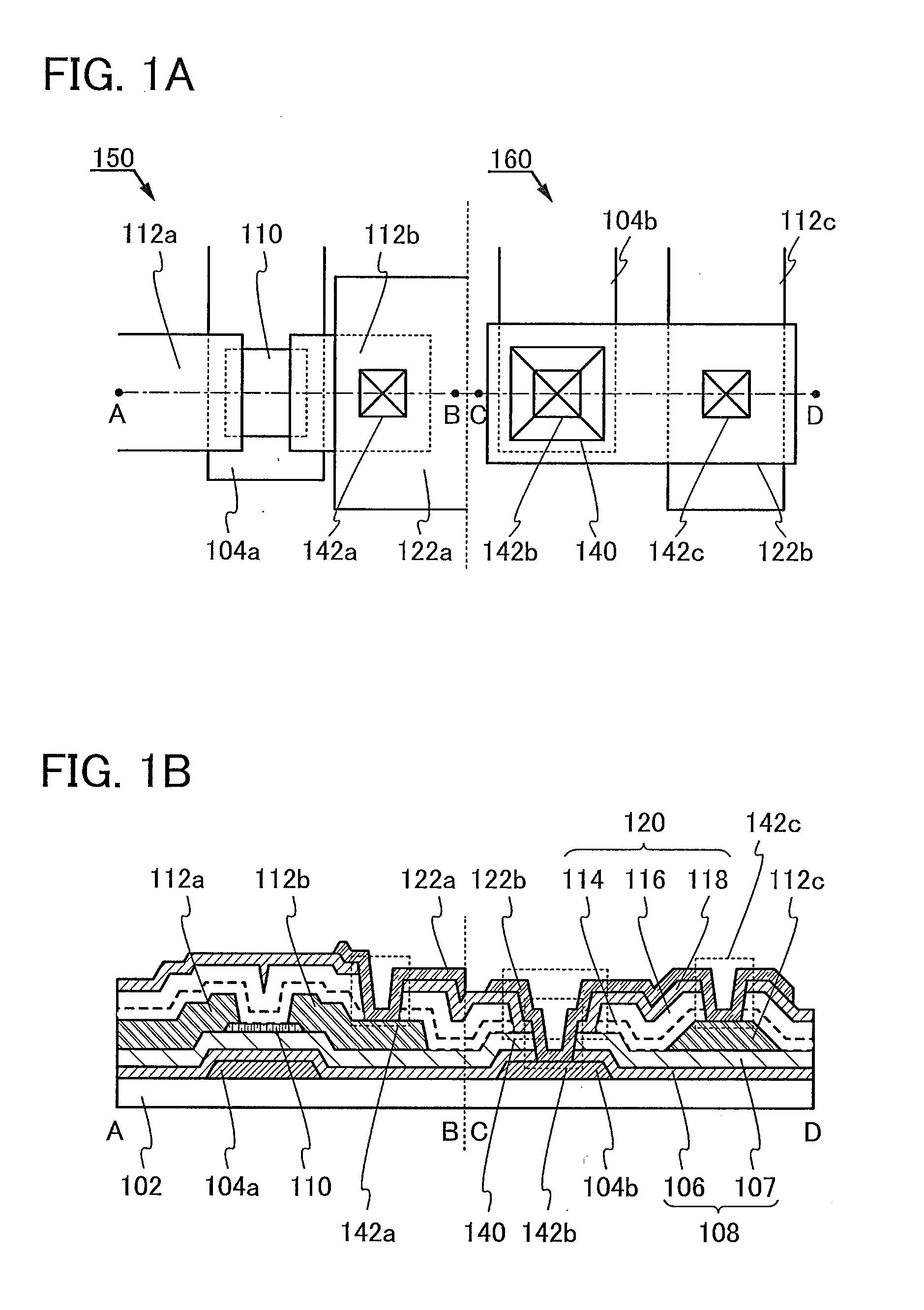
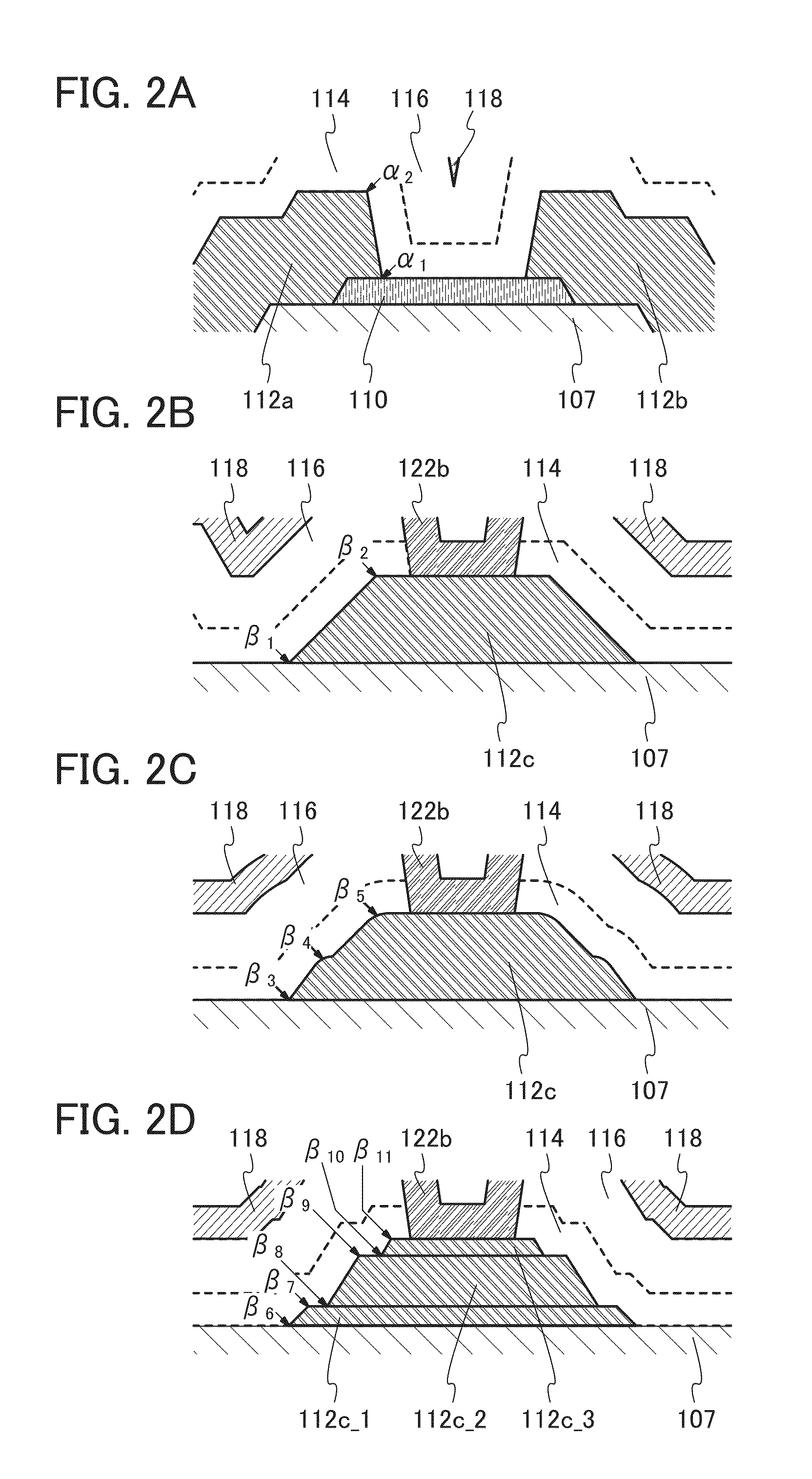
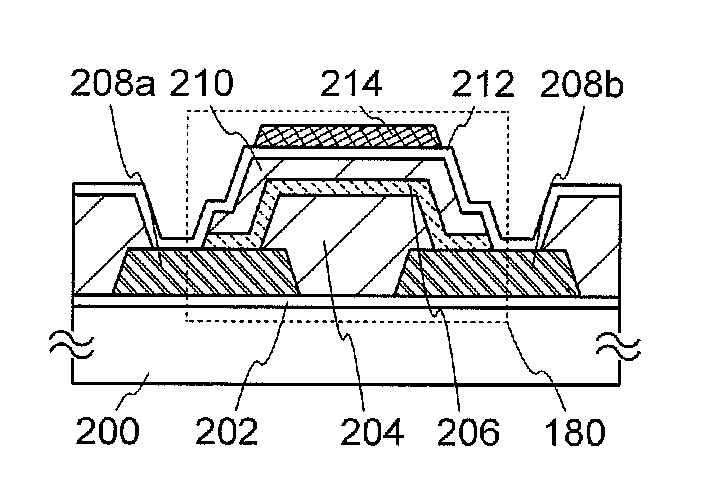
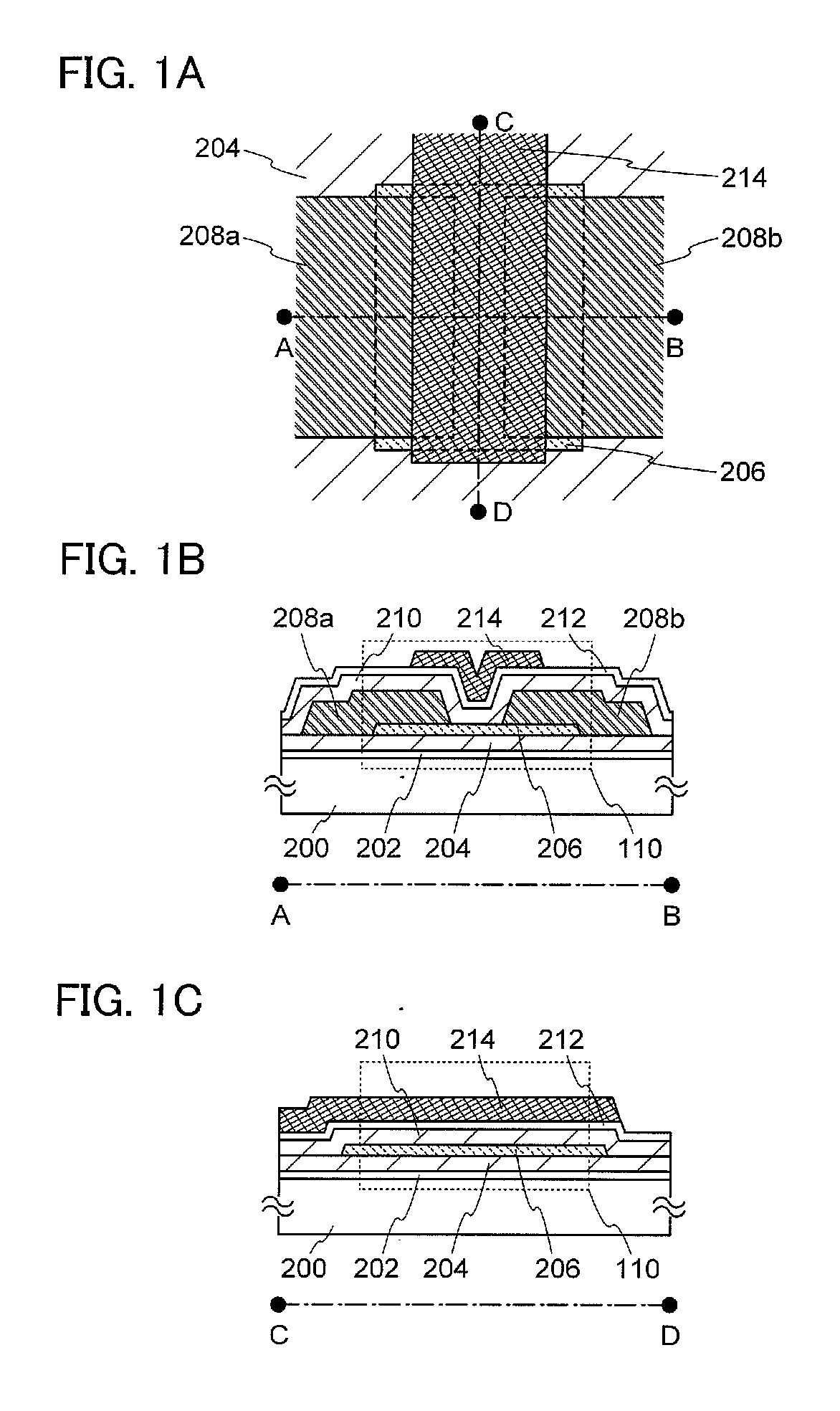
Patents
Literature
12807 results about "Power semiconductor device" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
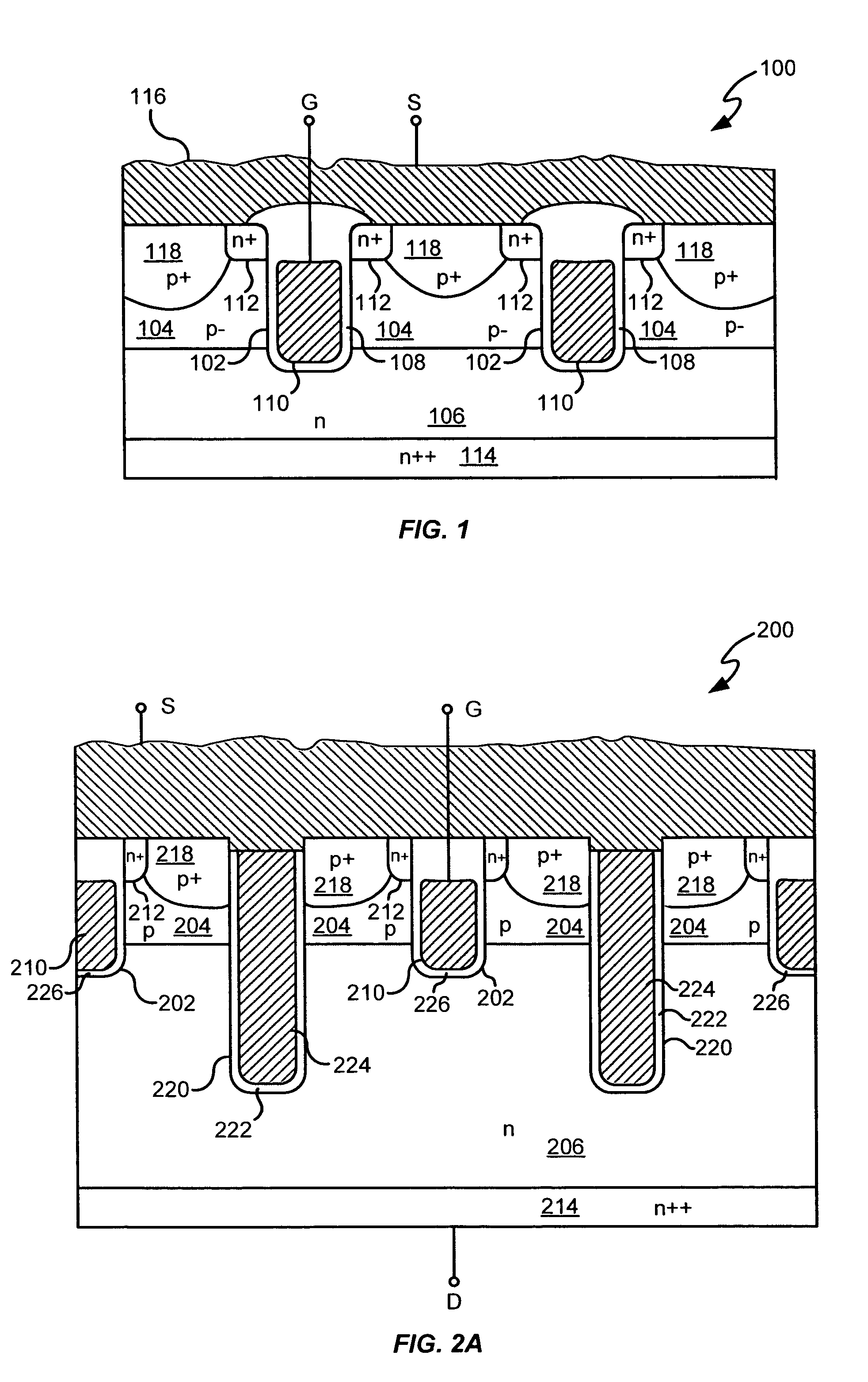
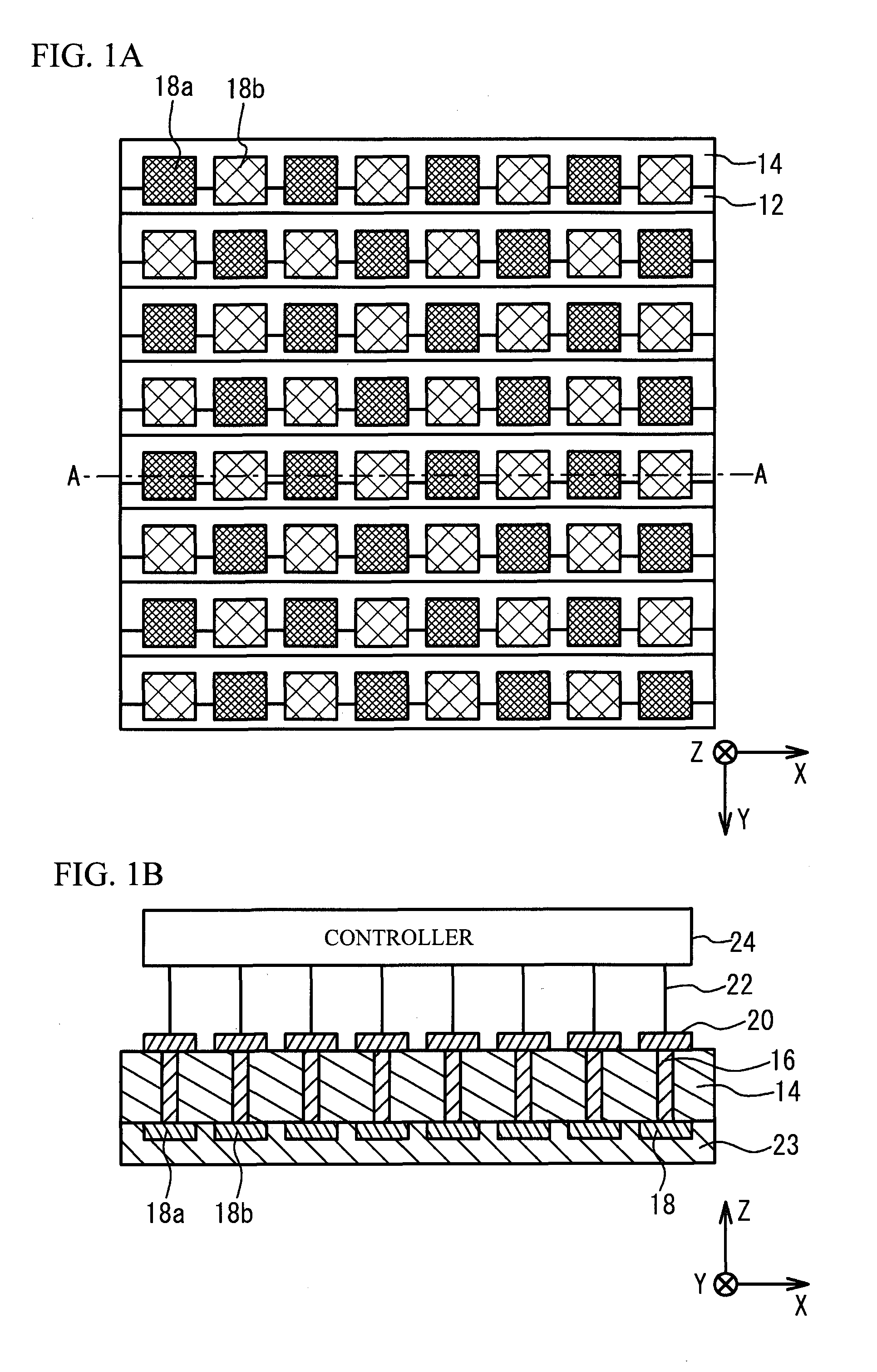
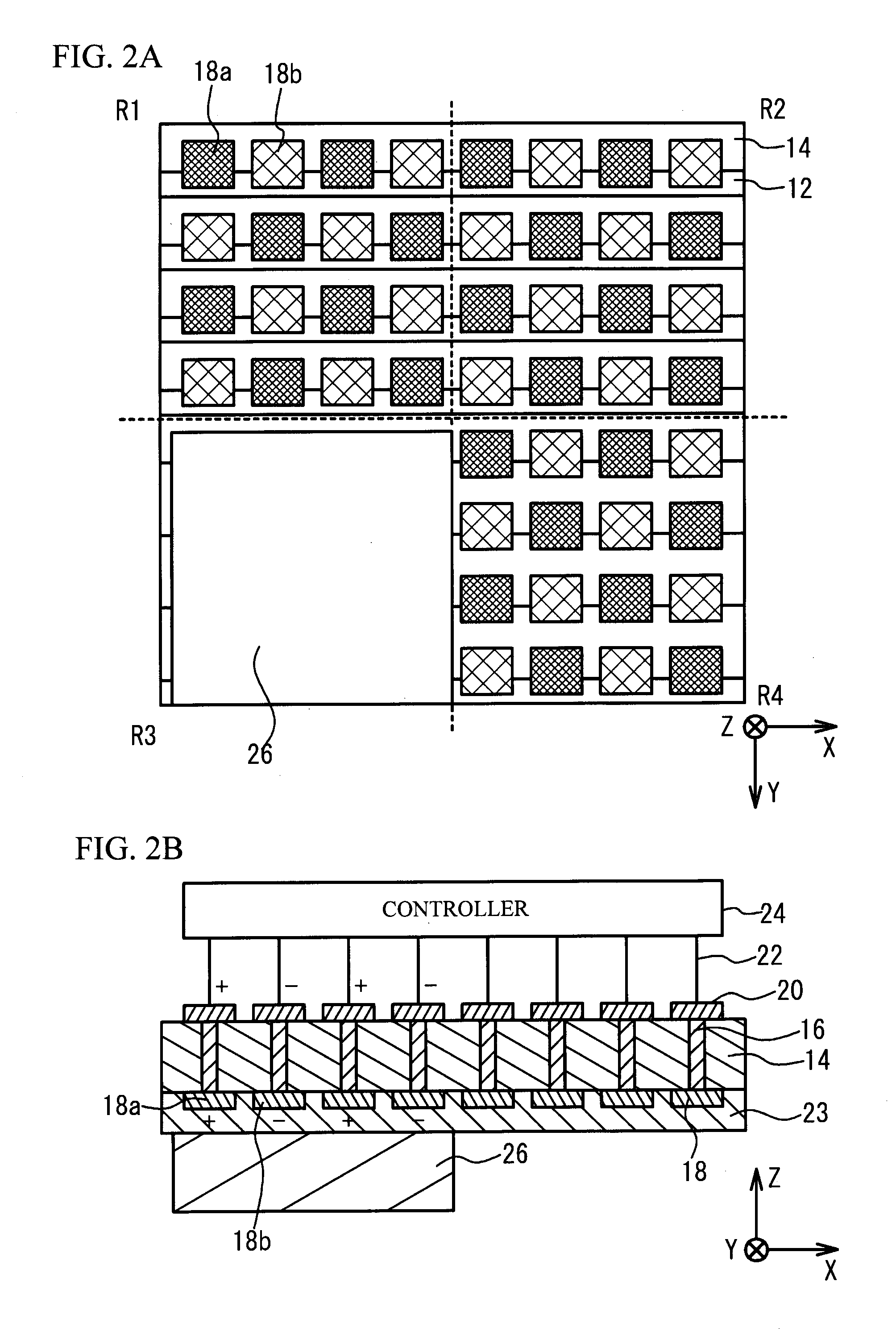
A power semiconductor device is a semiconductor device used as a switch or rectifier in power electronics (for example in a switch-mode power supply). Such a device is also called a power device or, when used in an integrated circuit, a power IC.
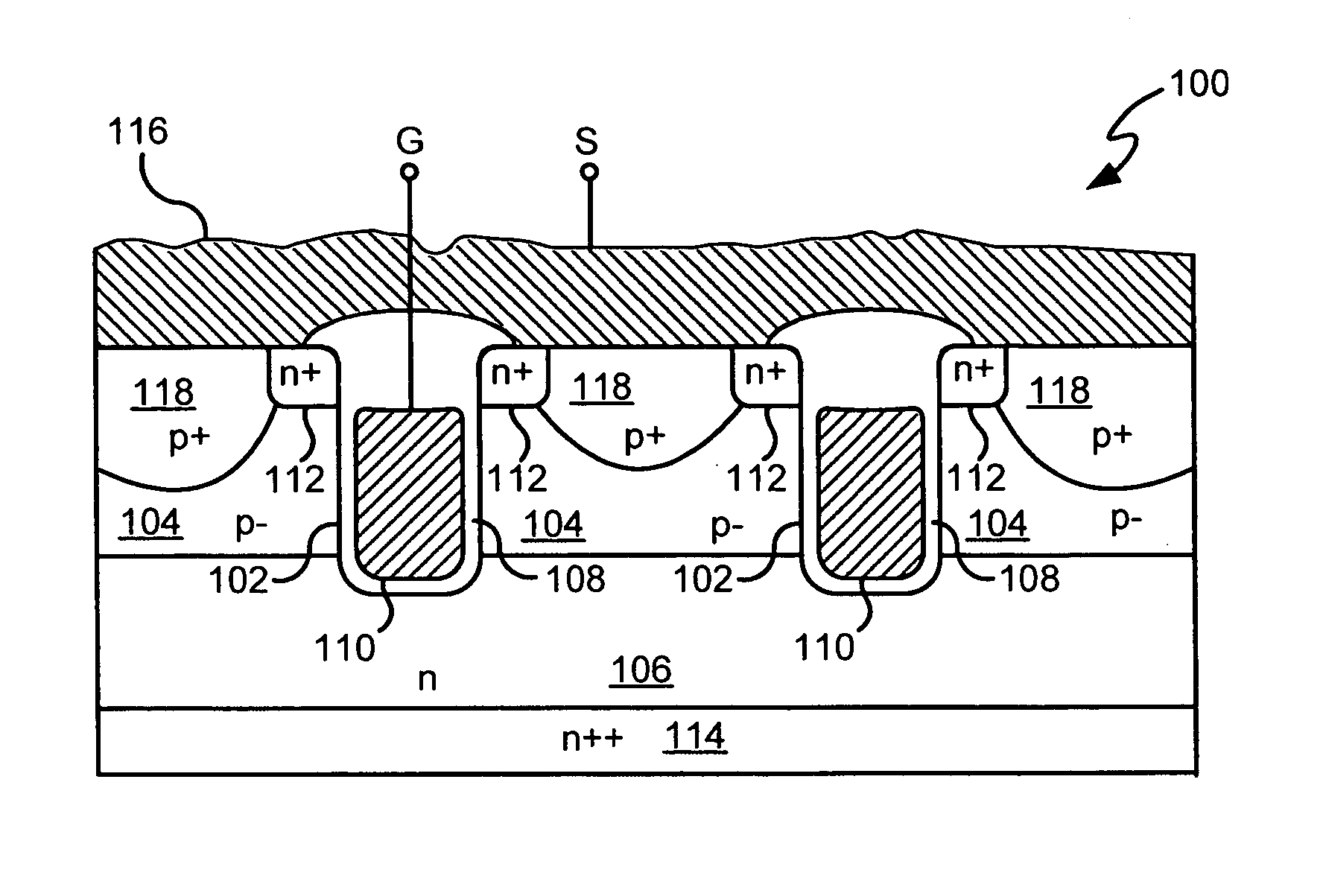
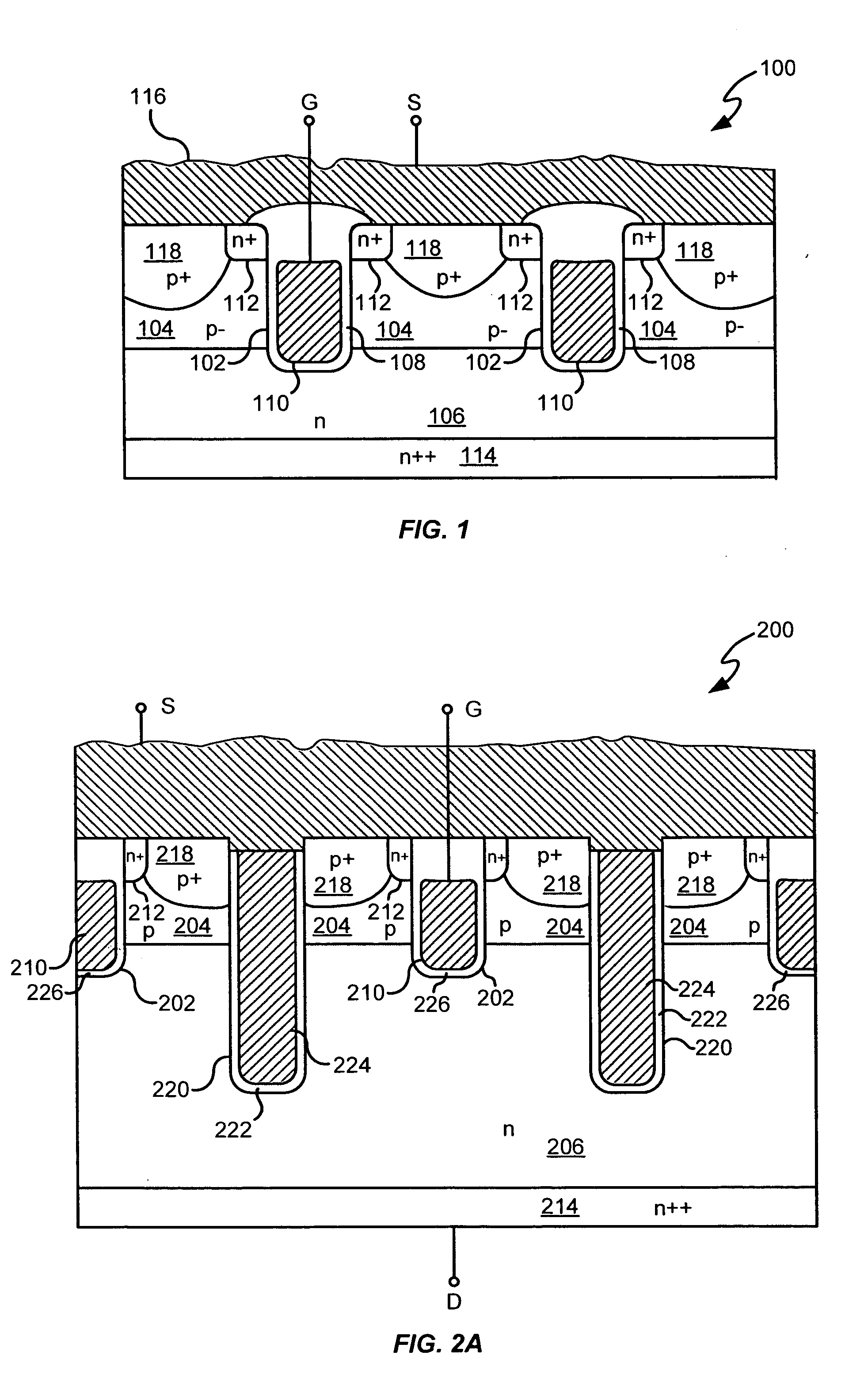
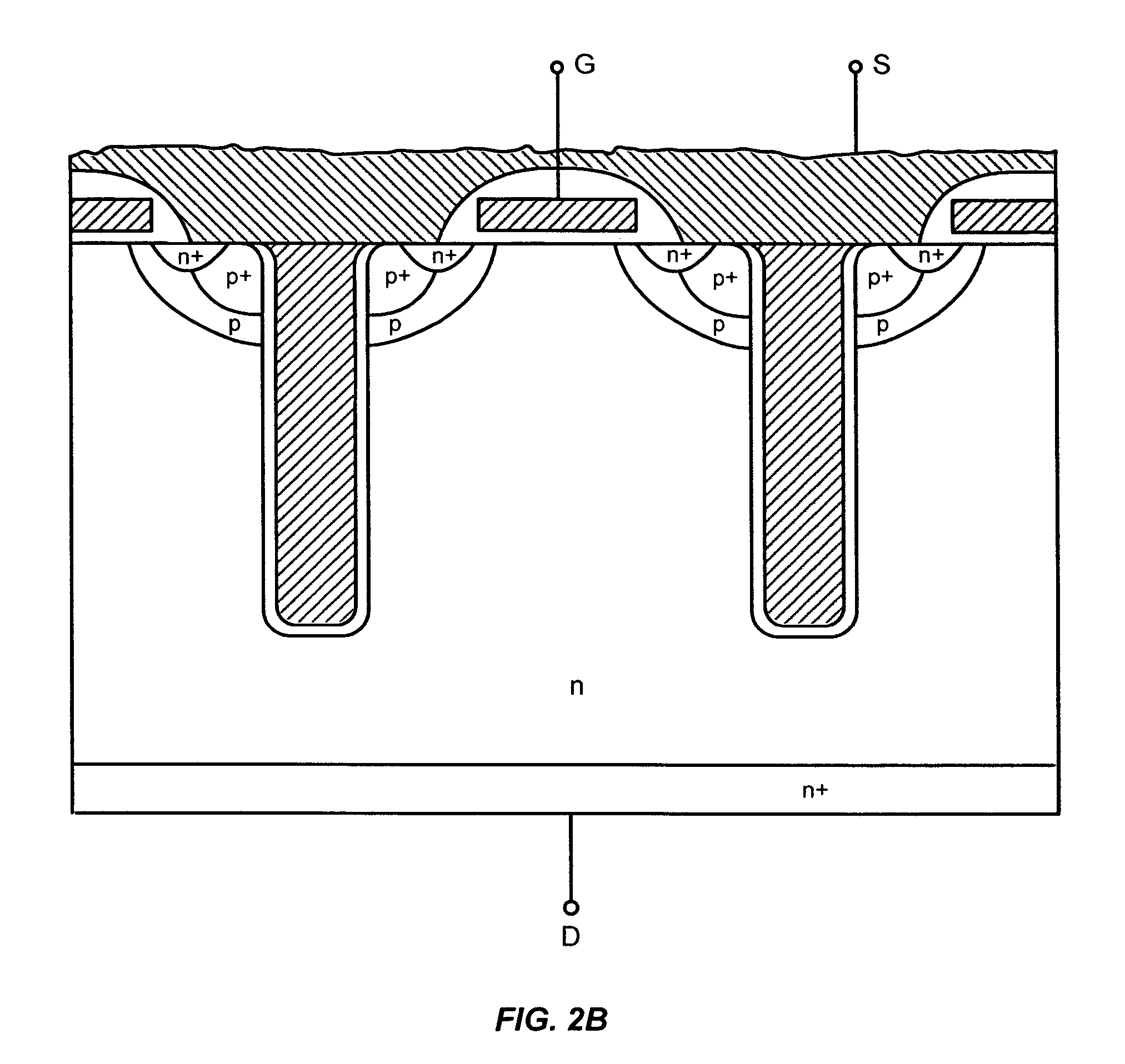
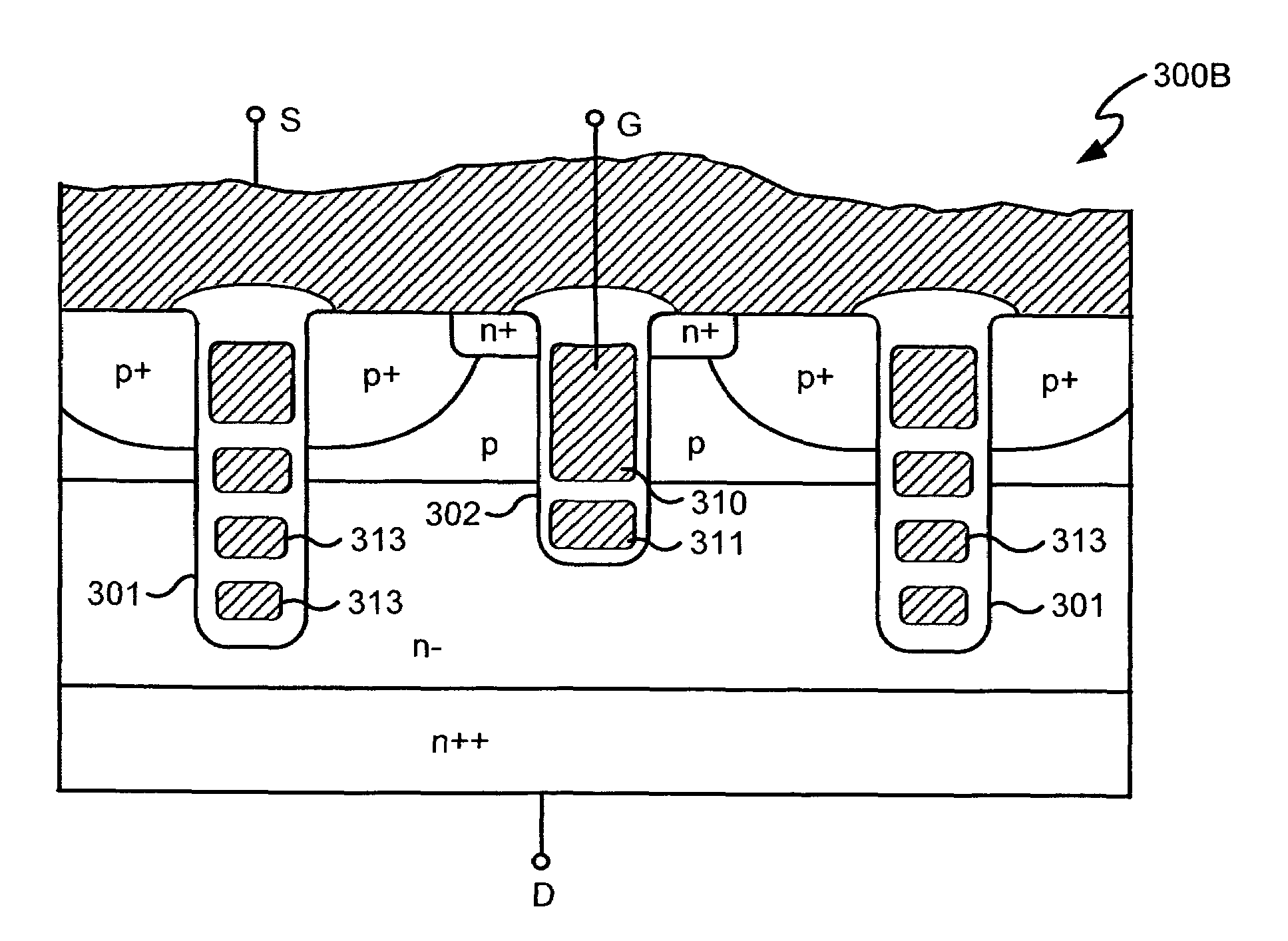
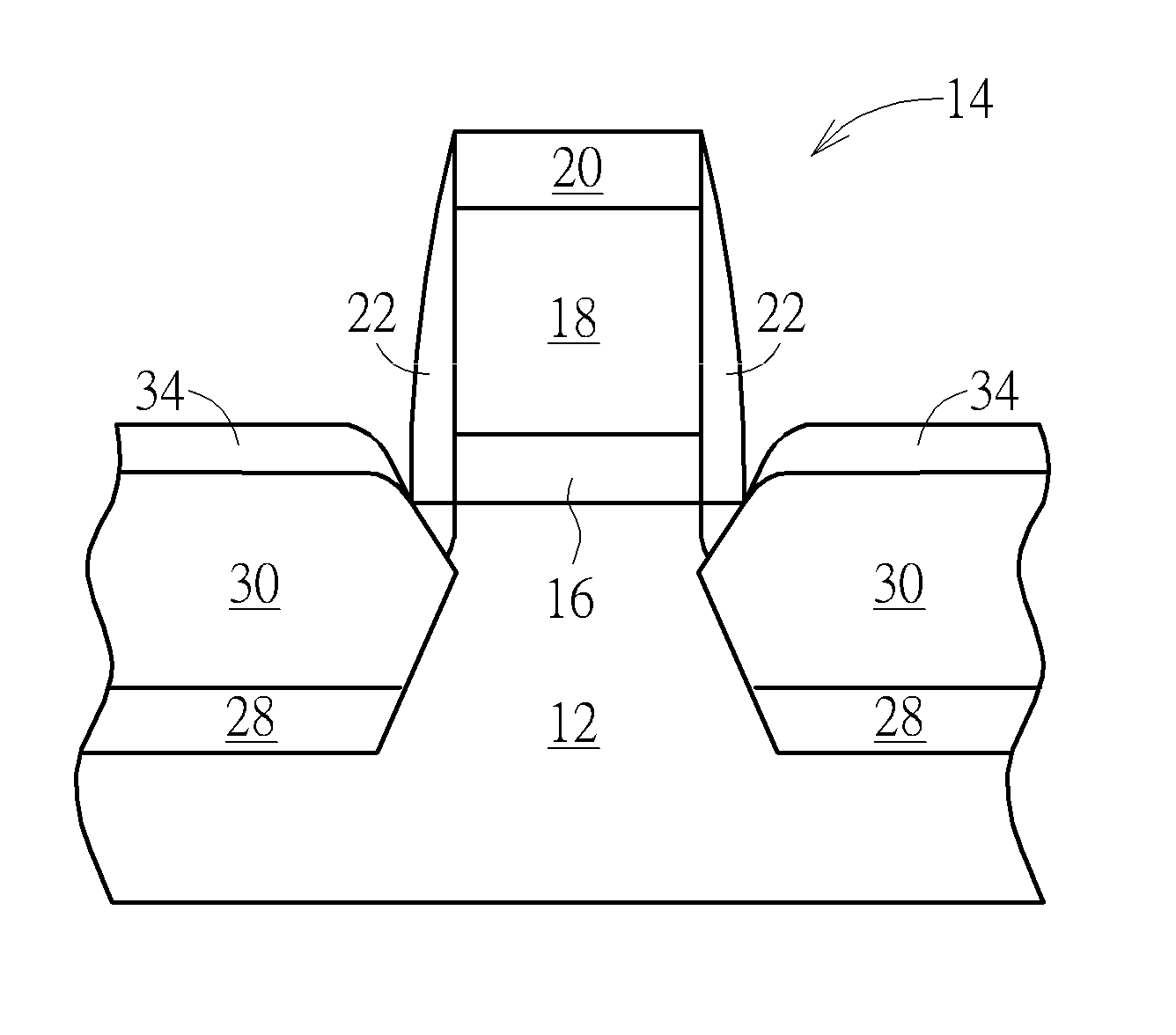
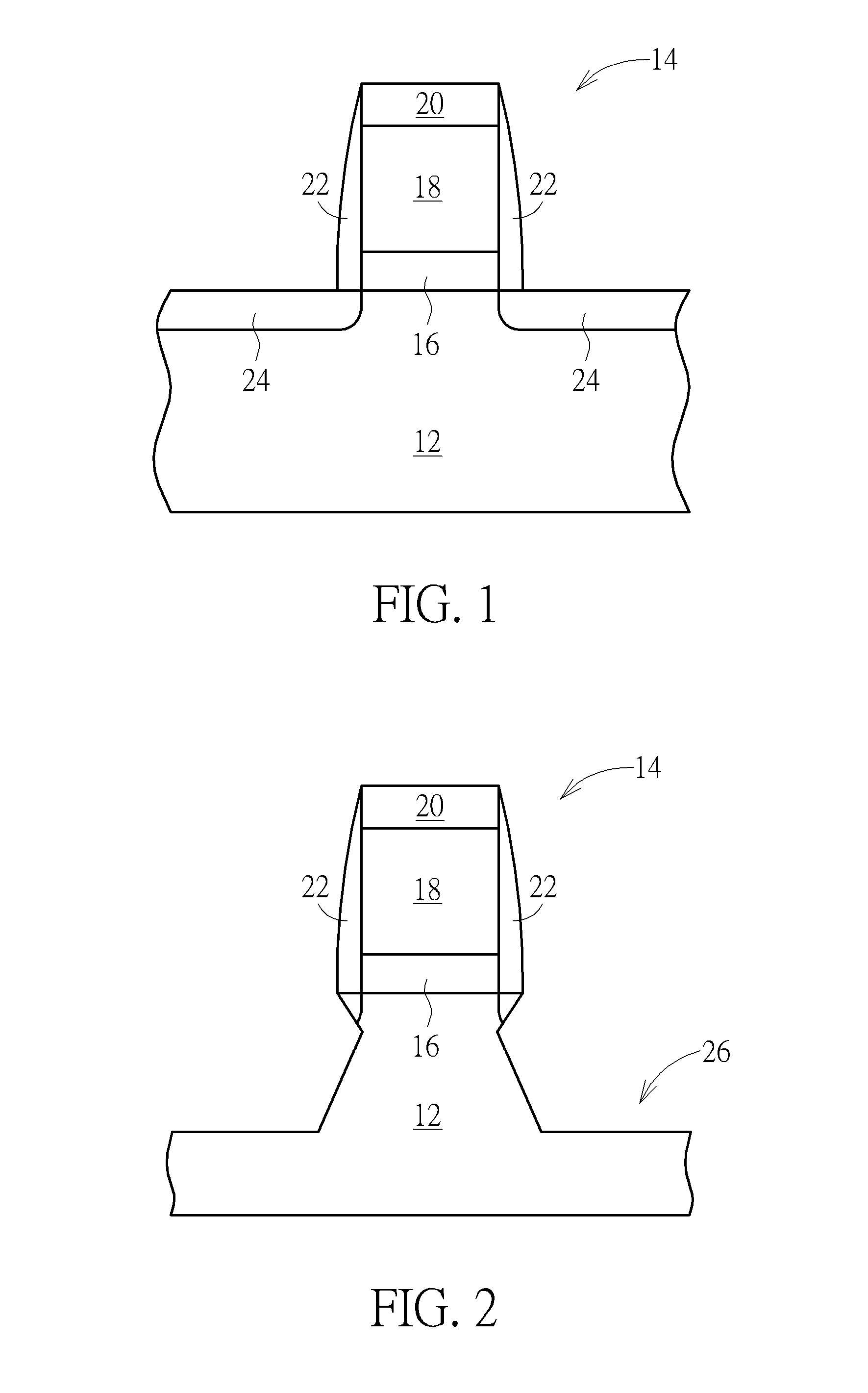
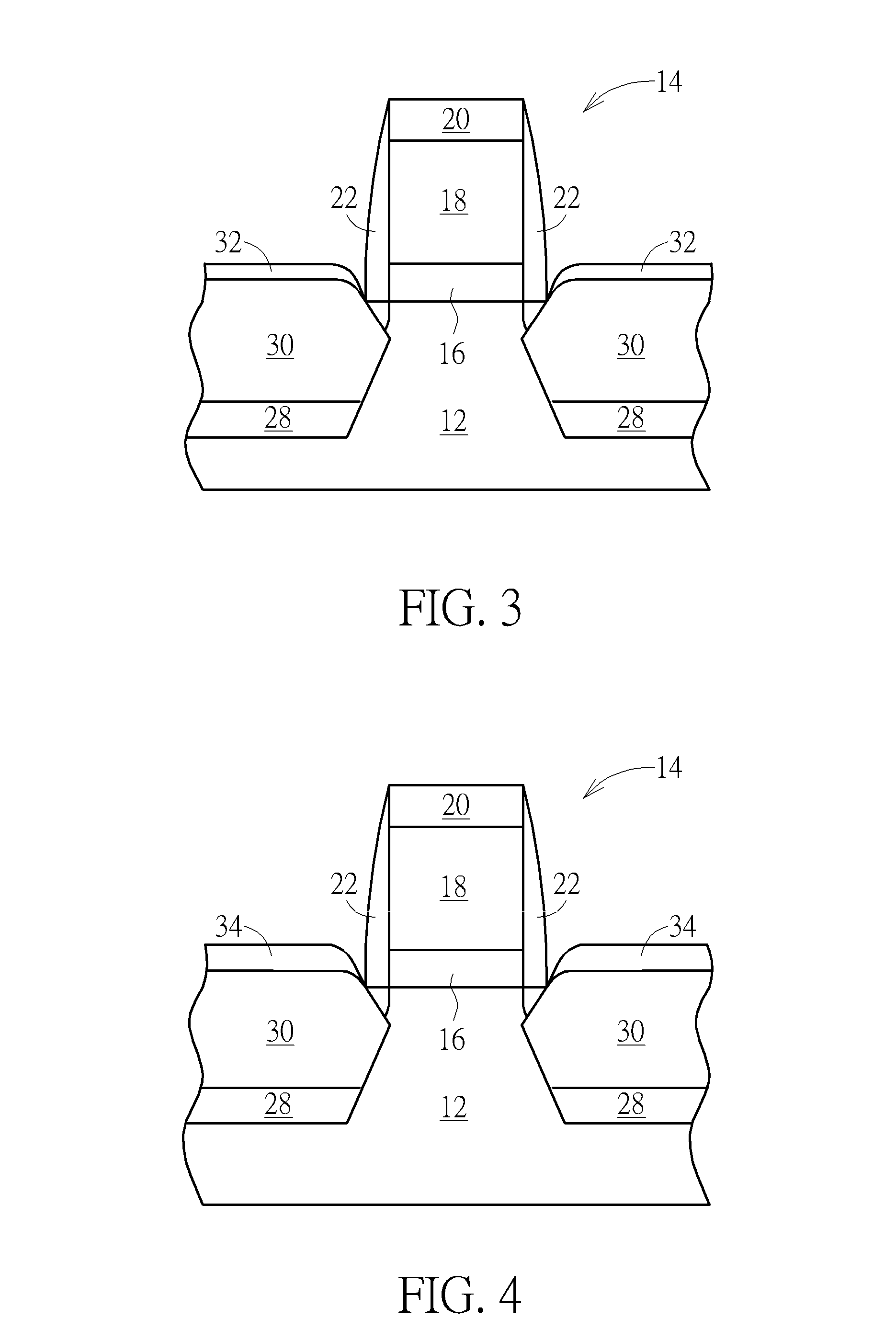
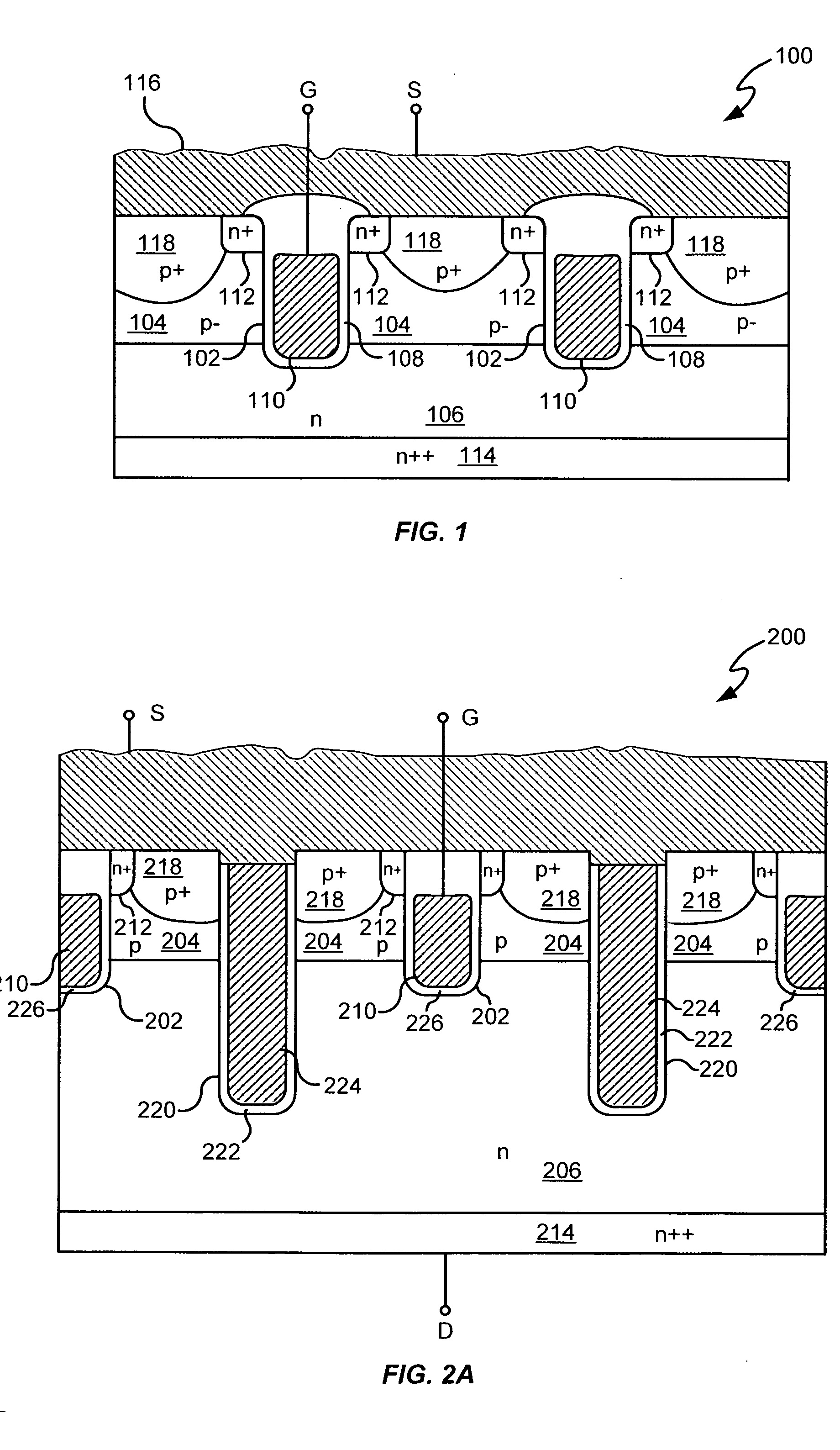
Power semiconductor devices and methods of manufacture
ActiveUS20050167742A1Improved voltage performanceFast switching speedEfficient power electronics conversionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringHigh voltage
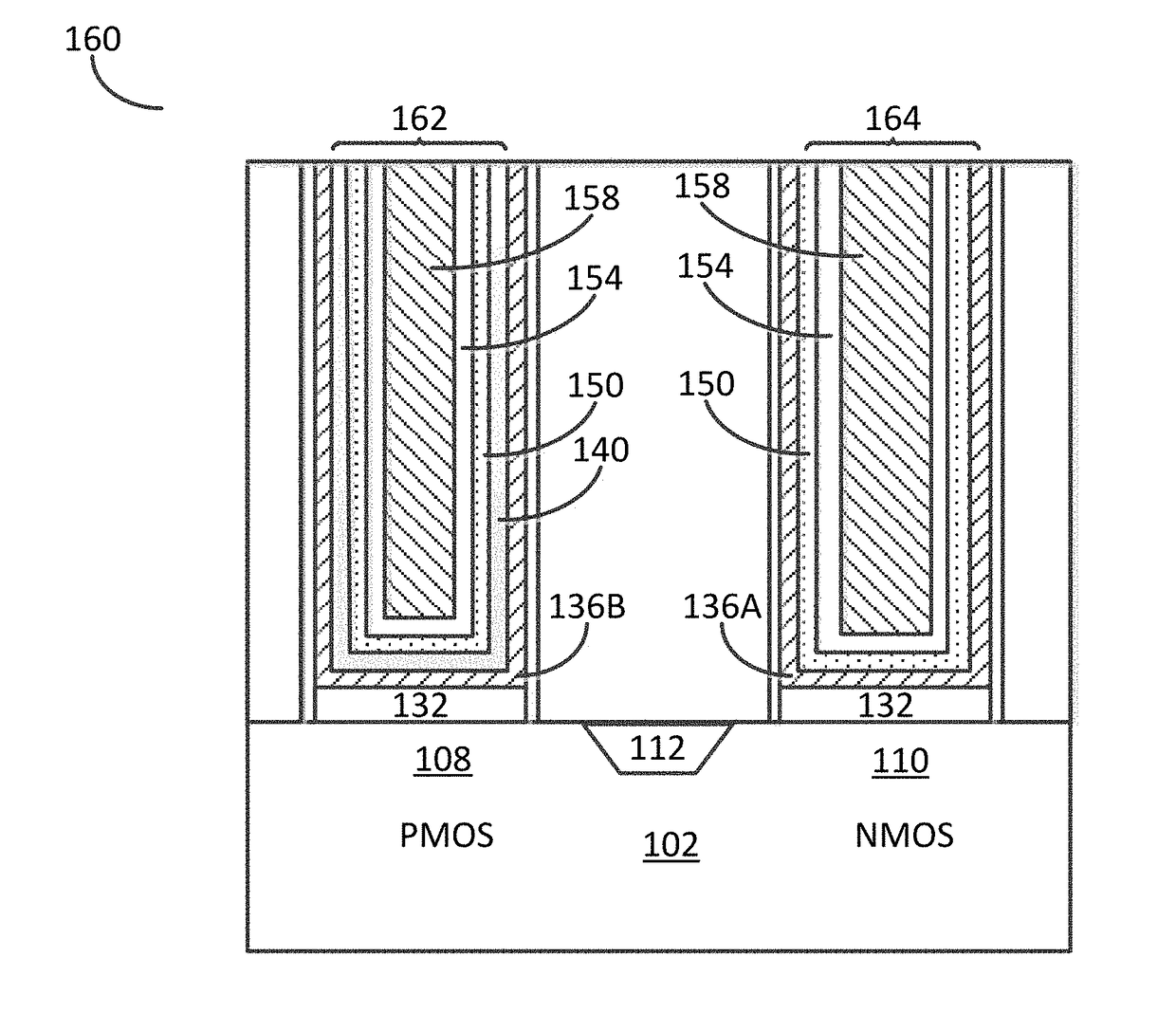
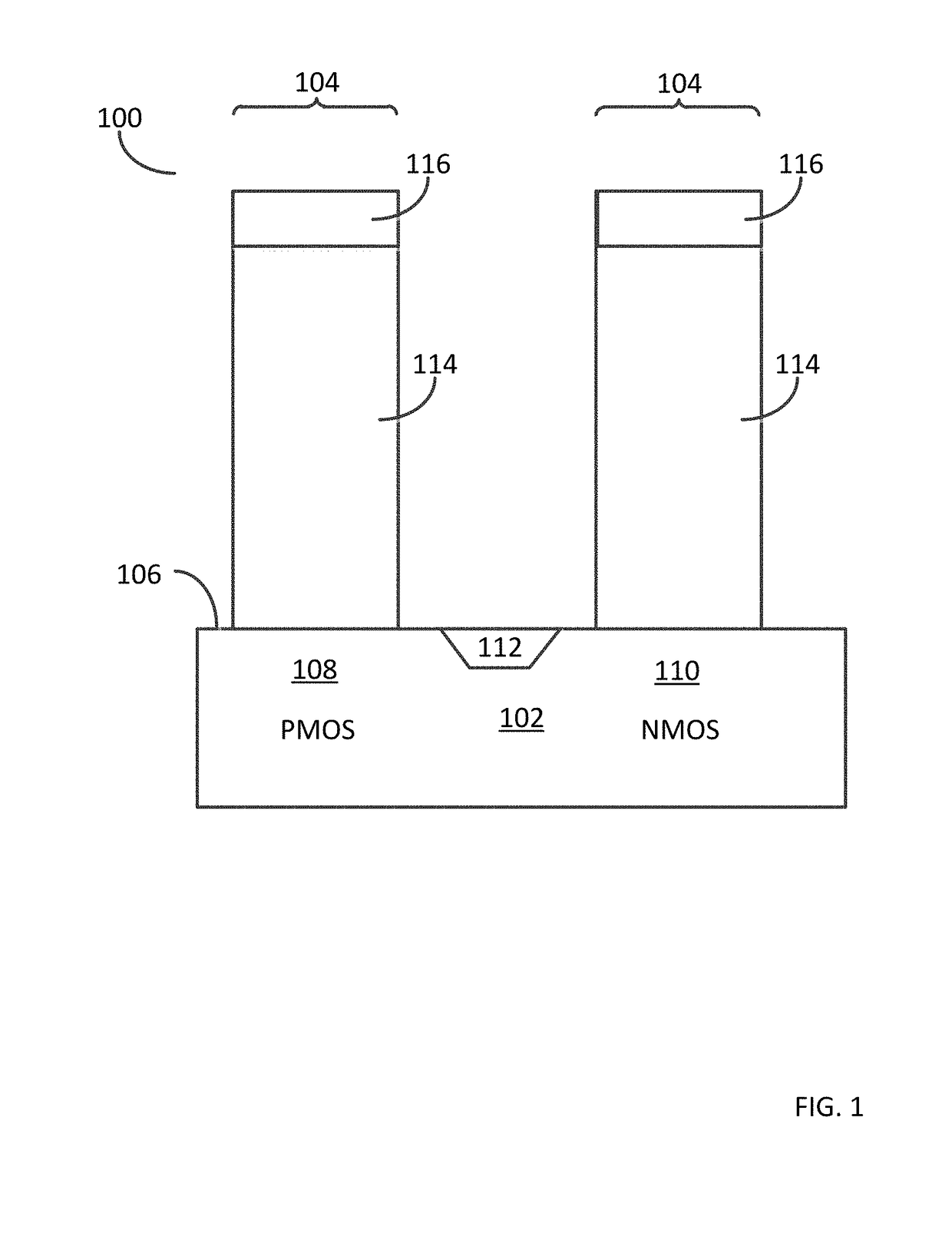
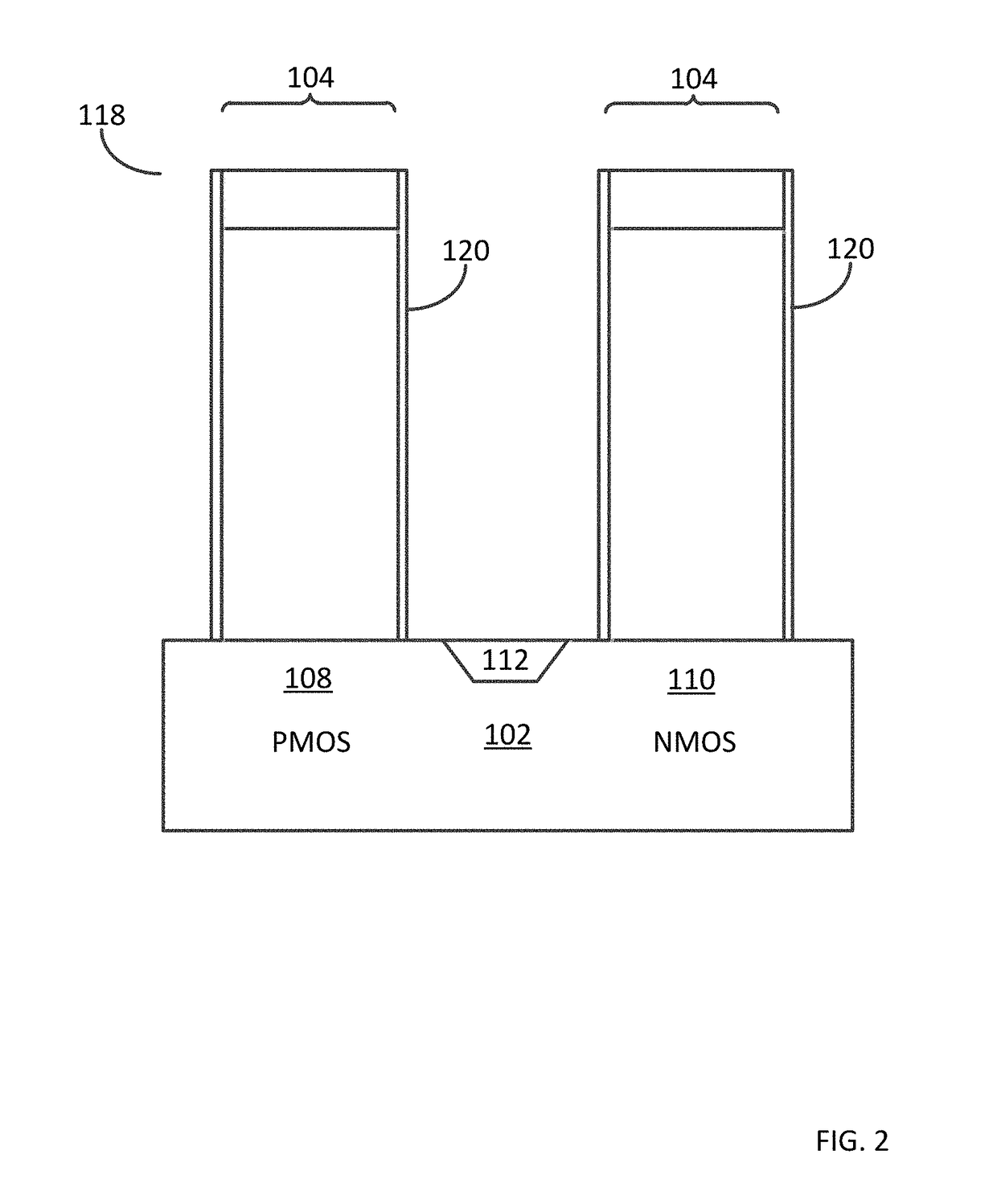
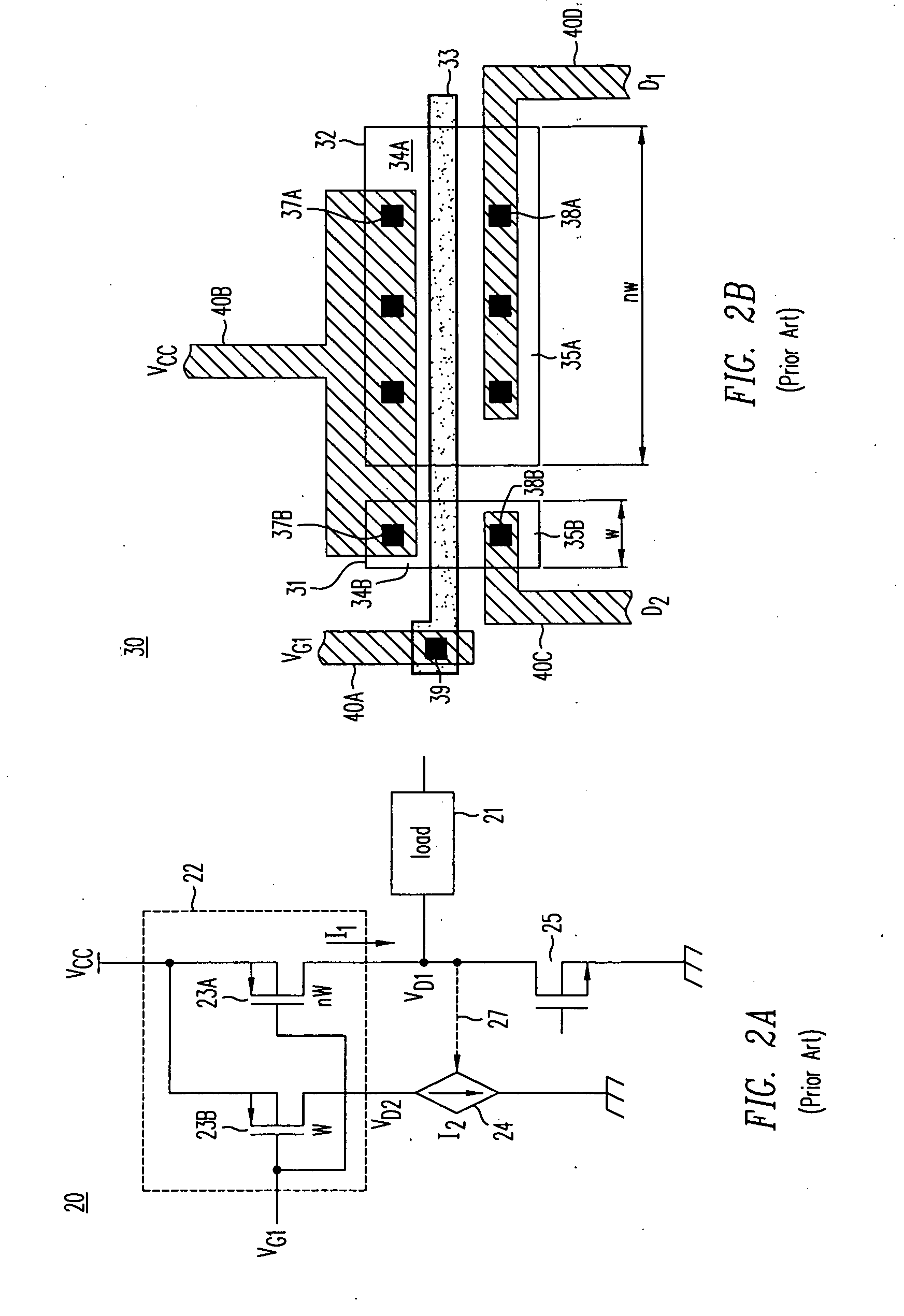
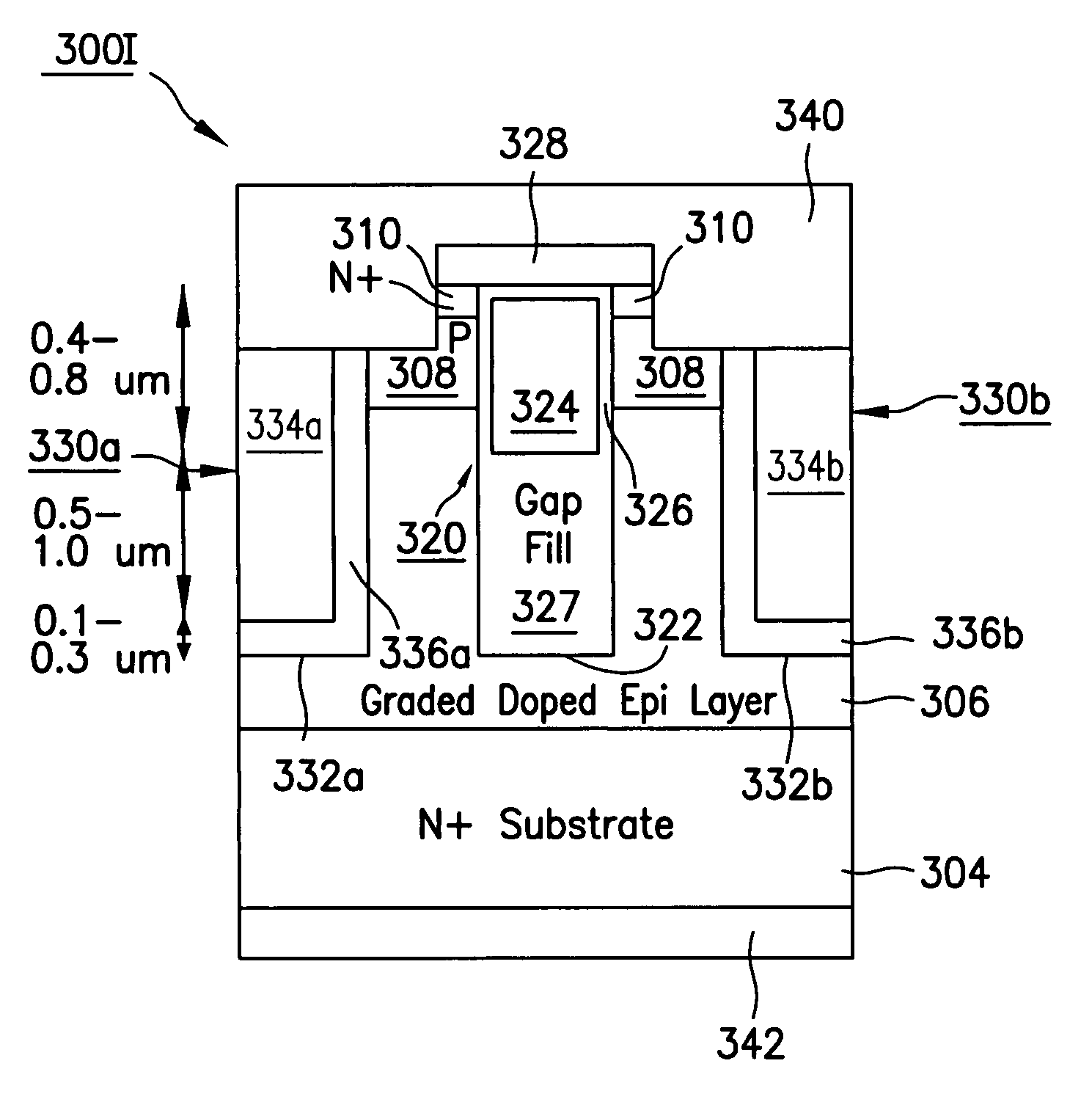
Various embodiments for improved power devices as well as their methods of manufacture, packaging and circuitry incorporating the same for use in a wide variety of power electronic applications are disclosed. One aspect of the invention combines a number of charge balancing techniques and other techniques for reducing parasitic capacitance to arrive at different embodiments for power devices with improved voltage performance, higher switching speed, and lower on-resistance. Another aspect of the invention provides improved termination structures for low, medium and high voltage devices. Improved methods of fabrication for power devices are provided according to other aspects of the invention. Improvements to specific processing steps, such as formation of trenches, formation of dielectric layers inside trenches, formation of mesa structures and processes for reducing substrate thickness, among others, are presented. According to another aspect of the invention, charge balanced power devices incorporate temperature and current sensing elements such as diodes on the same die. Other aspects of the invention improve equivalent series resistance (ESR) for power devices, incorporate additional circuitry on the same chip as the power device and provide improvements to the packaging of charge balanced power devices.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
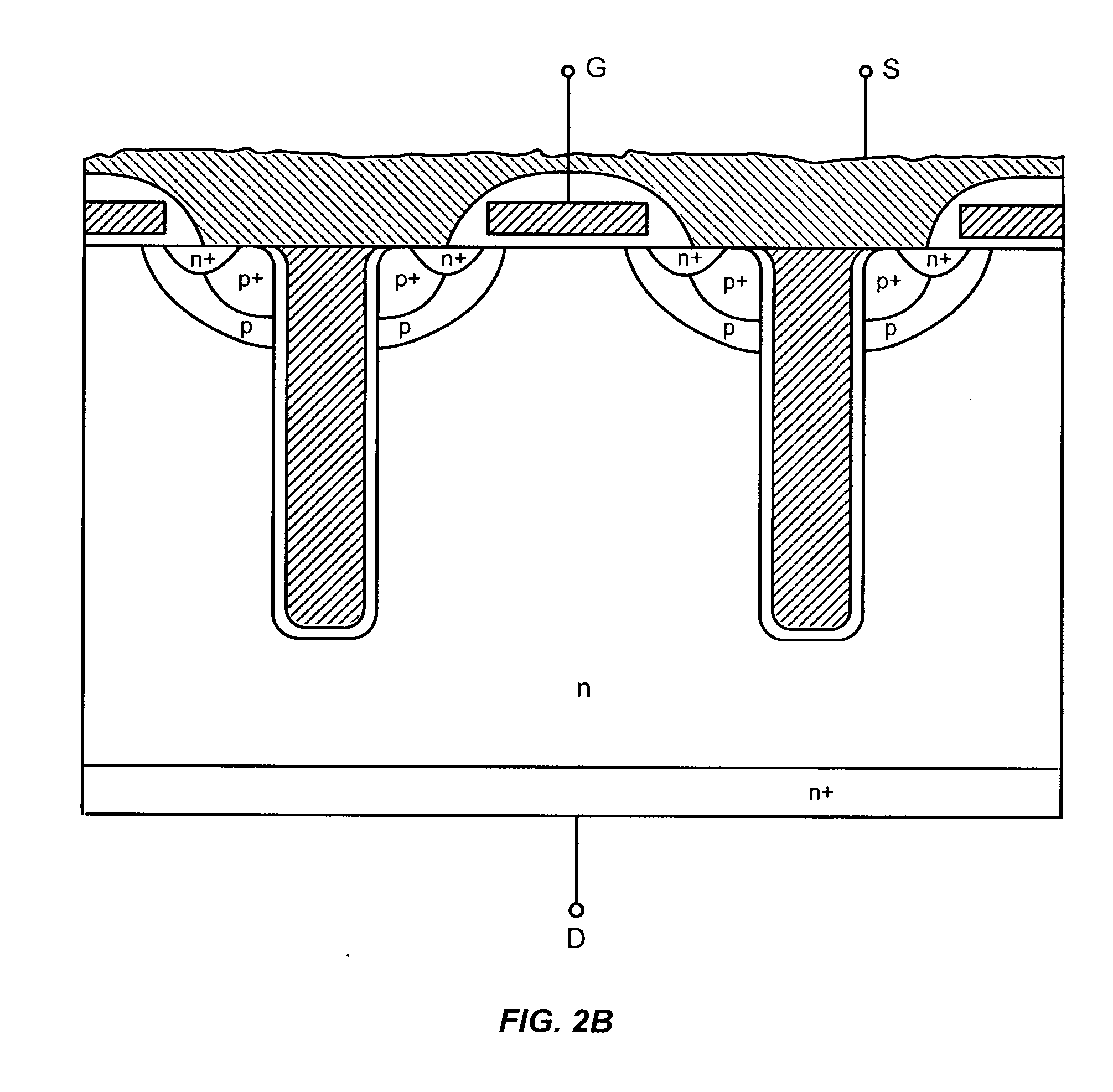
Power semiconductor devices and methods of manufacture
ActiveUS7345342B2Simple structureEasy to packEfficient power electronics conversionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringHigh pressure
Various embodiments for improved power devices as well as their methods of manufacture, packaging and circuitry incorporating the same for use in a wide variety of power electronic applications are disclosed. One aspect of the invention combines a number of charge balancing techniques and other techniques for reducing parasitic capacitance to arrive at different embodiments for power devices with improved voltage performance, higher switching speed, and lower on-resistance. Another aspect of the invention provides improved termination structures for low, medium and high voltage devices. Improved methods of fabrication for power devices are provided according to other aspects of the invention. Improvements to specific processing steps, such as formation of trenches, formation of dielectric layers inside trenches, formation of mesa structures and processes for reducing substrate thickness, among others, are presented. According to another aspect of the invention, charge balanced power devices incorporate temperature and current sensing elements such as diodes on the same die. Other aspects of the invention improve equivalent series resistance (ESR) for power devices, incorporate additional circuitry on the same chip as the power device and provide improvements to the packaging of charge balanced power devices.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Semiconductor device and method of making the same
ActiveUS20130037886A1Improve efficiencyImprove performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceEngineering
A semiconductor device includes a semiconductor substrate, at least a first fin structure, at least a second fin structure, a first gate, a second gate, a first source / drain region and a second source / drain region. The semiconductor substrate has at least a first active region to dispose the first fin structure and at least a second active region to dispose the second fin structure. The first / second fin structure partially overlapped by the first / second gate has a first / second stress, and the first stress and the second stress are different from each other. The first / second source / drain region is disposed in the first / second fin structure at two sides of the first / second gate.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20140191389A1Well formedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceCell region
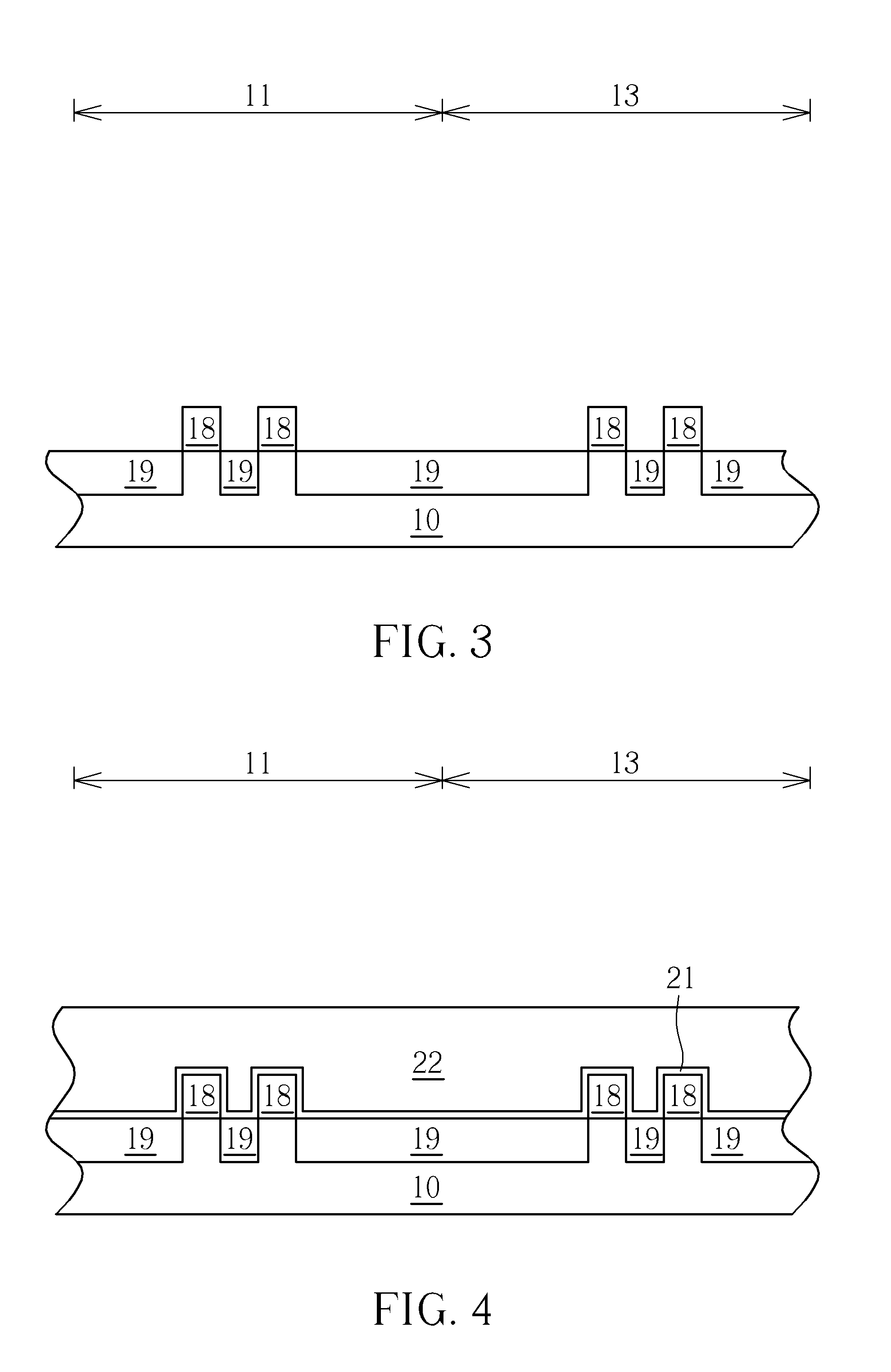
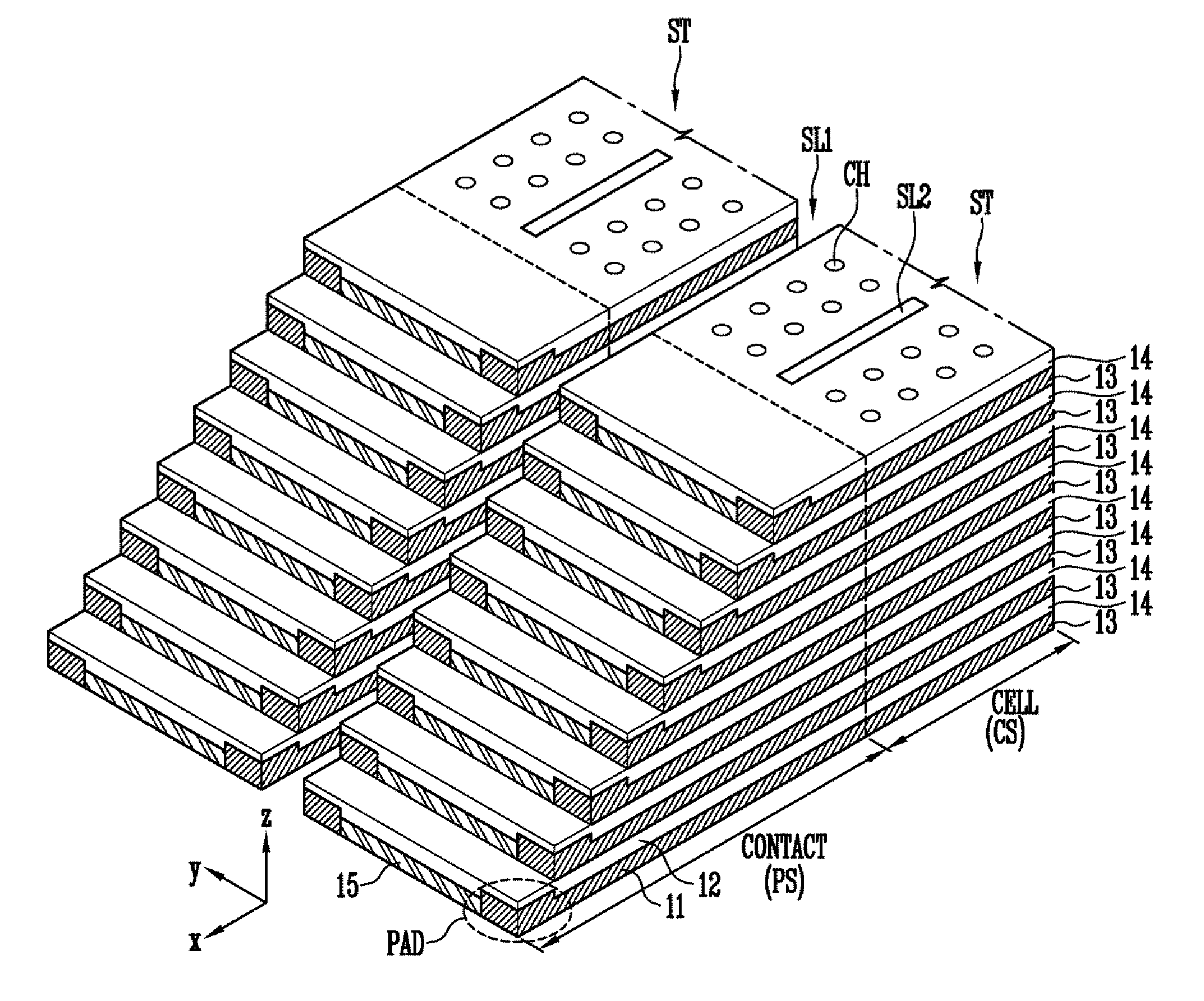
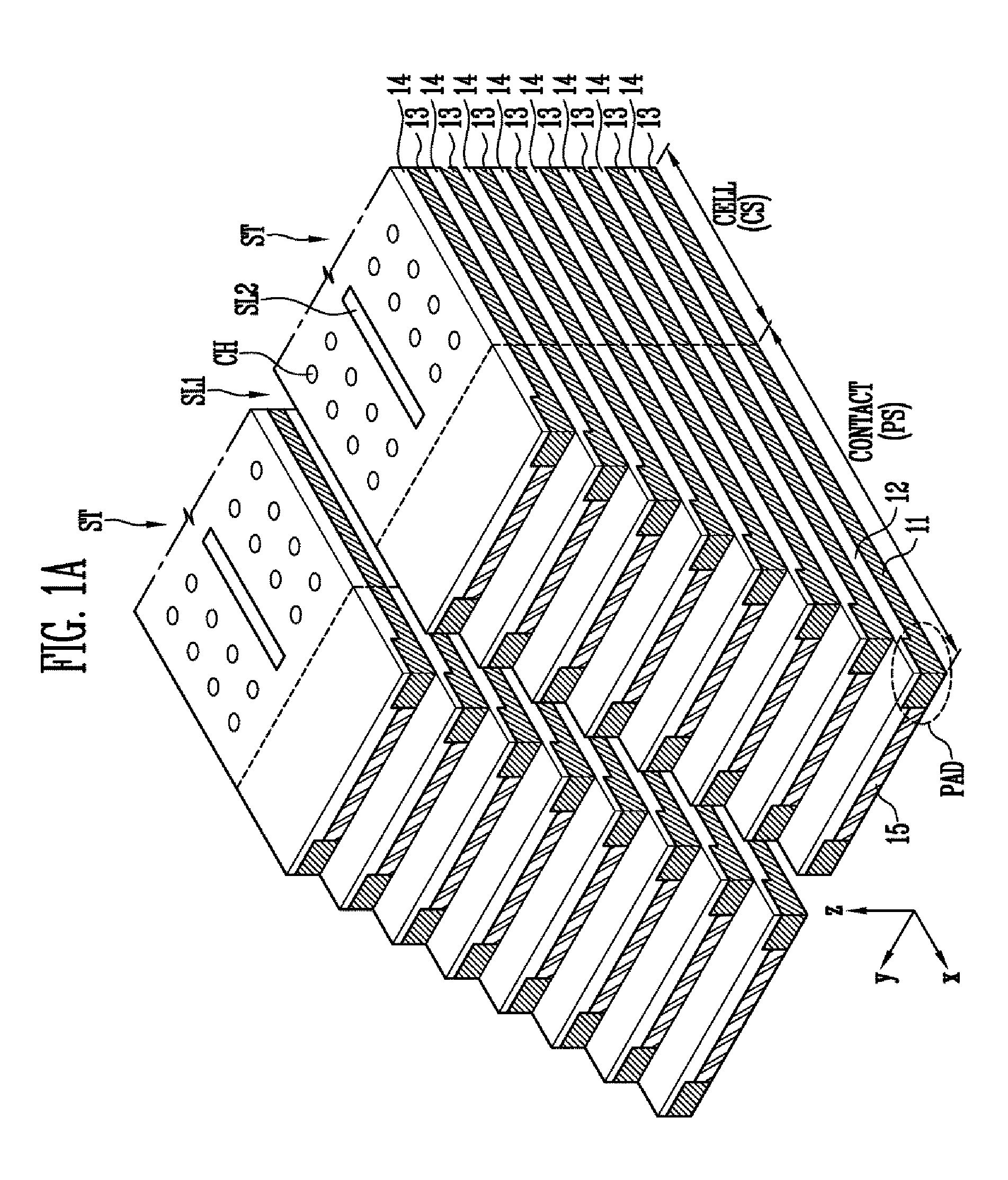
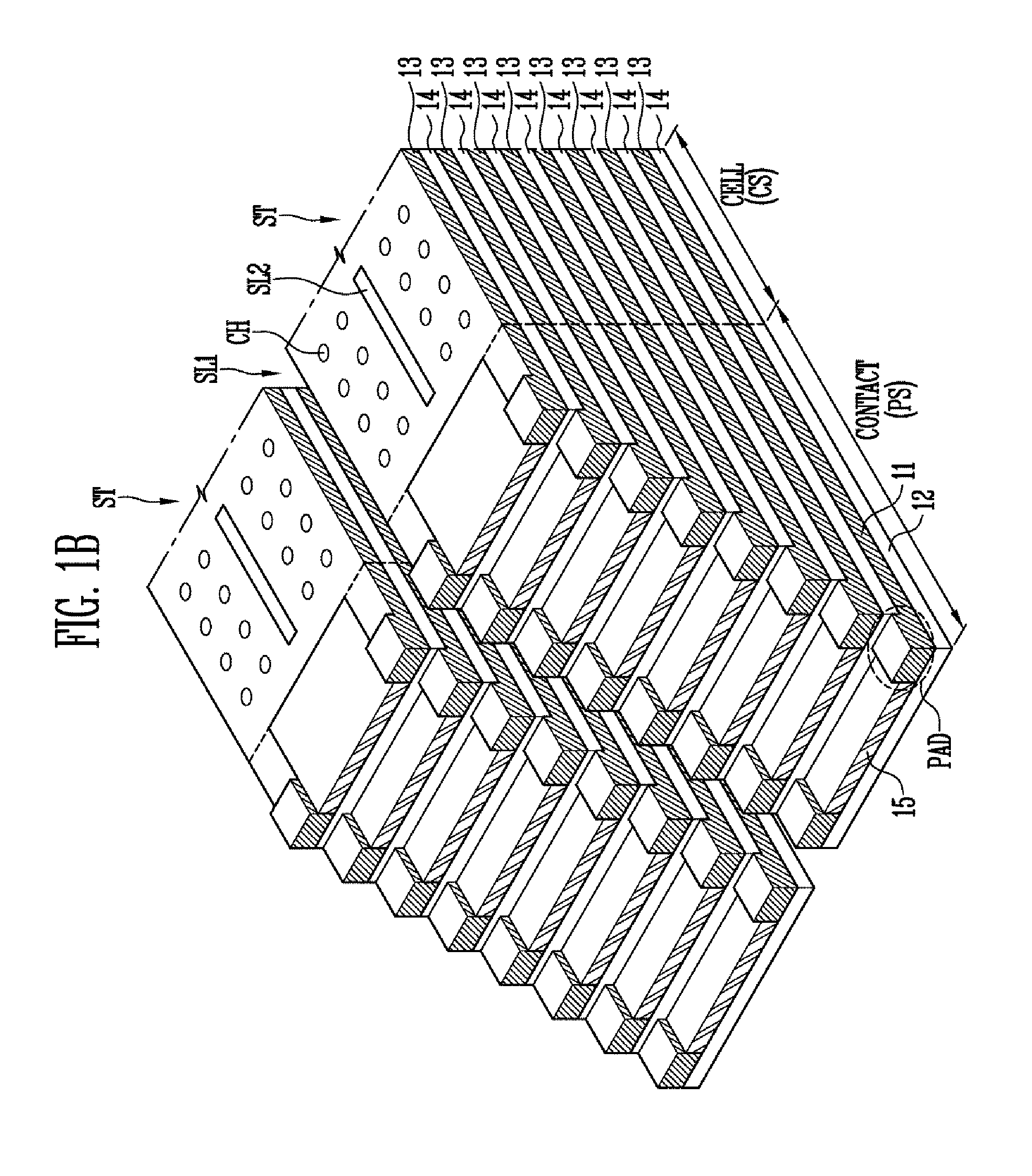
A semiconductor device includes a substrate in which a cell region and a contact region are defined, a pad structure including a plurality of first conductive layers and a plurality of first insulating layers formed alternately with each other in the contact region of the substrate, wherein an end of the pad structure is patterned stepwise, portions of the first conductive layers exposed at the end of the pad structure are defined as a plurality of pad portions, and the plurality of pad portions have a greater thickness than unexposed portions of the plurality of first conductive layers.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
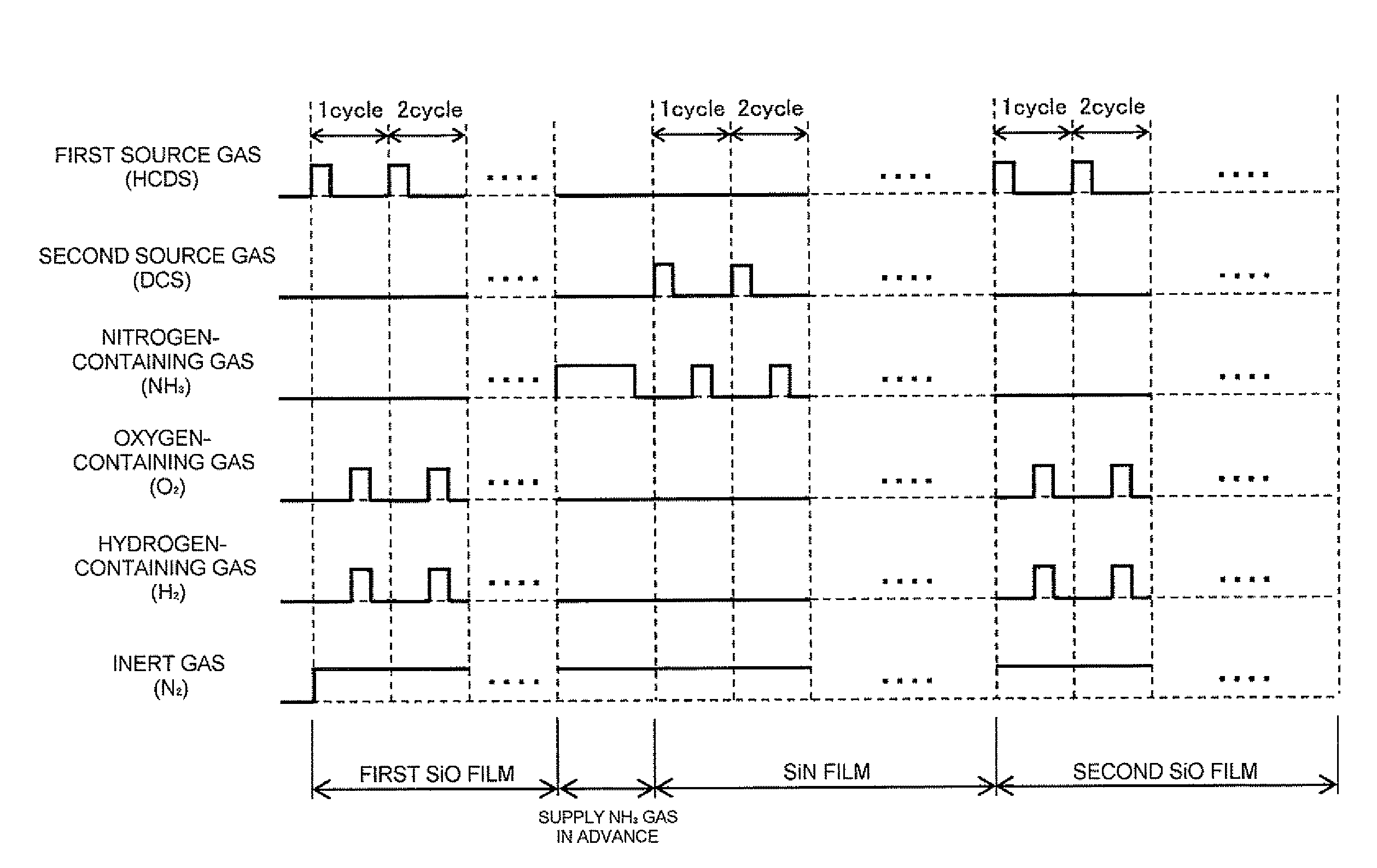
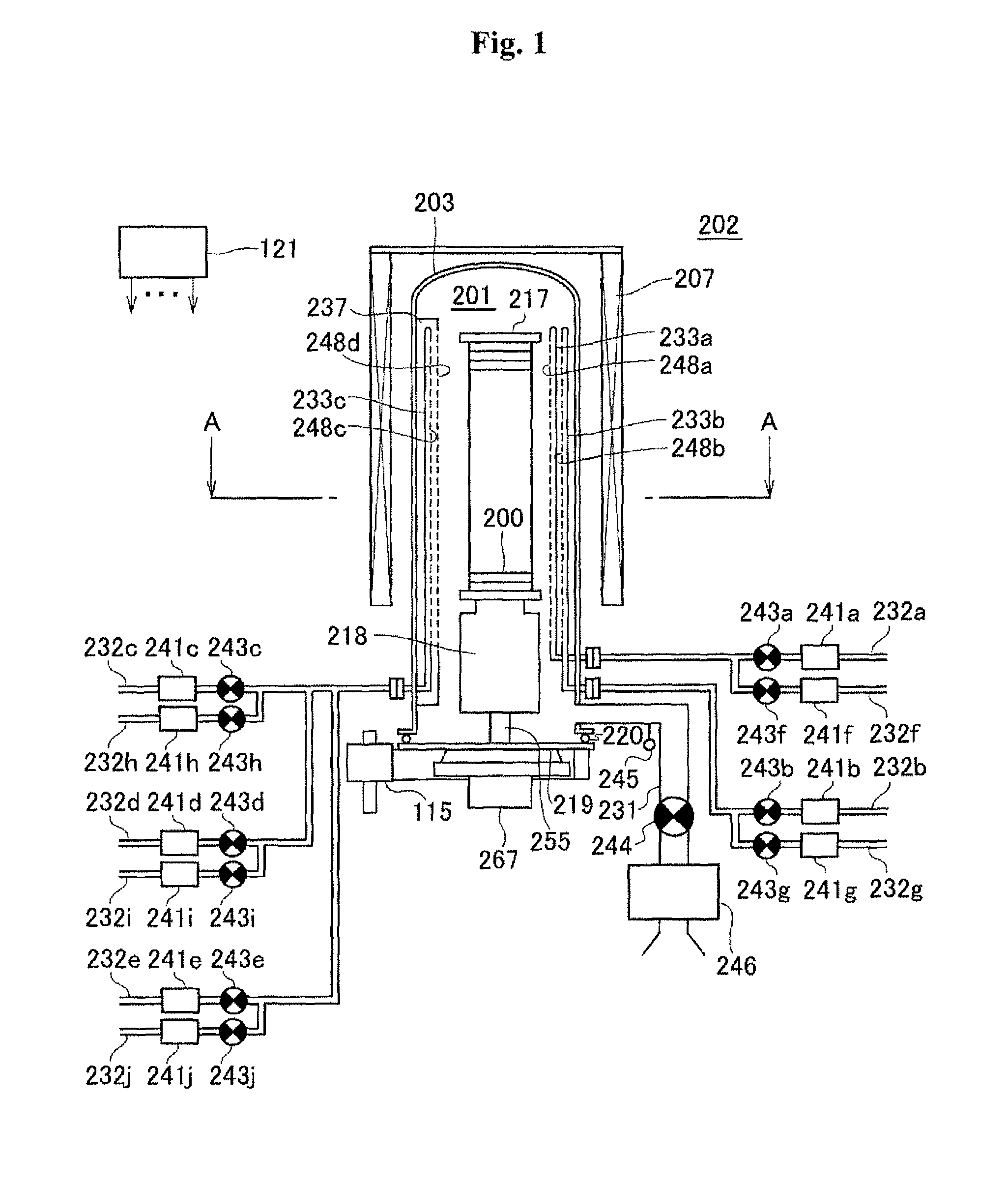
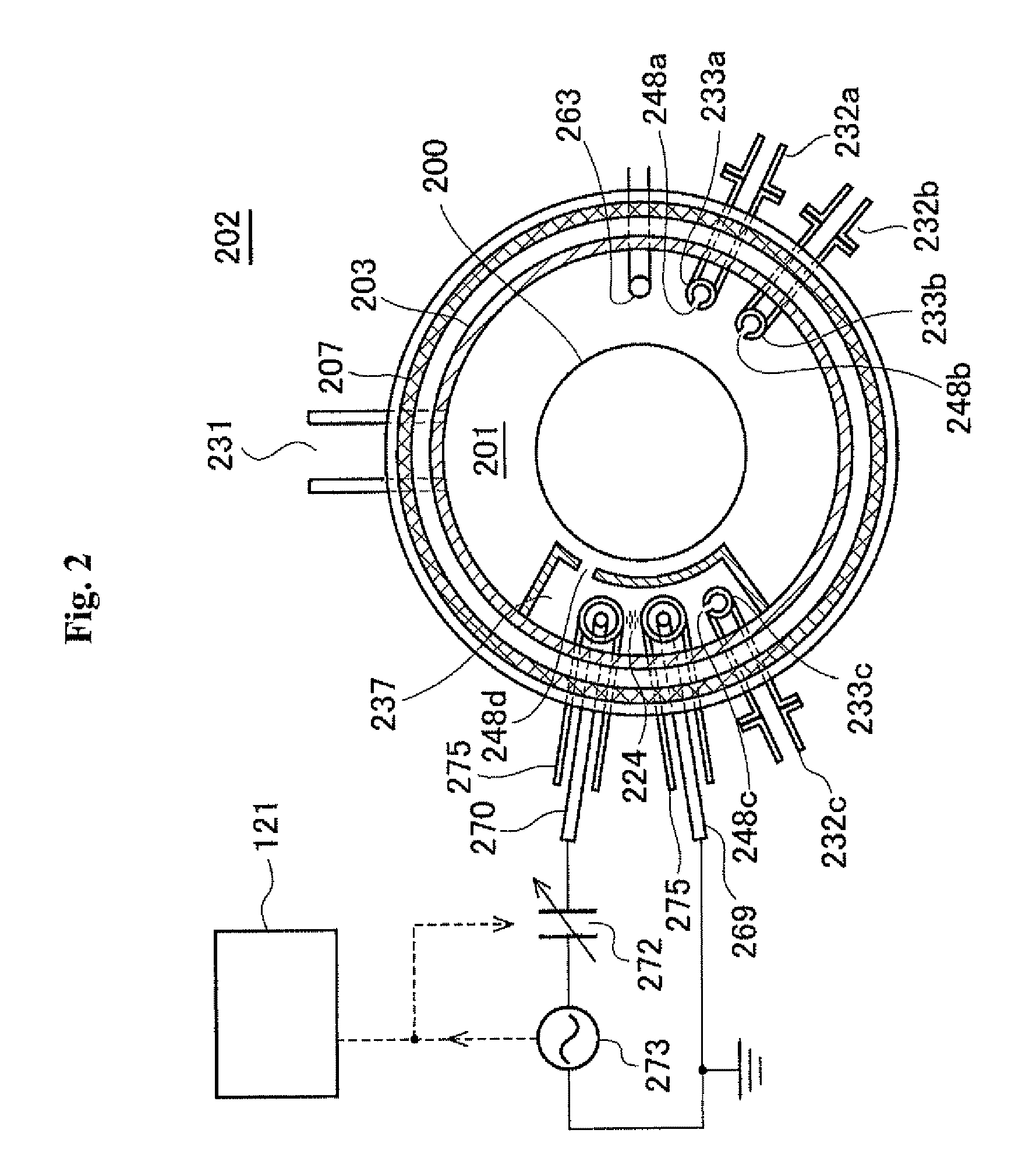
Method of manufacturing semiconductor device, method of processing substrate and non-transitory computer readable recording medium
ActiveUS9190264B2Increase productionEasy to operateLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPower semiconductor deviceEngineering
A semiconductor manufacturing method includes forming an oxide film on a substrate by performing a first cycle a predetermined number of times, including supplying a first source gas, an oxidizing gas and a reducing gas to the substrate heated to a first temperature in a process container under a sub-atmospheric pressure; forming a seed layer on a surface of the oxide film by supplying a nitriding gas to the substrate in the process container, the substrate being heated to a temperature equal to or higher than the first temperature and equal to or lower than a second temperature; and forming a nitride film on the seed layer formed on the surface of the oxide film by performing a second cycle a predetermined number of times, including supplying a second source gas and the nitriding gas to the substrate heated to the second temperature in the process container.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
System for heat treatment of semiconductor device
InactiveUS7989736B2Avoid damageIncrease temperatureFurnaces without endless coreSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectromotive forceSilicon thin film
Disclosed is a heat treatment system for semiconductor devices. The heat treatment system is used in a heat treatment process for semiconductor devices, such as a crystallization process for an amorphous silicon thin film or a dopant activation process for a poly-crystalline silicon thin film formed on a surface of a glass substrate of a flat display panel including a liquid crystal display (LCD) or an organic light emitting device (OLED). The heat treatment system transfers a semiconductor device after uniformly preheating the semiconductor device in order to prevent deformation of the semiconductor device during the heat treatment process, rapidly performs the heat treatment process under the high temperature condition by heating the semiconductor device using a lamp heater and induction heat derived from induced electromotive force, and unloads the semiconductor device after uniformly cooling the semiconductor device such that the semiconductor device is prevented from being deformed when the heat treatment process has been finished. The heat treatment system rapidly performs the heat treatment process while preventing deformation of the semiconductor device by gradually heating or cooling the semiconductor device.
Owner:VIATRON TECH INC
Semiconductor devices with varying threshold voltage and fabrication methods thereof
ActiveUS9748145B1Overcomes shortcomingEnhanced advantageTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPower semiconductor deviceDielectric layer
Semiconductor device fabrication methods are provided which include: providing a structure with at least one region and including a dielectric layer disposed over a substrate; forming a multilayer stack structure including a threshold-voltage adjusting layer over the dielectric layer, the multilayer stack structure including a first threshold-voltage adjusting layer in a first region of the at least one region, and a second threshold-voltage adjusting layer in a second region of the at least one region; and annealing the structure to define a varying threshold voltage of the at least one region, the annealing facilitating diffusion of at least one threshold voltage adjusting species from the first threshold-voltage adjusting layer and the second threshold-voltage adjusting layer into the dielectric layer, where a threshold voltage of the first region is independent of the threshold voltage of the second region.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20130320334A1Inhibited DiffusionLarge energy gapTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPower semiconductor devicePower flow
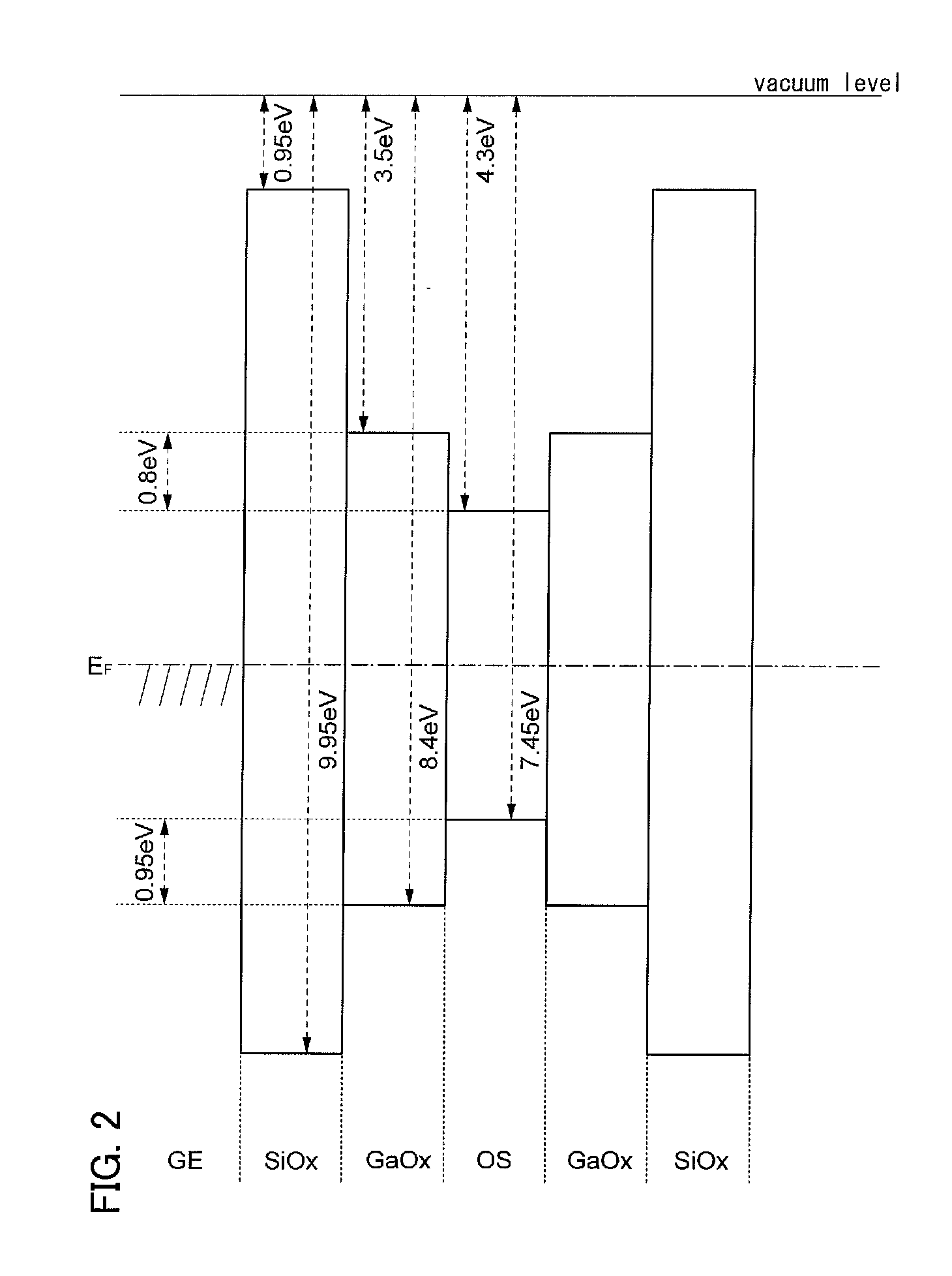
A highly reliable semiconductor device including an oxide semiconductor is provided by preventing a change in its electrical characteristics. A semiconductor device which includes a first oxide semiconductor layer which is in contact with a source electrode layer and a drain electrode layer and a second oxide semiconductor layer which serves as a main current path (channel) of a transistor is provided. The first oxide semiconductor layer serves as a buffer layer for preventing a constituent element of the source and drain electrode layers from diffusing into the channel. By providing the first oxide semiconductor layer, it is possible to prevent diffusion of the constituent element into an interface between the first oxide semiconductor layer and the second oxide semiconductor layer and into the second oxide semiconductor layer.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Methods for forming a semiconductor device and related semiconductor device structures
ActiveUS20180122709A1Well formedTransistorSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceGate dielectric
Methods for forming a semiconductor device and related semiconductor device structures are provided. In some embodiments, methods may include forming an NMOS gate dielectric and a PMOS gate dielectric over a substrate and forming a first work function metal over the NMOS gate dielectric and over the PMOS gate dielectric. In some embodiments, methods may also include, removing the first work function metal over the NMOS gate dielectric and forming a second work function metal over the NMOS gate dielectric and over the PMOS gate dielectric. In some embodiments, related semiconductor device structures may include an NMOS gate dielectric and a PMOS gate dielectric disposed over a semiconductor substrate. A PMOS gate electrode may be disposed over the PMOS gate dielectric and the PMOS gate electrode may include a first work function metal disposed over the PMOS gate dielectric and a second work function metal disposed over the first work function metal. A NMOS gate electrode may be disposed over the NMOS gate dielectric and the NMOS gate electrode may include the second work function metal.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
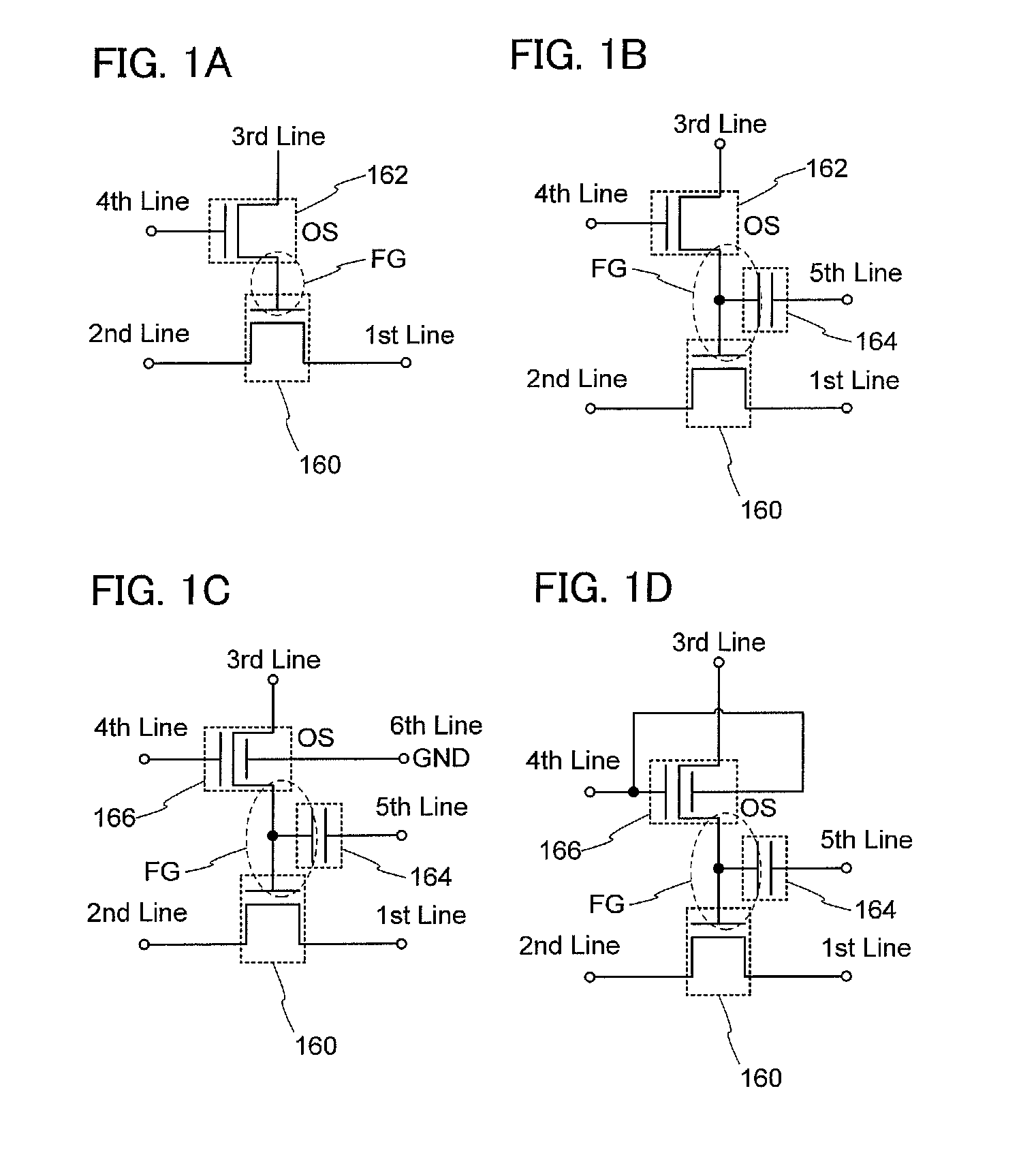
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20110134683A1Easily multivaluedNovel structureTransistorSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceDriver circuit
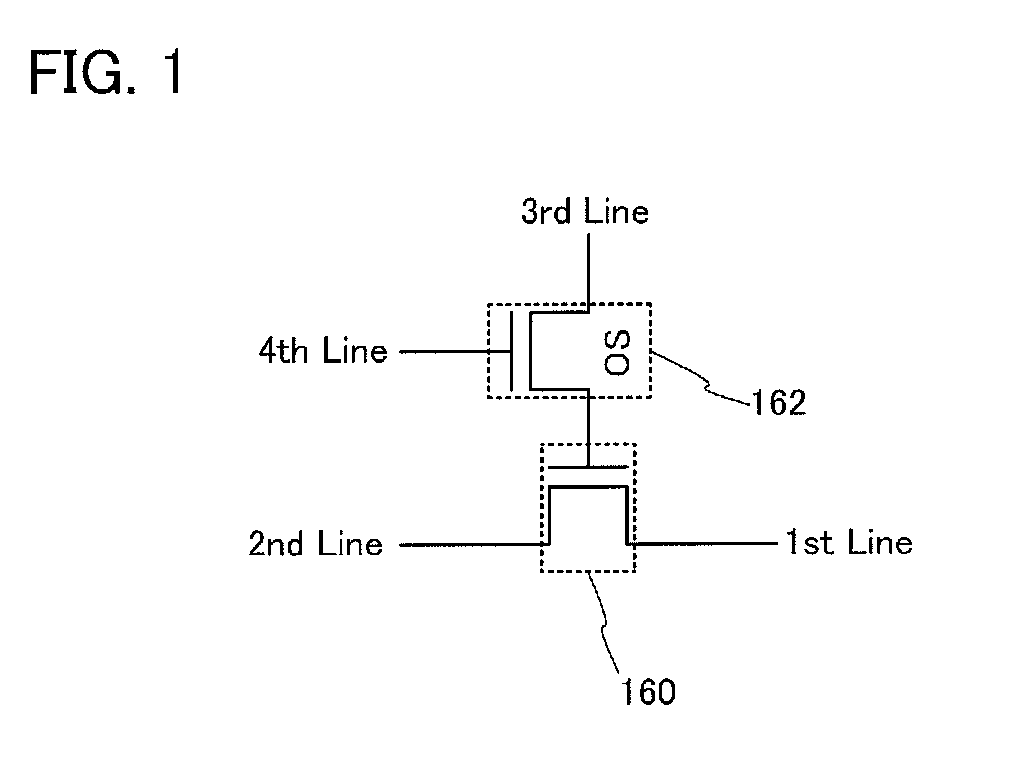
Disclosed is a semiconductor device functioning as a multivalued memory device including: memory cells connected in series; a driver circuit selecting a memory cell and driving a second signal line and a word line; a driver circuit selecting any of writing potentials and outputting it to a first signal line; a reading circuit comparing a potential of a bit line and a reference potential; and a potential generating circuit generating the writing potential and the reference potential. One of the memory cells includes: a first transistor connected to the bit line and a source line; a second transistor connected to the first and second signal line; and a third transistor connected to the word line, bit line, and source line. The second transistor includes an oxide semiconductor layer. A gate electrode of the first transistor is connected to one of source and drain electrodes of the second transistor.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
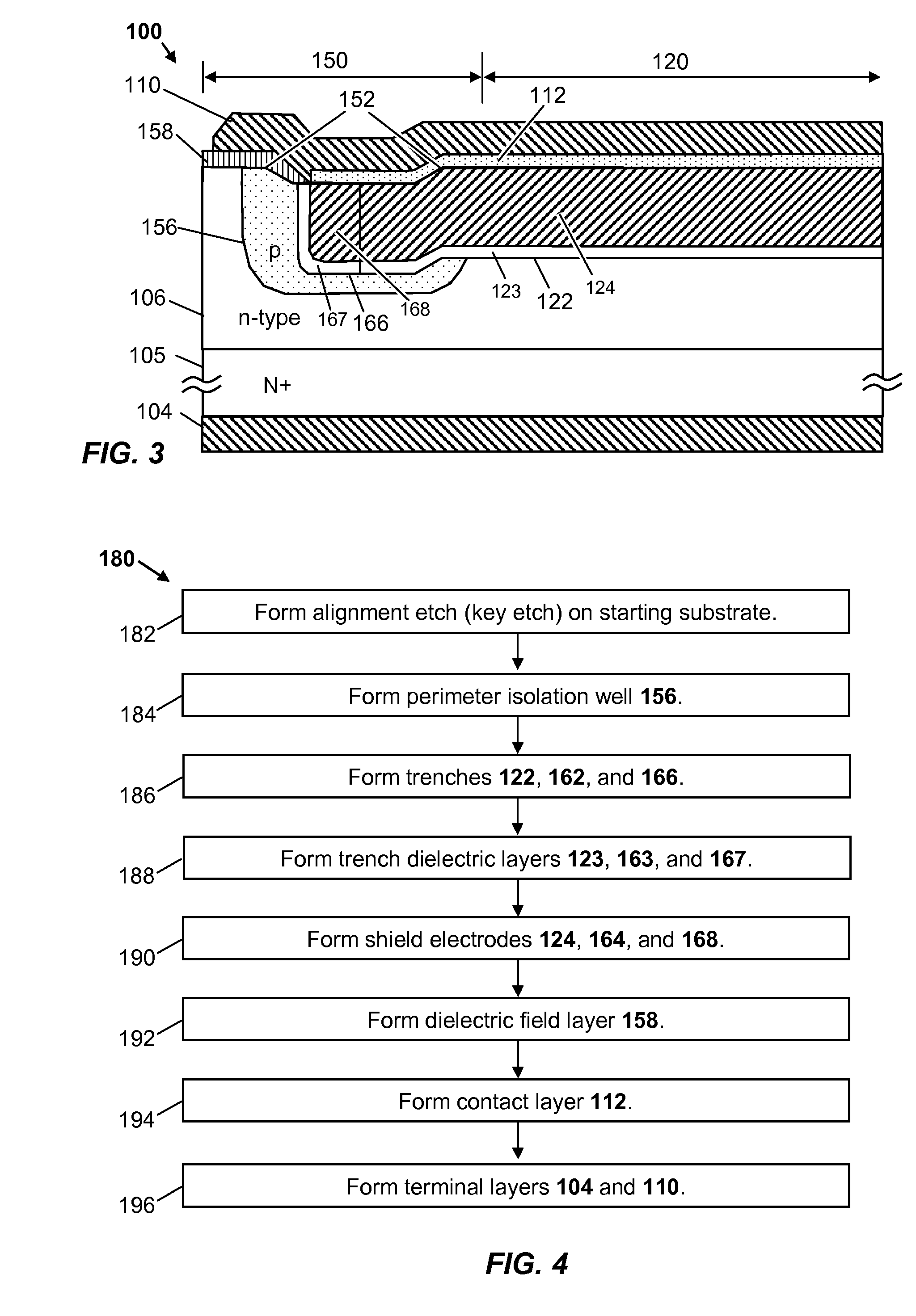
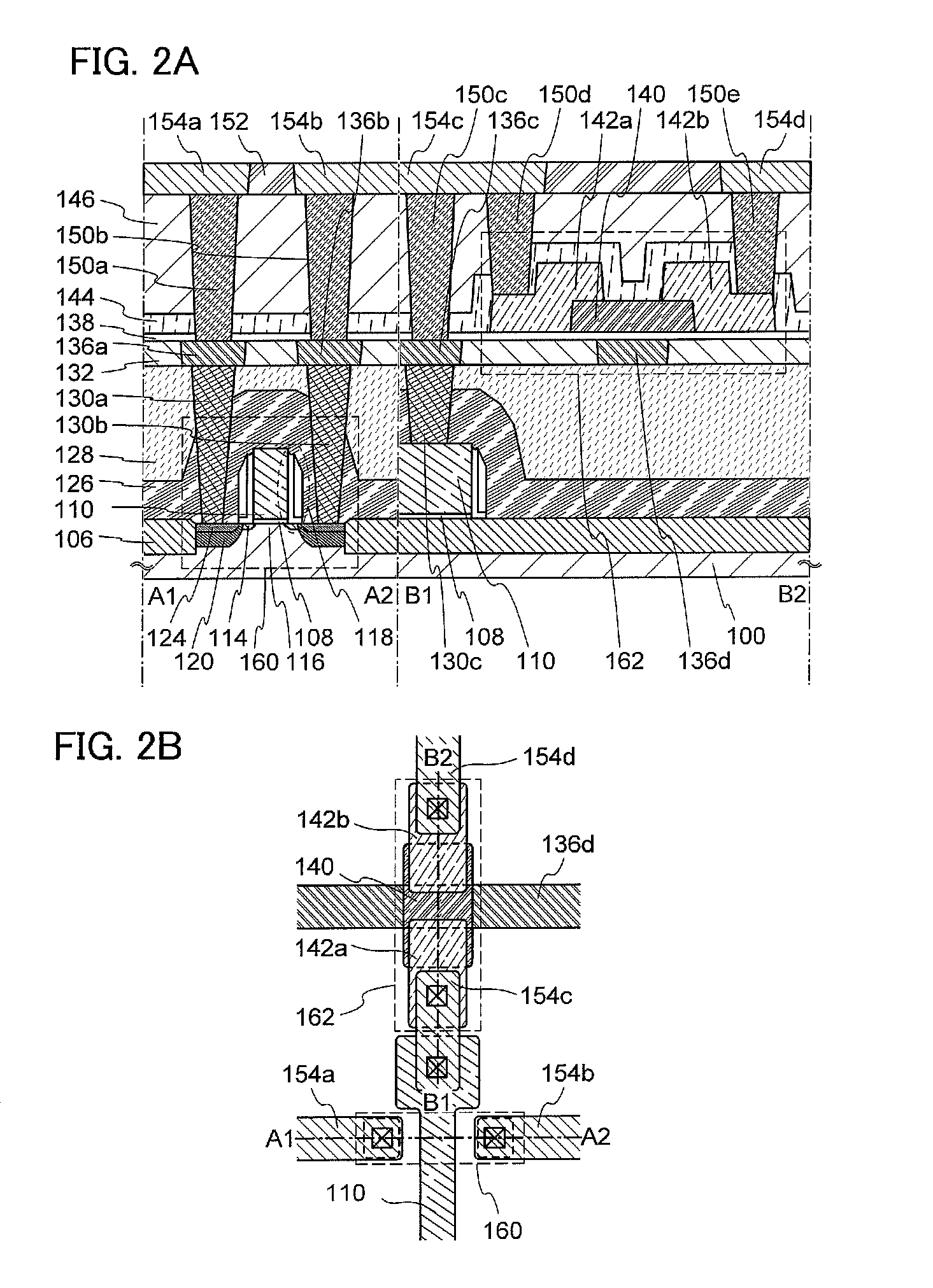
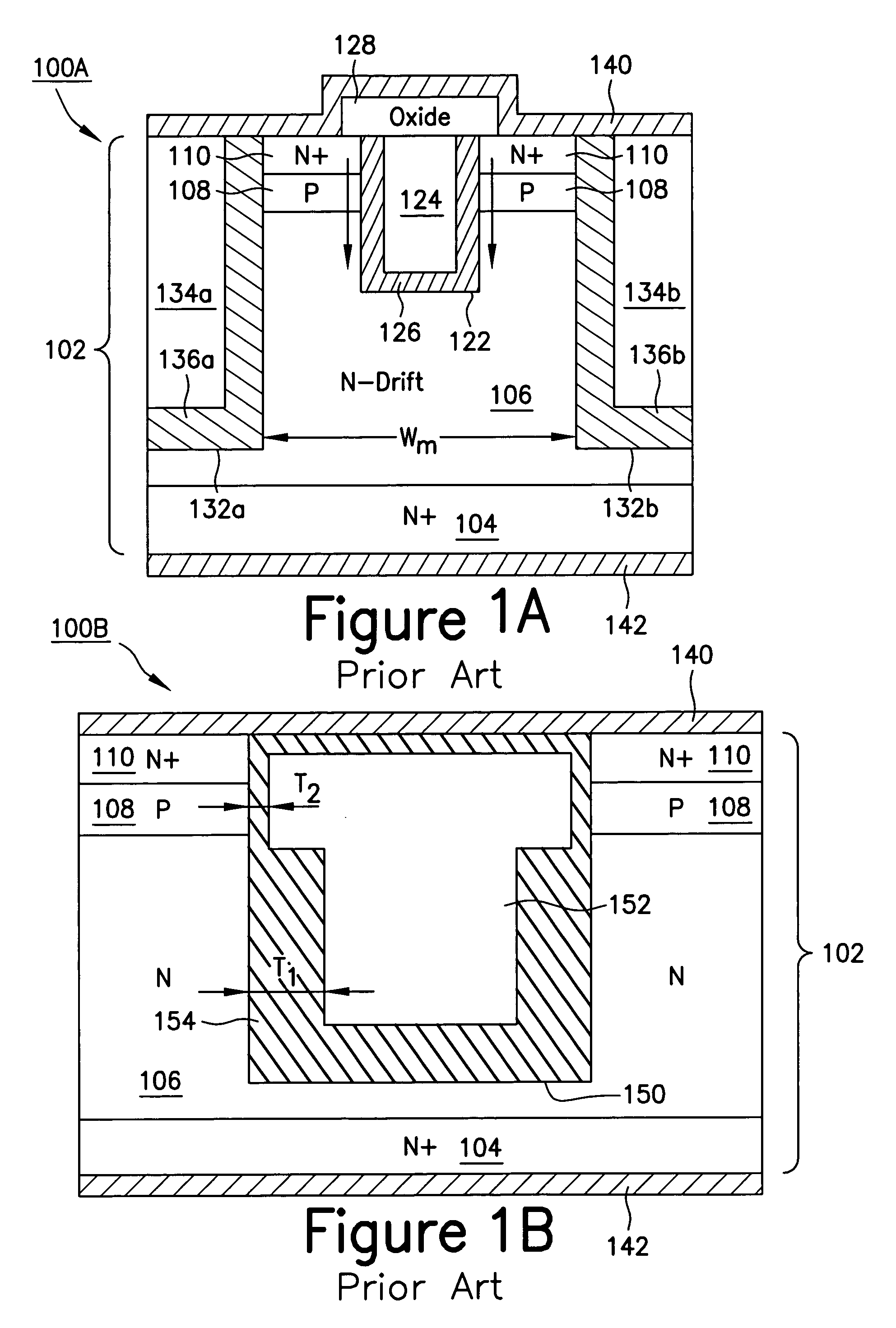
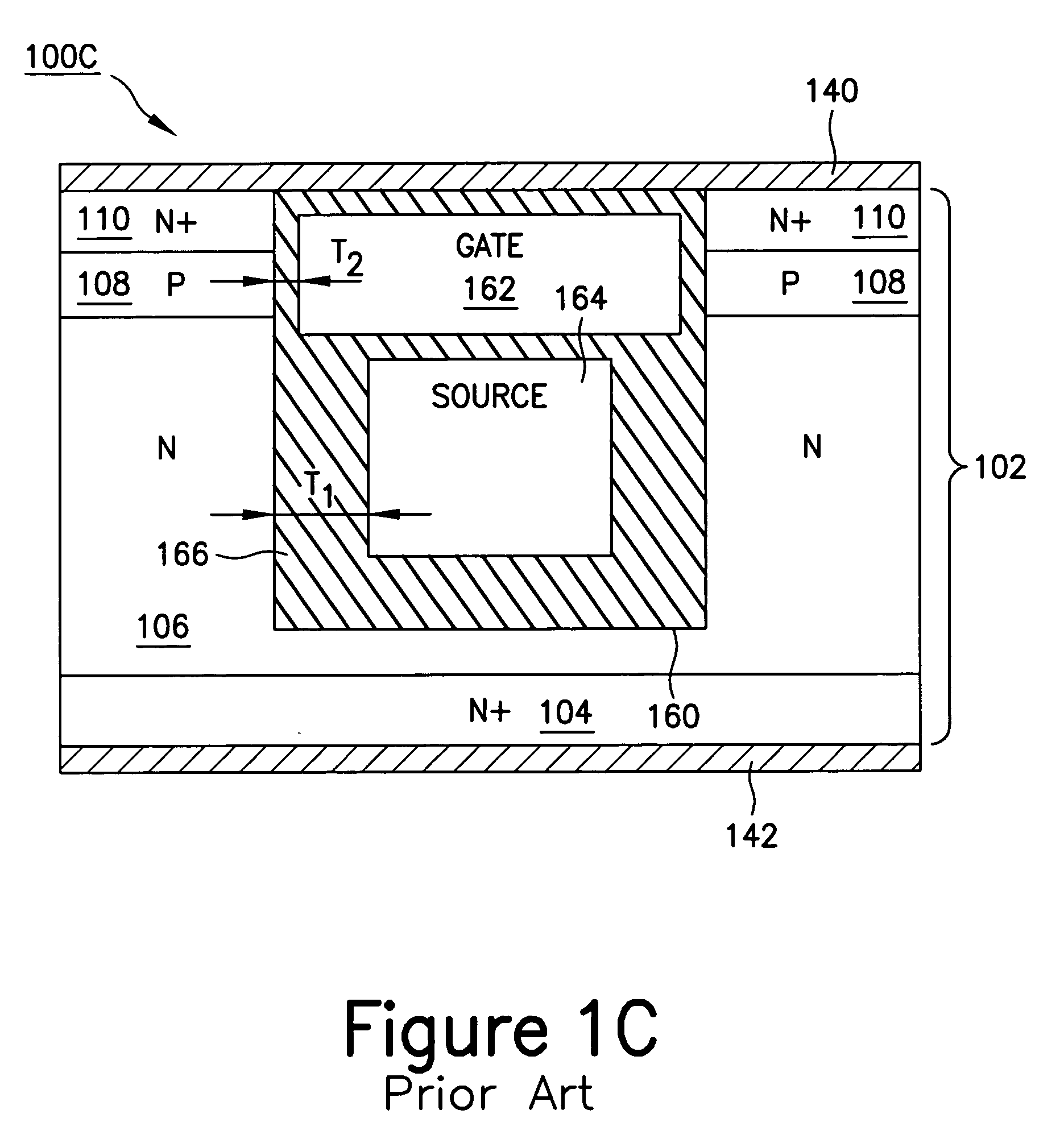
Structures and Methods for Improving Trench-Shielded Semiconductor Devices and Schottky Barrier Rectifier Devices
ActiveUS20100207205A1Improve breakdown voltageBreakdown voltage of deviceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPower semiconductor deviceSchottky barrier
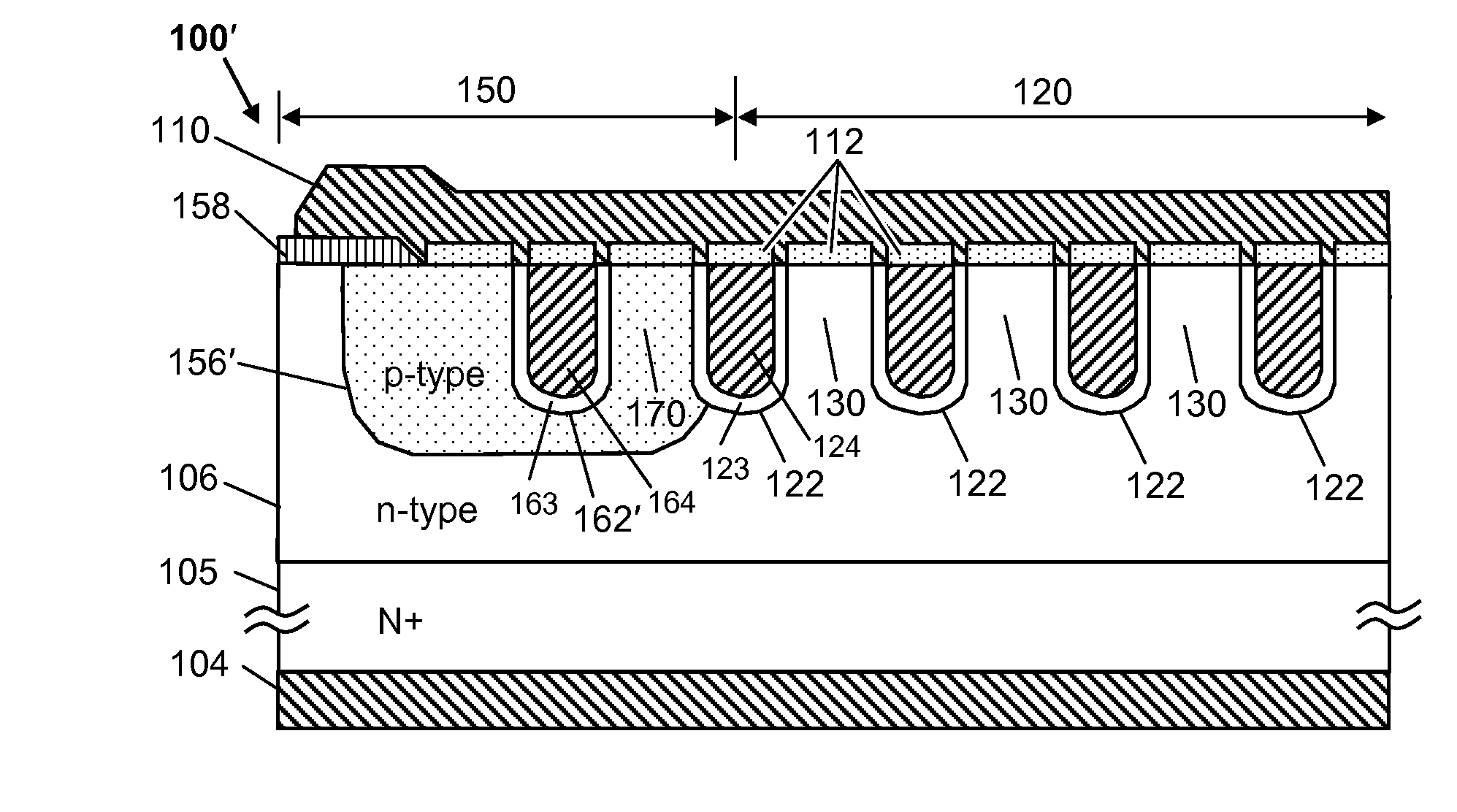
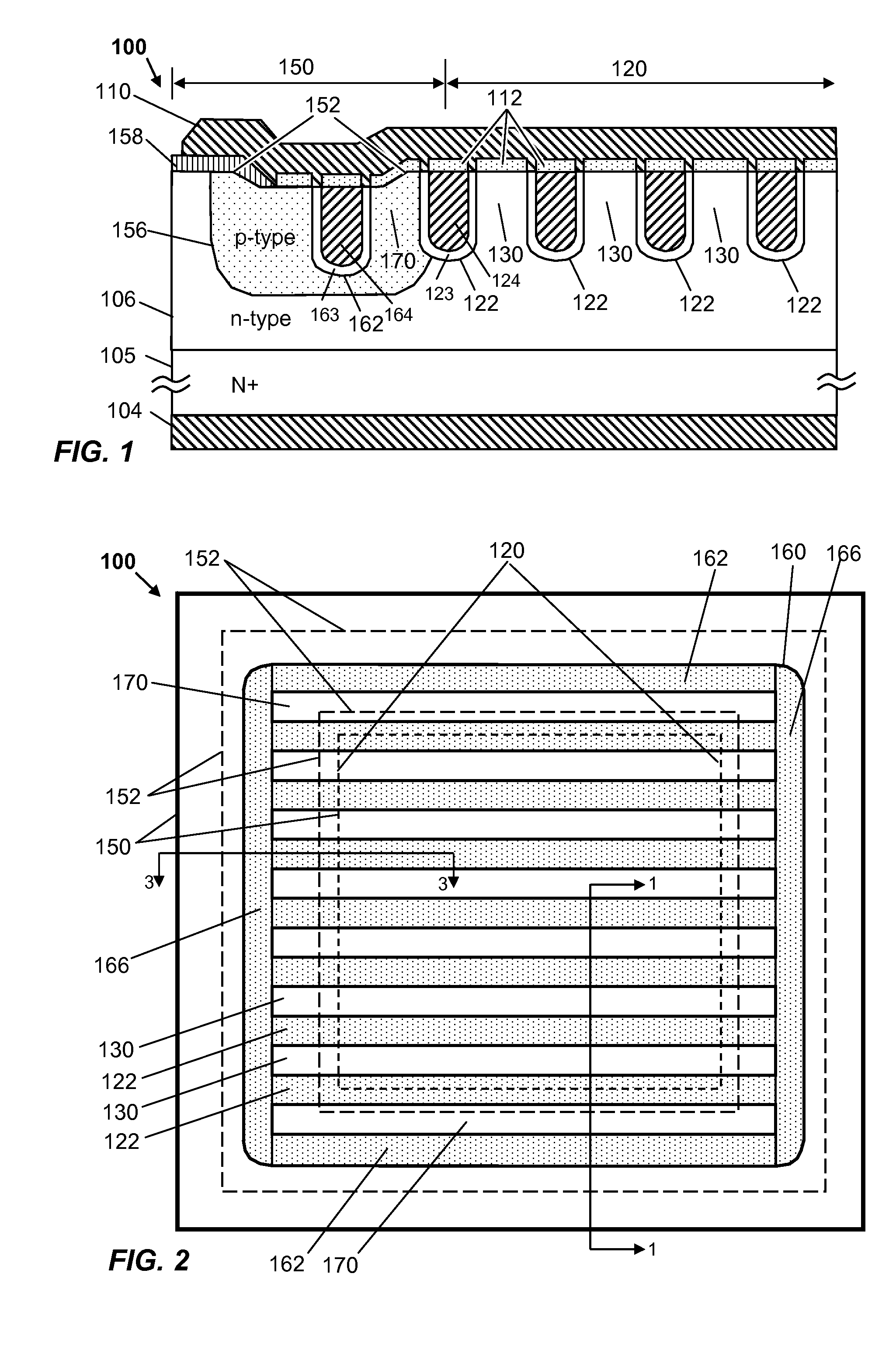
Various structures and methods for improving the performance of trench-shielded power semiconductor devices and the like are described.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20110128777A1Long storageReduce power consumptionSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesPower semiconductor deviceSemiconductor materials
The semiconductor device includes a first wiring; a second wiring; a third wiring; a fourth wiring; a first transistor having a first gate electrode, a first source electrode, and a first drain electrode; and a second transistor having a second gate electrode, a second source electrode, and a second drain electrode. The first transistor is formed on or in a substrate including a semiconductor material. The second transistor includes an oxide semiconductor layer.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device and method for fabricating the same
A method for fabricating semiconductor device is disclosed. The method includes the steps of: providing a substrate having a gate structure thereon; and forming a first epitaxial layer, a second epitaxial layer, and a silicide layer in the substrate adjacent to the gate structure. Preferably, the first epitaxial layer, the second epitaxial layer, and the silicide layer comprise SiGeSn.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
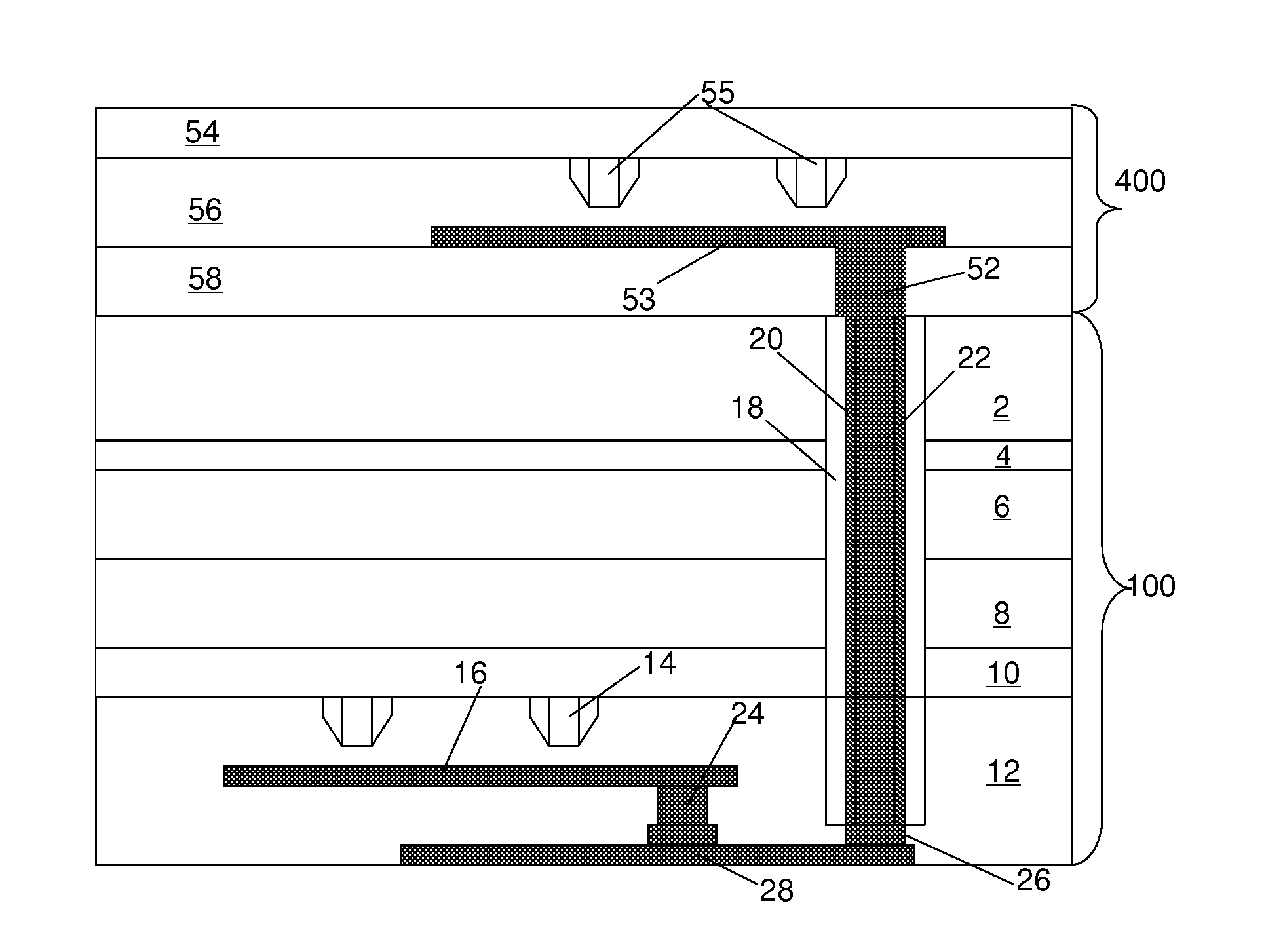
Power semiconductor devices and methods of manufacture
InactiveUS20060214221A1Improved voltage performanceFast switching speedTransistorEfficient power electronics conversionEngineeringHigh pressure
Various embodiments for improved power devices as well as their methods of manufacture, packaging and circuitry incorporating the same for use in a wide variety of power electronic applications are disclosed. One aspect of the invention combines a number of charge balancing techniques and other techniques for reducing parasitic capacitance to arrive at different embodiments for power devices with improved voltage performance, higher switching speed, and lower on-resistance. Another aspect of the invention provides improved termination structures for low, medium and high voltage devices. Improved methods of fabrication for power devices are provided according to other aspects of the invention. Improvements to specific processing steps, such as formation of trenches, formation of dielectric layers inside trenches, formation of mesa structures and processes for reducing substrate thickness, among others, are presented. According to another aspect of the invention, charge balanced power devices incorporate temperature and current sensing elements such as diodes on the same die. Other aspects of the invention improve equivalent series resistance (ESR) for power devices, incorporate additional circuitry on the same chip as the power device and provide improvements to the packaging of charge balanced power devices.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
3D integrated circuit structure, semiconductor device and method of manufacturing same
ActiveUS20110227158A1Improve performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMOSFETPower semiconductor device
The present invention discloses a semiconductor device. In one embodiment, the semiconductor device comprises a substrate, a diffusion stop layer formed on the substrate, an SOI layer formed on the diffusion stop layer, an MOSFET transistor formed on the SOI layer, and a TSV formed in a manner of penetrating through the substrate, the diffusion stop layer, the SOI layer, and a layer where the MOSFET transistor is located; and an interconnect structure connecting the MOSFET transistor and the TSV.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
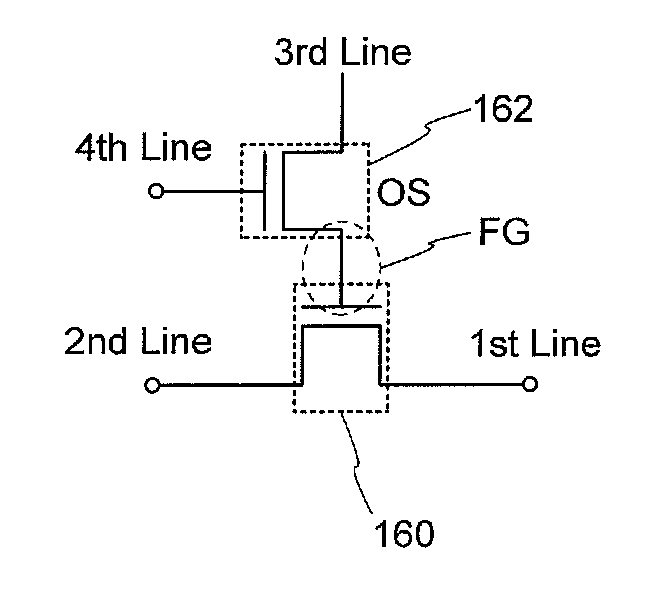
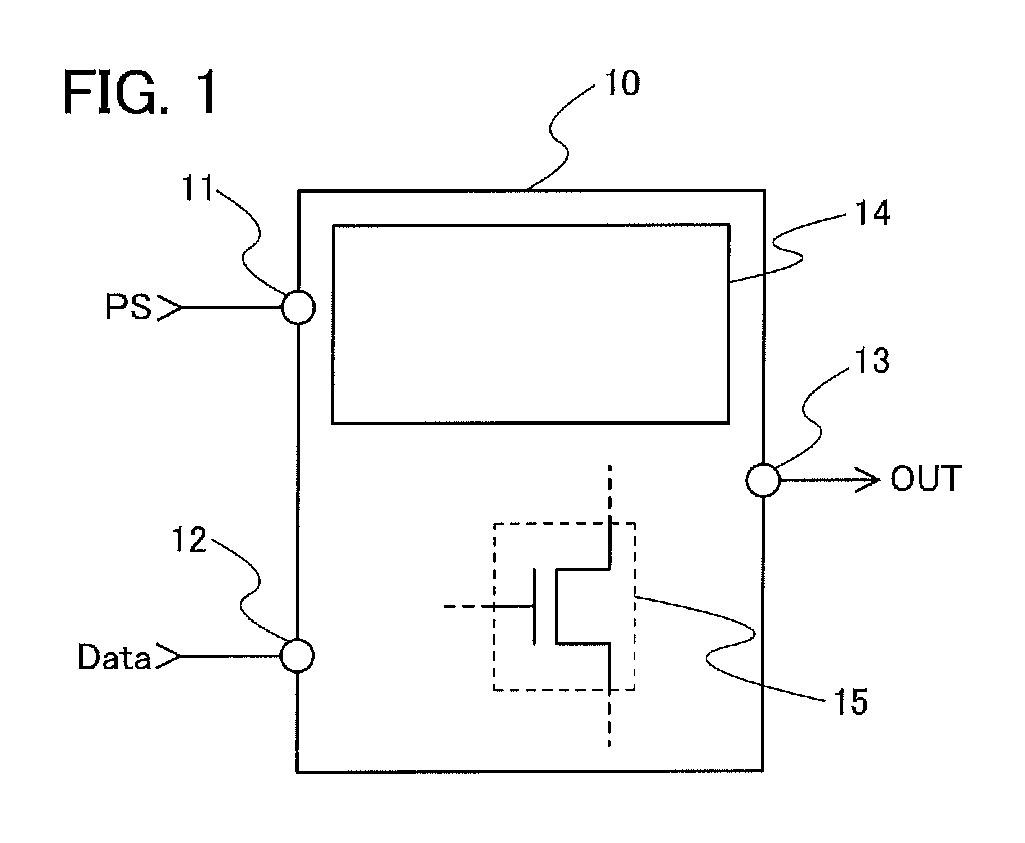
Nonvolatile latch circuit and logic circuit, and semiconductor device using the same
ActiveUS20110121878A1Wide operating temperature rangeGuaranteed uptimeTransistorSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceSemiconductor materials
To provide a novel nonvolatile latch circuit and a semiconductor device using the nonvolatile latch circuit, a nonvolatile latch circuit includes a latch portion having a loop structure where an output of a first element is electrically connected to an input of a second element, and an output of the second element is electrically connected to an input of the first element; and a data holding portion for holding data of the latch portion. In the data holding portion, a transistor using an oxide semiconductor as a semiconductor material for forming a channel formation region is used as a switching element. In addition, an inverter electrically connected to a source electrode or a drain electrode of the transistor is included. With the transistor, data held in the latch portion can be written into a gate capacitor of the inverter or a capacitor which is separately provided.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method for manufacturing semiconductor device, and semiconductor device
InactiveUS20120241919A1High precision transmissionSmall misalignmentSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPower semiconductor deviceSingle crystal
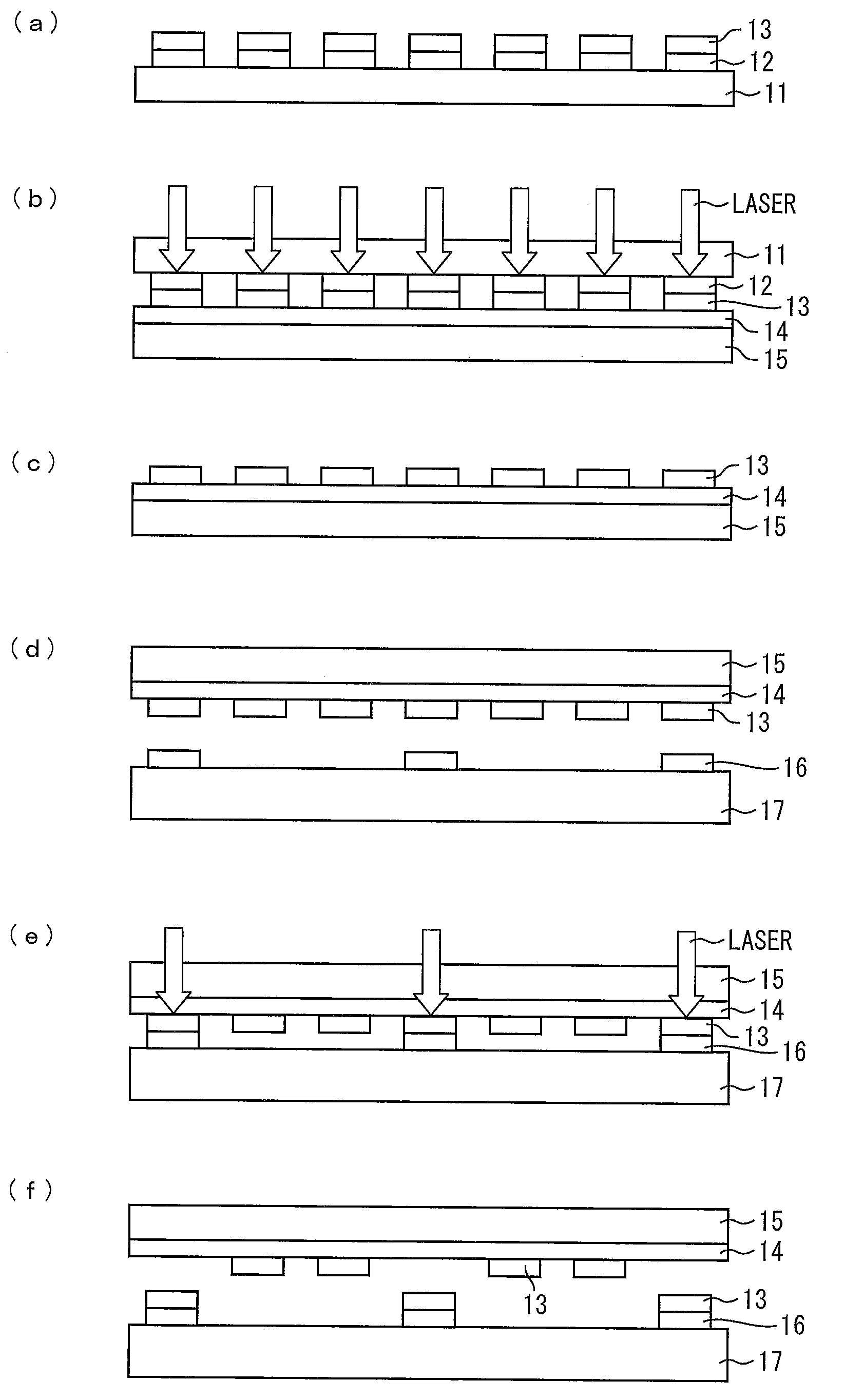
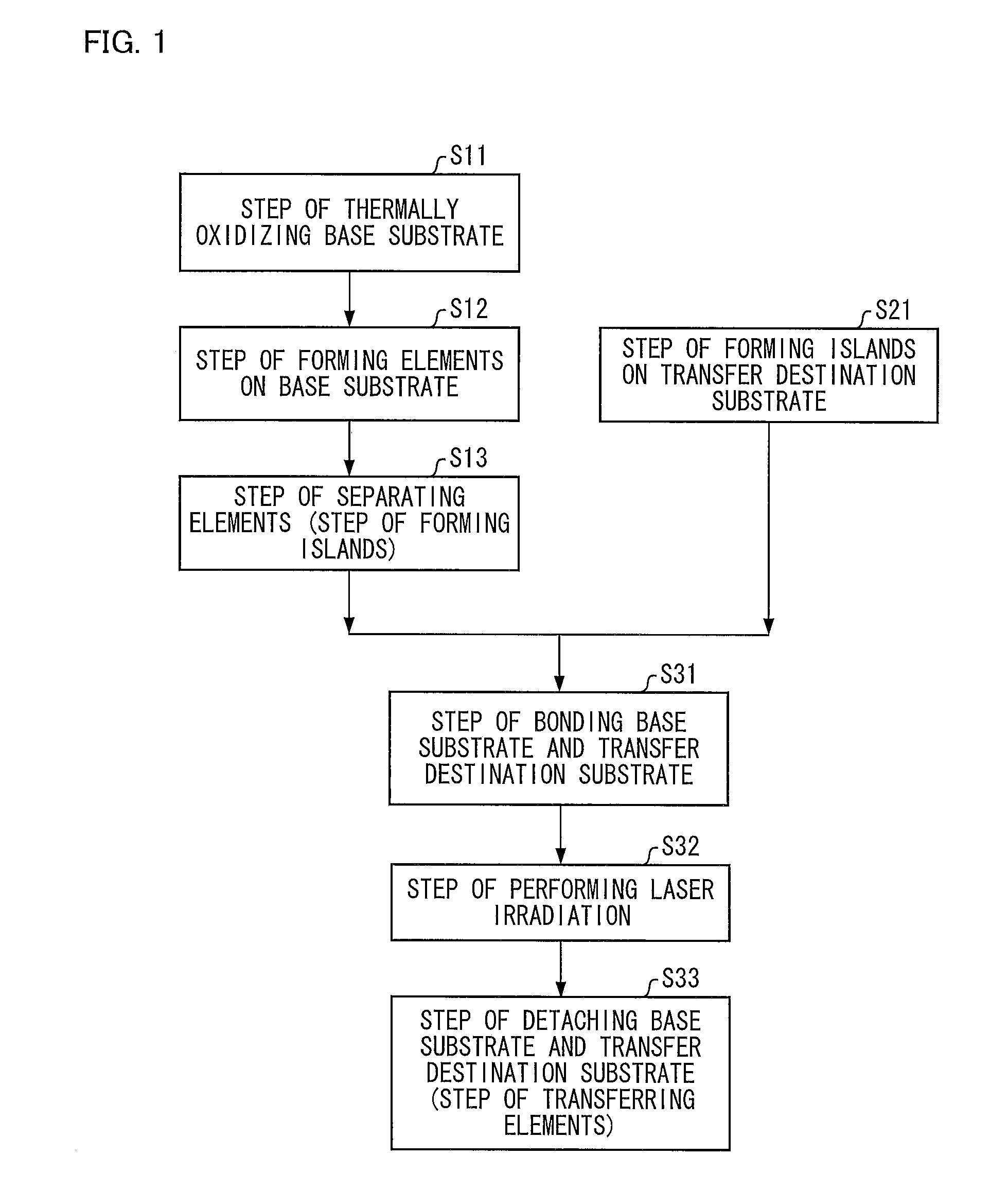
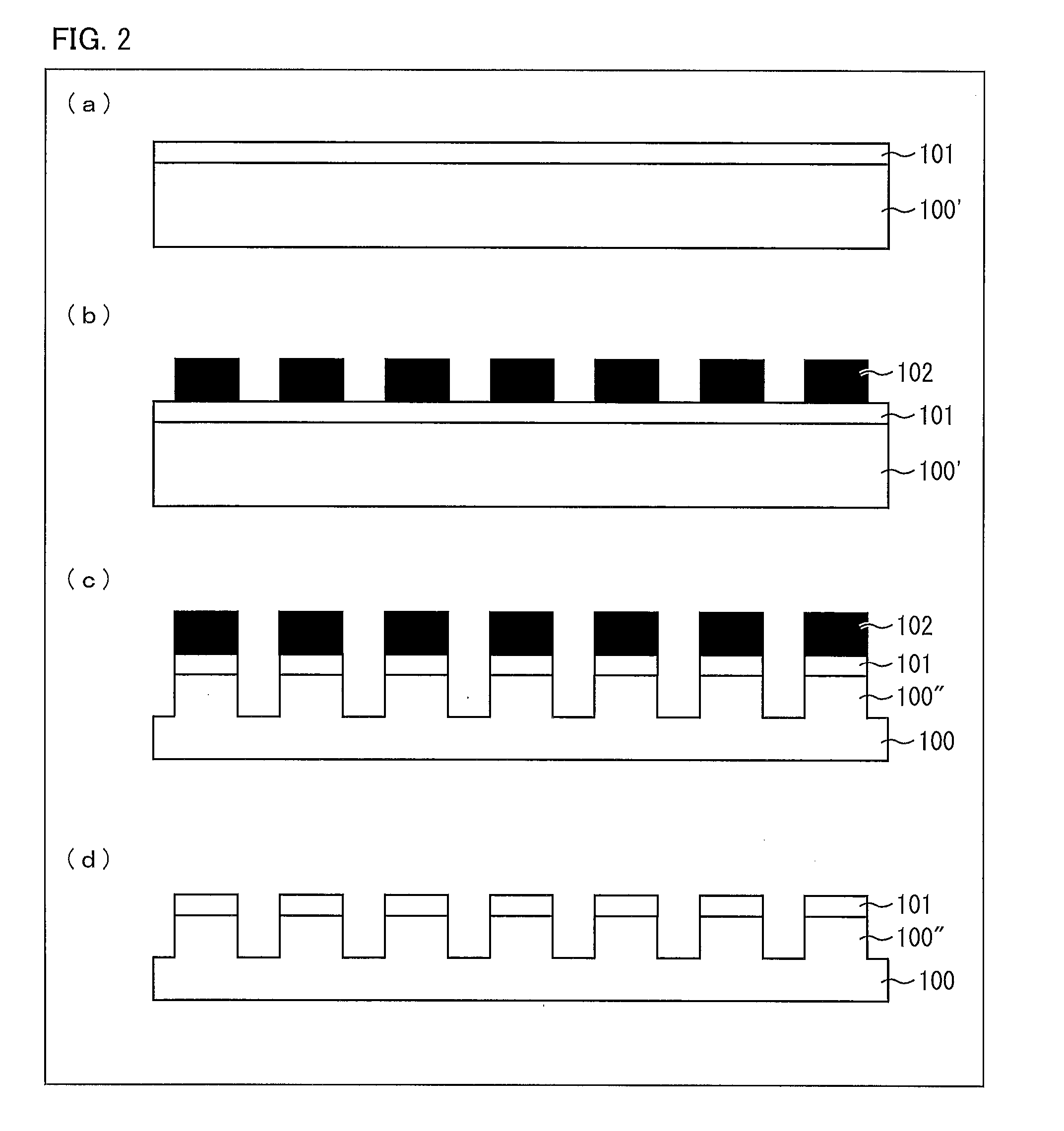
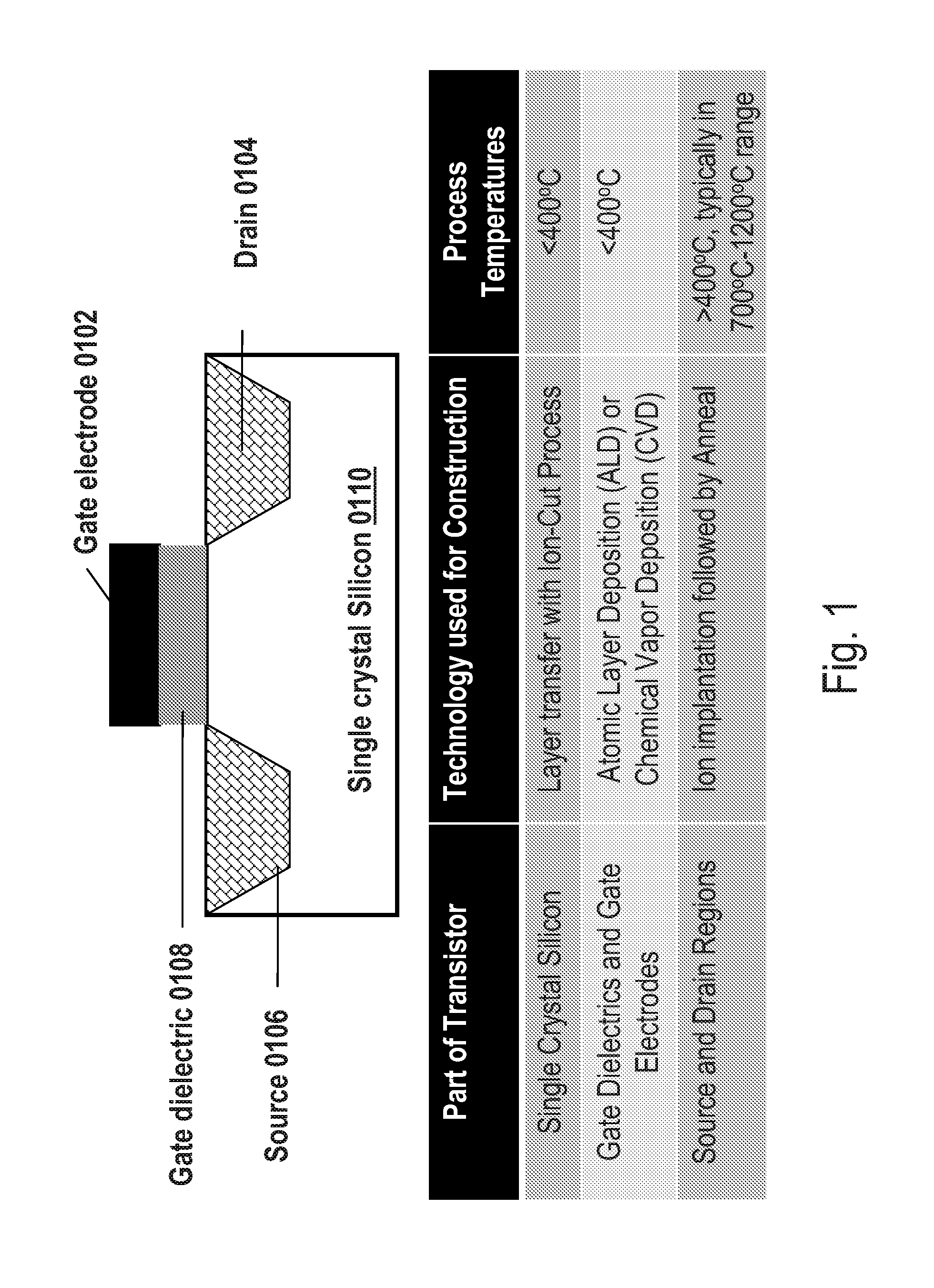
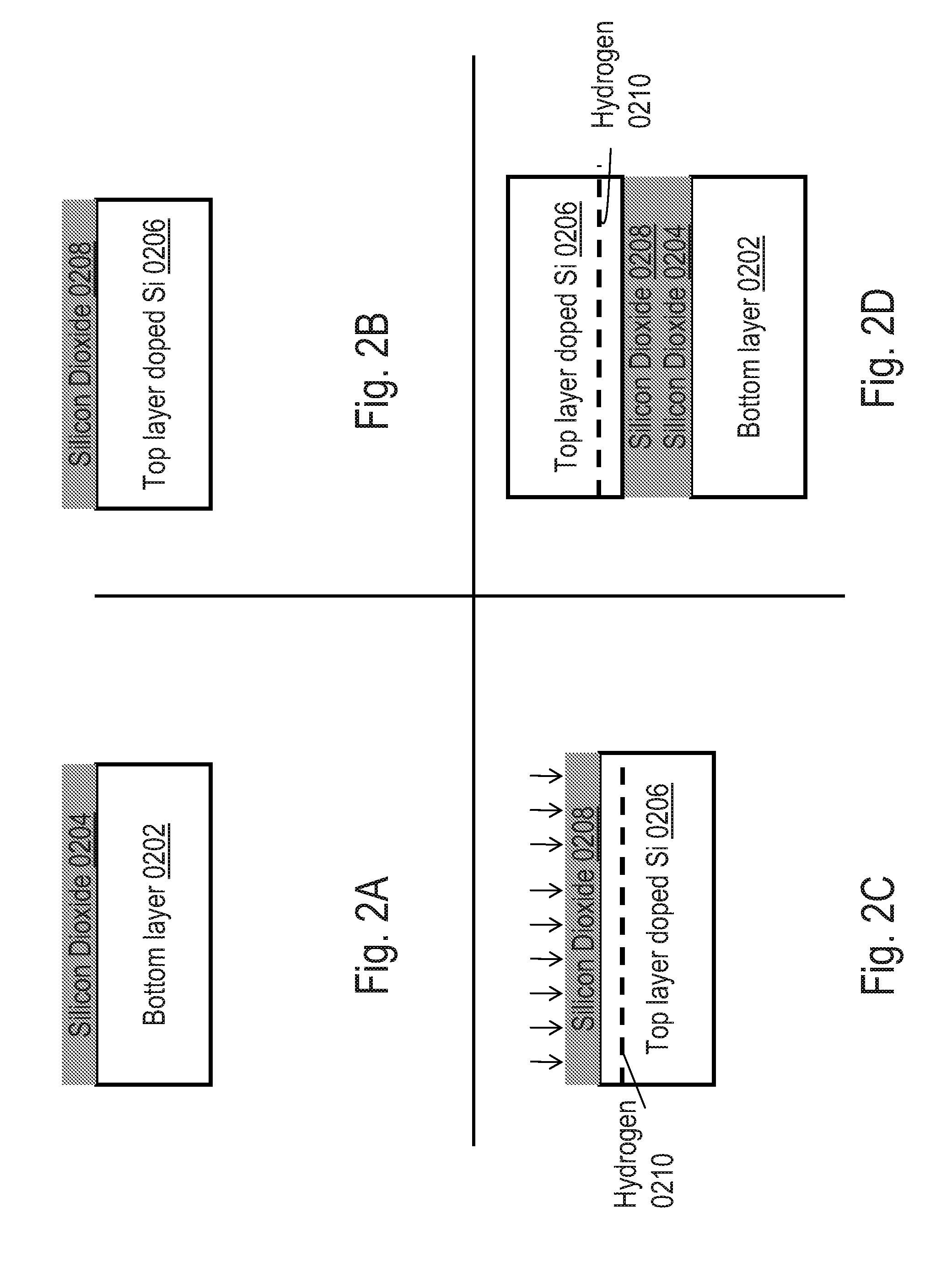
The present invention provides a method for selectively transferring elements such as monocrystalline Si thin films or elements made of monocrystalline Si from a base substrate (100) onto an insulating substrate without the use of an intermediate substrate. The base substrate (first substrate) (100) in which the elements are formed is selectively irradiated with a laser having a multiphoton absorption wavelength. Thus, elements to be transferred out of the elements and corresponding thin films on the base substrate (100) are transferred onto a transfer destination substrate (second substrate) (200).
Owner:SHARP KK
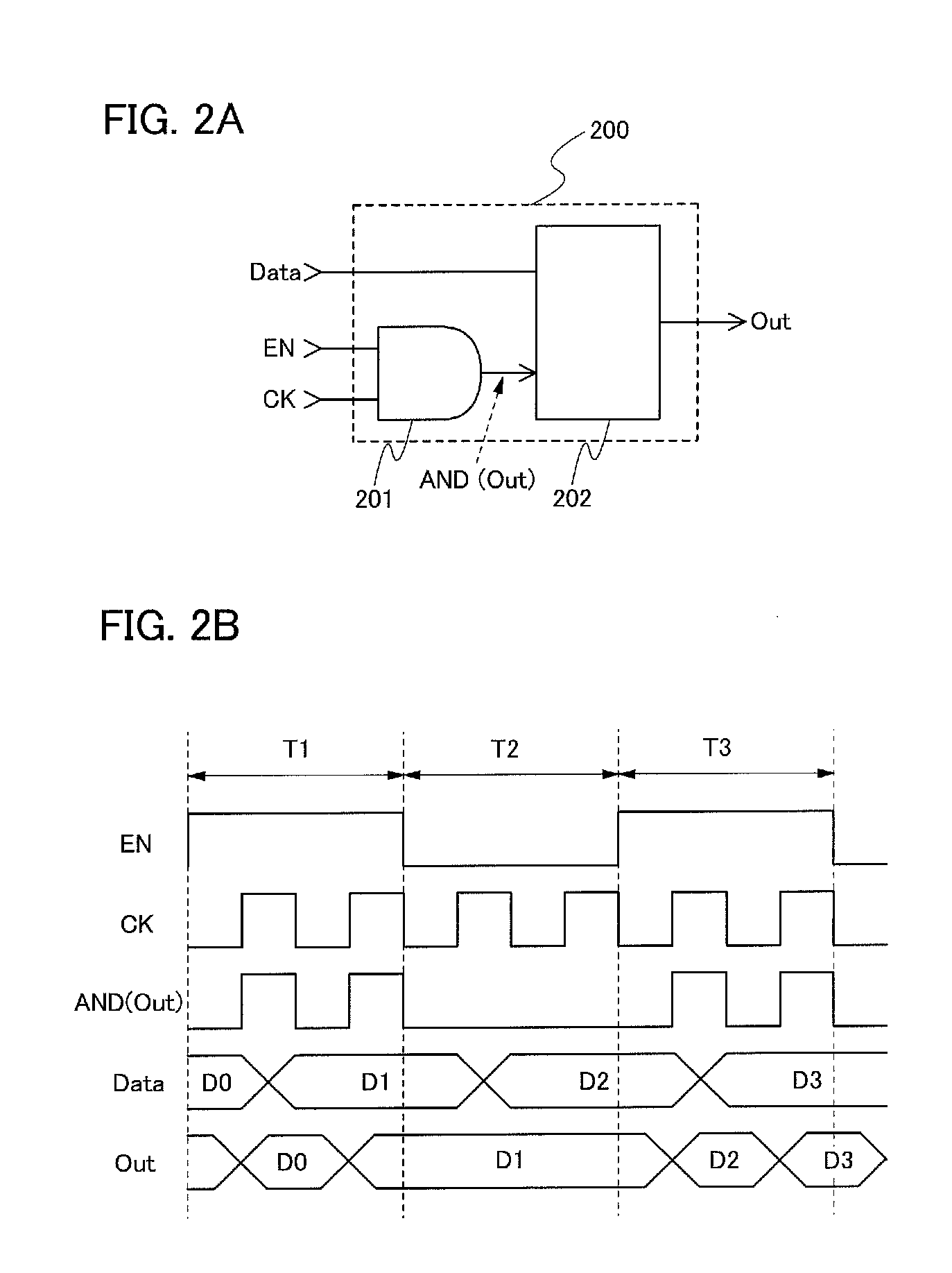
Logic circuit and semiconductor device
ActiveUS8207756B2Reduce dynamic power consumptionLeakage of highTransistorPower reduction by control/clock signalHydrogen concentrationPower semiconductor device
In a logic circuit where clock gating is performed, the standby power is reduced or malfunction is suppressed. The logic circuit includes a transistor which is in an off state where a potential difference exists between a source terminal and a drain terminal over a period during which a clock signal is not supplied. A channel formation region of the transistor is formed using an oxide semiconductor in which the hydrogen concentration is reduced. Specifically, the hydrogen concentration of the oxide semiconductor is 5×1019 (atoms / cm3) or lower. Thus, leakage current of the transistor can be reduced. As a result, in the logic circuit, reduction in standby power and suppression of malfunction can be achieved.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
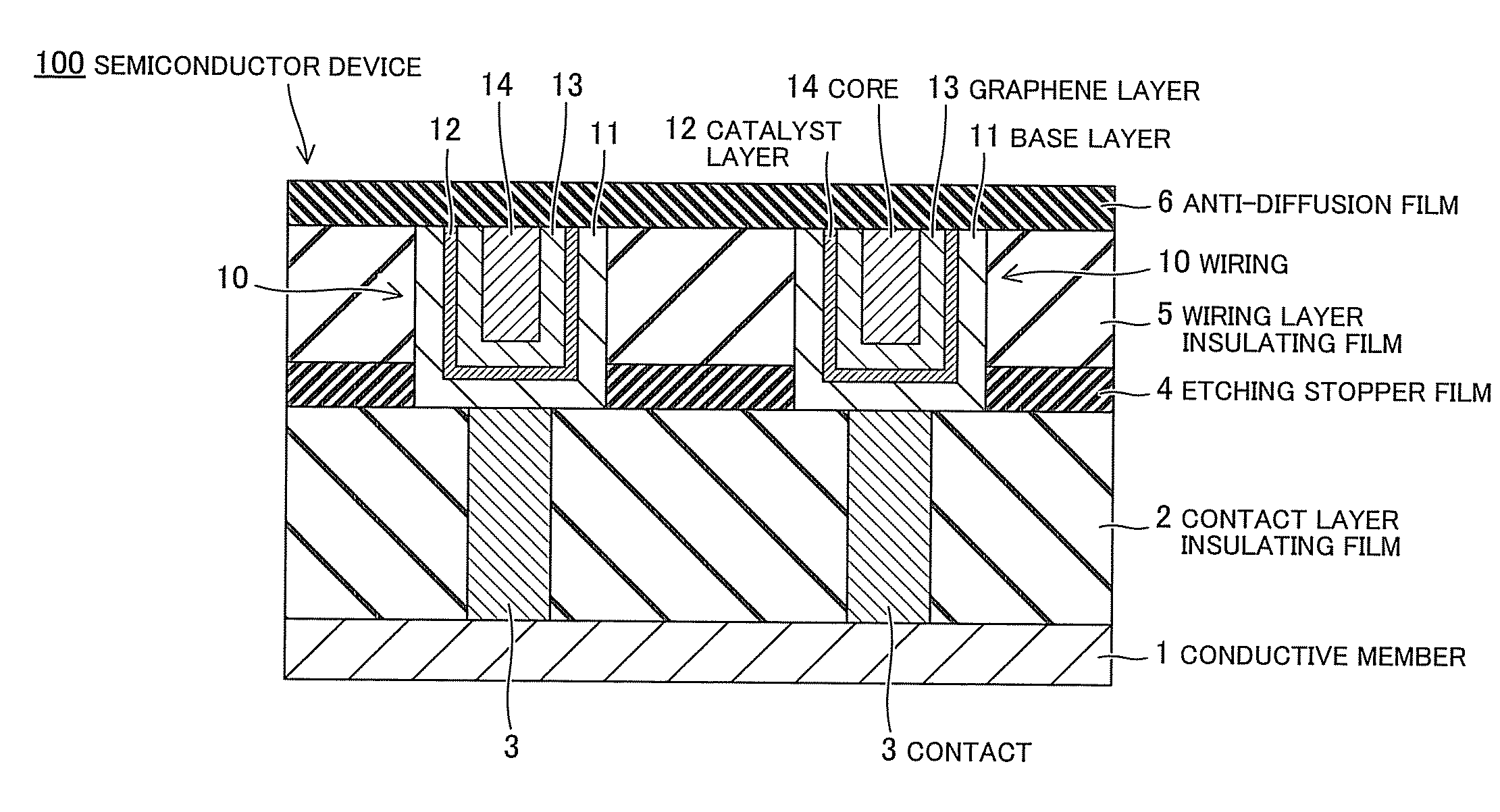
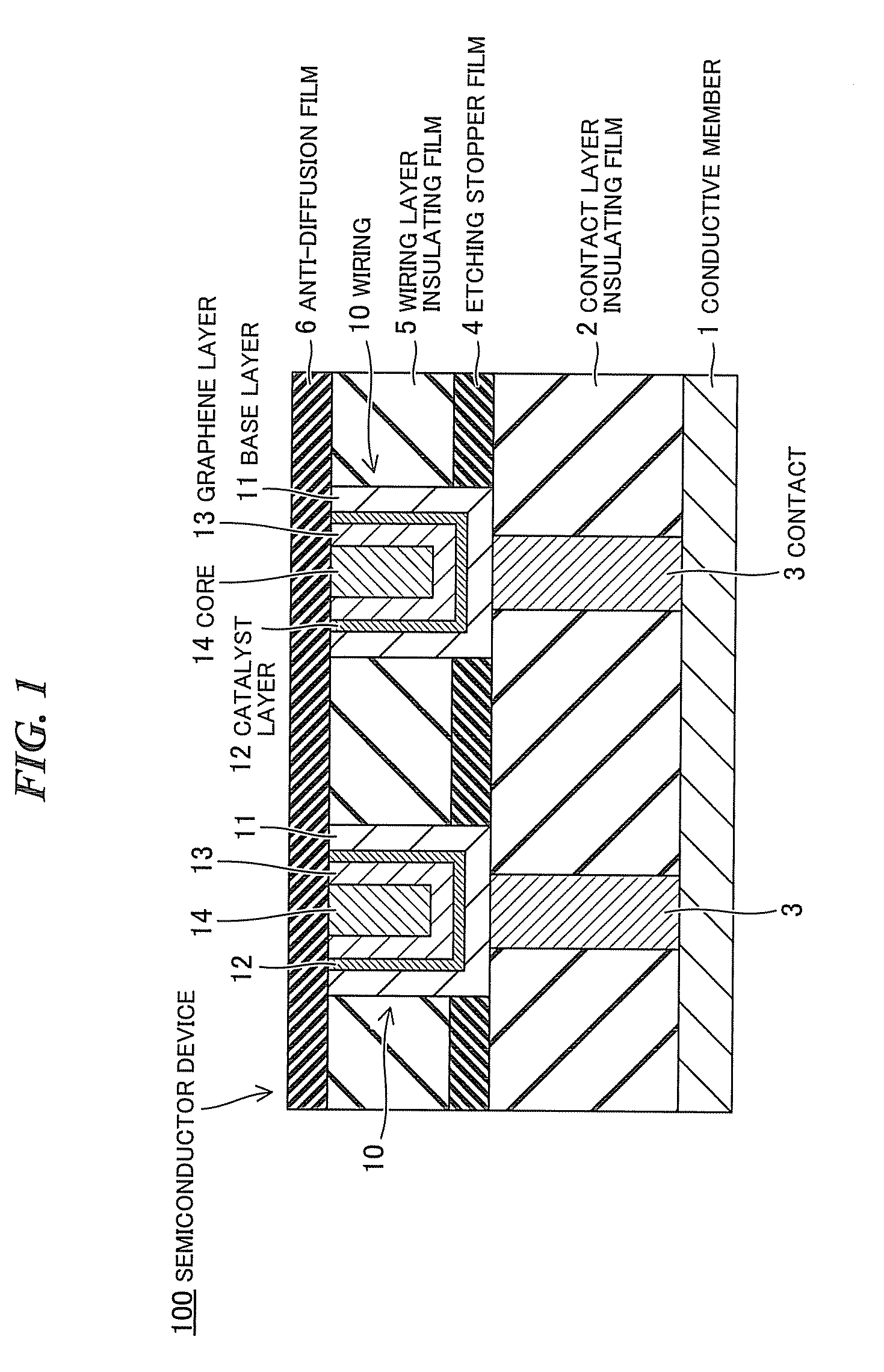
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20110006425A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceGraphene
A semiconductor device according to one embodiment includes: a semiconductor substrate; an insulating film provided on the semiconductor substrate and containing a wiring trench; a first catalyst layer provided directly or via another member on side and bottom surfaces of the wiring trench; and a first graphene layer provided in the wiring trench so as to be along the side and bottom surface of the wiring trench, the first graphene layer being provided on the first catalyst layer so as to be in contact with the first catalyst layer.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
ActiveUS20130009209A1Improve performanceReduce power consumptionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPower semiconductor deviceEngineering
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
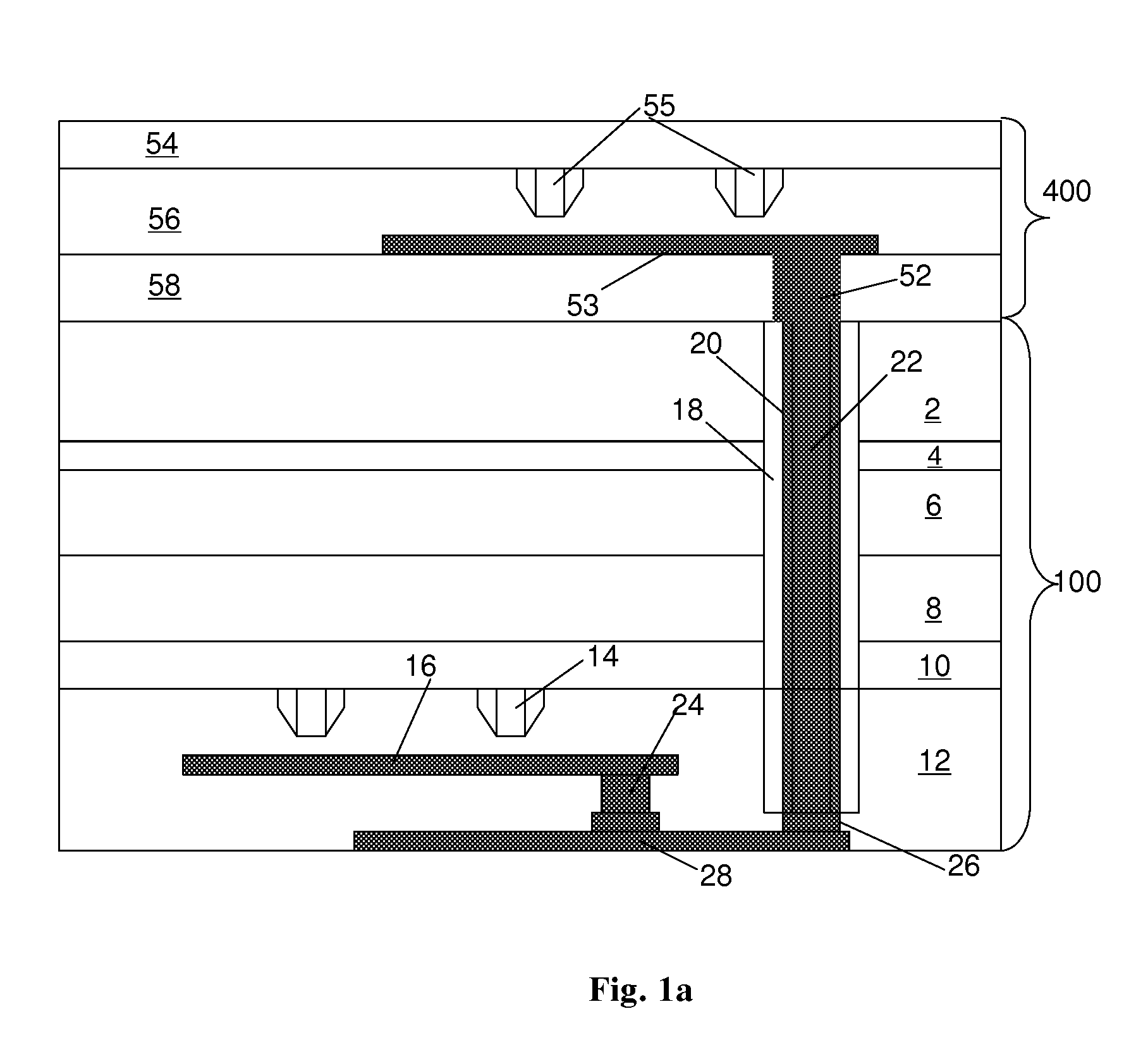
Power semiconductor devices and methods of manufacture
ActiveUS20060214222A1Improved voltage performanceFast switching speedTransistorEfficient power electronics conversionEngineeringHigh pressure
Various embodiments for improved power devices as well as their methods of manufacture, packaging and circuitry incorporating the same for use in a wide variety of power electronic applications are disclosed. One aspect of the invention combines a number of charge balancing techniques and other techniques for reducing parasitic capacitance to arrive at different embodiments for power devices with improved voltage performance, higher switching speed, and lower on-resistance. Another aspect of the invention provides improved termination structures for low, medium and high voltage devices. Improved methods of fabrication for power devices are provided according to other aspects of the invention. Improvements to specific processing steps, such as formation of trenches, formation of dielectric layers inside trenches, formation of mesa structures and processes for reducing substrate thickness, among others, are presented. According to another aspect of the invention, charge balanced power devices incorporate temperature and current sensing elements such as diodes on the same die. Other aspects of the invention improve equivalent series resistance (ESR) for power devices, incorporate additional circuitry on the same chip as the power device and provide improvements to the packaging of charge balanced power devices.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Electrostatic chuck and method of manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS20120134065A1Not always easySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMassive gravityPower semiconductor device
An electrostatic chuck device including: a plurality of adsorption areas having an electrode generating electrostatic attractive force; and a control portion controlling the electrostatic attractive force against each of the plurality of the adsorption areas independently of other adsorption areas.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
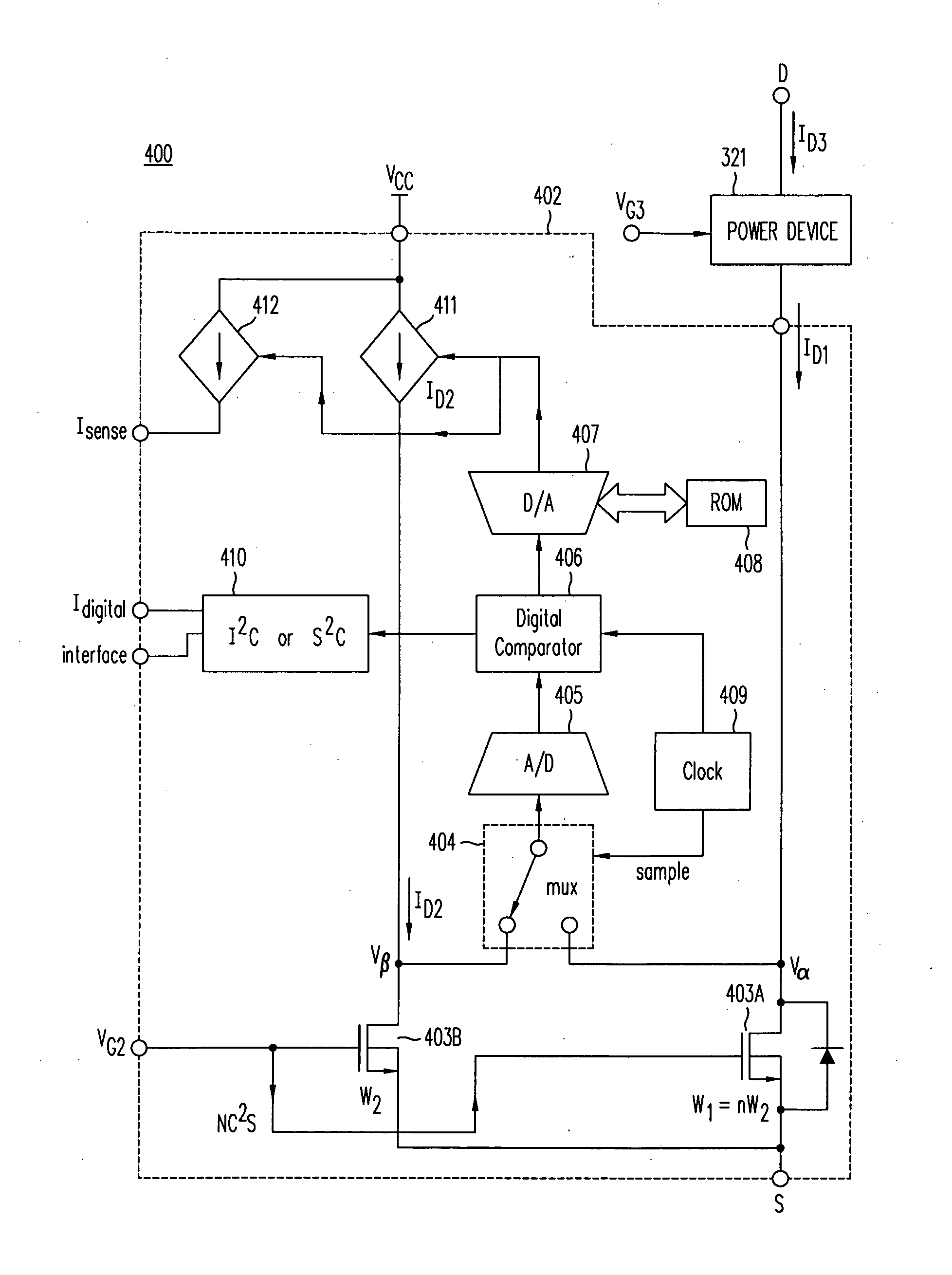
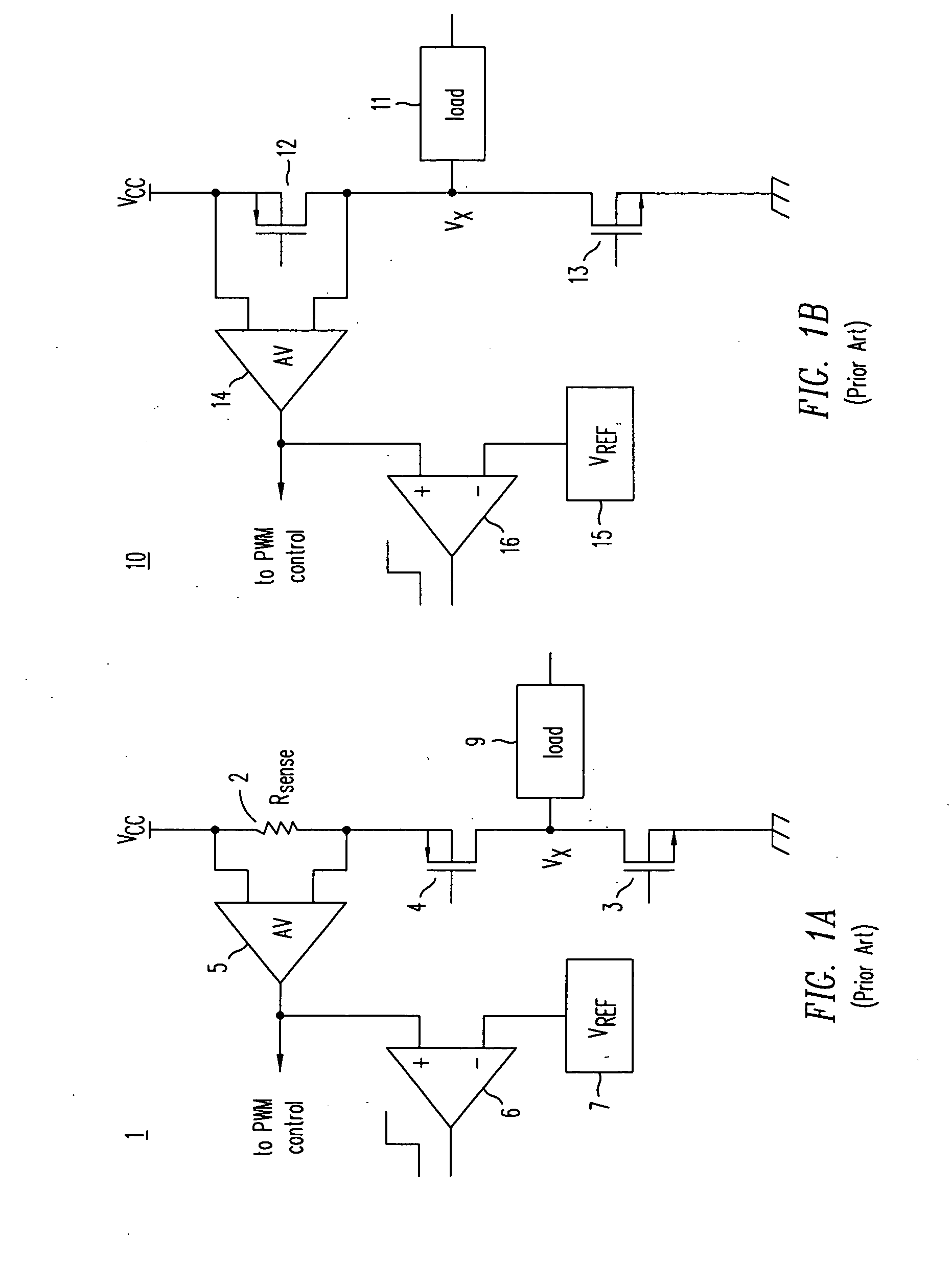
Cascode Current Sensor For Discrete Power Semiconductor Devices
InactiveUS20090039869A1Accurate detectionTransistorElectrical measurement instrument detailsMOSFETCascode
A cascode current sensor includes a main MOSFET and a sense MOSFET. The drain terminal of the main MOSFET is connected to a power device whose current is to be monitored, and the source and gate terminals of the main MOSFET are connected to the source and gate terminals, respectively, of the sense MOSFET. The drain voltages of the main and sense MOSFETs are equalized, in one embodiment by using a variable current source and negative feedback. The gate width of the main MOSFET is typically larger than the gate width of the sense MOSFET. Using the size ratio of the gate widths, the current in the main MOSFET is measured by sensing the magnitude of the current in the sense MOSFET. Inserting the relatively large MOSFET in the power circuit minimizes power loss.
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED
Semiconductor device and structure
ActiveUS20130122672A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPower semiconductor deviceEngineering
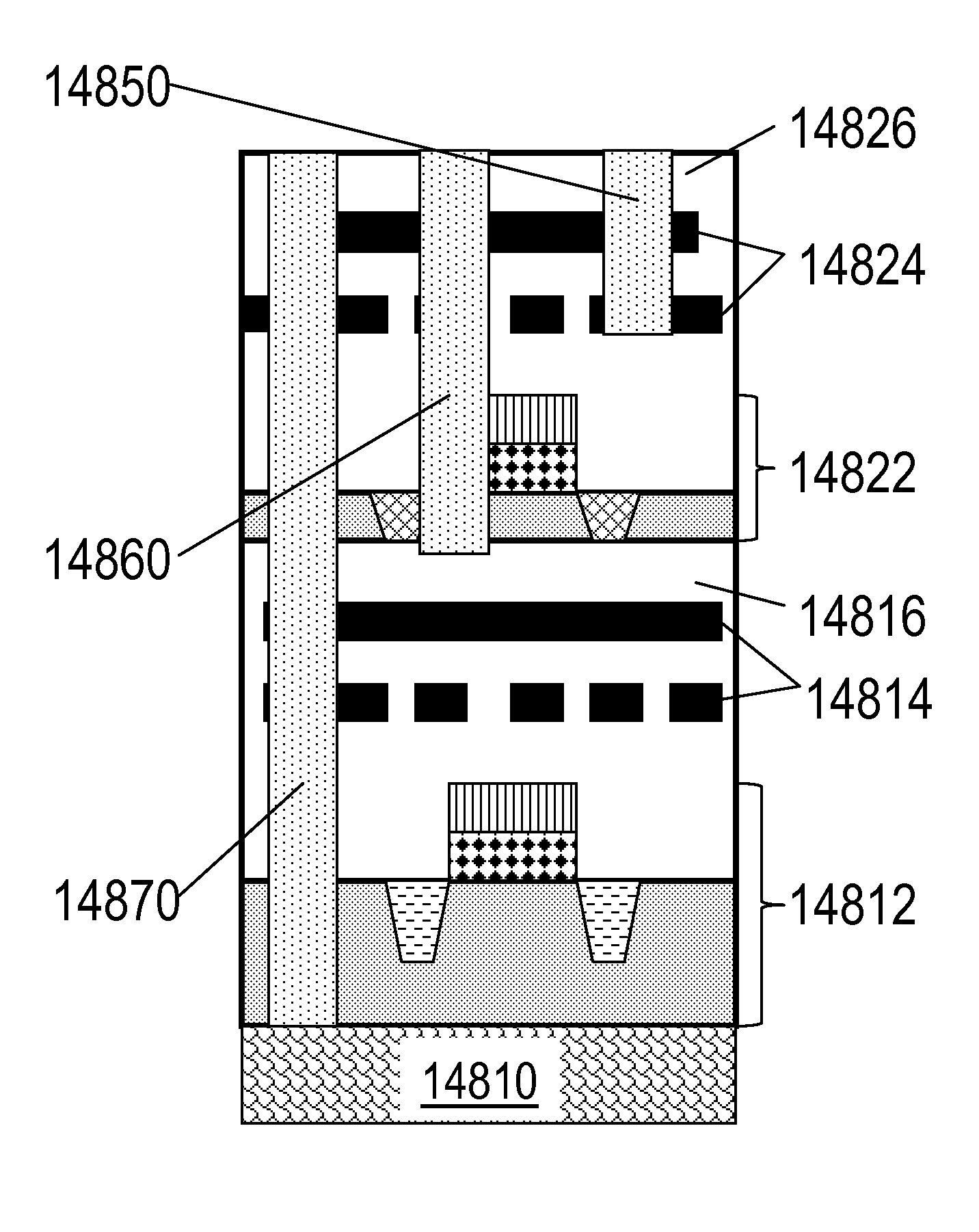
A method for formation of a semiconductor device including a first wafer including a first single crystal layer comprising first transistors and first alignment mark, the method including: implanting to form a doped layer within a second wafer; forming a second mono-crystalline layer on top of the first wafer by transferring at least a portion of the doped layer using layer transfer step, and completing the formation of second transistors on the second mono-crystalline layer including a step of forming a gate dielectric followed by second transistors gate formation step, wherein the second transistors are horizontally oriented.
Owner:MONOLITHIC 3D
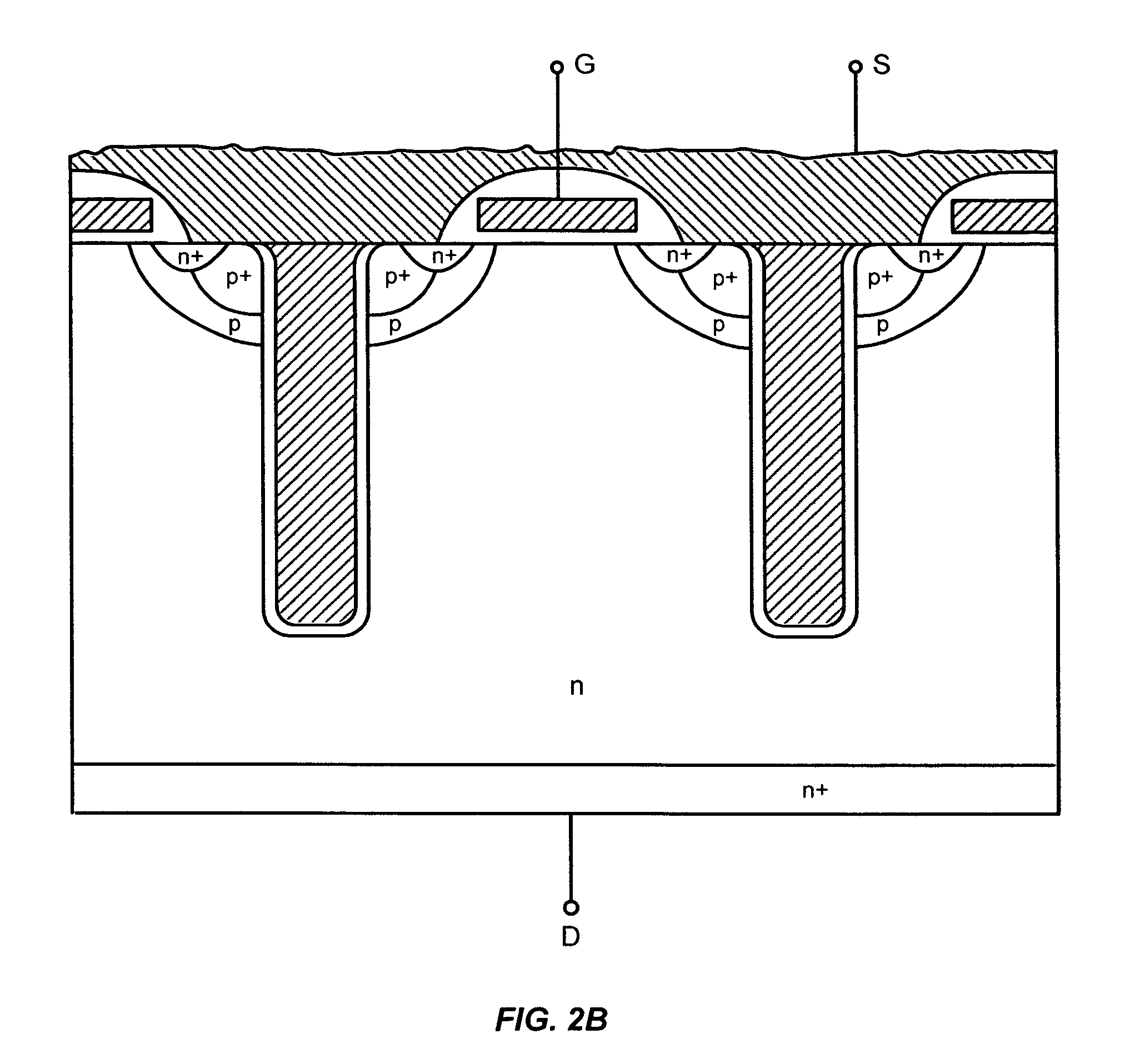
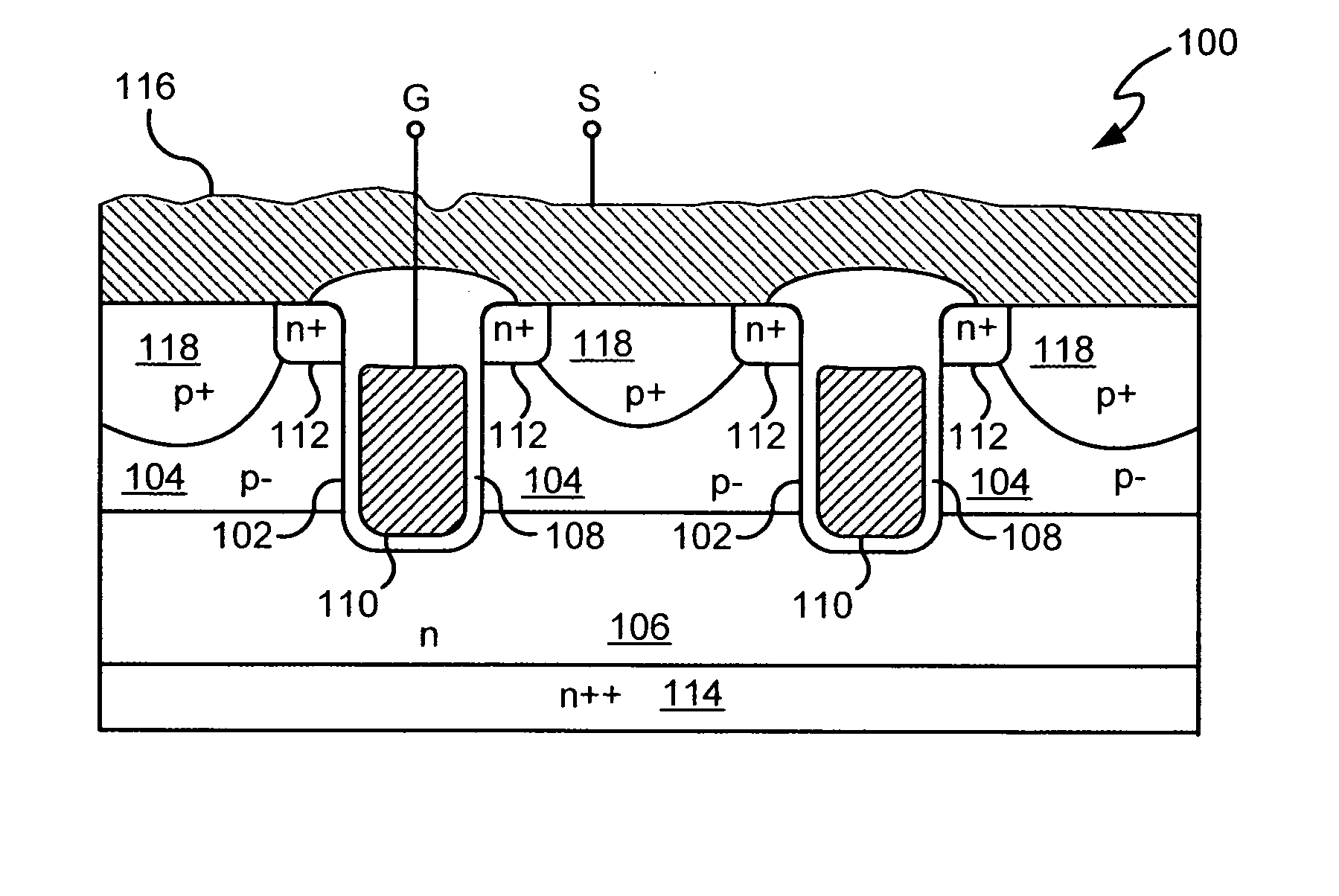
Power devices having trench-based source and gate electrodes
ActiveUS20060060916A1Improve breakdown voltageIncrease the on-resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiodePower semiconductor deviceDevice material
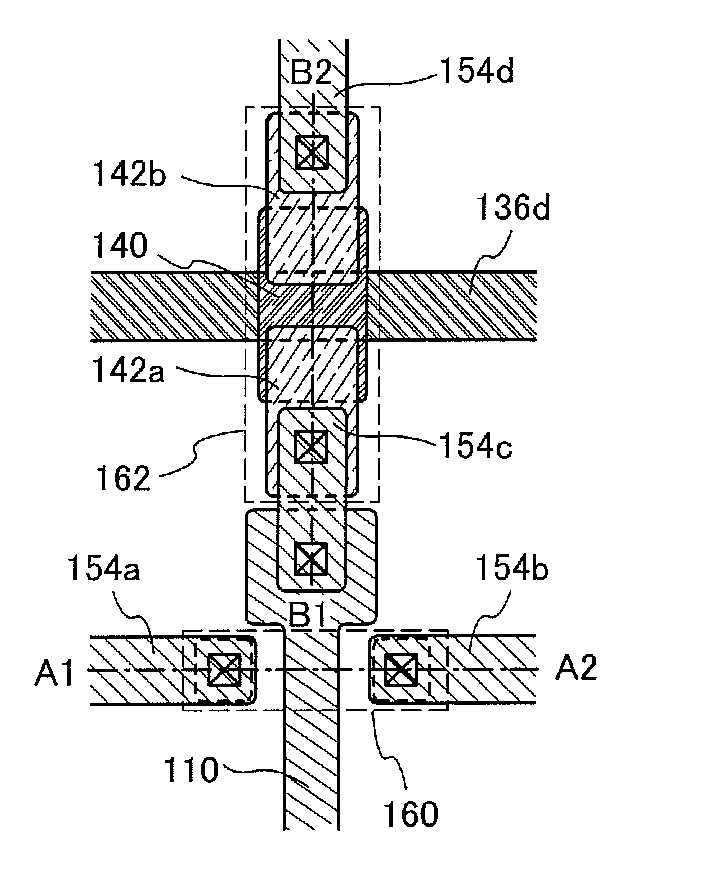
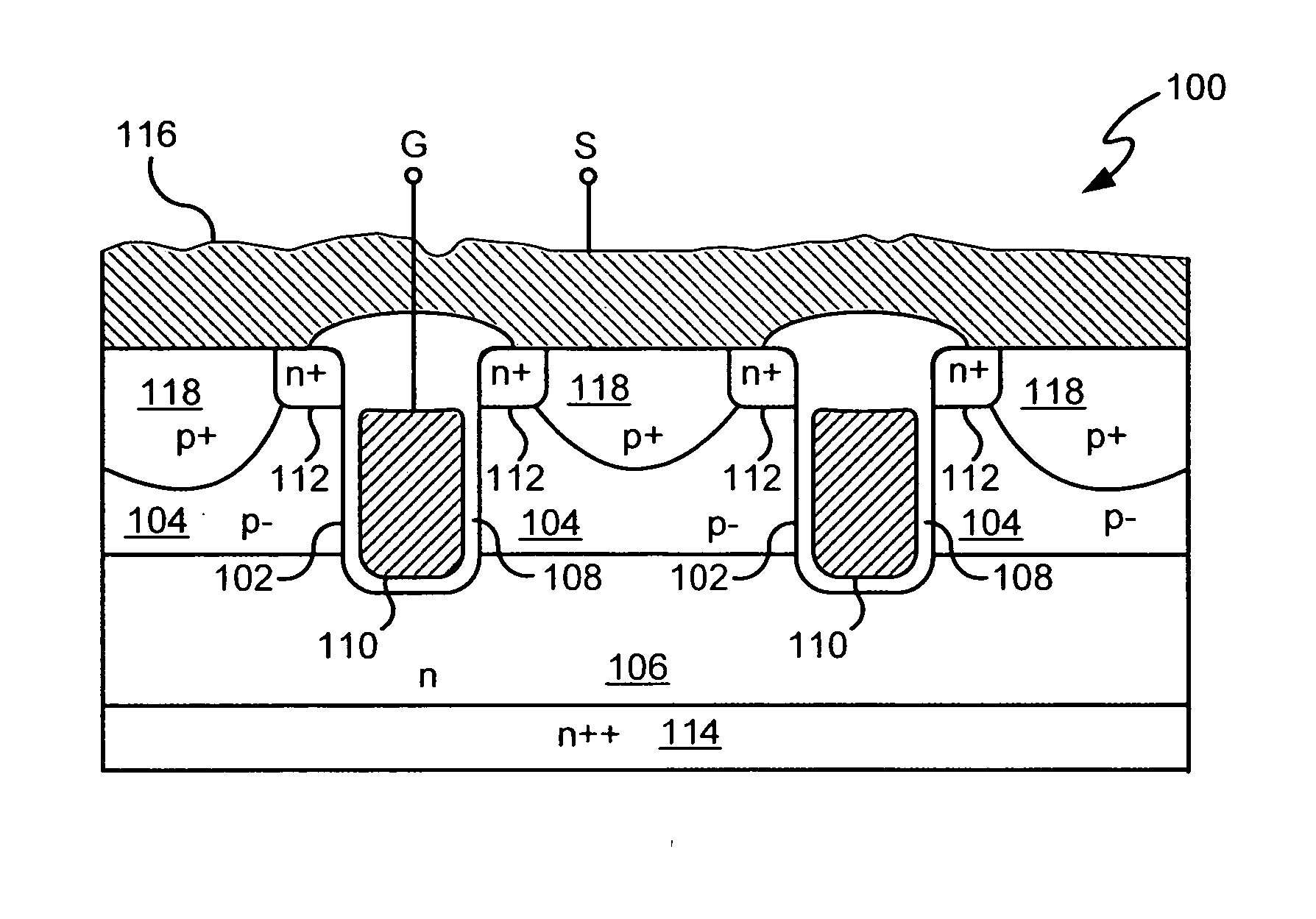
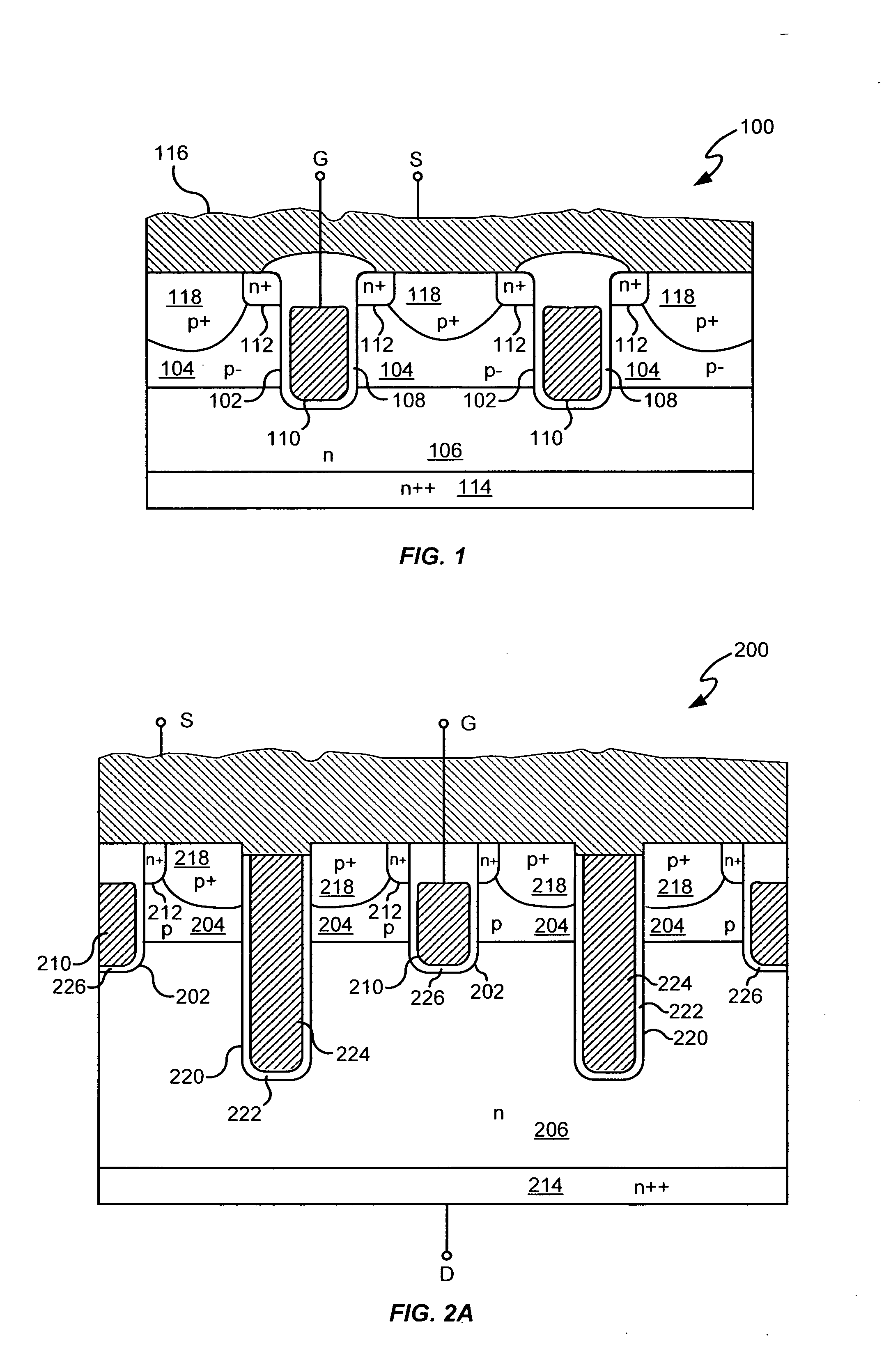
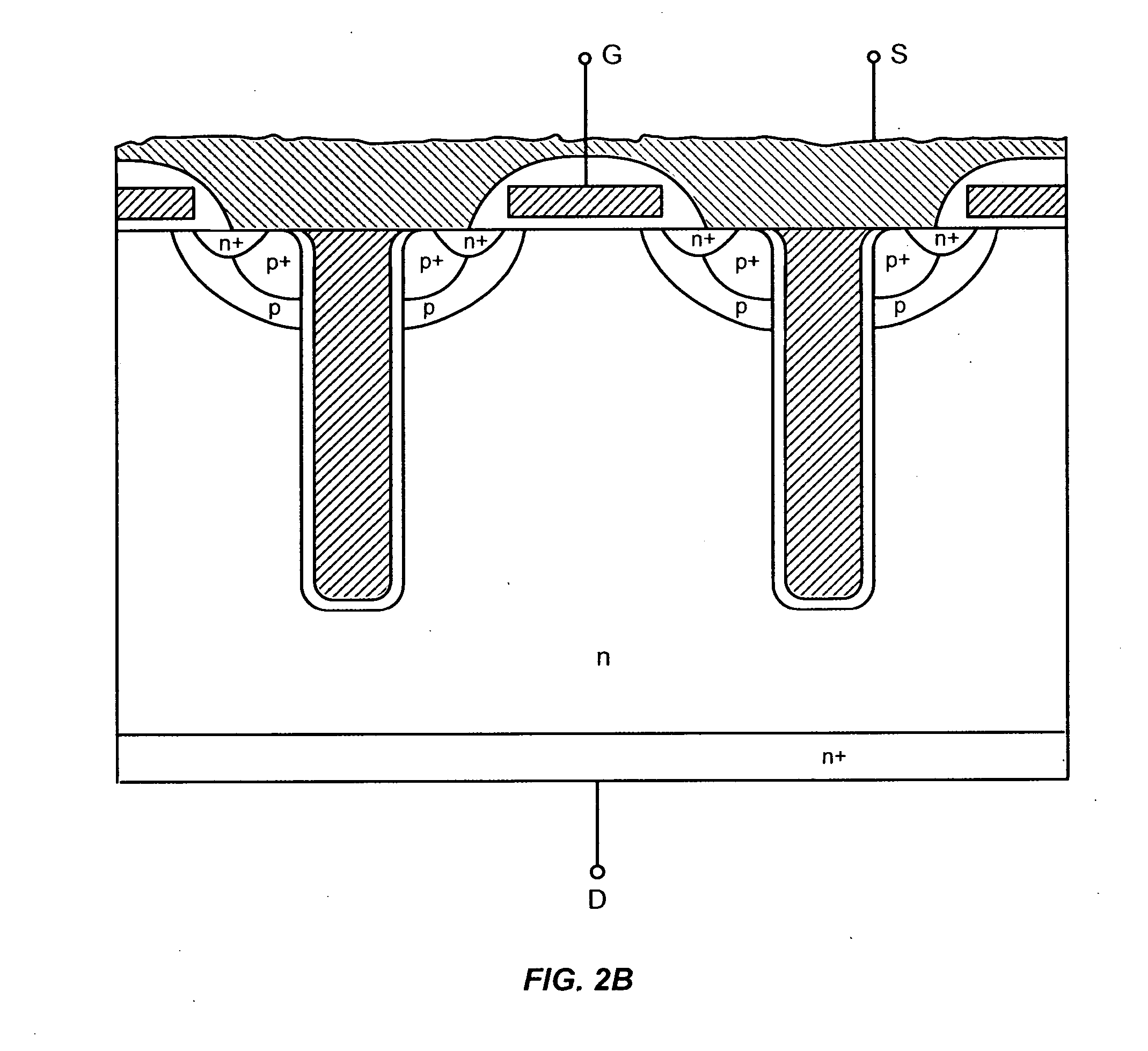
A power semiconductor device includes a plurality of trenches formed within a semiconductor body, each trench including one or more electrodes formed therein. In particular, according to embodiments of the invention, the plurality of trenches of a semiconductor device may include one or more gate electrodes, may include one or more gate electrodes or one or more source electrodes, or may include a combination of both gate and source electrodes formed therein. The trenches and electrodes may have varying depths within the semiconductor body.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
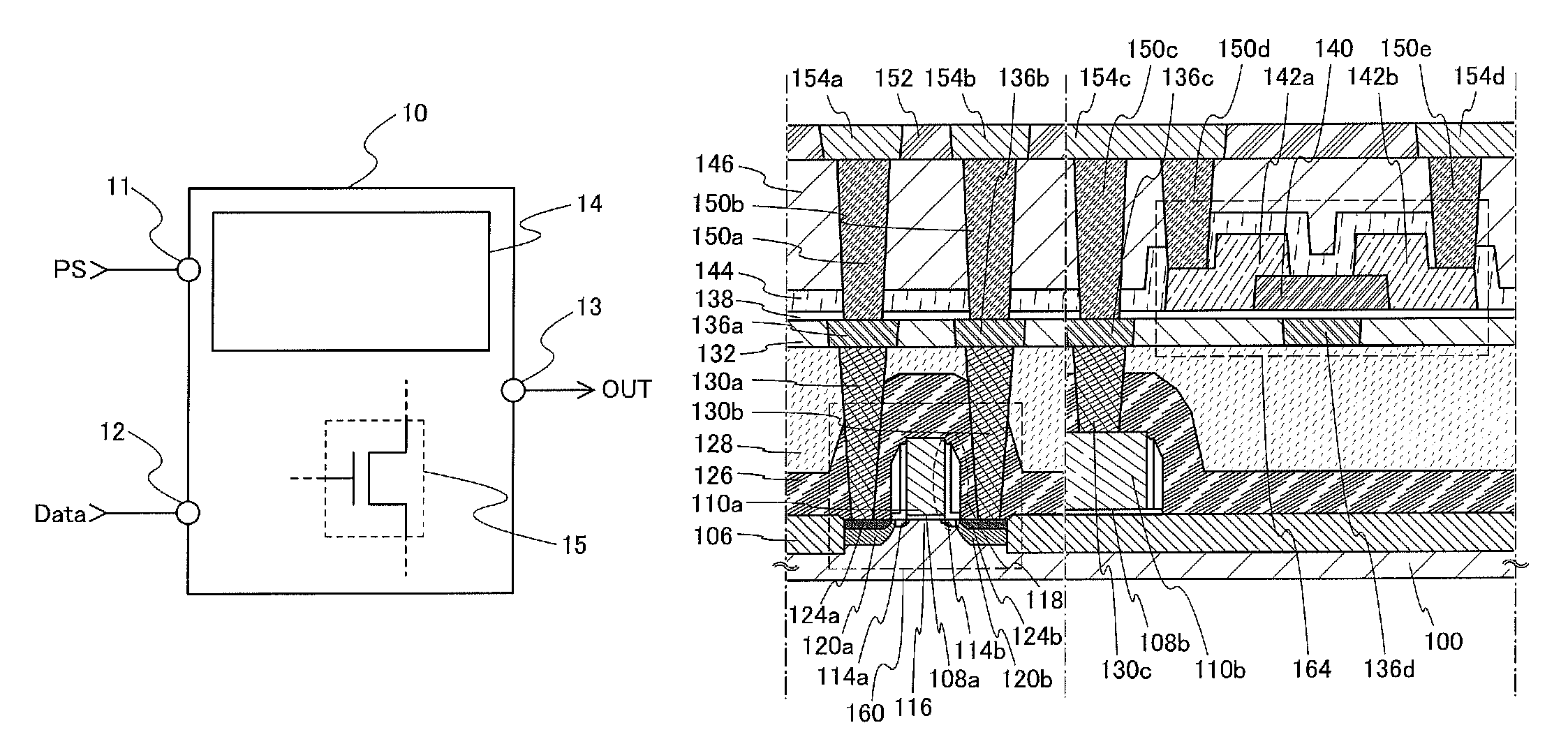
Semiconductor device and display device including the semiconductor device
ActiveUS20150014680A1Excellent electrical propertiesImprove featuresSolid-state devicesNon-linear opticsPower semiconductor deviceDisplay device
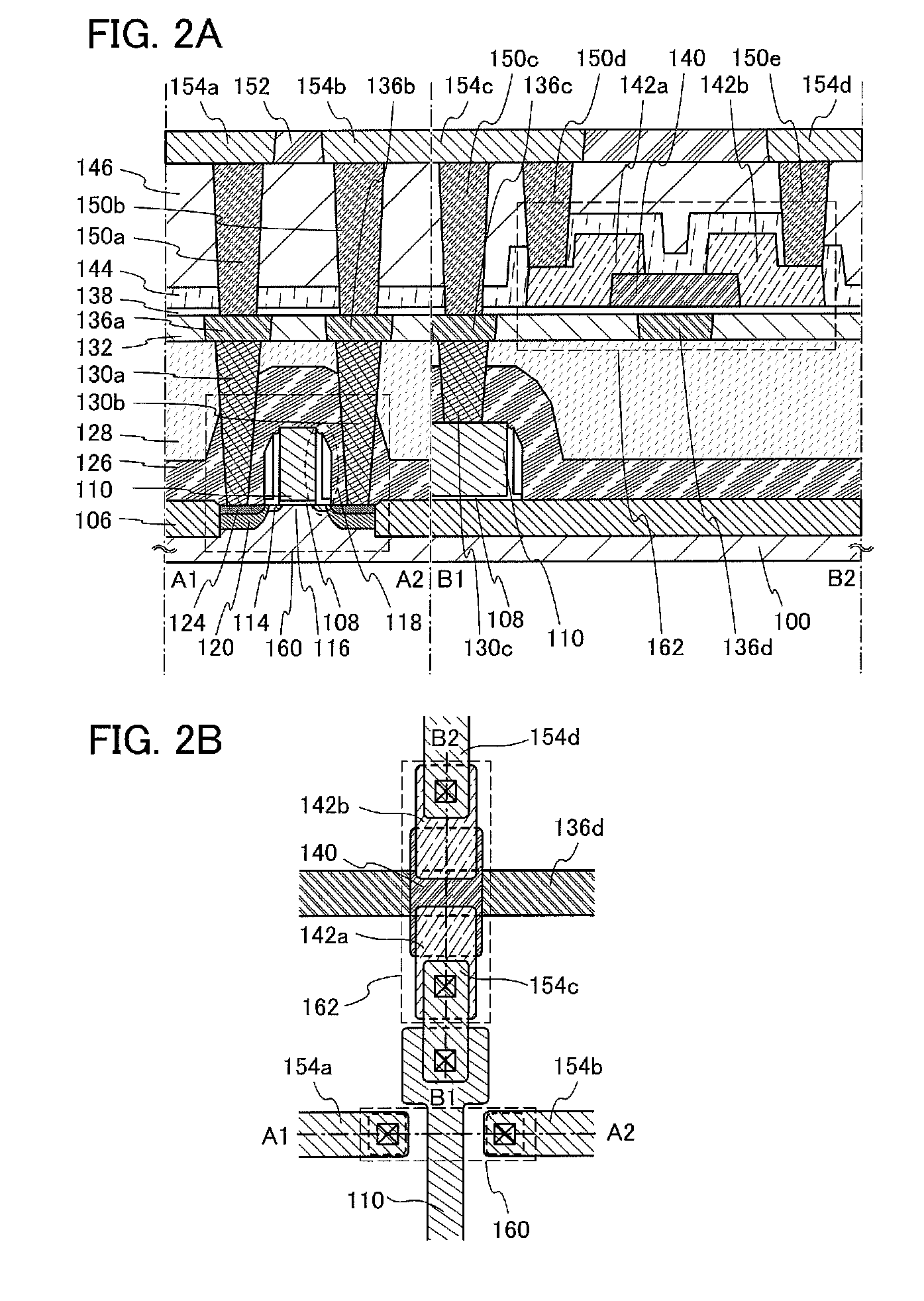
A semiconductor device including a transistor and a connection portion is provided. The transistor includes a gate electrode, a first insulating film over the gate electrode, an oxide semiconductor film over the first insulating film and at a position overlapping with the gate electrode, and source and drain electrodes electrically connected to the oxide semiconductor film; and the connection portion includes a first wiring on the same surface as a surface on which the gate electrode is formed, a second wiring on the same surface as a surface on which the source and drain electrodes are formed, and a third wiring connecting the first wiring and the second wiring. The distance between an upper end portion and a lower end portion of the second wiring is longer than the distance between an upper end portion and a lower end portion of each of the source and drain electrodes.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20110240990A1Improve reliabilityExcellent electrical propertiesTransistorSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceSemiconductor
An object is to stabilize electric characteristics of a semiconductor device including an oxide semiconductor to increase reliability. The semiconductor device includes an insulating film; a first metal oxide film on and in contact with the insulating film; an oxide semiconductor film partly in contact with the first metal oxide film; source and drain electrodes electrically connected to the oxide semiconductor film; a second metal oxide film partly in contact with the oxide semiconductor film; a gate insulating film on and in contact with the second metal oxide film; and a gate electrode over the gate insulating film.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20110193164A1Reduce parasitic capacitanceLarge thicknessSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPower semiconductor deviceGate dielectric
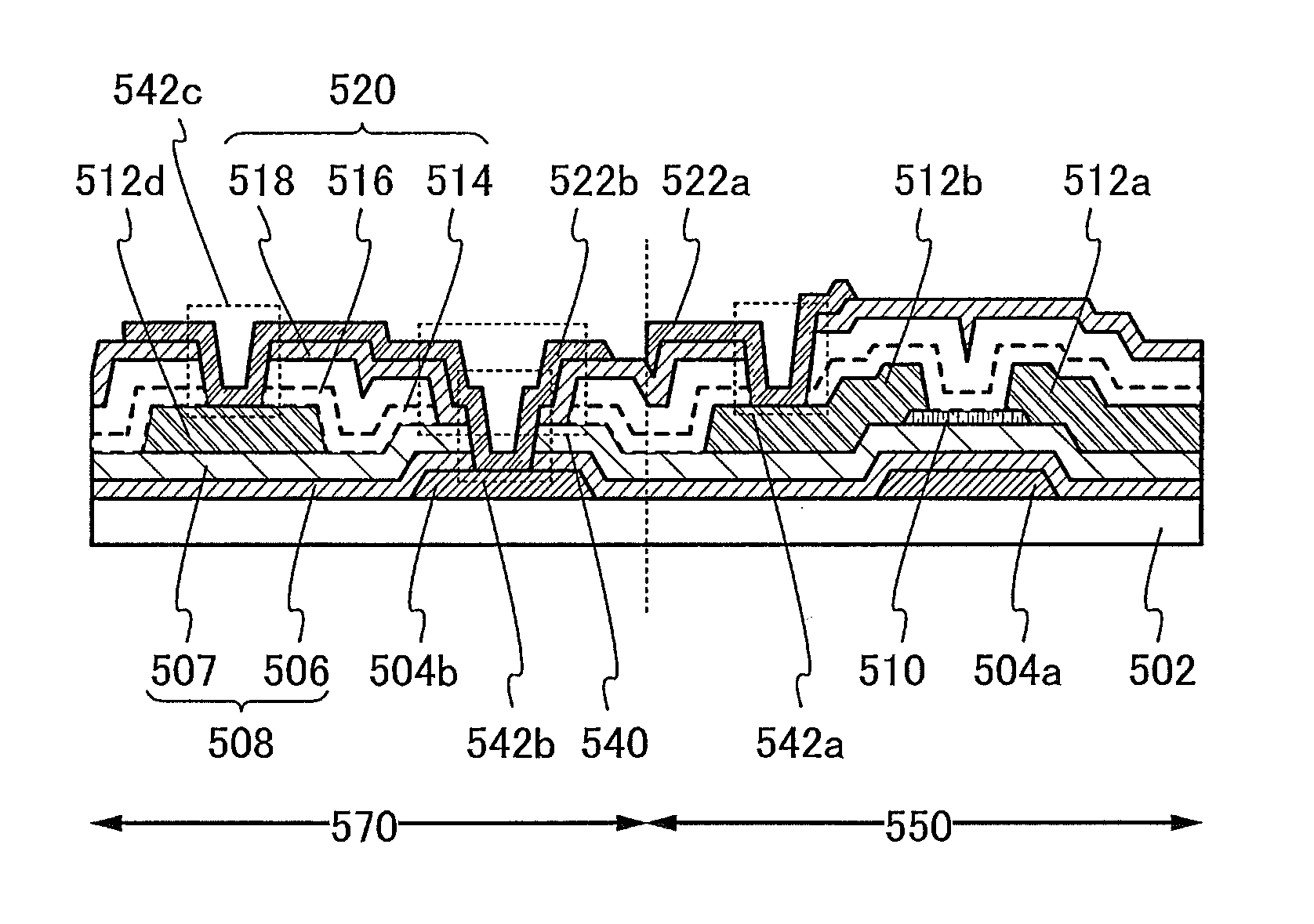
The present application discloses a semiconductor device formed on a SOI substrate which comprises a buried insulating layer and a semiconductor layer on the buried insulating layer and a method for manufacturing the same, wherein a fin of semiconductive material having two opposing sides perpendicular to a main surface of the SOI substrate is provided in the semiconductor layer, said semiconductor device comprising: a source region and a drain region provided at two ends of the fin respectively; a channel region provided at a central portion of the fin; and a stack of gate dielectric and gate conductor provided at one side of the fin, where the gate conductor is isolated from the channel region by the gate dielectric, wherein the gate conductor extends away from the one side of the fin in a direction parallel to the main surface of the SOI substrate. The semiconductor device has an improved short channel effect and a reduced parasitic capacitance and resistance, which contributes to an improved electrical property and facilitates scaling down of the transistor.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Semiconductor device, manufacturing method thereof, and electronic apparatus
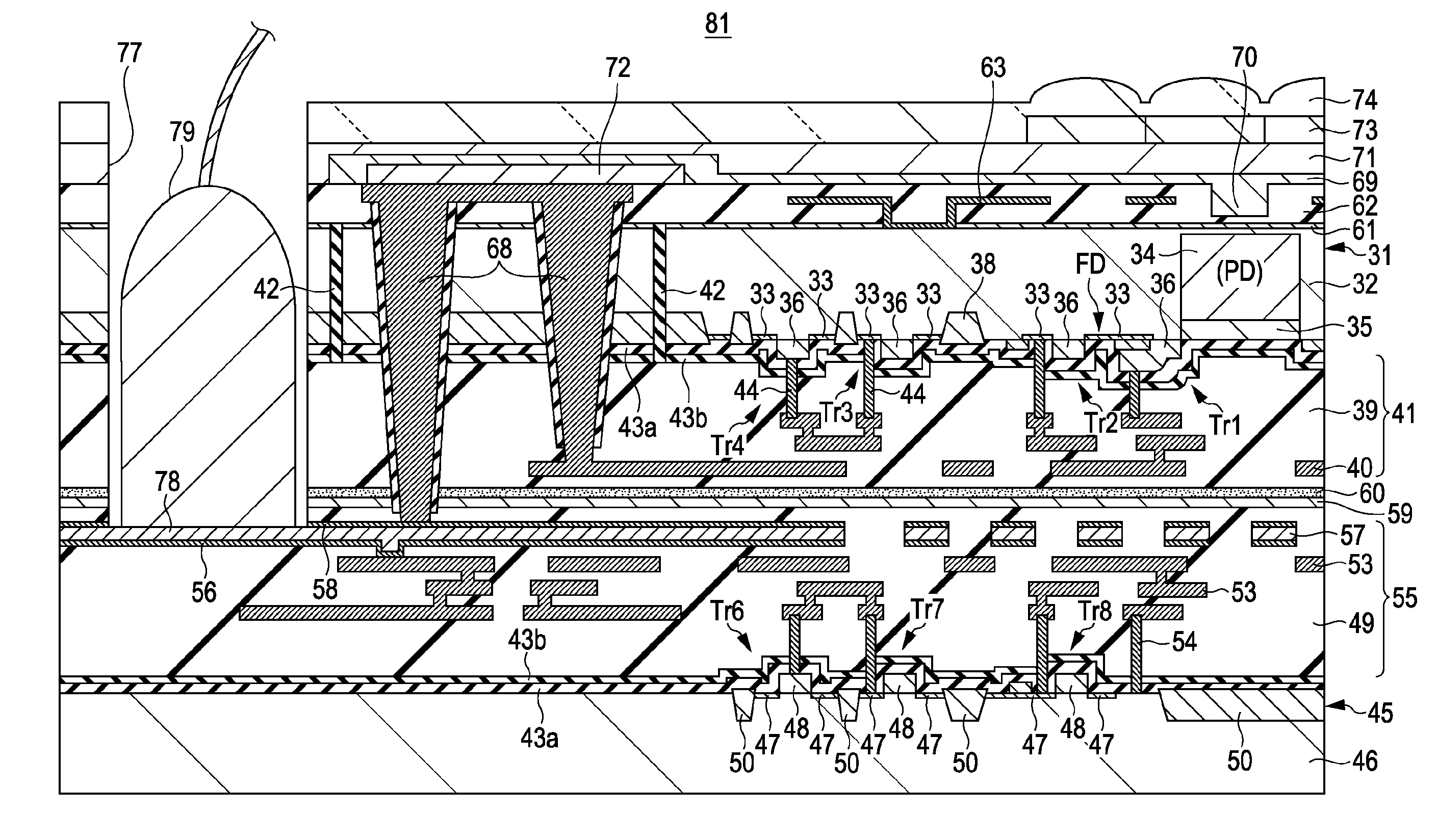
ActiveUS20110102657A1Improve batch productivityImprove performanceTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPower semiconductor deviceConductive materials
A semiconductor device having a first semiconductor section including a first wiring layer at one side thereof; a second semiconductor section including a second wiring layer at one side thereof, the first and second semiconductor sections being secured together with the respective first and second wiring layer sides of the first and second semiconductor sections facing each other; a conductive material extending through the first semiconductor section to the second wiring layer of the second semiconductor section and by means of which the first and second wiring layers are in electrical communication; and an opening, other than the opening for the conductive material, which extends through the first semiconductor section to the second wiring layer.
Owner:SONY CORP
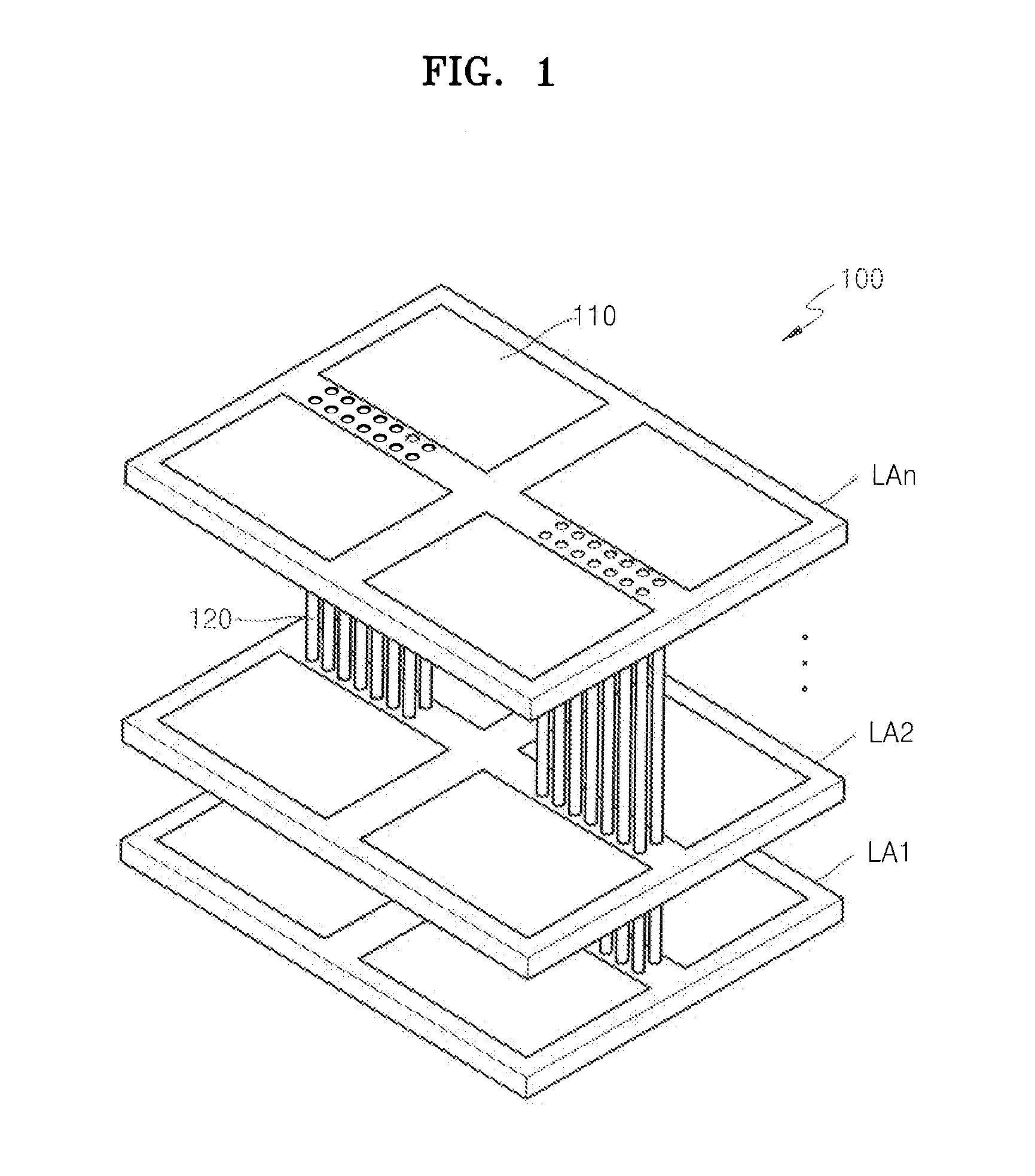
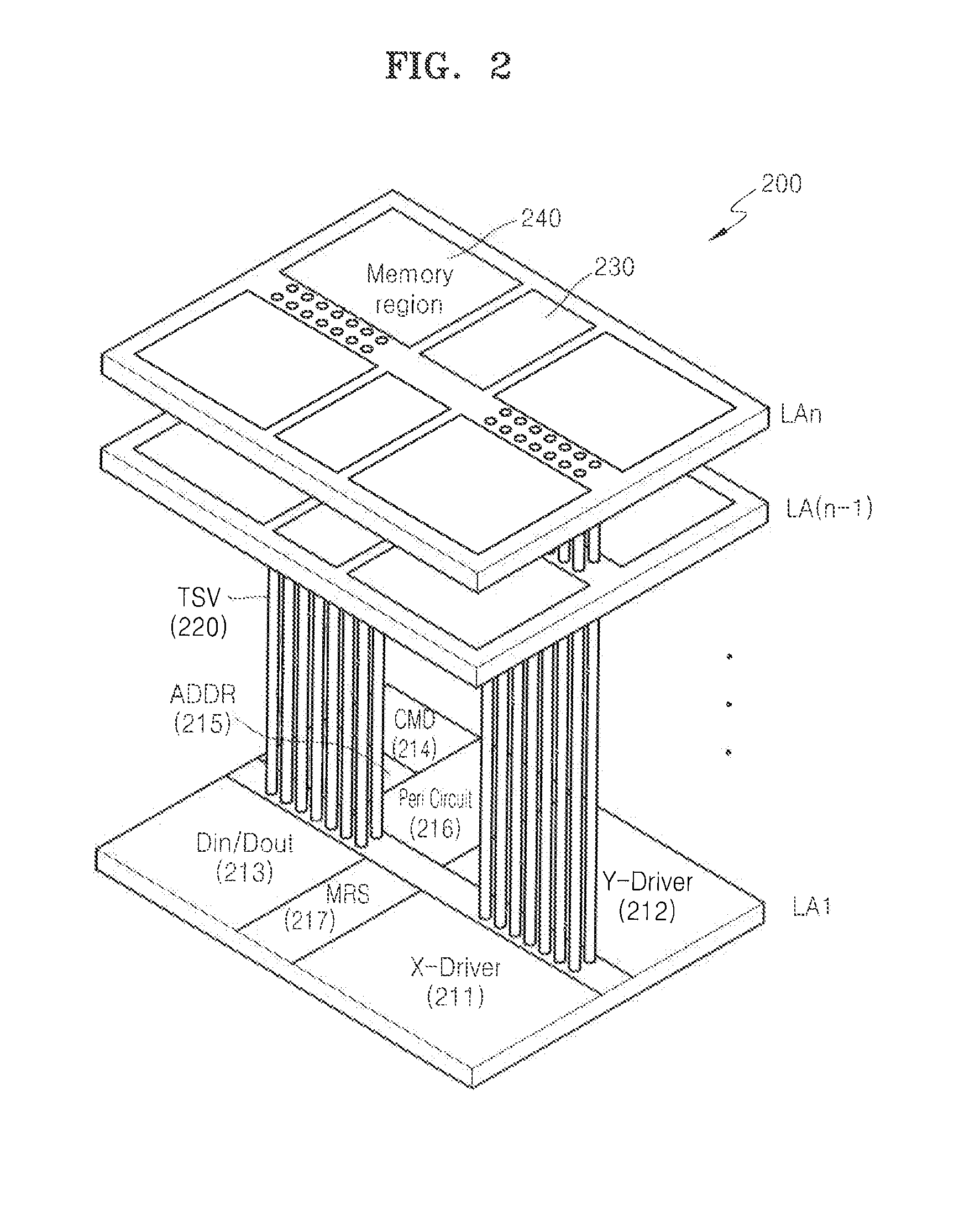
Semiconductor device having stacked structure including through-silicon-vias and method of testing the same
InactiveUS20120138927A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPower semiconductor deviceElectrical conductor
A semiconductor device having a stacked structure including through-silicon-vias (TSVs) and a method of testing the semiconductor device. The semiconductor device includes a first semiconductor layer, one or more second semiconductor layers stacked on the first semiconductor layer, and a plurality of input through-silicon-vias (TSVs) to transmit signals from a plurality of input pads, respectively. In a test mode, a test signal from the plurality of input pads is transmitted through at least two test paths, and the test signal transmitted through each of the test paths is output as a test result with respect to each of the plurality of input TSVs through an output pad.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com