Patents
Literature
46 results about "Floating body cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
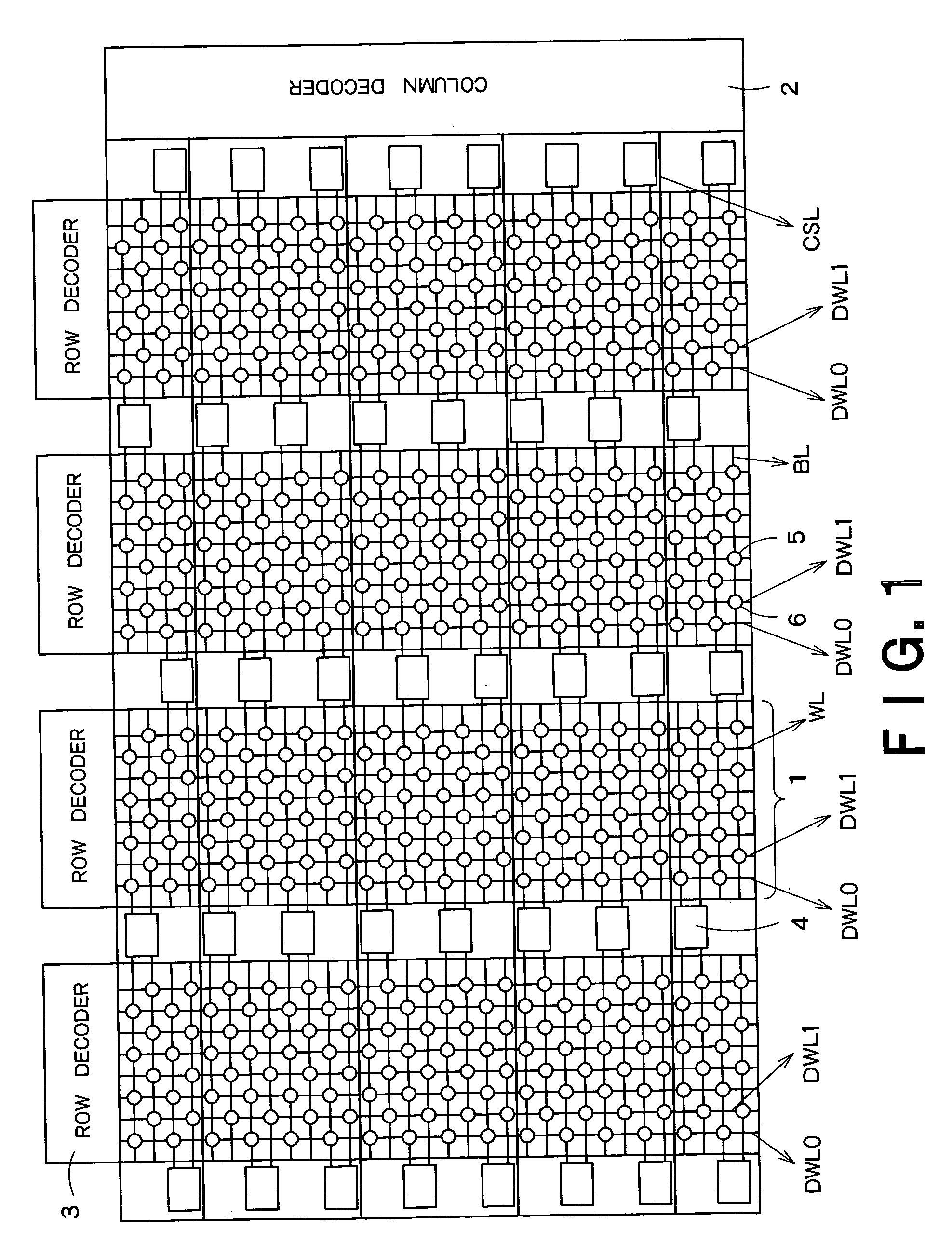
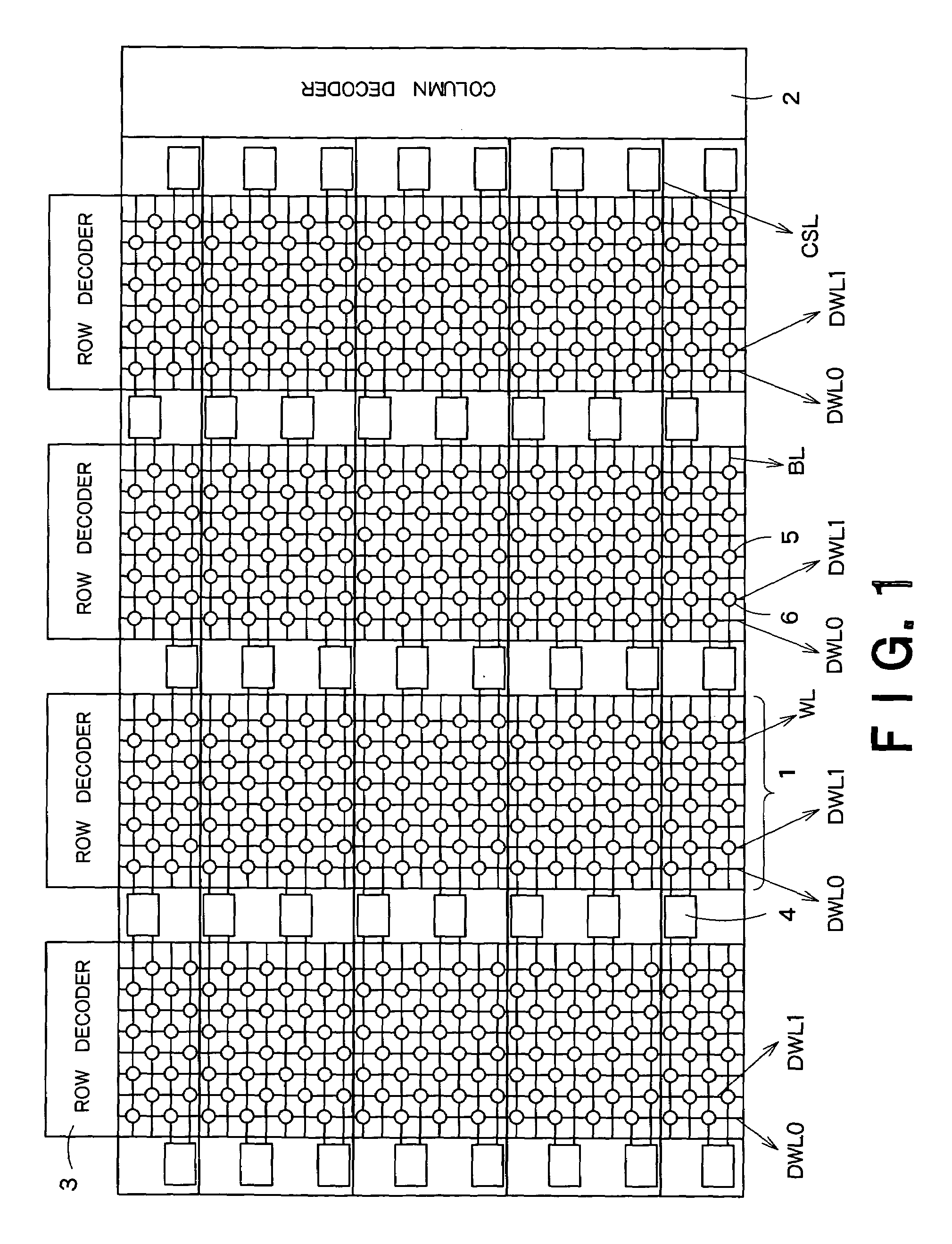
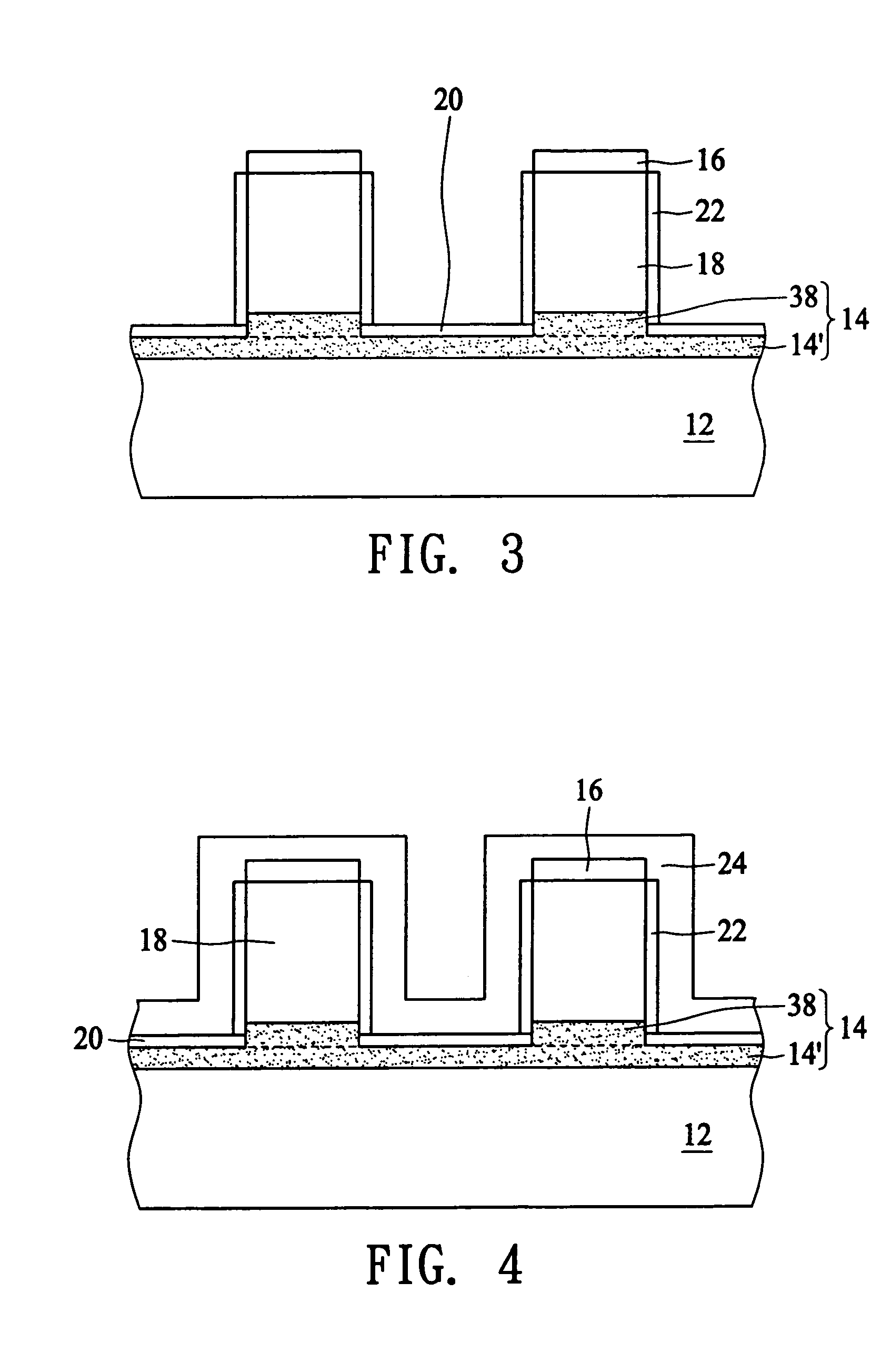
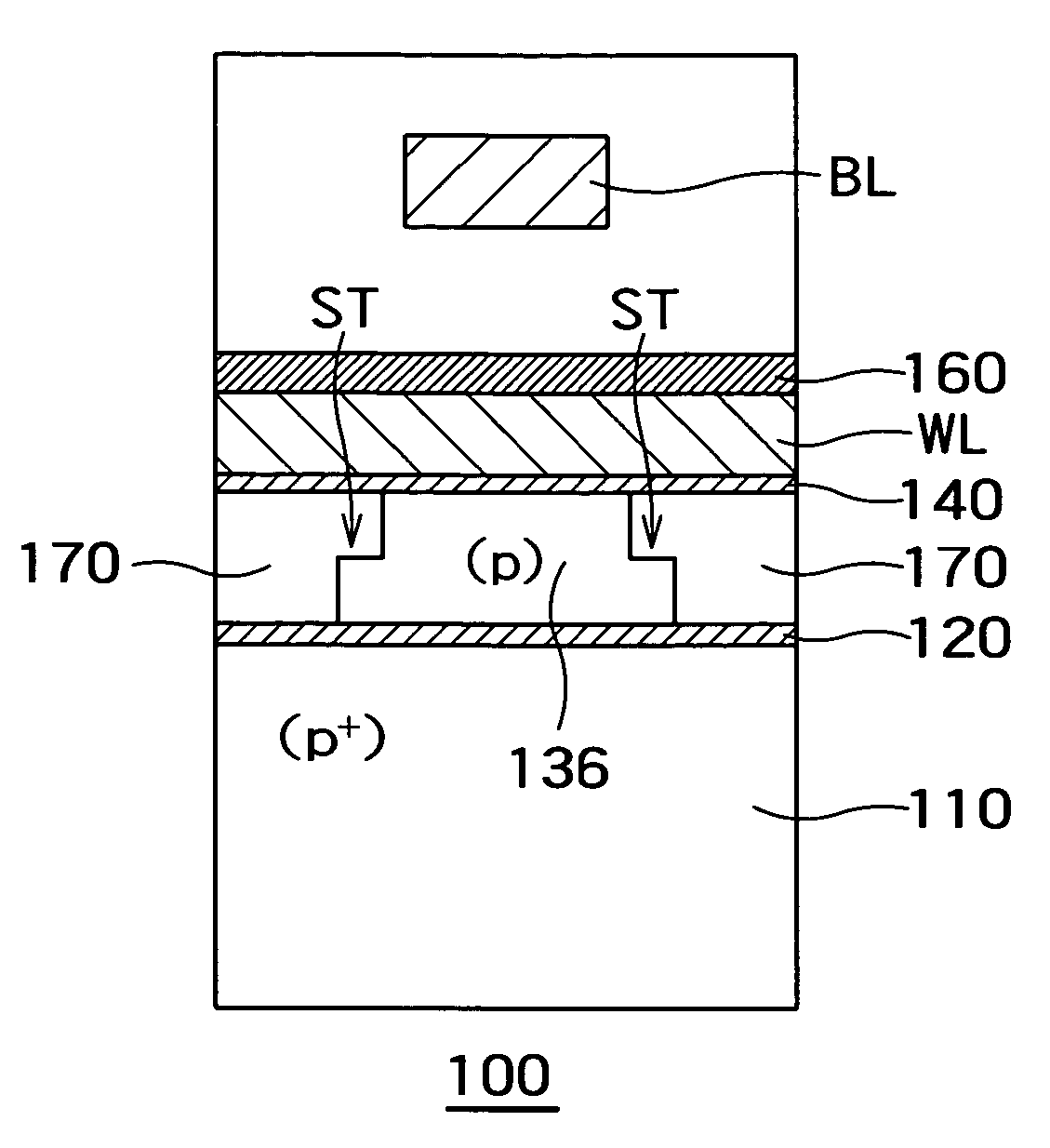
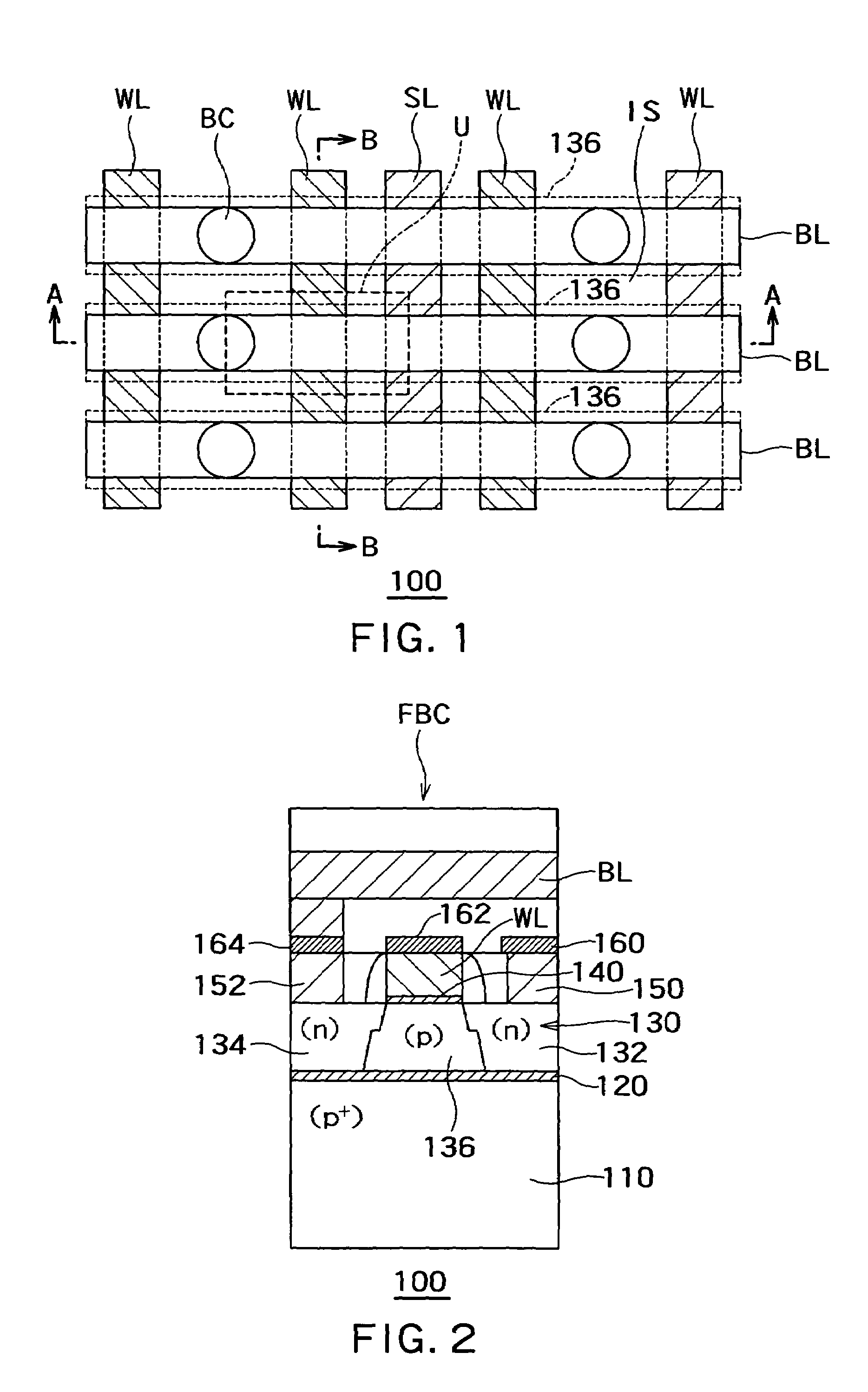
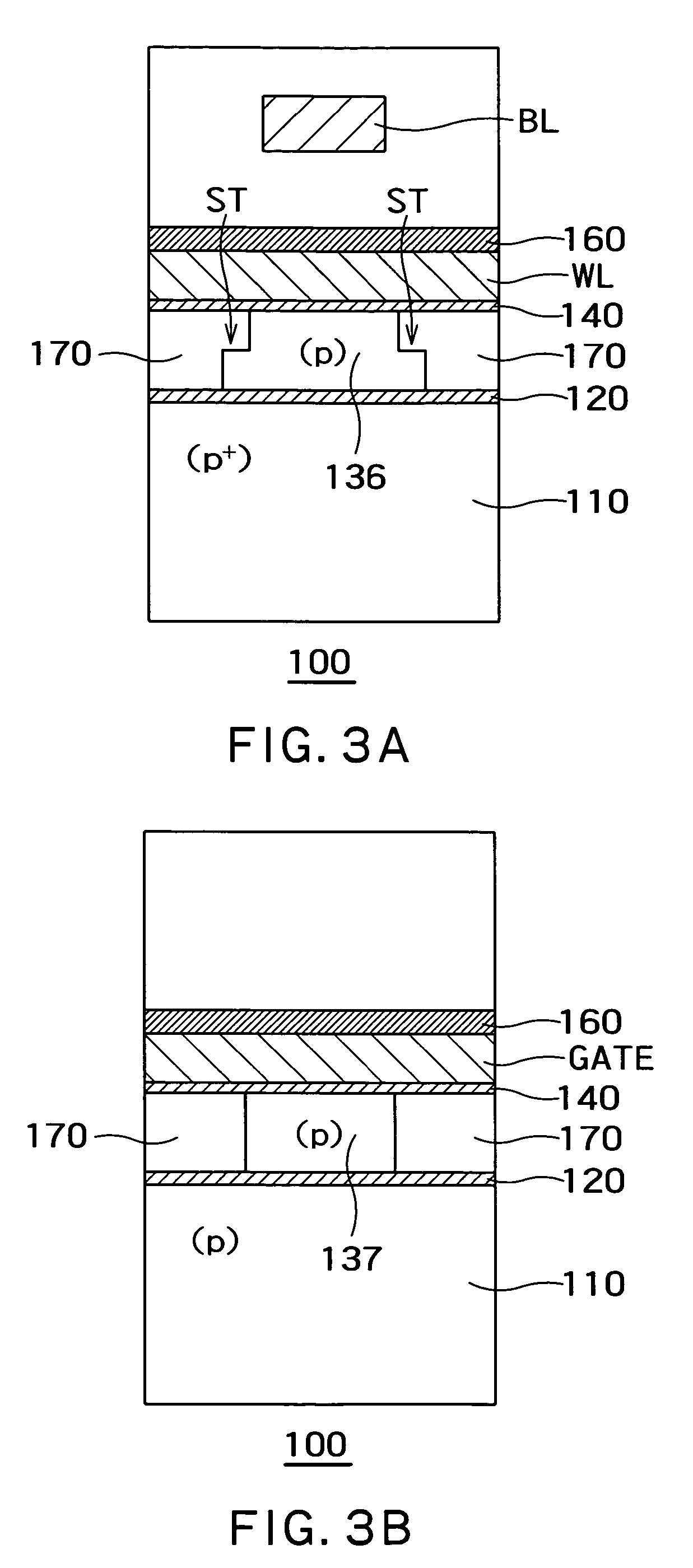
Floating body memory and method of fabricating the same
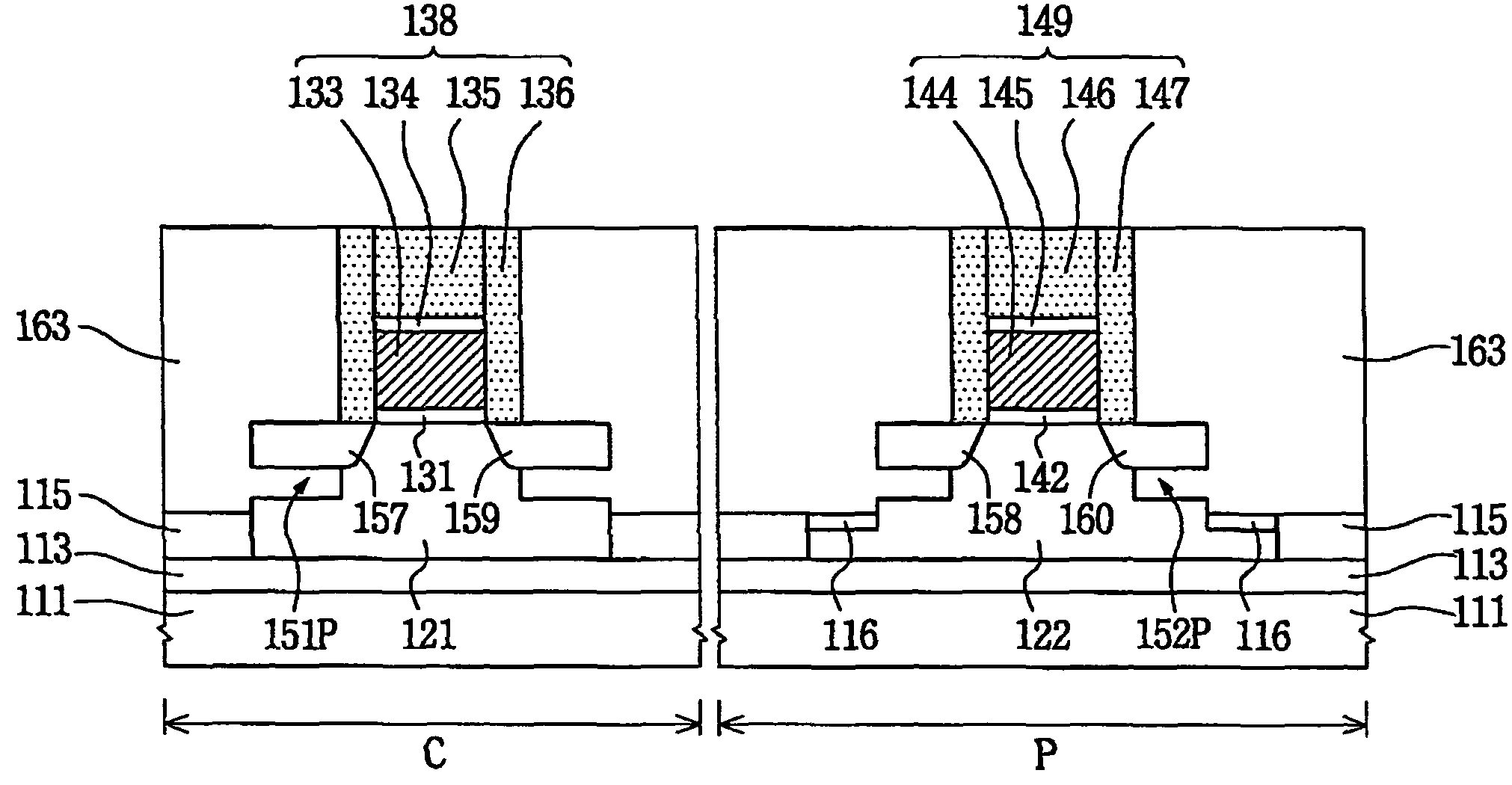
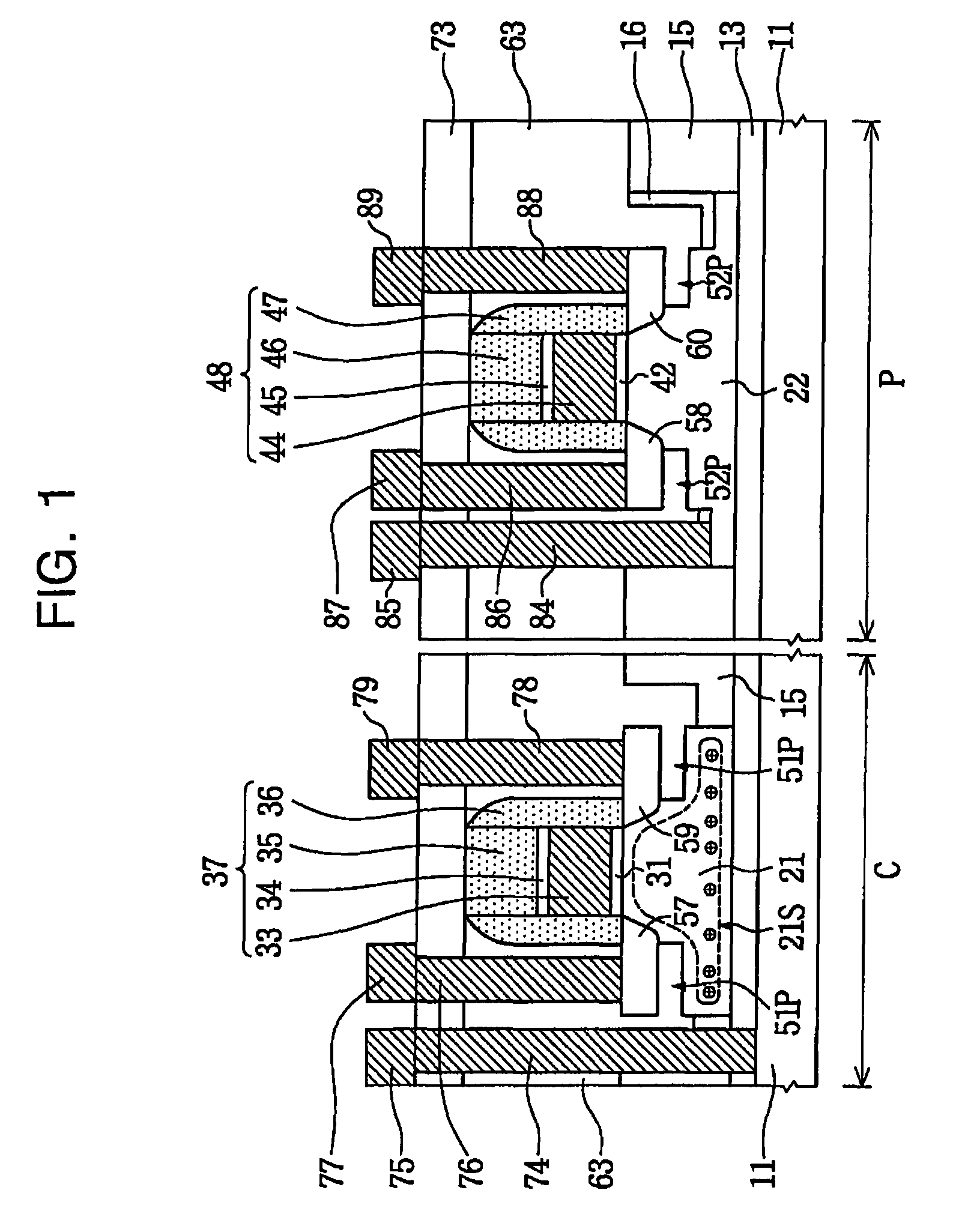
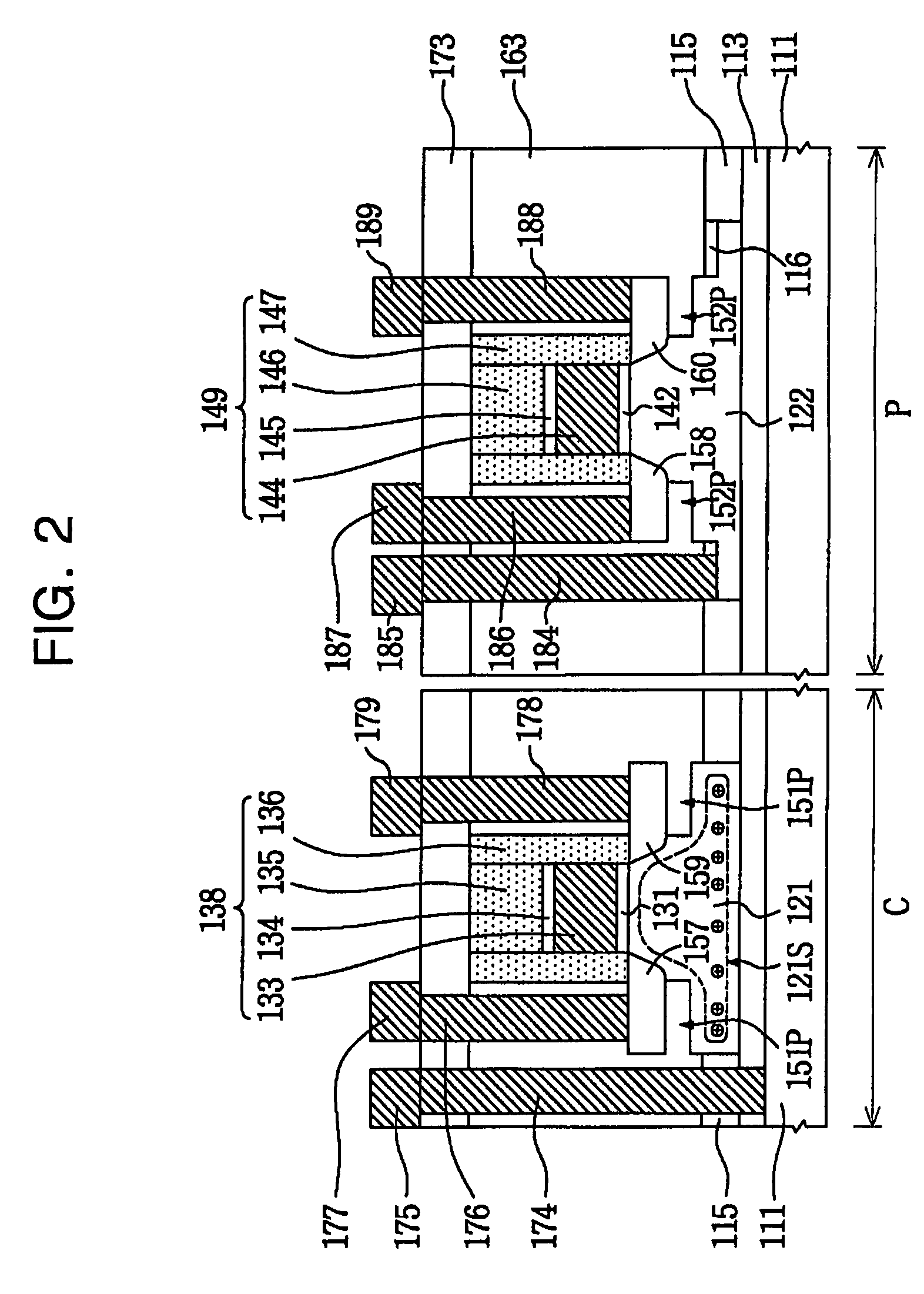
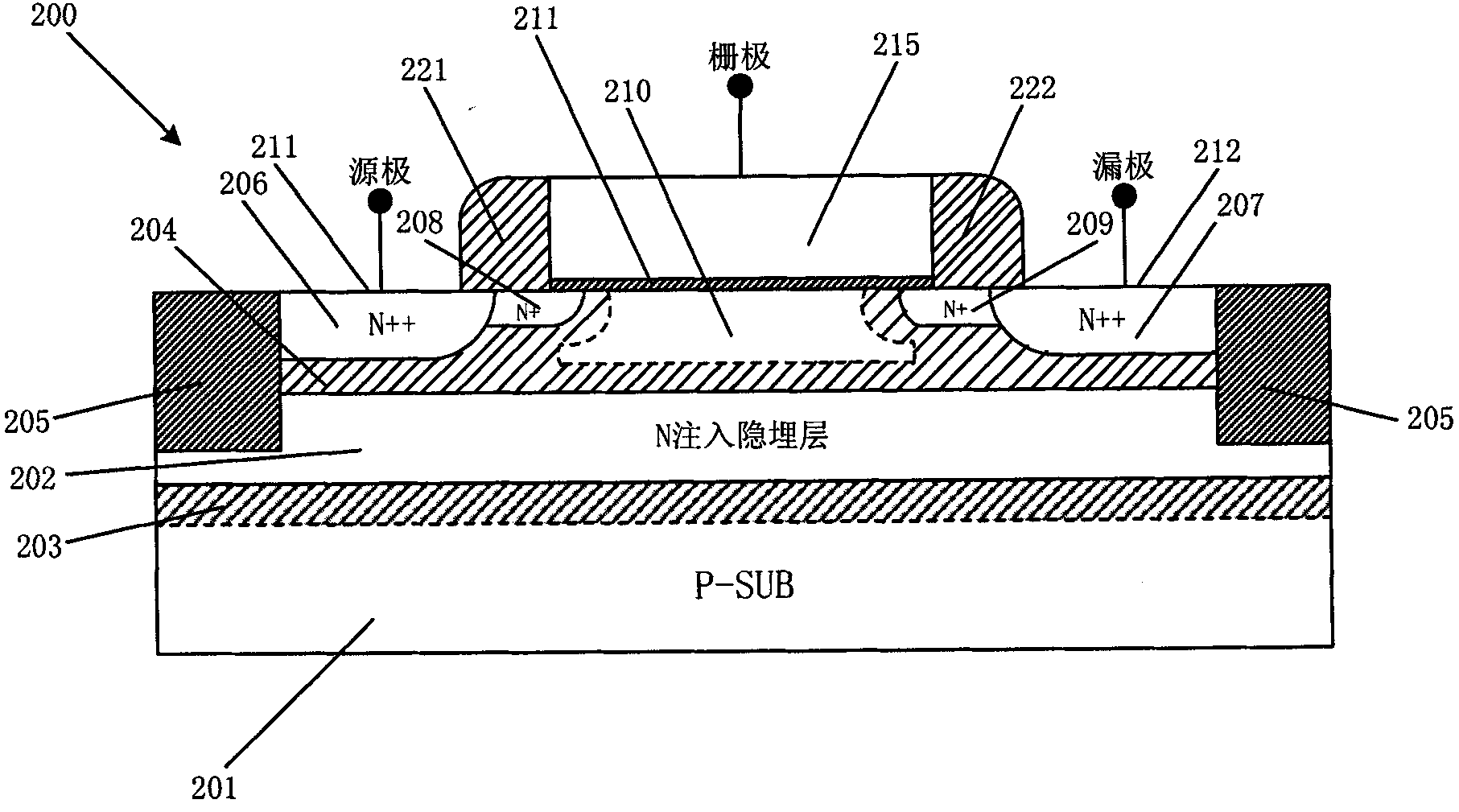
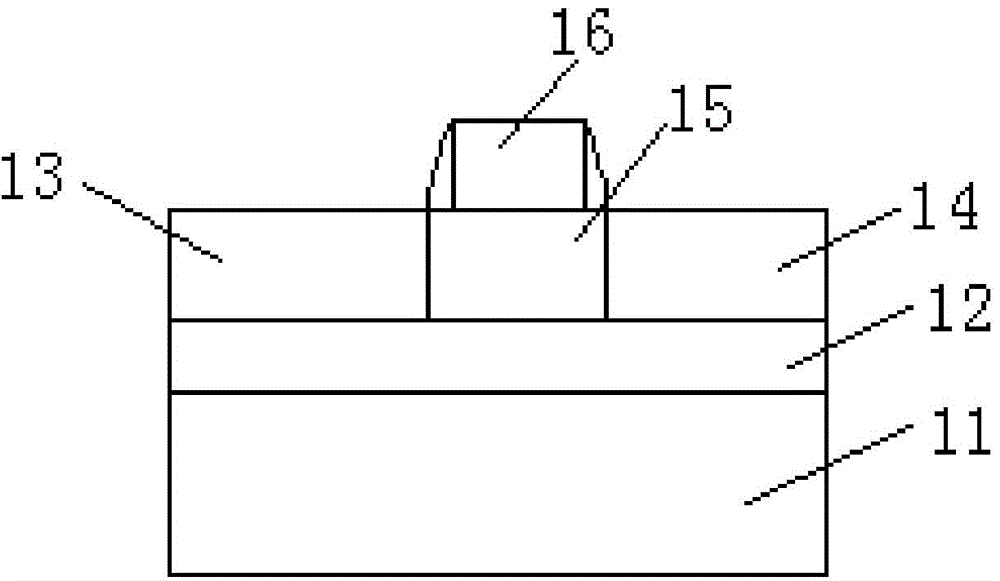
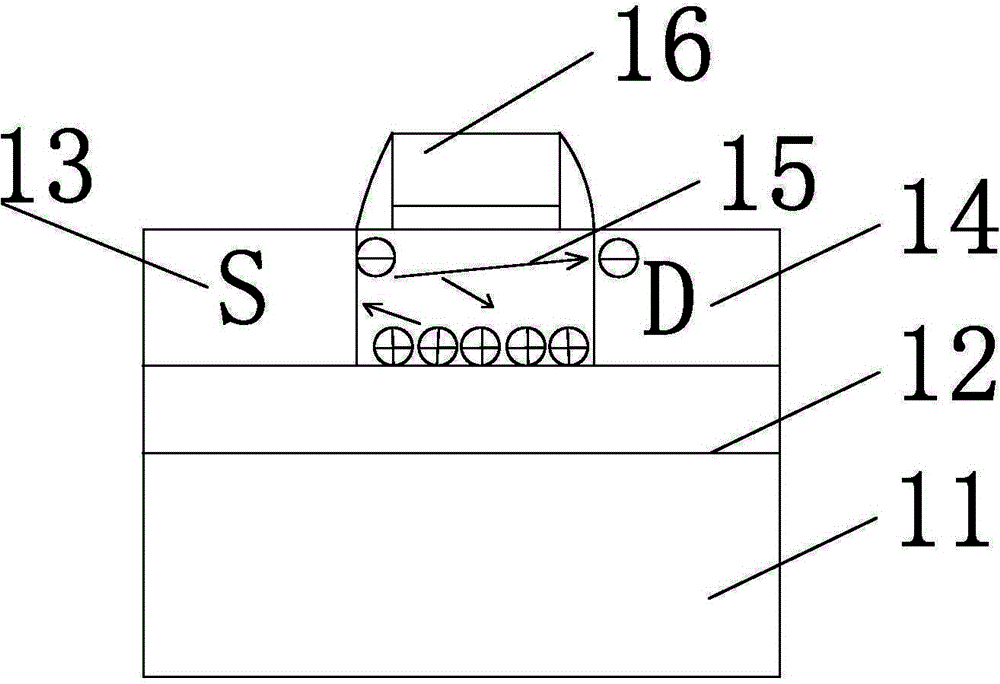
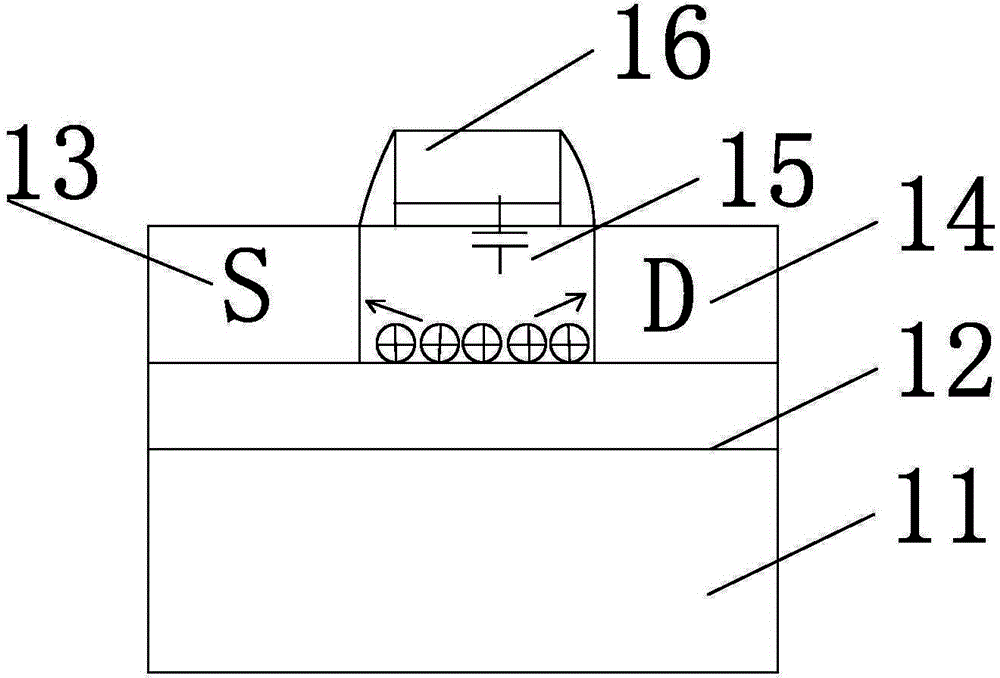
A floating body memory includes a semiconductor substrate having a cell region and a peripheral circuit region. A floating body cell is located in the cell region and a first floating body is located in the peripheral circuit region of the semiconductor substrate. A peripheral gate pattern is positioned on the first floating body. First source and drain regions are positioned at both sides of the peripheral gate pattern. First leakage shielding patterns are positioned between the first floating body and the first source and drain regions, the first source and drain regions contacting the first floating body. The first leakage shielding patterns may be positioned outside outer edges of the peripheral gate pattern.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
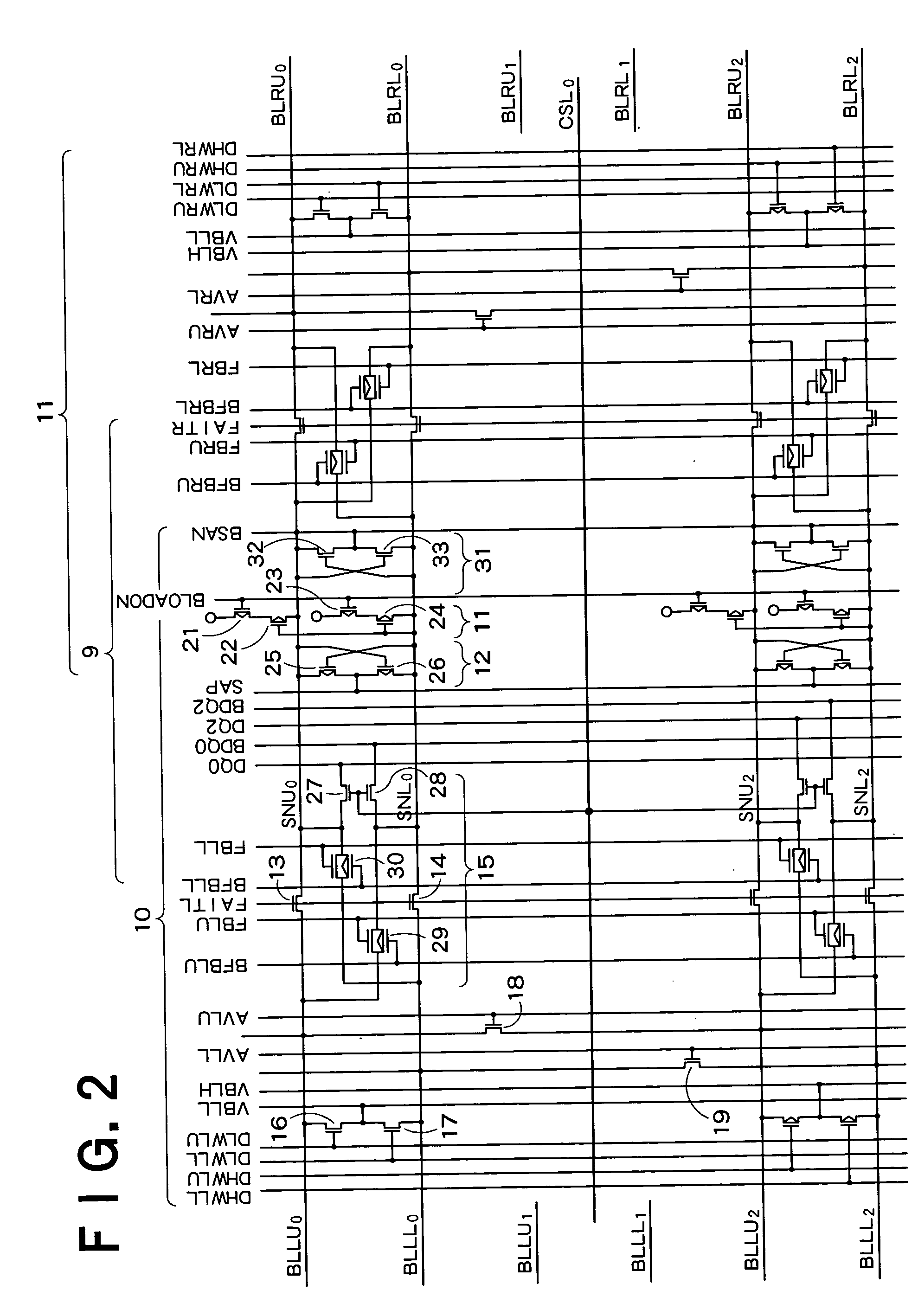
Semiconductor storage device
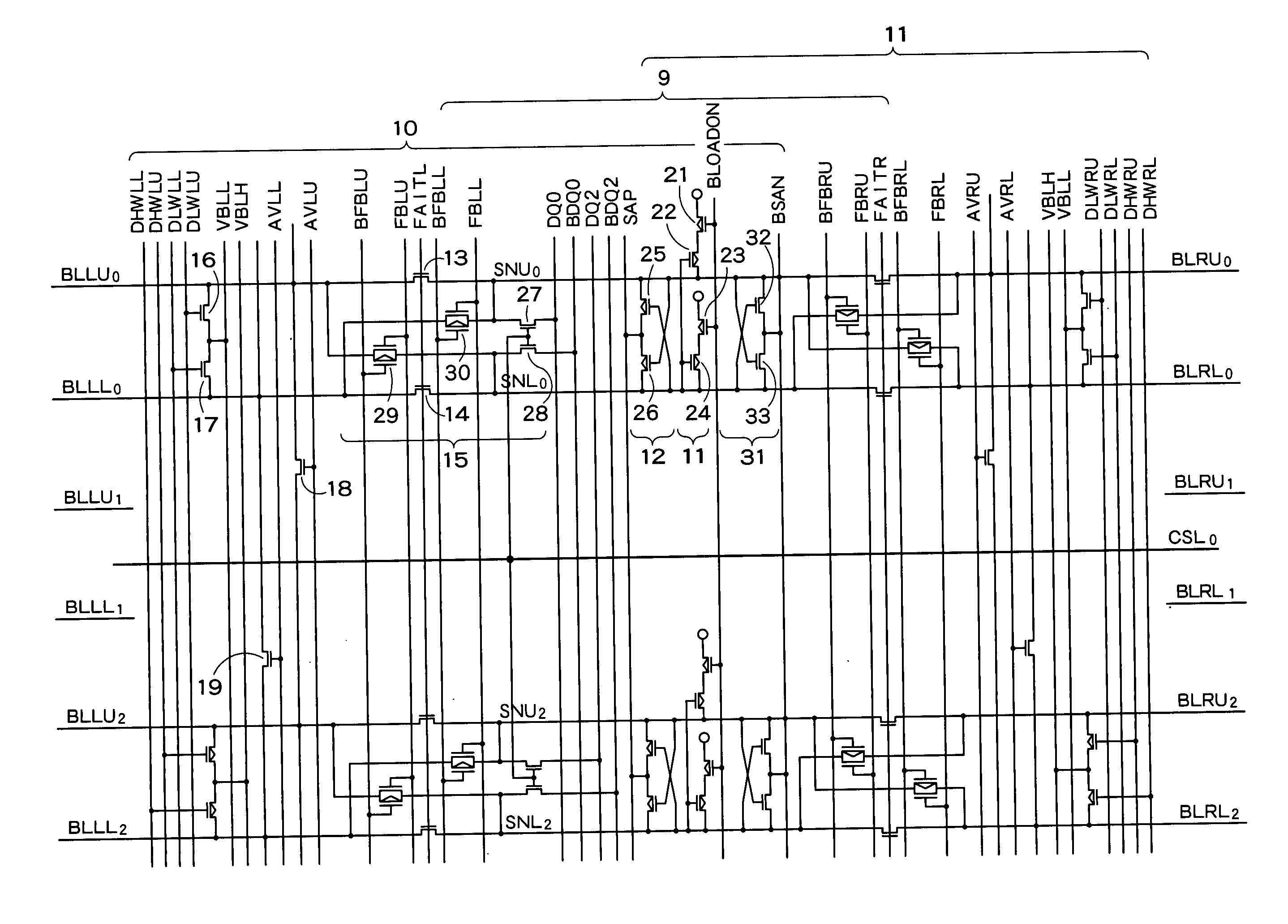
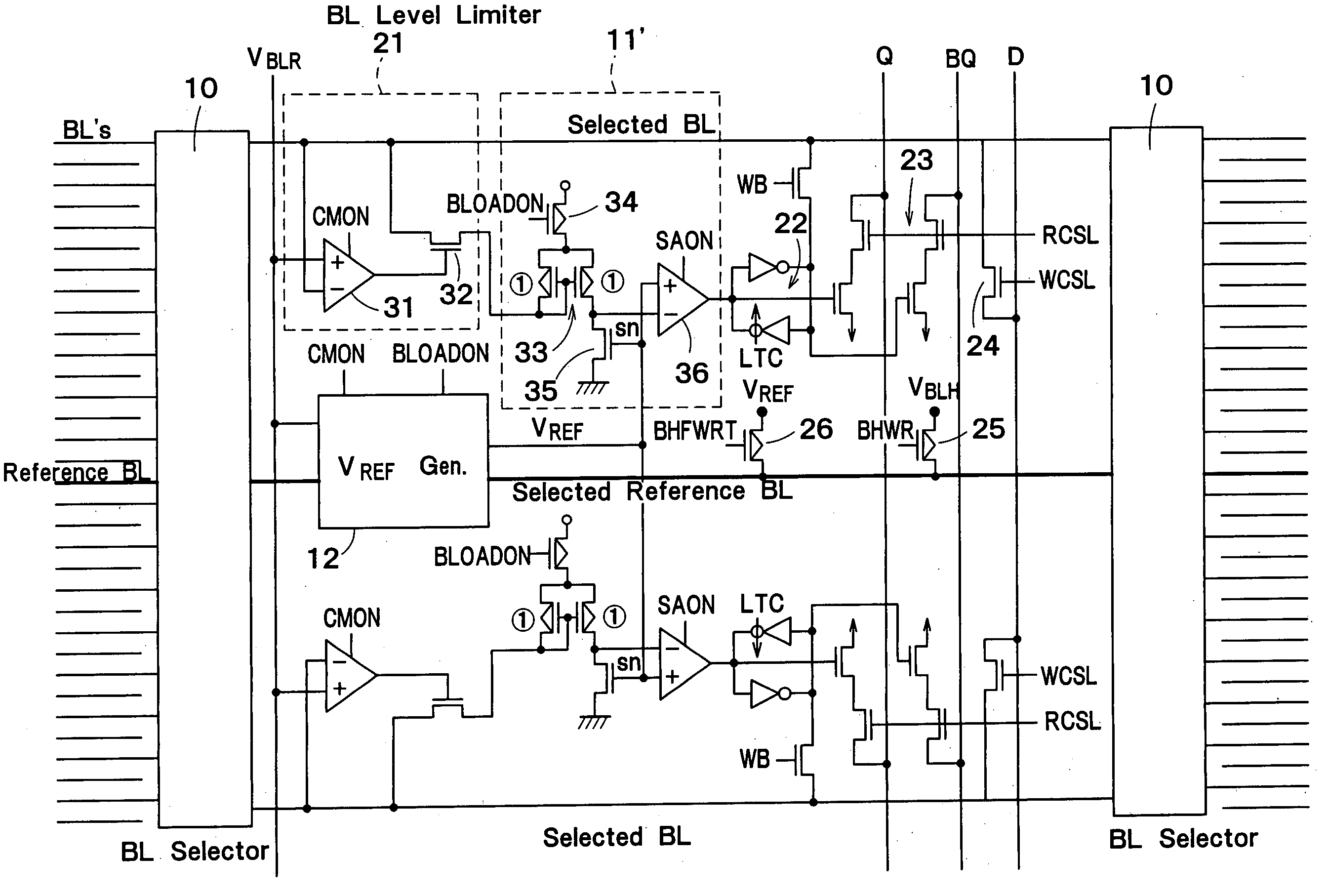
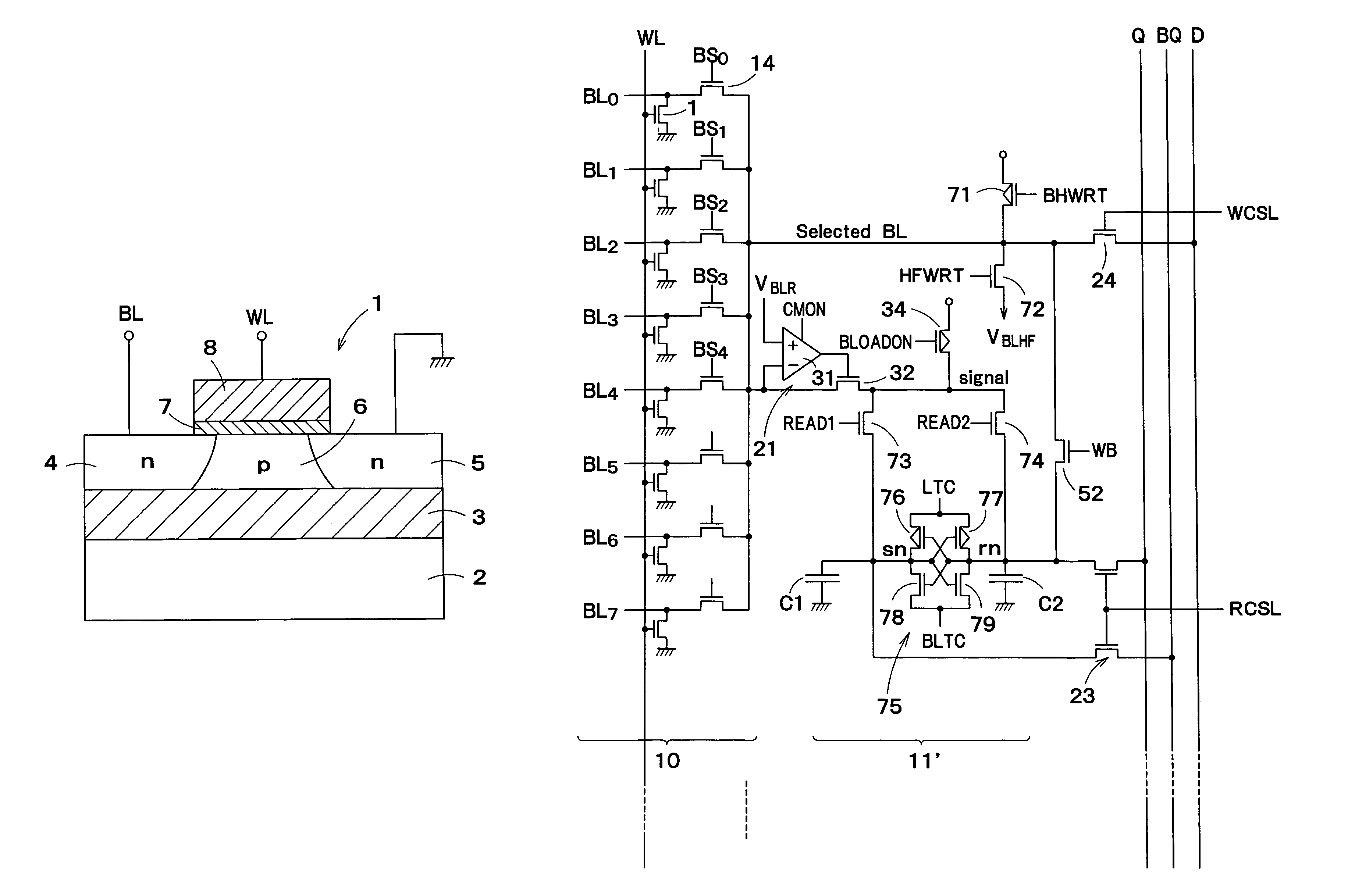
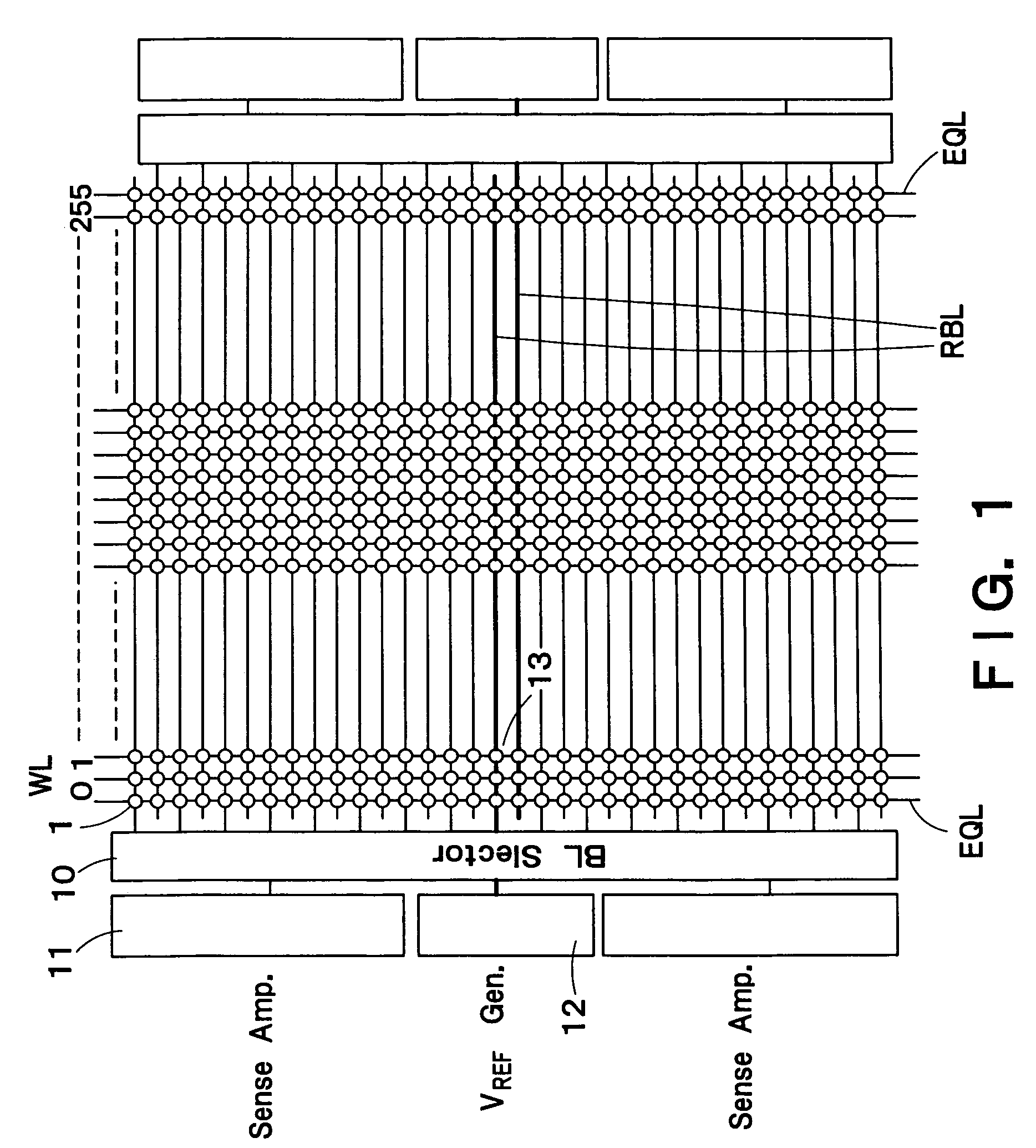
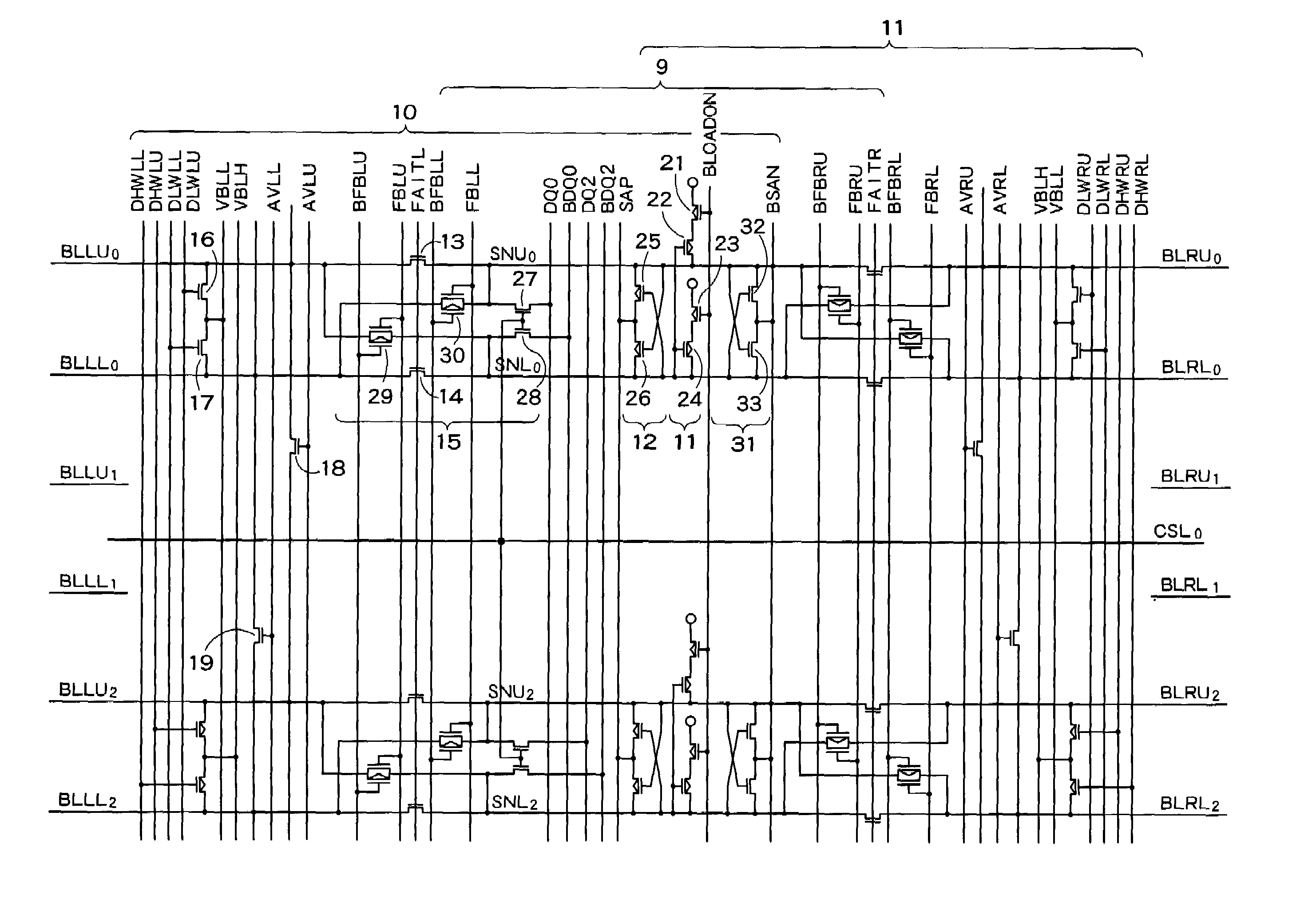
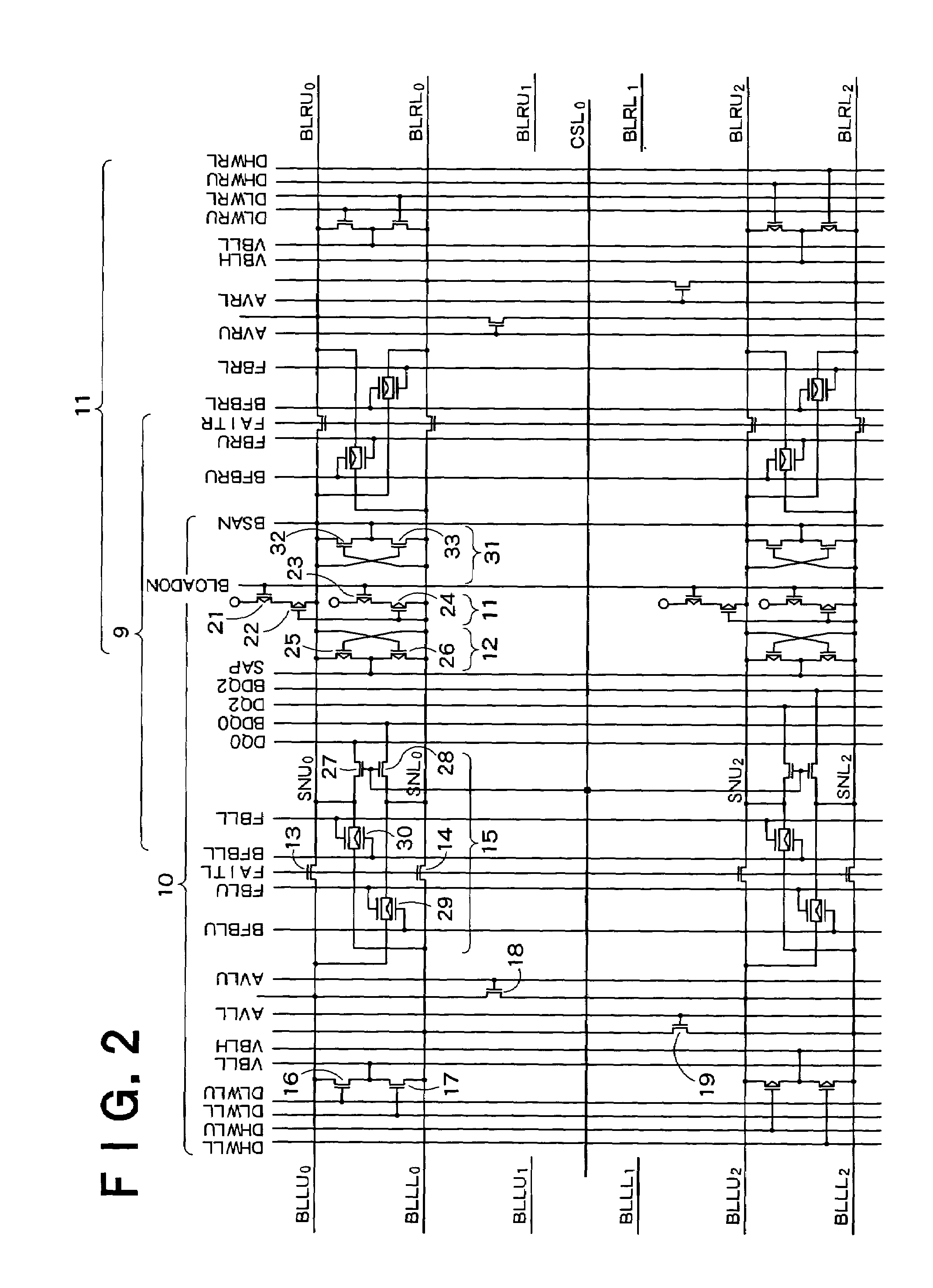
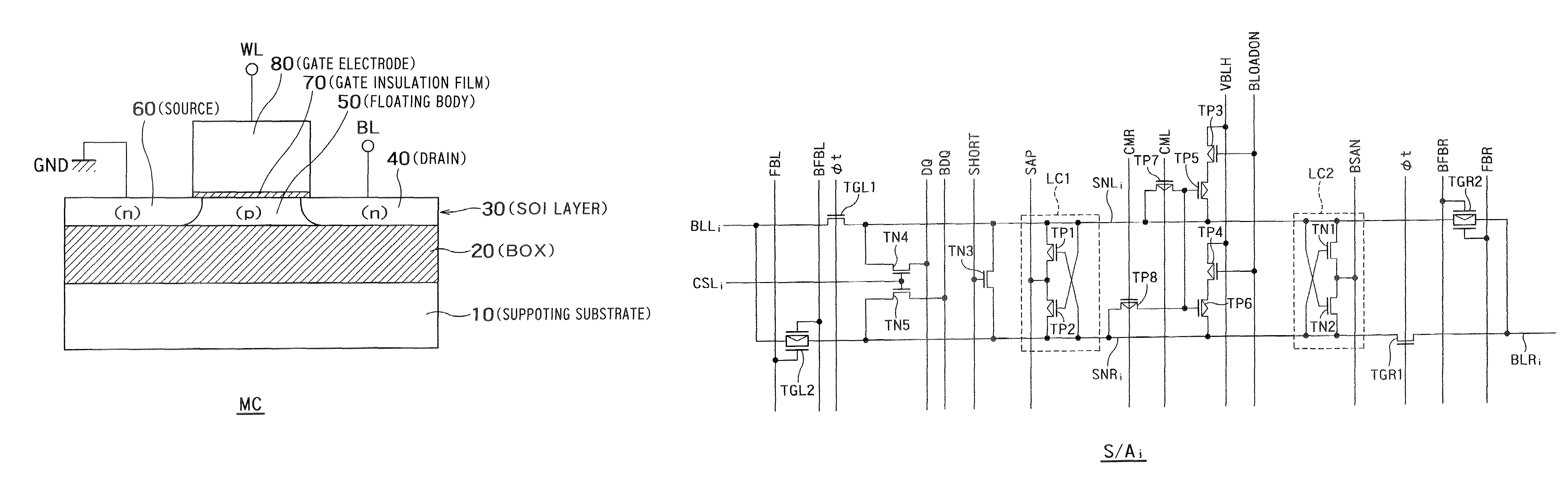
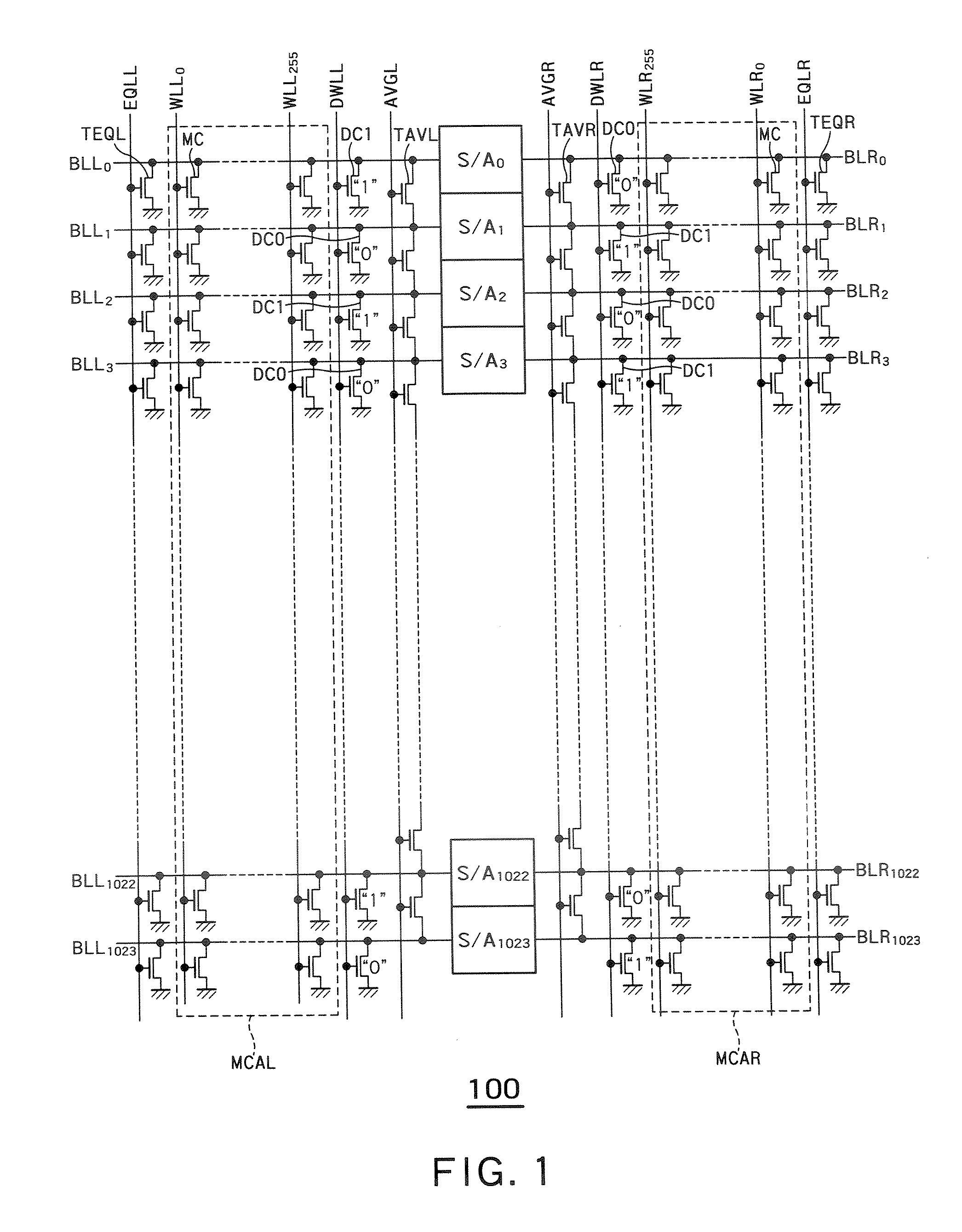
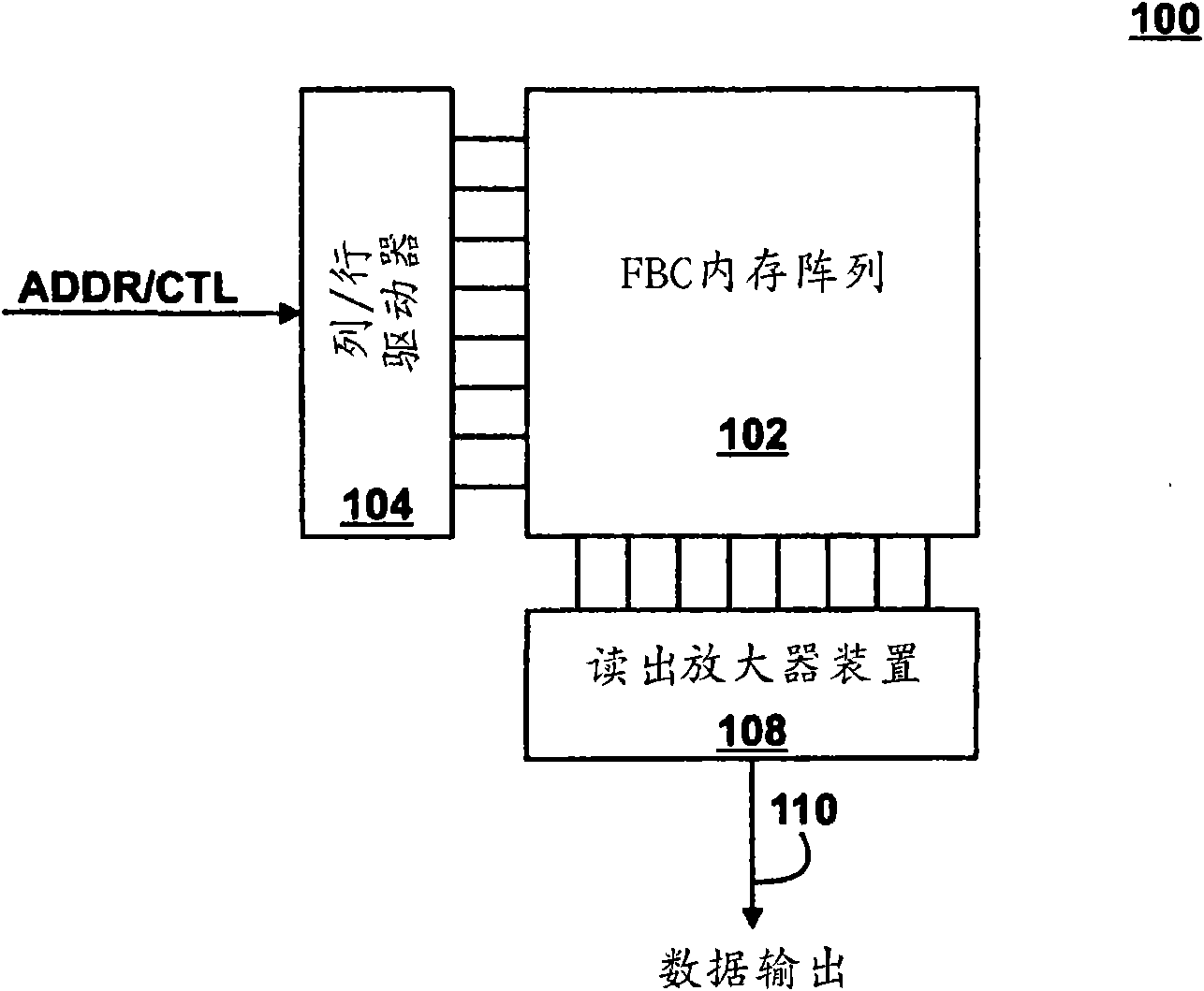
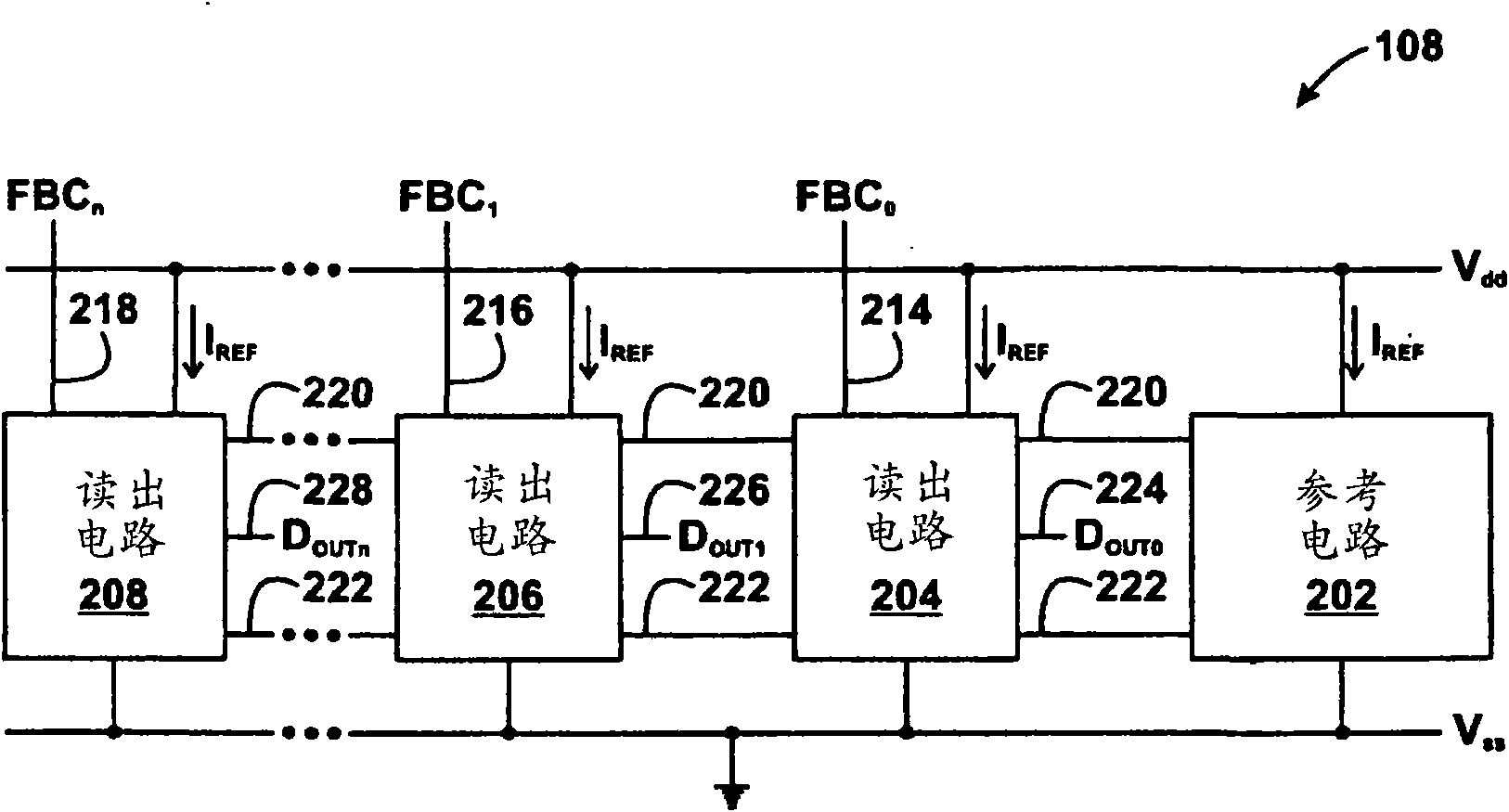
A semiconductor storage device according to one embodiment of the present invention, comprising: FBCs (Floating Body Cells) which store data by accumulating a majority carrier in a floating channel body; and sense amplifiers which perform control reading out data stored in said FBC, wherein each of said sense amplifier includes: a pair of sense nodes provided corresponding to a bit line pair to which said FBC is connected; a pair of load which flow currents through said pair of sense nodes; latch circuits which latch potentials of said pair of sense nodes when a potential difference between said pair of sense nodes reaches a predetermined value; and an output control circuit which outputs latched outputs of said latch circuits at a predetermined timing and feeds back the latched outputs to said bit line pair side to again write it into said FBC.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
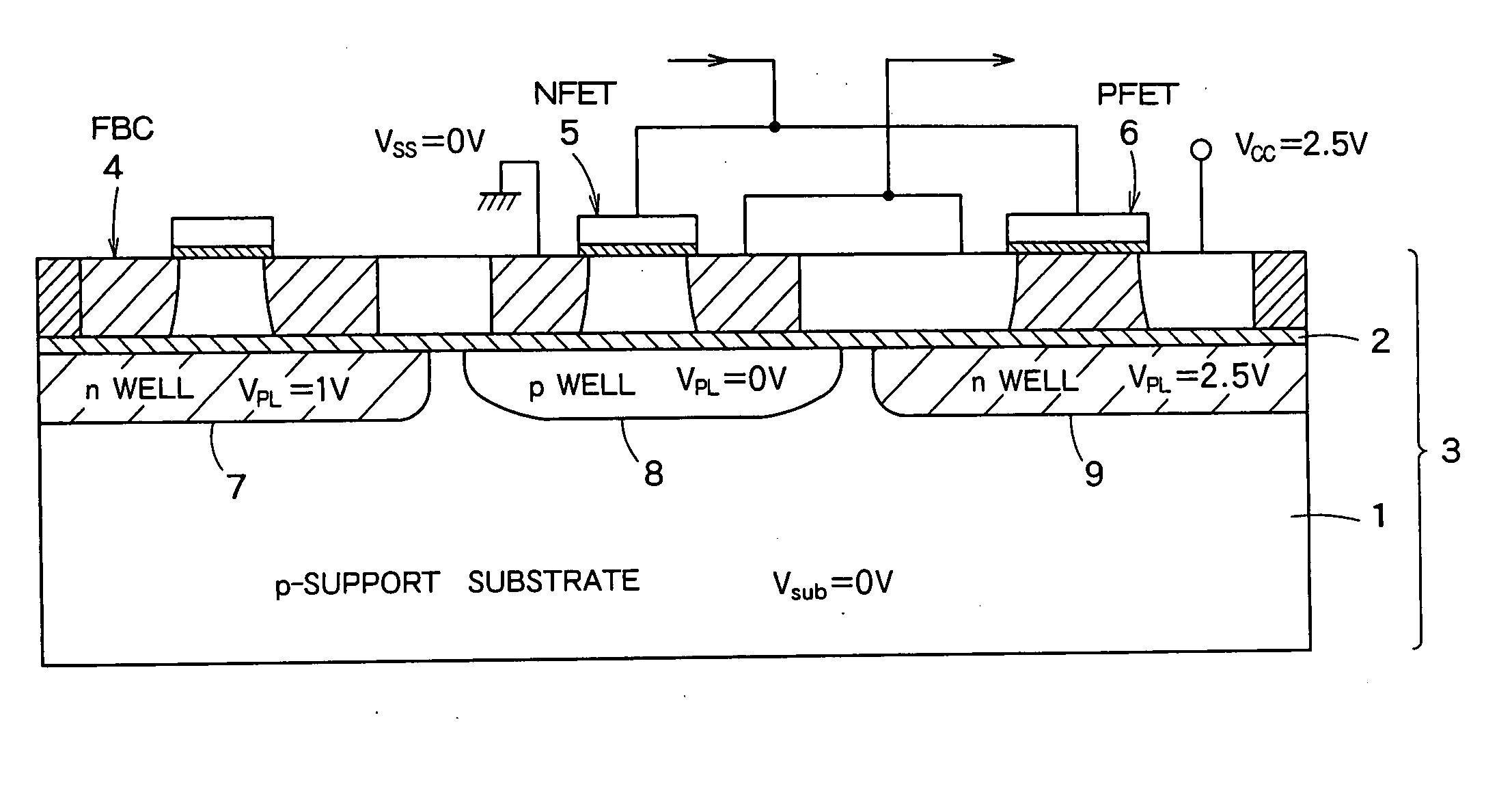
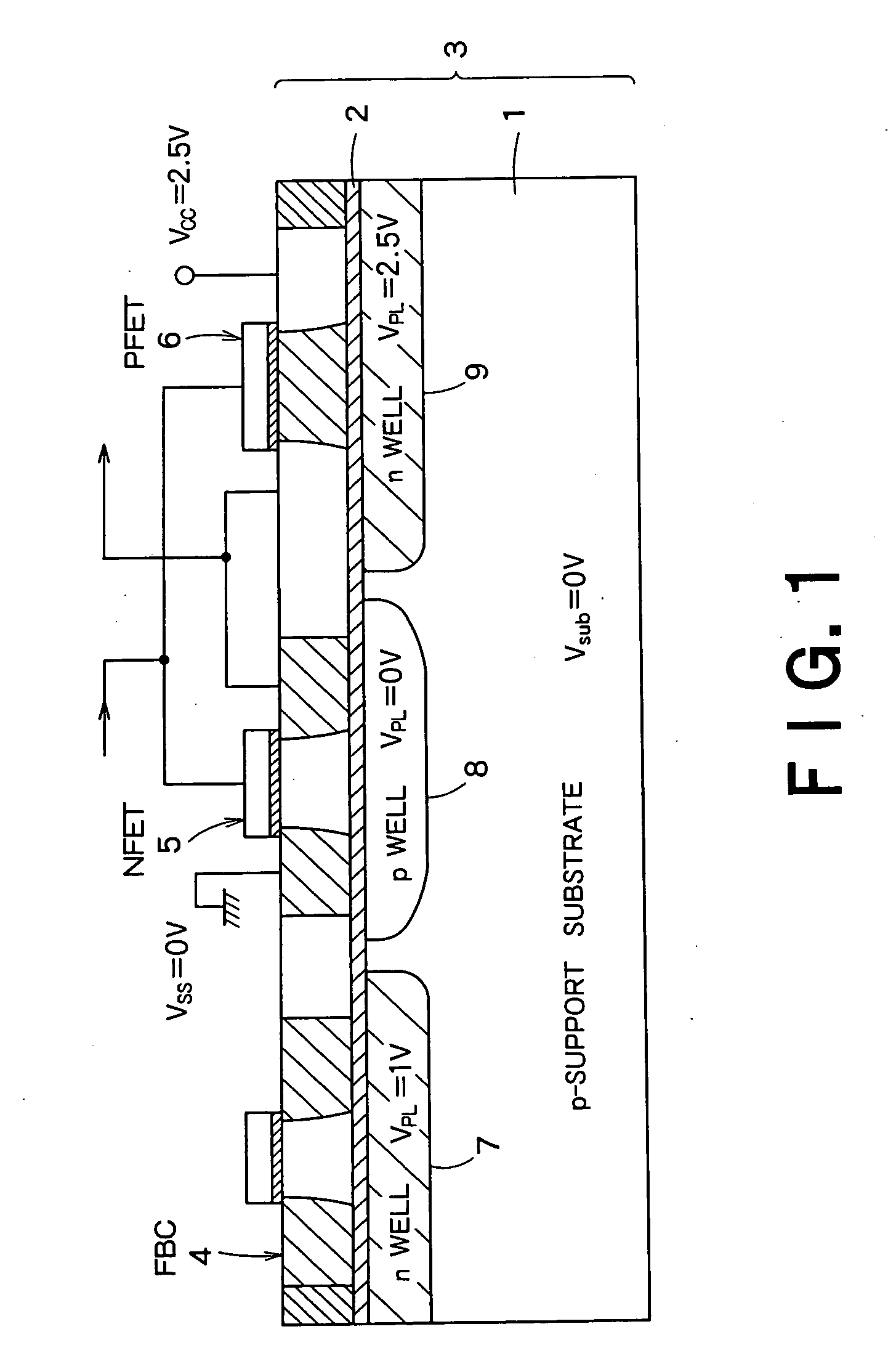
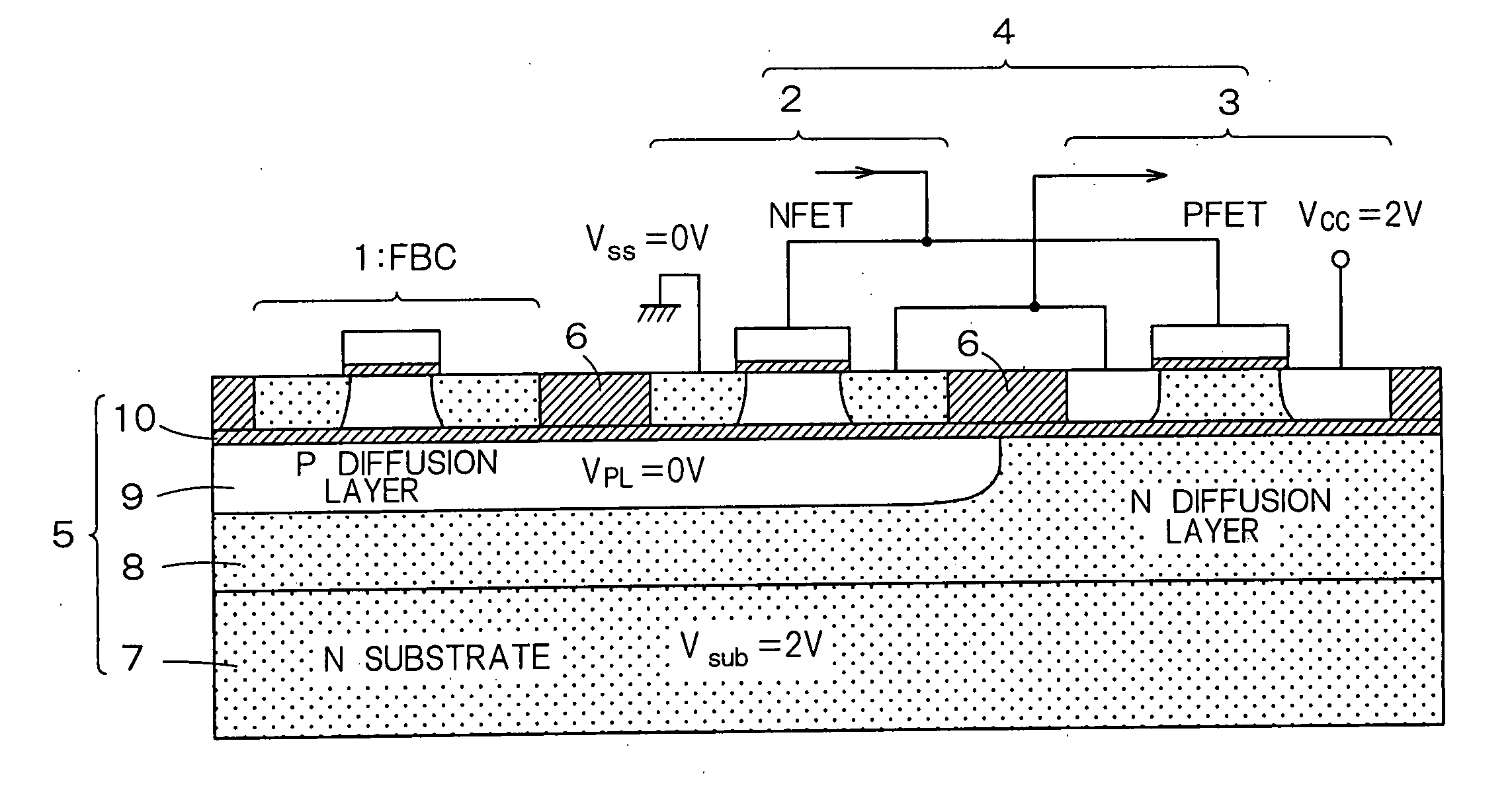
Semiconductor integrated device
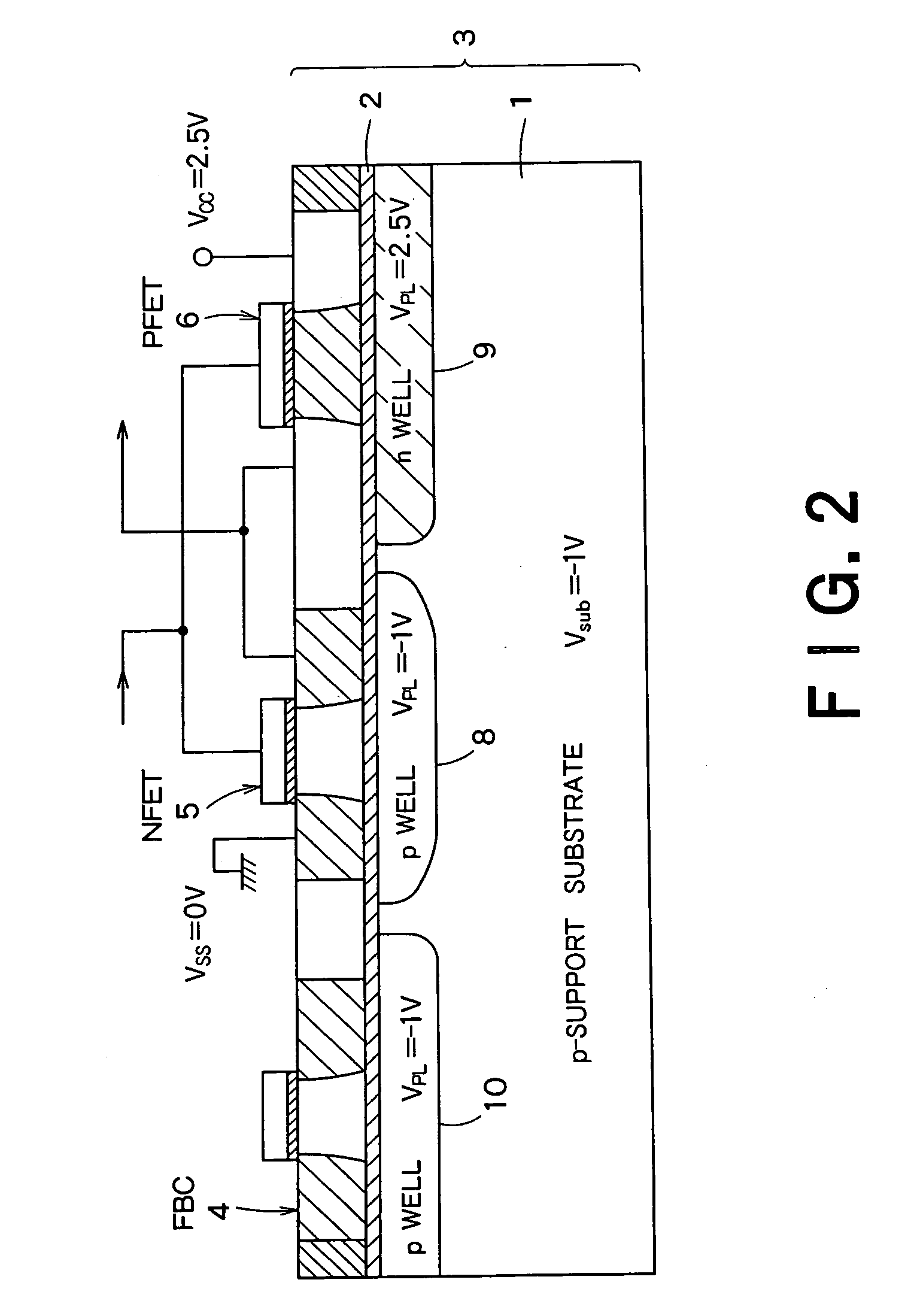
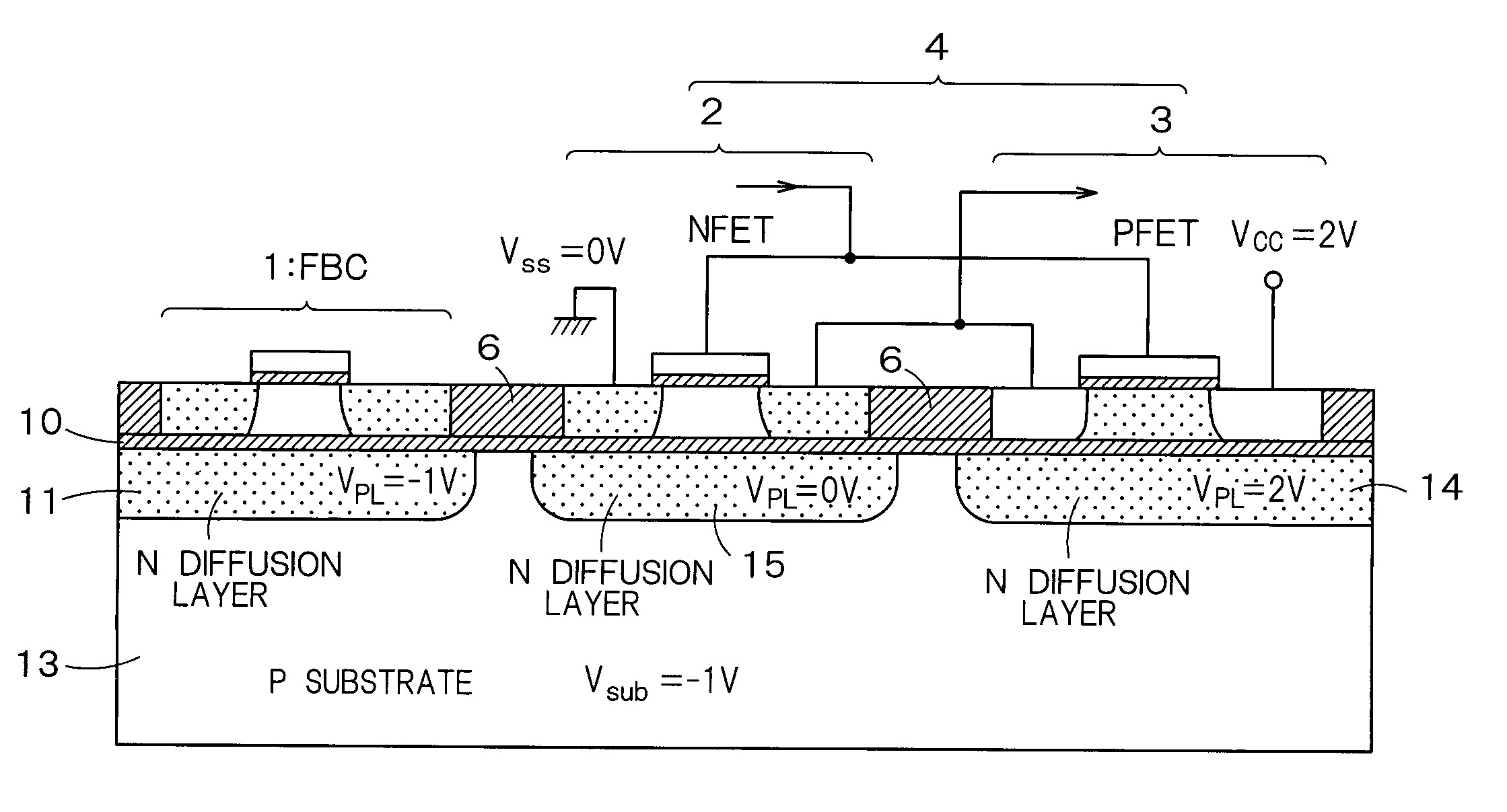
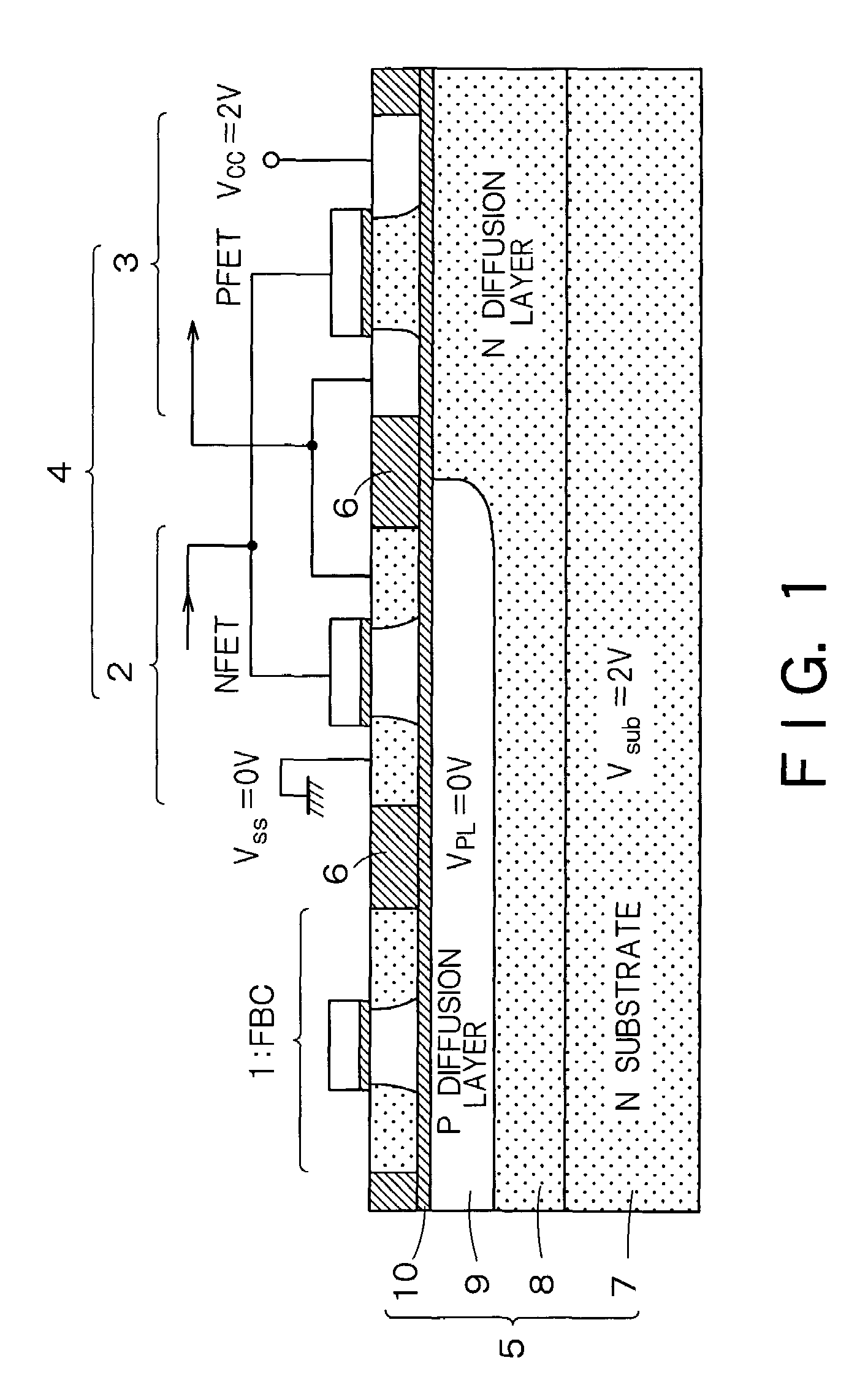
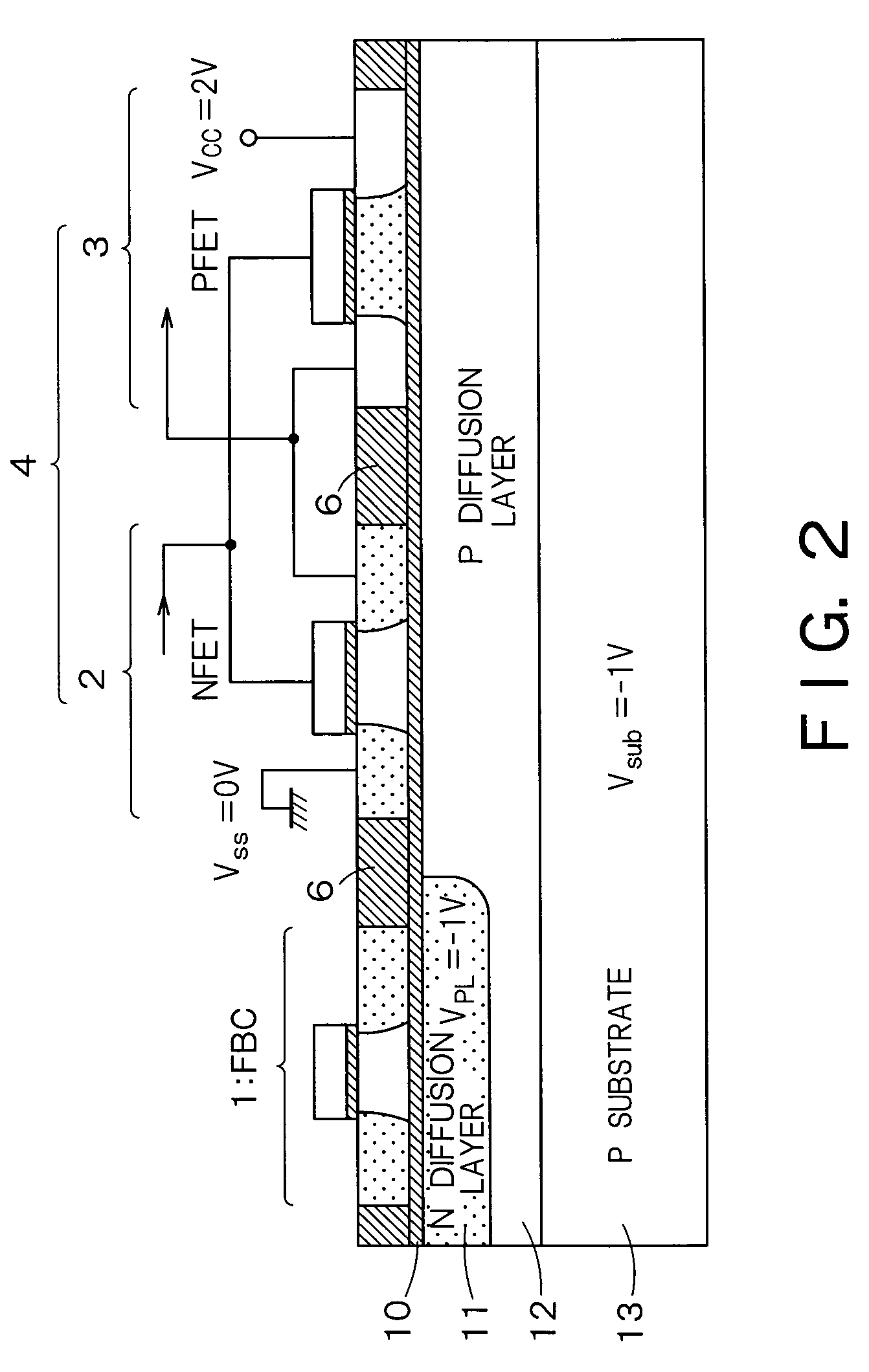
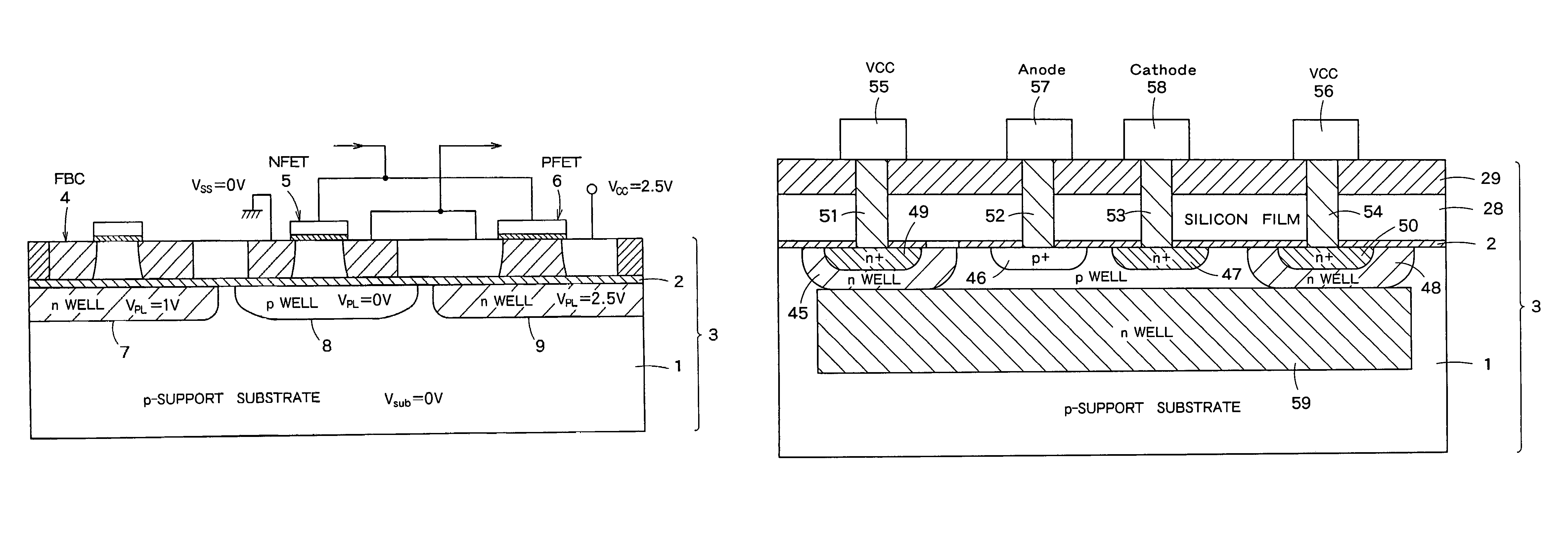
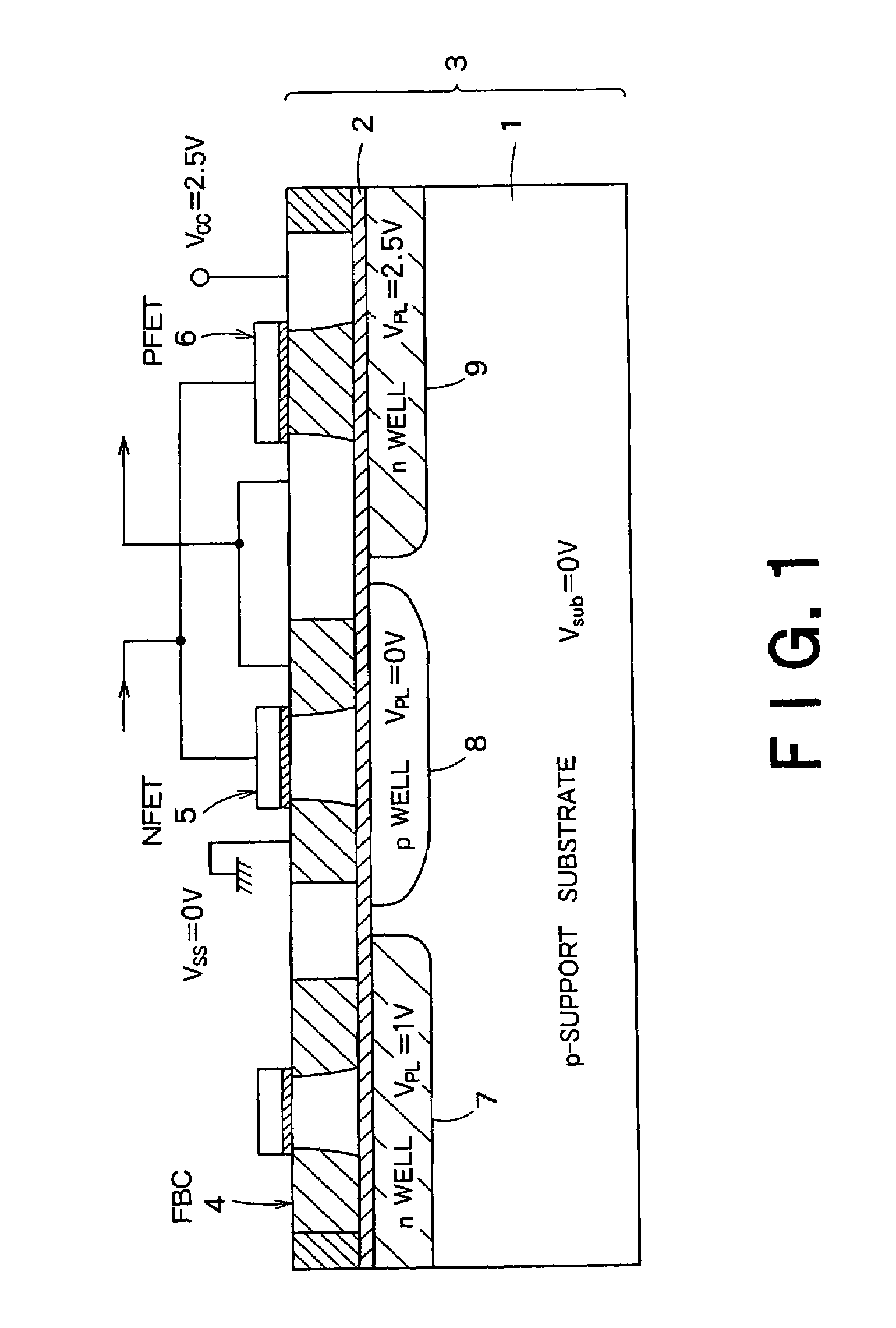
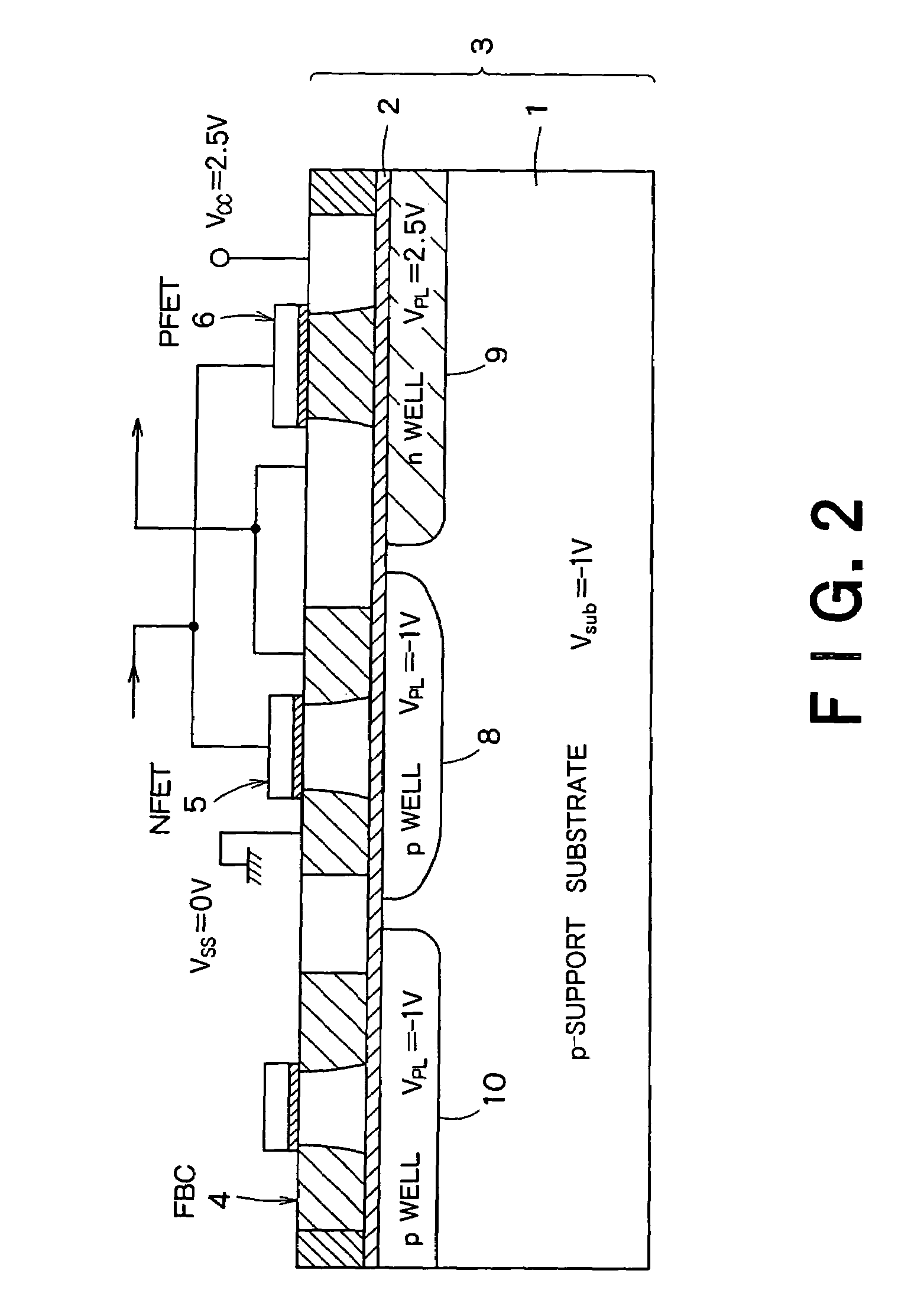
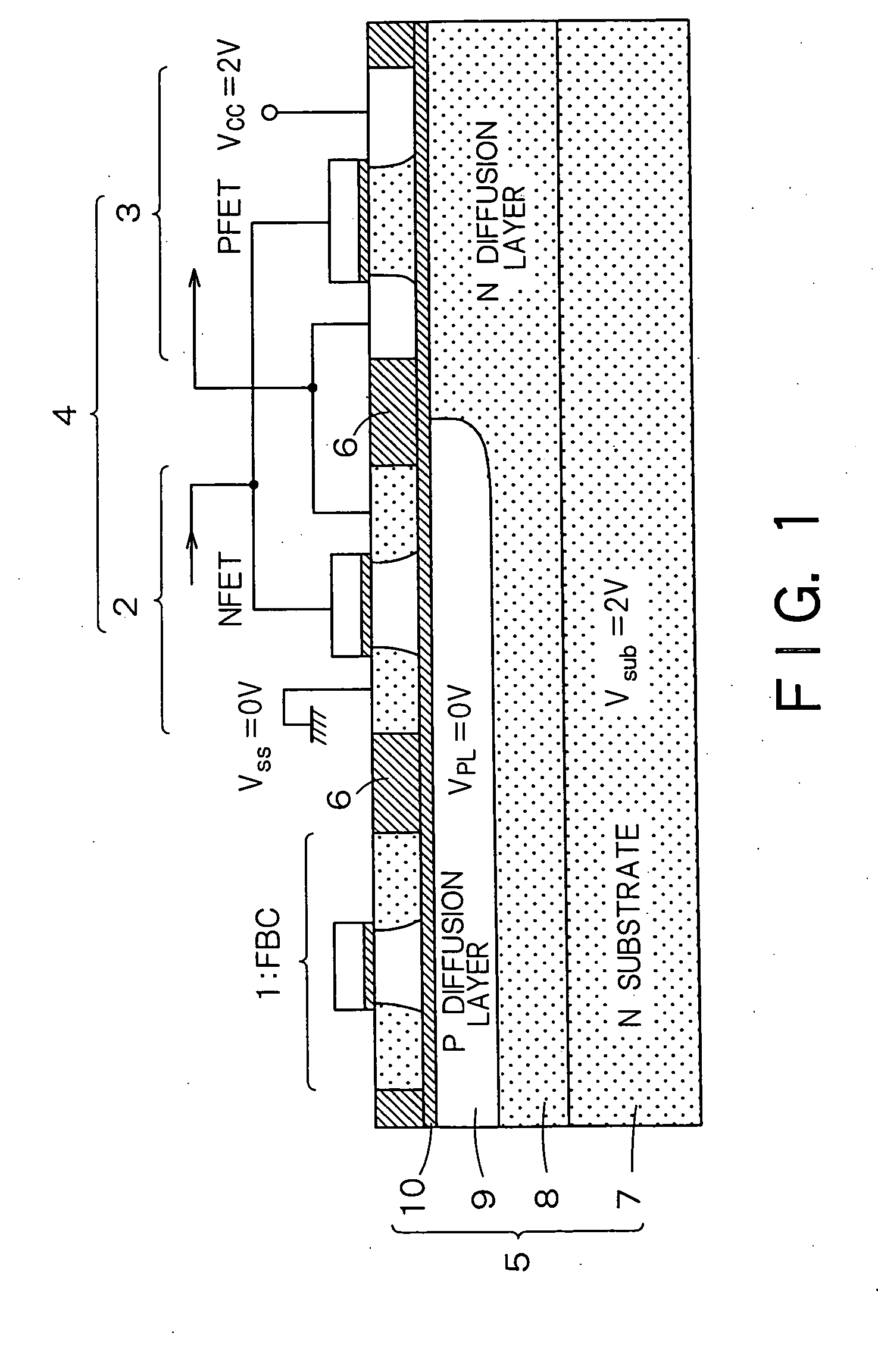
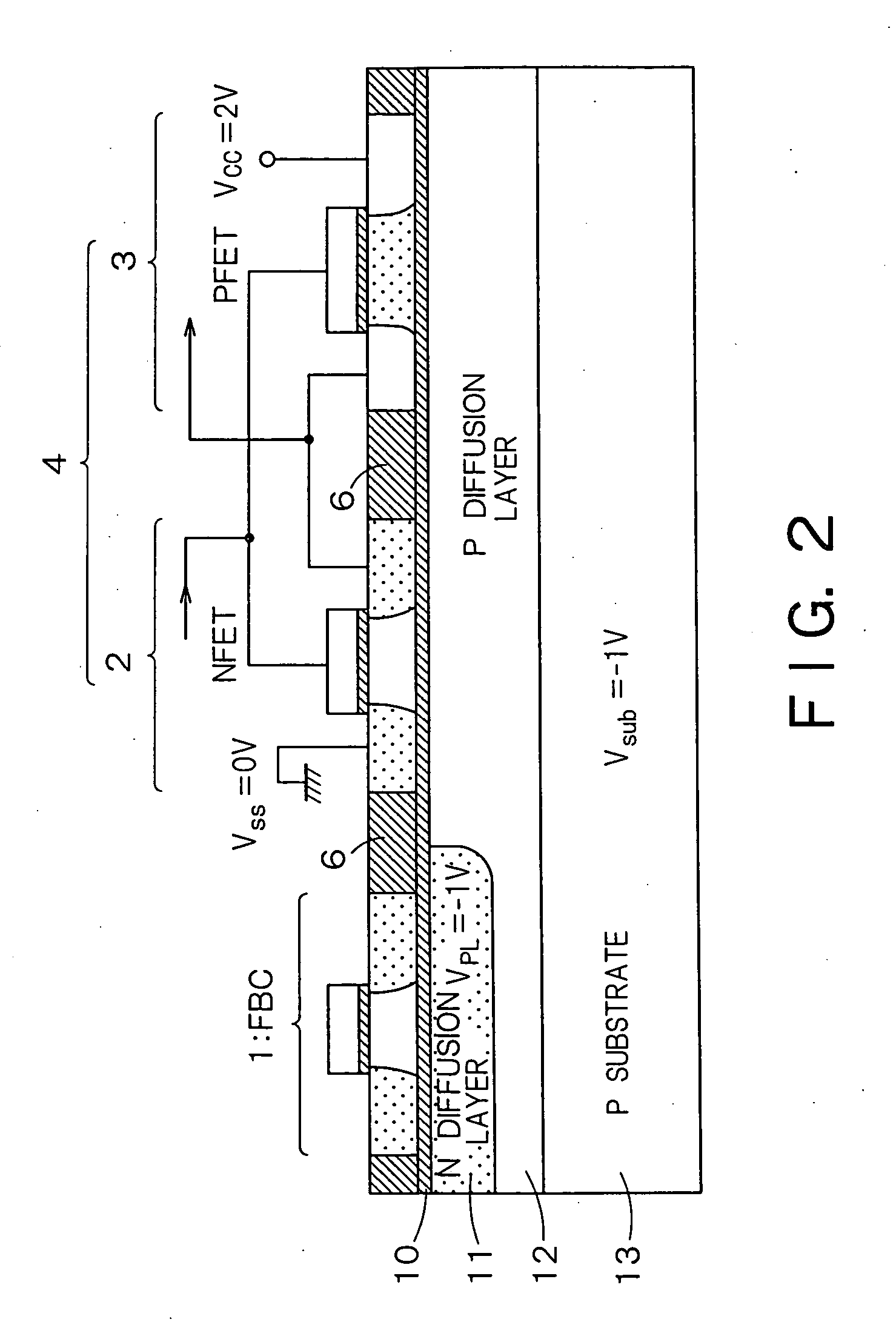
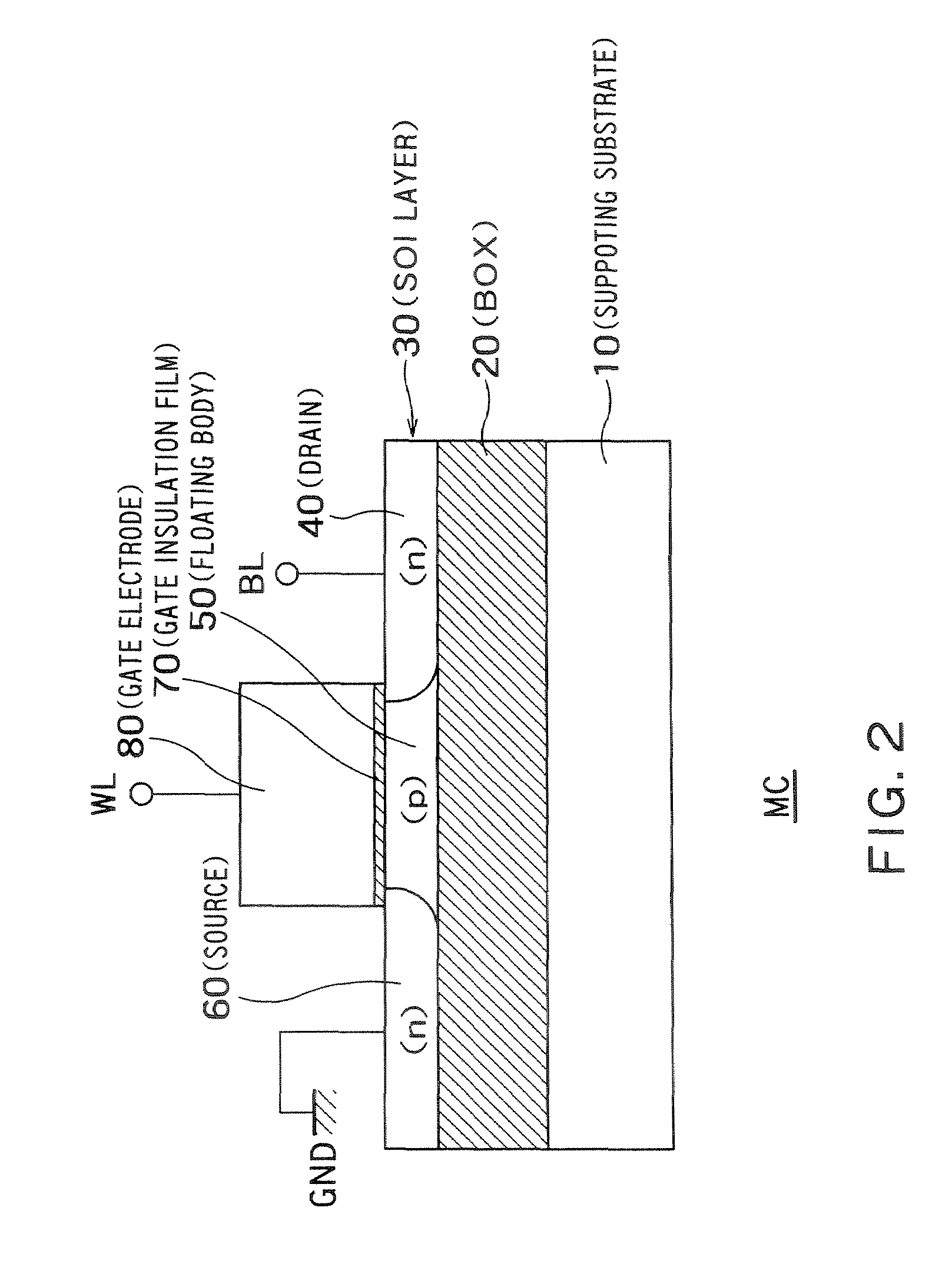
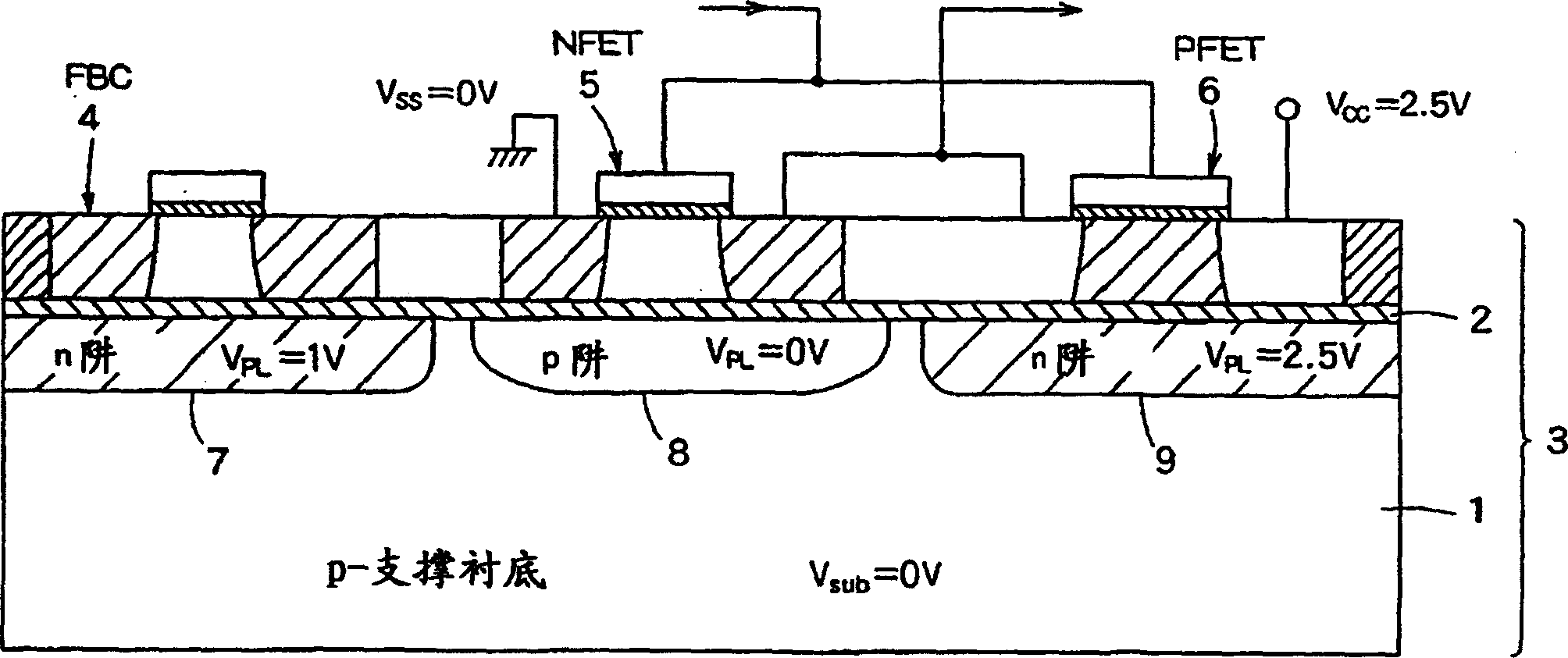
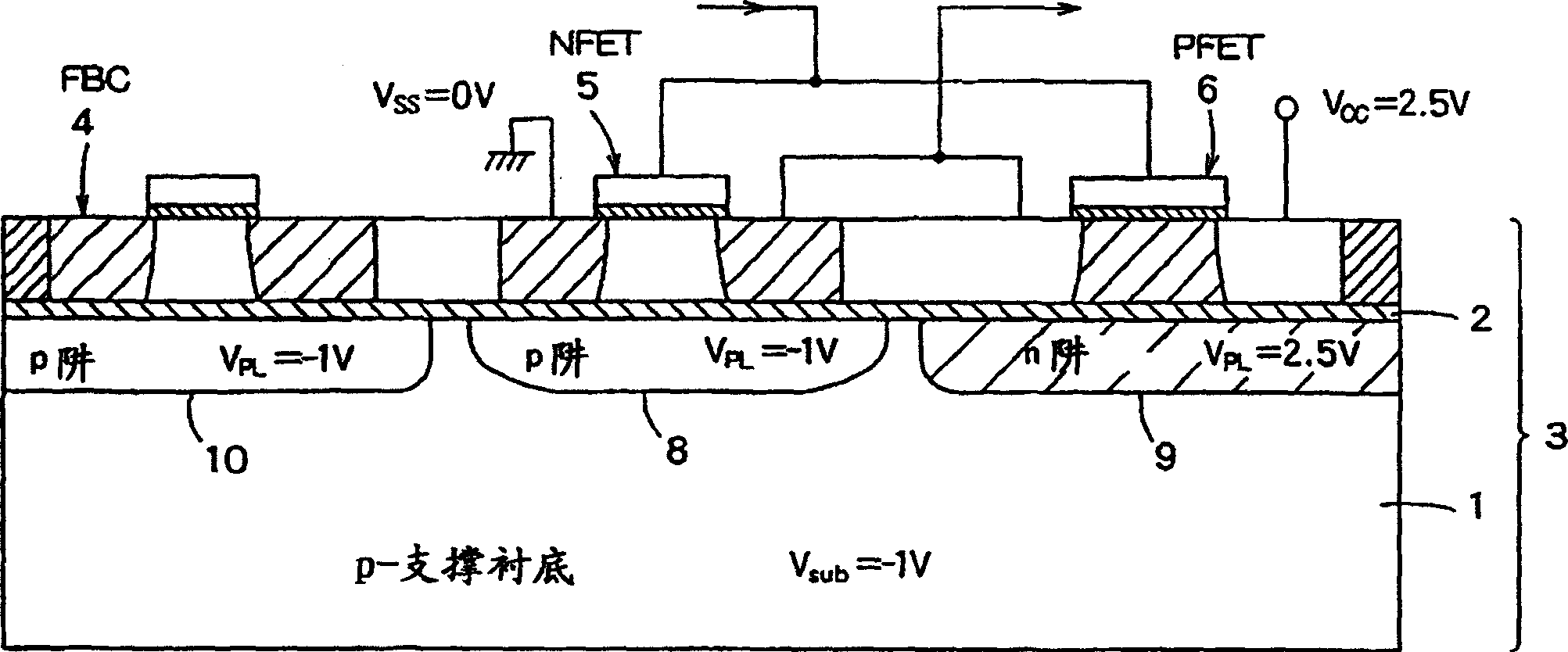
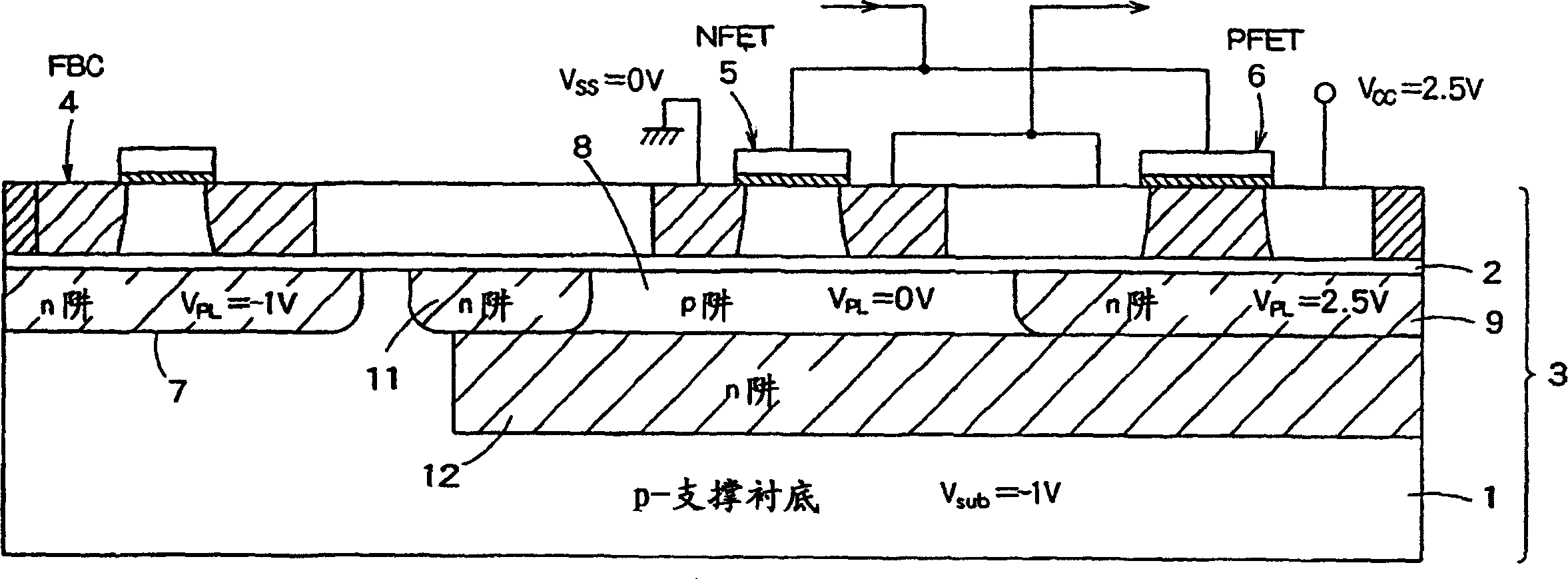
InactiveUS20060046408A1Prevent reversalSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSoi substrateEngineering
A semiconductor integrated apparatus, comprising: an SOI (Silicon On Insulator) substrate which has a support substrate and an embedded insulation film; an NMOSFET, a PMOSFET and an FBC (Floating Body Cell) formed on the SOI substrate separately from each other; a p type of first well diffusion region formed along the embedded insulation film in the support substrate below the NMOSFET; an n type of second well diffusion region formed along the embedded insulation film in the support substrate below the PMOSFET; and a conduction type of third well diffusion region formed along the embedded insulation film in the support substrate below the FBC.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Semiconductor integrated circuit device
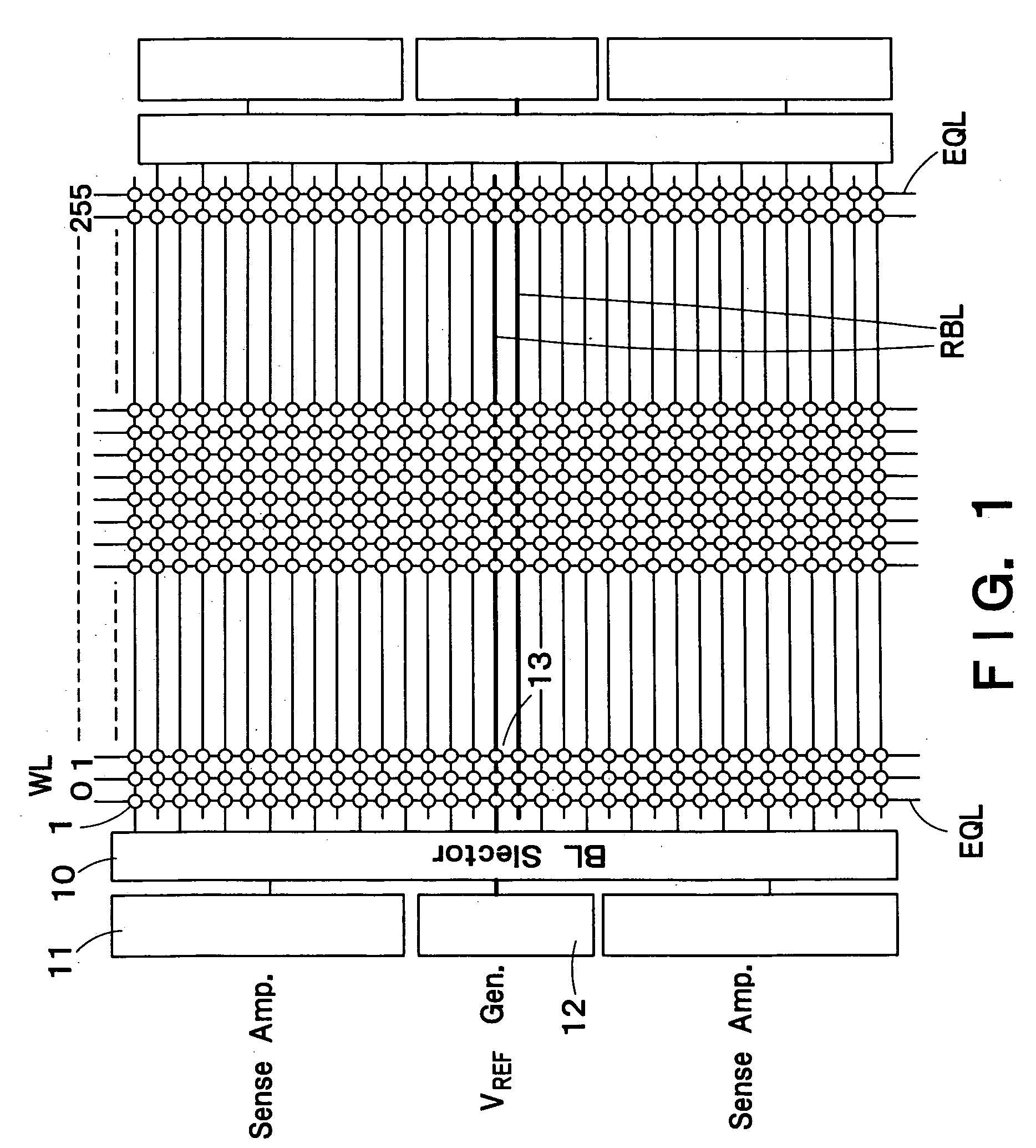
A semiconductor integrated circuit device, comprising: a semiconductor layer formed via an embedded insulation film on a substrate; an FBC (Floating Body Cell) which stores data by accumulating a majority carrier in a floating channel body formed on the semiconductor layer; a reference cell connected to a reference bit line, the reference cell having the same size, shape and electric properties as those of the FBC; an intermediate cell writing control circuit which performs control for writing intermediate potential which is less than data “1” and larger than data “0” in the channel body of the reference cell; and a sense amplifier which performs control for reading out data stored in a selected FBC based on the intermediate data read out from the reference cell.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
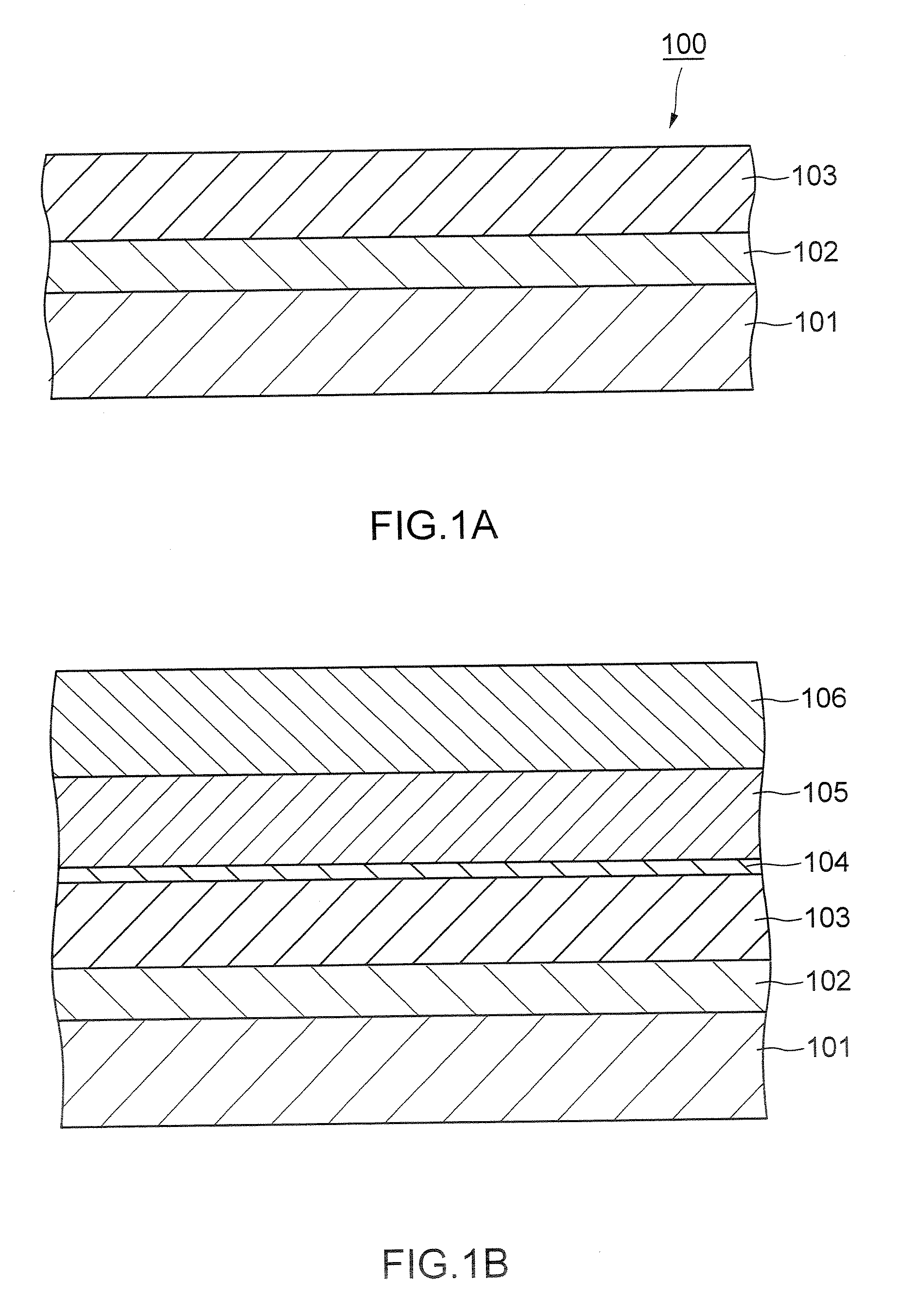
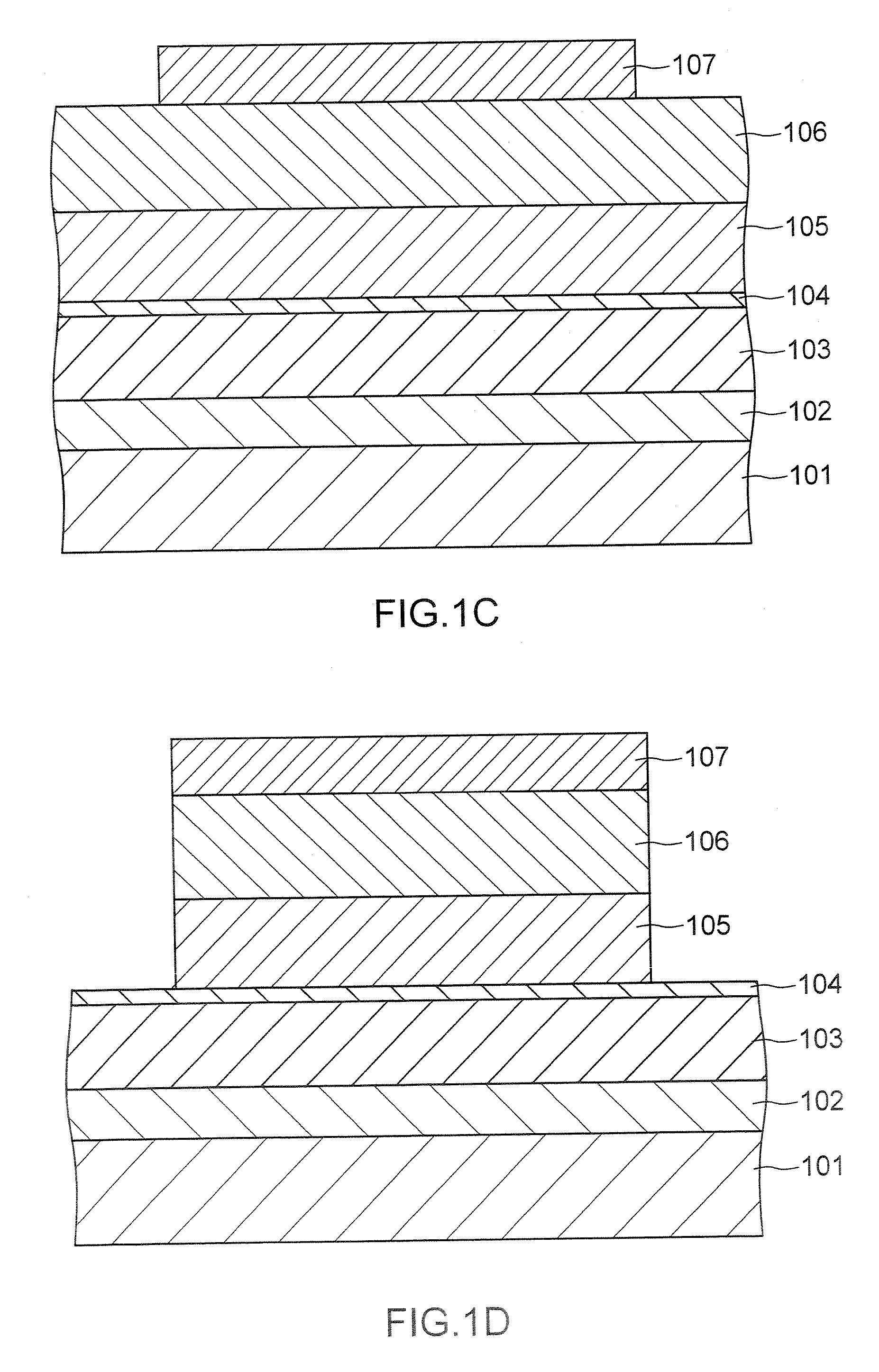
Dynamic random access memory structure and method for preparing the same
ActiveUS20070158719A1Improve integrityLong retention timeTransistorSolid-state devicesGate oxideEngineering physics
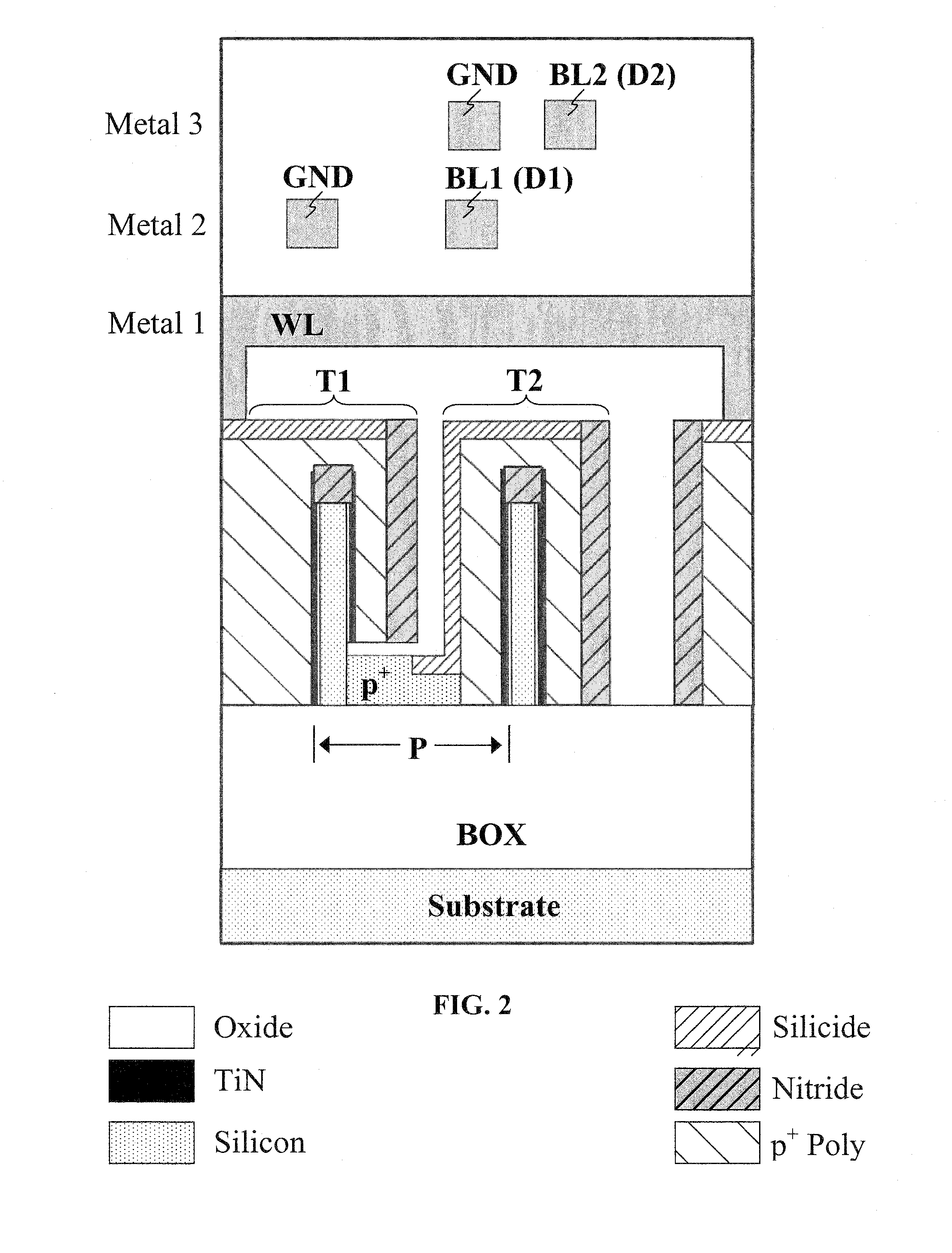
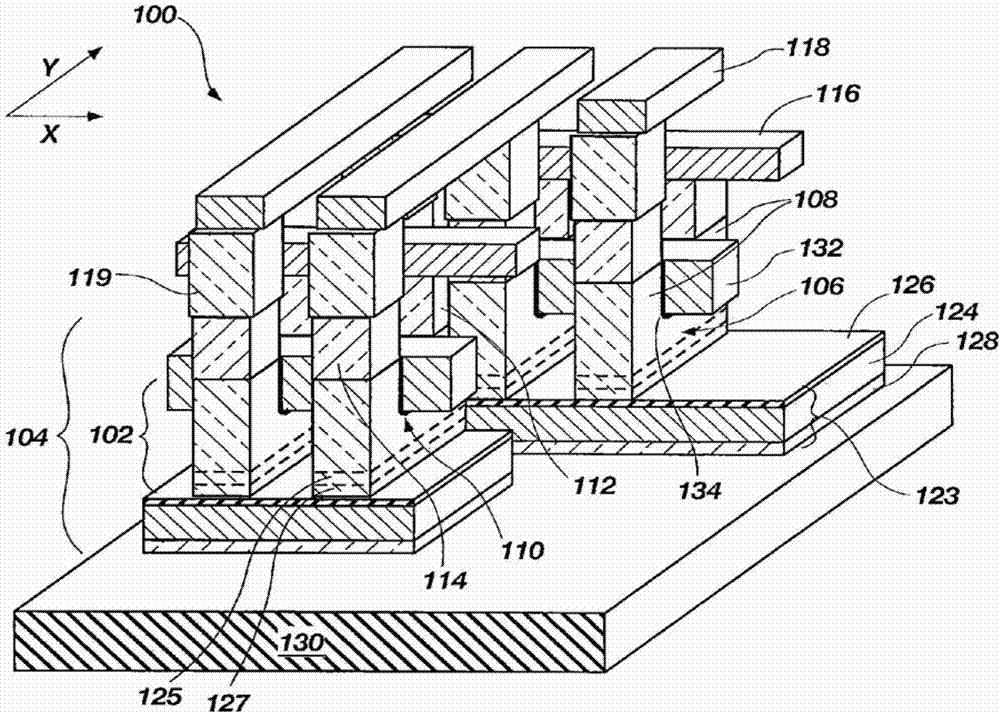
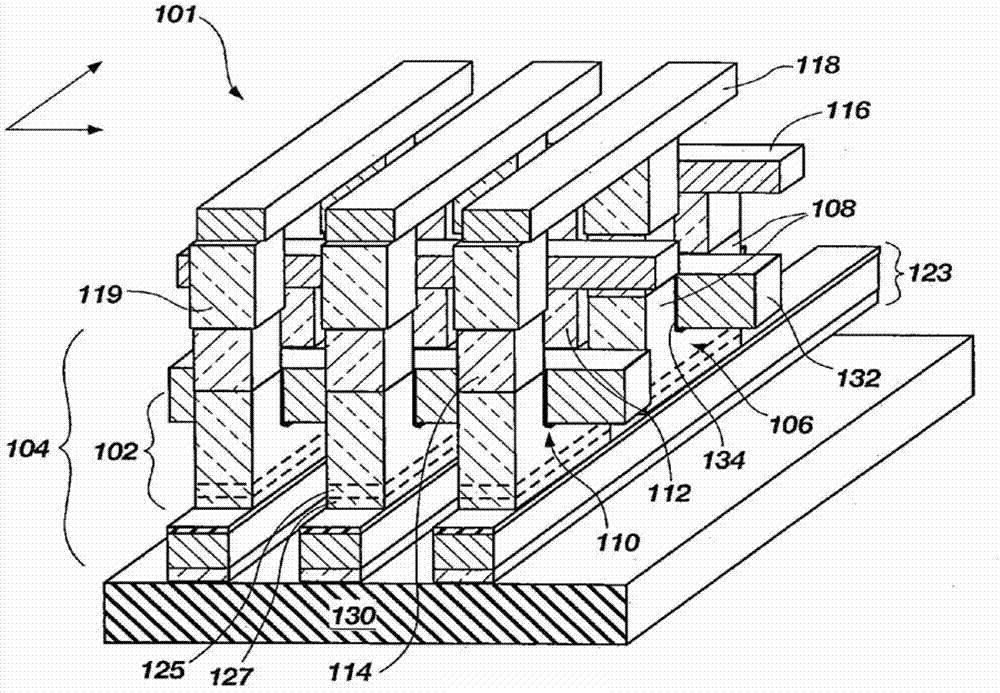
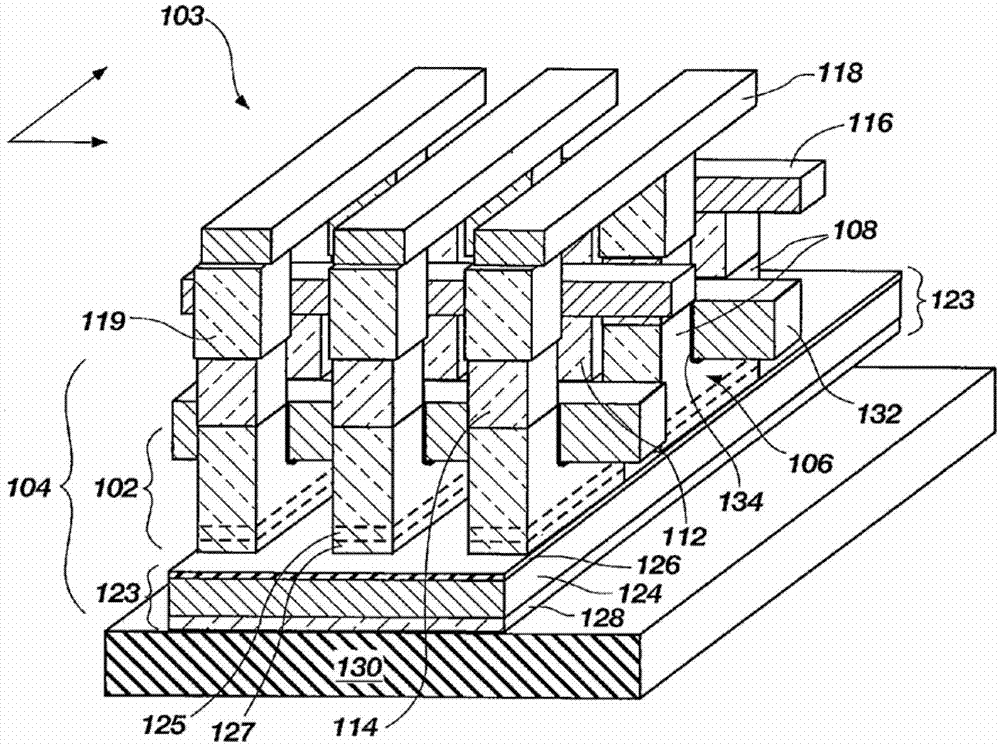
A dynamic random access memory structure having a vertical floating body cell includes a semiconductor substrate having a plurality of cylindrical pillars, an upper conductive region positioned on a top portion of the cylindrical pillar, a body positioned below the upper conductive portion in the cylindrical pillar, a bottom conductive portion positioned below the body in the cylindrical pillar, a gate oxide layer surrounding the sidewall of the cylindrical pillar and a gate structure surrounding the gate oxide layer. The upper conductive region serves as a drain electrode, the bottom conductive region serves as a source electrode and the body can store carriers such as holes. Preferably, the dynamic random access memory structure further comprises a conductive layer positioned on the surface of the semiconductor substrate to electrically connect the bottom conductive regions in the cylindrical pillars.
Owner:PROMOS TECH INC
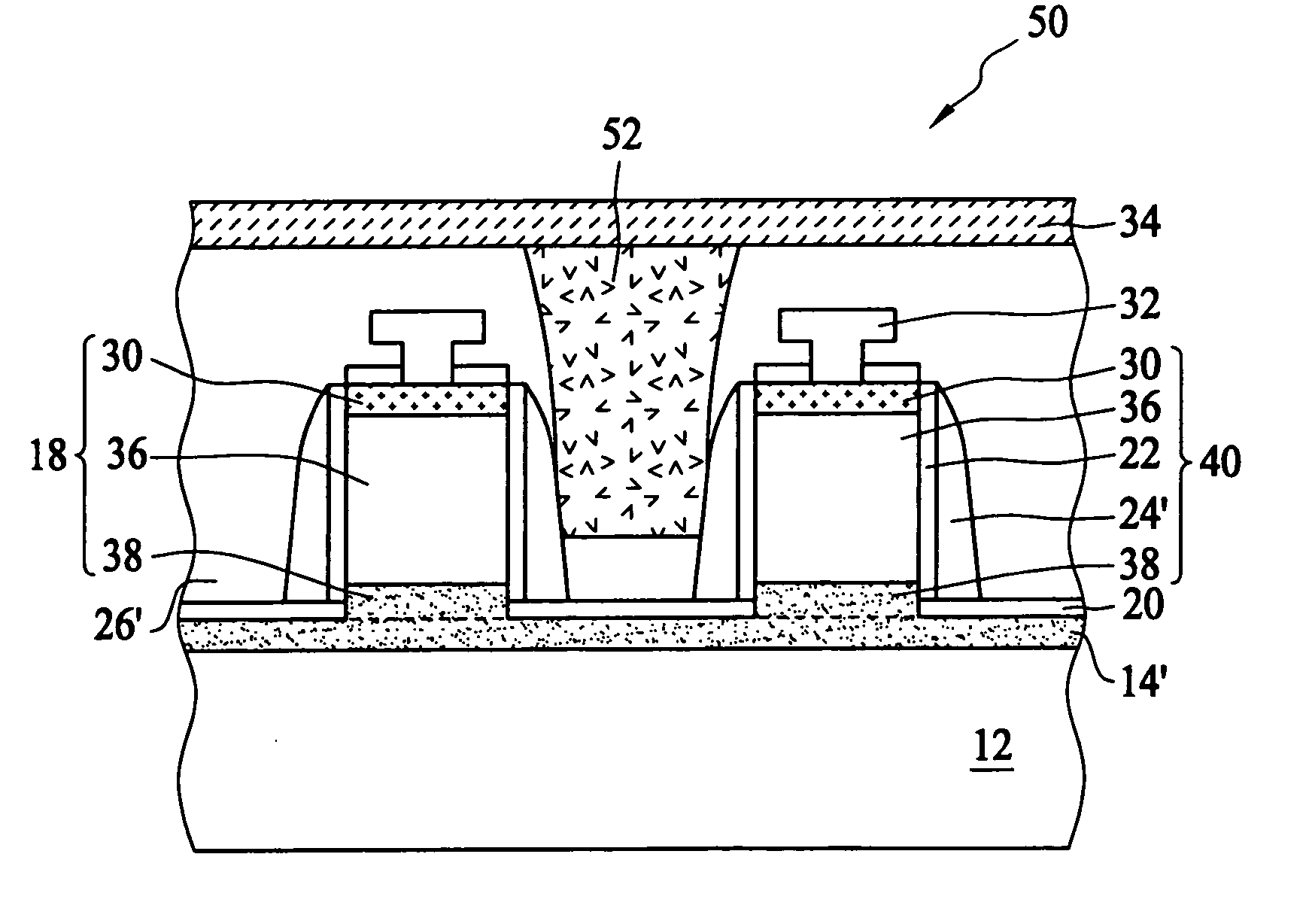
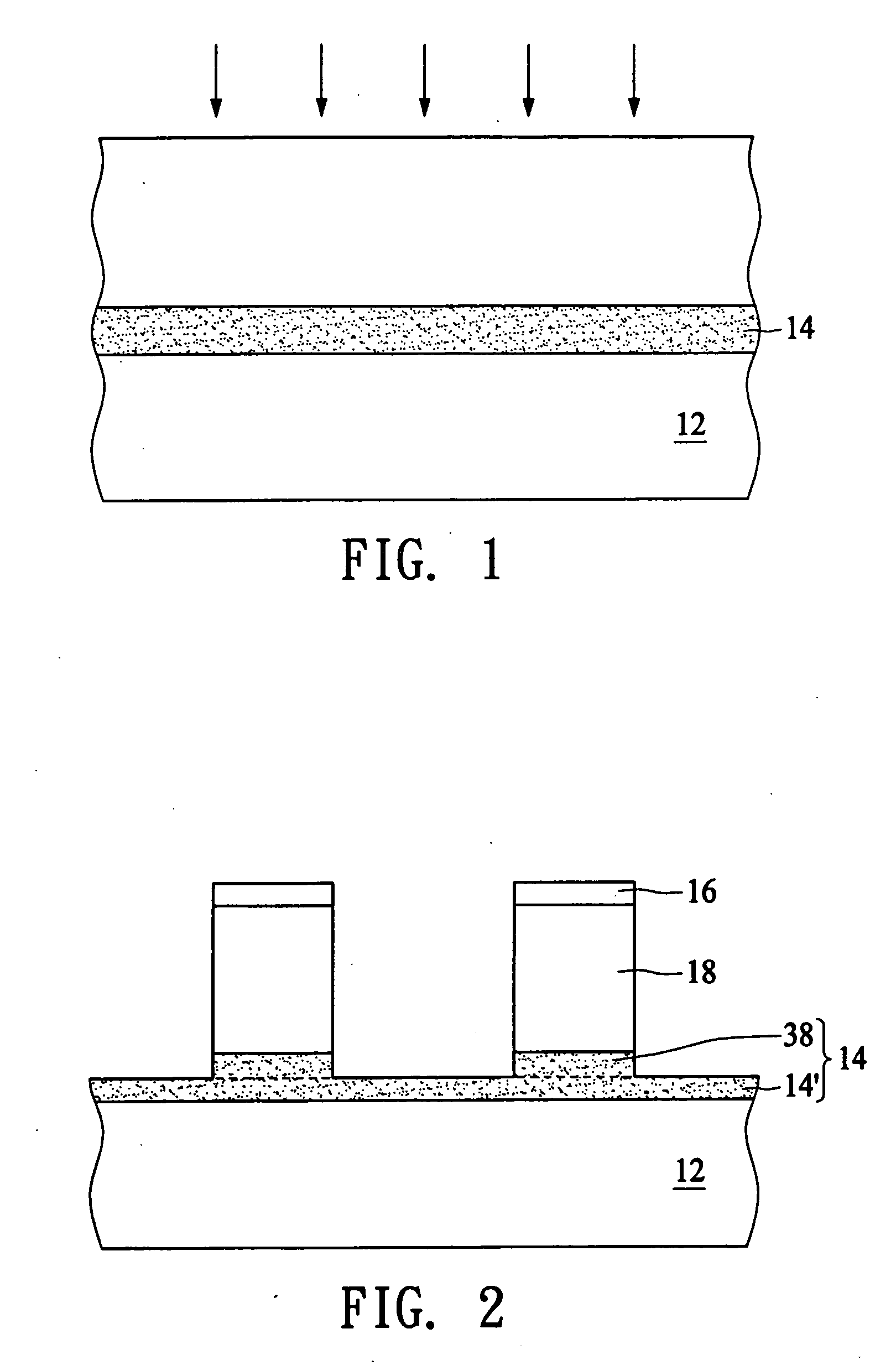
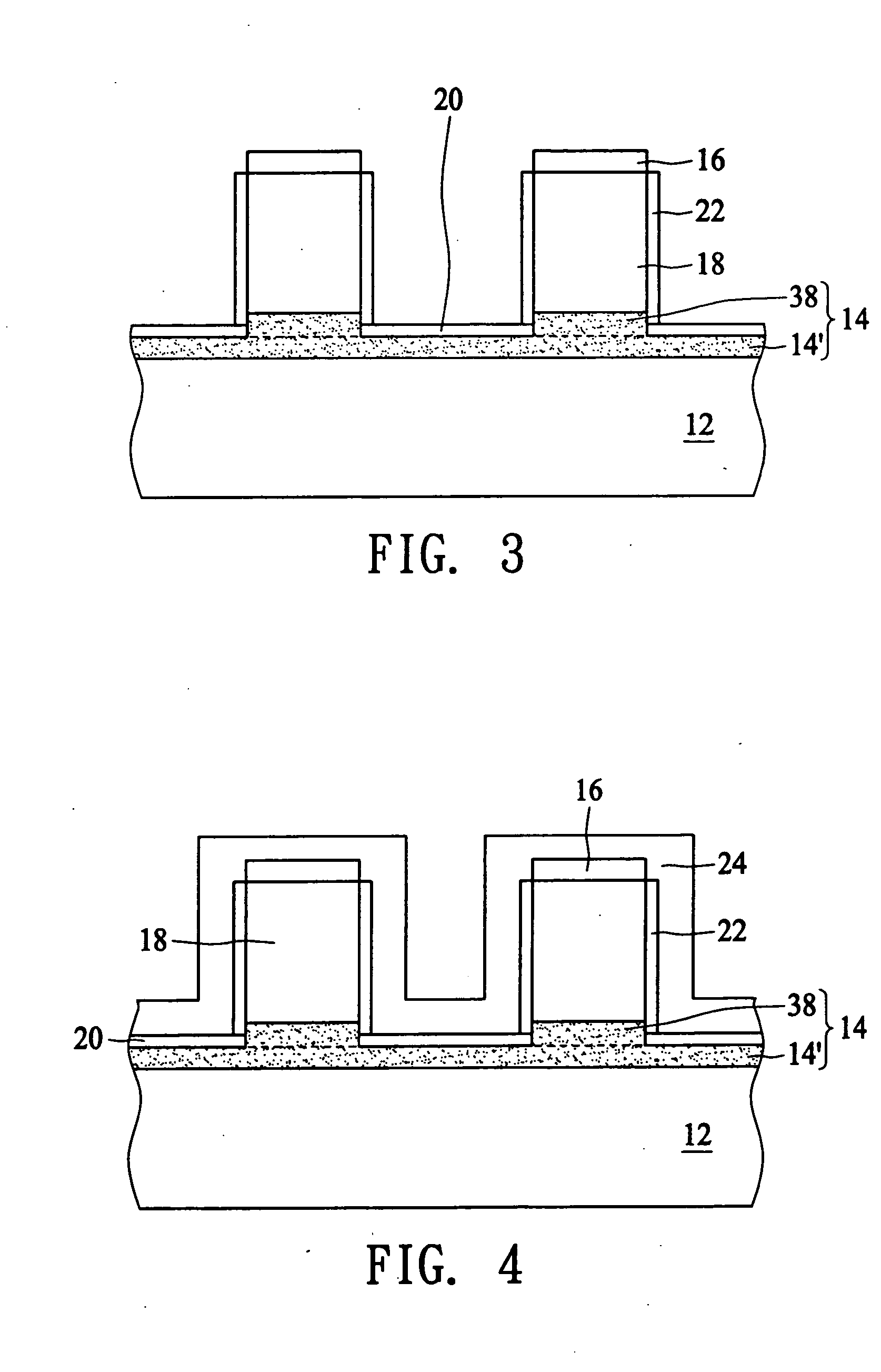
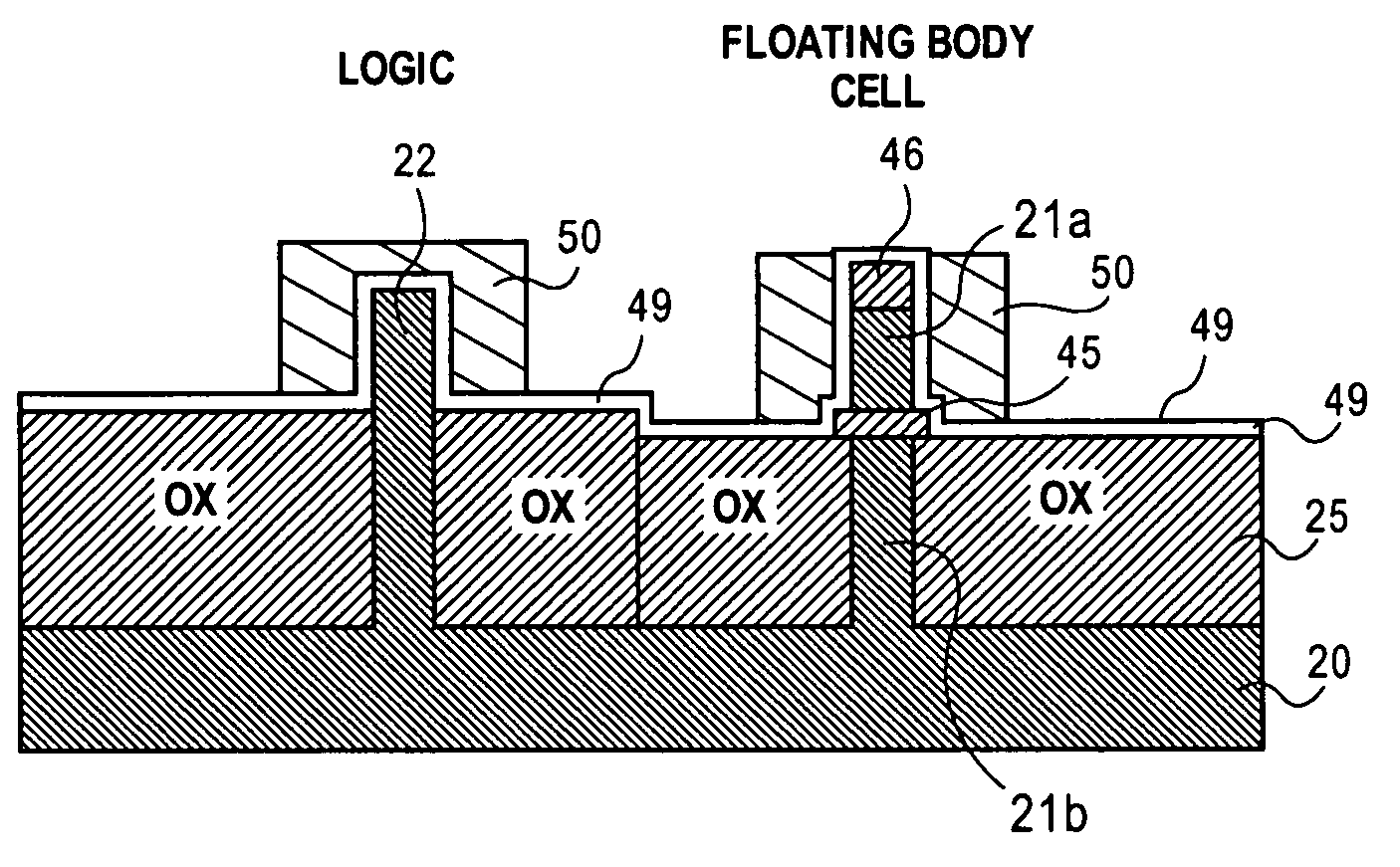
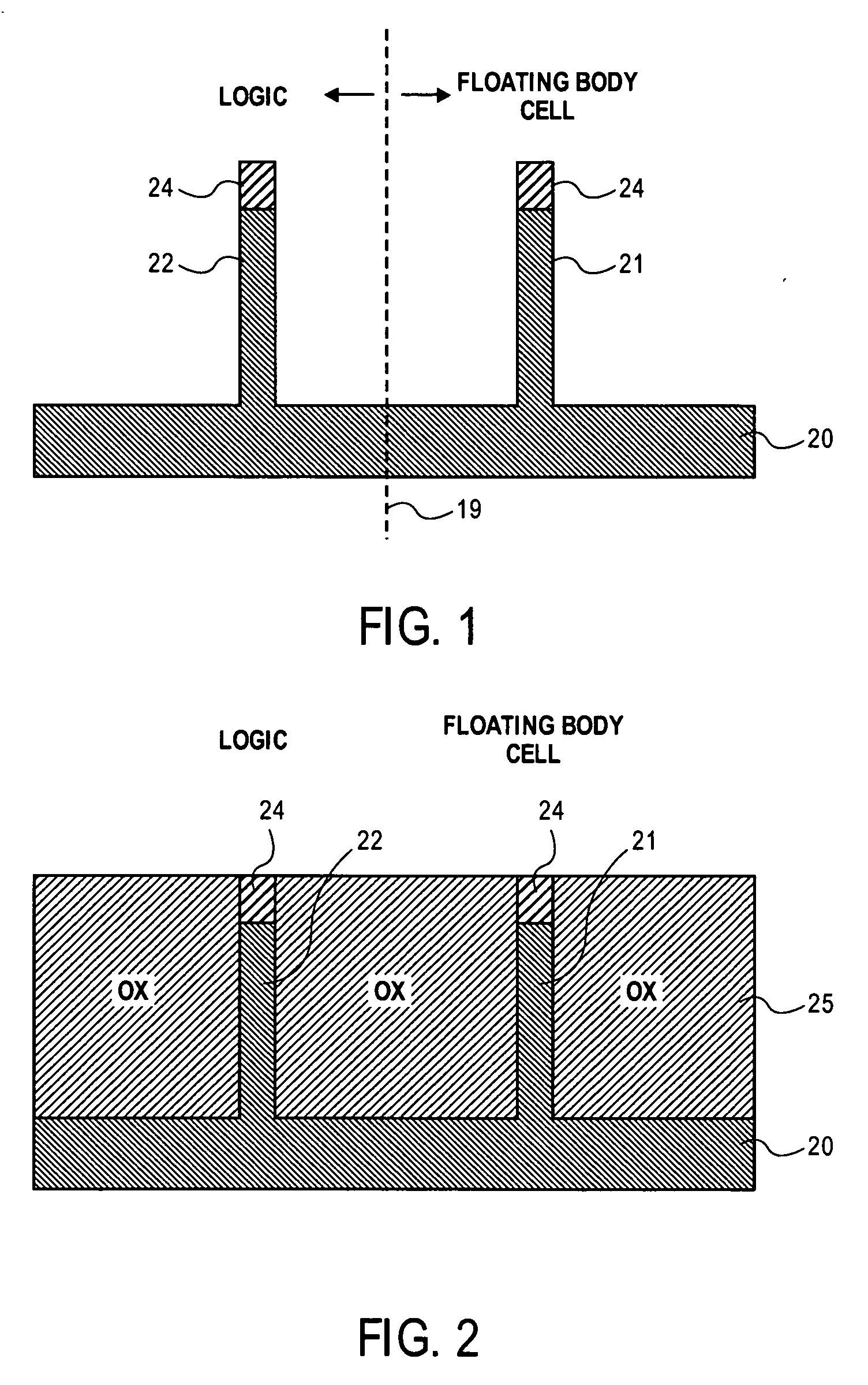
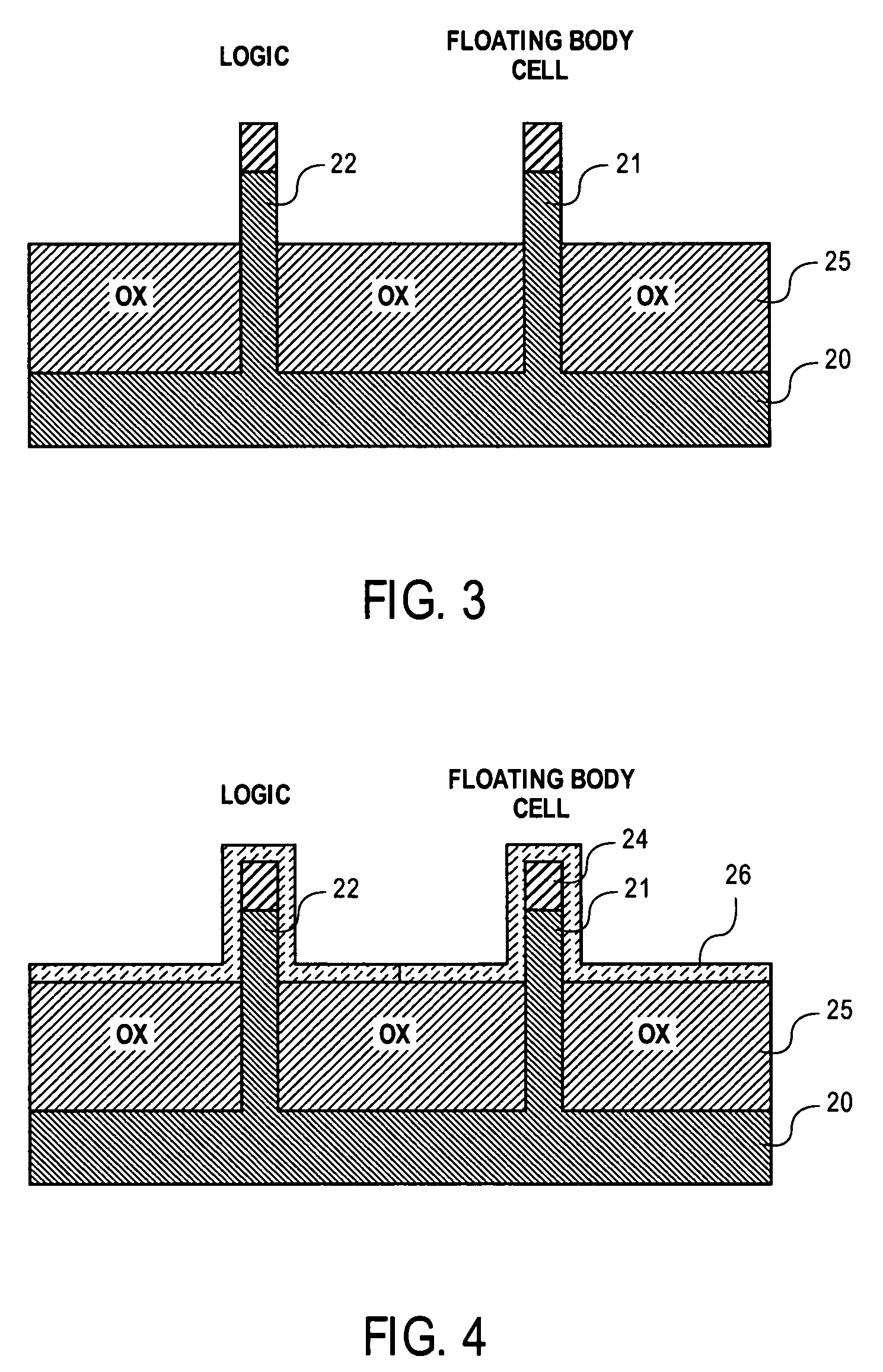
Method of combining floating body cell and logic transistors
An integrated circuit having both floating body cells and logic devices fabricated in a bulk silicon substrate is described. The floating body cells have electrically floating bodies formed by oxidizing a lower portion of the cell bodies to electrically isolate them from the substrate.
Owner:INTEL CORP
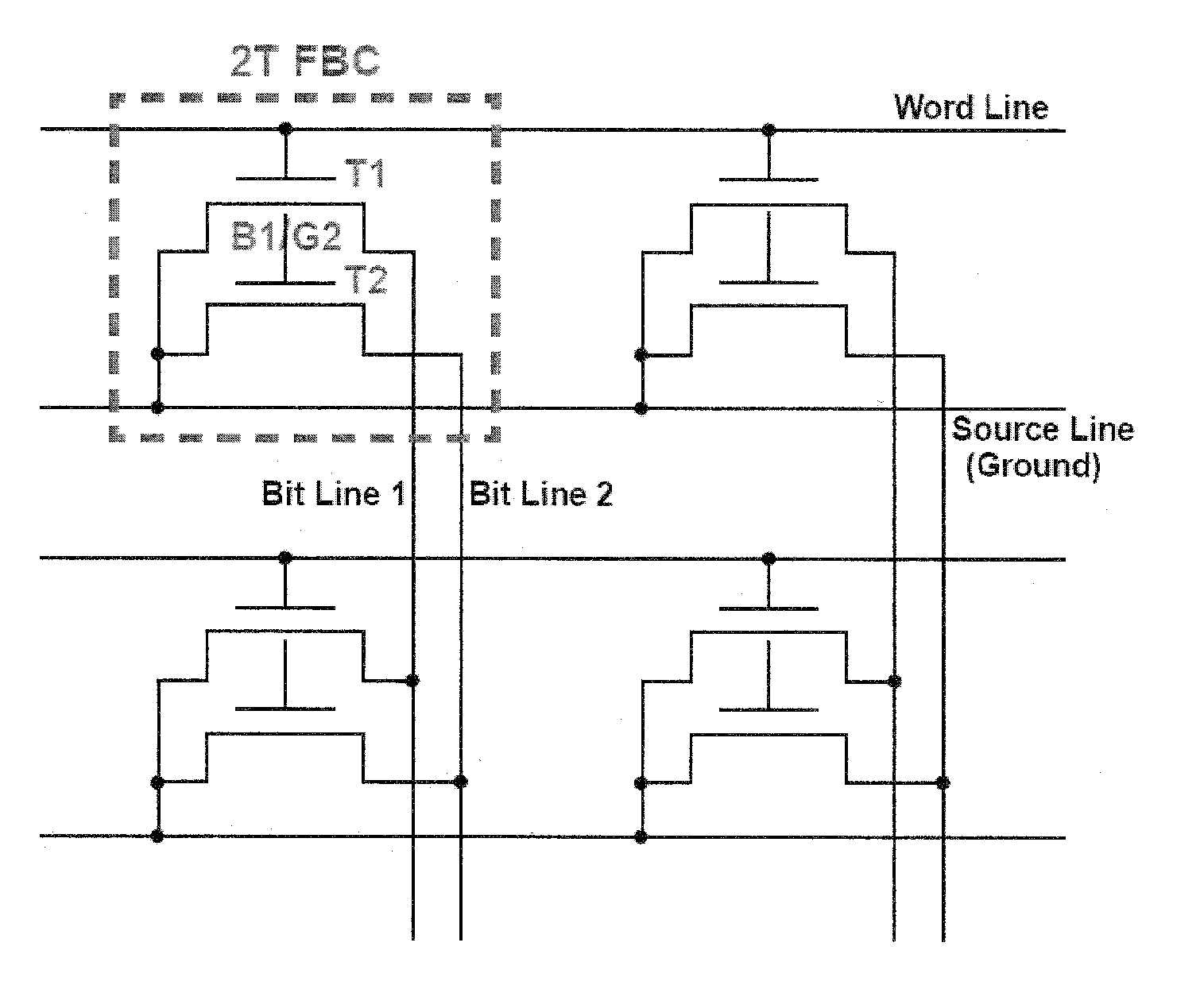
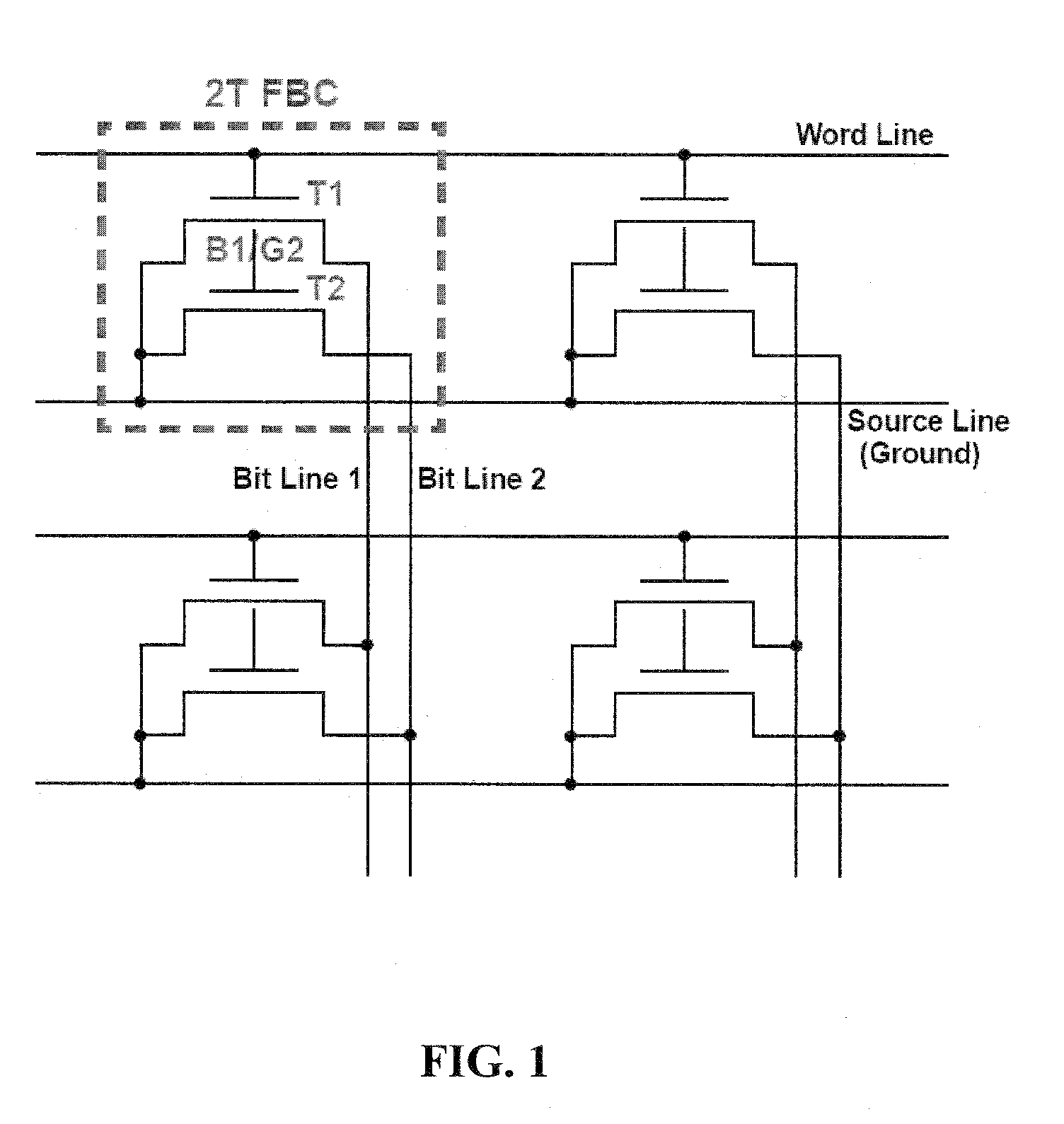
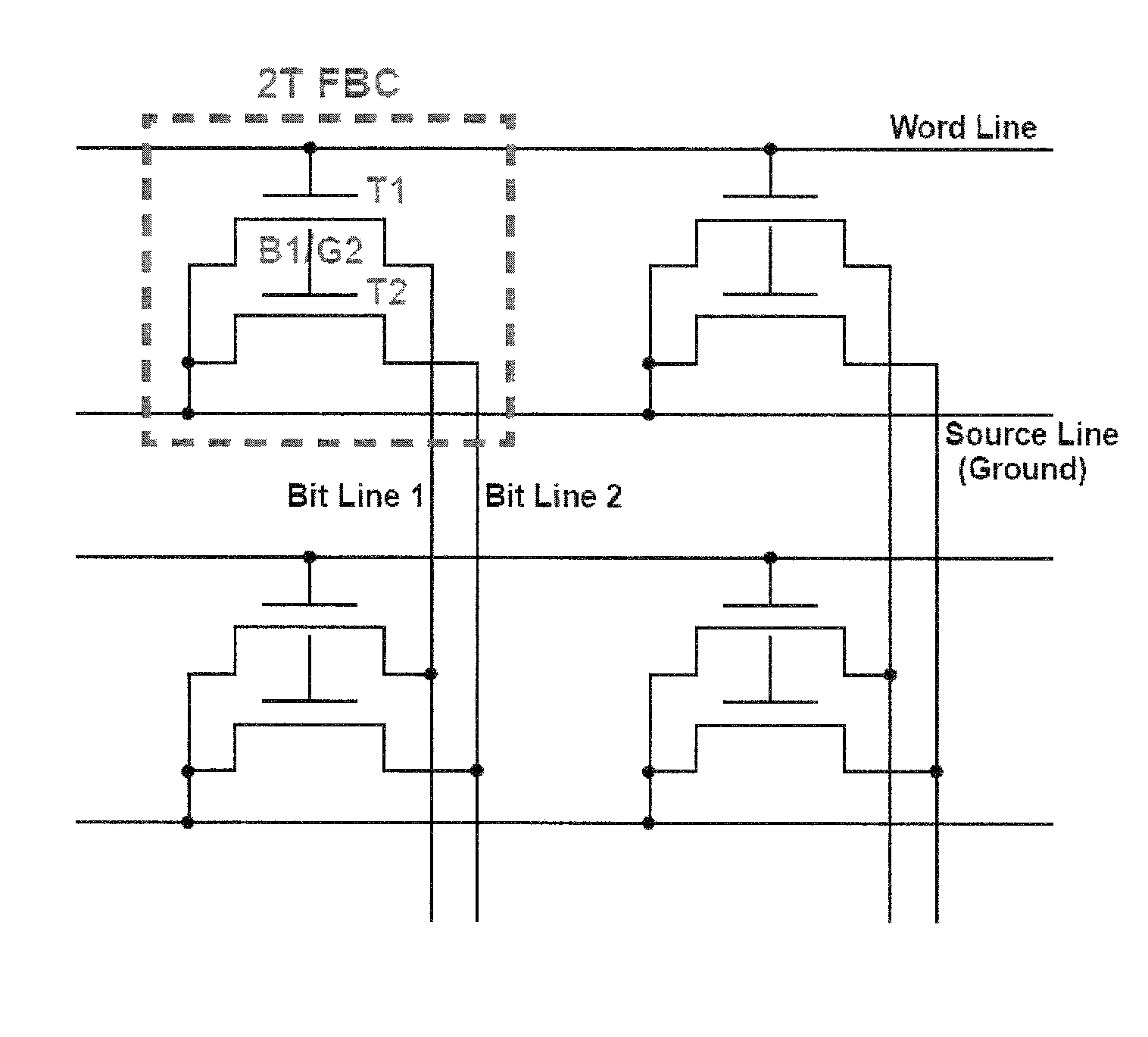
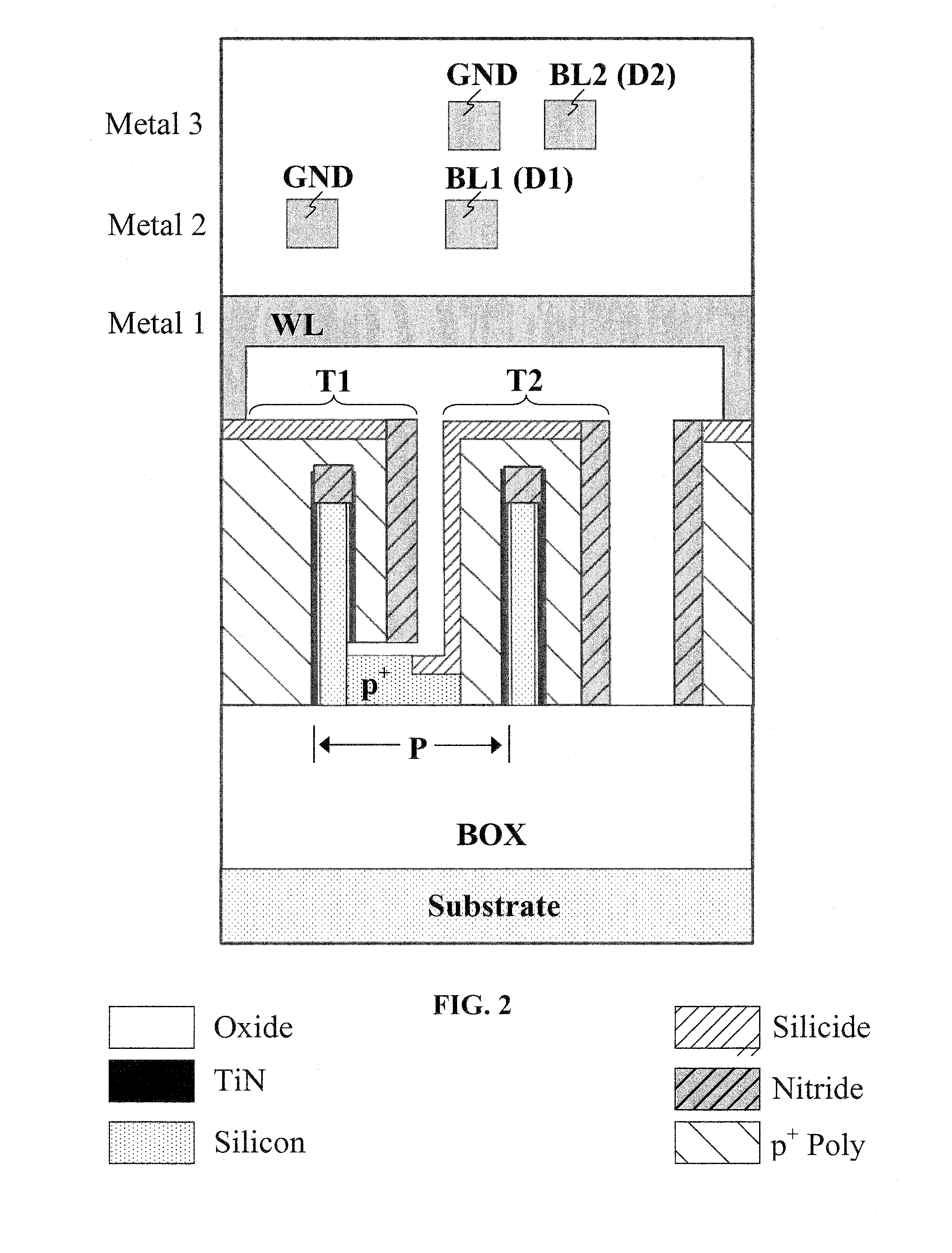
Two-Transistor Floating-Body Dynamic Memory Cell
InactiveUS20100329043A1Improve performanceImprove scalabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesHigh memoryBody dynamics
Embodiments relate to a two-transistor (2T) floating-body cell (FBC) for embedded-DRAM applications. Further embodiments pertain to a floating-body / gate cell (FBGC), which yields reduction in power dissipation, in addition to better signal margin, longer data retention, and higher memory density.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
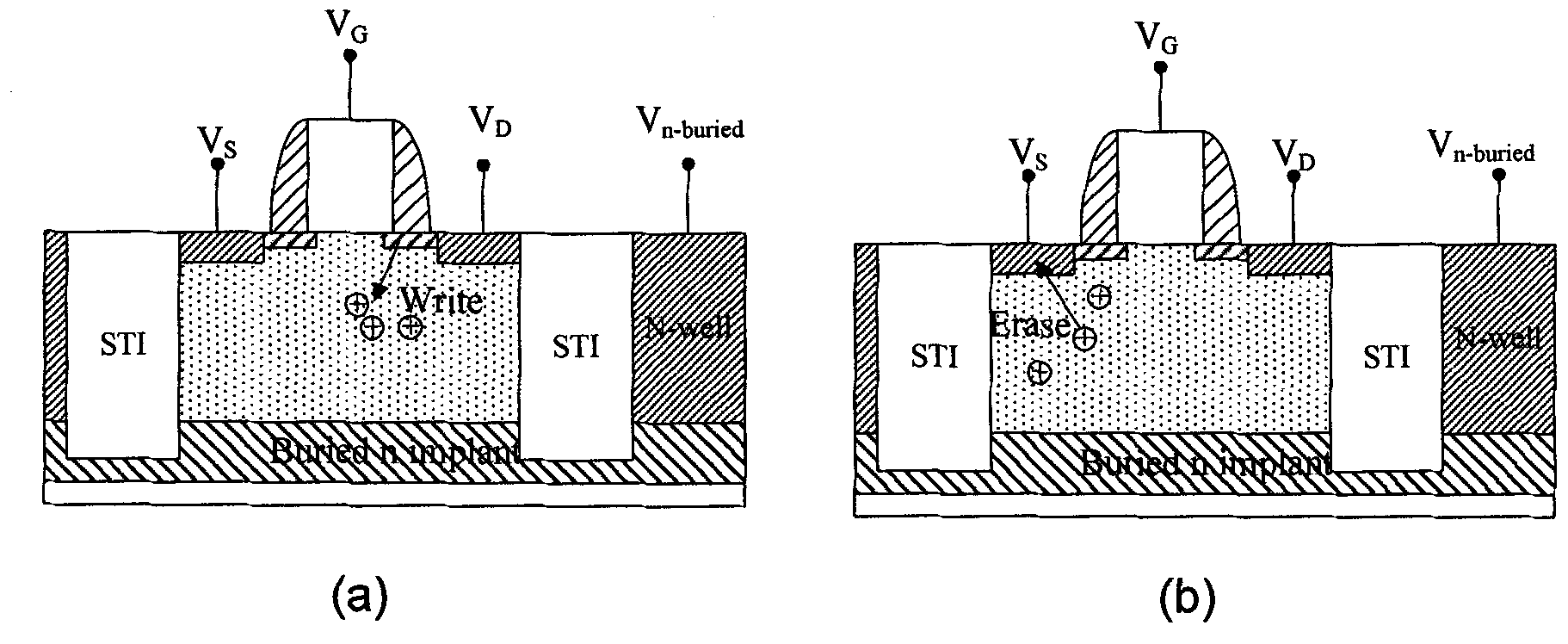
Asymmetric channel doping for improved memory operation for floating body cell (FBC) memory
An improved dynamic memory cell using a semiconductor fin or body is described. Asymmetrical doping is used in the channel region, with more dopant under the back gate to improve retention without significantly increasing read voltage.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Semiconductor storage device and semiconductor integrated circuit
A semiconductor storage device according to the present invention, comprising: a first semiconductor layer formed on a substrate via a buried insulation layer; an FBC (Floating Body Cell) having a channel body of floating type formed on the first semiconductor layer, a main gate which forms a channel at a first face side of the channel body, and an auxiliary gate formed to capacitively couple on a second face at an opposite side of the first face; a logic circuit formed on the first semiconductor layer, separate from the FBC by an insulation film, which transfers a signal for the FBC; a second semiconductor layer which locates below the FBC and is formed along an under face of the buried insulation film; and a third semiconductor layer which locates below the logic circuit and is formed along an under face of the buried insulation film, wherein the second and third semiconductor layers are set to be in a potential different from each other.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Floating body cell memory and reading and writing circuit thereof
A semiconductor integrated circuit device is provided, which includes a semiconductor layer formed via an embedded insulation film on a substrate and an FBC (Floating Body Cell) which stores data by accumulating a majority carrier in a floating channel body formed on the semiconductor layer.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
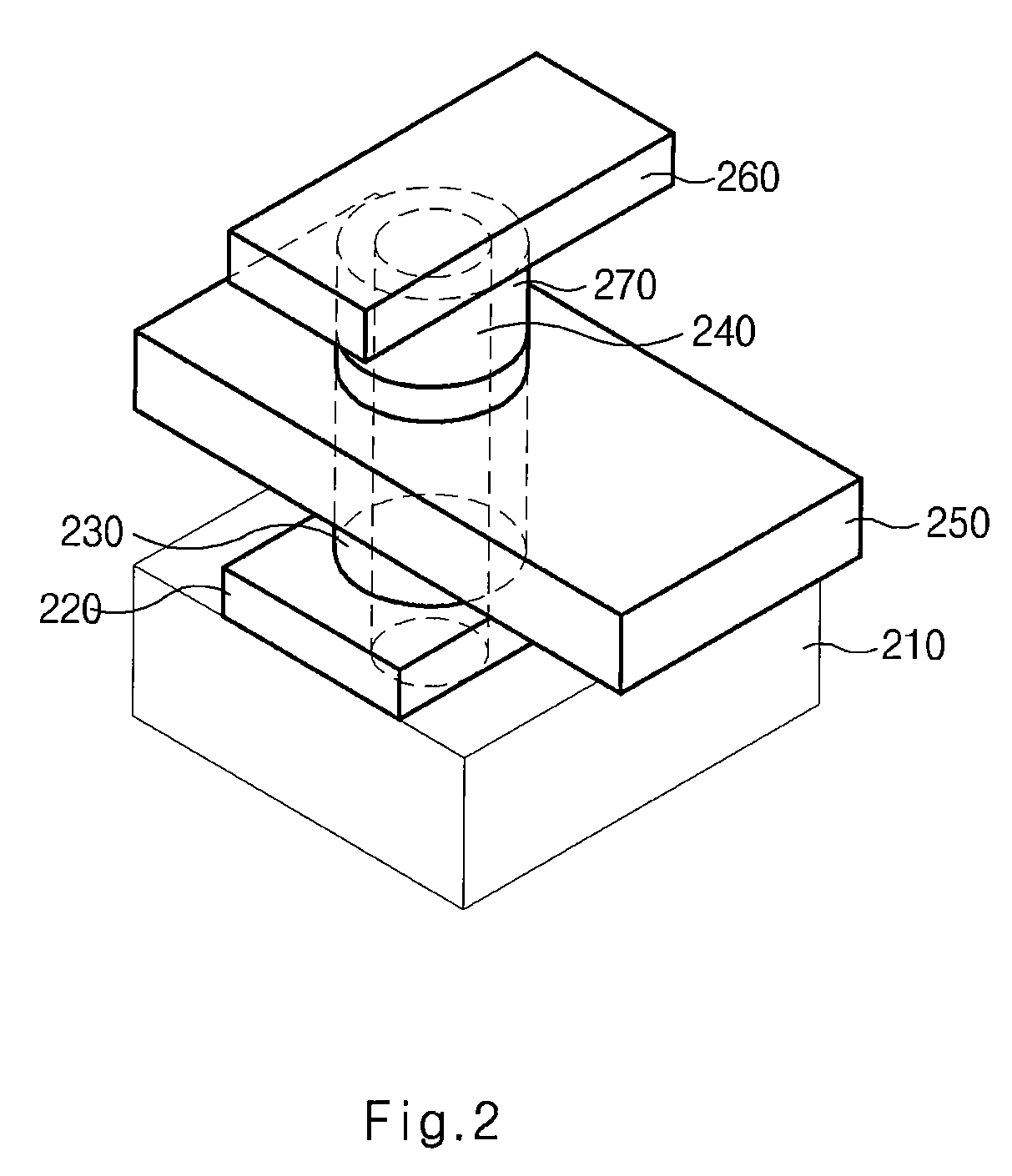
Vertical floating body cell of a semiconductor device and method for fabricating the same
A semiconductor device includes a tube-type channel formed over a semiconductor substrate. The tube-type channel is connected to first and second conductive lines. A bias electrode is formed in the tube-type channel. The bias electrode is connected to the semiconductor substrate. An insulating film is disposed between the tube-type channel and the bias electrode. A surrounding gate electrode is formed over the tube-type channel.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Asymmetric channel doping for improved memory operation for floating body cell (FBC) memory
An improved dynamic memory cell using a semiconductor fin or body is described. Asymmetrical doping is used in the channel region, with more dopant under the back gate to improve retention without significantly increasing read voltage.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Semiconductor storage device
InactiveUS7145811B2Not lower performanceRead-only memoriesDigital storageSemiconductor storage devicesExecution control
A semiconductor storage device according to one embodiment of the present invention, comprising: FBCs (Floating Body Cells) which store data by accumulating a majority carrier in a floating channel body; and sense amplifiers which perform control reading out data stored in said FBC, wherein each of said sense amplifier includes: a pair of sense nodes provided corresponding to a bit line pair to which said FBC is connected; a pair of load which flow currents through said pair of sense nodes; latch circuits which latch potentials of said pair of sense nodes when a potential difference between said pair of sense nodes reaches a predetermined value; and an output control circuit which outputs latched outputs of said latch circuits at a predetermined timing and feeds back the latched outputs to said bit line pair side to again write it into said FBC.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
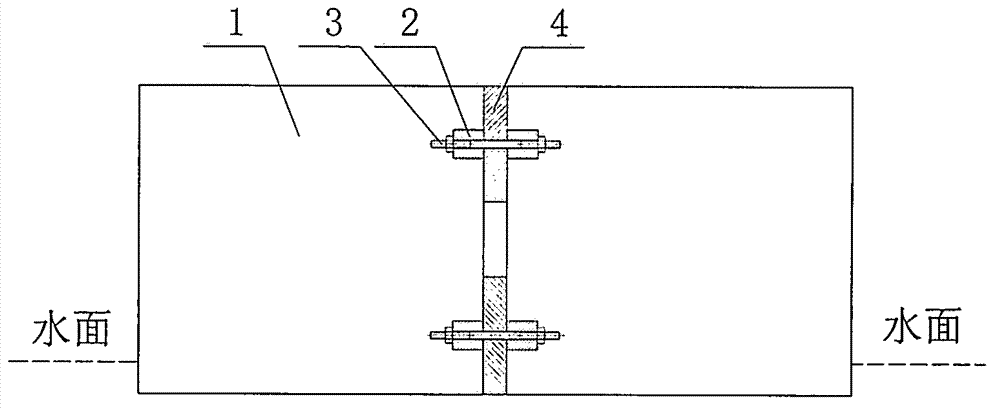
Floating structure connected by tension connector with adjustable length
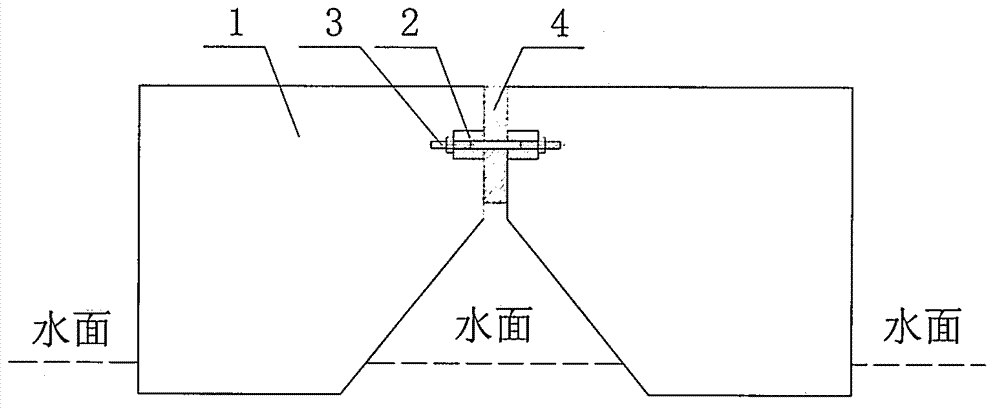
InactiveCN102787552AService life is no longer governed by the fatigue life of the jointManufacturing precision requirements are lowBridge structural detailsFloating bridgesPull forceEngineering
The invention discloses a floating structure connected by a tension connector with adjustable length. Floating body cells are connected by the tension connector with adjustable length, and elastic buffer material is installed among the floating body cells; a pull force is borne by the tension connector; a pressure is borne by the elastic buffer material and the floating body cells; and a shear force is borne by an inclined tension connector which forms an angle with a connection surface. Both a rigid joint and a hinge joint of the combined floating structure have certain elasticity and can bear a large wave load. Because the length of the tension connector can be adjusted and the requirement on the manufacturing precision of the floating body cells is low, bigger floating body cells can be used so that a bigger floating structure can be combined. Because of being not welded together with the floating body cells, the tension connector can be changed so that the service life of the floating structure is not limited by the fatigue life of the connector.
Owner:吴广怀
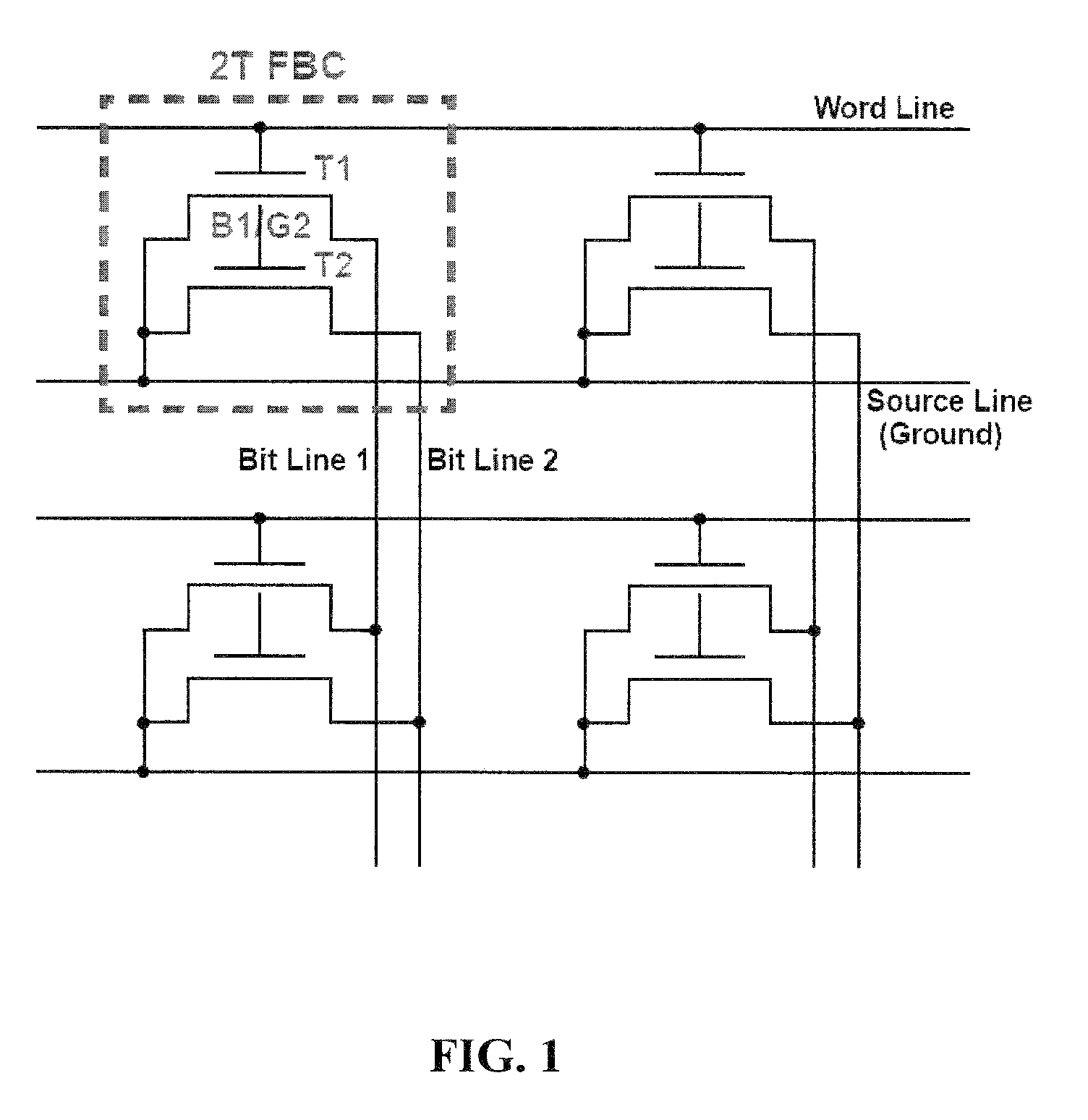
Two-transistor floating-body dynamic memory cell
InactiveUS8498140B2Improve performanceImprove scalabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesHigh memoryBody dynamics
Embodiments relate to a two-transistor (2T) floating-body cell (FBC) for embedded-DRAM applications. Further embodiments pertain to a floating-body / gate cell (FBGC), which yields reduction in power dissipation, in addition to better signal margin, longer data retention, and higher memory density.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
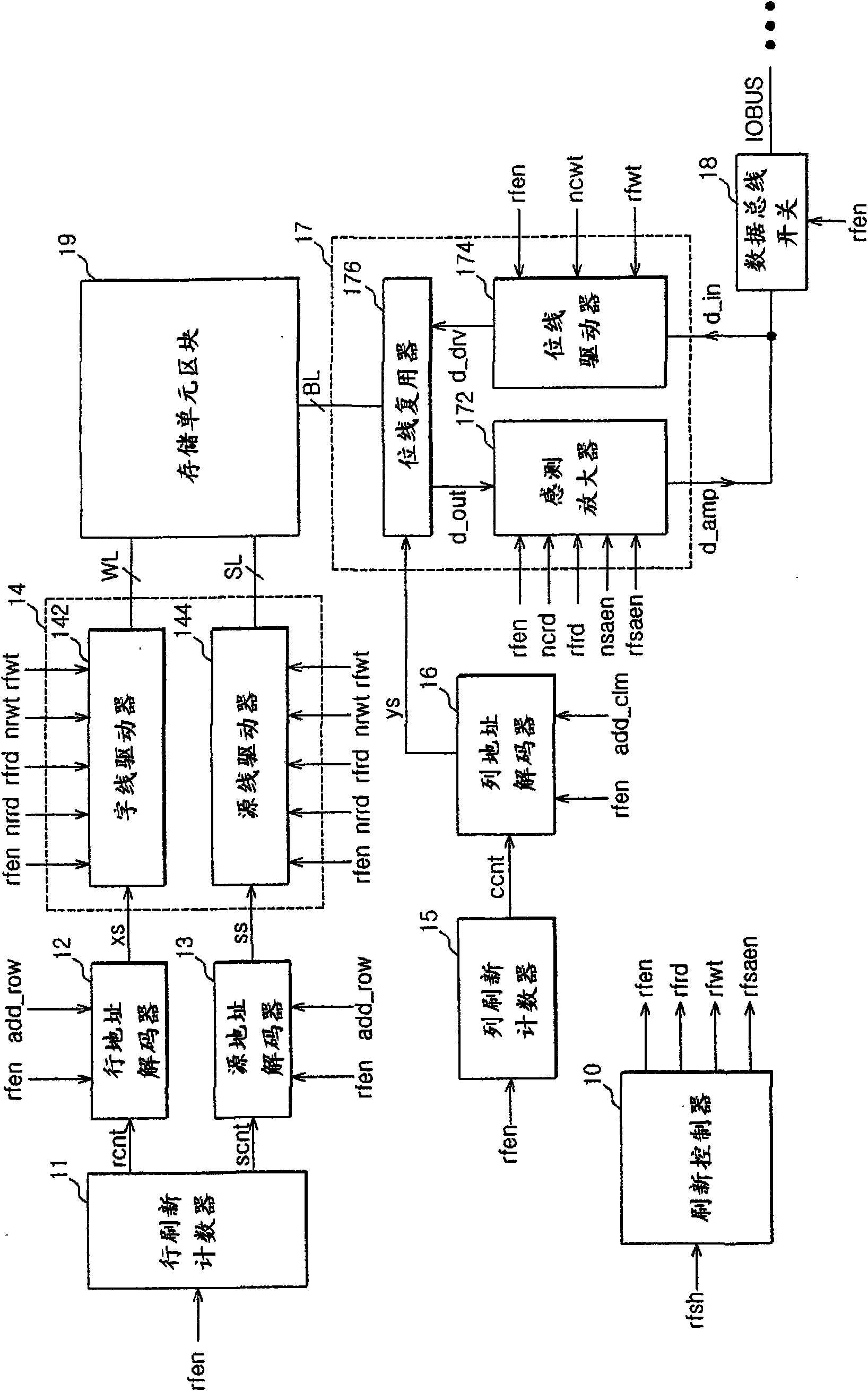
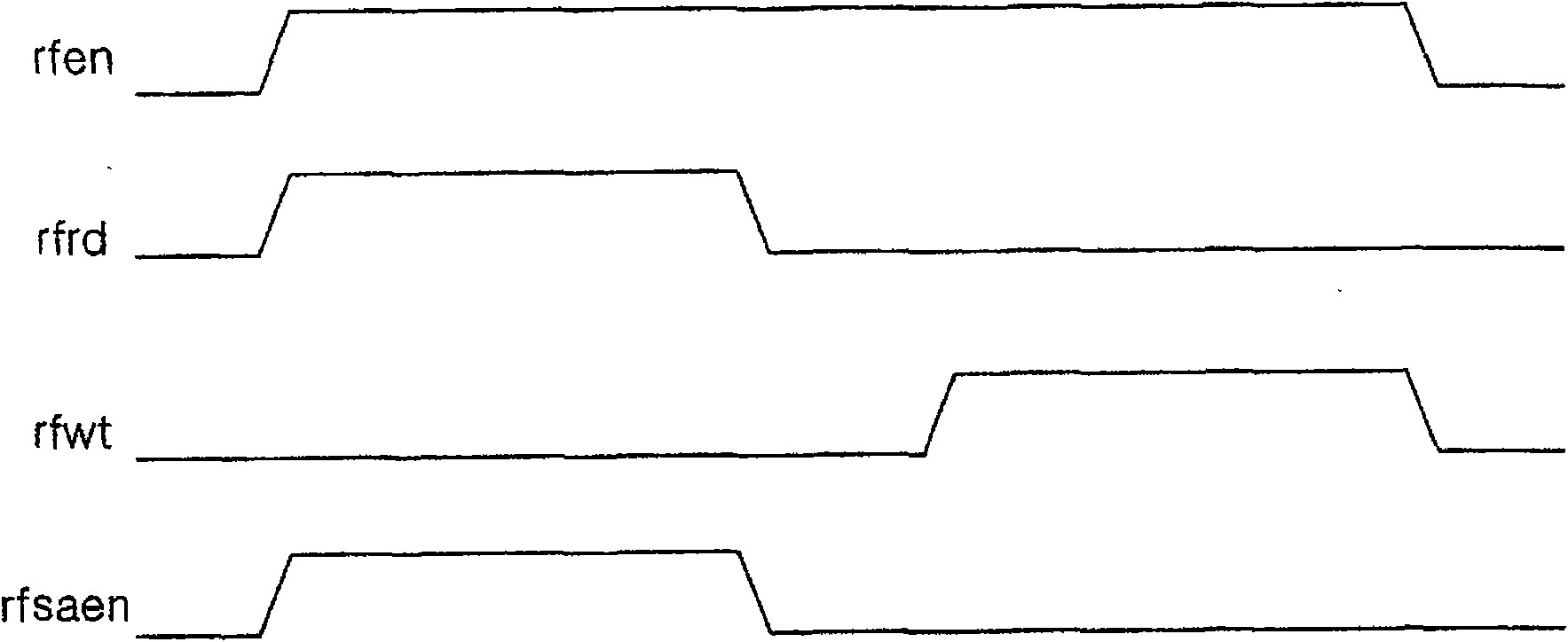
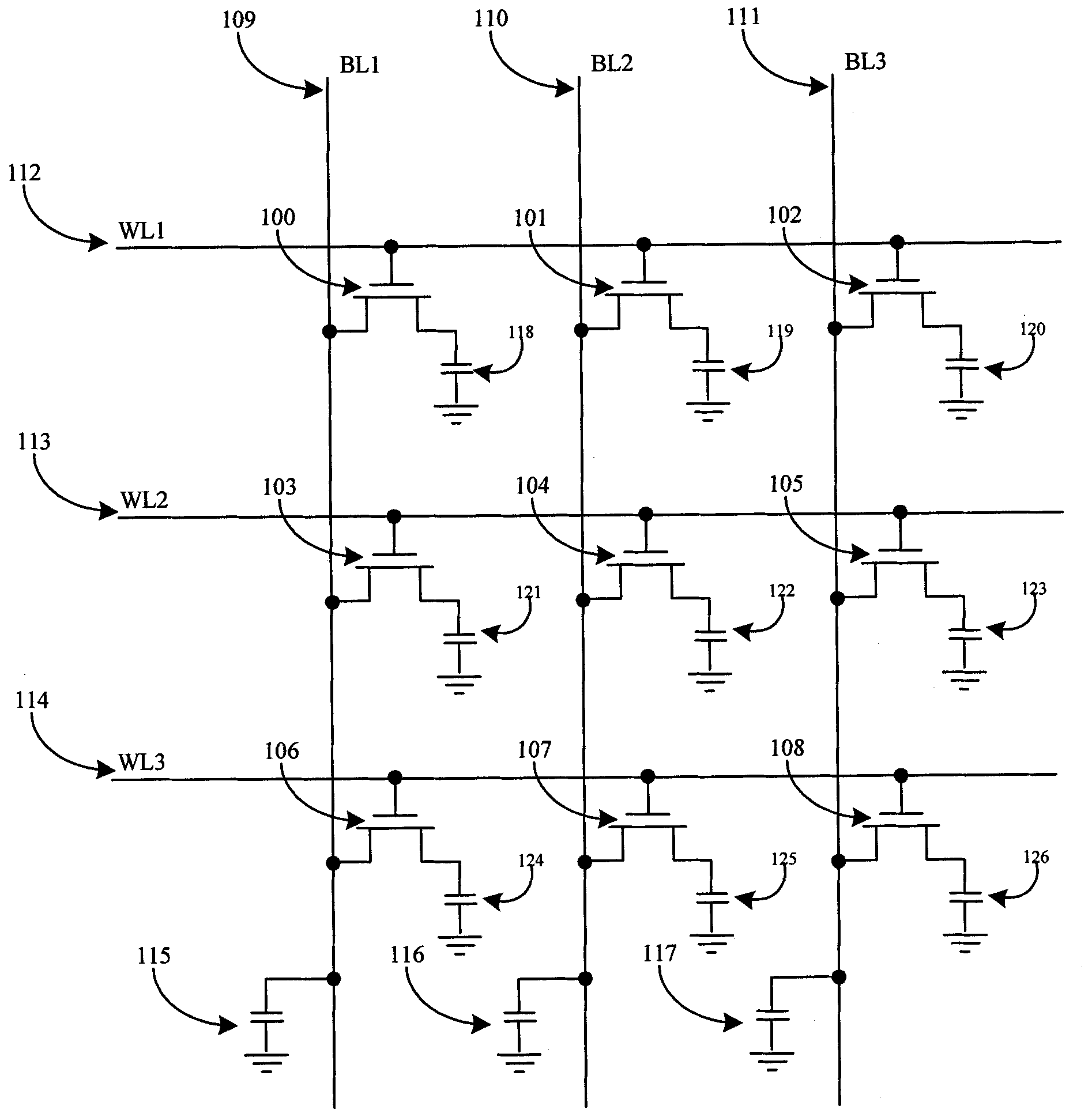
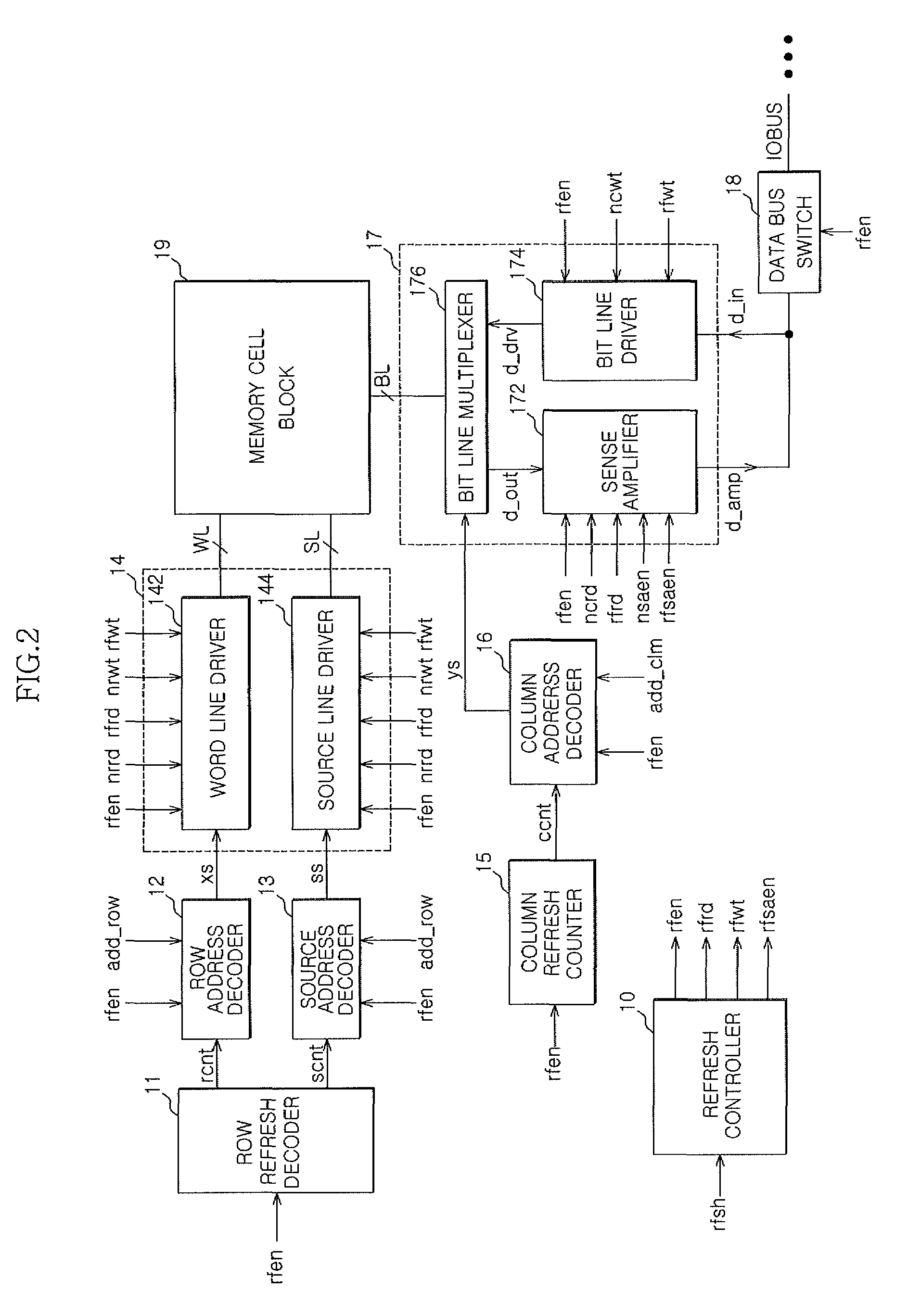
Semiconductor memory apparatus and refresh control method of the same
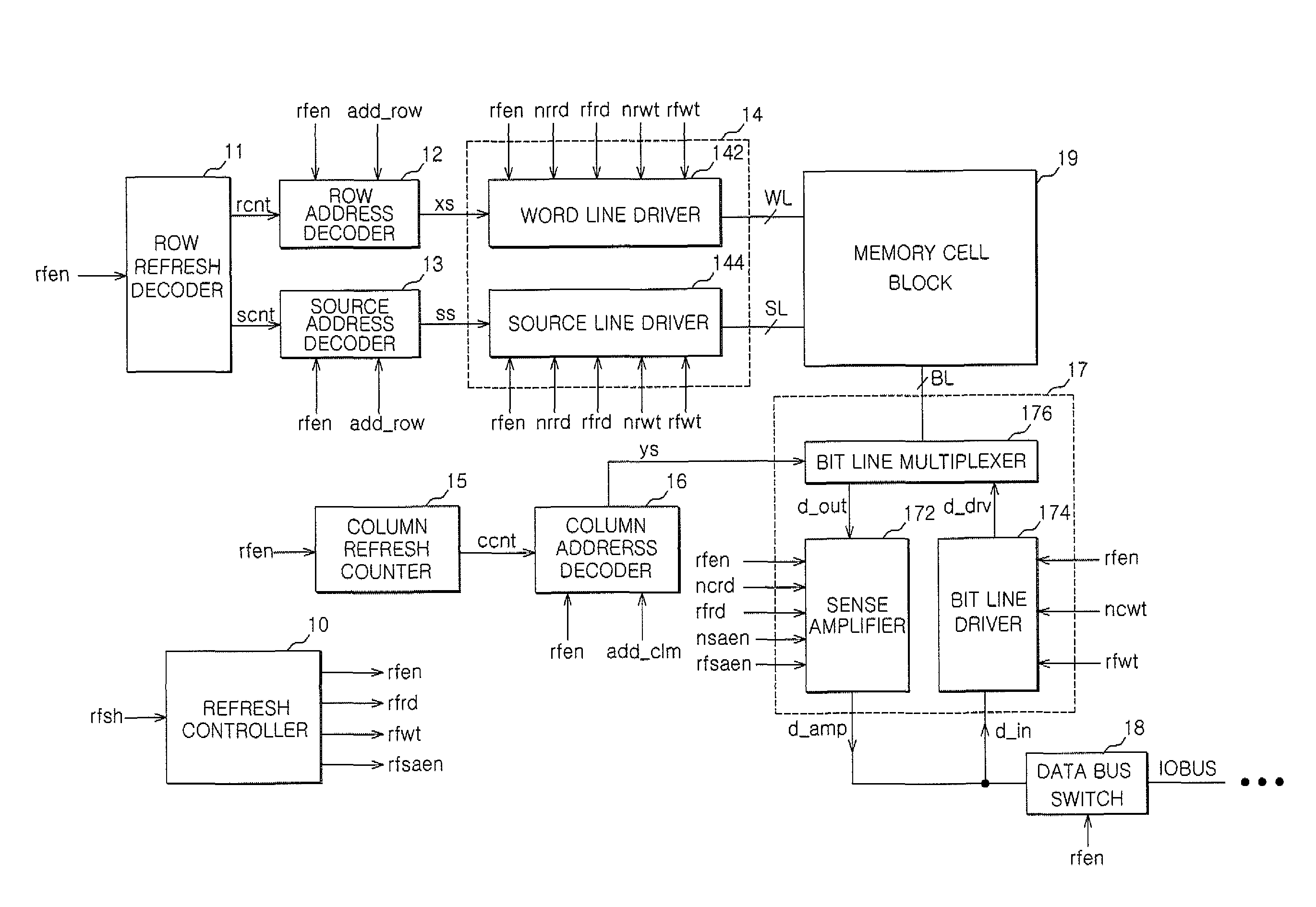
A semiconductor memory apparatus and a refresh control method are presented. The semiconductor memory apparatus includes a memory cell block composed of a multiplicity of floating body cell (FBC) transistors. Each FBC transistor has a gate connected to a word line, a drain connected to a bit line, and a source connected to a source line. FBC transistor pairs are formed by sharing the source lines in the plurality of the floating body cell transistors. When a refresh signal is enabled, the semiconductor memory apparatus is configured to read data stored in the memory cell block by enabling a refresh read signal and then configured to rewrite the read data in the memory cell block by enabling a refresh write signal.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Semiconductor integrated device
InactiveUS7244991B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSoi substrate
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Dynamic random access memory structure
ActiveUS7456458B2Avoid reorganizationLong retention timeTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringBody positions
Owner:PROMOS TECH INC
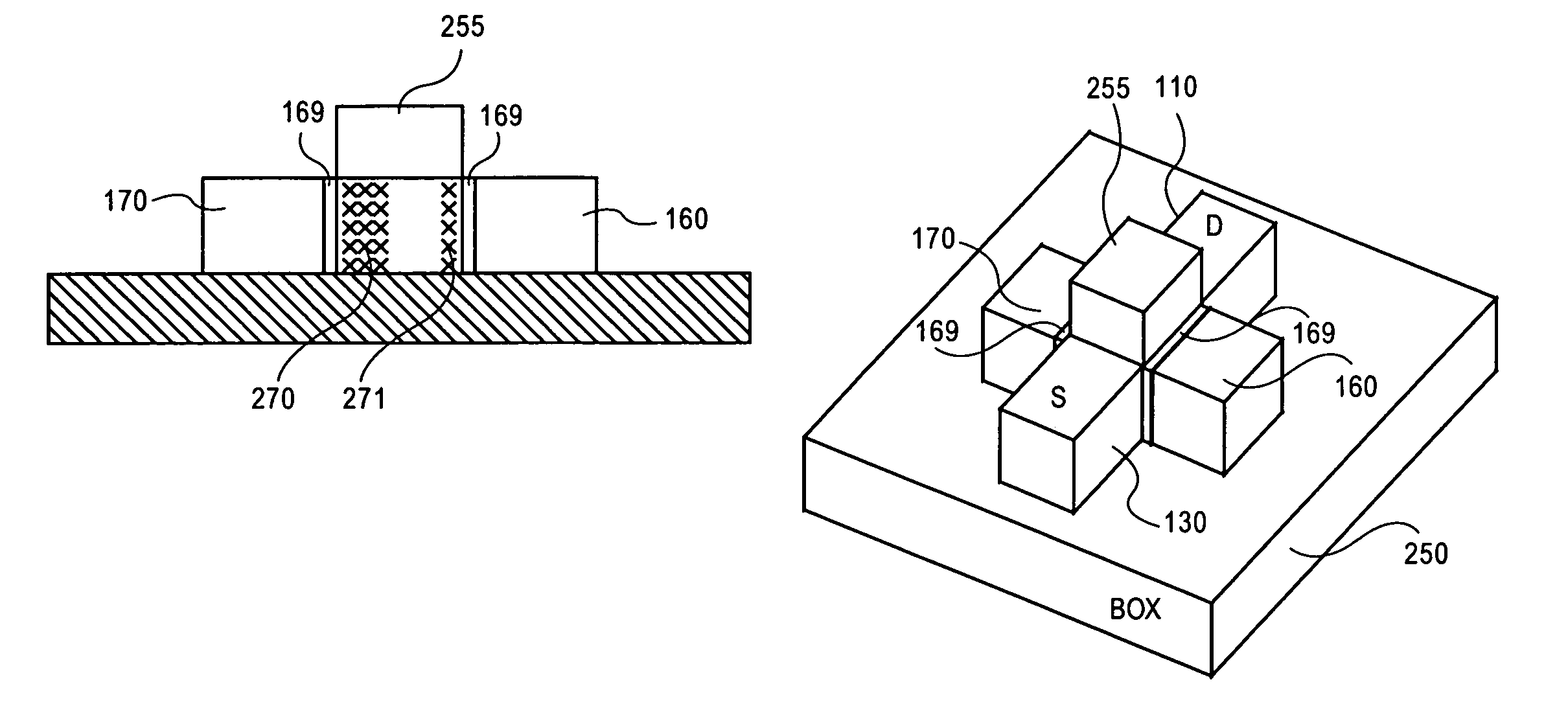
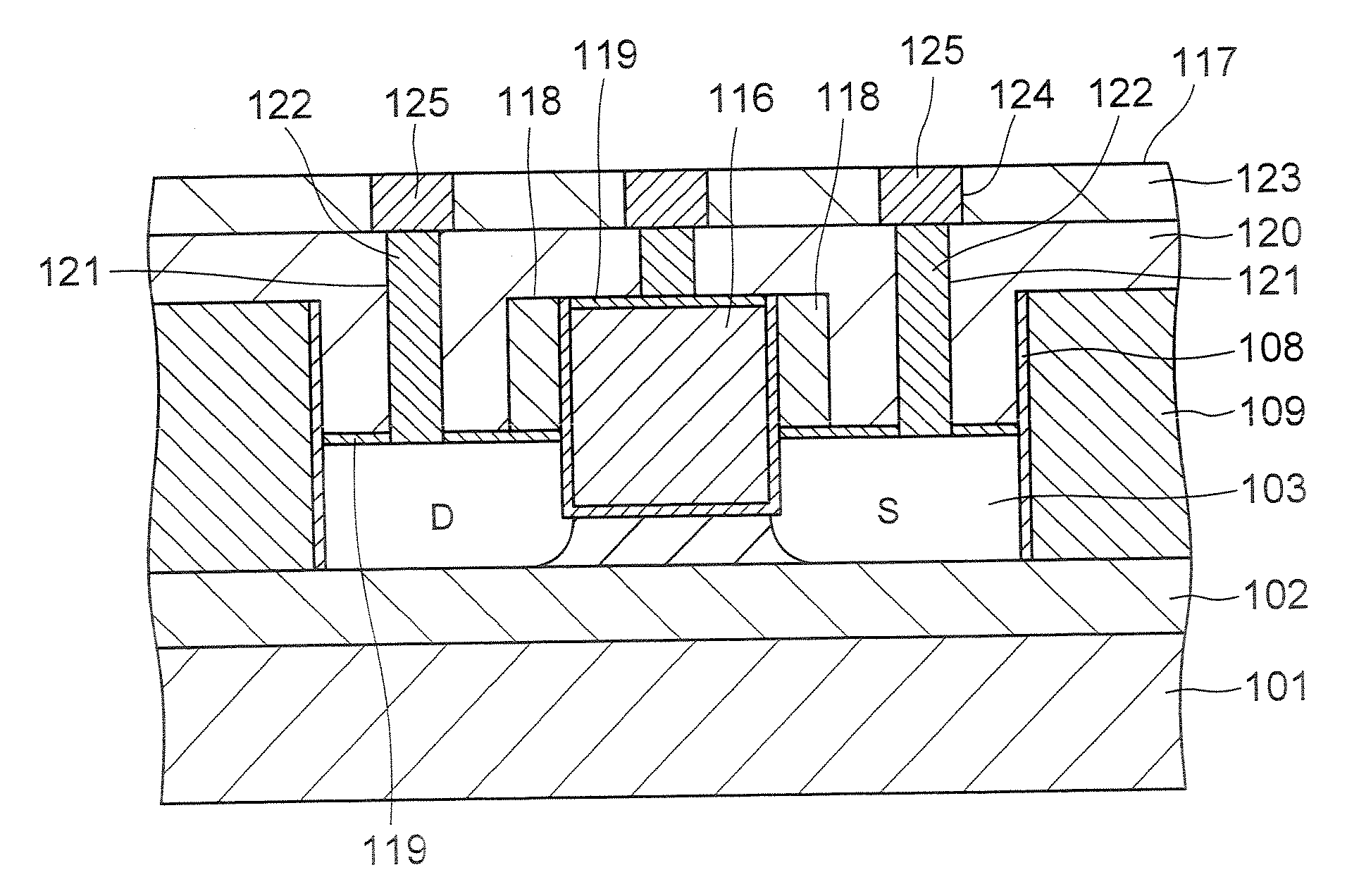
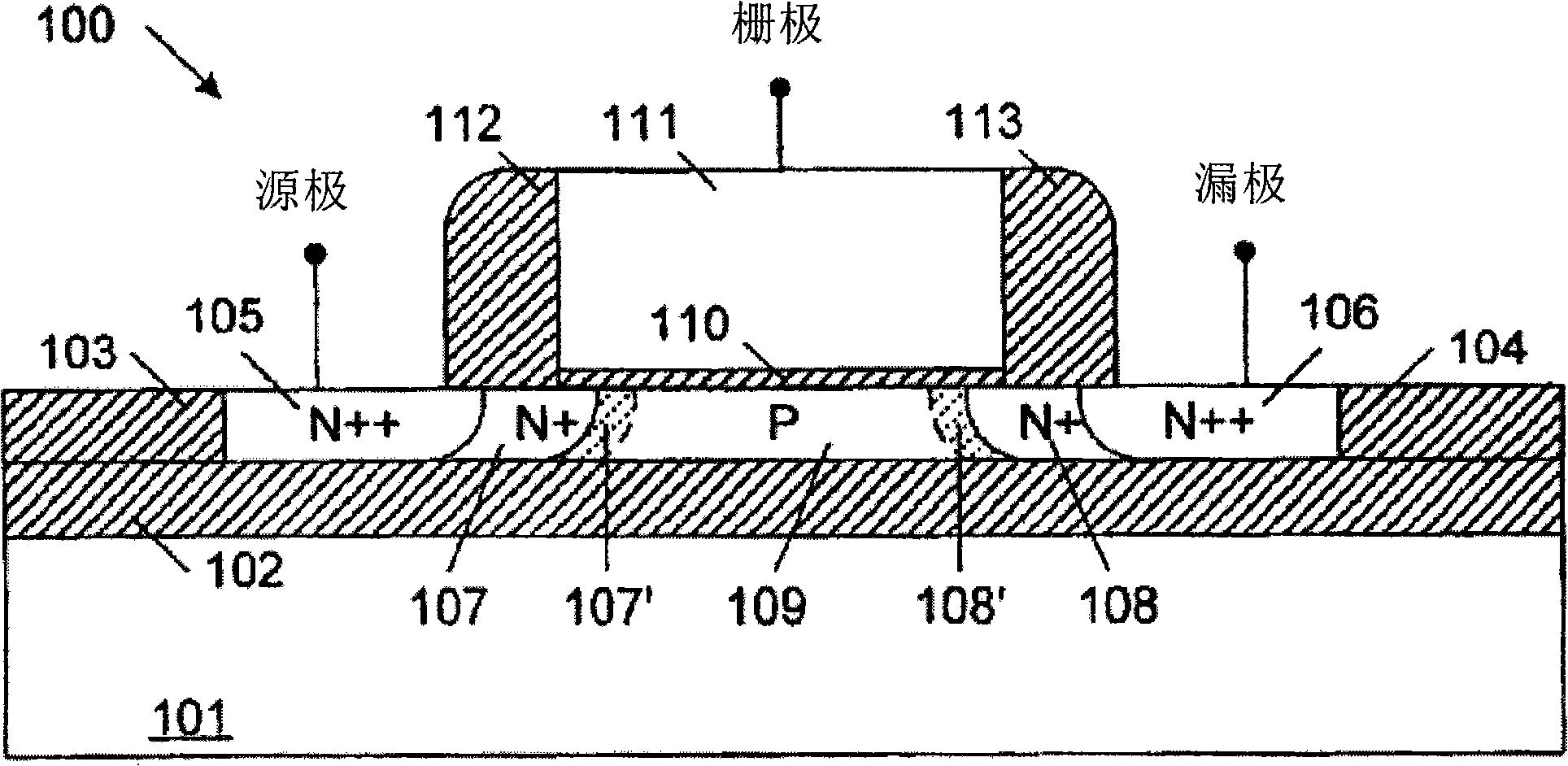
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method of the same
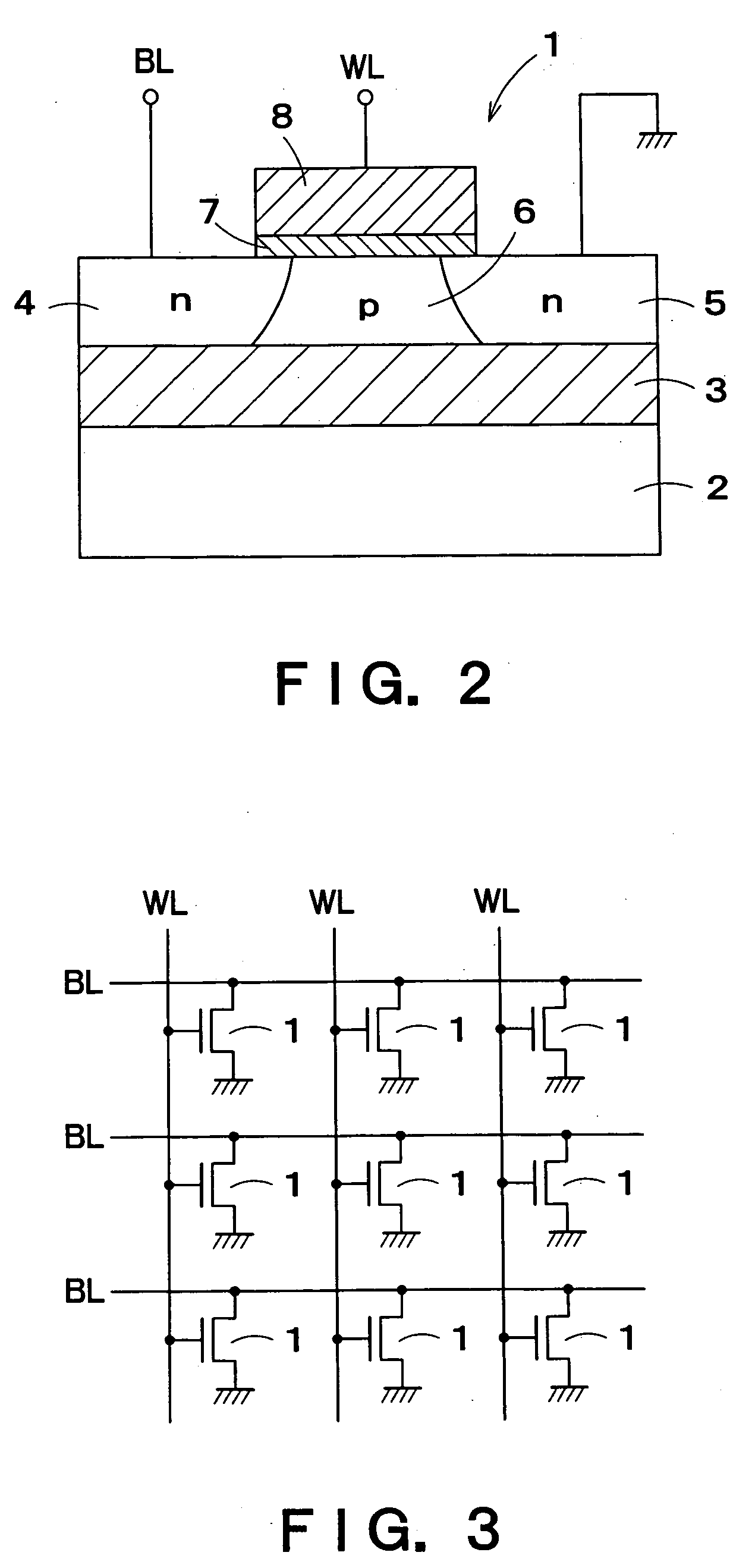
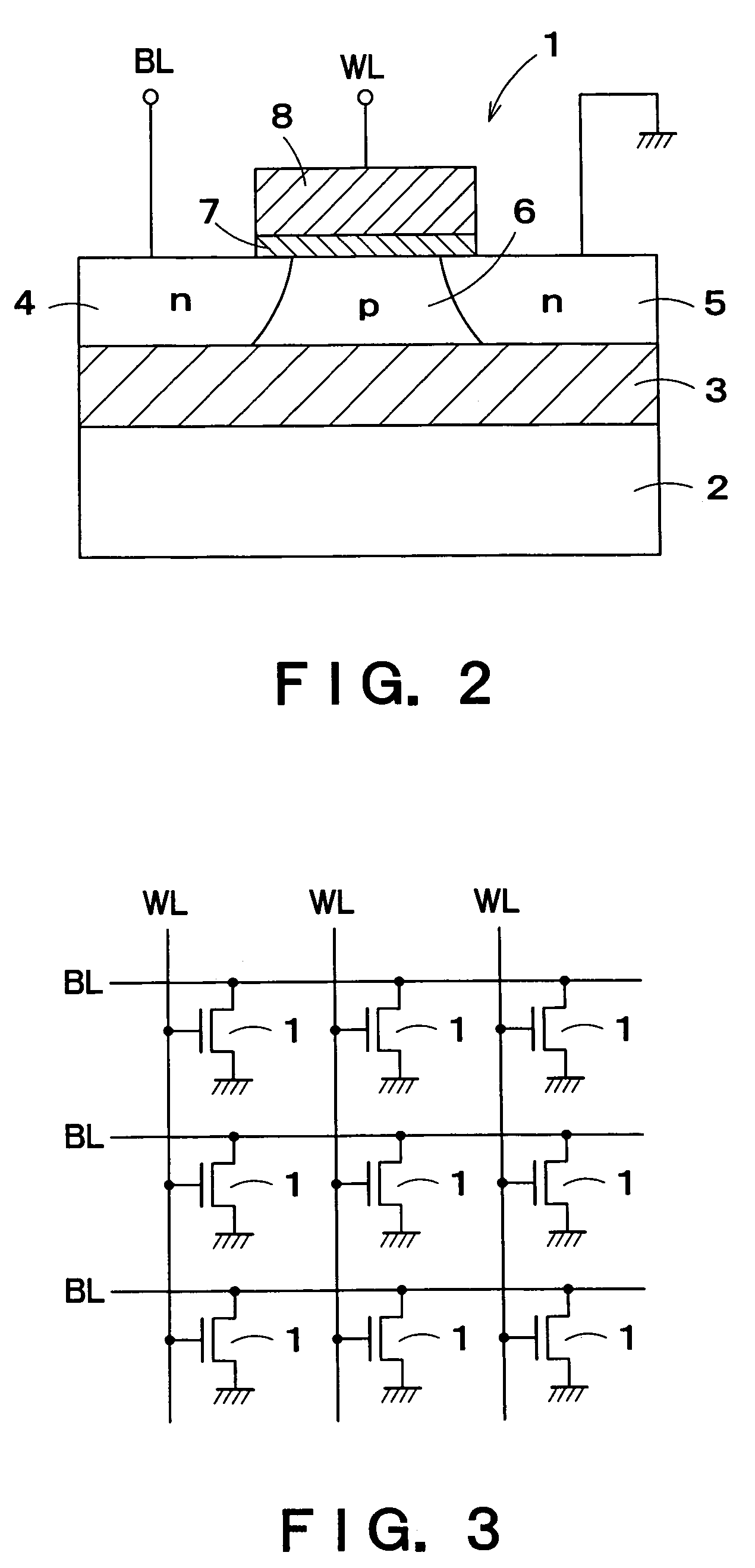
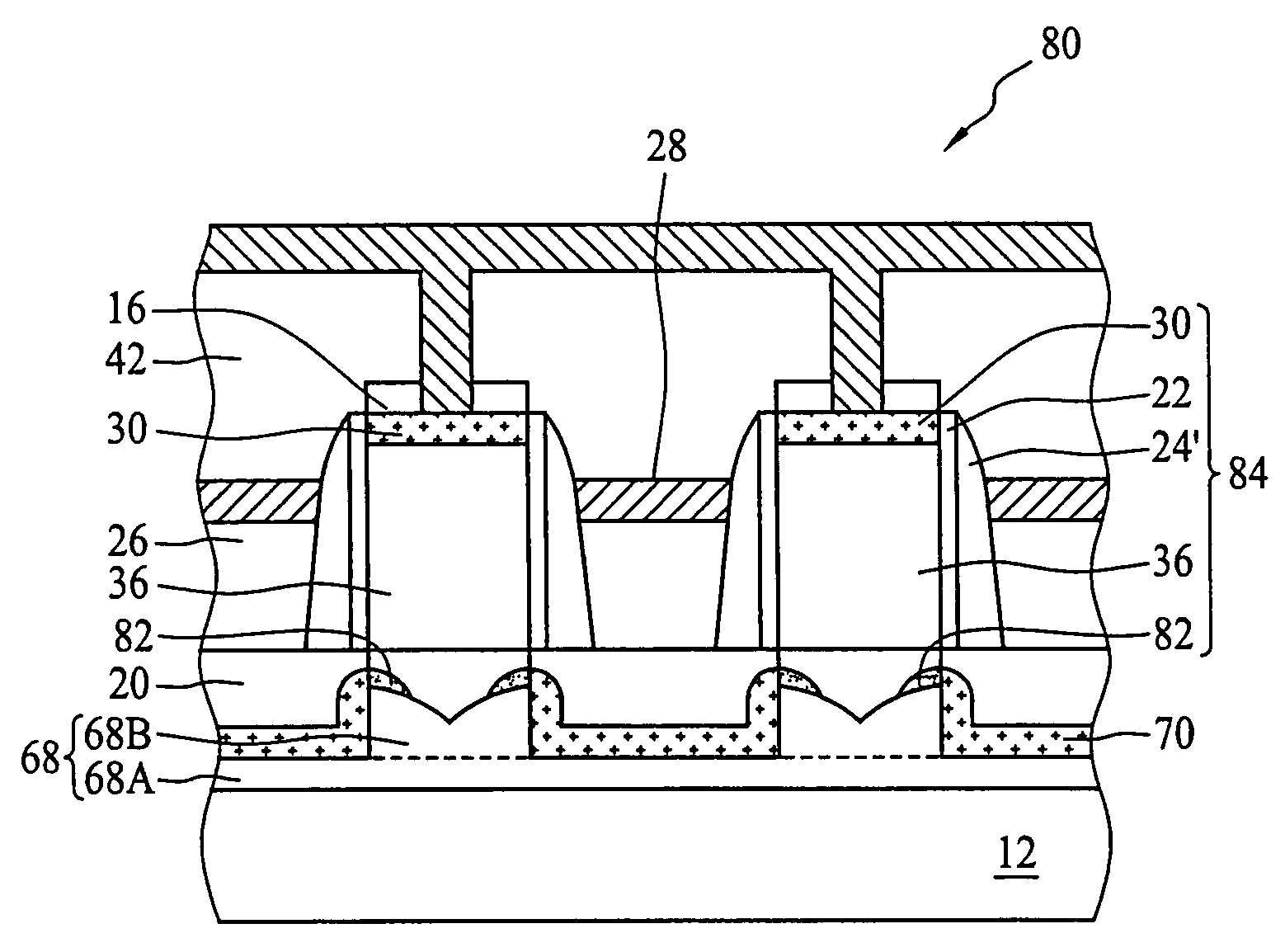
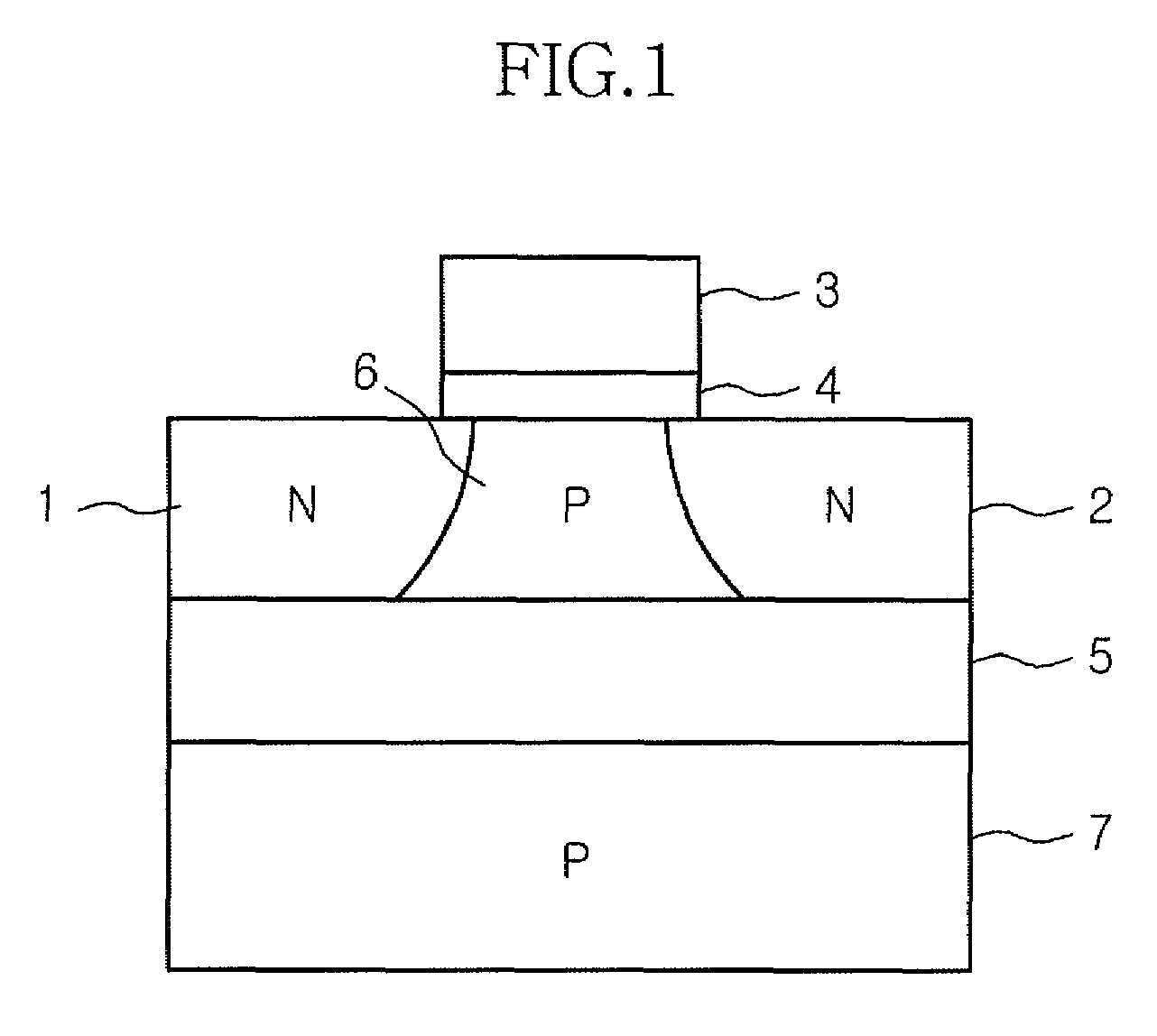
A semiconductor device comprises: a channel region of a transistor formed in a predetermined region of silicon layer formed on insulation film; a gate electrode formed on the channel region via gate insulation film; and source / drain regions formed in the silicon layer thicker than said channel region located out of the channel region, wherein the transistor is a memory element constituting the channel region as a floating body cell.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
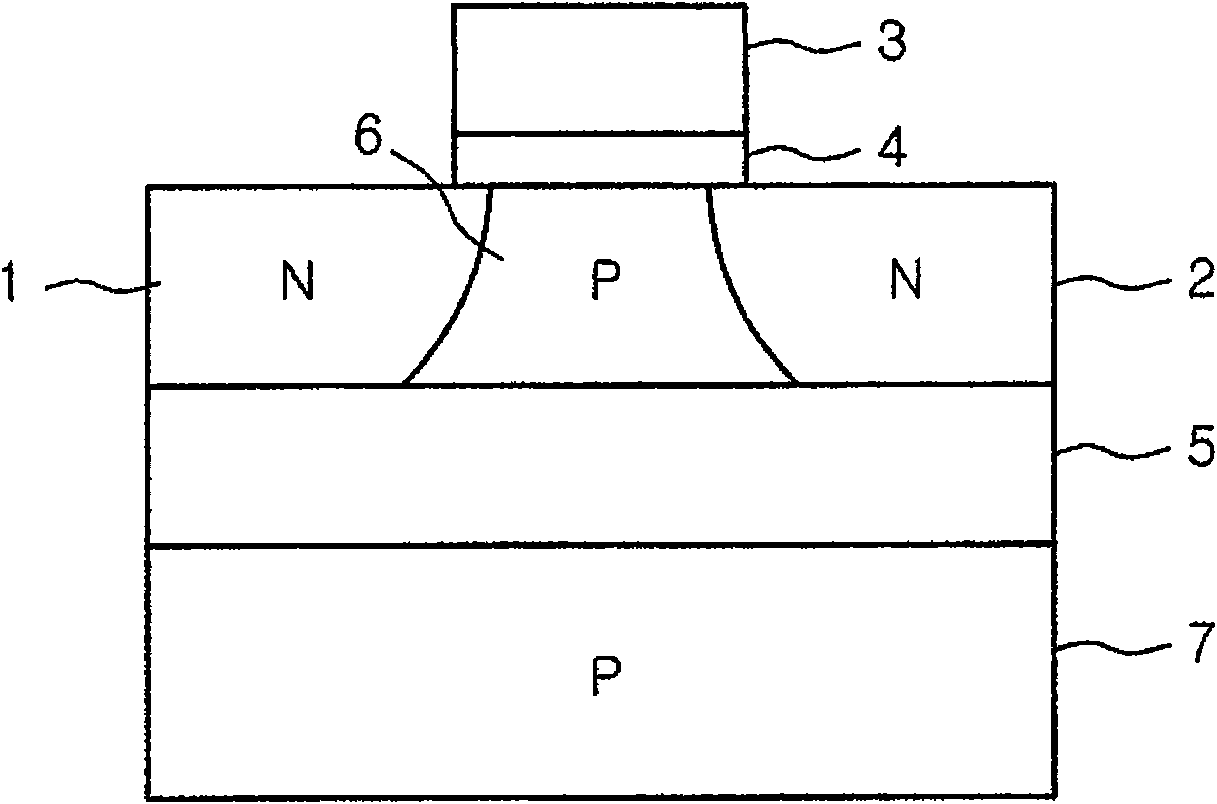
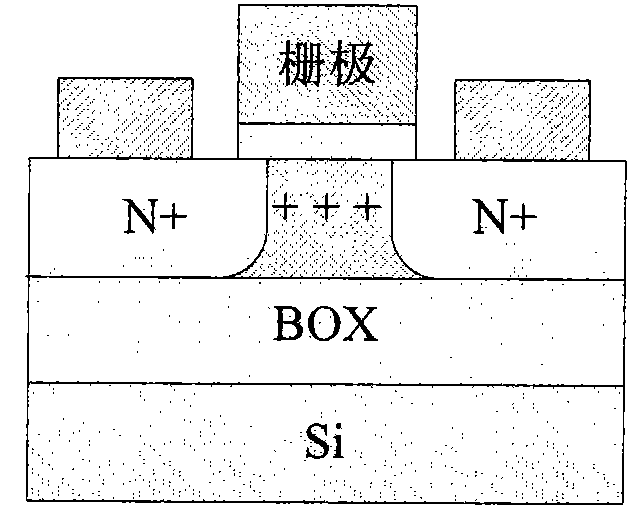
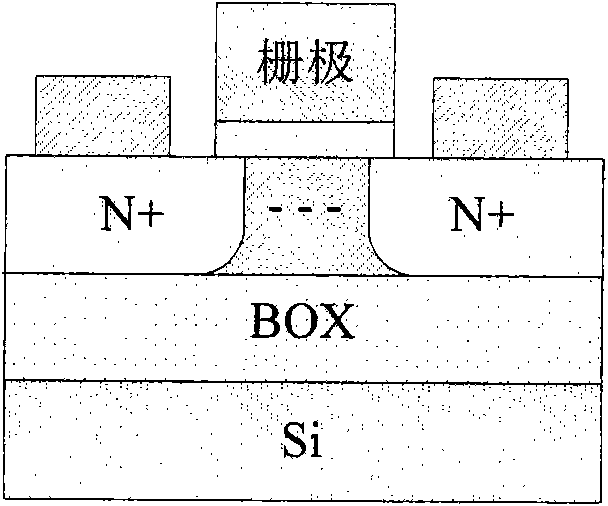
Floating body cell structure of dynamic random access memory and manufacturing technology thereof
InactiveCN101771051ASmall unit areaImprove reliabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesStatic random-access memoryManufacturing technology
The invention discloses a floating body cell structure of a dynamic random access memory and manufacturing technology thereof. The structure comprises an N type semiconductor area on a buried oxide layer (BOX), a P type semiconductor area on the N type semiconductor area and a gate area on the P type semiconductor area. Electric isolation areas are arranged around the P type semiconductor area and the N type semiconductor area. In the invention, isolated floating body gate diodes are employed as the storage nodes. Through tunneling among bands, the state that holes are accumulated in the floating body is defined as the first storage state. Through forward bias of PN junctions, the state that the holes are transmitted from the floating body or the electrons are injected into the floating body is defied as the second storage state. The two states lead to difference of the forward turn-on voltage of the floating body gate diodes (P+ / N+) and can be sensed through the current intensity. The gate diode (P+ / N+) floating body cell of the memory has high efficiency, low power consumption and high density and has the advantages of simple manufacturing technology, high integration density, low cost, high reliability, etc.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Semiconductor storage device and semiconductor integrated circuit
A semiconductor storage device according to the present invention, comprising: a first semiconductor layer formed on a substrate via a buried insulation layer; an FBC (Floating Body Cell) having a channel body of floating type formed on the first semiconductor layer, a main gate which forms a channel at a first face side of the channel body, and an auxiliary gate formed to capacitively couple on a second face at an opposite side of the first face; a logic circuit formed on the first semiconductor layer, separate from the FBC by an insulation film, which transfers a signal for the FBC; a second semiconductor layer which locates below the FBC and is formed along an under face of the buried insulation film; and a third semiconductor layer which locates below the logic circuit and is formed along an under face of the buried insulation film, wherein the second and third semiconductor layers are set to be in a potential different from each other.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Floating body cell (FBC) memory device with a sense amplifier for refreshing dummy cells
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Floating body cell structures, devices including same, and methods for forming same
Floating body cell structures including an array of floating body cells disposed on a back gate and source regions and drain regions of the floating body cells spaced apart from the back gate. The floating body cells may each include a volume of semiconductive material having a channel region extending between pillars, which may be separated by a void, such as a U-shaped trench. The floating body cells of the array may be electrically coupled to another gate, which may be disposed on sidewalls of the volume of semiconductive material or within the void therein. Methods of forming the floating body cell devices are also disclosed.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
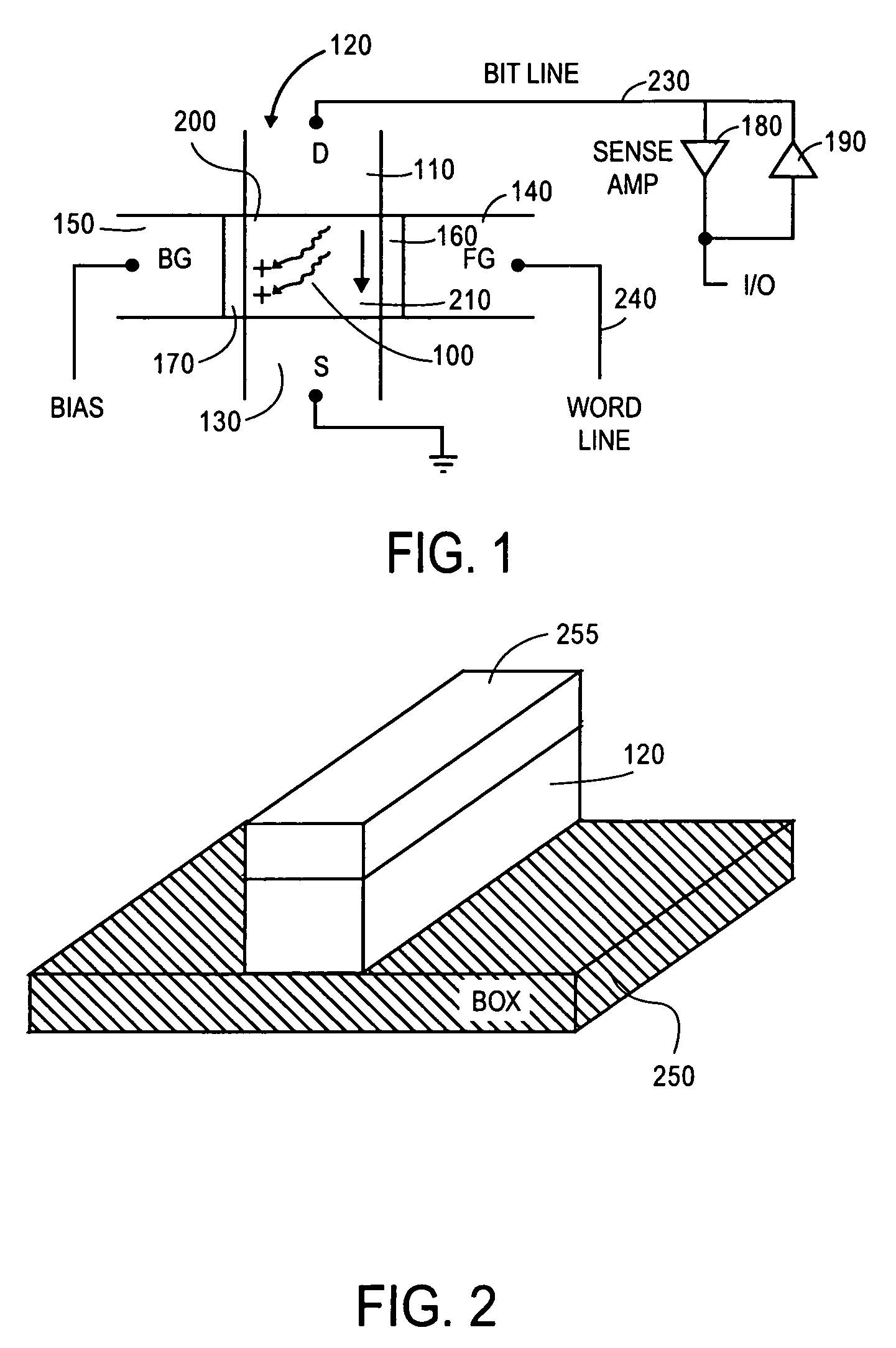
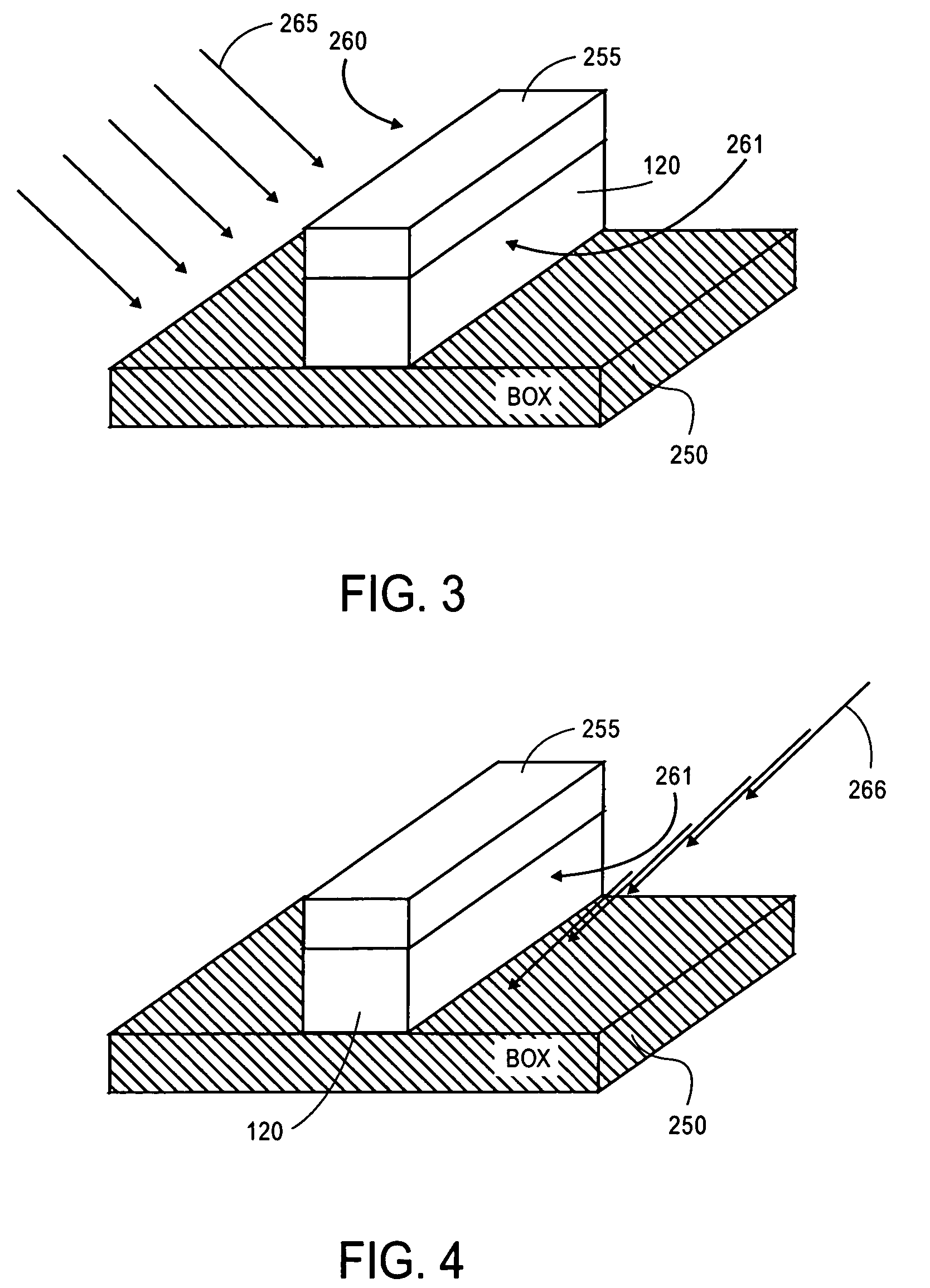
Floating body cell dynamic random access memory with optimized body geometry
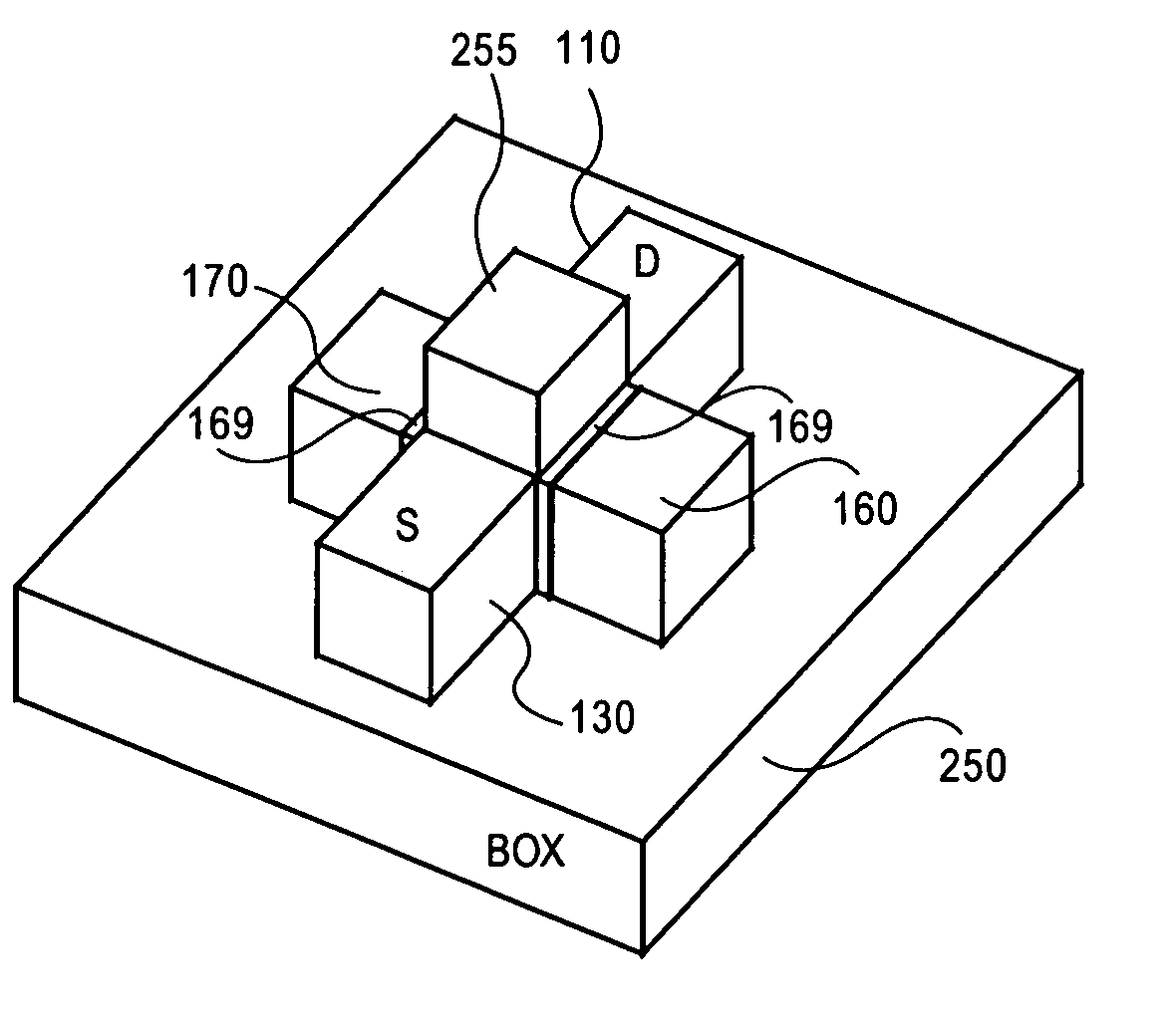
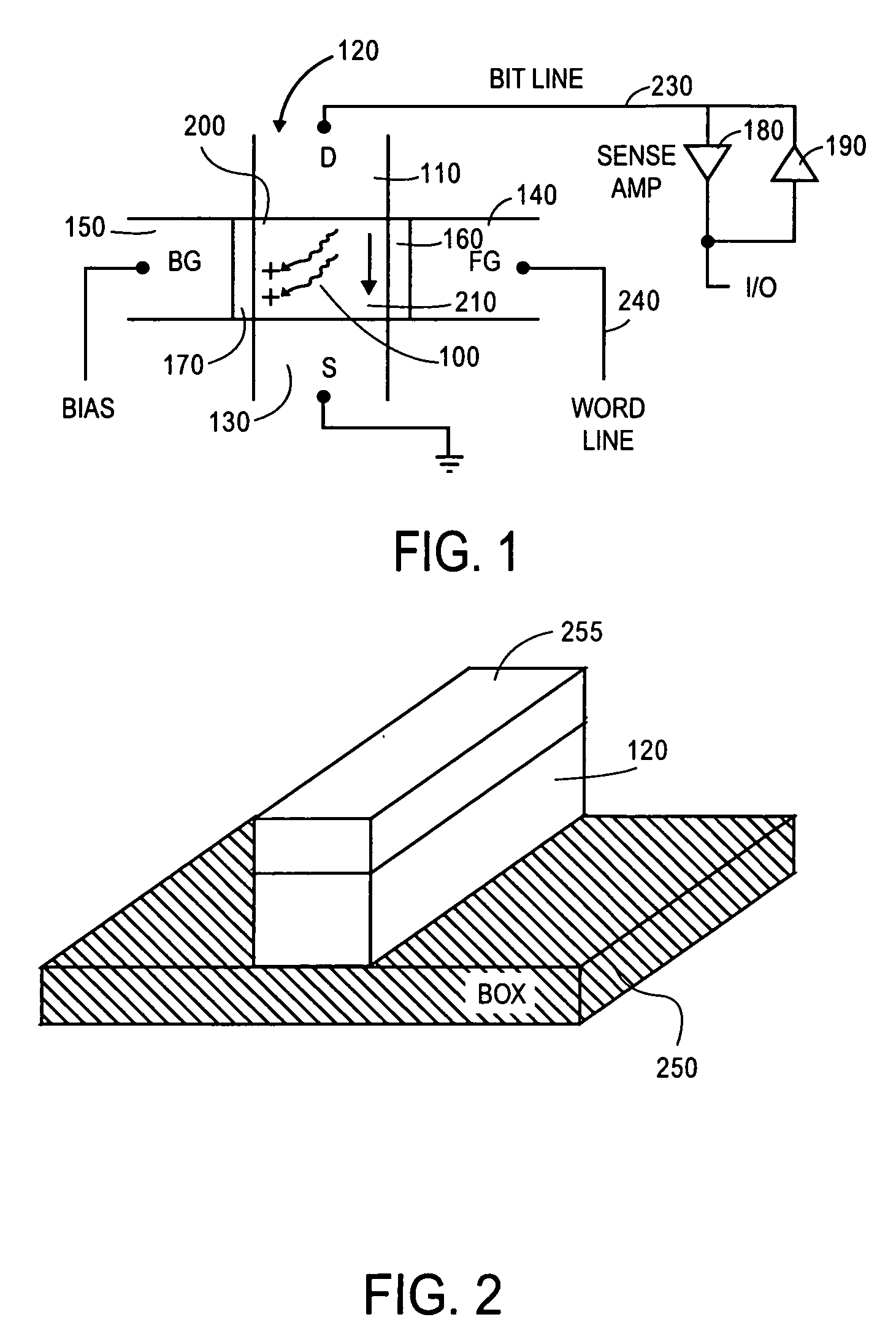
A semiconductor device includes a semiconductor substrate; a first insulation layer formed on the semiconductor substrate; a semiconductor layer insulated from the semiconductor substrate by the insulation layer; a source region of a first conduction type and a drain region of the first conduction type formed in the semiconductor layer; a body region of a second conduction type formed in the semiconductor layer between the source region and the drain region, said body region being capable of storing data by accumulating or releasing electric charge; a second insulation layer formed on the body region; a word line formed on the second insulation layer and insulated from the body region by the second insulation layer; and a bit line electrically connected to the drain region, wherein the area of the body region in contact with the first insulation layer is larger than the area thereof in contact with the second insulation layer.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method for refreshing bulk-silicon floating body cell transistor memory
The invention belongs to the technical field of dynamic random access memories, in particular to a method for refreshing a bulk-silicon floating body cell transistor memory, which comprises the step of: offsetting a voltage pulse on an implant layer of a bulk-silicon floating body cell (FBC) to ensure that a PN junction between the implant layer and a floating body cell region is weakly conductedso that the memory is changed from a strong 1 state into a weak 1 state or from a weak 0 state into a strong 0 state. The method has the characteristic of high refreshing reliability due to no utilization of a Charge Bumping effect. Meanwhile, for the FBC memory unit or memory, the read process does not exist in the refreshing process, thus a storage array of the FBC memory is integrally refreshed.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Semiconductor memory apparatus and refresh control method of the same
A semiconductor memory apparatus and refresh control method are presented. The semiconductor memory apparatus includes a memory cell block composed of a multiplicity of floating body cell (FBC) transistors. Each FBC transistor has a gate connected to a word line, a drain connected to a bit line, and a source connected to a source line. FBC transistor pairs are formed by sharing the source lines in the plurality of the floating body cell transistors. When a refresh signal is enabled, the semiconductor memory apparatus is configured to read data stored in the memory cell block by enabling a refresh read signal and then configured to rewrite the read data in the memory cell block by enabling a refresh write signal.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
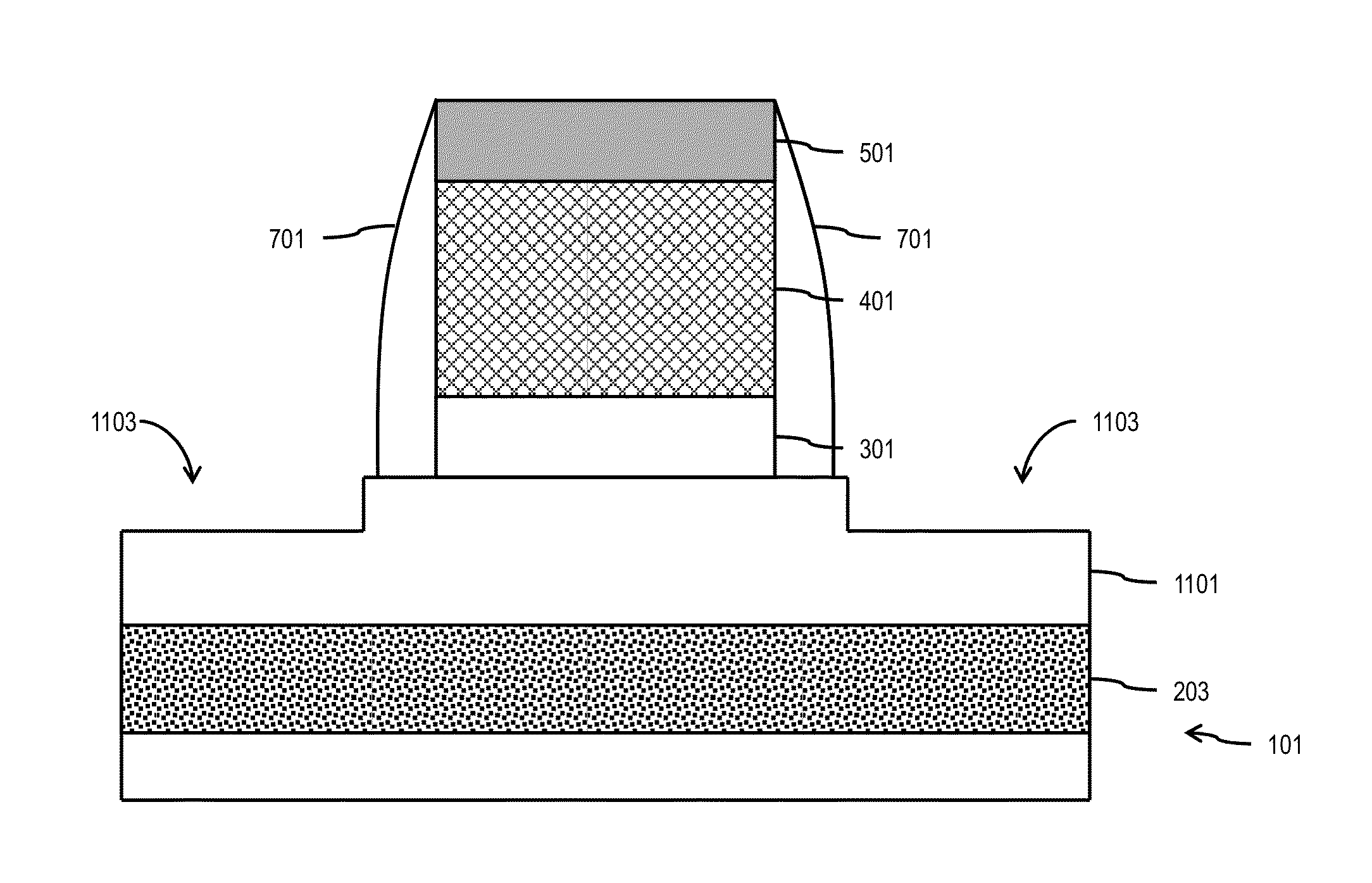
Floating body cell
ActiveUS20140167161A1Fast programmingLower refresh rateSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRefresh rateFloating body cell
Methods of forming a floating body cell (FBC) with faster programming and lower refresh rate and the resulting devices are disclosed. Embodiments include forming a silicon on insulator (SOI) layer on a substrate; forming a band-engineered layer surrounding and / or on the SOI layer; forming a source region and a drain region with at least one of the source region and the drain region being on the band-engineered layer; and forming a gate on the SOI layer, between the source and drain regions.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES SINGAPORE PTE LTD
Fin-like back gate storage structure and automatic refreshing method of floating body cells
InactiveCN103824861ASmall sizeHighly integratedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesCMOSStatic random-access memory
The invention provides a fin-like back gate storage structure and an automatic refreshing method of floating body cells. A back gate is arranged on the upper surface of a substrate, a back gate?oxide layer is arranged on the upper surface of the back gate, and a floating gate structure is arranged on the back gate?oxide layer. Data writing can be finished with small voltage. As the automatic floating body cell refreshing technology is adopted, the maintaining time is greatly increased, power consumption is significantly reduced, and integration is high as the size of the storage cell is excessively small. A static random access memory whose single tube storage structure replaces the original six-tube memory cell can greatly reduce the area of CMOS processer chip and is applied to a technology node of no less than 28 / 20 / 14nm, the cost is reduced obviously, and the power consumption is significantly reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI XINCHU INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
Semiconductor integrated device
A semiconductor integrated apparatus, comprising: an SOI (Silicon On Insulator) substrate which has a support substrate and an embedded insulation film; an NMOSFET, a PMOSFET and an FBC (Floating Body Cell) formed on the SOI substrate separately from each other; a p type of first well diffusion region formed along the embedded insulation film in the support substrate below the NMOSFET; an n type of second well diffusion region formed along the embedded insulation film in the support substrate below the PMOSFET; and a conduction type of third well diffusion region formed along the embedded insulation film in the support substrate below the FBC.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
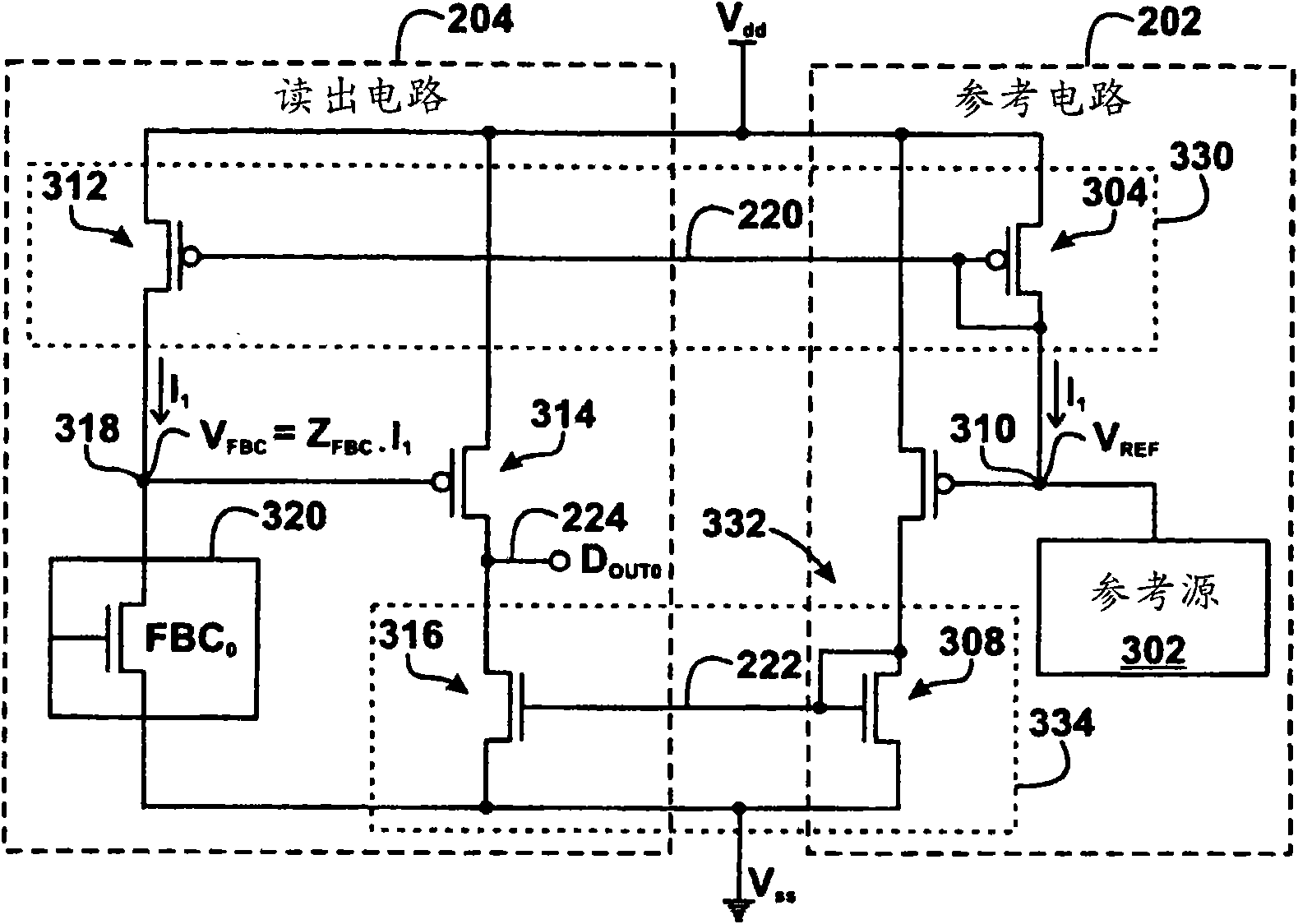
Sensing device for floating body cell memory and method thereof
A memory device includes a memory array and a sense amplifier. The memory array includes a floating body cell configured to store a bit value. The sense amplifier includes a bit output configured to provide an output voltage representative of the bit value and a reference source configured to provide a reference voltage. The sense amplifier further includes a current mirror configured to provide acurrent to the first floating body cell based on the reference voltage, and a differential amplifier circuit configured to determine the output voltage based on the reference voltage and a voltage across the floating body cell resulting from application of the current to the floating body cell.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com