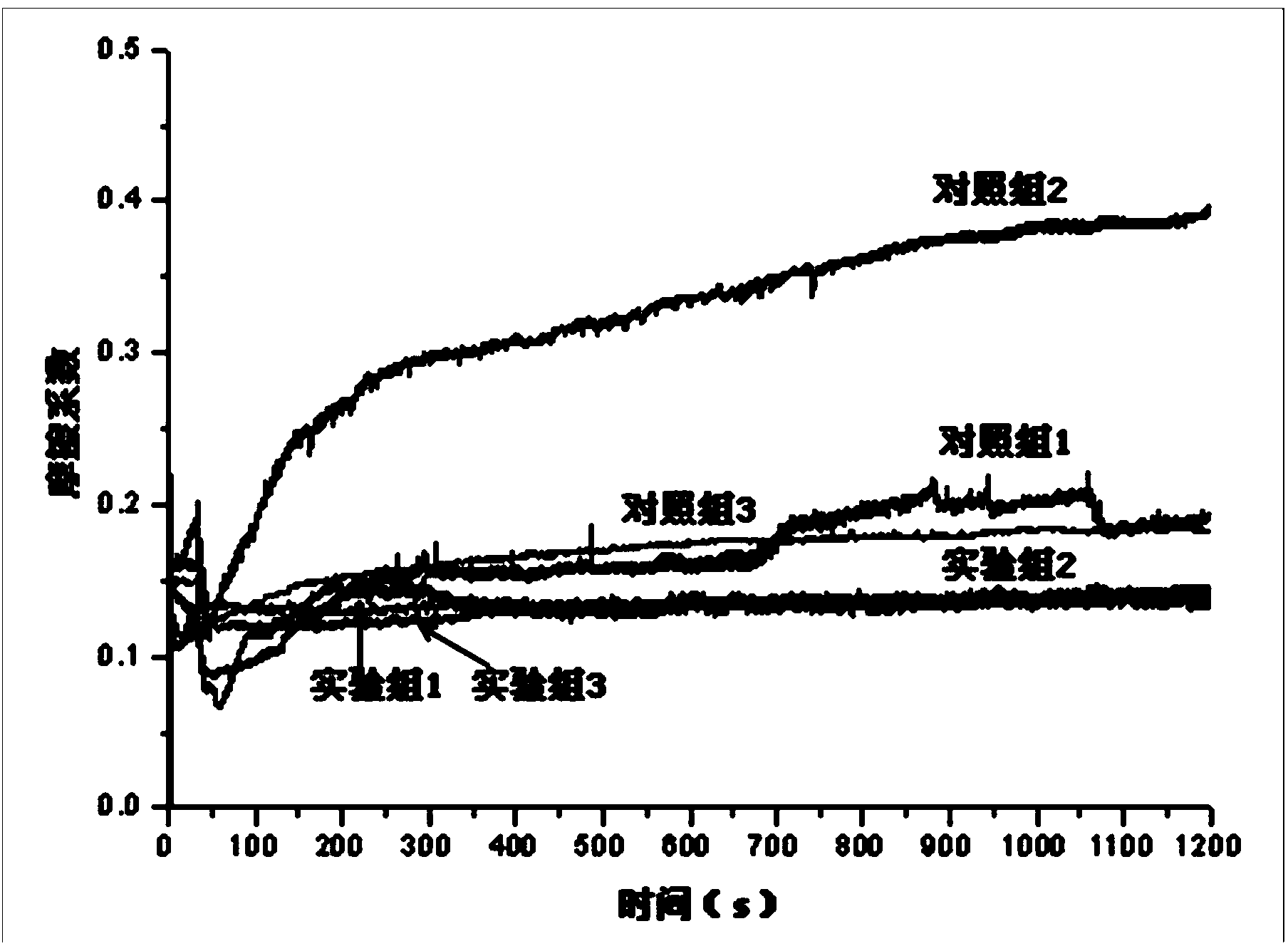
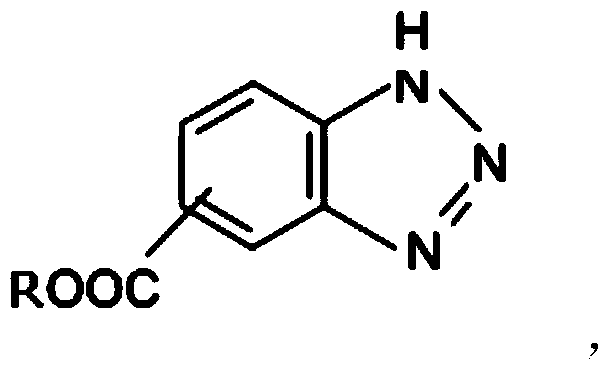
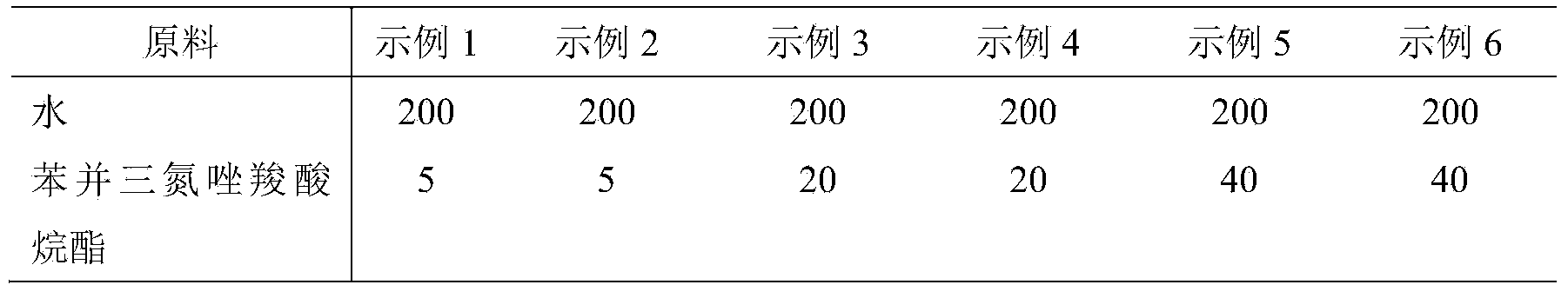
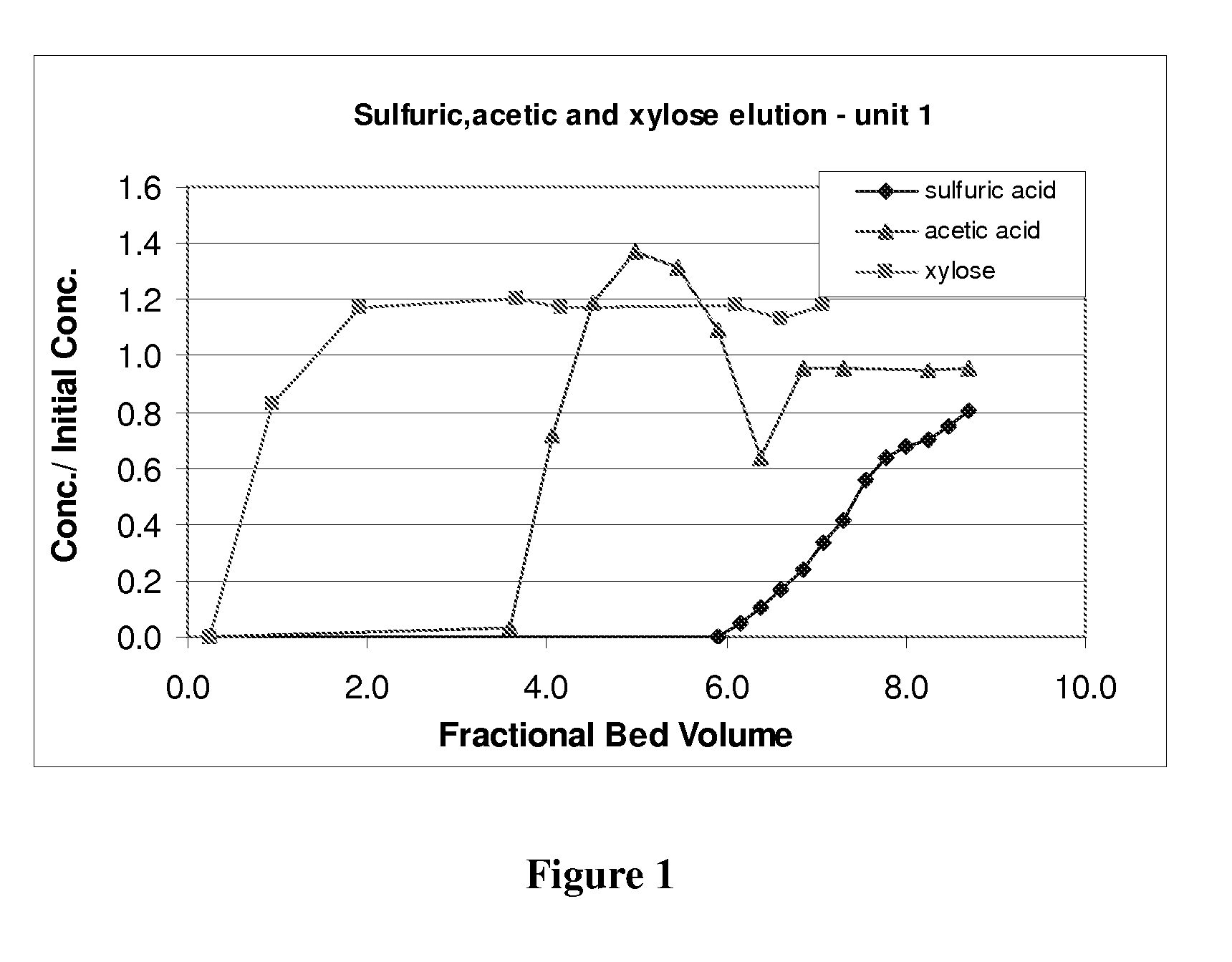
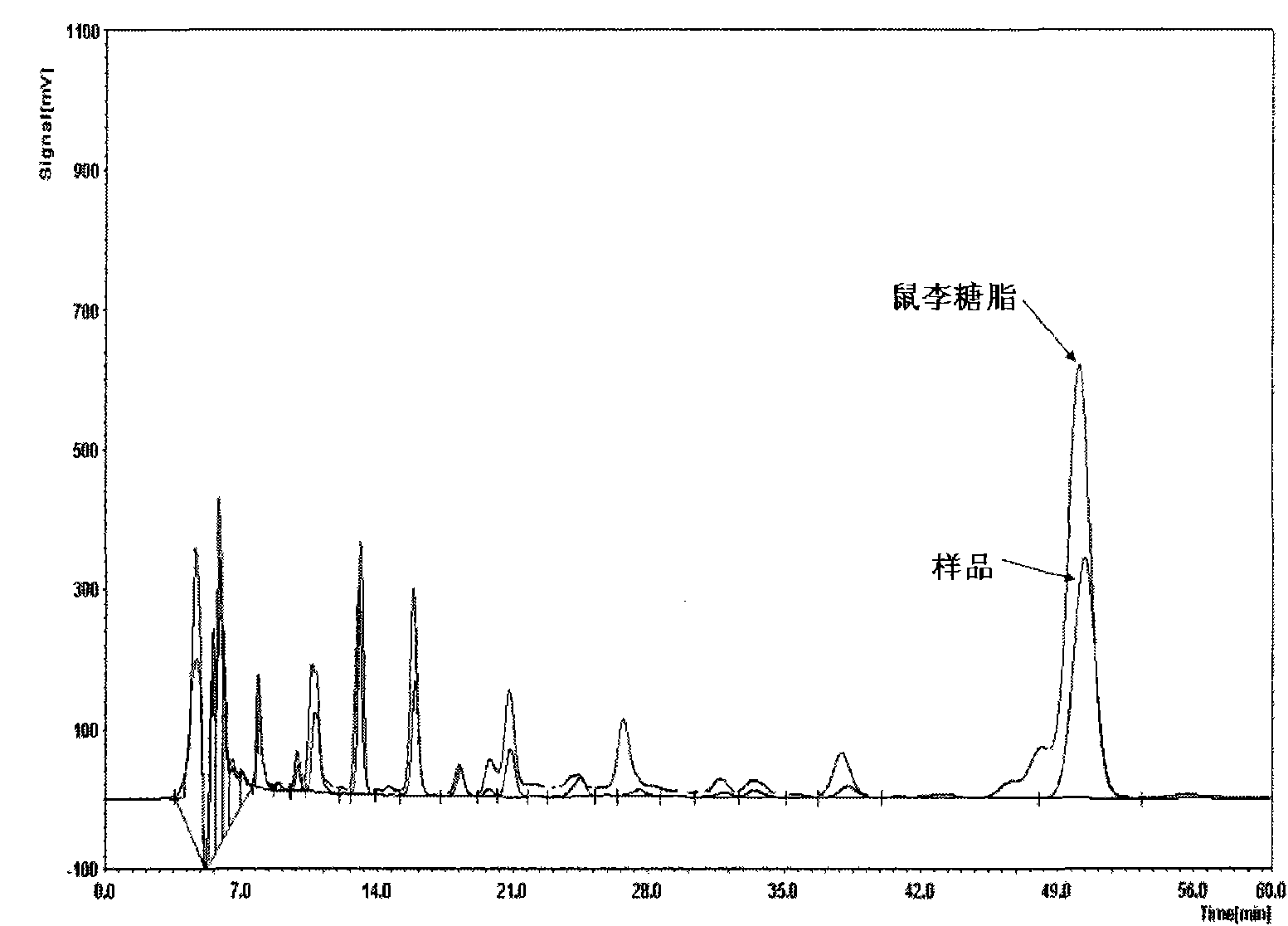
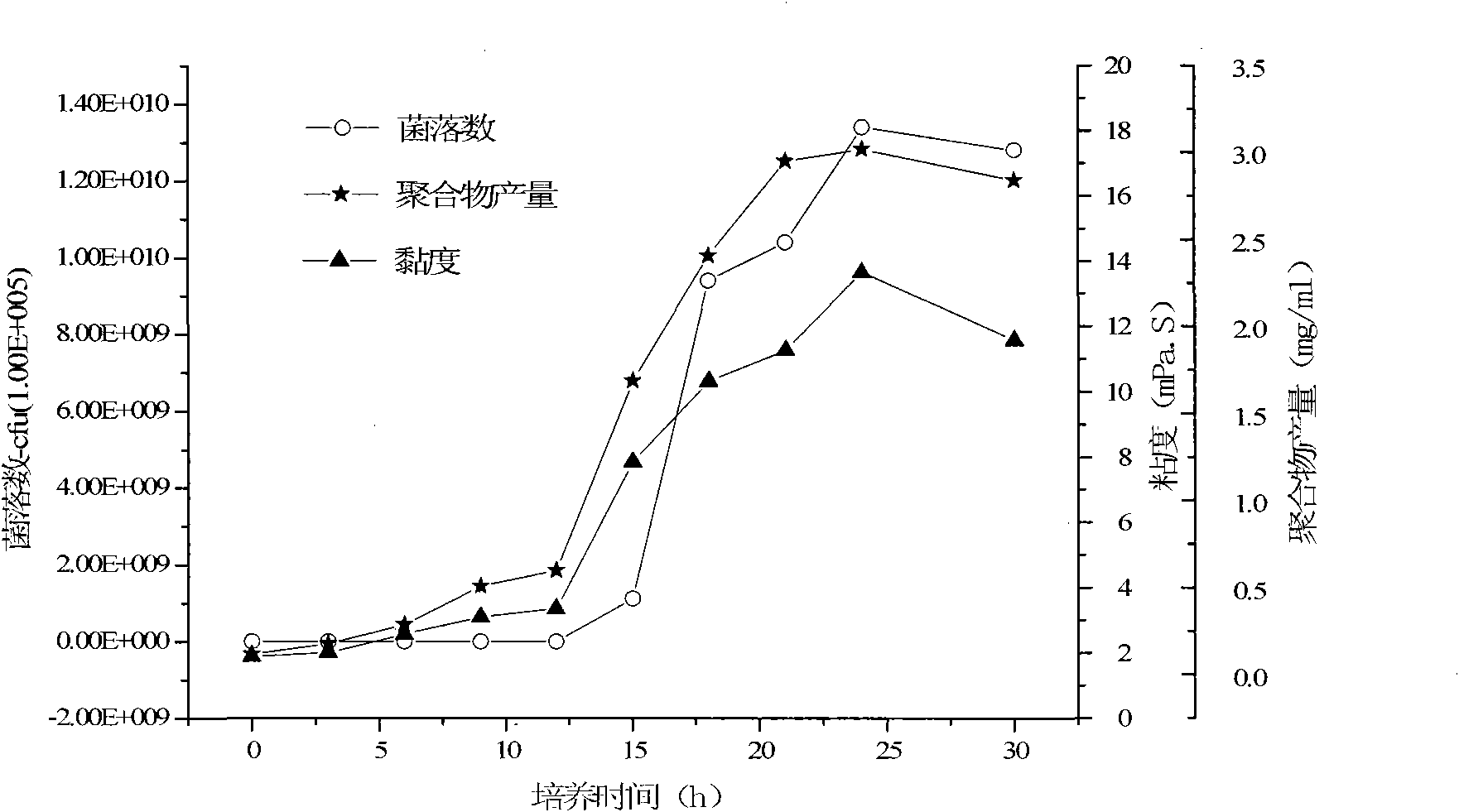
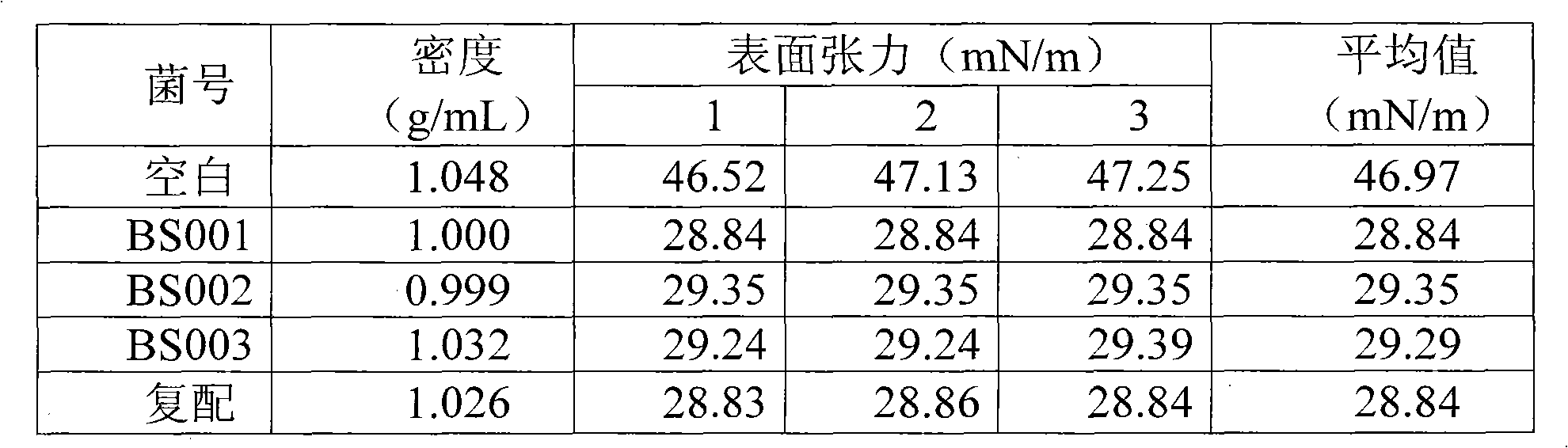
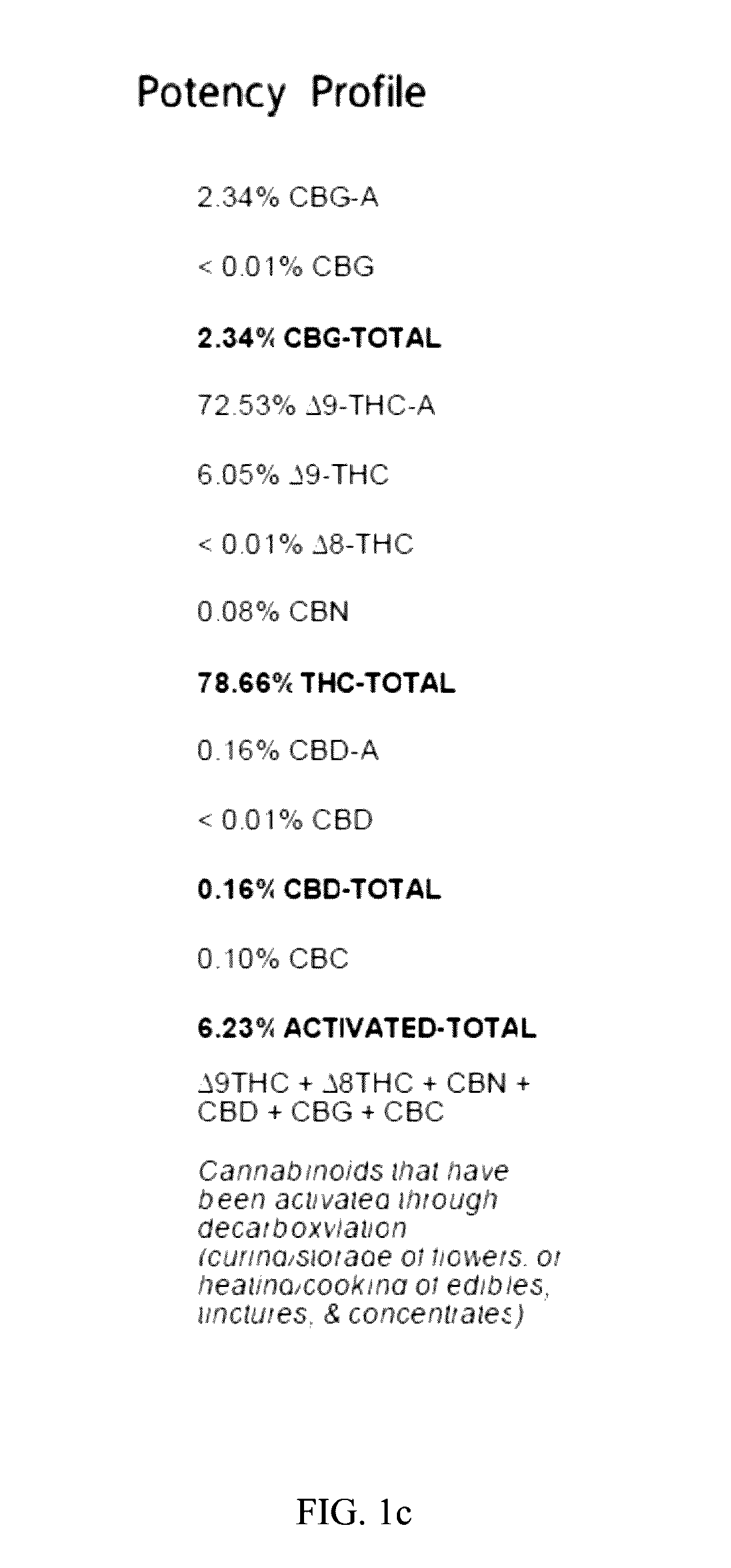Patents
Literature
354 results about "Organic Ester" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A chemical substance made when an acid and an alcohol combine and water is removed. Esters are found in essential oils (scented oils that come from plants).
Water soluble full-alloy metal grinding fluid
ActiveCN104017636ALubricity achievedImprove stabilityLubricant compositionOrganic EsterNonferrous metal
The invention discloses a water soluble full-alloy metal grinding fluid which belongs to the technical field of metal grinding fluids. The metal grinding fluid is prepared from the following components in percentage by weight: 5-40wt% of an antirust agent, 1-20wt% of a cleaning agent, 0.1-10wt% of a lubricating corrosion inhibitor, 1-20wt% of a penetrant, 1-20wt% of a solubilizer, 10-40wt% of a PH adjustor, 0.5-5wt% of a defoamer and the balance of water. Based on the total weight of the water soluble full-alloy metal grinding fluid, the pH value of the water soluble full-alloy metal grinding fluid is 7-11. The lubricating corrosion inhibitor is long chain nitrogen heterocyclic ring organic ester. The water soluble full-alloy metal grinding fluid has excellent lubricating, rust-preventing, cleaning and cooling performances and can be widely applied to grinding of ferrous metals and nonferrous metals.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Process for producing a paraffin-based object and such an object
The invention relates to a process for producing a paraffin-based object, especially a candle, with a proportion of a perfume which exceeds 10% by weight, in which the perfume is dissolved in a solvent containing an organic ester, and the solution is in turn added to or disolved in paraffin.
Owner:SCHUMANN SASOL SOUTH AFRICA
Bleed control solvents for pigmented and dye-based inks
InactiveUS6187086B1Reduce bleedingReduce rejectionDuplicating/marking methodsInksOrganic EsterWater soluble
Two classes of solvents, organic esters and diols and triols, help to reduce bleed between black (pigment-containing) inks and color (water-soluble dye-based) inks when used in formulating inks that contain self-dispersed pigments. The solvents help self-dispersed pigments to agglomerate by producing successful mutual collisions when the electrostatic potential is reduced with positively charged color inks. It appears that these solvents may be changing the dielectric constant of the ink, thereby reducing the repulsion potential of the pigment particles themselves.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Method of obtaining an organic salt or acid from an aqueous sugar stream
InactiveUS20080041366A1Low costPromote recoverySugar derivativesComponent separationOrganic acidOrganic Ester
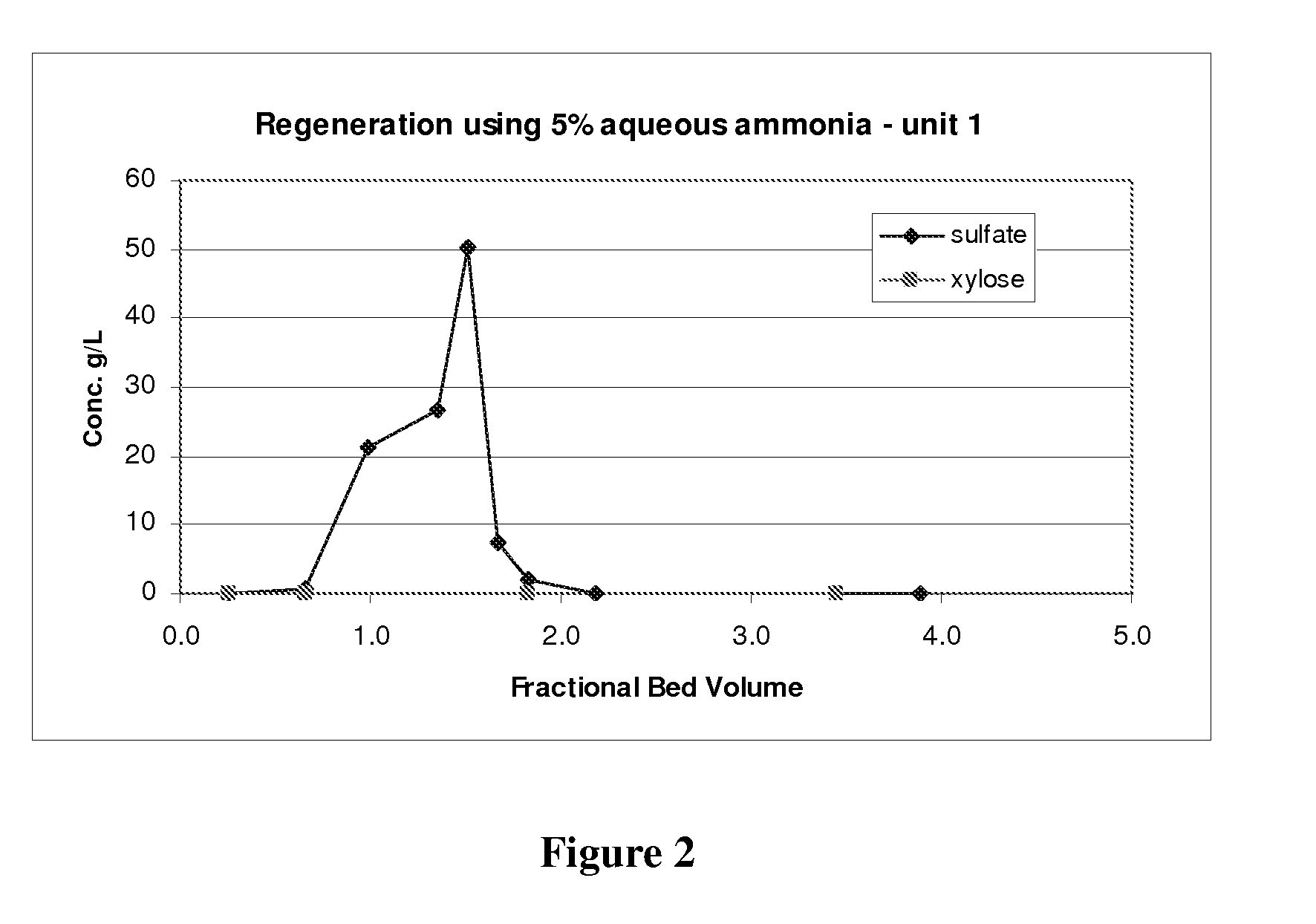
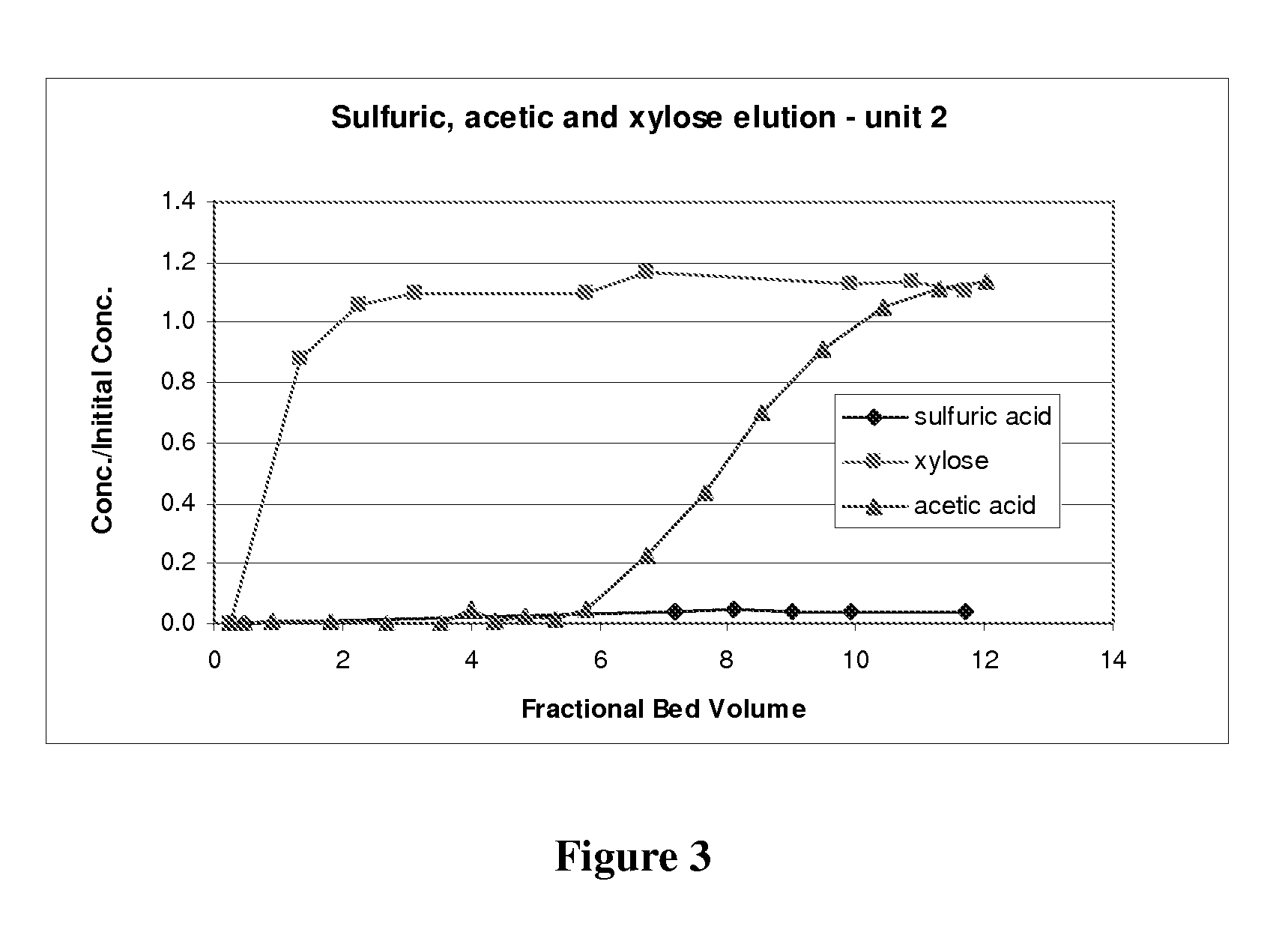
A process for obtaining one or more than one salt of an organic acid(s), or organic acid(s), from an aqueous sugar stream comprising one or more than one mineral acid and the organic acid(s) is provided. The process comprises introducing the aqueous sugar stream to a separation system comprising one or more beds of anion exchange resin and obtaining a stream therefrom comprising the sugar. The one or more beds of anion exchange resin are then regenerated in one or more stages to produce at least one product stream comprising the organic acid, a salt of the organic acid, or a combination thereof, and a separate outlet stream comprising the mineral acid, a salt of the mineral acid, or a combination thereof. The product stream is then recovered. The separation may be conducted with two separation units, or using a single anion exchange unit.
Owner:IOGEN ENERGY CORP
Method of treating subterranean formations by in-situ hydrolysis of organic acid esters
InactiveUS20090131285A1Improve applicabilityCost-effectiveFlushingDrilling compositionOrganic acidOrganic Ester
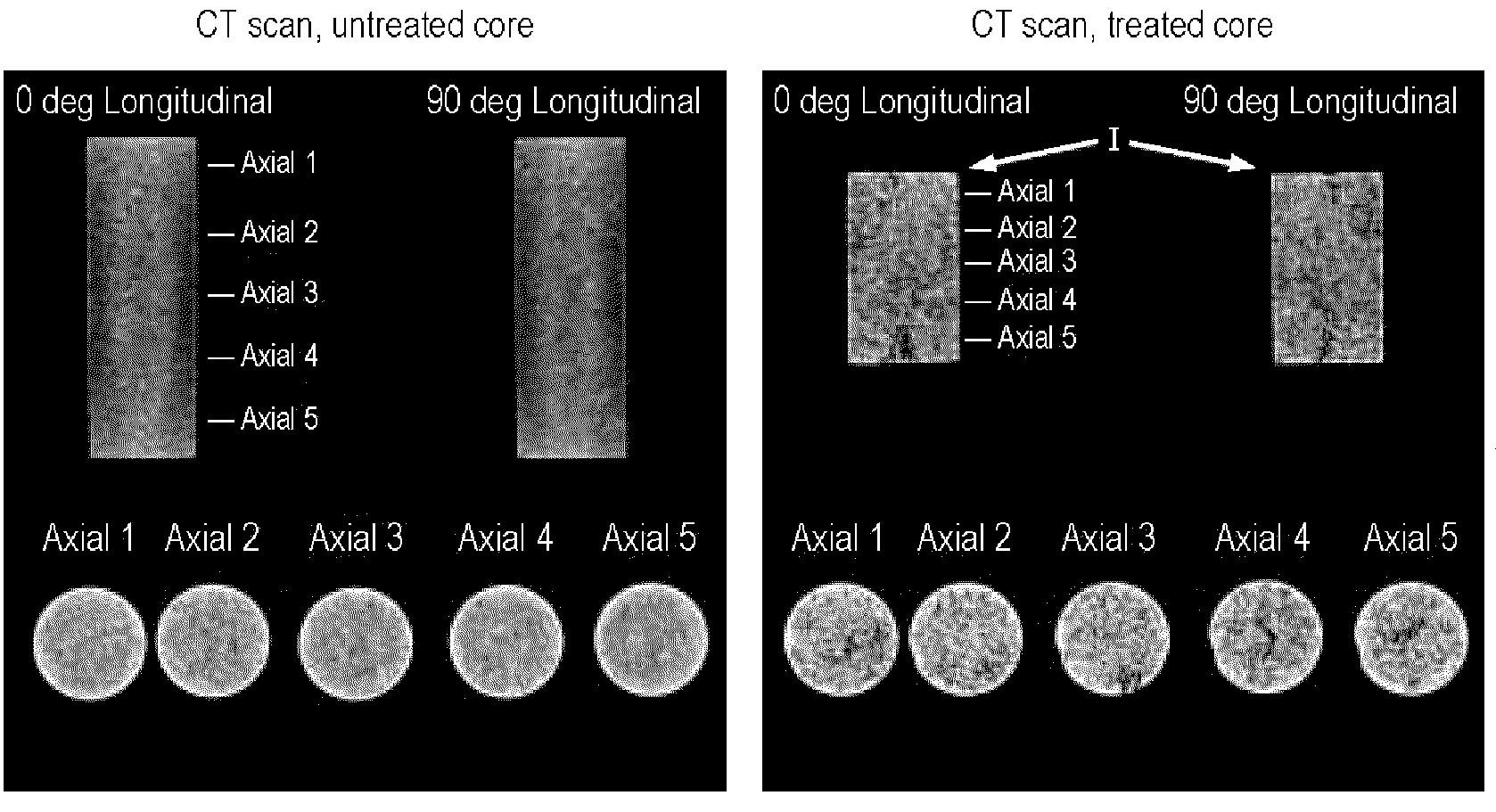
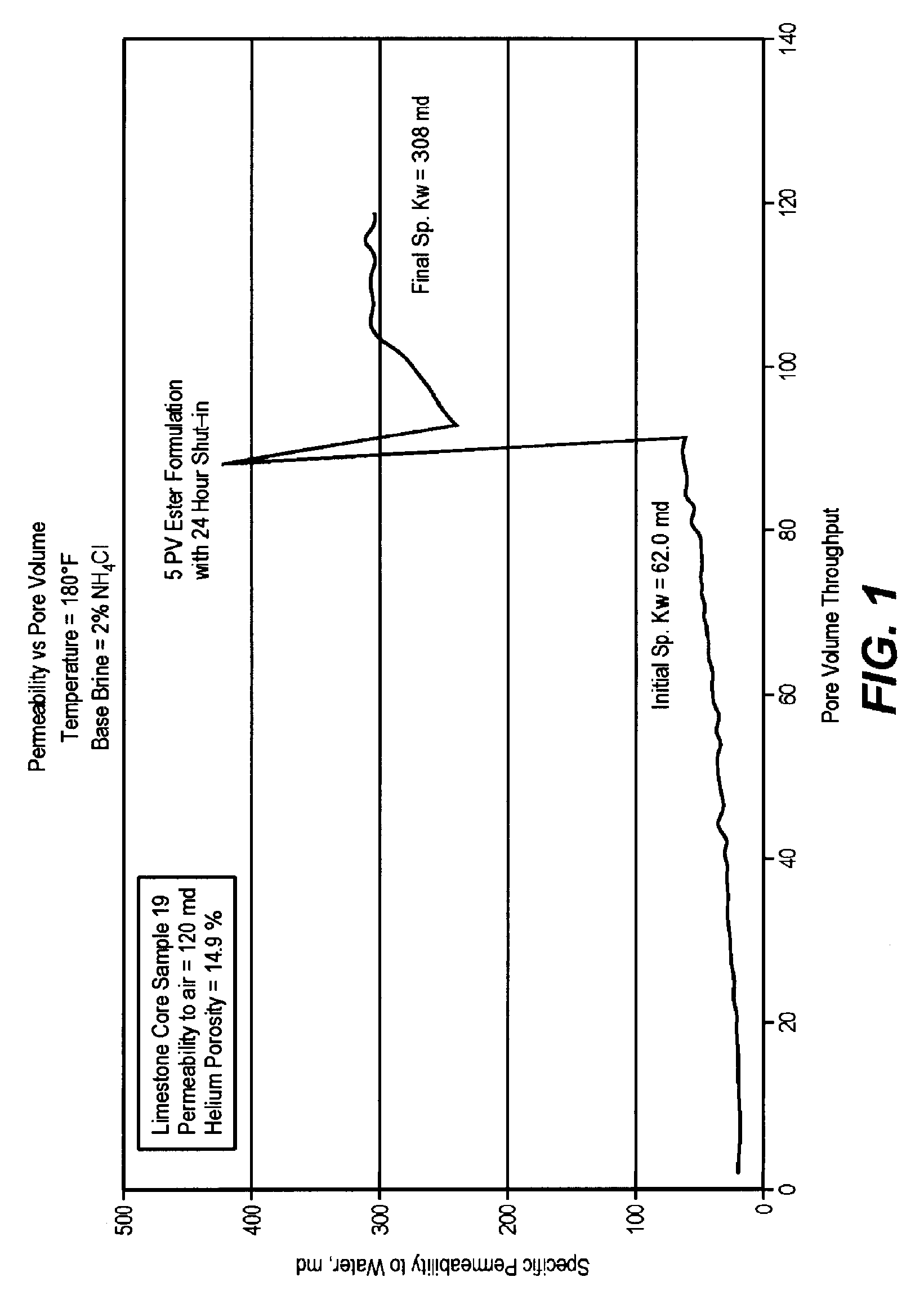
An oil or gas well penetrating a subterranean formation, such as a carbonate formation, is treated with a well treatment fluid which contains an organic ester. The fluid may be an oil-in-water emulsion of the organic ester and an emulsifier or a homogeneous solution of organic ester and a water / mutual solvent solution. Acid is produced in-situ by hydrolysis of the organic ester.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Moulding-grade wood-plastic composite and processing process
InactiveCN101024709AImprove high temperature fluidityExcellent formabilityCoatingsMoulding gradeStearic acid
The invention relates to an injection moulding wood plastic compound material and the process technology. It is made up from recycled P or HDPE or PVC 100 portions, wood flour 80-130 portions, chlorinated polyethylene 5-10 portions, polyethylene wax 0.5-5.0 portions, geoceric acid or stearate 1.0-5.0 portions, nanometer reinforcing agent 4.0-8.0 portions, organic esters flexibilizer 5.0-15.0 portions, and PE grafted by maleic anhydride 5.0-20 portions. Mixing the materials at low speed (300-600round / min), high speed (1500-2500 round / min), low speed (300-600 round / min) for 5-10min, 25-40min, and 5-10min, the premixed material would be gained. After being extruded from extruder, the moulding wood plastic compound material would be gained. It could be widely used in producing complex shaped products.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Fuel blends
A fuel additive composition containing ethanol, n-propanol or mixtures thereof together with a non-hydroxy fatty acid and organic ester is described. A miscible fuel blend composition containing the fuel additive composition and diesel oil, gas oil or a mixture thereof, as well as a process for preparing the fuel blend composition is also described.
Owner:VICTORIAN CHEM INT
System and method for extraction of chemicals from lignocellulosic materials
ActiveUS20140227161A1Oxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationFuranCellulose
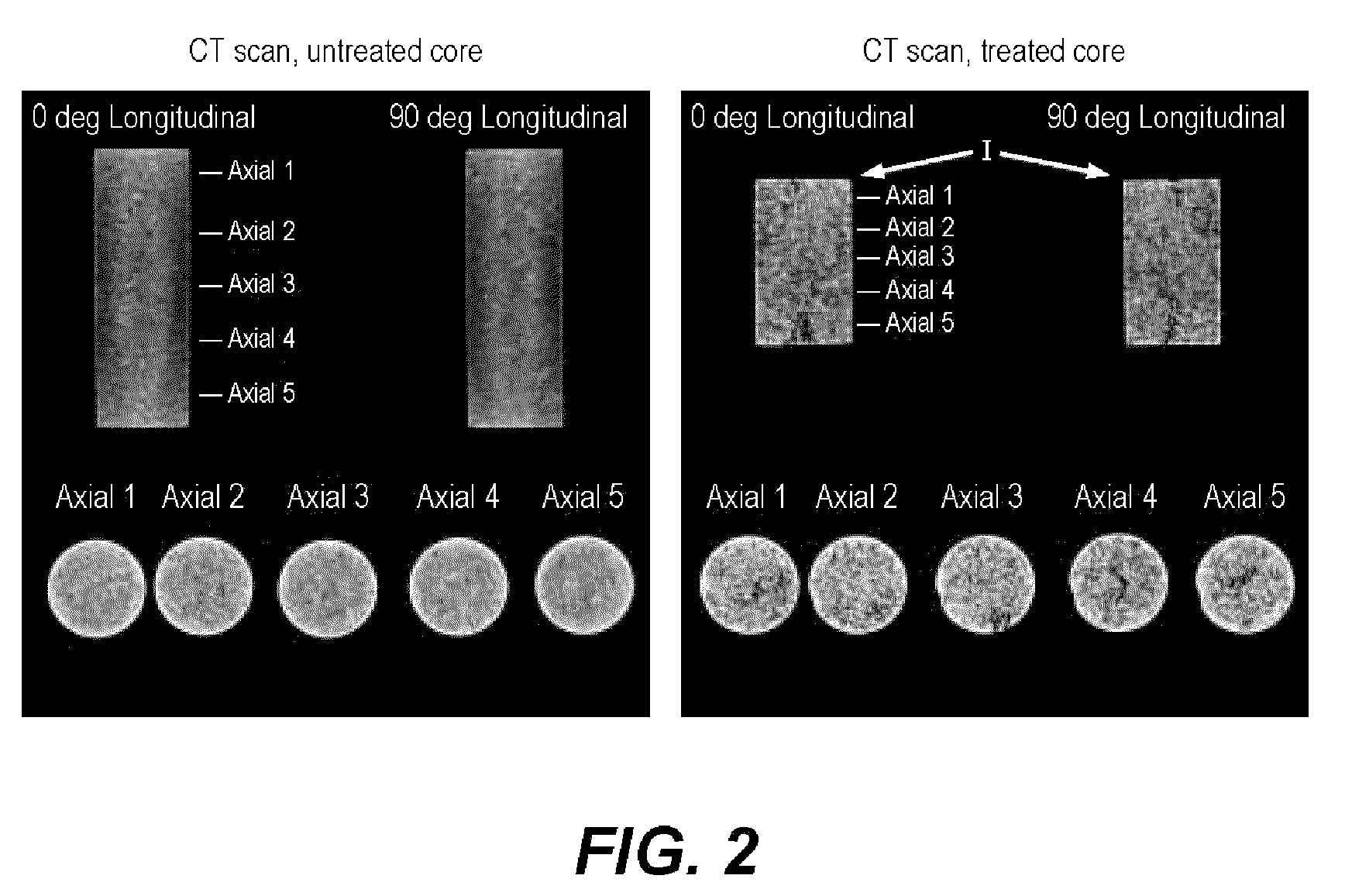
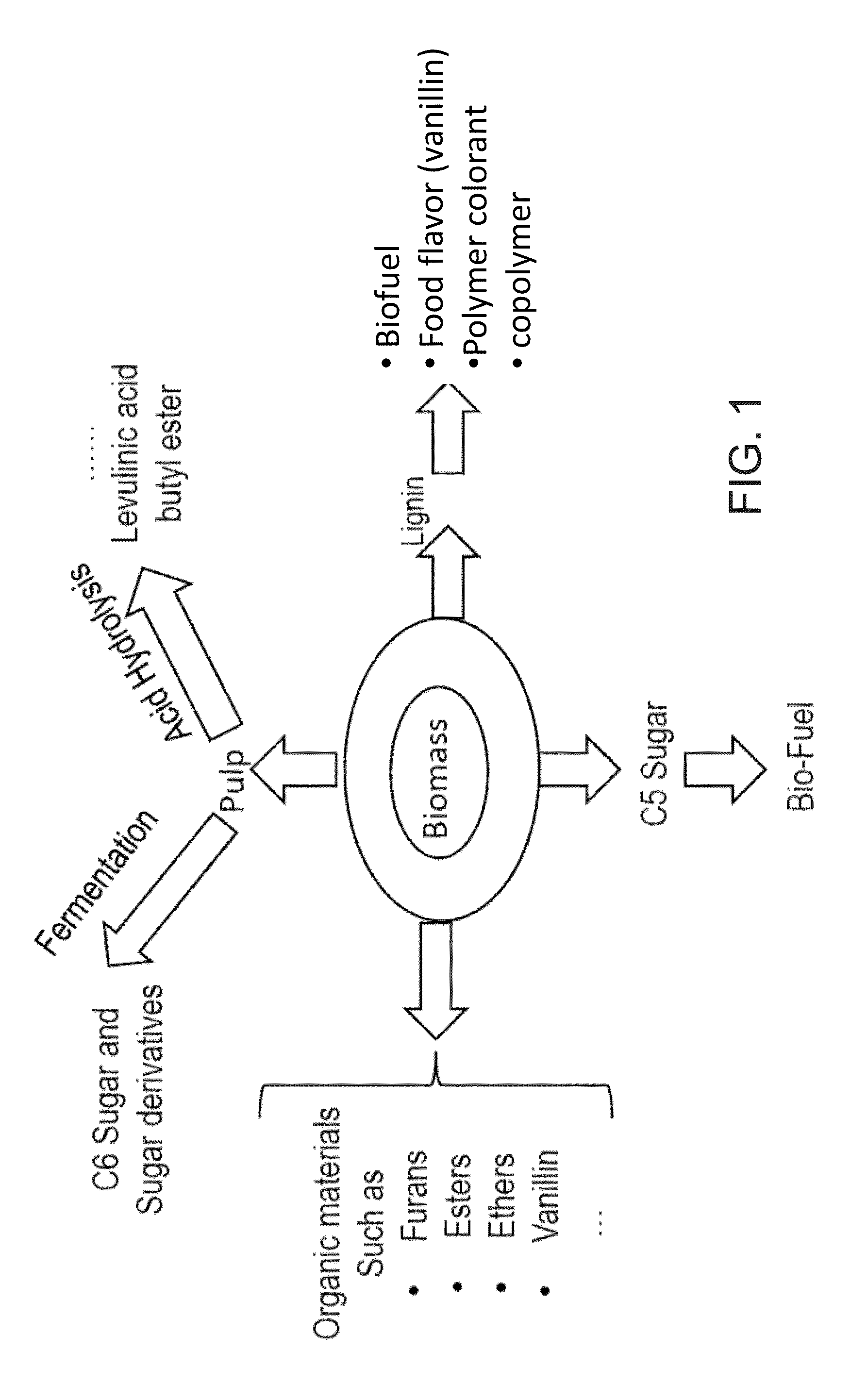
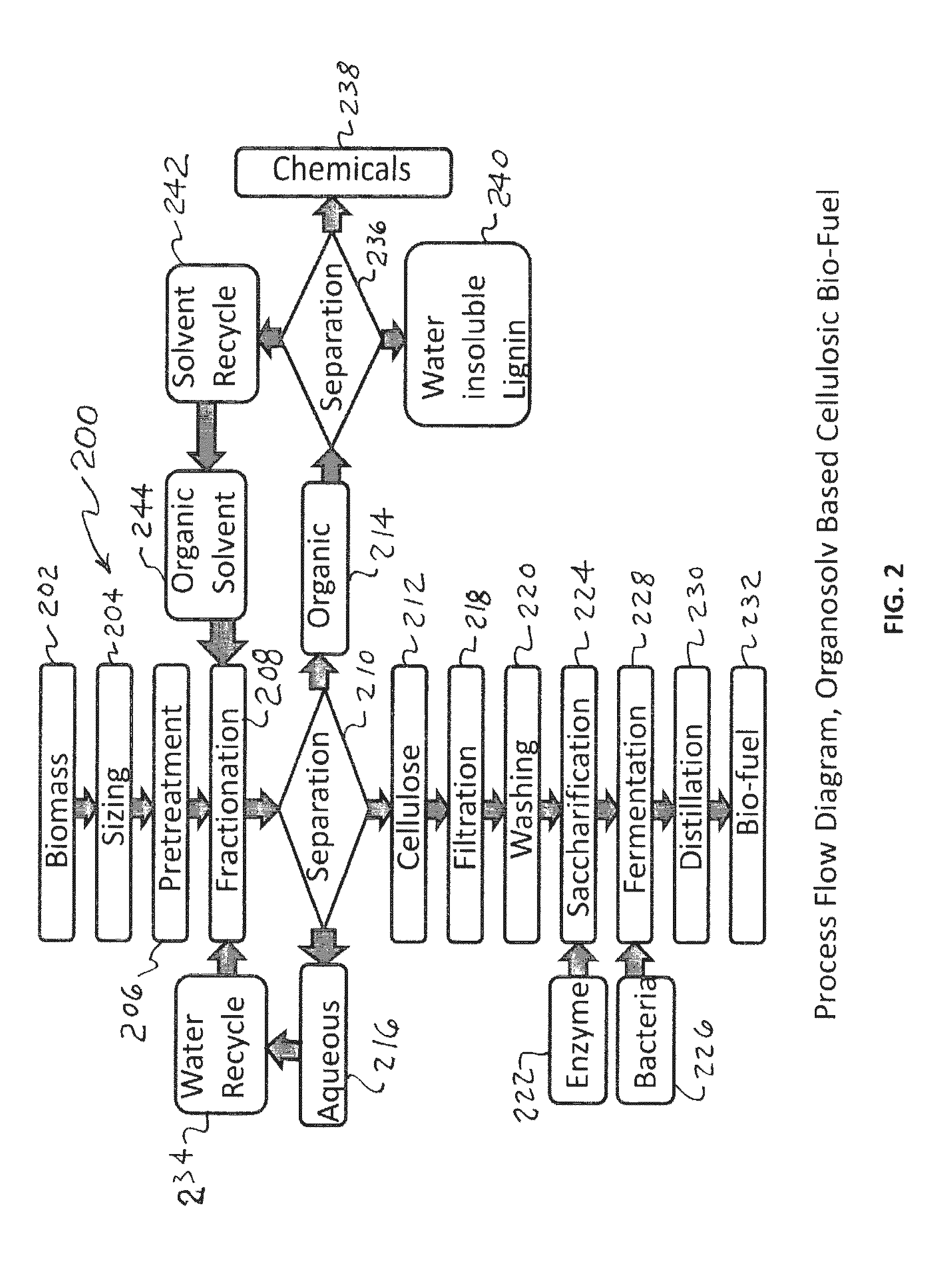
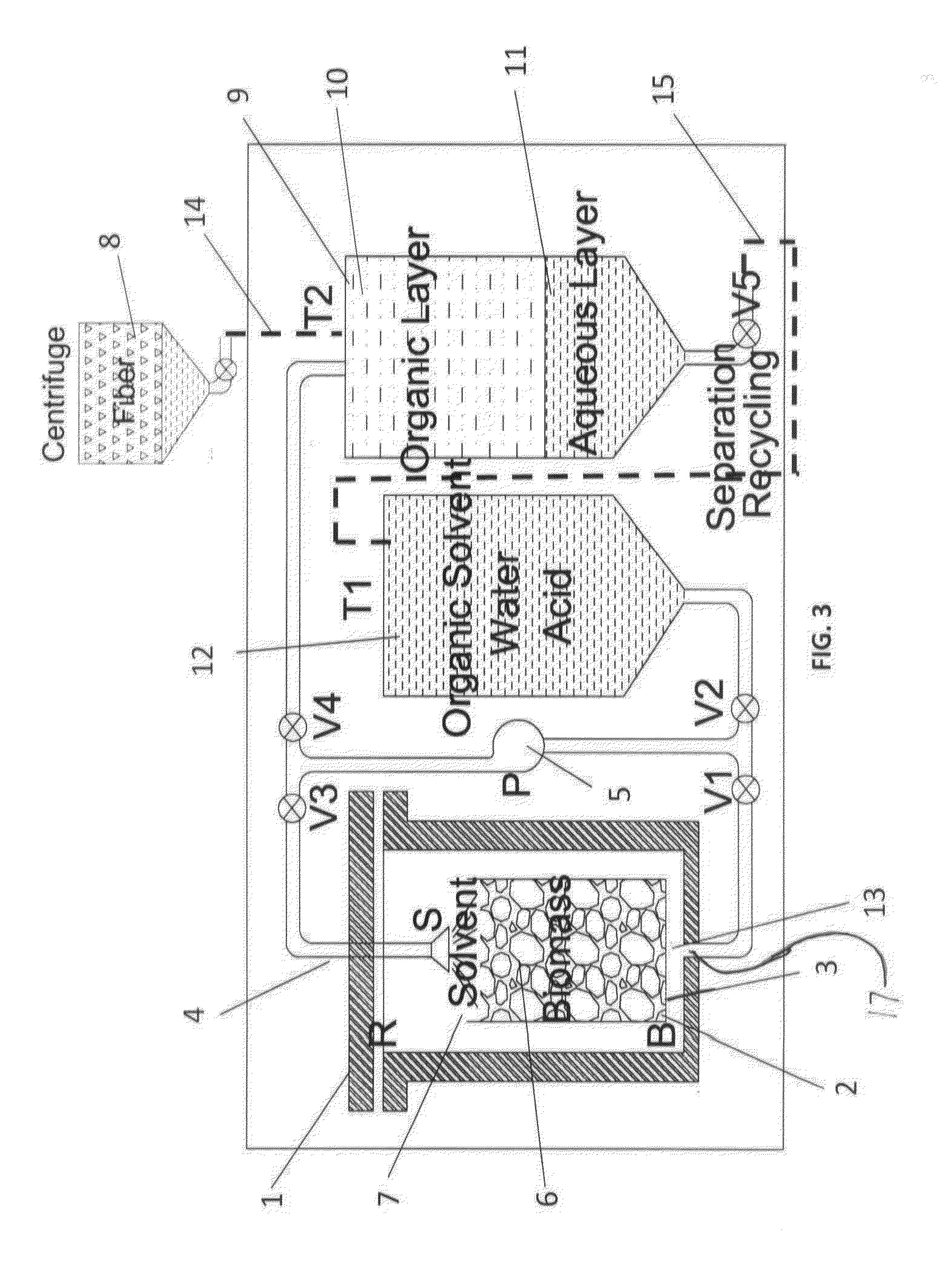
An organosolv process for producing bio-products by decomposing lignocellulosic materials comprises providing an initial lignin solvent with water, an acid, and a lignin dissolving chemical comprising at least one of an organic ester, butyl acetate, an organic furan, and furfural. The process also includes placing the lignin solvent in contact with a biomass to form a circulation solvent, and recycling at least a portion of the circulation solvent by circulating the circulation solvent back into contact with the biomass. The circulating of the circulation solvent occurs for a period of time, after which, the process then includes separating material such as chemicals and lignin from the circulation solvent. The chemicals can be recycled as new solvent or sold while lignin can be used as natural and renewable colorant for polymers such as poly lactic acid.
Owner:AMERICAN SCI & TECH
Micro-emulsion ink cleaning agent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101824243AReduce surface tensionNo pollutionChemical paints/ink removersOrganic EsterEmulsion
The invention discloses a micro-emulsion ink cleaning agent and a preparation method thereof, which belong to the technical field of printing ink cleaning. The cleaning agent comprises an anionic surfactant, a nonionic surfactant, cosurfactant, organic esters, a corrosion inhibitor, a penetrating agent and pure water. The micro-emulsion ink cleaning agent can be used for cleaning printers, inking rollers and rubber cloths, and has the advantages of quick ink dirt removing speed, good cleaning effect, low production cost, non-volatilization, non-inflammability and no pollution to the environment.
Owner:JIANGSU HAIXUN IND GROUP SHARE
Single-stage separation and esterification of cation salt carboxylates using electrodeionization
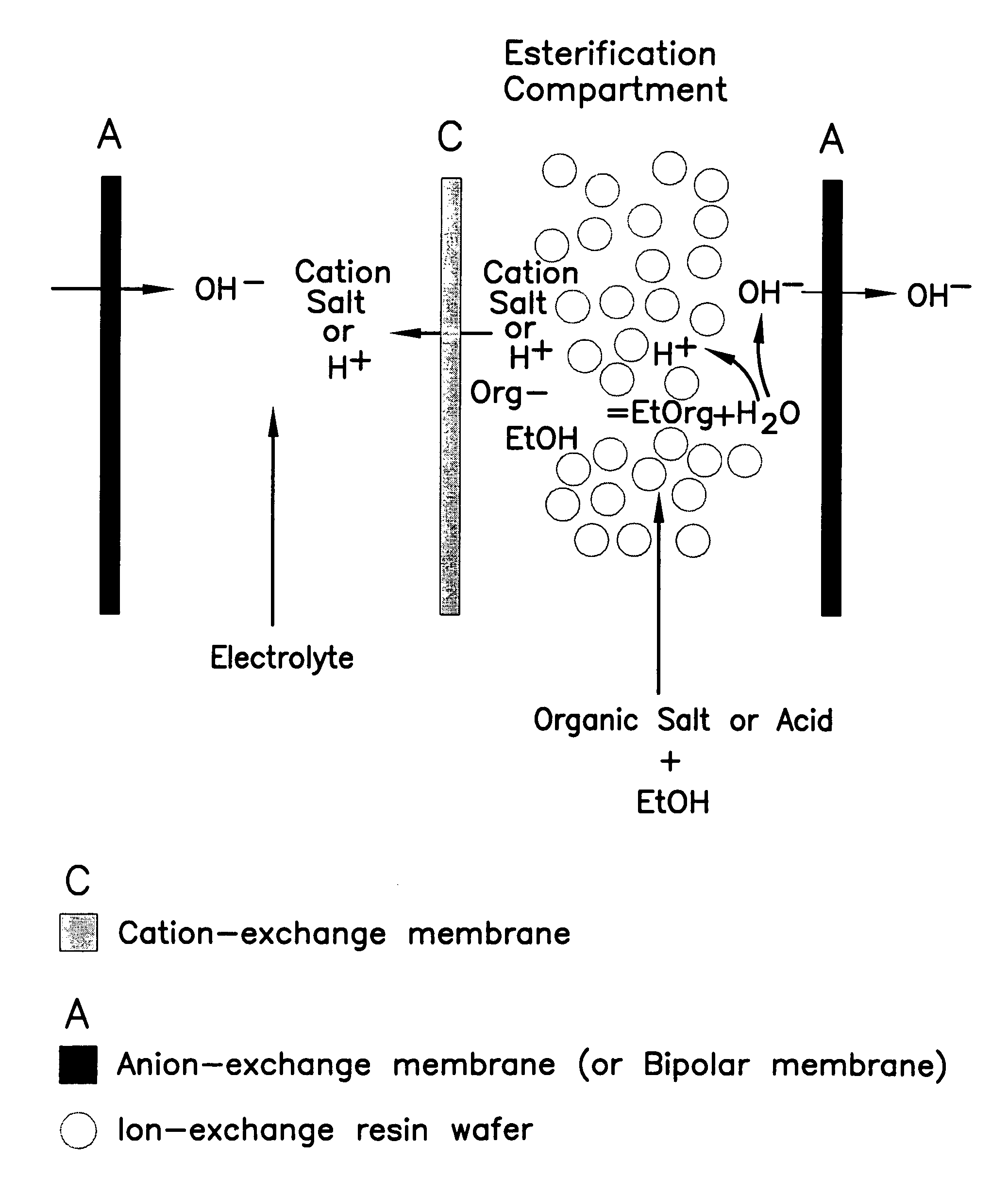
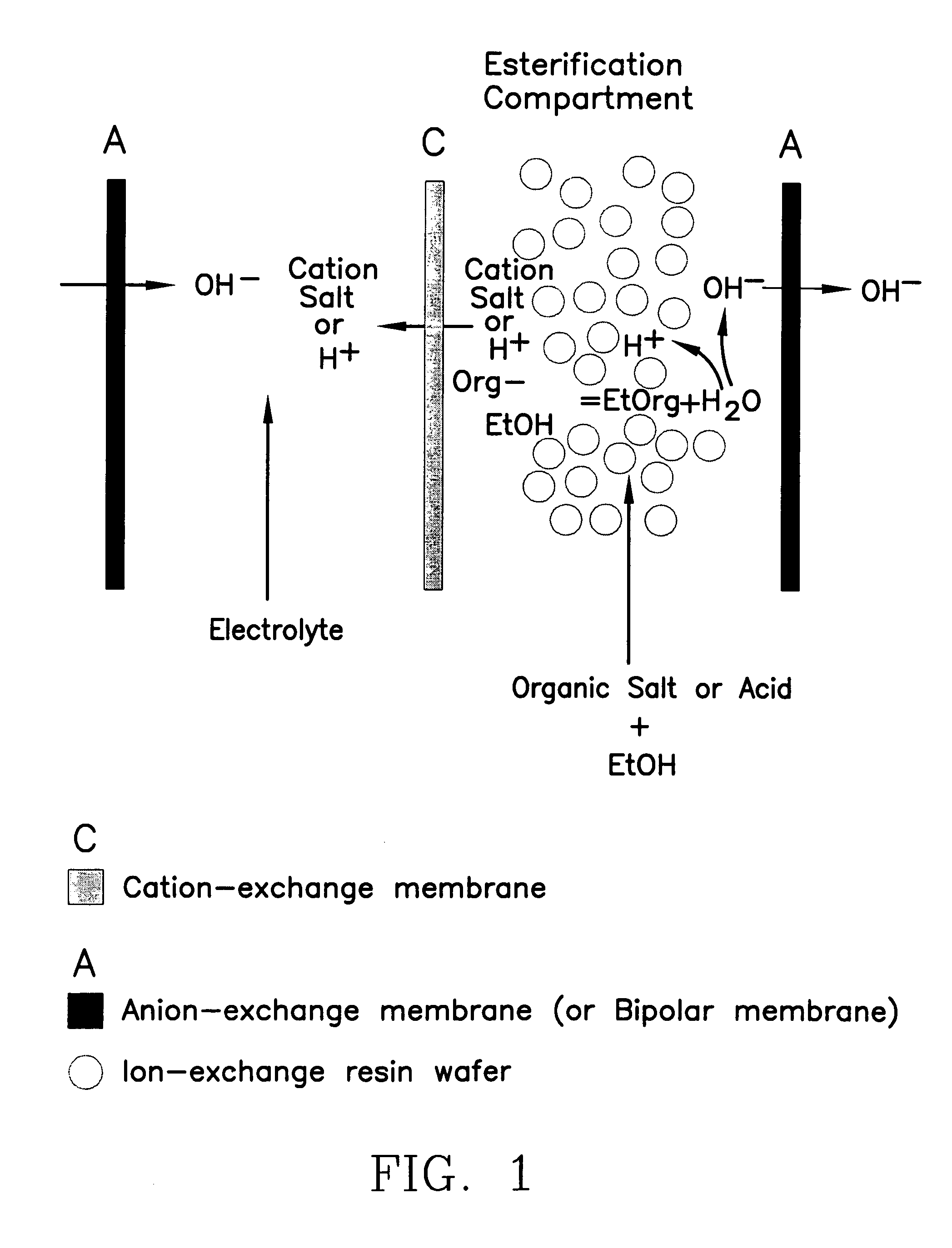
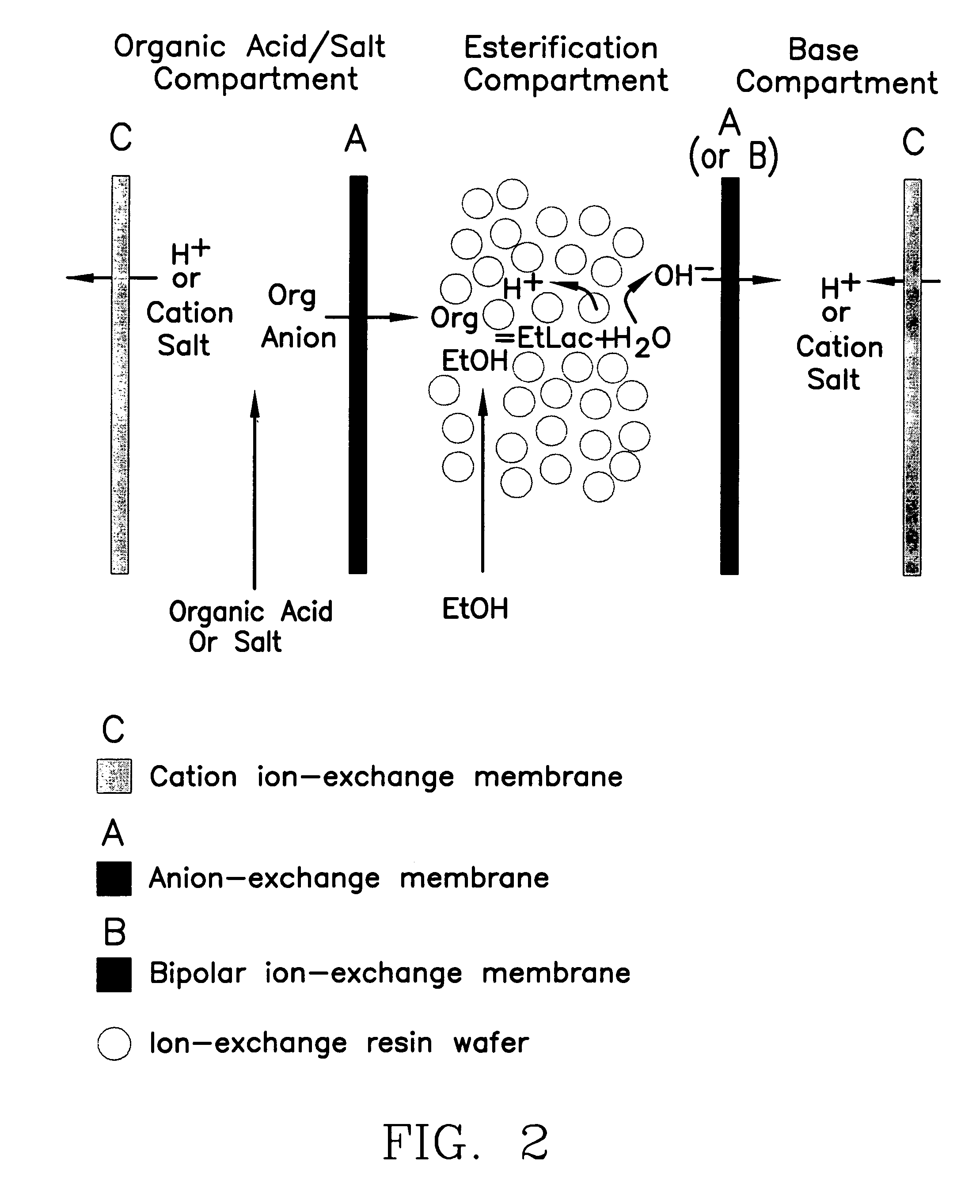
ActiveUS7141154B2Promote migrationSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementIon-exchange resinBioreactor
A method of and apparatus for continuously making an organic ester from a lower alcohol and an organic acid is disclosed. An organic acid or salt is introduced or produced in an electrode ionization (EDI) stack with a plurality of reaction chambers each formed from a porous solid ion exchange resin wafer interleaved between anion exchange membranes or an anion exchange membrane and a cation exchange membrane or an anion exchange membrane and a bipolar exchange membranes. At least some reaction chambers are esterification chambers and / or bioreactor chambers and / or chambers containing an organic acid or salt. A lower alcohol in the esterification chamber reacts with an anion to form an organic ester and water with at least some of the water splitting with the ions leaving the chamber to drive the reaction.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Method for the synthesis of organic acid esters of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural and their use
Method for the manufacture of organic acid esters of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural by reacting a fructose or glucose-containing starting material with an organic acid or its anhydride in the presence of a catalytic or sub-stoechiometric amount of solid acid catalyst. The catalysts are heterogeneous and may be employed in a continuous flow fixed bed reactor. The esters can be applied as a fuel or fuel additive.
Owner:FURANIX TECH BV
Liquid formula used for in-depth acidification of high temperature carbonate rock
ActiveCN102399550ASolve for reaction rateDeep acidificationDrilling compositionReaction rateFracturing fluid
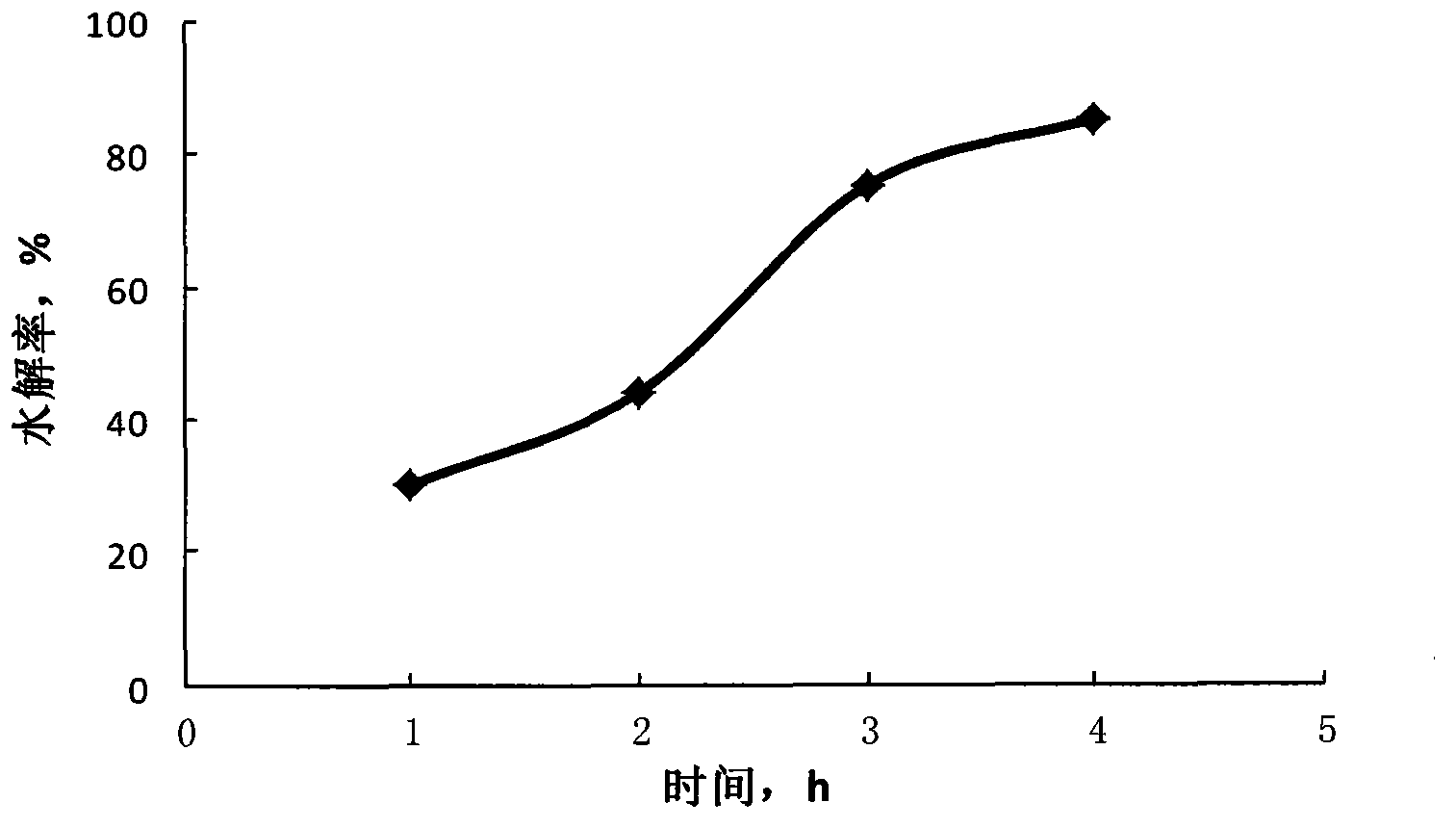
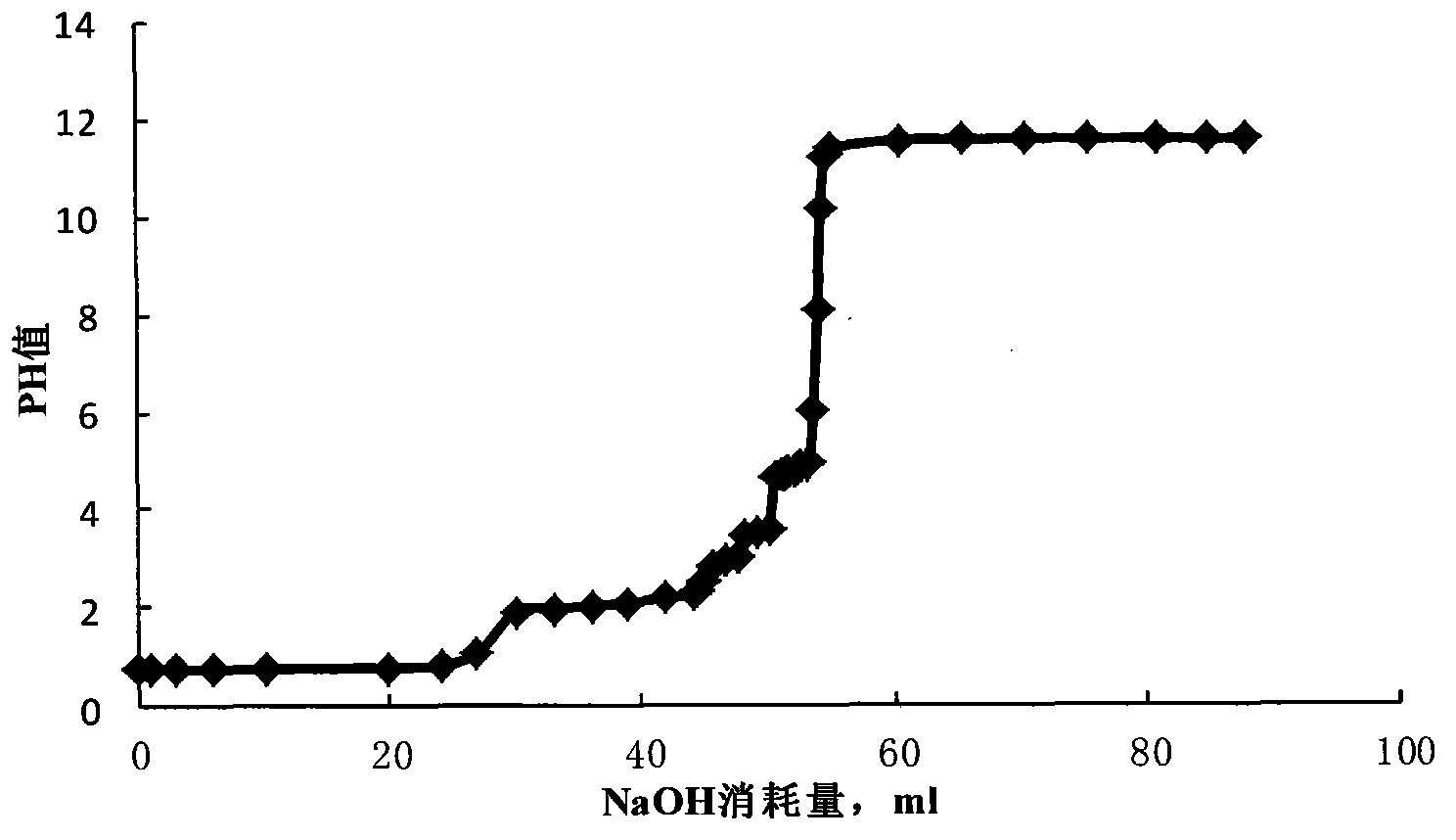
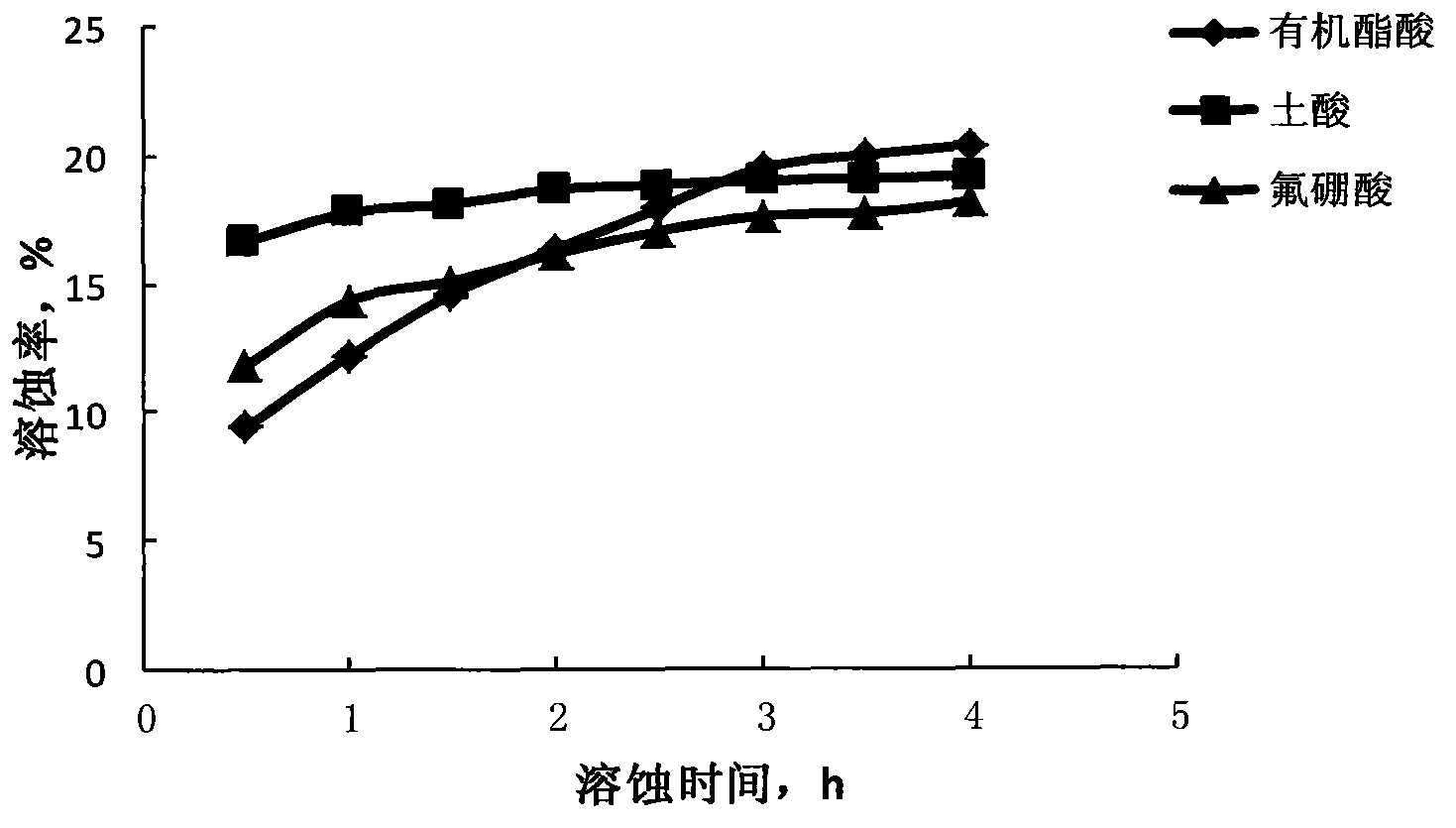
The invention relates to a liquid formula used for in-depth acidification of high temperature carbonate rock. The liquid formula is applicable at a temperature of 60 to 150 DEG C and comprises, on the basis of mass percentage, 10 to 50% of organic ester, 0 to 50% of halogen acid series, 0 to 45% of ammonium halide, 0 to 50% of formaldehyde or a mixture thereof and 0.1 to 5% of a surfactant. According to the invention, through adjusting of release of H<+> at 2.2 to 4 mol / L and generation of H<+> through hydrolysis at a temperature of 60 to 150 DEG C, the release speed of an acid solution is controlled to be in a range of 0.5 h to 6 h, which enables the problem of the reaction rate of a high temperature carbonate rock storage layer to be overcome and in-depth acidification to be realized; different addition amount of the liquid formula and different processes can be employed according to different formation conditions, and the liquid formula can be used for acidification, pickling and in-depth acid fracturing of carbonate rock and low molecular fracturing fluid acidic gel breakers; components in the liquid formula can be used individually according to different demands.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Method for making core with aeration ossification
InactiveCN101293271AWide variety of sourcesLow priceFoundry mouldsFoundry coresSoluble glassGlycerol
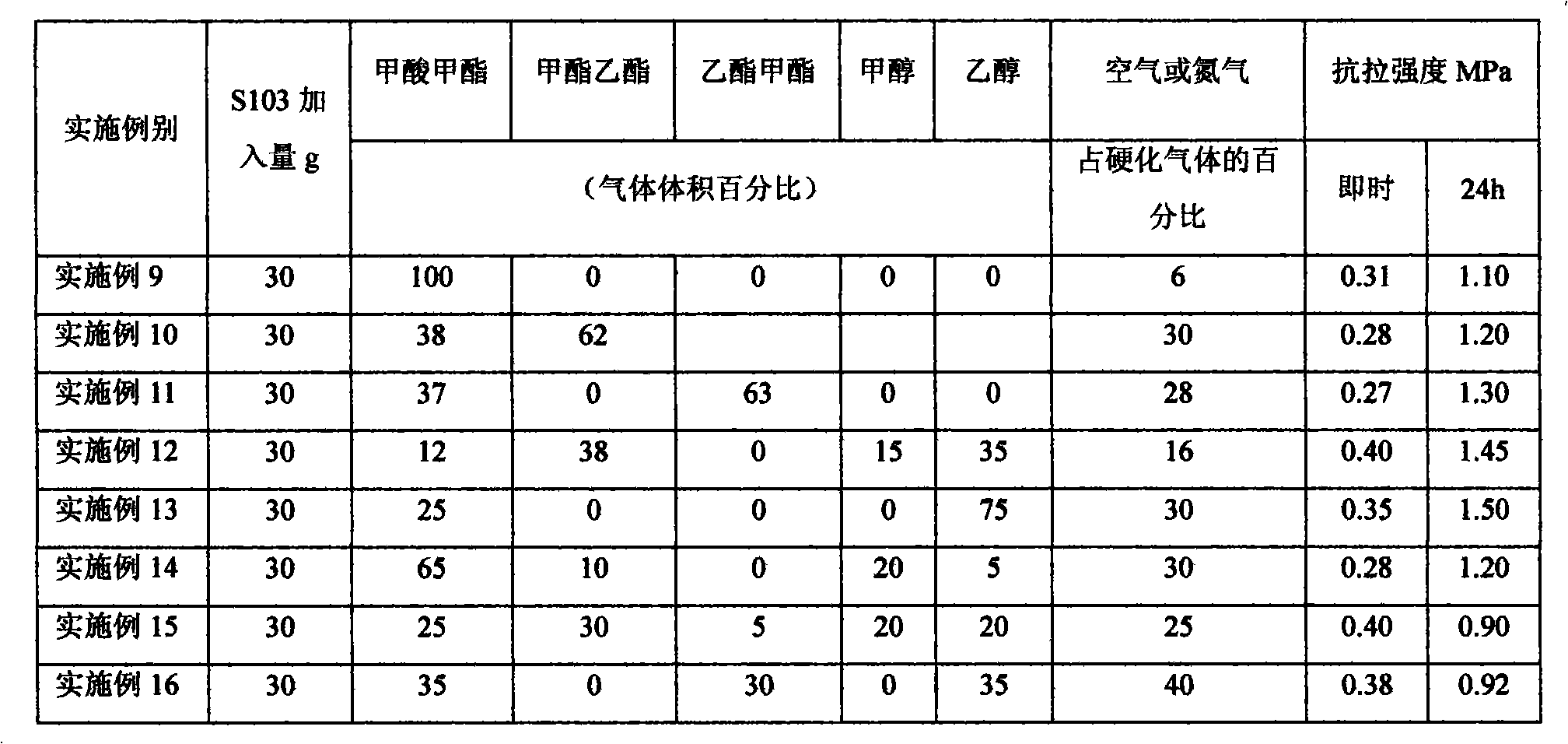
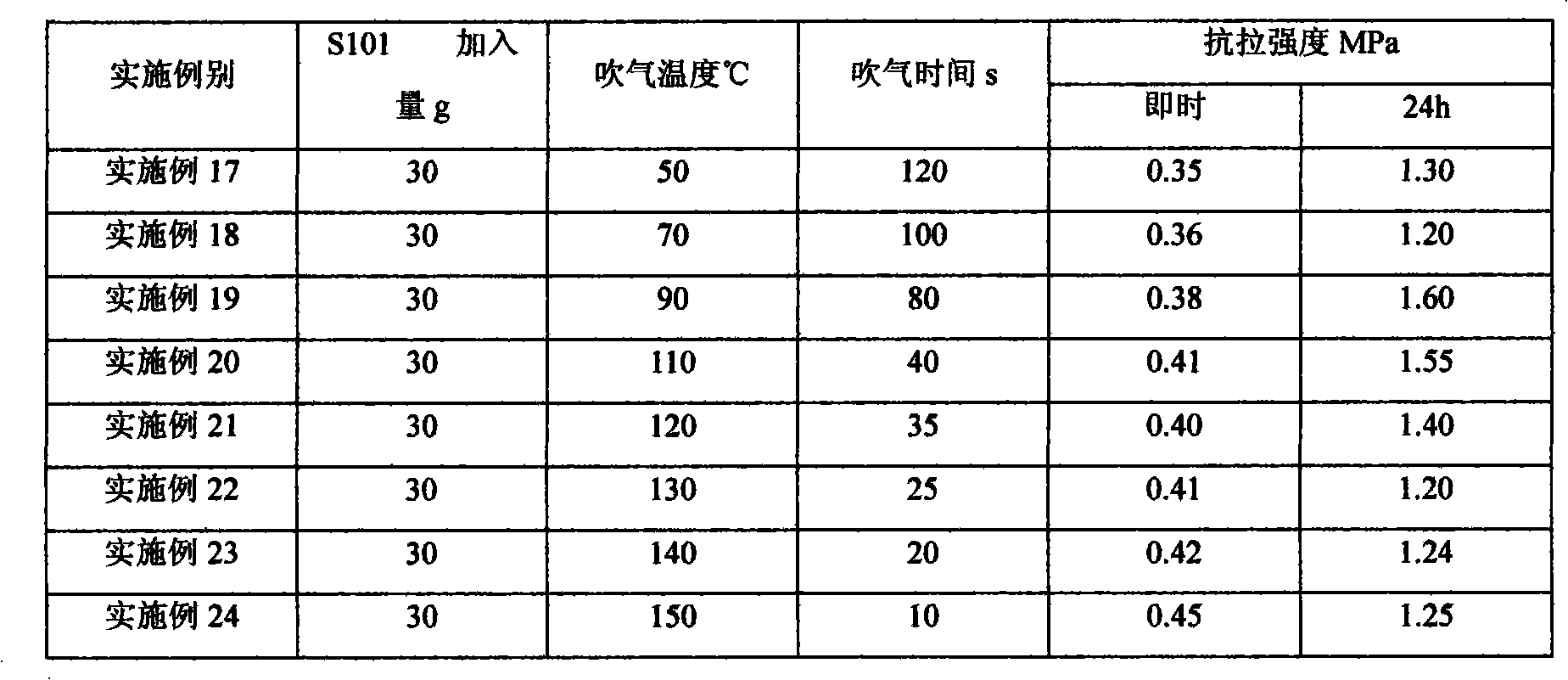
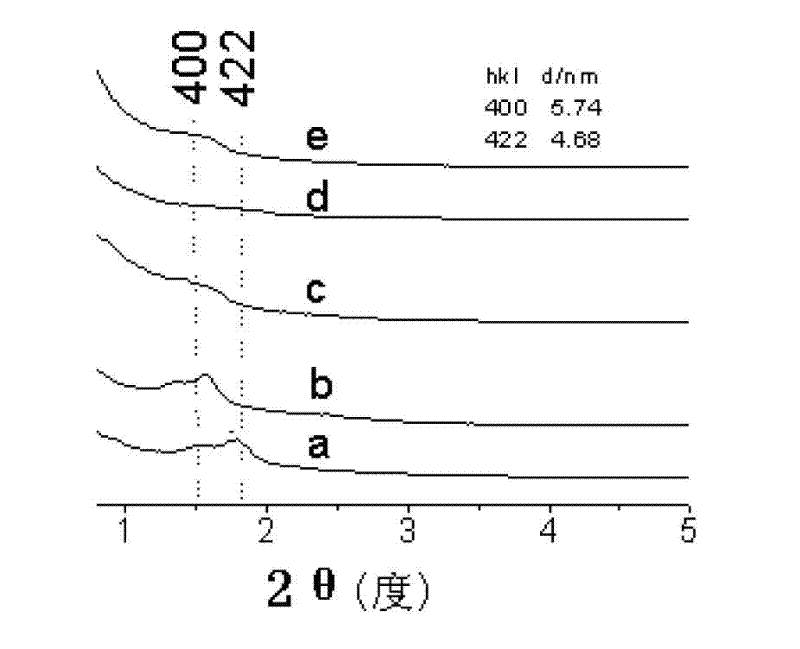
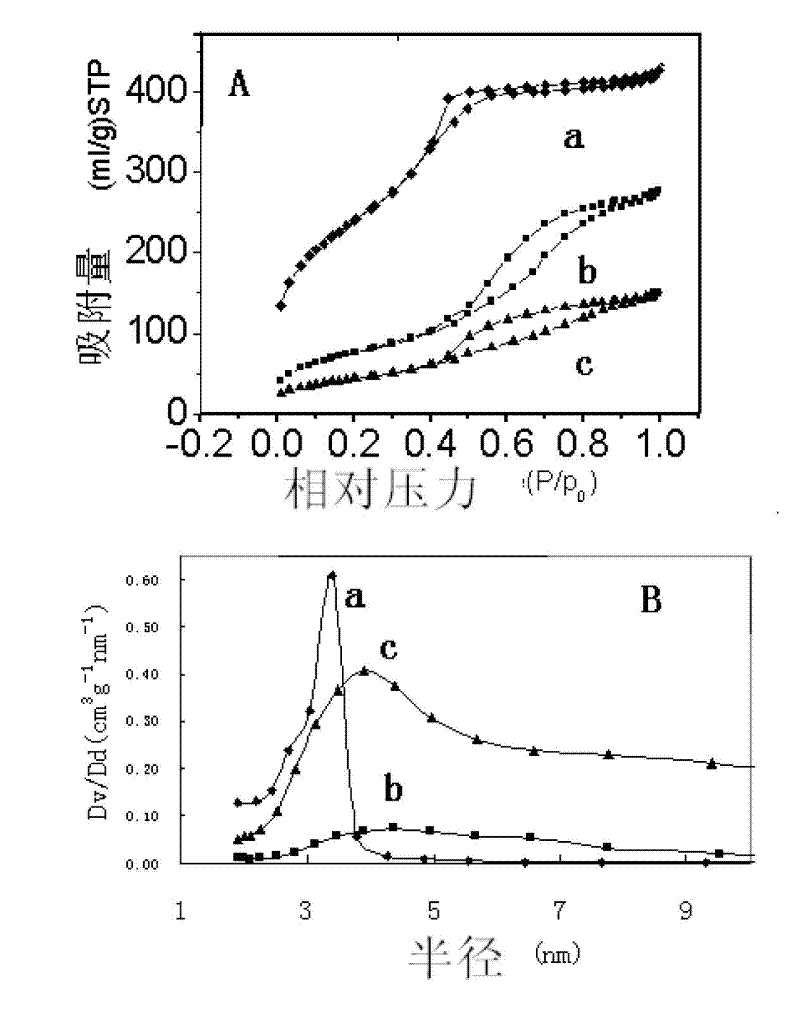
The invention discloses a core making method by gas-blowing hardening, which is characterized in that the mass percentage of mixing materials of the making core sand is as follows: 0.9-7.0 percent of soluble glass, 0.1-1.0 percent of moisture absorption resistant agent and raw sand for the rest; the used moisture absorption resistant agent can be triacetyl glycerine, diacetin, glycerol mono acetate bulk, diethylene glycol acetic ester, propylene glycol acetic ester, other polylol organic acid ester or the mixture thereof; the volume percentage of the blowing gas for hardening is as follows: 25-100 percent of C2-C4 organic ester and 0-75 percent of C1-C2 alcohols. The method of the invention has no toxicity and odor in production process, and the produced cores have better stripping strength.
Owner:SHENYANG HYATON FOUNDRY MATERIAL
Preparation method of composite ZnO-mesoporous silica nanomaterial
ActiveCN102250610AStable in natureExcellent optical propertiesWater/sewage treatment by irradiationMolecular sieve catalystsPtru catalystOrganosolv
The invention discloses a preparation method of a composite ZnO-mesoporous silica nanomaterial, namely a solvothermal in situ substitution method. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: uniformly mixing silicon-based molecular sieve powder, a ZnO precursor, a doping element and an organic solvent, adding the mixture into a high-pressure reaction kettle, and introducing a shielding gas to the reaction kettle for reaction; filtering the reaction mixture, washing, and drying to obtain dry powder; and heating and calcining the dry powder to obtain the composite ZnO-mesoporous silica nanomaterial. The composite ZnO-mesoporous silica nanomaterial prepared by the preparation method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of uniform ZnO loading, stable properties, excellent optical properties and catalytic properties and strong SHG (second harmonic generation) and TPL (two-photon luminescence) optical properties when used as an excellent catalyst for organic ester synthesis or as a laser nonlinear optical material, and is suitable for being prepared into a purple light-emitting material or a functional polymer additive. The preparation method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of wide and available raw materials, simplicity of operation and advantageous production cost.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Polymer-type water glass curing agent and application in water glass chemical grouting materials
InactiveCN101885591AResolution timeSolve the strength problemOther chemical processesBuilding constructionsSolubility(Hydroxyethyl)methacrylate
The invention relates to a polymer-type water glass curing agent with easily-controlled curing time and high toughness. The curing agent is mainly formed by polymerizing and copolymerizing double bonds-containing acids such as crylic acid, methacrylic acid and the like and double bonds-containing esters such as butyl methacrylate, vinyl acetate, hydroxy-ethyl methacrylate and the like by latex. The polymer-type water glass curing agent of the invention is a novel water-soluble water glass curing agent, which can control the curing time of the water-soluble grouting materials by controlling the content of carboxyl and ester group in a polymer. By using the curing agent, a water glass consolidating body has vey high compressive strength and toughness, synthetically overcomes the shortages of too fast curing time, high corrosiveness, low consolidating body strength and the like of an acid curing agent which is commonly used in the water glass grouting materials and the shortages of poor water solubility, slow curing time and the like of an organic ester curing agent, and can be widely applied in the field of anti-seepage stoppage engineering.
Owner:GUANGZHOU CHEM GROUTING CO LTD CAS
Cleaning agent for ink printed on surface of plastic and preparation method
This invention discloses a method for preparing cleaning agent for printing ink on plastic surface. The cleaning agent comprises: organic diluting agent 40-55 parts, organic ester 27-38 parts, ketone 15-23 parts, and nonvolatile component 1-3 parts. The method comprises: dissolving organic ester and ketone in organic diluting agent, mechanically stirring uniformly, then adding nonvolatile component, and mixing uniformly to obtain colorless and transparent cleaning agent. The cleaning agent has such advantages as high selectivity, good cleaning effect, and low solvent volatility, no matrix softening, low toxicity, low harm to human bodies, and simple formula, and can be used for cleaning printing ink on the surface of plastic plate or mackintosh surface, especially the surface of soft plastic package.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Aqueous strippable paint
The invention provides aqueous strippable paint. The aqueous strippable paint is composed of 0.2%-2.0% of organic ester parting agent, 0%-15% of water, 0.05%-2% of wetting agent, 0.05%-2% of defoaming agent, 0%-2.0% of ultraviolet stabilizing agent and absorbent composite, 0%-15% of inorganic filler, 0.05%-2.0% of rheological auxiliaries and balance waterborne polyurethane. The aqueous strippable paint can be applied to metal, plastic or oil varnish surfaces by means of brushing, spraying, roll painting and the like and is applicable to complex or bent surfaces. The aqueous strippable paint can be easily stripped off base materials once being dried to form a film, and no residue is remained on the surfaces.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Low residue anhydrous antiperspirant stick composition
InactiveUS20030113282A1Residue reductionHigh product deliveryCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsAntiperspirantsOrganic Ester
Disclosed are antiperspirant stick compositions that exhibit substantially less visible residue (whitening) upon application to the skin or after drying and which exhibit improved aesthetics and superior cosmetic properties. The compositions include a non-liquid organic ester emollient with a melting point between about 25° C. and about 60° C. (preferably isostearyl behenate); and an inert polymeric material (preferably a low molecular weight polyethylene; in addition to (a) a volatile (for example, cyclomethicone), (b) a non-volatile liquid emollient; (c) a gelling agent (for example, stearyl alcohol and hydrogenated castor oil); (d) at least one active antiperspirant material (for example, particulate antiperspirant aluminum zirconium tetrachlorohydrex salts); and (e) optionally other antiperspirant stick compatible materials.
Owner:CHURCH & DWIGHT CO INC
Systems and methods for cannabinoid and terpene extraction and purification
ActiveUS20170020944A1Ion-exchange process apparatusIon-exchanger regenerationOrganic EsterChlorophyll
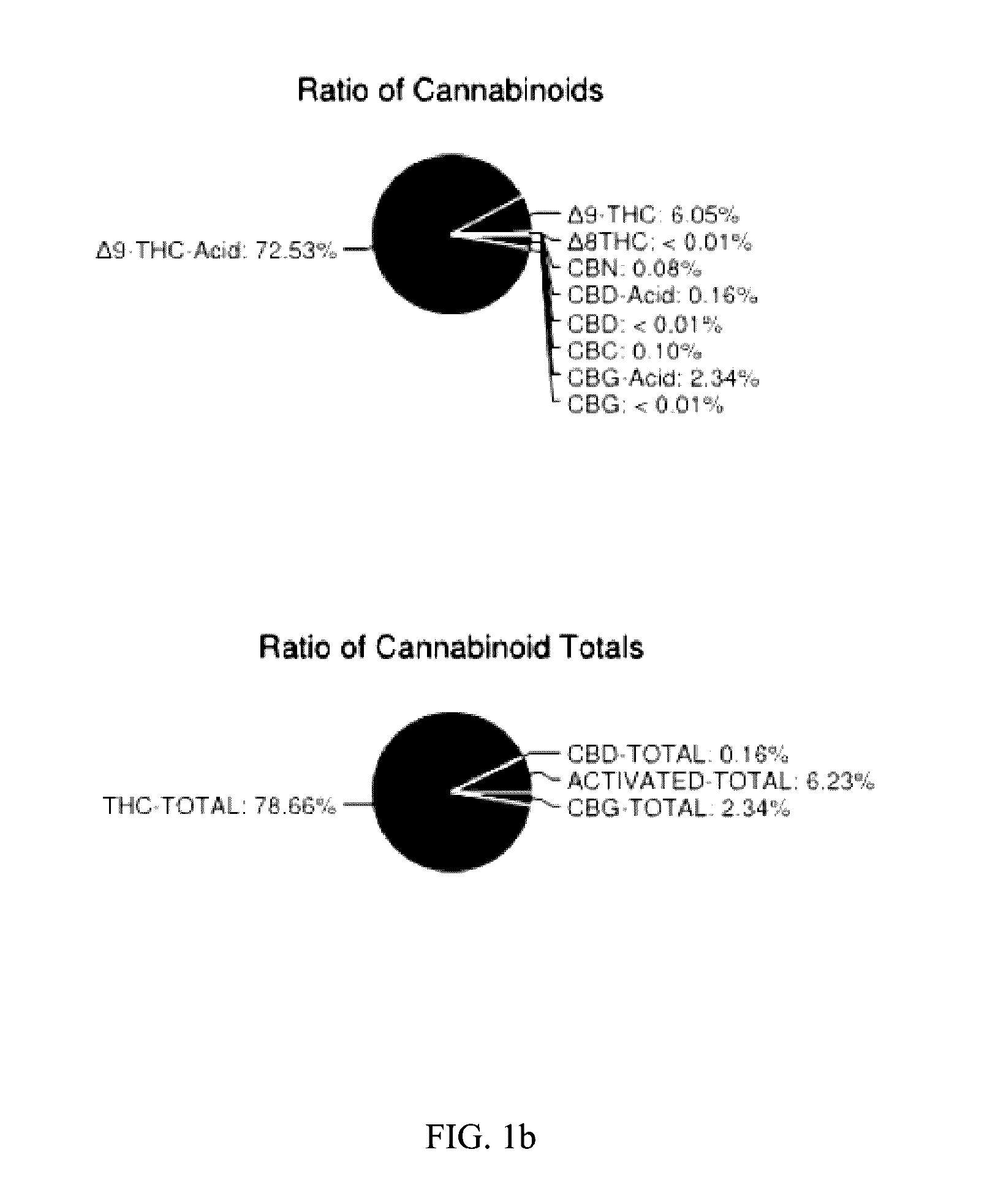
A method for preparing a purified cannabis extract may comprise extracting a crude extract from cannabis solids, dewatering the crude extract, removing chlorophyll from the crude extract, and distilling the crude extract thereby creating a purified cannabis extract. The extracting step may include contacting crude cannabis solids with an organic ester, thereby creating the crude extract and waste solids. The dewatering step may include contacting the crude extract with a solid dewatering agent and filtering the crude extract from the solid dewatering agent. The removing chlorophyll step may include contacting the crude extract with a solid absorbent agent, and filtering the crude extract from the solid absorbent agent.
Owner:EASY EXTRACTS LLC
Color masterbatch
The invention relates to color masterbatch. The color masterbatch is characterized by comprising, by weight, 75-85% of carriers, 5-6% of additives, 3-5% of dispersing agents, 2-3% of pearl powder, 1-2% of pigments, 1-2% of organic esters and 3-5% of paraffin, wherein the pigments comprise one or the mixture of phthalocyanine red, phthalocyanine blue, phthalocyanine green, sun-proof bright red, macromolecule red, macromolecule yellow, permanent yellow, permanent purple and azo red. The color masterbatch is the indispensable additive for colorization of plastic products, and for PVC products formed in an extrusion mode, the color masterbatch is assorted in variety and color, good in glossiness and high in controllability.
Owner:CHUZHOU HONGYUAN SPRAYING
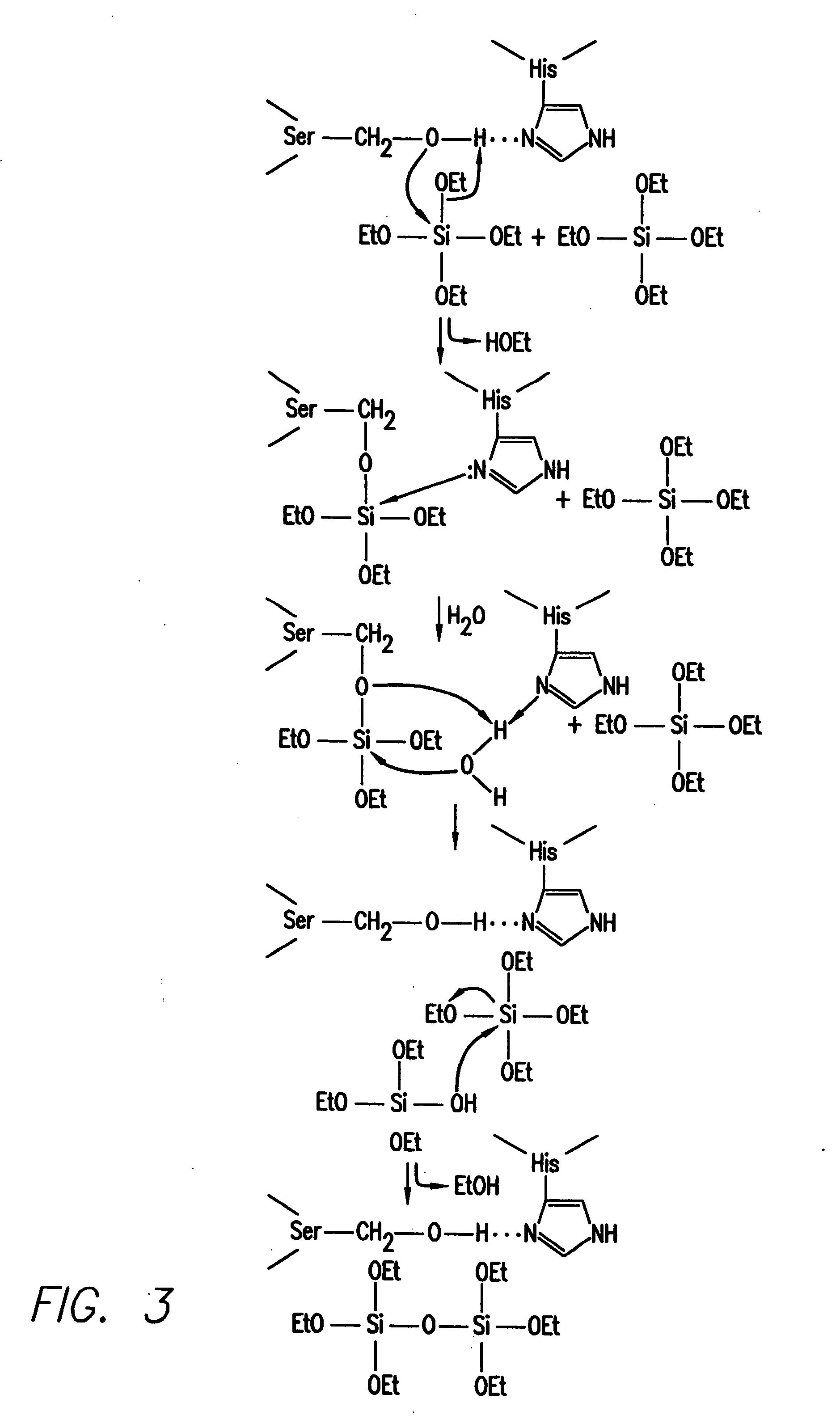
Methods, compositions, and biomimetic catalysts for the synthesis of silica, polysilsequioxanes, polysiloxanes, non-silicon metalloid-oxygen networks, polymetallo-oxanes, and their organic or hydrido conjugates and derivatives
InactiveUS20050090634A1SilicaOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPolymer networkNanostructure
The in vitro polymerization of silica, silicone, non-silicon metalloid-oxane and metallo-oxane polymer networks, by combining a catalyst and a substrate to polymerize the substrate to form silica, polysiloxanes, polymetalloid-oxanes polymetallo-oxanes (metal oxides), polyorganometalloid oxanes, polyorganometallo oxanes, and the polyhydrido derivatives thereof, at about neutral pH. The nanostructure-directing catalysts have a nucleophilic functionality and a hydrogen-bonding acceptor group, and include: silicateins, enzymes that work by a mechanism functionally related to that of the silicateins; self-assembling peptides related to those synthesized and demonstrated capable of acting as biomimetic substitutes for the silicateins; non-peptide-based synthetic polymers containing a nucleophilic group and a hydrogen bonding amine such that the polymer functions by a mechanism of action related to that of the silicateins; materials having such chemical functionality as a nucleophilic group and or a hydrogen bonding amine which, acting in concert with nanoconfinement and or chemical functionality of the surface or matrix to which the functionality is attached, acts catalytically by a mechanism related to that of the silicateins; and small-molecule non-polymeric biomimetic catalysts that operate by the same mechanism as silicateins. The substrate is selected from groups consisting of silicon alkoxides, non-silicon metalloid alkoxides or metal alkoxides, and any organic, organometallic or hydrido derivatives of the foregoing; inorganic and organic oxygen-containing chelates of silicon, non-silicon metalloids or metals and any organic, organometallic or hydrido derivatives of the foregoing; and inorganic and organic esters of the hydoxides of silicon, non-silicon metalloids or metals and any organic, organometallic or hydrido derivatives of the foregoing; and inorganic and organic hydolyzable salts, complexes or conjugates of the hydroxides of silicon, non-silicon metalloids or metals and any organic, organometallic and hydrido derivates of the foregoing.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Catalyst active component for ethylene polymerization or copolymerization and catalyst precursor comprising the active component and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101139407ANot easy to produceImprove copolymerization performanceBulk chemical productionElectron donorAccelerant
The present invention provides catalyst active components used in ethylene polymerization or polymerization, the catalyst precursors as well as the preparation method of the catalyst active components. The catalyst active components in the present invention comprise: magnesium compounds; titanium compounds Ti (OR) 4-n X n , where X is halogen, R is alkyl, n is O or an integer less than or equals 4; catalytic accelerant which is of chelate function and is of matching iron of [O,O] or[O,N]; Electron donor with silicon; Organic ester R'OH, where R' represents alkyl; and halogenated hydrocarbon. The catalyst precursors provided in the present invention are firm particles with high catalytic activity, stable dynamics and good polymerization and hydrogen-sensitive performance. The polyethylene products obtained from the catalyst precursors are particles of good shape, with the particle diameter evenly distributed. The density of the particles is high.
Owner:BEIJING JINDINGKE CHEM TECH
Organic denitrifier and denitrification method for processing high concentration ammonia-nitrogen waste water
The invention discloses an organic denitrifier for treating high concentration ammonia nitrogen wastewater and a denitrogenation method thereof; the organic denitrifier consists of 50%-80% of organic esters, 10%-50% of amines and 10%-50% of alkanes. 10-20ppm of the organic denitrifier is added into the high concentration ammonia nitrogen wastewater according to the proportion, and pH of the wastewater is adjusted with in the range of 9.0-10.4, then aeration is carried out for two hours; The organic denitrifier is only added into wastewater, ether in aeration tank or in aeration tower; the invention can be applied for eliminating high concentration inorganic ammonia nitrogen and organic nitrogen, especially for eliminating high concentration inorganic ammonia nitrogen. The concentration of the ammonia nitrogen wastewater can be reduced from 30000mg / L to below 0.5mg / L. The eliminating rate can reach 99.999%; and the required quantity of the denitrifier is small, the denitrogenation method can be applied simply.
Owner:溧阳常大技术转移中心有限公司
Composite bacterial agent and biological method for treating flow-back fracturing fluid to obtain oil displacement active water
InactiveCN101935615ACapable of recyclabilityWith oil displacement abilityFungiBacteriaMetaboliteFracturing fluid
The invention discloses a composite bacterial agent and a biological method for treating flow-back fracturing fluid to obtain oil displacement active water, which relate to biotransformation and reutilization technology of fracturing flow-back fluid. In the method, the fracturing flow-back fluid is treated by a microbial fermentation method, and a residual organic substance harmful to environment in the flow-back fluid is transformed into biological active water with certain function. The composite bacterial agent and the method are applied to reinjection water of water injection wells, reinjection water for single-well soaking, reinjection water for oil field blockage removal, reinjection water for other purposes, water for medicament preparation in a technical process and the like. The composite bacterial agent comprises biosurfactant, organic acid, organic ester, organic ketone, biogas and other metabolites produced by microbial metabolism of the fracturing flow-back fluid.
Owner:DALIAN BITEOMICS INC
Polymerizable compounds and compositions
InactiveUS20050043490A1Modest adhesionHigh fluoride ion releaseImpression capsMedical preparationsArylOrganic acid
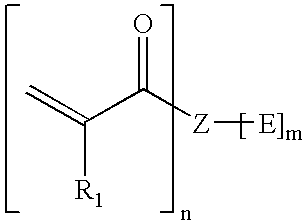
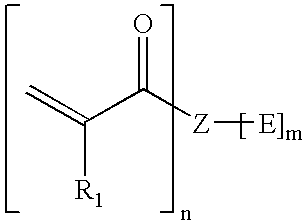
An esterified macromonomer within the scope of the general formula: wherein Z is an organic moiety, R1 is hydrogen or a substituted or unsubstituted alkyl having from 1 to 12 carbon atoms, oxyalkyl having from 1 to 12 carbon atoms, alkenyl having from 2 to 12 carbon atoms, cycloalkyl having from 5 to 12 carbon atoms, aryl having from 6 to 12 carbon atoms or aralkyl having from 7 to 12 carbon atoms, each E independently is a hydroxyl group, an organic ester moiety or an inorganic ester containing moiety and at least one E is an ester containing moiety, n and m each independently is an integer from 2 to 12. The esterified macromonomer is obtainable by esterification of at least a portion of the —OH groups of a macromonomer having at least one terminal double bond with at least one derivative of an inorganic or organic acid which introduces pendant groups exhibiting at least one acid moiety selected from the group of consisting of —COOH, —PO3H2, —SO3H, —BO2H or salts thereof. The number of the acid moieties is chosen such that a polymer obtained by polymerizing those monomers has an adhesive strength to dentine of at least 2 MPa.
Owner:KLEE JOACHIM E +1
Prepn process of solid super acidic catalyst
InactiveCN1421270AIncrease acidityHigh acid strengthPhysical/chemical process catalystsAlcoholOrganic Ester
The preparation process of solid acidic catalyst includes: dissolving organic ester in C1-C10 alcohol to prepare solution, mixing the ester alcohol solution with water solution of compound of Zr, Ti,Fe or Al, regulating the pH of the mixture solution with alkali solution to 6-11, ageing of the mixture in the temperature of room temperature to 100 deg.C for 1-24 hr, and filtering to obtain solid;water washing the solid, drying in 50-200 deg.c for 2-48 hr; dissolviong zirconium sulfate in the water solution of sulfuric acid of 1-15% concentration, soaking the solid in the solution, and roasting the product at 500-800 deg.c for 1-24 hr. The solid acidic catalyst of the present invention has high acidity, high reaction activity and high selectivity.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Retardance and low damage acid solution system for high temperature condensate oil gas reservoir acidification
The present invention discloses a retardance and low damage acid solution system for high temperature condensate oil gas reservoir acidification. The acid solution system is suitable for acidification modification of high temperature deep well, particularly condensate gas reservoir, and comprises the following components, by weight, 0.5-3 parts of hydrofluoric acid or 6-12 parts of fluoroboric acid, 8-10 parts of an organic ester, 0.01-0.05 part of a catalyst, 0.1-1 part of a corrosion inhibitor, 0.1-1 part of an iron ion stabilizer, 0.1-1 part of a clay stabilizer, 1-2 parts of a cleanup additive, and 80-100 parts of water. According to the present invention, effects of retardance and corrosion inhibition of the acid solution system can be well achieved at a high temperature, and water blocking can be released and acid solution backflow can be easily achieved with the finally produced methanol and the carbon dioxide.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Lithium ion battery gel electrolyte, monomer of lithium ion battery gel electrolyte, preparation method of monomer, and preparation method of lithium ion battery
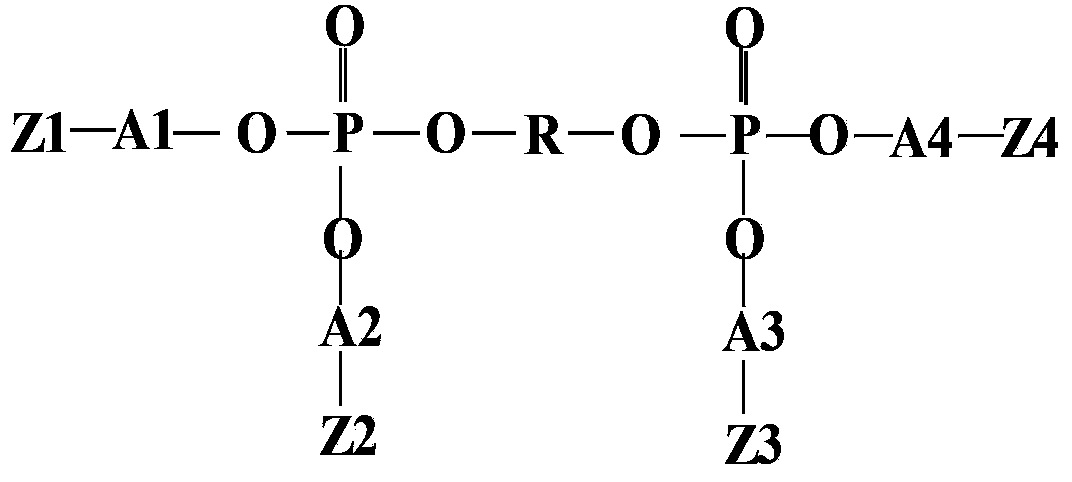
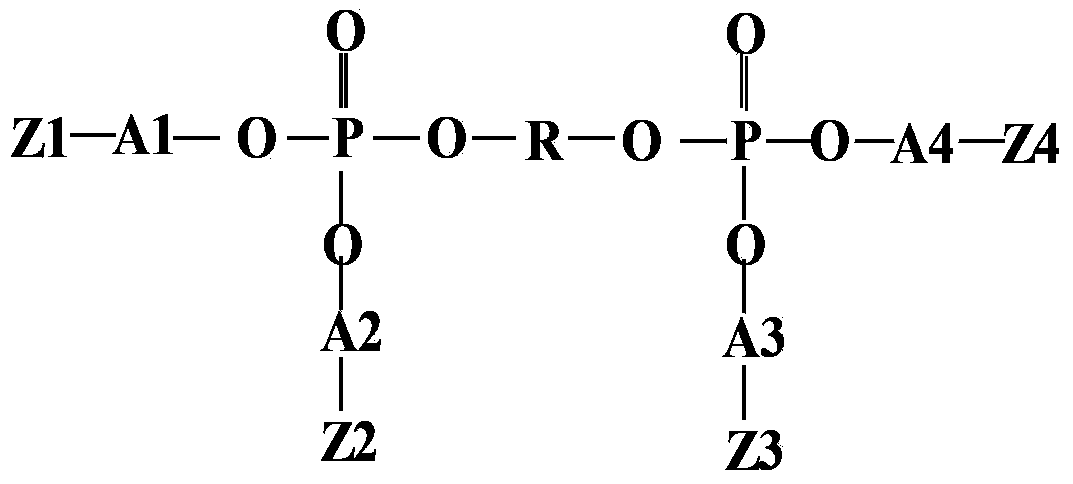
ActiveCN103441299AImprove securityImprove reliabilityFinal product manufactureElectrolyte accumulators manufactureEpoxyElectrolysis
The invention provides a monomer of a lithium ion battery gel electrolyte and a preparation method of the monomer, the lithium ion battery gel electrolyte and a preparation thereof, and a preparation method of a lithium ion battery. According to the general formula of the monomer, R represents the alkyl group of a dihydric alcohol, the alkyl group of a binary epoxy or the alkyl group of diglycidyl ether; A1, A2, A3 and A4 represent alkyl groups with 1 to 10 carbon atoms; and Z1, Z2, Z3 and Z4 represent organic esters with 1 to 10 carbon atoms, wherein the organic esters contain alkenyls. The preparation method of the monomer comprises following steps: phosphorous oxychloride is dissolved in an organic solvent; at least one of the dihydric alcohol, the binary epoxy or diglycidyl ether is added into the solution; an alkenyl ester and acid binding agent triethylamine are added into the mixture; catalyst triphenylphosphine corresponding to the selection of the binary epoxy may be added selectively; and the monomer of the lithium ion battery gel electrolyte is prepared by reaction under backflow of the organic solvent. Therefore, a safety risk that fire and blast of the lithium ion battery may be caused by strong oxidation conditions is lowered.
Owner:DONGGUAN AMPEREX TECH
Preparation of wood pulps with caustic pretreatment for use in the manufacture of cellulose acetates and other organic esters
A process for making cellulose acetate or cellulose esters which pretreats a wood pulp prior to acetylation or esterification is disclosed. The pretreatment of the wood pulp includes the mixture of wood pulp into a caustic solution to form a suspension of wood pulp. The suspension of wood pulp is separated from the caustic solution to form a cake. The cake is washed with an acid to obtain an acid and cellulose cake having a low water content. The acid and cellulose cake is then acetylated or esterifed to form cellulose acetate or other cellulose esters.
Owner:DEUT BANK AG NEW YORK BRANCH AS COLLATERAL AGENT
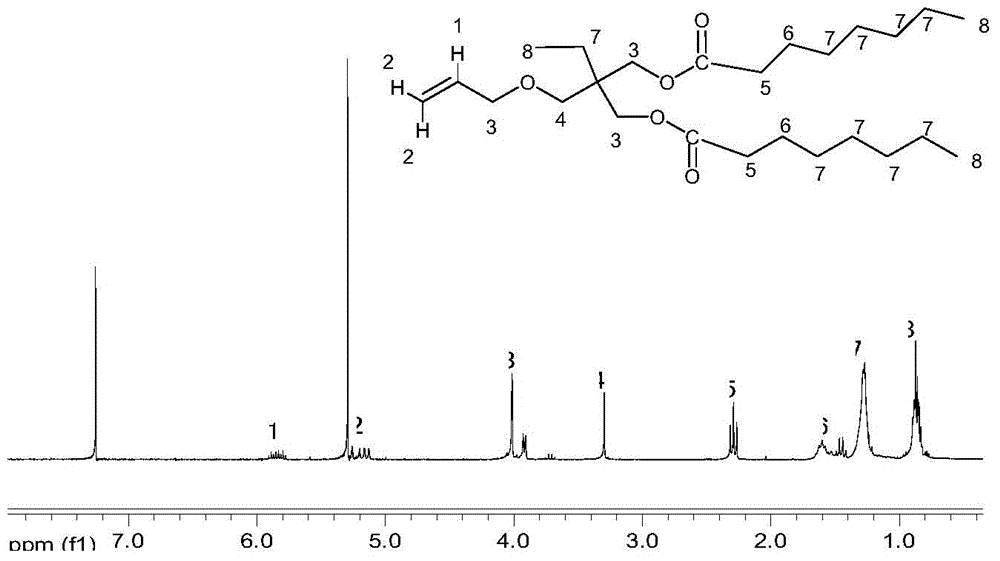
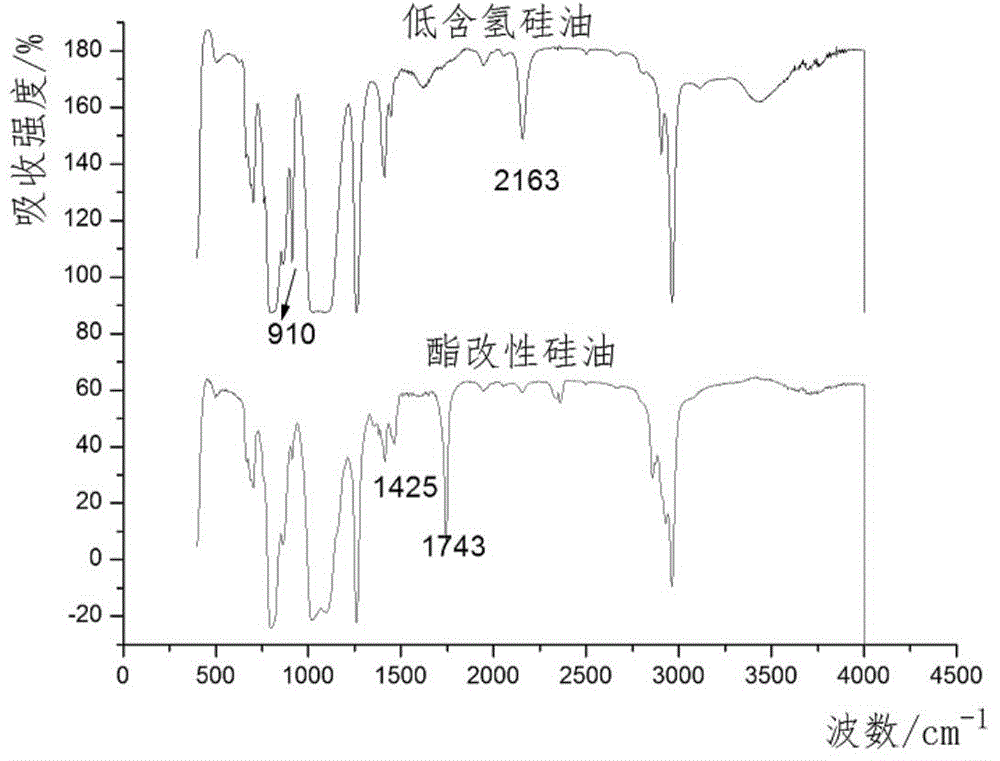
Polyol-ester-modified silicone oil and preparation method thereof, carbon fiber oil solution
The invention relates to polyol-ester-modified silicone oil and a preparation method thereof, a carbon fiber oil solution, particularly a polyol-ester-modified silicone oil and a preparation method thereof, and a carbon fiber oil solution using the polyol-ester-modified silicone oil as a key component, belonging to the technical field of organic high polymers. The polyol ester with favorable heat resistance is directly connected to the siloxane side chain to obtain the novel polyol-ester-modified silicone oil, and the novel polyol-ester-modified silicone oil is used as a necessary component of a low-silicon carbon fiber oil solution to basically avoid the possibility of microscopic phase separation between the polyol ester and silicone oil, thereby obtaining the oil solution product with favorable microscopic compatibility; and besides, the polyol-ester-modified silicone oil simultaneously contains the siloxane chain segment on the main chain and the polyol ester chain segment of the side chain, and thus, has favorable compatibility for other added silicone oil compounds and organic ester compounds, thereby being beneficial to lowering the cost and regulating the formula of the carbon fiber oil solution.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com