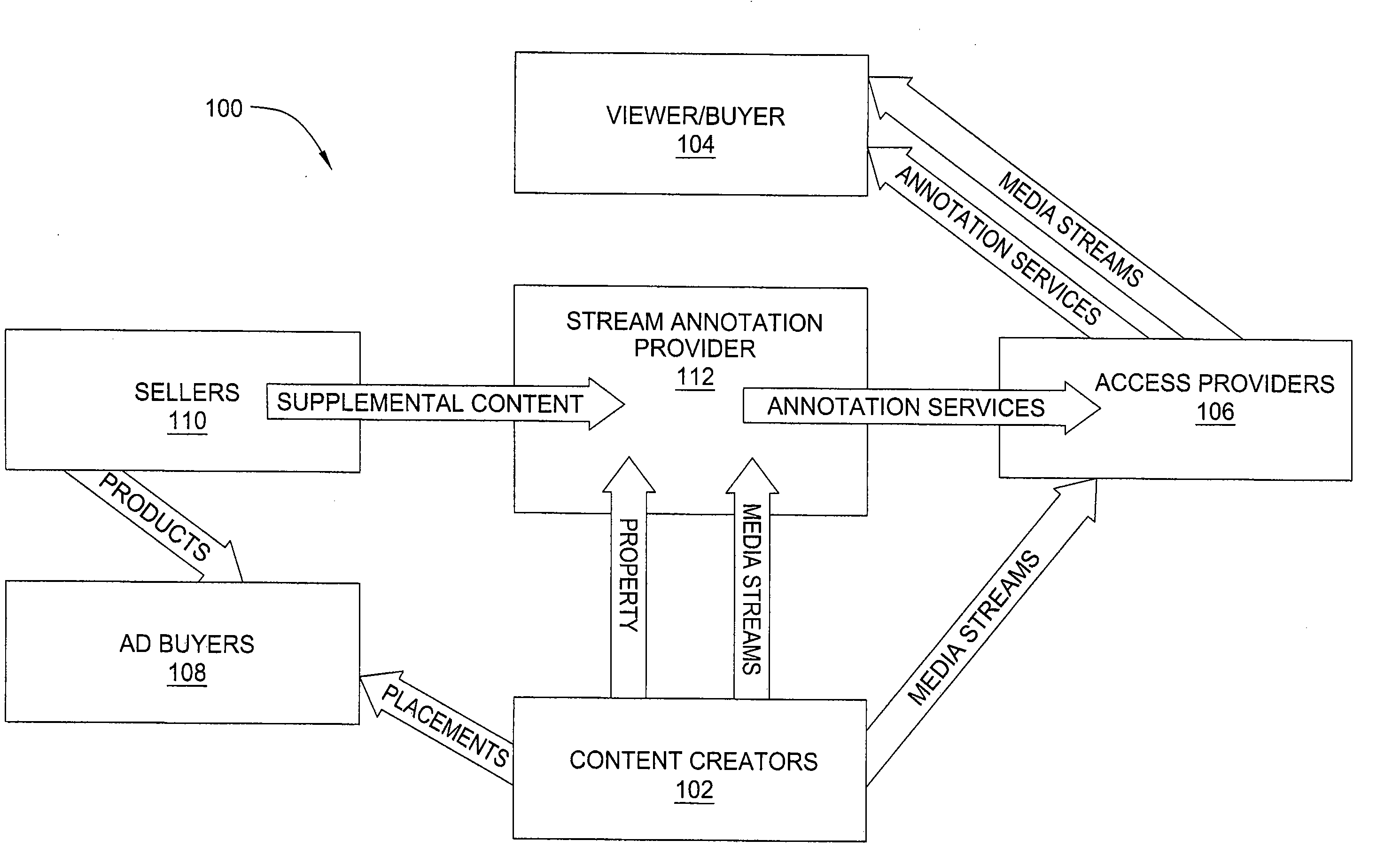
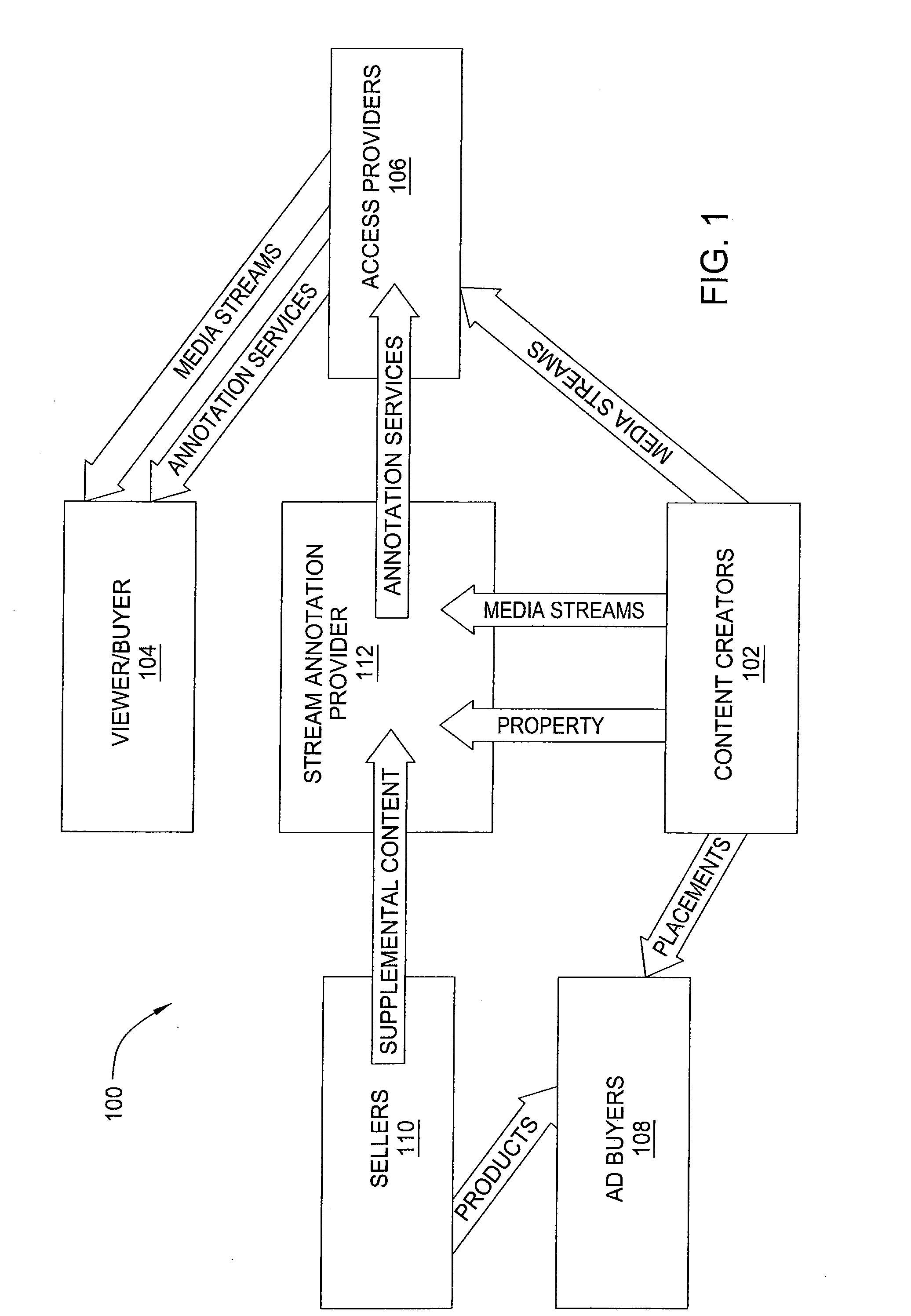
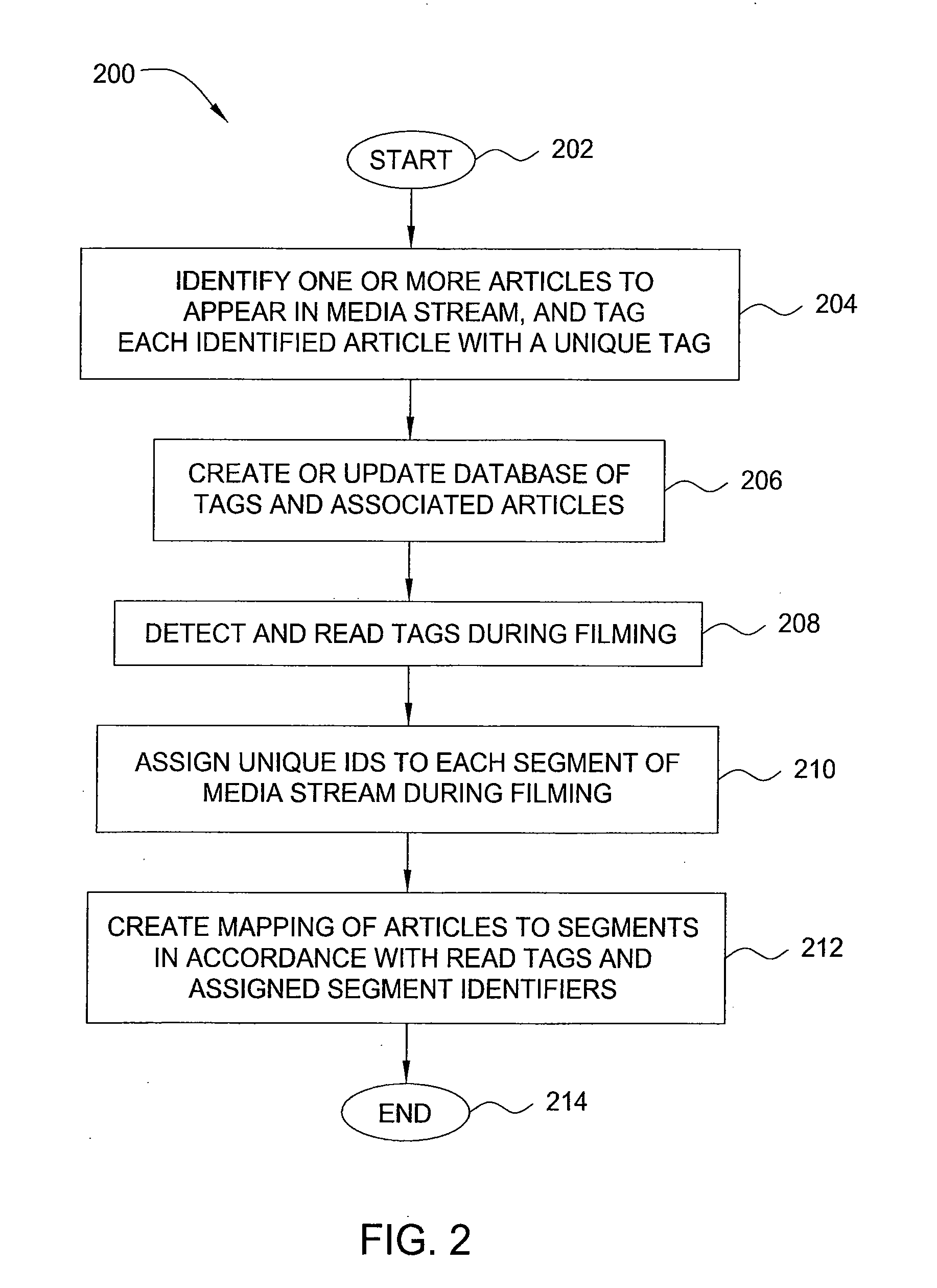
Method and apparatus for annotating media streams
InactiveUS20070250901A1Electronic editing digitised analogue information signalsDigital computer detailsHyperlinkComputer science
In one embodiment, the invention is a method and apparatus for annotating media streams. One embodiment of a method for facilitating creation of an annotated media stream by a user includes receiving the media stream from the user, mapping at least one item of supplemental content to at least a portion of the media stream to produce the annotated media stream, and storing the annotated media stream. In another embodiment, a method for distributing an annotated media stream provided by a user includes receiving the annotated media stream from the user, where the annotated media stream includes at least one item of supplemental content mapped to at least a portion of a media stream to produce the annotated media stream, storing the annotated media stream, receiving a request from a viewer to view the annotated media stream, and distributing the annotated media stream to the viewer. In another embodiment, a method for distributing an annotated media stream provided by a user includes distributing the annotated media stream to a viewer, where the annotated media stream includes at least one item of supplemental content mapped to at least a portion of a media stream to produce the annotated media stream, and collecting a commission when the annotated media stream is viewed by the viewer. In one embodiment, the collecting requires further action on a part of the viewer (such as selection of a hyperlink contained in the at least one item of supplemental content or consummation of a commercial transaction).
Owner:TOUT
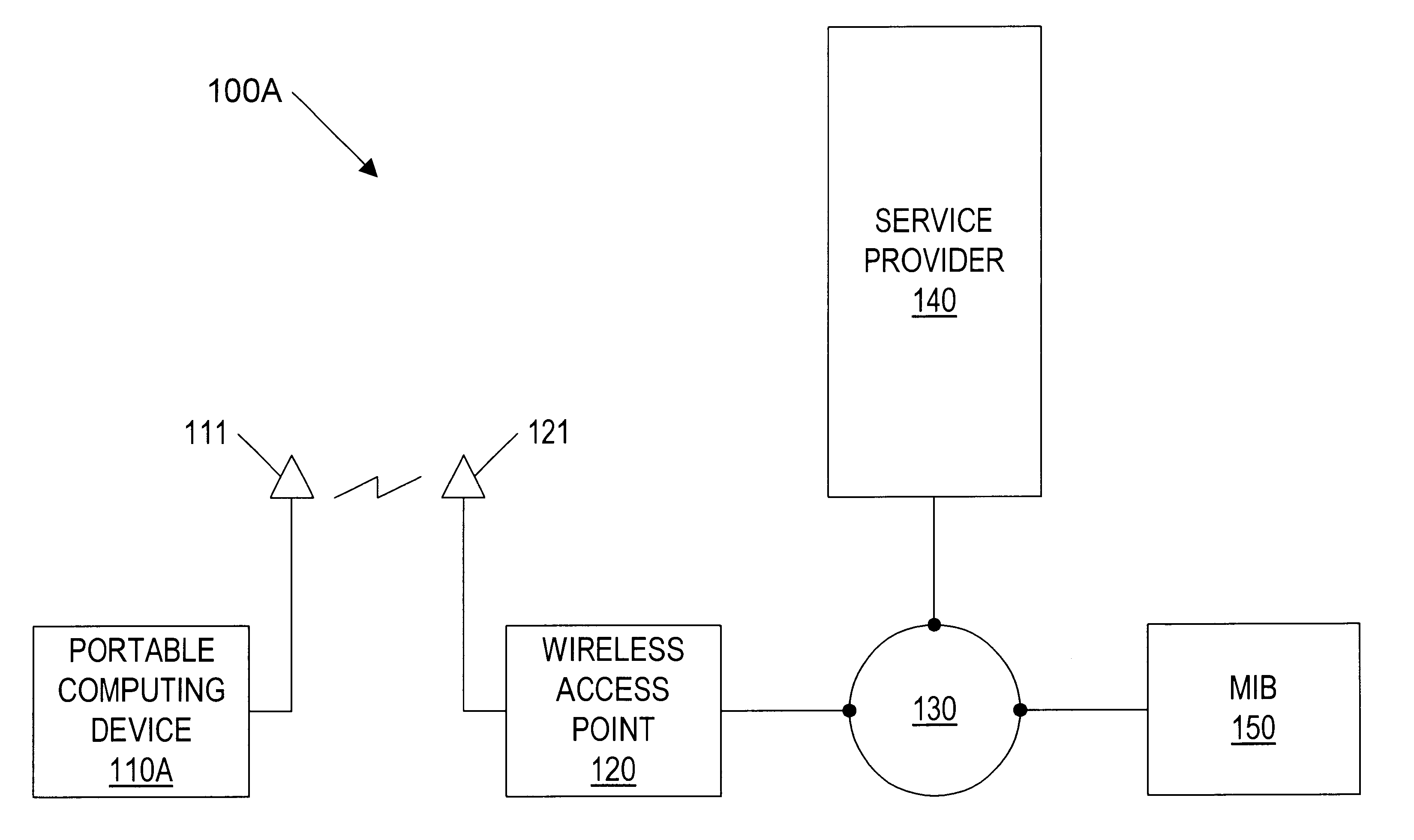
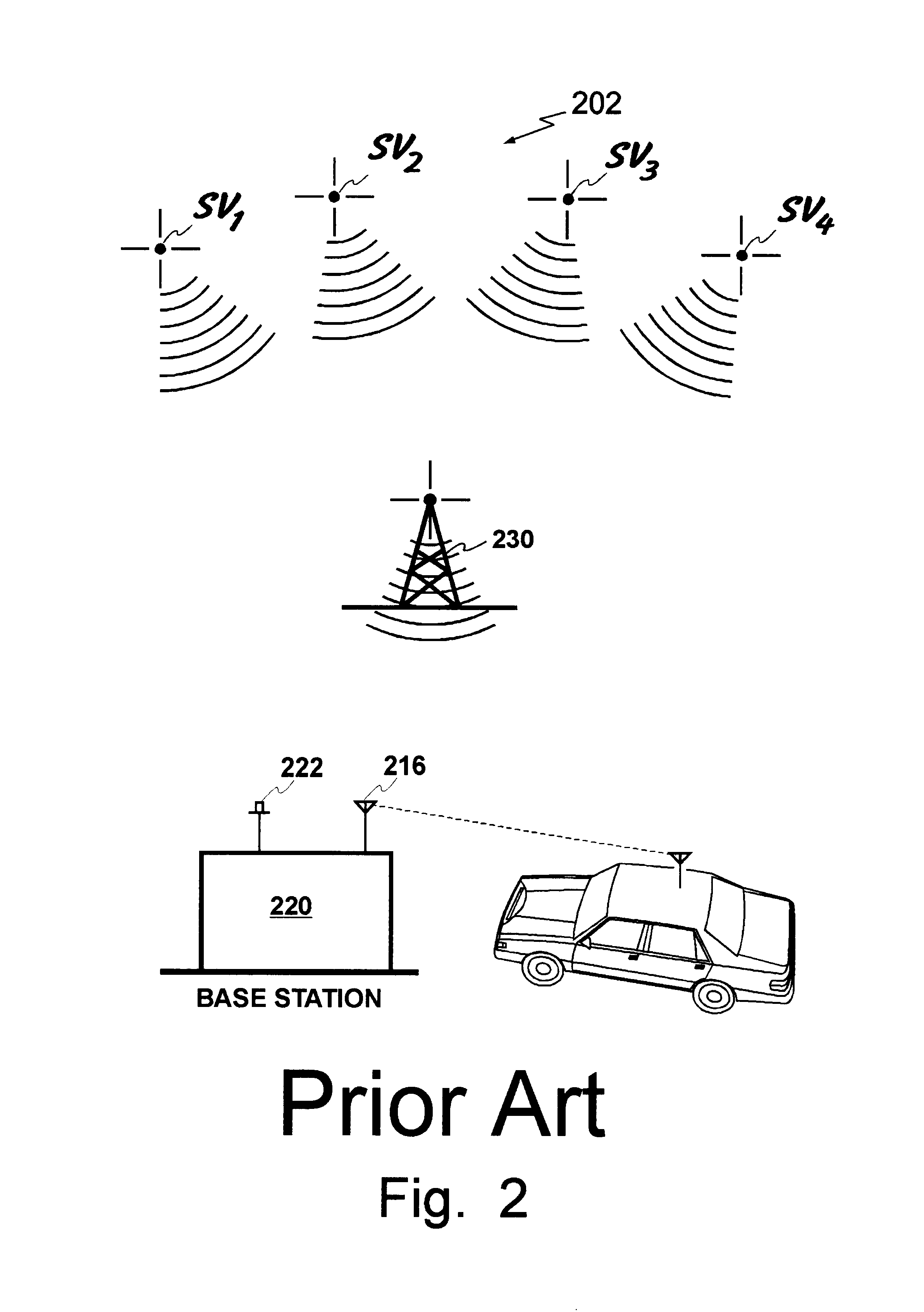
Geographic-based communication service system with more precise determination of a user's known geographic location
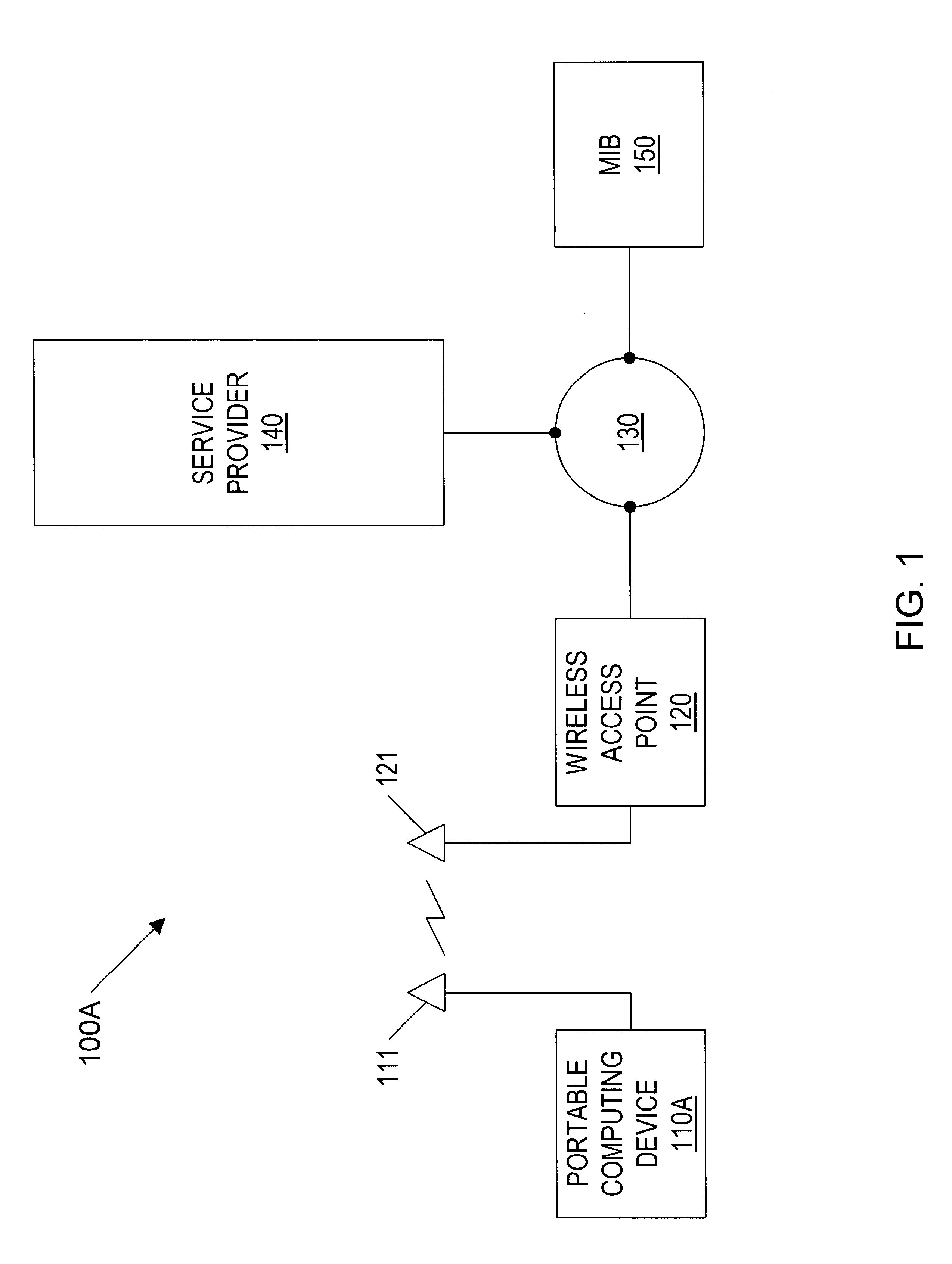
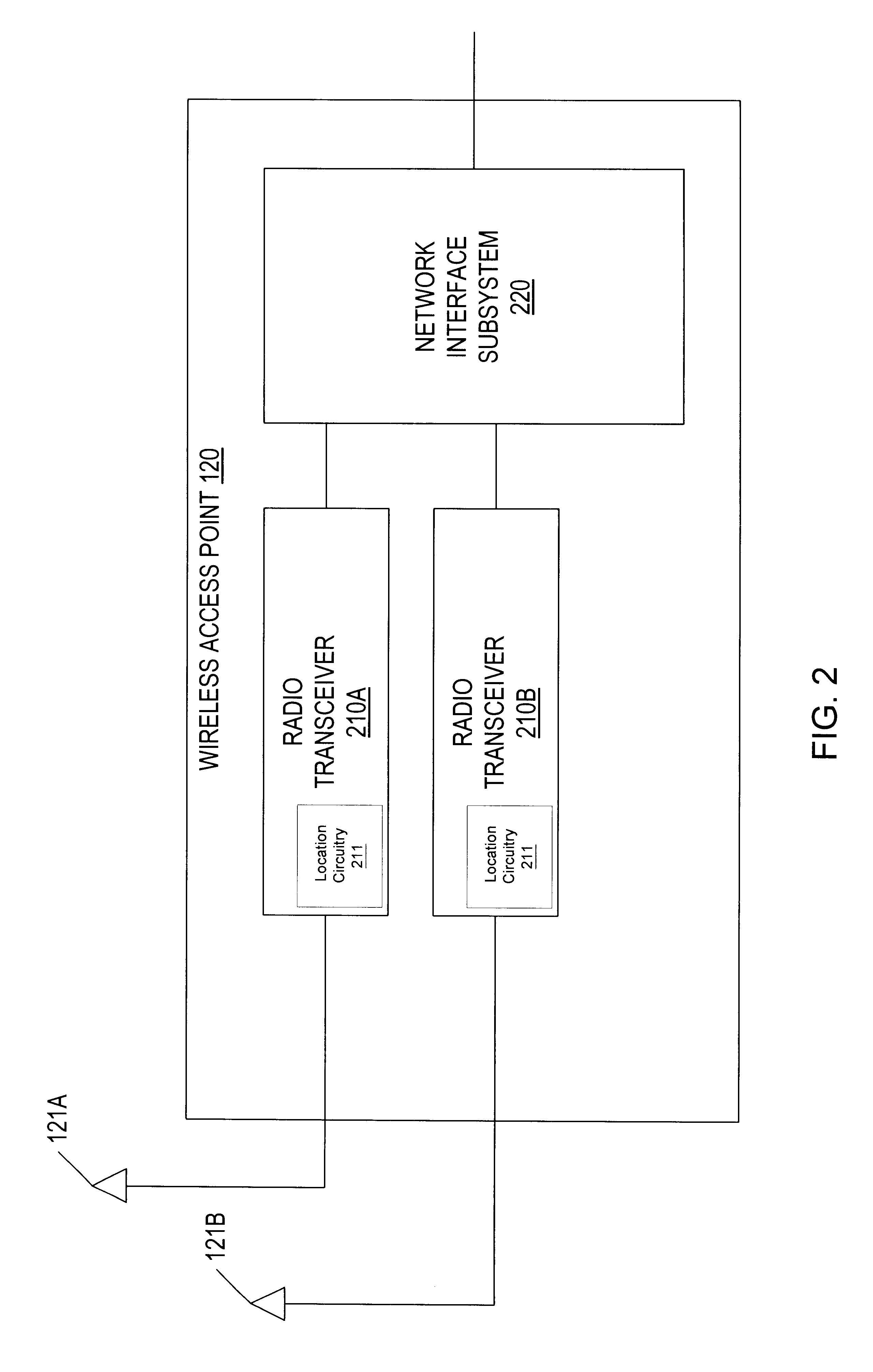
InactiveUS6414635B1Direction finders using radio wavesNetwork topologiesGeographic regionsGeolocation
A geographic based communications service system that includes a network and a plurality of access points connected to the network and arranged at known locations in a geographic region. One or more service providers or information providers may be connected to the network to provide services or information on the network. Content provided by the service providers may be based on the known geographic location of the user of a portable computing device (PCD). The known geographic location may be determined with a high degree of precision, using one or more access points and one of several different techniques. In one embodiment, the geographic location of the PCD may be determined within a radius of ten feet. Access points may be configured to determine the bearing of a signal received from a PCD, as well as the strength of the signal transmitted by the PCD. Access points may also be configured to send and receive signals with time stamps. These time stamps may be used to calculate signal travel time, thereby allowing a determination of the distance between an access point and a PCD. Each access point may include location circuitry. The location circuitry may include both analog and digital circuitry configured to perform the various methods used to determine the precise geographic location.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
Sensor assemblies
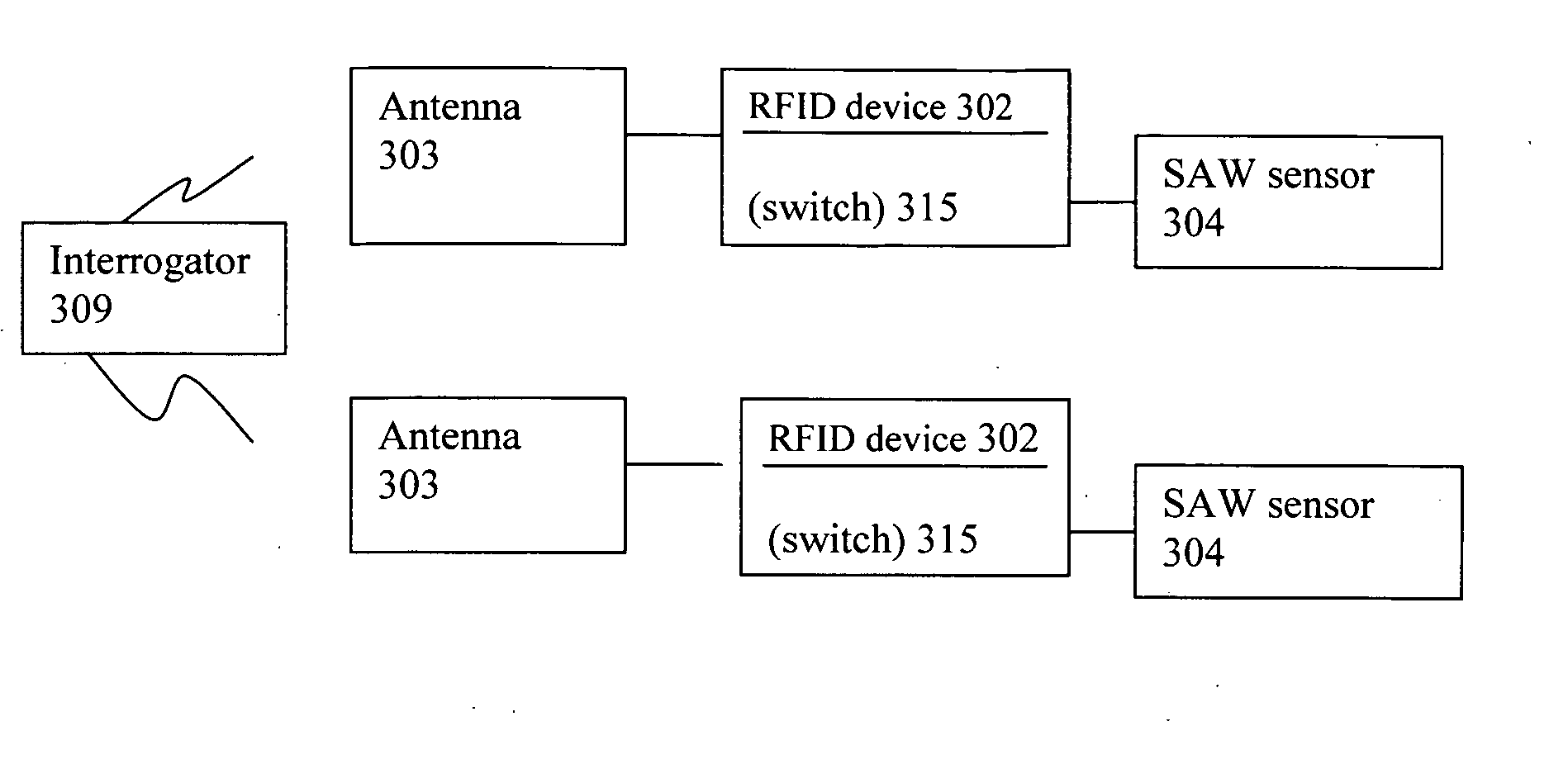
InactiveUS20060025897A1Low costPrecise positioningVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesRadio frequency signalPhysical quantity
Sensor assembly capable of obtaining and providing a measurement of a physical quantity, e.g., measurement of temperature and / or pressure of a vehicular tire, includes an antenna capable of receiving a radio frequency signal, a radio frequency identification (RFID) device coupled to the antenna, a sensor coupled to the RFID device arranged to generate a measurement of the physical quantity or quantities, and a switch coupled to the RFID device and arranged to connect or disconnect the sensor from a circuit with the antenna dependent on whether the antenna receives a particular signal associated with the RFID device. When the antenna receives the particular signal associated with the RFID device, the RFID device causes the switch to close and connect the sensor in the circuit with the antenna to enable the measurement generated by the sensor to be directed to and transmitted by the antenna.
Owner:AMERICAN VEHICULAR SCI
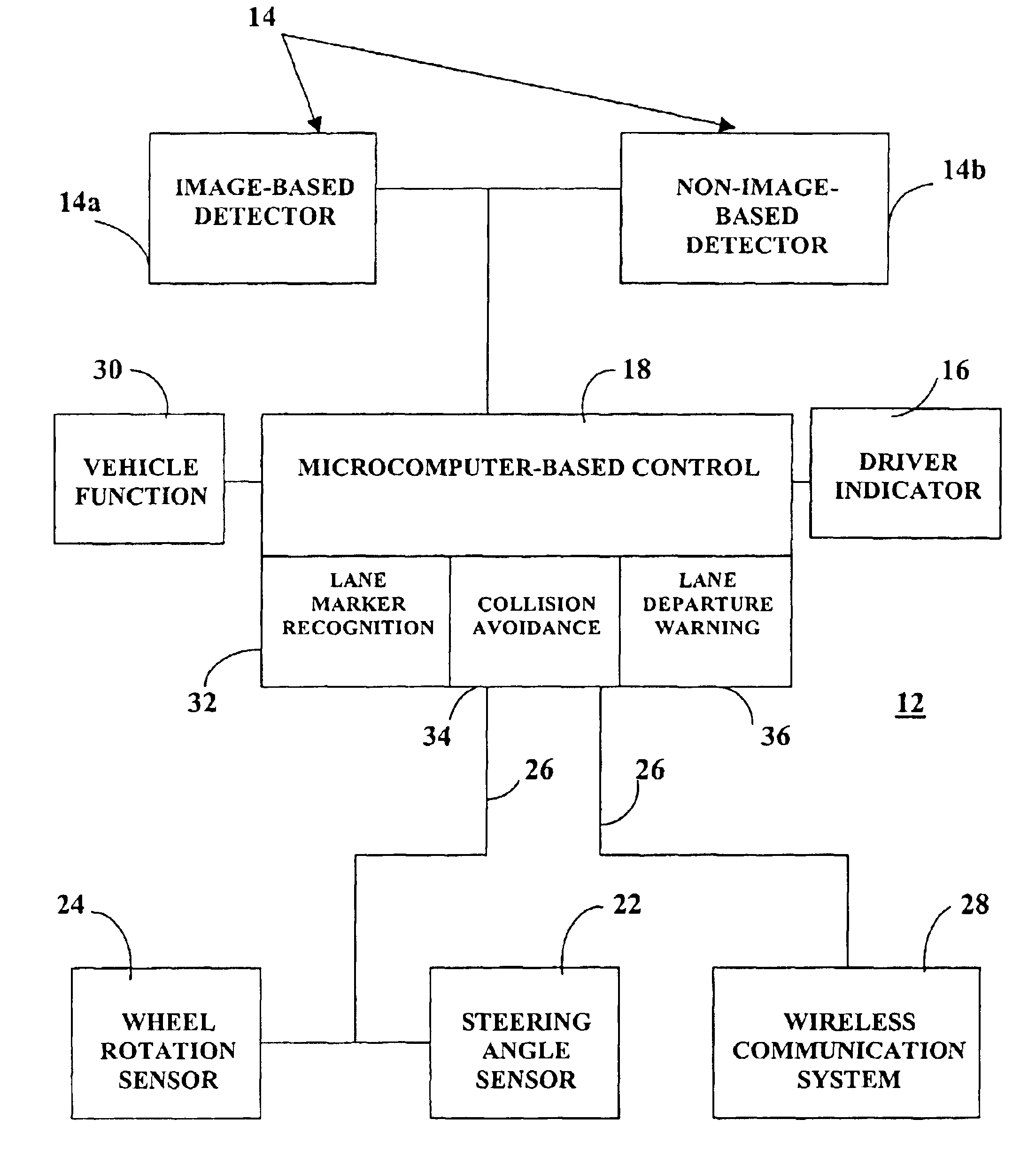
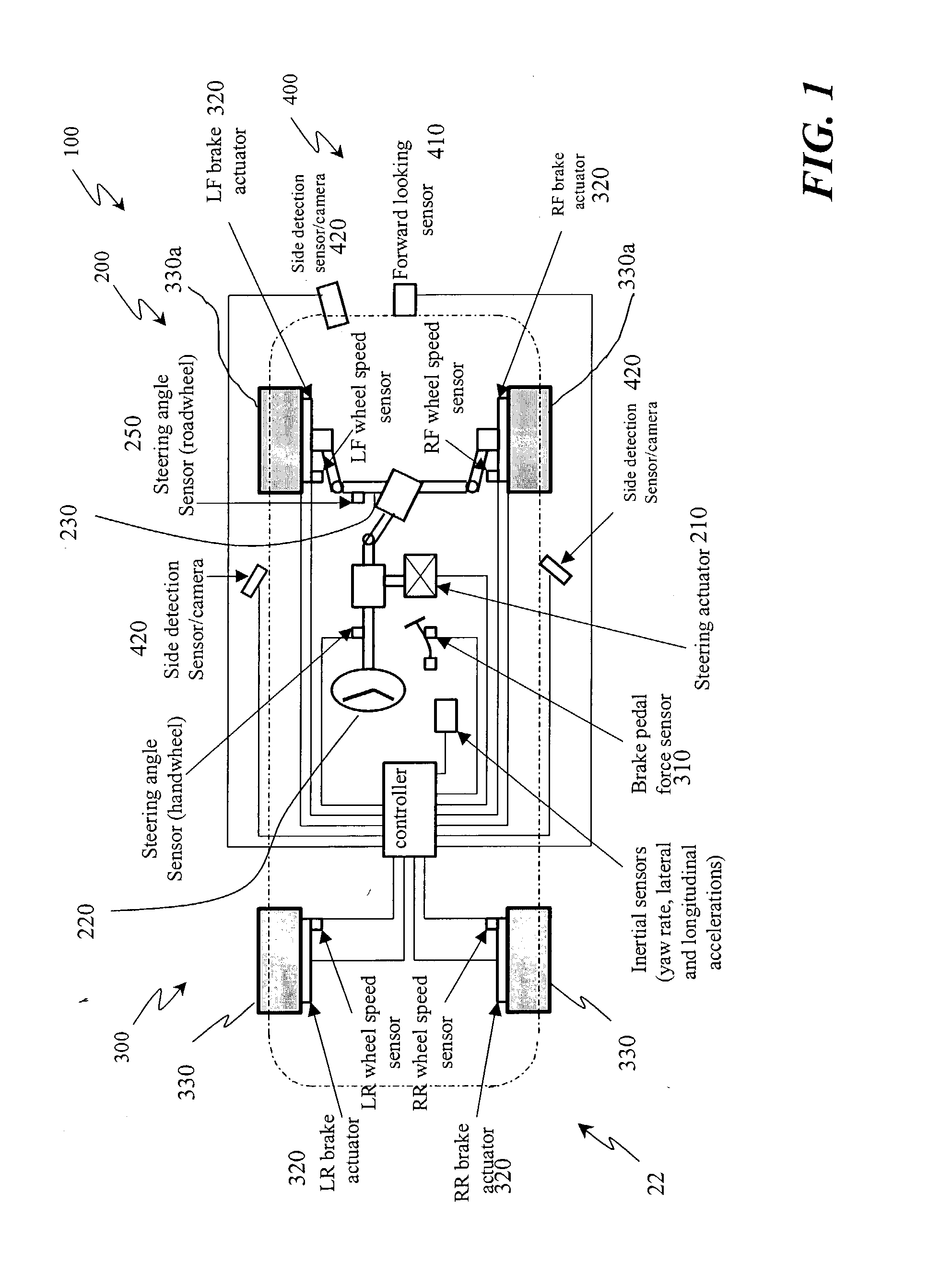
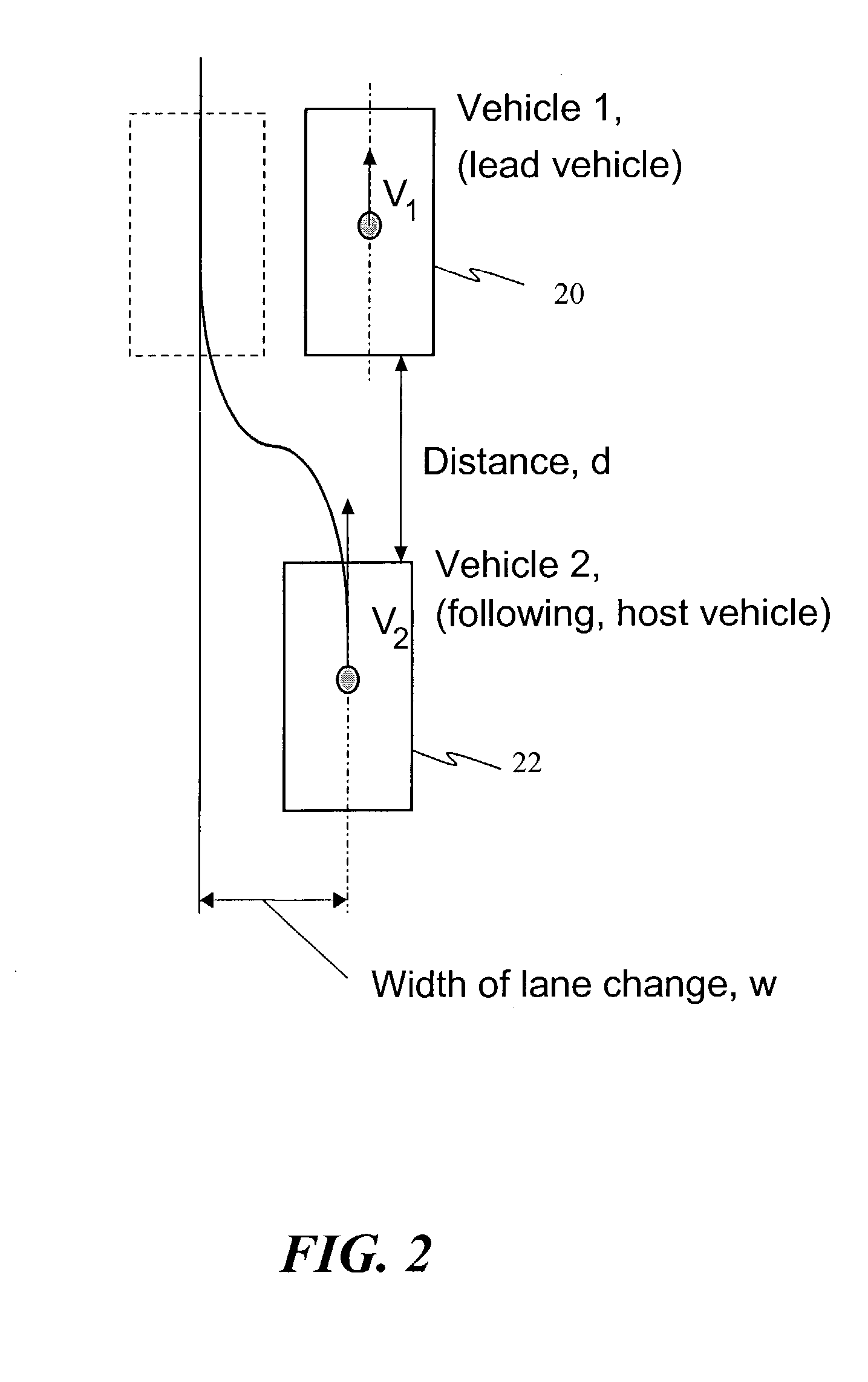
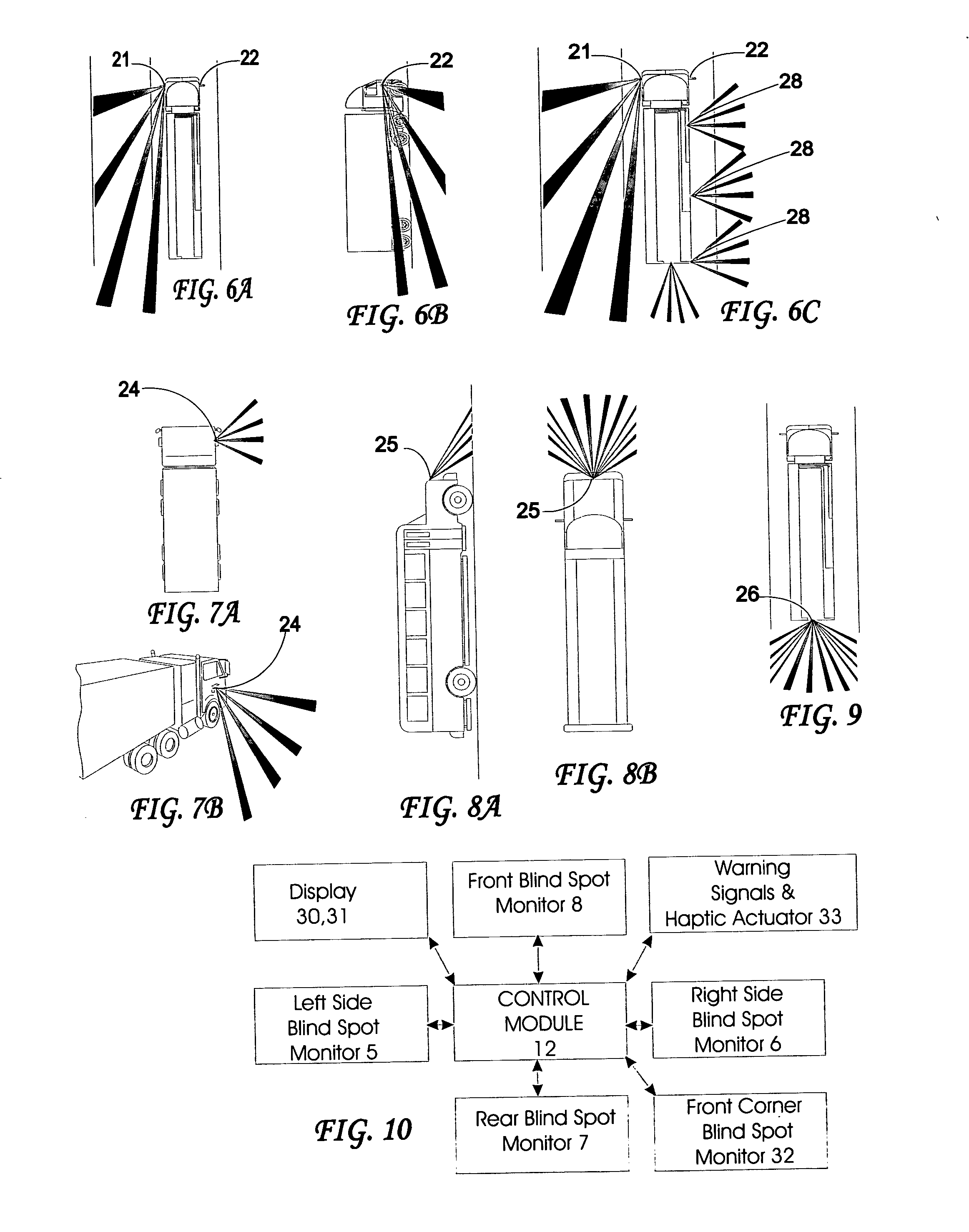
Automotive lane change aid
A vehicle lane change aid system includes a detector that is operative to detect the presence of an other vehicle adjacent the vehicle, an indicator for providing an indication that a lane change maneuver of the vehicle may affect the other vehicle and a control receiving movement information of the vehicle. The control develops a position history of the vehicle at least as a function of the movement information. The control compares the detected presence of the other vehicle with the position history and provides an indication when a lane change maneuver may affect the other vehicle.
Owner:MAGNA ELECTRONICS
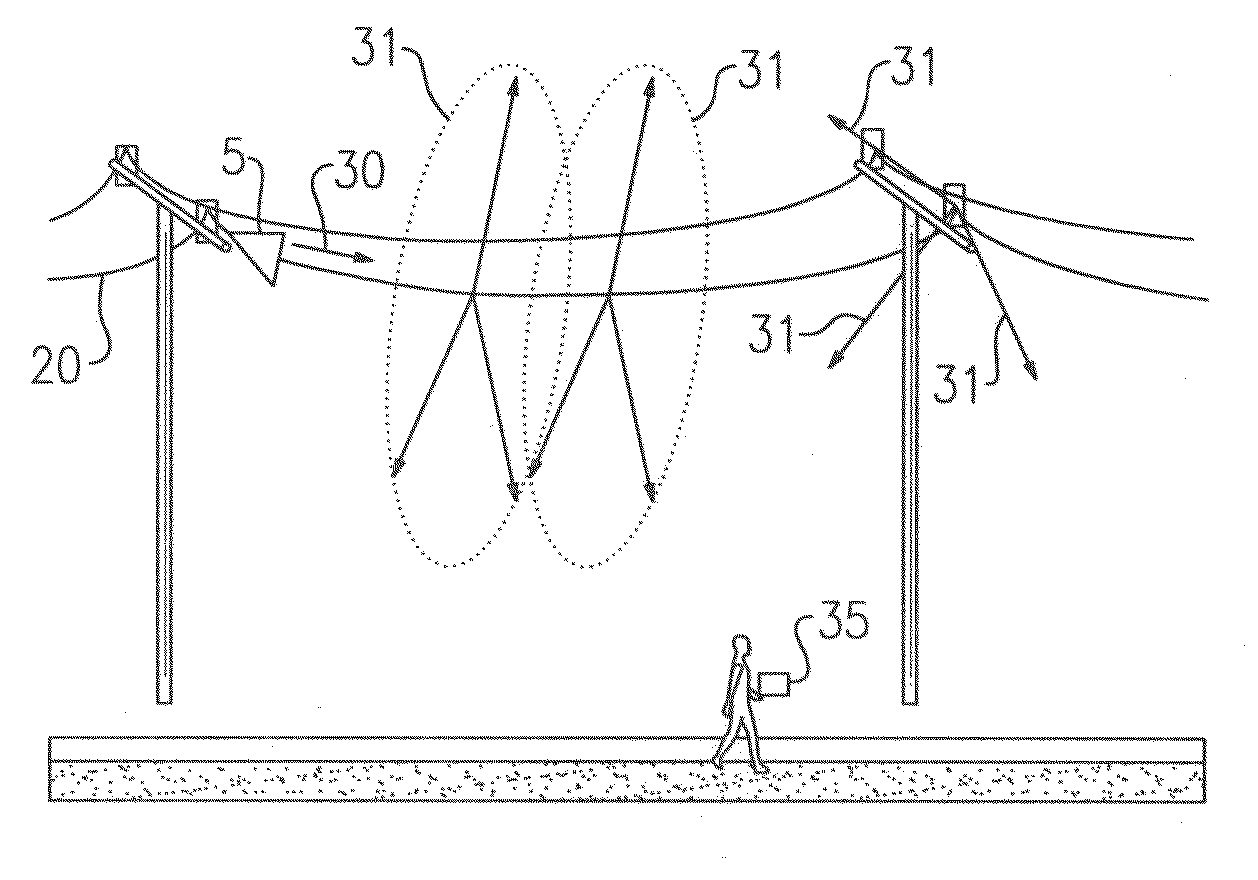
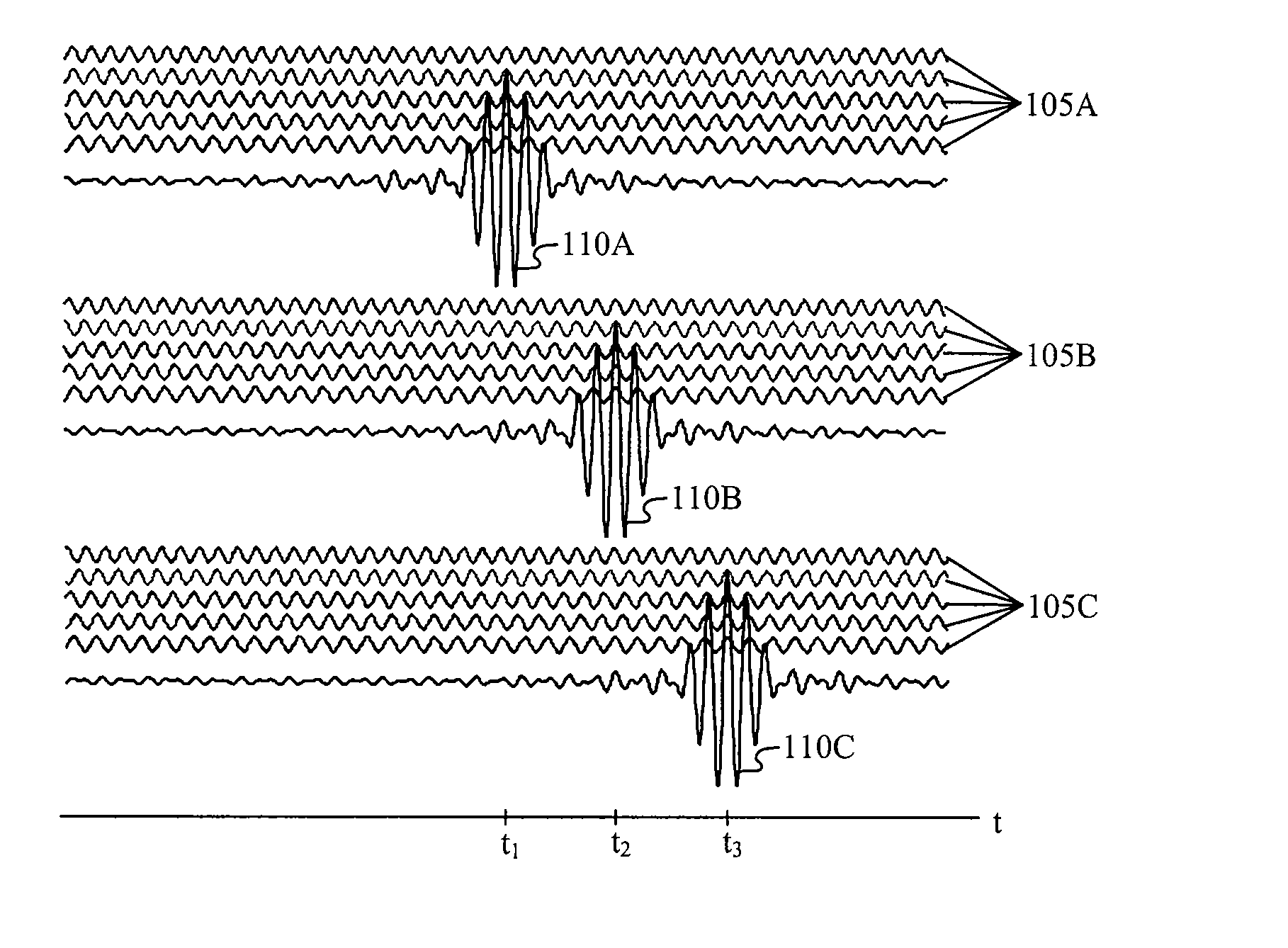
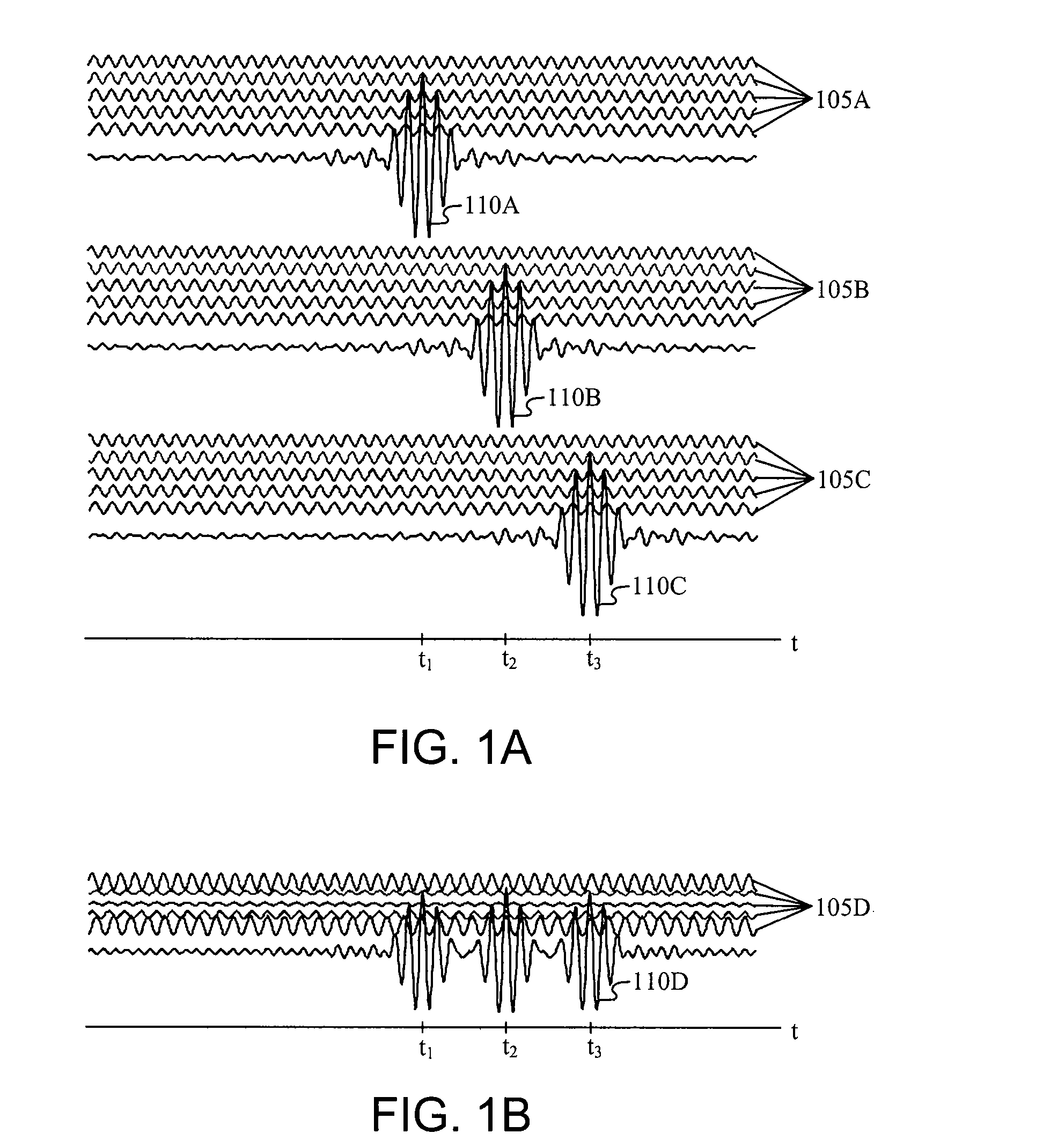
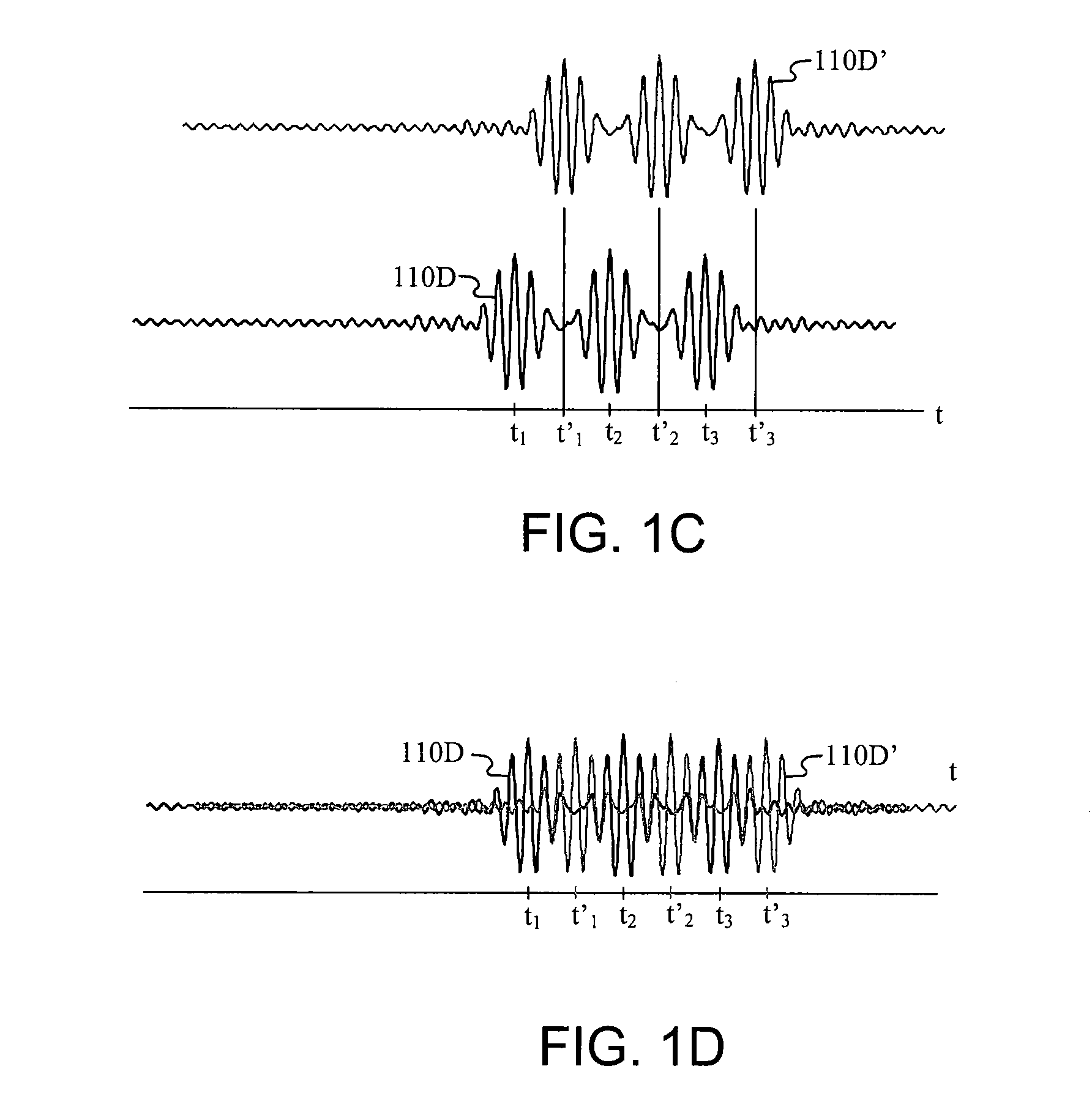
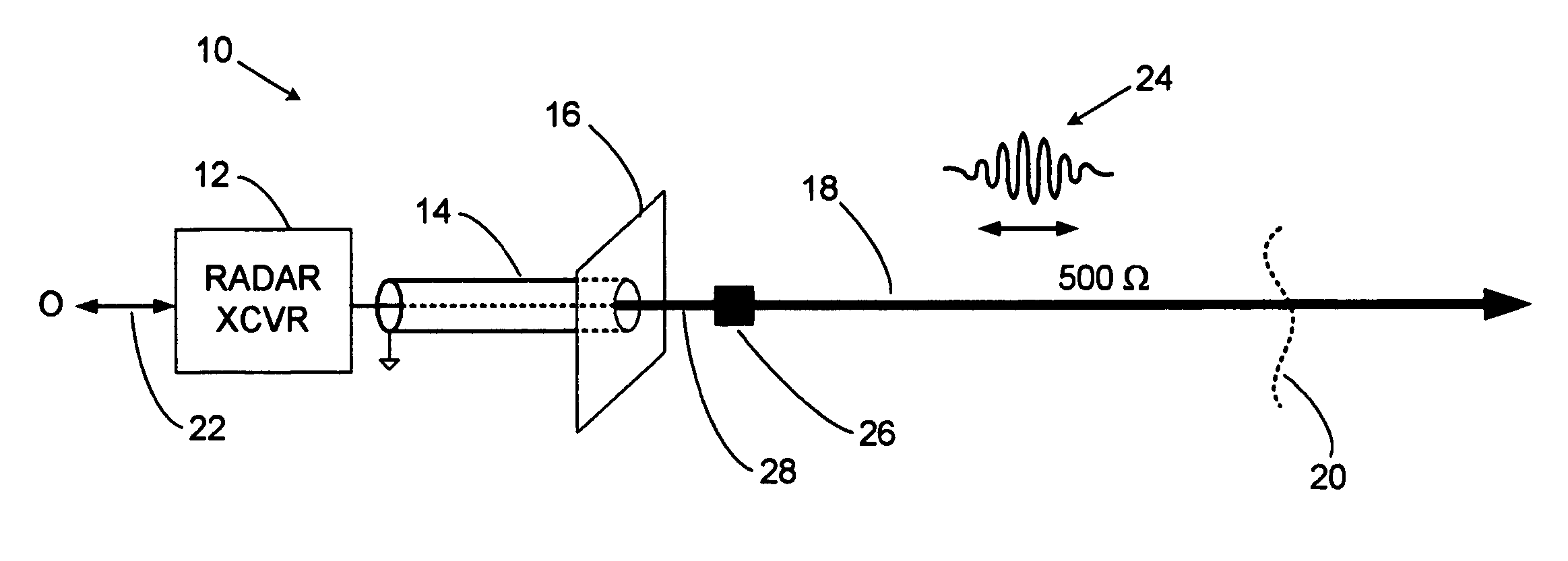
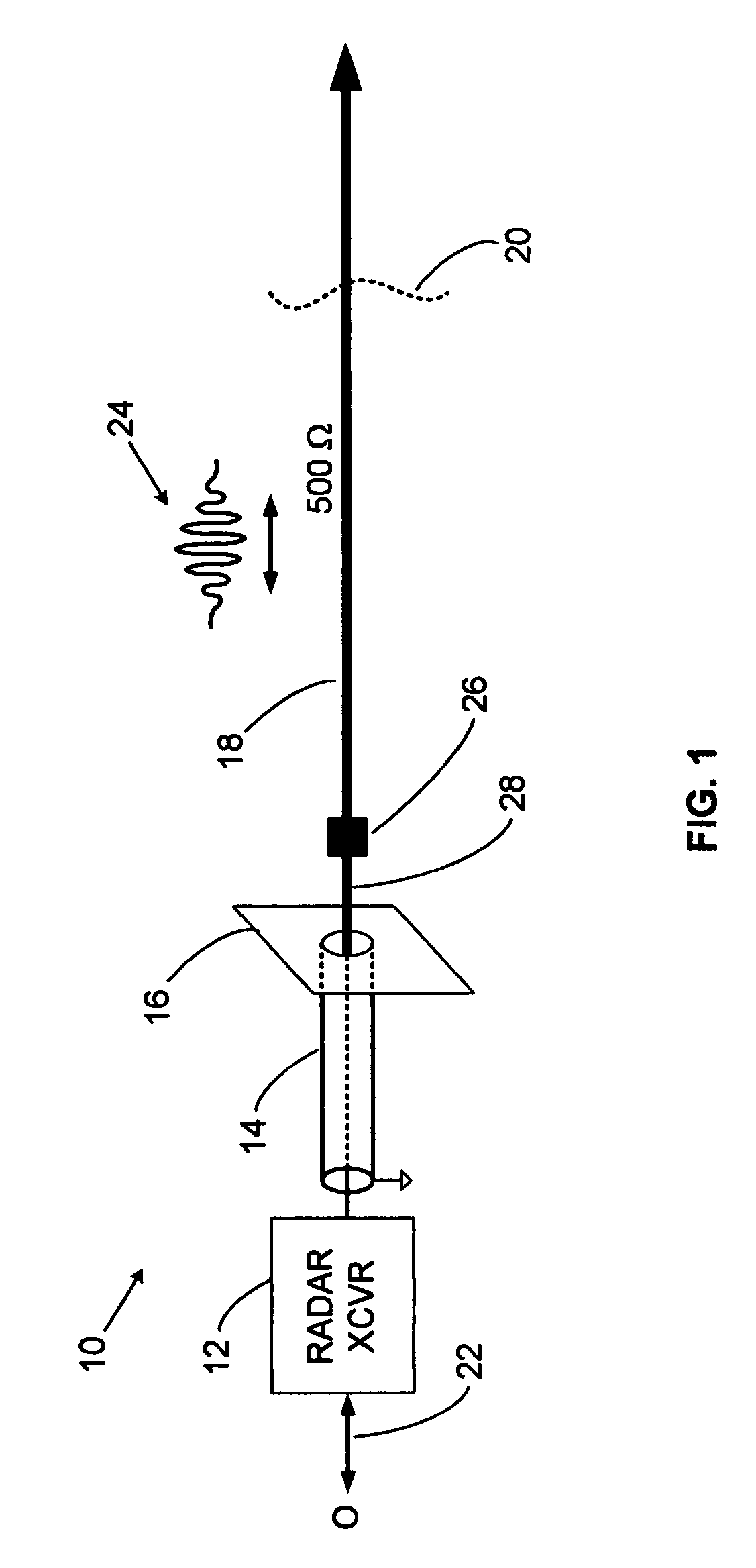
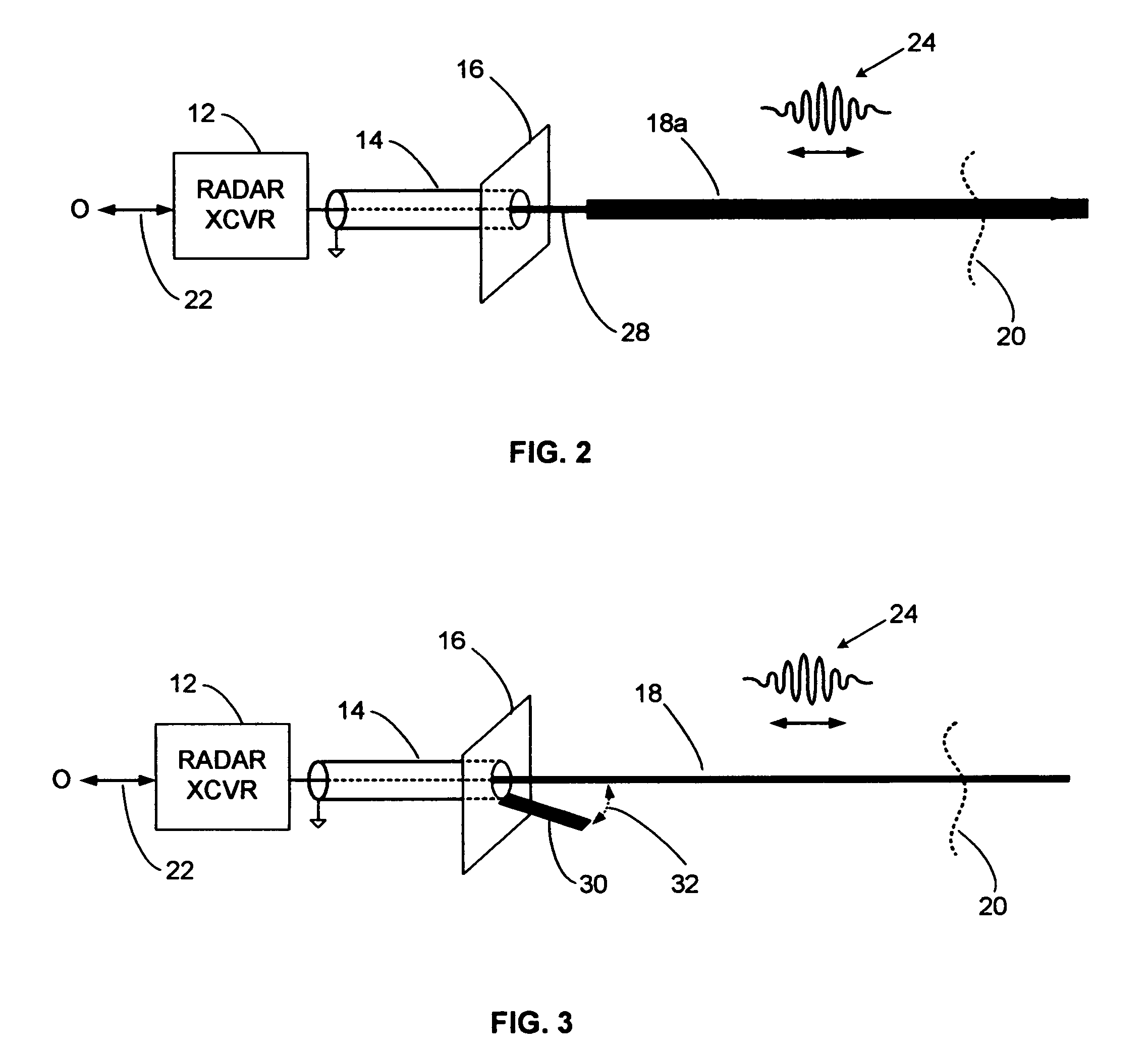
Conductive line communication apparatus and conductive line radar system and method
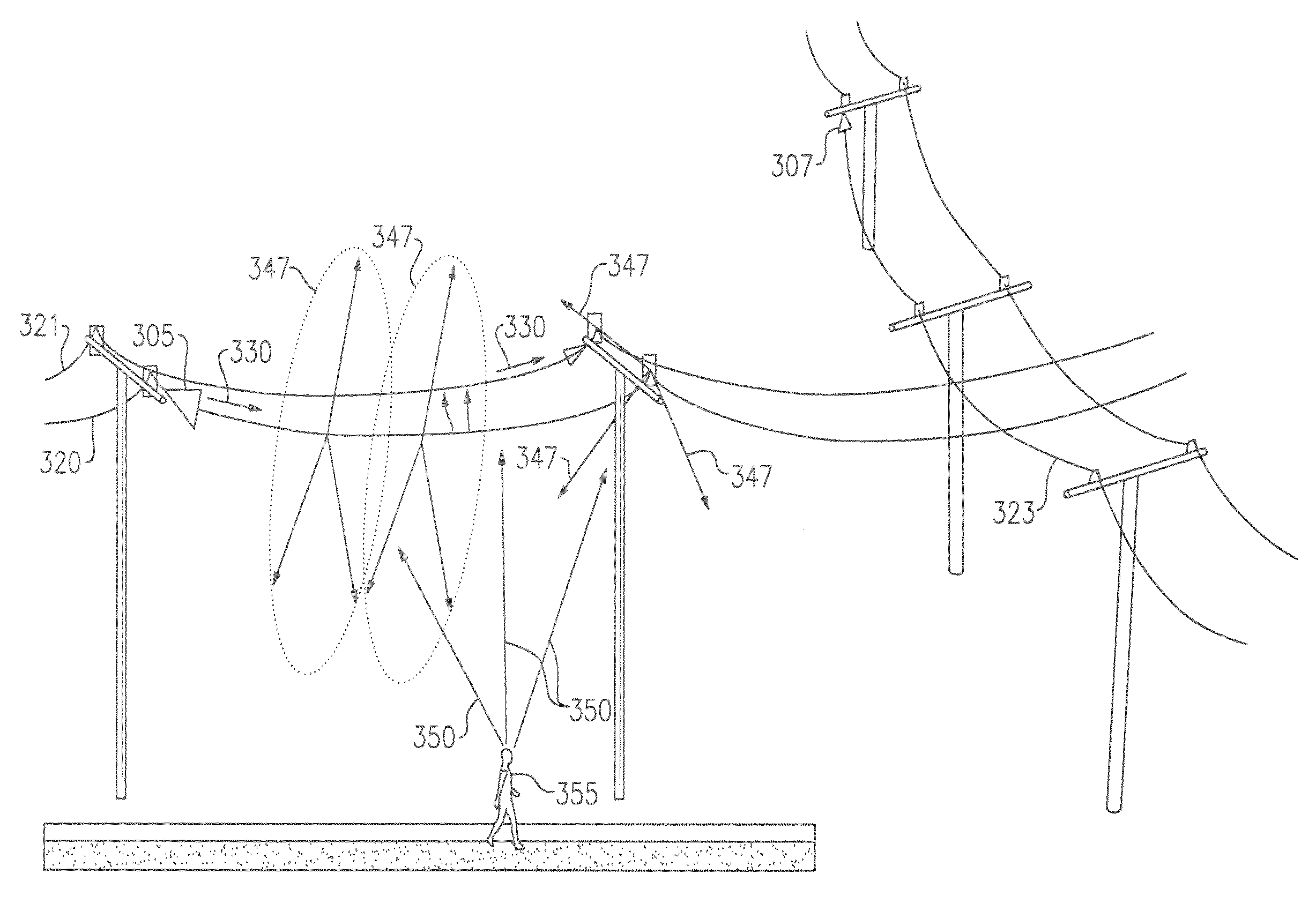
InactiveUS20110187578A1Increase heightAvoid interferenceDuplex signal operationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsTransceiver
A conductive line radar comprising at least one signal surface wave launcher, which comprises a signal surface wave transceiver, which is physically attached to a power line. The signal surface wave transceiver transmits a wave signal along the power line with another signal radiating from the wave signal in a plurality of directions along the power line. The at least one signal surface wave transceiver receives reflected signals from a target within a distance of the power line. The at least one signal surface wave launcher includes at least one RF communications transceiver and can be inductively powered from the power line.
Owner:SENSIS CORPORATION
Accident avoidance system
InactiveUS6370475B1Increase typeAvoid accidentsAnti-collision systemsPosition fixationAccident avoidancePositioning system
System and method for preventing vehicle accidents in which the absolute position of the vehicle is determined, e.g., using a satellite-based positioning system such as GPS, and the location of the vehicle relative to the edges of the roadway is then determined based on the absolute position of the vehicle and stored data relating to edges of roadways on which the vehicle may travel. A system or component within the vehicle is initiated, e.g., an alarm or warning system, or the operation of a system or component is affected, e.g., an automatic guidance system, if the location of the vehicle approaches close to an edge of the roadway or intersects with an edge of the roadway.
Owner:AMERICAN VEHICULAR SCI
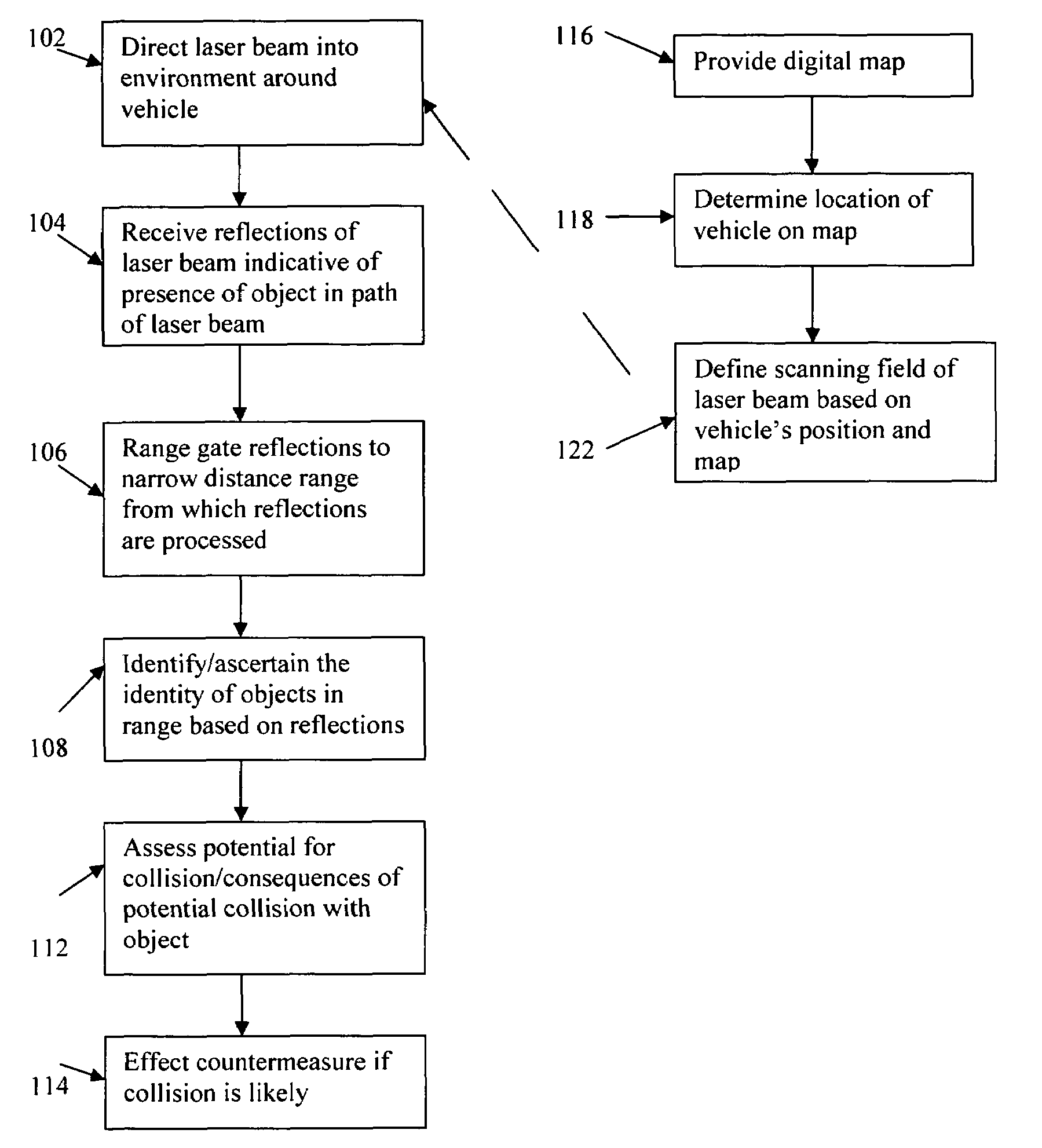
Method and system for detecting objects external to a vehicle
InactiveUS7202776B2Avoid collisionVehicle seatsInstruments for road network navigationRange gateLaser beams
Method and system for obtaining information about objects in the environment outside of and around a vehicle and preventing collisions involving the vehicle includes directing a laser beam from the vehicle into the environment, receiving from an object in the path of the laser beam a reflection of the laser beam at a location on the vehicle, and analyzing the received laser beam reflections to obtain information about the object from which the laser beam is being reflected. Analysis of the laser beam reflections preferably entails range gating the received laser beam reflections to limit analysis of the received laser beam reflections to only those received from an object within a defined (distance) range such that objects at distances within the range are isolated from surrounding objects.
Owner:AMERICAN VEHICULAR SCI
Method and arrangement for mapping a road
Arrangement and method for mapping a road during travel of a vehicle having two data acquisition modules arranged on sides of the vehicle, each including a GPS receiver and antenna for enabling the vehicle's position to be determined and a linear camera which provides one-dimensional images of an area on the respective side in a vertical plane perpendicular to the road such that information about the road is obtained from a view in a direction perpendicular to the road. A processor unit forms a map database of the road by correlating the vehicle's position and the information about the road. Instead of or in addition to the linear cameras, scanning laser radars are provided and transmit waves downward in a plane perpendicular to the road and receive reflected waves to provide information about distance between the laser radars and the ground for use in forming the database.
Owner:AMERICAN VEHICULAR SCI
Conductive line communication apparatus and conductive line radar system and method
InactiveUS8159385B2Eliminate the effects ofIncrease the areaDuplex signal operationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTransceiverRadar systems
A conductive line radar comprising at least one signal surface wave launcher, which comprises a signal surface wave transceiver, which is physically attached to a power line. The signal surface wave transceiver transmits a wave signal along the power line with another signal radiating from the wave signal in a plurality of directions along the power line. The at least one signal surface wave transceiver receives reflected signals from a target within a distance of the power line. The at least one signal surface wave launcher includes at least one RF communications transceiver and can be inductively powered from the power line.
Owner:SENSIS CORPORATION
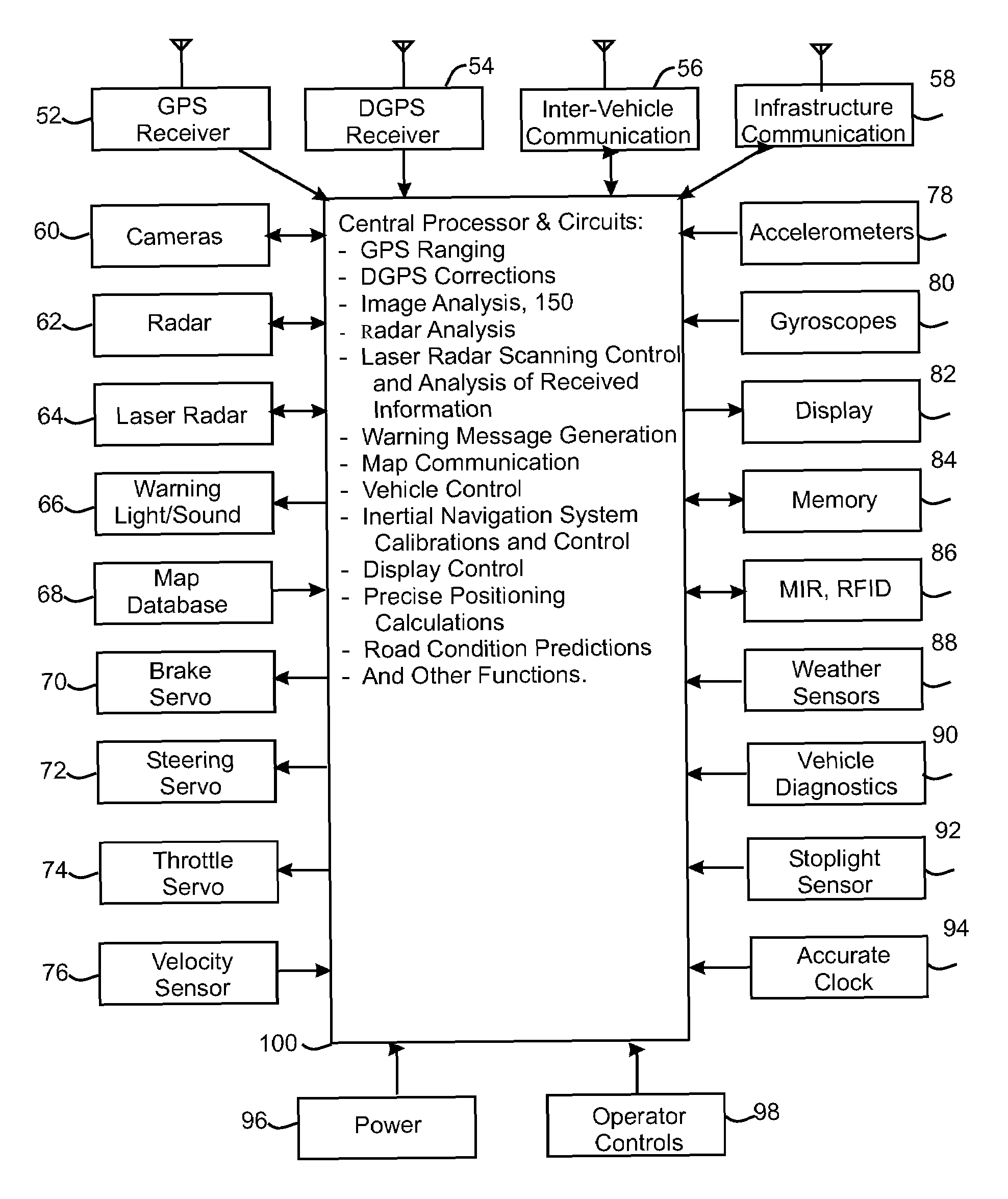
Navigation and control system for autonomous vehicles
ActiveUS20070219720A1Navigation instrumentsExternal condition input parametersControl systemLight beam
A navigation and control system including a sensor configured to locate objects in a predetermined field of view from a vehicle. The sensor has an emitter configured to repeatedly scan a beam into a two-dimensional sector of a plane defined with respect to a first predetermined axis of the vehicle, and a detector configured to detect a reflection of the emitted beam from one of the objects. The sensor includes a panning mechanism configured to pan the plane in which the beam is scanned about a second predetermined axis to produce a three dimensional field of view. The navigation and control system includes a processor configured to determine the existence and location of the objects in the three dimensional field of view based on a position of the vehicle and a time between an emittance of the beam and a reception of the reflection of the emitted beam from one of the objects.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
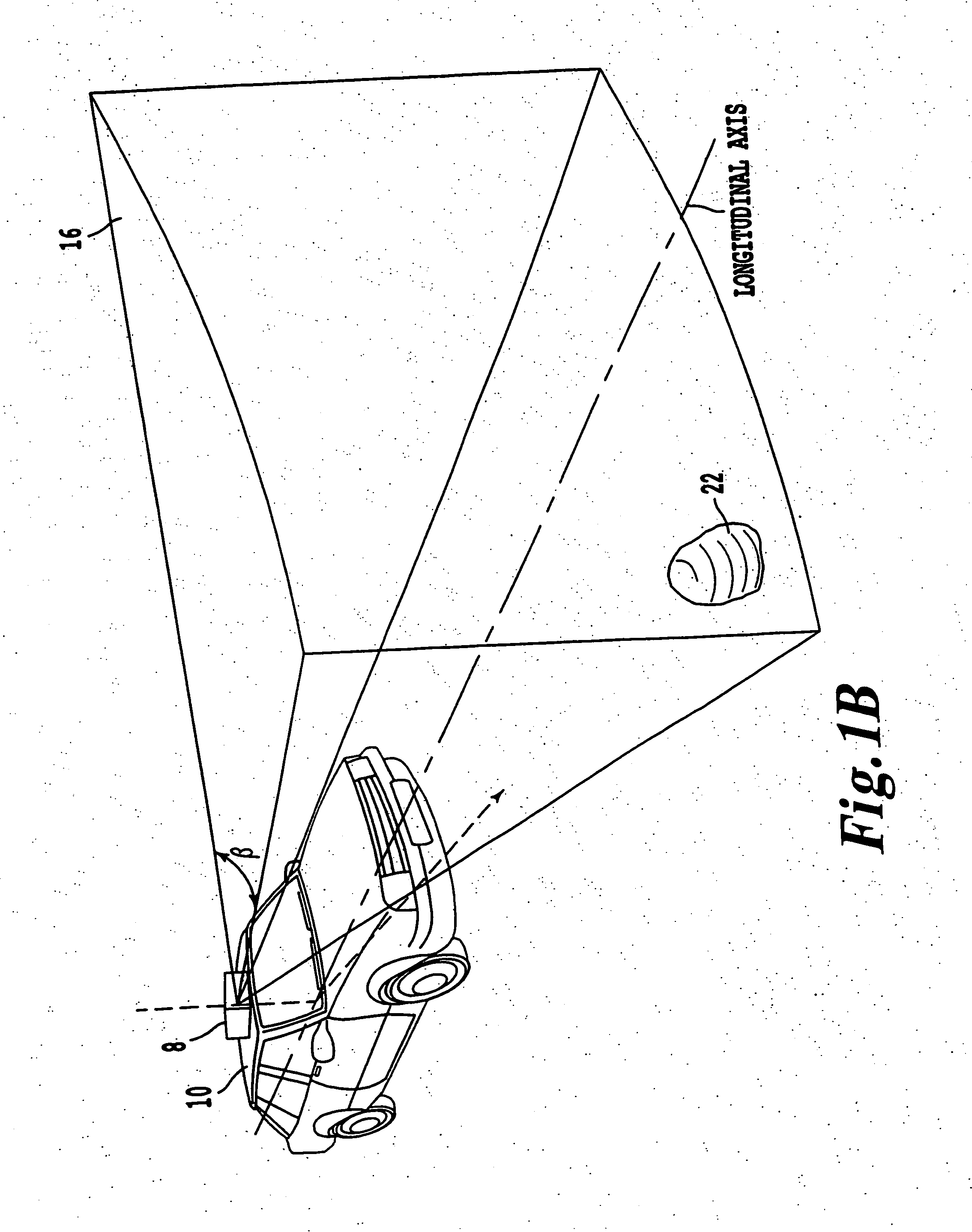
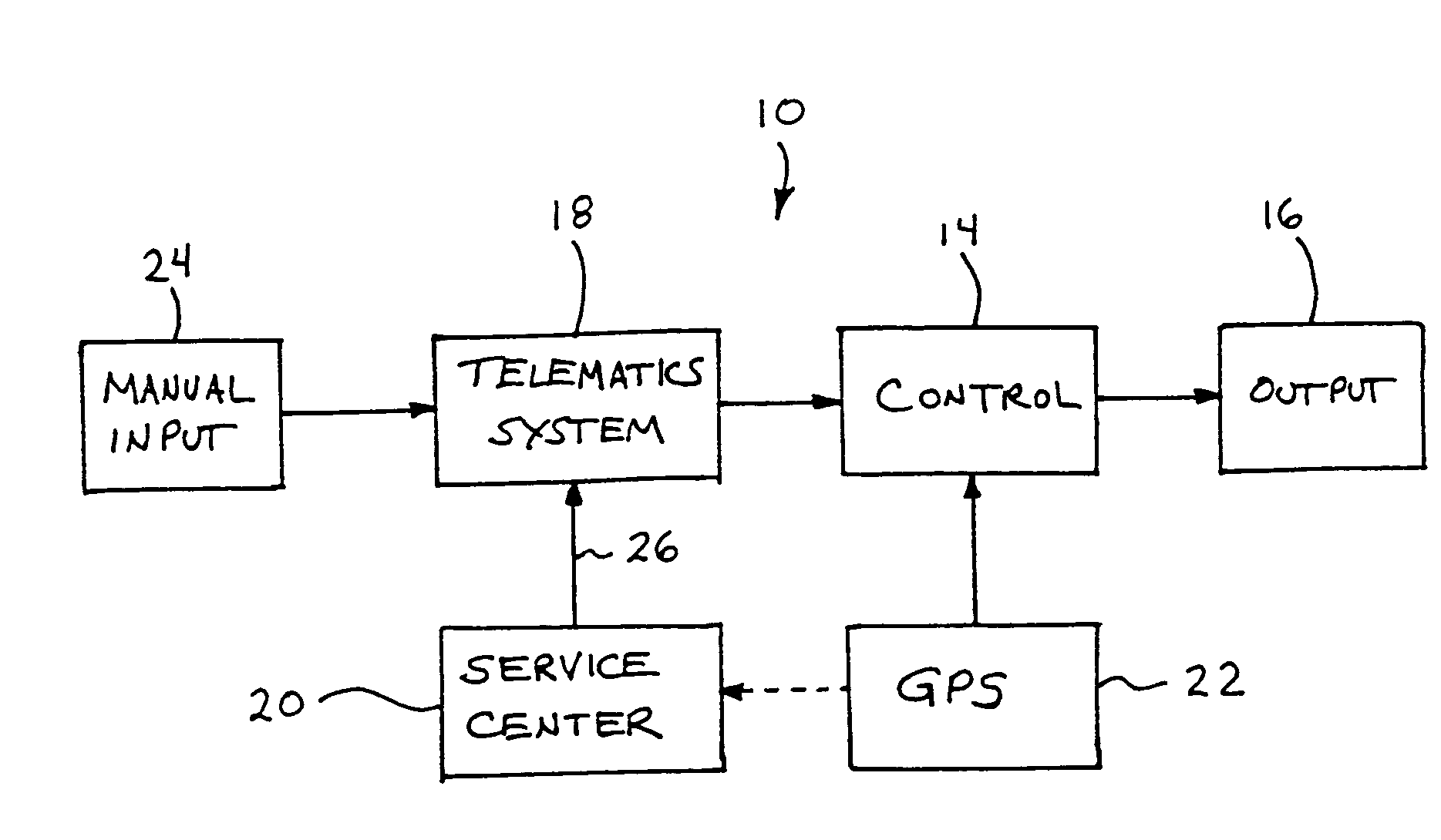
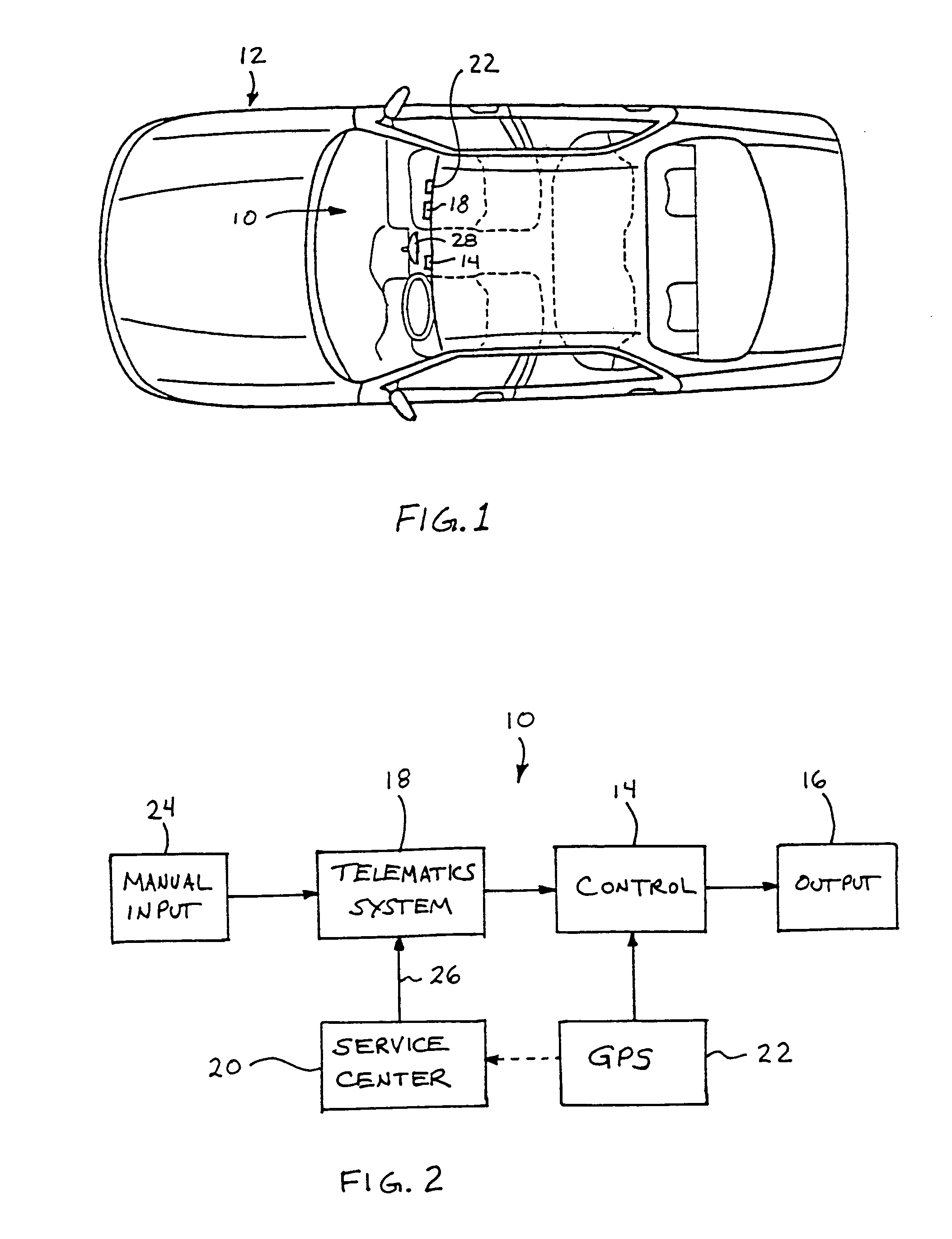
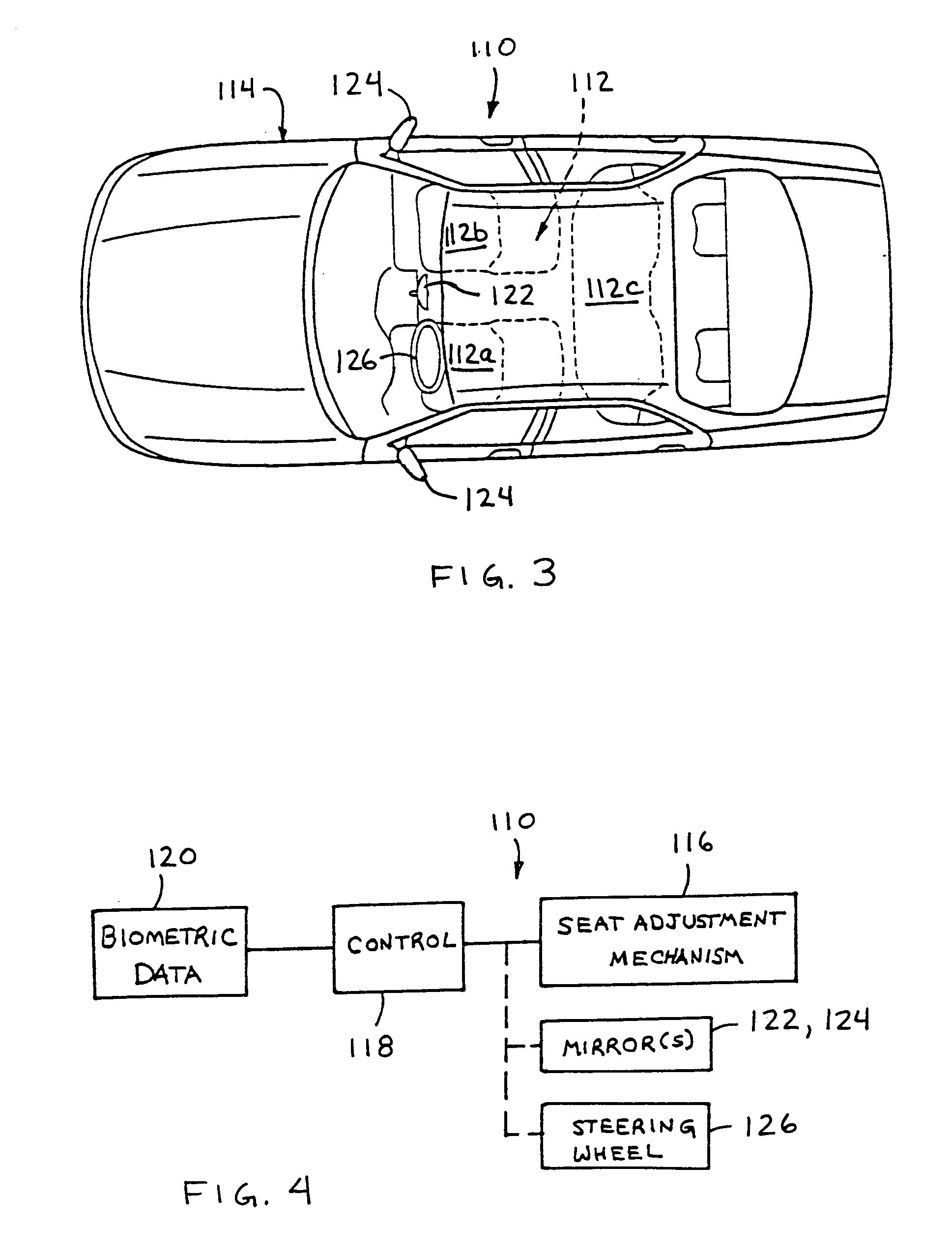
Vehicle navigation system for use with a telematics system
InactiveUS7167796B2Low costImage enhancementTelevision system detailsDriver/operatorService provision
A navigation system for a vehicle includes a vehicle-based telematics system, a vehicle-based global positioning system and a control. The telematics system is operable to receive a user input from a driver of the vehicle and to download directional information from an external service provider to the control in response to the user input and an initial geographic position of the vehicle. The directional information comprises at least two instructions with each of the instructions being coded or associated with or linked to a respective geographic location. The control is operable to provide an output corresponding to each of the instructions in response to a current actual geographic position of the vehicle. The control is operable to provide each instruction only when the then current actual geographic position of the vehicle at least generally corresponds to the particular geographic location associated with the instruction.
Owner:DONNELLY CORP
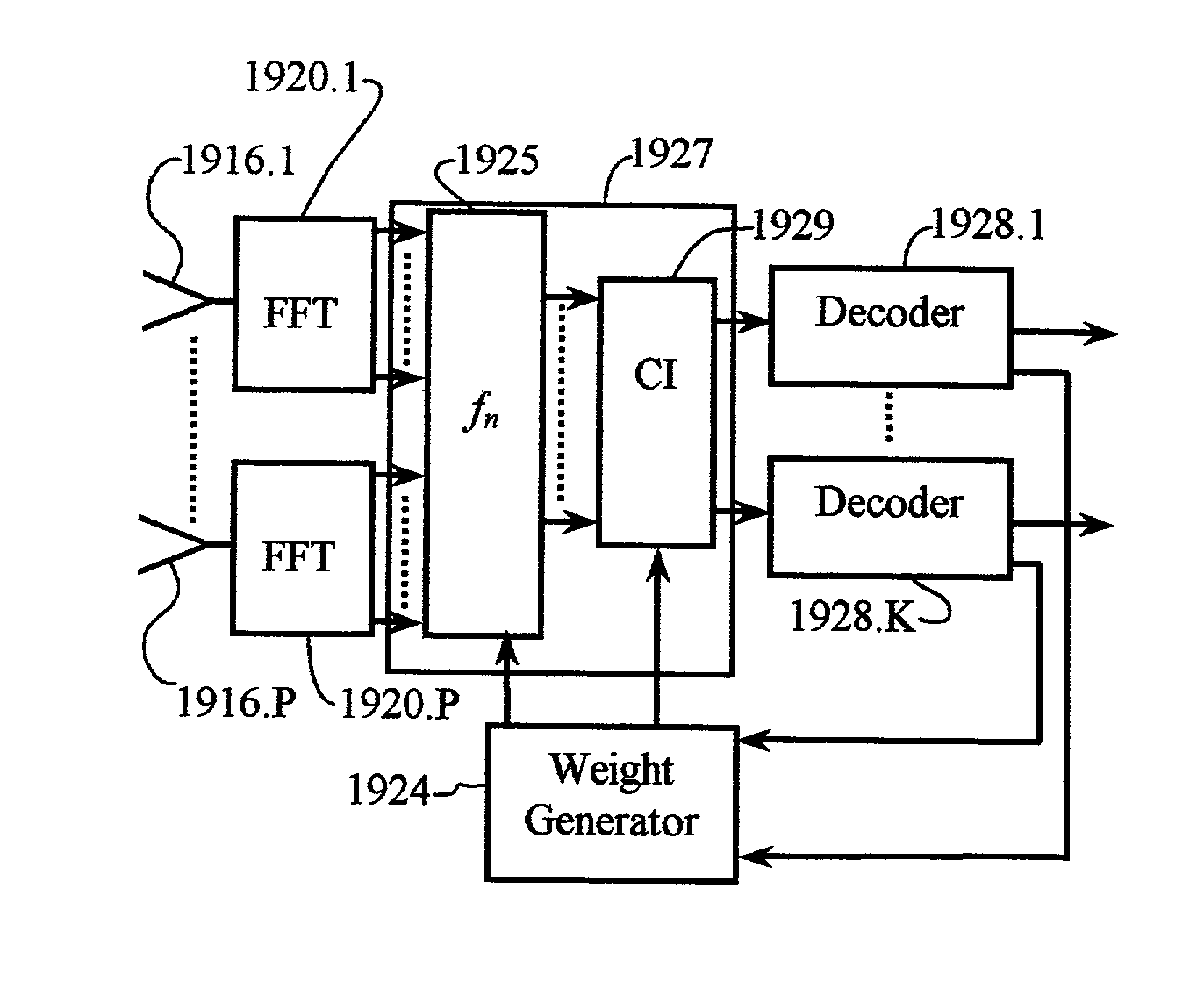
Multicarrier Sub-Layer for Direct Sequence Channel and Multiple-Access Coding
InactiveUS20070211786A1Low costImprove system performanceSecret communicationMultiplex code generationUltra-widebandTransmission protocol
Carrier Interferometry (CI) provides wideband transmission protocols with frequency-band selectivity to improve interference rejection, reduce multipath fading, and enable operation across non-continuous frequency bands. Direct-sequence protocols, such as DS-CDMA, are provided with CI to greatly improve performance and reduce transceiver complexity. CI introduces families of orthogonal polyphase codes that can be used for channel coding, spreading, and / or multiple access. Unlike conventional DS-CDMA, CI coding is not necessary for energy spreading because a set of CI carriers has an inherently wide aggregate bandwidth. Instead, CI codes are used for channelization, energy smoothing in the frequency domain, and interference suppression. CI-based ultra-wideband protocols are implemented via frequency-domain processing to reduce synchronization problems, transceiver complexity, and poor multipath performance of conventional ultra-wideband systems. CI allows wideband protocols to be implemented with space-frequency processing and other array-processing techniques to provide either or both diversity combining and sub-space processing. CI also enables spatial processing without antenna arrays. Even the bandwidth efficiency of multicarrier protocols is greatly enhanced with CI. CI-based wavelets avoid time and frequency resolution trade-offs associated with conventional wavelet processing. CI-based Fourier transforms eliminate all multiplications, which greatly simplifies multi-frequency processing. The quantum-wave principles of CI improve all types of baseband and radio processing.
Owner:GENGHISCOMM HLDG
Reflection free launcher for electromagnetic guide wire
InactiveUS7345623B2Easy to measureSmall sizeMachines/enginesLevel indicatorsEngineeringImpedance matching
Guided wave radar (GWR) pulses are launched onto an electromagnetic guide wire using a compact launcher that includes an impedance matching element. The impedance matching element produces reflections that cancel launcher reflections. Short range echoes can be accurately detected after impedance matching. GWR operation in small tanks and in tanks containing low dielectric constant materials, such as propane, can be enhanced with the compact impedance-matched launcher.
Owner:MCEWAN TECH
Multicarrier sub-layer for direct sequence channel and multiple-access coding
InactiveUS7430257B1Low costPolarisation/directional diversityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsUltra-widebandTransmission protocol
Carrier Interferometry (CI) provides wideband transmission protocols with frequency-band selectivity to improve interference rejection, reduce multipath fading, and enable operation across non-continuous frequency bands. Direct-sequence protocols, such as DS-CDMA, are provided with CI to greatly improve performance and reduce transceiver complexity. CI introduces families of orthogonal polyphase codes that can be used for channel coding, spreading, and / or multiple access. Unlike conventional DS-CDMA, CI coding is not necessary for energy spreading because a set of CI carriers has an inherently wide aggregate bandwidth. Instead, CI codes are used for channelization, energy smoothing in the frequency domain, and interference suppression. CI-based ultra-wideband protocols are implemented via frequency-domain processing to reduce synchronization problems, transceiver complexity, and poor multipath performance of conventional ultra-wideband systems. CI allows wideband protocols to be implemented with space-frequency processing and other array-processing techniques to provide either or both diversity combining and sub-space processing. CI also enables spatial processing without antenna arrays. Even the bandwidth efficiency of multicarrier protocols is greatly enhanced with CI. CI-based wavelets avoid time and frequency resolution trade-offs associated with conventional wavelet processing. CI-based Fourier transforms eliminate all multiplications, which greatly simplifies multi-frequency processing. The quantum-wave principles of CI improve all types of baseband and radio processing.
Owner:GENGHISCOMM HLDG
Dual mode tracking system
InactiveUS6353406B1Memory record carrier reading problemsCo-operative working arrangementsData warehouseDual mode
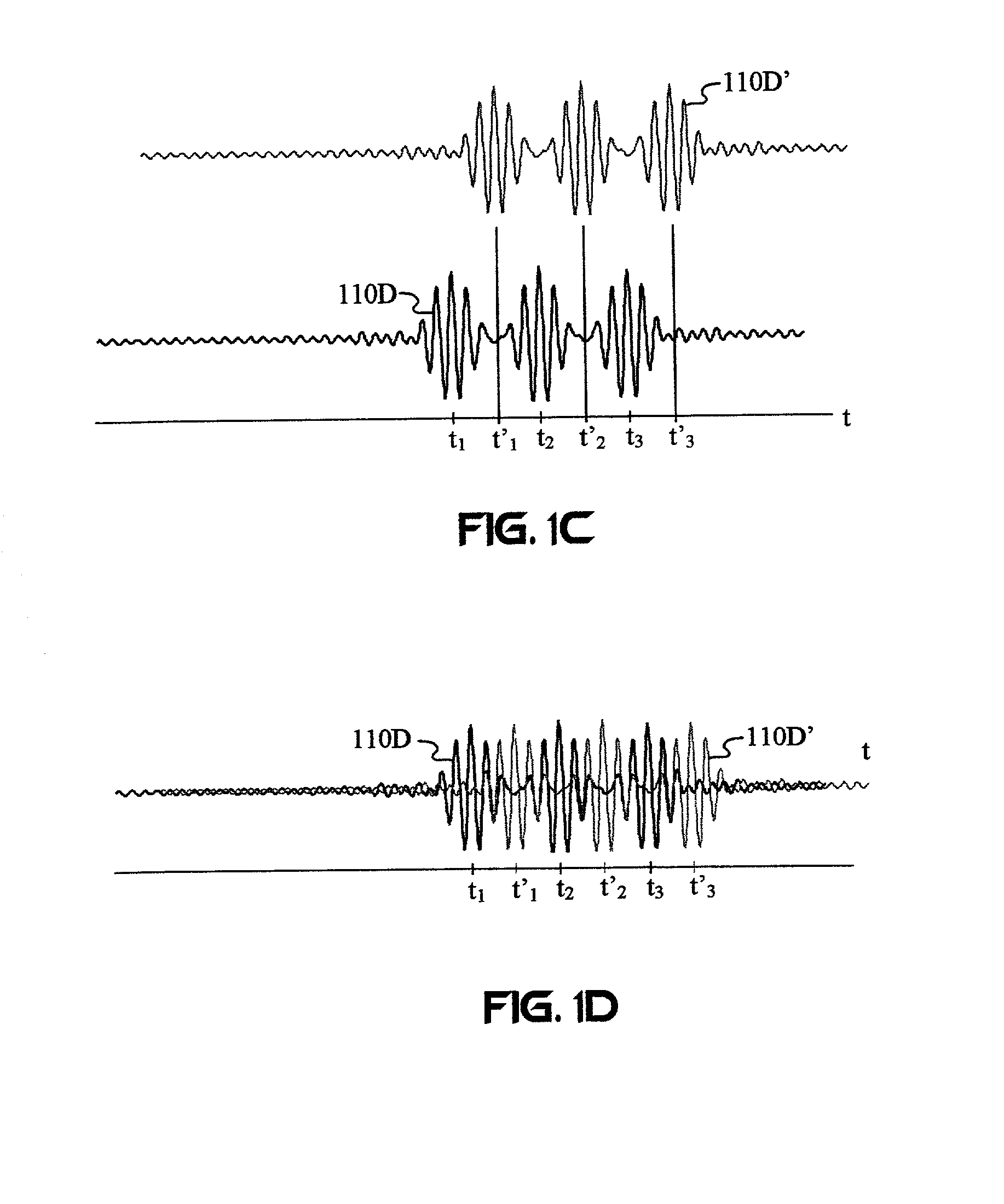
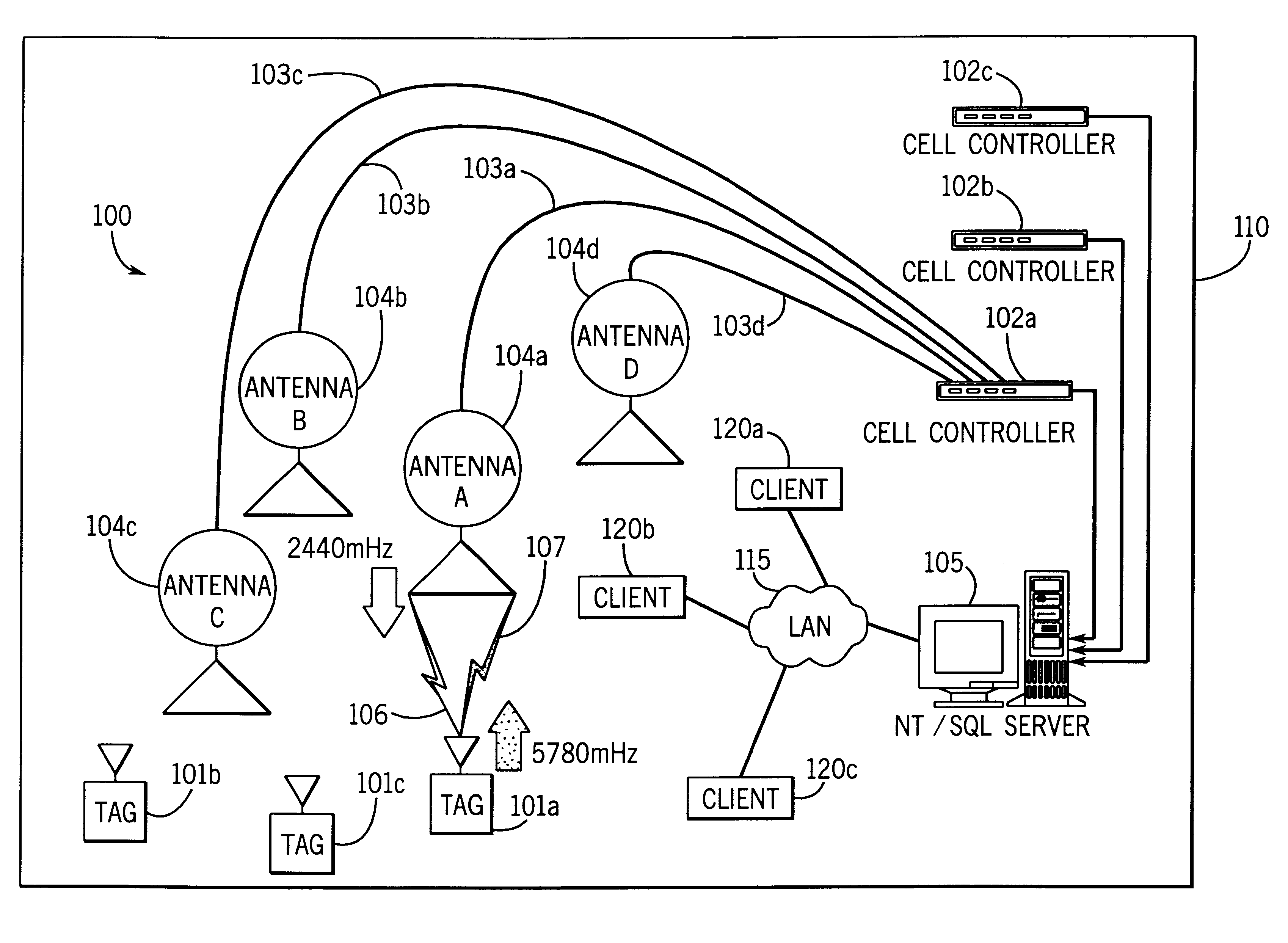
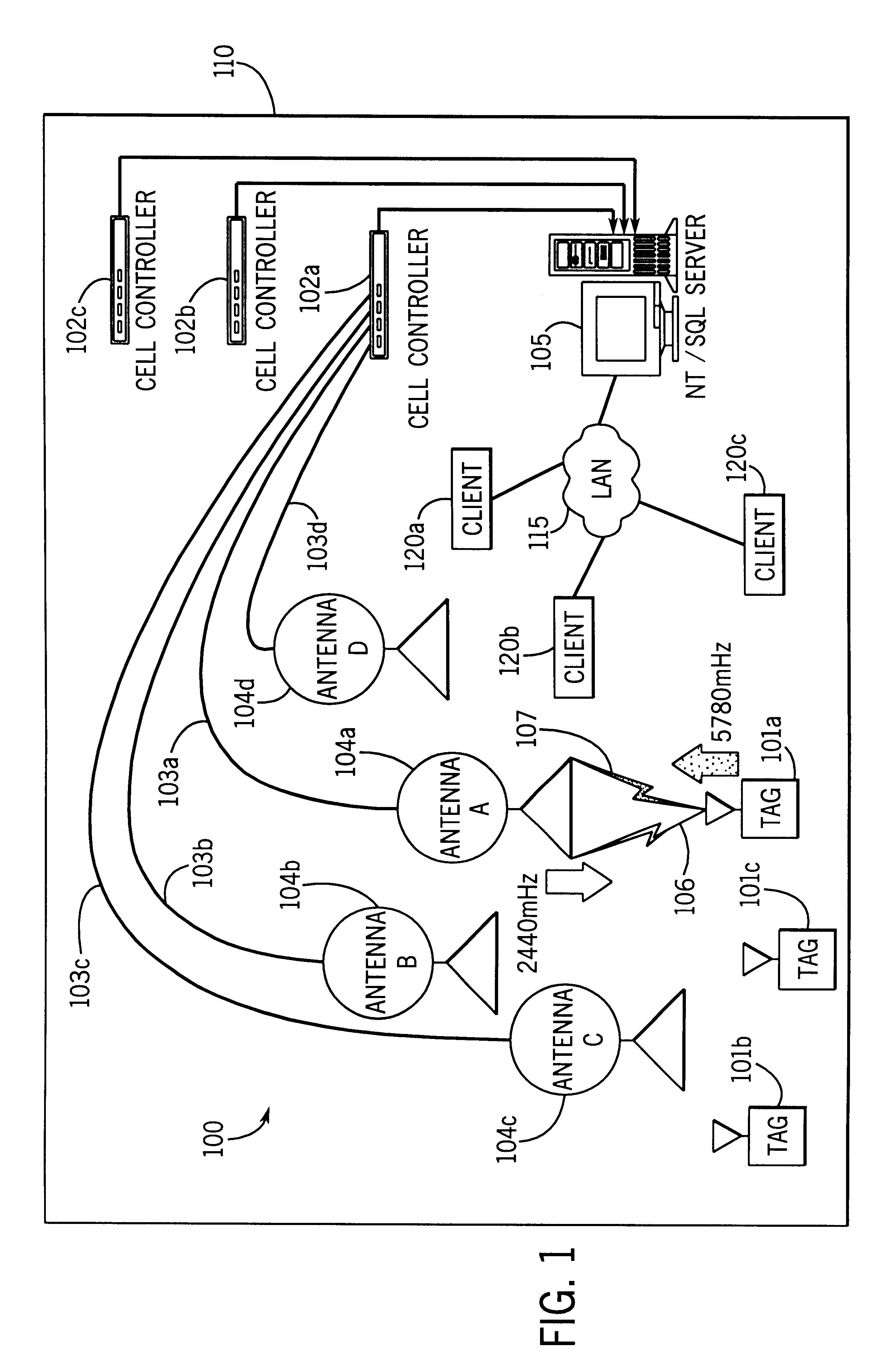
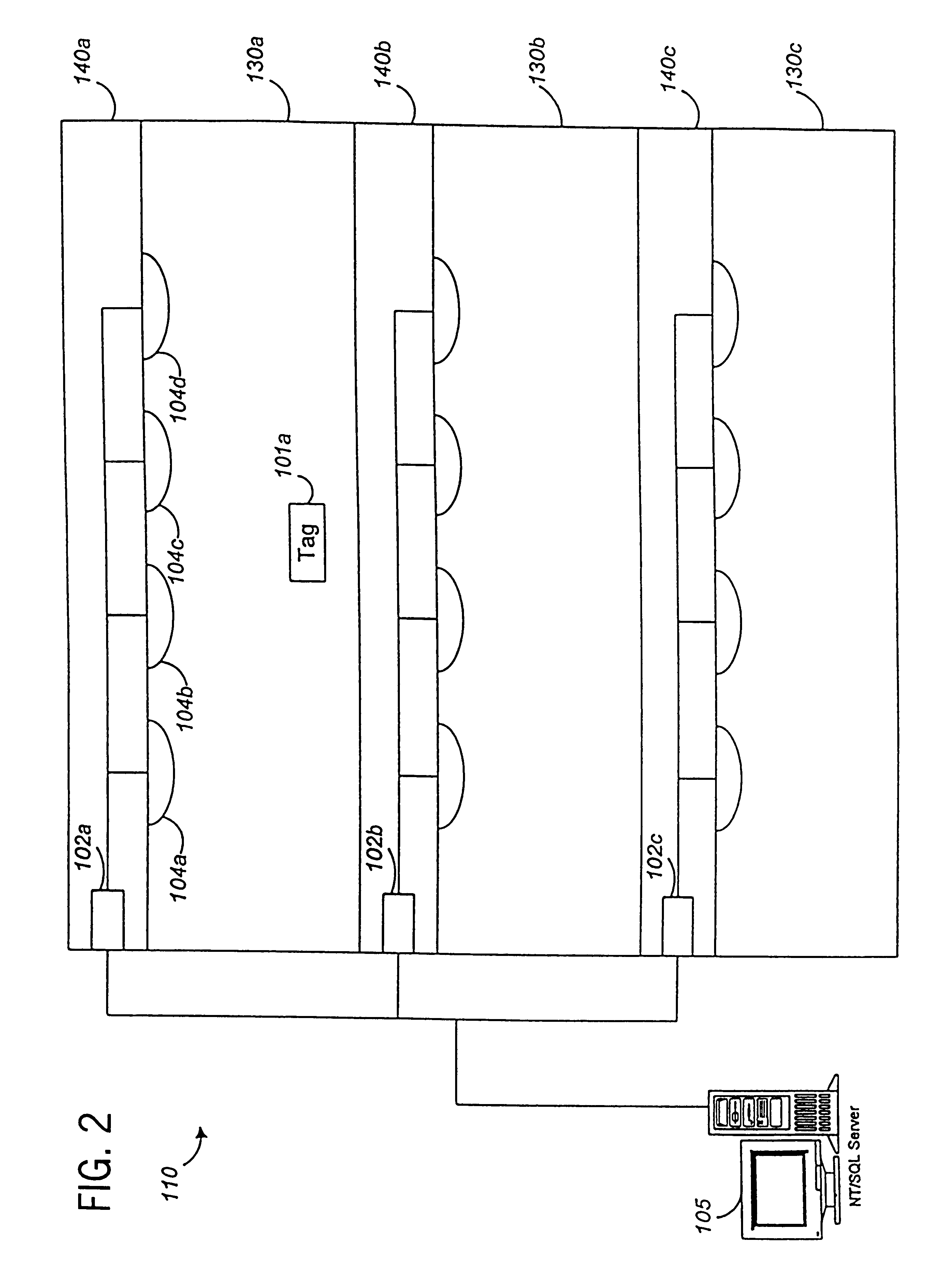
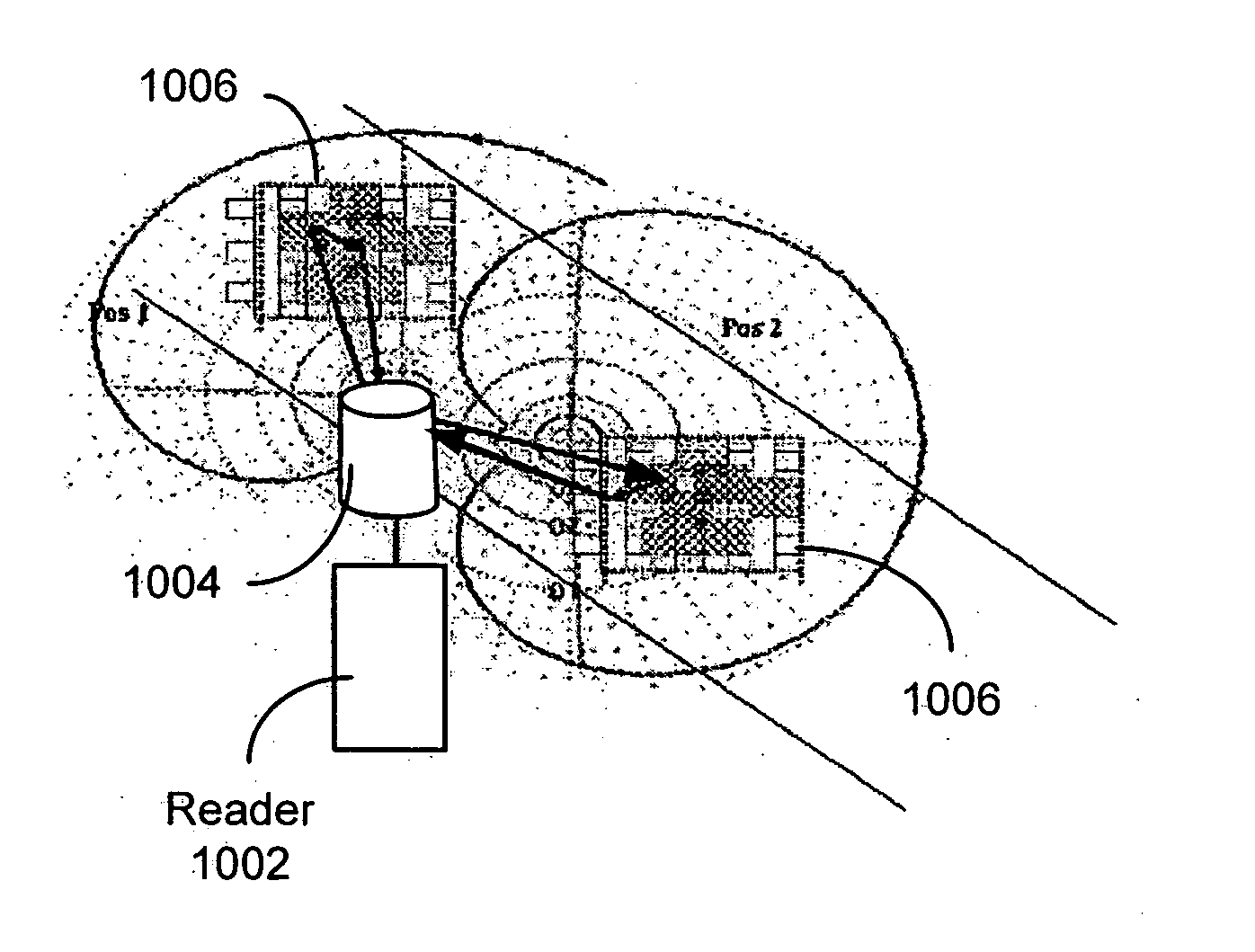
System for tracking mobile tags. Cell controllers with multiple antenna modules generate a carrier signal which is received by the tags. Tags shift the frequency of the carrier signal, modulate an identification code onto it, and transmit the resulting tag signal at randomized intervals. The antennas receive and process the response, and determine the presence of the tags by proximity and triangulation. The recursive-least squares (RLS) technique is used in filtering received signals. Distance of a tag from an antenna is calculated by measuring the round trip signal time. The cell controllers send data from the antenna to a host computer. The host computer collects the data and resolves them into positional estimates. Data are archived in a data warehouse, such as an SQL Server. Also disclosed is an article tracking system that supports both active and passive tags with a cell controller able to read both passive and active tag signals.
Owner:RF TECH +1
Scheduling in an RFID system having a coordinated RFID tag reader array
ActiveUS20060022800A1Improve reliabilityReduce the impactMemory record carrier reading problemsPosition fixationEmbedded systemWhole systems
A system and method of scheduling RFID tag interrogations by a plurality of RFID readers so as to mitigate the effects of interference within an RFID environment in which the readers are deployed, and to enhance the efficiency and reliability of the overall RFID system. The system includes a plurality of RFID receivers for receiving RFID tag data, a plurality of RFID tag interrogators for transmitting RF interrogation signals for interrogating RFID tags, and a controller for providing to at least one interrogator, at least one receiver, and at least one tag, a parameter associated with operational characteristics of the interrogator, the receiver, and the tag, respectively. The interrogator, the receiver, and the tag are operative, in response to receipt of the respective parameter, to modify its operational characteristics in accordance with the respective parameter, thereby avoiding interference at the receivers and the tags.
Owner:QUAKE GLOBAL +1
Method and system for detecting objects external to a vehicle
InactiveUS20050134440A1Avoid collisionAvoid and minimize effectVehicle seatsInstruments for road network navigationRange gateLaser beams
Method and system for obtaining information about objects in the environment outside of and around a vehicle and preventing collisions involving the vehicle includes directing a laser beam from the vehicle into the environment, receiving from an object in the path of the laser beam a reflection of the laser beam at a location on the vehicle, and analyzing the received laser beam reflections to obtain information about the object from which the laser beam is being reflected. Analysis of the laser beam reflections preferably entails range gating the received laser beam reflections to limit analysis of the received laser beam reflections to only those received from an object within a defined (distance) range such that objects at distances within the range are isolated from surrounding objects.
Owner:AMERICAN VEHICULAR SCI
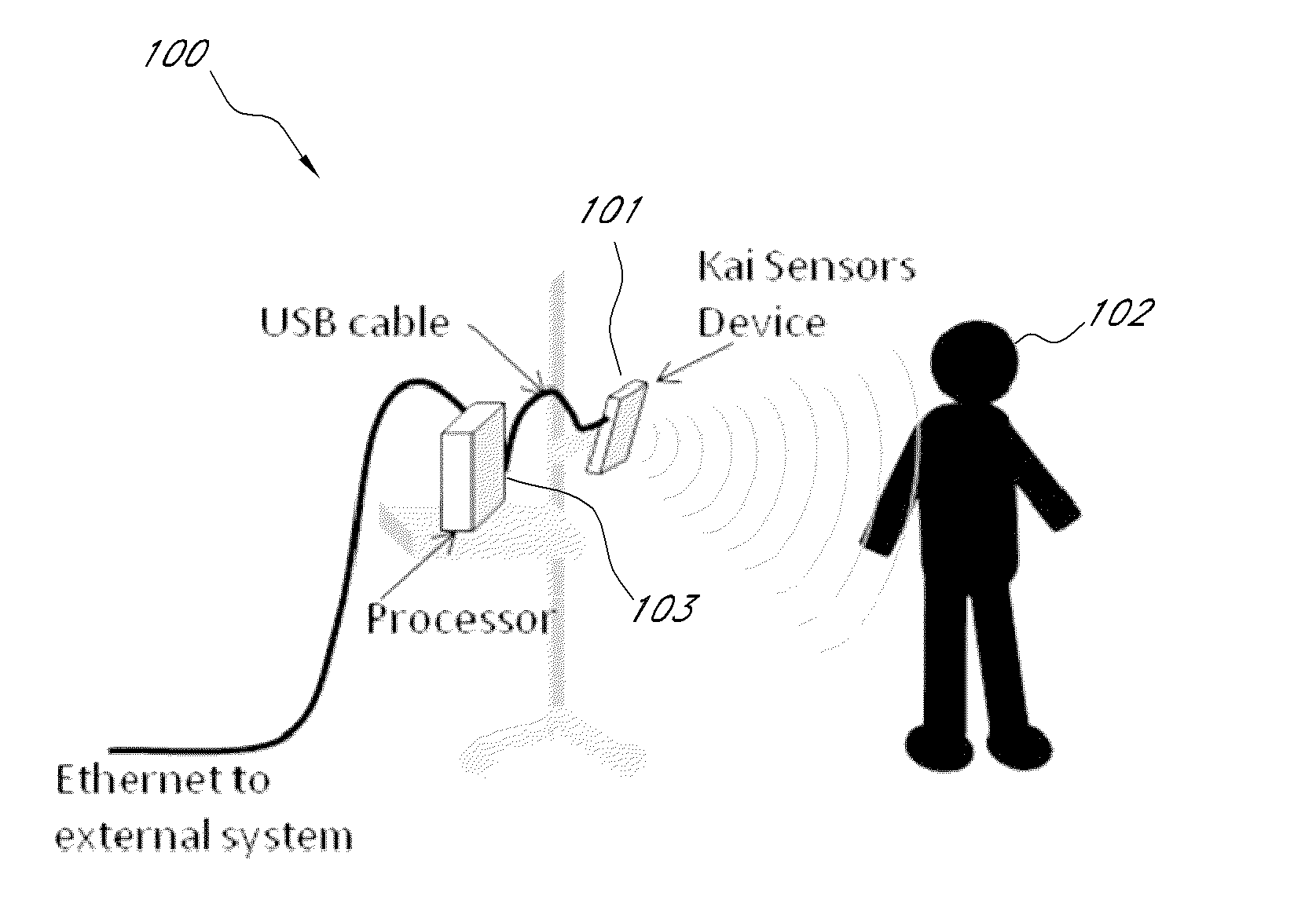
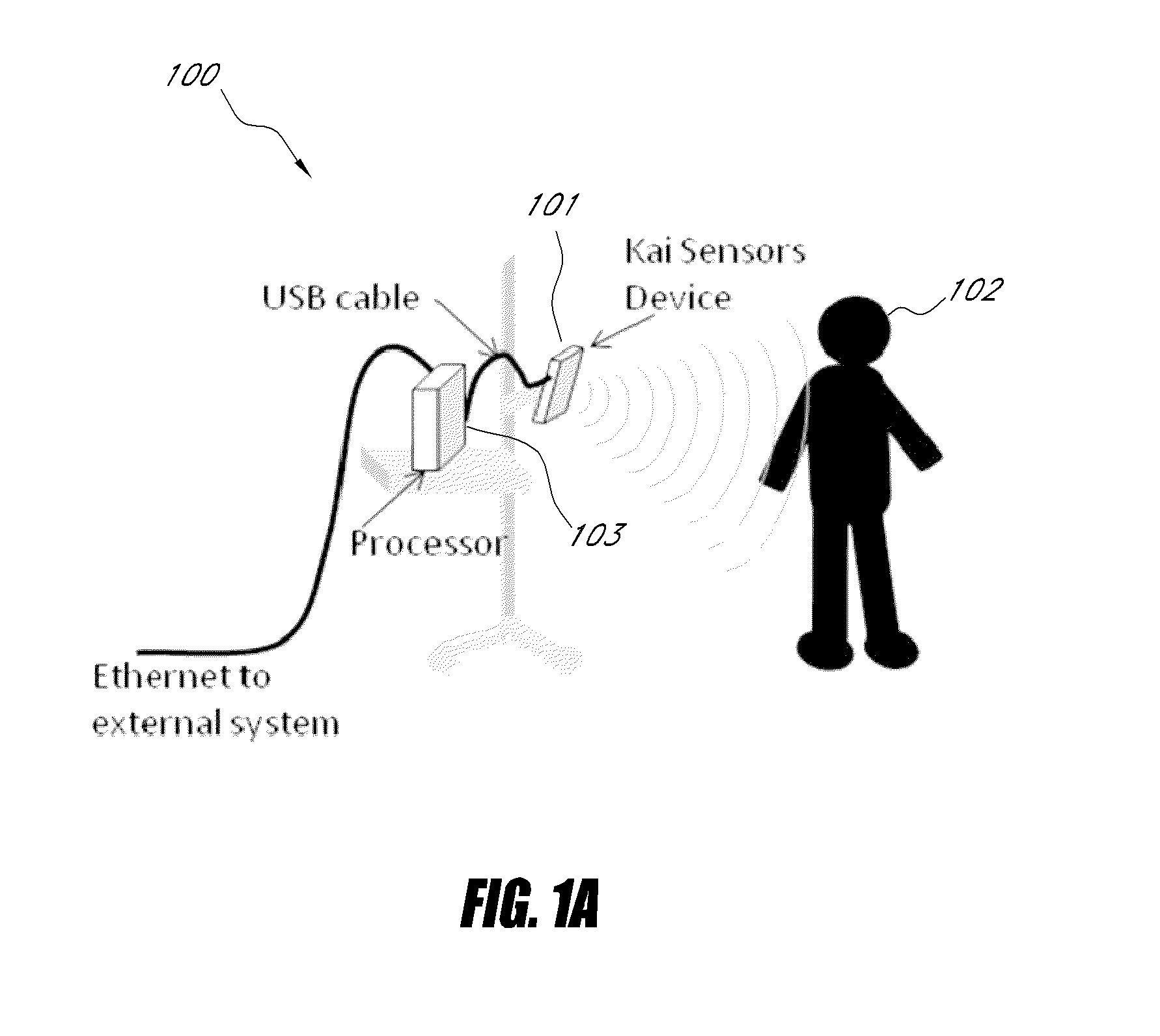
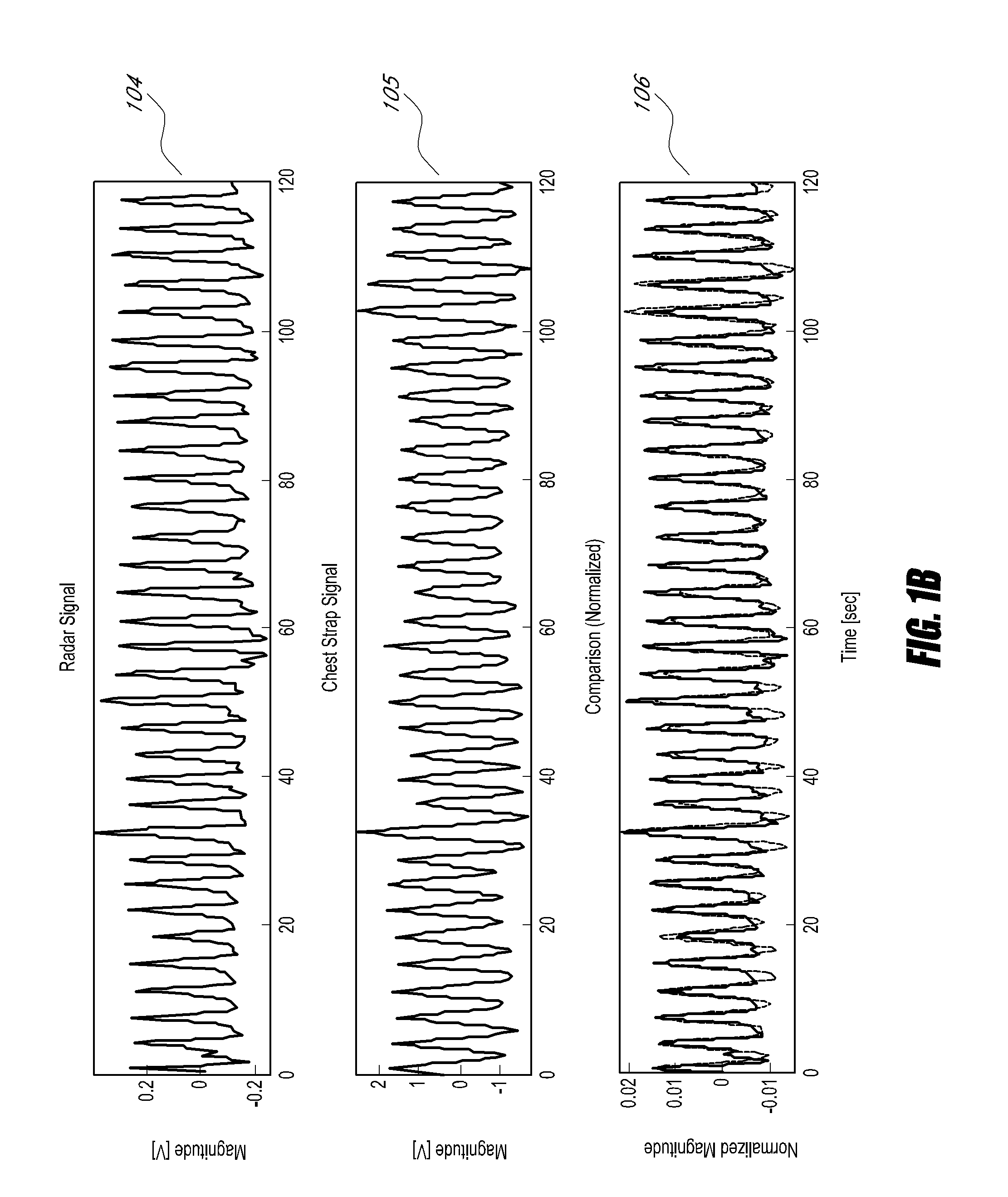
Non-contact physiologic motion sensors and methods for use
Owner:KAI MEDICAL
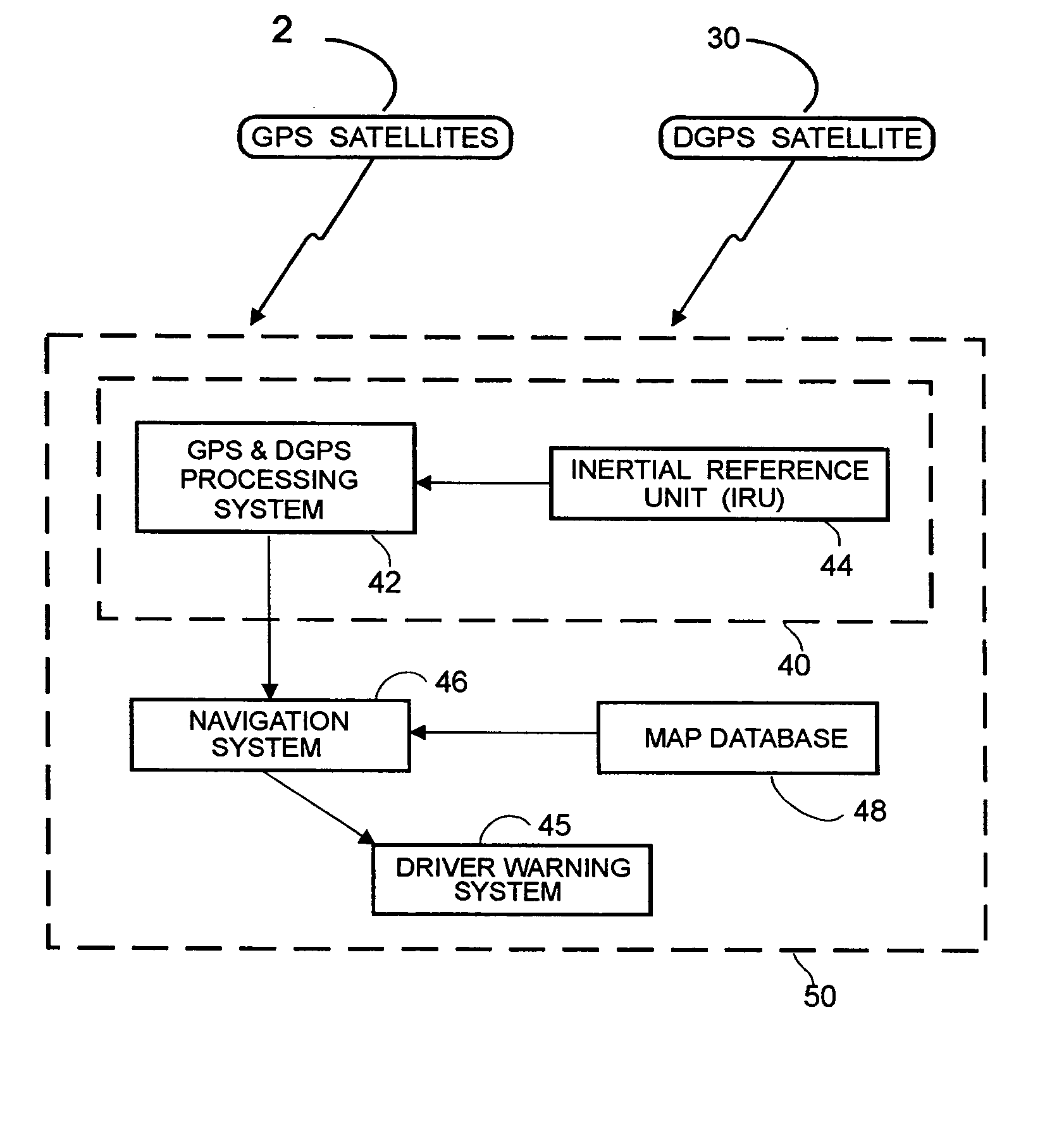
Method and system for controlling a vehicle
Apparatus for sensing a potential rollover situation involving a vehicle including an inertial reference unit including three accelerometers and three gyroscopes which provide data on vehicle motion, vehicle control devices arranged to affect control of the vehicle and a processor coupled to the inertial reference unit and the vehicle control devices. The processor includes an algorithm arranged to receive data from the inertial reference unit and control the vehicle control devices to apply the throttle, brakes and steering to prevent the rollover, optionally in consideration of the position of the vehicle as provided by a map database or location determining system.
Owner:AMERICAN VEHICULAR SCI
Intelligent station using multiple RF antennae and inventory control system and method incorporating same
ActiveUS7084769B2Boost RF signal strengthAntenna supports/mountingsCash registersControl systemEngineering
An inventory control system and method that tracks inventories of items with RFID tags, includes a reader unit and an intelligent station that tracks RFID tags to determine item information of items to be inventoried. The reader unit transmits and receives RF signals. The intelligent station includes a first RF antenna connected to the reader unit by a first transmission cable through a first switch, and one or more additional RF antennae connected to the reader unit by the same first transmission cable through additional switches. An inventory control processing unit receives item information from the intelligent stations to update inventory information regarding the items to be inventoried.
Owner:SENSORMATIC ELECTRONICS CORP
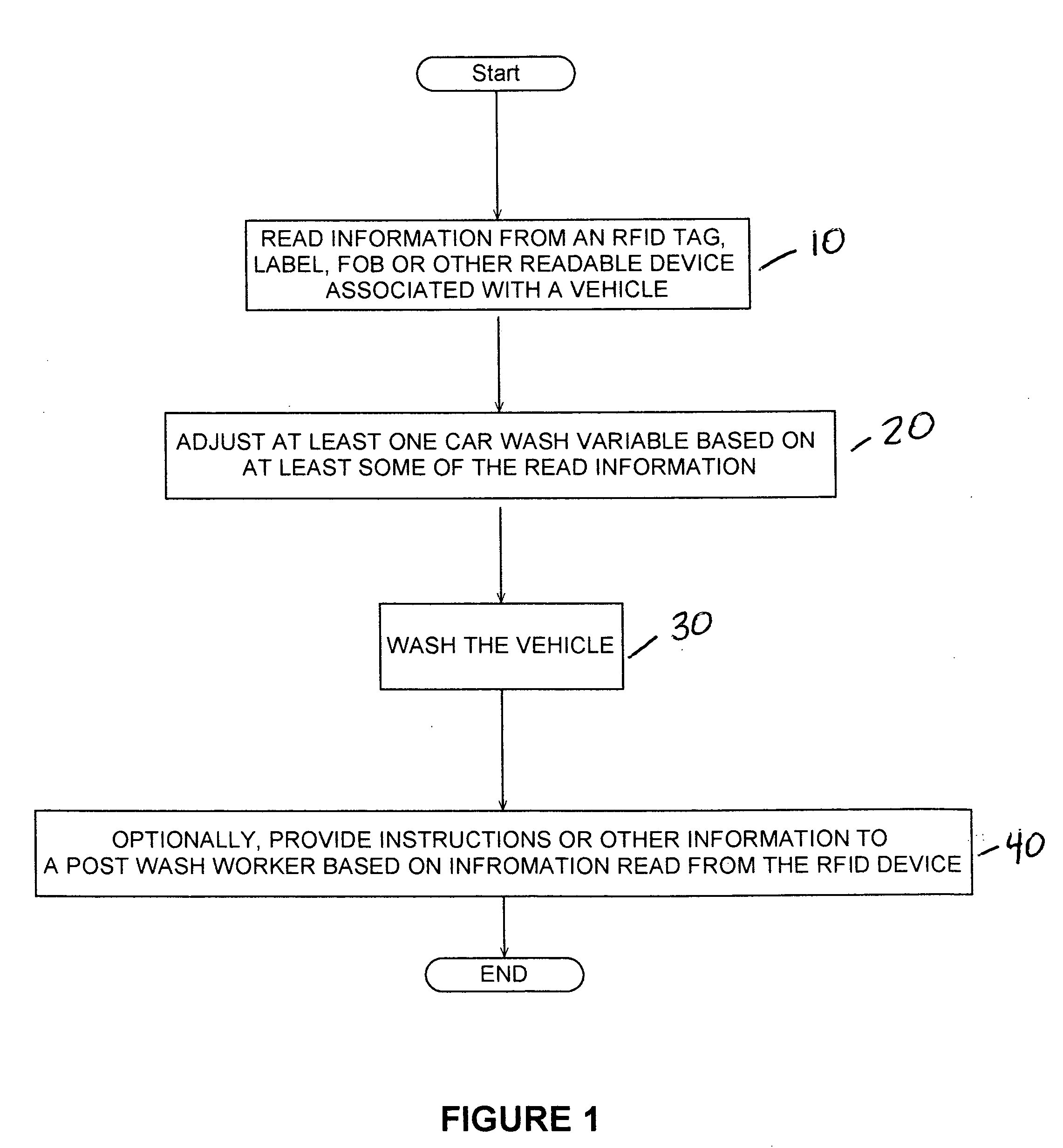
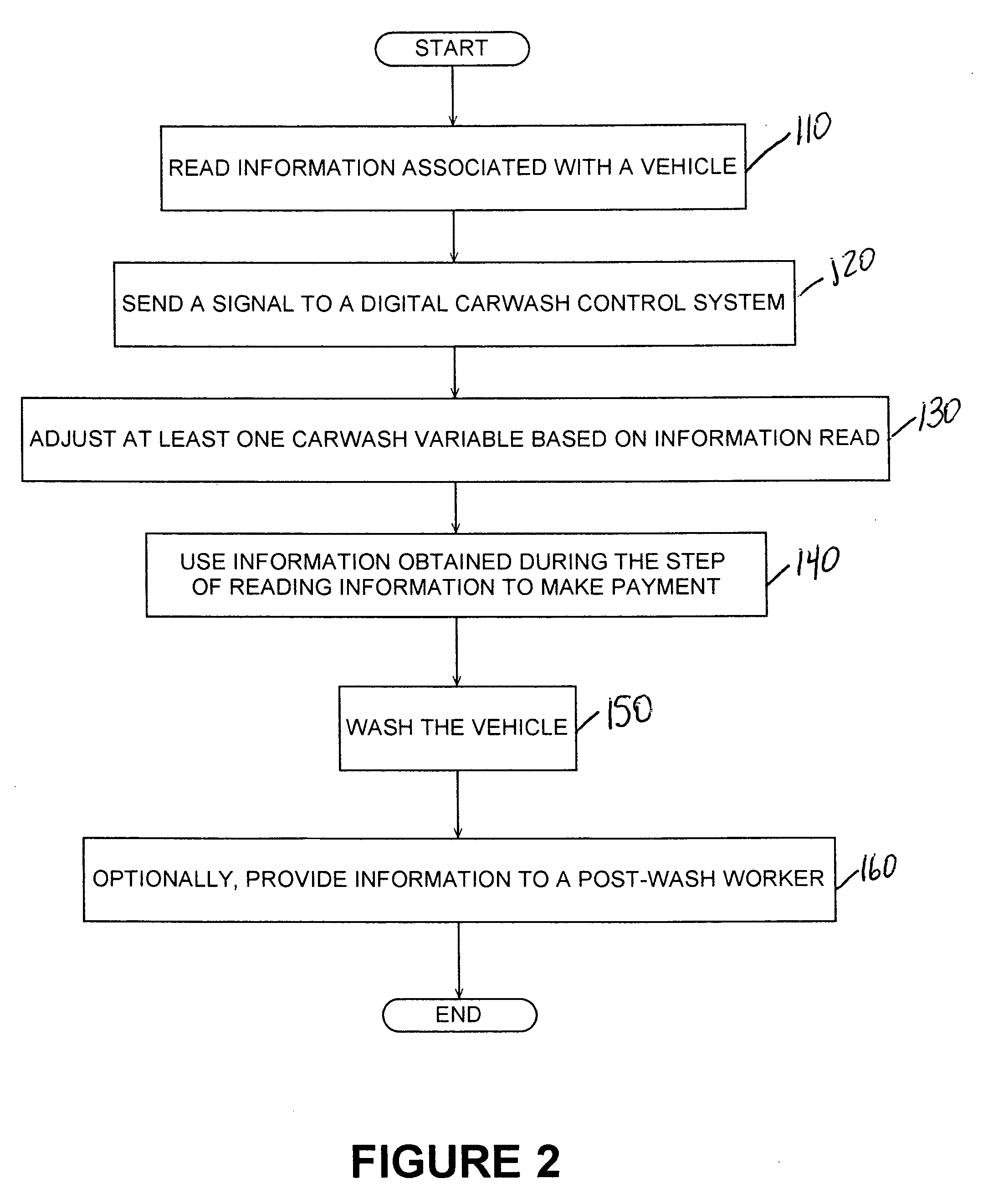
RFID applications
Applications of RFID technology include: RFID Tags on Automobiles in Parking Garages; RFID w / Toothbrushes; RFID Tags For Laundry Settings; RFID Tags Or Labels to Find a Mate; RFID To Identify The Value Of Coins; RFID Tags In The Doctors Office; RFID Tags Or Labels In Game Arcades; RFID With Prisoners; RFID Tags To Identify Soldiers; RFID Labels As Tags To Label Particular Components Of Aircraft or Other Structures; Car, Snowmobile, Boat, Etc. Ignition That Won't Start Without RFID Card; Car seats with RFID reader and memory; Air bags that adjust based on information on RFID; Car that keeps track of GPS info and knows whos driving based on RFID; RFID Smart Closet; Method of taking attendance; RFID on networked desks to monitor the location of individuals; Personal computer reads RFID to log you in and take you to favorite web page, load favorites list, etc.; RFID labels on Files; RFID address label versions of all label and sheet inventions; RFID sports tickets; Combination function invitation and RFID chip to allow admittance; Roll of tape with RFID built in; Schoolbus reads which kids getting on, keeps record; RFID on each car wheel; RFID key to operate common-area laundry; RFID to automatically adjust weights / treadmill settings in gym; RFID w / clothes measurements, save shelf space at store, get proper size; RFID keyring w / car information; Keep track of who's driving around neighborhood; RFID dental implant; RFID Thumbtack; RFID Doorstop; RFID identification of boats or ships at docks; RFID on cups w / specifics of favorite coffee drinks; RFID on bridges with RFID tanks on top of cars, to detect speeding; RFID on studs in a wall and RFID reader that acts as a stud finder; RFID tags or labels inside tires; RFID cards supplied with newspapers or magazines; RFID card that lights up a when the user reaches a particular location; RFID sports ticket w / automatic map generation to seat; RFID card to tell school cafeteria what lunch to prepare for particular student; student desk with slot to receive RFID card, desks on networks together, Central computing system can tell where any particular student is sitting at any given moment within the school; RFID readers on outdoor play equipment; Authentication of Expensive Items With RFID; Paintings or other art work with RFID label to be used to verify the number in a limited series; RFID on sports helmet or uniform; RFID chips in paint; RFID cards issued to airline passengers to identify type of drinks and meals for a particular passenger, etc.; Greeting Cards With RFID; Decorative Tiles With RFID Tags; RFID in Car Washes; and Adaptive Advertising Based on RFID Information.
Owner:HANSEN SCOTT ROBERT
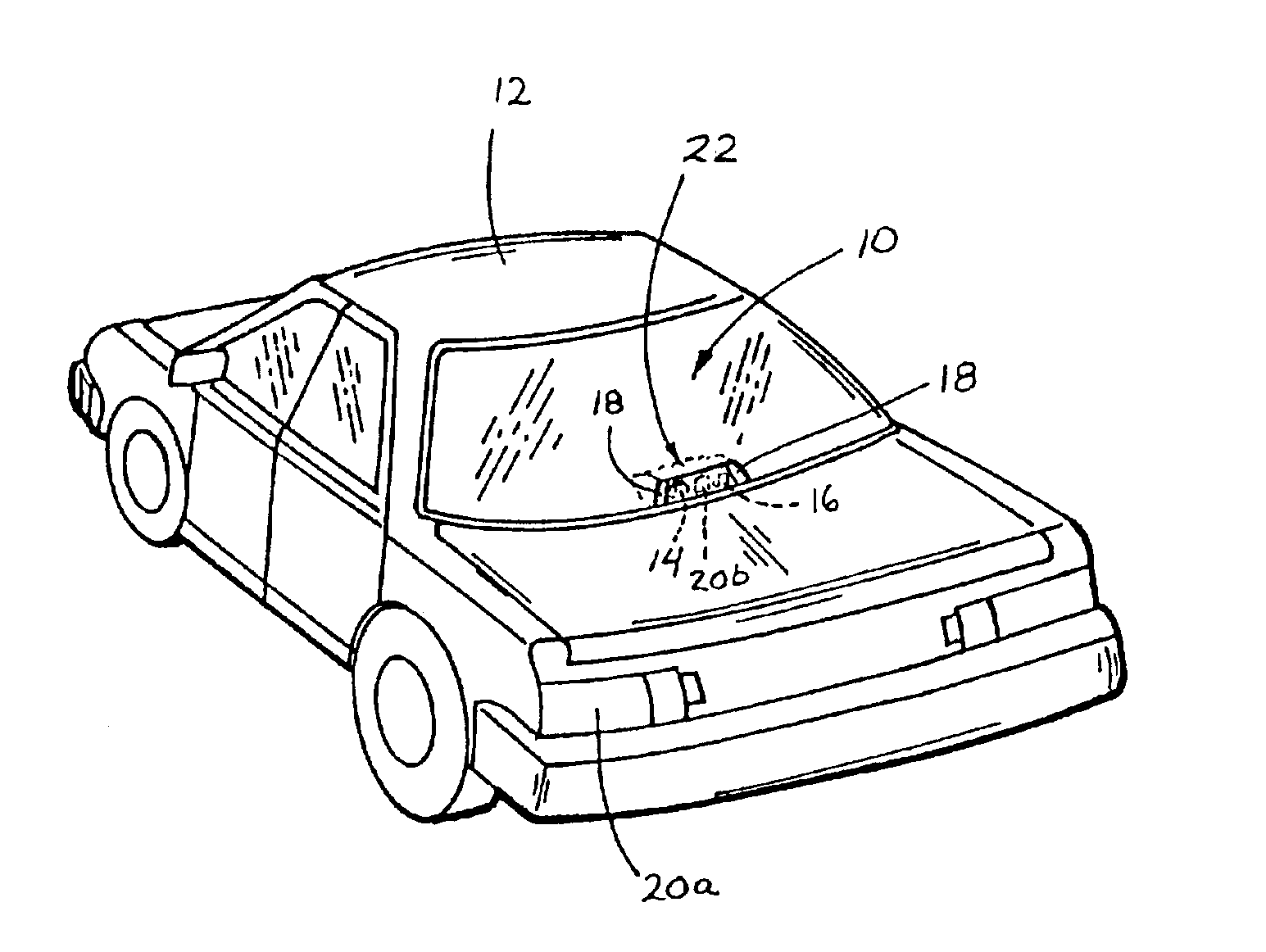
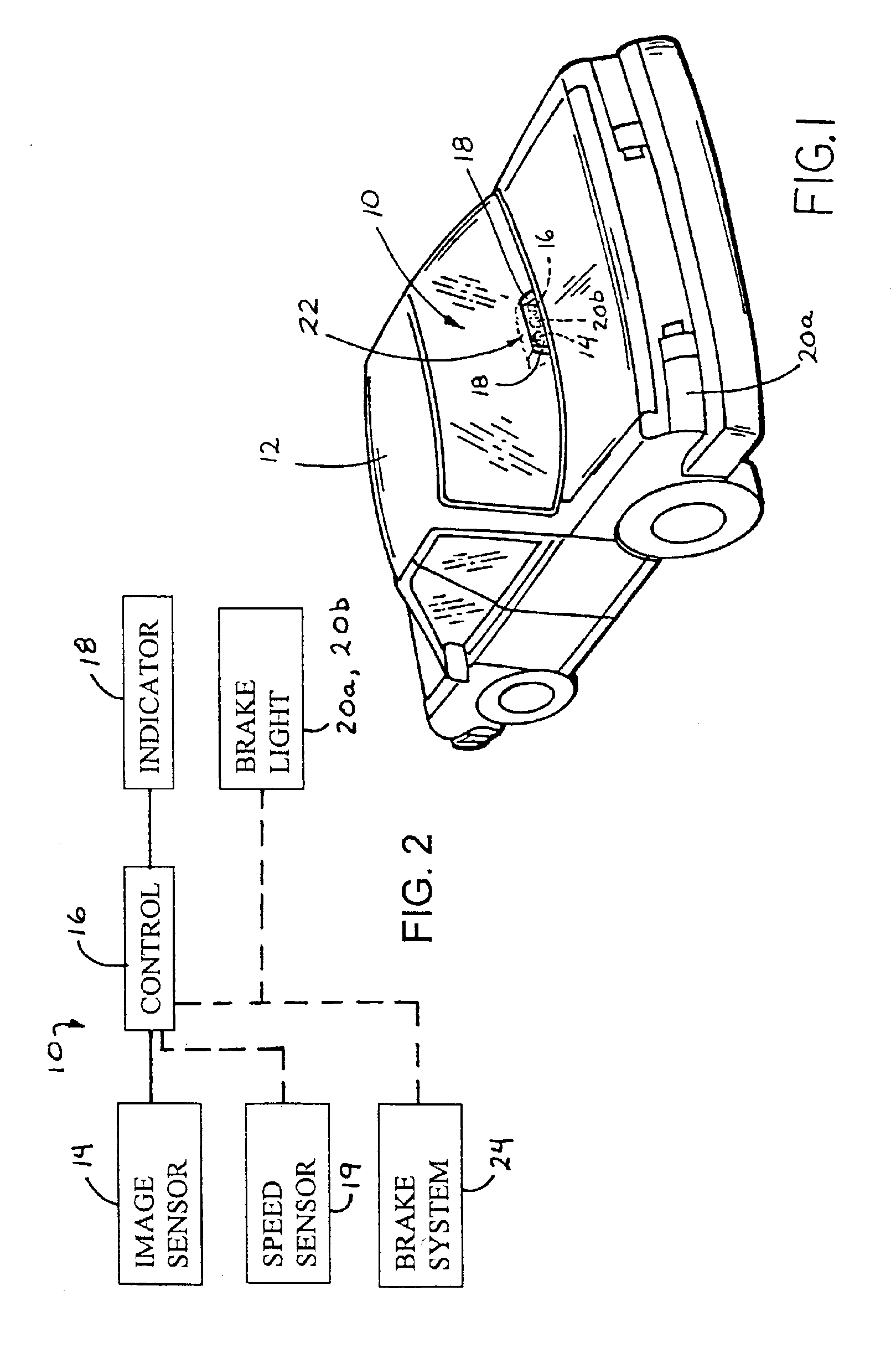
Driving separation distance indicator
ActiveUS7123168B2Digital data processing detailsRoad vehicles traffic controlImage captureAutomotive engineering
A driving separation indication system for a vehicle includes an imaging sensor, a control and at least one indicator. The control is operable to process an image captured by the imaging sensor representative of a scene occurring exteriorly of the subject vehicle and to detect another vehicle via processing of the image. The control is operable to determine a threshold interspacing distance in response to a speed of the subject vehicle, and is operable to determine a distance from the subject vehicle to the detected other vehicle. The control is operable to at least occasionally actuate the indicator in response to the distance from the subject vehicle to the other vehicle being less than or equal to the threshold interspacing distance. The control may generally continuously determine the speed of the vehicle and the threshold interspacing distance to provide an appropriate threshold interspacing distance.
Owner:DONNELLY CORP
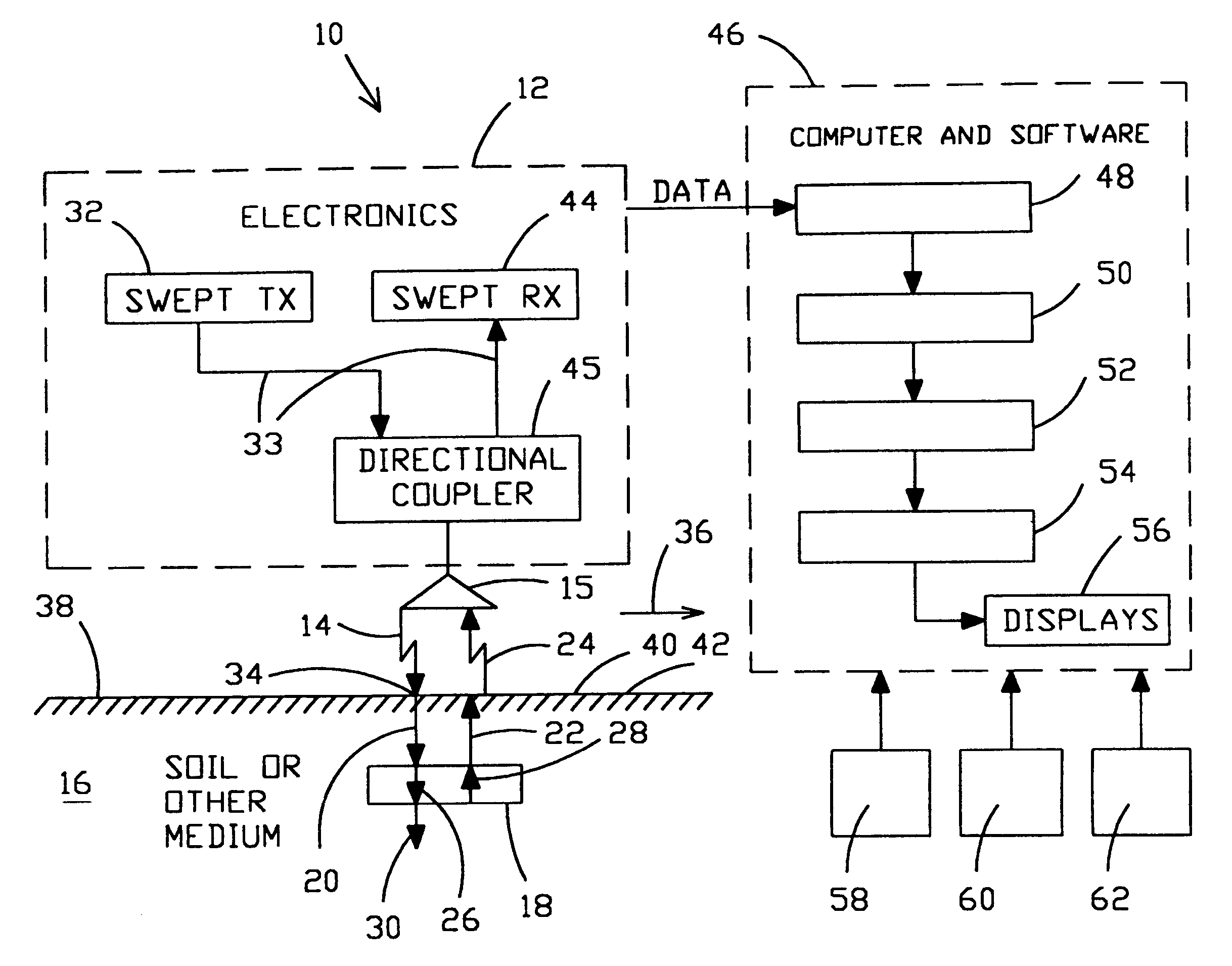
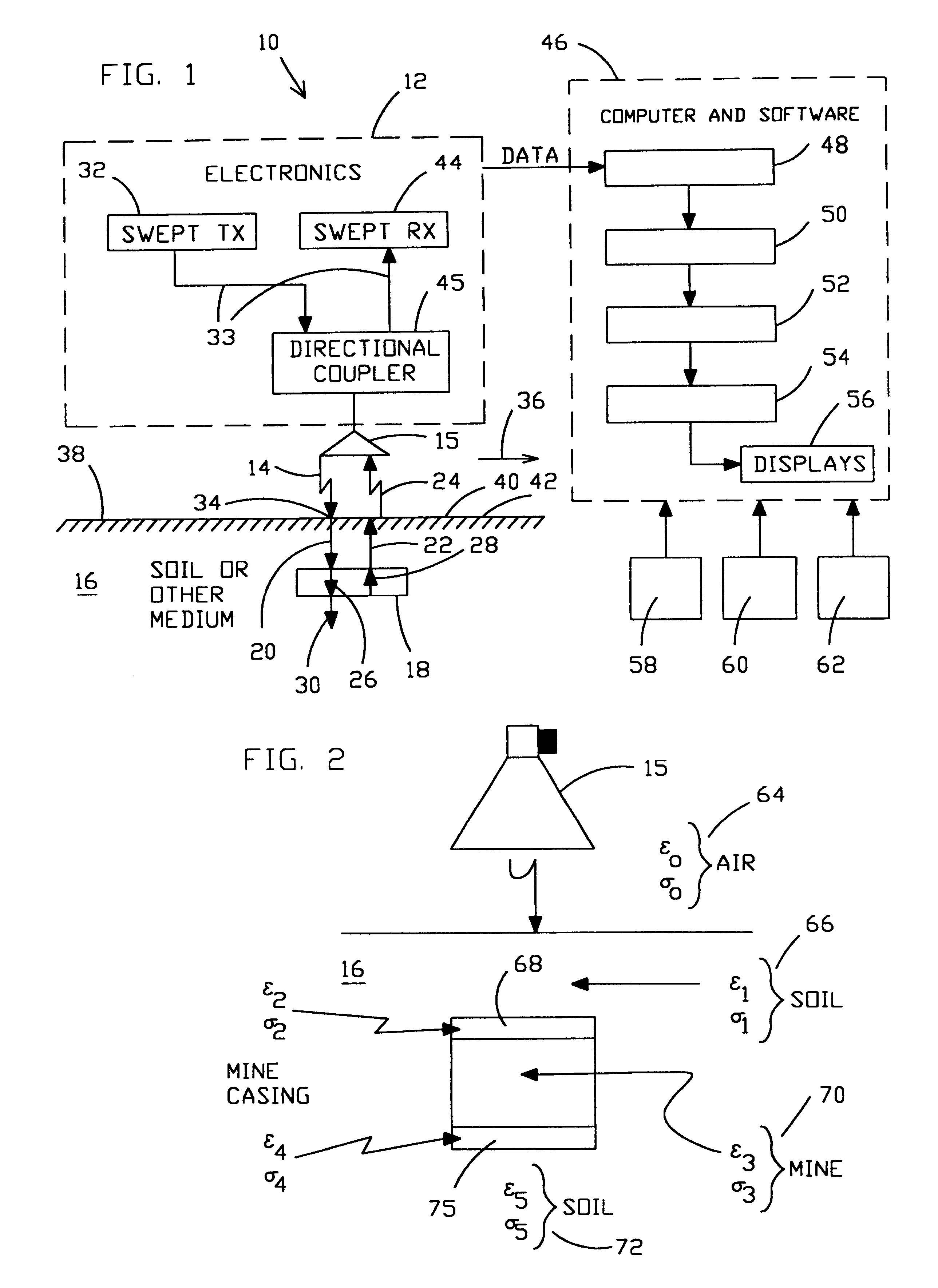
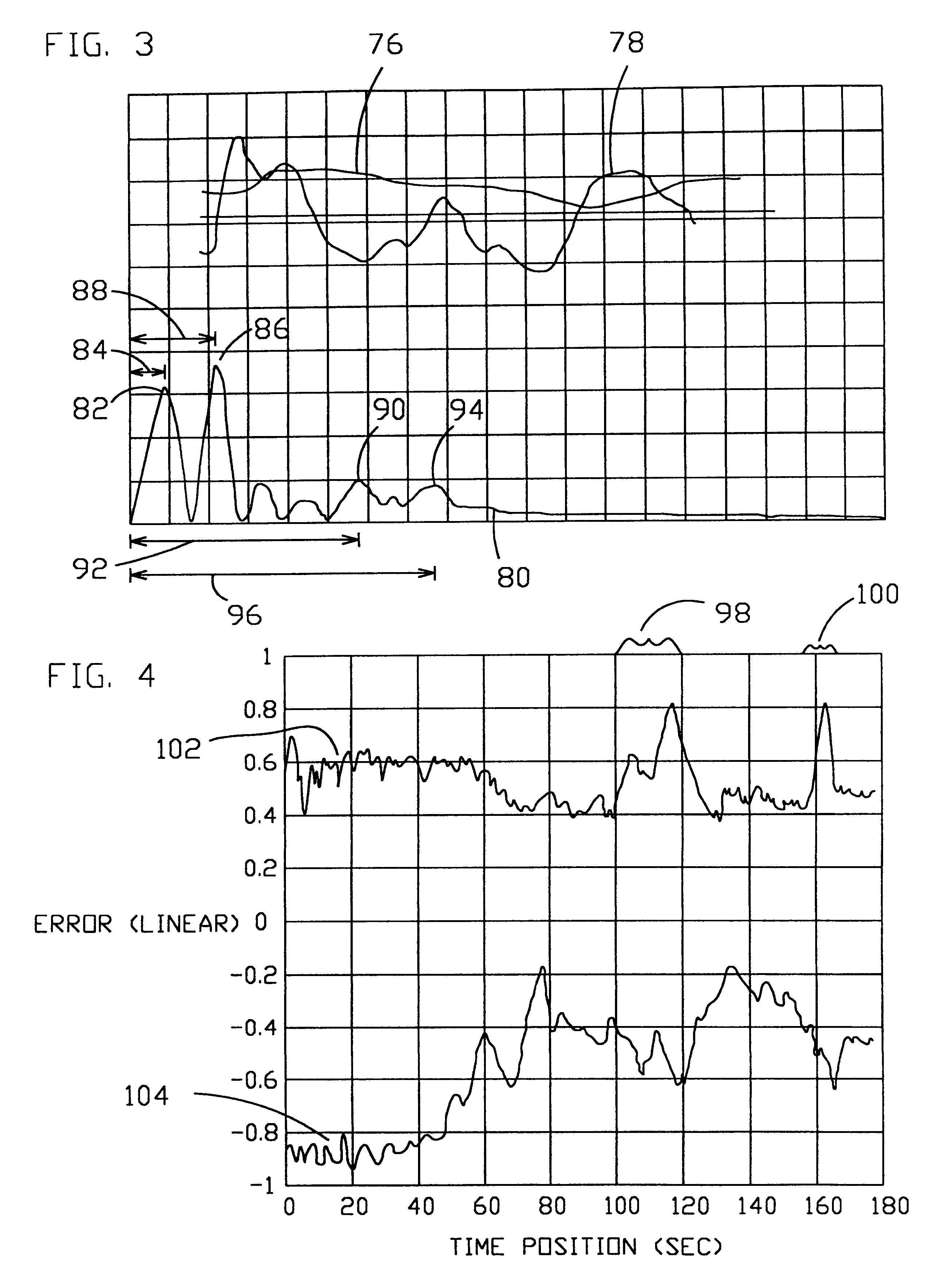
Method for locating a concealed object
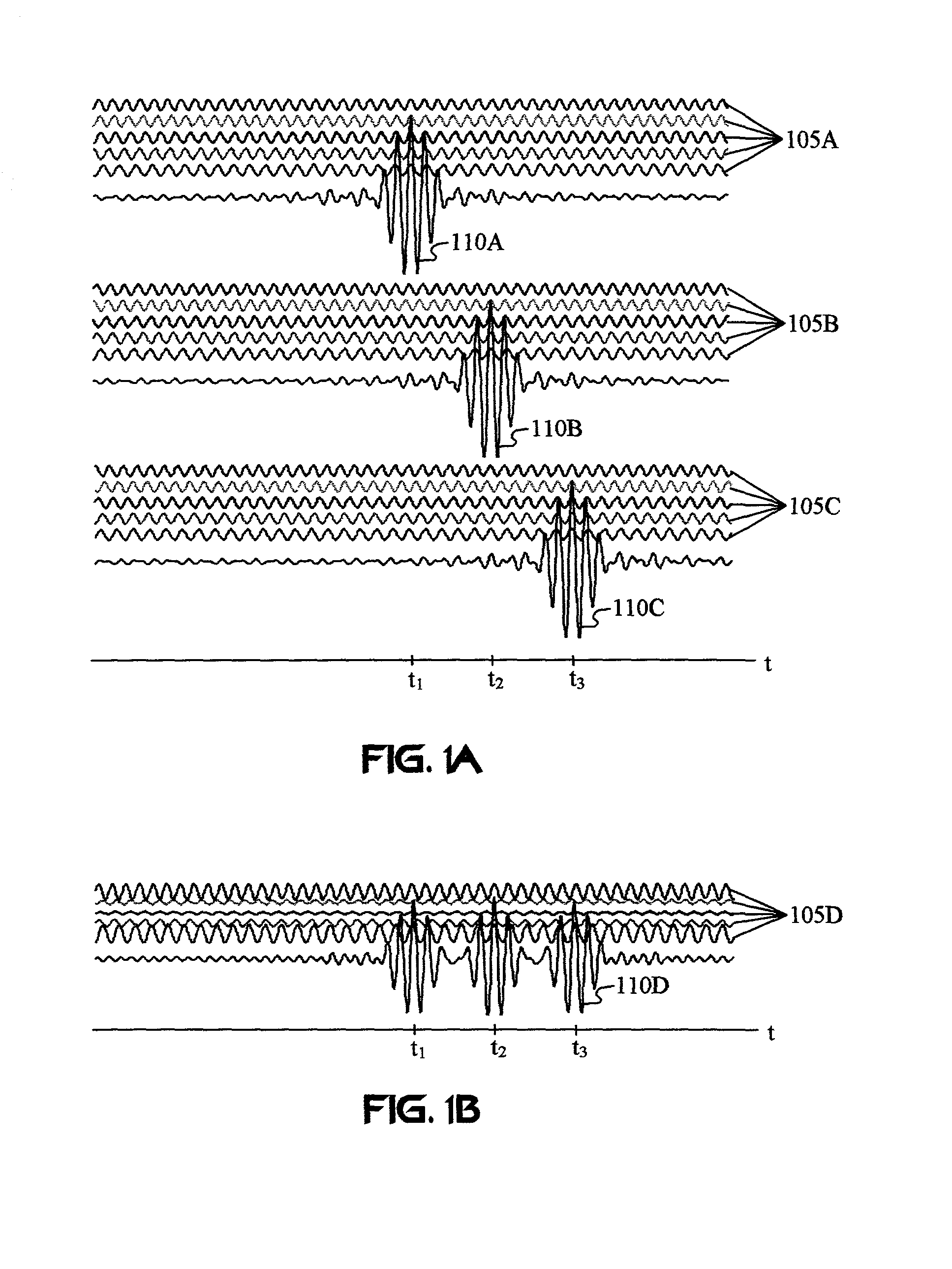
InactiveUS6501414B2Accurate detectionEnhance and preserve resolutionDefence devicesDetection using electromagnetic wavesTime delaysComplex filter
Apparatus and methods are disclosed for detecting anomalies in microwave penetrable material that may be used for locating plastic mines or pipes underneath the ground. A transmitter is positioned at a plurality of different positions above the ground. A microwave signal is transmitted that is stepped over a plurality of frequencies. At each position, a plurality of reflections are received corresponding to each of the plurality of frequencies that were transmitted. A complex target vector may be produced at each position that contains complex values corresponding to magnitude, phase, and time delay for each of the plurality of reflections received at that location. A complex reference data vector may be produced, either based on predetermined values or based on data from the received plurality of reflections. A comparison is made between the complex target vector and the complex reference data vector to produce a channel vector. In one embodiment, an operator may be applied to the channel vector such as a complex filter matrix or to add a complex conjugate. A response signal is produced and anomalies are detected by variations in the response signal with respect to the plurality of positions.
Owner:NASA
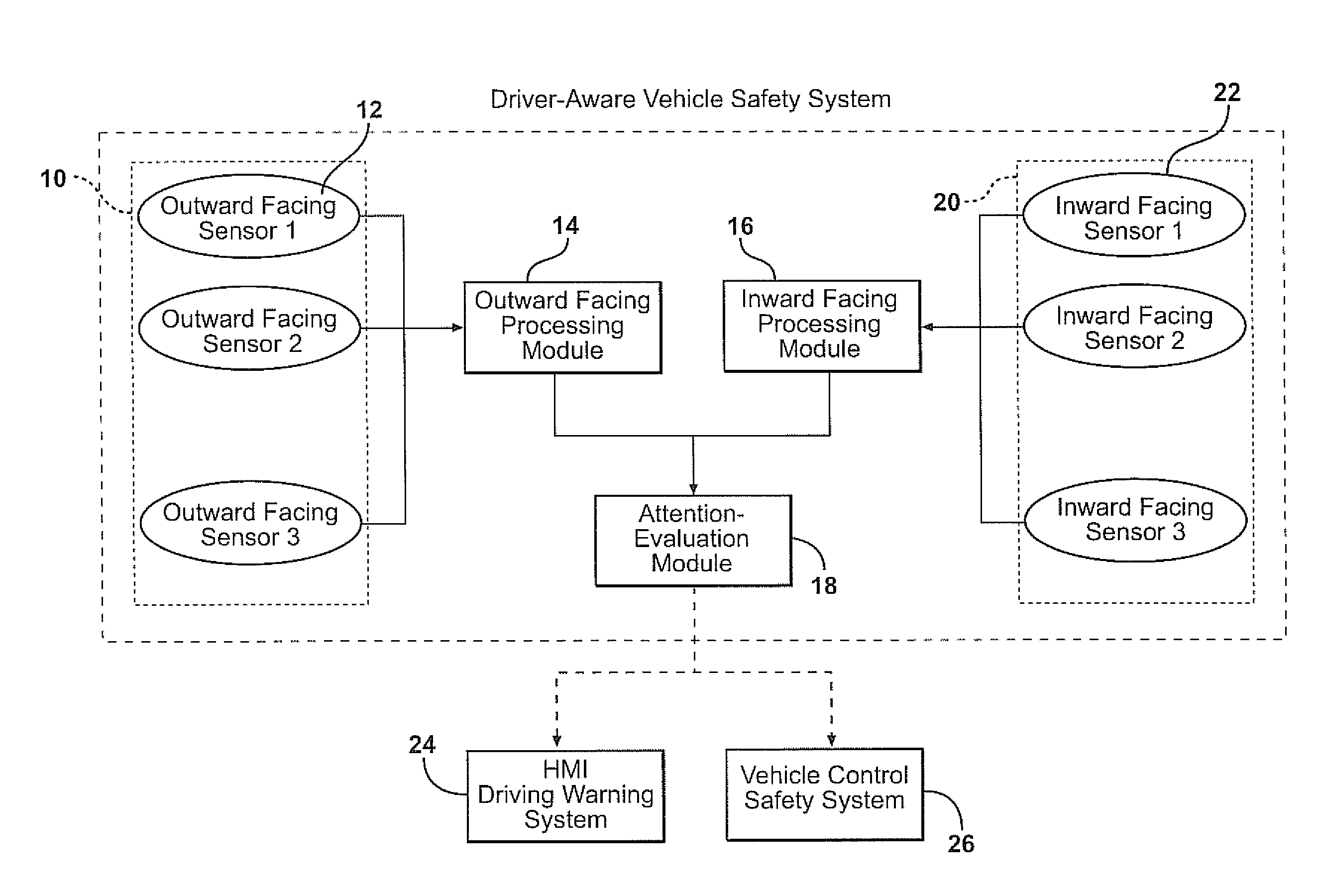
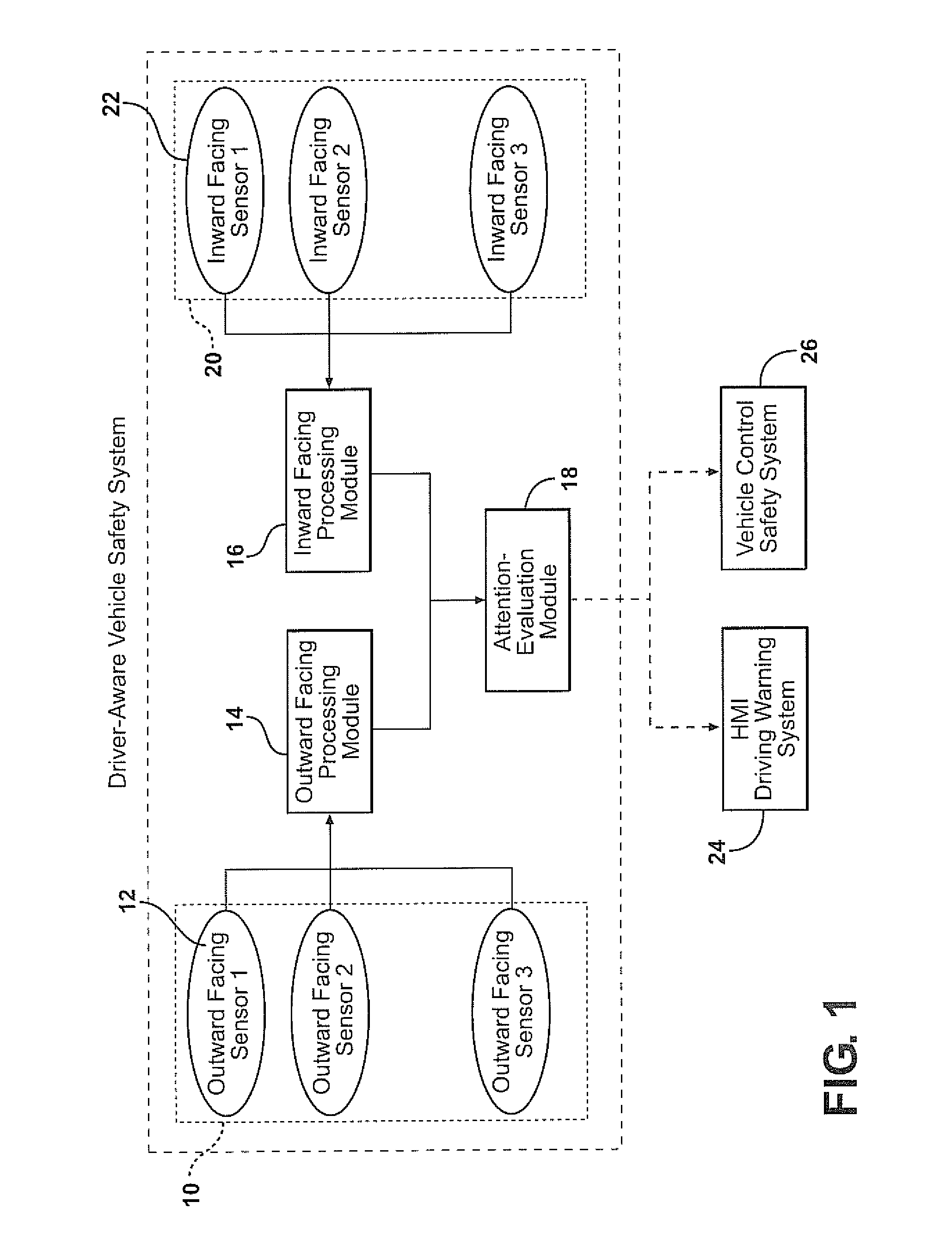
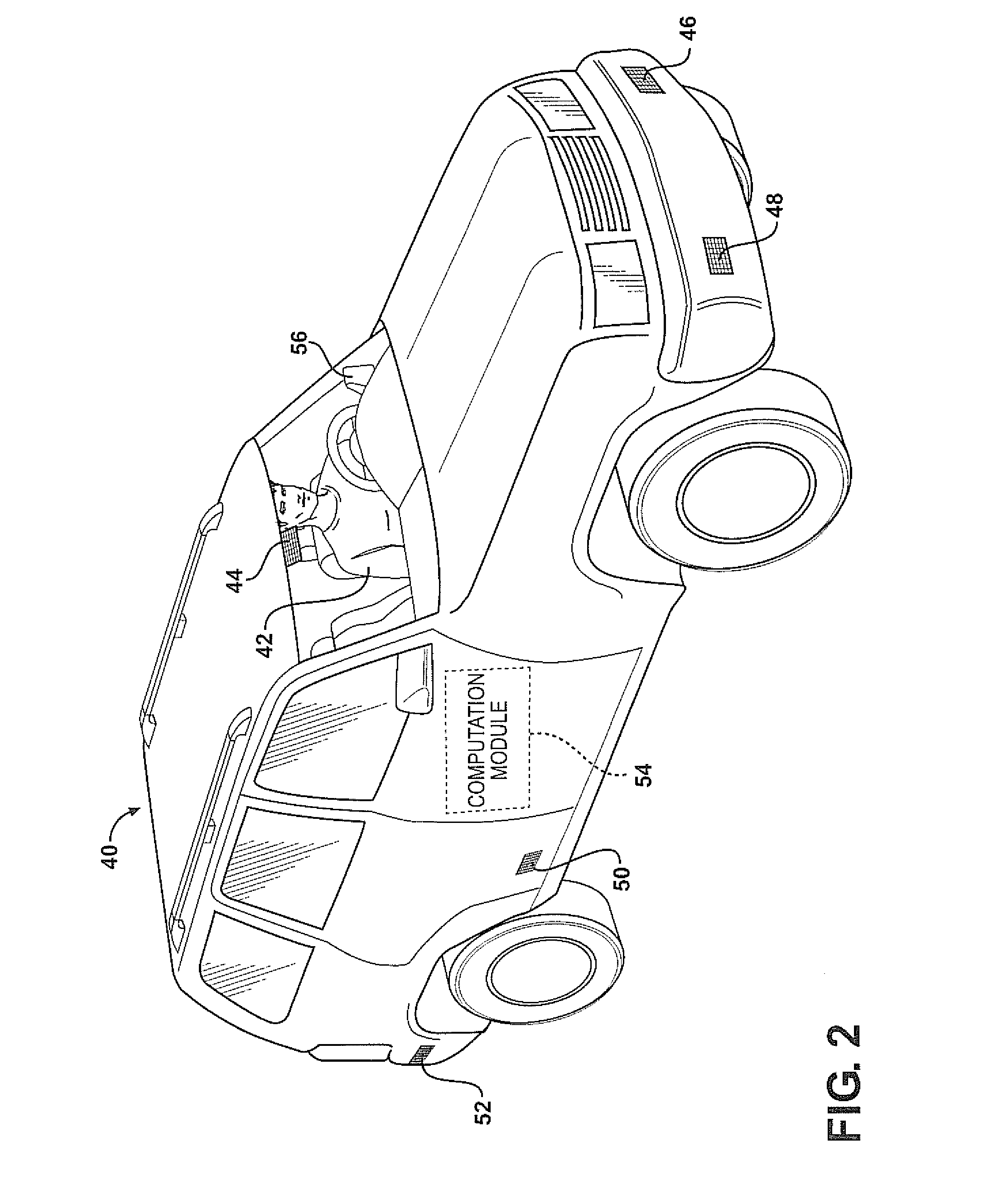
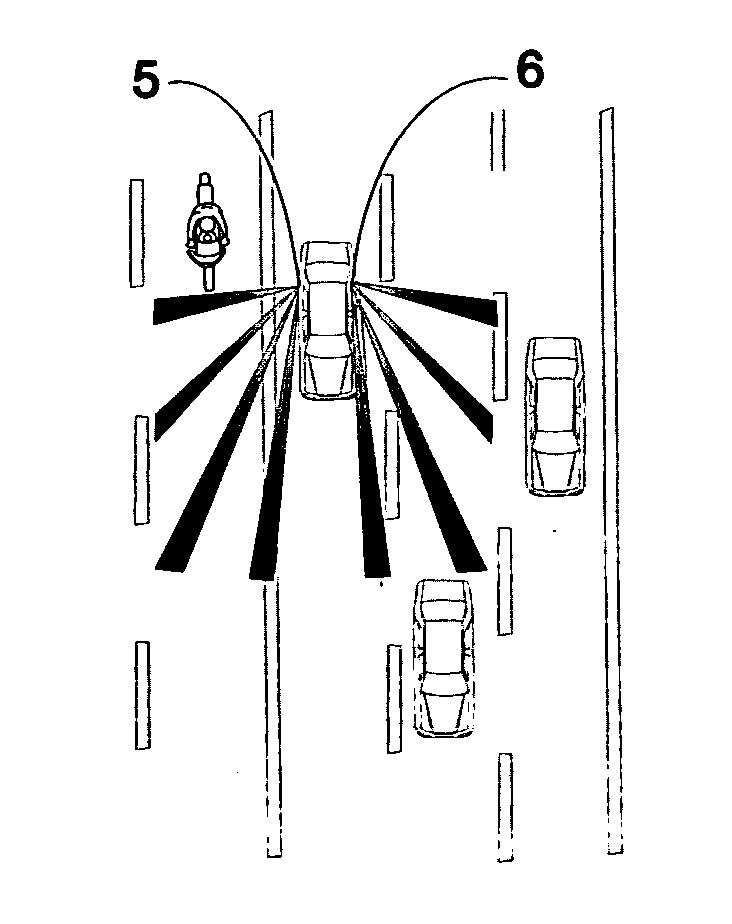
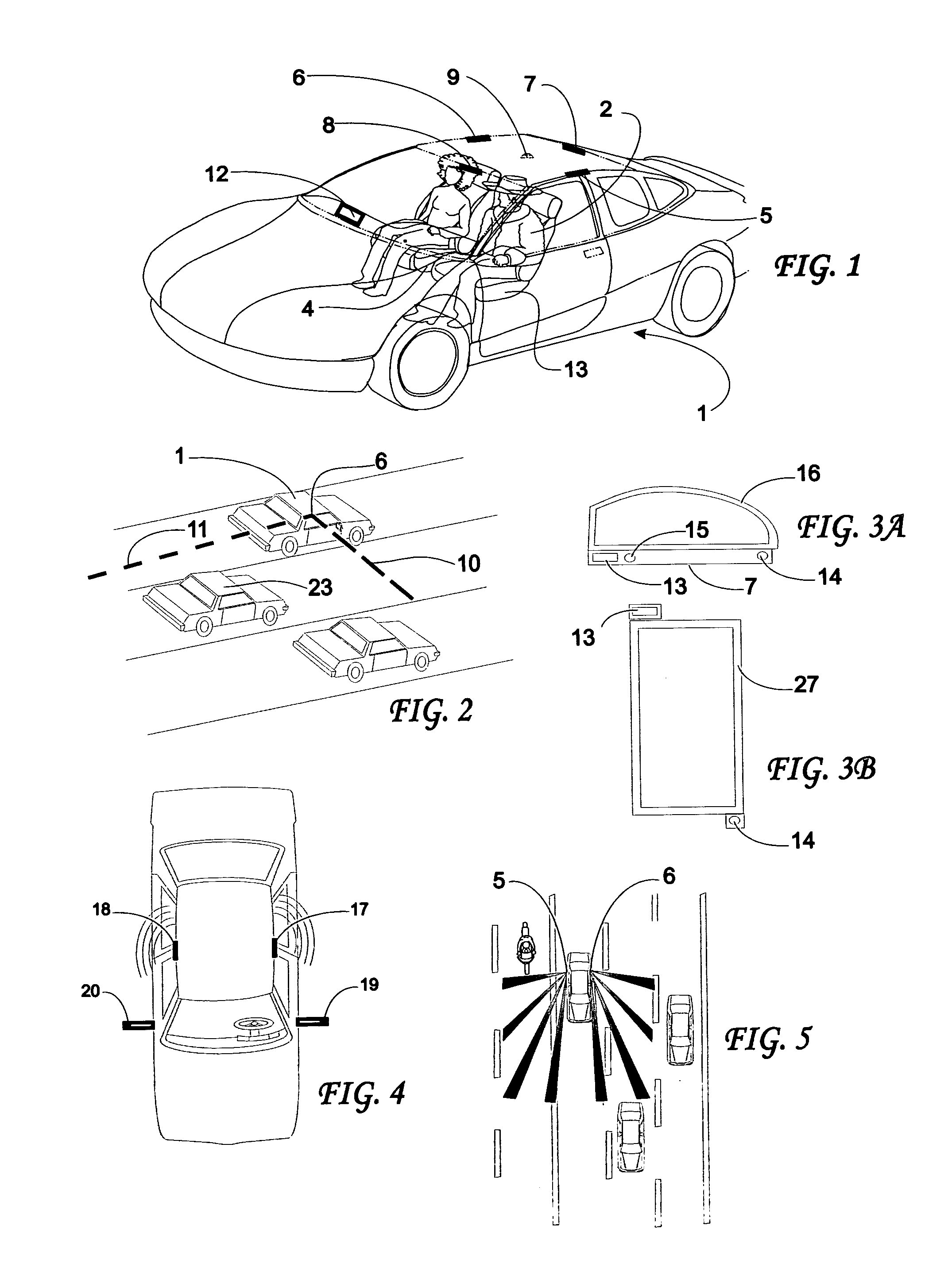
Combining driver and environment sensing for vehicular safety systems
ActiveUS20110169625A1Improve securityIncrease awarenessAnti-collision systemsCharacter and pattern recognitionDriver/operatorEngineering
An apparatus for assisting safe operation of a vehicle includes an environment sensor system detecting hazards within the vehicle environment, a driver monitor providing driver awareness data (such as a gaze track), and an attention-evaluation module identifying hazards as sufficiently or insufficiently sensed by the driver by comparing the hazard data and the gaze track. An alert signal relating to the unperceived hazards can be provided.
Owner:TOYOTA MOTOR CO LTD
Sensor assemblies
InactiveUS7089099B2Low costPrecise positioningVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesRadio frequency signalPhysical quantity
Sensor assembly capable of obtaining and providing a measurement of a physical quantity, e.g., measurement of temperature and / or pressure of a vehicular tire, includes an antenna capable of receiving a radio frequency signal, a radio frequency identification (RFID) device coupled to the antenna, a sensor coupled to the RFID device arranged to generate a measurement of the physical quantity or quantities, and a switch coupled to the RFID device and arranged to connect or disconnect the sensor from a circuit with the antenna dependent on whether the antenna receives a particular signal associated with the RFID device. When the antenna receives the particular signal associated with the RFID device, the RFID device causes the switch to close and connect the sensor in the circuit with the antenna to enable the measurement generated by the sensor to be directed to and transmitted by the antenna.
Owner:AMERICAN VEHICULAR SCI
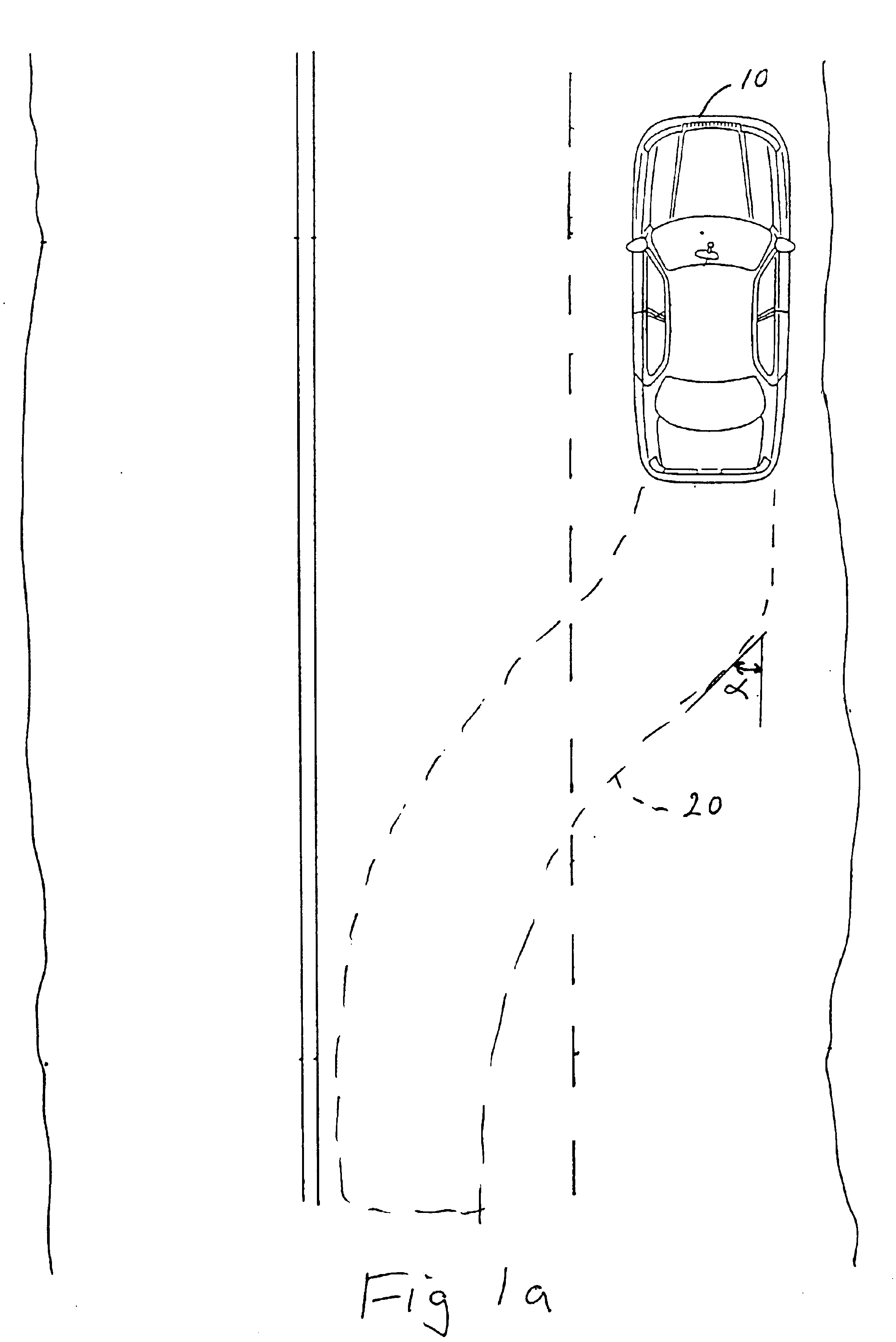
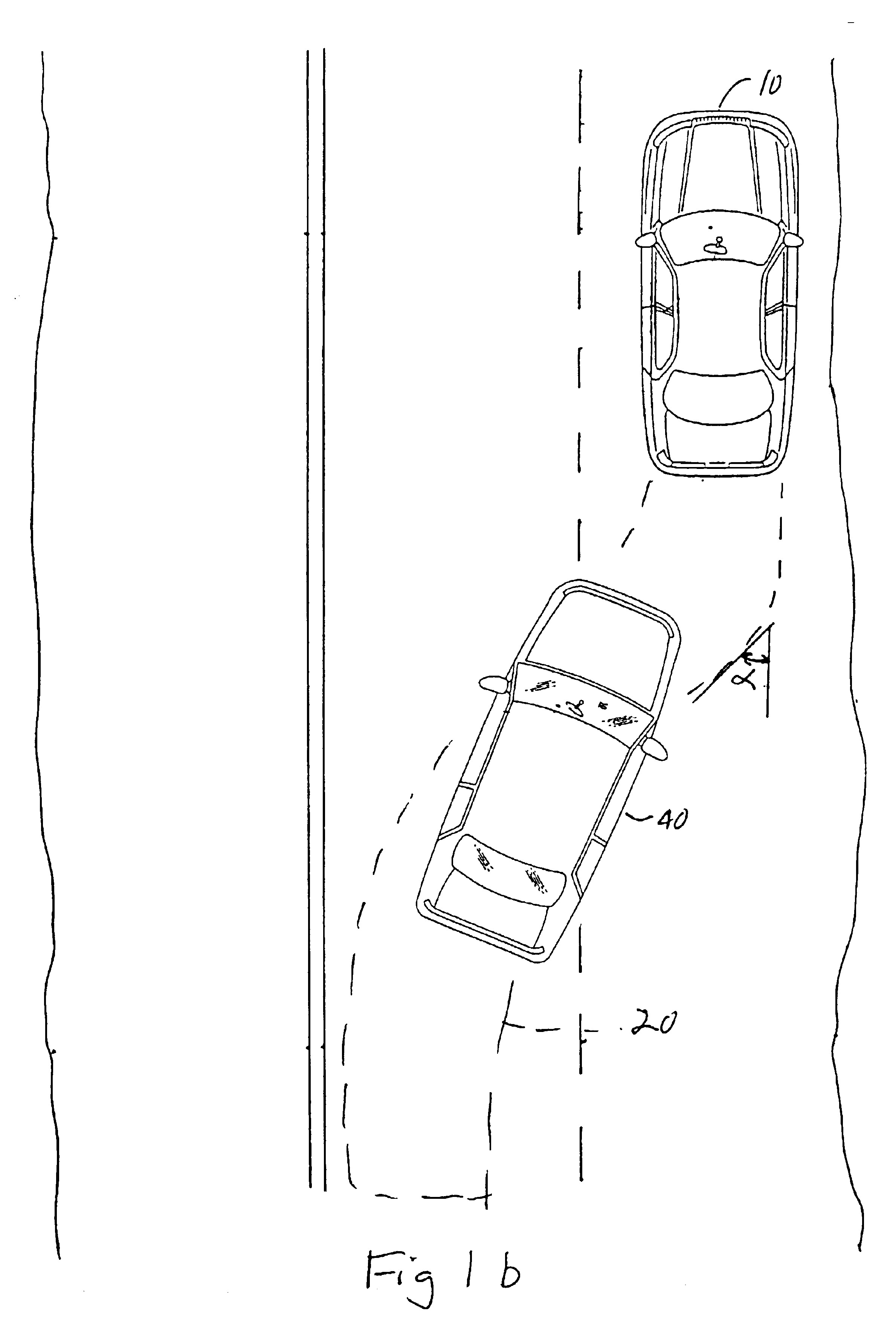
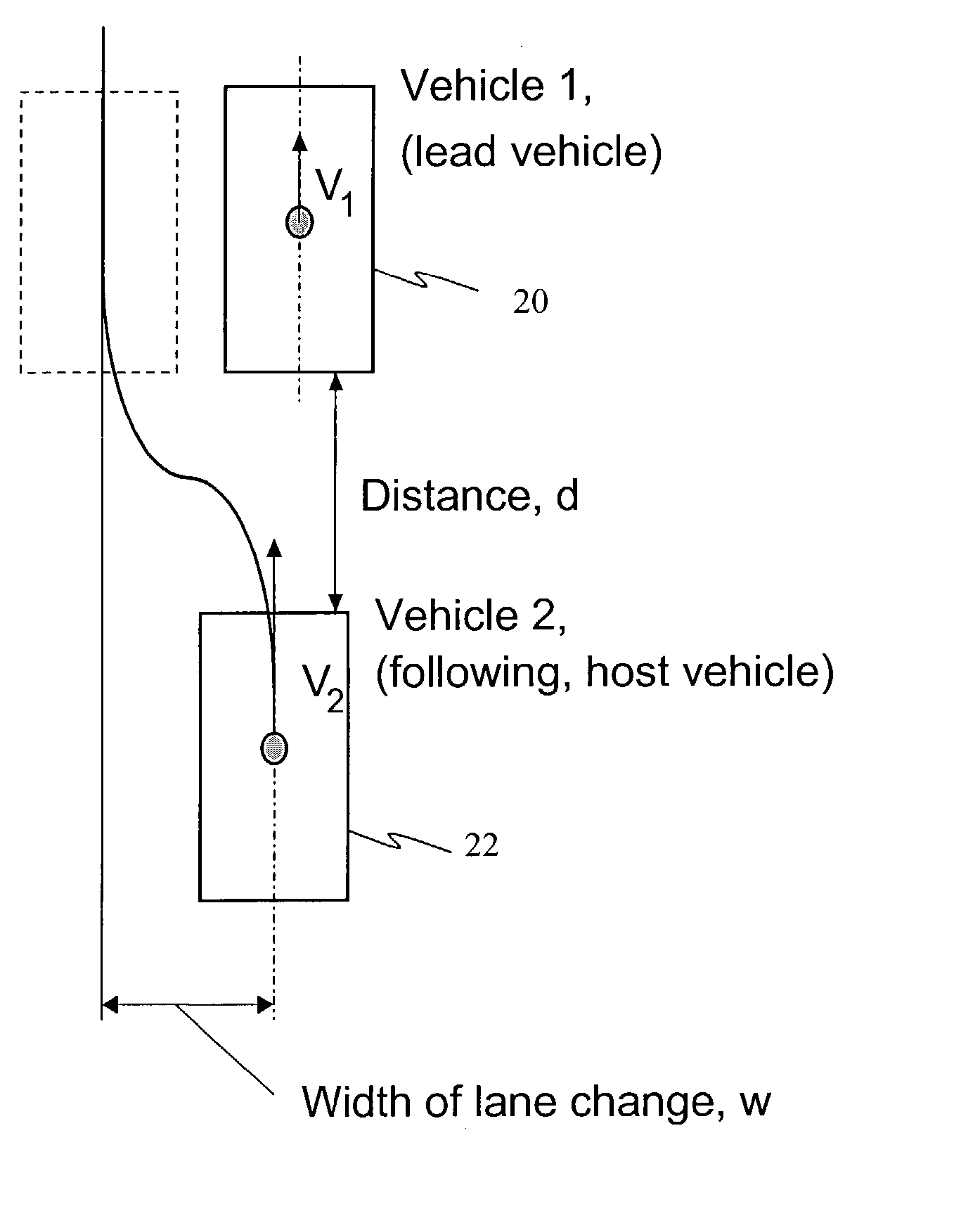
Method for recognizing a change in lane of a vehicle
InactiveUS6889161B2Accurate detectionReduce weightVehicle fittingsDigital data processing detailsImage resolutionAngular velocity
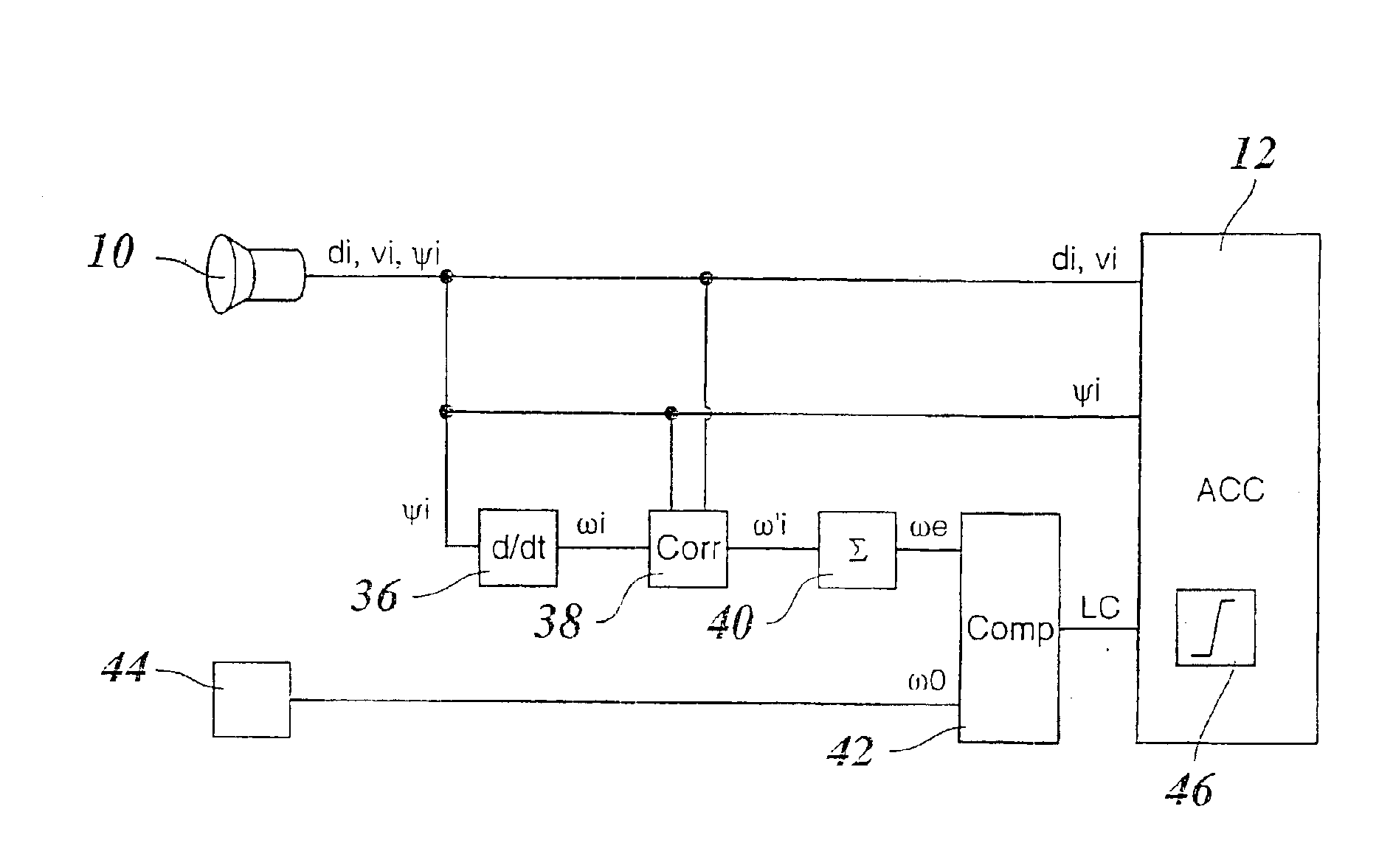
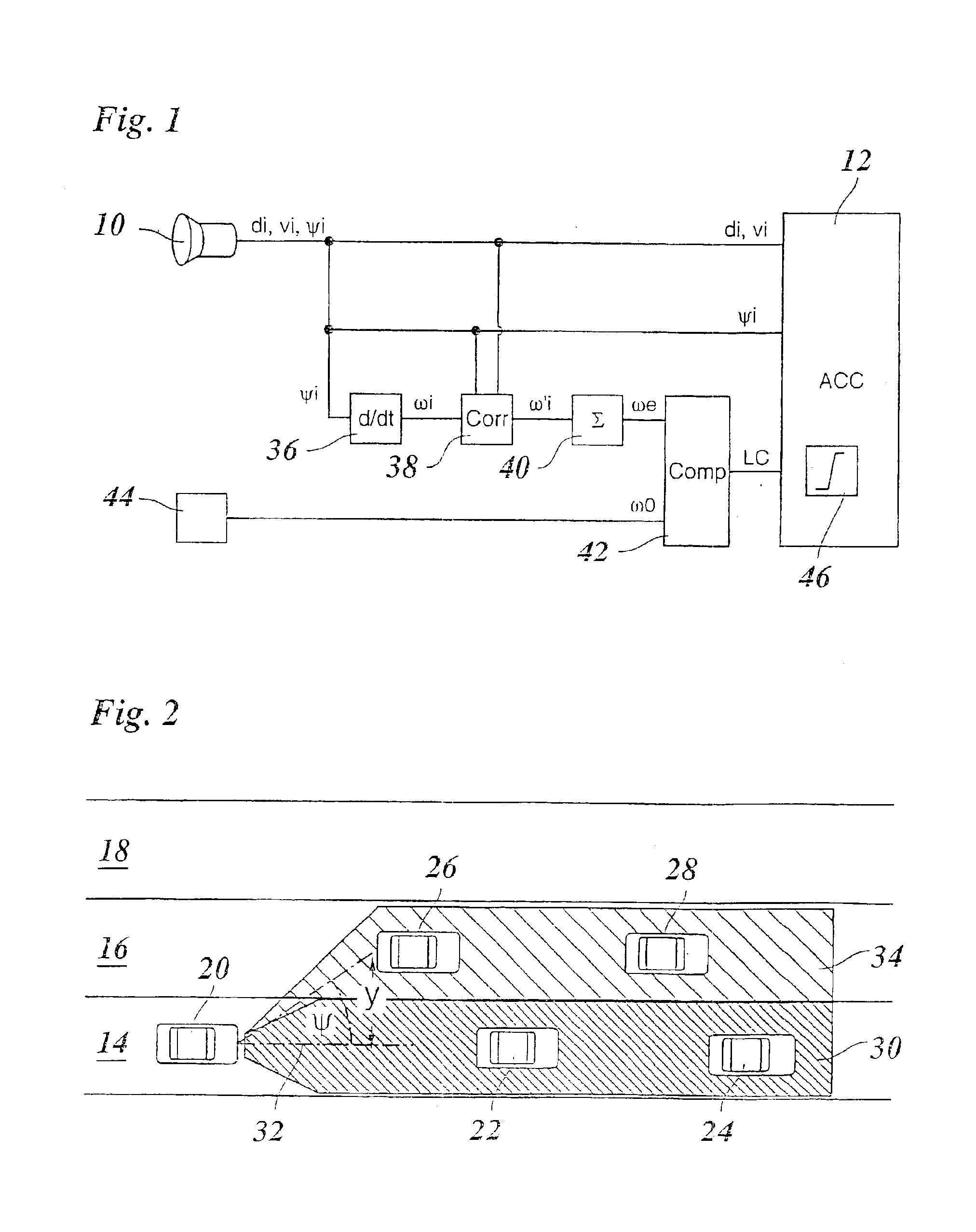
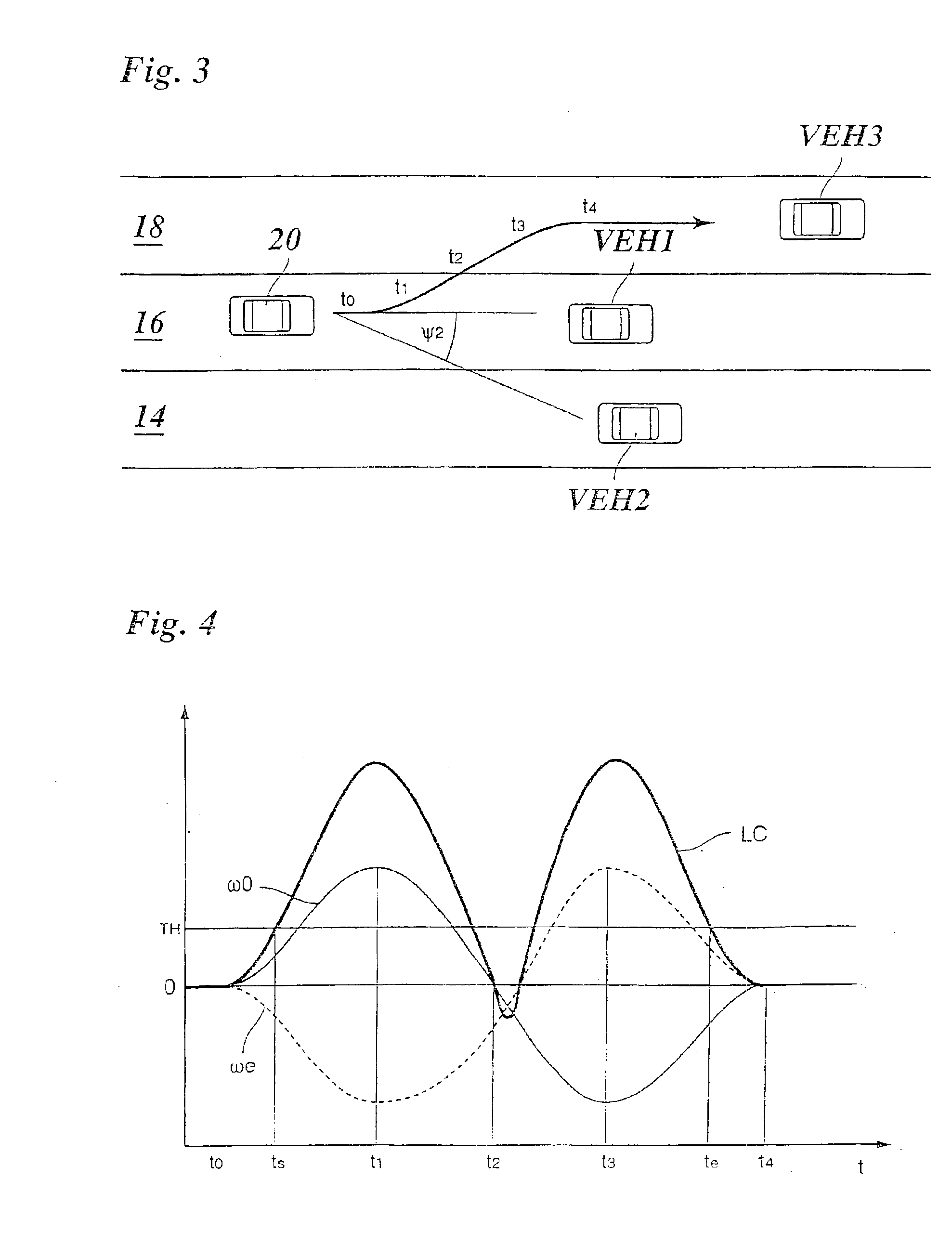
A method of detecting a lane change of a subject vehicle (20), having a locating device (10) which uses angular resolution for locating vehicles (VEH1, VEH2, VEH3) traveling in front, and a device (44) for determining the yaw rate (ω0) of the subject vehicle. The angular velocity (ωi) of at least one vehicle traveling in front relative to the subject vehicle (20) is measured using the locating device (10), and a lane change signal (LC) indicating the lane change is formed by comparing the measured angular velocity (ωi) to the yaw rate (ω0) of the subject vehicle.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
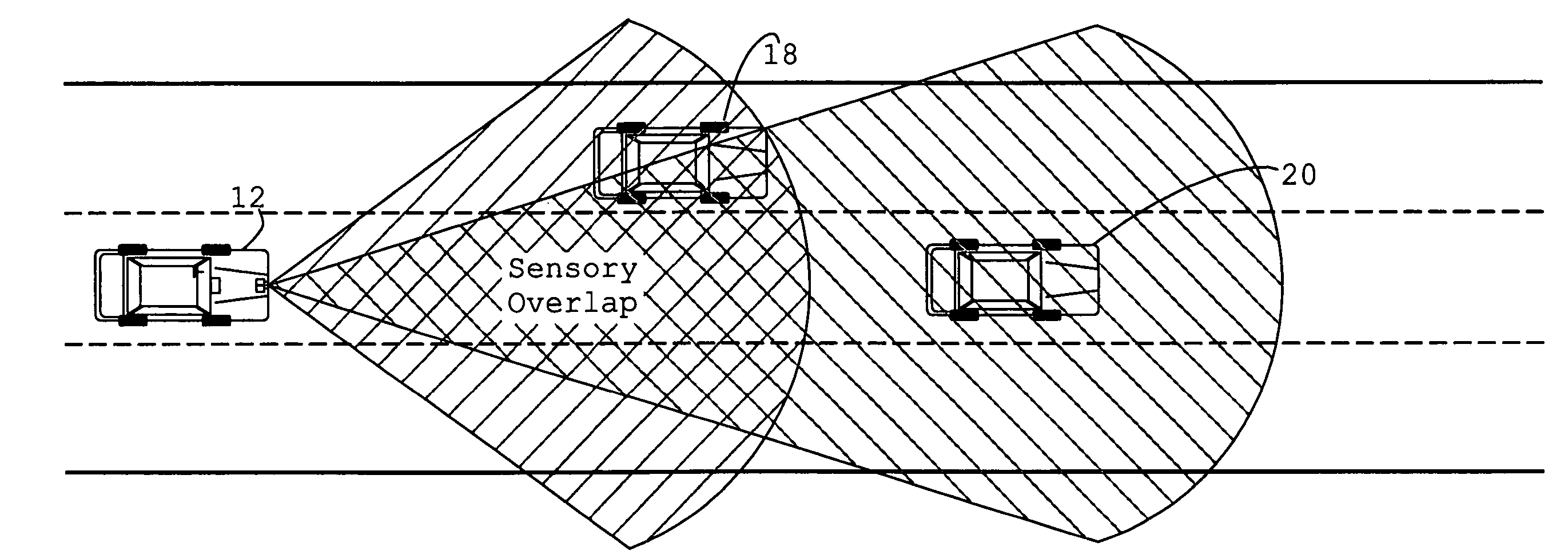
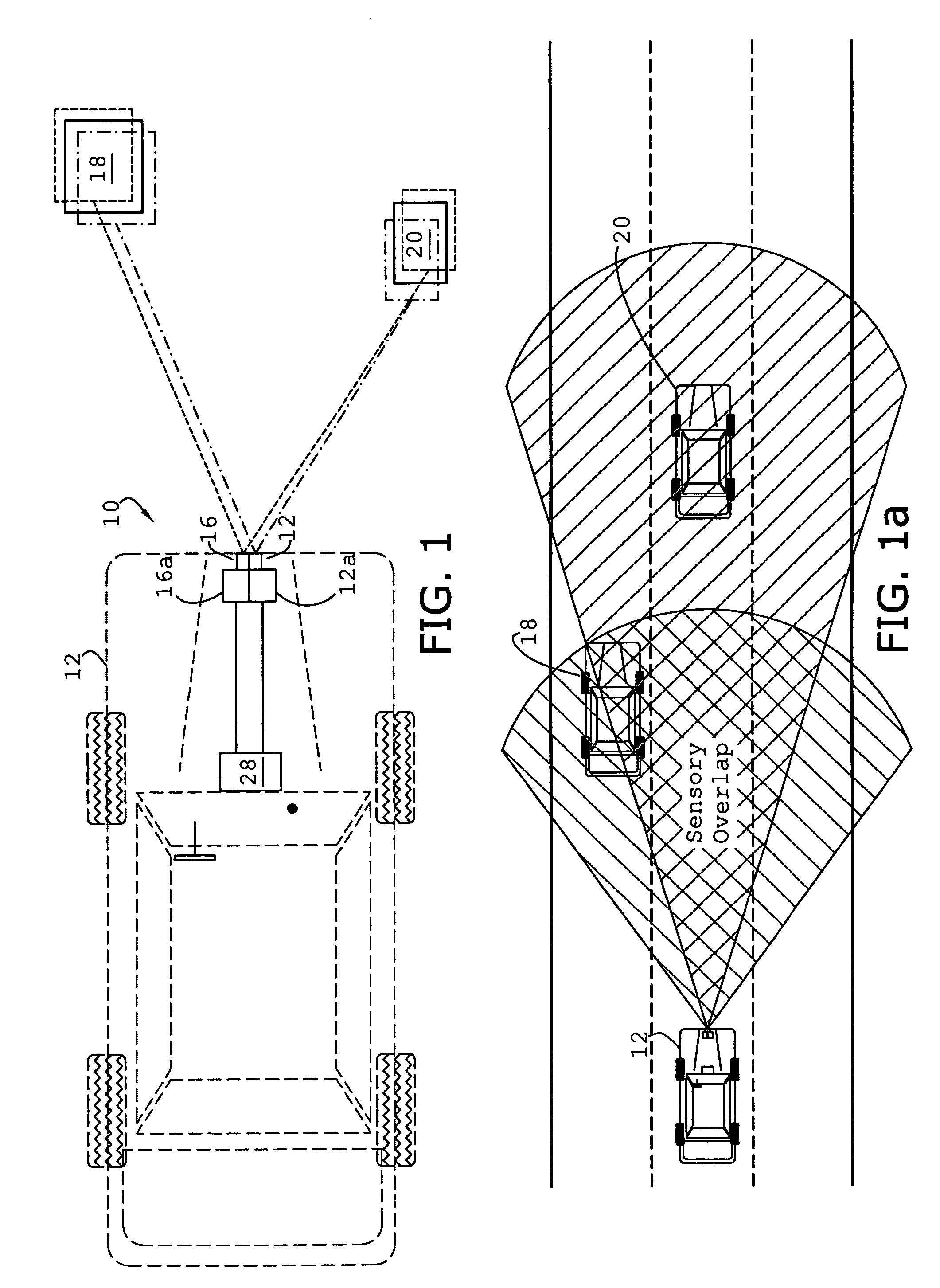
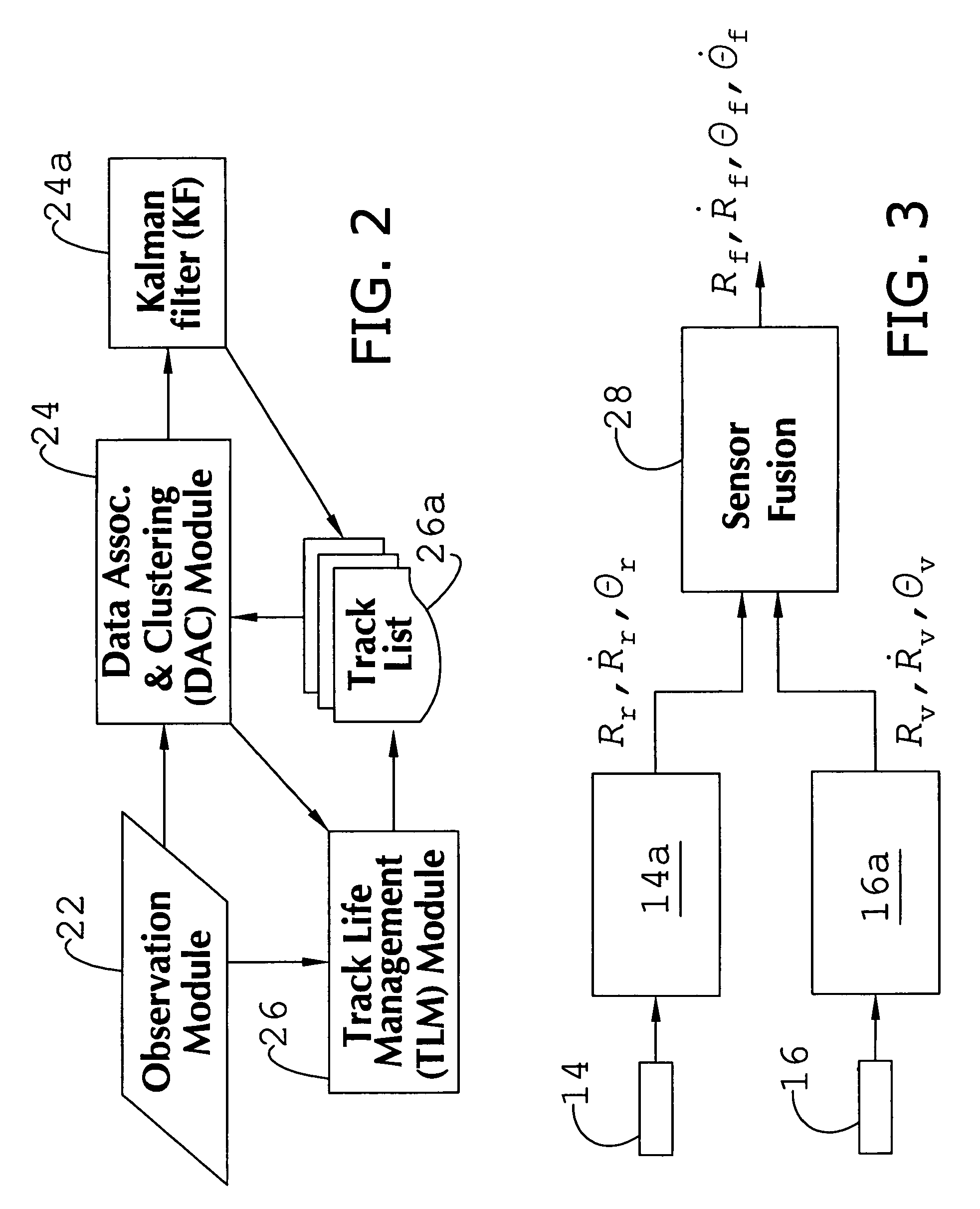
System and method of target tracking using sensor fusion
ActiveUS7460951B2Increasing precision and certaintyShorten the timeInstruments for road network navigationAnti-collision systemsSensor fusionEngineering
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Collision avoidance with active steering and braking
A method for collision avoidance using automated braking and steering comprising: determining an actual distance to an obstacle in a path of a vehicle; determining a relative velocity between the obstacle and the vehicle; determining a first distance sufficient to avoid collision by braking only; determining a second distance sufficient to avoid collision by combined braking and steering around the obstacle. The method also includes: applying braking if at least one of, the first distance exceeds the actual distance and the first distance is within a selected threshold of the actual distance. If the actual distance exceeds the second distance and a lane change is permitted, steering control to affect a lane change is applied.
Owner:BWI +1
Method for obtaining information about objects in a vehicular blind spot
InactiveUS20050195383A1Accurate identificationHigh resolutionOptical rangefindersAnti-theft devicesDisplay deviceComputer vision
Method for obtaining information about objects in an environment around a vehicle in which infrared light is emitted into a portion of the environment and received and the distance between the vehicle and objects from which the infrared light is reflected is measured. An identification of each object from which light is reflected is determined and a three-dimensional representation of the portion of the environment is created based on the measured distance and the determined identification of the object. Icons representative of the objects and their position relative to the vehicle are displayed on a display visible to the driver based on the three-dimensional representation. Additionally or alternatively to the display of icons, a vehicular system can be controlled or adjusted based on the relative position and optionally velocity of the vehicle and objects in the environment around the vehicle to avoid collisions.
Owner:AMERICAN VEHICULAR SCI
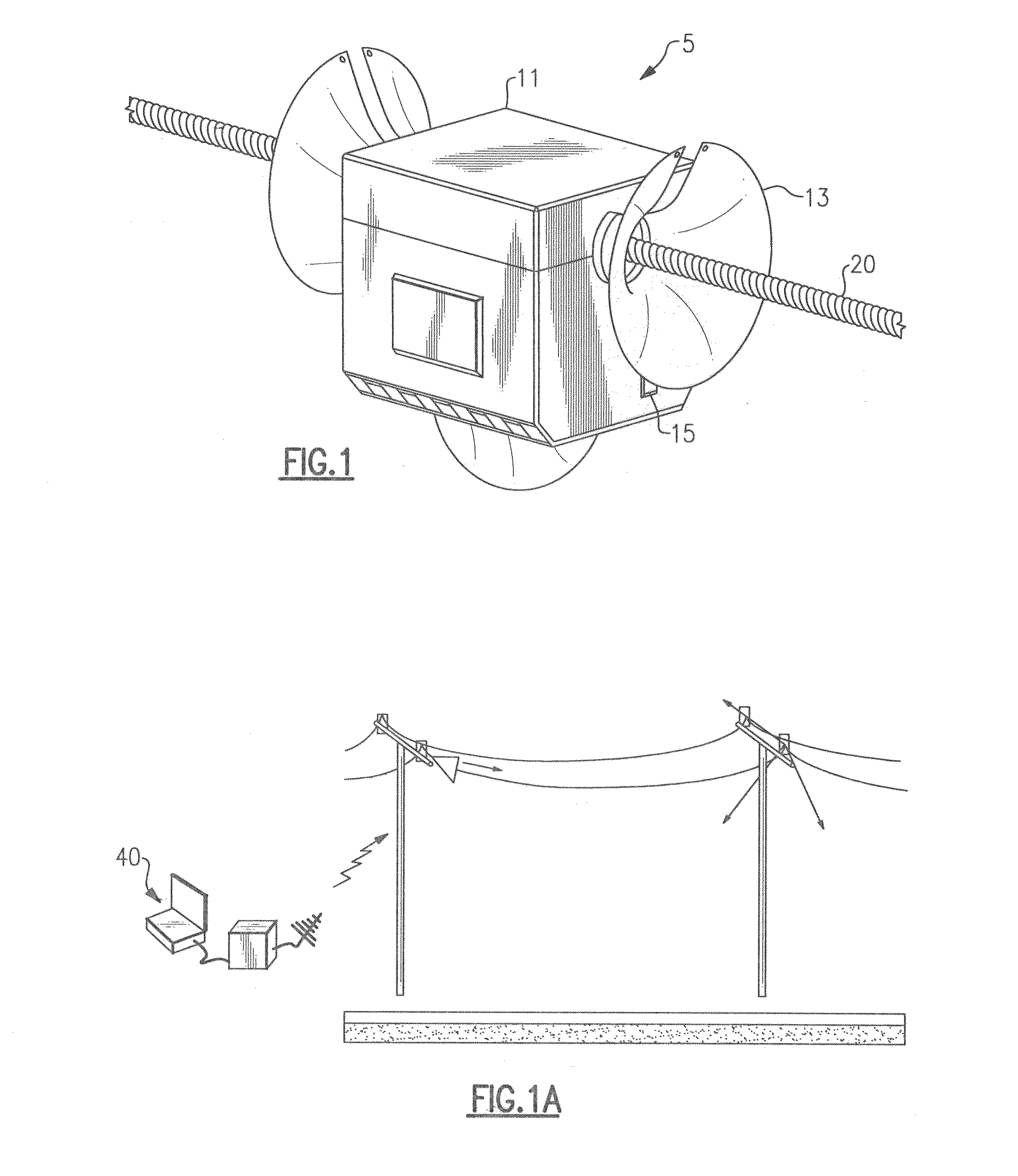
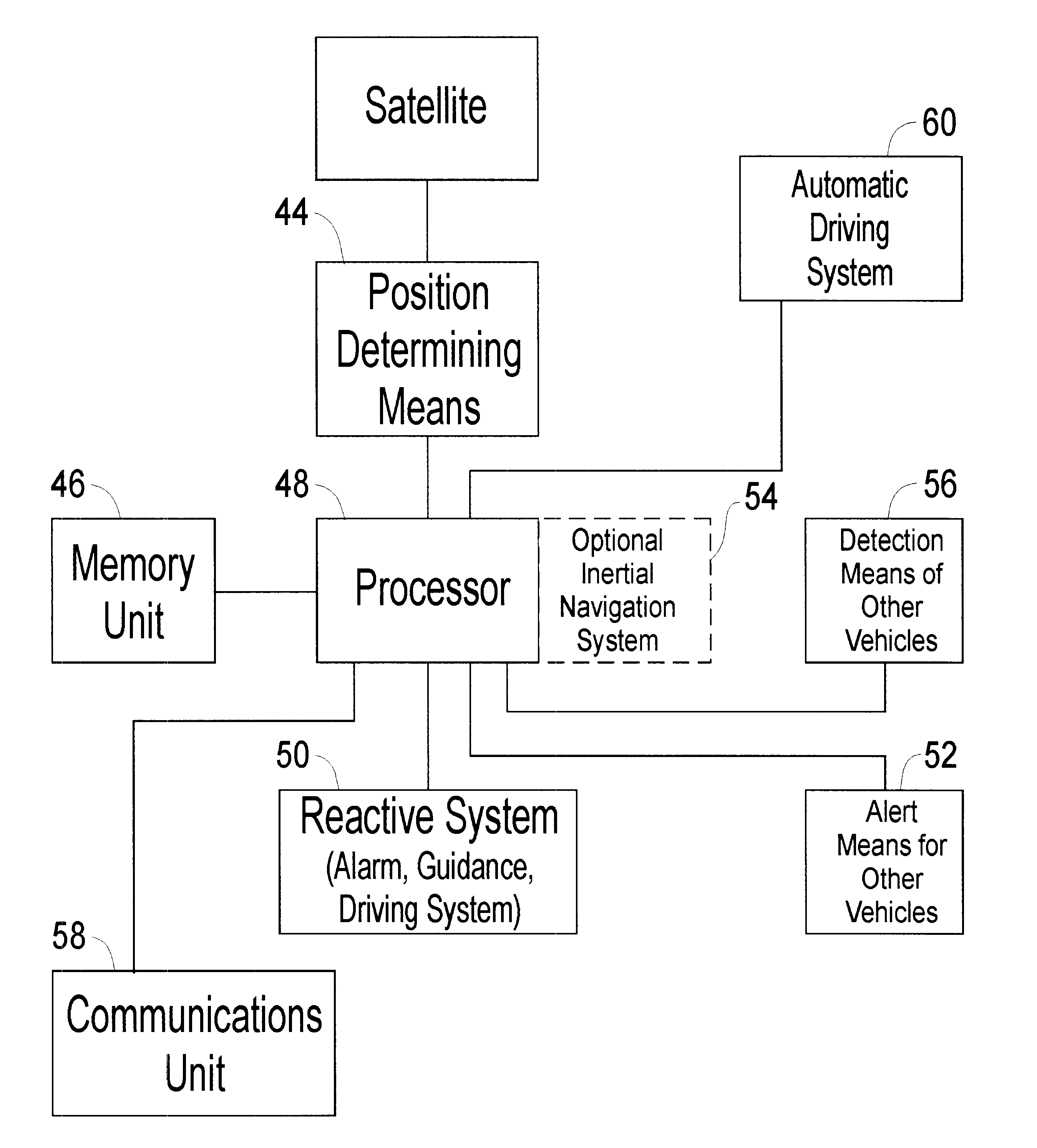
Accident avoidance systems and methods
InactiveUS7295925B2Avoid accidentsAvoid and minimize effectVehicle seatsAnalogue computers for vehiclesCommunications systemEngineering
Method and system for preventing accidents between first and second vehicles includes a positioning system arranged in each vehicle for determining the absolute position thereof, a memory unit arranged in the first vehicle for storing data about travel lanes, a communication system for transmitting the position of the second vehicle to the first vehicle, a receiver system arranged in the first vehicle for receiving position information from the second vehicle, a processor coupled to the positioning system, the receiver system and the memory unit in the first vehicle for predicting a collision between the vehicles based on the position of the vehicles and travel lane data, and a reactive component arranged in the first vehicle and coupled to the processor. The reactive component is arranged to initiate an action or change its operation when a collision is predicted by the processor, e.g., sound or indicate an alarm.
Owner:AMERICAN VEHICULAR SCI
Popular searches
Metadata multimedia retrieval Analogue secracy/subscription systems Using detectable carrier information Carrier indicating arrangements Two-way working systems Selective content distribution Special data processing applications Marketing Data switching by path configuration Location information based service
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com