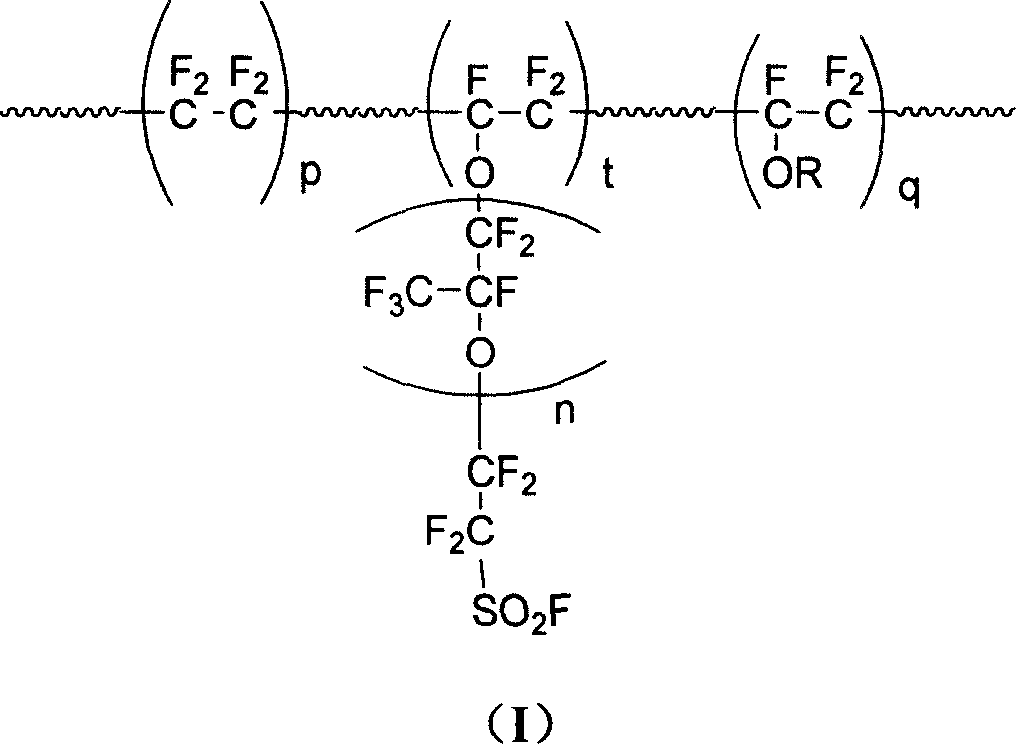
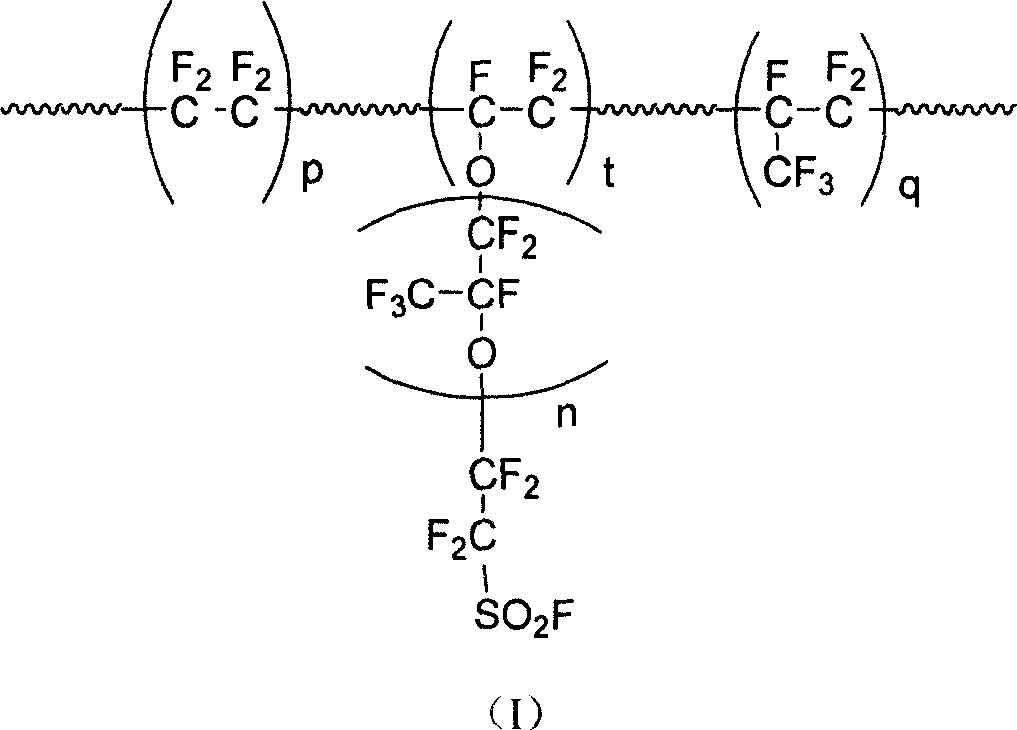
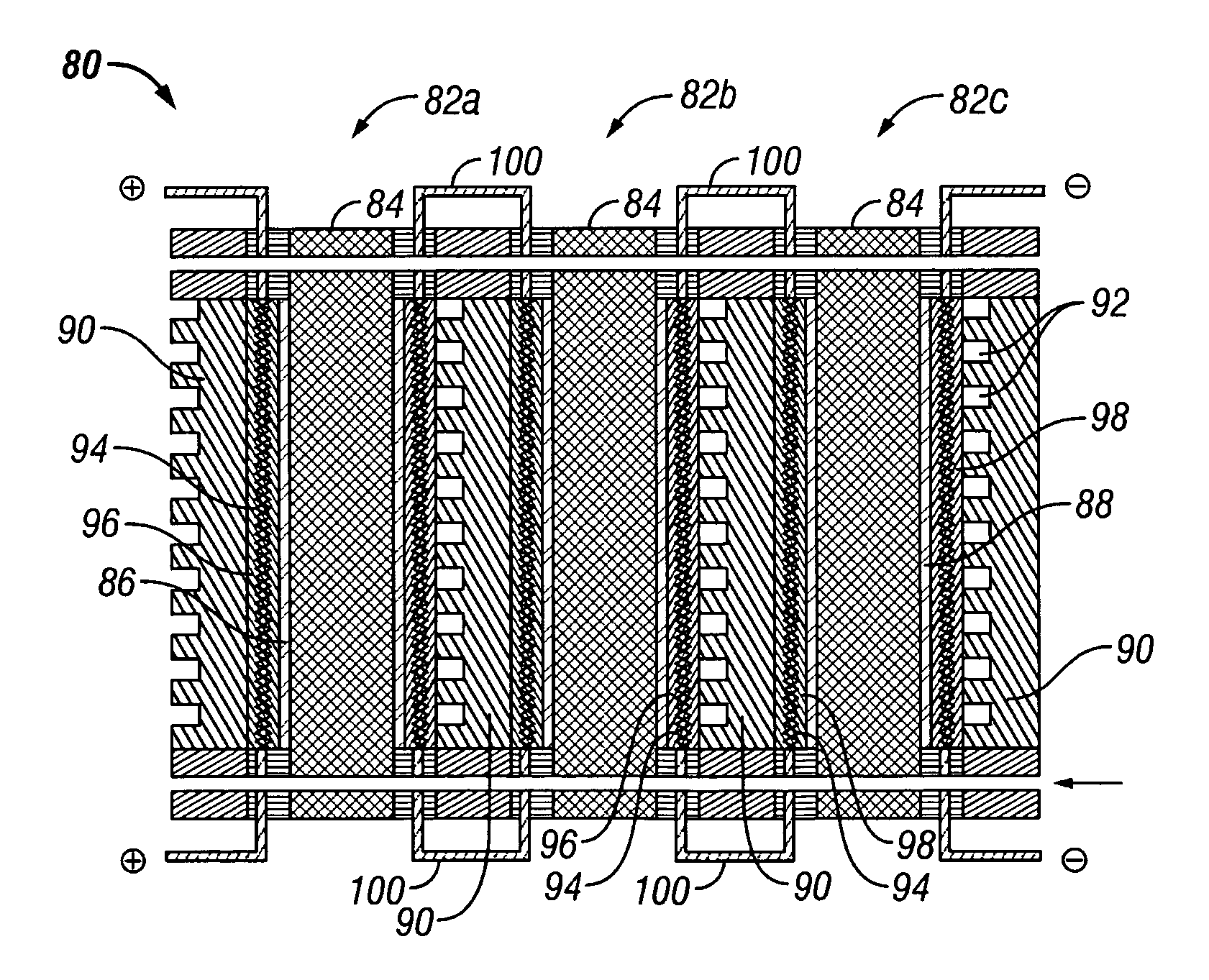
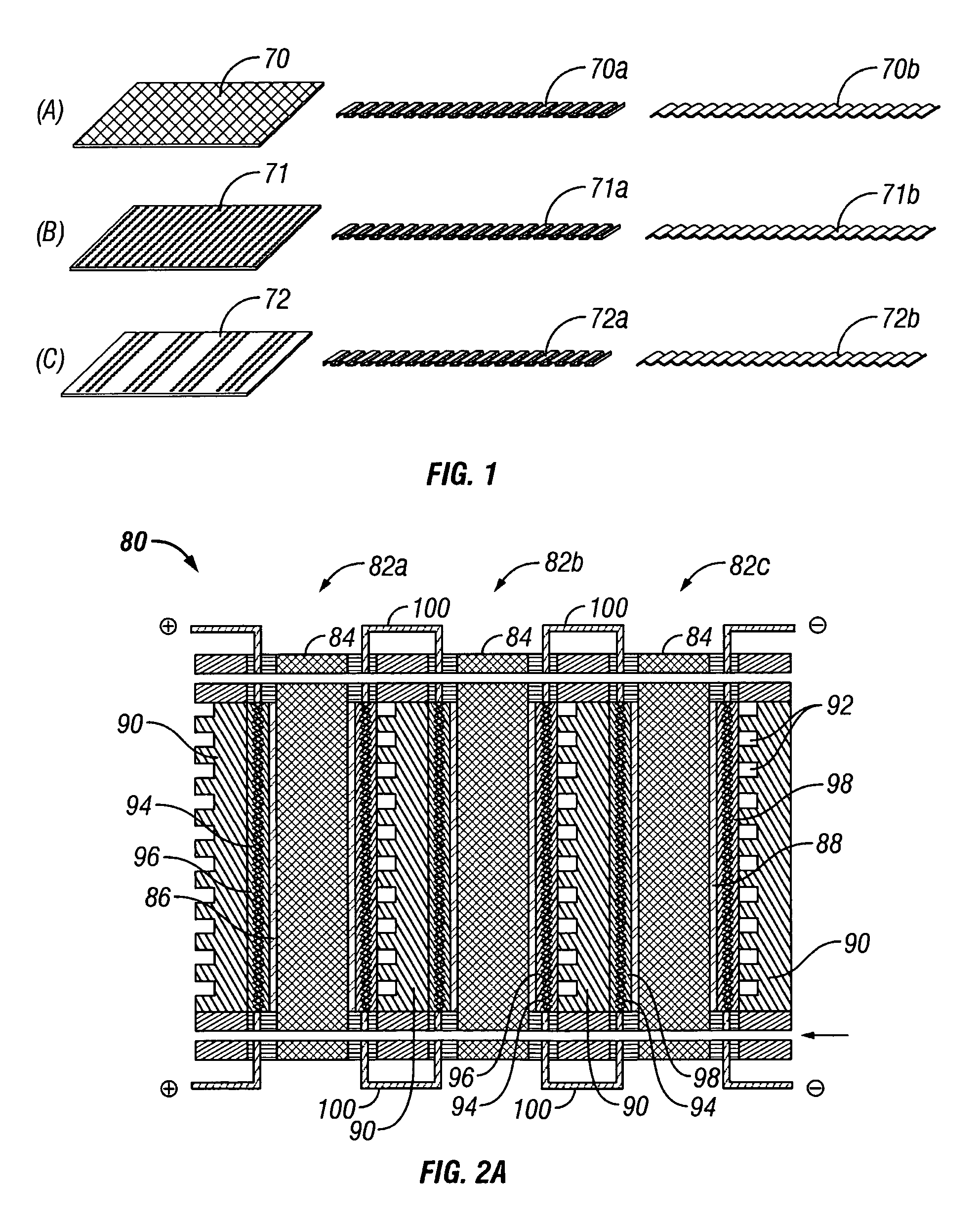
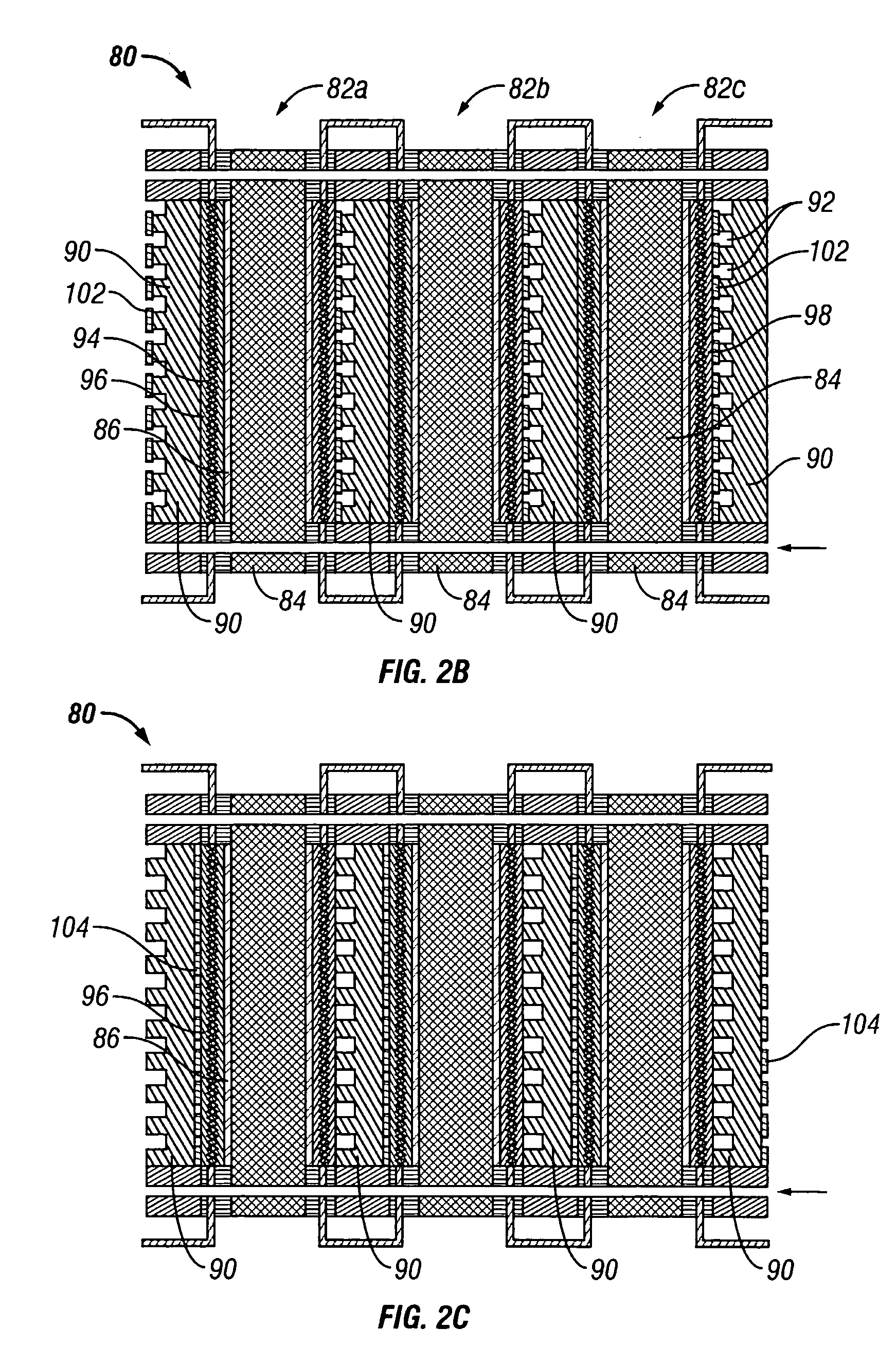
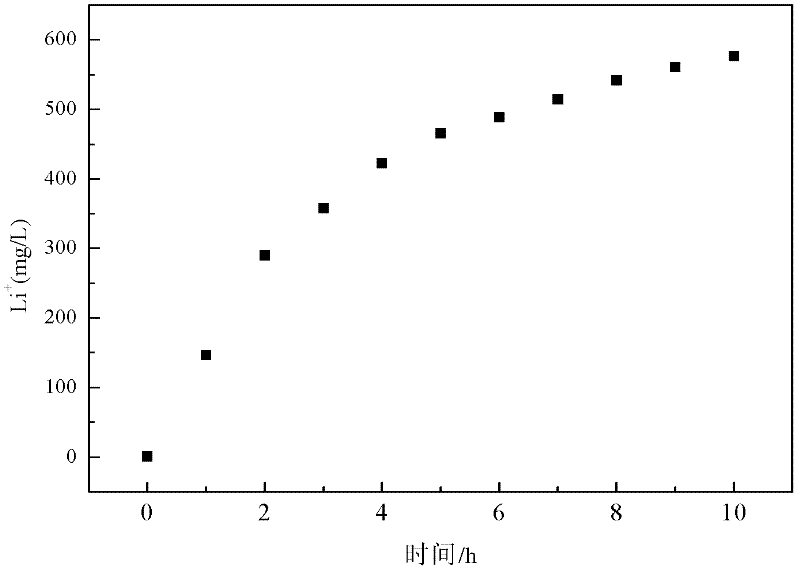
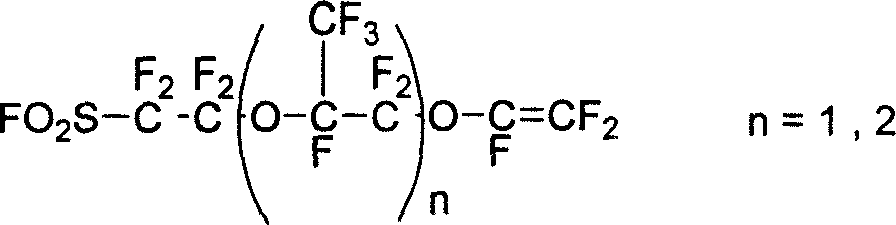Patents
Literature
3744 results about "Ion-exchange membranes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An ion-exchange membrane is a semi-permeable membrane that transports certain dissolved ions, while blocking other ions or neutral molecules. Ion-exchange membranes are therefore electrically conductive. They are often used in desalination and chemical recovery applications, moving ions from one solution to another with little passage of water.
Perfluorinated Membranes and Improved Electrolytes for Redox Cells and Batteries
ActiveUS20080292964A1Improve performanceReduce resistanceFinal product manufactureSecondary cellsSupporting electrolyteVanadyl ion
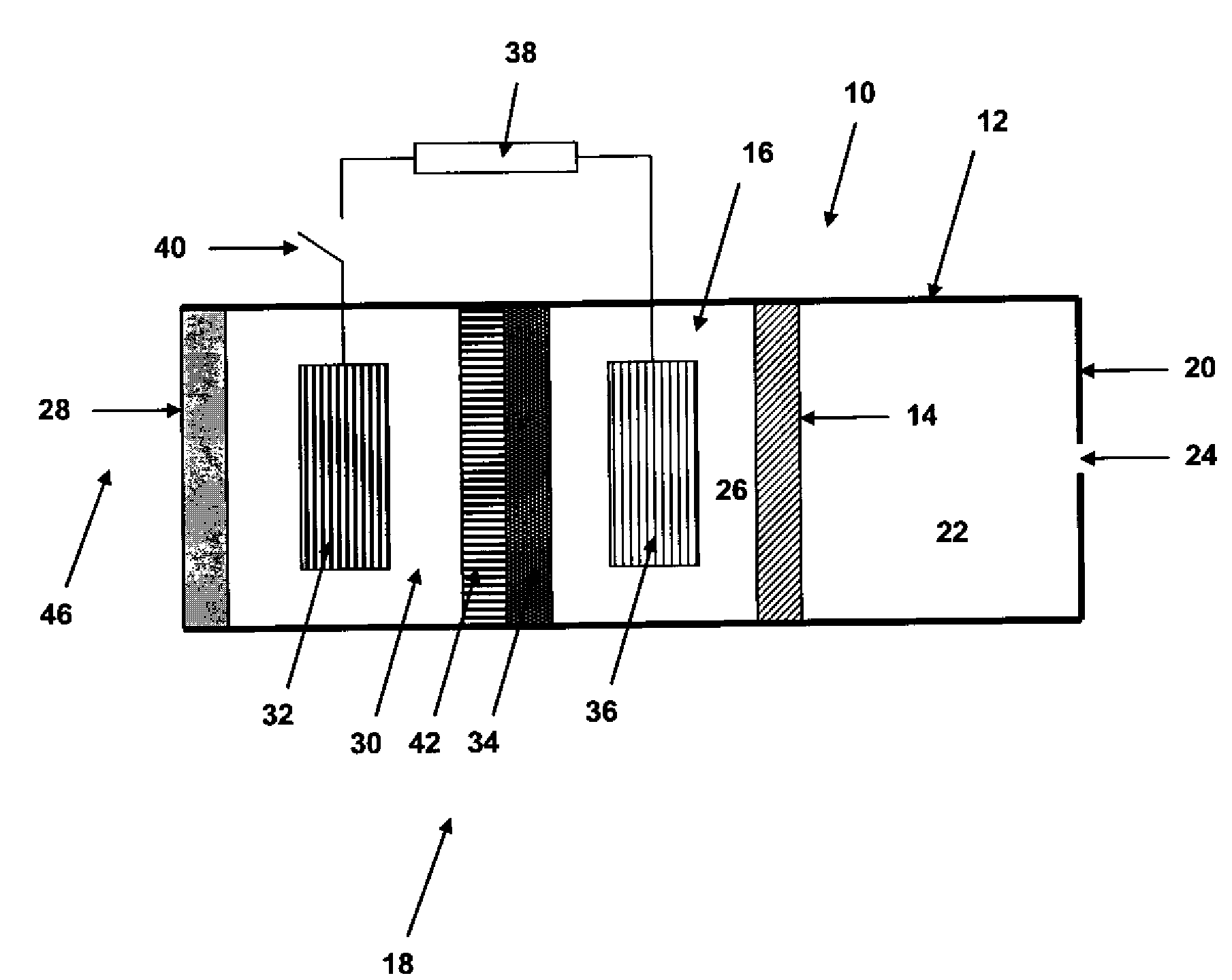
A vanadium redox cell having a positive half cell containing a positive half cell solution comprising a supporting electrolyte selected from H2SO4, HBr / HCl mixtures and one or more ions selected from the group vanadium (EI), Vanadium (IV), Vanadium (V), Br3 and Br2Cl; a negative half cell containing a negative half cell solution comprising a supporting electrolyte selected from H2SO4, HBr and HBr / HCl mixtures and one or more vanadium ions selected from the group Vanadium (II), Vanadium (III) and Vanadium (FV) and a perfluorinated cast cation exchange membrane or separator disposed between the positive and negative half cells and in contact with the positive and negative half cell solutions.
Owner:NEWSOUTH INNOVATIONS PTY LTD
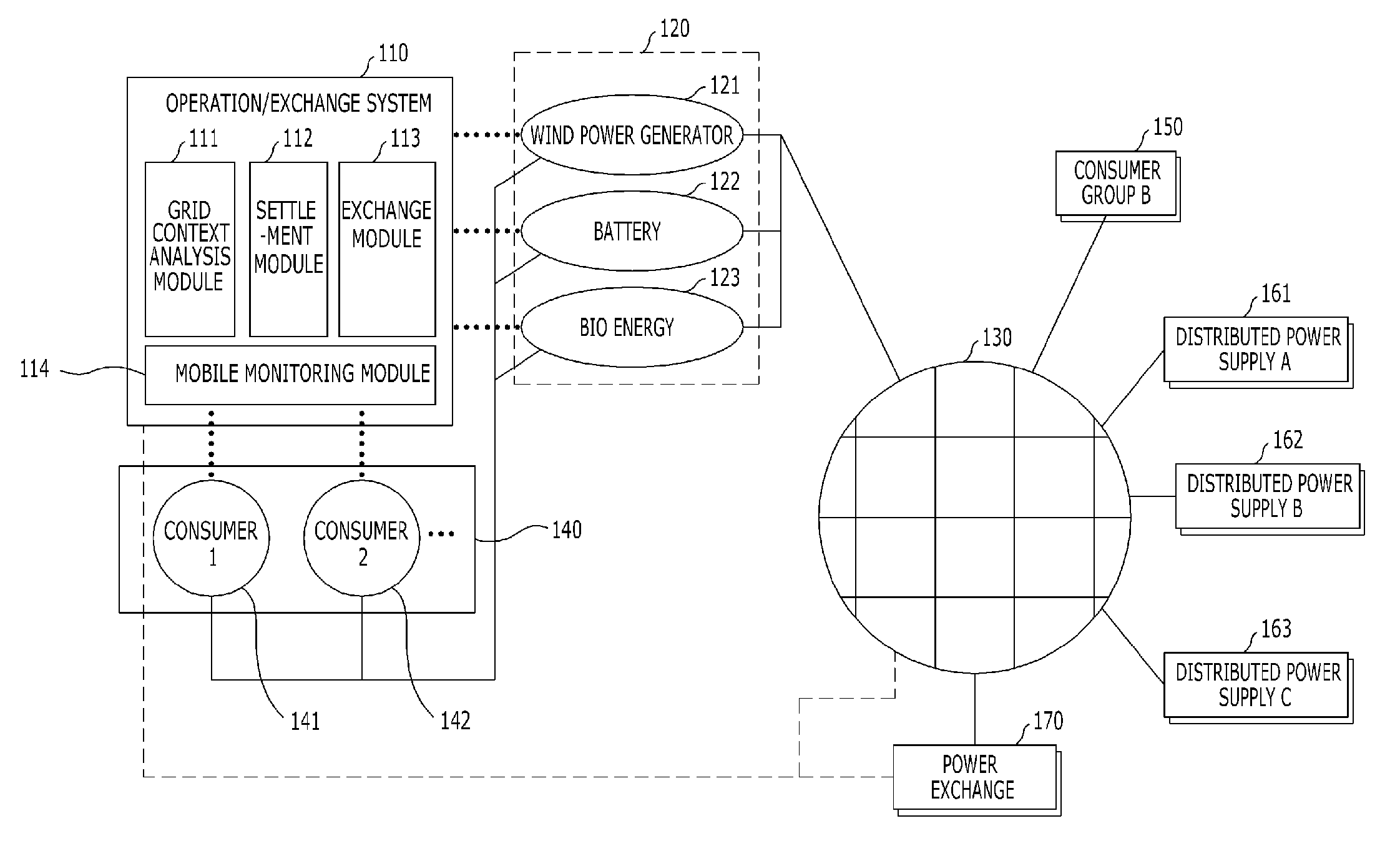
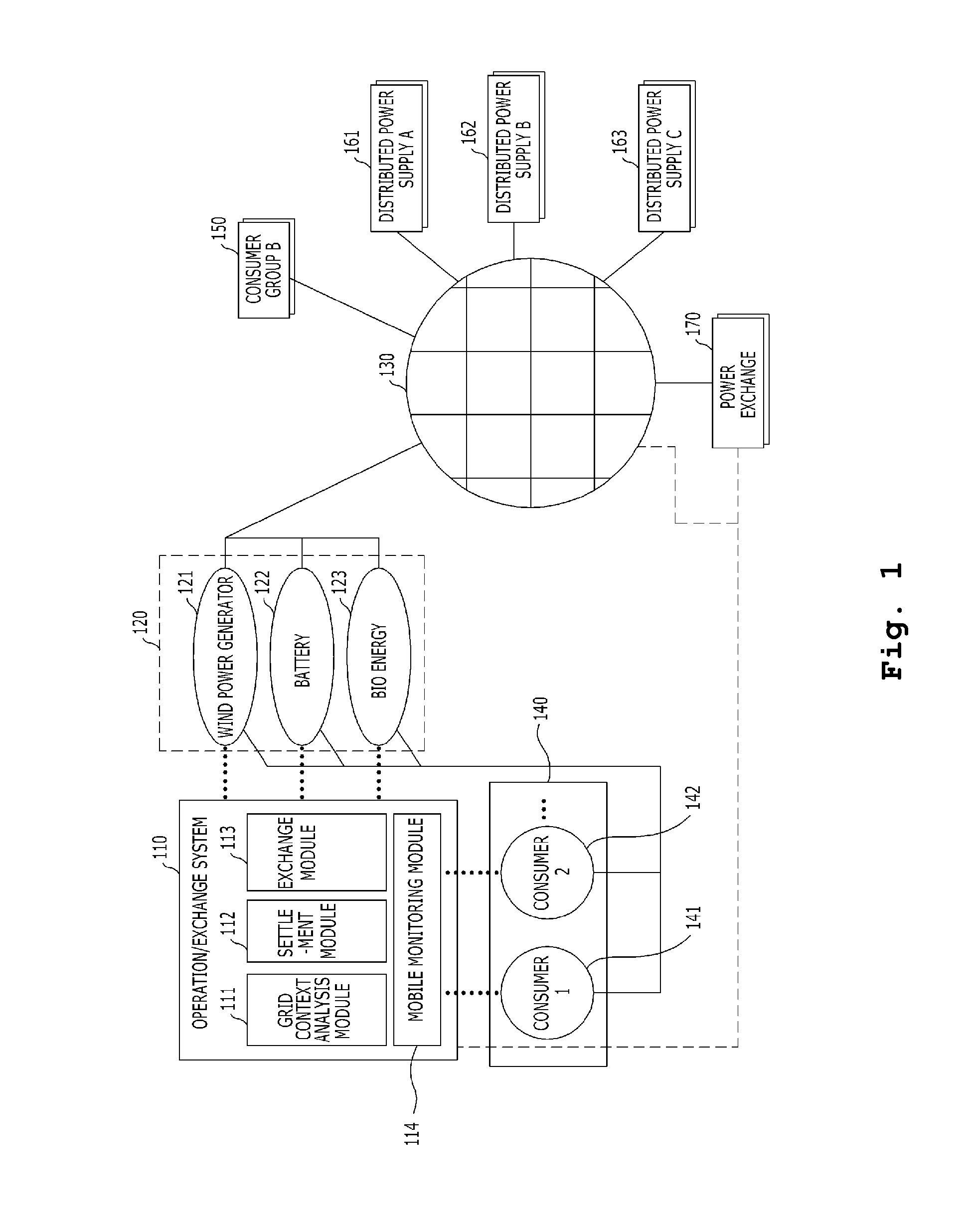
Power transaction system and transaction method of distributed power
InactiveUS20120205977A1Ac-dc network circuit arrangementsBuying/selling/leasing transactionsBiochemical engineeringComputer module
Provided are a CDI electrode and a method for manufacturing a module using the same. A hybridized electrode manufactured by the manufacturing method of the present invention can manufacture a CDI electrode capable of increasing adsorption efficiency and rate of ions and selectively adsorbing cation and anion, thereby simply and inexpensively manufacturing the CDI electrode module without using a cation-exchange membrane and an anion-exchange membrane.
Owner:ILJIN ELECTRONICS
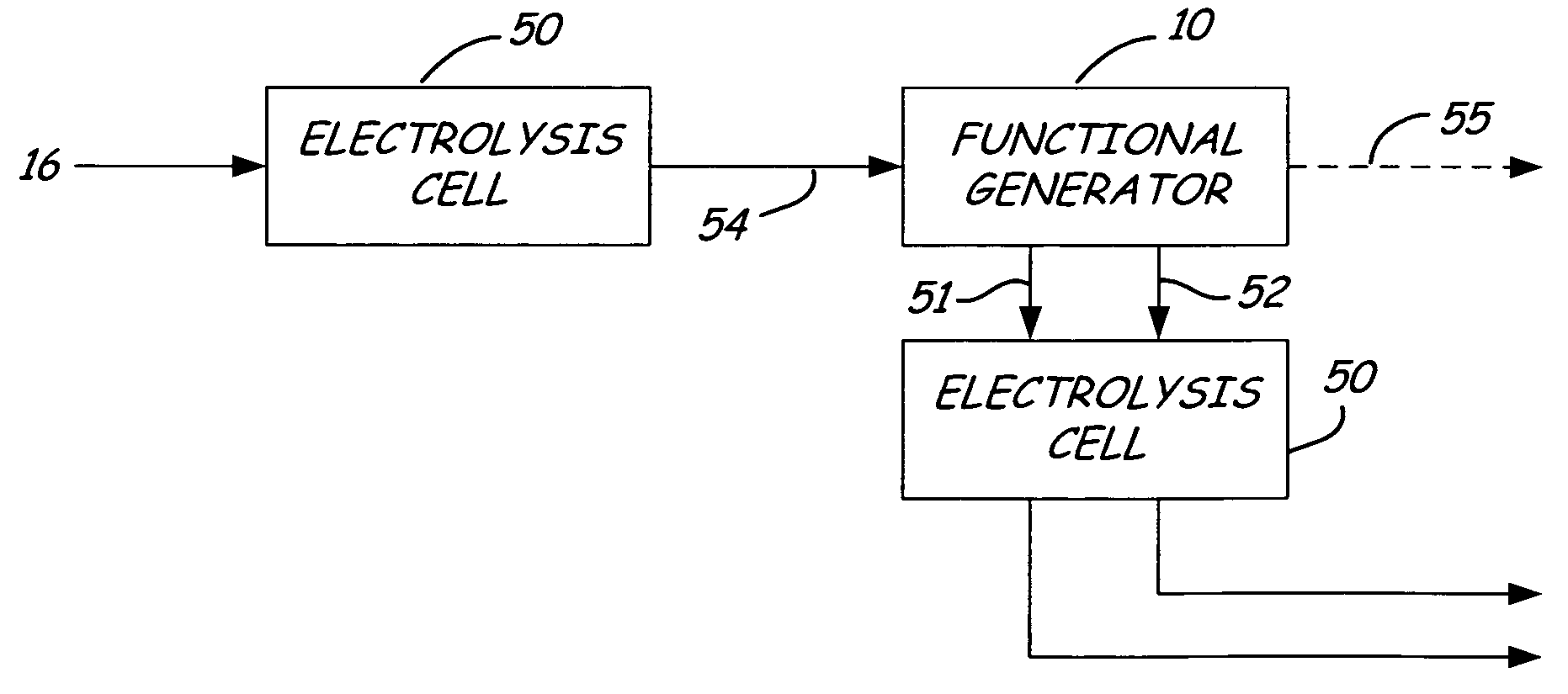
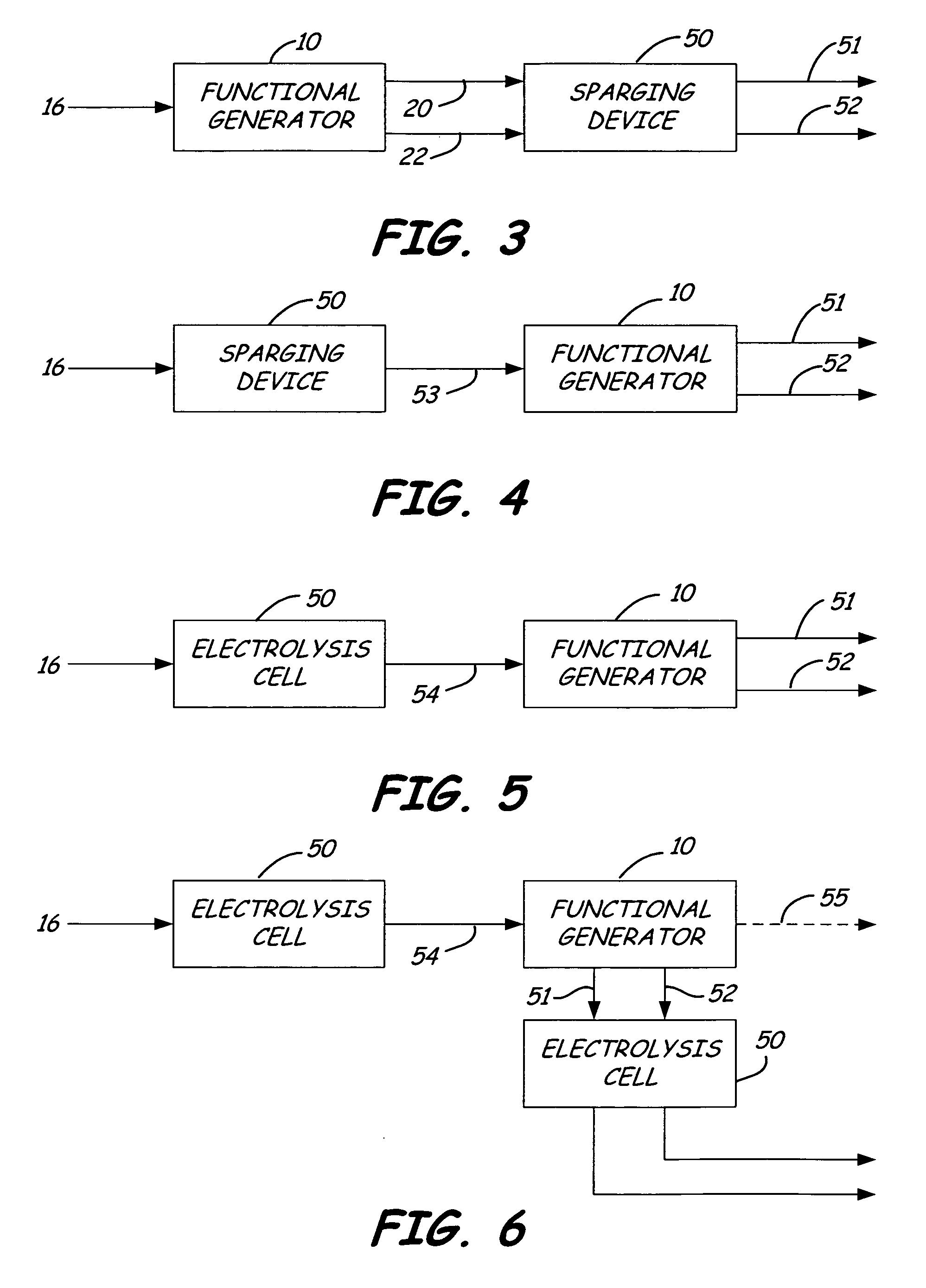
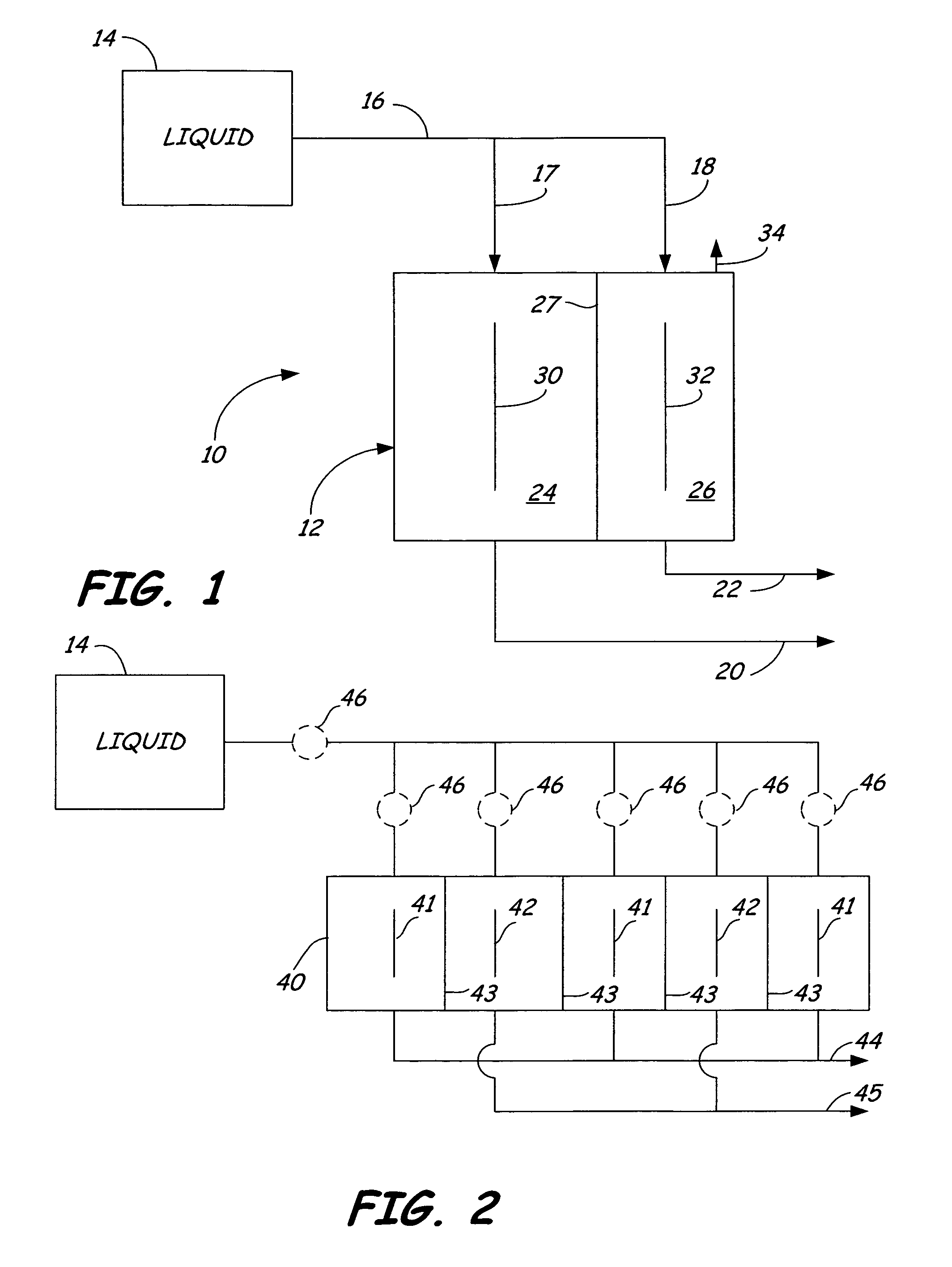
Cleaning apparatus having a functional generator for producing electrochemically activated cleaning liquid
An apparatus is provided, which includes a mobile body configured to travel over a surface, a source of a liquid, a liquid dispenser and a flow path from the liquid source to the liquid dispenser. A functional generator is coupled in the flow path, which comprises an anode chamber and a cathode chamber separated by an ion exchange membrane and which electrochemically activates the liquid from the liquid source which is passed through the functional generator.
Owner:TENNANT COMPANY
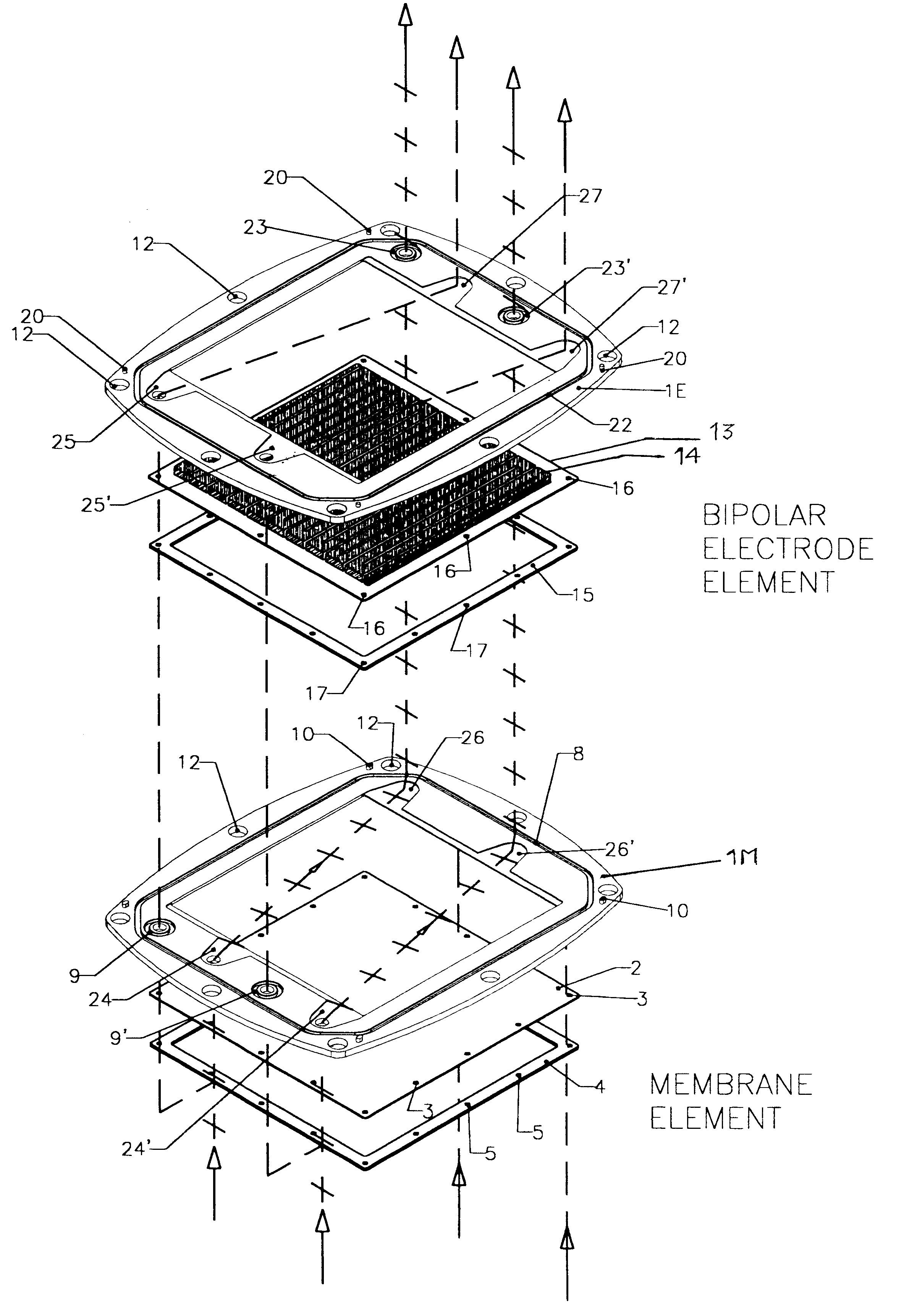
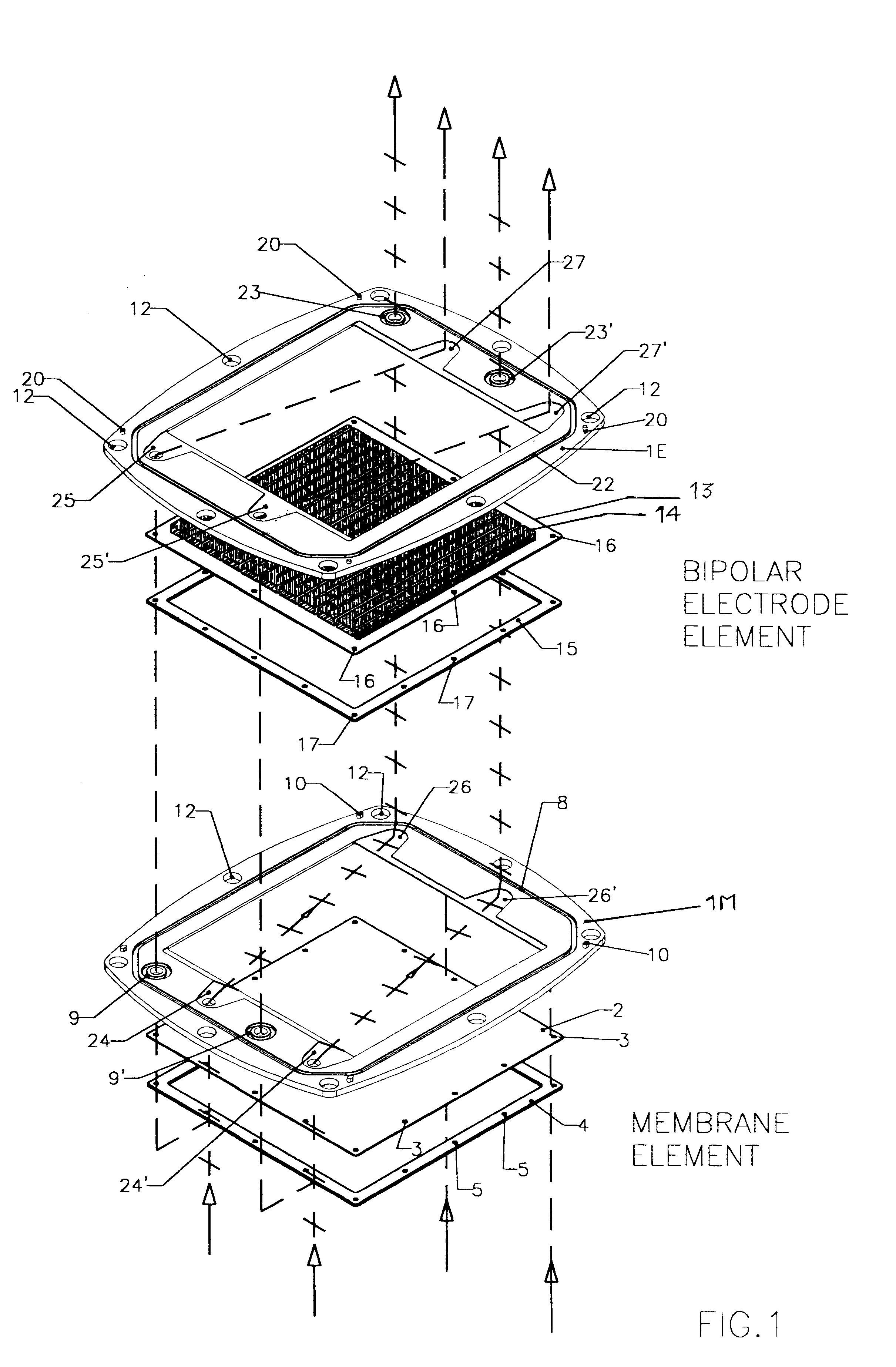
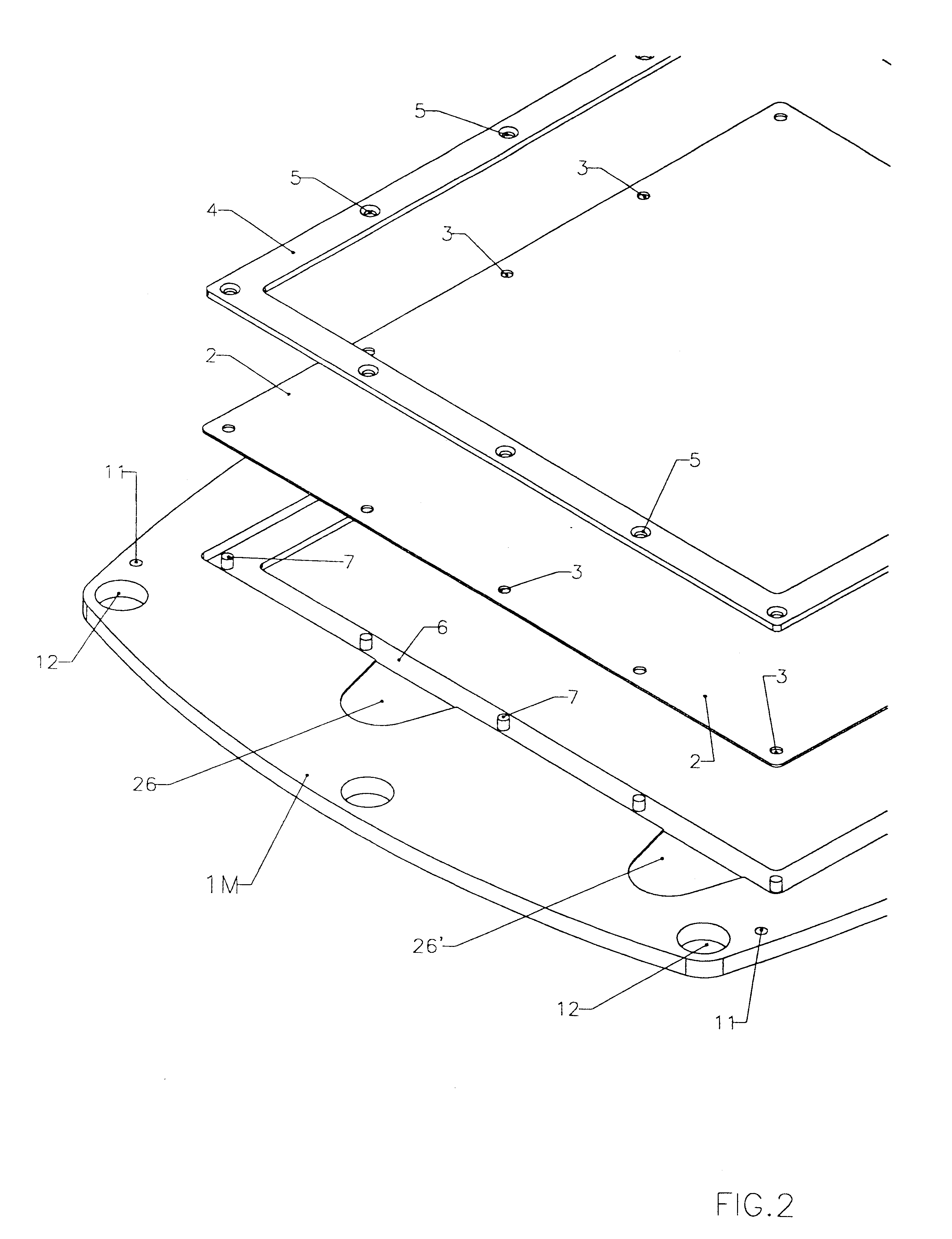
Membrane-separated, bipolar multicell electrochemical reactor
InactiveUS6555267B1Improve electrochemical performanceLower overall pressure dropFuel cells groupingFuel cell auxillariesPlastic materialsIon-exchange membranes
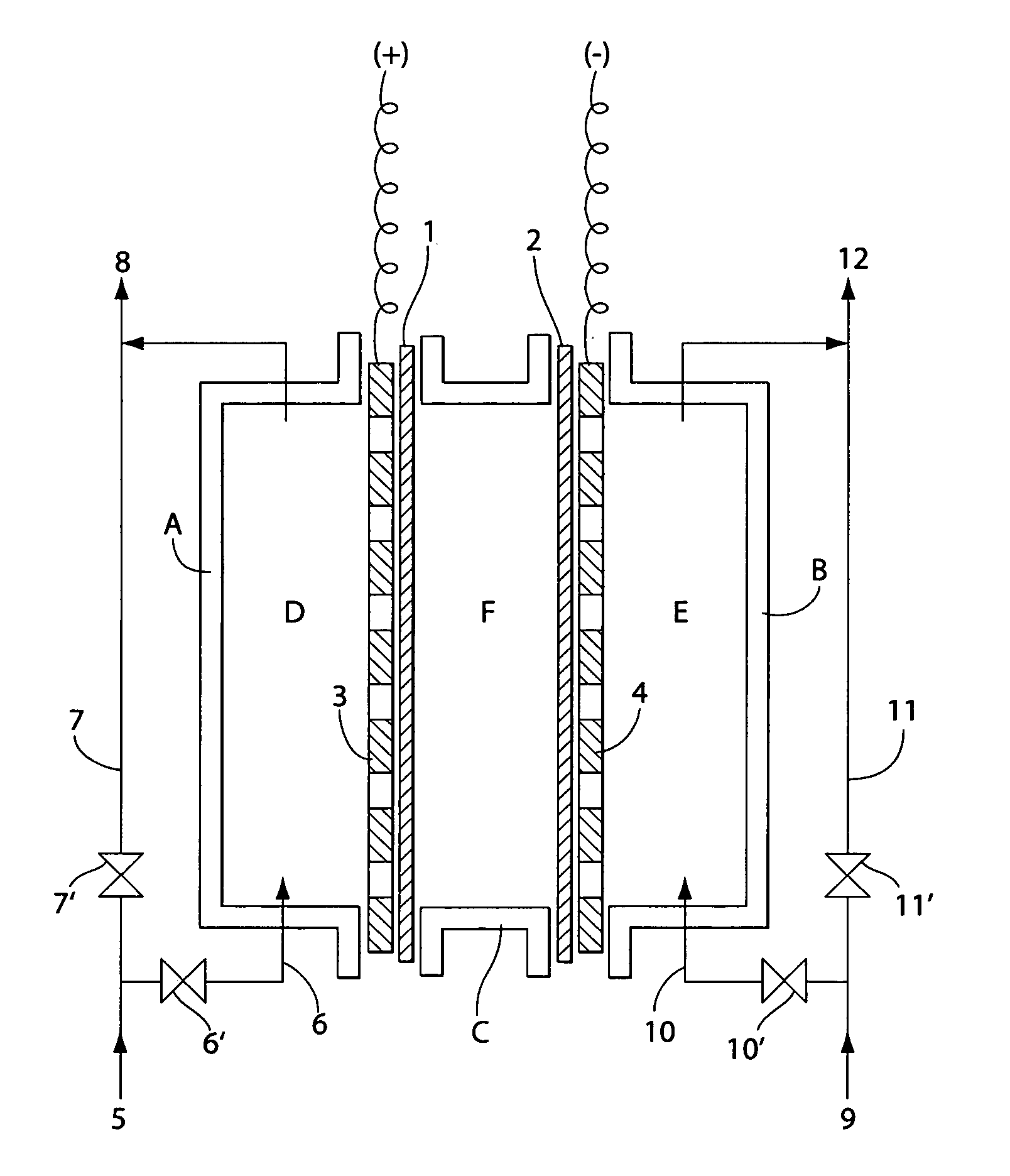
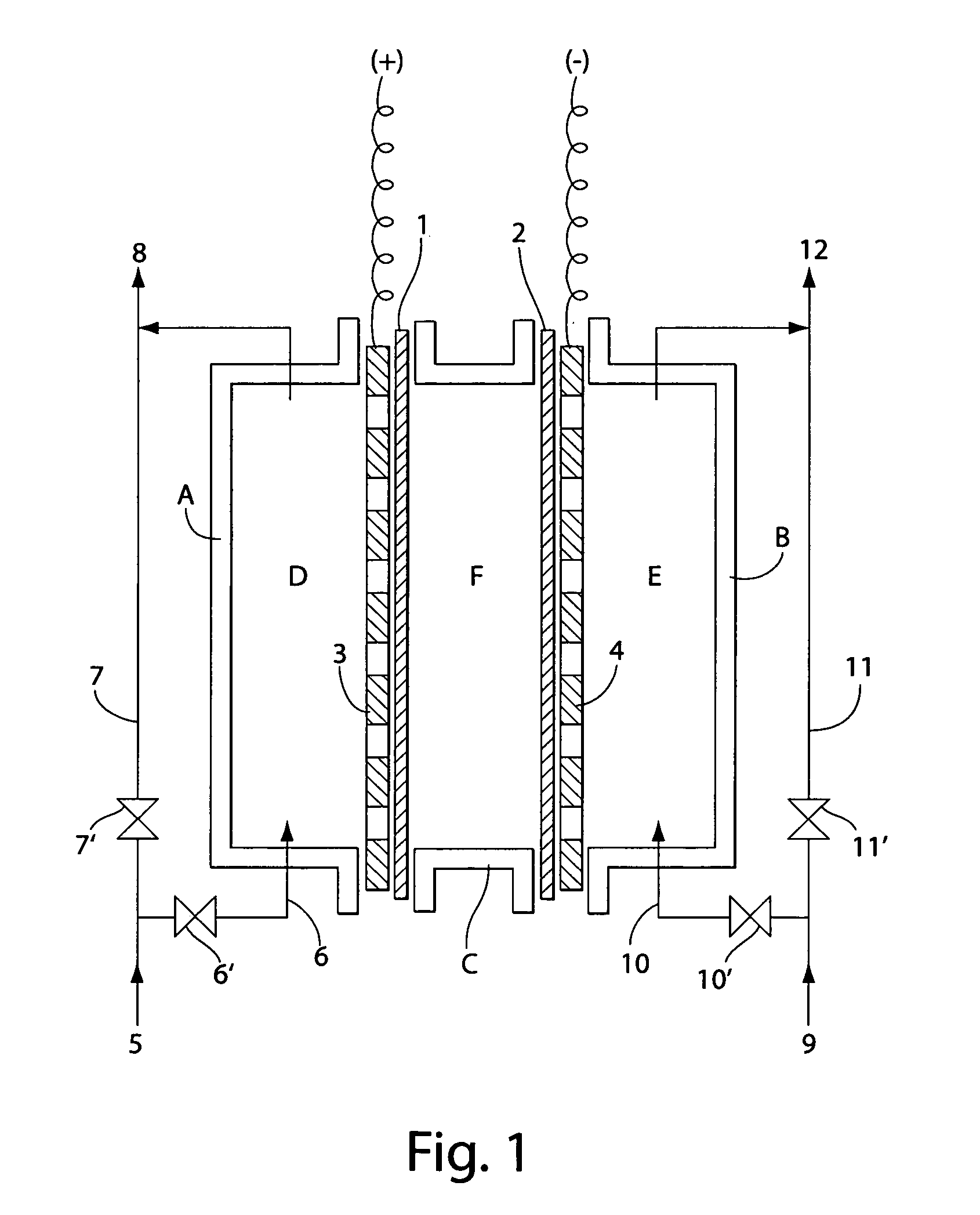
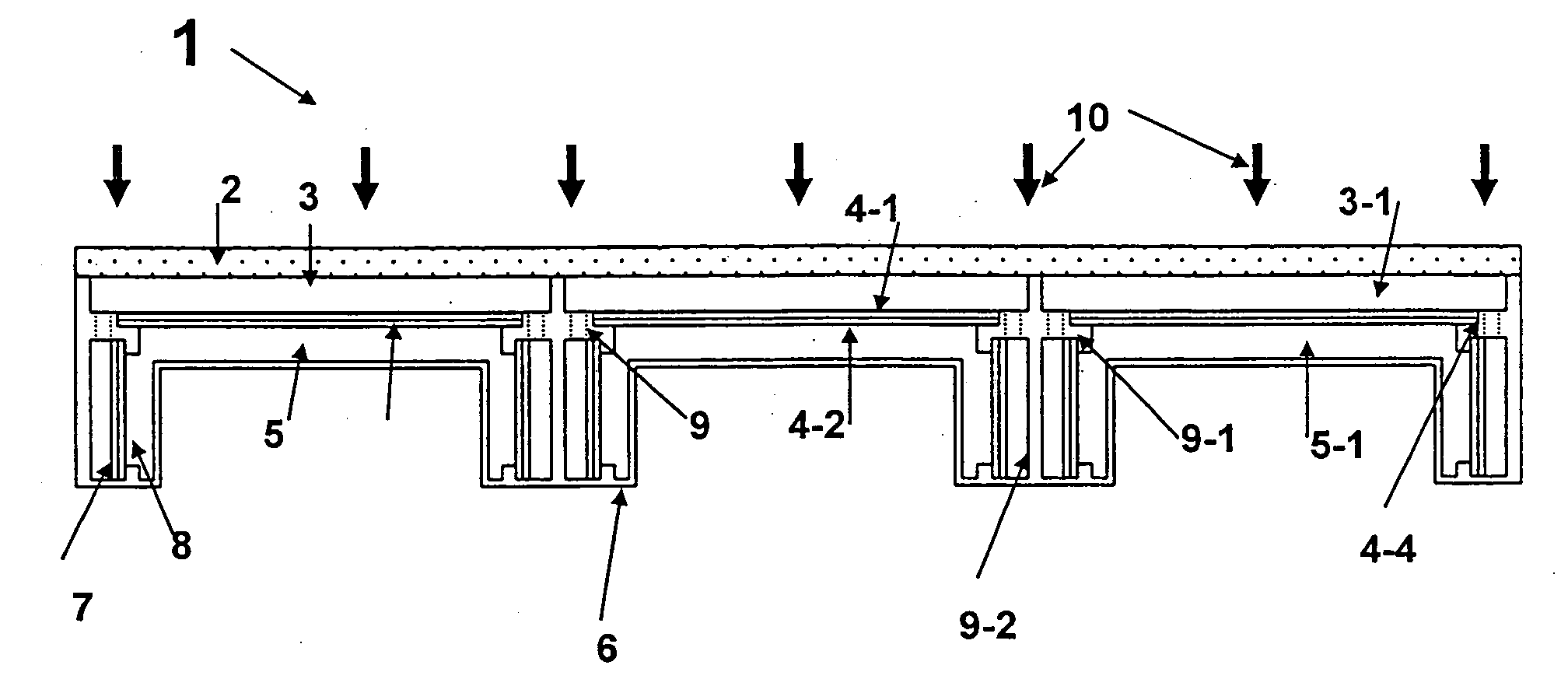
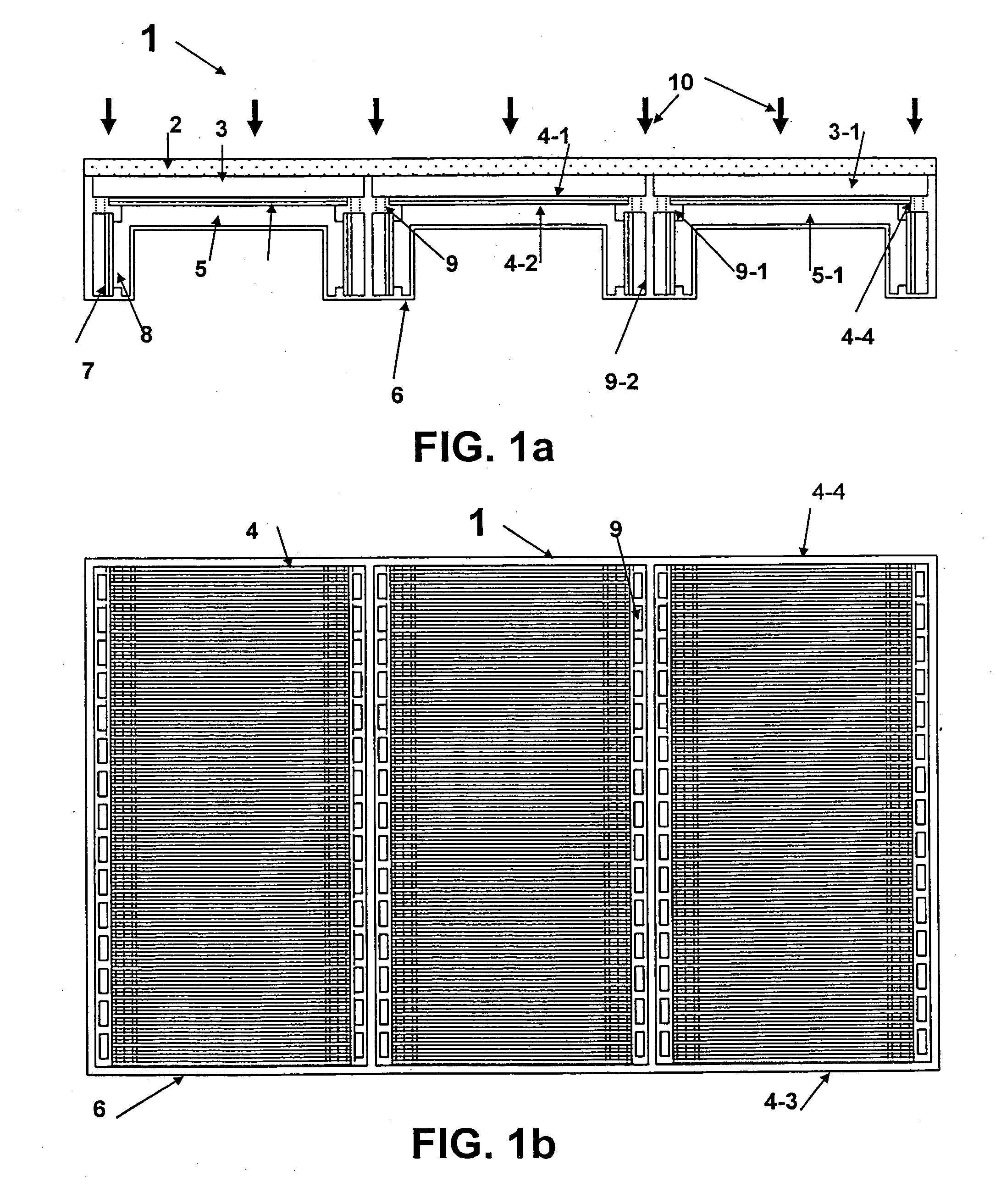
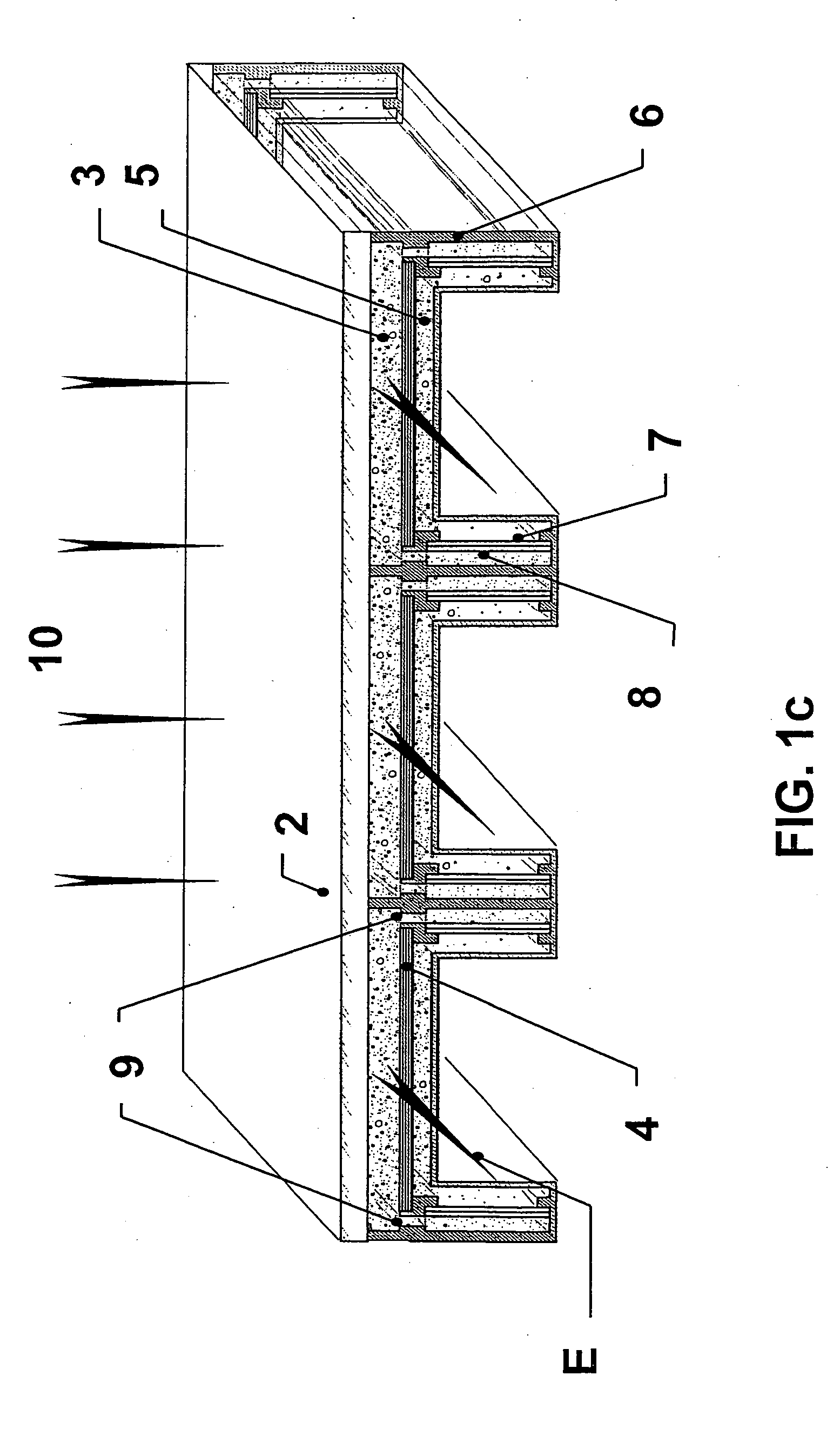
A multicell assembly is constituted by alternately stacking two types of pre-assembled elements: a bipolar electrode holding subassembly and a membrane holding subassembly. The alternate stack of elements is piled over a bottom end element and the stack is terminated by placing over the last membrane holding element a top end electrode element. Each bipolar plate electrode holding element and each ion exchange membrane separator holding element includes a substantially similar rectangular frame piece, made of an electrically nonconductive and chemically resistant material, typically of molded plastic material, having on its upper (assembly) face grooves for receiving O-ring type gasket means, and having through holes and recesses in coordinated locations disposed along two opposite sides of the rectangular frame forming, upon completion of the assembling, ducts for the separate circulation of the negative electrolyte and of the positive electrolyte through all the negative electrolyte flow chambers and all positive electrolyte flow chambers, respectively, in cascade.
Owner:SQUIRREL HLDG
Water transport method and assembly including a thin film membrane for the addition or removal of water from gases or liquids
A water transport assembly, is provided including a housing having a first chamber therein, which is accessible through an opening in the housing. The housing additionally includes a sample inlet port and a sample outlet port, both of which are in fluid communication with the first chamber. A flat ion exchange membrane is attached to the housing in a plane over the opening in the housing, to seal the opening in a vapor tight seal. Water will pass through the membrane based upon the vapor pressure on each side of the membrane, to either dry or humidify sample passing through the first chamber. When the flat ion exchange membrane is a flat, thin ion exchange membrane it is preferable that the thin ion exchange membrane have a thickness of between about 0.1 and about 3.0 mils.
Owner:GOLDSTEIN JAY
Fluid delivery device having an electrochemical pump with an ion-exchange membrane and associated method
InactiveUS20060116641A1Improve accuracySmall volumeMedical devicesPressure infusionEngineeringIon-exchange membranes
Owner:MICROLIN
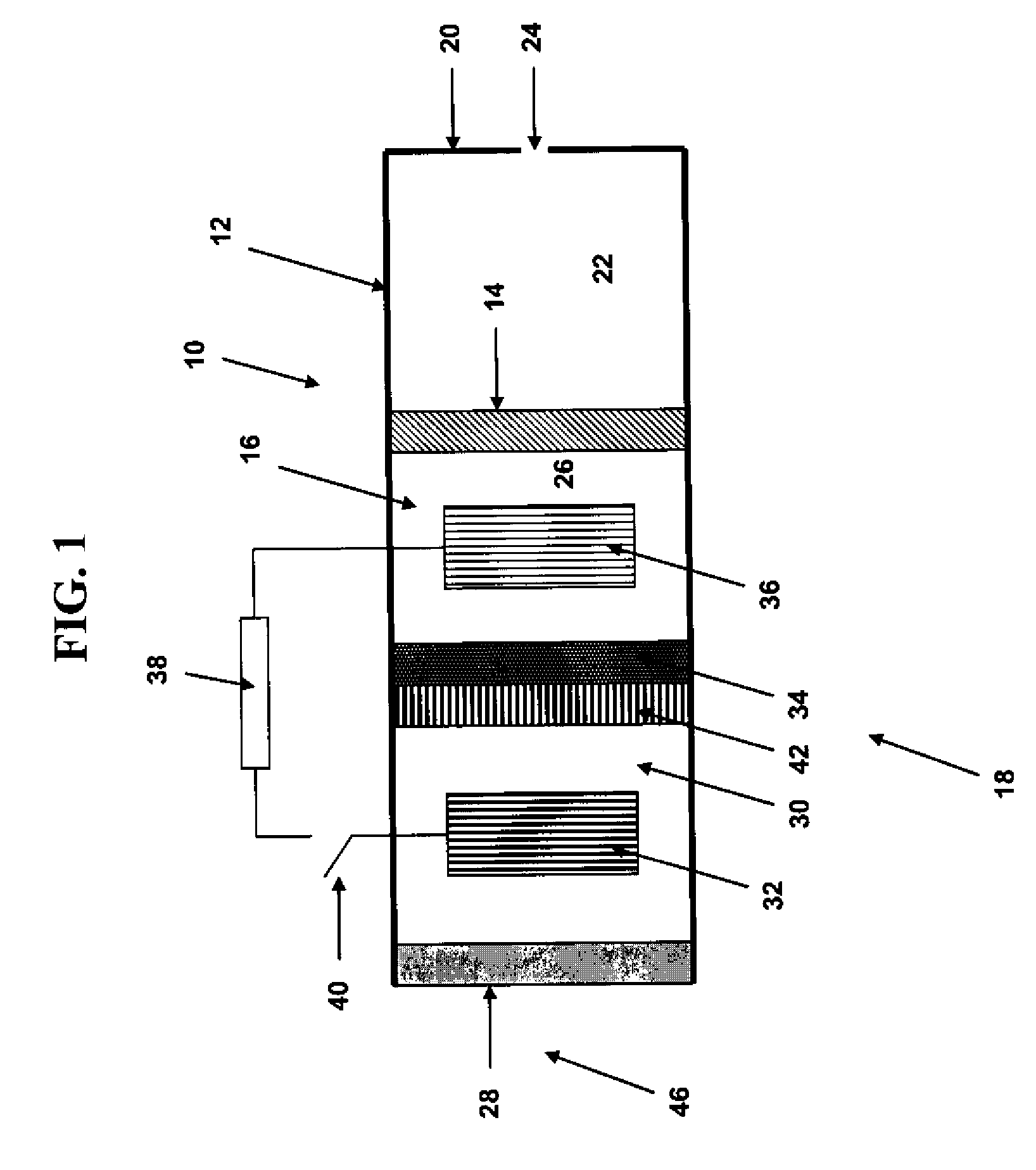
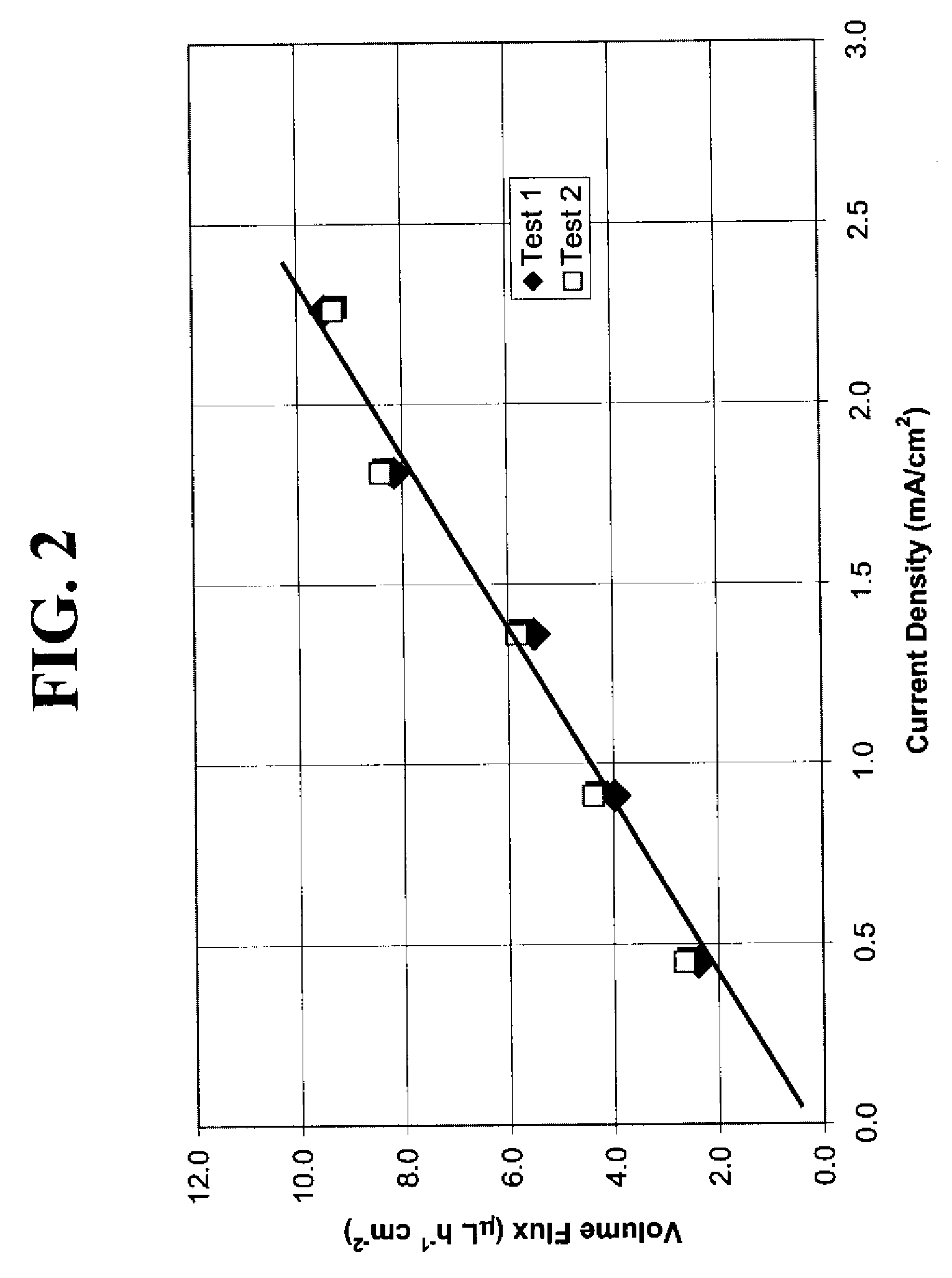
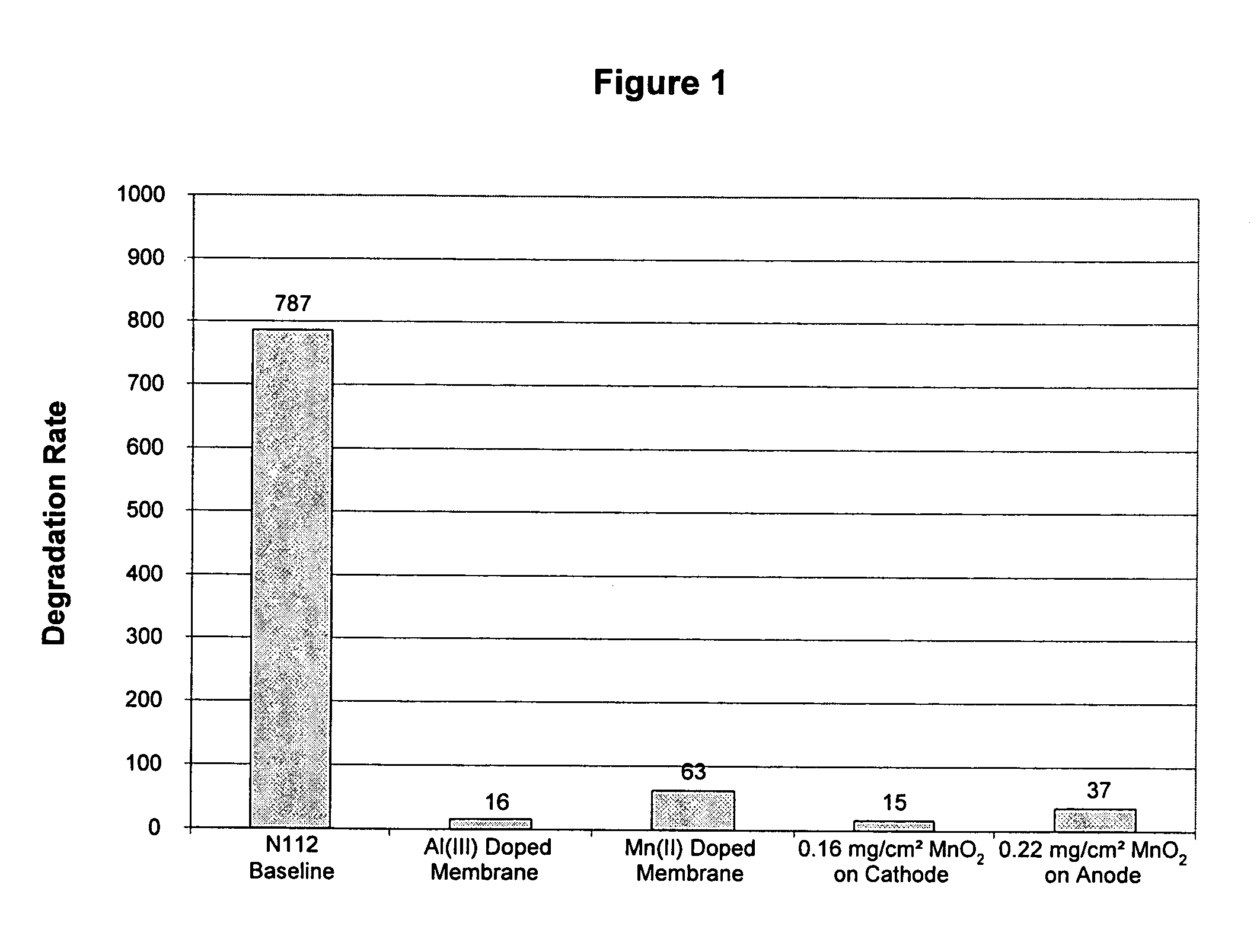
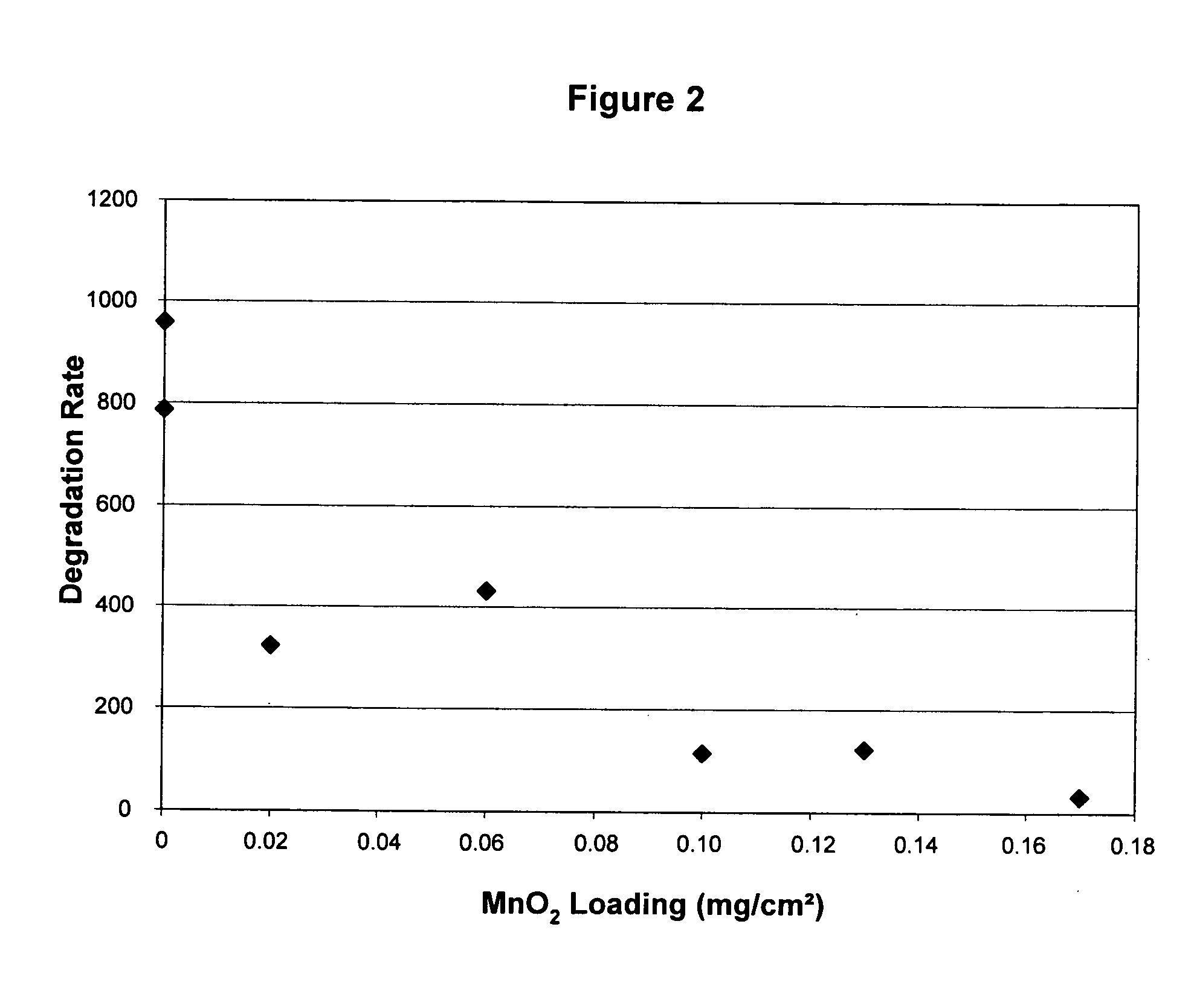
Reduced degradation of ion-exchange membranes in electrochemical fuel cells
ActiveUS20050136308A1Easy loadingIncreased susceptibilityFuel cells groupingIon-exchanger regenerationHydrogen peroxide breakdownScavenger
A significant problem in PEM fuel cell durability is in premature failure of the ion-exchange membrane and in particular by the degradation of the ion-exchange membrane by reactive hydrogen peroxide species. Such degradation can be reduced or eliminated by the presence of an additive in the anode, cathode or ion-exchange membrane. The additive may be a radical scavenger, a membrane cross-linker, a hydrogen peroxide decomposition catalyst and / or a hydrogen peroxide stabilizer. The presence of the additive in the membrane electrode assembly (MEA) may however result in reduced performance of the PEM fuel cell. Accordingly, it may be desirable to restrict the location of the additive to locations of increased susceptibility to membrane degradation such as the inlet and / or outlet regions of the MEA.
Owner:BDF IP HLDG
Method and apparatus for preventing scaling in electrodeionization units
InactiveUS6149788AAvoid mixingImprove conductivitySludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementElectricityIncreased tolerance
A method and apparatus is provided for inhibiting scaling in an electrodeionization system and, more particularly, for increasing tolerance to hardness in the feed water to an electrodeionization unit by inhibiting precipitation of scale-forming metallic cations contained in the feed water and thereby increasing efficiencies of the electrodeionization system. Water to be purified is passed through an electrodeionization unit in which the flow in the diluting compartment is countercurrent to the flow in the concentrating compartment. This is to impede the migration of scale-forming metallic cations from the diluting compartment, through the cation exchange membrane, into the concentrating compartment and towards the concentrating compartment side of the anion exchange membrane, thereby preventing scale formation on the anion exchange membrane. The electrodeionization unit may be further modified by dividing the concentrating compartments into first and second compartments by a porous diaphragm or ion-conducting membrane. The porous diaphragm or ion-conducting membrane effectively eliminates convective transport of scale-forming metallic cations from the cation exchange membrane side of the concentrating compartment to the anion exchange membrane side of the concentrating compartment, thereby inhibiting scale formation on the anion exchange membrane.
Owner:E CELL
Polymer of containing fluorin, and application as material of ion exchange fiber
InactiveCN101003588AIncrease the effective areaLower resistanceMelt spinning methodsVinyl etherAlkali ions
This invention discloses a fluorine-containing polymer and its application as ion exchange fiber material. The fluorine-containing polymer is a perfluoro resin containing sulfonylfluoride groups, and is shown in formula 1. The fluorine-containing polymer has ion exchange function, and is prepared by free radical copolymerization of perfluorosulfonyl vinyl ether, tetrafluoroethylene and hexafluoropropylene in the presence of dispersant, solvent and initiator. The dispersant / solvent is mixed solution of melamine derivative containing linear perfluoro hydrocarbon and water. The fluorine-containing polymer can be melt-spun into polymer fibers, which can be woven into fiber network that can be used as the reinforcing network material for ion exchange membranes and chlor-alkali ion membrane to reinforce and improve the ion exchange ability.
Owner:SHANDONG HUAXIA SHENZHOU NEW MATERIAL
Water management in bipolar electrochemical cell stacks
InactiveUS20060199061A1Reduce probabilityPromote loss of waterFuel cells groupingWater management in fuel cellsPolymer electrolytesLiquid water
A bipolar, filter press-like electrochemical cell stack comprising a plurality of electrochemical cells, where each electrochemical cell is supplied with a gaseous anodic reactant and either supplied with a gaseous cathodic reactant or produces a gaseous cathodic product, and where each electrochemical cell avoids drying out the ion exchange membrane polymer electrolyte, avoids flooding at the cathode, facilitates recovery of liquid water at the anode, and reduces water losses from at least one of the electrodes. A water retention barrier is variously positioned, such as between a gas diffusion electrode and a fluid flow field. The barrier may be either: (i) a thin, gas permeable, liquid water impermeable membrane; (ii) a thin, porous sheet of material; or (iii) a thin, substantially solid sheet of material except for a plurality of small through-holes that penetrate from one side of the sheet to an opposing side of the same sheet. The barrier is advantageously used at the cathode and facilitates air cooling of the cell.
Owner:LYNNTECH
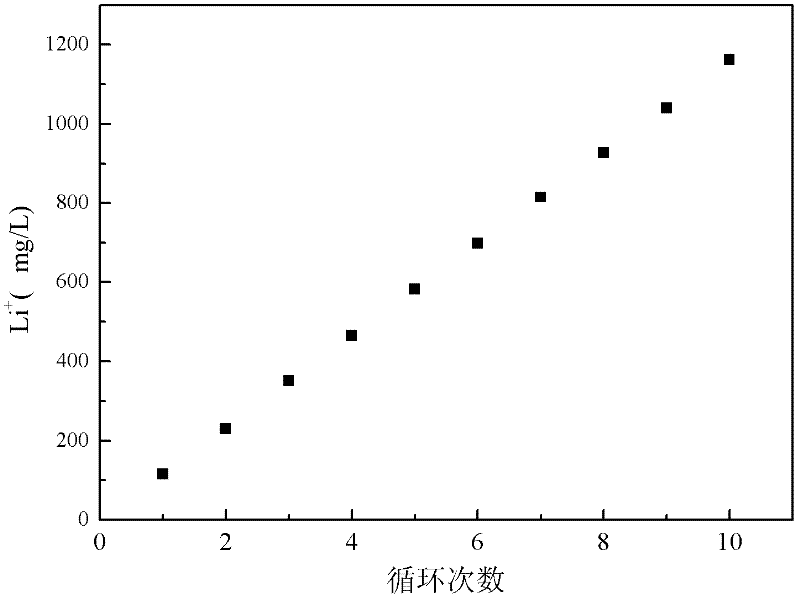
Method and device for separating magnesium and lithium and enriching lithium from salt lake brine
ActiveCN102382984AGood choiceImprove stabilityProcess efficiency improvementSupporting electrolyteIon-exchange membranes
The invention relates to a method and a device for separating magnesium and lithium and enriching the lithium from salt lake brine. The method comprises the following steps of: separating an electrodialyzing device into two areas by using an anion exchange membrane, namely a lithium salt chamber and a brine chamber, filling the salt lake brine in the brine chamber, and filling a supporting electrolyte solution which does not contain Mg<2+> in the lithium salt chamber; placing a conducting matrix coated by an ionic sieve in the brine chamber as a cathode; placing the conducting matrix coated by a lithium-embedded ionic sieve in the lithium salt chamber as an anode; under the driving of an external electric potential, embedding Li <1+> in the brine in the brine chamber into the ionic sieve to form the lithium-embedded ionic sieve, and recovering the lithium-embedded ionic sieve into the ionic sieve after the lithium-embedded ionic sieve in the lithium salt chamber releases the Li <1+> into a conducting solution; and discharging a liquid in the brine chamber after the lithium is embedded, adding the salt lake brine again, alternatively placing electrodes in the two chambers, and repeating and circulating operations. Through the method and the device for separating magnesium and lithium and enriching lithium in the salt lake brine, the separation of the lithium and other ions is effectively realized, and a lithium-enriched solution is synchronously obtained. The method has a short flow and low production cost, is simple to operate, can be operated continuously, and is easy to industrially apply.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Iontophoresis device
InactiveUS20050070840A1Improve performanceImprove convenienceElectrotherapyPharmaceutical delivery mechanismMembrane bodiesIon-exchange membranes
An iontophoresis device useful for administering an ionic drug by iontophoresis has an iontophoresis electrode section (active electrode section) and a ground electrode section (inactive electrode section) both of which are to be connected to a power source. The iontophoresis device includes elements (members) of both of the electrode sections are all formed of membrane bodies, and includes ion exchange membranes different in ion selectivity, one being selective to ions of the same species as charged ions of the ionic drug and the other to ions different in species from the charged ions of the ionic drug that are arranged in the iontophoresis electrode section, and at least an ion exchange membrane selective to ions opposite to the charged ions of the ionic drug is arranged in the ground electrode section. The iontophoresis device can administer the ionic drug stably over a long period of time at high transport efficiency.
Owner:TITI ELLEBEAU INC
Production of electrolytic water
InactiveUS7238272B2Prevent adhesionIncrease productivityCellsLiquid separation by electricityWater useElectrolysed water
Apparatus and methods are provided for producing electrolytic water using three chambers, rigid plates and ion exchange membranes. Benefits include reduced scale production and increased long-term bactericidal effects of the water produced.
Owner:ELECTROLYZER
Cluster ion exchange membrane and electrolyte membrane electrode connection body
InactiveUS20050095486A1High mechanical strengthImprove ionic conductivityIon-exchange process apparatusSolid electrolytesIon-exchange membranesMembrane configuration
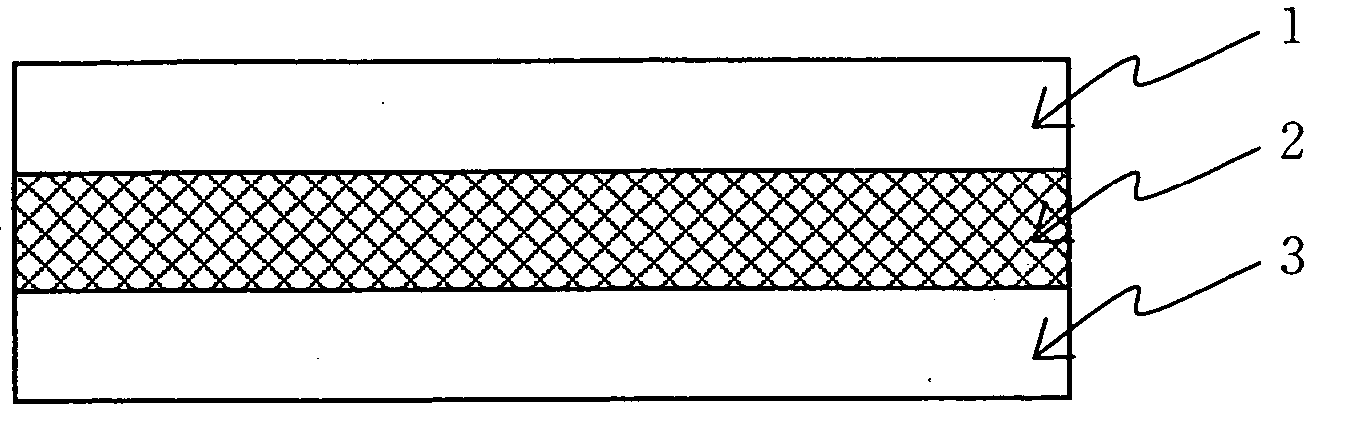
The present invention provides a composite ion exchange membrane which has high mechanical strength and is suitable for use as a solid polymer electrolyte membrane excellent in ionic conductivity and a method for its production. The invention is achieved by a composite ion exchange membrane including a composite layer comprising a support membrane with continuous voids formed of polybenzazole polymer, the support membrane being impregnated with ion exchange resin, and surface layers formed of ion exchange resin free of support membranes, the surface layers being formed on both surfaces of the composite layer so as to sandwich the composite layer therebetween.
Owner:TOYO TOYOBO CO LTD
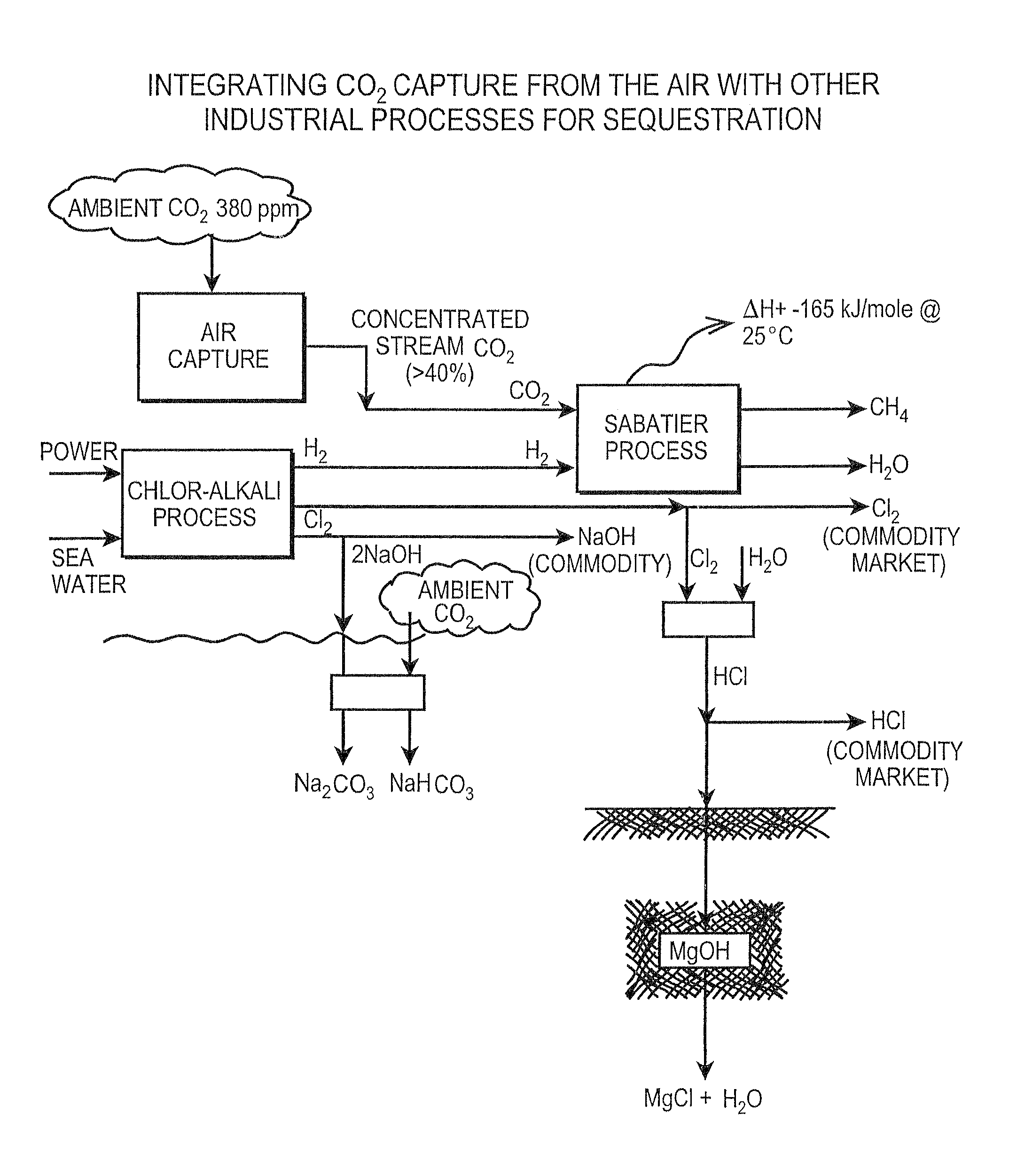
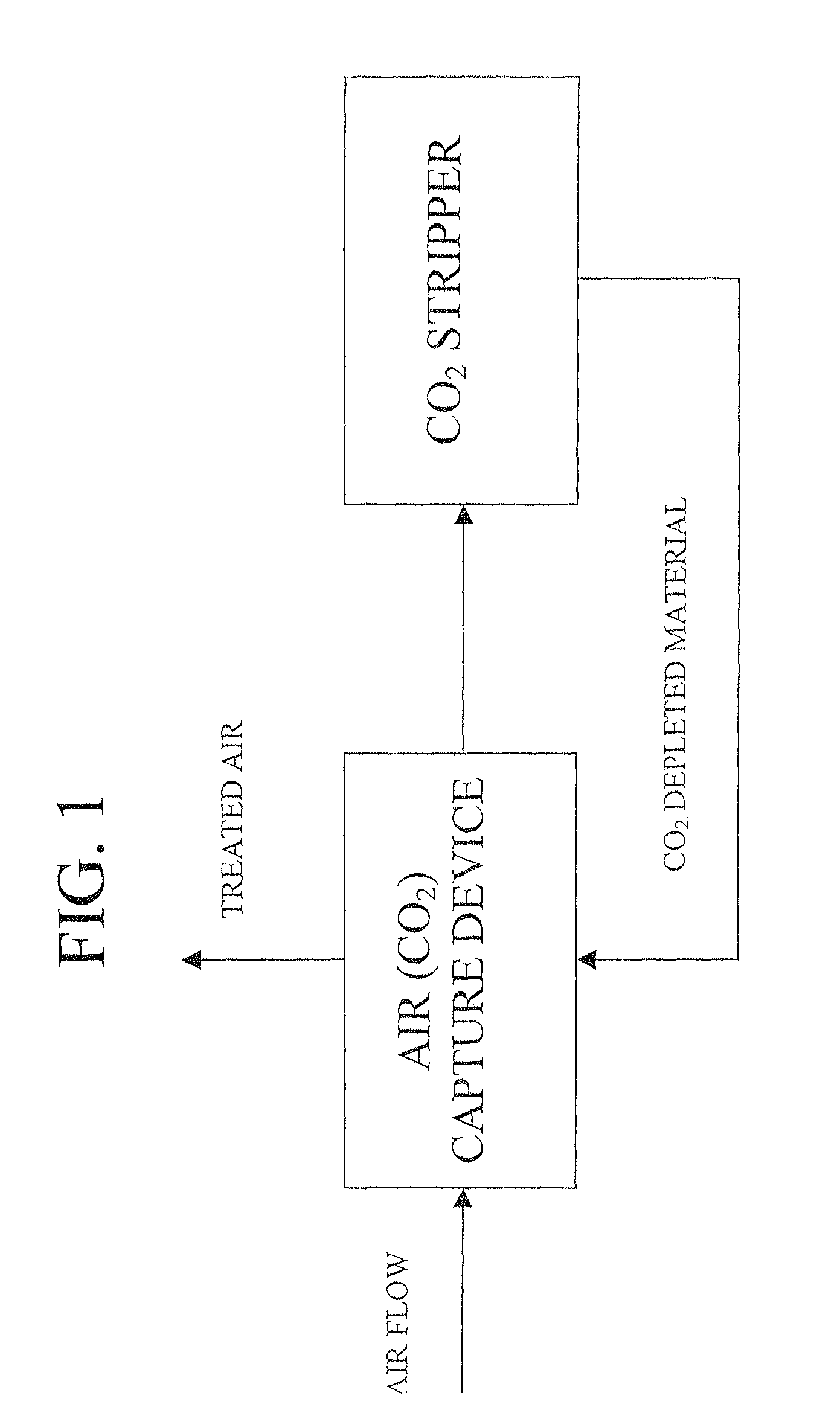
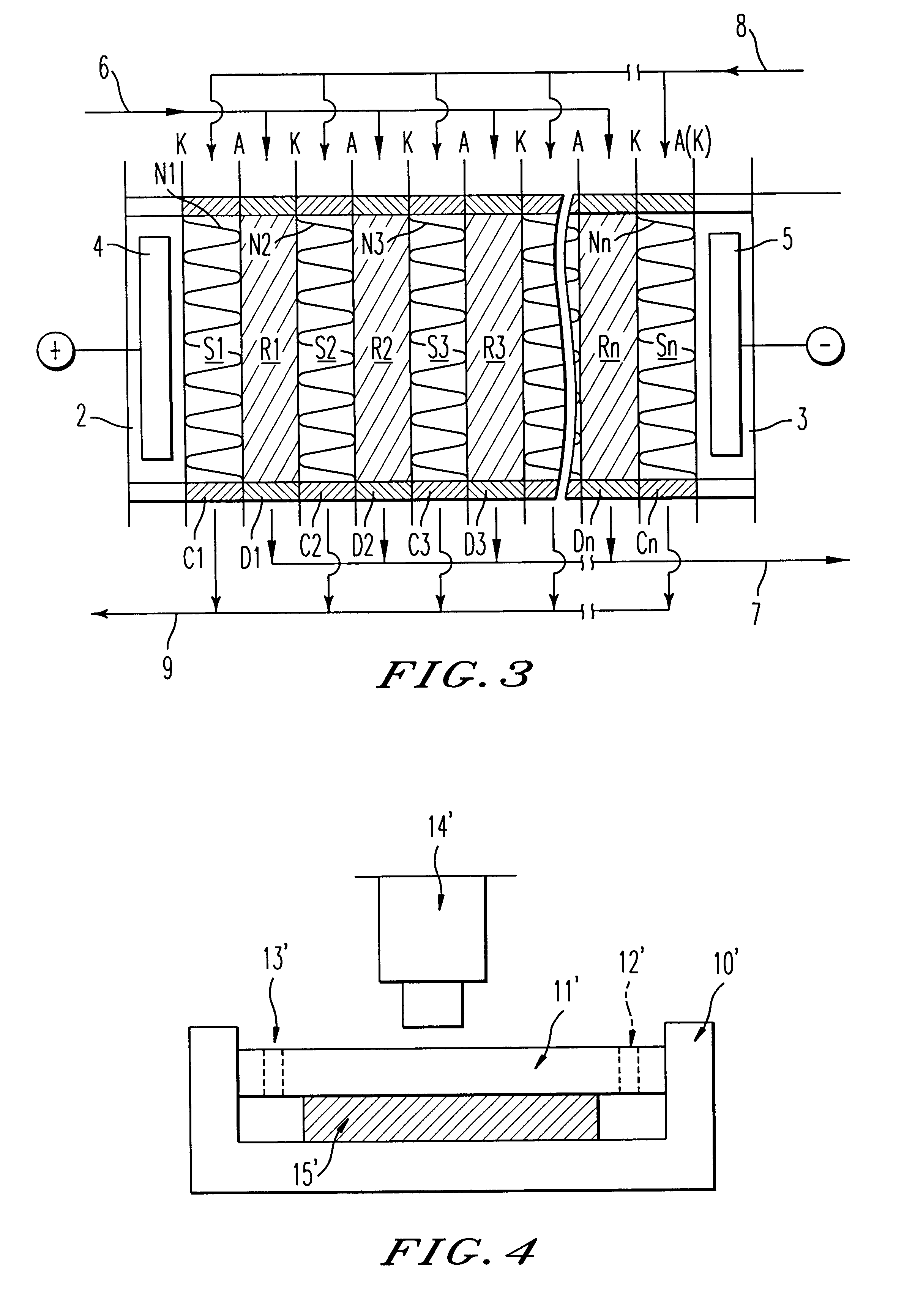
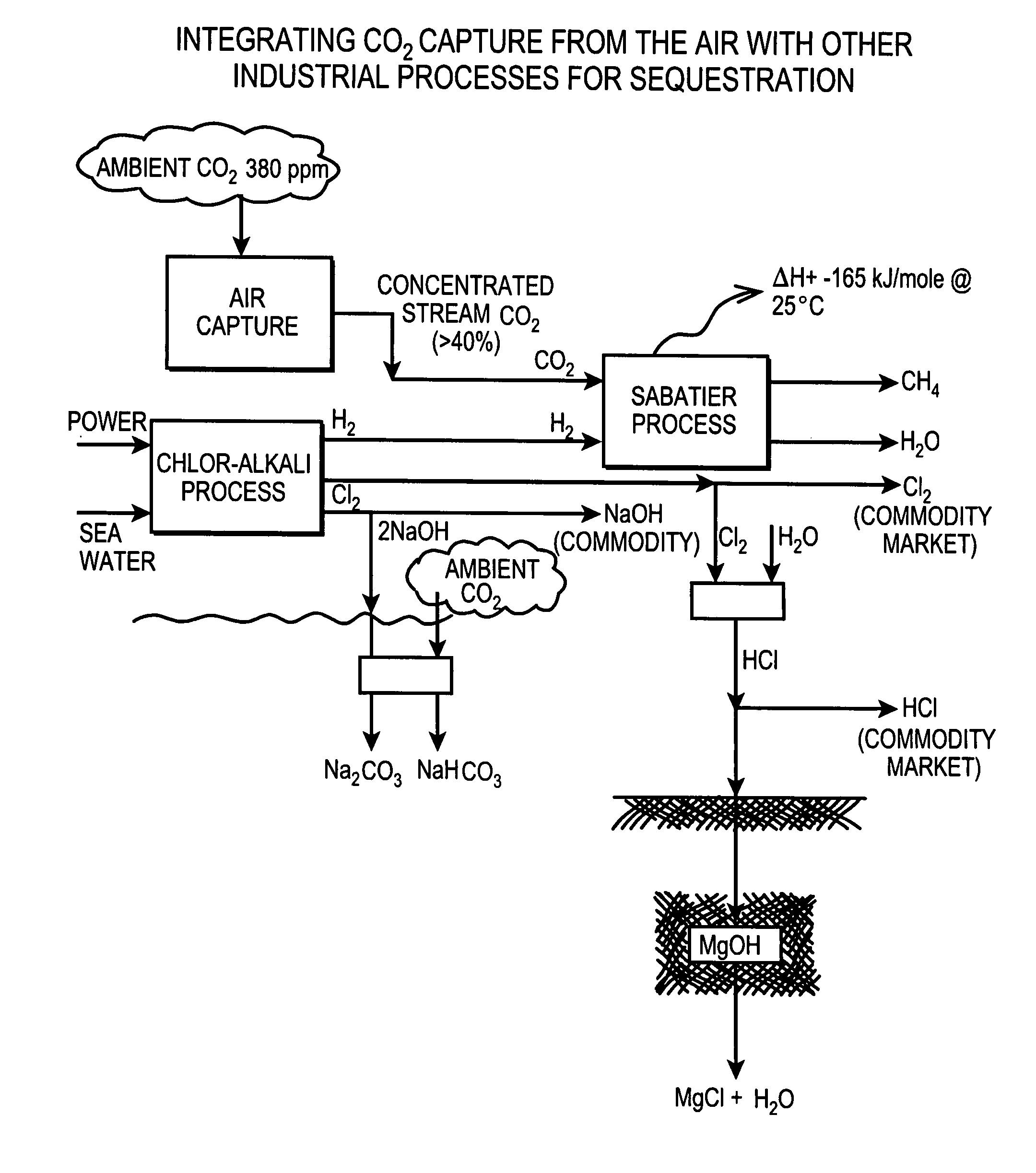
Air collector with functionalized ion exchange membrane for capturing ambient CO2
ActiveUS7993432B2Lower energy requirementsRepeatable air capture performanceMechanical apparatusElectrolysis componentsIon-exchange membranesAtmosphere
An apparatus for capture of CO2 from the atmosphere comprising an anion exchange material formed in a matrix exposed to a flow of the air.
Owner:CARBON SINK
Production of electrolytic water
InactiveUS20050189237A1Increase free chlorine production efficiencyPrevent adhesion of scaleCellsLiquid separation by electricityWater useElectrolysed water
Apparatus and methods are provided for producing electrolytic water using three chambers, rigid plates and ion exchange membranes. Benefits include reduced scale production and increased long-term bactericidal effects of the water produced.
Owner:ELECTROLYZER
Flow field plate for use in fuel cells
InactiveUS20050271909A1Improve manufacturabilityIncrease in sizeFuel cell auxillariesSolid electrolyte fuel cellsFuel cellsEngineering
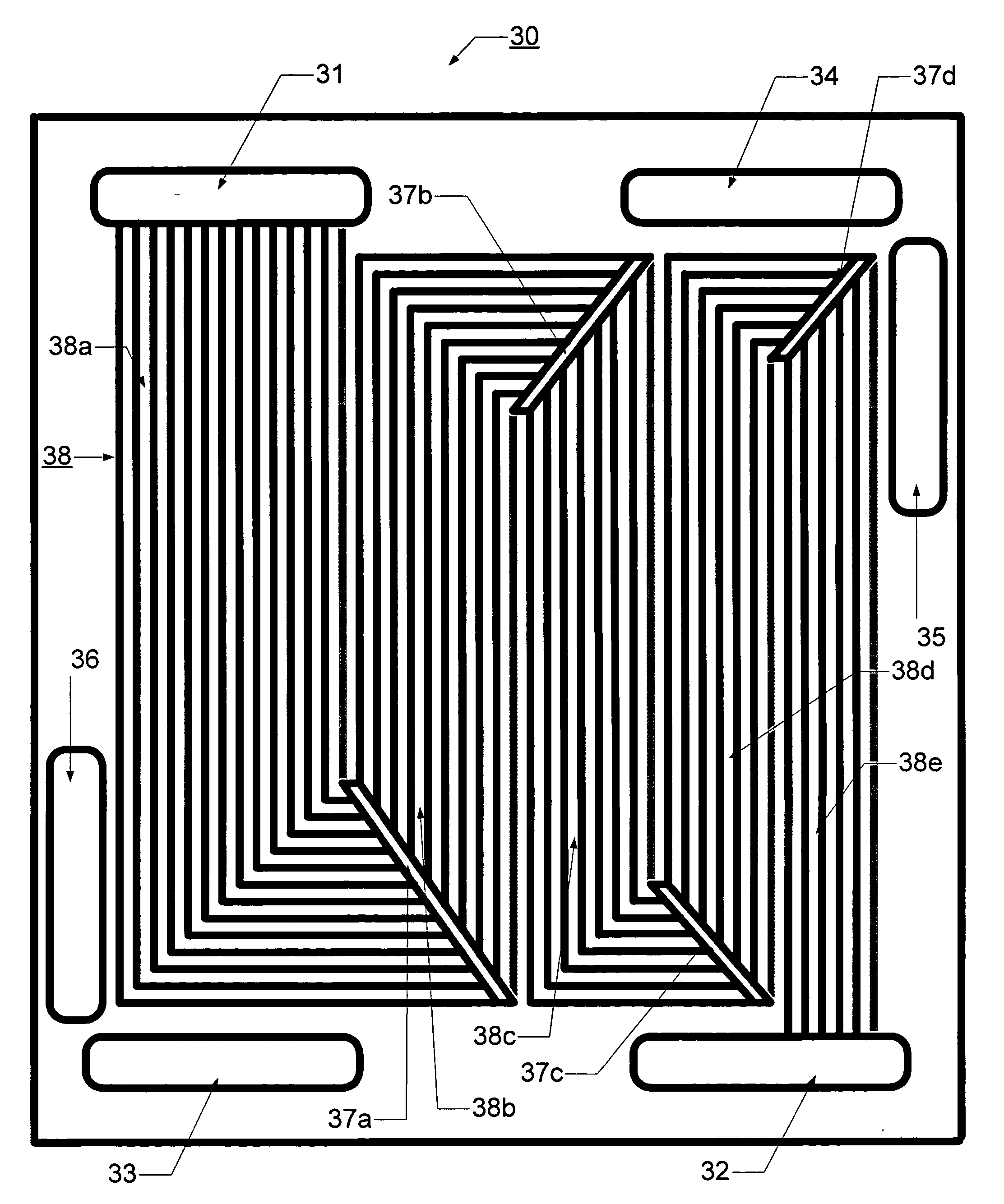
A method of flowing reactants over an ion exchange membrane in a fuel cell flow field plate is provided. The flow field plate is provided, comprising a network of flow channels in the plate bounded by an electrochemically active electrode, the network comprising a series of passages having parallel grooves, the passages being interconnected by a header providing a substantially even redistribution of fluid flow received from grooves of one passage to grooves of the next passage. A reactant fluid is supplied to create a flow across the network to achieve a desired reactant utilization, wherein a flow rate and a concentration of reactant molecules per active area of membrane in the grooves increase by less than 80% across the header.
Owner:HYTEON
Fluid delivery device having an electrochemical pump with an ion-exchange membrane and associated method
InactiveUS20060052768A1Improve accuracySmall volumeMedical devicesPressure infusionEngineeringIon-exchange membranes
Owner:MICROLIN
Method and apparatus for producing deionized water
InactiveUS6228240B1Improve the immunityPure waterSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementIon-exchange membranesChemistry
An apparatus for producing deionized water consisting essentially of an electrodialyzer having cation exchange membranes and anion exchange membranes alternately arranged between a cathode and an anode to form demineralizing compartments and concentrating compartments, and ion exchangers accommodated in the demineralizing compartments, wherein a pressure of from 0.1 to 20 kg / cm2 is exerted between the ion exchangers accommodated in the demineralizing compartments and the cation exchange membranes and anion exchange membranes defining the demineralizing compartments.
Owner:GE WATER
Air collector with functionalized ion exchange membrane for capturing ambient co2
ActiveUS20070217982A1Lower energy requirementsRepeatable air capture performanceMechanical apparatusElectrolysis componentsIon-exchange membranesAtmosphere
An apparatus for capture of CO2 from the atmosphere comprising an anion exchange material formed in a matrix exposed to a flow of the air.
Owner:CARBON SINK
Integrated photoelectrochemical cell and system having a liquid electrolyte
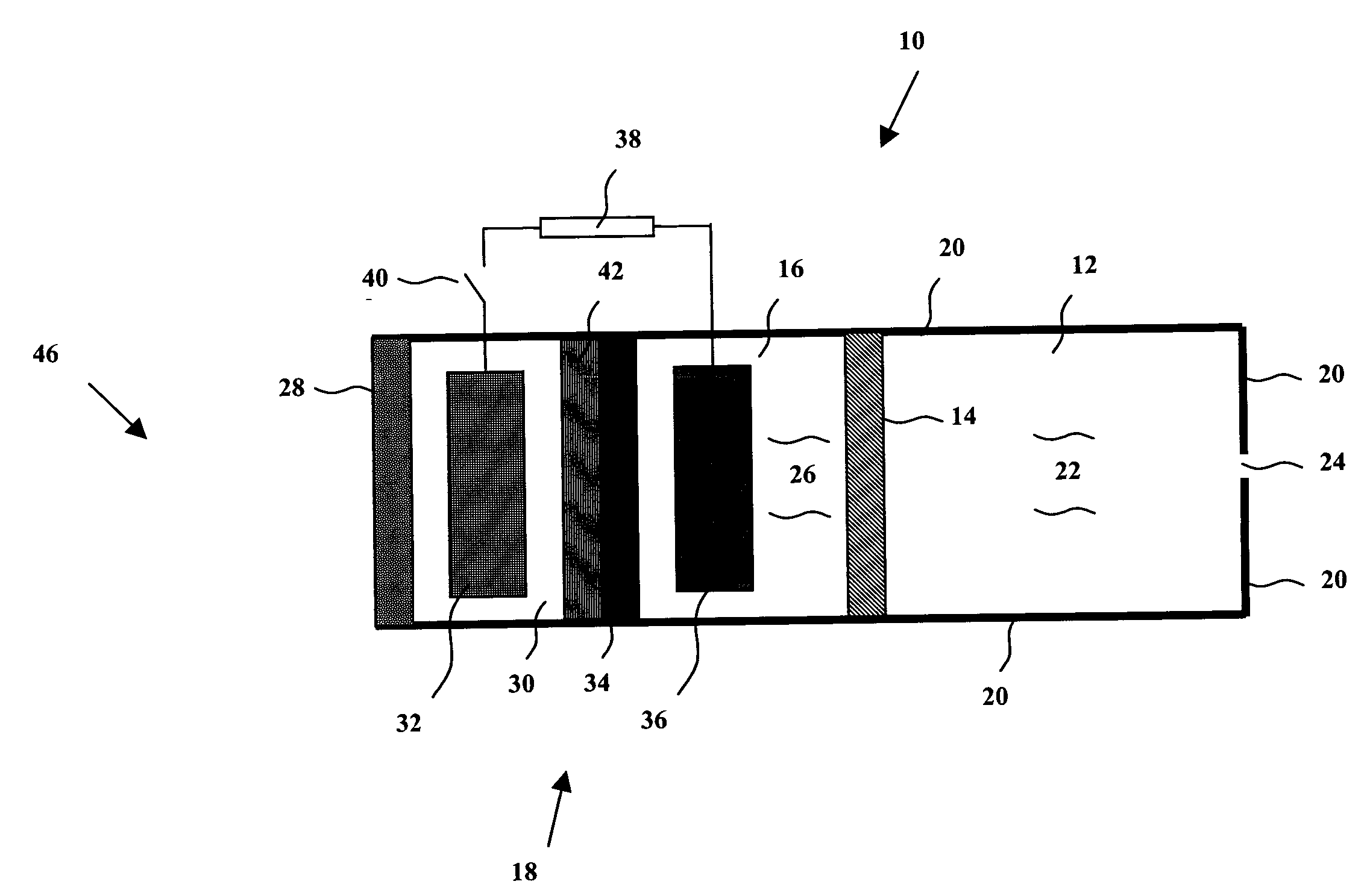
InactiveUS20050211290A1Improve hydrogen efficiencyImprove oxygen production efficiencyCellsLight-sensitive devicesHydrogenPhotoelectrochemical cell
An integrated photoelectrochemical (PEC) cell generates hydrogen and oxygen from water while being illuminated with radiation. The PEC cell employs a liquid electrolyte, a multi-junction photovoltaic electrode, and a thin ion-exchange membrane. A PEC system and a method of making such PEC cell and PEC system are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TOLEDO
Method for extracting alkali metal from salt lake brine and seawater through membrane extraction-back extraction
InactiveCN102312110AEfficient extractionEfficient enrichmentLiquid solutions solvent extractionRubidiumIon-exchange membranes
The invention discloses a method for extracting high-value alkali metal from salt lake brine or seawater through membrane extraction-back extraction. The method is implemented through continuous operation and comprises the following steps of: fixing an ion exchange blend membrane in a membrane component, allowing an organic solution containing an extracting agent to contact salt lake brine or seawater which contains alkali metal ions by a first ion exchange membrane, and allowing alkali metal ions to pass through the ion exchange membrane and be combined with the organic solution containing the extracting agent to obtain metal complex; then transmitting an organic solution of the metal complex to a second ion exchange membrane and allowing the organic solution of the metal complex to contact a back extraction solution by the second ion exchange membrane, and allowing the metal ions to pass through the ion exchange membrane to enter the back extraction solution; during membrane extraction-back extraction, and circulating feed liquid, the back extraction solution and the organic solution containing the extracting agent on one side of the first ion exchange membrane, on one side of the second ion exchange membrane and between the first and second ion exchange membranes; and performing back extraction until a certain concentration of the back extraction solution is reached, and separating lithium, rubidium or caesium precipitates to obtain the final product. The invention provides a high-efficiency, low-cost and feasible route for industrial production of alkali metal salts.
Owner:何涛 +1
Method of electrodynamics for restoring soil polluted by heavy metal
InactiveCN1695834AInhibited DiffusionMaintain fertilityContaminated soil reclamationHeavy metal compoundIon-exchange membranes
An electrodynamic method for repairing the soil polluted by heavy metal includes using ion exchange film to isolate cathode from said soil, inserting porous ceramic between said film and soil, controlling the pH value of soil by the H and OH ions generated by electrodes themsolves for speeding up the extraction of pollutants, depositing heavy metals in cathode solution, centrifugal purifying to obtain heavy metal compound, and using clean cathode solution to neutralizing soil.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for separating magnesium and concentrating lithium from brine in salt lake
ActiveCN1626443AHighly selective extractionEfficient separationMagnesium halidesLithium halidesLithiumSalt lake
Owner:QINGHAI INST OF SALT LAKES OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
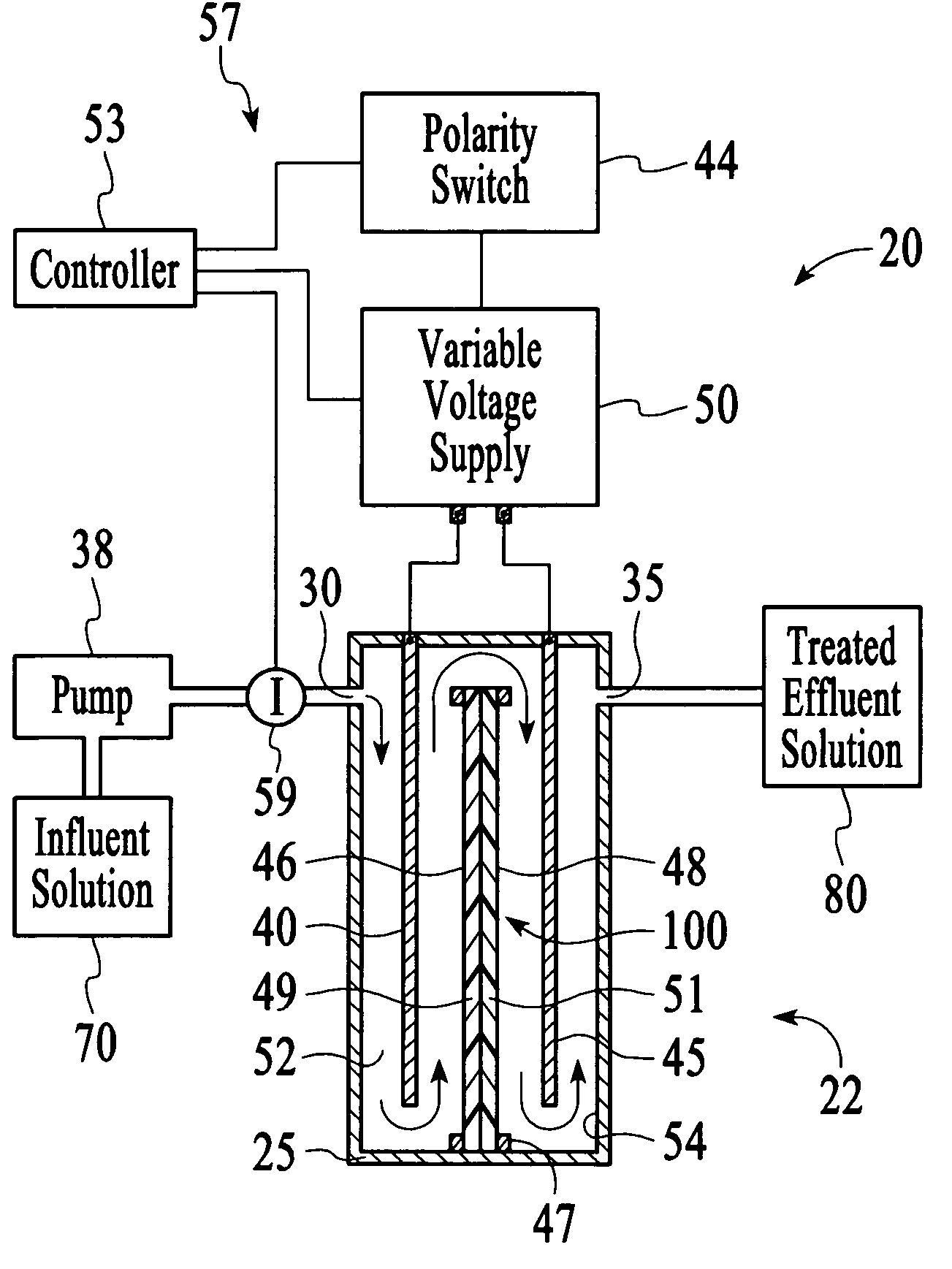
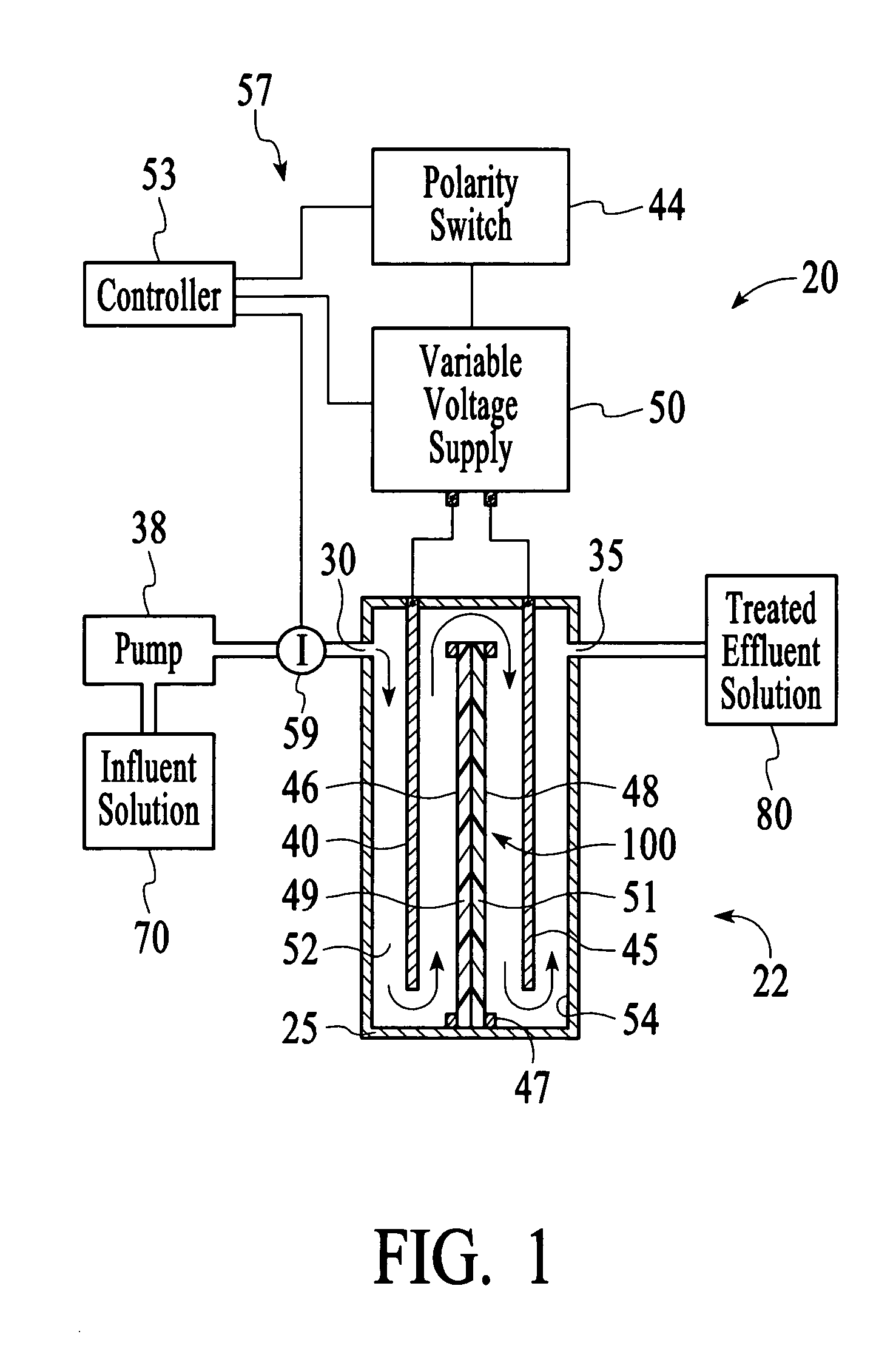
Selectable ion concentrations with electrolytic ion exchange
InactiveUS20050029124A1From normal temperature solutionsLiquid separation by electricityElectrolysisPhysical chemistry
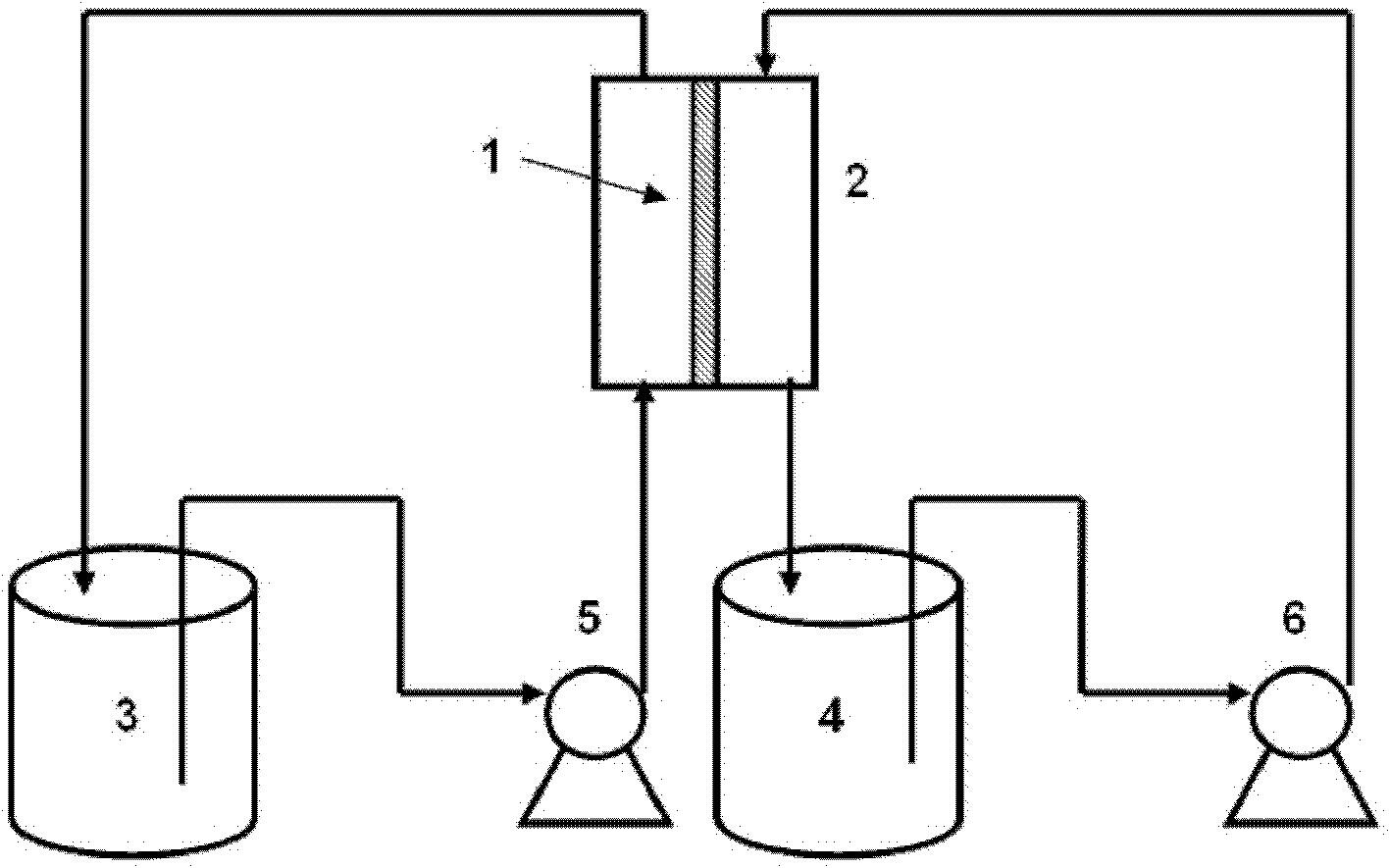
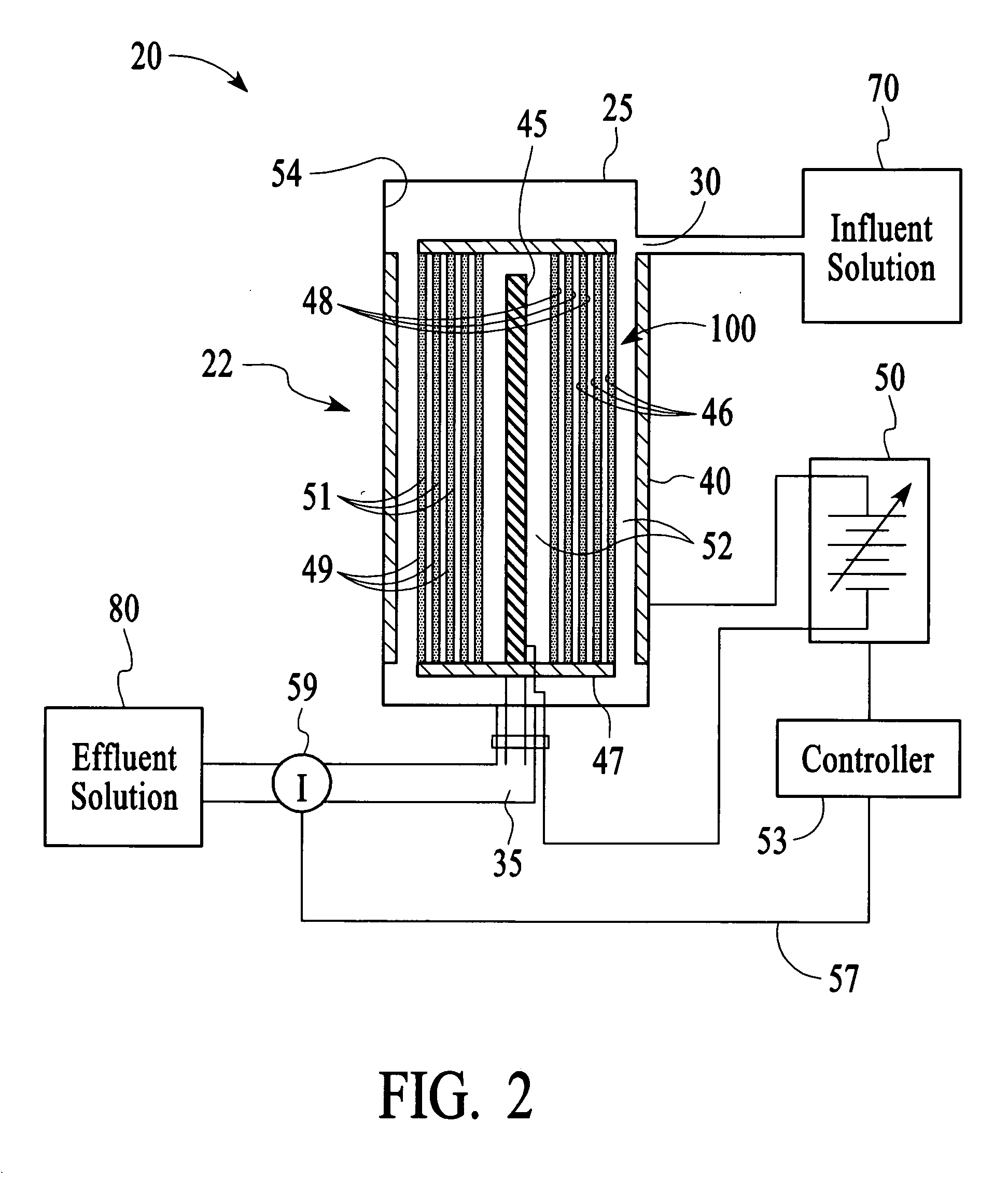
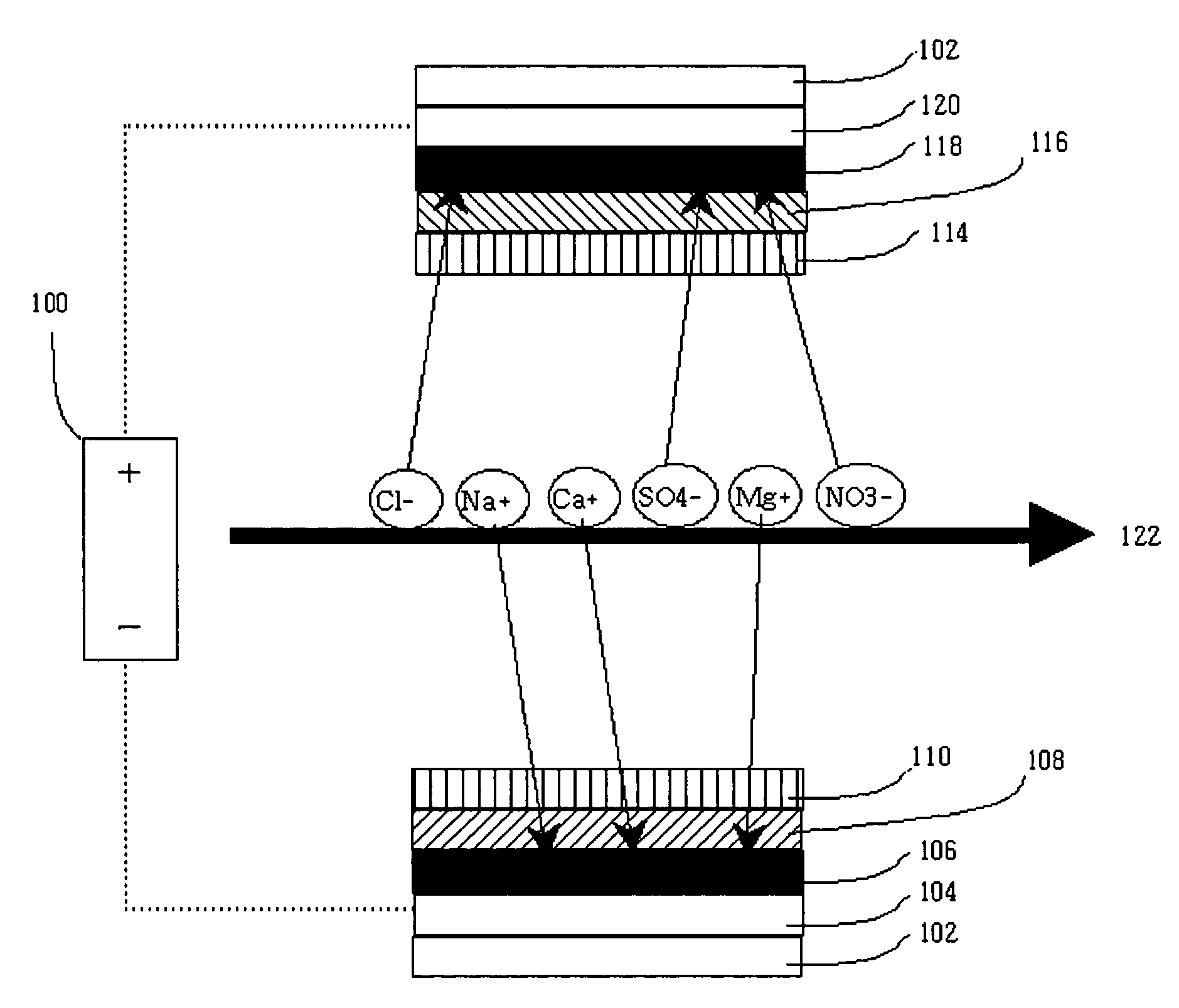
An apparatus to treat an influent solution comprising ions to obtain a selectable ion concentration in an effluent solution. The apparatus comprises an electrochemical cell comprising a housing comprising first and second electrodes. A water-splitting ion exchange membrane is between the first and second electrodes, the membrane comprising ananion exchange surface facing the first electrode, and an cation exchange surface facing the second electrode, or vice versa. The housing also has an influent solution inlet and an effluent solution outlet with a solution channel that allows influent solution to flow past both the anion and cation exchange surfaces of the water-splitting ion exchange membrane to form the effluent solution. A variable voltage supply is capable of maintaining the first and second electrodes at a plurality of different voltages during an ion exchange stage.
Owner:PINETICS INC +1
Submerged-type electrosorption-based water purification apparatus and method thereof
ActiveUS20070284313A1Improve efficiencyPromote recoverySeawater treatmentCell electrodesElectricityIndustrial effluent
Provided is a submerged-type, electrosorption-based desalination apparatus for water purification and method, comprising applying a DC voltage of 0.1 to 2.0 volts to a carbon electrode of the reactor to thereby adsorb inorganic ions on the carbon electrode, and reversely applying the same DC voltage having opposite polarity to recycle regeneration solution to the outside of the apparatus or into the treatment tank, thereby enhancing a recovery rate. In addition, in order to improve desalination efficiency, the reactor used in the desalination apparatus may be embodied in various forms of T-shaped, linear type, single, composite, and ion exchange membrane electrodes. Therefore, the present invention may be applied to remove inorganic ions from industrial wastewater, sea water, and brackish water, which contain large amounts of inorganic ions.
Owner:KOREA ELECTRIC POWER CORP
Method and apparatus for electrostatically coating an ion-exchange membrane or fluid diffusion layer with a catalyst layer
A method and apparatus for coating an ion-exchange membrane or fluid diffusion layer with a catalyst layer for use in an electrochemical fuel cell is disclosed, the method comprising the steps of electrostatically charging a catalyst slurry to yield an electrostatically-charged catalyst slurry, and applying the electrostatically-charged catalyst slurry onto a first surface of the ion-exchange membrane or fluid diffusion layer to form a first catalyst layer on the first surface.
Owner:BALLARD POWER SYSTEMS
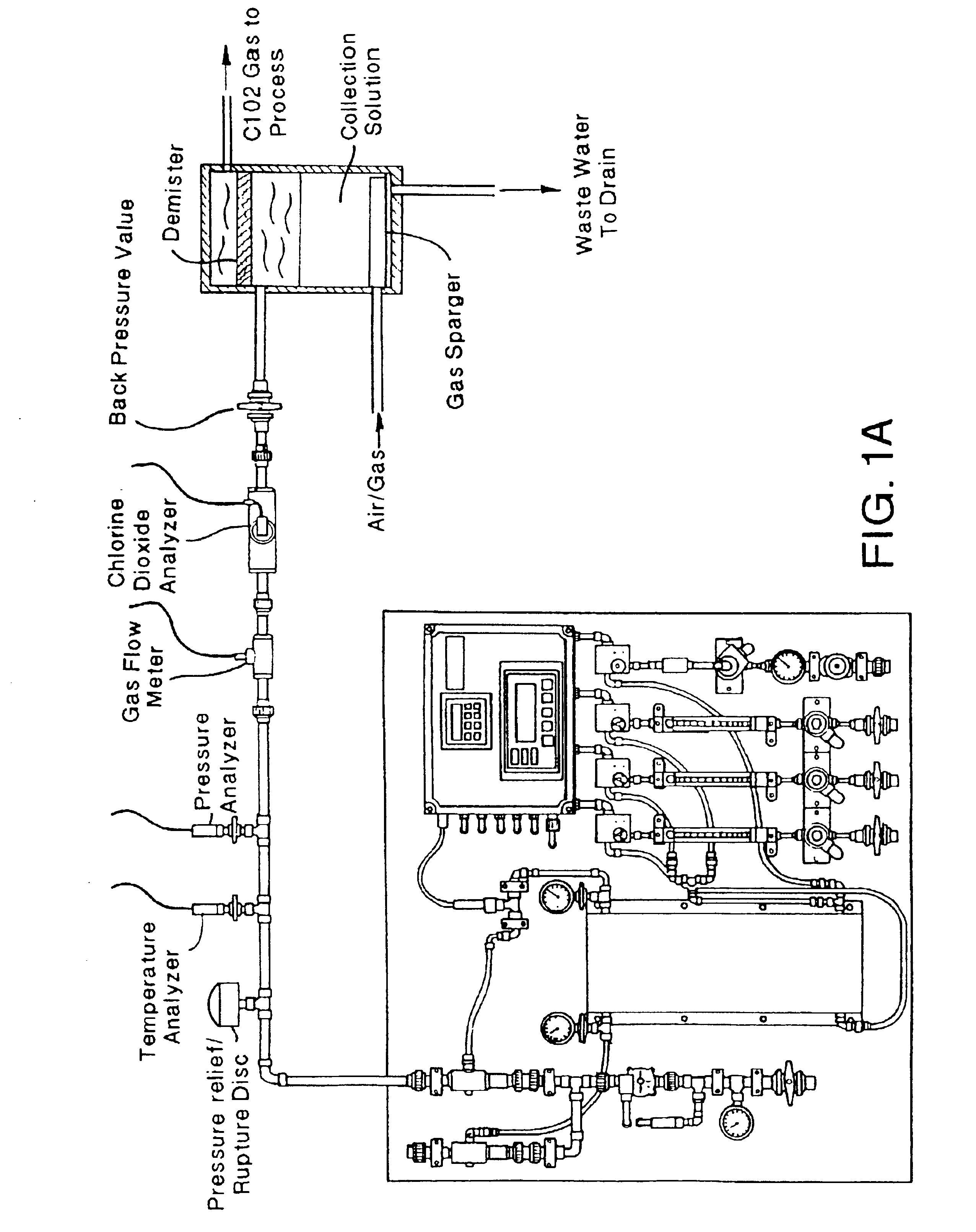
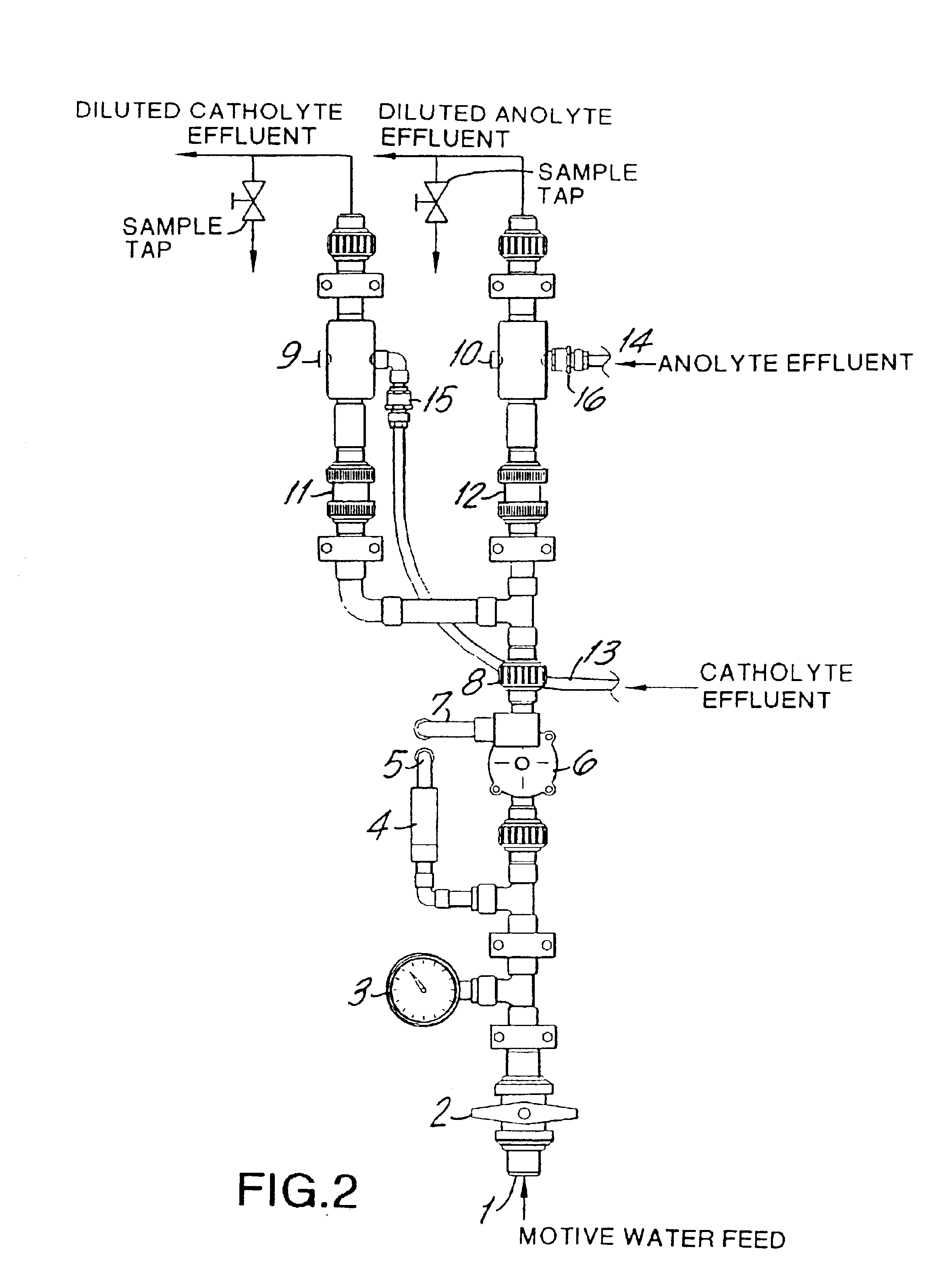
Generator for generating chlorine dioxide under vacuum eduction in a single pass
InactiveUS6881320B1Quickly and effectively evacuatesSecurity featureElectrolysis componentsAtomized substancesIon-exchange membranesChemistry
A vacuum operated electrolytic generator can be used to produce a chlorine dioxide solution or a mist of chlorine dioxide from a buffered aqueous alkali metal chlorite solution in one pass through an electrolytic cell. The cell contains a high surface area anode, a corrosion-resistant highly conductive cathode, and a cation ion exchange membrane between the anode and cathode. An eductor is used on the anolyte effluent line to create a vacuum and draw the anolyte through the cell. Either motive water or a motive inert gas (such as air) is used in the eductor. Preferably, an eductor is used in the catholyte effluent line. An ascending anolyte effluent line with a non-corrosive check valve leads from the cell to the anode eductor. Sensors are used to monitor the composition of the anolyte effluent and / or the anolyte feed. The final product is a chlorine dioxide solution when water is used for the eduction. The final product is a mist consisting essentially of gaseous chlorine dioxide, an inert gas, and water vapor when an inert gas is used for the eduction. The mist is useful for application crop, soils, produce such as vegetables, fruit, and tobacco, fields, storage cellars, and the like.
Owner:INT DIOXCIDE
Anion-exchange membrane and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20110281197A1Good alkali resistanceHigh ion exchange capacityIon-exchanger regenerationFinal product manufactureMonomer compositionQuaternary ammonium cation
Disclosed is an anion-exchange membrane which does not easily deteriorate even when used at high temperatures in a strong alkaline atmosphere. Also disclosed is a method for producing the anion-exchange membrane. The anion-exchange membrane is a microporous membrane which is composed of a water-insoluble resin and an anion-exchange resin filling the pores of the microporous membrane. The anion-exchange resin is composed of an anion-exchange resin wherein a quaternary ammonium salt group serving as an anion-exchange group is directly bonded to an aliphatic hydrocarbon chain, said anion-exchange resin being obtained by polymerizing and crosslinking a monomer composition which contains a crosslinking agent and a monomer component including a diallyl ammonium salt.
Owner:TOKUYAMA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com