Patents
Literature
9727 results about "Selection method" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Selection methods or screening devices include application blanks, employment interviews, aptitude tests, and personality test.
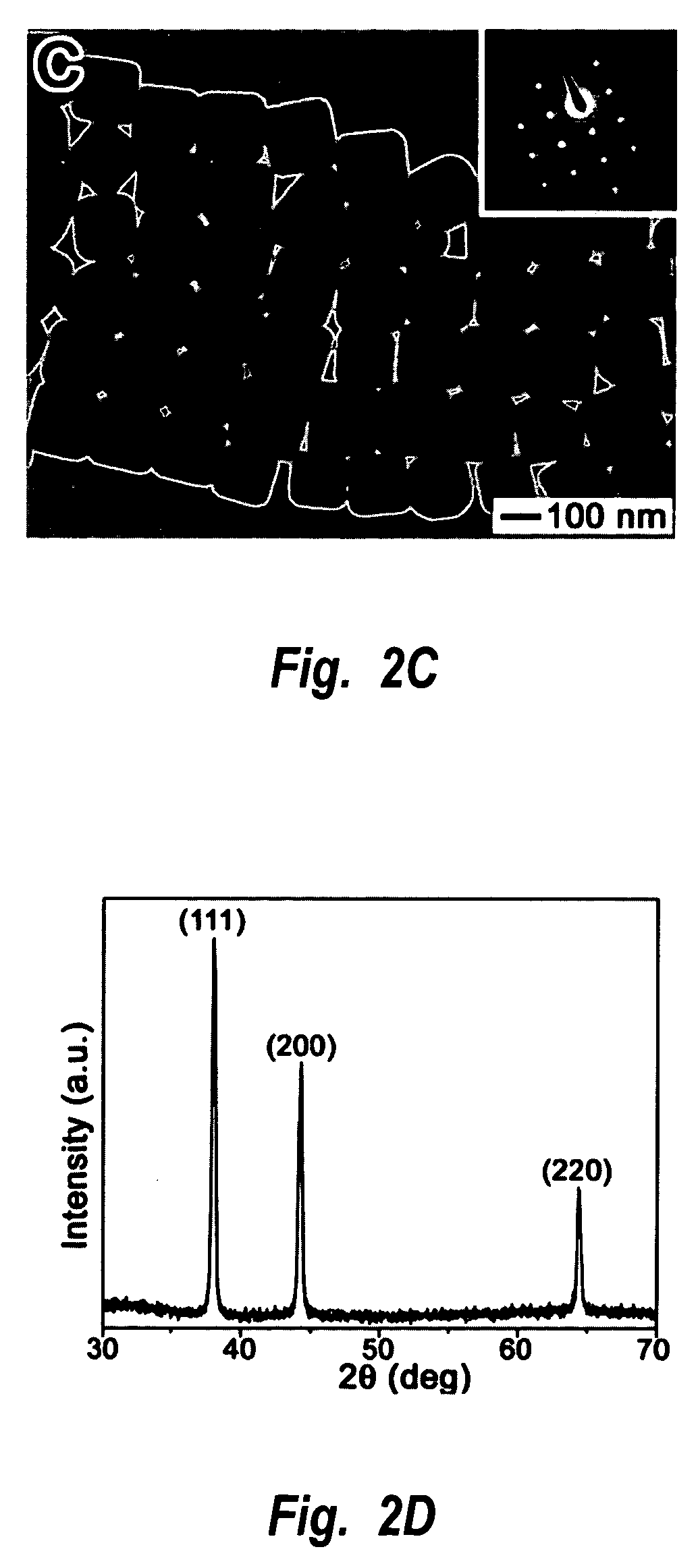
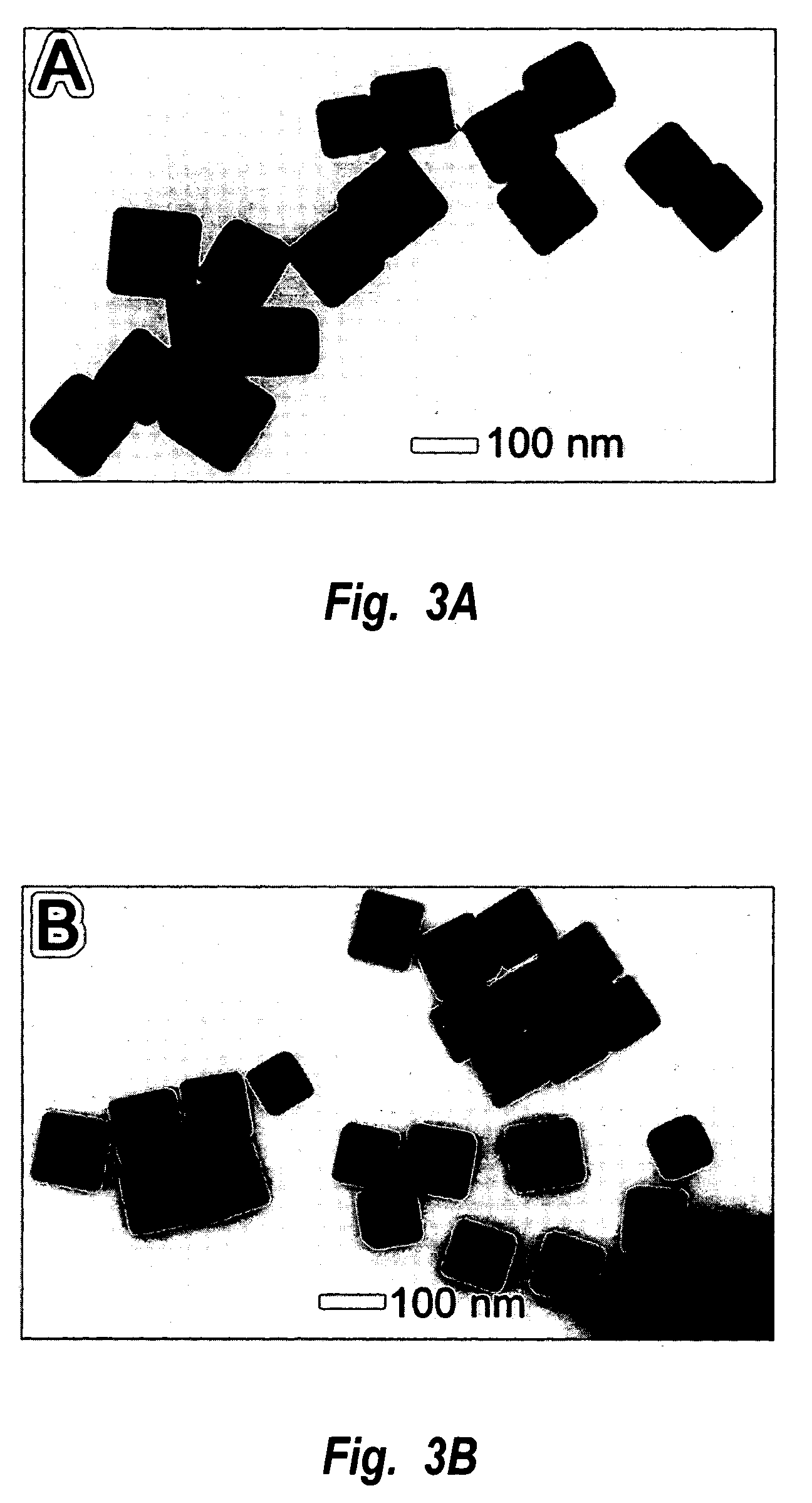
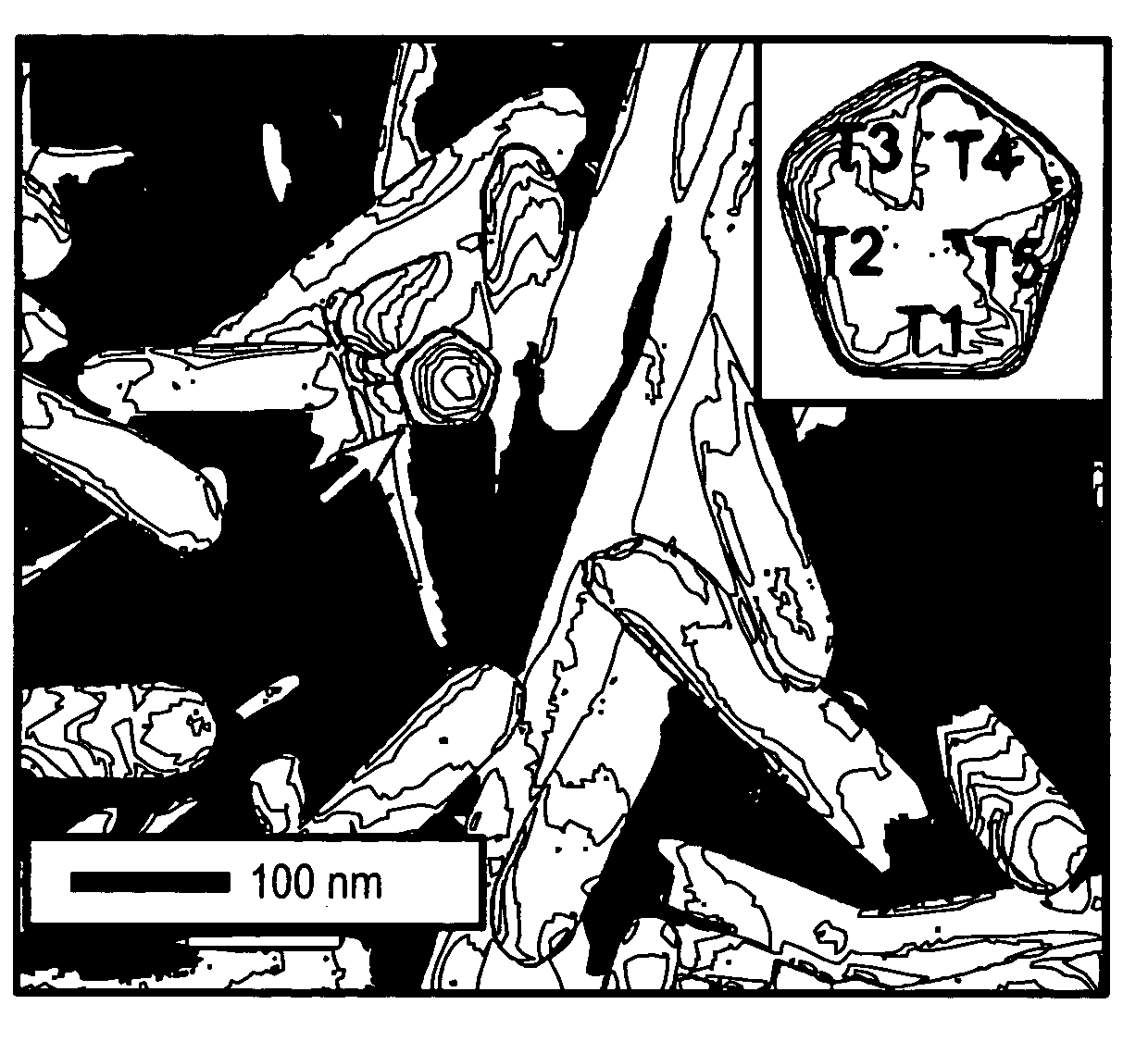
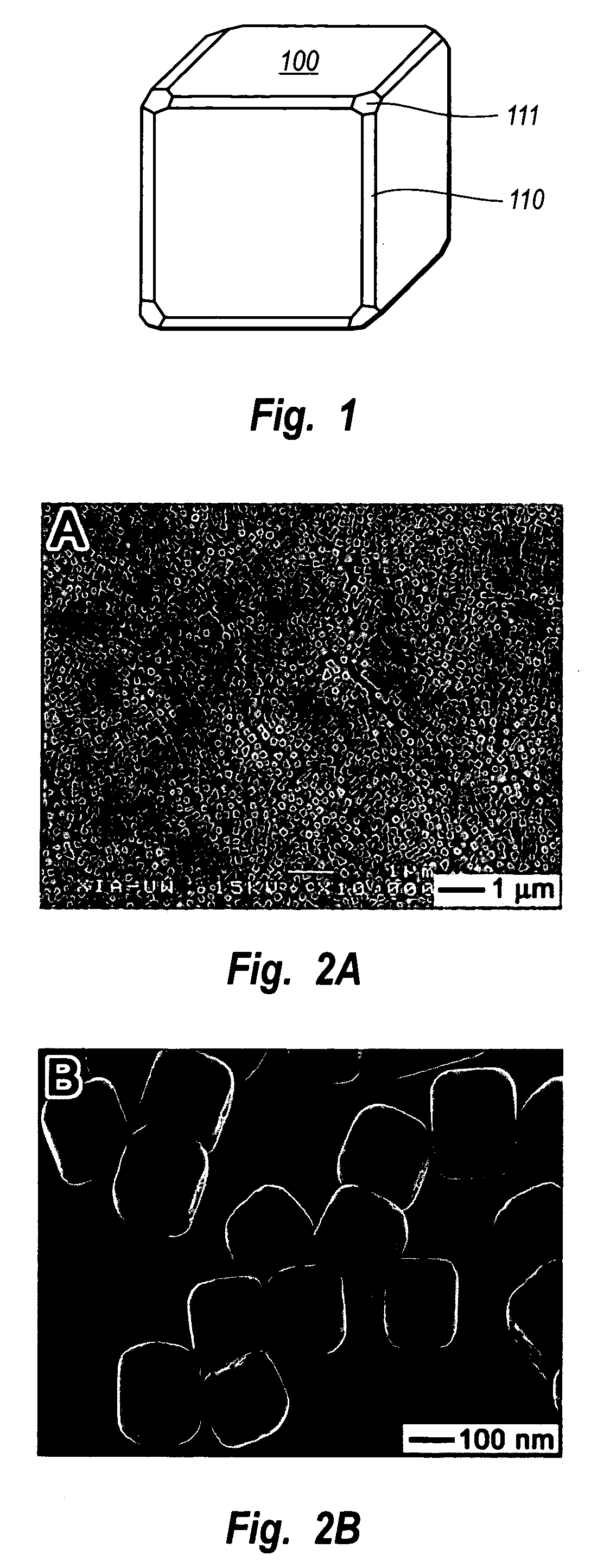
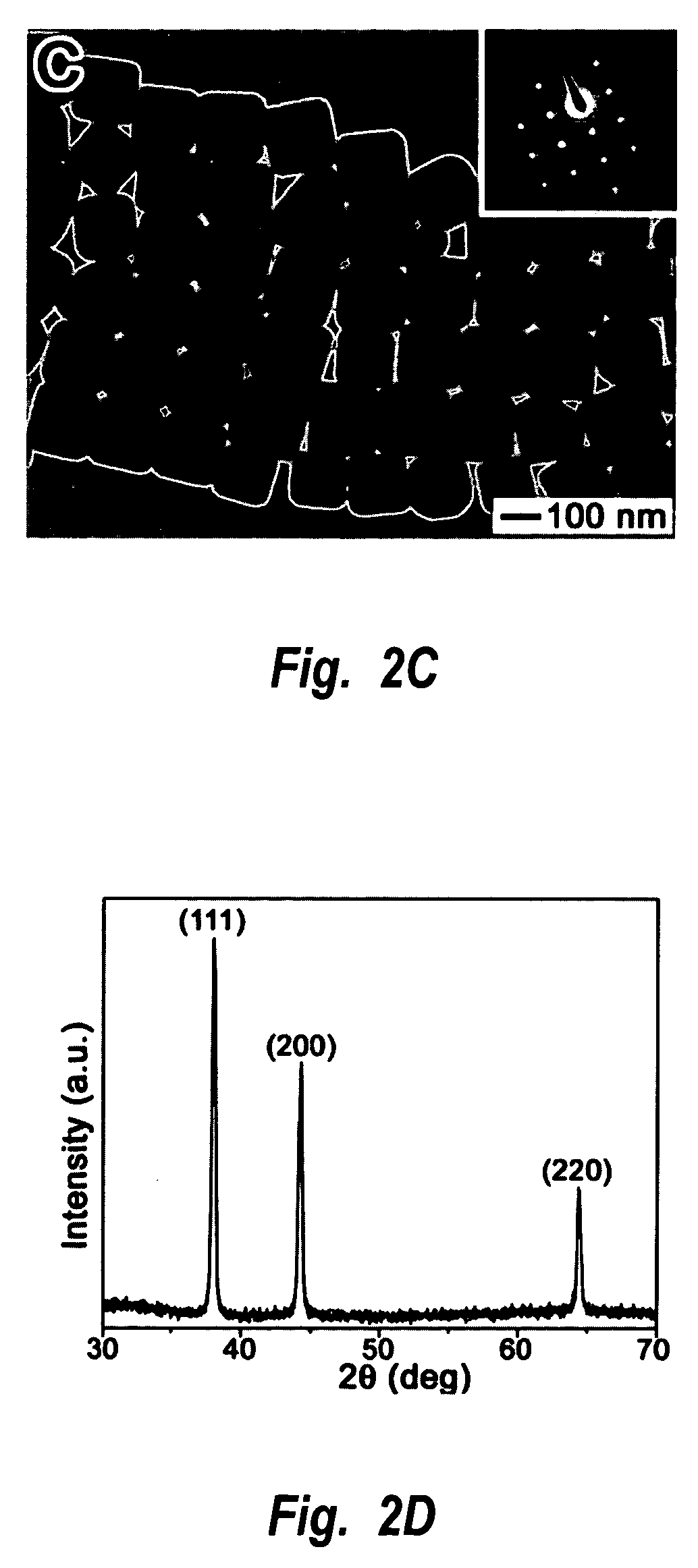
Methods of nanostructure formation and shape selection
Methods for forming nanostructures of various shapes are disclosed. Nanocubes, nanowires, nanopyramids and multiply twinned particles of silver may by formed by combining a solution of silver nitrate in ethylene glycol with a solution of poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) in ethylene glycol. Hollow nanostructures may be formed by reacting a solution of solid nanostructures comprising one of a first metal and a first metal alloy with a metal salt that can be reduced by the first metal or first metal alloy. Nanostructures comprising a core with at least one nanoshell may be formed by plating a nanostructure and reacting the plating with a metal salt.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
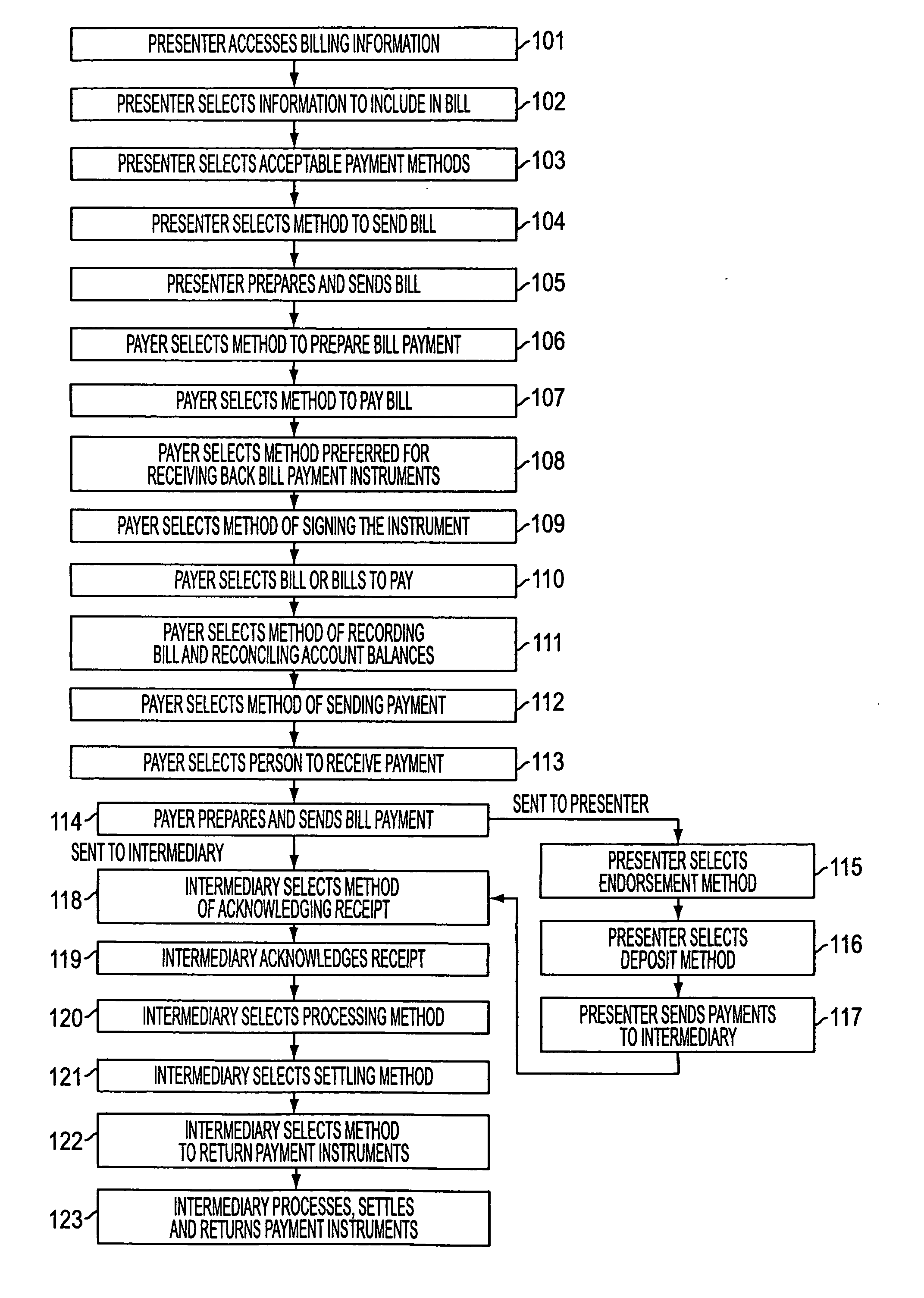
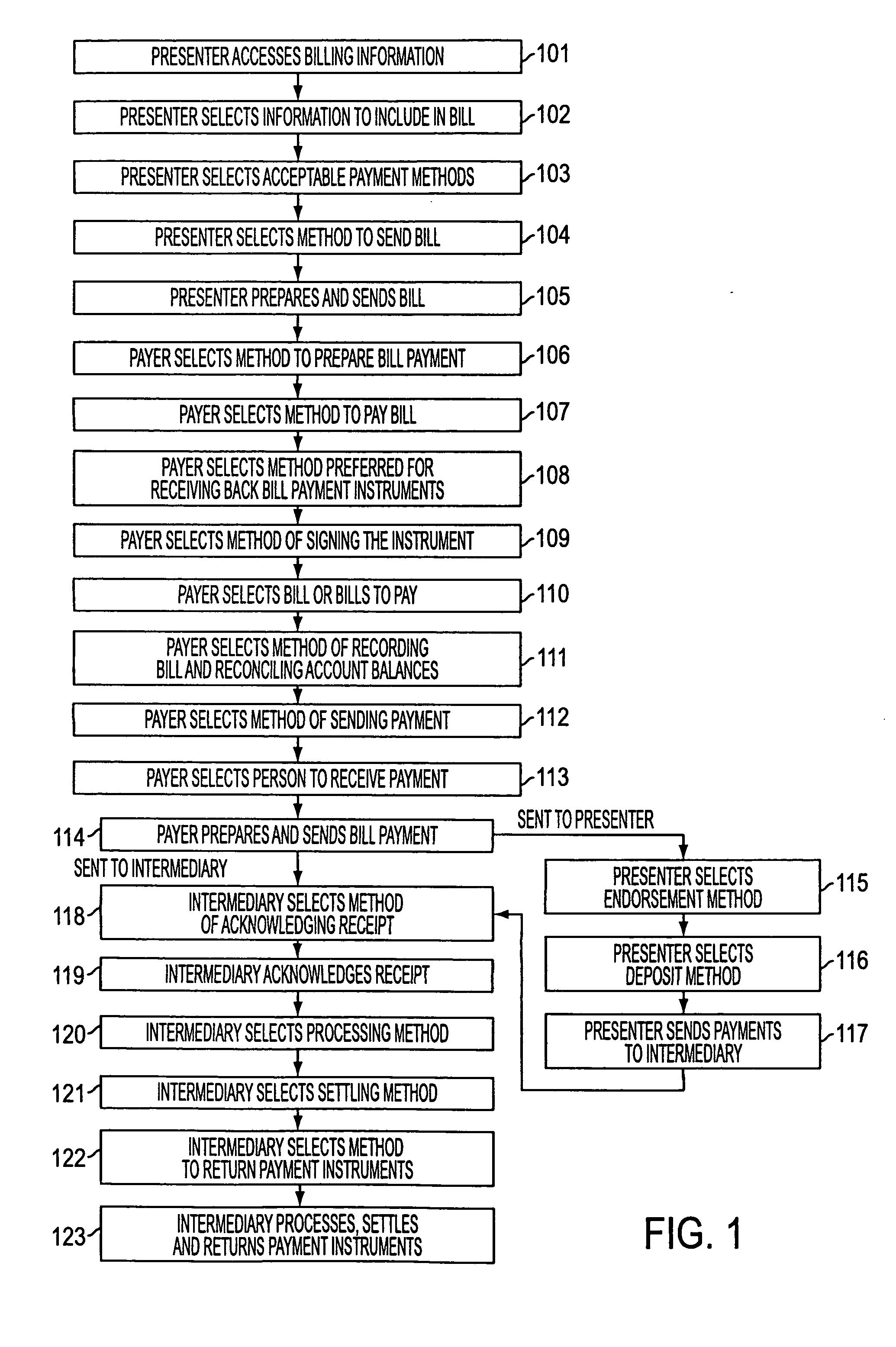
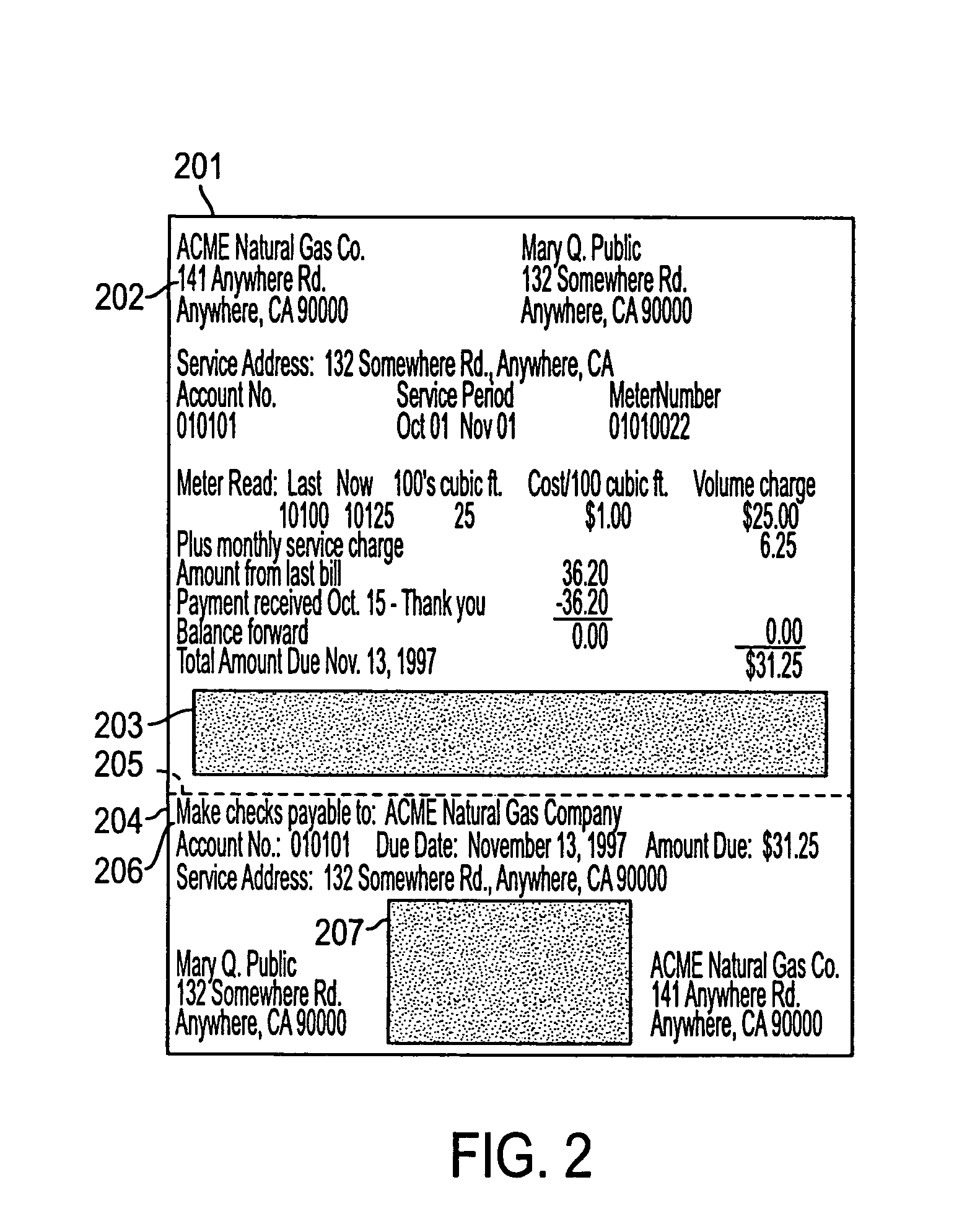
System and method for digital bill presentment and payment
InactiveUS20050033690A1Reduce complexityEnhanced interactionFinancePayment architectureCredit cardDigital data
A system of bill presentment and bill payment. The parties to the process, which typically include the bill presenter, bill payer, and bank, credit card company or other intermediary, select from a number of choices in the selection of information to include in the bill, preparation of the bill, acceptable payment methods, means to send the bill and bill payment instrument, means of signing the bill, bill payment instrument, receipt acknowledging deposit and payment, method of recording and reconciling payments, and further actions. An accumulation of choices by the involved parties can include digital information in each step that represents all of the significant data accumulated up to and including that step. That digital data preferably includes digital signatures of each party at each step so as to provide an audit trail in purely digital form. Where digital data is chosen for each step, the digital data can be electronic or, using machine readable code, printed on paper, regardless of the form chosen in prior or later steps.
Owner:ANTOGNINI WALTER GERARD +1
Single-molecule selection methods and compositions therefrom
InactiveUS20020034757A1Highly specific controlImprove complianceNanotechSugar derivativesNucleotideAdhesive
Single-molecule selection methods are provided for identifying target-binding molecules from diverse sequence and shape libraries. Complexes and imprints of selected target-binding molecules are also provided. The subject selection methods are used to identify oligonucleotide and nonnucleotide molecules with desirable properties for use in pharmaceuticals, drug discovery, drug delivery, diagnostics, medical devices, cosmetics, agriculture, environmental remediation, smart materials, packaging, microelectronics and nanofabrication. Single oligonucleotide molecules with desirable binding properties are selected from diverse sequence libraries and identified by amplification and sequencing. Alternatively, selected oligonucleotide molecules are identified by sequencing without amplification. Nonnucleotide molecules with desirable properties are identified by single-molecule selection from libraries of conjugated molecules or nucleotide-encoded nonnucleotide molecules. Alternatively, target-specific nonnucleotide molecules are prepared by imprinting selected oligonucleotide molecules into nonnucleotide molecular media. Complexes and imprints of molecules identified by single-molecule selection are shown to have broad utility as drugs, prodrugs, drug delivery systems, willfully reversible cosmetics, diagnostic reagents, sensors, transducers, actuators, adhesives, adherents and novel multimolecular devices.
Owner:MOLECULAR MACHINES
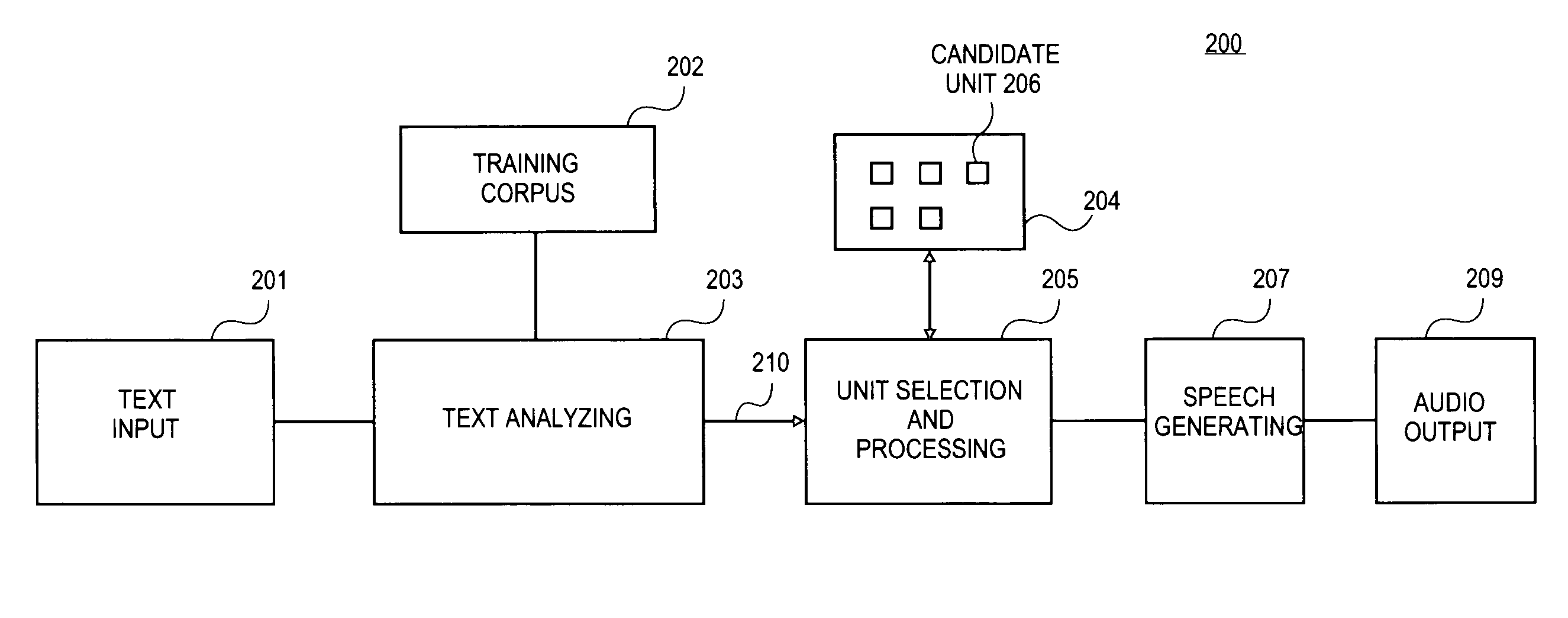
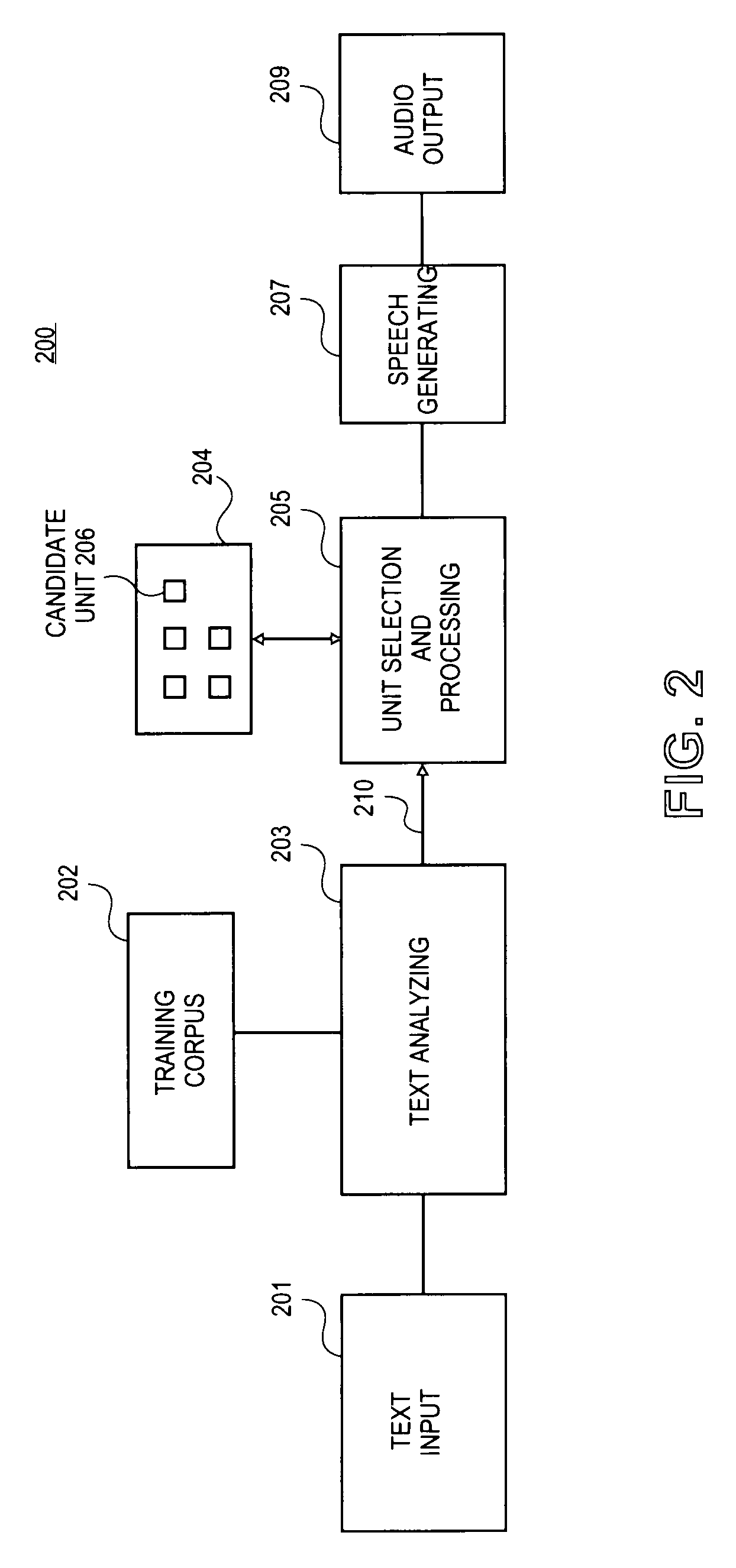
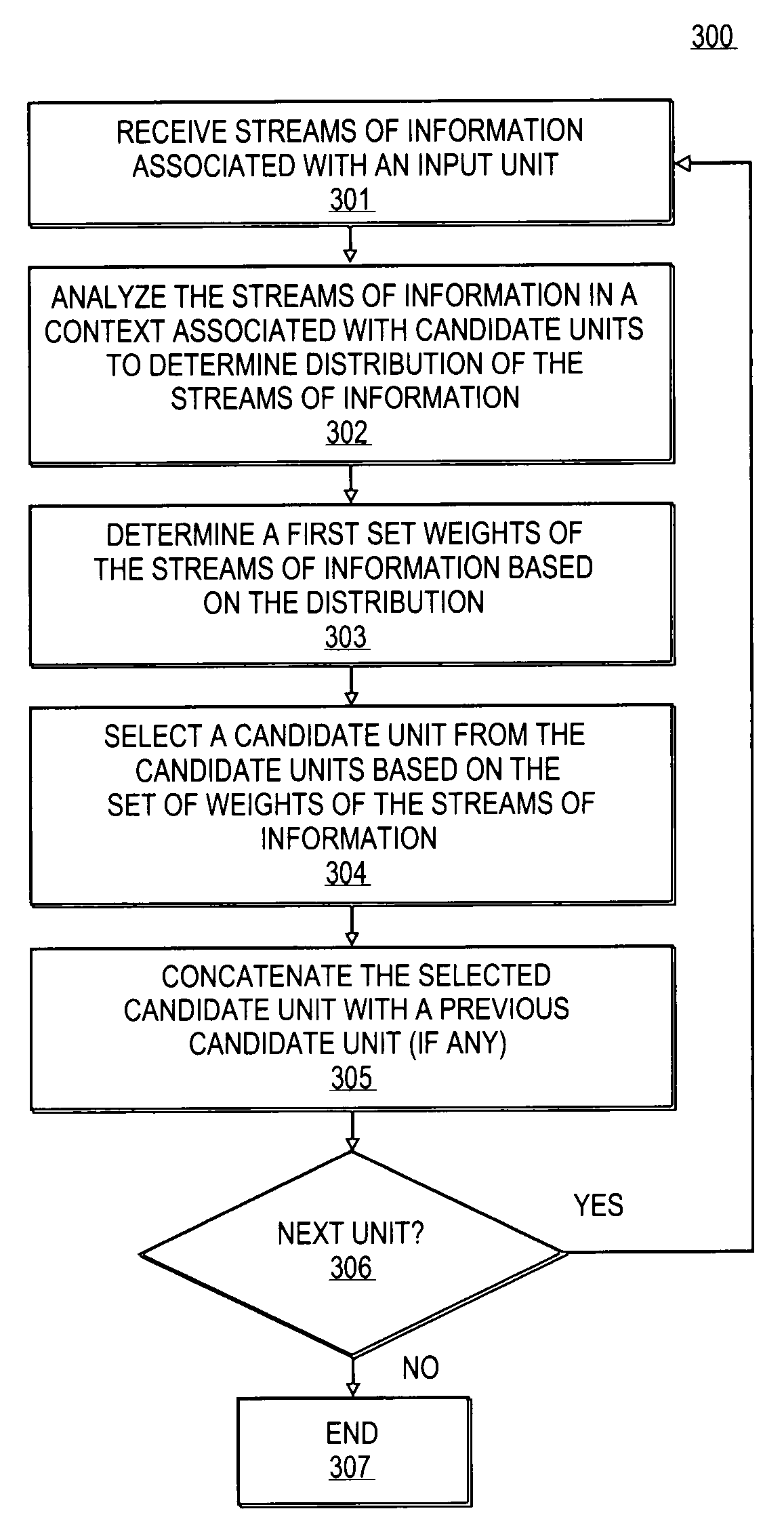
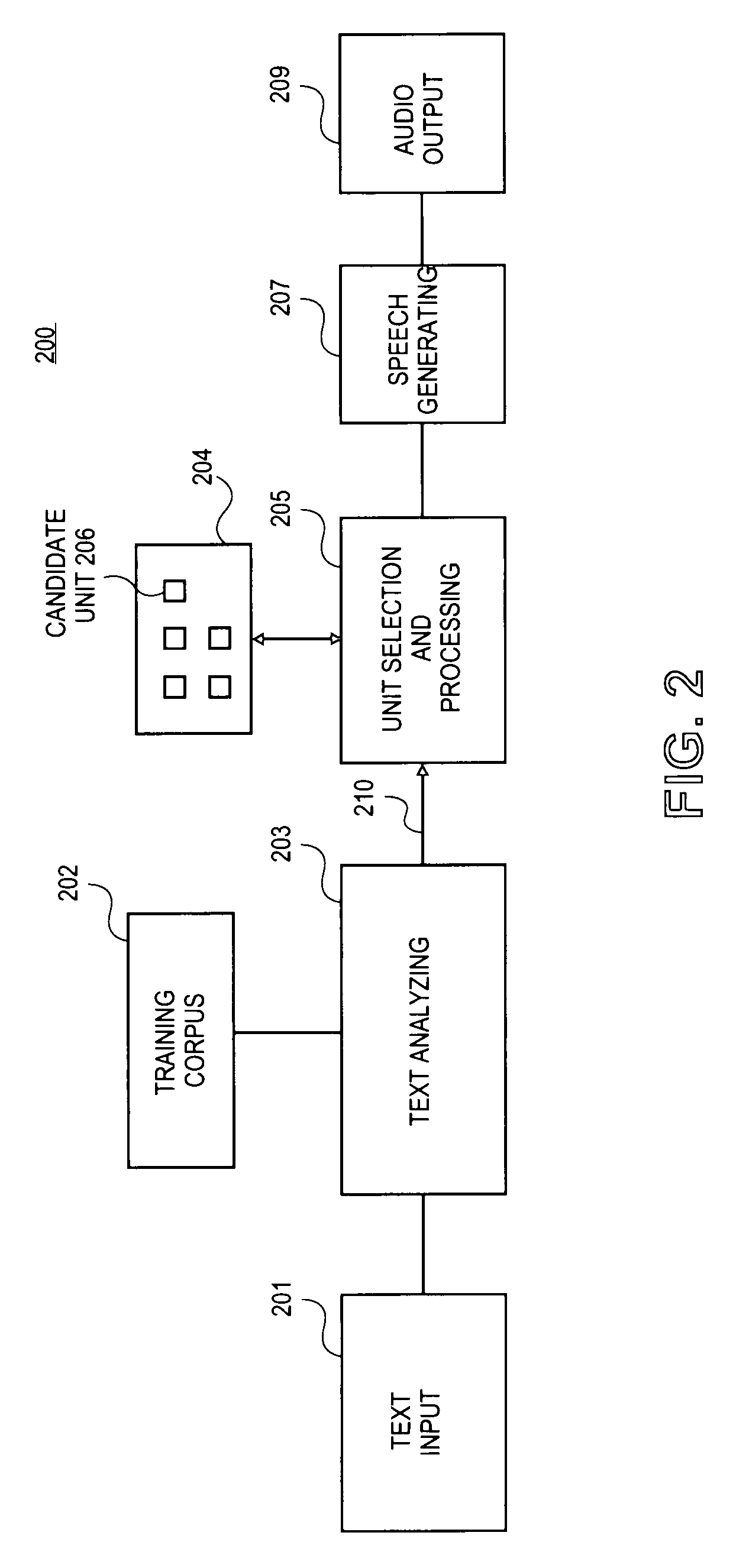
Context-aware unit selection
Methods and apparatuses to perform context-aware unit selection for natural language processing are described. Streams of information associated with input units are received. The streams of information are analyzed in a context associated with first candidate units to determine a first set of weights of the streams of information. A first candidate unit is selected from the first candidate units based on the first set of weights of the streams of information. The streams of information are analyzed in the context associated with second candidate units to determine a second set of weights of the streams of information. A second candidate unit is selected from second candidate units to concatenate with the first candidate unit based on the second set of weights of the streams of information.
Owner:APPLE INC
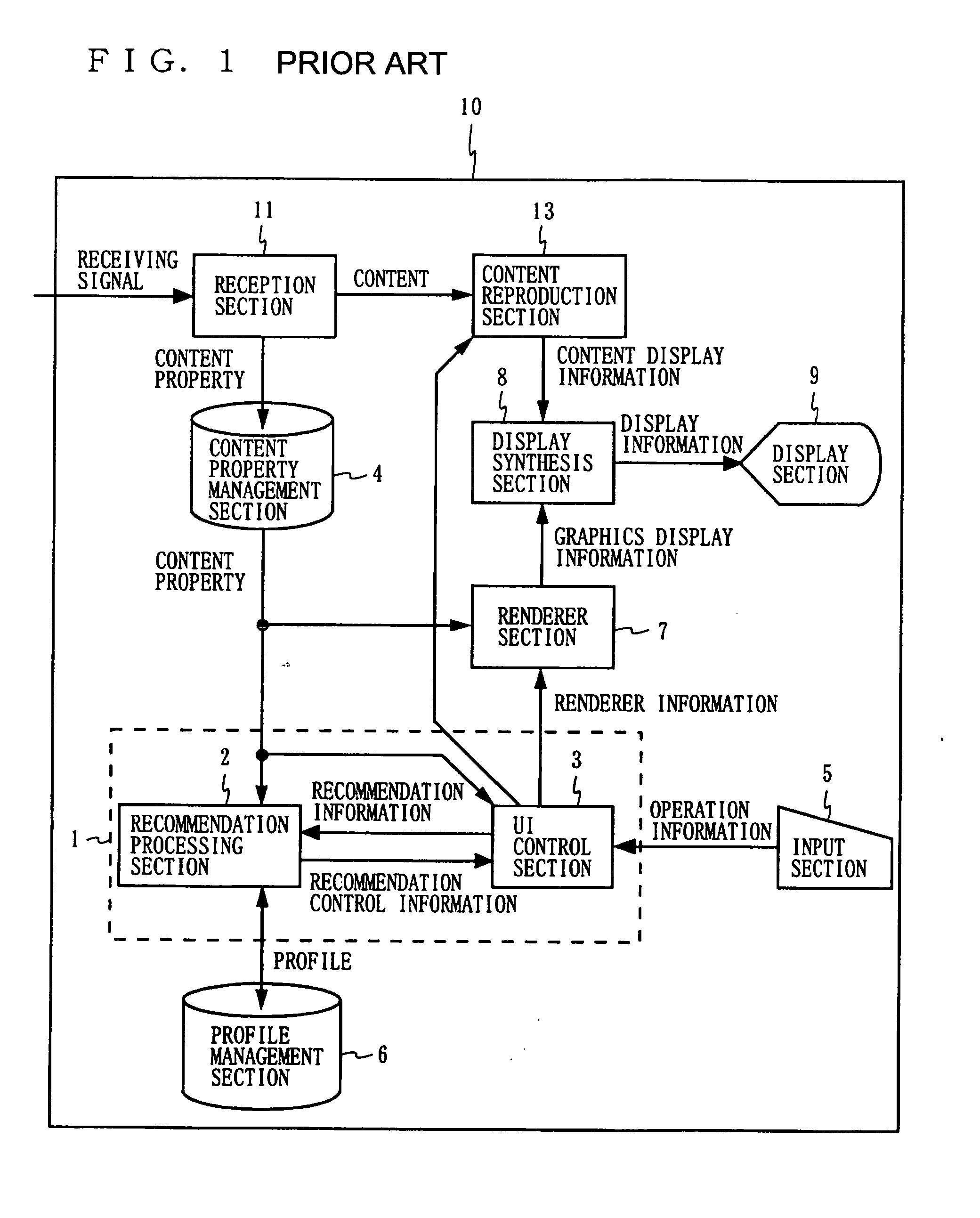
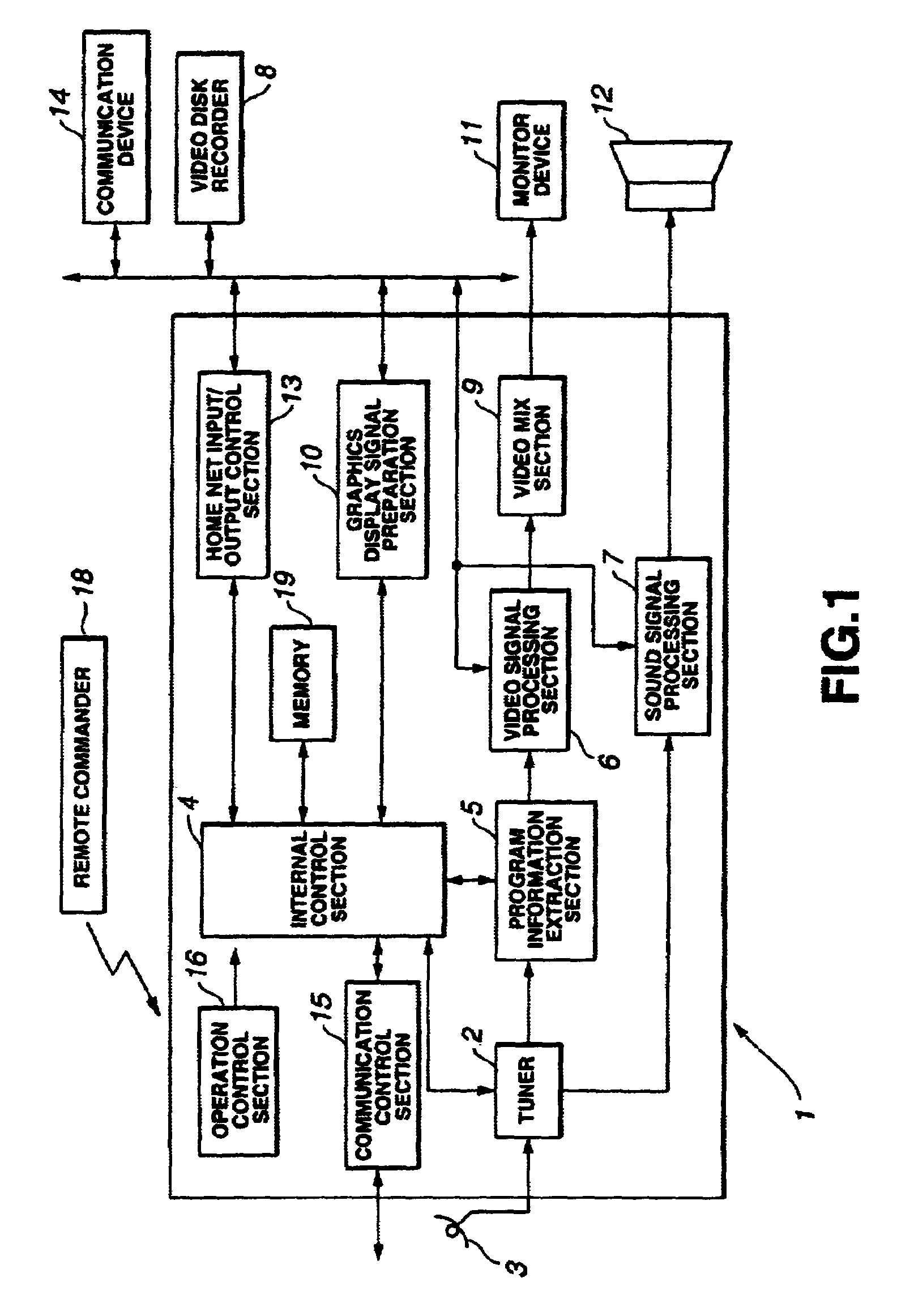
Information processing apparatus, information processing method, information processing program and storage medium containing information processing program
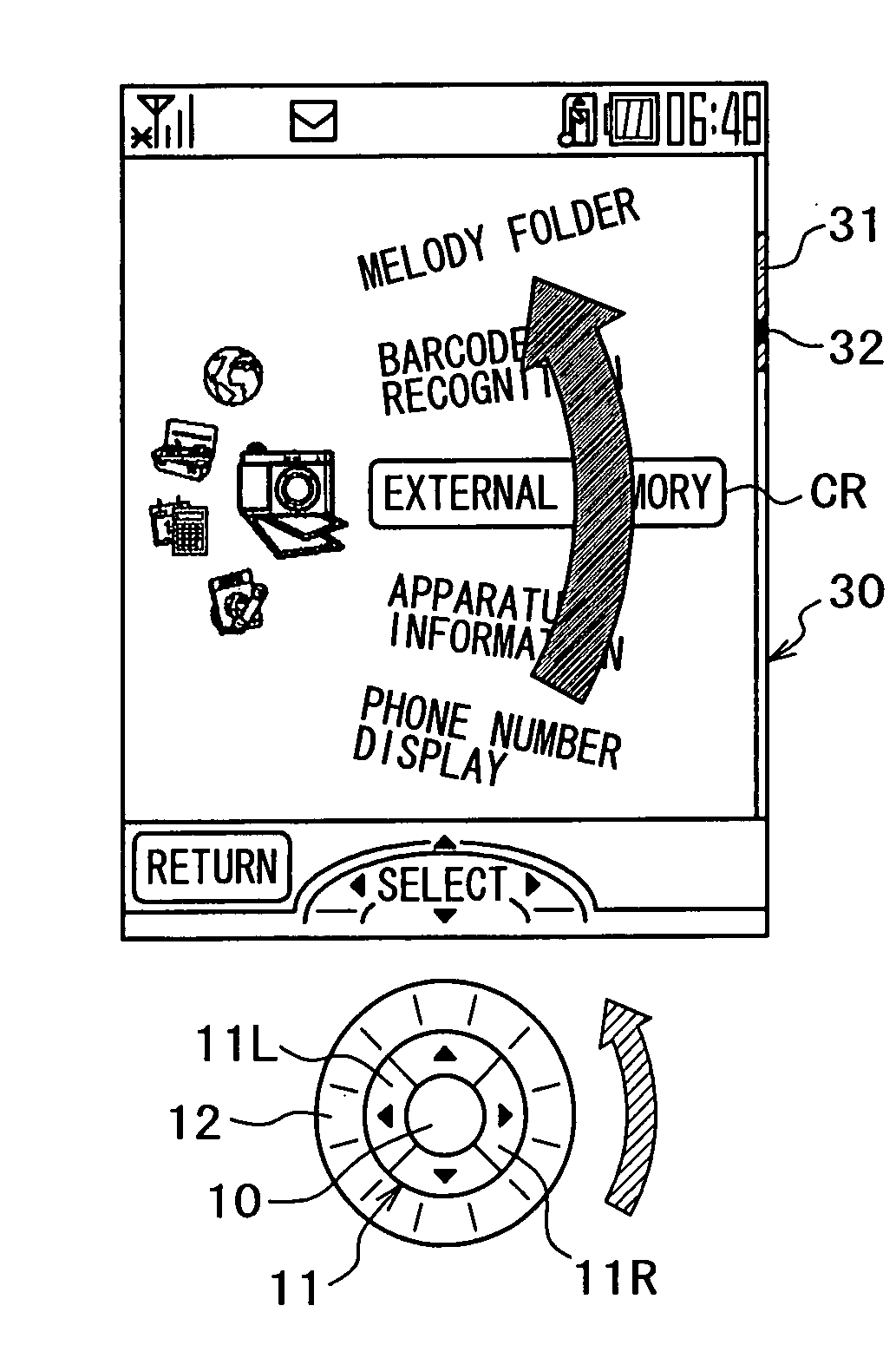
InactiveUS20050081164A1Satisfactory operabilityCathode-ray tube indicatorsTransmissionMoving speedSelection method
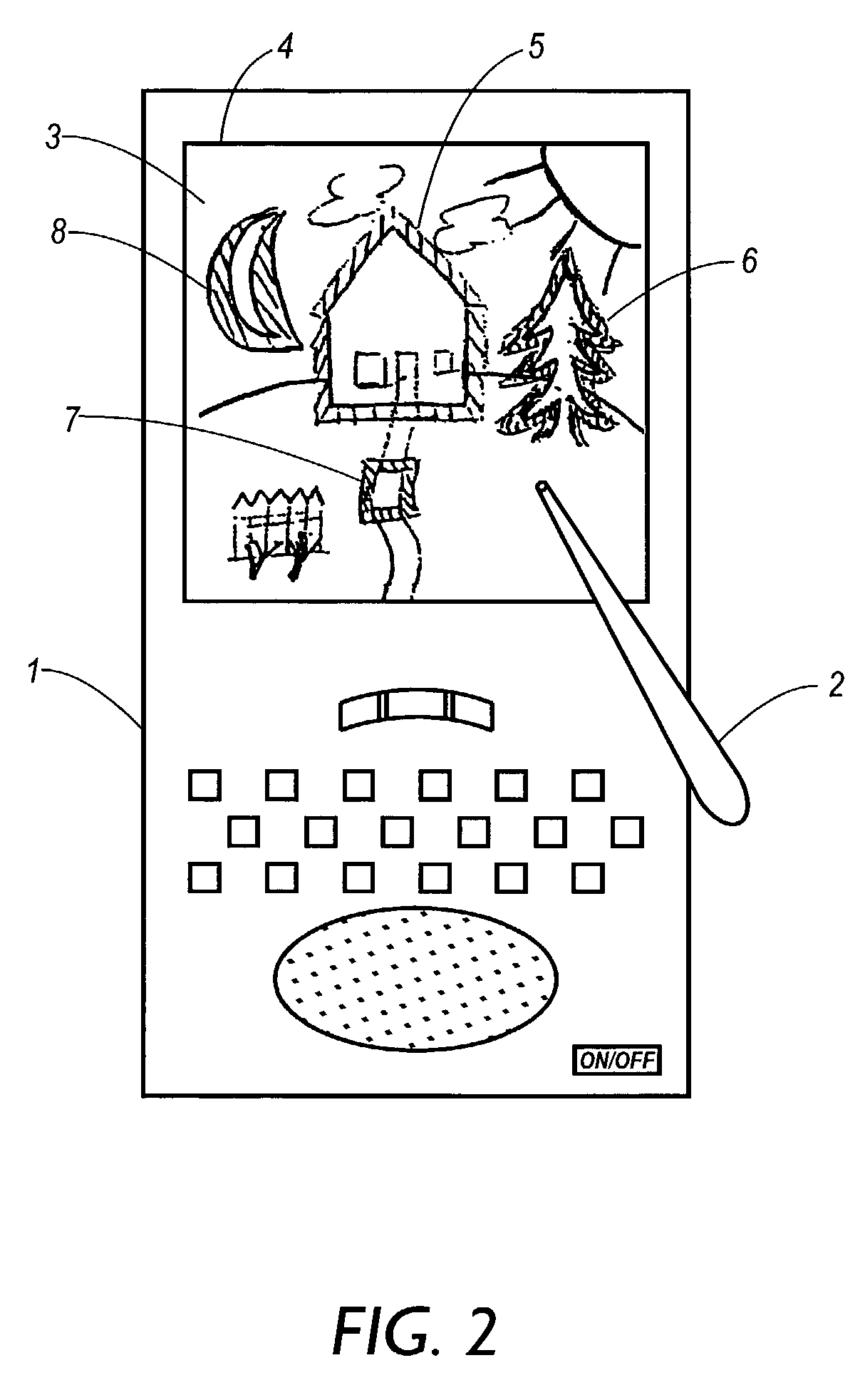
There is provided a novel menu selection method in a mobile phone. Also provided is a cursor displaying method with which a user can intuitively recognize a moving direction and moving speed. In addition, a novel scrollbar with which the user can recognize, in a case of displaying menus beyond a display screen, a range currently displayed on a display screen among all the menus and a current cursor position within the menus displayed on the current display screen.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
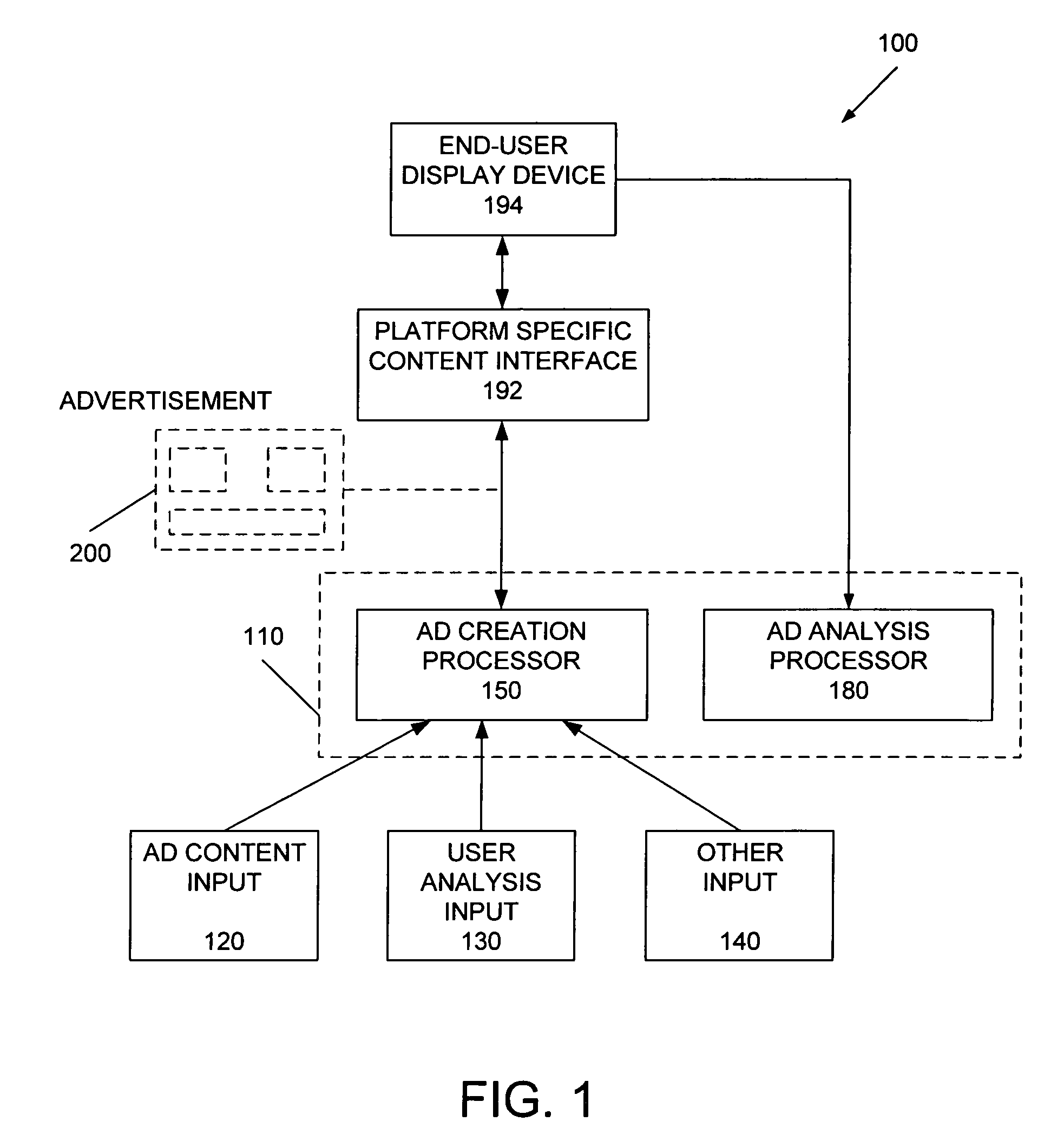
Method and apparatus for dynamic ad creation
The present invention provides methods and apparatus for selecting relating to content selection. In one aspect, the invention provides methods and apparatus for determining appropriate content based upon various other input data, particularly for individuals on whom personal data is already known. In another aspect of the invention provides method and apparatus for analyzing feedback statistics obtained from previously delivered content in order to update new content for delivery. Another aspect of the invention is combinations of content determination with the analysis of feedback statistics, preferably in real-time, to take into account not only individual preferences, but environmental and other factors. An embodiment of the present invention is directed toward personalized advertisements, with particularly preferred embodiments described that are implemented with an Internet media platform, an interactive digital television platform, as well as cross-platform implementations.
Owner:BOOK JOYCE A
Feedback mechanism for use with visual selection methods
InactiveUS6961912B2Enhance the imageEasy to browseDigital data processing detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsHyperlinkGraphics
A feedback mechanism usable with graphical user interface systems that do not have a cursor improves the usefulness of such graphical user interfaces. Locating, identifying and / or selecting hyperlink targets or active areas within a displayed image map or within a Web page is facilitated by providing distinctions to the hyperlink targets or active areas or by providing other locational indicators for a designated time period in response to a single user gesture. The distinctions or locational indicators may be provided in combination with other distinctions or locational indicators to further aid the hyperlink target or active area location, identification and / or selection process. After a designated time period expires, the distinctions, locational indicators, or their combination, are removed from the display without any additional user gesture. This increases the efficiency and convenience of locating, identifying and / or selecting hyperlink targets or active areas in a graphical user interface system.
Owner:XEROX CORP
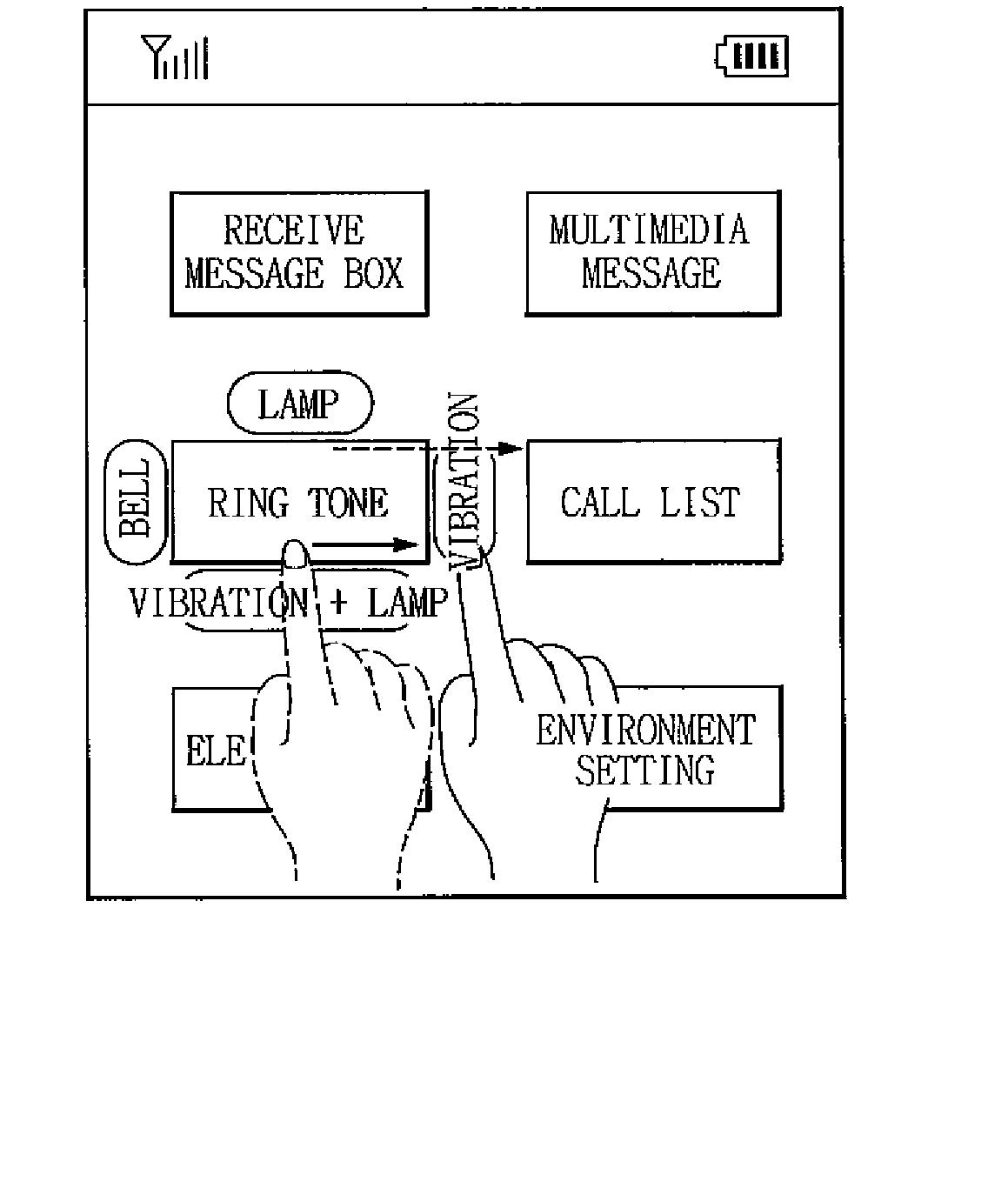
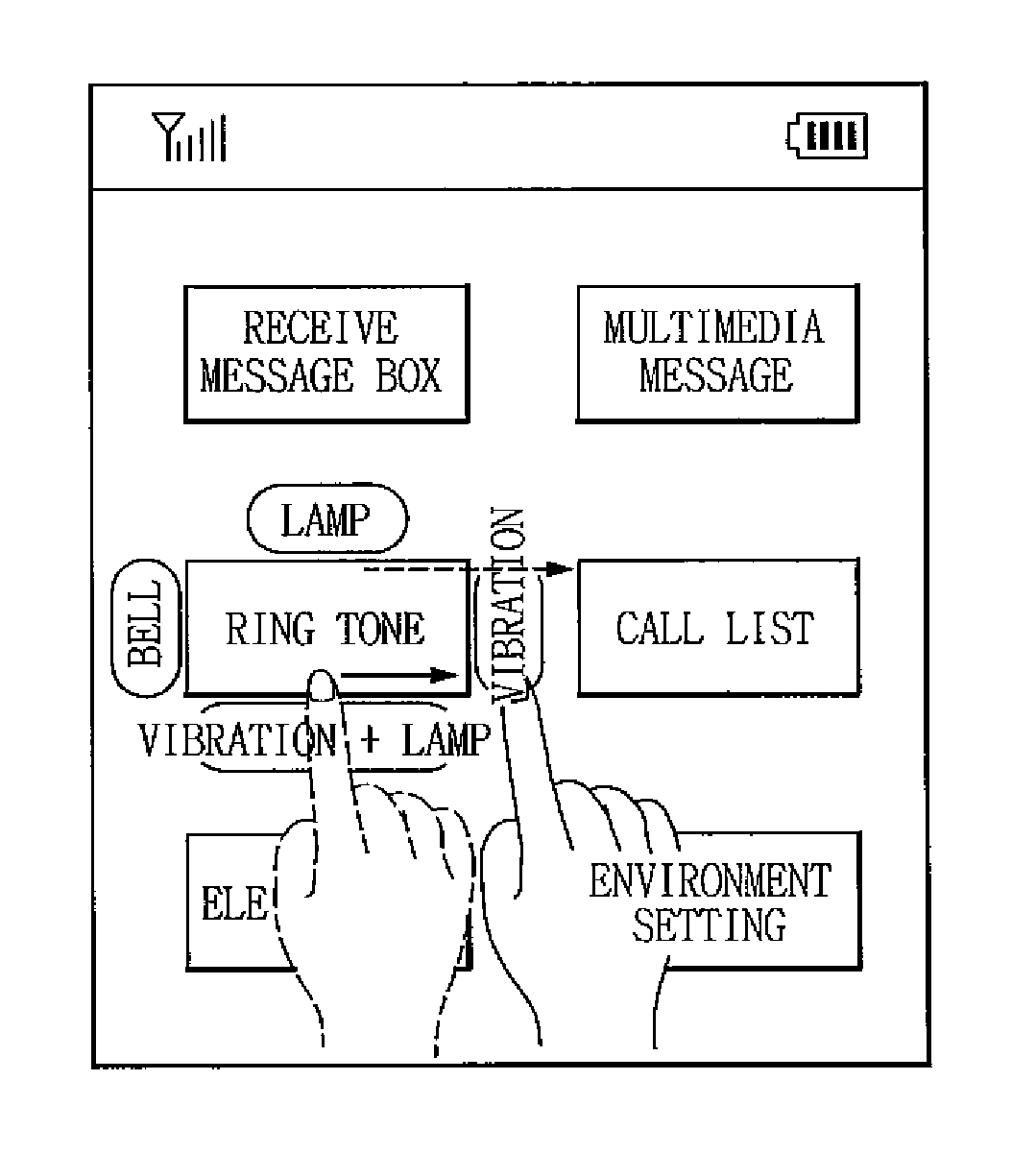
Mobile communication terminal and method of selecting menu and item
ActiveUS20080074399A1Choose simpleChoose accuratelySubstation equipmentTransmissionHuman–computer interactionSelection method
A menu selection method, which includes selecting a main menu displayed on a touch device of a terminal, displaying one or more sub-menus corresponding to the selected main menu, sensing a direction of a dragging operation on the touch device, and executing a corresponding sub-menu located in the sensed direction of the dragging operation.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Secure transaction system
InactiveUS20060191995A1Improve management efficiencyComplete banking machinesFinanceData fieldCentral database
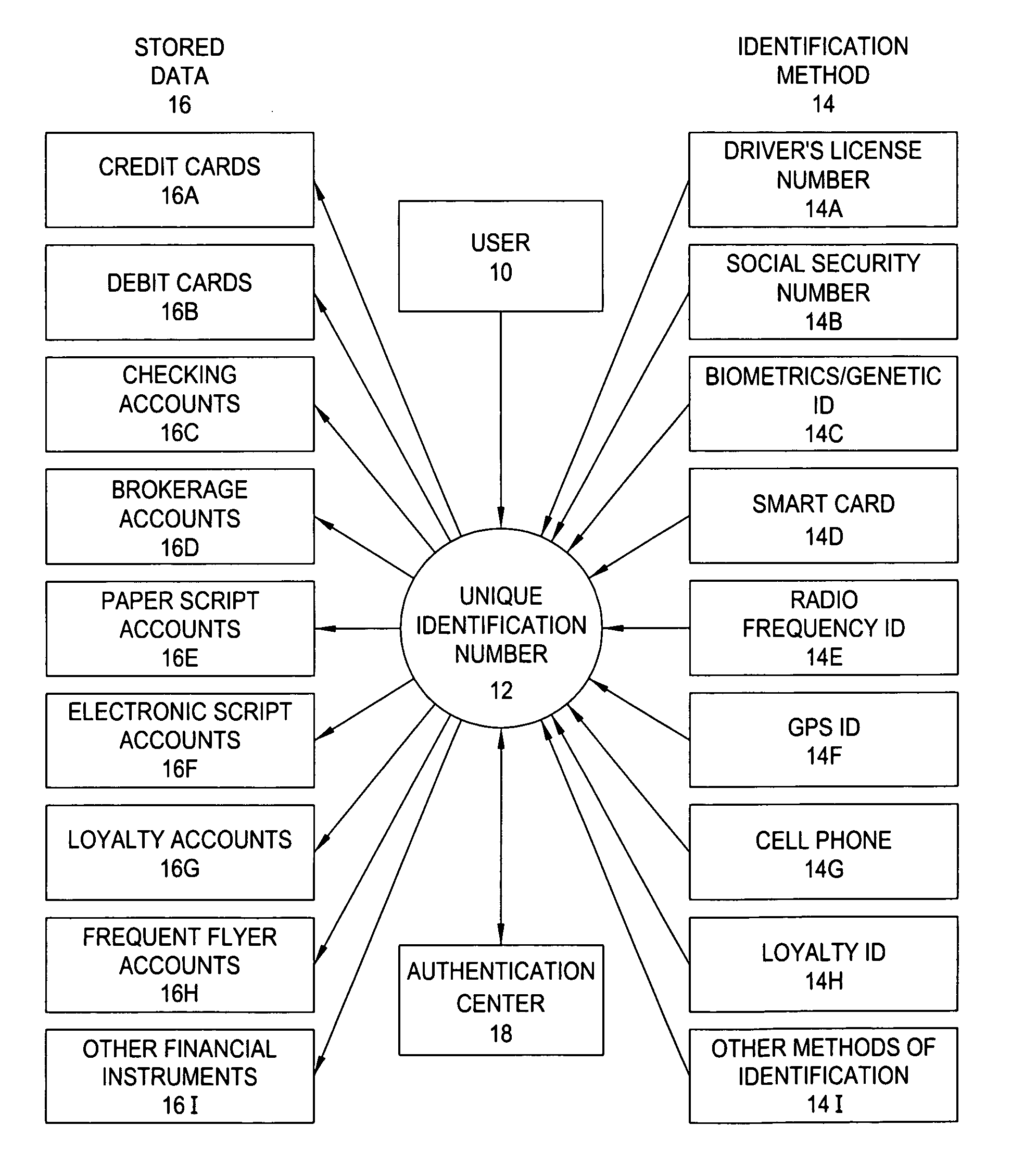
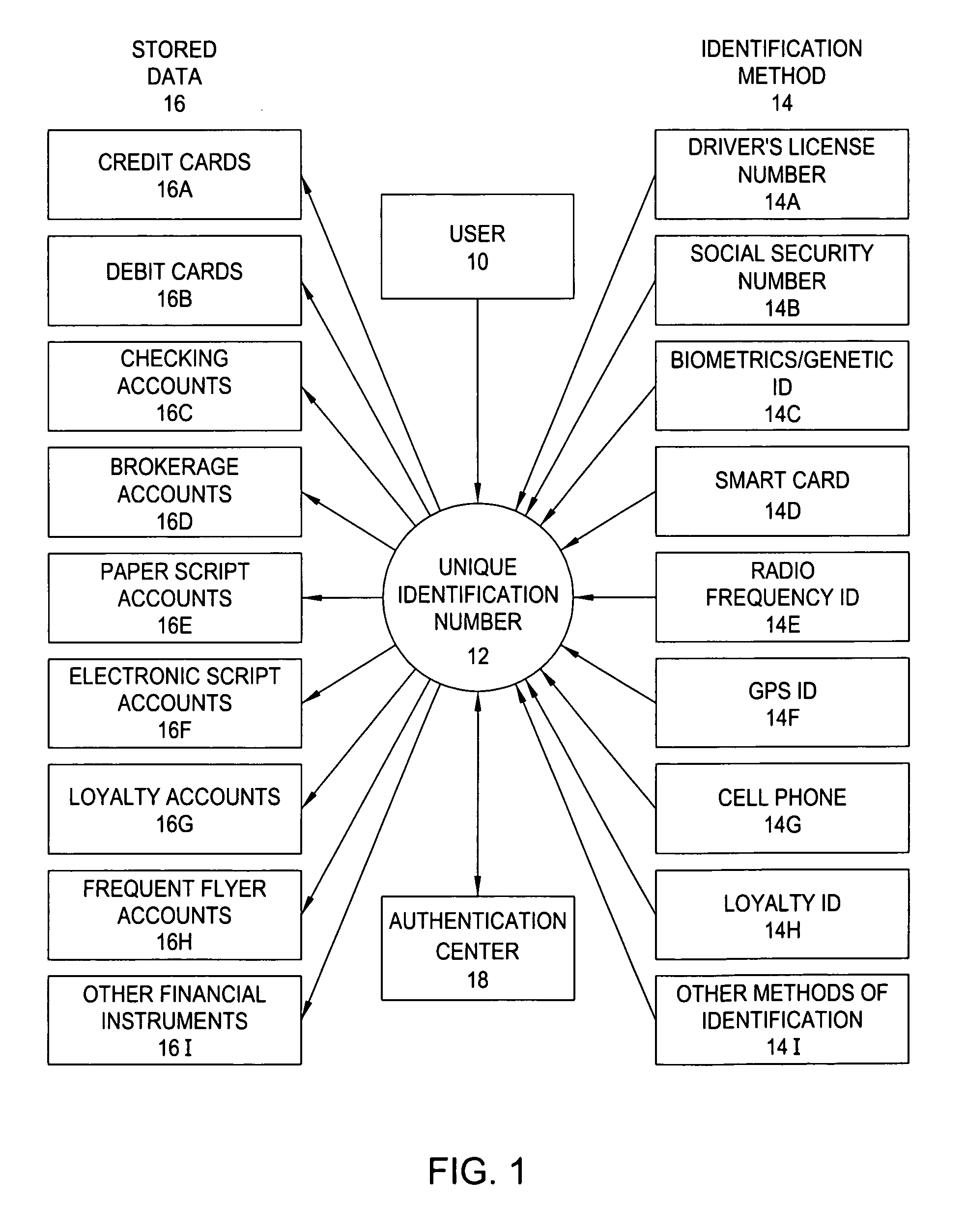
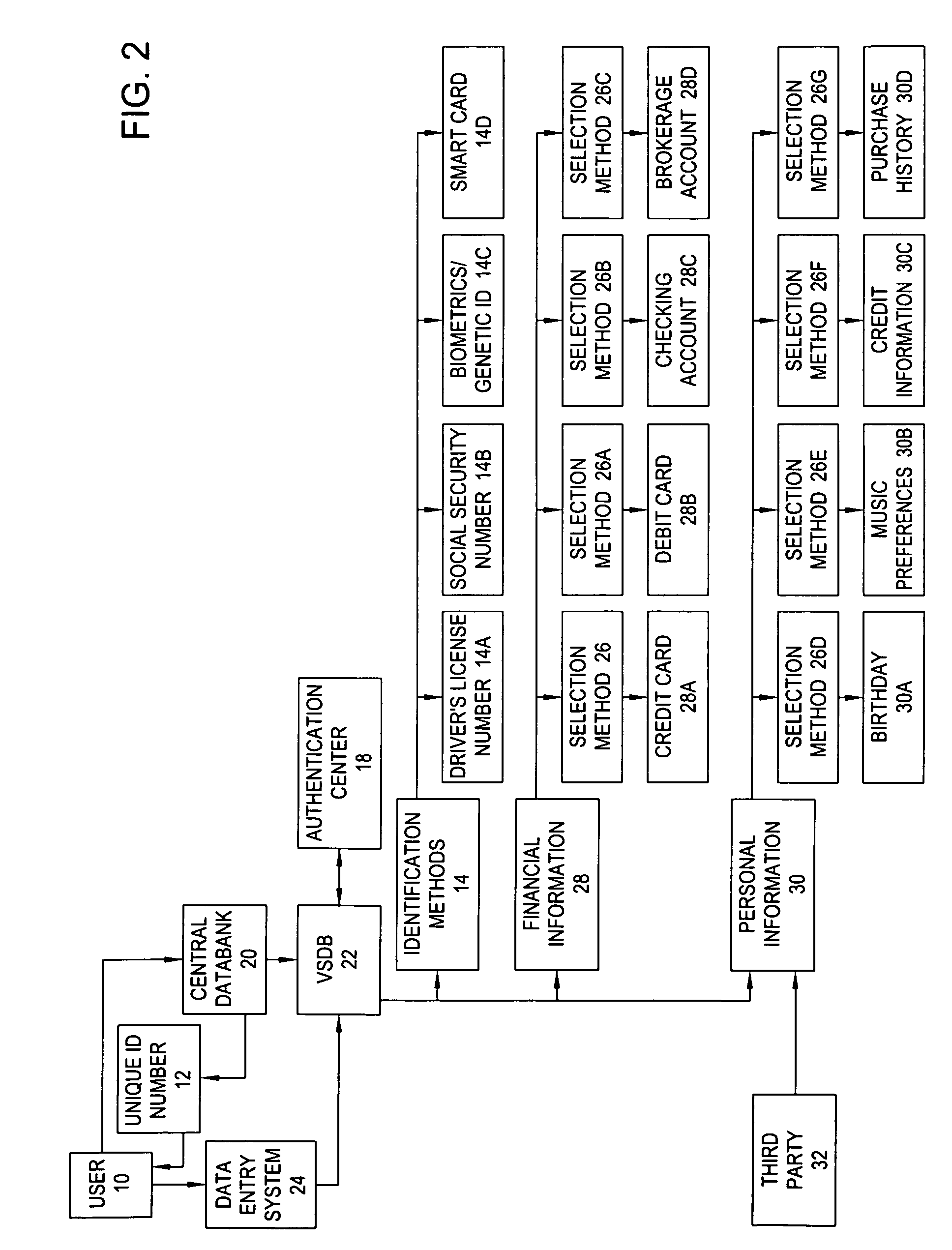
The system of the present invention comprises a personal Virtual Safety Deposit Box where users are able to enroll their identification methods, financial accounts and personal information. Once authenticated, this information is transferred to a master file within a central databank. Enrollment enables the user to link each item (collectively referred to as the “stored data”) to any one of the plurality of identification methods they enter. Thereafter, the user may employ their enrolled identification methods to select a desired one of the stored data fields. A secure intermediary uses the identification method and a selection method to determine which of the stored data fields the user desires to employ by accessing a database containing each of the stored data fields and the corresponding selection method. The selected field is activated and any relevant outside agencies are notified of the transaction and the transaction is concluded.
Owner:SOURCE
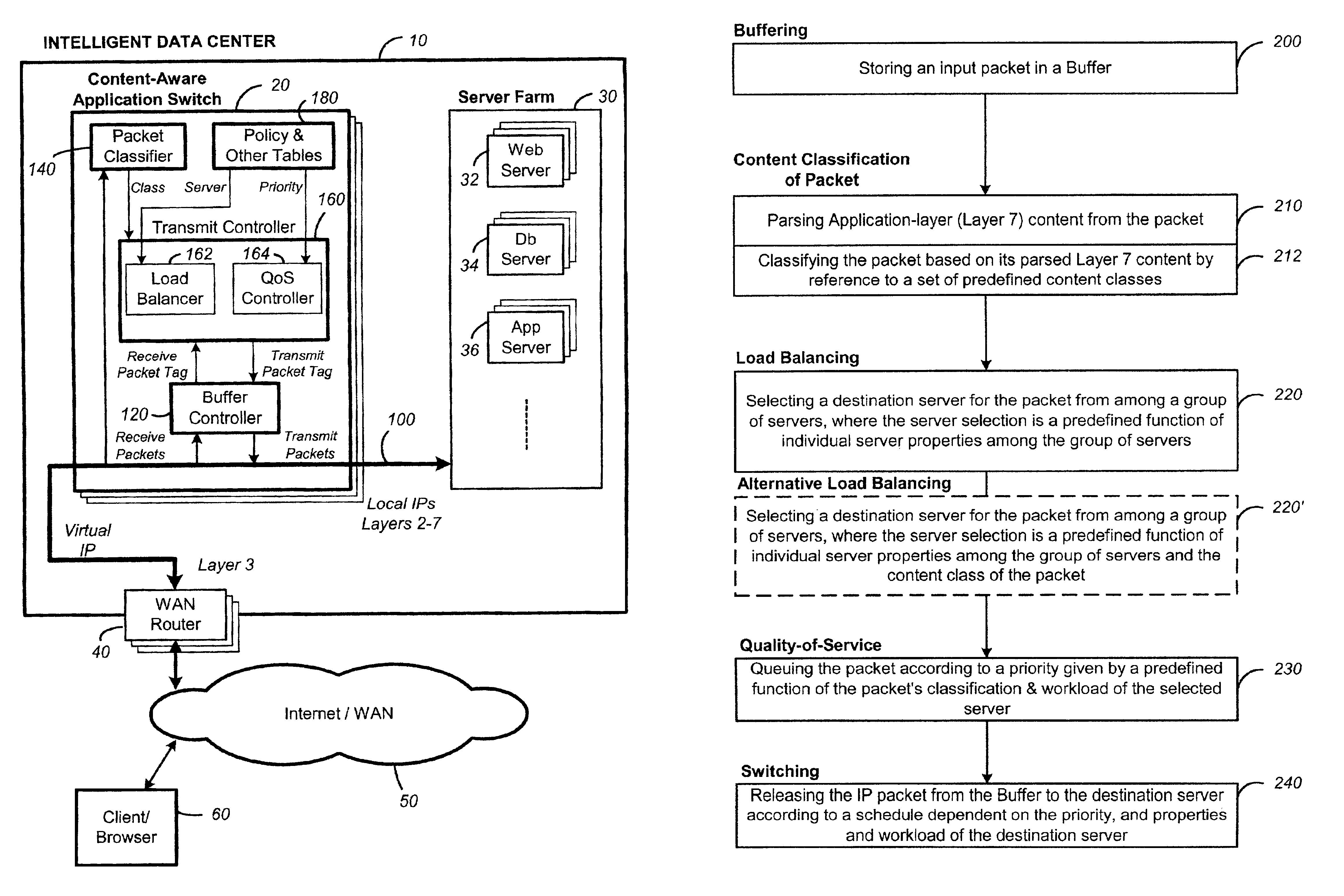
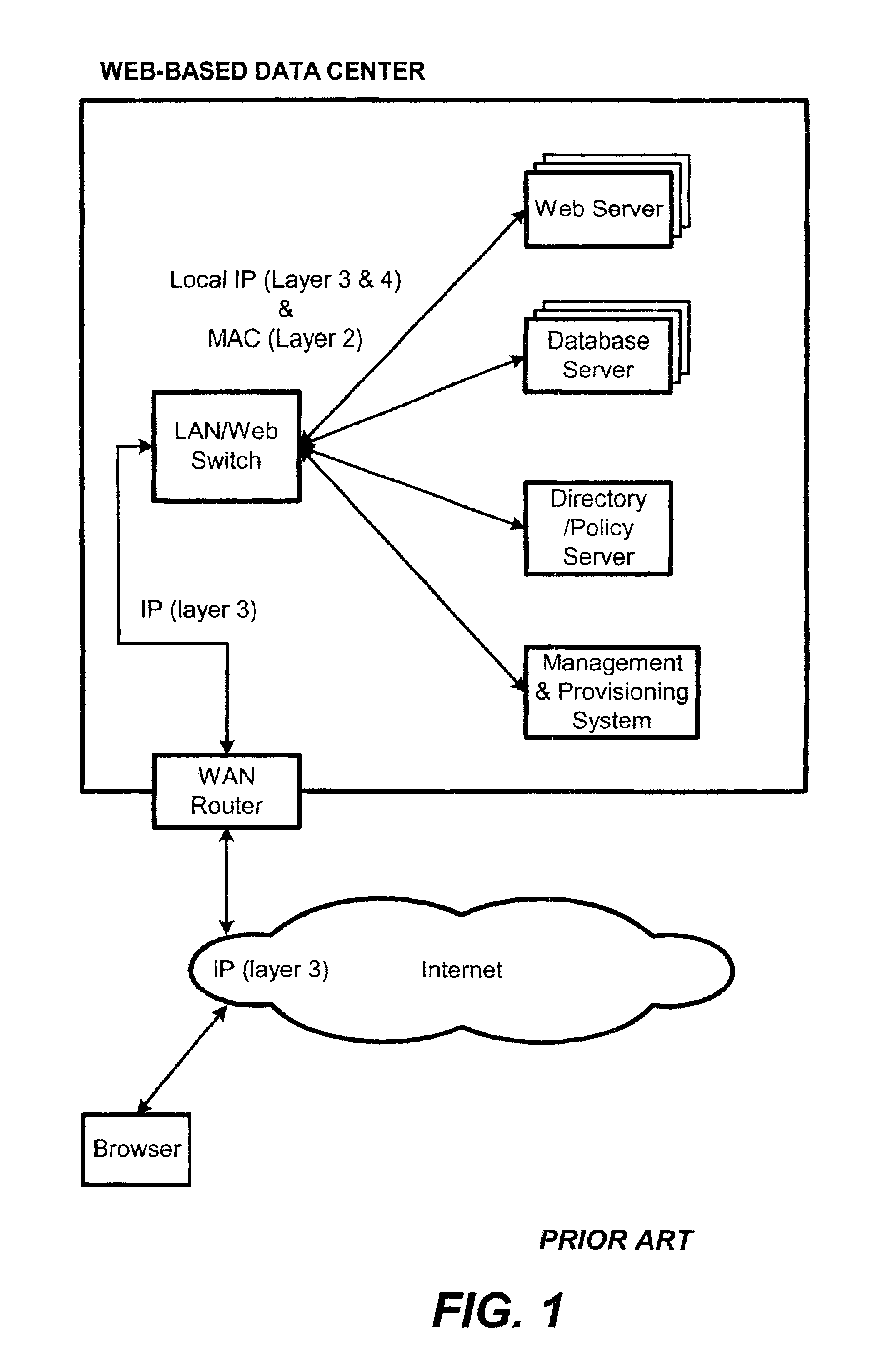
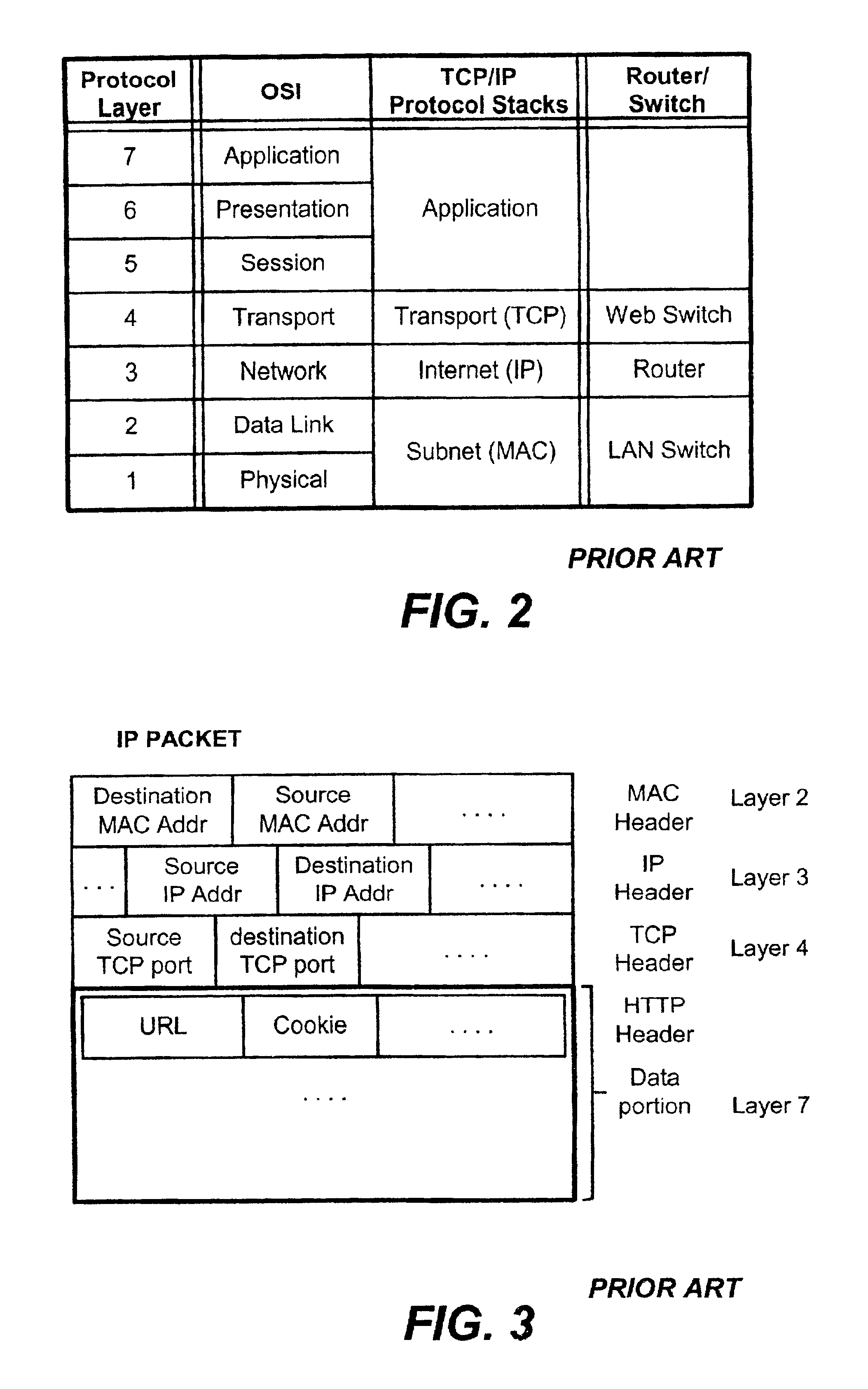
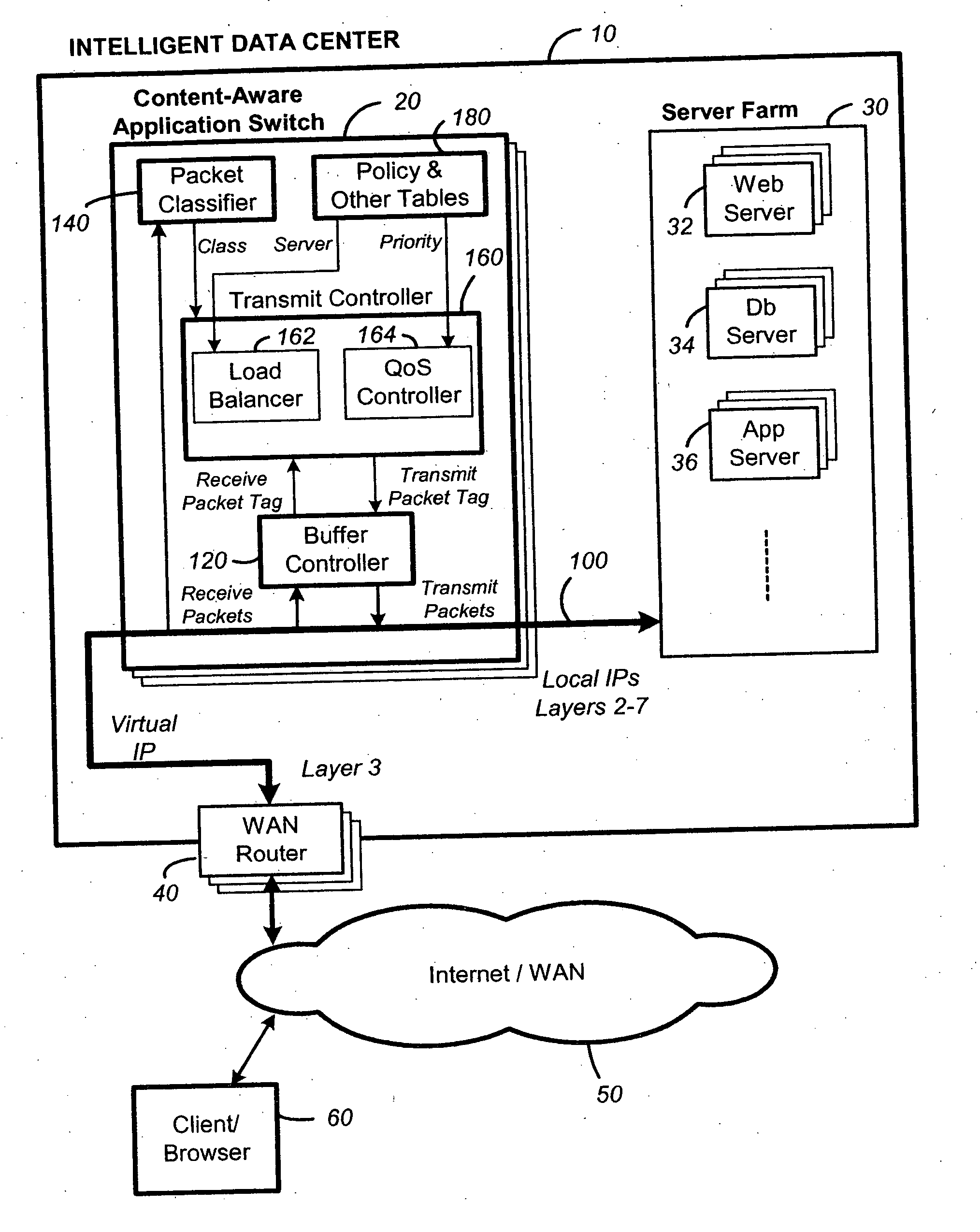
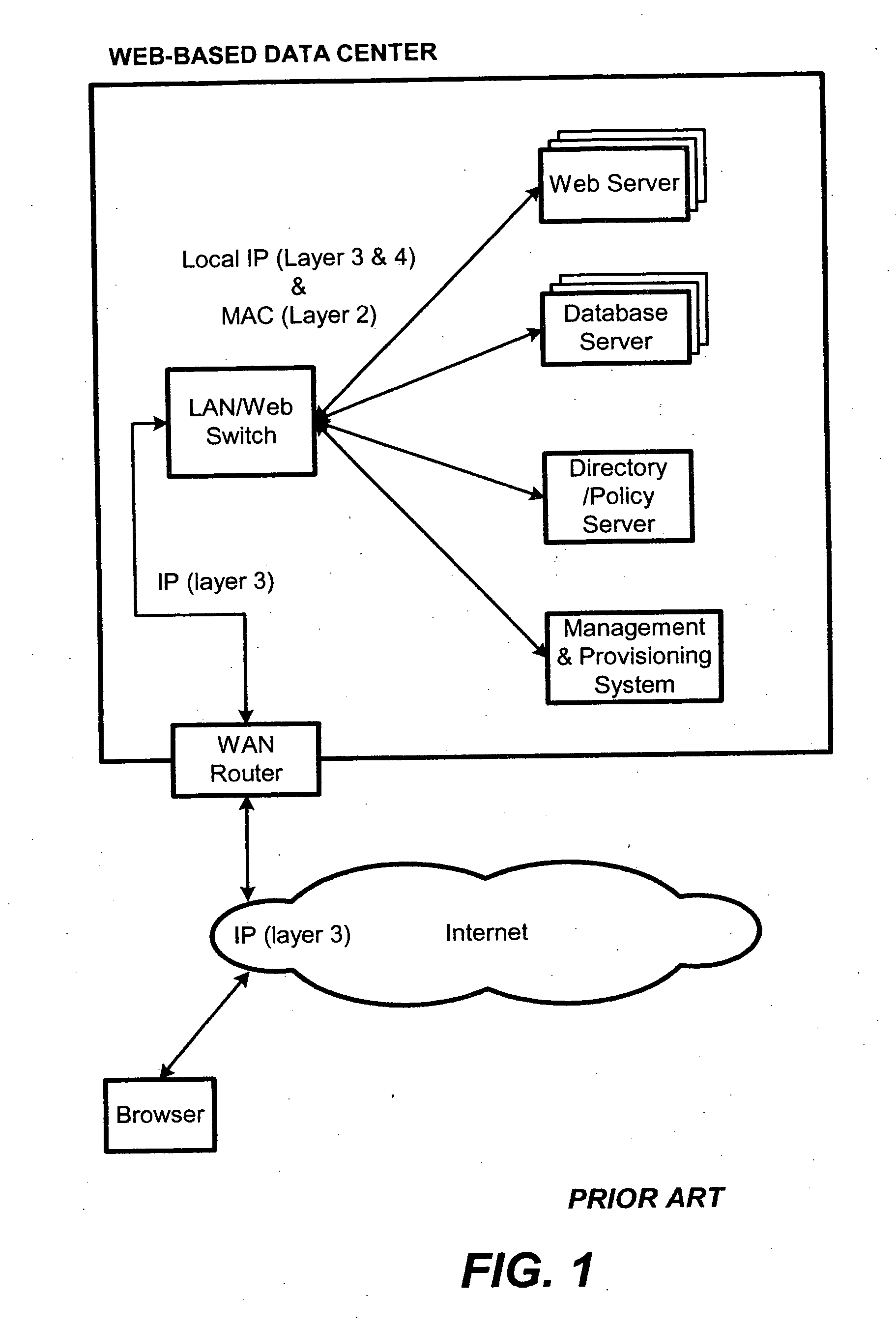
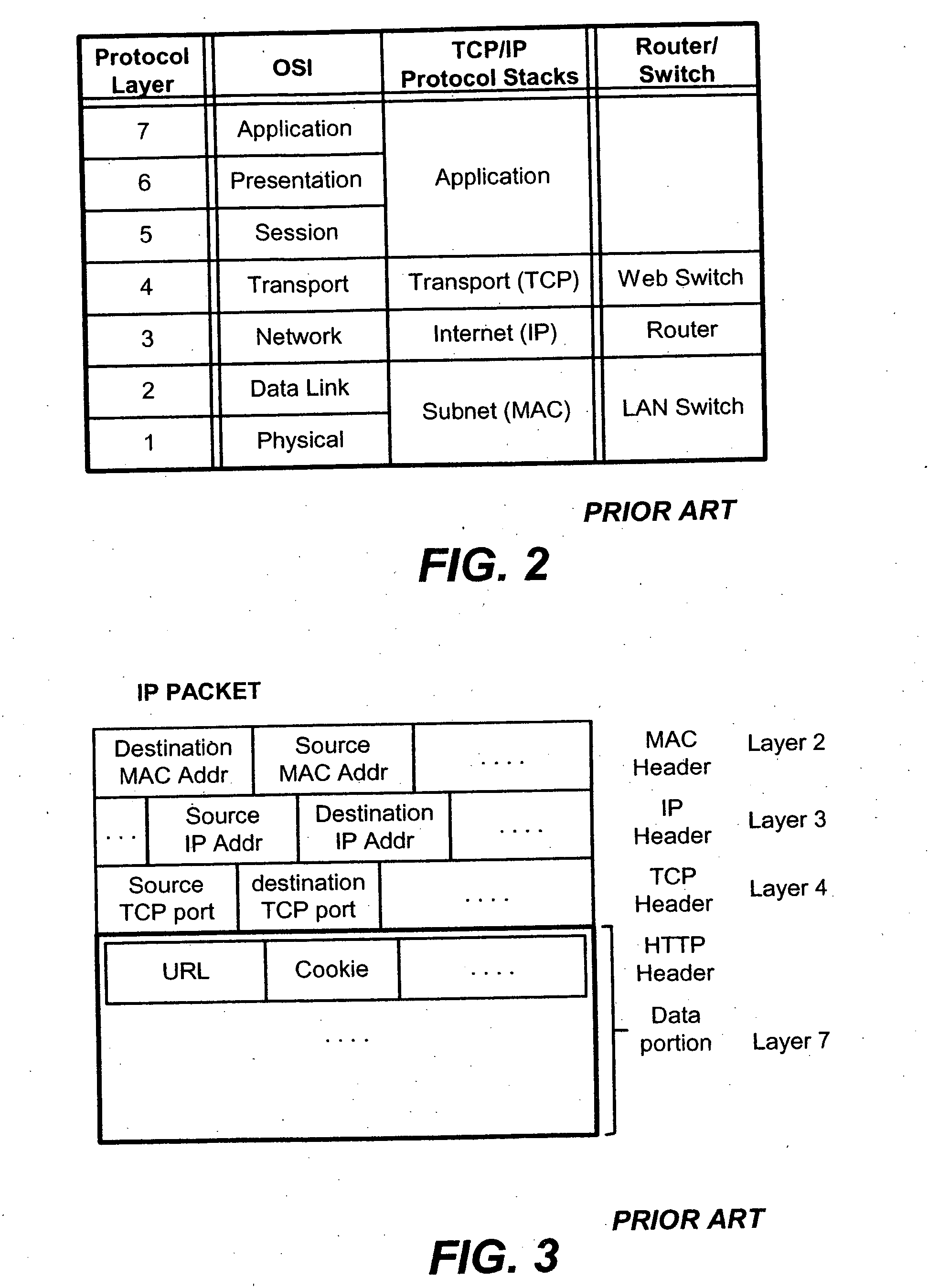
Content-aware application switch and methods thereof
InactiveUS6944678B2Easy to controlControl moreMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork connectionsQuality of serviceSlow-start
A content-aware application switch and methods thereof intelligently switch client packets to one server among a group of servers in a server farm. The switch uses Layer 7 or application content parsed from a packet to help select the server and to schedule the transmitting of the packet to the server. This enables refined load-balancing and Quality-of-Service control tailored to the application being switched. In another aspect of the invention, a slow-start server selection method assigned an initially boosted server load metric to a server newly added to the group of servers under load balancing. This alleviates the problem of the new server being swamped initially due to a very low load metric compared to that of others. In yet another aspect of the invention, a switching method dependent on Layer 7 content avoids delayed binding in a new TCP session. Layer 7 content is not available during the initial handshaking phase of a new TCP session. The method uses the Layer 7 content from a previous session as an estimate to help select the server and uses a default priority to scheduling the transmitting of the handshaking packets. Updated Layer 7 content available after the handshaking phase is then used to reset the priority for the transmit schedule and becomes available for use in load balancing of the next TCP session.
Owner:IBM CORP
Packet switch and method thereof dependent on application content
InactiveUS20060031374A1Easy to controlControl moreMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksData packQuality of service
A content-aware application switch and methods thereof intelligently switch client packets to one server among a group of servers in a server farm. The switch uses Layer 7 or application content parsed from a packet to help select the server and to schedule the transmitting of the packet to the server. This enables refined load-balancing and Quality-of-Service control tailored to the application being switched. In another aspect of the invention, a slow-start server selection method assigned an initially boosted server load metric to a server newly added to the group of servers under load balancing. This alleviates the problem of the new server being swamped initially due to a very low load metric compared to that of others. In yet another aspect of the invention, a switching method dependent on Layer 7 content avoids delayed binding in a new TCP session. Layer 7 content is not available during the initial handshaking phase of a new TCP session. The method uses the Layer 7 content from a previous session as an estimate to help select the server and uses a default priority to scheduling the transmitting of the handshaking packets. Updated Layer 7 content available after the handshaking phase is then used to reset the priority for the transmit schedule and becomes available for use in load balancing of the next TCP session.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Context-aware unit selection
Methods and apparatuses to perform context-aware unit selection for natural language processing are described. Streams of information associated with input units are received. The streams of information are analyzed in a context associated with first candidate units to determine a first set of weights of the streams of information. A first candidate unit is selected from the first candidate units based on the first set of weights of the streams of information. The streams of information are analyzed in the context associated with second candidate units to determine a second set of weights of the streams of information. A second candidate unit is selected from second candidate units to concatenate with the first candidate unit based on the second set of weights of the streams of information.
Owner:APPLE INC
Methods of nanostructure formation and shape selection
Methods for forming nanostructures of various shapes are disclosed. Nanocubes, nanowires, nanopyramids and multiply twinned particles of silver may by formed by combining a solution of silver nitrate in ethylene glycol with a solution of poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) in ethylene glycol. Hollow nanostructures may be formed by reacting a solution of solid nanostructures comprising one of a first metal and a first metal alloy with a metal salt that can be reduced by the first metal or first metal alloy. Nanostructures comprising a core with at least one nanoshell may be formed by plating a nanostructure and reacting the plating with a metal salt.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
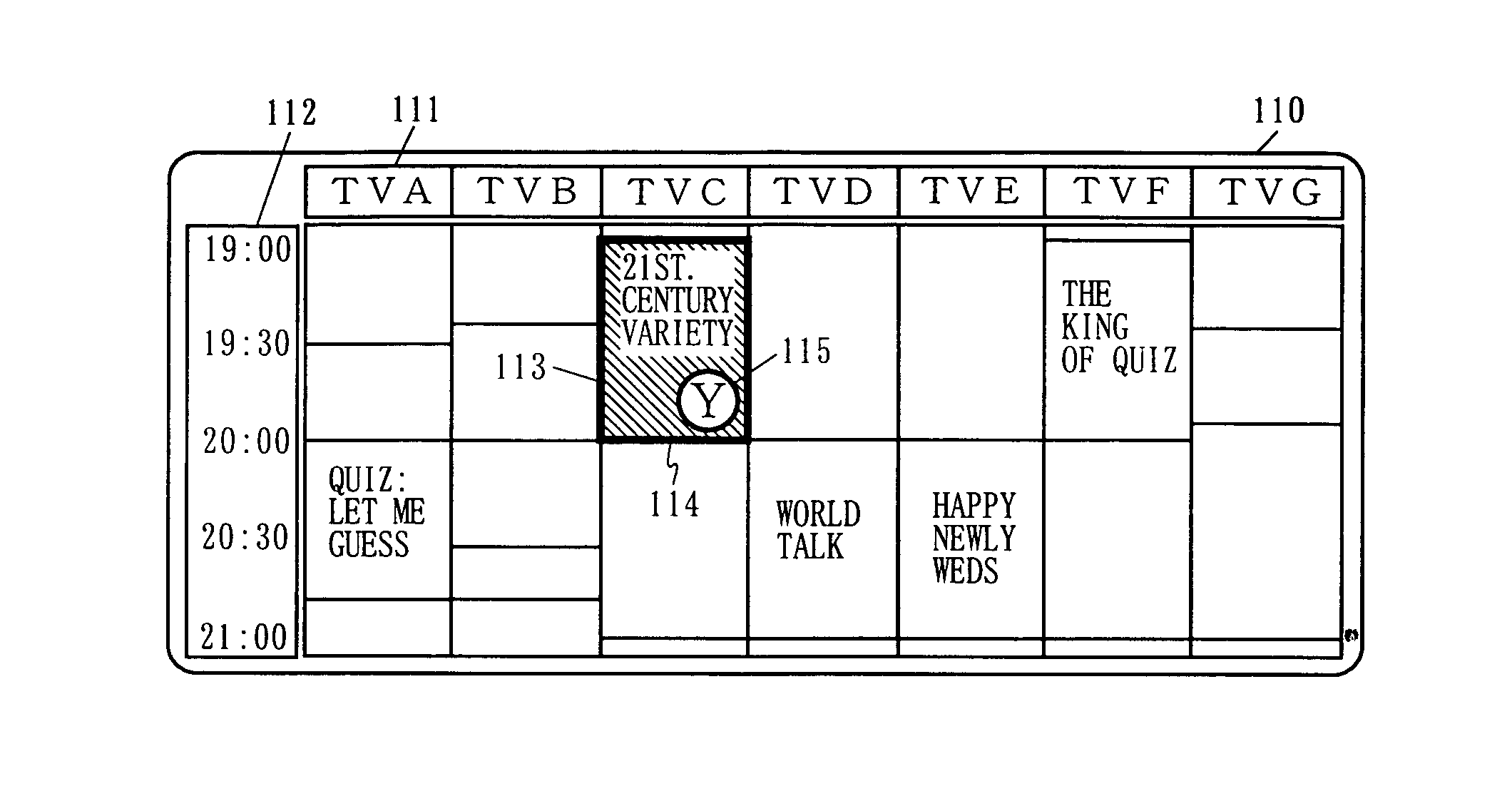
Content selection method and content selection device
InactiveUS20070039023A1Big burden to solveShorten the timeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsUser inputWorld Wide Web
A user inputs an evaluation of a content over an EPG, and specifies on a screen a search condition to search for a content. Based on the input, a content selection device evaluates contents, displays a content which is to be recommended by giving the content, which is to be recommended, a different indication in the EPG, and displays a list of contents which are to be recommended. By this, the present invention is able to offer a content, which is to be recommended, matching a preference of the user without burdening the user.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
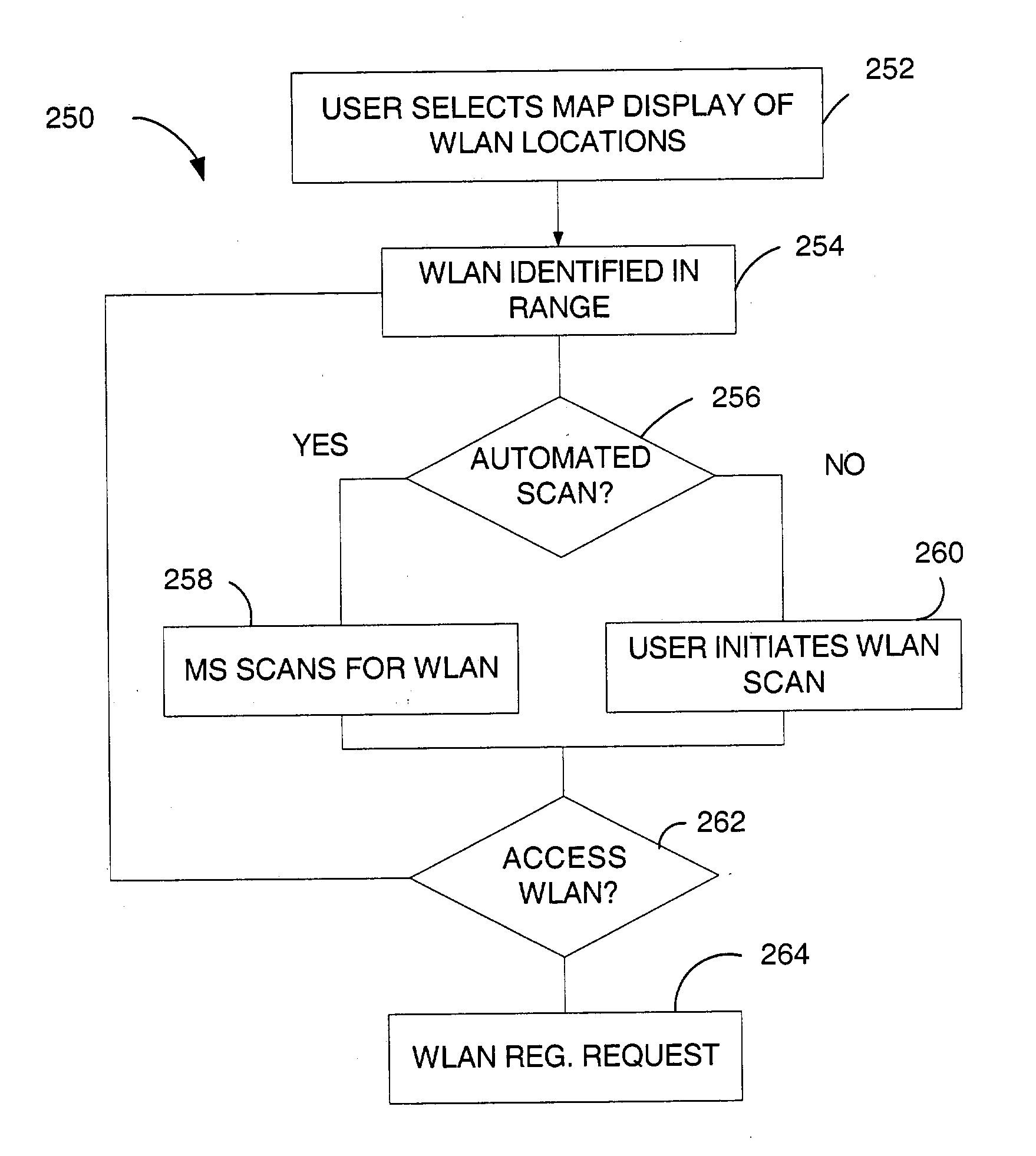
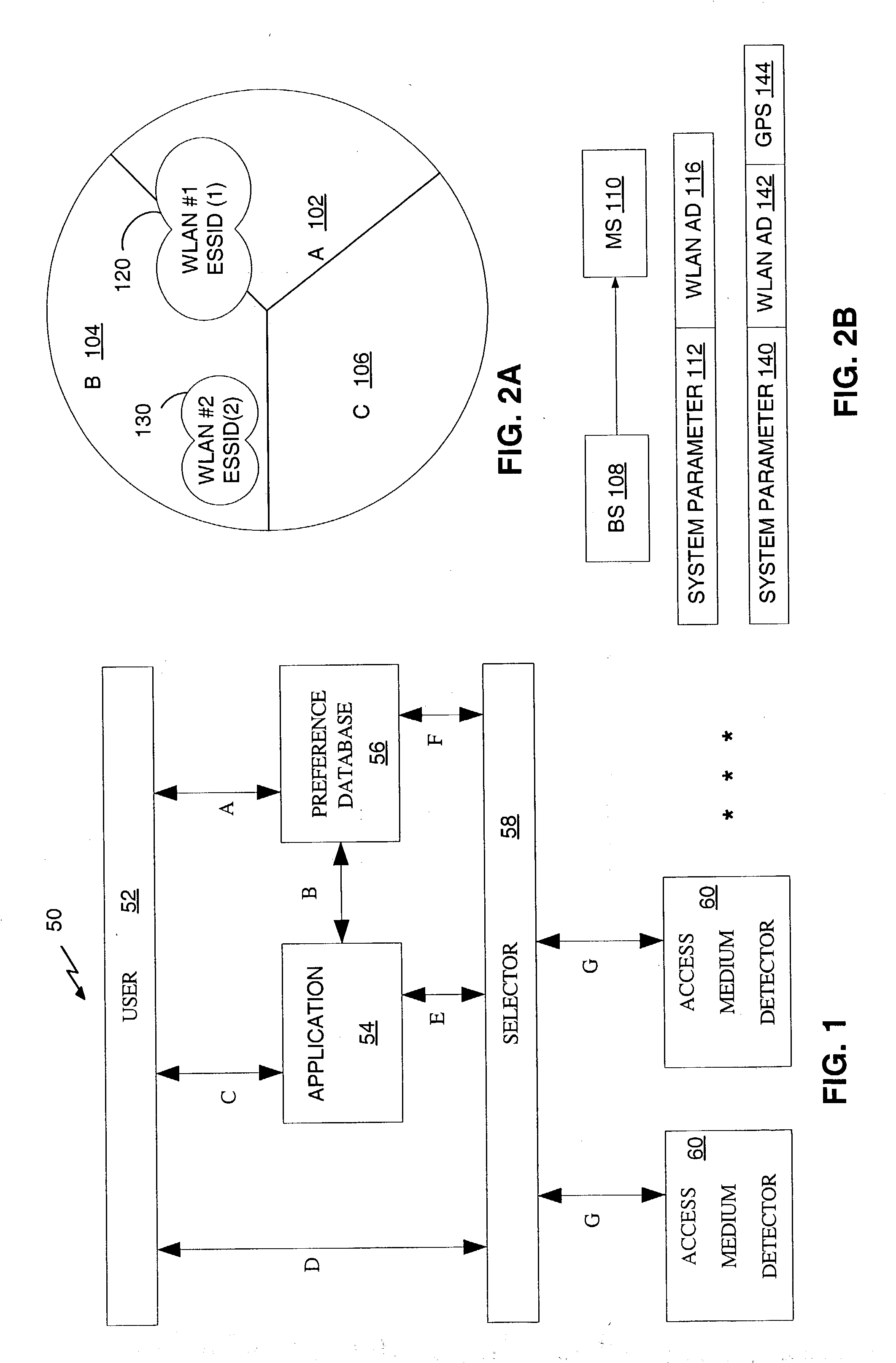
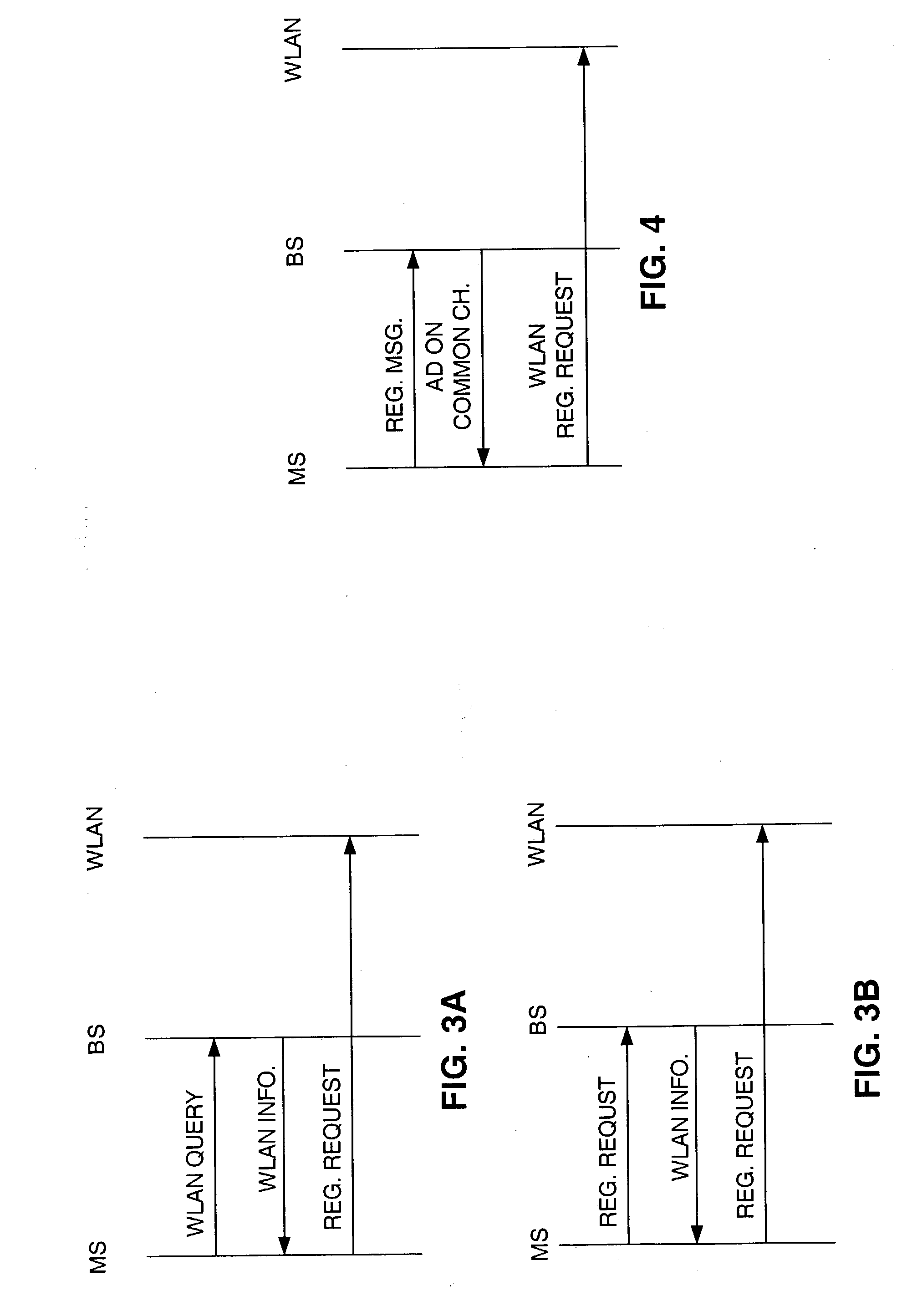
Wireless local access network system detection and selection
Method and apparatus for detection and selection of Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) service. A remote device includes a preference database for storing selection criteria for a plurality of access media. Access medium detector(s) determine accessibility of access media, and a selector selects one of the access media based on the selection criteria. The selection criteria indicate when on which to switch between access media.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Mobile communication terminal and method of selecting menu and item
ActiveUS7834861B2Choose simpleChoose accuratelySubstation equipmentTransmissionHuman–computer interactionSelection method
A menu selection method, which includes selecting a main menu displayed on a touch device of a terminal, displaying one or more sub-menus corresponding to the selected main menu, sensing a direction of a dragging operation on the touch device, and executing a corresponding sub-menu located in the sensed direction of the dragging operation.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
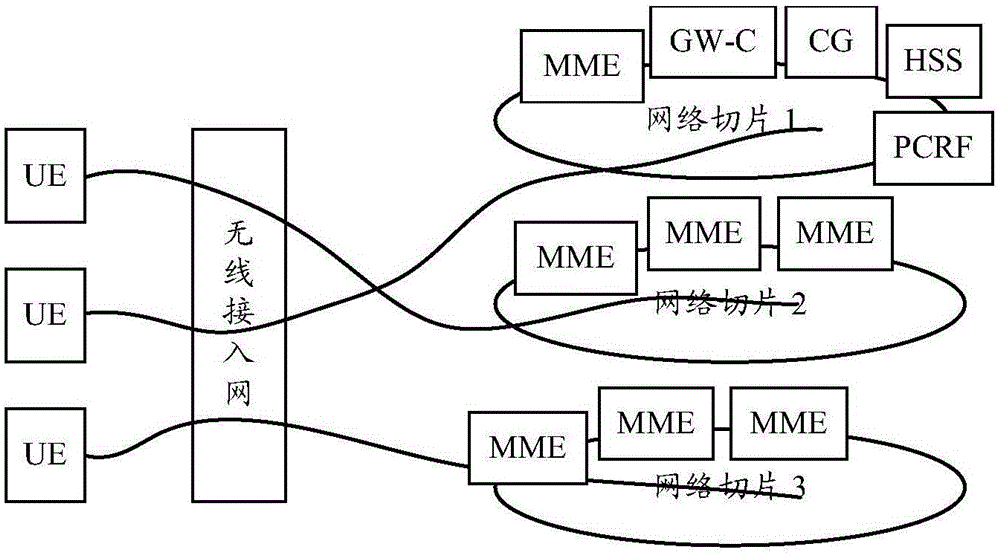
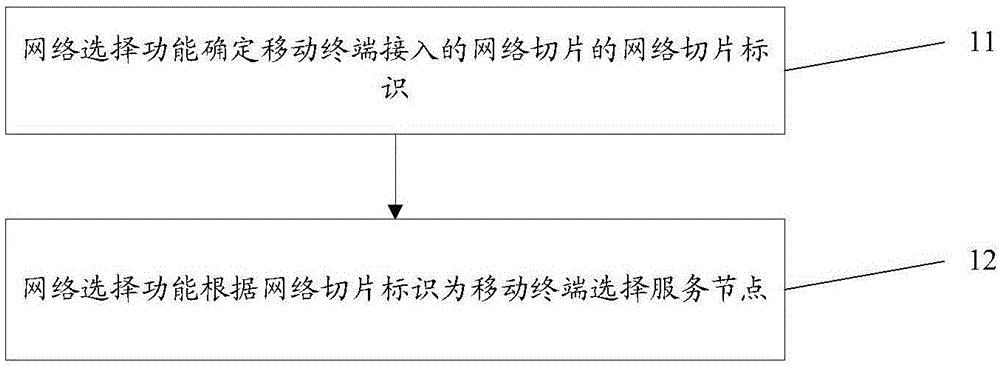
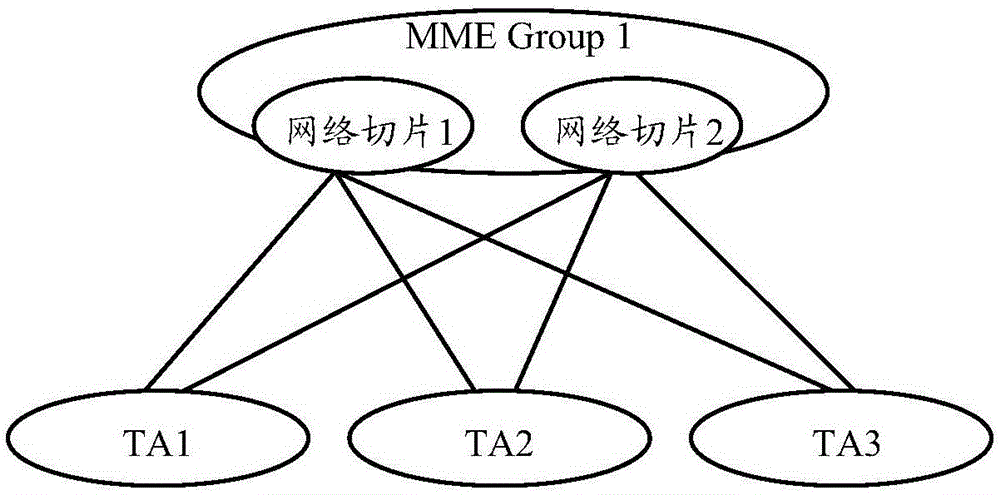
Method and system for selecting network slice
ActiveCN106375987ASolve the problem that network slice selection cannot be performedAssess restrictionConnection managementDistributed computingService provider
The invention discloses a method and system for selecting a network slice. The method comprises the following steps: a network selection function determining a network slice identification of the network slice accessed by a mobile terminal; and the network selection function, according to the network slice identification, selecting a service node for the mobile terminal. The disclosed method and system for selecting the network slice are applied to solving the problem of incapability of network slice selection when a service provider disposes multiple network slices in a conventional network.
Owner:ZTE CORP
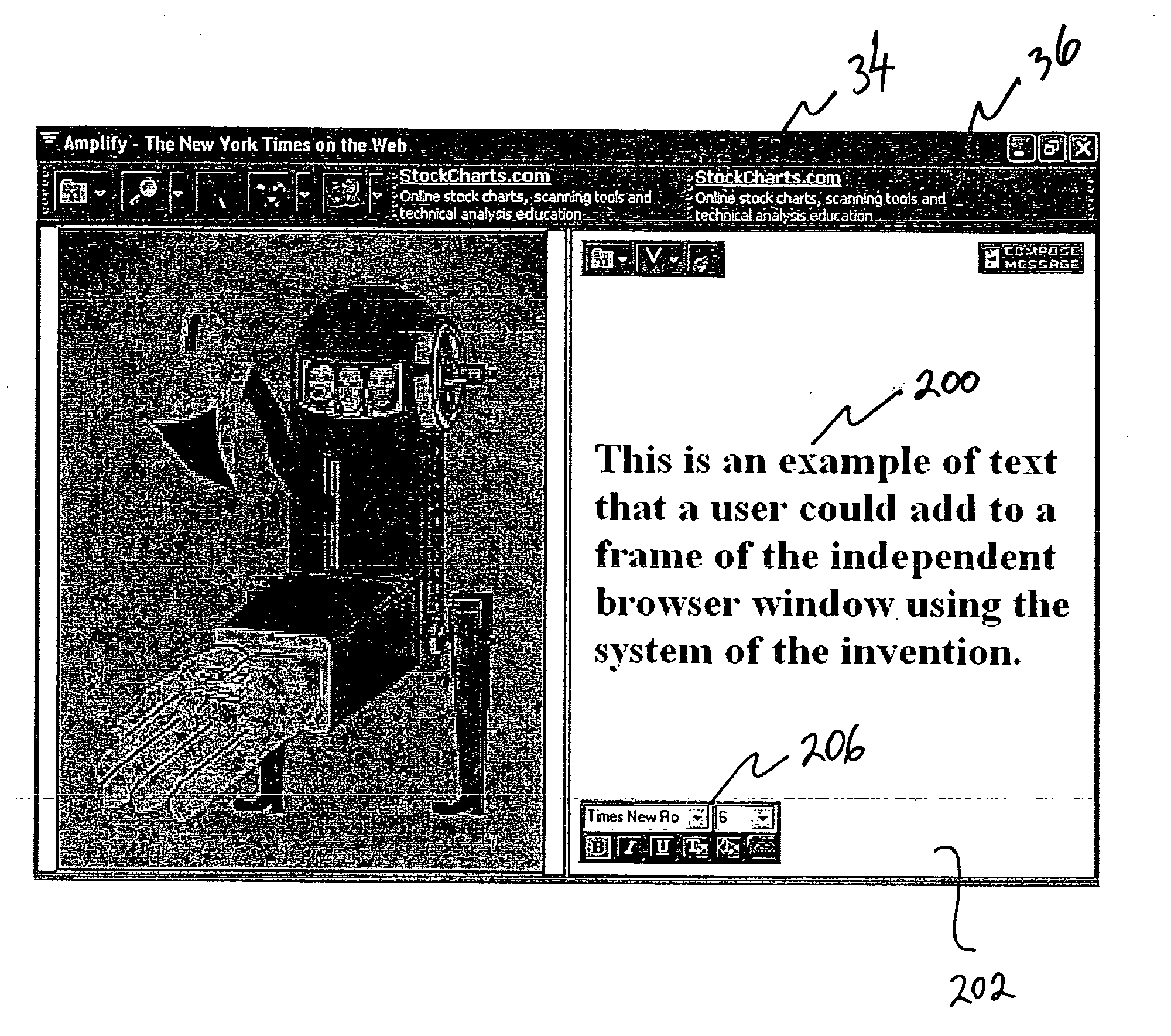
System, method and apparatus for selecting, displaying, managing, tracking and transferring access to content of web pages and other sources
ActiveUS20050246651A1Easy searchAdjustable sizeRecording carrier detailsRecord information storageAnimationThe Internet
A method, system and apparatus for selecting, displaying, managing, tracking and transferring access to content of Internet web pages and other sources along with custom text messages has programming permitting a user to create custom selections of selected image, animation, movie and text content items, and other types of content items from web pages or other sources from the same or different network sources containing multiple content items, along with user-supplied text messages, in an independent, resizable, rescalable browser window; permitting the user to transfer access to the custom selection of content items to a recipient; permitting the user or recipient to navigate quickly to a source of a content item in the custom selection; and permitting the user to define search keywords for performing searches related to content items in a custom selection; and other features. A method of tracking viewing and sharing activities of content items and custom selections of content items by users and recipients is also disclosed. A method of assisted content selection provides temporary borders around content items on mouseover.
Owner:SALESFORCE COM INC
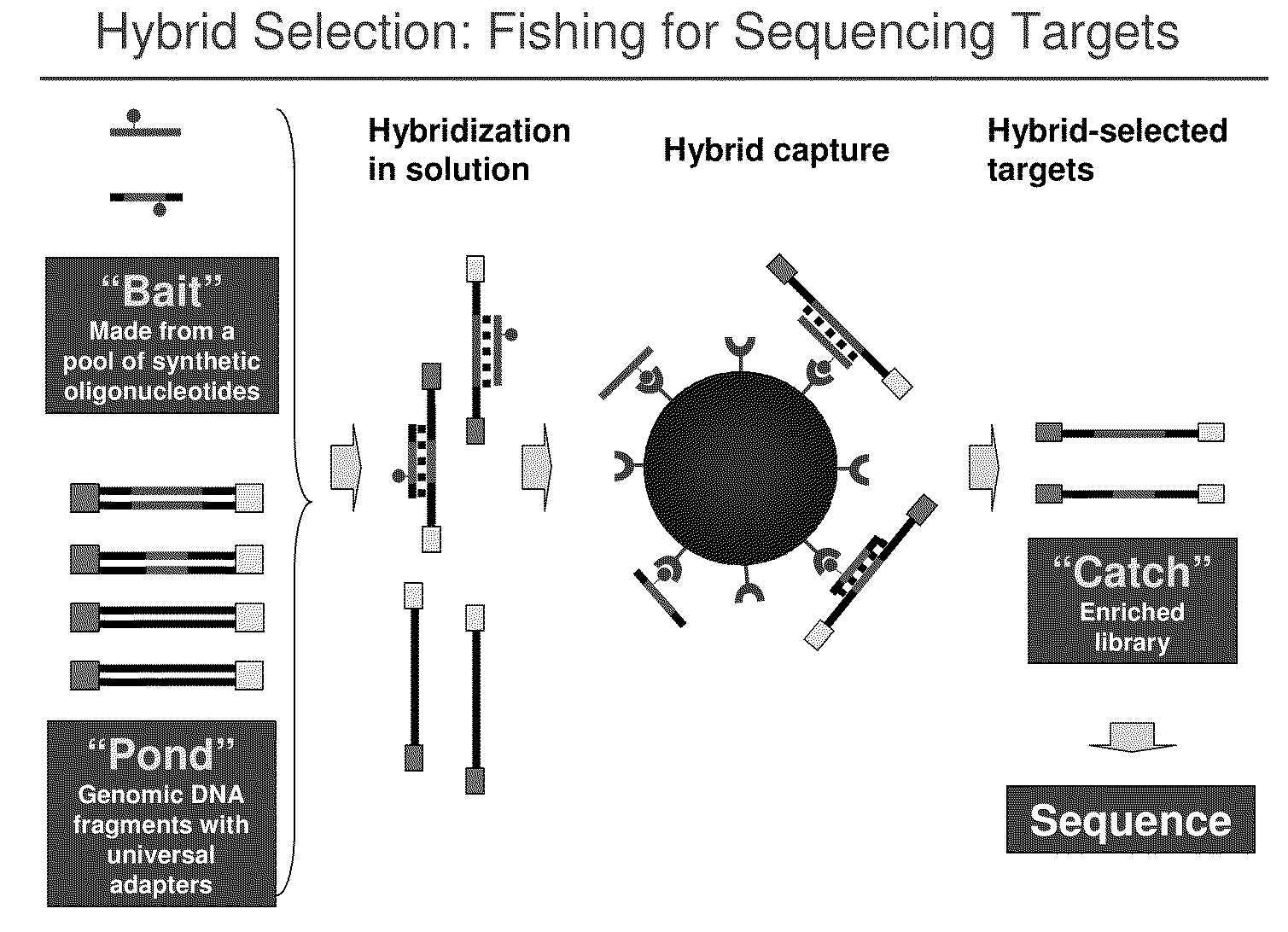
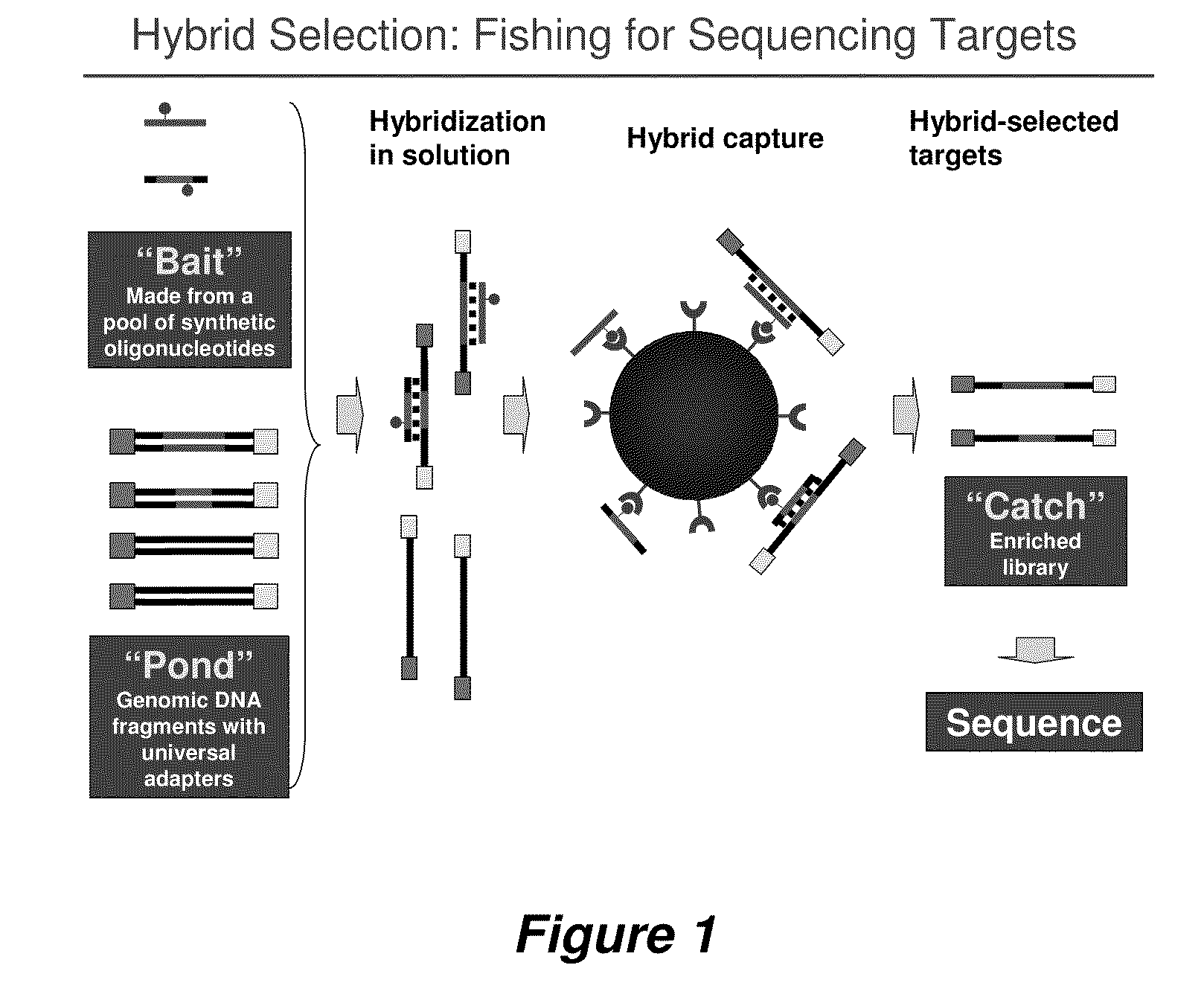
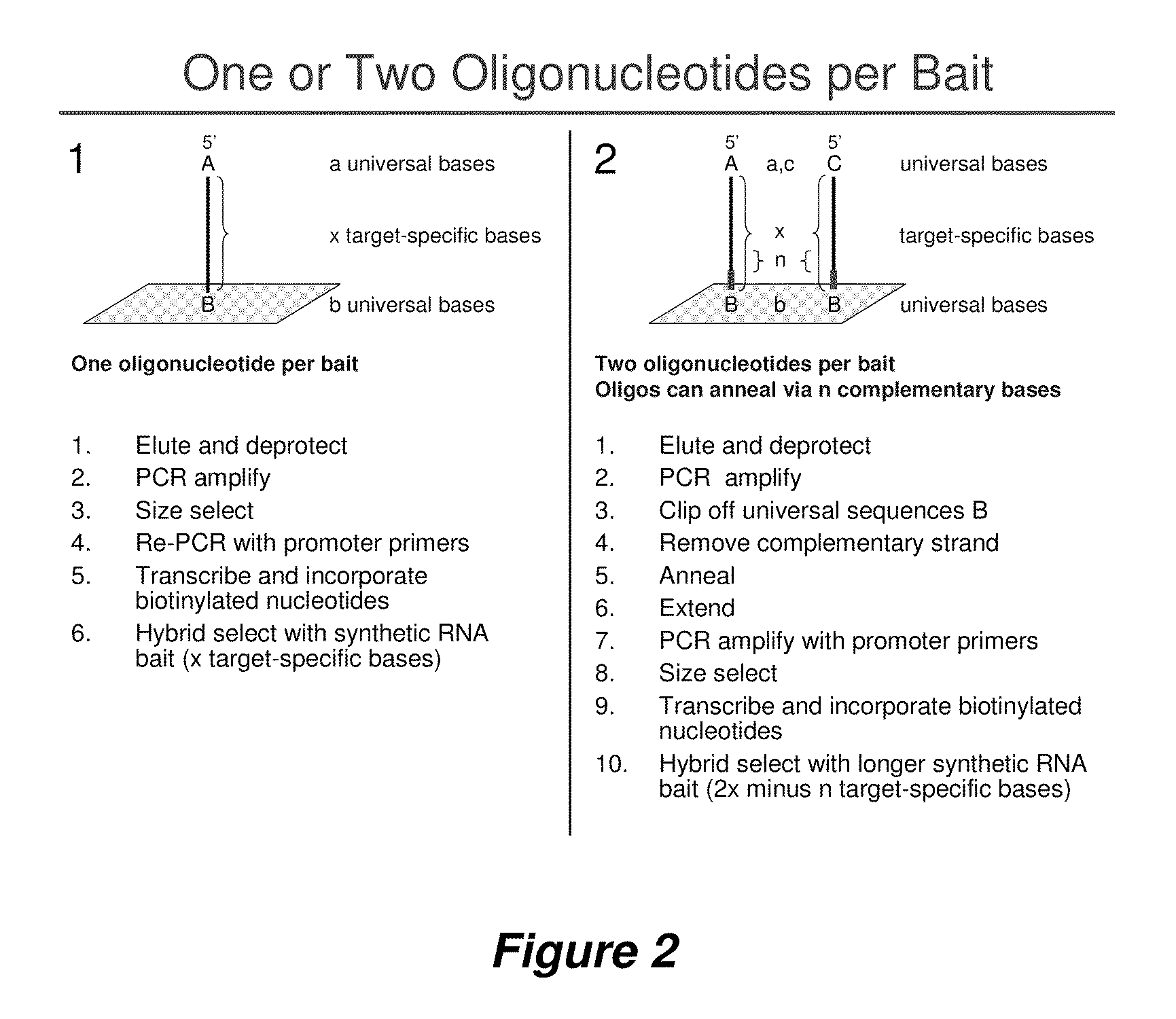
Selection of nucleic acids by solution hybridization to oligonucleotide baits
InactiveUS20100029498A1Minimize the differenceGood reproducibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningSolution hybridizationOligonucleotide
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +2
Automatic network selection methods and apparatus using a steered PLMN
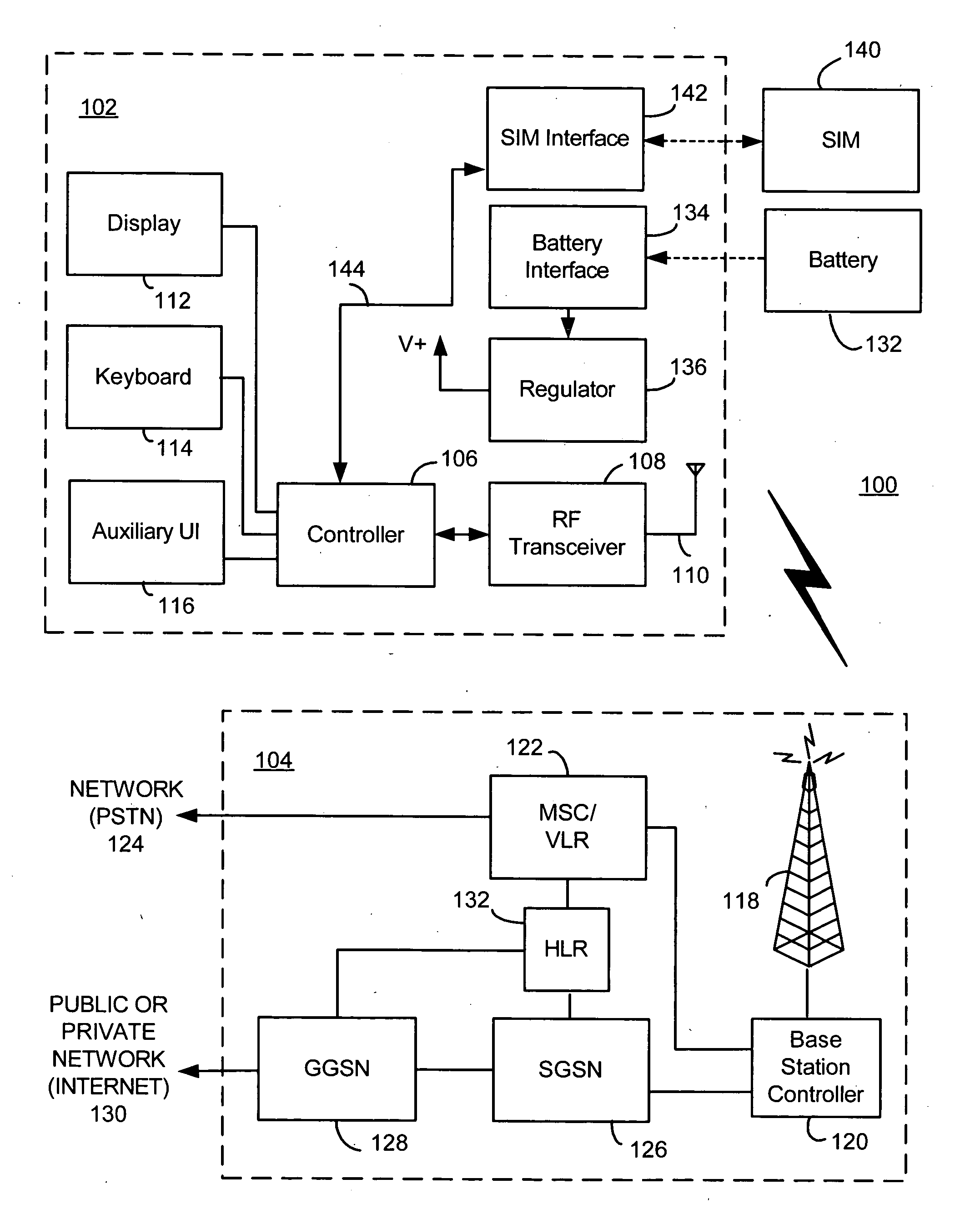
ActiveUS20070191006A1Assess restrictionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTelecommunicationsUser equipment
Methods and apparatus for automatically selecting a wireless communication network by user equipment using a “steered” PLMN are disclosed. A home network identification, a list of prioritized roaming network identifications, and a steered network identification are stored in memory (e.g. a SIM or USIM) of the user equipment. In an automatic network selection procedure, a scanning operation is performed to receive one or more network identifications corresponding to one or more available wireless communication networks in a coverage area. The user equipment attempts to select a wireless communication network in the coverage area by comparing the received network identifications from the scanning operation with the steered network identification. If a match between a received network identification and the steered network identification is identified, a wireless communication network corresponding to the received network identification that matches the steered network identification is selected and registered with by the user equipment. This procedure is performed in lieu of use of the list of prioritized roaming network identifications of the user equipment. By setting the steered network identification via an over-the-air programming procedure when necessary (e.g. on a per region basis), a home network operator may “steer” user equipment to any desired network immediately and efficiently.
Owner:LEPATENT (BEIJING) CONSULTING CORP LTD
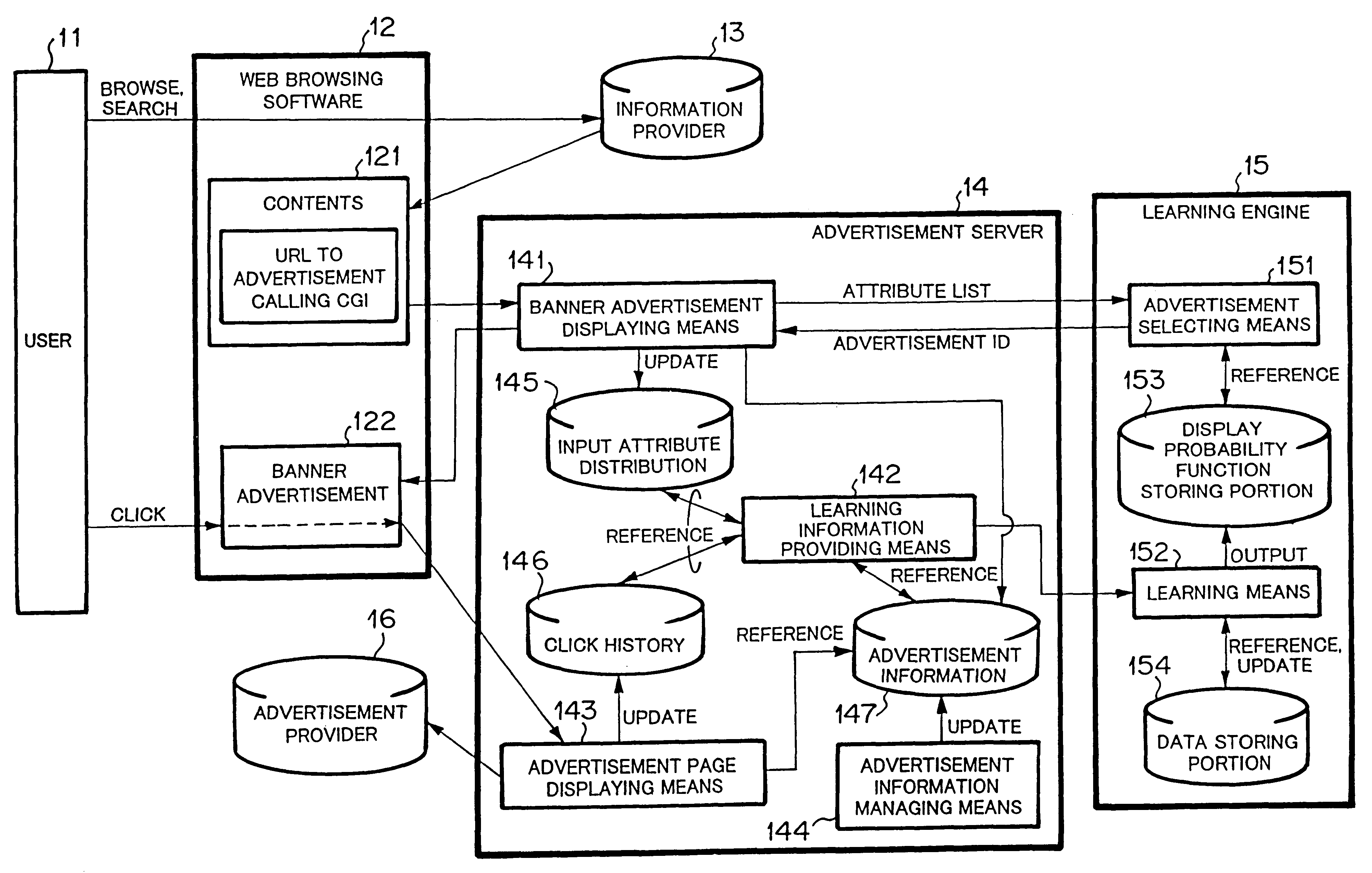
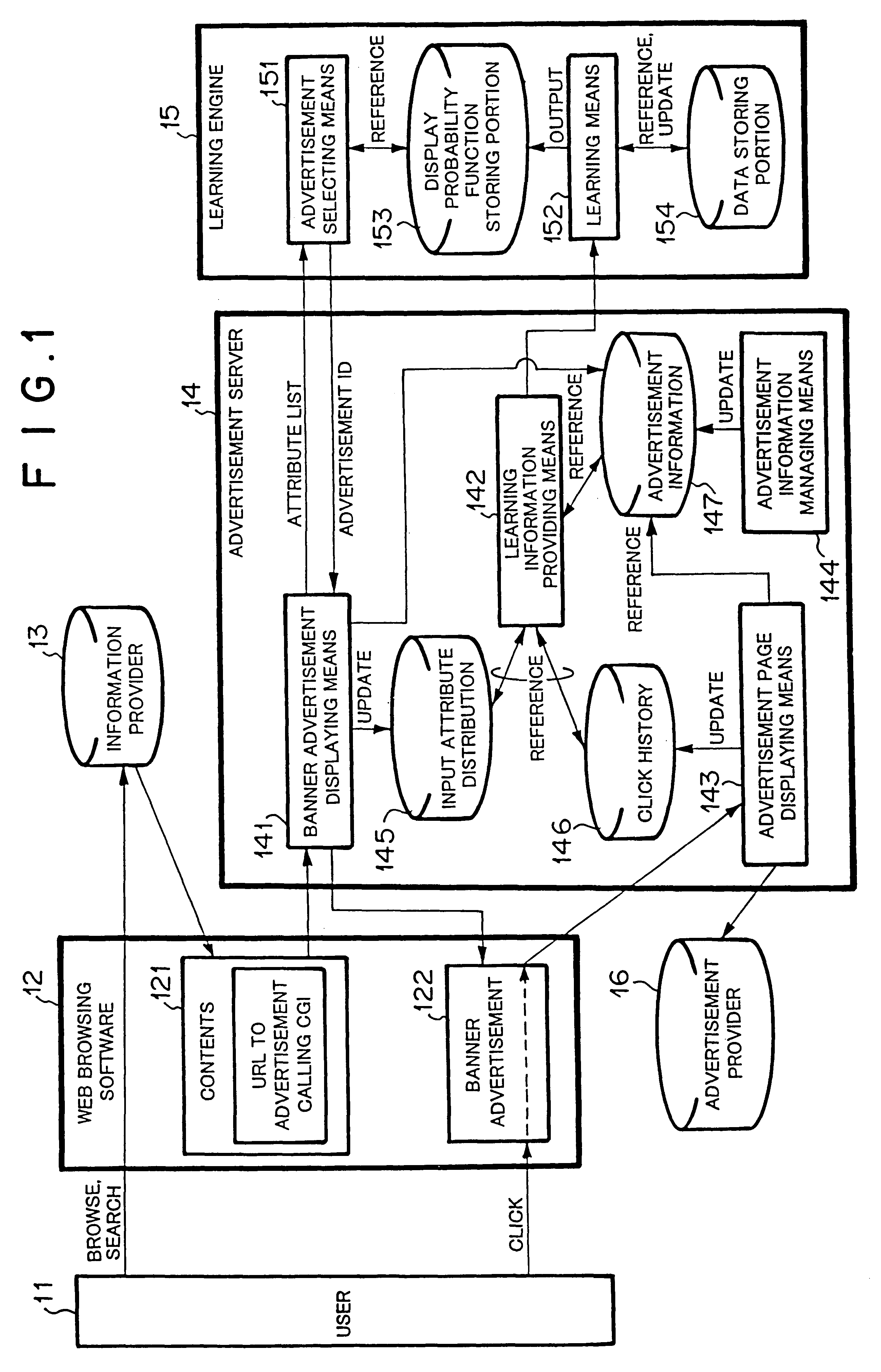
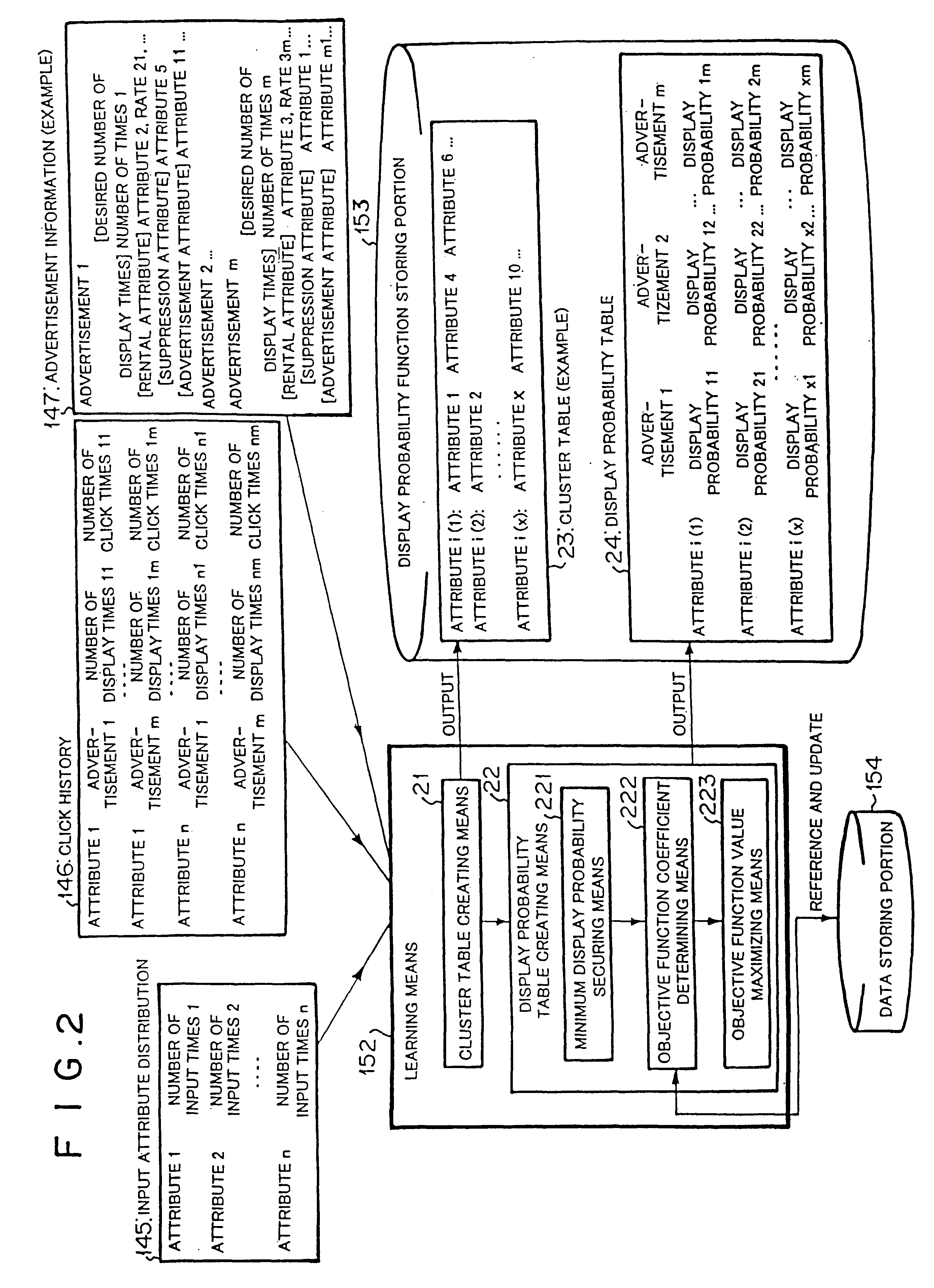
Banner advertisement selecting method
InactiveUS6591248B1Reduce in quantityImprove estimation accuracyAdvertisementsForecastingData miningClick-through rate
Owner:NEC CORP
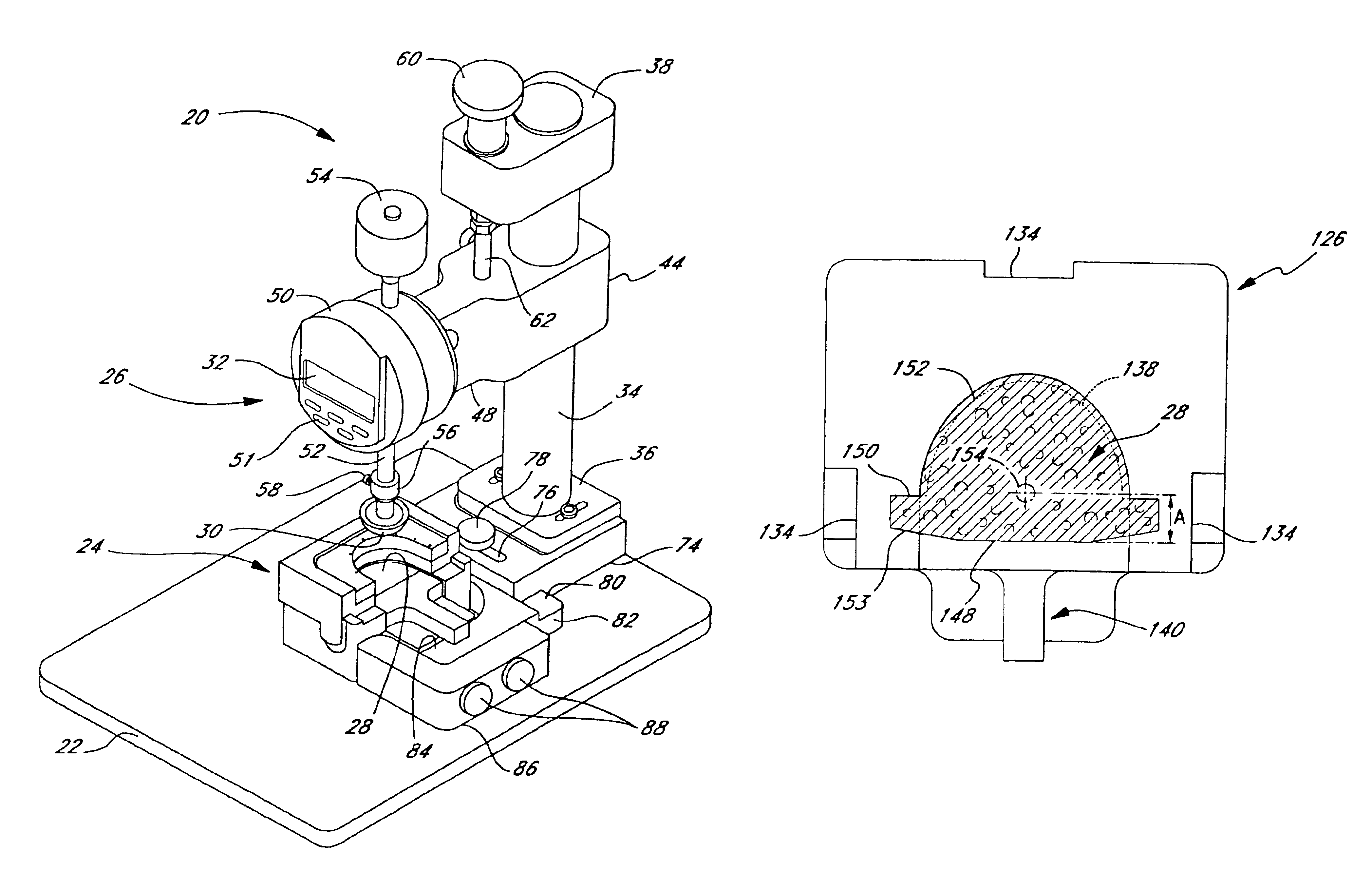
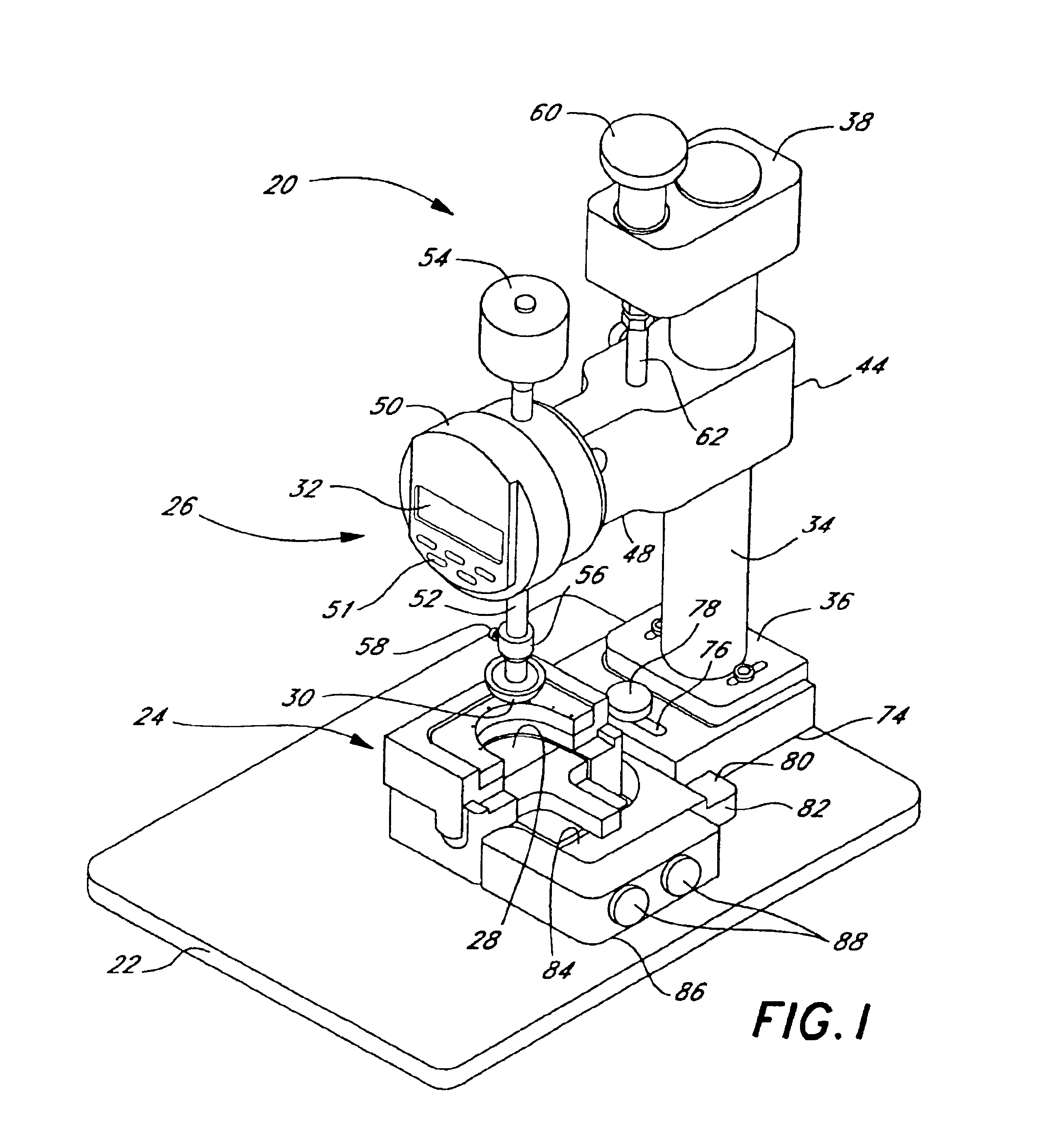
Methods of making bioprosthetic heart valves with strain matched leaflets
Heart valve leaflet selection methods and apparatuses which subject individual leaflets to loads and measure the resulting deflection to more reliably group leaflets of similar physical characteristics for later assembly in prosthetic heart valves. The deflection testing may be accomplished using a variety of test set ups which are designed to impart a load on the leaflet which simulates the actual loading within a heart valve. The results from a number of deflection tests are used to categorize individual leaflets, which data can be combined with other data regarding the characteristics of the leaflet to better select leaflets for assembly into a multi-leaflet heart valve. In one embodiment, the deflection test is combined with an intrinsic load test, and leaflets having similar deflection and intrinsic load values used in the same heart valve. One apparatus for testing the leaflets includes a frame for securing the arcuate cusp of the leaflet while the straight coapting edge remains free, to simulate the actual leaflet mounting configuration within the heart valve prosthesis. The frame may include a lower portion having a recess for the leaflet and plurality of receptor holes around the peripheral edge of the recess, and an upper portion having a plurality of needles which extend downward through the leaflet and into the receptor holes and secure the edges of the leaflet.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
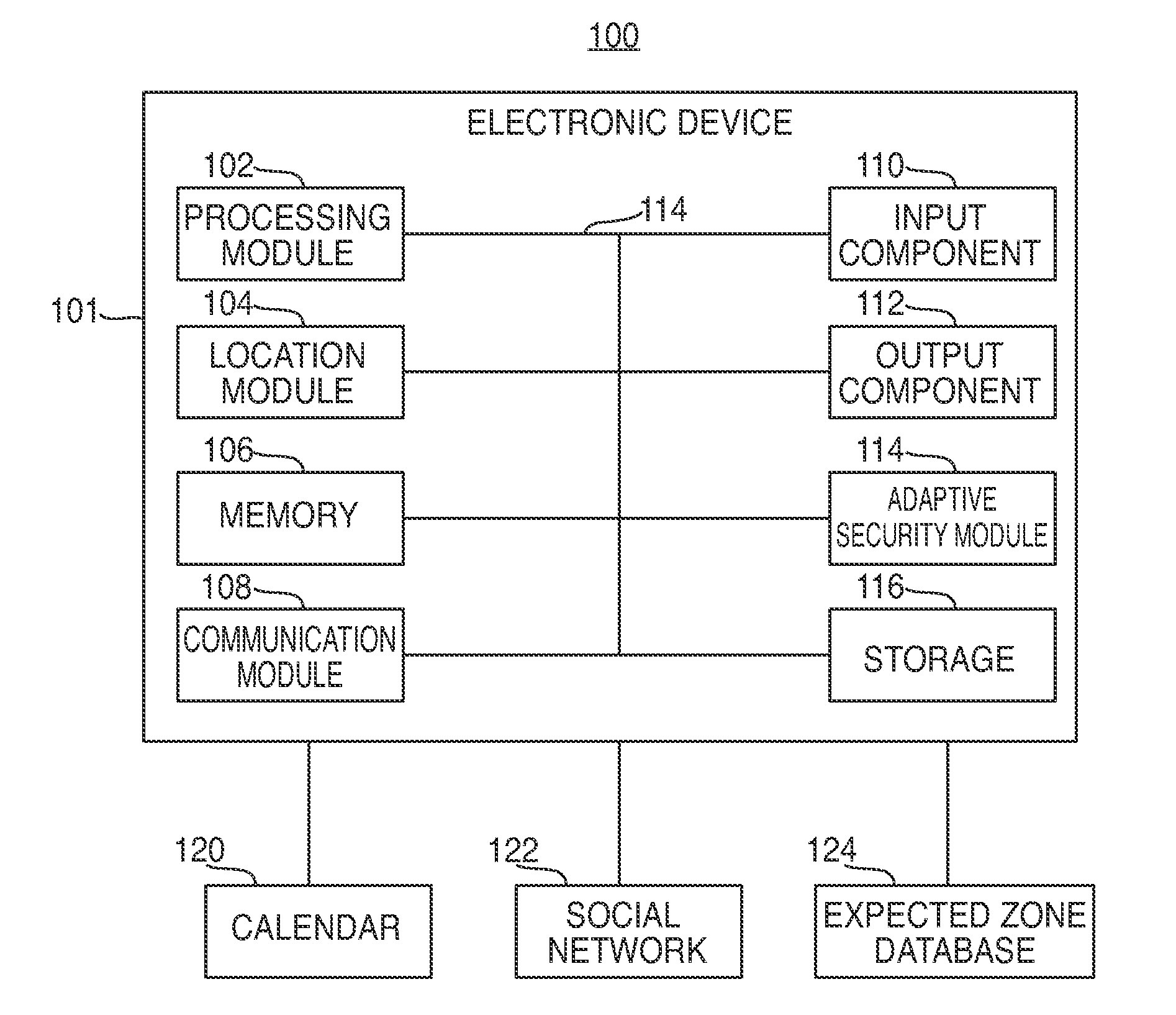
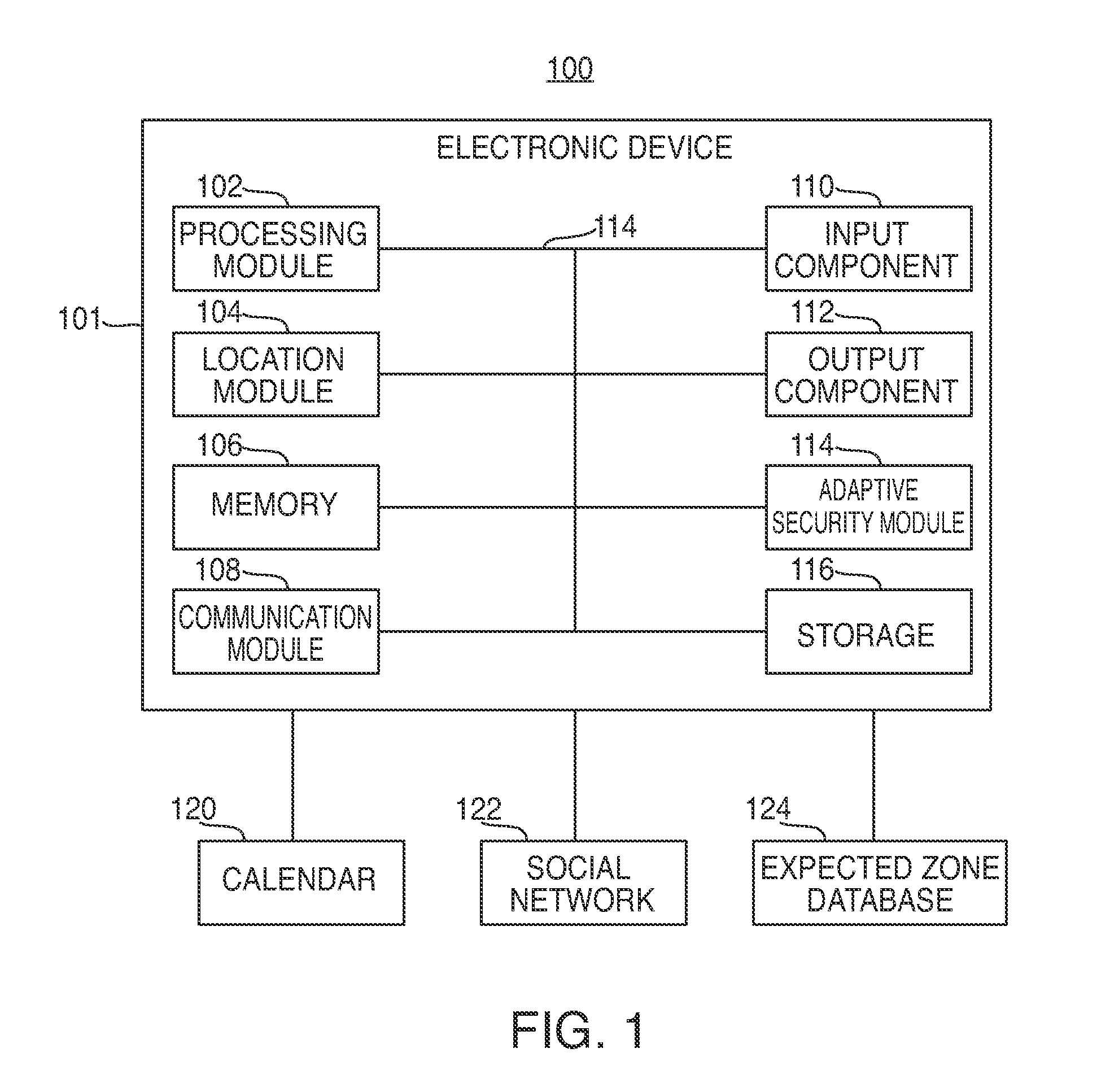
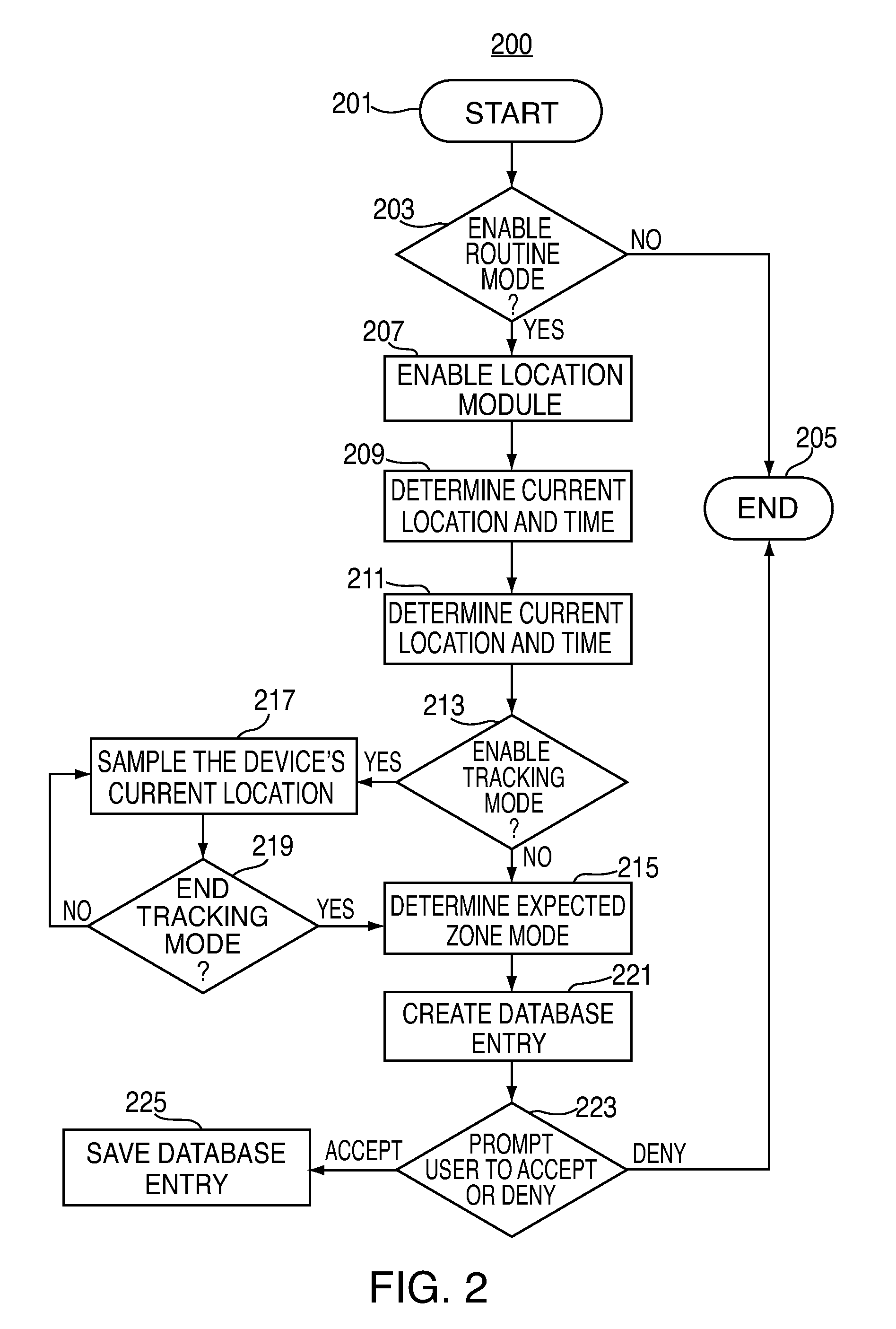
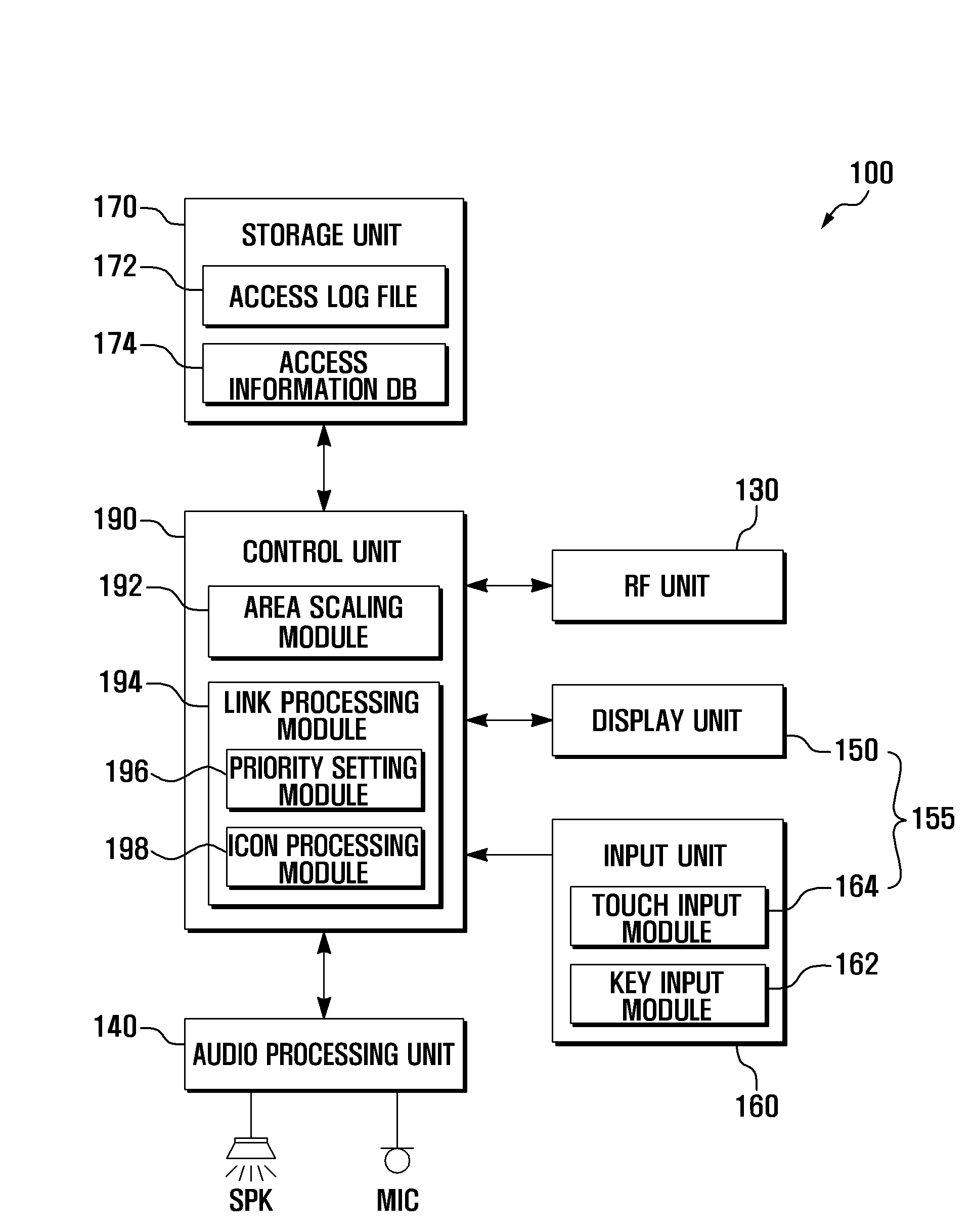
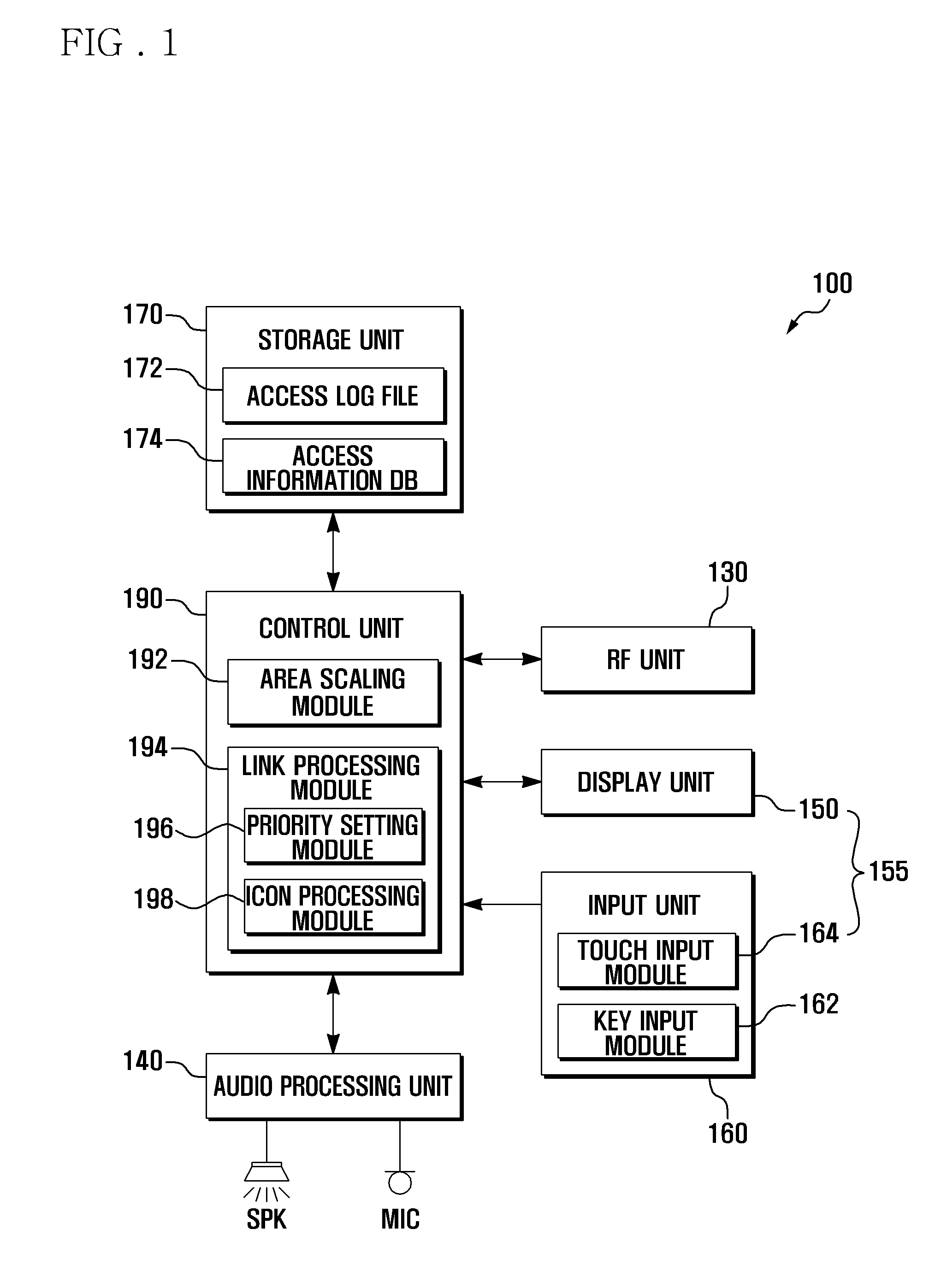
Electronic devices having adaptive security profiles and methods for selecting the same
ActiveUS20120284779A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationAdaptive securitySelf adaptive
Adaptive security profiles are supported on an electronic device. One or more security profiles may be automatically or selectively applied to the device based on the device's location and one or more geographic zone definitions. The security profiles may be used to determine the level of authentication or number of invalid authentication attempts for a particular feature or application or set of features or applications.
Owner:APPLE INC
Utilized-network selection method, communication system and mobile terminal
InactiveUS20050227692A1OptimizationAssess restrictionSubstation equipmentCommunications systemNetwork on
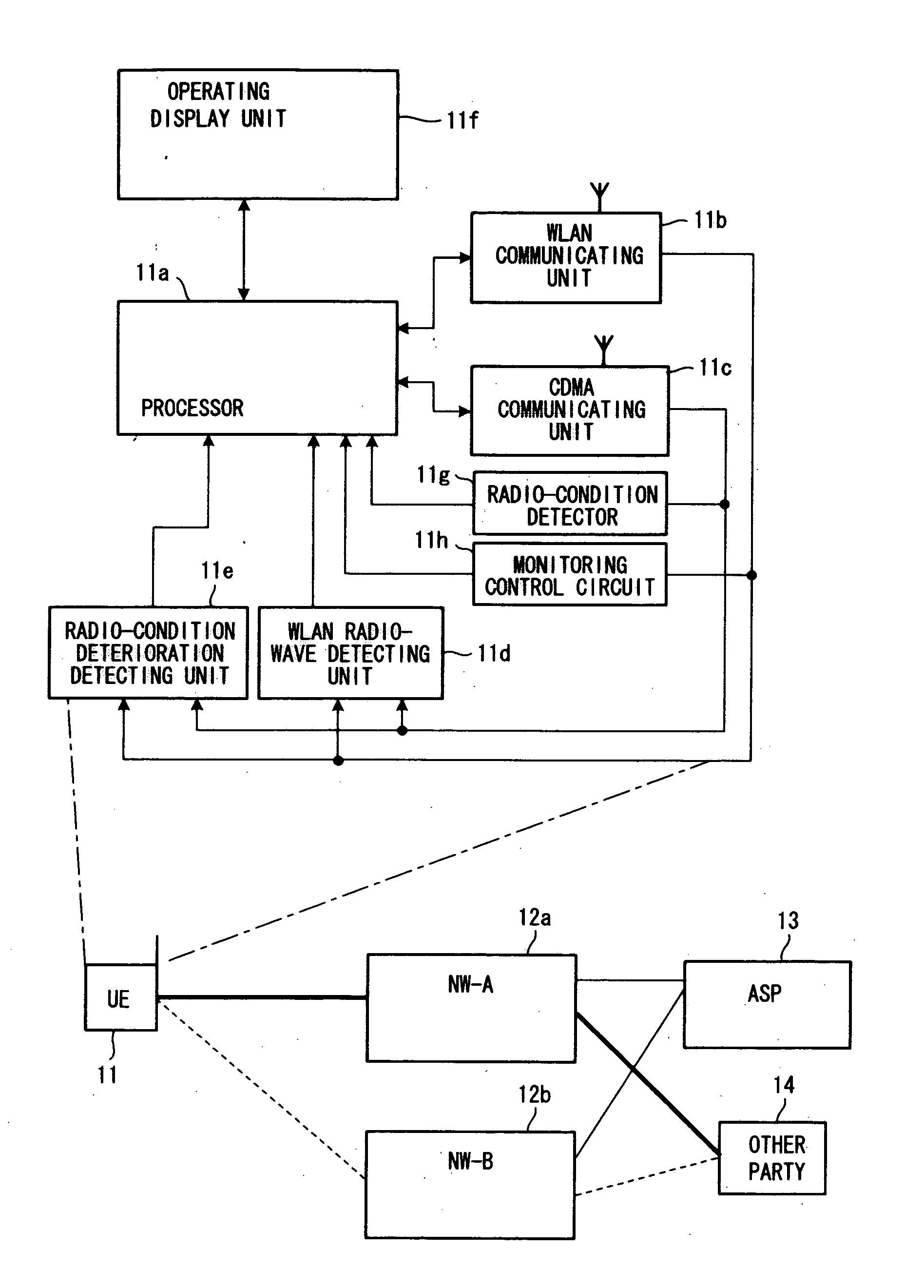
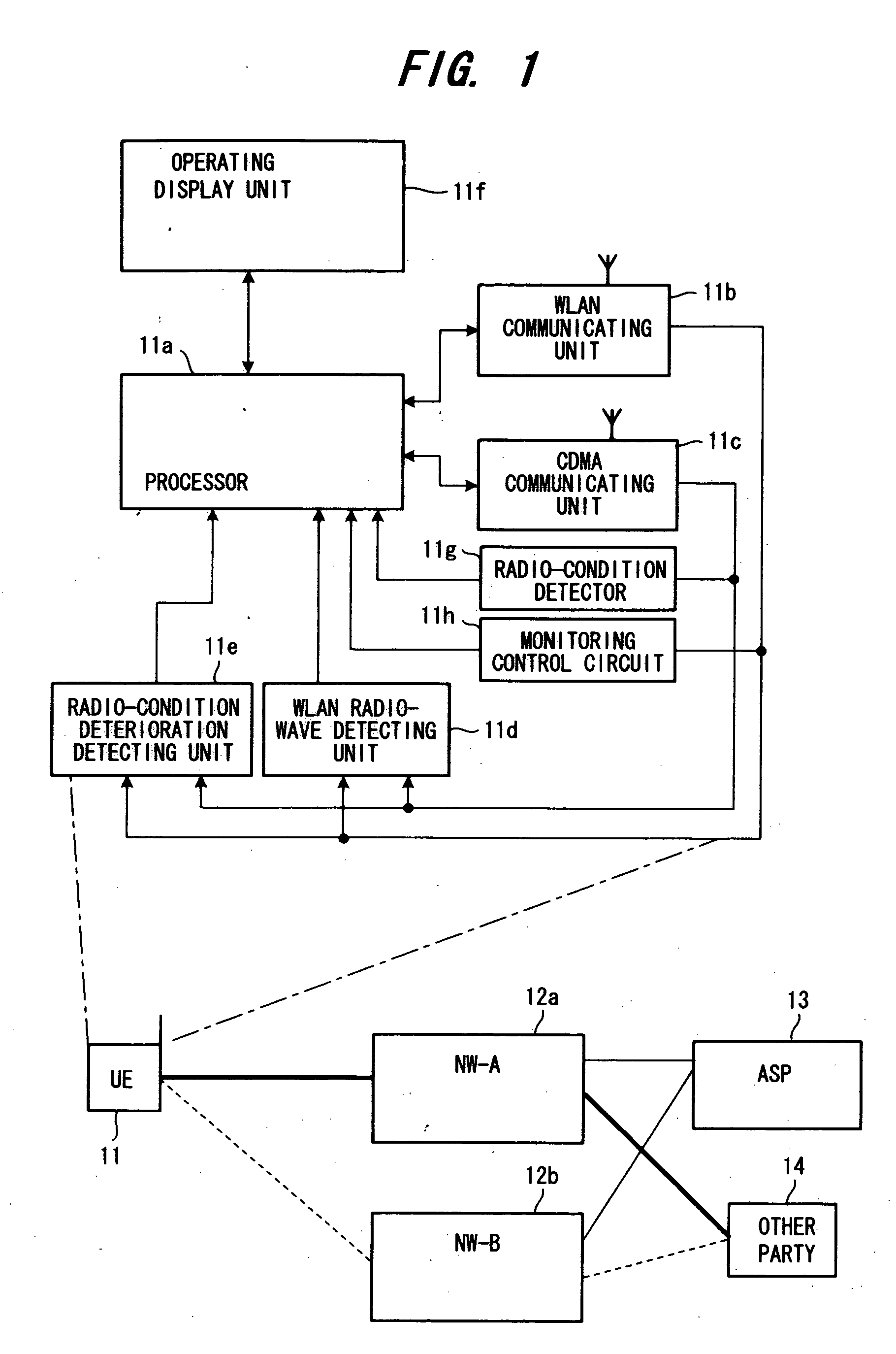
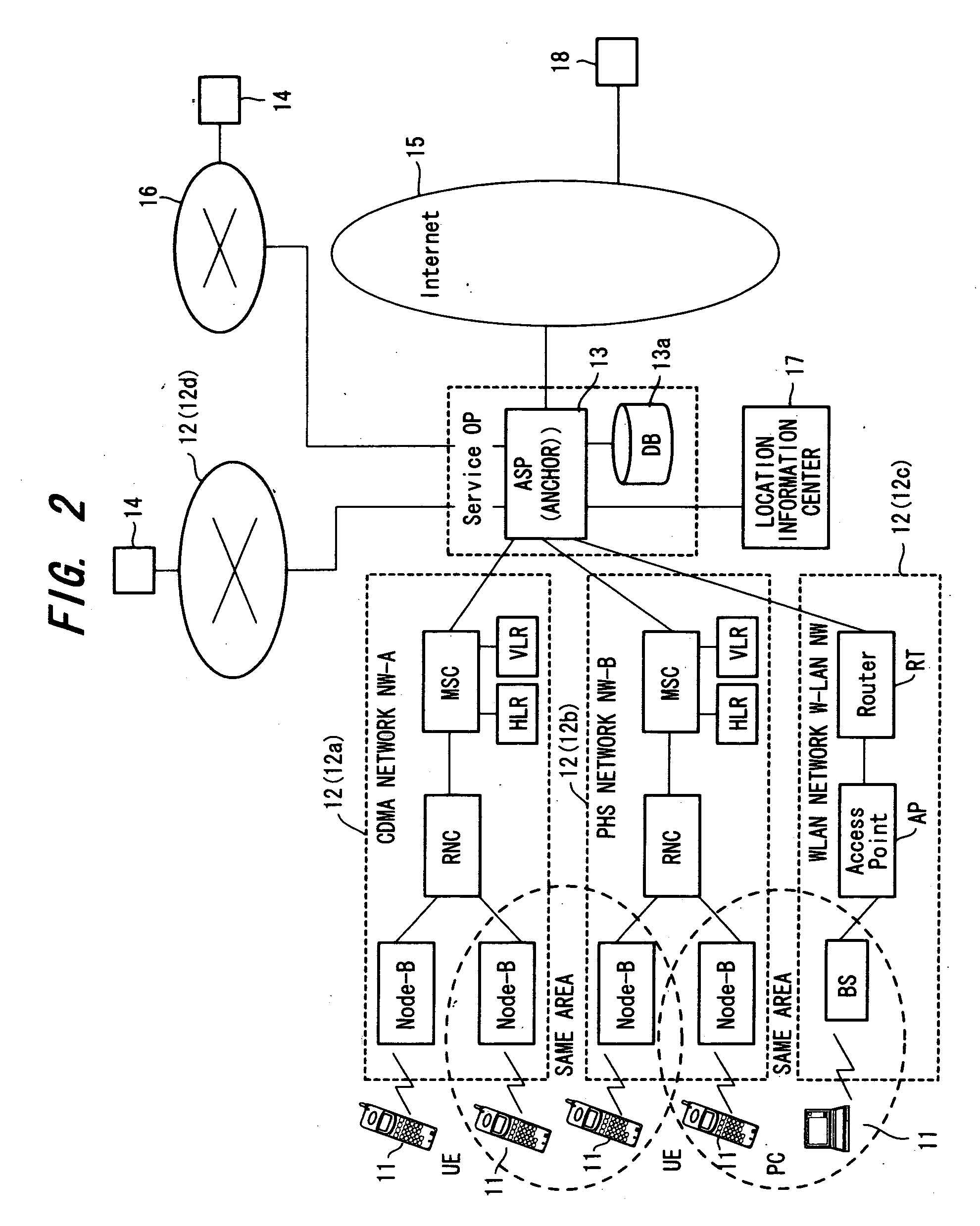
A mobile information terminal communicates with a terminal of another party by utilizing a prescribed network from among a plurality of networks. During communication with the other party by utilizing a first network, another network or deterioration of reception conditions is detected. When another network or deterioration of reception conditions is detected, a server system automatically selects a network for continuing communication (i.e., an ASP makes the selection automatically) or presents recommended networks on a display unit of the mobile information terminal so that the network for continuing communication may be selected on the side of the mobile information terminal and reported to the server system (i.e., the user makes the selection). Communication is continued via the selected network under the control of the server system.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
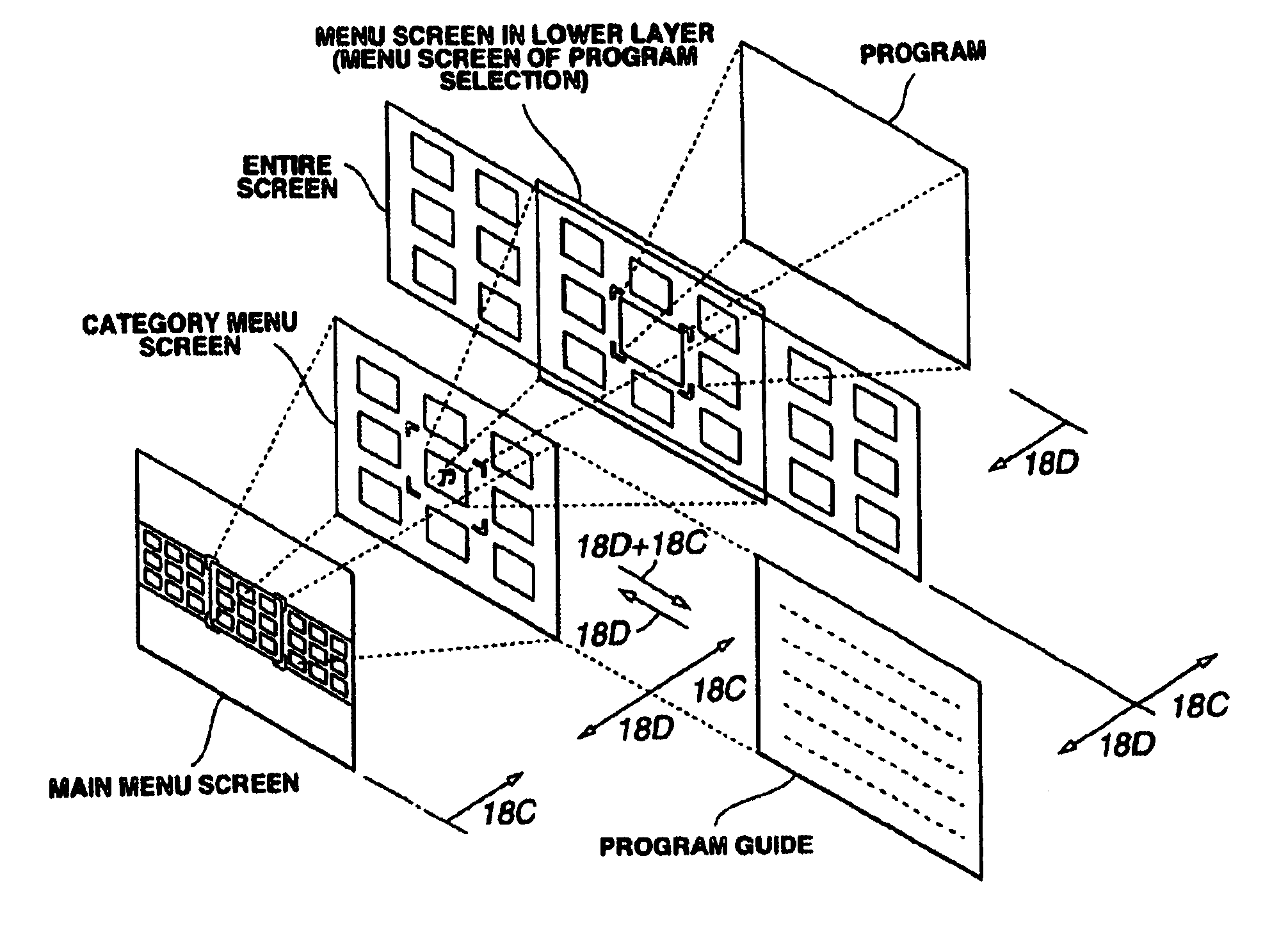
Information providing device and method
InactiveUS6978472B1Reduce the numberTelevision system detailsColor television detailsRemote controlSatellite broadcasting
The present invention relates to an information providing apparatus and an information providing apparatus. The display screen is switched to a predetermined display screen and receives processing on this predetermined display screen by operation of another operation key. Thus, in case where the present invention is applied to a set-top box for digital satellite broadcasting or the like to provide a large number of programs by various selection methods, the number of operation keys of a remote control device is prevented from being increased, so the operationality can be improved.
Owner:SONY CORP
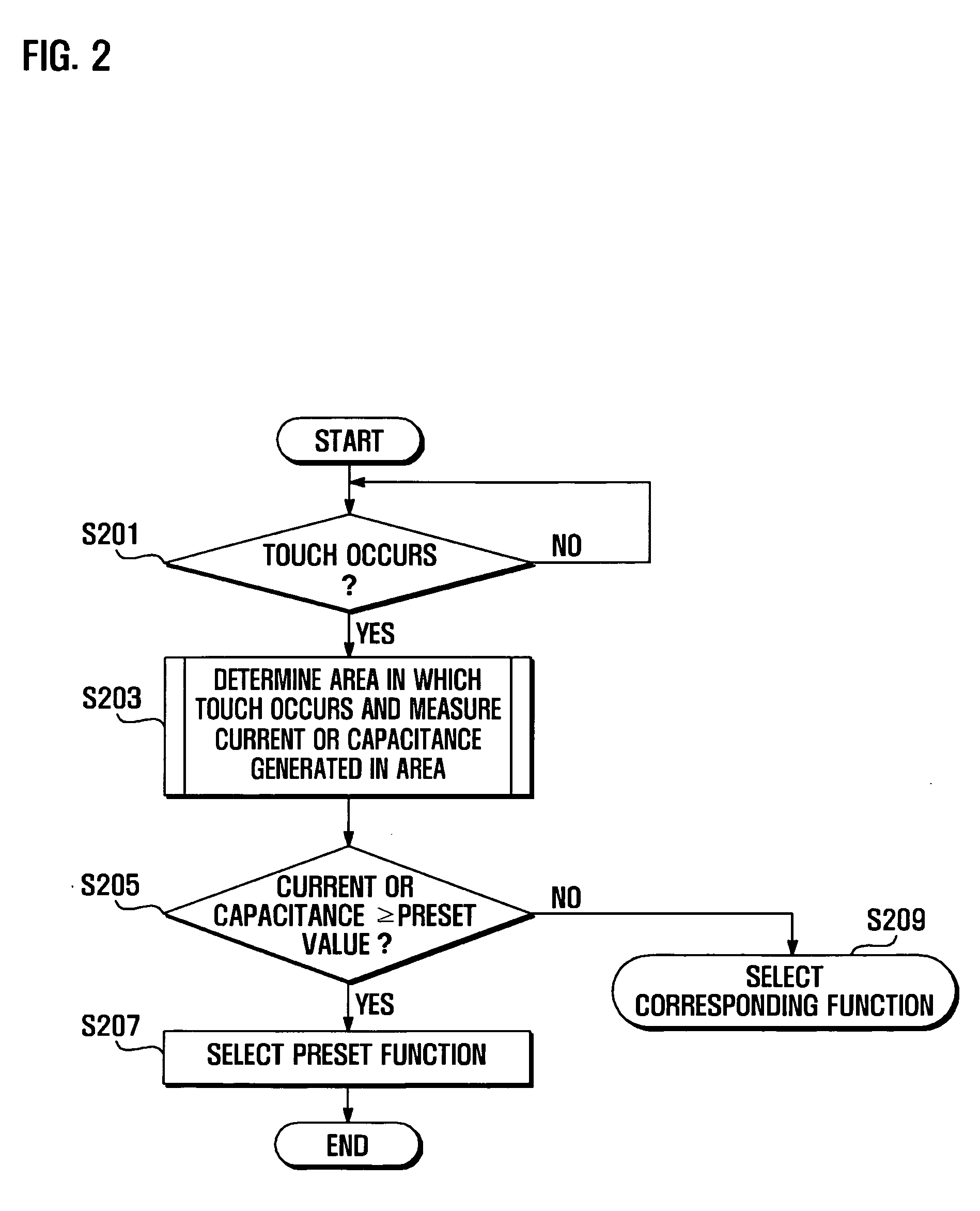
Hyperlink selection method using touchscreen and mobile terminal operating with hyperlink selection method
InactiveUS20090064047A1Choose accuratelyInput/output processes for data processingHyperlinkSelection method
A method of selecting one of a plurality of hyperlinks of a webpage viewed on a touchscreen of a mobile terminal is provided. A hyperlink selection method using a touchscreen includes detecting an occurrence of a touch event in which a touch point on the touchscreen displaying a webpage including a plurality of hyperlinks is touched, determining a number of hyperlinks involved in the touch event, displaying icons corresponding to the hyperlinks if the number of hyperlinks involved in the touch event is greater than or equal to two, and selecting an icon in response to movement of the touch point to one of the displayed icons.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Stock Portfolio Selection Device, Stock Portfolio Selection Method and Medium Storing Stock Portfolio Selection Program
InactiveUS20080249957A1Accurately valuateImproved business profitabilityFinanceStock portfolioCorrelation index
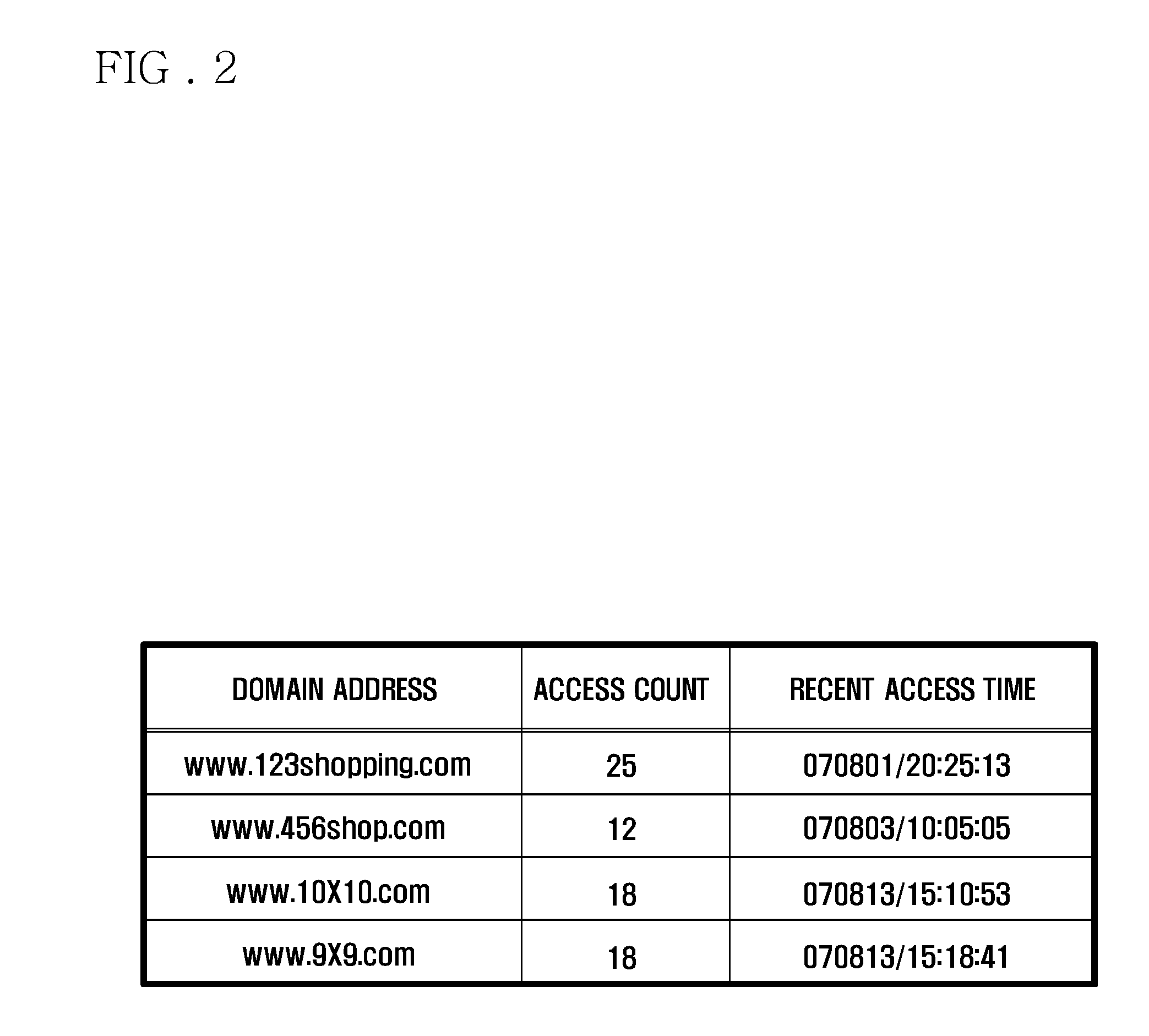
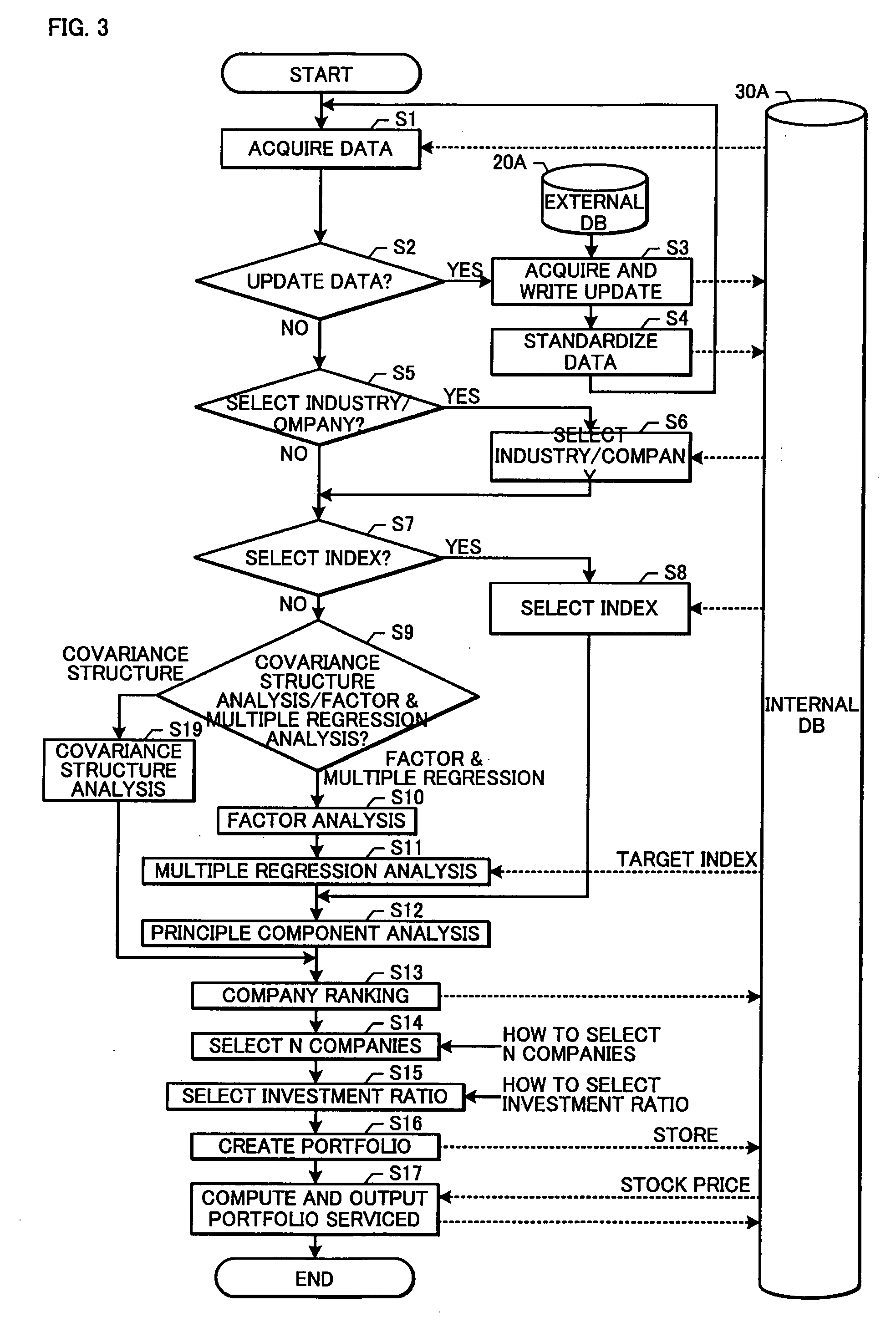
Upon selecting the stock portfolio, a plurality of corporate valuation index related data containing an intellectual asset related index is acquired (steps S1 to S6), analysis is performed with the acquired corporate valuation index related data and a company ranking corresponding to at least one prescribed index is created (steps S7 to S13 and S19), a prescribed number of companies is selected from the created company ranking (step S14), an investment ratio is selected in relation to each of the selected companies (step S15), and, based on the obtained distribution result of the investment ratio, a stock portfolio corresponding to the selected company is created and output (steps S16, S17). Therefore, a device for automatically selecting a more preferable stock portfolio based on the results upon performing a comprehensive valuation of companies using a corporate valuation index containing an intellectual asset related index is provided.
Owner:INTPROP BANK CORP (JP) +1
Mobile terminal and method of selecting lock function
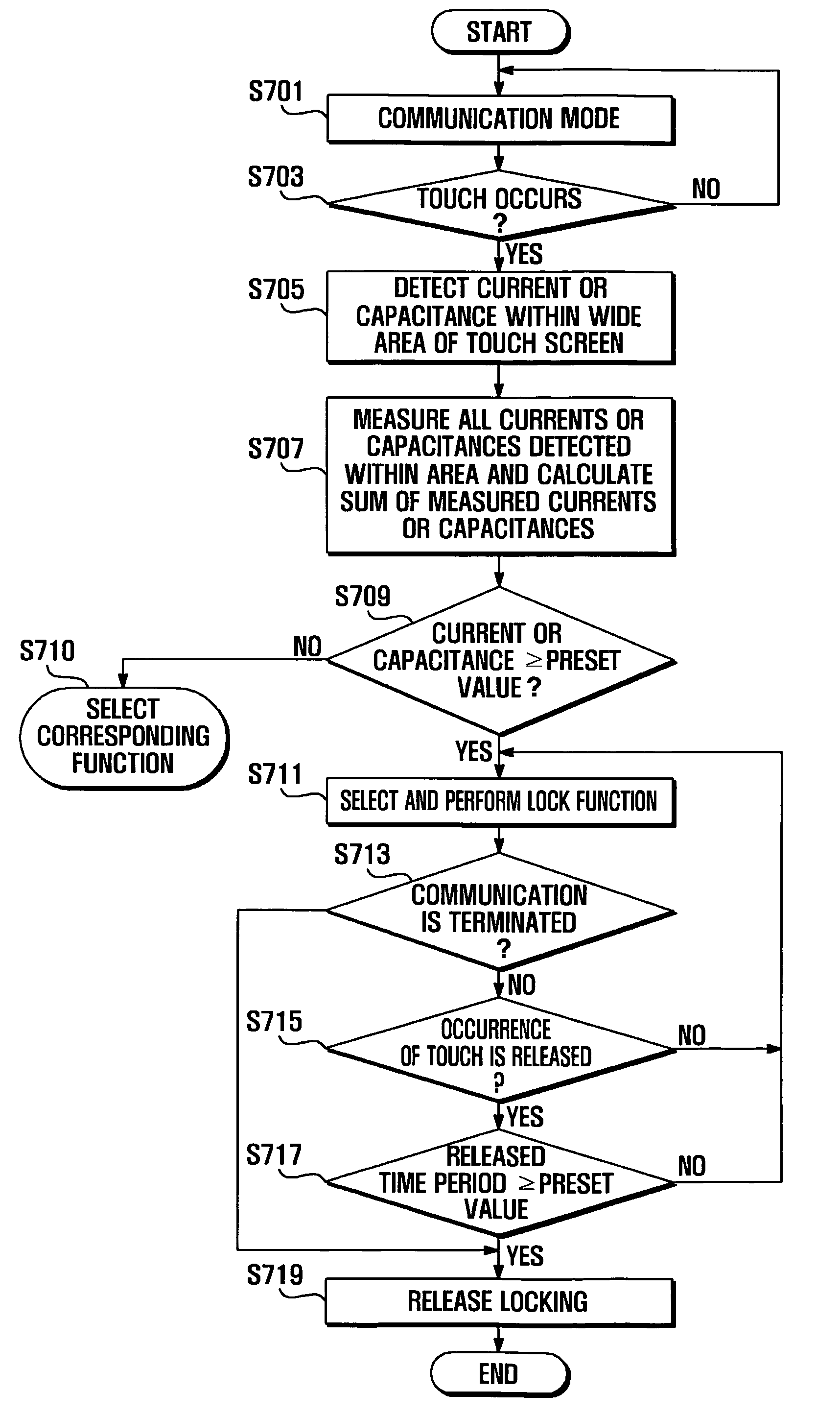
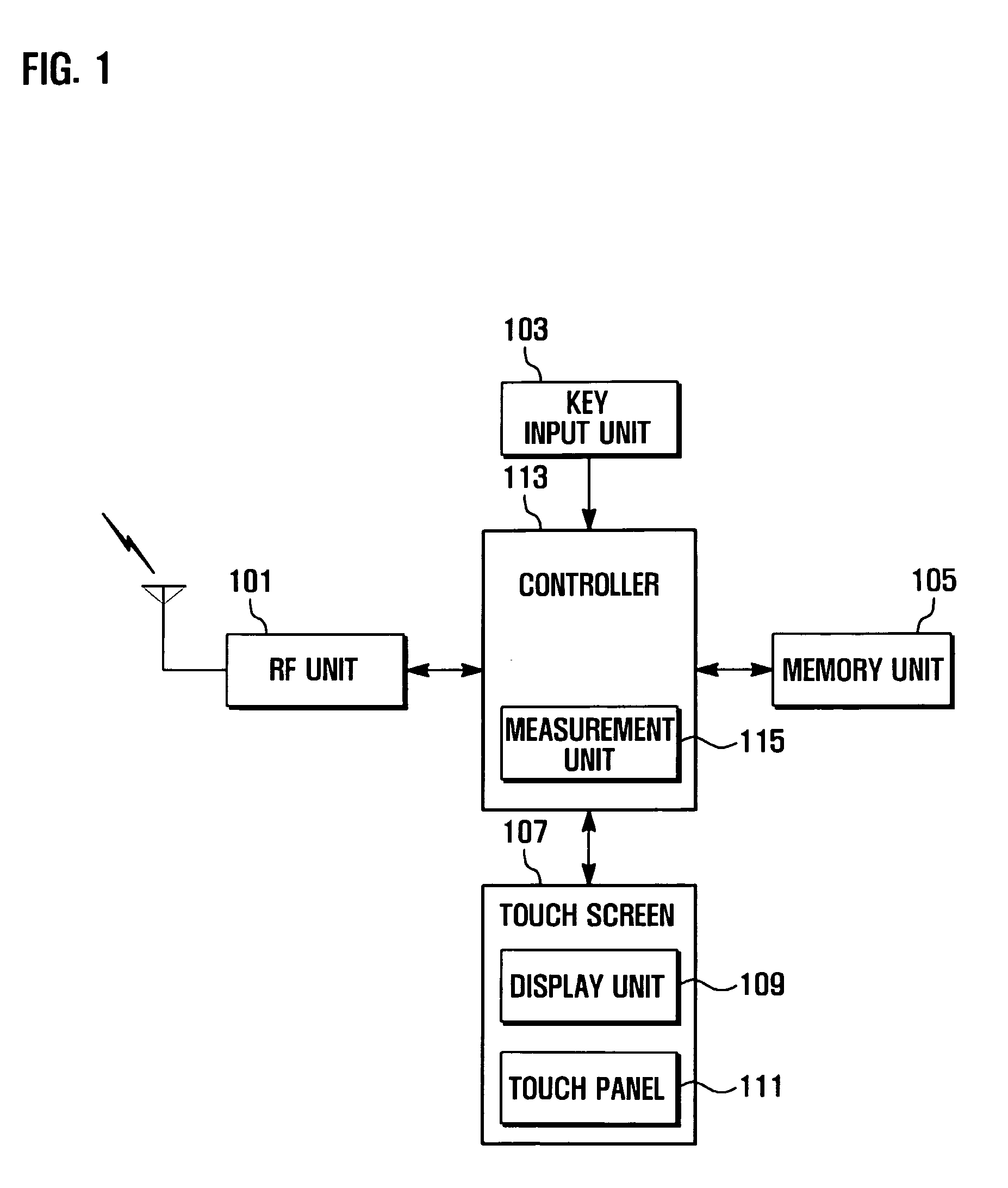
ActiveUS20090061823A1Unauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsCapacitanceTouchscreen
A mobile terminal and a method of selecting a lock function thereof are provided. The method of selecting a lock function of a mobile terminal having a touch screen includes: measuring, when at least one touch occurs on the touch screen, at least one of a pressure, a current, and a capacitance of an area of the touch screen in which the touch occurs; and selecting, if at least one of the measured pressure, current, and capacitance is greater than or equal to a preset value, a lock function. Thus, by touching the touch screen in such a manner that a high current or capacitance may be measured in a specific area of the mobile terminal, a user can easily perform a desired function, thereby improving user convenience.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
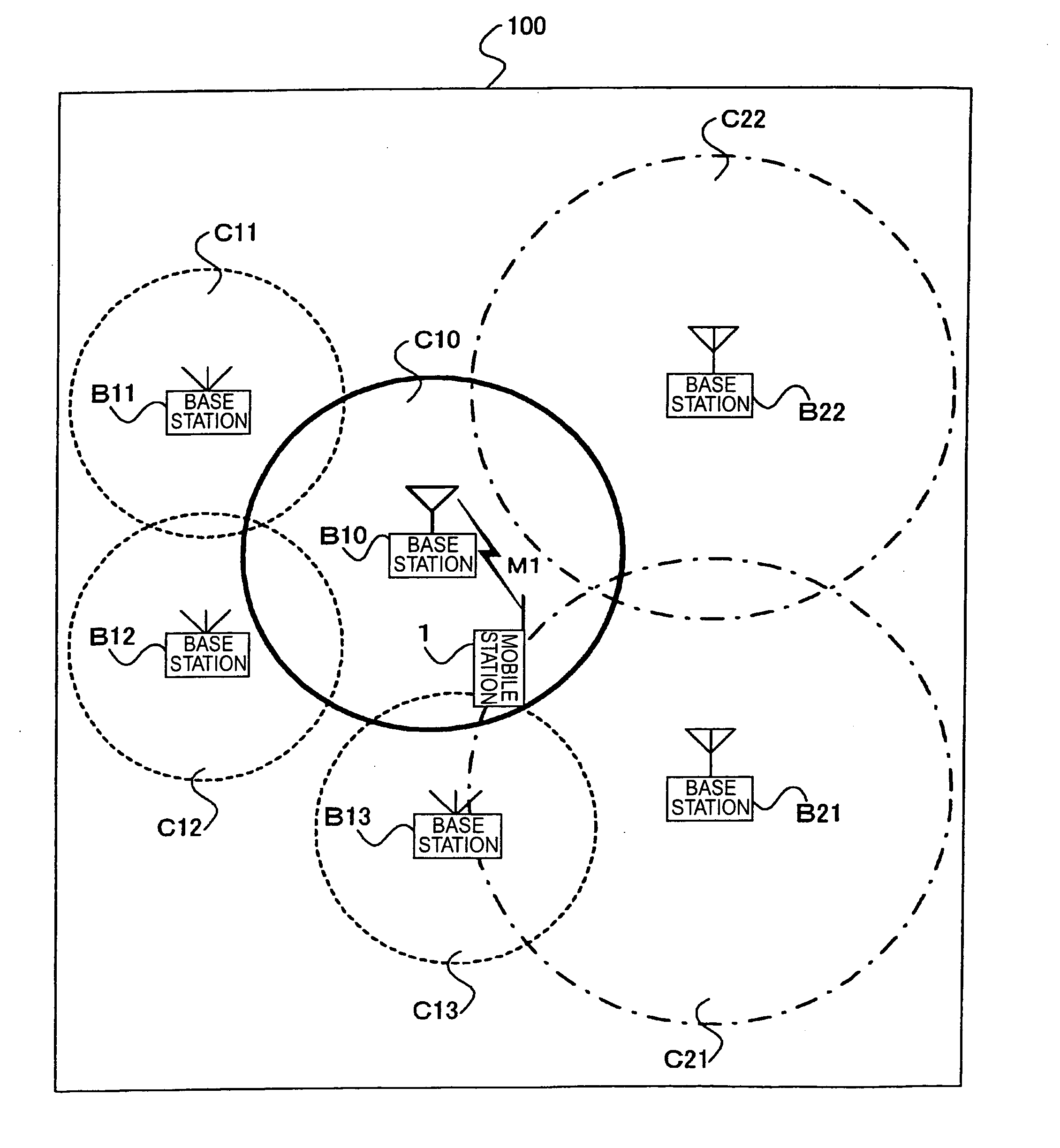
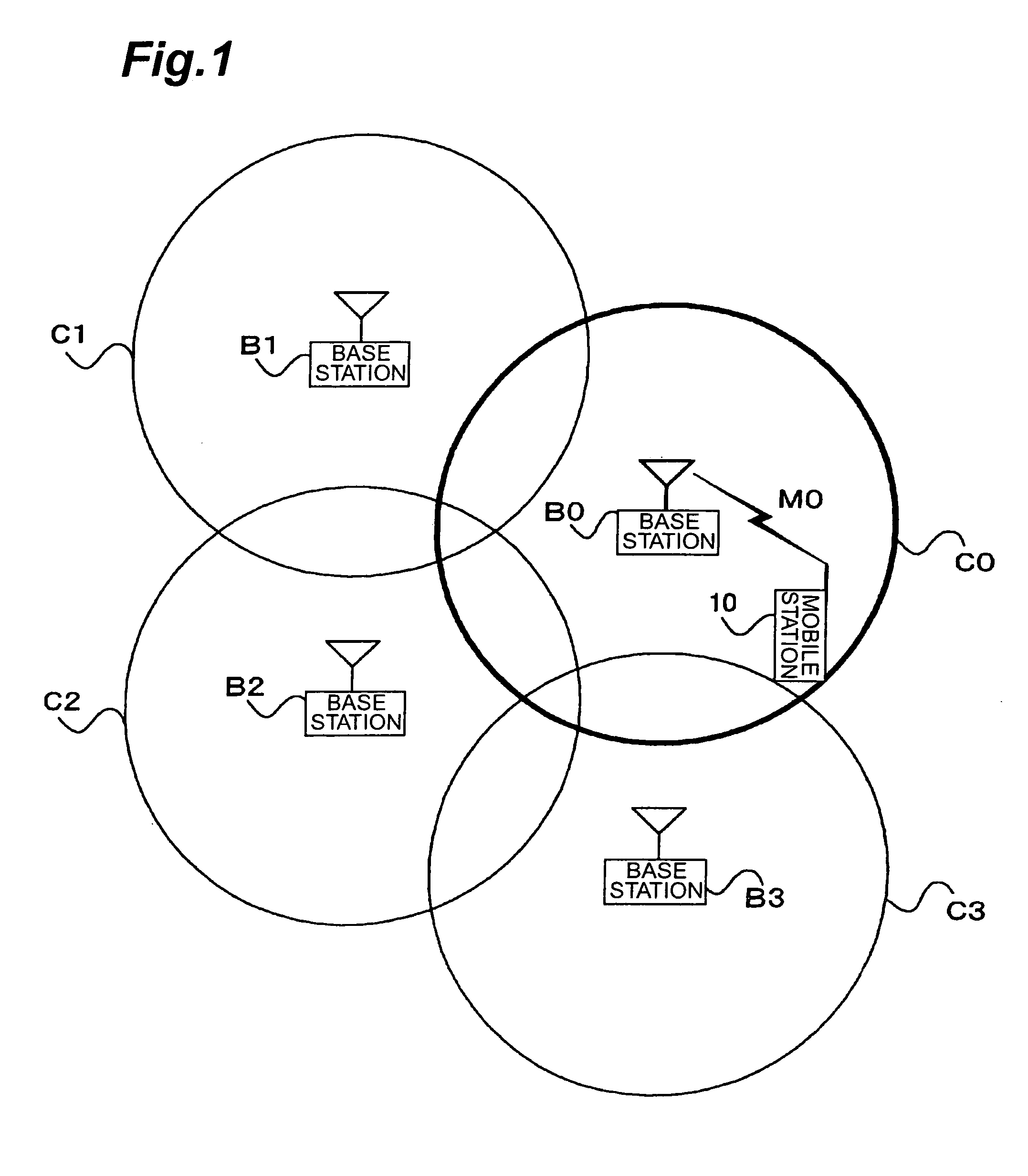
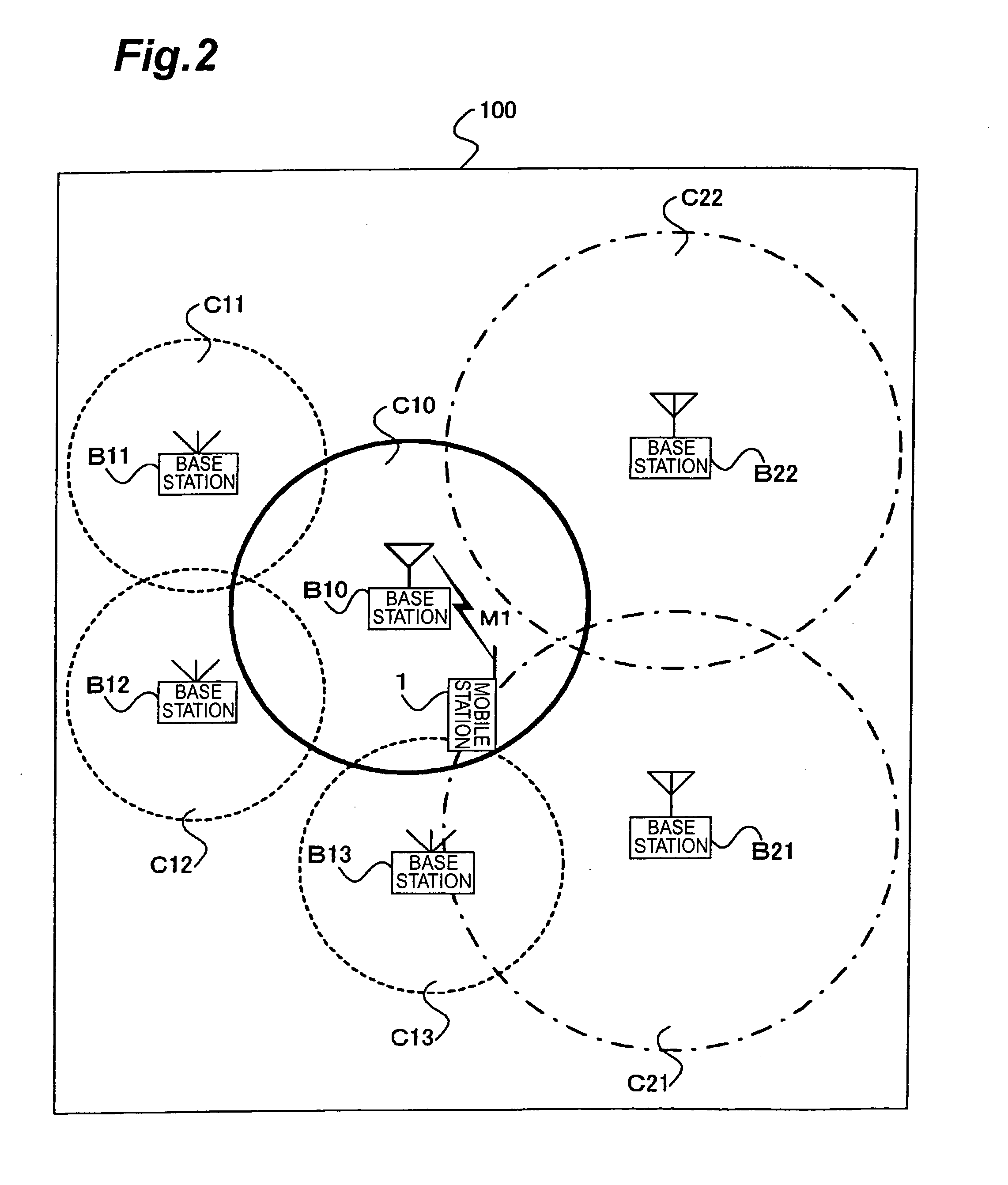
Mobile station, mobile communication system, and cell selection method
InactiveUS20050037798A1Stabilize good communication qualityCommunication quality is not deterioratedRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionCell selectionMobile station
In mobile communication system 100 according to the present invention, mobile station 1 is camped on cell C10 established by base station B10. In the cell C10, there exist indoor cells C11-C13 and outdoor cells C21, C22 as neighboring cells. Mobile station 1 measures received levels of cells C10-C13, C21, C22 and determines cell types of the respective cells, i.e., whether each cell is an indoor cell or not, based on broadcast information M1. Mobile station 1 selects a cell as a reselection target on the basis of the received levels and cell types.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
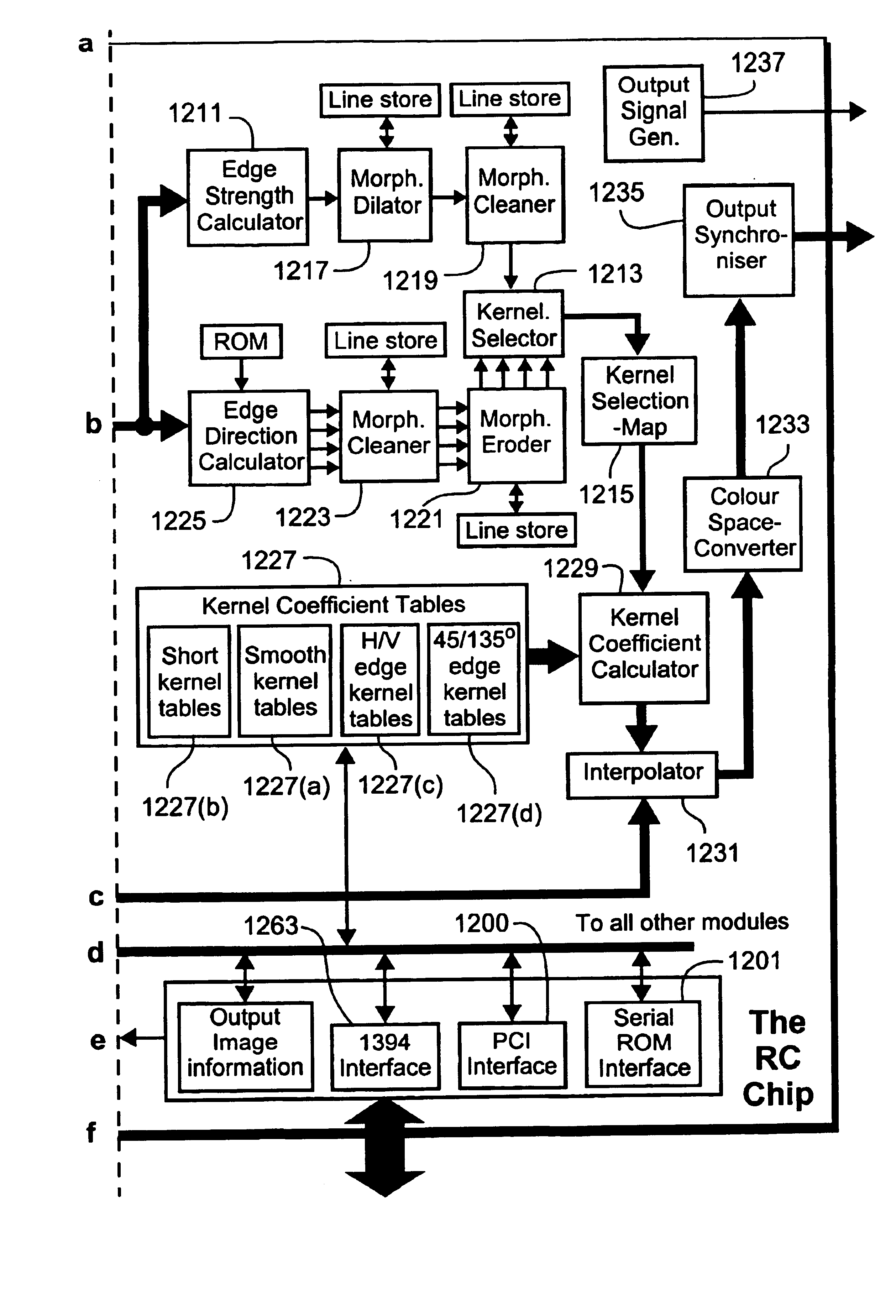
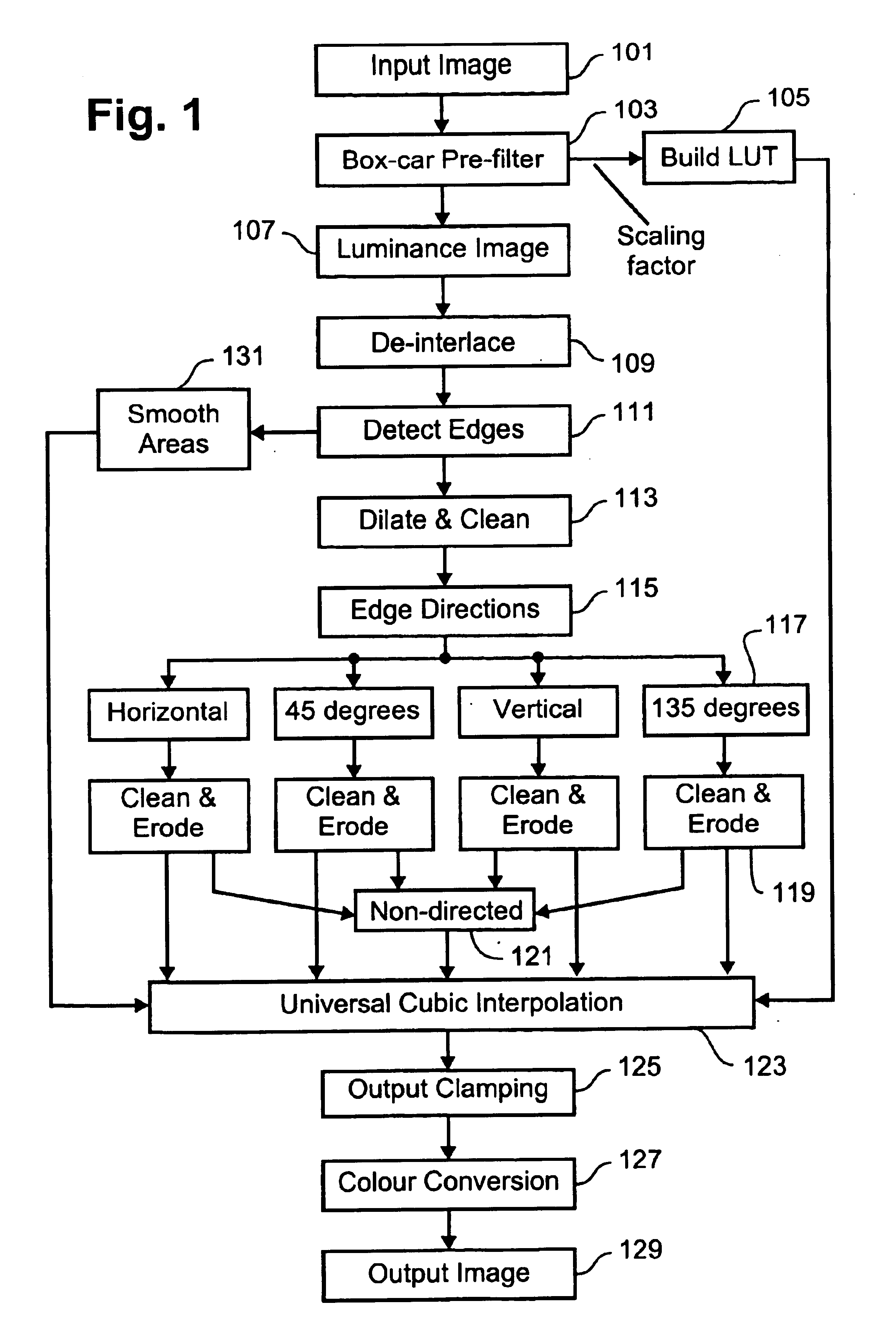
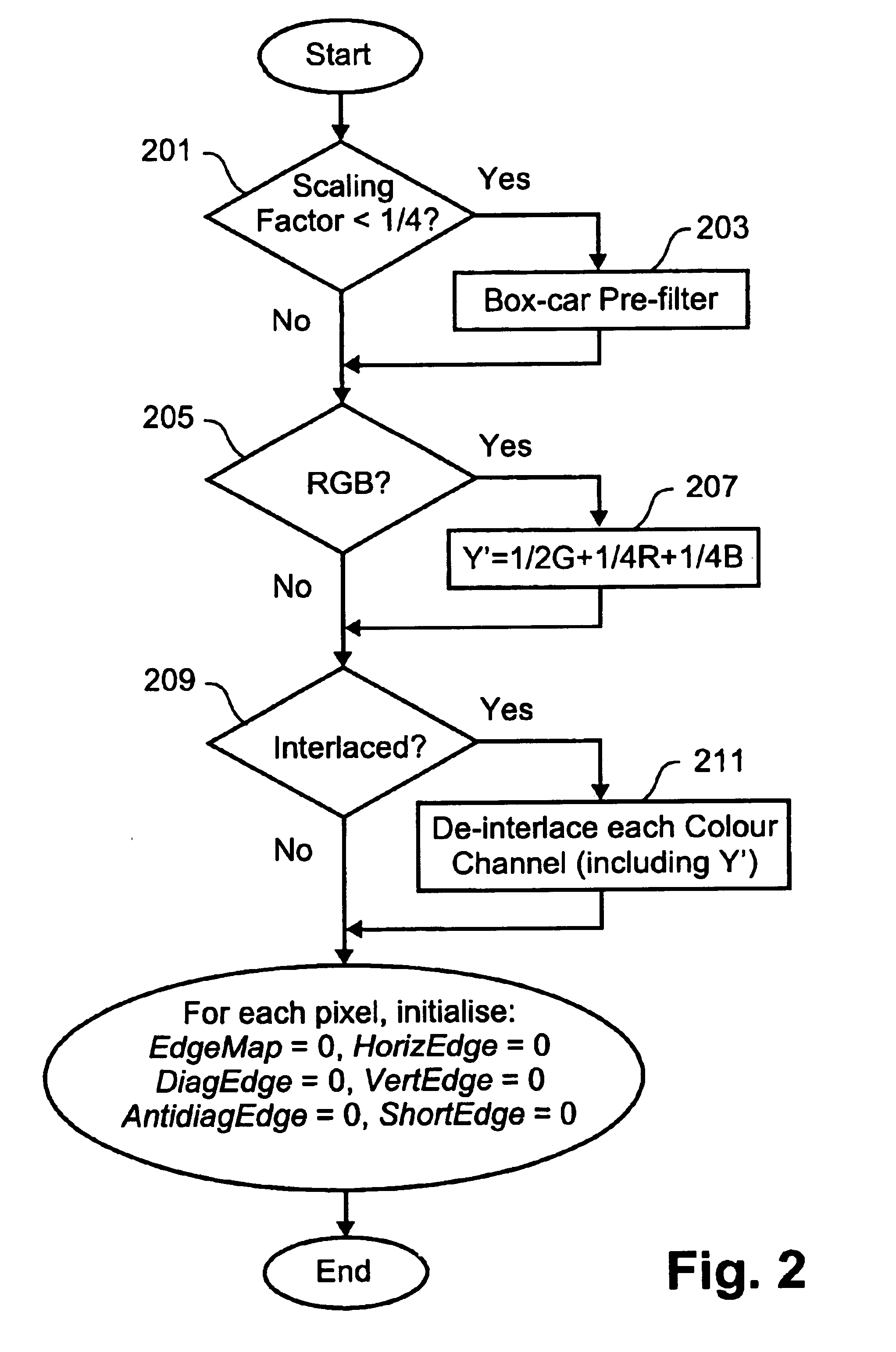
Method for kernel selection for image interpolation
InactiveUS6928196B1More disadvantageGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionEdge strength
A method and apparatus for determining edge information for image data comprising a mapping of discrete sample values are disclosed. An edge strength value is calculated for each of the discrete sample values of the image data to identify edge sample values, and an angle of orientation is stored for each of said edge sample values. The edge sample values and the stored angle of orientation for each of said discrete sample values are manipulated using a morphological process.
Owner:CANON KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com