Patents
Literature
328 results about "Vacuum level" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In physics, the vacuum level refers to the energy of a free stationary electron that is outside of any material (it is in a perfect vacuum). It may be taken as infinitely far away from a solid, or, defined to be near a surface. Its definition and measurement are often discussed in UPS literature, for example As the vacuum level is a property of the electron and free space, it is often used as the level of alignment for the energy levels of two different materials. The vacuum level alignment approach may or may not hold due to details of the interface. It is particularly important in the design of vacuum device components such as cathodes.
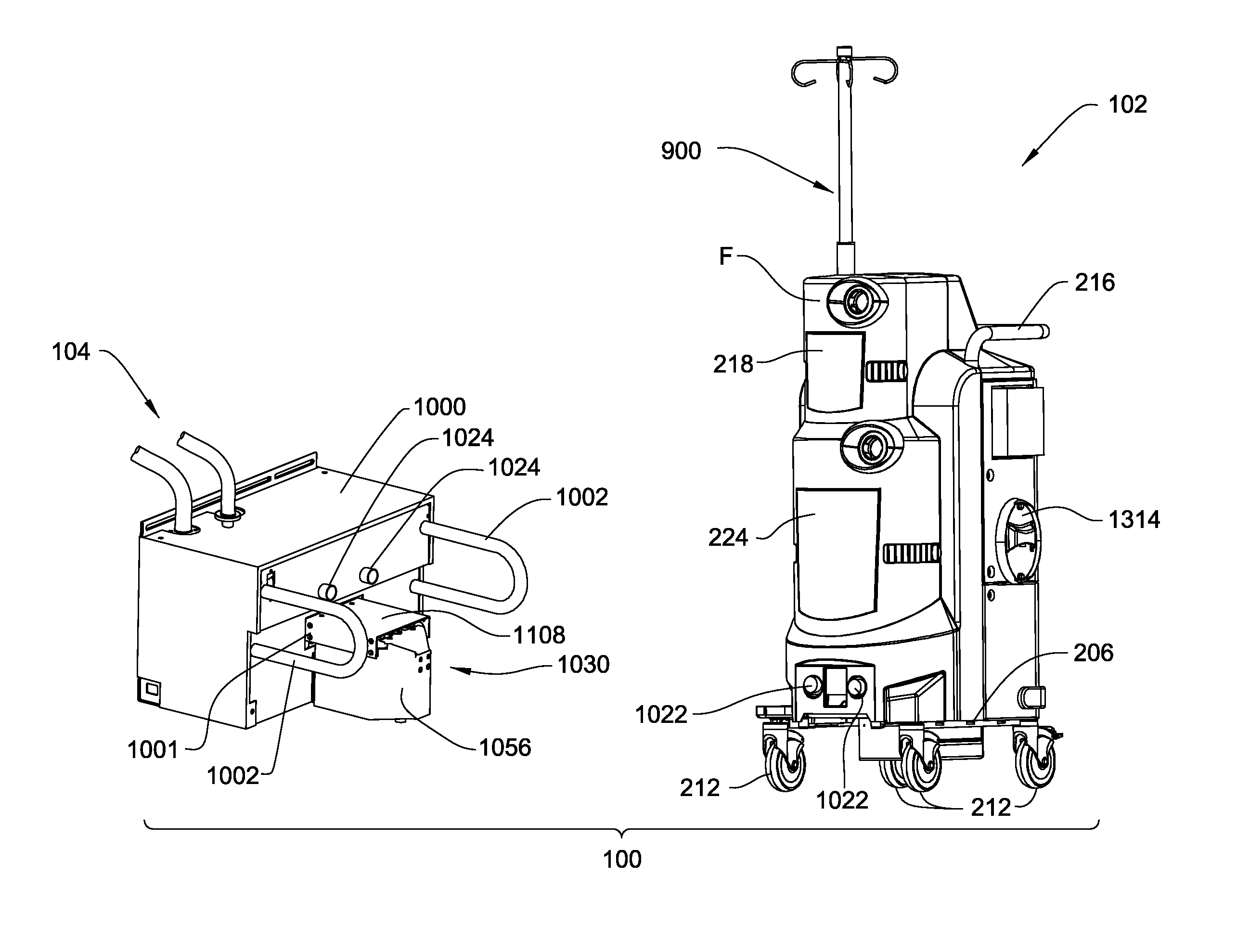
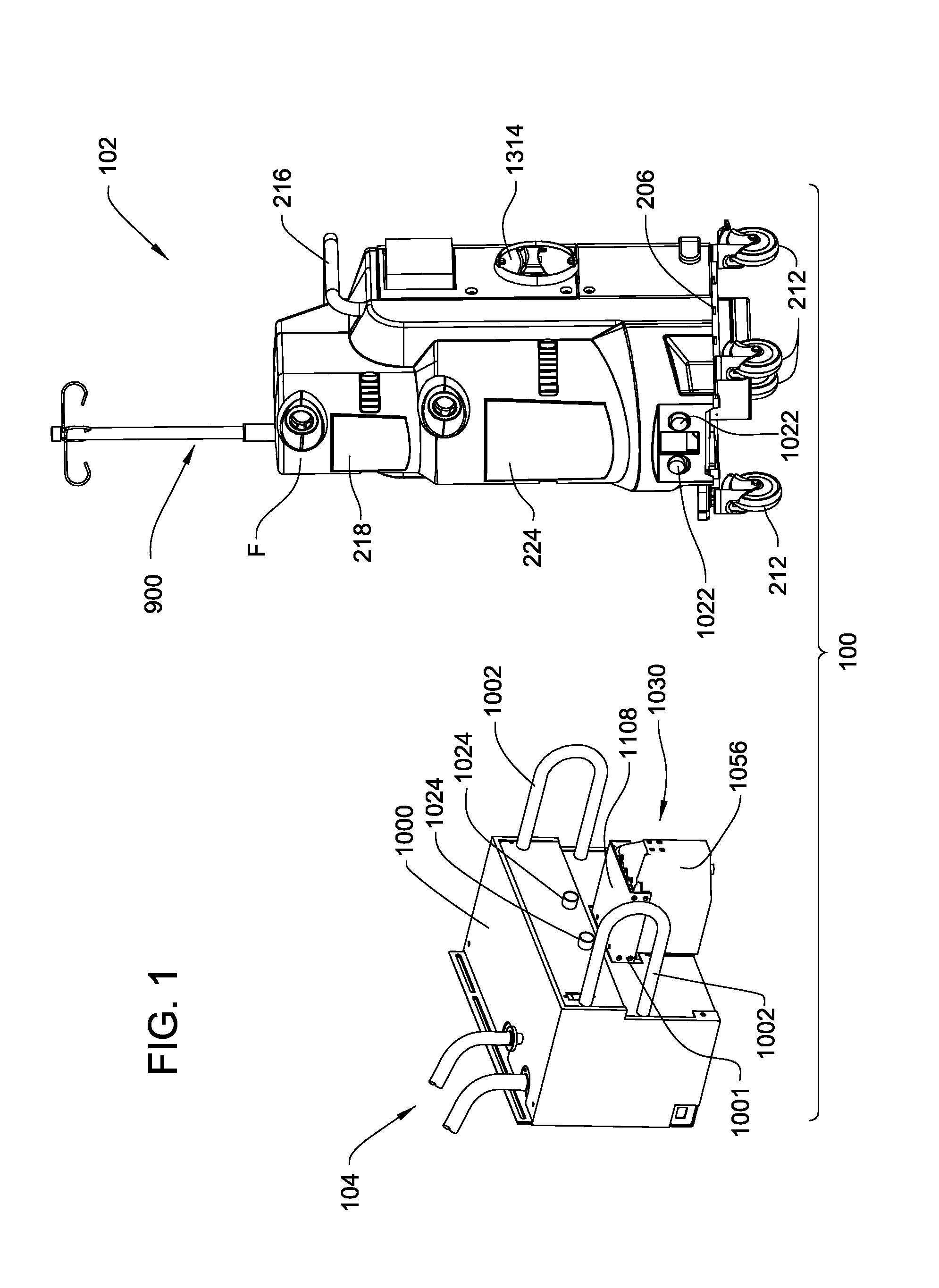
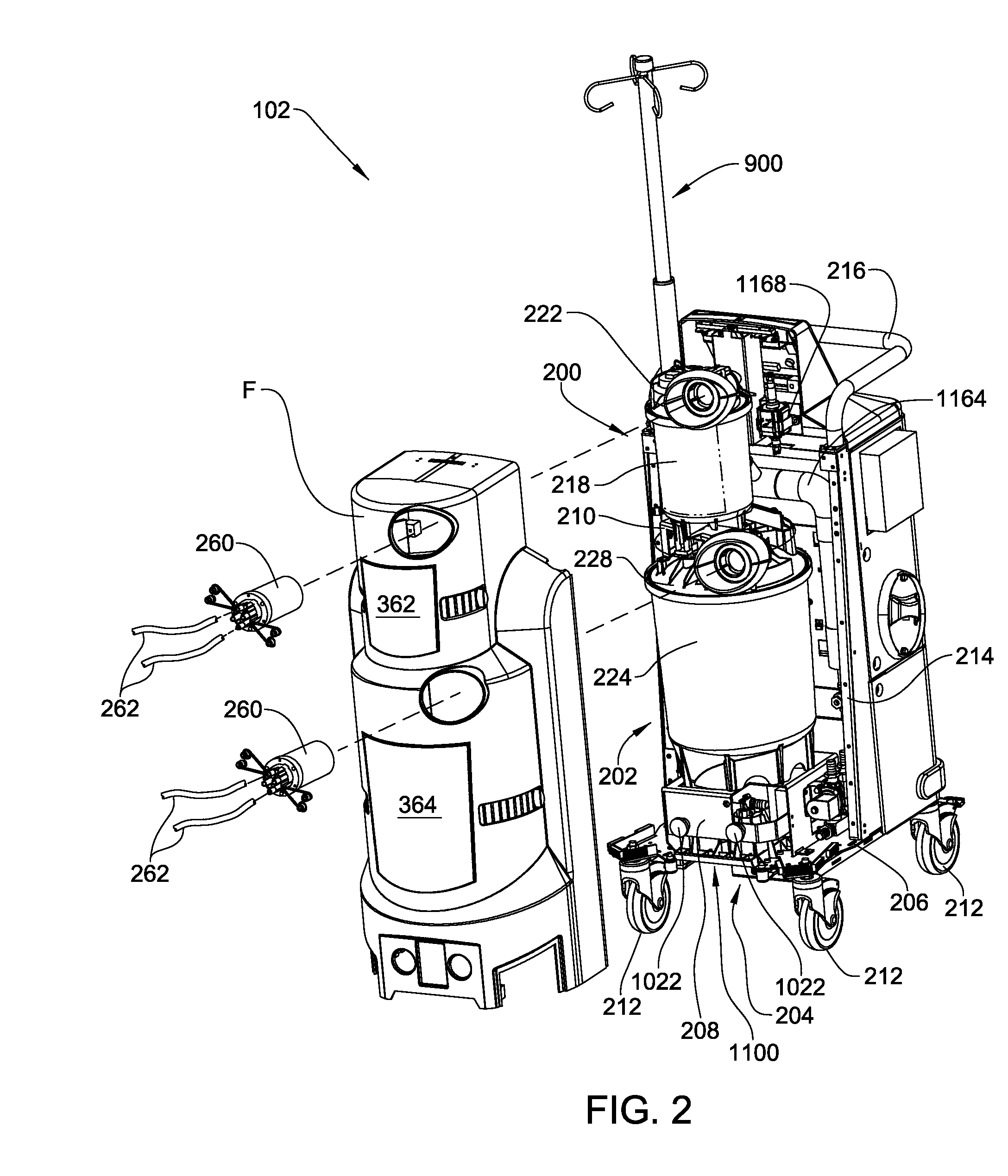
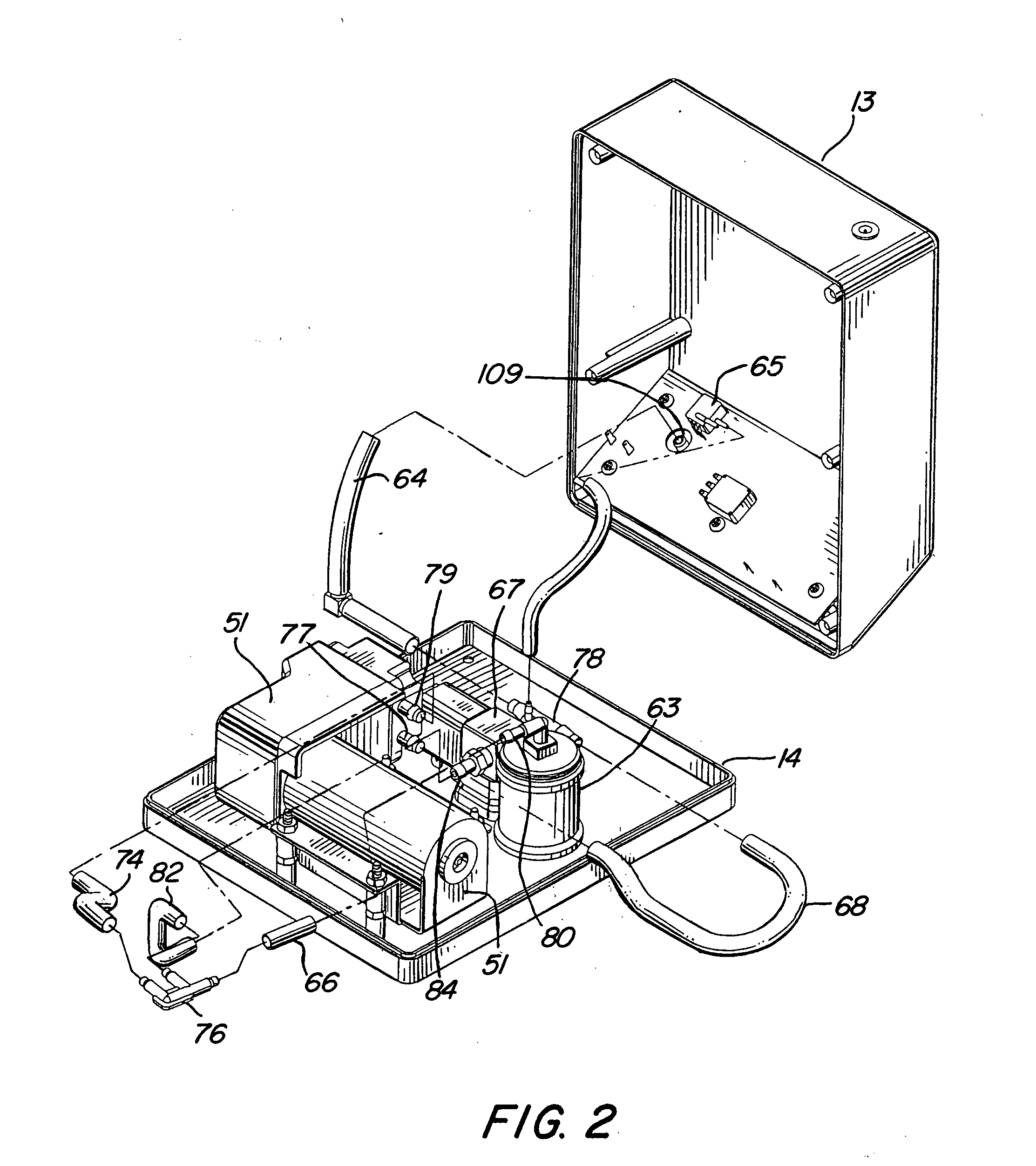
Medical/surgical waste collection unit including waste containers of different storage volumes with inter-container transfer valve and independently controlled vacuum levels
ActiveUS7621898B2Reduce in quantityLarge storage capacityMechanical apparatusDispersed particle filtrationDocking stationVacuum level
Owner:STRYKER CORP
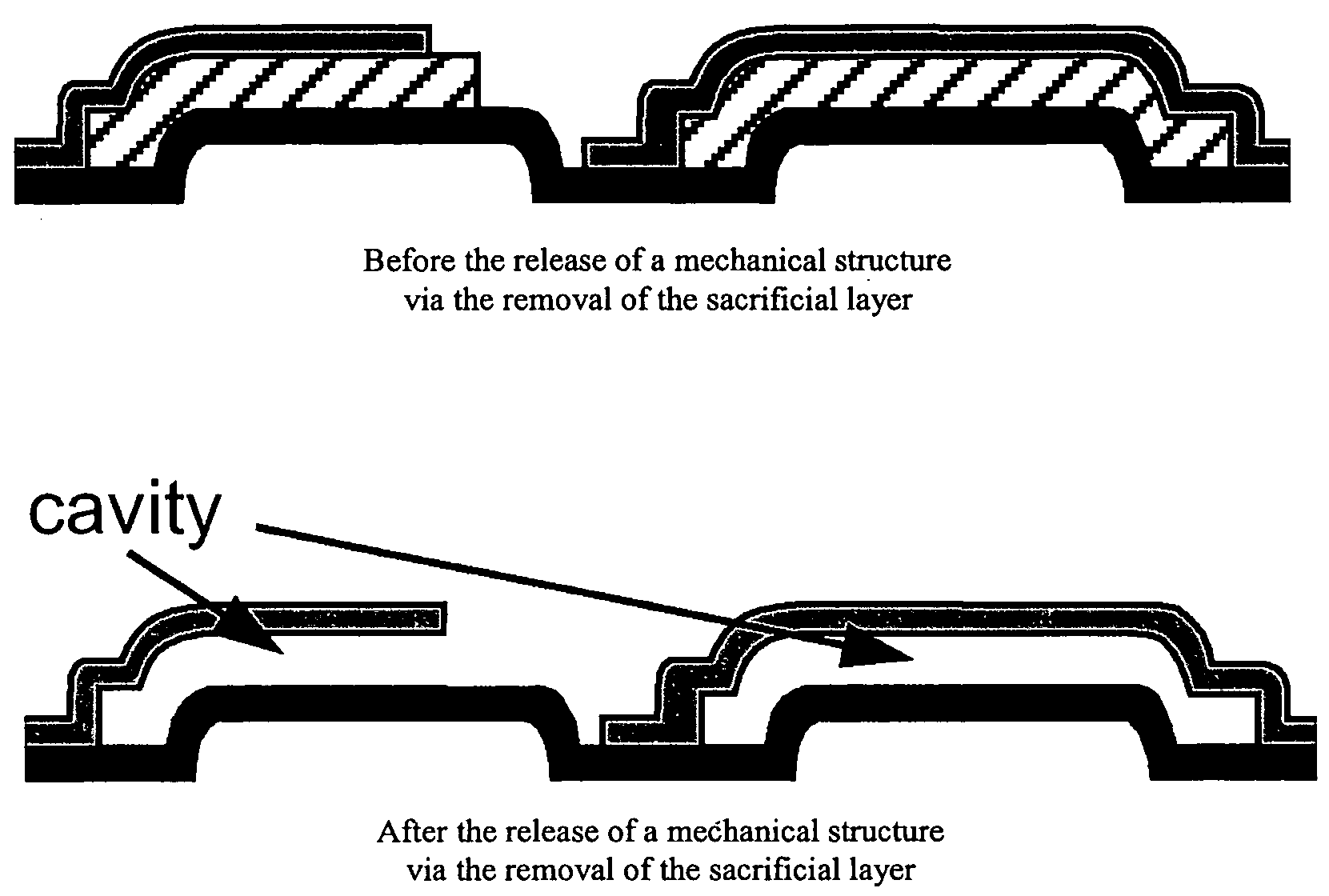
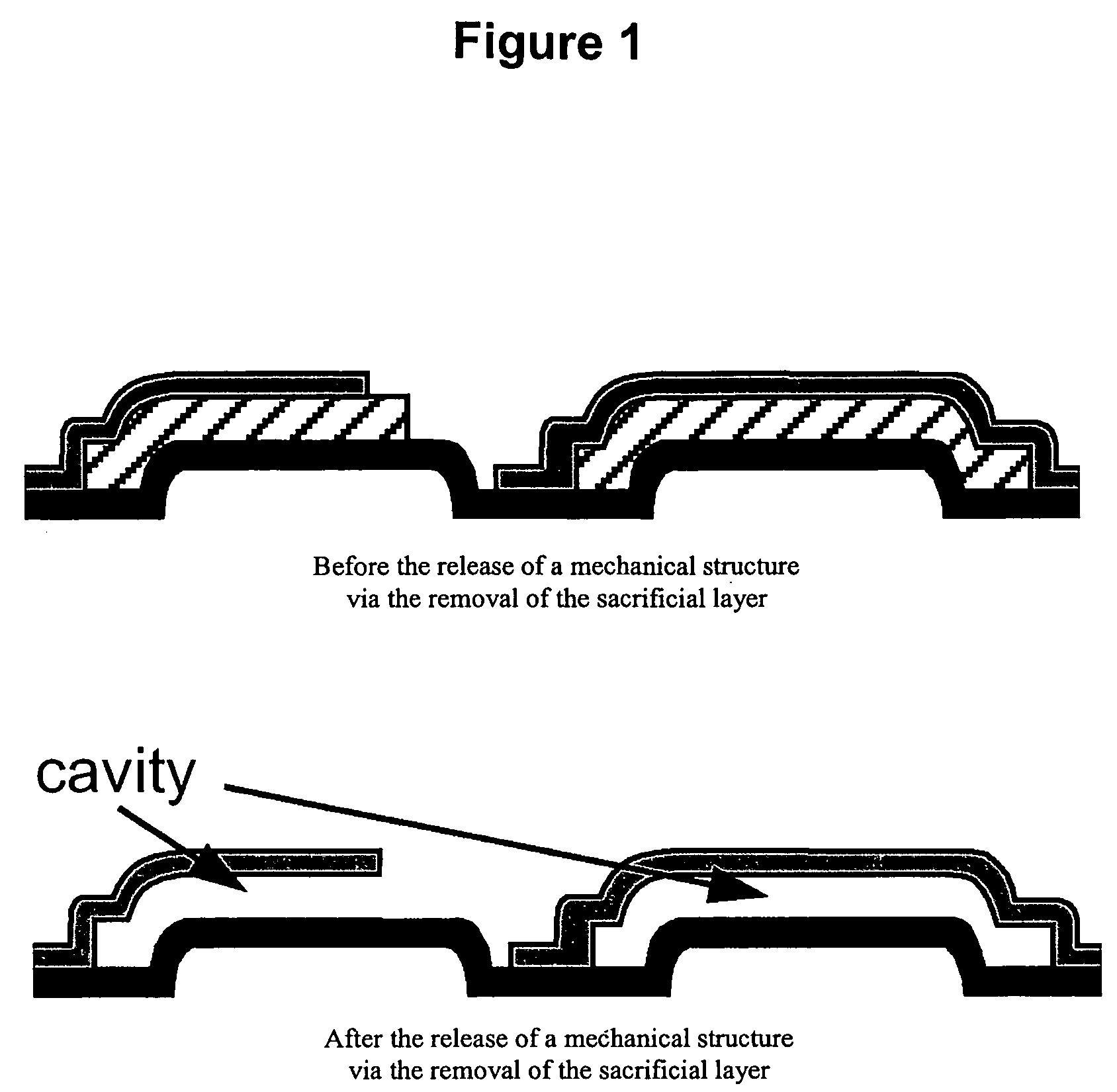
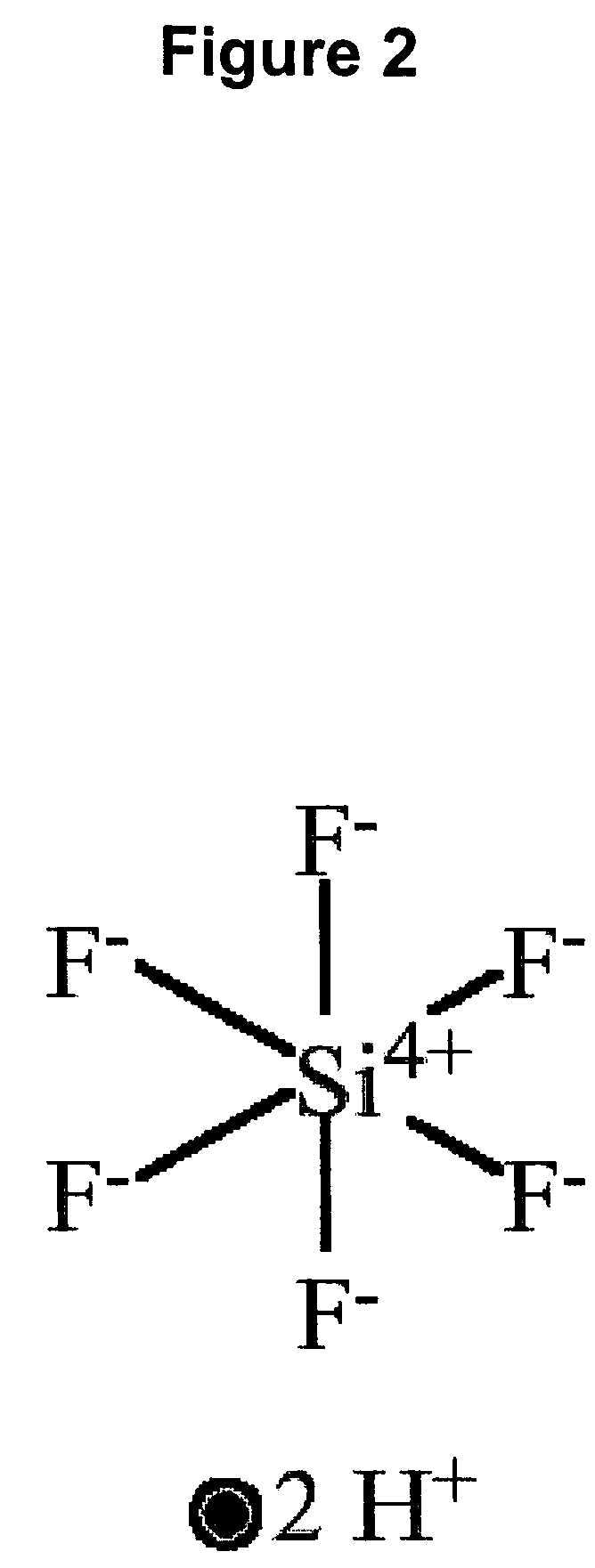
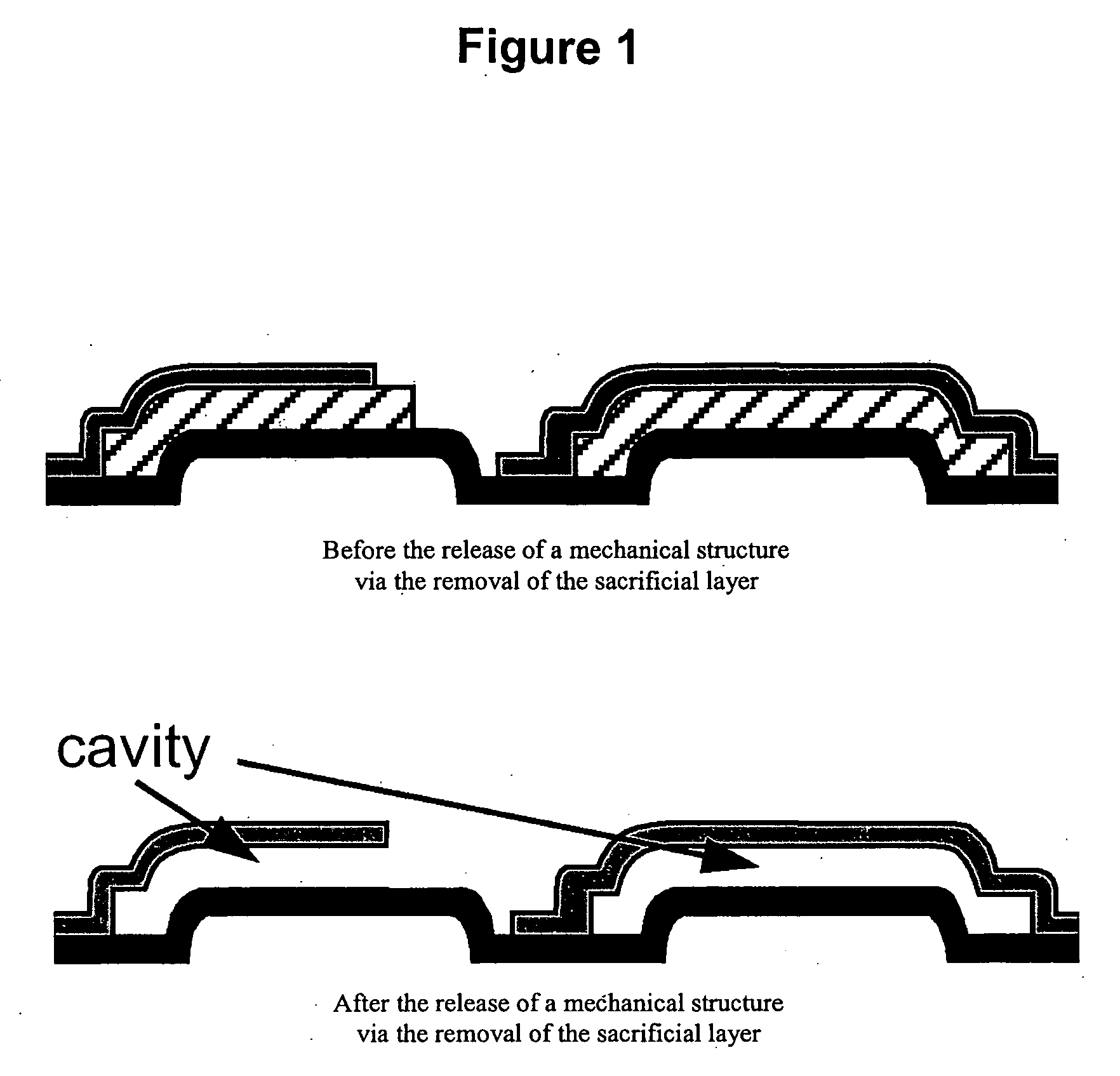
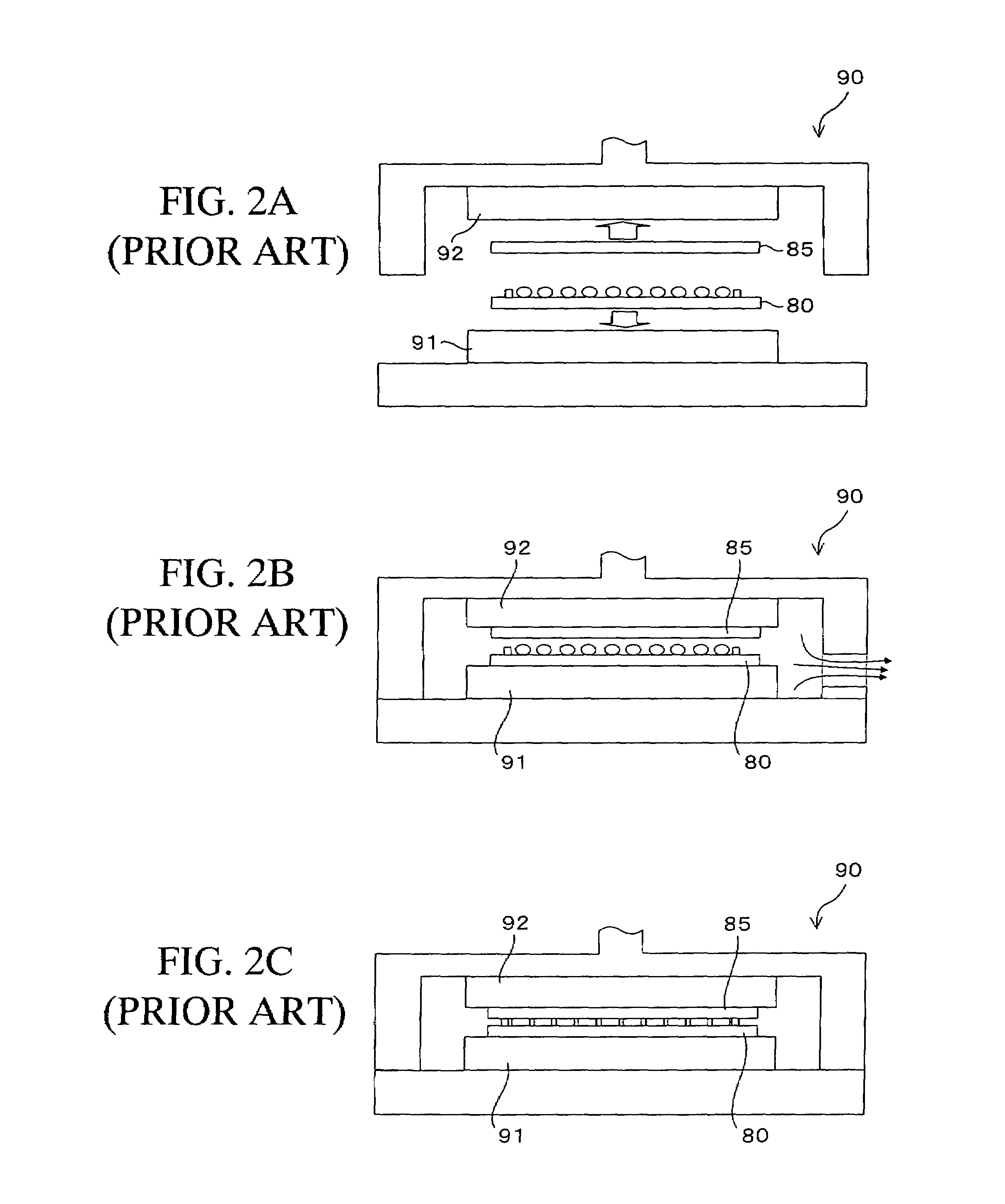
Anhydrous HF release of process for MEMS devices
ActiveUS7365016B2Prevent undesirable metal incompatibility effectDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhysical chemistryVacuum level
A method of etching a sacrificial oxide layer covering an etch-stop silicon nitride underlayer, involves exposing the sacrificial oxide to anhydrous HF at a temperature of less than about 100° C. and / or at vacuum level lower than 40 Torr; and subsequently performing an in-situ vacuum evaporation of etch by-products at a temperature of more than about 100° C. and at vacuum level lower than the 40 Torr without exposure to ambient air.
Owner:TELEDYNE DIGITAL IMAGING INC
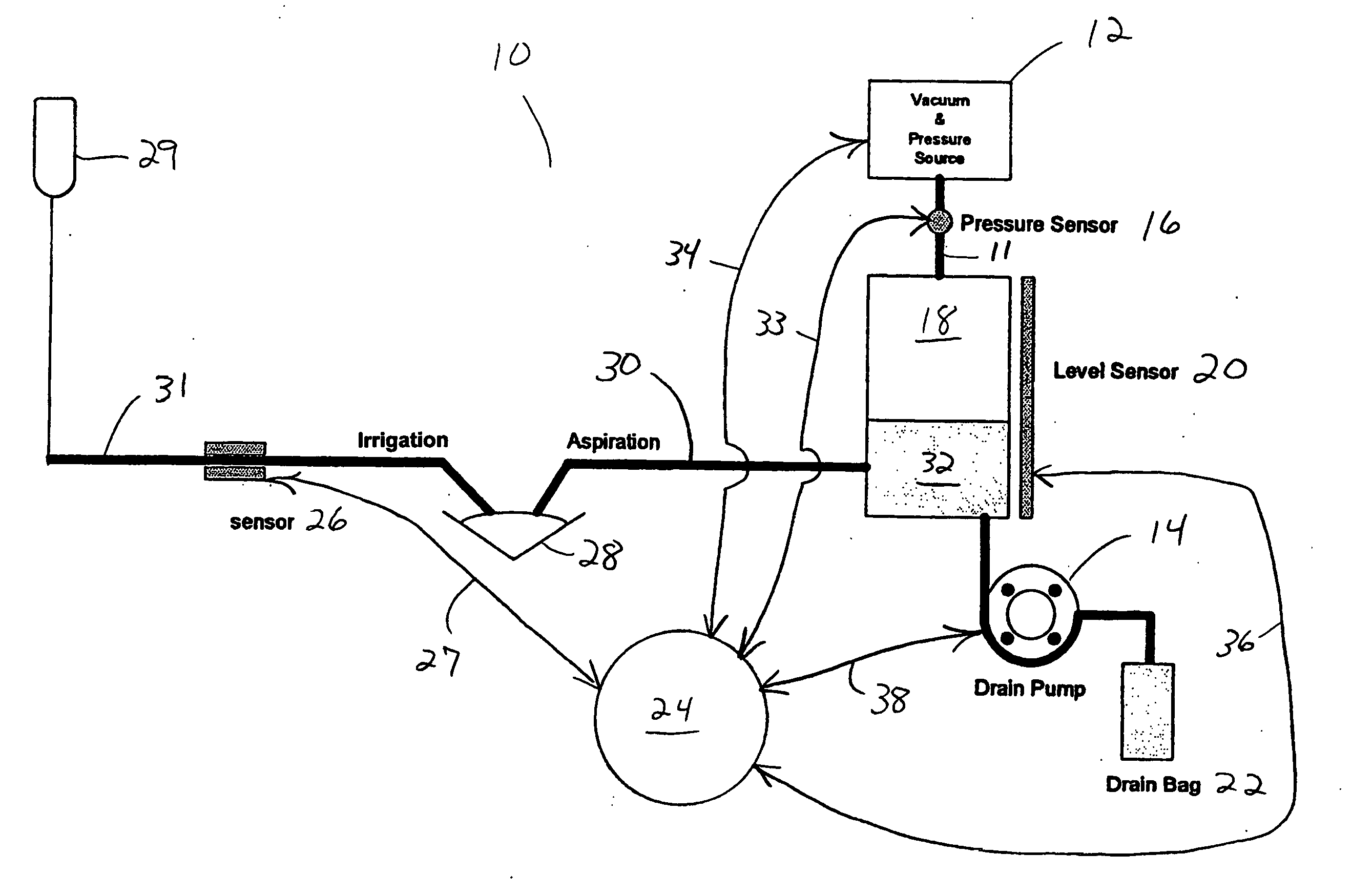
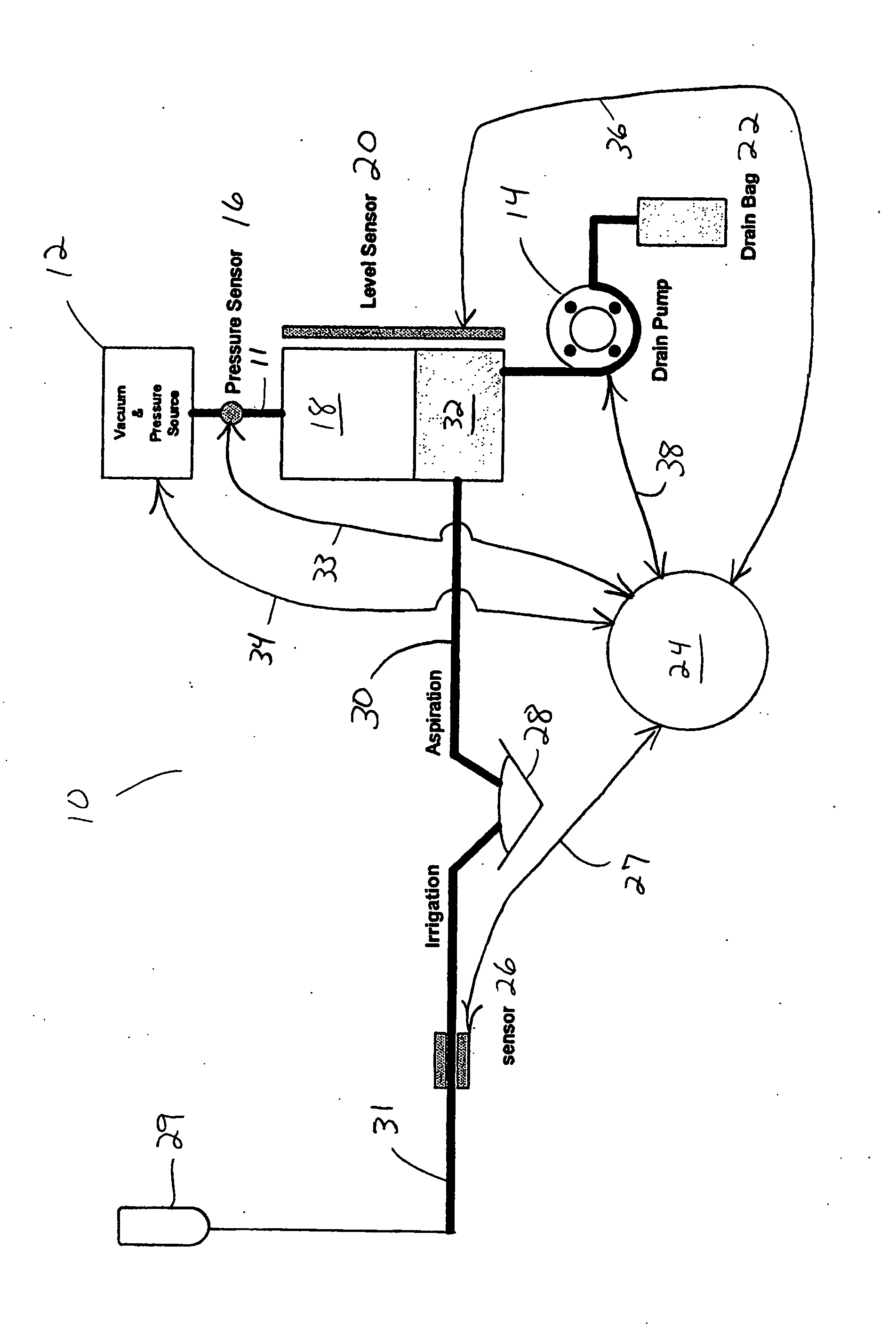
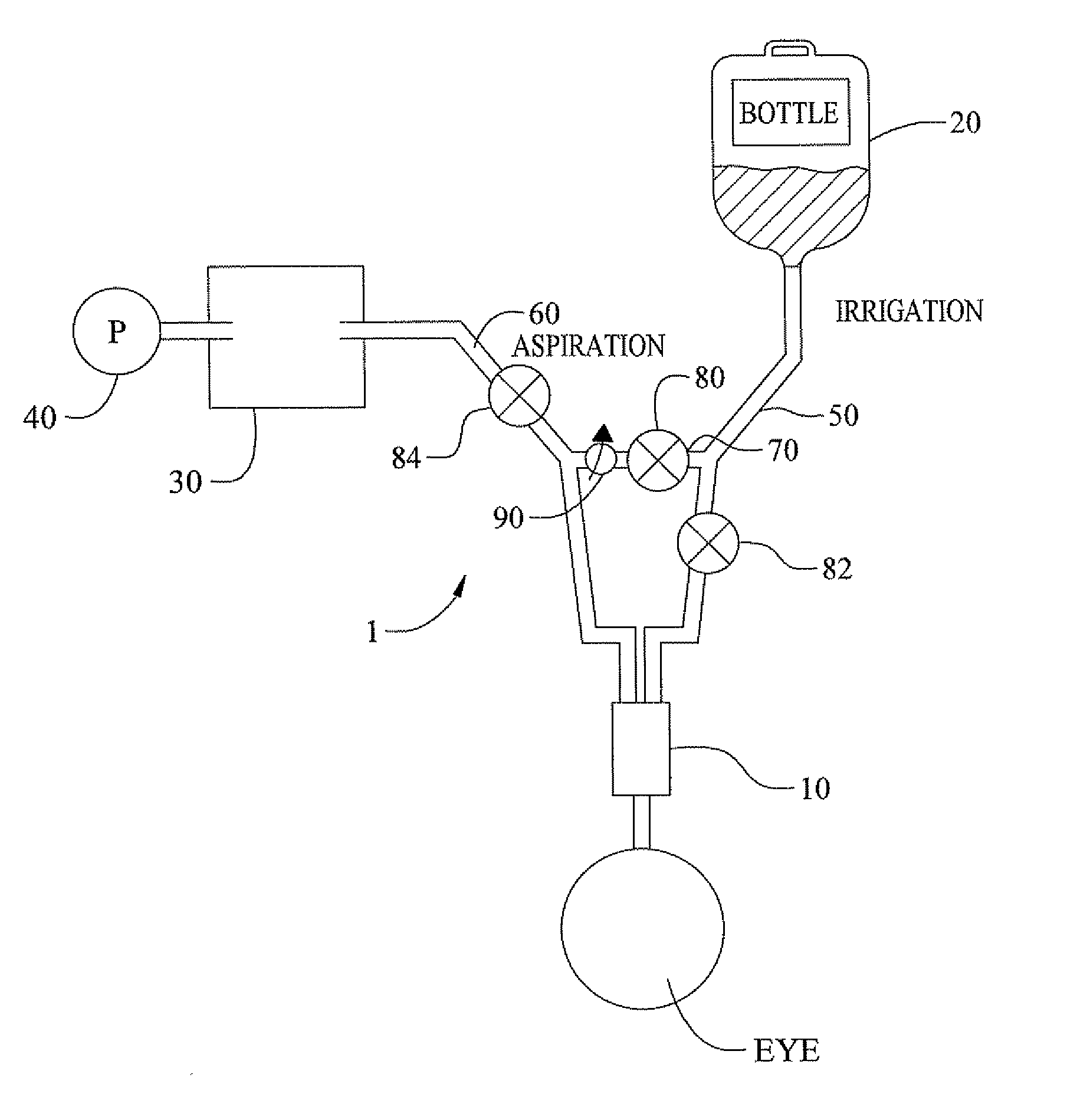
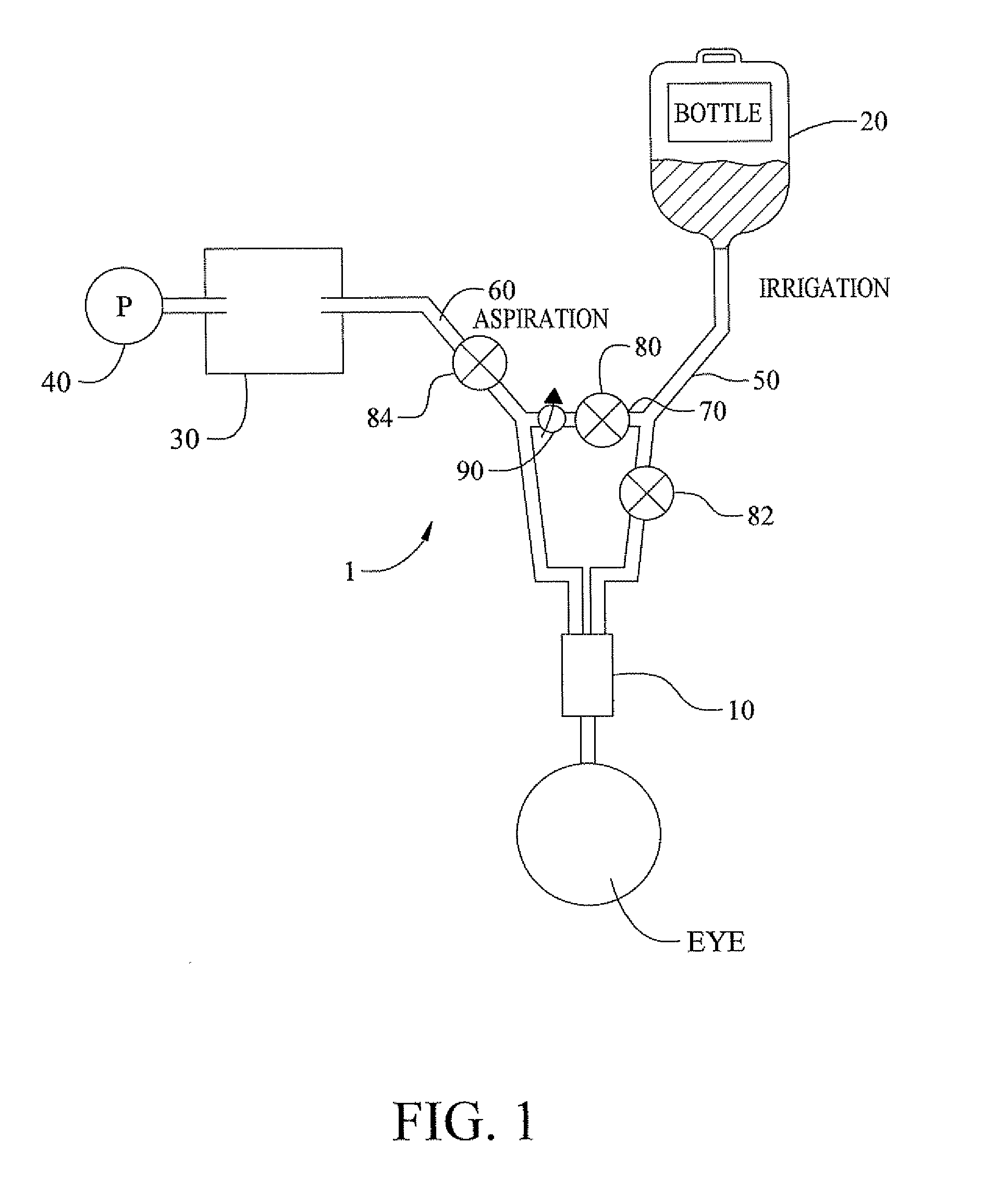
Method of controlling an irrigation/aspiration system
A dual pump aspiration system having both a vacuum level control loop and a flow rate control loop. The system can be operated either as a vacuum priority system or a flow rate priority system.
Owner:ALCON INC
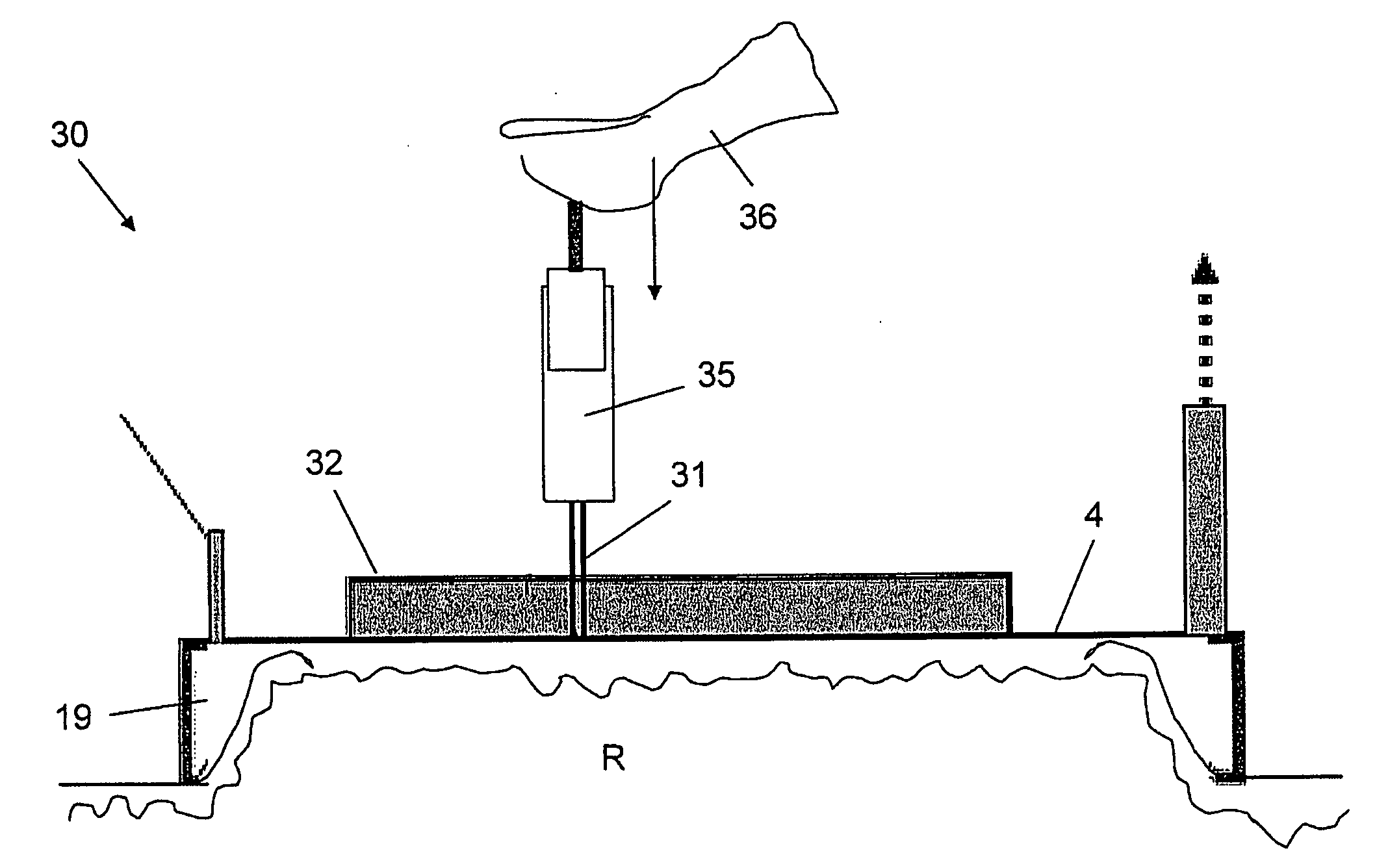
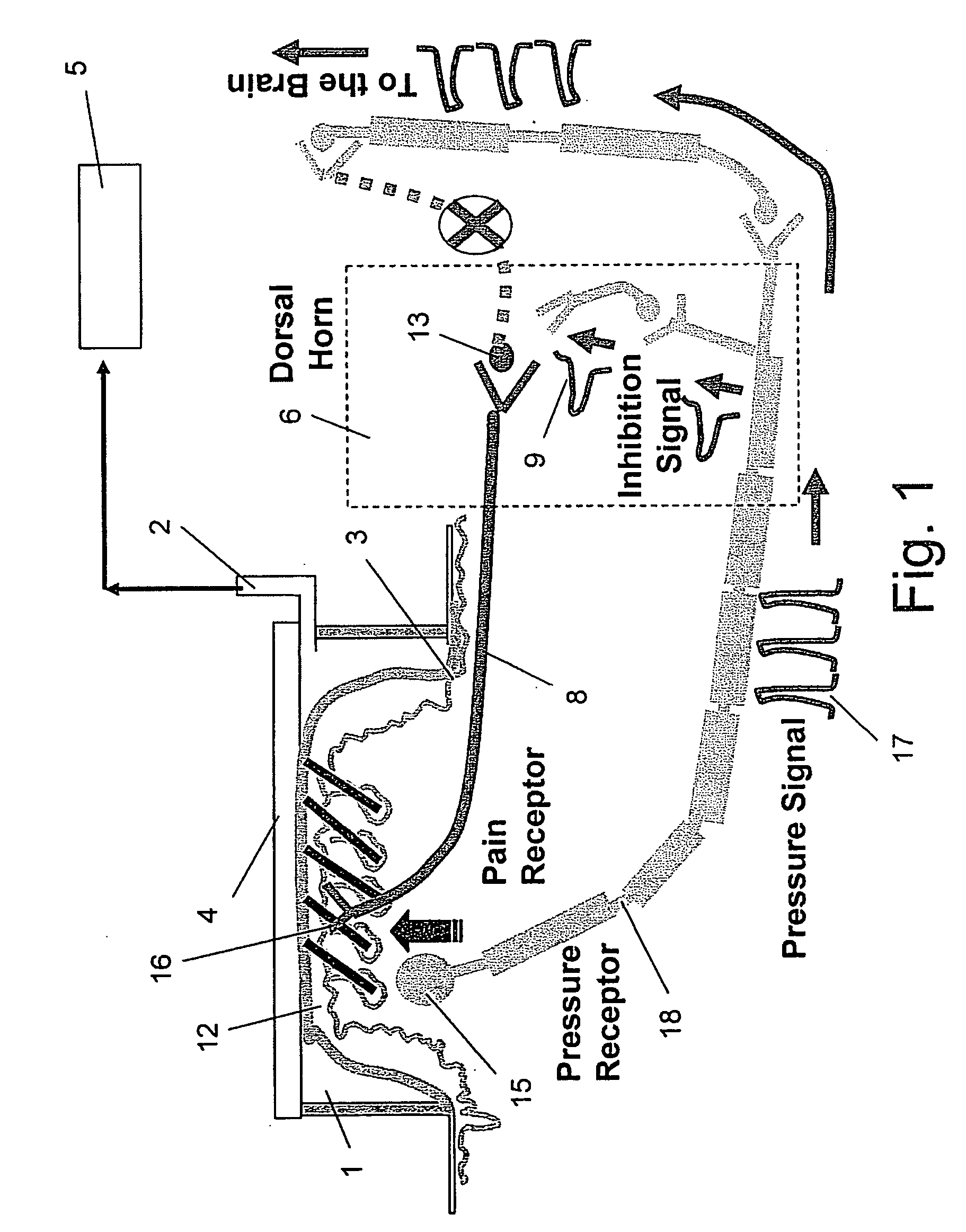
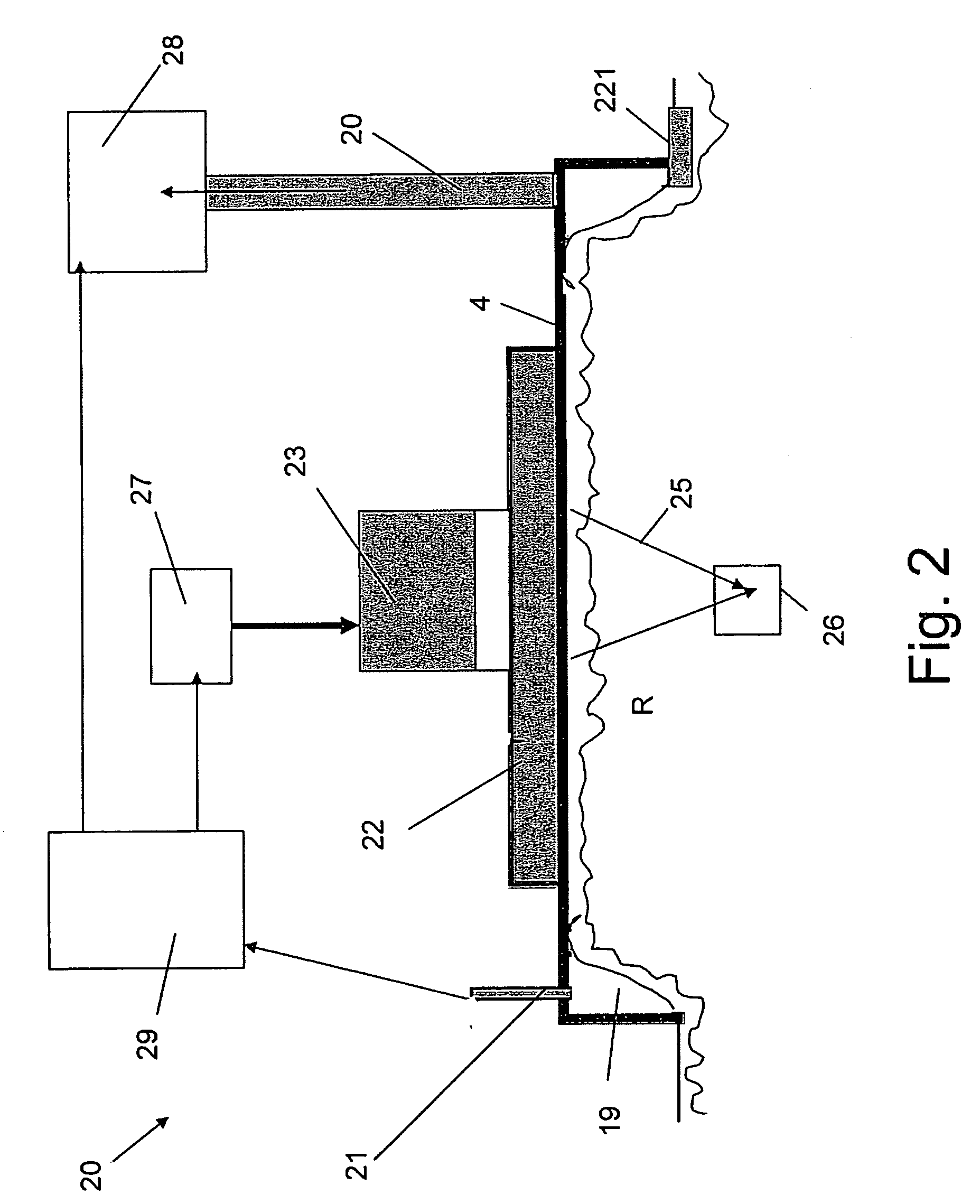
Apparatus and method for inhibiting pain signals transmitted during a skin related medical treatment
InactiveUS20060293722A1Improve skin appearanceChange effectUltrasound therapyElectrotherapyVacuum levelSKIN REGIONS
An apparatus adapted to inhibit pain signals generated by pain receptors in the skin during a skin related medical treatment such as an injection. An evacuation chamber is provided with an essentially rigid interface element larger than a threshold surface area through which a medical treatment can be administered to a selected skin region, one or more walls which are placeable in the vicinity of the skin region, an interior defined by the walls and by the interface element, and an opening at the bottom of the interior which is sealable by the skin region. A device generates a vacuum within the evacuation chamber interior to a level greater than the threshold vacuum level suitable for drawing the skin region through the opening towards, and in a compressing relation against, the interface element, to inhibit the transmission of a pain signal generated by pain receptors located within the skin region.
Owner:CANDELA CORP
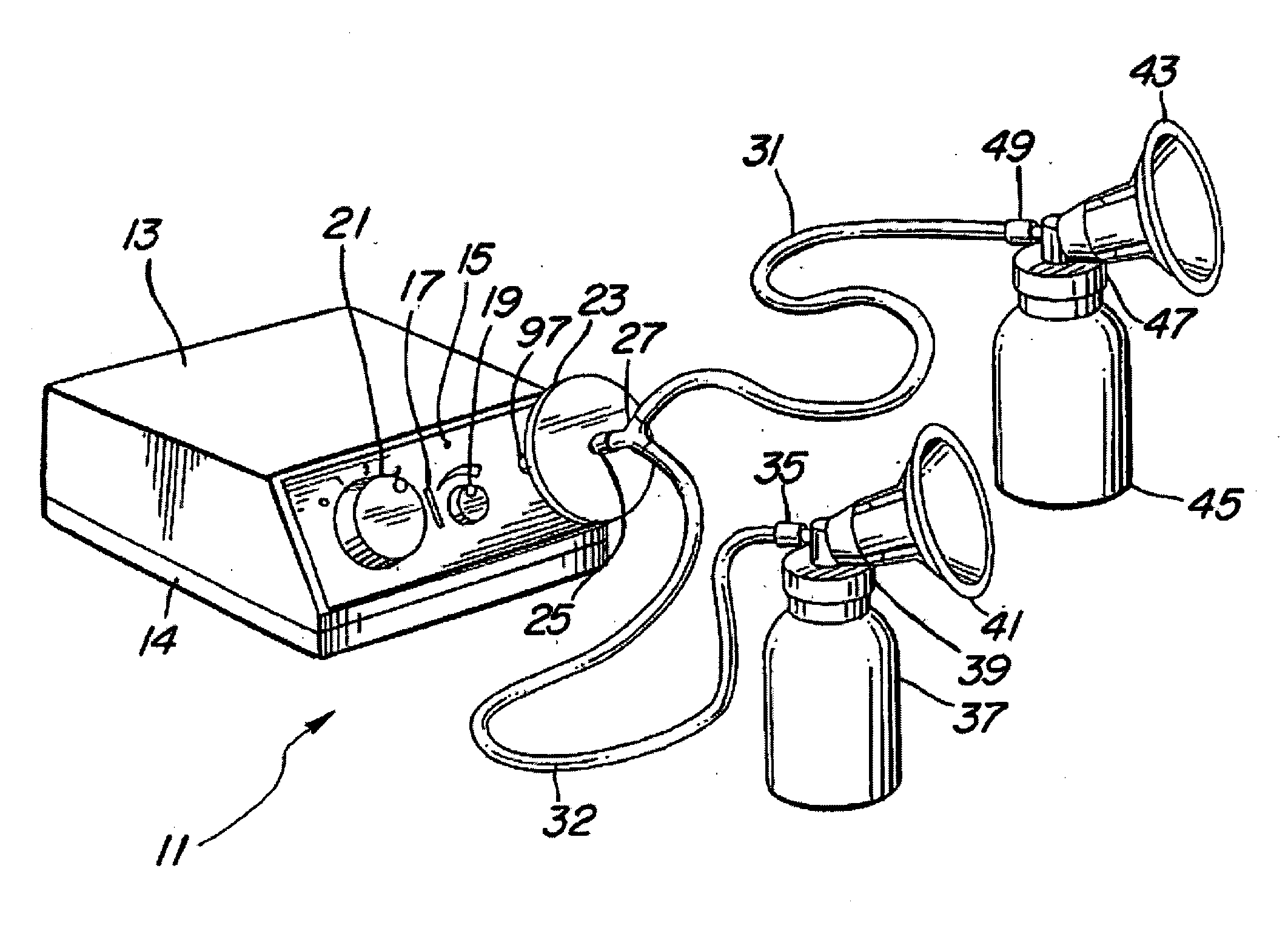
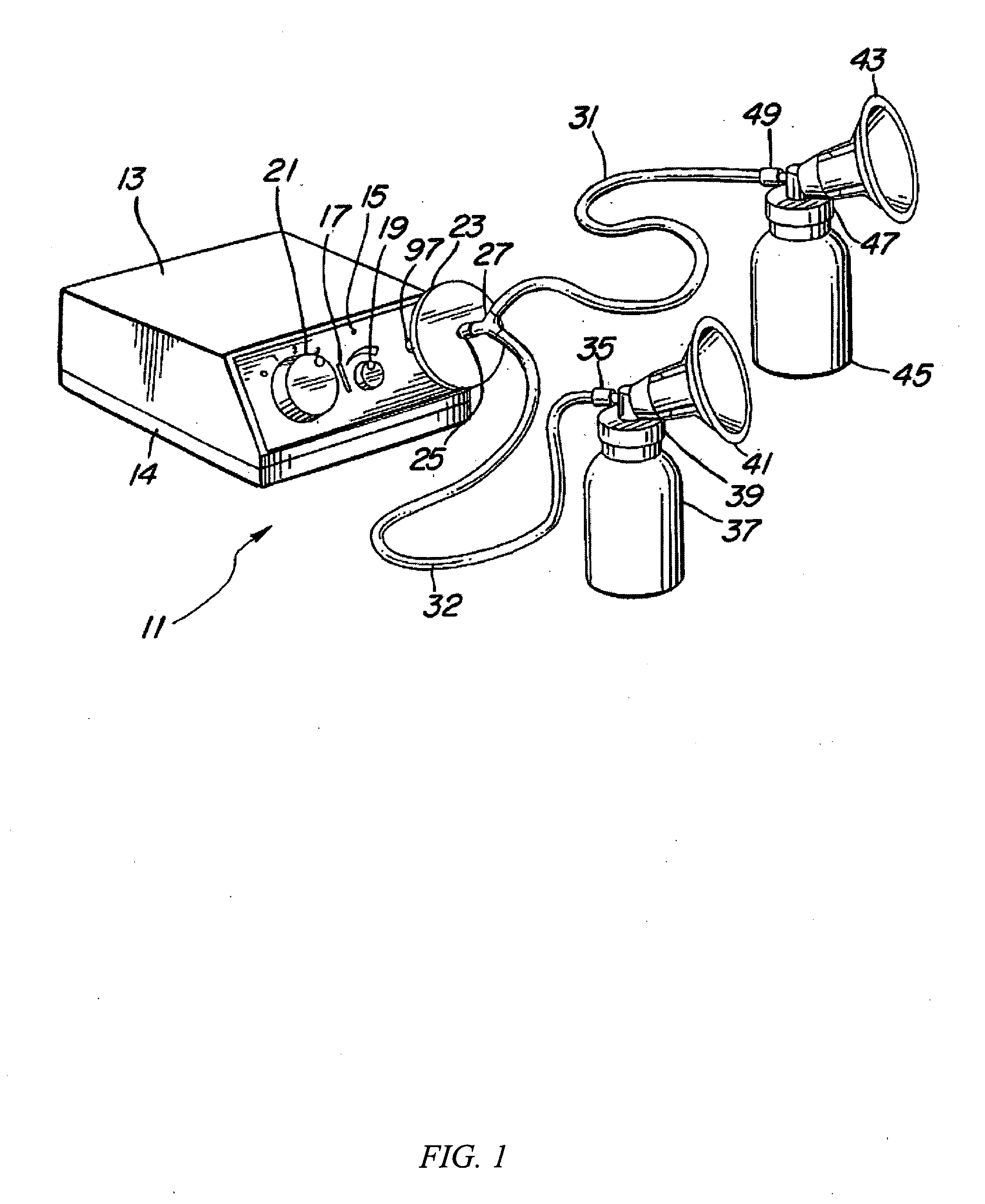
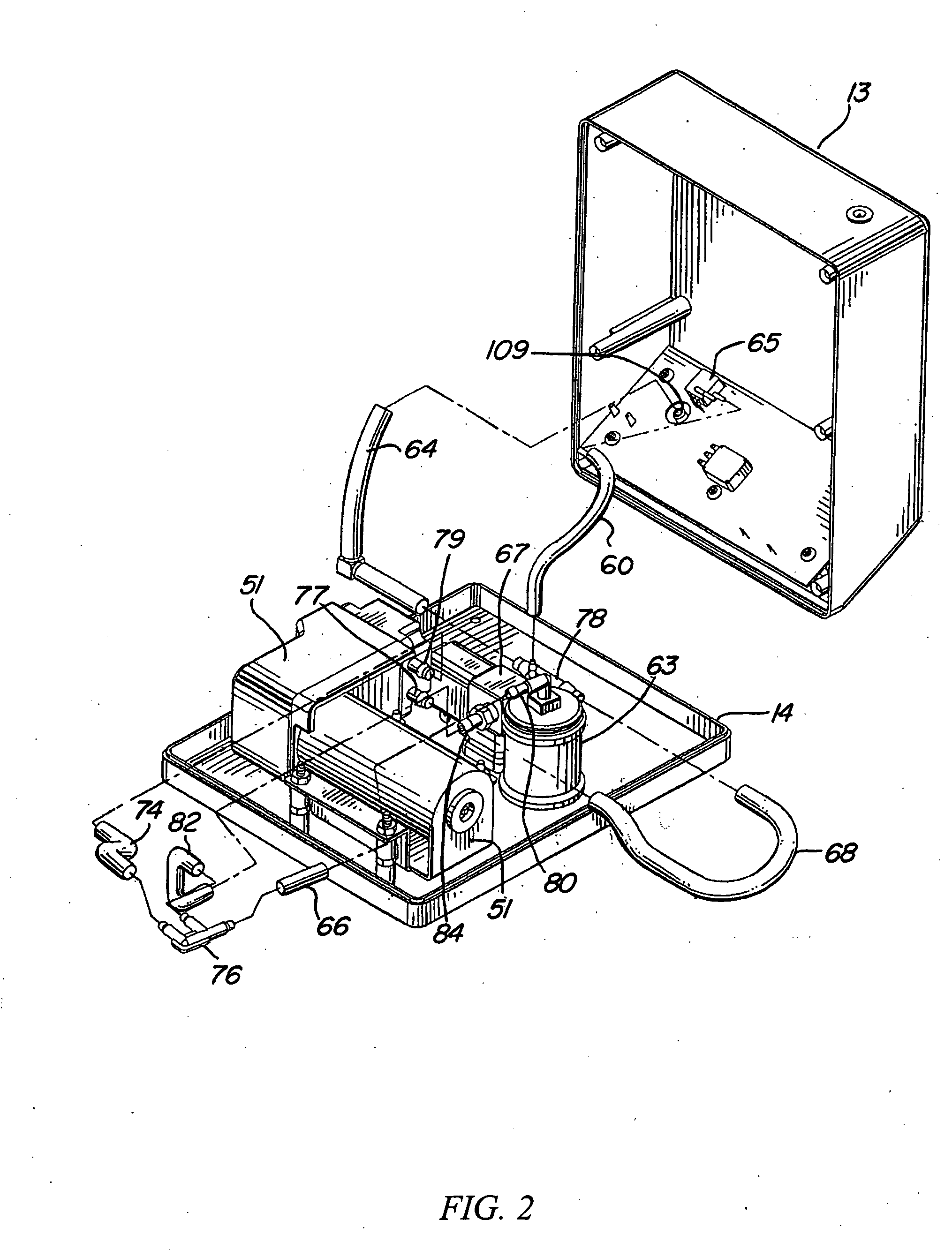
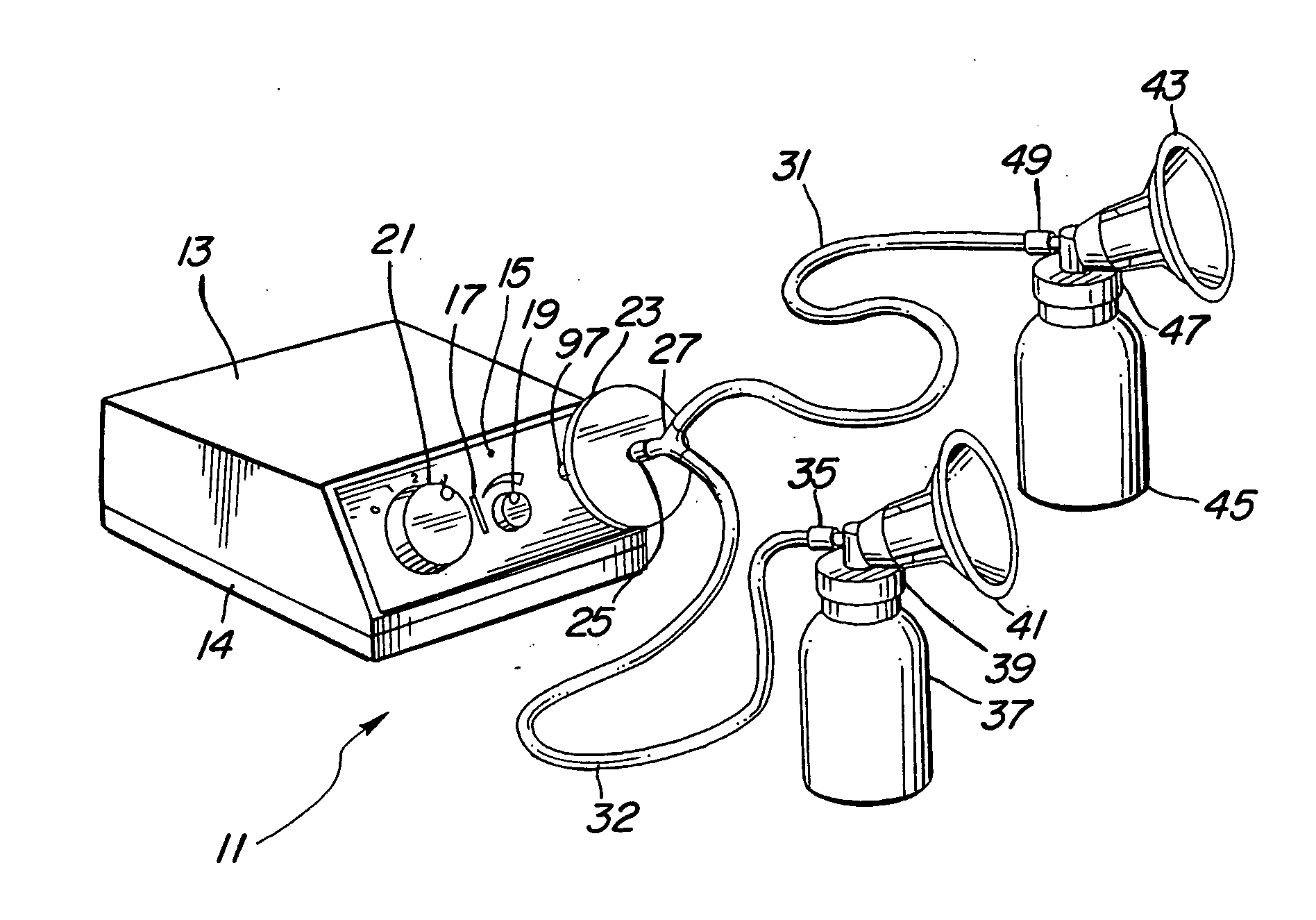
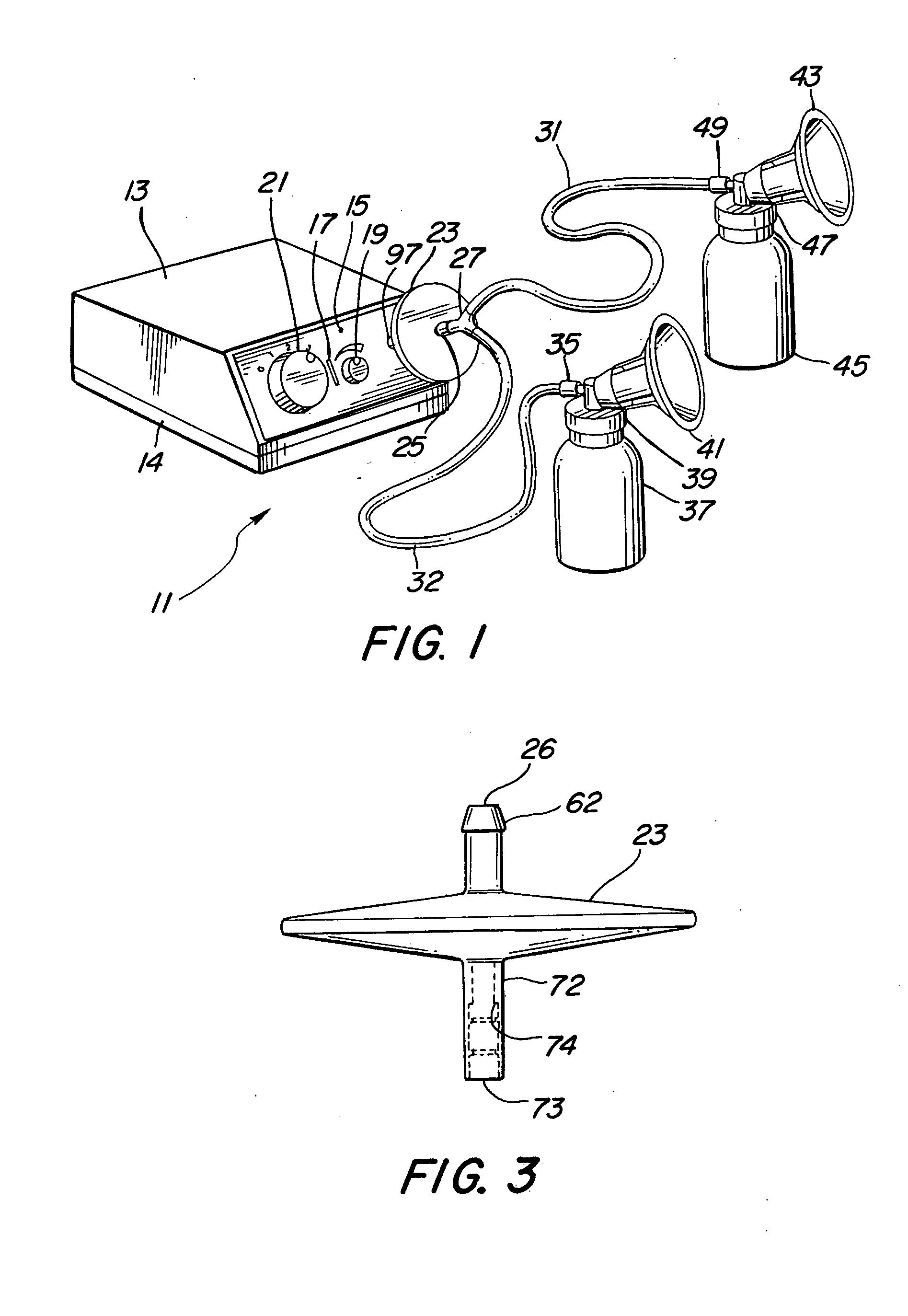
Programmable electric breast pump
A programmable electric breast pump system includes a vacuum pump pneumatically coupled to breast cups and a vacuum relief valve bypassing the vacuum pump. A controller receives command input from a vacuum level selector and a vacuum rate selector, and feedback from a pressure sensor measuring vacuum in the breast cups. In response, the controller cycles the relief valve between minimum and maximum vacuum setpoints to create a periodic vacuum pulse in the breast cups. By adjusting the vacuum min / max levels and vacuum rate, a user may change the strength of the pulse after let-down, or synchronize the frequency of the pulse with the natural refractory time of a lactating breast. Related methods for operating a breast pump mimic the suckling cycle of a nursing infant and may include steps for bypassing a vacuum pump with a vacuum relief valve, selecting a vacuum rate and a vacuum level, driving a vacuum pump at the selected vacuum rate, cycling the relief valve according to the vacuum level, and adjusting the vacuum level until the vacuum pulses in phase with a natural refractory time.
Owner:LIMERICK LTD
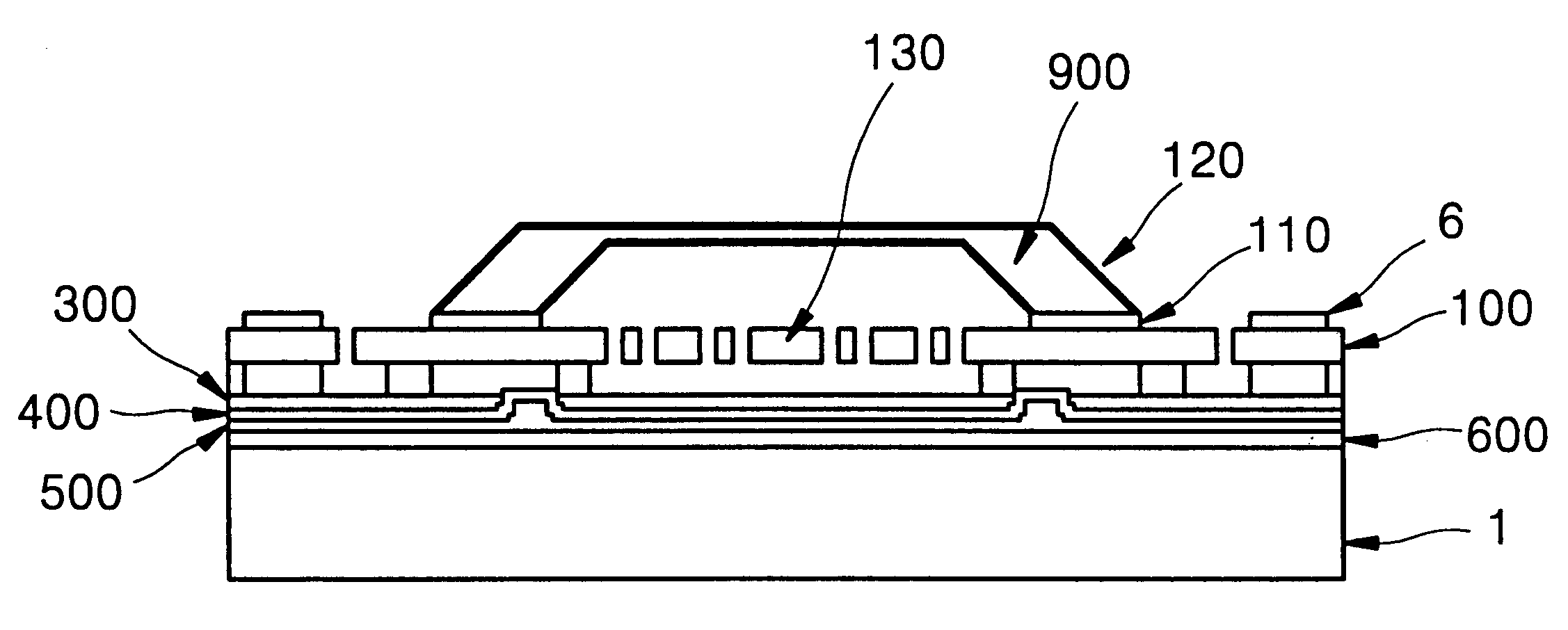
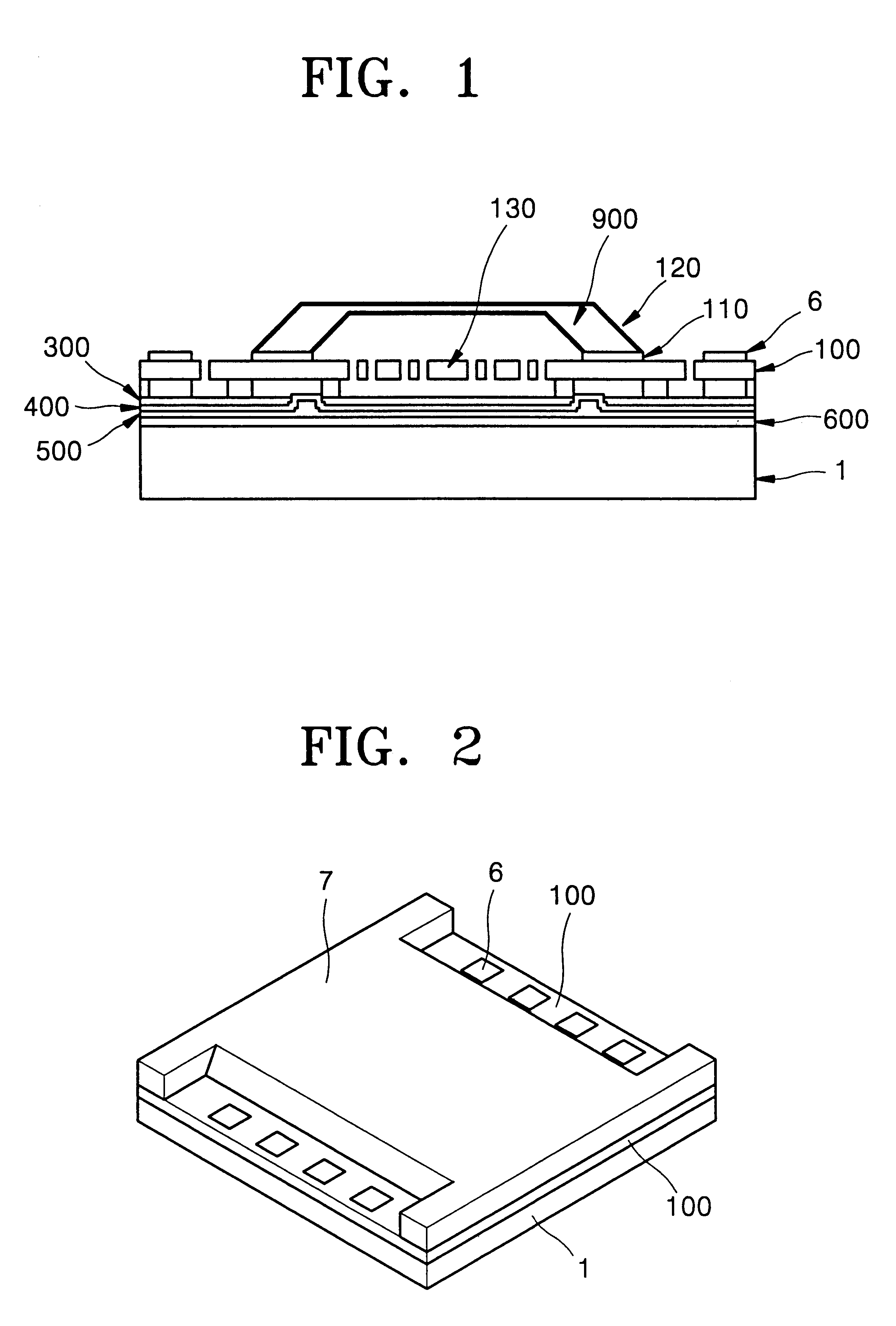
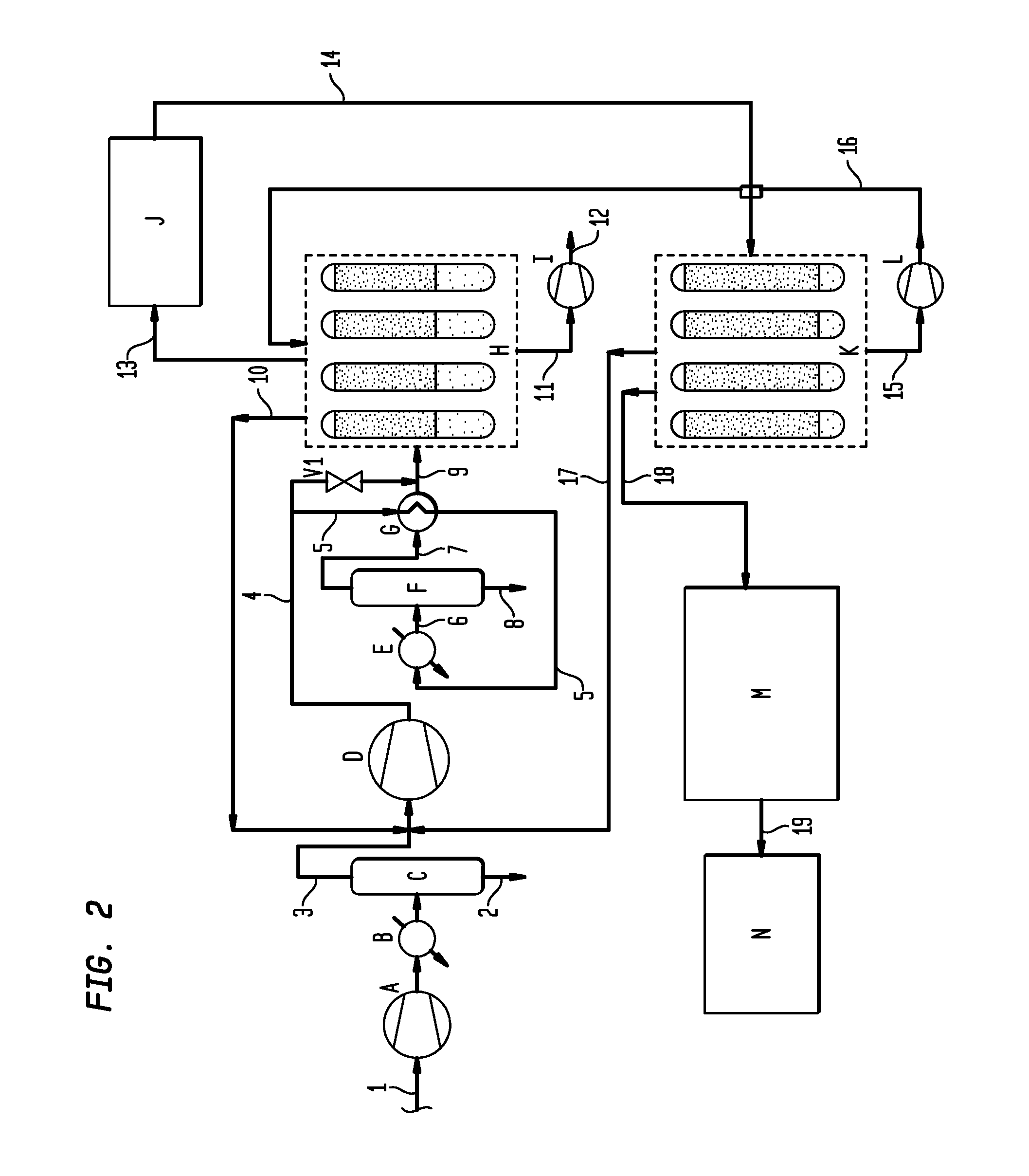
Method of fabricating micro electro mechanical system structure which can be vacuum-packed at wafer level
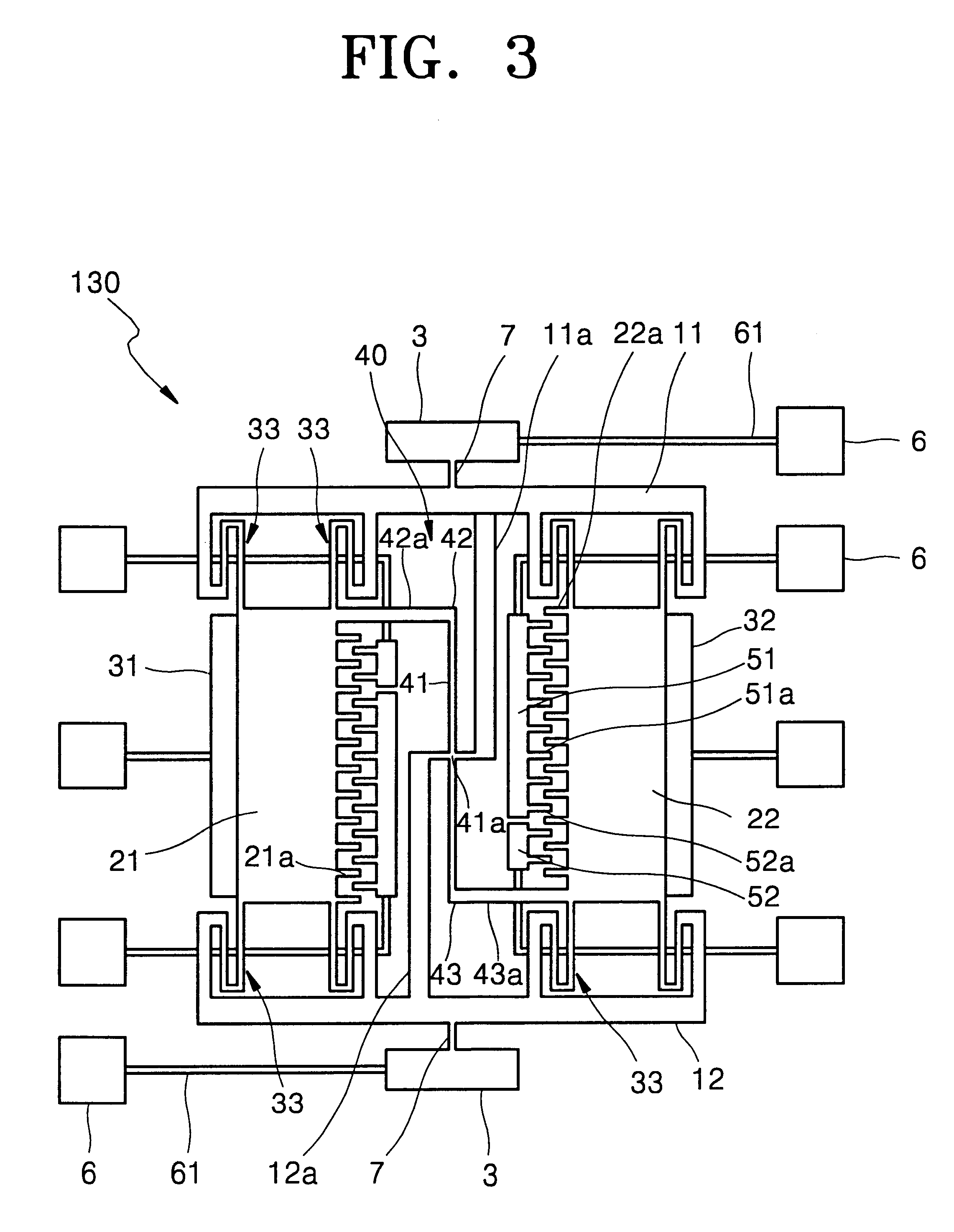
InactiveUS6391673B1Acceleration measurement using interia forcesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsVacuum packVacuum level
A method of fabricating a micro electromechanical system (MEMS) structure which can be vacuum-packaged at the wafer level is provided. The method includes the steps of forming a multilayered stack including a signal line on a first wafer; bonding a second wafer to the multilayered stack; polishing the first wafer to a predetermined thickness; forming a MEMS structure in a vacuum area of the first wafer and a pad outside the vacuum area, the MEMS structure and the pad being connected to the signal line; forming a structure in a third wafer to have space corresponding to the vacuum area of the MEMS structure; and bonding the third wafer to the polished surface of the first wafer in a vacuum state. For protection of the structure and maintaining a vacuum level required for operation, the fabricated structure is vacuum-packaged at the wafer level, thereby improving the yield of fabrication. In addition, since a special vacuum packaging process is not necessary, the fabrication can be simplified.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
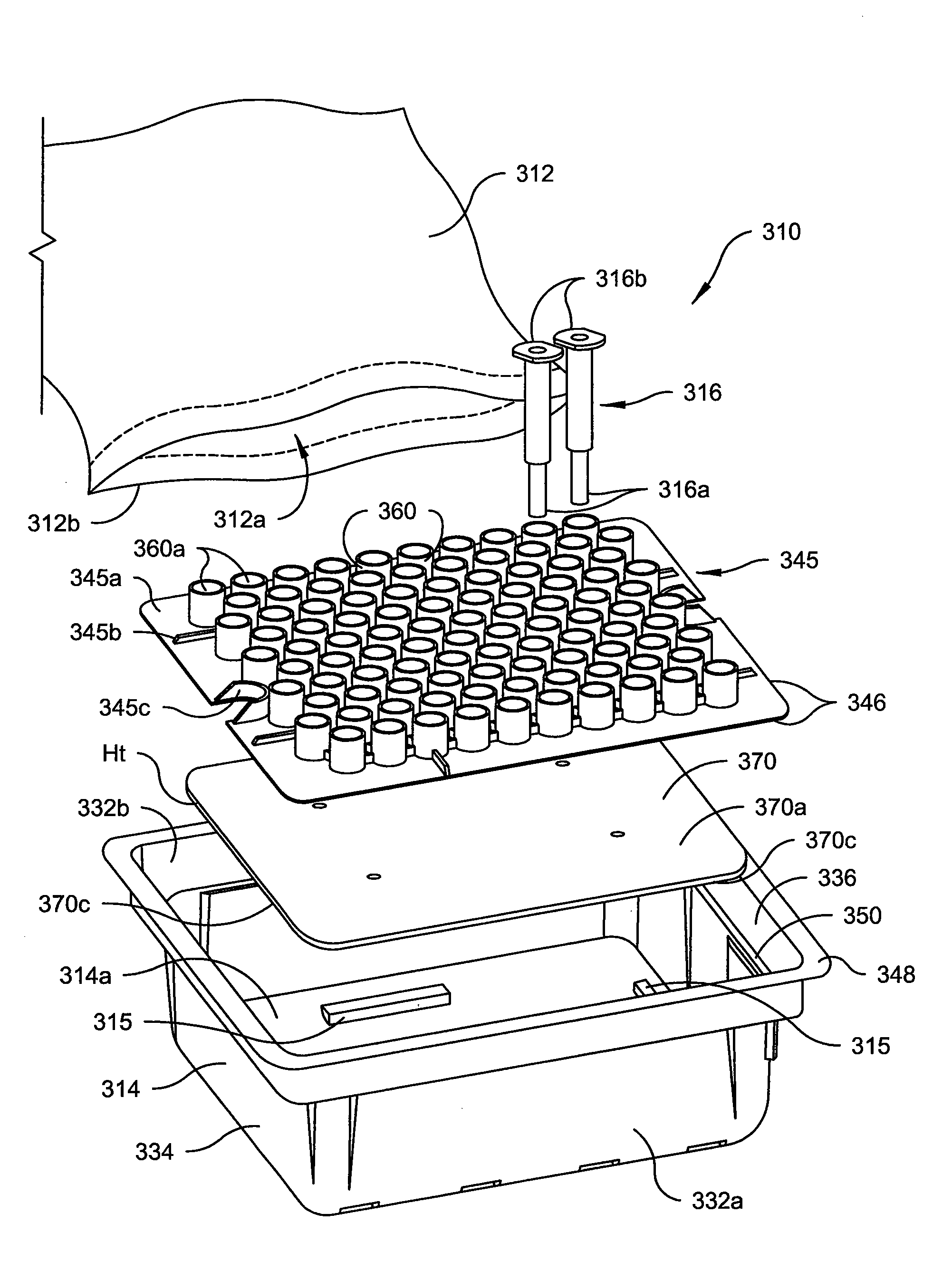
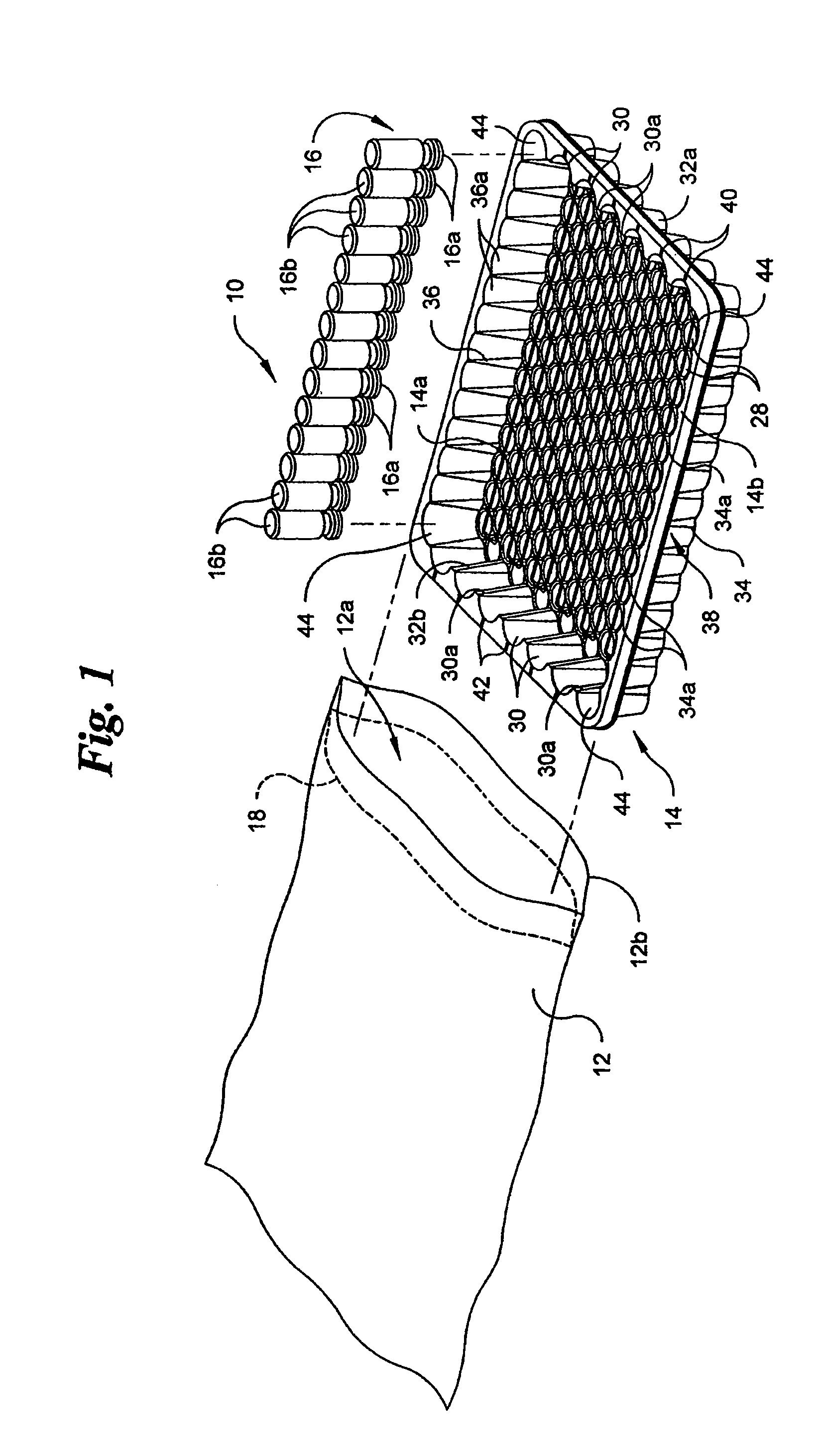
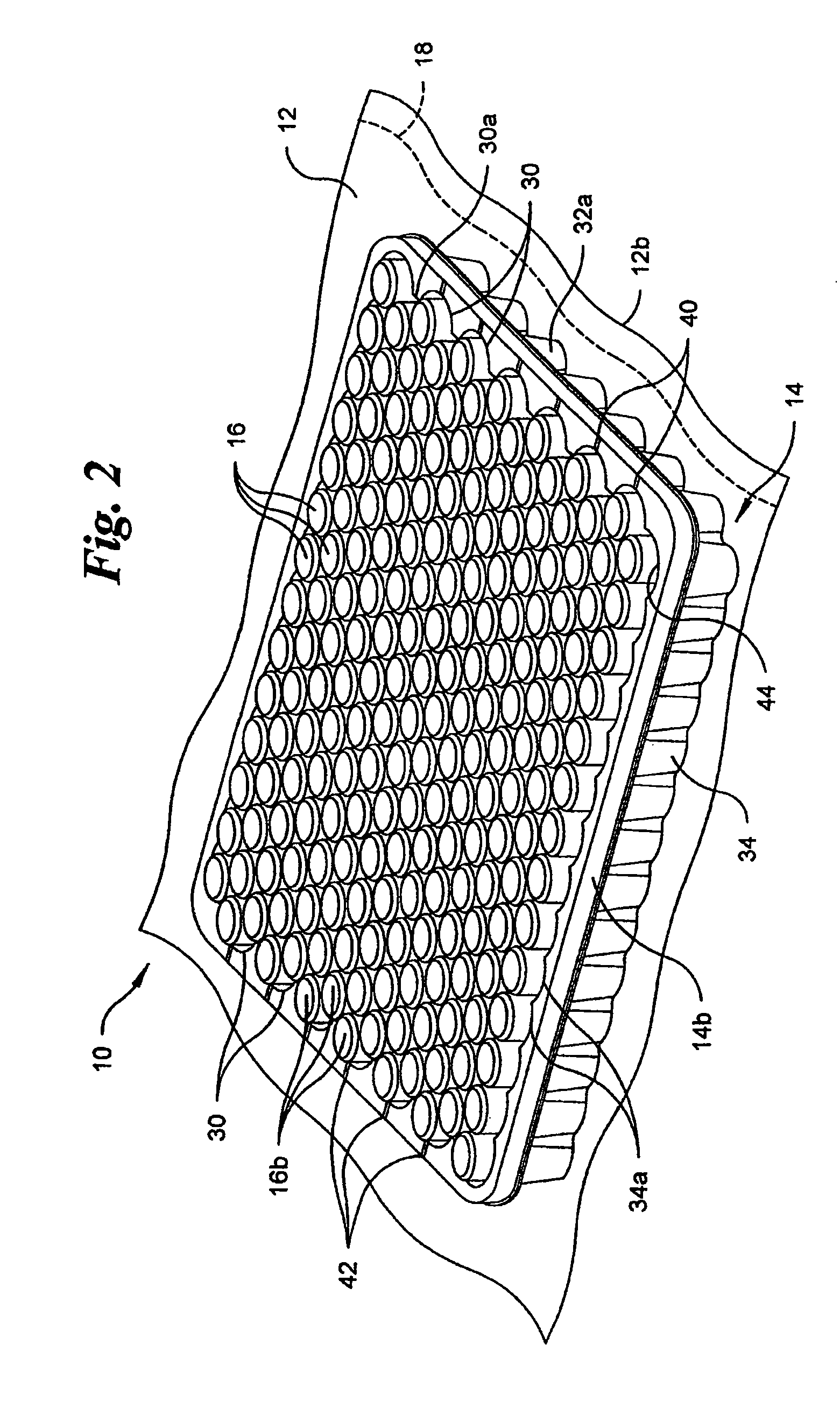
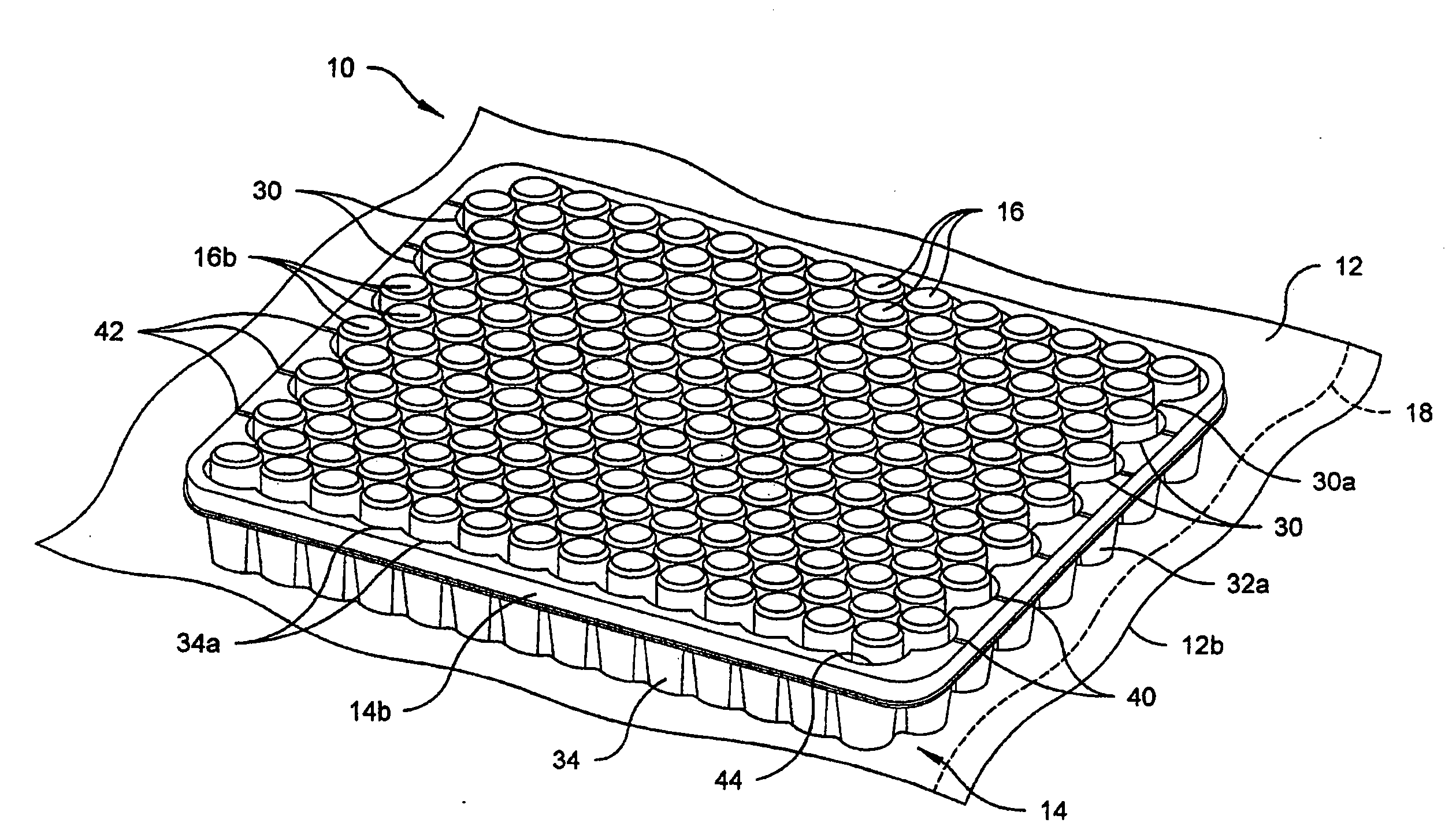
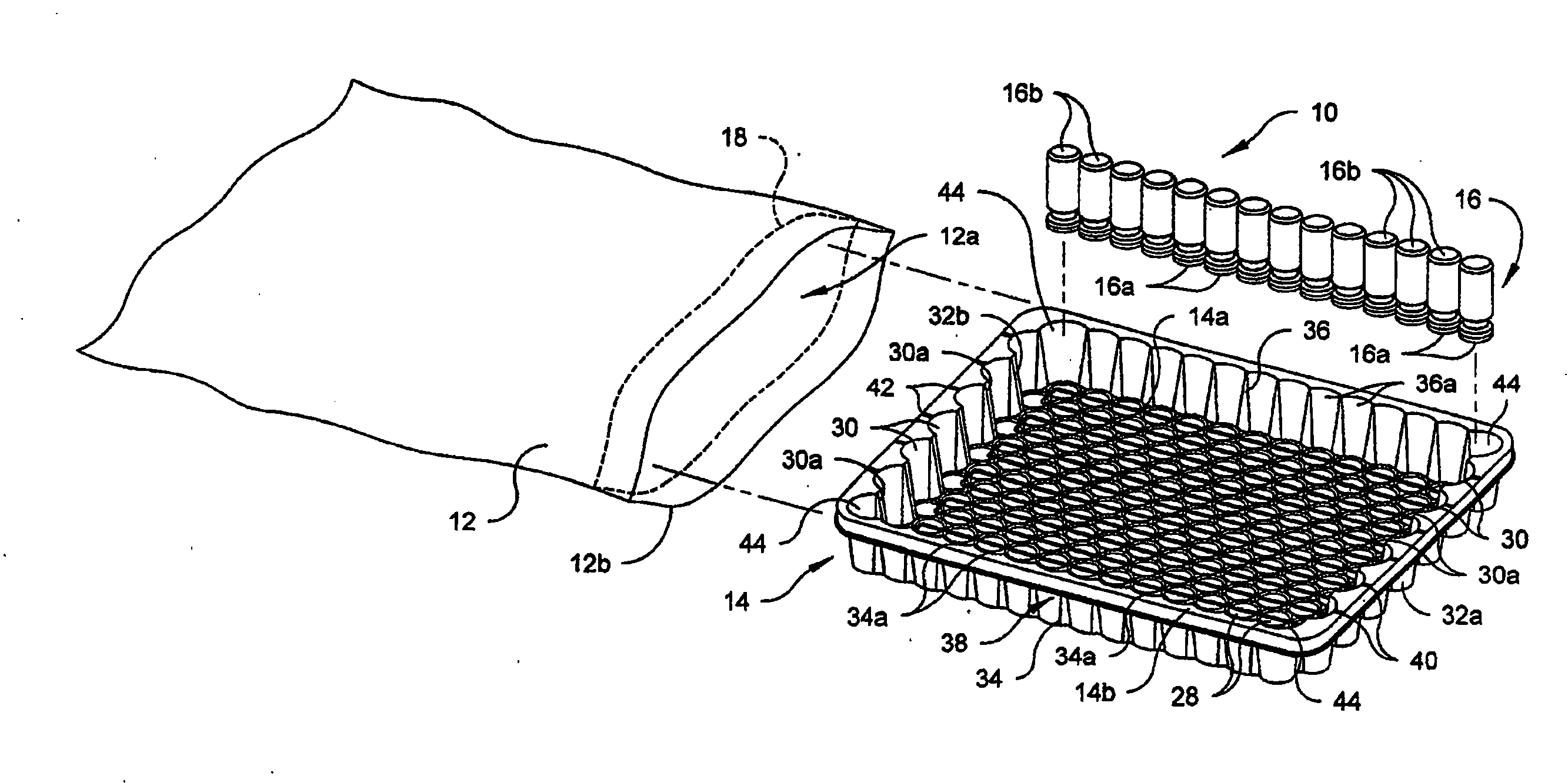
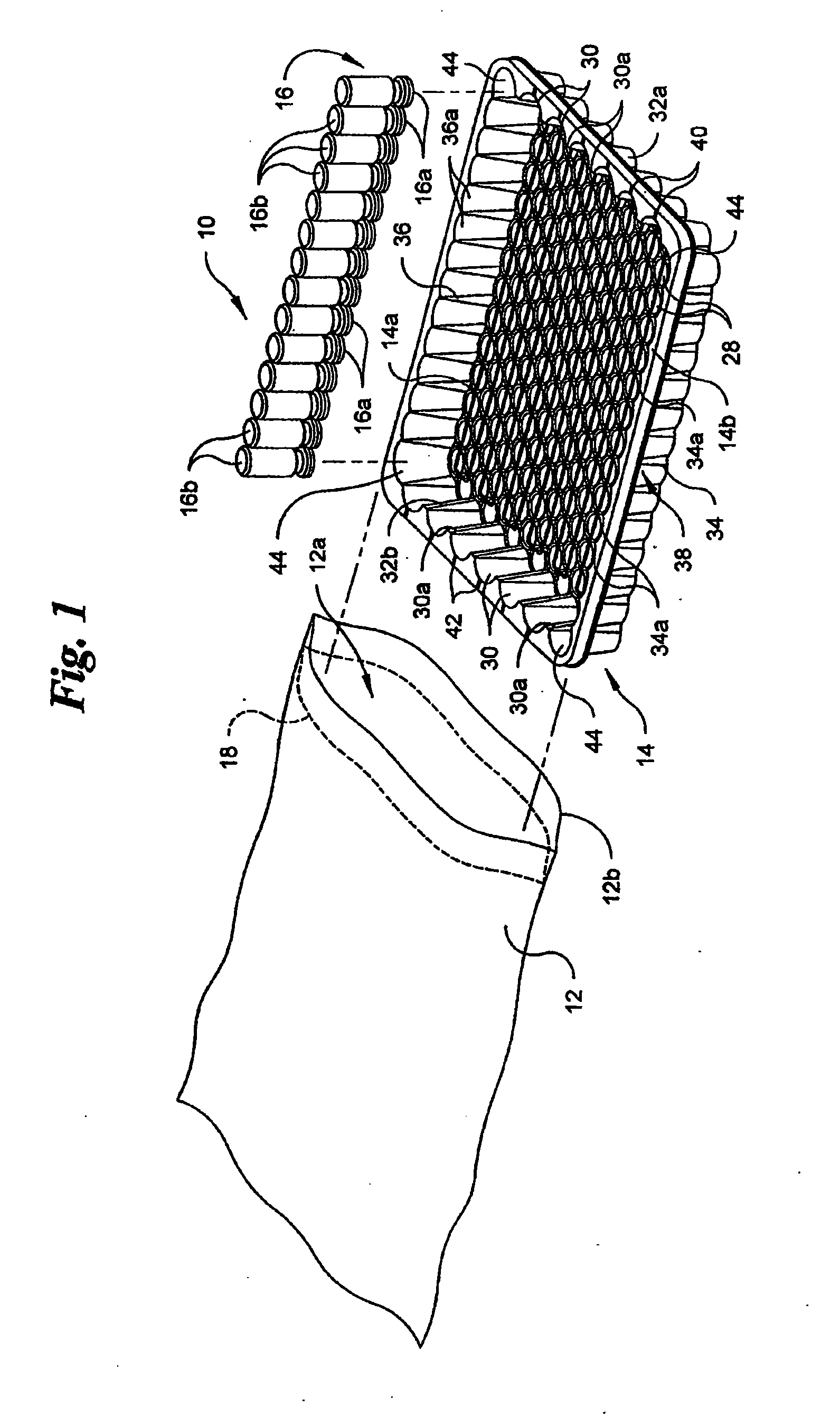
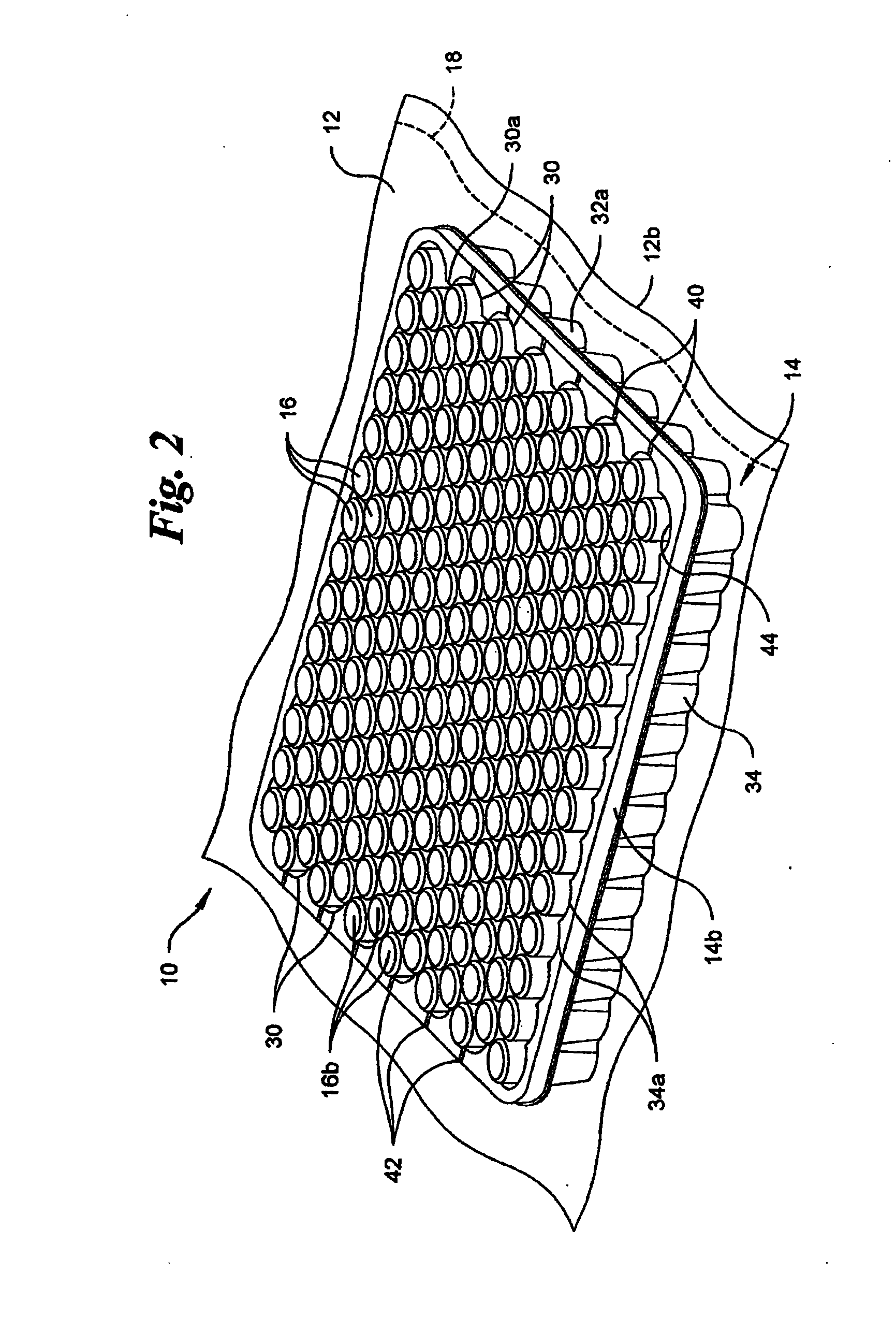
Vacuum package system
A vacuum packaging system for transporting a plurality of medical containers includes a plurality of medical containers each having a head side and a base side and a tray that receives and supports the medical containers. The tray includes opposing first and second sidewalls, opposing front and rear walls and a bottom floor. The walls extend generally vertically from the floor of the tray. At least one platform generally extends parallel to the floor of the tray. An air impervious flexible film defines an internal cavity. The air impervious flexible film completely surrounds the tray and the medical containers and the internal cavity is evacuated to and maintained at a predetermined vacuum level below atmospheric pressure. One of the head side and the base side of each medical container contacts a top surface of at least one platform when the medical containers are positioned in the tray.
Owner:WEST PHARM SERVICES INC +1
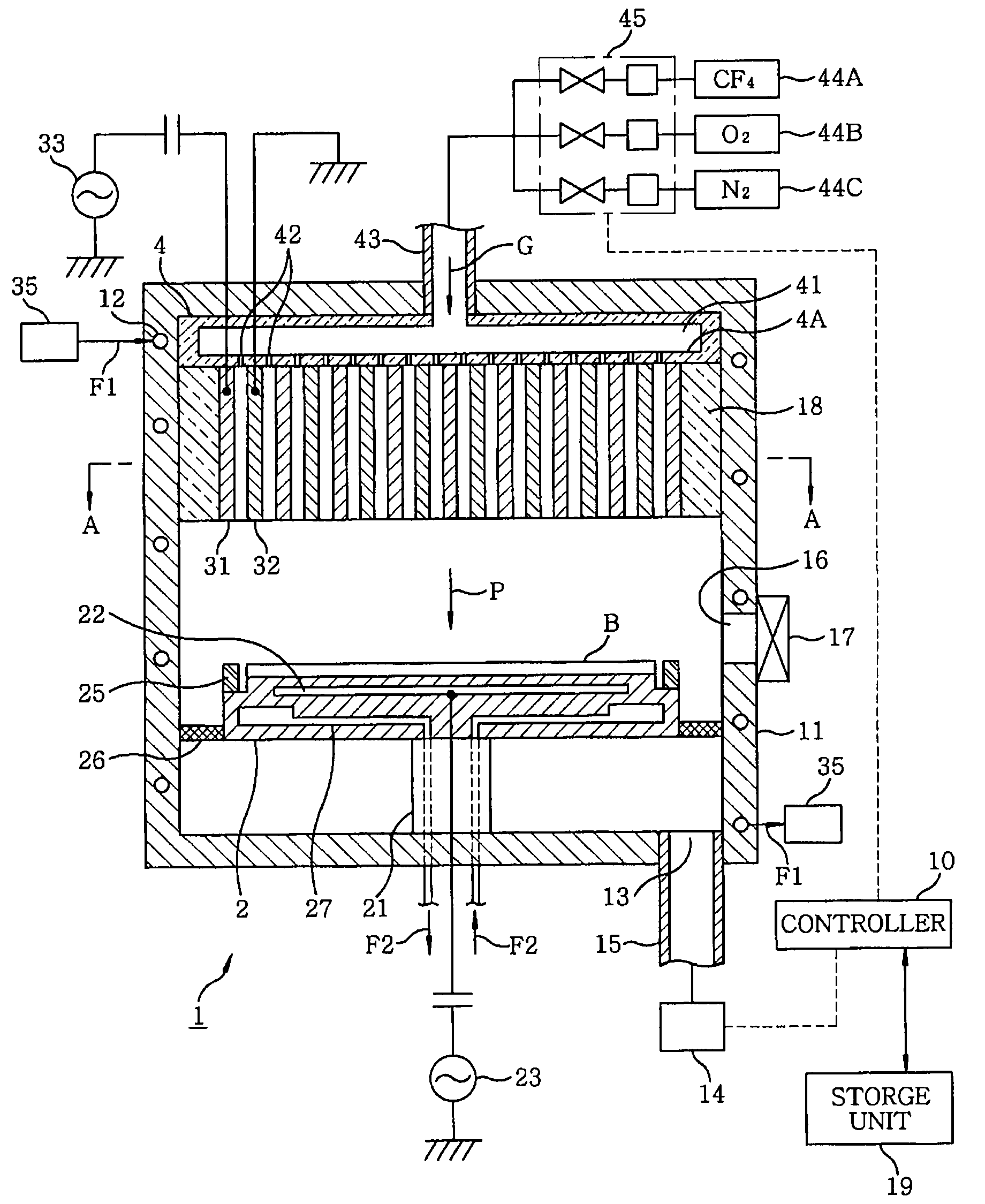
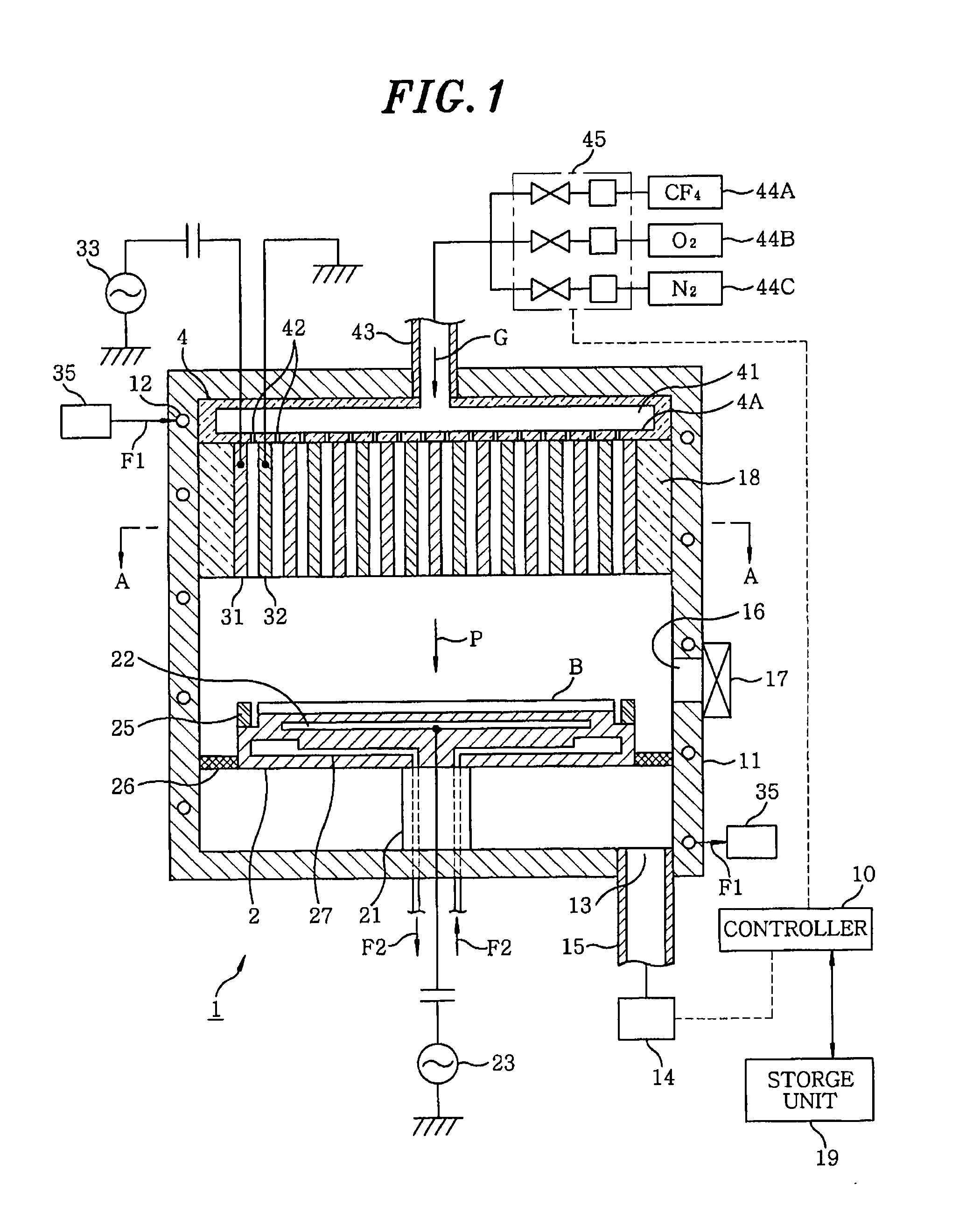
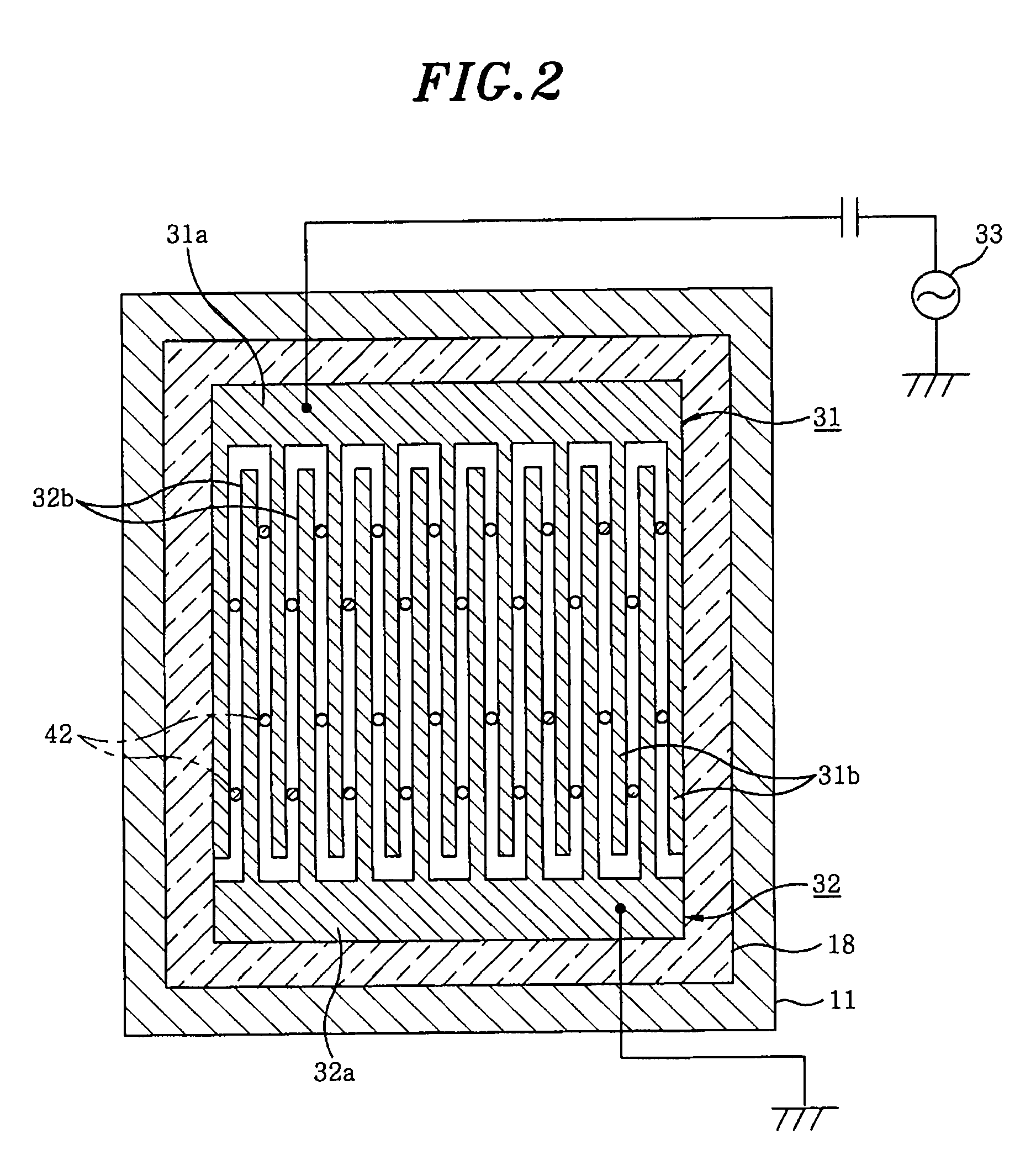
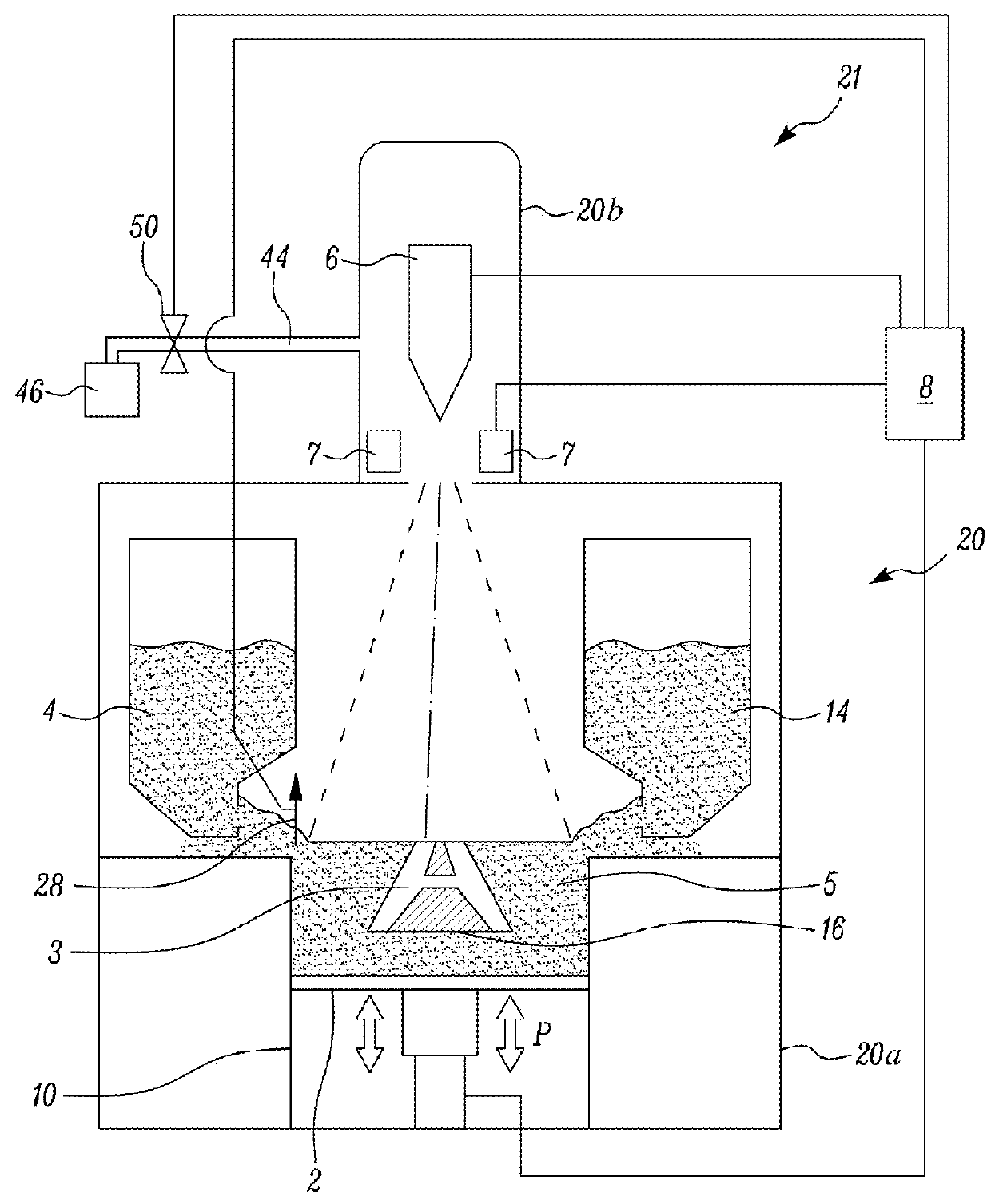
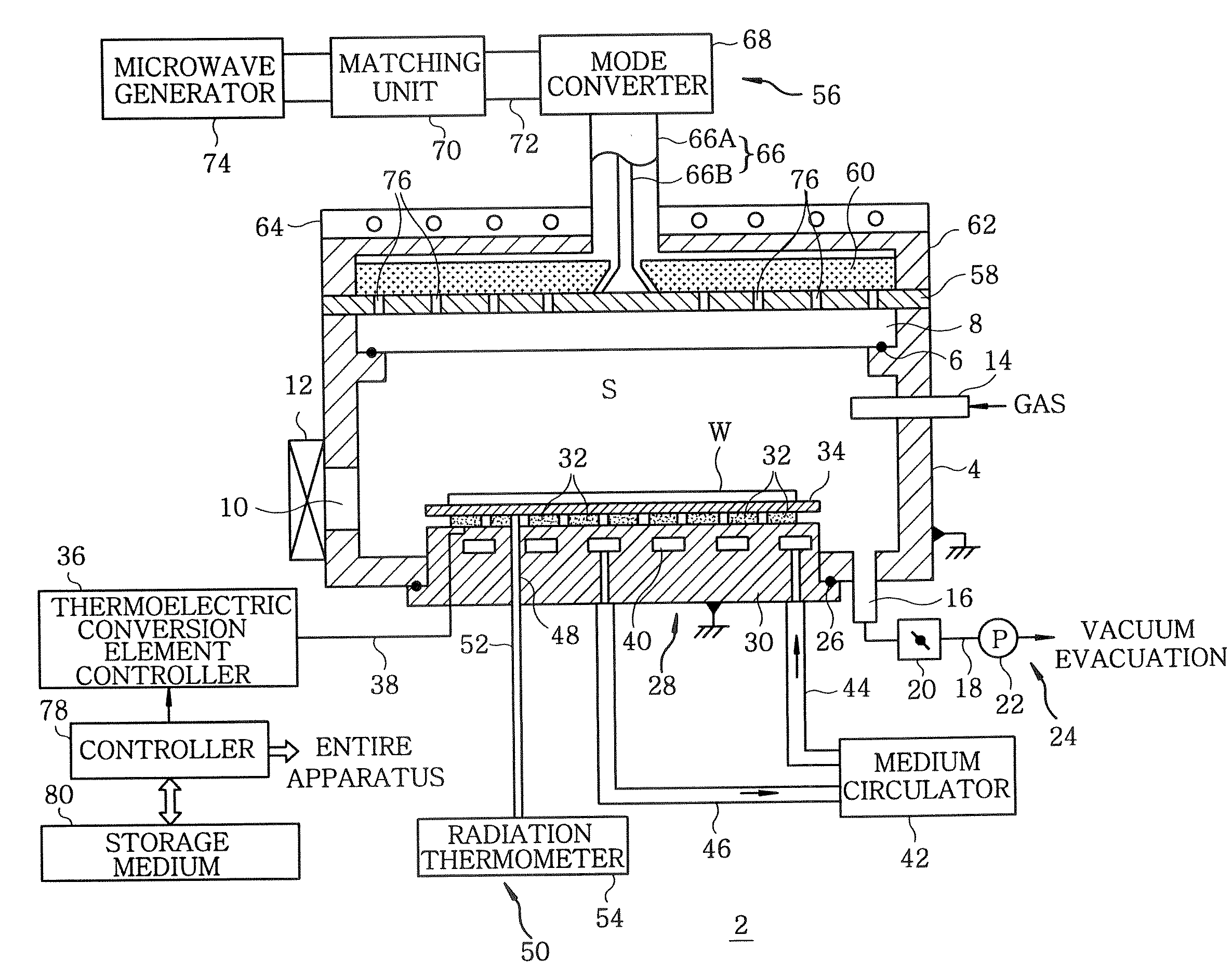
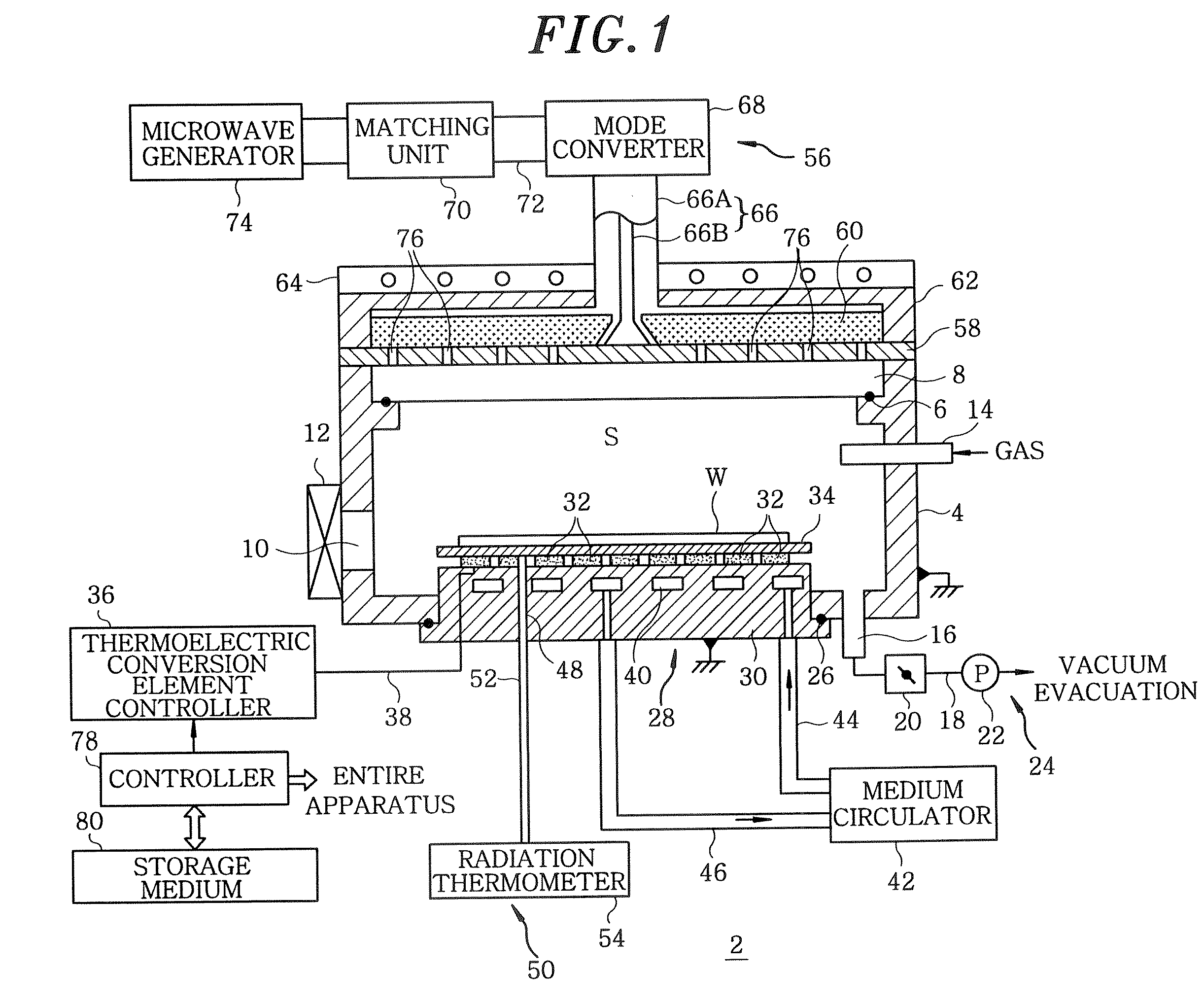
Plasma processing apparatus, plasma processing method and storage medium
InactiveUS20100006543A1Easy to control temperatureReduces temperature of electronLiquid surface applicatorsElectric discharge tubesElectron temperatureVacuum level
A plasma processing apparatus includes a first electrode and a second electrode so arranged in the upper portion of a processing chamber as to face a mounting table, a gas supply unit for supplying a processing gas between the first electrode and the second electrode, a RF power supply unit for applying a RF power between the first electrode and the second electrode for converting the process gas supplied between the electrodes into a plasma, and a gas exhaust unit for evacuating the inside of the processing chamber to a vacuum level from the lower portion of the processing chamber. Since the electron temperature in the plasma is low near a substrate on the mounting table, damage to the substrate caused by the plasma can be suppressed. In addition, since a metal can be used as a material for the processing chamber, the processing chamber can have good temperature controllability.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Vacuum package system
A vacuum packaging system for transporting a plurality of medical containers includes a plurality of medical containers each having a head side and a base side and a tray that receives and supports the medical containers. The tray includes opposing first and second sidewalls, opposing front and rear walls and a bottom floor. The walls extend generally vertically from the floor of the tray. At least one platform generally extends parallel to the floor of the tray. An air impervious flexible film defines an internal cavity. The air impervious flexible film completely surrounds the tray and the medical containers and the internal cavity is evacuated to and maintained at a predetermined vacuum level below atmospheric pressure. One of the head side and the base side of each medical container contacts a top surface of at least one platform when the medical containers are positioned in the tray.
Owner:WEST PHARM SERVICES INC +1
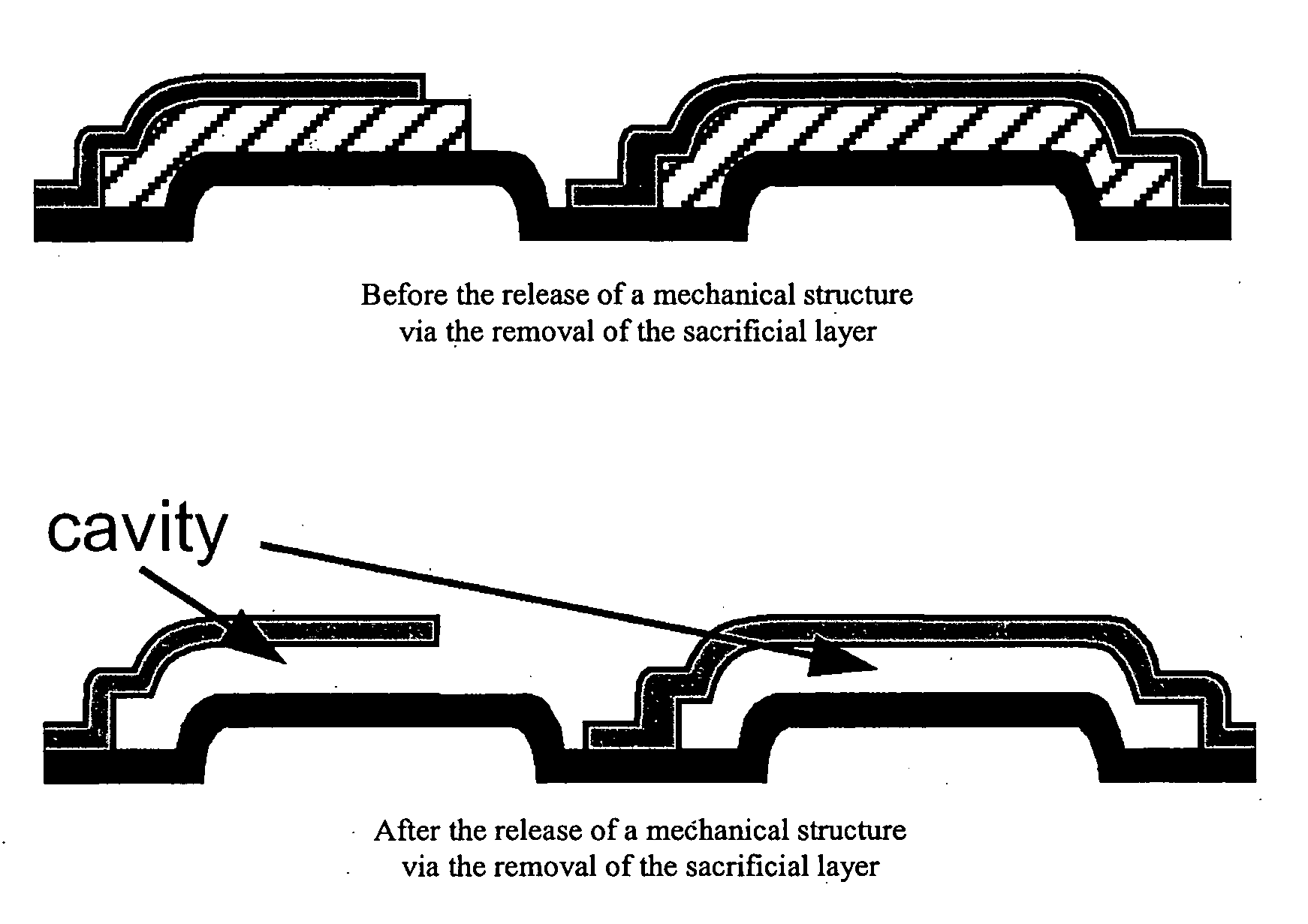
Microshells for multi-level vacuum cavities
Microshells for encapsulation of devices such as MEMS and microelectronics. In an embodiment, the microshells include a planar perforated pre-sealing layer, below which a non-planar sacrificial layer is accessed, and a sealing layer to close the perforation in the pre-sealing layer after the sacrificial material is removed. The sealing layer may include a nonhermetic layer to physically occlude the perforation and a hermetic layer over the nonhermetic occluding layer to seal the perforation as a function of the dimension of the perforation to form cavities having different vacuum levels on the same substrate.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Propulsion-Release Safety Vacuum Release System
InactiveUS20030106147A1Reliably release and push awayNew designGymnasiumSwimming poolsPositive pressureFiltration
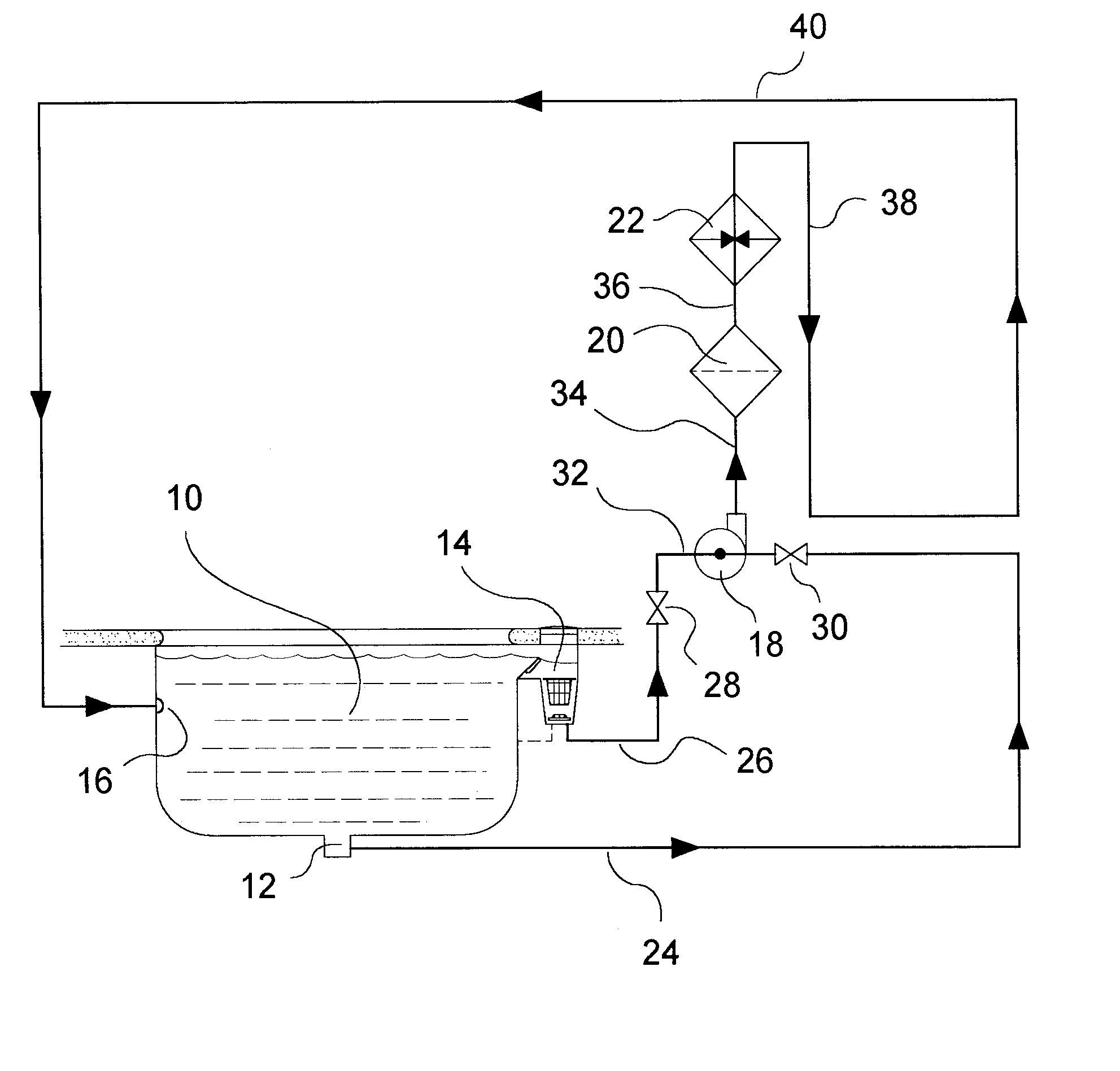
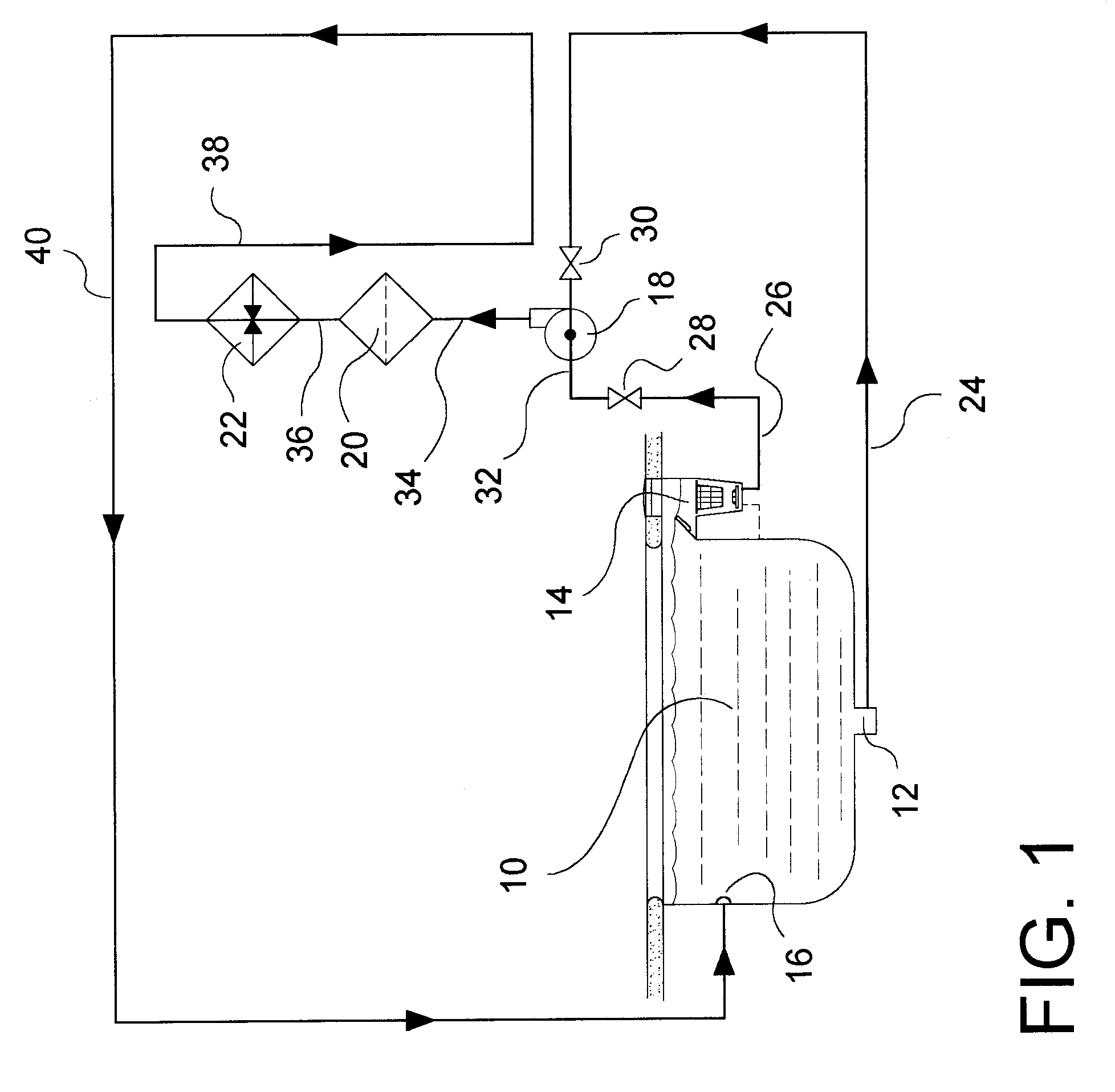
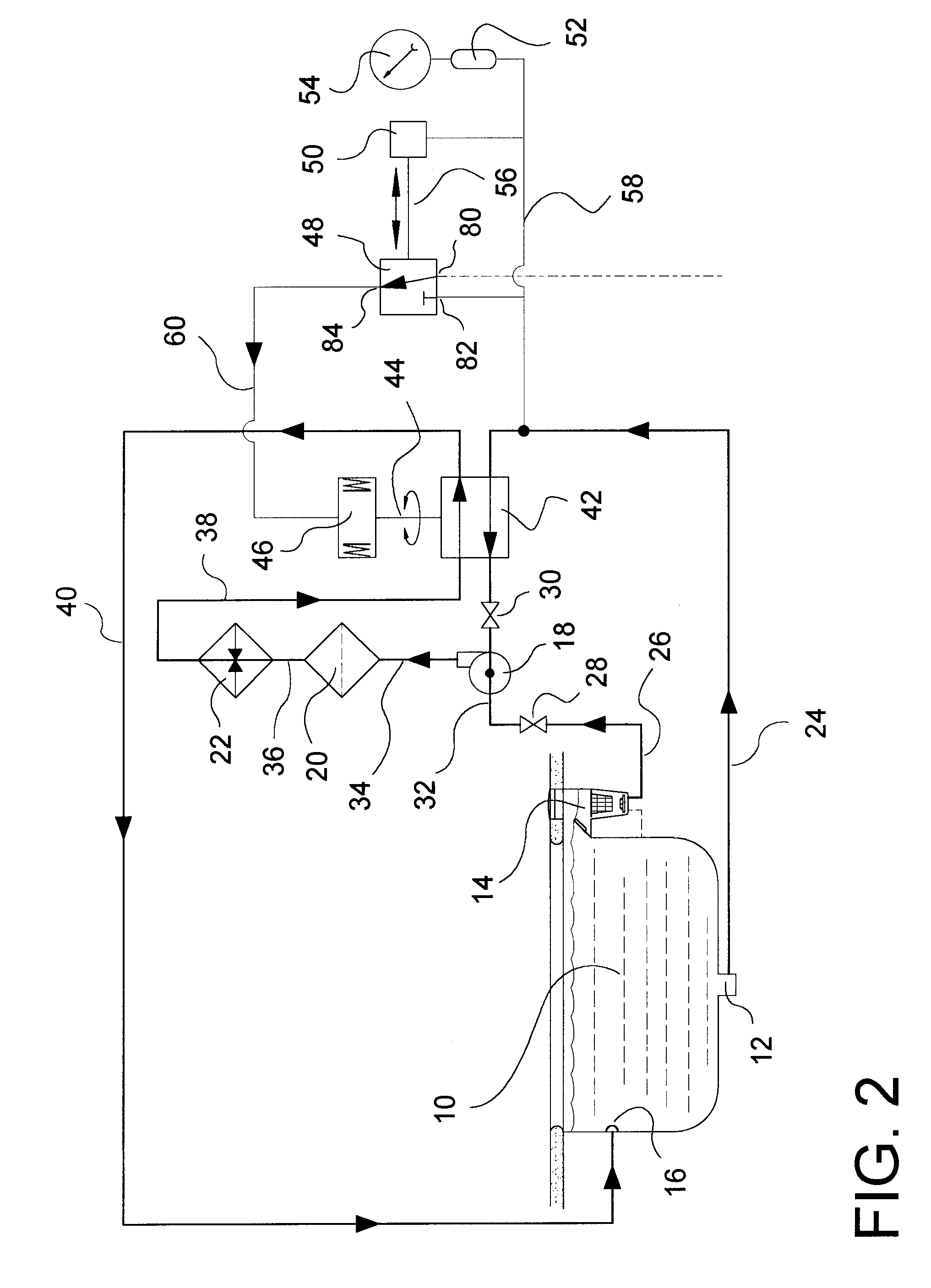
Abstract of Disclosure A propulsion-release safety vacuum release system (SVRS) for swimming pools monitors vacuum level in a suction pipe and reverses flow within the suction pipe if vacuum level exceeds a predetermined level. Thus, if a bather becomes entrapped on a suction outlet such as the pool main drain, the SVRS system not only releases the vacuum but also pushes away the suction-entrapped bather. In response to an elevated vacuum level, a vacuum-monitoring device actuates an automatic valve, which reverses fluid communications between the influent and effluent conduits of the pump and filter system. In this process, the suction pipe is converted from vacuum (negative pressure) to positive pressure. Thereafter, the automatic valve system automatically resets the SVRS to the original or normal flow configuration. The SVRS functions without interrupting operation of the swimming pool filtration system.
Owner:COHEN JOSEPH D +1
MEMS RF switch
A capacitance coupled, transmission line-fed, radio frequency MEMS switch and its fabrication process using photoresist and other low temperature processing steps are described. The achieved switch is disposed in a low cost dielectric housing free of undesired electrical effects on the switch and on the transmission line(s) coupling the switch to an electrical circuit. The dielectric housing is provided with an array of sealable apertures useful for wet, but hydrofluoric acid-free, removal of switch fabrication employed materials and also useful during processing for controlling the operating atmosphere surrounding the switch—e.g. at a pressure above the high vacuum level for enhanced switch damping during operation. Alternative arrangements for sealing an array of dielectric housing apertures are included. Processing details including plan and profile drawing views, specific equipment and materials identifications, temperatures and times are also disclosed.
Owner:US SEC THE AIR FORCE THE
MEMS RF switch integrated process
InactiveUS7381583B1Electrostatic/electro-adhesion relaysSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrofluoric acidCapacitance
A capacitance coupled, transmission line-fed, radio frequency MEMS switch and its fabrication process using photoresist and other low temperature processing steps are described. The achieved switch is disposed in a low cost dielectric housing free of undesired electrical effects on the switch and on the transmission line(s) coupling the switch to an electrical circuit. The dielectric housing is provided with an array of sealable apertures useful for wet, but hydrofluoric acid-free, removal of switch fabrication employed materials and also useful during processing for controlling the operating atmosphere surrounding the switch—e.g. at a pressure above the high vacuum level for enhanced switch damping during operation. Alternative arrangements for sealing an array of dielectric housing apertures are included. Processing details including plan and profile drawing views, specific equipment and materials identifications, temperatures and times are also disclosed.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESETNED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE
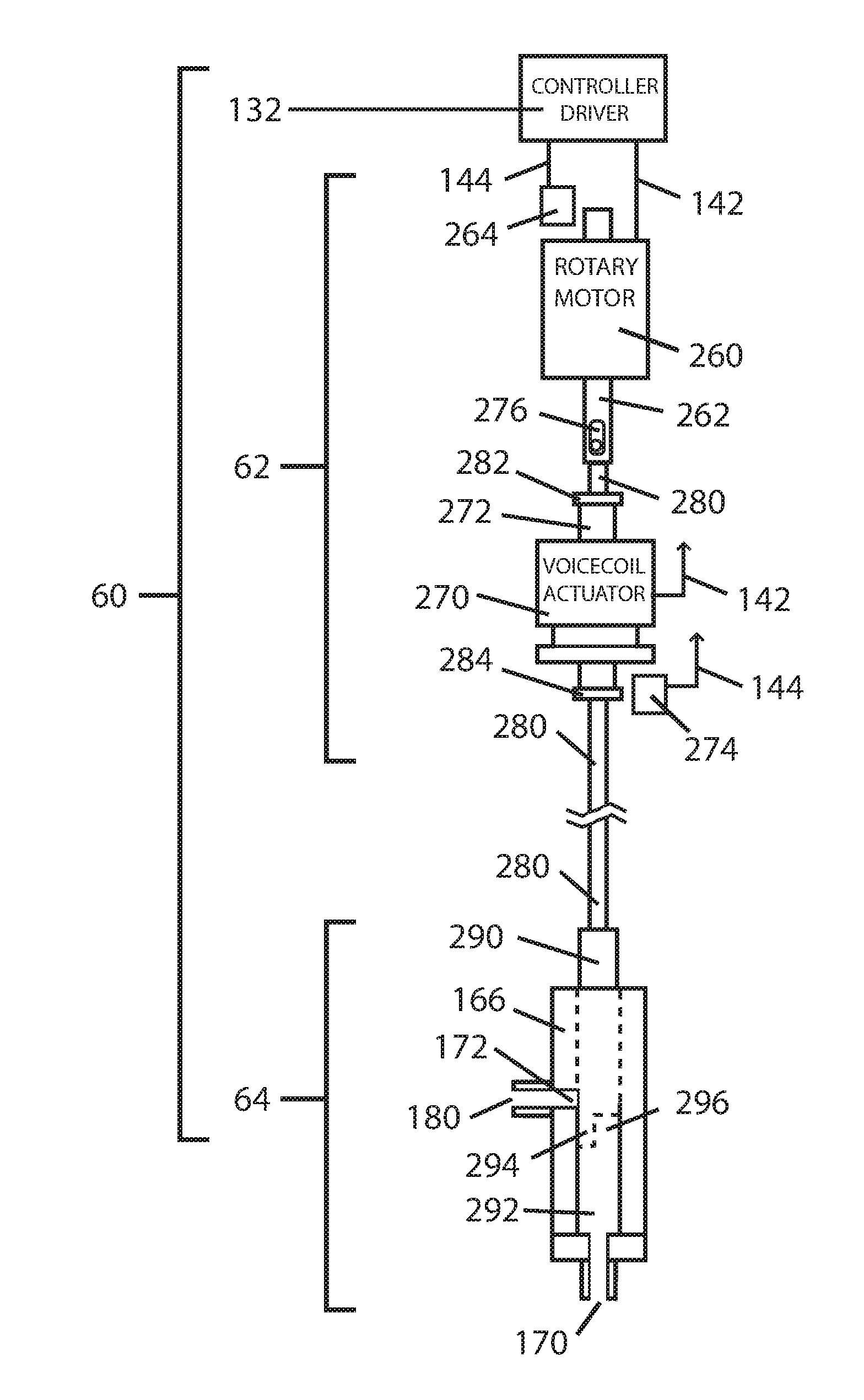
Electrical breast pump
ActiveUS20050043677A1Easily engageableMilking pumpIntravenous devicesCollection systemControl system
A vacuum control system controls the amount of time that pressure is applied to a breast and the amount of time no pressure is applied to the breast, independent of the vacuum level. The amount of time that pressure is applied to a breast and the amount of vacuum applied to the breast cups can be varied by the user. A disposable biological filter isolates the pump from the breast cups. The biological filter is packaged in a housing that has an O-ring push-in connector to connect the collection system to the pump. The vacuum applied to the breast cups is monitored. The control system maintains the vacuum at a level set by the user. A second higher level is used as a safety threshold. The control system shuts down the pump when this higher level is sensed. The breast cup is constructed to provide a controlled collapse when vacuum is applied to mimic the suckling of an infant.
Owner:KELLY PATRICIA A +1
Enhanced additive manufacturing
InactiveUS20160052079A1Shorten the timeSmall volumeAdditive manufacturing apparatusElectric discharge tubesBeam sourceVacuum level
Various embodiments of the present invention relate to a method for operating an additive manufacturing apparatus in which a three-dimensional article is formed. Said method comprising the steps of: providing a vacuum chamber having at least a first and a second section, wherein said first and second sections are openly connected to each other, providing a predetermined vacuum level inside said vacuum chamber, providing a layer of powder material on a work table in said first section of said vacuum chamber, directing an electron beam from said at least one electron beam source provided in said second section over said work table to fuse in first selected locations according to said model to form a first cross section of said three-dimensional article, purging said second section with a dry gas when said vacuum chamber is open for prohibiting ambient air into said second section.
Owner:ARCAM AB
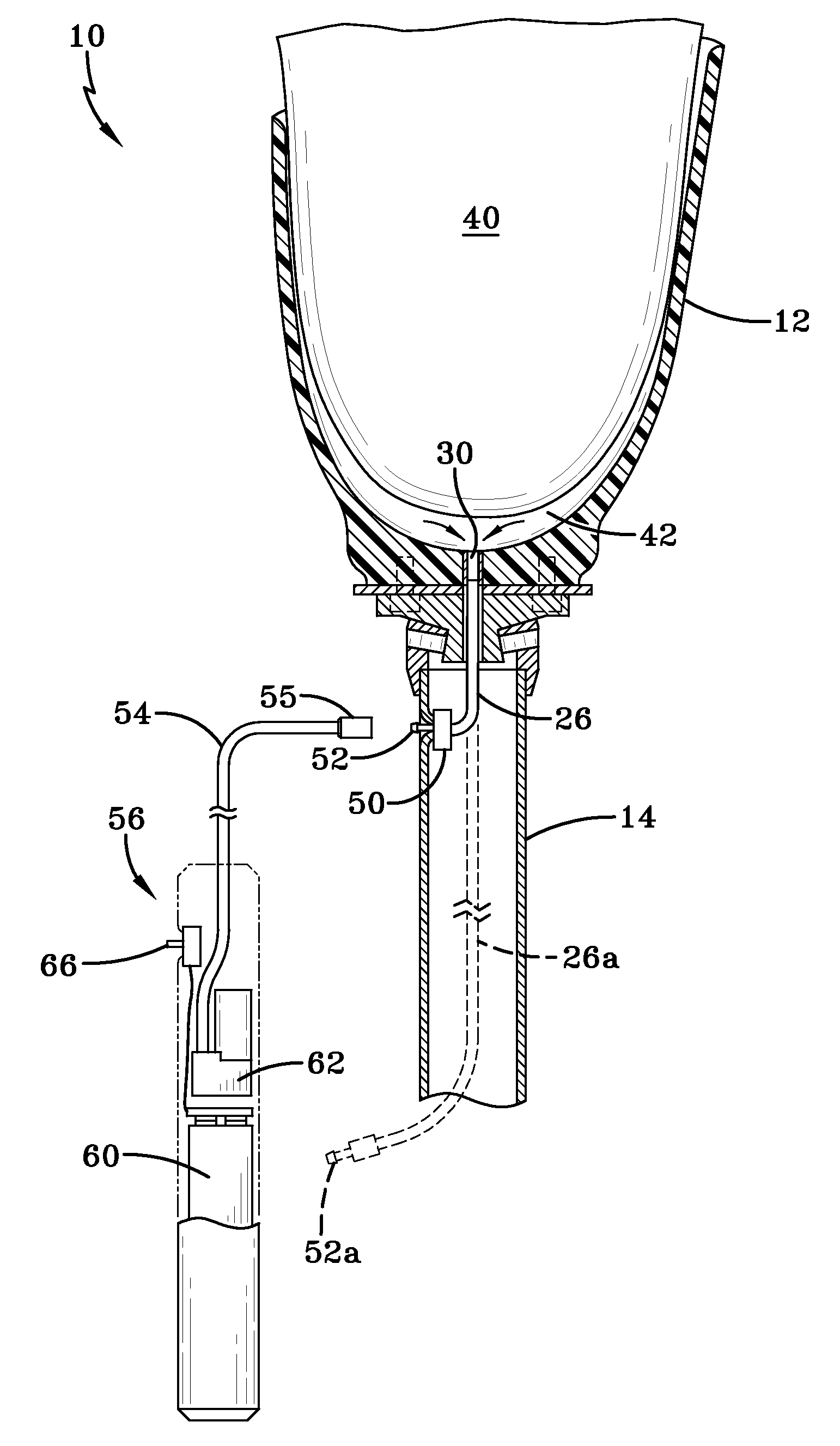
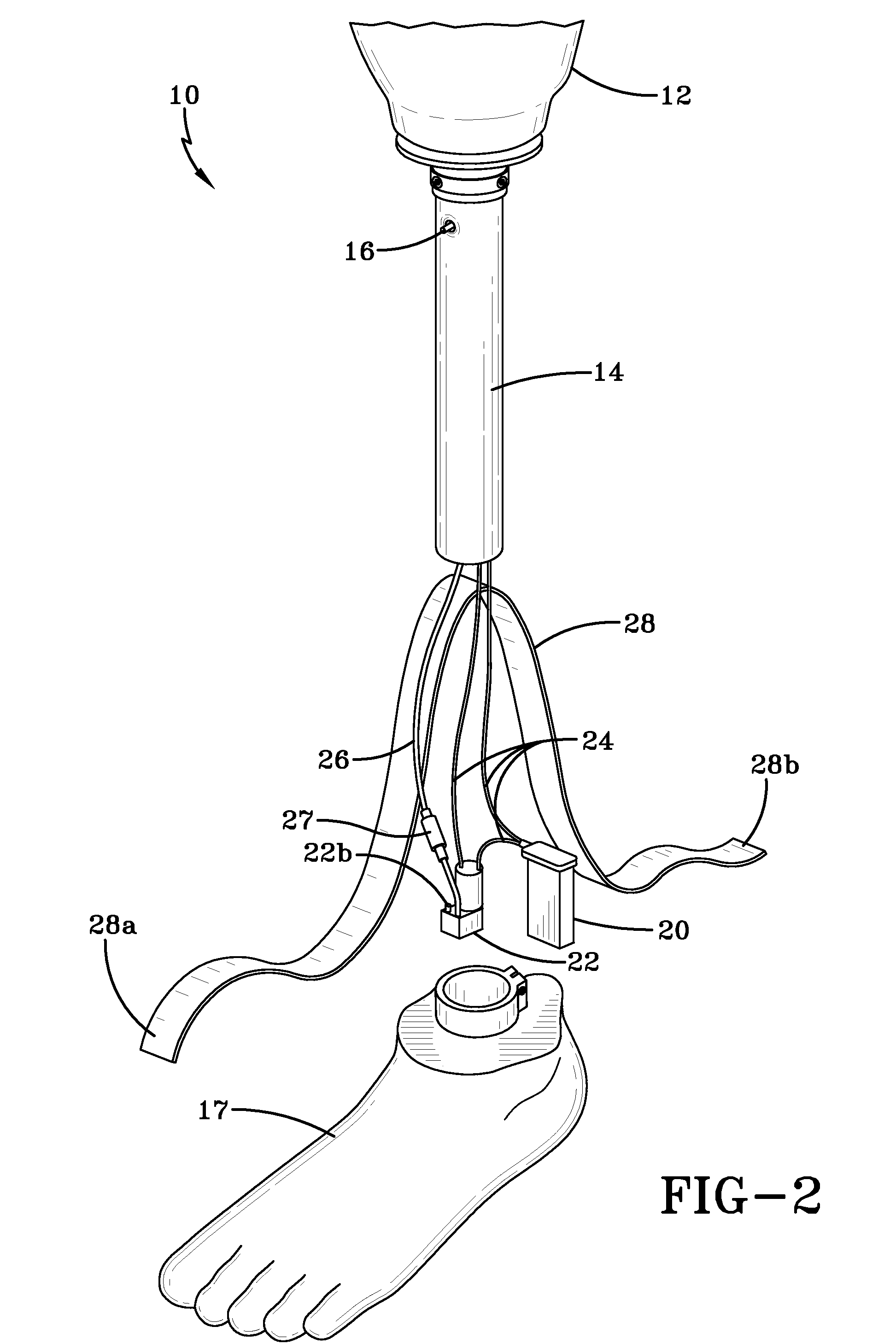
Prosthetic device utilizing electric vacuum pump
ActiveUS20080243266A1Easy to useReadily incorporated into/onto prosthesisArtificial legsArtificial handsControl systemVacuum level
Prosthetic devices having vacuum components operative to evacuate the interior of a prosthetic socket thereof, and control systems for use therewith. The evacuation devices preferably include at least an electrically powered vacuum pump and associated power source, and a vacuum accumulator connected to the vacuum pump. Associated control systems may be of various designs and may employ wired or wireless communication. Control of an evacuation device may be based on vacuum level, residual limb volume, residual limb motion, user activity level or other device parameters.
Owner:WILLOWWOOD GLOBAL LLC
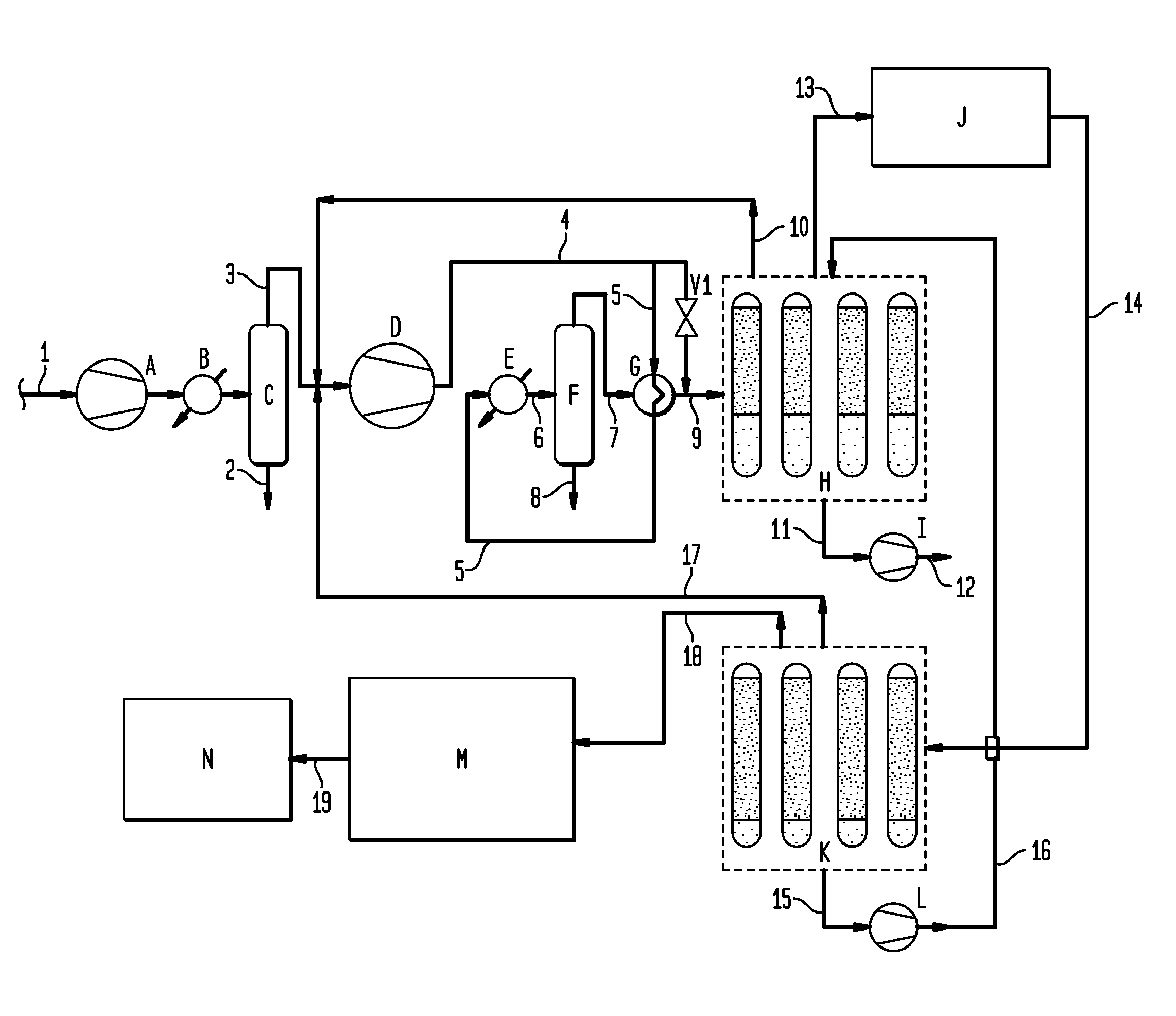
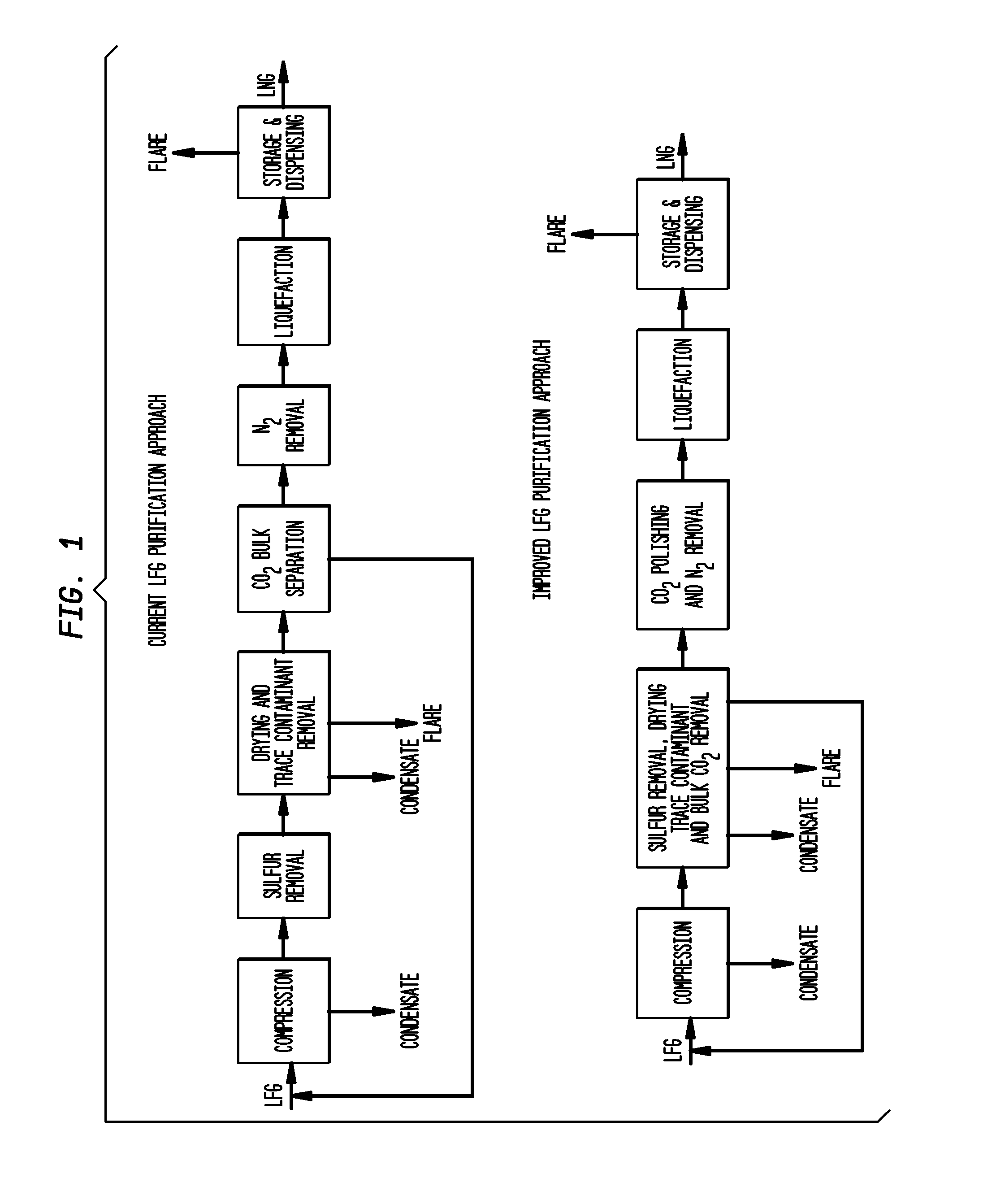
Gas purification processes
InactiveUS20110185896A1Reduce and eliminate needEasy to controlGas treatmentGaseous fuelsVacuum levelAir purification
A method for removing contaminants from a natural gas stream such as a biogas / landfill gas stream. The natural gas stream is fed to a first adsorption unit for removal of certain contaminants and then to a second adsorption unit for the removal of additional contaminants. Alternatively, a membrane stage may be employed between the adsorption units. The method utilizes the external purge to enhance pressure swing adsorption working capacity so that the vacuum level required for regeneration is not as high.
Owner:LINDE AG
Field effect transistor
ActiveUS20110309411A1Reduce FET characteristicReduce the impactTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical conductorIndium
An insulating film is provided over one surface of a first semiconductor layer including a first oxide semiconductor including indium as a main component, and a second semiconductor layer including an i-type second oxide semiconductor is provided in contact with the other surface. The energy difference between a vacuum level and a Fermi level in the second oxide semiconductor is larger than that in the first oxide semiconductor. In the first semiconductor layer, a region in the vicinity of the junction surface with the second oxide semiconductor which satisfies the above condition is a region having an extremely low carrier concentration (a quasi-i-type region). By using the region as a channel, the off-state current can be reduced. Further, a drain current of the FET flows through the first oxide semiconductor having a high mobility; accordingly, a large amount of current can be extracted.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Insulating film, method for manufacturing semiconductor device, and semiconductor device
ActiveUS20130264563A1Excellent electrical propertiesReduce the amount of oxygenTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHigh frequency powerVacuum level
In a semiconductor device including a transistor including an oxide semiconductor film and a protective film over the transistor, an oxide insulating film containing oxygen in excess of the stoichiometric composition is formed as the protective film under the following conditions: a substrate placed in a treatment chamber evacuated to a vacuum level is held at a temperature higher than or equal to 180° C. and lower than or equal to 260° C.; a source gas is introduced into the treatment chamber so that the pressure in the treatment chamber is set to be higher than or equal to 100 Pa and lower than or equal to 250 Pa; and a high-frequency power higher than or equal to 0.17 W / cm2 and lower than or equal to 0.5 W / cm2 is supplied to an electrode provided in the treatment chamber.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Vehicle Braking Control
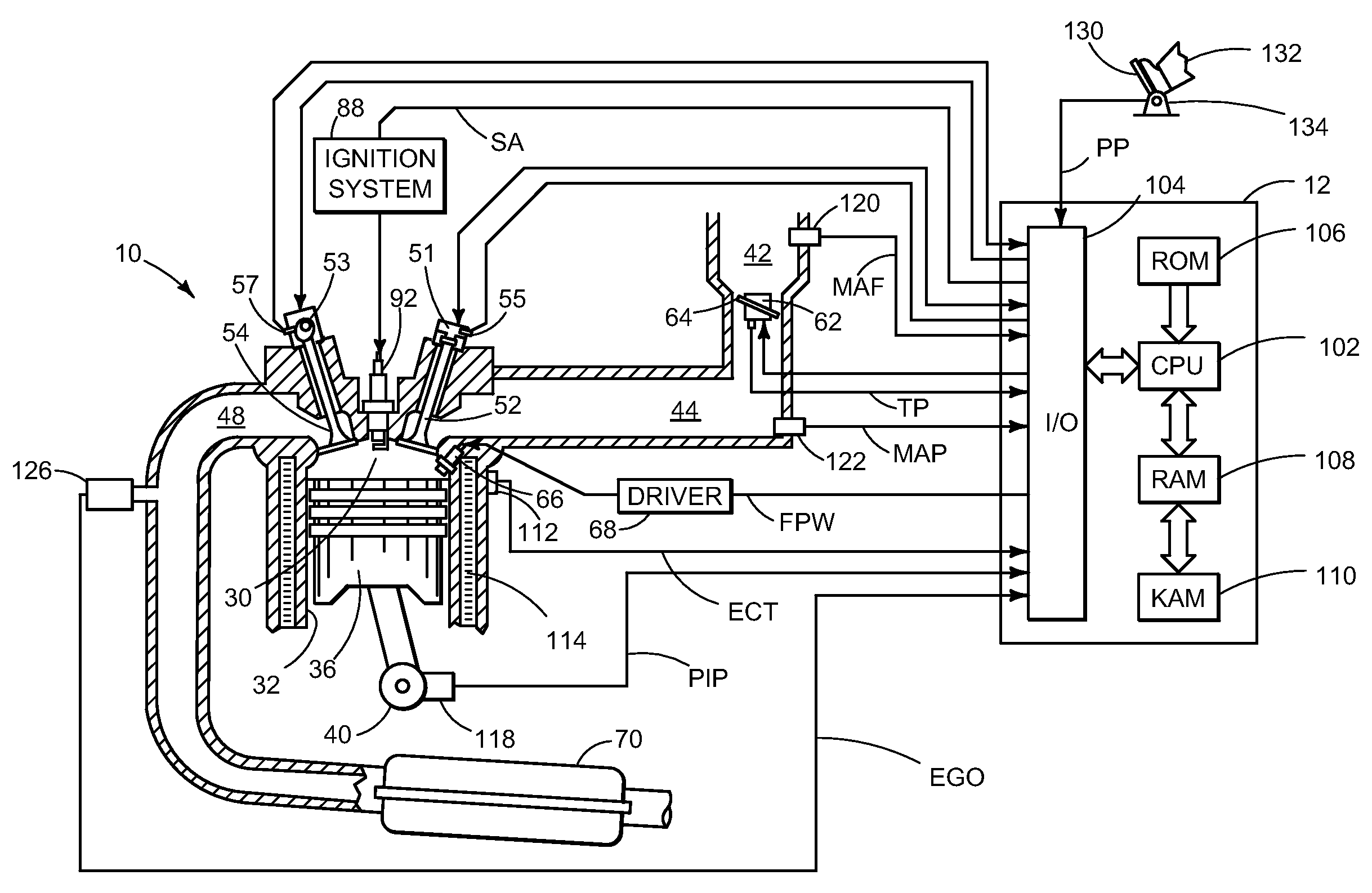
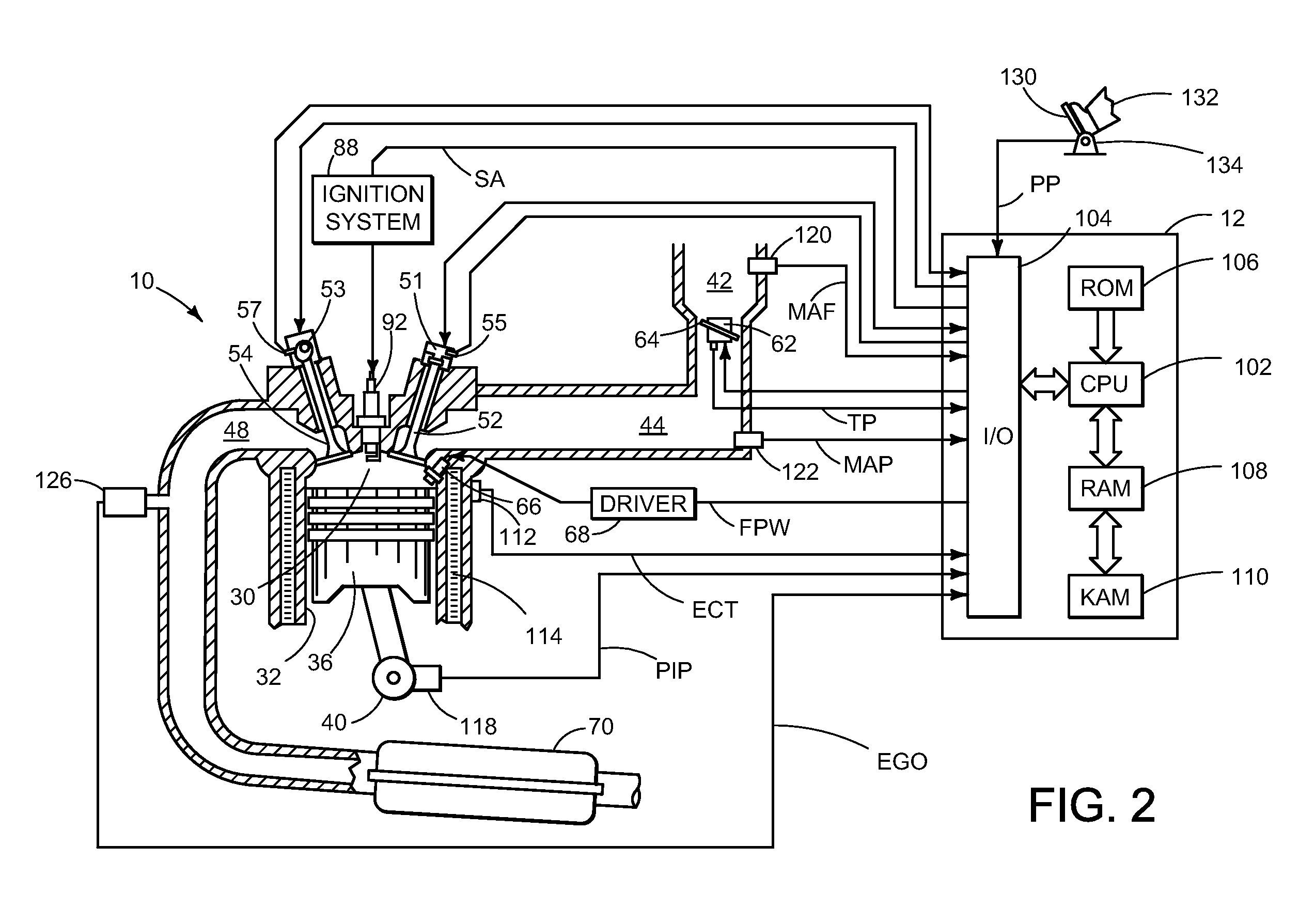
ActiveUS20080041336A1Increased intake manifold vacuumEasy to controlElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust valveVacuum level
A method of operating an engine for a vehicle having at least a first cylinder, the method comprising of operating the first cylinder to provide at least one of compression braking and expansion braking by holding one of an intake valve and an exhaust valve of the first cylinder closed while opening, closing, and opening the other of the intake valve and the exhaust valve during a cycle of the first cylinder and during a first vacuum level of an intake manifold upstream of the first cylinder; and operating the first cylinder to provide at least one of compression braking and expansion braking by operating both the intake valve and the exhaust valve of the first cylinder during a cycle of the first cylinder to allow at least some air to flow through the first cylinder during a second vacuum level of the intake manifold.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Anhydrous HF release of process for MEMS devices
ActiveUS20060211163A1Prevent undesirable metal incompatibility effectDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhysical chemistryVacuum level
A method of etching a sacrificial oxide layer covering an etch-stop silicon nitride underlayer, involves exposing the sacrificial oxide to anhydrous HF at a temperature of less than about 100° C. and / or at vacuum level lower than 40 Torr; and subsequently performing an in-situ vacuum evaporation of etch by-products at a temperature of more than about 100° C. and at vacuum level lower than the 40 Torr without exposure to ambient air.
Owner:TELEDYNE DIGITAL IMAGING INC
Method of manufacturing liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS6970227B2Improve display qualityHigh yieldNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayVacuum level
A plurality of main seal patterns and dummy seal patterns are formed by a sealant on one of substrates. The plurality of main seal patterns individually enclose each of a plurality of display areas. The dummy seal patterns individually enclose the plurality of main seal patterns, and sides of the dummy seal patterns facing sides of the one substrate are all interconnected. These formations enable constant vacuum levels to be maintained the inside and the outside of the main seal patterns when the inside of a chamber of an assembling device is recovered to atmospheric pressure. Therefore, distortion of substrates is impeded in the vicinity of the main seal patterns, and degradation of display quality can be prevented.
Owner:SHARP KK
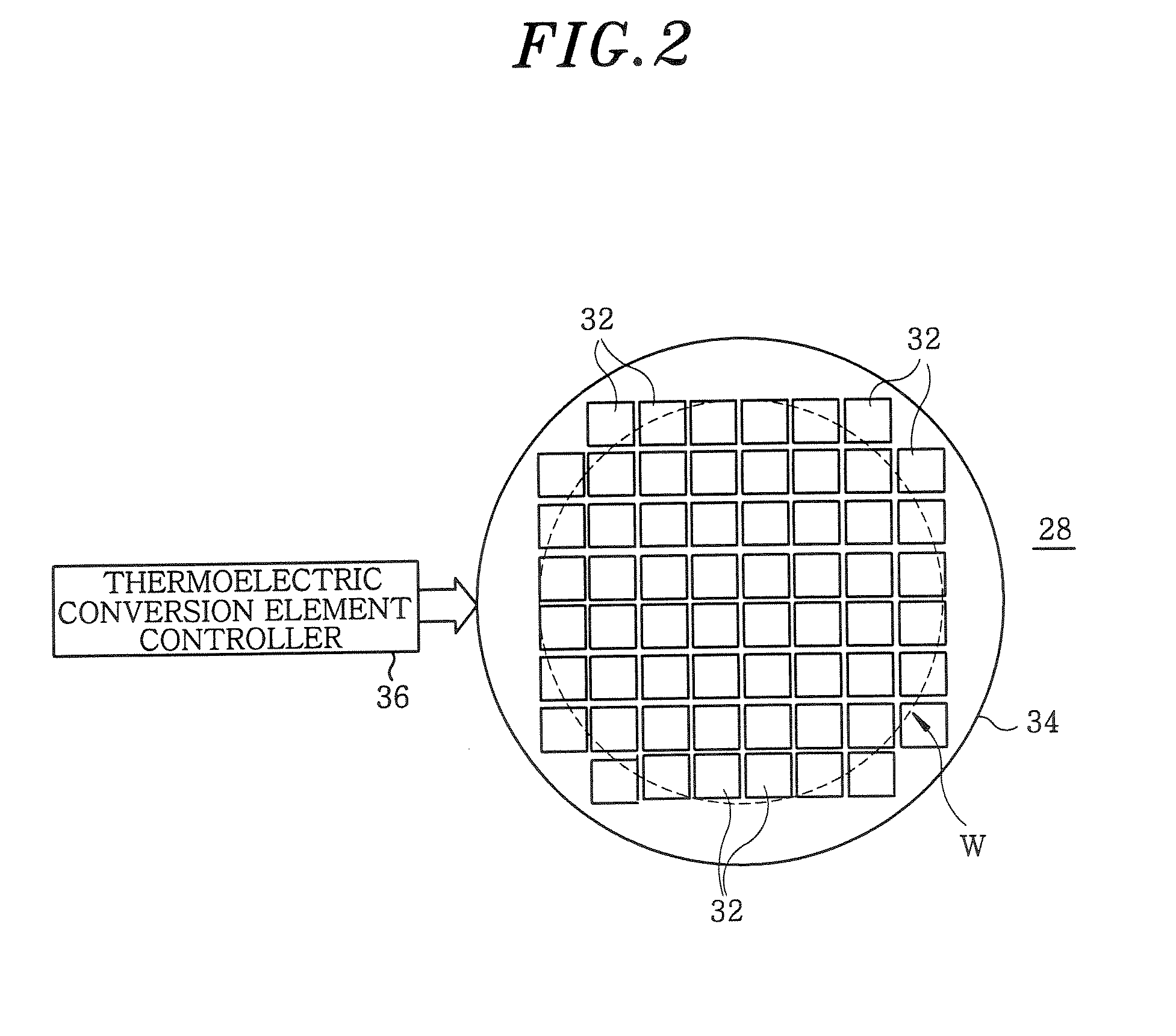
Heat treating apparatus, heat treating method and storage medium
InactiveUS20070224839A1Temperature can be raised and loweredImprove efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicrowave heatingElectromagnetic electron waveVacuum level
A heat treating apparatus, which performs a specified heat treatment on a target object, includes a processing chamber accommodating therein the target object; a mounting table for mounting thereon the target object; a vacuum exhaust system for vacuum evacuating the processing chamber; an electromagnetic wave supply unit for irradiating an electromagnetic wave onto the target object to heat the target object; and a controller for controlling the heat treating apparatus such that the electromagnetic wave is irradiated onto the target object at a high vacuum level at which plasma is not generated. Further, a heat treating method performs a specified heat treatment on a target object, wherein the target object is accommodated in a processing chamber capable of being vacuum evacuated, and the target object is heated by irradiating an electromagnetic wave thereon at a high vacuum level at which plasma is not generated in the processing chamber.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Vacuum Package System
A vacuum packaging system for transporting a plurality of medical containers includes a plurality of medical a tray that receives and supports the medical containers. The tray includes opposing first and second side walls, opposing side and rear walls and a bottom floor. The walls extend generally perpendicularly from the bottom floor of the tray to a top edge thereof. A nesting plate is removably mountable in the tray and includes a plurality of generally cylindrical sleeves each receiving one of the plurality of medical containers. A support surface within the tray generally extends parallel to and spaced a predetermined distance from the bottom floor of the tray and receives and supports the nesting plate. An air impervious flexible film defines an internal cavity and completely surrounds the tray and the medical containers. The internal cavity is evacuated to and maintained at a predetermined vacuum level below atmospheric pressure.
Owner:WEST PHARM SERVICES INC +1
Precision orifice safety device
InactiveUS20100030134A1Easy to controlLower Level RequirementsMedical devicesIntravenous devicesRefluxVacuum level
A safety device in a fluid vent conduit for reducing vacuum level in an aspiration conduit of an ophthalmic surgical system. The device includes an orifice having an inlet for receiving a flow of fluid from an irrigation source. The orifice further has an outlet for directing the flow of fluid into the aspiration conduit. The orifice has a cross-sectional area sufficiently large to ensure an acceptable amount of fluid flows into the aspiration conduit, to reduce the vacuum level in the aspiration conduit, to an acceptable level in an acceptable amount of time and to provide adequate reflux. The cross-section area is sufficiently small to restrict the flow of fluid to allow enough fluid to continue to flow from the irrigation source to a handpiece at a surgical site.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
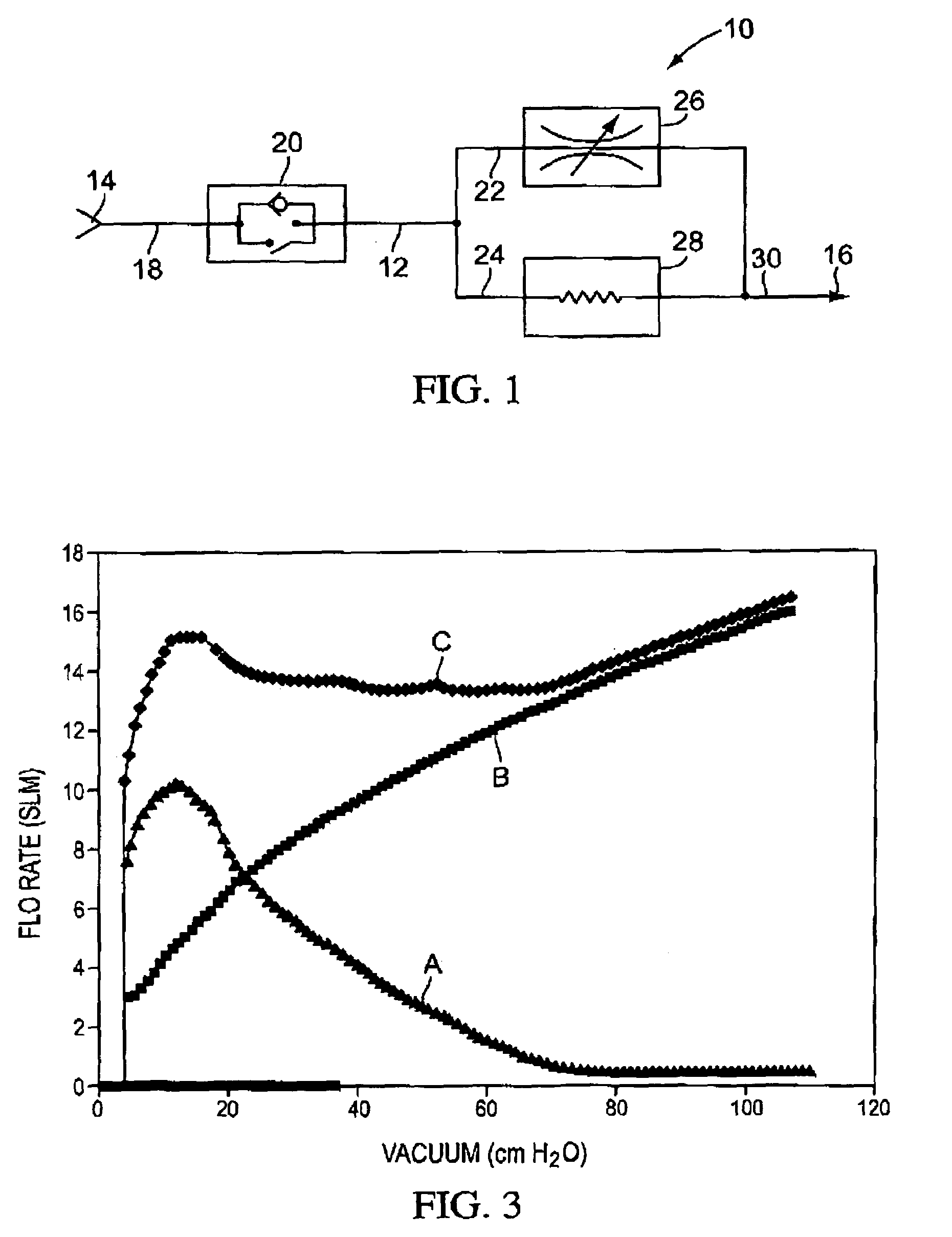
Flow regulator for aerosol drug delivery and methods
InactiveUS7185651B2Sufficient flow rateEasy to useRespiratorsLiquid surface applicatorsVacuum levelEngineering
An aerosolization device comprises a housing having a mouthpiece, and a flow path arrangement in fluid communication with the mouthpiece. The flow path arrangement has a flow regulating valve and a threshold valve, where the threshold valve is configured to open at a first vacuum level and to close at a second vacuum level that is less than the first vacuum level. The housing includes a region that is adapted to hold a powder in fluid communication with the flow path arrangement so that air drawn through the mouthpiece opens the threshold valve once the first vacuum level is exceeded and remains open until the vacuum falls below the second vacuum level. The flow rate of the air drawn through the mouthpiece is regulated by the flow regulating valve to remain within a certain range while the threshold valve remains open.
Owner:NOVARTIS FARMA
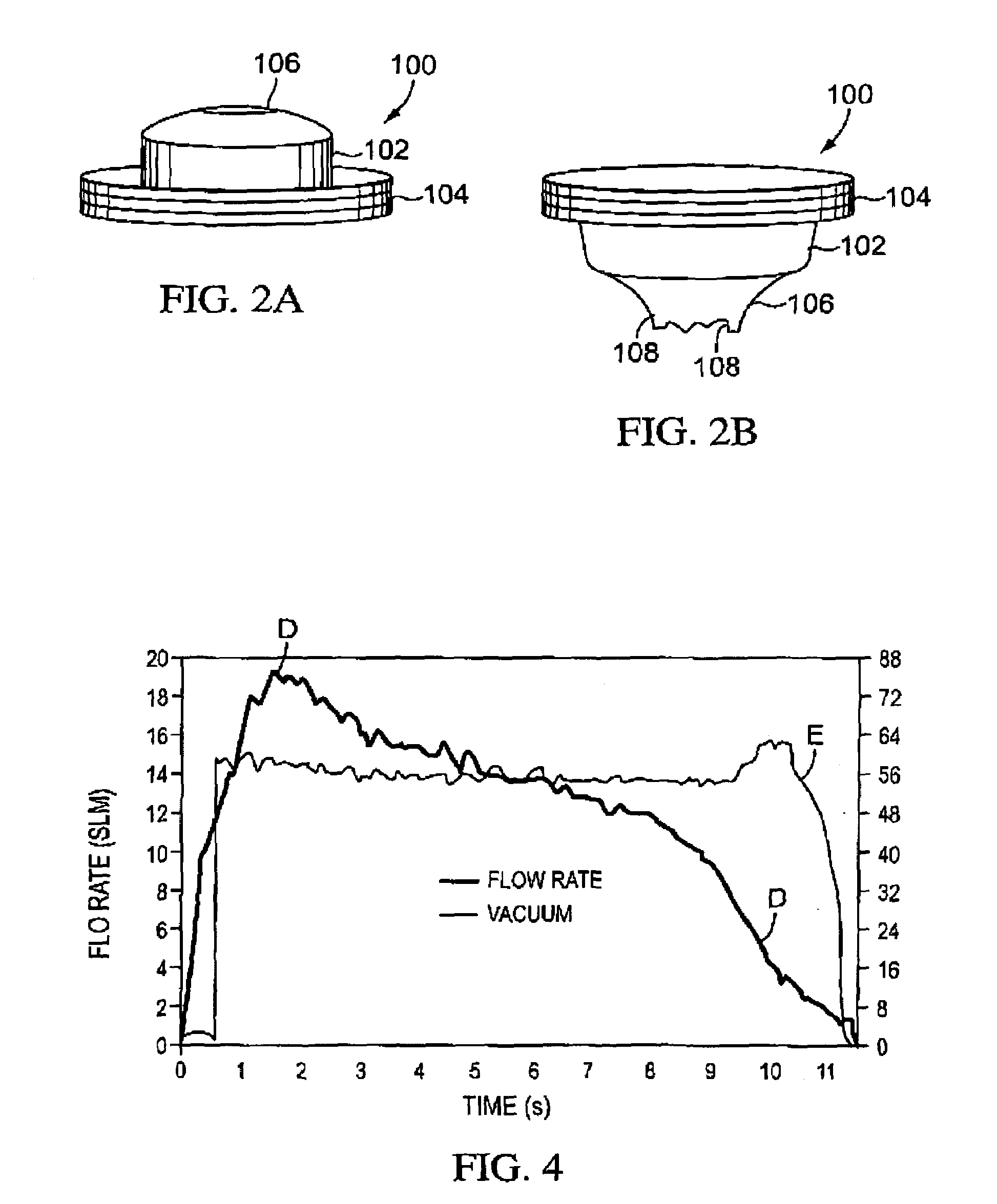
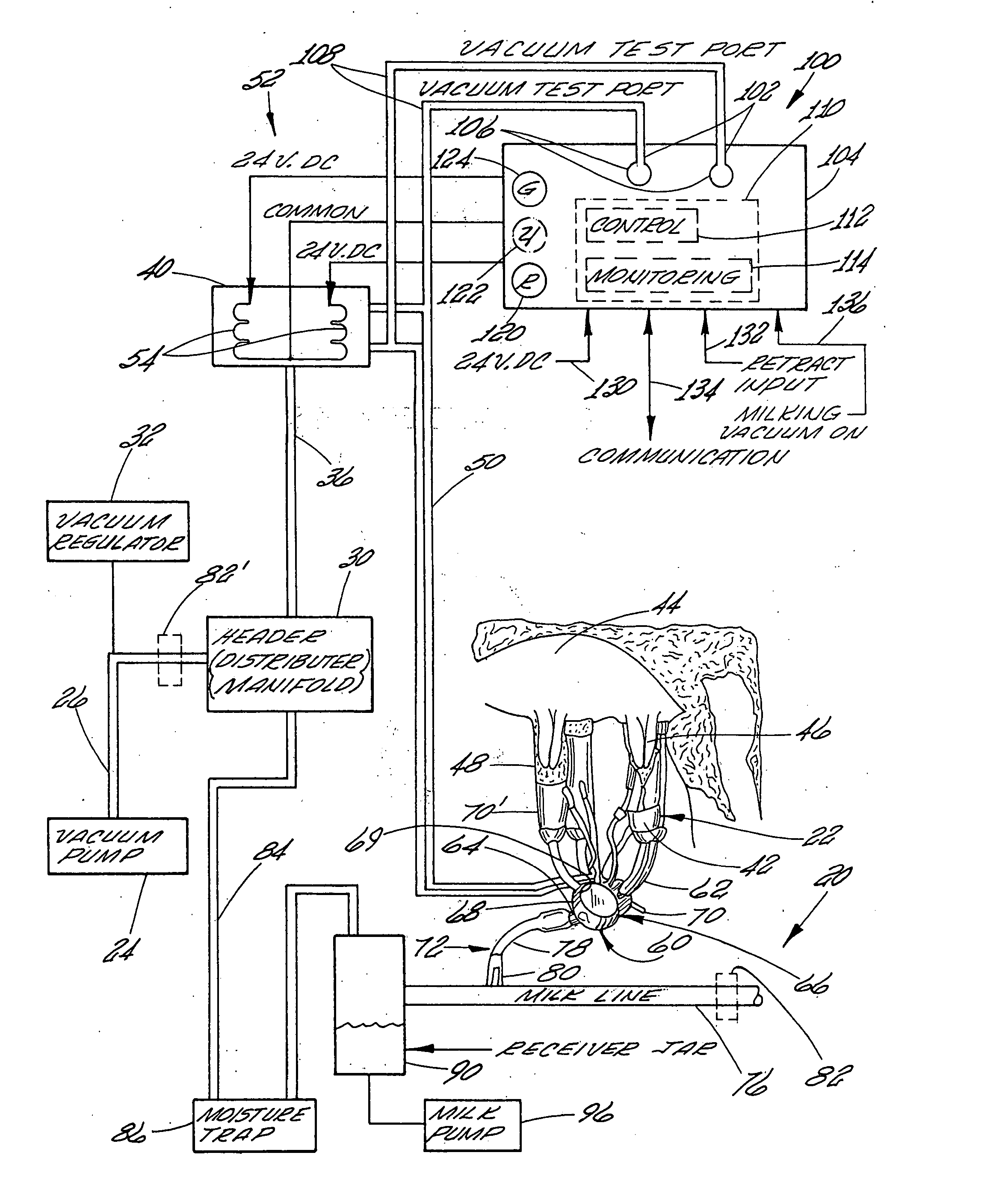
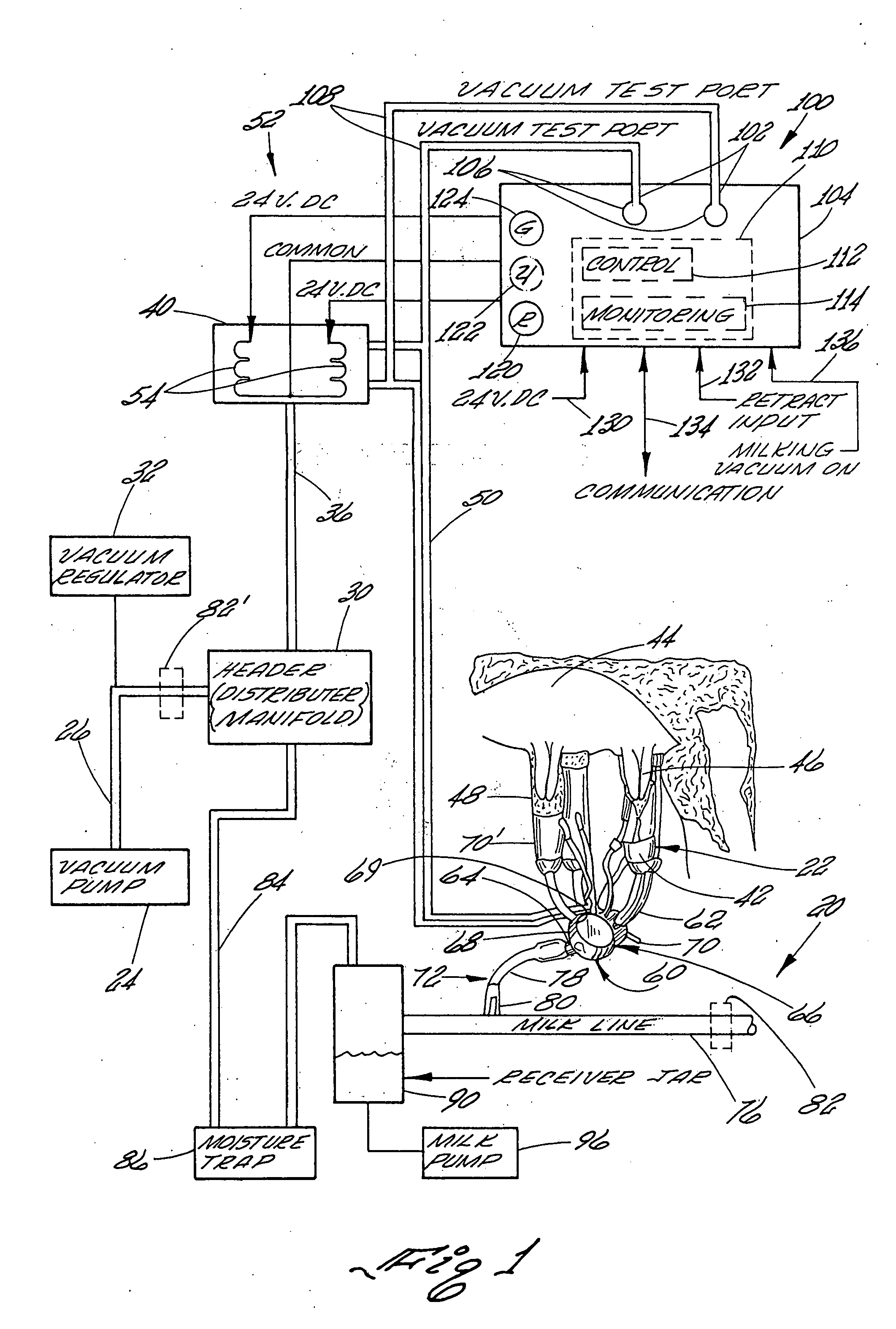
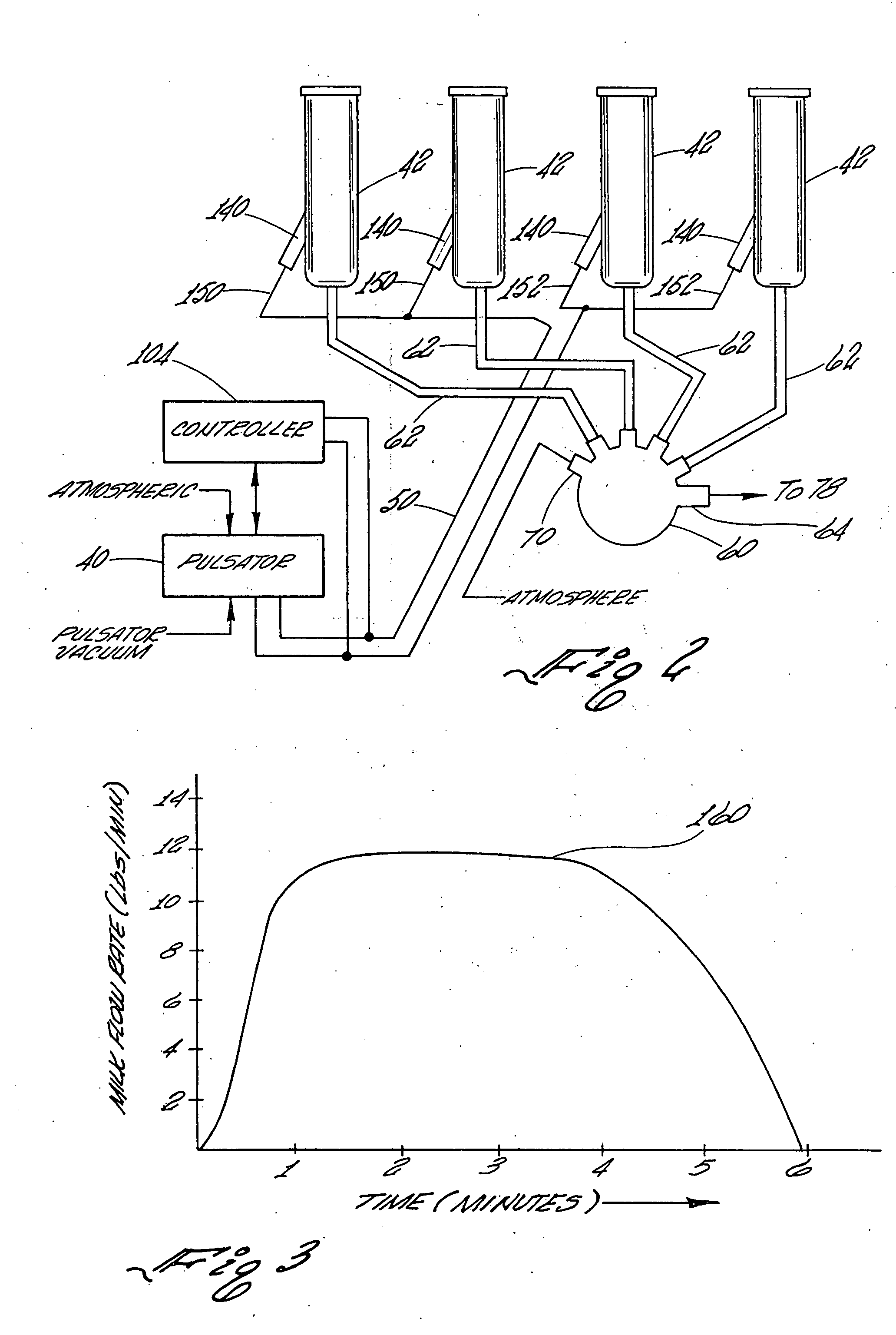
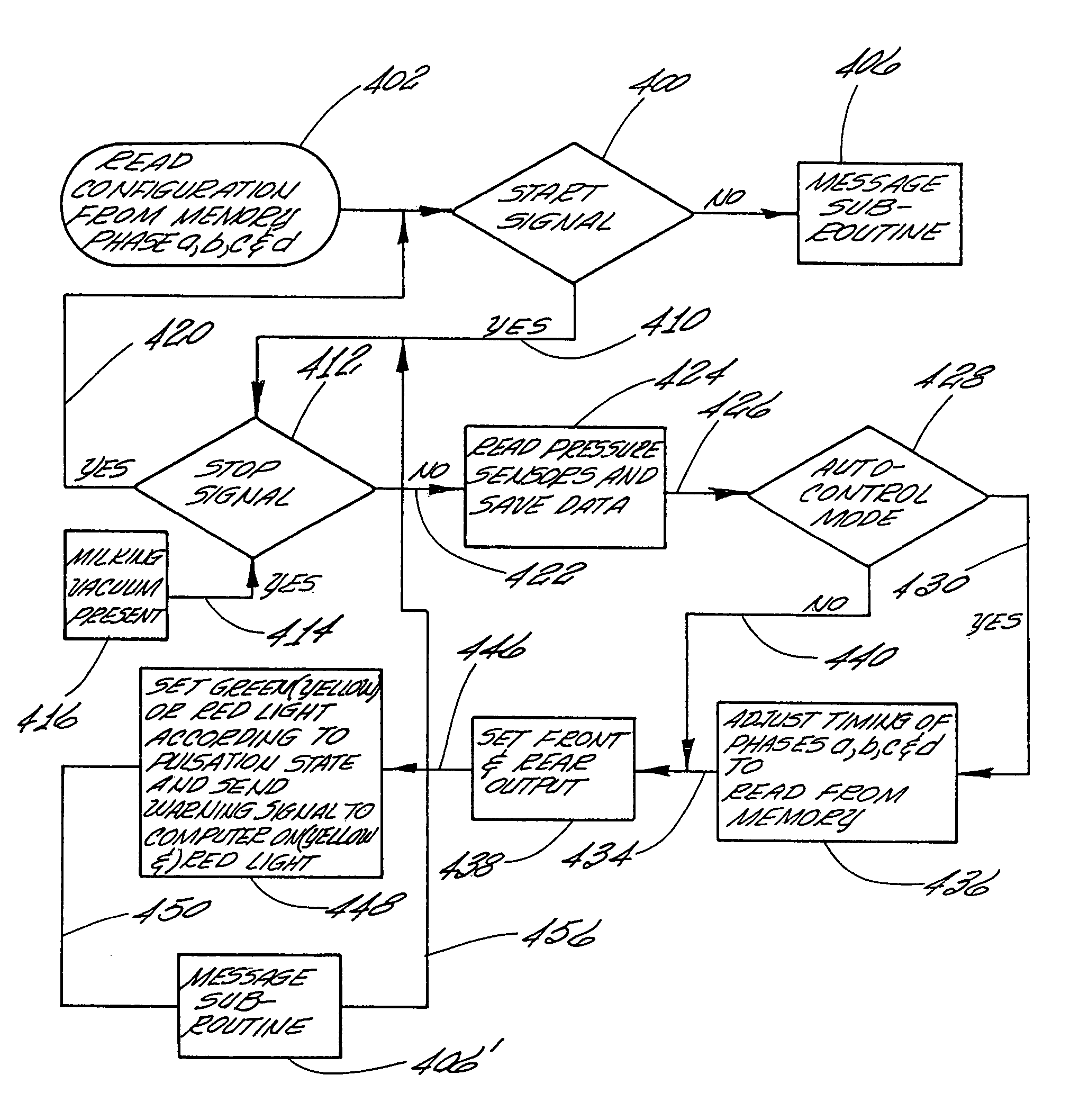
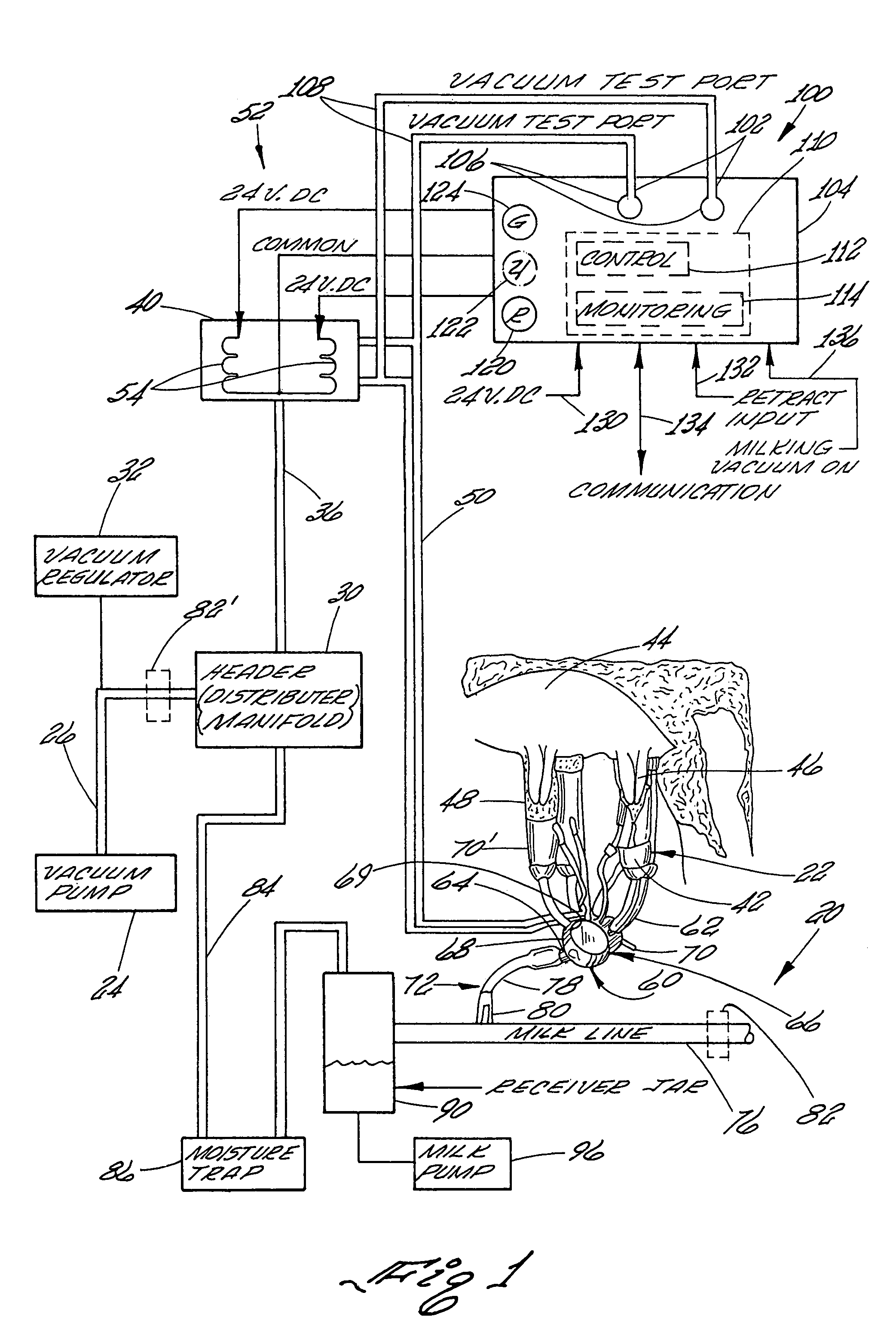
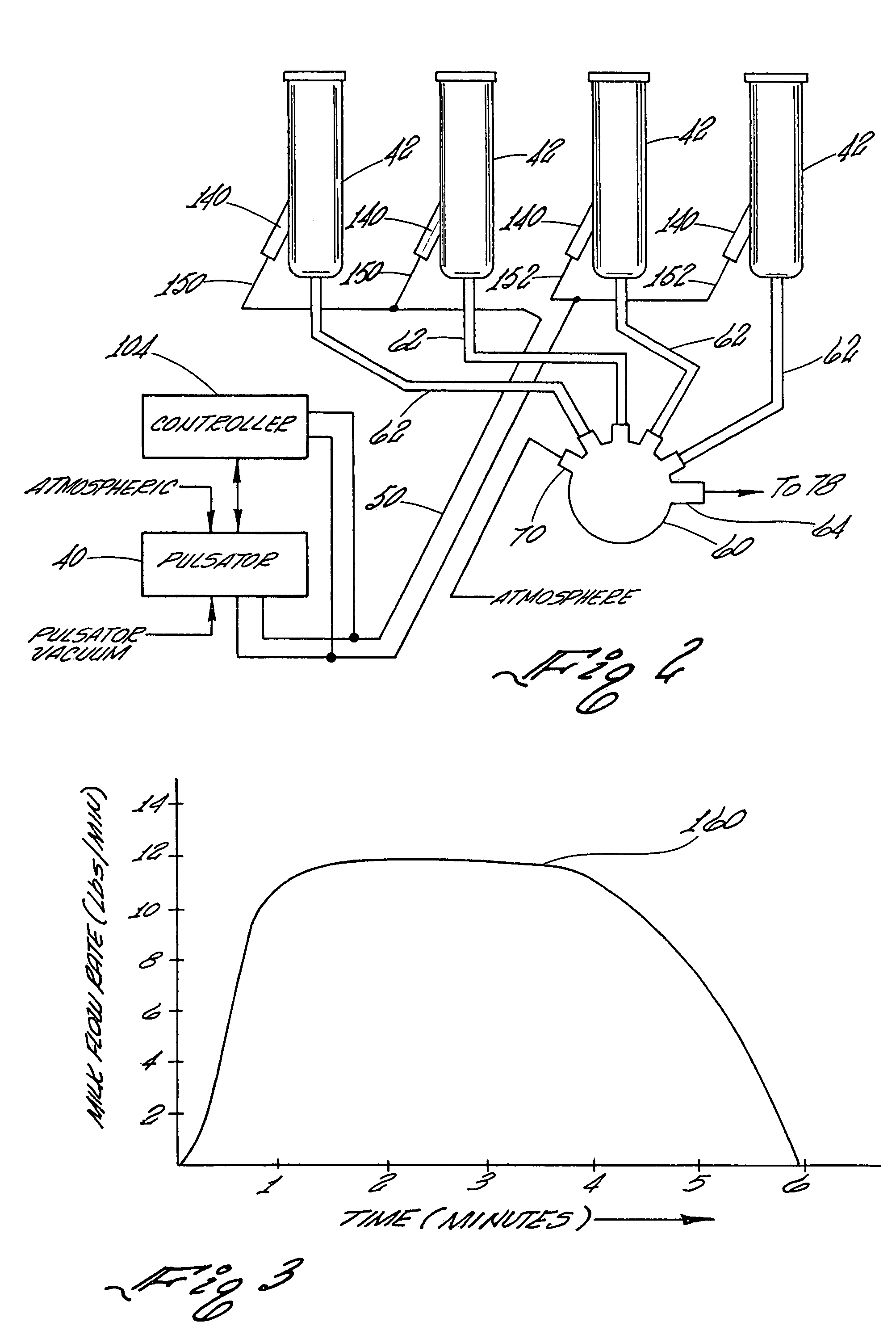
Controller for monitoring and controlling pulsators in a milking system
A controller for monitoring and controlling an operating pulsator in a milking system is shown. The controller comprises a first sensor operatively connected to a designated pulsator for receiving a pulsating vacuum therefrom. The controller produces a first signal representing the pulsating vacuum level. A processor is operatively connected to the first sensor for receiving the first signal. The processor includes a comparator for comparing the first signal to a stored reference signal representing a predetermined vacuum range of pulsating vacuum levels programmed as acceptable for milking systems pulsators. The processor generates at least one control signal when the designated pulsator pulsating vacuum level is at a vacuum level outside of the predetermined vacuum range. A control circuit signals that the designated pulsator pulsating vacuum level is outside the range of pulsating vacuum levels programmed as acceptable for the milking system pulsators.
Owner:TECH HLDG
Controller for monitoring and controlling pulsators in a milking system
A controller for monitoring and controlling an operating pulsator in a milking system is shown. The controller comprises a first sensor operatively connected to a designated pulsator for receiving a pulsating vacuum therefrom. The controller produces a first signal representing the pulsating vacuum level. A processor is operatively connected to the first sensor for receiving the first signal. The processor includes a comparator for comparing the first signal to a stored reference signal representing a predetermined vacuum range of pulsating vacuum levels programmed as acceptable for milking systems pulsators. The processor generates at least one control signal when the designated pulsator pulsating vacuum level is at a vacuum level outside of the predetermined vacuum range. A control circuit signals that the designated pulsator pulsating vacuum level is outside the range of pulsating vacuum levels programmed as acceptable for the milking system pulsators.
Owner:TECH HLDG
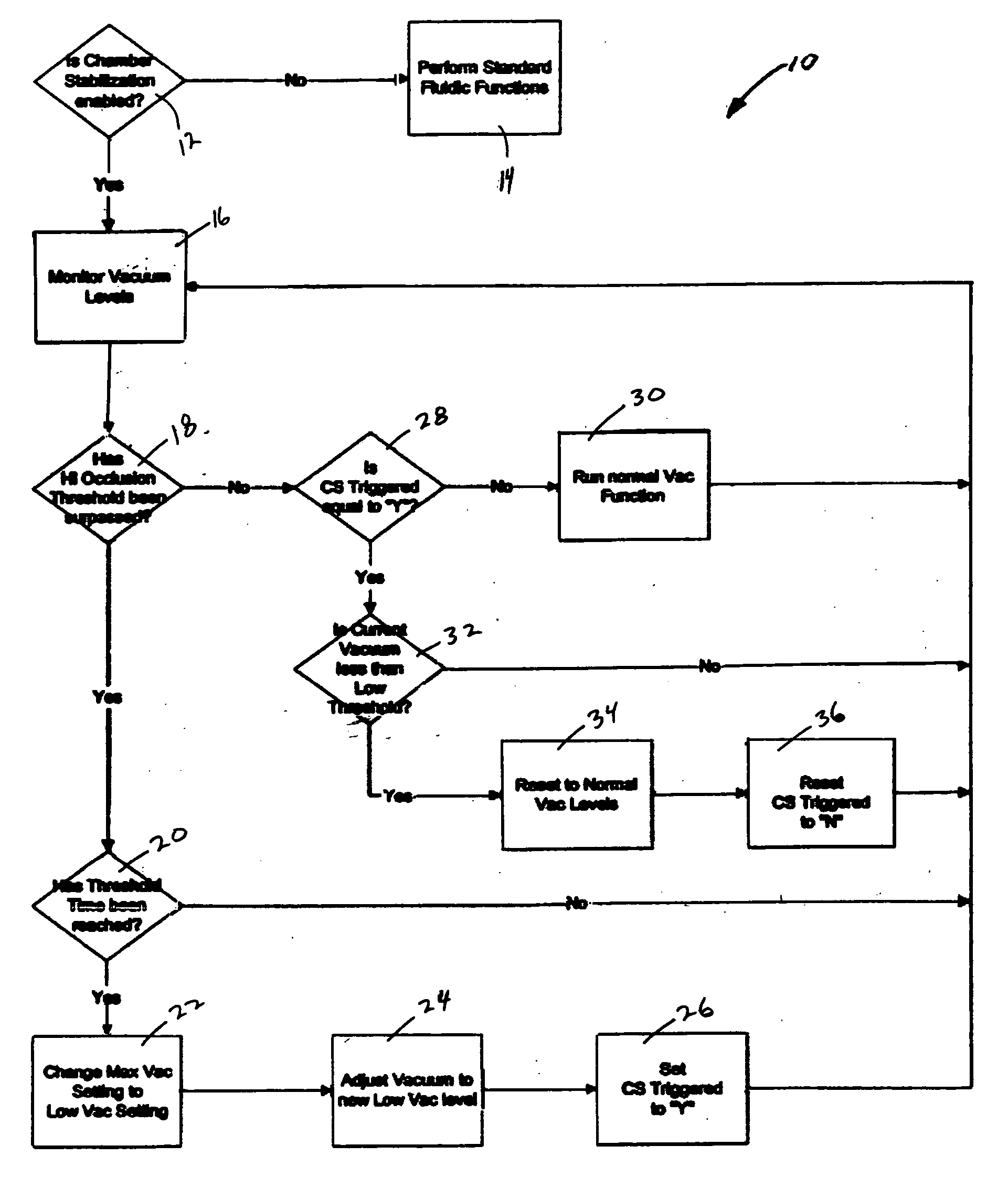
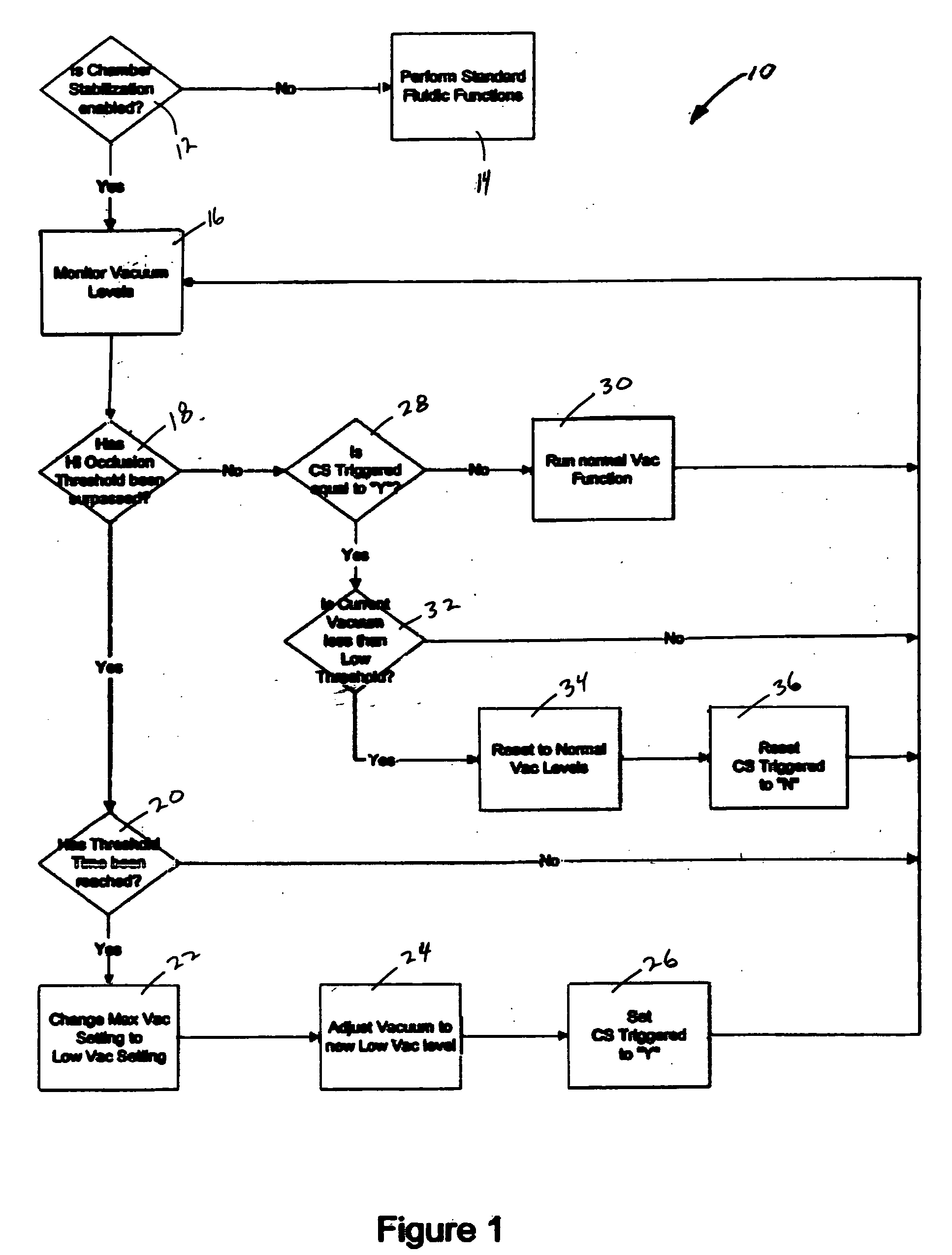
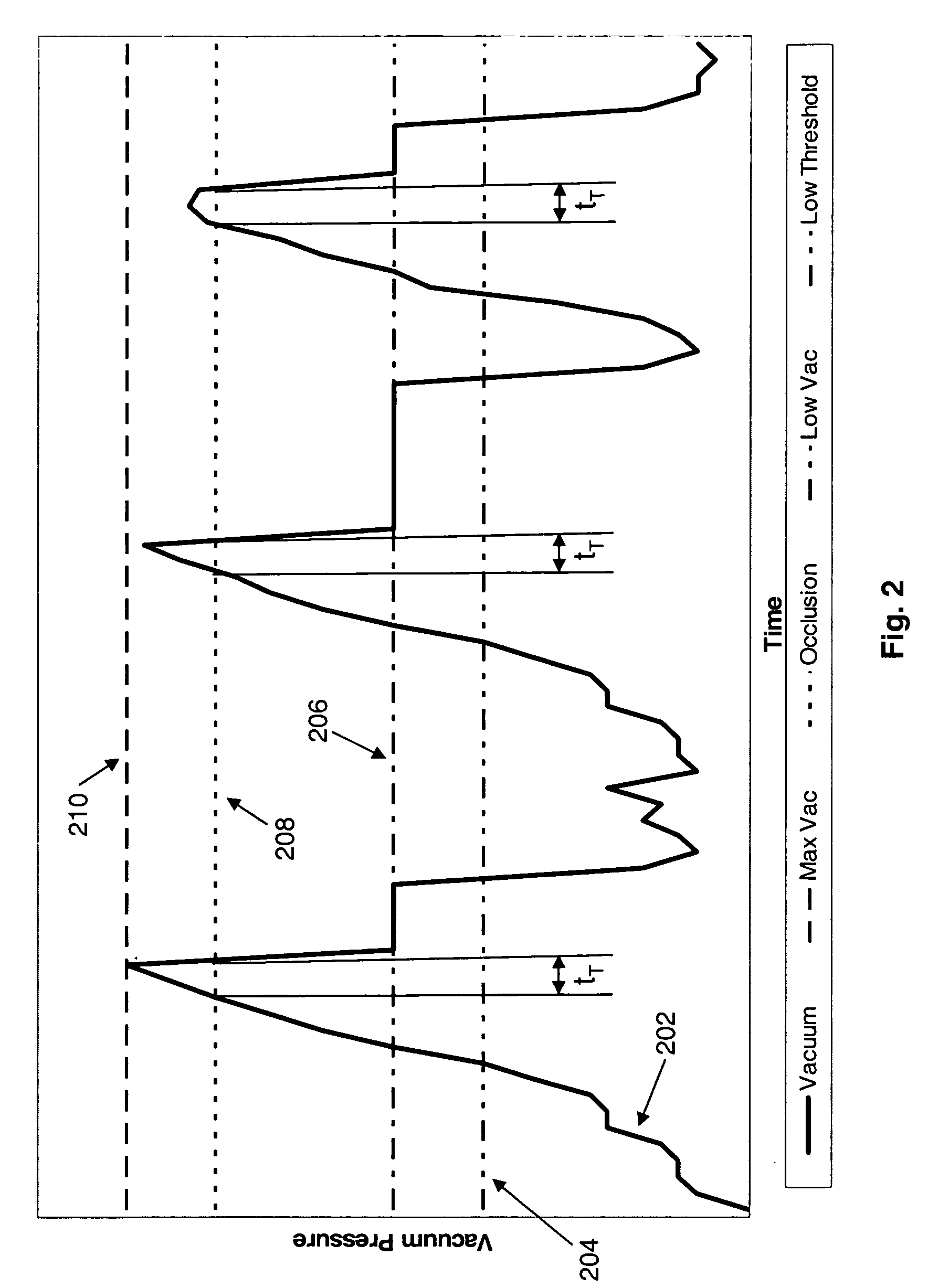
Application of vacuum as a method and mechanism for controlling eye chamber stability
A method for operating a surgical system including a control unit having a vacuum sensor and / or a flow rate sensor, the method including placing a handpiece in an operative relationship with an eye for a surgical procedure and thereafter supplying irrigation fluid to the handpiece while applying a vacuum to the handpiece to aspirate the irrigation fluid from the eye through the handpiece. During fluid aspiration, a vacuum level and / or flow rate is sensed which corresponds to an occlusion of the handpiece and from the sensed vacuum level and / or flow rate, a duration of the occlusion is determined. In response to the determined duration of occlusion, at least one of the handpiece parameters is varied.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON SURGICAL VISION INC
Cyclic aperture flow regulator system
ActiveUS20160128869A1Prevent post-occlusion instabilityReduce the cross-sectional areaEye surgerySurgeryControl flowVacuum level
A cyclic aperture flow regulator system is disclosed to control flow exiting from a body cavity during surgery in a way that post-occlusion surges are effectively suppressed. The system is composed by an adjustable fluid aperture installed in a fluid path connecting the aspiration port of a surgical probe with a vacuum source, the probe to be inserted in a body cavity. The cross-sectional area of the fluid aperture can be modified by the action of an actuator portion driven by a controller. The controller commands the actuators in the actuator portion to modify the cross-sectional area of the adjustable fluid aperture in cycles. Each cycle of aperture dimension fluctuation includes at least one segment where the fluid aperture cross-sectional area is substantially reduced. The segment of each cycle where the cross-sectional area of the fluid aperture is substantially reduced can optionally include a transient complete closure of the aperture. The cycles of fluid aperture fluctuation are programmed to occur at a rate fast enough to produce a substantially steady flow, with minimum flow ripple and pressure ripple. Flow rate across the cyclic aperture flow regulator system is a function of the vacuum level of the vacuum source and can be regulated by adjusting the level of the vacuum. Flow rate across the cyclic aperture flow regulator system is also a function of the RMS value of the cross-sectional area of the fluid aperture and can be regulated by adjusting the amplitude of the waveform of each cycle.
Owner:ALCON INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com