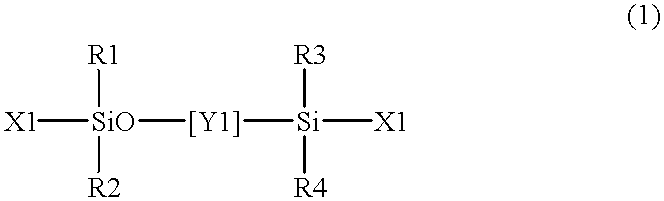
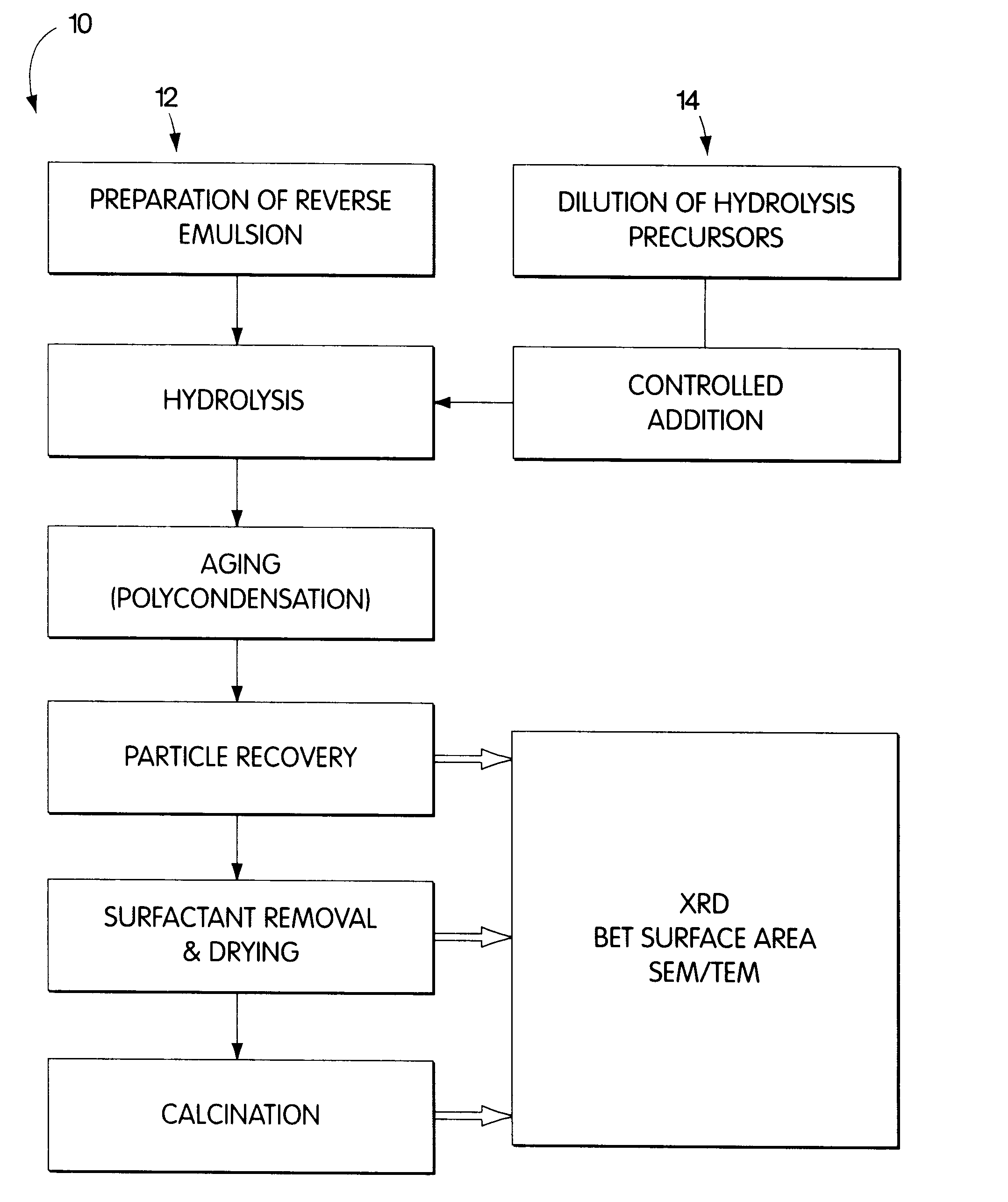
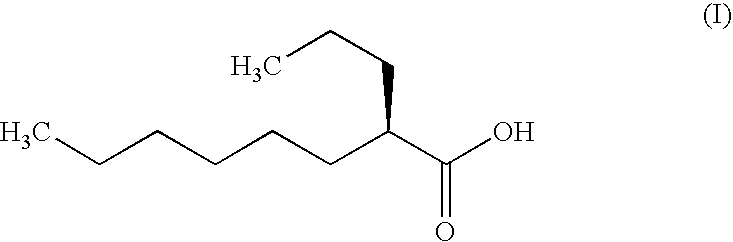
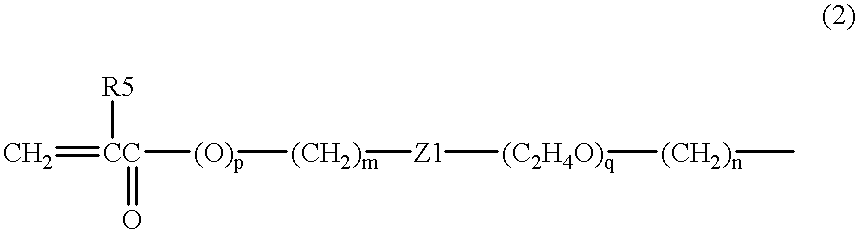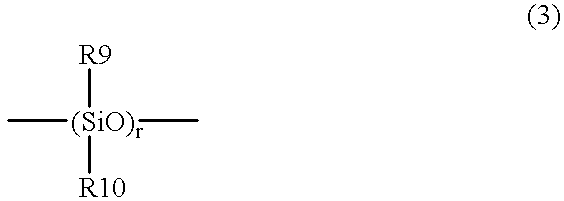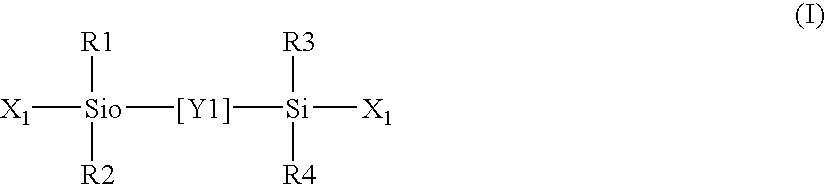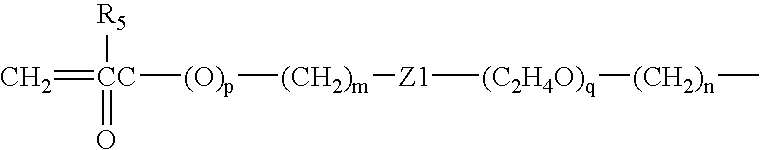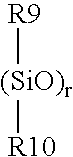Patents
Literature
29459 results about "Water content" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Water content or moisture content is the quantity of water contained in a material, such as soil (called soil moisture), rock, ceramics, crops, or wood. Water content is used in a wide range of scientific and technical areas, and is expressed as a ratio, which can range from 0 (completely dry) to the value of the materials' porosity at saturation. It can be given on a volumetric or mass (gravimetric) basis.
Long wearable soft contact lens
The present invention relates to a soft contact lens, and provides a contact lens which shows small and stable contact angle to water at its surface in water as well as in air, little deposition in wearing, high oxygen permeability, no adhesion of lens to a cornea and superior extended-wearing characteristics. The present invention provides a hydrogel soft contact lens which has contact angle at a lens surface in a range of 10-50° by the captive bubble method in water and 30-90° by the sessile drop method in air, oxygen permeability of not less than 30 and water content of not less than 5%, and also a hydrogel soft contact lens consisting of a polymer comprising a hydrophilic siloxanyl monomer shown by a specified general formula.
Owner:COOPERVISION INT LTD
Synthesis of nanometer-sized particles by reverse micelle mediated techniques
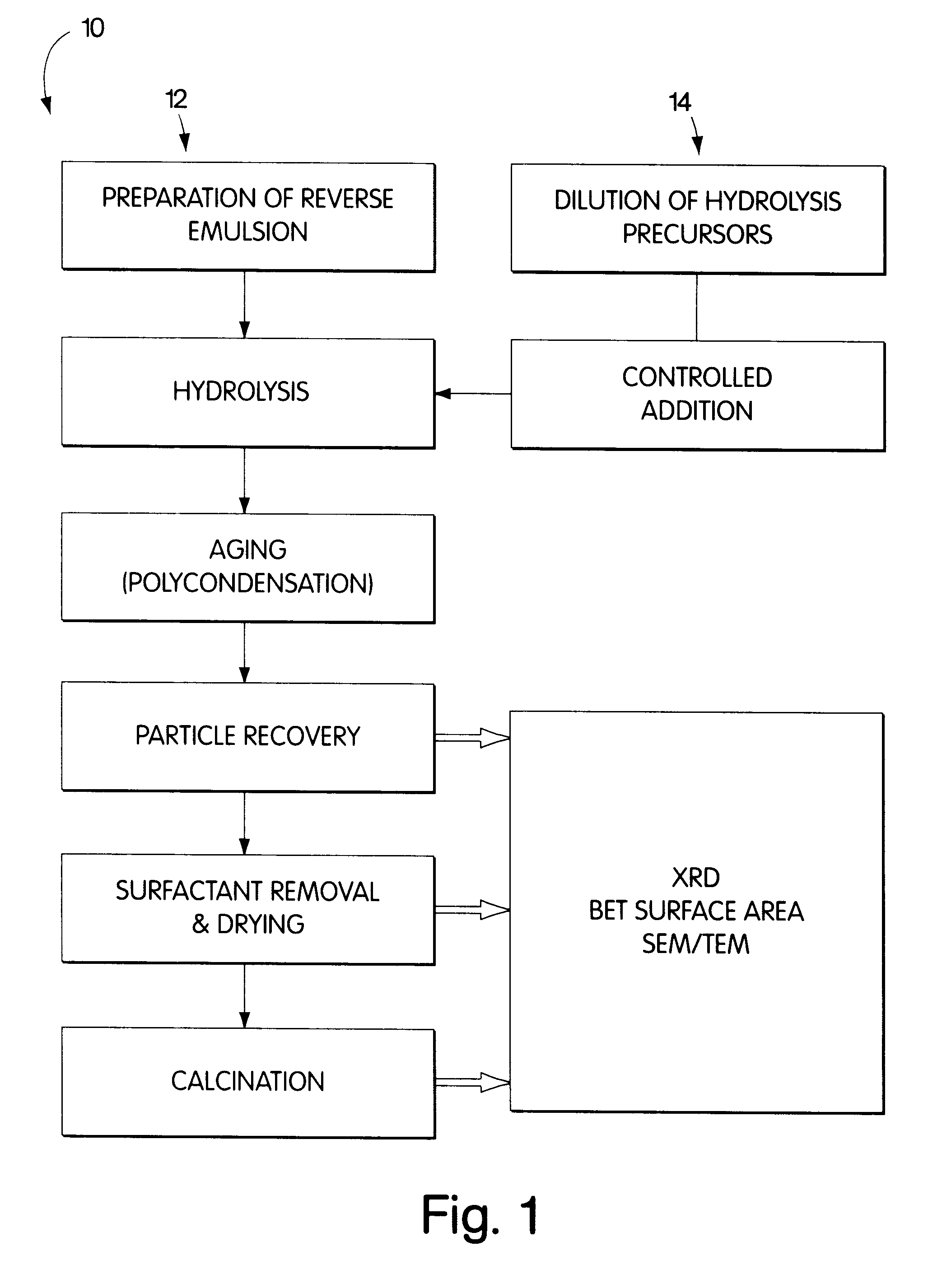
The present invention relates to a method of producing particles having a particle size of less than 100 nm and surface areas of at least 20 m2 / g where the particles are free from agglomeration. The method involves synthesizing the particles within an emulsion having a 1-40% water content to form reverse micelles. In particular, the particles formed are metal oxide particles. The particles can be used to oxidize hydrocarbons, particularly methane.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Silicone hydrogel contact lens
Ophthalmically compatible contact lenses include lens bodies configured for placement on a cornea of an animal or human eye. The lens bodies are made of a hydrophilic silicon-containing polymeric material. The lens bodies have oxygen permeabilities, water content, surface wettabilities, flexibilities, and / or designs to be worn by a lens wearer even during sleep. The present lenses can be worn on a daily basis, including overnight, or can be worn for several days, such as about thirty days, without requiring removal or cleaning.
Owner:COOPERVISION INT LTD
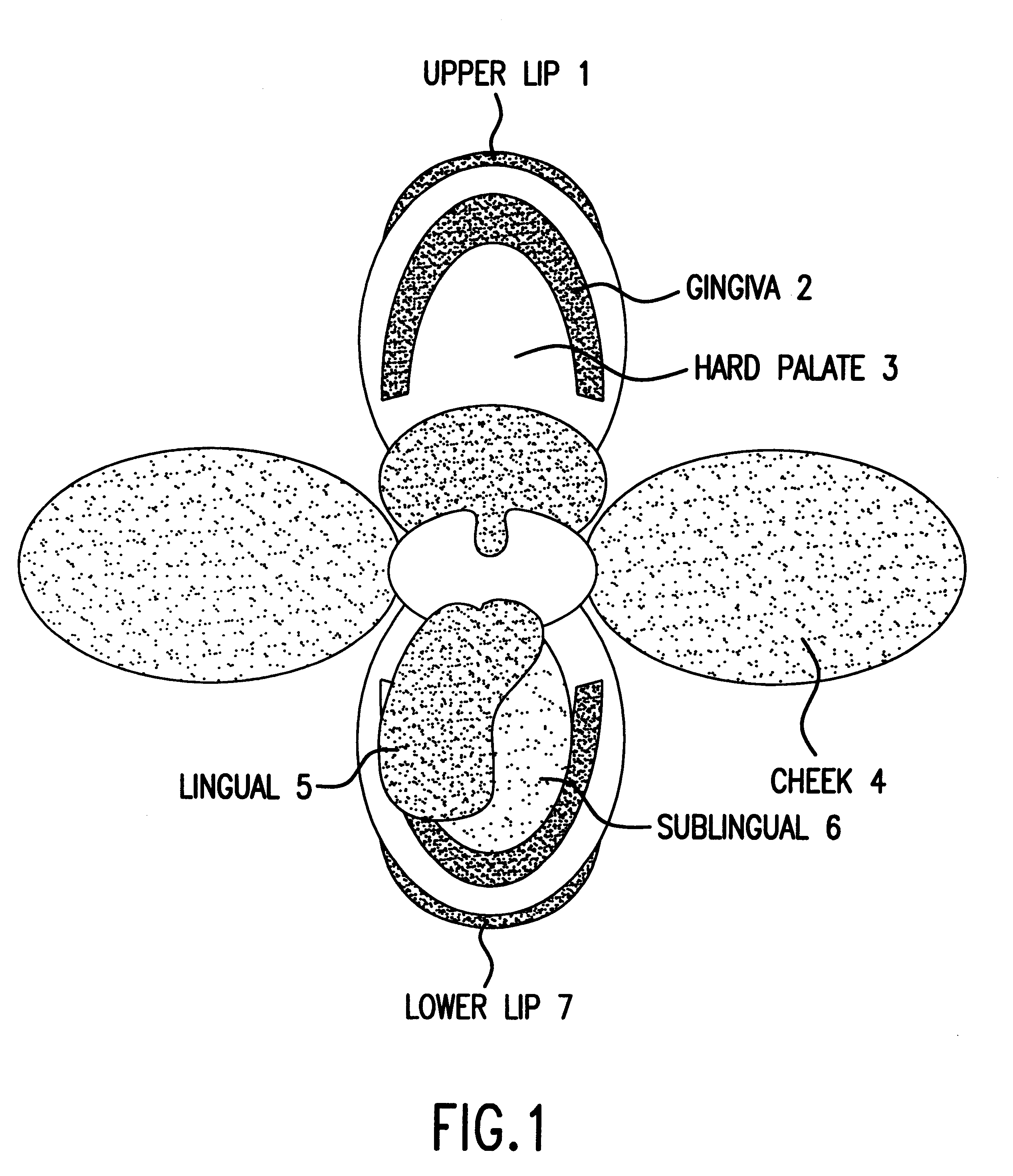
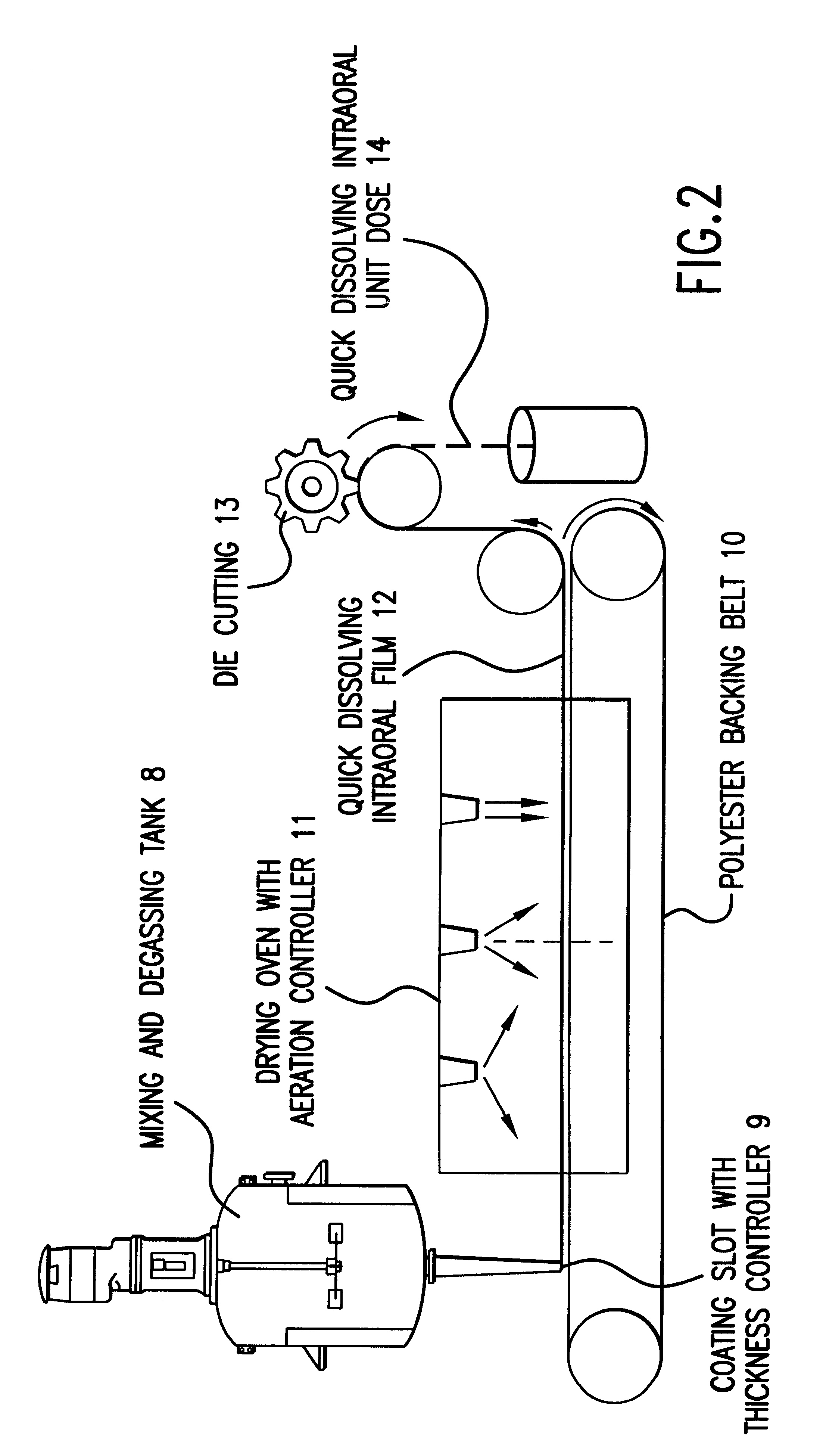
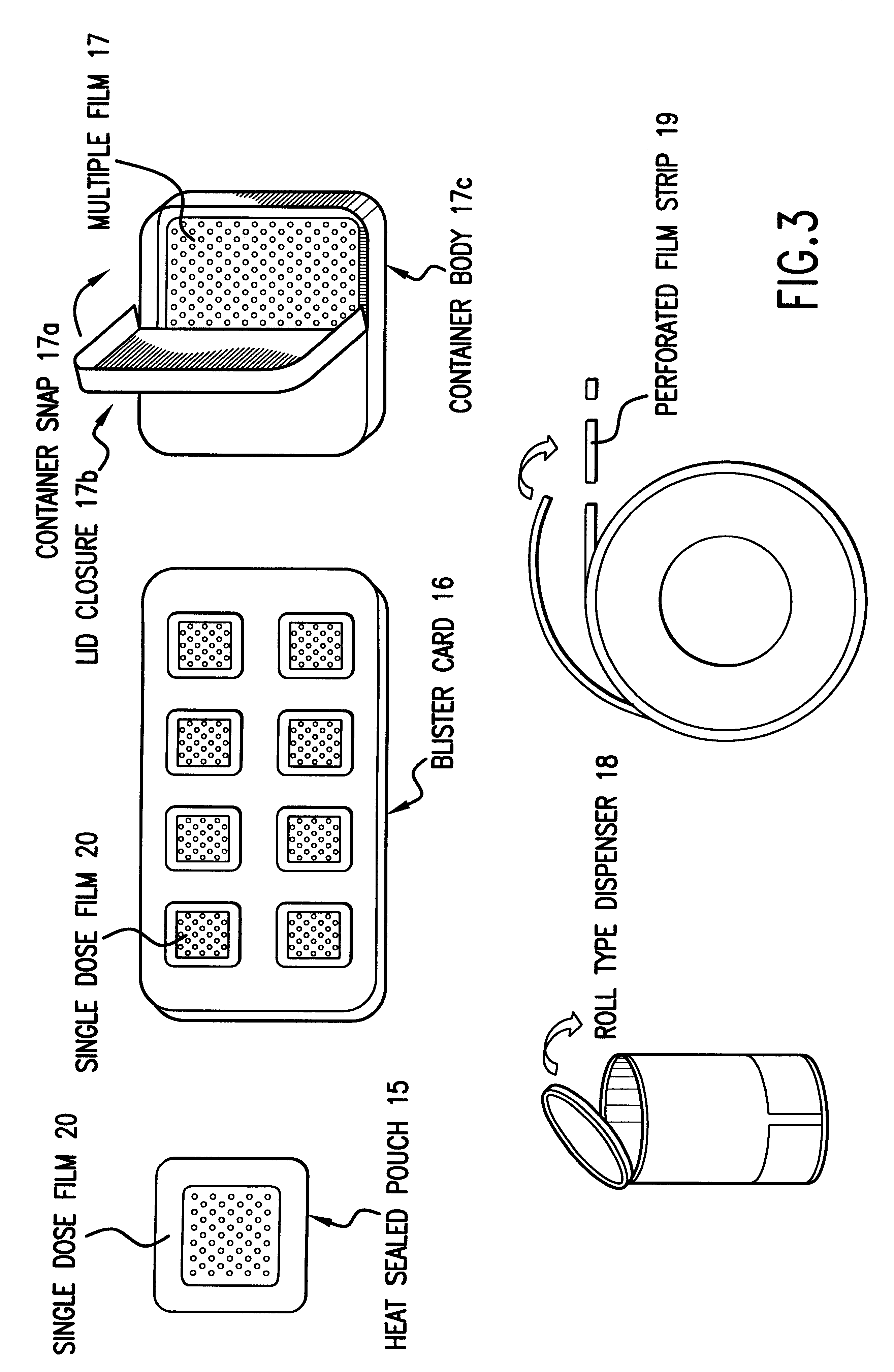
Compositions and methods for mucosal delivery
Mucosal surface-coat-forming film dosage units containing a water-soluble hydrocolloid, an effective dose of an active agent and a mucosal adhesion enhancer; wherein the active agent is encapsulated within a polymer which is chemically or physically distinct from the hydocolloid; wherein the mucosal adhesion enhancer is a starch graft copolymer; wherein the film exhibits a dry tack value of less than 3.5 g, a wet tack of greater than 35 g, a gelation temperature that is greater than 70° C. for a 2% polymer solution, a dry film thickness of less than 20 mil, a water content of 0.5 to 10%, a tensile strength greater than 1500 psi, a modulus in the range of 35,000 to 300,000 psi, a % elongation of less than 20%, a tear probagation resistance of 0.001 to 1 N, and a dissolution time in the range of 1 to 600 seconds upon application to an oral mucosal surface.
Owner:THALLIUM HLDG CO LLC
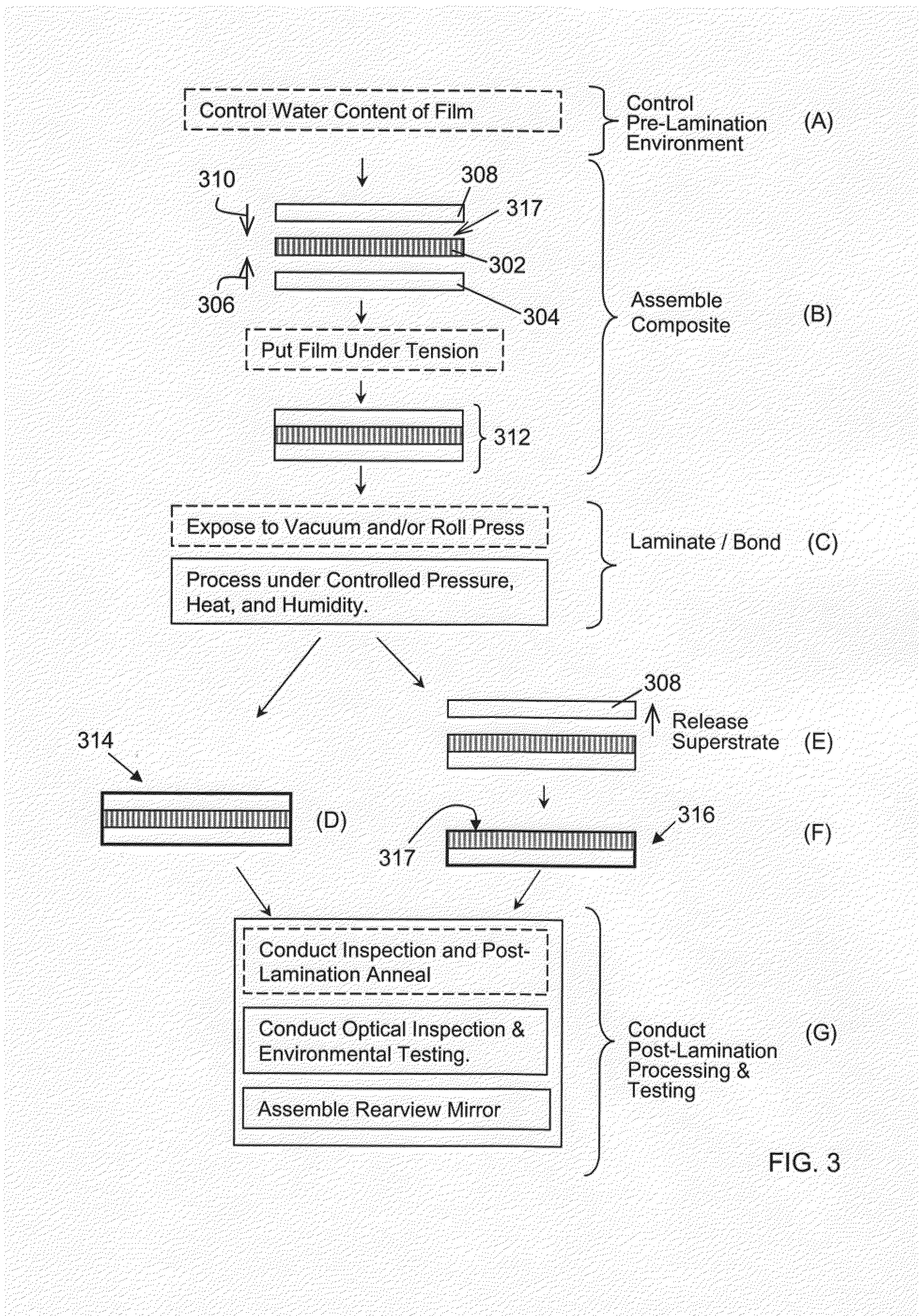
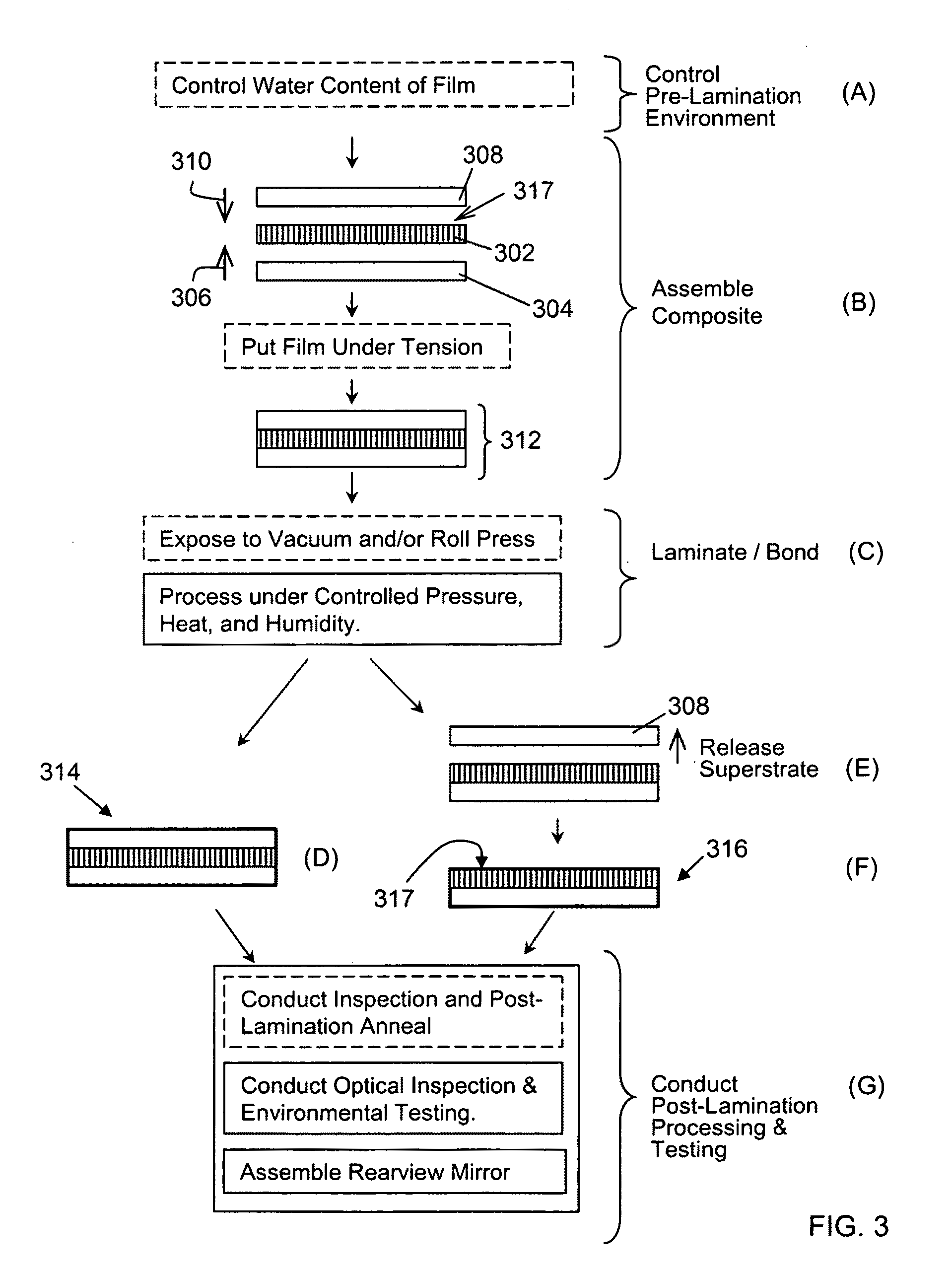
Rearview Mirror Assemblies With Anisotropic Polymer Laminates
ActiveUS20100277786A1High strengthAdequate flatness of filmPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsLower limitGlass transition
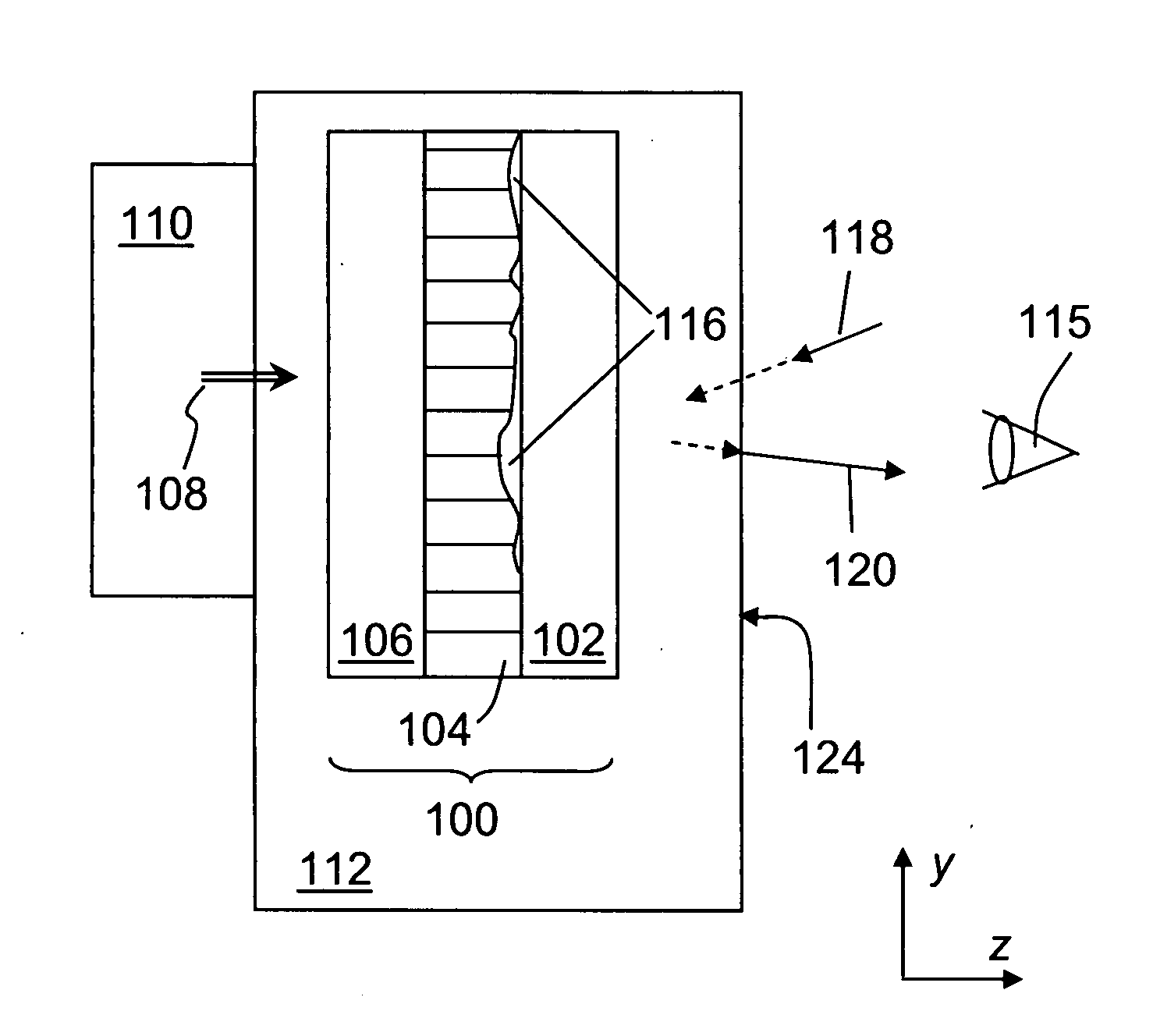
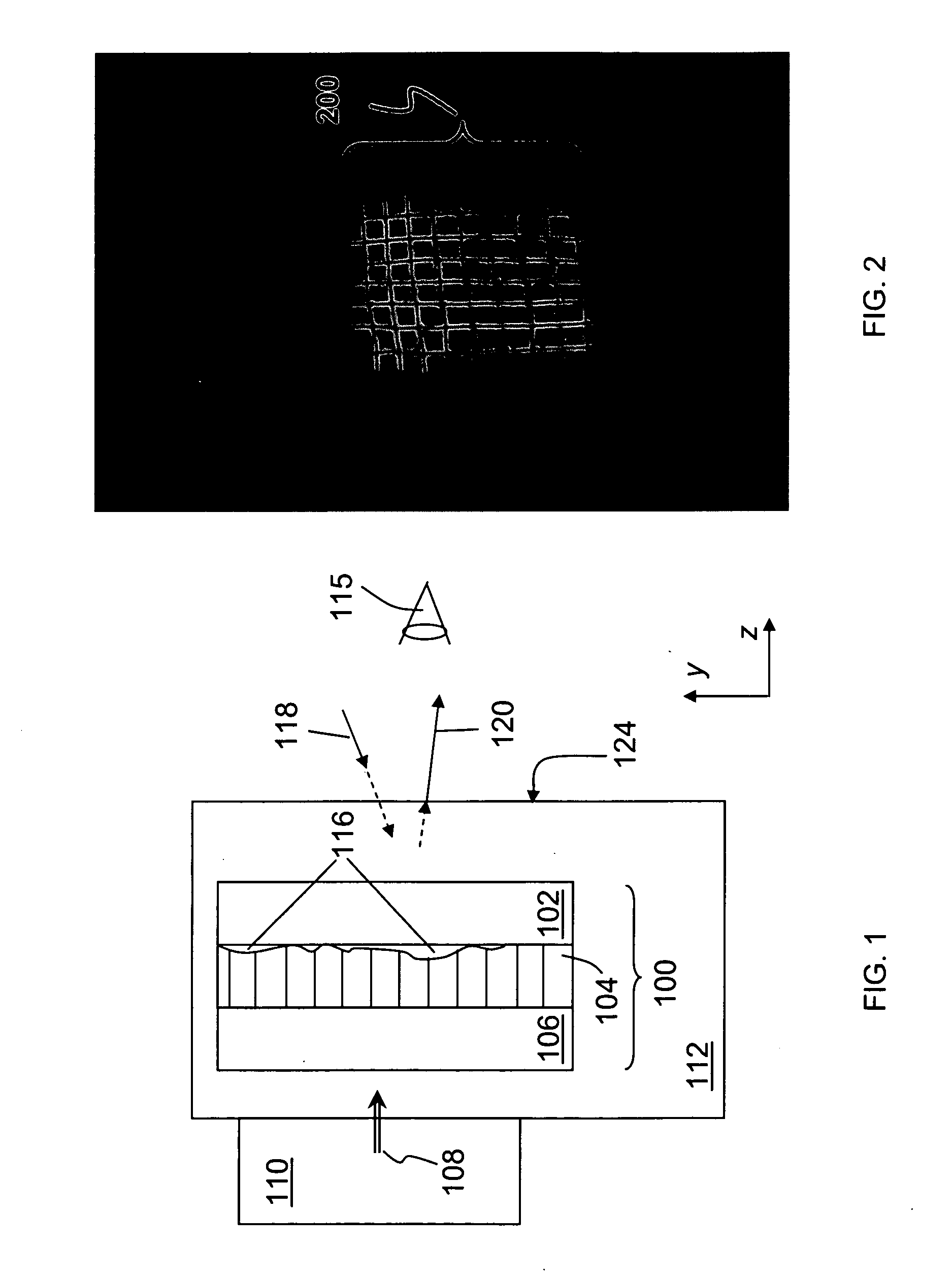
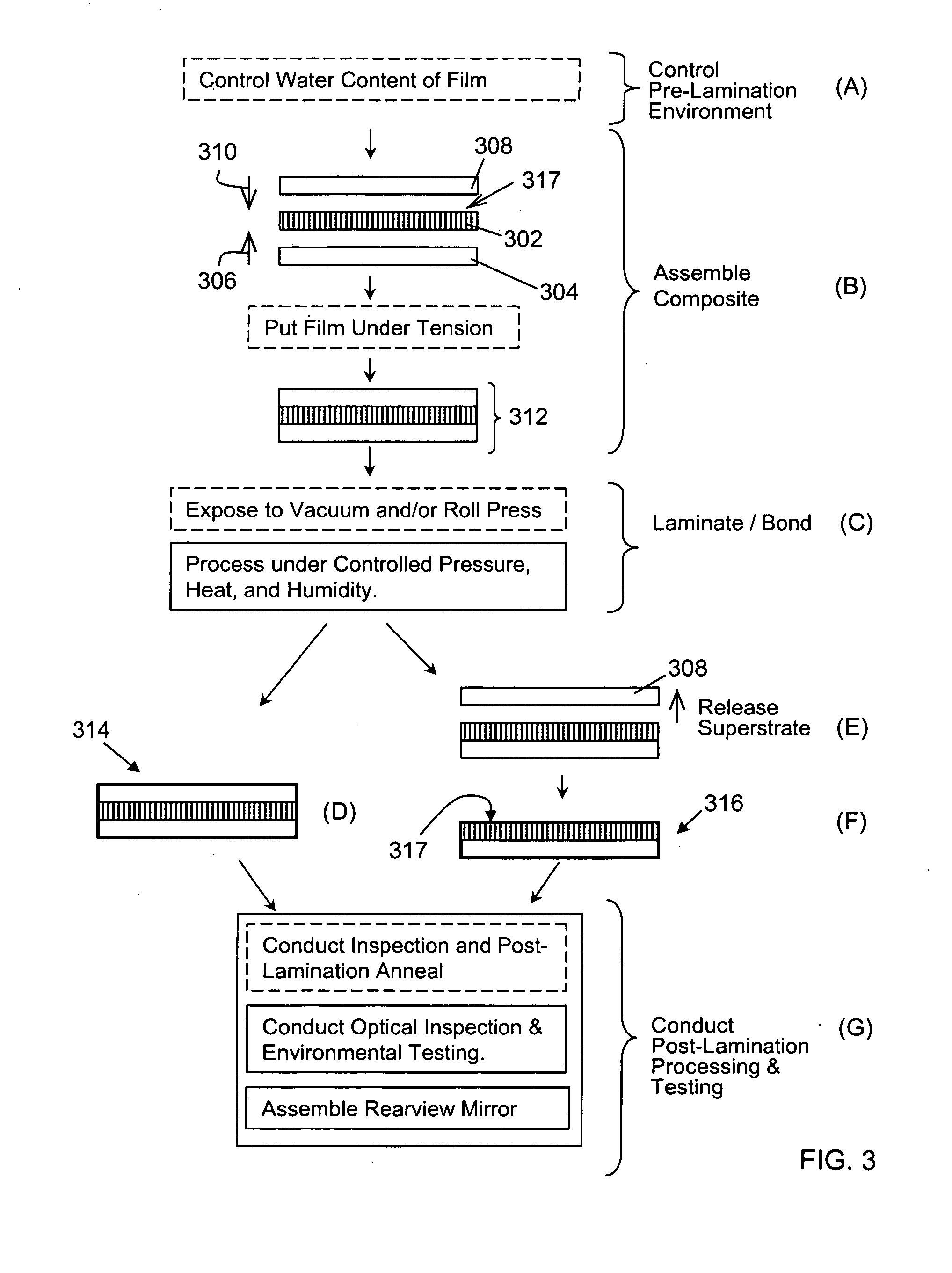
Anisotropic film laminates for use in image-preserving reflectors such as rearview automotive mirror assemblies, and related methods of fabrication. A film may comprise an anisotropic layer such as a light-polarizing layer and other functional layers. The film having controlled water content is heated under omnidirectional pressure and vacuum to a temperature substantially equal to or above a lower limit of a glass-transition temperature range of the film so as to be laminated to a substrate. The laminate is configured as part of a mirror structure so as to increase contrast of light produced by a light source positioned behind the mirror structure and transmitted through the mirror structure towards a viewer. The mirror structure is devoid of any extended distortion and is characterized by SW and LW values less than 3, more preferably less than 2, and most preferably less than 1.
Owner:GENTEX CORP
Polymorphous forms of rifaximin, processes for their production and use thereof in medicinal preparations
Crystalline polymorphous forms of the rifaximin (INN) antibiotic named rifaximin α and rifaximin β, and a poorly crystalline form named rifaximin γ have been discovered. These forms are useful in the production of medicinal preparations for oral and topical use and can be obtained by means of a crystallization process carried out by hot-dissolving the raw rifaximin in ethyl alcohol and by causing the crystallization of the product by the addition of water at a determinate temperature and for a determinate period of time. The crystallization is followed by drying carried out under controlled conditions until a specific water content is reached in the end product.
Owner:ALFASIGMA SPA
Rearview Mirror Assemblies With Anisotropic Polymer Laminates
ActiveUS20090296190A1High strengthAdequate flatness of filmMirrorsSynthetic resin layered productsLower limitWing mirror
Anisotropic film laminates for use in image-preserving reflectors such as rearview automotive mirror assemblies, and related methods of fabrication. A film may comprise an anisotropic layer such as a light-polarizing layer and other functional layers. The film having controlled water content is heated under omnidirectional pressure and vacuum to a temperature substantially equal to or above a lower limit of a glass-transition temperature range of the film so as to be laminated to a substrate. The laminate is configured as part of a mirror structure so as to increase contrast of light produced by a light source positioned behind the mirror structure and transmitted through the mirror structure towards a viewer. The mirror structure is devoid of any extended distortion and is characterized by SW and LW values less than 3, more preferably less than 2, and most preferably less than 1.
Owner:GENTEX CORP
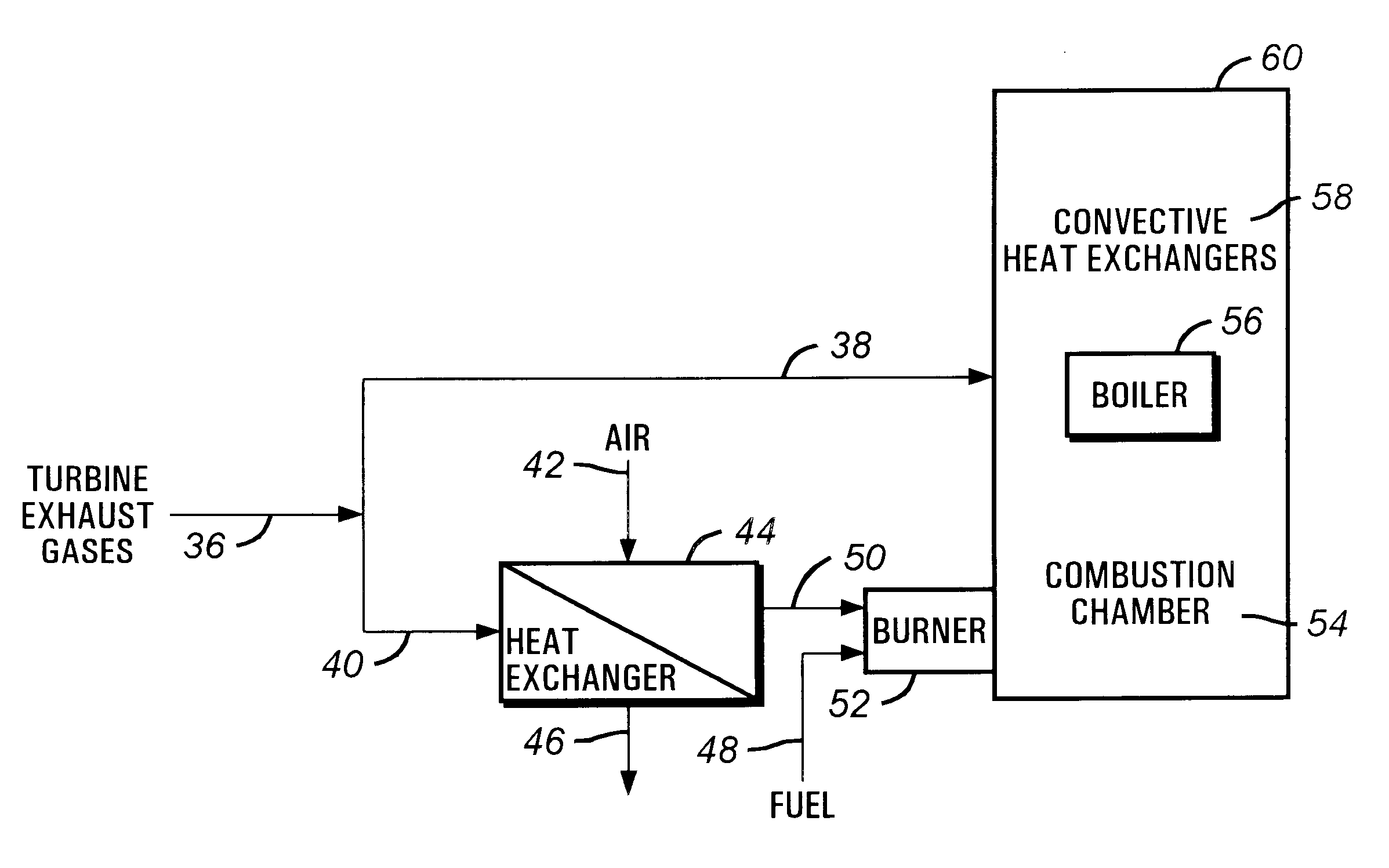
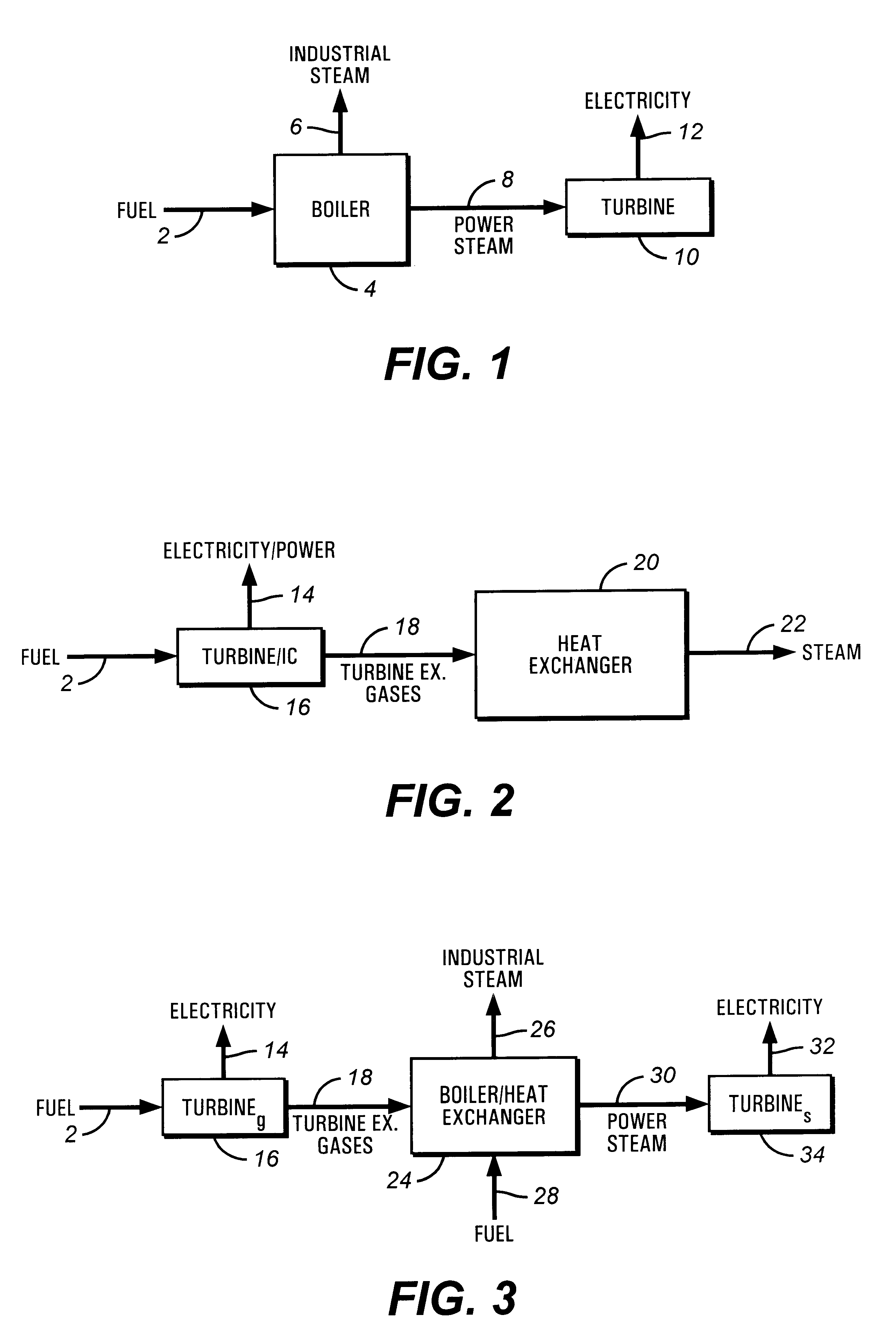
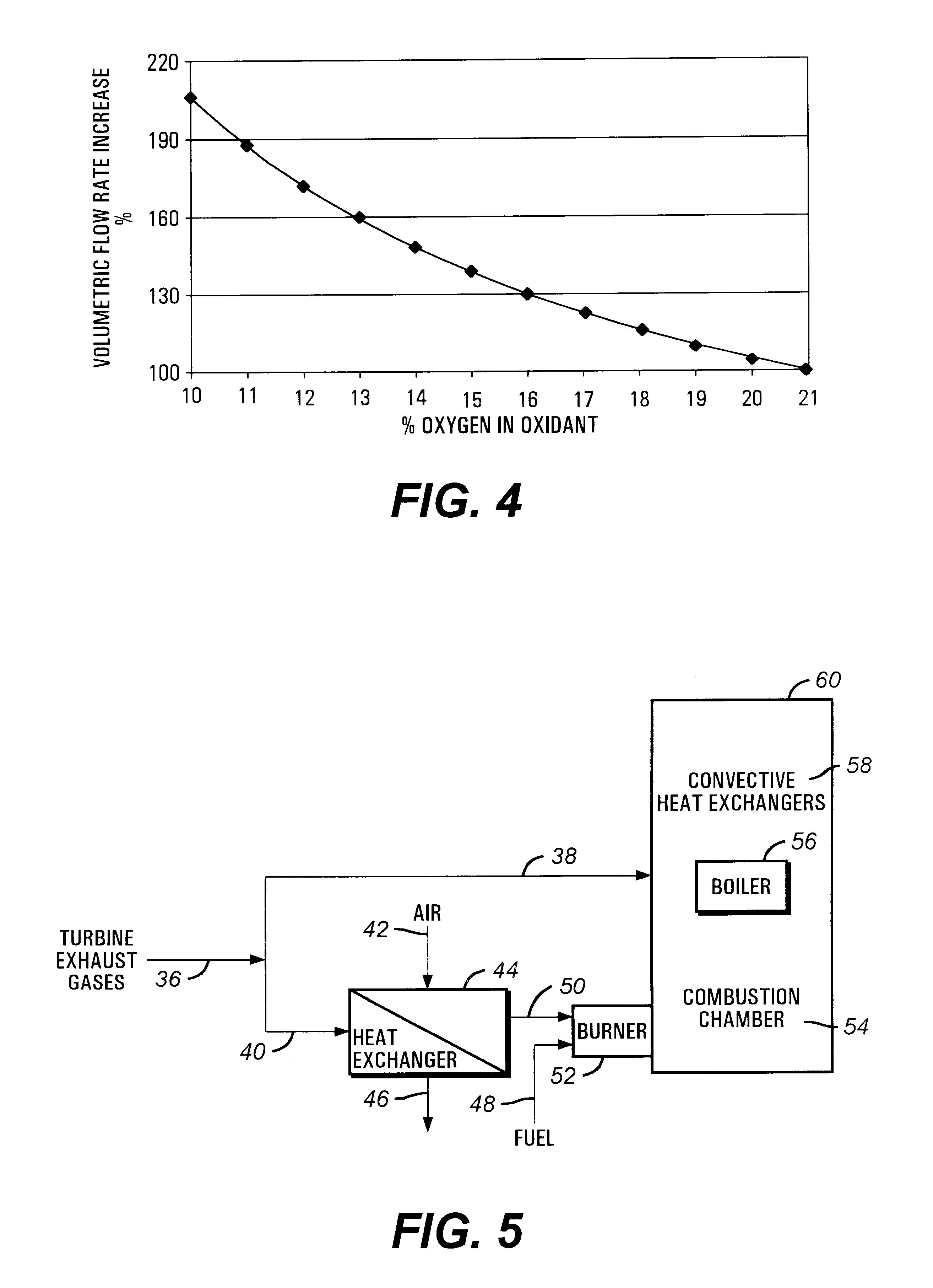
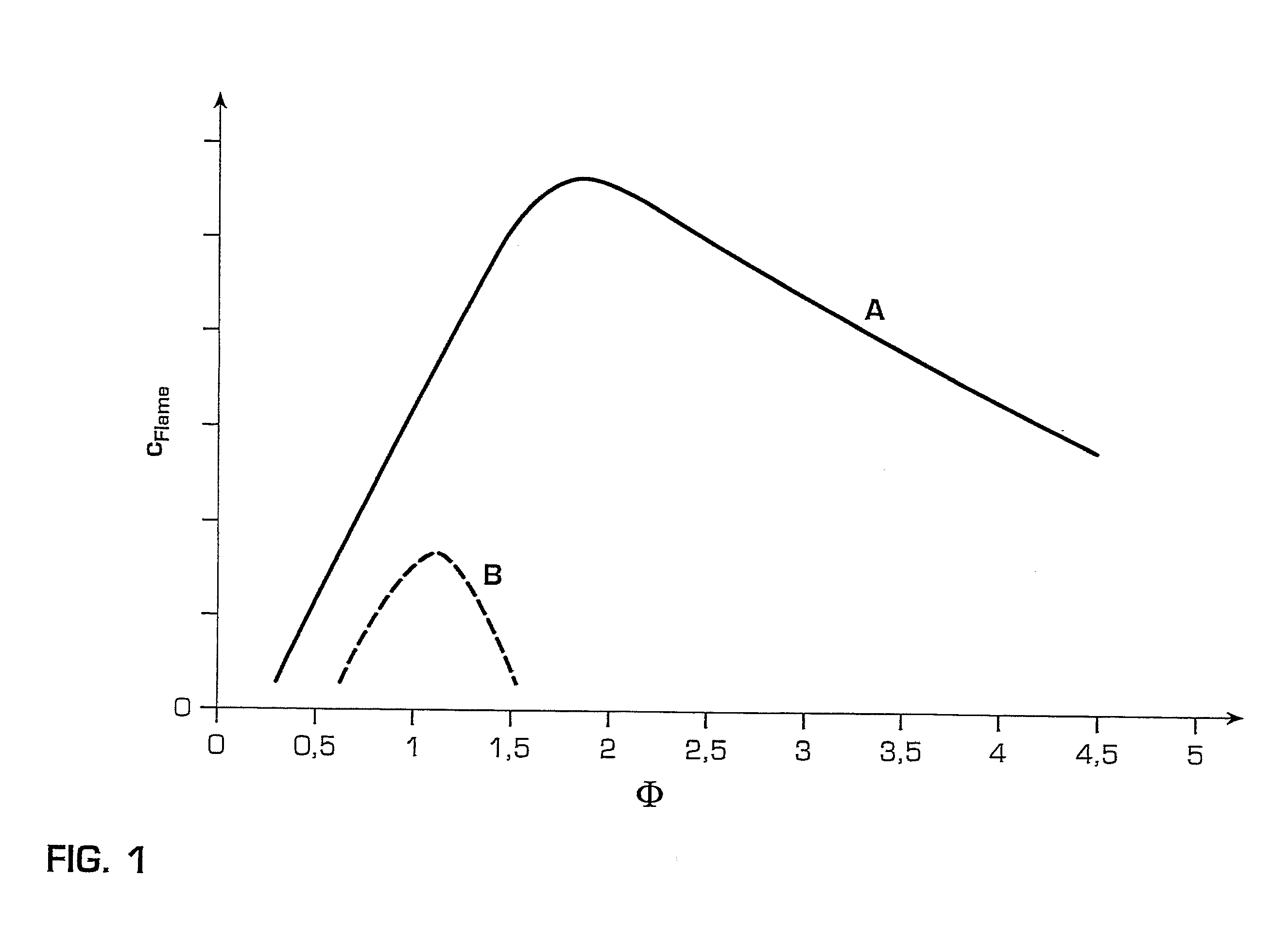
Oxidant control in co-generation installations
InactiveUS6247315B1Steam regenerationIndirect carbon-dioxide mitigationControl system designCogeneration
This invention is related to so-called combined cycle co-generation installations, and it addresses present concerns of the industry. Among these, combustion stability, corrosion (due to large water content in the flue gases), large heat transfer areas, and the like. In some embodiments, an additional heat exchanger is added to heat combustion air with a portion of the exhaust gases resulting from an engine, preferably a gas turbine. As a result, the efficiency of the cycle will improve, the oxidant will be enriched by above 50% oxygen, the combustion process will be enhanced, and the dimensions of the boiler may be reduced. It is considered that the combustion air will require between 10% and 80% of the total flue gas volume, more preferably between 20% and 40%. This is the portion of the flue gases sent through the heat exchanger. A control system designed to optimize the flow of the different streams is also presented. Other inventive embodiments forego heat exchanges in lieu of precise control of two flows of exhaust gas, with preferred addition of additional oxidant to the boiler bumers.
Owner:LAIR LIQUIDE SA POUR LETUDE & LEXPLOITATION DES PROCEDES GEORGES CLAUDE +1
Silicone hydrogels comprising desirable water content and oxygen permeability
The present invention relates to a process comprising the steps of reacting a reactive mixture comprising at least one silicone-containing component, at least one hydrophilic component, and at least one diluent to form an ophthalmic device having an advancing contact angle of less than about 80°; and contacting the ophthalmic device with an aqueous extraction solution at an elevated extraction temperature, wherein said at least one diluent has a boiling point at least about 10° higher than said extraction temperature.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Gas Turbine Installation with Flue Gas Recirculation
A method and installation are disclosed which can, for example, provide for reliable, low-Nox-emission operation of a gas turbine installation with hydrogen-rich fuel gas. An exemplary gas turbine installation includes an arrangement for flue gas recirculation into a compressor inlet and for fuel gas dilution. Oxygen content in combustion air can be reduced by recirculation of recooled flue gas, and the fuel gas can be diluted with compressed flue gas. The oxygen reduction in the combustion air can lead to minimum residual oxygen in the flue gas which can be used for fuel gas dilution. As a result of the flue gas recirculation, water content in the combustion air can be increased by feedback of the water which results as a combustion product. The oxygen reduction, increased water content, and fuel dilution can reduce the flame velocity of hydrogen-rich fuel gases and enable a robust, reliable and low-emission combustion.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC TECH GMBH
Polymer wood composite
InactiveUS6015612AHigh modulusHigh compressive strengthWood working apparatusRecord information storageFiberThermoplastic
The invention relates to a composition comprising a polymer and wood fiber composite that can be used in the form of a linear extrudate or thermoplastic pellet to manufacture structural members. The polymer and wood fiber composite structural members can be manufactured in an extrusion process or an injection molding process. The linear extrudate or pellet can have a cross-section of any arbitrary shape, or can be a regular geometric. The pellet can have a cross-section shape having a volume of at least about 12 mm3. Preferably the pellet is a right cylindrical pellet having a minimum radius of about 1.5 mm and a minimum length of 1 mm weighing at least 14 mg. The invention also relates to an environmentally sensitive recycle of waste streams. The polymer and wood fiber composite contains an intentional recycle of a waste stream comprising polymer flakes or particles or wood fiber. The waste stream can comprises, in addition to polymer such as polyvinyl chloride or wood fiber, adhesive, paint, preservative, or other chemical stream common in the wood-window or door manufacturing process, or mixtures thereof. The initial mixing step before extrusion of the composite material insures substantial mixing and melt contact between molten polymer and wood fiber. The extruded pellet comprises a consistent proportion of polymer, wood fiber and water. During the extrusion, water is removed intentionally to dry the material to a maximum water content of less than about 10 wt-% based on the pellet weight. To make a structural unit, the pellet is introduced into an extruder or injection molding apparatus wherein, under conditions of temperature and pressure, the composite pellet material is shaped into a useful cross-section. Alternatively, the extruded thermoplastic mass, in the form of a elongated linear extrudate without a pelletizing step, can be immediately directed after formation into an extruder or injection molding apparatus.
Owner:ANDERSEN CORPORATION
Rearview Mirror Assemblies with Anisotropic Polymer Laminates
ActiveUS20100110553A1High strengthAdequate flatness of filmMirrorsNon-linear opticsLower limitWing mirror
Anisotropic film laminates for use in image-preserving reflectors such as rearview automotive mirror assemblies, and related methods of fabrication. A film may comprise an anisotropic layer such as a light-polarizing layer and other functional layers. The film having controlled water content is heated under omnidirectional pressure and vacuum to a temperature substantially equal to or above a lower limit of a glass-transition temperature range of the film so as to be laminated to a substrate. The laminate is configured as part of a mirror structure so as to increase contrast of light produced by a light source positioned behind the mirror structure and transmitted through the mirror structure towards a viewer. The mirror structure is devoid of any extended distortion and is characterized by SW and LW values less than 3, more preferably less than 2, and most preferably less than 1.
Owner:GENTEX CORP
Advanced compatible polymer wood fiber composite
InactiveUS6210792B1Improve compatibilityGood material compatibilitySynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsThermoplasticFiber
The invention relates to a composition comprising a thermoplastic polymer and wood fiber composite that can be used in the form of a linear extrudate or thermoplastic pellet to manufacture structural members. The polymer, the fiber or both can be modified to increase compatibility. The wood fiber composite structural members can be manufactured in an extrusion process or an injection molding process. The linear extrudate or pellet can have a cross-section of any arbitrary shape, or can be a regular geometric. The pellet can have a cross-section shape having a volume of at least about 12 mm3. Preferably the pellet is a right cylindrical pellet having a minimum radius of about 1.5 mm and a minimum length of 1 mm weighing at least 14 mg. The invention also relates to an environmentally sensitive recycle of waste streams. The polymer and wood fiber composite contains an intentional recycle of a waste stream comprising polymer flakes or particles or wood fiber. The waste stream can comprises, in addition to polymer such as polyvinyl chloride or wood fiber, adhesive, paint, preservative, or other chemical stream common in the wood-window or door manufacturing process, or mixtures thereof. The initial mixing step before extrusion of the composite material insures substantial mixing and melt contact between molten polymer and wood fiber. The extruded pellet comprises a consistent proportion of polymer, wood fiber and water. During the extrusion, water is removed intentionally to dry the material to a maximum water content of less than about 10 wt-% based on the pellet weight. To make a structural unit, the pellet is introduced into an extruder or injection molding apparatus wherein, under conditions of temperature and pressure, the composite pellet material is shaped into a useful cross-section. Alternatively, the extruded thermoplastic mass, in the form of a elongated linear extrudate without a pelletizing step, can be immediately directed after formation into an extruder or injection molding apparatus.
Owner:ANDERSEN CORPORATION
Sucralose-containing composition and edible products containing the composition
A composition which is obtained by causing a specific compound to be present together with sucralose. The composition provides a sucralose in a stable form, more particularly, a sucralose which is still stable and thus is significantly suppressed with respect to the decrease in sweetness and discoloration (browning blackening), even when it is subjected to a warming treatment under a condition wherein temperature is high and especially water content is low and / or pH is low. The stabilized sucralose-containing composition can be used a sweetener by itself and as a compound with a food or a drug.
Owner:SAN EI GEN F F I
Cementing compositions and application of such compositions to cementing oil wells or the like
InactiveUS6874578B1Improve mechanical propertiesReduce penetrationFluid removalDrilling compositionPolymer sciencePortland cement
Method of well cementing with a foamed slurry having a very low water content. When based on ordinary cement, the solid fraction of the slurry includes (by volume) 20-35% Portland cement, 35-65% particles ranging from 200 μm to 600 μm, and 5% to 25% of fine particles in the range 0.5 μm to 5 μm and the water content is less than 50% by volume. When based on micro-cement, the solid fraction includes (by volume) 50-75% micro-cement, 15-40% fine particles in the range 0.5 μm to 5 μm, and 0-20% particles in the rang 3 nanometers to 60 nanometers and the water content is less than 72% by volume.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Coated powder particles for producing three-dimensional bodies by means of a layer constituting method
InactiveUS20060251535A1Good storage stabilityHigh distinctnessAdditive manufacturing apparatusTransportation and packagingOrganic solventLaser light
The invention relates a powder material consisting of coated particles for a powder-based rapid generative prototyping methods, in particular by compressing a 3D binder. Said powder material consists of individual plastic, metal and / or ceramic particles and / or granules. A coating essentially consists of an adhesive agent which can be activated by a liquid binder, light or laser light, and of sinterable or glass-forming fine-grained material. Said invention also relates to a method for compressing 3D binder with the aid of an organic solvent having a water content less than 45% and to sintered bodies, in particular for moulding or precision mechanical engineering, which are fixed to each other by sintering or glass formation from a fine grained material.
Owner:PFEIFER ROLF +2
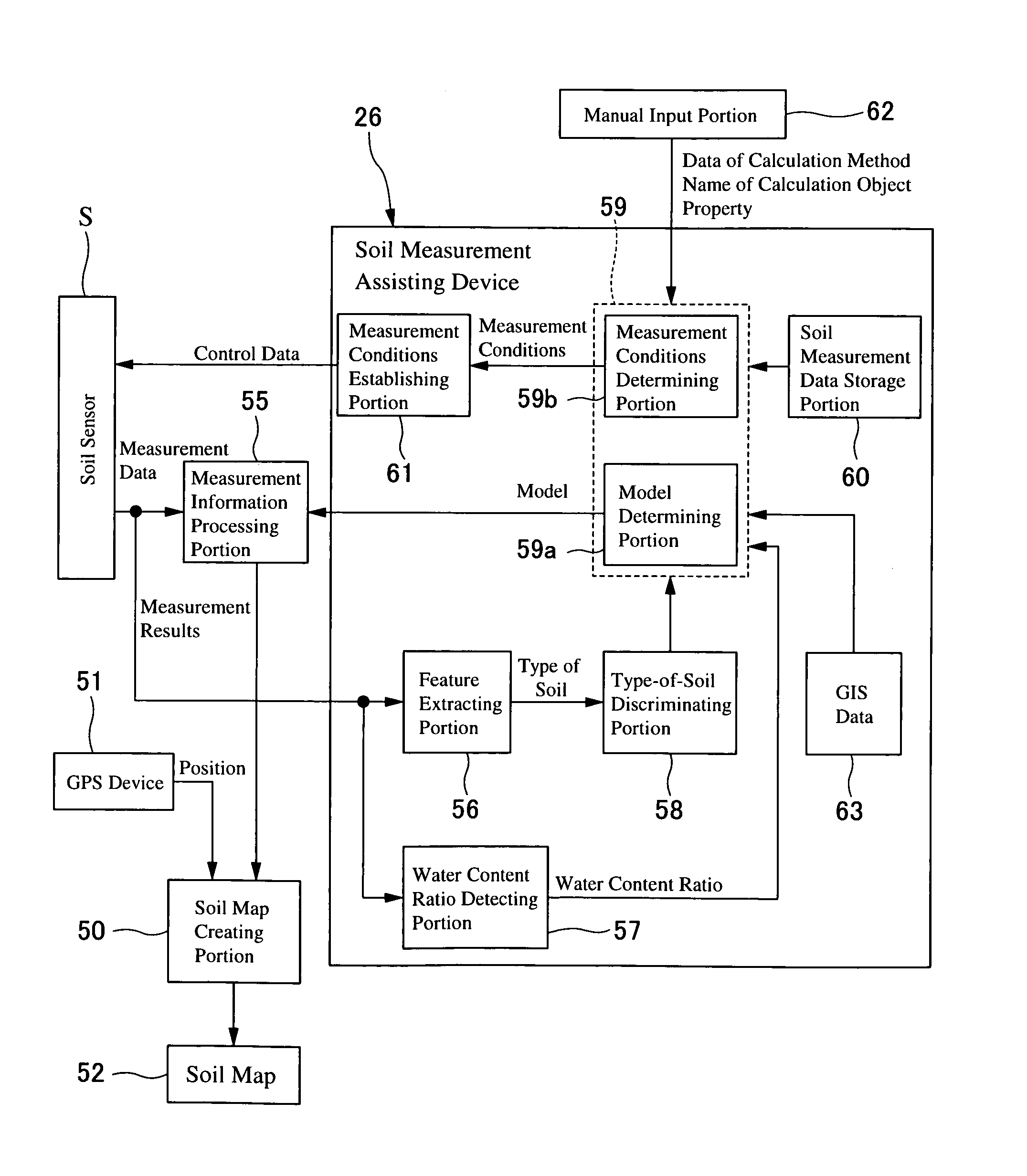
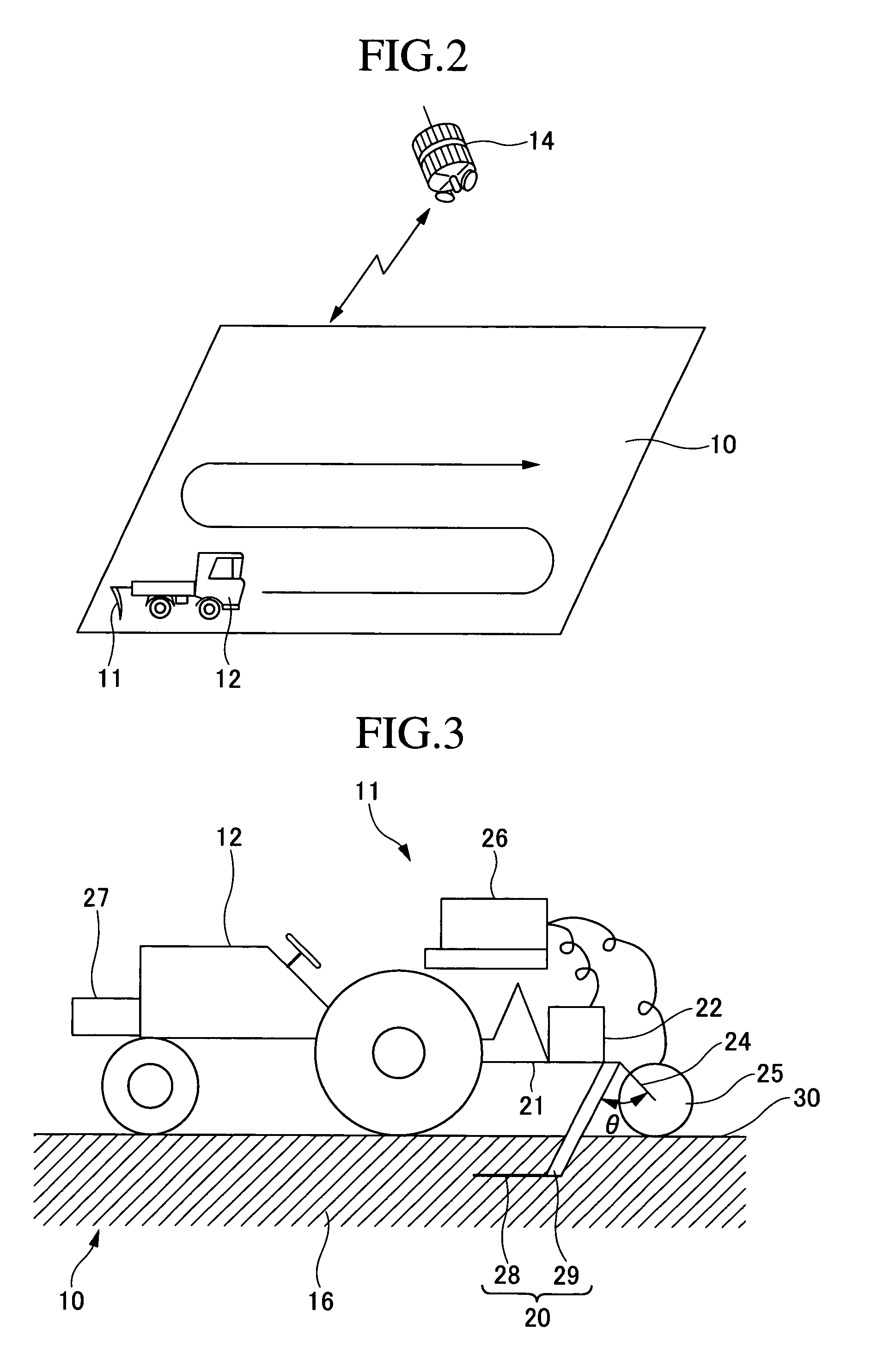
Soil measuring instrument, soil measurement assisting device and method, recorded medium on which a program is recorded, recorded medium on which data is recorded, application amount controller, application amount determining device, method for them, and farm working determination assisting system
InactiveUS6937939B1Increased harvest amountIncrease volumeRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationInformation processingSoil type
A model for determining the type of soil, the water content of a soil, and the soil properties, and a soil measurement data storage portion (60) to store therein measurement data necessary to carry out the model and correlated with specific measurement conditions are provided. The water content is measured by a water content measuring portion (57) on the basis of the measurement data fed from a soil sensor (S). The type of soil is determined by a feature extracting portion (56) and a type-of-soil determining portion (58), and the determined type of soil is sent to a determining portion (59). The determining portion (59) determines corresponding conditions and a model according to the type of soil and water content of the measured place received and sets them in a predetermined processing portion. The soil sensor feeds measurement data meeting the measurement conditions to a measurement information processing portion (55), and the processing portion (55) determines the soil properties according to the determined model.
Owner:NAT UNIV CORP TOKYO UNIV OF AGRI & TECH
Production process for hydrophilic polymer
InactiveUS6207796B1Low residual monomer contentIncrease production capacityWater contentProduction rate
The present invention provides a production process to obtain a hydrophilic polymer, having a low residual monomer content, with good productivity while keeping the properties of a hydrogel polymer resultant from polymerization. In a drying process for a hydrogel polymer, the hydrogel polymer is dried under normal pressure at a material temperature of not higher than 90° C. until the water content of the hydrogel polymer reduces to 15~40 weight %, and then the hydrogel polymer is kept for not shorter than 10 minutes either in a state where the change of the water content of the hydrogel polymer is within 5 weight % and where the material temperature is in the range of 70~120° C. or in a state where the water content of the hydrogel polymer is in the range of 15~40 weight % and where the material temperature is in the range of 70~120° C., and then the hydrogel polymer is finish-dried.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
Ion mineralization stabilizer for treating soil with heavy metal pollution and application method thereof
InactiveCN102766465AWide range of raw materialsEasy to obtainContaminated soil reclamationOrganic fertilisersSulfurPhosphor
The invention discloses ion mineralization stabilizer for treating soil with heavy metal pollution and an application method thereof. The ion mineralization stabilizer comprises, by weight percent, 5-30% of sulfur-based compound, 10-50% of phosphor-based compound, 10-50% of calcium-based compound, and 10-30% of silicon-based compound. The materials are respectively ground into powders with particle size not less than 200 meshes, and the powders are proportionally mixed well. The application method of the ion mineralization stabilizer for treating soil with heavy metal pollution includes: detecting arsenic content and leaching toxicity of the soil to be treated, placing the ion mineralization stabilizers in different proportions on the surface of the soil to be treated according to pollution level, well mixing to form mixed soil by ploughing and stirring, adding water to keep the water content of the mixed soil no less than 25%, covering the mixed soil with moisturizing material, curing for at least 5 days to keep heavy metals in the mixed soil to form stable minerals.
Owner:YONKER ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
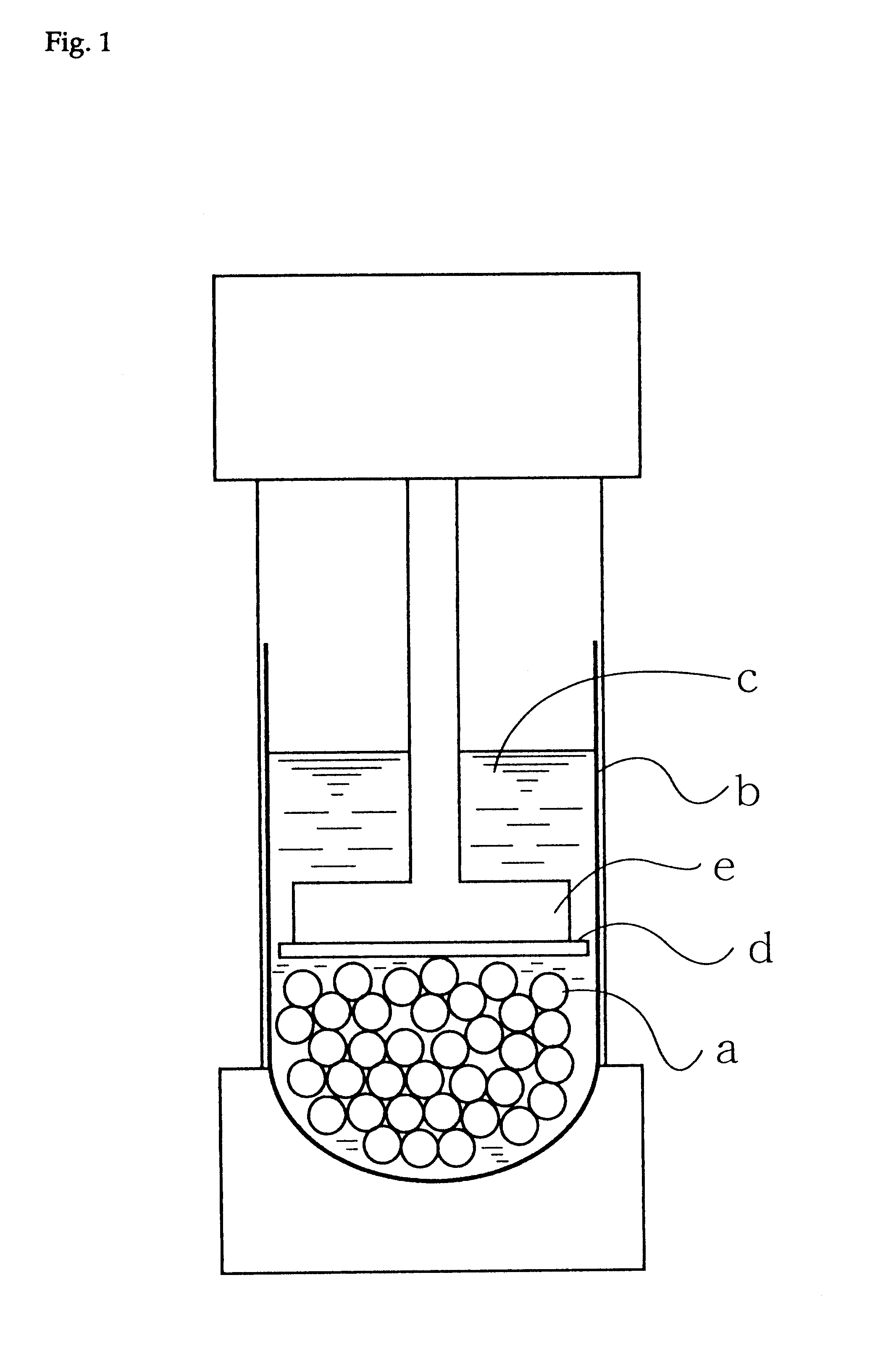
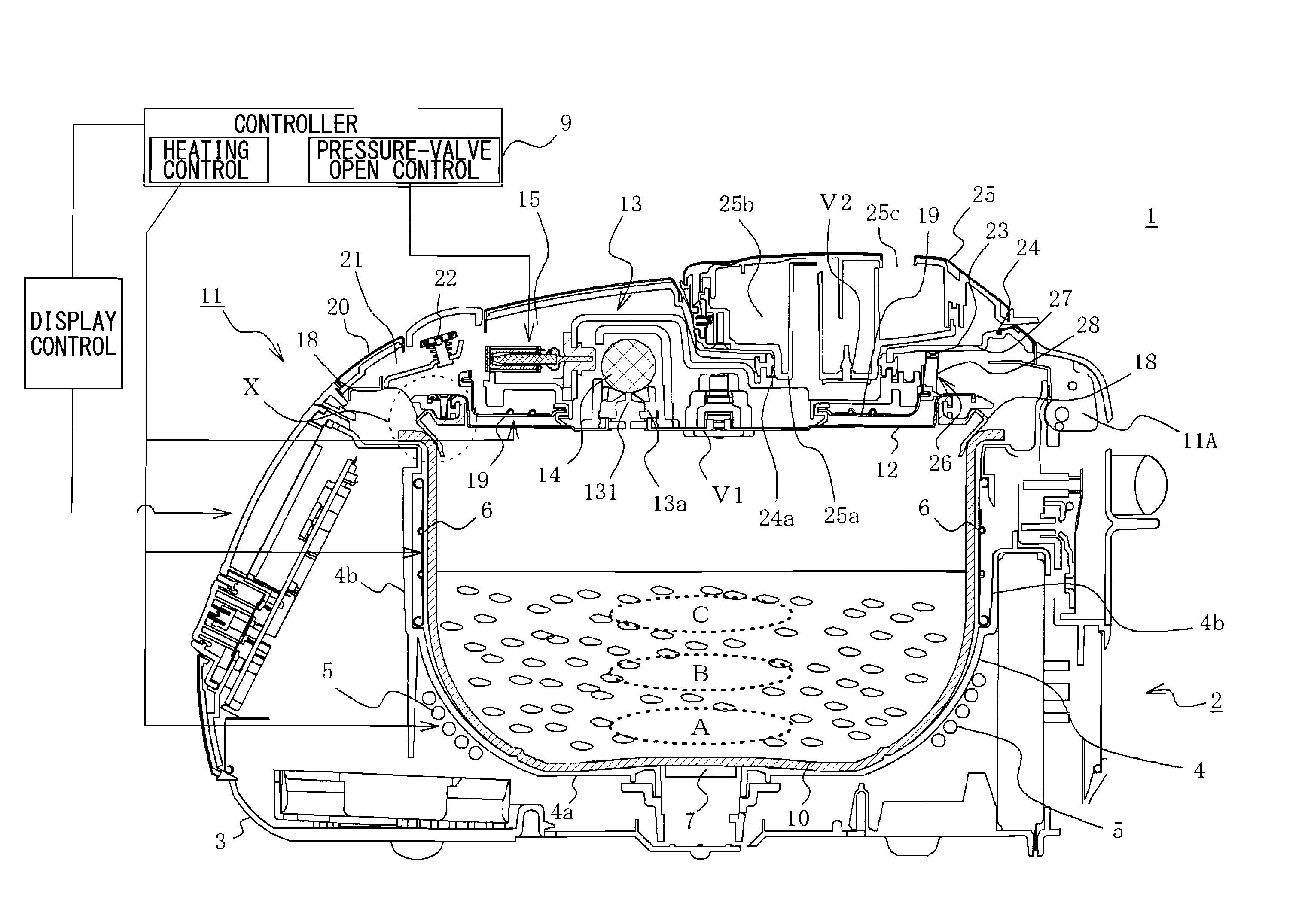
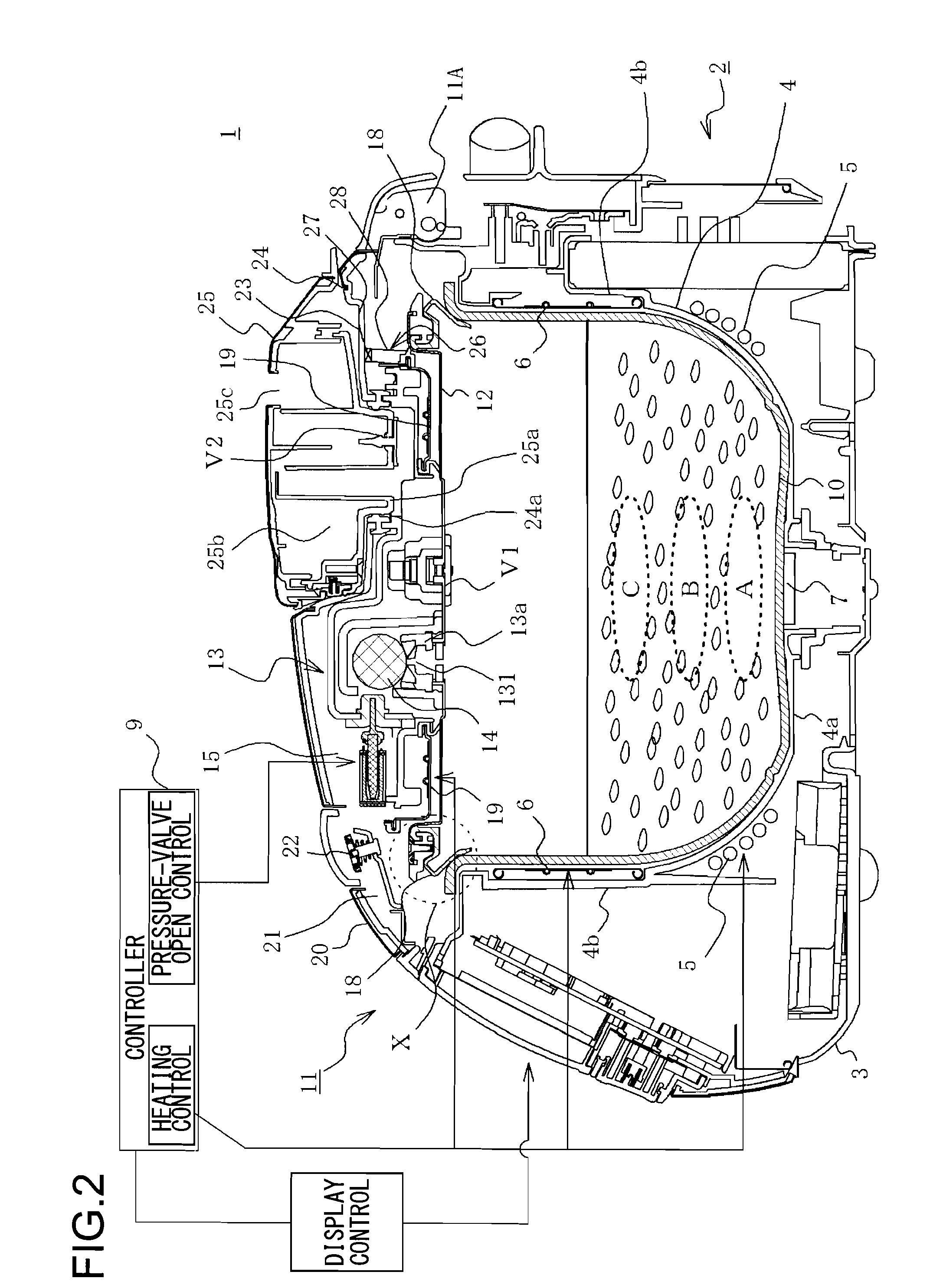
Electric rice cooker and method of cooking rice
InactiveUS20110003048A1Increase moistureUneven water absorptionBoiling over preventionMilk treatmentInternal pressureEngineering
An electric rice cooker capable of increasing the water content of rice by a simple structure. The electric rice cooker (1) has a pot (10) in which food substances to be cooked including water and rice are contained, heating device (5, 6, 19) for heating the food substances to be cooked in the pot, a lid (11) for closing the opening of the pot, and a controller (9) for performing rice cooking steps including a water absorption step for allowing the rice to absorb the water by controlling the heating devices. The controller (9) raises the internal pressure of the pot (10) to 1.05-1.18 atm in the water absorbing step to allow the rice to absorb the water.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD +1
Methods for integrated fast pyrolysis processing of biomass
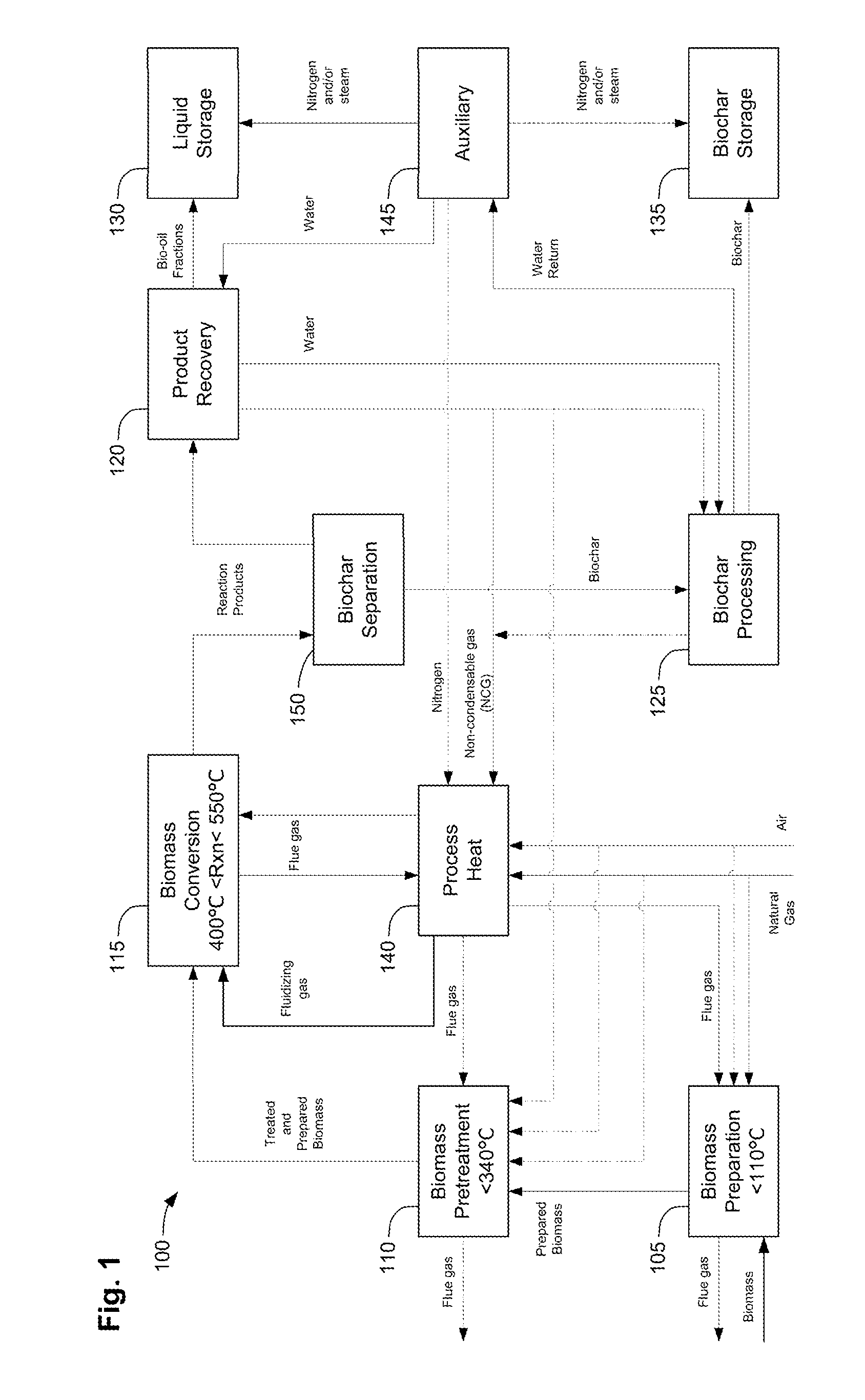
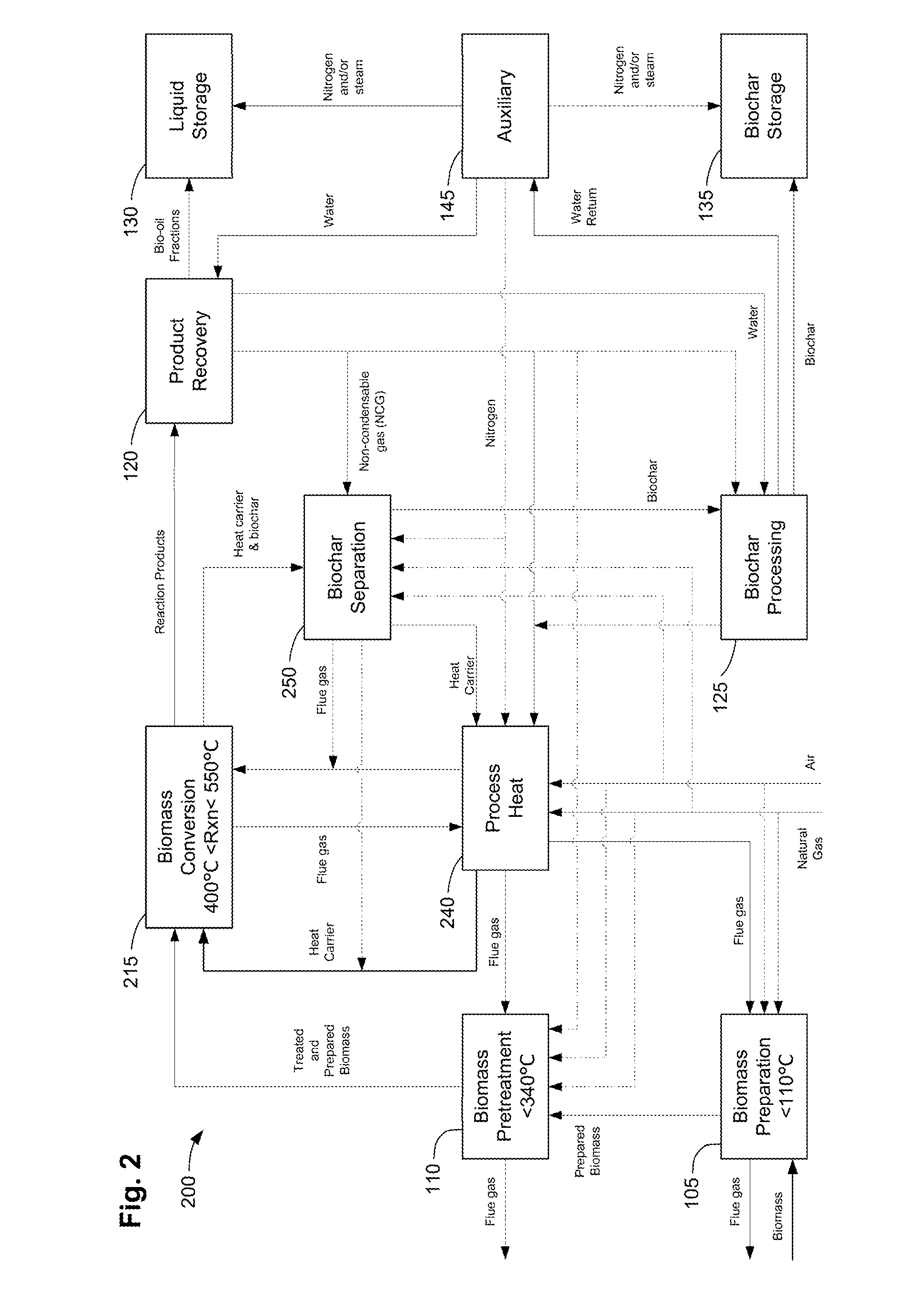
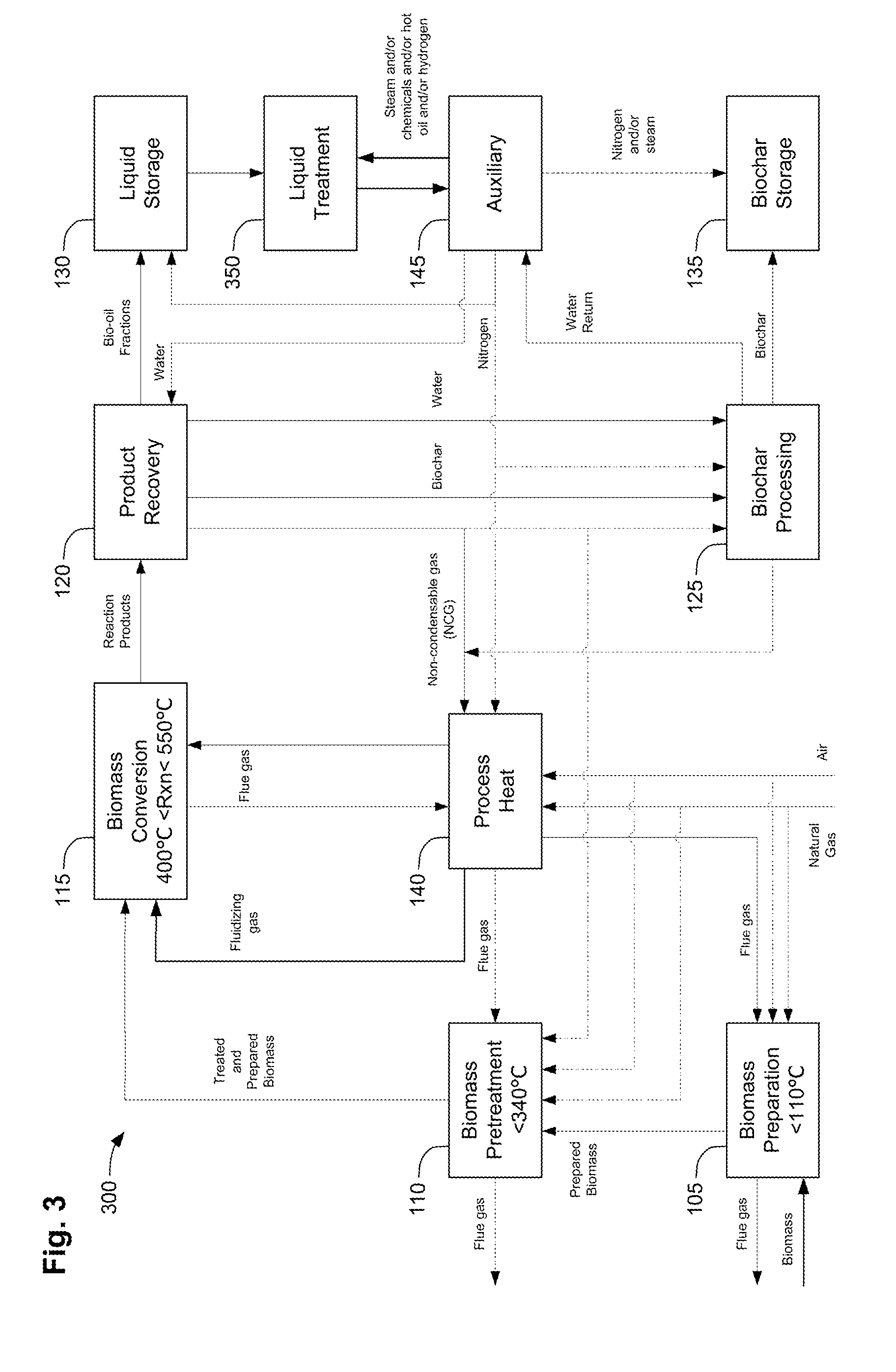
ActiveUS20110258914A1Improve collection efficiencyMinimizes water contentDirect heating destructive distillationBiofuelsPre treatmentSafe handling
Methods, process, apparatus, equipment, and systems are disclosed for converting biomass into bio-oil fractions for chemicals, materials, feedstocks and fuels using a low-cost, integrated fast pyrolysis system. The system improves upon prior art by creating stable, bio-oil fractions which have unique properties that make them individually superior to conventional bio-oil. The invention enables water and low-molecular weight compounds to be separated into a final value-added fraction suitable for upgrading or extracting into value-added chemicals, fuels and water. Initial bio-oil fractions from the process are chemically distinct, have low-water content and acidity which reduces processing costs normally associated with conventional bio-oil post-production upgrading since fewer separation steps, milder processing conditions and lower auxiliary inputs are required. Biochar is stabilized so that it can be handled safely. The integrated fast pyrolysis process includes biomass storage, preparation, pretreatment, and conversion, product recovery and processing to create and store stable biochar and bio-oil fractions.
Owner:AVELLO BIOENERGY
Solvent system of hardly soluble drug with improved dissolution rate
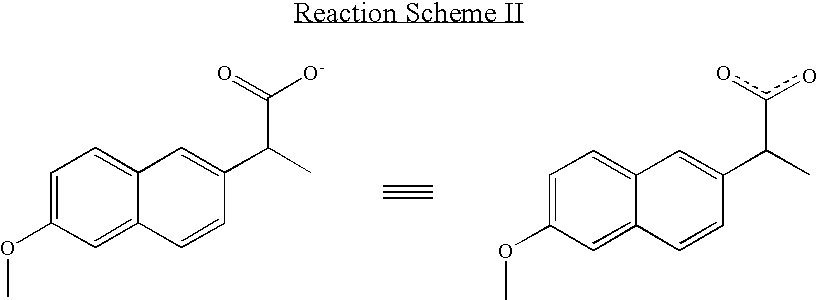
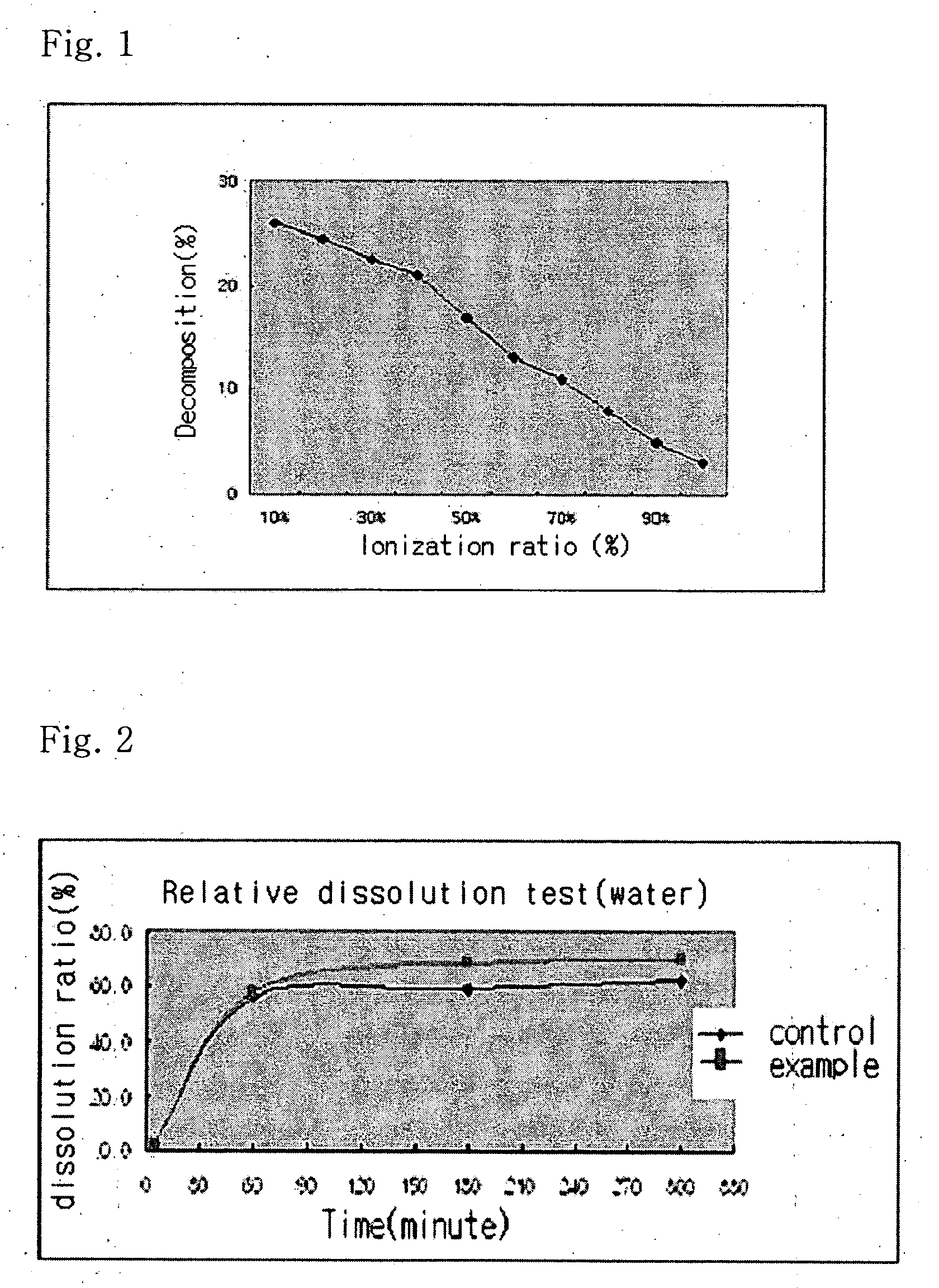
InactiveUS20040157928A1Good disintegrationPromote dissolutionBiocideAntipyreticDissolutionIonization
The present invention relates to a solvent system with improved disintegration degree and dissolution ratio of a hardly soluble drug by highly concentrating the drug through partial ionization, and by establishing optimal conditions for enhancing bioavailability of the drug, such as the co-relation between the acid drug and the accompanied components, ionization degree of a solvent system, use of an appropriate cation acceptance, water content, selection of optimal mixing ratio of the respective components and use of specific surfactants, and to a pharmaceutical preparation comprising the same. The solvent system of the invention has advantages in that it can enhance bioavailability by improving the disintegration degree and dissolution ratio of a hardly soluble drug and also provide a capsule with a sufficiently small volume to permit easy swallowing.
Owner:R & P KOREA
Scar and rosacea and other skin care treatment composition and method
ActiveUS20090068128A1Increase moistureRemoved from skinCosmetic preparationsBiocideMedicineSkin surface
The present invention relates generally to composition and methods for topical application to skin. More particularly, it relates to treatment of scars and rosacea, and other aspects of skin care. A composition is disclosed having a skin toner for cleansing a skin surface, removing dead skin cells, restoring alkali balance, and shrinking skin pores; and a skin moisturizer for increasing water content in the external layers of the skin.
Owner:WADDINGTON TAUNA ANN
Conversion of municipal solid waste to high fuel value
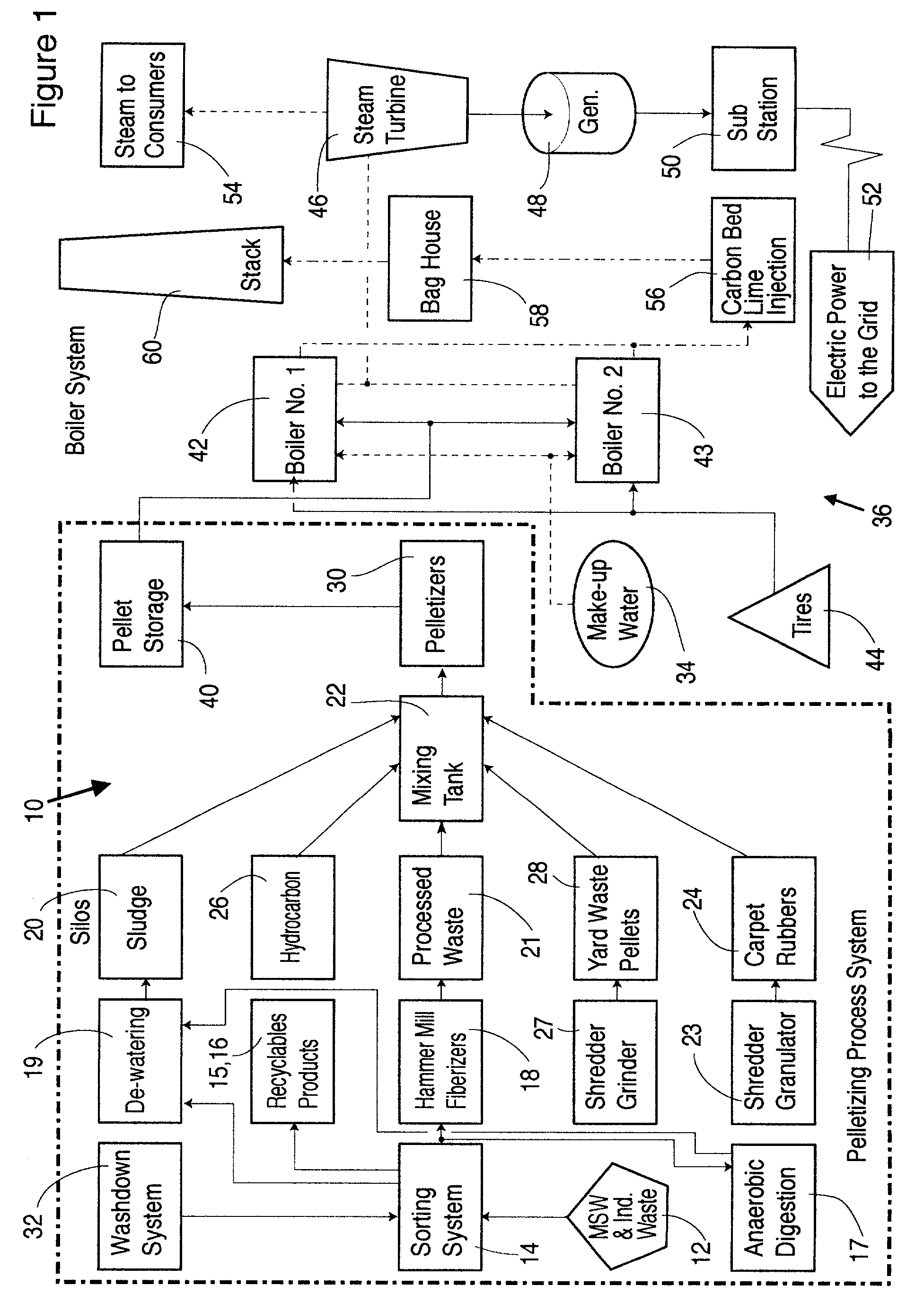
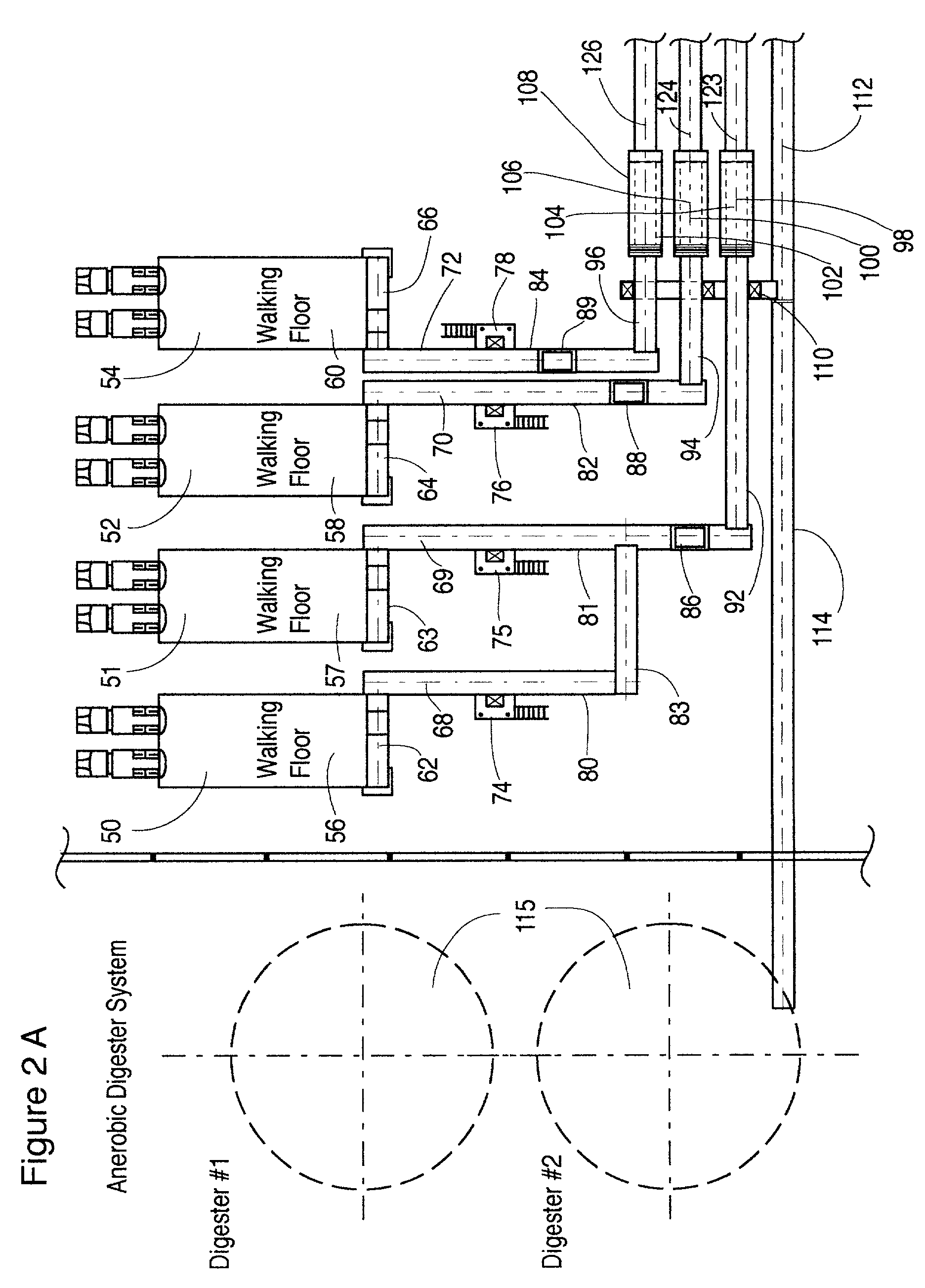
InactiveUS7252691B2Increasing value of such fuelHigh fuel valueBiofuelsSolid fuelsEnvironmental engineeringUrban solid waste
A combustible pellet comprising municipal solid waste. The pellet has a water content of less than 10% by weight and a fuel value of at least 10,000 BTU. A process for the forming of a combustible pellet from municipal solid wastes, comprising the steps of removing solid hazardous waste from said municipal solid waste; subjecting the municipal solid waste so obtained to at least one step to separate recyclable products therefrom; and subjecting the resultant product to a shredding and a pulverizing step. A fluff with a water content of less than 10% by weight is obtained. The fluff is compacted to form a combustible pellet.
Owner:SENTINEL WASTE INT
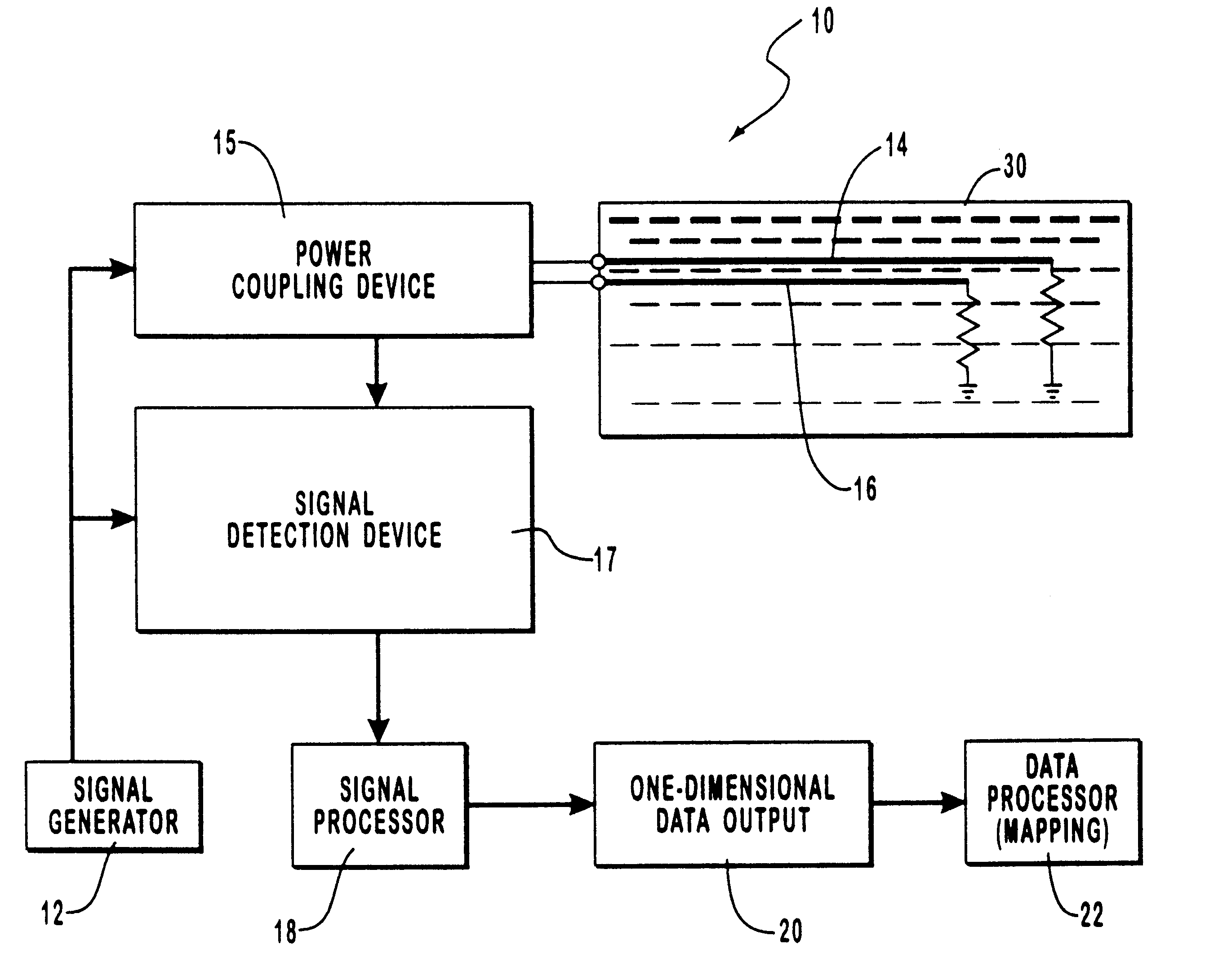
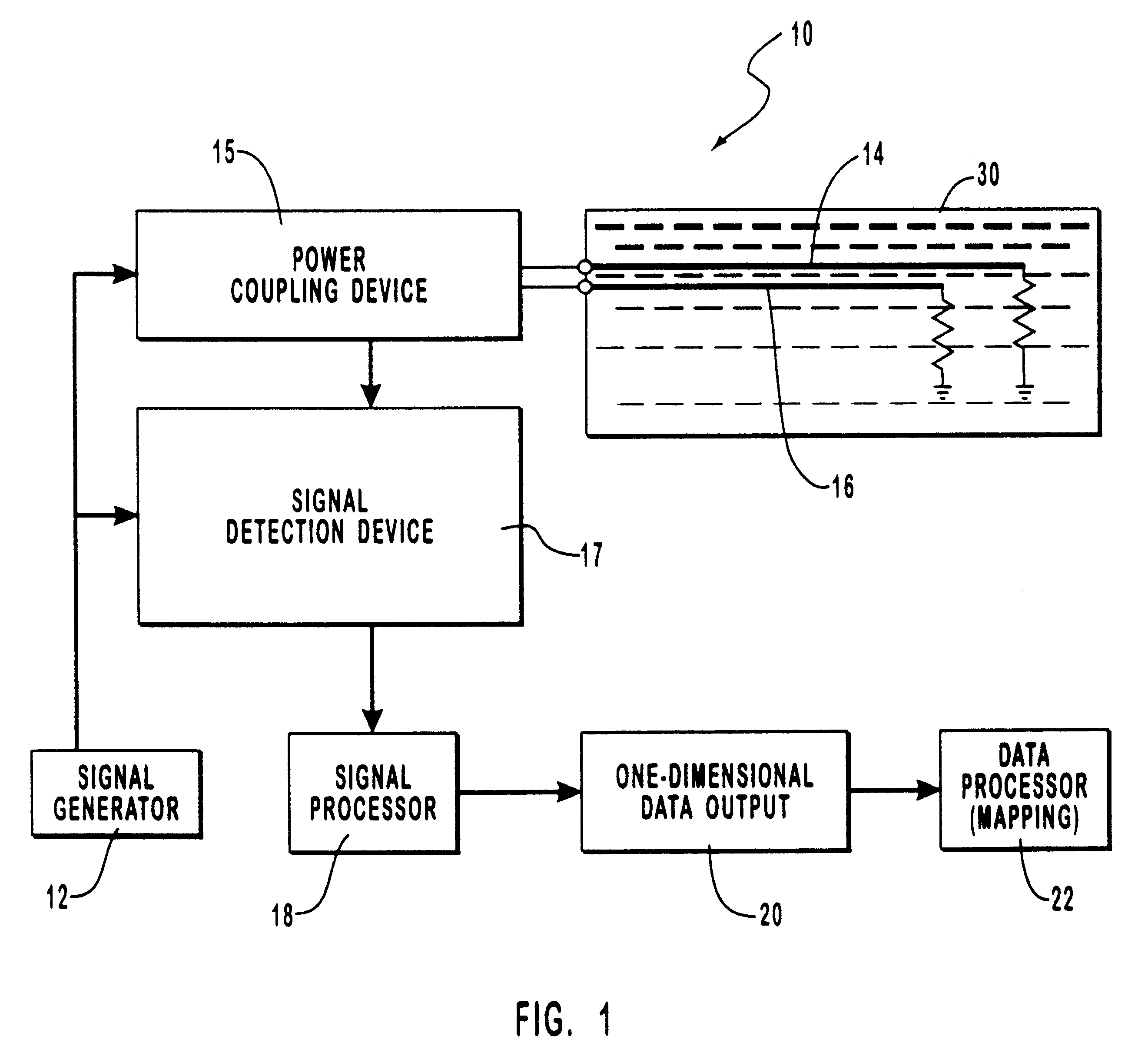
System and method for monitoring water content or other dielectric influences in a medium
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC +1
System for testing physical model for large-scale landslides under action of multiple factors
ActiveCN102331489ASmall sizeHigh precisionEarth material testingUsing optical meansRainfall simulationStress measures
The invention discloses a system for testing a physical model for large-scale landslides under the action of multiple factors, which comprises a reservoir level fluctuation simulation unit, a landslide experiment slot section, an artificial rainfall simulation unit and a measuring unit, wherein the landslide experiment slot section comprises a horizontal slot section and a slope slot section, the horizontal slot section and the slope slot section are respectively paved with a slope body consisting of sand-soil mixtures, and the rear end of the horizontal slot section is hinged with the front end of the slope slot section; the slope slot section is composed of more than two slot sections which are sequentially hinged end to end, and the bottom of each slot section is provided with a lifting unit which can adjust the dip angle of the slot section; the rear end of the slope slot section is provided with a Malpighian-tube rear-edge water-replenishing unit; and the measuring unit comprises a deformation measuring part and a stress measuring part, wherein the deformation measuring part is used for measuring the deformation process of the slope body, and the stress measuring part is used for measuring the water pressure and water content of a pore of the slope body. By using the system disclosed by the invention, the changing regularity of each measurable physical quantity of a landslide in different development stages can be grasped accurately, thereby providing a possibility for better developing the studies on key parameters of landslides in different evolution stages.
Owner:INST OF MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Magnetic biological carrier and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102225806APromote recoveryRealize dynamic regenerationSustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentResource utilizationEngineering
The invention discloses a magnetic biological carrier and a preparation method thereof. The raw materials of the magnetic biological carrier comprise aggregate, iron oxide, a binder and a reducing agent. The preparation method of the magnetic biological carrier comprises the following steps of: mixing the aggregate, iron oxide and the reducing agent, crushing, screening with a 60-mesh sieve to obtain a mixed material, adding water which is 30-60% of the mixed material by weight to the binder, stirring for dissolving the binder to obtain a binder solution, then mixing the binder solution with the mixed material, uniformly stirring, granulating and shaping to obtain 2-10 mm granules, drying the granules till the water content of the granules is less than 10%, and calcining at the temperature of 350-1100 DEG C for 0.2-10 hours to obtain the magnetic biological carrier. The magnetic biological carrier provided by the invention can be applied to the deep treatment of secondary treatment water of domestic sewage, meets the requirements of landscape water replenishing and circulating cooling water treatment, and can be used for realizing the deep treatment and resource utilization of industrial wastewater.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Low water content, high refractive index, flexible, polymeric compositions
InactiveUS6852793B2Ideal physical propertyHigh refractive indexOrganic dyesIntraocular lensHydrophilic monomerRefractive index
Optically transparent, relatively high refractive index polymeric compositions and ophthalmic devices such as intraocular lenses and corneal inlays made therefrom are described herein. The preferred polymeric compositions are produced through the polymerization of one or more copolymers with one or more hydrophilic monomers and optionally one or more aromatic-based monomers, hydrophobic monomers or a combination thereof.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Capsule Stable Against Mastication
InactiveUS20080057115A1Good disintegrationExcellent pharmaceutical preparationAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderSlice thicknessMedicine
The present invention relates to a soft capsule which is easily disintegrated in the stomach, wherein the contents thereof are not easily leaked at the time of mastication, which is obtained by providing a soft capsule comprising (2R)-2-propyloctanoic acid or a salt thereof with at least one property, preferably all properties, selected from (A) wherein it has a strength of 150 to 400 N by a cracking test; (B) wherein it has a disintegration time of 3 to 10 minutes by the disintegration test stipulated in Japanese Pharmacopoeia; (C) wherein the capsule shell has a shell thickness of 0.05 to 0.50 mm; (D) wherein the capsule shell has a first seam thickness of 0.10 to 0.55 mm; (E) wherein the capsule shell has a second seam thickness of 0.05 to 0.50 mm; (F) wherein the capsule shell has a water content of 5.0 to 9.0%.
Owner:ONO PHARMA CO LTD
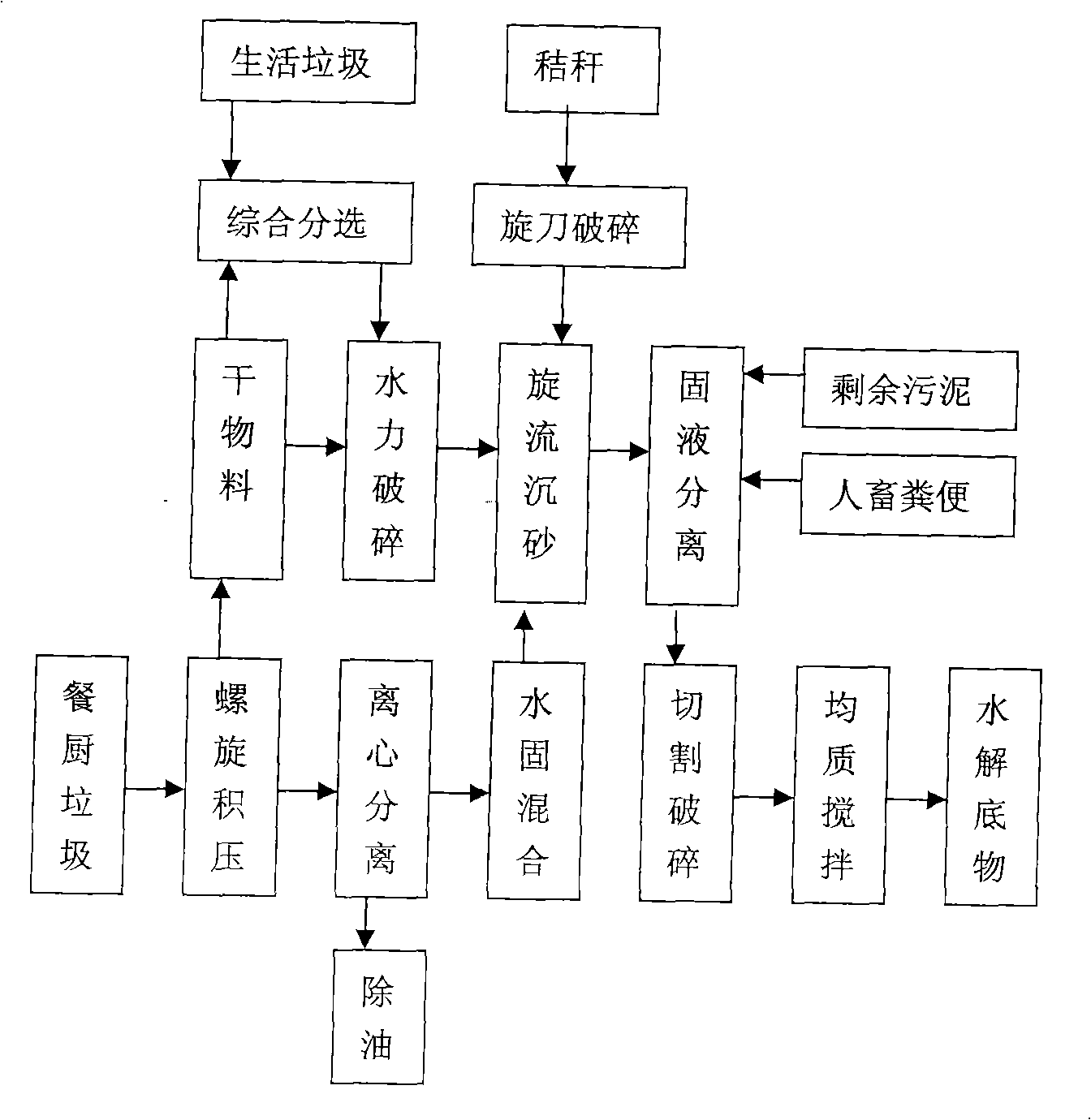
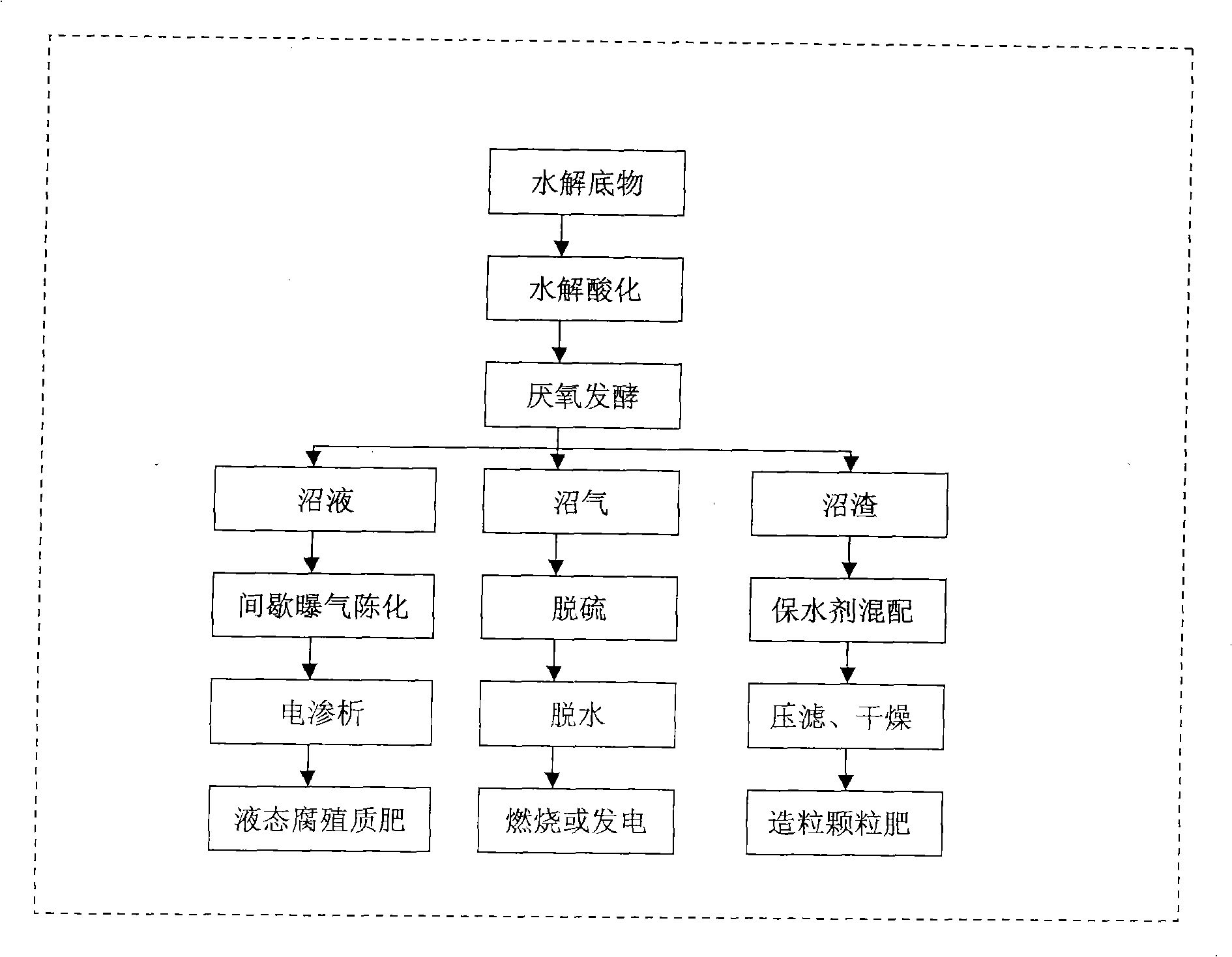
Combined anaerobic fermentation process for organic solid wastes
InactiveCN101337838AReduce consumptionImprove mass transfer efficiencyBio-organic fraction processingClimate change adaptationSludgeAnimal feces
The invention discloses a combined anaerobic fermentation method of organic solid wastes. The organic solid wastes used for the combined anaerobic fermentation include domestic wastes, excess sludge, feces, kitchen waste, straws, etc. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out different pre-processing processes to obtain organic materials with a granularity less than 5 mm; passing through a cutting pump, adjusting the C / N ratio, adjusting the water content, etc. to obtain a homogeneous fermentation substrate with a solid holdup of 2 to 10%; hydrolyzing and acidifying the fermentation substrate in the presence of a hydrolase; fermenting for a period of 15 to 25 days under the condition of stirring at a middle temperature of 32-38 DEG C to obtain biogas, which can be used for energy supply or output of a system; aging and desalting the biogas liquid to obtain a liquid humic acid fertilizer; and processing the biogas residues to a granular humic acid fertilizer. The fermentation substrate has proper C / N ratio to obviate feedback suppression of the substrate during the fermentation of a single material and simultaneously can enhance the hydrolysis effects of celluloses, lignin, hemicelluloses, etc. The method has the advantages of easy flow pattern control, low energy consumption, and no generation of sewages, and can obtain the high-quality biogas fluid and the high-quality granular humic acid fertilizer.
Owner:鄂尔多斯市城市矿产研究开发有限责任公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com