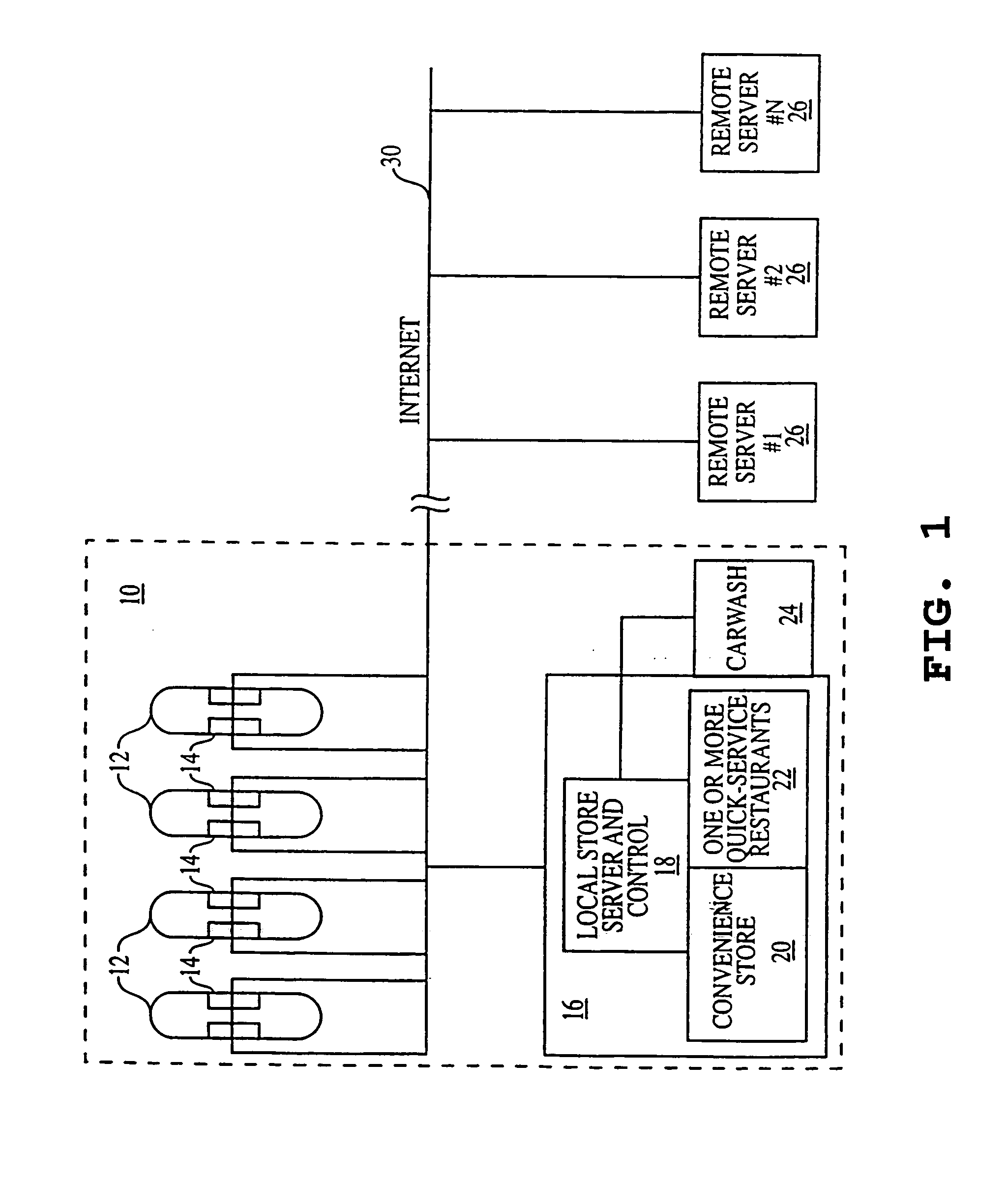
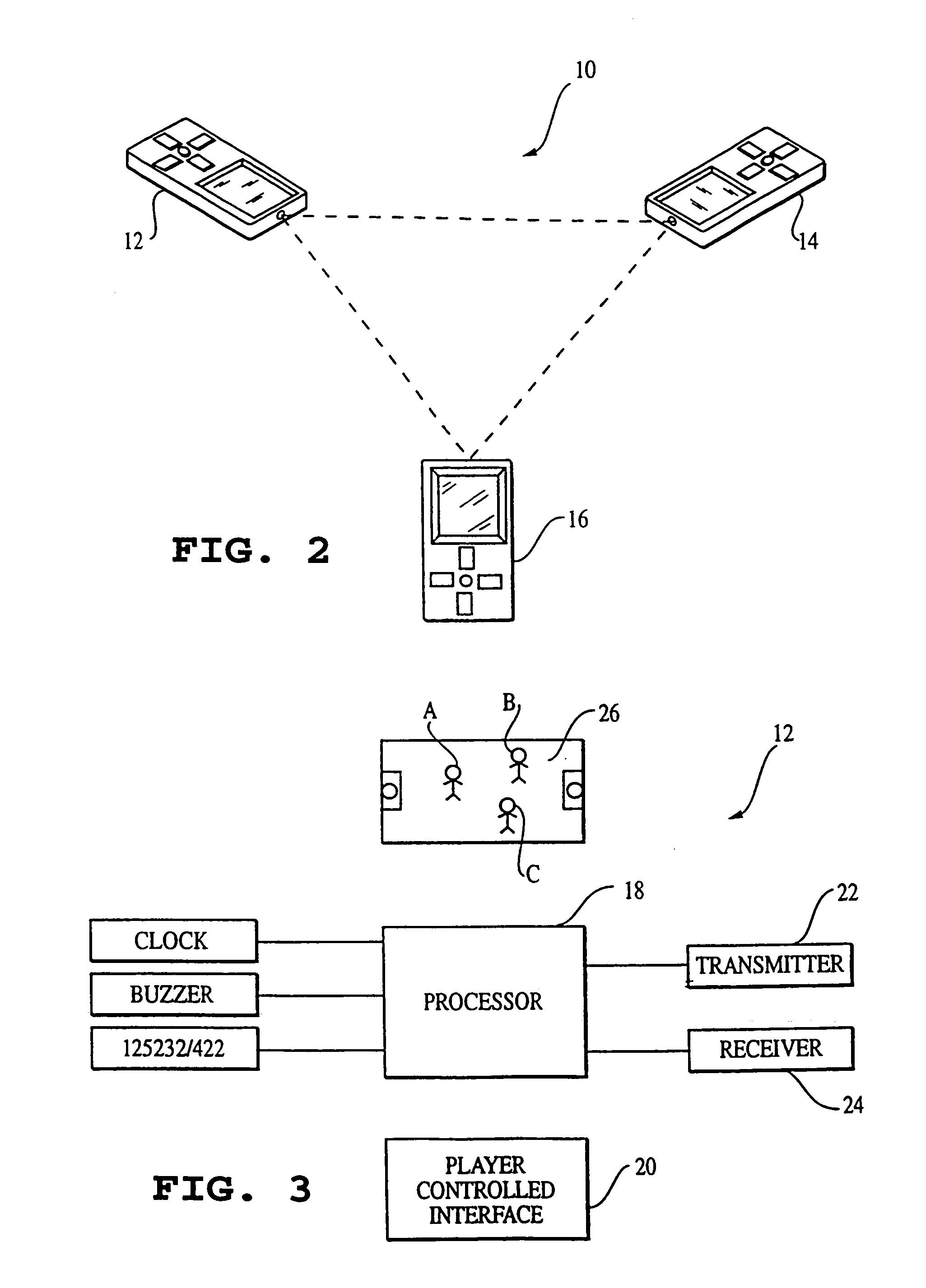
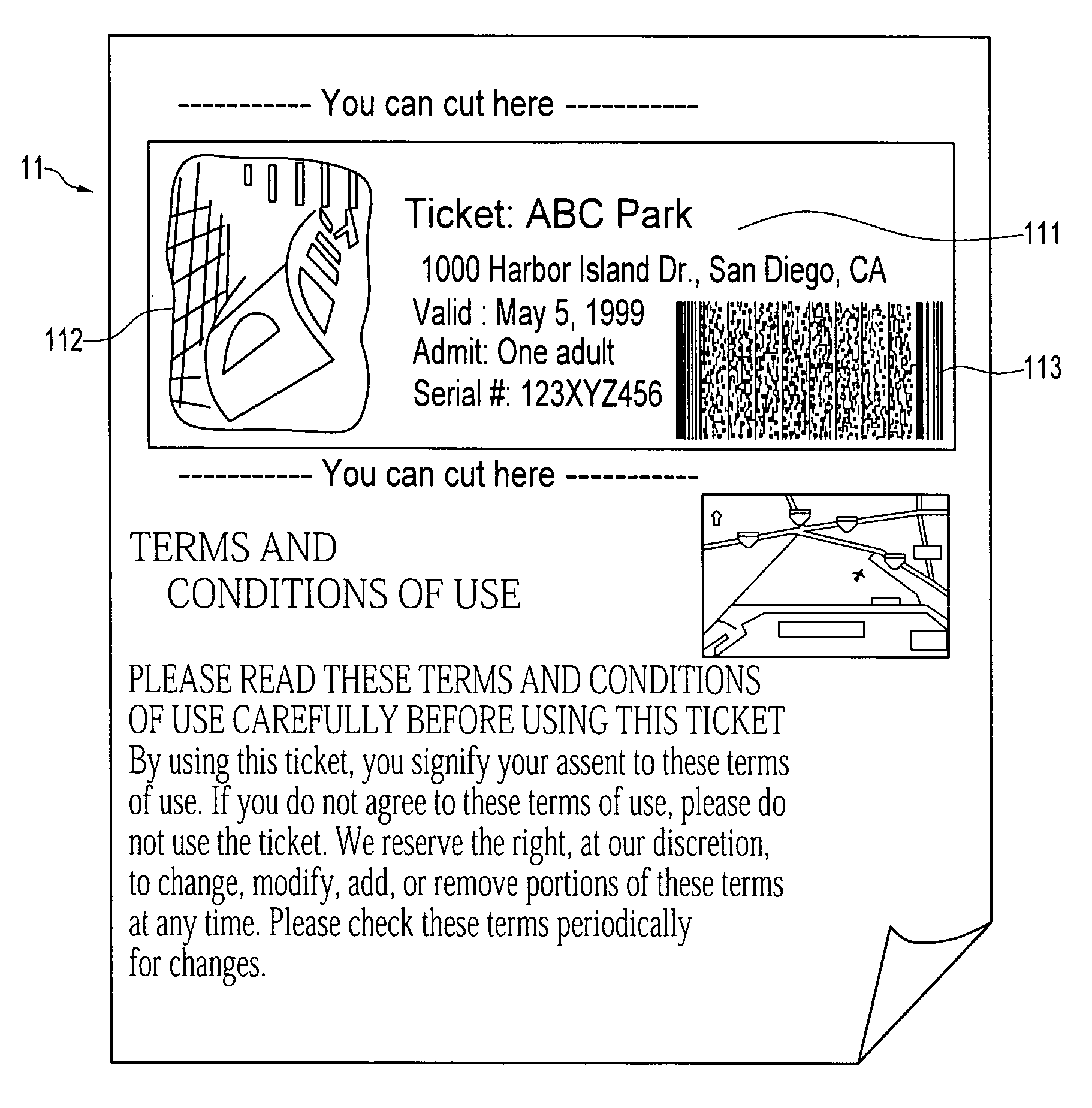
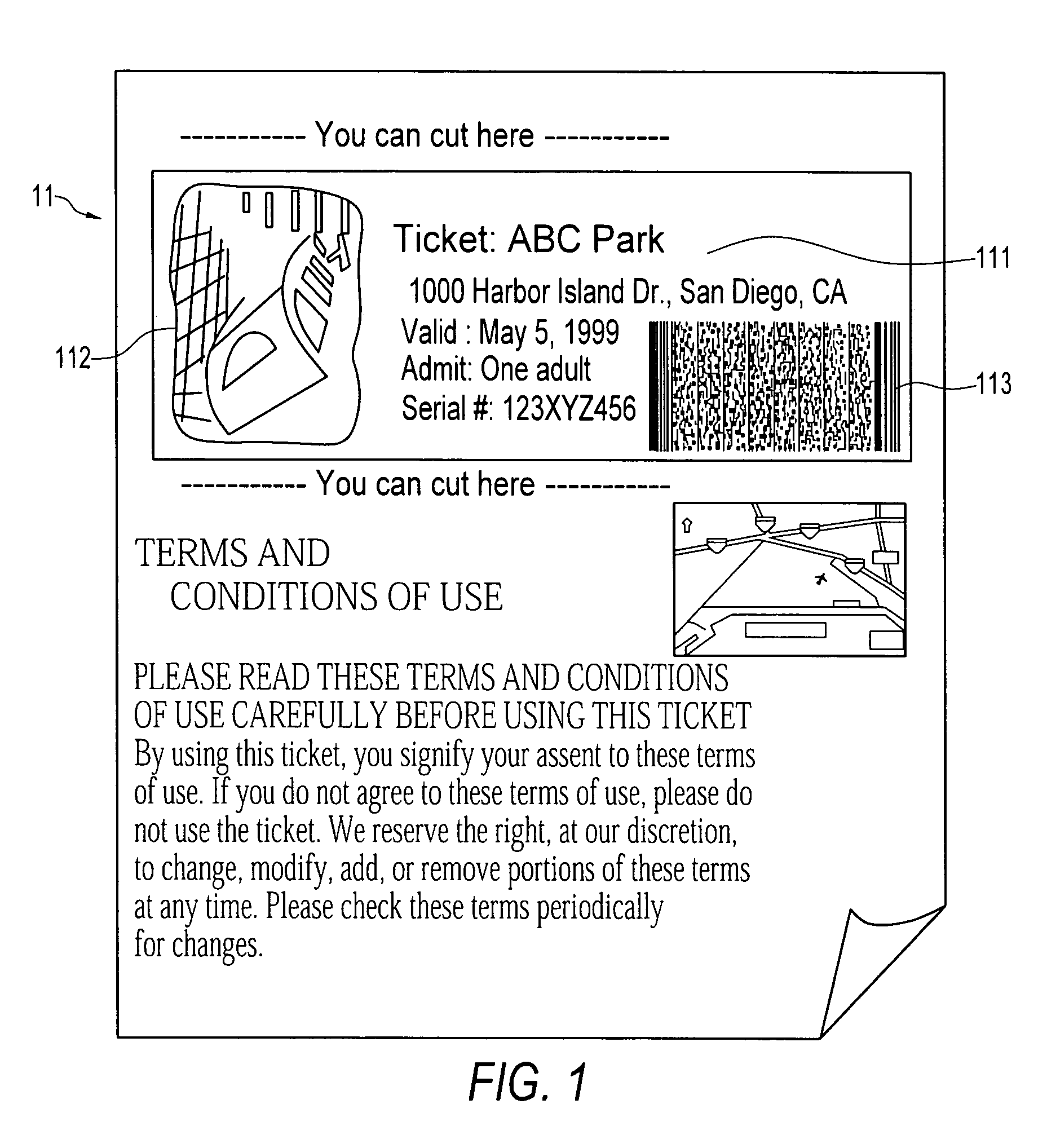
Patents
Literature
1383 results about "Ticket" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In IT security, a ticket is a number generated by a network server for a client, which can be delivered to itself, or a different server as a means of authentication or proof of authorization, and cannot easily be forged. This usage of the word originated with MIT's Kerberos protocol in the 1980s. Tickets may either be transparent, meaning they can be recognized without contacting the server that generated them; or opaque, meaning the original server must be contacted to verify that it issued the ticket.
Systems and Methods for Facilitating Distributed Authentication
ActiveUS20070107048A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationApplication serverClient-side
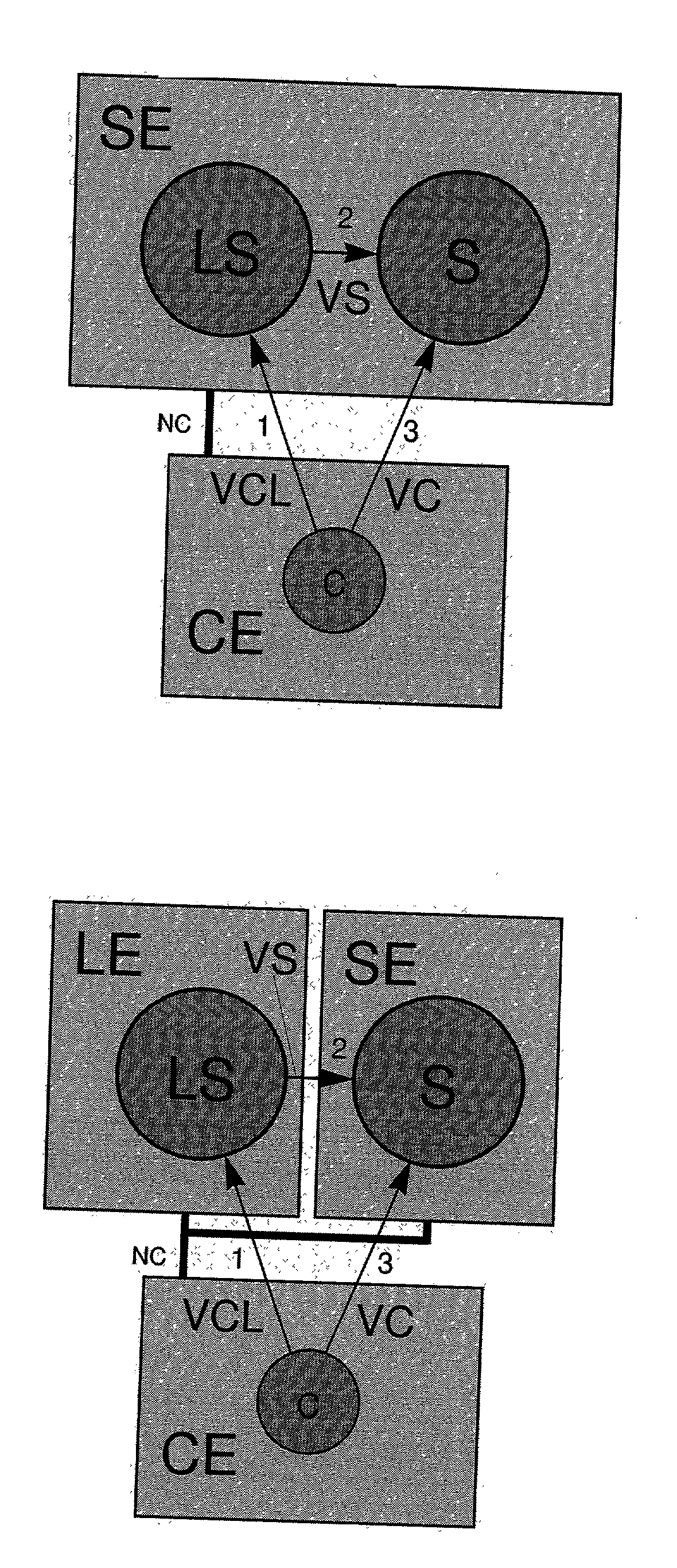
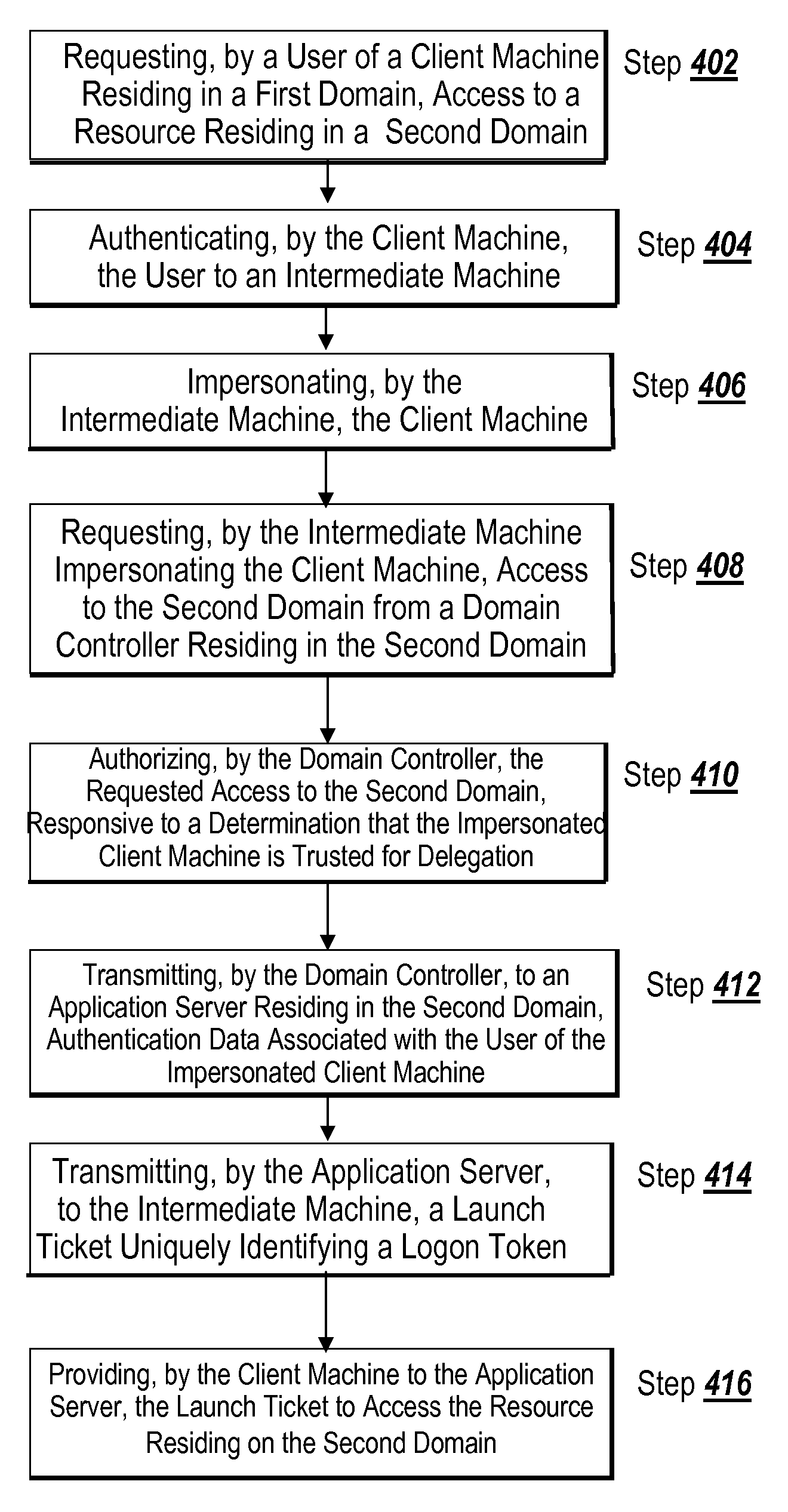
A method for facilitating distributed authentication includes the step of requesting, by a user of a client machine residing in a first domain, access to a resource residing in a second domain. The client machine authenticates the user to an intermediate machine. The intermediate machine impersonates the client machine. The intermediate machine impersonating the client machine requests access to the second domain from a domain controller residing in the second domain. The domain controller authorizes the requested access, responsive to a determination that the impersonated client machine is trusted for delegation. The domain controller transmits to an application server residing in the second domain, authentication data associated with the impersonated client machine. The application server transmits, to the intermediate machine, a launch ticket uniquely identifying a logon token. The client machine provides, to the application server, the launch ticket to access the resource residing in the second domain.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
System and method for reallocating and/or upgrading and/or selling tickets, other even admittance means, goods and/or services
InactiveUS7162454B1To offer comfortIncrease the fun of activitiesTicket-issuing apparatusFinancePoint of saleAdmittance
A method, system, server architecture and / or tangible medium upgrade and award admittance of events to an event customer, preferably via a data communication network. The method includes, for example, receiving a communication from the event customer, the communication including a request to obtain admittance to at least one event, the communication also including an identifier associated with the event customer, admitting the event customer at the point of sale system after verification of the request, and updating a database indicating that the request was processed. The method also includes determining first predetermined criteria associated with the event indicative of at least one other event customer not attending the event, releasing an allocation associated with the at least one other event customer, and notifying at least another of the event customers to perform the upgrade and / or reallocation. Various optional embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES ASSETS 186 LLC
System and method for delivering and examining digital tickets
InactiveUS7093130B1Cost effectiveModest appearanceTicket-issuing apparatusUser identity/authority verificationTicketThe Internet
A digital ticket is procured by a client ticket consumer upon, preferably, the Internet from and by staged interaction with a ticket provider server. The digital ticket becomes embodied in a tangible transportable data storage medium, normally a 2-D bar code printed on paper by the consumer, or on the consumer's flexible disk or smart card, containing Sign(s,I||hash(R))||R where (1) R is a number having its origin in the computer of the ticket consumer, which number R is appended to (2) a number Sign(s,I||hash(R)). This number Sign(s,I||hash(R)) was earlier computed in the computer of the ticket provider as a digital signature using signature key s of a number hash(R) combined with event information I, and was subsequently communicated across the communications network to the computer of the ticket consumer. The number hash(R) was itself even earlier computed in the computer of the ticket consumer as a one-way function of random number R, which computed one-way function was subsequently communicated to the computer of the ticket provider. The number R is private to the ticket consumer and not public; the digital signature key s is private to the ticket provider.The digital ticket is redeemed by (1) transporting the transportable storage medium within which the Sign(s,I||hash(R))||R is written to the particular selected event; (2) tendering the digital ticket for verification and for admission; (3) reading the Sign(s,I||hash(R))||R to an event computer and extracting the number R; (4) decrypting the remaining Sign(s, I||hash(R)) with verification key v of the ticket producer to get hash(R) and I; (5) re-calculating from R, with the same one-way function previously used, a re-calculated hash(R); then, having this recalculated hash(R) to hand; (6) comparing the re-calculated hash(R) to the extracted hash(R). The (4) decrypting will work, producing a proper I for the selected event, and the (6) comparing will be equal, only for a legitimate ticket.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method and system for authorizing a client computer to access a server computer
InactiveUS7089585B1Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsAuthorization certificateHash function
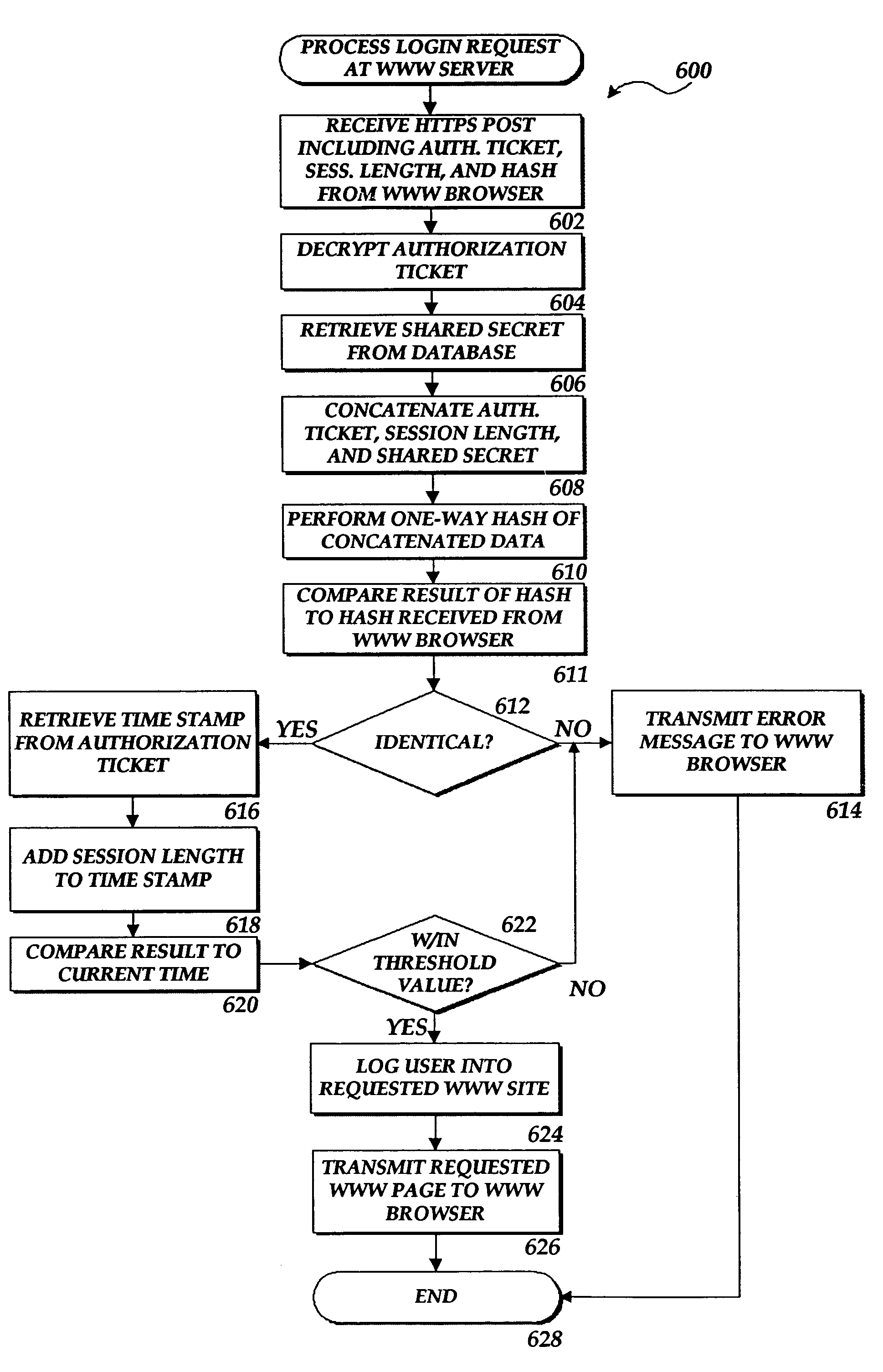
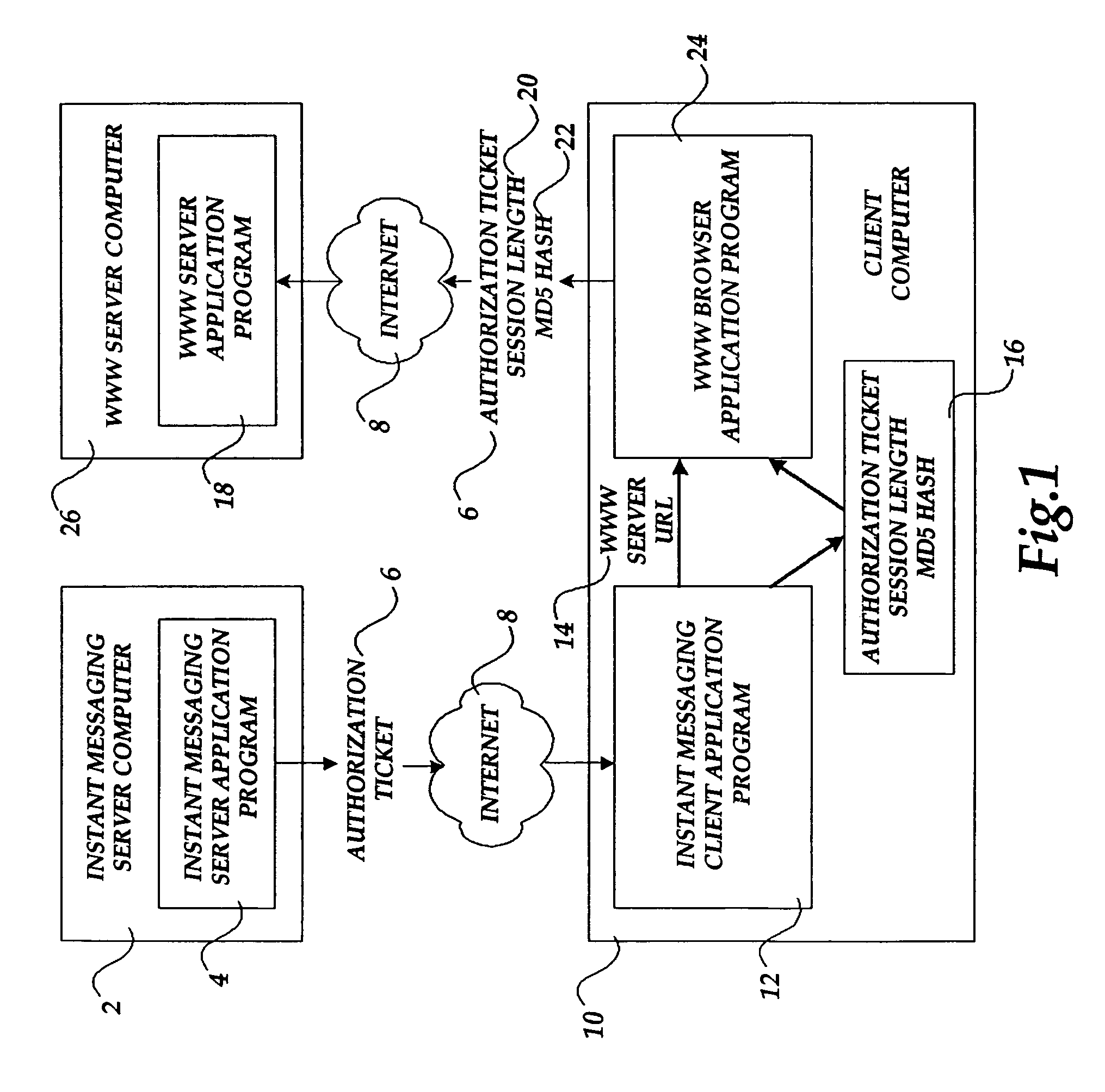
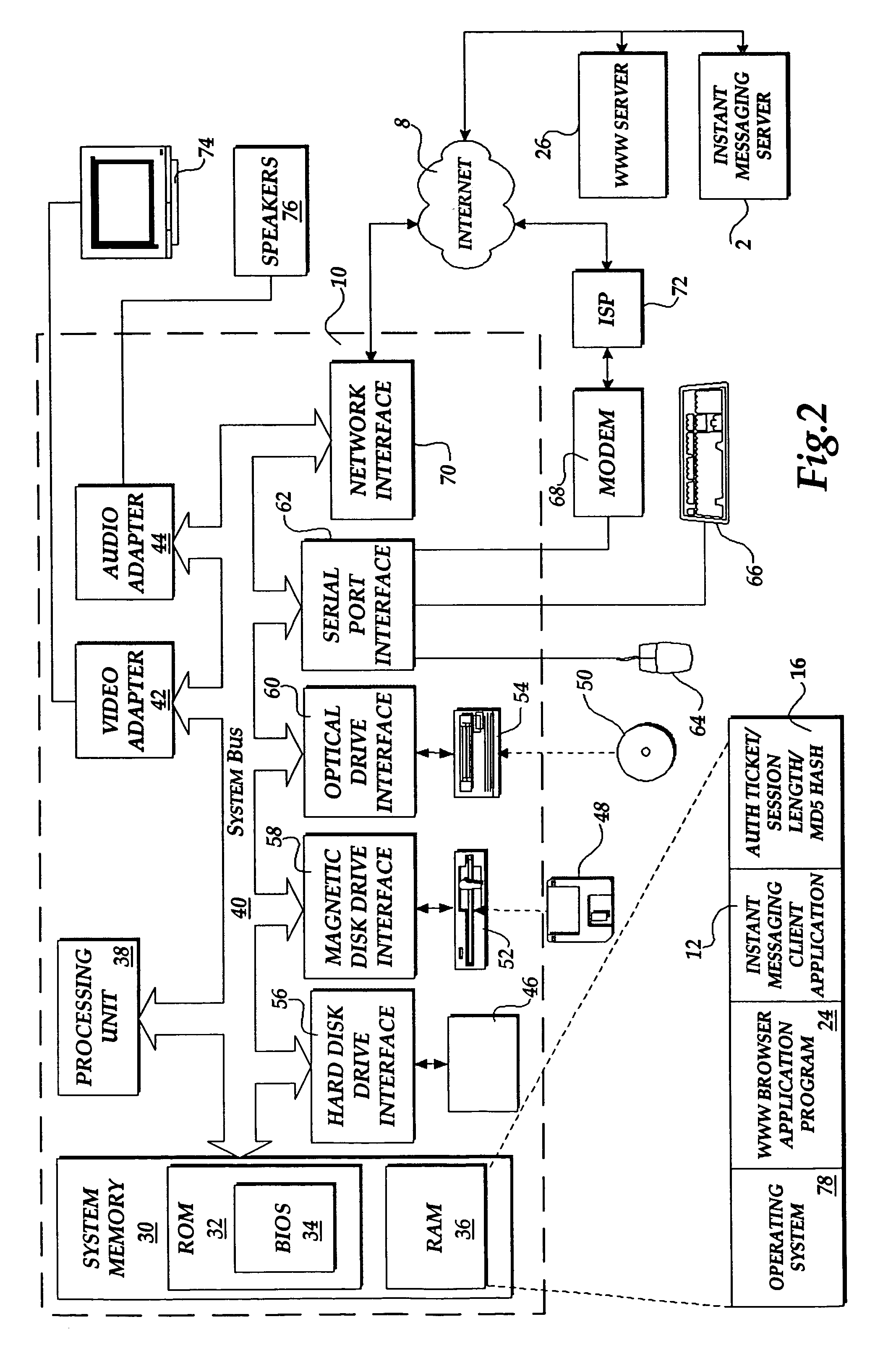
The present invention includes a client computer, a first server computer, and a second server computer. The first server provides an authorization ticket containing a time stamp to the client computer when the client computer is authorized to access the first server. An elapsed time counter is started at the client computer when access is provided to the first server. When a request is received at the client computer to access the second server, the client computer determines the session length based upon the elapsed time counter. The client computer calculates a hash value for the authorization ticket, the session length, and a secret shared with the second server computer. The client computer transmits a login request to the second server including the authorization ticket, the session length, and the hash. The second server decrypts the authorization ticket and retrieves a copy of the shared secret. The second server executes a hash function on the authorization ticket, the session length, and the shared secret. The second server then compares the computed hash to the hash value received from the second client application. If the two hash values are identical, the second server retrieves the time stamp from the authorization ticket and adds the session length to the time stamp. The second server then compares the resulting value to the current time. If the resulting value and the current time are within a preset threshold value, the client computer is provided.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and method for distributed computation based upon the movement, execution, and interaction of processes in a network
InactiveUS6016393AResource allocationInterprogram communicationDistributed Computing EnvironmentEngineering
A distributed computing environment in which agent processes direct their own movement through a computer network. Place processes provide a computing context within which agent processes are interpreted. An agent process controls its movement from one place process to another within the network by using a ticket. An agent process which moves from one place process to another transports definitions of classes of which objects included in the agent process are members. An agent process which moves from one place process to a second place process avoids unnecessary transportation of objects included in the agent process by substituting equivalent objects which are found in the second place process. An agent process sends clones of the agent process to several place processes simultaneously. If two clones travel along paths which are coextensive for an initial portion thereof, a single clone is transported along the initial portion of the paths and other clones are formed from the single clone, thereby avoiding transferring redundant information along communications media. Two agent processes, which occupy a single place process, interact by exchanging references to one another. The single place process ensures that neither agent process receives a reference to the other agent process without simultaneously giving to the other agent process a reference to the former agent process. Unauthorized or inadvertent excessive use of network resources by an agent process, or a place process, is prevented by associating with each process a permit which defines various capabilities and resource allowances of the process.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
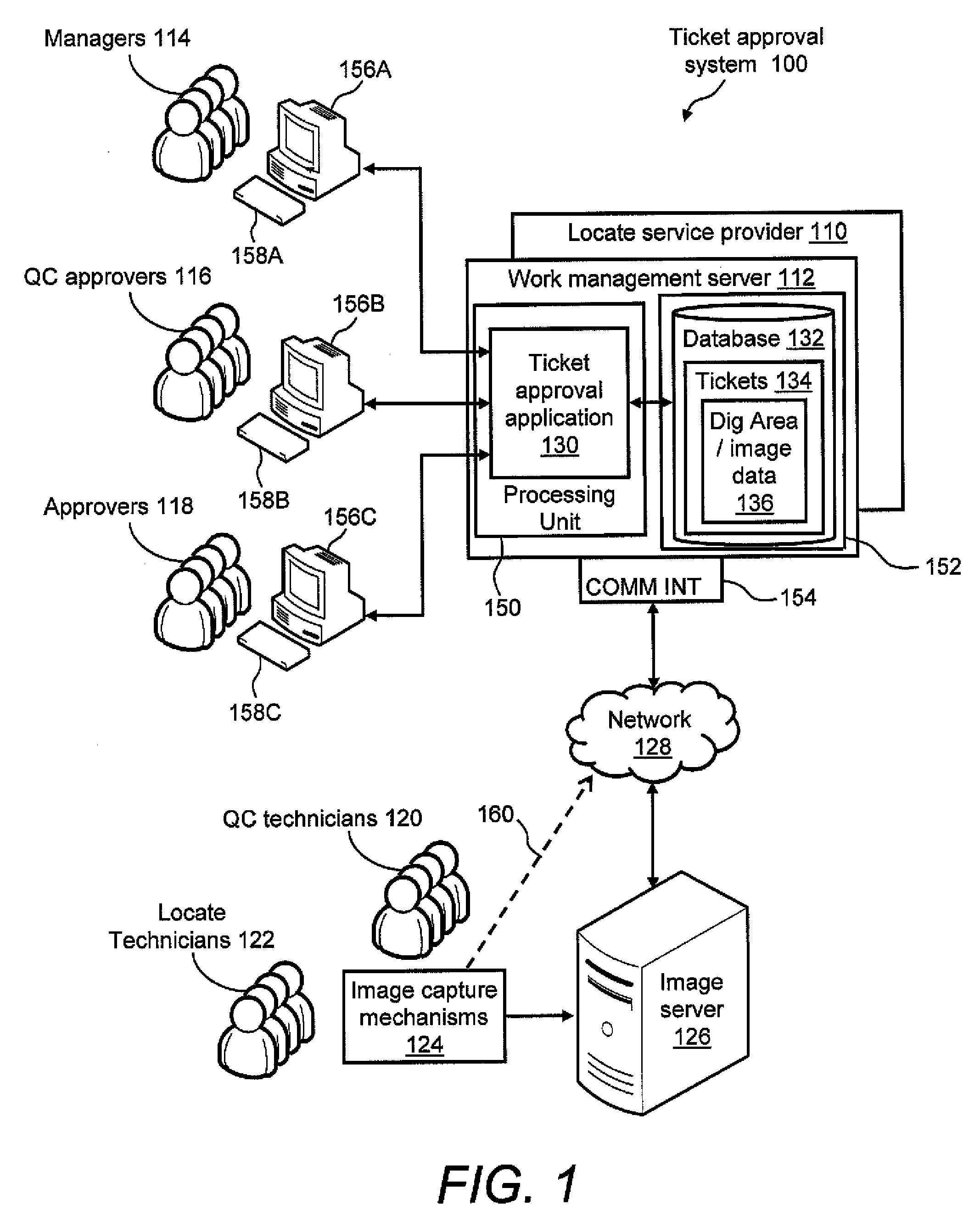
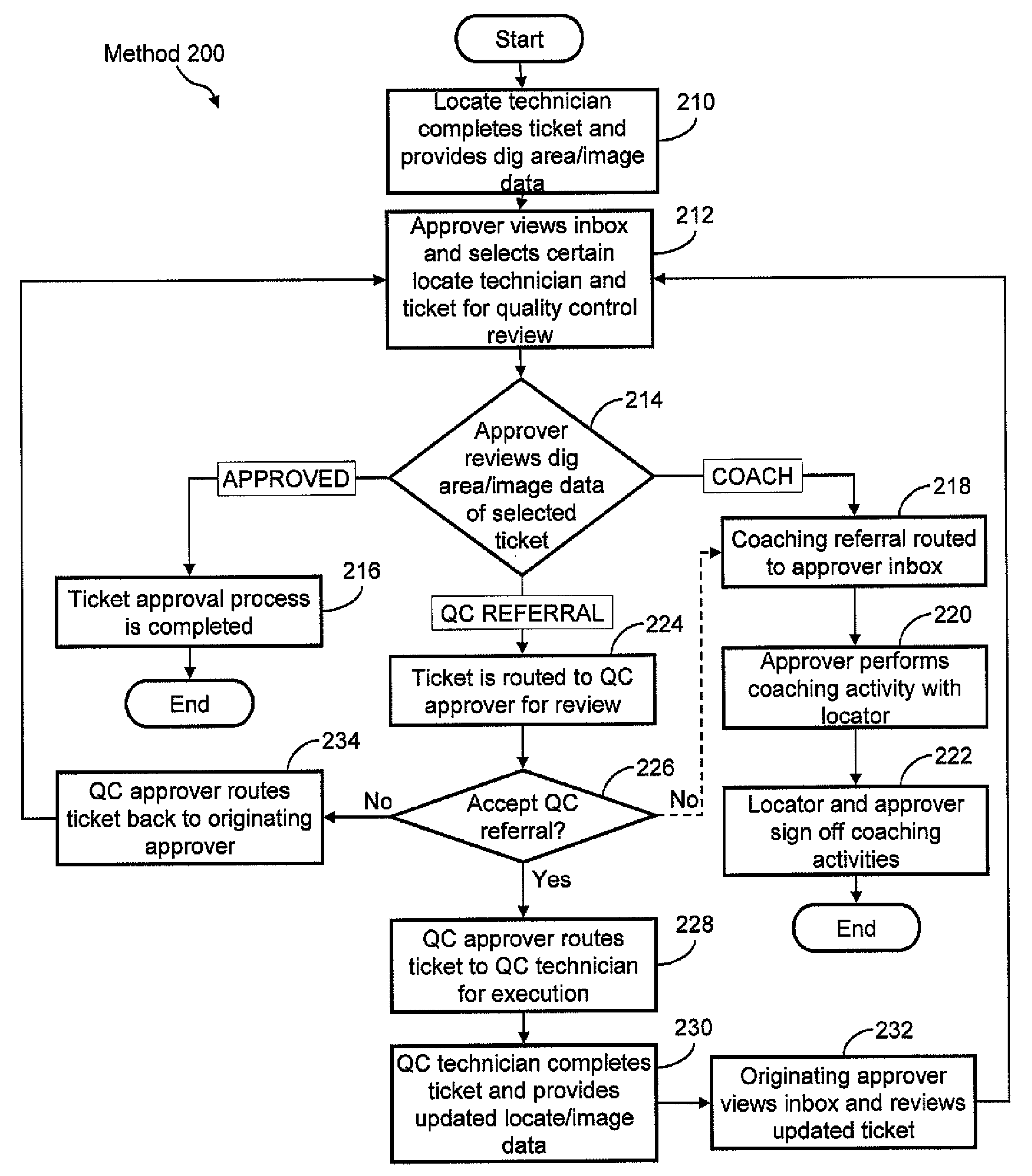
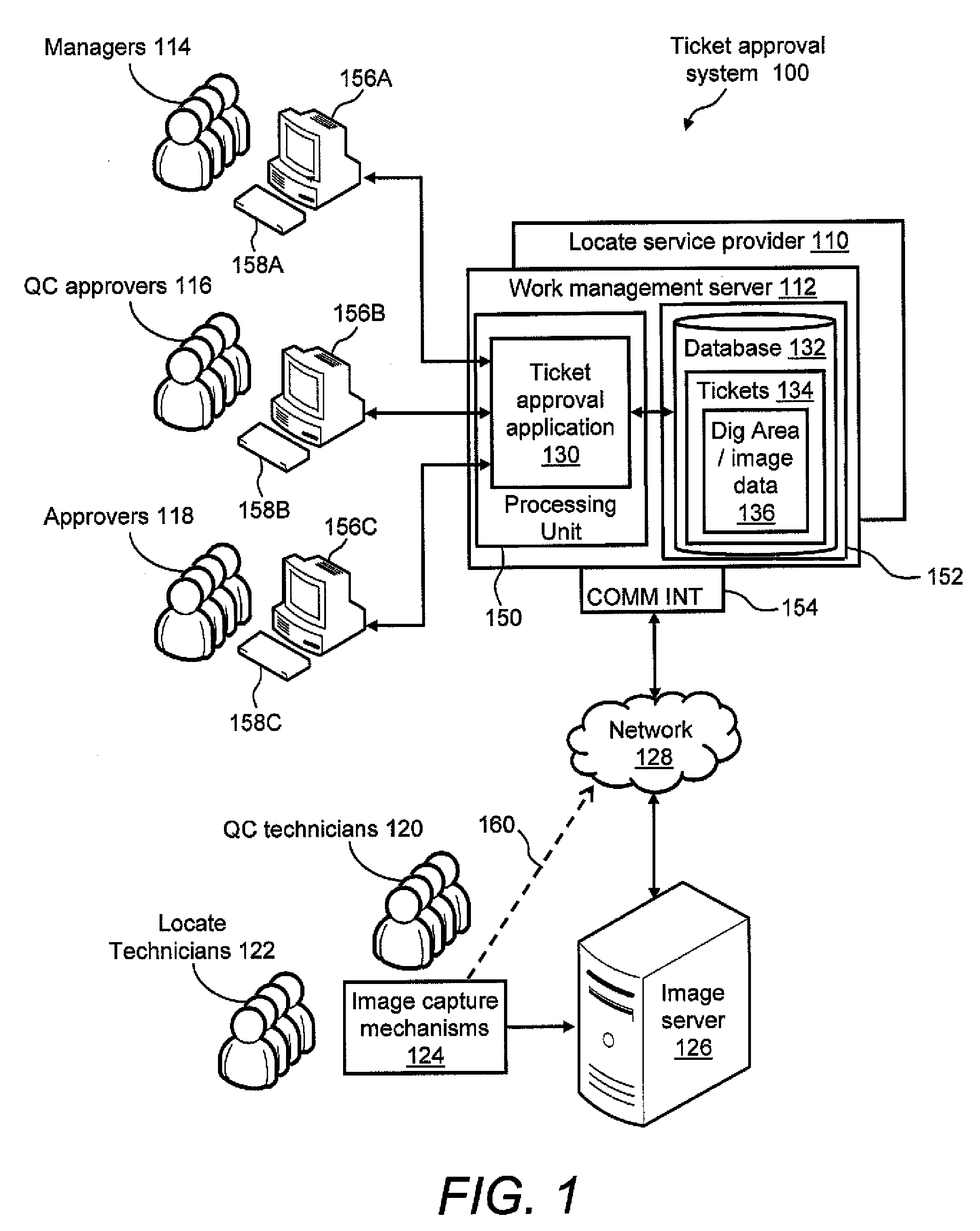
Ticket approval system for and method of performing quality control in field service applications
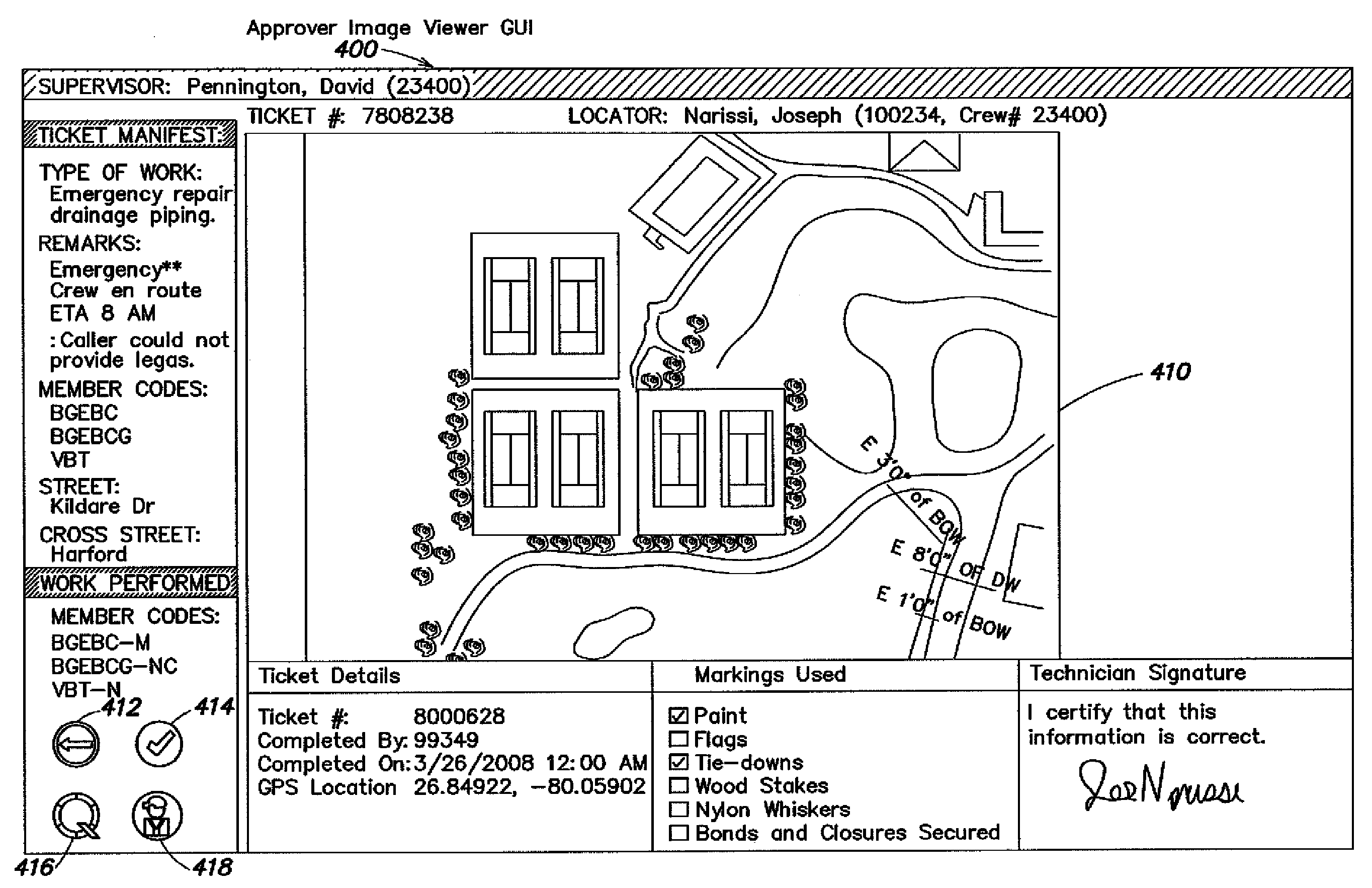
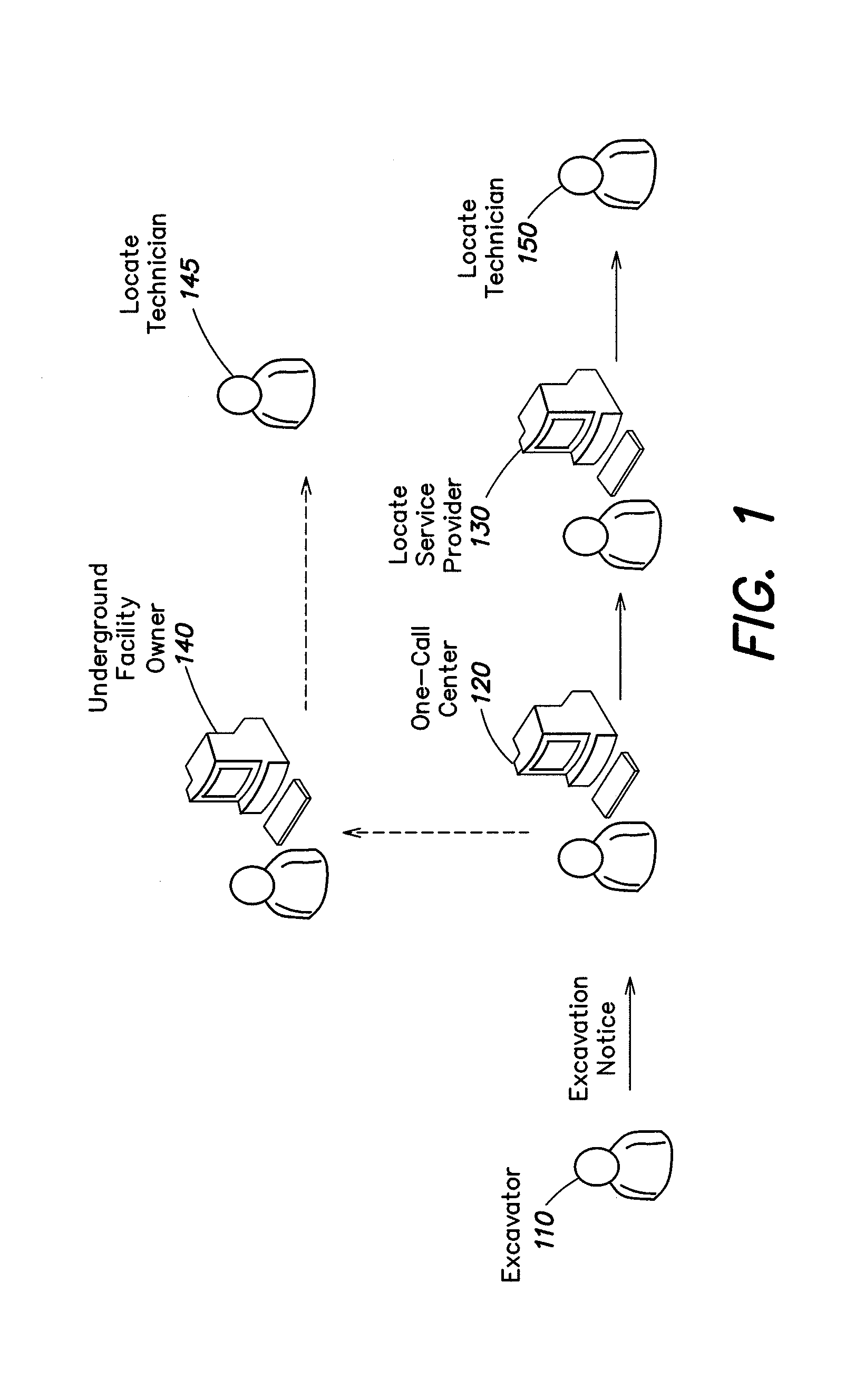
Methods and apparatus for assessing a locate and marking operation. Ticket information is received regarding the locate and marking operation prior to performance. Following performance, a locate manifest is received that includes a digital image associated with a dig area for which the operation was performed. One or more electronic indications are provided, based at least in part on a comparison of the ticket information and the locate manifest, of a quality assessment of the locate and marking operation. The electronic indication(s) indicate one of: 1) a satisfactory operation; 2) an unsatisfactory operation requiring further quality control assessment and / or at least partial re-performance; or 3) a satisfactory operation, but nonetheless requiring technician coaching. An electronic record is generated of the quality assessment of the locate and marking operation based on the electronic indication(s).
Owner:CERTUSVIEW TECH LLC
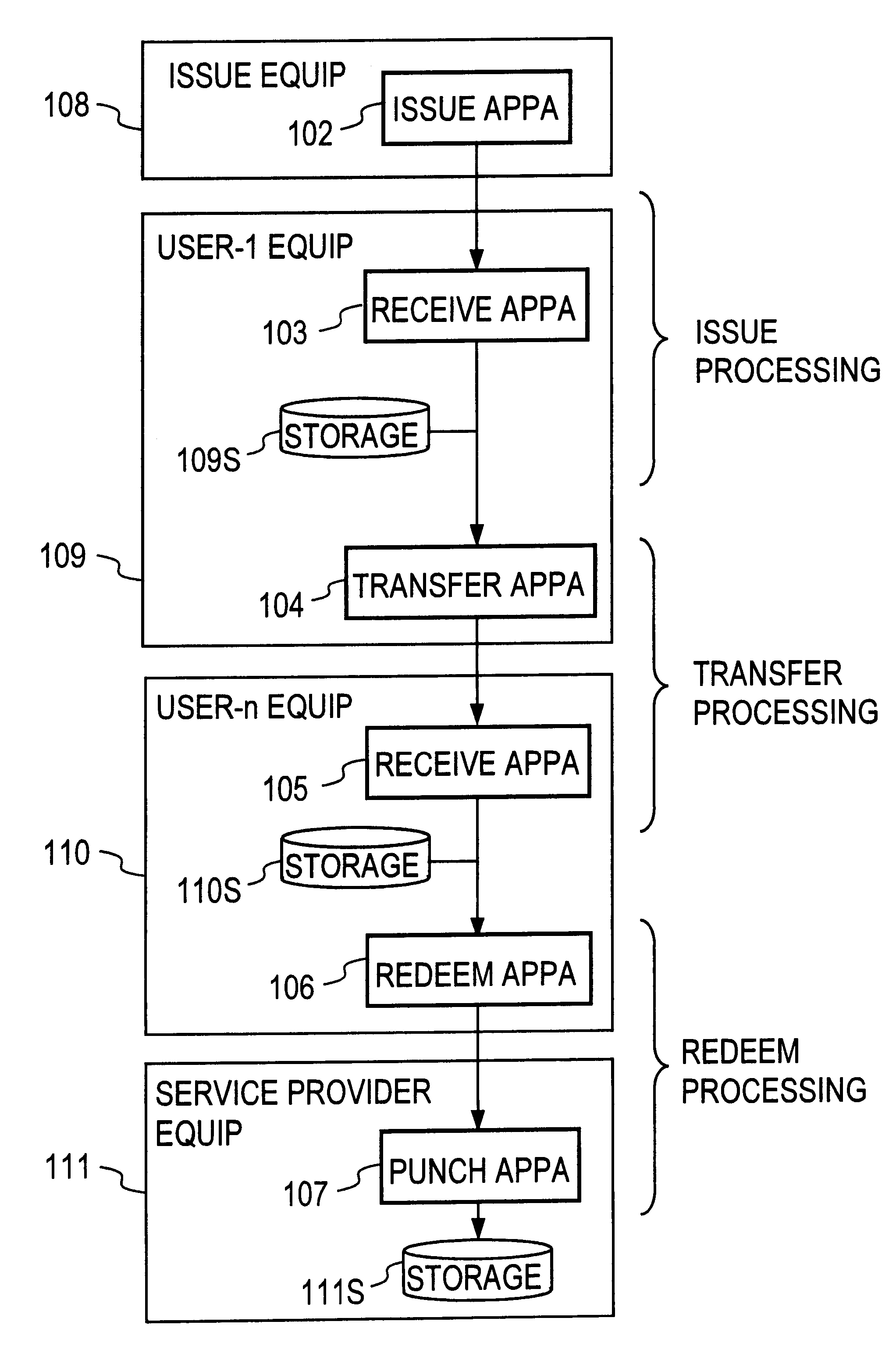
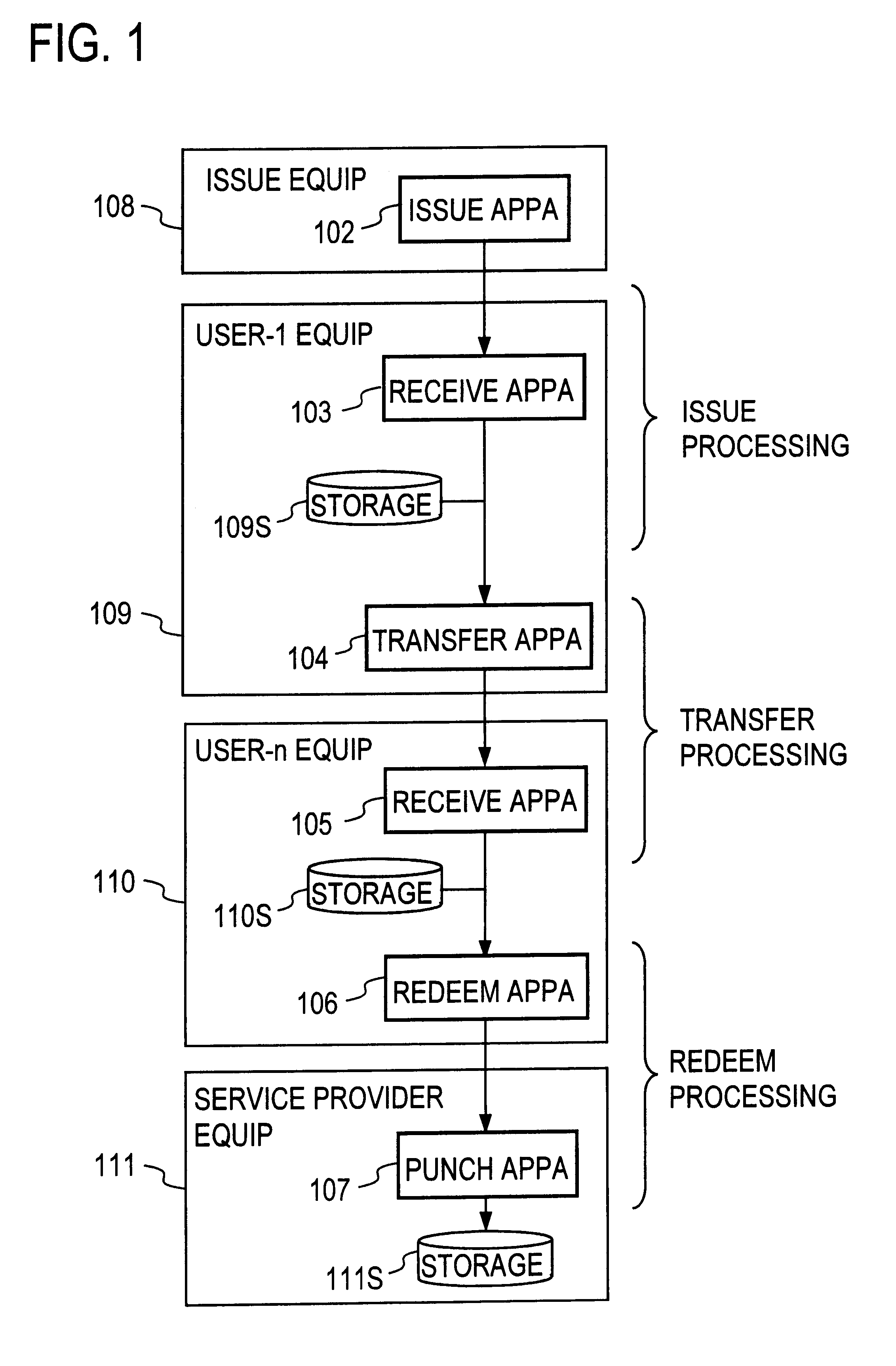
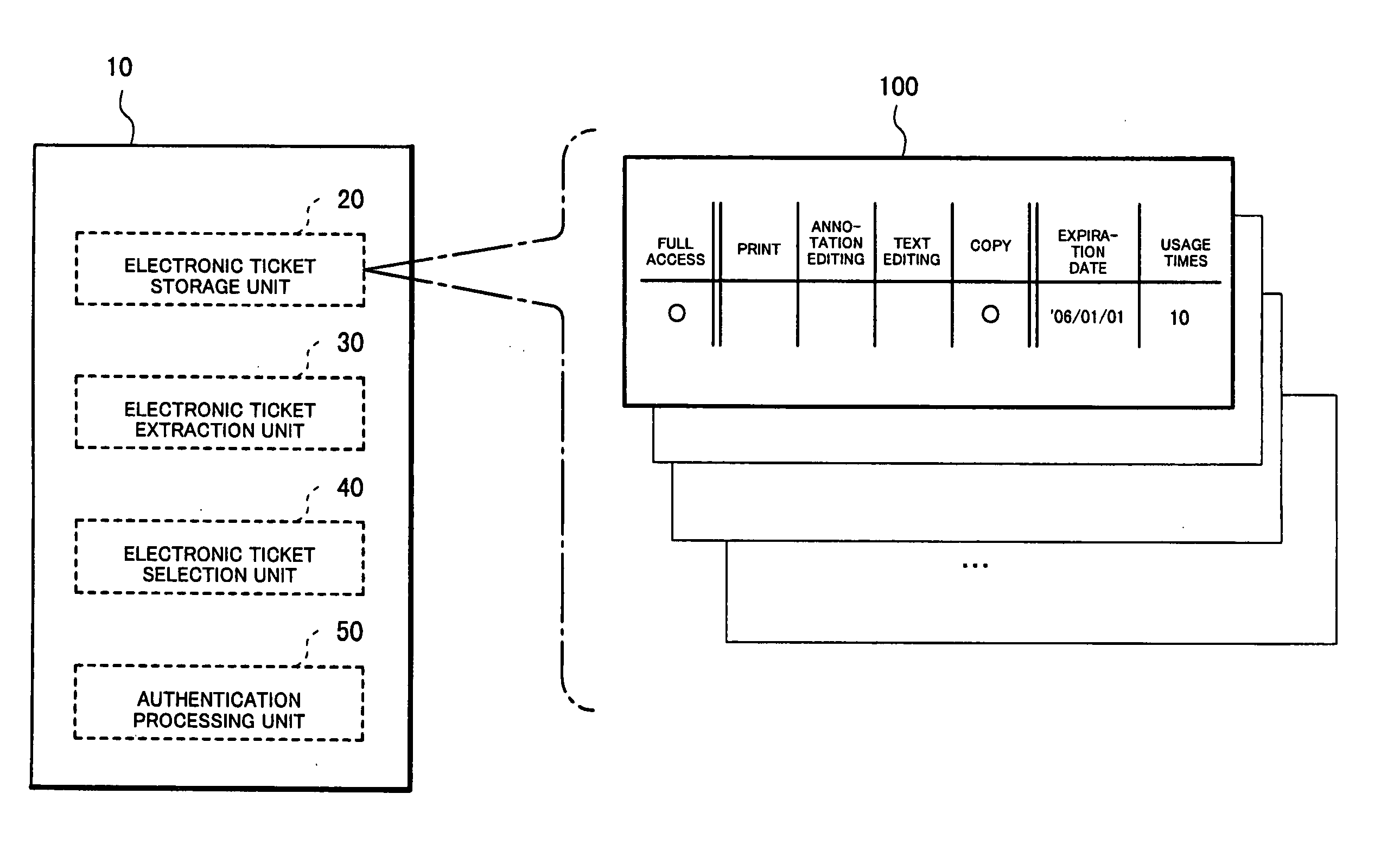
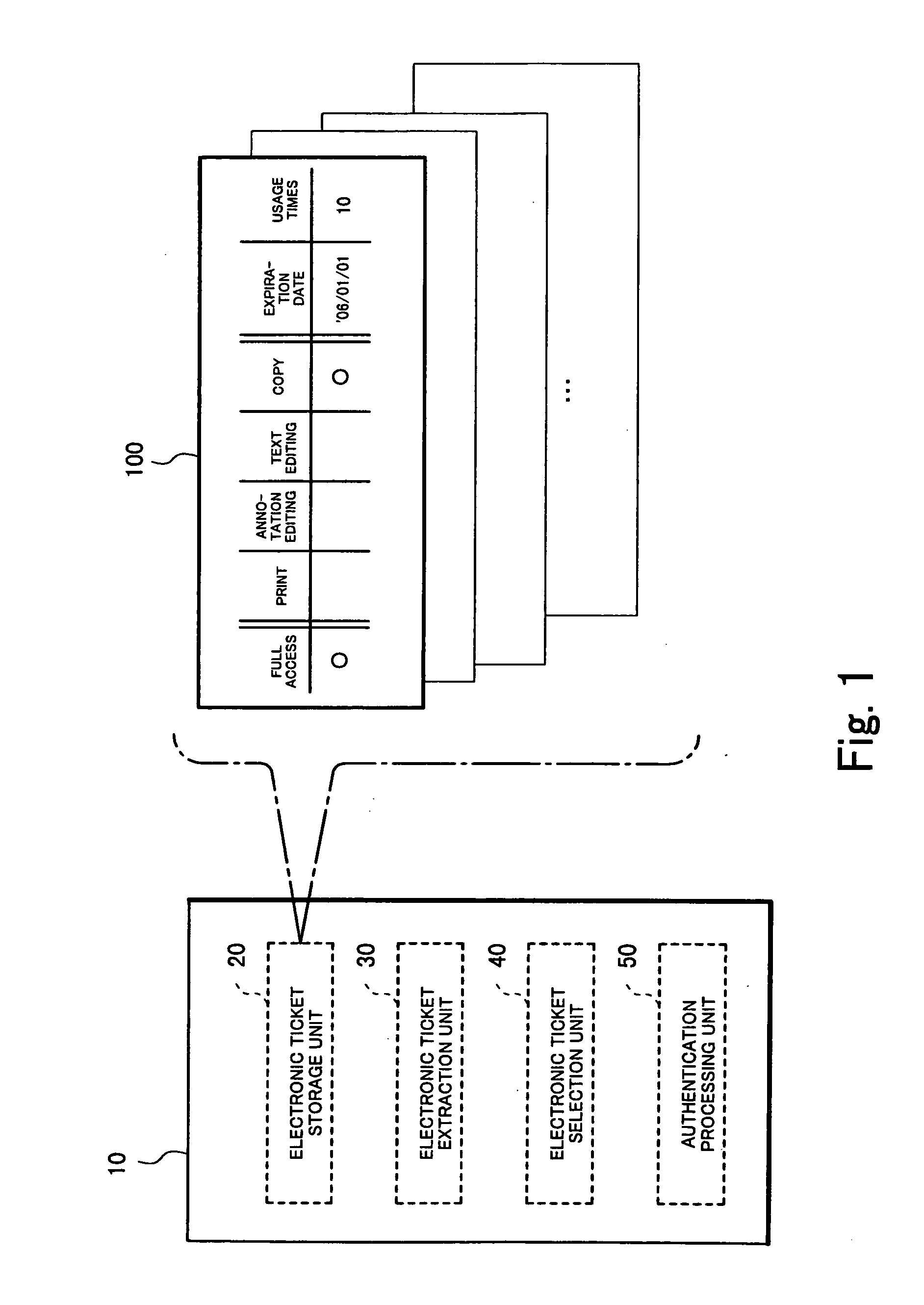
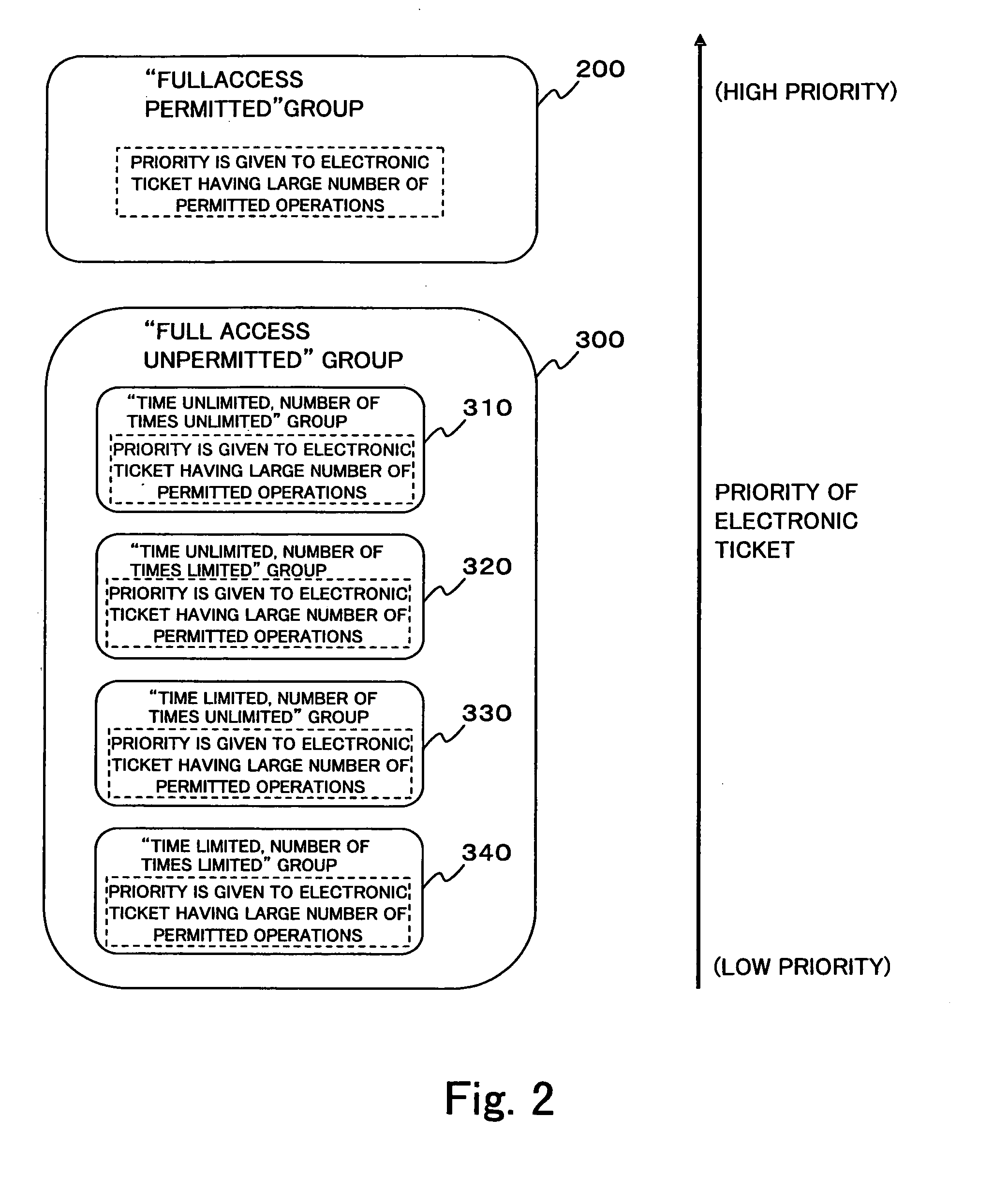
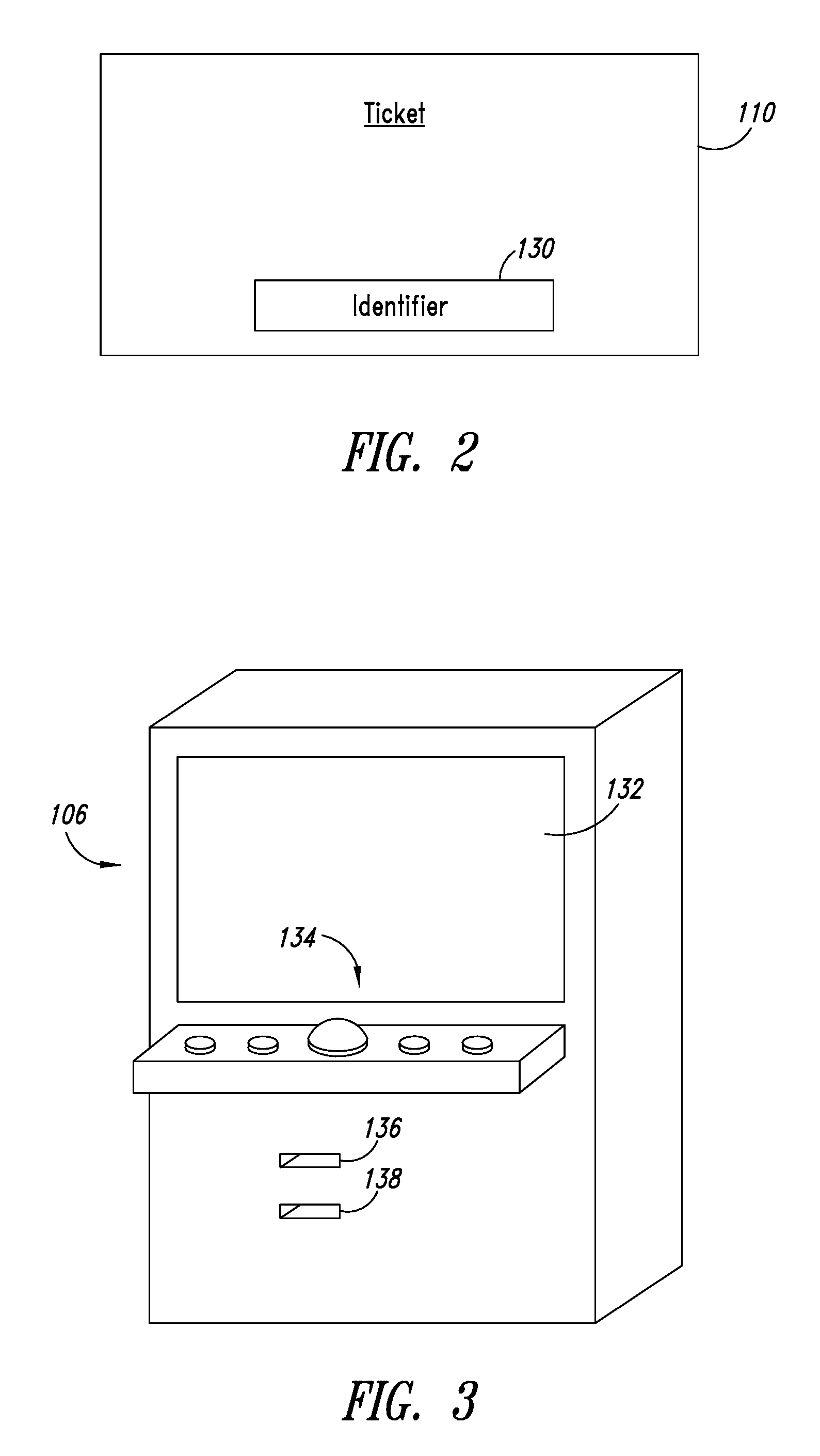
Recording medium with electronic ticket definitions recorded thereon and electronic ticket processing methods and apparatuses
InactiveUS6842741B1Easy to useComplete banking machinesTicket-issuing apparatusDatabaseRecording media
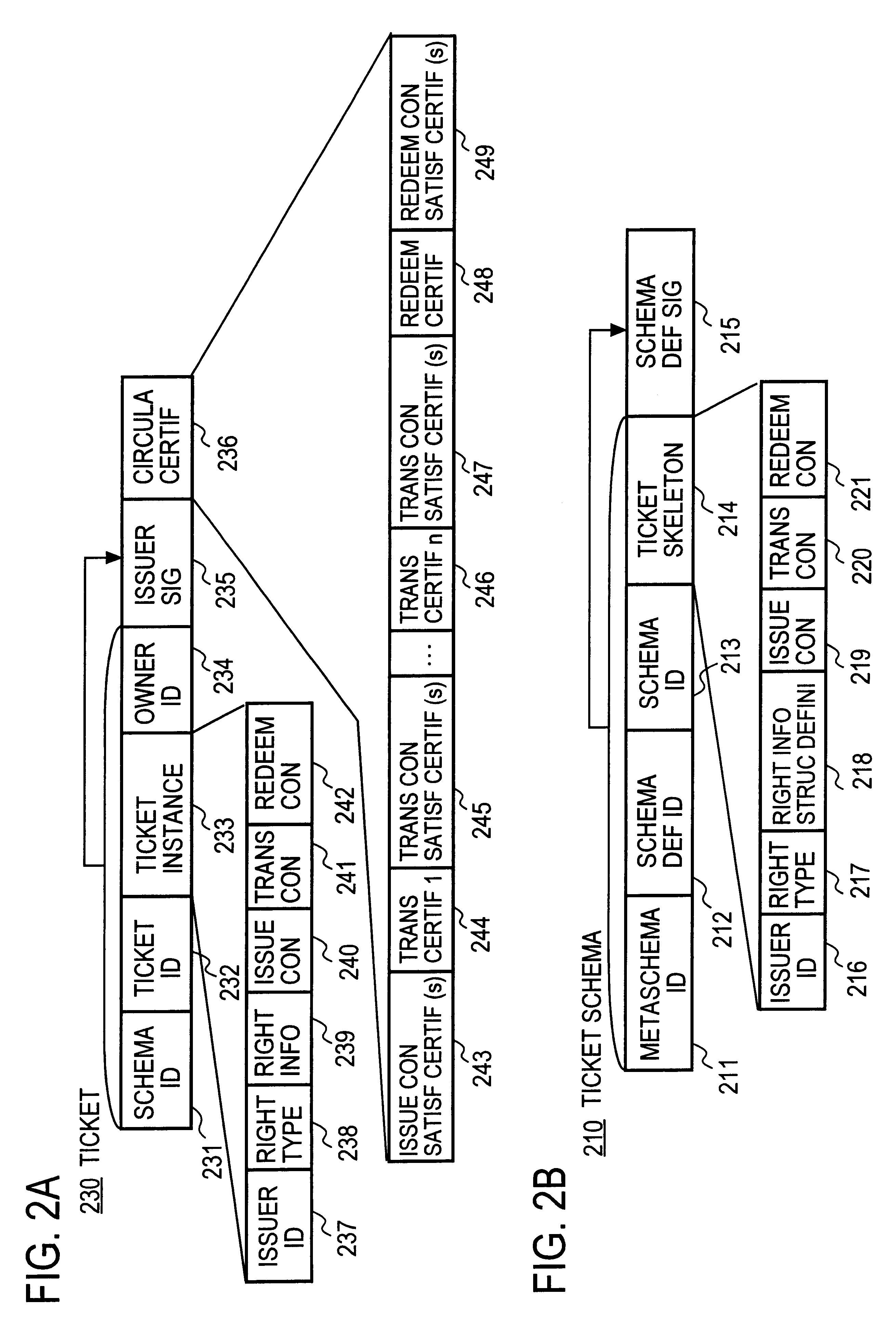
An electronic ticket comprises a ticket ID 233, an issuer ID 237, right information 239 of the electronic ticket, and issue, transfer and redeem conditions 240, 241 and 242, the entire block of these pieces of information being attached with an issuer's signature 235. In each of the issue, transfer and redeem conditions there are recorded ticket schema ID's which specify the types of tickets that the ticket sender and receiver are required to possess, and in each phase of the issue, transfer and redeem transactions it is verified whether these conditions are satisfied.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
System and method for application authorization
ActiveUS7805755B2Reduced promptingDigital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionPasswordApplication software
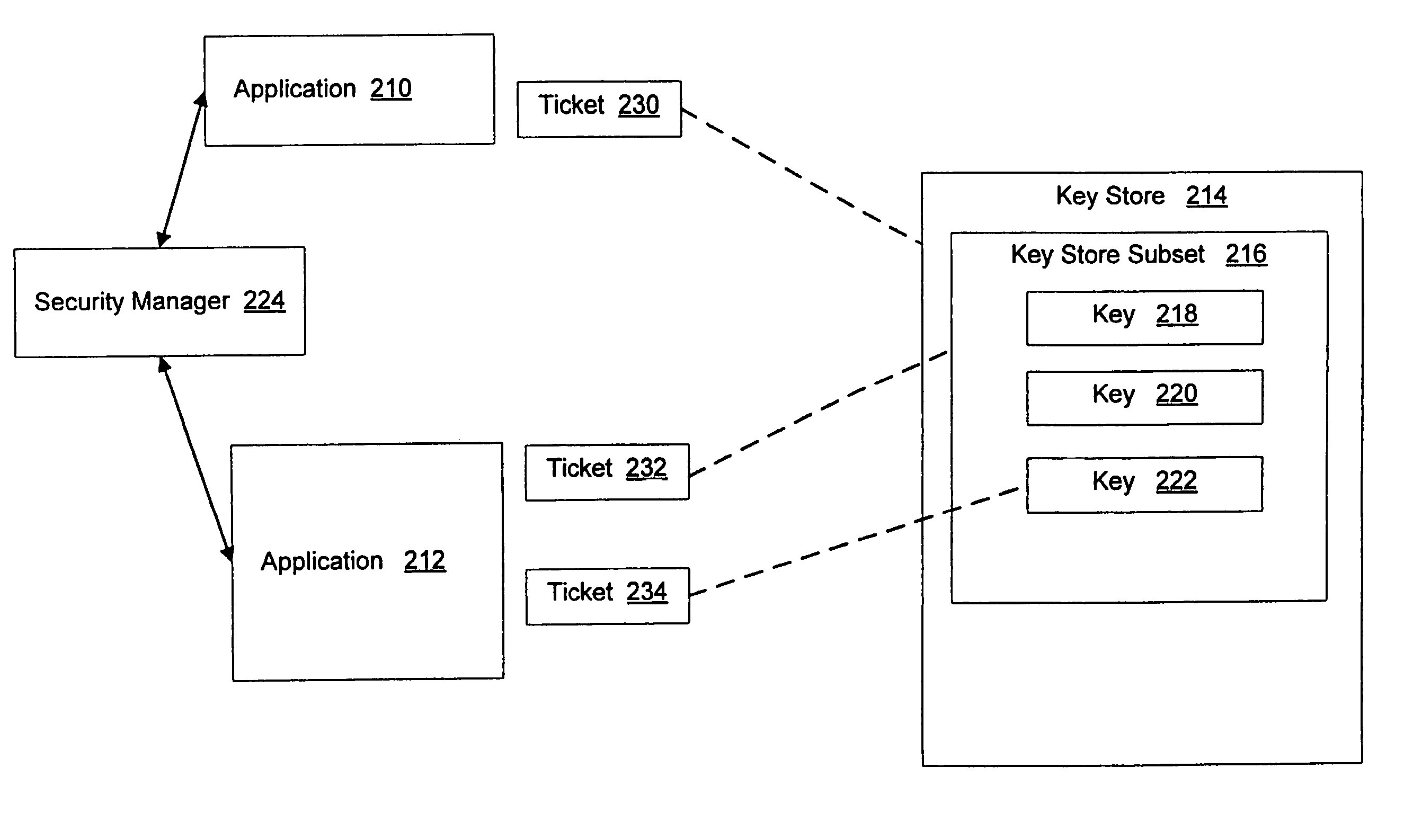
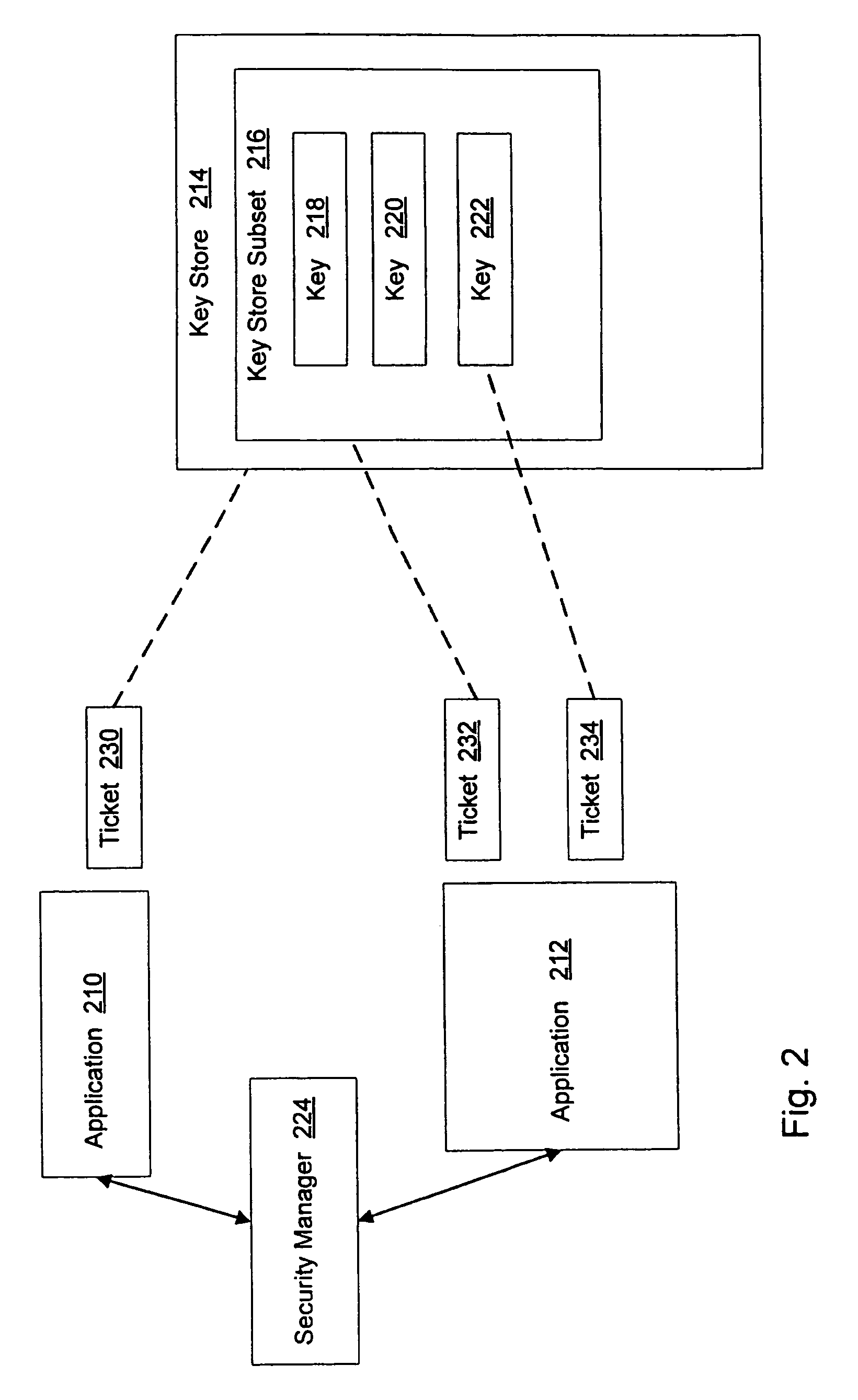
A method and system for authorization of applications executing on a device having a key store. Applications obtain an application-level ticket to permit access to one or more key values located in the key store. Each ticket is securely associated with an application and being generated on the determination that the application is a trusted application. Tickets are potentially associated with one key value in the key store, with a subset of key values in the key store, or with all key values in the key store. Access to key values by an application is possible independently of a user providing a password for each such access.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
System and methods of determining computational puzzle difficulty for challenge-response authentication
InactiveUS20110231913A1Low costEnsure correct executionDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsGeographic siteComputational intelligence
Computational puzzles are parameterized by a difficulty variable which may be assigned based on at least one component from the group of components: time component, location component, reputation component, usage component, content component, and social networking component. For example, in one embodiment, the proof-of-work puzzle comprises a location component directed by the geographic location of the client that can be applied to any web transaction or application. One such application involves online ticket sales including those that employ purchasing robots. Another application involves accessing and using webmail.
Owner:THE OREGON STATE BOARD OF HIGHER EDUCATION ACTING BY & THROUGH PORTLAND STATE UNIV
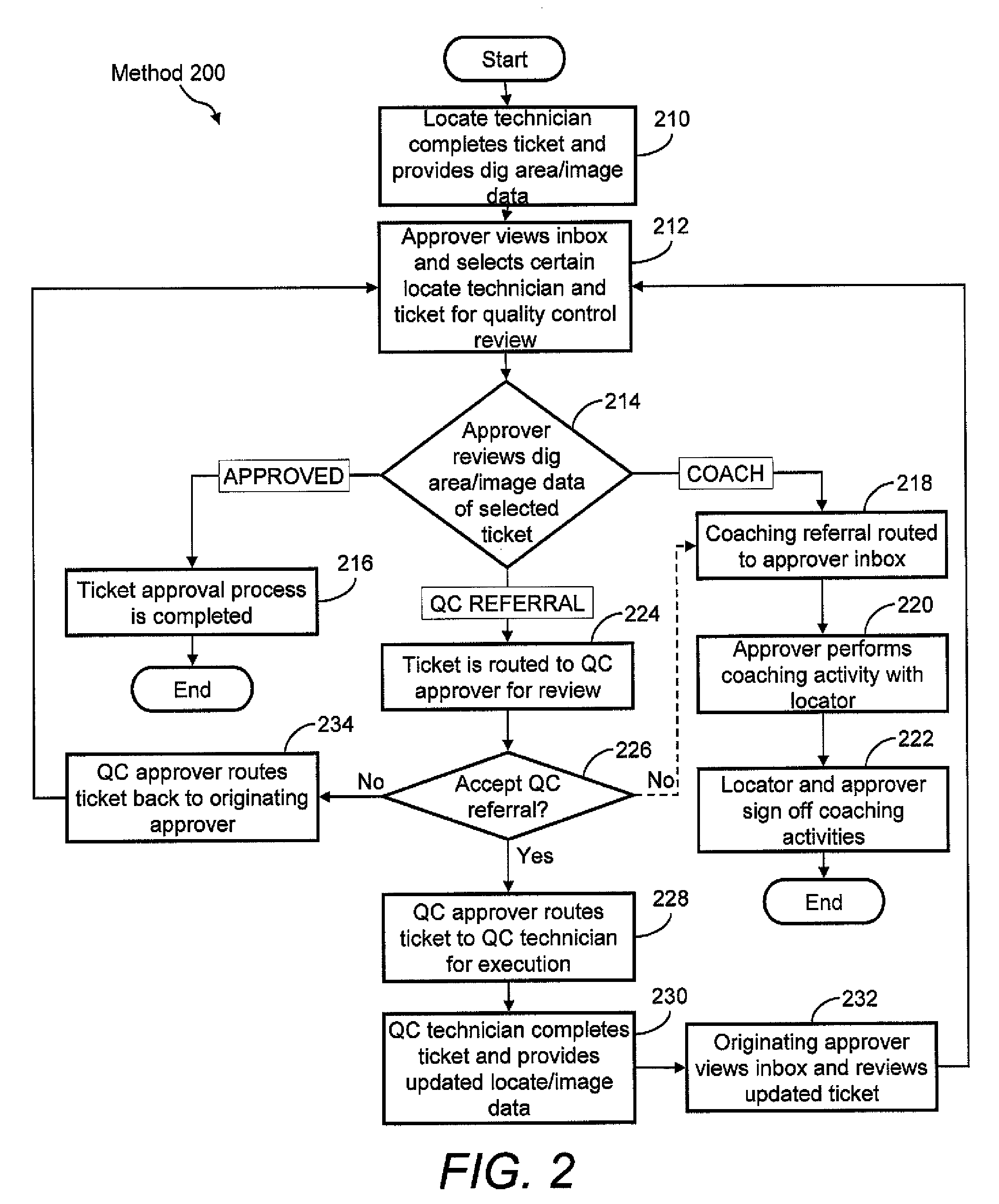
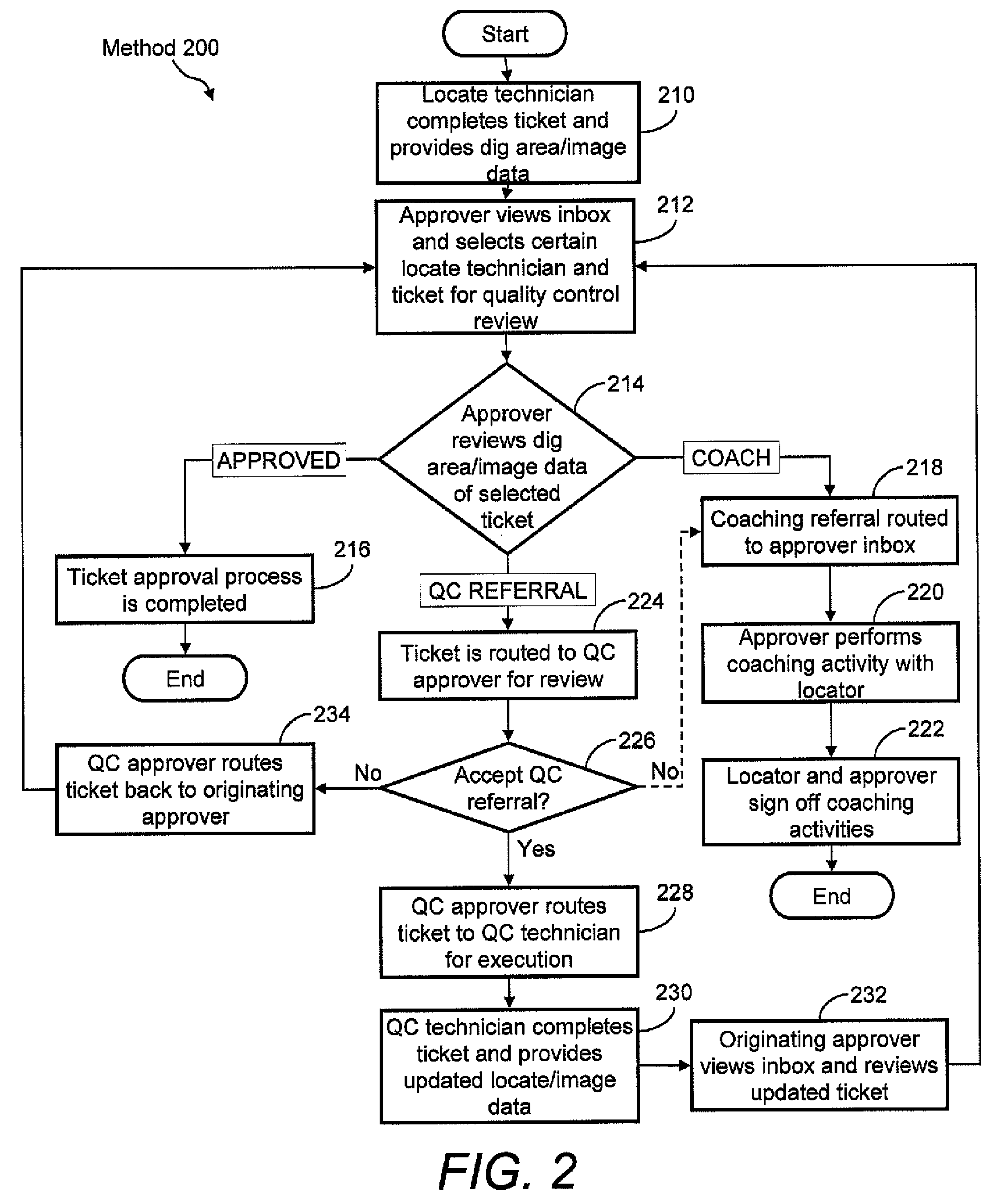
Ticket approval system for and method of performing quality control in field service applications
Methods for overseeing and assessing a locate and marking operation. A ticket is received including ticket information regarding the operation, and a first locate technician is dispatched to perform the operation pursuant to the ticket information. A locate manifest is received that includes at least one digital image associated with a dig area in which the locate technician performed the operation. The locate manifest is compared to the ticket information, and a determination is made if the operation is 1) satisfactory, 2) unsatisfactory and requires further quality control assessment and / or at least partial re-performance, or 3) satisfactory but the first locate technician requires coaching. One or more electronic indications of one of 1), 2) and 3) are provided so as to generate an electronic record of a quality assessment of the locate and marking operation.
Owner:CERTUSVIEW TECH LLC
Electronic System and Apparatuses Coupling Ticketing on Mobile Devices with Event Sponsorship and Interaction
The instant disclosure is a continuation in part of this inventor's previously disclosed US and PCT patent applications that claim operating systems, apparatuses and mobile phone devices for live event and common carrier electronic ticketing, event interaction and the end-to-end production, editing, authenticated distribution and management of event-associated Recordings. It now adds placement of at least one of a logo, message, icon, ad or public service announcement on an electronic ticket, entry pass, admission / placed bet or other receipt and on event-related Recordings as a technological production solution for global brands and program sponsors that is independent of placing ads on search engine Websites and their links.
Owner:GURVEY AMY R
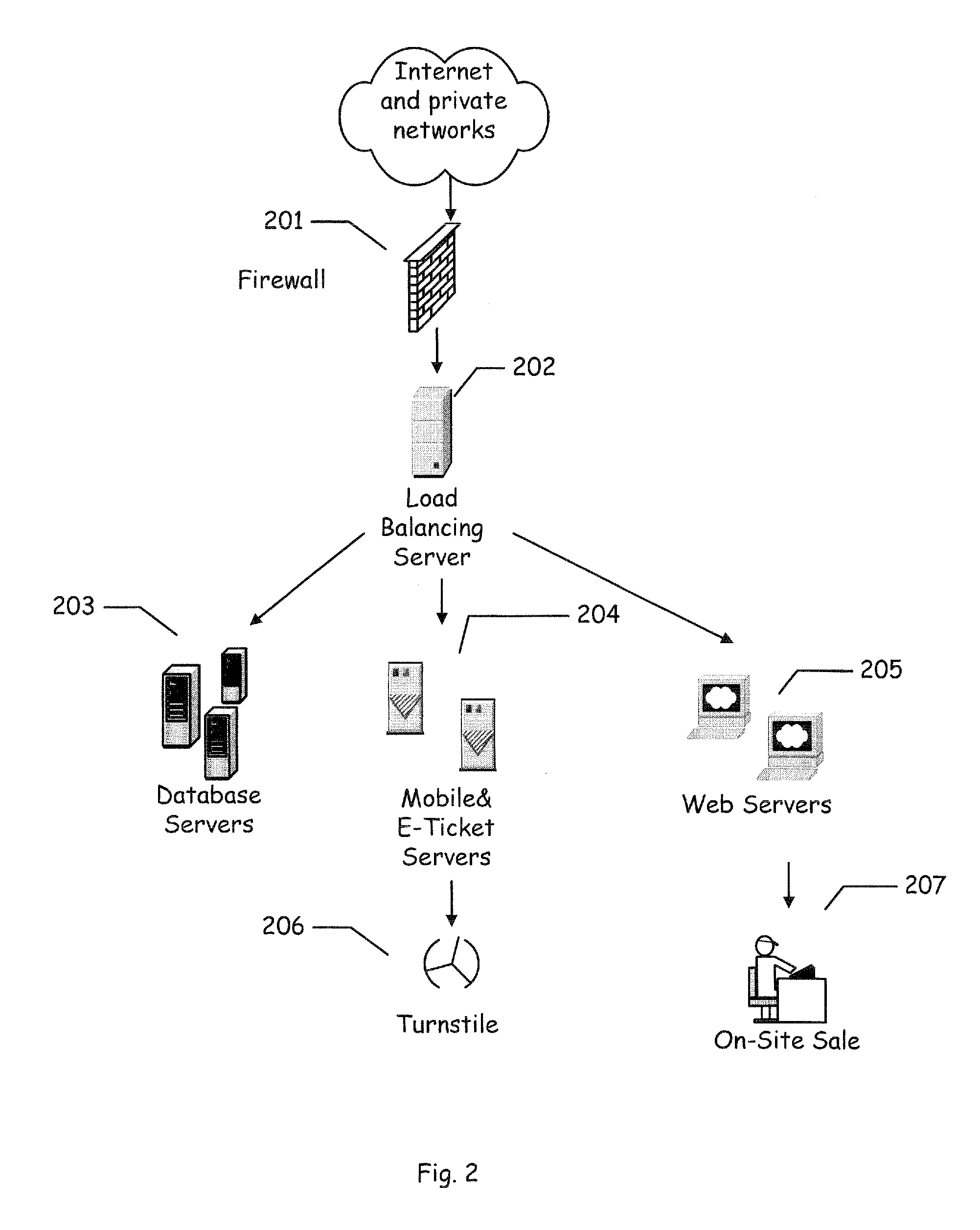
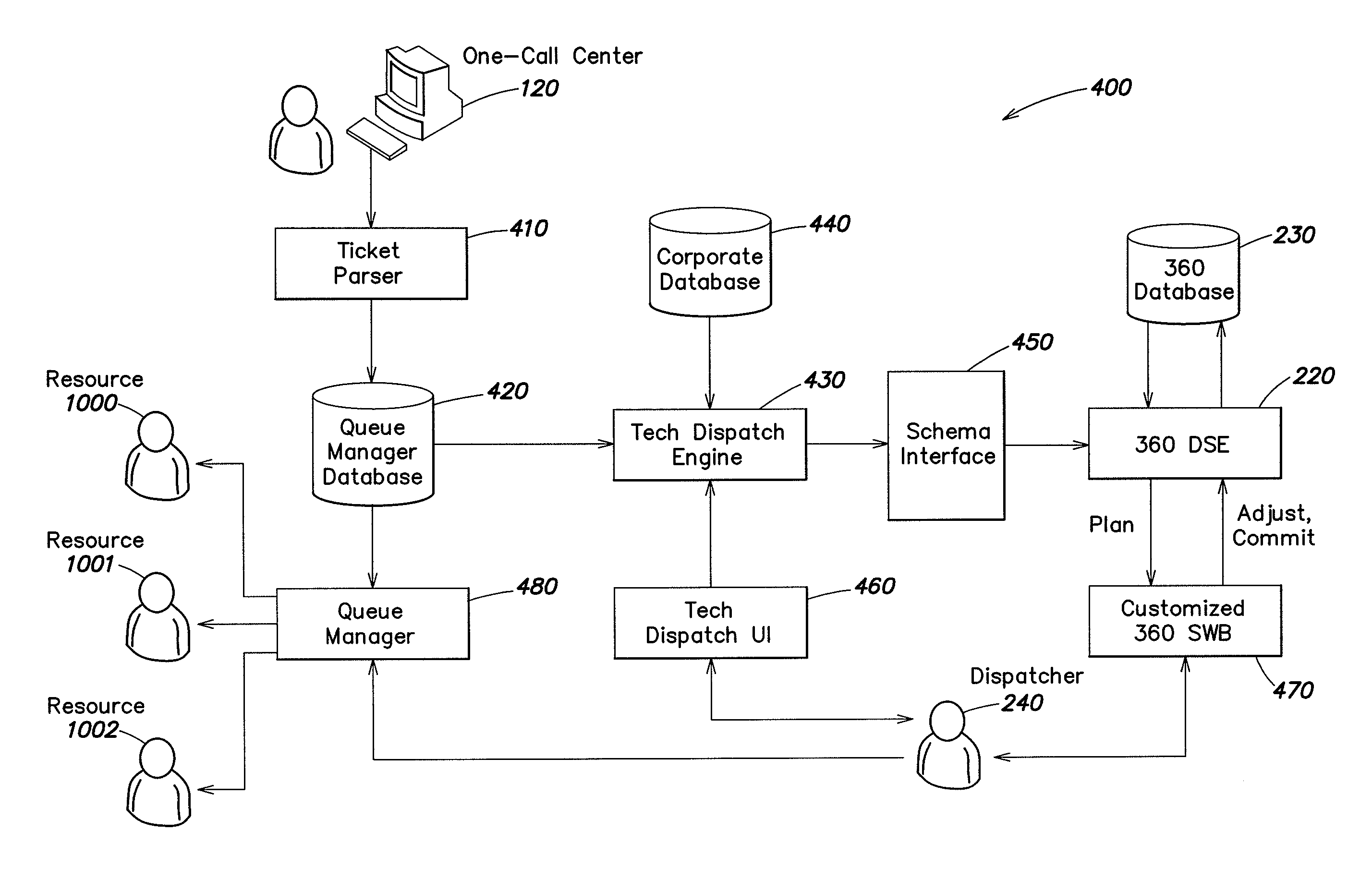
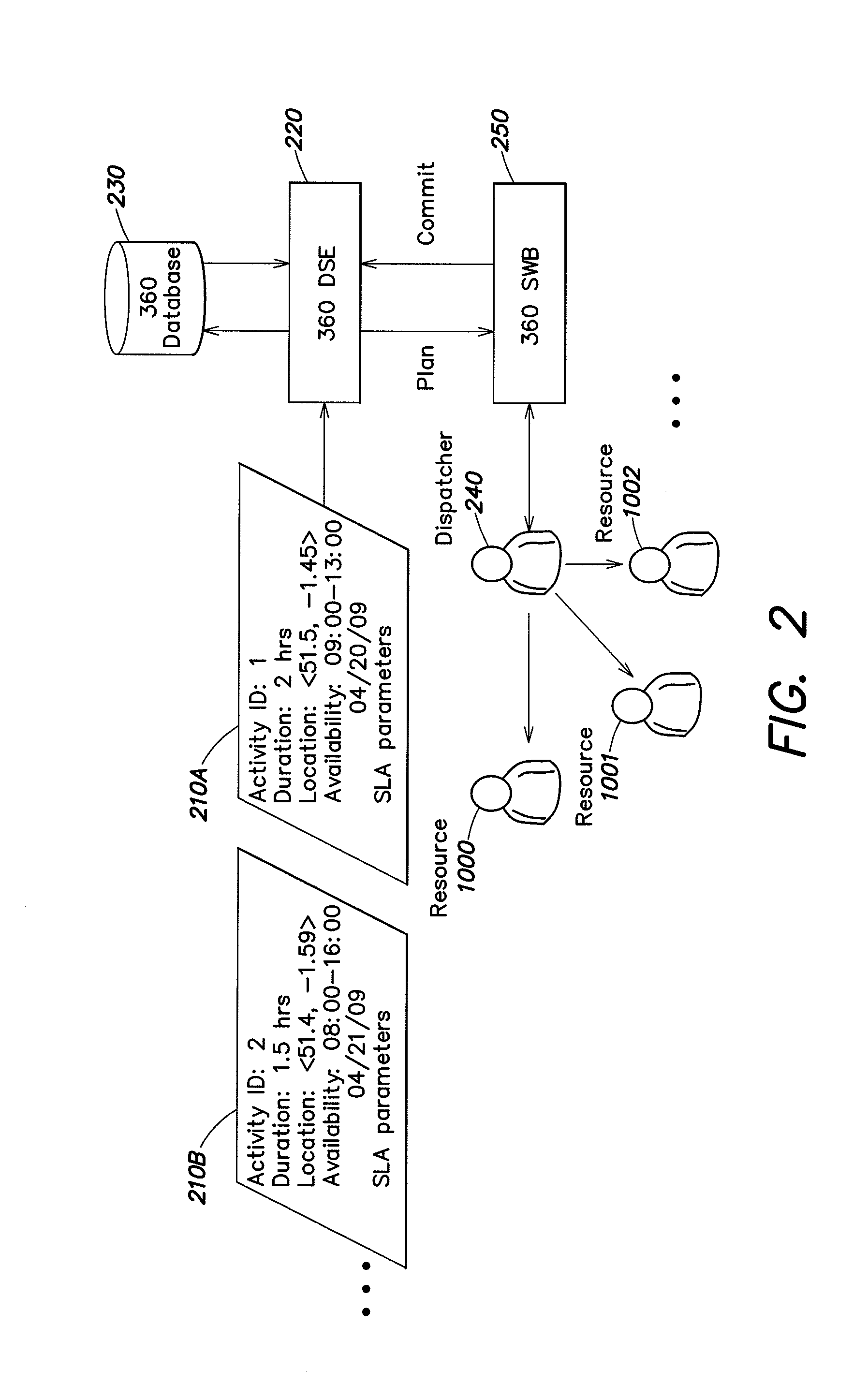
Methods, apparatus, and systems for dispatching service technicians
ActiveUS8612276B1The degree of freedom becomes largerQuality improvementInstrumentsResource informationField service
Scheduling of activities for field service technicians may be improved by modifying availability constraints associated with appointment windows for activities. Activities may be scheduled based on a performance deadline and relevant shift times of the resources to whom the activity may be allocated, as well as a variety of parameters relating to activities, resources and / or relevant environmental conditions (e.g., weather, traffic). An activity may be moved from one calendar day to another, a location constraint at the beginning and / or the end of a technician's shift may be removed or modified, and / or information updates may be provided in real time or near real time (e.g., every five minutes or less) throughout a work day to facilitate scheduling. In one example for scheduling dispatch of locate technicians for locate operations, ticket information relating to locate request tickets, as well as resource information relating to available technicians, may be extracted from a ticket database and a resource / technician database to provide appropriate inputs to a scheduling engine, based at least in part on matching available resources to performance deadlines associated with locate requests.
Owner:CERTUSVIEW TECH LLC
Method of transmitting and reproducing content processed by various DRM systems
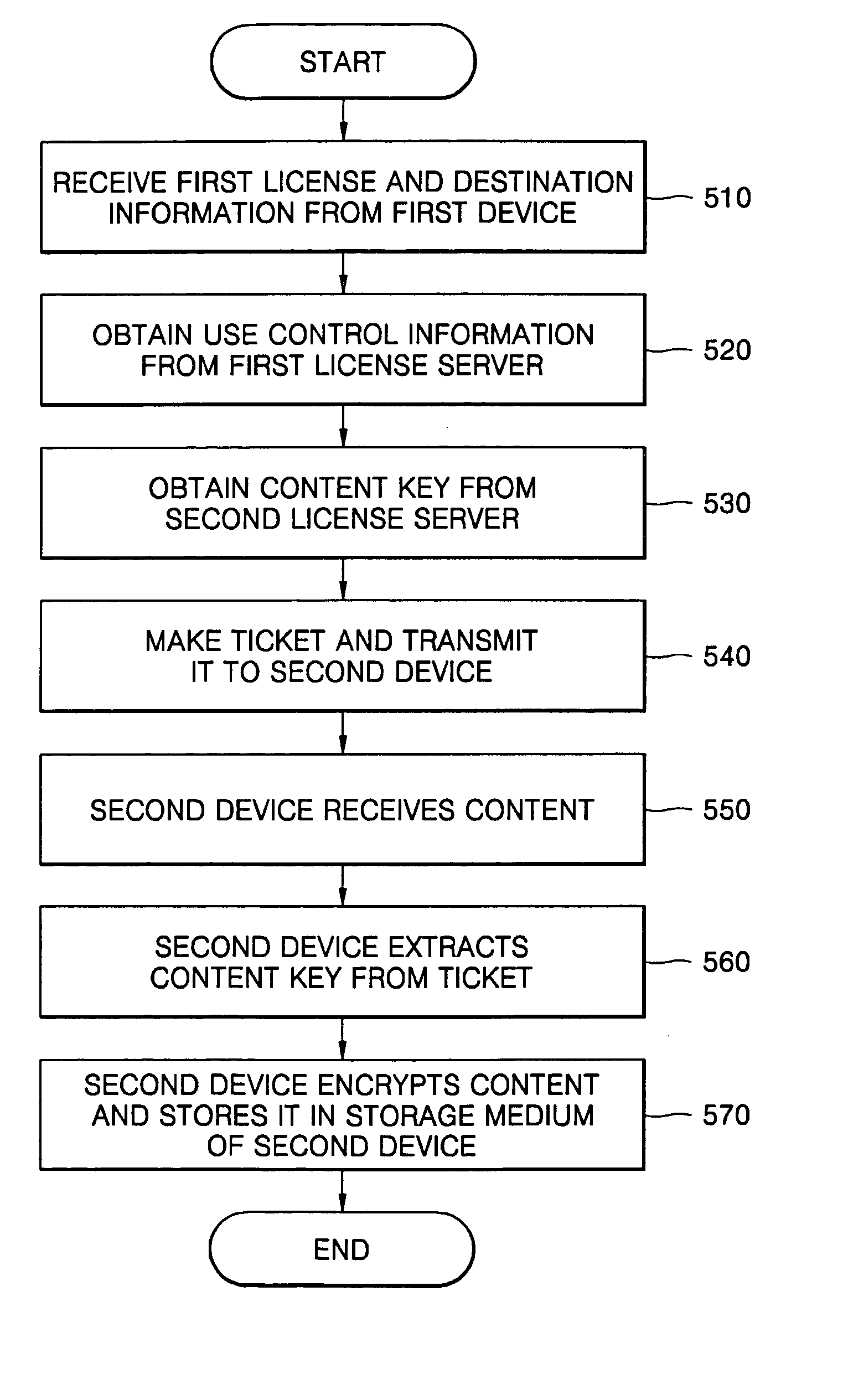
ActiveUS20060026691A1Load minimizationDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationTicketEngineering
Provided is a method of transmitting content processed according to first digital rights management (DRM) to a device that uses second DRM. The method includes generating a ticket using a first license server and a second license server, the first license server issuing a first license for use in the first DRM and the second license server issuing a second license for use in the second DRM; the second device obtaining a second content key required to process the content using the ticket and the second DRM; and the second device receiving the content from the first device and processing the content using the second content key and the second DRM. The ticket includes use control information that specifies a restriction of use of the content, and the second content key required to process the content using the second DRM.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
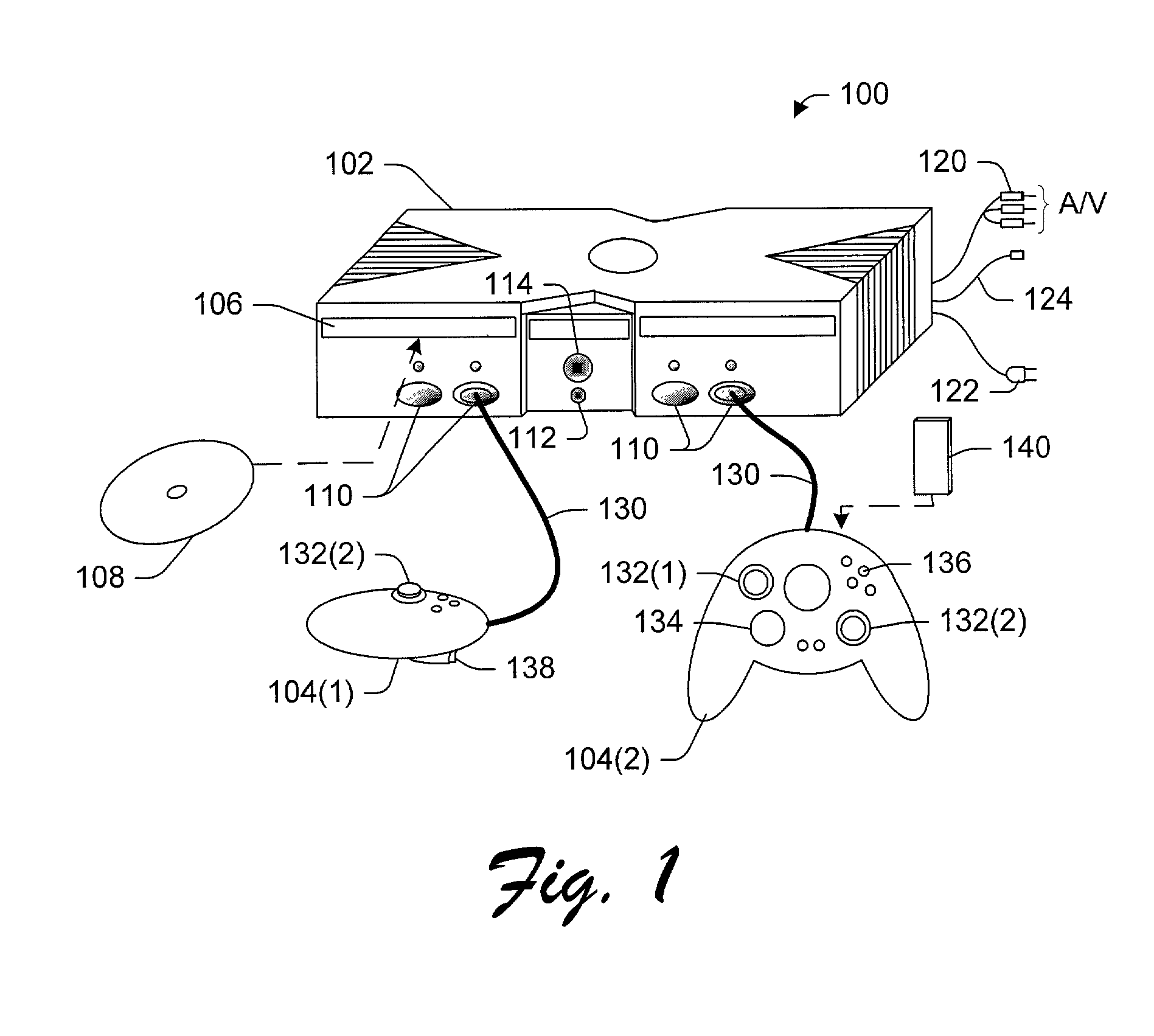
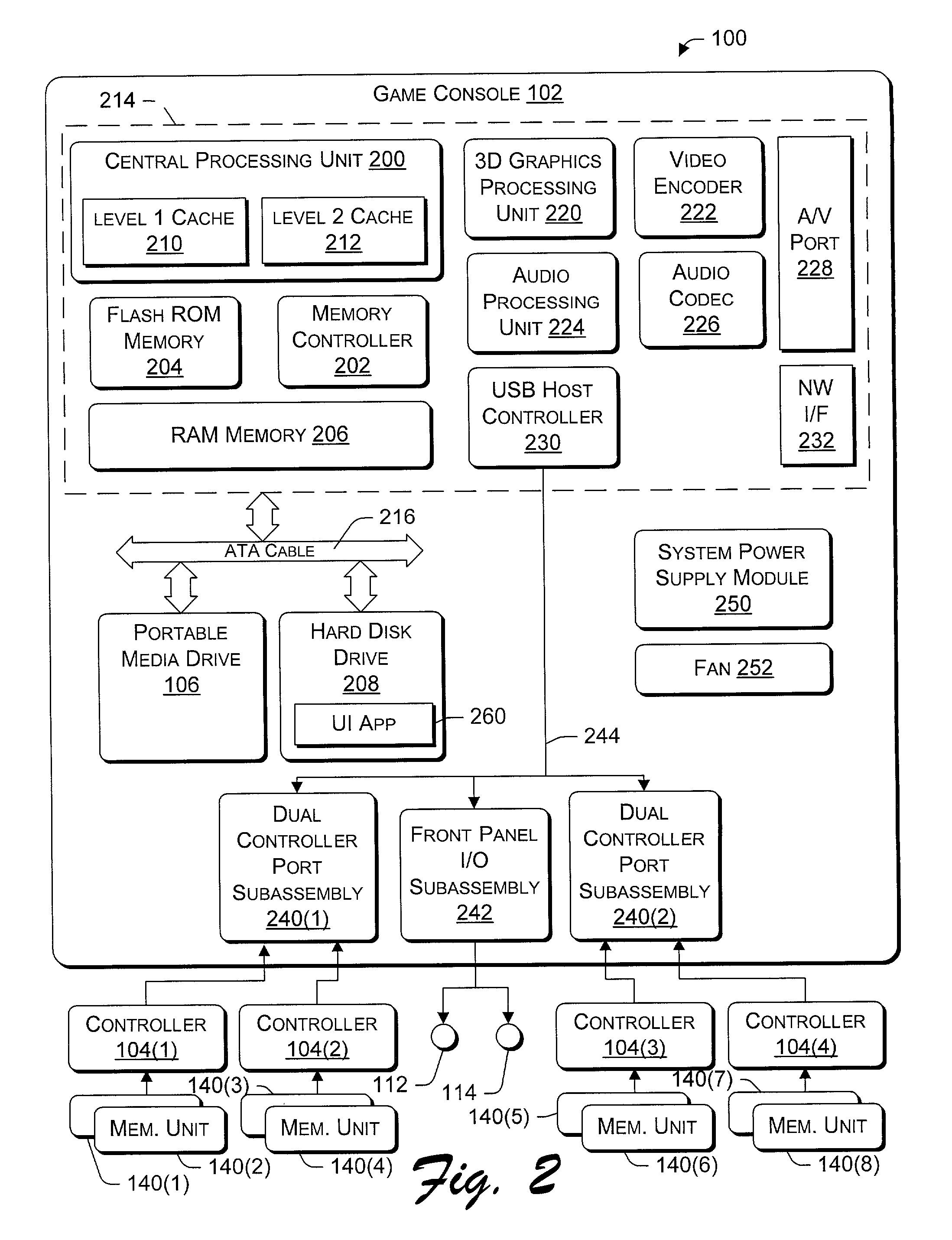
Multiple user authentication for online console-based gaming
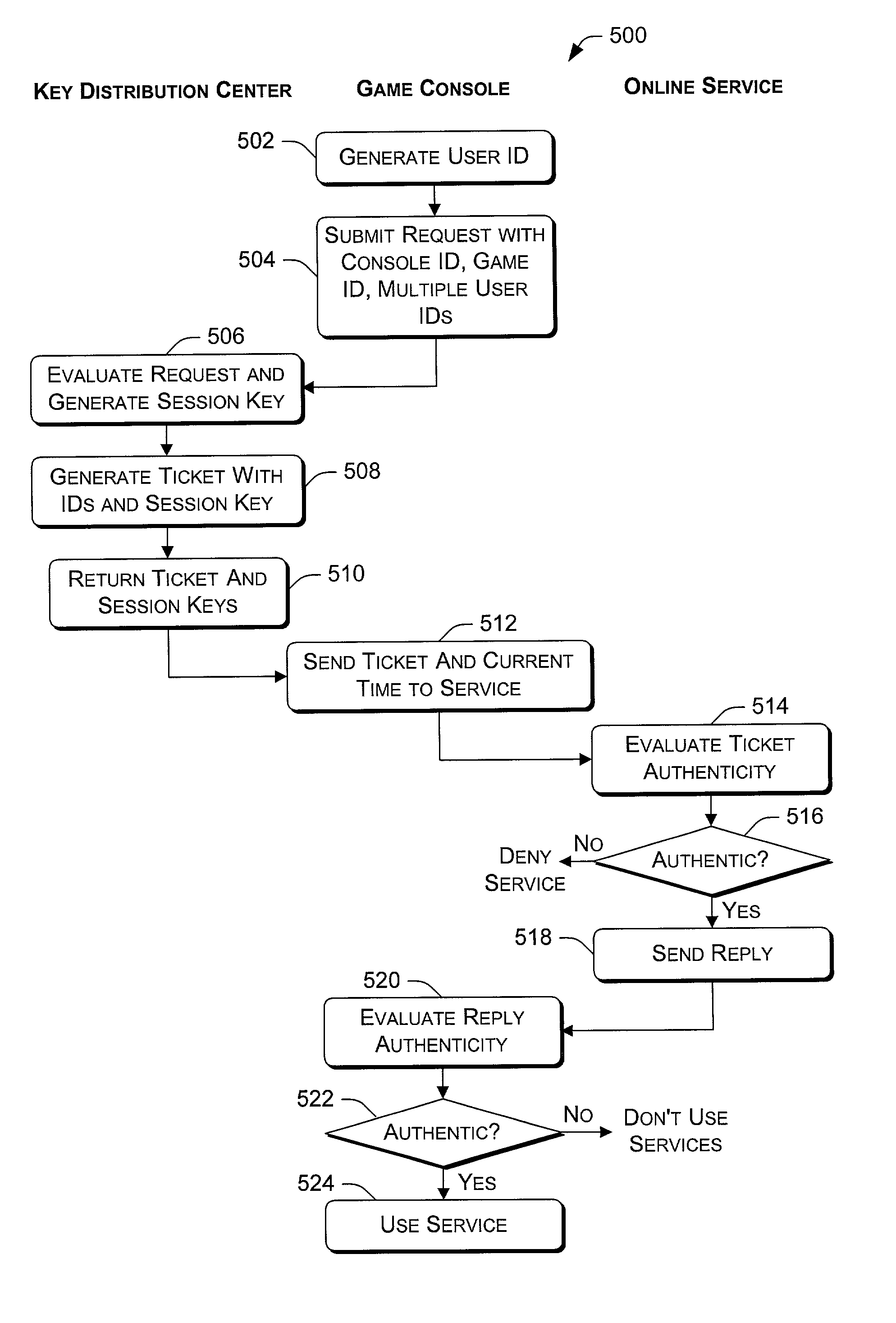
InactiveUS20020126846A1Key distribution for secure communicationData processing applicationsTicketInternet privacy
A console-based multi-user authentication process allows multiple users of a game console to be authenticated together in a single request / reply exchange with an authentication entity. The results of which is the possession of a single ticket that can be used to prove authenticity of multiple authentication principals to one or more online services. Also described is a handshake process that can be used to initially establish an authentication account for each game console, in which the account creation server can trust that a genuine game console is making the request.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Medium storing program selecting electronic ticket, electronic ticket processing apparatus and electronic ticket selection method
InactiveUS20060188097A1Digital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsInformation retrievalSelection method
One or more computer-readable media on which is stored a program for selecting an optimum electronic ticket among a plurality of electronic tickets for imparting rights of use of content, the stored program causing a computer to execute functions comprising: extracting a plurality of electronic tickets corresponding to a content; and selecting the optimum electronic ticket among the extracted electronic tickets by comparing conditions of use of content included in the respective extracted electronic tickets.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
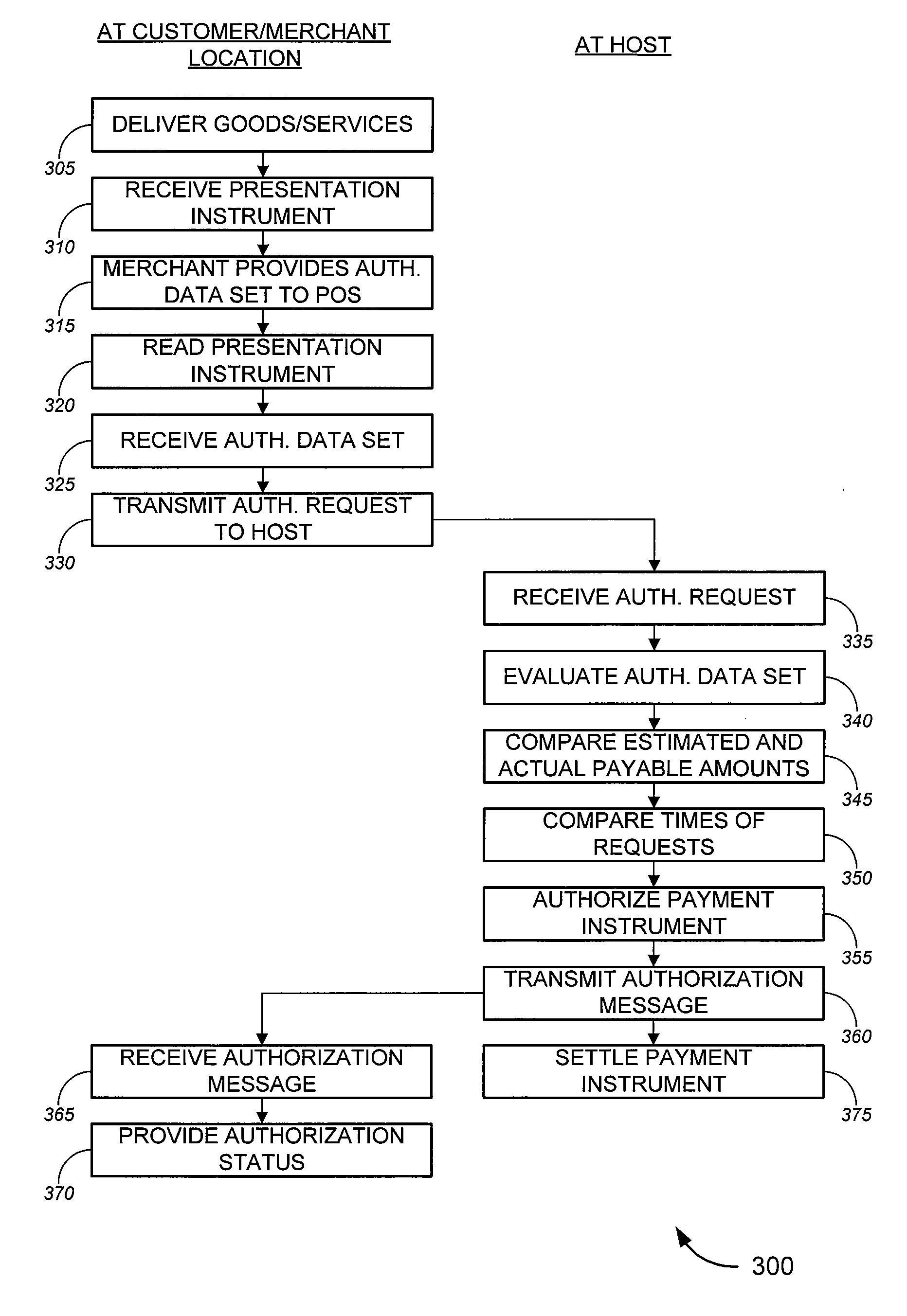
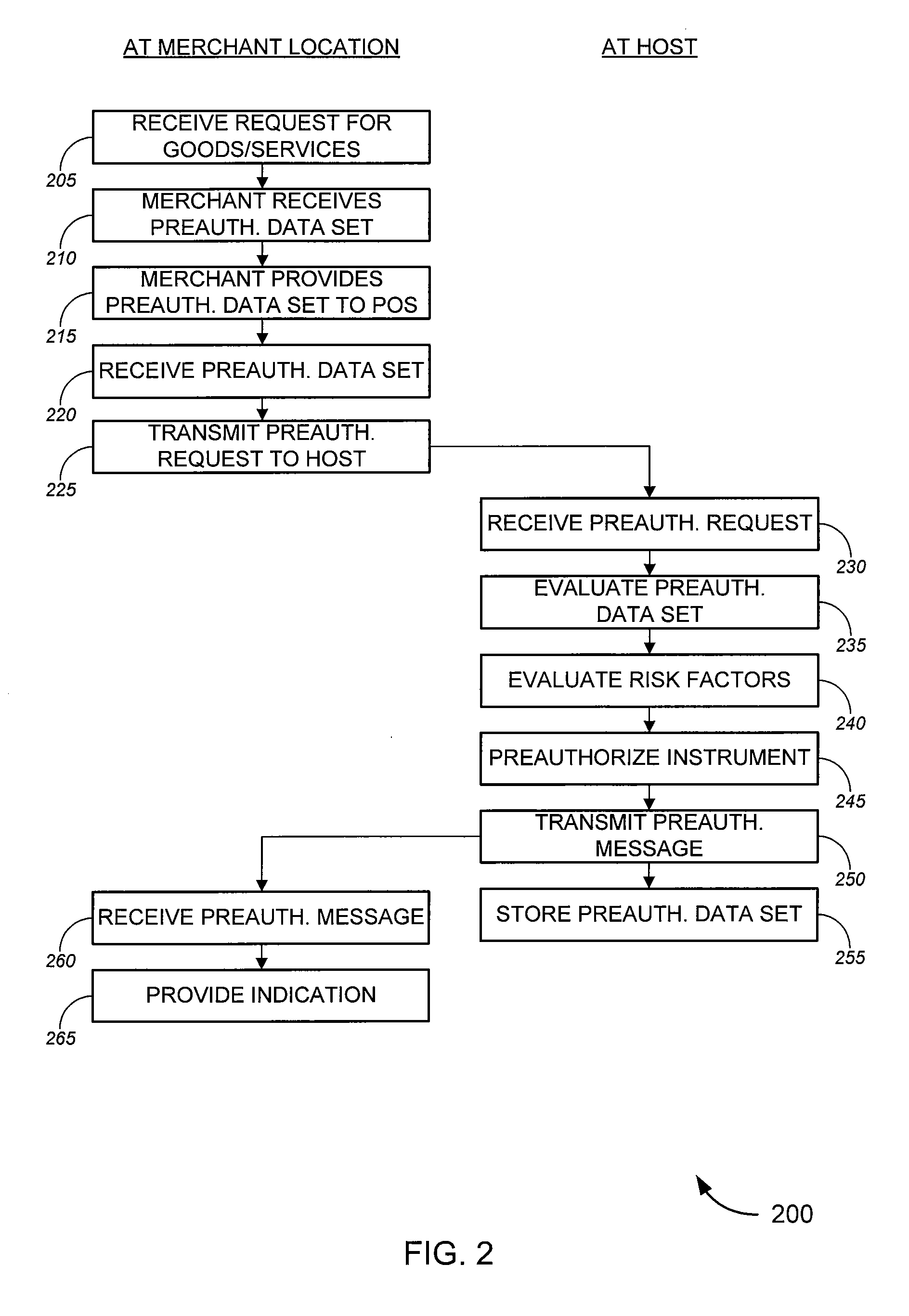
Personal check acceptance systems and methods
Tools for facilitating the acceptance of personal checks and other presentation instruments. The tools, in some aspects, allow for preauthorization of a personal check (or other presentation instrument) prior to the merchant receiving the actual check, allowing a merchant, for example, to accept an order by phone, obtain details about the check that will be used to pay for the order, obtain preauthorization to accept the check, and arrange for delivery of the order. Upon delivering the order, the merchant can receive the check, and then obtain a full authorization to accept the check. The full authorization can be based primarily on the preauthorization, giving the merchant assurance that the check will in fact be authorized. In some cases, the tools of the invention also settle the check; in a particular aspect, the check can be settled without requiring the merchant to deposit the check.
Owner:FIRST DATA
Systems and methods for proxying encrypted traffic to protect origin servers from internet threats
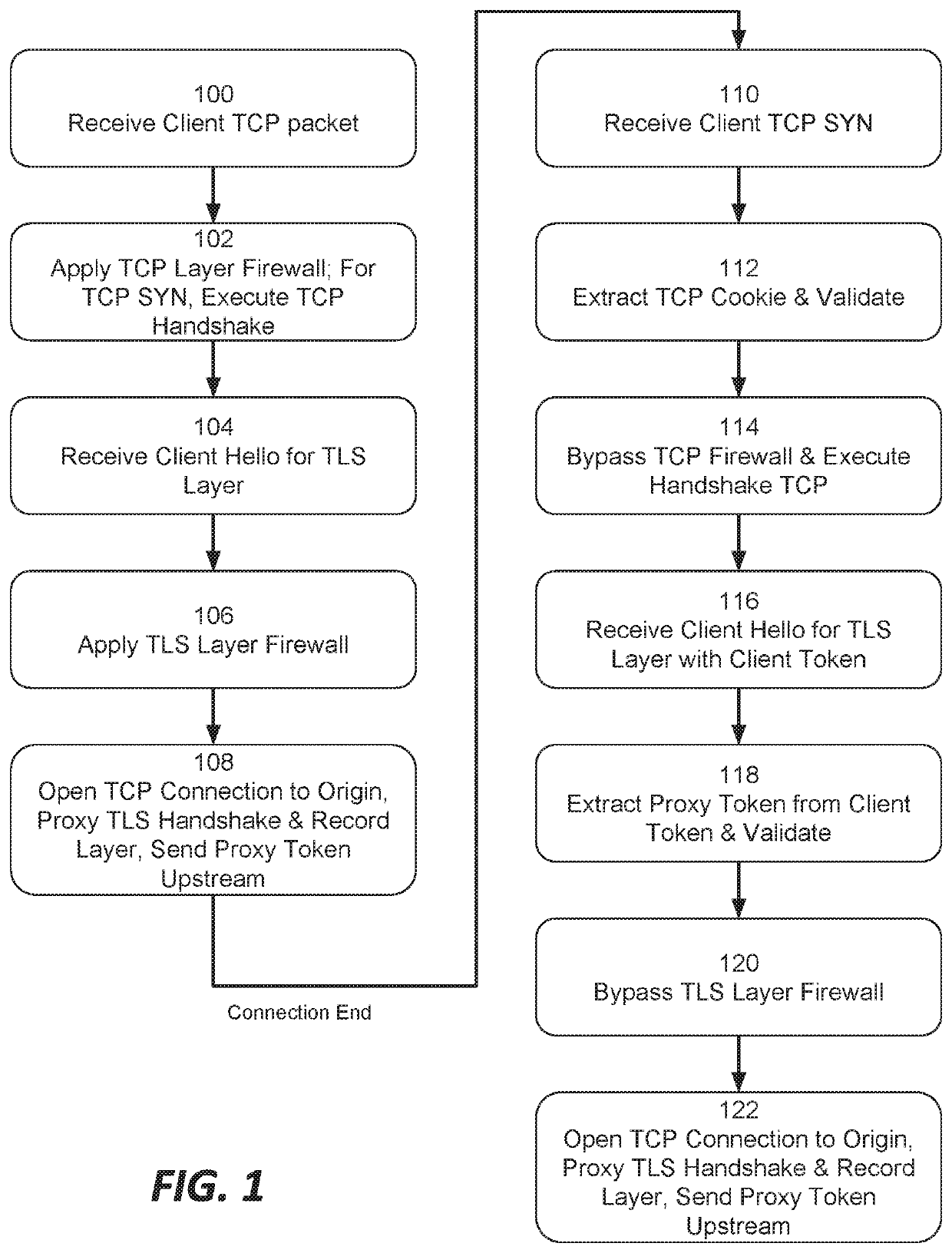
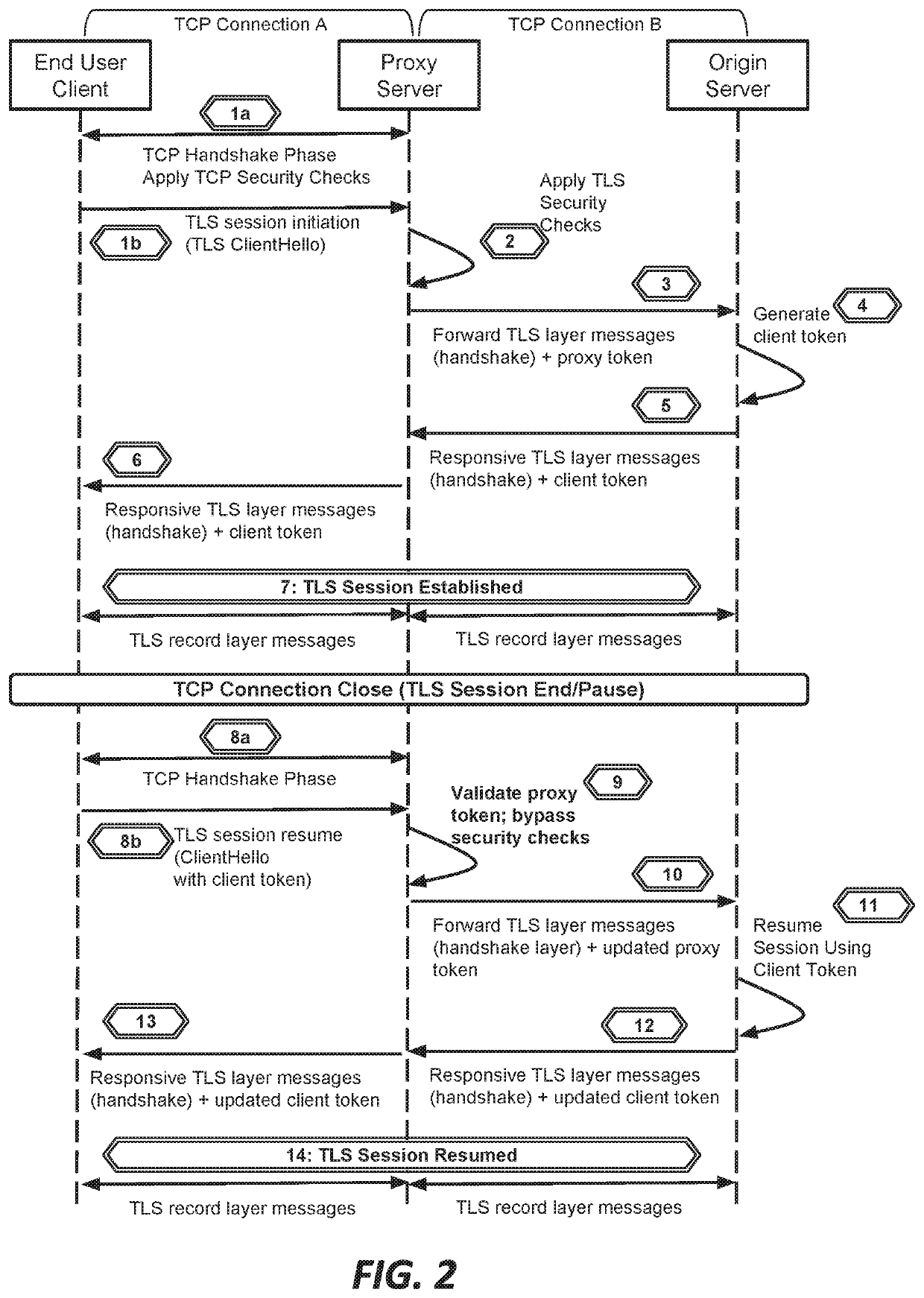
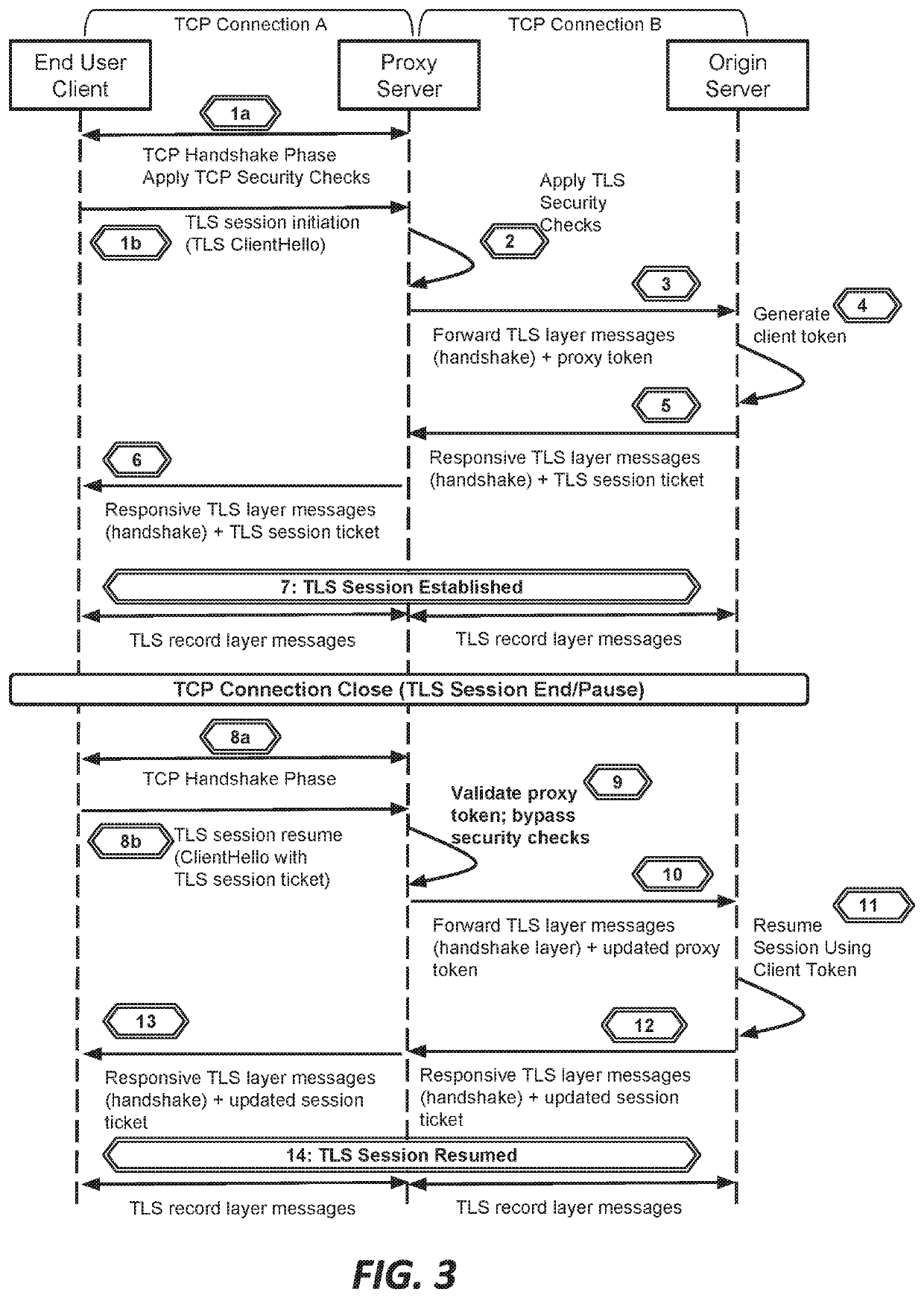
This document describes, among other things, systems and methods for more efficiently resuming a client-to-origin TLS session through a proxy layer that fronts the origin in order to provide network security services. At the time of an initial TLS handshake with an unknown client, for example, the proxy can perform a set of security checks. If the client passes the checks, the proxy can transmit a ‘proxy token’ upstream to the origin. The origin can incorporate this token into session state data which is passed back to and stored on the client, e.g., using a TLS session ticket extension field, pre-shared key extension field, or other field. On TLS session resumption, when the client sends the session state data, the proxy can recover its proxy token from the session state data, and upon successful validation, bypass security checks that it would otherwise perform against the client, thereby more efficiently handling known clients.
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
Device control using job ticket scoring
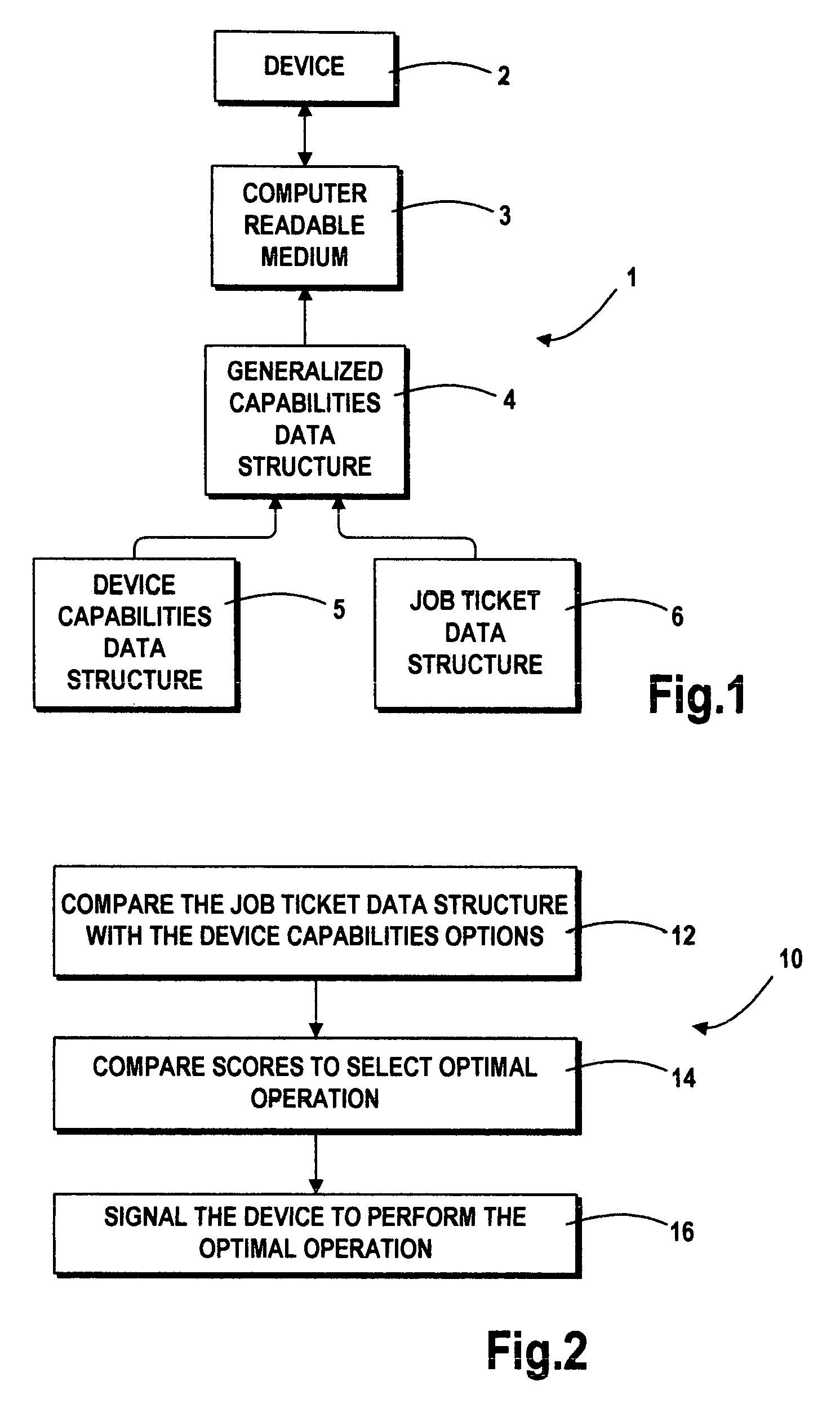
ActiveUS6975820B2Electrographic process apparatusDigital output to print unitsXML schemaComputer printing
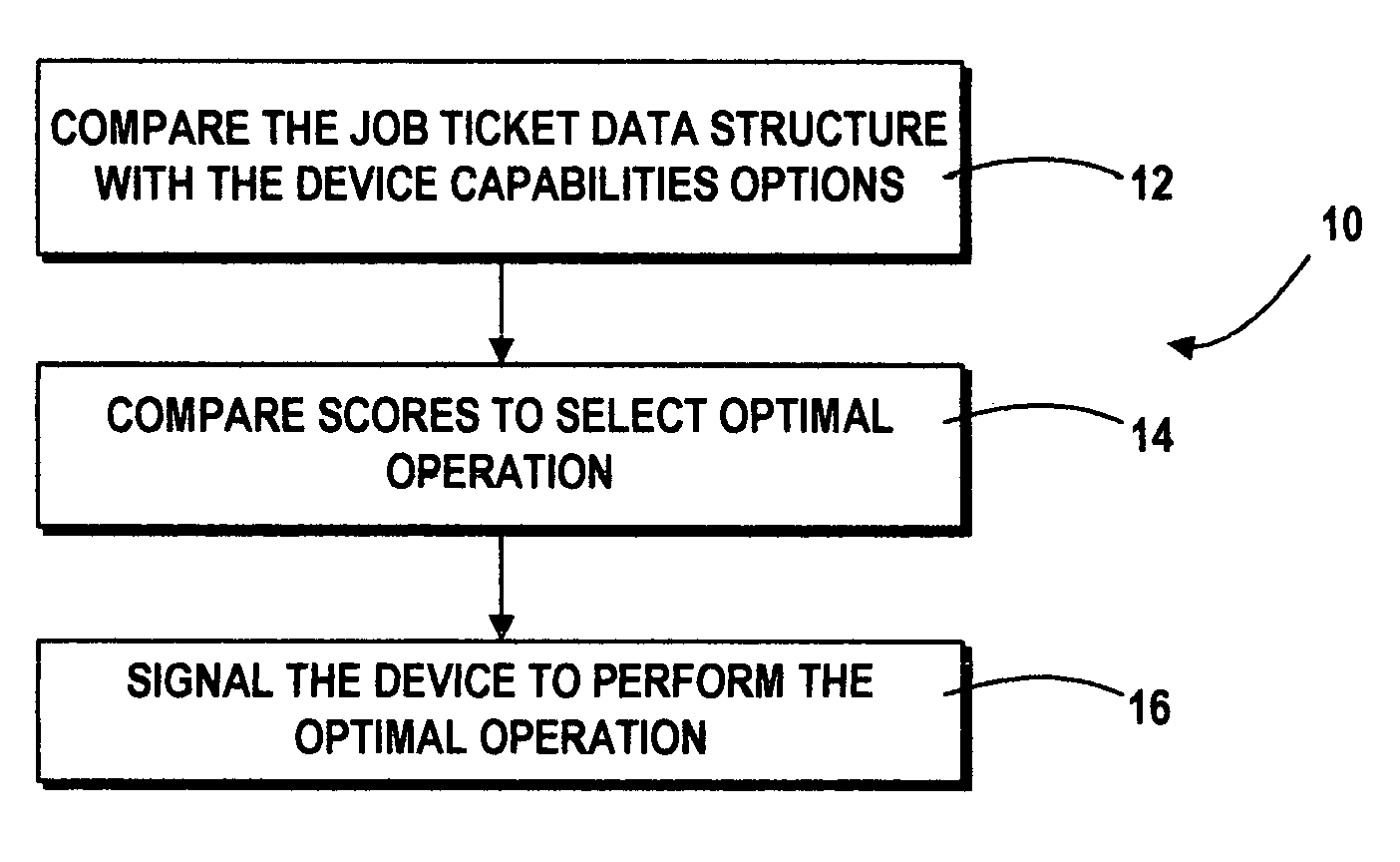
A method for controlling a device capable of performing an operation in response to a job ticket includes comparing the job ticket with options within the capabilities of the device for fulfilling the job. One such device is a printer coupled to a computer for printing text and the like in accordance with such a job ticket. The job configuration and the options defining the plurality of operations preferably are stored in data structures, most preferably XML files validated under an XML schema defining options for a universe of similar operations. Each comparison of the job configuration with a device capability option results in a score. These scores are compared to obtain an optimal or preferred option which best approximates the job ticket within the capabilities of the device.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Systems, methods, and devices for providing purchases of instances of game play at a hybrid ticket/currency game machine
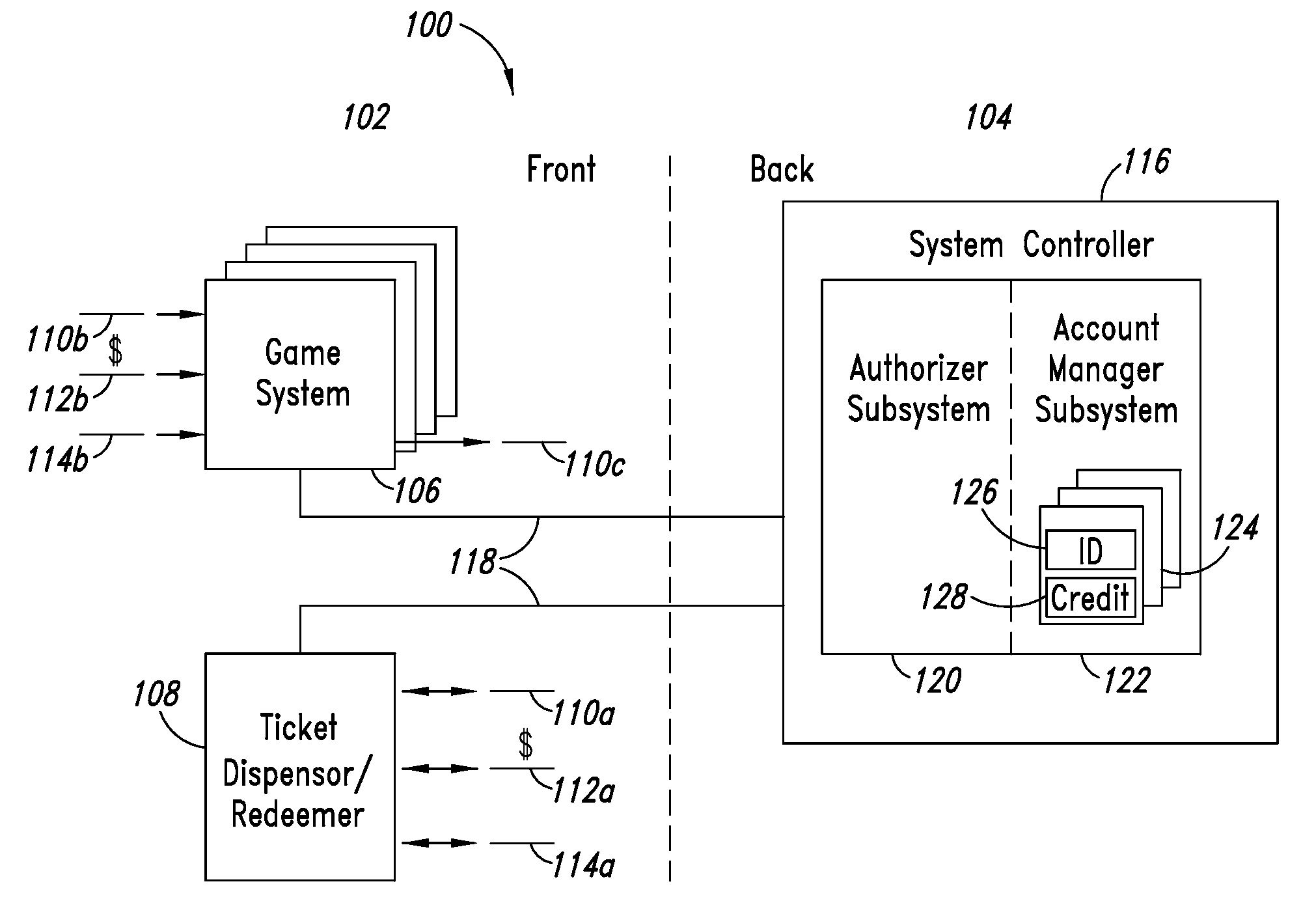
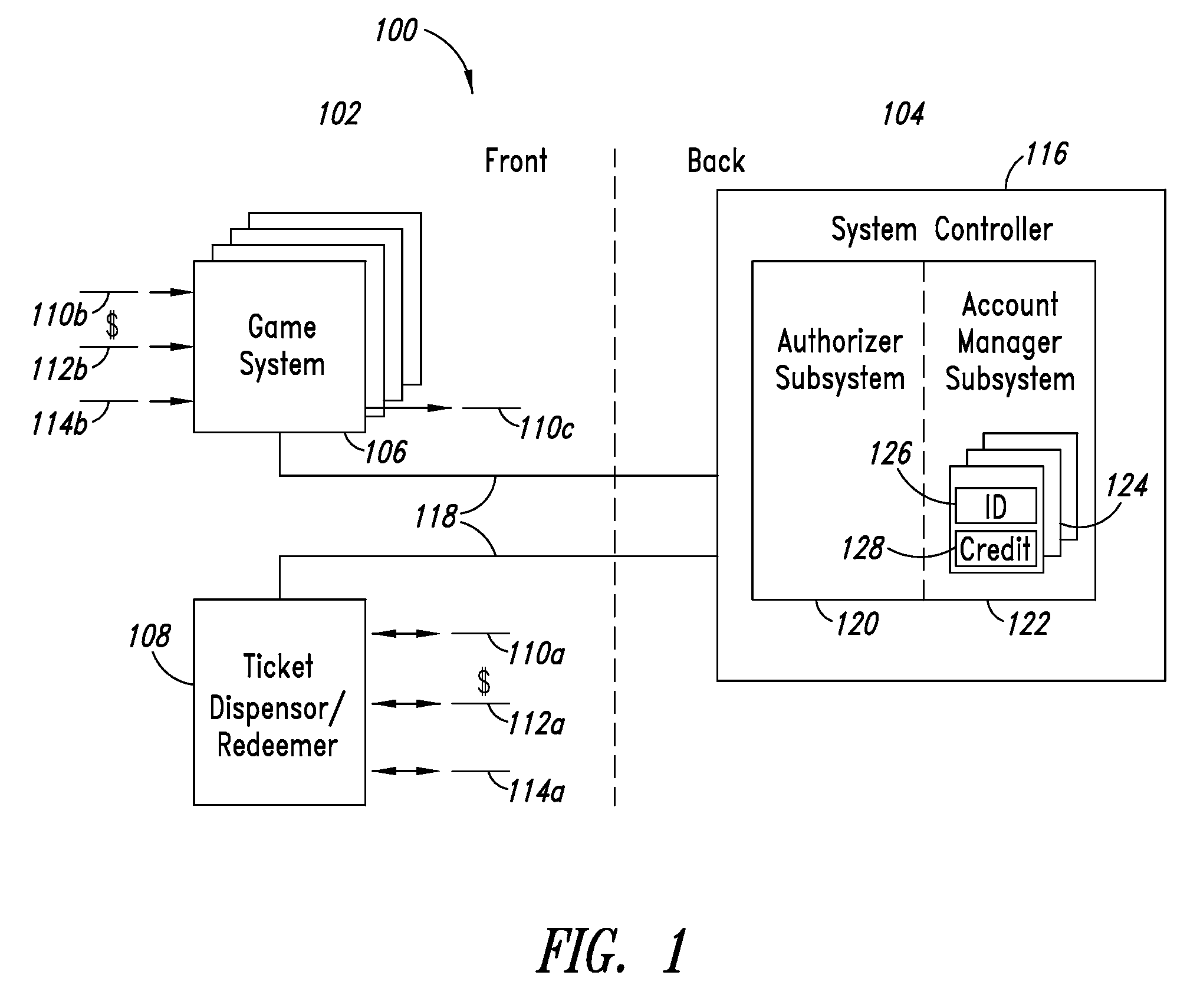
ActiveUS20090170594A1Payment architectureApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingSystems approachesAuthorization
Systems, methods, and devices may be capable of allowing a player to purchase an instance of game play at a game system with a pre-paid ticket or with another item of value. The game system may determine a denomination of a unit of a currency and generate a session request indicative of the denomination. The game system may also determine a ticket code of a ticket and generate a session request indicative of the ticket code. A remote authorizer may provide the game system with game authorization indicative of a number of entertainment credits in response to receiving a session request.
Owner:LNW GAMING INC
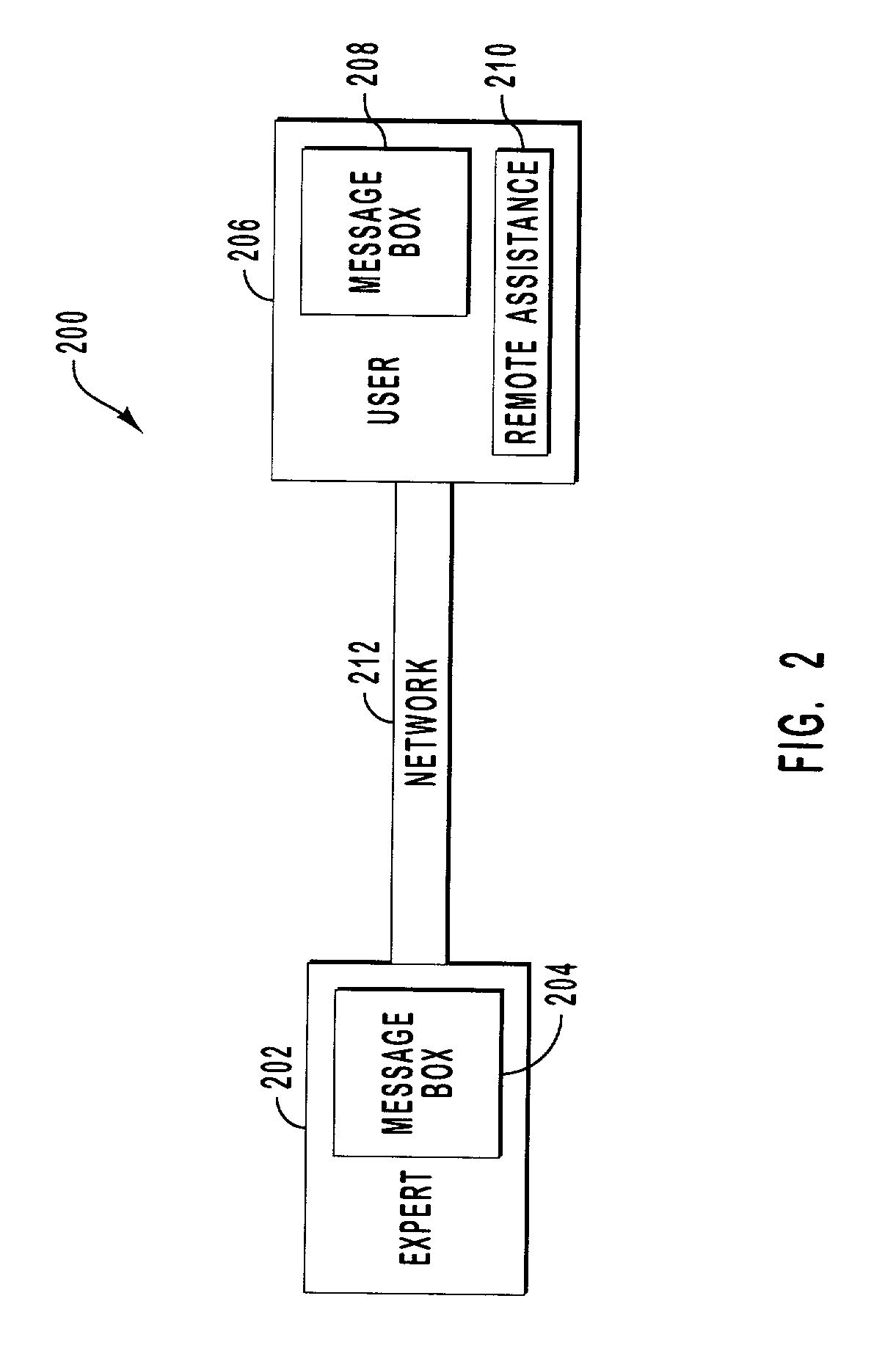
Remote assistance
InactiveUS6973482B2Overcome limitationsTrouble in viewingUnauthorized memory use protectionHardware monitoringPasswordRemote assistance
Systems and methods for remote assistance. A user computer is able to generate a ticket that includes temporary credentials for a remote assistance account of the user computer. The ticket is escalated to an expert, who activates the ticket and requests a connection with the user using the encrypted credentials. The user can accept this request if the credentials are validated and provide the expert with a view of the user's desktop. The expert, if necessary, can request control of the user computer and the user can either grant or deny this request. If granted, the user computer can unilaterally terminate the control that was provided to the expert. Because the credentials in the ticket are encrypted, the expert does not know the actual password to the remote assistance account and can only access the user computer interactively.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
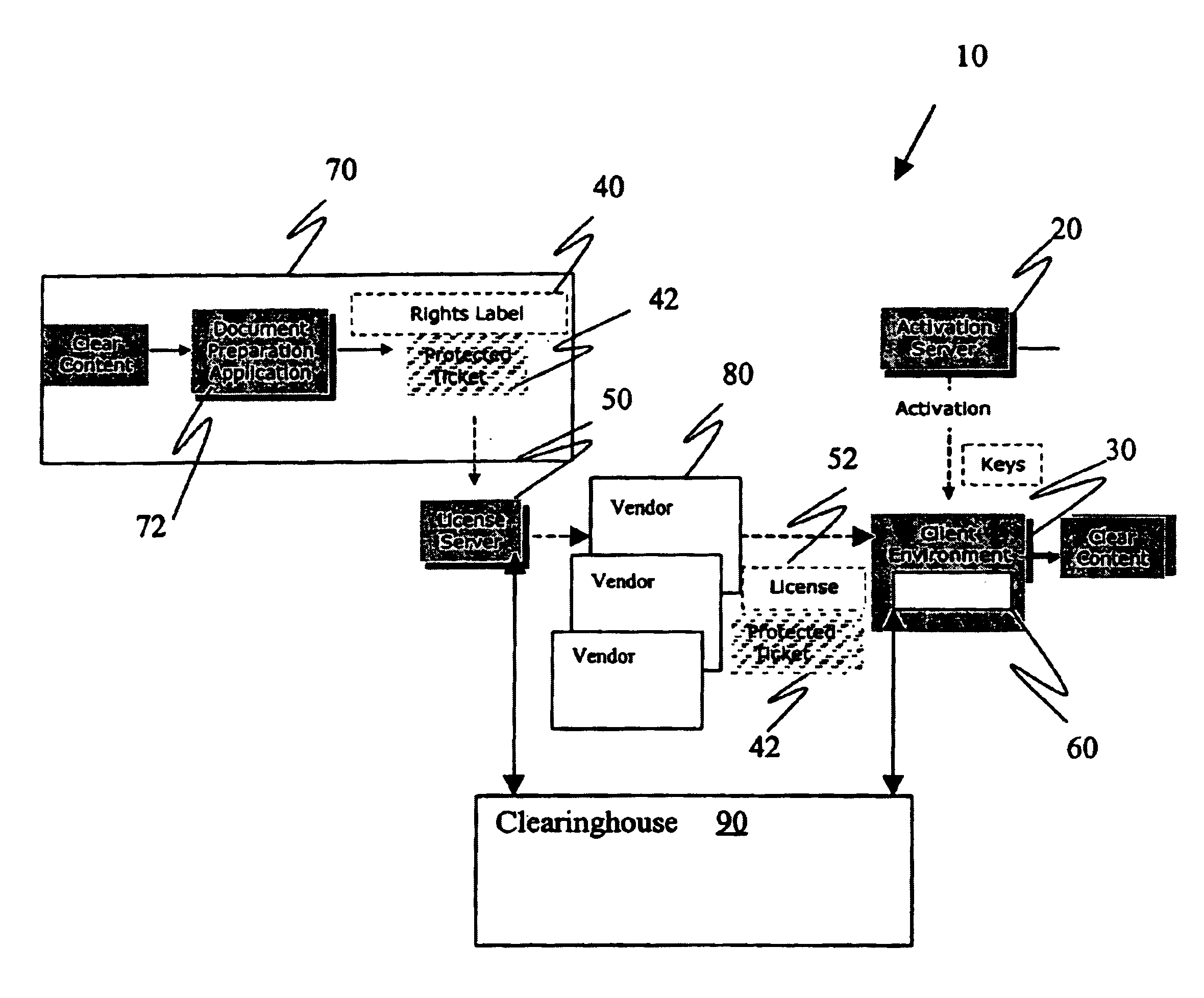
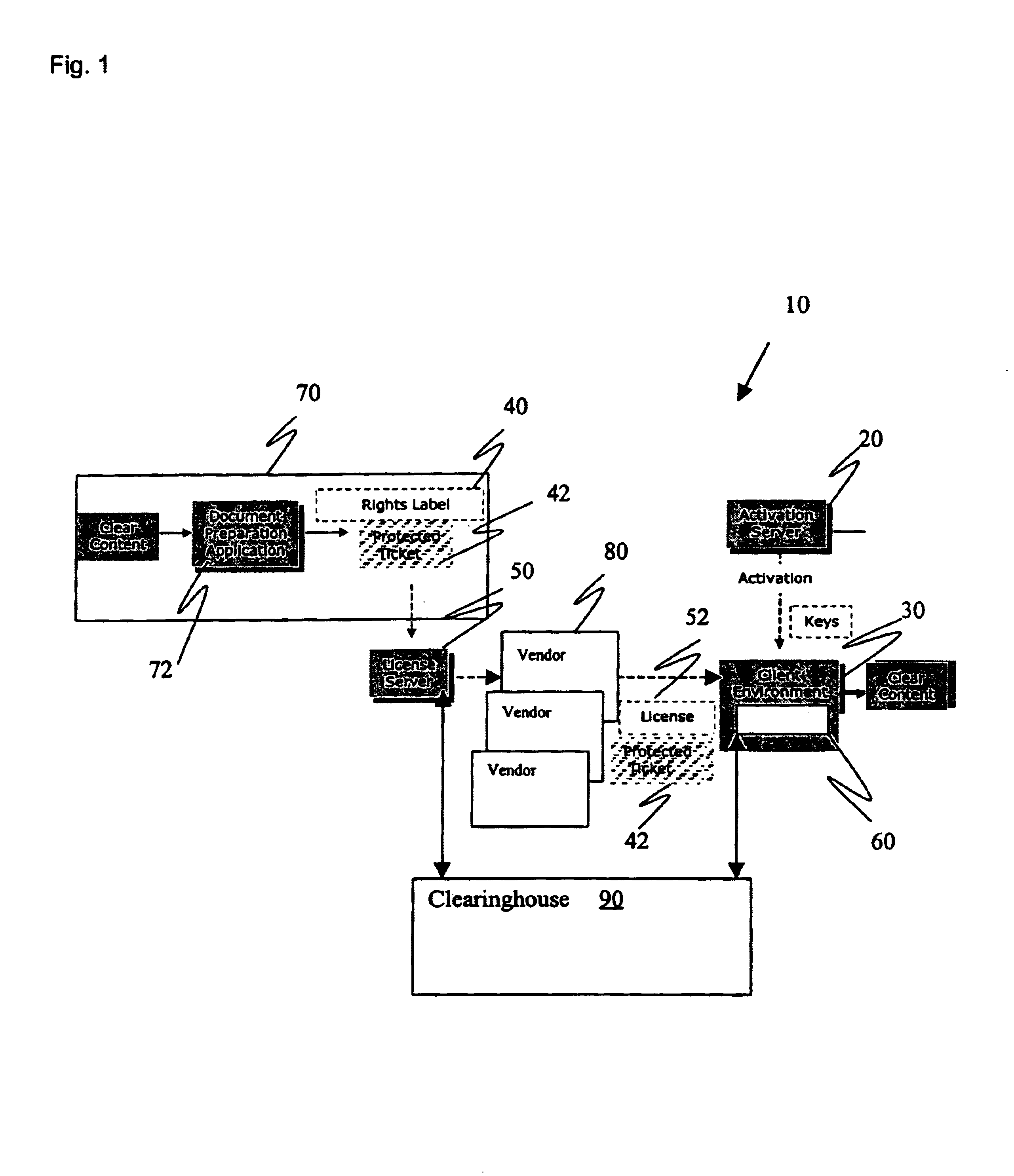
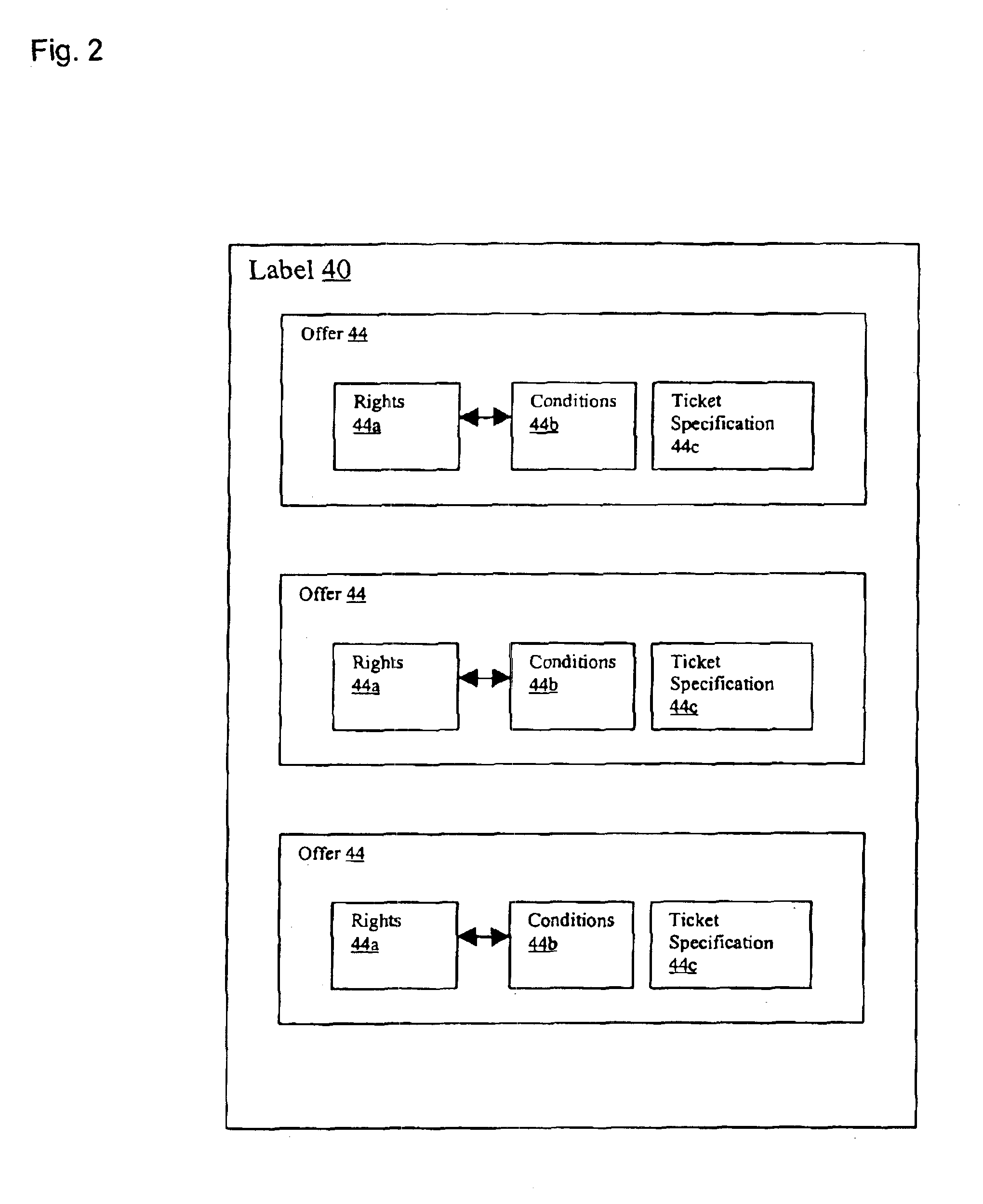
Method and apparatus for distributing enforceable property rights
InactiveUS6954738B2Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsLicenseComputer security
An enforceable property right and a system for controlling the manner of use of an item in accordance with usage rights. The enforceable property right includes an item ticket having a security mechanism incorporated therein and specifying an item for which the item ticket can be redeemed and a license associated with the item ticket. The license includes usage rights specifying a manner of use for redeeming the item ticket and a mechanism for unlocking said security mechanism.
Owner:CONTENTGUARD HLDG
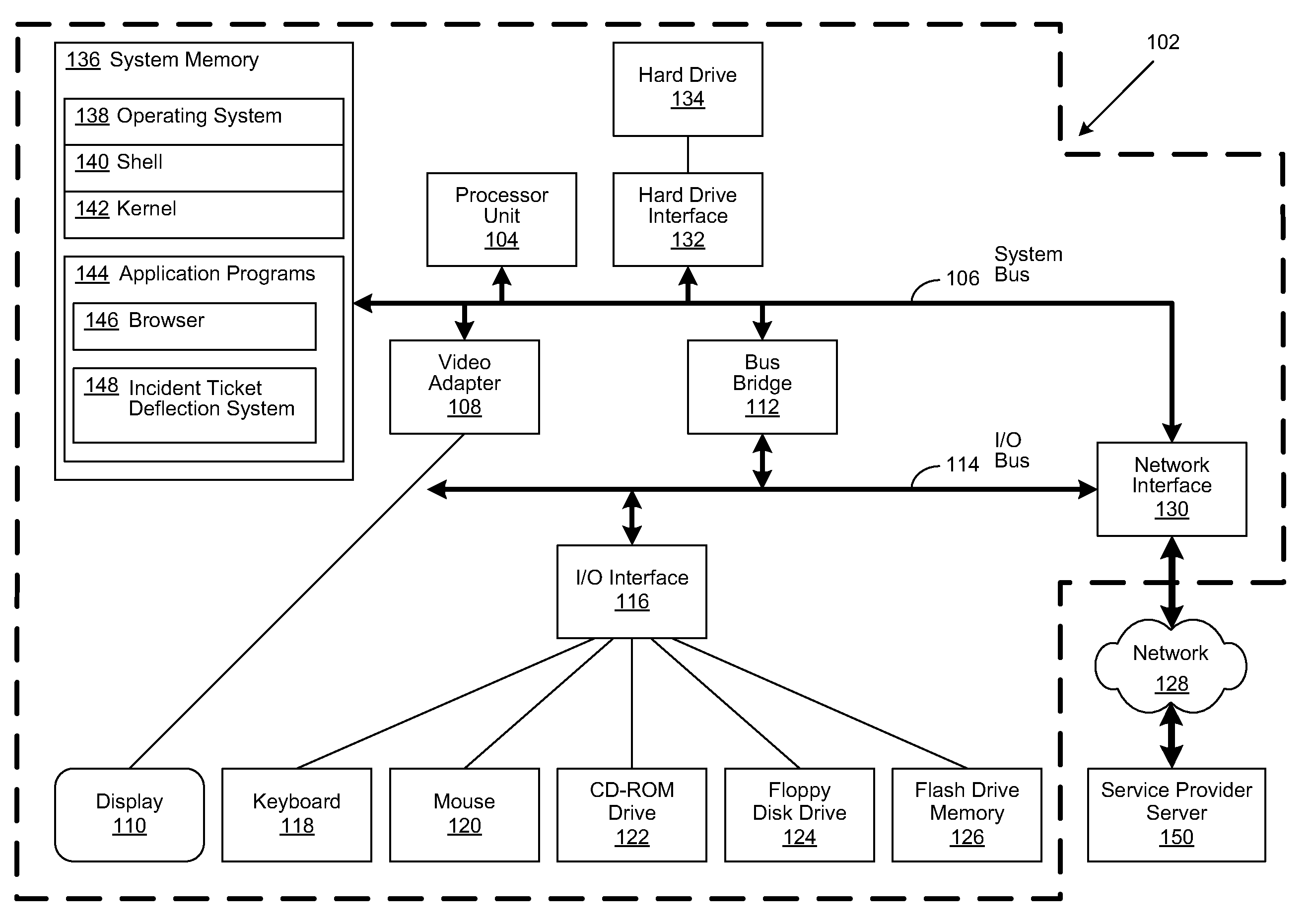
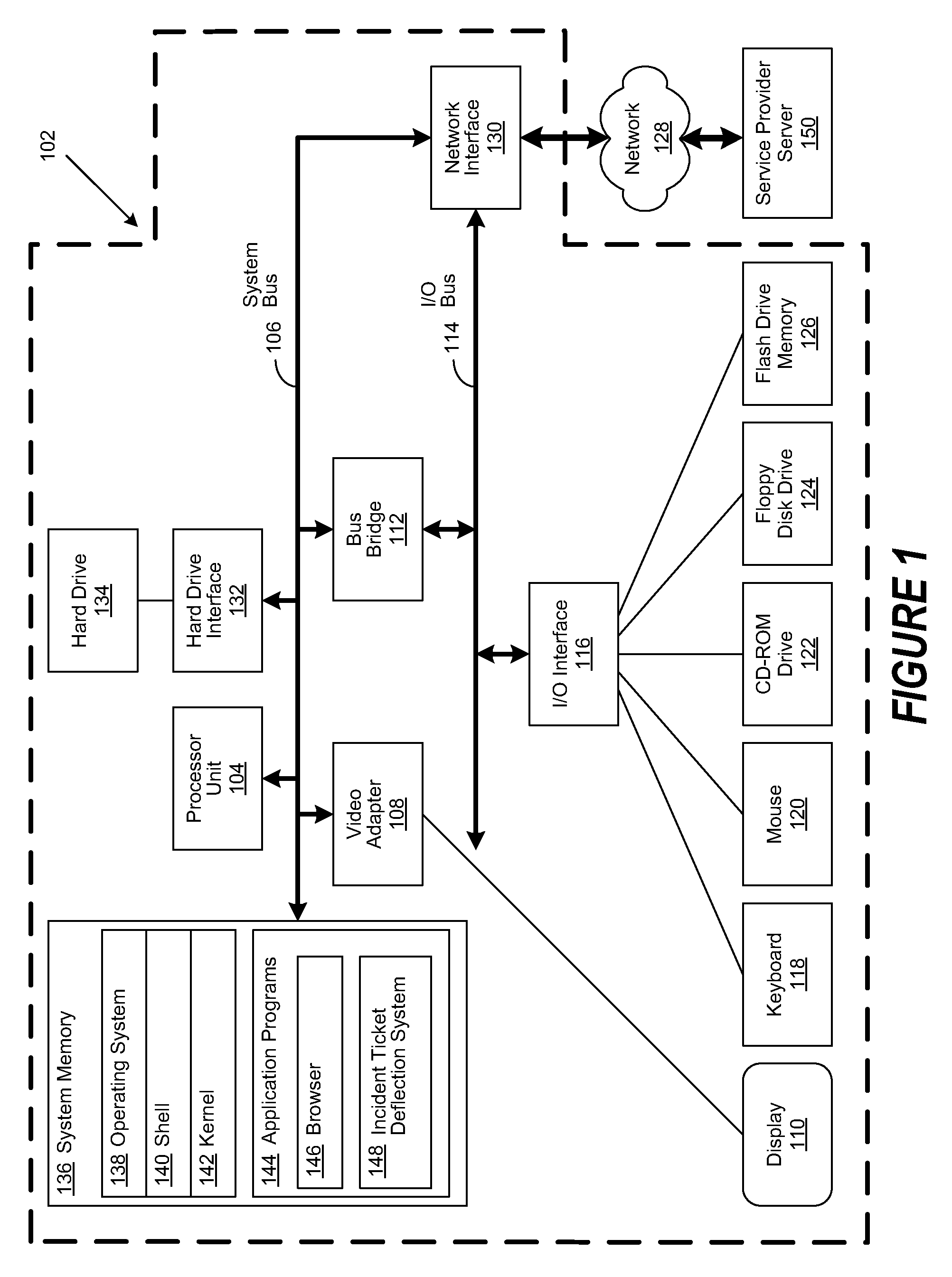
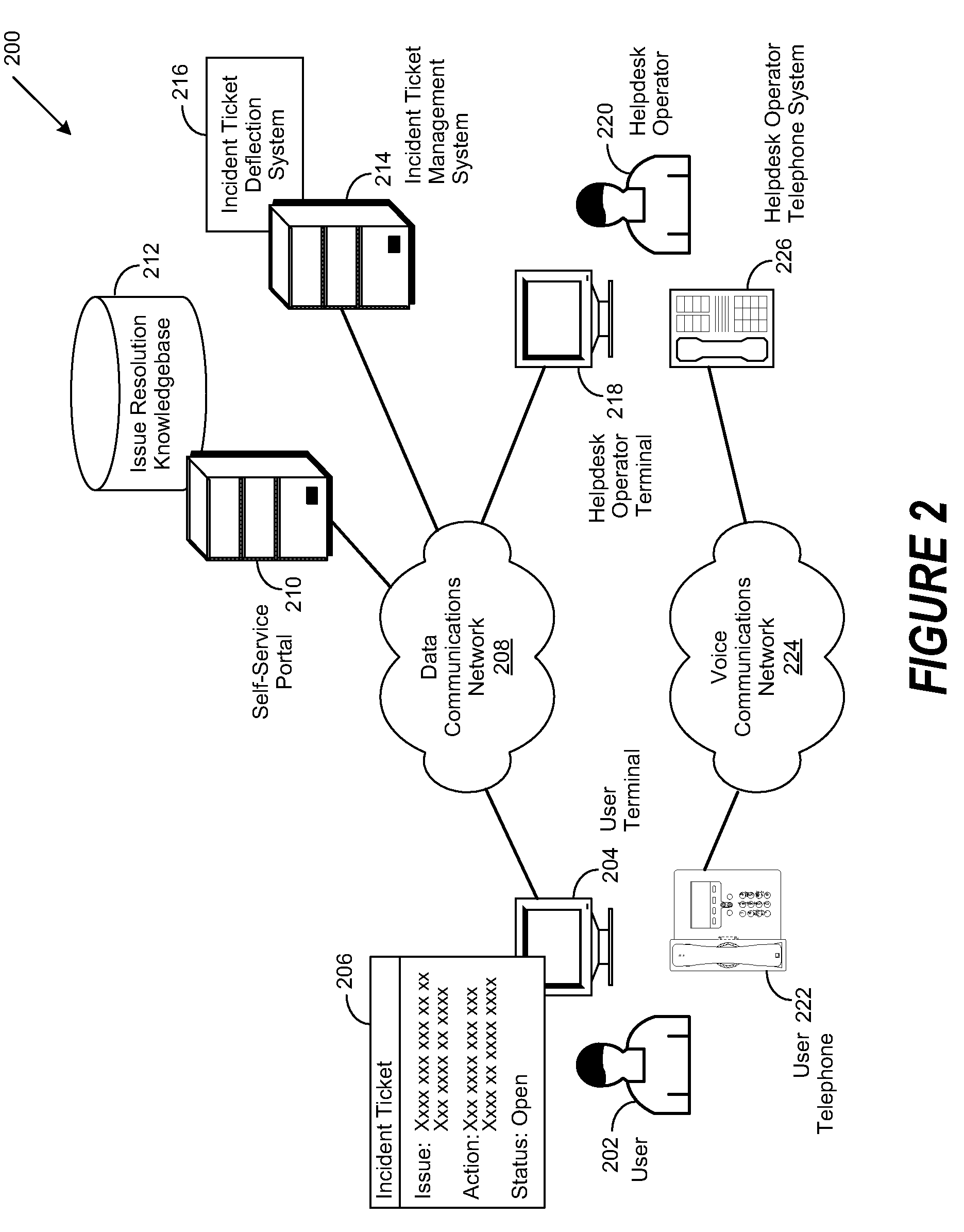
Technique to Deflect Incident Ticket Submission in Real-Time
A method, system and computer-usable medium are disclosed for reducing the amount of human interaction involved in the resolution of incident tickets. A user interacts with a self-service portal to generate an incident ticket to resolve an issue. The generated incident ticket is routed by the self-service portal to an incident ticket management system for processing. The incident ticket management system accepts the incident ticket and in turn routes it to an incident ticket deflection system (ITDS). The ITDS analyzes the resolution state of the issue and generates relevant search queries that are submitted to an issue resolution knowledgebase. The results of the search queries are then returned to the ITDS, which compares them to captured interactions of the user with the self-service portal. Irrelevant query results or those that match the captured user interactions are disregarded. The remaining query results are used by the ITDS to generate remedial actions for the user to perform. If the remedial actions do not resolve the user's issue, then the incident ticket is escalated to a helpdesk operator. When received by the helpdesk operator, the incident ticket is populated with the captured user interactions with the self-service portal, the recommended remedial actions for the user to perform, and the current resolution status of the user's issue. The helpdesk operator then uses the information contained in the escalated incident ticket to facilitate the resolution of the user's issue.
Owner:IBM CORP
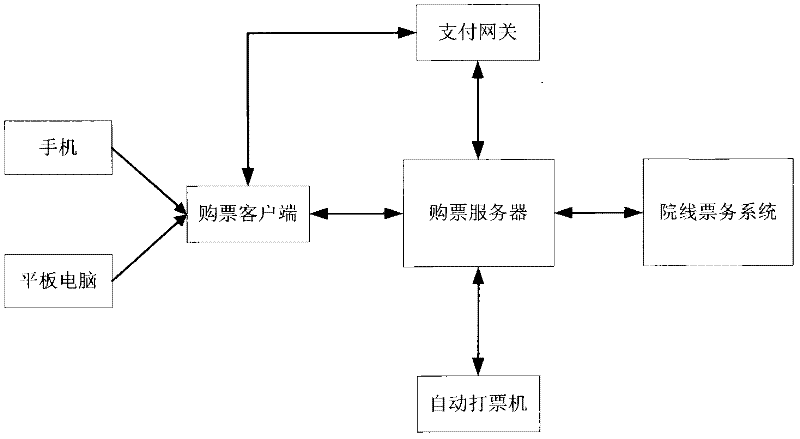
Self-service system and method for selecting seat and buying cinema ticket of mobile phone
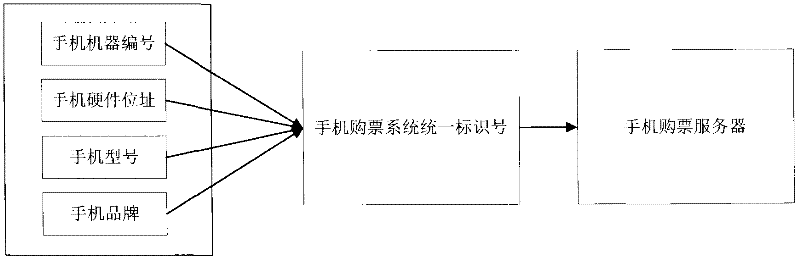
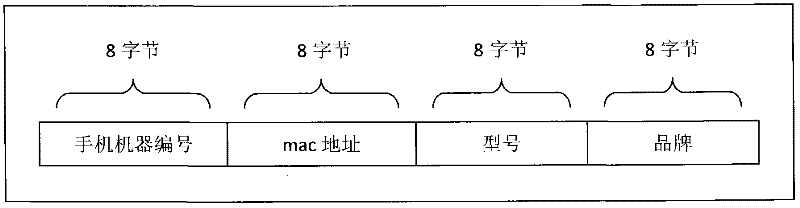
InactiveCN102609867AConvenient and fast ticket purchaseQuick ticketReservationsPayment architectureTicketEngineering
Ticket buying client sides are installed in a mobile phone and a panel personal computer by a user, and once the ticket buying client sides are installed, a system unique identification number is built for the mobile phone according to information such as the machine number of the mobile phone, the mac (media access control) address, namely the hardware address, the model and the brand. The ticket buying client side on the mobile phone is connected with a ticket buying client server by virtue of the wireless internet or the mobile internet, the user inquires and selects the cinema of which the ticket is needed to be bought and the showing member of the film by virtue of the ticket buying client side, and selects the position and number of the seat which is needed to be bought on the client side, and after selecting, on-line payment is performed through connecting the ticket buying client side with an on-line payment gateway; after the payment is completed, the ticket is successfully bought; and the ticket buying server returns the relevant information of the bought cinema ticket back to the ticket buying client side, and a relevant ticket buying certificate is generated on the client side. The user can directly exchange the cinema ticket by virtue of a counter or directly issues the ticket by virtue of an automatic ticket printer when going to the cinema with the ticket buying certificate.
Owner:北京华宏天下信息技术有限公司
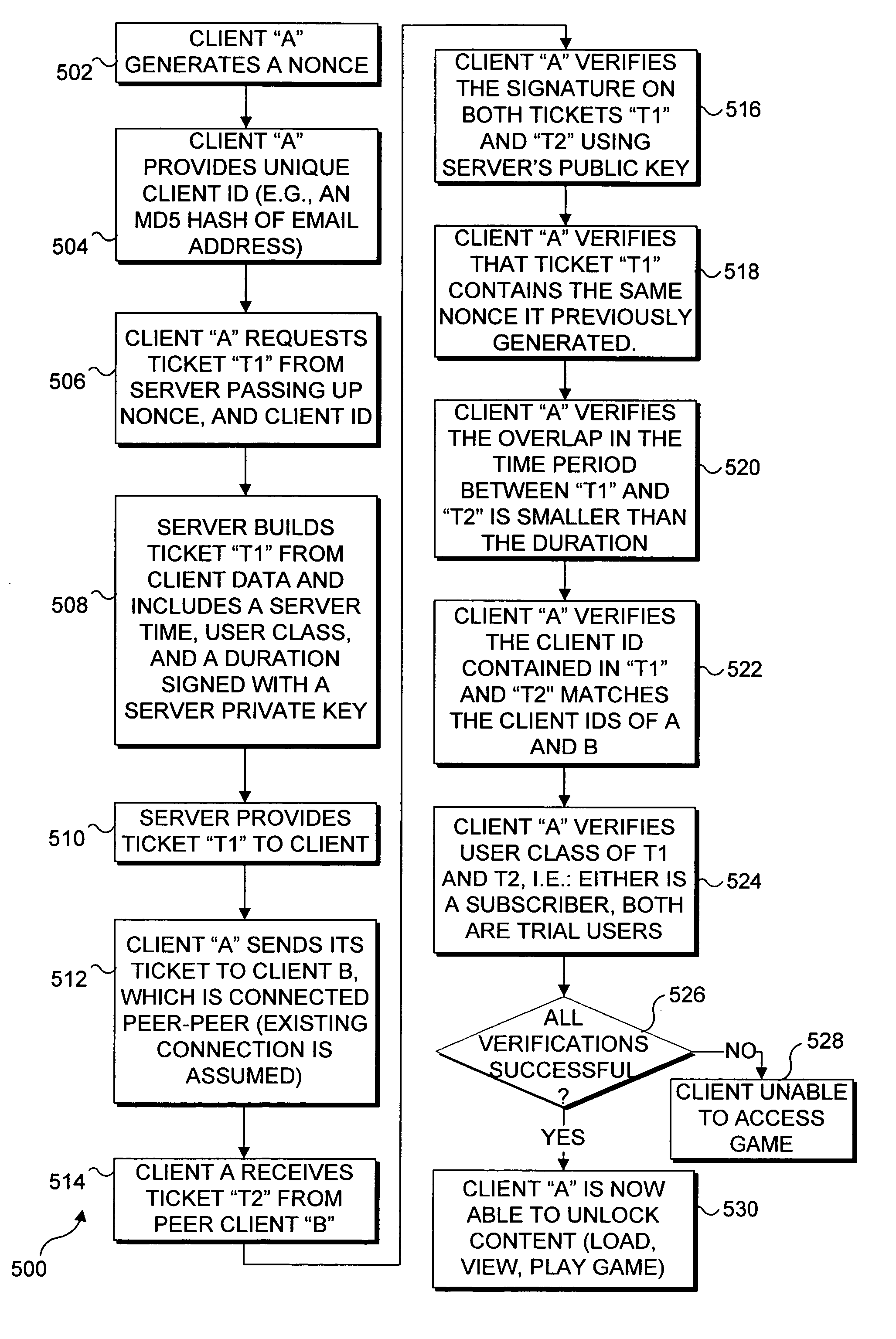
Trial-before-purchase subscription game infrastructure for peer-peer networks
InactiveUS20060123117A1Safety managementEnabling useDigital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionDigital signatureClient-side
A game or other software program is made accessible for execution by clients on a peer-peer network only after a plurality of verifications are made to ensure that control of the software is maintained. With a request sent to a server to access the software, a client includes a nonce and an ID of the user. The server digitally signs a portion of a ticket that is returned to the client, which includes the nonce, a time stamp, and the ID. The ticket is required to access the software. The clients are required to exchange the tickets, verify the digital signature on the portion of each ticket, and use the information therein to confirm that the tickets are current, issued by the correct server, issued to the proper users, and received from the users who are intended to execute the software.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
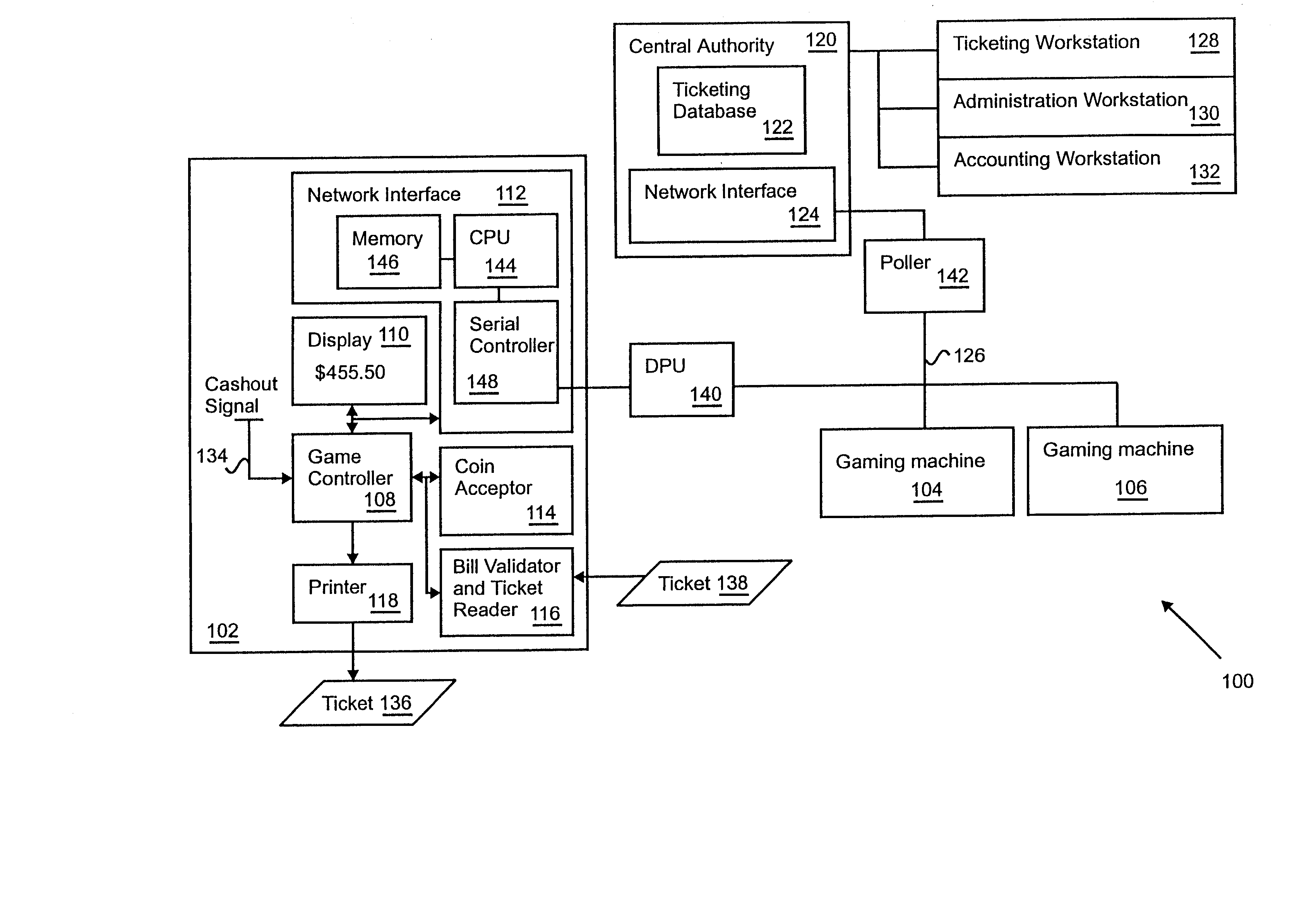
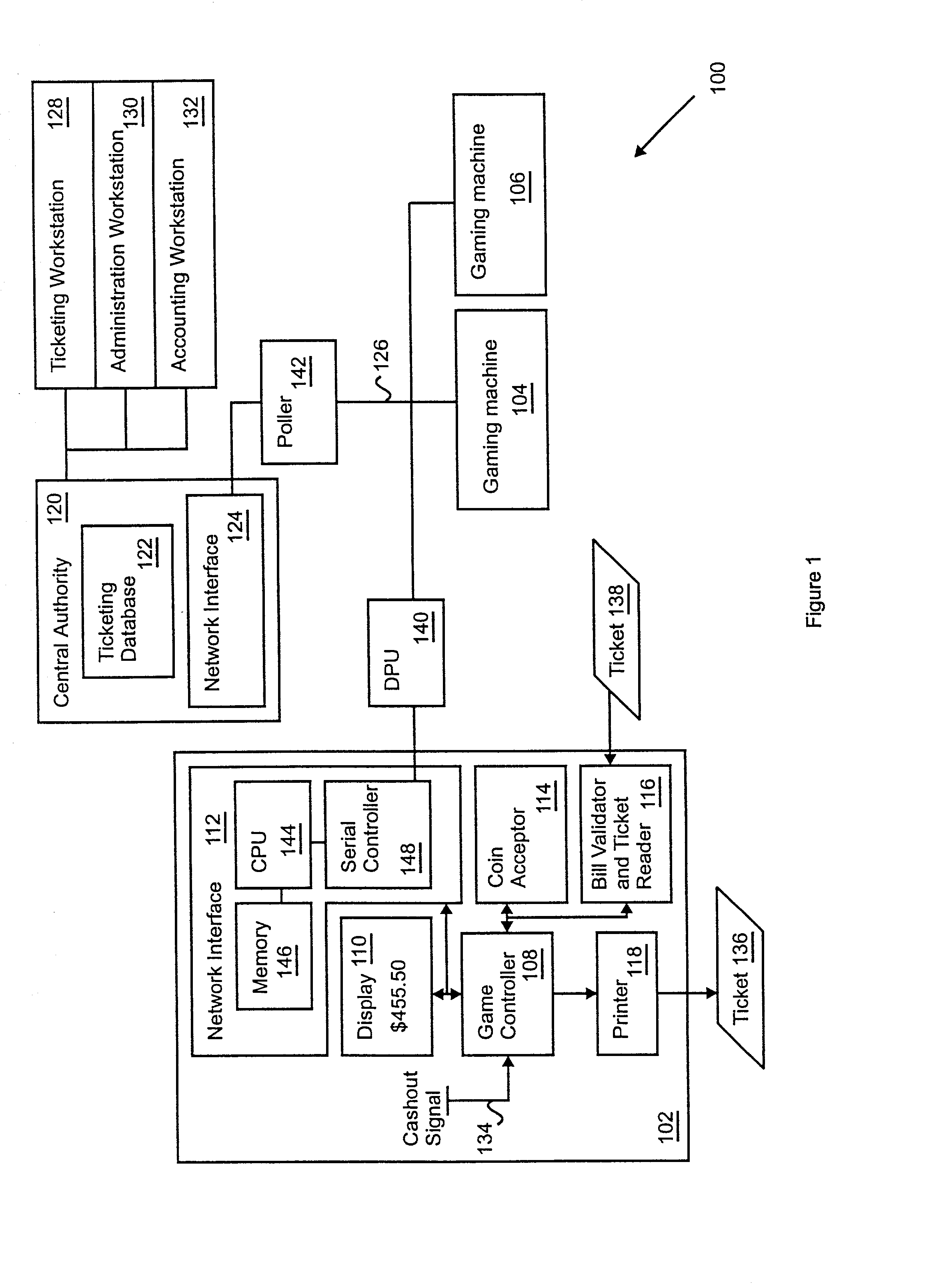
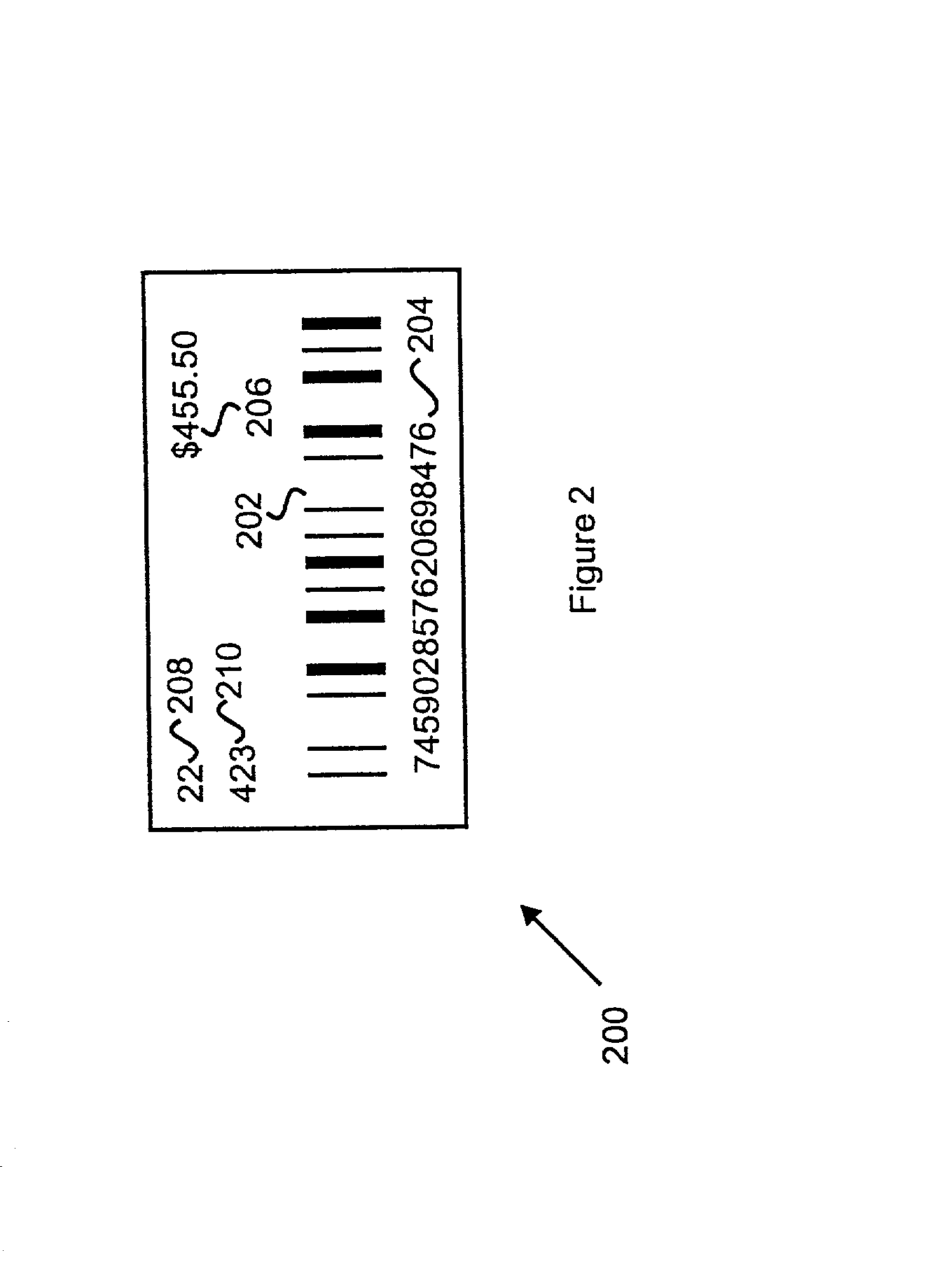
Apparatus and method for a cashless actuated gaming system
A gaming machine adapted to print validated tickets for a game player includes a microprocessor for controlling game operation (e.g., slot machine operation) and including a cashout signal input, a network interface coupled to the microprocessor for communicating with a central authority, and a memory in the network interface that stores a pre-loaded ticket validation number received from the central authority. In addition, a ticket printer is coupled to the microprocessor for printing a ticket that includes pending credit indicia and pre-loaded ticket validation indicia in response to a cashout signal on the cashout signal input. After the ticket is printed, the gaming machine obtains a new pre-loaded validation number in preparation for the next ticket printing event.
Owner:ARISTOCRAT TECH INC
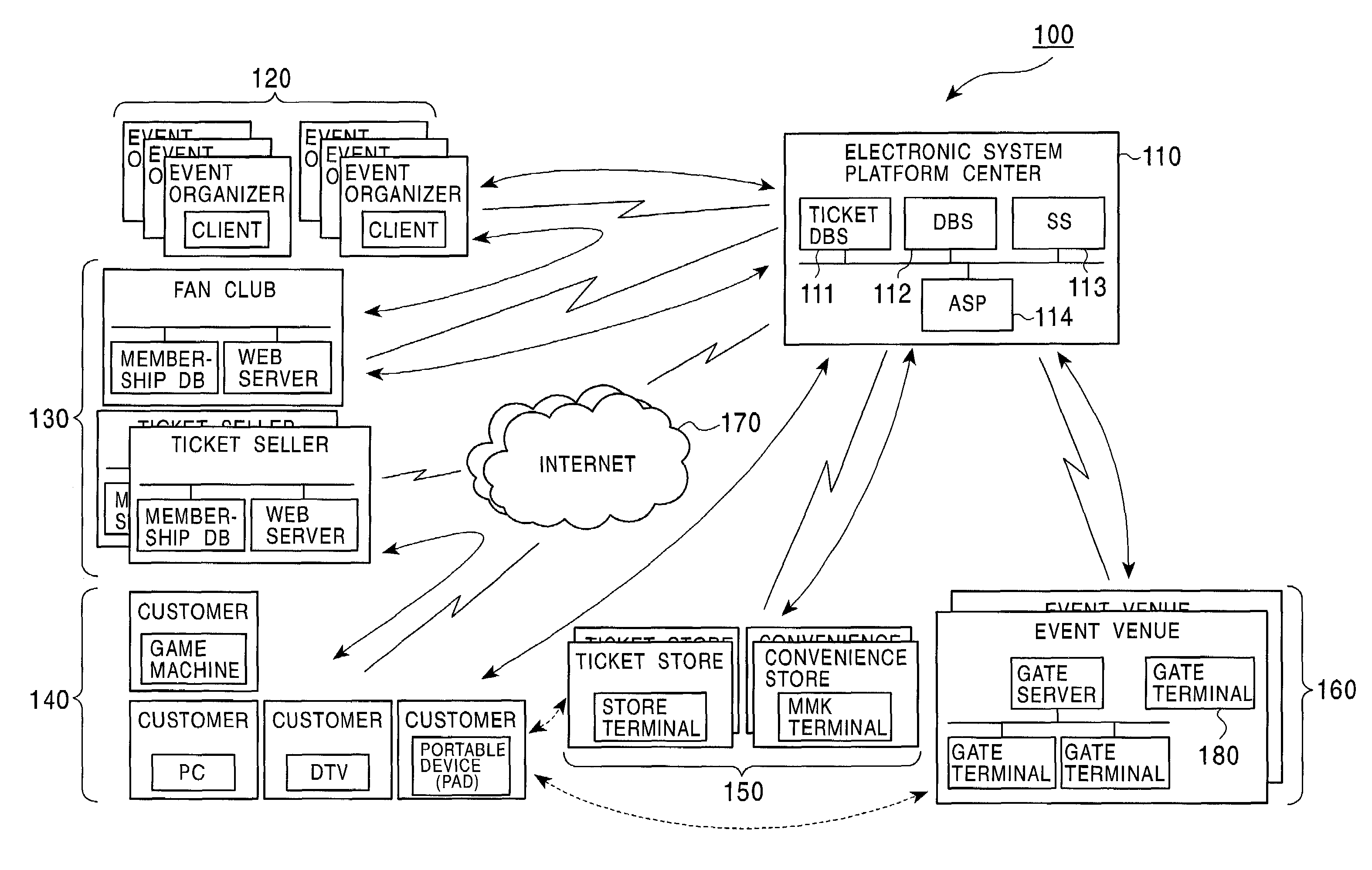
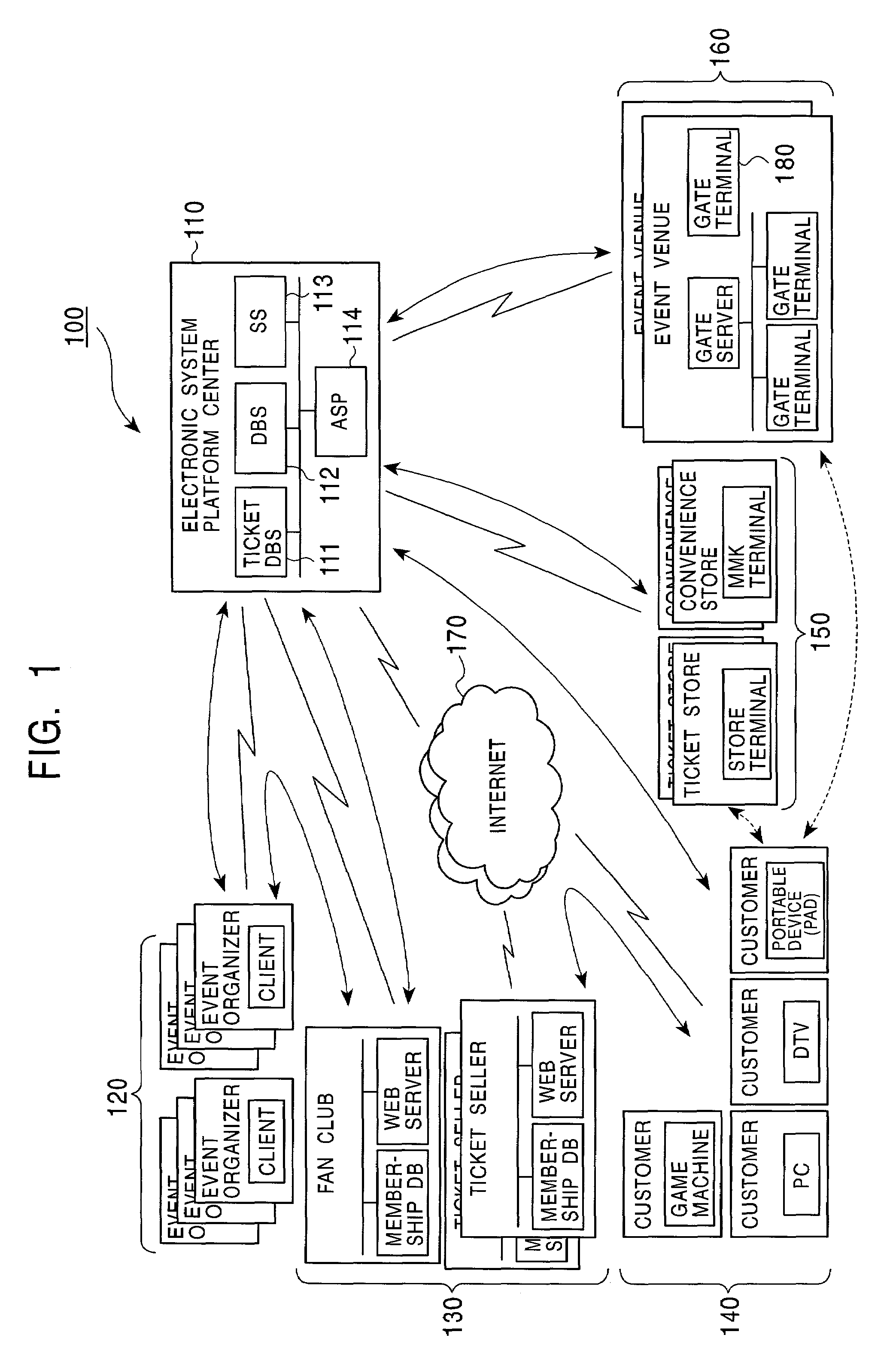
Apparatus, system and method for electronic ticket management and electronic ticket distribution authentication
An electronic ticket management system includes an event organizer for planning an event, an electronic ticket seller for distributing electronic ticket information which authenticates the right to attend the event, an information storage chip for storing the electronic ticket information, and an electronic ticket platform center for managing the distribution of the electronic ticket information. The electronic ticket platform center forms an electronic ticket information master based on event information registered by the event organizer, and relates ticket issuing information registered by the electronic ticket seller to the electronic ticket information master. The electronic ticket platform center also issues the tickets by writing the electronic ticket information into the corresponding information storage chip based on ticket issuing information. A determination as to whether the user is permitted to enter the event venue is made according to the integrity of the event information stored in the information storage chip.
Owner:SONY CORP
Invisible services
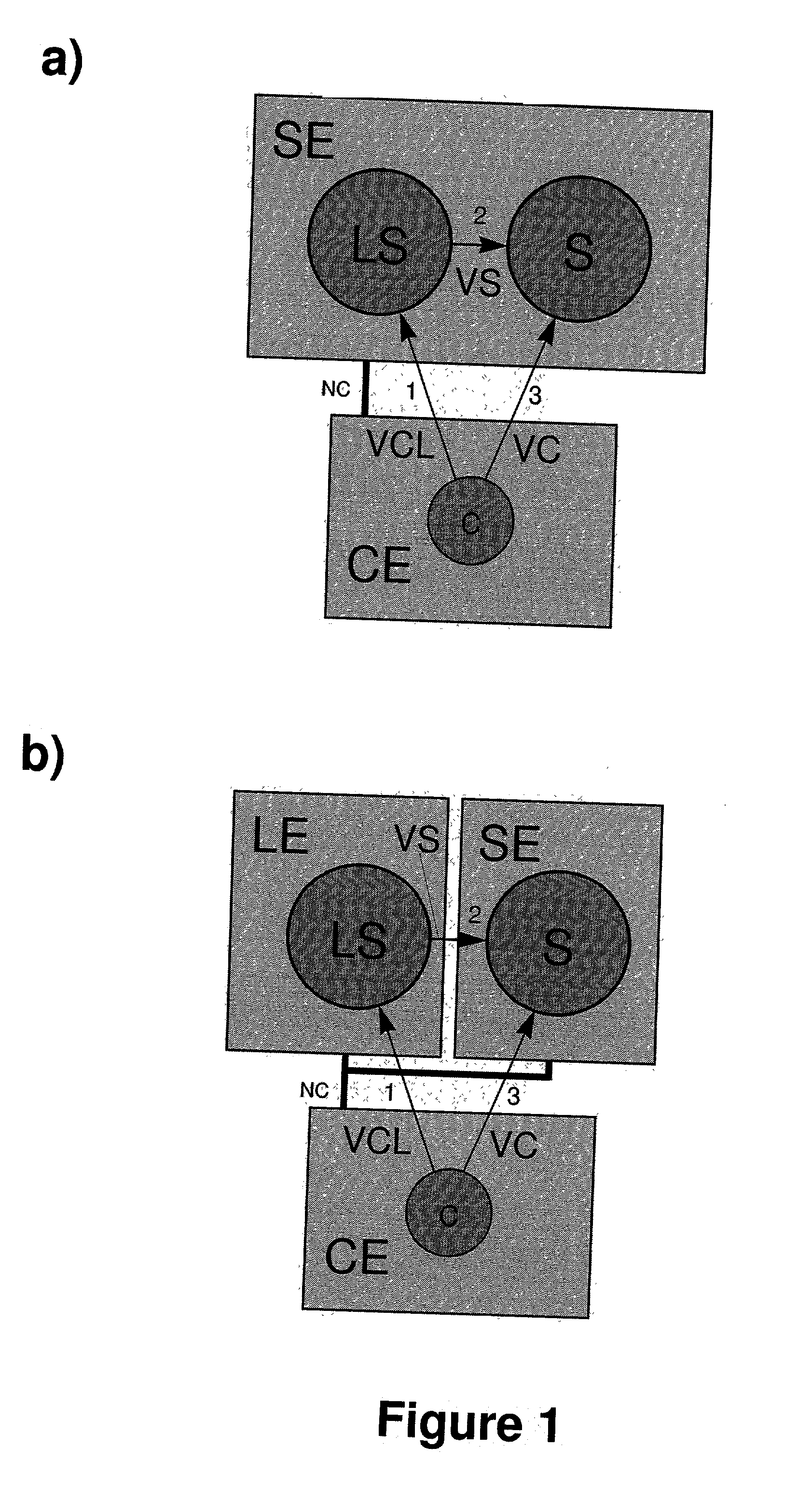
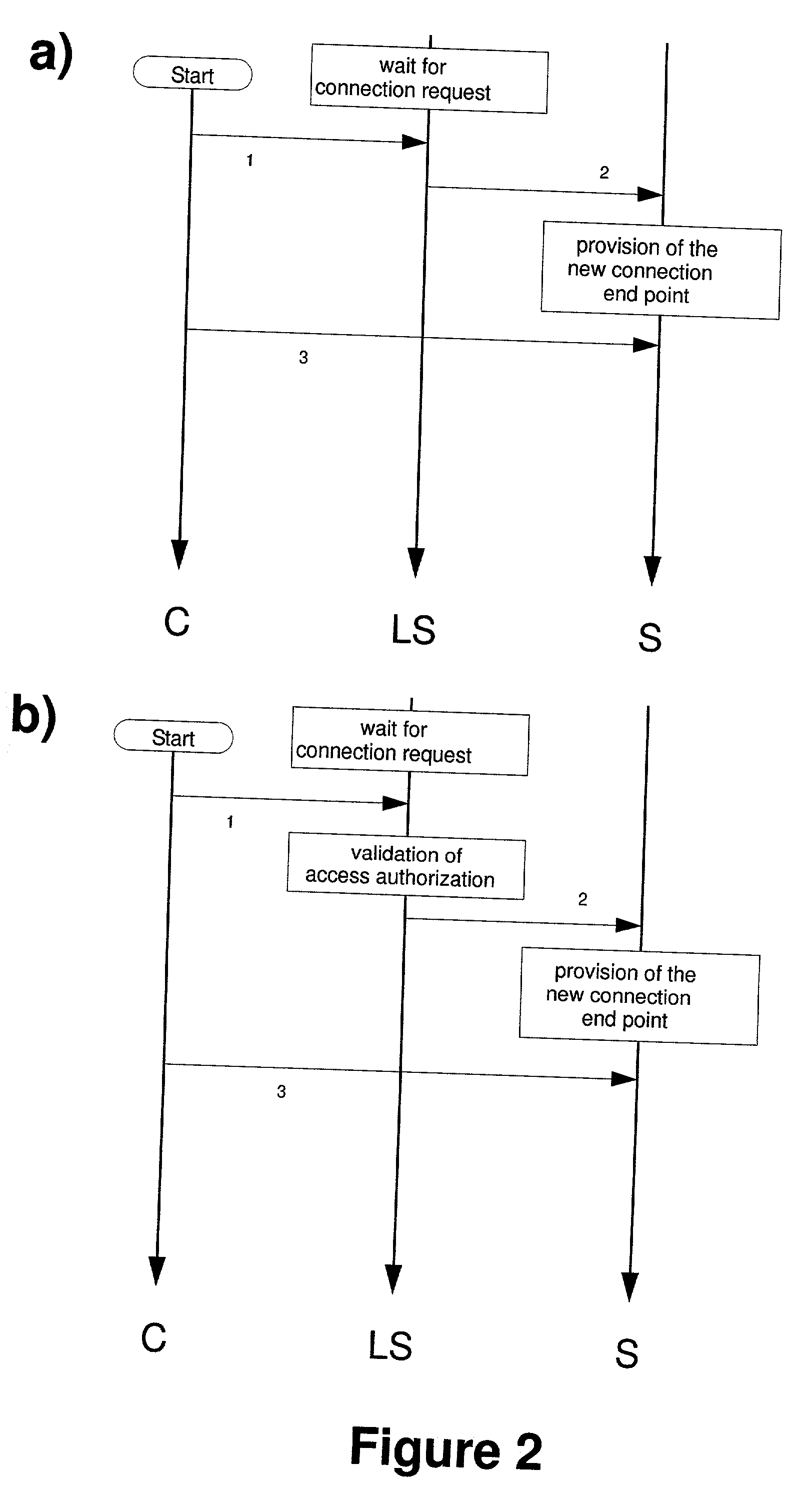
InactiveUS20020194505A1Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsClient-sidePort scan
The presented inventions concern communication systems with services. The services provided by the presented systems are invisible to port scans, allowing security critical data to be stored on units without any permanently open connection endpoints. Existing network systems according to the client / server-principle require the permanent provision of open connection endpoints to be accessible on a 24h base. The large number of services implies a large number of open connection endpoints, where each open connection endpoint presents a potential point-of-attack for malicious clients. The object of the present invention is to securely provide services in communication systems. The present invention overcomes the prior art by triggerable invisible services, which during normal operation do not provide any permanently open connection endpoint. Connection endpoints are only opened after prior client authentication and authorization validated by an independent logon sub-system. Connection endpoints can be opened for previously authenticated and authorized clients either on the service side during a predefined short time interval or on the client side. If opened on the client side, the invisible service is triggered to initiate the connection build-up to the open connection endpoint on the client side. Services opening temporary connection endpoints are for port scan during normal operation invisible. Services connecting to connection endpoints opened on the client side, at no time provide any open connection endpoints and are therefore for port scan absolutely invisible. In networks on the base of TCP / IP the id of an opened connection endpoint (port) may be selected pseudo or absolutely randomly. In addition, it is possible to dynamically select the service unit out of a set of multiple service units in dependence of the actual system load distribution "load balancing", connection quality, geographical, topological or other criteria. After the establishment of a connection between an invisible service and a client, both partners may authenticate each other using random access data (tickets).
Owner:MUSCHENBORN HANS JOACHIM
Preemptive weighted round robin scheduler
InactiveUS20060176807A1Error preventionTransmission systemsClassification schemeDistributed computing
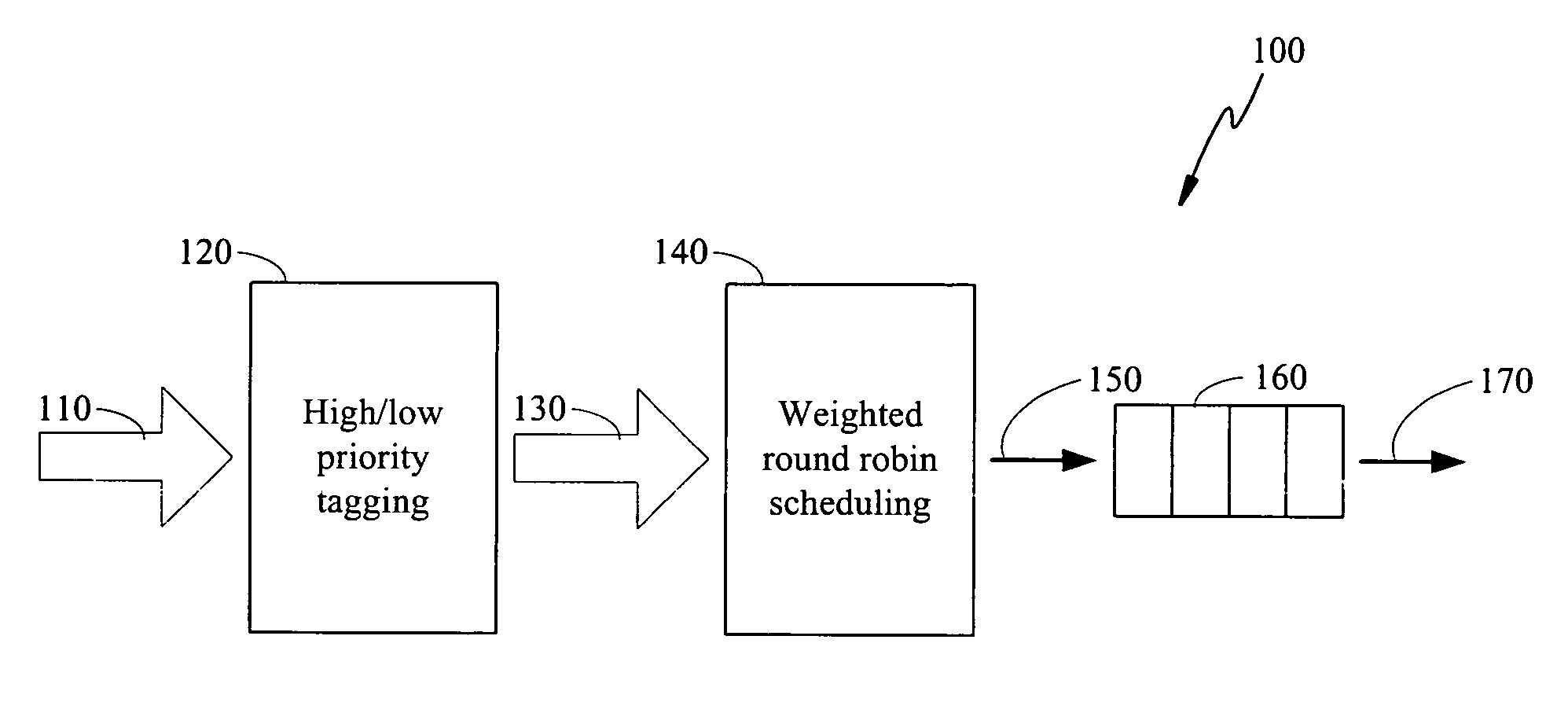
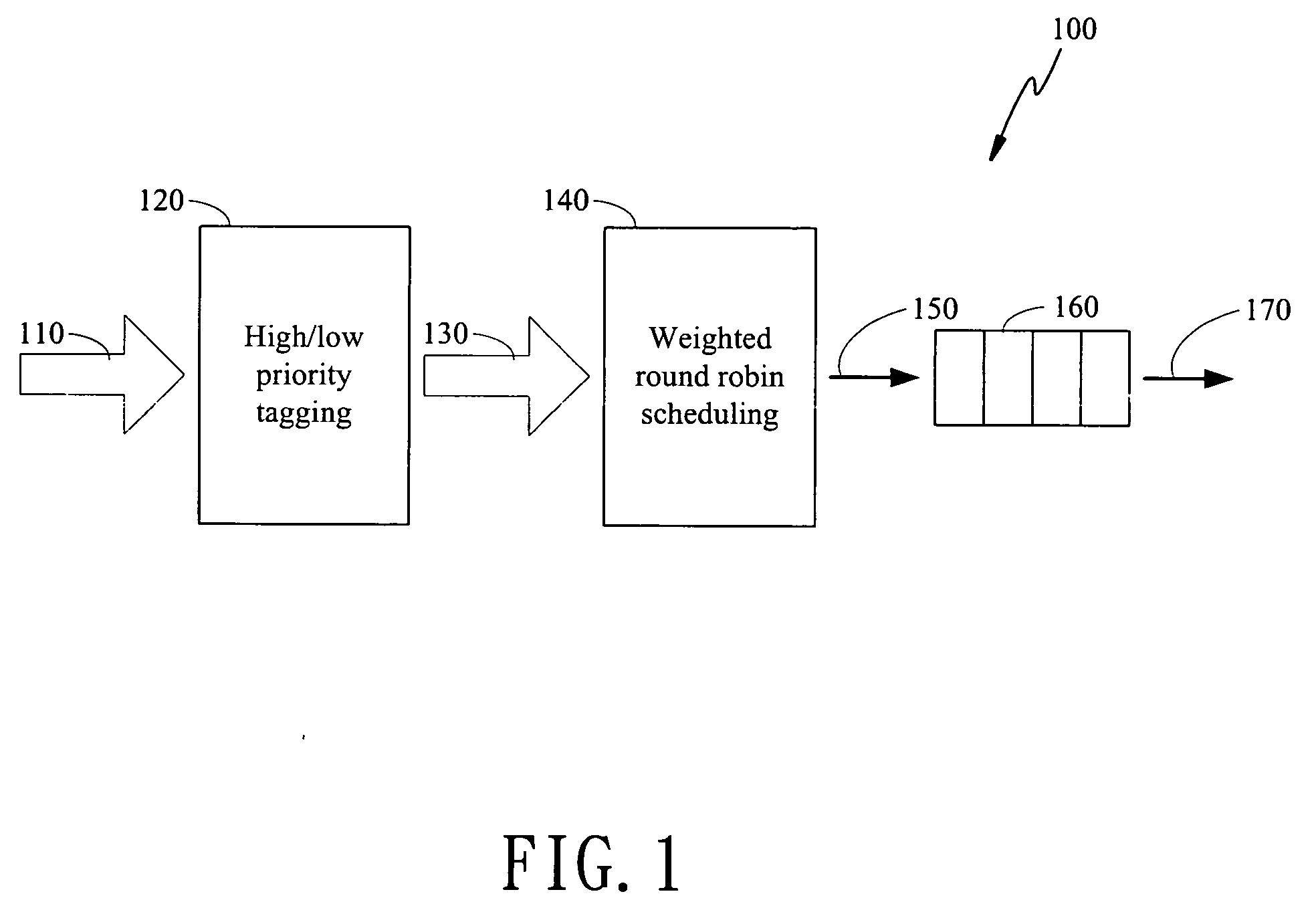
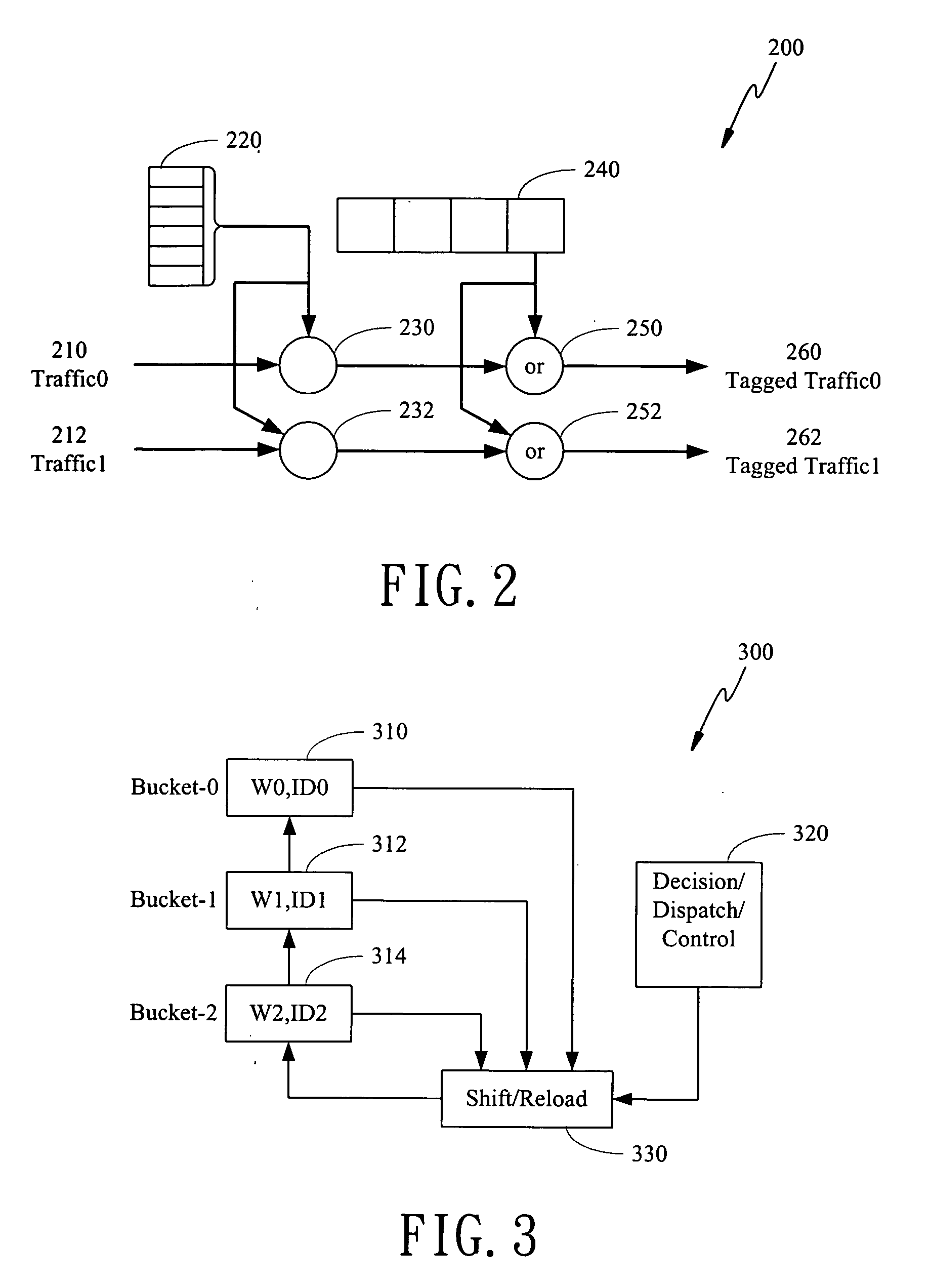
The present invention is to disclose a scheduler which comprising a priority tagging module for receiving a plurality of information chucks, a plurality of output lines, and a WRR (weighted round robin) module. In this regards, each information chucks are tagged with a priority tag by said priority tagging module according to a priority classification scheme. In addition, the WRR module further comprises a bucket list, which has a plurality of buckets, and a control module. Each bucket stores a ticket, which comprises an identification representing one of the plurality of output lines and an associated weight value of the represented output line. Besides, the control module receives the tagged information chucks from the priority tagging module and schedules the tagged information chucks into the plurality of output lines according to a scheduling scheme based on said bucket list.
Owner:RETI CORP
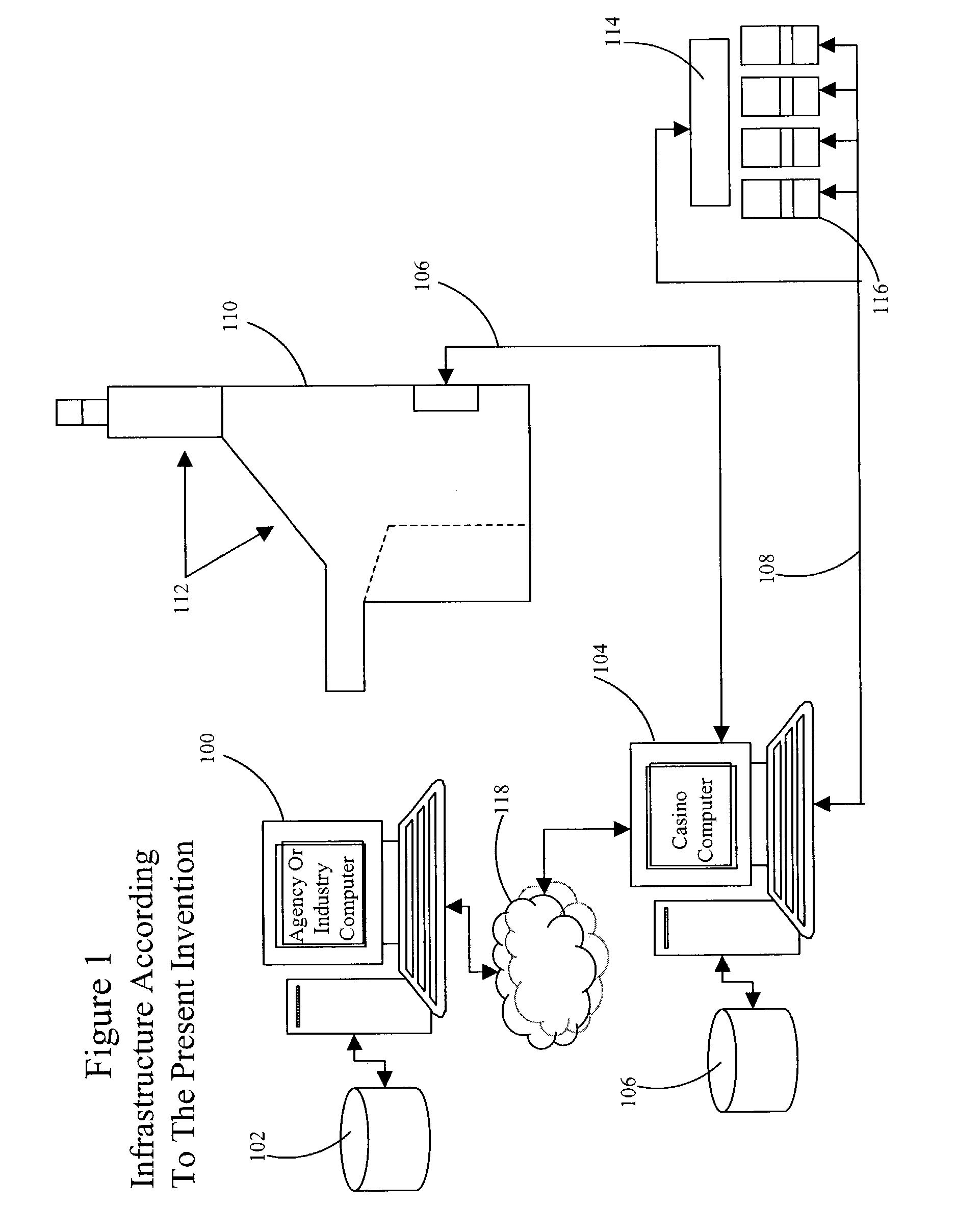
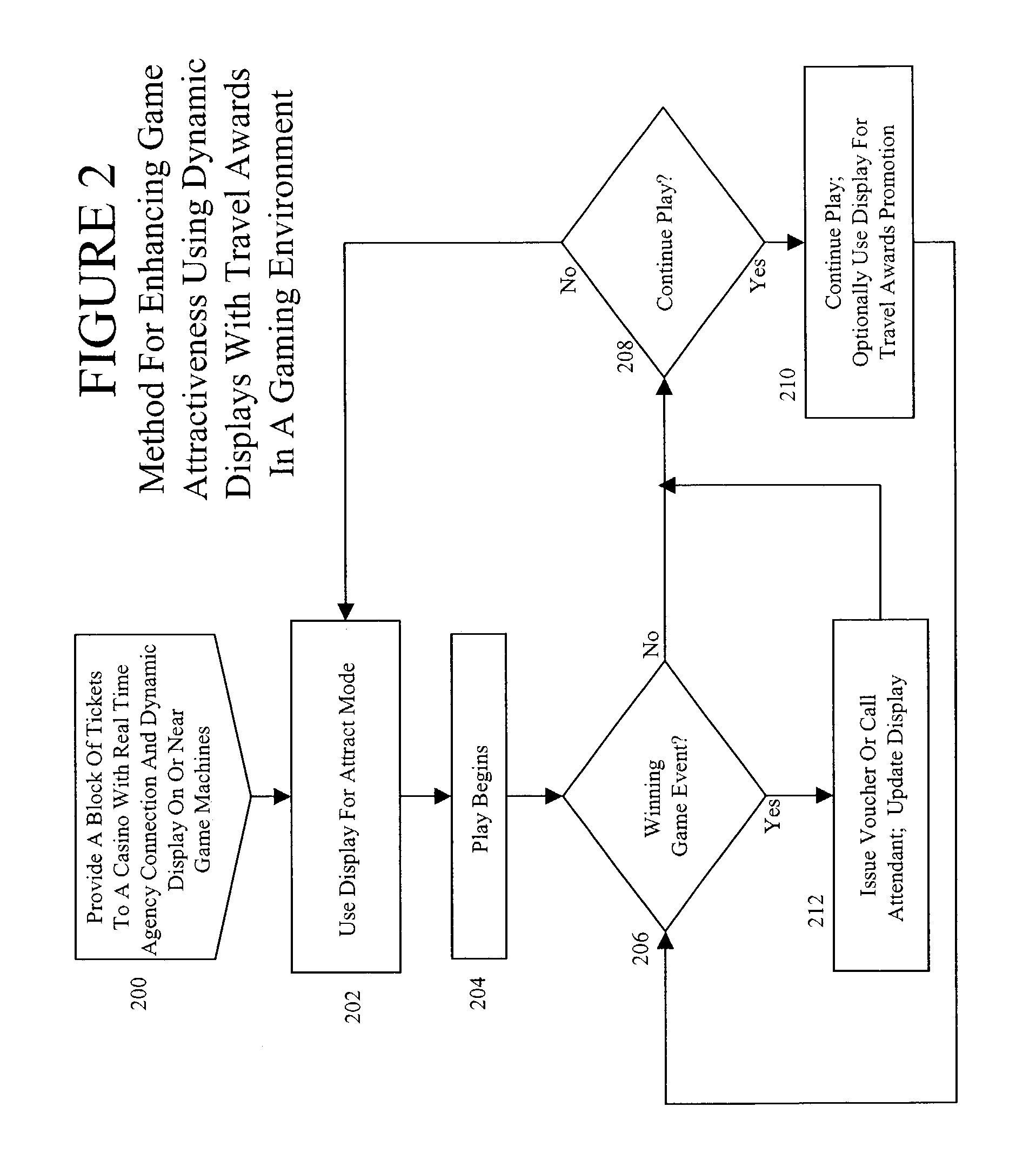
System and method for using time-sensitive tickets as player awards in gaming machines
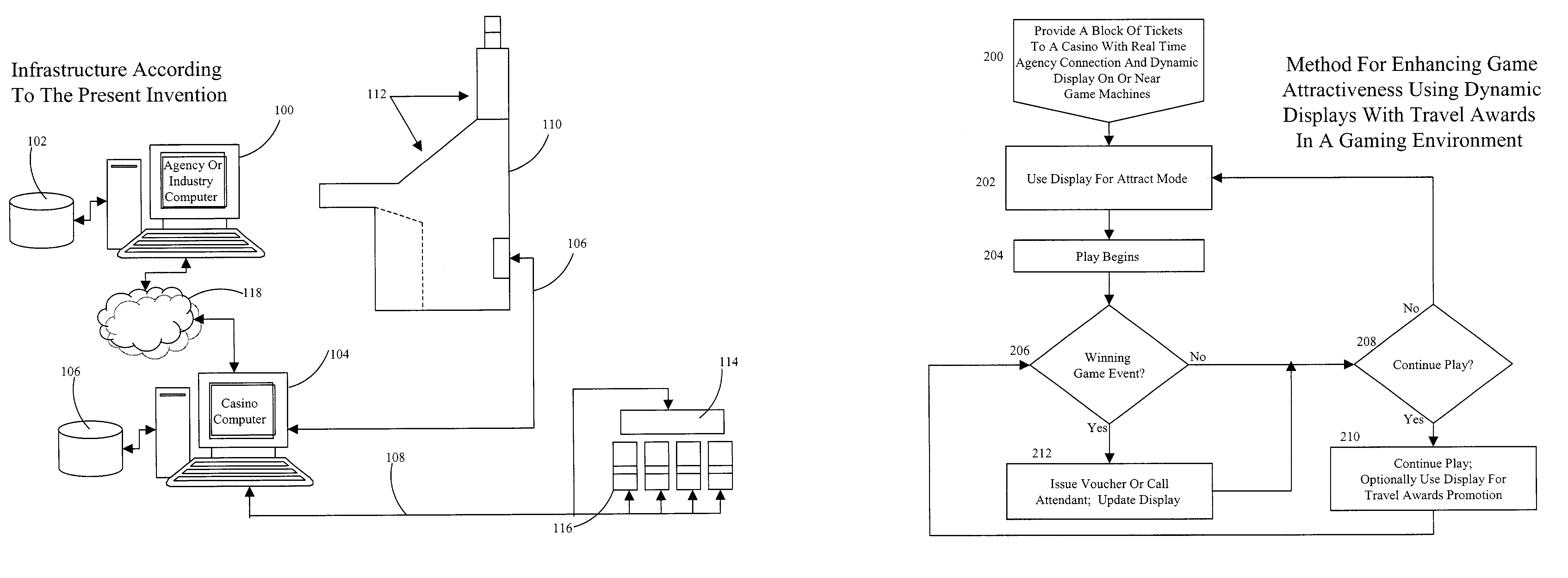
InactiveUS7137889B1Precise managementReduce lossesDiscounts/incentivesReservationsPima indiansTime sensitive
A new system and method for use in dynamic gaming environments such as Nevada-style casinos and Amerindian casinos is presented that enables using time-sensitive tickets as prizes. Block of tickets for a future event are allocated to a casino, which constitutes a “found” market (the ticket seller expends no funds for the tickets sold to the casino). This block may also be sold through normal reseller channels; the allocated block acts as a cap to the number of tickets potentially channeled through a casino rather than being a casino exclusive. This enables the casino to purchase the tickets at a steeper discount rates than is otherwise possible, and by associating tickets with payout events on games or progressives (instead of cash awards), enables time-sensitive tickets to be awarded as prizes on an on-going basis.
Owner:BALLY GAMING INC
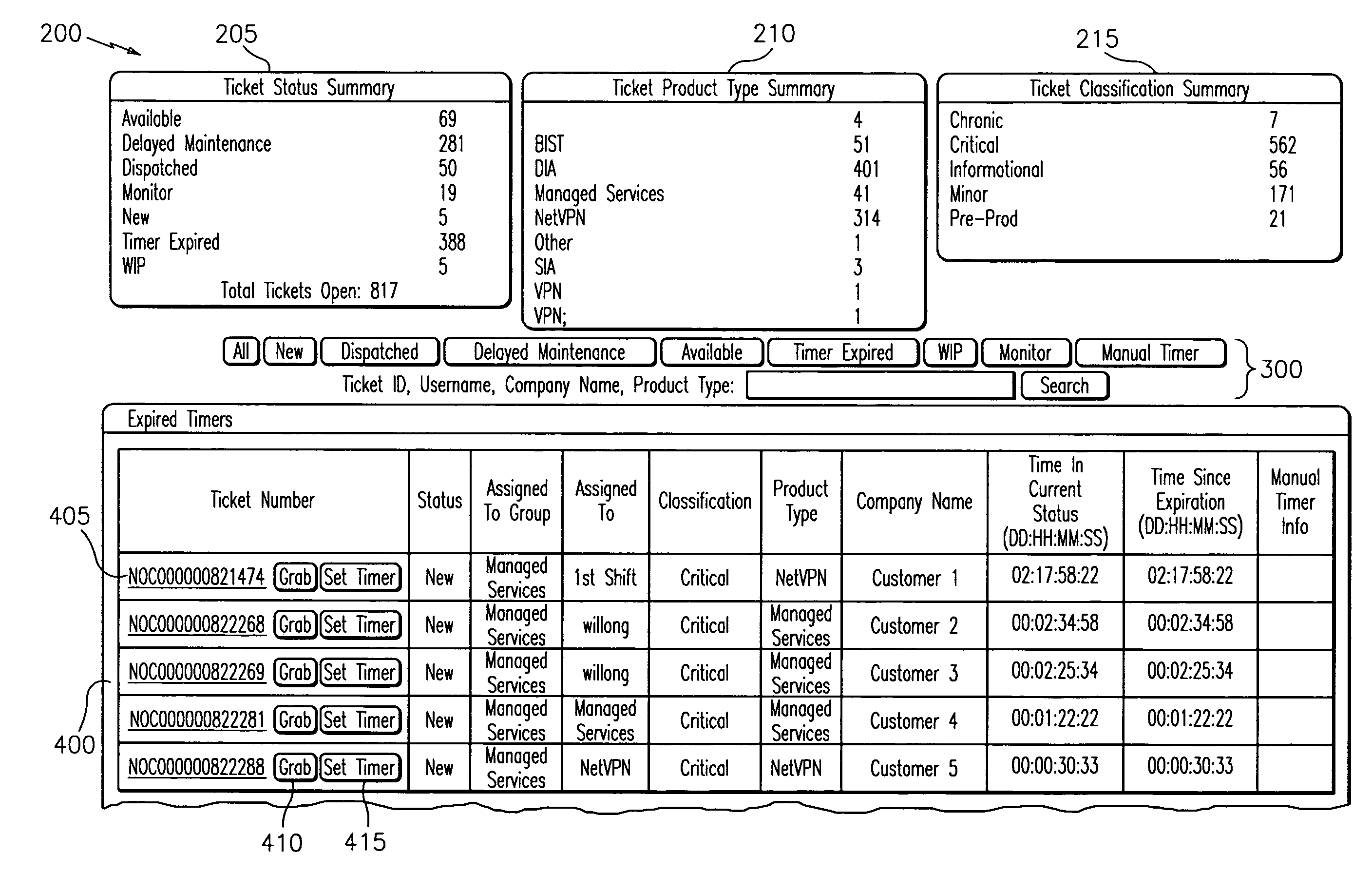
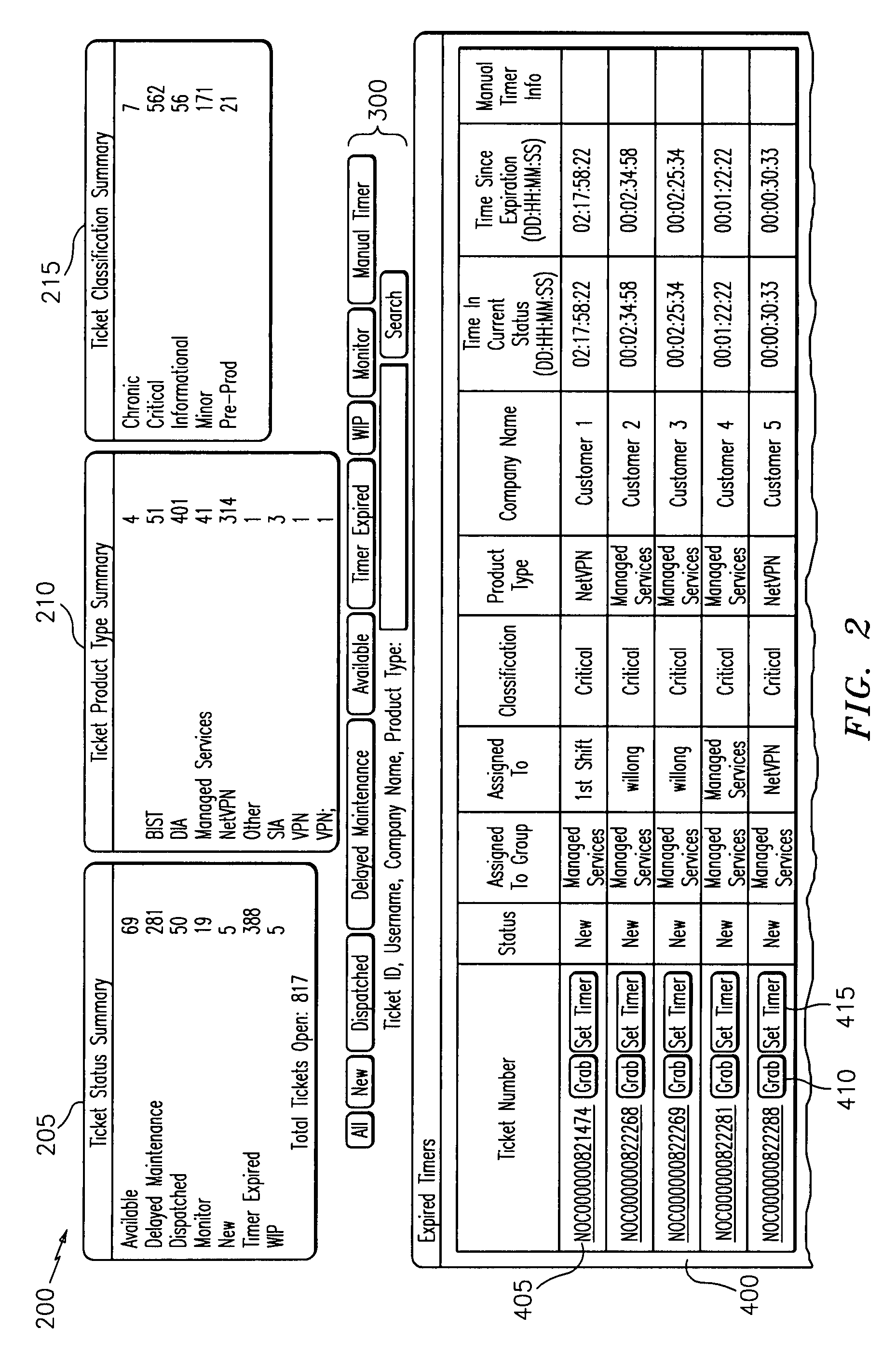
Systems, methods, website and computer products for service ticket consolidation and display
Systems, methods, website and computer products for service ticket consolidation and display. Exemplary embodiments include a service ticket display method, including generating a service ticket from a ticket service application, storing the service ticket in a database, accessing the ticket from the database through a ticket display application and displaying service ticket data on an interface coupled to the ticket display application. Additional exemplary embodiments include a service ticket display system, including a central server, a service ticket process residing on the server for generating service tickets, a database coupled to the server, a service ticket display process residing on the server for managing the service tickets and a display coupled to the server and database for accessing and displaying the service tickets on an interface in response to request to display consolidated ticket status.
Owner:BOSTON CHRISTOPHER
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com