Patents
Literature
57 results about "Body memory" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Body memory (BM) is a hypothesis that the body itself is capable of storing memories, as opposed to only the brain. While experiments have demonstrated the possibility of cellular memory there are currently no known means by which tissues other than the brain would be capable of storing memories.
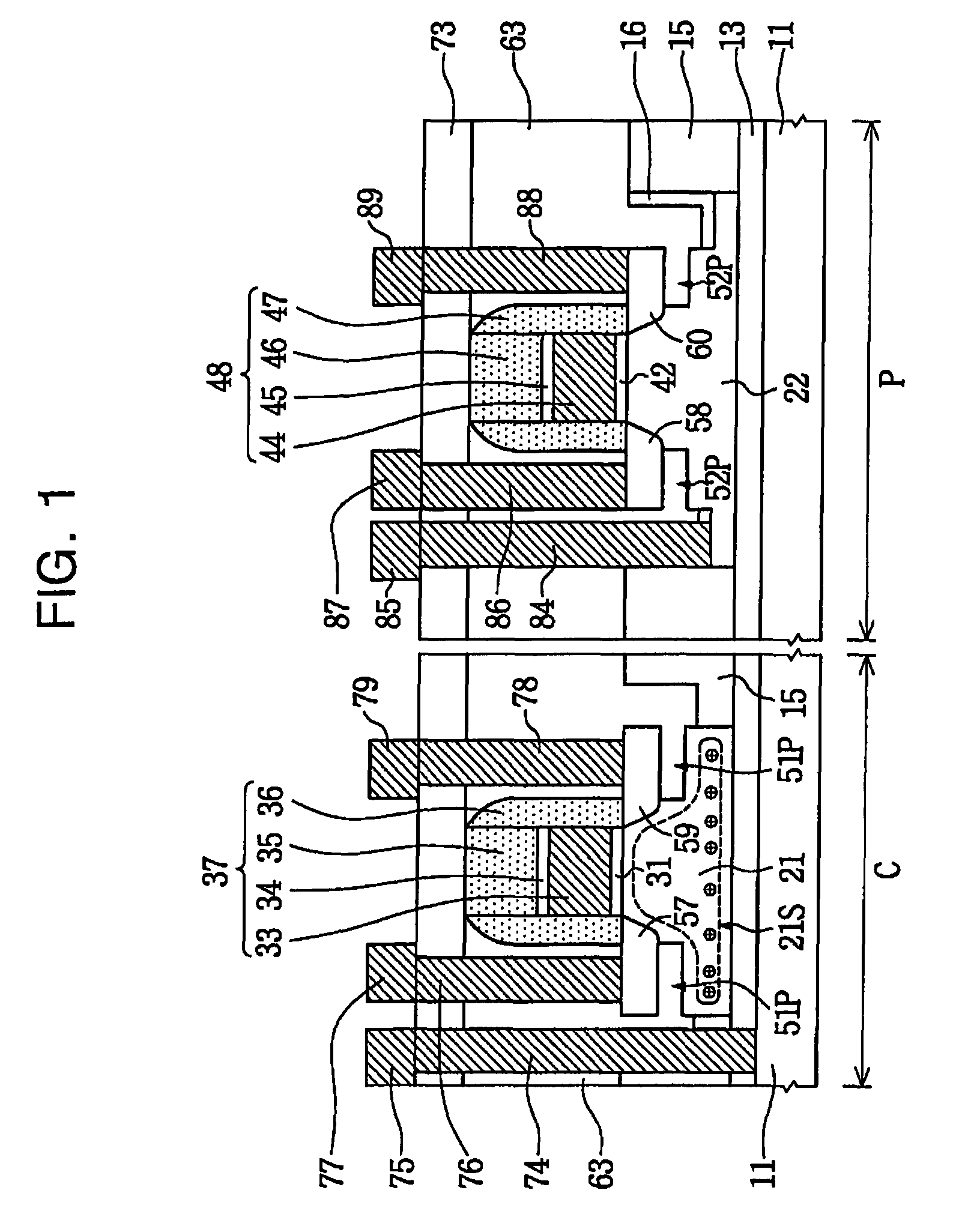
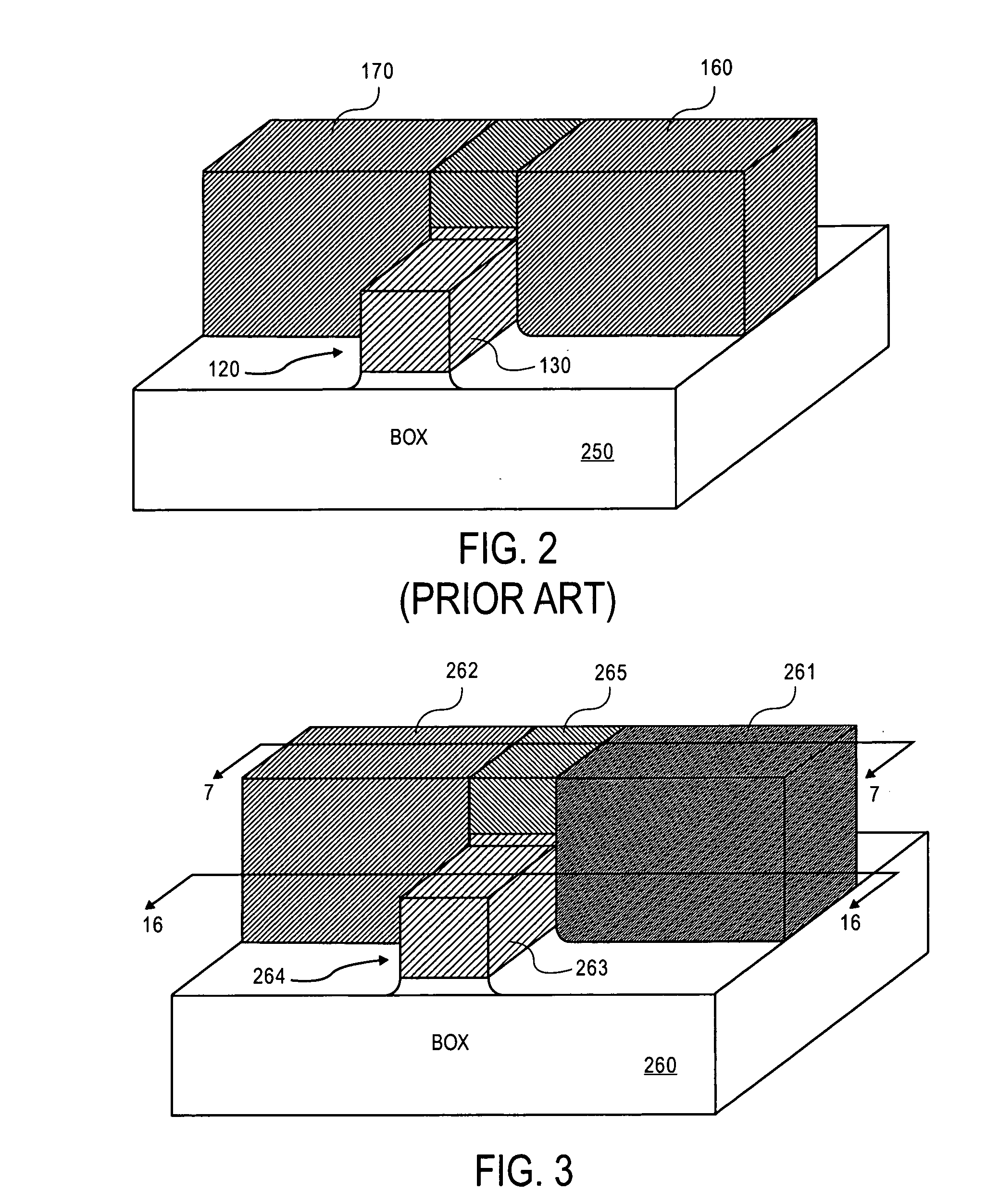
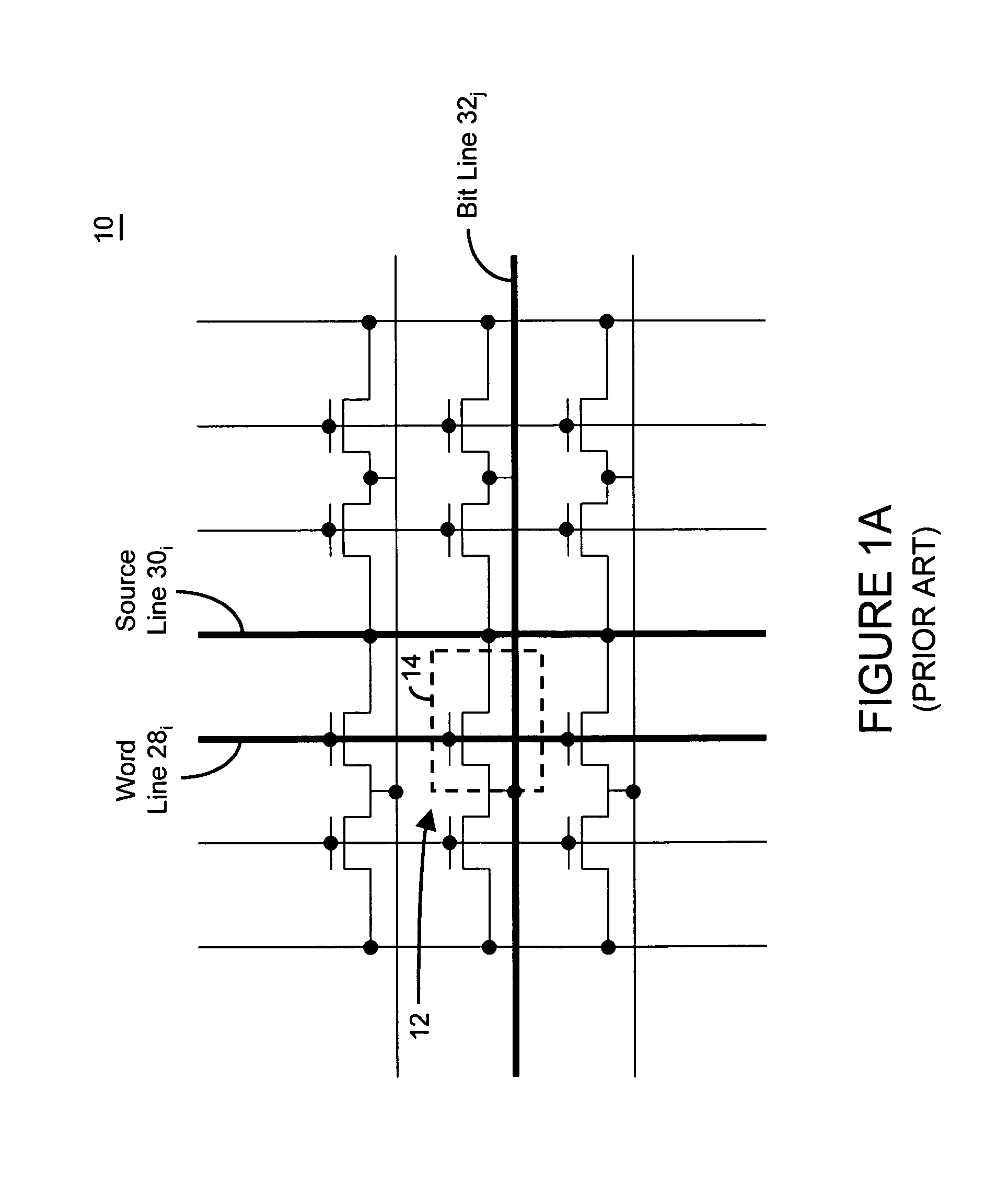
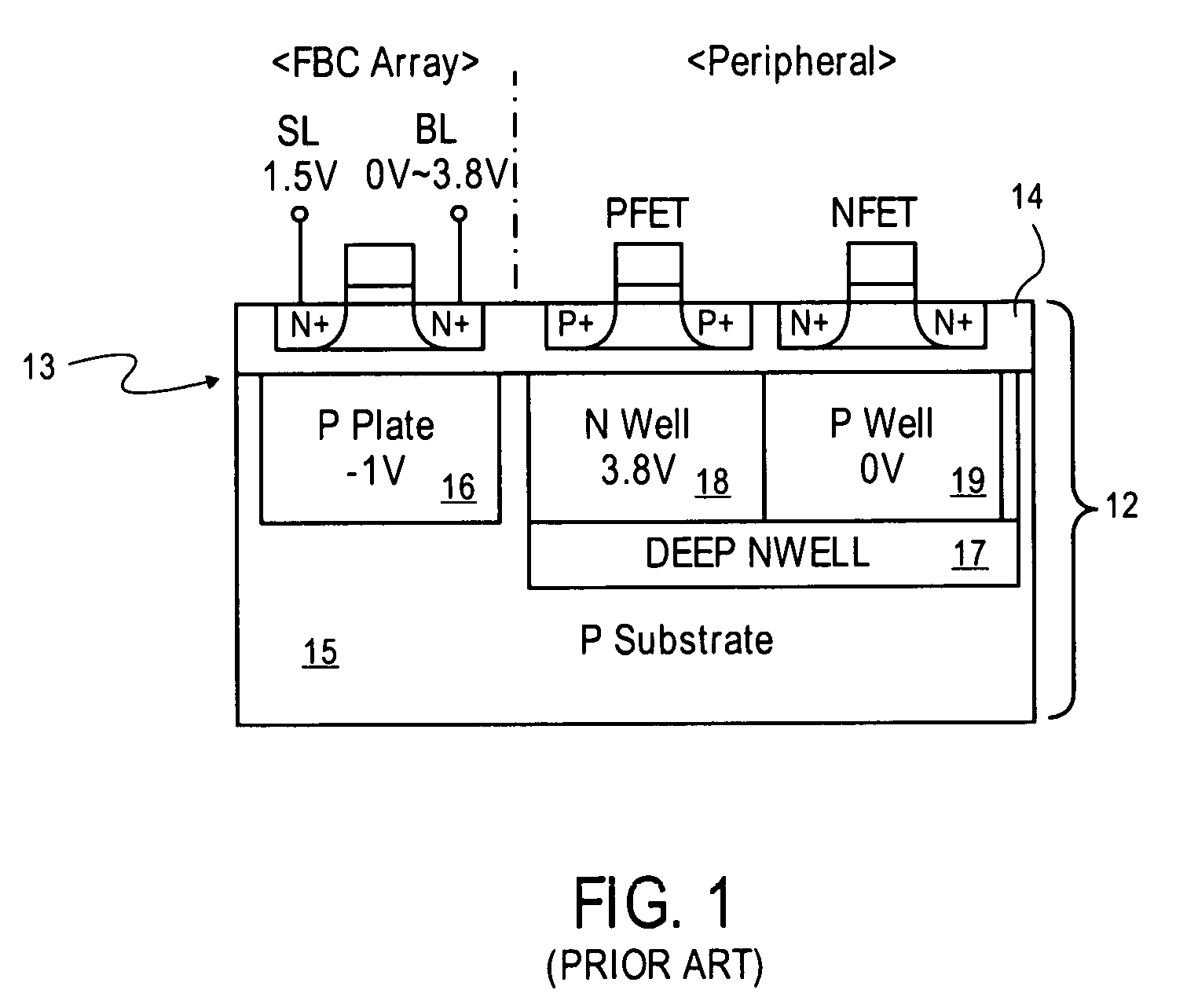
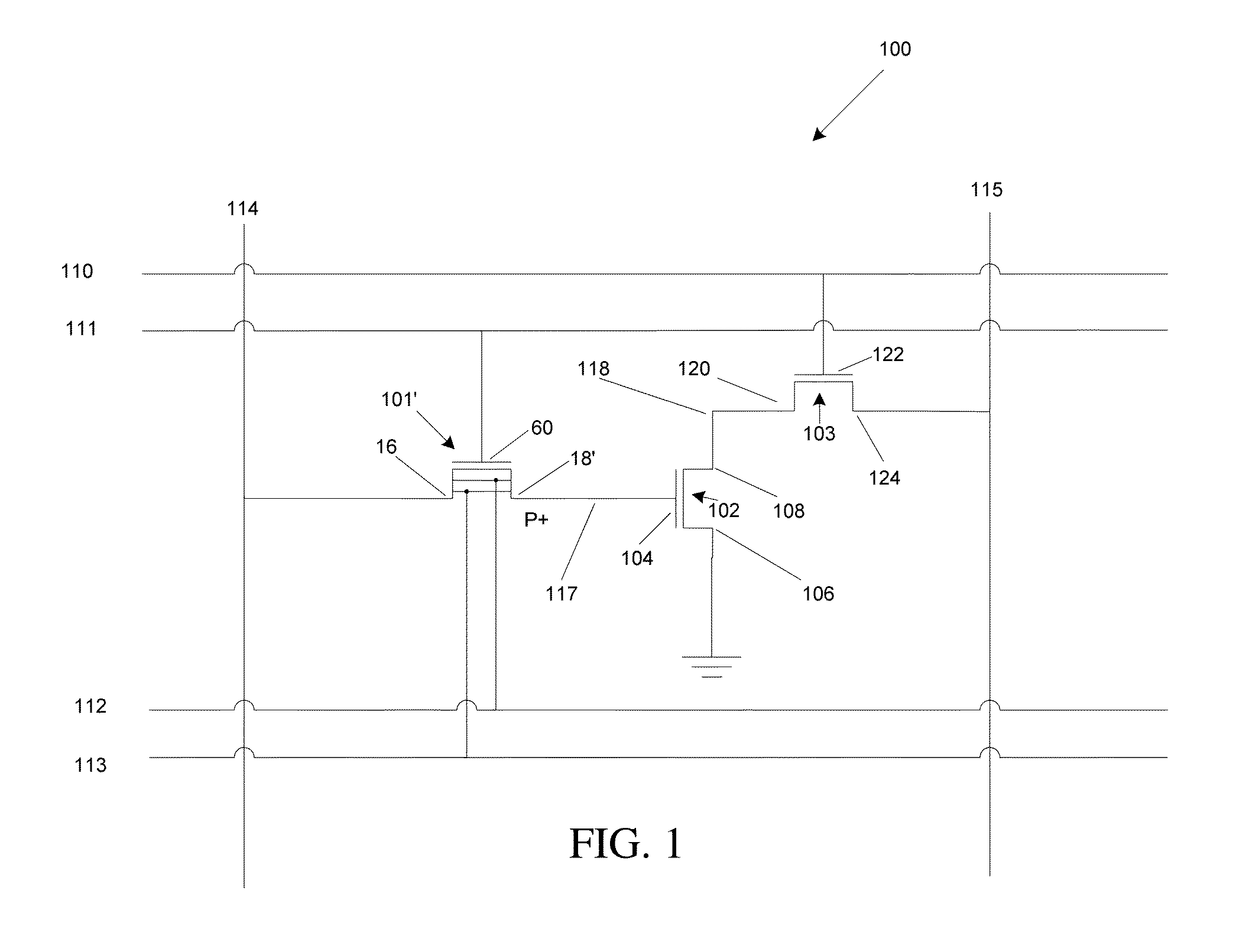
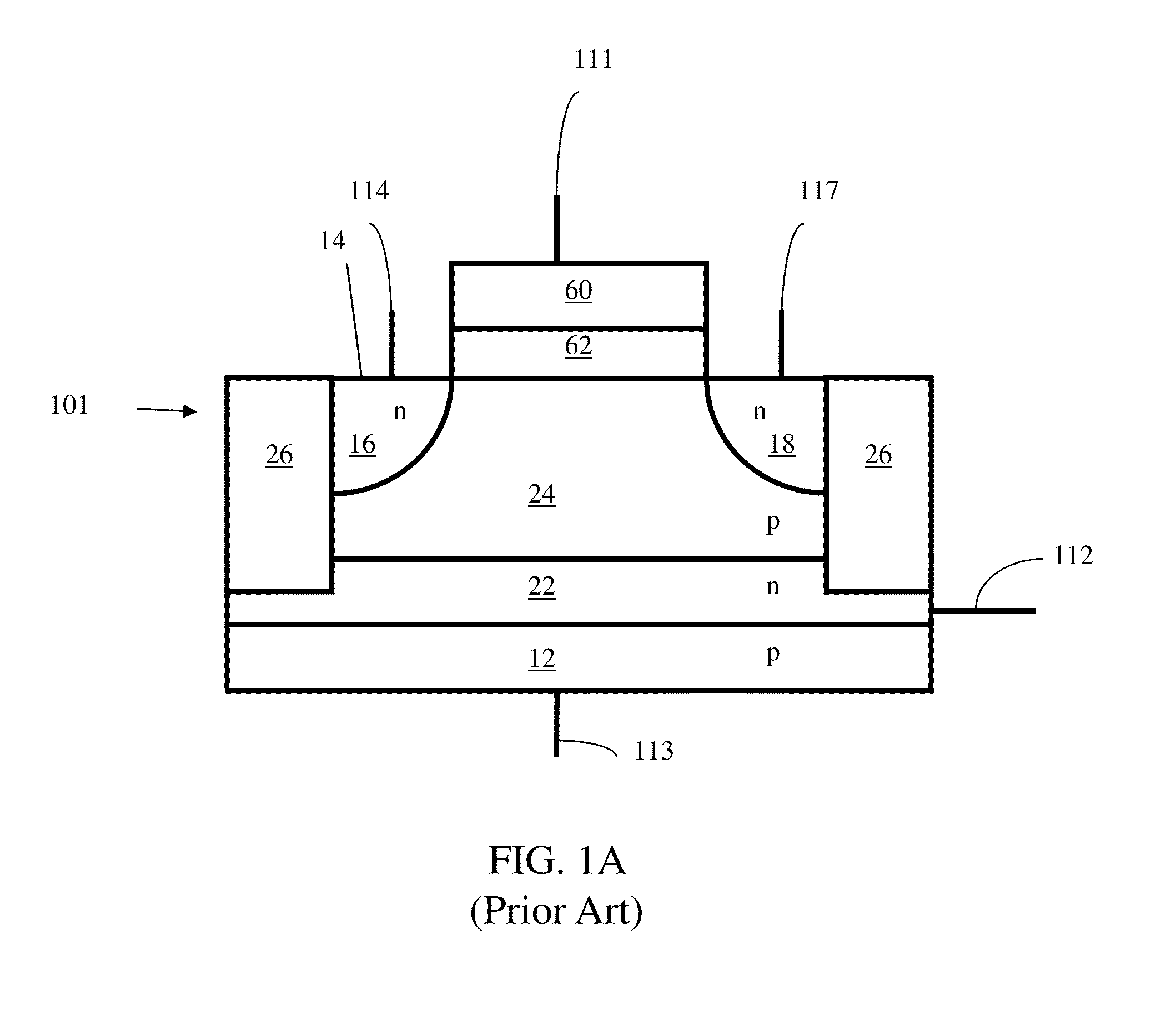
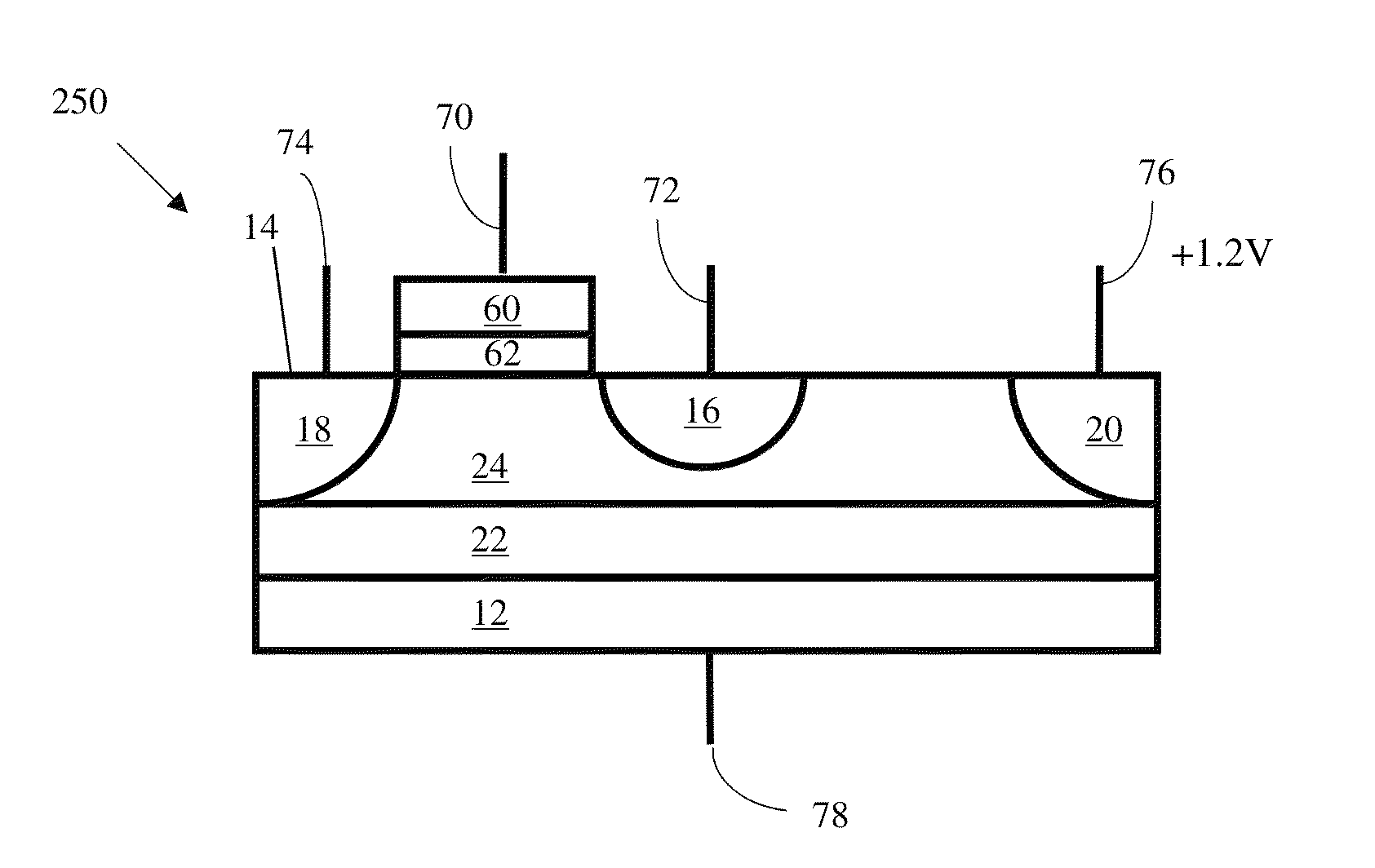
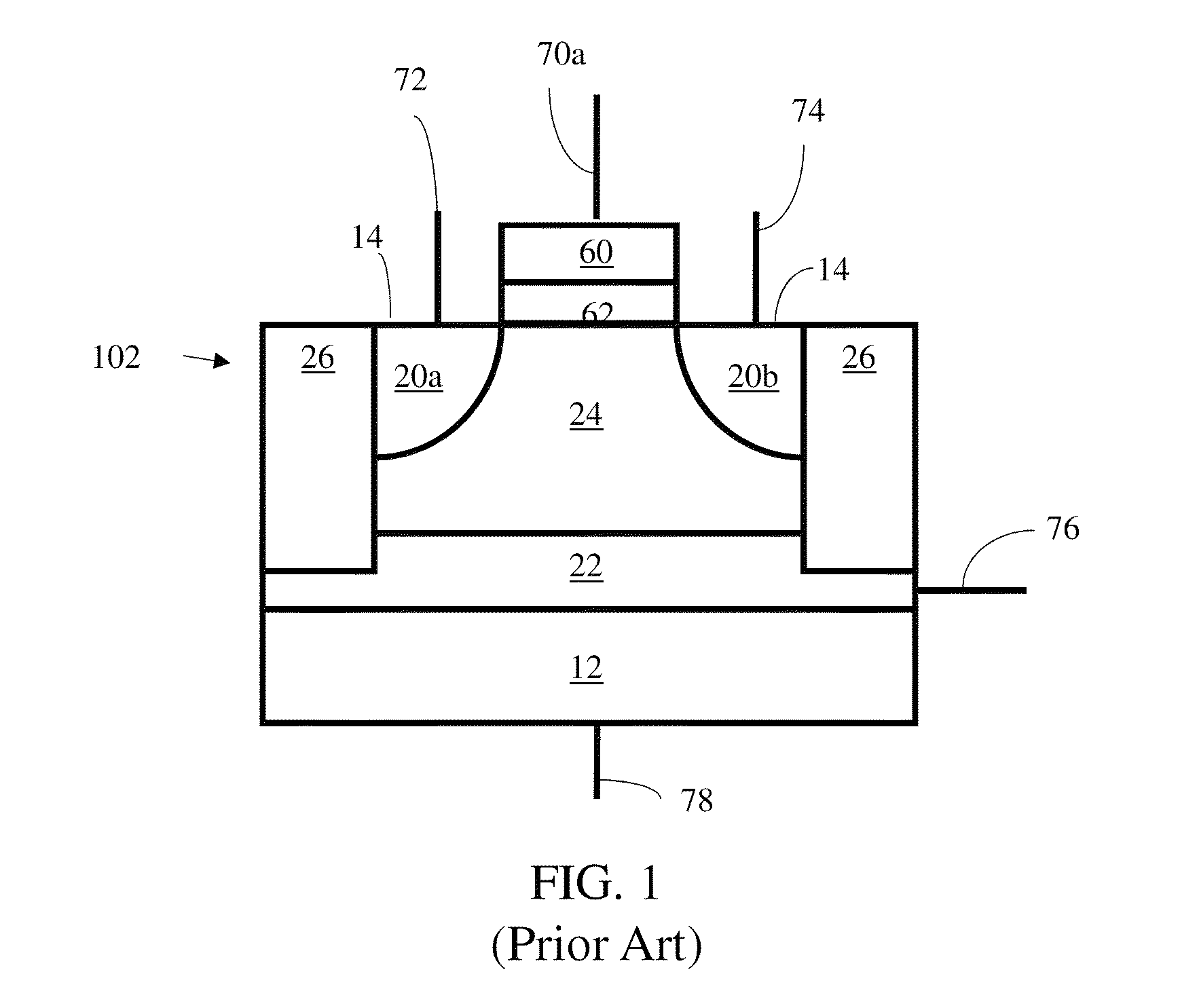
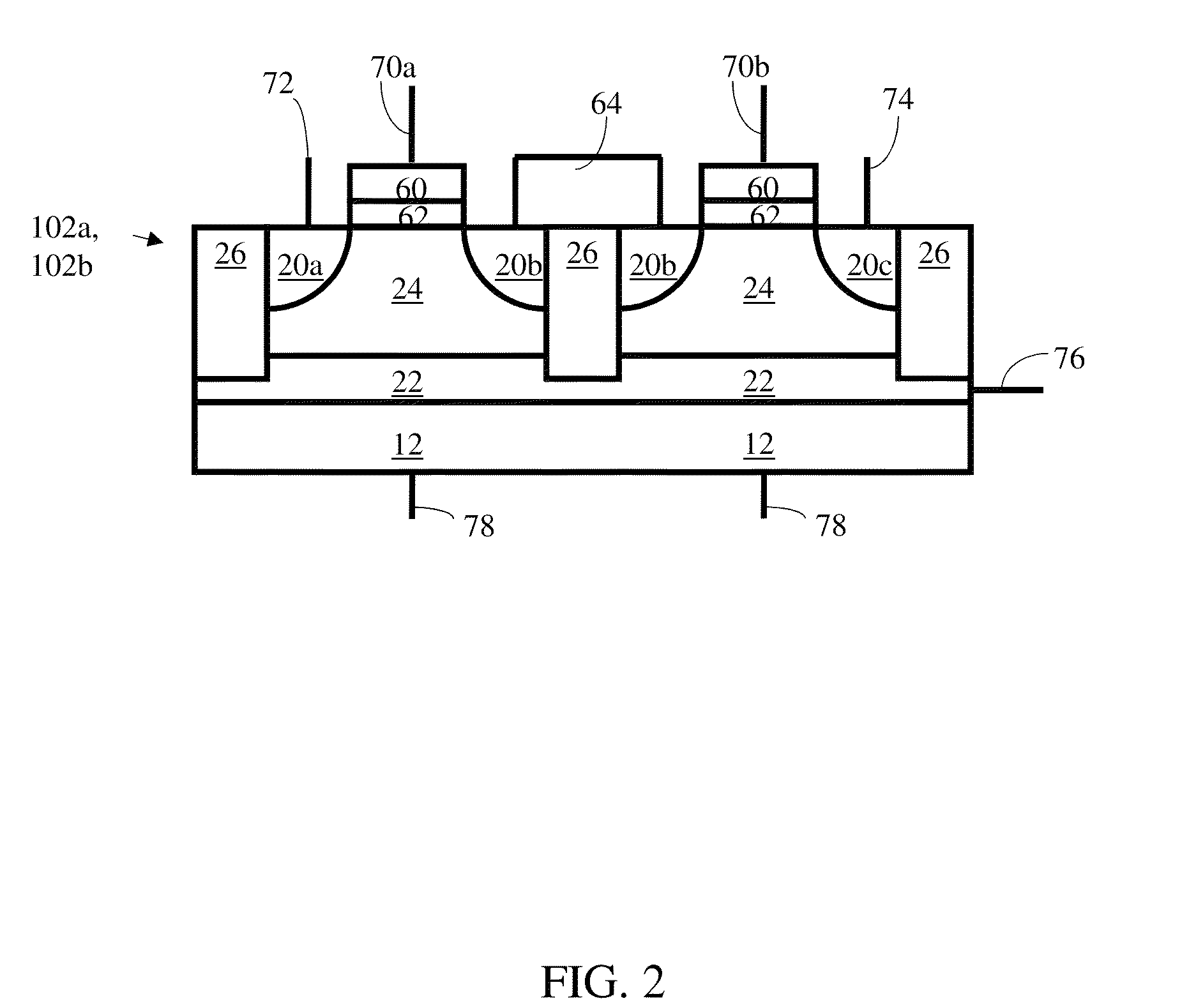
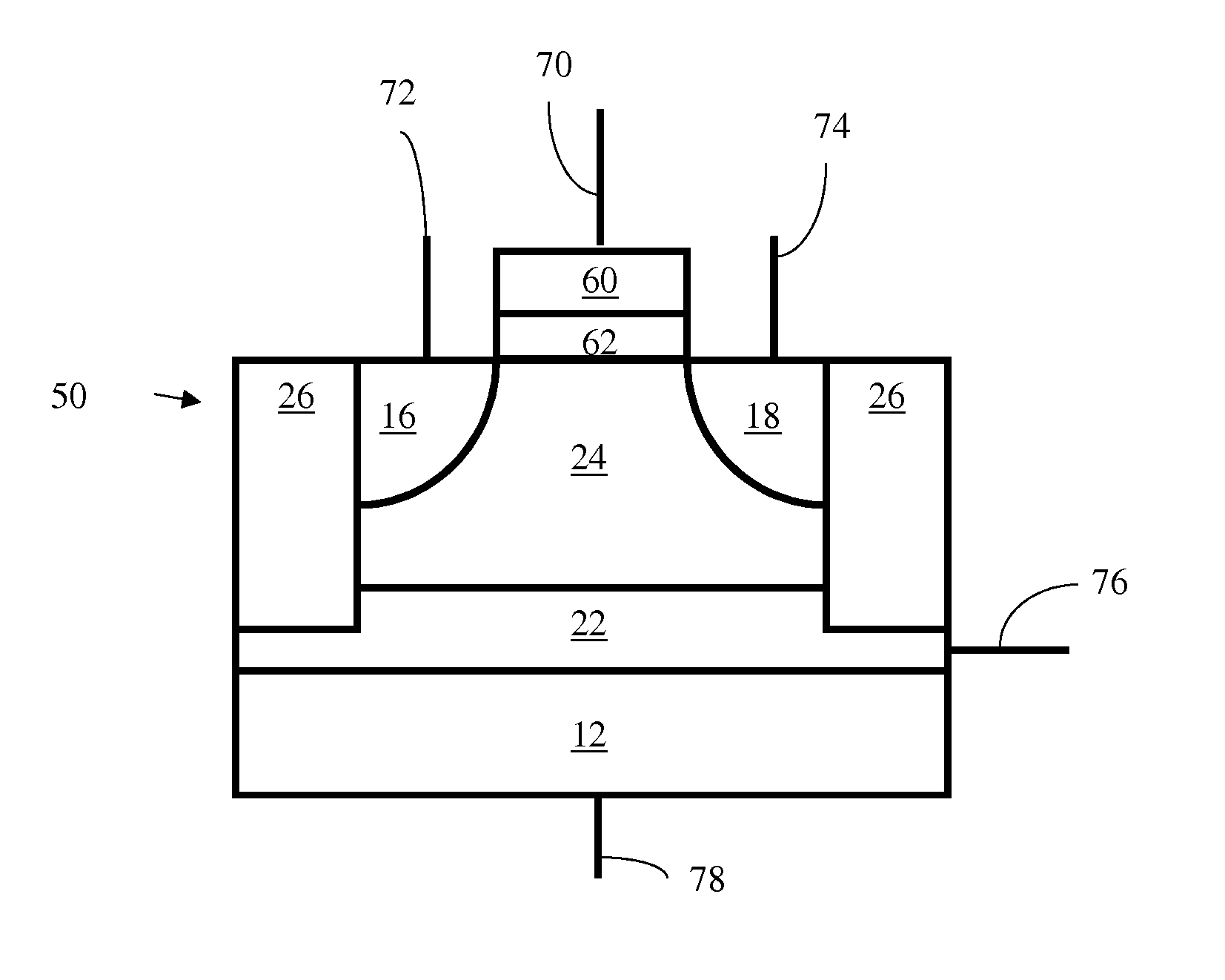
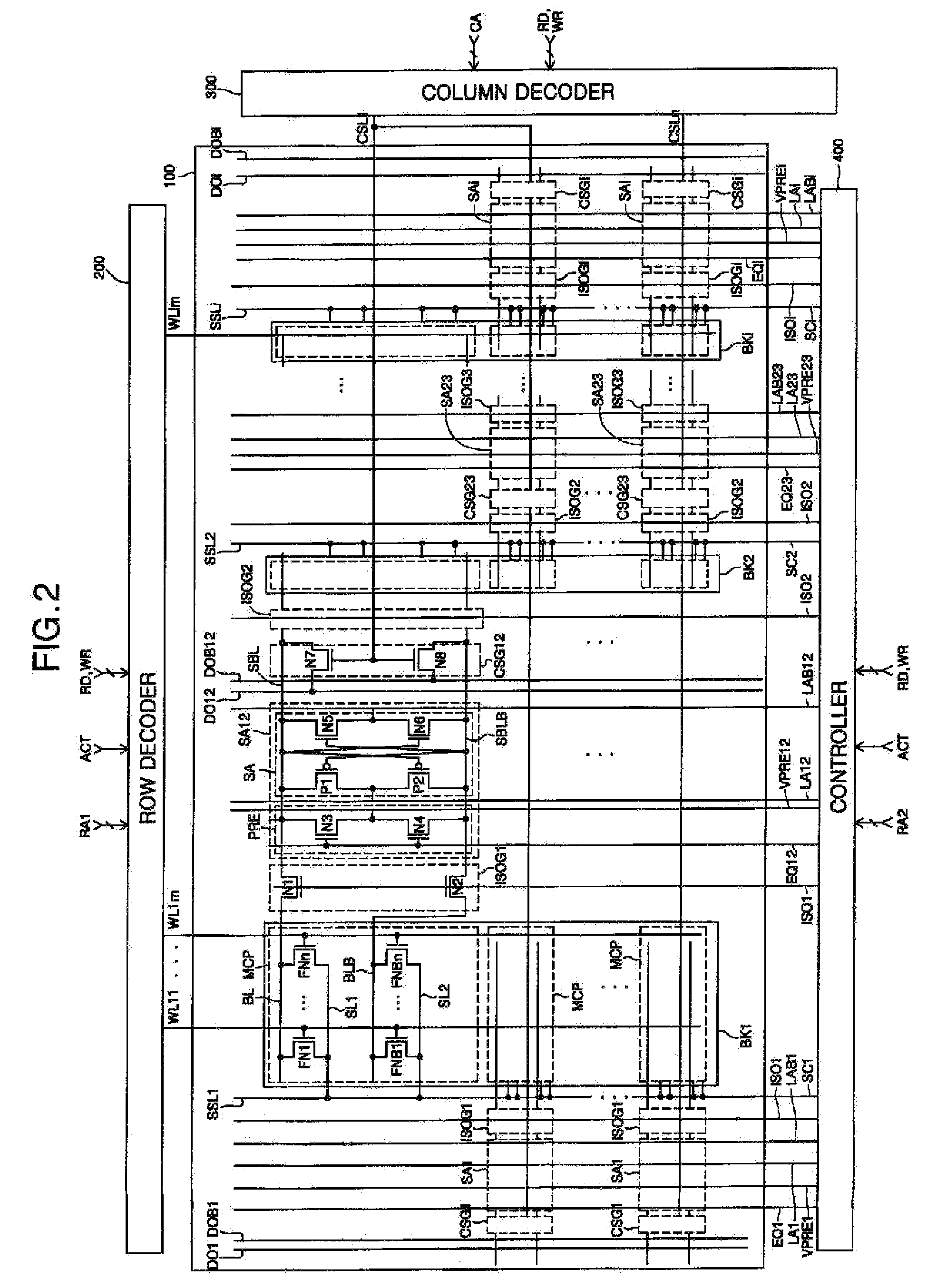
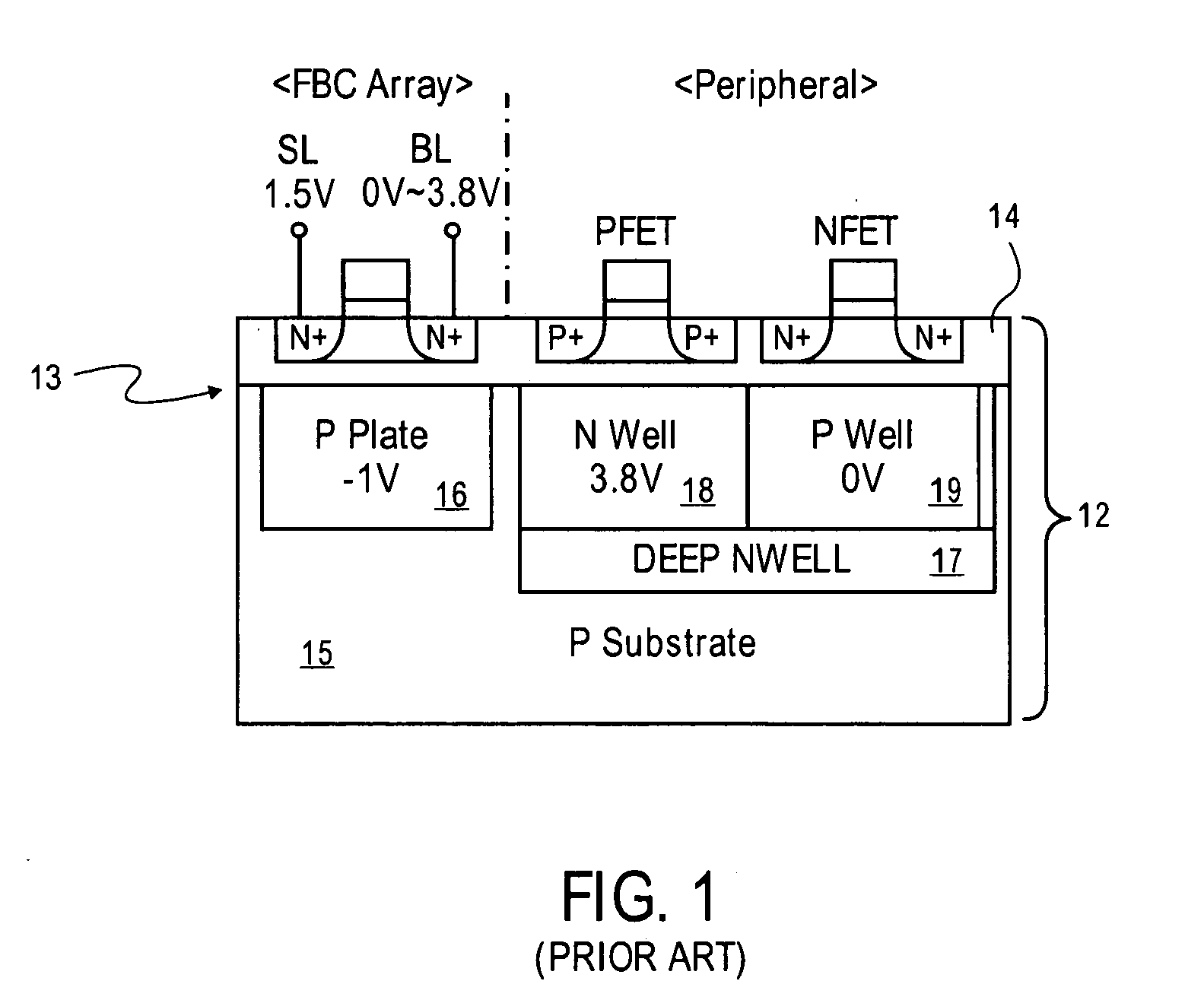
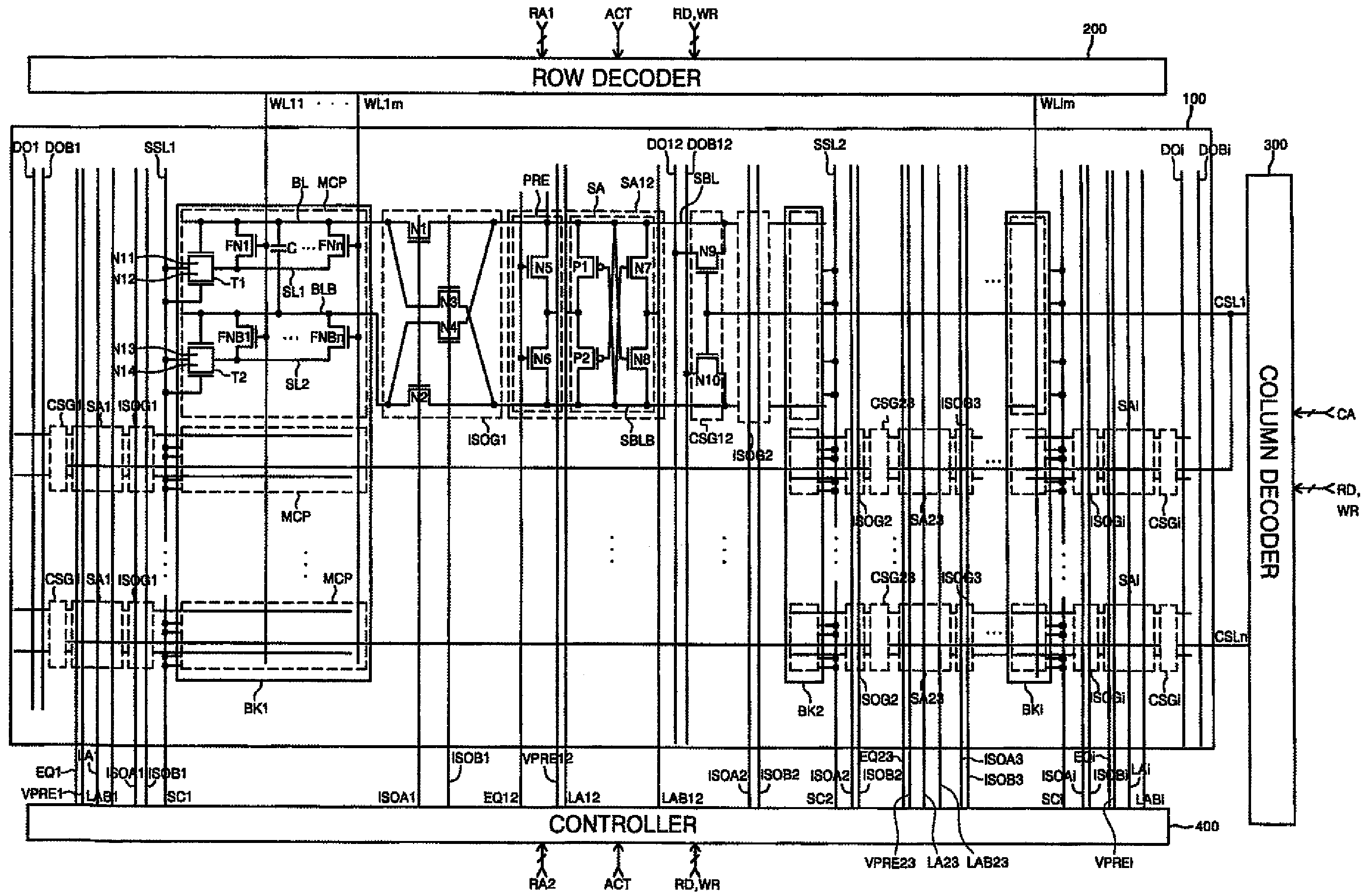
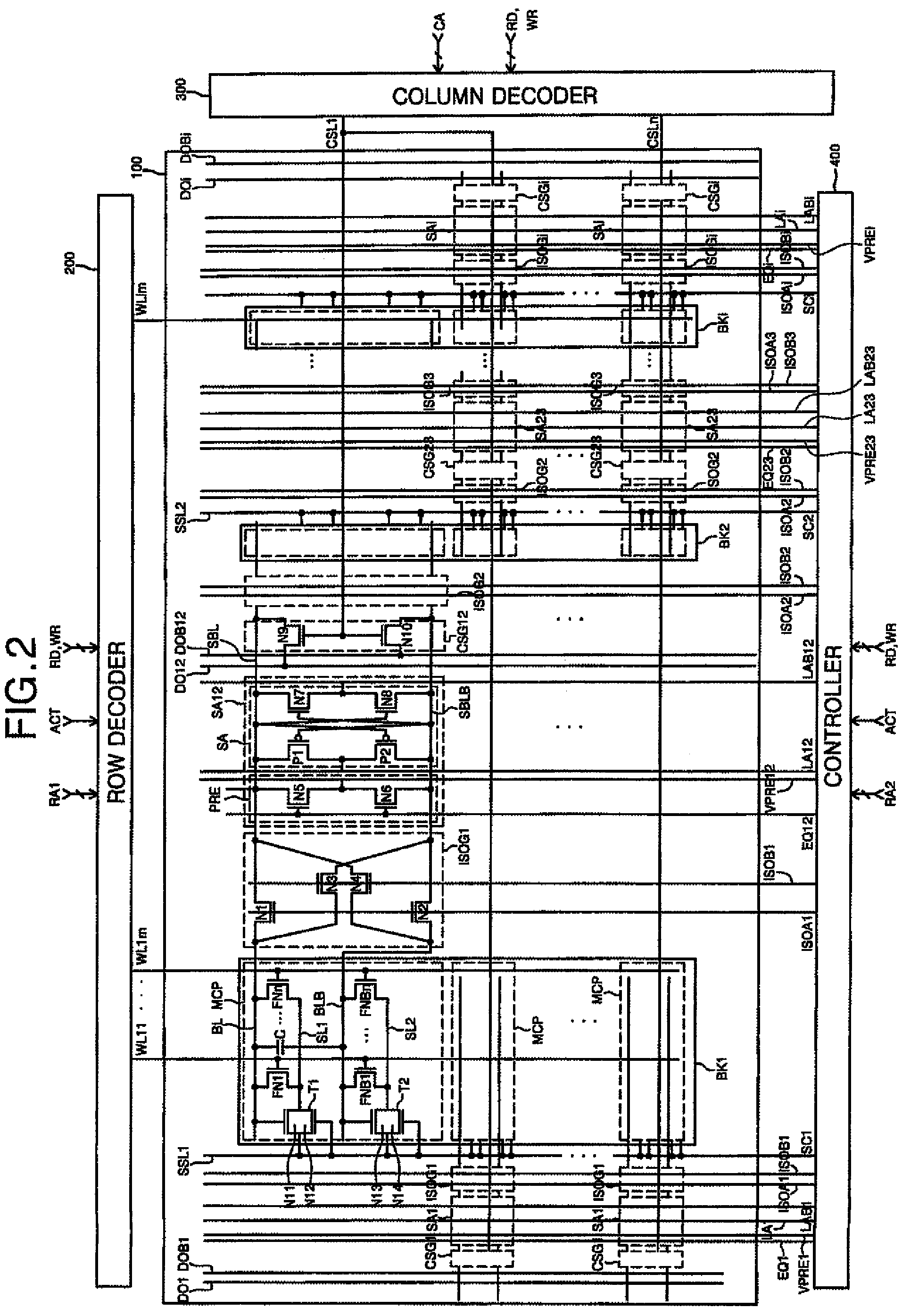
Low power programming technique for a floating body memory transistor, memory cell, and memory array
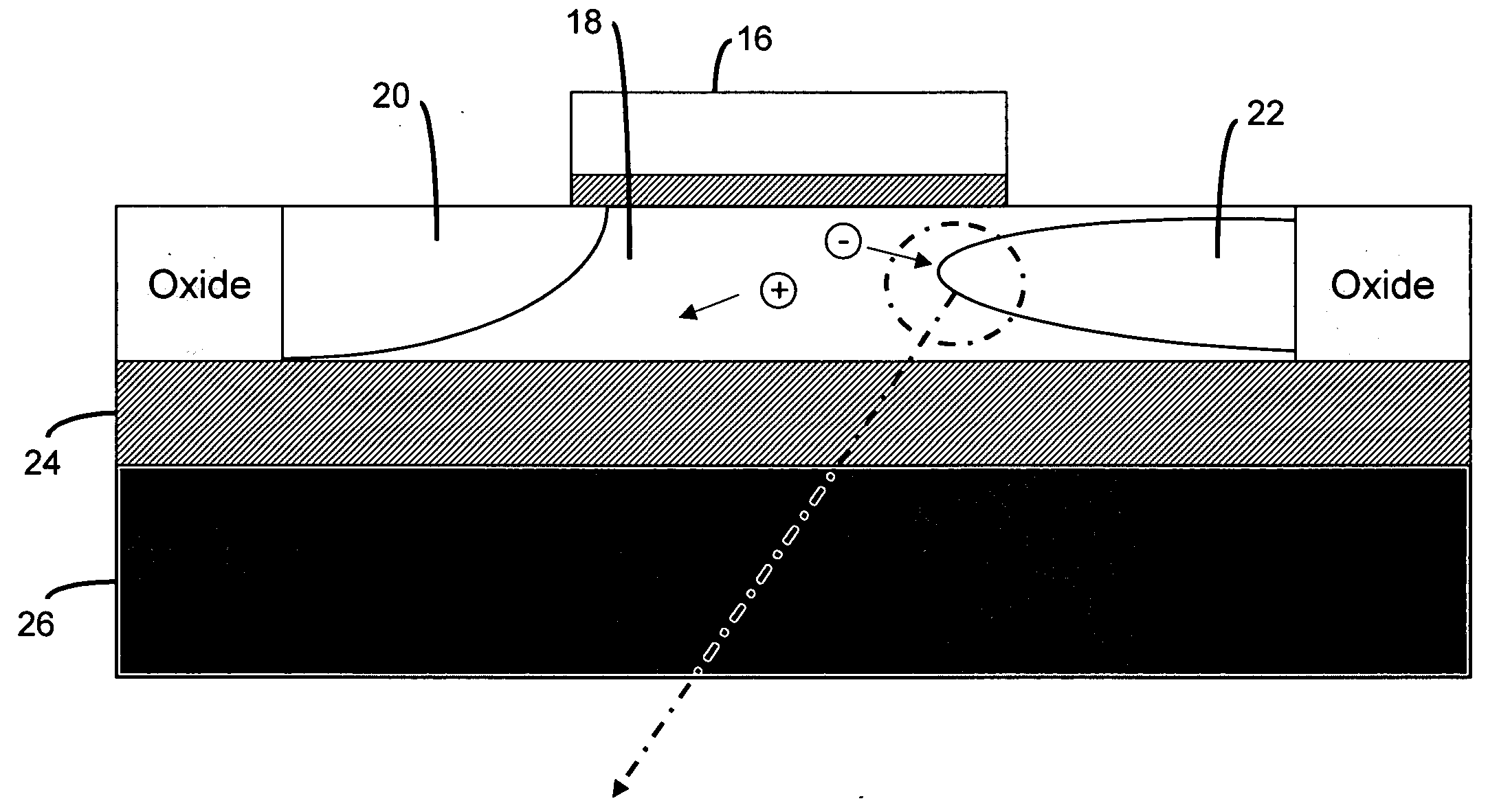
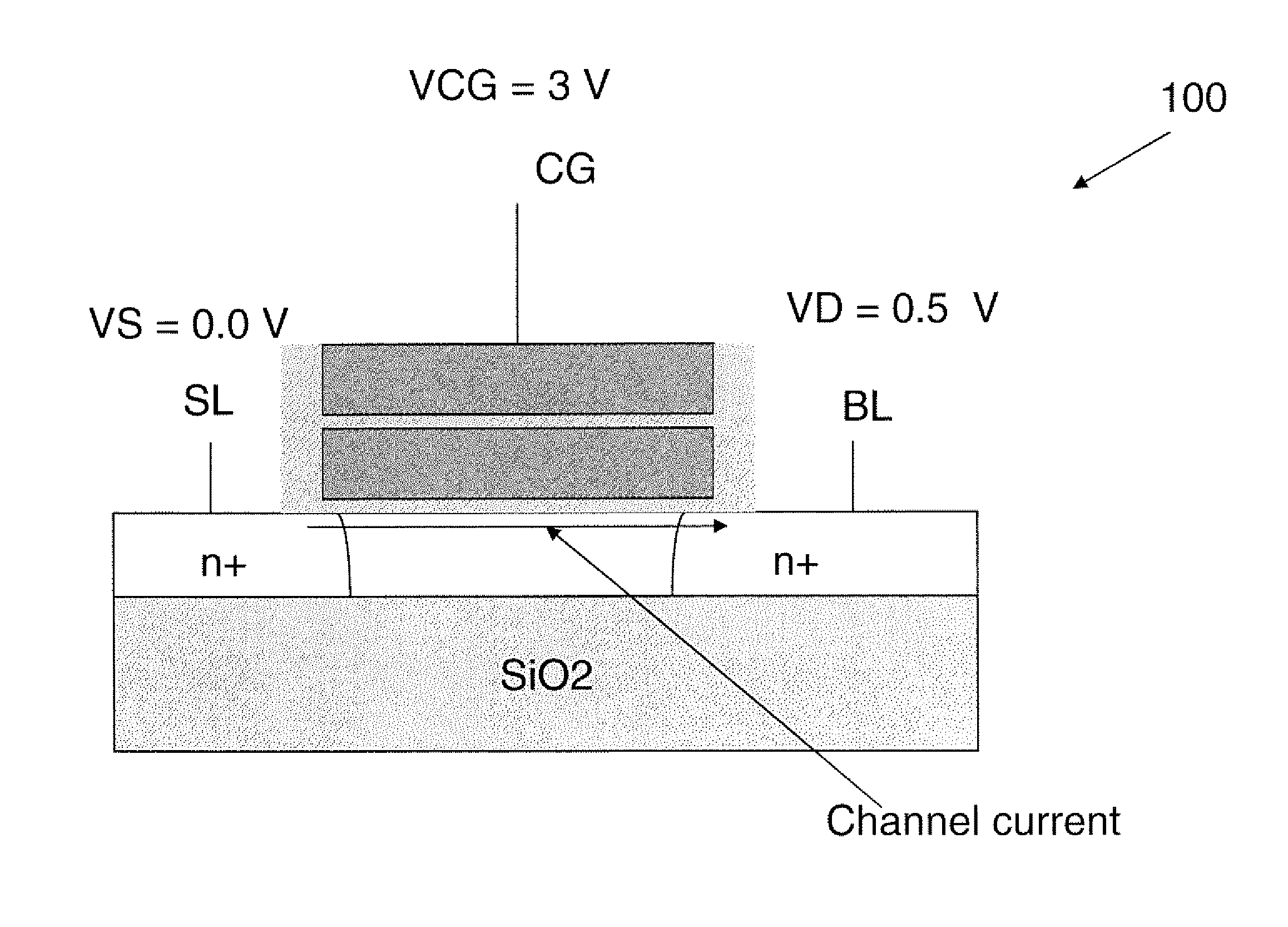
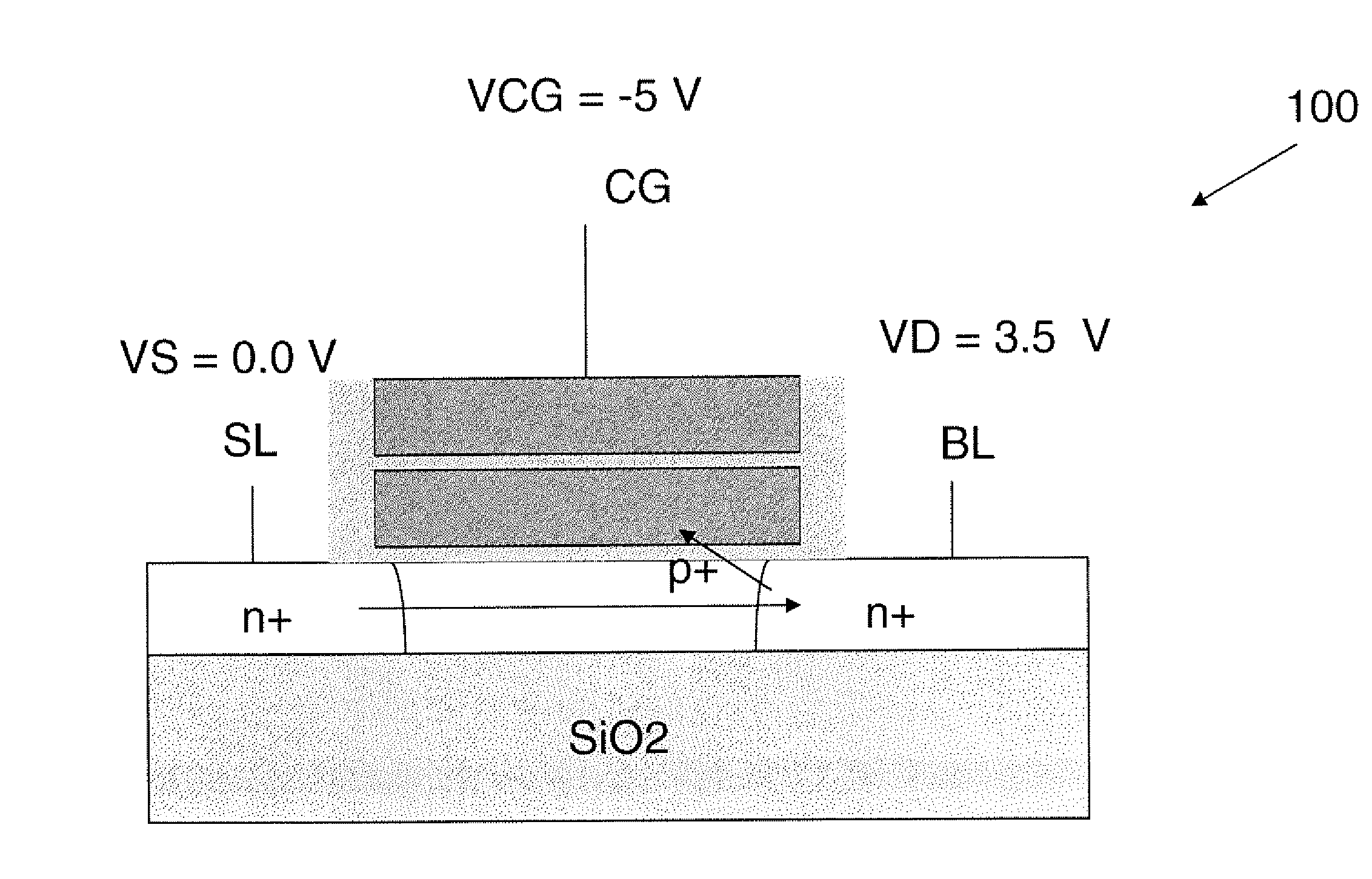
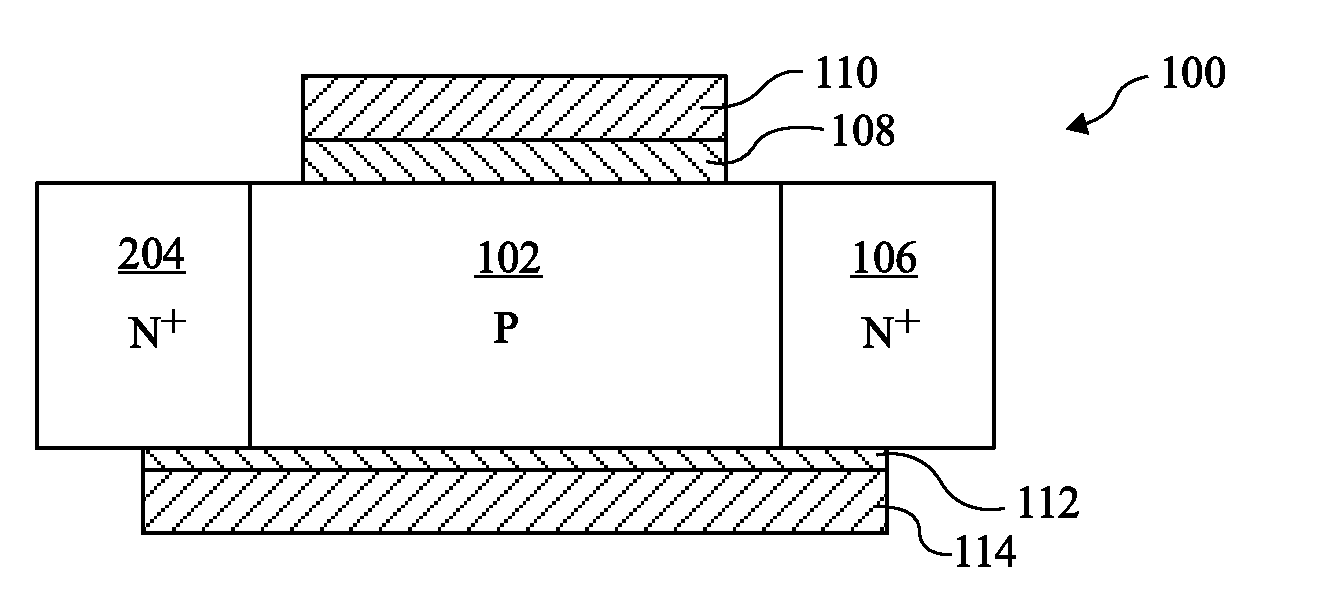
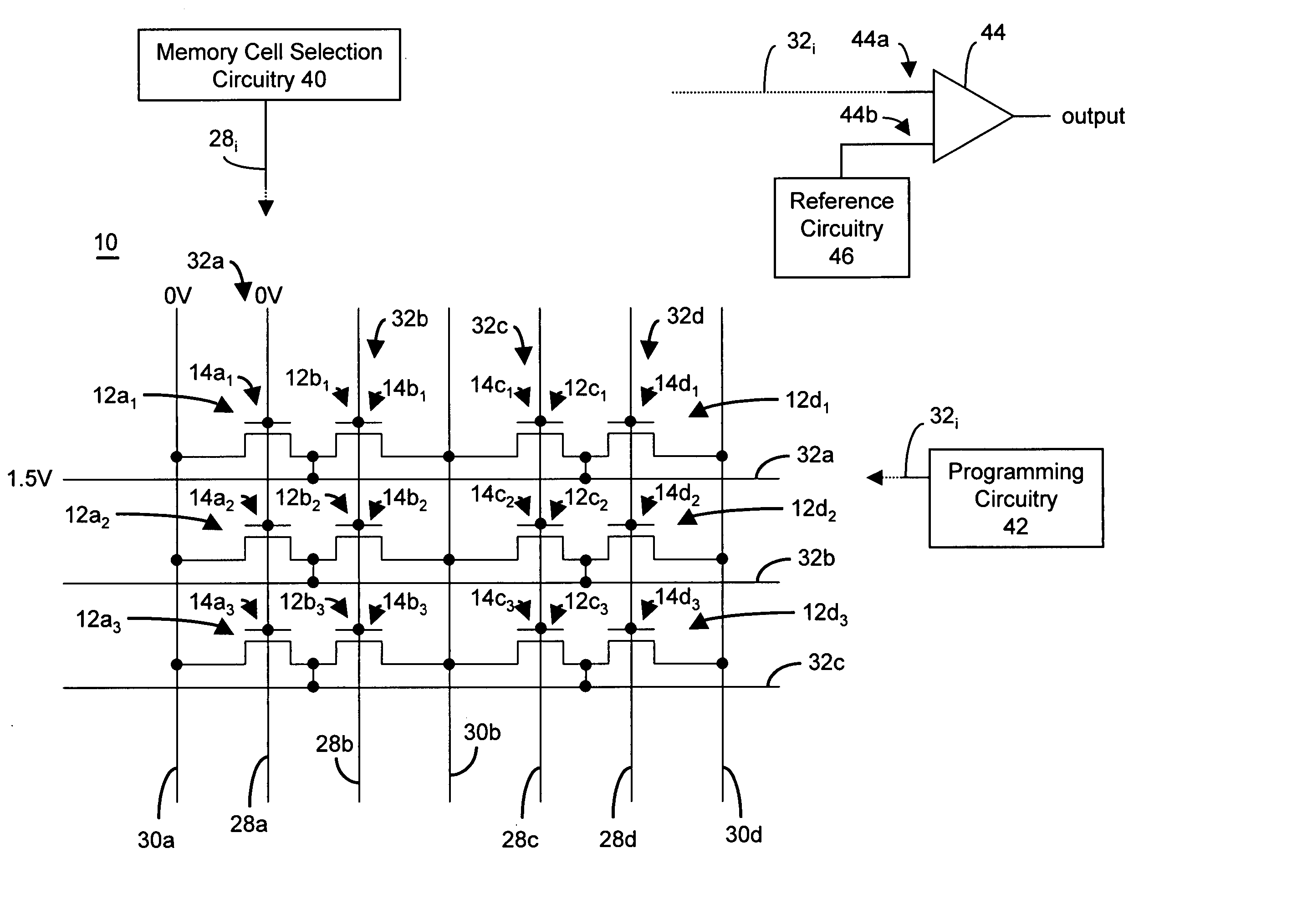
There are many inventions described and illustrated herein. In one aspect, the present invention is directed to a memory cell, architecture, and / or array and / or technique of writing or programming data into the memory cell (for example, a technique to write or program a logic low or State “0” in a memory cell employing an electrically floating body transistor. In this regard, the present invention programs a logic low or State “0” in the memory cell while the electrically floating body transistor is in the “OFF” state or substantially “OFF” state (for example, when the device has no (or practically no) channel and / or channel current between the source and drain). In this way, the memory cell may be programmed whereby there is little to no current / power consumption by the electrically floating body transistor and / or from memory array having a plurality of electrically floating body transistors.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
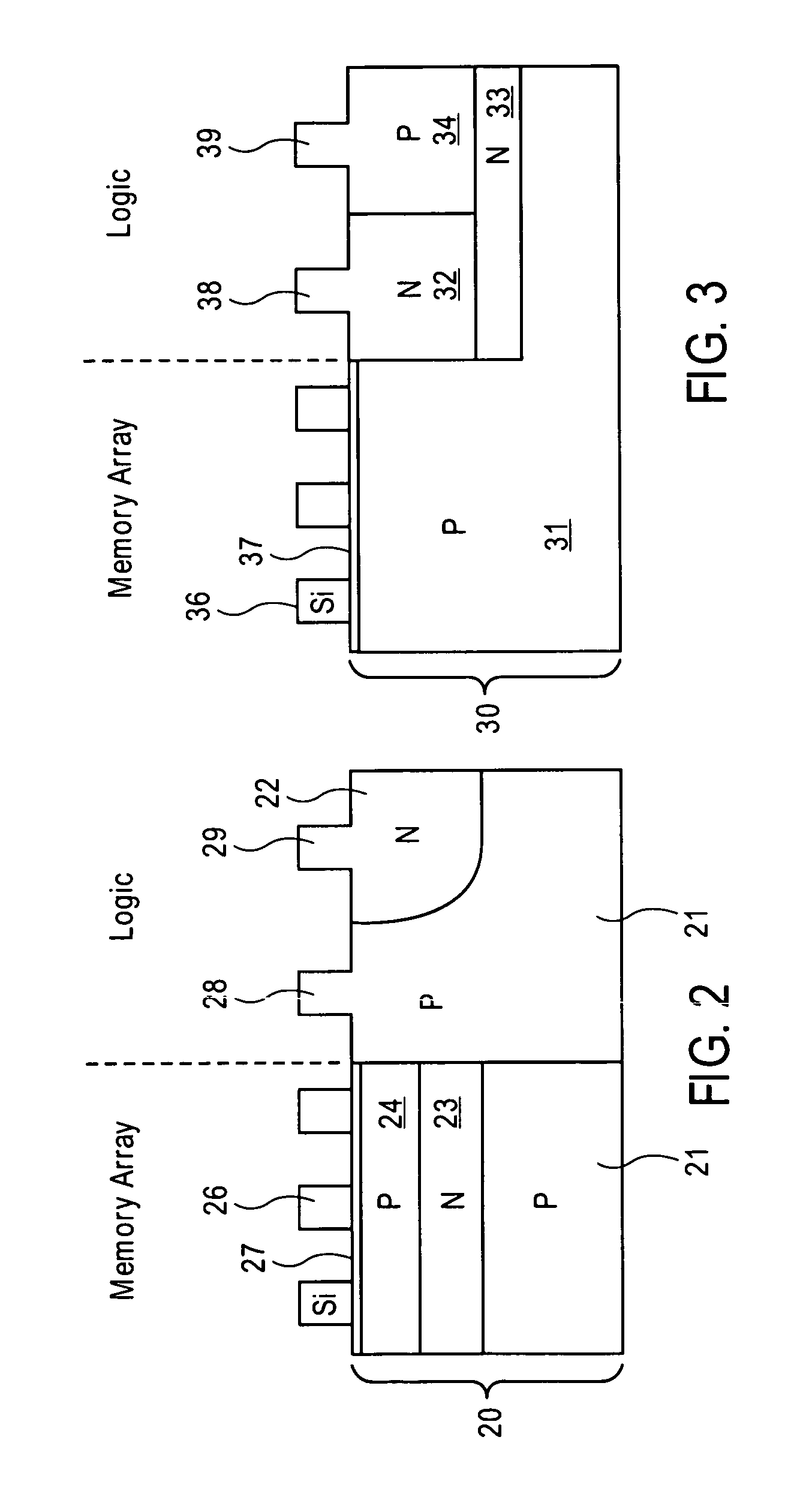
Floating body memory and method of fabricating the same
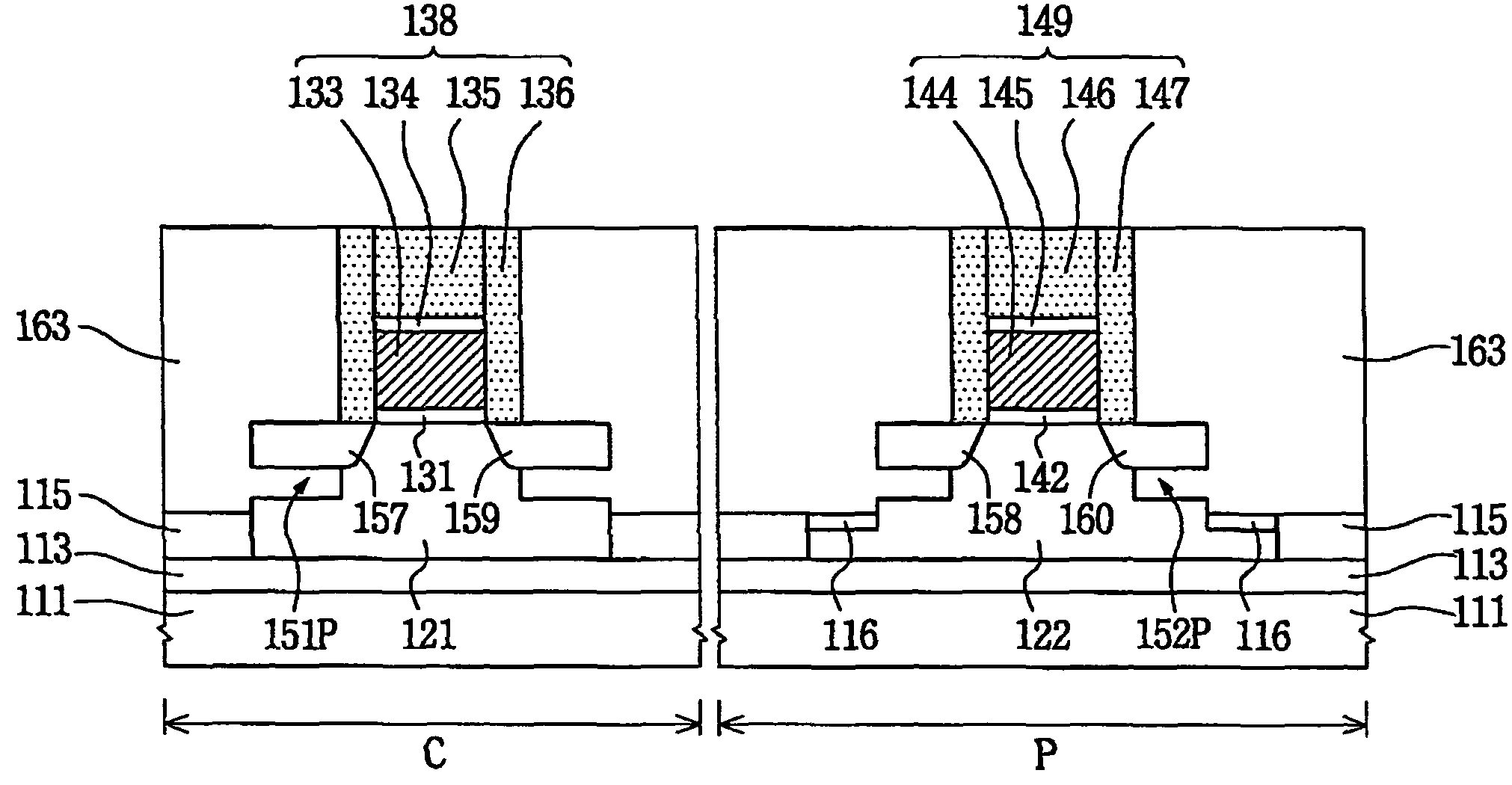
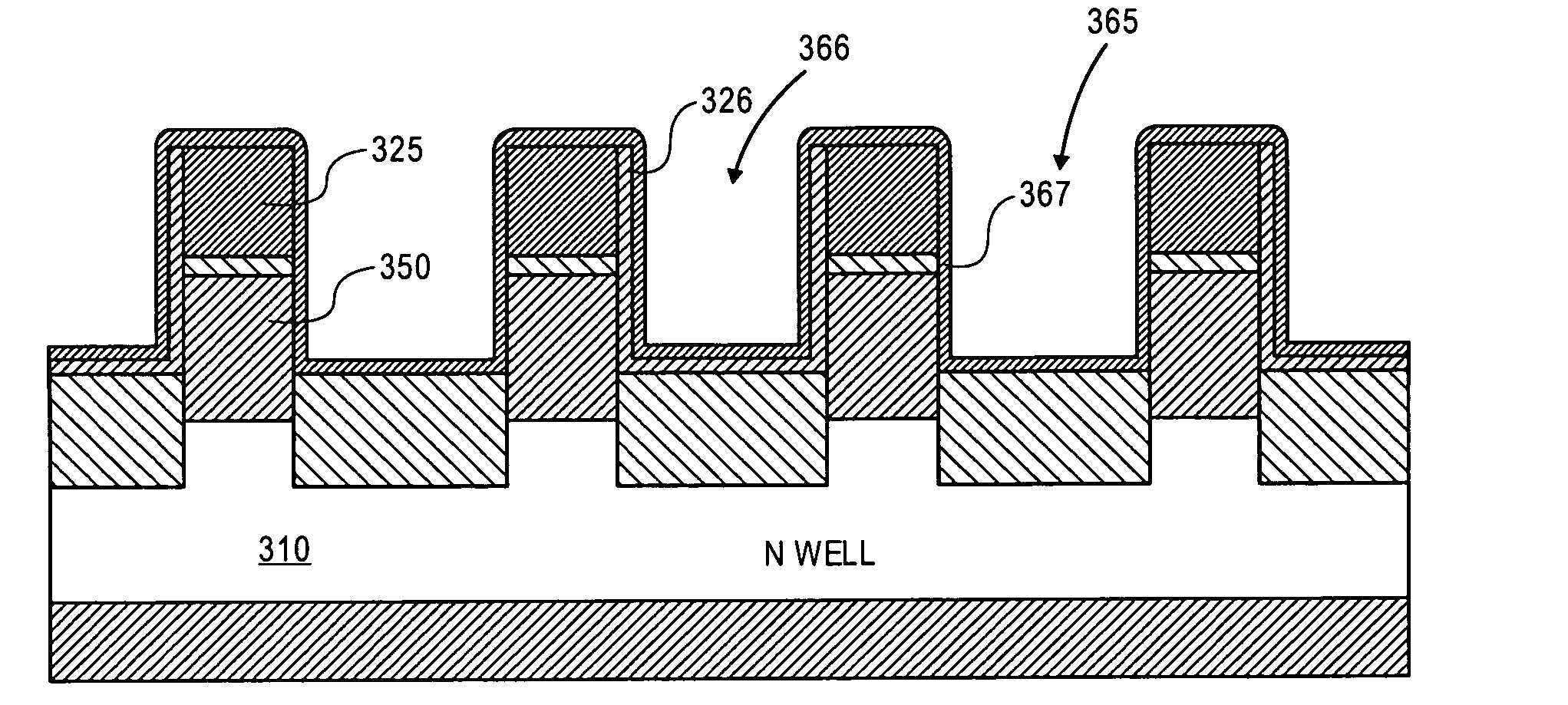
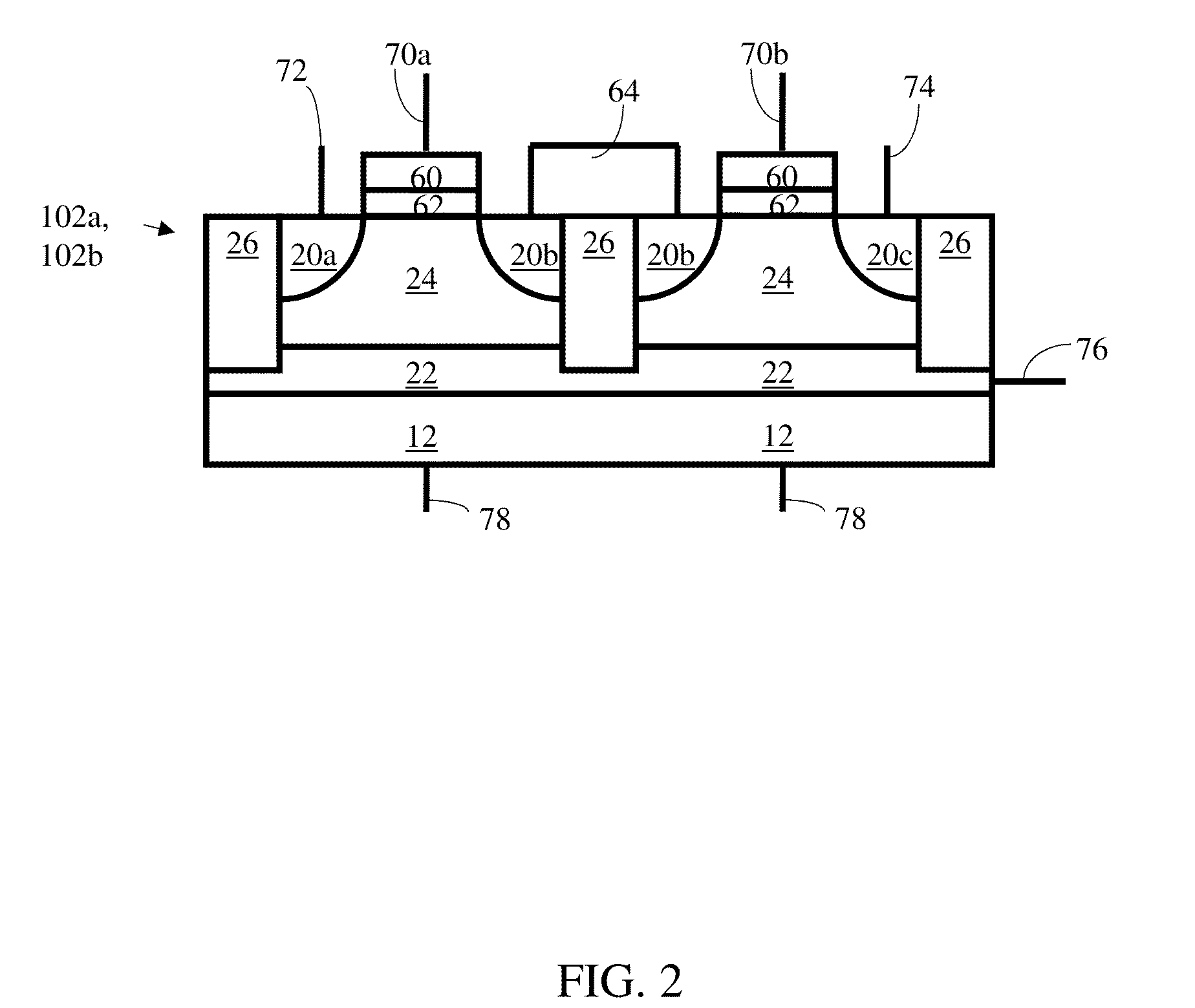
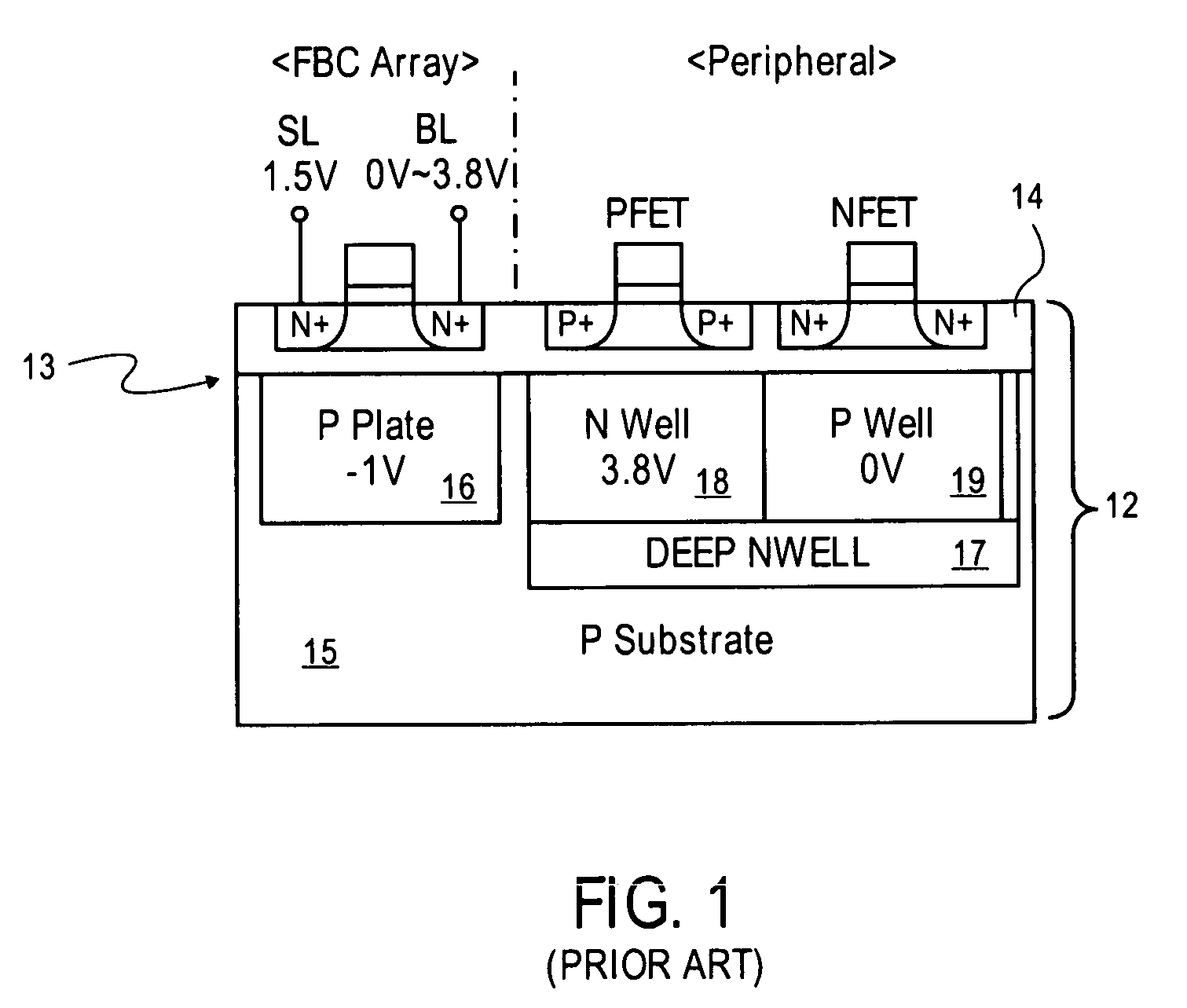
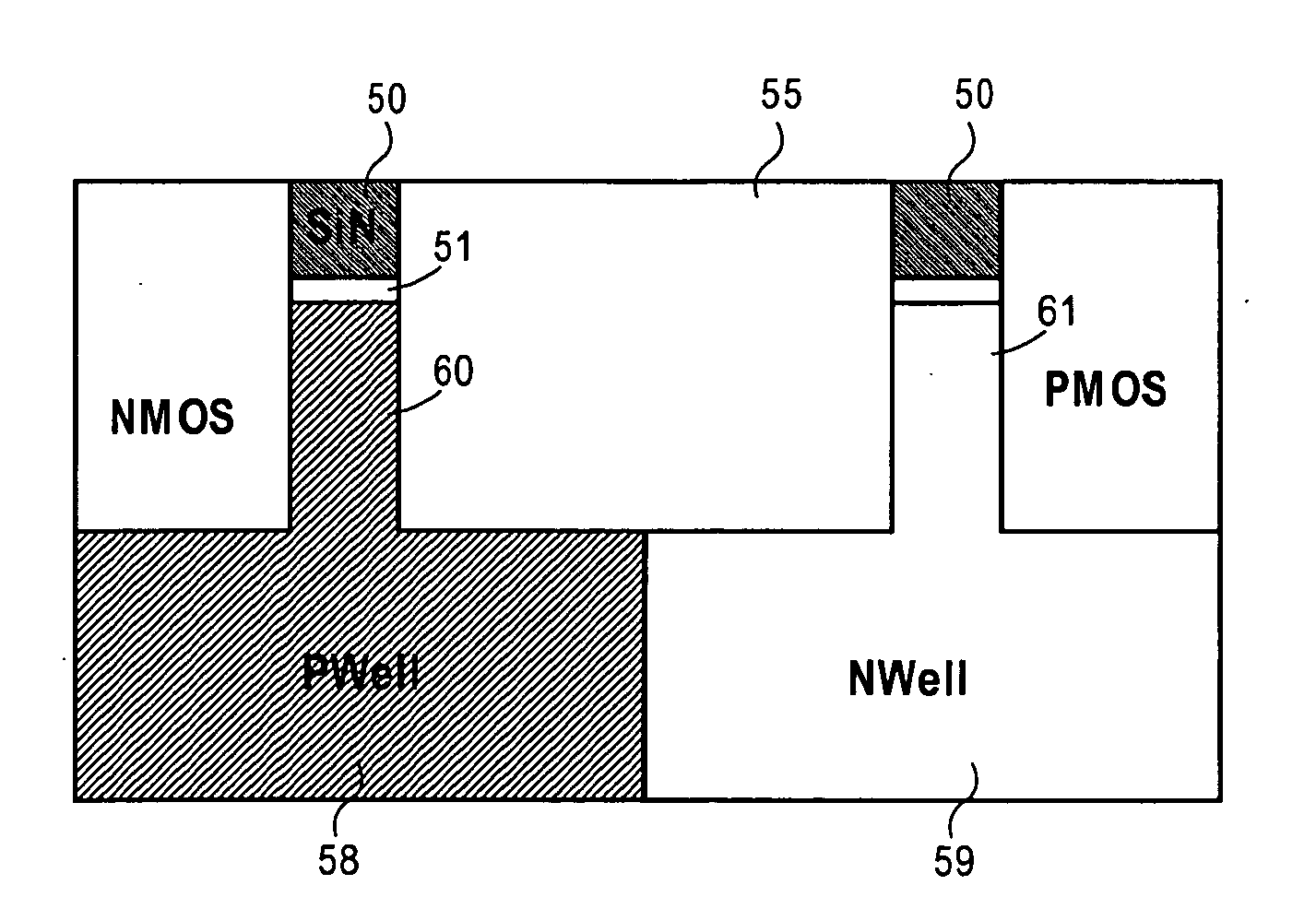
A floating body memory includes a semiconductor substrate having a cell region and a peripheral circuit region. A floating body cell is located in the cell region and a first floating body is located in the peripheral circuit region of the semiconductor substrate. A peripheral gate pattern is positioned on the first floating body. First source and drain regions are positioned at both sides of the peripheral gate pattern. First leakage shielding patterns are positioned between the first floating body and the first source and drain regions, the first source and drain regions contacting the first floating body. The first leakage shielding patterns may be positioned outside outer edges of the peripheral gate pattern.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Floating body memory cell having gates favoring different conductivity type regions
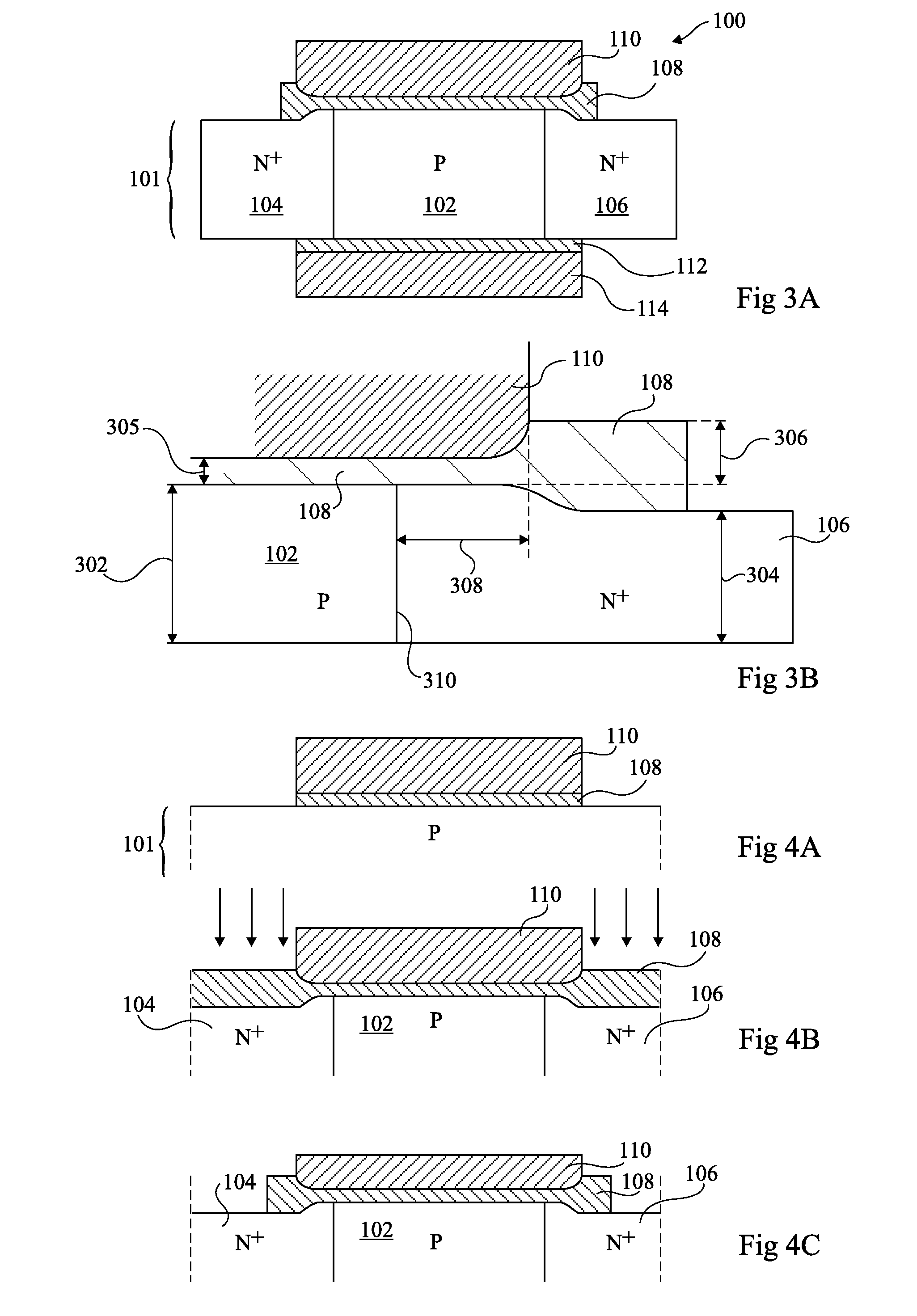
A method for fabricating floating body memory cells (FBCs), and the resultant FBCs where gates favoring different conductivity type regions are used is described. In one embodiment, a p type back gate with a thicker insulation is used with a thinner insulated n type front gate. Processing, which compensates for misalignment, which allows the different oxide and gate materials to be fabricated is described.
Owner:INTEL CORP
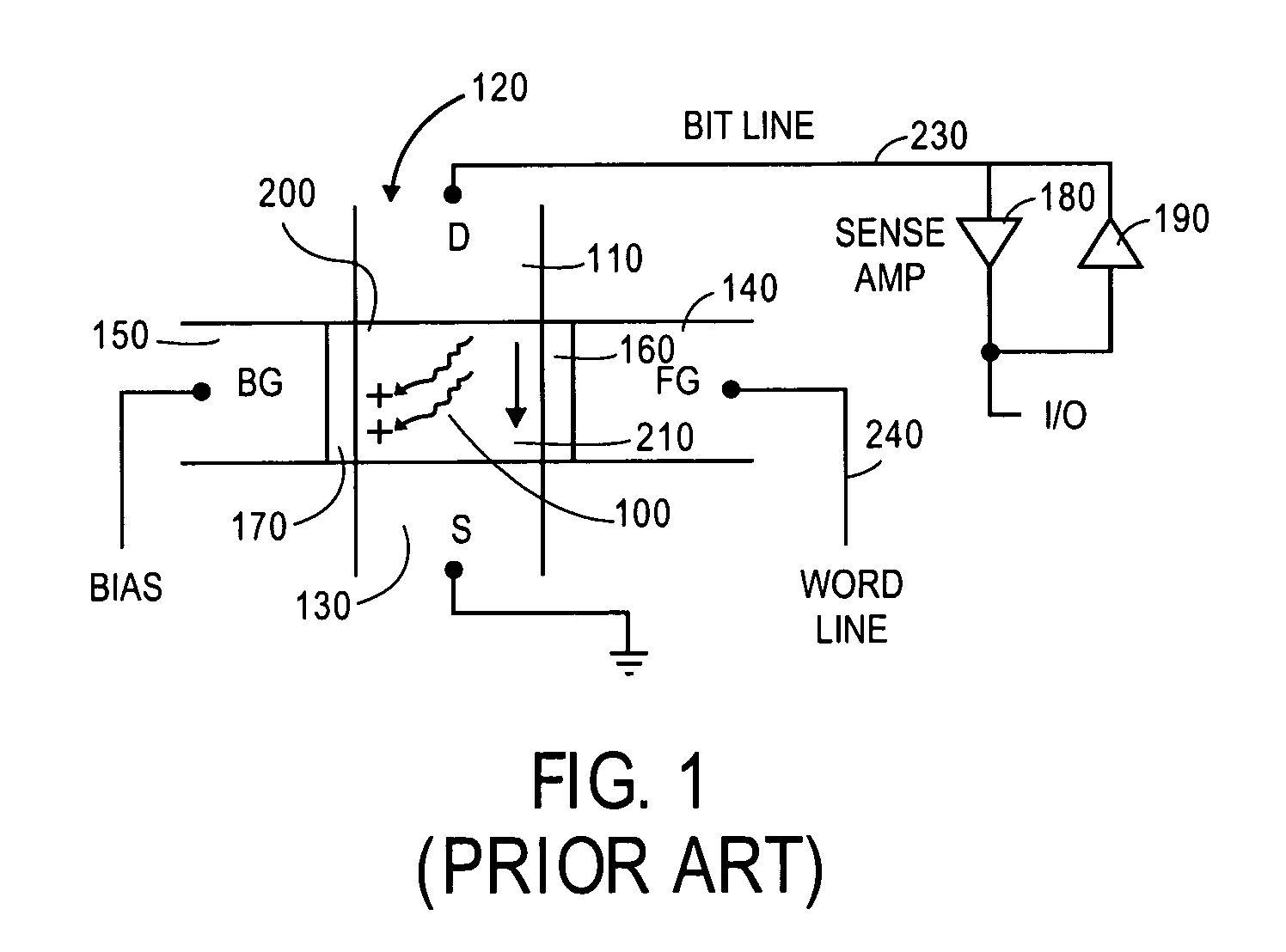
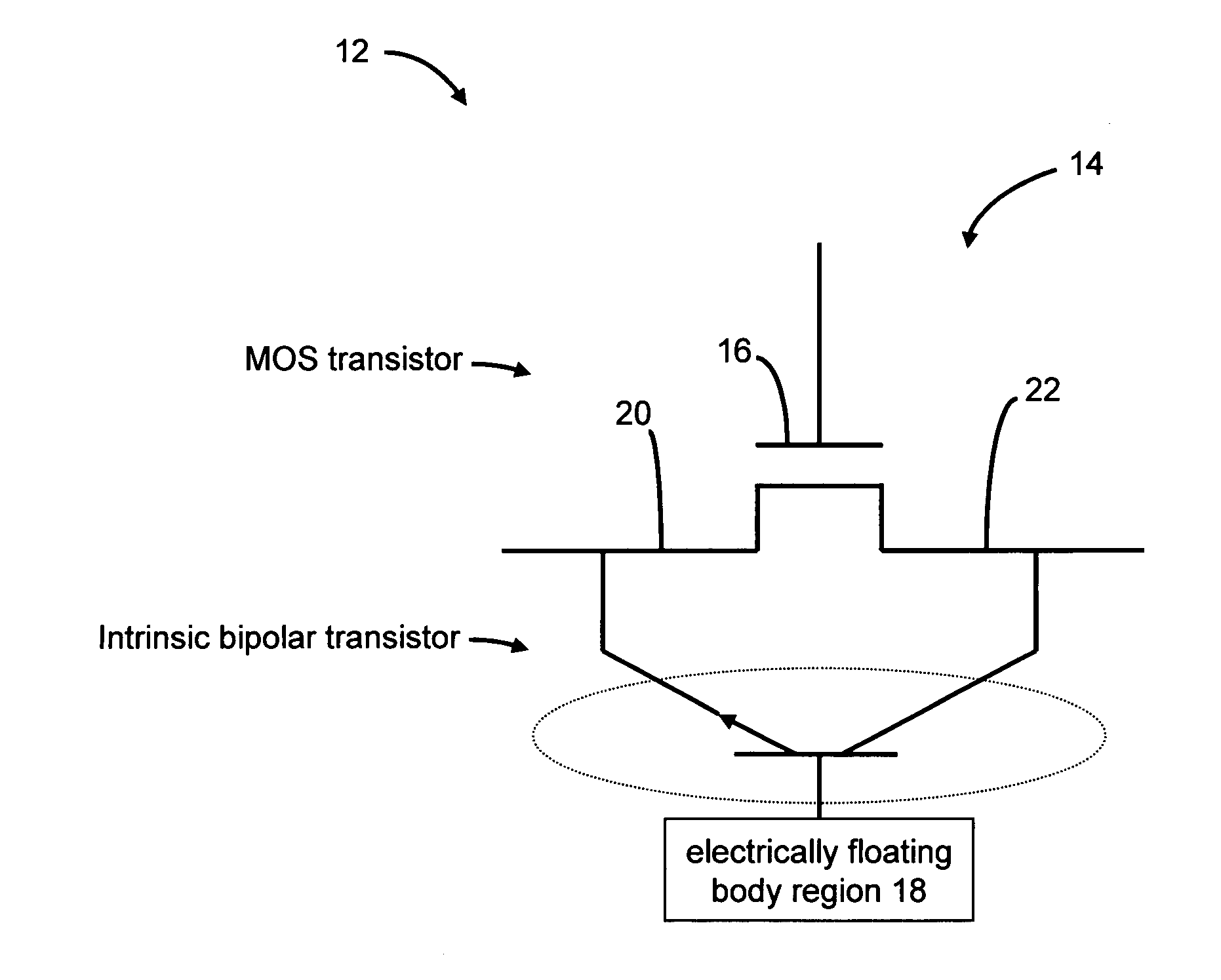
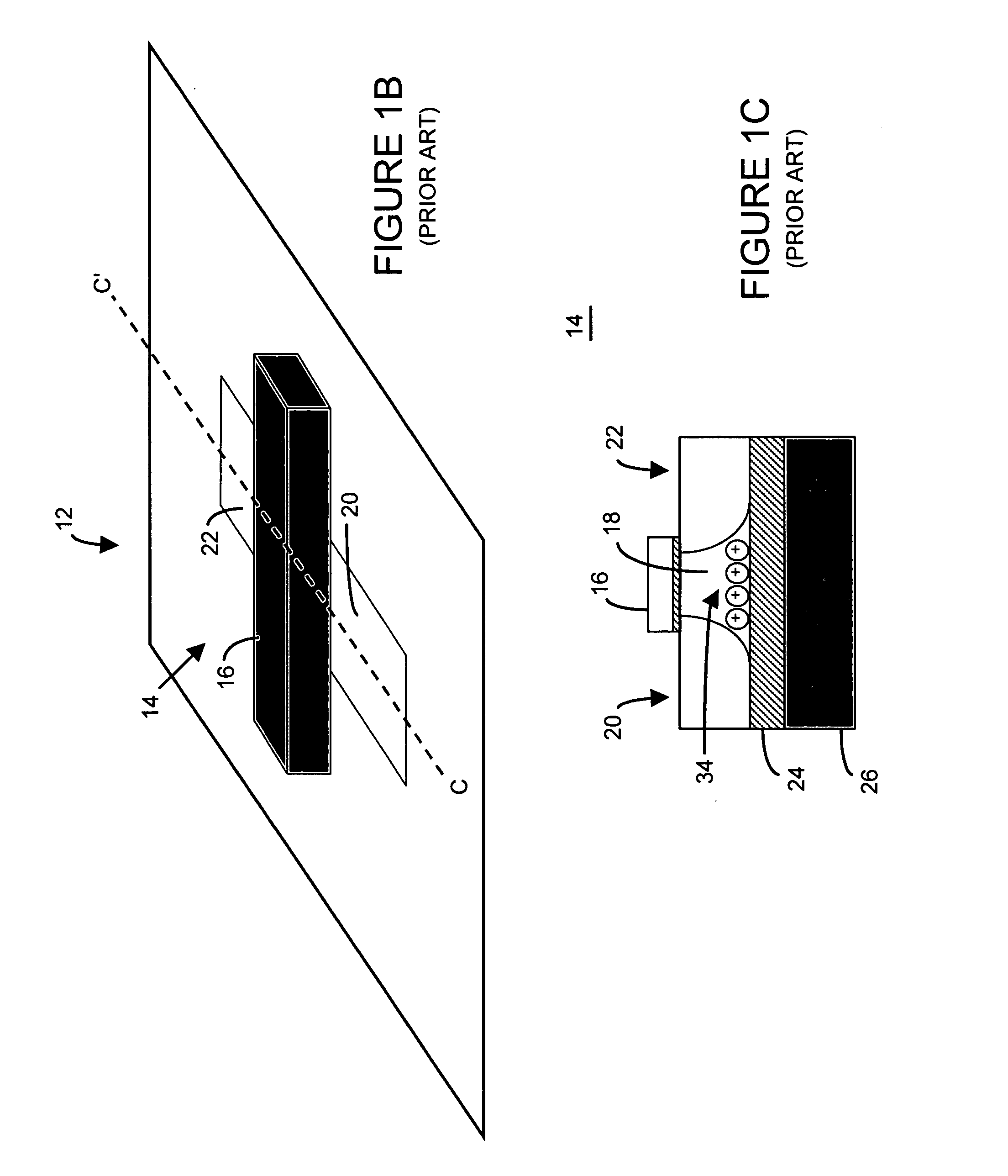
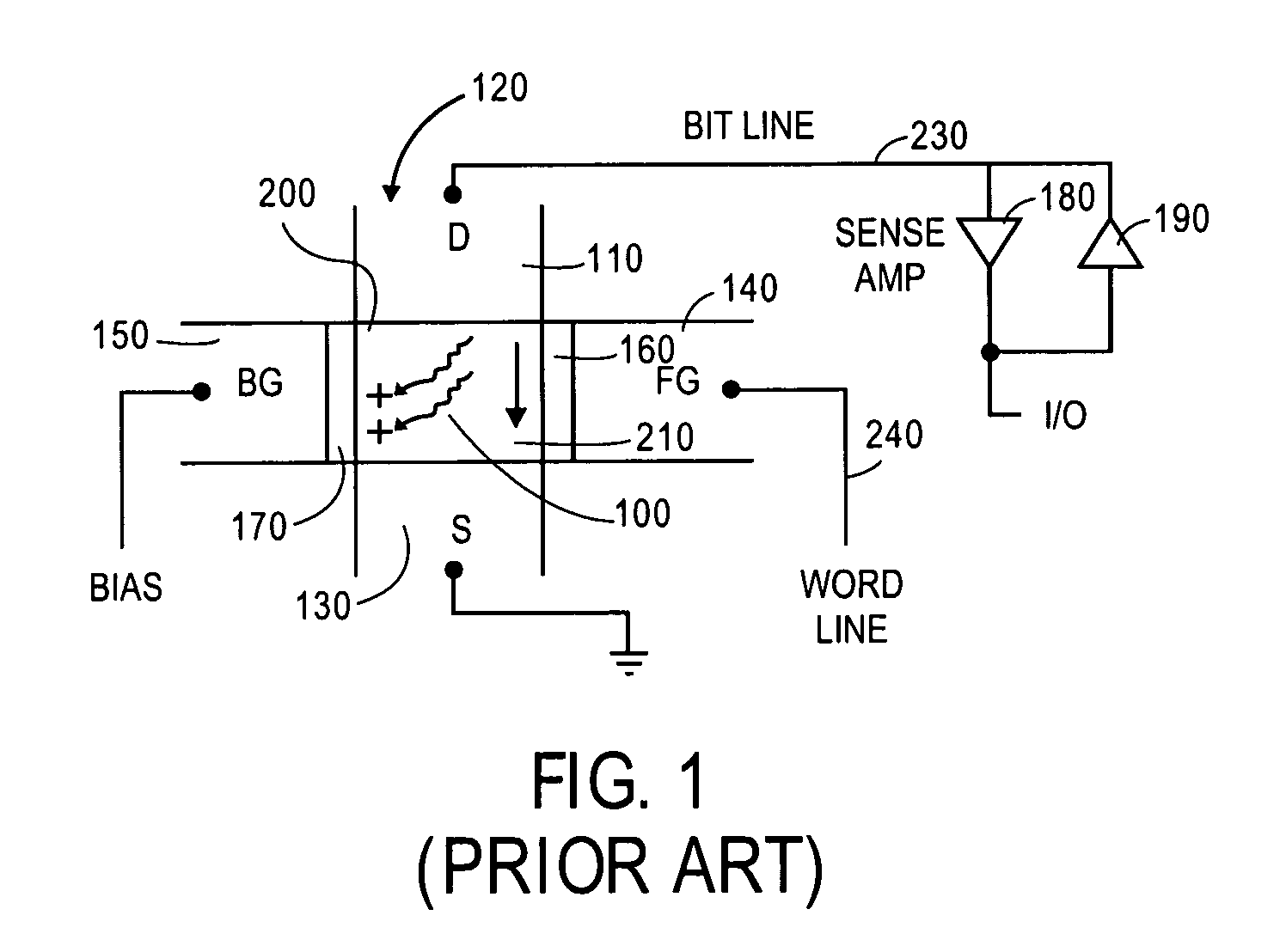
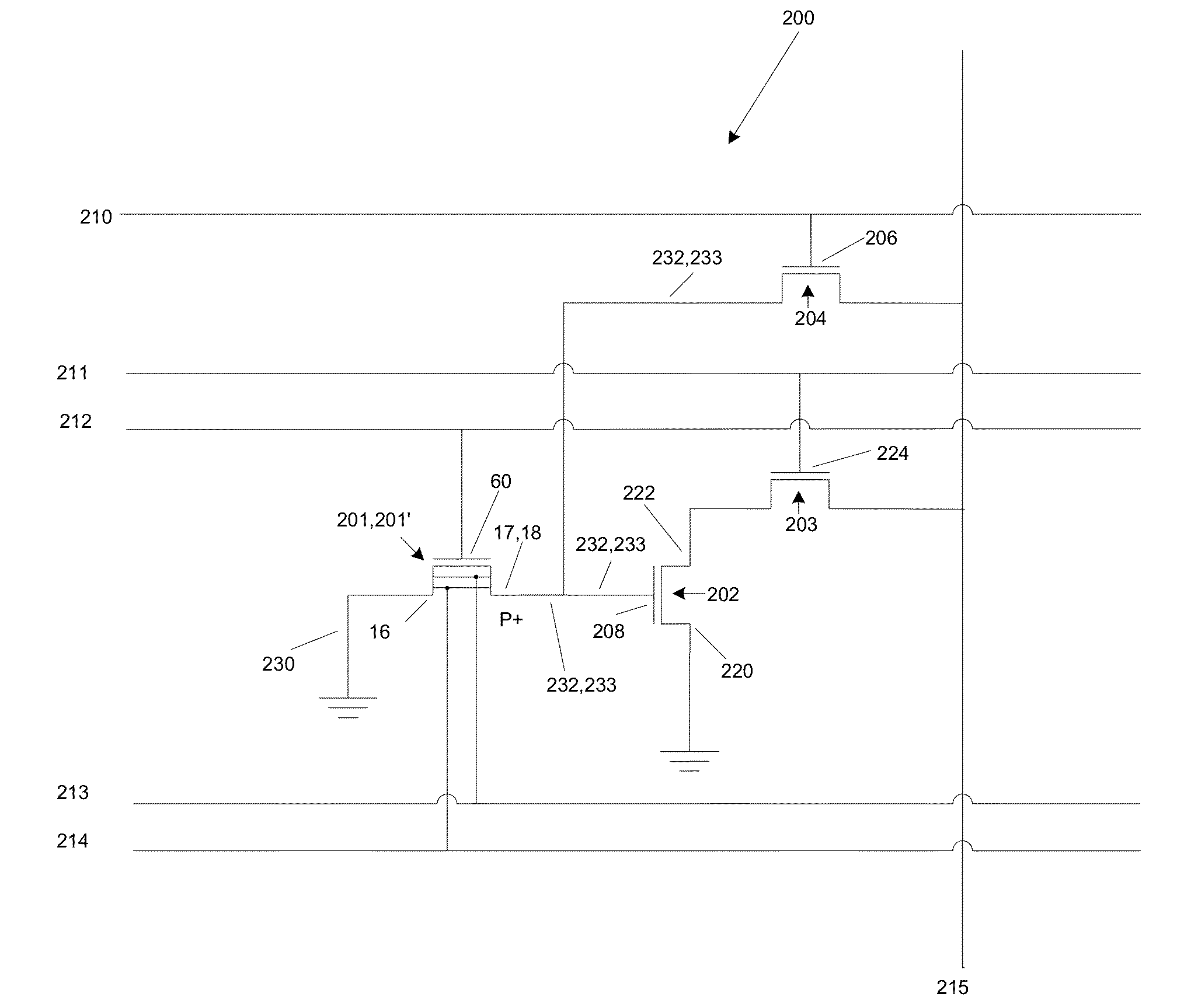
Bipolar reading technique for a memory cell having an electrically floating body transistor
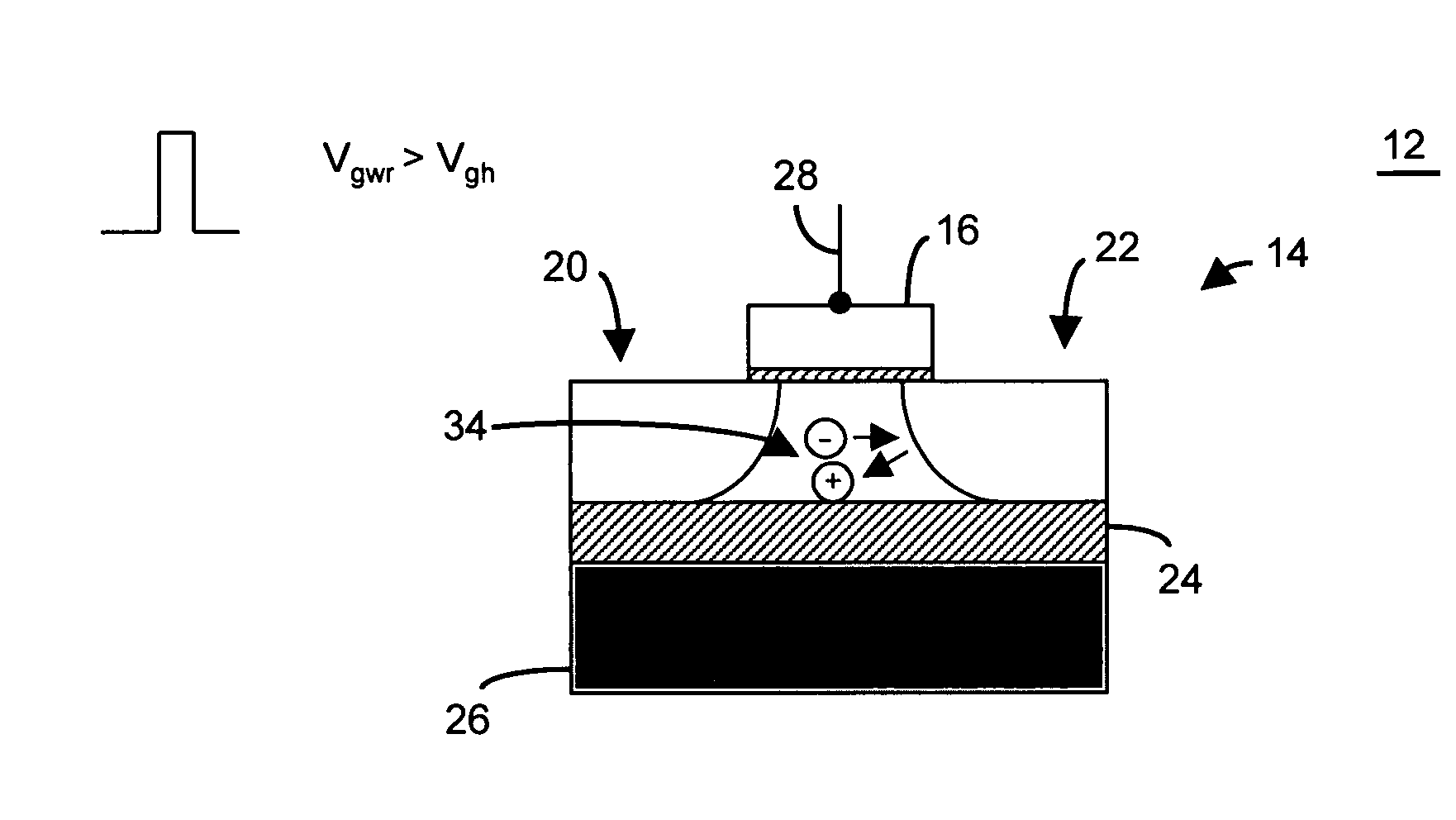
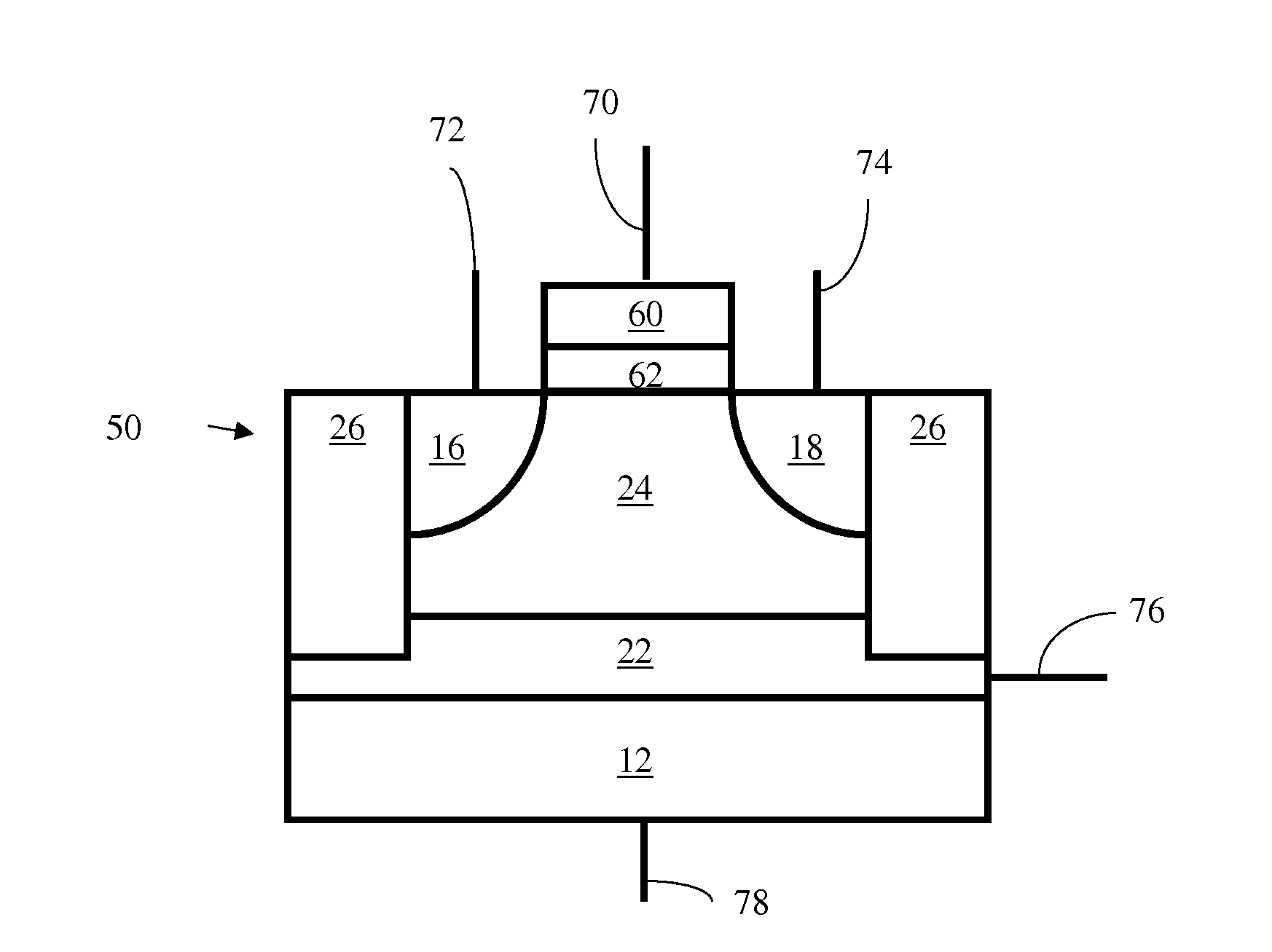
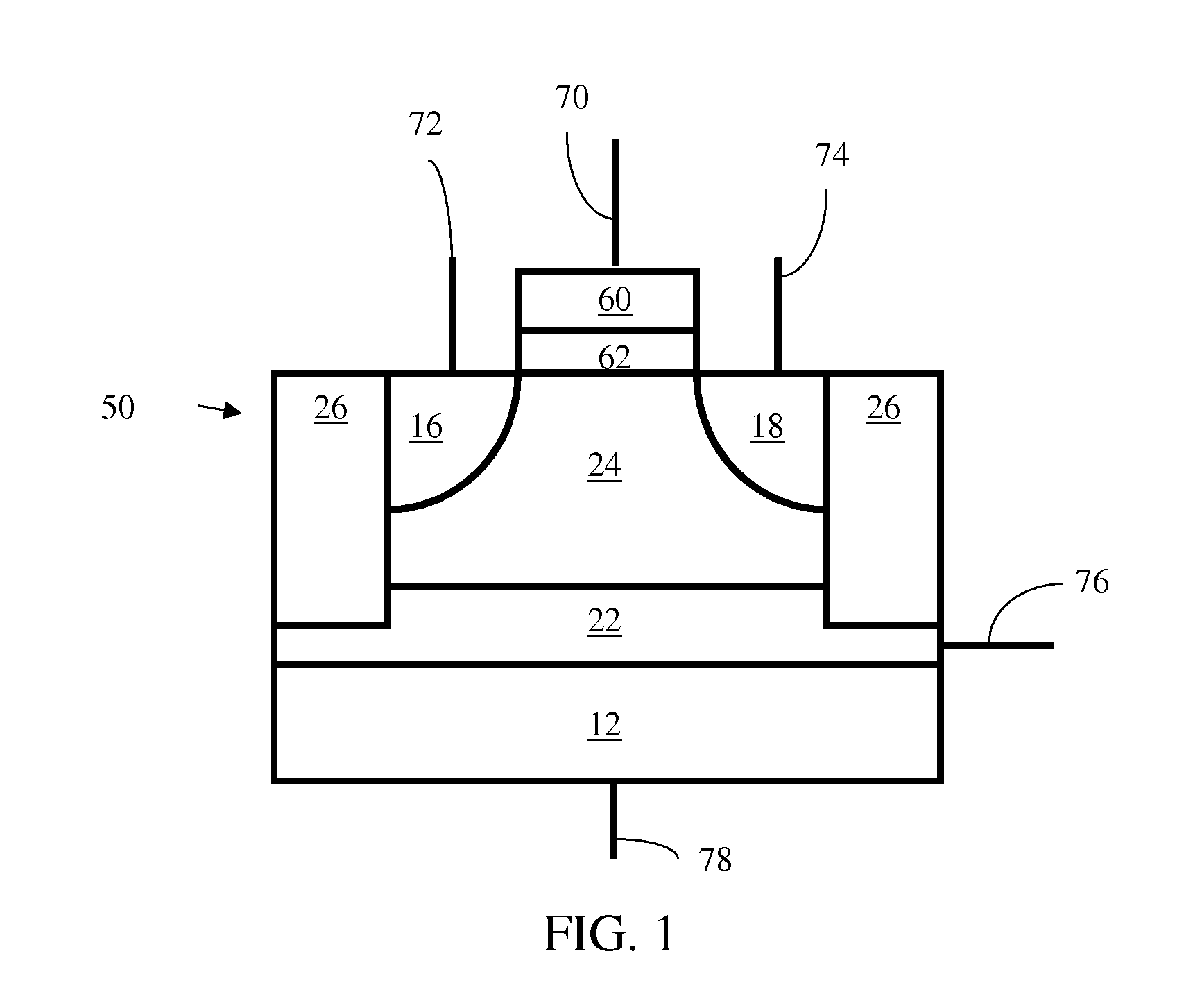
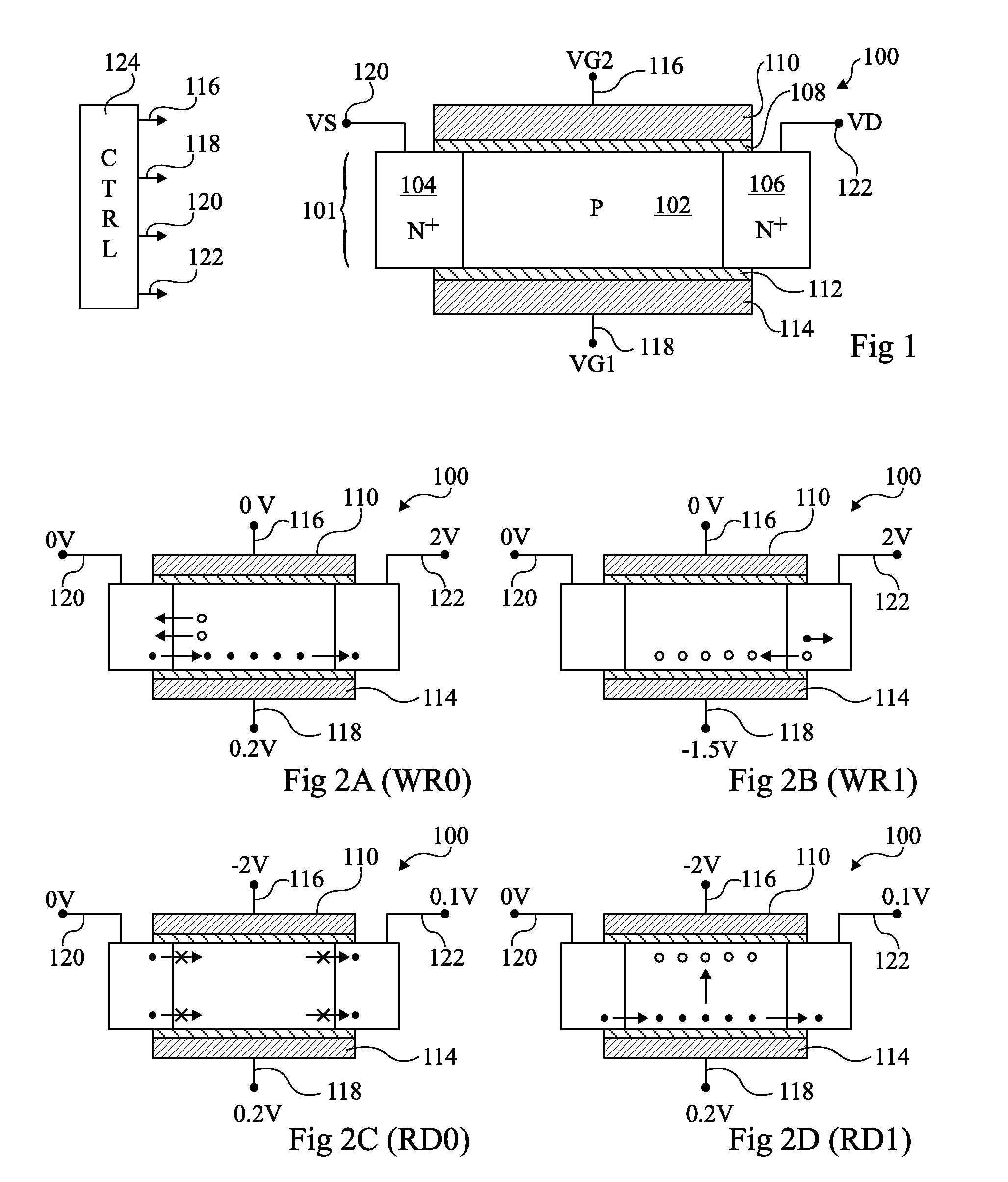
A technique of sampling, sensing, reading and / or determining the data state of a memory cell of a memory cell array (for example, a memory cell array having a plurality of memory cells which consist of an electrically floating body transistor). In one embodiment, the present inventions are directed to a memory cell, having an electrically floating body transistor, and / or a technique of reading the data state in such a memory cell. In this regard, the present inventions employ the intrinsic bipolar transistor current to read and / or determine the data state of the electrically floating body memory cell (for example, whether the electrically floating body memory cell is programmed in a State “0” and State “1”). During the read operation, the data state is determined primarily by or sensed substantially using the bipolar current responsive to the read control signals and significantly less by the interface channel current component, which is negligible relatively to the bipolar component. The bipolar transistor current may be very sensitive to the floating body potential due to the high gain of the intrinsic bipolar transistor. As such, the programming window obtainable with the bipolar reading technique may be considerably higher (for example, up two orders of magnitude higher) than the programming window employing a conventional reading technique (which is based primarily on the interface channel current component.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Semiconductor device with floating gate and electrically floating body
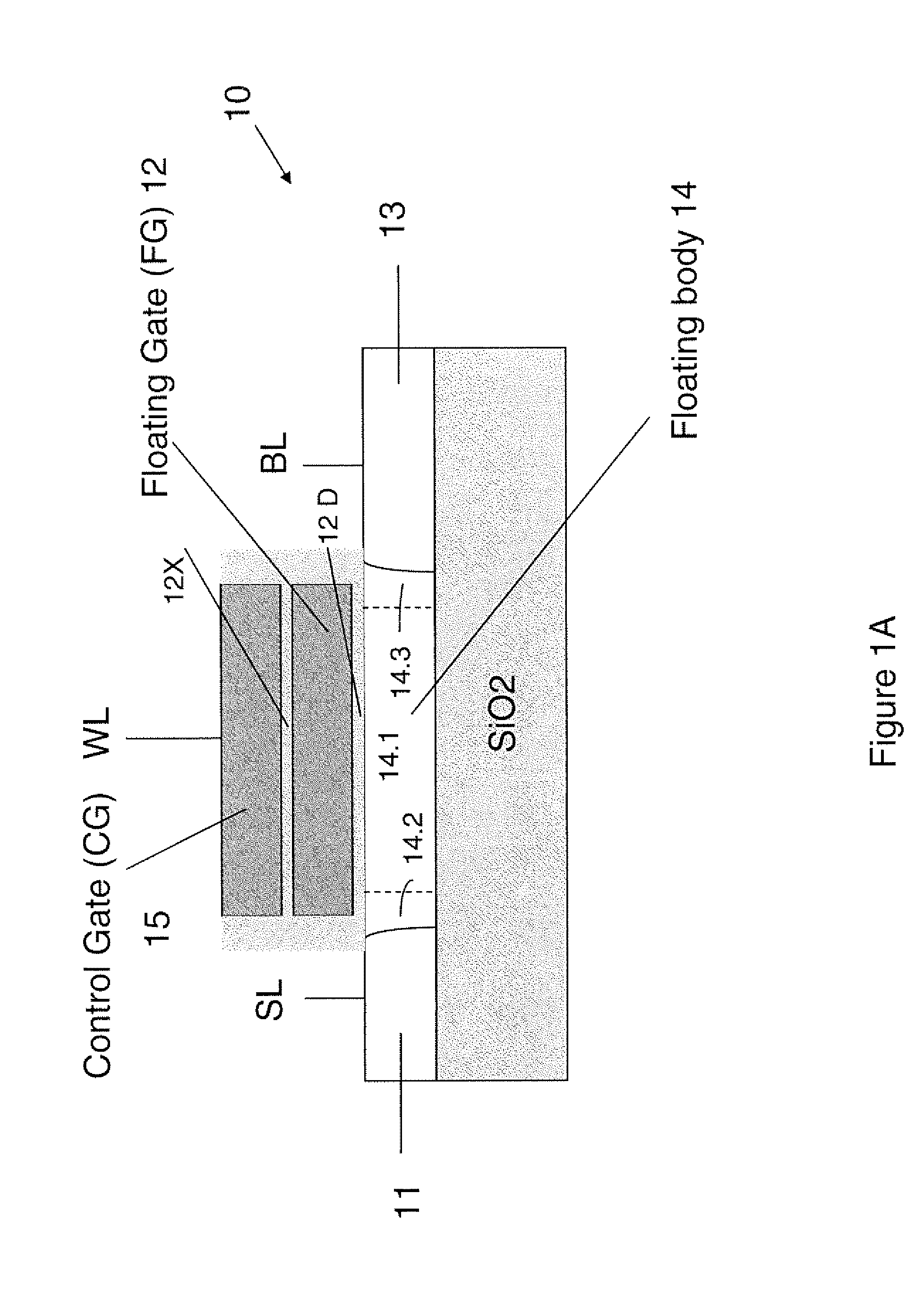
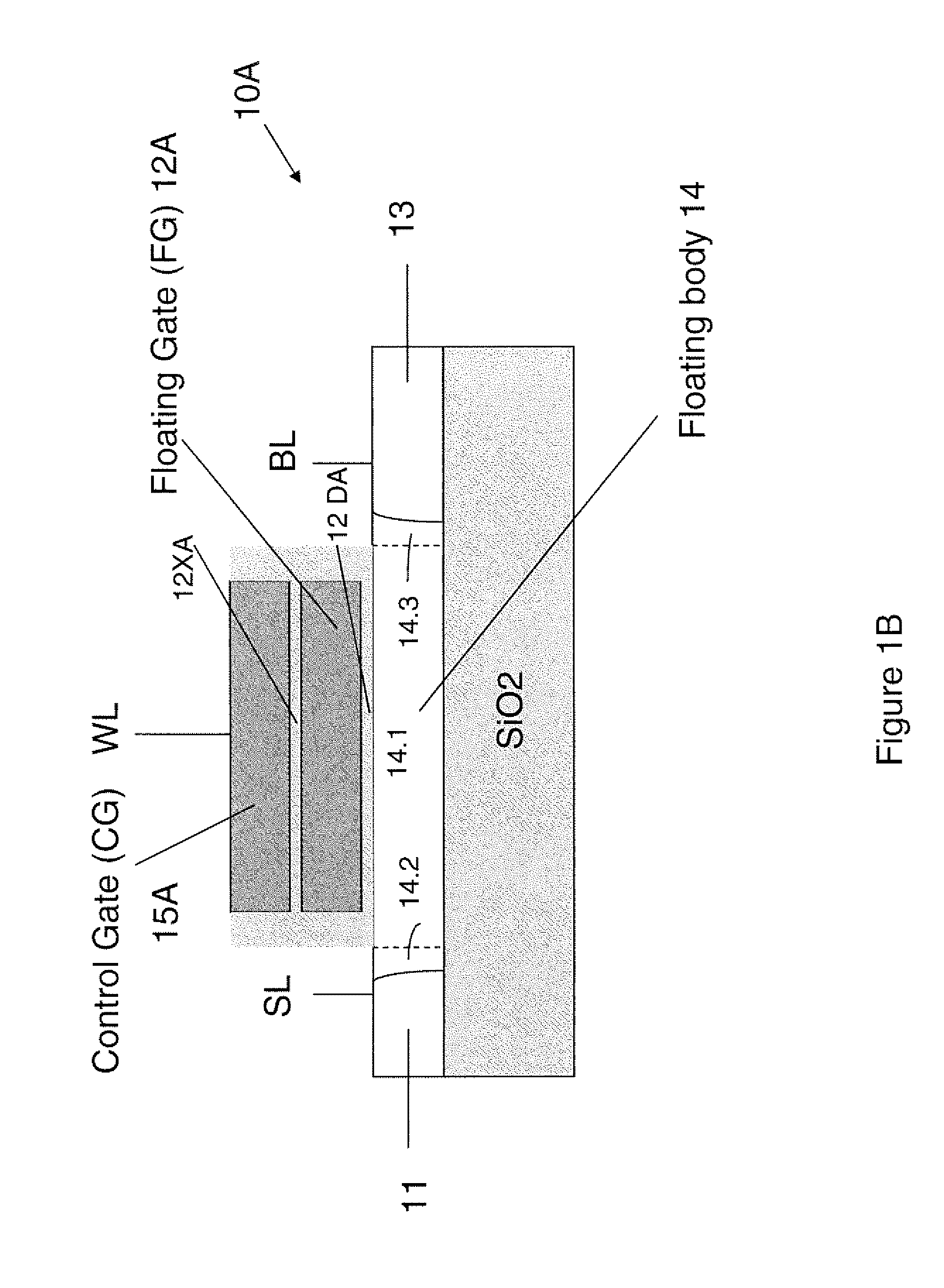
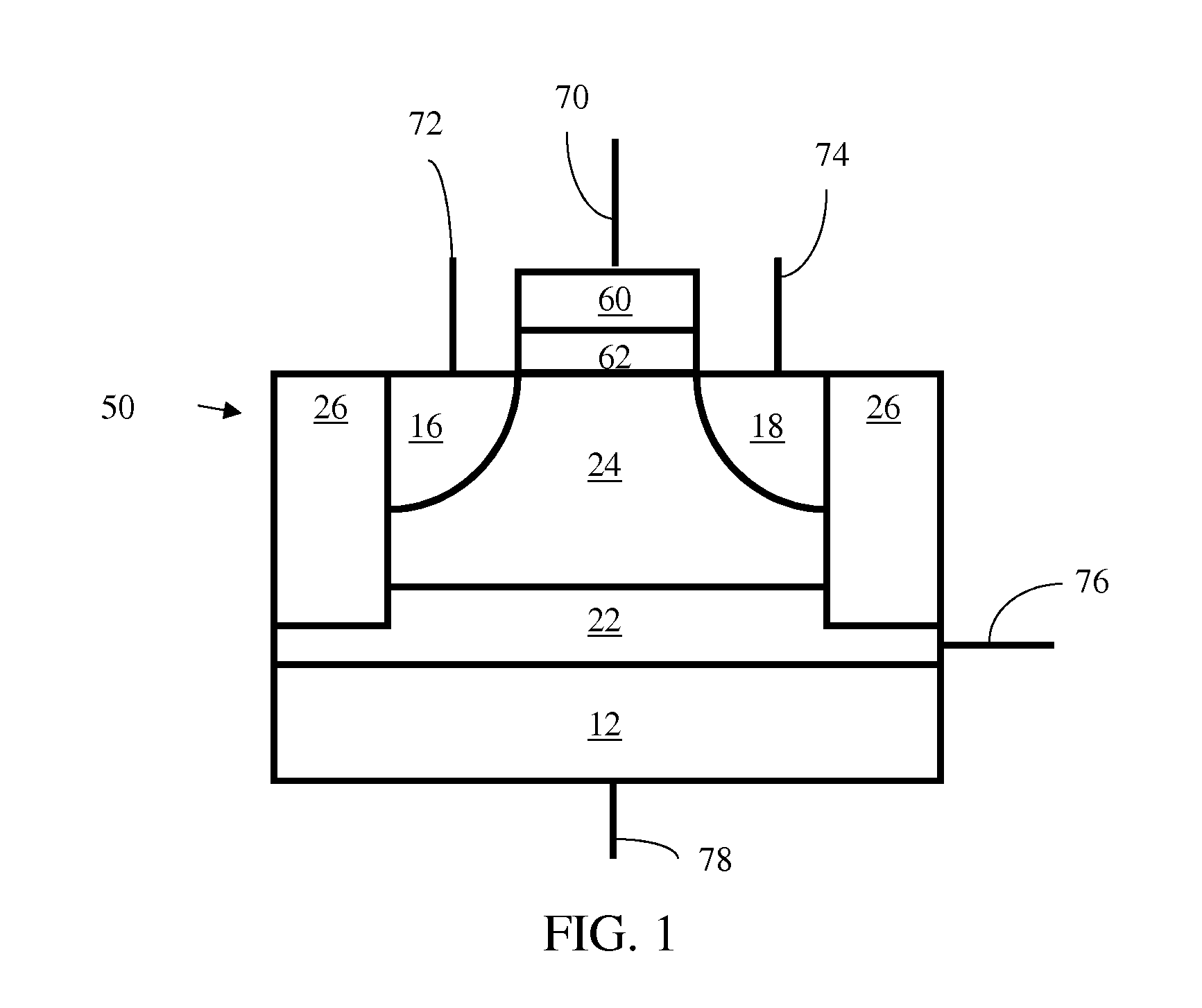
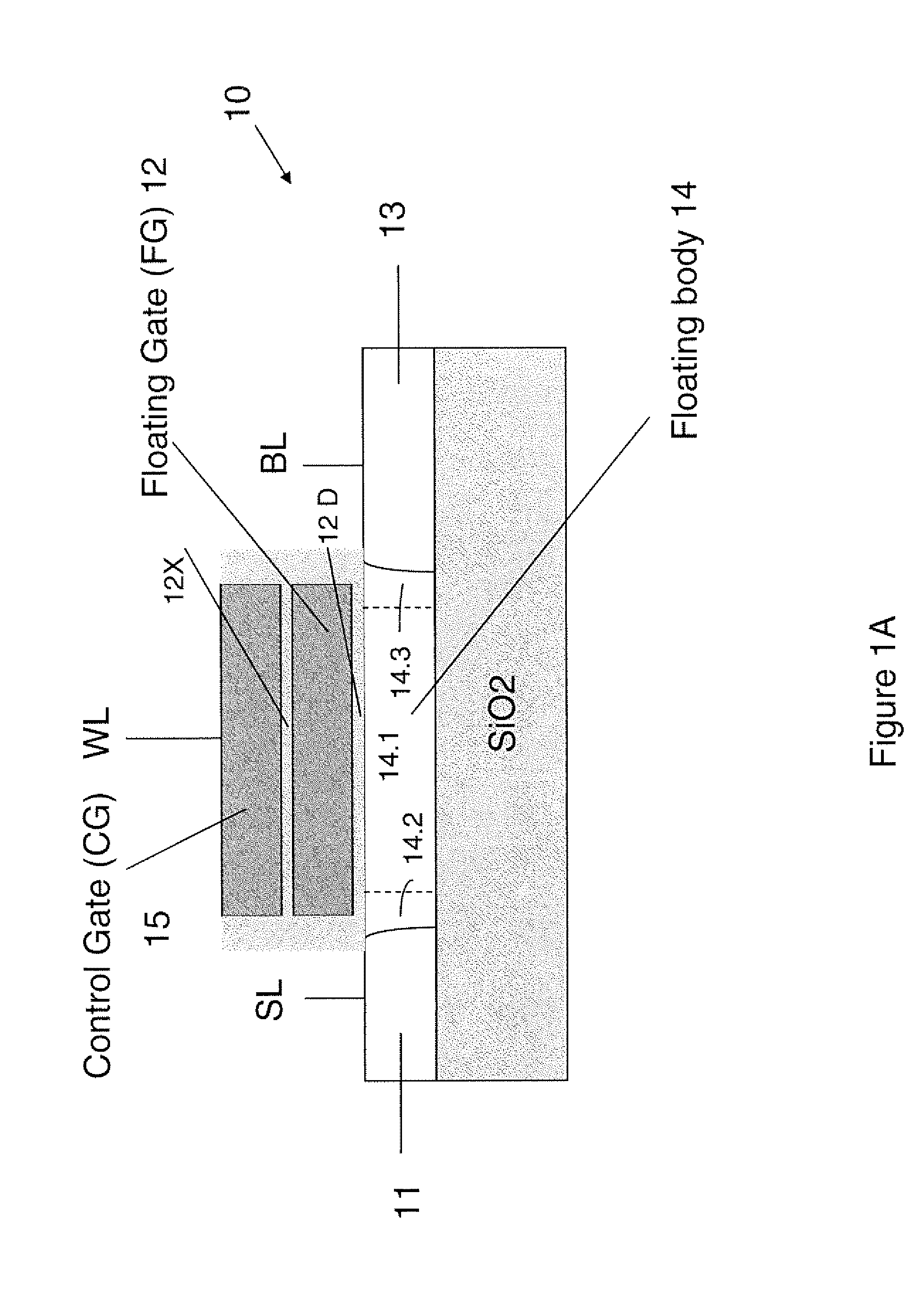
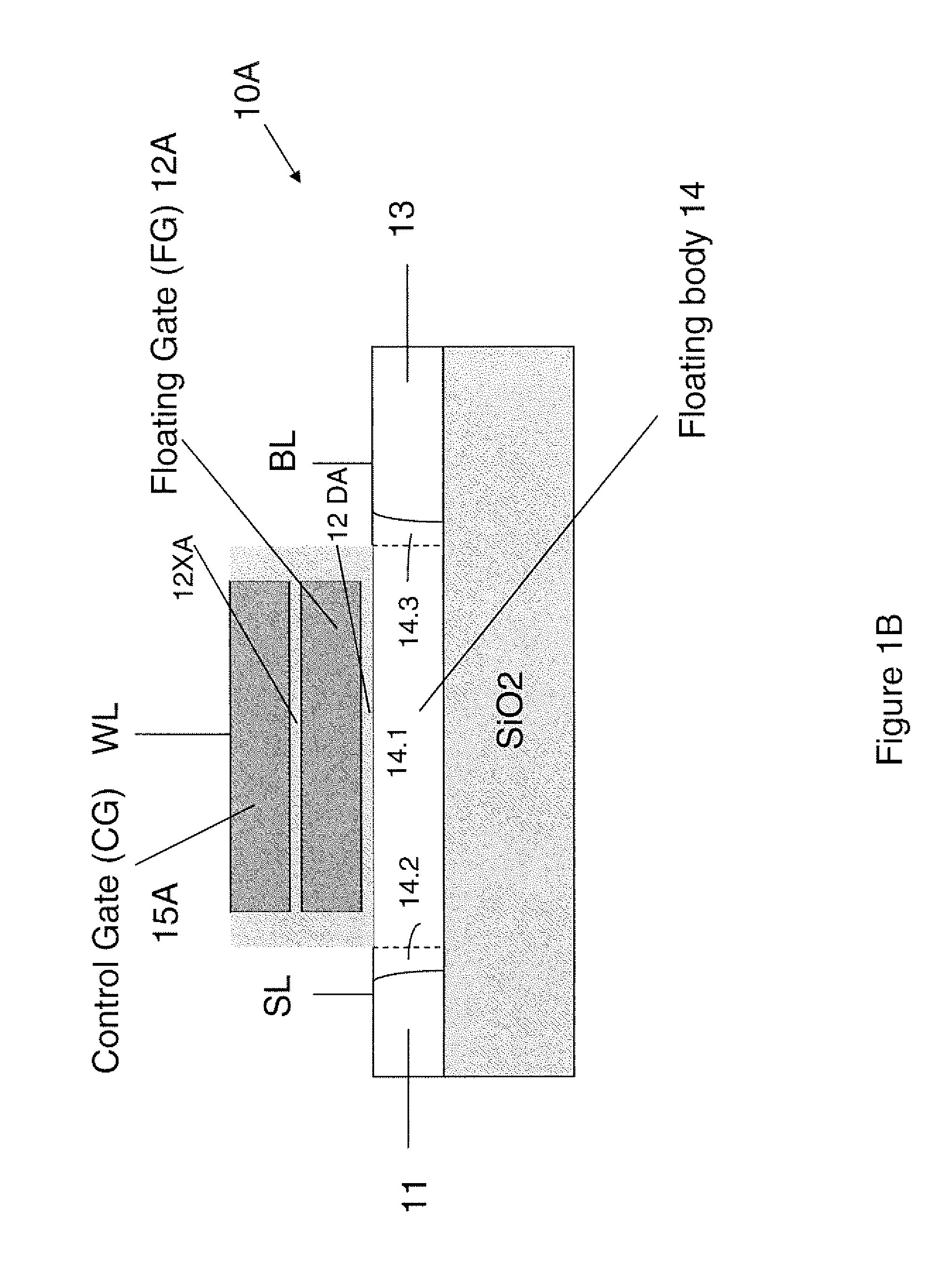
Techniques for providing floating body memory devices are disclosed. In one particular exemplary embodiment, the techniques may be realized as a semiconductor device comprising a floating gate, a control gate disposed over the floating gate, a body region that is electrically floating, wherein the body region is configured so that material forming the body region is contained under at least one lateral boundary of the floating gate, and a source region and a drain region adjacent the body region.
Owner:OVONYX MEMORY TECH LLC
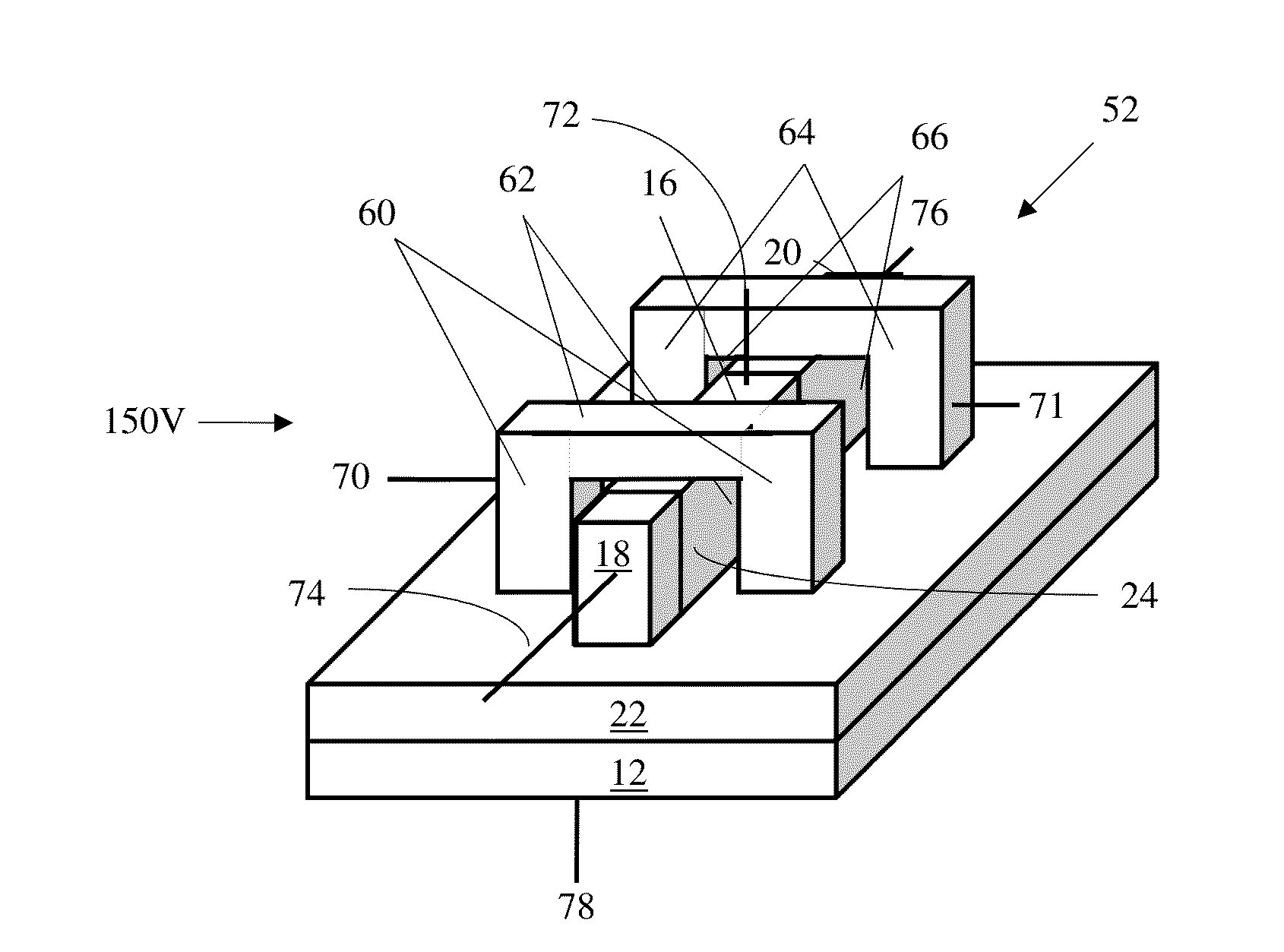
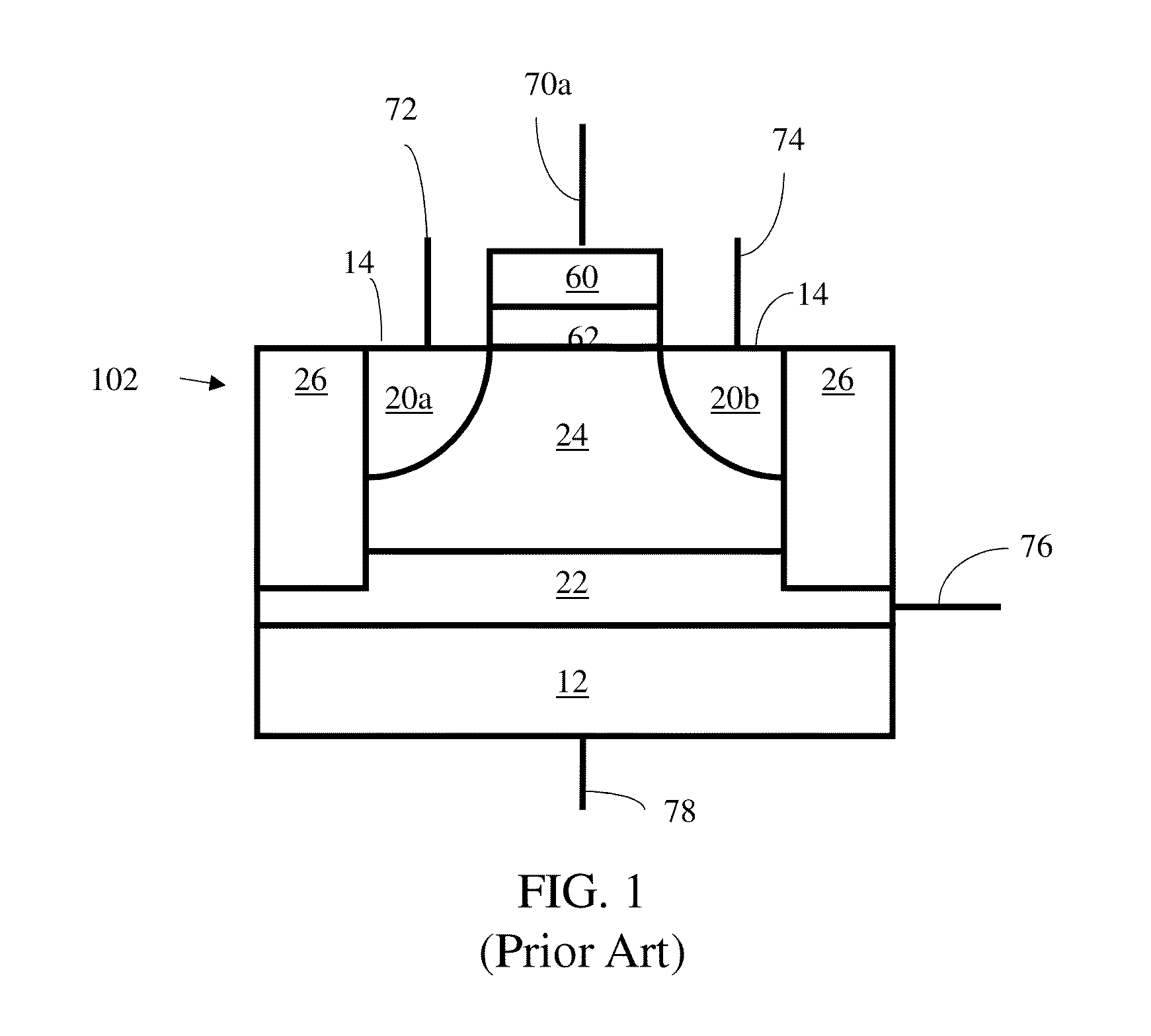
Electrically floating body memory cell and array, and method of operating or controlling same
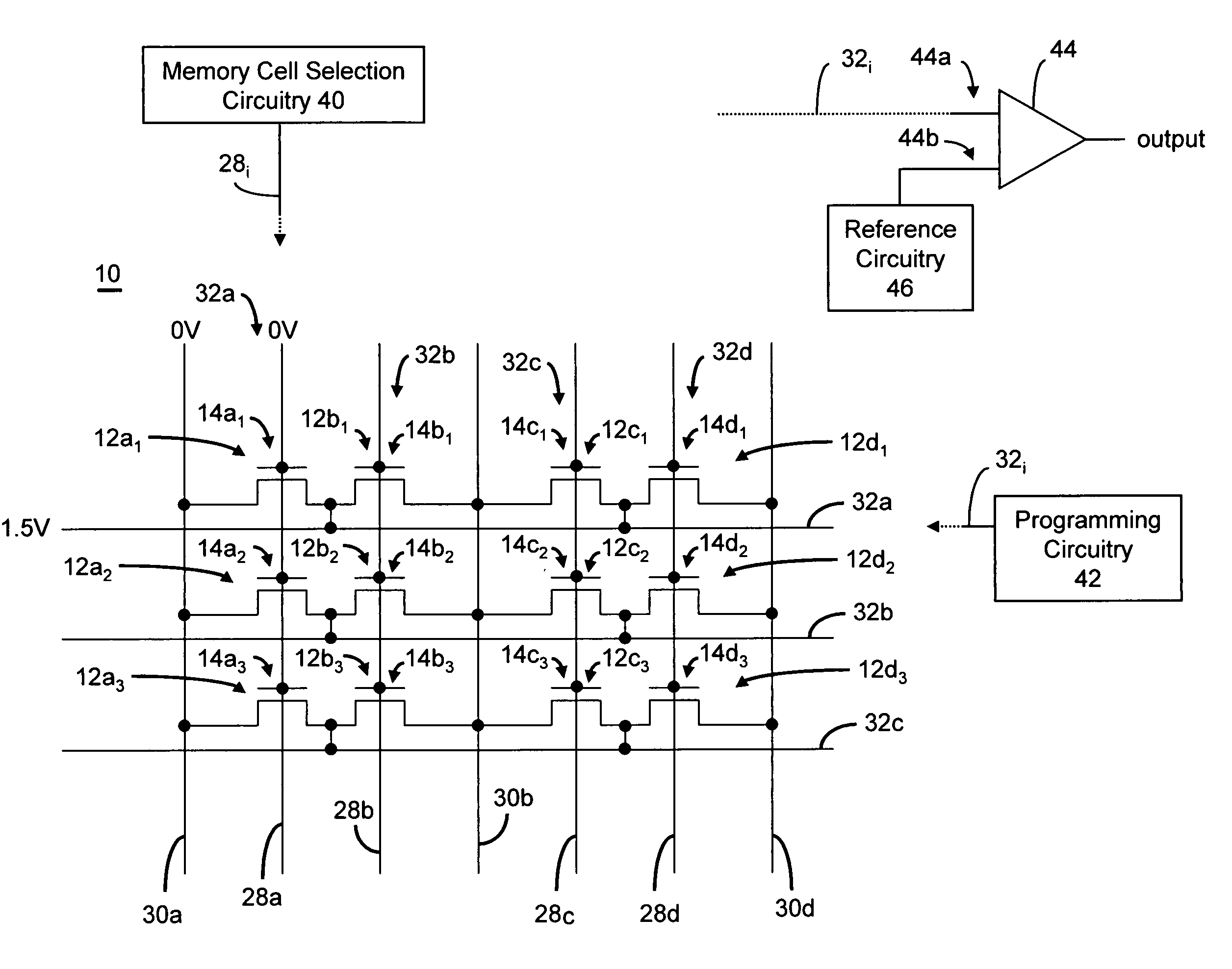
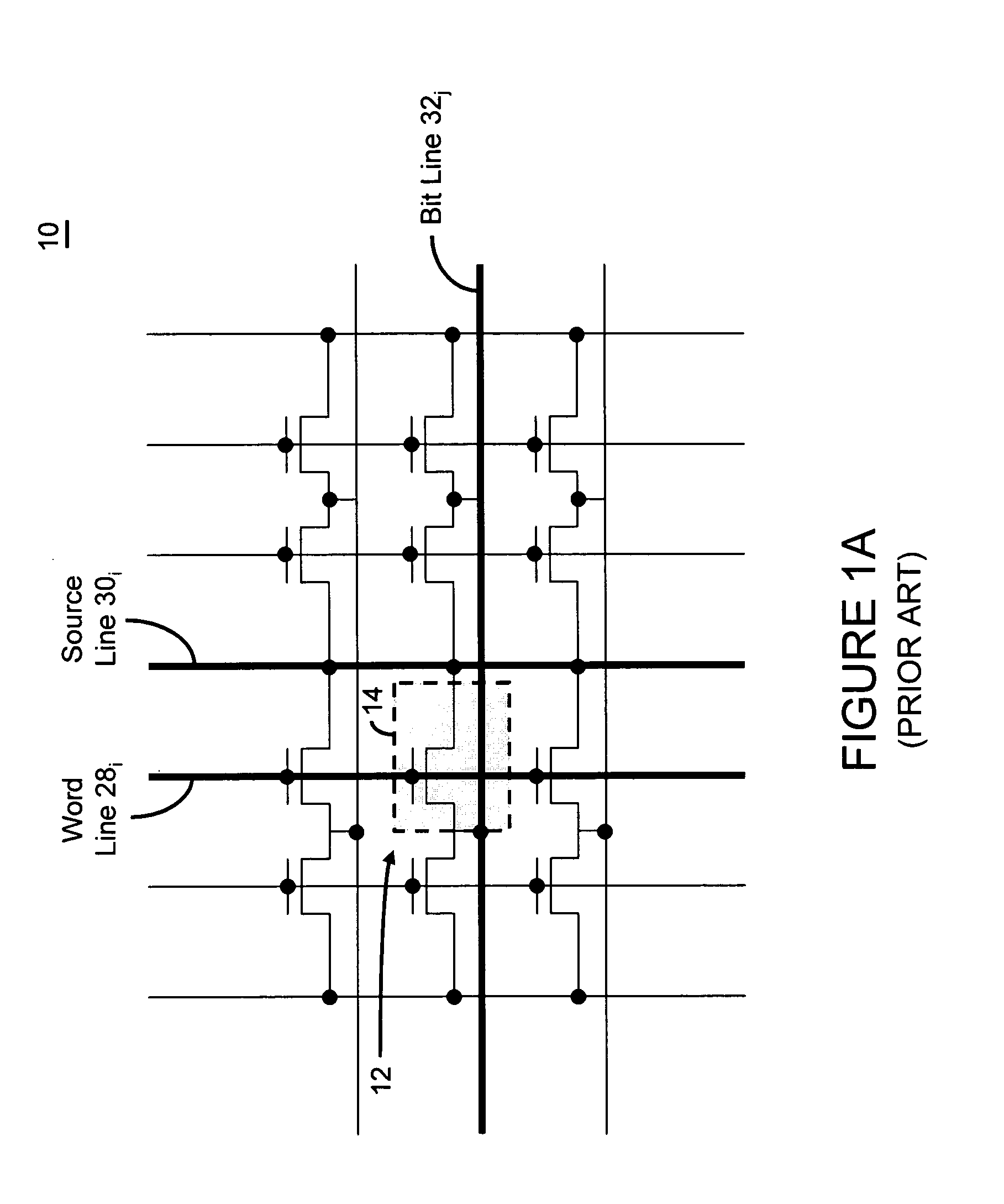
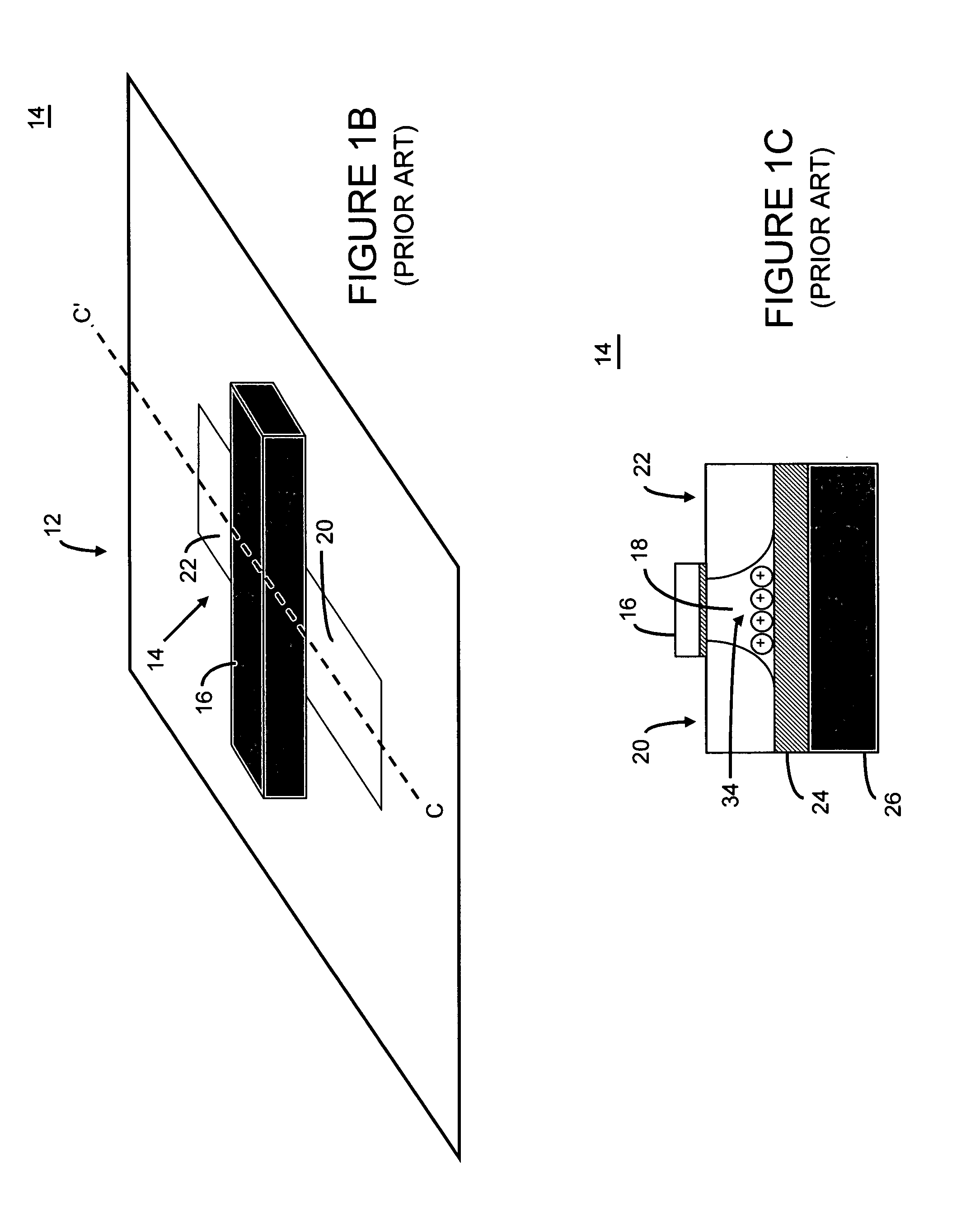
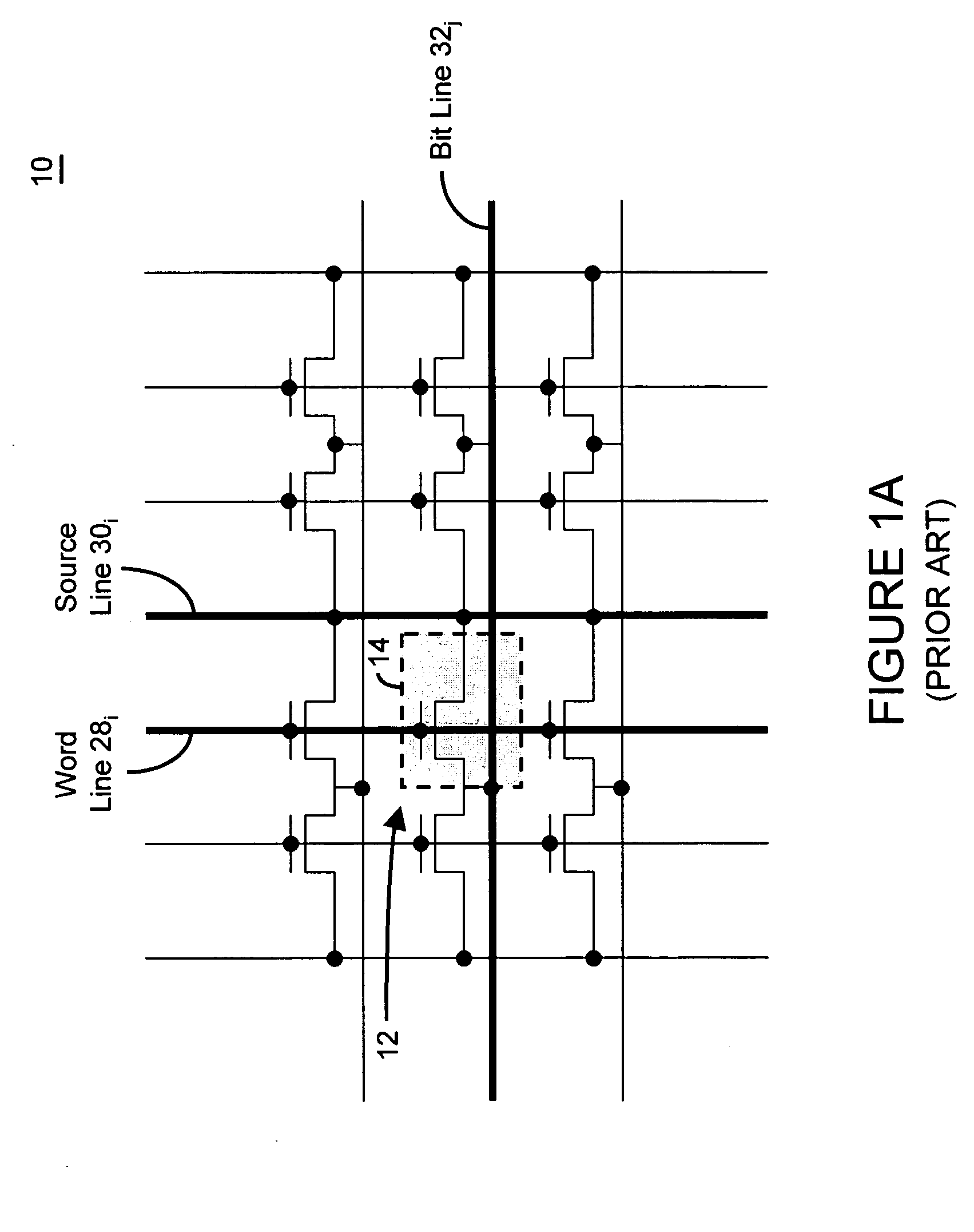
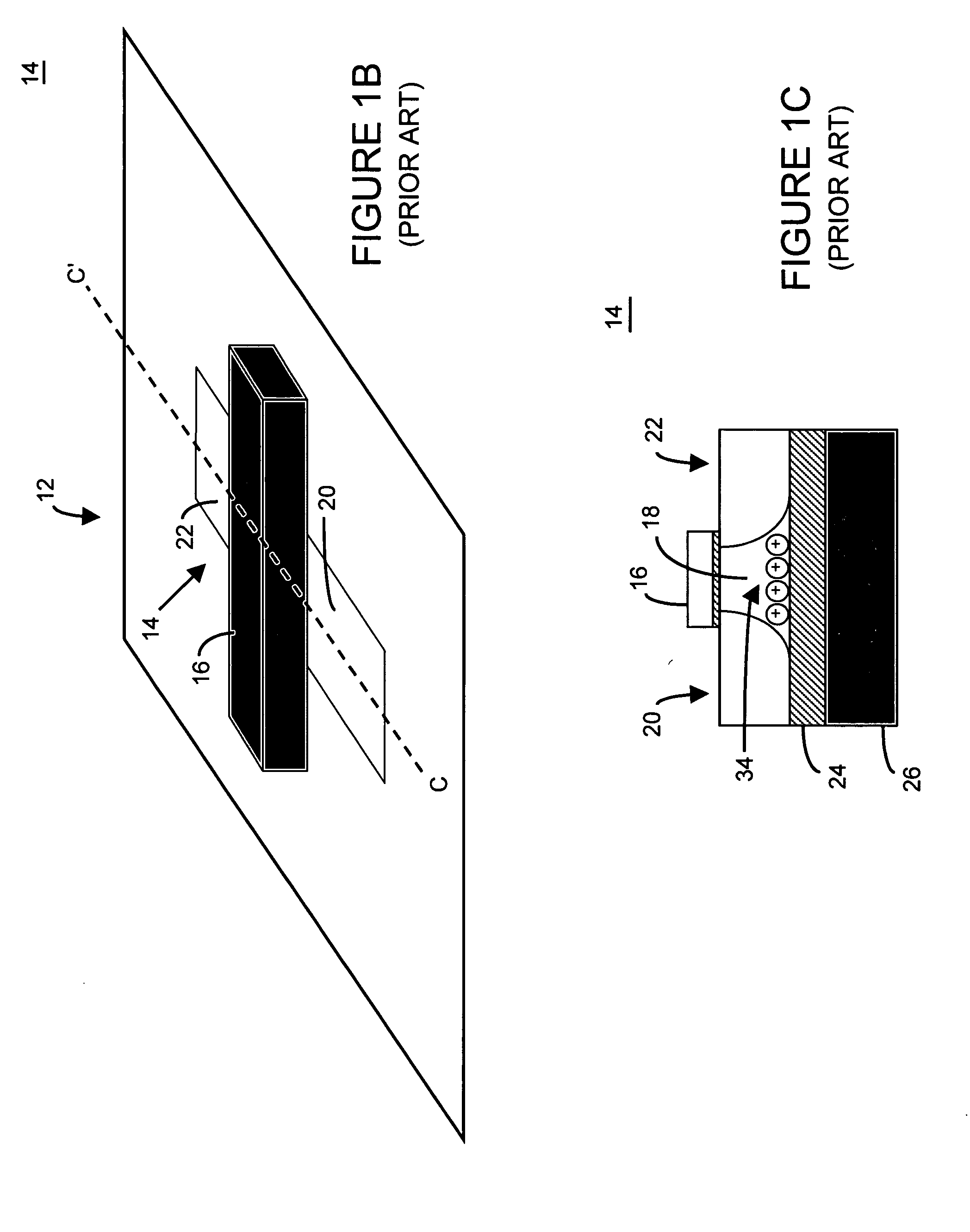
An integrated circuit having a memory cell and / or memory cell array including a plurality of memory cells (as well as techniques for reading, controlling and / or operating, the memory cell, and / or memory cell array). Each memory cell includes at least one transistor having an electrically floating body transistor and an active access element. The electrically floating body region of the transistor forms a storage area or node of the memory cell wherein an electrical charge which is representative of a data state is stored in the electrically floating body region. The active access element is coupled to the electrically floating body transistor to facilitate programming of the memory cell and to provide a relatively large amount of majority carriers to the storage area or node of the memory cell during a write operation. The memory cell and / or memory cell array of the present inventions may be incorporated in an integrated circuit device, for example, a logic device (such as, for example, a microcontroller or microprocessor) or may comprise a portion of a memory device (such as, for example, a discrete memory).
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
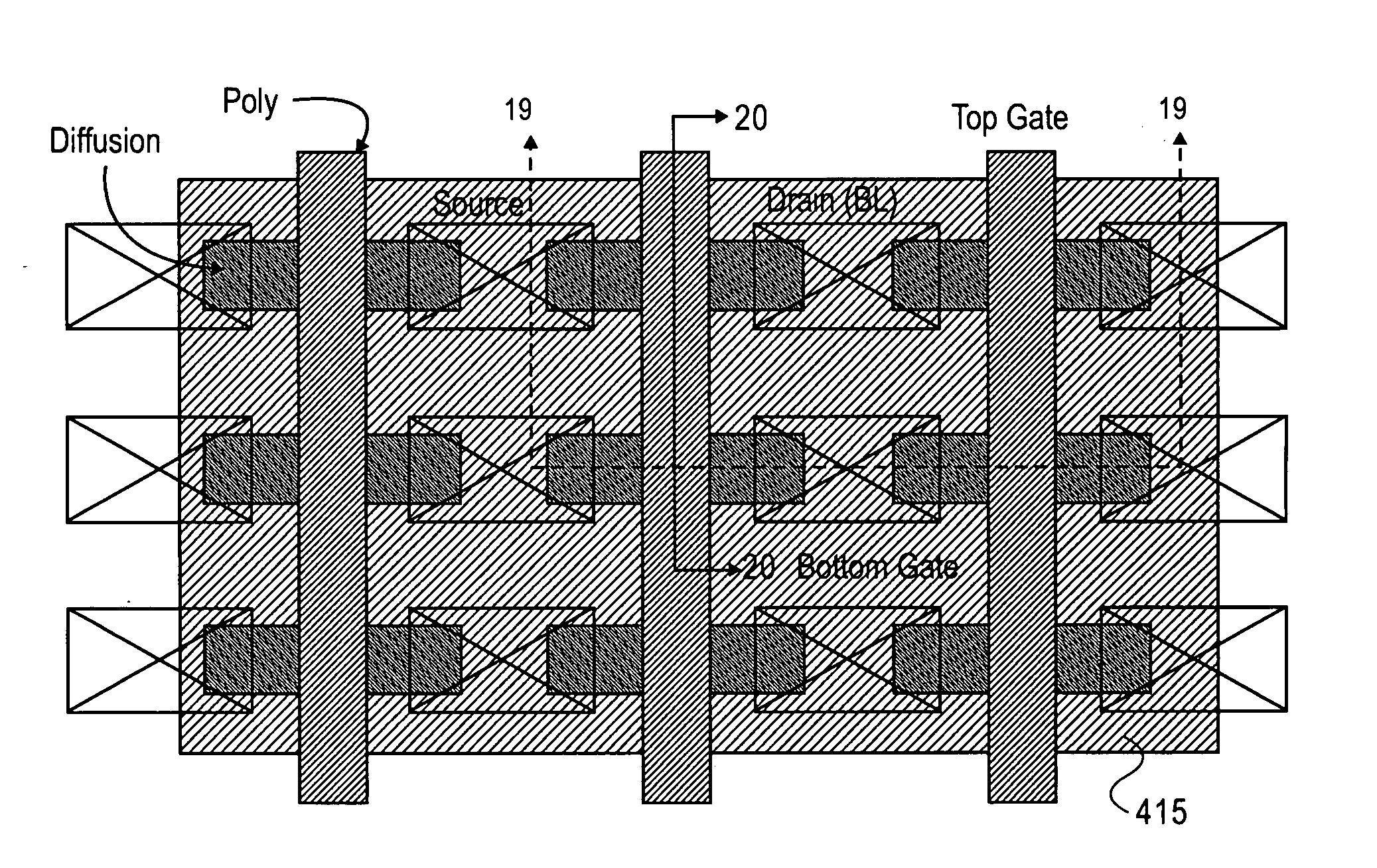
NAND String Utilizing Floating Body Memory Cell
NAND string configurations and semiconductor memory arrays that include such NAND string configurations are provided. Methods of making semiconductor memory cells used in NAND string configurations are also described.
Owner:ZENO SEMICON
Systems and Methods for Reducing Standby Power in Floating Body Memory Devices
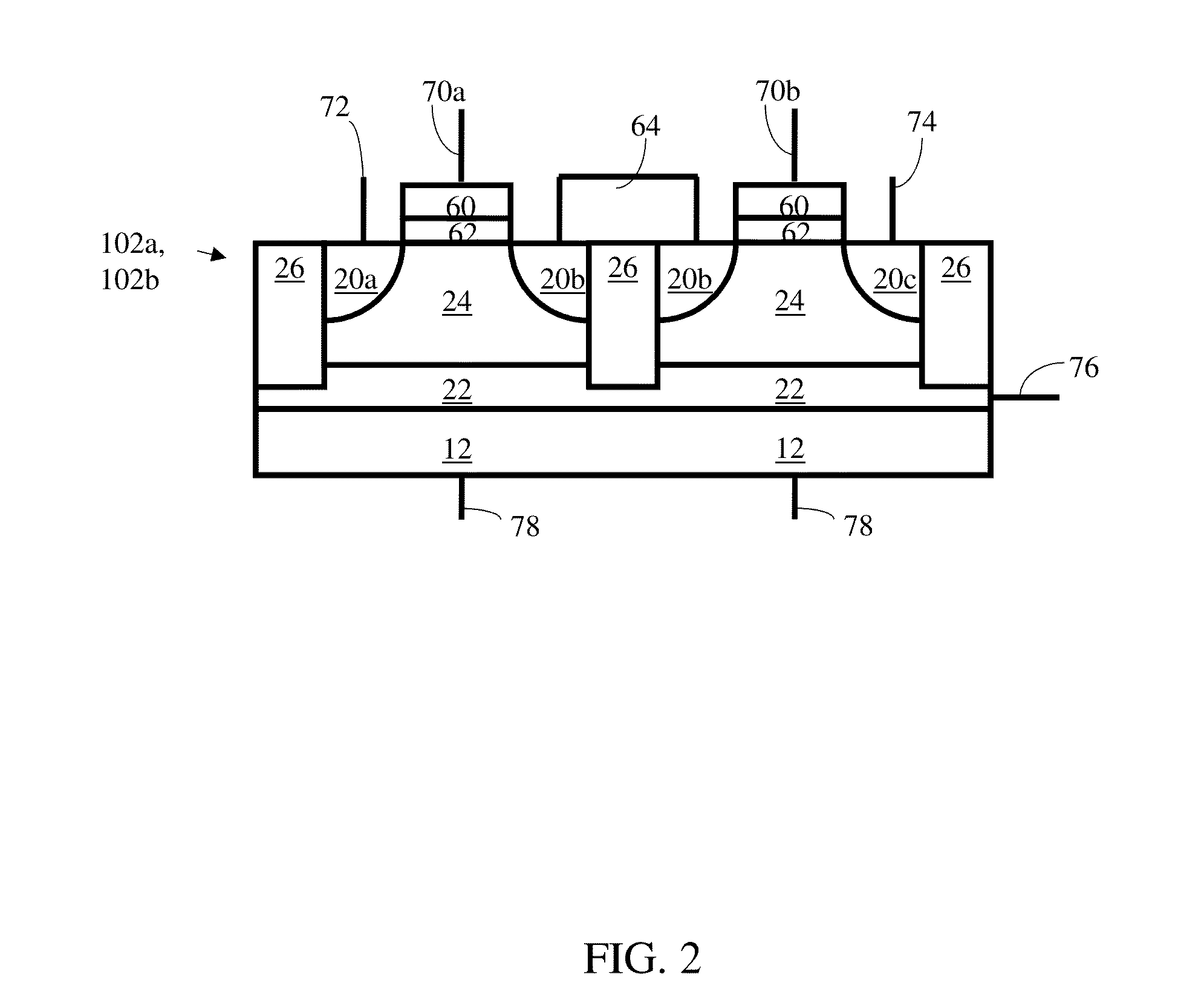
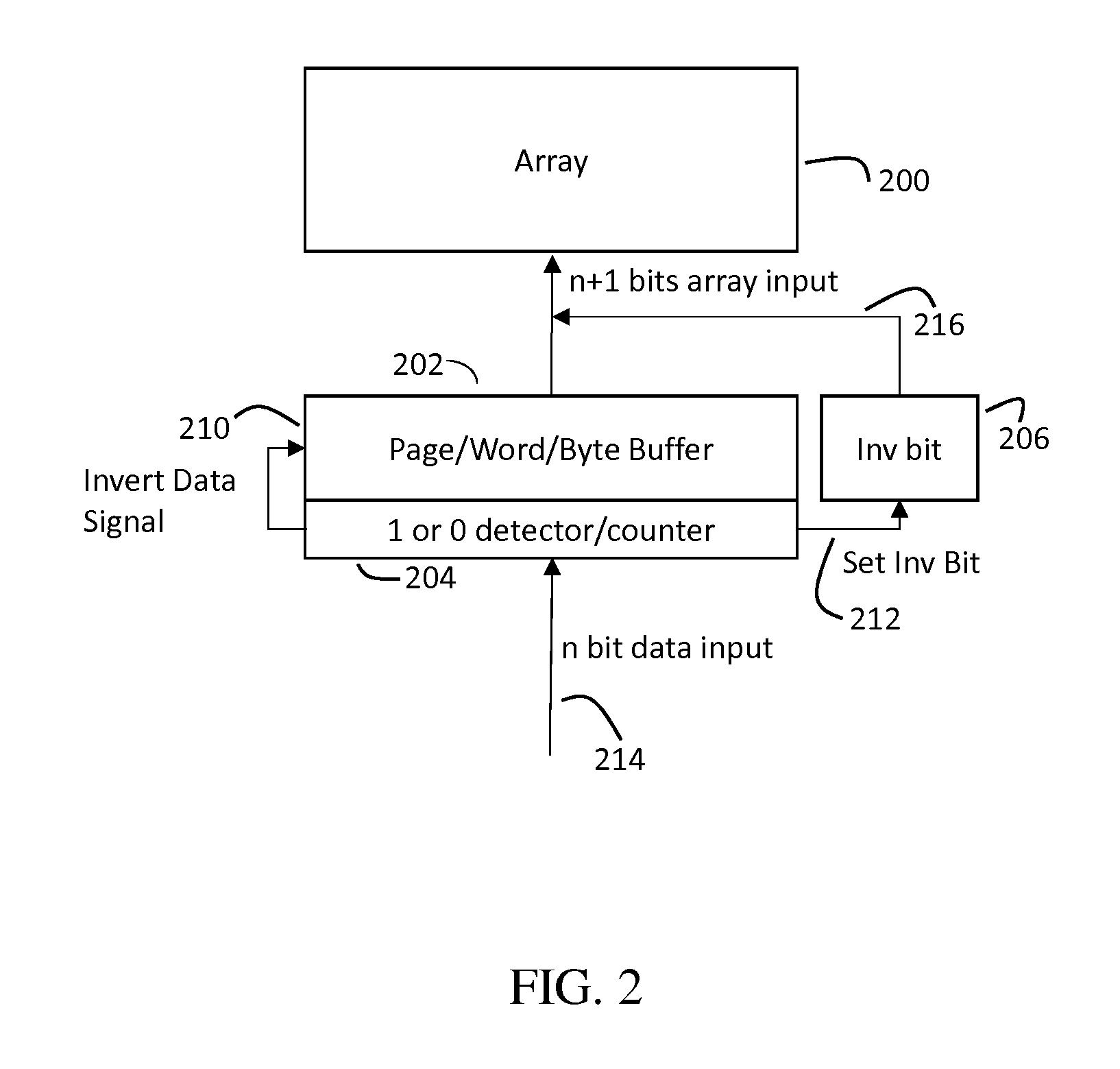
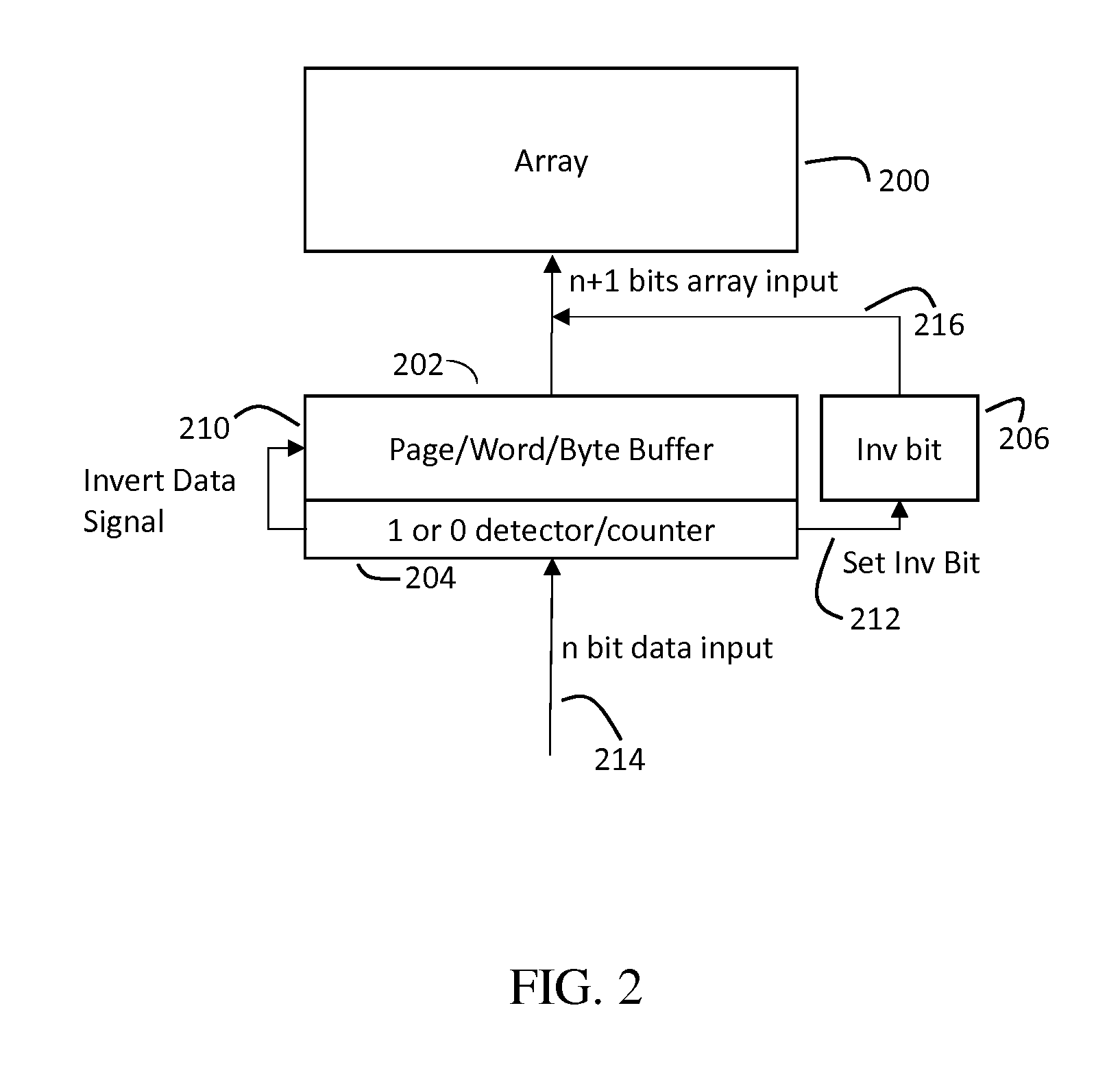
Methods, devices, arrays and systems for reducing standby power for a floating body memory array. One method includes counting bits of data before data enters the array, wherein the counting includes counting at least one of: a total number of bits at state 1 and a total number of all bits; a total number of bits at state 0 and the total number of all bits; or the total number of bits at state 1 and the total number of bits at state 0. This method further includes detecting whether the total number of bits at state 1 is greater than the total number of bits at state 0; setting an inversion bit when the total number of bits at state 1 is greater than the total number of bits at state 0; and inverting contents of all the bits of data before writing the bits of data to the memory array when the inversion bit has been set.
Owner:ZENO SEMICON
Scalable floating body memory cell for memory compilers and method of using floating body memories with memory compilers
Owner:ZENO SEMICON
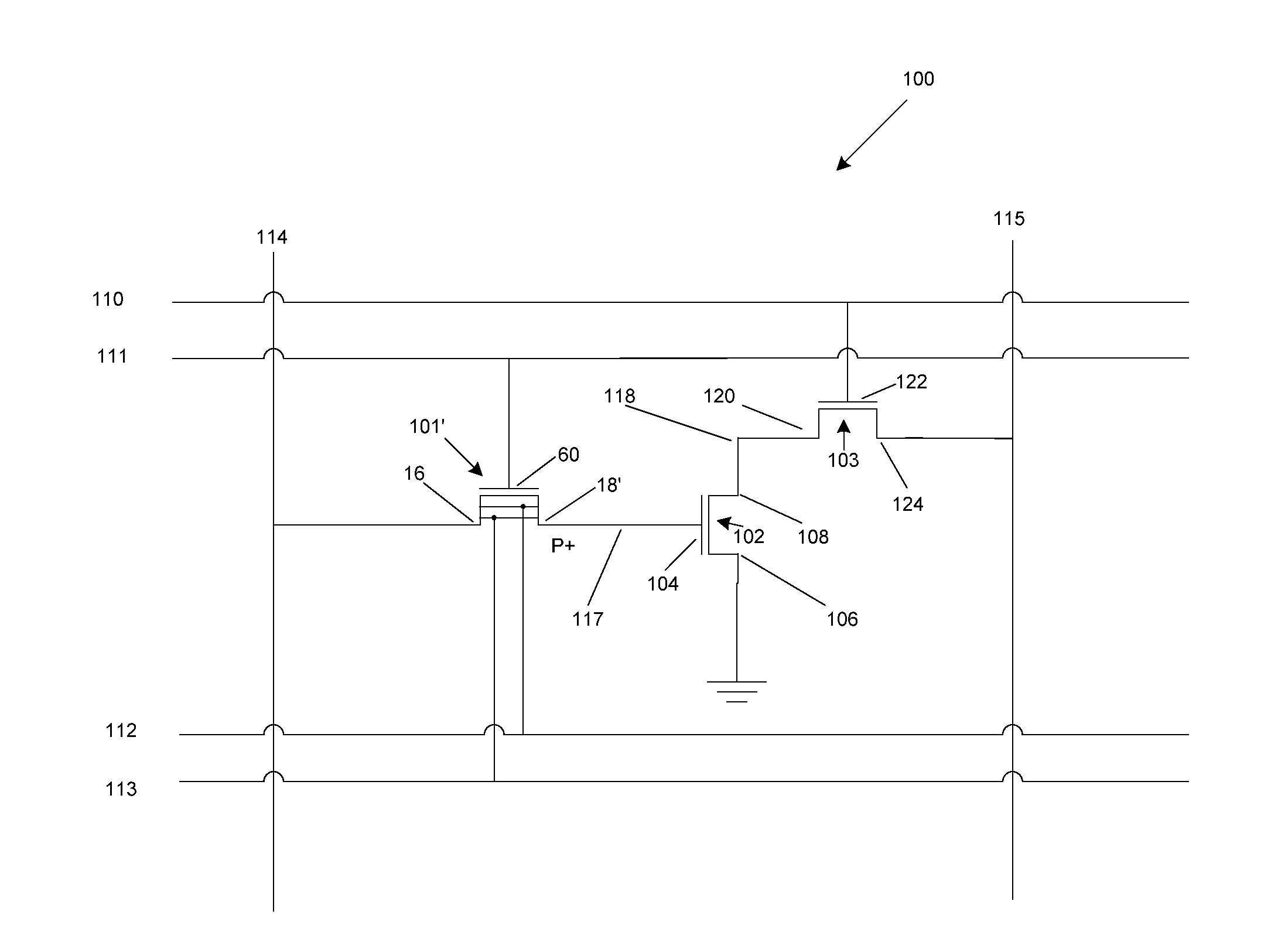
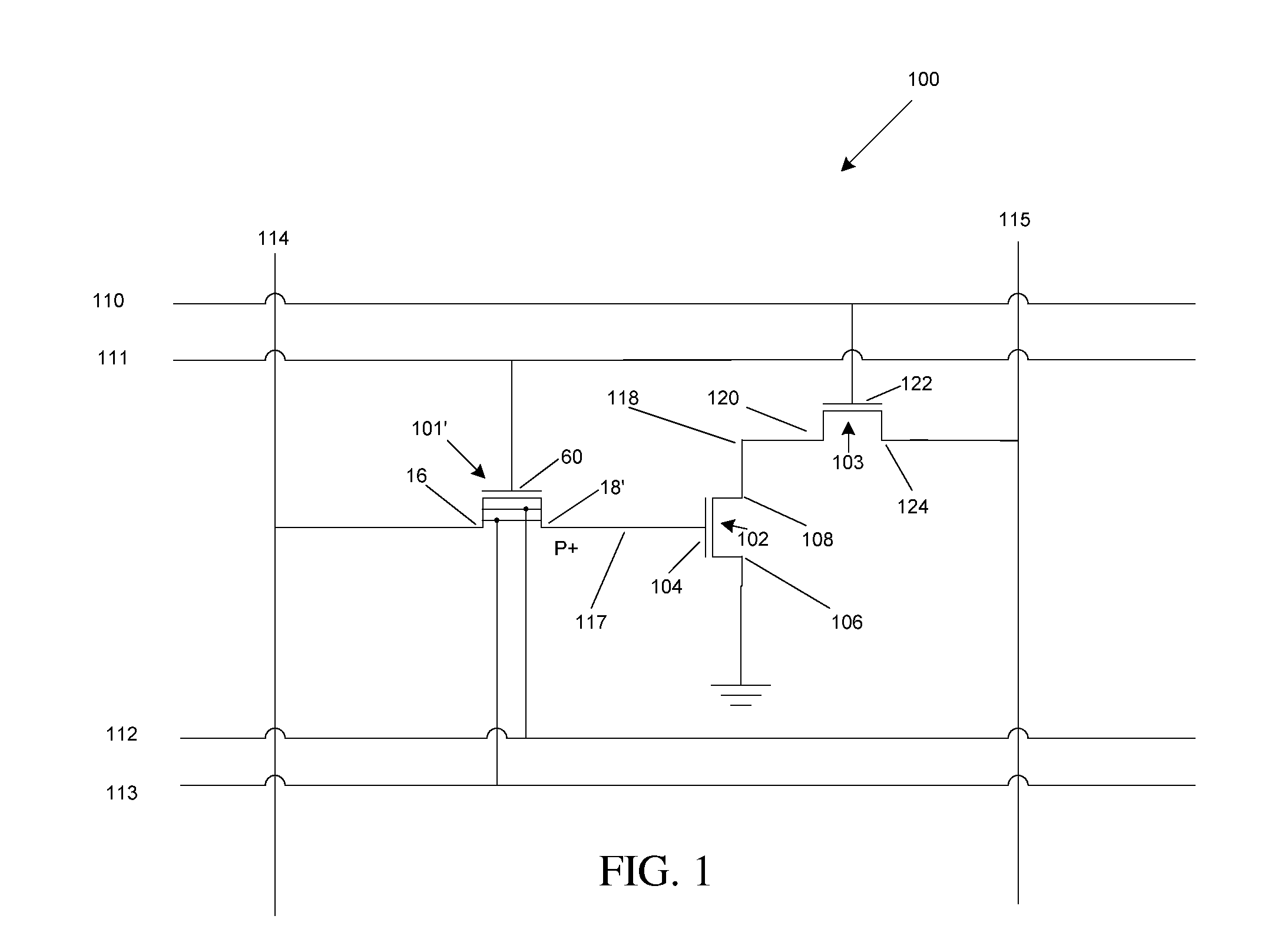
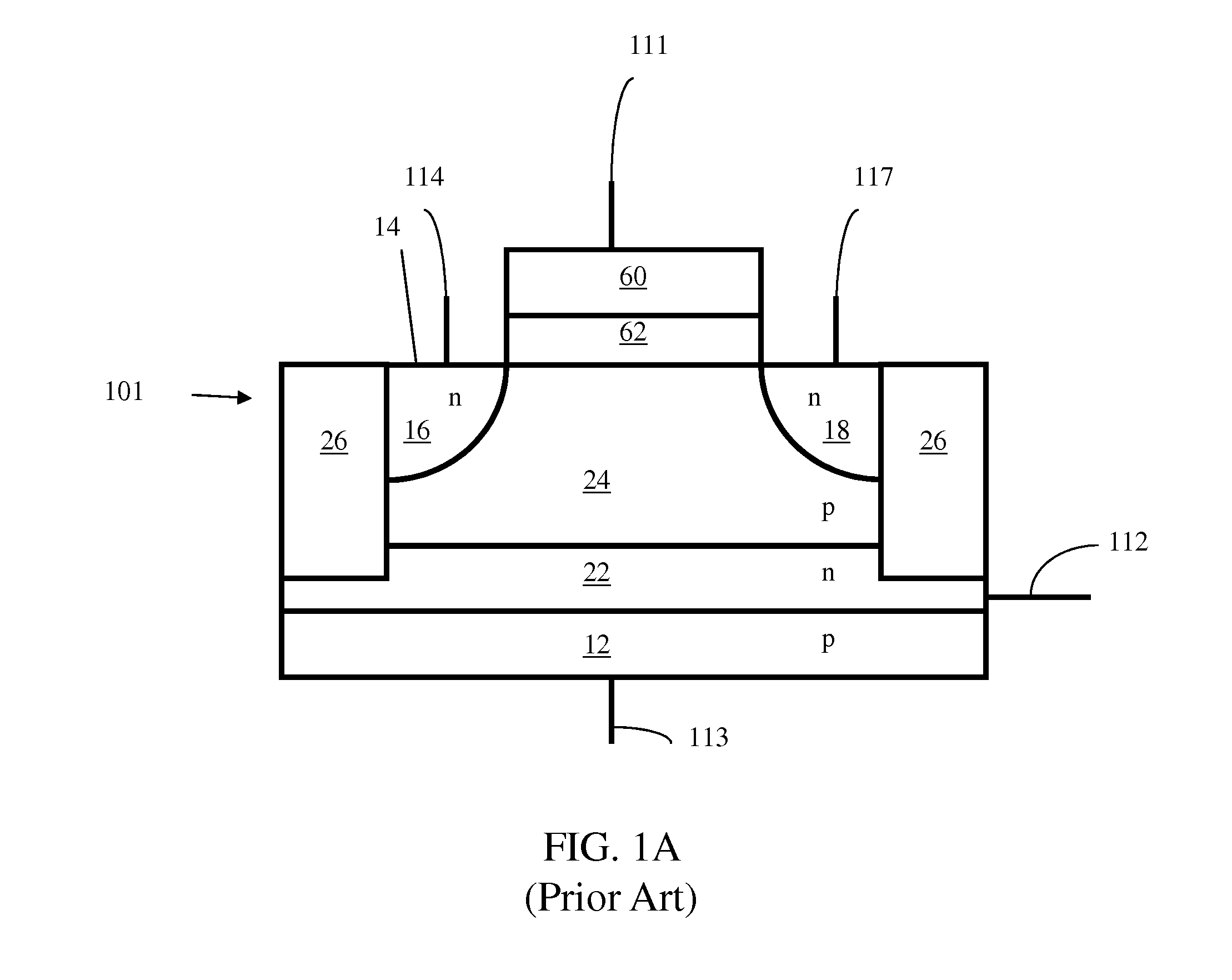
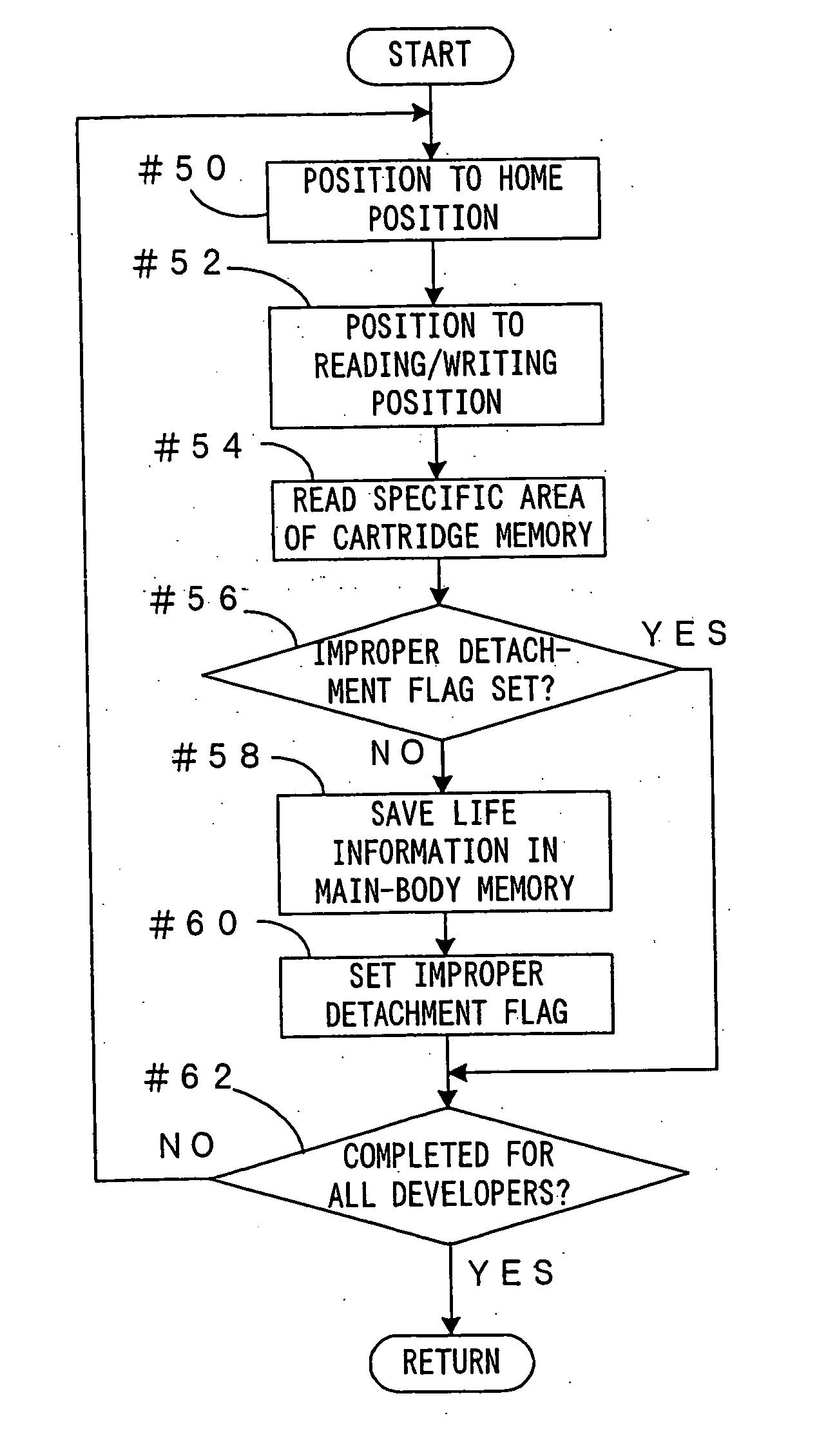
Image forming apparatus and a storage controlling method for information on an improper detachment of a developer cartridge to be written in a cartridge storage means
When an apparatus is turned on, one developer is positioned to a reading / writing position (Step #52) and a specific area of a cartridge memory is read (Step #54) to judge whether or not an improper detachment flag is set (Step #56). Unless the improper detachment flag is set (NO in Step #56), the improper detachment flag is set in the specific area of the cartridge memory (Step #60) after information on life saved in the cartridge memory is read and written in a main-body memory (Step #58).
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Floating body memory cell having gates favoring different conductivity type regions
A method for fabricating floating body memory cells (FBCs), and the resultant FBCs where gates favoring different conductivity type regions are used is described. In one embodiment, a p type back gate with a thicker insulation is used with a thinner insulated n type front gate. Processing, which compensates for misalignment, which allows the different oxide and gate materials to be fabricated is described.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Scalable floating body memory cell for memory compilers and method of using floating body memories with memory compilers
Owner:ZENO SEMICON
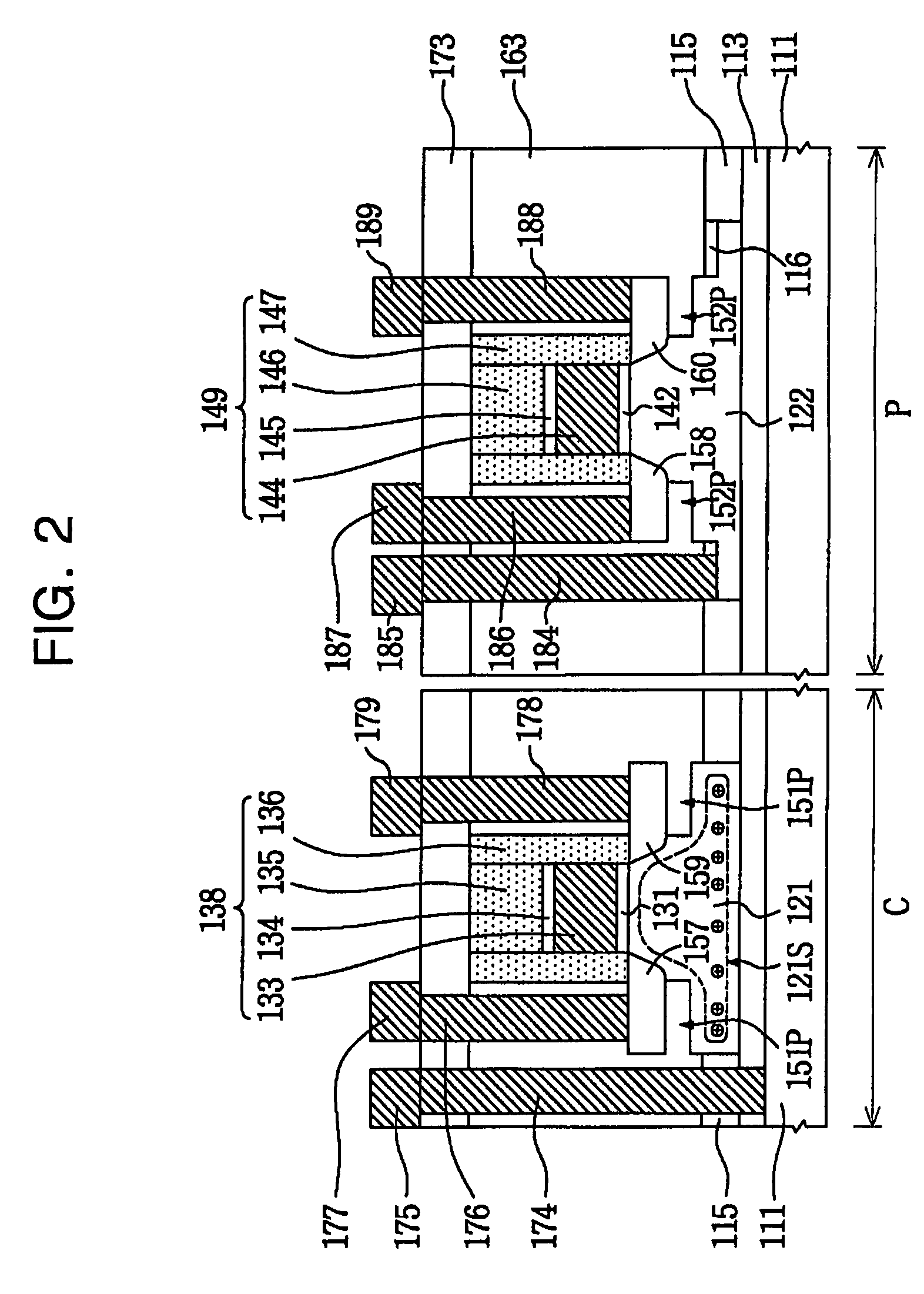
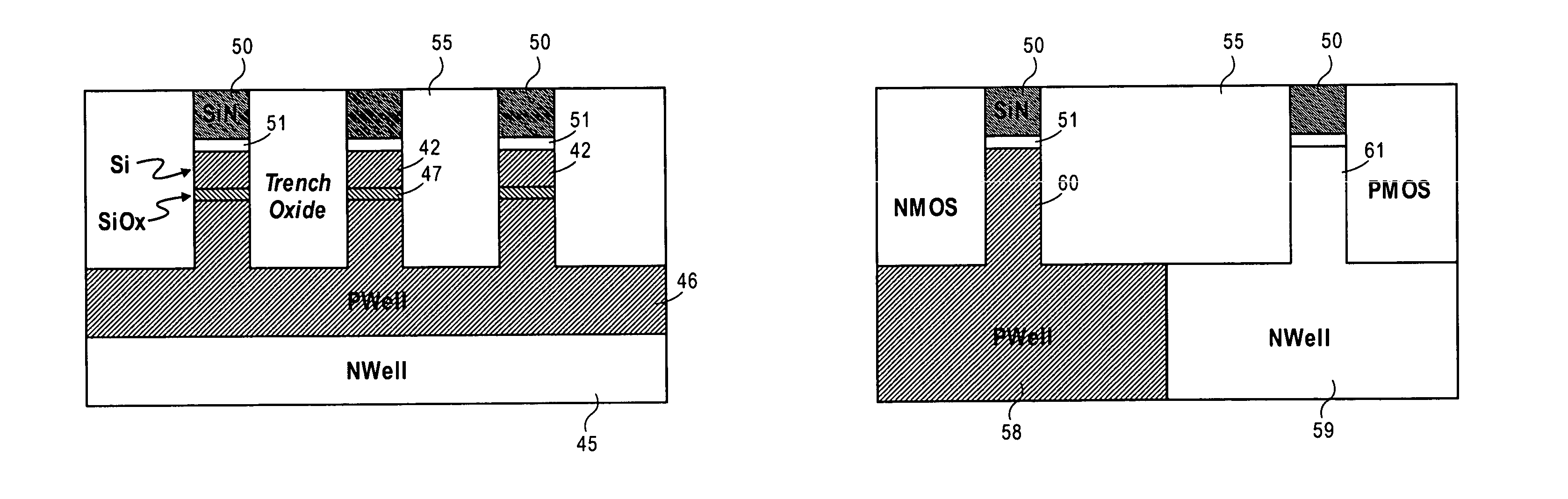
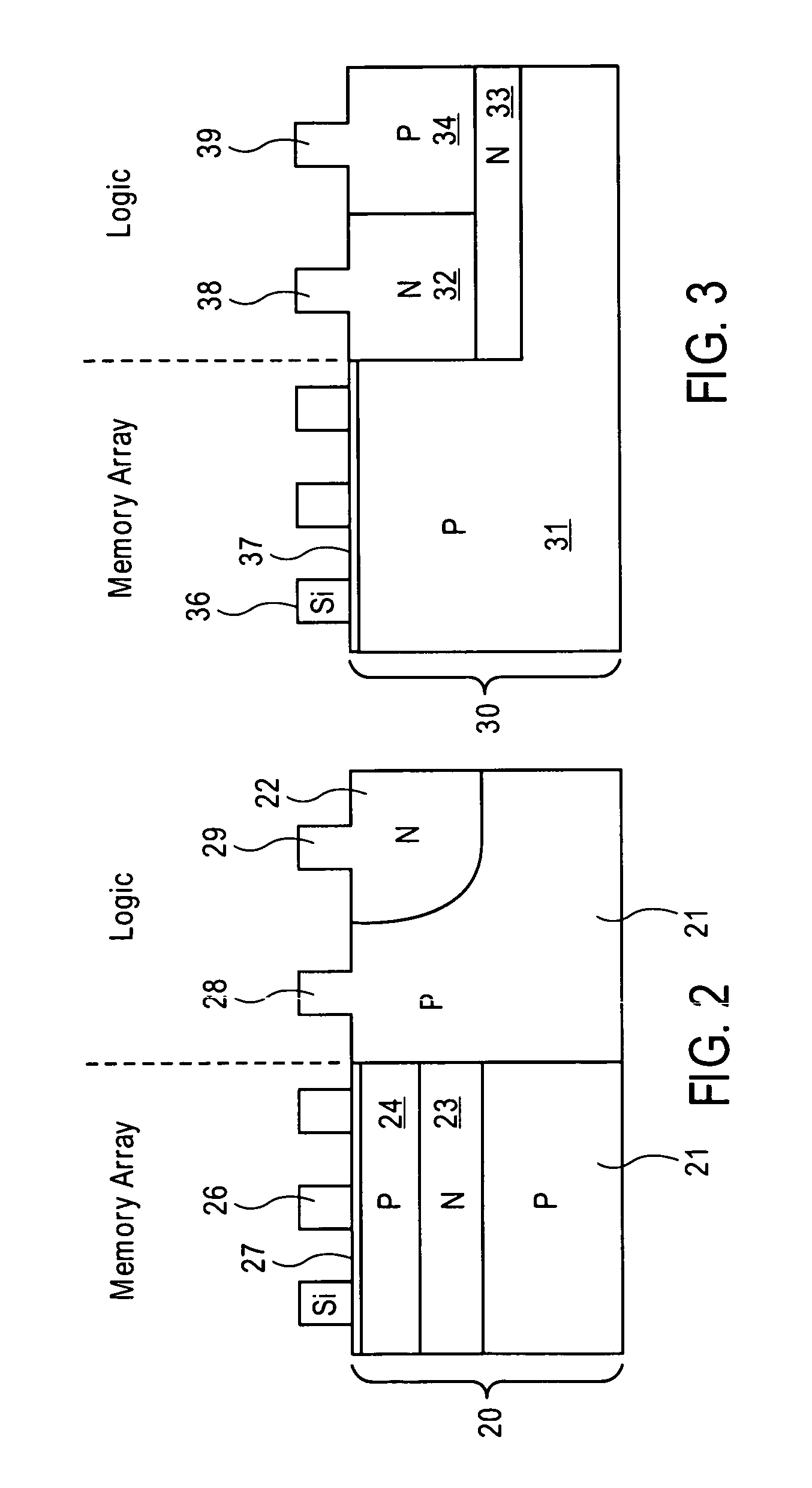
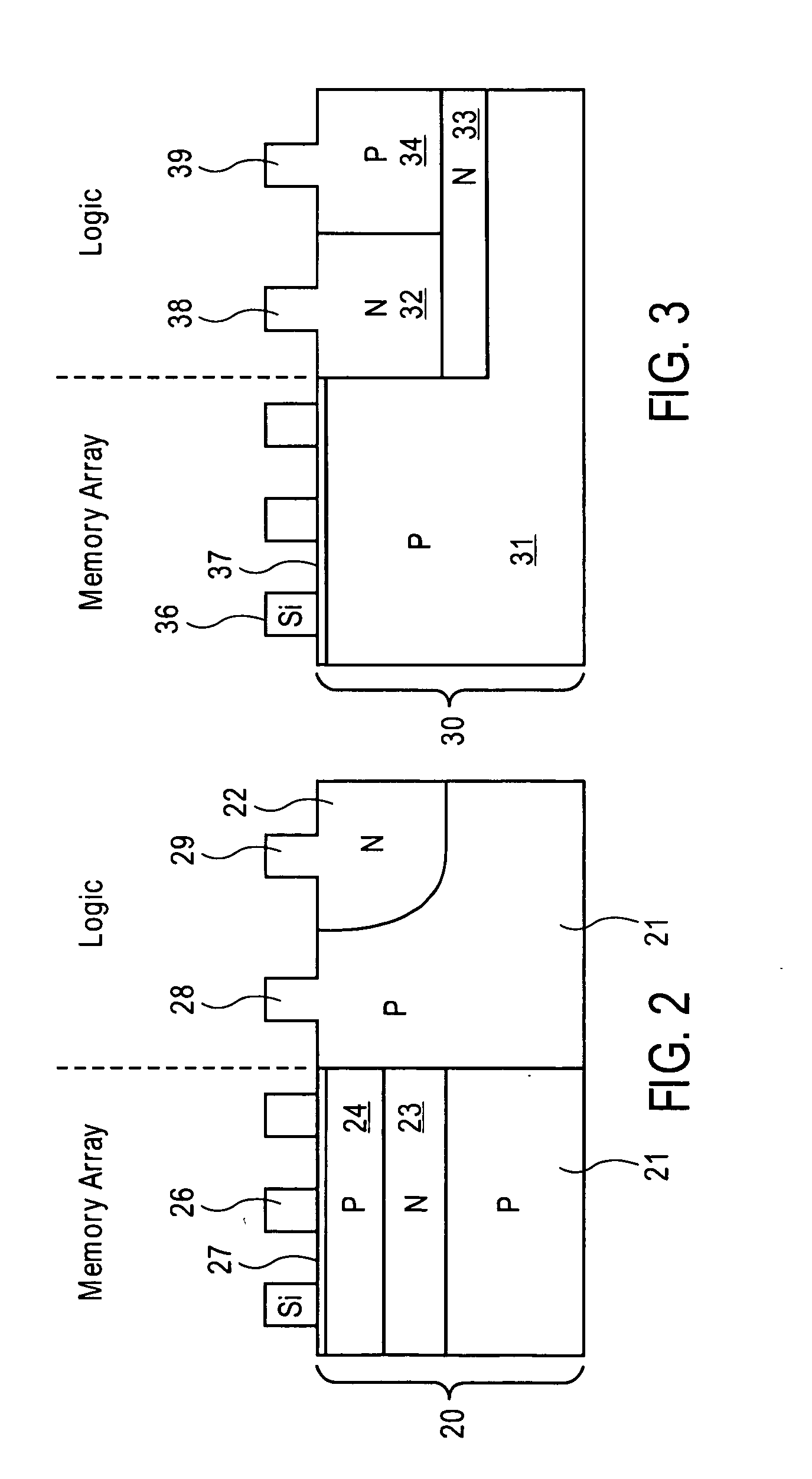
Integration of a floating body memory on SOI with logic transistors on bulk substrate
ActiveUS7592209B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTransistor arraySoi substrate
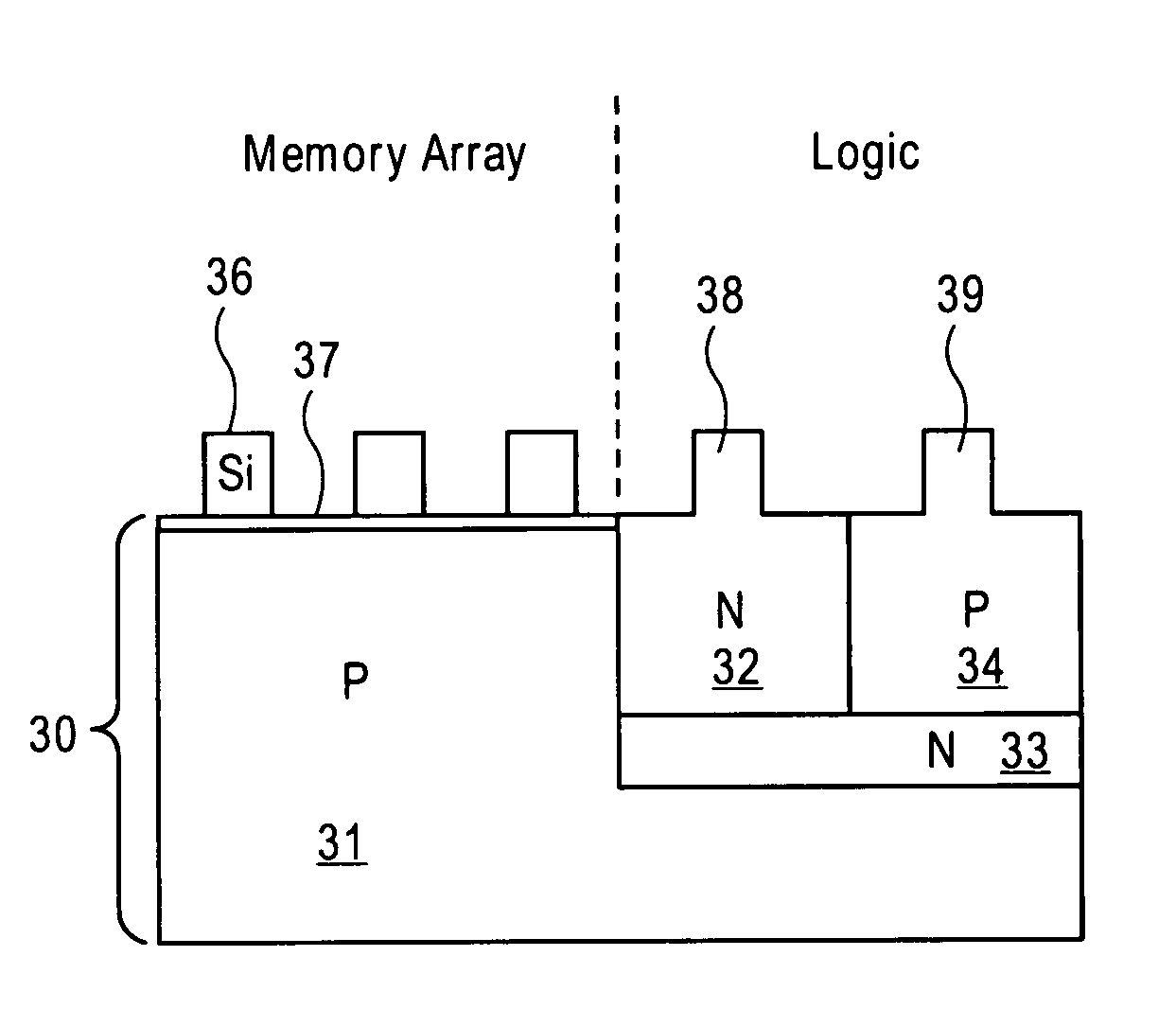
A method and the resultant memory is described for forming an array of floating body memory cells and logic transistors on an SOI substrate. The floating bodies for the cells are formed over the buried oxide, the transistors in the logic section are formed in the bulk silicon.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Scalable floating body memory cell for memory compilers and method of using floating body memories with memory compilers
ActiveUS20160148675A1Improve scalabilityDigital storageCAD circuit designParallel computingBody memory
Owner:ZENO SEMICON
NAND String Utilizing Floating Body Memory Cell
NAND string configurations and semiconductor memory arrays that include such NAND string configurations are provided. Methods of making semiconductor memory cells used in NAND string configurations are also described.
Owner:ZENO SEMICON
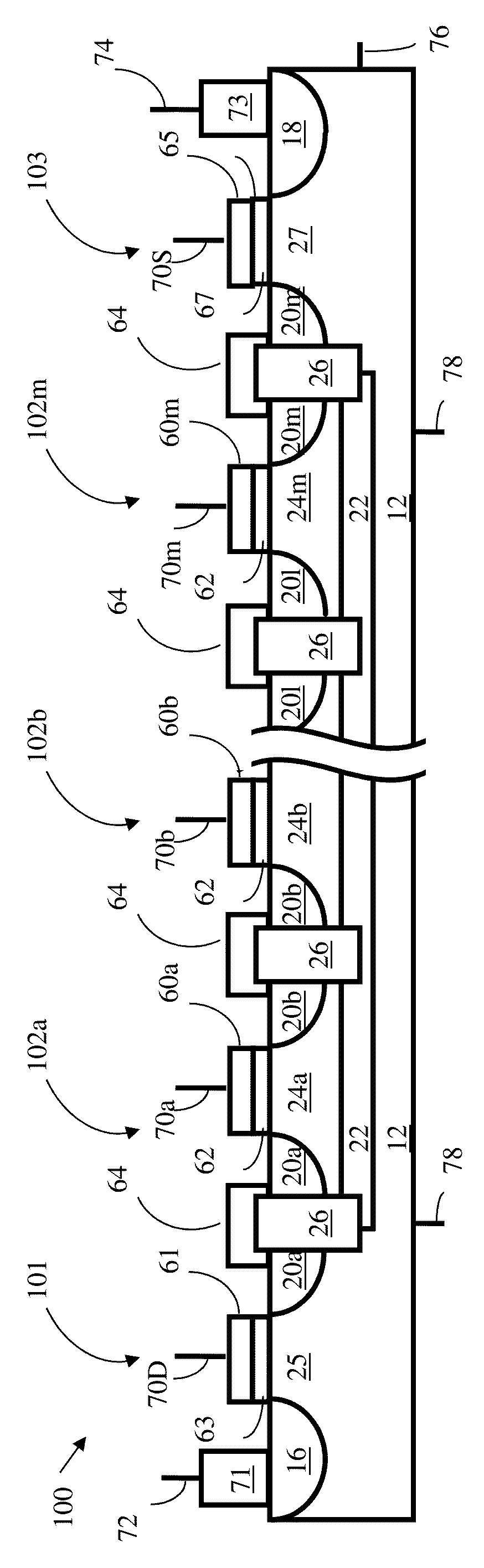
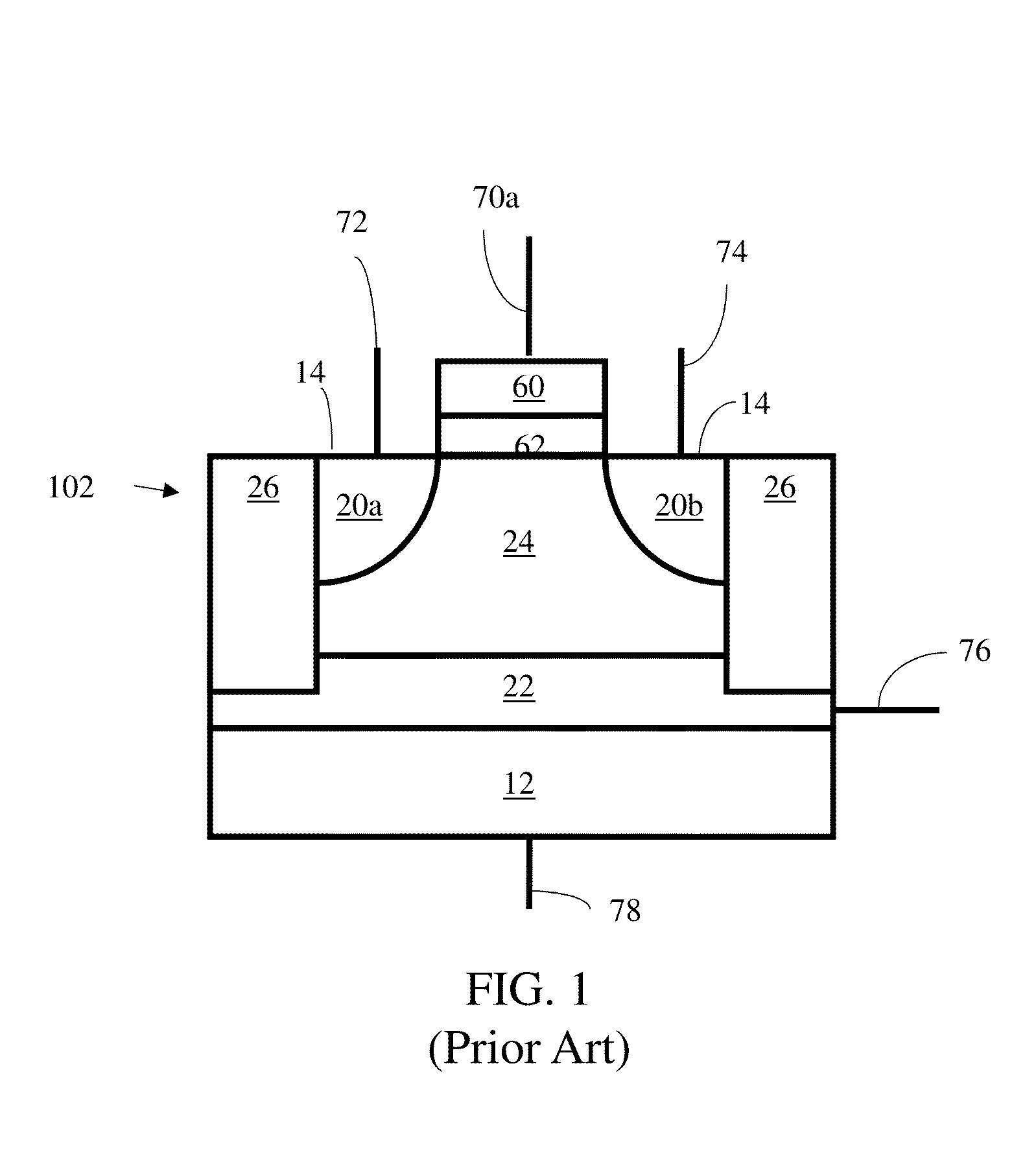
Low power programming technique for a floating body memory transistor, memory cell, and memory array
There are many inventions described and illustrated herein. In one aspect, the present invention is directed to a memory cell, architecture, and / or array and / or technique of writing or programming data into the memory cell (for example, a technique to write or program a logic low or State “0” in a memory cell employing an electrically floating body transistor. In this regard, the present invention programs a logic low or State “0” in the memory cell while the electrically floating body transistor is in the “OFF” state or substantially “OFF” state (for example, when the device has no (or practically no) channel and / or channel current between the source and drain). In this way, the memory cell may be programmed whereby there is little to no current / power consumption by the electrically floating body transistor and / or from memory array having a plurality of electrically floating body transistors.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
NAND string utilizing floating body memory cell
NAND string configurations and semiconductor memory arrays that include such NAND string configurations are provided. Methods of making semiconductor memory cells used in NAND string configurations are also described.
Owner:ZENO SEMICON
Systems and methods for reducing standby power in floating body memory devices
Methods, devices, arrays and systems for reducing standby power for a floating body memory array. One method includes counting bits of data before data enters the array, wherein the counting includes counting at least one of: a total number of bits at state 1 and a total number of all bits; a total number of bits at state 0 and the total number of all bits; or the total number of bits at state 1 and the total number of bits at state 0. This method further includes detecting whether the total number of bits at state 1 is greater than the total number of bits at state 0; setting an inversion bit when the total number of bits at state 1 is greater than the total number of bits at state 0; and inverting contents of all the bits of data before writing the bits of data to the memory array when the inversion bit has been set.
Owner:ZENO SEMICON
Semiconductor device with floating gate and electrically floating body
Techniques for providing floating body memory devices are disclosed. In one particular exemplary embodiment, the techniques may be realized as a semiconductor device comprising a floating gate, a control gate disposed over the floating gate, a body region that is electrically floating, wherein the body region is configured so that material forming the body region is contained under at least one lateral boundary of the floating gate, and a source region and a drain region adjacent the body region.
Owner:OVONYX MEMORY TECH LLC
Information display system
InactiveCN1725828AReduce power consumptionTelevision system detailsStatic indicating devicesComputer hardwareInformation display systems
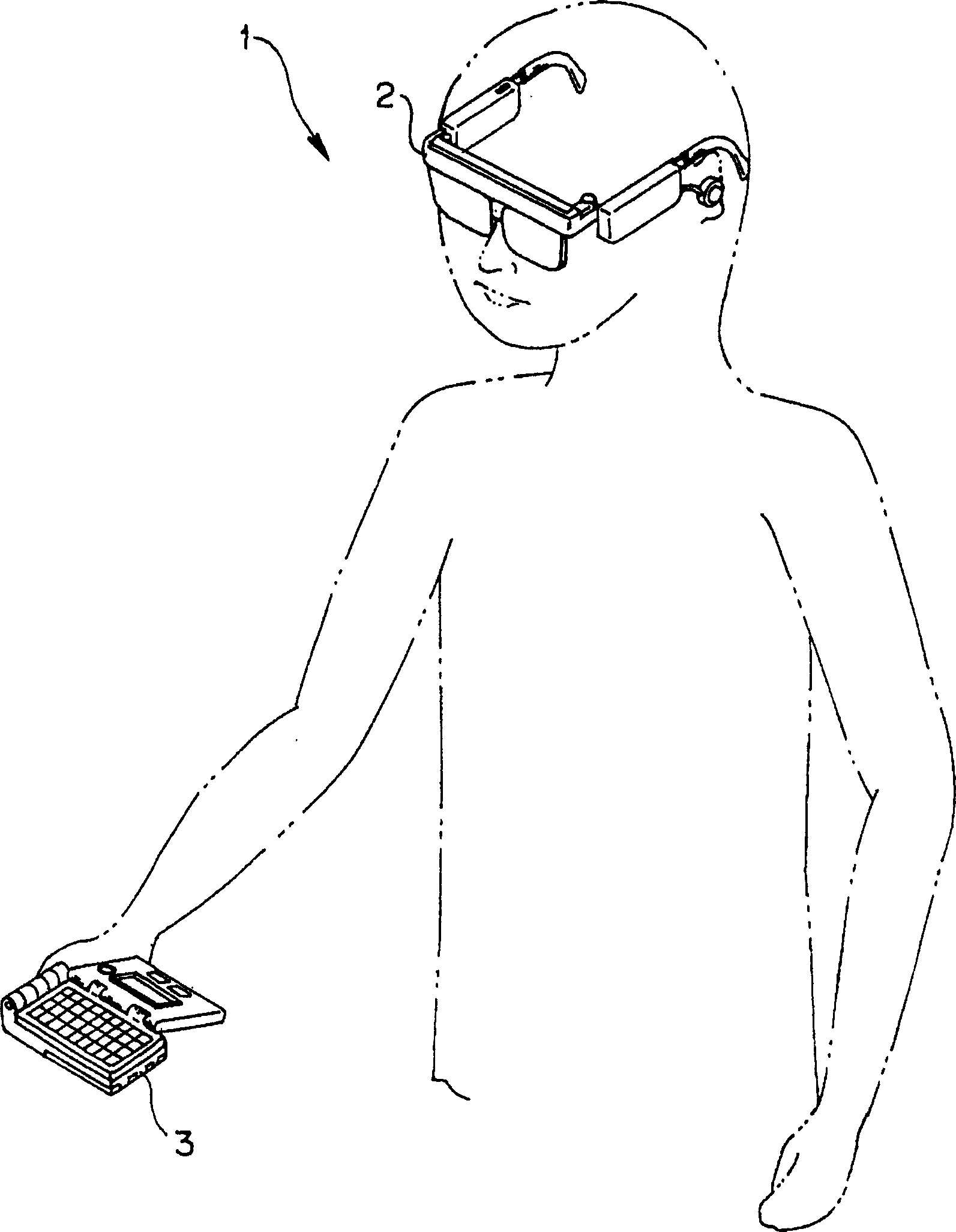
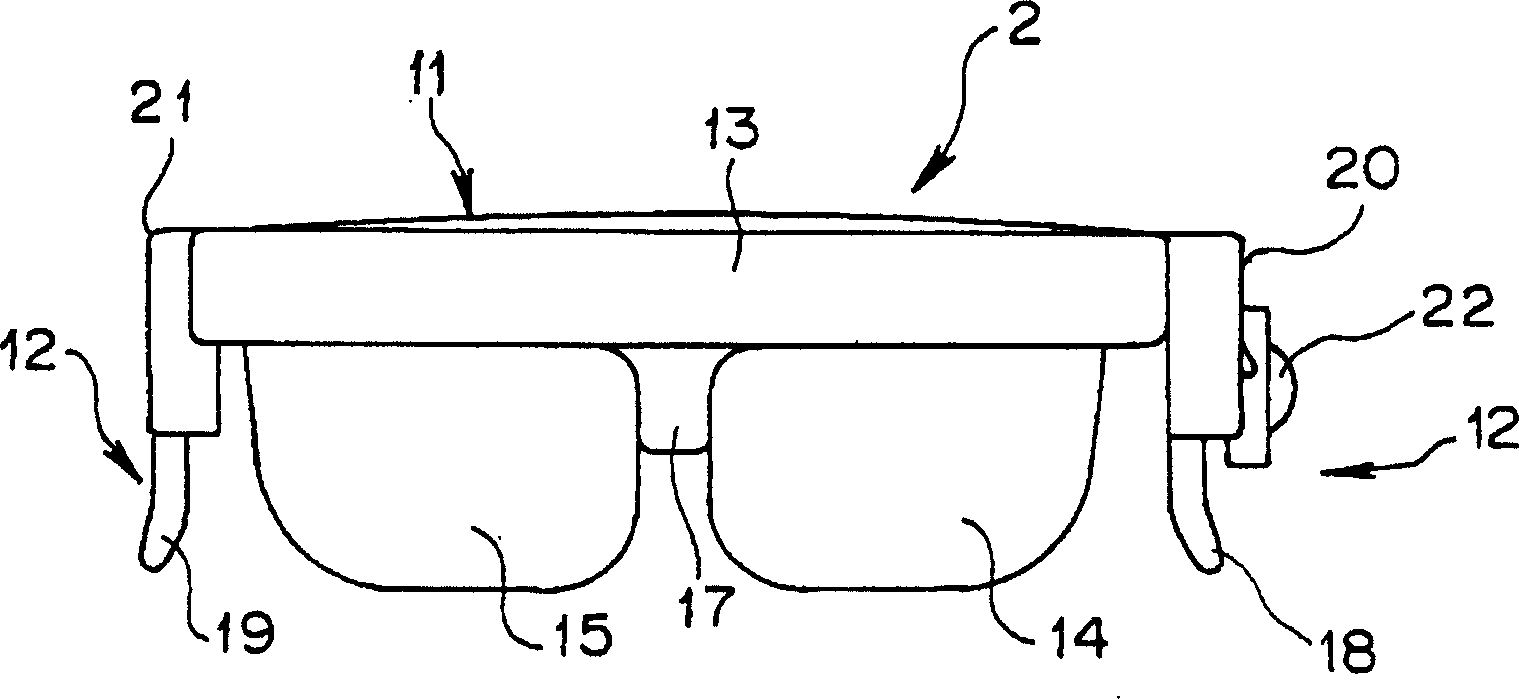
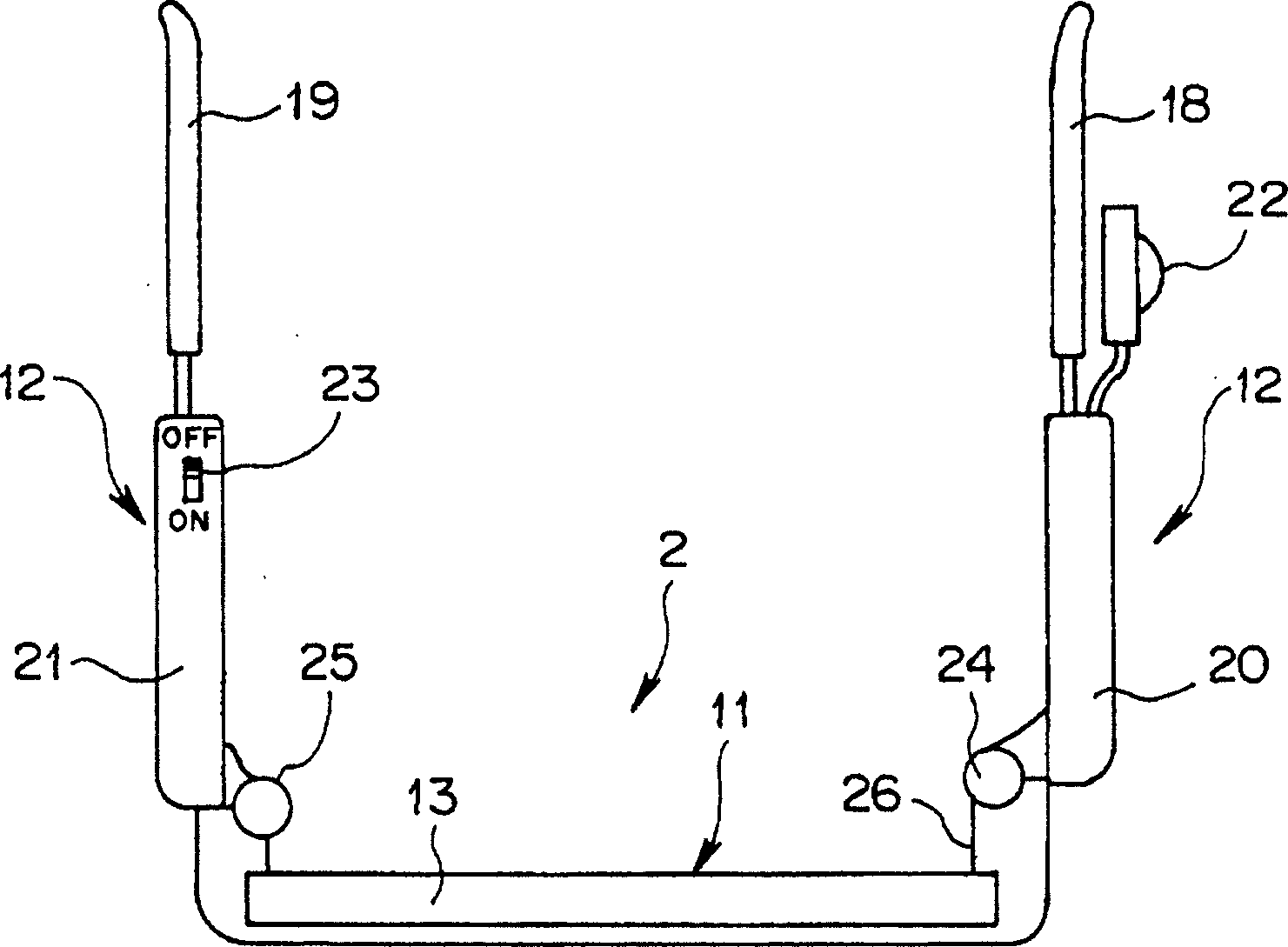
The present invention provides an information display system capable of enabling a user to observe information even when a head fitting part is detached from his (or her) head part and capable of suppressing useless power consumption without requiring complicated operation. The information display system is provided with: the head fitting part 2 for enabling a user to observe an image as a virtual image by projecting display data to user's eyes; and a body 3 comprising a hard disk 85 and a recording memory 83 for storing original display information, a body memory 78 for temporarily storing display data read out from these memories 85, 83 and converted, an LCD 51 for performing display based on the display data and a second operation switch 73 including a display change-over switch for alternatively selecting display by the heat fitting part or display by the LCD 51.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Double-gate floating-body memory device
A memory device is provided comprising a transistor having a floating body positioned between source and drain regions, the floating body being sandwiched between first and second insulated gates each comprising a gate electrode. A control circuit is arranged to program the state of said floating body to have an accumulation or depletion of majority carriers by applying one of first and second voltage levels between the first gate and at least one of the source and drain regions, and to retain the programmed state of said floating body by applying a third voltage level to the second gate. The voltages are switched over a time duration shorter than 100 ns.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
Integration of a floating body memory on SOI with logic transistors on bulk substrate
ActiveUS20080111190A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTransistor arraySoi substrate
A method and the resultant memory is described for forming an array of floating body memory cells and logic transistors on an SOI substrate. The floating bodies for the cells are formed over the buried oxide, the transistors in the logic section are formed in the bulk silicon.
Owner:INTEL CORP
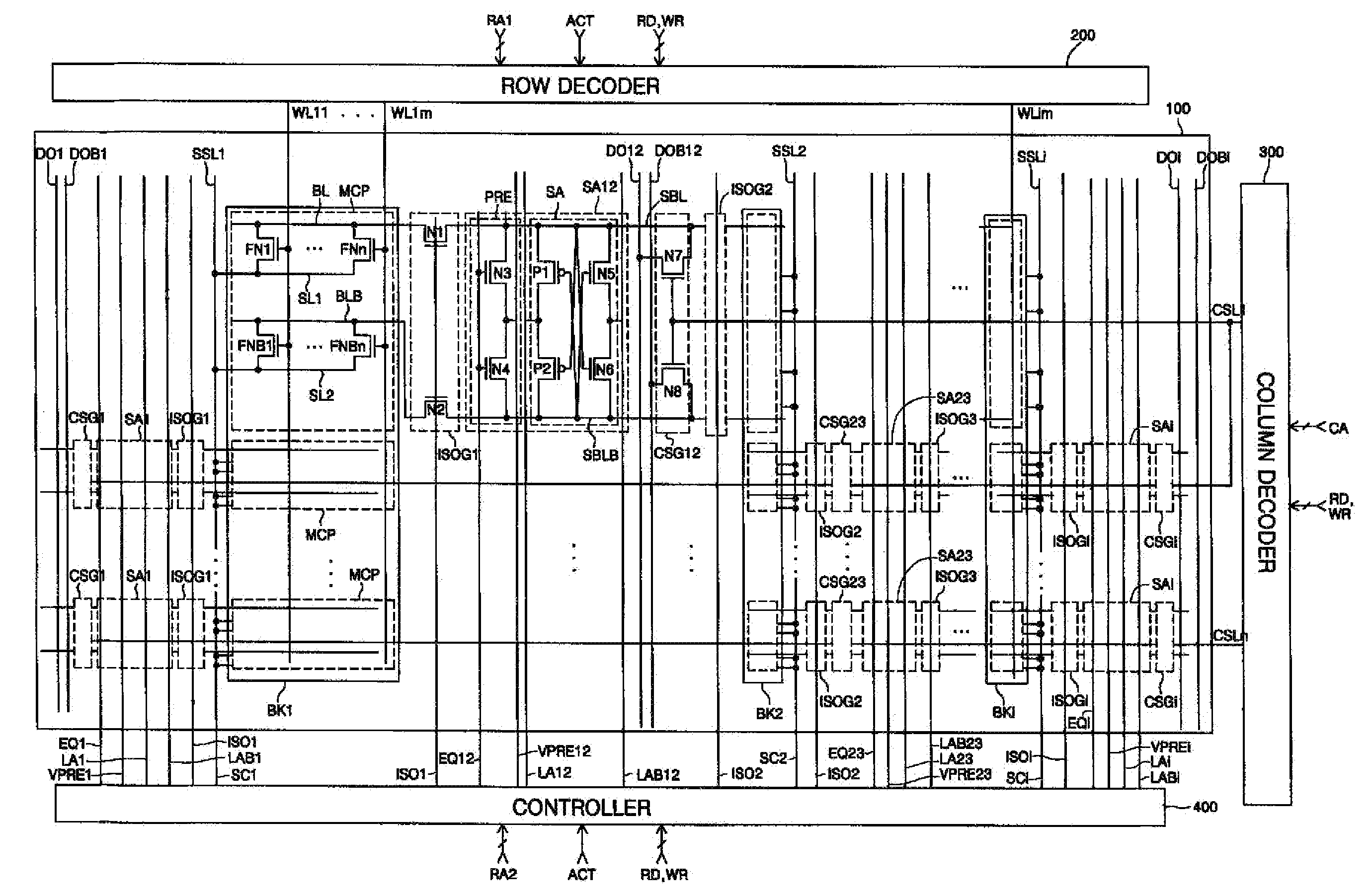
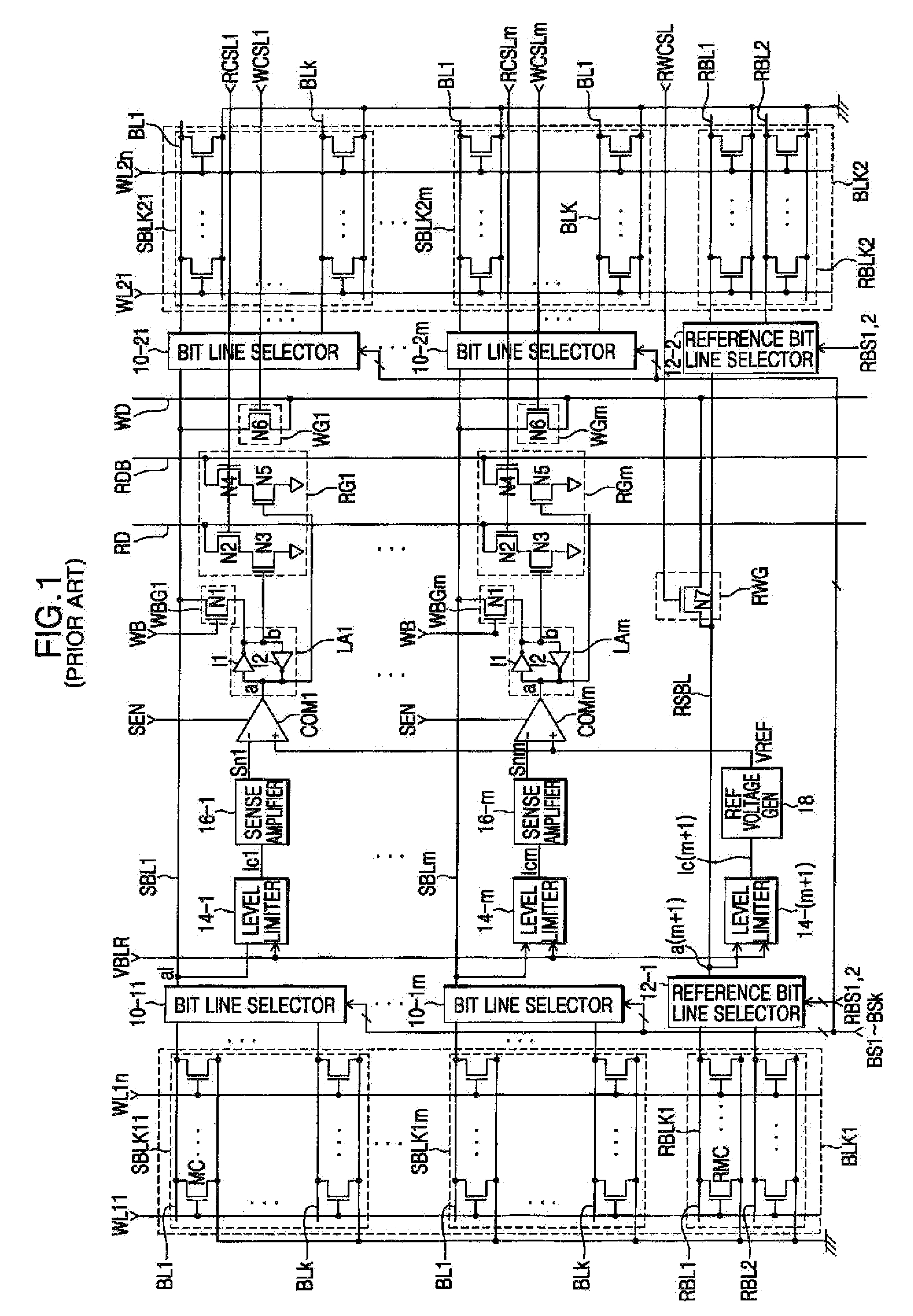
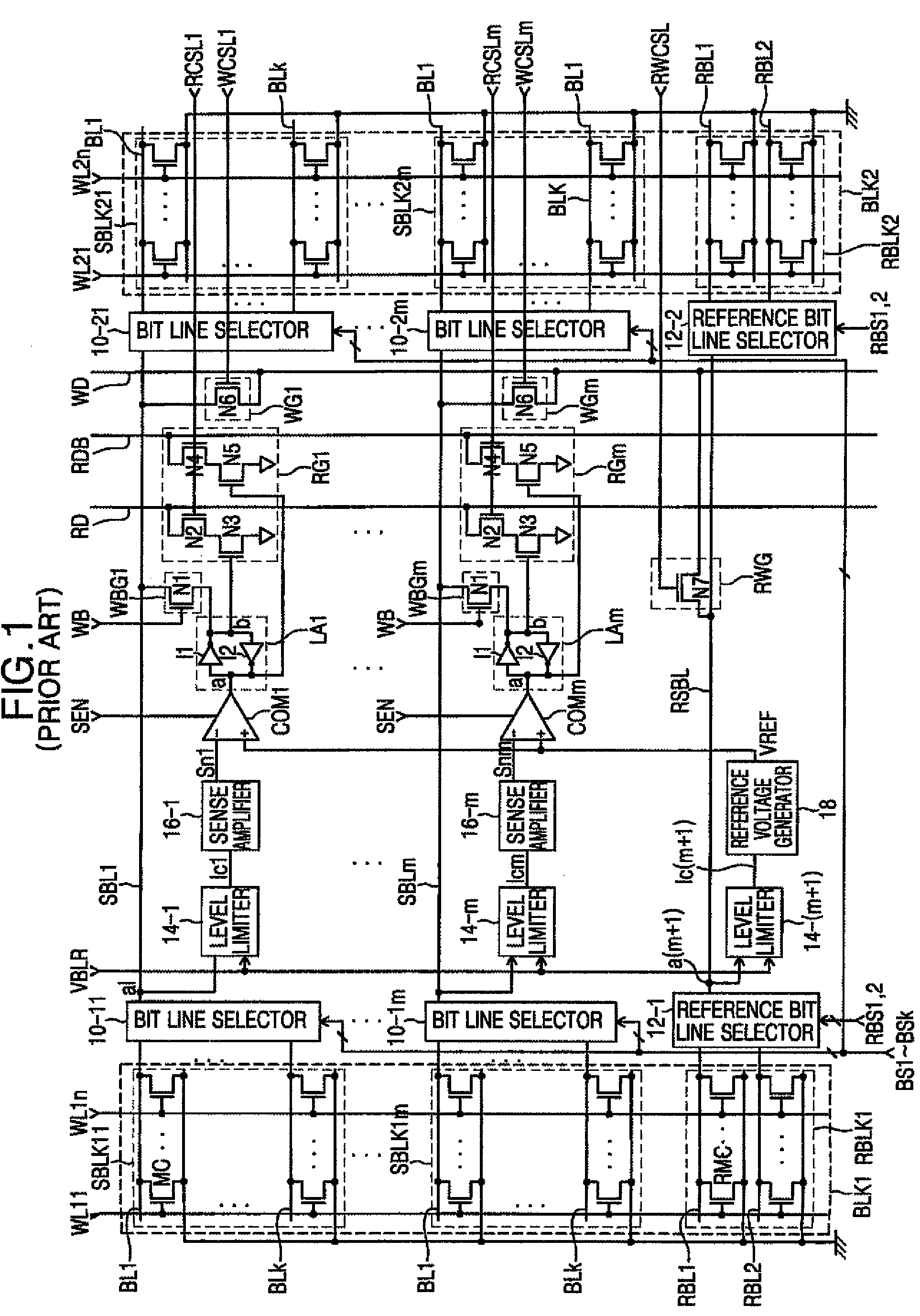
Semiconductor memory device including floating body memory cells and method of operating the same
A semiconductor memory device includes first and second memory cells having floating bodies, each of which includes a gate connected to a word line and an electrode connected to a common source line to store data. A controller applies a first voltage to the common source line, a negative second voltage to the word line, a third voltage as a first sense enable control voltage and the first voltage as a second sense enable control voltage during a first write period of a write operation. The controller also applies a fourth voltage to the common source line and the first voltage to the word line during a second write period of the write operation. The sensing portion amplifies a bit line and an inverted bit line to the third voltage or the first voltage, respectively, during the first write period in response to the first and second sense enable control voltages.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Image forming unit and displaying unit
Owner:CANON KK
Low power programming technique for a floating body memory transistor, memory cell, and memory array
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Intergration of a floating body memory on soi with logic transistors on bulk substrate
InactiveUS20100006941A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSoi substrateBody memory
A method and the resultant memory is described for forming an array of floating body memory cells and logic transistors on an SOI substrate. The floating bodies for the cells are formed over the buried oxide, the transistors in the logic section are formed in the bulk silicon.
Owner:INTEL CORP
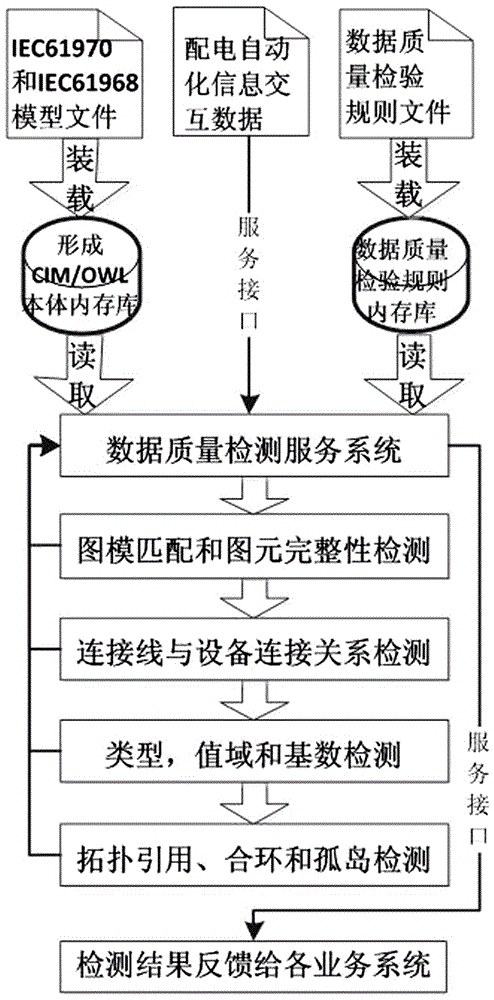
Data quality detection method based on IEC61968
ActiveCN105956107ASave loading and unloading timeImprove interactive data qualityObject oriented databasesResourcesMemory bankService mode
The invention discloses a data quality detection method based on IEC61968. The method comprises the steps that a data quality service system forms device objects in IEC61968 and IEC61970 model files into CIM / OWL body objects and loads the CIM / OWL body objects to a body memory bank; the data quality service system loads data quality detection rules to a rule memory bank; the data quality service system receives power distribution automation information interaction data through a service interface; the data quality service system detects the received power distribution automation information interaction data step by step according to service rules and body models; and the data quality service system forms detection results and feeds back the results to each service system. According to the method, the automatic data quality detection method for improving the data quality detection efficiency is provided through adoption of a service mode, therefore, the data interaction efficiency of power distribution automation switching buses can be greatly improved, and the data quality of an interaction service system can be improved.
Owner:NANJING GUODIAN NANZI POWER GRID AUTOMATION CO LTD
Semiconductor memory device comprising floating body memory cells and related methods of operation
A semiconductor device comprising floating body memory cells performs read and write operations by selectively connecting bit lines and inverted bit lines to sense bit lines and inverted sense bit lines.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
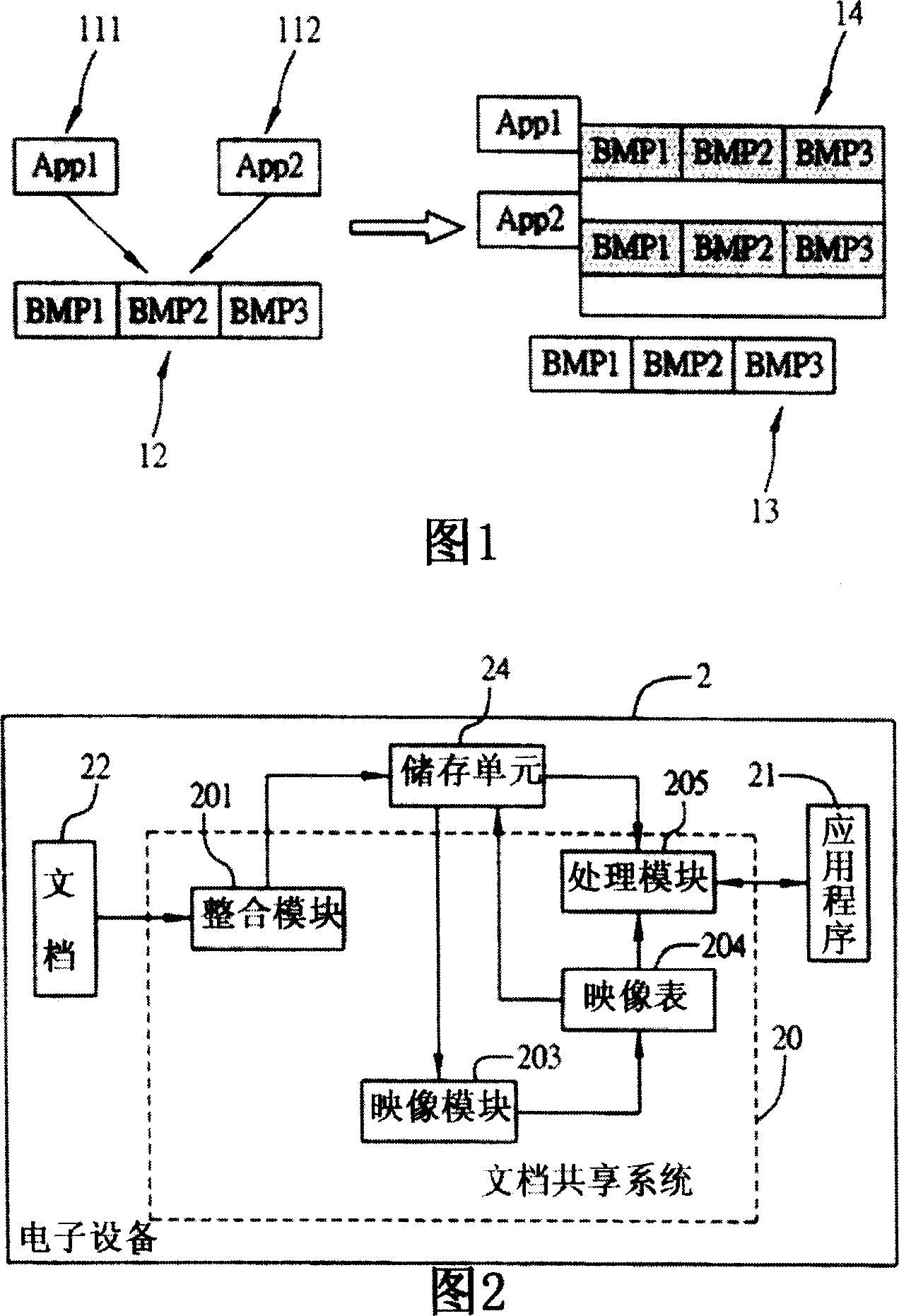
Method and system for sharing document
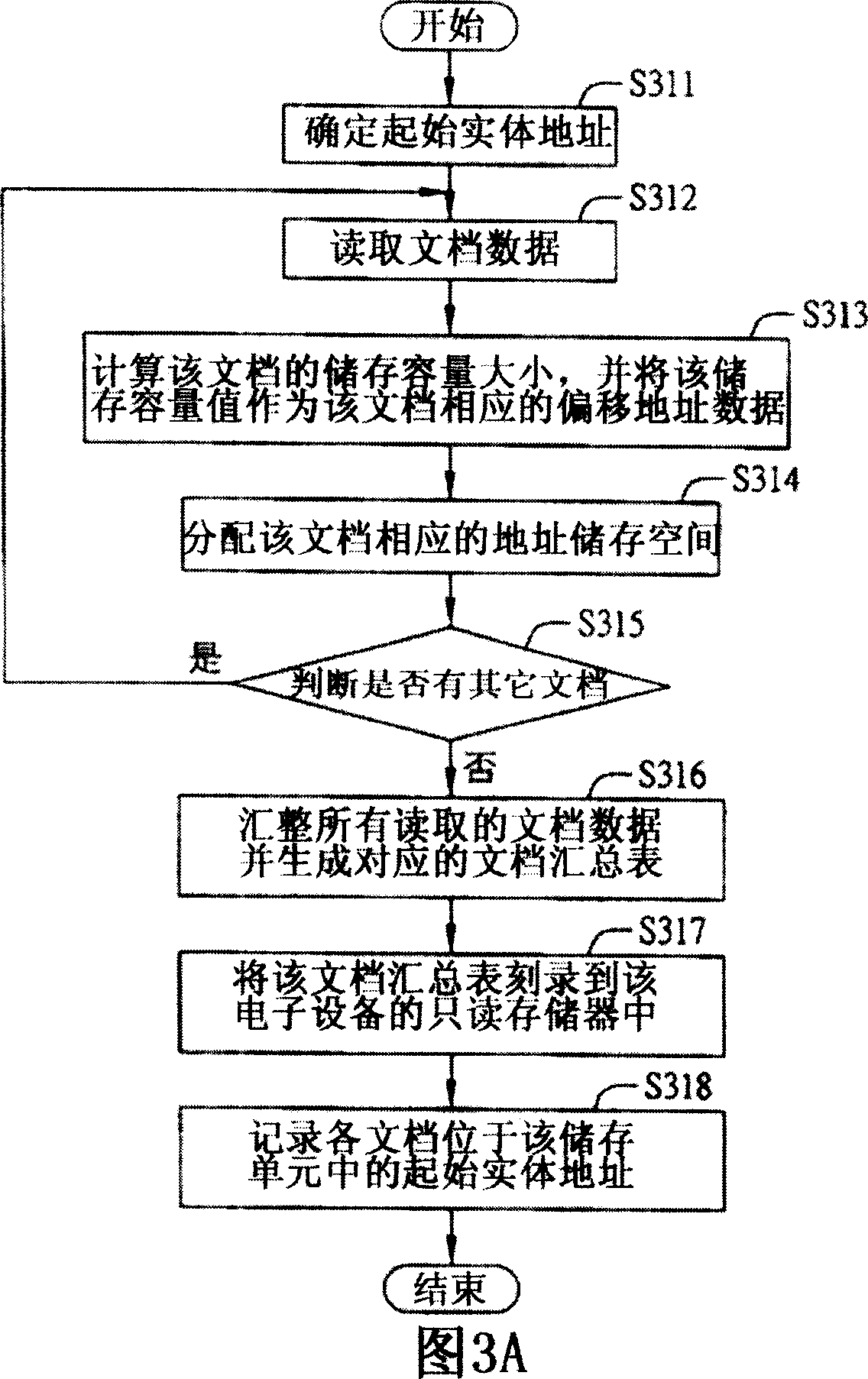
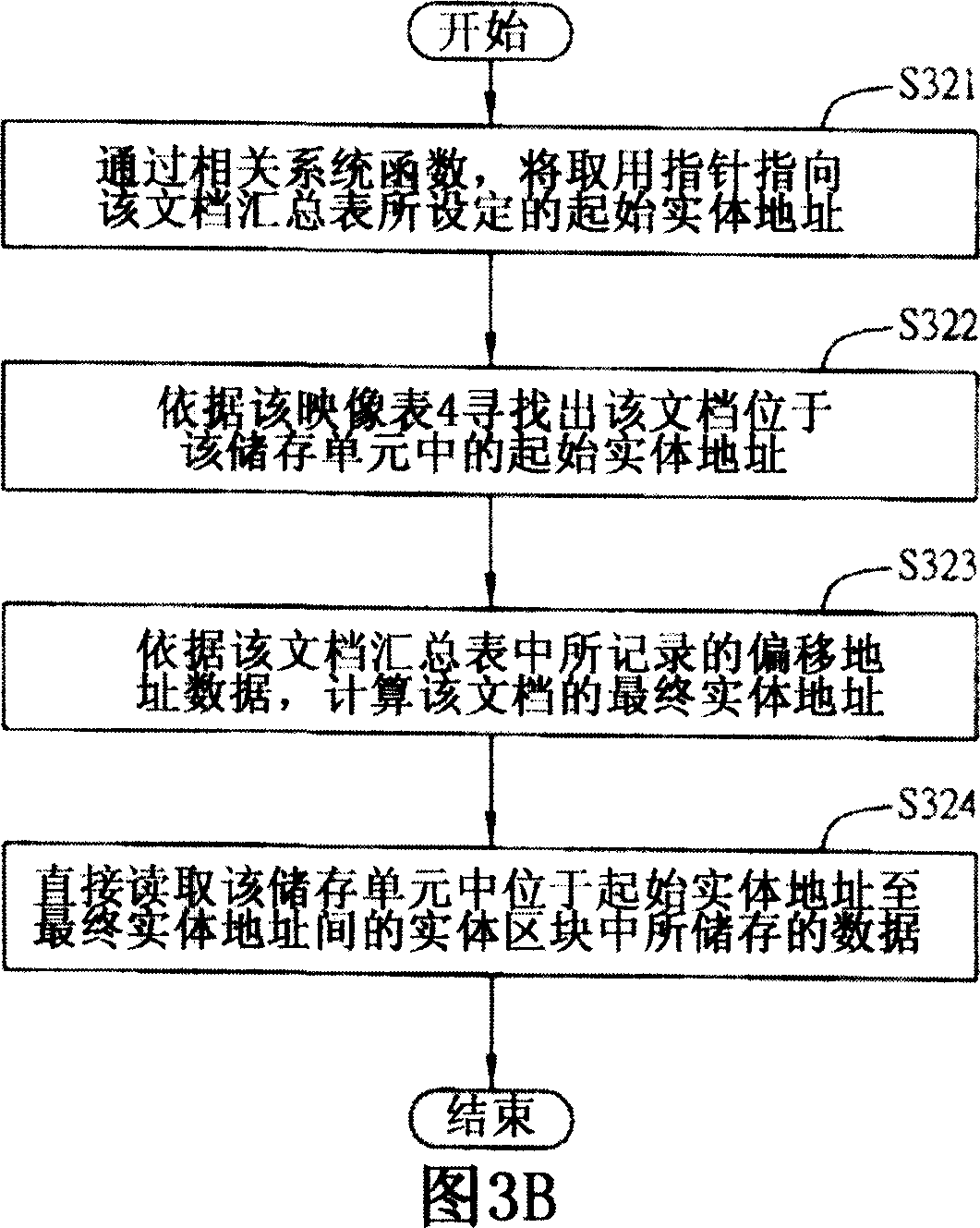
InactiveCN1952931AImprove reading speedSave storage spaceMultiprogramming arrangementsSpecial data processing applicationsFile systemProcess module
This invention relates to file common method and system applied in multiple program electron device, wherein, the file system comprises the following parts: integration module to integrate electron device needed files and to store special memory unit; mapping module to record and store unit each file relative body memory address and establishing relative mapping list; process module to find relative body memory address according to application program to take program to execute relative operation relative files.
Owner:INVENTEC CORP
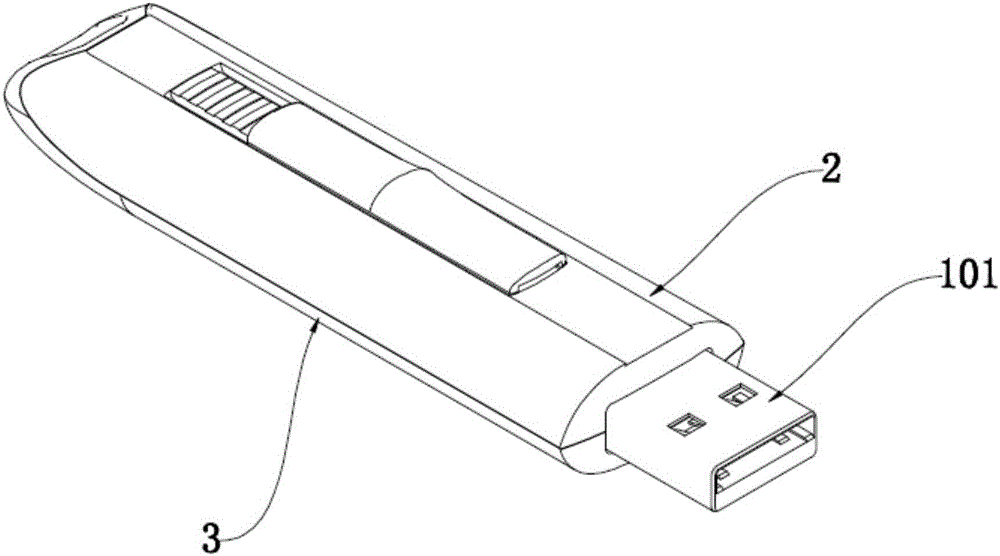
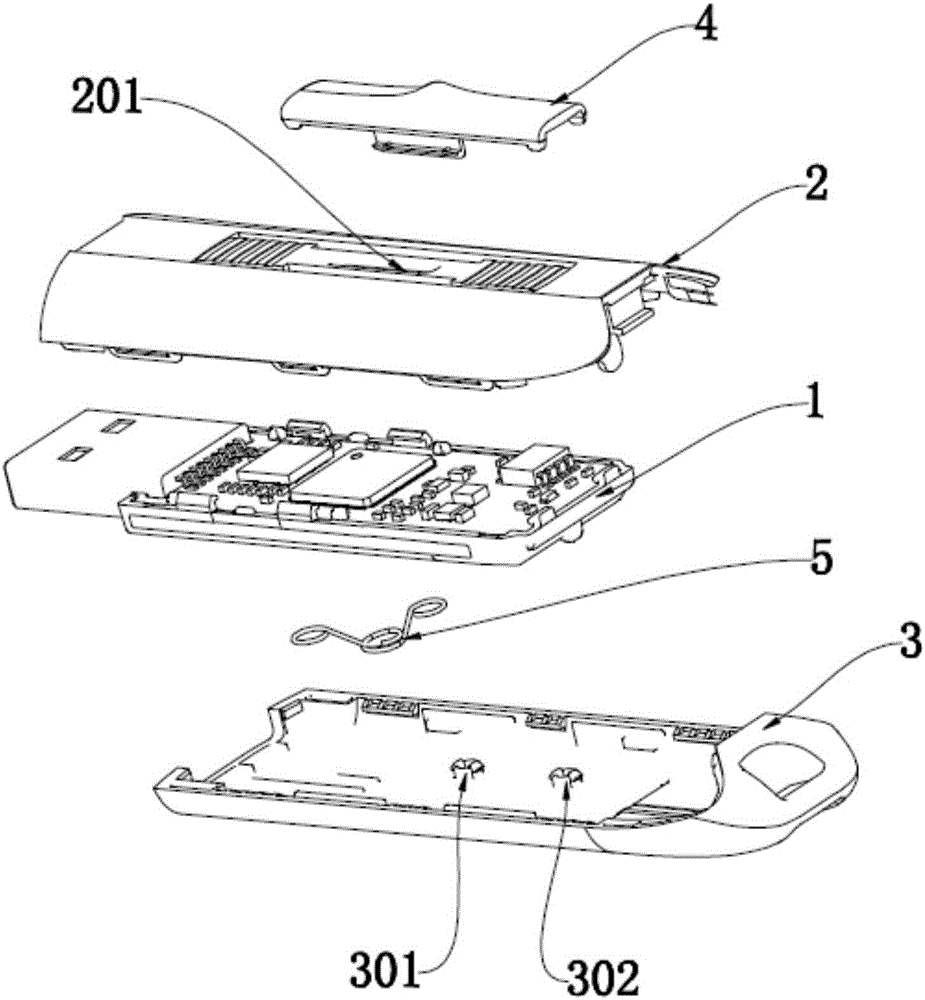
Pushing type telescopic flash drive
InactiveCN105930897AWon't pop upEasy to push and pullRecord carriers used with machinesPush pullEngineering
The invention discloses a pushing type telescopic flash drive, which comprises a memory housing with an opening on one end and a memory body positioned in the memory housing. The memory housing comprises a first housing and a second housing, wherein the first housing and the second housing are each provided with a slide rail for the memory body to slide back and forth, the first housing is detachably connected with the second housing, the first housing is provided with a push-pull member, and the first housing is provided with a push-pull slot allowing the push-pull member to move back and forth on the upper surface thereof. The push-pull member, after penetrating through the push-pull slot, is connected with the memory body. The memory body is connected to the second housing through an elastic member. The memory body is entirely housed in the memory housing, and the memory body and the connecting plug of the memory body are effectively protected. A backward elastic force is applied to the memory body through the elastic member to ensure that the body memory may not pop out under the condition of natural gravity or slight swinging force. Push-pull means is convenient and fast, and the slide rail type movement ensures low resistance force.
Owner:东江精创注塑(深圳)有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com