Patents
Literature
189 results about "Mastication" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Chewing or mastication is the process by which food is crushed and ground by teeth. It is the first step of digestion, and it increases the surface area of foods to allow a more efficient break down by enzymes. During the mastication process, the food is positioned by the cheek and tongue between the teeth for grinding. The muscles of mastication move the jaws to bring the teeth into intermittent contact, repeatedly occluding and opening. As chewing continues, the food is made softer and warmer, and the enzymes in saliva begin to break down carbohydrates in the food. After chewing, the food (now called a bolus) is swallowed. It enters the esophagus and via peristalsis continues on to the stomach, where the next step of digestion occurs.
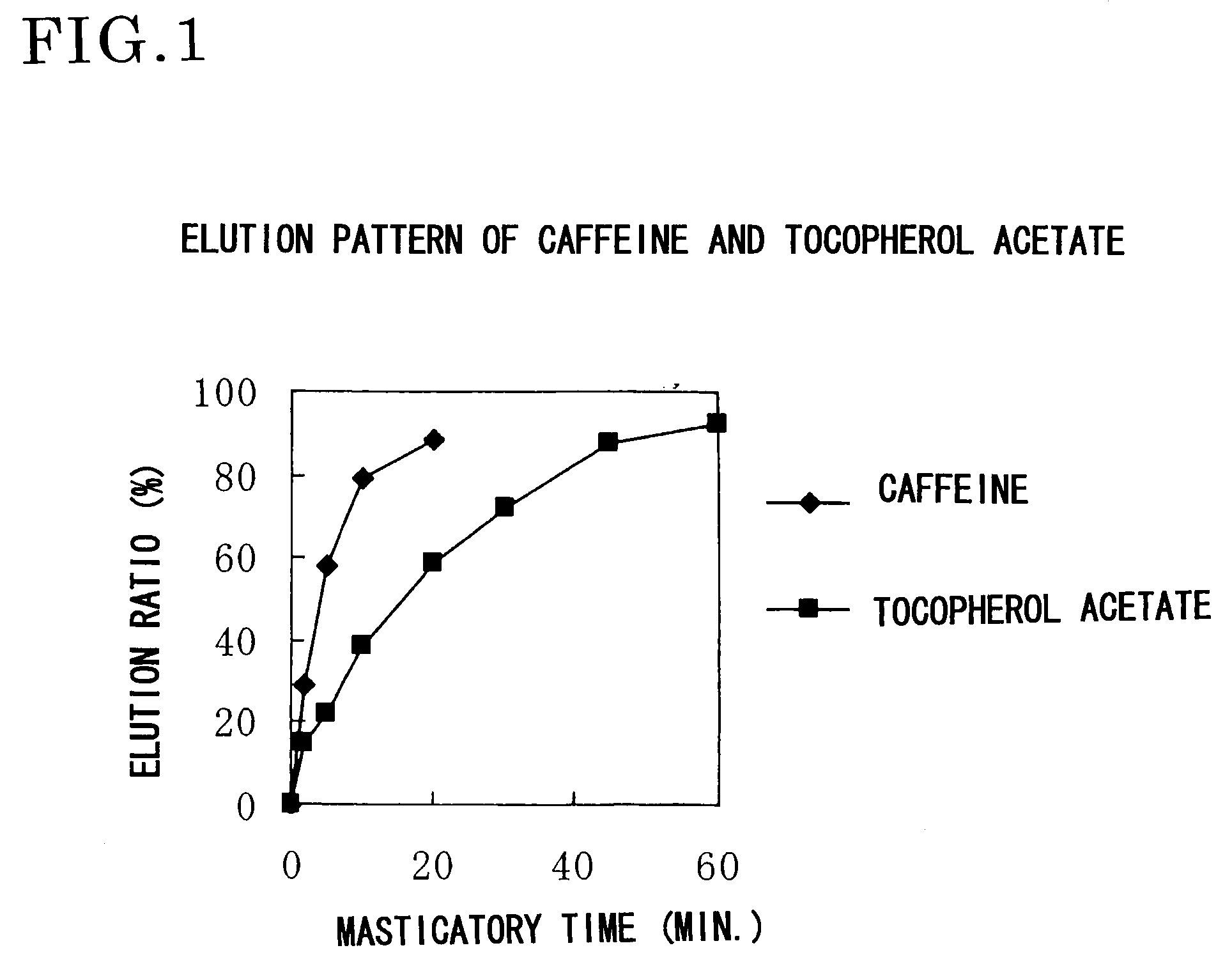
Capsule Stable Against Mastication
InactiveUS20080057115A1Good disintegrationExcellent pharmaceutical preparationAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderSlice thicknessMedicine
The present invention relates to a soft capsule which is easily disintegrated in the stomach, wherein the contents thereof are not easily leaked at the time of mastication, which is obtained by providing a soft capsule comprising (2R)-2-propyloctanoic acid or a salt thereof with at least one property, preferably all properties, selected from (A) wherein it has a strength of 150 to 400 N by a cracking test; (B) wherein it has a disintegration time of 3 to 10 minutes by the disintegration test stipulated in Japanese Pharmacopoeia; (C) wherein the capsule shell has a shell thickness of 0.05 to 0.50 mm; (D) wherein the capsule shell has a first seam thickness of 0.10 to 0.55 mm; (E) wherein the capsule shell has a second seam thickness of 0.05 to 0.50 mm; (F) wherein the capsule shell has a water content of 5.0 to 9.0%.
Owner:ONO PHARMA CO LTD
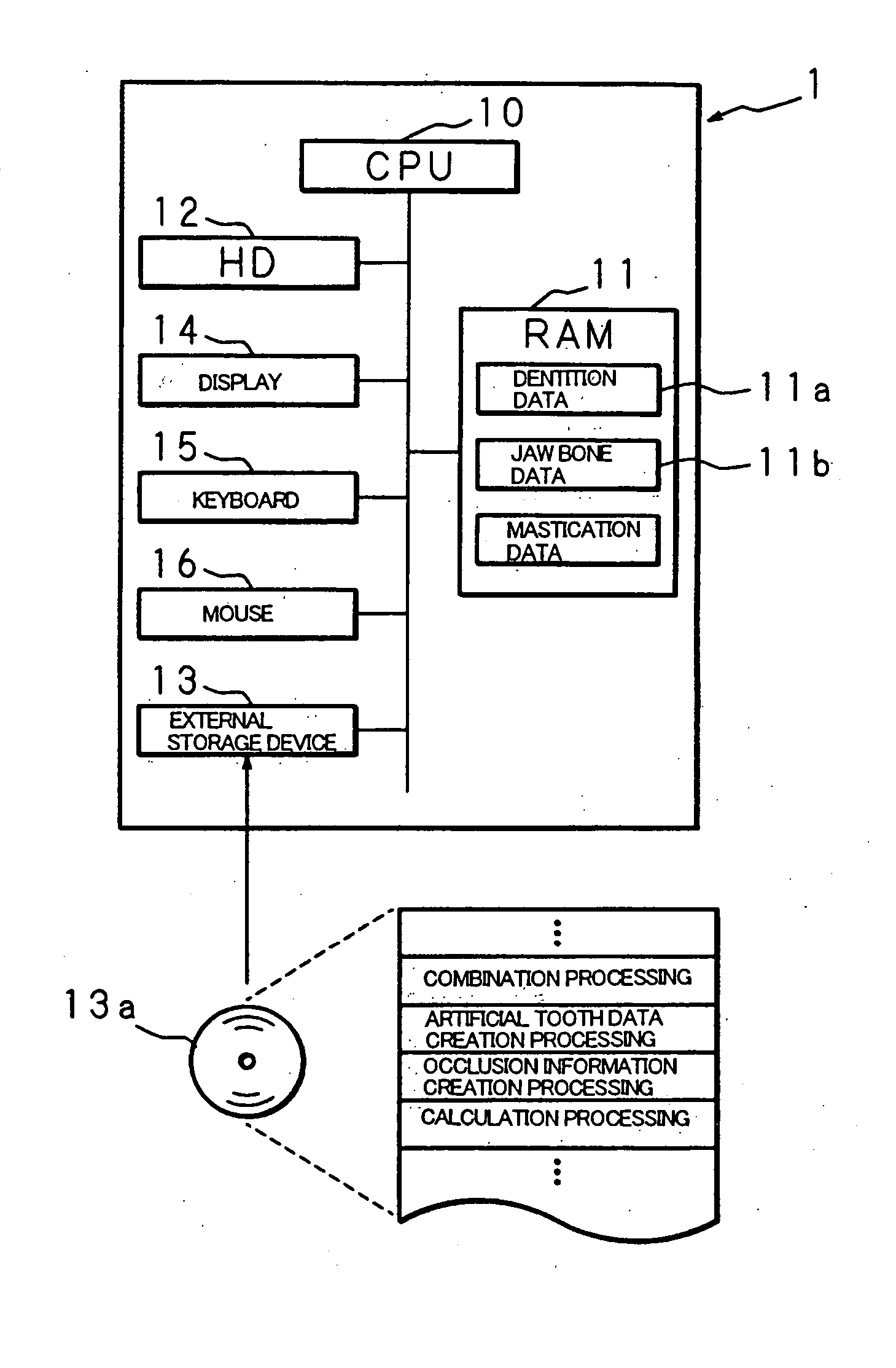
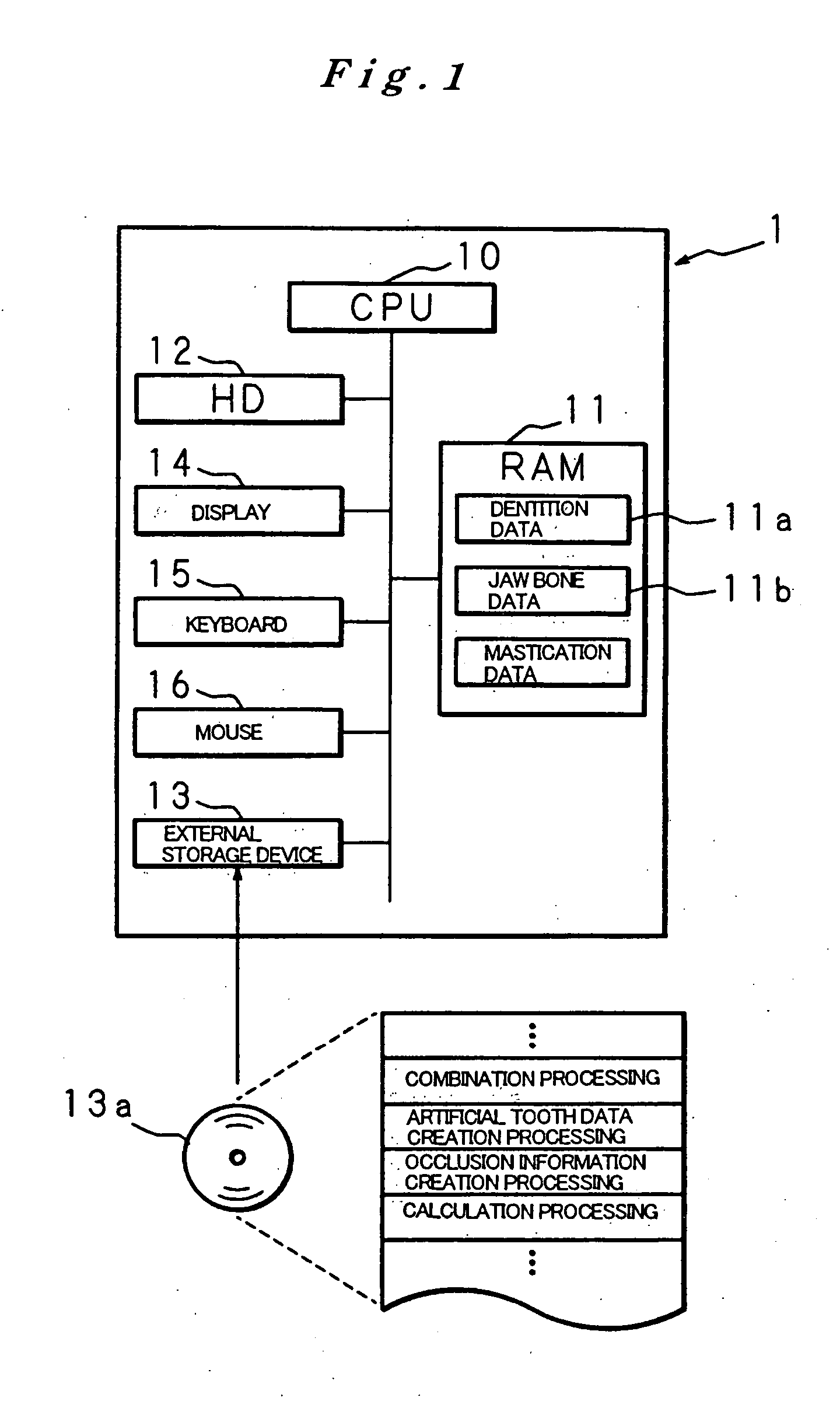
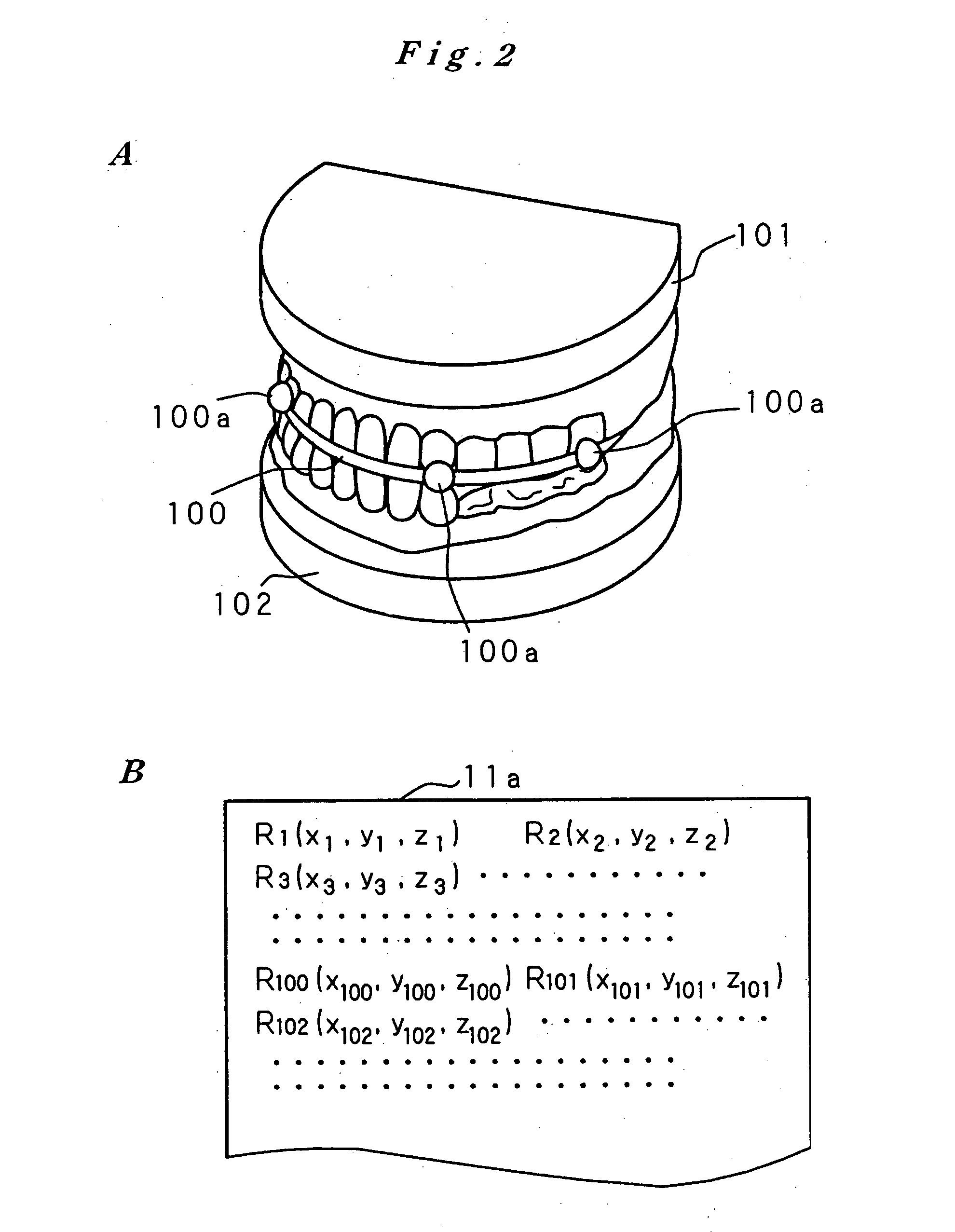
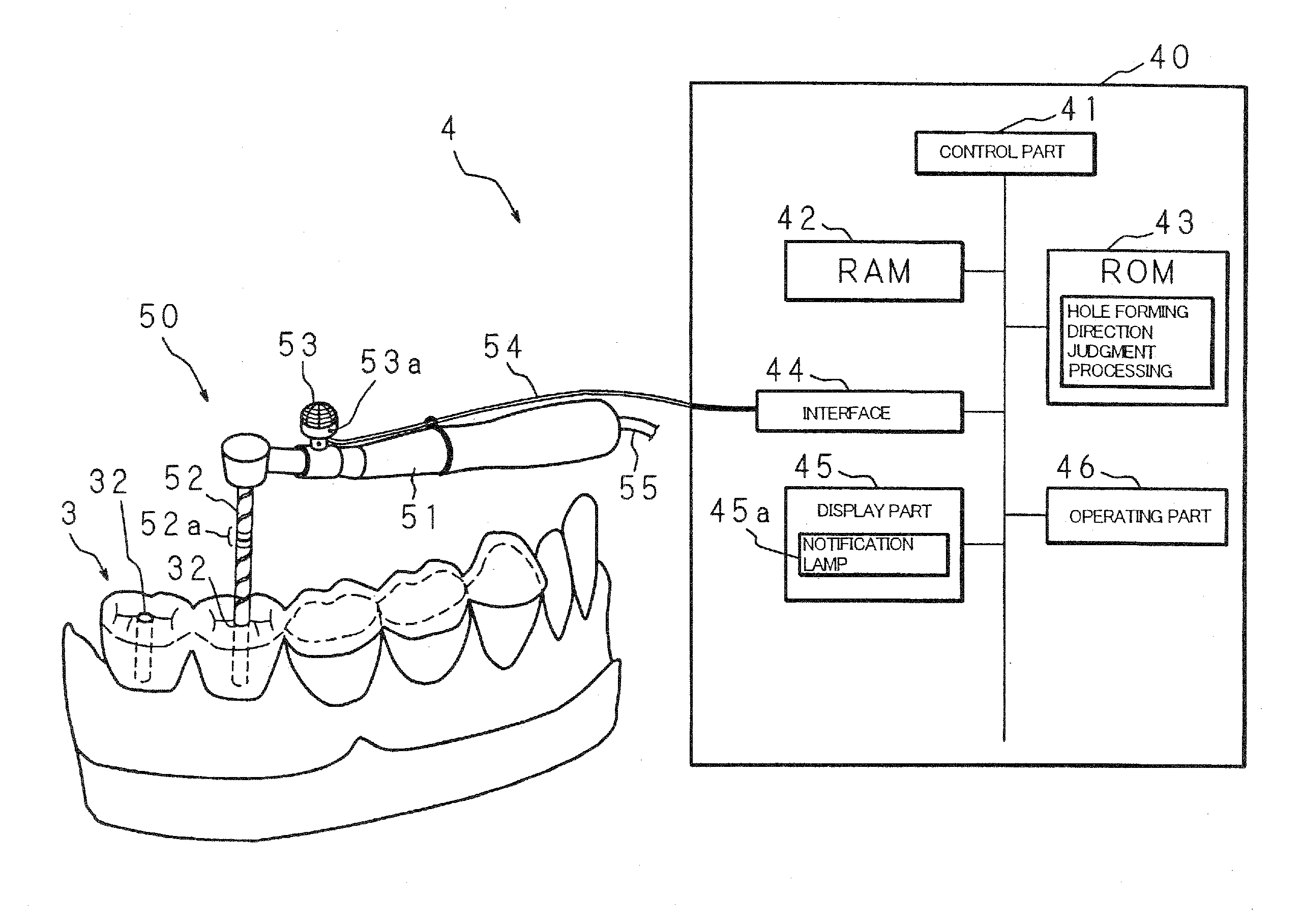
Artificial tooth root implantation position determining instrument, artificial tooth root implantation position determining method, guide member manufacturing device, sensor, drill, artificial tooth manufacturing device, computer program, and recorded medium
InactiveUS20060127848A1Reduce loadEasy to manufactureDental implantsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesLocation determinationTooth root
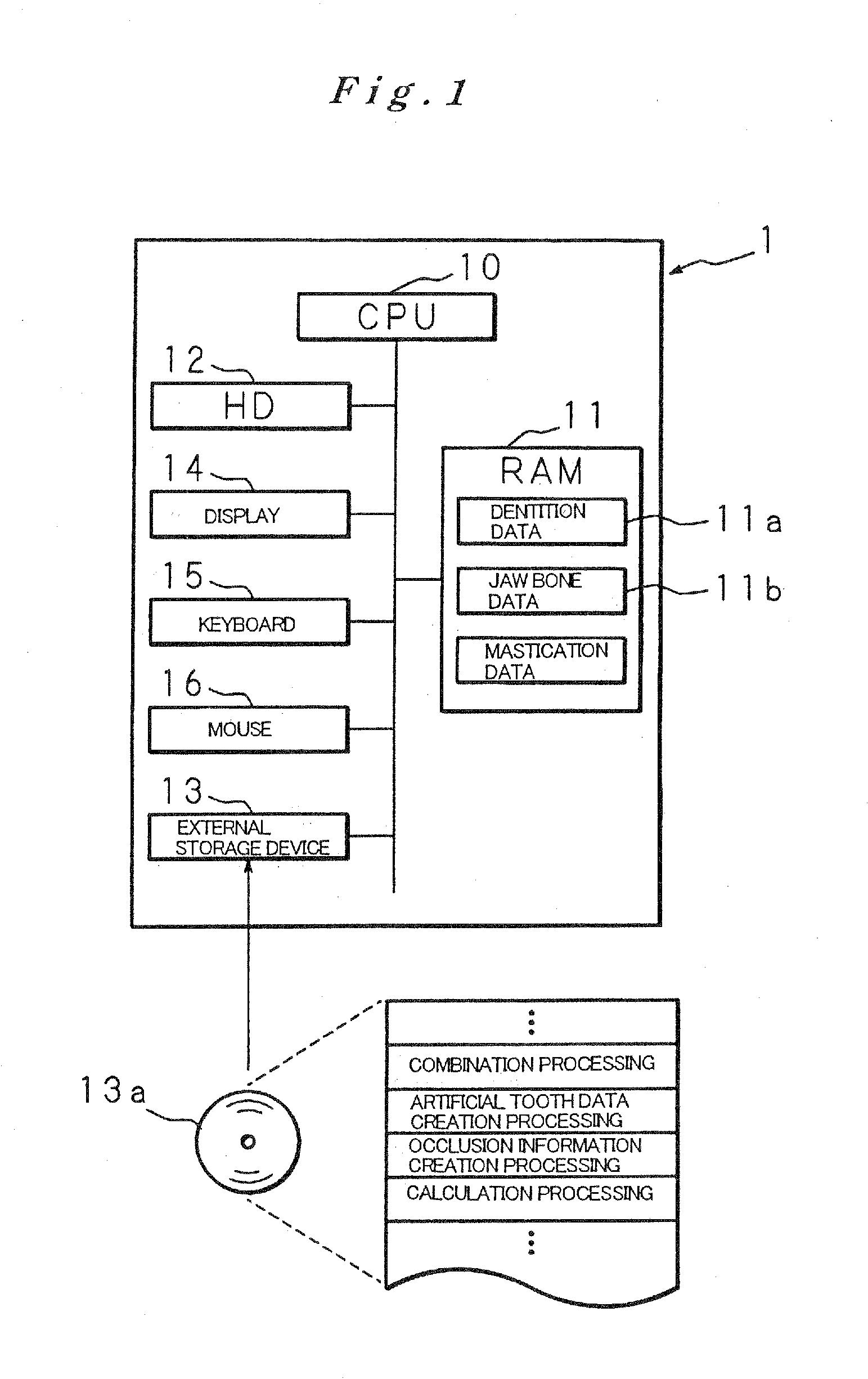
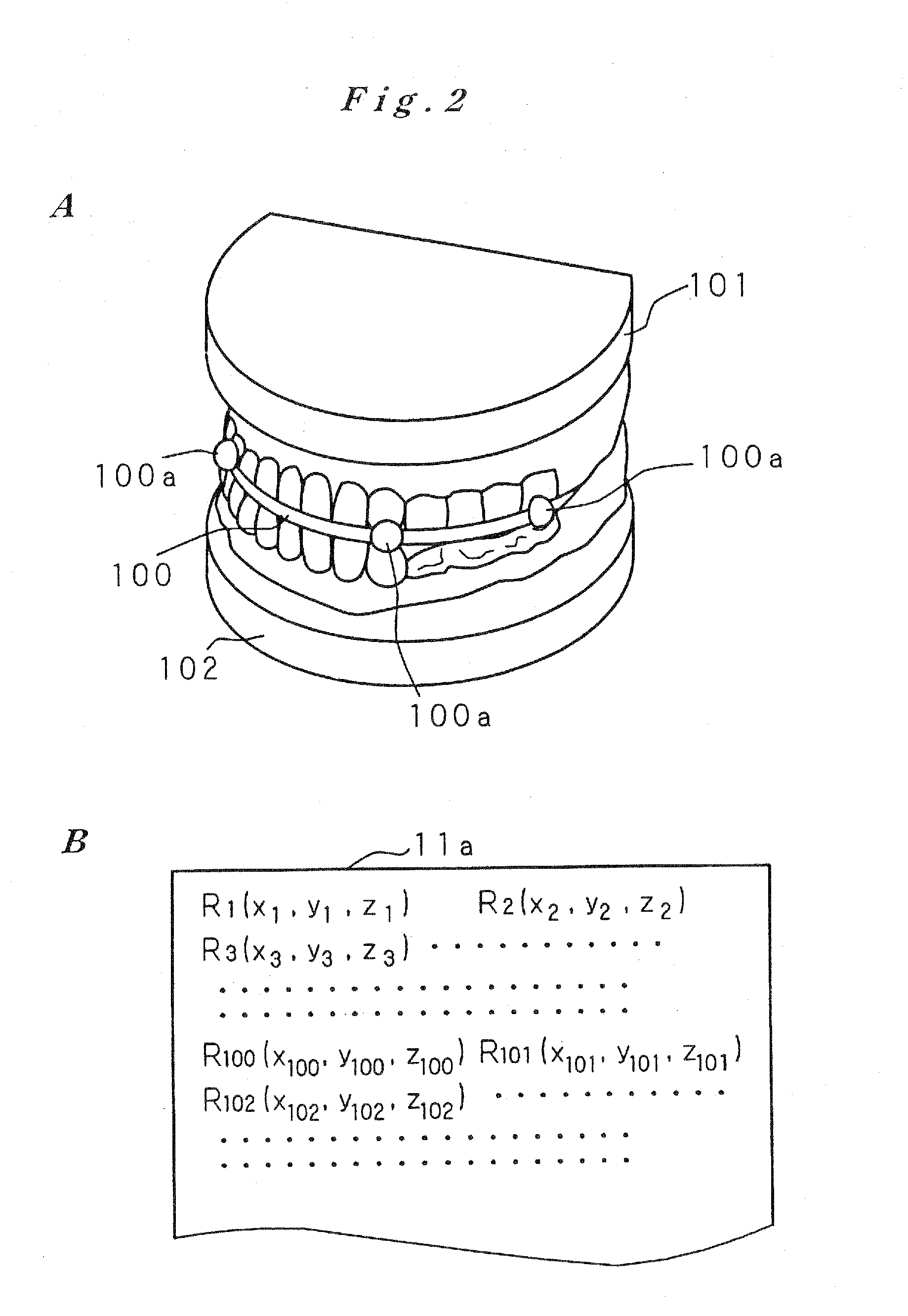
Dentition three-dimensional data and jaw-bone three-dimensional data are collected from a patient and they are combined. According to the combined data, dental crown data for making up for data on a lost tooth and occlusion data on a dental crown represented by the dental crown data are created. When an occlusion force according to the occlusion data is exerted on the occlusion face of a dental crown, a mechanical evaluation factor is produced in a jaw bone. The mechanical evaluation factor produced near the place where an artificial tooth root supporting a dental crown is to be implanted is calculated. The implantation place is determined so that the mechanical evaluation factor may be smaller and the mechanical load on the jaw bone from the opposed tooth during mastication may be lighter.
Owner:CAT CORP
Artificial Tooth Root Implantation Position Determining Instrument, Artificial Tooth Root Implantation Position Determining Method, Guide Member Manufacturing Device, Sensor, Drill, Artificial Tooth Manufacturing Device, Computer Program, and Recording Medium
InactiveUS20100173260A1Reduce loadEasy to manufactureDental implantsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesTooth rootMastication
Dentition three-dimensional data and jaw-bone three-dimensional data are collected from a patient and they are combined. According to the combined data, dental crown data for making up for data on a lost tooth and occlusion data on a dental crown represented by the dental crown data are created. When an occlusion force according to the occlusion data is exerted on the occlusion face of a dental crown, a mechanical evaluation factor is produced in a jaw bone. The mechanical evaluation factor produced near the place where an artificial tooth root supporting a dental crown is to be implanted is calculated. The implantation place is determined so that the mechanical evaluation factor may be smaller and the mechanical load on the jaw bone from the opposed tooth during mastication may be lighter.
Owner:CAT CORP
Active lactic acid bacteria beverage and method for producing the same
ActiveCN101467558AImprove suspension stabilityIncrease varietyMilk preparationStabilizing AgentsRaw material
The invention provides a kind of active lactobacillus beverage containing mastication particles. According to the total weight of active lactobacillus beverage as reference, the raw materials comprise 25-75% of milk, 3-20% of particle sauce, 0.2-0.7% of stabilizing agent and appropriate water by weight; the beverage contains live lactobacillus with concentration of 1*106cfu / ml or above. The active lactobacillus beverage in the invention contains masticatory particles, abundant product types and taste, cool taste and good stability.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA YILI INDUSTRIAL GROUP CO LTD
Fiber reinforced rubber
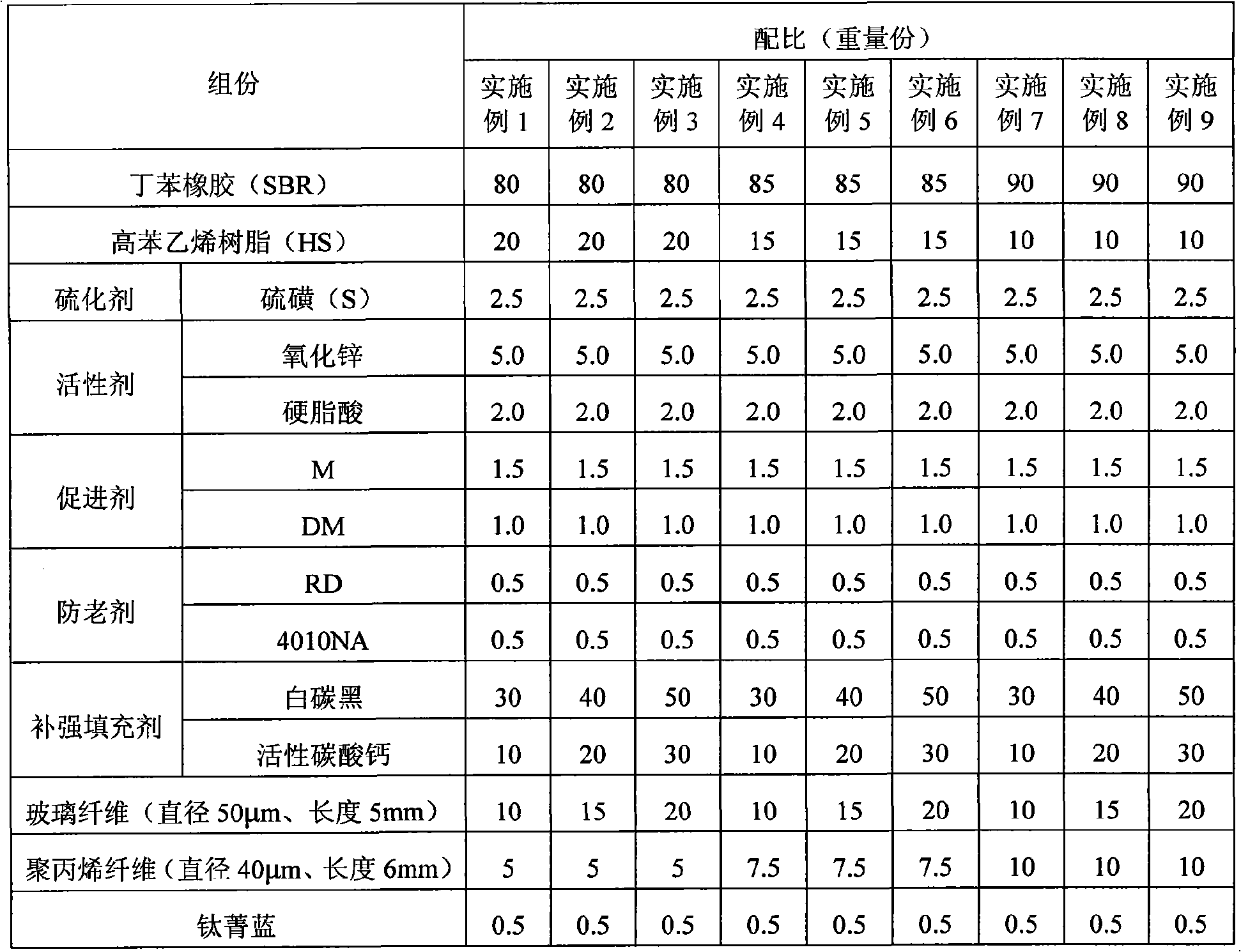
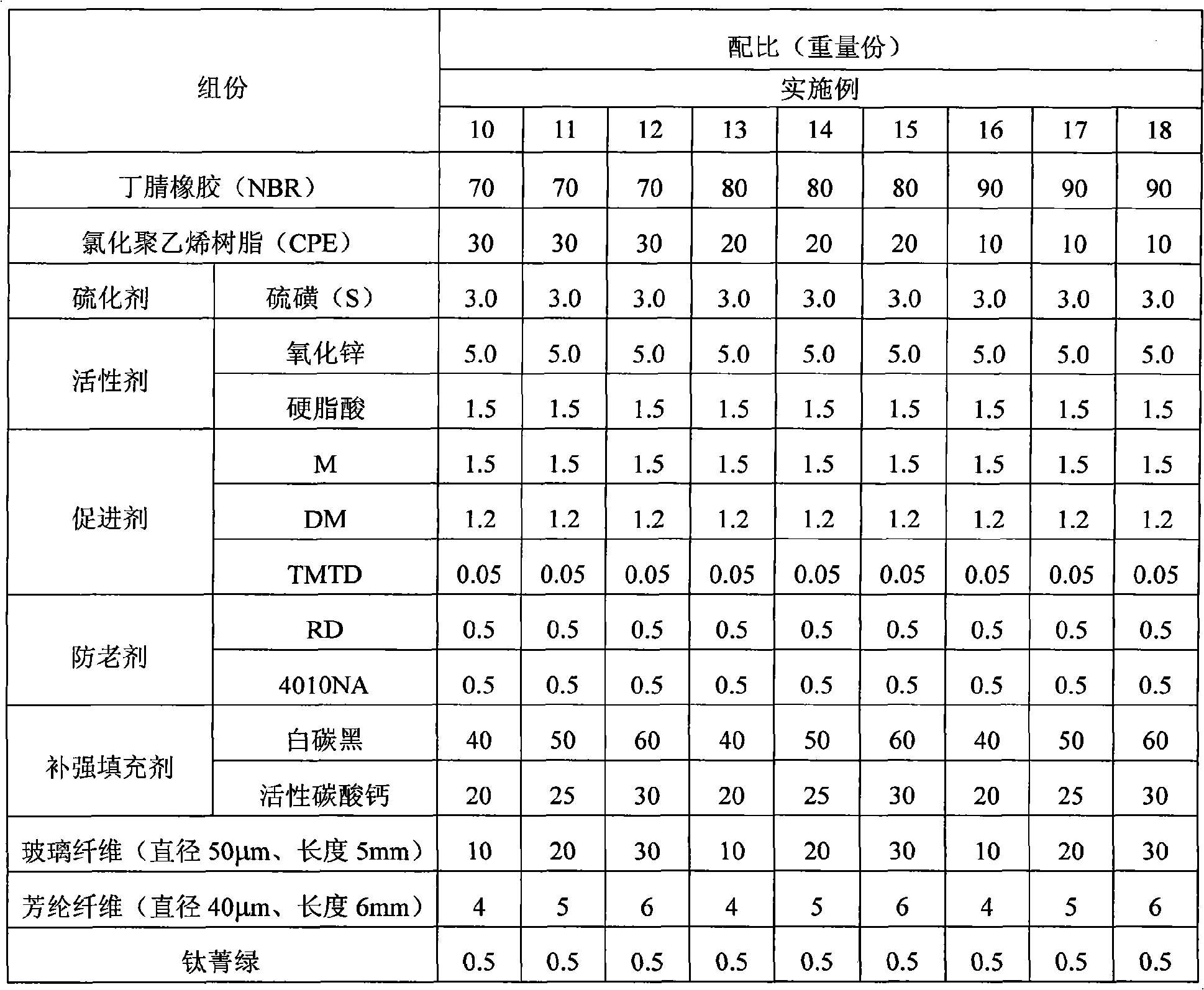
The invention relates to a fiber reinforced rubber, for which the strength can be remarkably improved, the permanent compression set can be reduced and the anti-tear performance of rubber sheet can be enhanced. A method for preparing the fiber reinforced rubber comprises the following steps: a. mastication of rubber; b. reinforcing filler, fiber and accessory ingredient are added into the rubber for mixing; wherein, the fiber and the reinforcing filler is evenly mixed to prepare pre-dispersoid, and the pre-dispersoid is added into the rubber. As a preferred proposal, the method adopts styrene-butadiene rubber, nitrile rubber and neoprene which have the good properties of wearing resistance, pressure resistance, oil and water resistance and air tightness resistance as the rubber. The rubber sheet produced by the method can work under ultra-high temperature and pressure in various media for a long time with the maximum working temperature being 300 DEG C, and maintains good elasticity, less compressive deformation and excellent physical and mechanical properties which are reduced by not more than 20% compared with those at the normal temperature.
Owner:南京固柏橡塑制品有限公司
Mastication detection device and mastication detection method
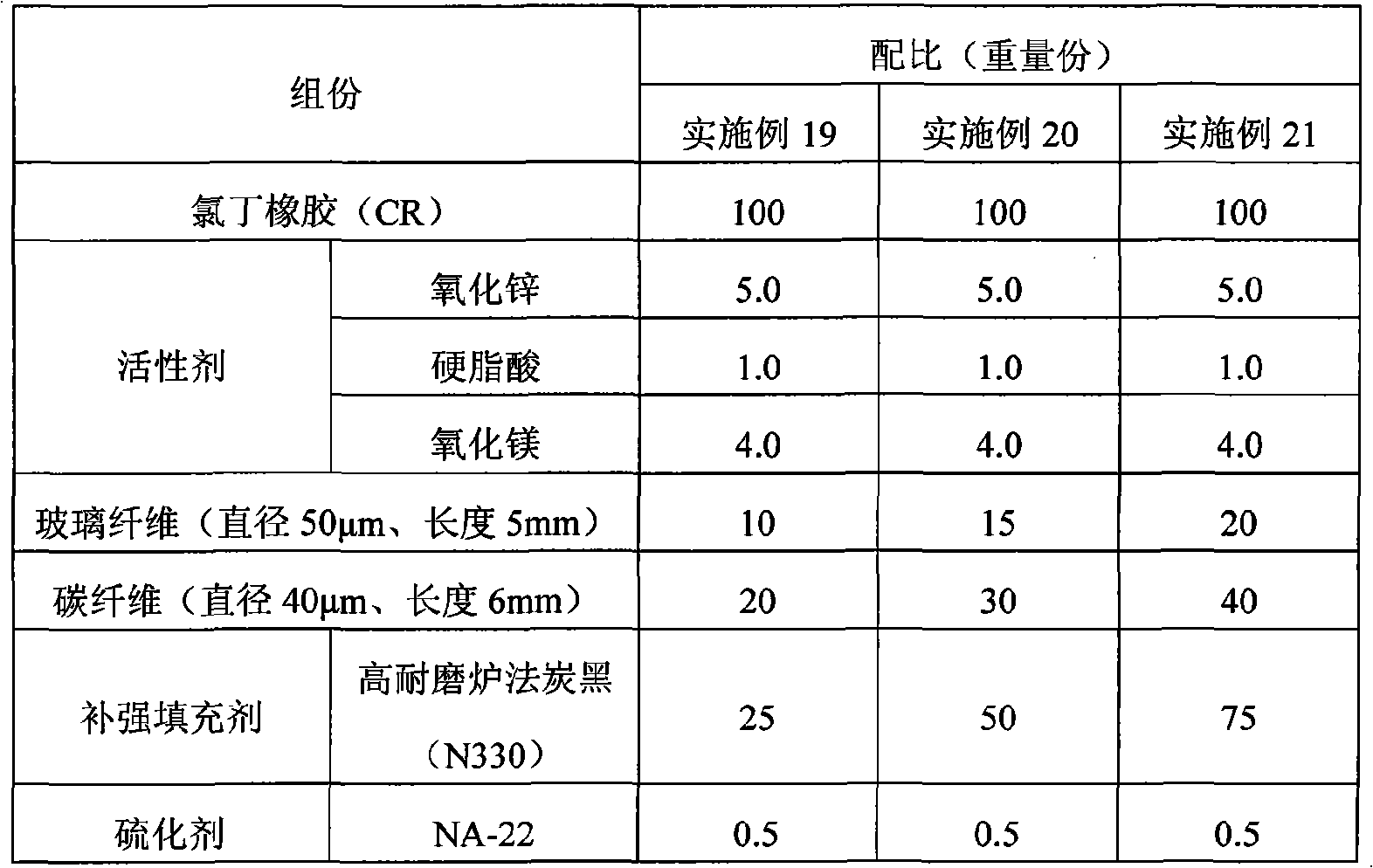
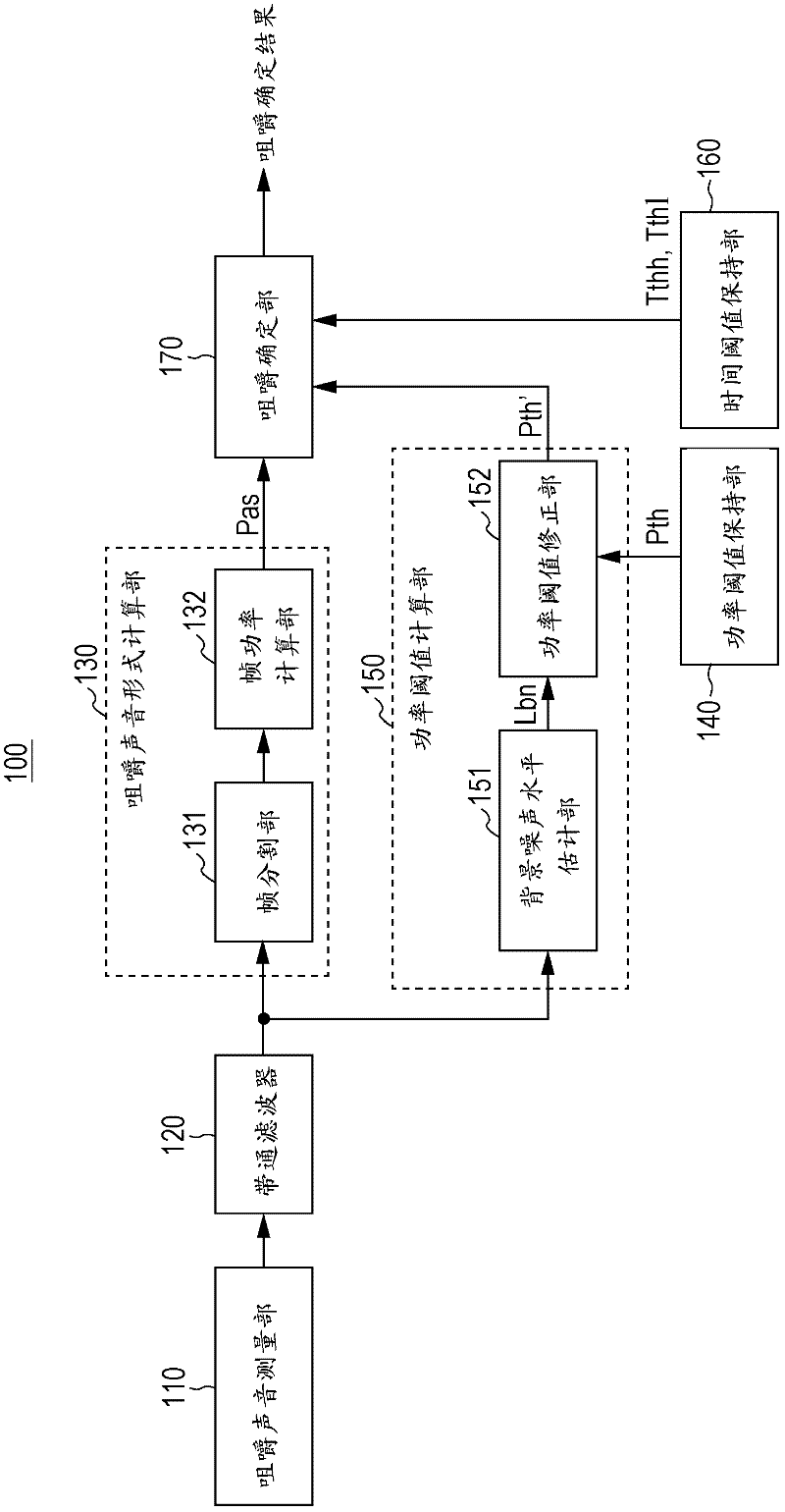
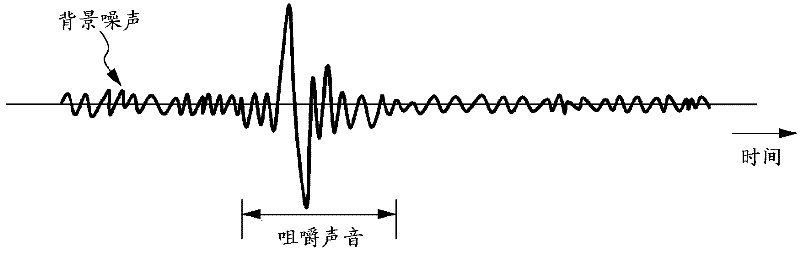
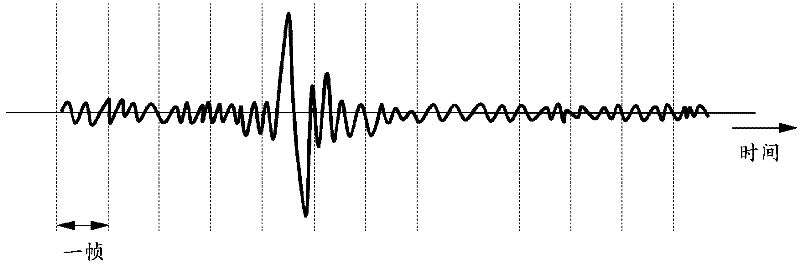
InactiveCN102670206AHigh-precision detectionStethoscopeDiagnostic recording/measuringInformation processingAudio signal flow
A mastication detection device and a mastication detection method are disclosed. The invention relates to an information processing apparatus and a method for providing logic for processing information. In one implementation, an information processing apparatus may include a receiving unit configured to receive an audio signal associated with a motion of a human mandible over a time period. The information processing apparatus may also include a determination unit configured to determine whether the motion of the human mandible corresponds to mastication, based on at least a power of the received audio signal during the time period.
Owner:SONY CORP
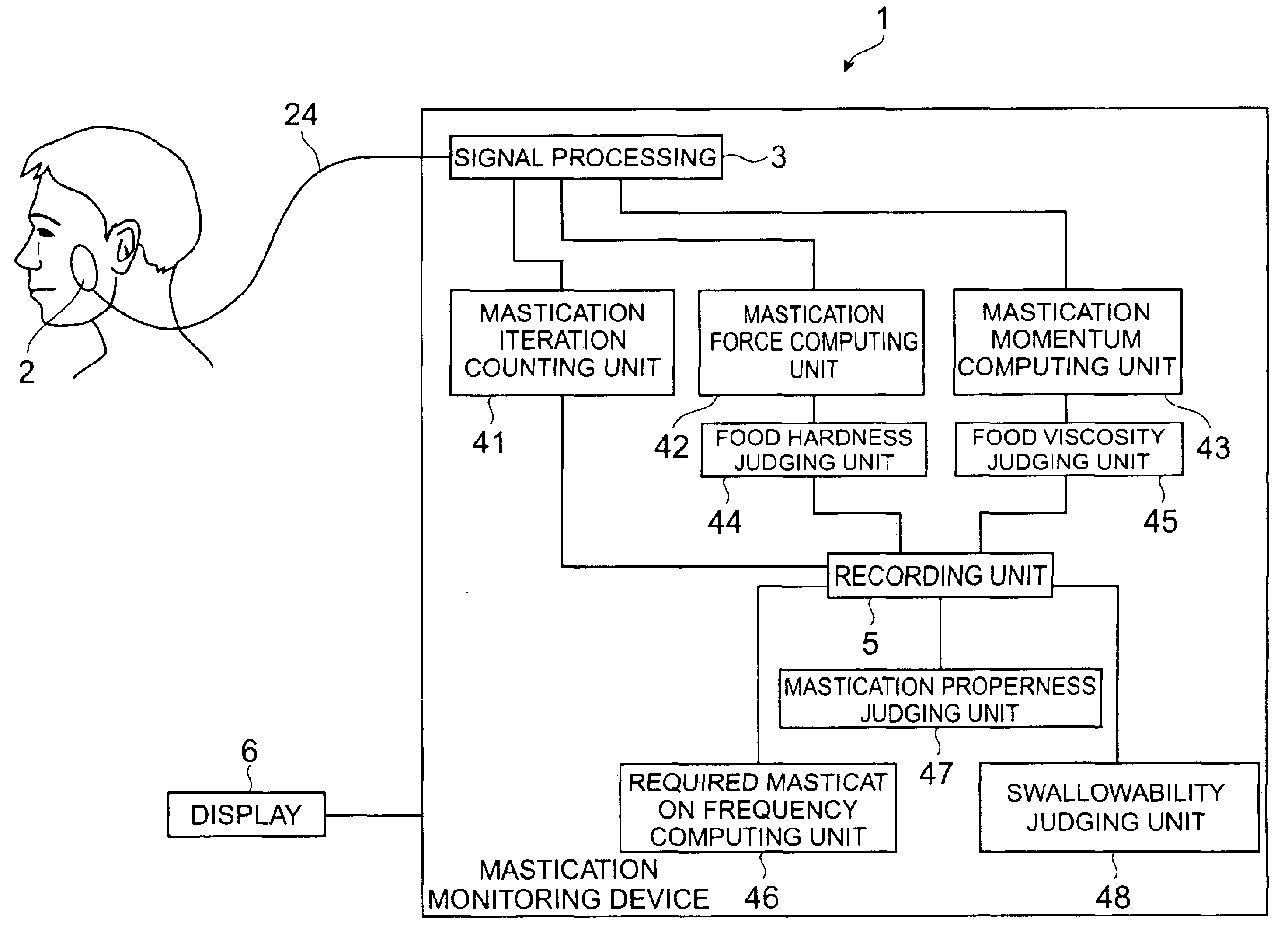
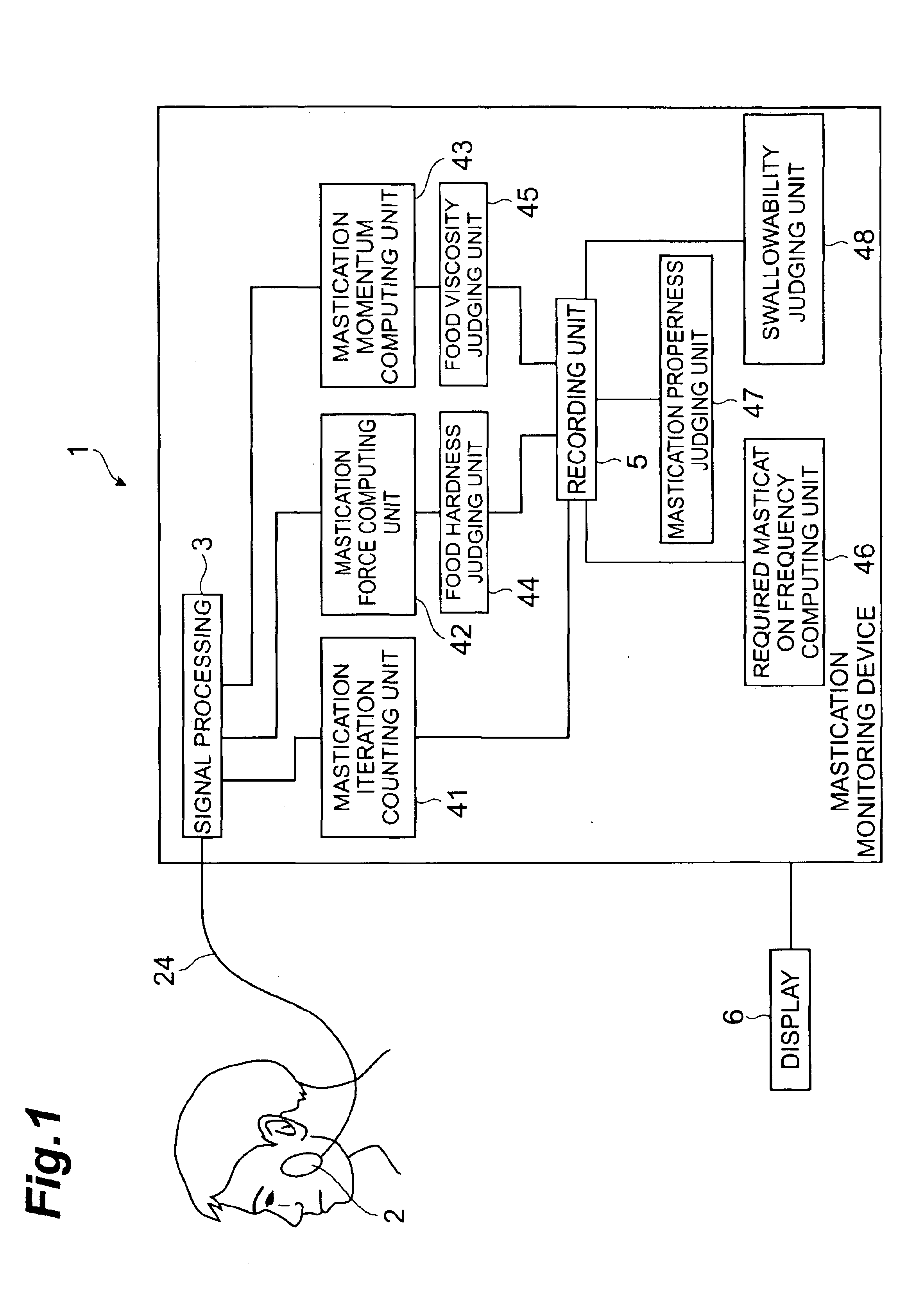
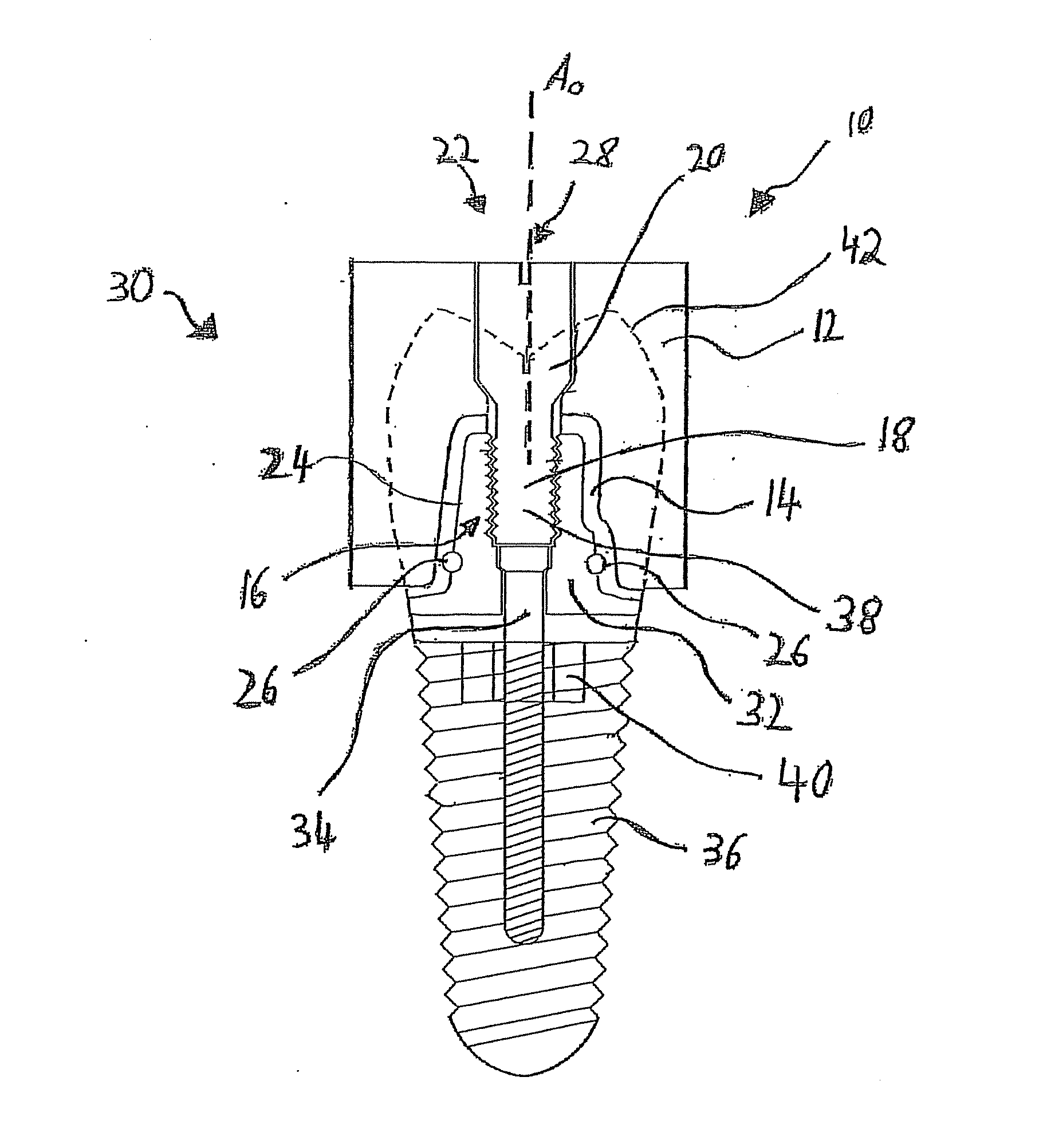
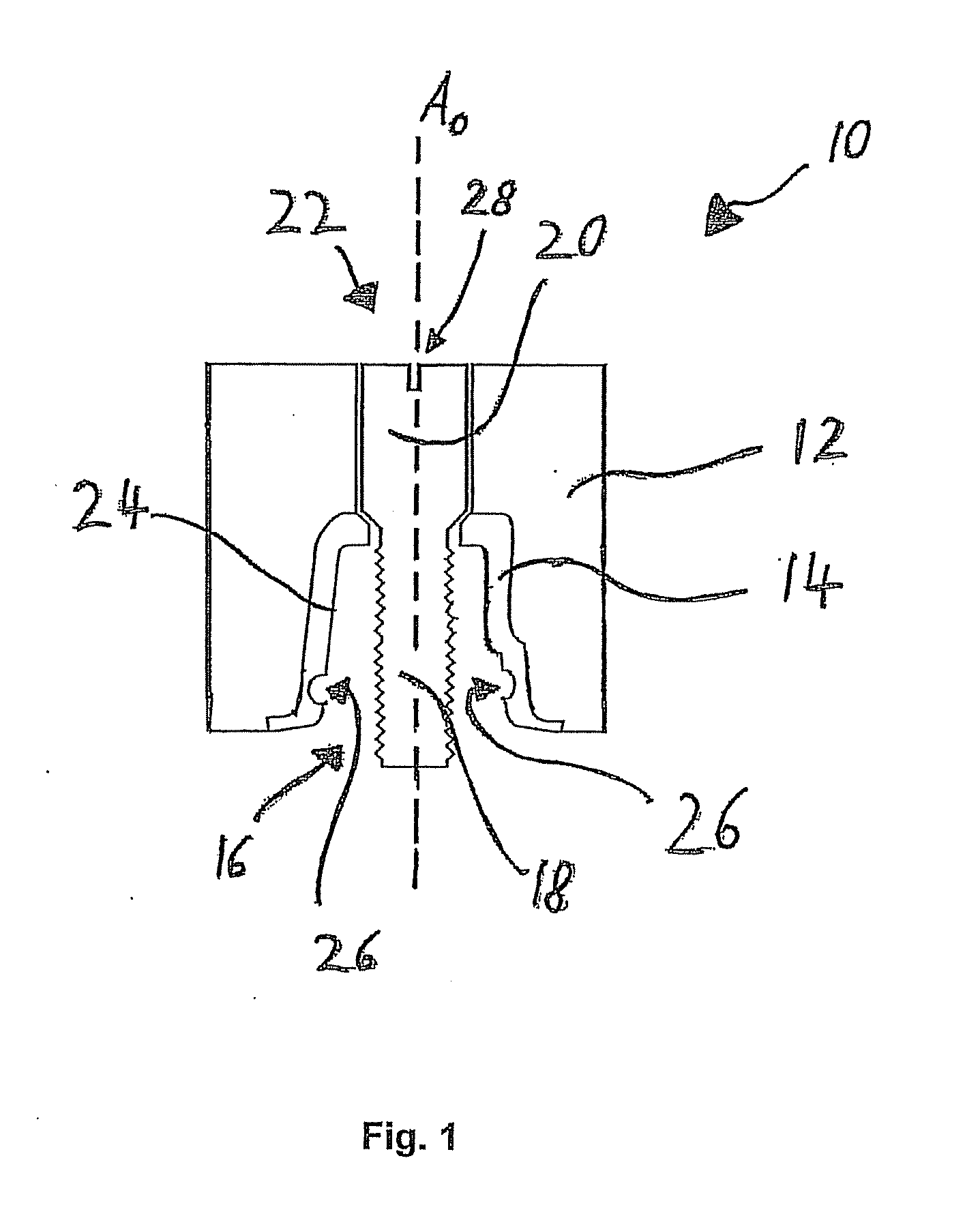
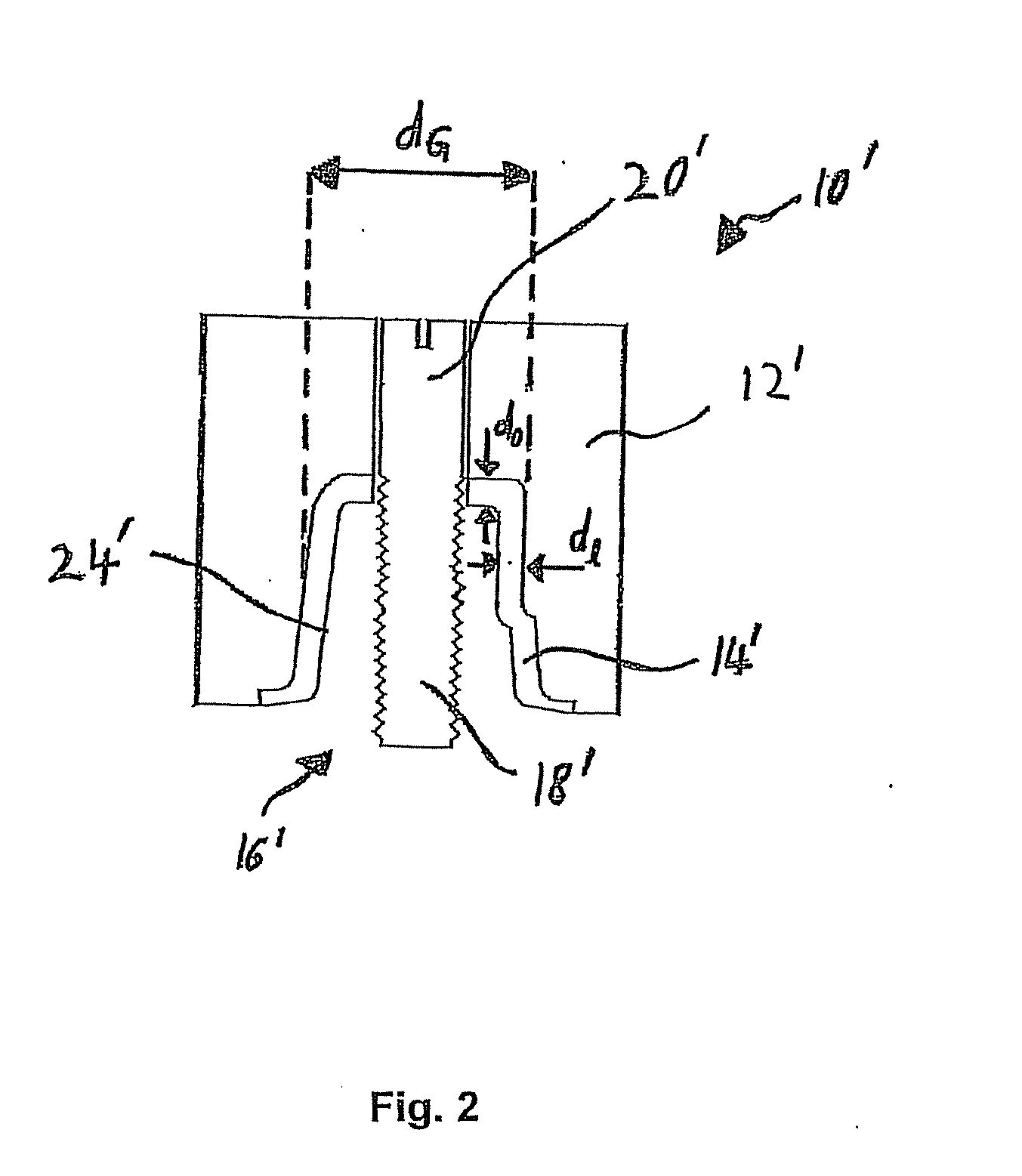
Mastication monitoring device
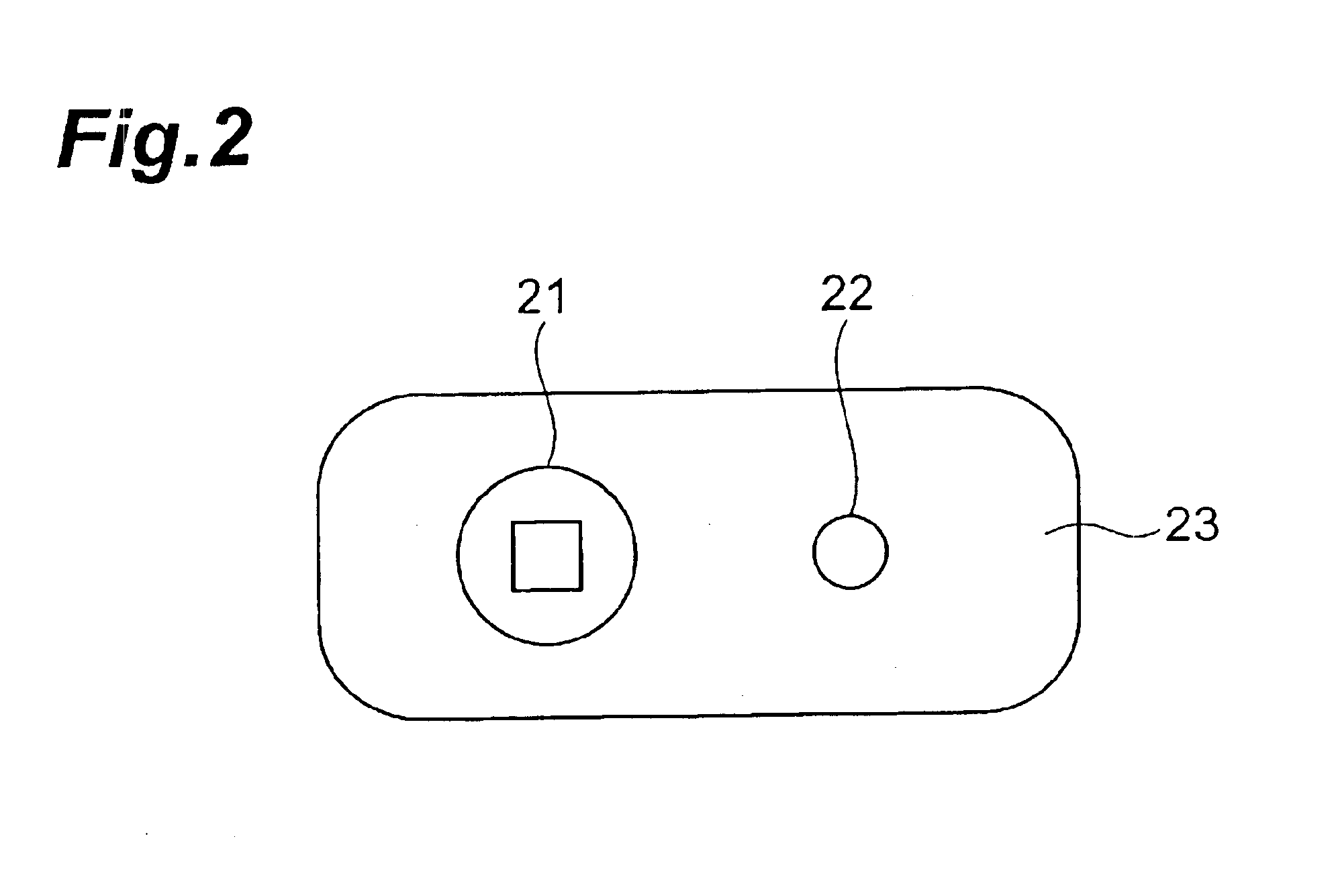
InactiveUS6893406B2Accurate bilateral mastication force balanceAccurate measurementSurgeryPerson identificationMoving averagePhotodetector
A mastication monitoring device 1 is provided with a probe 2 which is attached to a cheek in order to detect the concentration of reduced hemoglobin in the masticatory muscles. A photodetector 22 of the probe 2 detects light scattered in the masticatory muscles and delivers a signal of the amount of light received to a signal processing unit 3. The signal processing unit 3 computes the reduced hemoglobin concentrations (time-series changes) from the signals of the amount of light received, and further computes outputs S (time-series changes) corresponding to the time-series changes in the reduced hemoglobin concentrations. A mastication iteration counting unit 41 detects peaks in periodical changes of Sd which is the difference between the output S and the moving average value Sma of the output S and counts the peaks in periodical changes of Sd as the mastication iterations.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
Chewable electrolyte tablet
InactiveUS20060068005A1Avoid stomach irritationTotal calories lowBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsMedicineIrritation
A chewable electrolyte tablet. The chewable electrolyte tablet includes an agent to prevent stomach irritation, a flavoring agent, a sweetening agent, or a combination thereof to enable the tablet to be palatable and, therefore, ingested through simple mastication and without the need for water, thereby permitting the amount of water to be regulated. The tablet may be used to deliver electrolytes, amino acids and / or vitamins. Select embodiments of the tablet contain substantially no carbohydrates, thereby reducing the caloric content of the tablet. In other embodiments, the tablet provides a sustained release of nutrients over time.
Owner:PAL LAB
Rubber composition for sidewall, insulation or breaker cushion, production method thereof, and pneumatic tire
InactiveUS20110184118A1Improve fuel economyHigh flex crack growth resistanceSpecial tyresRolling resistance optimizationEngineeringChewing food
The present invention provides a rubber composition for a sidewall, an insulation, or a breaker cushion, which can achieve both excellent fuel economy (low heat build-up) and high flex crack growth resistance while having processability excellent enough to eliminate the need for mastication, and also provides a pneumatic tire produced using the rubber composition. The present invention relates to a rubber composition for a sidewall, an insulation, or a breaker cushion, including: a rubber component that contains a modified natural rubber with a phosphorus content of 200 ppm or less; and carbon black and / or a white filler.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Chewing gum compositions
InactiveUS6926916B1Shorten the timeHigh smooth teeth feelCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsParticulatesPolymeric surface
The present invention relates to chewing gum composition comprising a polymeric surface active agent. A second aspect of this invention relates to a crunchy chewing gum wherein the crunchy texture is provided by particulate polyphosphate particles within the formulation and which lasts through the initial minutes of mastication. The chewing gum composition may also contain a cationic material and or an orally active metallic ion. The chewing gum composition will provide surface conditioning effects on a subject's teeth and or oral mucosa and the crunchy texture is used as a sensate to reinforce these effects. The surface conditioning effects can be measured through in vitro or in vivo testing. The in vitro testing shows a total surface energy and or a lewis base score to increase immediately after treatment with the chewing gum and then decrease over time. The in vivo testing shows a water contact angle of the oral mucosa to decrease after treatment with the chewing gum composition and / or a significantly higher smooth teeth feel relative to other chewing gum compositions. The present invention also relates to methods of providing surface conditioning effects to a subject comprising administering to the subject a chewing gum comprising a polymeric surface active agent. The present invention also relates to methods of reducing astringency of a chewing gum containing an orally active metallic ion without significantly reducing the efficacy of the metallic ion.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Special compound enzymic preparation for softening areca nut
The invention relates to a special compound enzymic preparation for softening areca nut, which is characterized by comprising the following components by weight percent: 15-20 percent of hemicellulase, 10-15 percent of cellulose, 10-15 percent of pectinase, 25-45 percent of beta- glucanase and 20-25 percent of purified water. The special compound enzymic preparation for softening areca nut can cause decentralization and defibrination of the areca nut cellulose by applying a biotechnology via the action of the biological enzyme so that the cellulose microcrystalline structure is disorganized resulting in denaturation, the macromolecule structure of the areca nut fibre is hydrolyzed into micromolecule to cause fibrous fracture, and the aim of softening areca nut fibre and improving the mastication and mouth feel is achieved. The invention achieves the softening effect by adopting the biotechnology to substitute the traditional process which uses chemical measures such as lime water and the like, ensures safety and no peculiar smell, keeps the pleasant sensation of mastication and does not damage the oral cavity.
Owner:吴鹏
Rubber composition for inner liner and pneumatic tire
InactiveUS20110178235A1Excellent low heat build-upHigh flex crack growth resistanceSpecial tyresPolymer scienceChewing food
The present invention provides a rubber composition for an inner liner, which can achieve both excellent low heat build-up and high flex crack growth resistance while having processability excellent enough to eliminate the need for mastication, and further has good air impermeability, and also provides a pneumatic tire produced using the rubber composition. The present invention relates to a rubber composition for an inner liner, including: a rubber component that contains a modified natural rubber with a phosphorus content of 200 ppm or less, and carbon black and / or a white filler.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Sheath material for optical fiber cable, and production process thereof
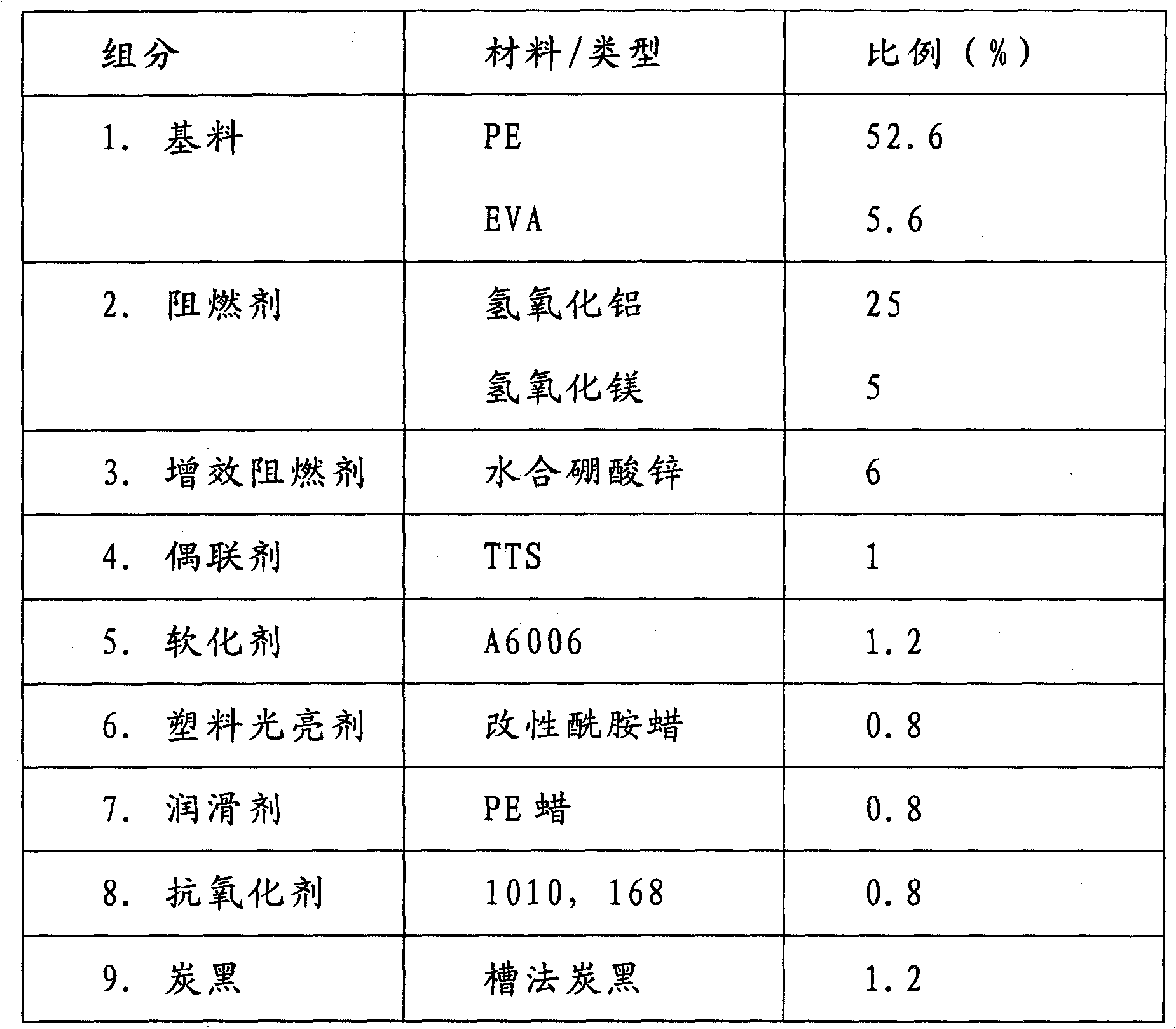
InactiveCN102807693AMeet the use requirementsImprove performanceFibre mechanical structuresPolymer sciencePolyolefin
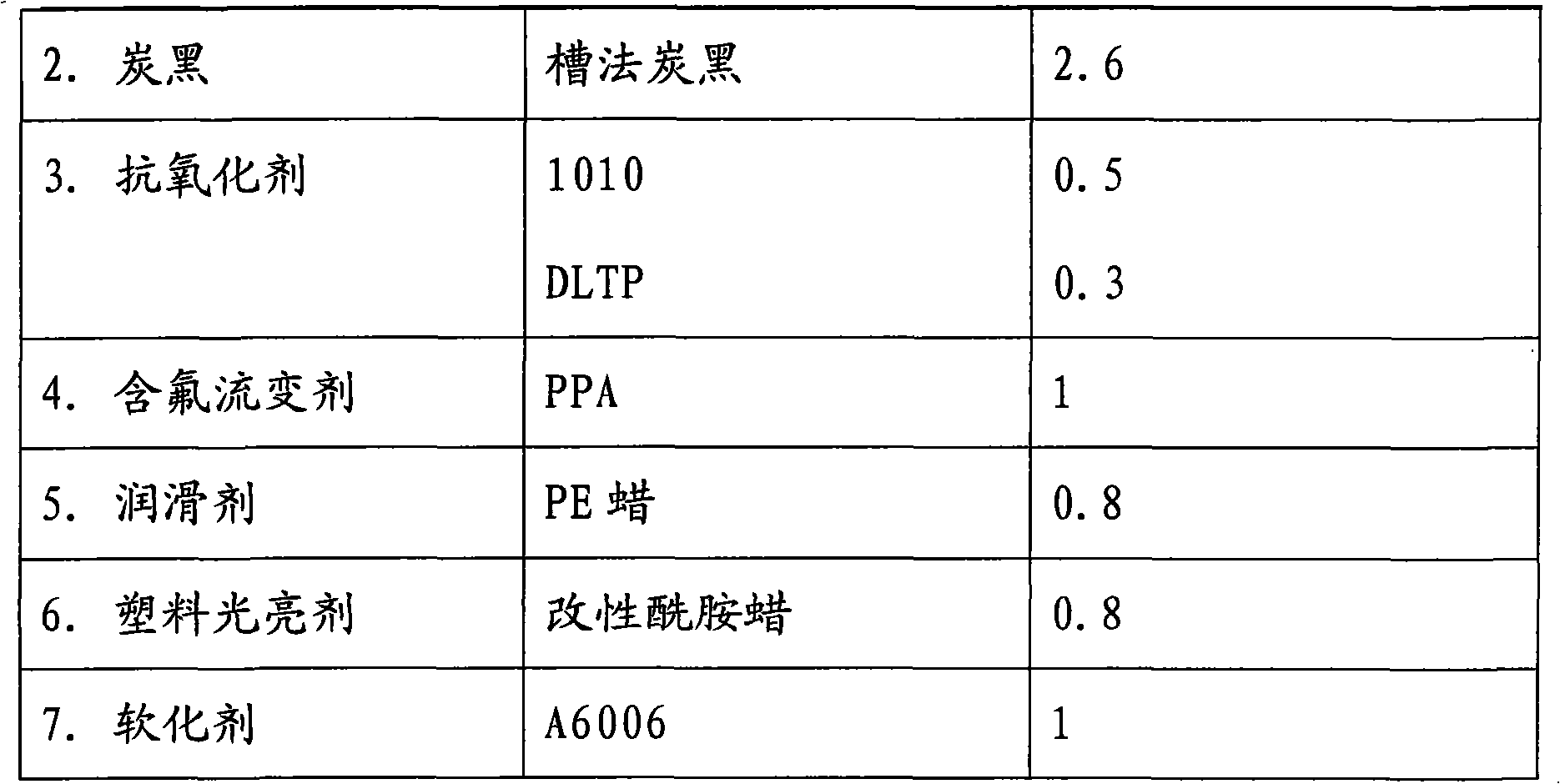
The present invention relates to a sheath material for an optical fiber cable, and a production process thereof. The sheath material comprises, by weight, 85-95% of a polyolefin base material, 2.35-2.85% of carbon black, 0.5-1% of an antioxidant, and 0.8-1% of an additive, wherein the polyolefin base material comprises a polyethylene base material and a modifier, and the additive comprises a fluorine-containing rheological agent PPA, a lubricant, a plastic brightening agent and a softener. During production, carbon black is made into a masterbatch; PPA is made into a masterbatch by using a polyethylene base material; the carbon black masterbatch, the PPA masterbatch, an antioxidant, a plastic brightening agent and a softener are mixed; the mixed material is added to EVA to mix; the resulting mixture is added to polyethylene to mix, and then mastication extrusion is performed through a plastic extruder. According to the present invention, high and medium density polyethylene is adopted as a base material for the optical fiber cable sheath, such that a chemical performance is stable; and various auxiliary materials are added to the polyethylene base material, such that performances of the optical fiber cable sheath are improved, and various use requirements of the optical fiber cables are met.
Owner:JIANGSU NANFANG COMM TECH
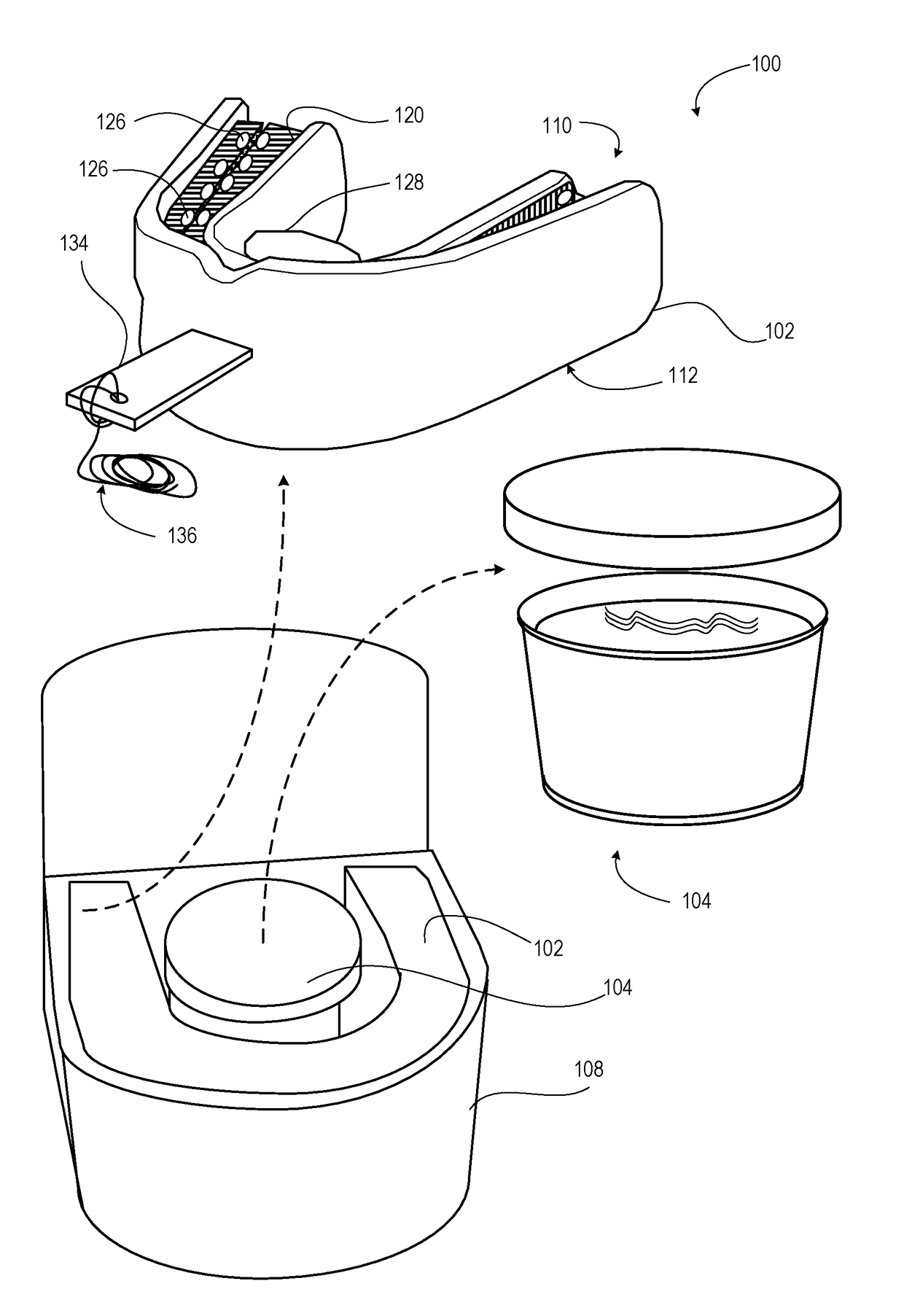
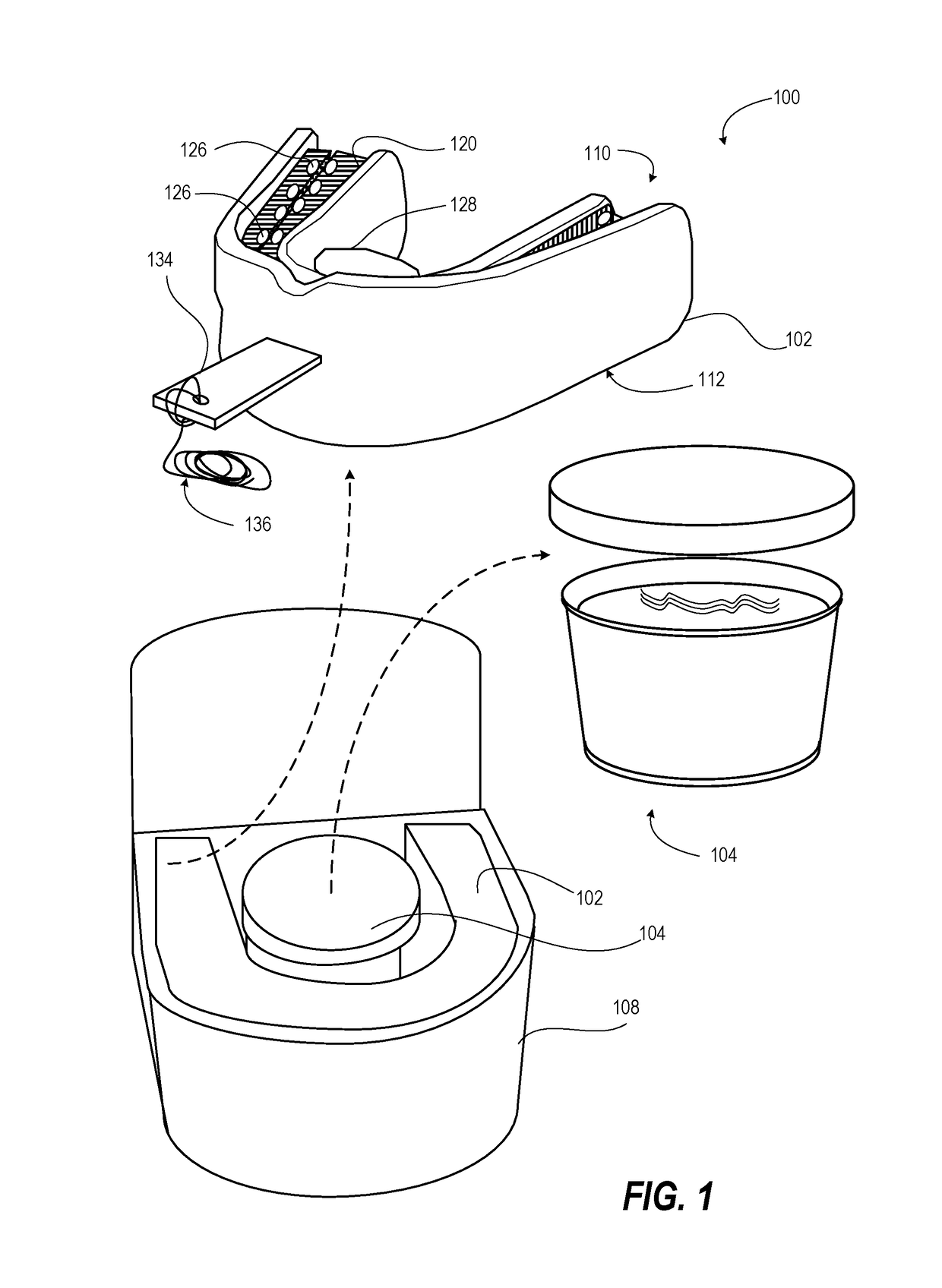
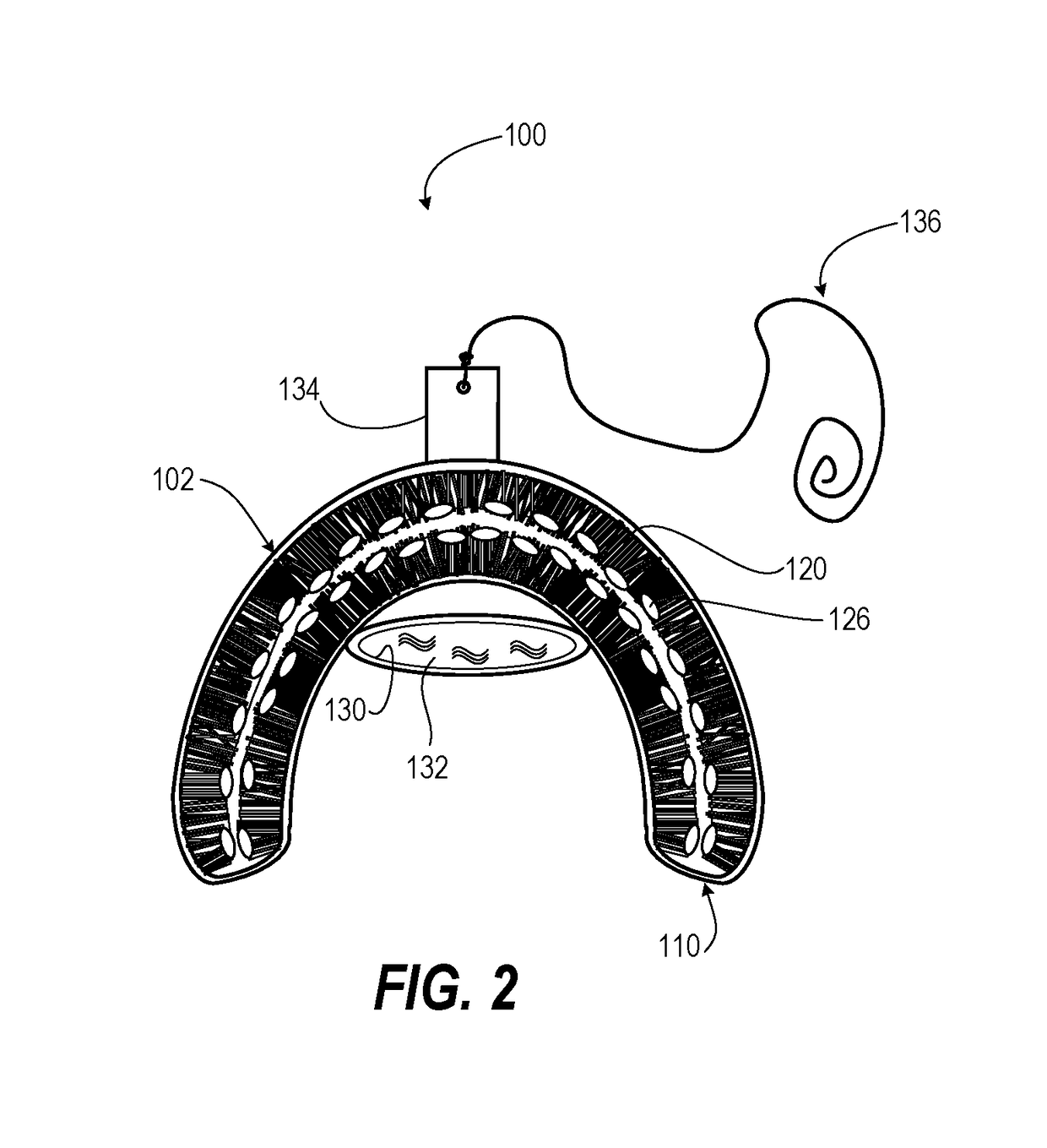
Teeth cleaning travel kit
A teeth cleaning travel kit includes toothbrushing mouthpiece that has two inverted channels dimensioned to receive upper and lower bites of dental arches of a user, the channels being integral with one another. Teeth-cleaning bristles inwardly project within the two inverted channels to bear inwardly against teeth and gums of the user, wherein the channels and teeth-cleaning bristles are configured such that mastication produces relative brushing movement of the teeth-cleaning bristles over the teeth and gums. An oral hygiene promoting product is attached to one of the two inverted channels and the teeth-cleaning bristles that is released by action of the user's mouth. The teeth cleaning travel kit also includes a vessel that contains a rinsing fluid and kit packaging that contains the toothbrushing mouthpiece and vessel.
Owner:BRUSH LLC
Functional Masticatory Material, Method Of Producing The Same And Method Of Using The Same
InactiveUS20090169682A1Increase the number ofExtension of timeMilk preparationBaking mixturesMasticationChemistry
Tableting or granulating is conducted using prolamine, wheat gluten and a functional material or materials as raw materials. The functional masticatory product has elasticity and extensibility through inclusion of saliva during mastication, has edibility and has mastication time longer than that of gummi candy. Thus, varied mastication time longer than that of gummi candy can be provided and the functional material or materials can be sufficiently ingested without depending on natures of the same such as water solubility.
Owner:MEIJI PHARMA
Spout for drinking container
A spout for attachment to bottles, cups or other drinking vessels and containers having a dome shaped enclosure and a set of stability ribs. The stability ribs specifically ensuring that fluid flow through the fluid conduit remains as laminar as possible, and prevents the fluid conduit from collapse if a high amount of suction or mastication is provided by a user of the drinking vessel or container.
Owner:SAKULSACHA CHAWARIN +1
Green pawpaw mastication tablet and producing method thereof
The invention relates to a green papaya chewing tablet made from natural plant fruit papaya, which mainly contains the materials of green papaya powder, sweetener and adhesives; the preparation method comprises following steps: making green papaya powder first; mixing the green papaya powder with other materials; making the mixture into particle materials; drying the particle materials with low temperature; squashing the particle materials into tablets; finally packing the tablets to obtain the product. The green papaya chewing tablet has the advantages of strengthening spleen and stomach, helping digestion, relieving constipation, detoxicating and deswelling, improving lactation, preserving continence, preventing tooth decay, anti-tumor, reducing weight, enlarging breast, and being suitable for general population, more particularly for the female friends.
Owner:广西科学院生物研究所有限责任公司
Blank and process for producing a dental restoration by subtractive machining
InactiveUS20150216635A1High natural appearanceHigh strengthDental implantsWashersAngular orientationImplant retainer
A blank is provided for producing a dental prosthesis (tooth crown) comprising a mechanically processable material block and a holder connected thereto for clamping in an automatic processing tool. Said block is provided with a subgingival anatomic implant connecting part which is protrusively arranged thereon and in which an implant fixture for fixing it to the implant head is formed. The holder is arranged on the surface of the block arrangement side and the implant fixture to a surface on the implant side, thereby making it possible to work the blank by means of a computer-controlled conventional tool. A threaded channel which is embodied in the centre of the block in a parallel direction with respect to the surface on the fixation side, the angular orientation of the mastication surface of the tooth crown with respect to the occlusion vertical and the subgingival anatomic implant connecting part make it possible to fix the prosthetic element (tooth crown) directly to the implant without an abutment and with correct orientation in the row of teeth.
Owner:JOSEF SCHWEIGER
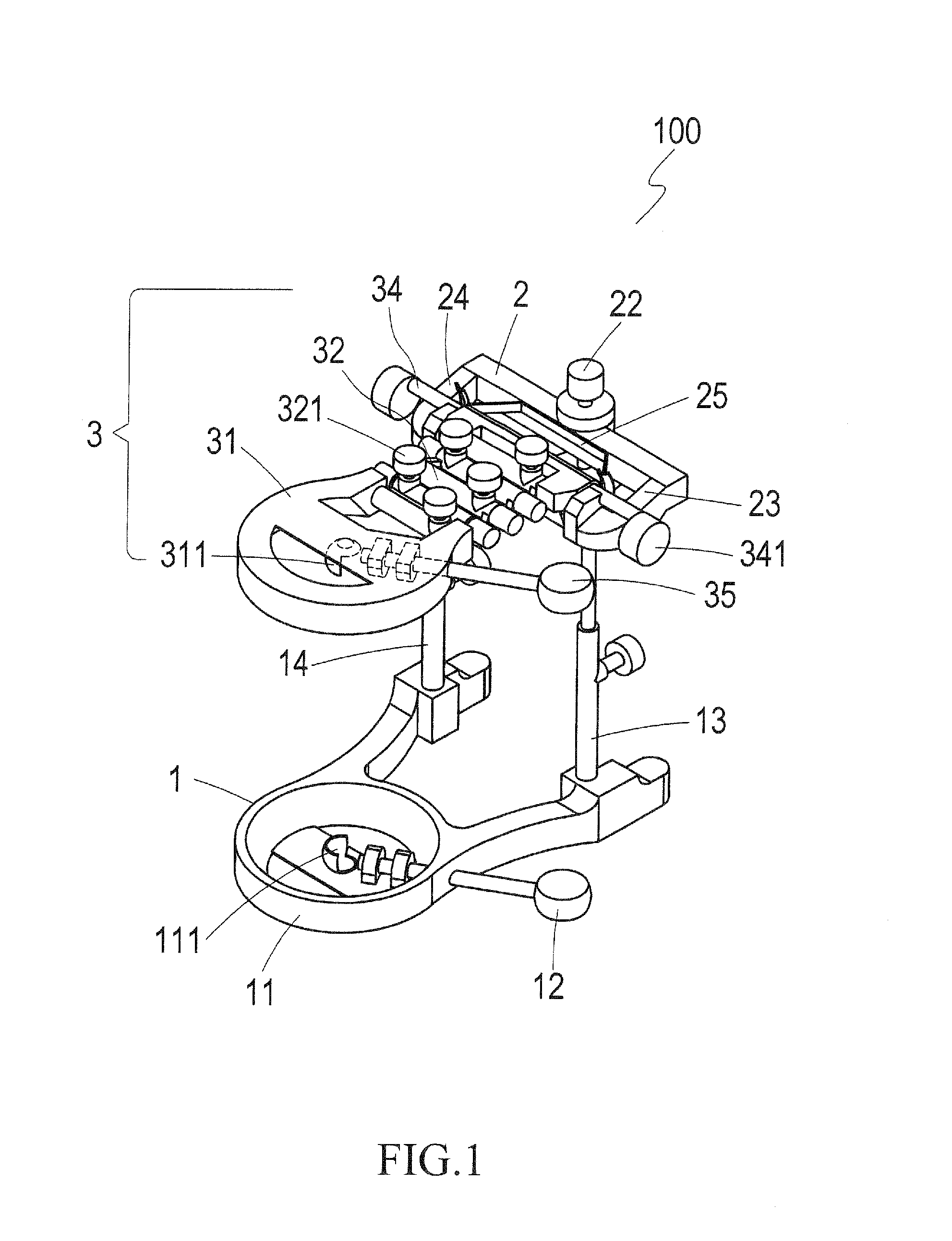
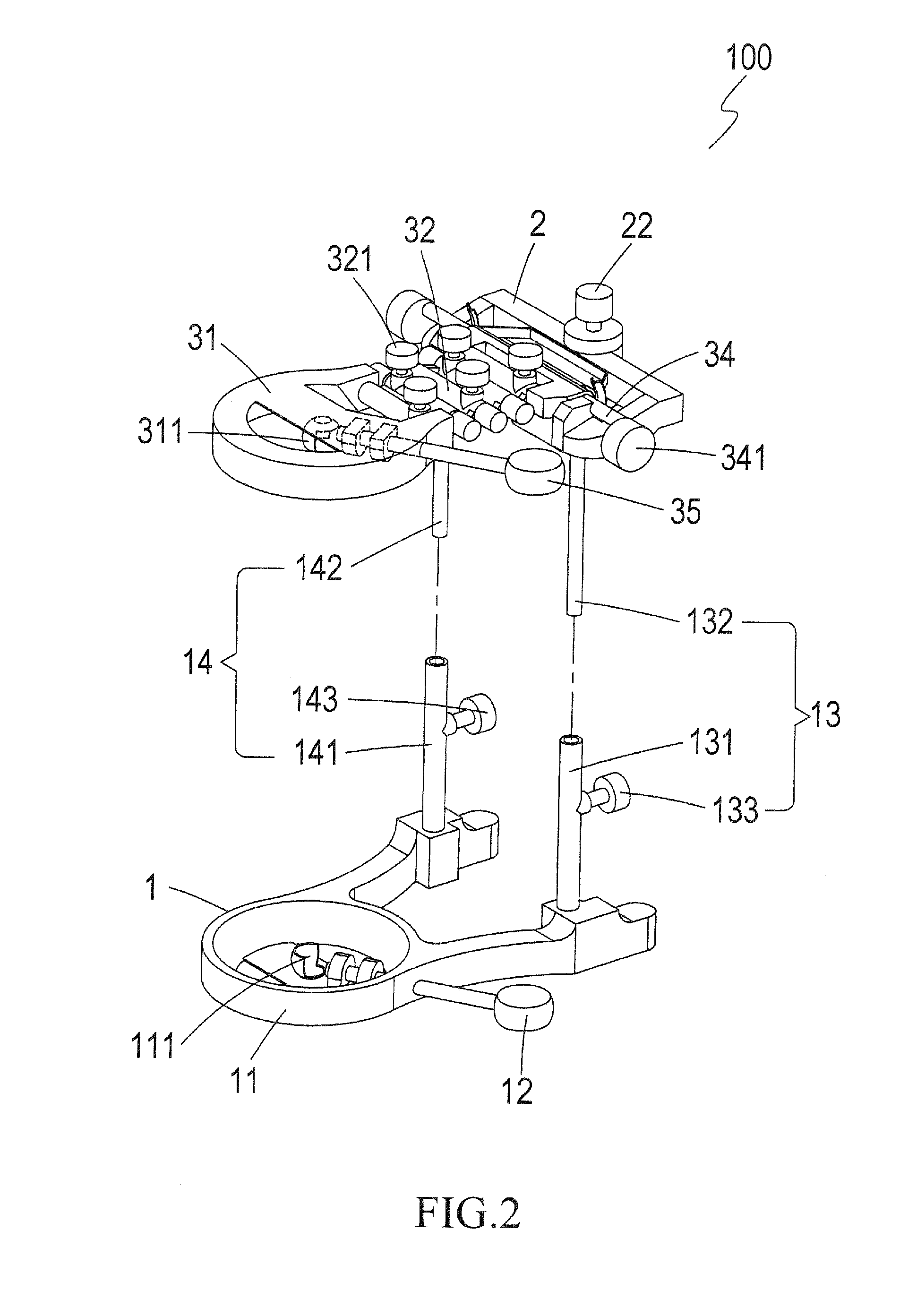
Articulator
InactiveUS20120164595A1The result is accurateVarious sizesDental articulatorsEducational modelsOcclusal AdjustmentDental Articulators
A denture articulator is provided for coupling denture casts to allow for occlusal adjustment of the casts. The articulator includes a base, a cross bar, and a top. The casts are mounted to the top and base by cast holder seats or cast retainer seats for simulation of mastication and occlusal adjustment. The top allows a user to adjust the vertical location of the cast and also allows the user to adjust the elevation of the cast.
Owner:SU CHIH CHIANG
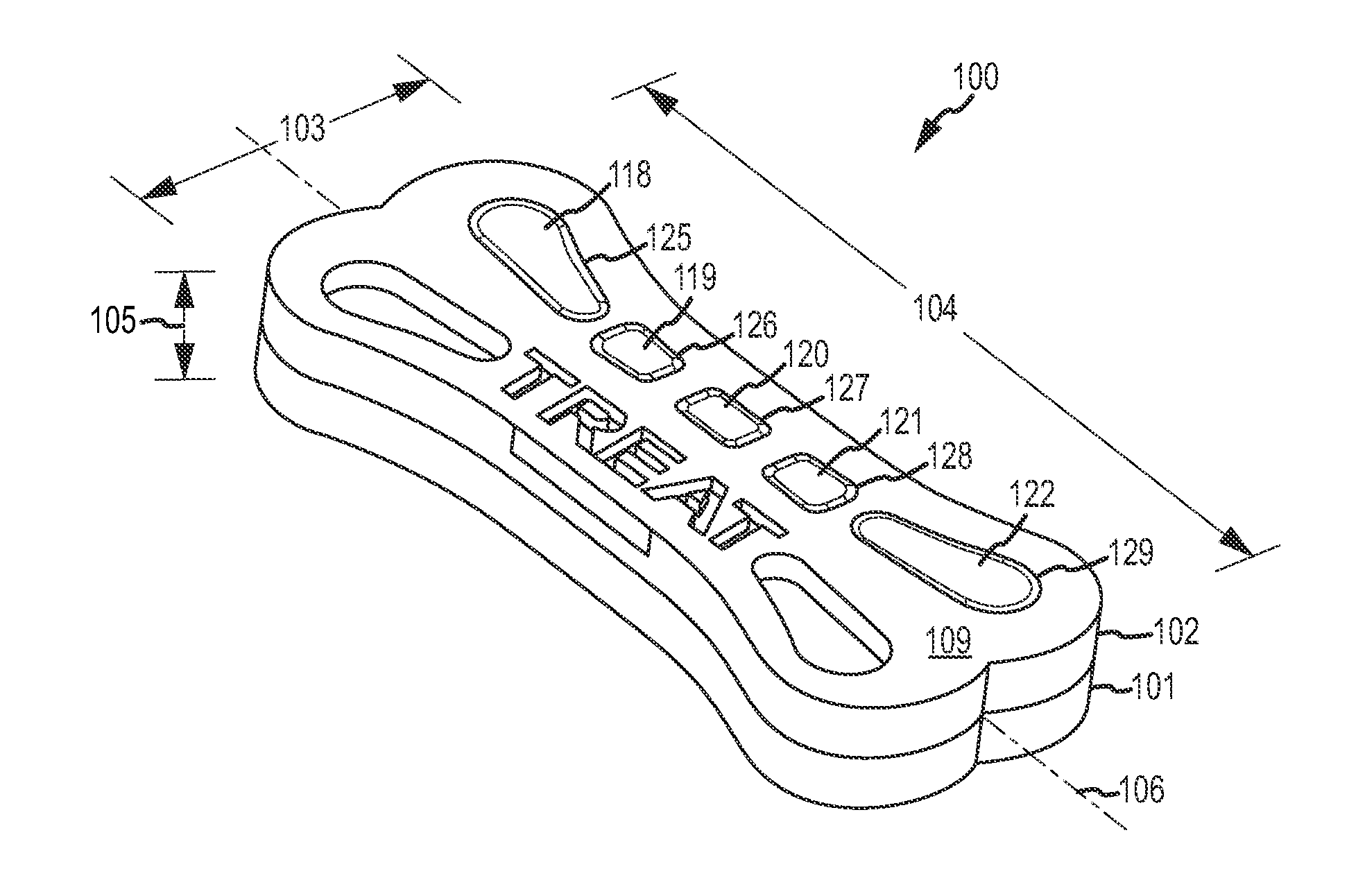
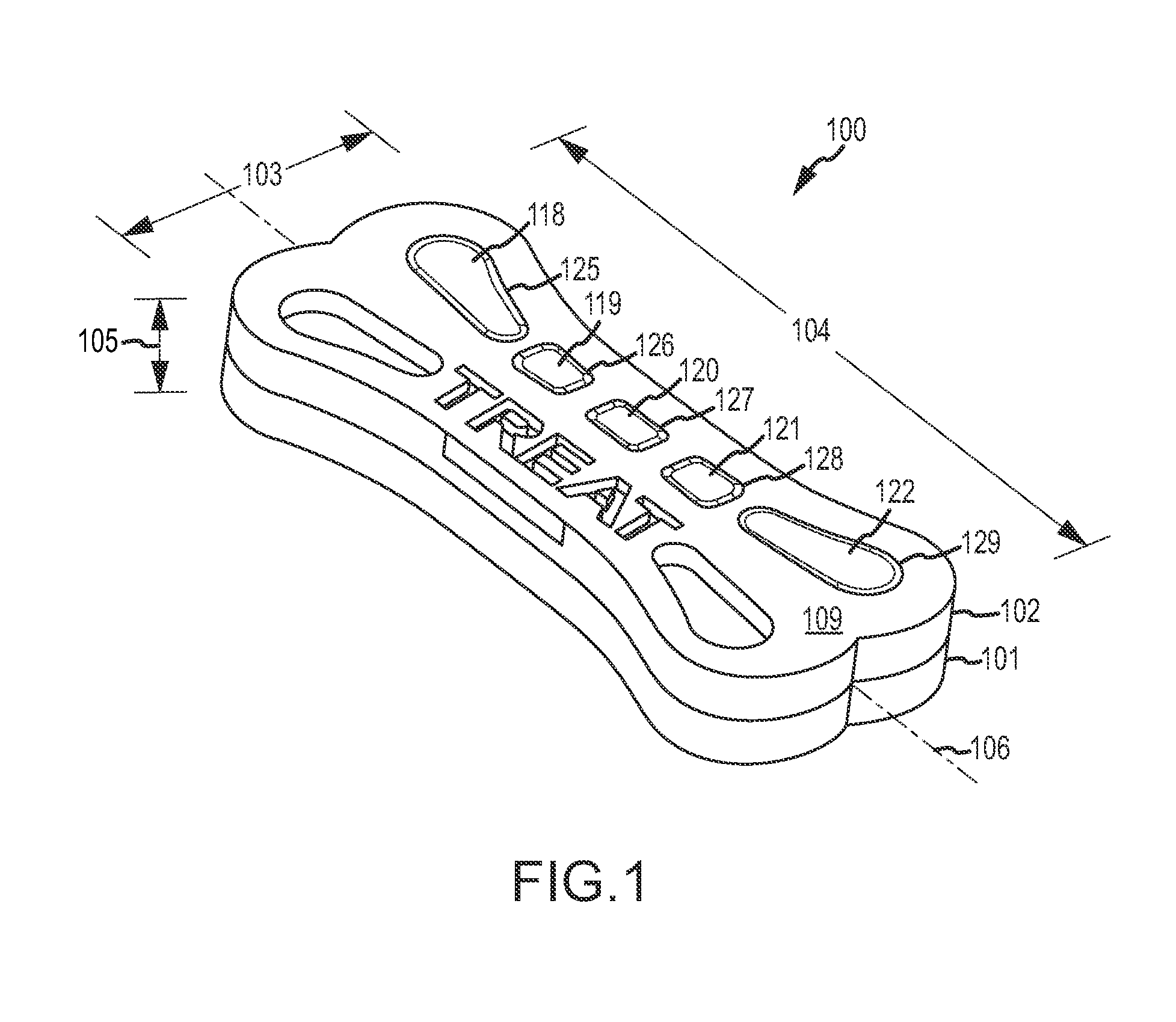
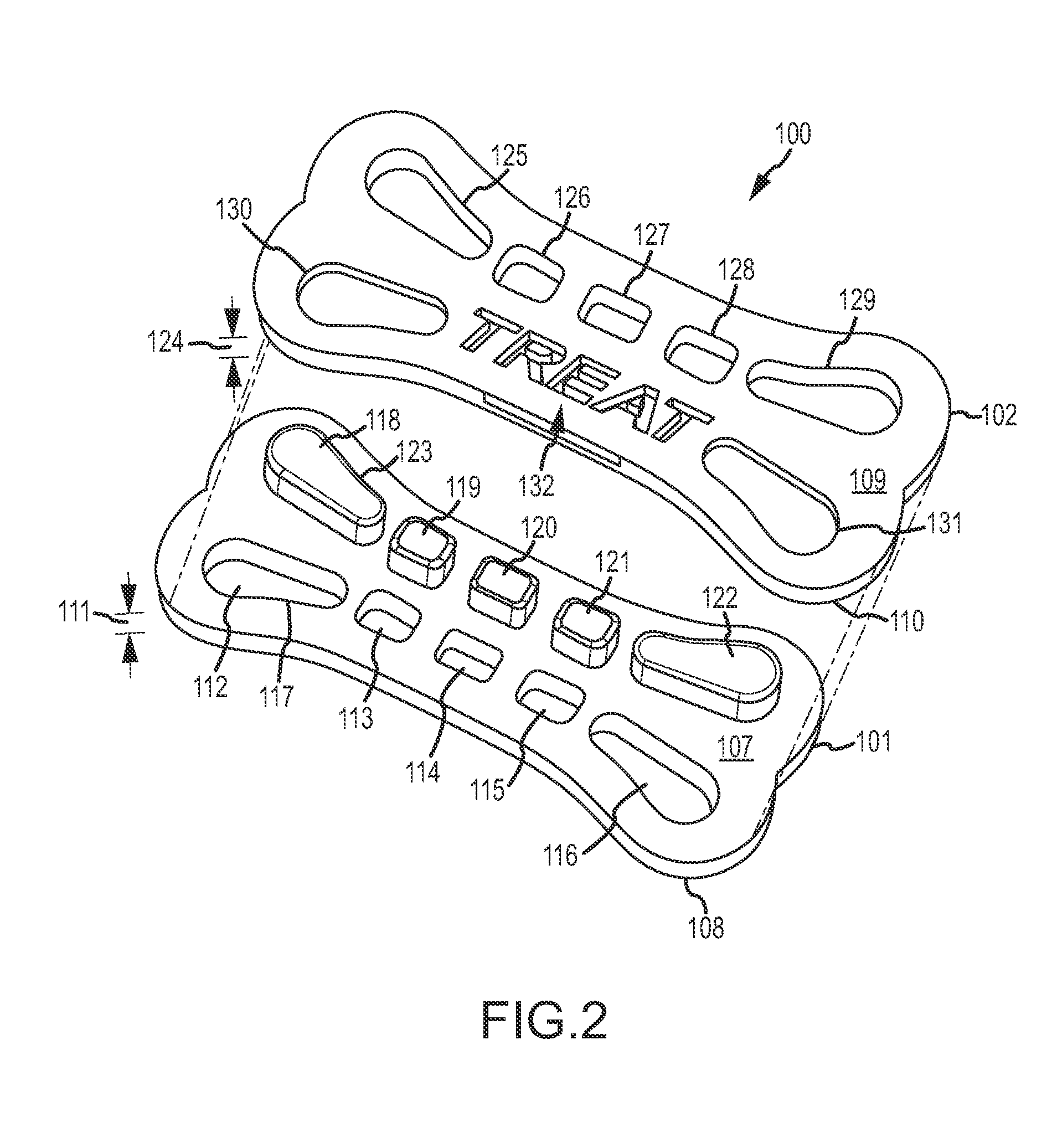
Pet Food Product with Interlocking Feature
InactiveUS20130189397A1Extended treatment timeAvoid separationMilk preparationMeat/fish preservationEngineeringDental cleaning
A pet food product with multiple layers and at least one of the layers includes protrusions that extend into another layer. The protrusions provide a mechanical interlock between layers providing increased resistance to delamination while the pet food product is being masticated. One of the layers may primarily provide palatability while another layer may provide therapy such as dental cleaning. The ability to resist delamination during mastication may result in prolonged delivery of the therapy as the pet chews on the pet food product to experience the palatability of the palatable layer.
Owner:JELCER IP
Ferrum replenishing jelly and its preparation technology
InactiveCN101142974AChange formEasy to takeHeavy metal active ingredientsFood preparationFlavorTrace element
The invention relates to iron supplementing jelly and preparation process and provides iron supplementing jelly which can supplement trace element iron necessary for human body and has no need of mastication due to appropriate flavor, with easy preparation, low cost, easy carrying and taking. The invention comprises the following components: jelly sandwich particle and outer jelly; the composition and weight shares of jelly sandwich particle are as follows: iron of 0.1 to 2 shares, folate of 0 to 1 shares, jelly powder or food glue of 20 to 60 shares, filler of 1 to 5 shares, sweetener and / or edible taste correcting substance of 0.5 to 5 shares, edible flavor of 0.1 to 5 shares and water of 20 to 70 shares, and the composition and weight shares of outer jelly ingredient are as follows: jelly powder or food glue of 15 to 50 shares, filler of 1 to 5 shares, sweetener and / or edible taste correcting substance of 0.5 to 5 shares, food flavor of 0.1-5 shares and water of 20 to 70 shares. The product provided by the invention is suitable for various crowds.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV
Low smoke halogen-free flame retardant sheath material for optical fiber cable, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102807695AStrong toughnessIncrease elasticityFibre mechanical structuresEnvironmental resistancePolyolefin
The invention relates to a low smoke halogen-free flame retardant sheath material for an optical fiber cable, and a preparation method thereof. Components of the material comprise a polyolefin base material, a flame retardant, an antioxidant, carbon black and an additive, wherein the carbon black is channel black, the base material is PE added with EVA, the antioxidant adopts a phenol antioxidant as a main antioxidant and adopts a phosphite antioxidant as a synergetic antioxidant, the additive comprises a coupling agent, a lubricant, a brightening agent, a lubricant and a synergistic flame retardant, and the flame retardant is a hydrated metal oxide. The preparation method comprises: making the carbon black into masterbatch; carrying out a modification treatment on the flame retardant with the coupling agent; mixing the carbon black masterbatch, the antioxidant, the brightening agent and an softener, and then adding the mixed material to the coupling agent-modified flame retardant to mix; adding the resulting mixture to a plastic extruder to carry out mastication extrusion to obtain the finished product. The flame retardant sheath material of the present invention has characteristics of low smoke, low toxicity, no halogen, environmental protection, low cost, and good comprehensive performance.
Owner:JIANGSU NANFANG COMM TECH
Spout for drinking container
A spout for attachment to bottles, cups or other drinking vessels and containers having a dome shaped enclosure and a set of stability ribs. The stability ribs specifically ensuring that fluid flow through the fluid conduit remains as laminar as possible, and prevents the fluid conduit from collapse if a high amount of suction or mastication is provided by a user of the drinking vessel or container.
Owner:SAKULSACHA CHAWARIN +1
Production method of anti-bacterial SBR (styrene butadiene rubber) foaming material
The invention relates to a production method of an anti-bacterial SBR (styrene butadiene rubber) foaming material. The ingredients includes, by weight parts, 20 to 40 parts of natural rubber, 60 to 80 parts of main SBR materials, 10 to 15 parts of process / operation auxiliaries, 20 to 30 parts of vulcanization / foaming auxiliaries, 40 to 50 parts of processing oil and 120 to 150 parts of reinforcing filler. The production method includes steps of firstly, masticating; secondly, mixing; thirdly, opening smelting; fourthly, fine smelting; fifthly, open smelting secondarily; sixthly, extruding; seventhly, vulcanizing and eighthly, foaming. The production method is characterized in that 3 to 5 parts of nanometer silver powder are added into the ingredients according to mass ratio, the first step of the production method includes feeding the natural rubber and the nanometer silver powder into an open smelting machine or a fine smelting machine to realize mastication, and the second step of the production method includes feeding a primary product of the first step, the main SBR and the process / operation auxiliaries into the fine smelting machine to mix. The production method of the anti-bacterial SBR foaming material has the advantages that anti-bacterial nanometer silver powder can prevent physiological breeding of bacteria while original characteristics of the foaming material are kept.
Owner:丁金标
Natural collagen pet chew and nutrient and flavor agent delivery method
InactiveUS7921814B1Add flavorEnhance healthy propertyAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsAcetic acidChewing food
A method of producing an enriched, natural collagen pet chew by means of vacuum sealing impregnation technology to add nutrients, flavoring, and / or anti-microbial agents to a natural, but demineralized, canine bone chew. A pet mastication article is soaked in acetic acid to reveal a flexible, chewable collagen structure. After the collagen structure is soaked and rinsed, nutrients and other agents are infused into the porous structure of the bone by means of vacuum impregnation.
Owner:COSMIC PET LLC
Rubber composition for sidewall, insulation or breaker cushion, production method thereof, and pneumatic tire
InactiveUS8623956B2Eliminate needImprove economySpecial tyresRolling resistance optimizationEngineeringChewing food
The present invention provides a rubber composition for a sidewall, an insulation, or a breaker cushion, which can achieve both excellent fuel economy (low heat build-up) and high flex crack growth resistance while having processability excellent enough to eliminate the need for mastication, and also provides a pneumatic tire produced using the rubber composition. The present invention relates to a rubber composition for a sidewall, an insulation, or a breaker cushion, including: a rubber component that contains a modified natural rubber with a phosphorus content of 200 ppm or less; and carbon black and / or a white filler.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Intraoral orthodontic corrector
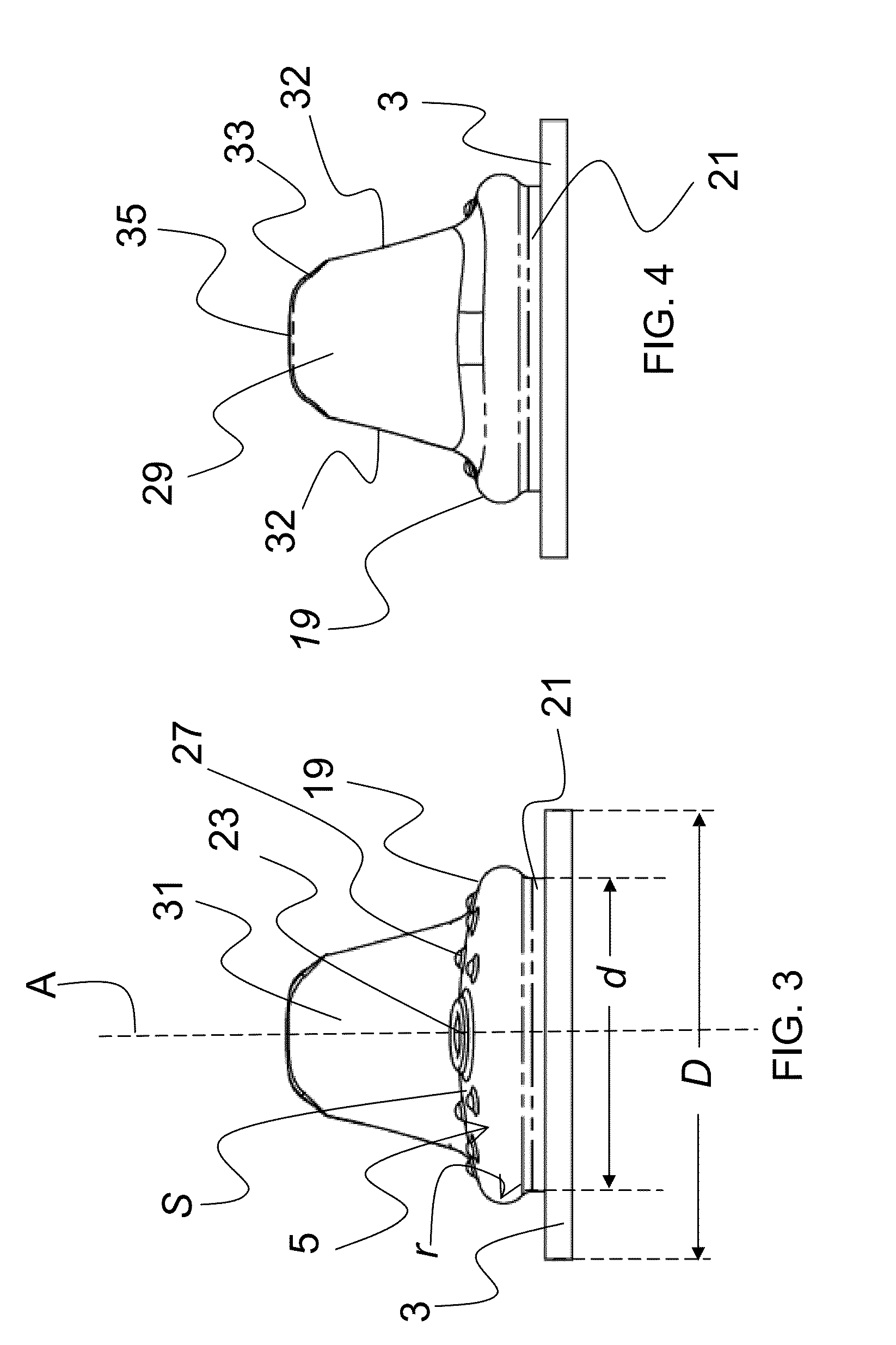
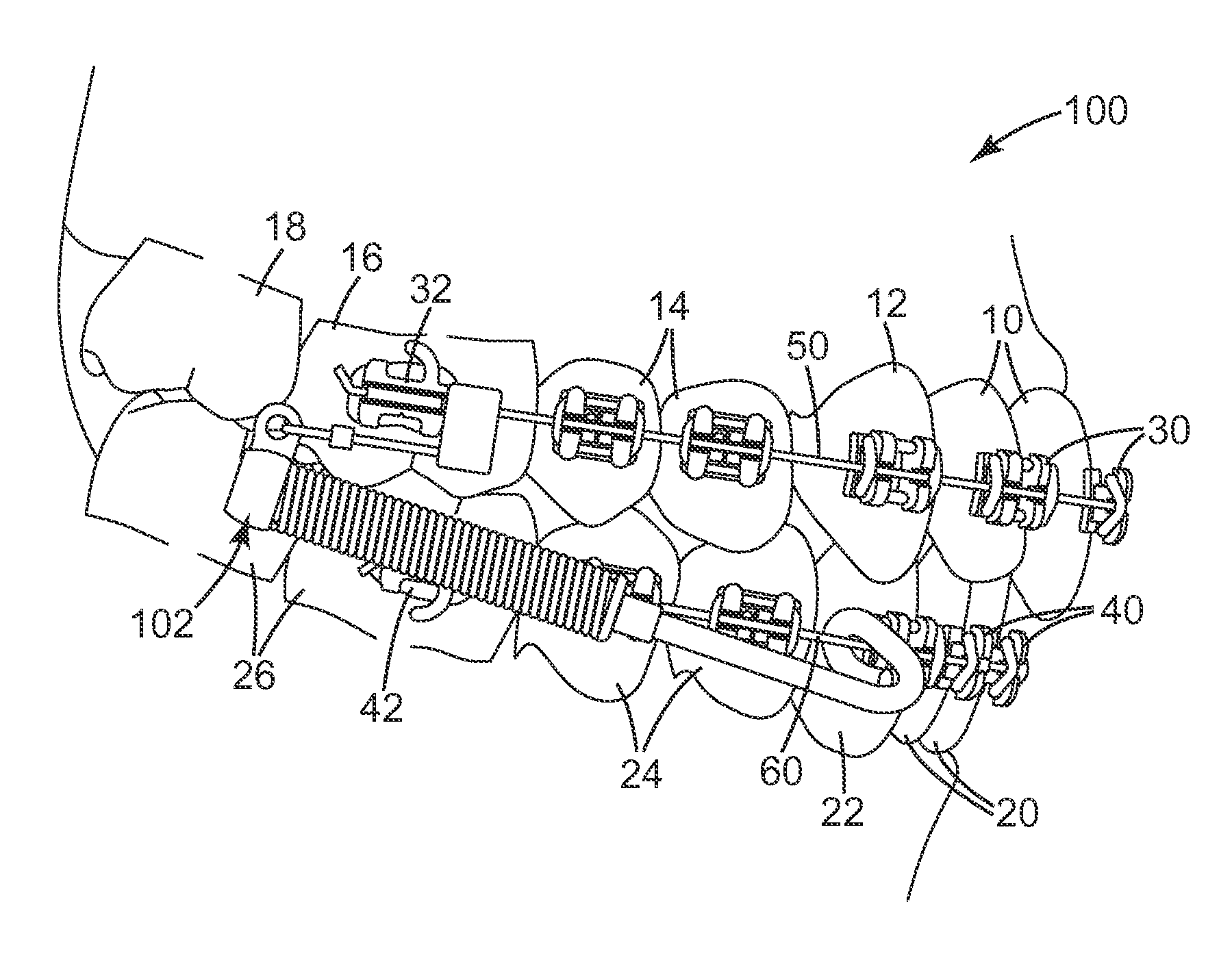
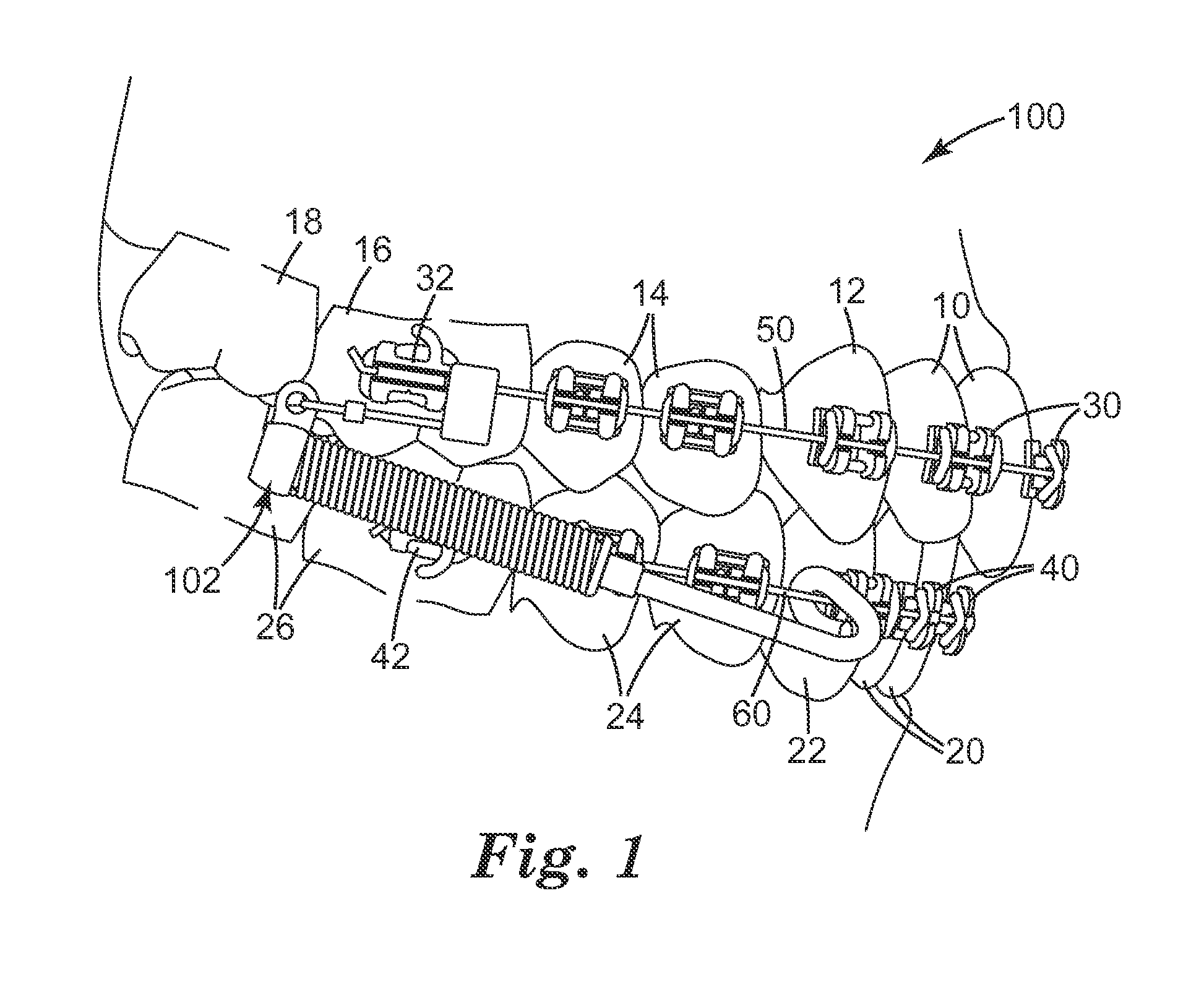
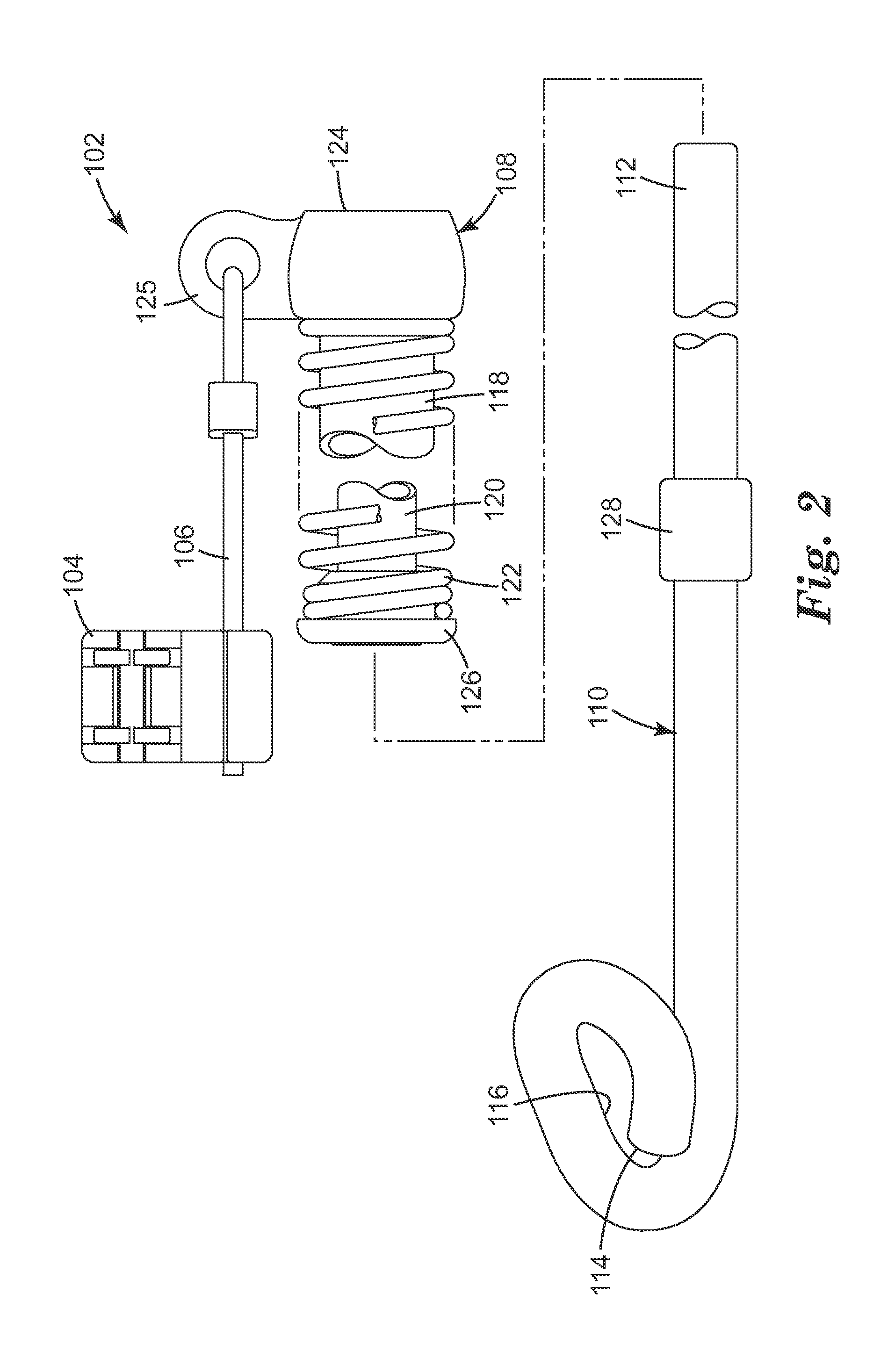
Provided are orthodontic corrector devices, related assemblies and methods which direct forces within the oral cavity. These corrector devices and assemblies include a flexible cantilever which is coupled to both a connector component and a force module. The cantilever acts to isolate adjacent components from mastication forces encountered during treatment. By resiliently deflecting in response to these inadvertent forces, the cantilever reduces the likelihood of device breakage and bond failure. Upon removal of these forces, the cantilever returns to its original orientation thereby maintaining the proper alignment of the corrector. Advantageously, the cantilever also allows the force module to be positioned further in the distal direction thereby enabling a greater range of connection options.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Interface system using mastication myoelectricity
InactiveCN101981533AInput/output for user-computer interactionDiagnostic recording/measuringMaximum amplitudeHuman–computer interaction
The invention provides an interface system using mastication myoelectricity. The interface system enabling quick menu selection without special mastication or repetition of highlight even in any situation that myoelectricity is produced during e.g., conversation or a meal in the daily life of the user. The interface system includes an output unit for visually presenting an operation menu of a device, a measuring unit for measuring the mastication myoelectricity of the user, a menu presenting unit for sequentially presenting each of the menu items contained in the operation menu through the output unit, an amplitude calculating unit for determining the maximum amplitude of the potential waveform of the mastication myoelectricity, a latent time calculating unit for determining the latent time at which the potential waveform takes on a maximum amplitude from when each of the menu items is highlighted, and a judging unit for judging whether or not the maximum amplitude is larger than a predetermined threshold and whether or not the latent time is within a range of about 200 ms after the highlight. The menu presenting unit executes the processing corresponding to the highlighted menu item depending on the result of the judgment made by the judging unit.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Oil-in-water-type emulsion gel food
The object of the present invention is to produce a masticable food, composed of an oil-in-water-type emulsion gel which has a shape-retaining property and an oil-holding property before mastication and from which oil and fat oozes during mastication to make swallowing smooth, by using any oil and fat. An oil-in-water-type emulsion gel food containing oil droplets having a particle diameter of 50-800 μm is used. Preferably, the oil and fat is vegetable oil or fish oil, the food is a heat-sterilized food, and the gel is a soybean protein gel crosslinked by a protein corsslinking enzyme.
Owner:FUJI OIL CO LTD
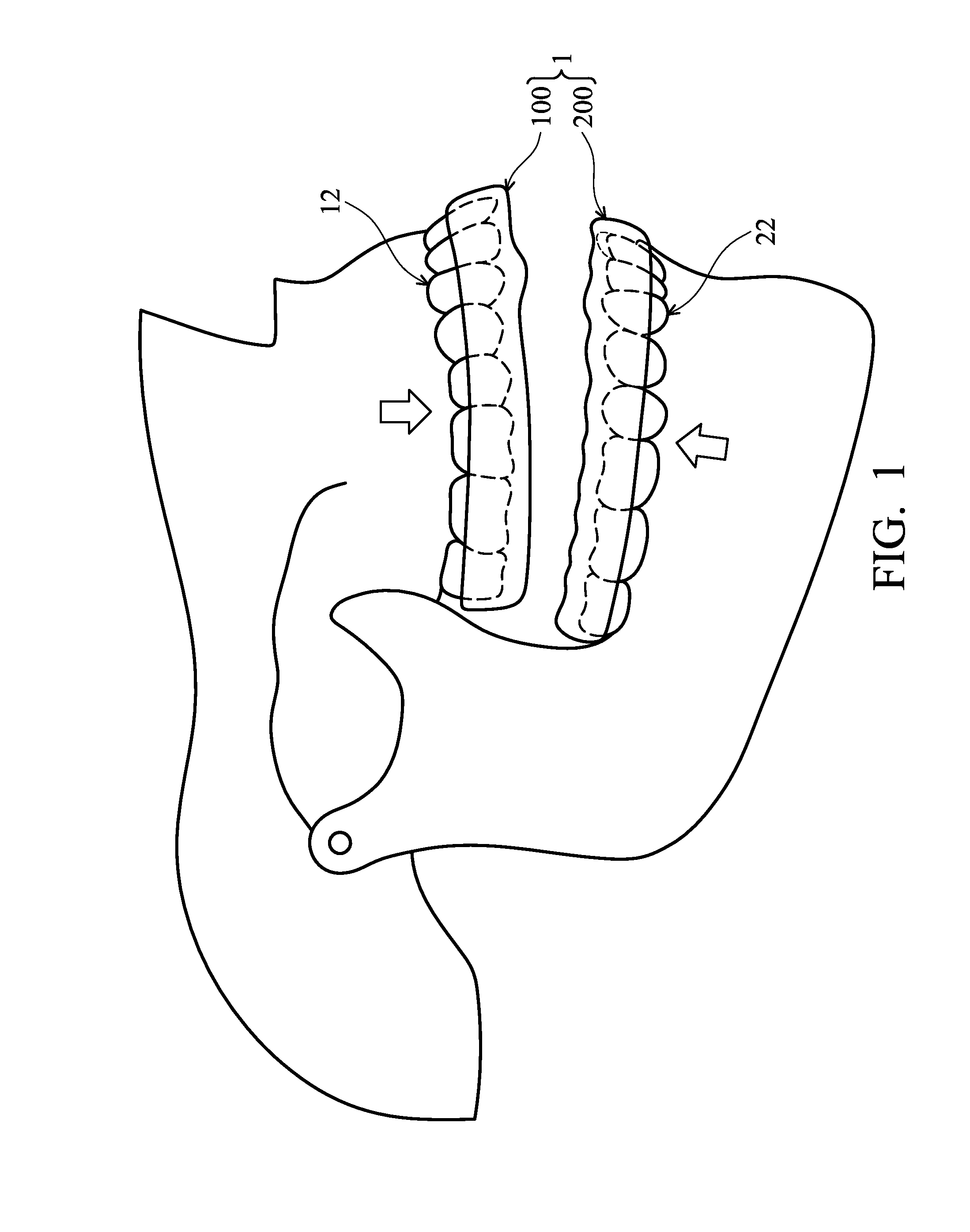
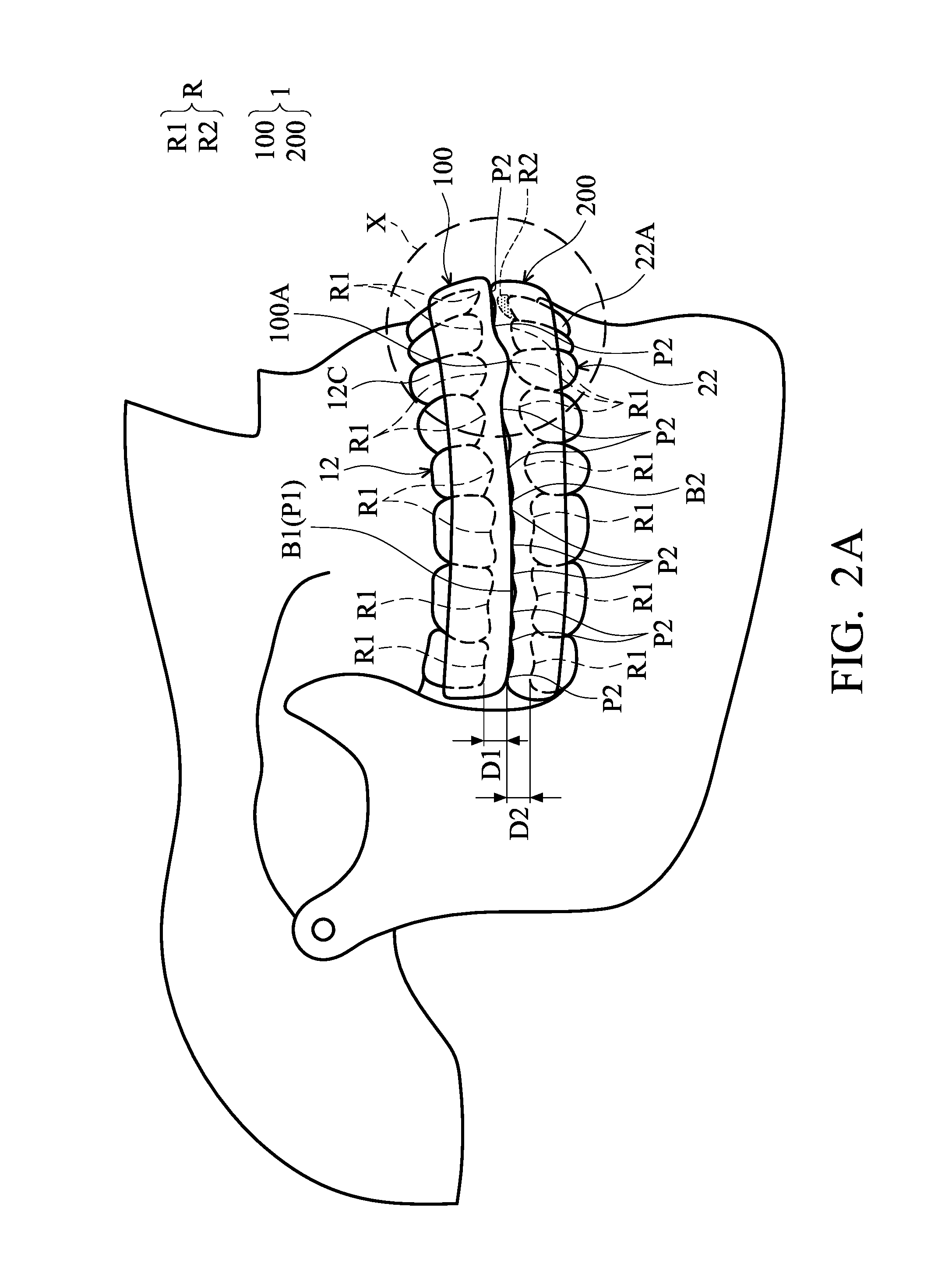
Masticatory orthodontic correction device
A masticatory orthodontic correction device includes at least one correction unit with a rigid body. The correction unit is worn on a maxillary or mandibular dental arch of a patient during mastication, and the shape of the correction unit is maintained without deformation when accommodating teeth. At least one first recess is formed in the correction unit and has a shape which leaves a first space around a first tooth of the maxillary or mandibular dental arch. The first tooth is a tooth in malposition requiring correction, and the first space allows the first tooth to move therein during mastication. At least one buffering member is formed in the first space for transmitting and buffering force between the first recess and the first tooth. The orthodontic correction function of the device is active under occlusal loads generated during mastication.
Owner:HUNG CHENG HSIANG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com