Patents
Literature
1014results about How to "Prevent reversal" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Hair Color Smoothing Compositions and Methods
InactiveUS20150034119A1Prevent reversalCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsOrganic chemistryDisulfide bond
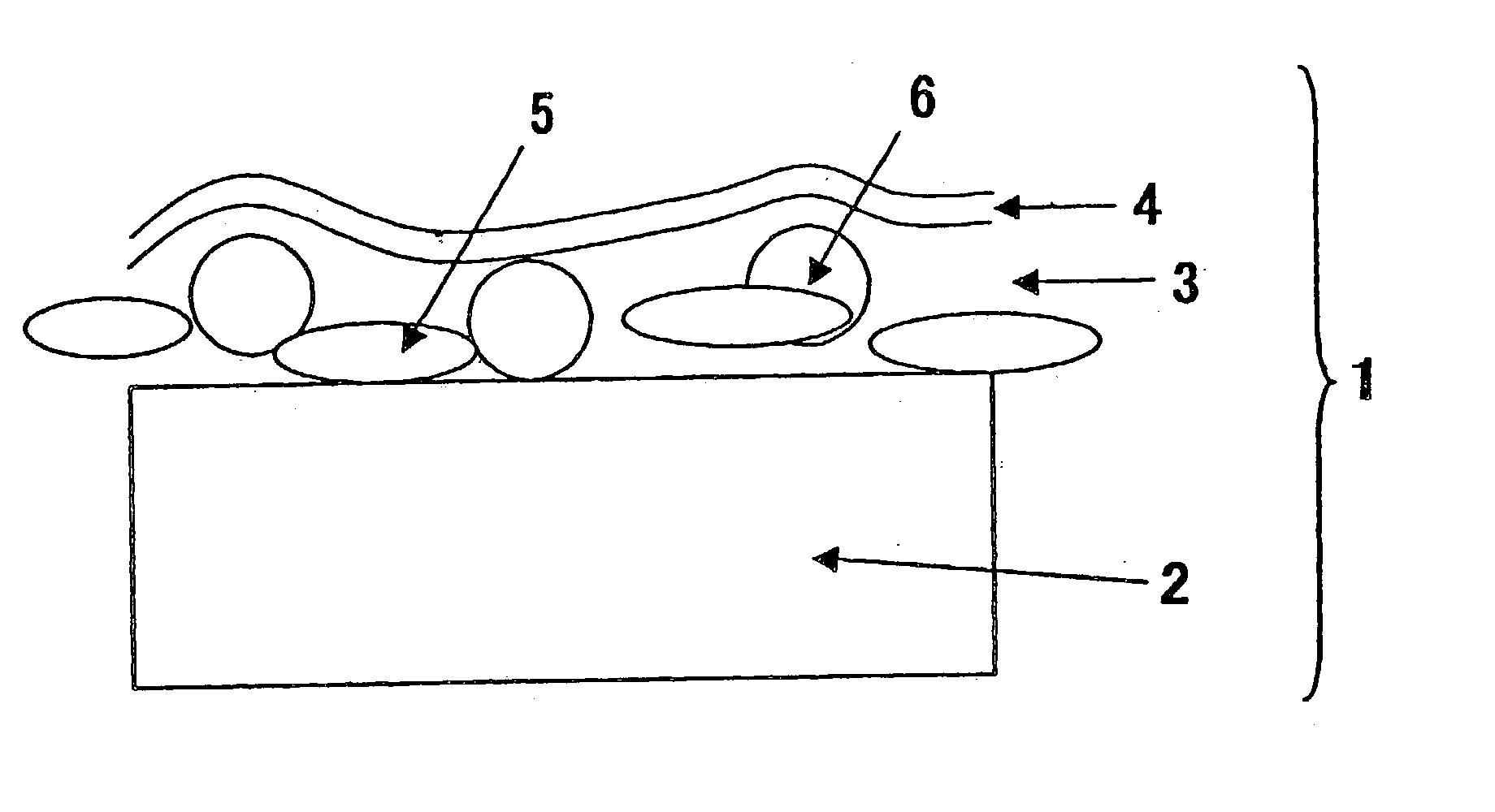
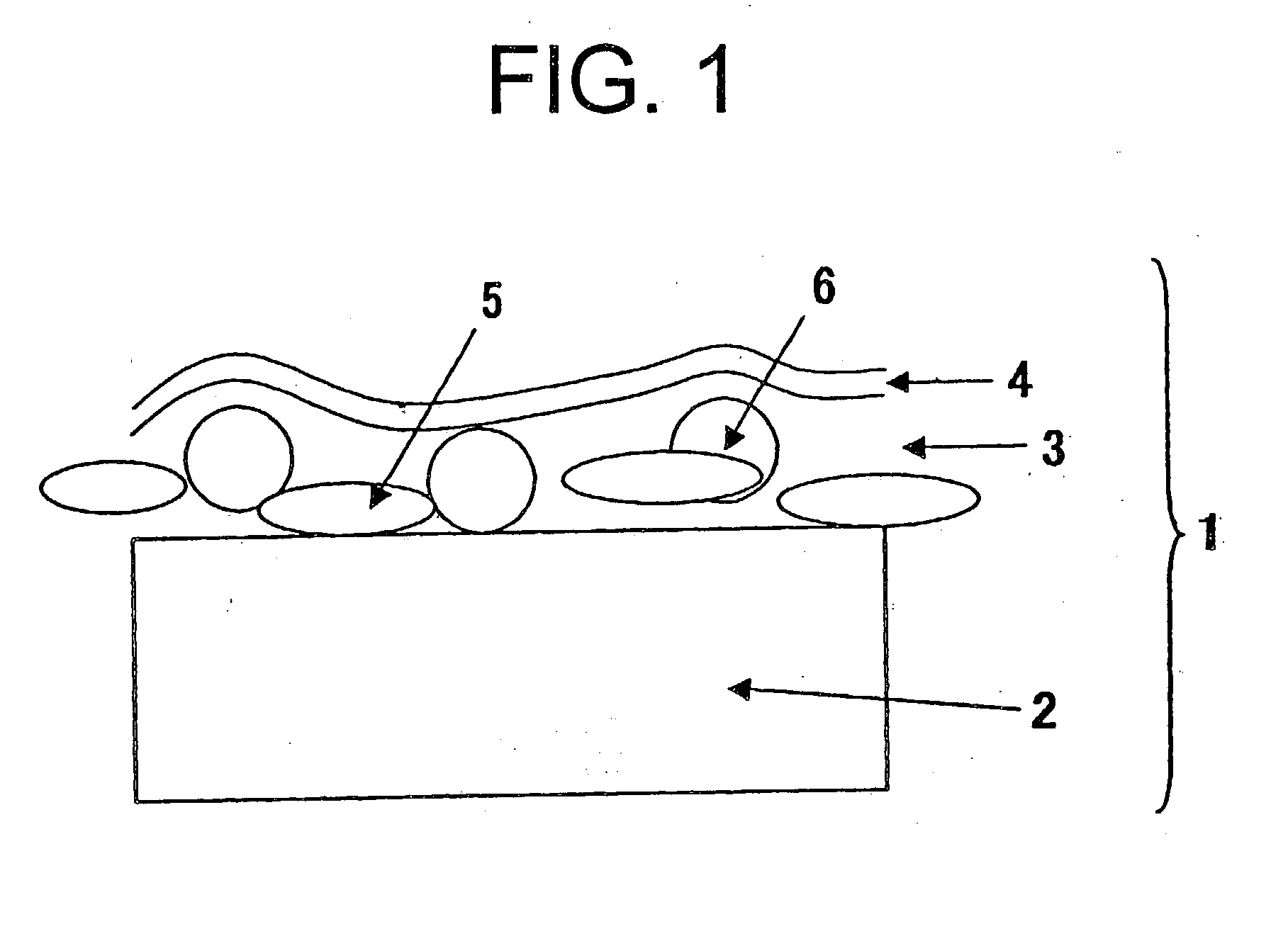
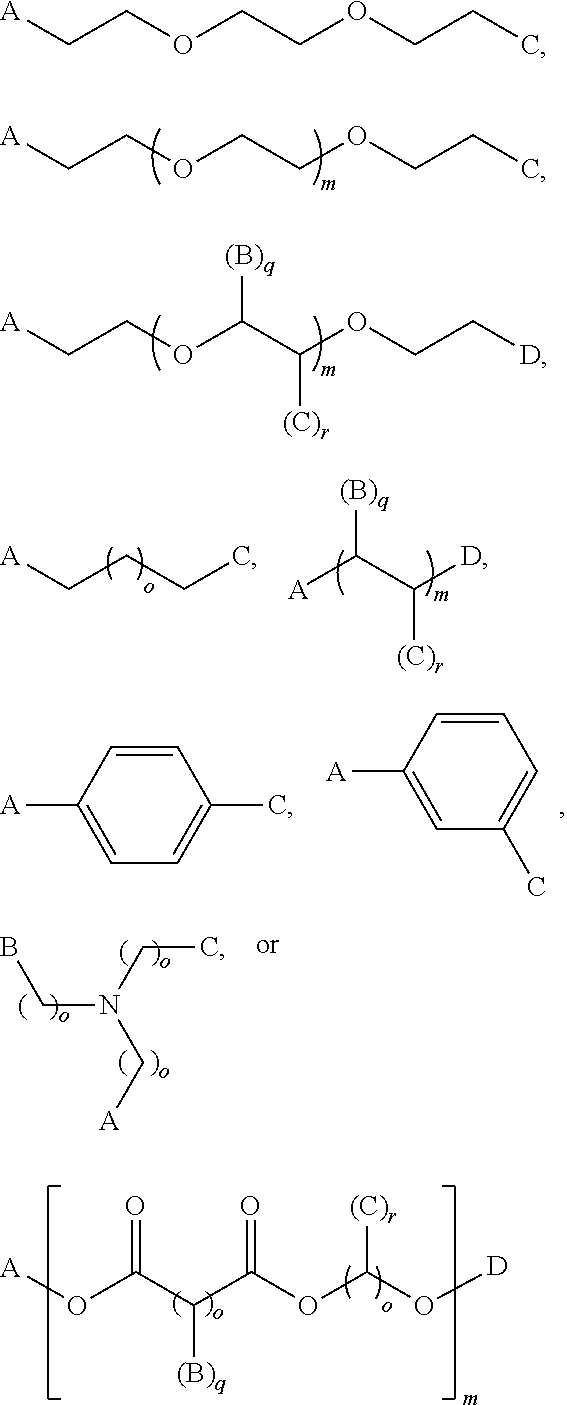
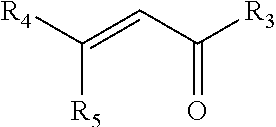
Compositions, kits, and methods for rebuilding the disulfide bonds in hair that is damaged due to a hair coloring treatment are disclosed. The compositions contain one or more compounds that covalently crosslink at least two thiol groups in the hair. The compositions may be applied subsequent to a hair coloring treatment or simultaneously with a hair coloring treatment. Under normal hair washing conditions, the covalent crosslinks formed are not succeptable to reduction or hydrolysis. Use of the crosslinking compositions prevent the reversion of the hair's disulfide bonds to its reduced state, for at least one week, preferably at least three months, more preferably at least one year, most preferably at least greater than one year, after at least one application of the composition.
Owner:LIQWD
Power plant
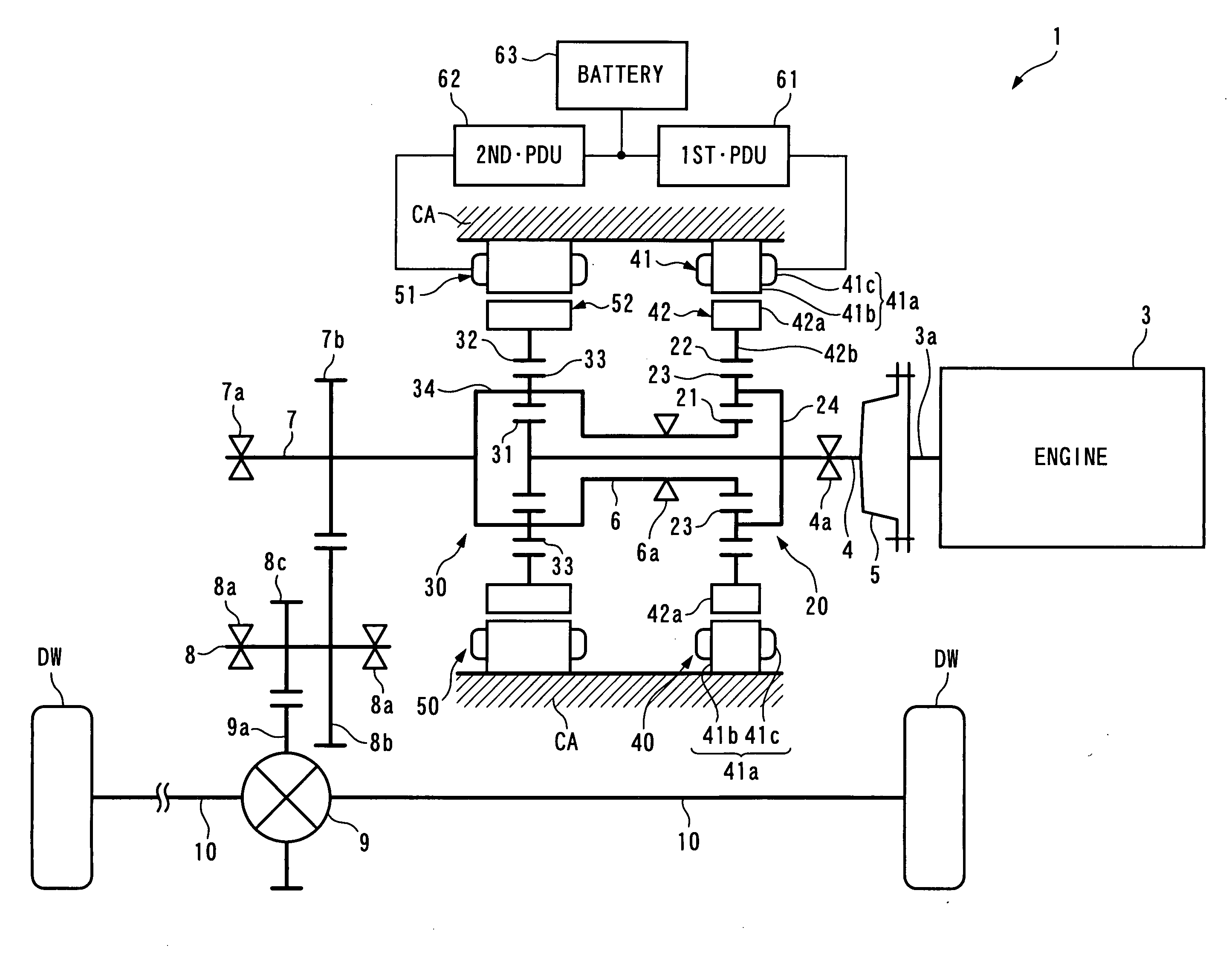
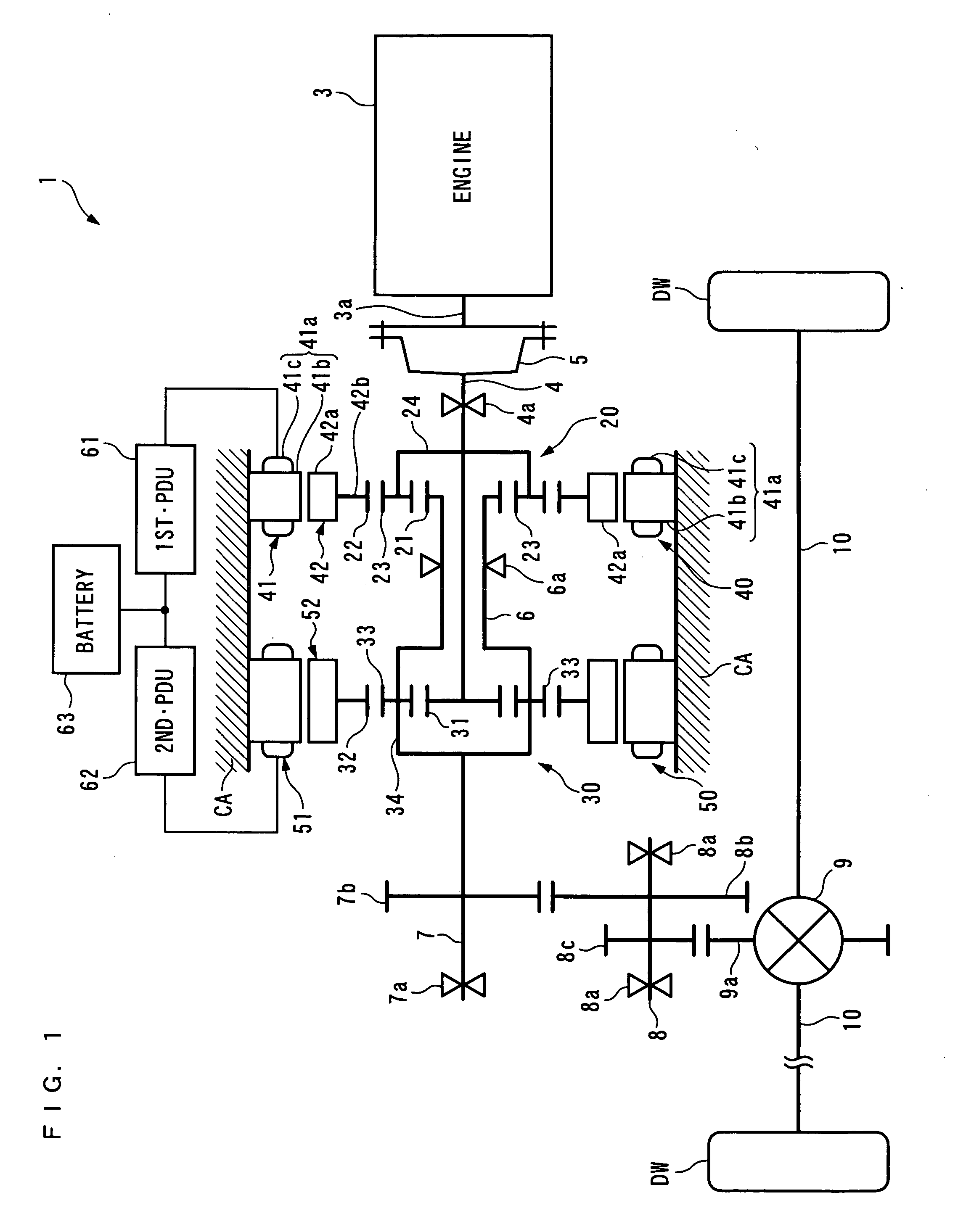
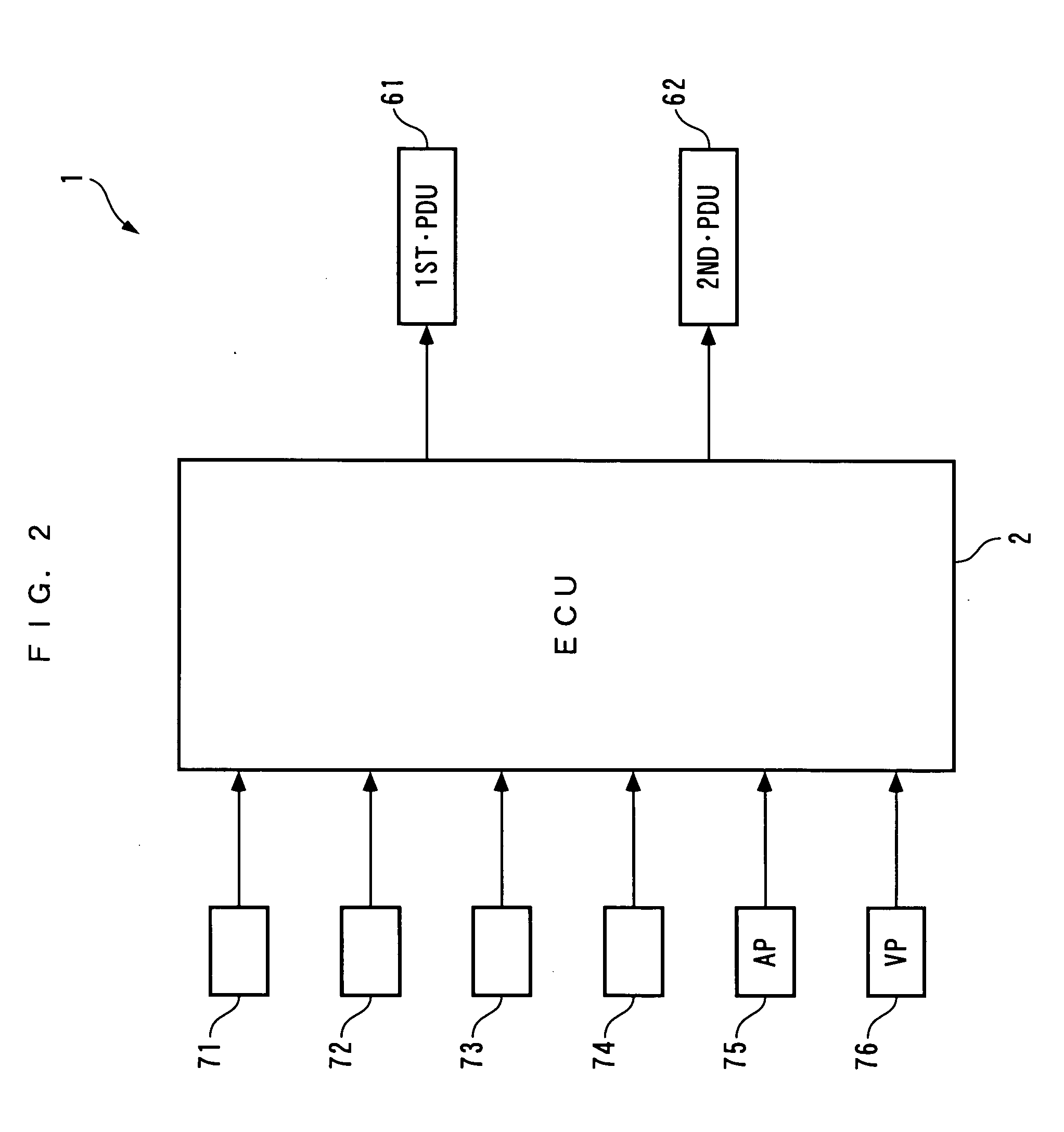
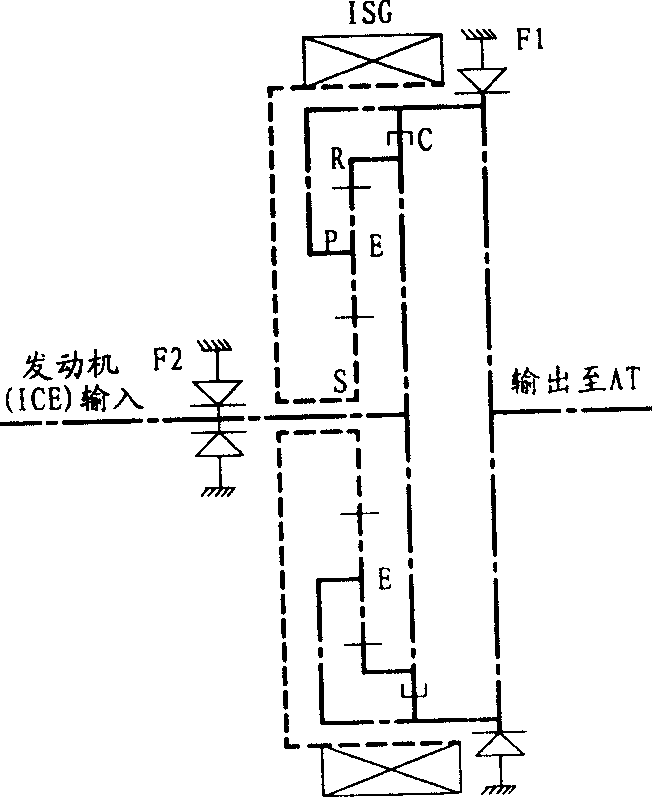
ActiveUS20100029428A1Reduce size and costMake smallEngine controllersTransmission elementsAutomotive engineeringPower station
To provide a power plant which is capable of reducing power passing through a distributing and combining device, thereby making it possible to attain reduction of the size and manufacturing costs of the power plant and enhance driving efficiency of the same. The power plant 1 for driving driven parts DW and DW includes a prime mover 3, a first distributing and combining device 20 having first, second and third elements 21, 24 and 22, a second distributing and combining device 30 having fourth, fifth and sixth elements 31, 34 and 32, and speed-changing devices 40, 50, 2, 61 and 62 which are connected to the third and sixth elements 22 and 32 and are capable of changing the relationship between the rotational speed of the third element and that of the sixth element 32. The second and fourth elements 24 and 31 are mechanically connected to an output shaft 3a of the prime mover 3, and the first and fifth elements 21 and 34 are mechanically connected to the driven parts DW and DW.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
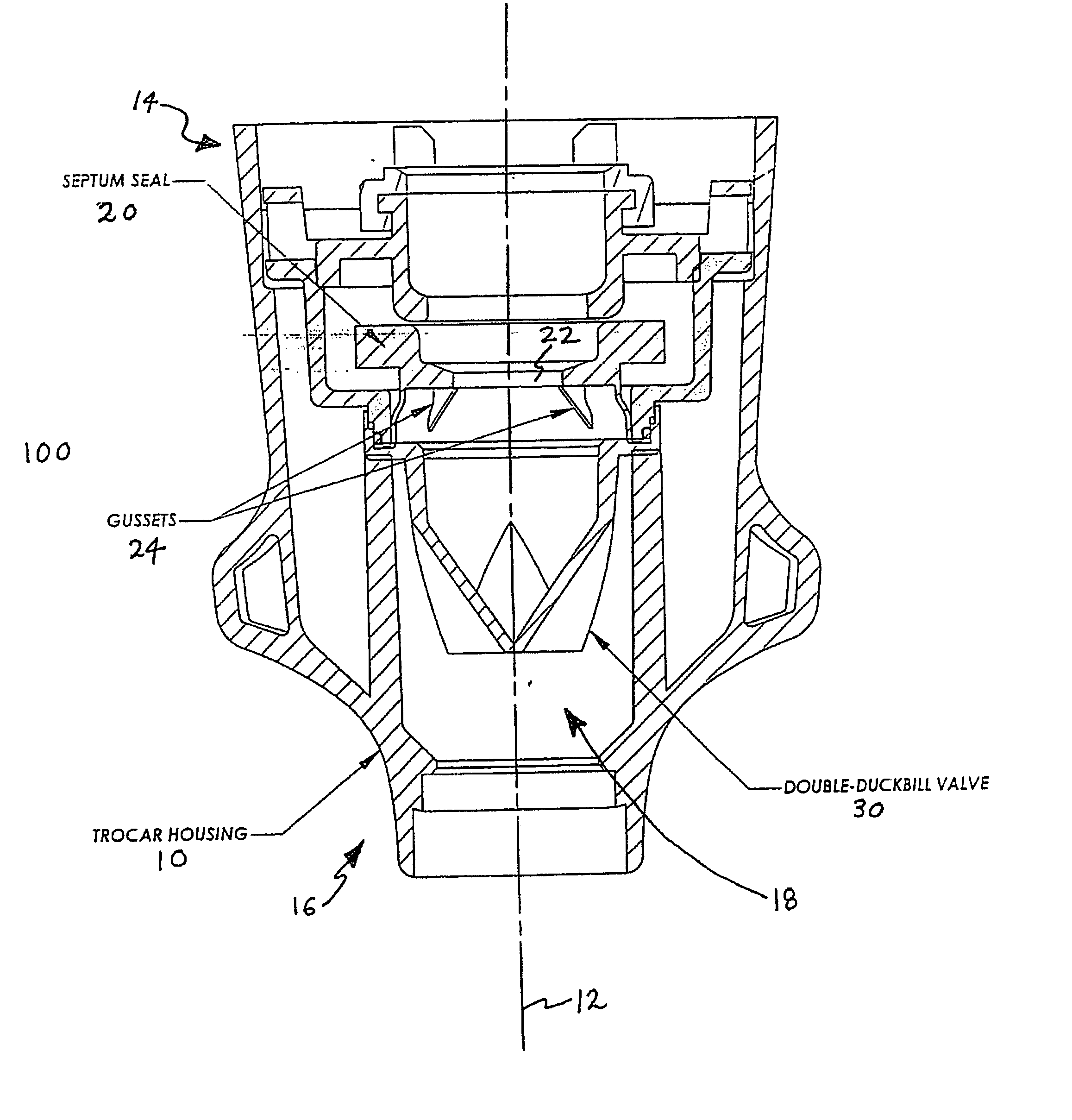
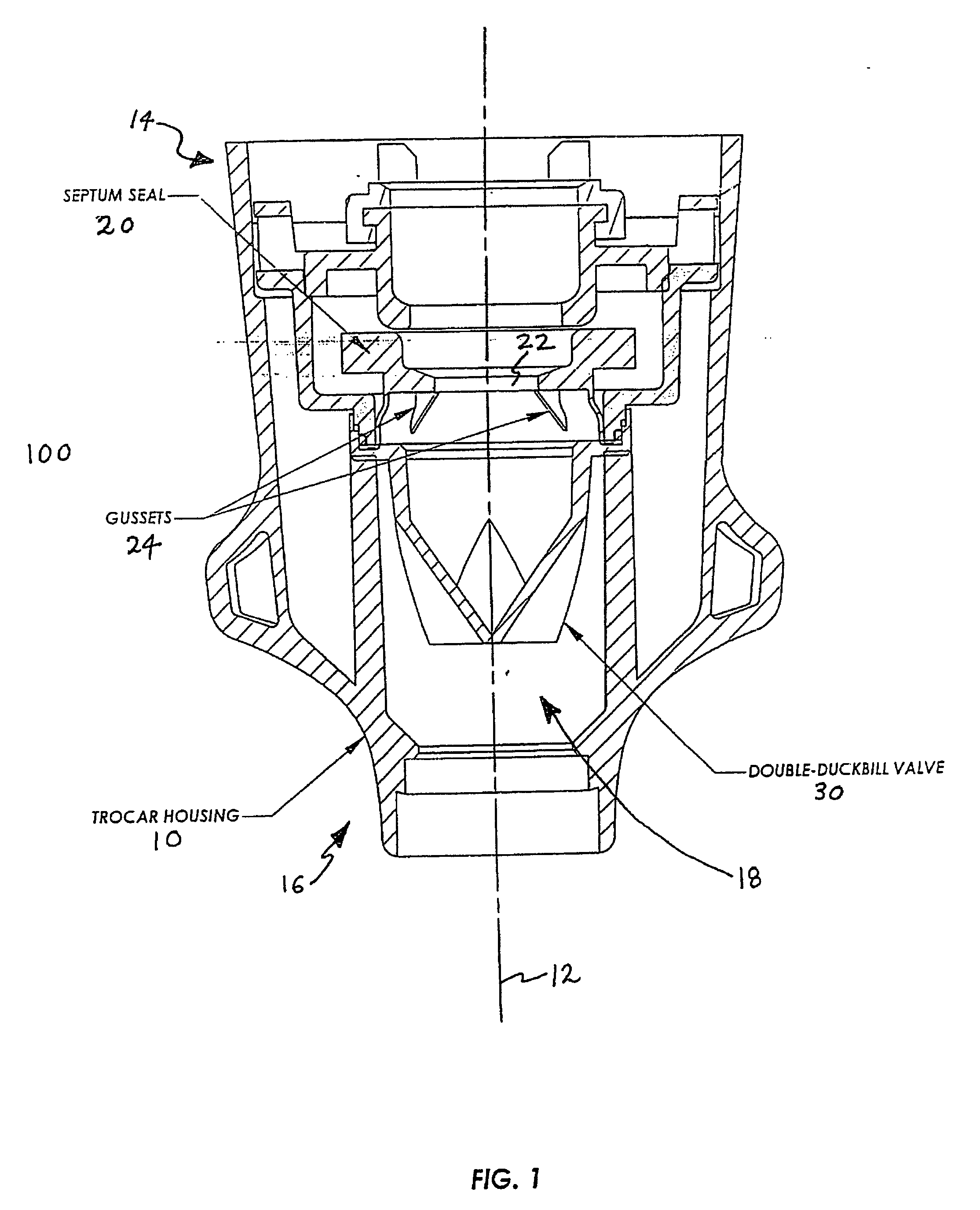
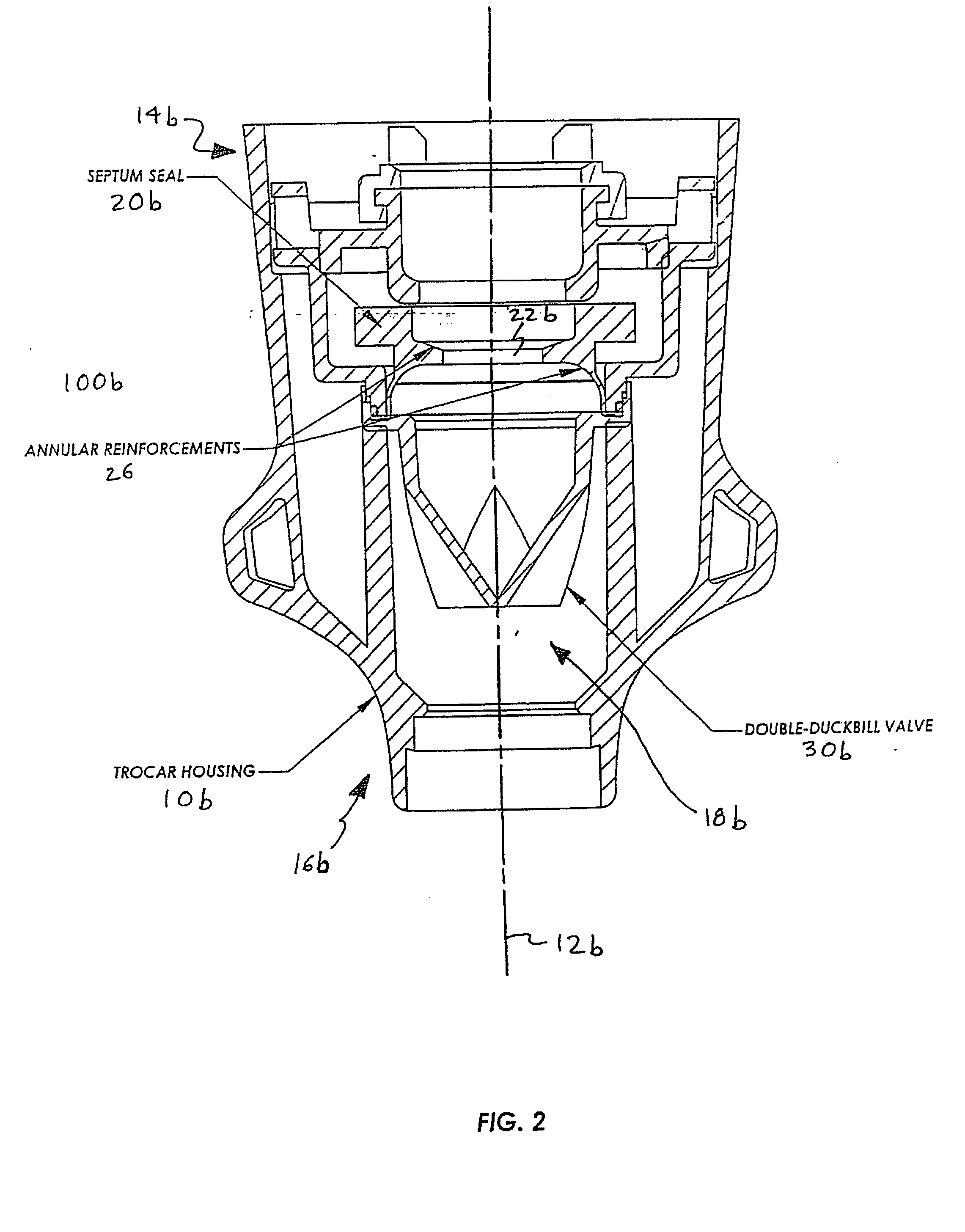
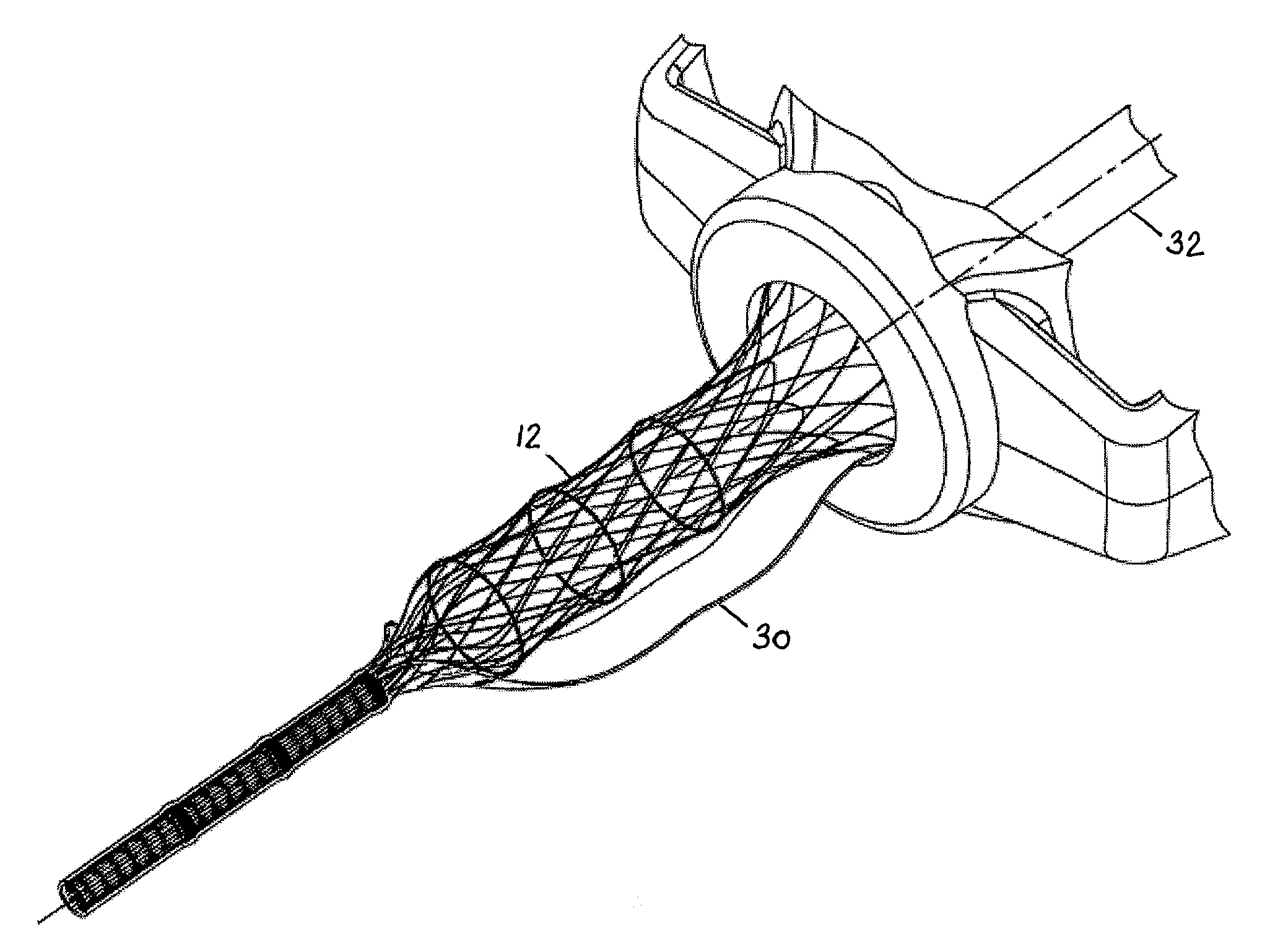
Anti-inversion trocar seal
The invention is directed to a trocar seal adapted to form a seal around a surgical instrument, the trocar seal comprising a housing having an axis extending between a proximal end and a distal end and forming a working channel sized and configured to receive the surgical instrument; an elastomeric septum seal having a proximal face and a distal face, the septum seal being disposed in the housing and extending transverse to the axis of the housing across the working channel; portions of the septum seal defining a hole having a diameter less than or equal to the diameter of the surgical instrument so that during insertion of the instrument along the working channel the septum seal forms a seal with the instrument; and at least one structure formed integrally with or proximate to the septum seal to prevent inversion of the septum seal upon withdrawal of the surgical instrument. The septum seal or the housing may further comprise a sidewall to include the structure extending from the sidewall to the distal face of the seal to tether the seal distally. The structure may be integrally formed with the proximal face of the septum seal to reinforce the seal, or the structure may be integrally formed with the distal face of the septum seal to tether the seal distally. The structure may be an annular reinforcement or rib, and is formed so as to allow side-to-side movement or floatation of the seal. The trocar seal may further comprise a plurality of radially extending ribs formed on the proximal or distal face of the septum seal to reinforce the seal. The trocar seal may further comprise a tensile element formed on the distal face of the septum seal.
Owner:MINEBEA CO LTD +1
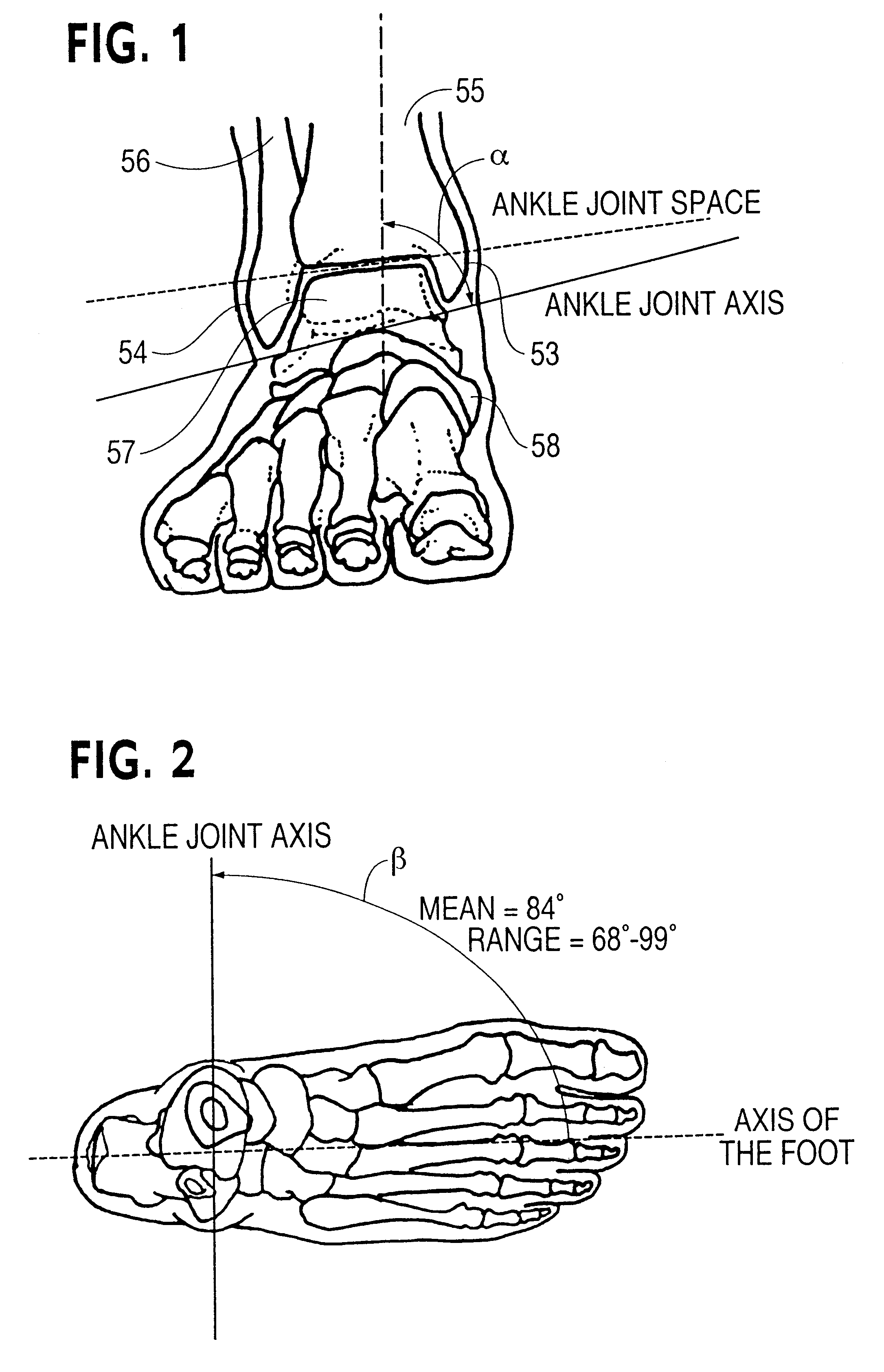
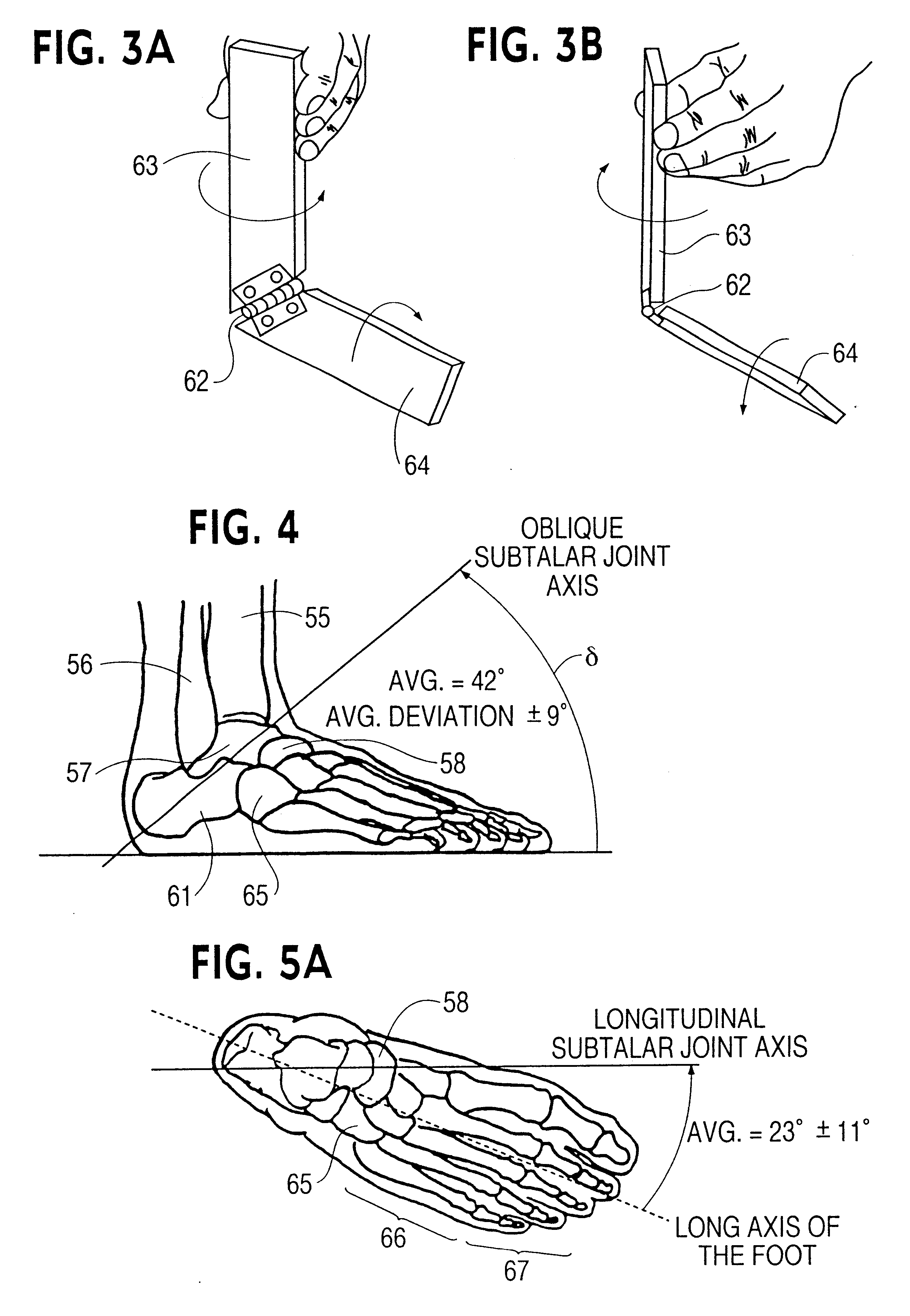
Shoe, ankle orthosis and method for protecting the ankle
InactiveUS6270468B1Prevent reversalEasy to controlFeet bandagesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesSacroiliac jointKnee orthosis
An improved athletic shoe, ankle orthosis and method for protecting the ankle against injury, limit subtalar joint motion of the ankle by controlling the motions of segments of the subtalar joint fore and aft of the subtalar joint while permitting motion of the foot about the ankle joint. A supporting structure a part of or connected to the shoe or orthosis is preferably in the form of a heel-sole counter provided about the heel and at least a portion of the foot forward of the subtalar joint. The supporting structure has a semi-rigid shape retaining character which is not collapsible vertically and which together with the shoe or orthosis limits torsional movement of the foot about the longitudinal axis of the subtalar joint as seen in a top plan view thereof by an upwardly extending portion thereof which acts as a torsion bar that is, in turn, secured to the lower leg. Preferably, the torsion bar has directional properties for resisting bending which are most rigid in a direction orthogonal or nearly orthogonal to the longitudinal axis of the subtalar joint. In a disclosed embodiment of the shoe motion of the midtarsal joint is also limited by the supporting structure to aid in limiting subtalar joint motion and shoe rollover. The shoe is secured to the foot by way of a strap arrangement which applies a force to the foot in a direction which, together with the heel-sole counter opposes the subtalar joint motion in supination.
Owner:TOWNSEND BARRY W +1
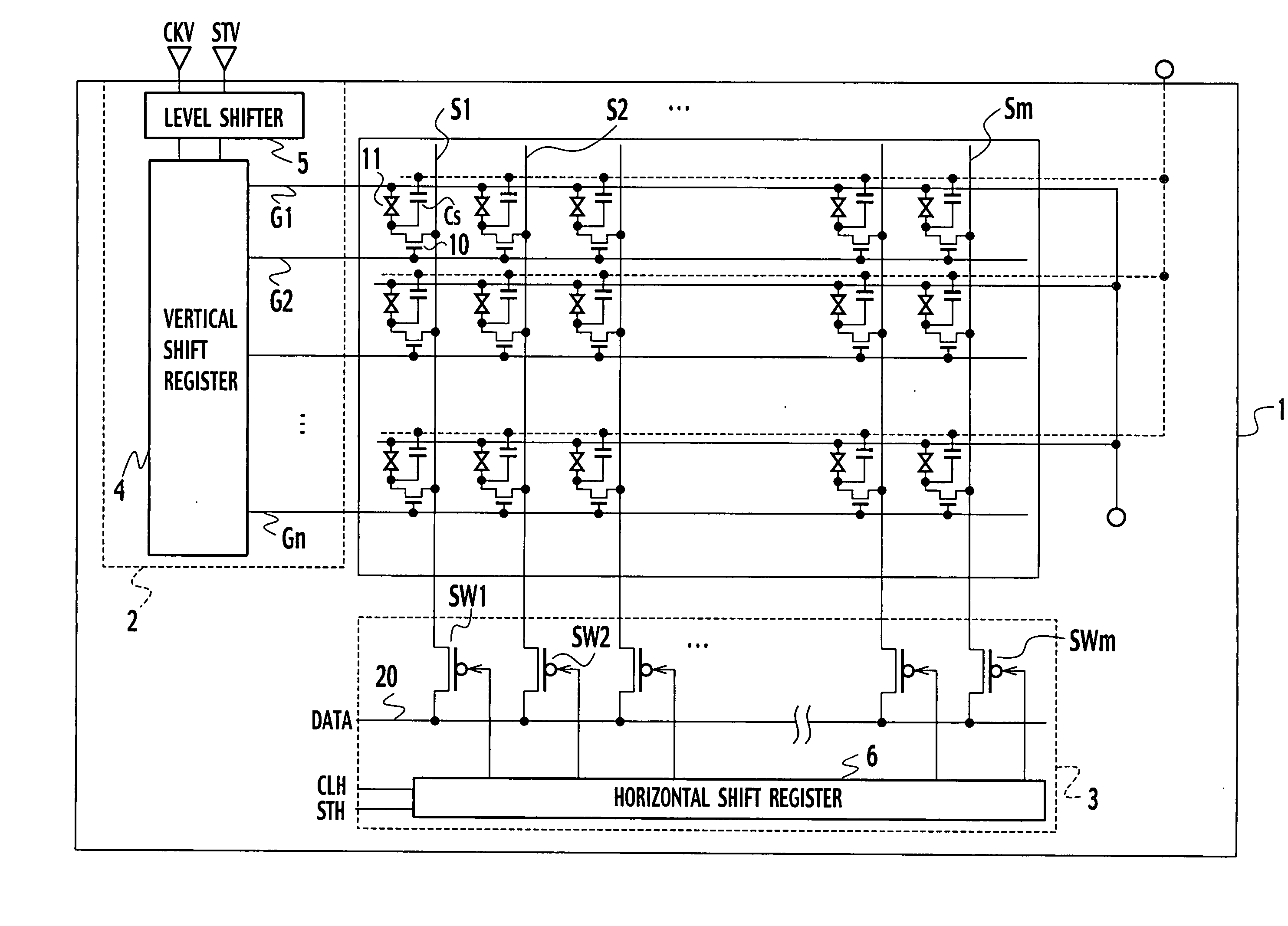
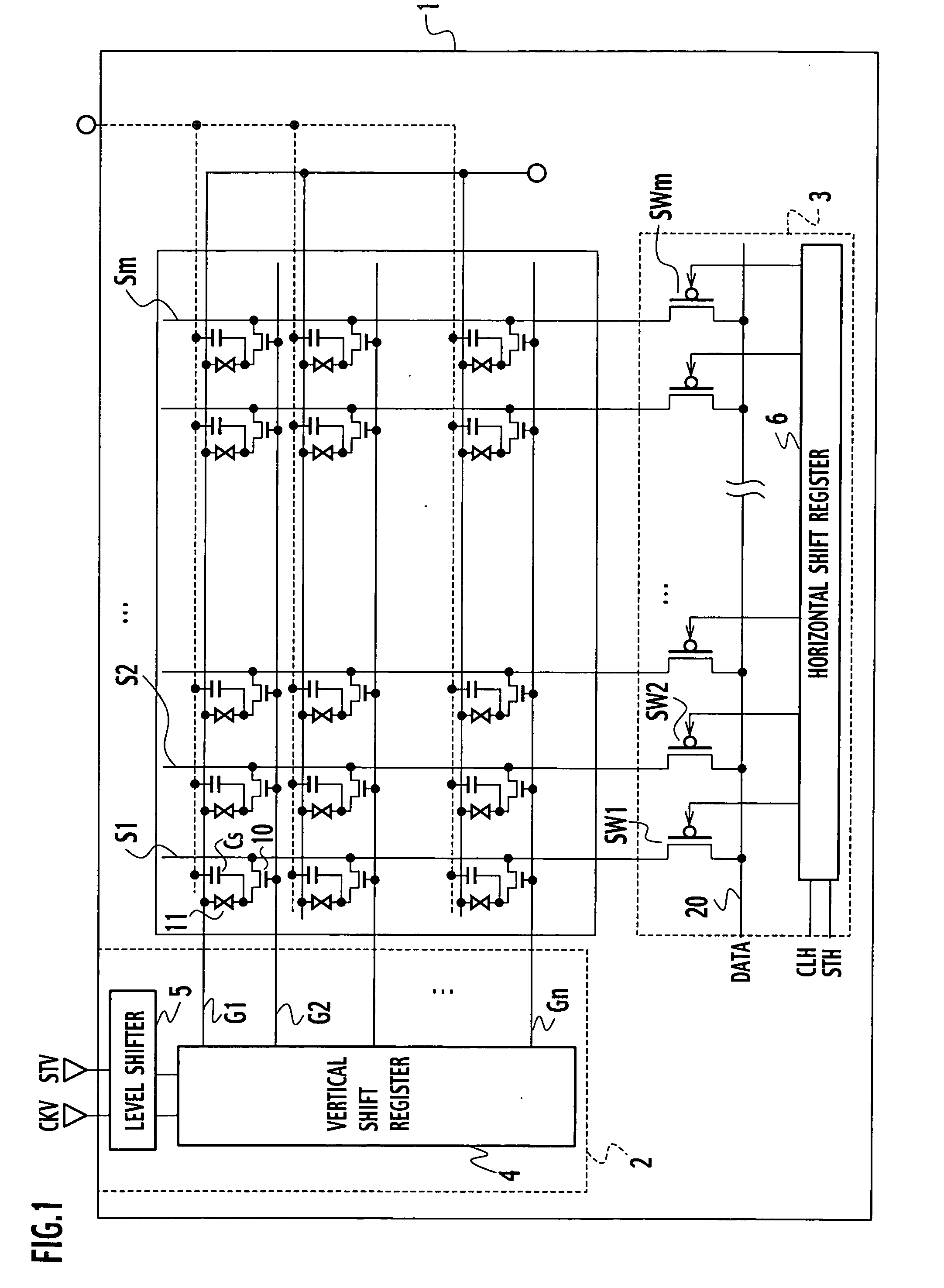
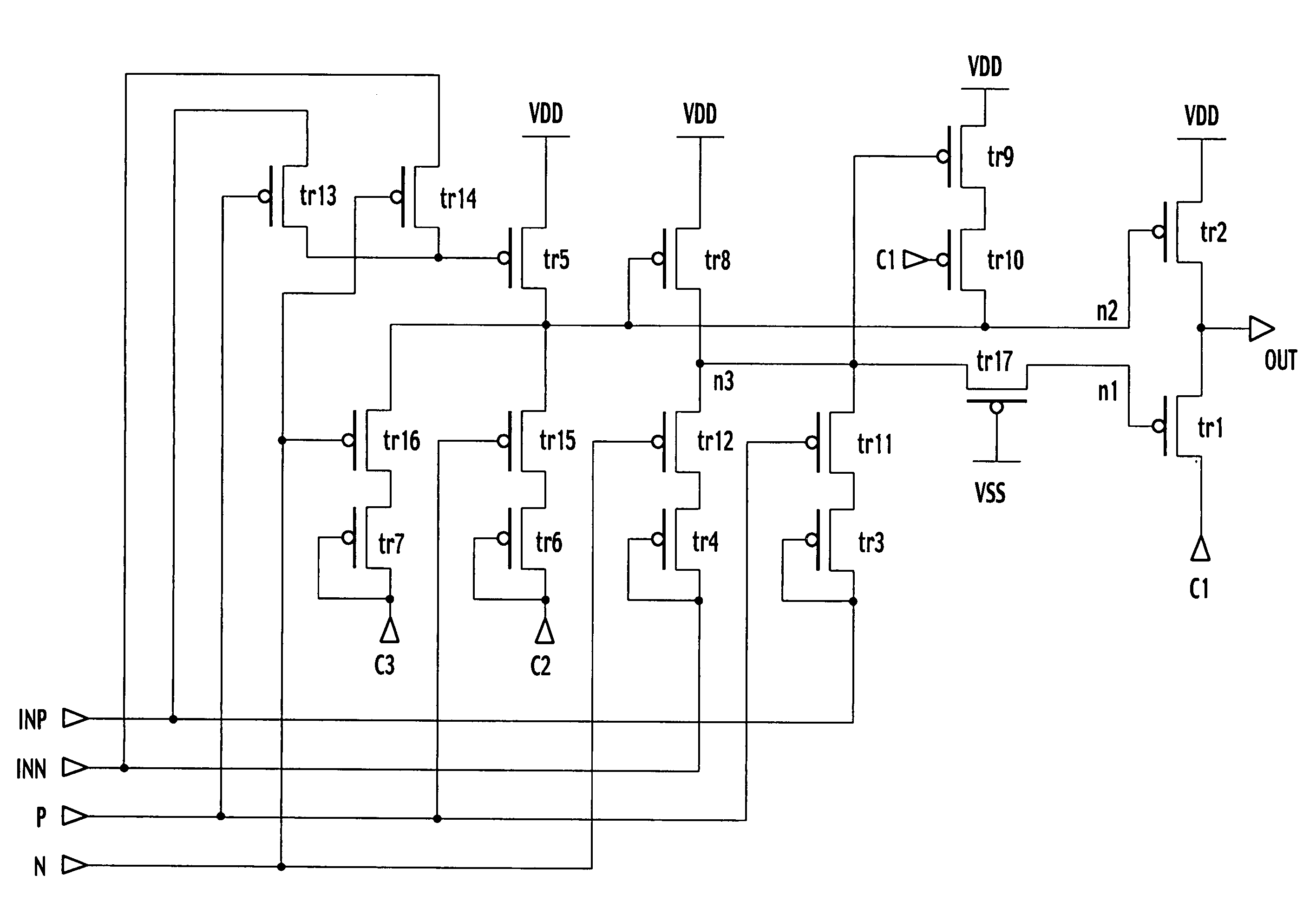
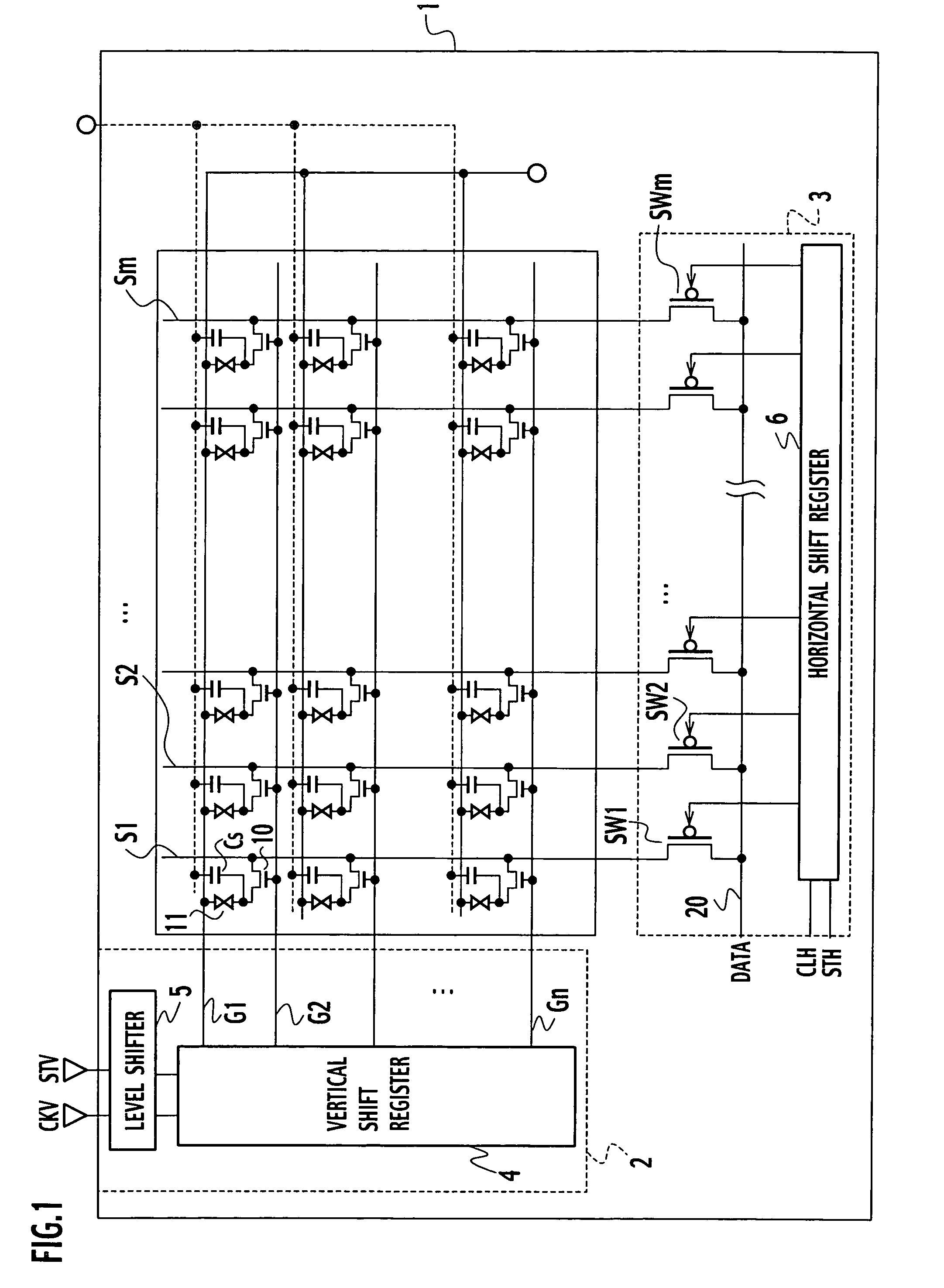
Bidirectional shift register shifting pulse in both forward and backward directions
ActiveUS20040104882A1Prevent reversalRaise the potentialStatic indicating devicesDigital storageShift registerEngineering
In forward direction pulse shift, by turning off a sixteenth transistor, a through-current is prevented from flowing between the fifth transistor and the seventh transistor. In backward direction pulse shift, by turning off the fifteenth transistor, a through-current is prevented from flowing between the fifth and sixth transistors. Thus, a potential variation in an output signal of a shift register between the forward direction pulse shift and the backward direction pulse shift is prevented.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY CENT INC
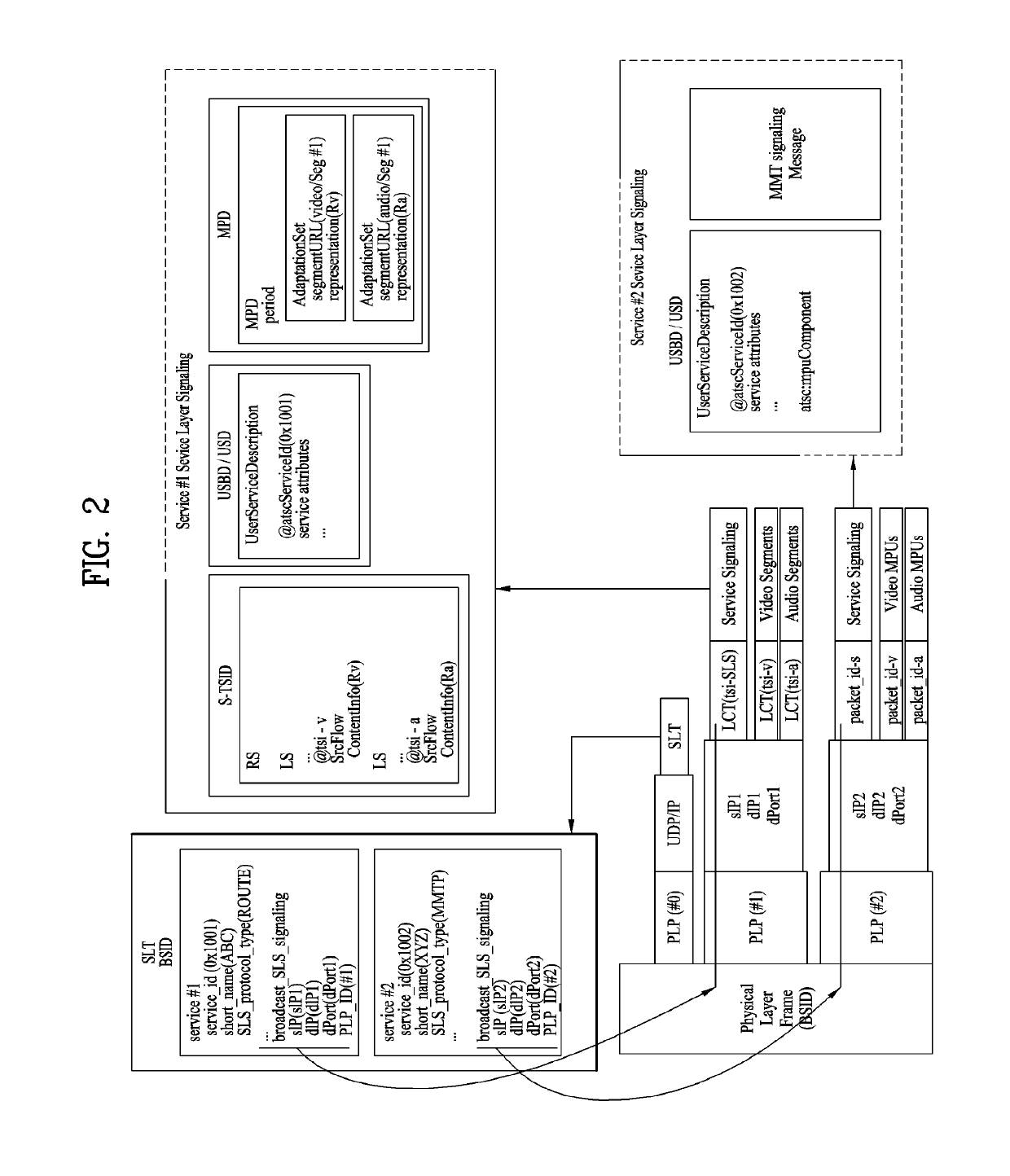
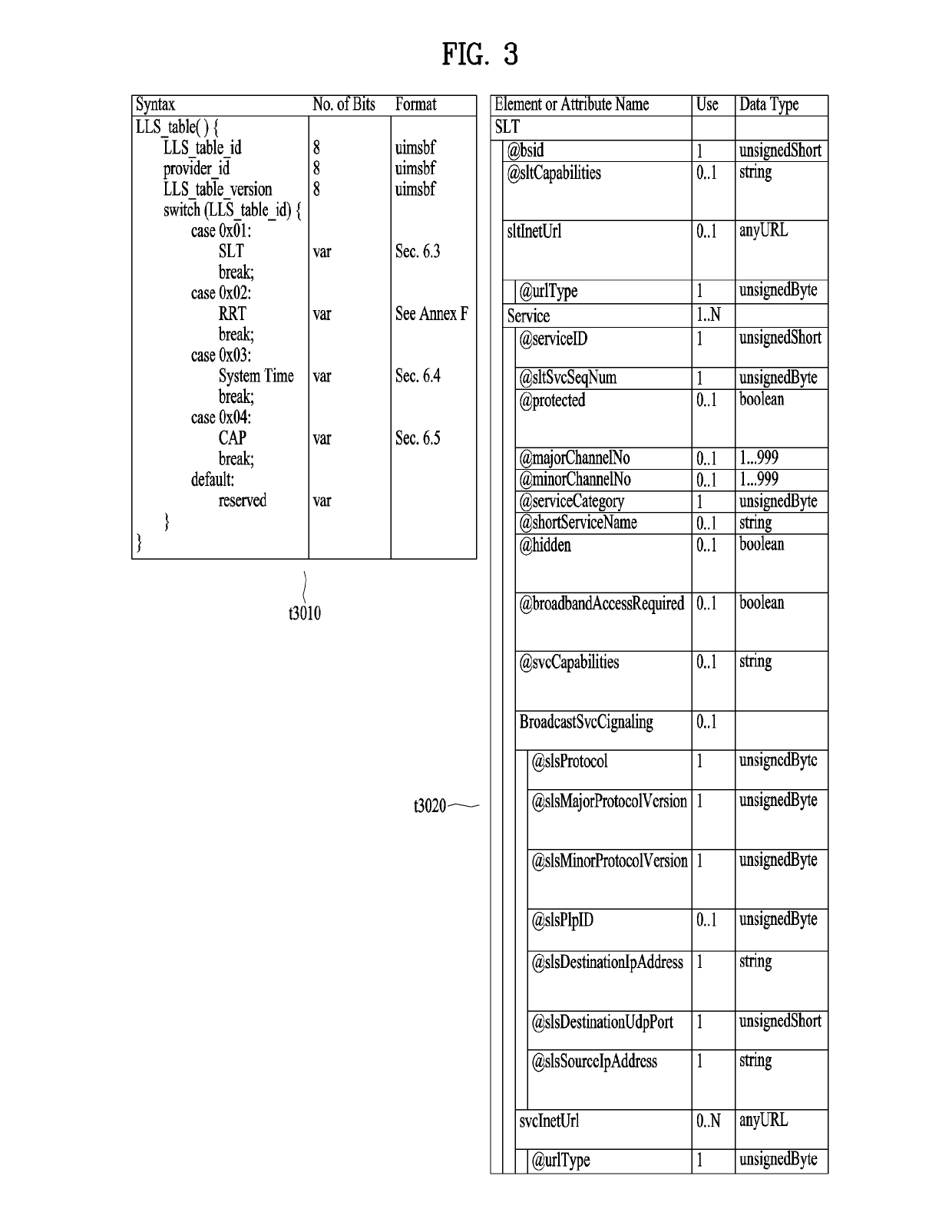
Broadcast signal transmission method, broadcast signal reception method, broadcast signal transmission apparatus, and broadcast signal reception apparatus
ActiveUS20190158894A1Prevent reversalHigh saturationTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsTelecommunicationsMetadata
Disclosed is a color volume mapping method. A broadcast signal transmission method according to an embodiment of the present invention may comprise the steps of: encoding video data and metadata for the video data; generating a broadcast signal including the encoded video data and metadata; and transmitting the generated broadcast signal.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Bidirectional shift register shifting pulse in both forward and backward directions
ActiveUS7098882B2Prevent reversalRaise the potentialStatic indicating devicesDigital storageShift registerEngineering
In forward direction pulse shift, by turning off a sixteenth transistor, a through-current is prevented from flowing between the fifth transistor and the seventh transistor. In backward direction pulse shift, by turning off the fifteenth transistor, a through-current is prevented from flowing between the fifth and sixth transistors. Thus, a potential variation in an output signal of a shift register between the forward direction pulse shift and the backward direction pulse shift is prevented.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY CENTRAL CO LTD
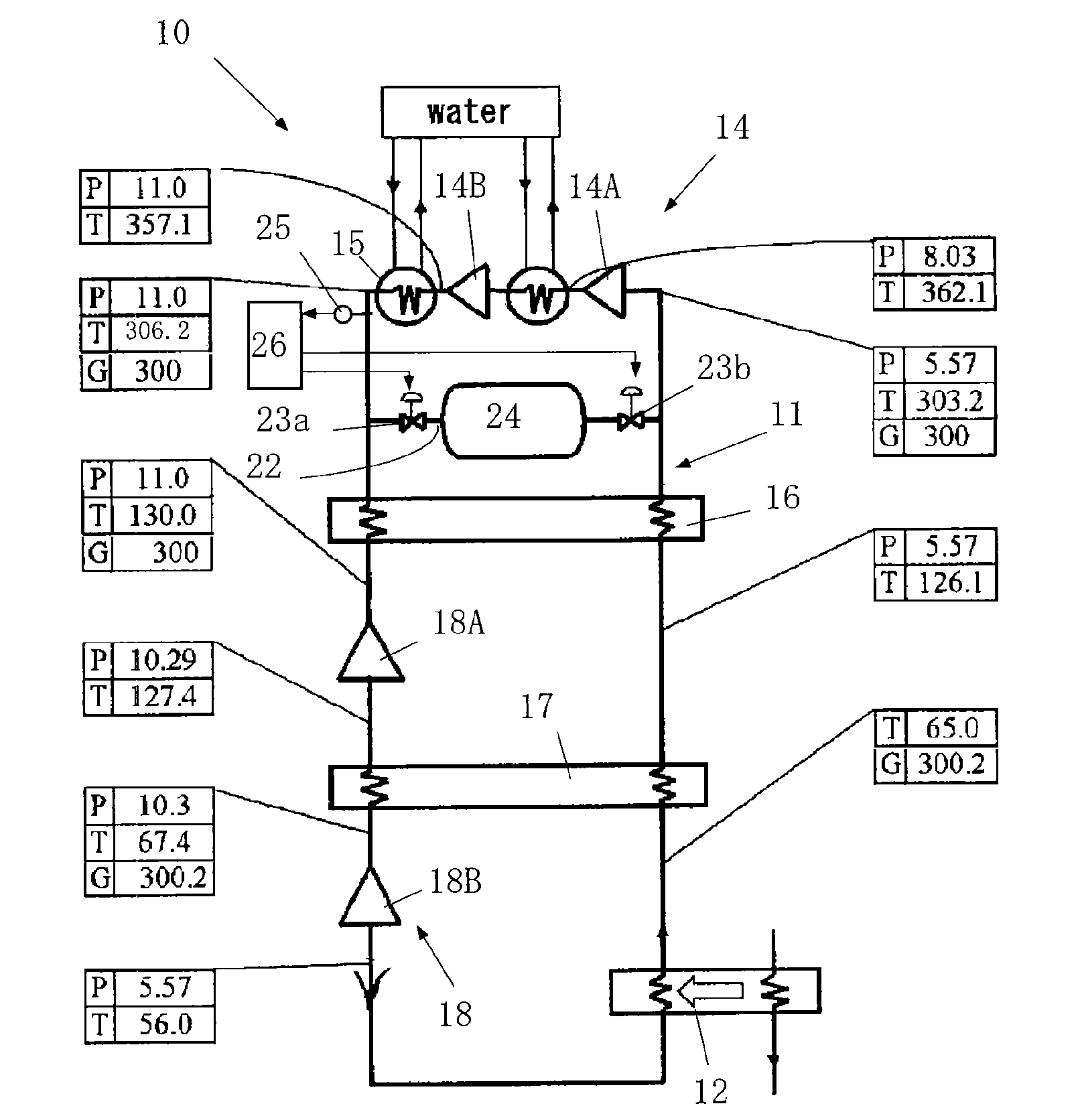
Cryogenic refrigerator and control method therefor
InactiveUS20100275616A1Smooth rotationPrevent reversalSolidificationLiquefactionClosed loopRoom temperature
A cryogenic refrigerator (10) which generates a cryogenic temperature by compressing and expanding a working gas in a closed loop (11). The cryogenic refrigerator comprises a bypass line (22) allowing a high-pressure portion and a low-pressure portion to communicate with each other, a gas storage tank (24) located midway in the bypass line and having pressure regulation valves (23a, 23b) on the high-pressure side and the low-pressure side, respectively, and a pressure control unit (26) controlling the pressure regulation valves. The pressure control unit (26) controls the pressure regulation valves (23a, 23b) so that the pressure in the gas storage tank (24) is equal to the pressure in the closed loop at room temperature and in a stopped state and so that the pressure in the gas storage tank (24) is between the pressures in the high-pressure portion and in the low-pressure portion and is close to the pressure in the low-pressure portion in an operating state.
Owner:IHI CORP
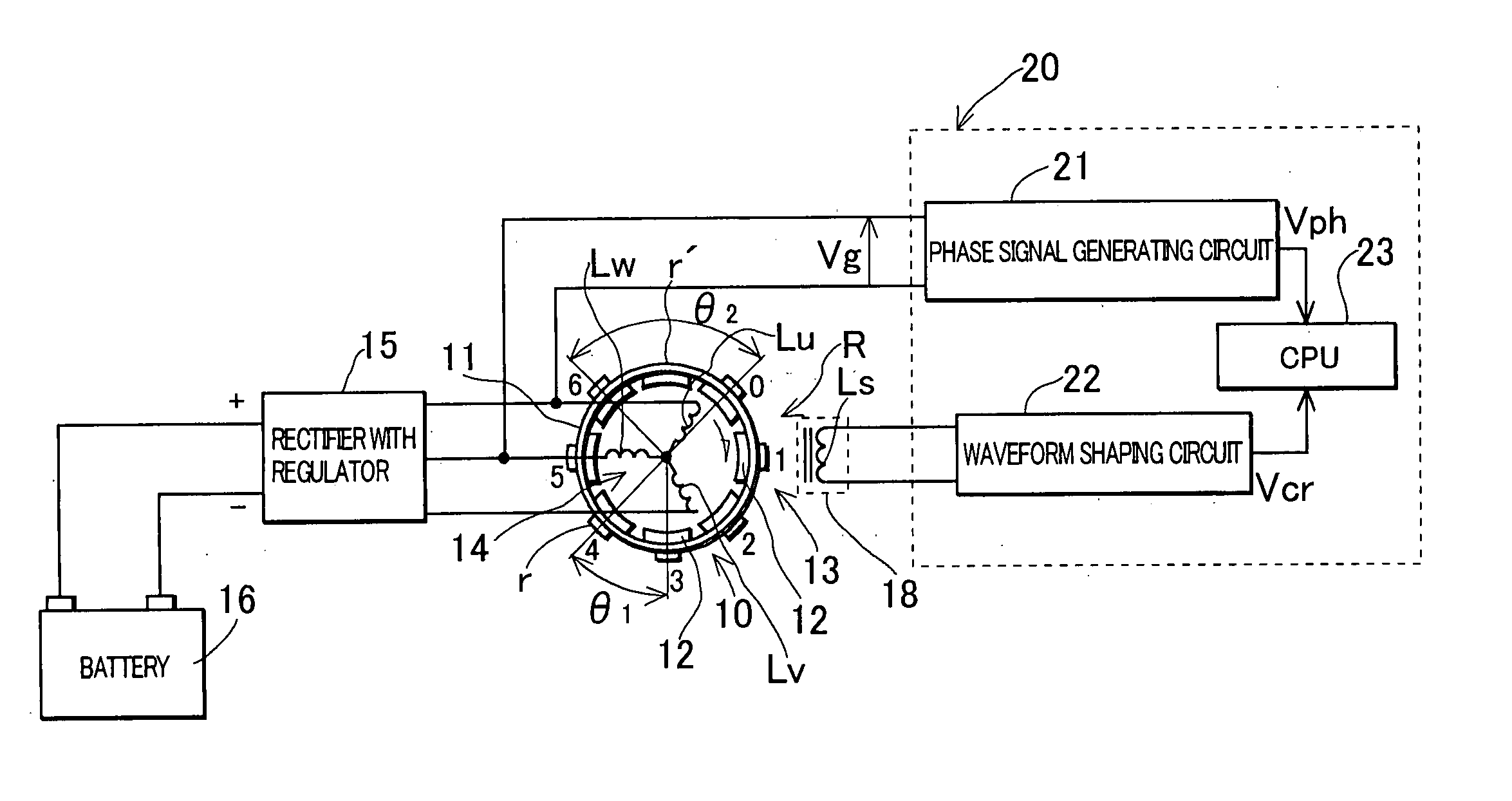
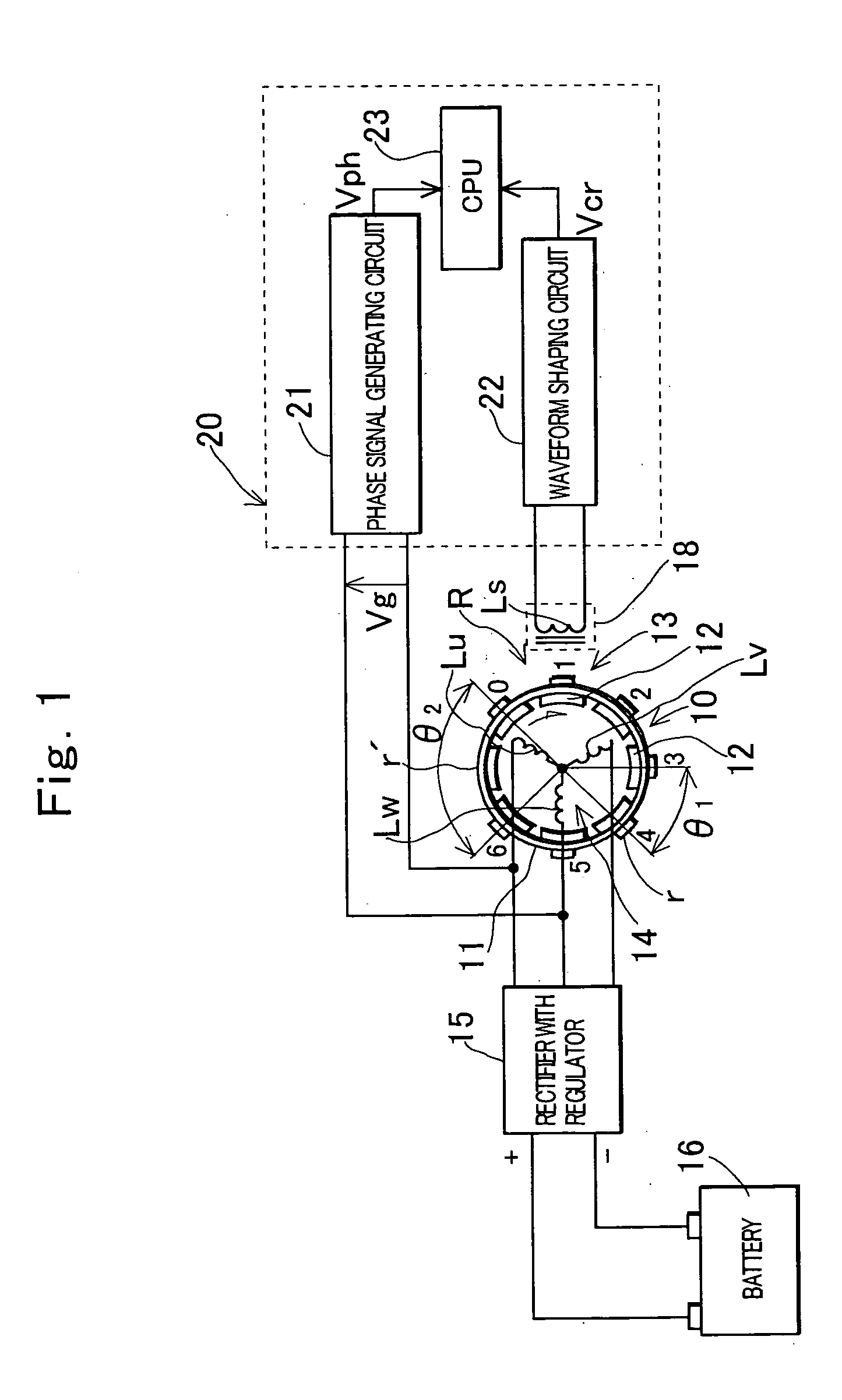
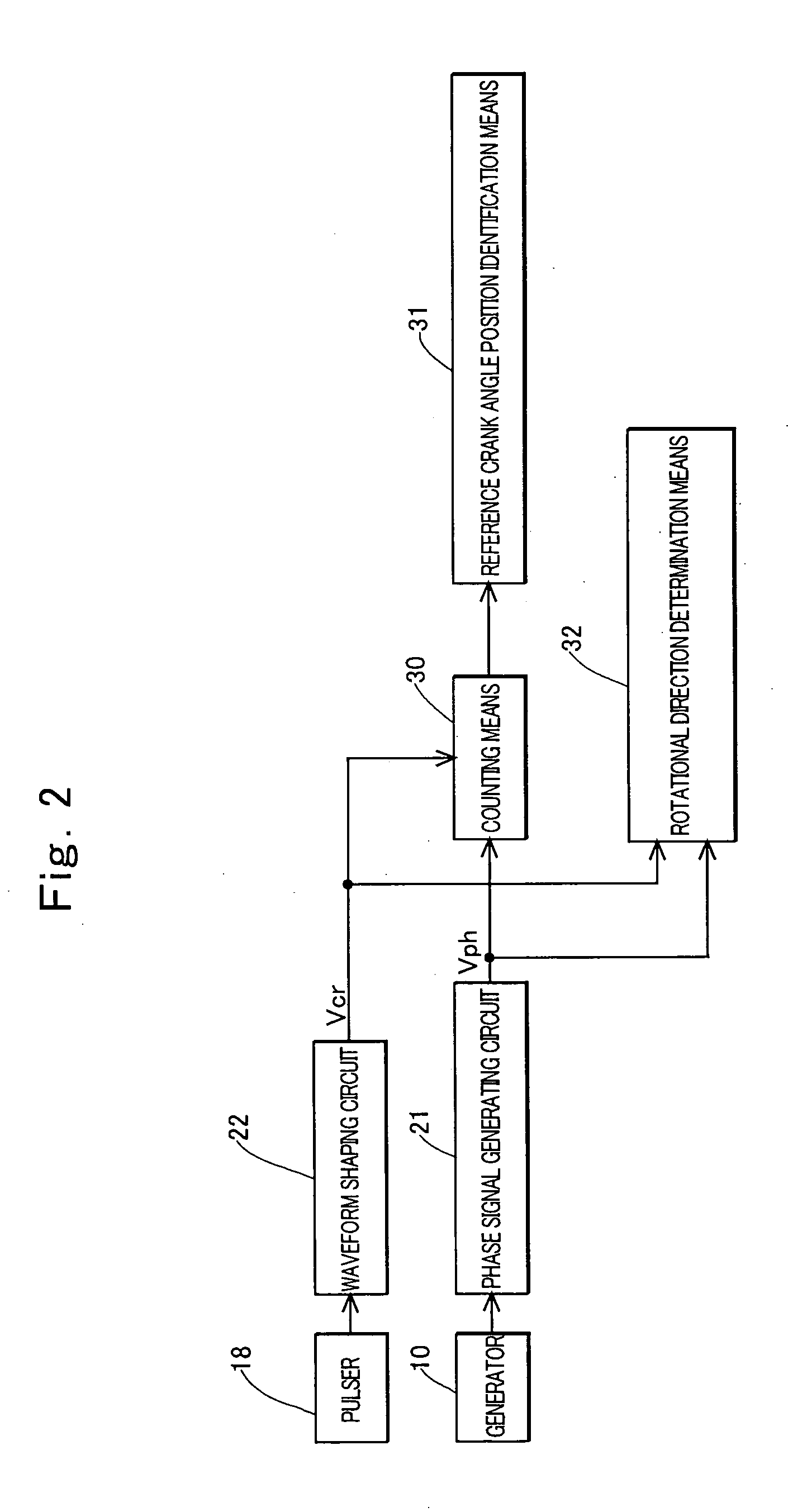
Engine rotation information detection device
ActiveUS20050120782A1Prevent reversalEasy to controlElectrical controlEngine testingEngineeringSignal generator
An engine rotation information detection device including: a generator that rotates in synchronization with an engine to output an AC voltage; a pulse signal generator that detects reluctors of a rotor having many reluctors and one reluctor missing portion to generate a pulse; counting means that counts the number of detections of a zero point of a waveform of the AC voltage in each detection section, the detection section being a section between a crank angle position where the pulse signal generator detects an edge of each reluctor and a crank angle position where the pulse signal generator detects a next reluctor; and reference crank angle position identification means that specifies a detection section including the reluctor missing portion from a count value counted by the counting means and identifies a pulse generated at a reference crank angle position based on the specified detection section.
Owner:MAHLE INT GMBH
Fortified confectionery delivery systems and methods of preparation thereof
InactiveUS6673380B2Great tasteImprove textureConfectioneryAnimal feeding stuffDelivery systemCarbohydrate
Chewy confectionery products, and processes for producing said products, are provided as delivery systems for minerals such as calcium. The carbohydrates of the fortified confectionery products include at least one reducing sugar and one non-reducing sugar in a weight ratio of about 1:0.2 to about 1:1 reducing sugar:non-reducing sugar. The chewy confectionery products offer a matrix for about 0.2 wt. % to 45 wt. % of a fortifying component while maintaining a smooth and soft texture.
Owner:HEARTLAND CONSUMER PROD
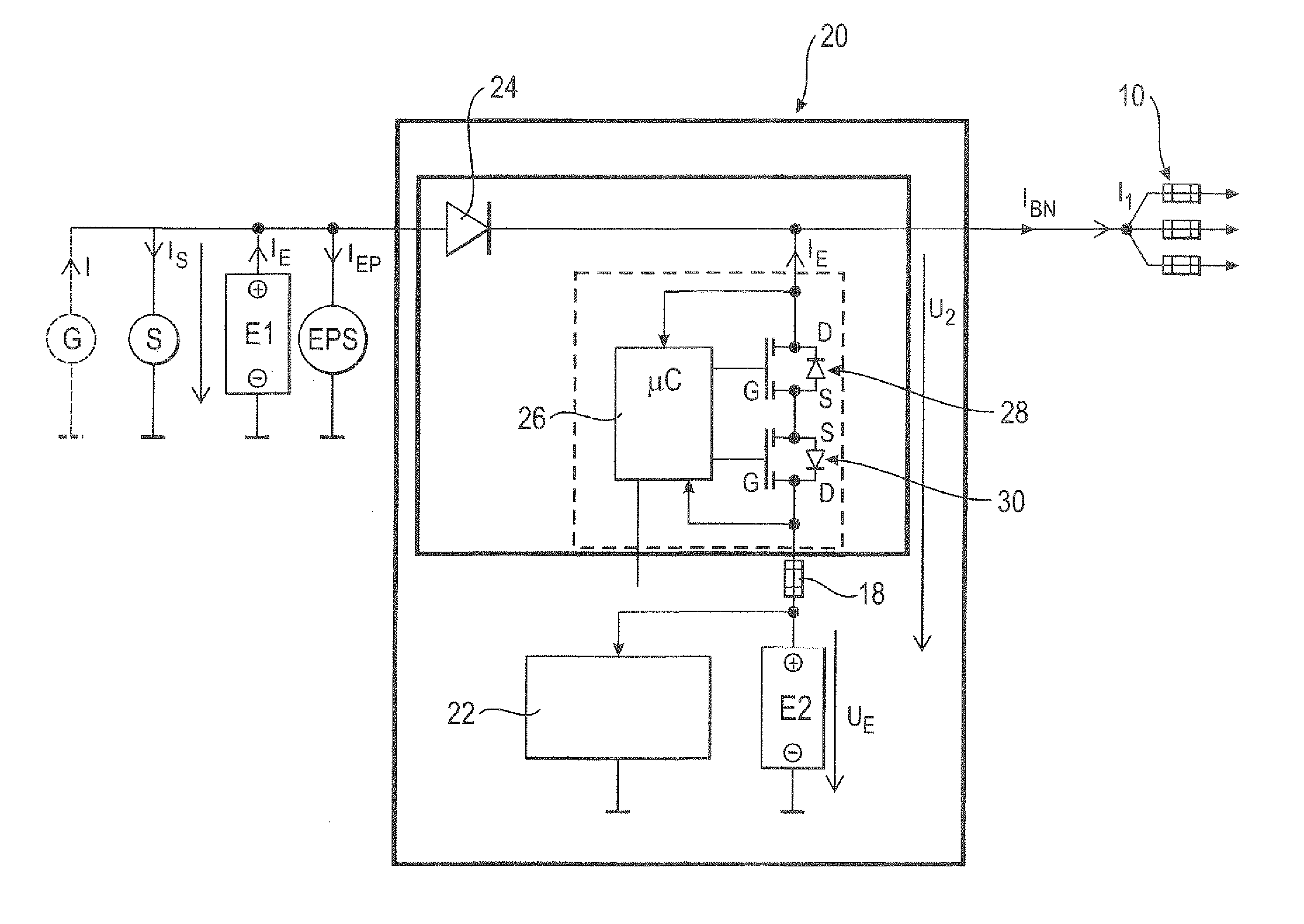
Circuit for voltage stabilization in an onboard power supply
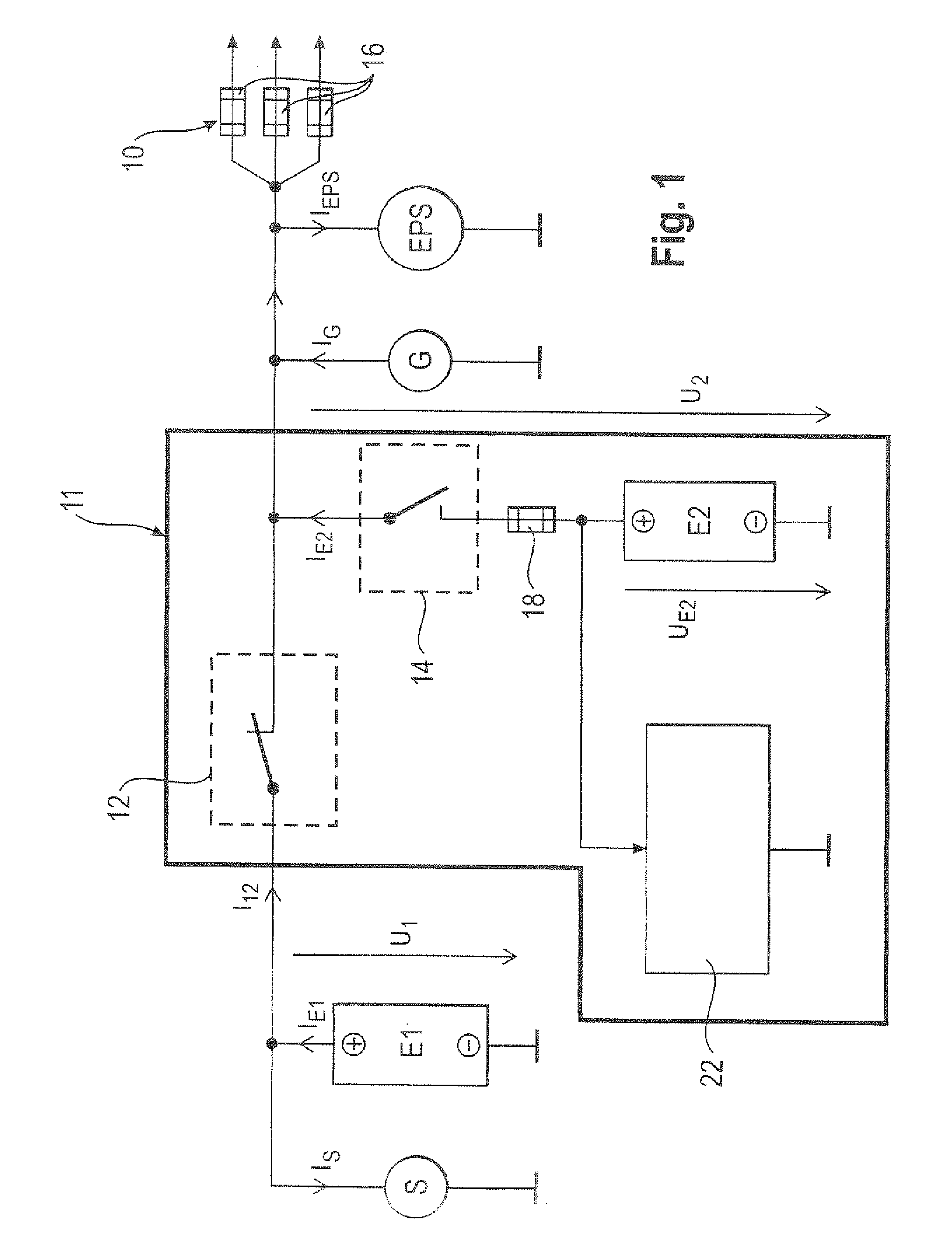
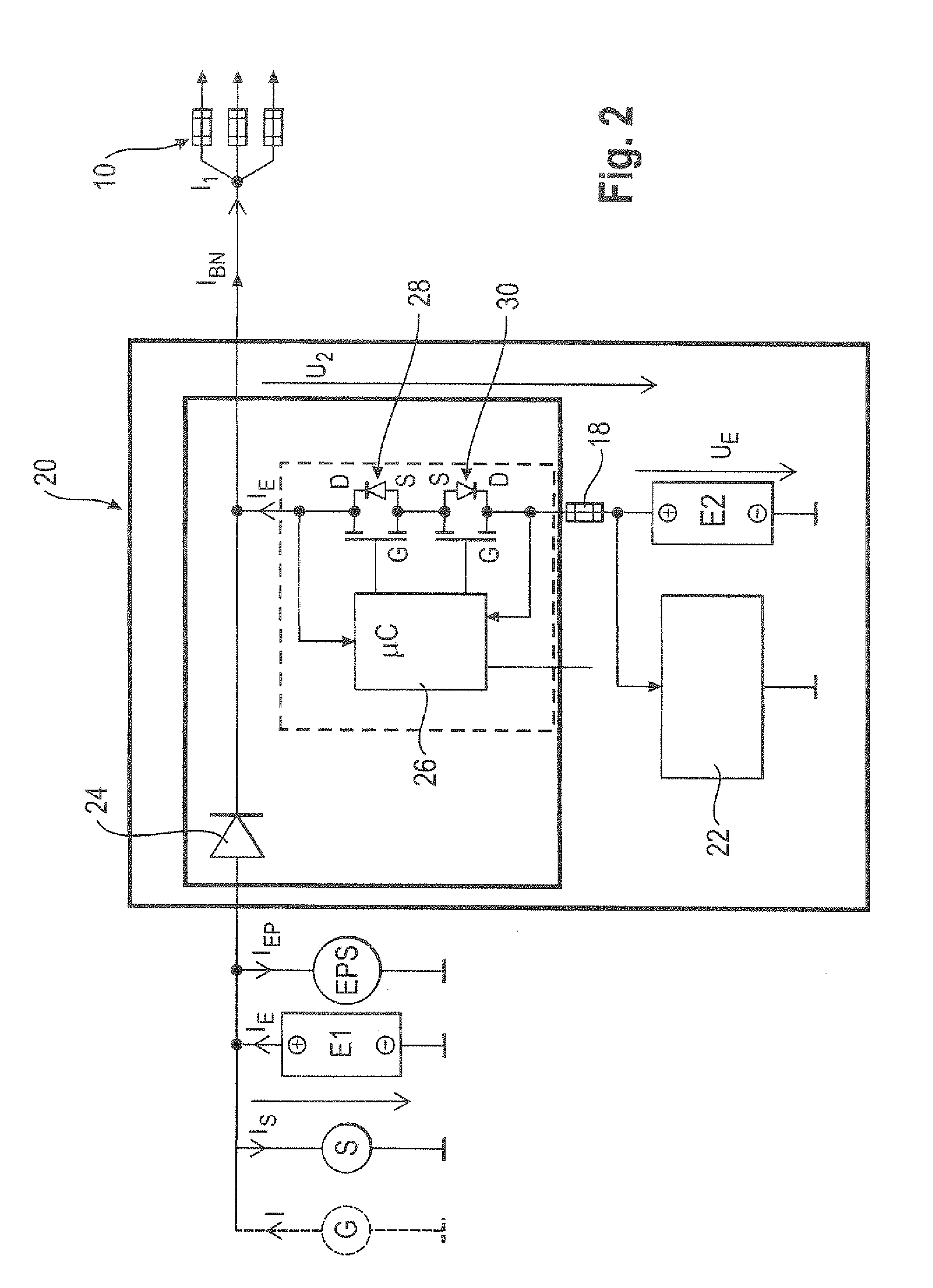
ActiveUS20110012424A1Improve storage densityShort release timeBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric devicesMobile vehicleElectricity
The invention relates to a circuit (20, 50) for voltage stabilization in an onboard power supply (10), particularly for motor vehicles, which is electrically connected between the onboard power supply (10) to be stabilized and a first energy store (E1). The circuit (20, 50) comprises a diode element (24) which contains a plurality of semiconductor switches (34) connected in parallel, a pilot and control circuit (33) which determines the level of a current flowing through the diode element (24) and controls the semiconductor switches (34) of the diode element (24) on the basis of the determined current level, and a second energy store (E2) which is electrically connected to the diode element (24) and to the onboard power supply (10).
Owner:LISA DRAXLMAIER GMBH
Electrohydraulic energy-regenerative type shock absorber
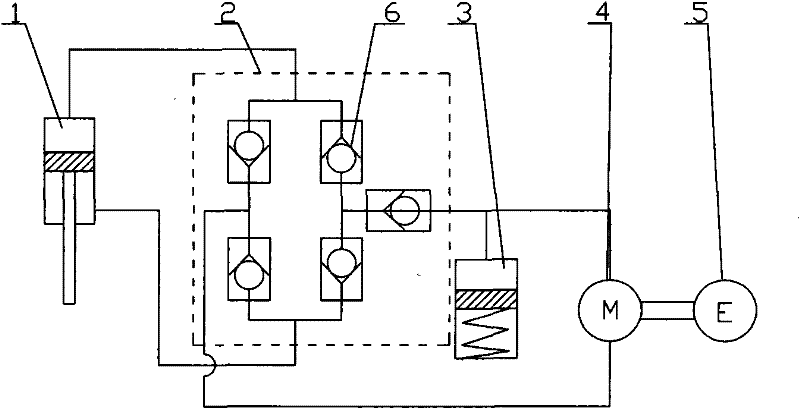
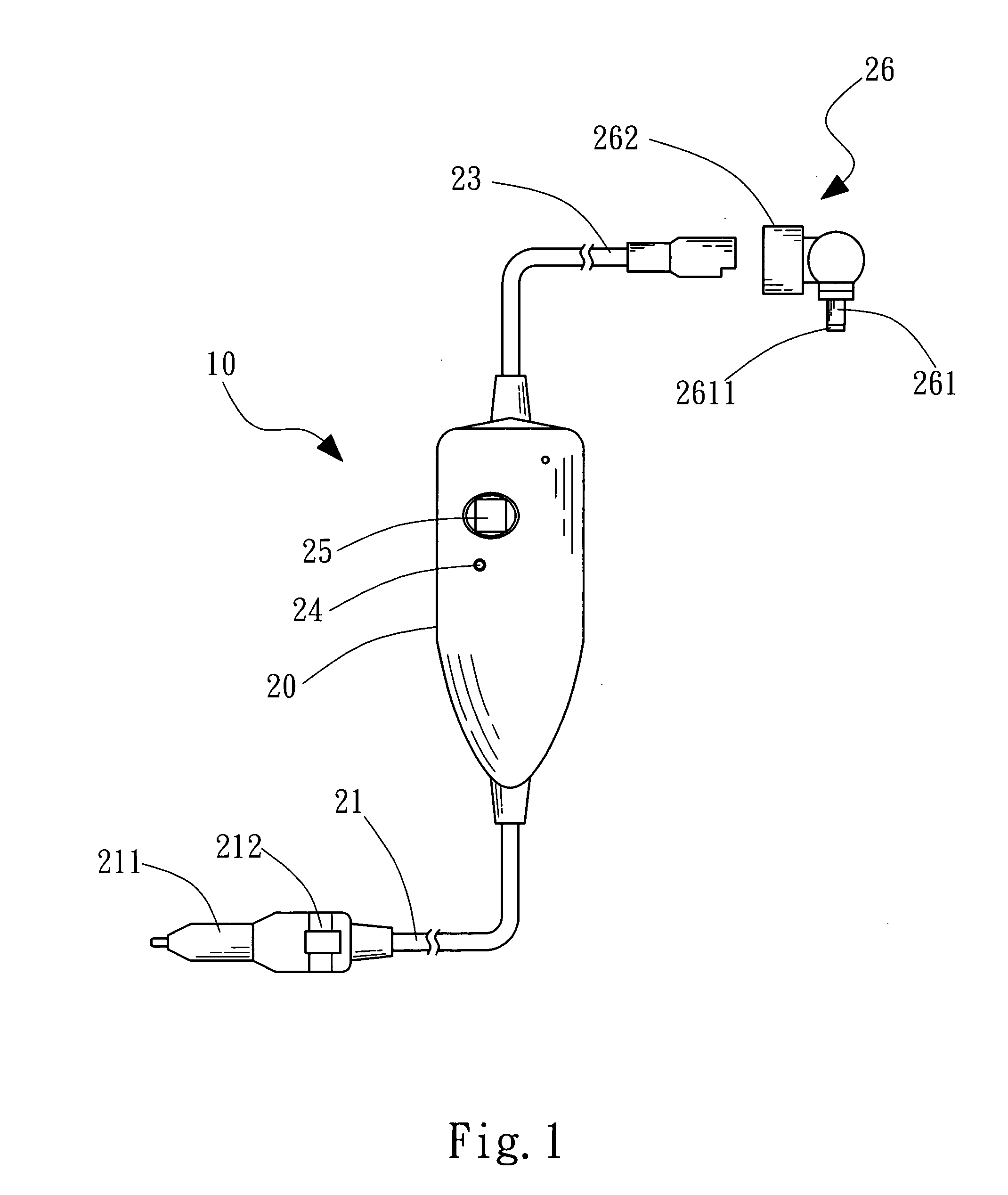
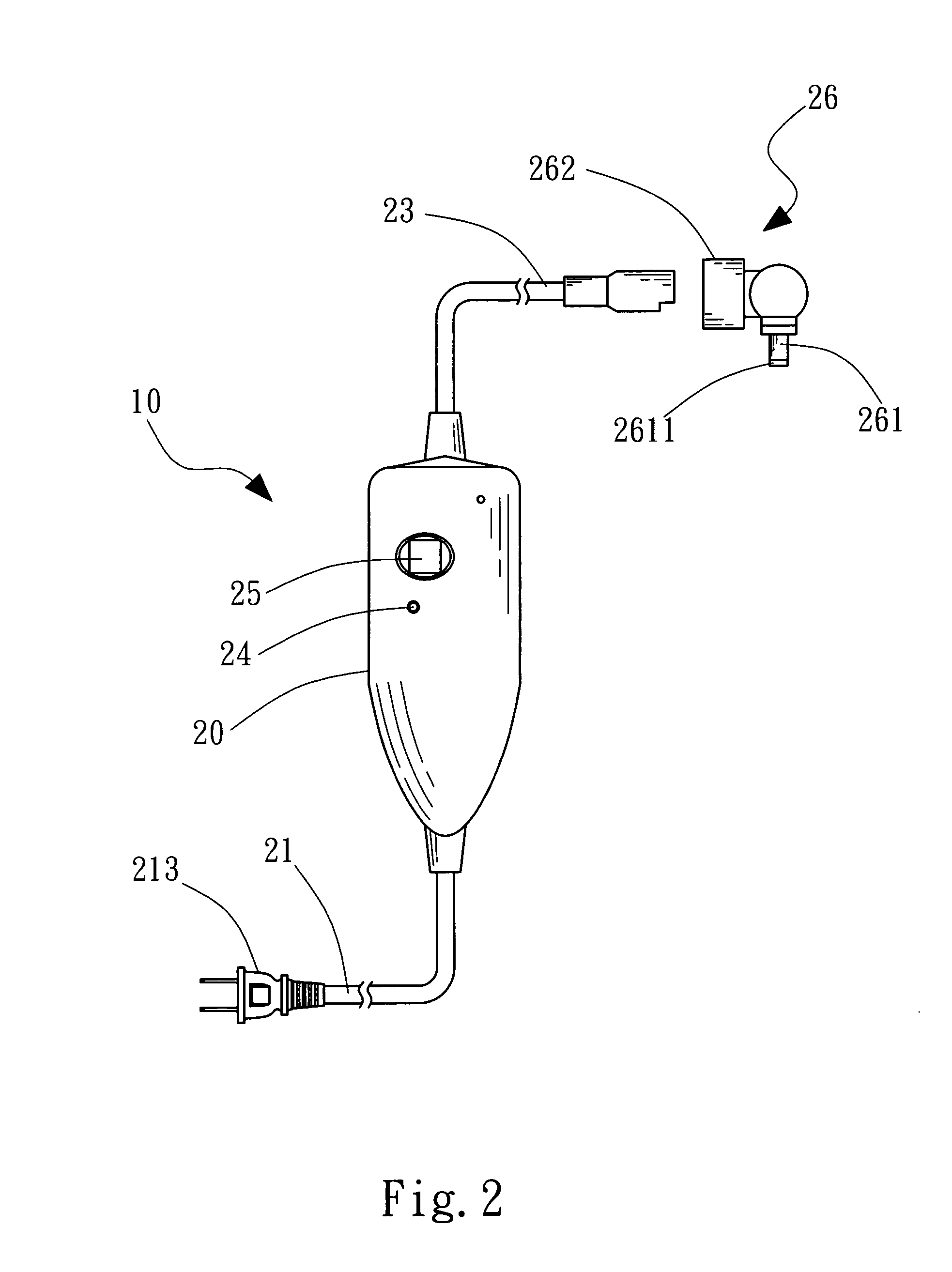
ActiveCN101749353APrevent reversalExtend your lifeLiquid based dampersMechanical energy handlingHydraulic motorDrive shaft
The invention relates to an electrohydraulic energy-regenerative type shock absorber, which comprises a hydraulic circuit, a working chamber and a piston, wherein the working chamber is divided into a piston working cavity and an accumulating power-generating cavity by a partition plate (13), and the piston is positioned in the piston working cavity and is connected with an external upper mounting base (7) through a piston push rod (8); a hydraulic motor (4) is positioned in the energy storage power-generating cavity and is connected with an external rotary generator (5) through a driving shaft, and an accumulator (3) is positioned in the accumulating power-generating cavity and is positioned below the partition plate (13); and the hydraulic circuit and a plurality of one-way valves (6) form a hydraulic rectifier bridge, and the hydraulic circuit adopts the method that an external pipeline is arranged outside the piston or the piston is designed to form internal and external cavities. The invention has simple structure, fewer components and small volume, can allow the energy generated by vehicle vibration to be fully used for doing work, can effectively recover vibration energy, has better shock absorbing effect than the existing shock absorber, and also prolongs the service life of the generator.
Owner:武汉经开科创运营有限公司
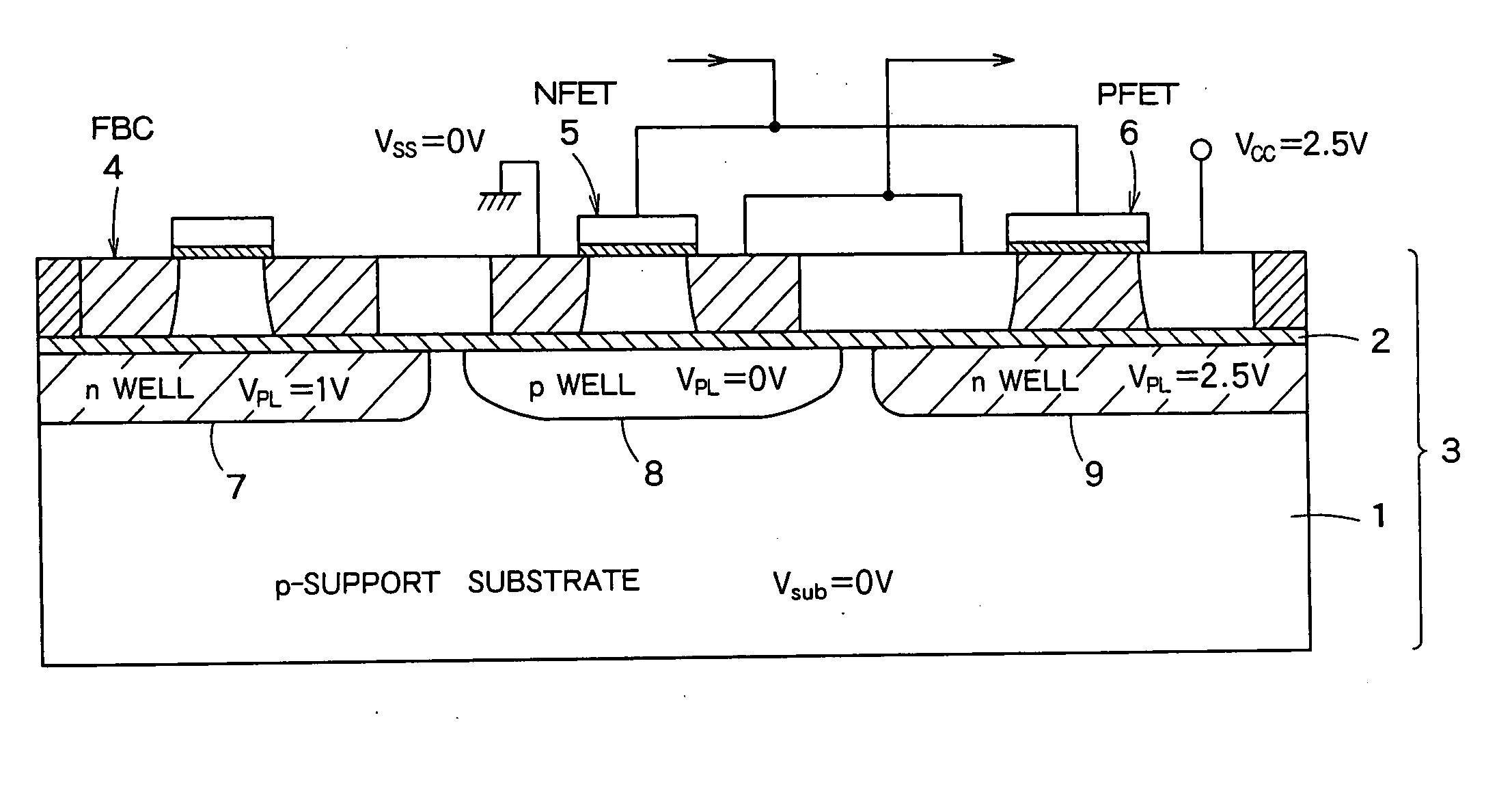
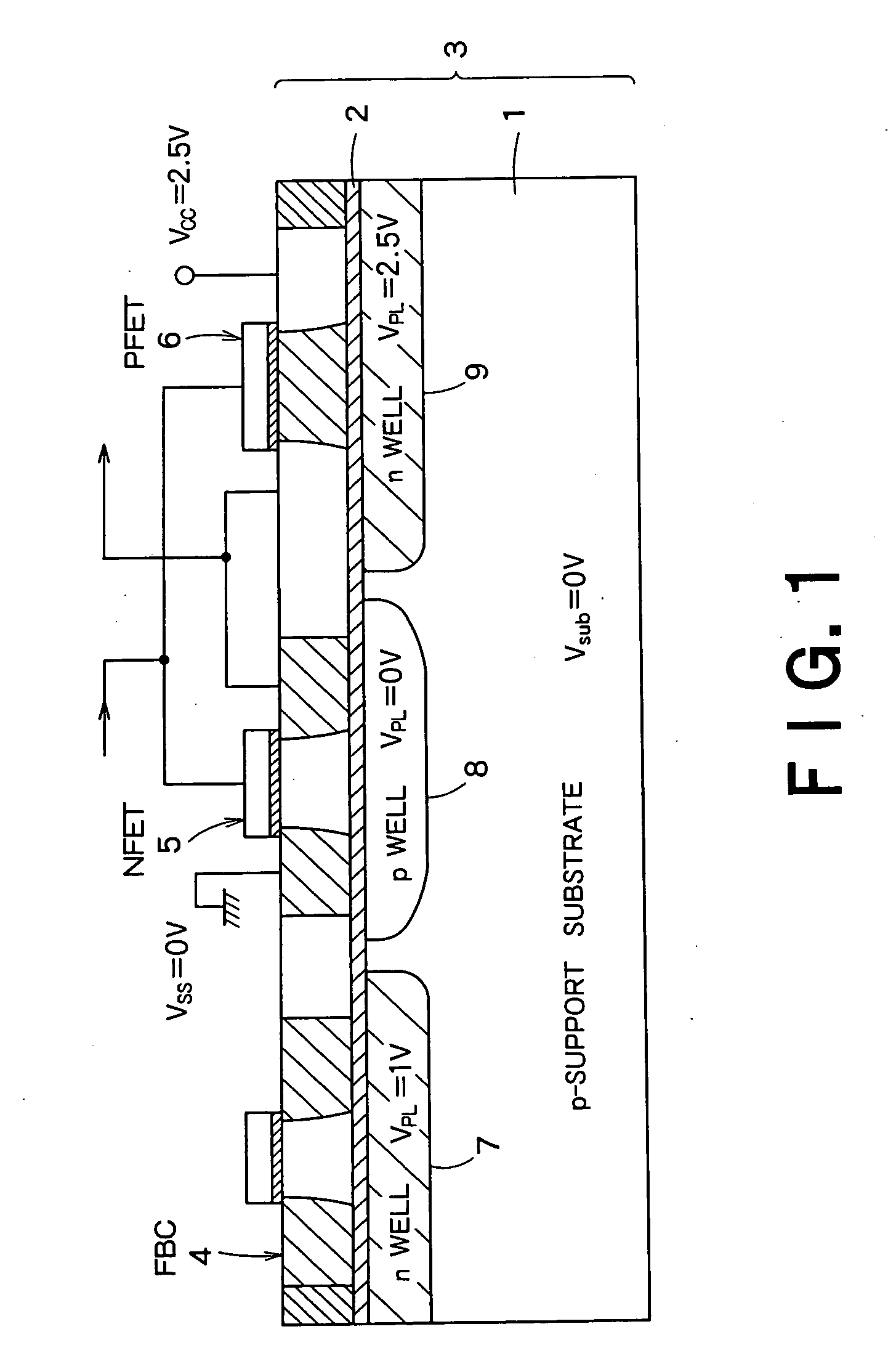
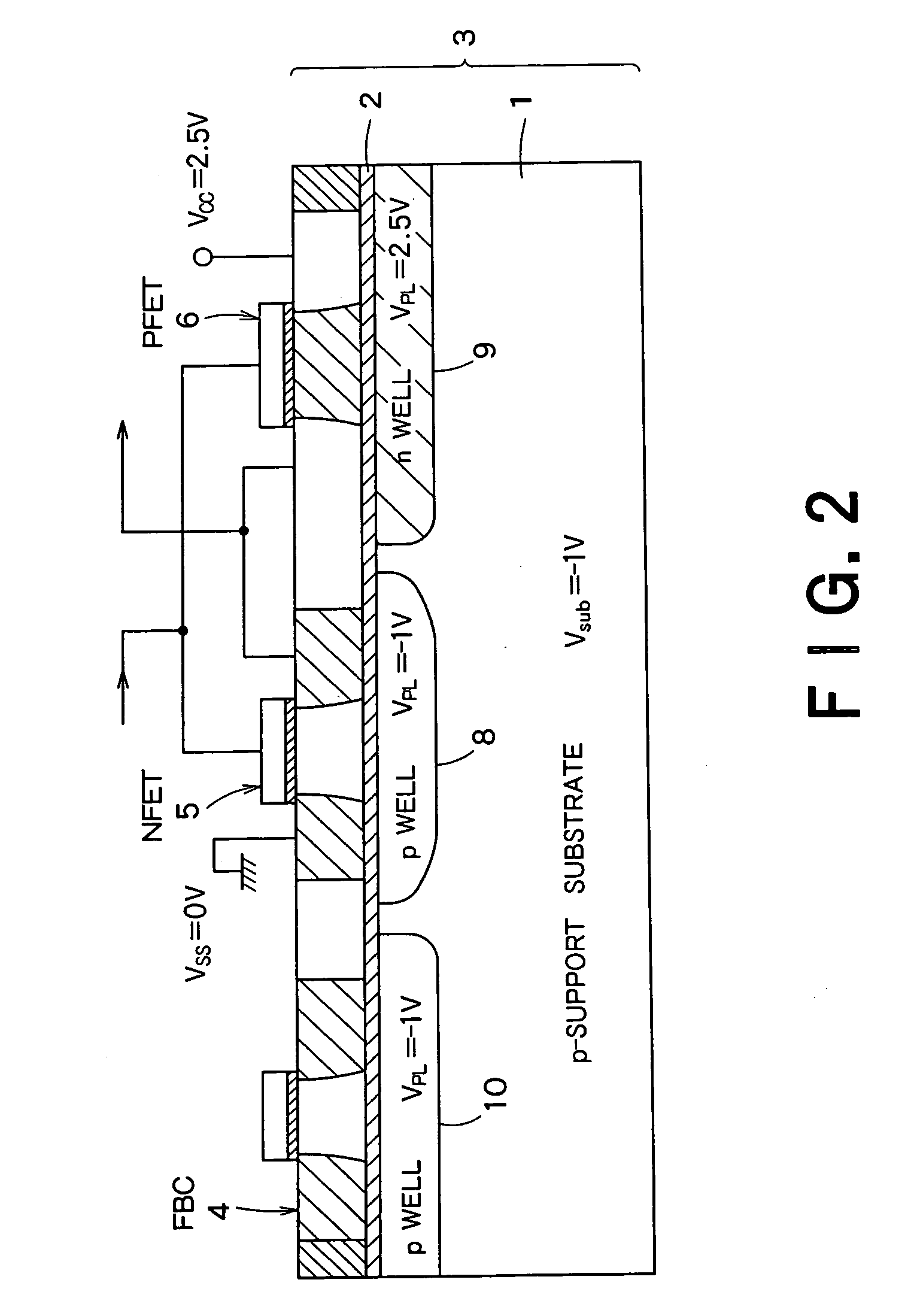
Semiconductor integrated device
InactiveUS20060046408A1Prevent reversalSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSoi substrateEngineering
A semiconductor integrated apparatus, comprising: an SOI (Silicon On Insulator) substrate which has a support substrate and an embedded insulation film; an NMOSFET, a PMOSFET and an FBC (Floating Body Cell) formed on the SOI substrate separately from each other; a p type of first well diffusion region formed along the embedded insulation film in the support substrate below the NMOSFET; an n type of second well diffusion region formed along the embedded insulation film in the support substrate below the PMOSFET; and a conduction type of third well diffusion region formed along the embedded insulation film in the support substrate below the FBC.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Diffusing film comprising transparent resin and scatterers
InactiveUS20030147140A1Controlled surface roughnessImprove viewing angle characteristicsDiffusing elementsPolarising elementsRefractive indexPolymer chemistry
A diffusing film comprises a transparent resin in which scatterers are dispersed. The difference between the refractive index of the transparent resin and that of the scatterers is in the range of 0.04 to 1.5. The scatterers are flat particles having sizes of 0.1 to 50 mum.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Compositions and Kits for Hair and Skin
InactiveUS20150037270A1Improved conditioning benefitImprove dry strengthCosmetic preparationsHair removalHair straighteningDisulfide bonding
Compositions, kits, and methods for repairing bonds, for example, disulfide bonds, in hair or on the skin are disclosed. The compositions provide improved conditioning benefit for dry hair or moisturize the skin. The compositions also provide a long lasting moisturized feel and smooth feel to the skin or hair, without feeling greasy. The compositions contain one or more compounds that covalently crosslink at least two thiol groups in the hair or on the skin. Use of the crosslinking compositions prevents reversion of the repaired bonds to their reduced (thiol) state, for at least one week, one month, six months, or one year, after a single application of the composition. Improved methods of styling hair, for example permanent hair waving, hair curling, and hair straightening are also provided.
Owner:LIQWD
Flexible cannula devices and methods
InactiveUS20100312189A1Prevent reversalEfficient insertionCannulasInfusion syringesCannula deviceAbdominal trocar
Various devices and methods are provided for dilating tissue. In one embodiment, a trocar cannula is provided and includes an elongate tubular member defining an inner lumen extending therethrough and configured to receive a surgical instrument therethrough. The tubular member is configured to radially expand to increase an inner diameter of the inner lumen and thereby dilate tissue. In one embodiment, the tubular member has an expansion element incorporated therein and the expansion element is configured to maintain the tubular member in a radially expanded position when no instrument is disposed within the inner lumen.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC +1
Diffusion film comprising transparent substrate and diffusion layer
InactiveUS20050063062A1Widen perspectiveReduce image qualityDiffusing elementsPolarising elementsDiffusionOptoelectronics
A diffusion film comprises a transparent substrate and a diffusion layer. The diffusion layer shows a specific scattered light profile measured by a goniophotometer. In the scattered light profile, a ratio of an intensity of scattered light at an angle of 30° to an intensity of transmitted light at an angle of 0° is 0.01 to 0.2%.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Generator for generating chlorine dioxide under vacuum eduction in a single pass
InactiveUS6881320B1Quickly and effectively evacuatesSecurity featureElectrolysis componentsAtomized substancesIon-exchange membranesChemistry
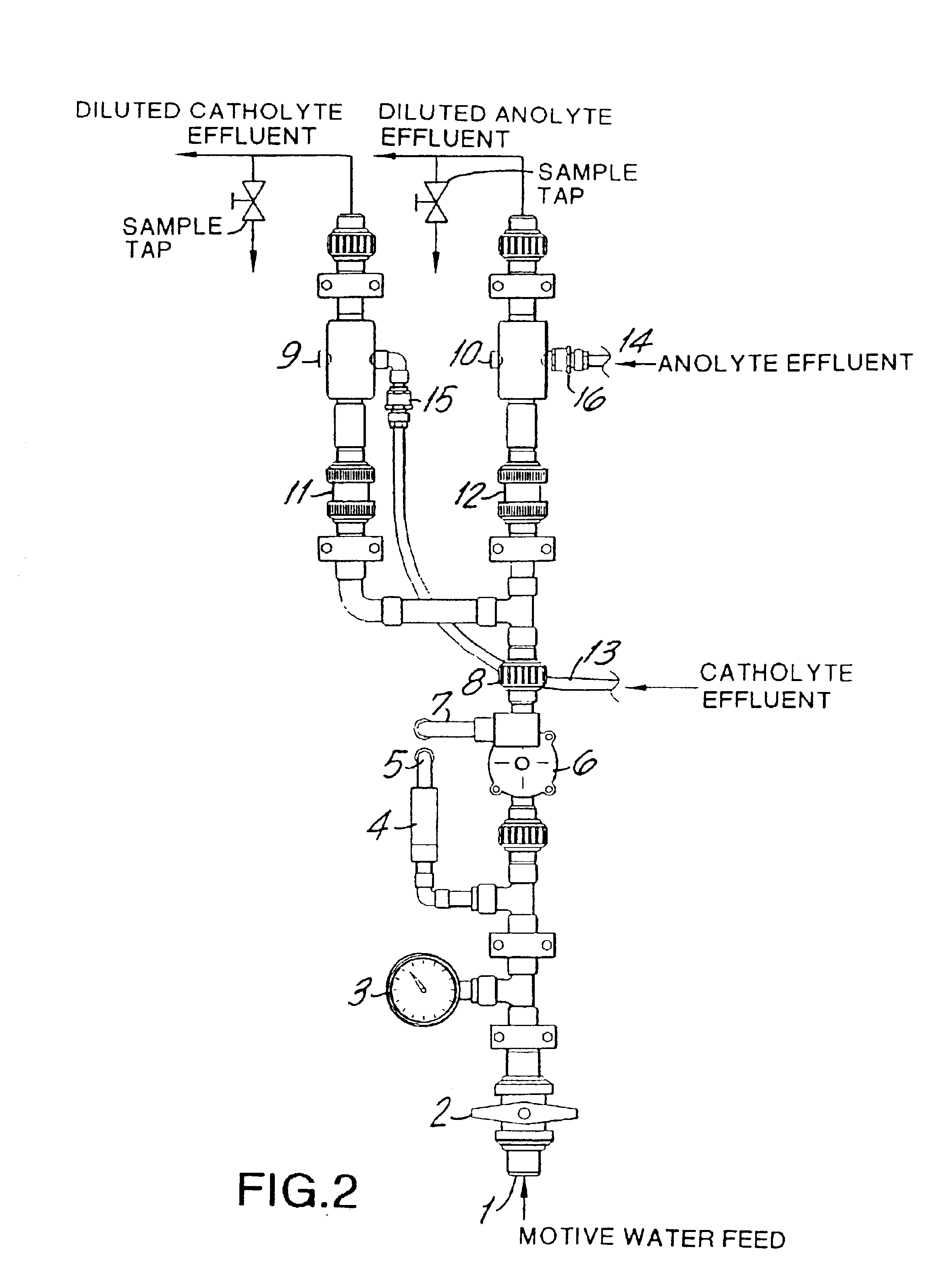
A vacuum operated electrolytic generator can be used to produce a chlorine dioxide solution or a mist of chlorine dioxide from a buffered aqueous alkali metal chlorite solution in one pass through an electrolytic cell. The cell contains a high surface area anode, a corrosion-resistant highly conductive cathode, and a cation ion exchange membrane between the anode and cathode. An eductor is used on the anolyte effluent line to create a vacuum and draw the anolyte through the cell. Either motive water or a motive inert gas (such as air) is used in the eductor. Preferably, an eductor is used in the catholyte effluent line. An ascending anolyte effluent line with a non-corrosive check valve leads from the cell to the anode eductor. Sensors are used to monitor the composition of the anolyte effluent and / or the anolyte feed. The final product is a chlorine dioxide solution when water is used for the eduction. The final product is a mist consisting essentially of gaseous chlorine dioxide, an inert gas, and water vapor when an inert gas is used for the eduction. The mist is useful for application crop, soils, produce such as vegetables, fruit, and tobacco, fields, storage cellars, and the like.
Owner:INT DIOXCIDE
Surgical sutures having collapsible tissue anchoring protrusions and methods therefor
Owner:ETHICON INC
Diffusing film comprising transparent resin and scatterers
InactiveUS6710923B2Prevent surfaceWiden perspectiveDiffusing elementsPolarising elementsRefractive indexPolymer chemistry
A diffusing film comprises a transparent resin in which scatterers are dispersed. The difference between the refractive index of the transparent resin and that of the scatterers is in the range of 0.04 to 1.5. The scatterers are flat particles having sizes of 0.1 to 50 mum.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
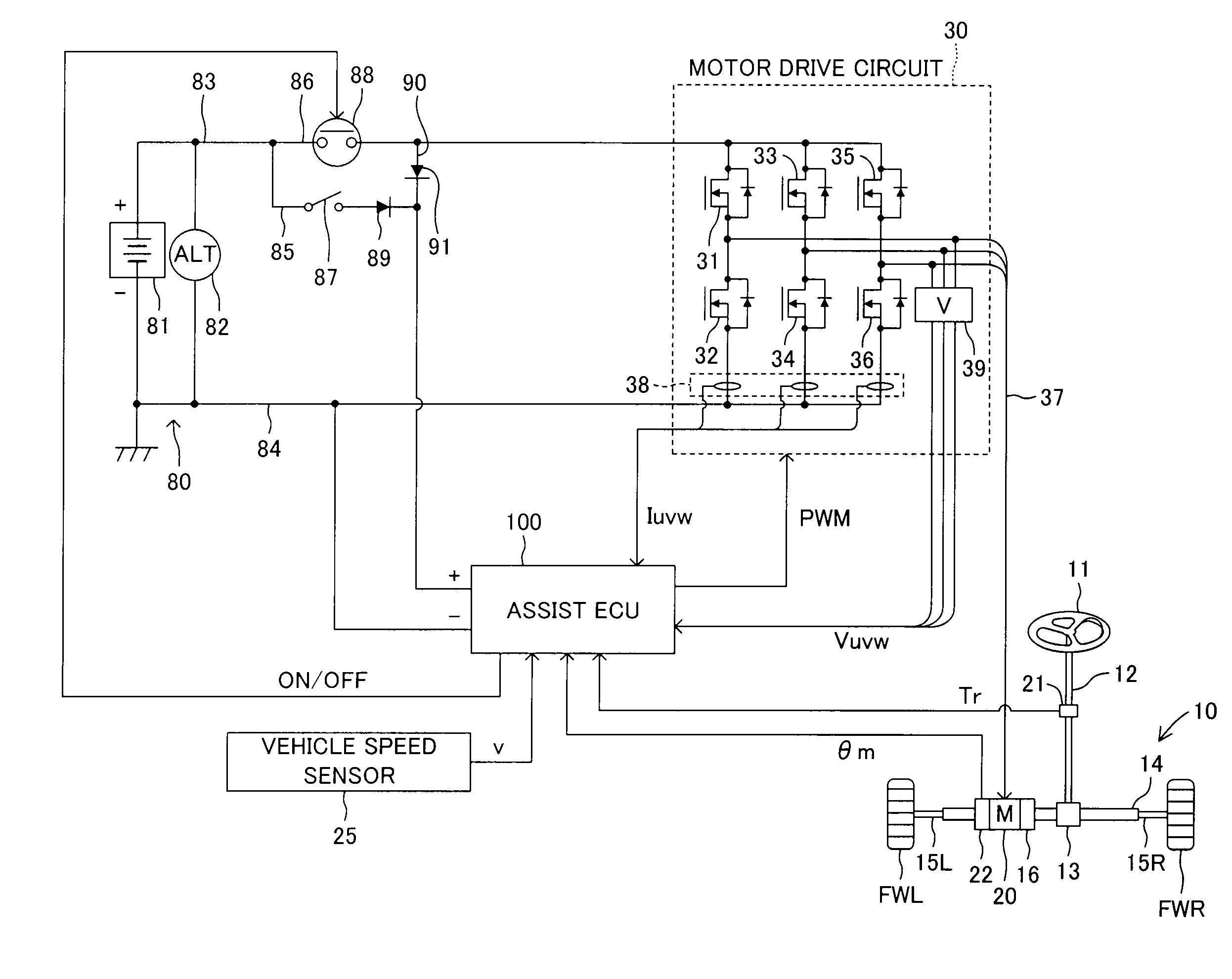
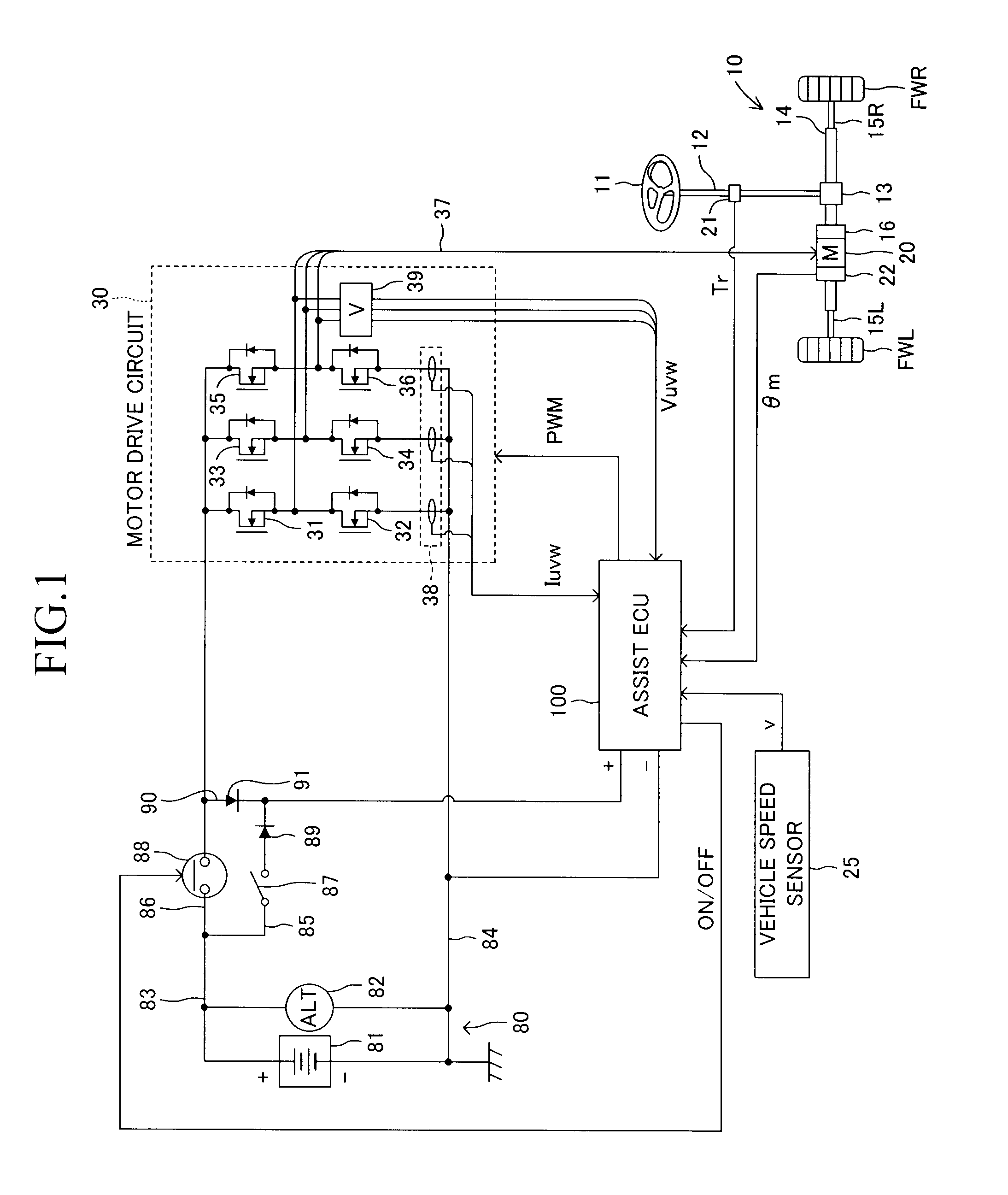
Electric power steering apparatus
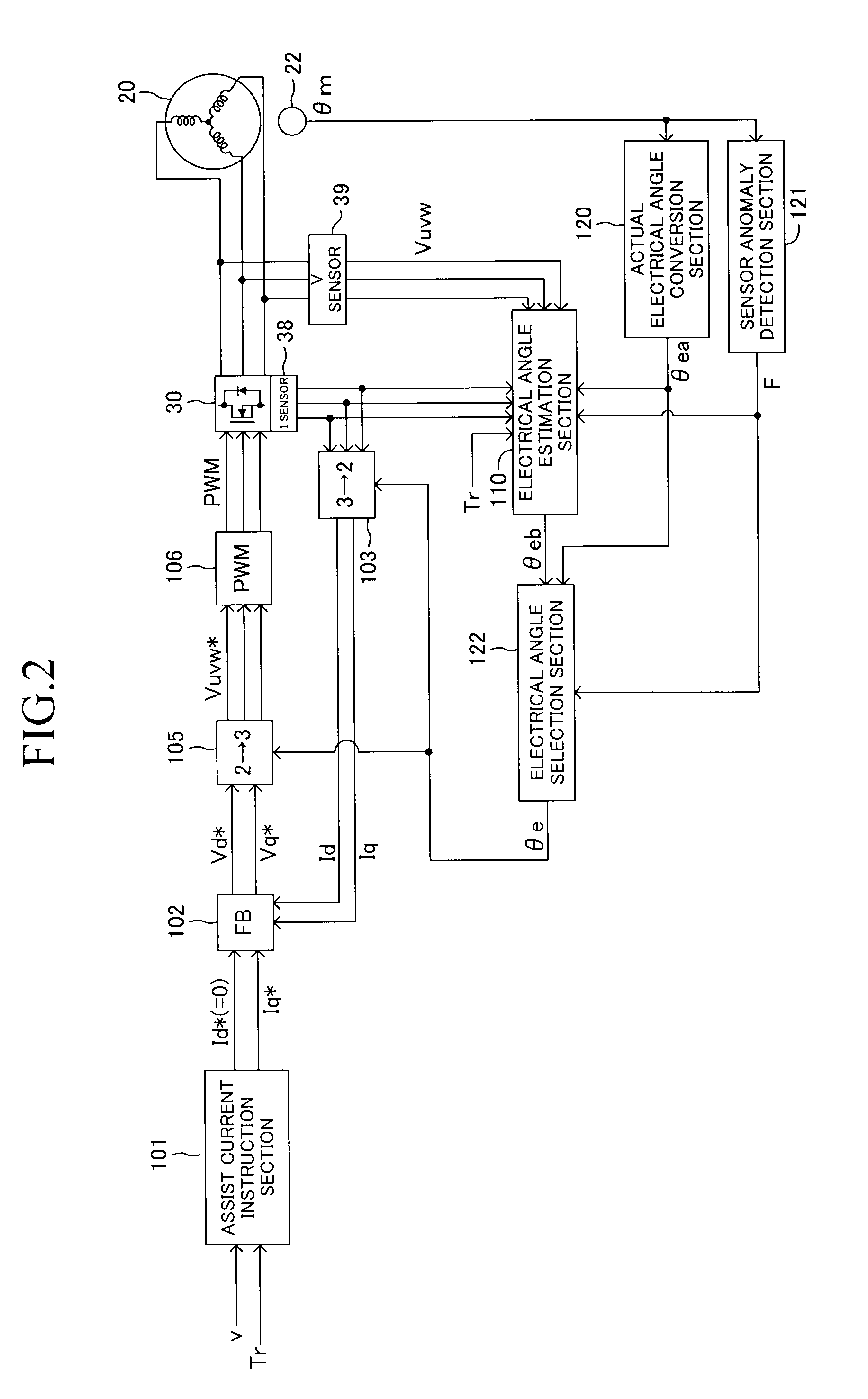
ActiveUS20120211299A1Restraining loss of synchronismLow assist performanceTorque ripple controlDigital data processing detailsAngular rangeSynchronism
An electrical angle estimation section calculates an estimative electrical angle on the basis of an inductive voltage generated in a motor, and obtains an estimative electrical angle by correcting the estimative electrical angle by an electrical angle correction amount. On the basis of a detection value which represents the difference in electrical angle between the q-axis and the δ-axis calculated by an electrical-angle-error detection section, an electrical-angle-correction-amount computation section calculates an electrical angle correction amount such that the electrical angle of the δ-axis falls within a prescribed angular range, which lags behind the q-axis in terms of electrical angle. Thus, when sensorless control is performed, a phenomenon in which the motor loses synchronism can be restrained.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
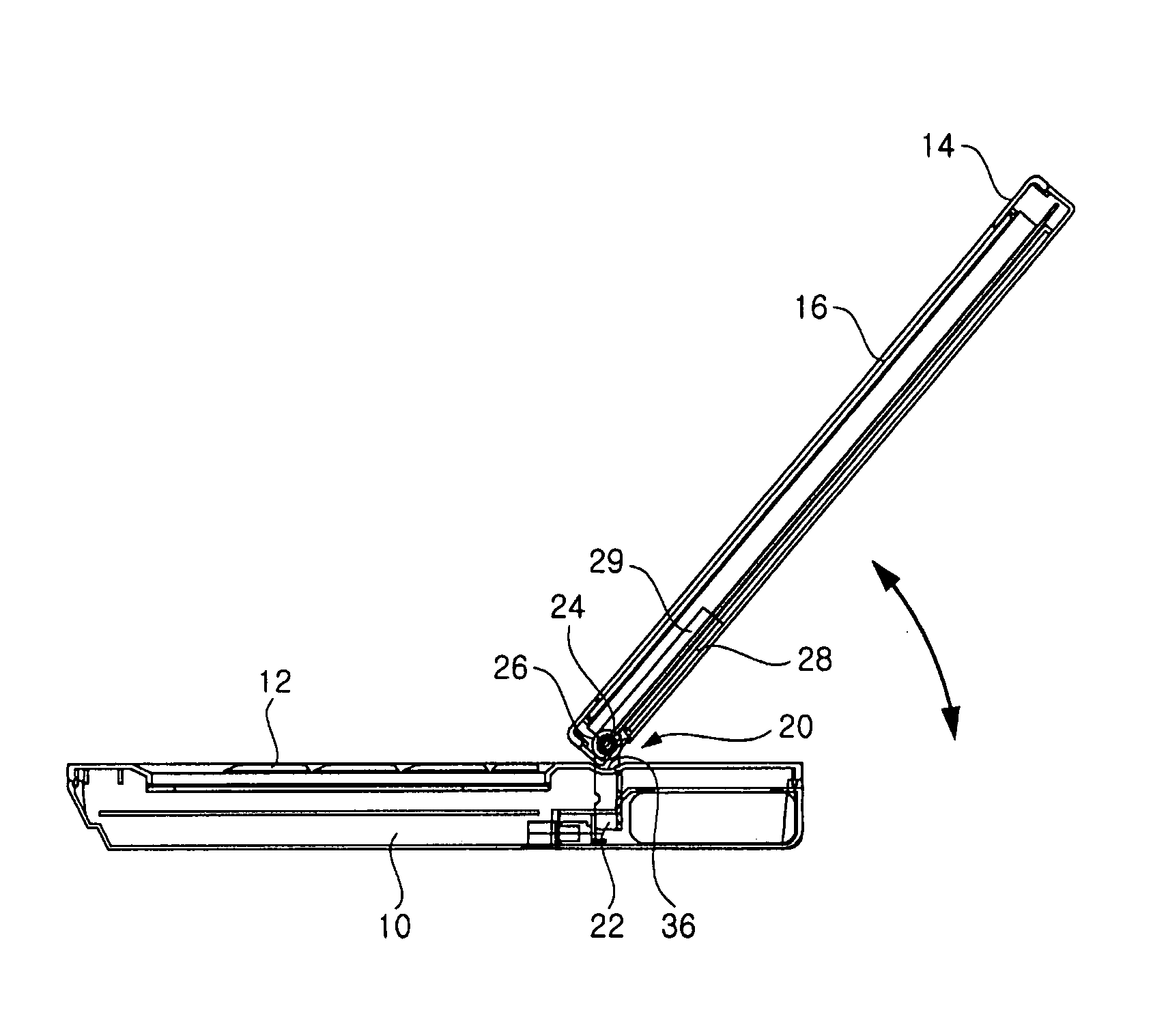
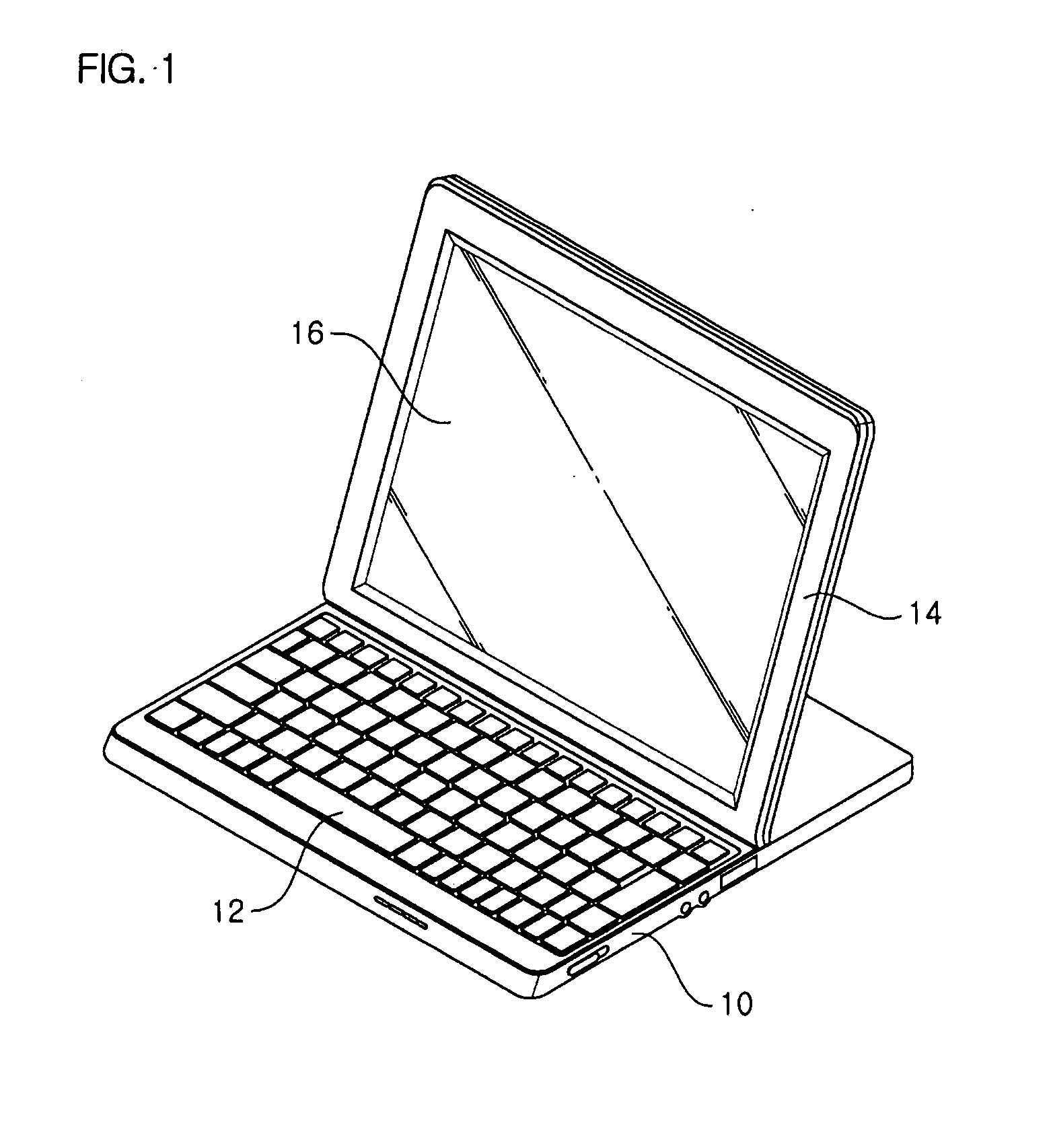
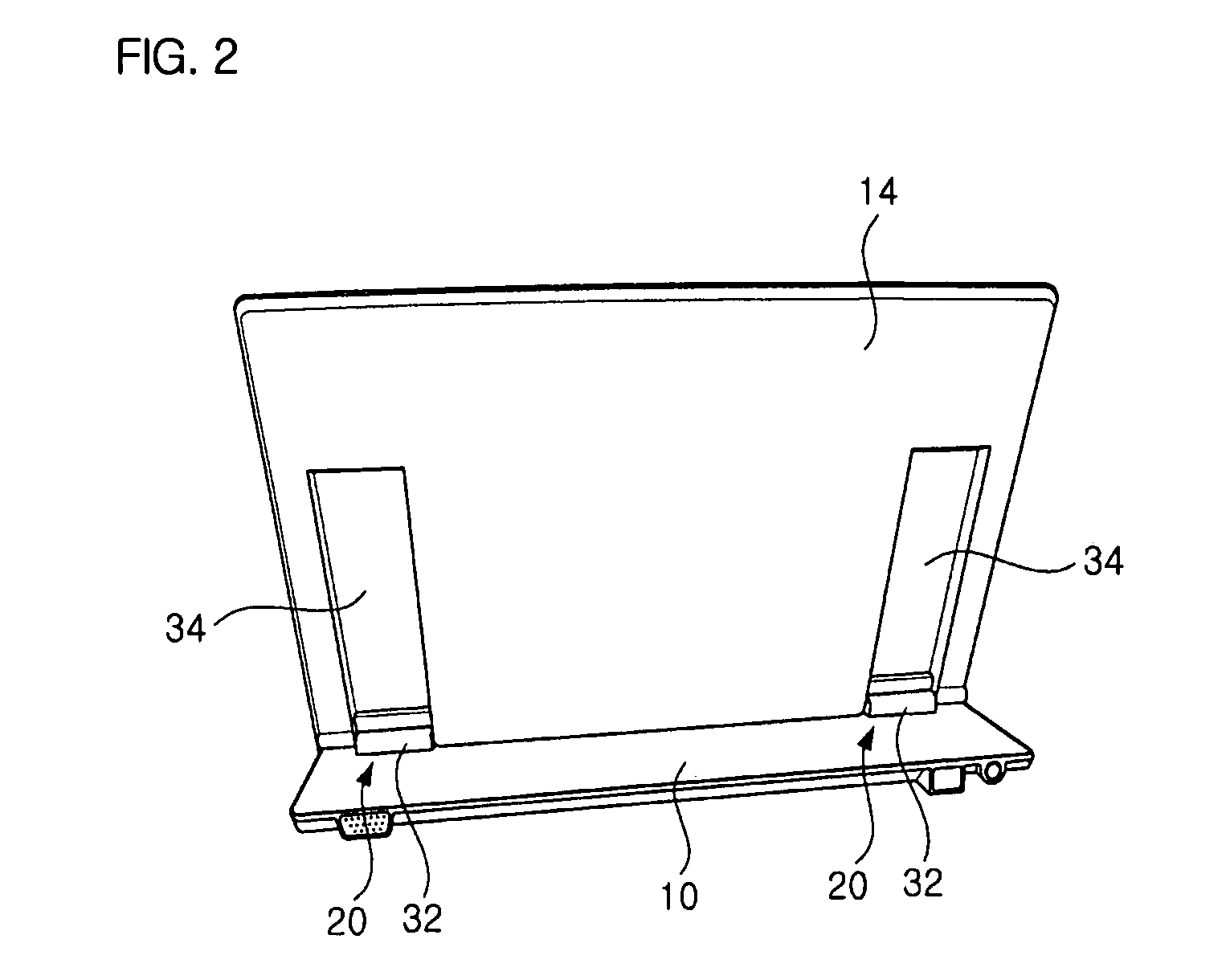
Hinge assembly and mobile device having the same
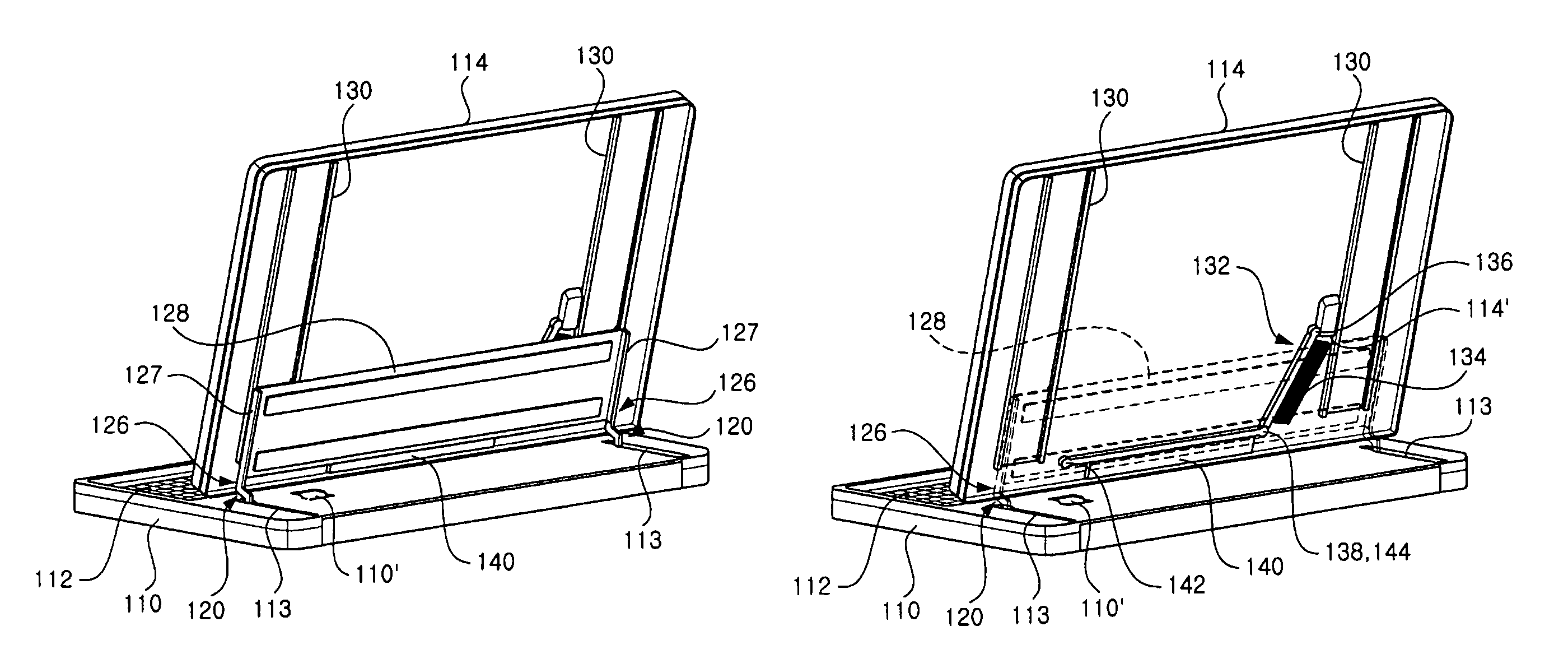
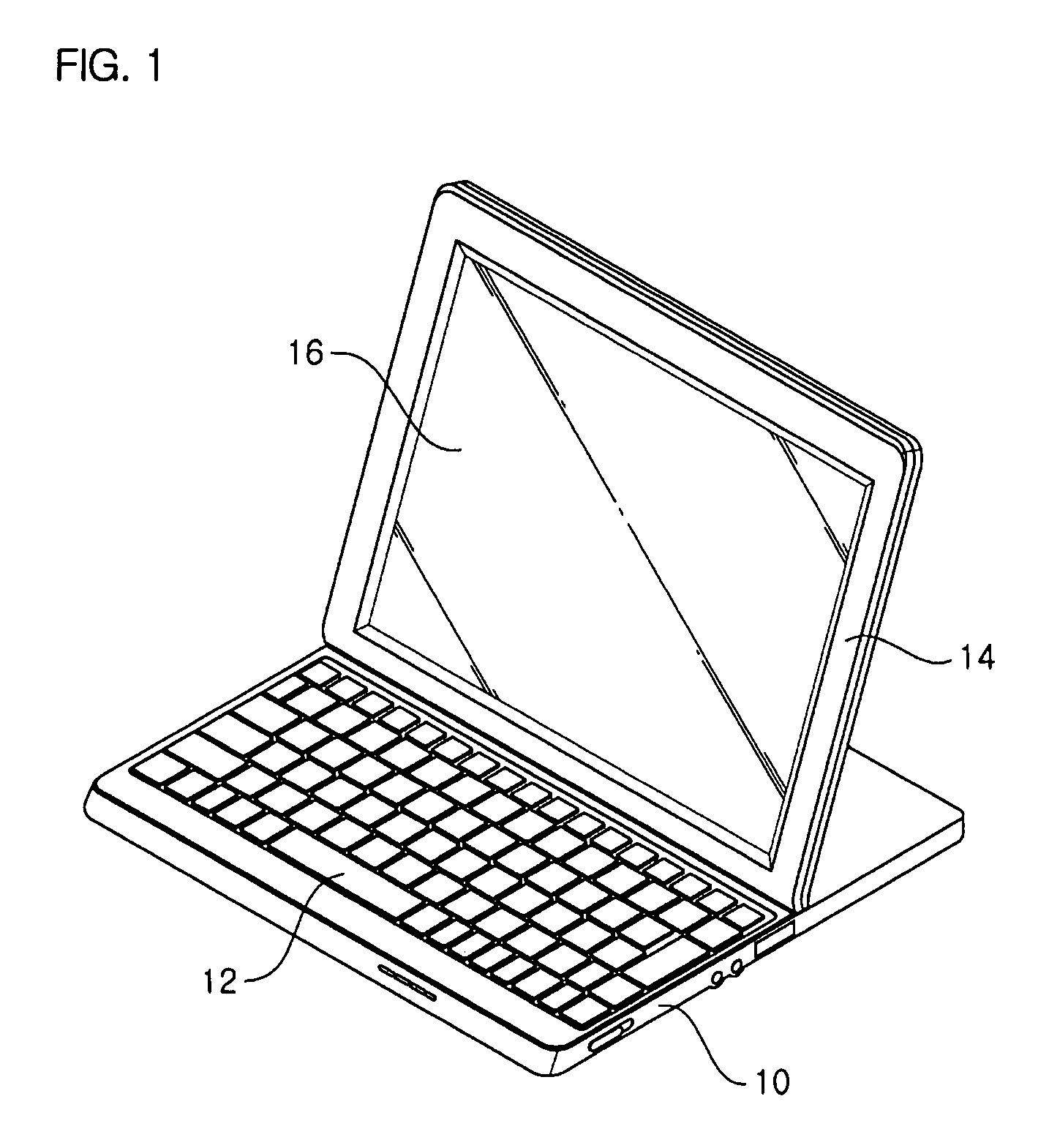
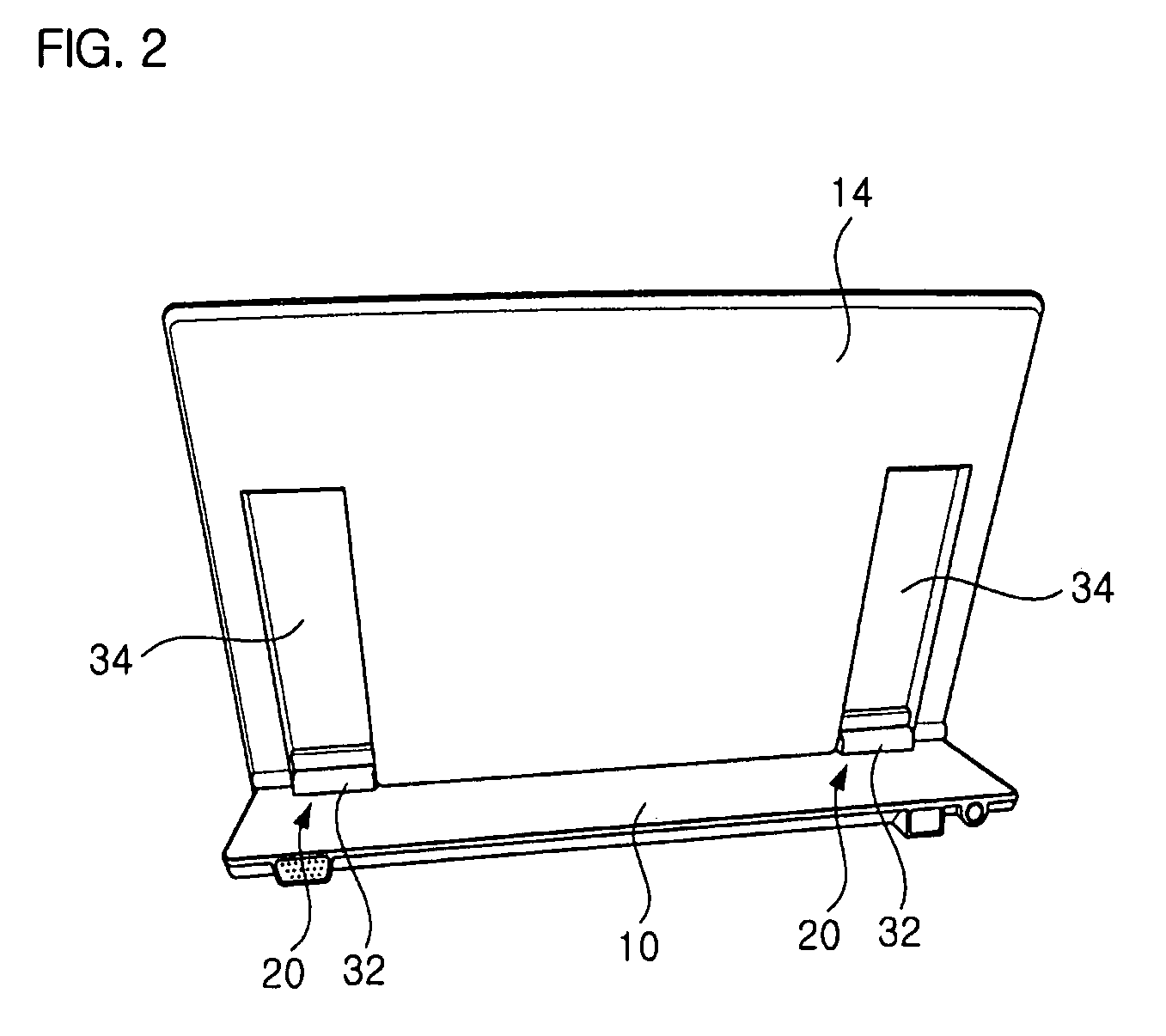
InactiveUS7725988B2Smooth rotationPrevent reversalDetails for portable computersHingesEngineeringMobile device
Disclosed are a hinge assembly and a mobile device having the hinge assembly. In the mobile device, a rotation portion 14 slides and rotates on a base portion 10, so as to be inclined to the base portion 10. For this reason, the rotation portion 14 is connected to the base portion by means of the hinge assembly 20 so as to slide and rotate on the base portion 10. The rotation portion 14 slides on the base portion by a predetermined distance, and then rotates to be inclined at a desired angle with respect to the base portion 10. The rotation portion 14 easily rotates with respect to the base portion of the mobile device, so that the status of the mobile device can be easily converted. Further, when the status of the mobile device is converted, the front, rear, left and right of a display screen is not changed. As a result, the mobile device should not have a structure of changing a display direction of the display screen. Further, there is an advantage in that an electric connection between the base portion and the rotation portion by means of a connection link mechanism can be stably achieved.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Hinge assembly and mobile device having the same
InactiveUS20070186380A1Smooth rotationPrevent reversalDetails for portable computersHingesEngineeringMobile device
Disclosed are a hinge assembly and a mobile device having the hinge assembly. In the mobile device, a rotation portion 14 slides and rotates on a base portion 10, so as to be inclined to the base portion 10. For this reason, the rotation portion 14 is connected to the base portion by means of the hinge assembly 20 so as to slide and rotate on the base portion 10. The rotation portion 14 slides on the base portion by a predetermined distance, and then rotates to be inclined at a desired angle with respect to the base portion 10. The rotation portion 14 easily rotates with respect to the base portion of the mobile device, so that the status of the mobile device can be easily converted. Further, when the status of the mobile device is converted, the front, rear, left and right of a display screen is not changed. As a result, the mobile device should not have a structure of changing a display direction of the display screen. Further, there is an advantage in that an electric connection between the base portion and the rotation portion by means of a connection link mechanism can be stably achieved.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
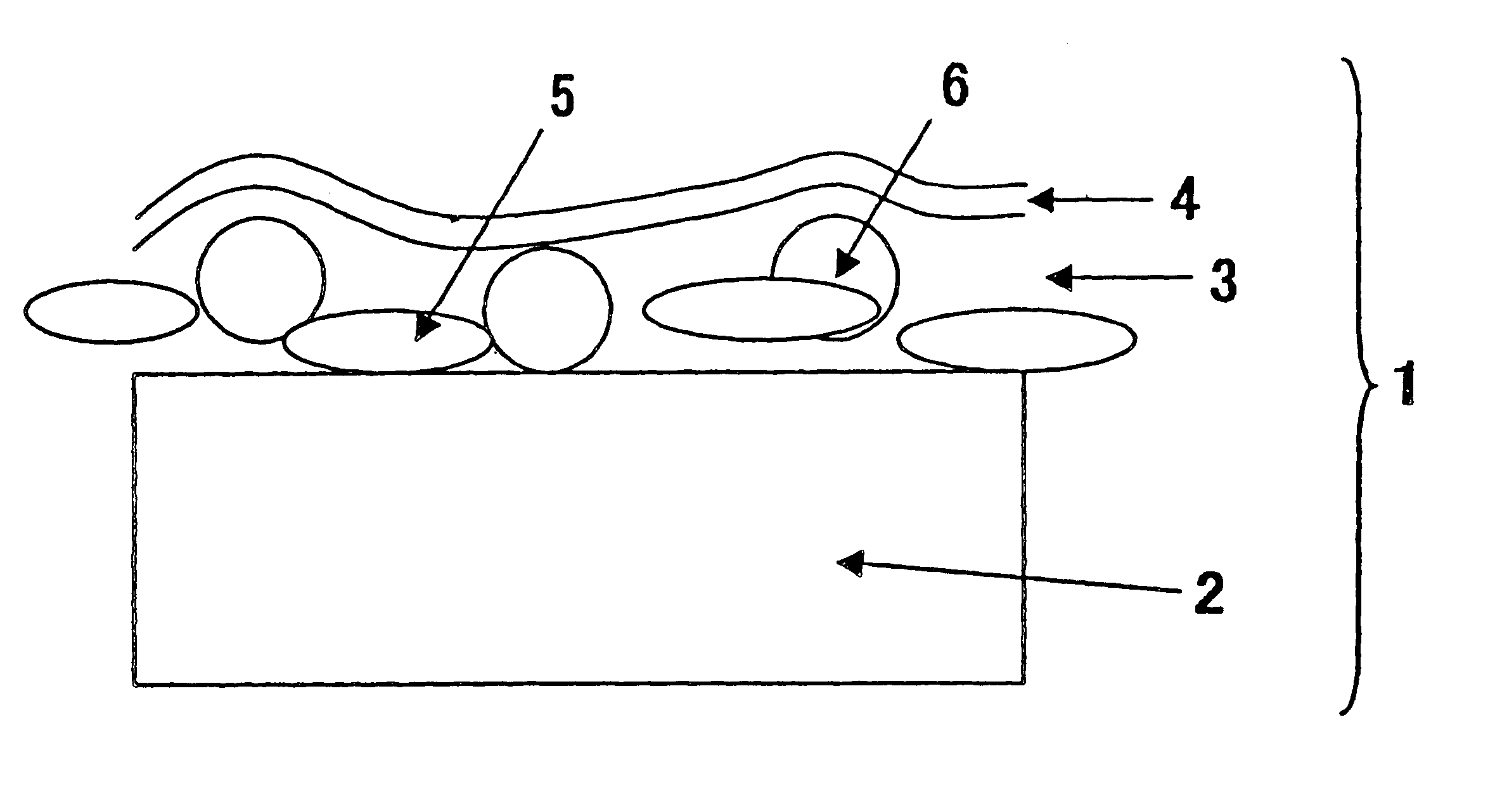
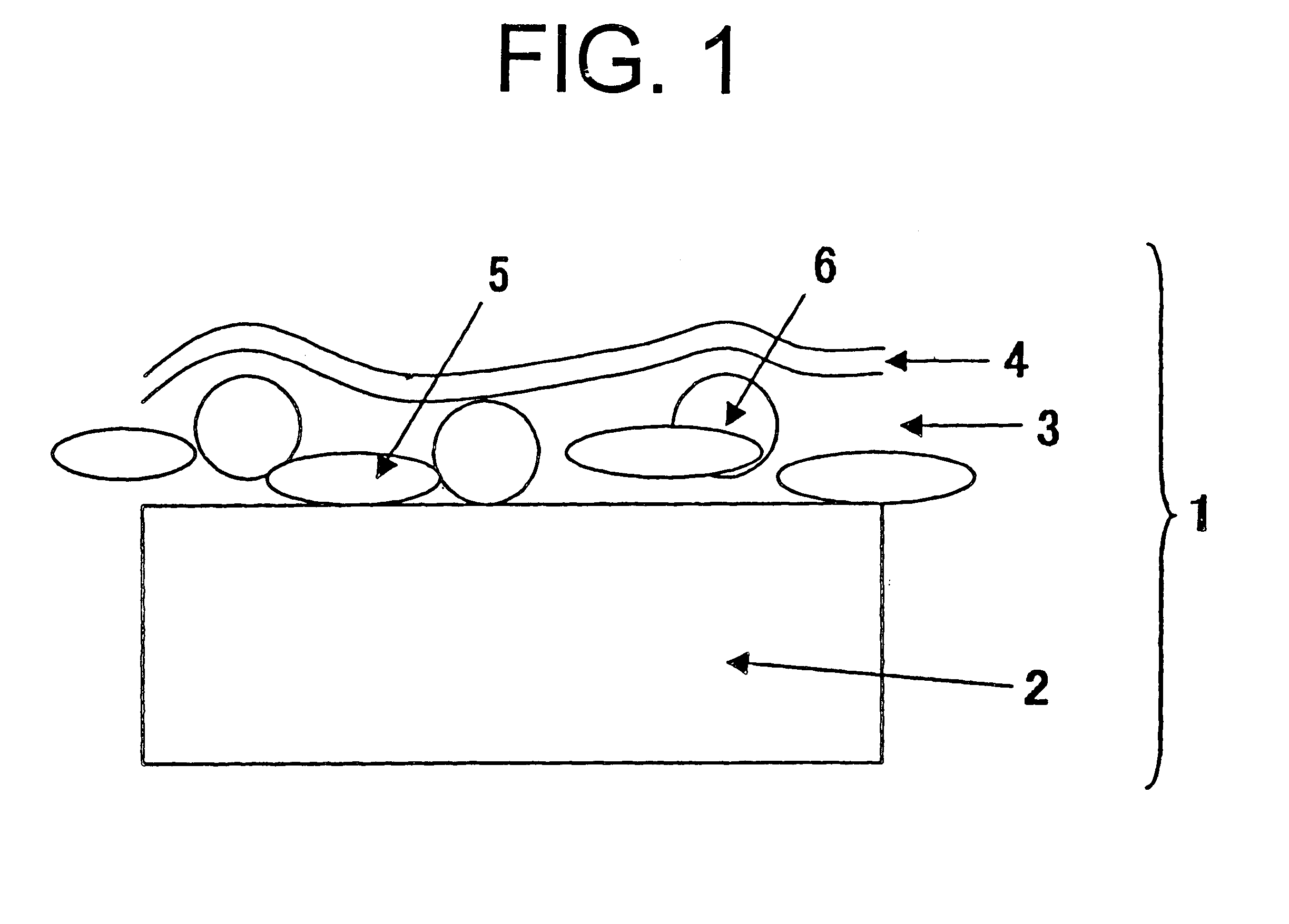
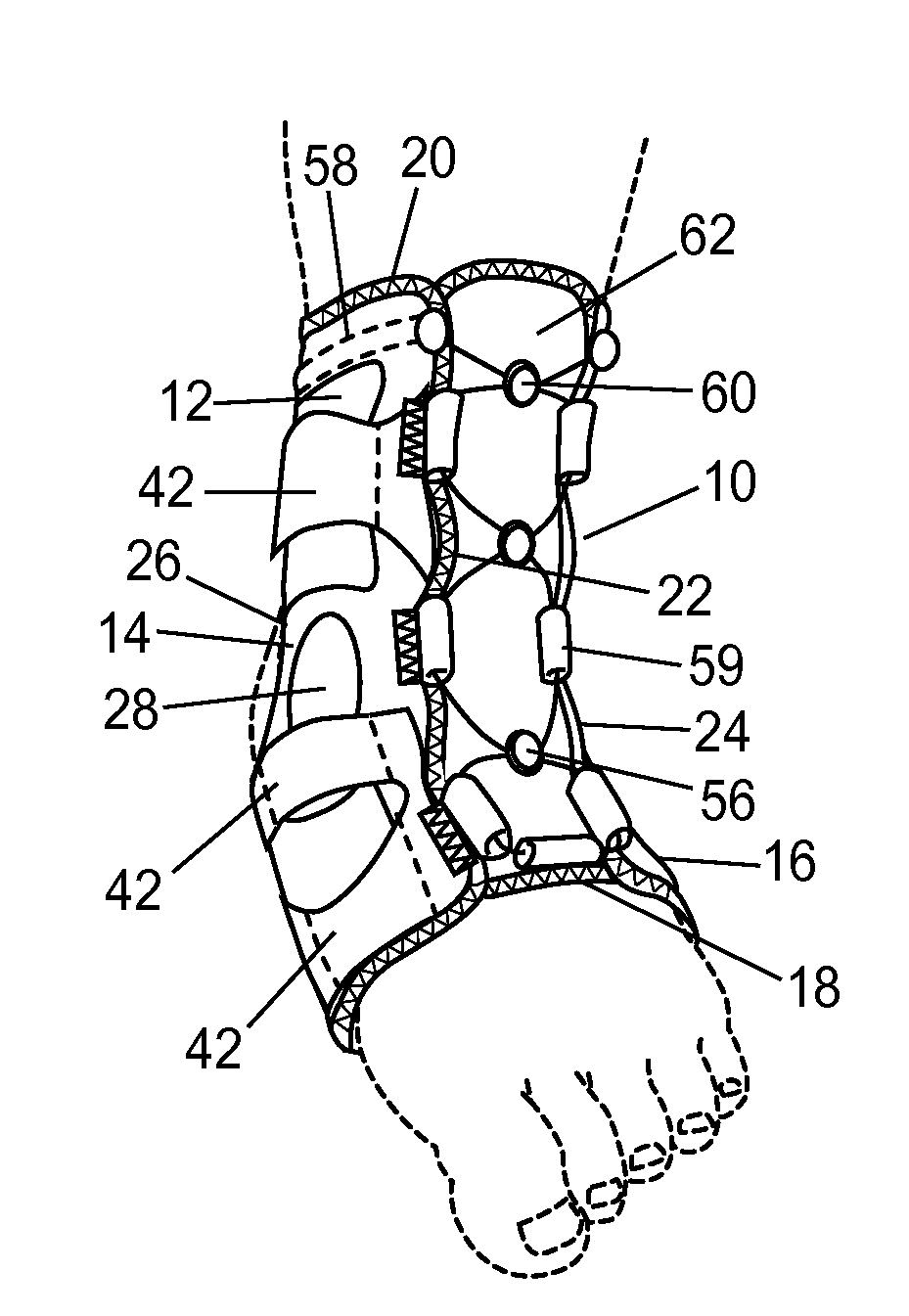
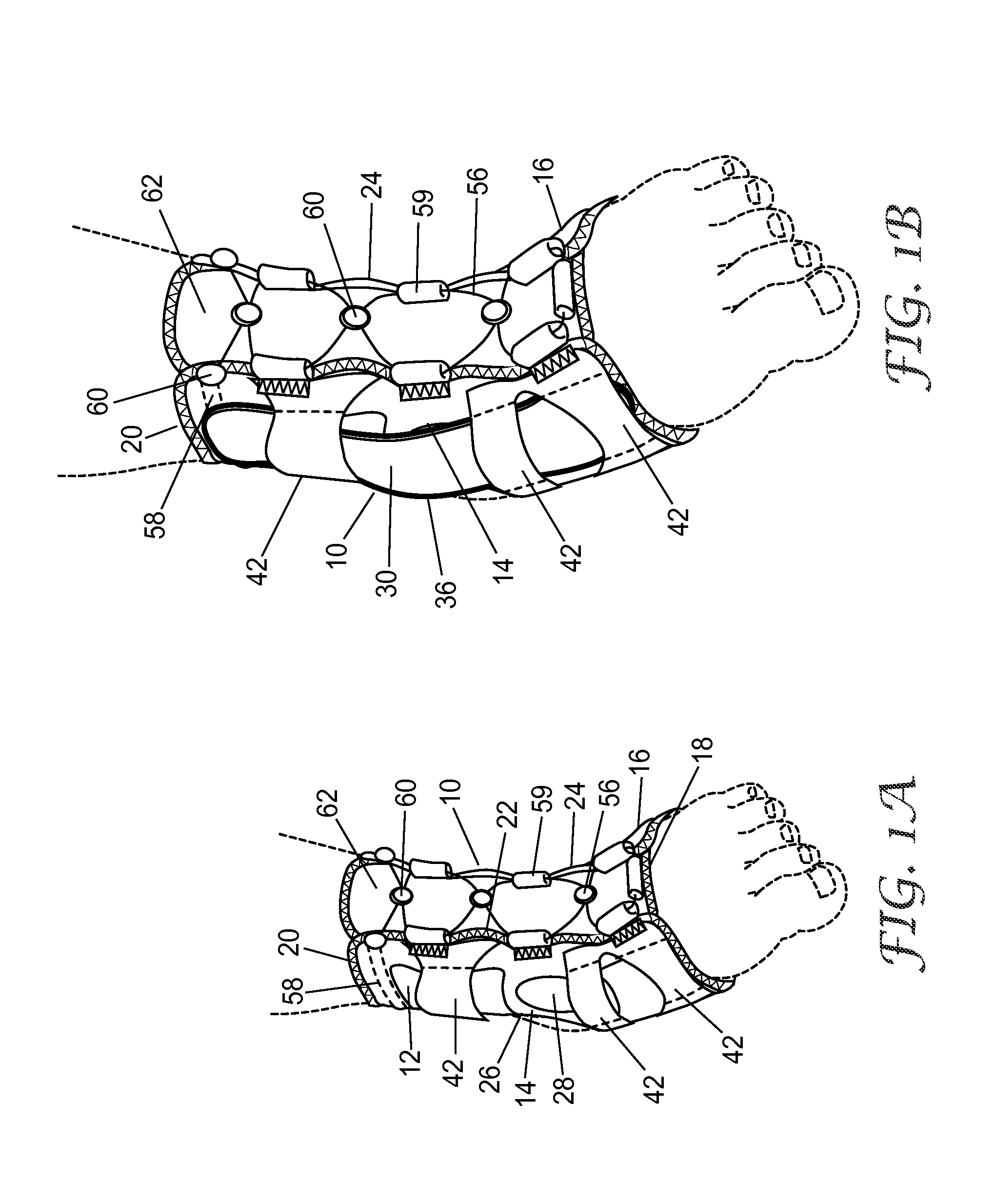
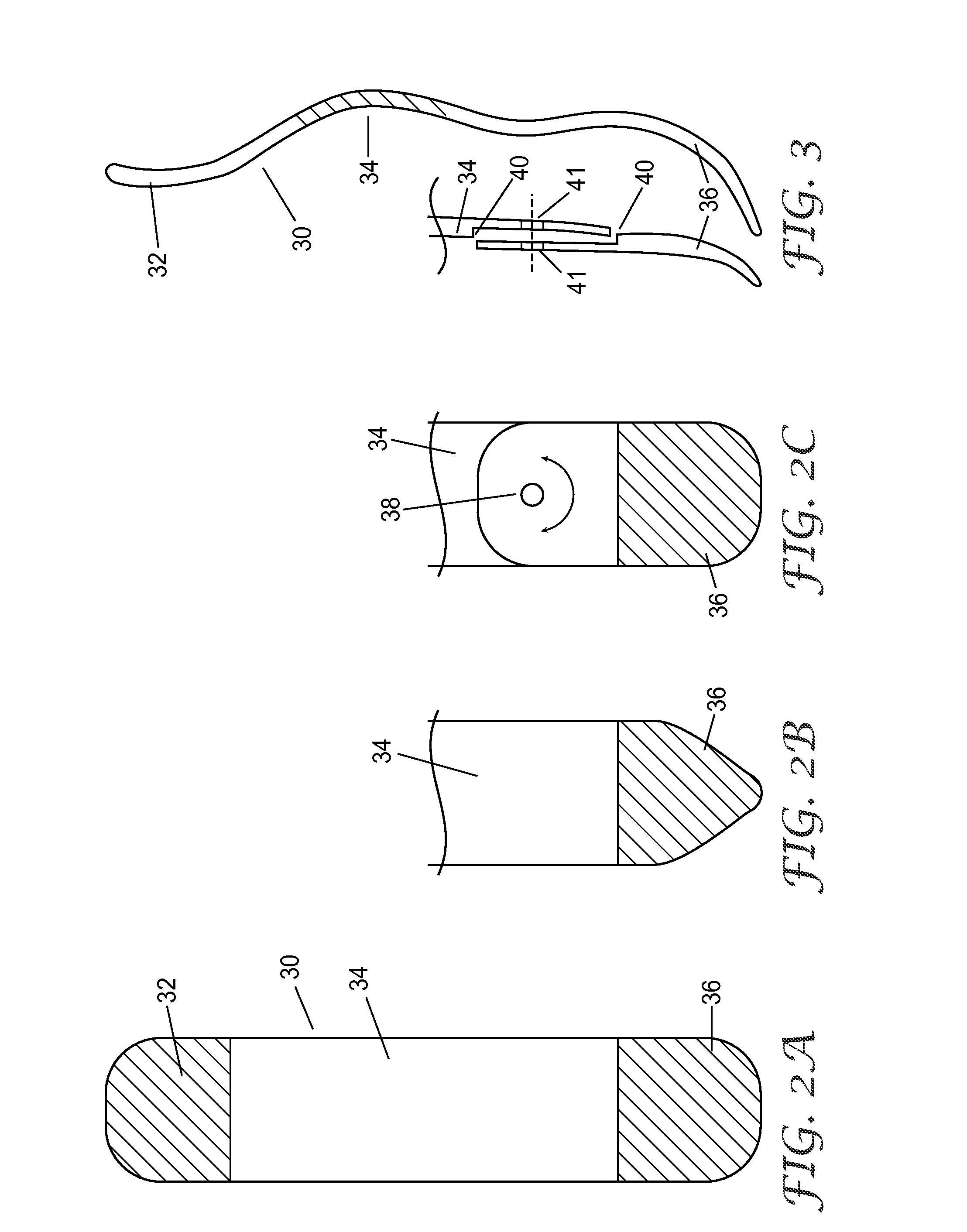
Ankle support with splint and method of using same
According to one embodiment, an orthopedic support for supporting a portion of a wearer's anatomy is provided. For example, the orthopedic support may be an ankle brace comprising a sheet of flexible material configured to at least partially enclose a wearer's ankle and a splint coupled to the sheet of material. The splint is configured to be positioned on a medial side of the wearer's ankle when the sheet of material is secured on the wearer's ankle and includes an undulating profile configured to conform to at least a portion of the medial side of the wearer's ankle and resist inversion of the ankle
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
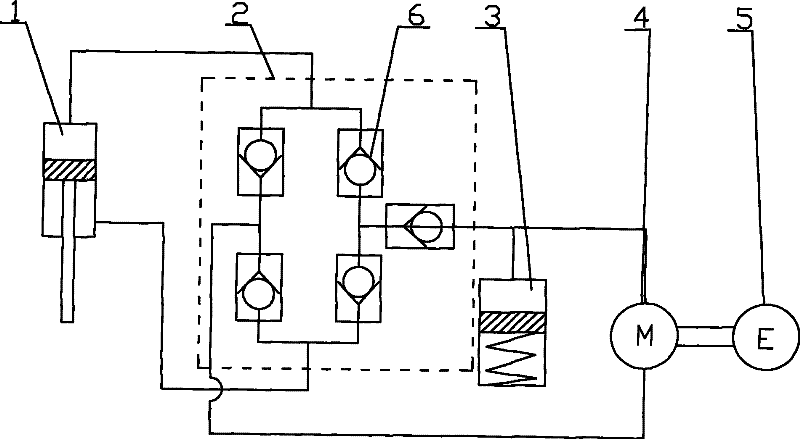
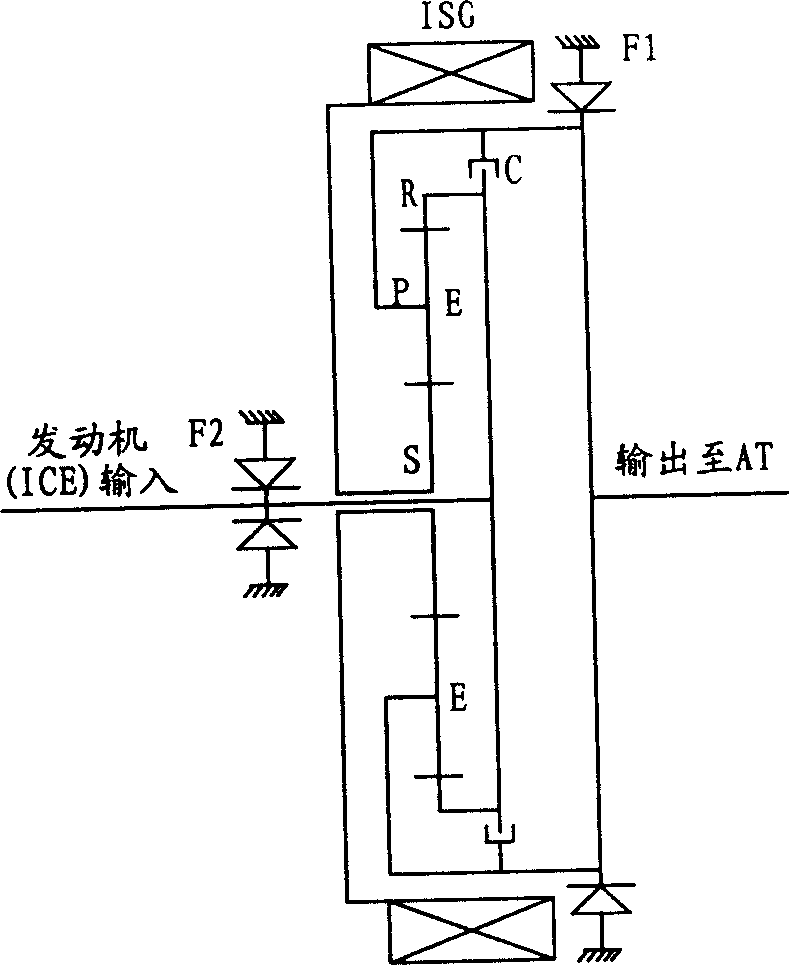
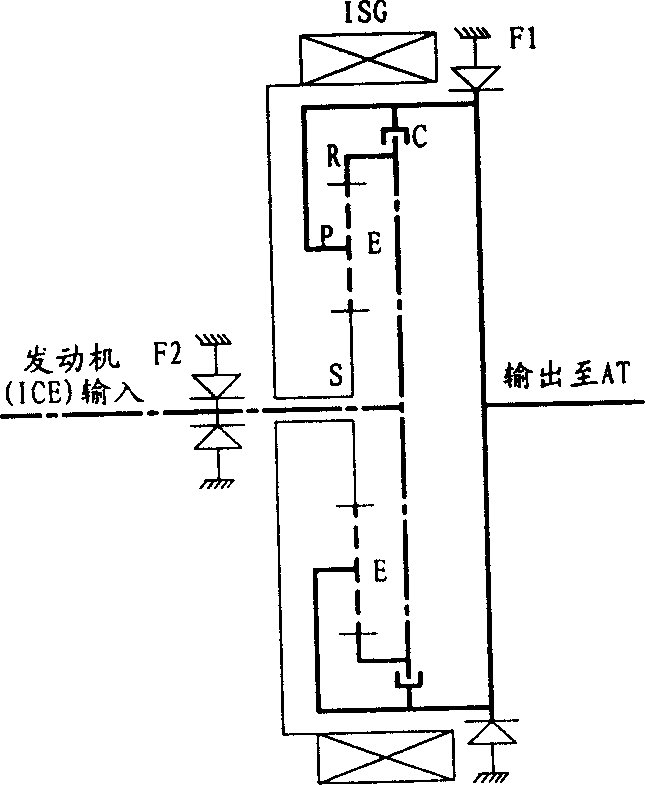
Power driving device for mixed power vehicle
InactiveCN1888483APrevent reversalAchieve power transmissionToothed gearingsGearing controlAutomatic transmissionHybrid electrical vehicle
A power transmission for mixed power vehicles located between an engine and an automatic speed variator consists of a generator, a clutch, a one-way clutch and a planetary gear mechanism consisting of a solar wheel, a planet wheel, a planetary frame and a gear ring. The planet wheel is externally engaged with the solar wheel and internally engaged with the gear ring separately. The output shaft of the engine is connected with the gear ring through a flange, the rotor of the generator is connected with the central shaft of the solar wheel through a spline and the planetary frame is connected with the input shaft of the automatic speed variator through a flange. On the output shafts of the engine and the planetary frame is disposed the one-way clutch separately and between the gear ring and the planetary frame is disposed the clutch.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Drive system of a utility vehicle
InactiveUS7044257B2Avoid drivingPrevent reversalGearing controlMotor depositionControl signalEngineering
A drive system for use in utility vehicles, such as agricultural forage harvesters and combines, includes a hydrostatic transmission having a pump driven by a main engine of the vehicle and having first and second motors respectively coupled to front and rear axles of the vehicle by way of first and second differential gear sets. The pump and one or both of the motors have a variable displacement determined by positioning respective swash plates through the agency of a lever, in the case of the pump, and by electronic devices, in the case of the motors, the electronic devices acting in response to control signals sent by a control arrangement, which in turn, operates in response to signals produced by pressure sensors associated with the motors and by signals produced by speed sensors associated with output shafts of the hydraulic motors. The control arrangement has a memory for storage of data, such as maximum legal ground speed and the ratio of the speeds of the axles as results from a given wheel size, and uses this information for controlling the hydrostatic transmission such that the vehicle does not exceed the speed, and the front and rear axles are driven so as to produce the same ground speed.
Owner:DEERE & CO
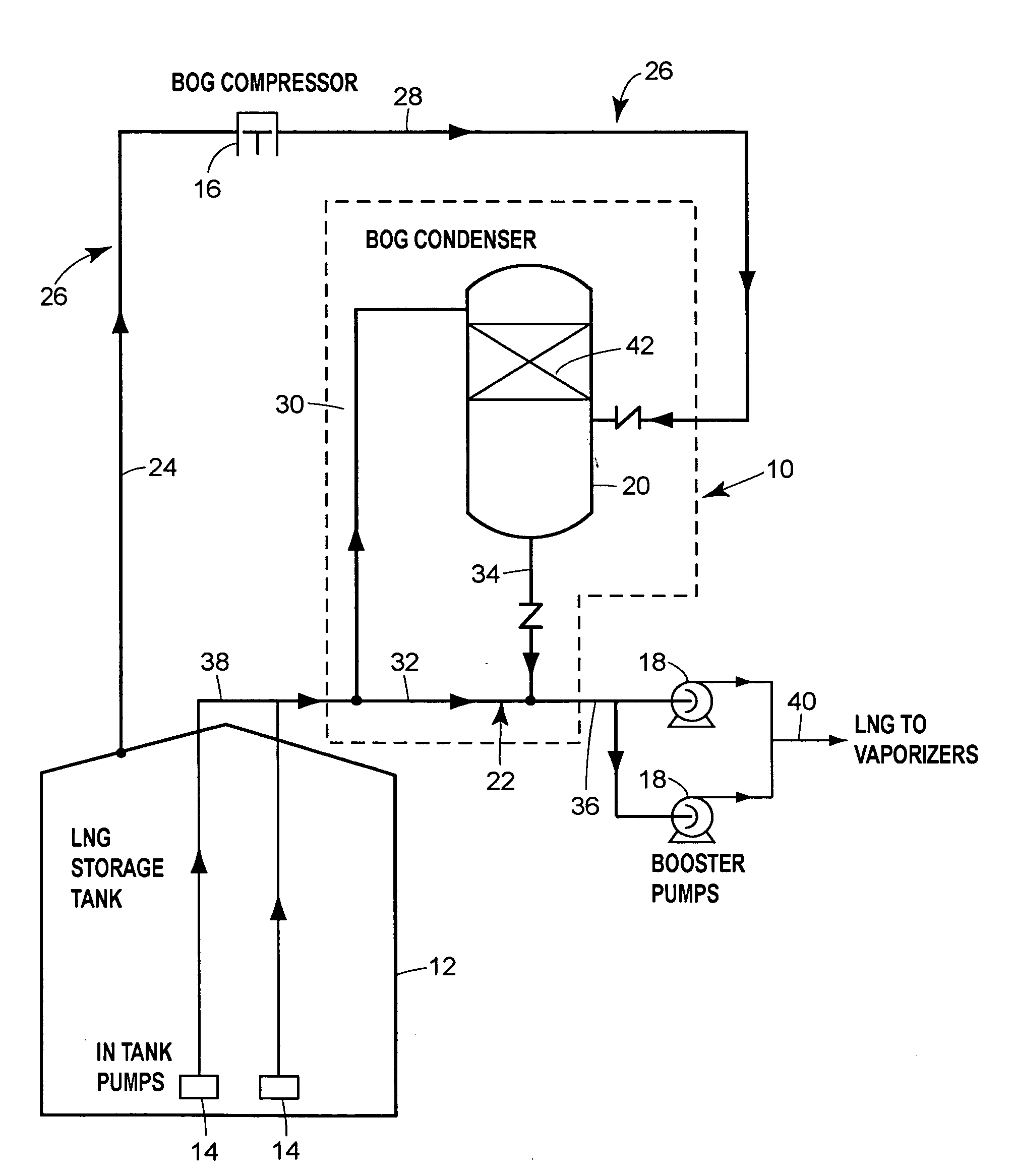
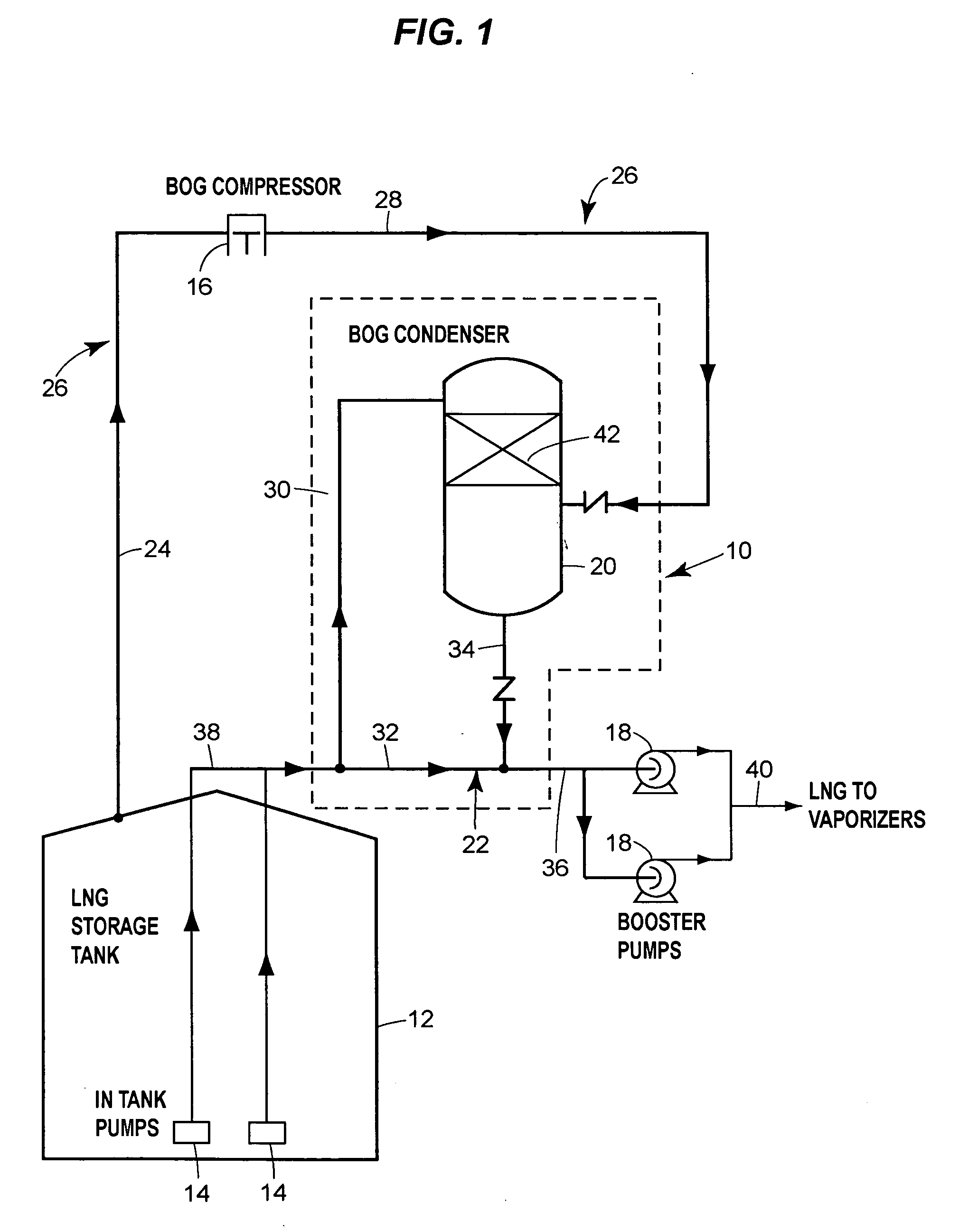
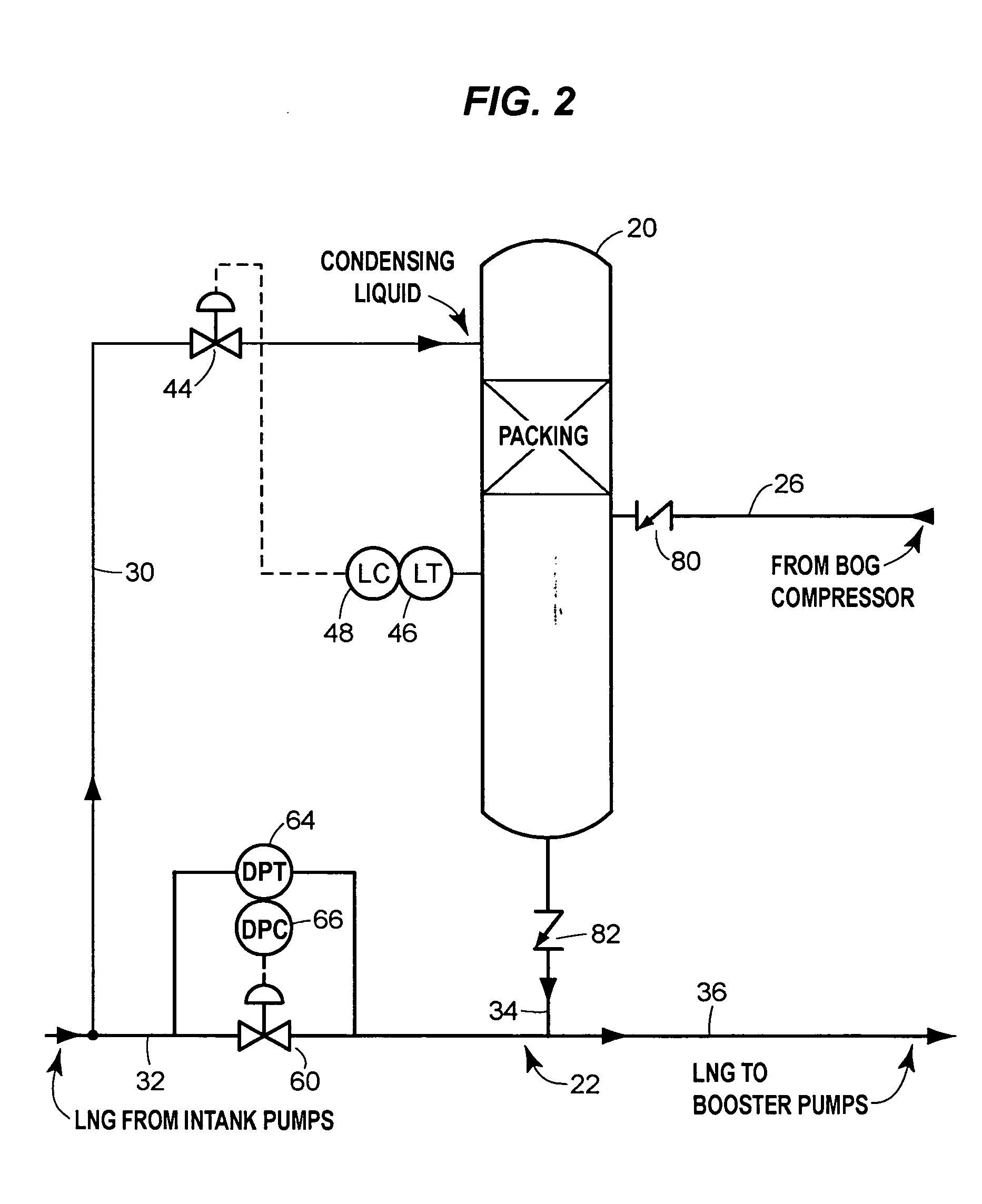
Boil-off gas condensing assembly for use with liquid storage tanks
The assembly includes a boil-off gas line that carries storage tank boil-off gas to a condenser that uses condensing liquid from the liquid send-out line to condense the gas. A level control valve on the condensing liquid line actively controls the flow of condensing liquid based on the liquid level in the condenser. A check valve prevents liquid from the send-out line from flowing into the condenser through the condensate line that discharges condensate from the condenser to the send-out line.
Owner:CHICAGO BRIDGE & IRON CO
Battery charger with multiple functions
InactiveUS20050151506A1Prevent reversalCircuit monitoring/indicationDifferent batteries chargingEngineeringVoltage range
The present invention relates to a battery charger with multiple functions comprises a charging unit and at least two adaptive connectors. The charging unit controls output voltages via software and has a display screen showing set voltages. A voltage select button provides convenience of voltage setting by touch button (or keys), the adaptive connector between the main charger and a charged device sets limited output voltages range, providing end user to select required voltages for various products. End users can power / charge many electrical products with one charger only.
Owner:KENNEDY ROSALIA +1
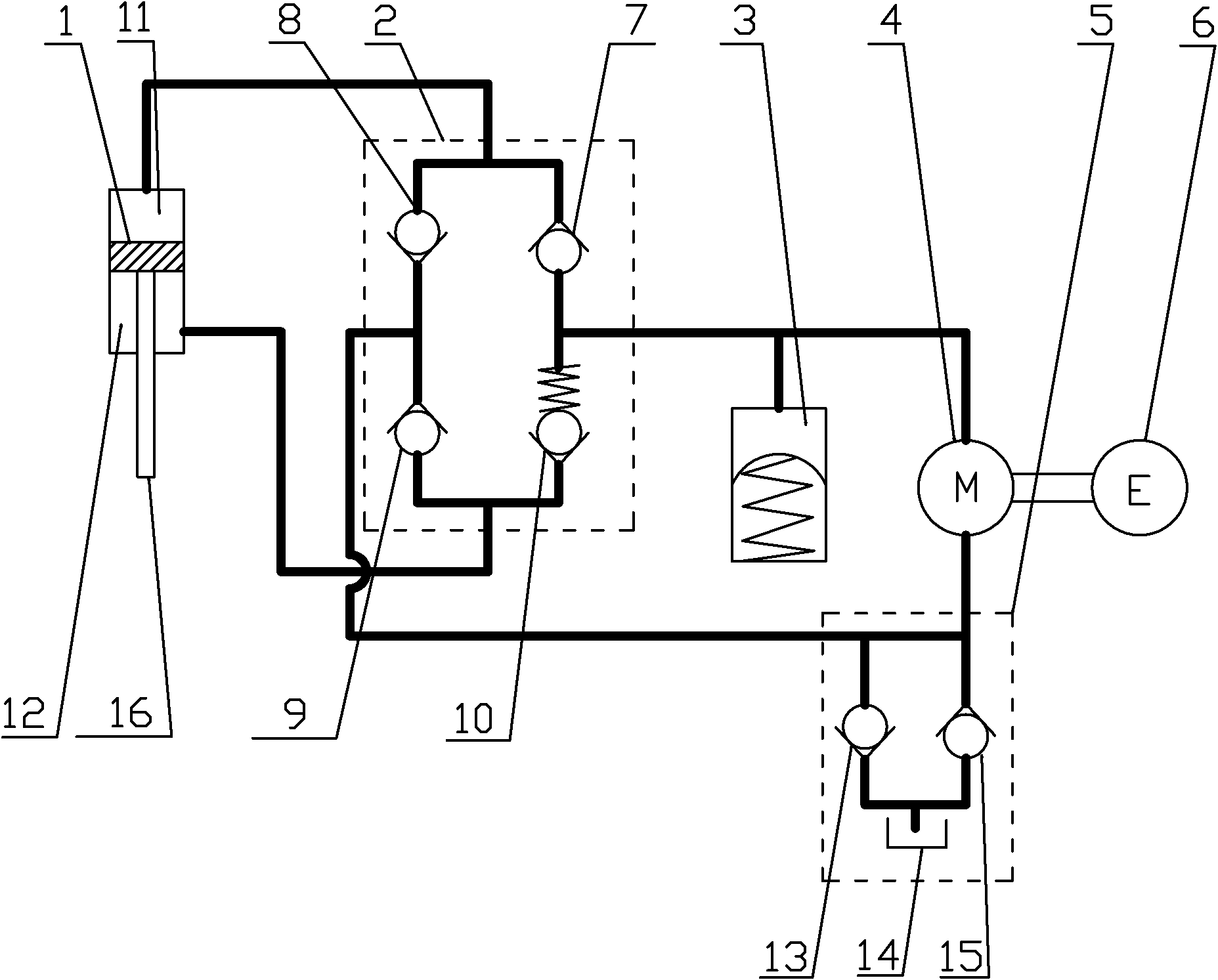
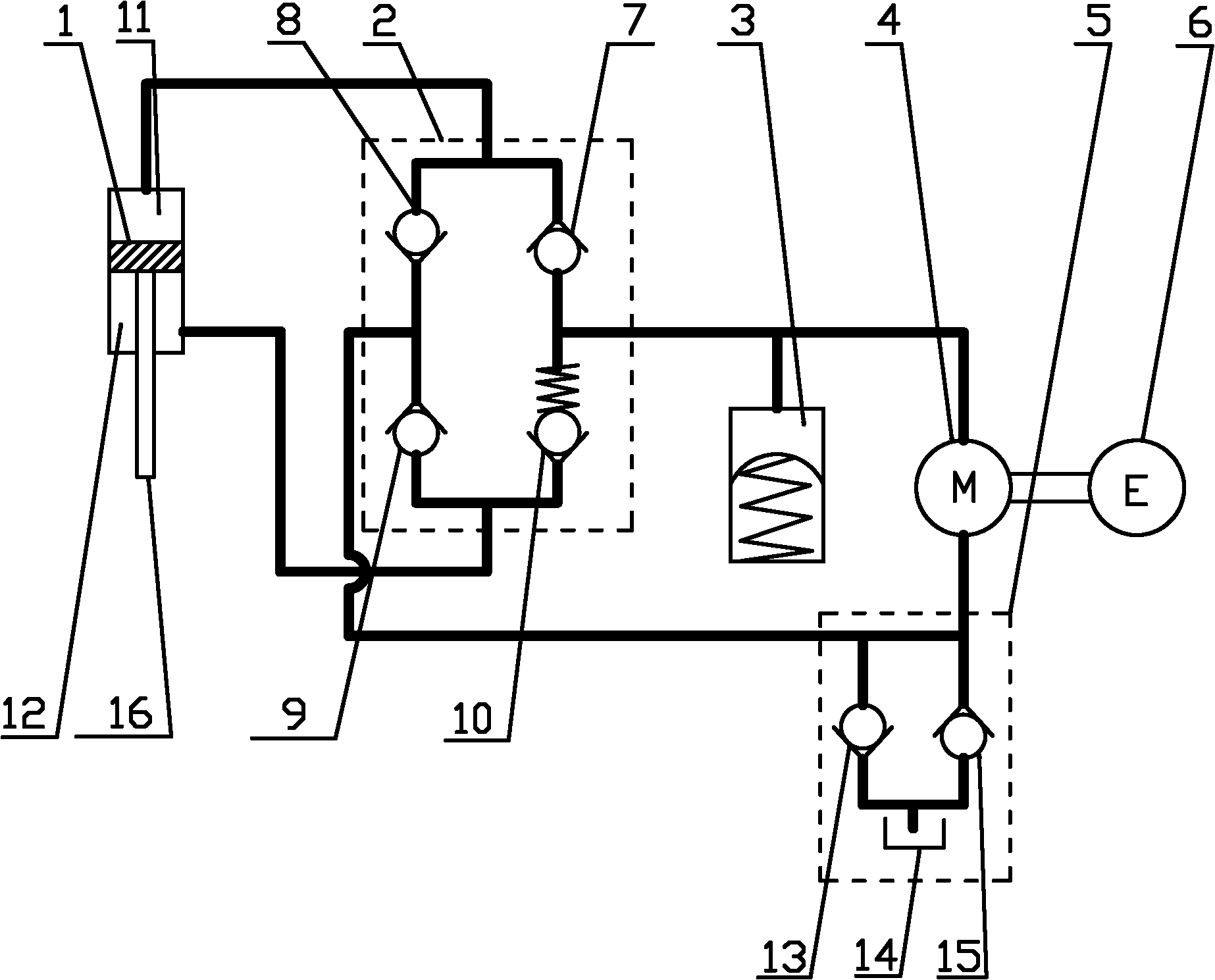
Electrohydraulic energy regenerative vibration absorber
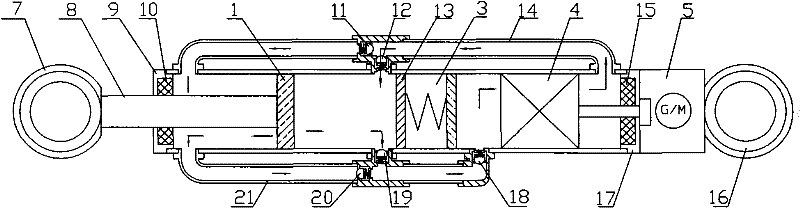
The invention relates to an electrohydraulic energy regenerative vibration absorber, which comprises a piston, a hydraulic check bridge, an accumulator, a hydraulic motor and a rotary generator. A vibration absorber cavity is divided into a rodless cavity (11) and a rod cavity (12) by a piston and a piston push rod (16); the two cavities are provided with an oil outlet and an oil inlet respectively; each oil outlet and each oil inlet are provided with a one-way valve; the one-way valve and a pipeline which is connected with the one-way valve form the hydraulic check bridge; the accumulator is connected in parallel on a connecting pipeline between two oil outlets and an oil inlet of the hydraulic motor; a volume conversion bridge (5) is connected in parallel on a pipeline between the oil outlet of the hydraulic motor and two oil inlets of the vibration absorber cavity; and the volume conversion bridge consists of two one-way valves and an oil tank which is connected with the one-way valves. The electrohydraulic energy regenerative vibration absorber meets the damping force requirement of an automobile vibration absorber, and can convert the ground vibration into direction-invariable rotary movement to drive the generator to generate power and actively control the damping of the vibration absorber by controlling the generator load.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
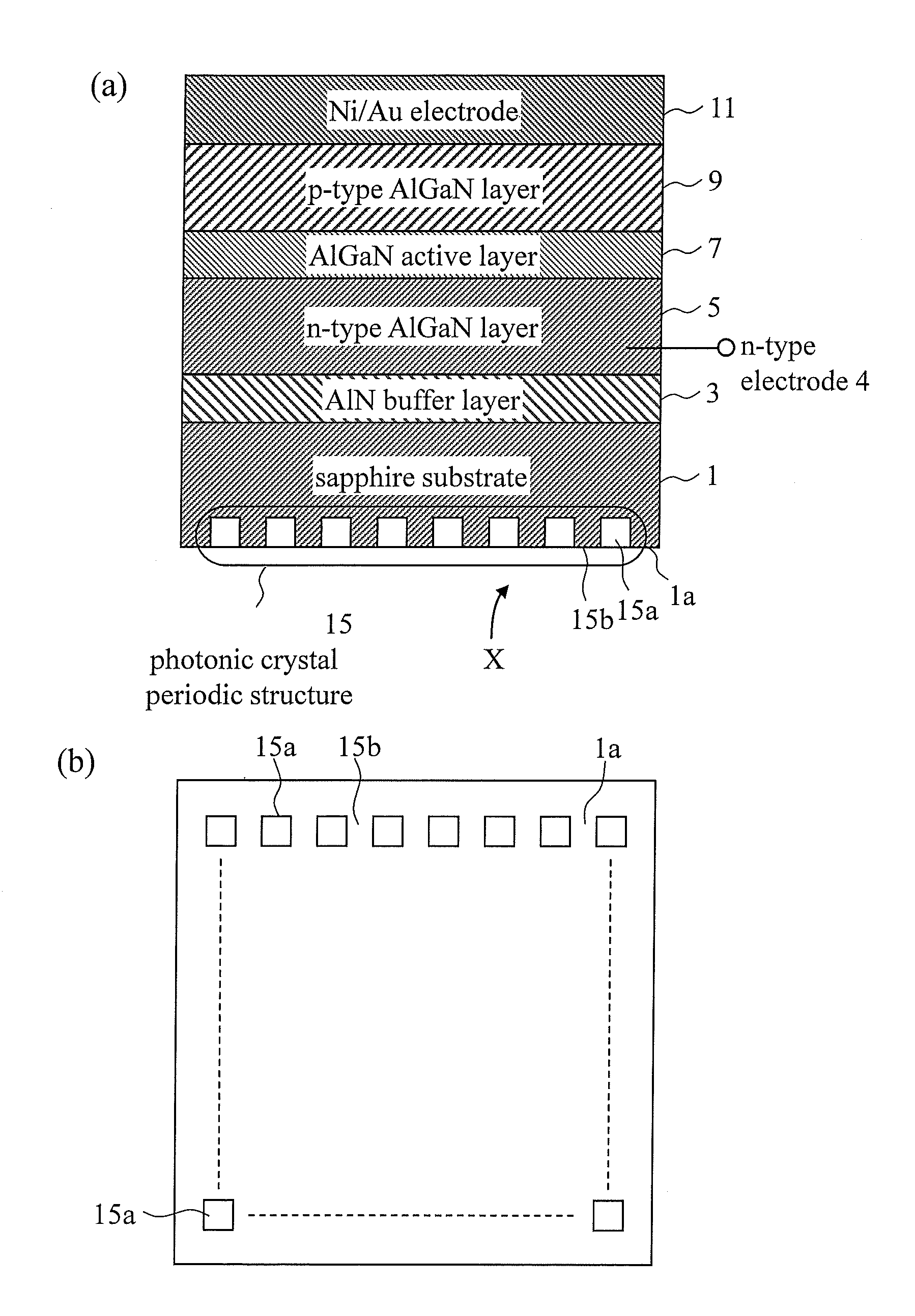
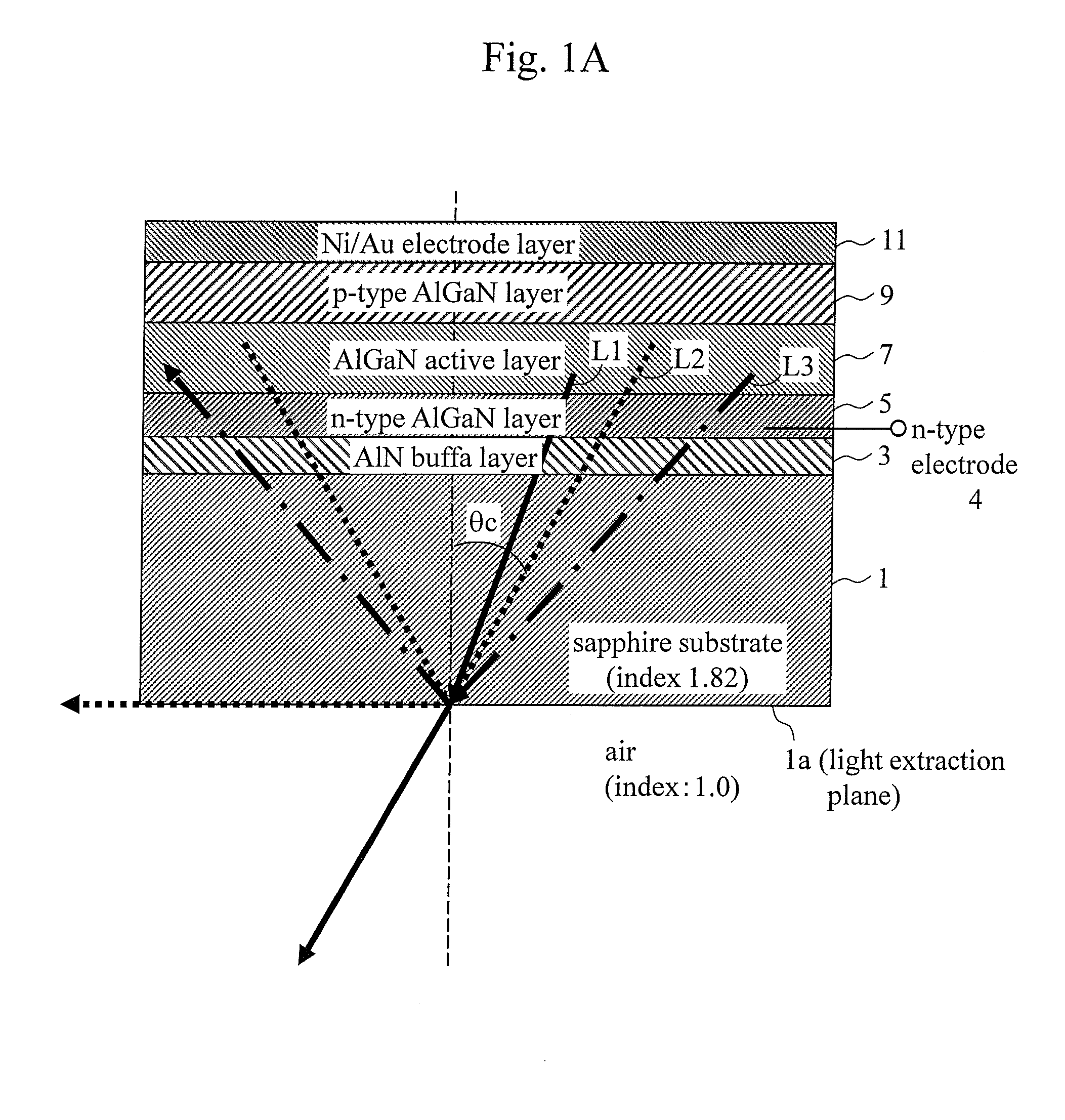
Light emitting element and method for manufacturing same
ActiveUS20140167066A1Low efficiencyHigh light transmittanceSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotonic bandgapRefractive index
A semiconductor light emitting element including, in a light extraction layer thereof, a photonic crystal periodic structure including two systems (structures) with different refractive indices. An interface between the two systems (structures) satisfies Bragg scattering conditions, and the photonic crystal periodic structure has a photonic band gap.
Owner:MARUBUN +3
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com