Patents
Literature
352 results about "Electrodeionization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
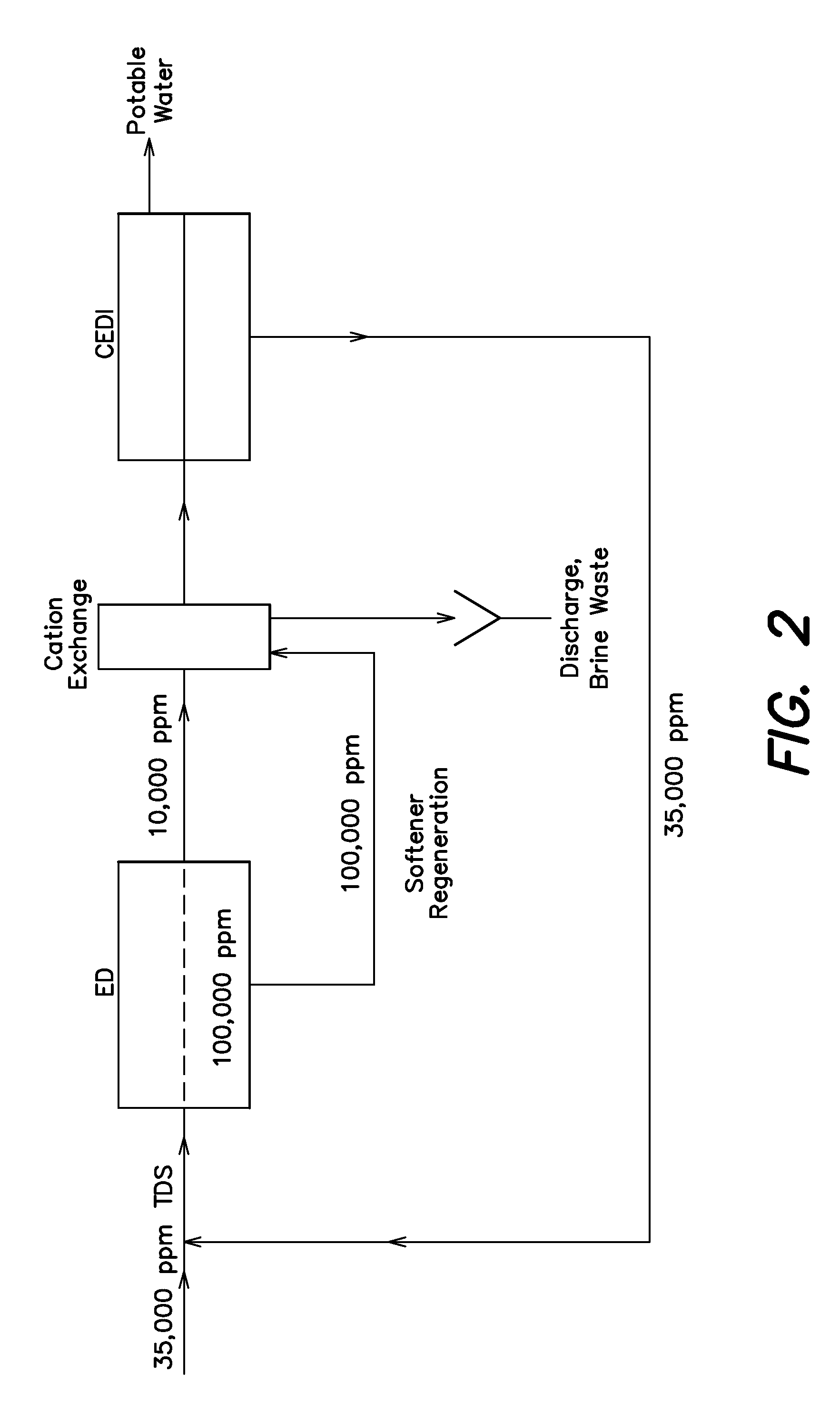
Electrodeionization (EDI) is a water treatment technology that utilizes electricity, ion exchange membranes and resin to deionize water and separate dissolved ions (impurities) from water. It differs from other water purification technologies in that it is done without the use of chemical treatments and is usually a polishing treatment to reverse osmosis (RO). There are also EDI units that are often referred to as continuous electrodeionization (CEDI) since the electric current regenerates the resin mass continuously. CEDI technique can achieve very high purity, with conductivity below 0.1 μS/cm.
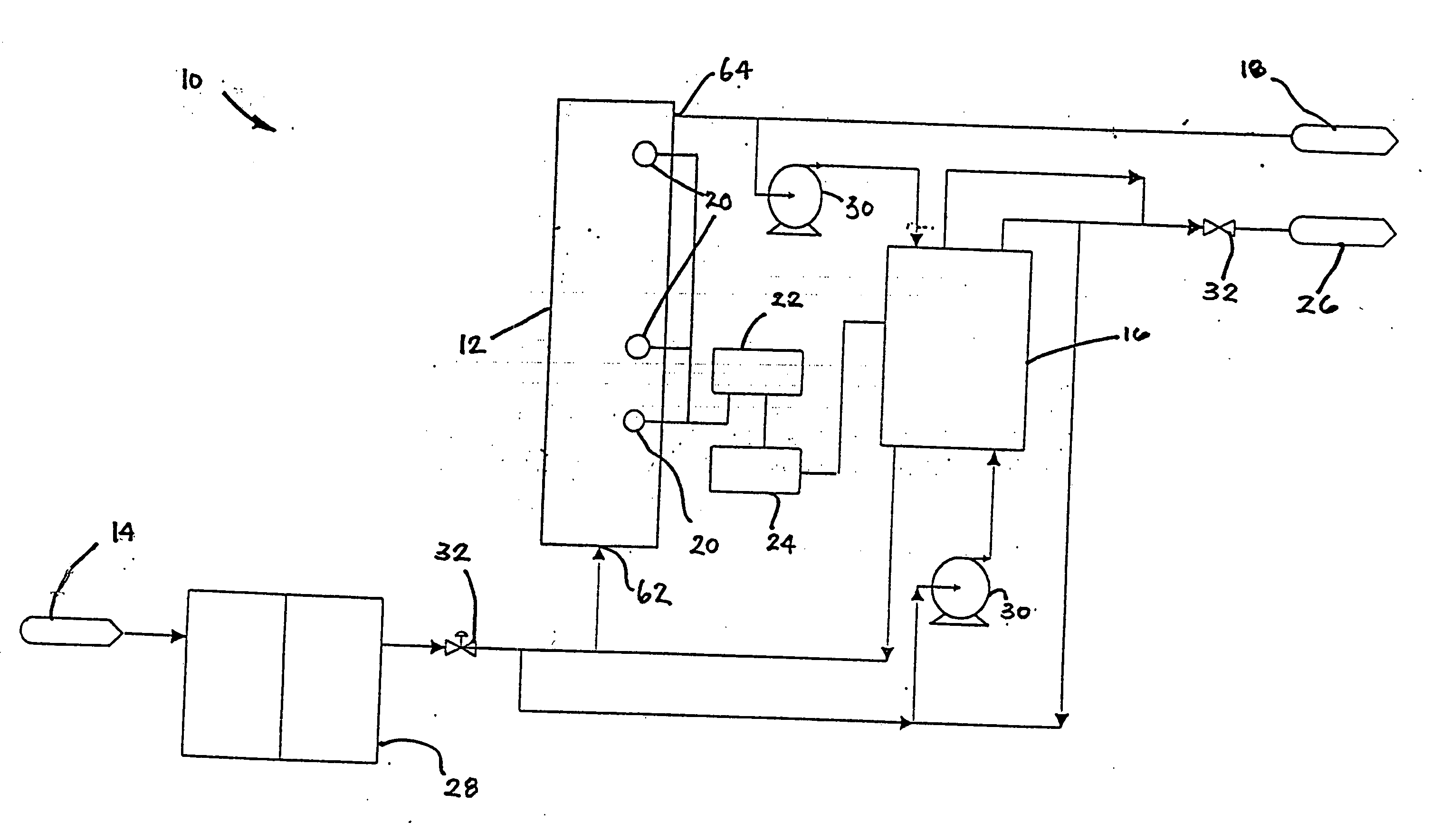
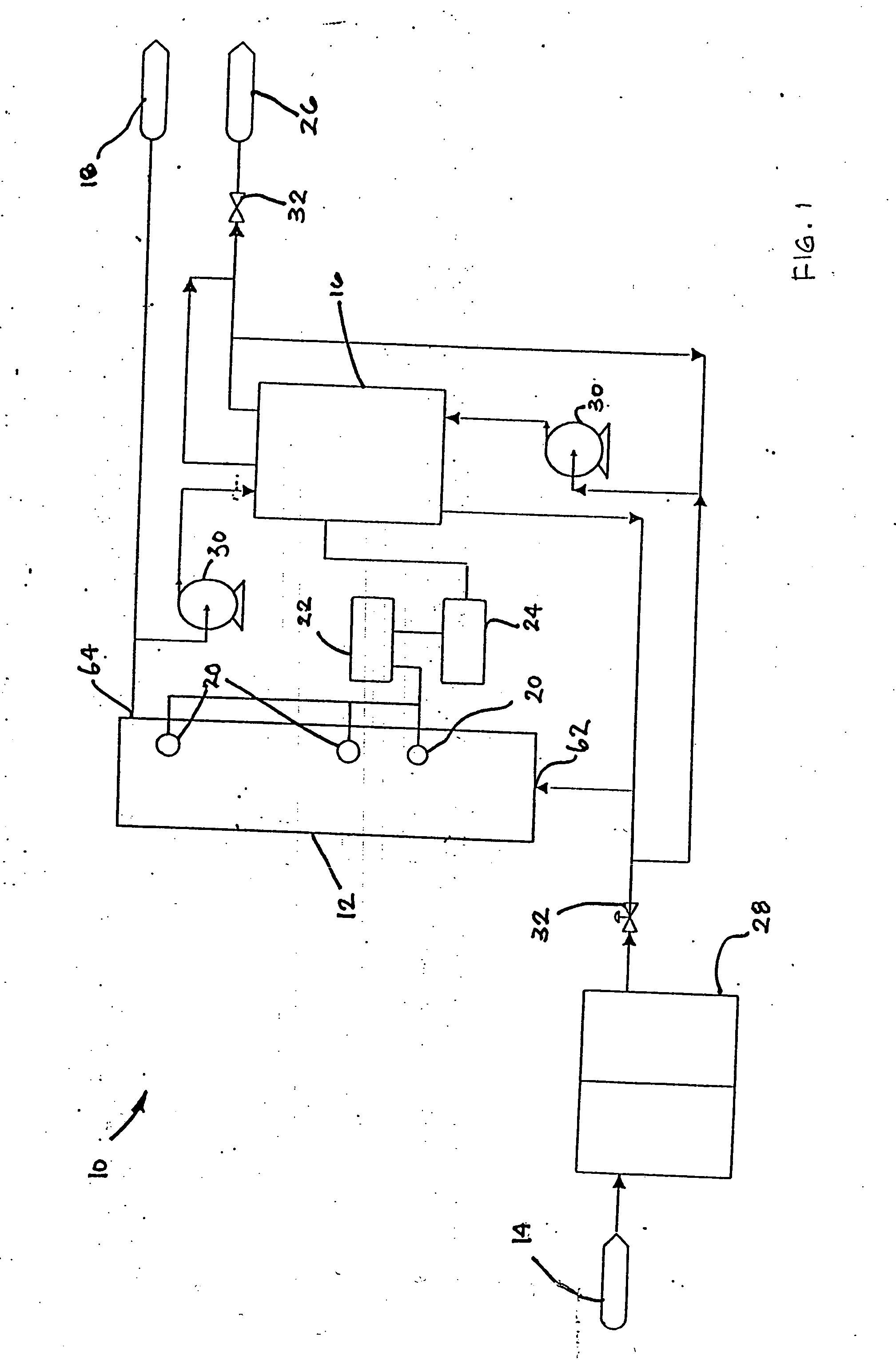
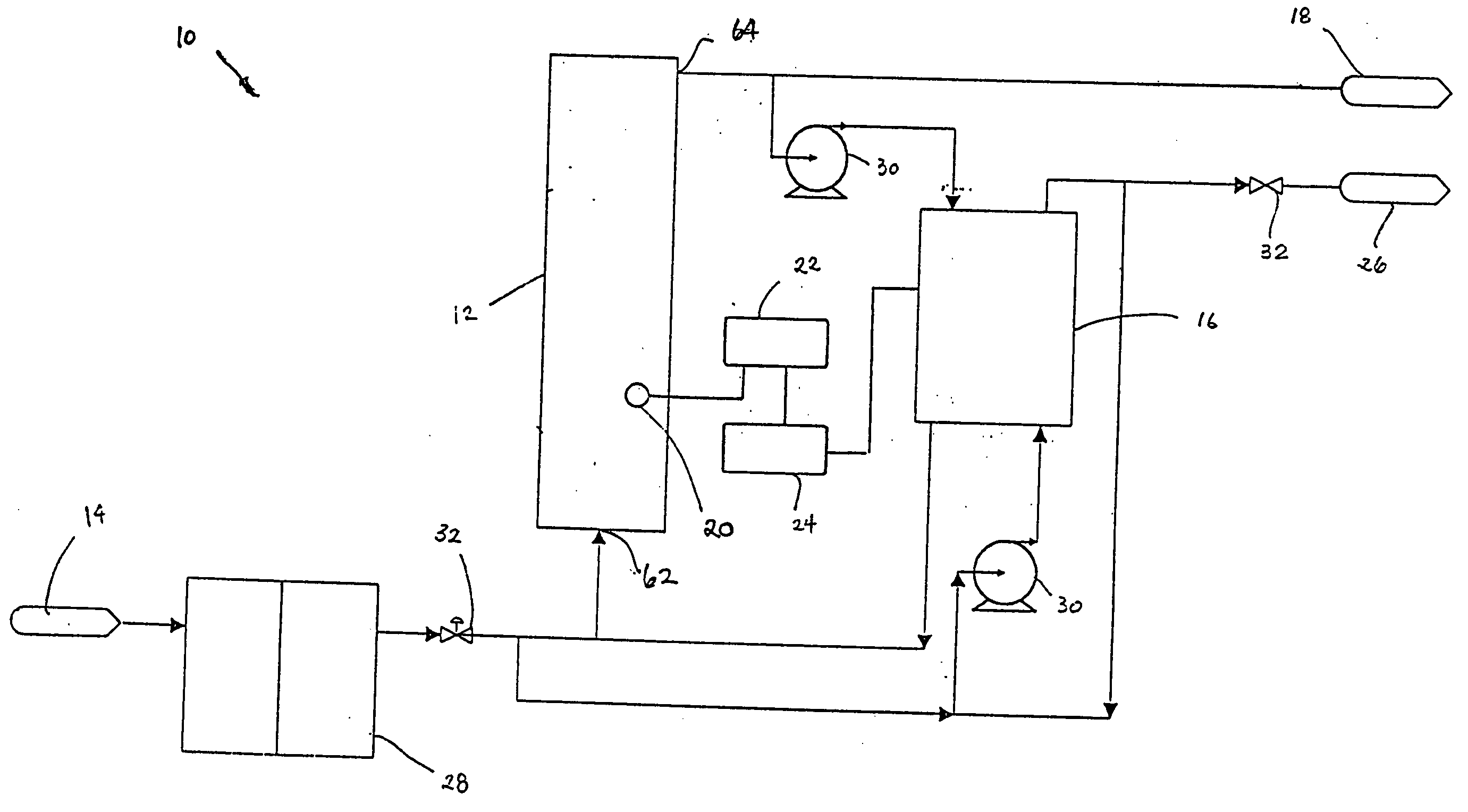
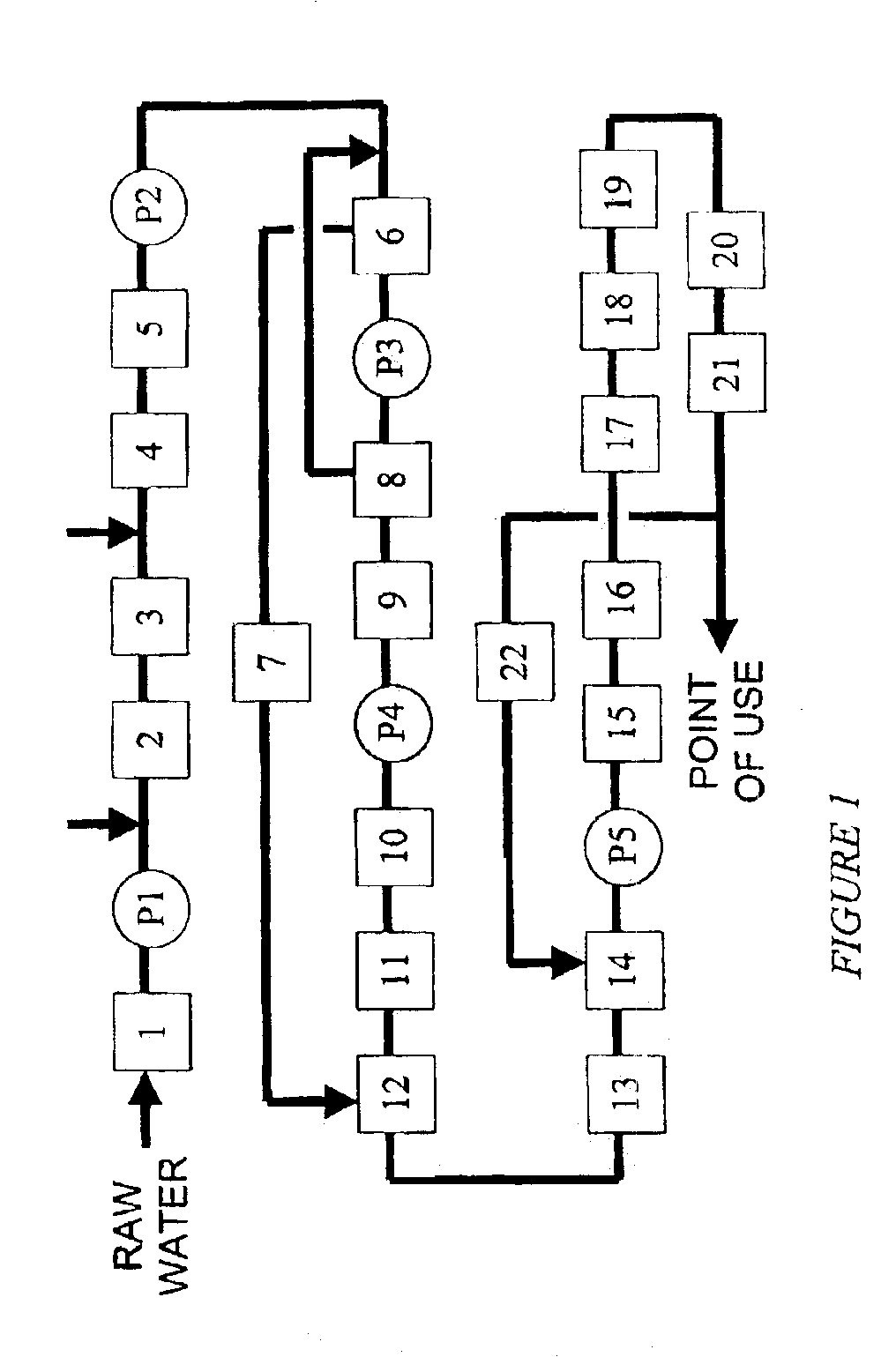
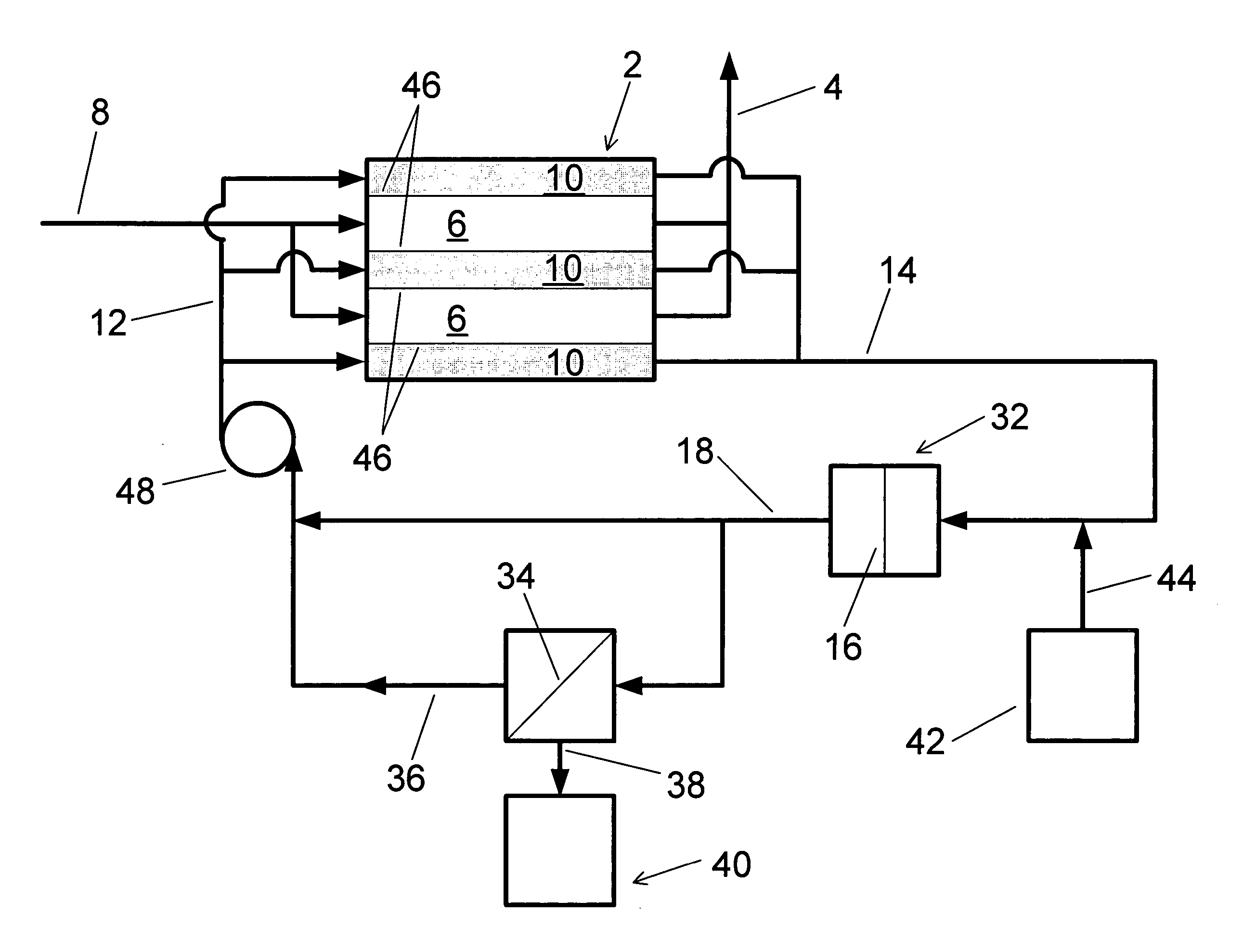
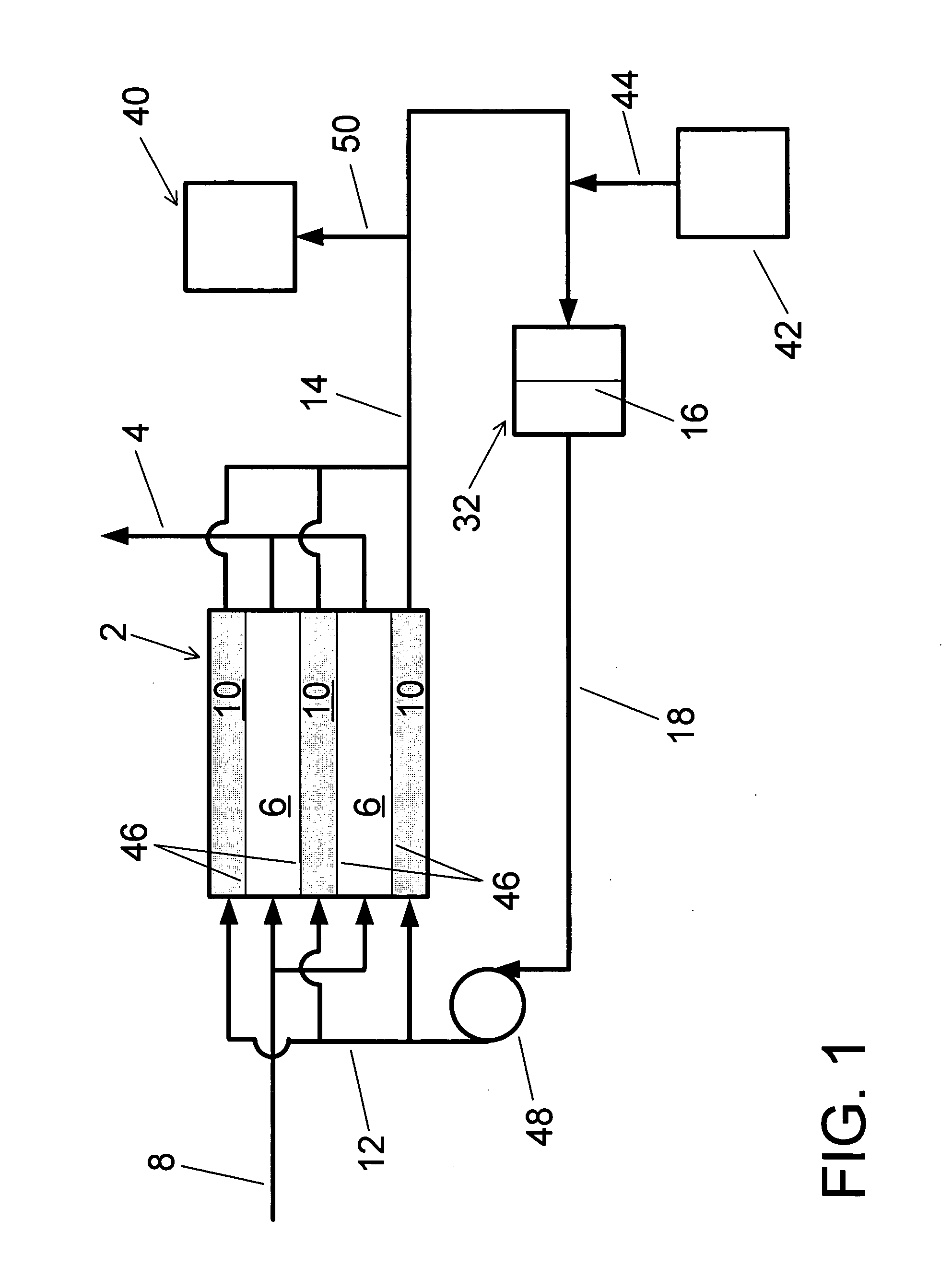
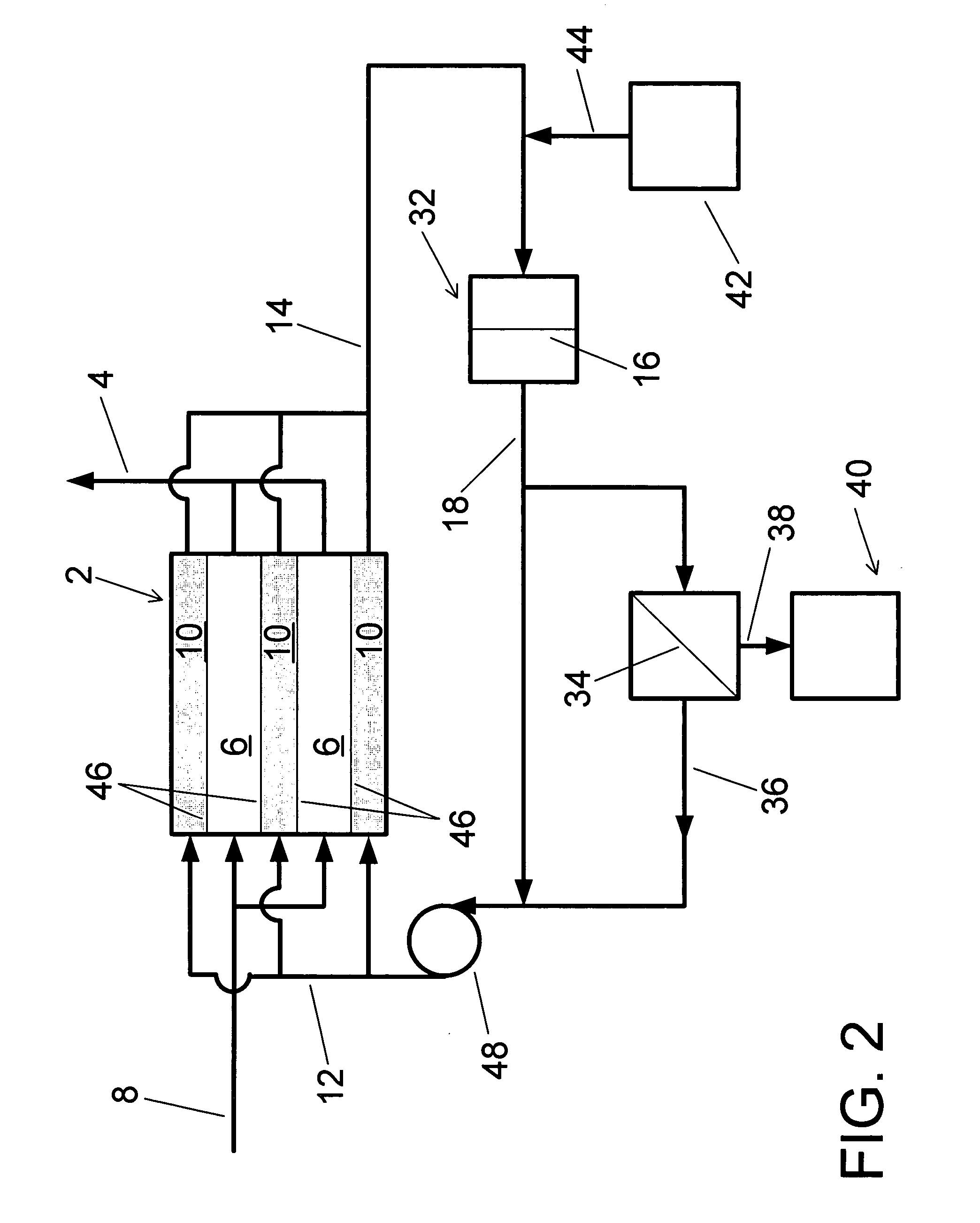
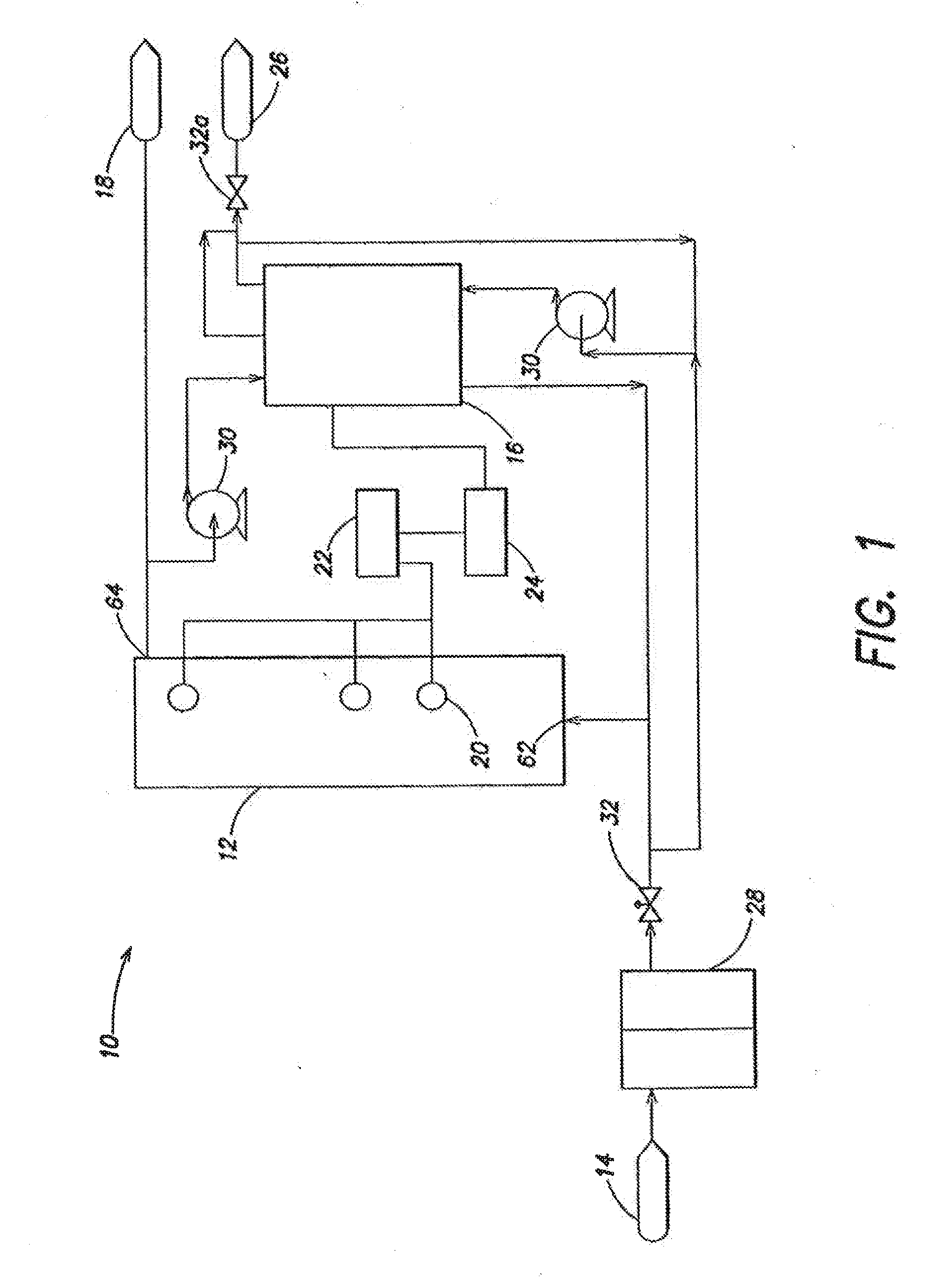
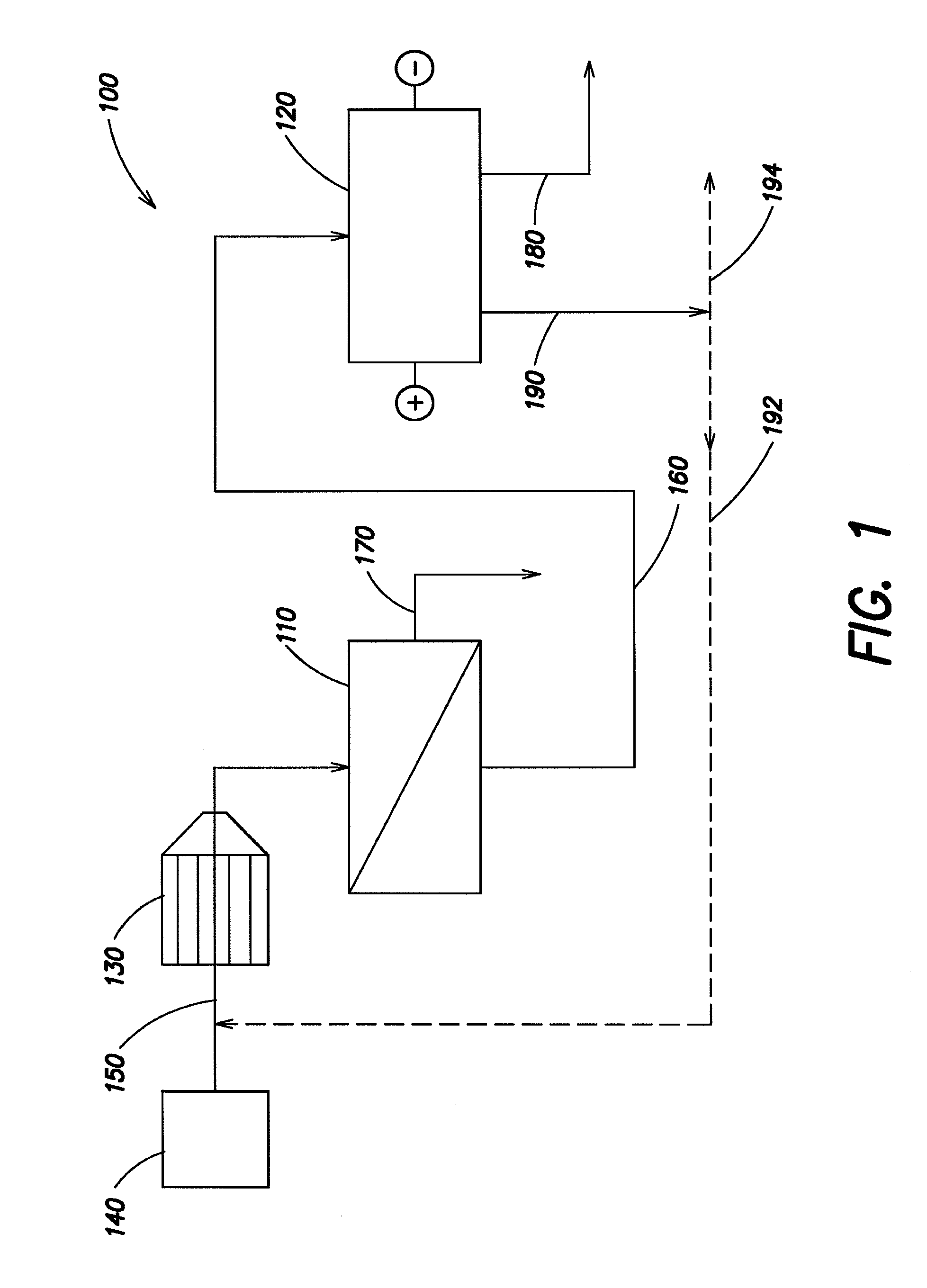
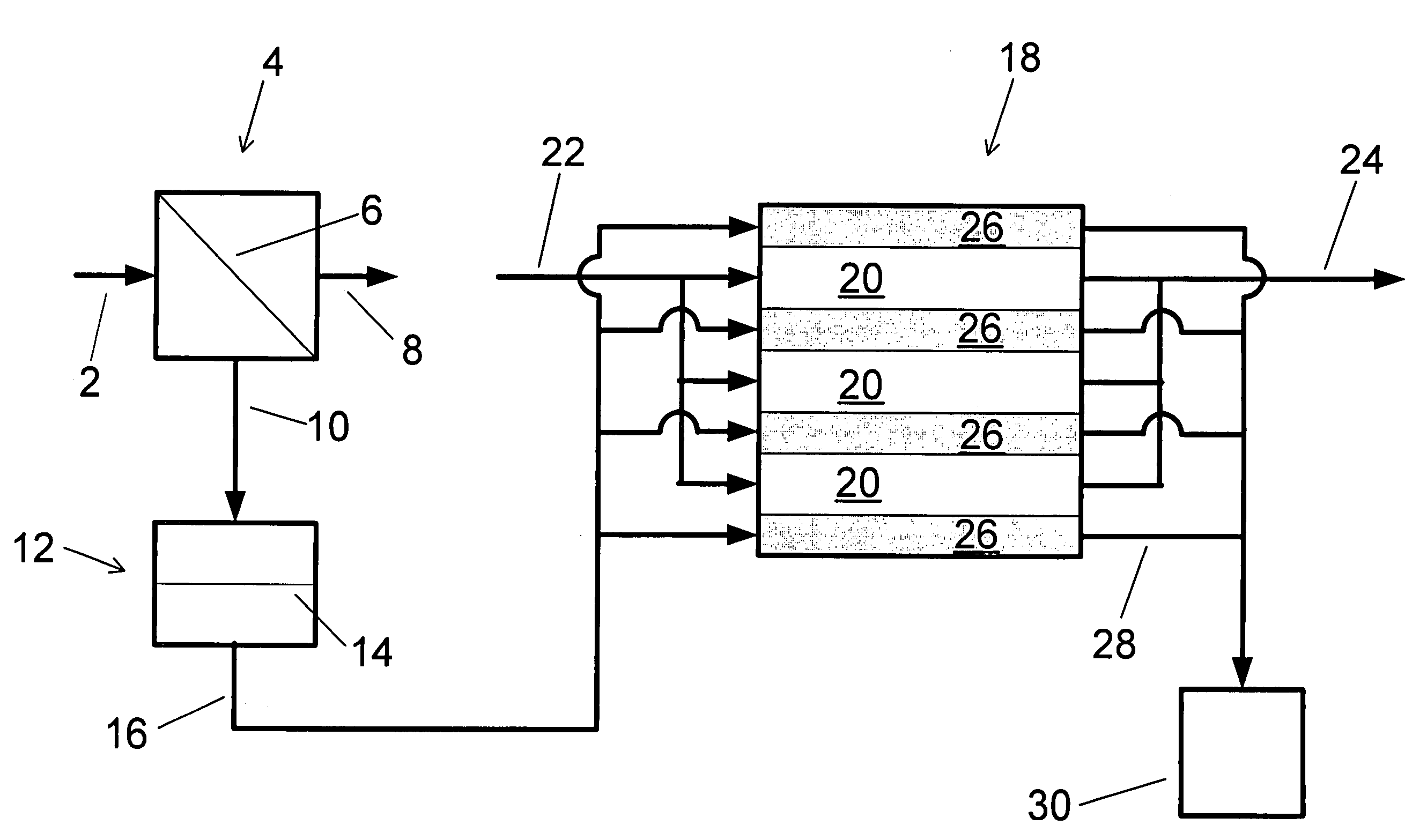
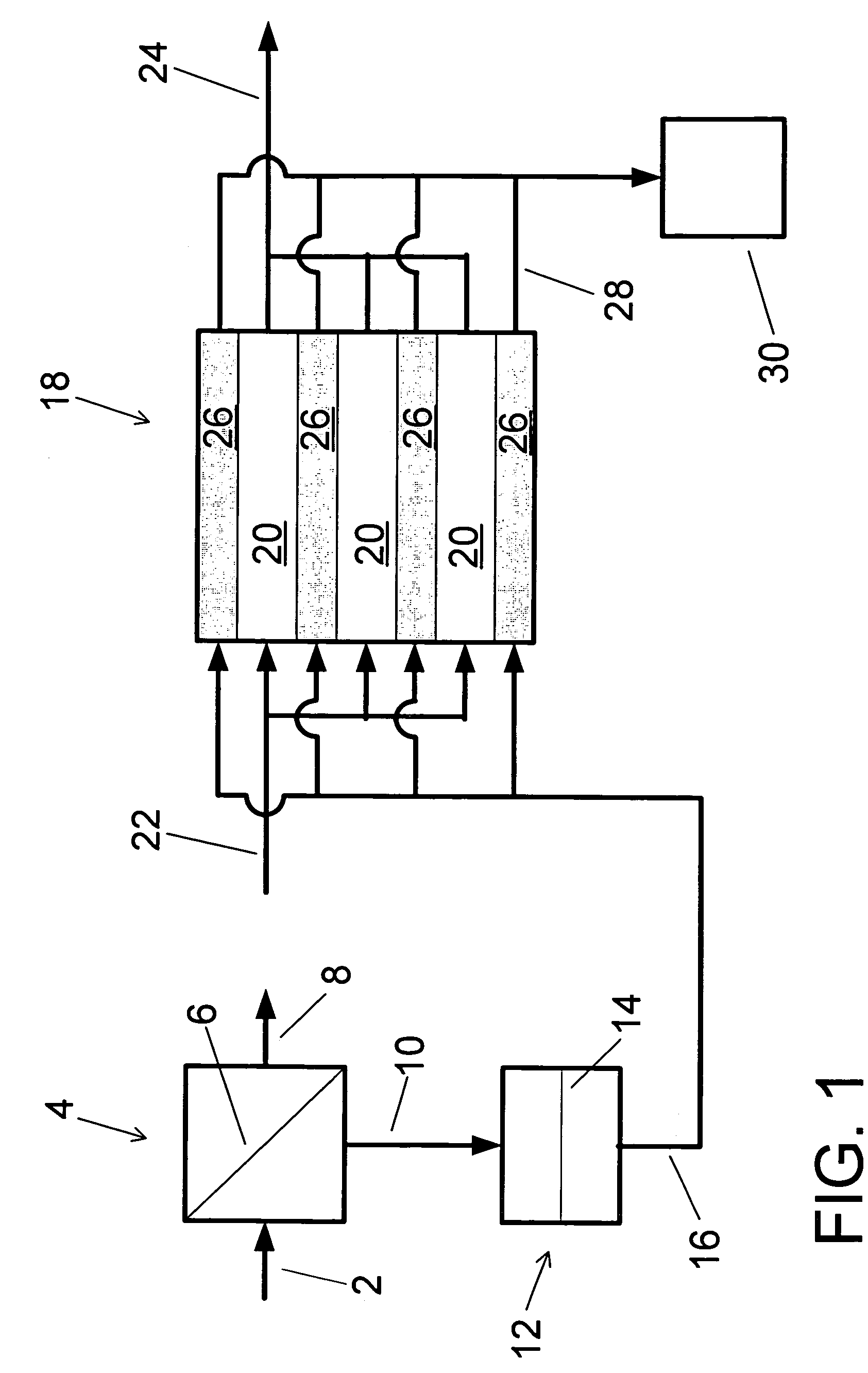
Water treatment system and method
ActiveUS20050103722A1Water treatment parameter controlIon-exchange column/bed processesWater treatment systemWater source
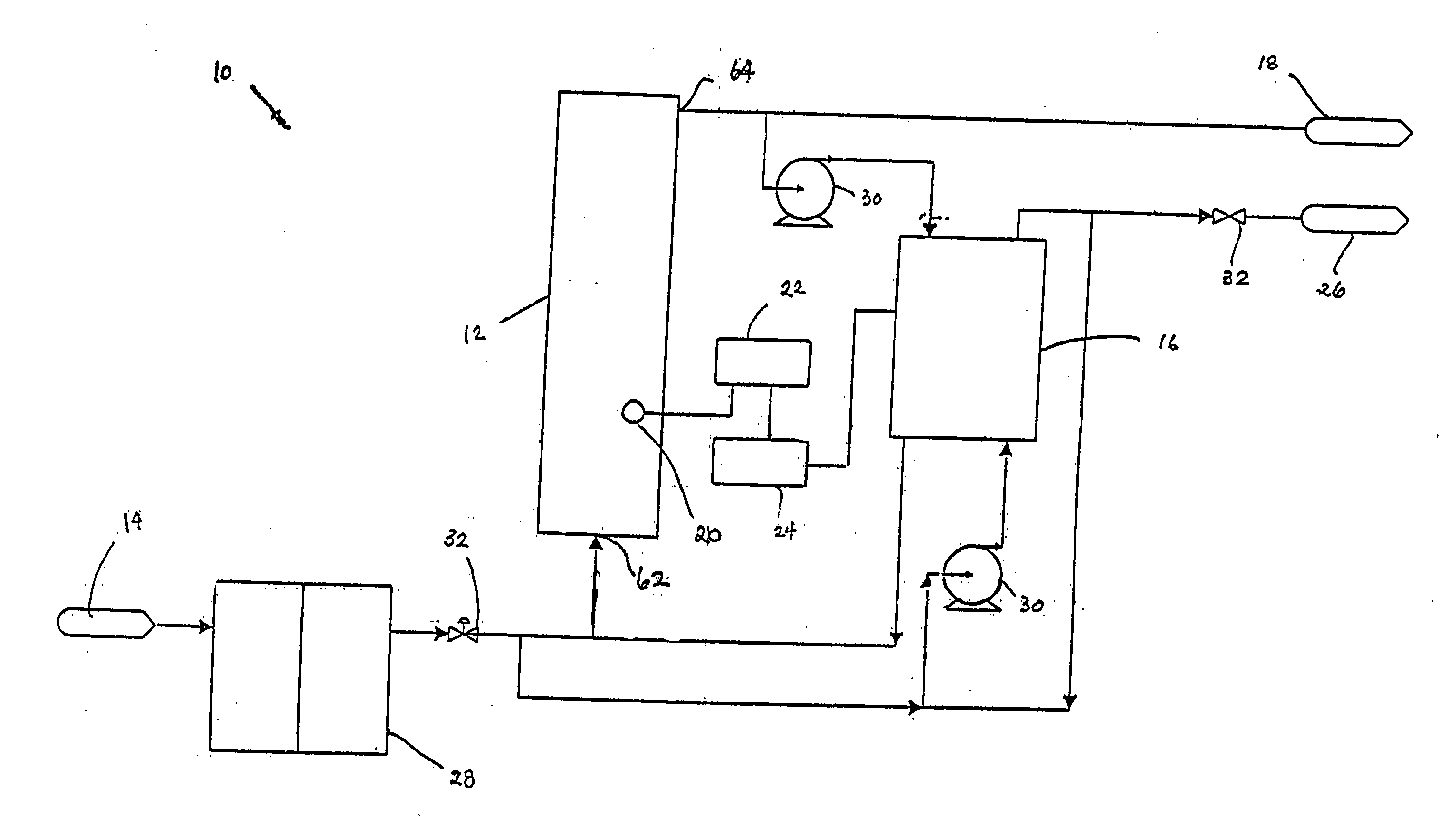
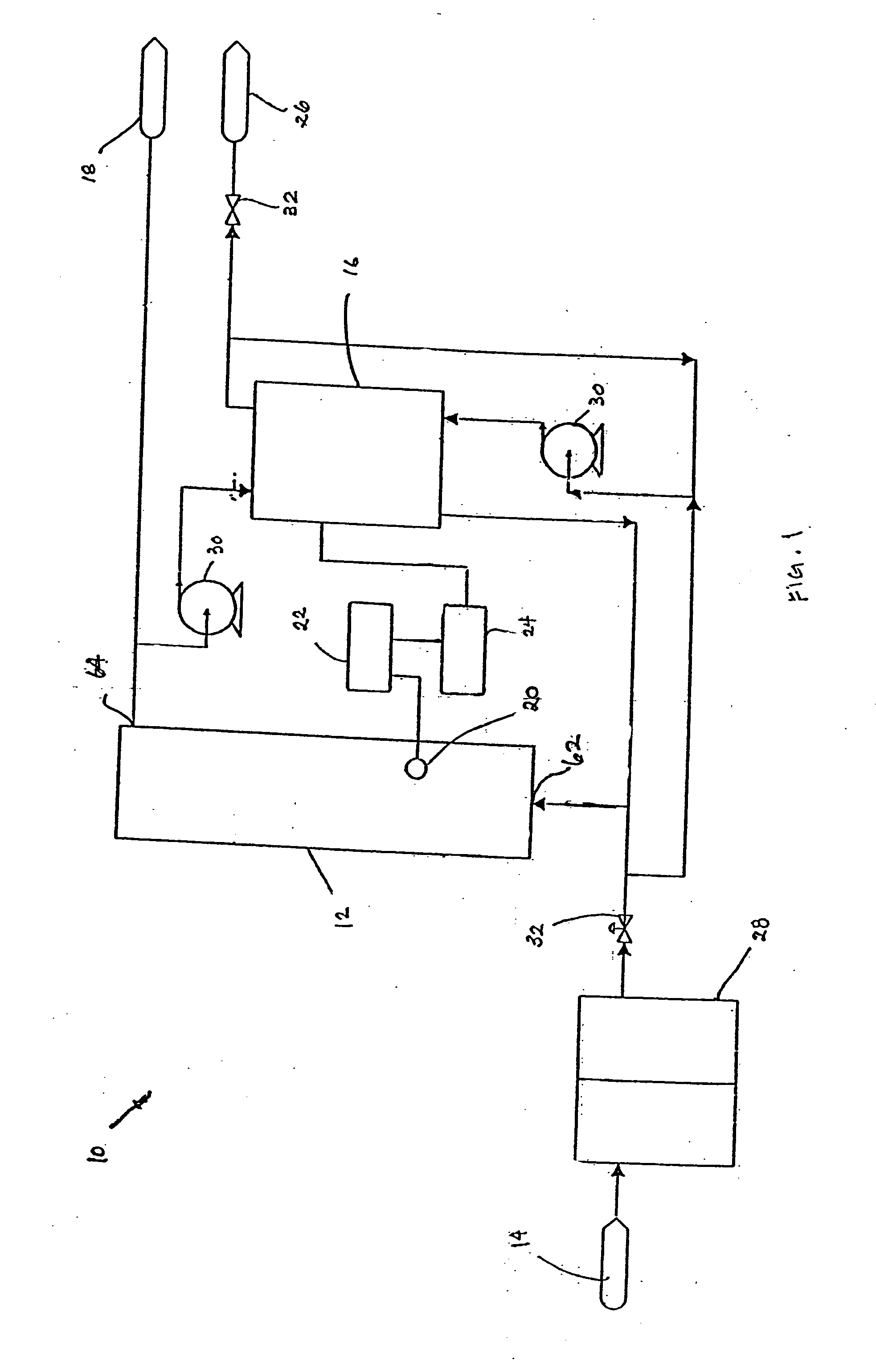
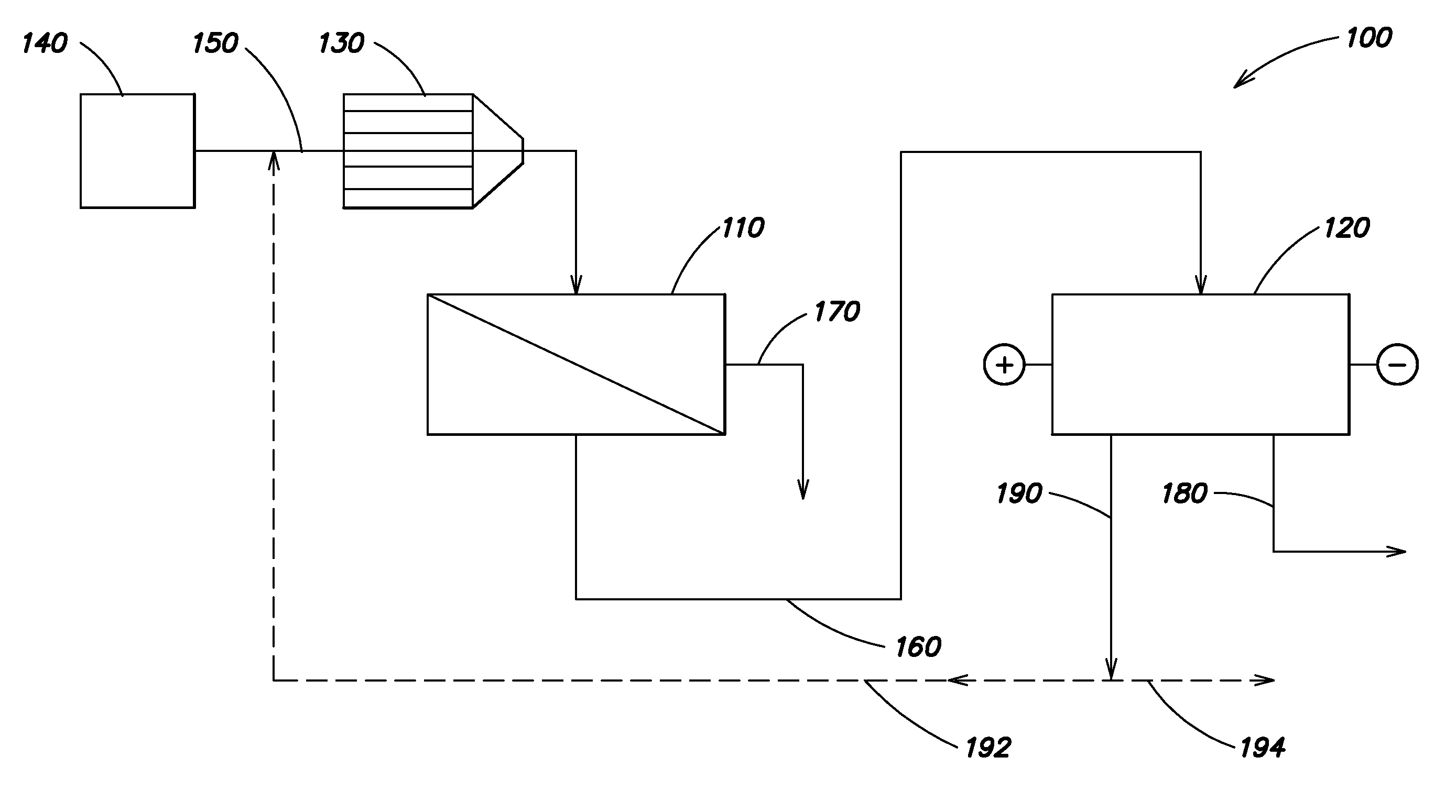
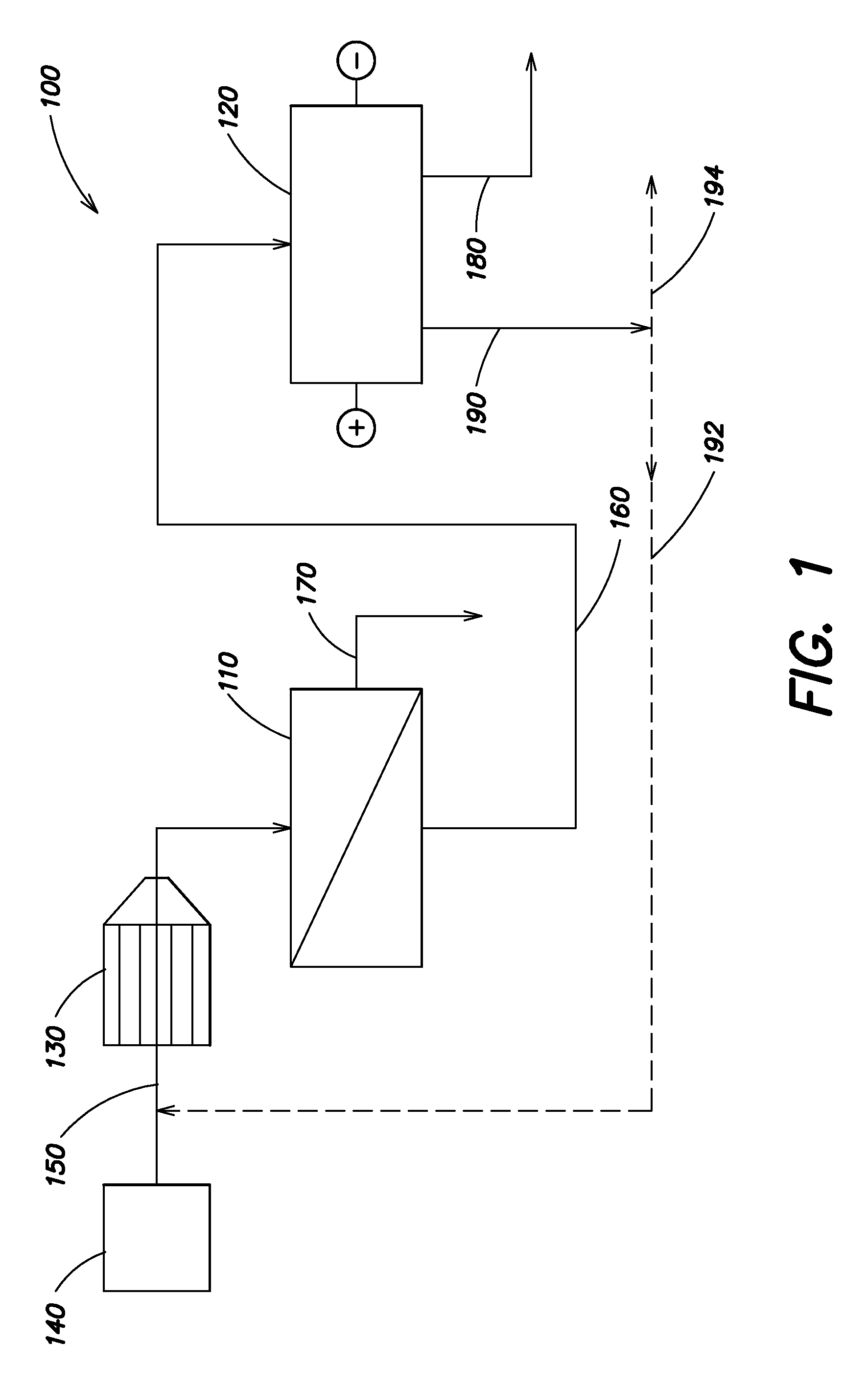
A water treatment system provides treated or softened water to a point of use by removing a portion of any hardness-causing species contained in water from a point of entry coming from a water source, such as municipal water, well water, brackish water and water containing foulants. The water treatment system typically treats the water containing at least some undesirable species before delivering the treated water to a point of use. The water treatment system has a reservoir system in line with an electrochemical device such as an electrodeionization device. The water treatment system has a sensor or a set of sensors for measuring at least one property of the water or an operating condition of the treatment system. The water treatment system also has a controller for adjusting or regulating at least one operating parameter of the treatment system or a component of the water treatment system to optimize the operation and performance of the system or components of the system to supply water tailored to quality requirements.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
Water treatment system and method
InactiveUS20050103717A1Water treatment parameter controlWater/sewage treatment by electrochemical methodsElectricityWater treatment system
A water treatment system provides treated water to a point of use by removing at least a portion of any hardness-causing species contained in water from a water source, such as municipal water, well water, brackish water and water containing foulants. The water treatment system typically receives water from the water source or a point of entry and purifies the water containing at least some undesirable species before delivering the treated water to a point of use. The water treatment system has a pressurized reservoir system in line with an electrochemical device such as an electrodeionization device. The water treatment system can have a controller for adjusting or regulating at least one operating parameter of the treatment system or a component of the water treatment system.
Owner:SIEMENS WATER TECH HLDG CORP
Method and apparatus for preventing scaling in electrodeionization units
InactiveUS6149788AAvoid mixingImprove conductivitySludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementElectricityIncreased tolerance
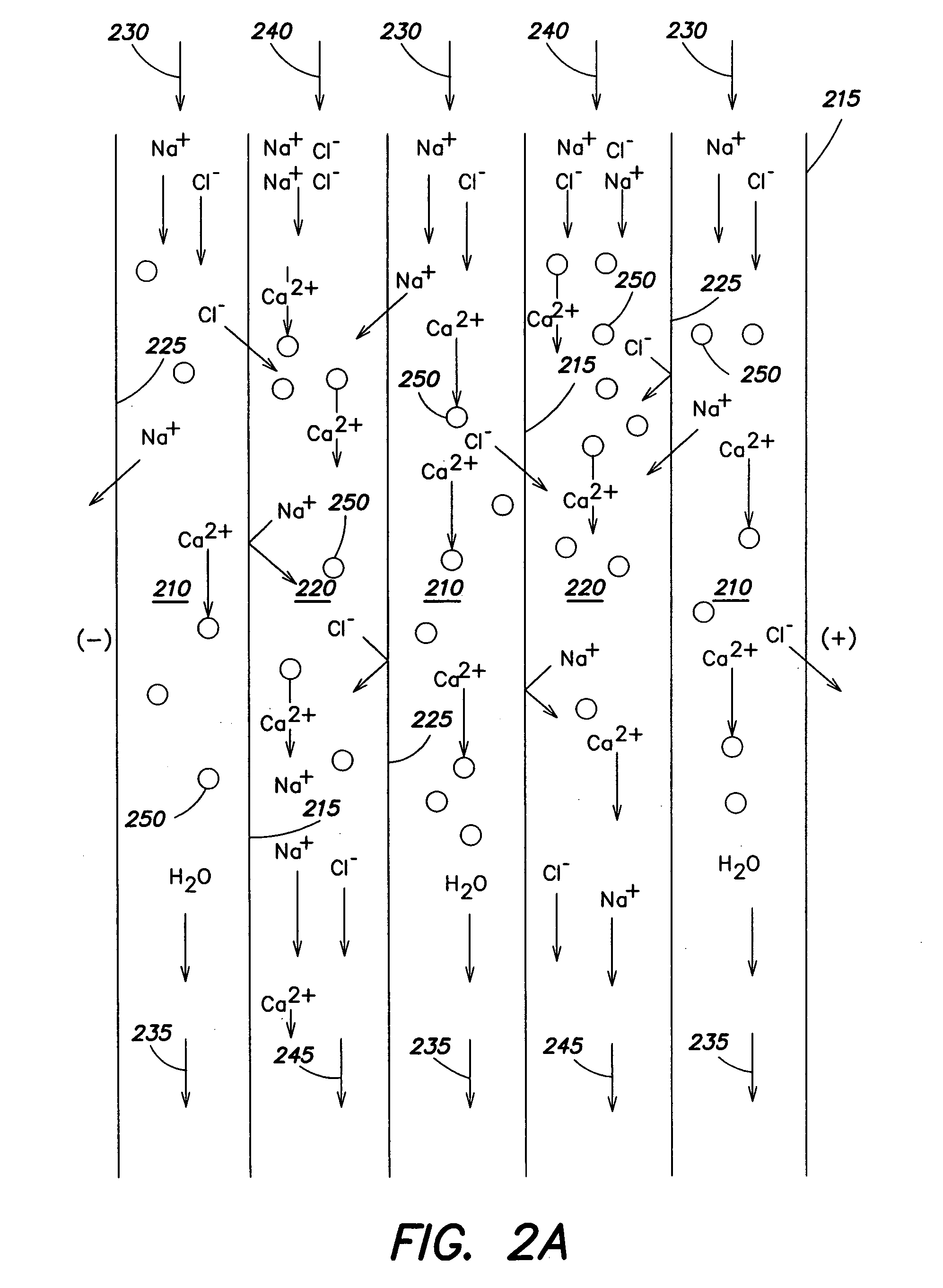
A method and apparatus is provided for inhibiting scaling in an electrodeionization system and, more particularly, for increasing tolerance to hardness in the feed water to an electrodeionization unit by inhibiting precipitation of scale-forming metallic cations contained in the feed water and thereby increasing efficiencies of the electrodeionization system. Water to be purified is passed through an electrodeionization unit in which the flow in the diluting compartment is countercurrent to the flow in the concentrating compartment. This is to impede the migration of scale-forming metallic cations from the diluting compartment, through the cation exchange membrane, into the concentrating compartment and towards the concentrating compartment side of the anion exchange membrane, thereby preventing scale formation on the anion exchange membrane. The electrodeionization unit may be further modified by dividing the concentrating compartments into first and second compartments by a porous diaphragm or ion-conducting membrane. The porous diaphragm or ion-conducting membrane effectively eliminates convective transport of scale-forming metallic cations from the cation exchange membrane side of the concentrating compartment to the anion exchange membrane side of the concentrating compartment, thereby inhibiting scale formation on the anion exchange membrane.
Owner:E CELL
Water treatment system and method
ActiveUS20050103630A1Inhibit migrationPromote migrationSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementWater sourceSoftened water
The present invention is directed to a water treatment or purification system and method for providing treated water in industrial, commercial and residential applications. The treatment system provides treated or softened water to a point of use by removing at least a portion of any hardness-causing species contained in water from a water source, such as municipal water, well water, brackish water and water containing foulants. The water treatment system includes an electrochemical device, such as an electrodeionization device, that can have at least one compartment that generates and traps hydrogen ions which can be used in another compartment of the electrochemical device such as, an electrode compartment, to reduce or at least dissolve any scale. Other applications of the system would be in the treatment and processing of foods and beverages, sugars, various industries such as the chemical, pharmaceutical, waste water treatment and power generating industries.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
Apparatus and method for continuous electrodeionization
InactiveUS6929748B2Volume/mass flow measurementFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsElectricityWastewater
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH PTE LTD
Method for treating radioactive wastewater
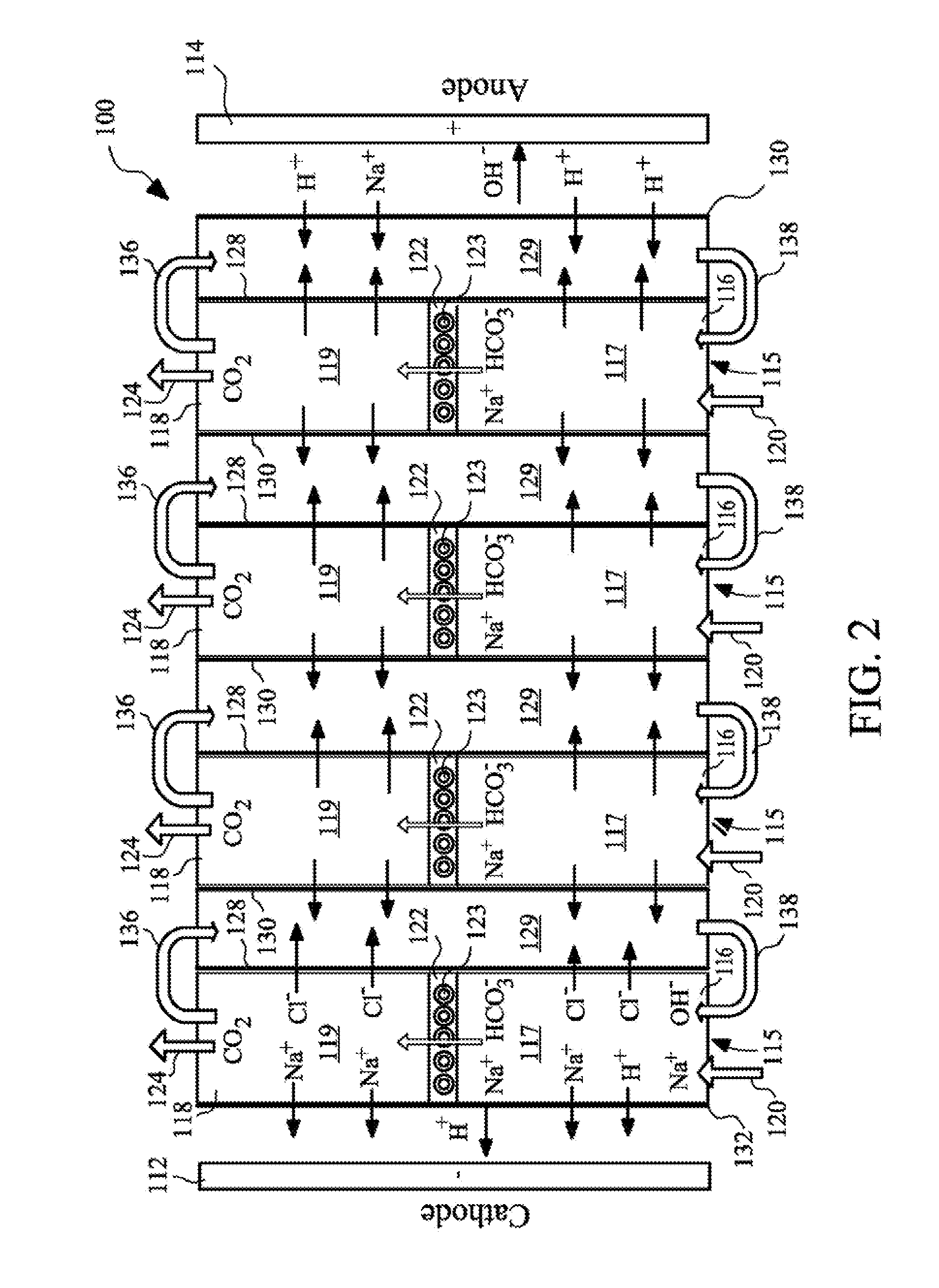
ActiveCN103177784AImprove processing precisionReduce competitionGeneral water supply conservationRadioactive contaminantsStrong acidsIon exchange
The invention discloses a method for treating radioactive wastewater. The method for treating the radioactive wastewater comprises the steps of firstly carrying out reverse osmosis treatment on the radioactive wastewater, then enabling the radioactive wastewater to enter a continuous electrodeionization unit to be treated, and further removing radionuclide so as to enable treated wastewater to reach discharge requirements; and respectively filling different mixed ion exchange resin in a plain water chamber and a thick water chamber in a continuous electrodeionization membrane stack of the continuous electrodeionization unit, wherein mixed ion exchange resin filled in the plain water chamber comprises, by volume ratio, 30%-60% of strong-acid cation exchange resin, 40%-60% of strong-base anion exchange resin, and 0%-30% of weak-base anion exchange resin, mixed ion exchange resin filled in the thick water chamber comprises, by volume ratio, 20%-50% of strong-acid cation exchange resin, and the balance strong-base anion exchange resin. A weak dissociation polymer portion is used for improving selectivity of continuous electrodeionization membrane stack to trace amount radionuclide, radionuclide with extremely concentration can be effectively removed, and the method for treating the radioactive wastewater ensures that the final discharged water satisfies the discharge requirements.
Owner:BEIJING QINGHE CHAOHUA TECH CO LTD
Method of disinfecting a deionized water producing apparatus and method of producing deionized water
InactiveUS6461512B1Prevent proliferationQuality improvementVolume/mass flow measurementFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsWater flowIon exchange
A deionized water producing apparatus includes a pretreatment apparatus having a reverse osmosis apparatus, and an electrodeionization apparatus having a diluting compartment filled with an ion exchanger. In order to disinfect the deionized water producing apparatus, hot water of higher than 80° C. is flown through the pretreatment apparatus, and hot water of higher than 60° C. is flown through the electrodeionization apparatus. Hot water flowing thorough the electrodeionization apparatus is gradually heated at a rate of 0.1-10° C. / min.
Owner:KURITA WATER INDUSTRIES LTD
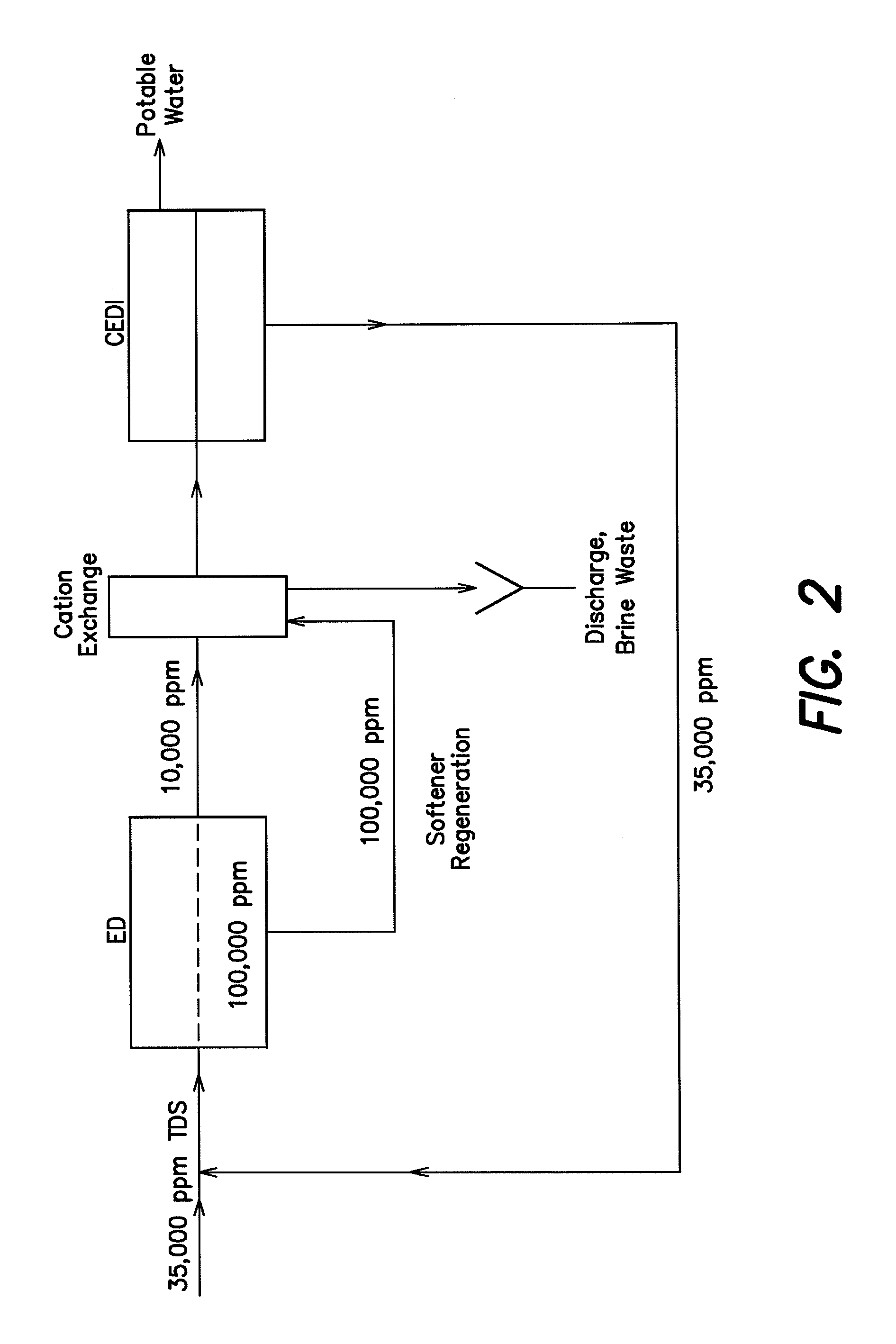
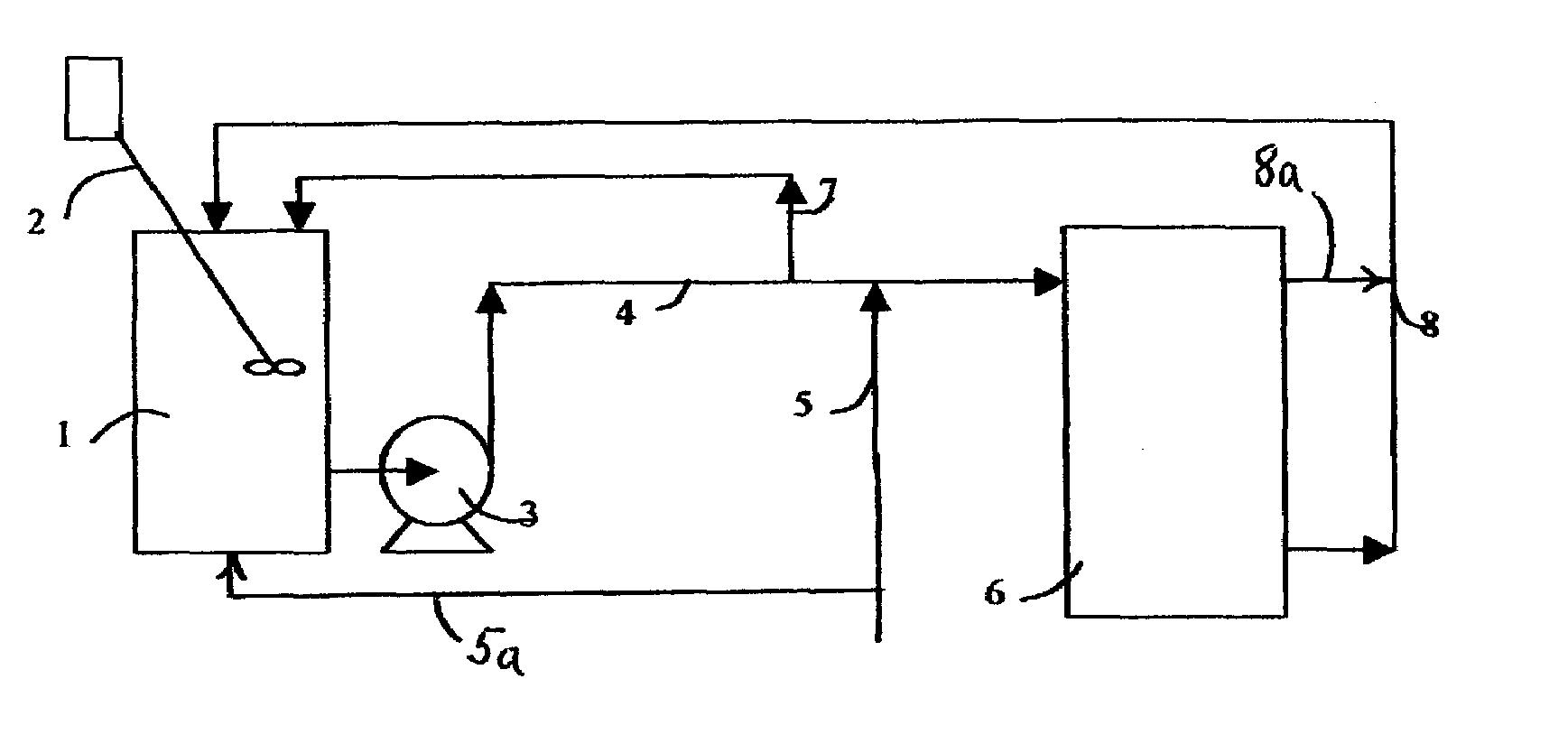
Low energy system and method of desalinating seawater
InactiveUS20100282689A1Reduce power consumptionLower energy requirementsGeneral water supply conservationSeawater treatmentWater desalinationHandling system
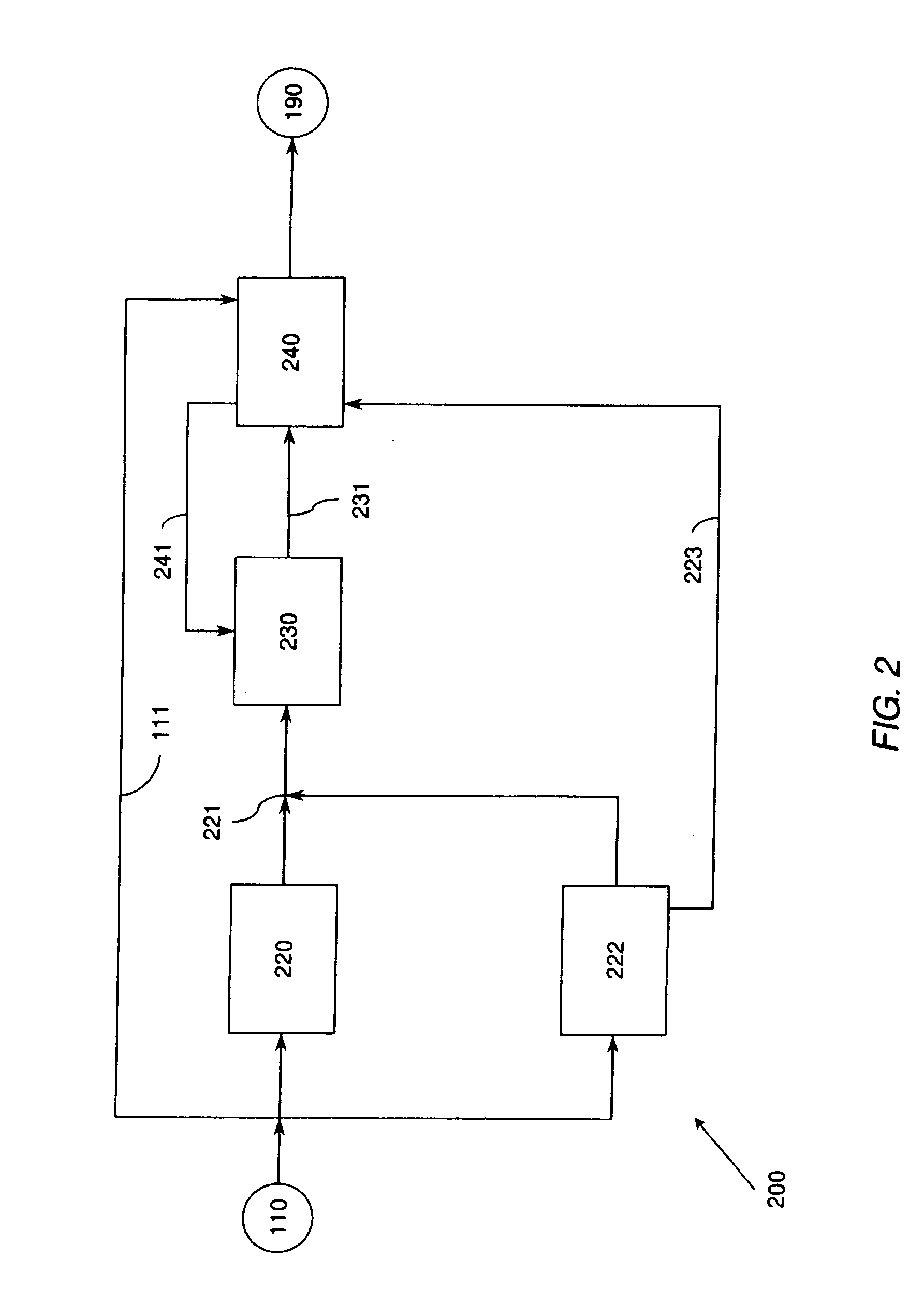
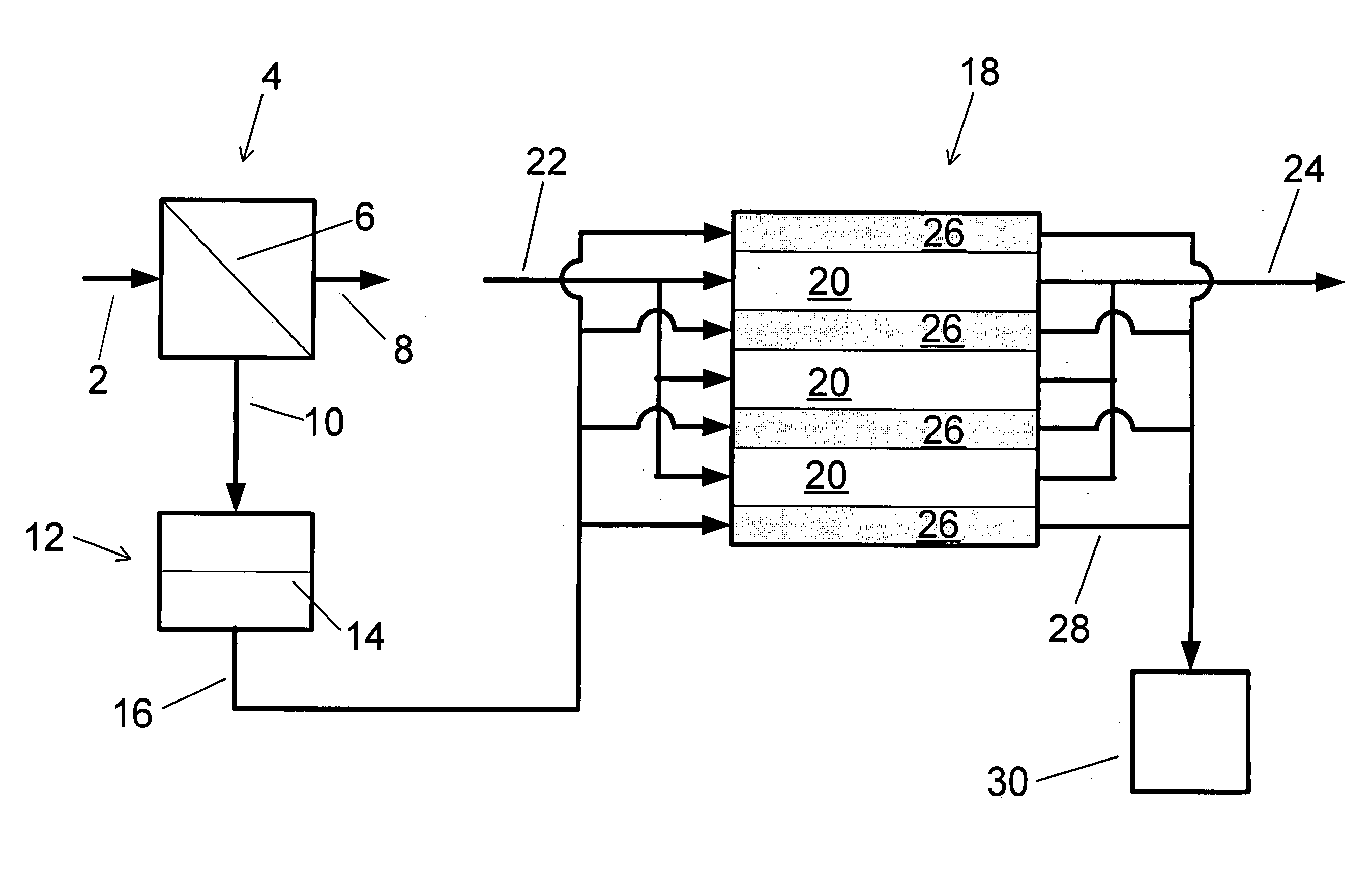
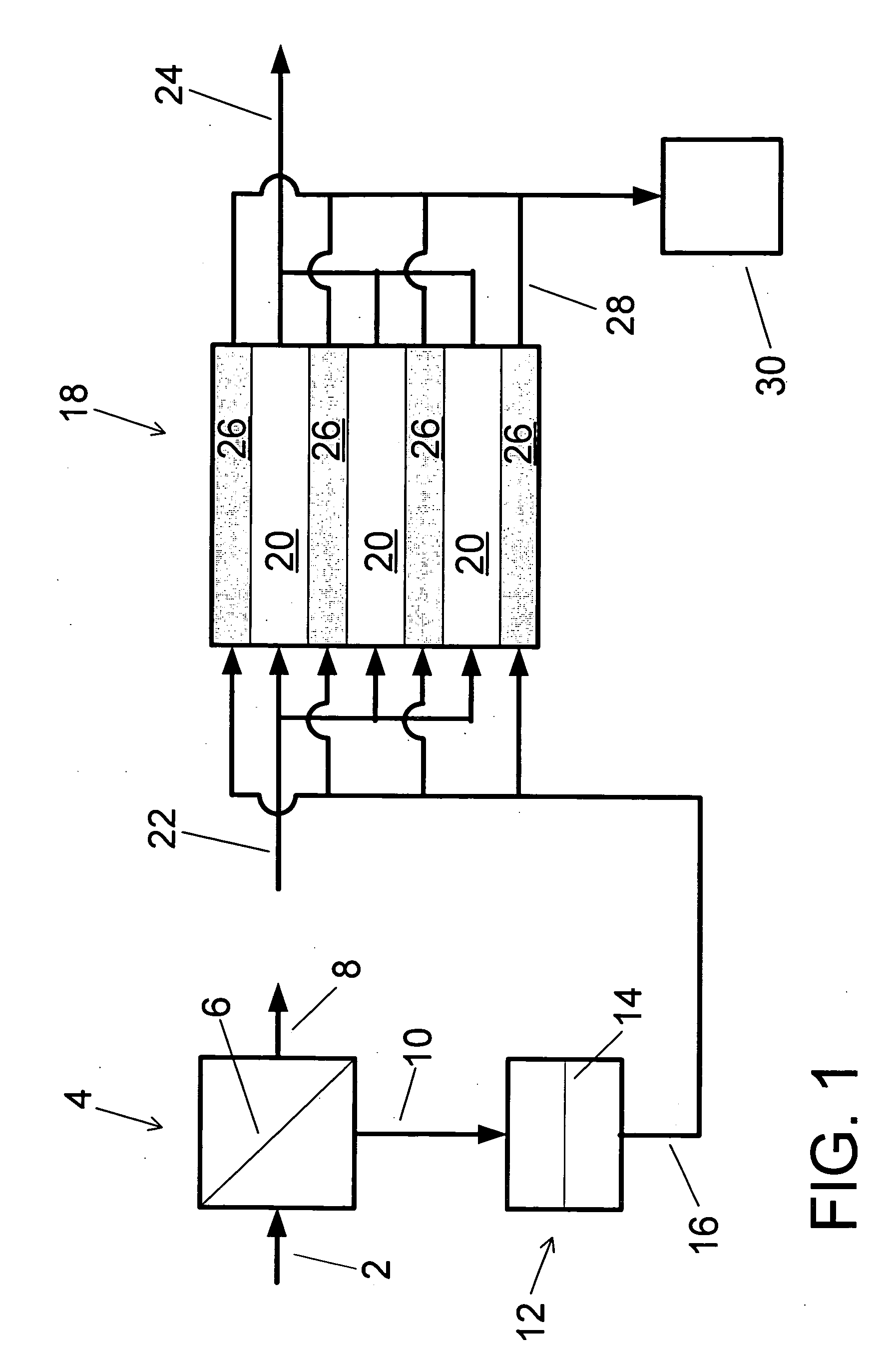
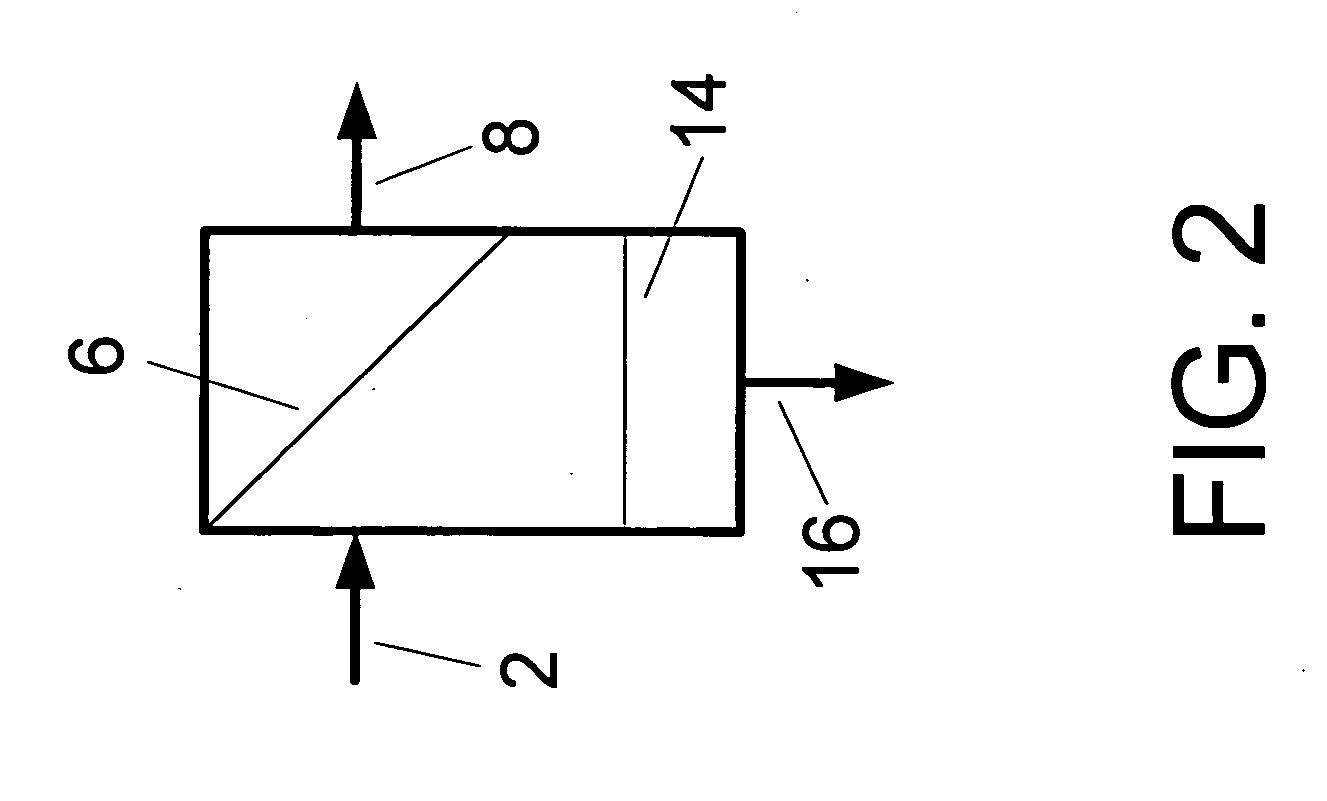
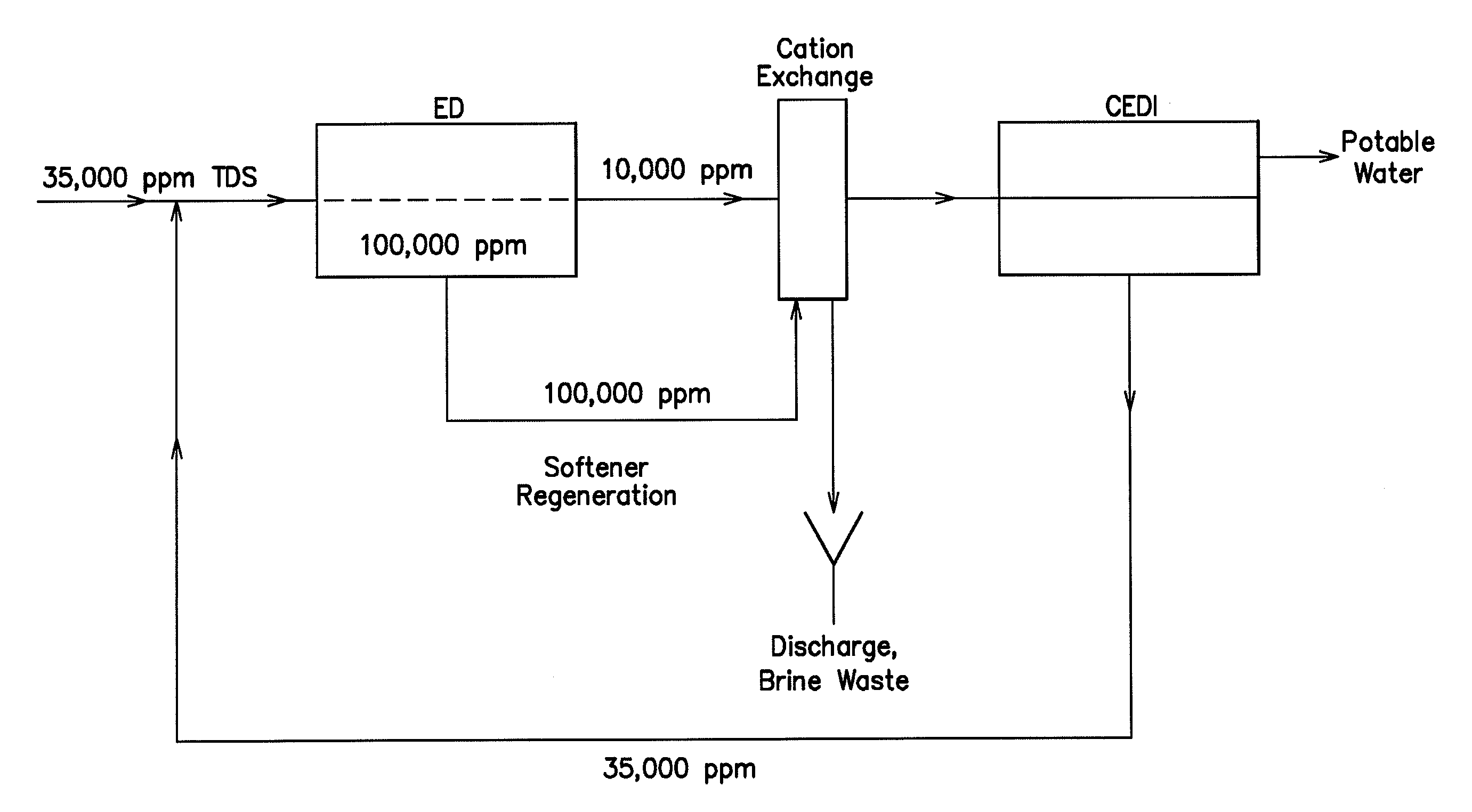
A low energy water treatment system and method is provided. The system has at least one electrodialysis device that produces partially treated water and a brine byproduct, a softener, and at least one electrodeionization device. The partially treated water stream can be softened by the softener to reduce the likelihood of scale formation and to reduce energy consumption in the electrodeionization device, which produces water having target properties. At least a portion of the energy used by the electrodeionization device can be generated by concentration differences between the brine and seawater streams introduced into compartments thereof. The brine stream can also be used to regenerate the softener.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
Method and apparatus for desalination
ActiveUS20080067125A1Reduce total dissolved solidReduce concentrationGeneral water supply conservationSeawater treatmentDesalinationFresh water
A method and apparatus for purifying water are provided. A feed water such as seawater can be fed to a filter such as a microporous or nanofiltration membrane to produce a permeate that can, in turn, be fed to an electrodeionization system to produce fresh water.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
Concentrate recycle loop with filtration module
InactiveUS20060091077A1Increase flow rateVolume/mass flow measurementFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsFiltration membraneMineralogy
Water purification systems include a concentrate filtration membrane and an electrodeionization unit. A concentrate effluent stream from the electrodeionization unit is filtered in the concentrate filtration membrane; the filtered concentrate effluent stream is provided to concentrating compartments of the electrodeionization unit.
Owner:ECOLOCHEM
Water treatment system and method
InactiveUS20110120886A1Reduce likelihood of formationPrevent scalingCellsWater treatment parameter controlElectricityWater treatment system
A water treatment system provides treated water to a point of use by removing at least a portion of any hardness-causing species contained in water from a water source, such as municipal water, well water, brackish water and water containing foulants. The water treatment system typically receives water from the water source or a point of entry and purifies the water containing at least some undesirable species before delivering the treated water to a point of use. The water treatment system has a pressurized reservoir system in line with an electrochemical device such as an electrodeionization device. The water treatment system can have a controller for adjusting or regulating at least one operating parameter of the treatment system or a component of the water treatment system. The electrochemical device can be operated at a low current and low flow rate to minimize water splitting or polarization, which minimizes scale formation.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
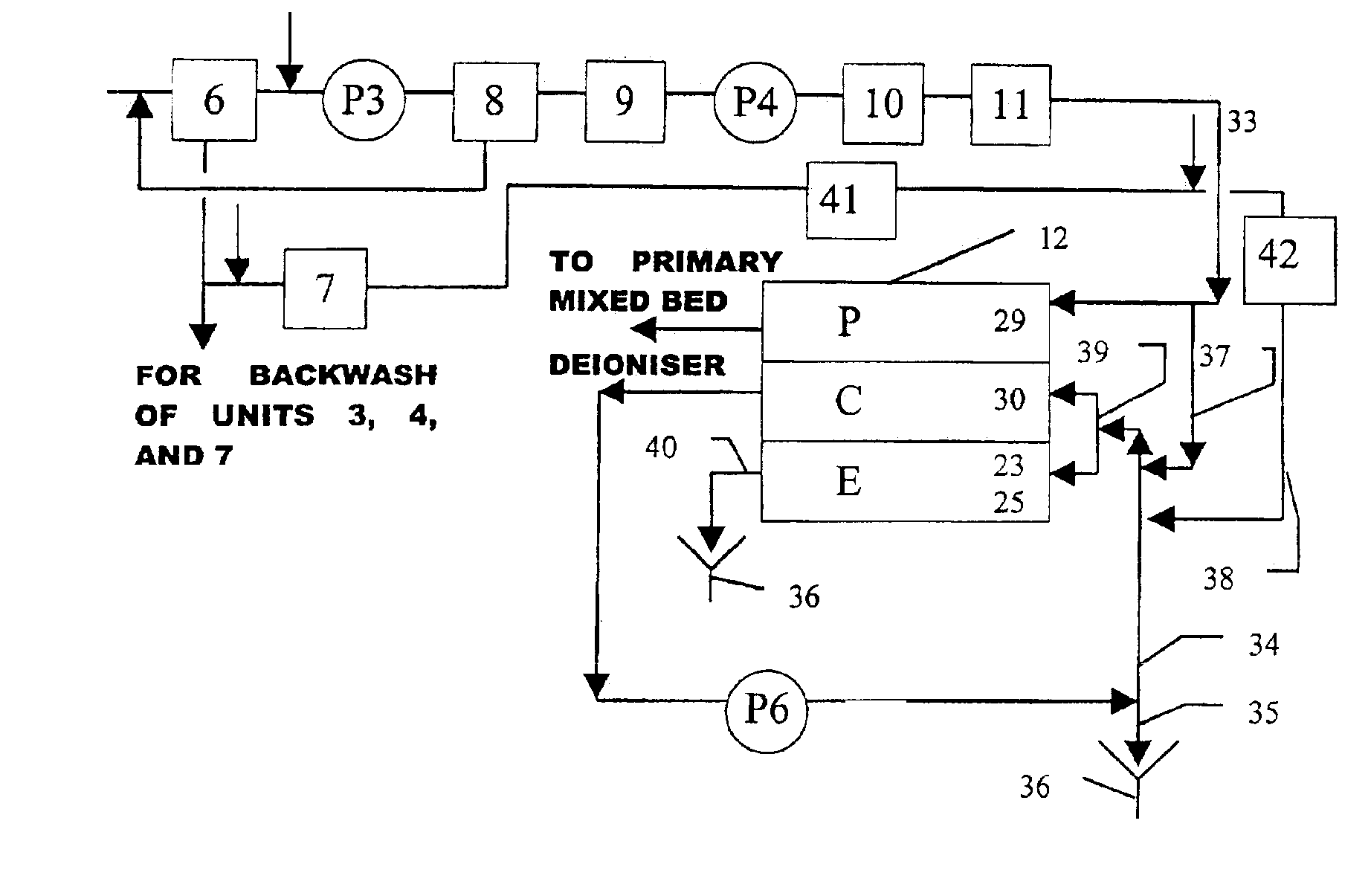
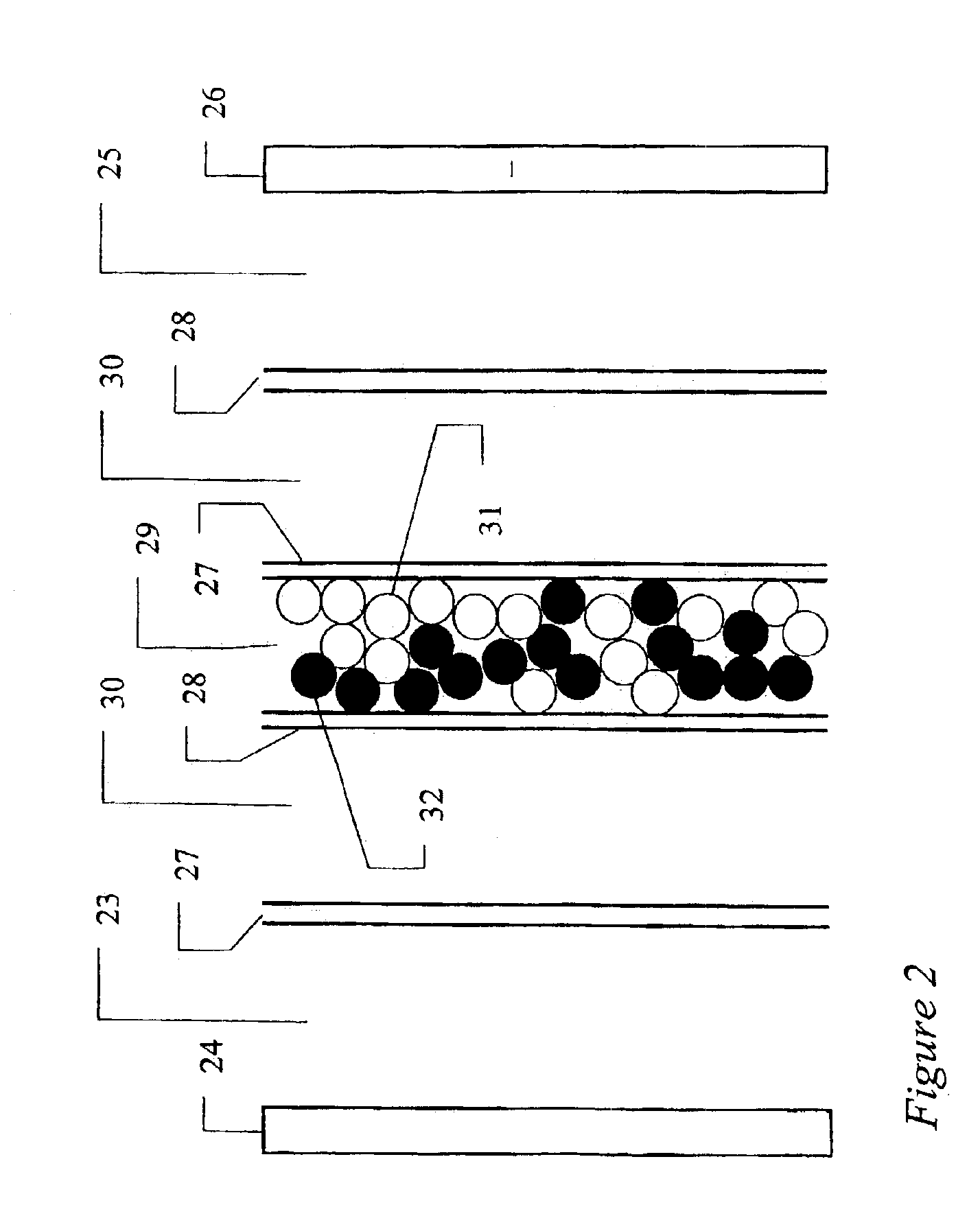
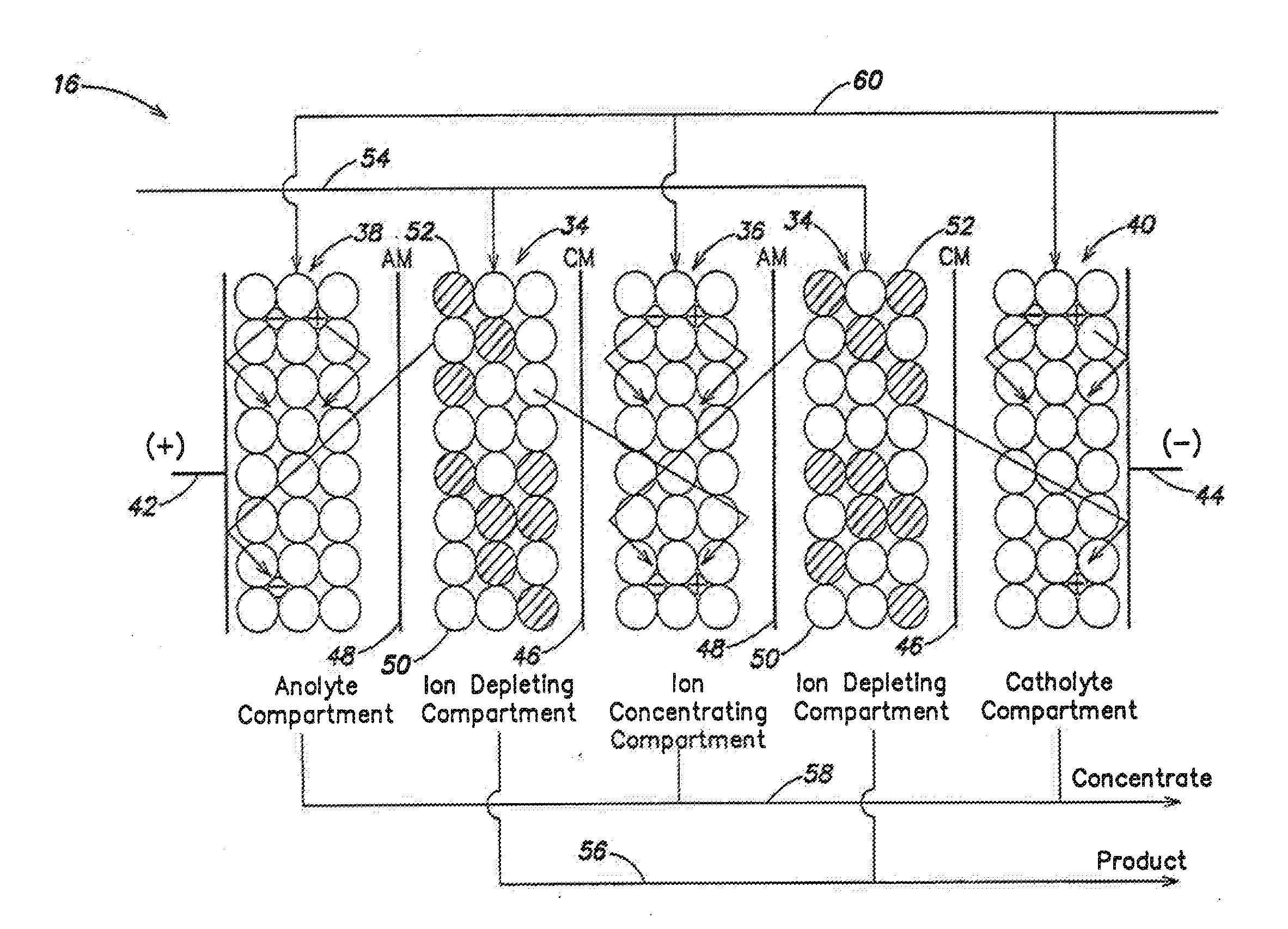
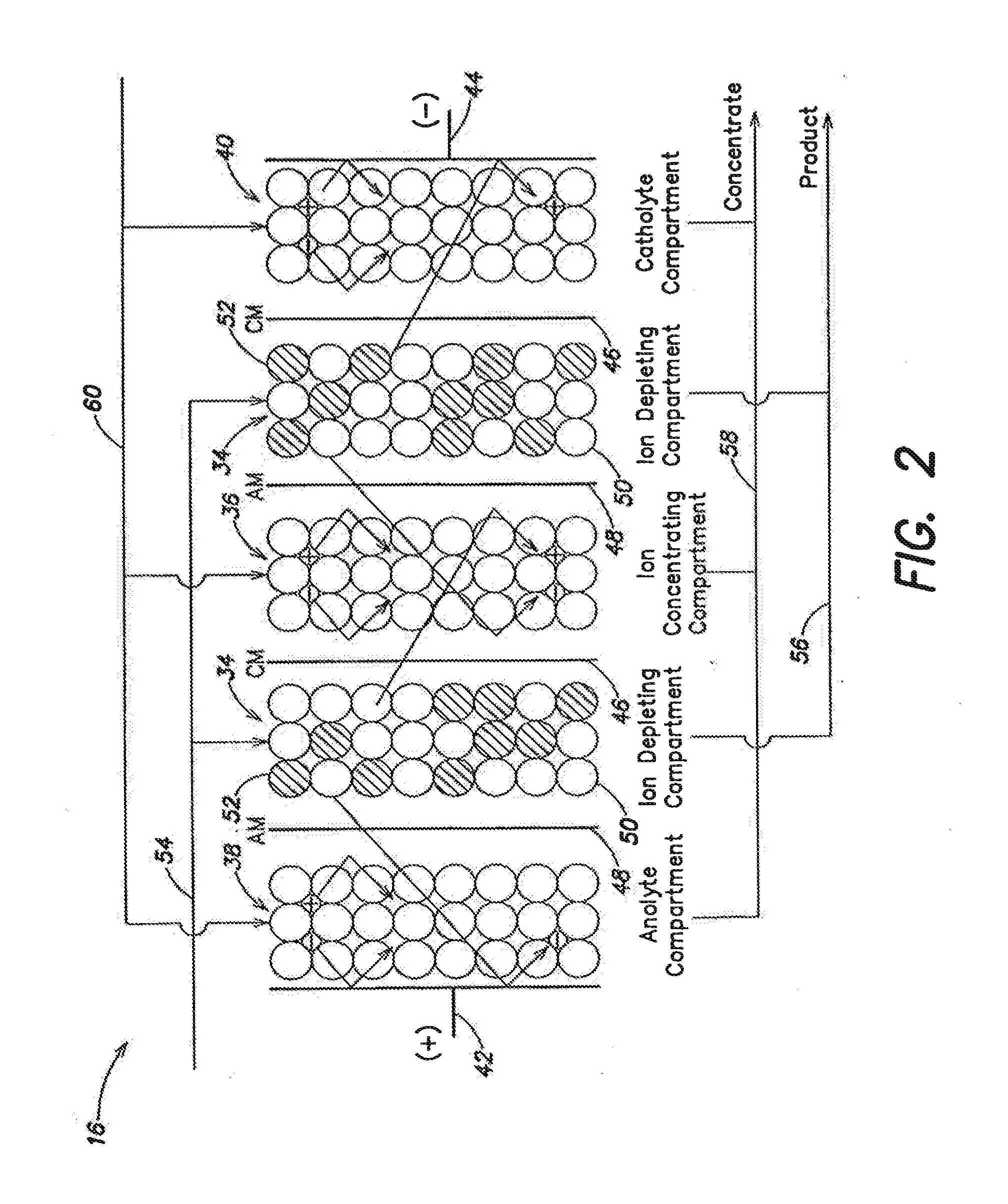
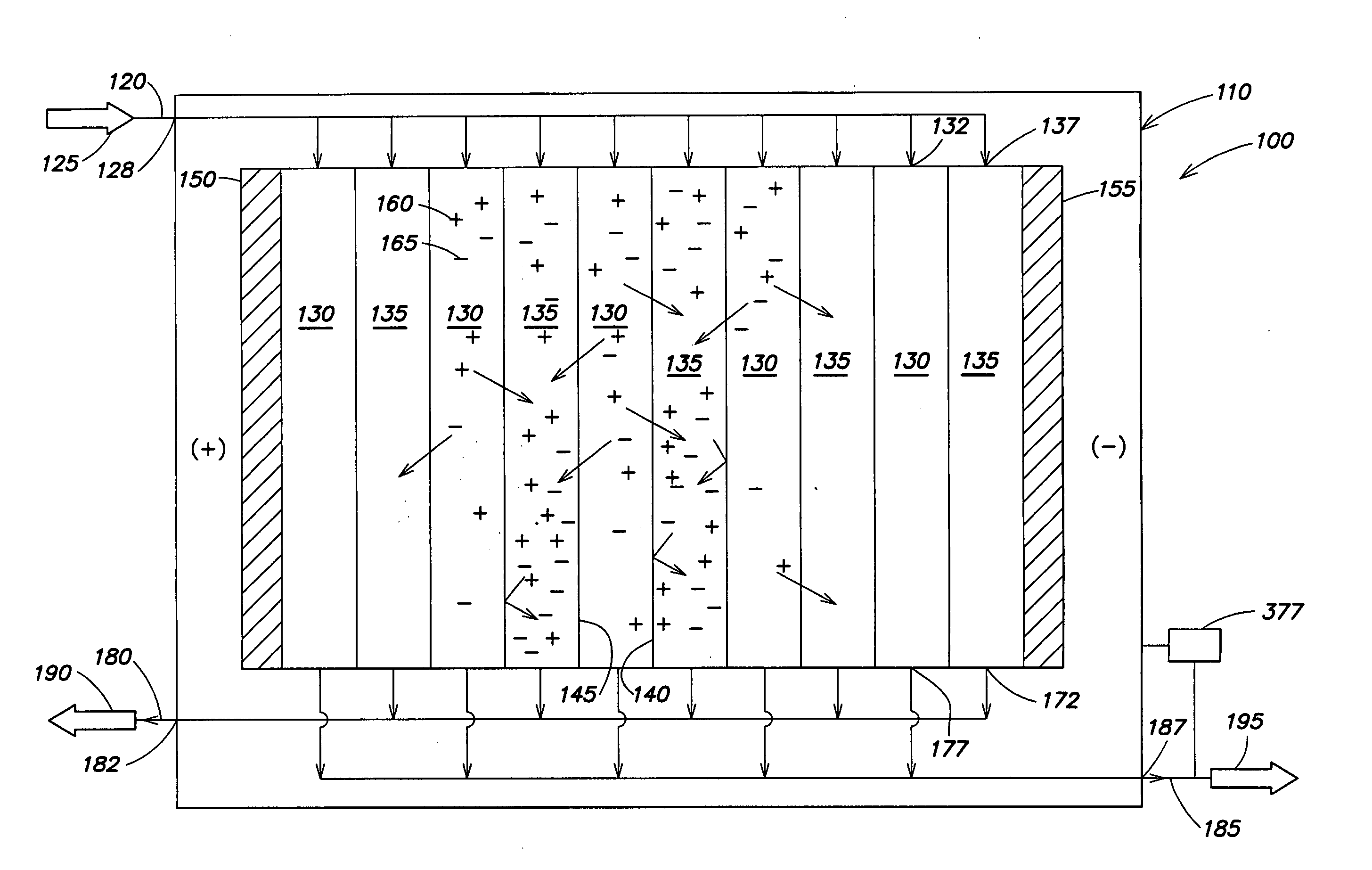
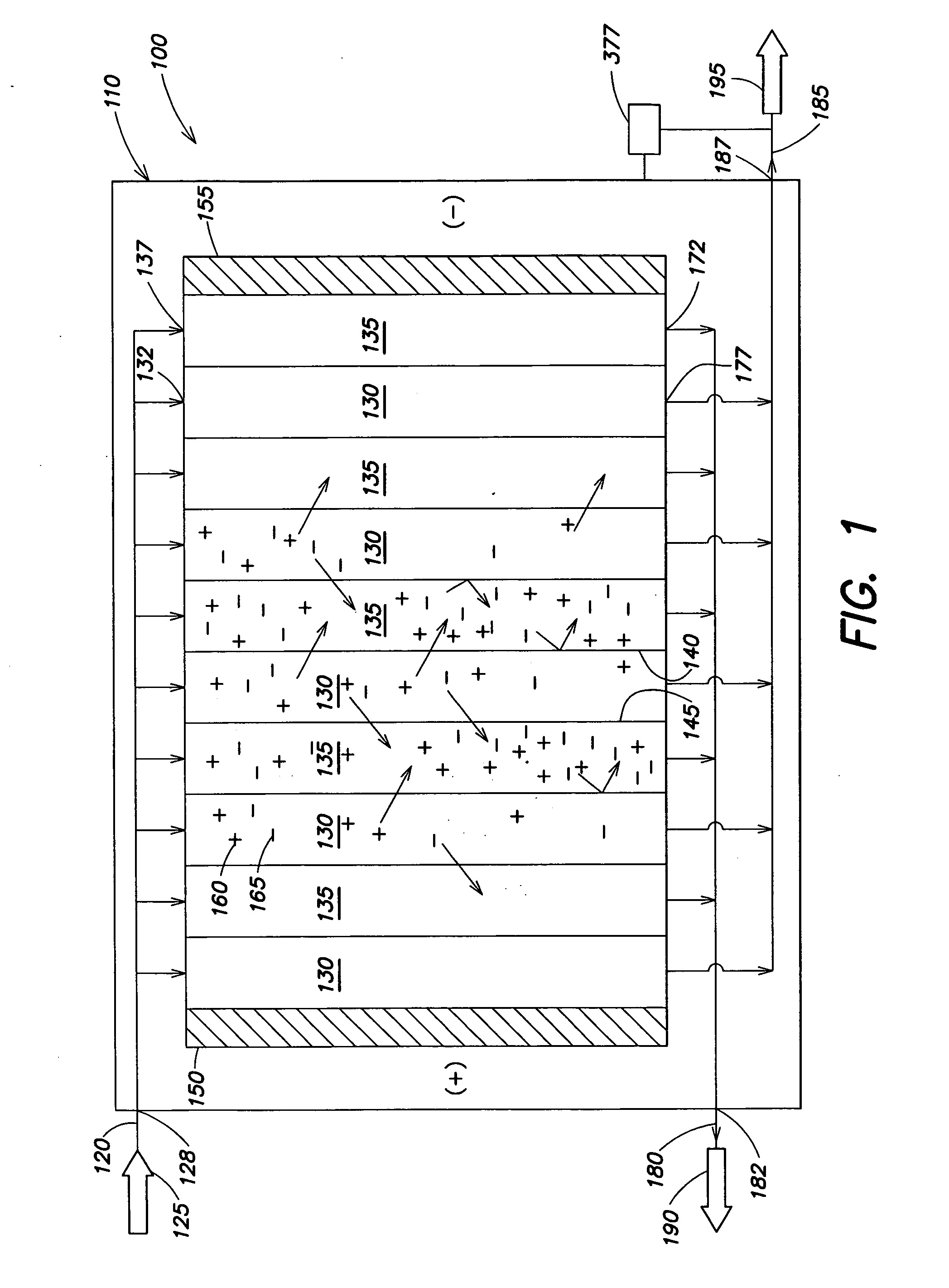
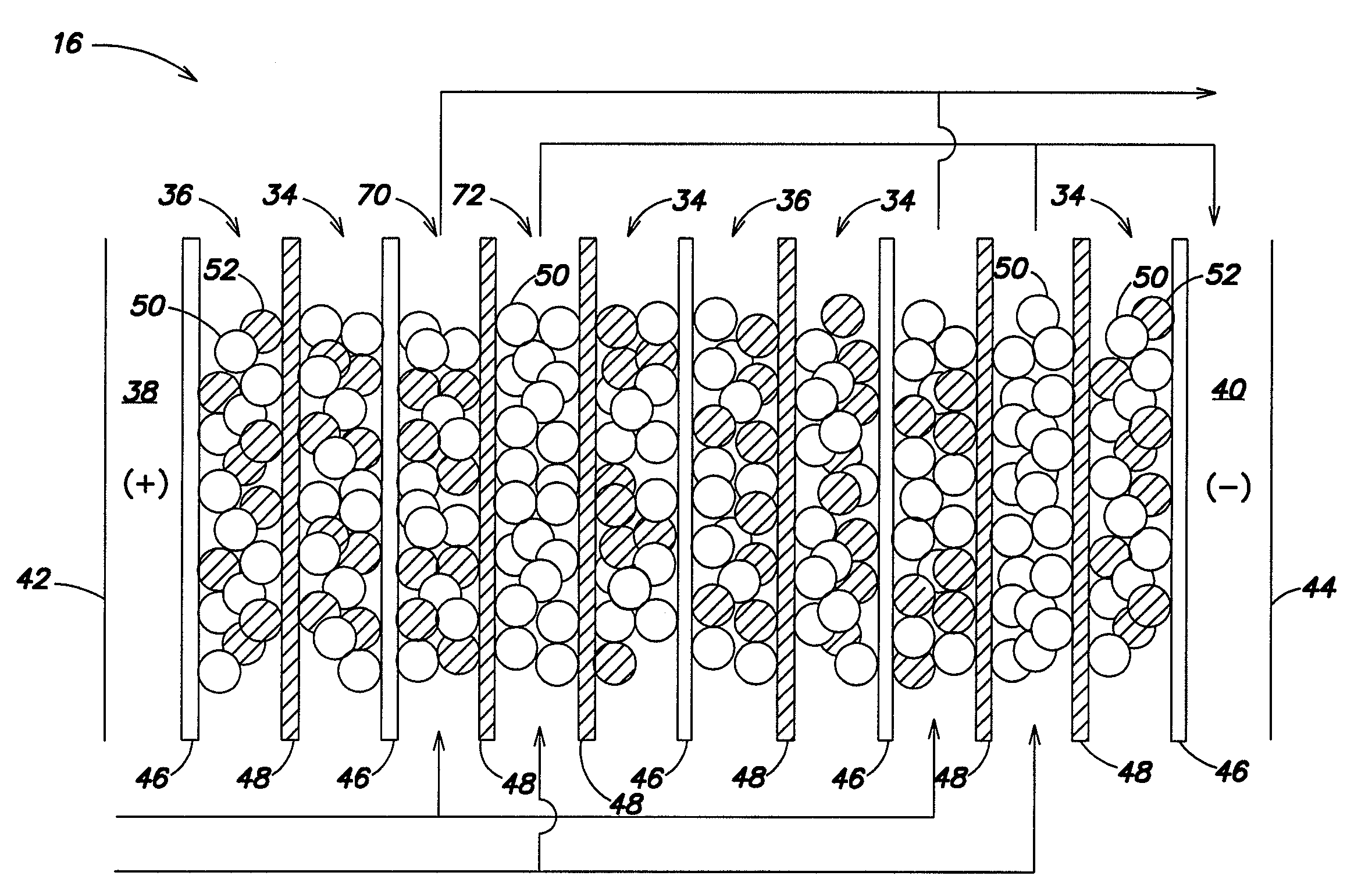
Arrangement of ion exchange material within an electrodeionization apparatus
An electrodeionization apparatus is provided comprising an ion-concentrating compartment partially bounded by an anion permeable membrane and also partially bounded by a cation permeable membrane, and a first ion exchange material domain disposed within the ion-concentrating compartment, wherein the first ion exchange material domain is contiguous with at least a portion of an ion-concentrating compartment side surface of one of the anion permeable membrane and the cation permeable membrane, and is spaced apart from the other one of the one of the anion permeable membrane and the cation permeable membrane. In the case where the one of the anion permeable membrane and the cation permeable membrane, having the at least a portion of an ion-concentrating compartment side surface with which the first ion exchange material domain is contiguous, is an anion permeable membrane, the first ion exchange material domain is an anion exchange material predominant domain. In the case where the one of the anion permeable membrane and the cation permeable membrane, having the at least a portion of an ion-concentrating compartment side surface with which the first ion exchange material domain is contiguous, is a cation permeable membrane, the first ion exchange material domain is a cation exchange material predominant domain.
Owner:BL TECH INC
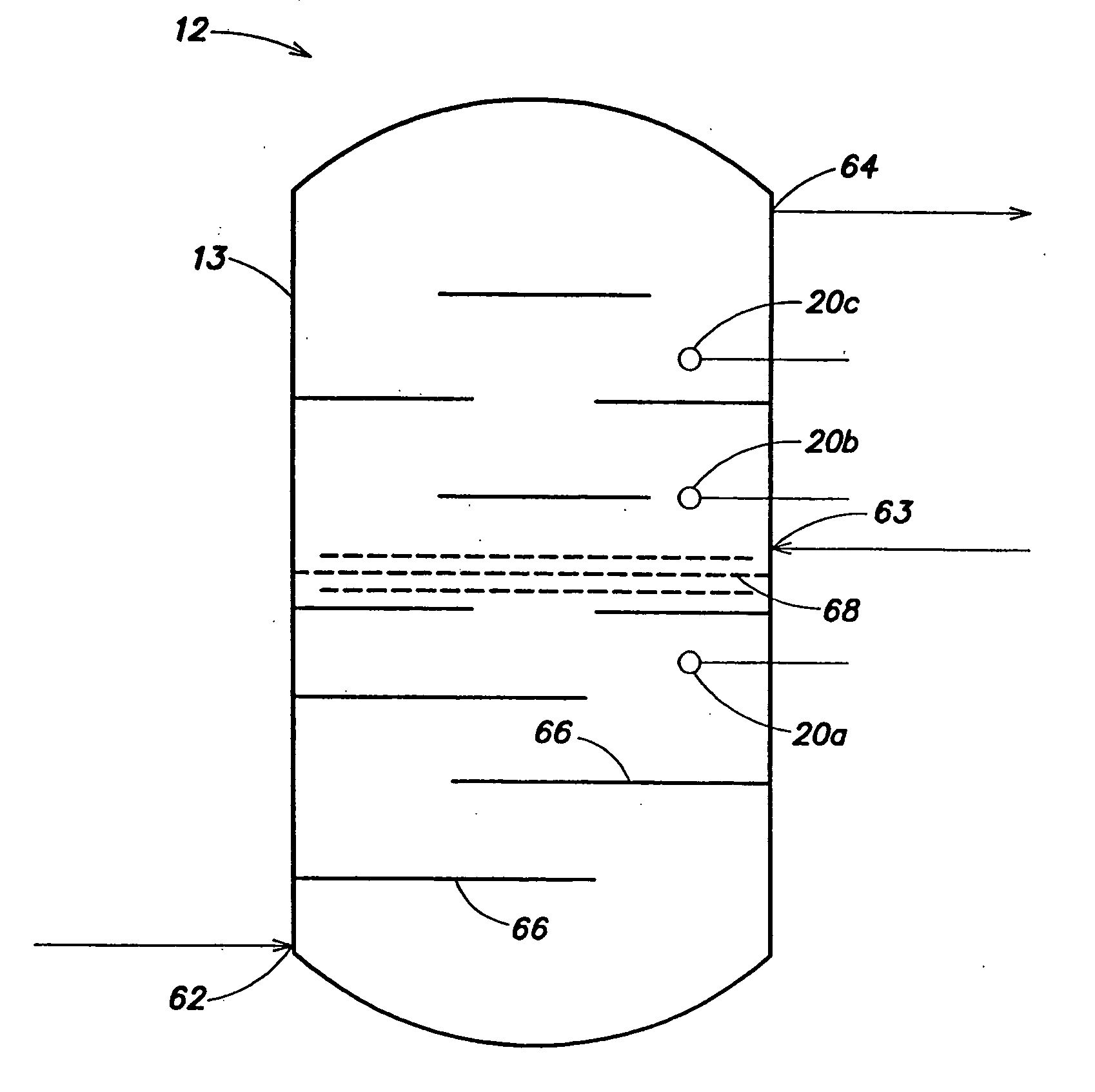
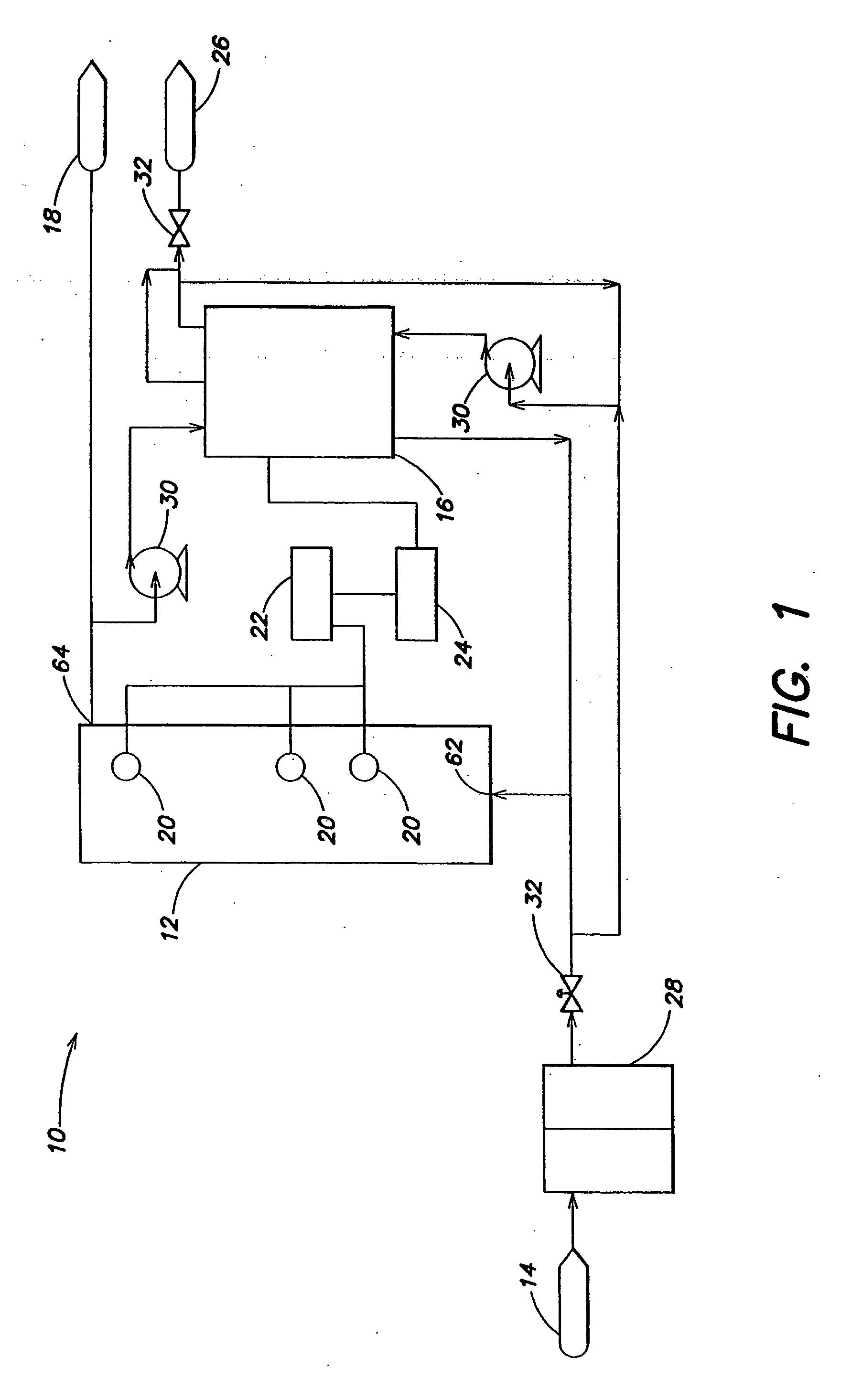
Sparse media edi apparatus and method
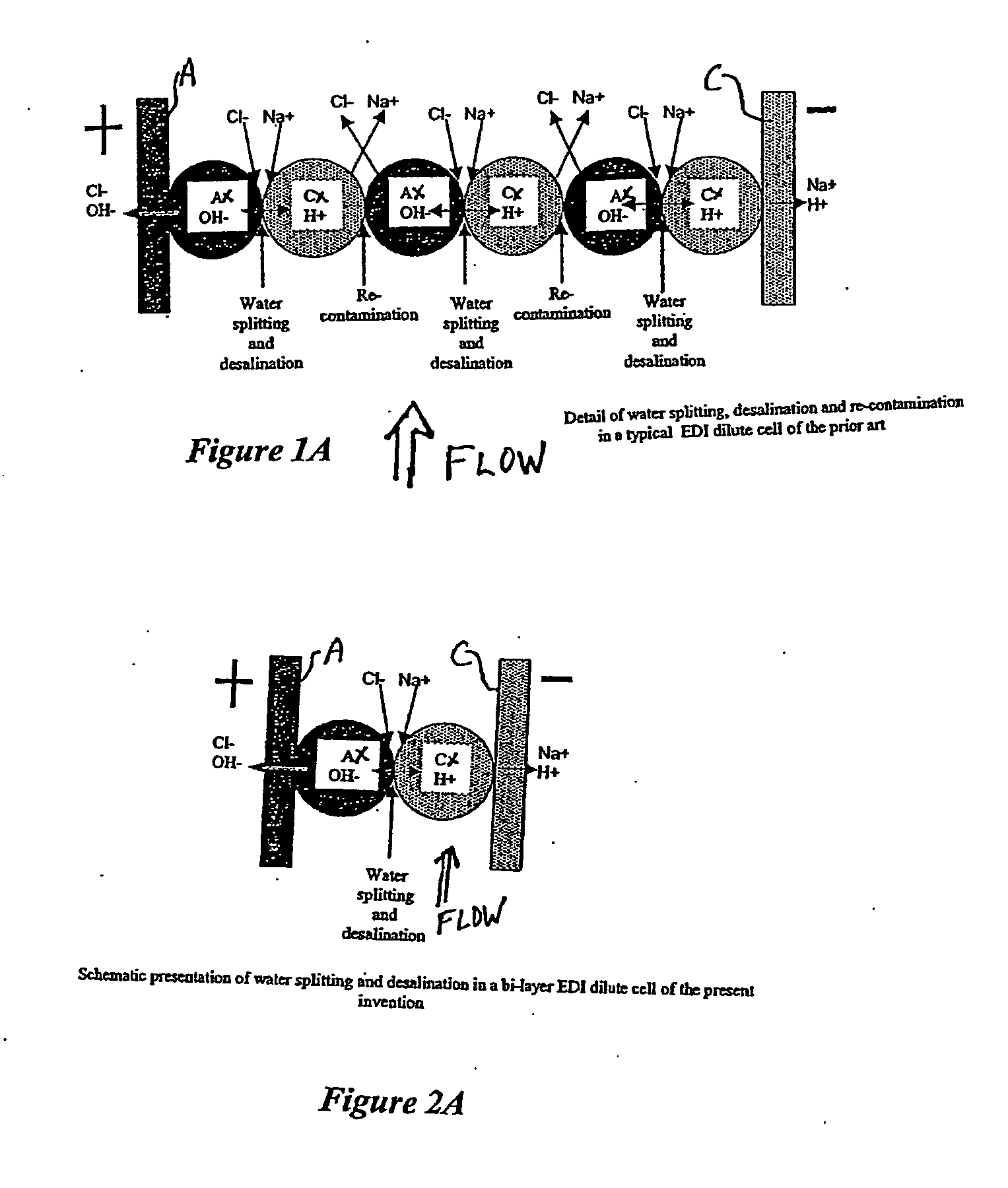
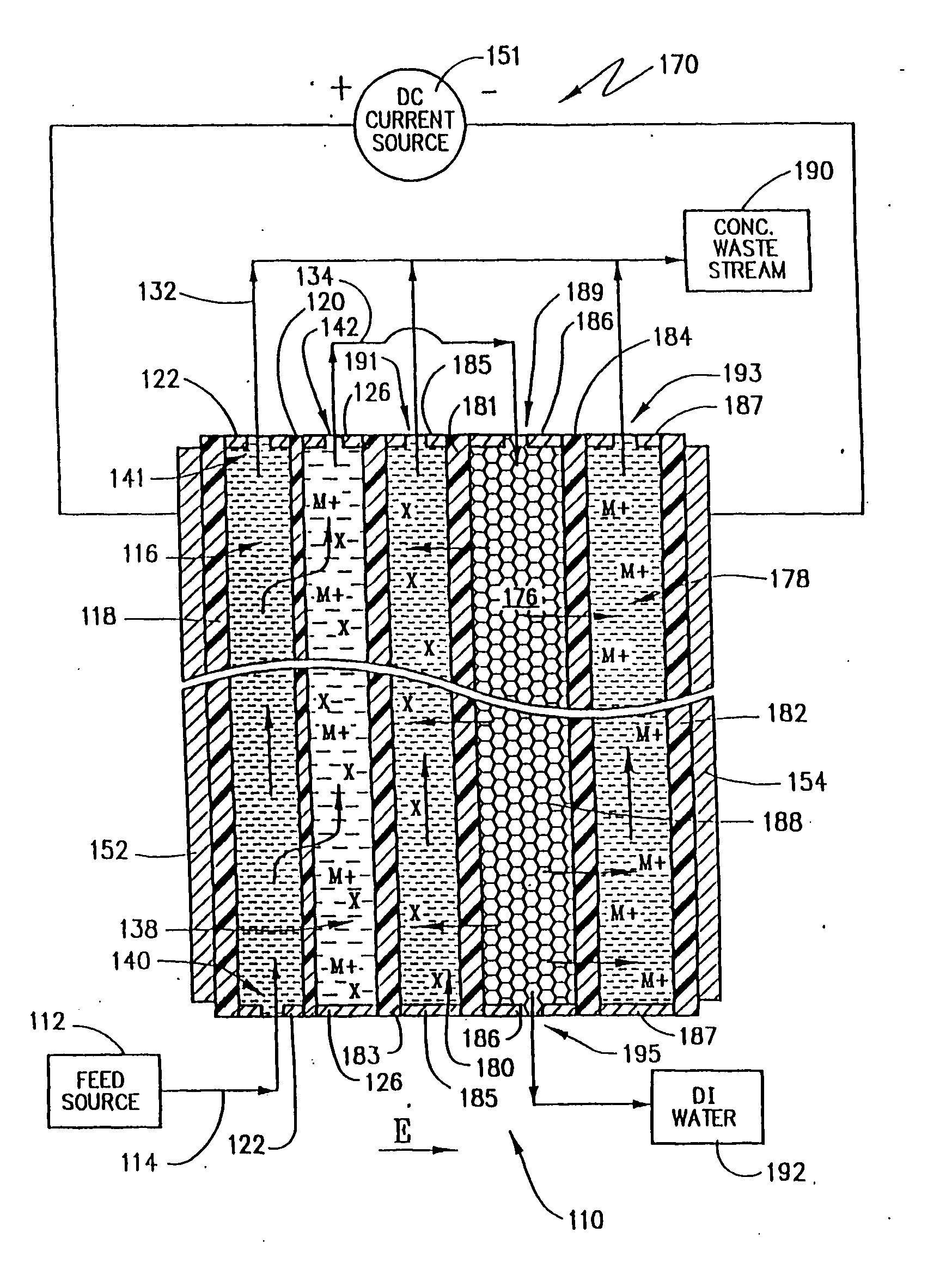
An electrodeionization, (EDI) apparatus has flow cells with a sparse distribution of ion exchange (IX) material or beads. The beads extend between membranes defining opposed walls of the cell to separate and support the membranes, and form a layer substantially free of bead-to-bead dead-end reverse junctions. The beads enhance capture of ions from surrounding fluid in dilute cells, and do not throw salt when operating current is increased. In concentrating cells, the sparse bead filling provides a stable low impedance bridge to enhanced power utilization in the stack. A monotype sparse filling may be used in concentrate cells, while mixed, layered, striped, graded or other beads may be employed in dilute cells. Ion conduction paths are no more than a few grains long and the lower packing density permits effective fluid flow. A flow cell thickness may be below one millimeter, and the beads may be discretely spaced, form a mixed or patterned monolayer, or form an ordered bilayer, and a mesh having a lattice spacing comparable to or of the same order of magnitude as resin grain size, may provide a distributed open support that assures a stable distribution of the sparse filling, and over time maintains the initial balance of uniform conductivity and good through-flow. The cells or low thickness and this resin layers relax stack size and power supply constraints, while providing treatment efficiencies and process stability. Reduced ion migration distances enhance the ion removal rate without reducing the product flow rate. The sparse resin bed may be layered, graded along the length of the path, striped or otherwise patterned. Inter-grain ion hopping is reduced or eliminated, thus avoiding the occurrence of salt-throwing which occurs at reverse bead junctions of prior art constructions. Conductivity of concentrate cells is increased, permitting more compact device construction, allowing increases in stack cell number, and providing more efficient electrical operation without ion additions. Finally, ion storage within beads is greatly reduces, eliminating the potential for contamination during reversal operation. Various methods of forming sparse beds and assembling the stacks are disclosed.
Owner:IONICS INC
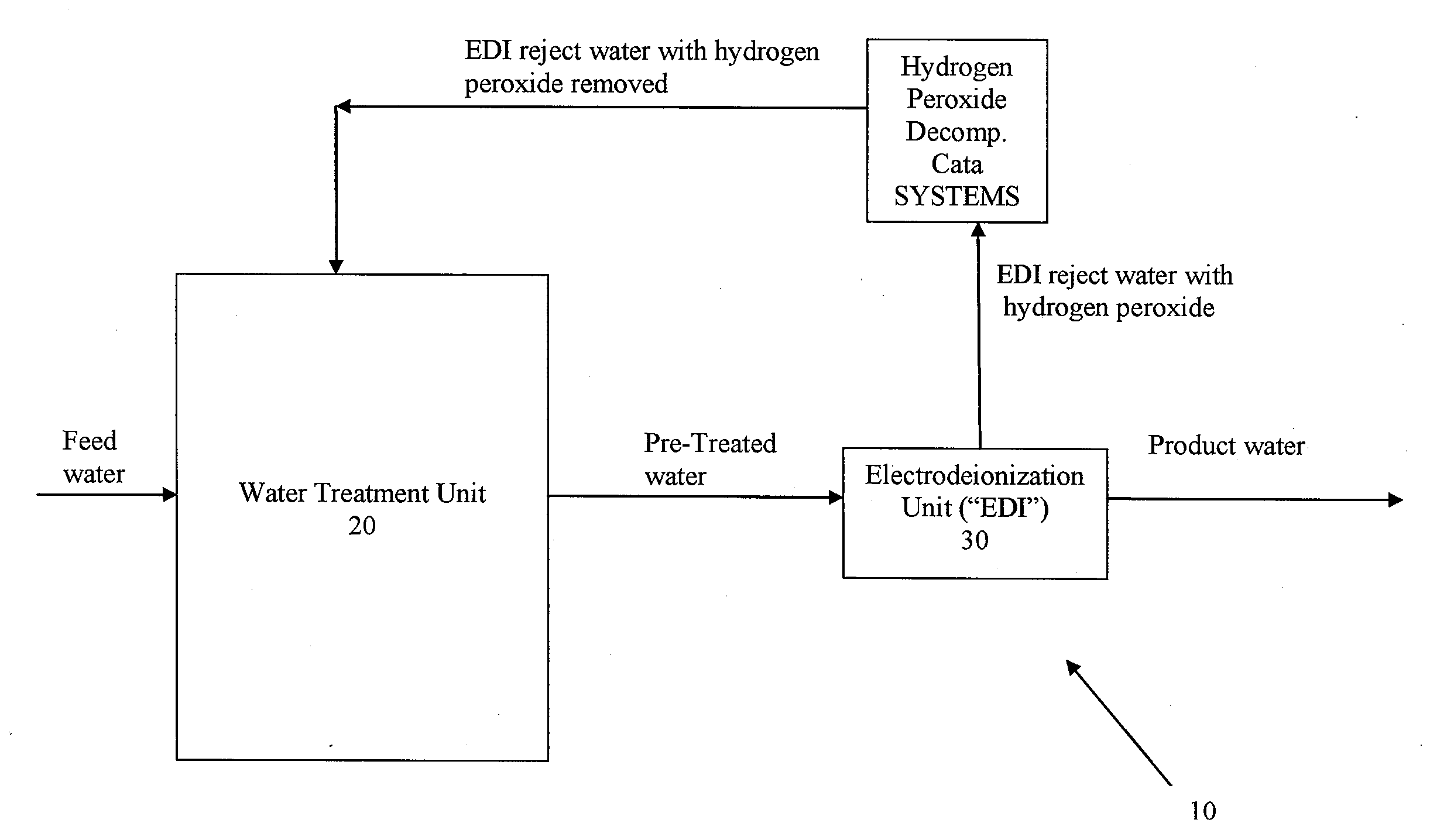
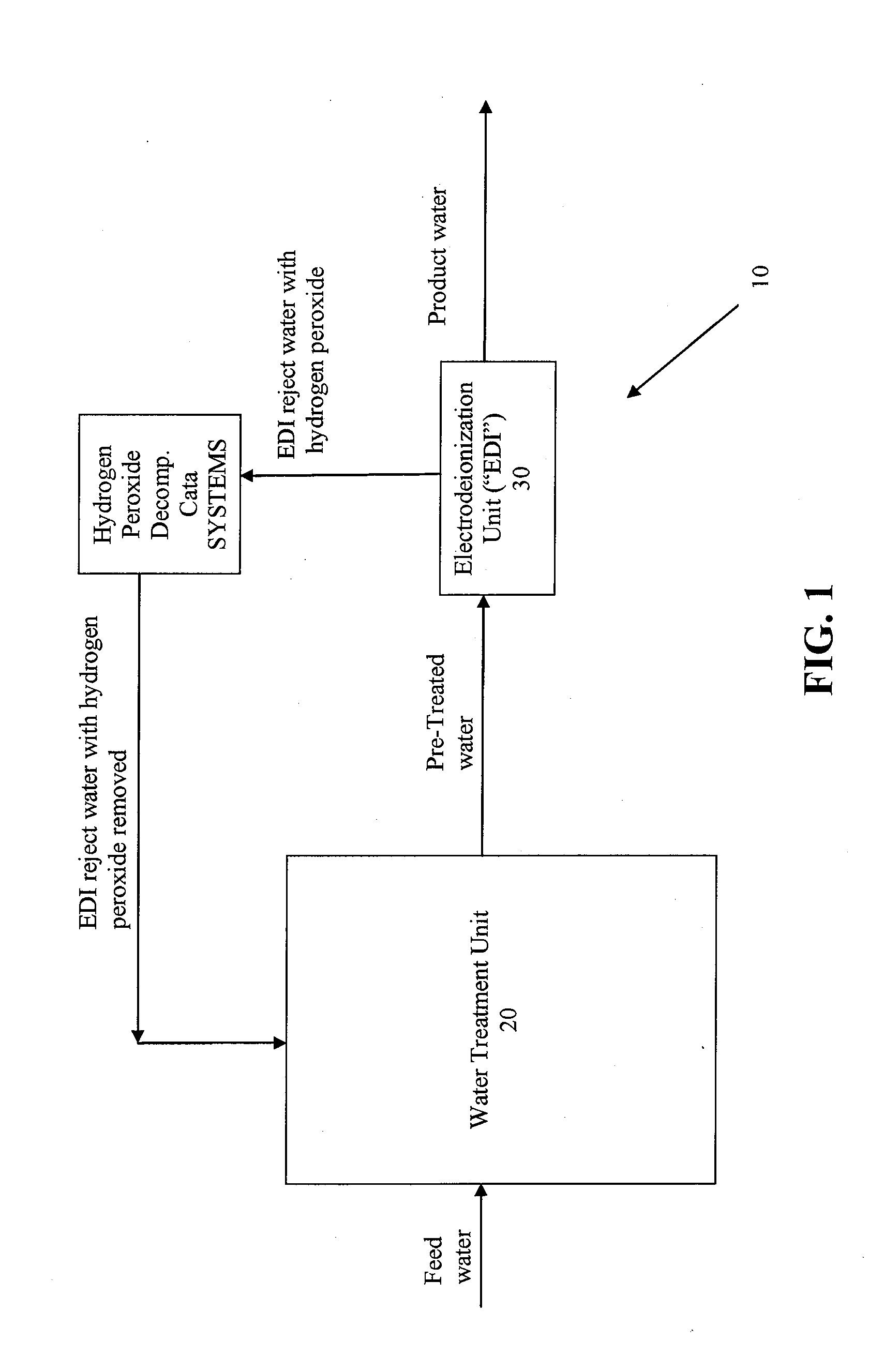
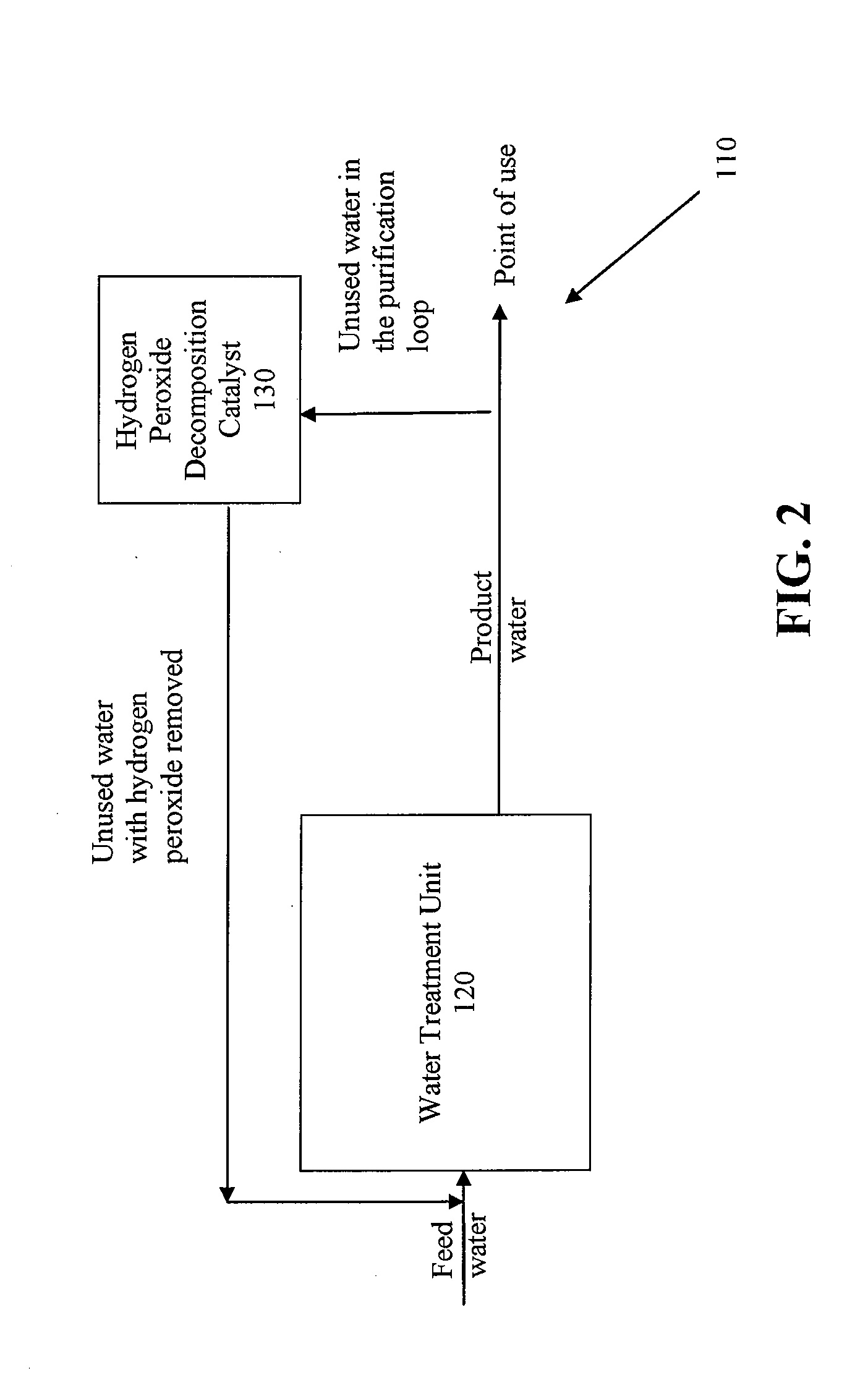
Systems and methods for removing hydrogen peroxide from water purification systems
ActiveUS20110284377A1Inhibition formationReduce water consumptionSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementHydrogen peroxide breakdownElectricity
Systems and methods for removing hydrogen peroxide from water purification systems are provided. In a general embodiment, the present disclosure provides a water purification system including a water treatment unit, an electrodeionization unit and a hydrogen peroxide decomposition catalyst in fluid connection with the electrodeionization unit. The water purification system can be fluidly connected to a renal treatment system.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
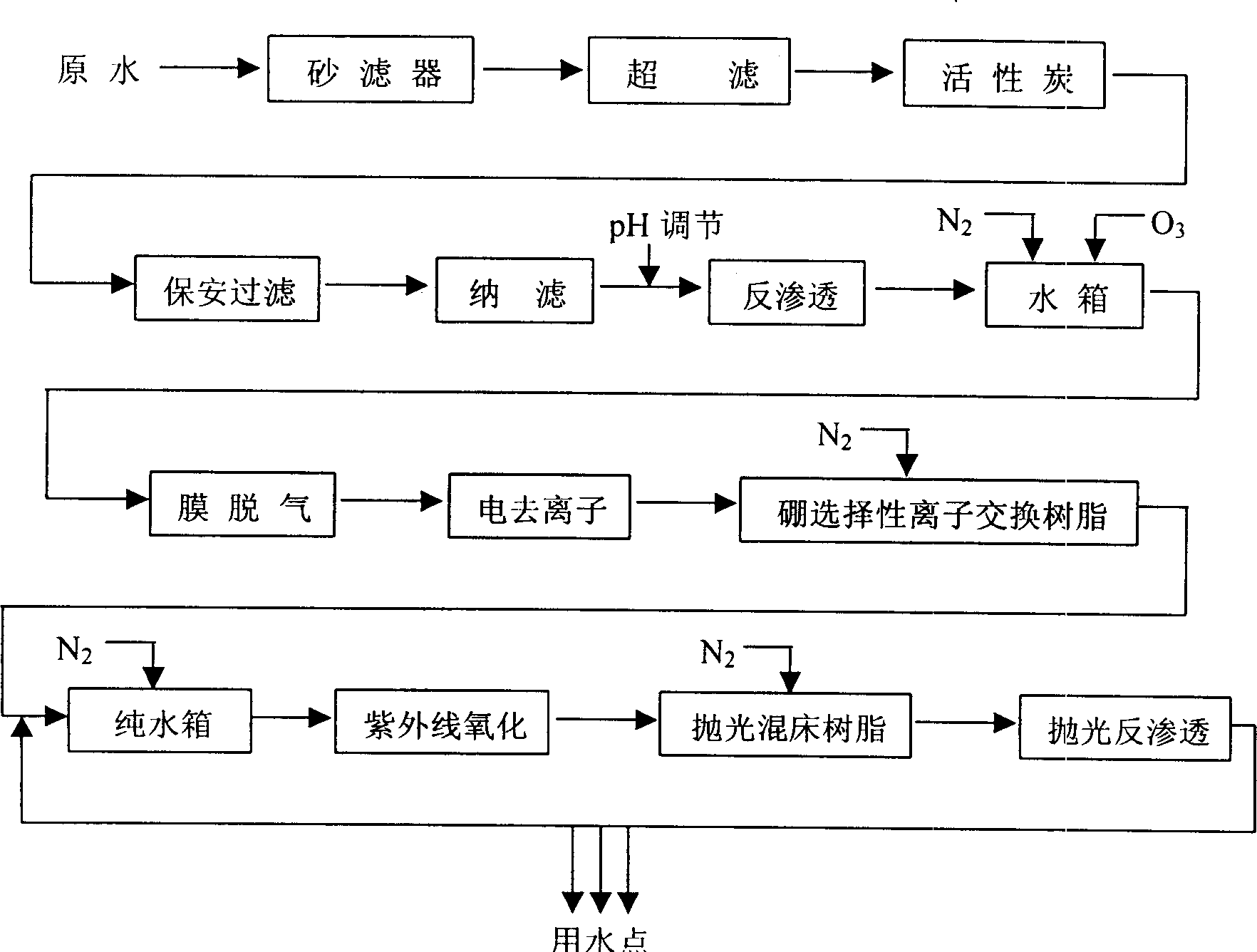
Producing process and technology for electronic grade water by intergrated film process
InactiveCN1408653AEfficient removalContinuous removalMultistage water/sewage treatmentEnvironmental engineeringPre treatment
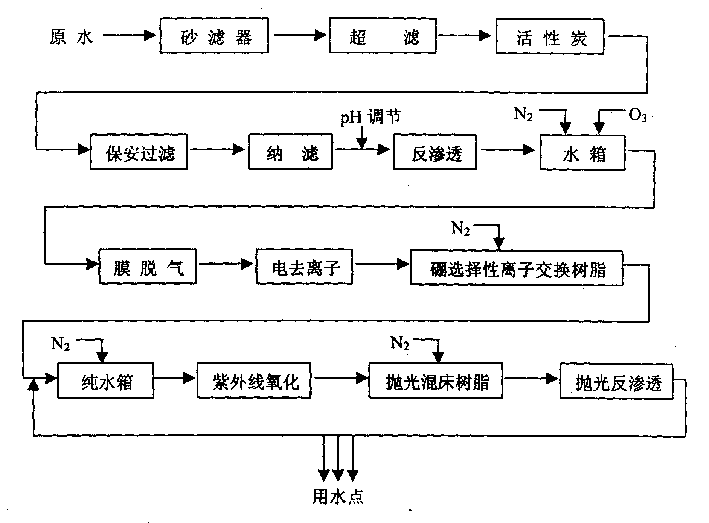
In the production process, tap water as material water is treated in four parts including pre-treatment unit, the first water purifying system, the second water purifying system and the end film filtering treatment system to prepare electronic level super-pure water. For the treating process, the pre-treatment unit includes sand filtering, superfiltering, active carbon adsorption and nanofiltering; the first water purifying system consists of reverse osmosis, film deairing, electrically deionizing, selective ion exchange resin to eliminate boron impurity and other units; the second water purifying sytem consists of ultraviolet lamp oxidation and polishing mixed bed resin; and the end film filtering treatment is polished reverse osmosis film treatment. The water purifying system has high efficiency, and low cost.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Regeneration of adsorption media within electrical purification apparatuses
The present disclosure generally relates to methods, systems, and devices for electrically purifying liquids containing species such as minerals, salts, ions, organics, and the like. One aspect of the invention provides an electrical purification apparatus, including an electrodeionization device. The electrodeionization device may be run in any suitable fashion, for example, continuously or essentially continuously, intermittently, upon demand, with periodic reversals of polarity. In another aspect, methods of regenerating media within an electrical purification device are provided, for example, exposing the media to one or more eluting solutions, and / or selectively desorbing ions, organics, and / or other species from the media by exposing the media to certain eluting conditions. In yet another aspect, methods of selectively removing one or more ions, organics, and / or other species from a liquid to be purified are provided, by selective removal of one or more ions, or organics, and the like from solution that can easily precipitate, and / or cause scaling or fouling to occur. In still another aspect, the invention provides a method of treating a solution containing ions, organics, and / or other species using an electrical purification apparatus in a continuous or semi-continuous fashion, while also performing regeneration of media contained within the apparatus.
Owner:SIEMENS WATER TECH HLDG CORP
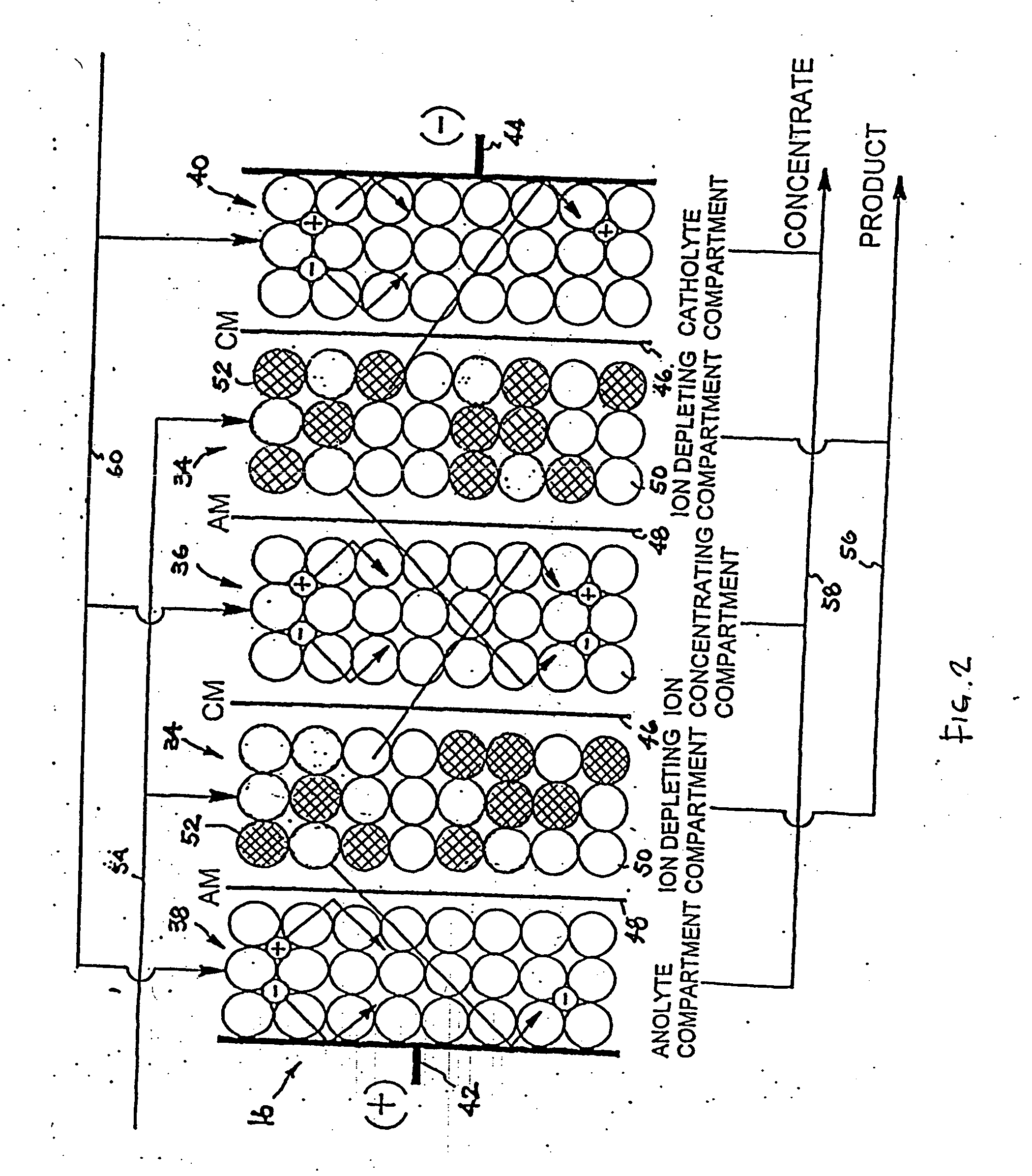
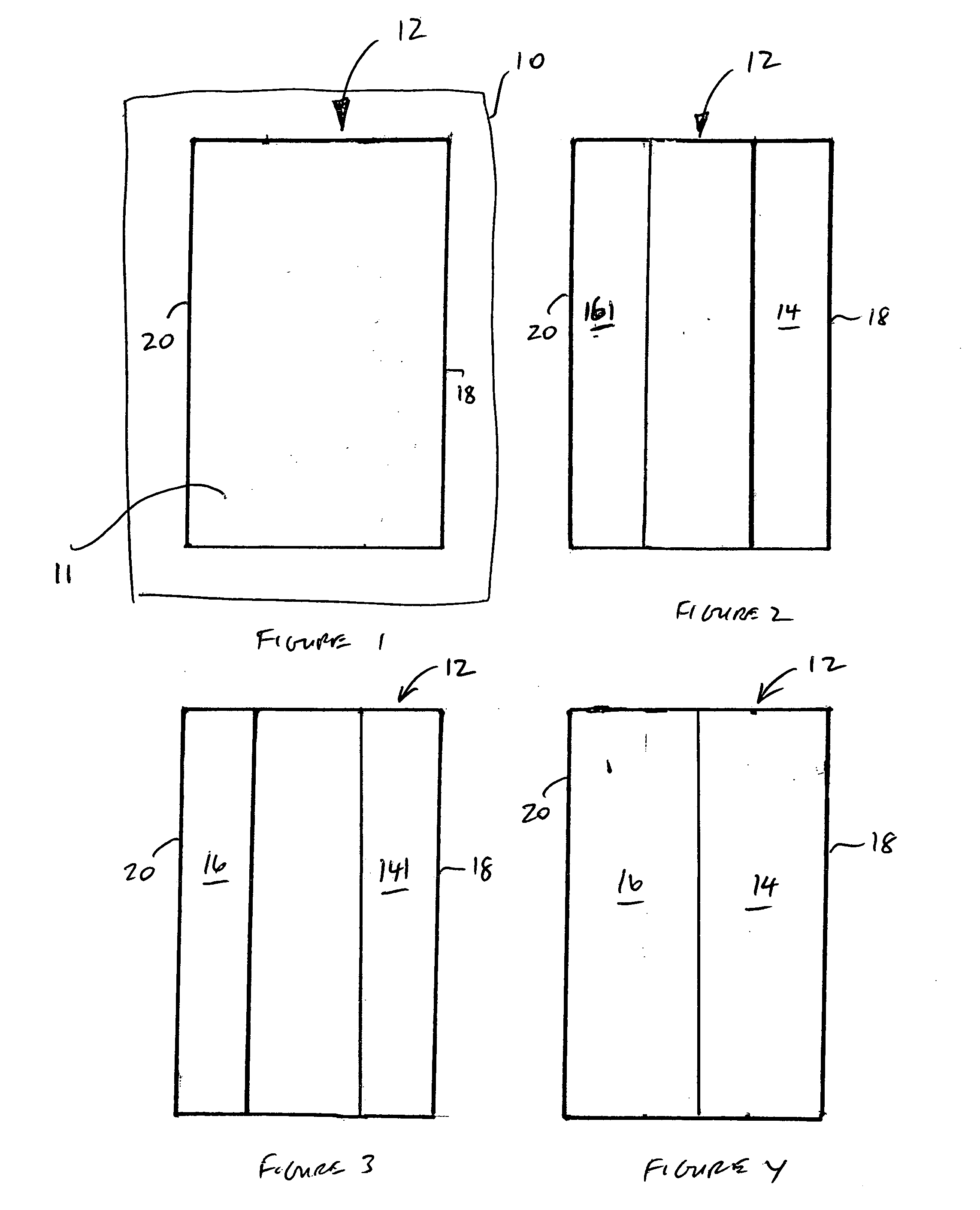
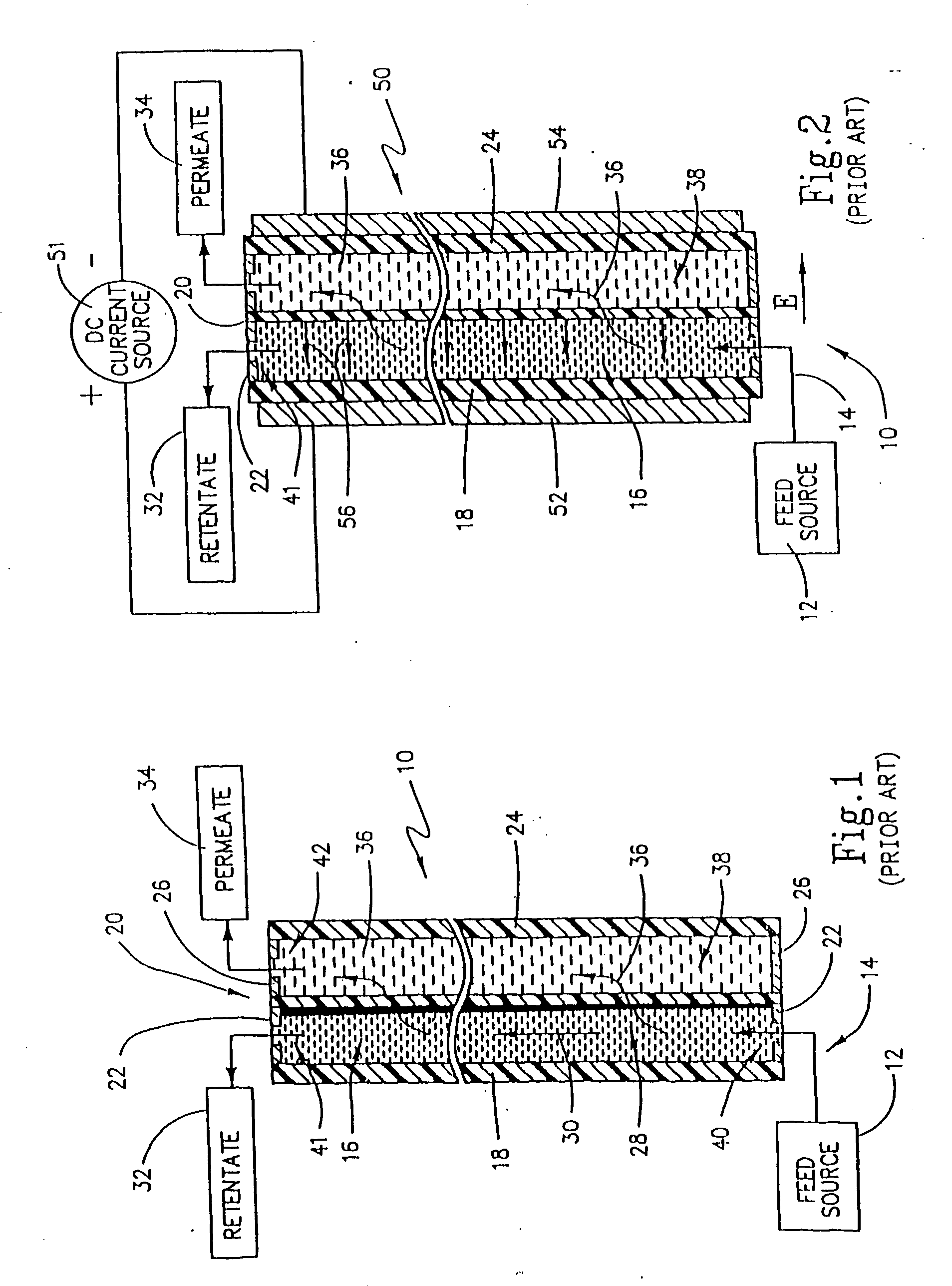
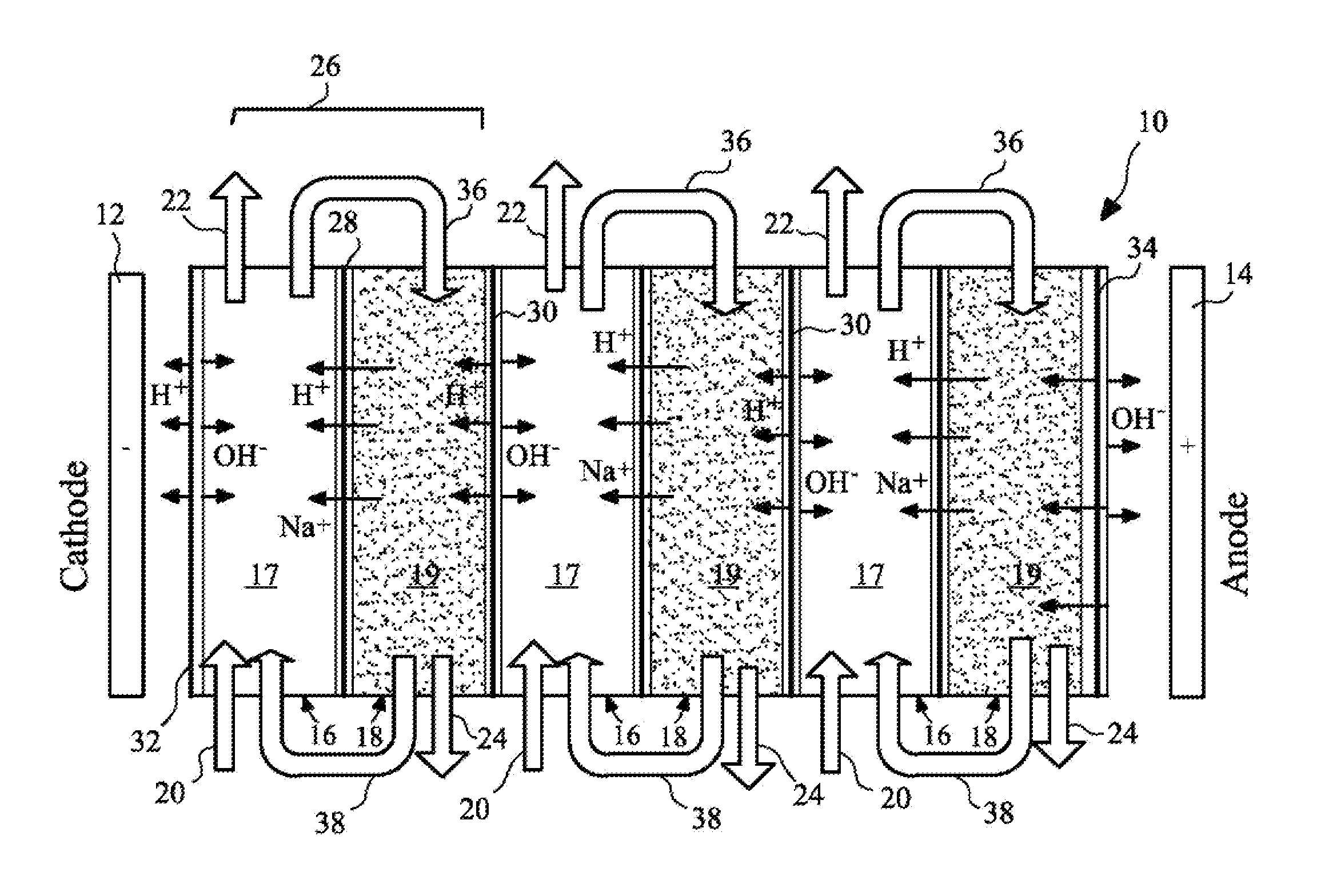
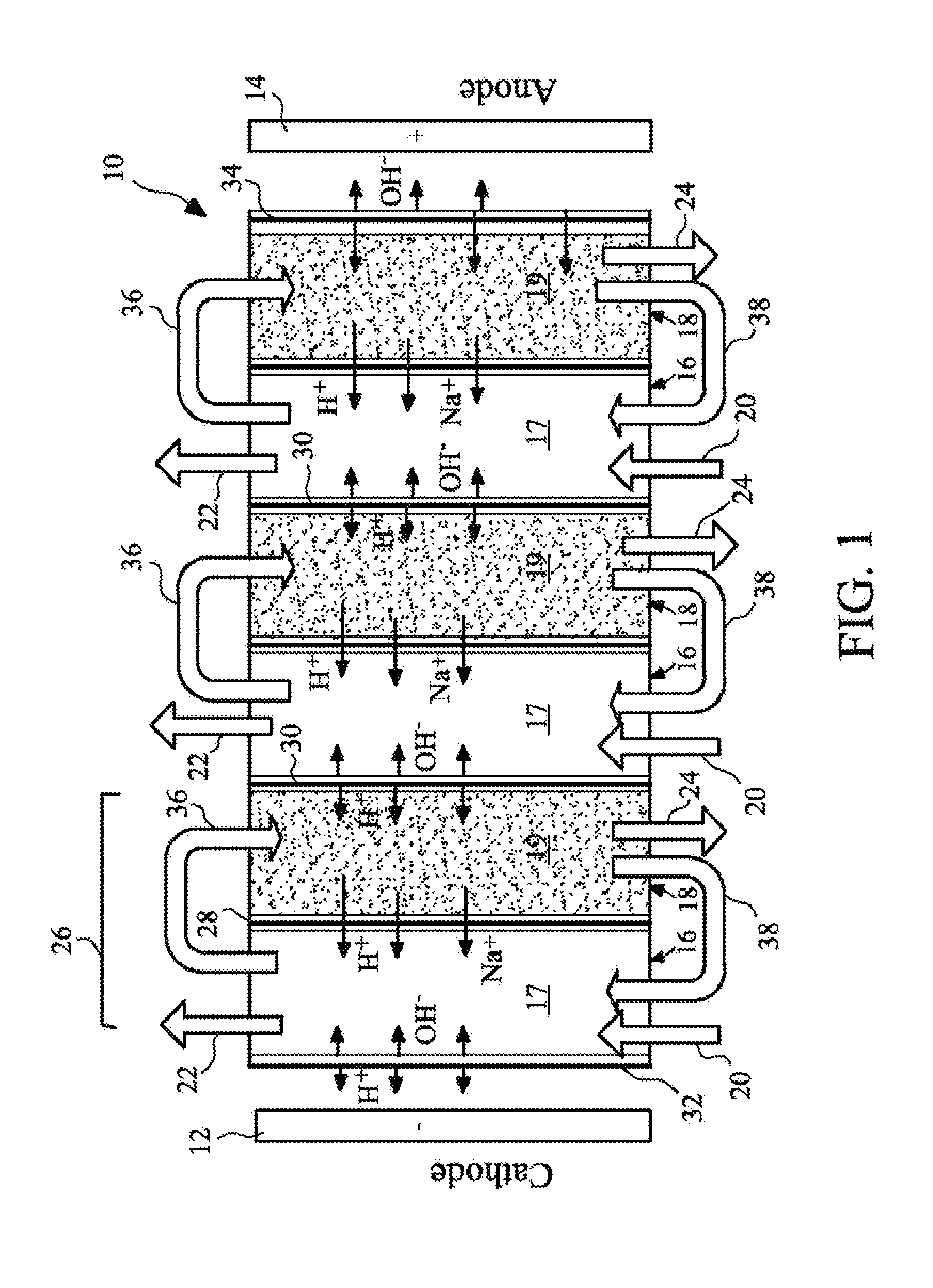
Method and apparatus for electrodeionization of water
InactiveUS6733646B2Reduce concentrationImprove efficiencyGeneral water supply conservationVolume/mass flow measurementActivated carbonWater flow
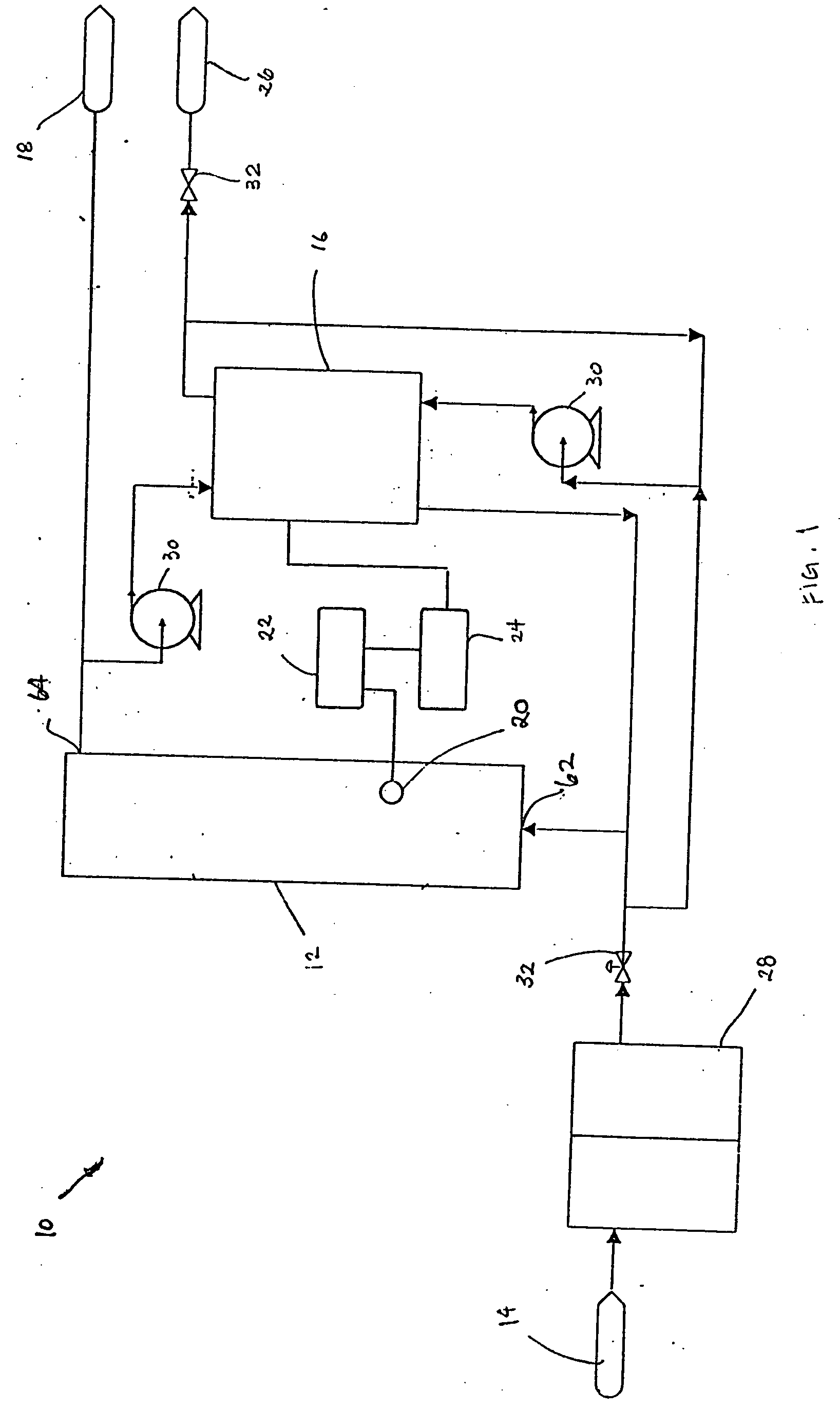
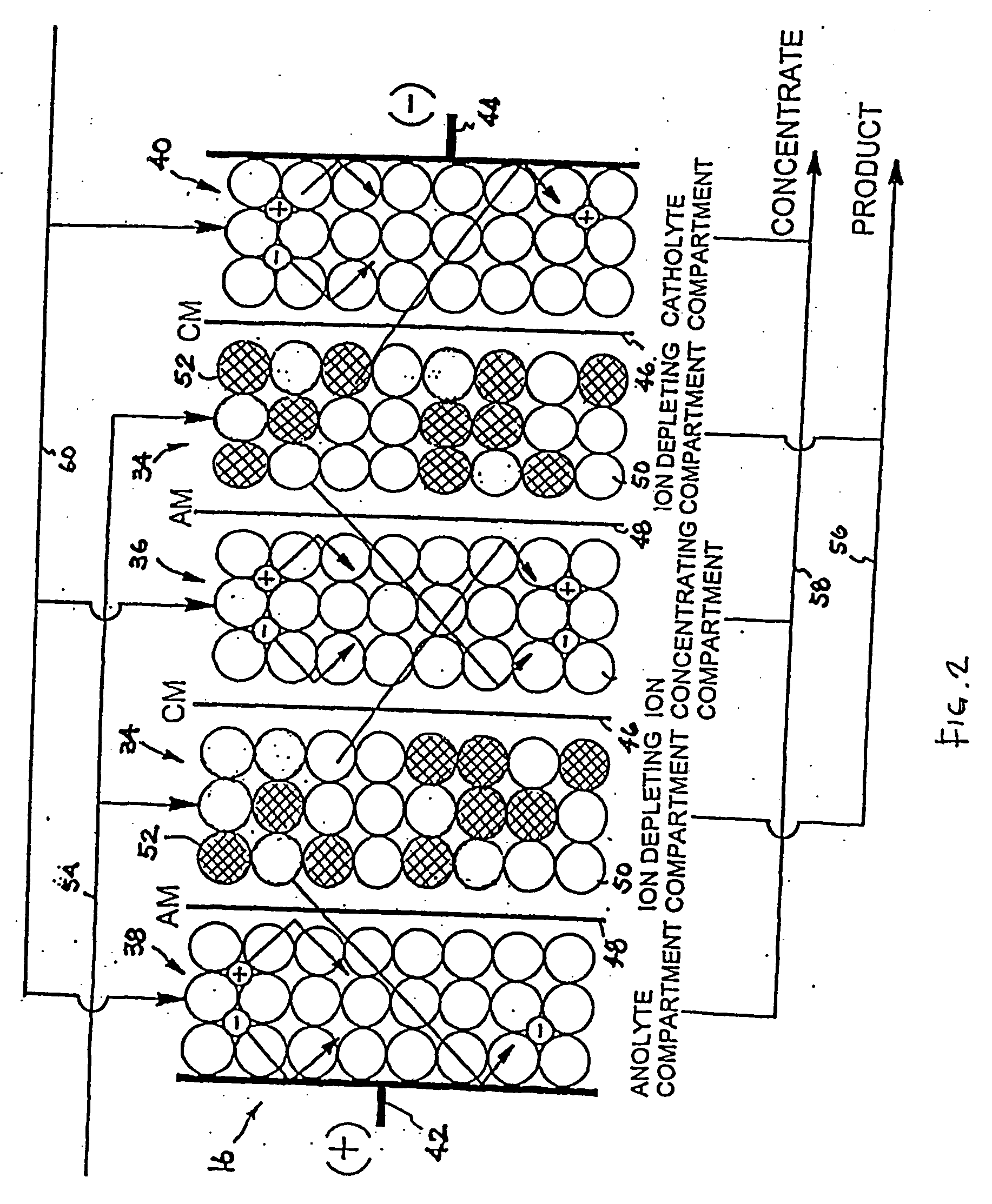
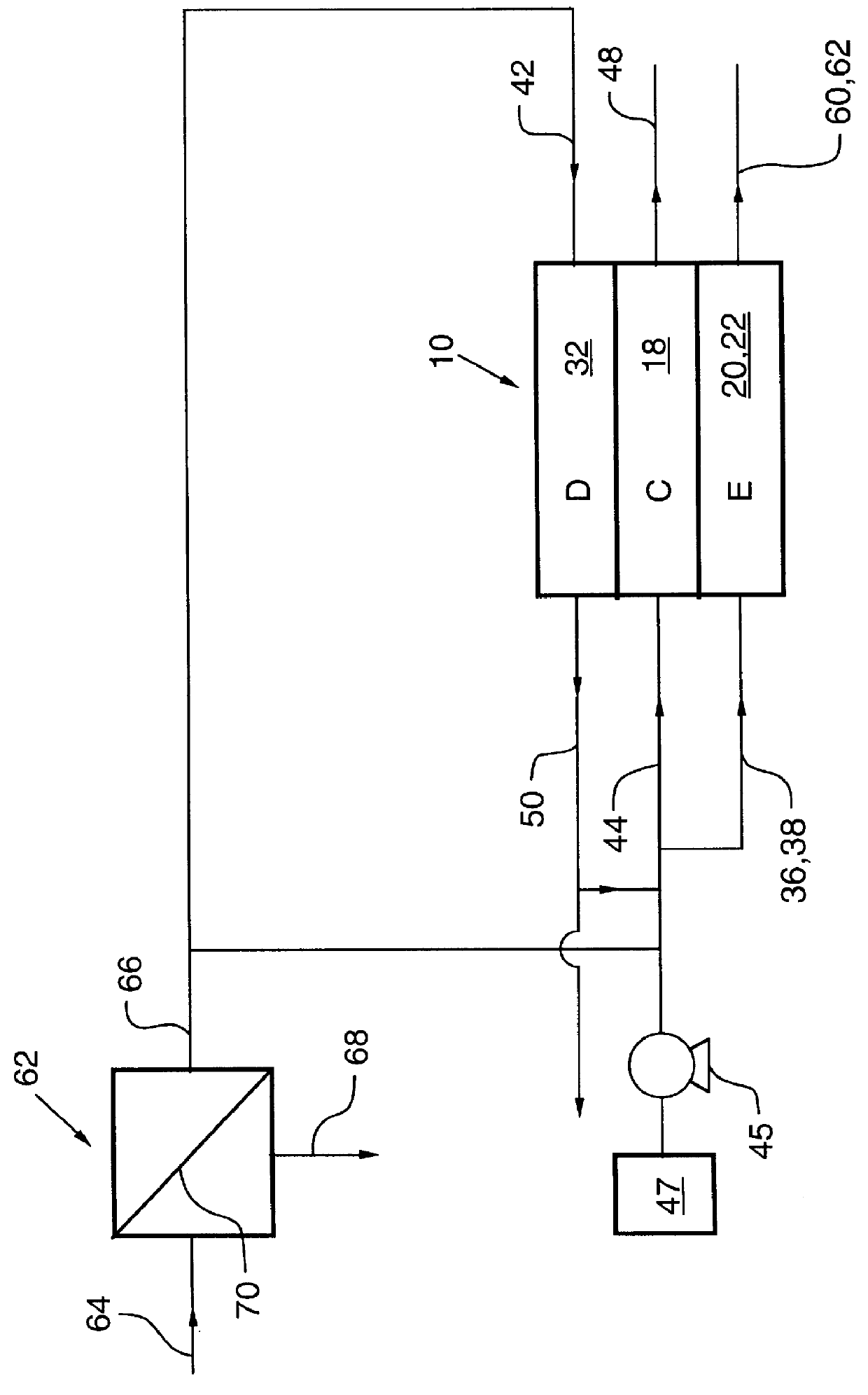
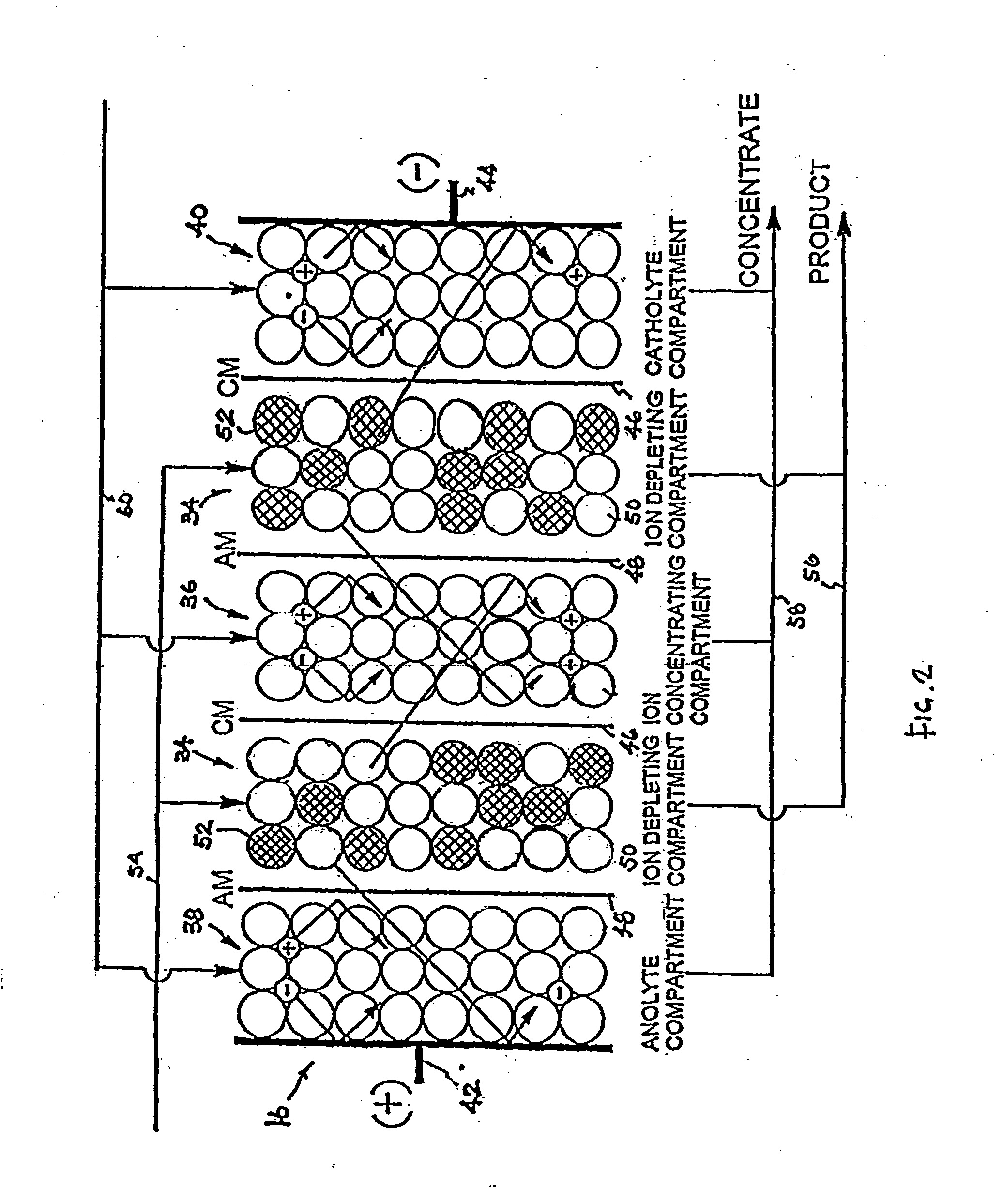
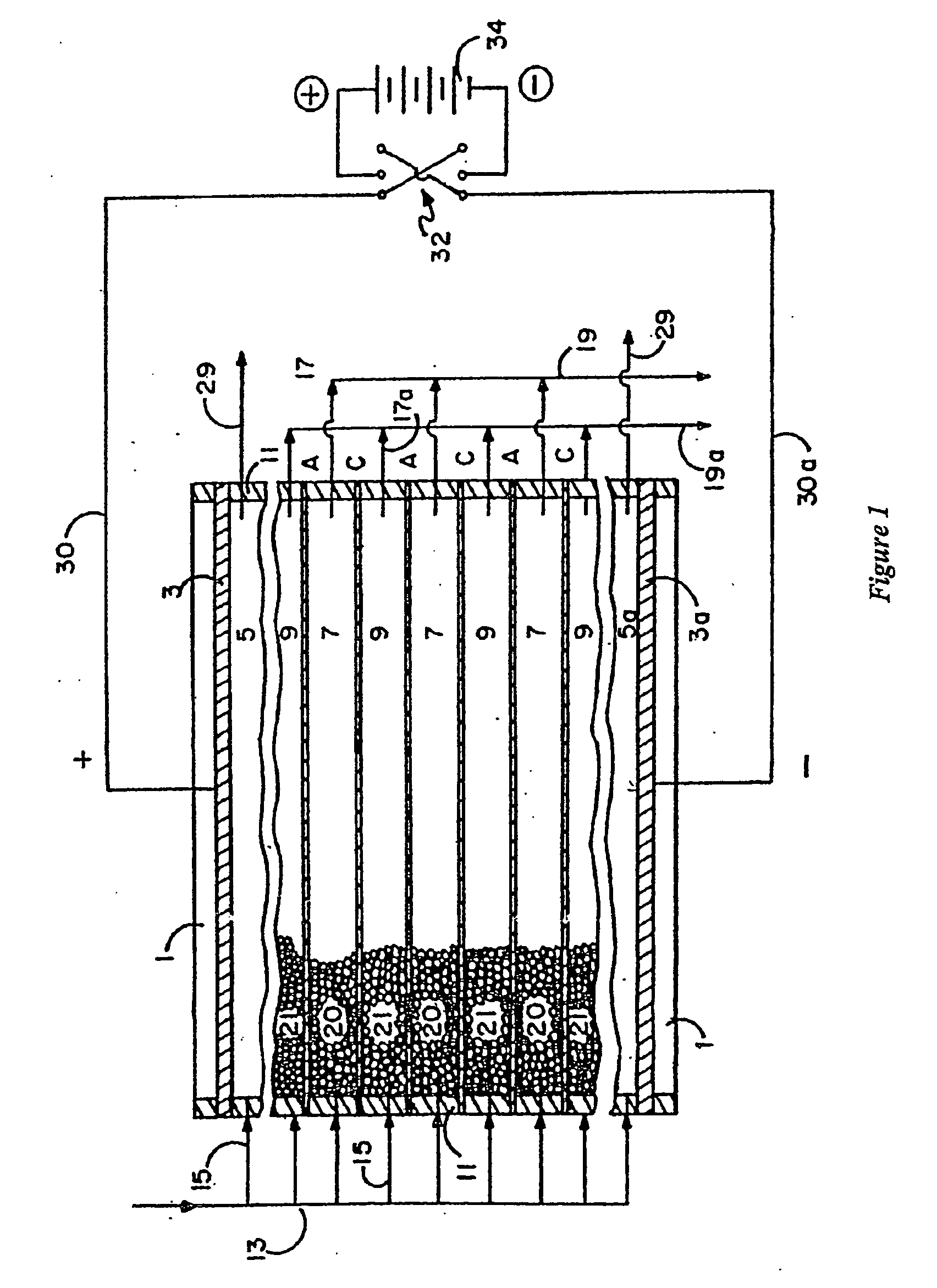
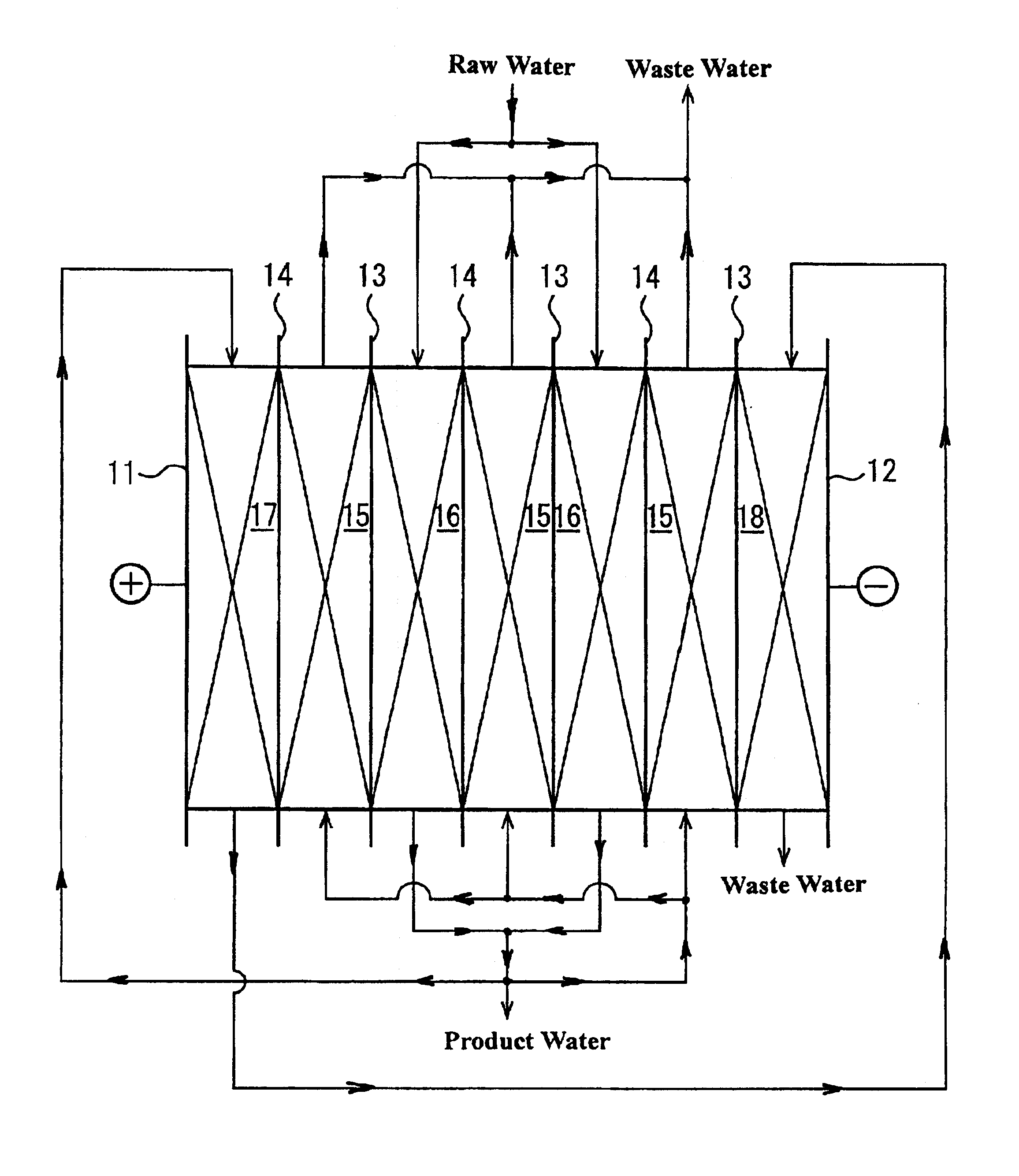
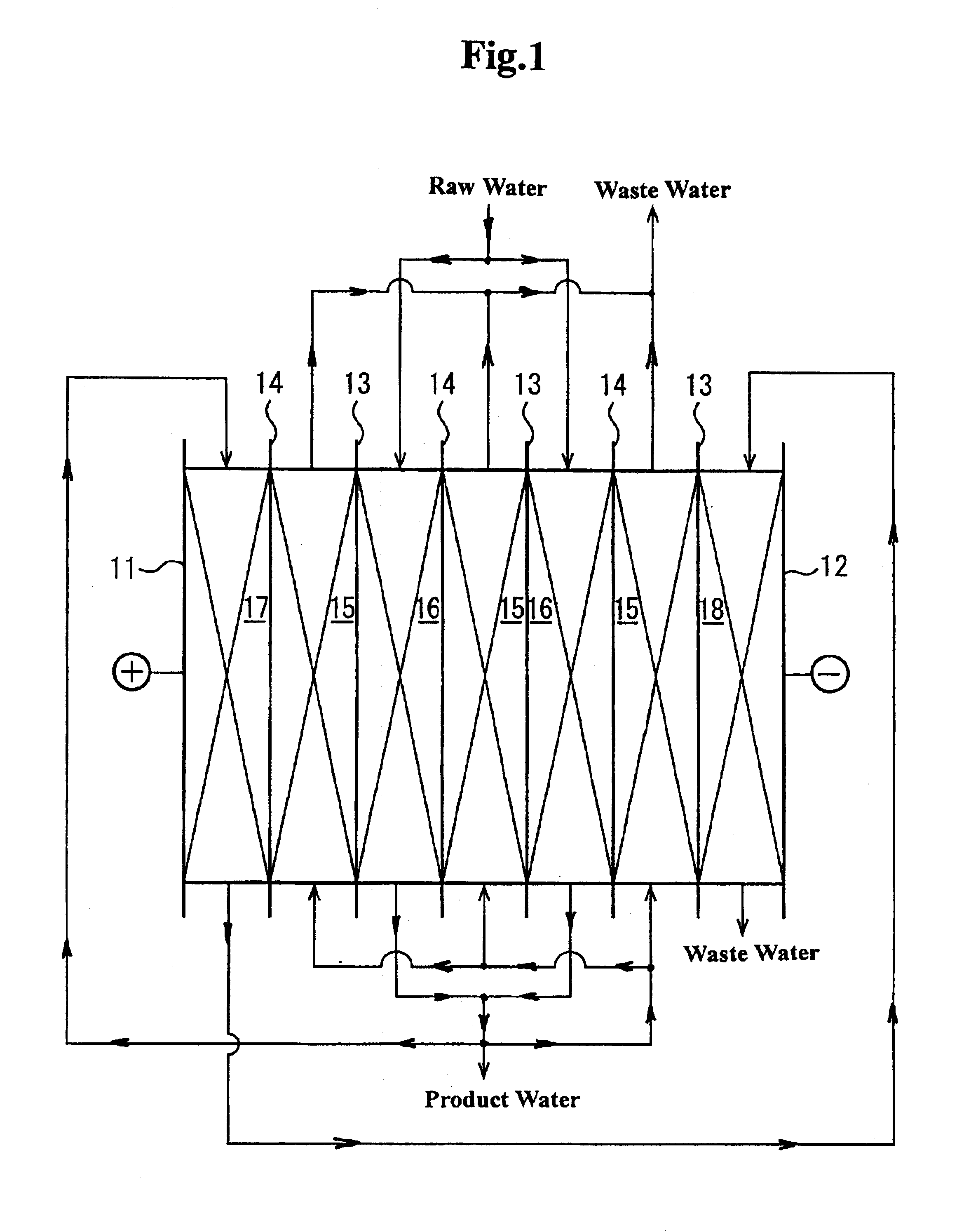
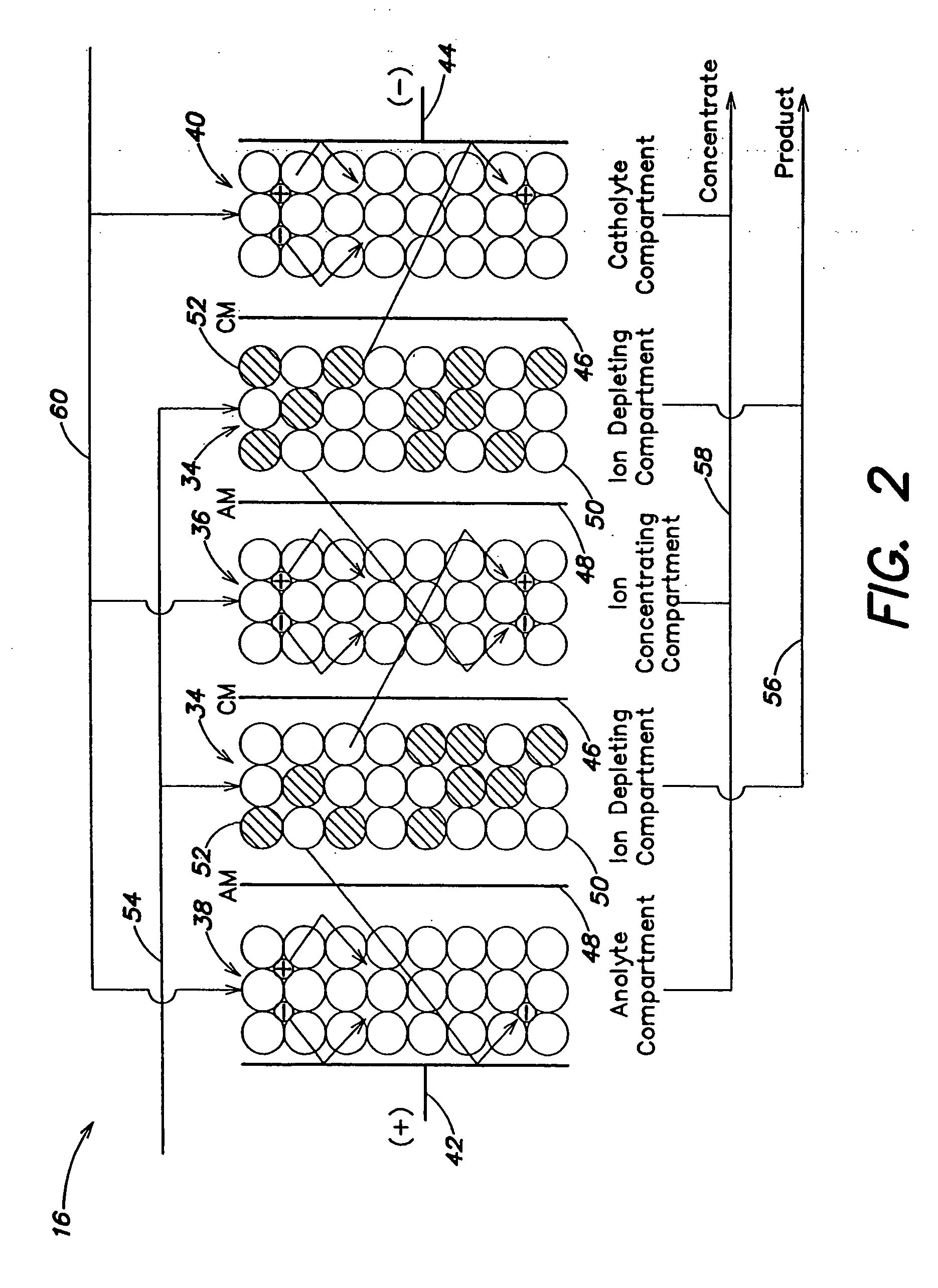
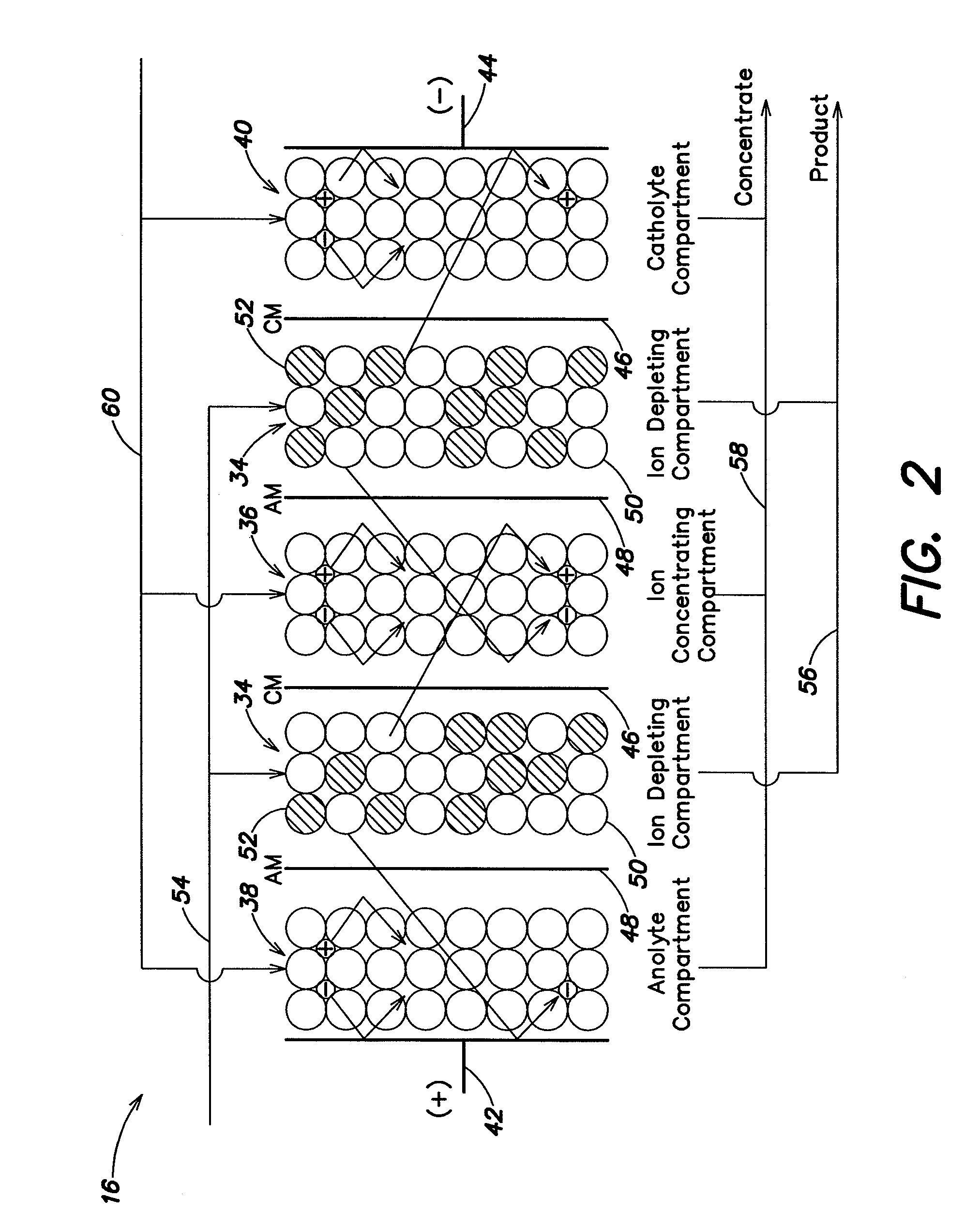
An electrodeionization apparatus has an anolyte compartment 17 having an anode 11, a catholyte compartment 18 having a cathode 12, concentrating compartments 15, and desalting compartments 16. The concentrating compartments 15 and the desalting compartments 16 are alternately formed between the anolyte compartment 17 and the catholyte compartment 18 by alternately arranging a plurality of anion-exchange membranes 13 and a plurality of cation-exchange membranes 14. The desalting compartments 16 are filled with ion-exchanger and the concentrating compartments 15 are filled with ion-exchanger, activated carbon, or electric conductor. Electrode water flows into the anolyte compartment 17 and the catholyte compartment 18. Concentrated water is introduced into the concentrating compartments 15. Raw water is fed into the desalting compartment 16 to produce the deionized water from the desalting compartment 16. Water containing silica or boron at a lower concentration than the raw water is introduced into the concentrating compartments 15 as the concentrated water in a direction from a side near an outlet for the deionized water toward a side near an inlet for the raw water of the desalting compartments 16. At least a part of concentrated water flowing out of the concentrating compartments 15 is discharged out of a circulatory system.
Owner:KURITA WATER INDUSTRIES LTD
Fractional deionization process
InactiveUS6896814B2Easy to disassembleEfficient removalElectrolysis componentsIon-exchanger regenerationElectricityIonic strength
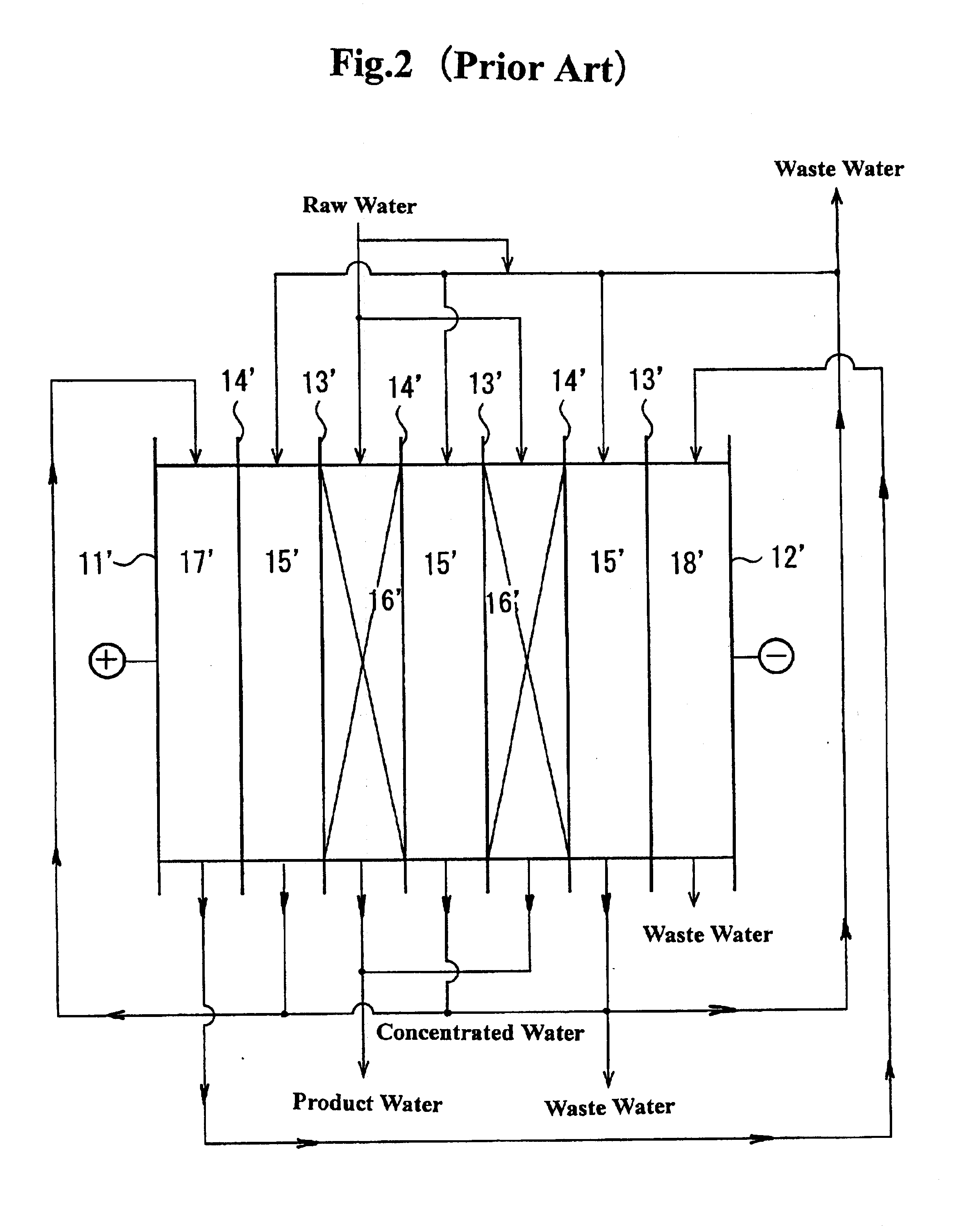
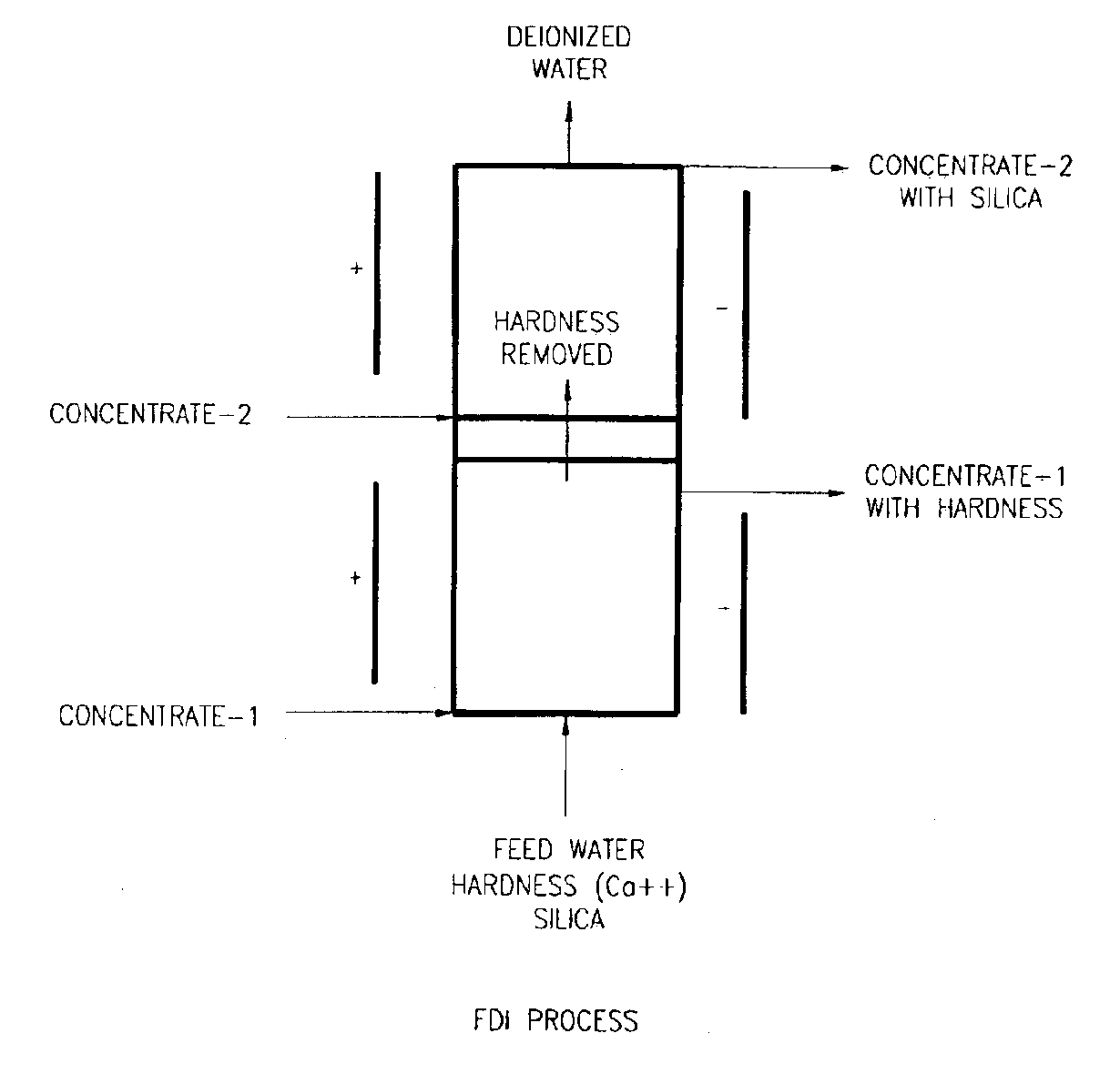
A liquid treatment process is described for sequential removal of ionic species of progressively decreasing ionic strength without precipitation or “scaling.” An aspect of the invention includes dual electrodeionization operations. The first electrodeionization operation is performed at a voltage calculated to remove strongly ionized species such as calcium and magnesium from the feed water without scaling. The product of the first electrodeionization operation is then subjected to a second electrodeionization operation. The second electrodeionization operation is performed at a voltage greater than the first electrodeionization operation, and is designed to remove more weakly ionized species such as silica and carbon dioxide, preventing scaling. More than two successive electrodeionization operations may be performed if desired. Multiple electrodeionization operations may occur in a single electrodeionization stack or in multiple electrodeionization stacks.
Owner:AQUATECH INT LLC
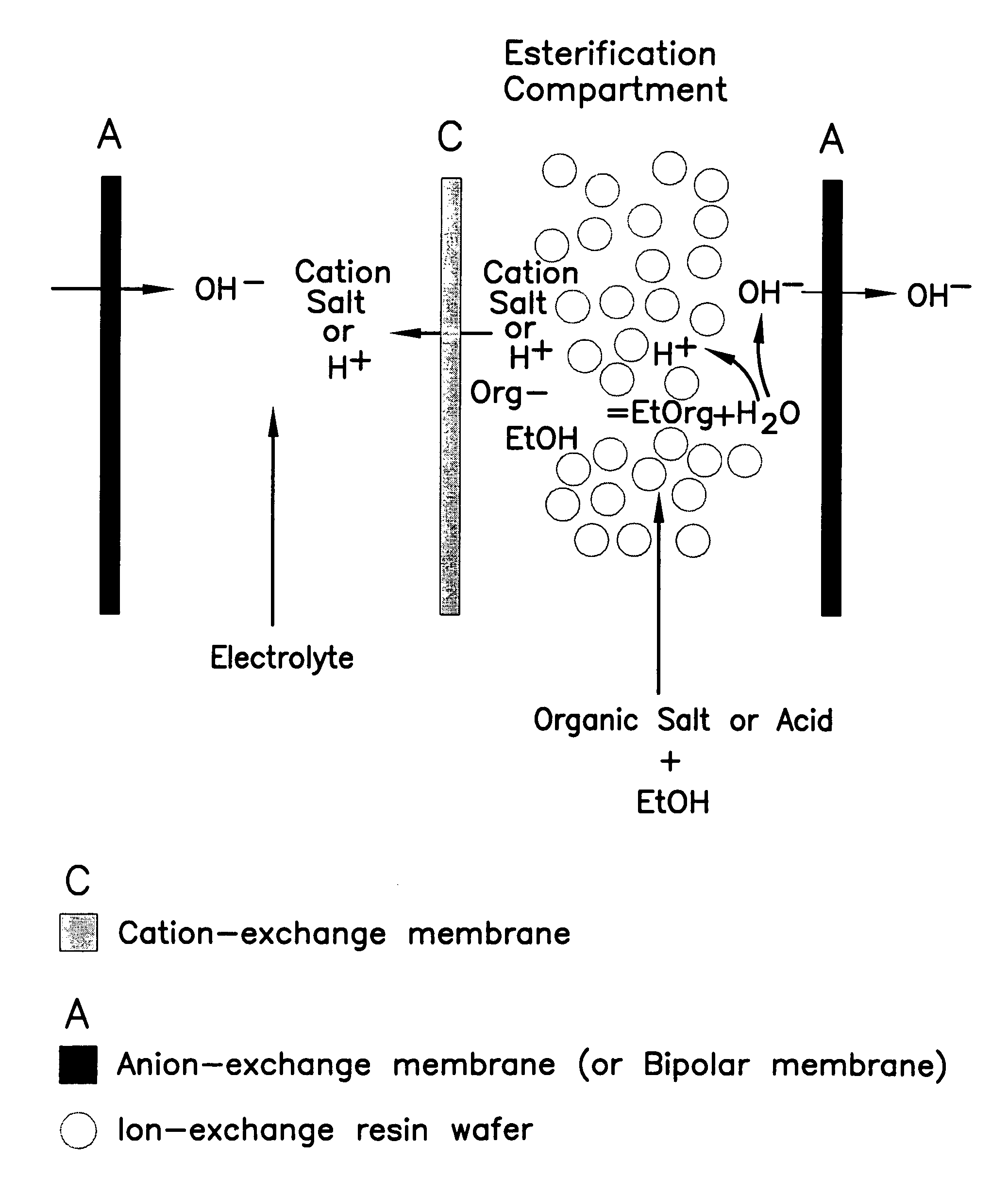
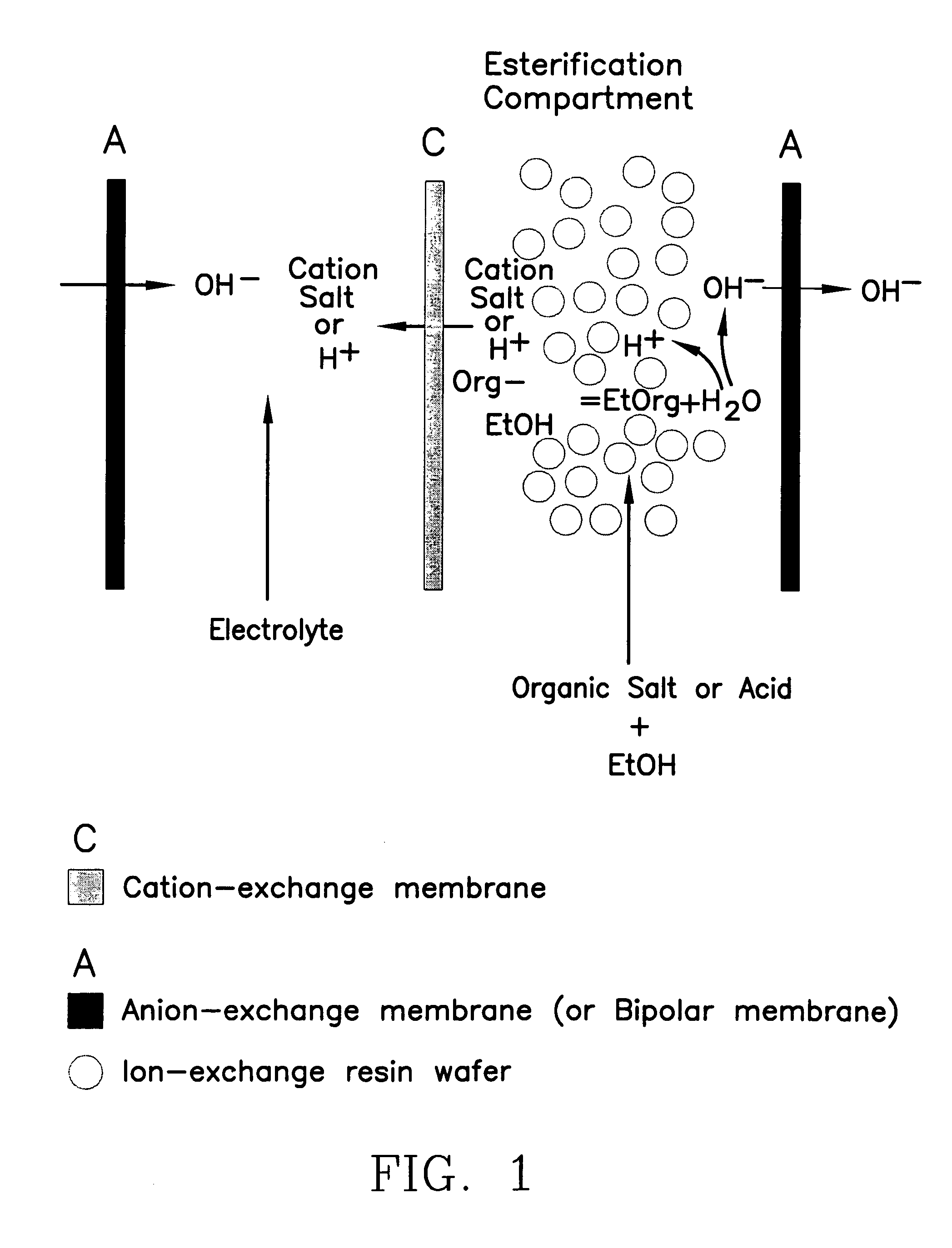
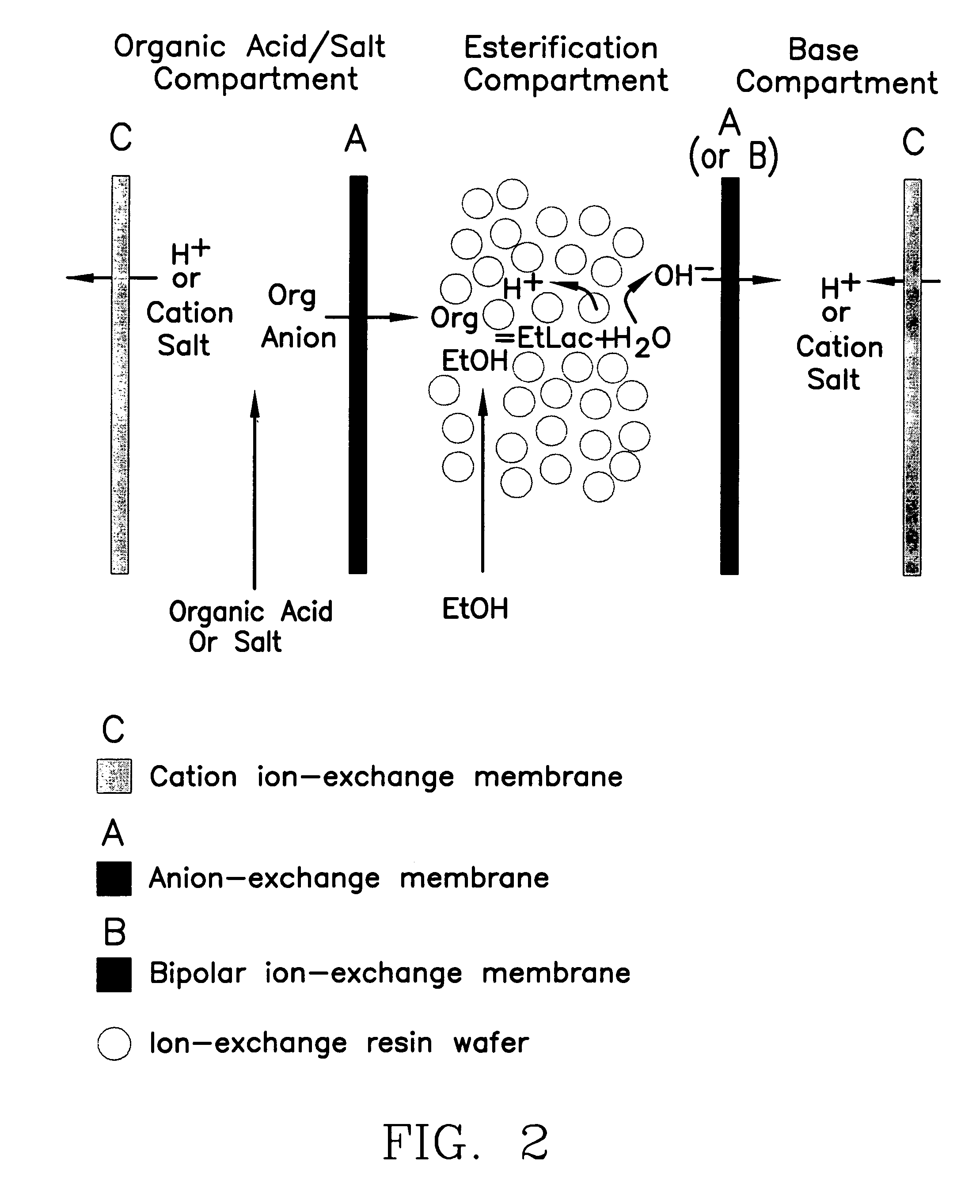
Single-stage separation and esterification of cation salt carboxylates using electrodeionization
ActiveUS7141154B2Promote migrationSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementIon-exchange resinBioreactor
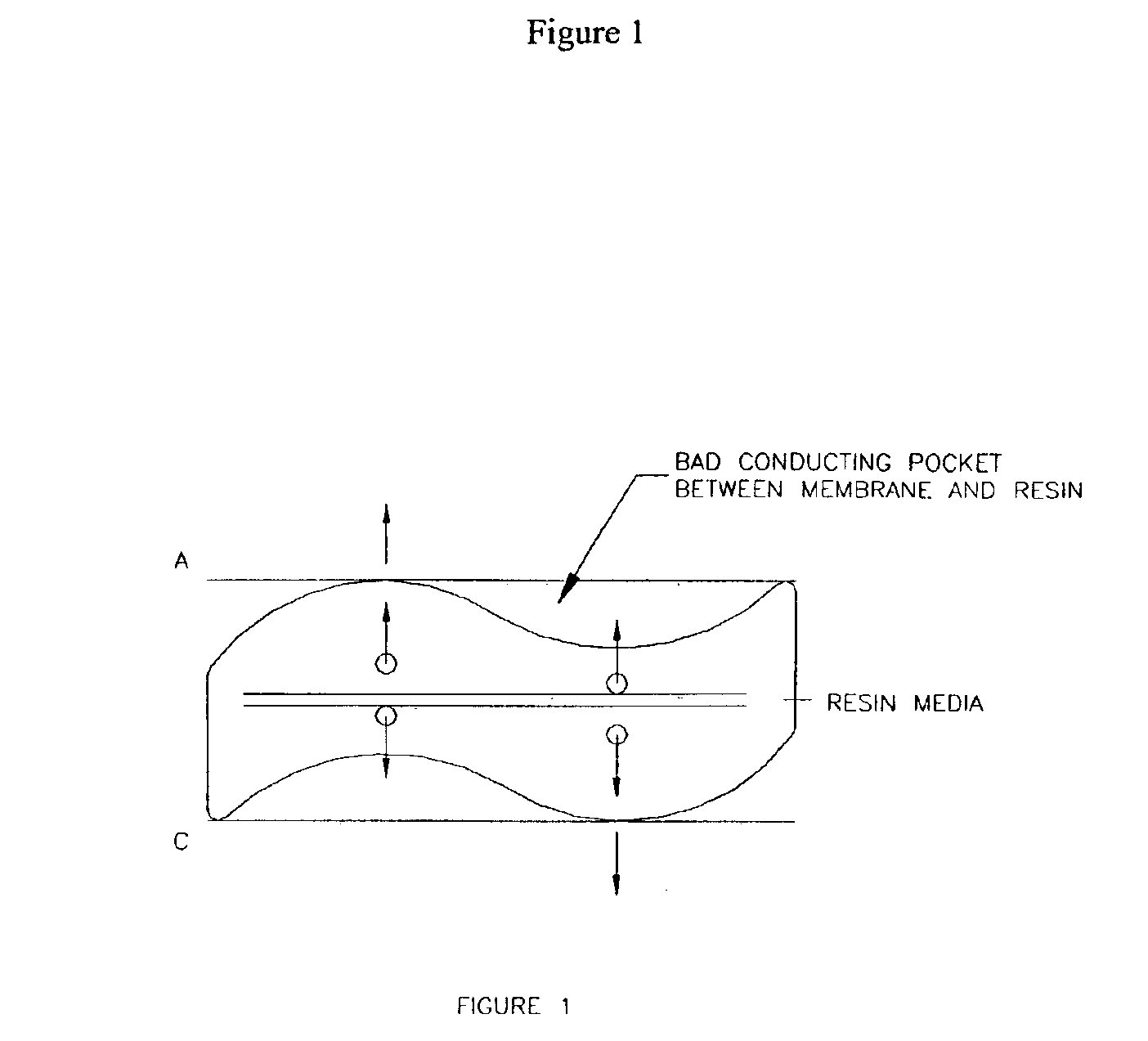
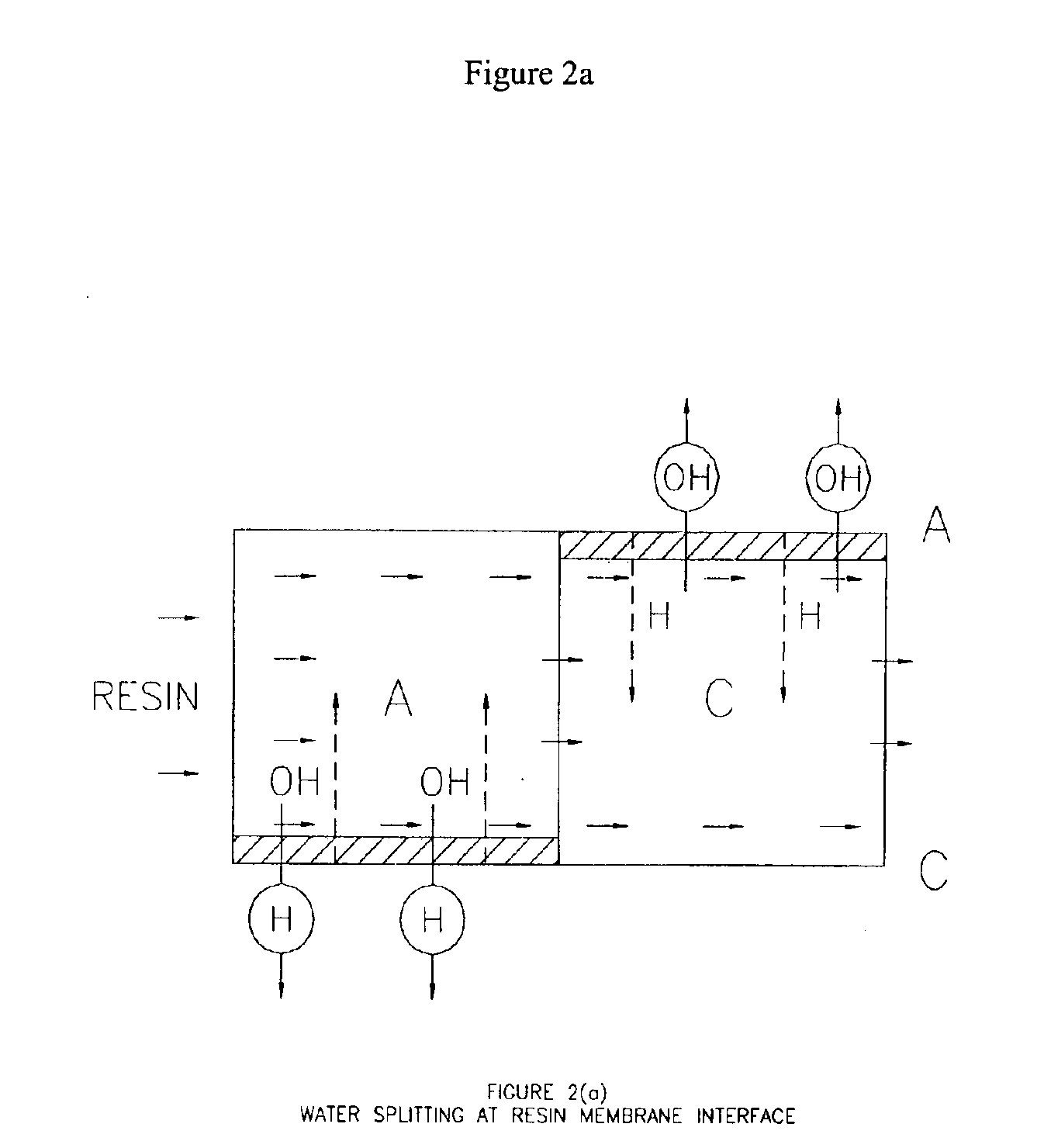
A method of and apparatus for continuously making an organic ester from a lower alcohol and an organic acid is disclosed. An organic acid or salt is introduced or produced in an electrode ionization (EDI) stack with a plurality of reaction chambers each formed from a porous solid ion exchange resin wafer interleaved between anion exchange membranes or an anion exchange membrane and a cation exchange membrane or an anion exchange membrane and a bipolar exchange membranes. At least some reaction chambers are esterification chambers and / or bioreactor chambers and / or chambers containing an organic acid or salt. A lower alcohol in the esterification chamber reacts with an anion to form an organic ester and water with at least some of the water splitting with the ions leaving the chamber to drive the reaction.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
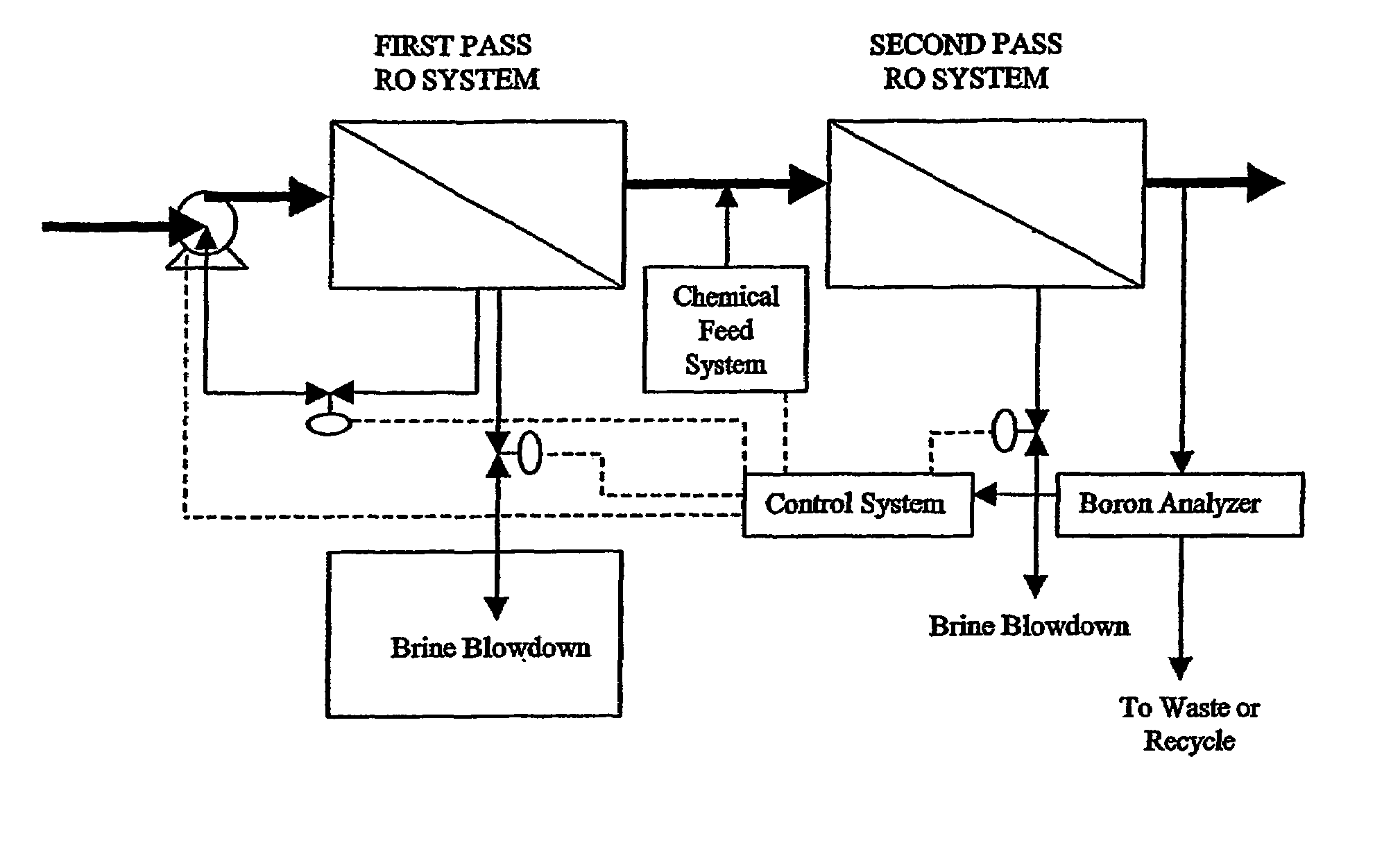
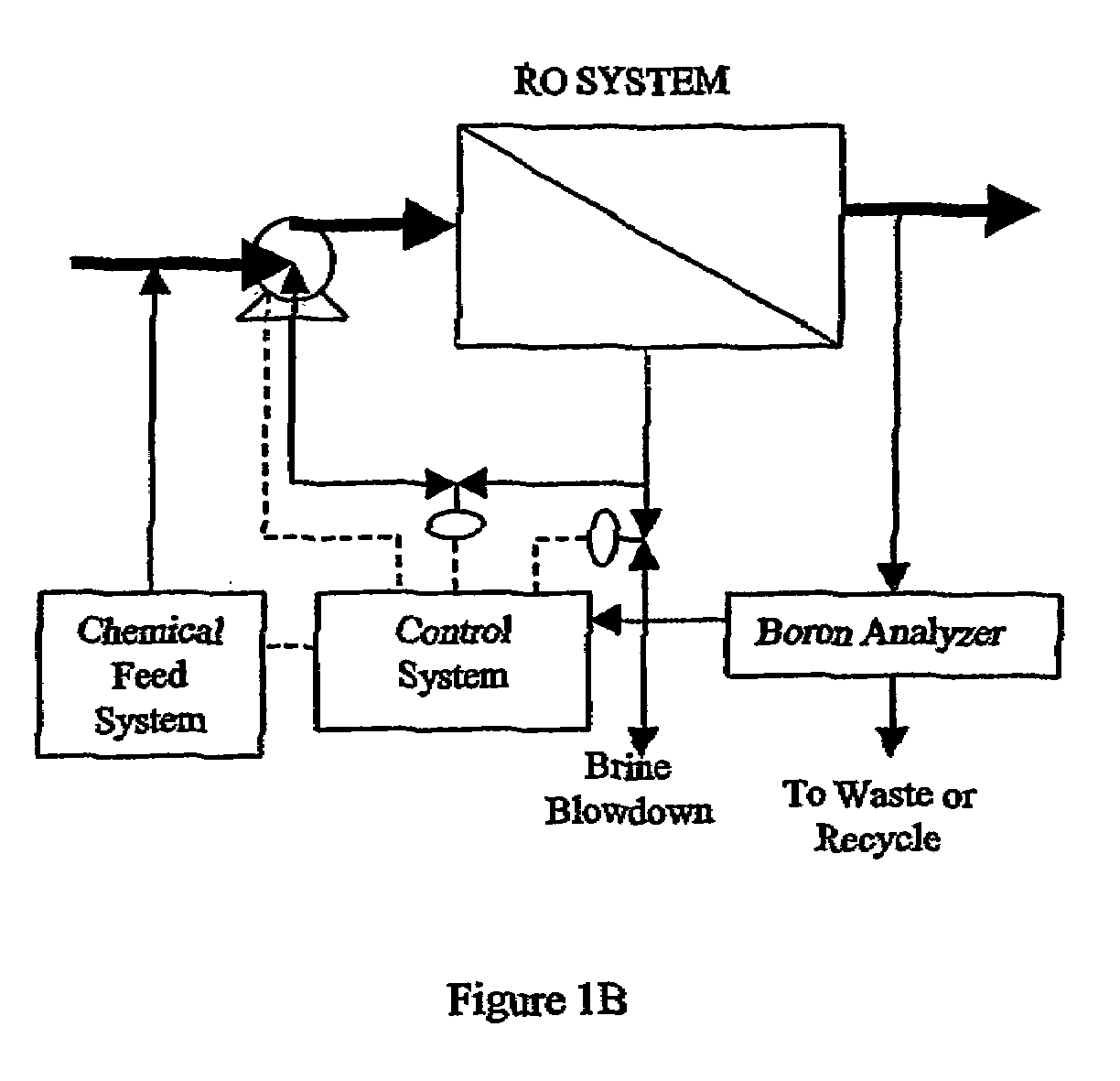
Control of water treatment system with low level boron detection
ActiveUS7264737B2Improve electricity efficiencyOptimize overall demineralizationSolvent extractionScale removal and water softeningWater treatment systemEngineering
A water treatment system and method including a membrane-based boron removal unit includes a boron analyzer for detecting the concentration of boron in a treatment stream. The boron removal unit can be a reverse osmosis (RO) or electrodeionization (EDI) treatment unit. A controller responds to the detected boron concentration to control an operation of the RO or EDI units. In an EDI system, the controller may adjust current or voltage supplied to match current to changes in ionic load and maintain a portion of the dilute cell in a substantially regenerated state. In an RO system, the controller may control the high pressure side flow rate, the brine blowdown rate, the product water permeation rate, pH, or feed rate of chemicals in response to the detected boron concentration value.
Owner:IONICS INC
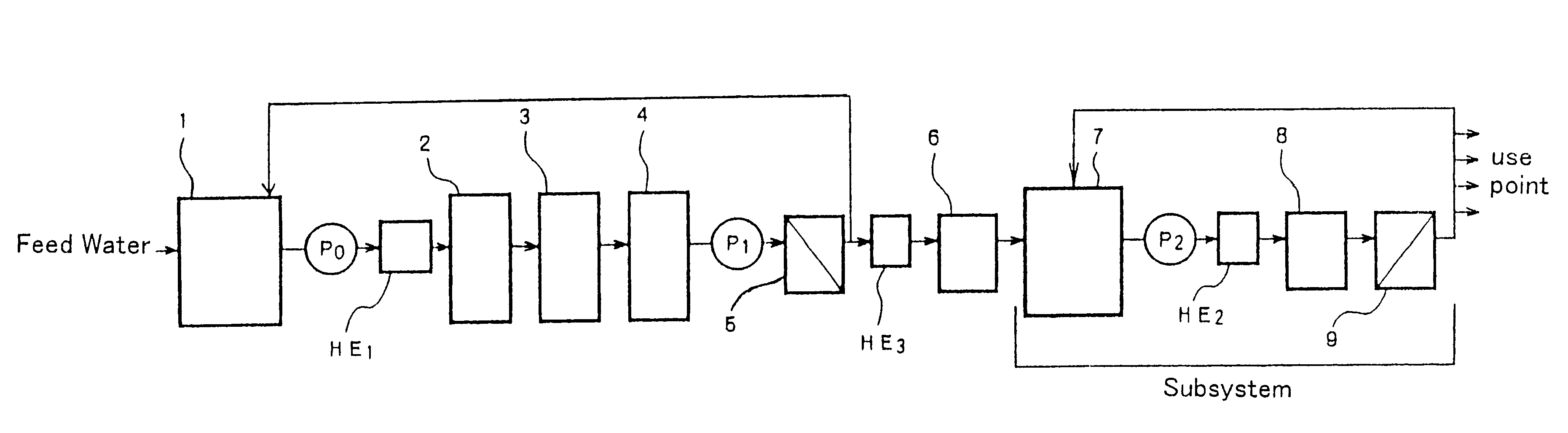
Water purification system and method using reverse osmosis reject stream in an electrodeionization unit
InactiveUS20050247631A1Efficient energy consumptionSimple designFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsIsotope separationTreatment unitElectrodeionization
Water purification systems include a reverse osmosis unit, a treatment unit, and an electrodeionization unit. A reverse osmosis reject stream from the reverse osmosis unit is treated in the treatment unit and provided to concentrating compartments of the electrodeionization unit.
Owner:ECOLOCHEM
Method and apparatus for desalination
ActiveUS20100089756A1Reduce concentrationGeneral water supply conservationSeawater treatmentDesalinationFresh water
A method and apparatus for purifying water are provided. A feed water such as seawater can be fed to a filter such as a microporous or nanofiltration membrane to produce a permeate that can, in turn, be fed to an electrodeionization system to produce fresh water.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
Water treatment system and method
InactiveUS20060157422A1Sludge treatmentLiquid separation by electricityWater treatment systemWater source
A water treatment system provides treated or softened water to a point of use by removing a portion of any hardness-causing species contained in water from a point of entry coming from a water source, such as municipal water, well water, brackish water and water containing foulants. The water treatment system typically treats the water containing at least some undesirable species before delivering the treated water to a point of use. The water treatment system has a reservoir system in line with an electrochemical device such as an electrodeionization device. The water treatment system has a sensor or a set of sensors for measuring at least one property of the water or an operating condition of the treatment system. The water treatment system also has a controller for adjusting or regulating at least one operating parameter of the treatment system or a component of the water treatment system to optimize the operation and performance of the system or components of the system to supply water tailored to quality requirements.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
Low energy system and method of desalinating seawater
InactiveUS20110180477A1Reduce energy consumptionGeneral water supply conservationSeawater treatmentIon exchangeEnergy expenditure
A low energy system and process for seawater desalination wherein the system has at least an electrodialysis apparatus that produces partially desalinated water and a brine by-product, an ion exchange softener, and at least one electrodeionization apparatus. The softener treats the partially desalinated water stream to remove or reduce the amount of scaling material in order to maintain deionization apparatus efficiency and reduce energy consumption. The softener has the capability of removing a higher ratio of calcium ions to magnesium ions than is in the partially desalinated stream, thereby reducing softener size and energy use. The deionization apparatus produces product water of the desired properties. The brine stream may be used to regenerate the softener.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
Method of ion chromatography wherein a specialized electrodeionization apparatus is used
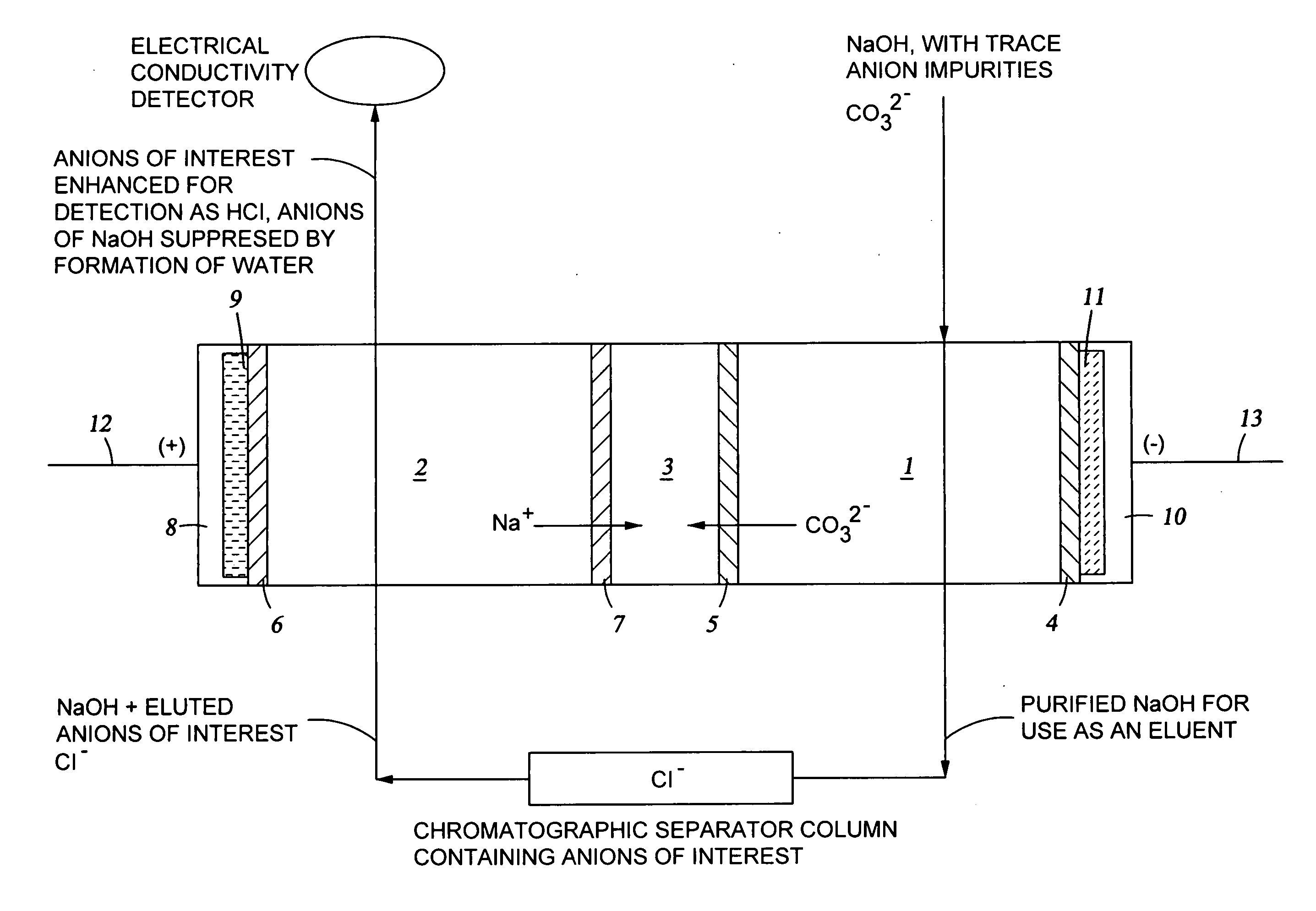
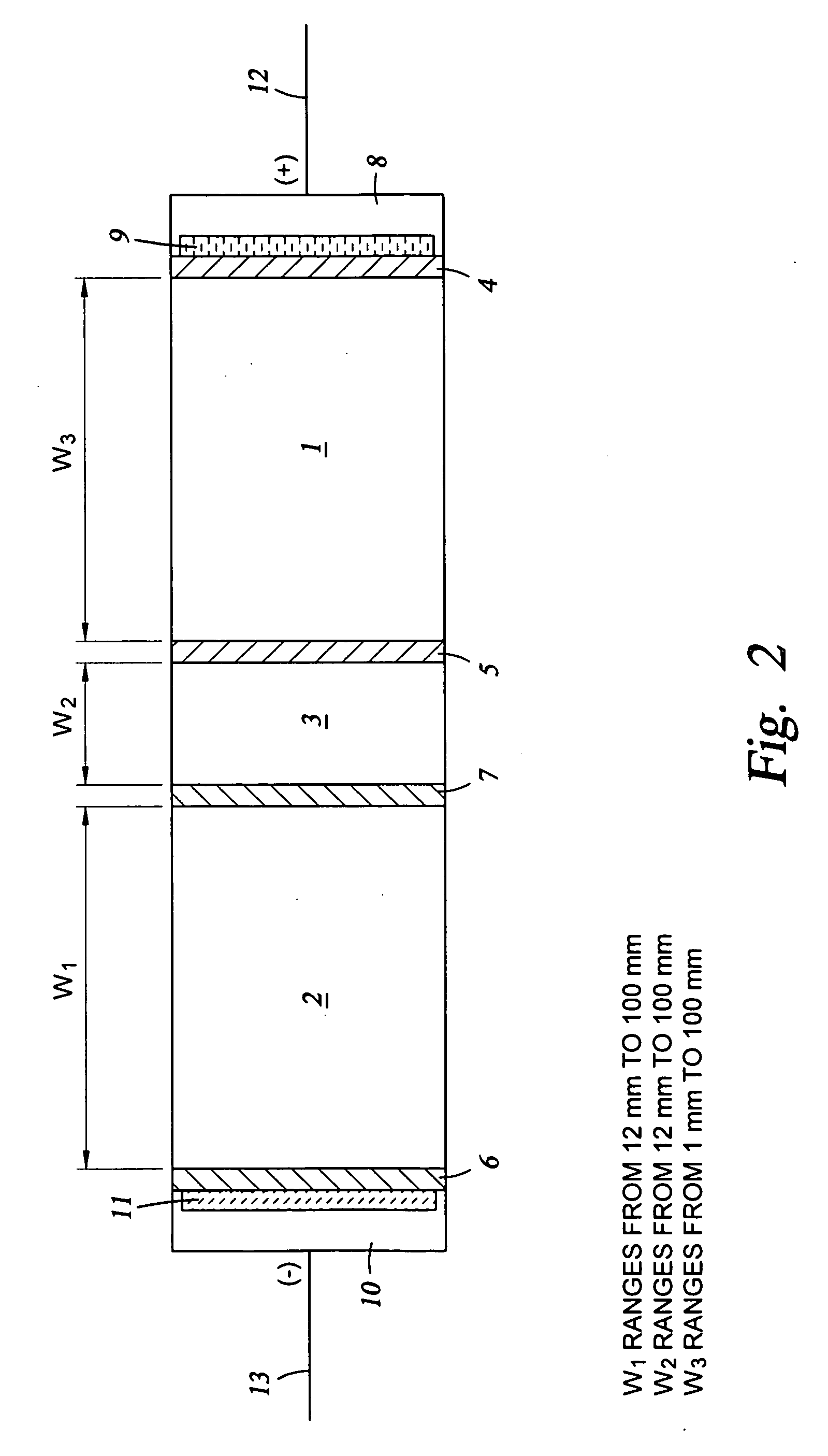
The present invention pertains to a method of ion chromatography wherein a specialized electrodeionization (EDI) apparatus is used for (1) the preparation of a pure acid or pure base for use as an eluent in a chromatographic separation column and / or (2) for ion suppression (or neutralization) of the acid or base after it has been used to elute ions from a chromatographic separation column. Methods for trace ion removal, acid and base neutralization, and ion suppression using a specialized EDI apparatus are also described. The methods described herein allow for the ion suppression of samples containing chloride, nitrate, and other electrochemically active anions, without causing damage to the suppressor.
Owner:TROVION PTE
Electrophoretic cross-flow filtration and electrodeionization method for treating effluent waste and apparatus for use therewith
InactiveUS20060254919A1Efficient purificationEfficient methodSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementSuspended particlesElectrophoresis
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for purifying effluent wastewater utilizing electrophoretic cross-flow filtration and electrode ionization. The method first comprises filtering the water in a cross-flow direction with a filter membrane in the presence of an electric field that is operative to drive suspended particles away from a surface of the filter membrane. The permeate containing dissolved solids is next passed through a mixture of at least one cation-exchange resin and at least one anion-exchange resin disposed between a cation-selective membrane and an anion-selective membrane in the presence of an electric field. The electric field drives cations in the permeate through the cation-selective membrane, and drives anions in the permeate through the anion-selective membrane, thereby to form deionized water. The apparatus includes cell modules adapted to be used in plate-and-frame or radial flow configurations.
Owner:EDWARDS VACUUM INC
Water treatment system and method
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
Water purification system and method using reverse osmosis reject stream in an electrodeionization unit
InactiveUS7470366B2Energy efficiencySimple designFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsIsotope separationReverse osmosis plantTreatment unit
Water purification systems include a reverse osmosis unit, a treatment unit, and an electrodeionization unit. A reverse osmosis reject stream from the reverse osmosis unit is treated in the treatment unit and provided to concentrating compartments of the electrodeionization unit.
Owner:ECOLOCHEM
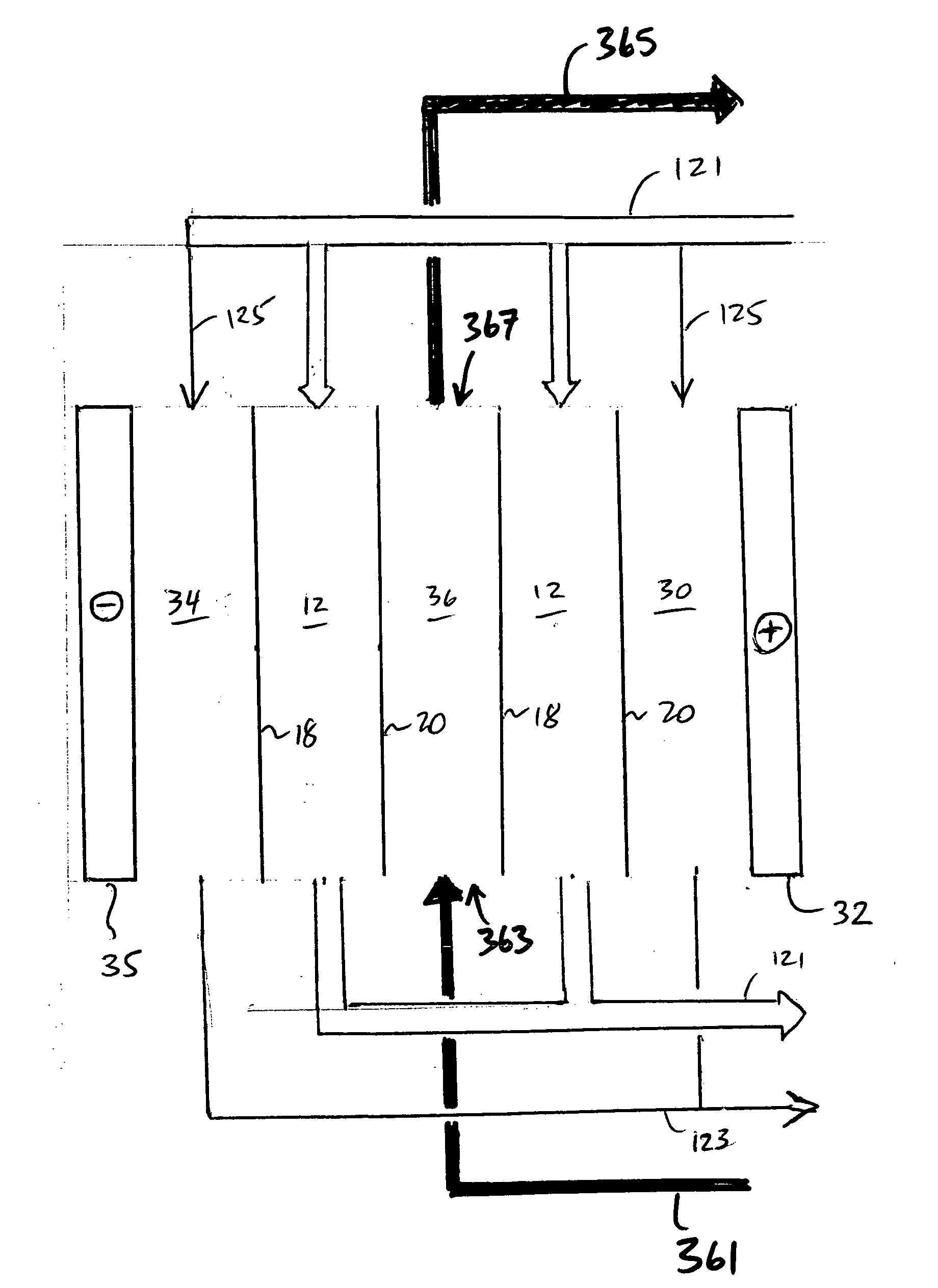
Carbon dioxide capture using resin-wafer electrodeionization
ActiveUS20100300894A1High methane contentReducing greenhouse gas emissionLiquid separation by electricityCarbon compoundsElectricityIon-exchange membranes
The present invention provides a resin-wafer electrodeionization (RW-EDI) apparatus including cathode and anode electrodes separated by a plurality of porous solid ion exchange resin wafers, which when in use are filled with an aqueous fluid. The apparatus includes one or more wafers comprising a basic ion exchange medium, and preferably includes one or more wafers comprising an acidic ion exchange medium. The wafers are separated from one another by ion exchange membranes. The fluid within the acidic and / or basic ion exchange wafers preferably includes, or is in contact with, a carbonic anhydrase (CA) enzyme to facilitate conversion of bicarbonate ion to carbon dioxide within the acidic medium. A pH suitable for exchange of CO2 is electrochemically maintained within the basic and acidic ion exchange wafers by applying an electric potential across the cathode and anode.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
EDI and related stacks and method and apparatus for preparing such
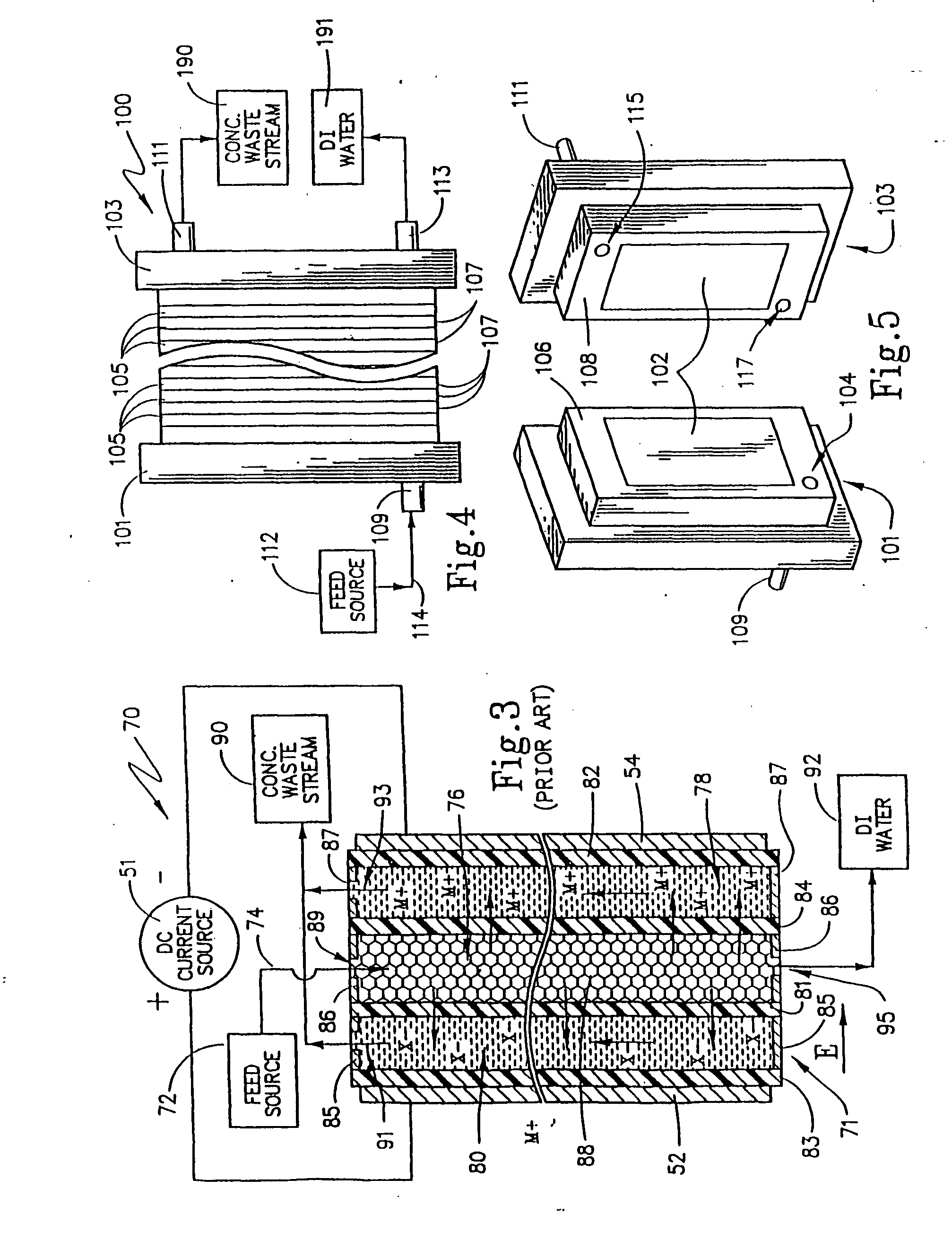
InactiveUS7094325B2Easy to controlEasy constructionSludge treatmentIon-exchanger regenerationParticulatesElectricity
Apparatus and method are disclosed for introducing ion exchange or other particulates into compartments of an already-assembled electrodeionization or comparable stack by modulating a flow of slurry into the compartments with slugs of gas such as air. The air propels liquid through the cells, scavenging ponded liquid so that the particulates (which are retained, e.g., by a strainer or obstruction, in compartment of the apparatus) are deposited as well-packed beds to fill the compartments. Pressurized air filling protocols may deliver discrete slugs of slurry between bursts of air, and the direction of filling may be periodically reversed to diminish particle bed non-homogeneities or settling gradients that arise during transport. The slugs of air may be applied in the direction of slurry flow, in the reverse direction, or both. Different slurries may be transported in a sequence to form layered and packed beds of enhanced utility. An apparatus of the invention has filled compartments of enhanced packing, and is ported or has its passages arranged so that ion exchange material may be filled, or may be replenished by a fluidized flow according to a method of this invention.
Owner:UBS AG STAMFORD BRANCH AS COLLATERAL AGENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com