Patents
Literature
9655 results about "Semiconductor device modeling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Semiconductor device modeling creates models for the behavior of the electrical devices based on fundamental physics, such as the doping profiles of the devices. It may also include the creation of compact models (such as the well known SPICE transistor models), which try to capture the electrical behavior of such devices but do not generally derive them from the underlying physics. Normally it starts from the output of a semiconductor process simulation.
Semiconductor device and method of making the same
ActiveUS20130037886A1Improve efficiencyImprove performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceEngineering
A semiconductor device includes a semiconductor substrate, at least a first fin structure, at least a second fin structure, a first gate, a second gate, a first source / drain region and a second source / drain region. The semiconductor substrate has at least a first active region to dispose the first fin structure and at least a second active region to dispose the second fin structure. The first / second fin structure partially overlapped by the first / second gate has a first / second stress, and the first stress and the second stress are different from each other. The first / second source / drain region is disposed in the first / second fin structure at two sides of the first / second gate.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20180047749A1Reduce chargeAvoid chargingSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantCharge carrier
Disclosed are a semiconductor device and a manufacturing method thereof. According to the semiconductor device and the manufacturing method thereof according to exemplary embodiments of the present invention, after the dopant source layer is uniformly deposited on a channel layer of the device with the 3-demensional vertical structure by the plasma-enhanced atomic layer deposition (PEALD) method, the deposited dopant source layer is heat-treated so that the dopants are diffused into the channel layer to function as charge carriers, thereby preventing the charges in the channel layer from being reduced. According to the exemplary embodiments of the present invention, the diffusion speed and concentration of the dopant may be controlled by forming the barrier layer between the channel layer and the dopant source layer.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Semiconductor devices with varying threshold voltage and fabrication methods thereof
ActiveUS9748145B1Overcomes shortcomingEnhanced advantageTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPower semiconductor deviceDielectric layer
Semiconductor device fabrication methods are provided which include: providing a structure with at least one region and including a dielectric layer disposed over a substrate; forming a multilayer stack structure including a threshold-voltage adjusting layer over the dielectric layer, the multilayer stack structure including a first threshold-voltage adjusting layer in a first region of the at least one region, and a second threshold-voltage adjusting layer in a second region of the at least one region; and annealing the structure to define a varying threshold voltage of the at least one region, the annealing facilitating diffusion of at least one threshold voltage adjusting species from the first threshold-voltage adjusting layer and the second threshold-voltage adjusting layer into the dielectric layer, where a threshold voltage of the first region is independent of the threshold voltage of the second region.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Film forming method, semiconductor device, manufacturing method thereof and substrate processing apparatus therefor
InactiveUS8785311B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsSilanes
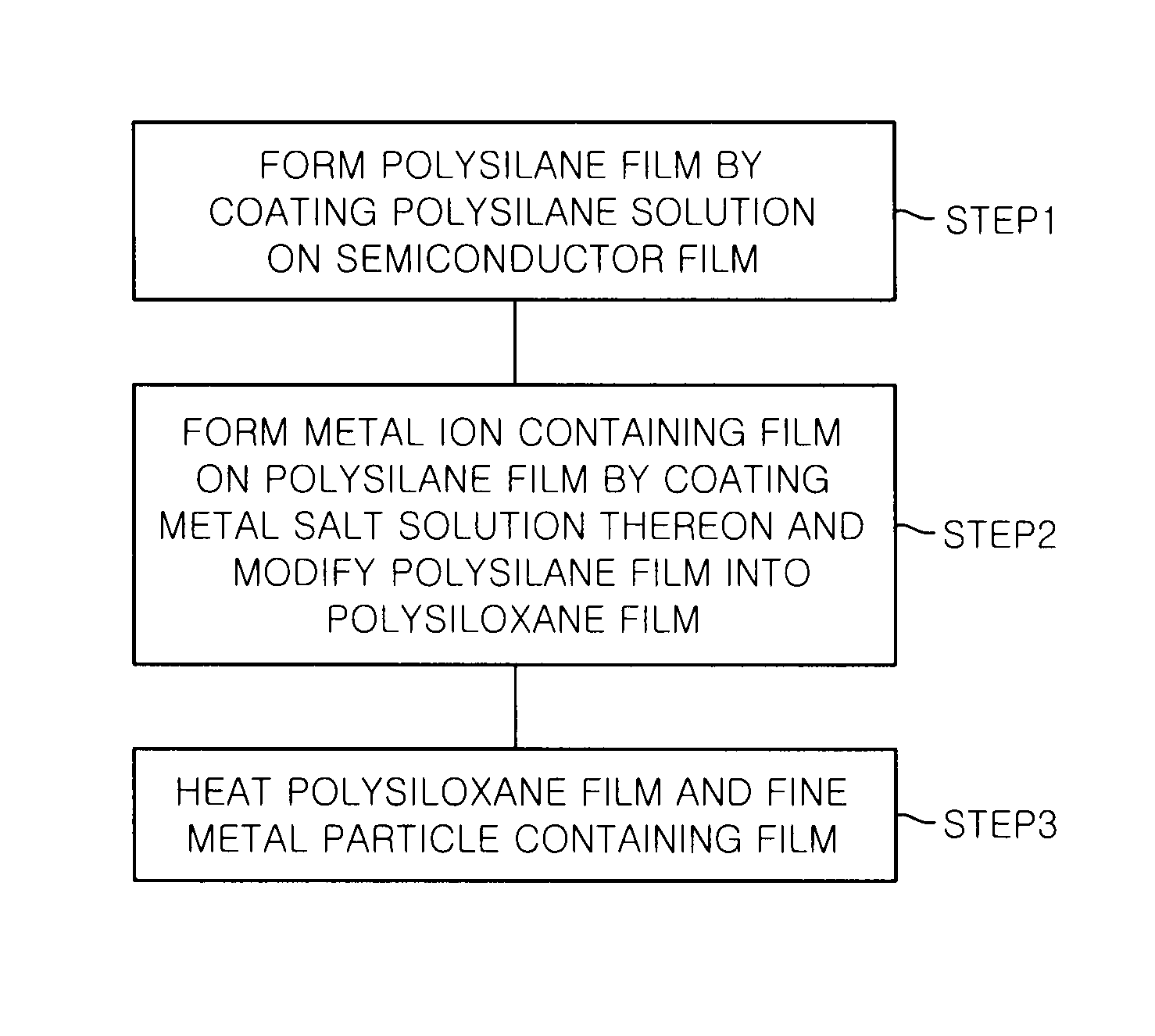
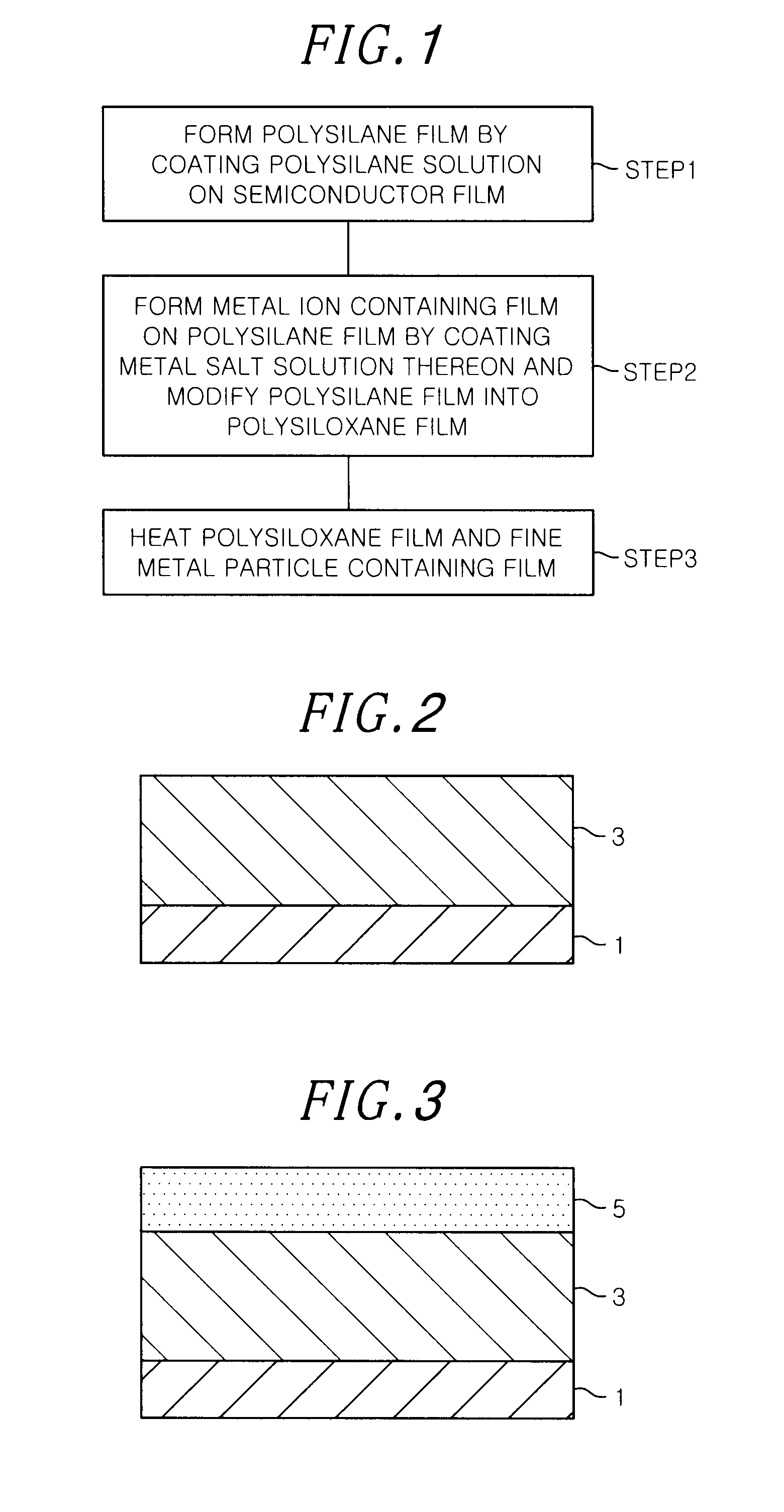
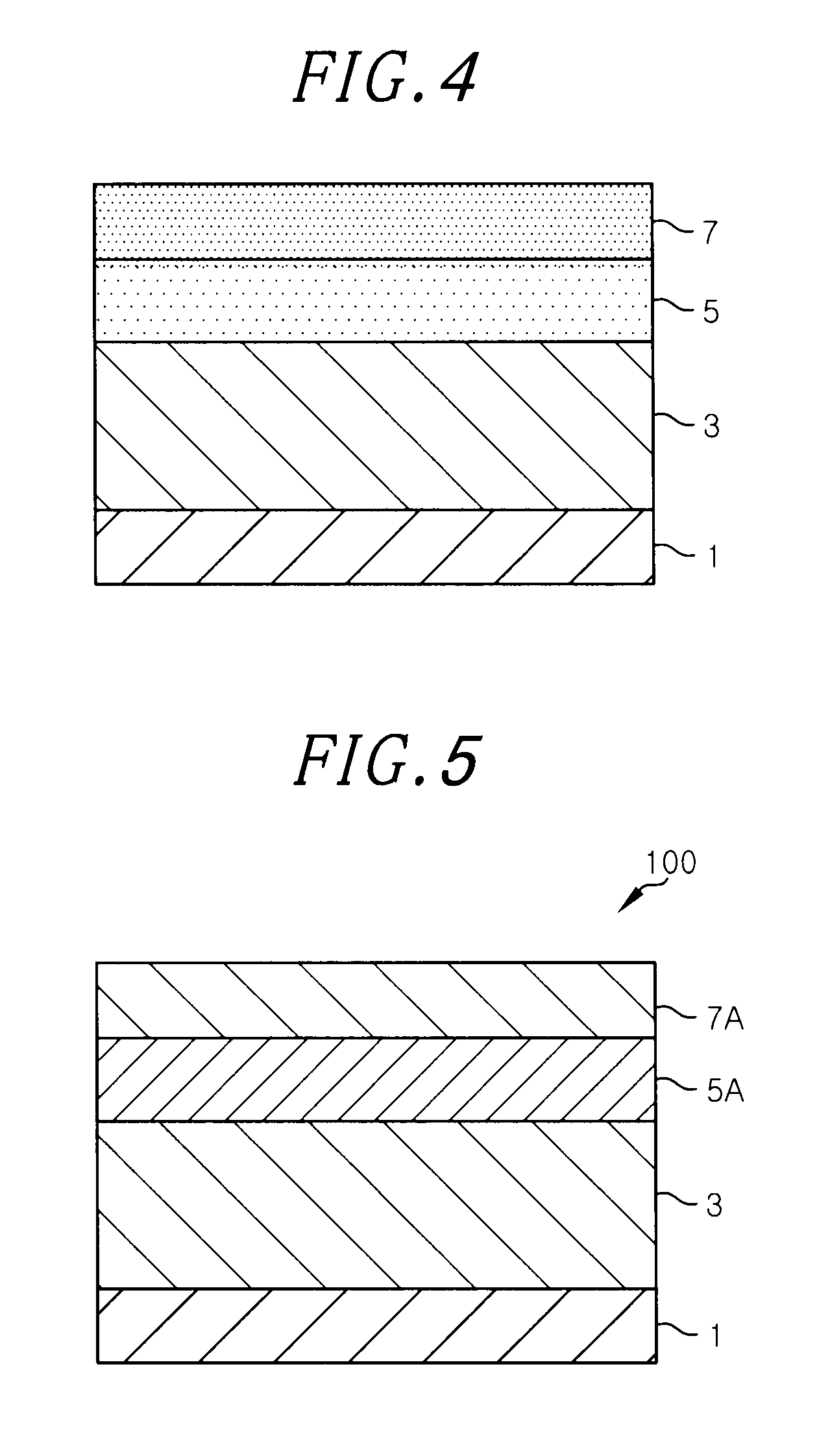
In a method for forming a stacked substrate of a MOS (Metal Oxide Semiconductor) structure including an oxide film serving as a gate insulating film formed on a semiconductor material layer having a film or substrate shape; and a conductive film serving as a gate electrode formed on the oxide film, a polysilane film on the semiconductor material layer is formed by coating a polysilane solution on a surface of a substrate to which the semiconductor material layer is exposed. A film containing metal ions is formed on the polysilane film by coating a metal salt solution thereon, and the polysilane film and the film containing metal ions are respectively modified into a polysiloxane film and a film containing fine metal particles to form the stacked substrate.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20130320334A1Inhibited DiffusionLarge energy gapTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPower semiconductor devicePower flow
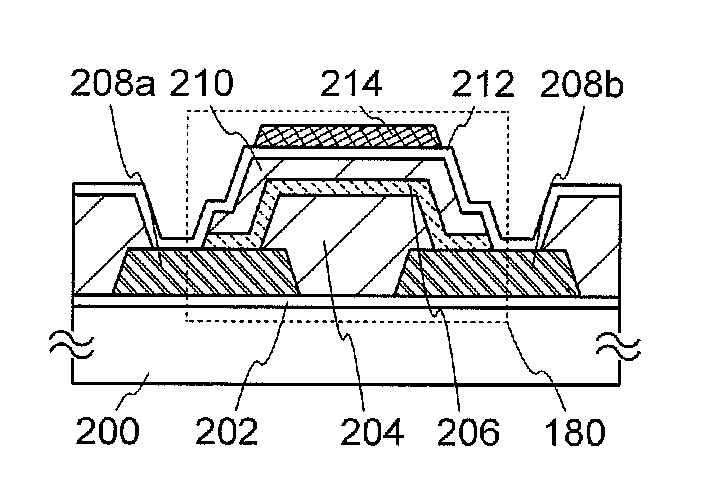
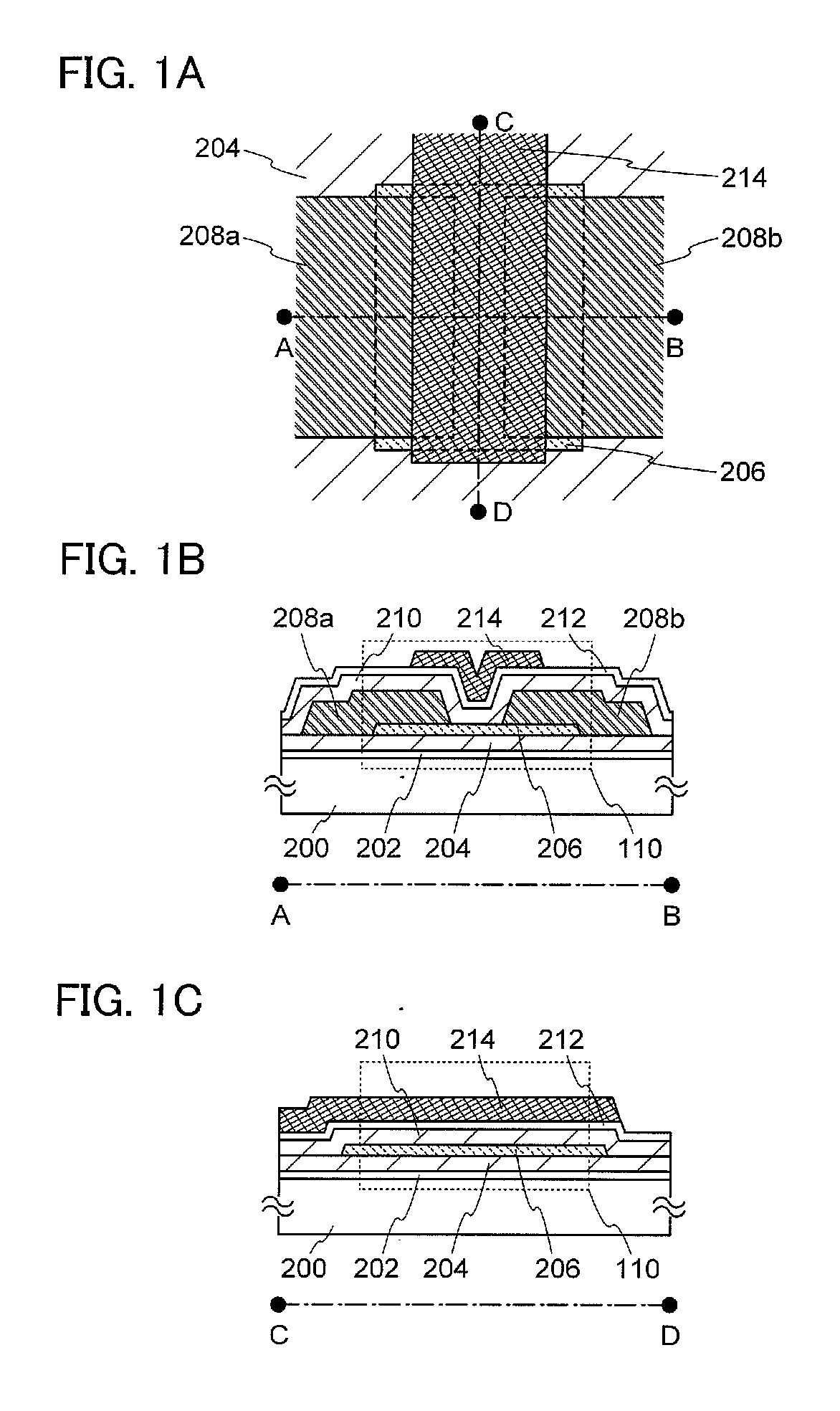
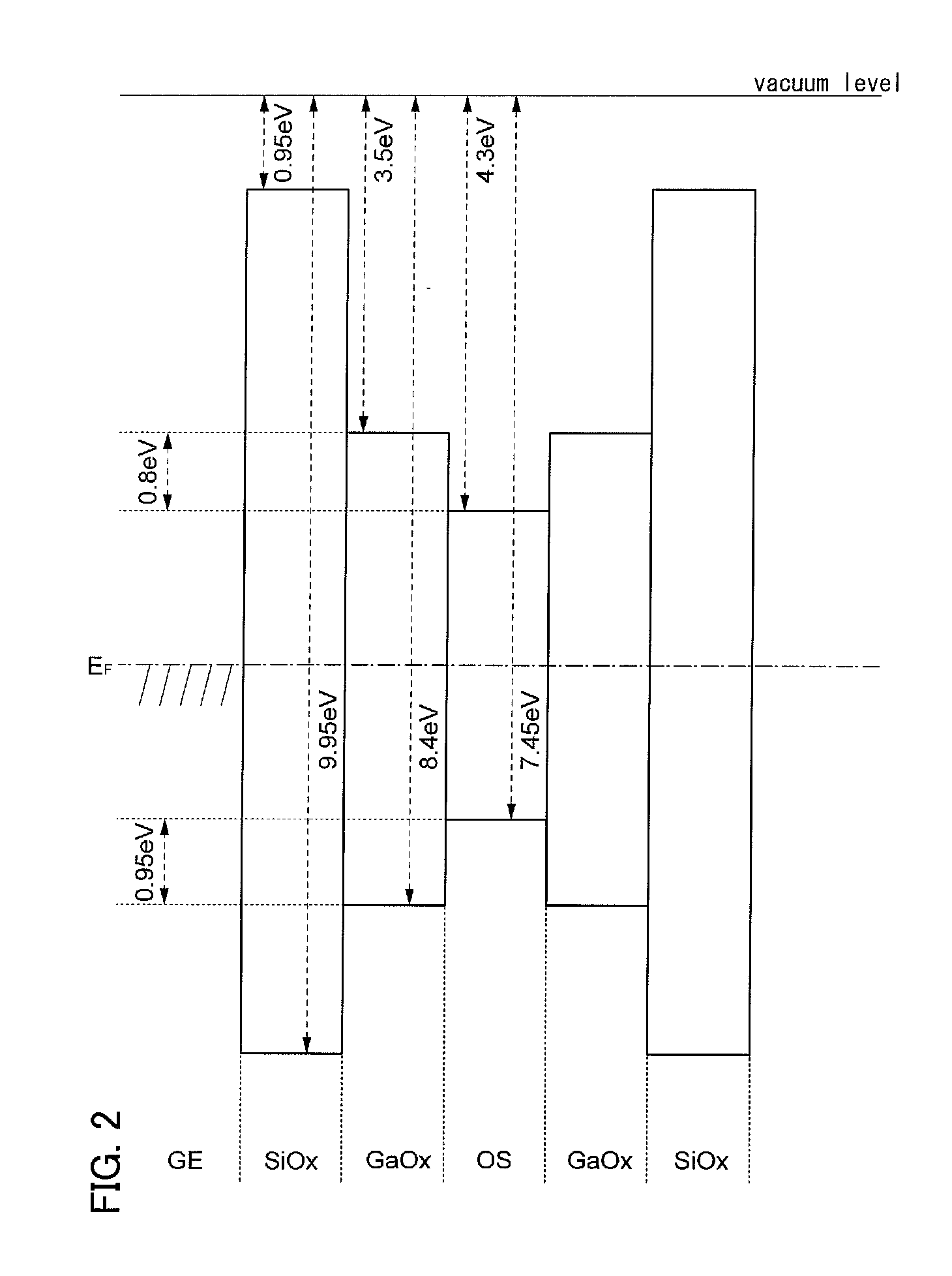
A highly reliable semiconductor device including an oxide semiconductor is provided by preventing a change in its electrical characteristics. A semiconductor device which includes a first oxide semiconductor layer which is in contact with a source electrode layer and a drain electrode layer and a second oxide semiconductor layer which serves as a main current path (channel) of a transistor is provided. The first oxide semiconductor layer serves as a buffer layer for preventing a constituent element of the source and drain electrode layers from diffusing into the channel. By providing the first oxide semiconductor layer, it is possible to prevent diffusion of the constituent element into an interface between the first oxide semiconductor layer and the second oxide semiconductor layer and into the second oxide semiconductor layer.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Methods for forming a semiconductor device and related semiconductor device structures
ActiveUS20180122709A1Well formedTransistorSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceGate dielectric
Methods for forming a semiconductor device and related semiconductor device structures are provided. In some embodiments, methods may include forming an NMOS gate dielectric and a PMOS gate dielectric over a substrate and forming a first work function metal over the NMOS gate dielectric and over the PMOS gate dielectric. In some embodiments, methods may also include, removing the first work function metal over the NMOS gate dielectric and forming a second work function metal over the NMOS gate dielectric and over the PMOS gate dielectric. In some embodiments, related semiconductor device structures may include an NMOS gate dielectric and a PMOS gate dielectric disposed over a semiconductor substrate. A PMOS gate electrode may be disposed over the PMOS gate dielectric and the PMOS gate electrode may include a first work function metal disposed over the PMOS gate dielectric and a second work function metal disposed over the first work function metal. A NMOS gate electrode may be disposed over the NMOS gate dielectric and the NMOS gate electrode may include the second work function metal.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Method for manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS20110318888A1High crystallinityExcellent electrical propertiesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingHydrogenEngineering
A method for manufacturing a semiconductor device comprises the steps of forming a seed over the insulating film by introducing hydrogen and a deposition gas into a first treatment chamber under a first condition and forming a microcrystalline semiconductor film over the seed by introducing hydrogen and the deposition gas into a second treatment chamber under a second condition: a second flow rate of the deposition gas is periodically changed between a first value and a second value; and a second pressure in the second treatment chamber is higher than or equal to 1.0×102 Torr and lower than or equal to 1.0×103 Torr.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method of manufacturing semiconductor device
ActiveUS20070238321A1Improve reliabilityVariation in electrical propertyTransistorElectrostatic cleaningEngineeringSemiconductor
Provided is a method of manufacturing a semiconductor device. After a semiconductor wafer is placed over a wafer stage with which a dry cleaning chamber of a film forming apparatus is equipped, dry cleaning treatment is given over the surface of the semiconductor wafer with a reducing gas. Then, the semiconductor wafer is heat treated at a first temperature of from 100 to 150° C. by using a shower head kept at 180° C. The semiconductor wafer is then vacuum-transferred to a heat treatment chamber, wherein the semiconductor wafer is heat treated at a second temperature of from 150 to 400° C. A product remaining over the main surface of the semiconductor wafer is thus removed. The present invention makes it possible to manufacture a semiconductor device having improved reliability and production yield by reducing variations in the electrical properties of a nickel silicide layer.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor device
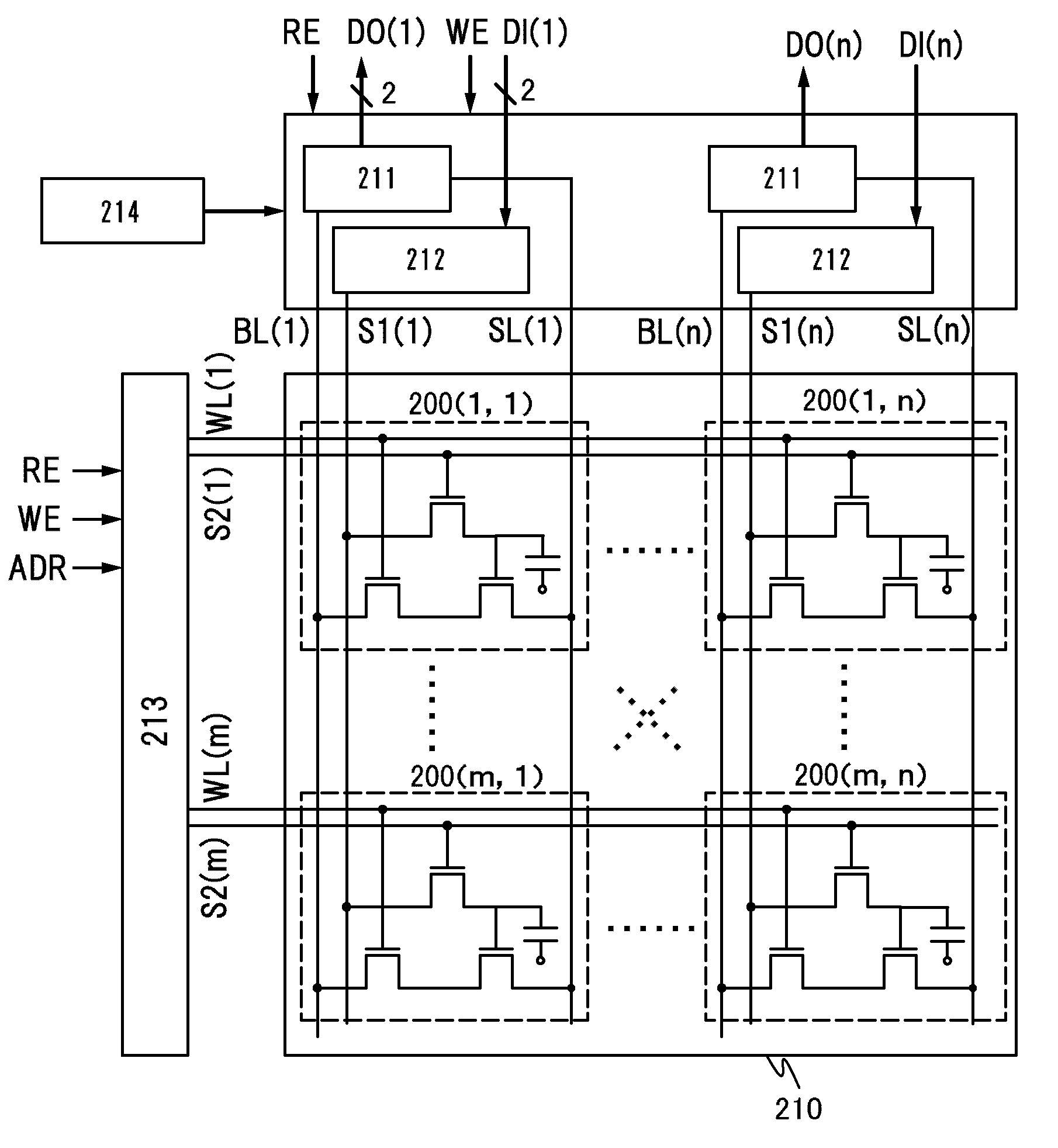
InactiveUS20110128777A1Long storageReduce power consumptionSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesPower semiconductor deviceSemiconductor materials
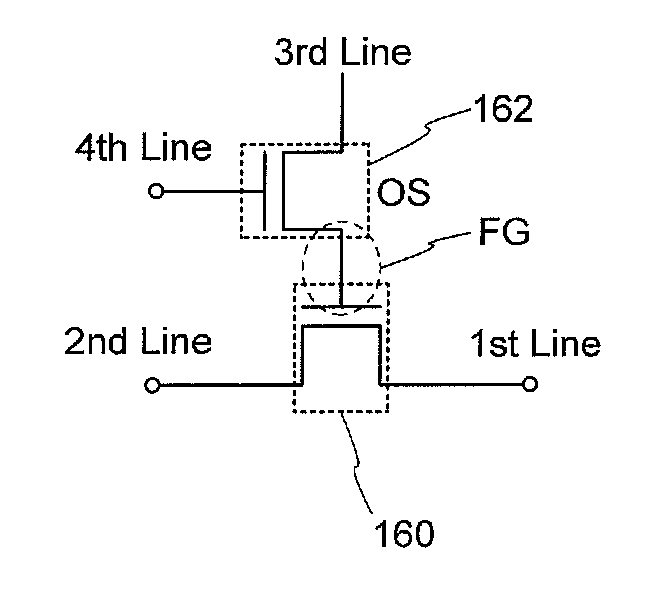
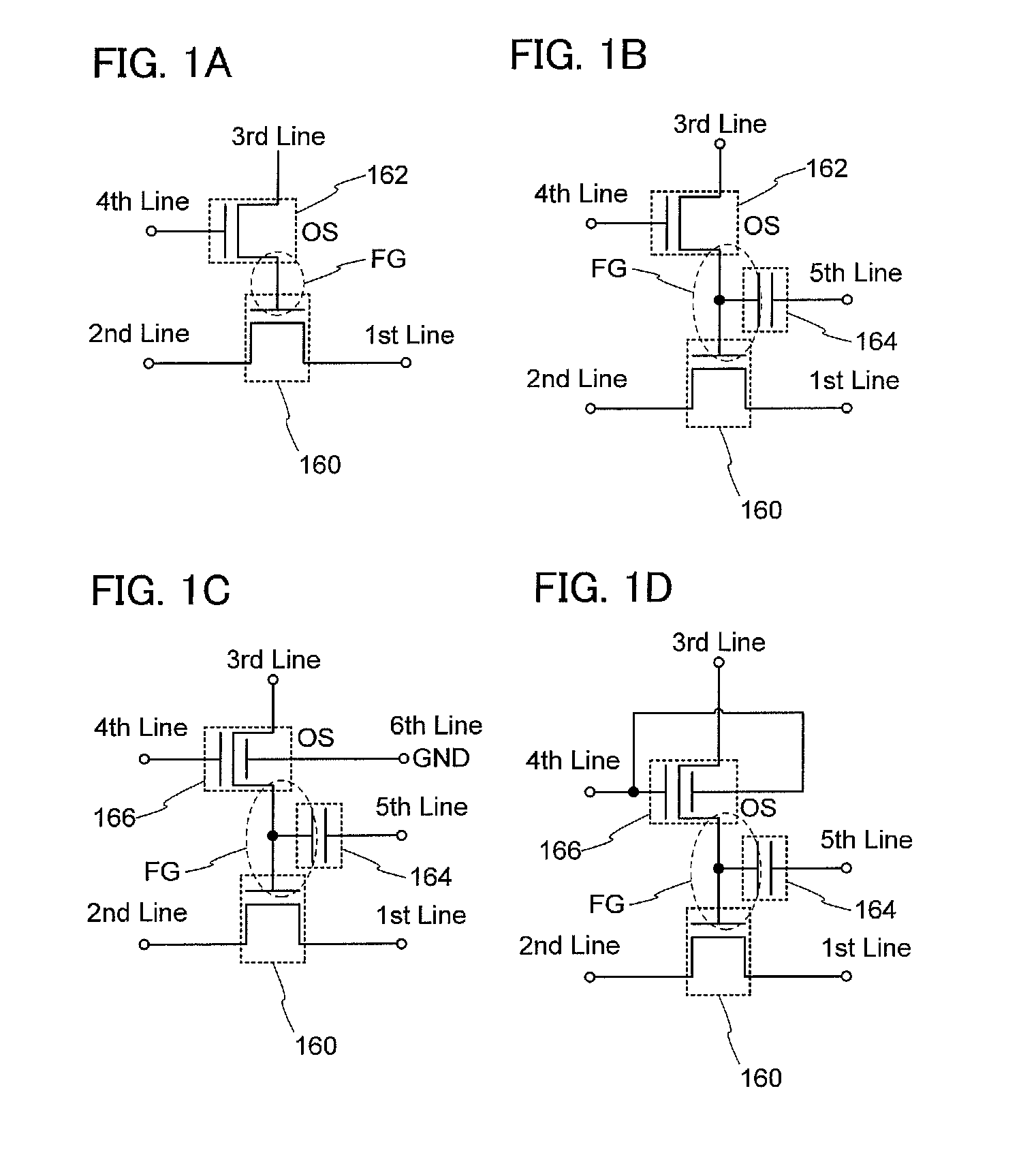
The semiconductor device includes a first wiring; a second wiring; a third wiring; a fourth wiring; a first transistor having a first gate electrode, a first source electrode, and a first drain electrode; and a second transistor having a second gate electrode, a second source electrode, and a second drain electrode. The first transistor is formed on or in a substrate including a semiconductor material. The second transistor includes an oxide semiconductor layer.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device and method for fabricating the same
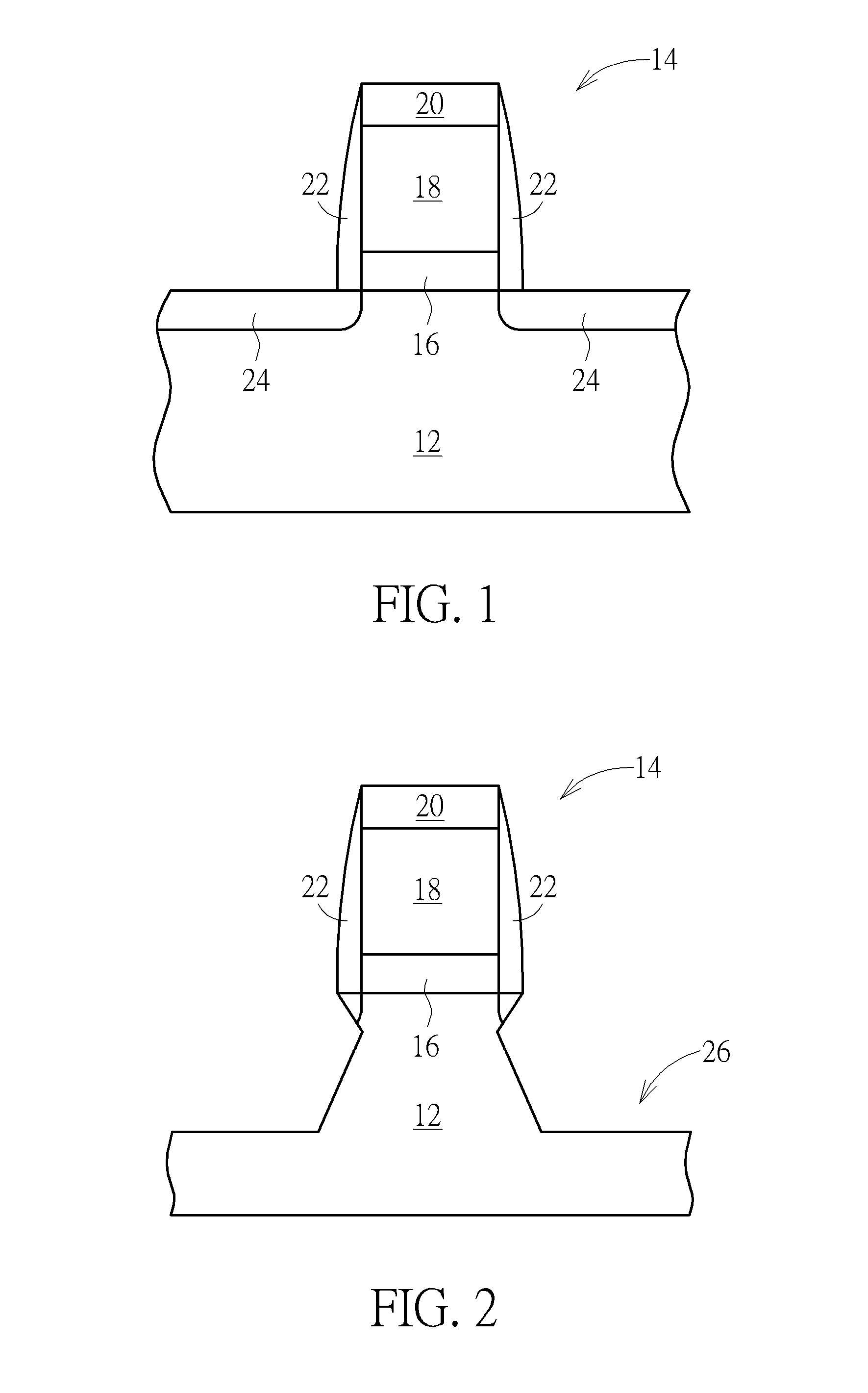
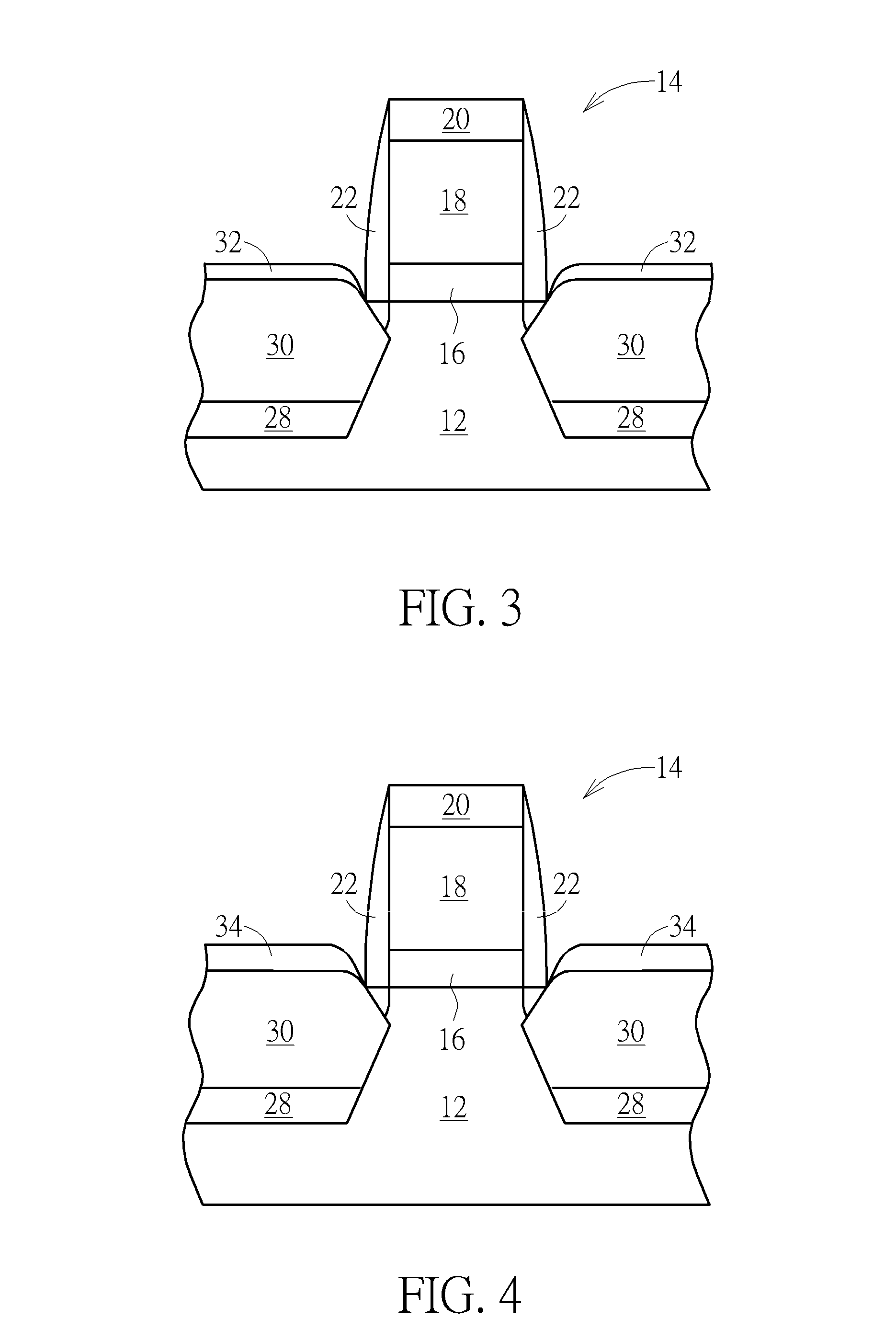
A method for fabricating semiconductor device is disclosed. The method includes the steps of: providing a substrate having a gate structure thereon; and forming a first epitaxial layer, a second epitaxial layer, and a silicide layer in the substrate adjacent to the gate structure. Preferably, the first epitaxial layer, the second epitaxial layer, and the silicide layer comprise SiGeSn.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Method for fabricating semiconductor device
ActiveUS20150187908A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSemiconductorSemiconductor device
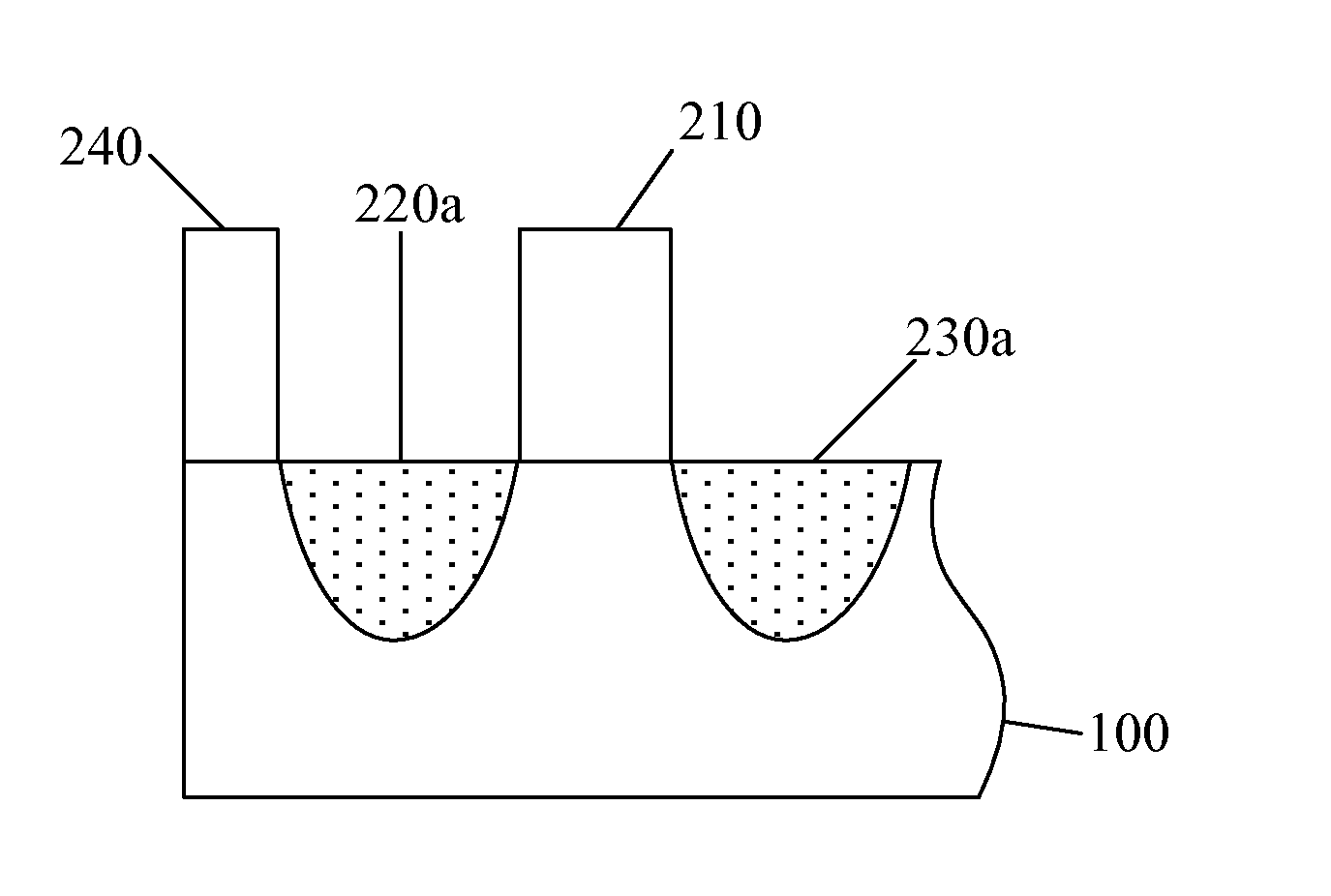
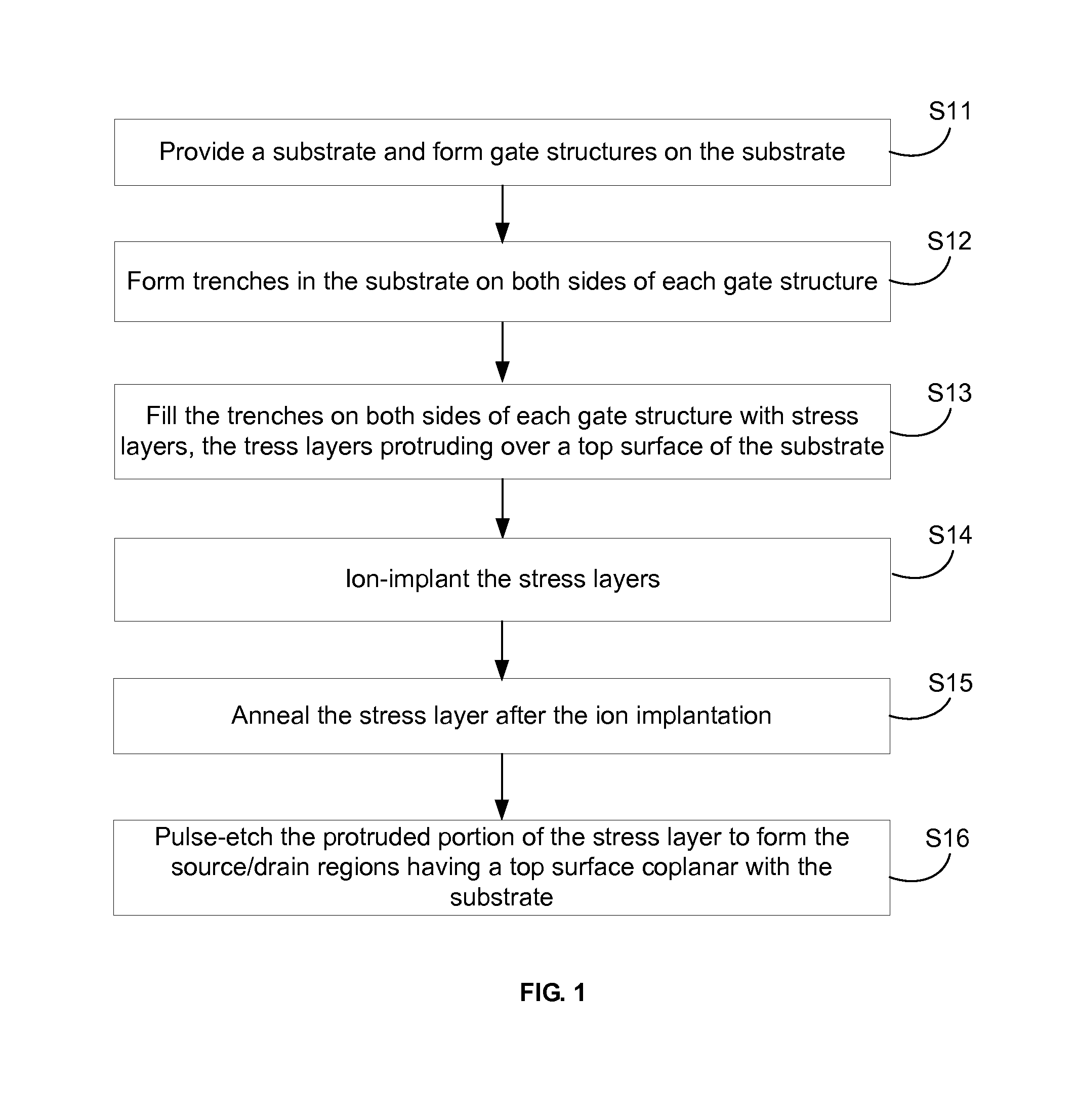
Methods for fabricating semiconductor devices are provided. Gate structures are formed on a top surface of a substrate to form semiconductor devices. Trenches are formed in the substrate on both sides of each gate structure of each semiconductor device. The trenches on the both sides of each gate structure are filled with stress layers, the stress layers in the substrate protruding over the top surface of the substrate The stress layers are ion-doped and annealed on the both sides of each gate structure, and are pulse-etched to form a source region and a drain region of each gate structure. The pulse-etching is controlled such that the source regions and the drain regions of the plurality of semiconductor devices have a top surface coplanar with the top surface of the substrate.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
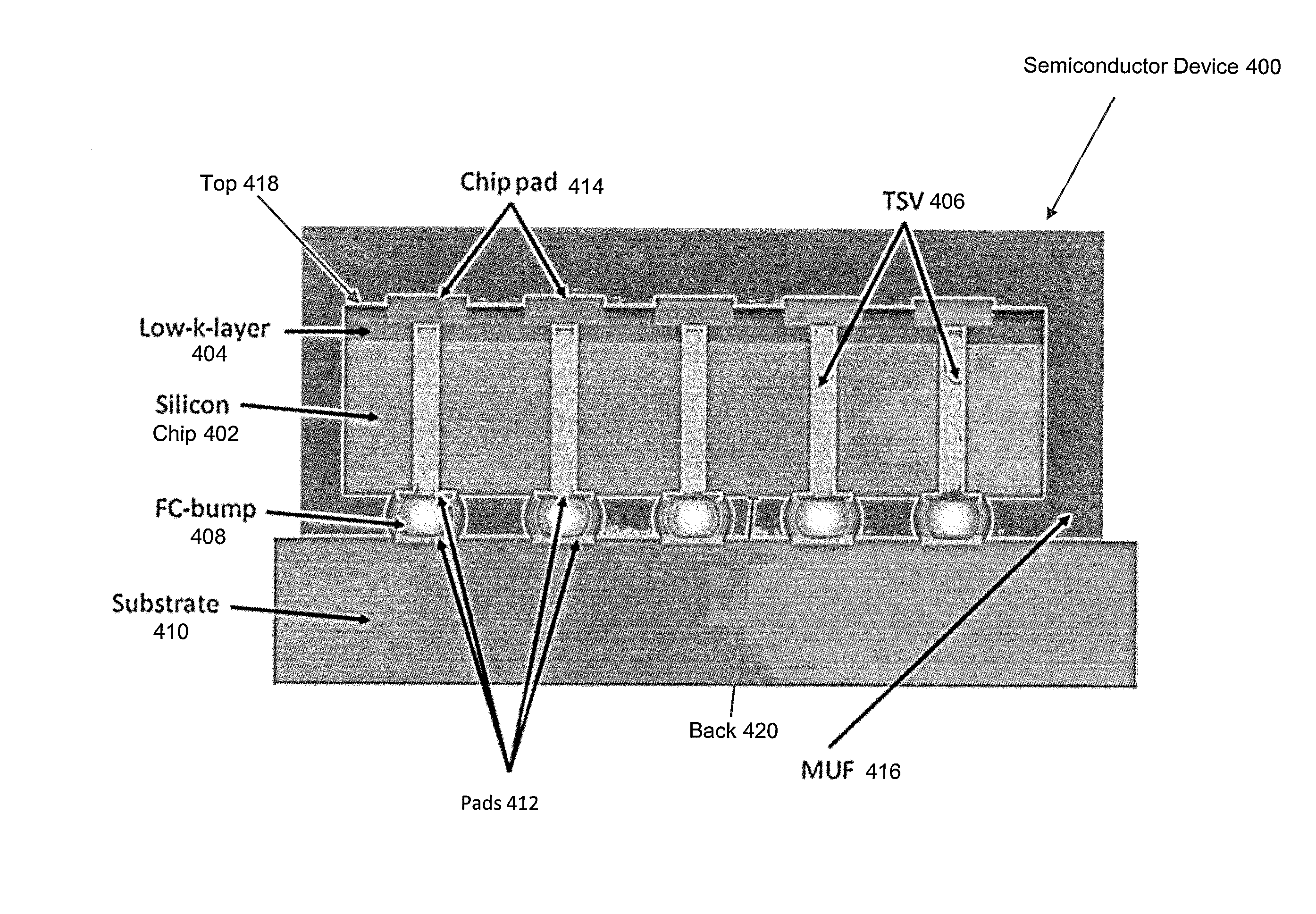
3D integrated circuit structure, semiconductor device and method of manufacturing same
ActiveUS20110227158A1Improve performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMOSFETPower semiconductor device
The present invention discloses a semiconductor device. In one embodiment, the semiconductor device comprises a substrate, a diffusion stop layer formed on the substrate, an SOI layer formed on the diffusion stop layer, an MOSFET transistor formed on the SOI layer, and a TSV formed in a manner of penetrating through the substrate, the diffusion stop layer, the SOI layer, and a layer where the MOSFET transistor is located; and an interconnect structure connecting the MOSFET transistor and the TSV.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
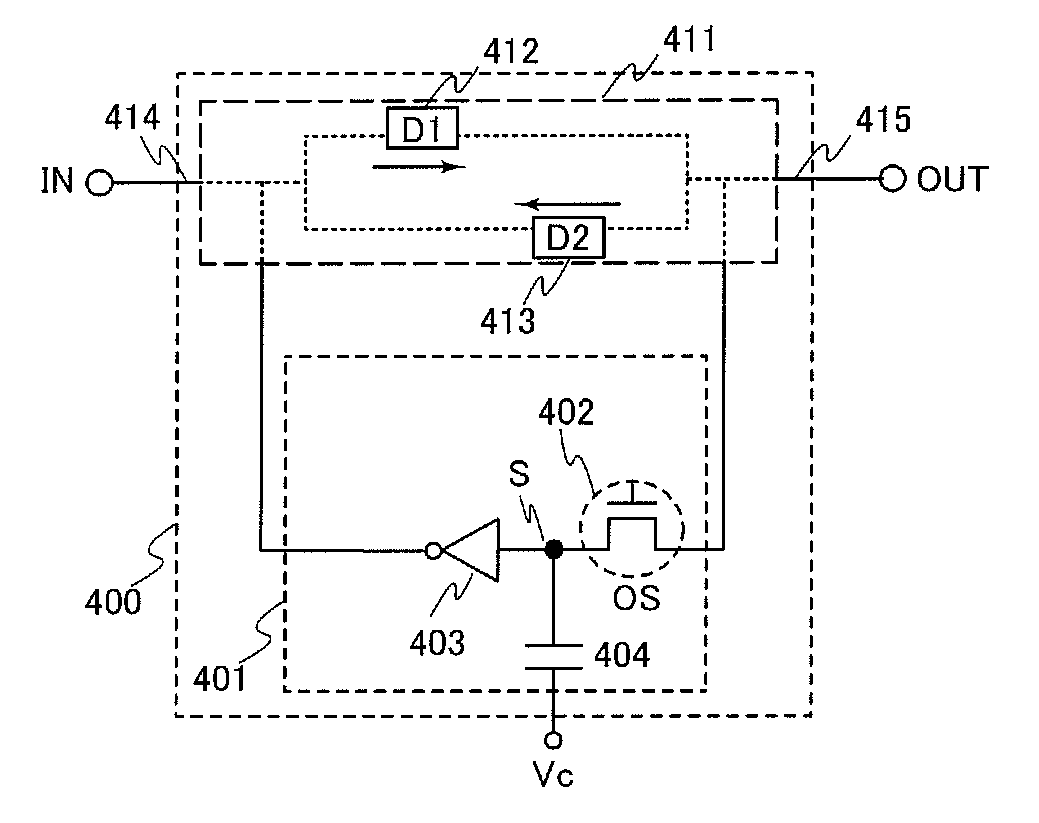
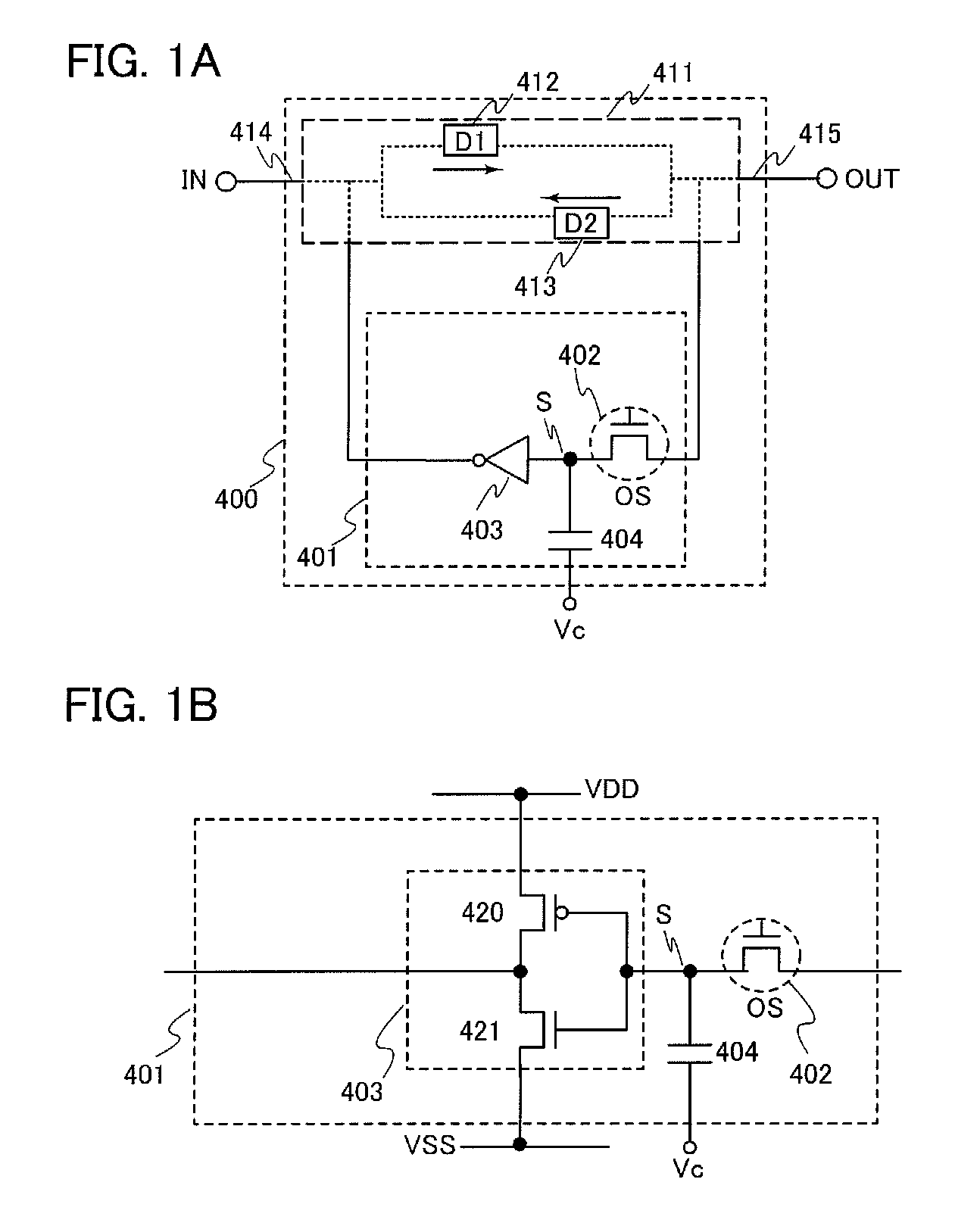
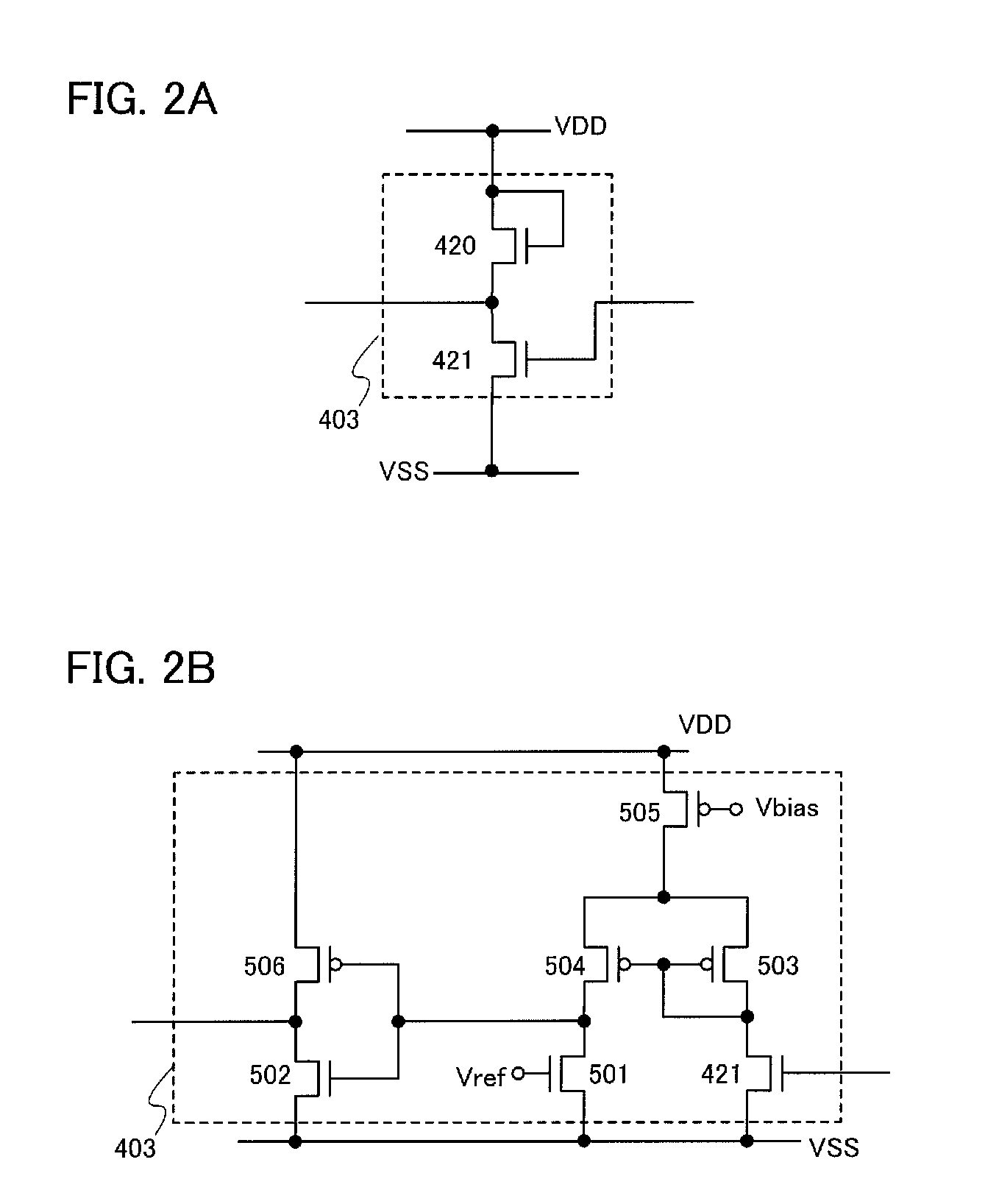
Nonvolatile latch circuit and logic circuit, and semiconductor device using the same
ActiveUS20110121878A1Wide operating temperature rangeGuaranteed uptimeTransistorSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceSemiconductor materials
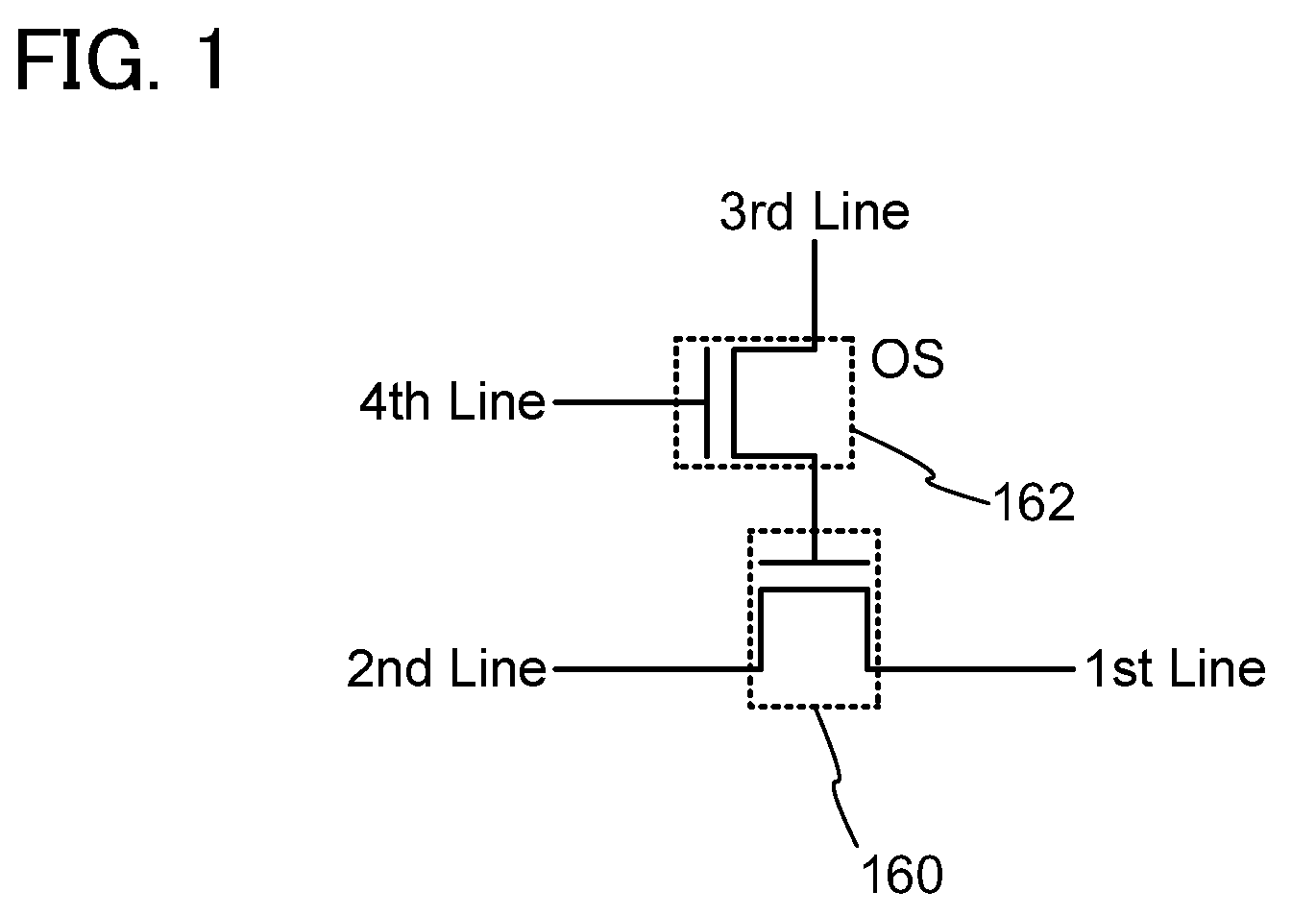
To provide a novel nonvolatile latch circuit and a semiconductor device using the nonvolatile latch circuit, a nonvolatile latch circuit includes a latch portion having a loop structure where an output of a first element is electrically connected to an input of a second element, and an output of the second element is electrically connected to an input of the first element; and a data holding portion for holding data of the latch portion. In the data holding portion, a transistor using an oxide semiconductor as a semiconductor material for forming a channel formation region is used as a switching element. In addition, an inverter electrically connected to a source electrode or a drain electrode of the transistor is included. With the transistor, data held in the latch portion can be written into a gate capacitor of the inverter or a capacitor which is separately provided.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
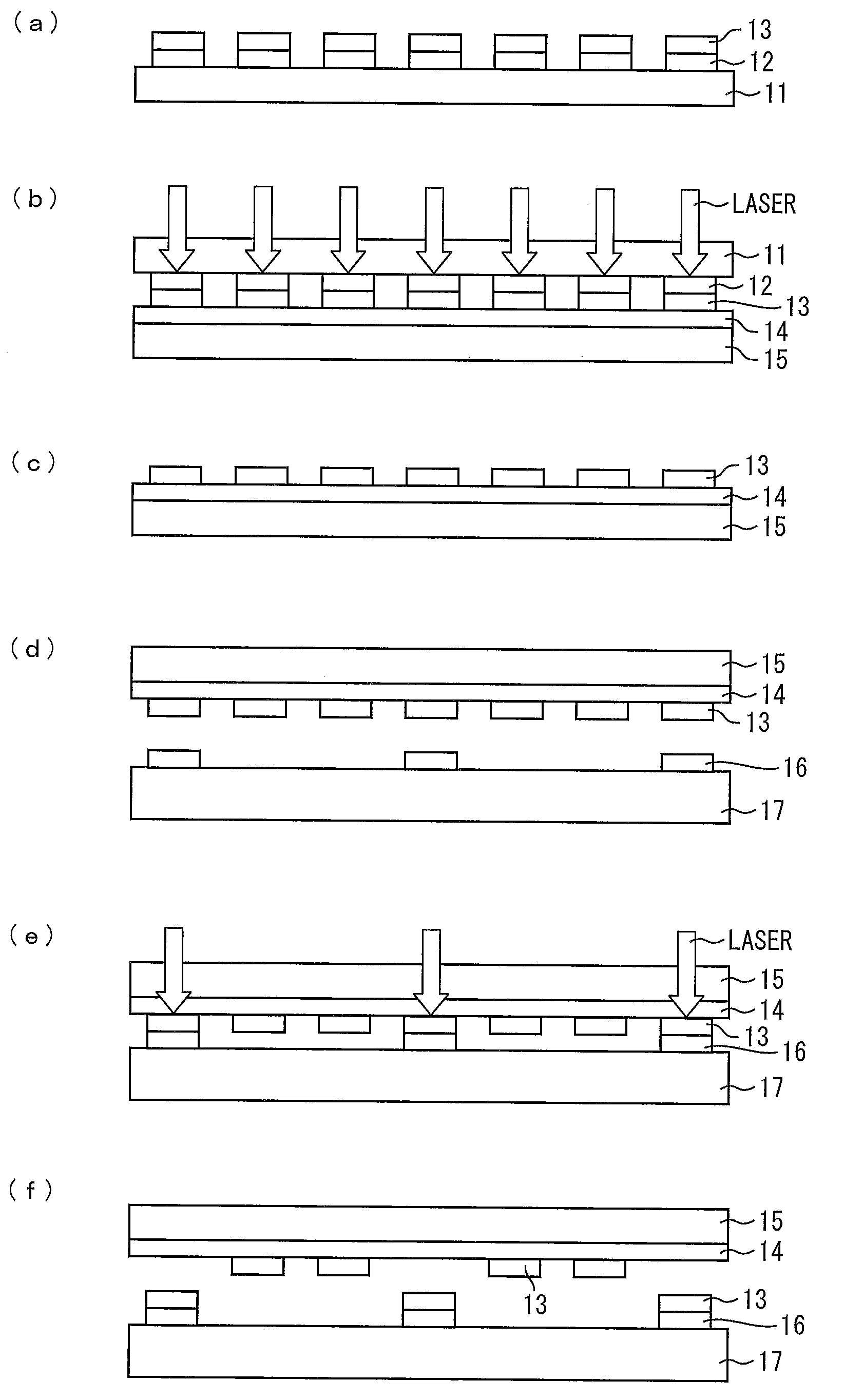
Method for manufacturing semiconductor device, and semiconductor device
InactiveUS20120241919A1High precision transmissionSmall misalignmentSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPower semiconductor deviceSingle crystal
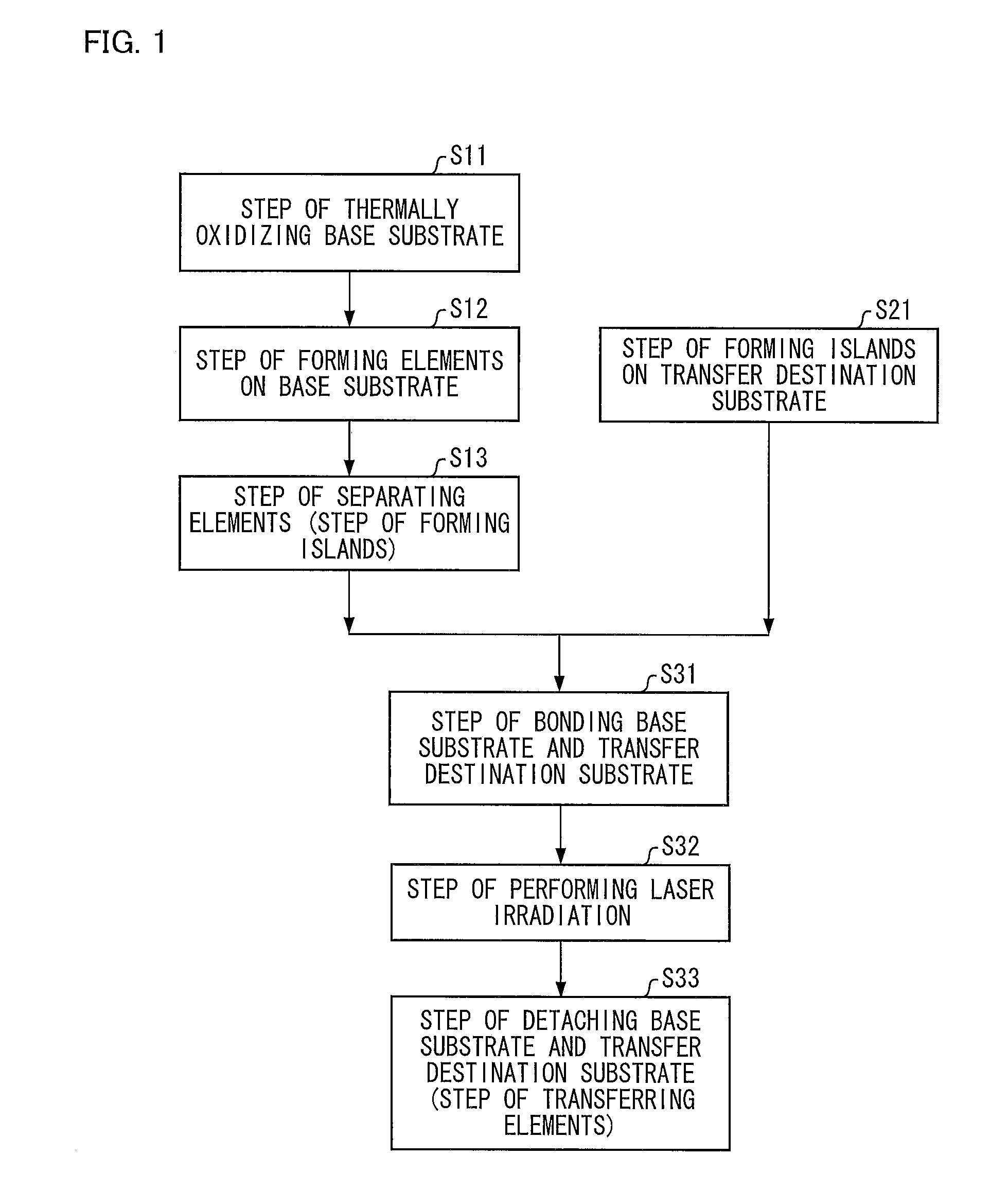
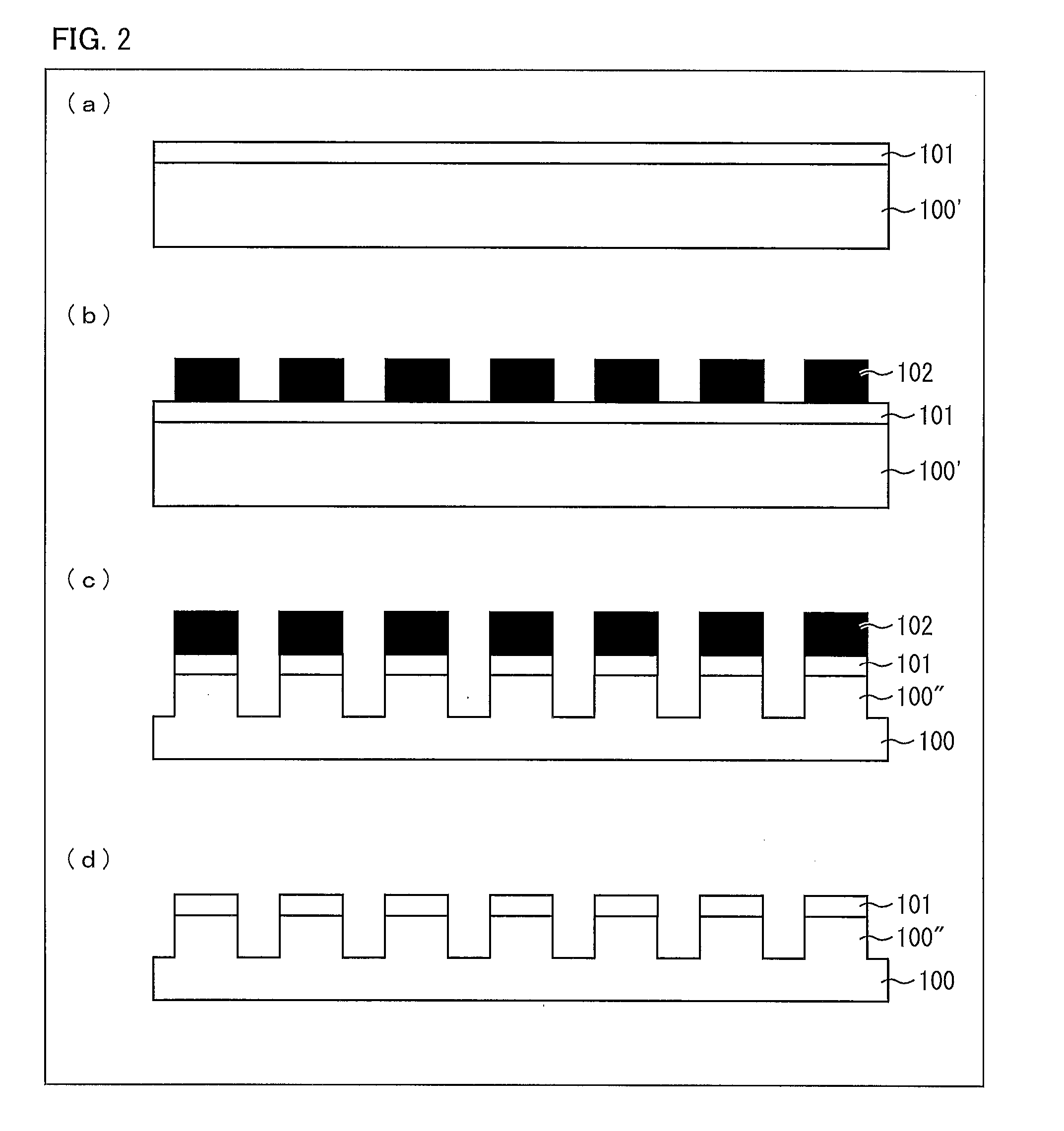
The present invention provides a method for selectively transferring elements such as monocrystalline Si thin films or elements made of monocrystalline Si from a base substrate (100) onto an insulating substrate without the use of an intermediate substrate. The base substrate (first substrate) (100) in which the elements are formed is selectively irradiated with a laser having a multiphoton absorption wavelength. Thus, elements to be transferred out of the elements and corresponding thin films on the base substrate (100) are transferred onto a transfer destination substrate (second substrate) (200).
Owner:SHARP KK
Semiconductor device
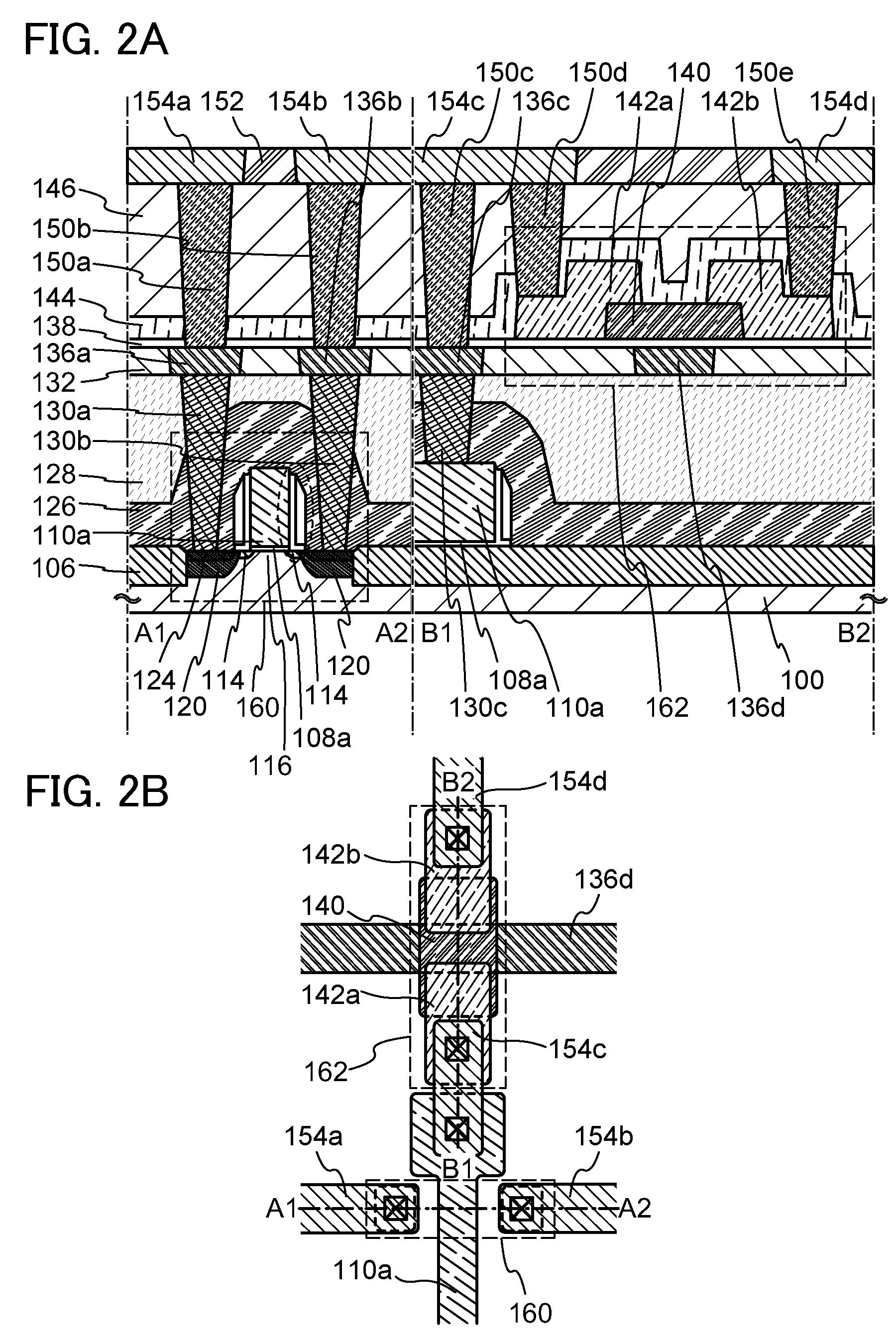
ActiveUS20110240991A1Stable electrical characteristicsExcellent electrical propertiesTransistorElectroluminescent light sourcesHydrogenOxygen
The oxide semiconductor film has the top and bottom surface portions each provided with a metal oxide film containing a constituent similar to that of the oxide semiconductor film. An insulating film containing a different constituent from the metal oxide film and the oxide semiconductor film is further formed in contact with a surface of the metal oxide film, which is opposite to the surface in contact with the oxide semiconductor film The oxide semiconductor film used for the active layer of the transistor is an oxide semiconductor film highly purified to be electrically i-type (intrinsic) by removing impurities such as hydrogen, moisture, a hydroxyl group, and hydride from the oxide semiconductor and supplying oxygen which is a major constituent of the oxide semiconductor and is simultaneously reduced in a step of removing impurities.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20110024751A1Reduce manufacturing costEasily brokenTransistorSolid-state devicesBottom gateSemiconductor
In a bottom-gate thin film transistor using the stack of the first oxide semiconductor layer and the second oxide semiconductor layer, an oxide insulating layer serving as a channel protective layer is formed over and in contact with part of the oxide semiconductor layer overlapping with a gate electrode layer. In the same step as formation of the insulating layer, an oxide insulating layer covering a peripheral portion (including a side surface) of the stack of the oxide semiconductor layers is formed.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Substrate for semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS7902660B1Thin thicknessAvoid warpingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectricitySolder ball
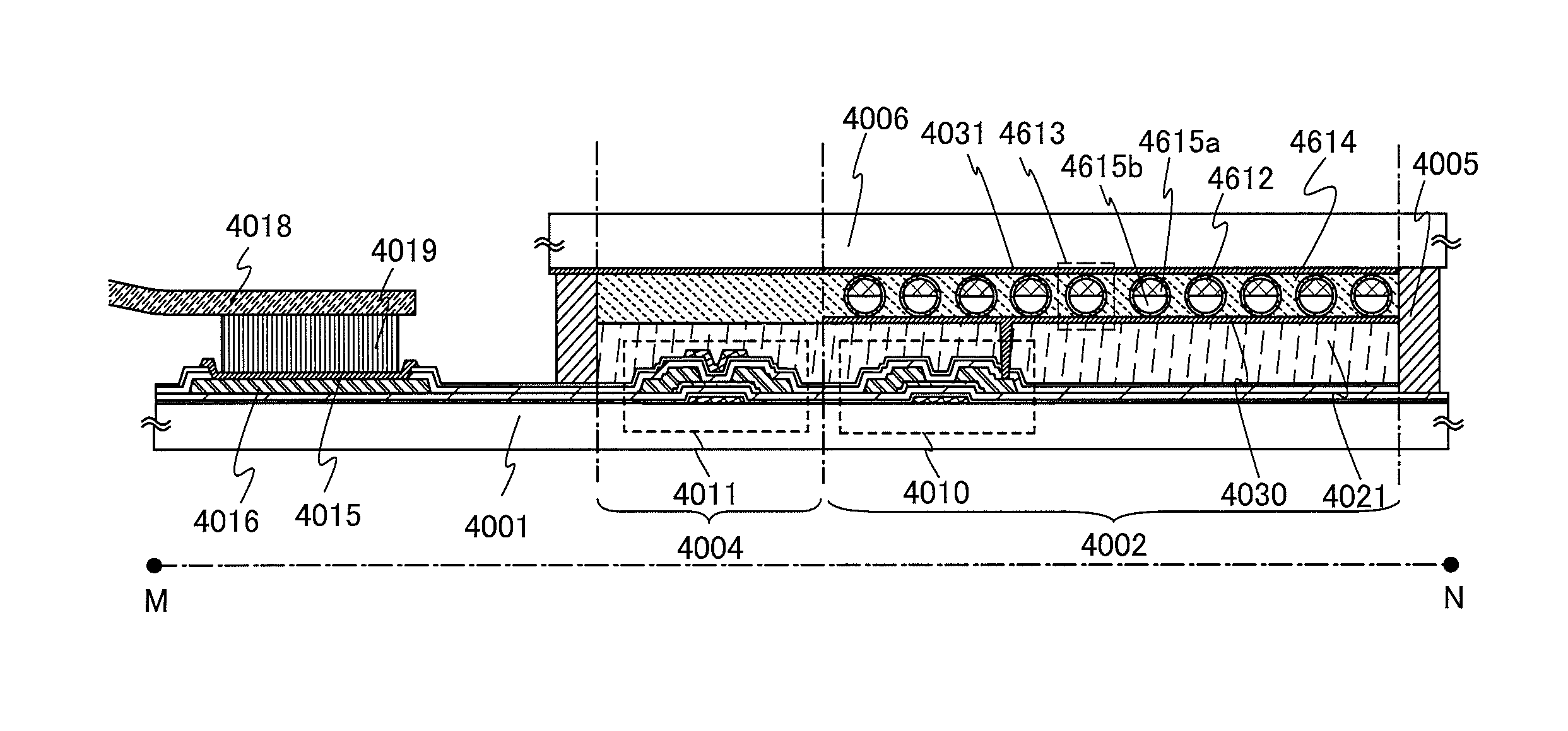
A substrate for a semiconductor device and a manufacturing thereof, and a semiconductor device using the same and a manufacturing method thereof are disclosed. For example, in the substrate according to the present invention, a core is eliminated, so that the substrate has a very thin thickness, as well, the length of electrically conductive patterns becomes shorter, whereby the electrical efficiency thereof is improved. Moreover, since a carrier having a stiffness of a predetermined strength is bonded on the substrate, it can prevent a warpage phenomenon during the manufacturing process of the semiconductor device. Furthermore, the carrier is removed from the substrate, whereby a solder ball fusing process or an electrical connecting process of the semiconductor die can be easily performed.
Owner:AMKOR TECH SINGAPORE HLDG PTE LTD
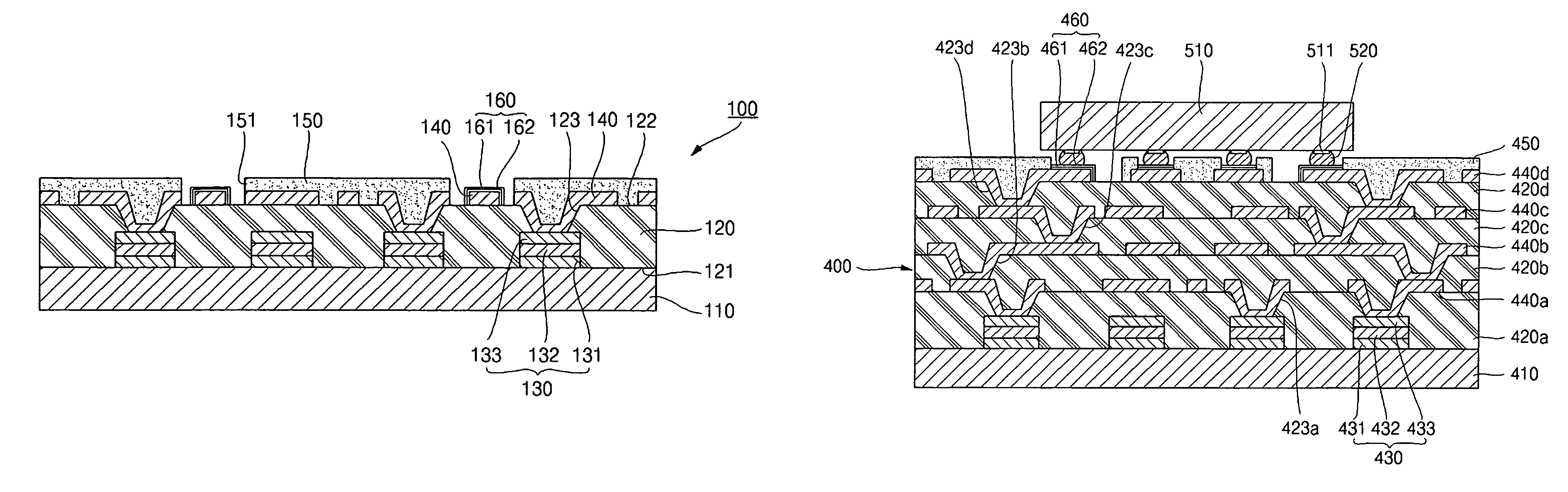
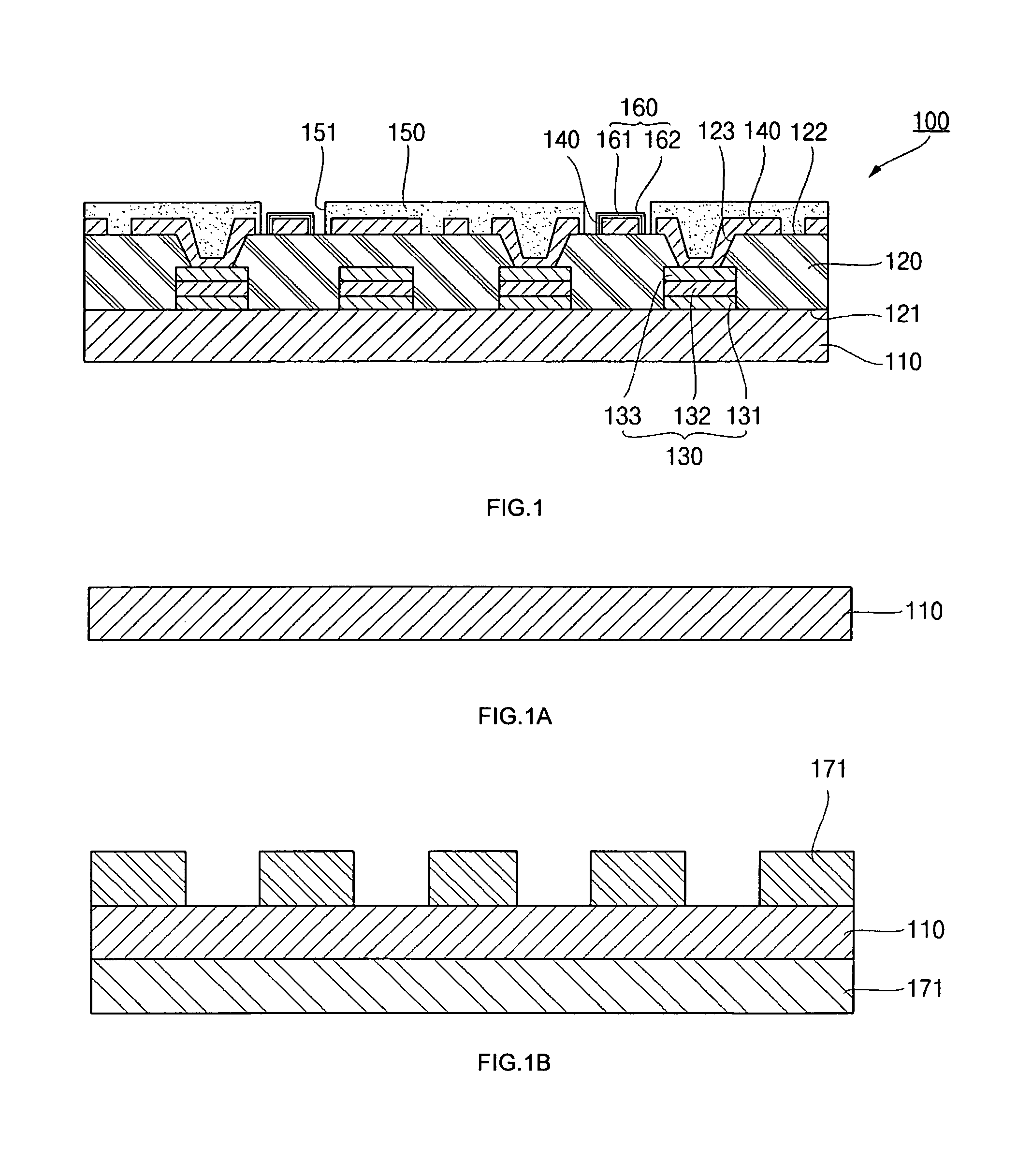
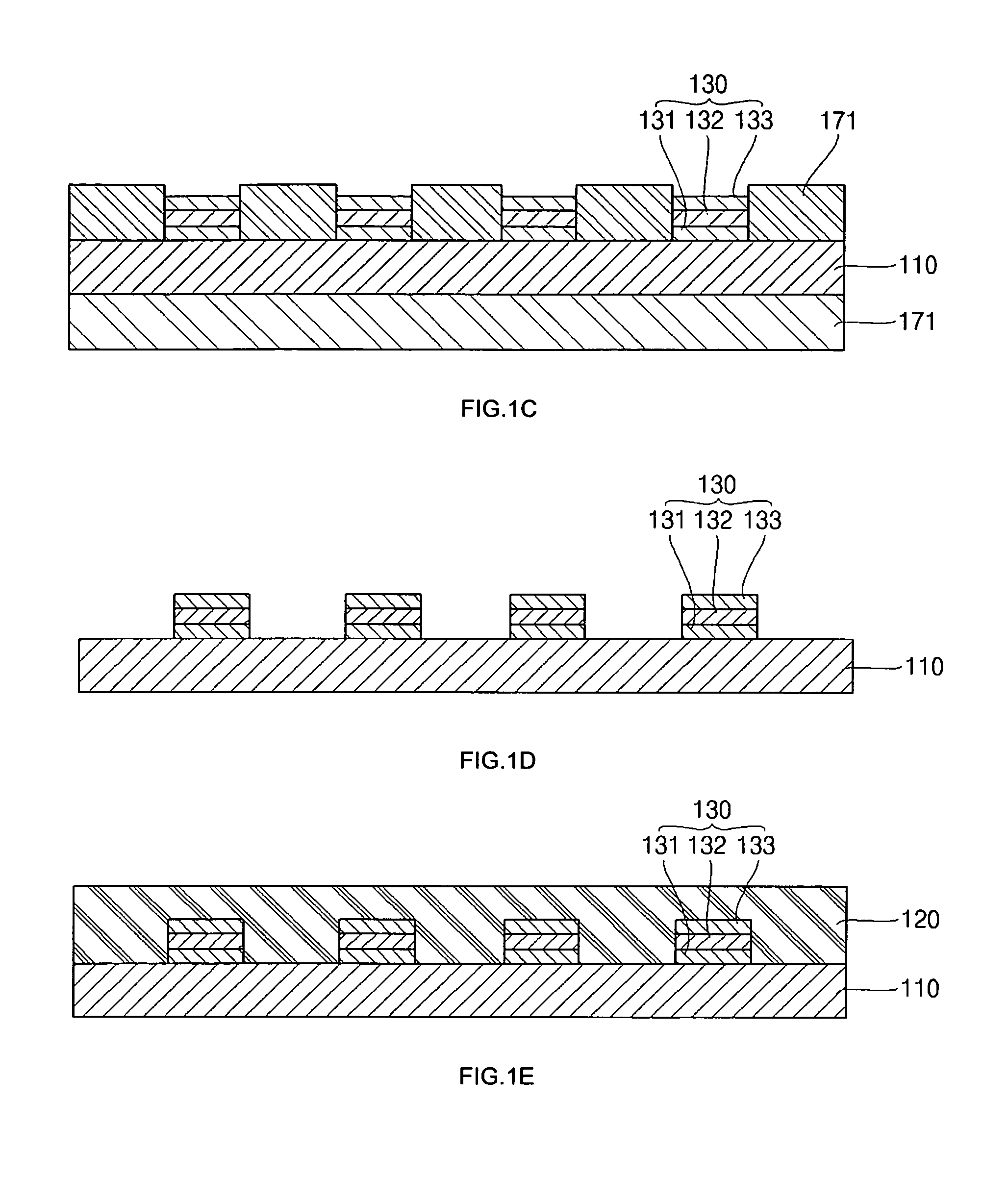
Semiconductor device with chip having low-k-layers
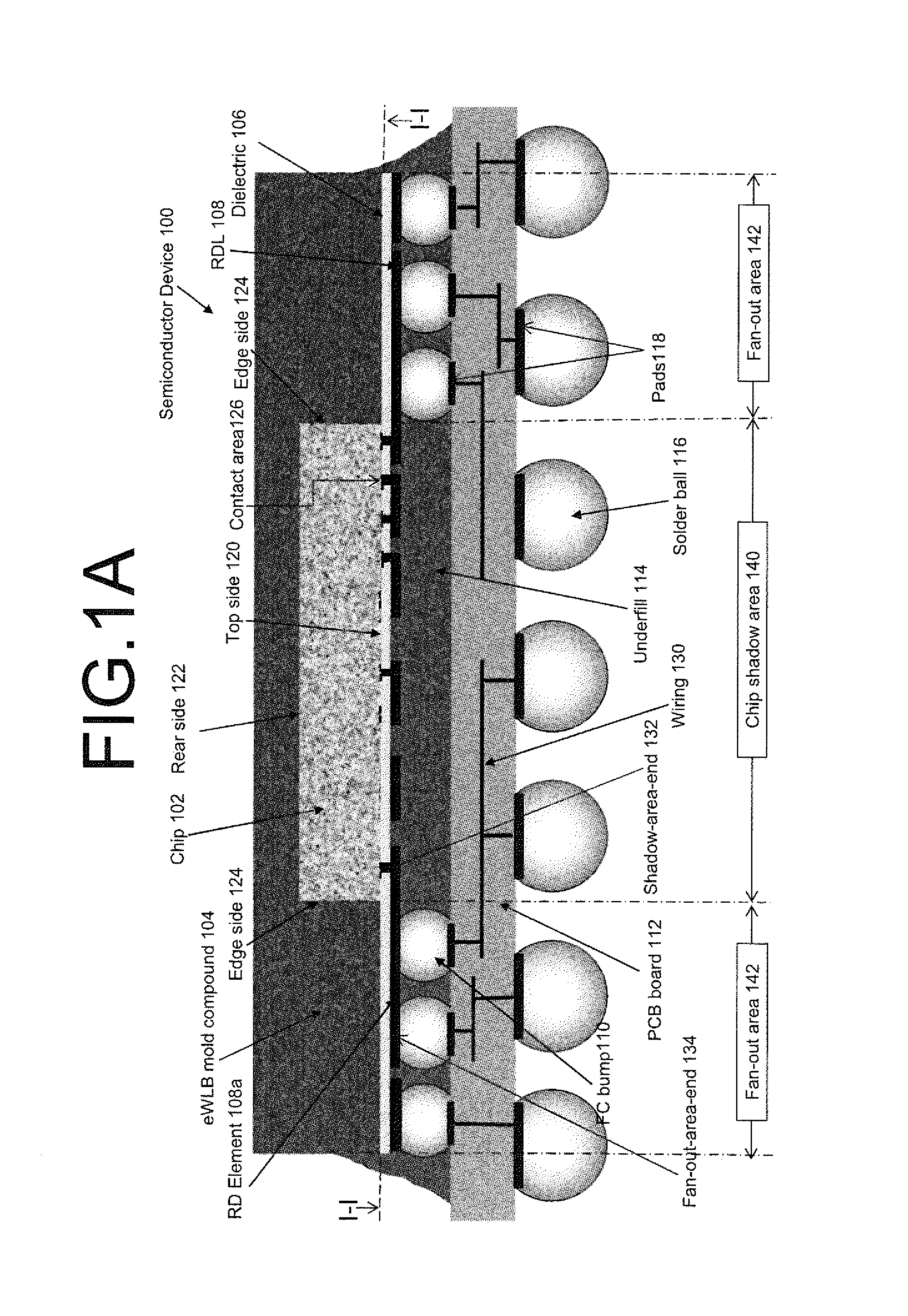
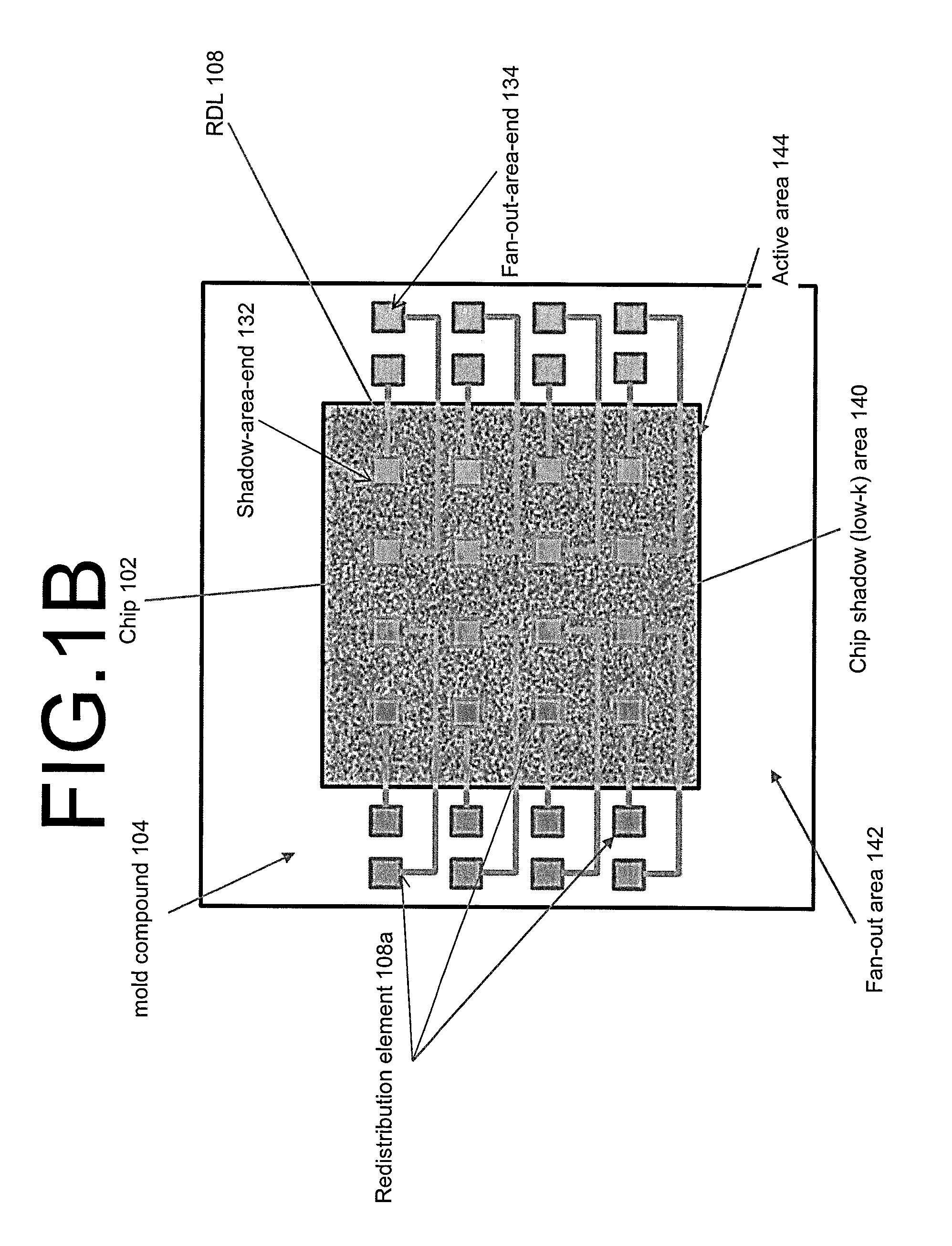
ActiveUS20140197530A1Firm packagingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesRedistribution layerSemiconductor chip
A semiconductor device is described having at least one semiconductor chip, the chip having an active area on a top side thereof, the active area formed at least in part of low-k material, said low-k material defining a low-k subarea of said active area; an embedding material, in which said at least one semiconductor chip is embedded, at least part of the embedding material forming a coplanar area with said active area; at least one contact area within the low-k subarea; a redistribution layer on the coplanar area, the redistribution layer connected to said contact areas; at least one first-level interconnect, located outside said low-k subarea, the first-level interconnect electrically connected to at least one of said contact areas via the redistribution layer.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
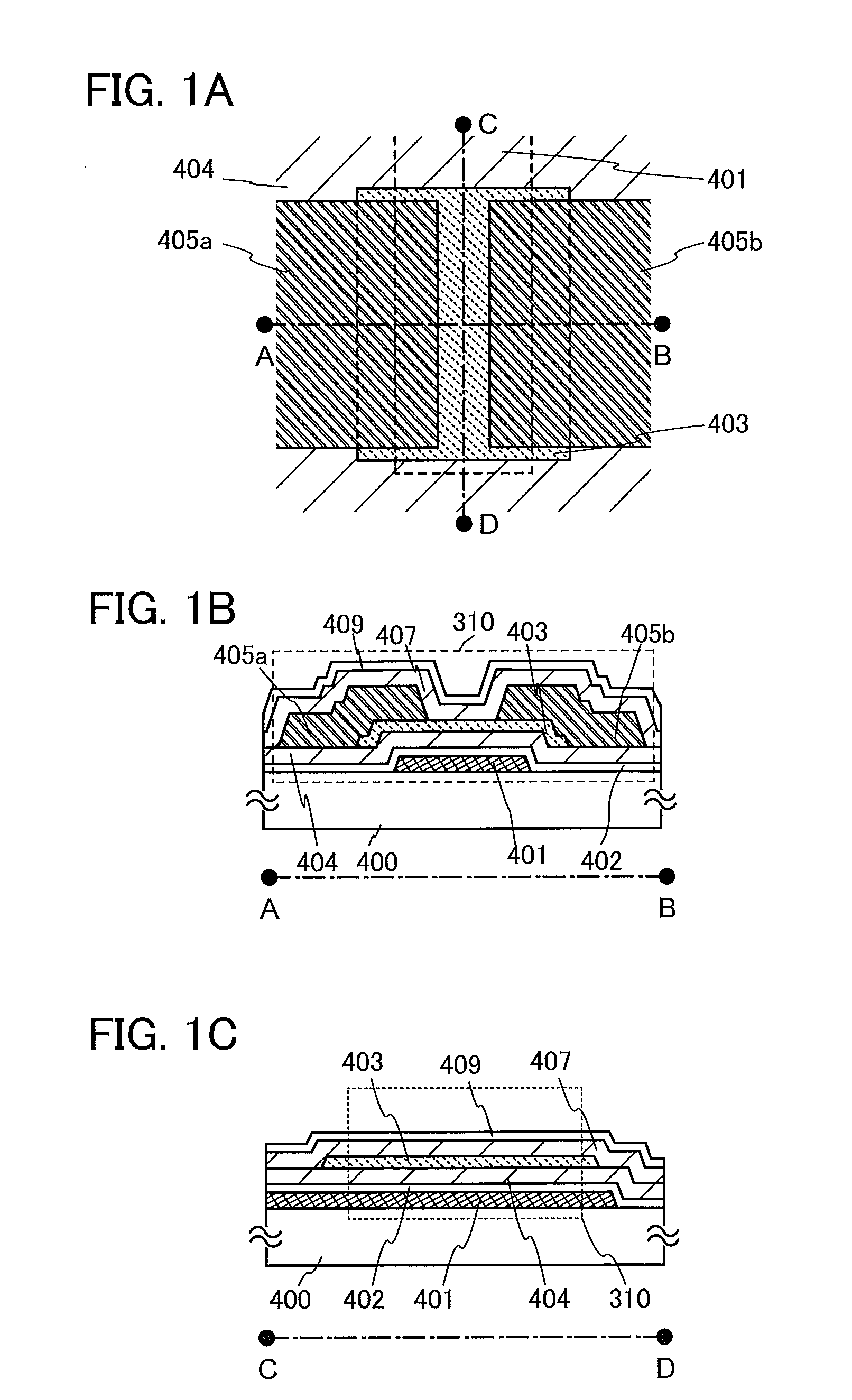
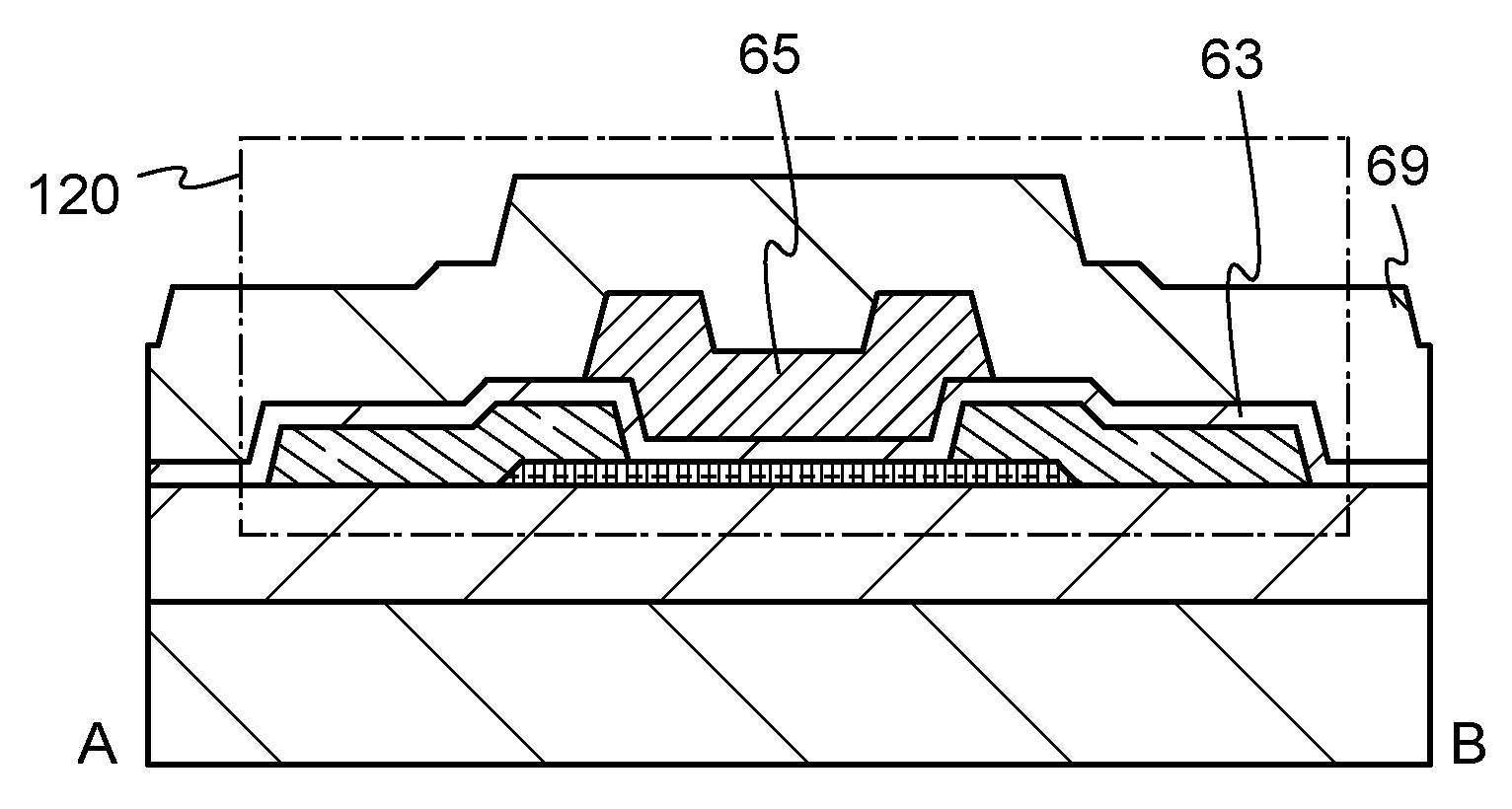
ActiveUS20110031491A1Reduce parasitic capacitanceOff-current can be reducedTransistorStatic indicating devicesBottom gateParasitic capacitance
An object is to provide a semiconductor device having a structure in which parasitic capacitance between wirings can be efficiently reduced. In a bottom gate thin film transistor using an oxide semiconductor layer, an oxide insulating layer used as a channel protection layer is formed above and in contact with part of the oxide semiconductor layer overlapping with a gate electrode layer, and at the same time an oxide insulating layer covering a peripheral portion (including a side surface) of the stacked oxide semiconductor layer is formed. Further, a source electrode layer and a drain electrode layer are formed in a manner such that they do not overlap with the channel protection layer. Thus, a structure in which an insulating layer over the source electrode layer and the drain electrode layer is in contact with the oxide semiconductor layer is provided.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device
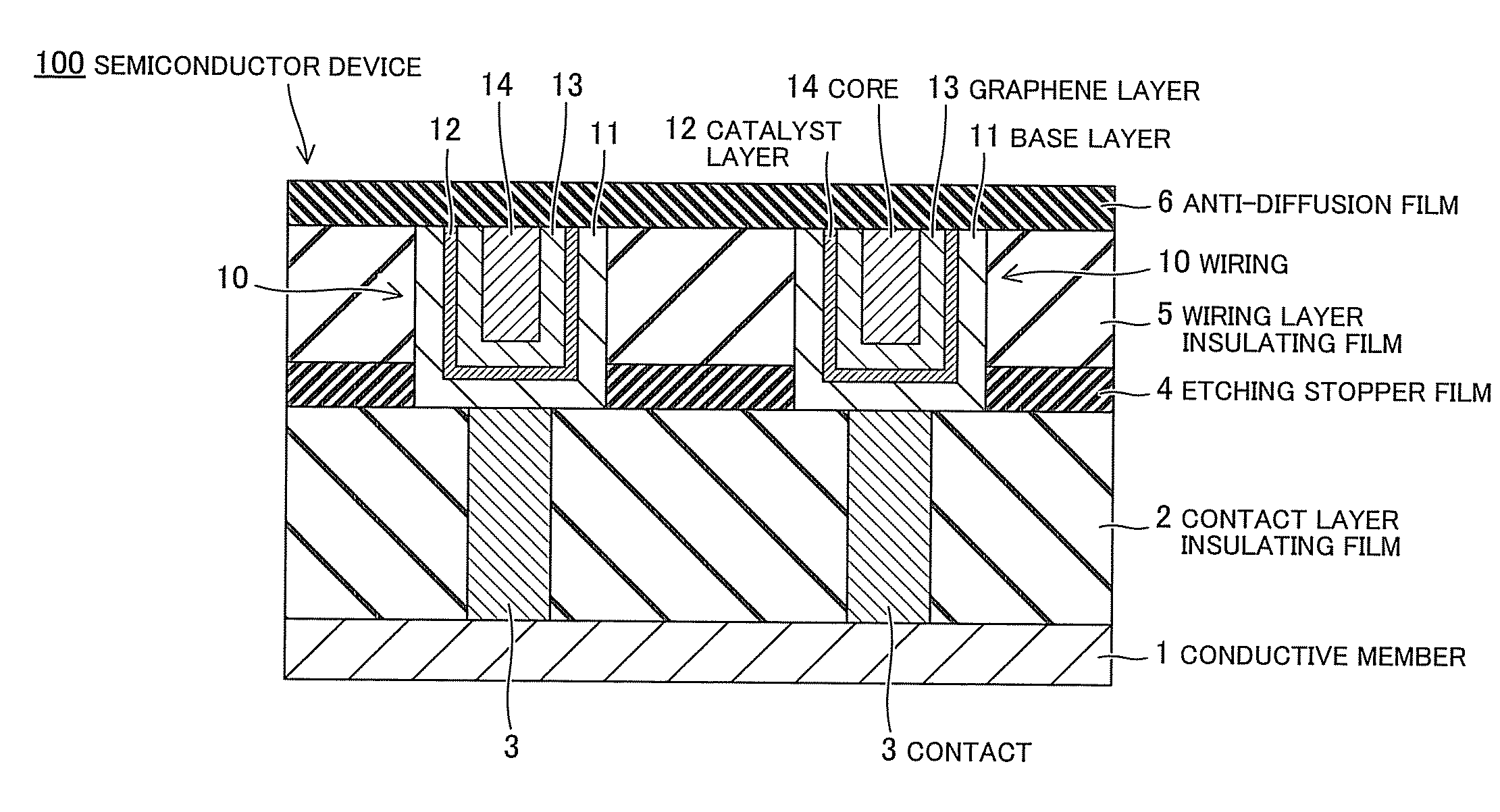
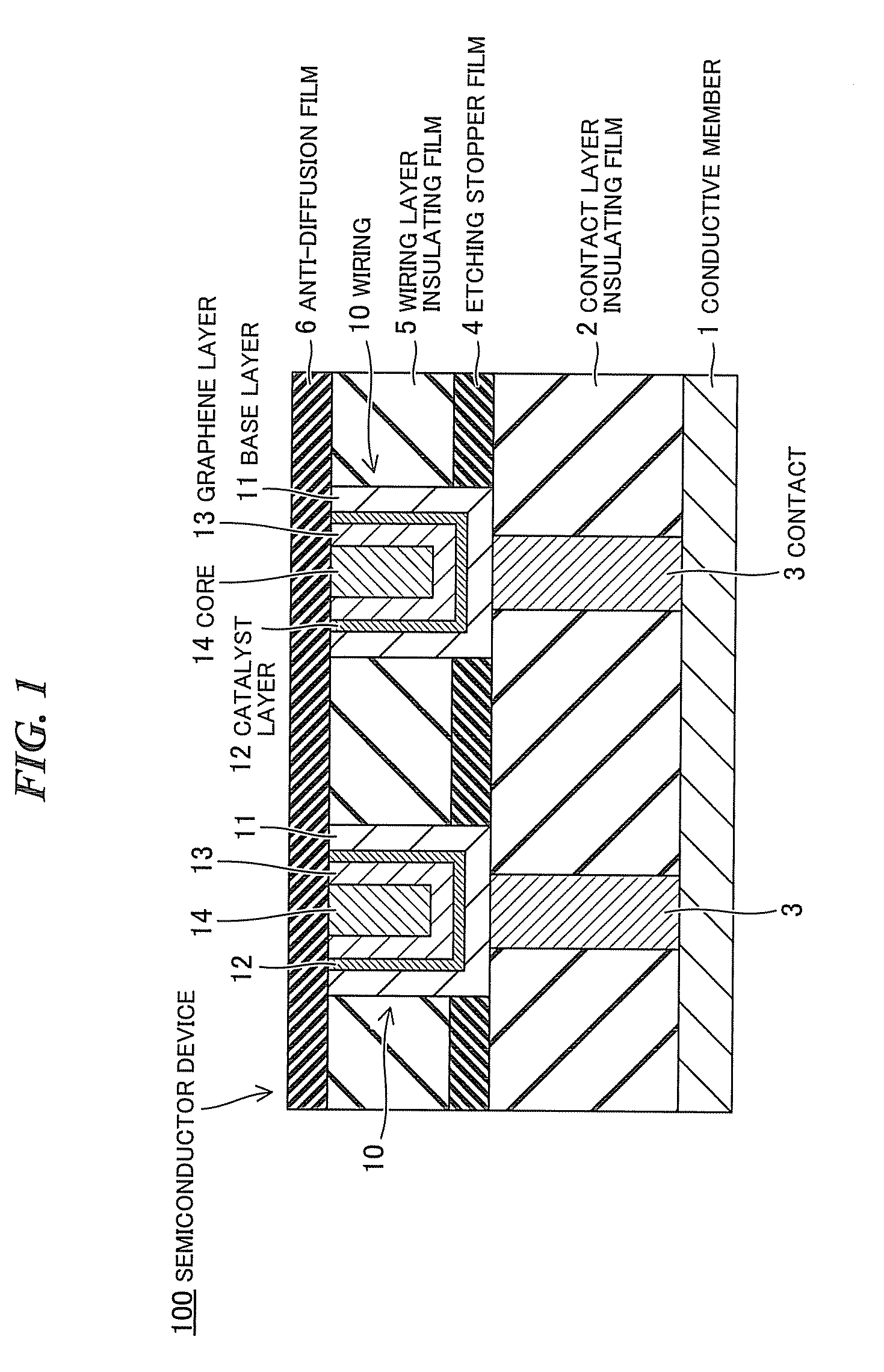
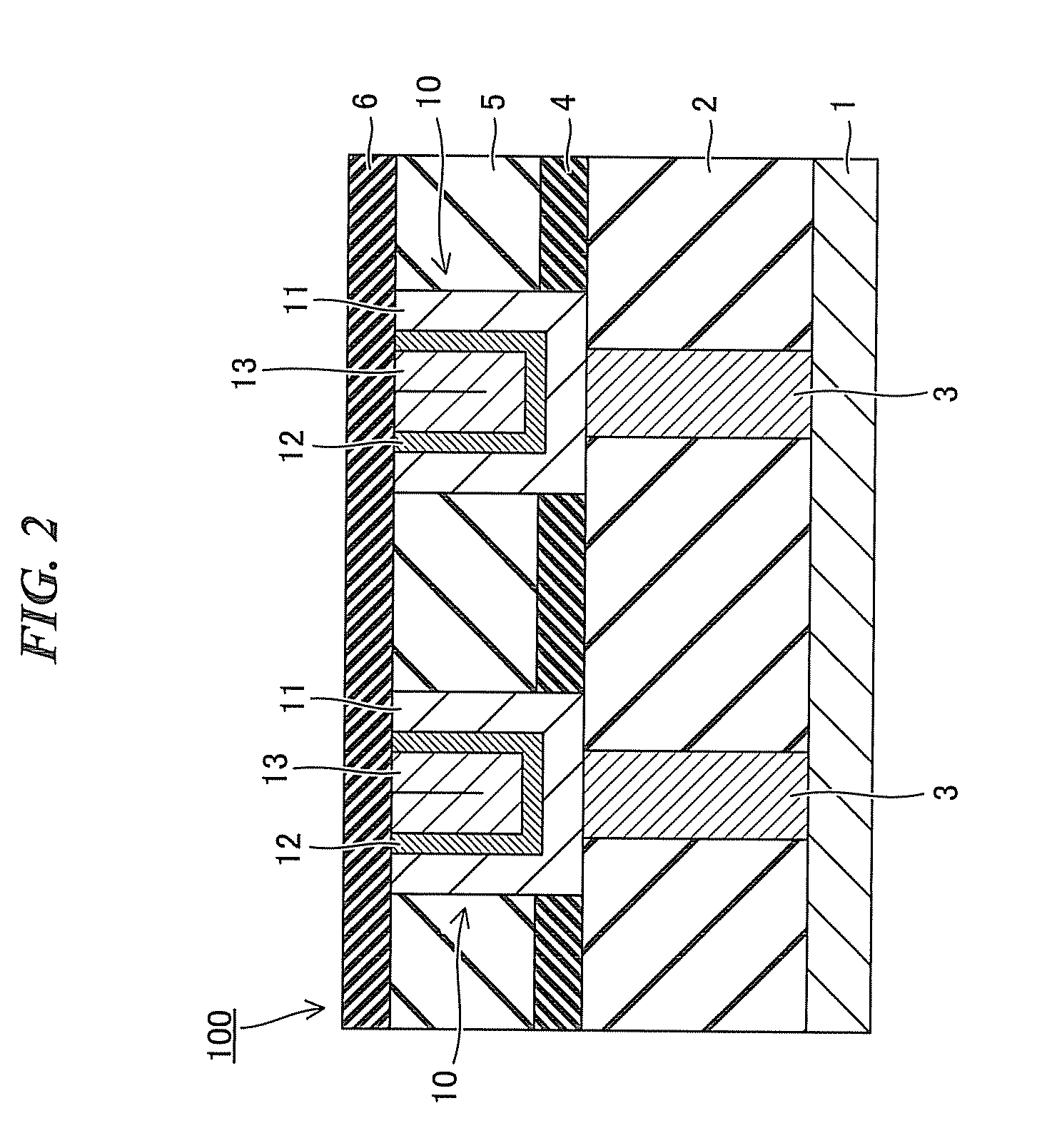
ActiveUS20110006425A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceGraphene
A semiconductor device according to one embodiment includes: a semiconductor substrate; an insulating film provided on the semiconductor substrate and containing a wiring trench; a first catalyst layer provided directly or via another member on side and bottom surfaces of the wiring trench; and a first graphene layer provided in the wiring trench so as to be along the side and bottom surface of the wiring trench, the first graphene layer being provided on the first catalyst layer so as to be in contact with the first catalyst layer.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
ActiveUS20130009209A1Improve performanceReduce power consumptionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPower semiconductor deviceEngineering
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Electrostatic chuck and method of manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS20120134065A1Not always easySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMassive gravityPower semiconductor device
An electrostatic chuck device including: a plurality of adsorption areas having an electrode generating electrostatic attractive force; and a control portion controlling the electrostatic attractive force against each of the plurality of the adsorption areas independently of other adsorption areas.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
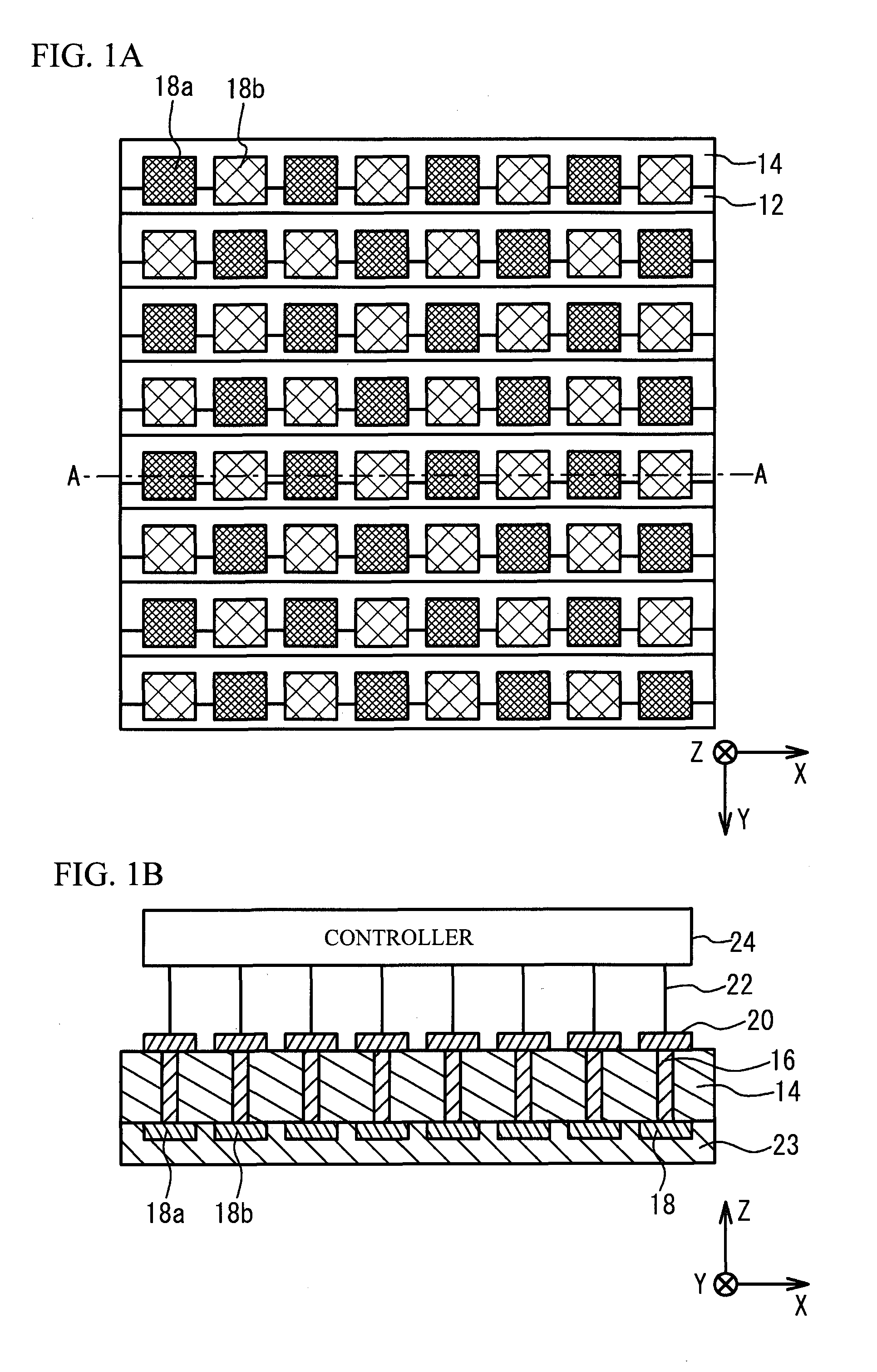
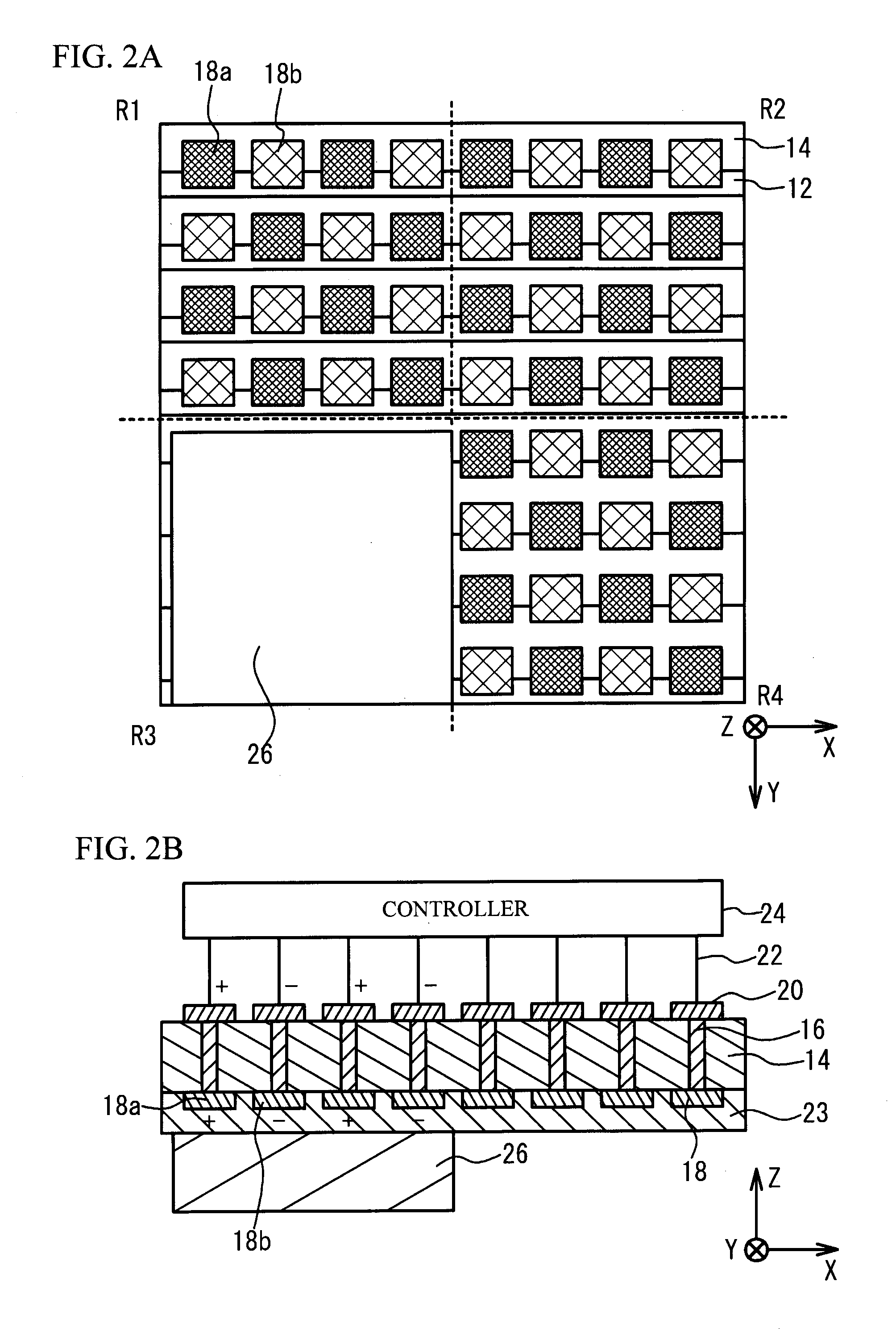
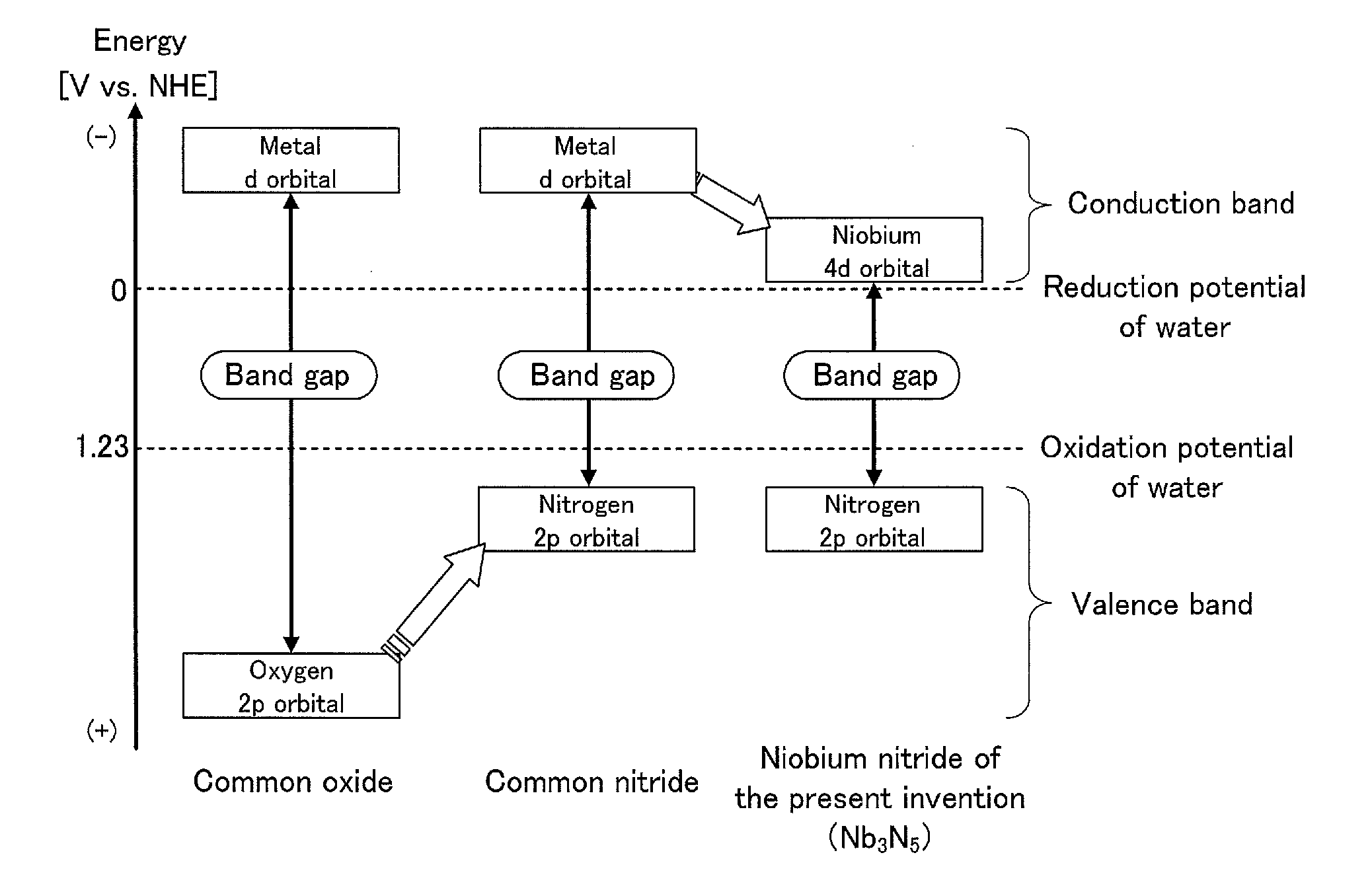
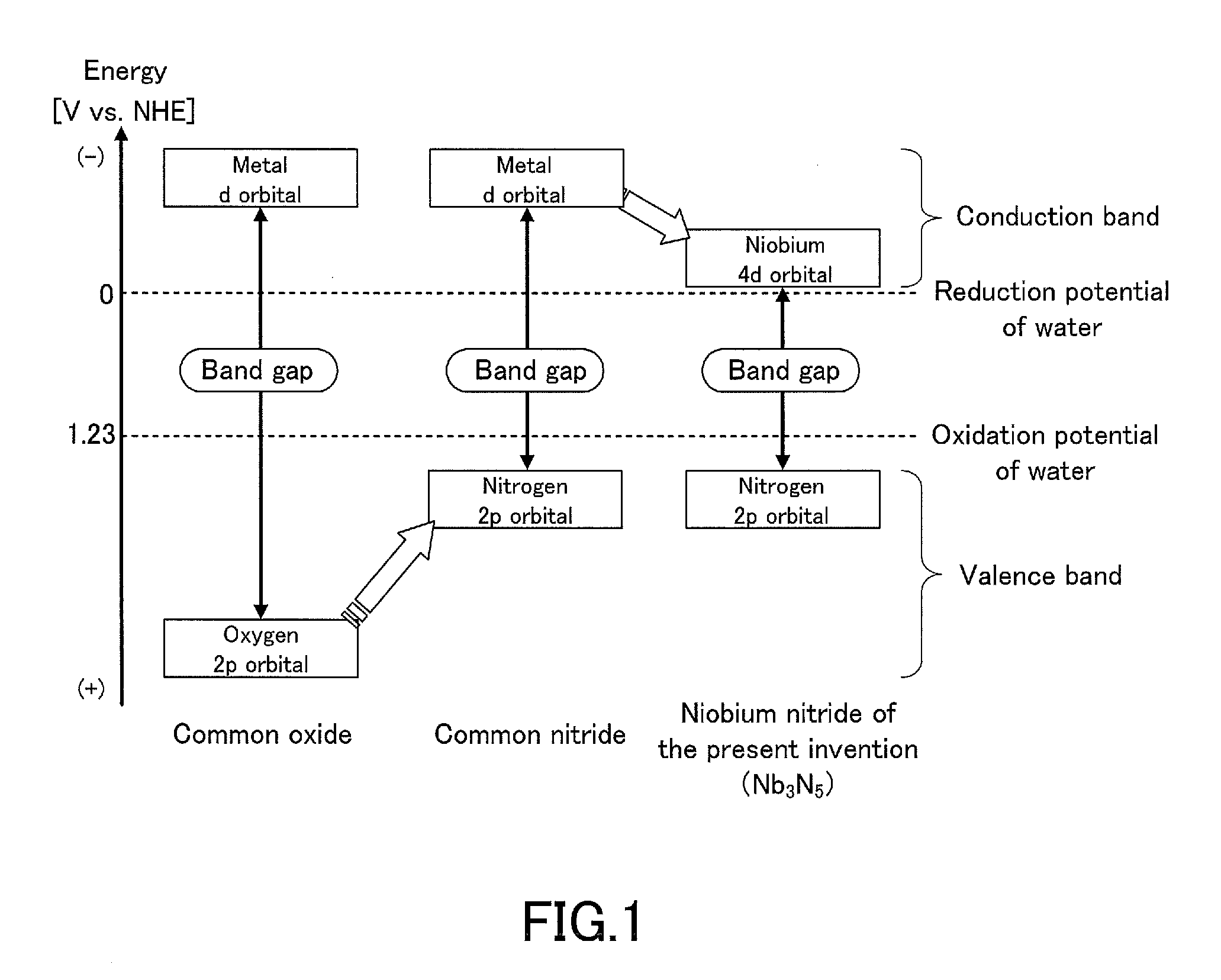
Niobium nitride and method for producing same, niobium nitride-containing film and method for producing same, semiconductor, semiconductor device, photocatalyst, hydrogen generation device, and energy system
The present invention is a niobium nitride which has a composition represented by the composition formula Nb3N5 and in which a constituent element Nb has a valence of substantially +5. The method for producing the niobium nitride of the present invention includes the step of nitriding an organic niobium compound by reacting the organic niobium compound with a nitrogen compound gas.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Semiconductor device and display device including the semiconductor device
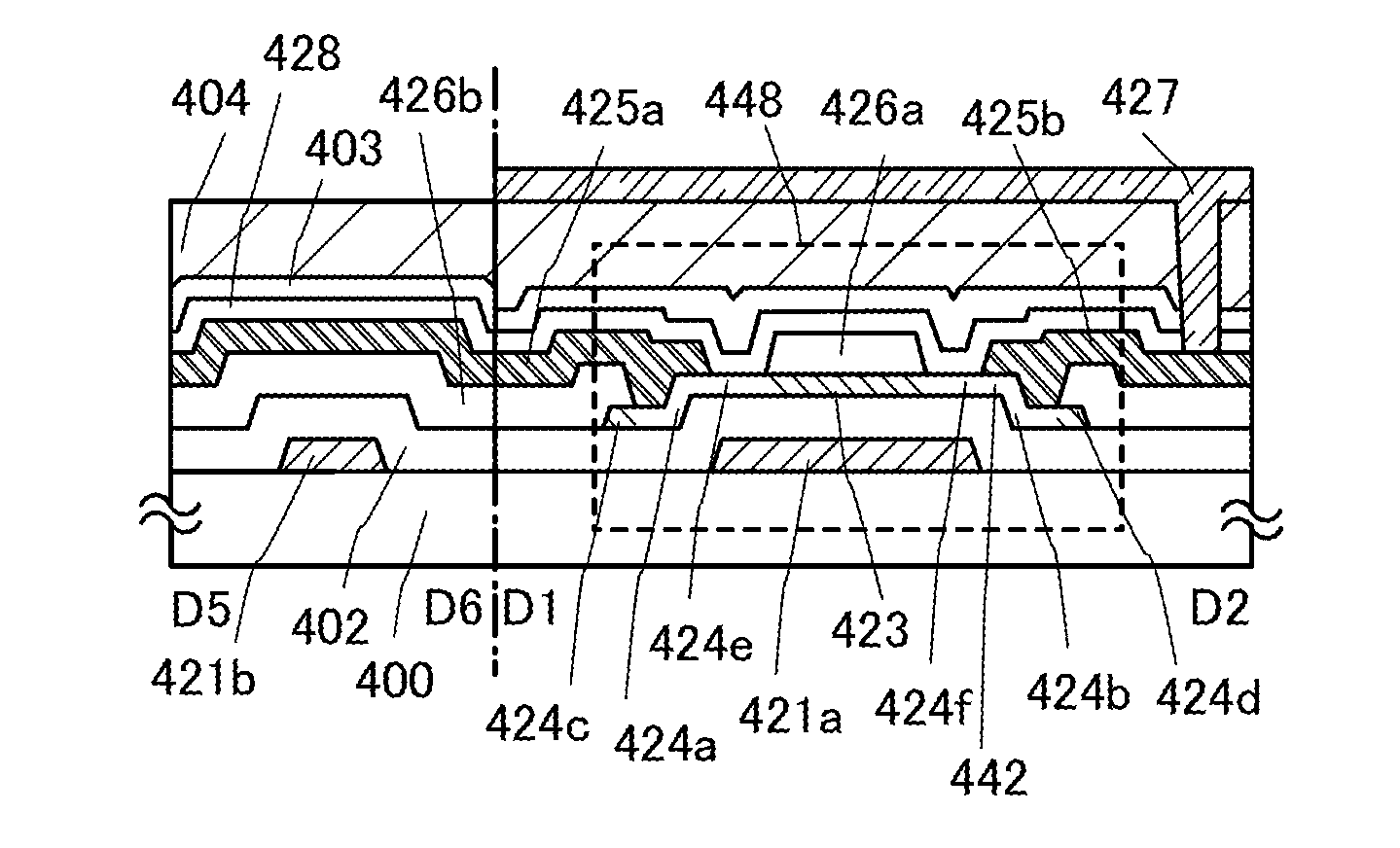
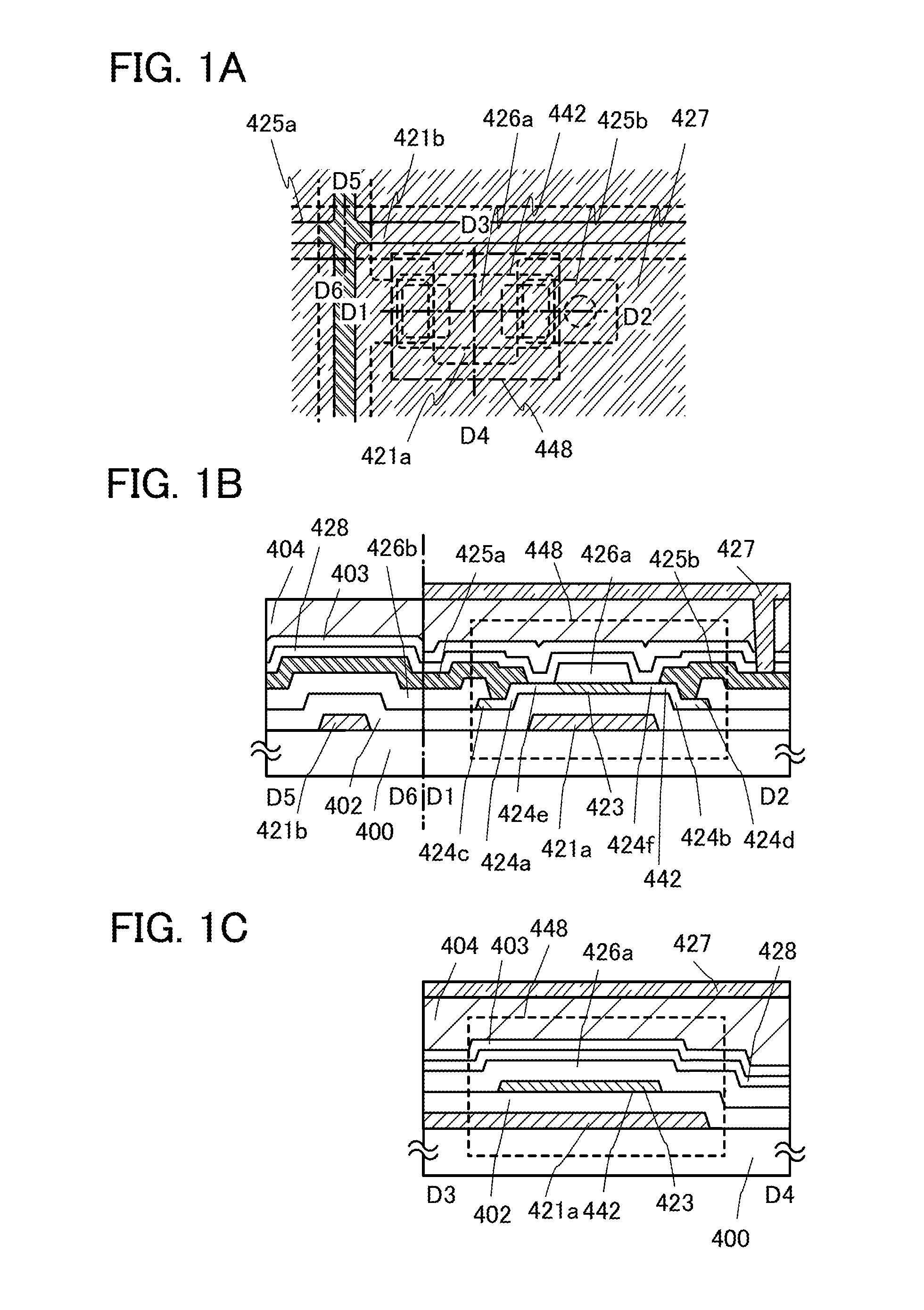
ActiveUS20150014680A1Excellent electrical propertiesImprove featuresSolid-state devicesNon-linear opticsPower semiconductor deviceDisplay device
A semiconductor device including a transistor and a connection portion is provided. The transistor includes a gate electrode, a first insulating film over the gate electrode, an oxide semiconductor film over the first insulating film and at a position overlapping with the gate electrode, and source and drain electrodes electrically connected to the oxide semiconductor film; and the connection portion includes a first wiring on the same surface as a surface on which the gate electrode is formed, a second wiring on the same surface as a surface on which the source and drain electrodes are formed, and a third wiring connecting the first wiring and the second wiring. The distance between an upper end portion and a lower end portion of the second wiring is longer than the distance between an upper end portion and a lower end portion of each of the source and drain electrodes.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20110240990A1Improve reliabilityExcellent electrical propertiesTransistorSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceSemiconductor
An object is to stabilize electric characteristics of a semiconductor device including an oxide semiconductor to increase reliability. The semiconductor device includes an insulating film; a first metal oxide film on and in contact with the insulating film; an oxide semiconductor film partly in contact with the first metal oxide film; source and drain electrodes electrically connected to the oxide semiconductor film; a second metal oxide film partly in contact with the oxide semiconductor film; a gate insulating film on and in contact with the second metal oxide film; and a gate electrode over the gate insulating film.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20110193164A1Reduce parasitic capacitanceLarge thicknessSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPower semiconductor deviceGate dielectric
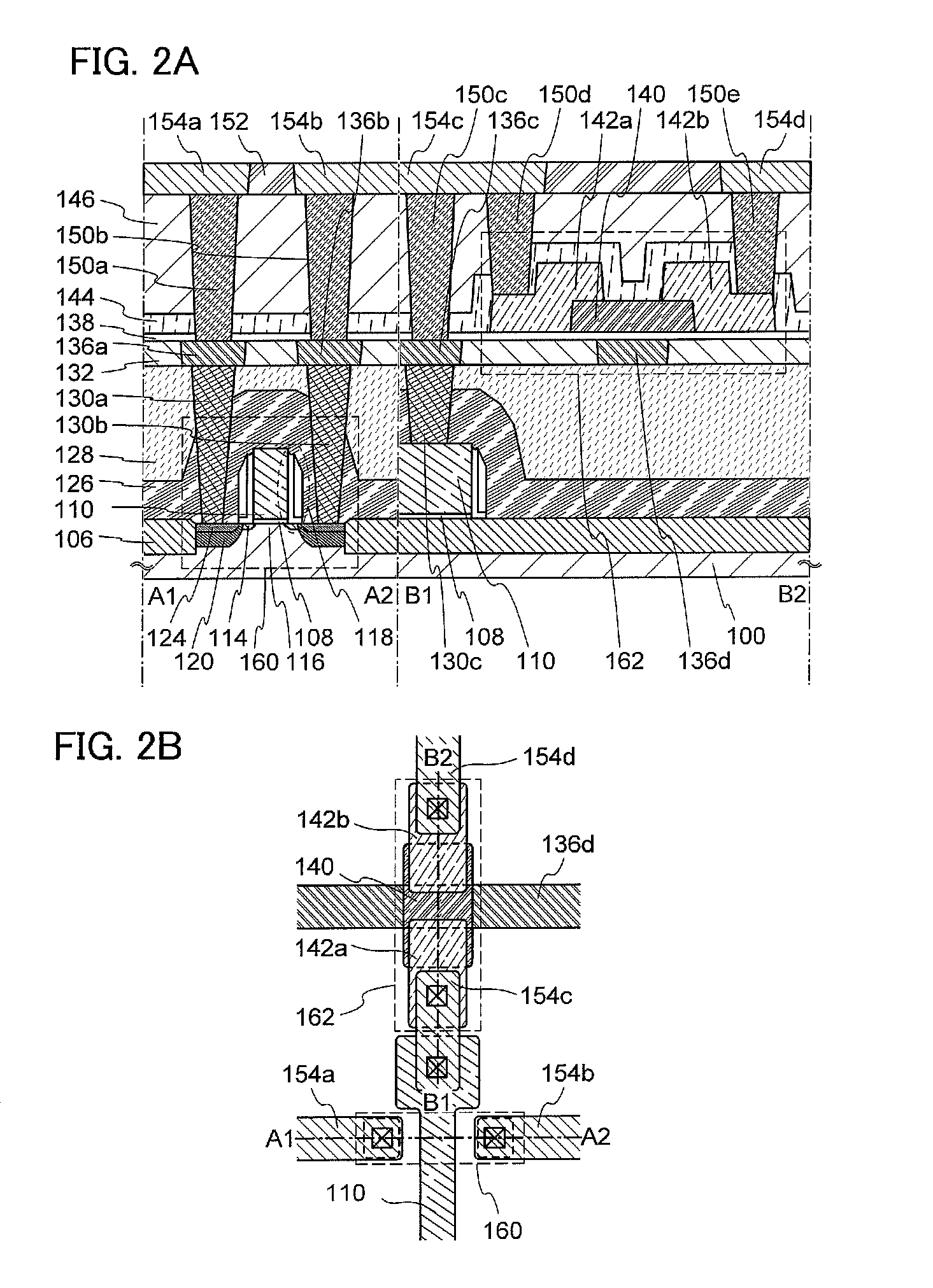
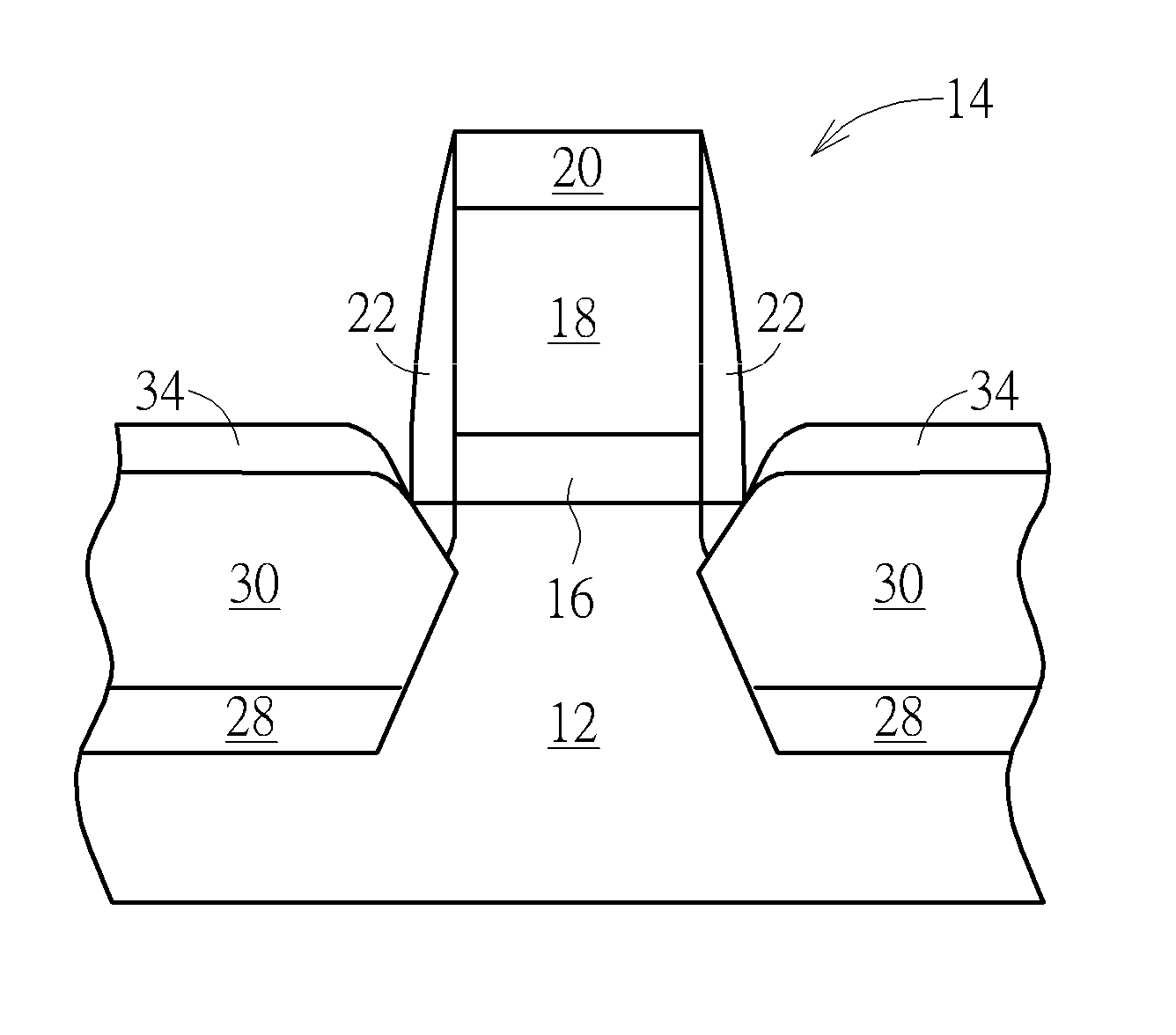
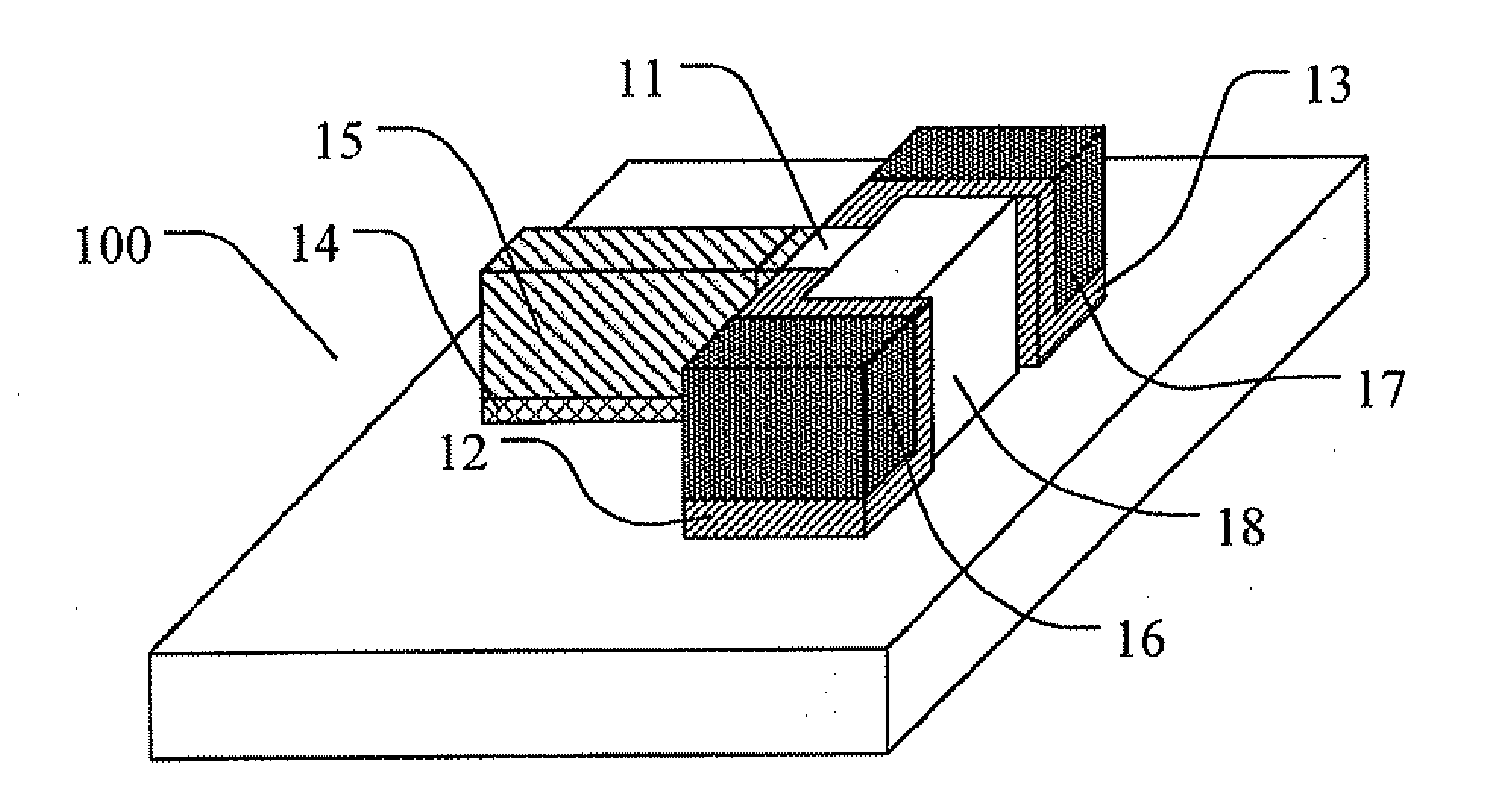
The present application discloses a semiconductor device formed on a SOI substrate which comprises a buried insulating layer and a semiconductor layer on the buried insulating layer and a method for manufacturing the same, wherein a fin of semiconductive material having two opposing sides perpendicular to a main surface of the SOI substrate is provided in the semiconductor layer, said semiconductor device comprising: a source region and a drain region provided at two ends of the fin respectively; a channel region provided at a central portion of the fin; and a stack of gate dielectric and gate conductor provided at one side of the fin, where the gate conductor is isolated from the channel region by the gate dielectric, wherein the gate conductor extends away from the one side of the fin in a direction parallel to the main surface of the SOI substrate. The semiconductor device has an improved short channel effect and a reduced parasitic capacitance and resistance, which contributes to an improved electrical property and facilitates scaling down of the transistor.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Semiconductor device with floating gate and electrically floating body
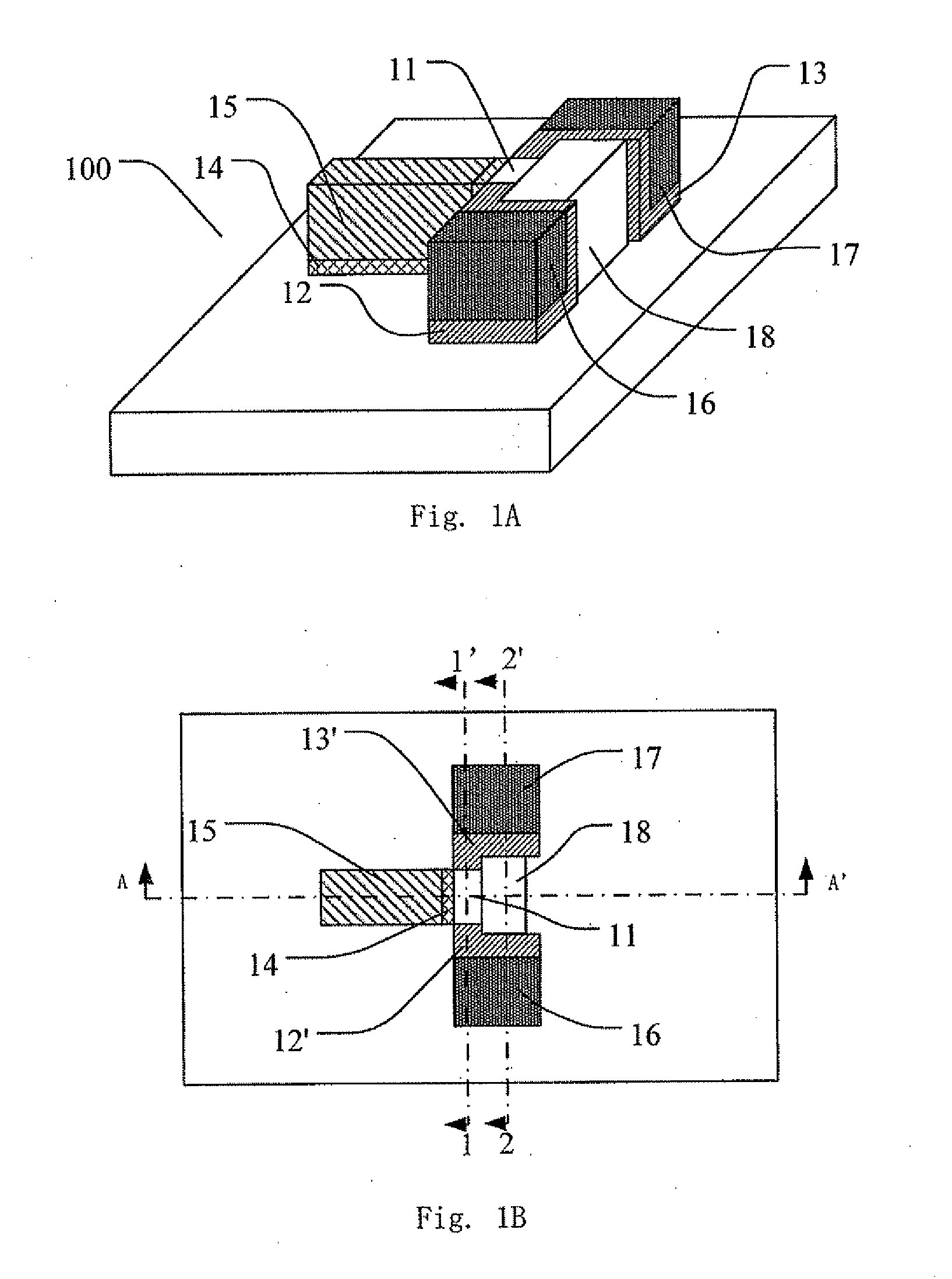
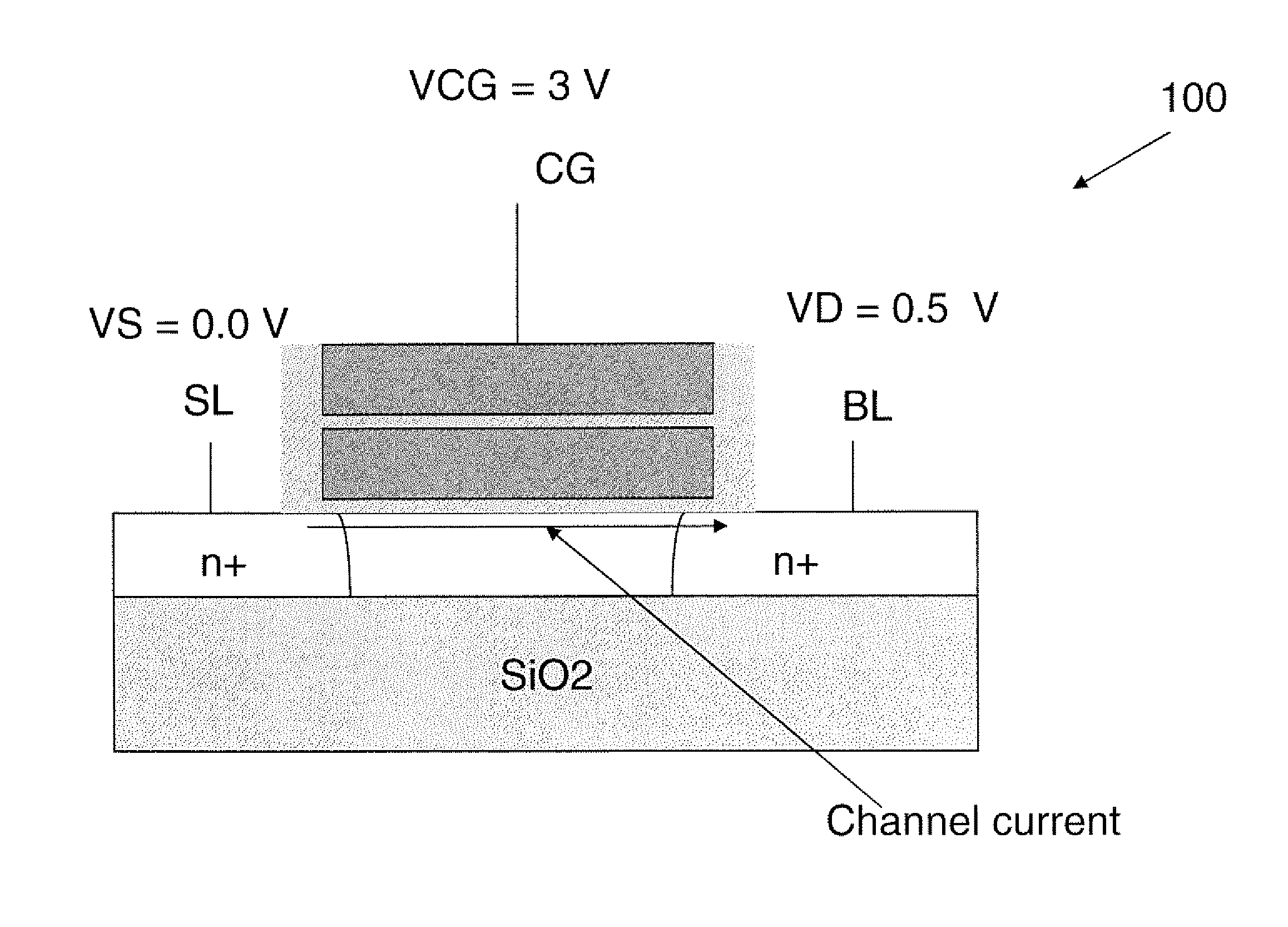
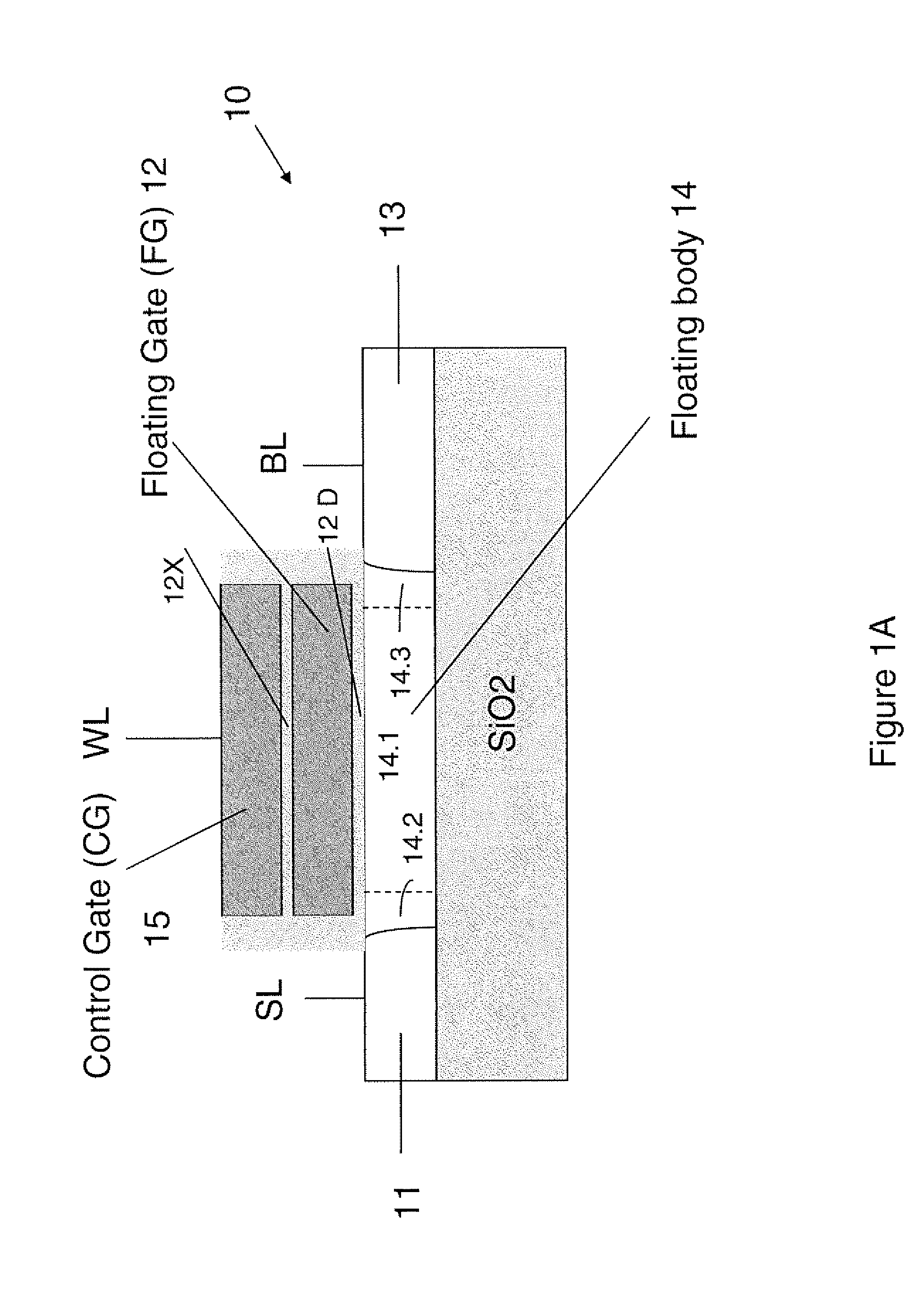
Techniques for providing floating body memory devices are disclosed. In one particular exemplary embodiment, the techniques may be realized as a semiconductor device comprising a floating gate, a control gate disposed over the floating gate, a body region that is electrically floating, wherein the body region is configured so that material forming the body region is contained under at least one lateral boundary of the floating gate, and a source region and a drain region adjacent the body region.
Owner:OVONYX MEMORY TECH LLC
Semiconductor device and production method
ActiveUS20110303973A1Limitation on gate lengthReduce metal pollutionTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPower semiconductor deviceSilicon
The semiconductor device according to the present invention is an nMOS SGT and is composed of a first n+ type silicon layer, a first gate electrode containing metal and a second n+ type silicon layer arranged on the surface of a first columnar silicon layer positioned vertically on a first planar silicon layer. Furthermore, a first insulating film is positioned between the first gate electrode and the first planar silicon layer, and a second insulating film is positioned on the top surface of the first gate electrode. In addition, the first gate electrode containing metal is surrounded by the first n+ type silicon layer, the second n+ type silicon layer, the first insulating film and the second insulating film.
Owner:UNISANTIS ELECTRONICS SINGAPORE PTE LTD
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20110122670A1Limitation number of operationEasily multivalued informationTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHemt circuitsSemiconductor
An object of the present invention is to provide a semiconductor device combining transistors integrating on a same substrate transistors including an oxide semiconductor in their channel formation region and transistors including non-oxide semiconductor in their channel formation region. An application of the present invention is to realize substantially non-volatile semiconductor memories which do not require specific erasing operation and do not suffer from damages due to repeated writing operation. Furthermore, the semiconductor device is well adapted to store multivalued data. Manufacturing methods, application circuits and driving / reading methods are explained in details in the description.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method for manufacturing semiconductor device
ActiveUS20120064664A1Stable electrical characteristicsReduce the amount of variationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectroluminescent light sourcesCrystalline oxidePower semiconductor device
An object is to manufacture a semiconductor device including an oxide semiconductor film, which has stable electric characteristics and high reliability. A crystalline oxide semiconductor film is formed, without performing a plurality of steps, as follows: by utilizing a difference in atomic weight of plural kinds of atoms included in an oxide semiconductor target, zinc with low atomic weight is preferentially deposited on an oxide insulating film to form a seed crystal including zinc; and tin, indium, or the like with high atomic weight is deposited on the seed crystal while causing crystal growth. Further, a crystalline oxide semiconductor film is formed by causing crystal growth using a seed crystal with a hexagonal crystal structure including zinc as a nucleus, whereby a single crystal oxide semiconductor film or a substantially single crystal oxide semiconductor film is formed.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com