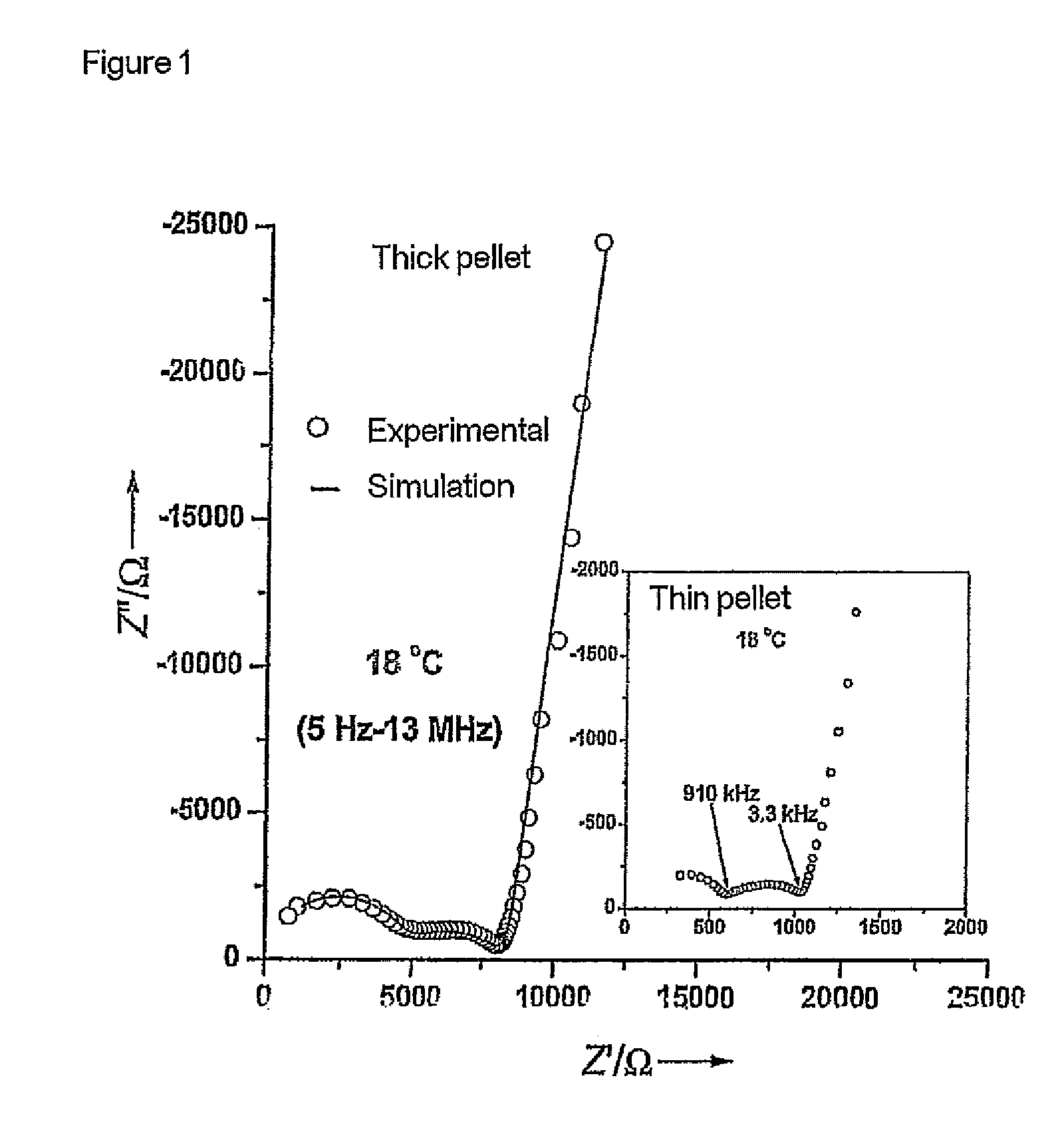
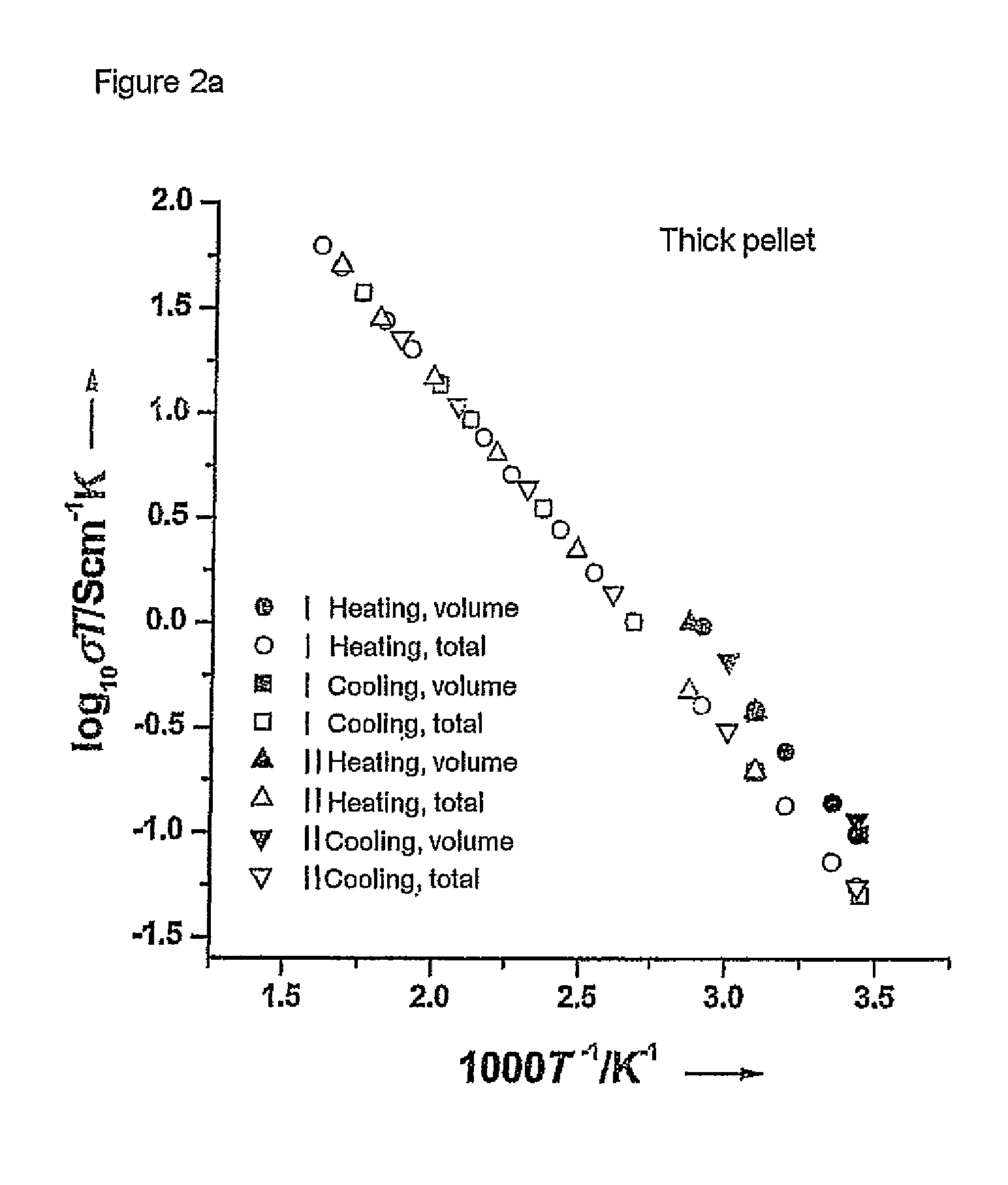
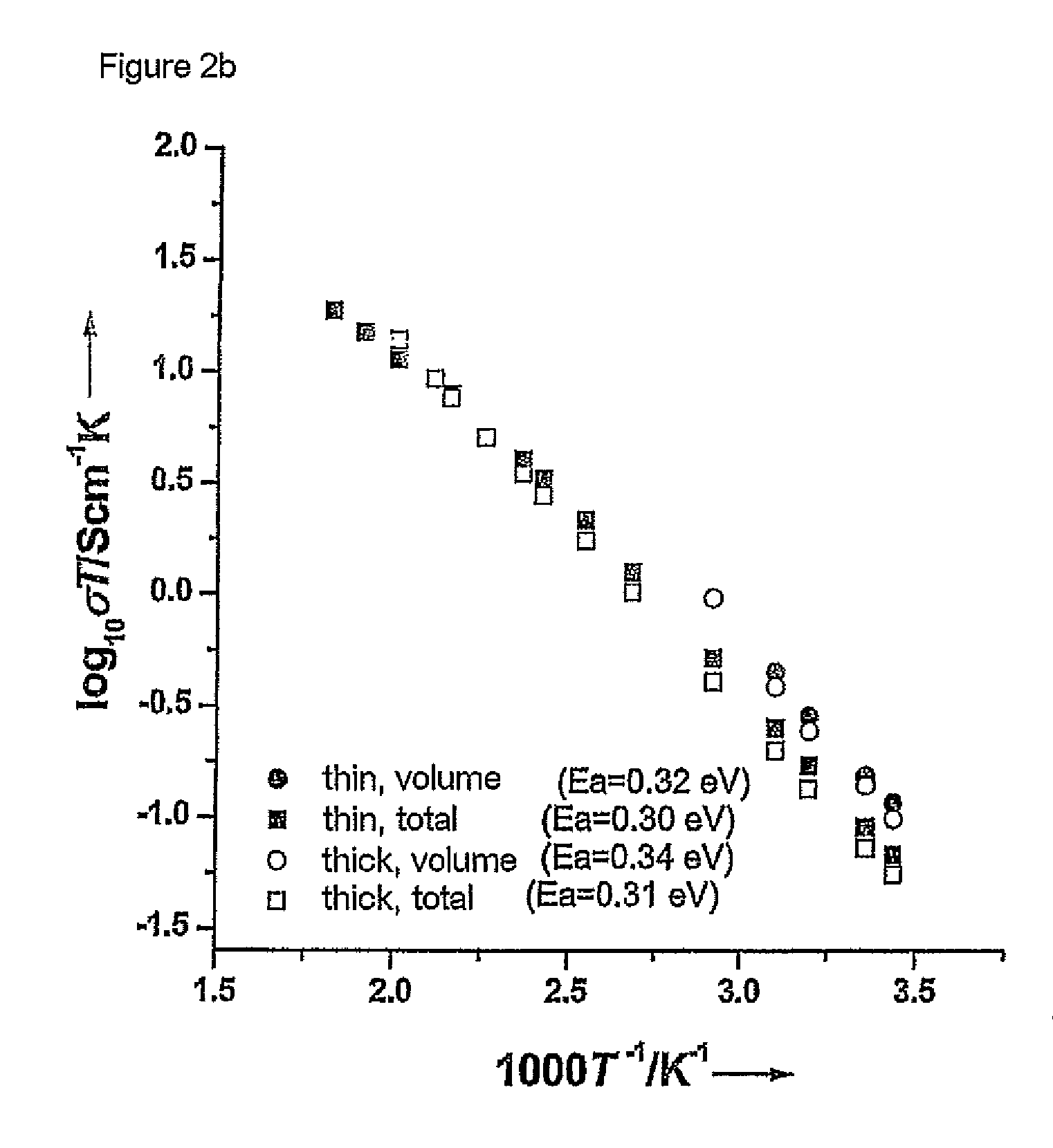
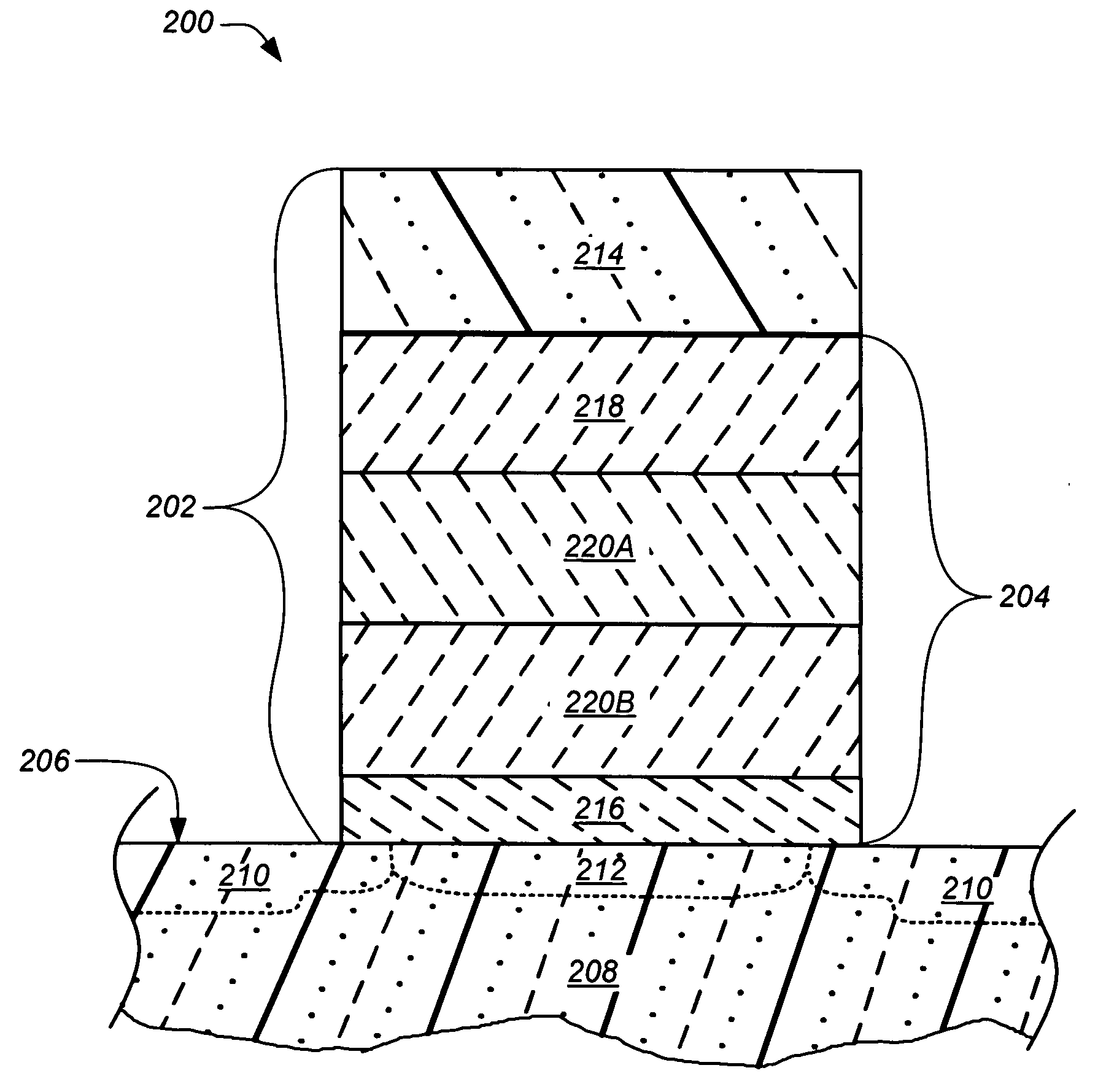
Patents
Literature
157 results about "Stoichiometric composition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Composition stoichiometry refers to the atomic makeup of a molecule. For instance, we can say that one molecule of glucose has 6 carbon atoms, or we can say, equivalently, that one mole of glucose has 6 moles of carbon atoms.
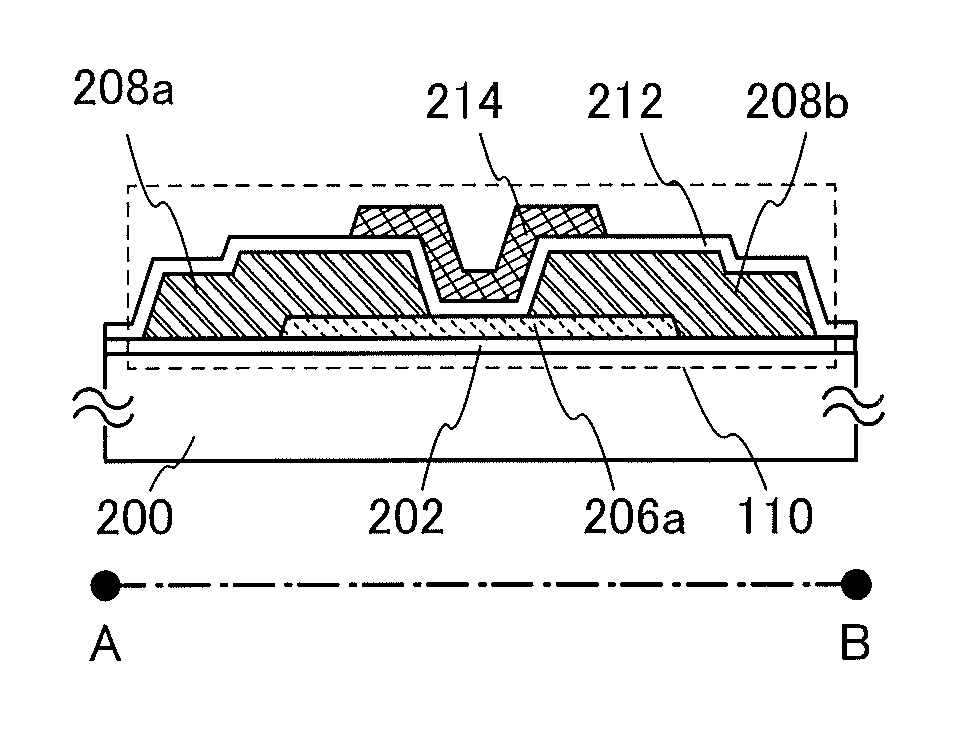
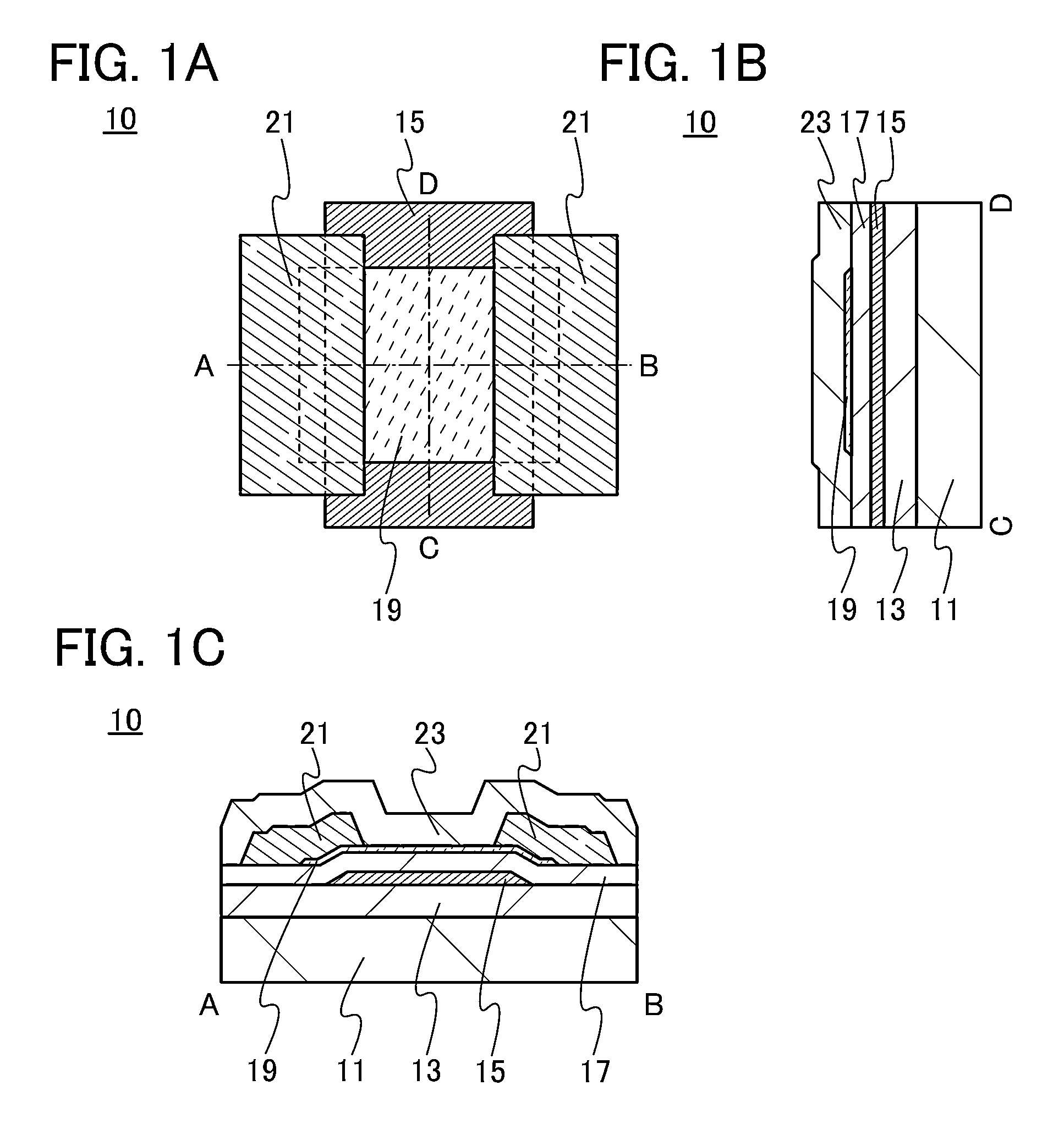
Solid ion conductor which has a garnet-like crystal structure and has the stoichiometric composition L7+XAXG3-XZr2O12
ActiveUS8658317B2Easily employedImprove ionic conductivityFinal product manufactureCell electrodesElectrical conductorCrystal structure
The invention is directed to a solid ion conductor which has a garnet-like crystal structure and has the stoichiometric composition L7+xAxG3−xZr2O12, whereinL is in each case independently a monovalent cation,A is in each case independently a divalent cation,G is in each case independently a trivalent cation,0≦x≦3 andO can be partly or completely replaced by divalent or trivalent anion.
Owner:BASF AG
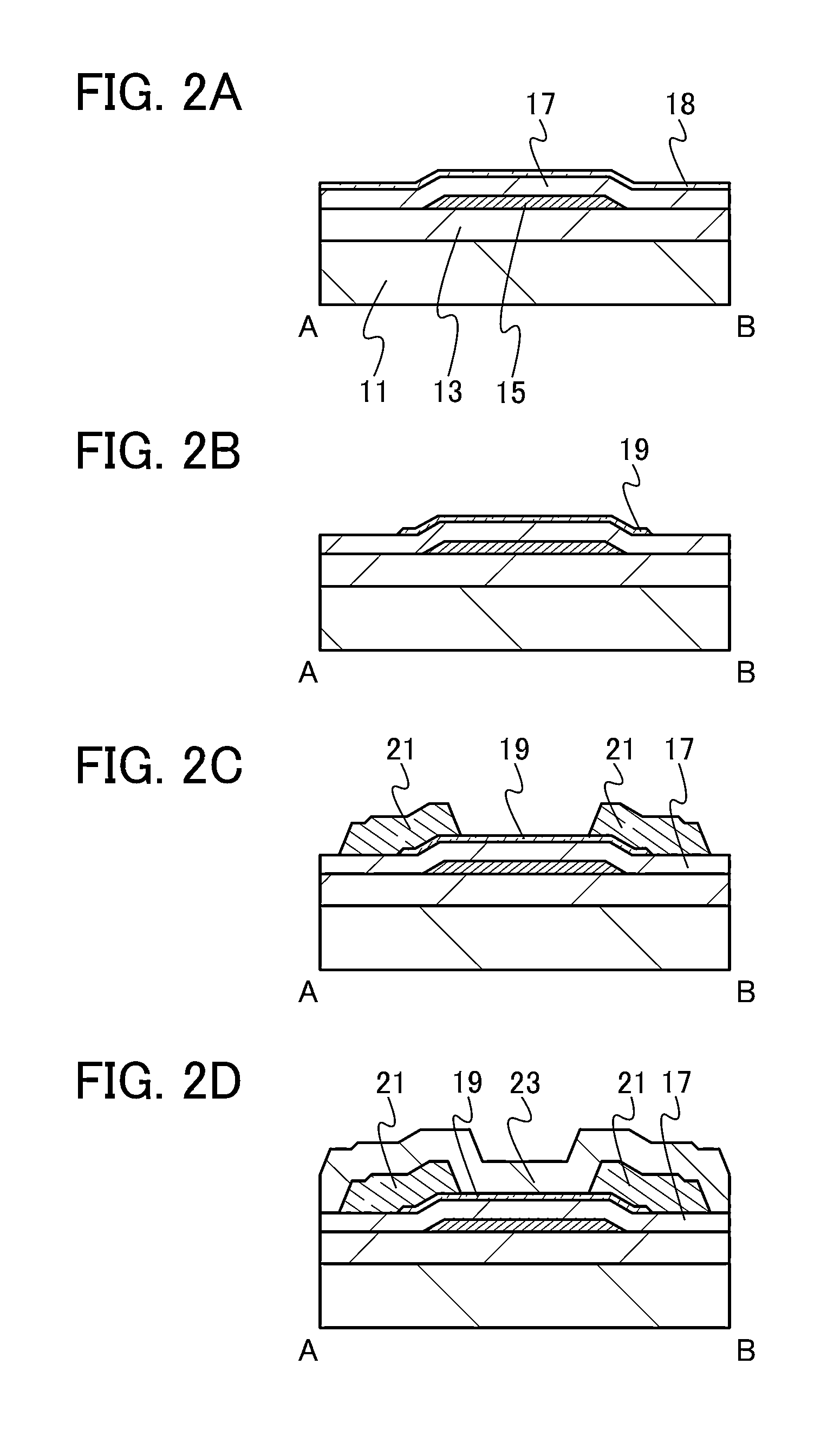
Oxide-nitride-oxide stack having multiple oxynitride layers
InactiveUS20090179253A1Read-only memoriesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitrogenSilicon oxide
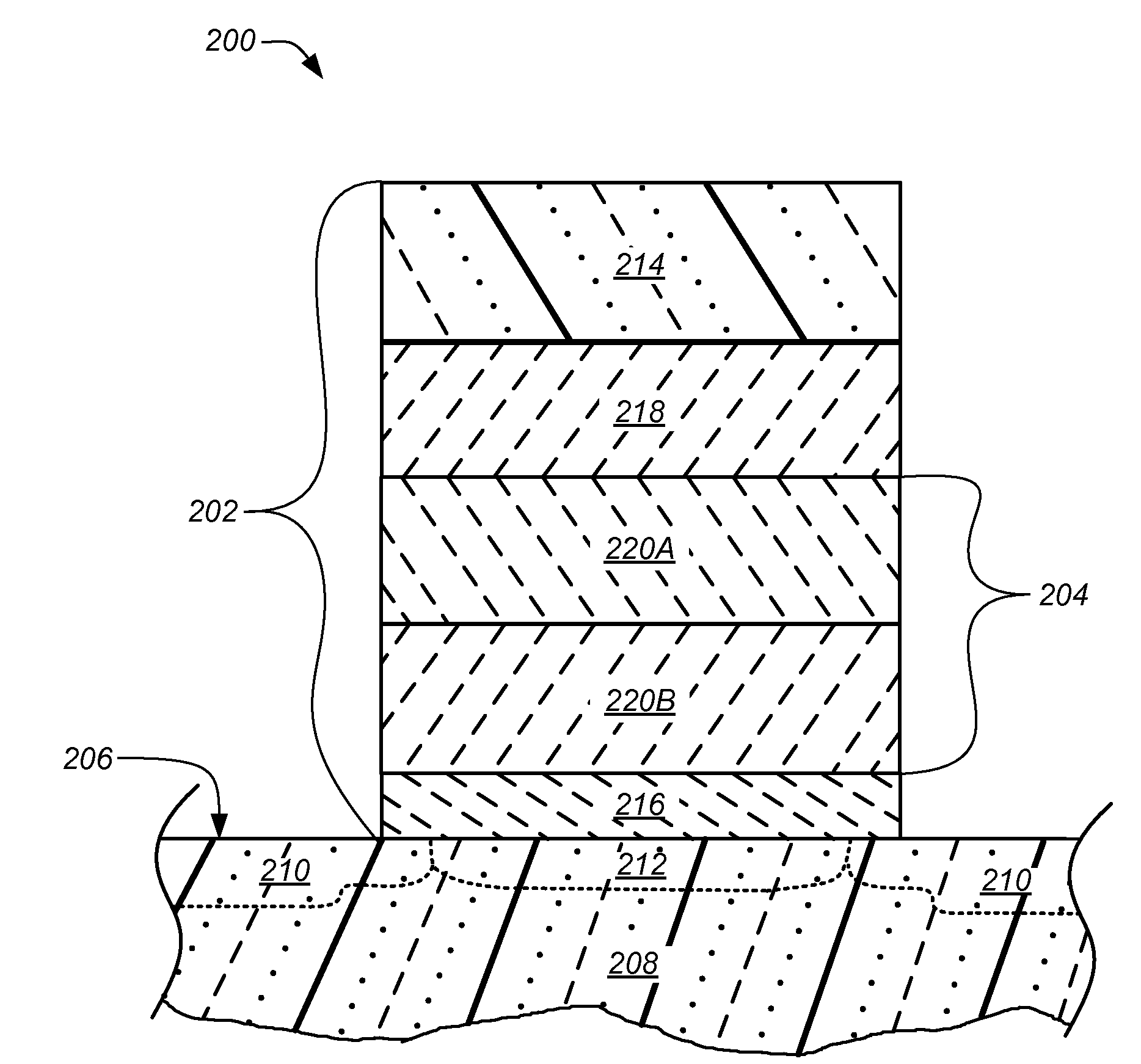
A semiconductor device including an oxide-nitride-oxide (ONO) structure having a multi-layer charge storing layer and methods of forming the same are provided. Generally, the method involves: (i) forming a first oxide layer of the ONO structure; (ii) forming a multi-layer charge storing layer comprising nitride on a surface of the first oxide layer; and (iii) forming a second oxide layer of the ONO structure on a surface of the multi-layer charge storing layer. Preferably, the charge storing layer comprises at least two silicon oxynitride layers having differing stoichiometric compositions of Oxygen, Nitrogen and / or Silicon. More preferably, the ONO structure is part of a silicon-oxide-nitride-oxide-silicon (SONOS) structure and the semiconductor device is a SONOS memory transistor. Other embodiments are also disclosed.
Owner:LONGITUDE FLASH MEMORY SOLUTIONS LTD
Defect-free group iii - nitride nanostructures and devices using pulsed and non-pulsed growth techniques
InactiveUS20110140072A1Laser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialCrystallinity
Exemplary embodiments provide semiconductor devices including high-quality (i.e., defect free) Group III—Nitride nanostructures and uniform Group III—Nitride nanostructure arrays as well as their scalable processes for manufacturing, where the position, orientation, cross-sectional features, length and the crystallinity of each nanostructure can be precisely controlled. A pulsed growth mode can be used to fabricate the disclosed Group III—Nitride nanostructures and / or nanostructure arrays providing a uniform length of about 0.01-20 micrometers (μm) with constant cross-sectional features including an exemplary diameter of about 10 nanometers (nm)-500 micrometers (μm). Furthermore, core-shell nanostructure / MQW active structures can be formed by a core-shell growth on the non-polar sidewalls of each nanostructure and can be configured in nanoscale photoelectronic devices such as nanostructure LEDs and / or nanostructure lasers to provide tremendously-high efficiencies. Additional growth mode transitions from the pulsed to the non-pulsed growth mode and subsequent transitions from non-pulsed to pulsed growth mode are employed in order to incorporate certain group III—Nitride compounds more efficiently into the nanostructures and form devices of the designed shape, morphology and stochiometric composition. In addition, high-quality group III—Nitride substrate structures can be formed by coalescing the plurality of group III—Nitride nanostructures and / or nanostructure arrays to facilitate the fabrication of visible LEDs and lasers.
Owner:NANOCRYSTAL CORP
Method of manufacturing semiconductor device and substrate processing apparatus
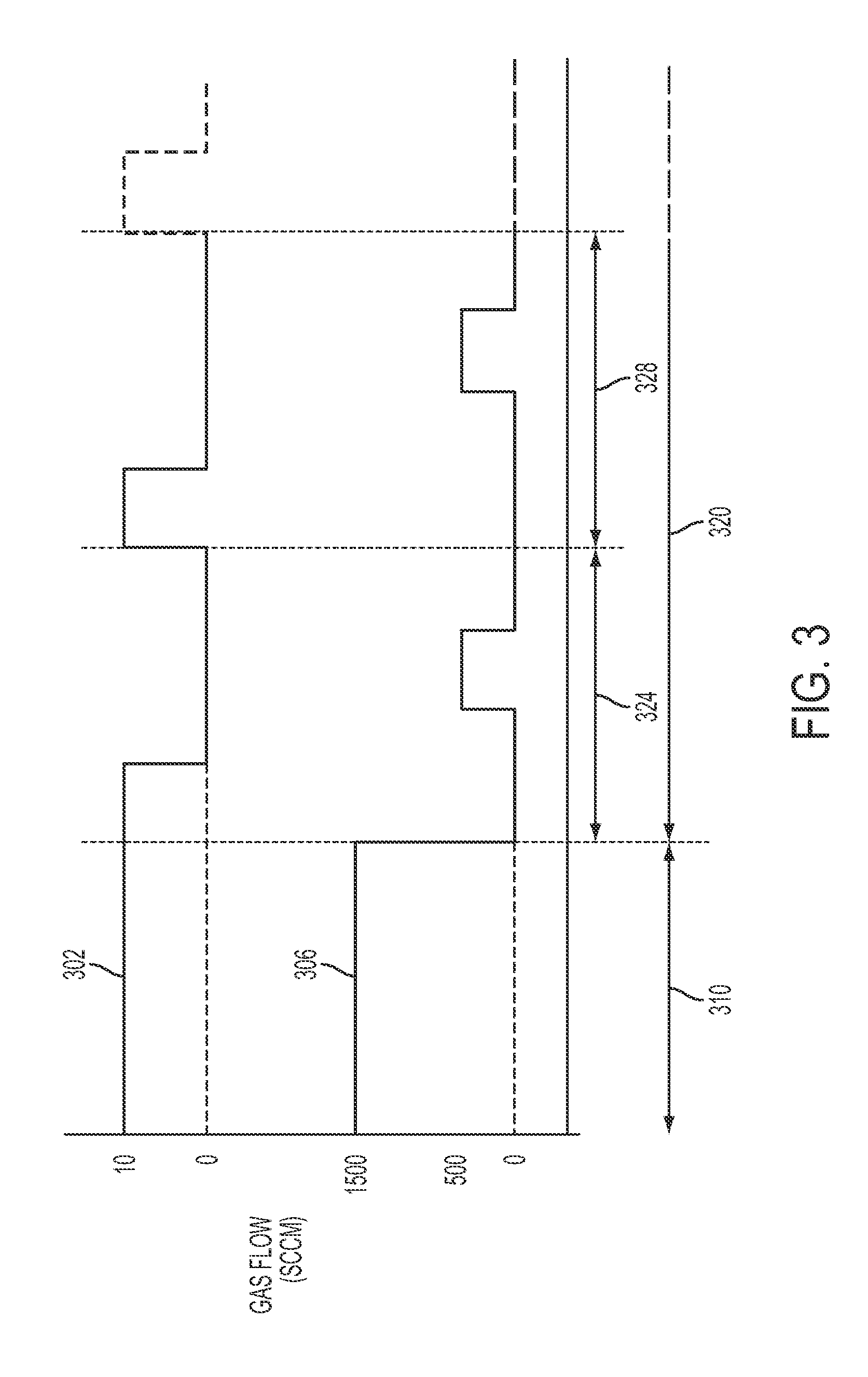
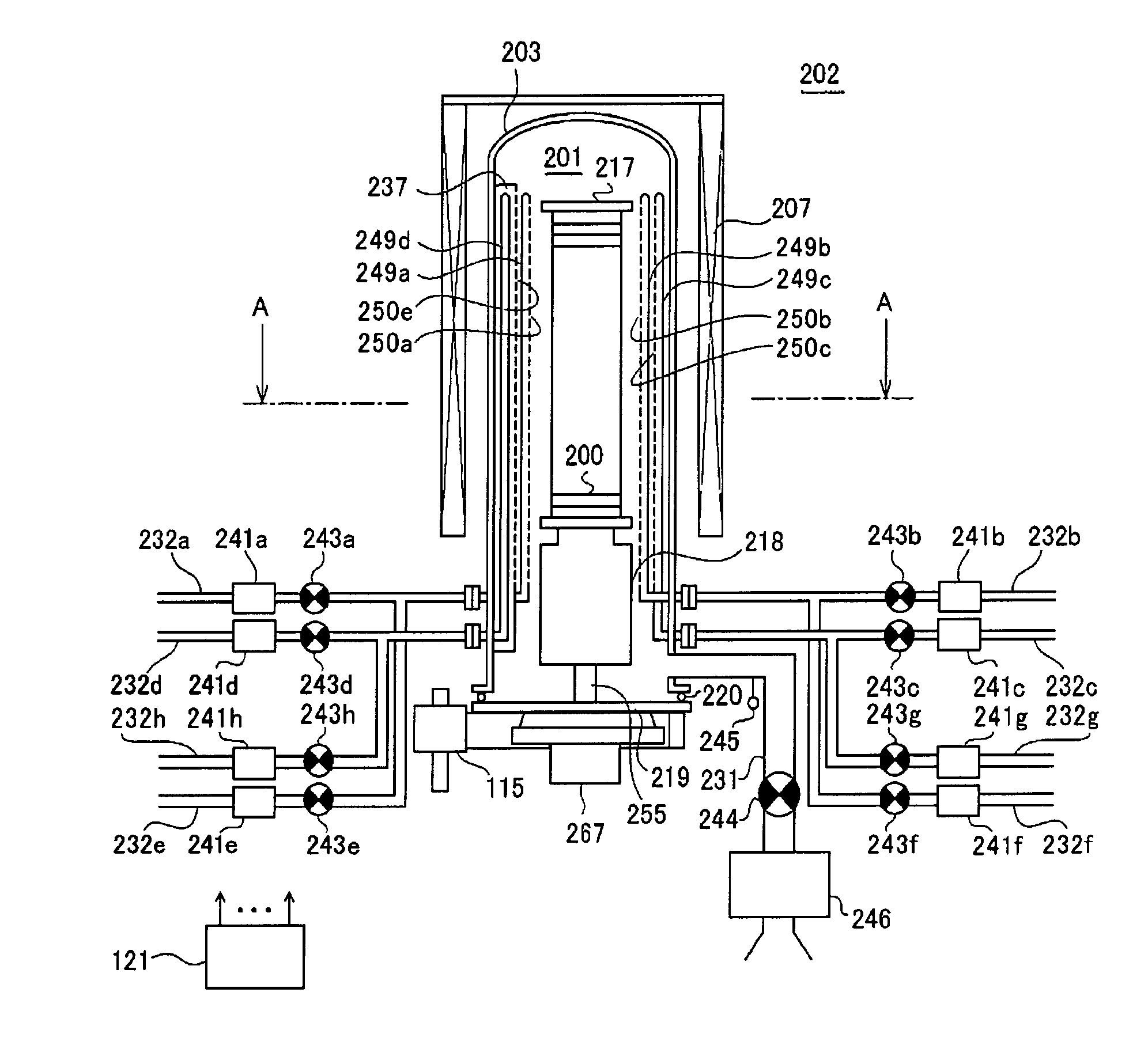
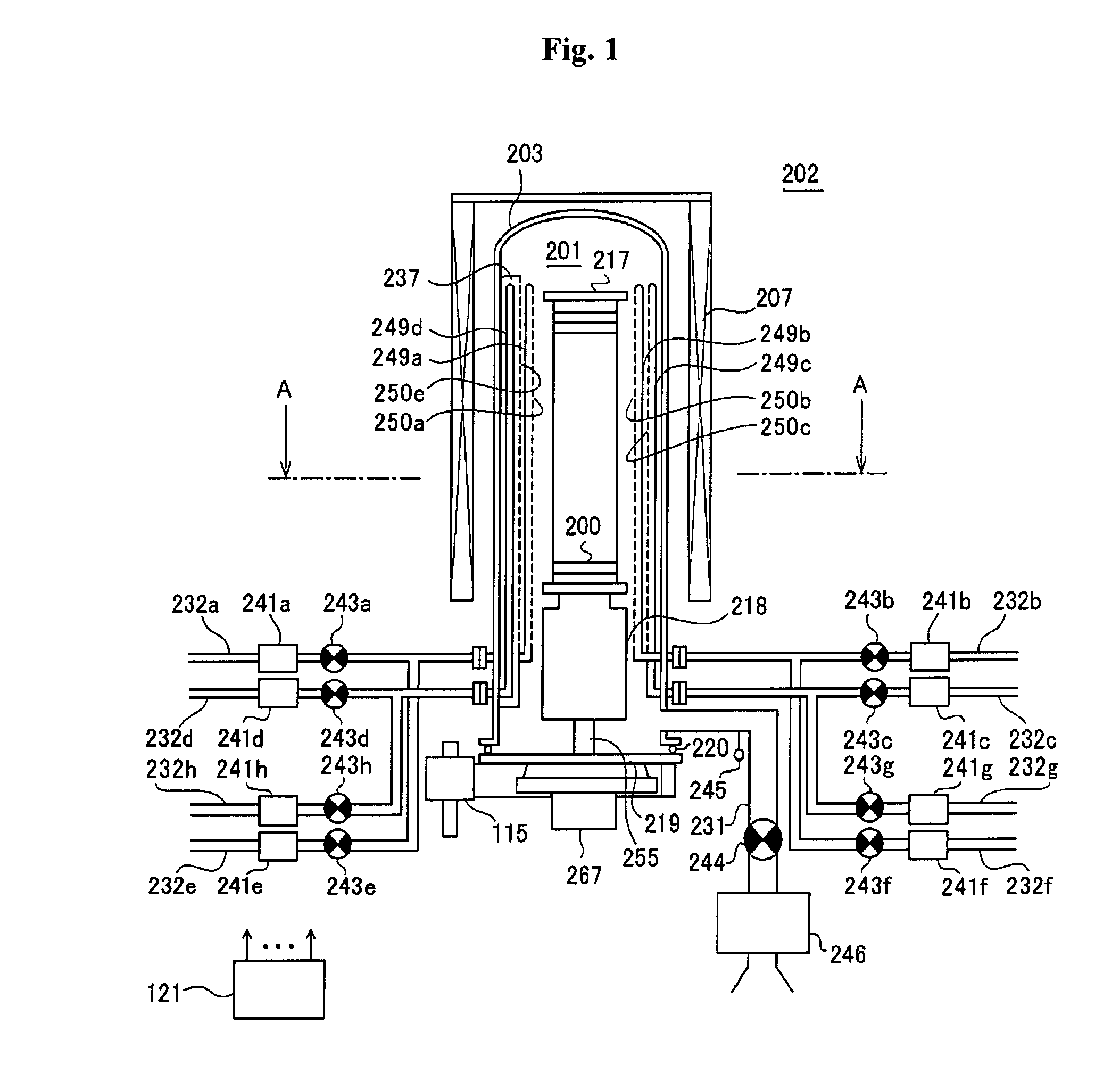
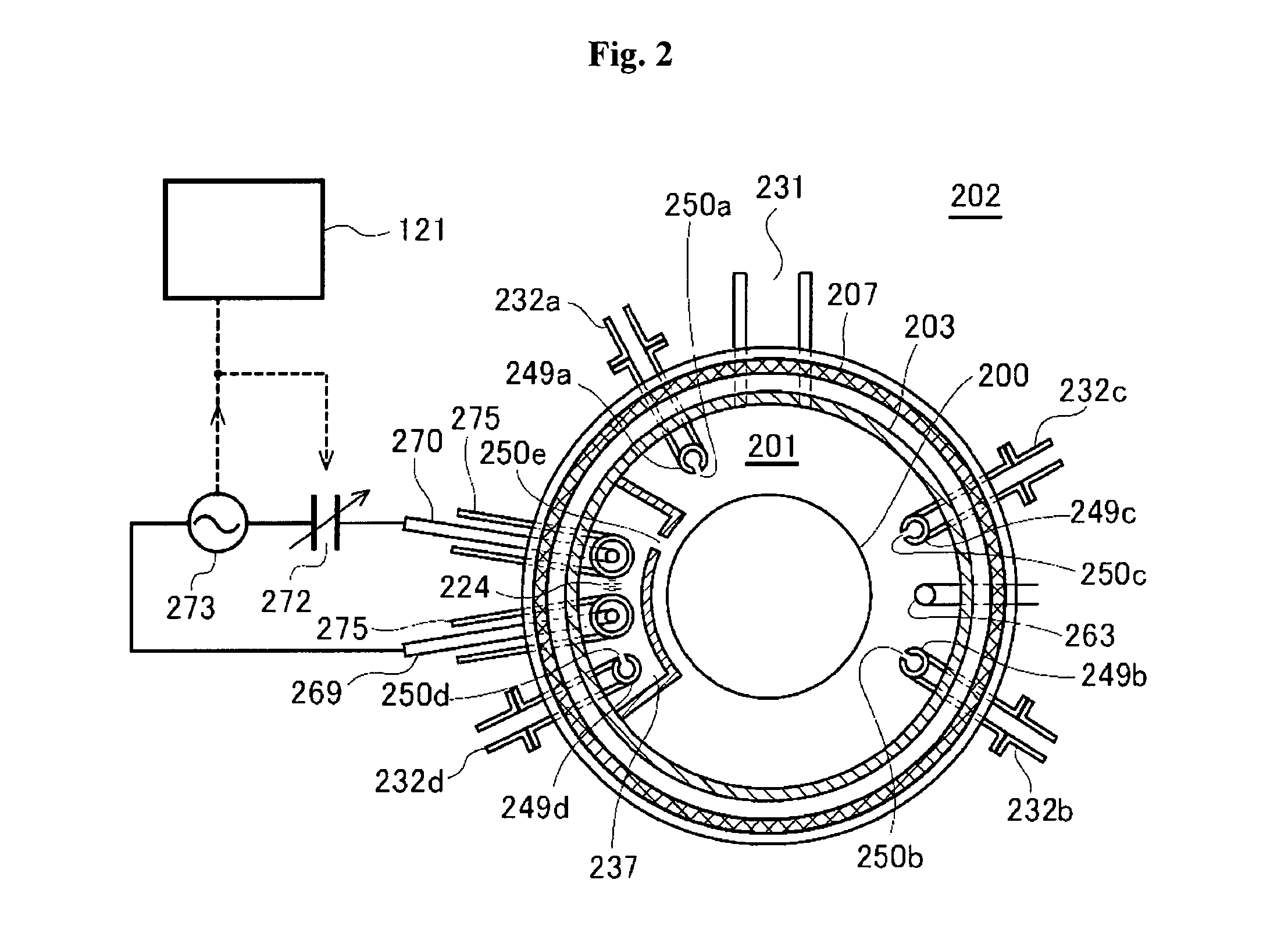
ActiveUS20100130024A1Quality improvementLiquid surface applicatorsVacuum evaporation coatingEngineeringGas supply
Provided are a method of manufacturing a semiconductor device and a substrate processing apparatus. The method includes: forming a first layer including a first element on a substrate by supplying a gas containing the first element; forming a second layer including first and second elements by supplying a gas containing the second element to modify the first layer; and forming a thin film having a predetermined thickness by setting the forming of the first layer and the forming of the second layer to one cycle and repeating the cycle at least once. Pressure, or pressure and a gas supply time in one process of the forming of the first layer and the forming of the second layer are controlled to be higher or longer, or lower or shorter than pressure, or pressure and a time in the one process when the thin film having a stoichiometric composition is formed.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Insulating film, method for manufacturing semiconductor device, and semiconductor device
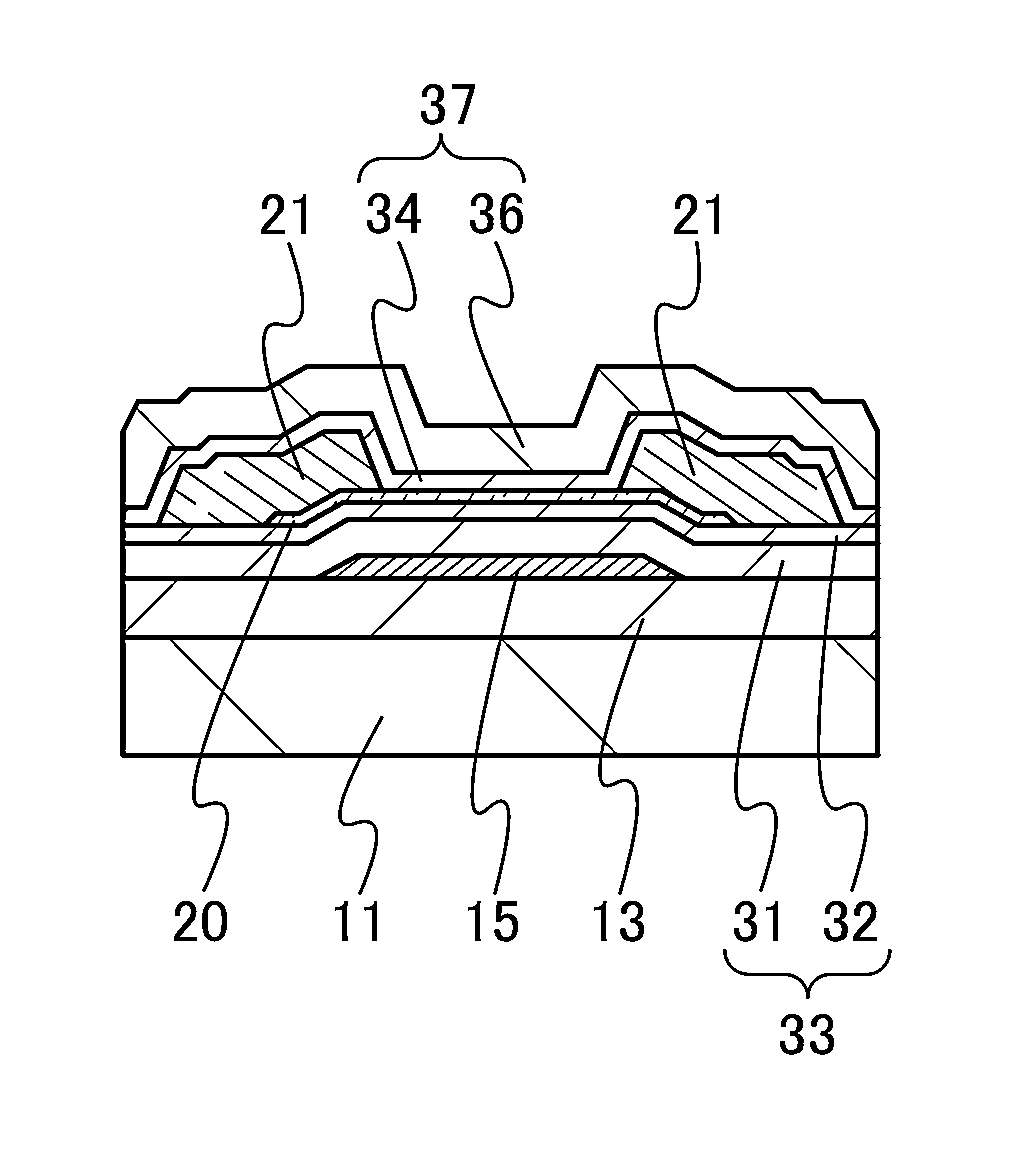
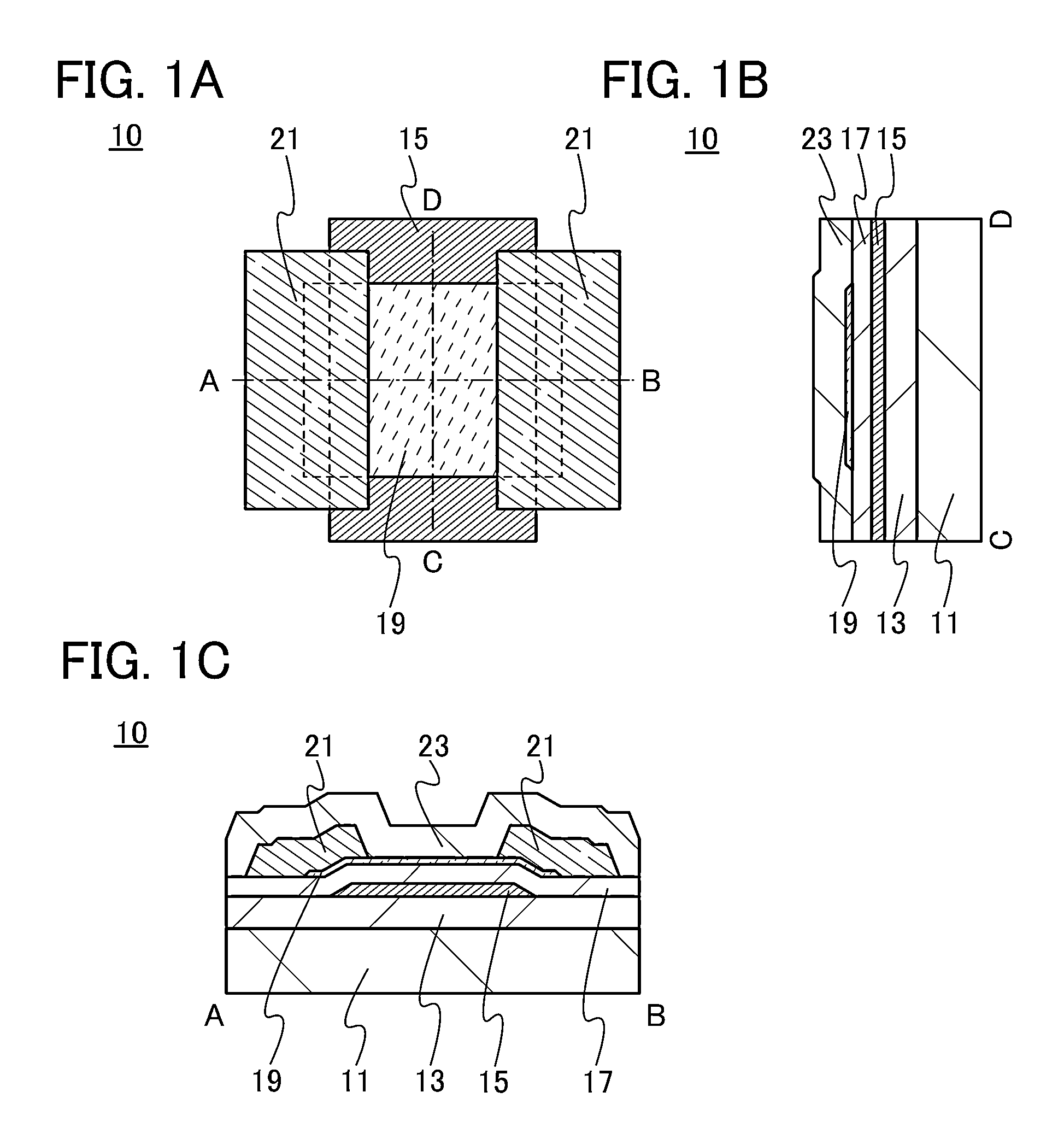
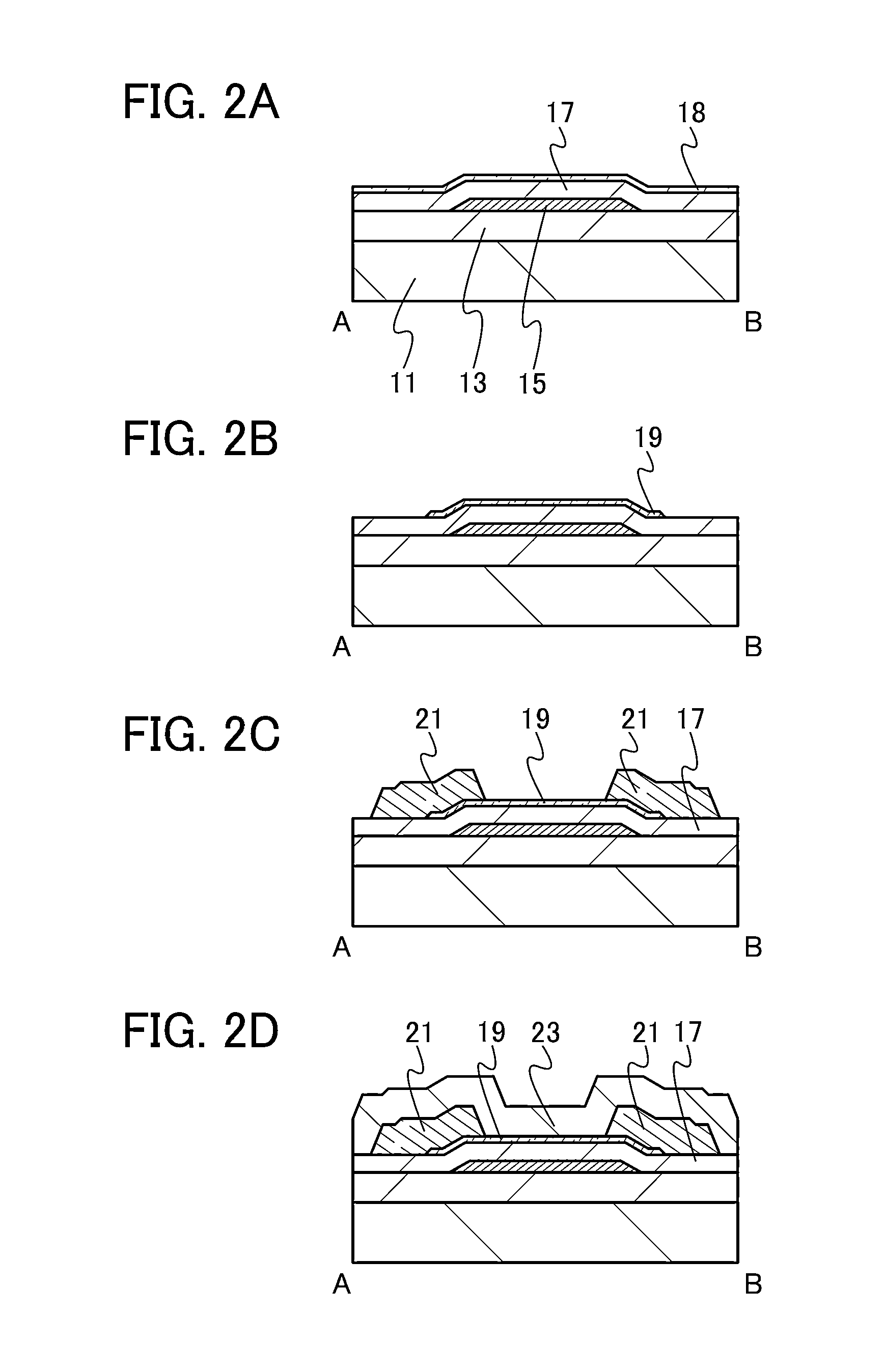
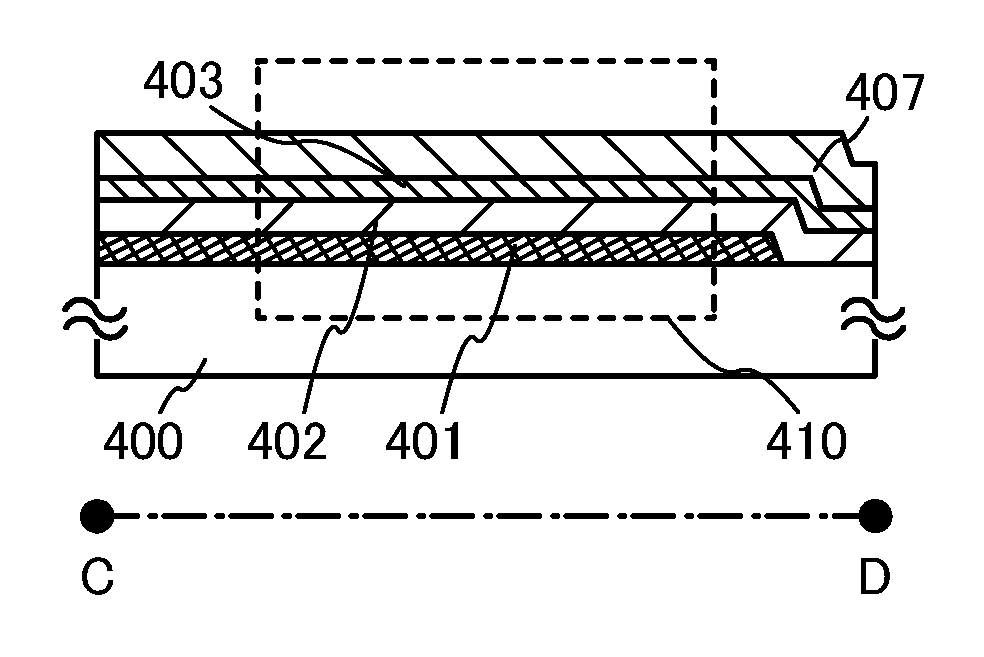
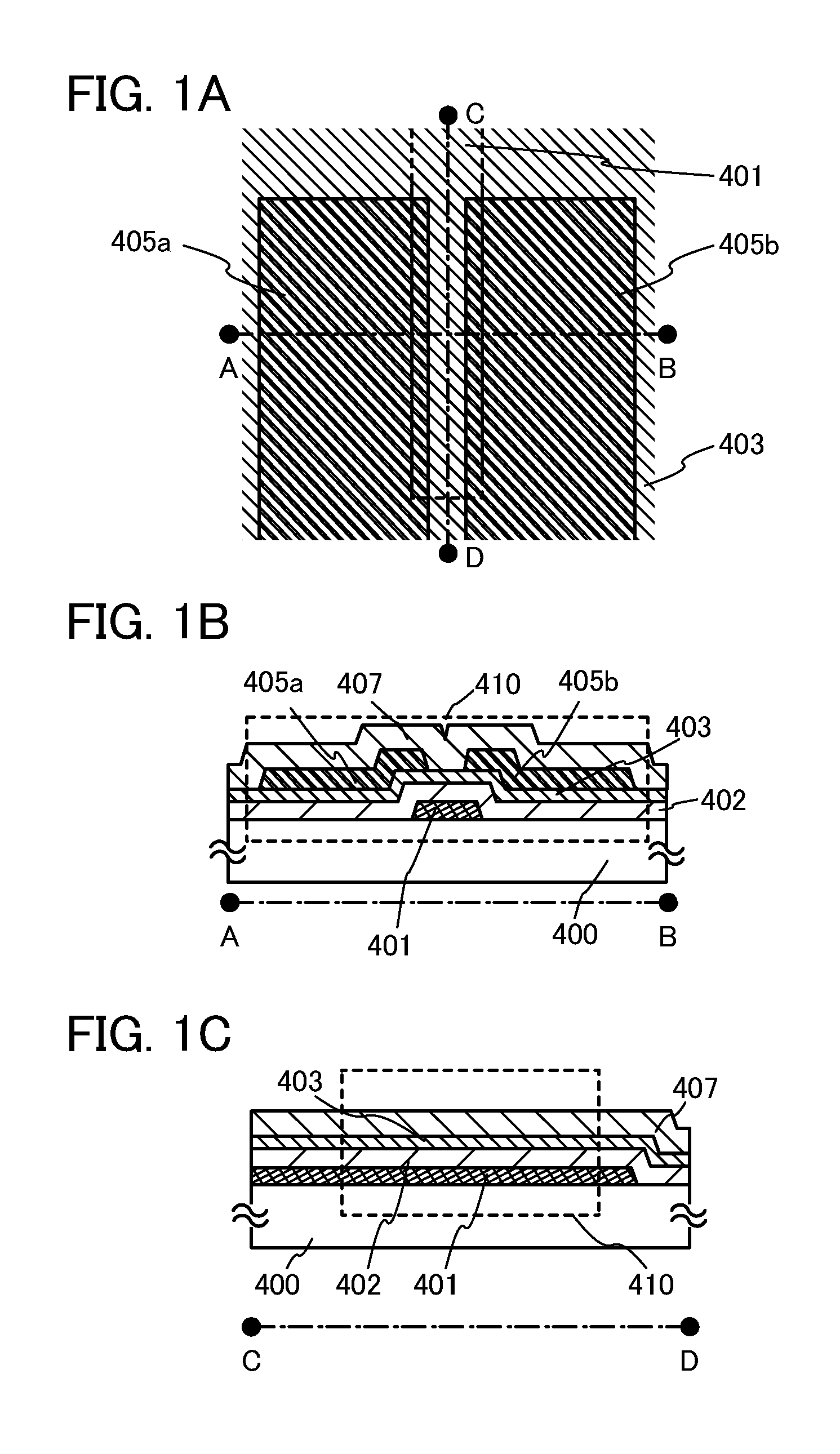
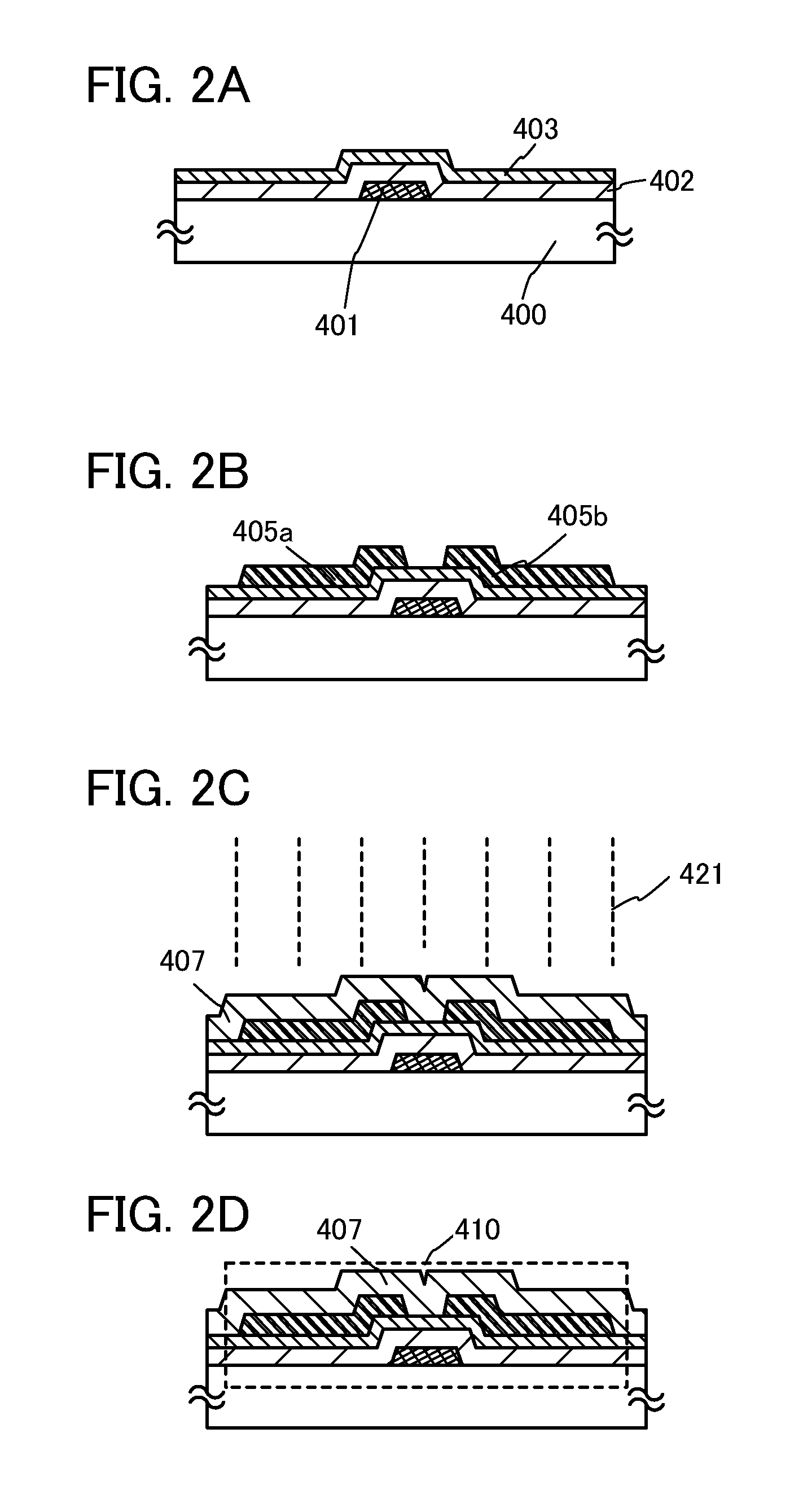
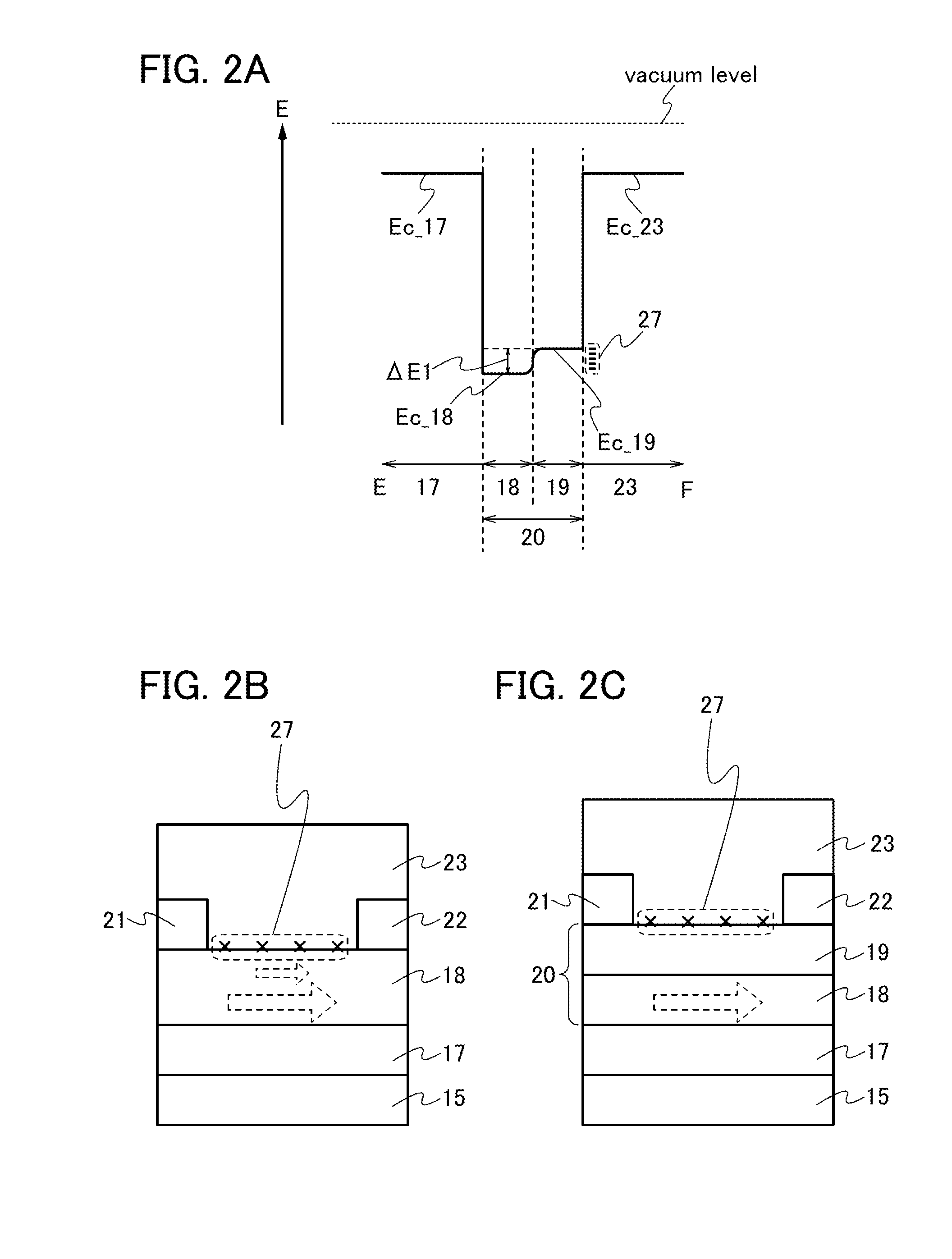
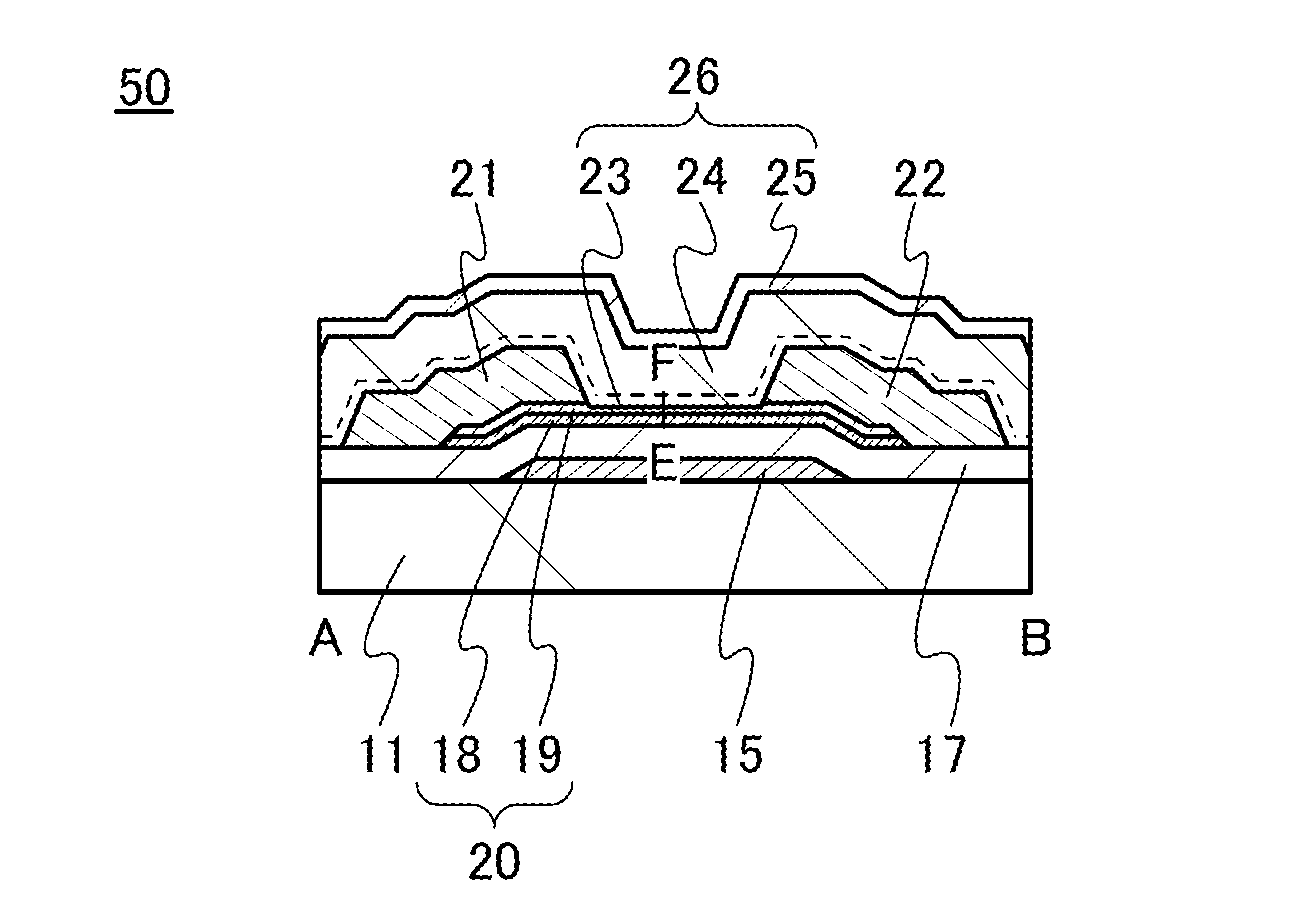
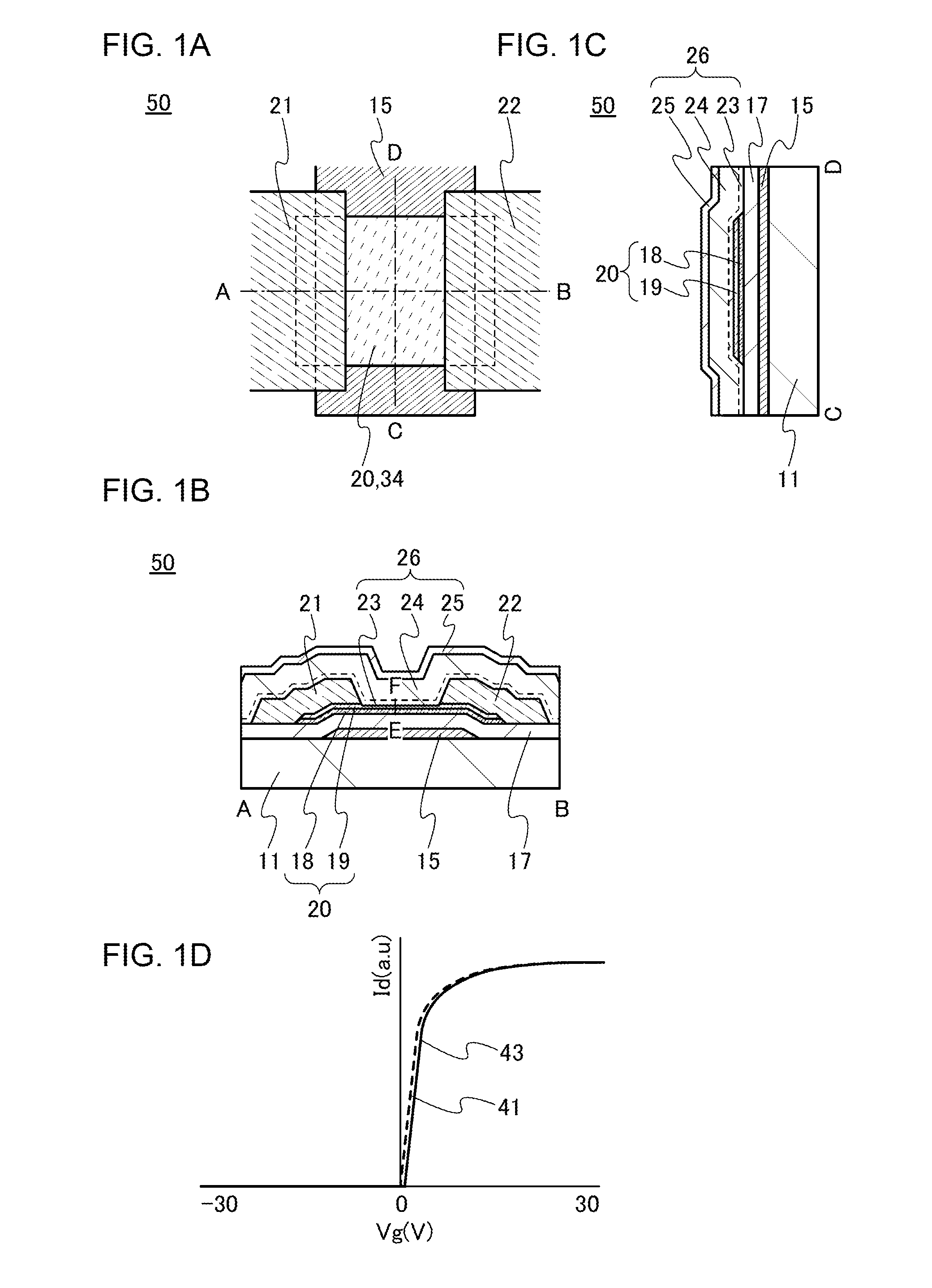
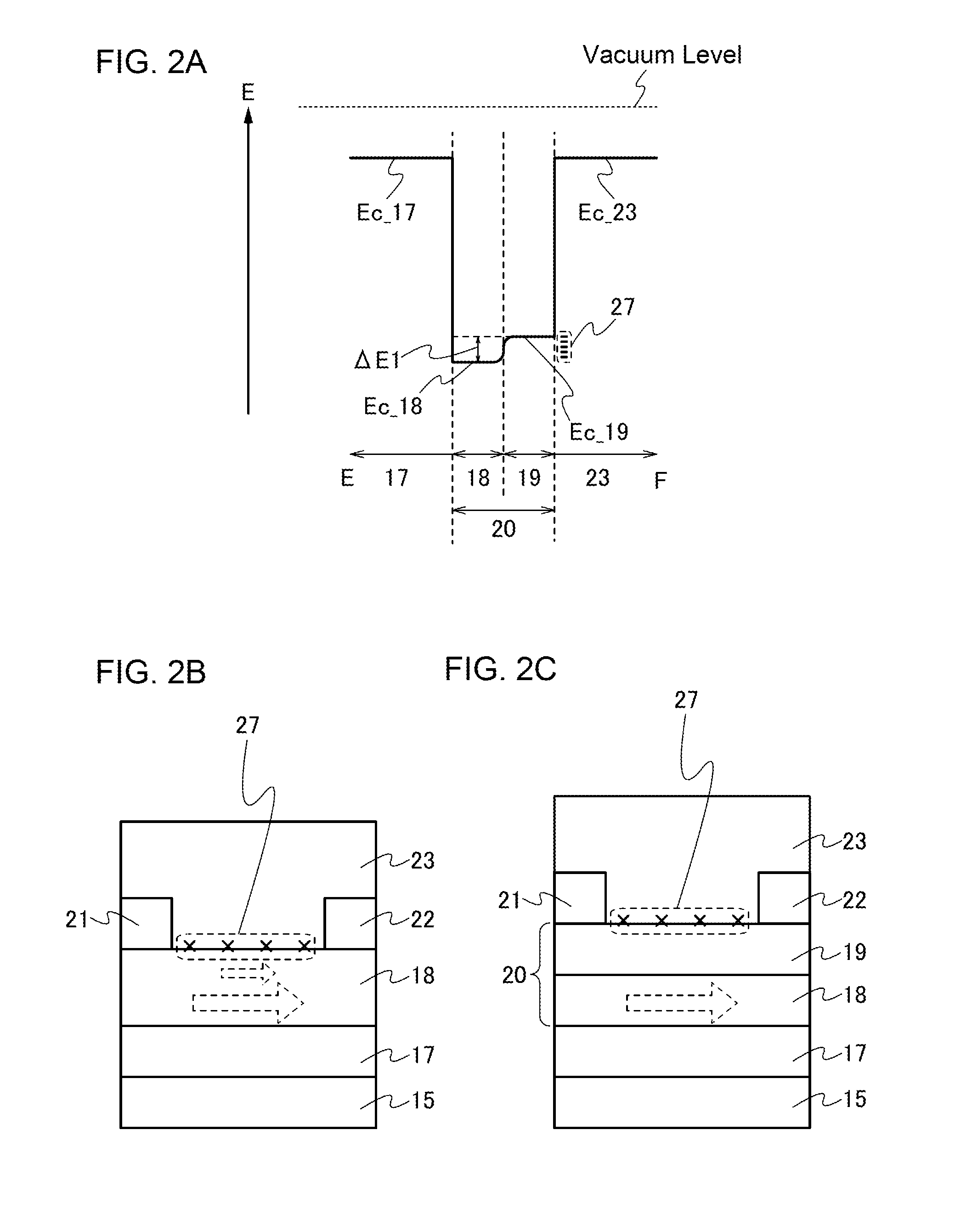
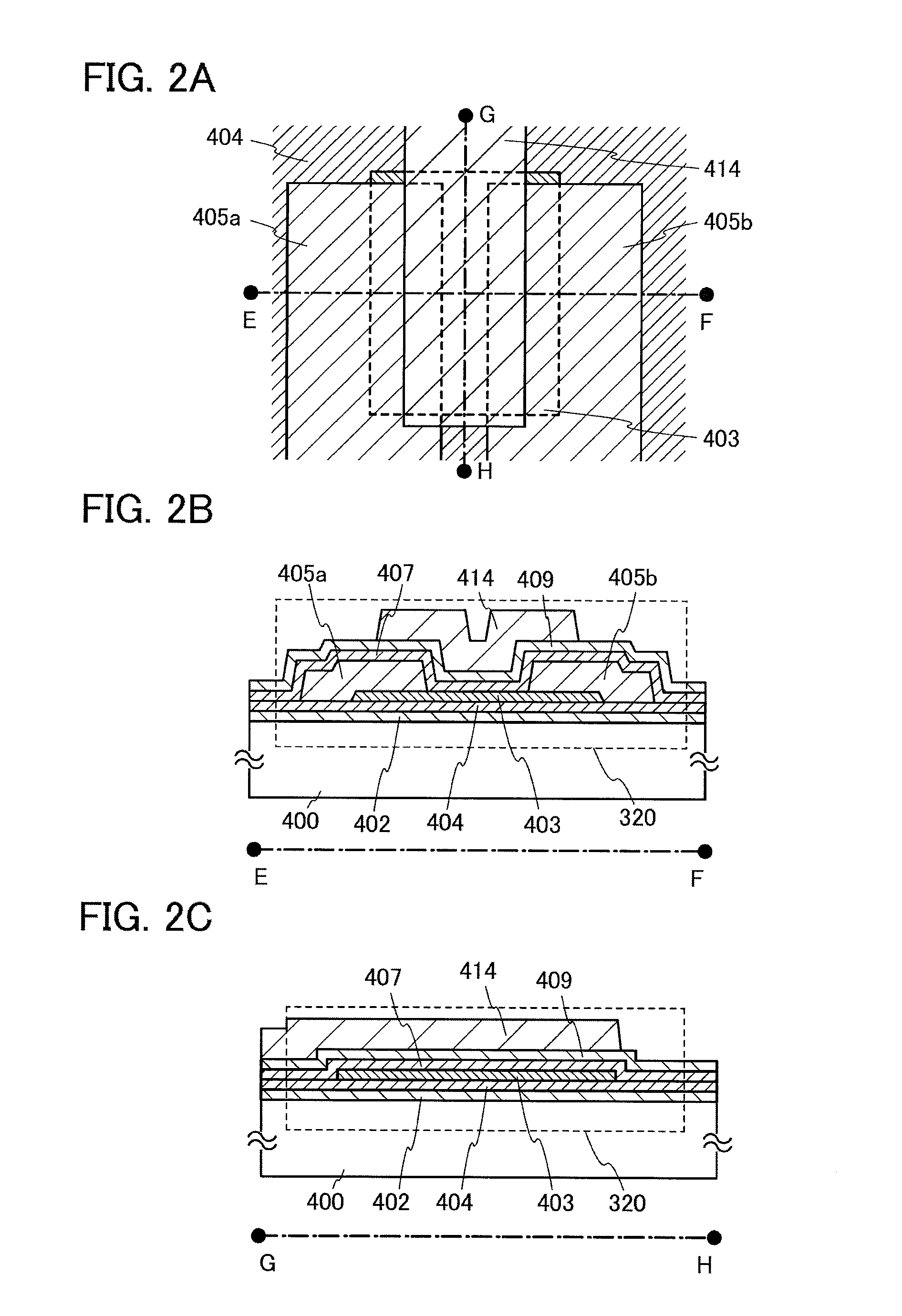
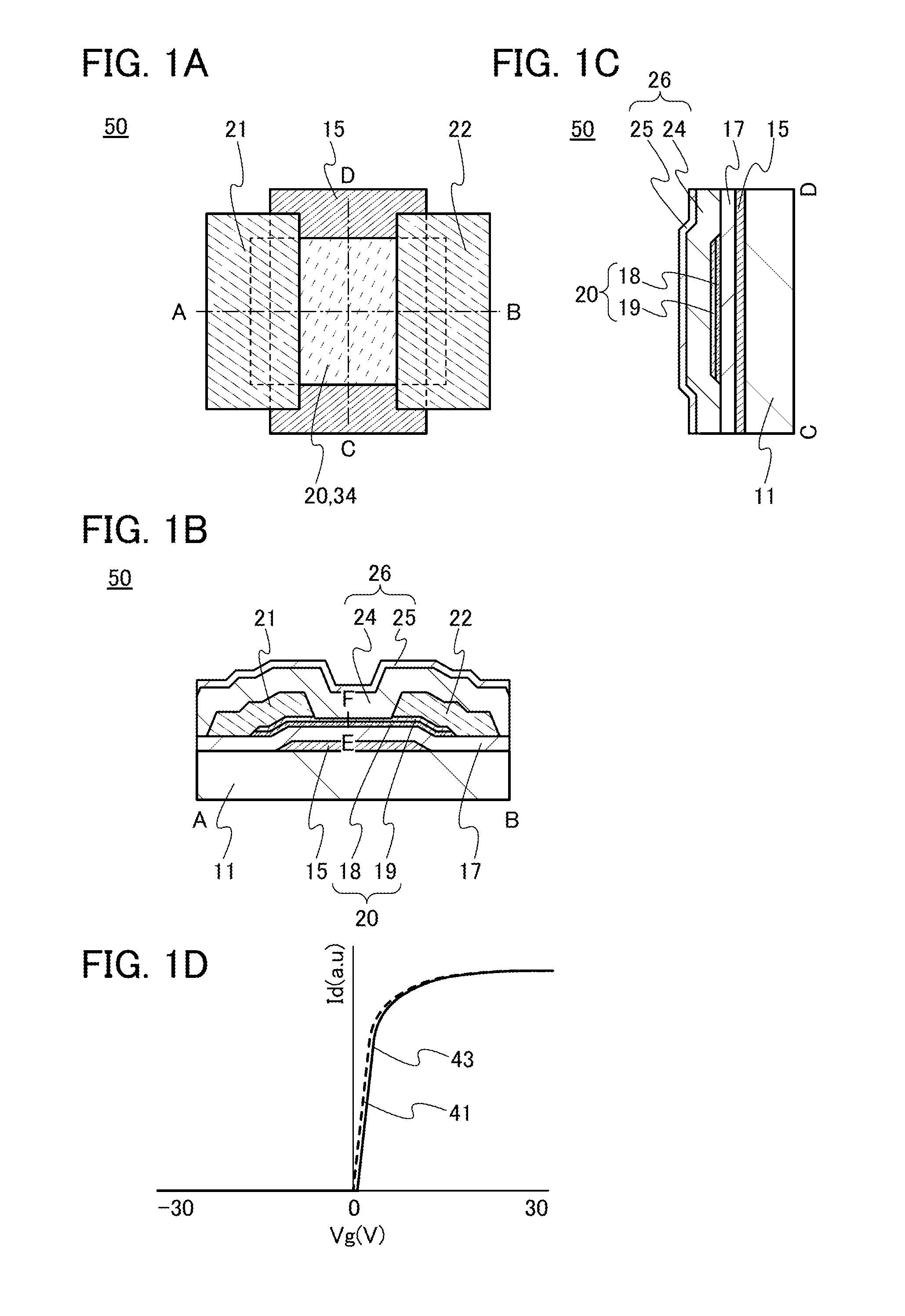
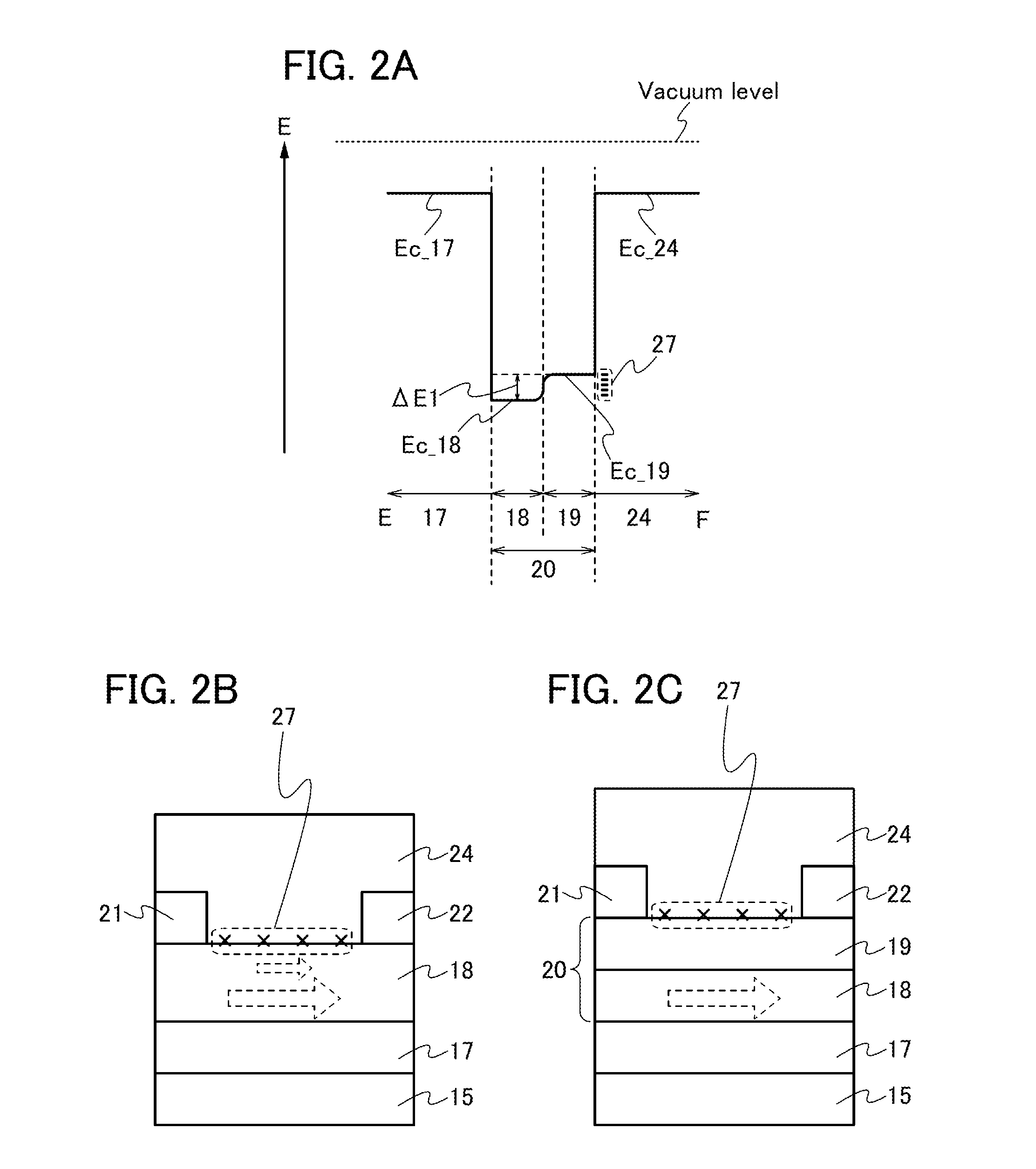
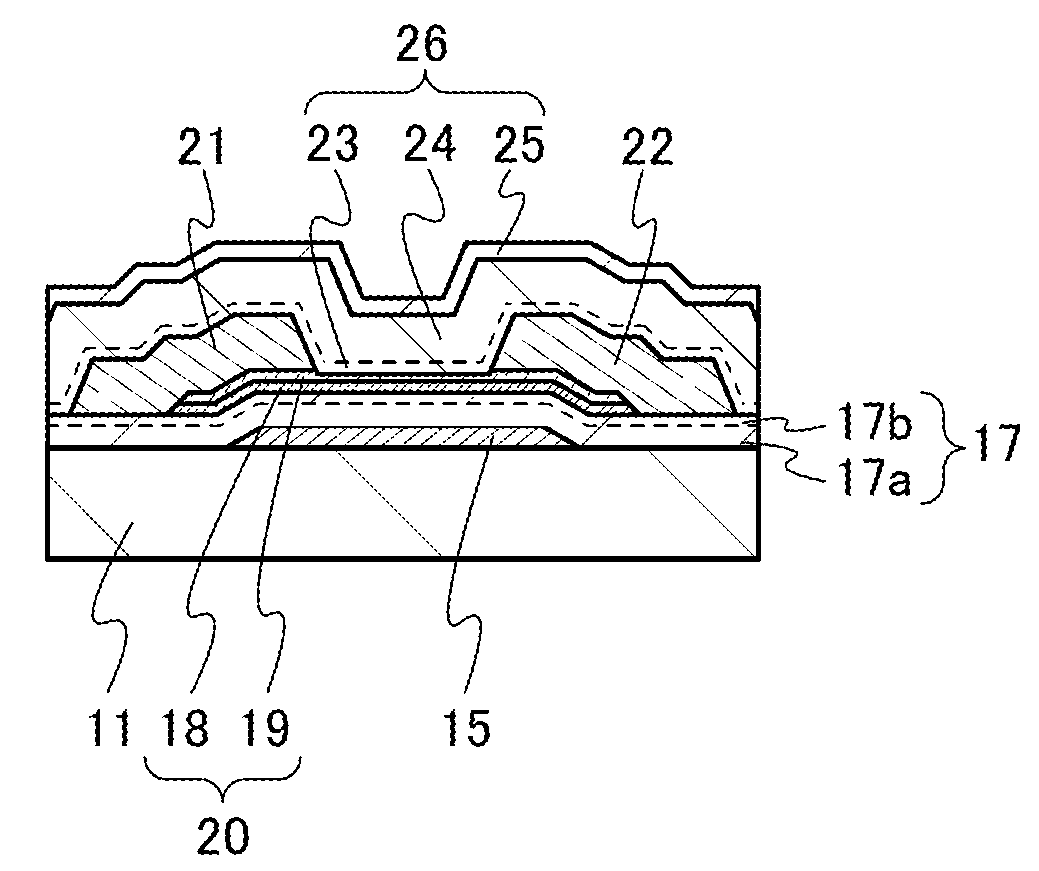
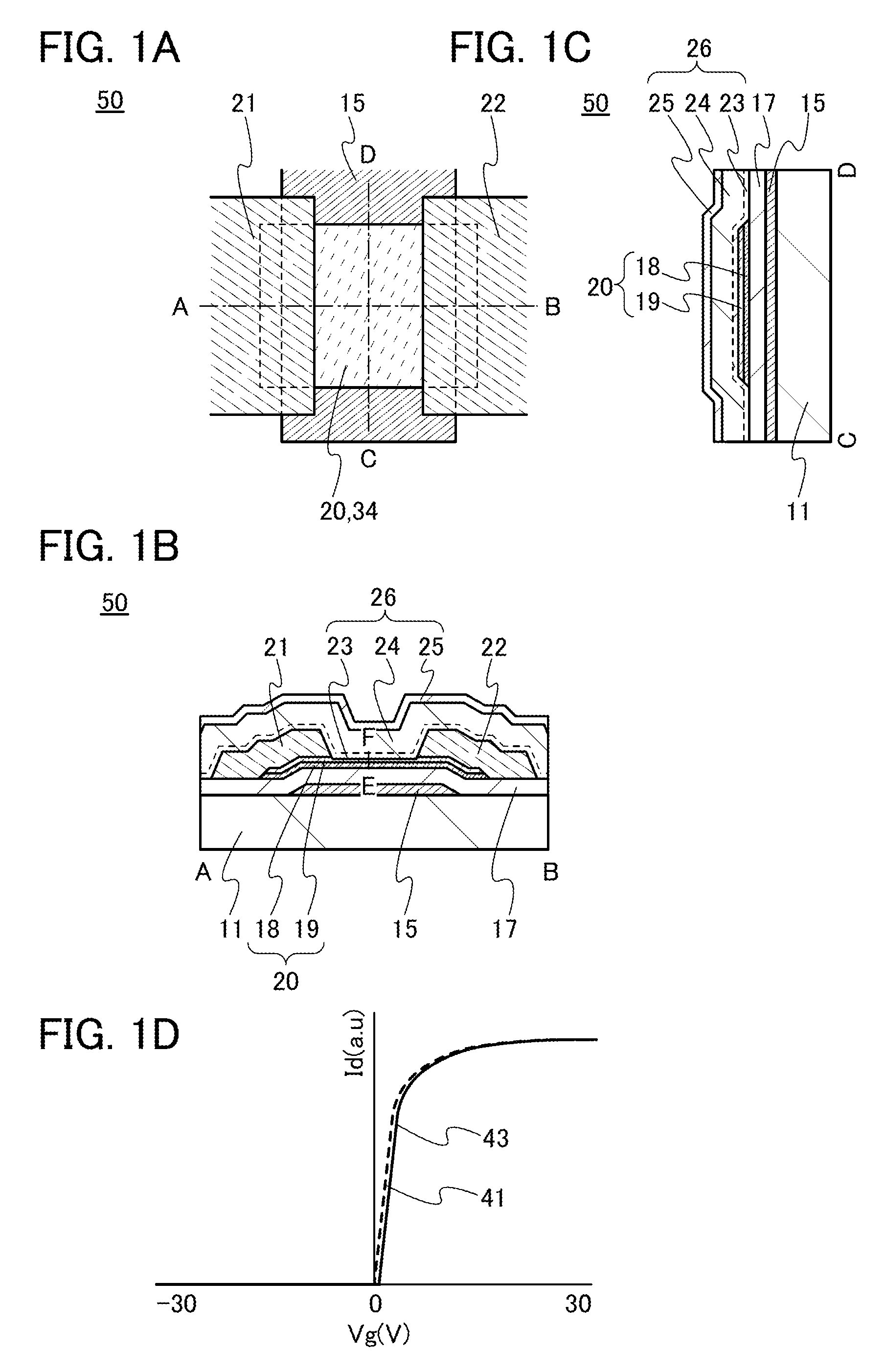
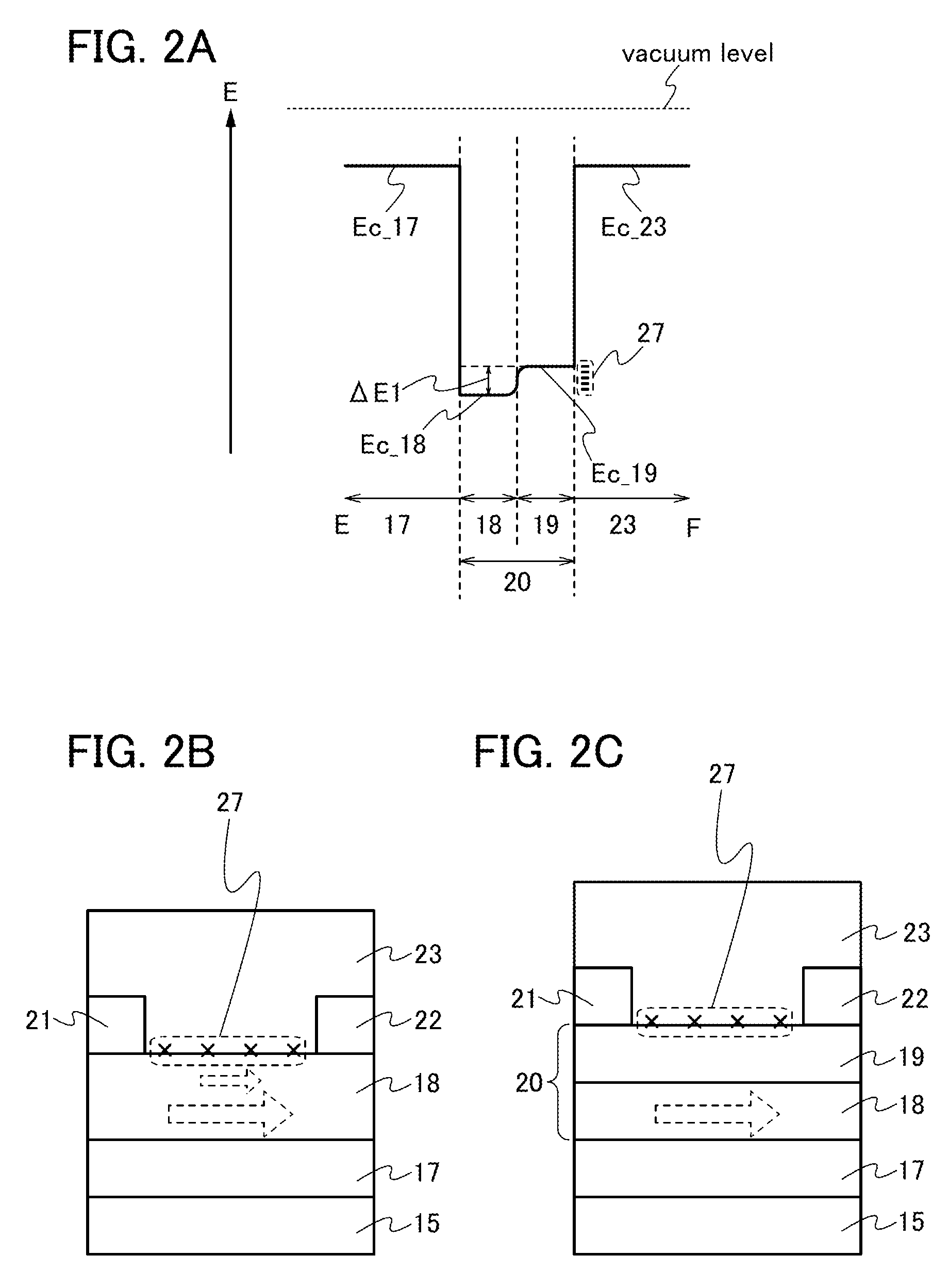
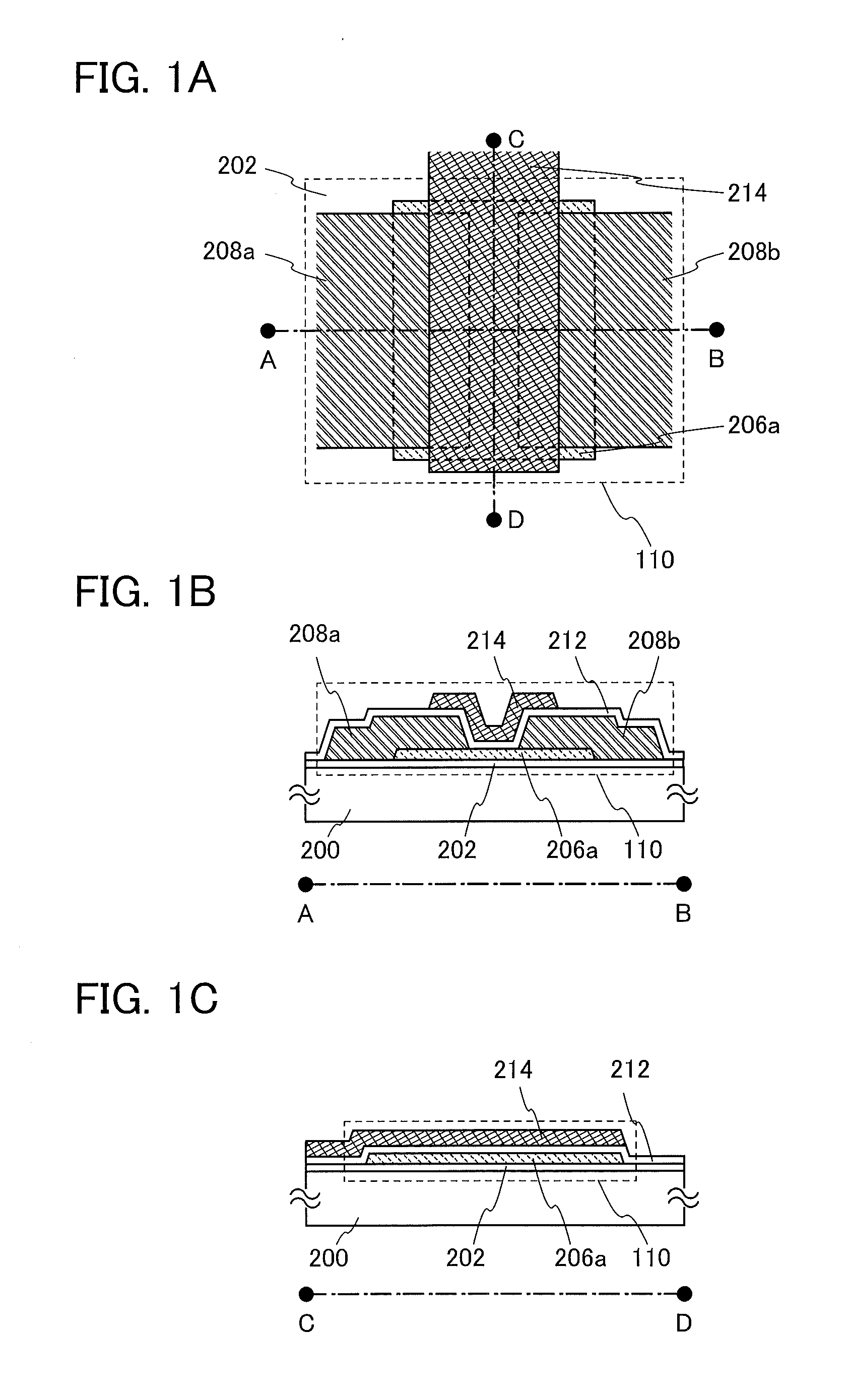
ActiveUS20130264563A1Excellent electrical propertiesReduce the amount of oxygenTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHigh frequency powerVacuum level
In a semiconductor device including a transistor including an oxide semiconductor film and a protective film over the transistor, an oxide insulating film containing oxygen in excess of the stoichiometric composition is formed as the protective film under the following conditions: a substrate placed in a treatment chamber evacuated to a vacuum level is held at a temperature higher than or equal to 180° C. and lower than or equal to 260° C.; a source gas is introduced into the treatment chamber so that the pressure in the treatment chamber is set to be higher than or equal to 100 Pa and lower than or equal to 250 Pa; and a high-frequency power higher than or equal to 0.17 W / cm2 and lower than or equal to 0.5 W / cm2 is supplied to an electrode provided in the treatment chamber.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method of manufacturing semiconductor device
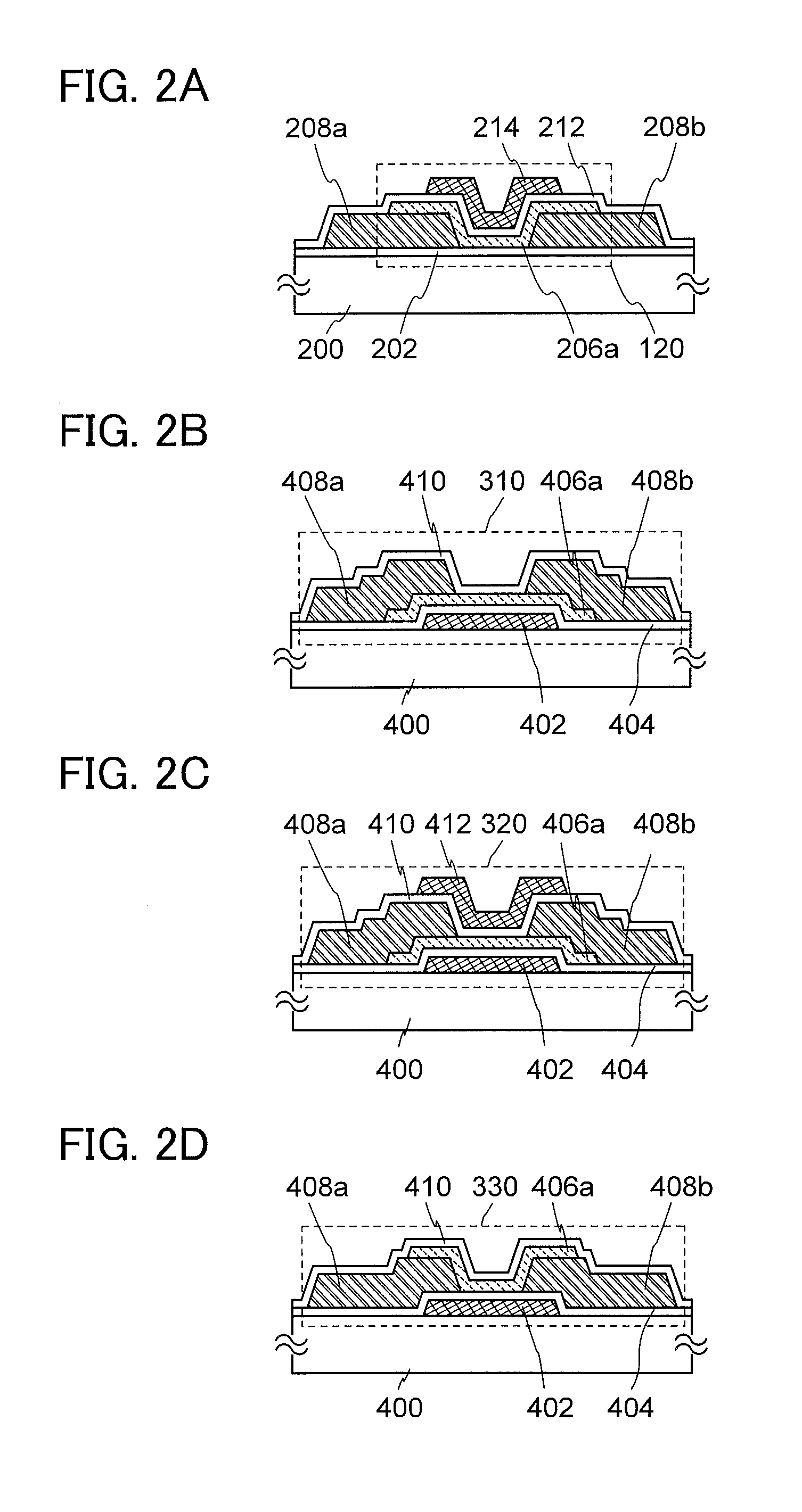
ActiveUS20120231580A1Increasing oxide thicknessLess fluctuationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBias temperature stressSemiconductor
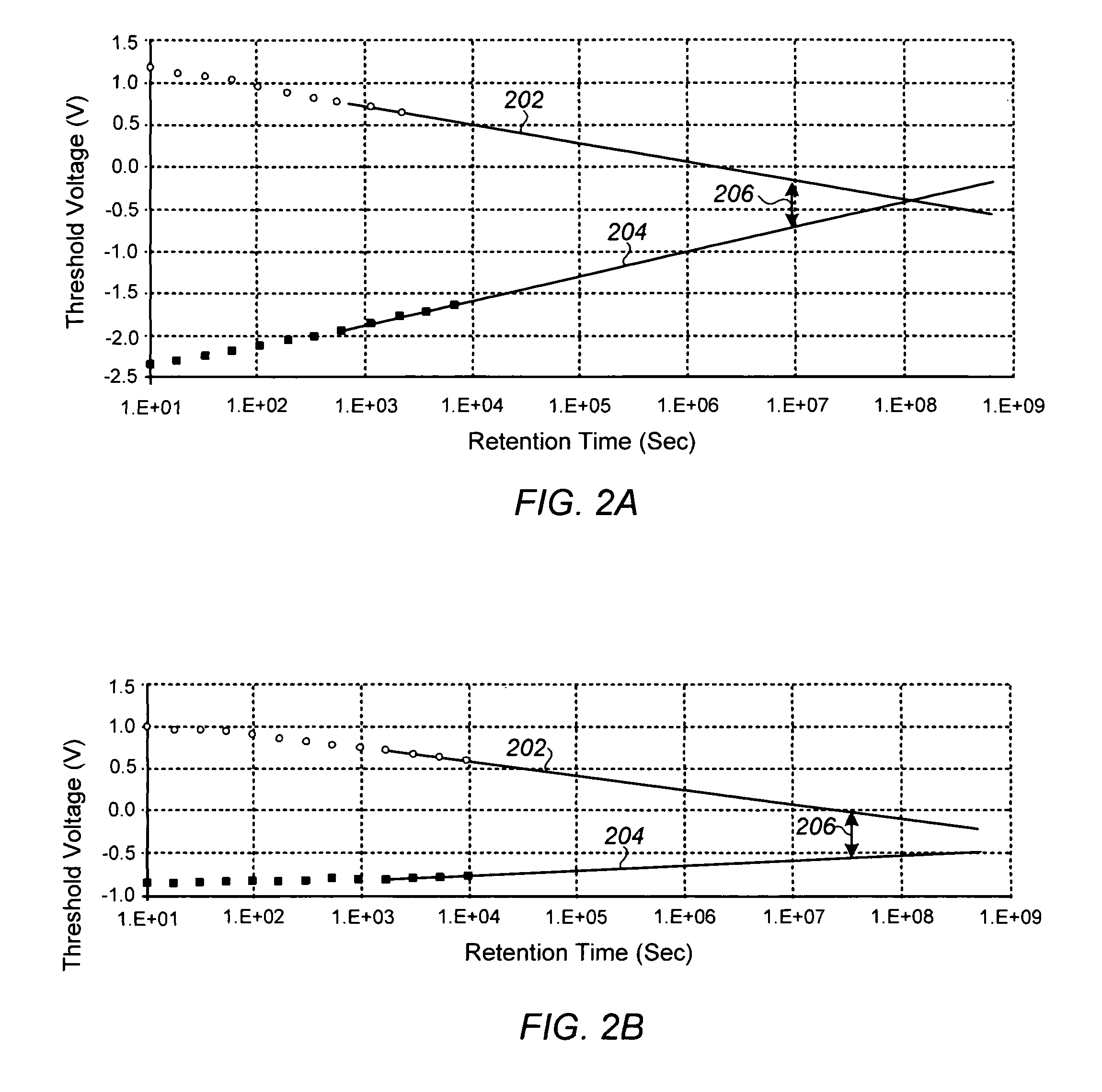
In a manufacturing process of a transistor including an oxide semiconductor film, oxygen doping treatment is performed on the oxide semiconductor film, and then heat treatment is performed on the oxide semiconductor film and an aluminum oxide film provided over the oxide semiconductor film. Consequently, an oxide semiconductor film which includes a region containing more oxygen than a stoichiometric composition is formed. The transistor formed using the oxide semiconductor film can have high reliability because the amount of change in the threshold voltage of the transistor by a bias-temperature stress test (BT test) is reduced.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
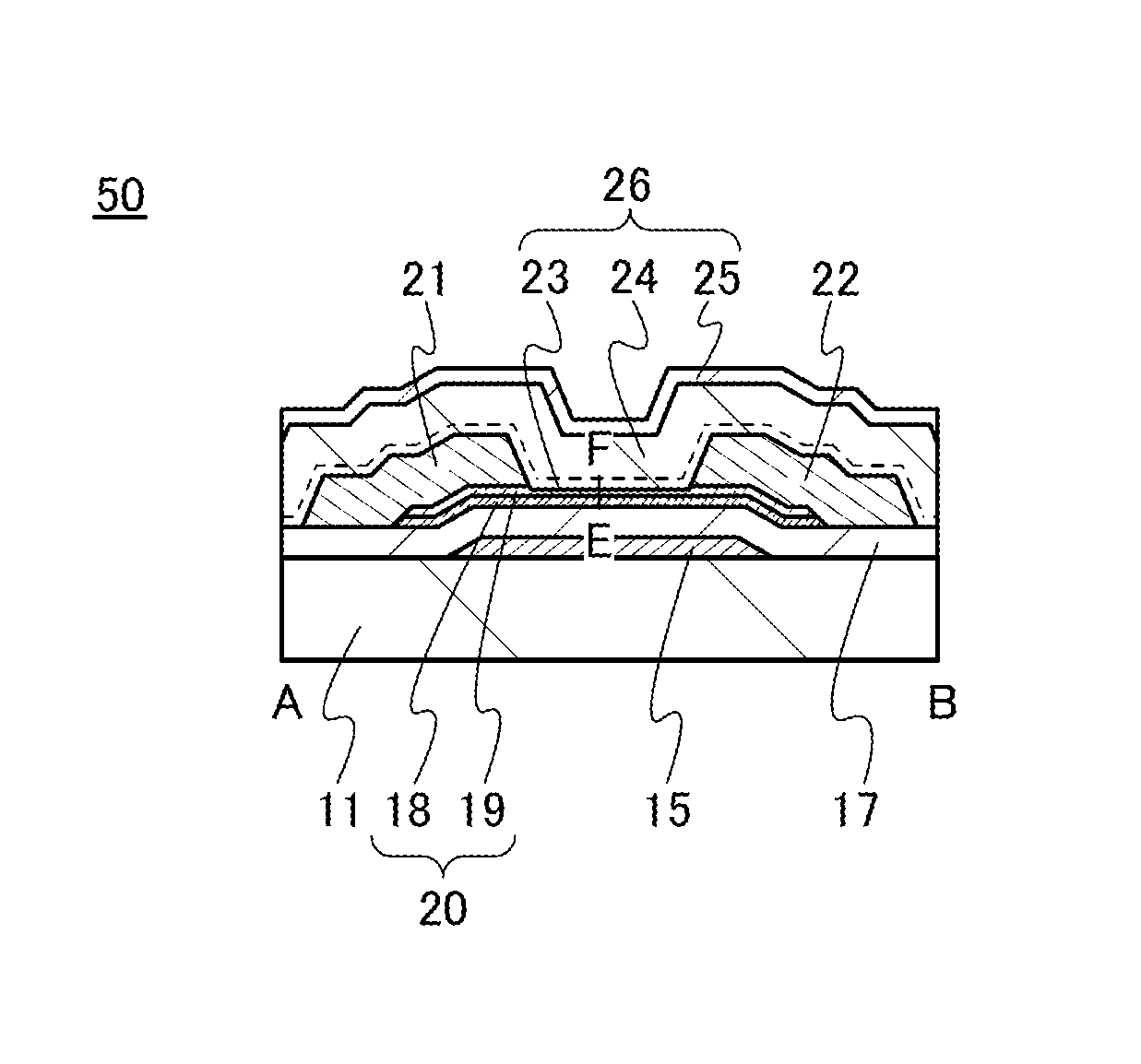
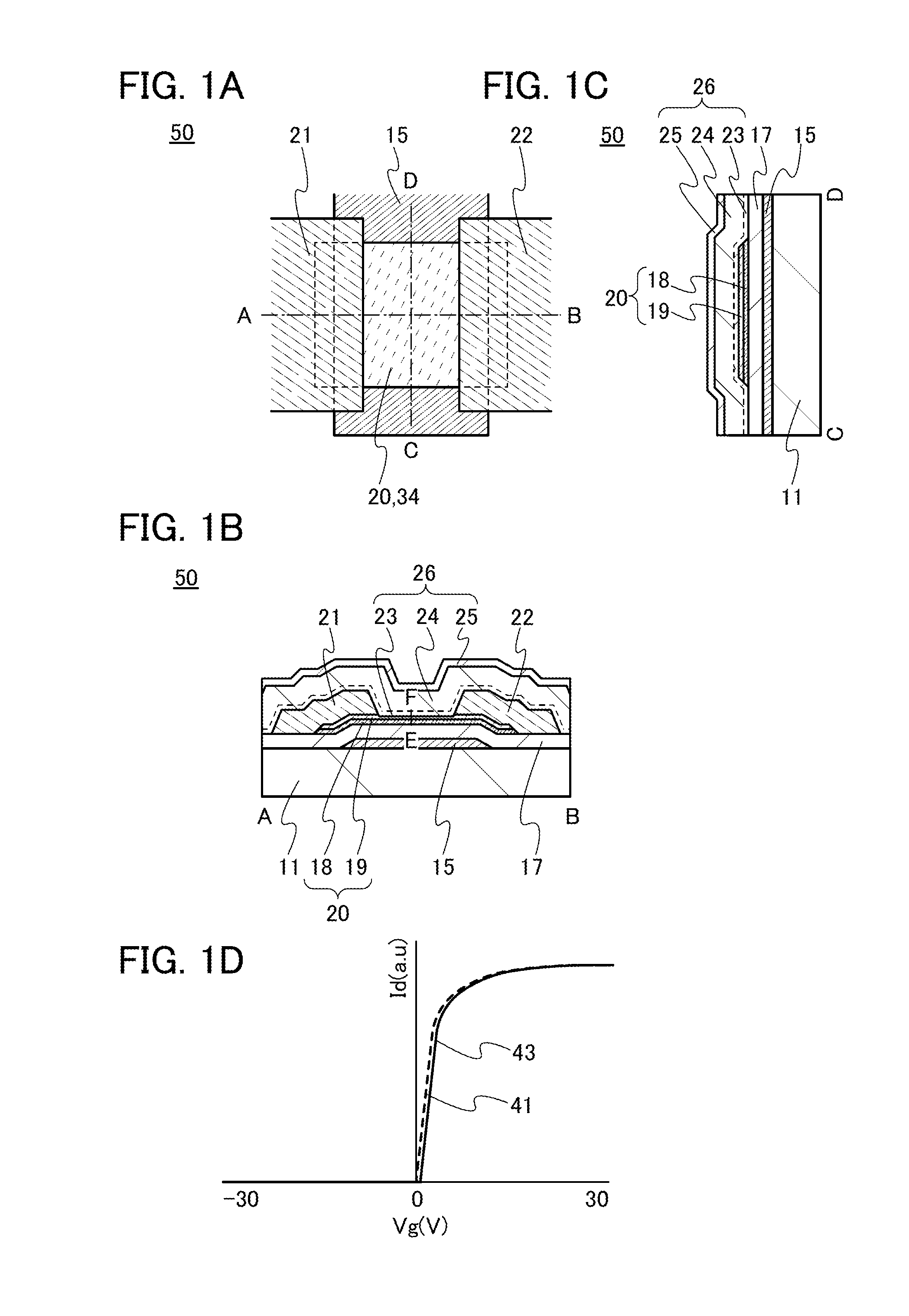
ActiveUS20140110707A1Improve featuresImprove reliabilityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialSemiconductor
In a semiconductor device including a transistor including a gate electrode formed over a substrate, a gate insulating film covering the gate electrode, a multilayer film overlapping with the gate electrode with the gate insulating film provided therebetween, and a pair of electrodes in contact with the multilayer film, a first oxide insulating film covering the transistor, and a second oxide insulating film formed over the first oxide insulating film, the multilayer film includes an oxide semiconductor film and an oxide film containing In or Ga, the oxide semiconductor film has an amorphous structure or a microcrystalline structure, the first oxide insulating film is an oxide insulating film through which oxygen is permeated, and the second oxide insulating film is an oxide insulating film containing more oxygen than that in the stoichiometric composition.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
One-dimensional illumination apparatus and imaging apparatus
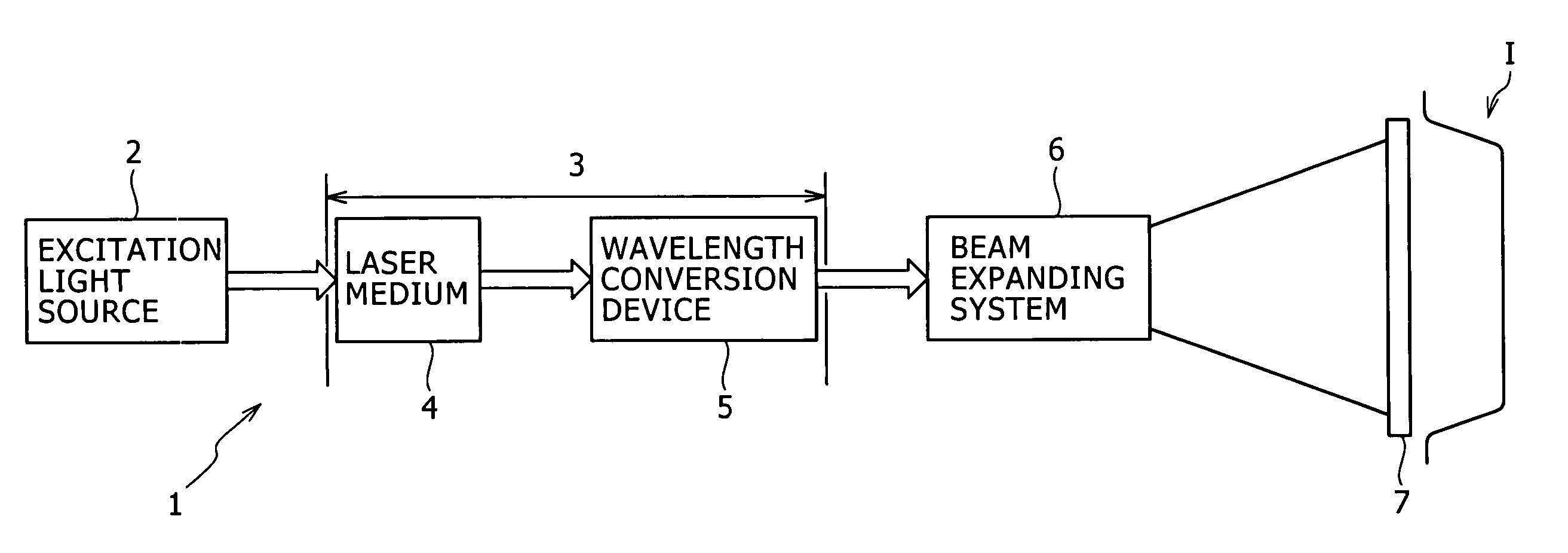
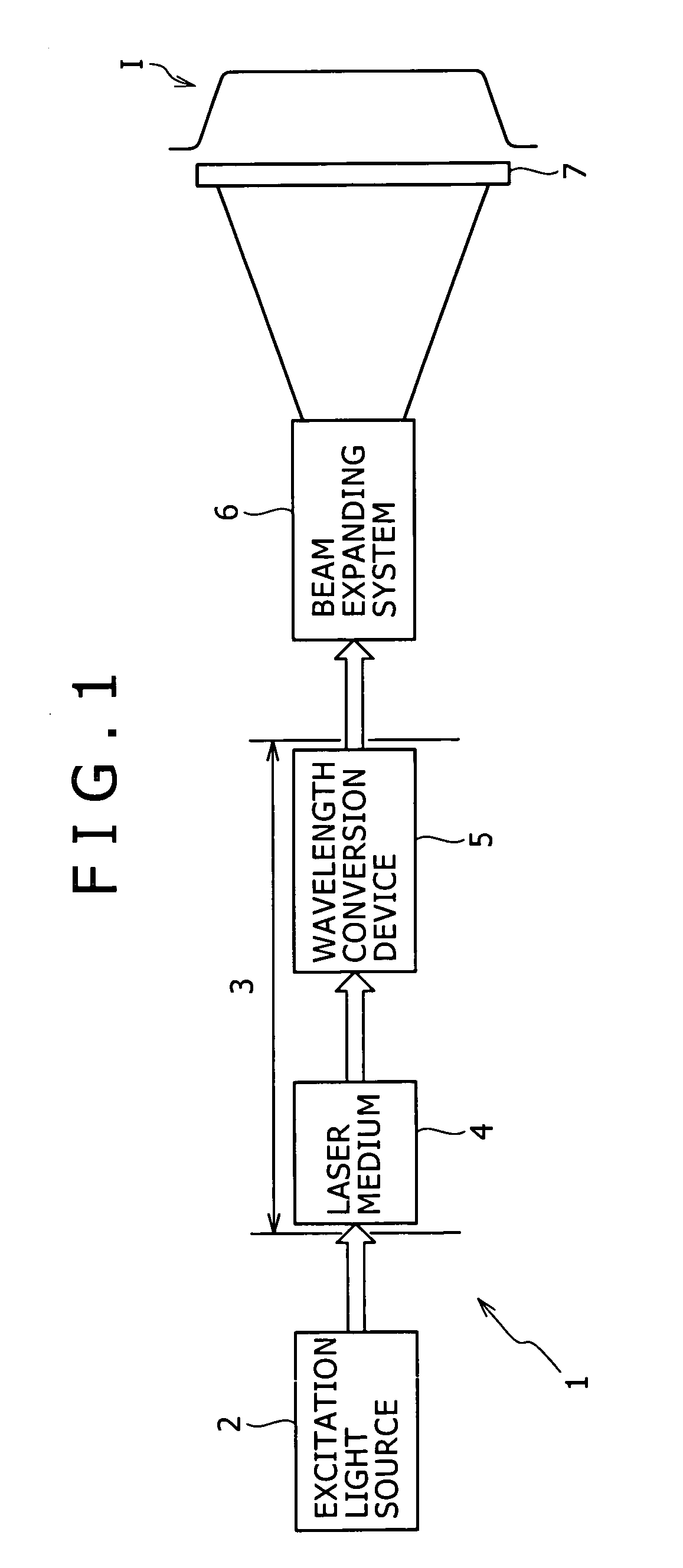
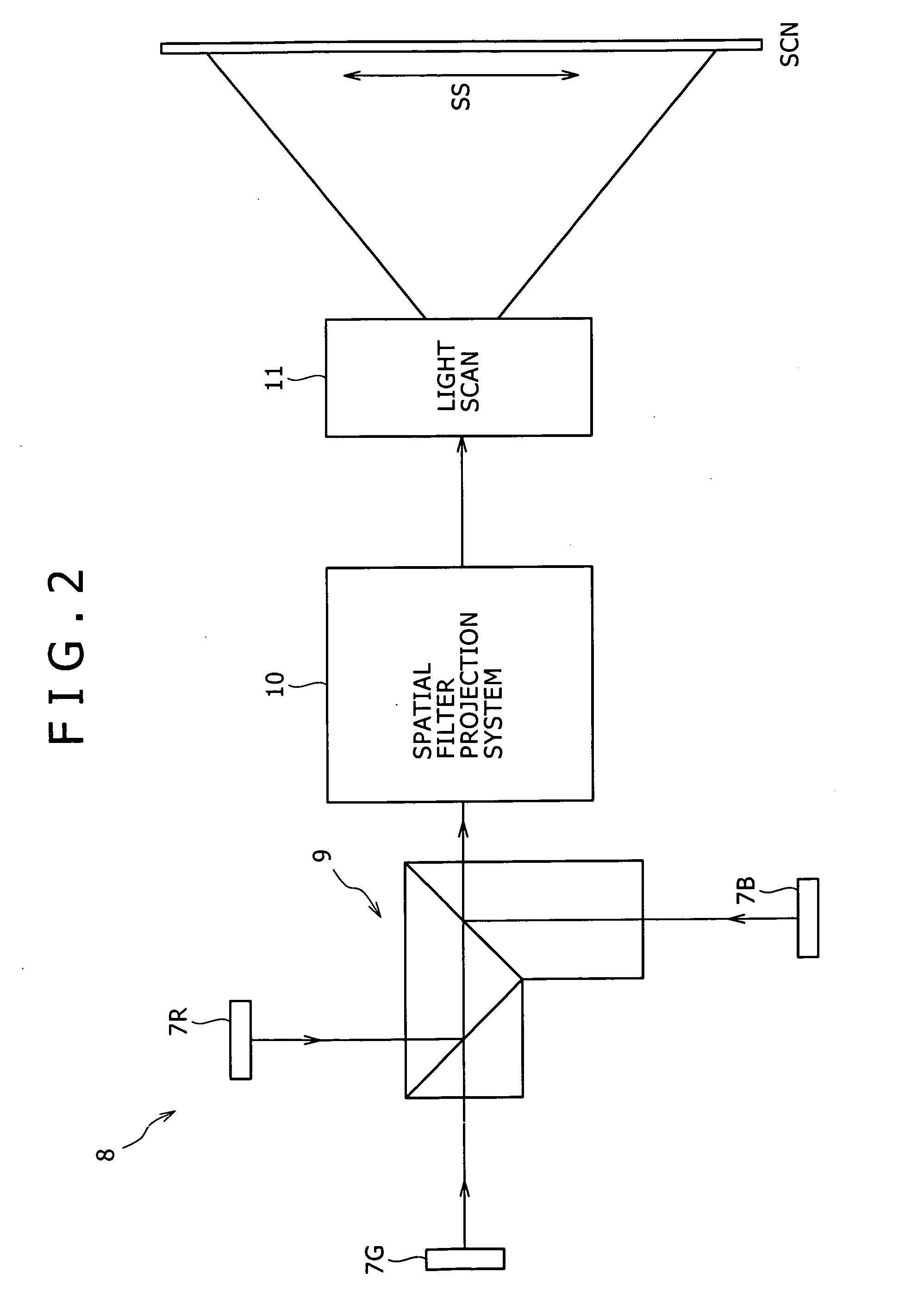
InactiveUS7545837B2High in output and efficiencyReduce speckle noiseSemiconductor laser arrangementsPicture reproducers using projection devicesNonlinear optical crystalLight equipment
Owner:SONY CORP
Rare-earth doped alkaline-earth silicon nitride phosphor, method for producing and radiation converting device comprising such a phosphor
InactiveUS20100288972A1A large amountImprove conversion efficiencyLuminescent compositionsRare-earth elementAlkaline earth metal
The invention relates to a method of manufacturing a rare-earth doped alkaline-earth silicon nitride phosphor of a stoichiometric composition. Said method comprising the step of selecting one or more compounds each comprising at least one element of the group comprising the rare-earth elements (RE), the alkaline-earth elements (AE), silicon (Si) and nitrogen (N) and together comprising the necessary elements to form the rare-earth doped alkaline-earth silicon nitride phosphor (AE2Si5N8:RE). The method further comprises the step of bringing the compounds at an elevated temperature in reaction for forming the rare-earth doped alkaline-earth silicon nitride phosphor (AE2Si5N8:RE). In such a method normally a small amount of oxygen, whether intentionally or not-intentionally added, will be incorporated in the rare-earth doped alkaline-earth silicon nitride phosphor (AE2Si5N8:RE). According to the invention the creation of defects by formation of a non-stoichiometric oxygen containing phosphor is at least partly prevented by partly substituting for the ions (AE, Si, N) of the alkaline-earth silicon nitride phosphor (AE2Si5N8:RE) suitable further elements of the periodic system by which vacancies are created, filled or annihilated resulting in the formation of a modified alkaline-earth silicon nitride phosphor (AE2Si5N8:RE) having a stoichiometric composition. In this way a modified phosphor is obtained having excellent and stable optical properties. The invention further relates to a modified phosphor obtainable by the above-mentioned method and a radiation converting device comprising such a phosphor.
Owner:LEUCHTSTOFFWERK BREITUNGEN +1
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20140110705A1Reduce eye fatigueImprove featuresTransistorSolid-state devicesDevice materialEngineering
To reduce defects in an oxide semiconductor film in a semiconductor device. To improve the electrical characteristics and the reliability of a semiconductor device including an oxide semiconductor film. In a semiconductor device including a transistor including a gate electrode formed over a substrate, a gate insulating film covering the gate electrode, a multilayer film overlapping with the gate electrode with the gate insulating film provided therebetween, and a pair of electrodes in contact with the multilayer film, a first oxide insulating film covering the transistor, and a second oxide insulating film formed over the first oxide insulating film, the multilayer film includes an oxide semiconductor film and an oxide film containing In or Ga, the first oxide insulating film is an oxide insulating film through which oxygen is permeated, and the second oxide insulating film is an oxide insulating film containing more oxygen than that in the stoichiometric composition.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Electrode Which Has Been Coated With A Solid Ion Conductor Which Has A Garnet-Like Crystal Structure And Has The Stoichiometric Composition L7+XAXG3-XZr2O12
ActiveUS20140205910A1Stable crystal structureGood chemical stabilityHybrid capacitor electrodesElectrolytic capacitorsCrystal structureStoichiometric composition
The invention is directed to an electrode which has been coated with the solid ion conductor which has a garnet-like crystal structure and has the stoichiometric composition L7+xAxG3−xZr2O12, whereinL is in each case independently a monovalent cation,A is in each case independently a divalent cation,G is in each case independently a trivalent cation,0≦x≦3 andO can be partly or completely replaced by divalent or trivalent anion.
Owner:BASF SE
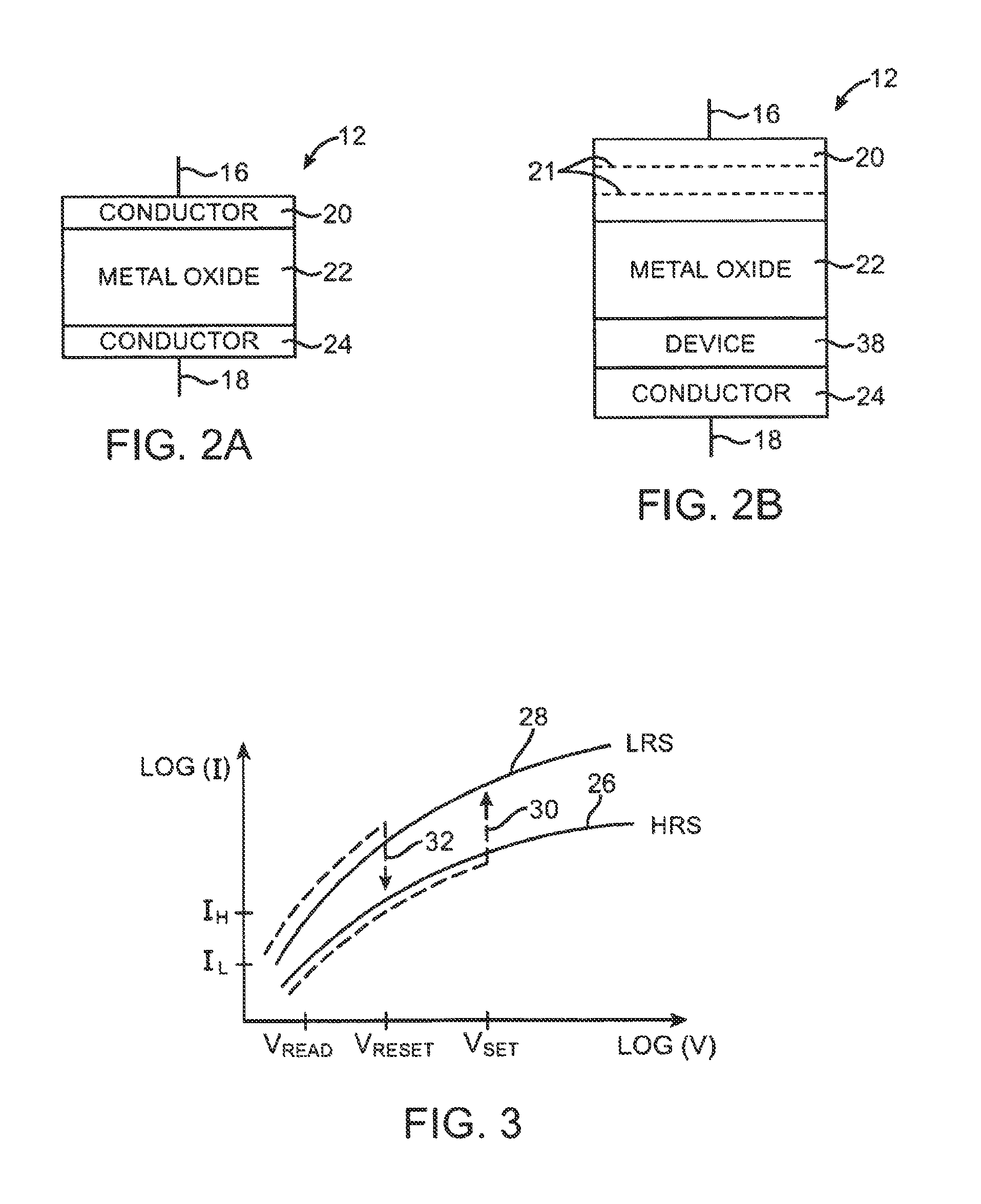
Semiconductor device including oxide semiconductor and metal oxide
ActiveUS8878173B2Stable electrical characteristicsImprove reliabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesOxygenSemiconductor
An object is to provide a semiconductor device including an oxide semiconductor, which has stable electrical characteristics and improved reliability. In a transistor including an oxide semiconductor film, insulating films each including a material containing a Group 13 element and oxygen are formed in contact with the oxide semiconductor film, whereby the interfaces with the oxide semiconductor film can be kept in a favorable state. Further, the insulating films each include a region where the proportion of oxygen is higher than that in the stoichiometric composition, so that oxygen is supplied to the oxide semiconductor film; thus, oxygen defects in the oxide semiconductor film can be reduced. Furthermore, the insulating films in contact with the oxide semiconductor film each have a stacked structure so that films each containing aluminum are provided over and under the oxide semiconductor film, whereby entry of water into the oxide semiconductor film can be prevented.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Stoichiometric Lithium Cobalt Oxide and Method for Preparation of the Same
ActiveUS20070218363A1Sensitive to process parameterLarge fluctuationsPrimary cell to battery groupingElectrode manufacturing processesHigh temperature storageLithium metal
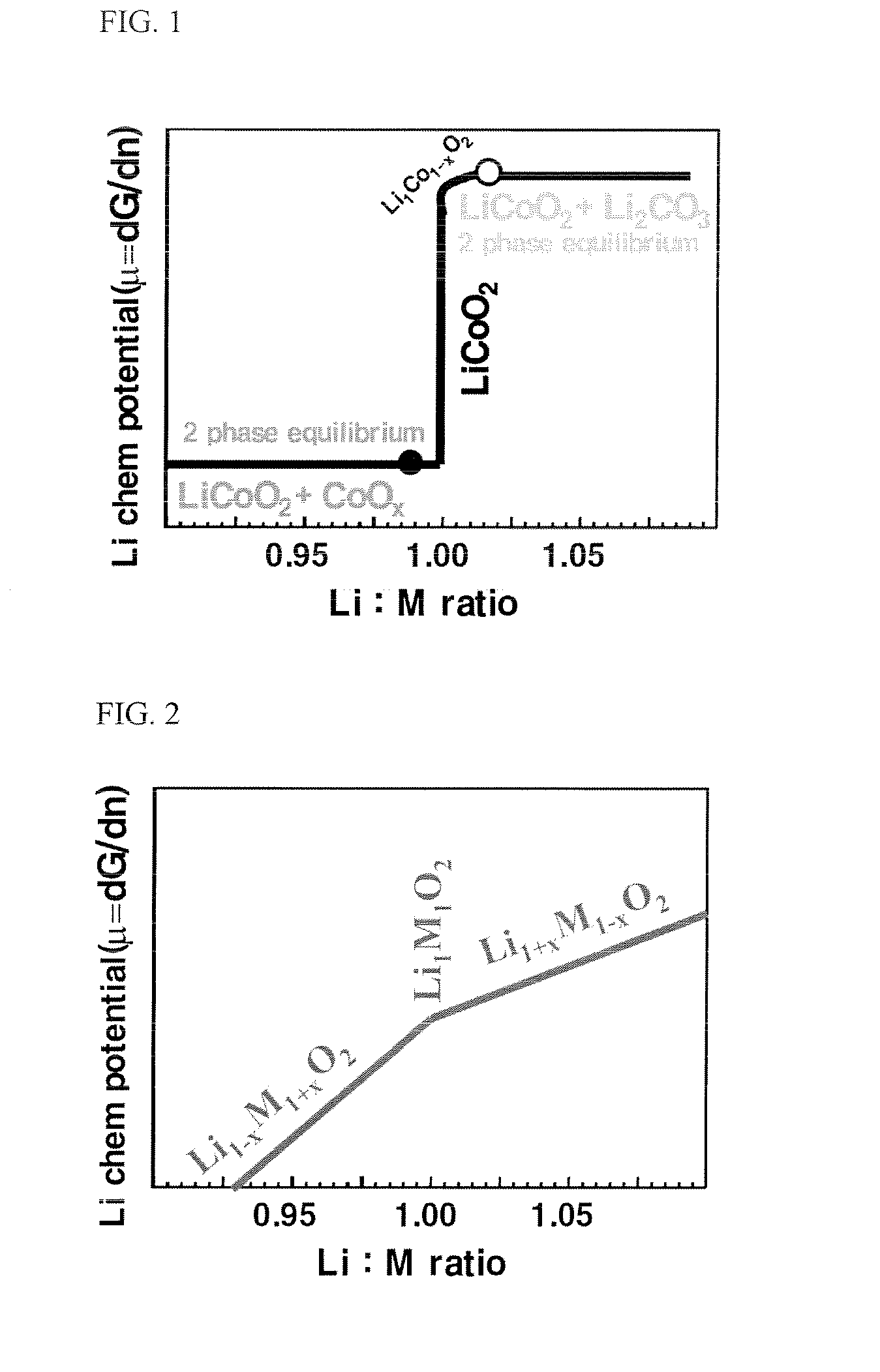
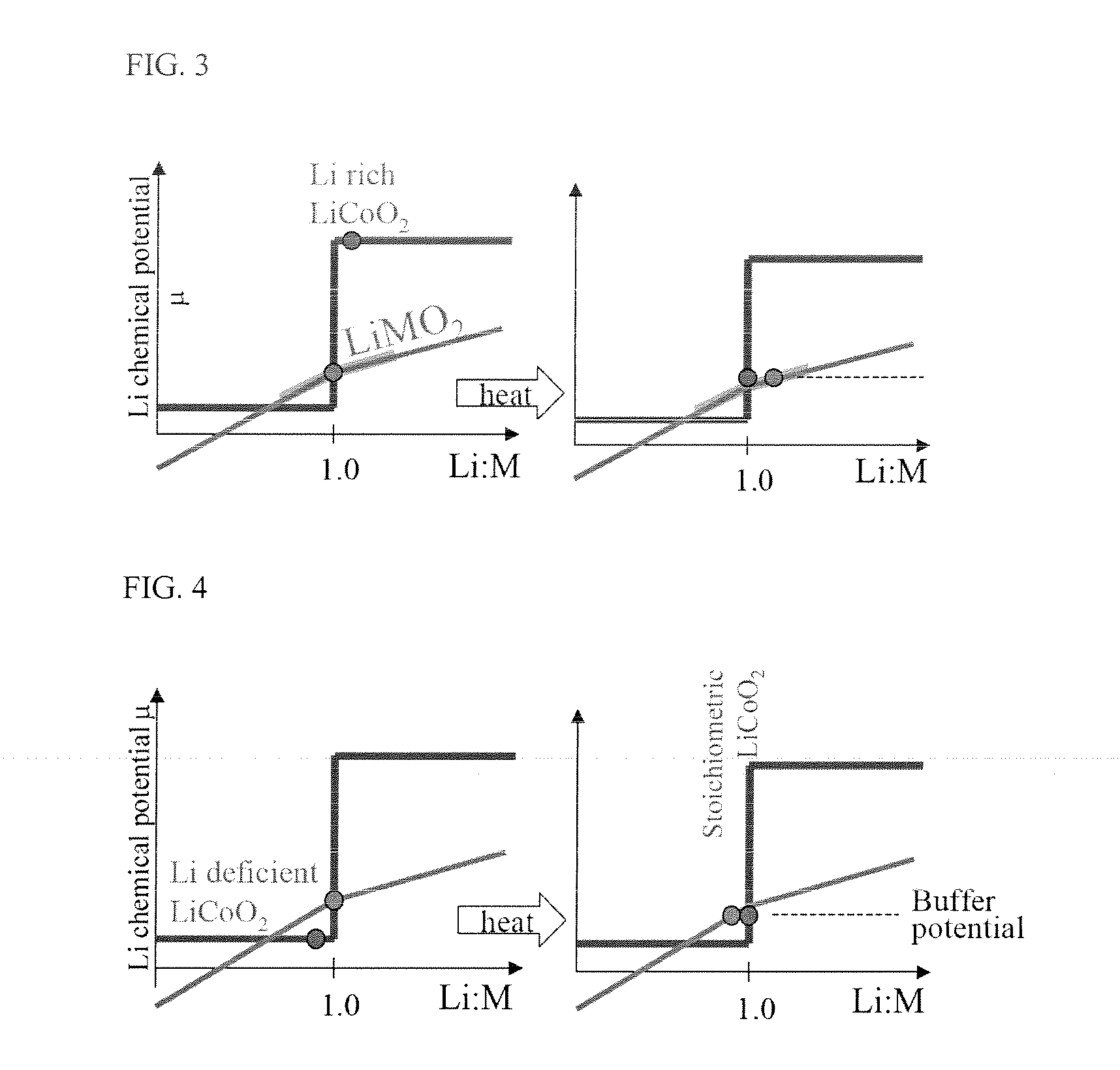
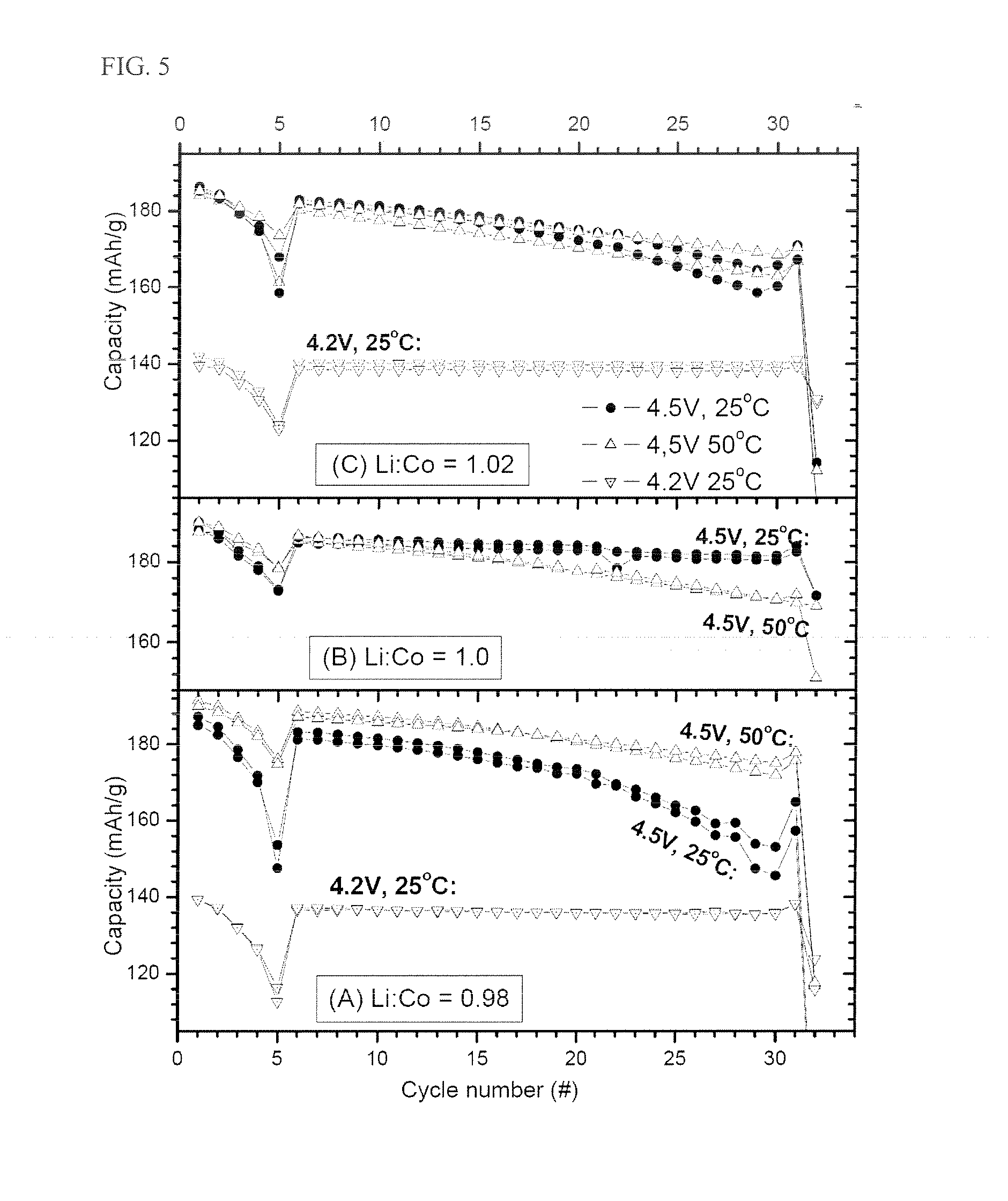
The present invention provides a LiCoO2-containing powder comprising LiCoO2 having a stoichiometric composition via heat treatment of a lithium cobalt oxide and a lithium buffer material to make equilibrium of a lithium chemical potential therebetween: a lithium buffer material which acts as a Li acceptor or a Li donor to remove or supplement Li-excess or Li-deficiency, coexisting with a stoichiometric lithium metal oxide; and a method for preparing a LiCoO2-containing powder. Further, provided is an electrode comprising the above-mentioned LiCoO2-containing powder as an active material, and a rechargeable battery comprising the same electrode.The present invention enables production of a LiCoO2 electrode active material which has improved high-temperature storage properties and high-voltage cycling properties, and is robust in composition fluctuation in the production process. Therefore, the present invention provides advantages such as reduction of time and labor required for quality control and process management in the mass-production of the electrode active material, and decreased production costs of LiCoO2.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
Method of manufacturing semiconductor device
ActiveUS8828794B2Stable electrical characteristicsImprove reliabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesBias temperature stressSemiconductor
In a manufacturing process of a transistor including an oxide semiconductor film, oxygen doping treatment is performed on the oxide semiconductor film, and then heat treatment is performed on the oxide semiconductor film and an aluminum oxide film provided over the oxide semiconductor film. Consequently, an oxide semiconductor film which includes a region containing more oxygen than a stoichiometric composition is formed. The transistor formed using the oxide semiconductor film can have high reliability because the amount of change in the threshold voltage of the transistor by a bias-temperature stress test (BT test) is reduced.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20140110708A1Improve featuresImprove reliabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringOxygen
A semiconductor device includes a transistor including a gate electrode over a substrate, a gate insulating film covering the gate electrode, a multilayer film overlapping with the gate electrode with the gate insulating film provided therebetween, and a pair of electrodes in contact with the multilayer film, and an oxide insulating film covering the transistor. The multilayer film includes an oxide semiconductor film and an oxide film containing In or Ga, the oxide insulating film contains more oxygen than that in the stoichiometric composition, and in the transistor, by a bias-temperature stress test, threshold voltage does not change or the amount of the change in a positive direction or a negative direction is less than or equal to 1.0 V, preferably less than or equal to 0.5 V.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Oxynitride bilayer formed using a precursor inducing a high charge trap density in a top layer of the bilayer
ActiveUS8067284B1Increase the number ofSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesTrappingNitrogen oxide
A semiconductor device including a bilayer charge storing layer and methods of forming the same are provided. Generally, the method includes: (i) forming a first layer of the bilayer charge storing layer; and (ii) forming a second layer formed on a surface of the first layer, the second layer including an oxynitride charge trapping layer. Preferably, the first layer includes a substantially trap free oxynitride layer. More preferably, the oxynitride charge trapping layer includes a significantly higher stoichiometric composition of silicon than that of the first layer. In certain embodiments, the oxynitride charge trapping layer has a concentration of carbon selected to increase the number of traps therein. Other embodiments are also disclosed.
Owner:LONGITUDE FLASH MEMORY SOLUTIONS LTD
Piezoelectic element and method for manufacturing the same, and ink jet head and ink jet recording apparatus using the piezoelectric element
ActiveUS20050162047A1Easy accessHighly reliable piezoelectricPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device material selectionLead zirconate titanatePiezoelectric thin films
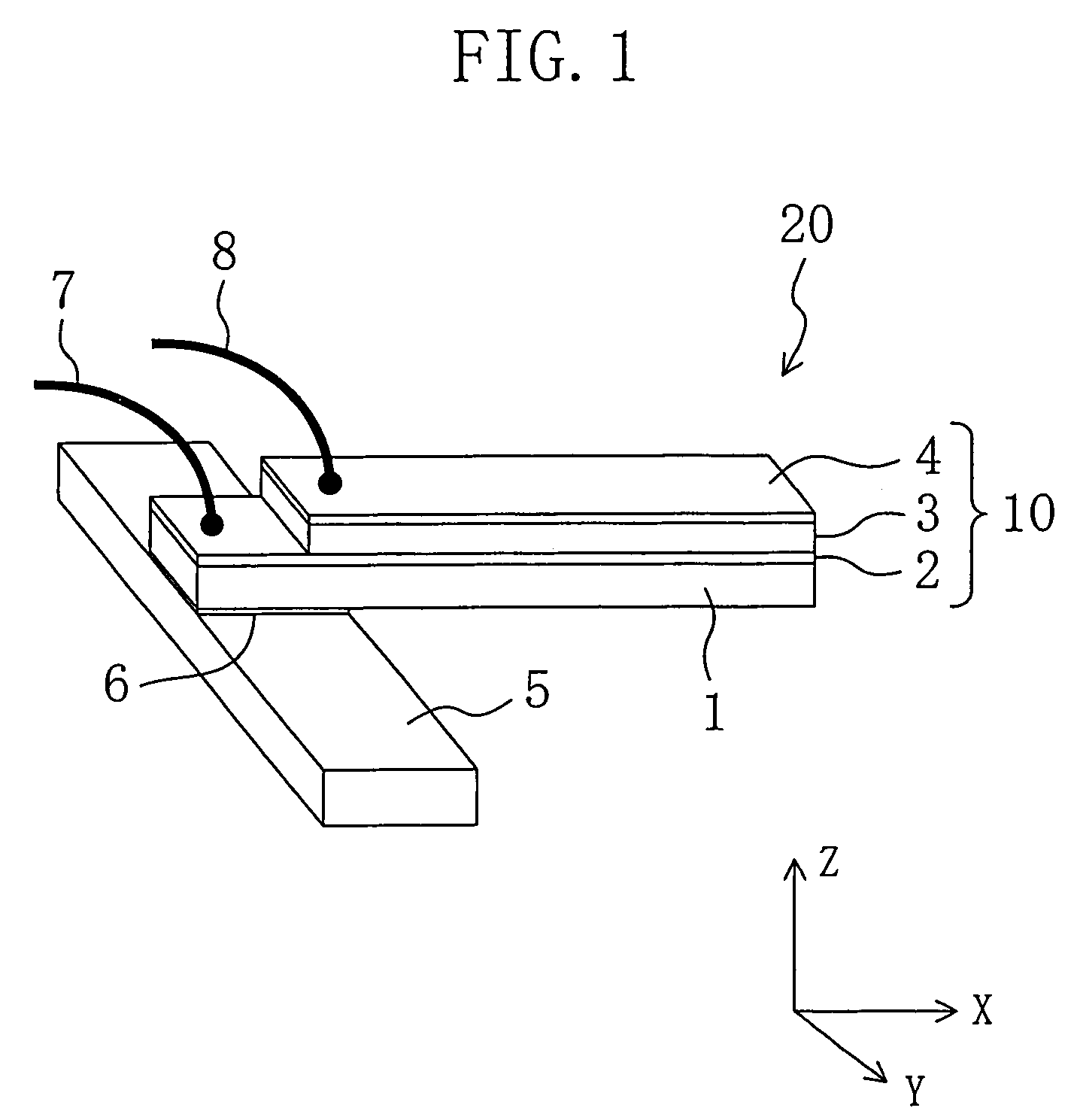
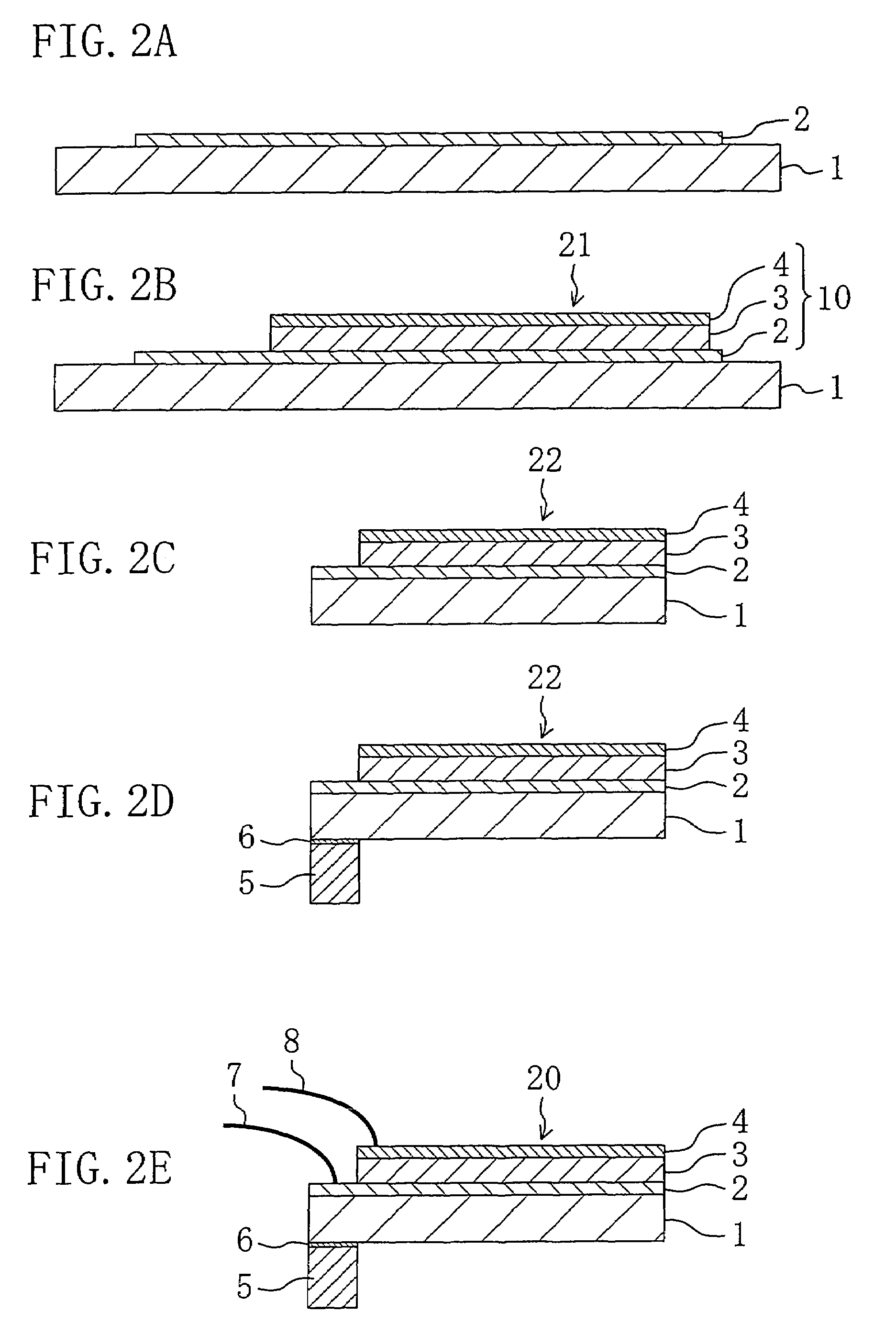
A lead content in a piezoelectric thin film (3) of a piezoelectric element (20) is made smaller as compared to stoichiometric composition. More specifically, the piezoelectric thin film (3) is made of lead zirconate titanate expressed as Pb(1−x)(Zr(1−s)Tis)O3(0<s<1) or lead-zirconate-titanate-based oxide expressed as (Pb(1−x−y)Ay)(Zr(1−t)TisBt)O3(0<s<1, 0<t<1−s) where A is a substitutive metal ion in an A-site in the perovskite crystalline structure and B is a substitutive metal ion in a B-site in the perovskite crystalline structure. The value of x, which indicates a deficiency in Pb content in each composition, is more than 0 but not more than 0.15.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
One-dimensional illumination apparatus and imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20050238071A1High in output and efficiencyReduce speckle noiseSemiconductor laser arrangementsPicture reproducers using projection devicesNonlinear optical crystalLight equipment
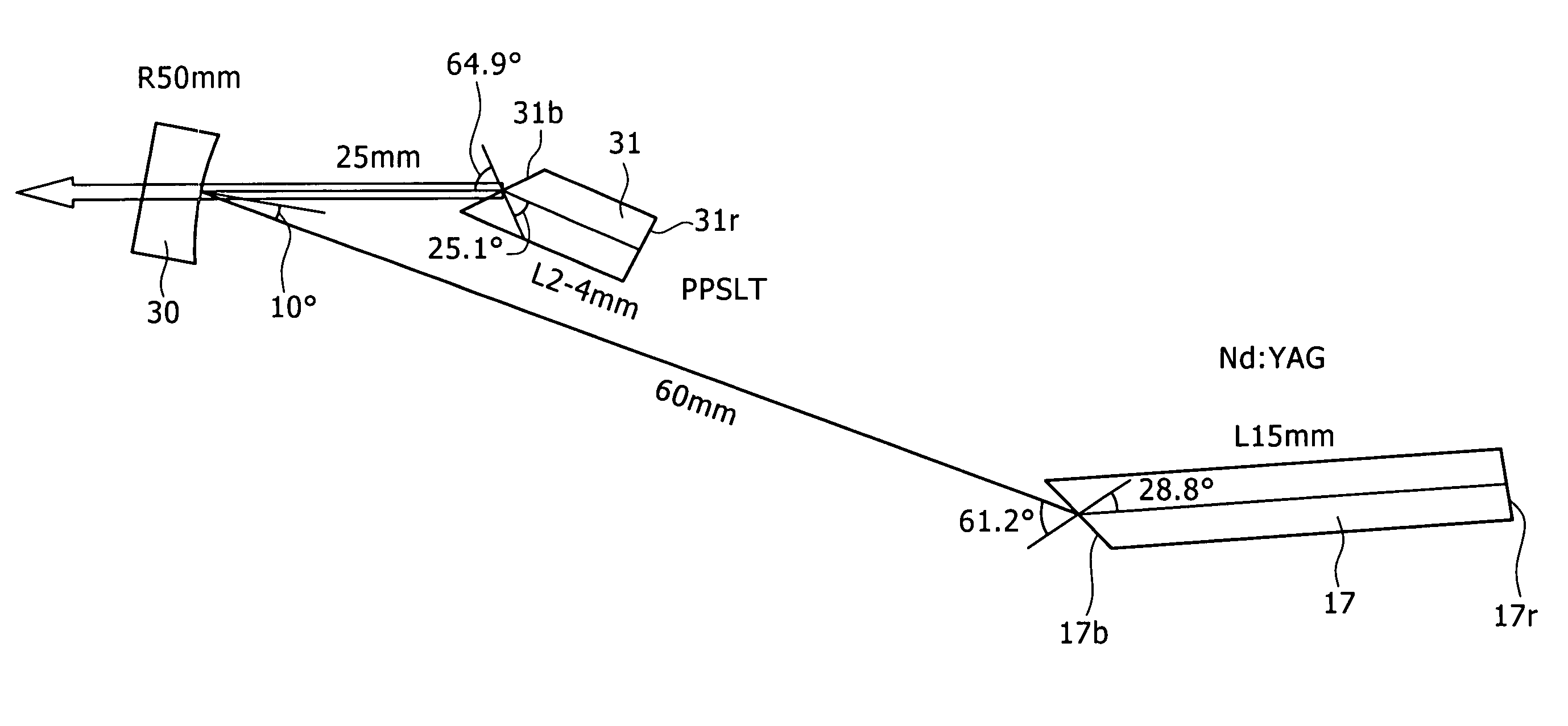
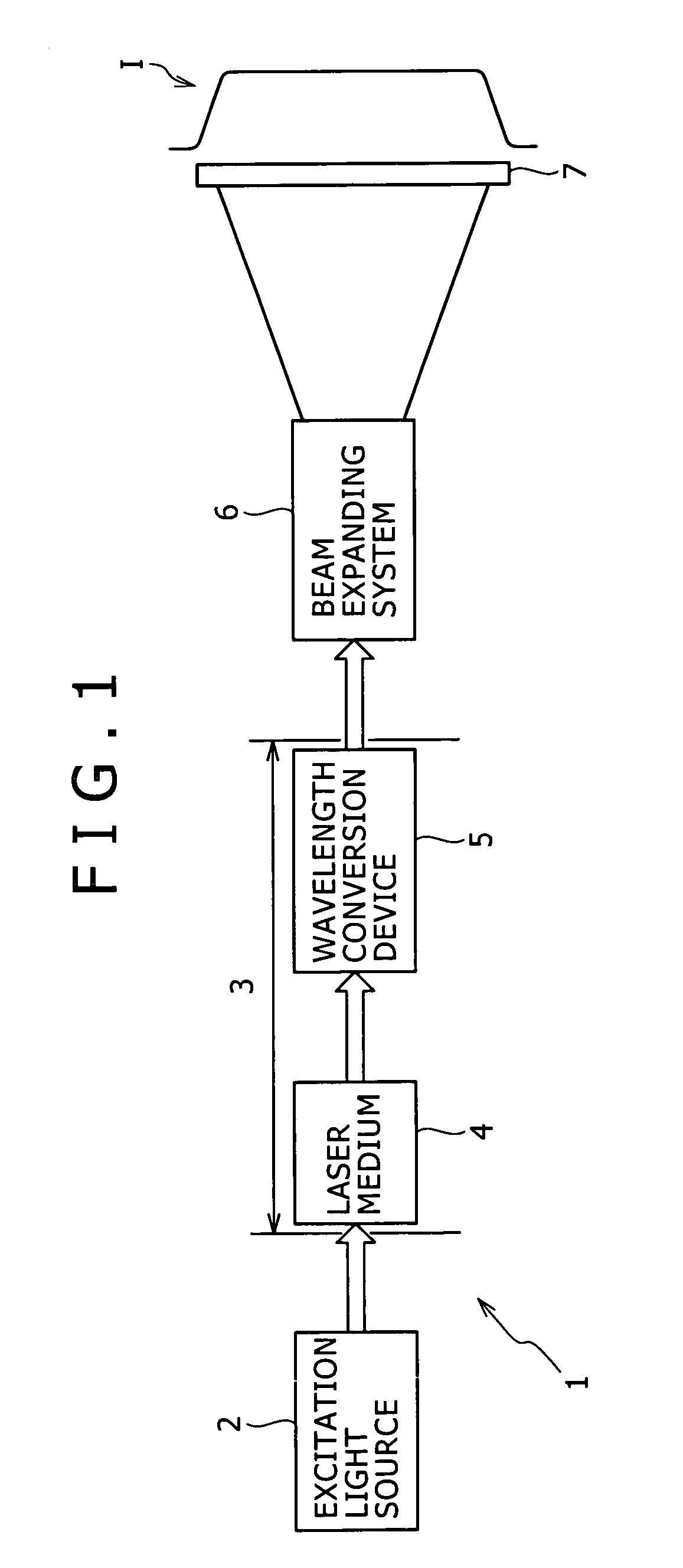
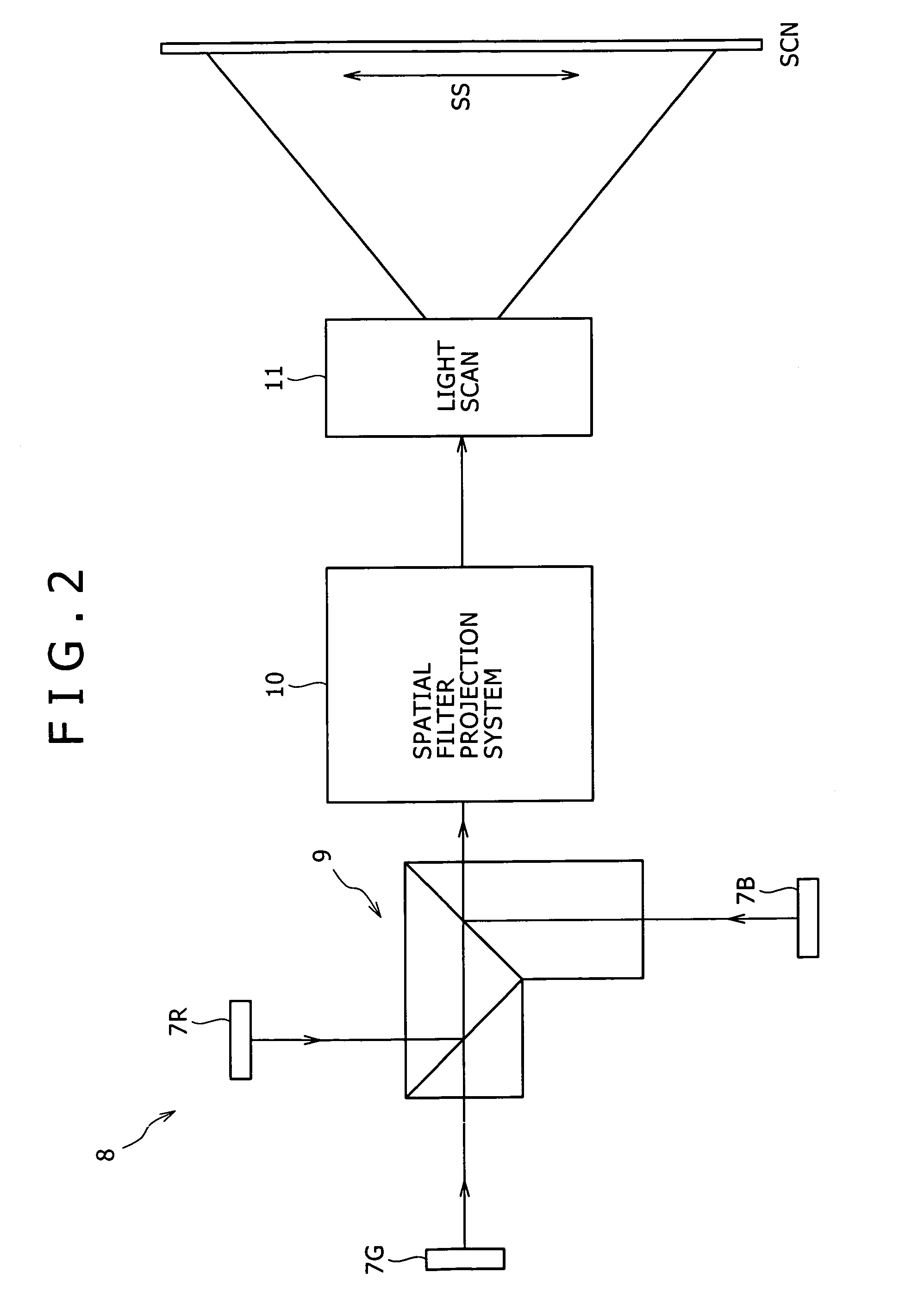
A one-dimensional transverse multiple mode laser is used for a one-dimensional illumination apparatus. A pumping light source, and a laser medium and a wavelength conversion device (nonlinear optical crystal or a nonlinear optical device) which are disposed in a resonator, are provided, and the nonlinear optical crystal or a nonlinear optical device is irradiated with a line beam obtained by exciting the laser medium in an elliptic transverse mode pattern. Then, a one-dimensional light modulation device is irradiated with the wavelength-converted line beam, and scanning with the beam modulated by the modulation device is conducted to produce a two-dimensional image. For example, in a green illumination optical system, in the case where the nonlinear optical device for obtaining visible rays through second harmonic generation from IR rays oscillated by a solid state laser medium has a periodical poling structure, stoichiometric composition periodical poling lithium tantalate having been subjected to vapor transport equilibration is used, whereby reliability is enhanced and a reduction in cost can be achieved through mass production.
Owner:SONY CORP
Oxide-nitride-oxide stack having multiple oxynitride layers
A semiconductor device including a silicon-oxide-oxynitride-oxide-silicon structure and methods of forming the same are provided. Generally, the structure comprises: a tunnel oxide layer on a surface of a substrate including silicon; a multi-layer charge storing layer including an oxygen-rich, first oxynitride layer on the tunnel oxide layer in which the stoichiometric composition of the first oxynitride layer results in it being substantially trap free, and an oxygen-lean, second oxynitride layer on the first oxynitride layer in which the stoichiometric composition of the second oxynitride layer results in it being trap dense; a blocking oxide layer on the second oxynitride layer; and a silicon containing gate layer on the blocking oxide layer. Other embodiments are also disclosed.
Owner:LONGITUDE FLASH MEMORY SOLUTIONS LTD
Methods for fabricating memory devices
InactiveUS6410412B1Increase energy densitySolve the small densityTransistorNanoinformaticsPulse energy densitySemiconductor
Methods for fabricating memory devices having a multi-dot floating gate ensuring a desirable crystallization of a semiconductor film without ruining the flatness of the surface of the polycrystallized silicon layer and a tunnel oxide film, allowing desirable semiconductor dots to be produced, and allowing production of the memory devices having a multi-dot floating gate with ease and at low costs even when a substrate is made of glass or plastic. Such a method for fabricating memory devices includes steps for forming on a substrate a semiconductor film and treating said semiconductor film by a first laser annealing so as to have a polycrystalline structure; forming on the semiconductor film a semiconductor dot forming film having a non-stoichiometric composition with an excessive content of a semiconductor element; and dispersing semiconductor dots within the semiconductor dot forming film by a second laser annealing thereby to produce semiconductor dots; in which a pulse energy density of the laser used for the first laser annealing is larger than a pulse energy density of the laser used for the second laser annealing.
Owner:SONY CORP
Transition metal oxide bilayers
ActiveUS8569104B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSputteringOptoelectronics
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC +2
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS9287411B2Reduce defectsImprove featuresTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPower semiconductor deviceDevice material
In a semiconductor device including a transistor including a gate electrode formed over a substrate, a gate insulating film covering the gate electrode, a multilayer film overlapping with the gate electrode with the gate insulating film provided therebetween, and a pair of electrodes in contact with the multilayer film, a first oxide insulating film covering the transistor, and a second oxide insulating film formed over the first oxide insulating film, the multilayer film includes an oxide semiconductor film and an oxide film containing In or Ga, the oxide semiconductor film has an amorphous structure or a microcrystalline structure, the first oxide insulating film is an oxide insulating film through which oxygen is permeated, and the second oxide insulating film is an oxide insulating film containing more oxygen than that in the stoichiometric composition.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Piezoelectric element and method for manufacturing the same, and ink jet head and ink jet recording apparatus using the piezoelectric element
ActiveUS7348715B2Highly reliable piezoelectricEasy to getPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device material selectionLead zirconate titanateStoichiometric composition
A lead content in a piezoelectric thin film (3) of a piezoelectric element (20) is made smaller as compared to stoichiometric composition. More specifically, the piezoelectric thin film (3) is made of lead zirconate titanate expressed as Pb(1-x)(Zr(1-s)Tis)O3(0<s<1) or lead-zirconate-titanate-based oxide expressed as (Pb(1-x-y)Ay)(Zr(1-s-t)TisBt)O3(0<s<1, 0<t<1-s) where A is a substitutive metal ion in an A-site in the perovskite crystalline structure and B is a substitutive metal ion in a B-site in the perovskite crystalline structure. The value of x, which indicates a deficiency in Pb content in each composition, is more than 0 but not more than 0.15.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Optical information recording medium and method for manufacturing the same
A recording layer included in an optical information recording medium of the present invention includes: a mixture of a low oxide Te-O-M (M denotes at least one element selected from the group consisting of a metallic element, a metalloid element, and a semiconductor element) or a low oxide A-O (A denotes at least one element selected from the group consisting of Sb, Sn, In, Zn, Mo and W; and a material X (X denotes at least one compound selected from the group consisting of a fluoride, a carbide, a nitride and an oxide). Herein the low oxide refers to an oxide whose composition ratio of oxygen element is smaller than a composition ratio of oxygen element according to a stoichiometric composition.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Lead-free piezoelectric ceramic composition wherin Cu is contained in (KxA1-x)y(Nb1-zBz)O3perovskite compound, and process of preparing the same
InactiveUS6884364B2Improve sintering performanceImprove sinterabilityPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device material selectionAbnormal grain growthSecondary component
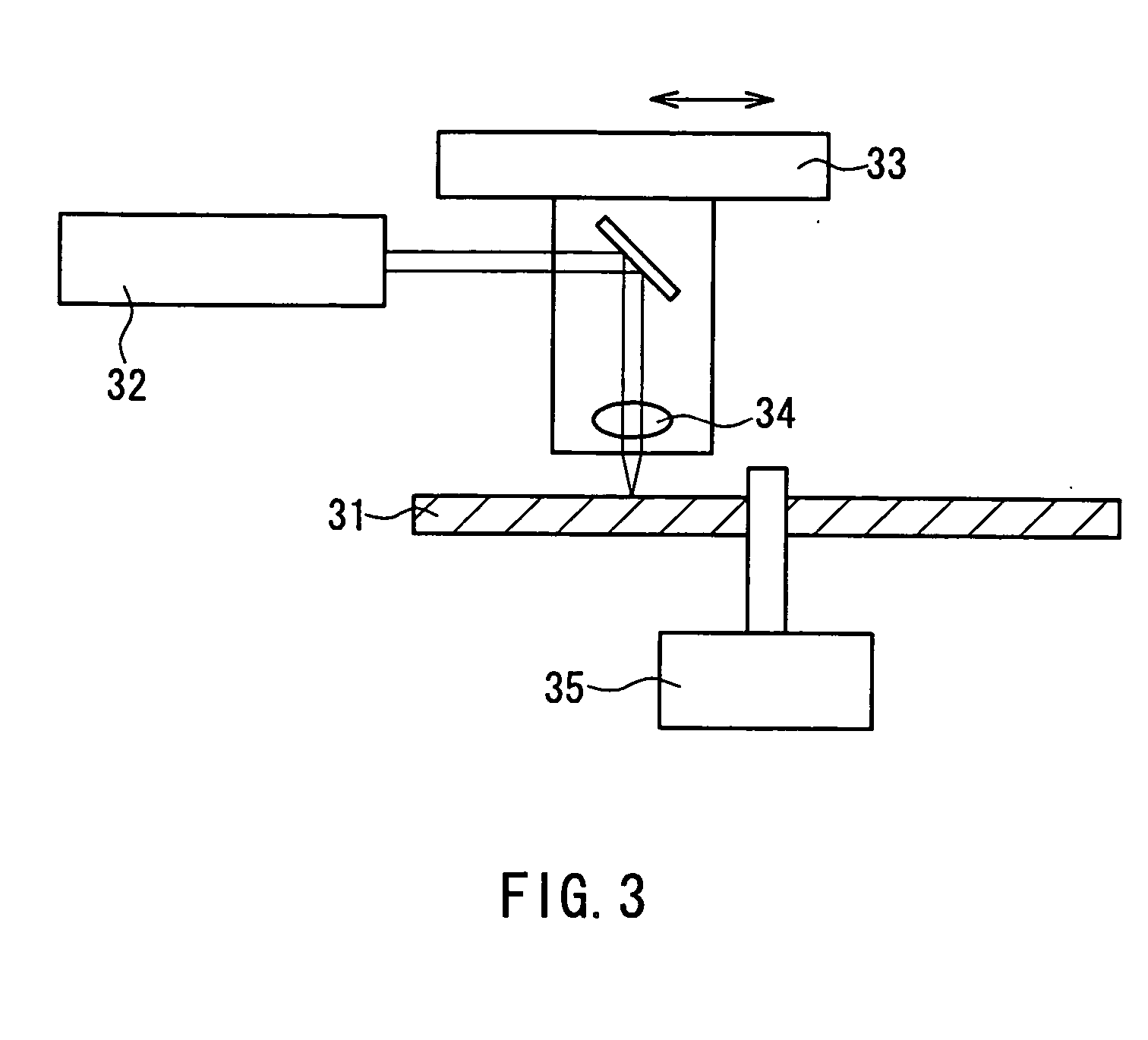
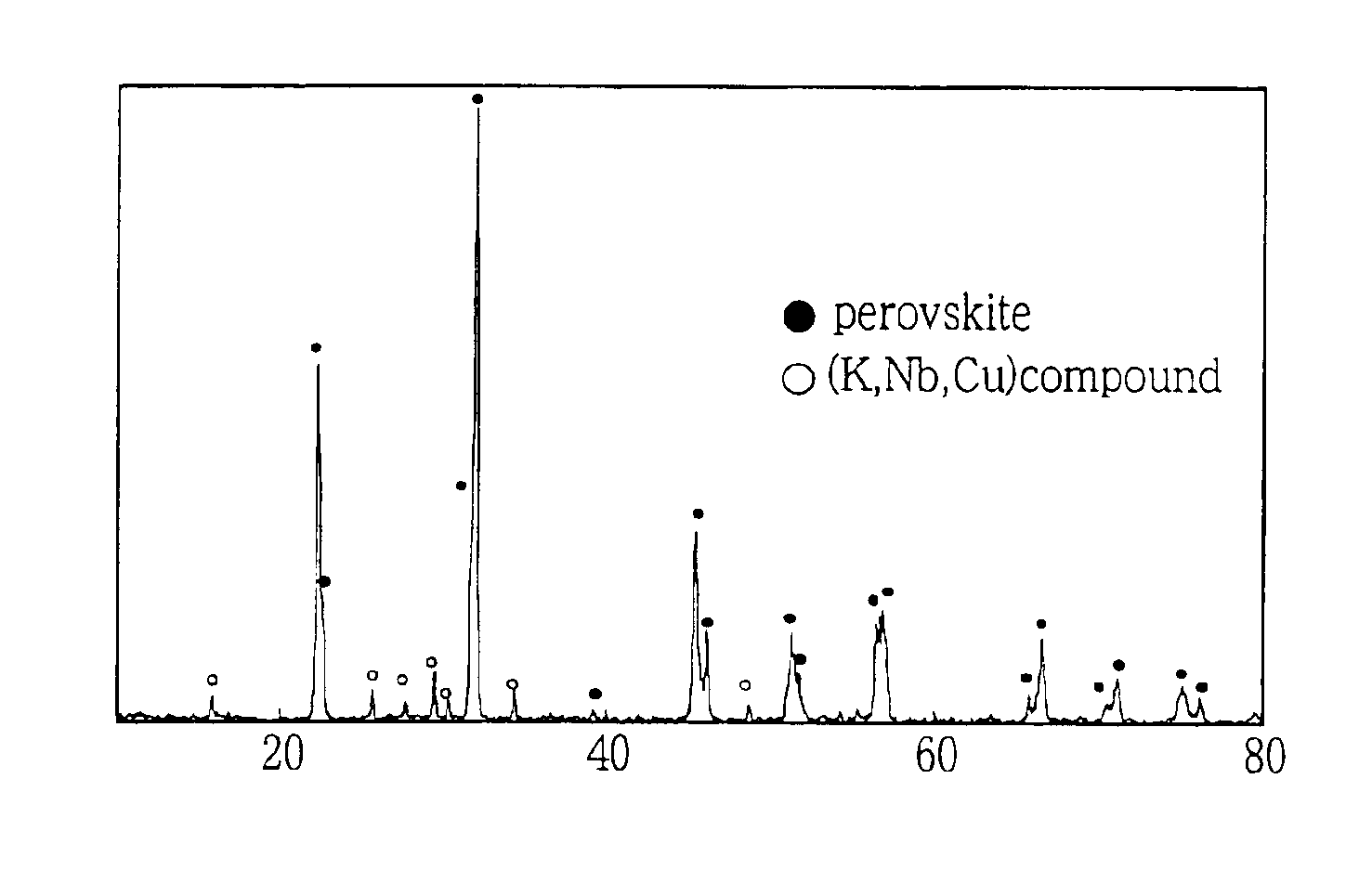
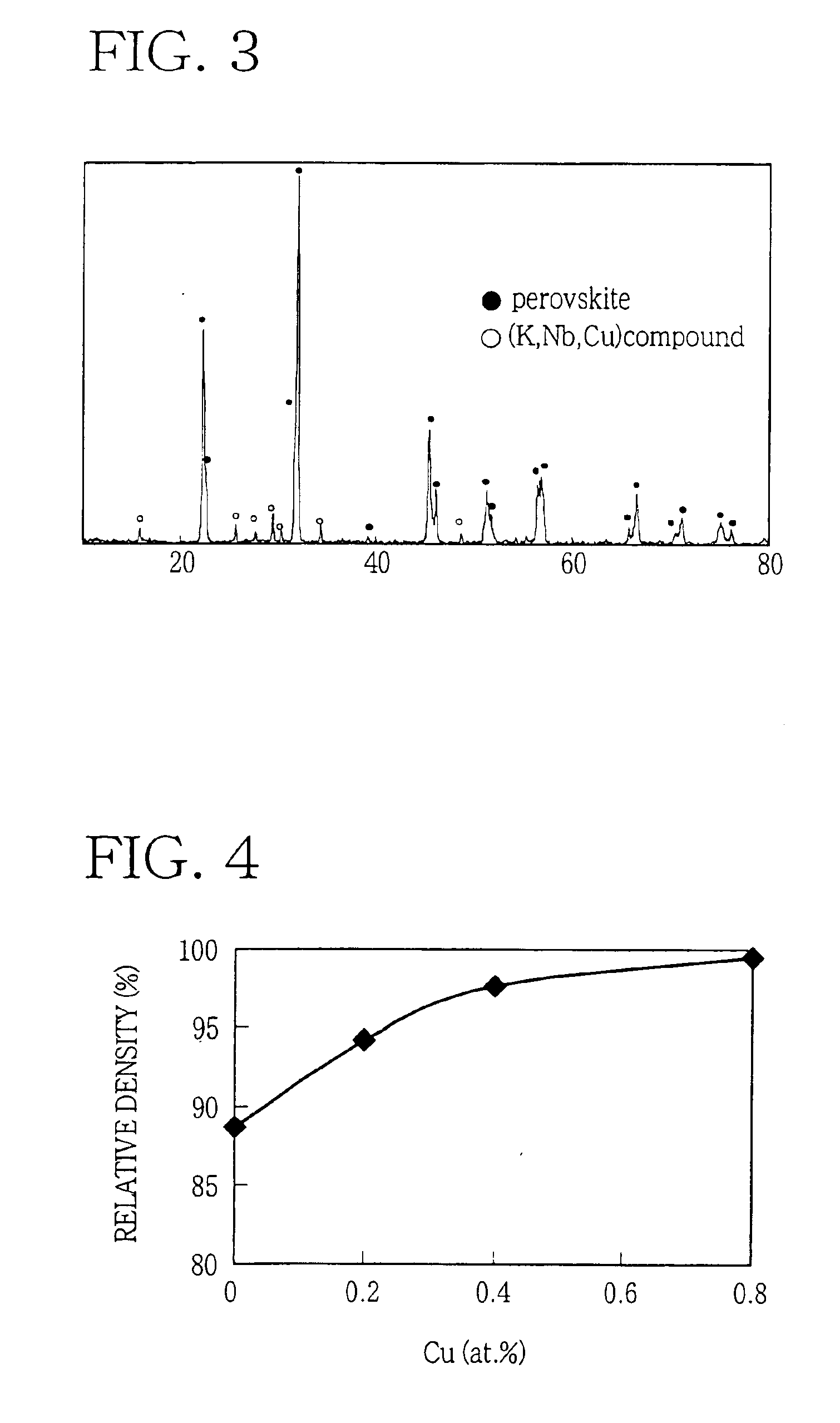
A lead-free piezoelectric ceramic composition wherein a suitable amount of Cu is contained in a perovskite compound of a non-stoichiometric composition represented by a formula (KxA1-x)y(Nb1-zBz)O3, wherein “A” represents at least one of Na and Bi, while “B” represents at least one of Ta and Ti, and wherein 0<x≦1, 0<y<1, and 0≦z≦1, so that by-products such as KaCubNbcOd and KaCubTacOd are produced as a result of reaction of (Nb1-zBz) with Cu in the process of calcination of a starting material, and the by-products restrict melting and abnormal grain growth of (KxNa1-x)(Nb1-zTaz) O3 during firing of a calcined body, thereby improving sinterability of the fired body, while restricting volatilization of alkali components and melting of KNbO3, thereby increasing the density and improving the piezoelectric properties of the fired body. The ceramic composition is prepared by firing a starting composition including the perovskite composition as a primary component, and a secondary component in the form of at least one of compounds KaCubNbcOd, KeCufTagOh and KiCujTikOl.
Owner:NORITAKE CO LTD +1
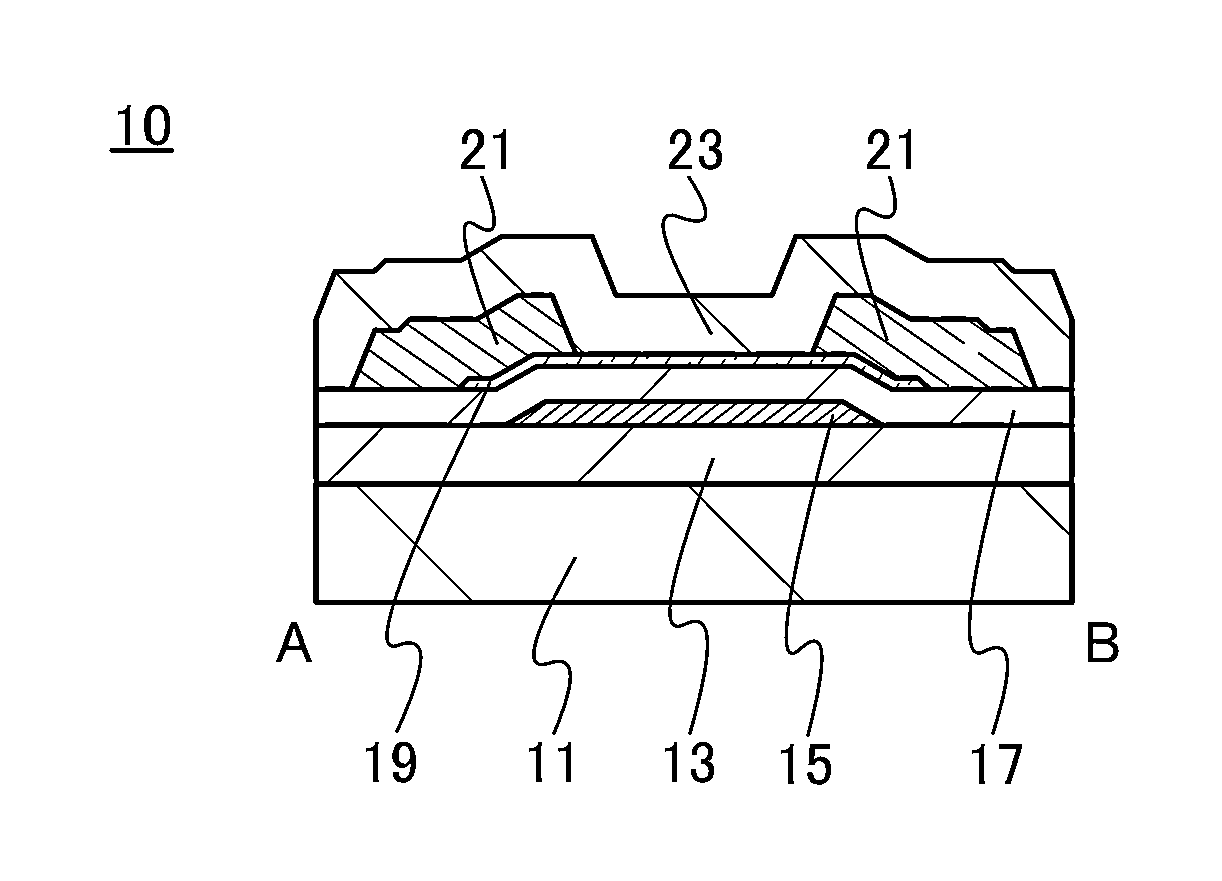
Semiconductor Device
ActiveUS20110303914A1Reduce in quantityDefects due to oxygen deficiency are sufficiently reducedSemiconductor devicesOxygenSemiconductor
One object is to provide a semiconductor device including an oxide semiconductor with improved electrical characteristics. The semiconductor device includes a first insulating film including an element of Group 13 and oxygen; an oxide semiconductor film partly in contact with the first insulating film; a source electrode and a drain electrode electrically connected to the oxide semiconductor film; a gate electrode overlapping with the oxide semiconductor film; and a second insulating film partly in contact with the oxide semiconductor film, between the oxide semiconductor film and the gate electrode. Further, the first insulating film including an element of Group 13 and oxygen includes a region where an amount of oxygen is greater than that in a stoichiometric composition ratio.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Insulating film, method for manufacturing semiconductor device, and semiconductor device
ActiveUS8901556B2Reduce resistanceReduce the amount requiredTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsTectorial membraneHigh frequency power
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Variable resistive element, and non-volatile semiconductor memory device
InactiveUS20130193396A1Well formedEfficient use ofSolid-state devicesBulk negative resistance effect devicesLow voltageEngineering
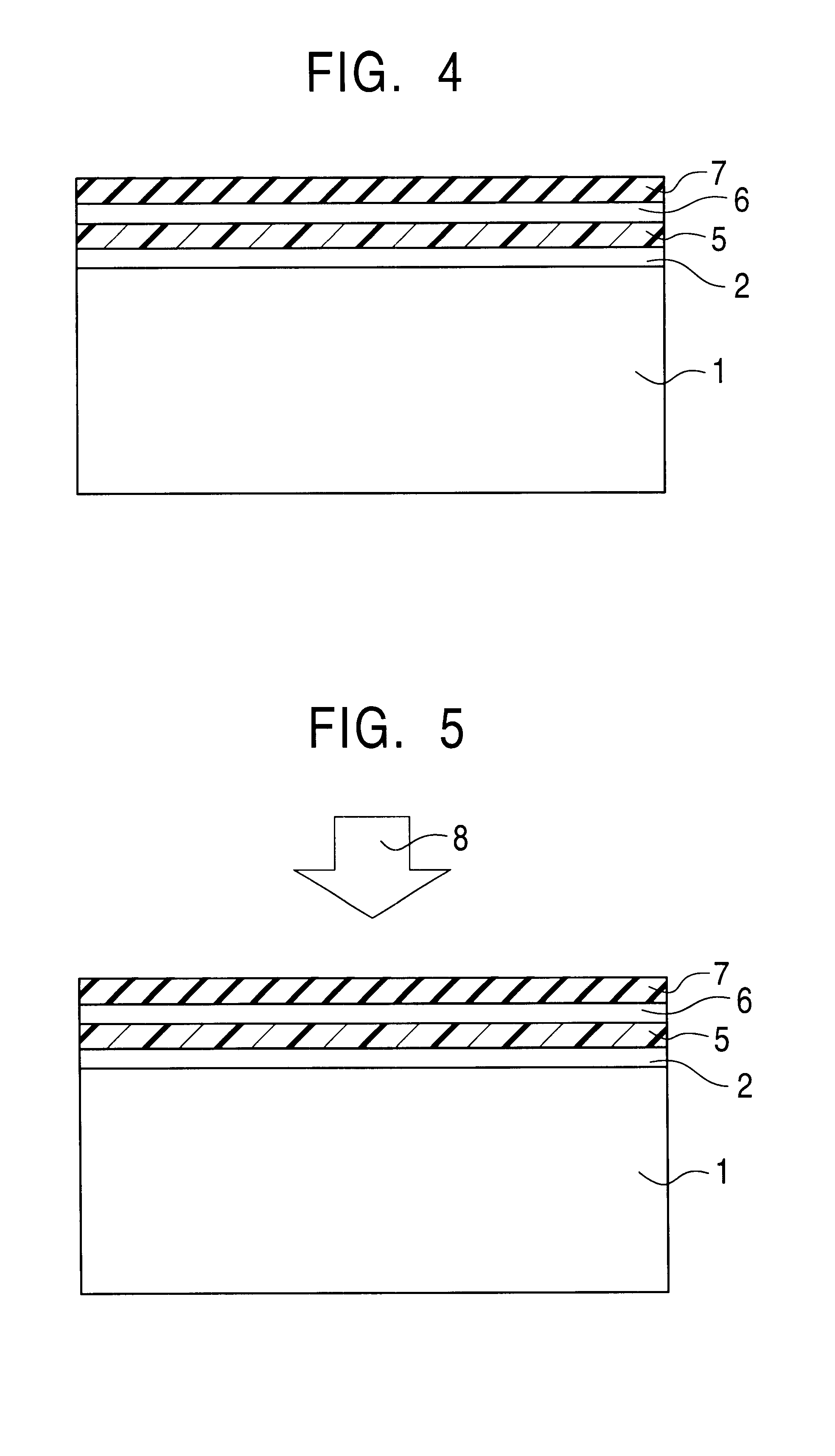
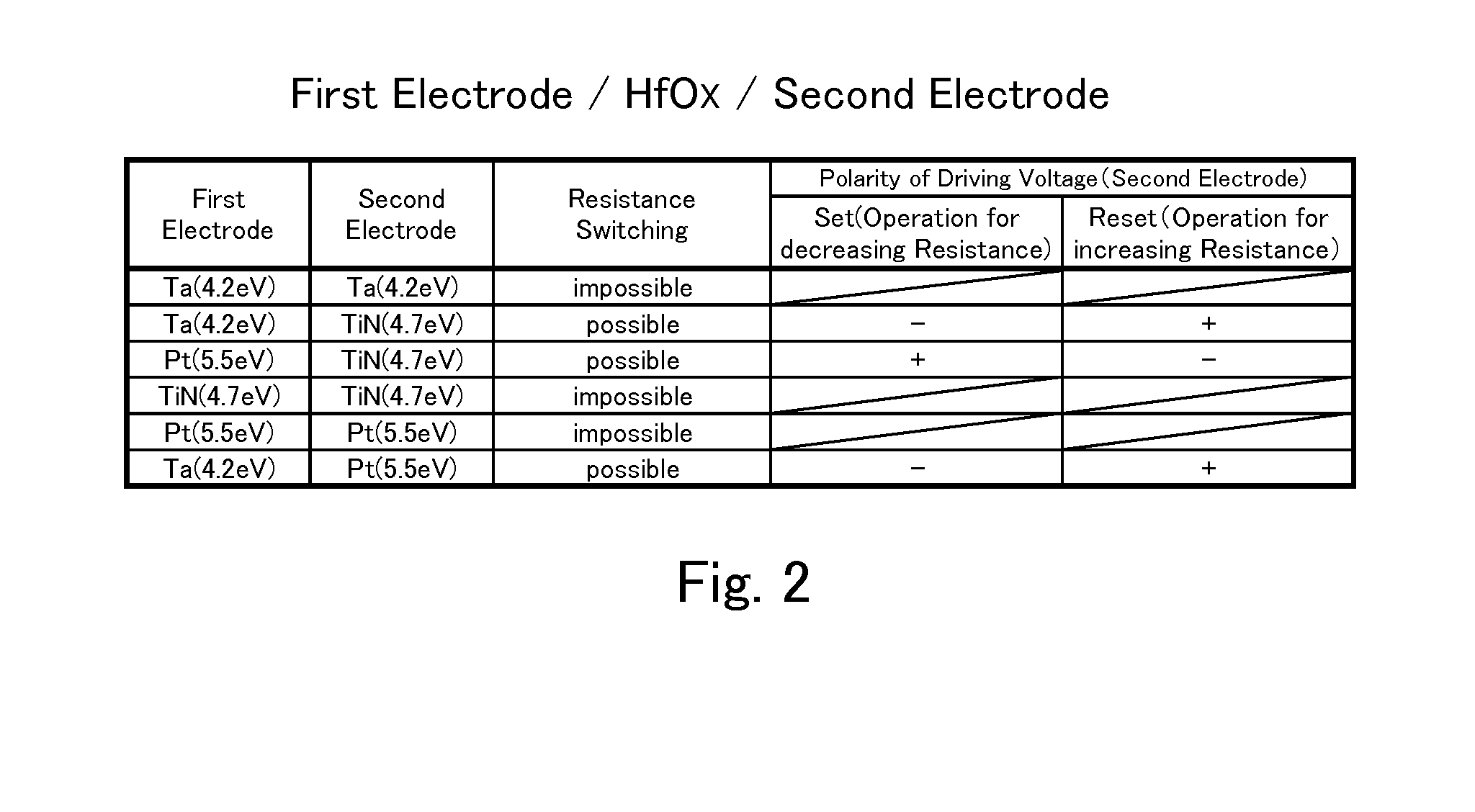
A variable resistive element that performs a forming action at small current and a stable switching operation at low voltage and small current, and a low-power consumption large-capacity non-volatile semiconductor memory device including the element are realized. The element includes a variable resistor between first and second electrodes. The variable resistor includes at least two layers, which are a resistance change layer and high-oxygen layer, made of metal oxide or metal oxynitride. The high-oxygen layer is inserted between the first electrode having a work function smaller than the second electrode and the resistance change layer. The oxygen concentration of the metal oxide of the high-oxygen layer is adjusted such that the ratio of the oxygen composition ratio to the metal element to stoichiometric composition becomes larger than the ratio of the oxygen composition ratio to the metal element of the metal oxide forming the resistance change layer to stoichiometric composition.
Owner:SHARP KK +1
Method for manufacturing semiconductor device
ActiveUS20120252160A1Low densityIncreasing oxide thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSilicon oxideOxygen
In a method for manufacturing a transistor including an oxide semiconductor layer, a gate electrode is formed and then an aluminum oxide film, a silicon oxide film, and the oxide semiconductor film are successively formed in an in-line apparatus without being exposed to the air and are subjected to heating and oxygen adding treatment in the in-line apparatus. Then, the transistor is covered with another aluminum oxide film and is subjected to heat treatment, so that the oxide semiconductor film from which impurities including hydrogen atoms are removed and including a region containing oxygen at an amount exceeding that in the stoichiometric composition ratio. The transistor including the oxide semiconductor film is a transistor having high reliability in which the amount of change in threshold voltage of the transistor by the bias-temperature stress (BT test) can be reduced.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
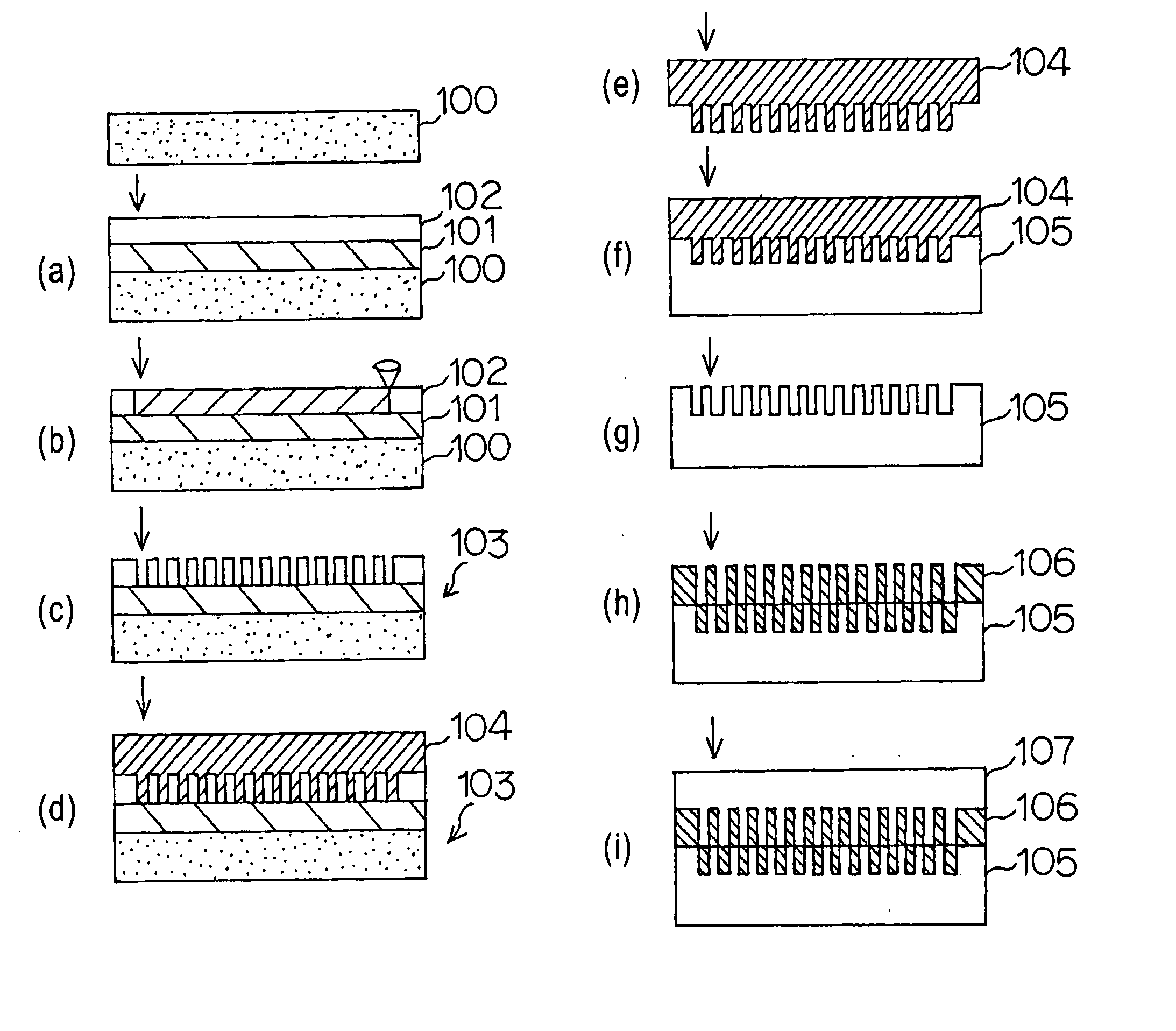
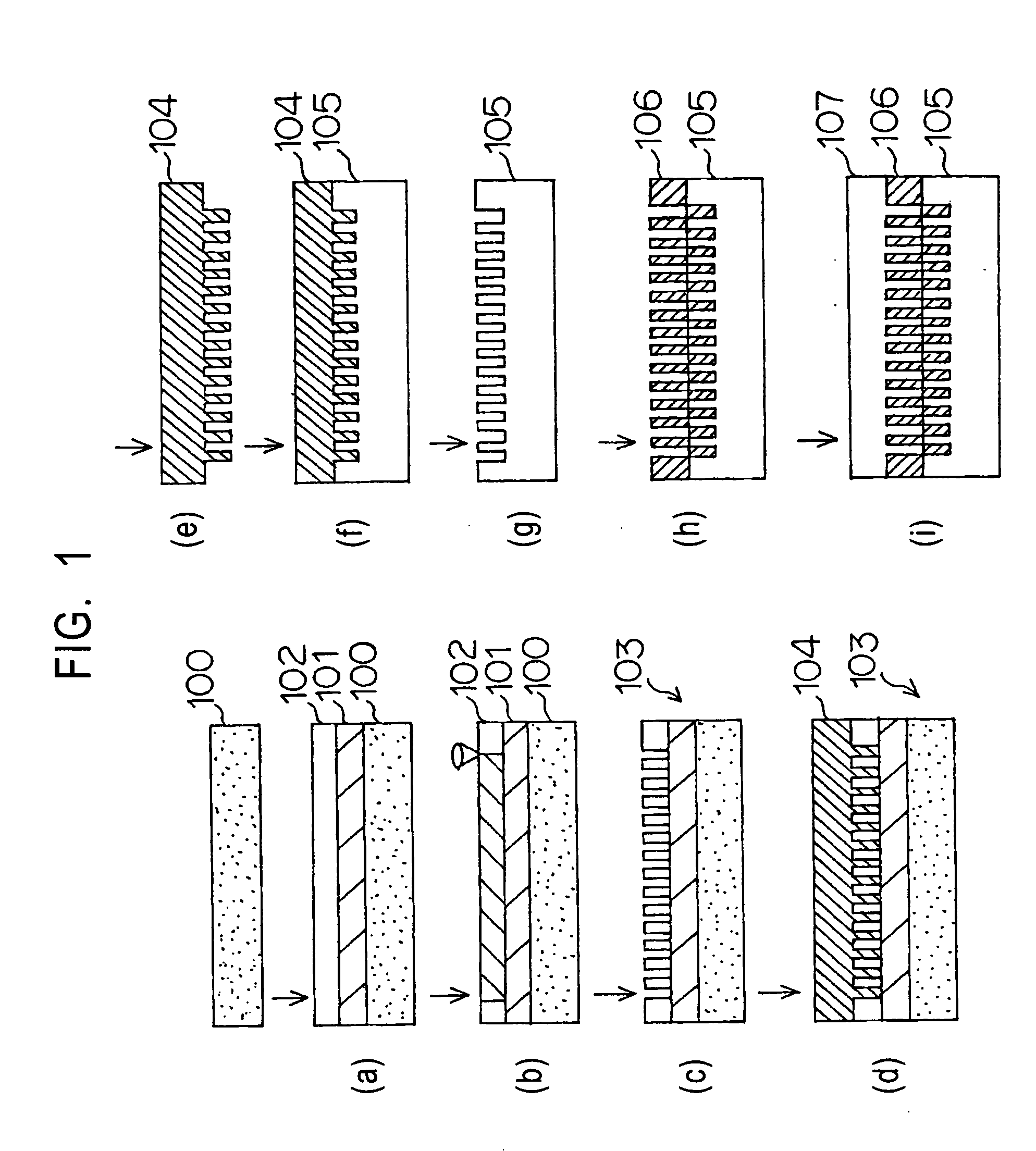
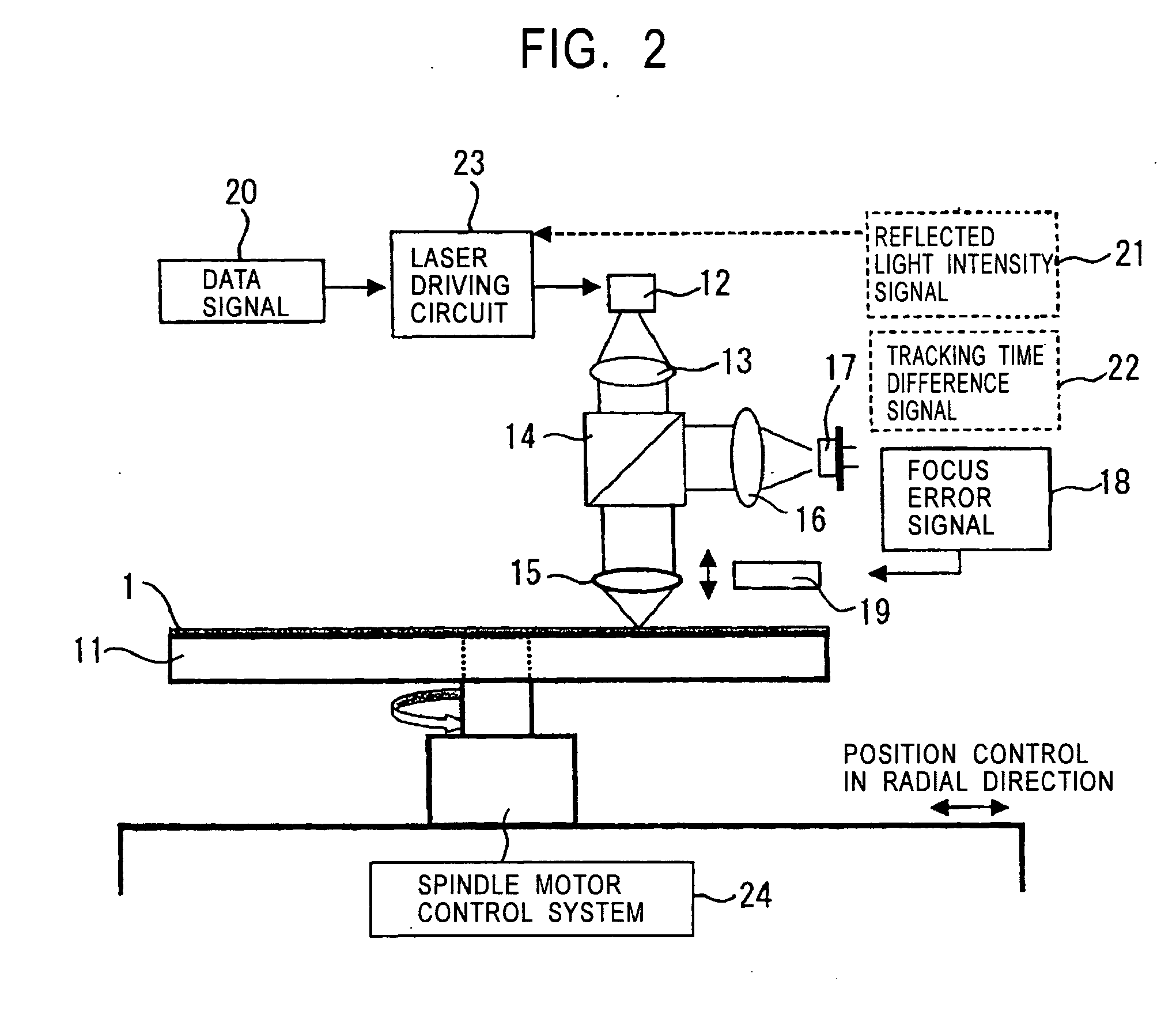
Method of producing optical disk-use original and method of producing optical disk
InactiveUS20050226999A1Improve accuracyReduce molecular weightRecord carriersPhotosensitive materialsResistOxygen content
A method for manufacturing an optical disc master using an existing exposure system, and a method for manufacturing an optical disc having higher recording capacity. The method for manufacturing an optical disc, using a master to produce the optical disc having an irregular pattern thereon, the master being produced by the steps of forming a resist layer composed of a resist material including an incomplete oxide of a transition metal such as W or Mo on a substrate, the oxygen content of the incomplete oxide being smaller than the oxygen content of the stoichiometric composition corresponding to a valence of the transition metal; selectively exposing the resist layer with laser according to a recording signal pattern; and developing the resist layer to form the predetermined irregular pattern.
Owner:SONY CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com