Patents
Literature
2132 results about "Microelectronics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Microelectronics is a subfield of electronics. As the name suggests, microelectronics relates to the study and manufacture (or microfabrication) of very small electronic designs and components. Usually, but not always, this means micrometre-scale or smaller. These devices are typically made from semiconductor materials. Many components of normal electronic design are available in a microelectronic equivalent. These include transistors, capacitors, inductors, resistors, diodes and (naturally) insulators and conductors can all be found in microelectronic devices. Unique wiring techniques such as wire bonding are also often used in microelectronics because of the unusually small size of the components, leads and pads. This technique requires specialized equipment and is expensive.
Atomic layer deposition using metal amidinates
ActiveUS20060141155A1Improve conductivityReduce the temperatureGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsHydrogenWater vapor
Metal films are deposited with uniform thickness and excellent step coverage. Copper metal films were deposited on heated substrates by the reaction of alternating doses of copper(I) NN′-diisopropylacetamidinate vapor and hydrogen gas. Cobalt metal films were deposited on heated substrates by the reaction of alternating doses of cobalt(II) bis(N,N′-diisopropylacetamidinate) vapor and hydrogen gas. Nitrides and oxides of these metals can be formed by replacing the hydrogen with ammonia or water vapor, respectively. The films have very uniform thickness and excellent step coverage in narrow holes. Suitable applications include electrical interconnects in microelectronics and magnetoresistant layers in magnetic information storage devices.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
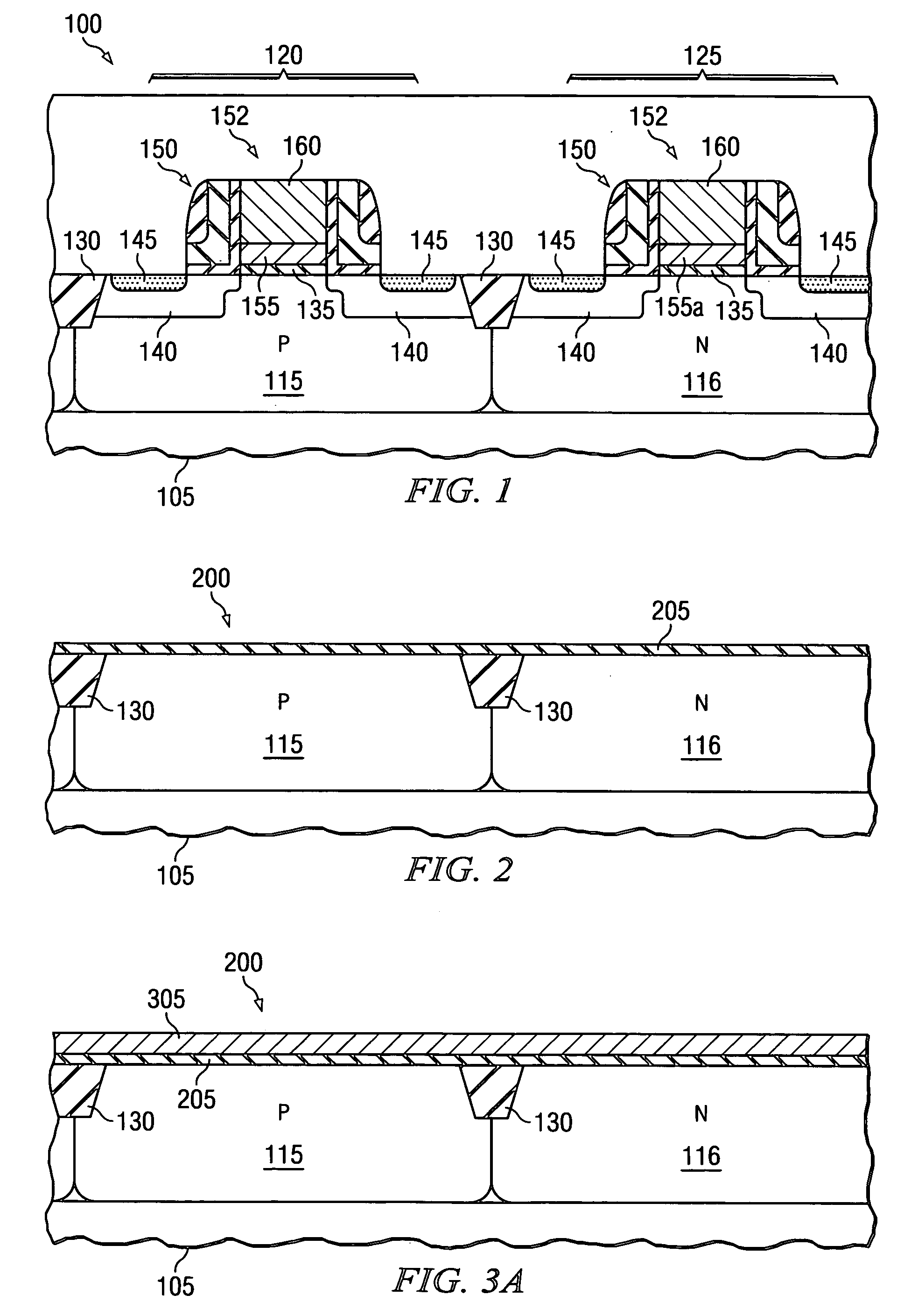
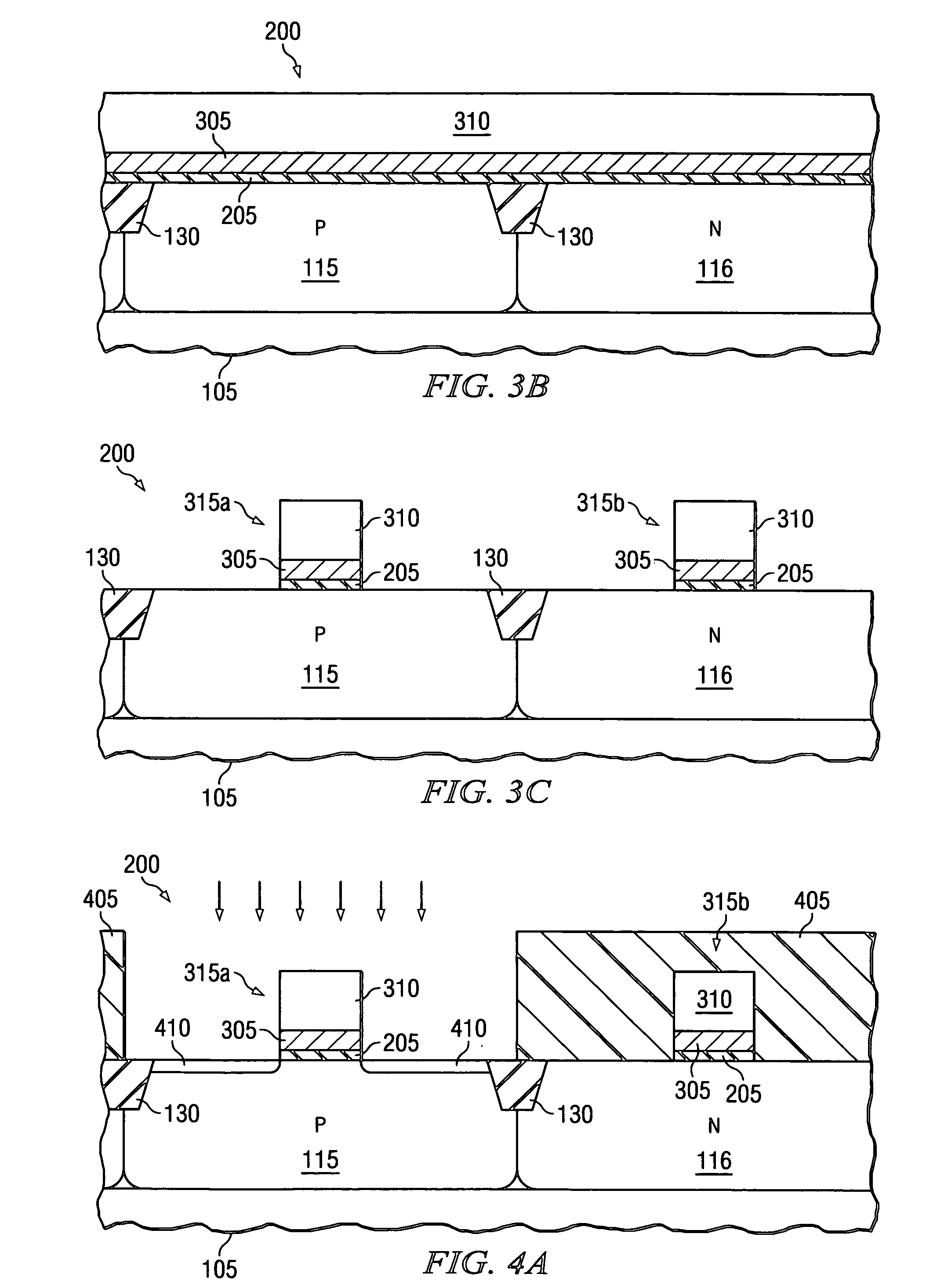
Process for manufacturing dual work function metal gates in a microelectronics device
ActiveUS20070037343A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricWork function
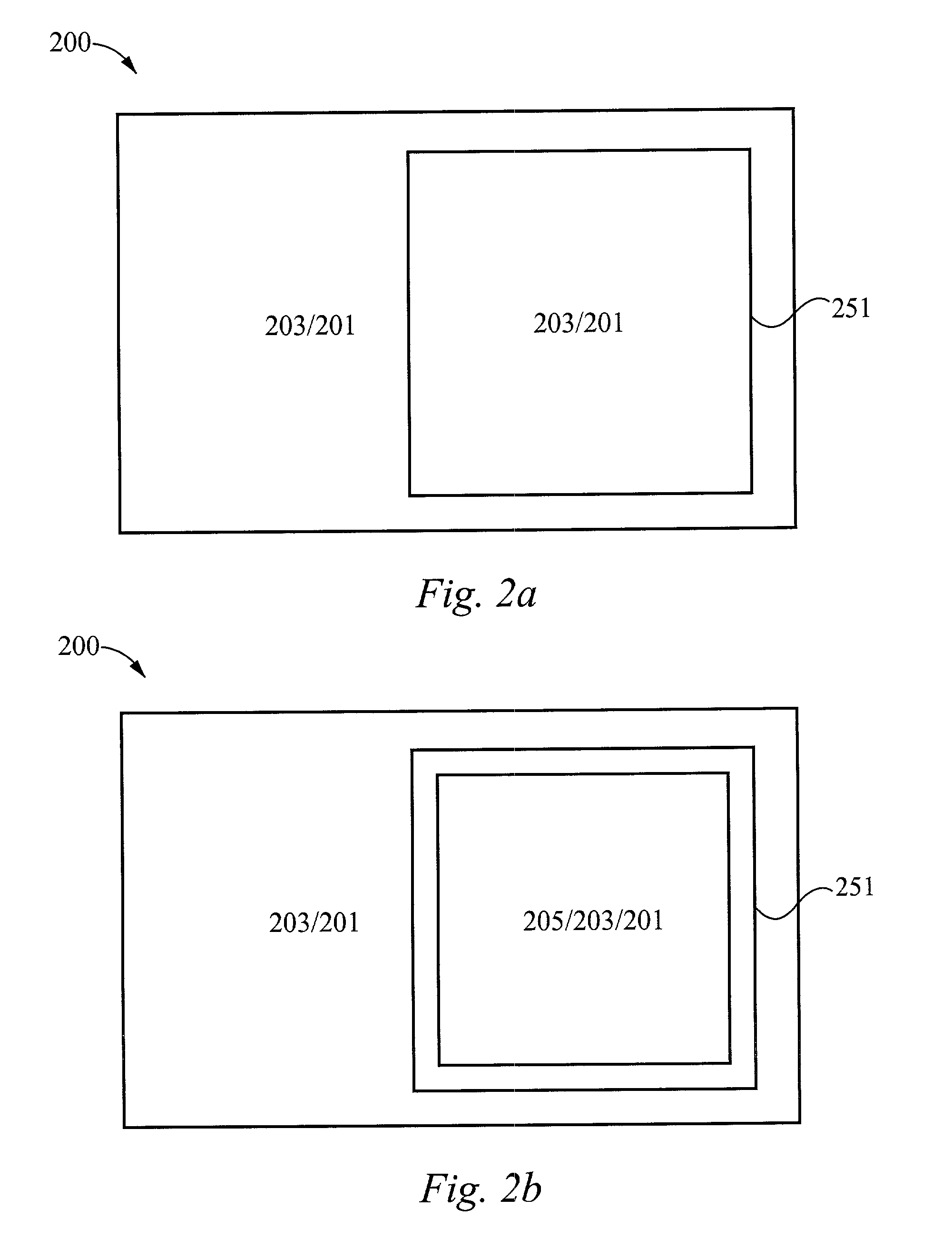
The present invention provides a method of forming a dual work function metal gate microelectronics device 200. In one aspect, the method includes forming nMOS and pMOS stacked gate structures 315a and 315b. The nMOS and pMOS stacked gate structures 315a and 315b each comprise a gate dielectric 205, a first metal layer, 305 located over the gate dielectric 205 and a sacrificial gate layer 310 located over the first metal layer 305. The method further includes removing the sacrificial gate layer 310 in at least one of the nMOS or pMOS stacked gate structures, thereby forming a gate opening 825 and modifying the first metal layer 305 within the gate opening 825 to form a gate electrode with a desired work function.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Atomic layer deposition using metal amidinates
ActiveUS20090291208A1Good step coverageImprove conductivityGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsCopper organic compoundsHydrogenWater vapor
Metal films are deposited with uniform thickness and excellent step coverage. Copper metal films were deposited on heated substrates by the reaction of alternating doses of copper(I) NN′-diispropylacetamidinate vapor and hydrogen gas. Cobalt metal films were deposited on heated substrates b the reaction of alternating doses of cobalt(II) bis(N,N′-diispropylacetamidinate) vapor and hydrogen gas. Nitrides and oxides of these metals can be formed by replacing the hydrogen with ammonia or water vapor, respectively. The films have very uniform thickness and excellent step coverage in narrow holes. Suitable applications include electrical interconnects in microelectronics and magnetoresistant layers in magnetic information storage devices.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Vapor deposition of tungsten nitride
ActiveUS20060125099A1Uniform thicknessImprove efficiencyMirrorsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectrical conductorGas phase
Tungsten nitride films were deposited on heated substrates by the reaction of vapors of tungsten bis(alkylimide)bis(dialkylamide) and a Lewis base or a hydrogen plasma. For example, vapors of tungsten bis(tert-butylimide)bis(dimethylamide) and ammonia gas supplied in alternate doses to surfaces heated to 300° C. produced coatings of tungsten nitride having very uniform thickness and excellent step coverage in holes with aspect ratios up to at least 40:1. The films are metallic and good electrical conductors. Suitable applications in microelectronics include barriers to the diffusion of copper and electrodes for capacitors. Similar processes deposit molybdenum nitride, which is suitable for layers alternating with silicon in X-ray mirrors.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
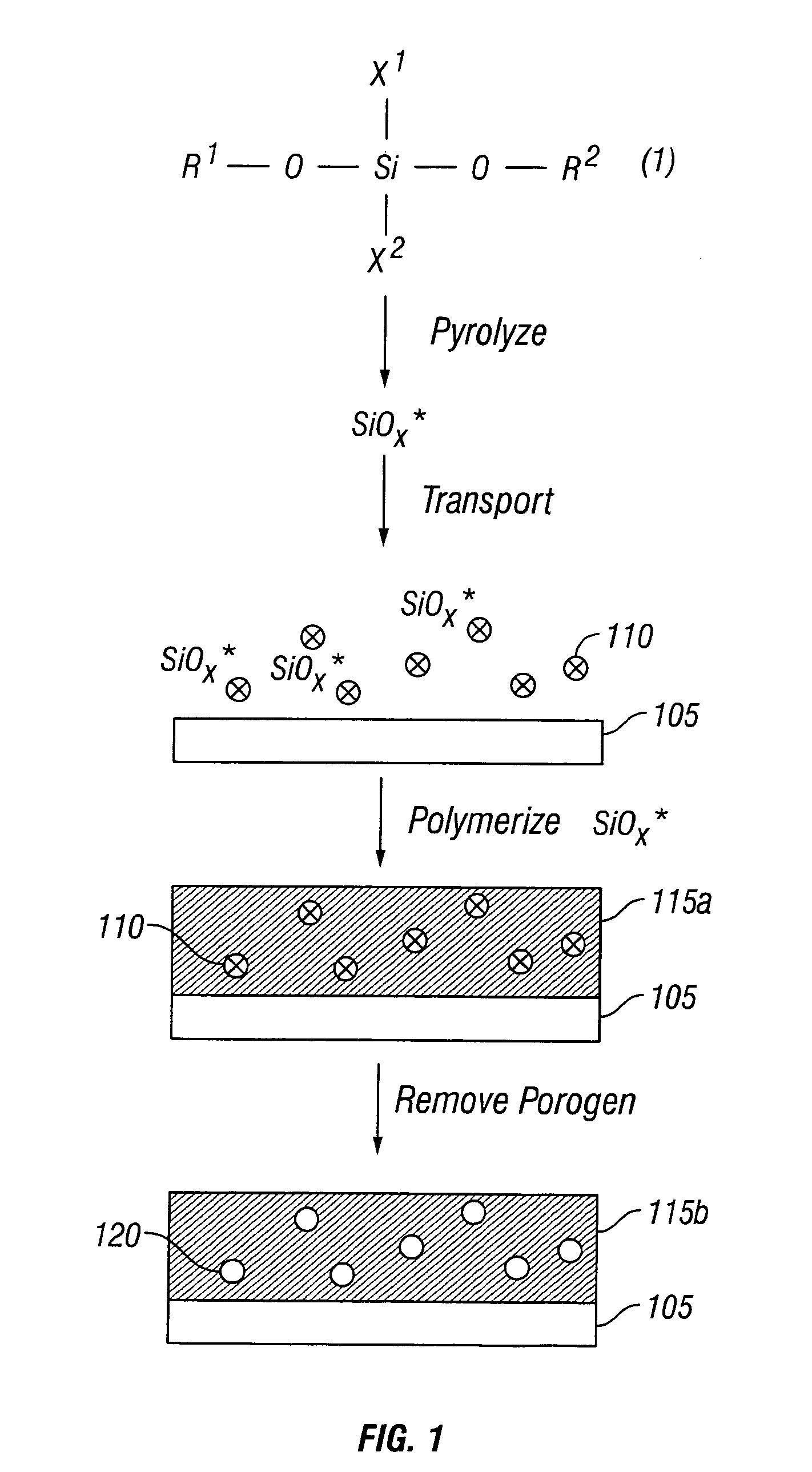
Apparatus, precursors and deposition methods for silicon-containing materials
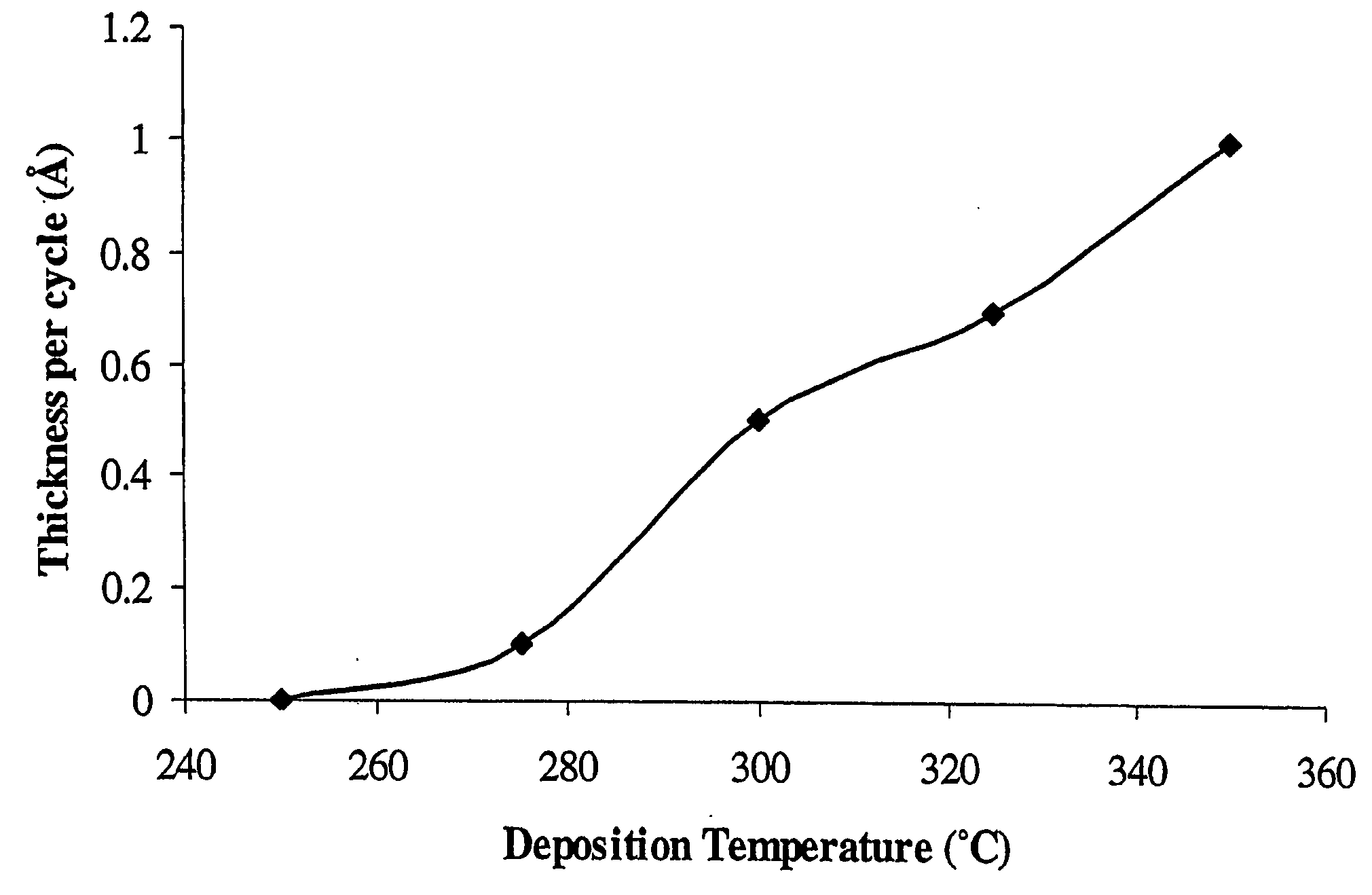
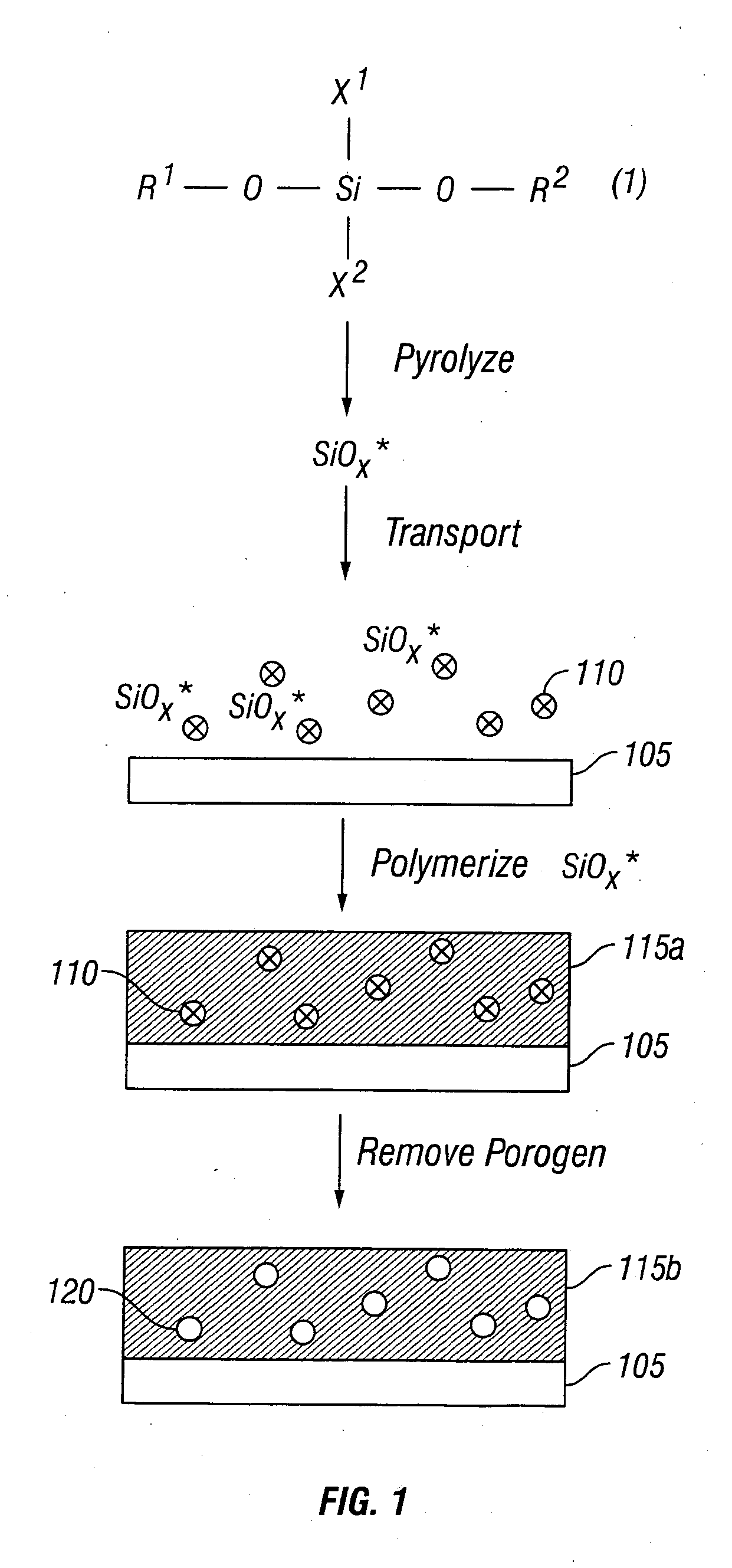
A method for making a Si-containing material comprises transporting a pyrolyzed Si-precursor to a substrate and polymerizing the pyrolyzed Si-precursor on the substrate to form a Si-containing film. Polymerization of the pyrolyzed Si-precursor may be carried out in the presence of a porogen to thereby form a porogen-containing Si-containing film. The porogen may be removed from the porogen-containing Si-containing film to thereby form a porous Si-containing film. Preferred porous Si-containing films have low dielectric constants and thus are suitable for various low-k applications such as in microelectronics and microelectromechanical systems.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
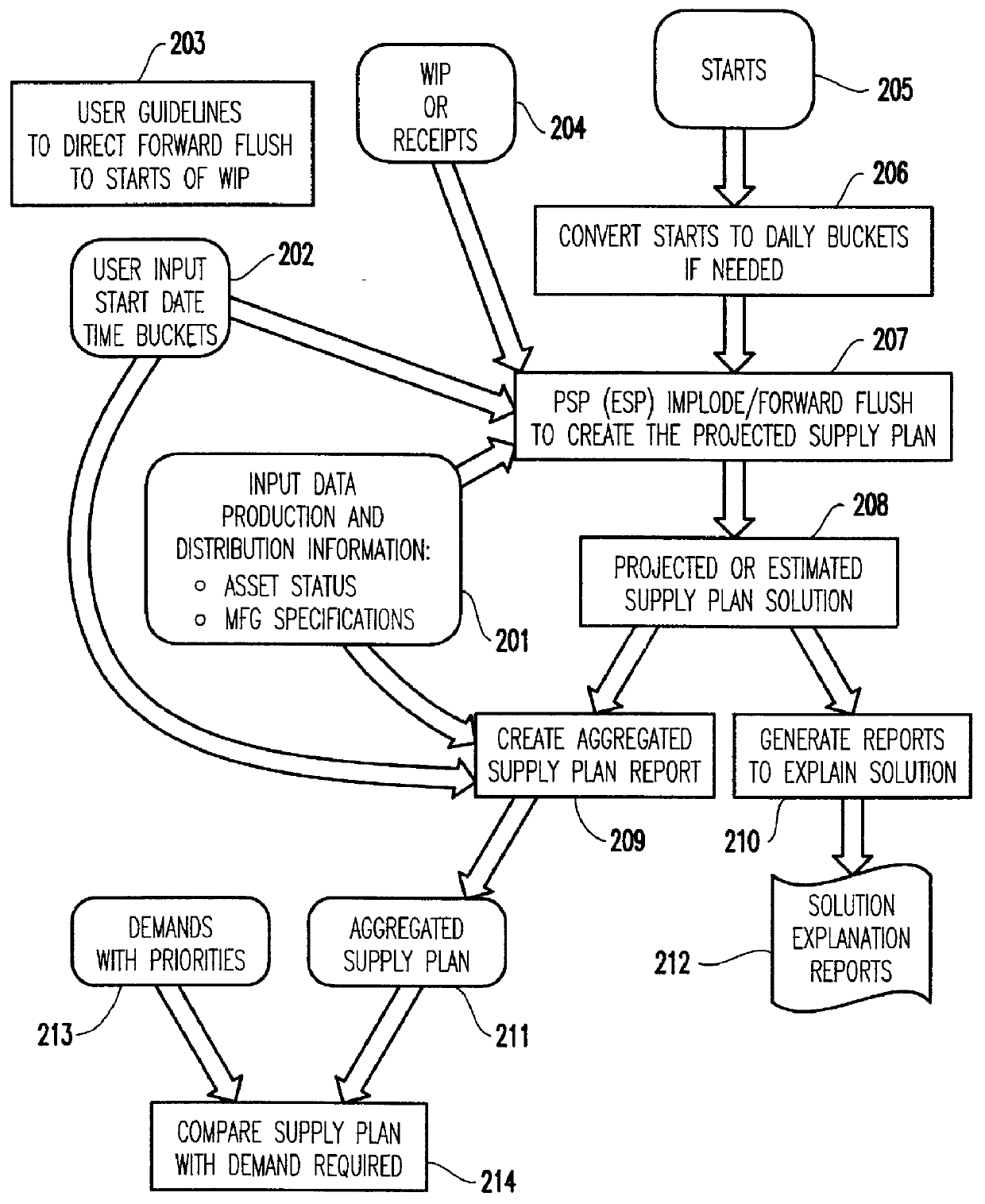
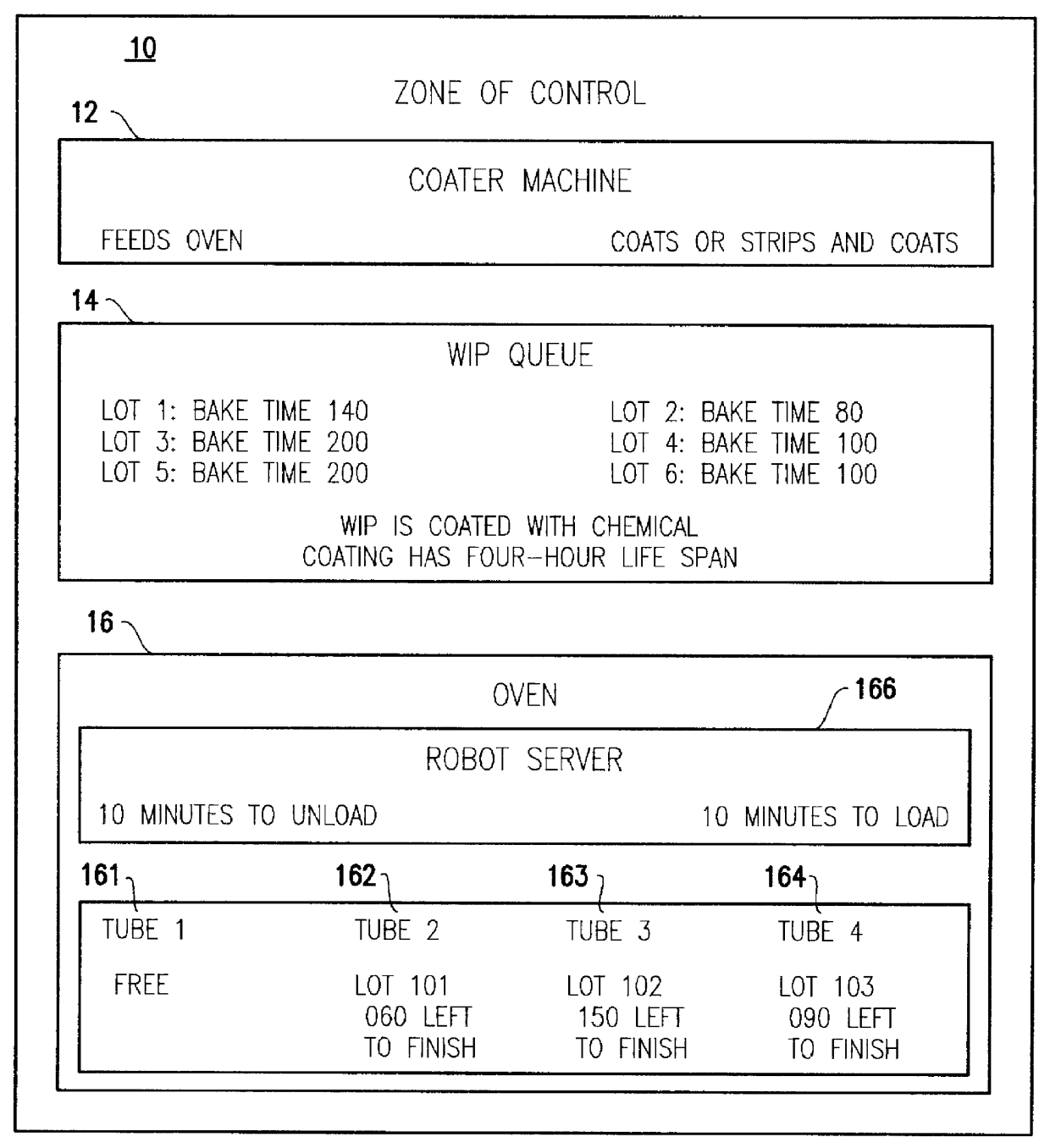
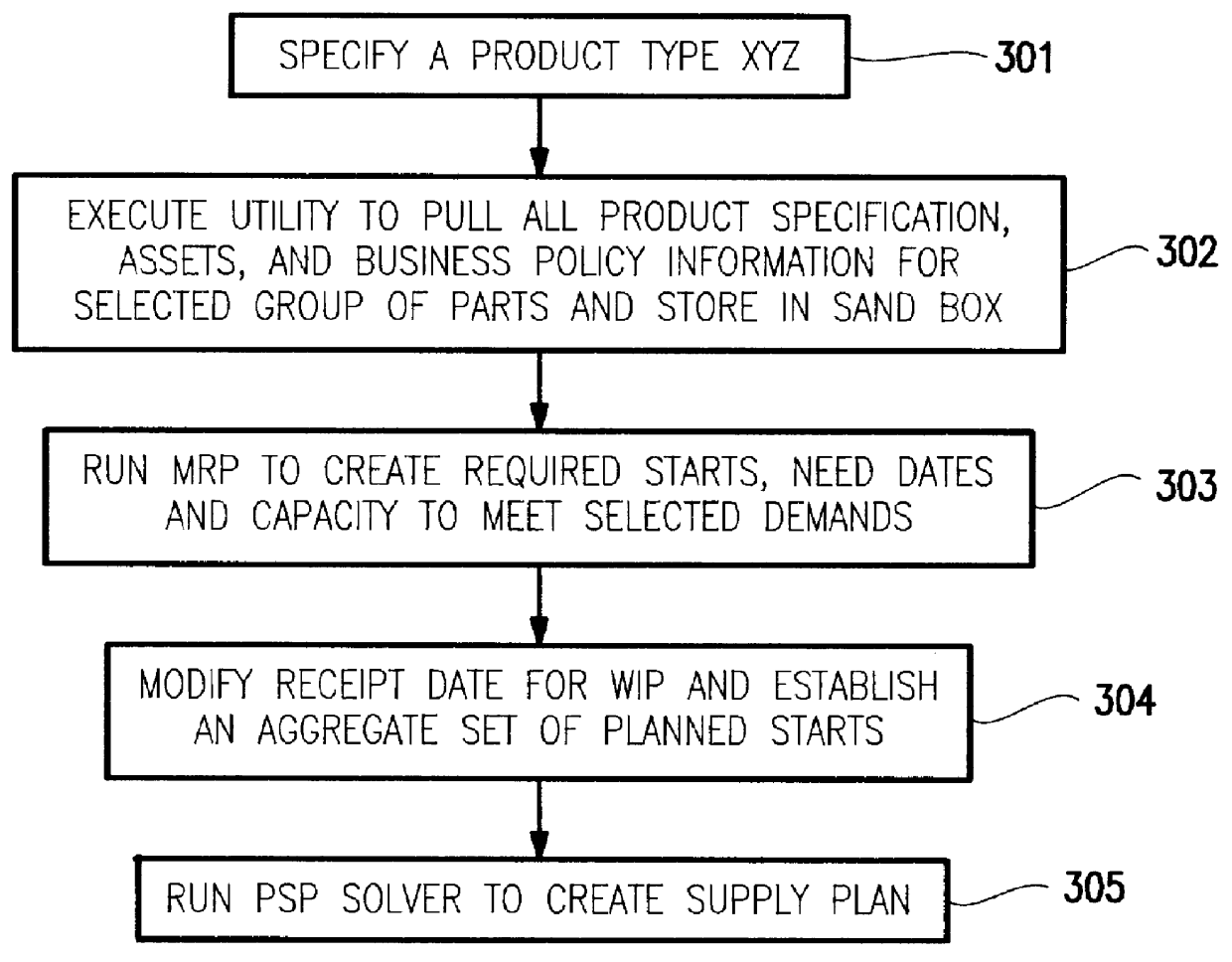
Projected supply planning matching assets with demand in microelectronics manufacturing
A computer-implemented decision-support tool serves as a solver to generate a projected supply planning (PSP) or estimated supply planning (ESP) match between existing assets and demands across multiple manufacturing facilities within the boundaries established by the manufacturing specifications and process flows and business policies to determine what supply can be provided over what time-frame by manufacturing and establishes a set of actions or guidelines for manufacturing to incorporate into their manufacturing execution system to ensure that the delivery commitments are met in a timely fashion. The PSP or ESP tool resides within a data provider tool that pulls the required production and distribution information. PSP matching is driven directly by user-supplied guidelines on how to flow or flush assets "forward" to some inventory or holding point. After the supply plan is created, the analyst compares this plan against an expected demand profile.
Owner:INDUCTIVE AUTOMATION LLC
Assist layers for EUV lithography
ActiveUS8968989B2Reduce negative impactMaterial nanotechnologyPhotosensitive materialsElectronic structureLithographic artist
The present invention provides novel methods of fabricating microelectronics structures, and the resulting structures formed thereby, using EUV lithographic processes. The method involves utilizing an assist layer immediately below the photoresist layer. The assist layer can either be directly applied to the substrate, or it can be applied to any intermediate layer(s) that may be applied to the substrate. The preferred assist layers are formed from spin-coatable, polymeric compositions. The inventive method allows reduced critical dimensions to be achieved with improved dose-to-size ratios, while improving adhesion and reducing or eliminating pattern collapse issues.
Owner:BREWER SCI
High mobility heterojunction complementary field effect transistors and methods thereof
InactiveUS7057216B2High hole mobilitySimilar current carrying capabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesHeterojunctionPresent day
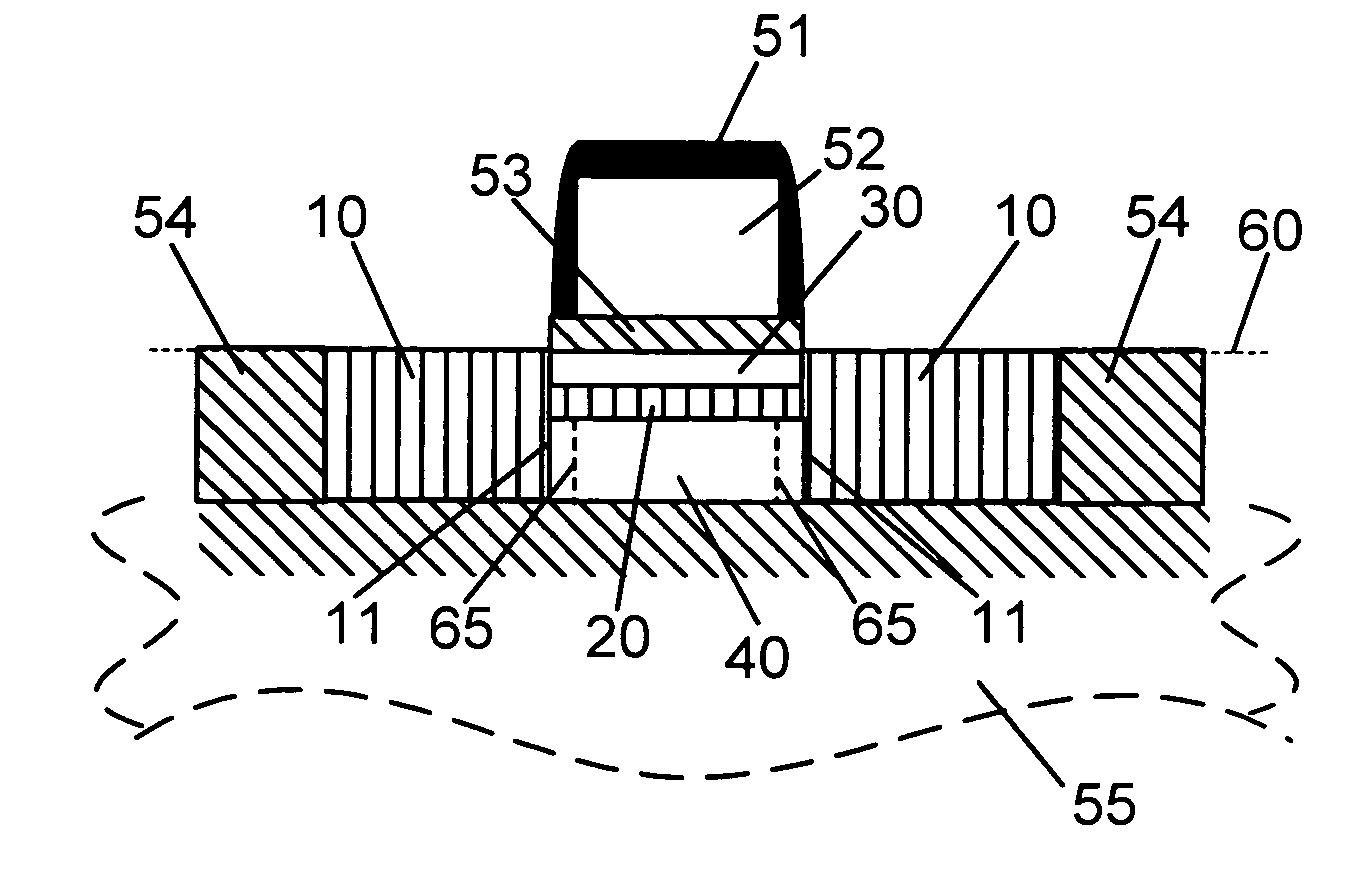
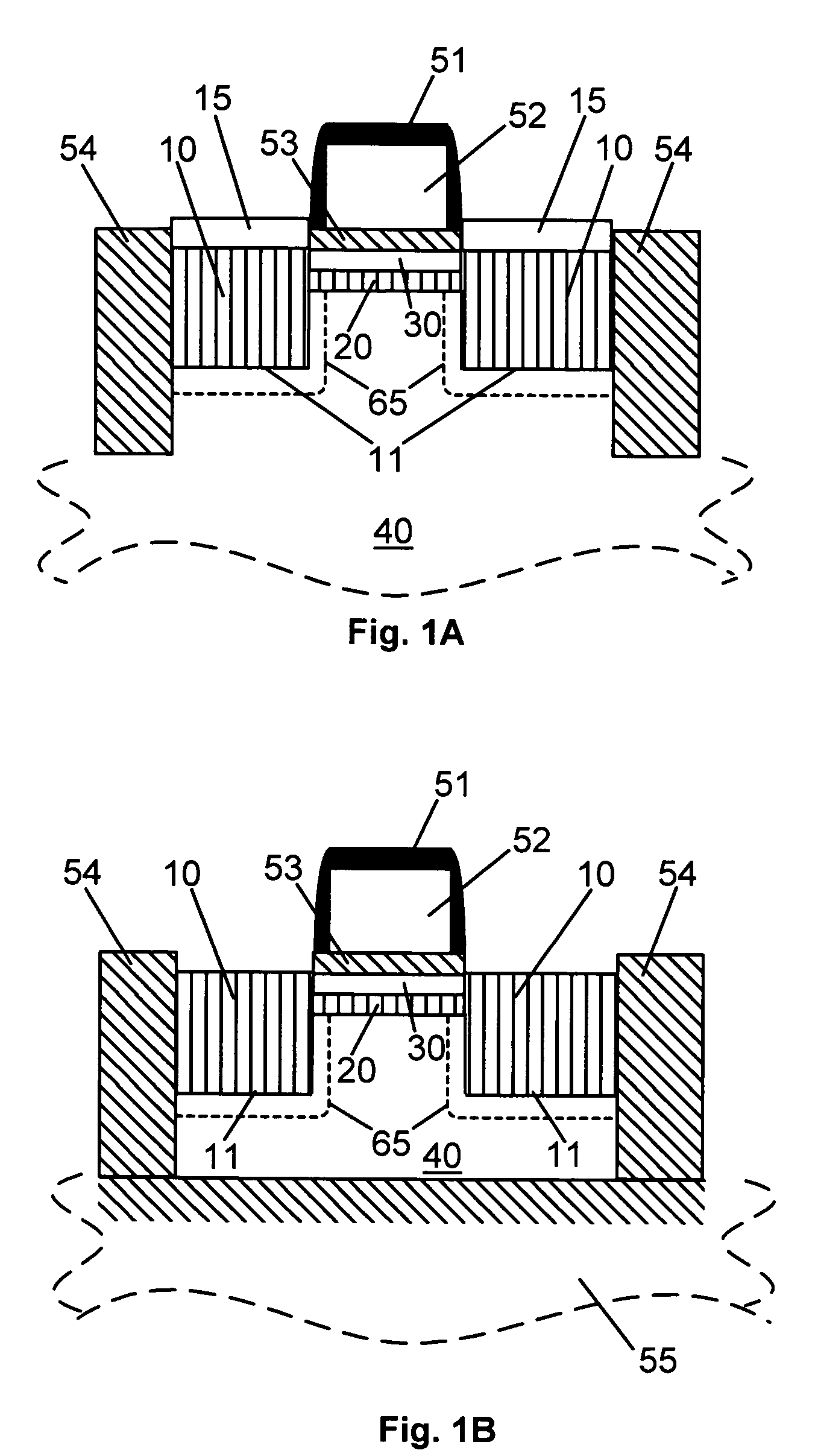
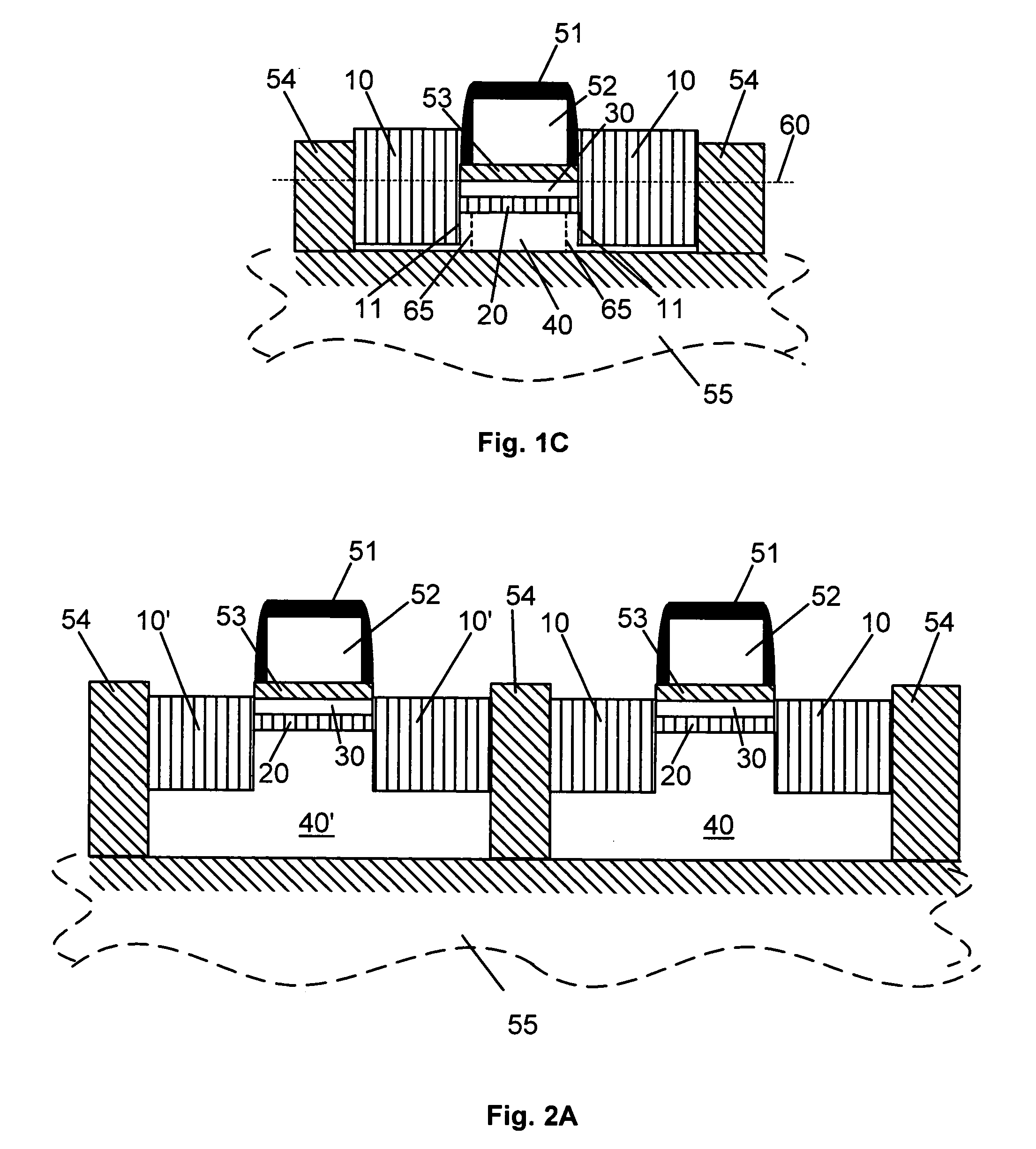
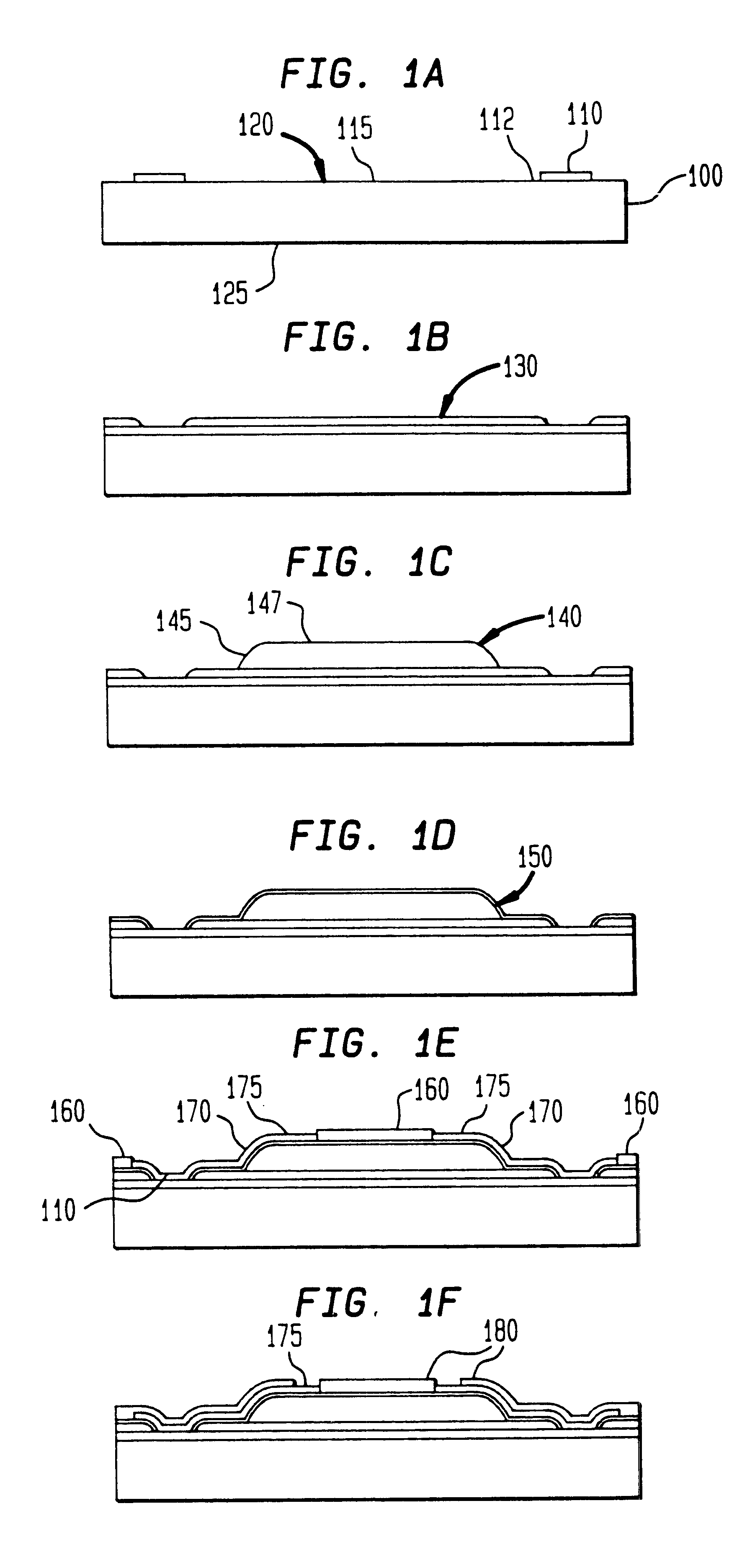
In all representative embodiments presented, the Ge concentration in the source and drain 10 and the SiGe epitaxial channel layer 20 is in the 15% to 50% range, preferably between about 20% to 40%. The SiGe thicknesses in the source / drain 10 are staying below the critical thickness for the given Ge concentration. The critical thickness is defined such that above it the SiGe will relax and defects and dislocations will form. The thickness of the SiGe epitaxial layer 20 typically is between about 5nm and 15nm. The thickness of the epitaxial Si layer 30 is typically between about 5nm and 15nm. FIG. 1A shows an embodiment where the body is bulk Si. These type of devices are the most common devices in present day microelectronics. FIGS. 1B and 1C show representative embodiment of the heterojunction source / drain FET device when the Si body 40 is disposed on top of an insulating material 55. This type of technology is commonly referred to as silicon on insulator (SOI) technology. The insulator material 55 usually, and preferably, is SiO2. FIG. 1B shows an SOI embodiment where the body 40 has enough volume to contain mobile charges. Such SOI devices are called partially depleted devices. FIG. 1C shows an SOI embodiment where the volume of the body 40 is insufficient to contain mobile charges. Such SOI devices are called fully depleted devices. For devices shown in FIG. 1B and 1C there is, at least a thin, layer of body underneath the source and drain 10. This body material serves as the seed material onto which the epitaxial SiGe source and drain 10 are grown. In an alternate embodiment, shown in FIG. 1D. for extremely thin fully depleted SOI devices, one could grow the source and drain 10 laterally, from a lateral seeding, in which case the source and drain 10 would penetrate all the way down to the insulating layer 55.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
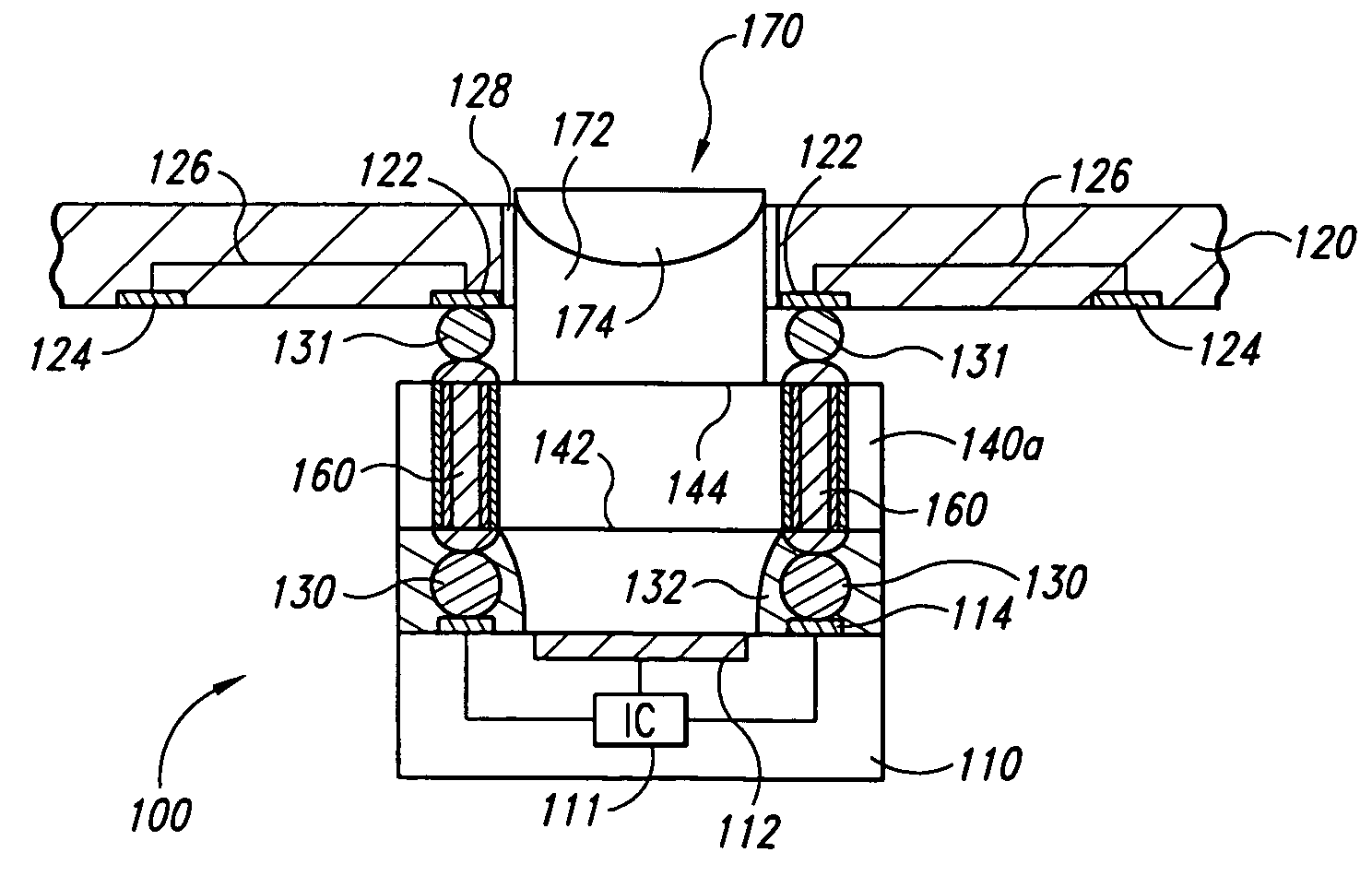
Integrated circuit packages including high density bump-less build up layers and a lesser density core or coreless substrate
In some embodiments, integrated circuit packages including high density bump-less build up layers and a lesser density core or coreless substrate are presented. In this regard, an apparatus is introduced having a first element including a microelectronic die having an active surface and at least one side, an encapsulation material adjacent said at least one microelectronic die side, wherein said encapsulation material includes at least one surface substantially planar to said microelectronic die active surface, a first dielectric material layer disposed on at least a portion of said microelectronic die active surface and said encapsulation material surface, a plurality of build-up layers disposed on said first dielectric material layer, and a plurality of conductive traces disposed on said first dielectric material layer and said build-up layers and in electrical contact with said microelectronic die active surface; and a second element coupled to the first element, the second element including a substrate having a plurality of dielectric material layers and conductive traces to conductively couple conductive contacts on a top surface with conductive contacts on a bottom surface, said conductive contacts on said top surface conductively coupled with said conductive traces of said first element. Other embodiments are also disclosed and claimed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Stabilized alkaline compositions for cleaning microelectronic substrates
InactiveUS6599370B2Eliminate contaminationLong lastingInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsLighting and heating apparatusWater solubleSURFACTANT BLEND
The invention provides aqueous alkaline compositions useful in the microelectronics industry for stripping or cleaning semiconductor wafer substrates by removing photoresist residues and other unwanted contaminants. The compositions typically contain (a) one or more metal ion-free bases at sufficient amounts to produce a pH of about 10-13 and one or more bath stabilizing agents having at least one pKa in the range of 10-13 to maintain this pH during use; (b) optionally, about 0.01% to about 5% by weight (expressed as % SiO2) of a water-soluble metal ion-free silicate; (c) optionally, about 0.01% to about 10% by weight of one or more chelating agents; (d) optionally, about 0.01% to about 80% by weight of one or more water-soluble organic co-solvents; and (e) optionally, about 0.01% to about 1% by weight of a water-soluble surfactant.
Owner:AVANTOR PERFORMANCE MATERIALS LLC
Edge connect wafer level stacking
ActiveUS20080083976A1Low costSmall sizeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringElectronic component
A method of making a stacked microelectronic package by forming a microelectronic assembly by stacking a first subassembly including a plurality of microelectronic elements onto a second subassembly including a plurality of microelectronic elements, at least some of the plurality of microelectronic elements of said first subassembly and said second subassembly having traces that extend to respective edges of the microelectronic elements, then forming notches in the microelectronic assembly so as to expose the traces of at least some of the plurality of microelectronic elements, then forming leads at the side walls of the notches, the leads being in electrical communication with at least some of the traces and dicing the assembly into packages. Additional embodiments include methods for creating stacked packages using substrates and having additional traces that extend to both the top and bottom of the package.
Owner:TESSERA INC
Stacked microelectronic assemblies with central contacts
ActiveUS20050116358A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectronic componentMicroelectronics
A stacked microelectronic assembly includes a dielectric element and a first and second microelectronic element stacked one on top of the other with the first microelectronic element underlying at least a portion of the second microelectronic element. The first microelectronic element and the second microelectronic element have front surfaces on which exposed on a central region of the front surface are contacts. A spacer layer may be provided under a portion of the second microelectronic element opposite a portion of the second microelectronic element overlying the first microelectronic element. Additionally, a third microelectronic element may be substituted in for the spacer layer so that the first microelectronic element and the third microelectronic element are underlying opposing sides of the second microelectronic element.
Owner:TESSERA INC
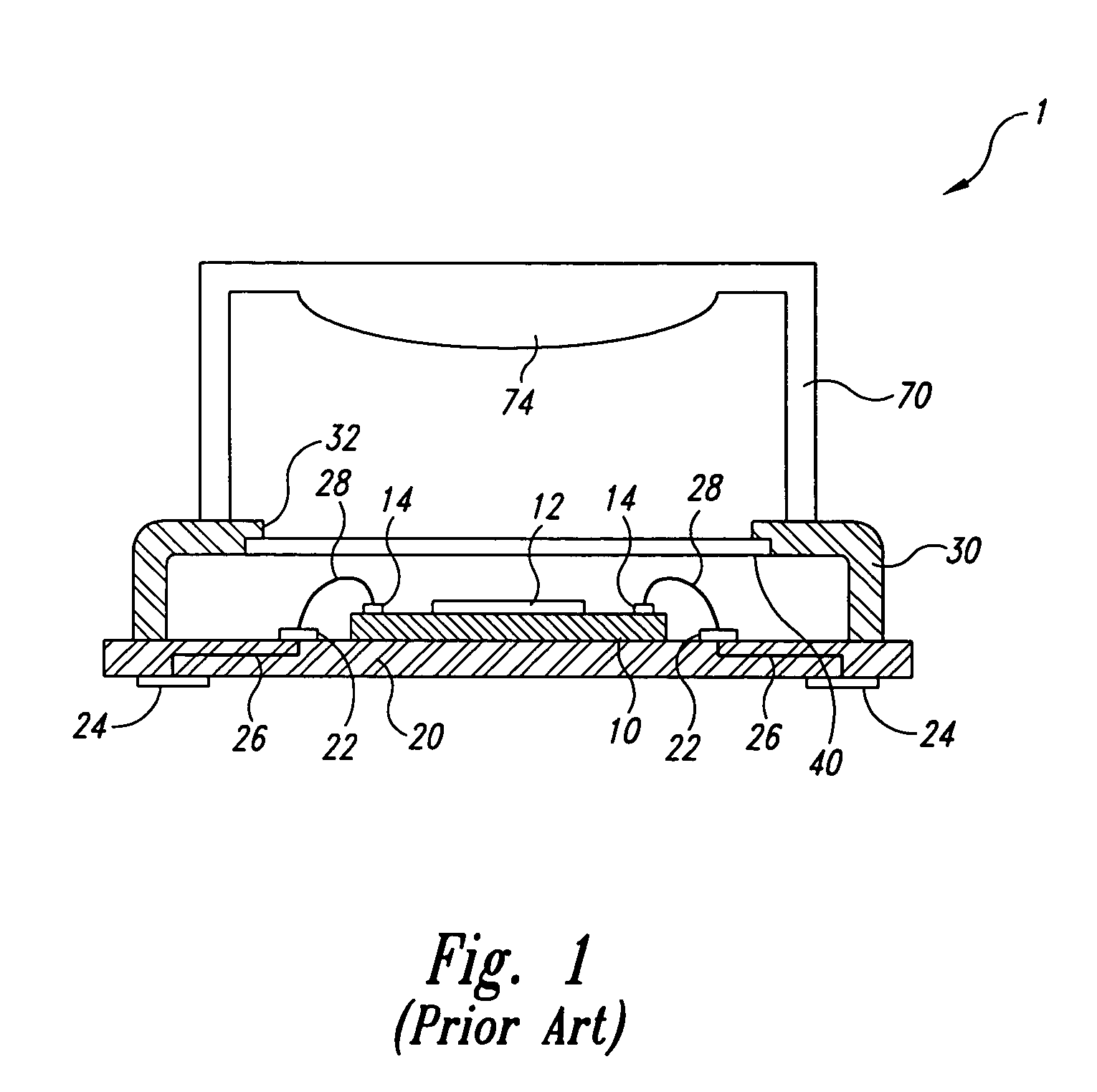
Microelectronic package having a compliant layer with bumped protrusions
InactiveUS6847101B2Minimizing overall package sizeImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMicroelectronics
Owner:TESSERA INC
Microelectronic mechanical system and methods
InactiveUS20040053434A1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNoble gasSilicon oxide
The current invention provides for encapsulated release structures, intermediates thereof and methods for their fabrication. The multi-layer structure has a capping layer, that preferably comprises silicon oxide and / or silicon nitride, and which is formed over an etch resistant substrate. A patterned device layer, preferably comprising silicon nitride, is embedded in a sacrificial material, preferably comprising polysilicon, and is disposed between the etch resistant substrate and the capping layer. Access trenches or holes are formed in to capping layer and the sacrificial material are selectively etched through the access trenches, such that portions of the device layer are release from sacrificial material. The etchant preferably comprises a noble gas fluoride NGF2x (wherein Ng=Xe, Kr or Ar: and where x=1, 2 or 3). After etching that sacrificial material, the access trenches are sealed to encapsulate released portions the device layer between the etch resistant substrate and the capping layer. The current invention is particularly useful for fabricating MEMS devices, multiple cavity devices and devices with multiple release features.
Owner:SILICON LIGHT MACHINES CORP
Alkaline, post plasma etch/ash residue removers and photoresist stripping compositions containing metal-halide corrosion inhibitors
InactiveUS20070060490A1Avoiding consequenceAvoid expensesDetergent mixture composition preparationElectrostatic cleaningAlkaline earth metalMetal halides
The invention provides alkaline compositions useful in the microelectronics industry for stripping or cleaning semiconductor wafer substrates by removing photoresist residues and other unwanted contaminants. The compositions contain (a) one or more bases and (b) one or more metal corrosion inhibiting metal halides of the formula: WzMXy where M is a metal selected from the group Si, Ge, Sn, Pt, P, B, Au, Ir, Os, Cr, Ti, Zr, Rh, Ru, and Sb; X is a halide selected from F, Cl, Br and I; W is selected from H, to an alkali or alkaline earth metal, and a metal ion-free hydroxide base moiety; y is a numeral of from 4 to 6 depending on the metal halide; and z is a numeral of 1, 2 or 3.
Owner:AVANTOR PERFORMANCE MATERIALS INC
Polyphenylene oligomers and polymers
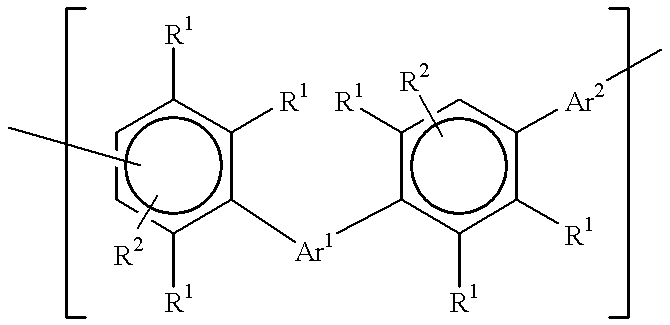
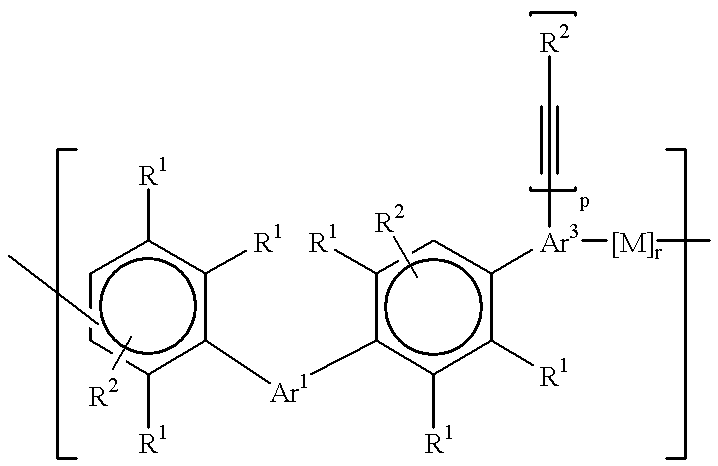
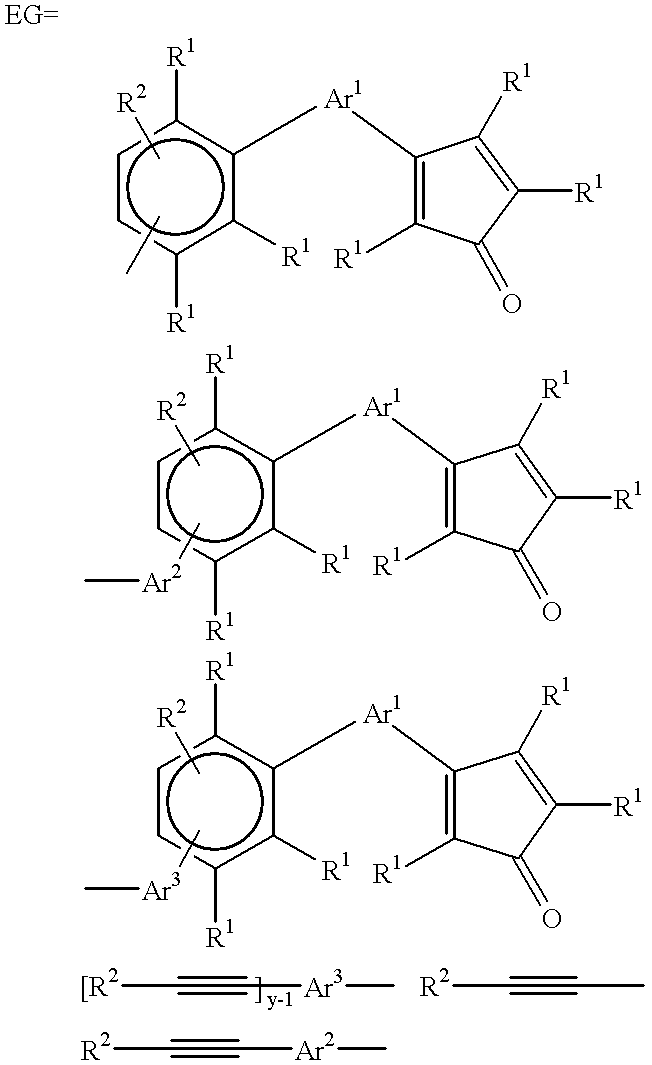
An oligomer, uncured polymer or cured polymer comprising the reaction product of one or more polyfunctional compounds containing two or more cyclopentadienone groups and at least one polyfunctional compound containing two or more aromatic acetylene groups wherein at least some of the polyfunctional compounds contain three or more reactive groups. Such oligomers and uncured polymers may be cured to form cured polymers which are useful as dielectrics in the microelectronics industry, especially for dielectrics in integrated circuits.
Owner:THE DOW CHEM CO
Microbolometer infrared sensors
InactiveUS6359276B1High mechanical strengthReduce residual stressSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansThermal isolationMicrobolometer
A microbolometer infrared sensor utilizes a porous silicon bridge as its thermal isolating and mechanical supporting structure. Porous silicon formed from single crystal silicon on lightly doped p-type silicon has a thermal conductivity lower than silicon dioxide and silicon nitride, and, therefore, when used as a mechanical supporting structure, can offer better thermal isolation performance. The porous silicon layer can be fabricated much thicker than silicon dioxide and silicon nitride membranes since there is almost no residual stress therein. A thicker porous silicon bridge has higher mechanical support strength. The porous silicon process is a low temperature process. It facilitates a fabrication strategy of microelectronics first and micromechanics last.
Owner:TU XIANG ZHENG
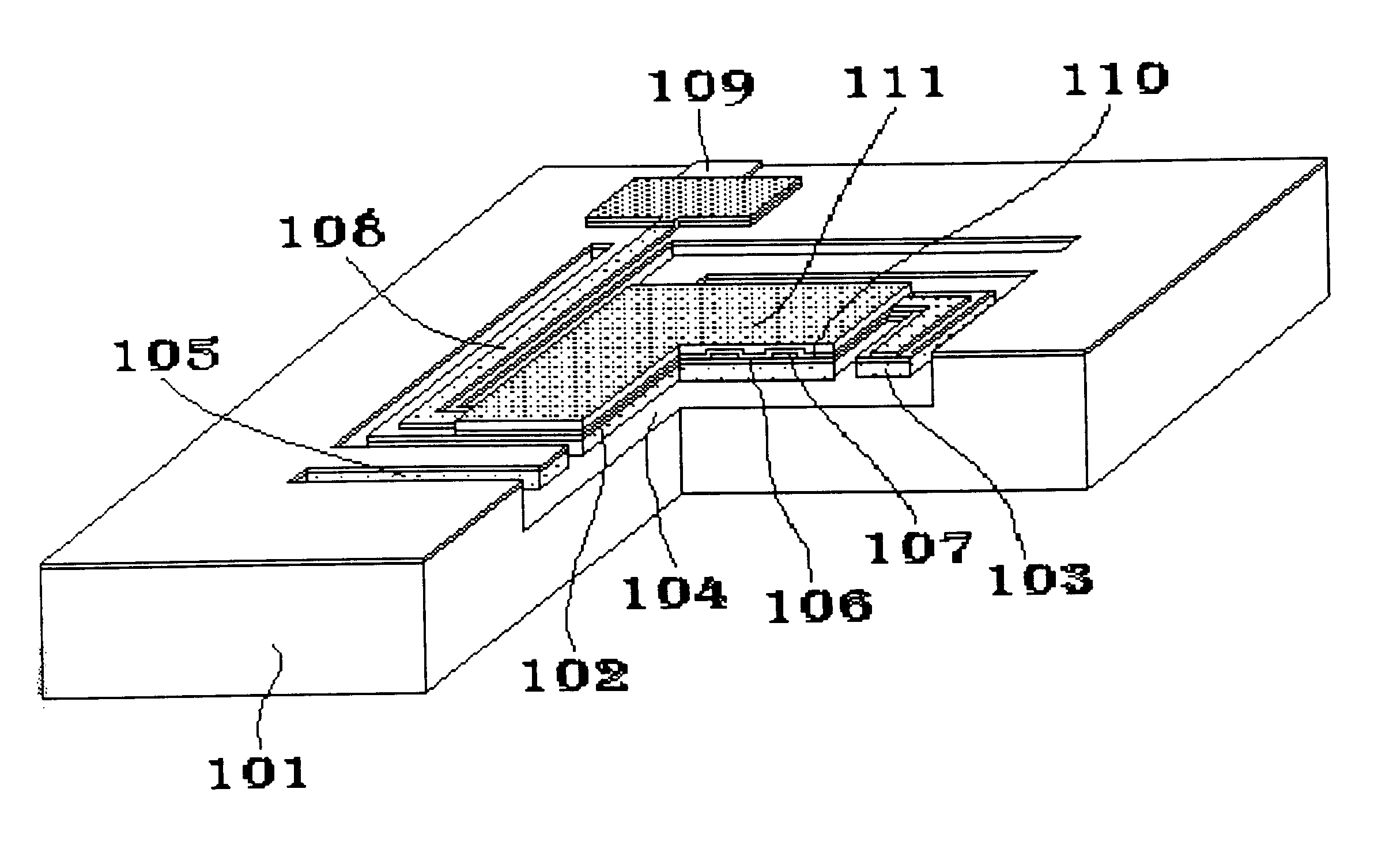
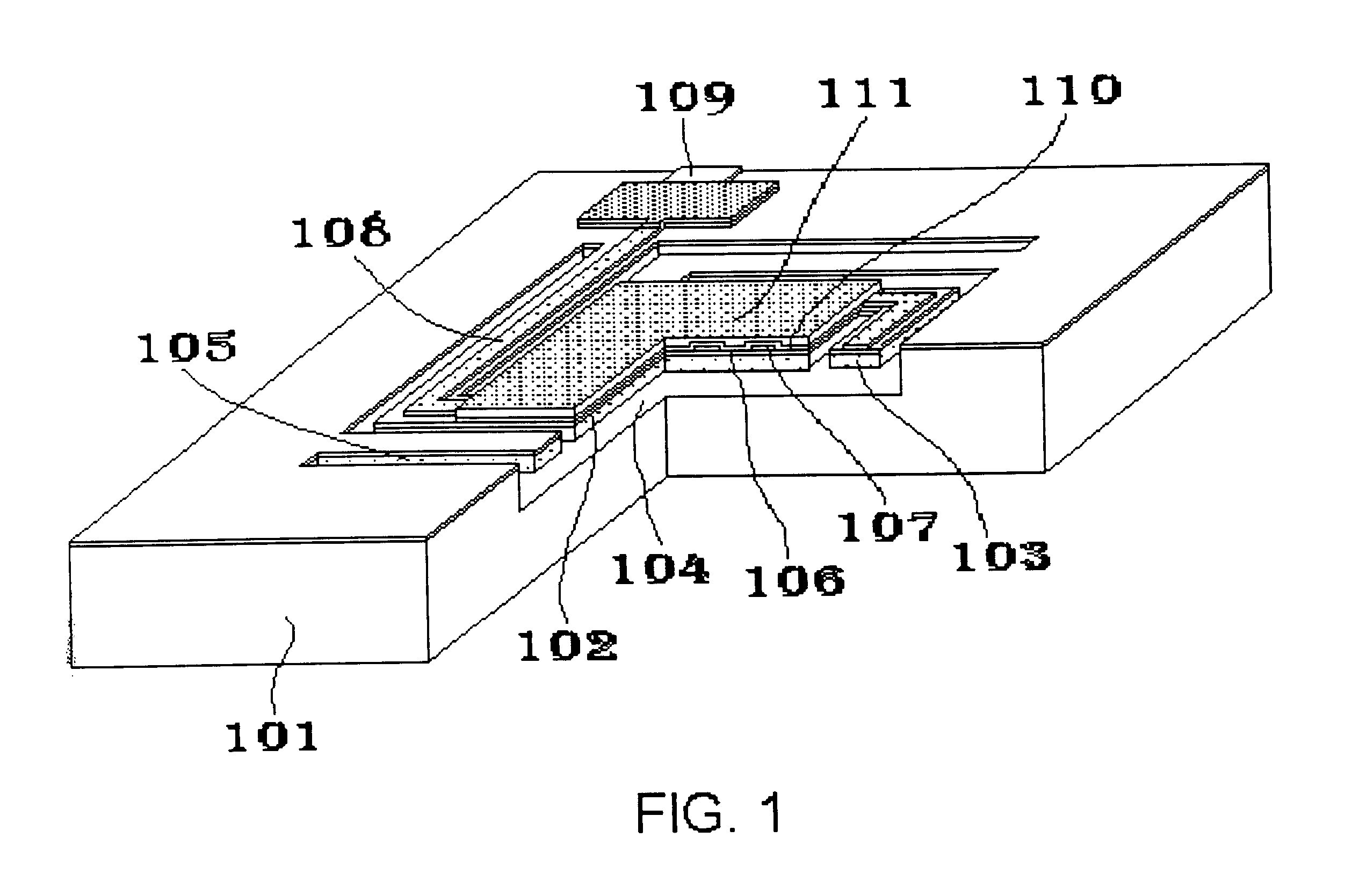
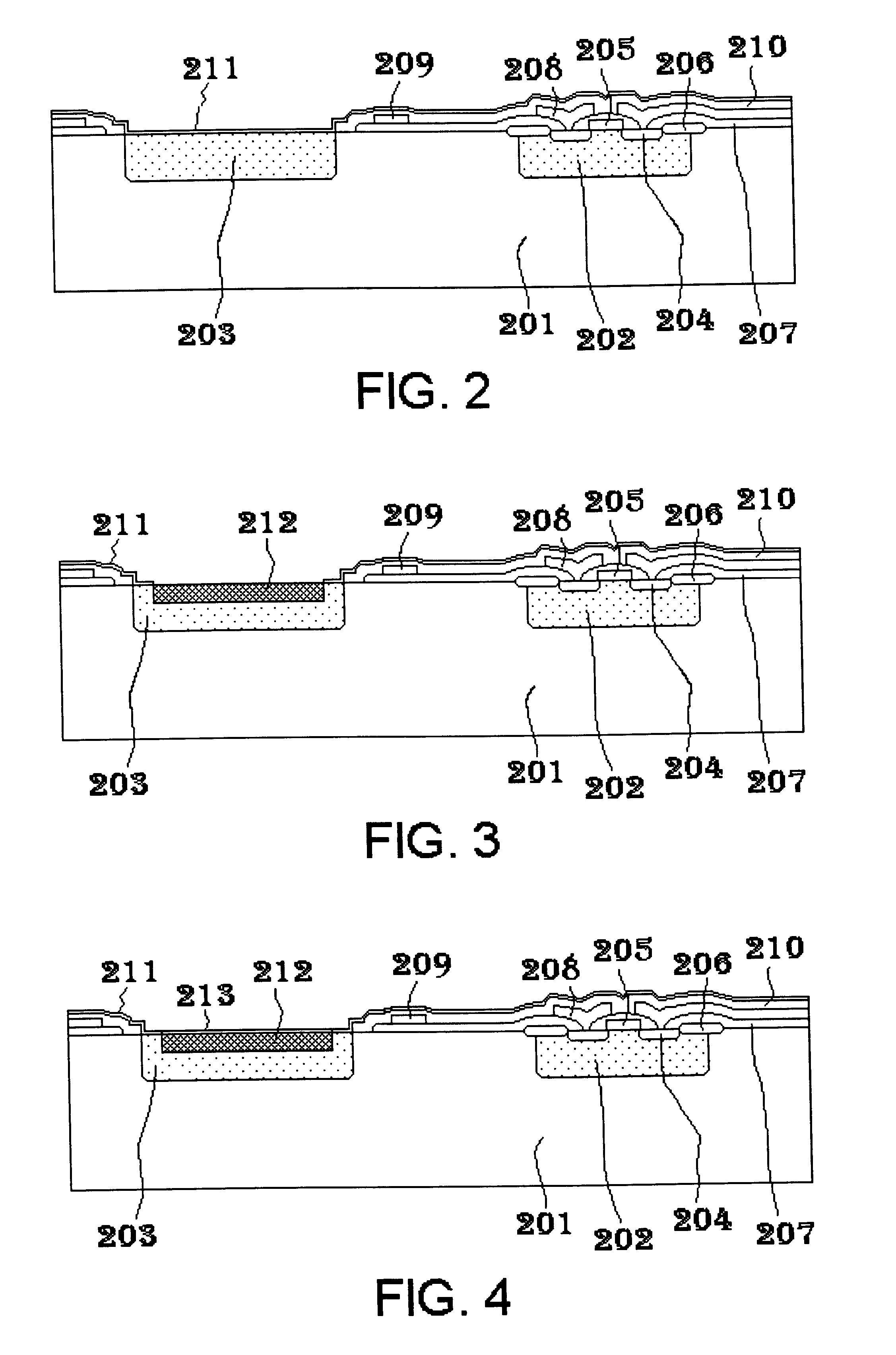
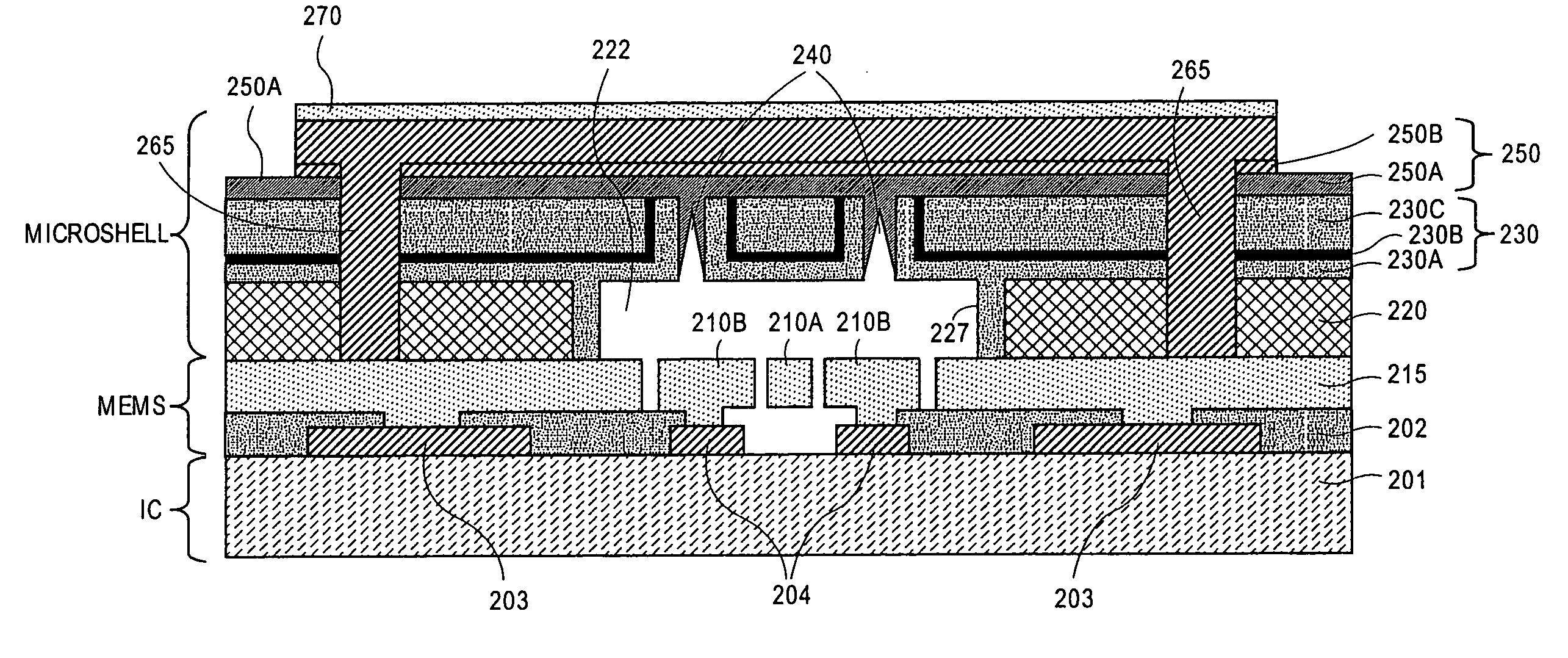
Planar microshells for vacuum encapsulated devices and damascene method of manufacture
ActiveUS7923790B1Acceleration measurement using interia forcesSolid-state devicesMaterial PerforationMetal
Low temperature, multi-layered, planar microshells for encapsulation of devices such as MEMS and microelectronics. The microshells include a planar perforated pre-sealing layer, below which a non-planar sacrificial layer is accessed, and a sealing layer to close the perforation in the pre-sealing layer after the sacrificial material is removed. In an embodiment, the pre-sealing layer has perforations formed with a damascene process to be self-aligned to the chamber below the microshell. The sealing layer may include a nonhermetic layer to physically occlude the perforation and a hermetic layer over the nonhermetic occluding layer to seal the perforation. In a particular embodiment, the hermetic layer is a metal which is electrically coupled to a conductive layer adjacent to the microshell to electrically ground the microshell.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Metal amides of cyclic amines
ActiveUS20160152649A1Improve thermal stabilityImprove conductivityIron group organic compounds without C-metal linkagesNickel organic compoundsGermanideMetal silicide
Compounds, and oligomers of the compounds, are synthesized with cyclic amine ligands attached to a metal atom. These compounds are useful for the synthesis of materials containing metals. Examples include pure metals, metal alloys, metal oxides, metal nitrides, metal phosphides, metal sulfides, metal selenides, metal tellurides, metal borides, metal carbides, metal silicides and metal germanides. Techniques for materials synthesis include vapor deposition (chemical vapor deposition and atomic layer deposition), liquid solution methods (sol-gel and precipitation) and solid-state pyrolysis. Suitable applications include electrical interconnects in microelectronics and magnetoresistant layers in magnetic information storage devices. The films have very uniform thickness and high step coverage in narrow holes.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
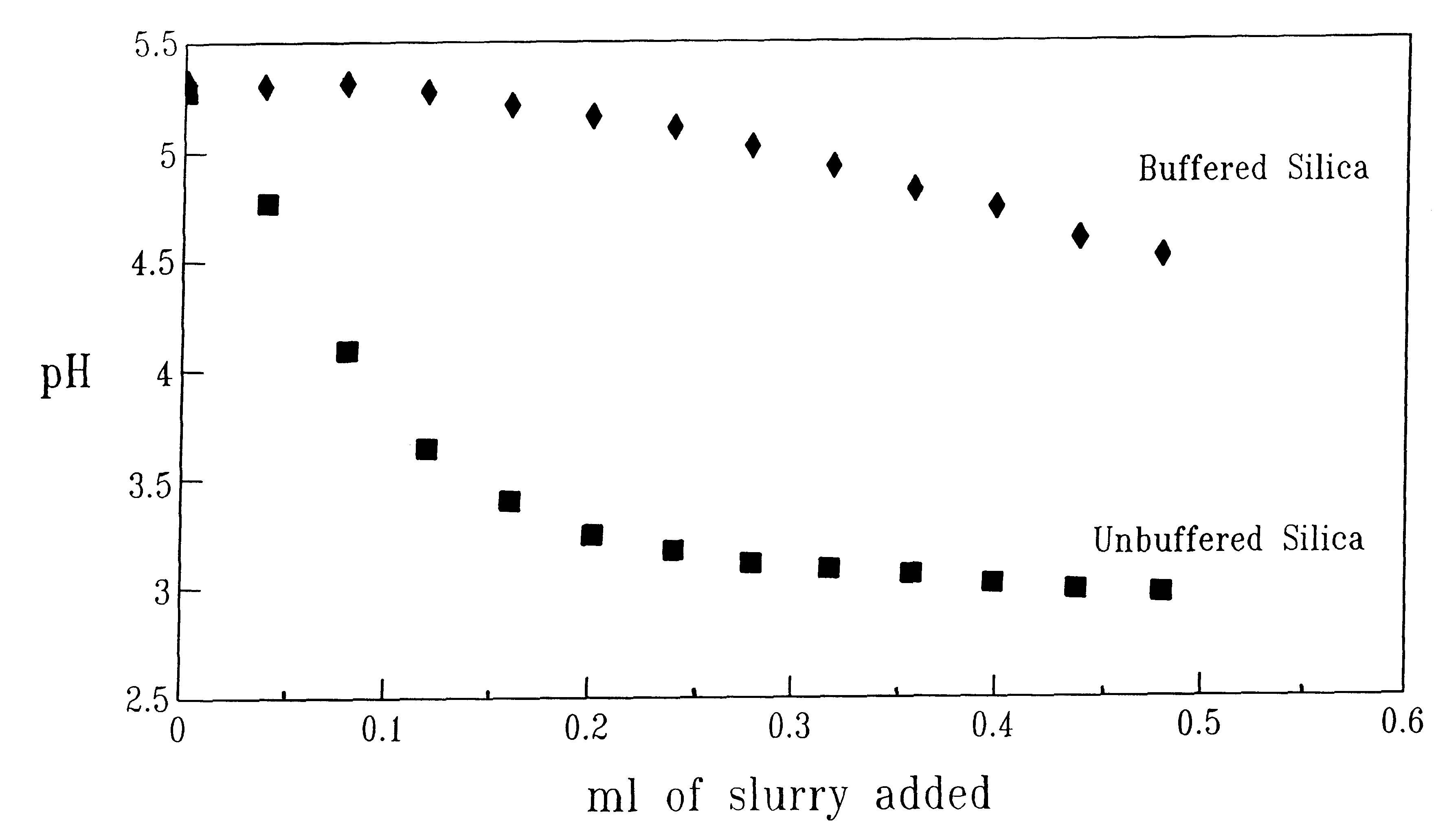
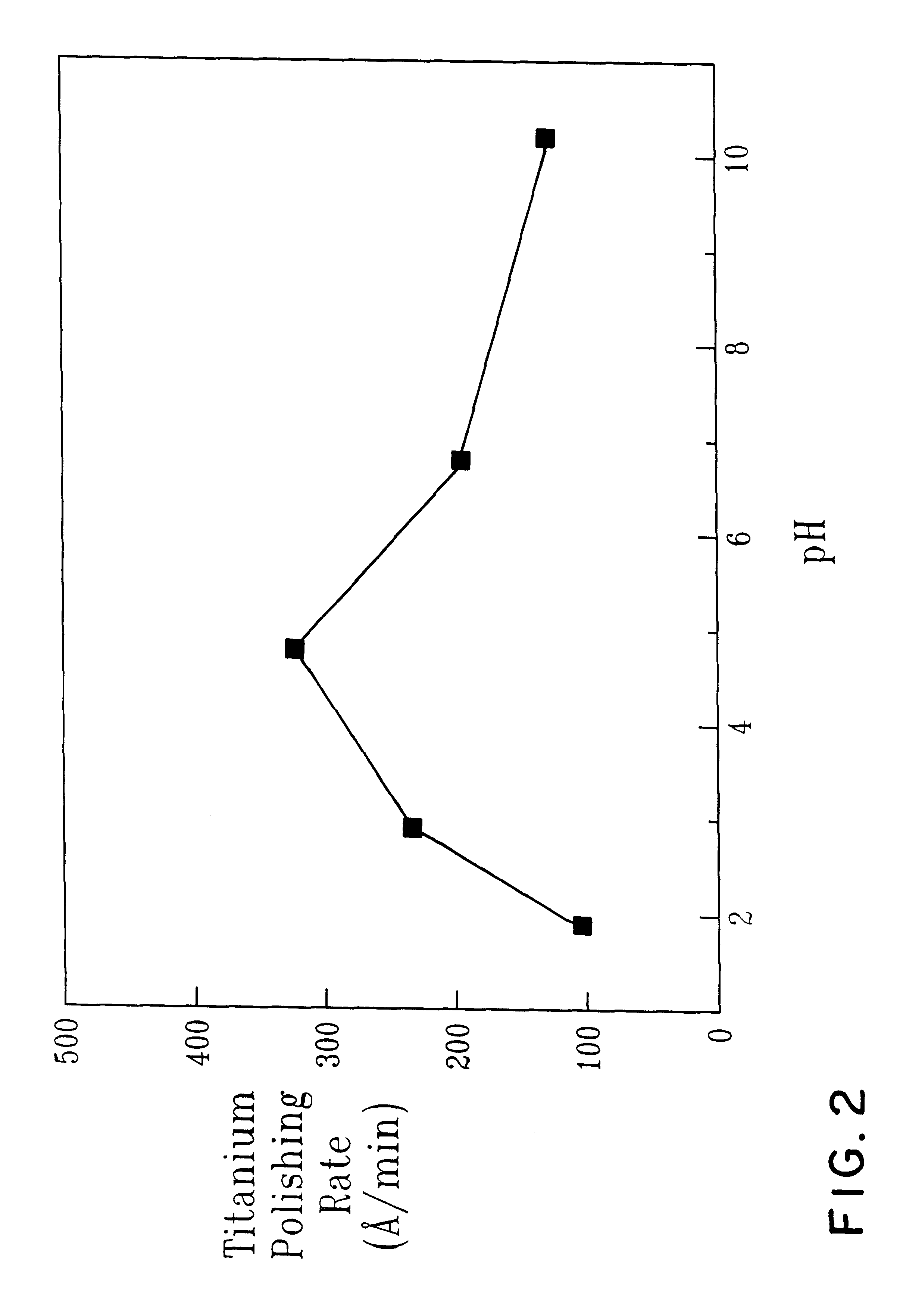
pH-buffered slurry and use thereof for polishing
InactiveUS6190237B1Other chemical processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPh bufferingSlurry
A slurry containing abrasive particles and a pH buffering component comprising at least one acid or salt thereof and at least one base is especially useful for polishing surfaces, including those used in microelectronics.
Owner:IBM CORP
Controlled lens antenna apparatus and system
Present configuration concerns microelectronics; for instance, compact antenna devices applied in mobile communications and other equipment operating in millimeter range. The controlled lens antenna apparatus may include antenna elements in an integrated circuit configured to transmit beams. The apparatus may also include a dielectric lens antenna configured to generate a plane wave based in the beams transmitted. The apparatus may include a plate configured to deflect the generated plane wave at a random angle.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Process for controlling etching parameters
InactiveUS6027842AEasy and inexpensive to utilizeElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistEngineering
Focus and exposure parameters may be controlled in a lithographic process for manufacturing microelectronics by creating a complementary tone pattern of shapes and spaces in a resist film on a substrate. Corresponding dimensions of the resist shape and space are measured and the adequacy of focus or exposure dose are determined as a function of the measured dimensions. Etching parameters may also be controlled by creating a complementary tone pattern of etched shapes and spaces on a substrate. Corresponding dimensions of the etched shape and space are measured and the adequacy of etching parameters are determined as a function of the measured dimensions.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Microshells for multi-level vacuum cavities
Microshells for encapsulation of devices such as MEMS and microelectronics. In an embodiment, the microshells include a planar perforated pre-sealing layer, below which a non-planar sacrificial layer is accessed, and a sealing layer to close the perforation in the pre-sealing layer after the sacrificial material is removed. The sealing layer may include a nonhermetic layer to physically occlude the perforation and a hermetic layer over the nonhermetic occluding layer to seal the perforation as a function of the dimension of the perforation to form cavities having different vacuum levels on the same substrate.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Stacked microelectronic assemblies with central contacts
ActiveUS7061121B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringElectronic component
A stacked microelectronic assembly includes a dielectric element and a first and second microelectronic element stacked one on top of the other with the first microelectronic element underlying at least a portion of the second microelectronic element. The first microelectronic element and the second microelectronic element have front surfaces on which exposed on a central region of the front surface are contacts. A spacer layer may be provided under a portion of the second microelectronic element opposite a portion of the second microelectronic element overlying the first microelectronic element. Additionally, a third microelectronic element may be substituted in for the spacer layer so that the first microelectronic element and the third microelectronic element are underlying opposing sides of the second microelectronic element.
Owner:TESSERA INC
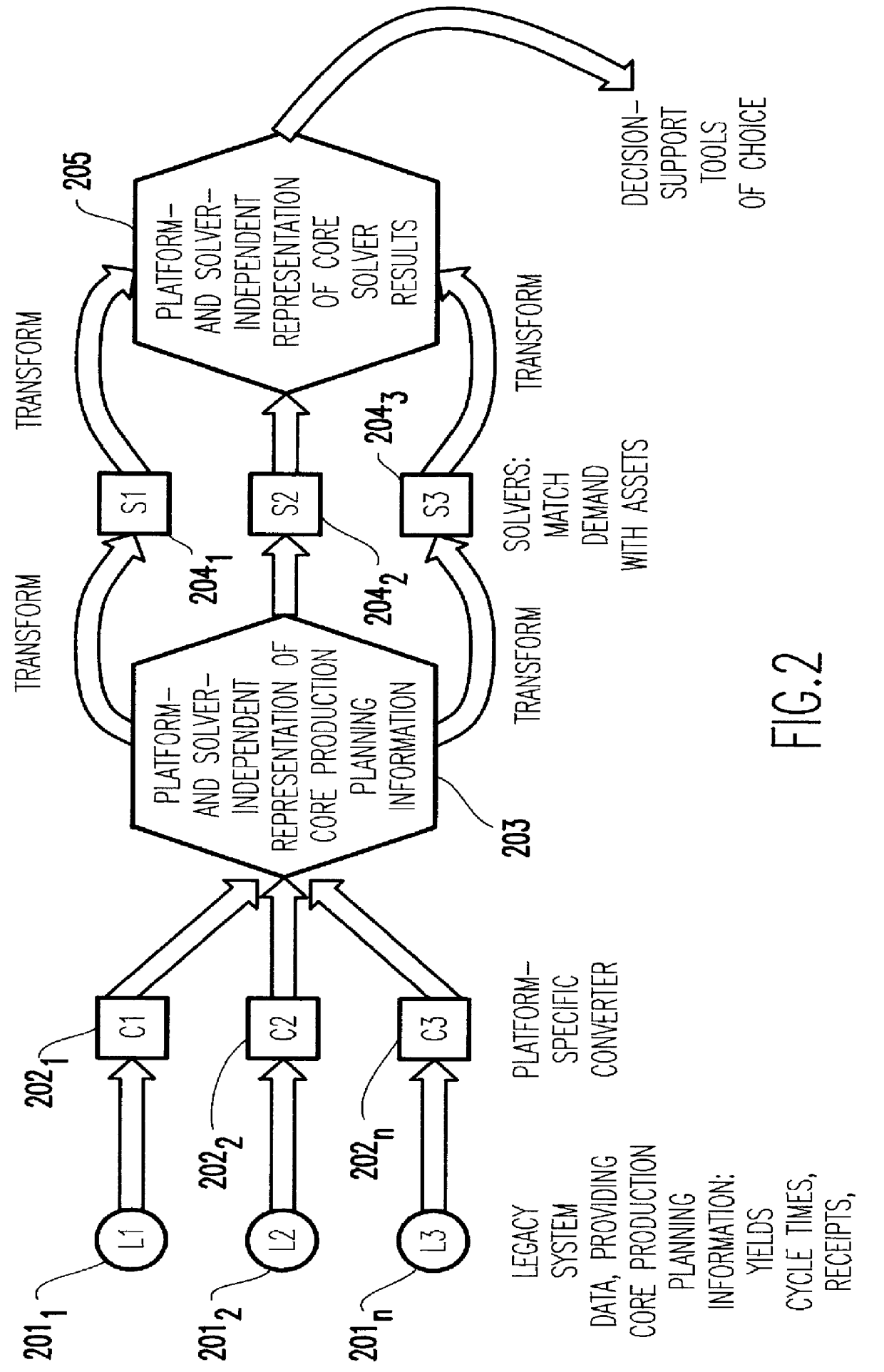
Method to provide common support for multiple types of solvers for matching assets with demand in microelectronics manufacturing
InactiveUS6041267ATotal factory controlSpecial data processing applicationsWorking environmentMaterial requirements planning
A computer implemented decision support tool serves as a vehicle to enable a user to execute within a common work environment, from common production information files, and at the discretion of the user one of three types of matching between existing assets and demands across multiple manufacturing facilities within boundaries established by manufacturing specifications and process flows and business policies. The tool provides an environment which permits the user to easily gain the advantages of a synergistic relationship between the three types of matching. The tool directly supports three types of matching: (1) material requirements planning (MRP) type of matching, (2) best can do (BCD) type of matching, and (3) projected supply planning (PSP) type of matching.
Owner:IBM CORP
Apparatus, precursors and deposition methods for silicon-containing materials
A method for making a Si-containing material comprises transporting a pyrolyzed Si-precursor to a substrate and polymerizing the pyrolyzed Si-precursor on the substrate to form a Si-containing film. Polymerization of the pyrolyzed Si-precursor may be carried out in the presence of a porogen to thereby form a porogen-containing Si-containing film. The porogen may be removed from the porogen-containing Si-containing film to thereby form a porous Si-containing film. Preferred porous Si-containing films have low dielectric constants and thus are suitable for various low-k applications such as in microelectronics and microelectromechanical systems.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Versatile maskless lithography system with multiple resolutions
InactiveUS20060012766A1Quick selectionEasy to combinePhotomechanical apparatusPhotographic printingSpatial light modulatorImage resolution
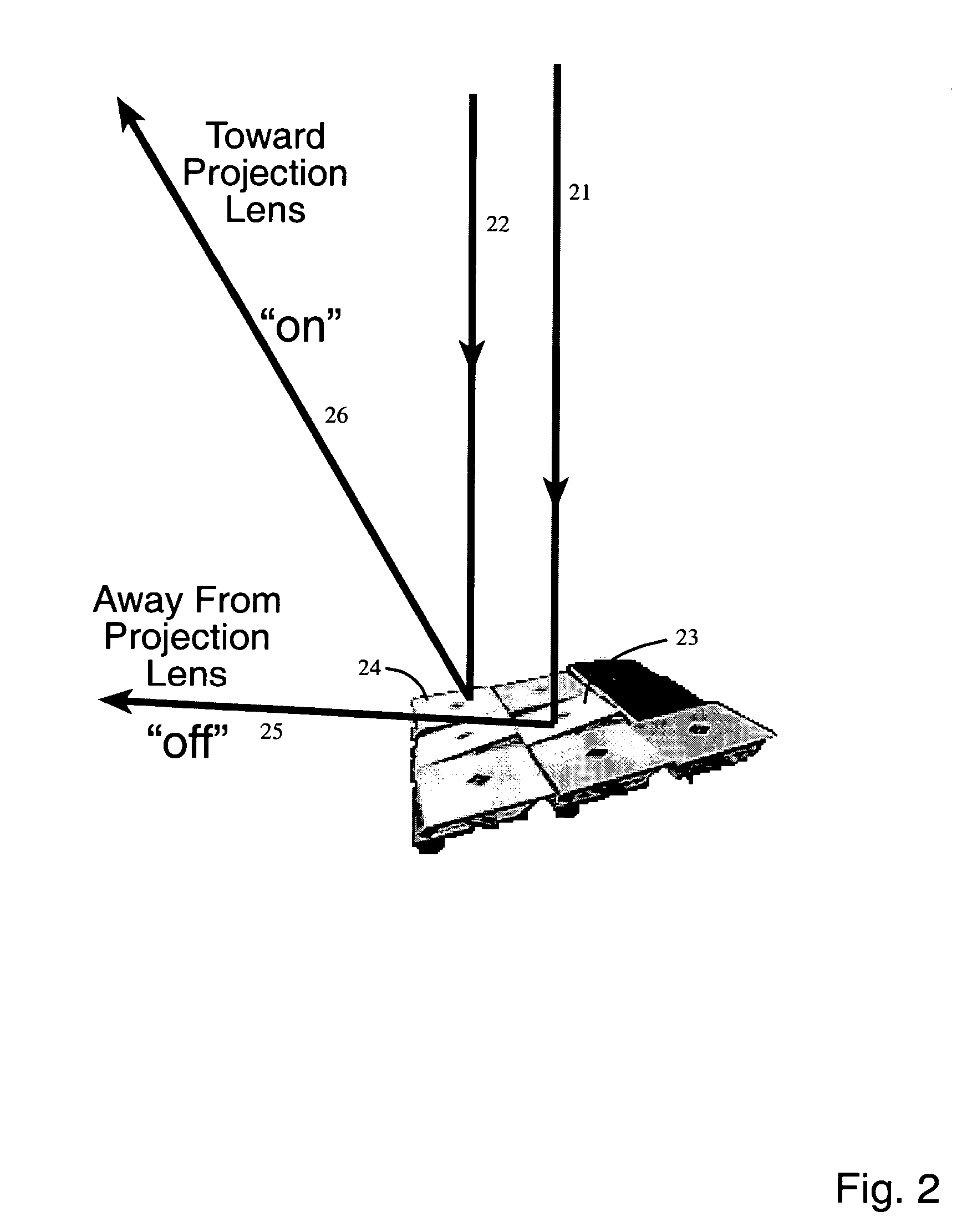
A versatile maskless patterning system with capability for selecting rapidly among a plurality of projection lenses mounted on a turret. This provides the ability to rapidly select multiple choices for resolution and enables optimization of the combination of the imaging resolution and exposure throughput, making possible cost-effective fabrication of microelectronics packaging products. A preferred embodiment uses a digital micromirror device array spatial light modulator as a virtual mask. Another preferred embodiment use multiple closely spaced digital micromirror device array spatial light modulators to enhance throughput.
Owner:ANVIK CORP
Packaged microelectronic imaging devices and methods of packaging microelectronic imaging devices
ActiveUS20060043509A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIntegrated circuitElectrical contacts
Microelectronic imaging devices and methods of packaging microelectronic imaging devices are disclosed herein. In one embodiment, a microelectronic imaging device includes a microelectronic die having an integrated circuit, an image sensor electrically coupled to the integrated circuit, and a plurality of bond-pads electrically coupled to the integrated circuit. The imaging device further includes a cover over the image sensor and a plurality of interconnects in and / or on the cover that are electrically coupled to corresponding bond-pads of the die. The interconnects provide external electrical contacts for the bond-pads of the die. The interconnects can extend through the cover or along a surface of the cover.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
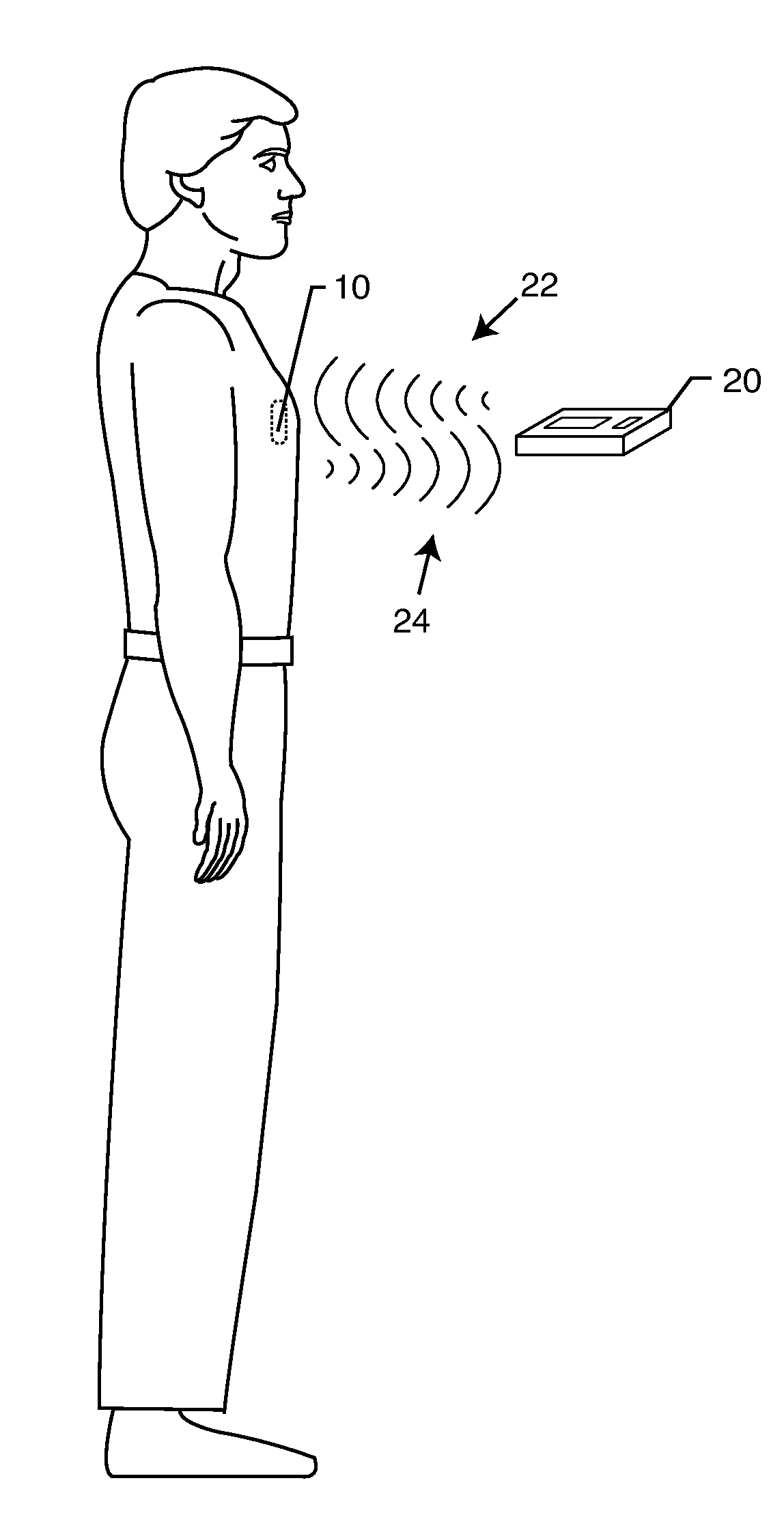
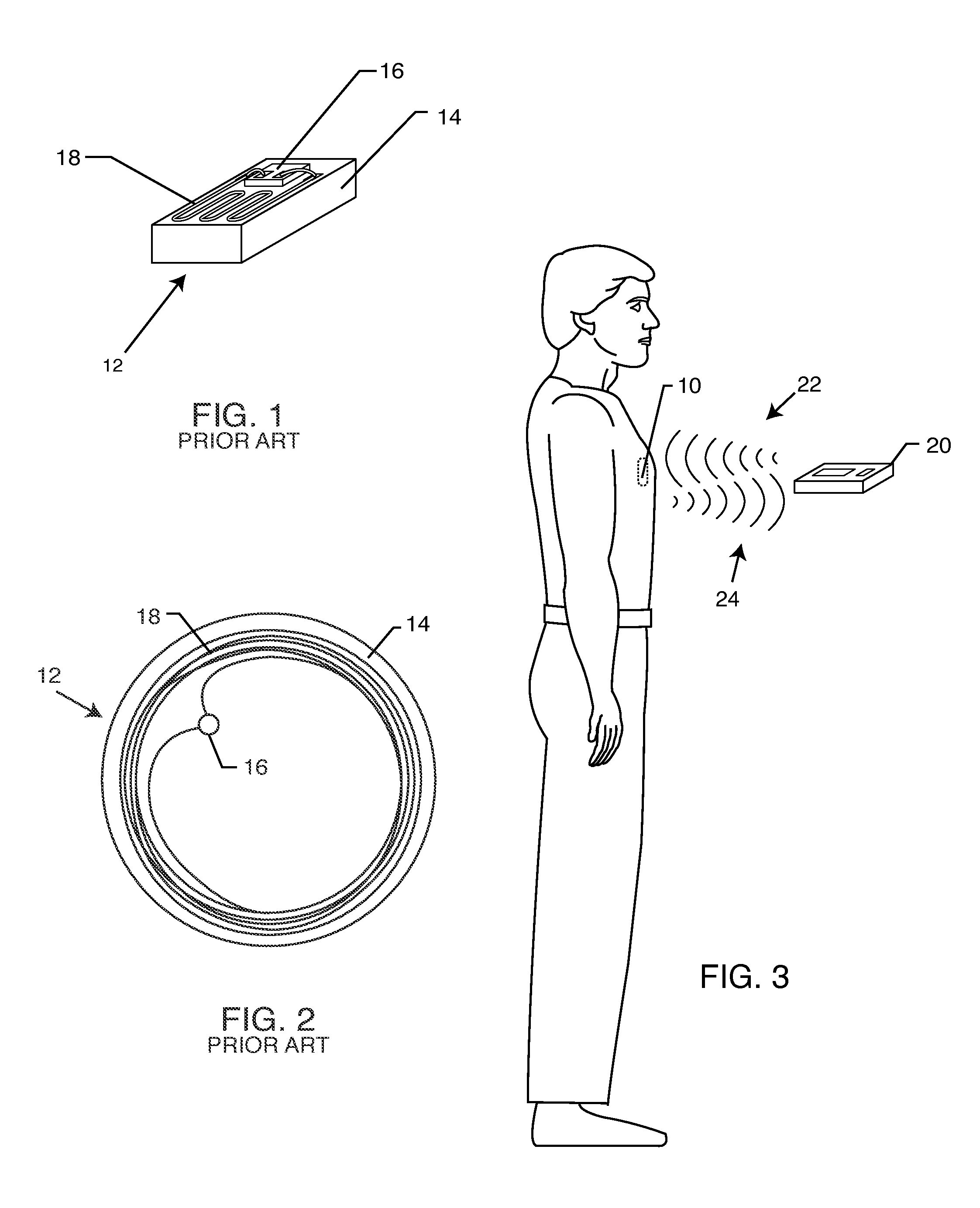
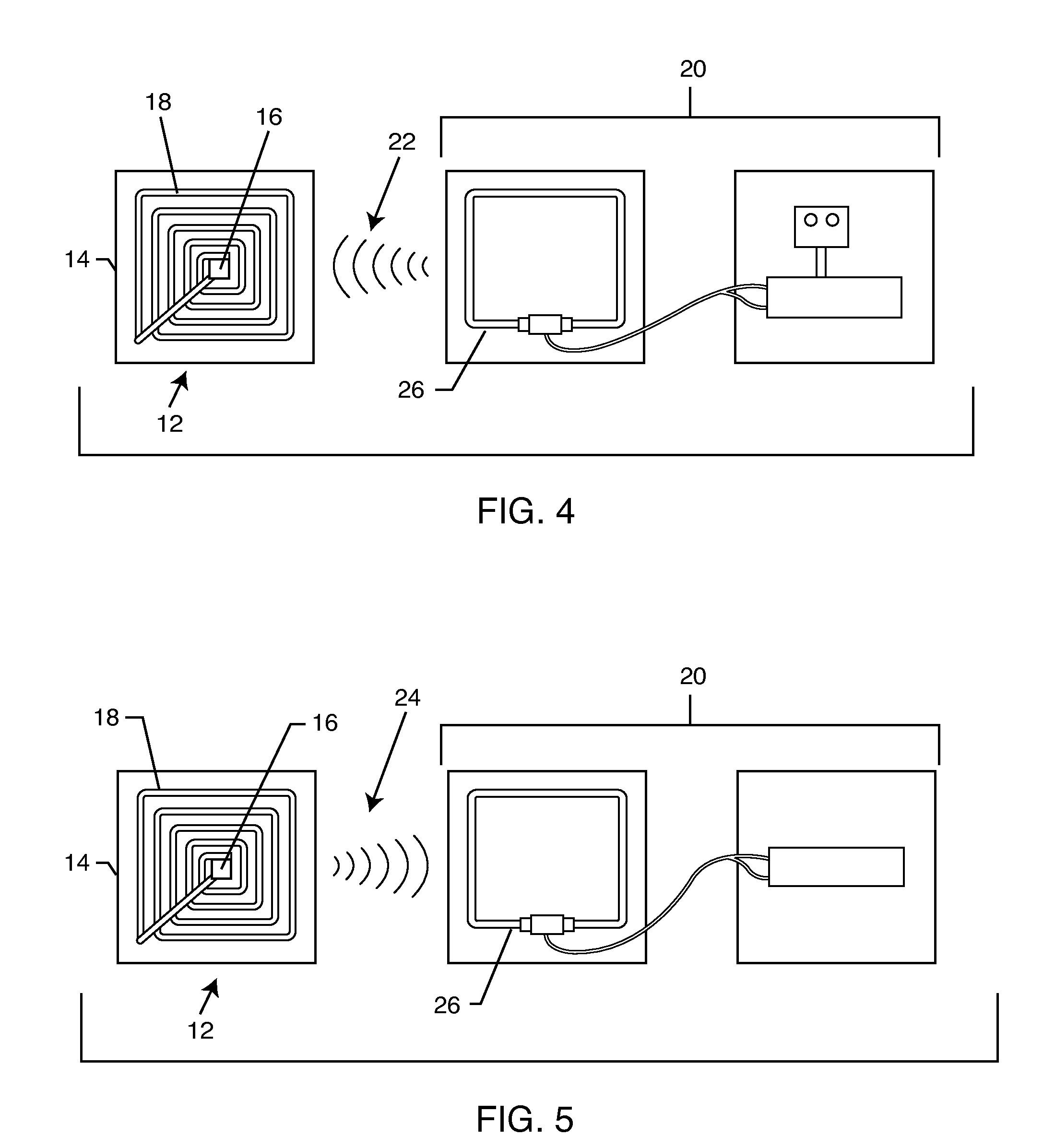
Hermetically sealed RFID microelectronic chip connected to a biocompatible RFID antenna
An implantable radio frequency identification (RFID) tag includes a hermetically sealed biocompatible housing for an active implantable medical device (AIMD), an RFID microelectronics chip is disposed within the housing, and a biocompatible antenna extends from the RFID microelectronic chip and exteriorly of the housing. In a preferred form of the invention, the antenna is disposed within a header block of the AIMD, and the RFID chip is disposed within the AIMD housing.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
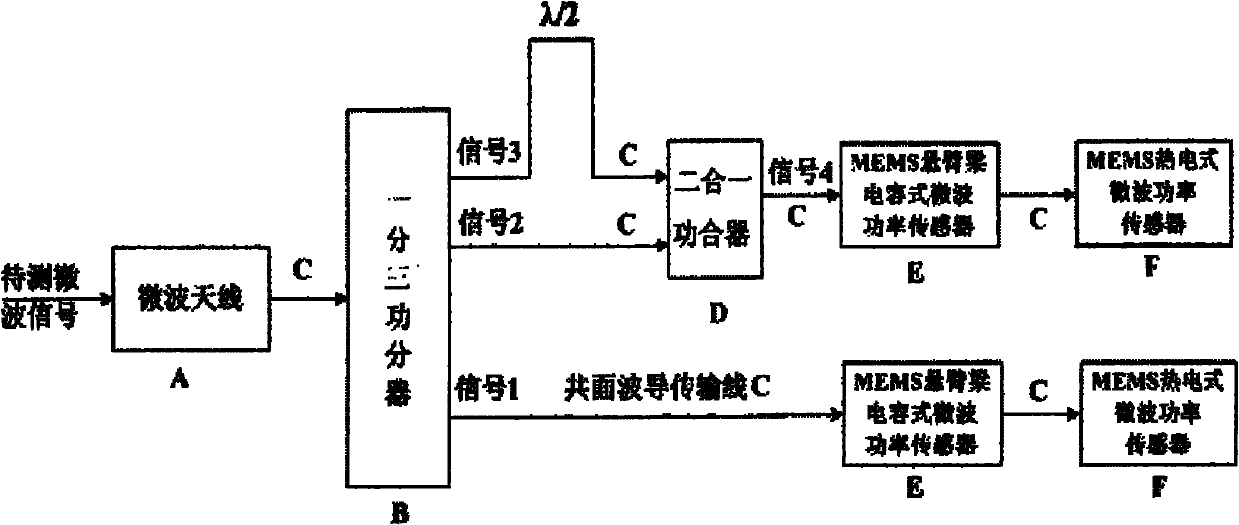
Wireless-receiving system for detecting microelectronic mechanical microwave frequency and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101788605ARealize wireless receptionTo achieve the purpose of wireless detectionTelevision system detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPower combinerPhase difference
The invention relates to a wireless-receiving system for detecting microelectronic mechanical microwave frequency and a preparation method thereof. The wireless-receiving system for detecting the microelectronic mechanical microwave frequency has quite simple structure, large measurement magnitude range, no direct-current power consumption and easy integration. In the system for detecting the microelectronic mechanical microwave frequency, gallium arsenide is used as a substrate, wherein a microwave antenna (A), a one-three power splitter (B), a coplanar waveguide transmission line (C), a two-in-one power combiner (D), an MEMS cantilever capacitive microwave power sensor (E) and an MEMS thermoelectric microwave power sensor (F) are designed on the substrate; and then a phase difference between a signal 3 and a signal 2 after the signal 3 passes through the coplanar waveguide transmission line with the length of lambda / 2 can be determined according to a law of cosines. Because the phase difference corresponds to the frequency of the signal, the frequency of the signal can be measured.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com