Patents
Literature
998 results about "Mechanical load" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
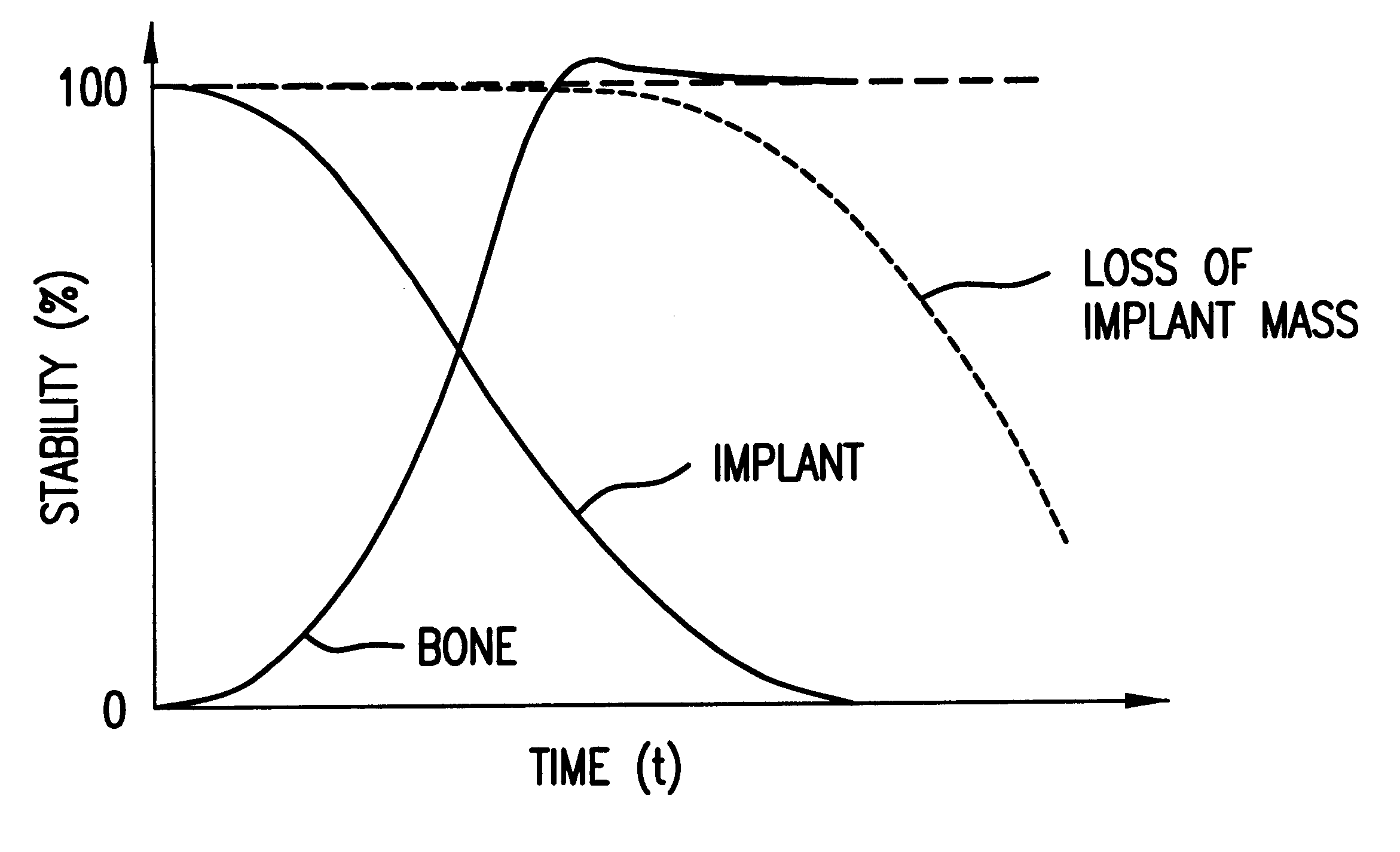
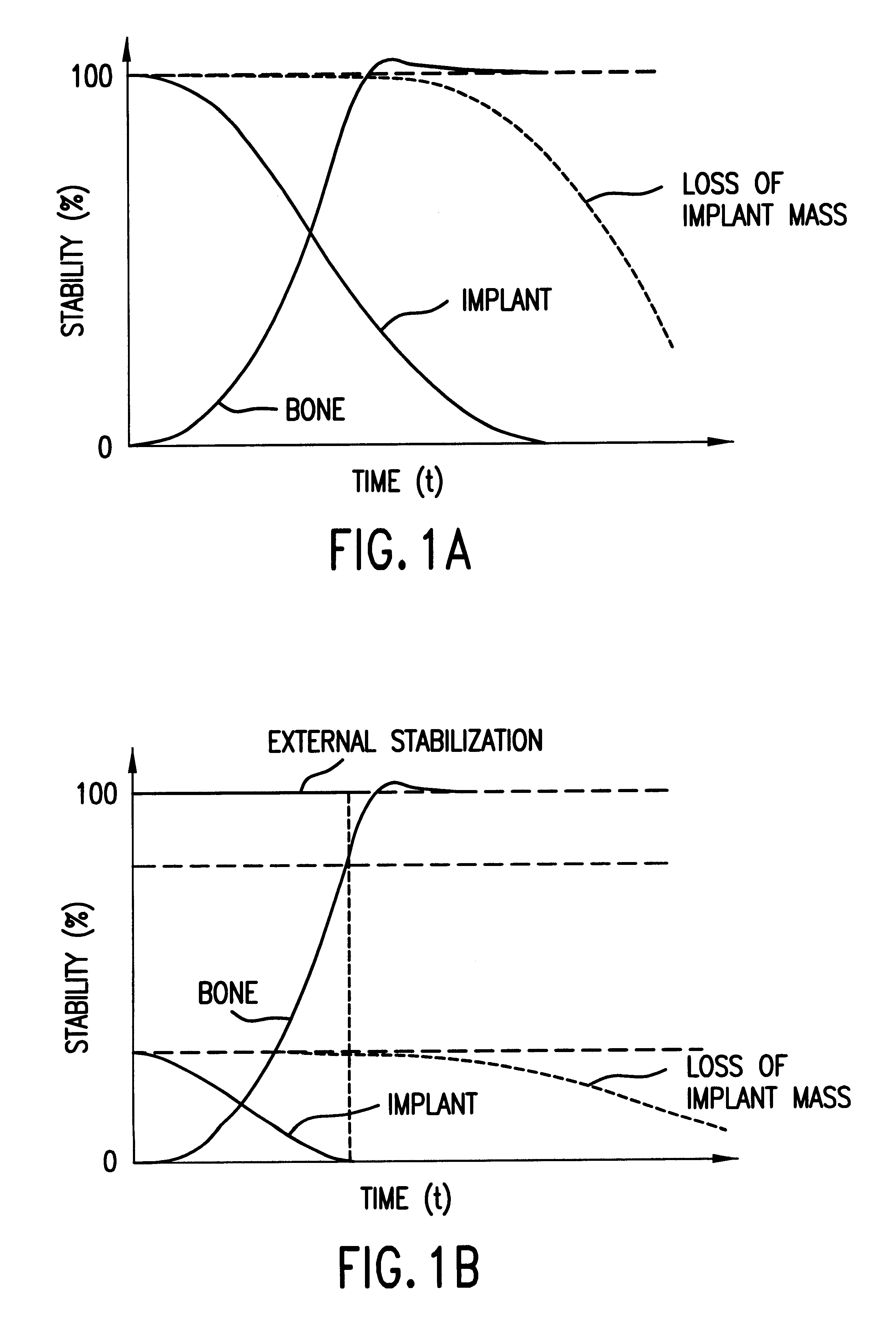
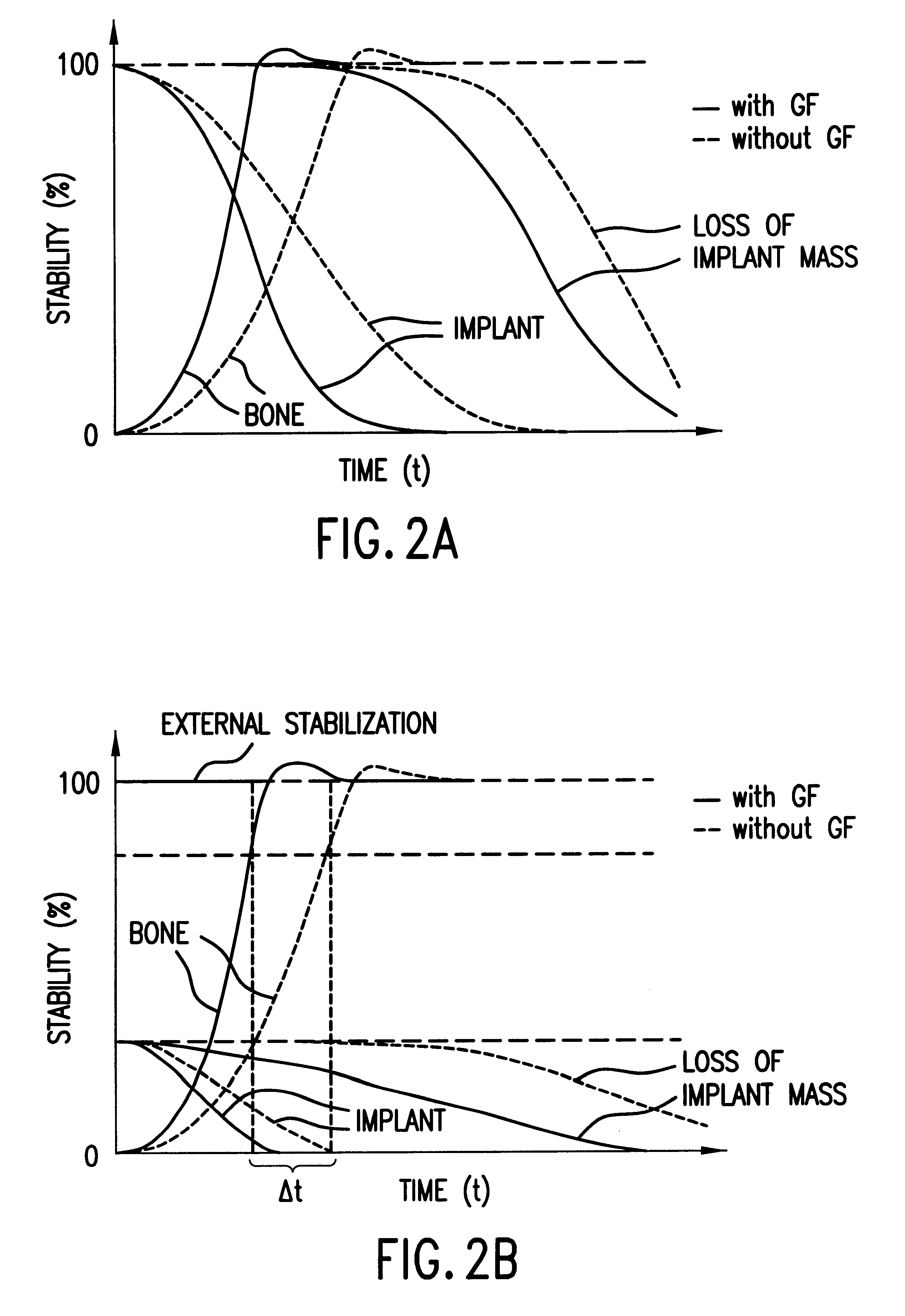
Load, in mechanics, is the external mechanical resistance against which a machine, such as a motor or engine, acts. The load can often be expressed as a curve of force versus speed.
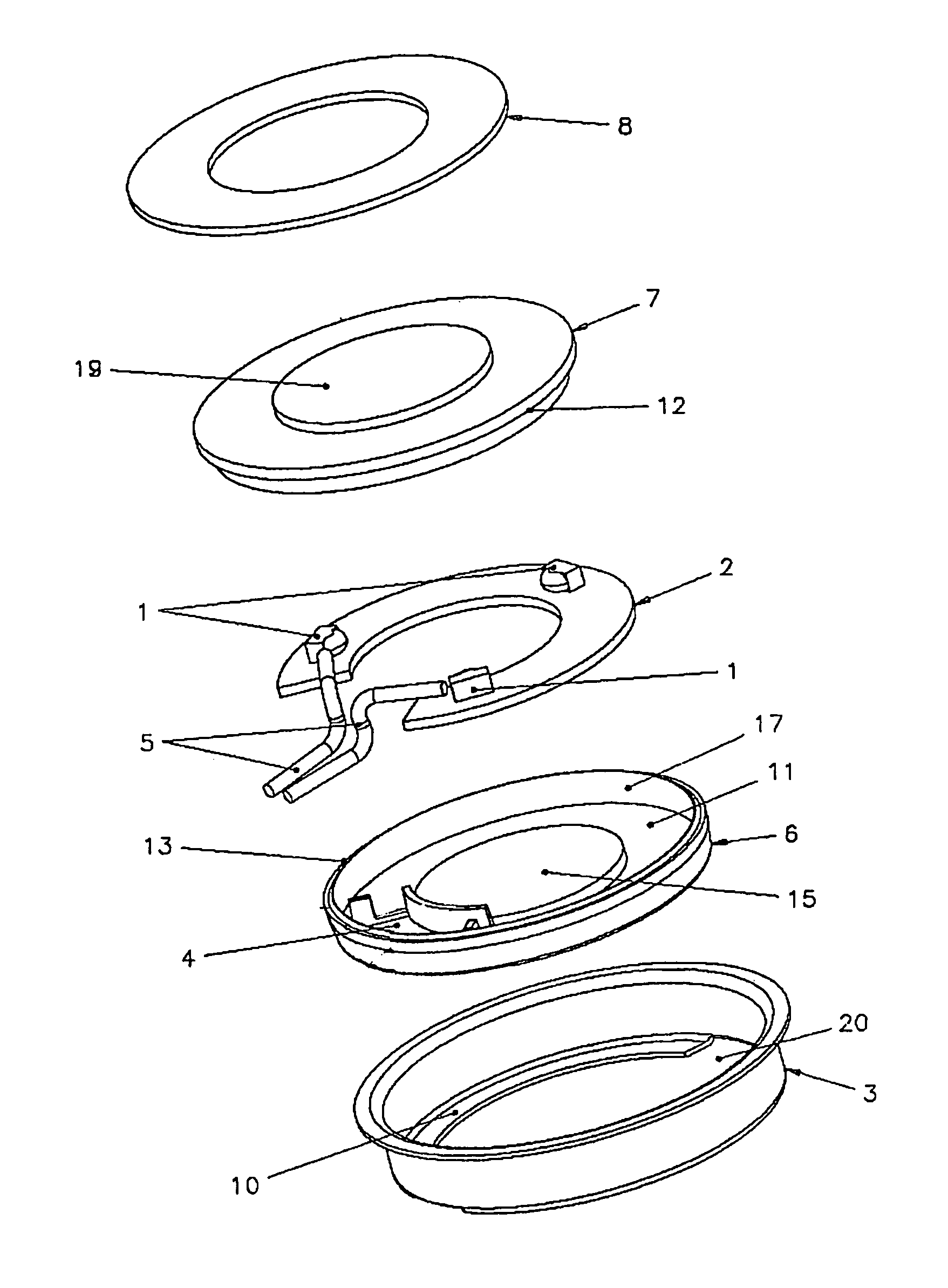
Porous Substrates for Implantation
InactiveUS20100137990A1Easy to integrateGood biocompatibilitySuture equipmentsDental implantsPorous substrateAnimal body
A porous substrate or implant for implantation into a human or animal body constructed from a structural material and having one or more regions which when implanted are subjected to a relatively lower mechanical loading. The region(s) are constructed with lesser mechanical strength by having a lesser amount of structural material in said region(s) relative to other regions. This is achieved by controlling pore volume fraction in the regions. A spacer is adapted to define an open-cell pore network by taking a model of the required porous structure, and creating the spacer to represent the required porous structure using three-dimensional modelling. Material to form the substrate about the spacer in infiltrated the scaffold structure formed.
Owner:NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF IRELAND
Wind dam electric generator and method
InactiveUS6984899B1Constant windmill shaft rotational speedWind motor controlEngine fuctionsAir volumeEngineering
A vertical axis windmill is provided wherein the amount of wind directed to blades in the power producing part of rotation and the mechanical load of multiple generators is controlled by a feedback control to maintain a relatively constant rotational frequency of the shaft of the windmill. In a preferred embodiment, two wind foils extend radially outwardly from the blades to thereby provide a scoop capable of pulling in more air than would normally be received by the blades. The wind foils then direct the wind flow to the power producing part of rotation of the blades for maximum power output, when necessary. The wind foils can close to control the wind flow to the blades. The generating capacity of a plurality of generators is also controlled in response to shaft rotation to maintain substantially constant shaft rotation.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Three-dimensionally reinforced multifunctional nanocomposites
ActiveUS20070128960A1Improve structural reinforcementSimple structureMaterial nanotechnologySynthetic resin layered productsFiberGeometric stability
A three-dimensional composite reinforcement, a three-dimensionally reinforced multifunctional nanocomposite, and methods of manufacture of each are disclosed. The three dimensional reinforcement comprises a two dimensional fiber cloth upon which carbon nanotubes have been grown, approximately perpendicular to the plane of the fiber cloth. The nanocomposite comprises the three-dimensional reinforcement and a surrounding matrix material. Examples illustrate improvements in the through-thickness mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties of the nanocomposite, in addition to substantial improvements in geometrical stability upon temperature changes and vibrational damping, compared to baseline composites reinforced with the two-dimensional fiber cloth alone. Embodiments of the nanocomposite may also be configured to perform multiple functions simultaneously, such as bearing a thermal or mechanical load simultaneously or bearing a mechanical load while also monitoring the state of damage within the nanocomposite.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST +1
Method and system for real-time prognosis analysis and usage based residual life assessment of turbine engine components and display
ActiveUS20110137575A1Low costFacilitate decisionsPlug gaugesTesting dielectric strengthCombustion chamberOff design
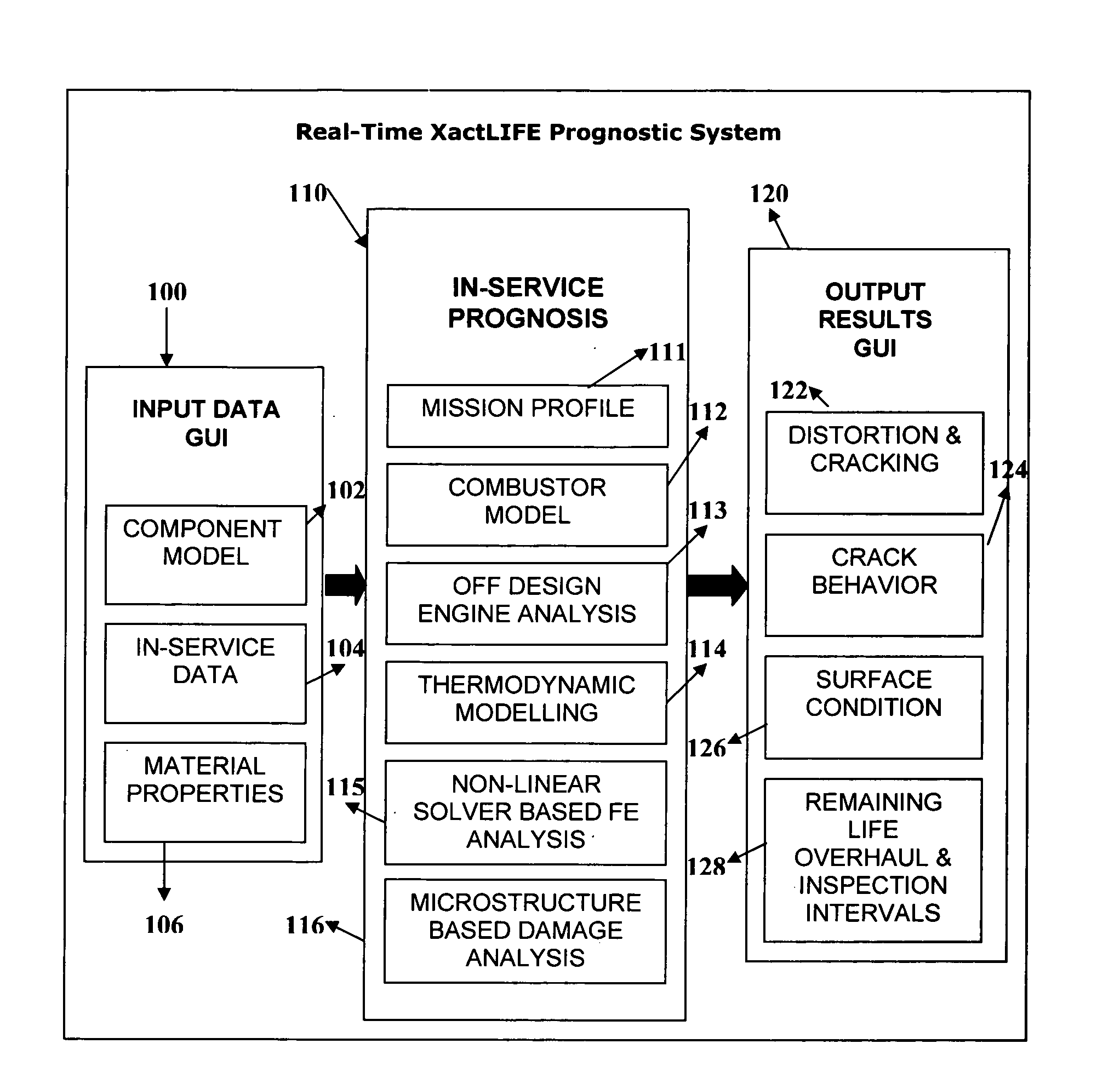
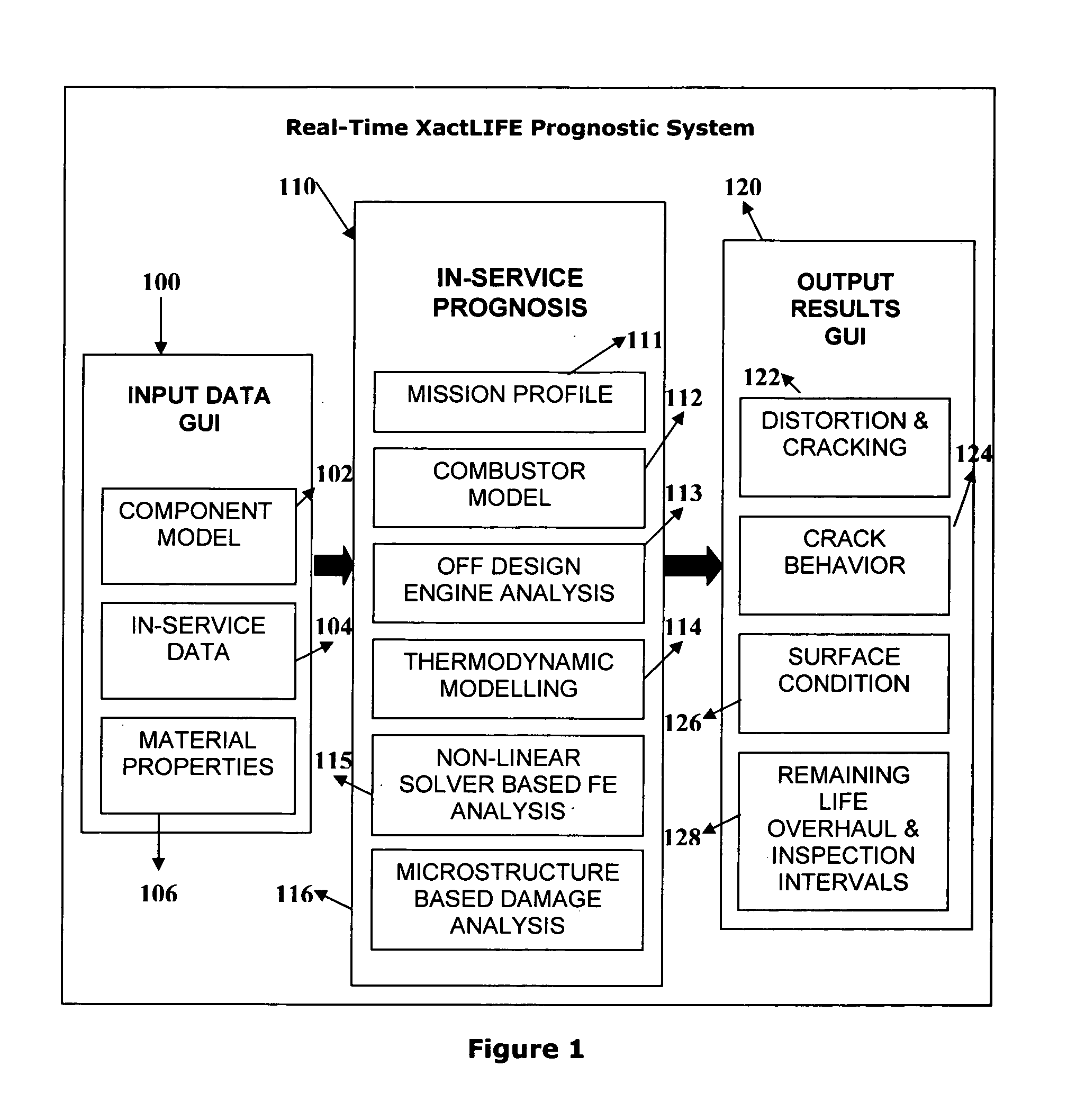
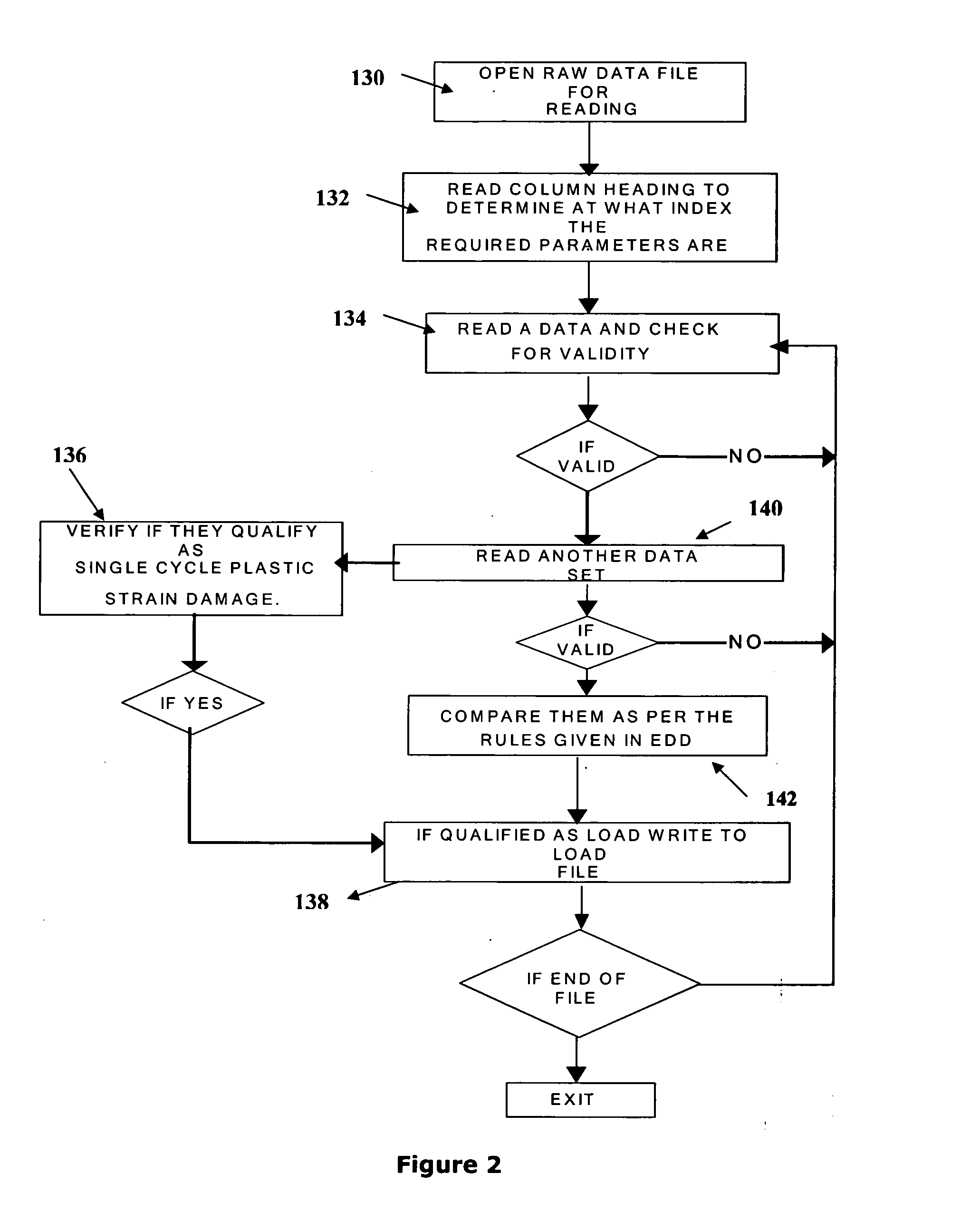
A method and system for performing continuous (real-time) physics based prognostics analysis as a function of actual engine usage and changing operating environment. A rule-based mission profile analysis is conducted to determine the mission variability which yields variability in the type of thermal-mechanical loads that an engine is subjected to during use. This is followed by combustor modeling to predict combustion liner temperatures and combustion nozzle plane temperature distributions as a function of engine usage which is followed by off-design engine modeling to determine the pitch-line temperatures in hot gas path components and thermodynamic modeling to compute the component temperature profiles of the components for different stages of the turbine. This is automatically followed by finite element(FE) based non-linear stress-strain analysis using an real-time FE solver and physics based damage accumulation, life consumption and residual life prediction analyses using microstructural modeling based damage and fracture analysis techniques.
Owner:KOUL ASHOK
Telemetric orthopaedic implant
ActiveUS8486070B2Accurate predictionAccurately prescribeInternal osteosythesisBone implantPlastic surgeryElectronic component
An instrumented orthopaedic implant, such as an intramedullary (IM) nail, is disclosed. The implant has the capacity to provide an accurate measurement of the applied mechanical load across the implant. The implant includes sensors and associated electronic components located in recesses on the outer surface of the implant. The implant houses the sensing apparatus, the interface circuitry, the data transmitter, and the power receiver. The hermetically sealed housing is adapted for implantation in the body of a patient. The implant is used with a controller which communicates with it by telemetry, and there is an acting unit connected to the electronic components which is adapted to carry out a function based upon a condition detected by the sensors.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
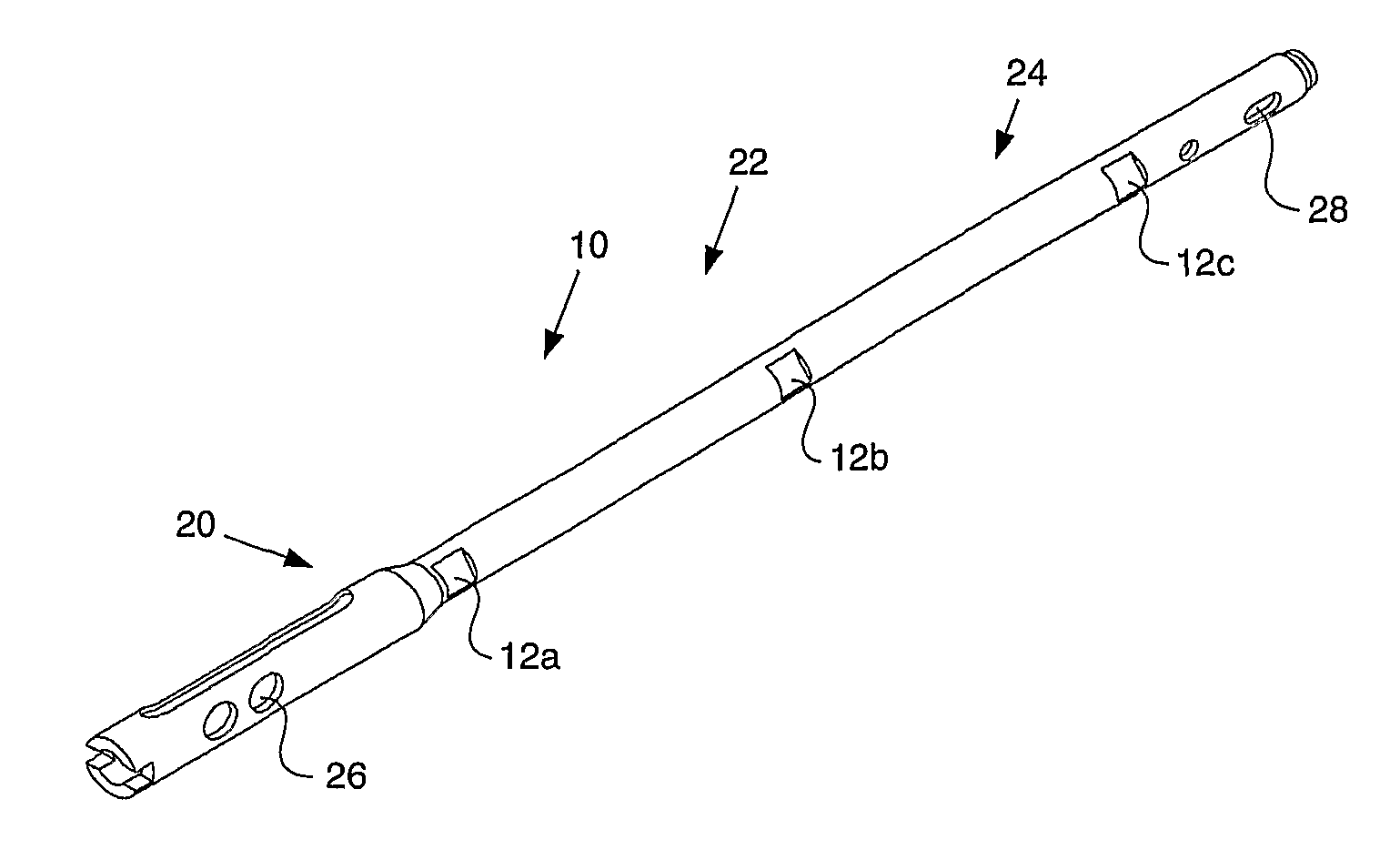
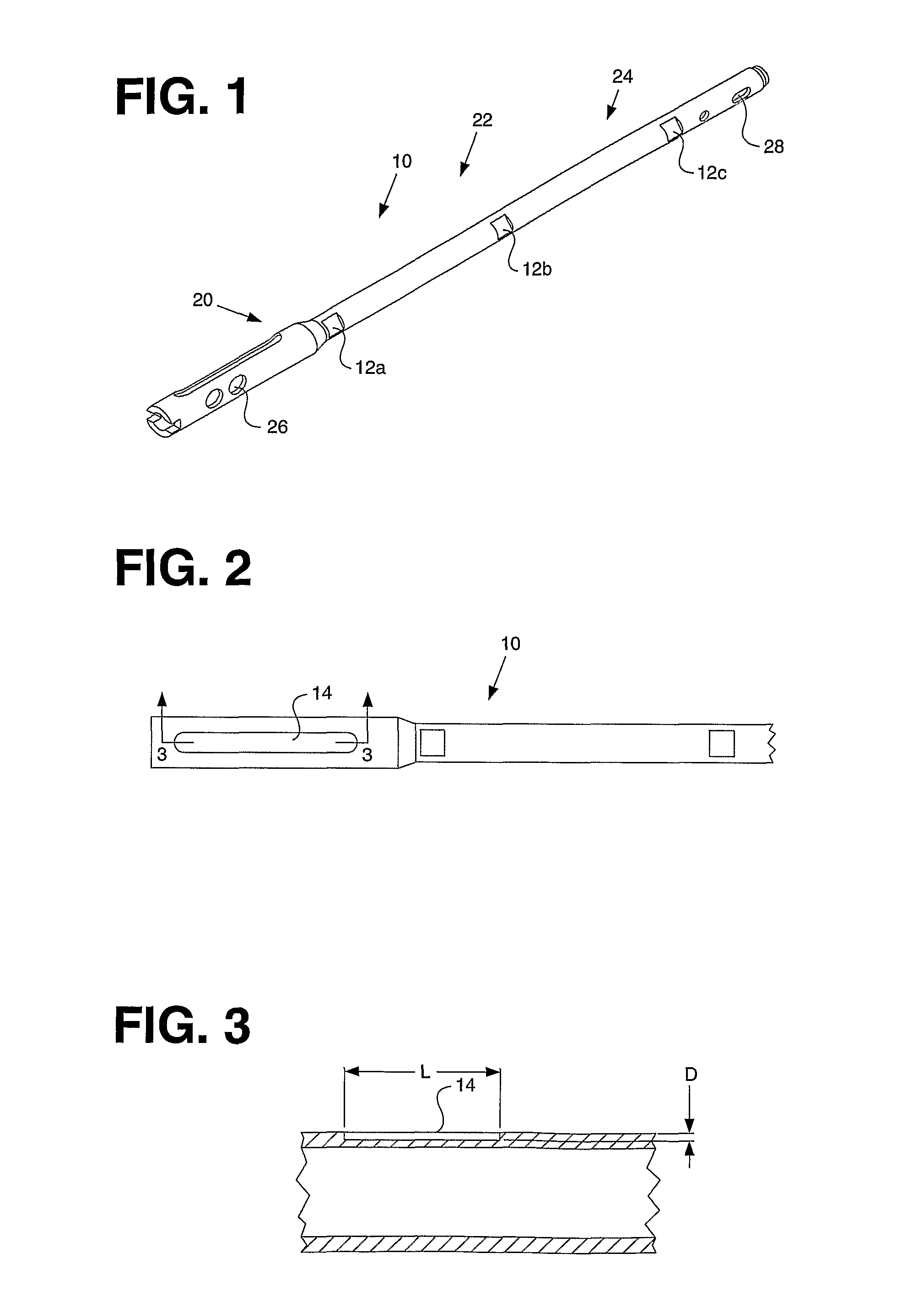
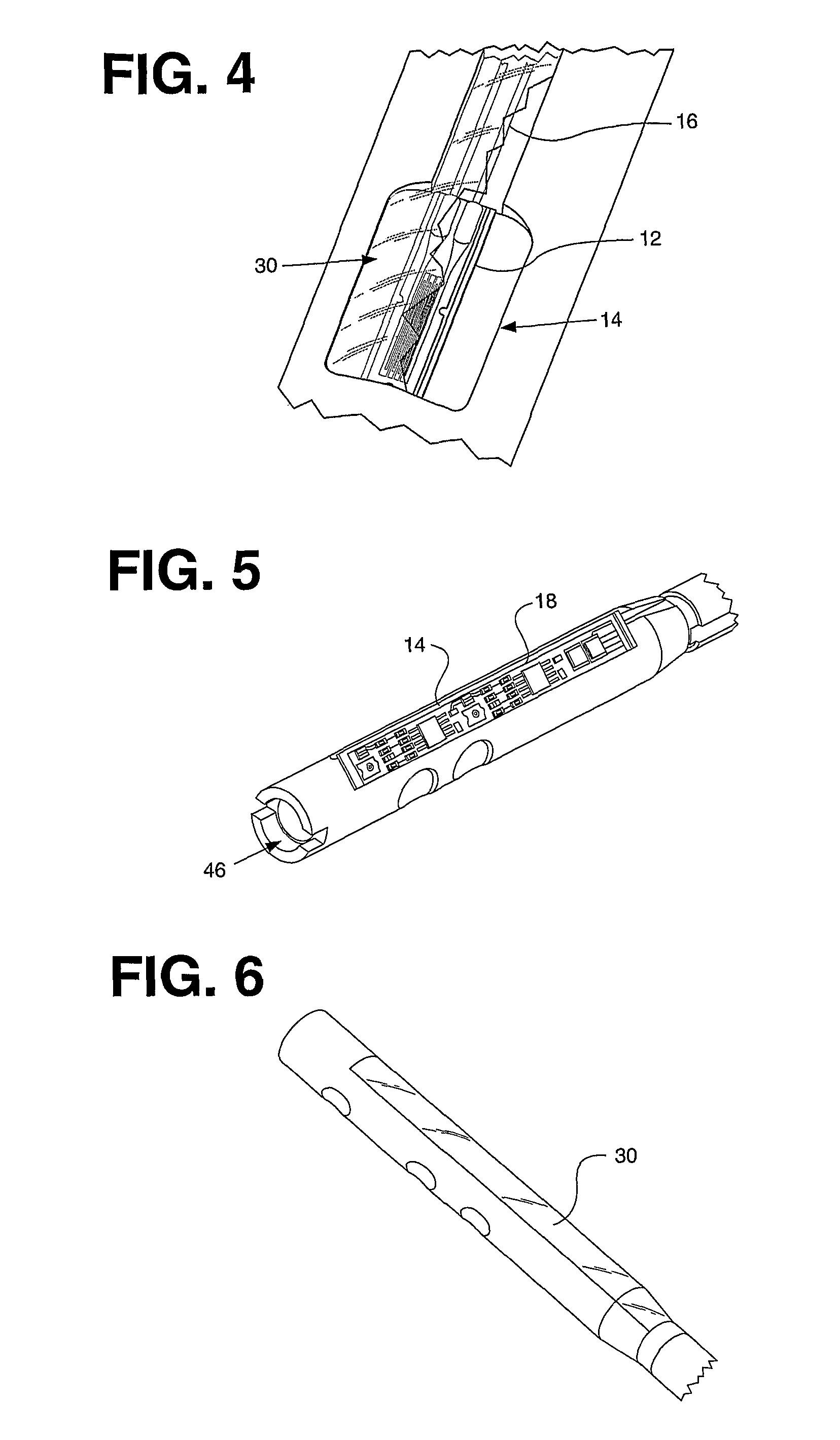
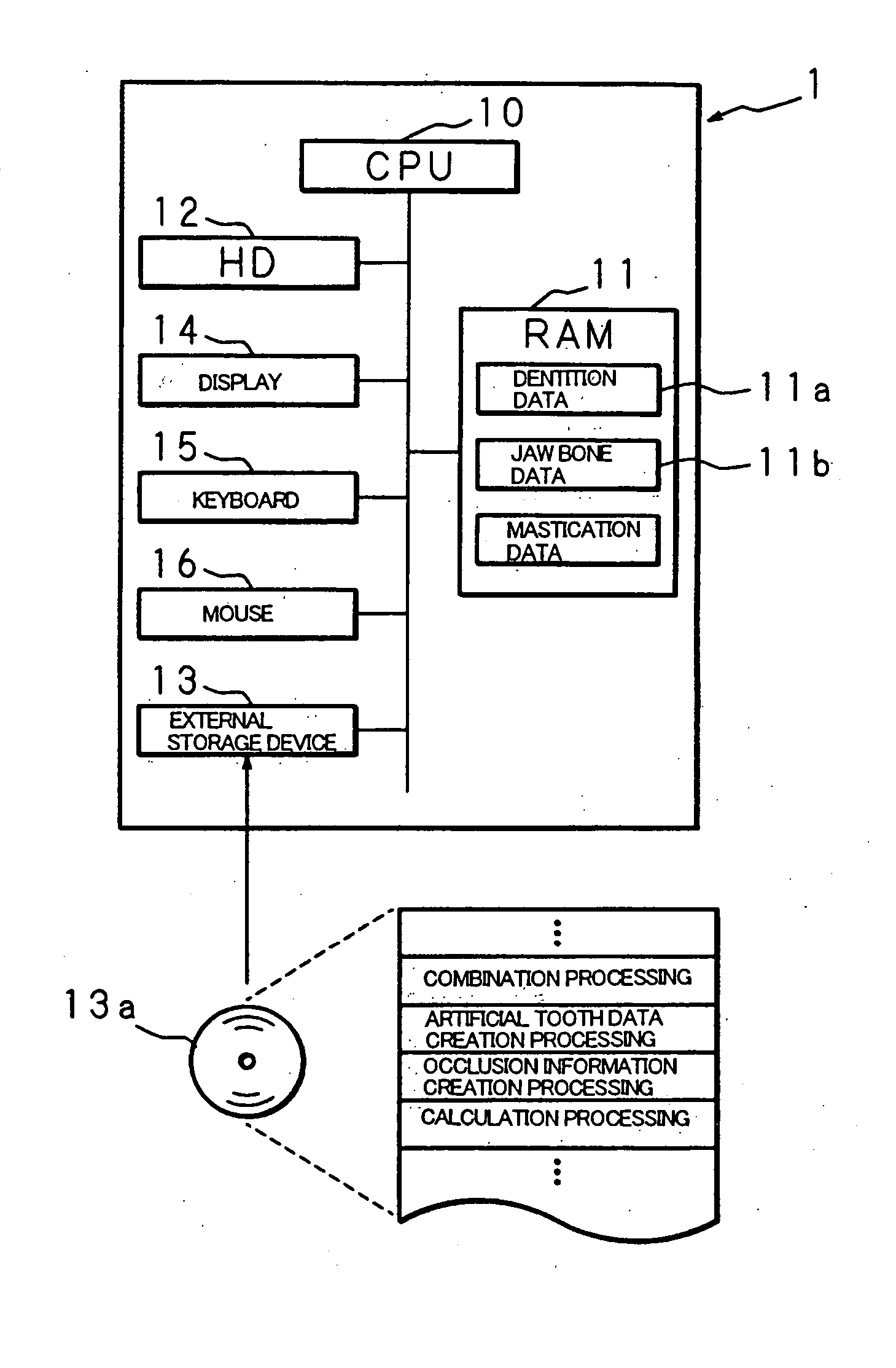
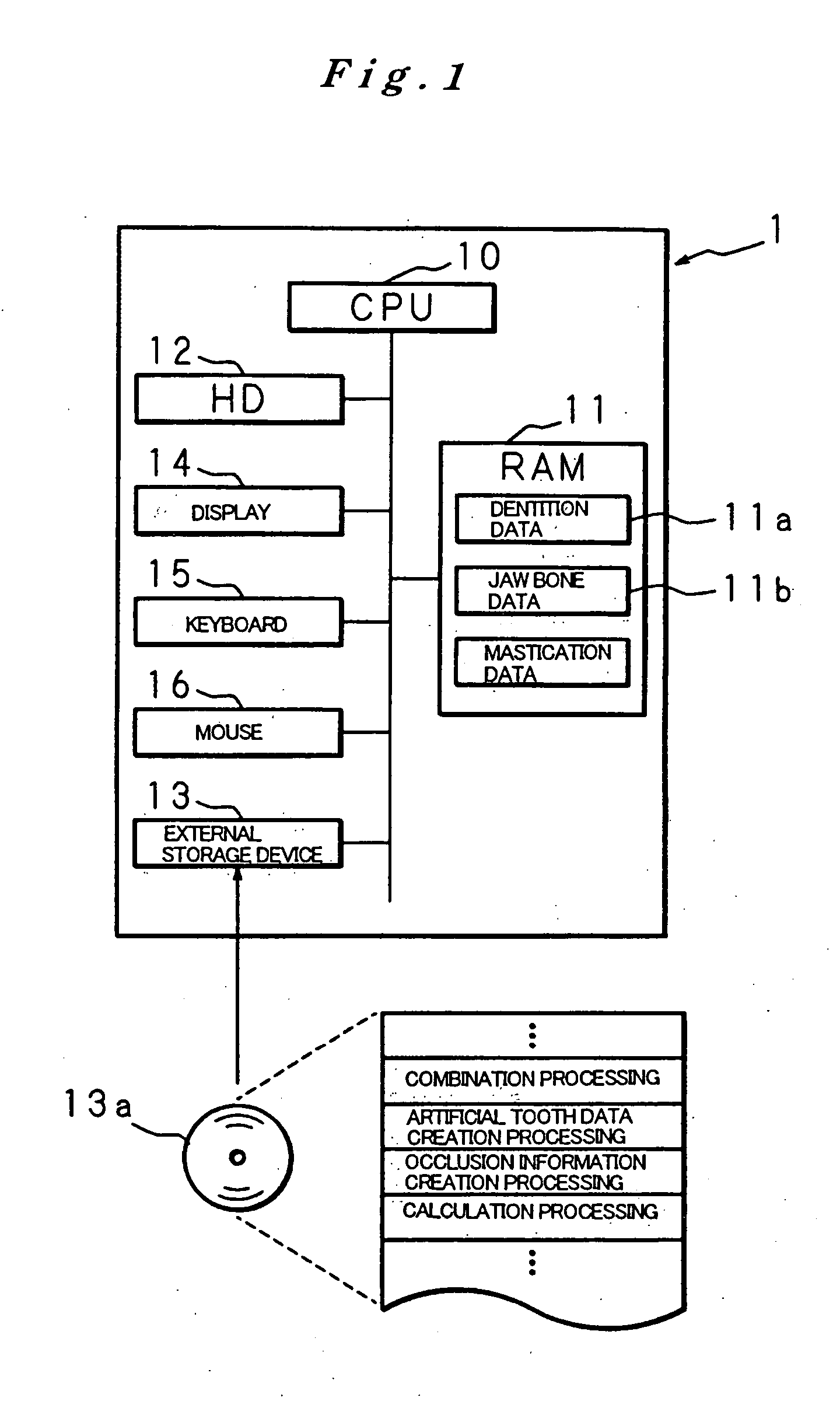
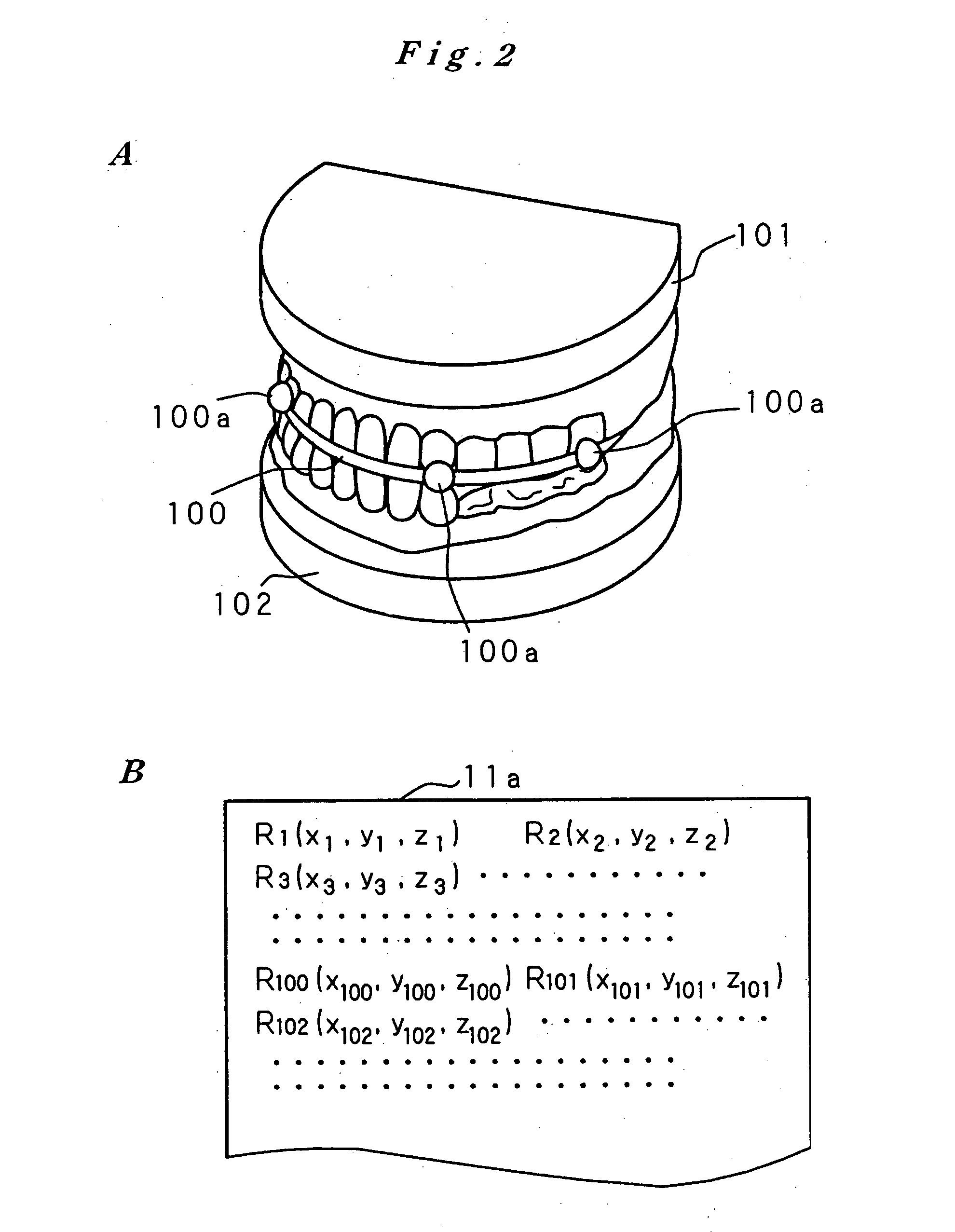
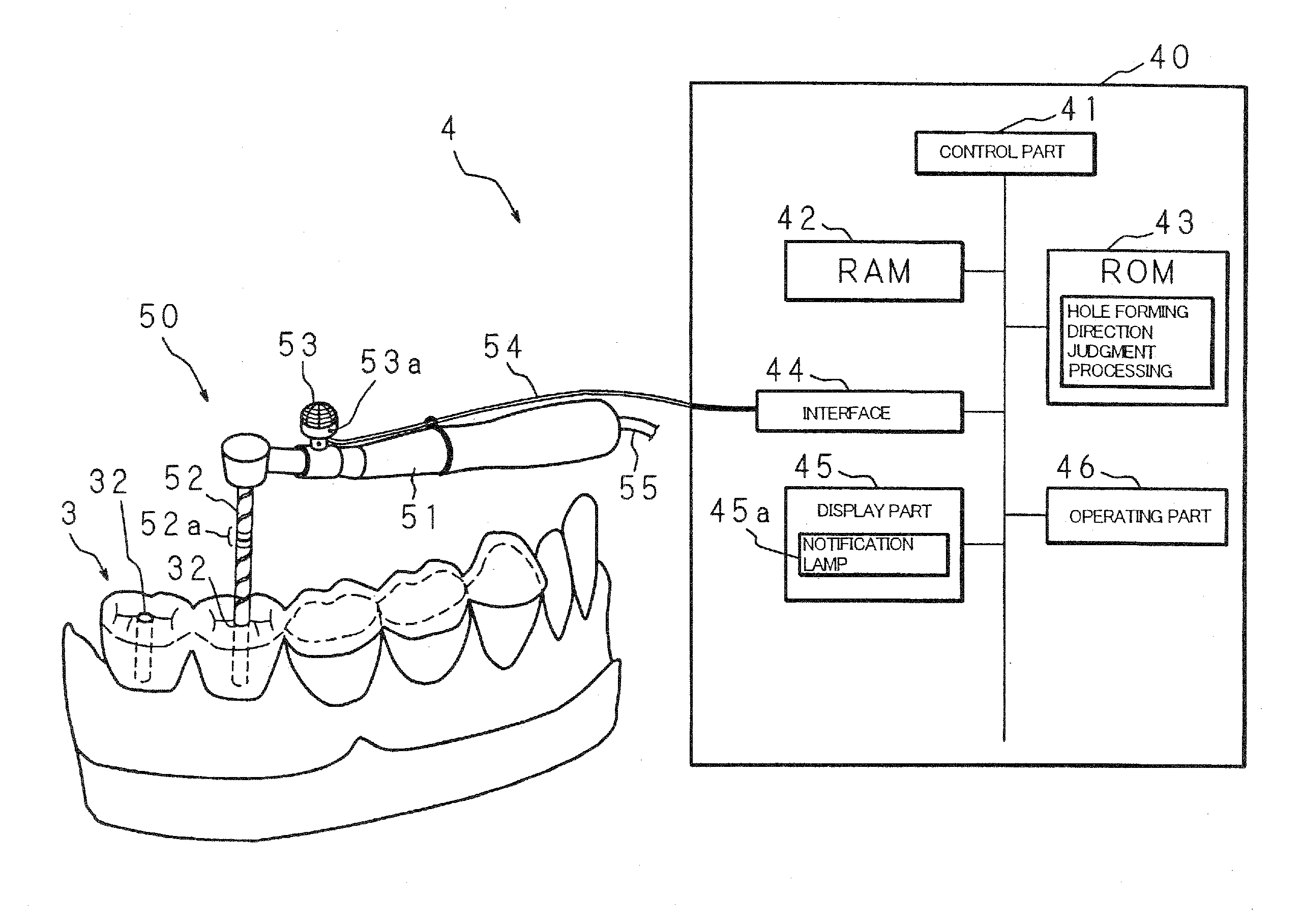
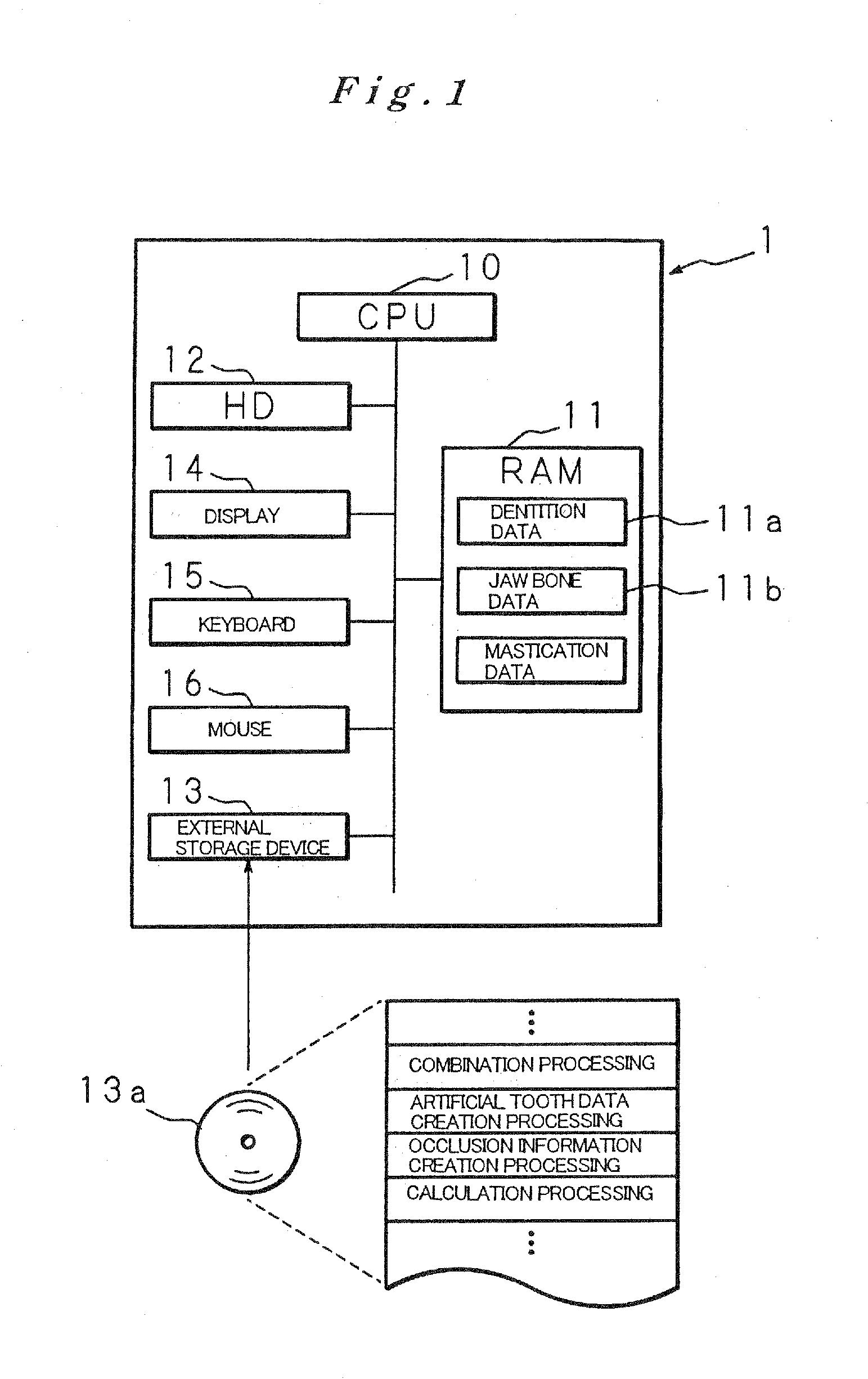
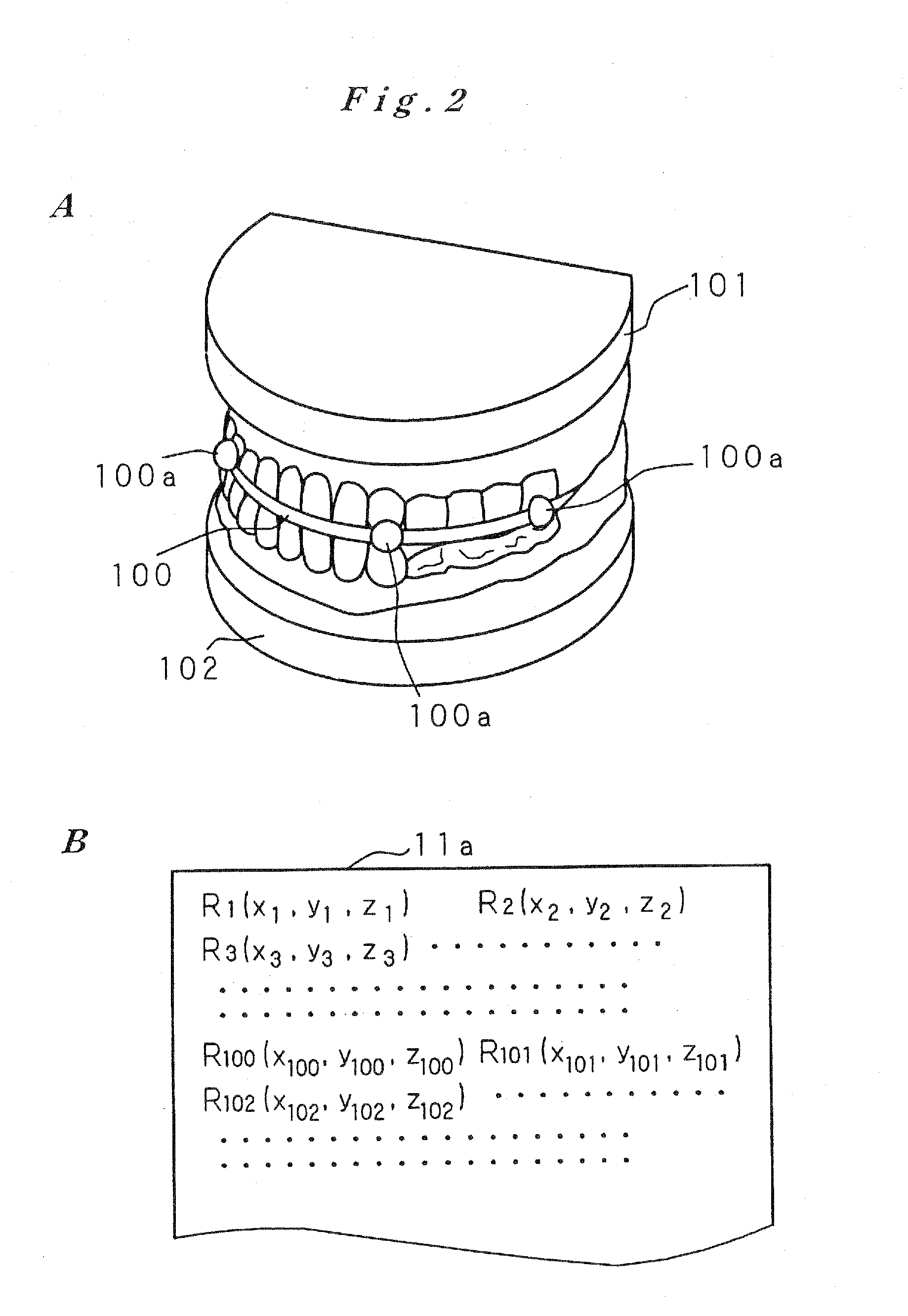
Artificial tooth root implantation position determining instrument, artificial tooth root implantation position determining method, guide member manufacturing device, sensor, drill, artificial tooth manufacturing device, computer program, and recorded medium
InactiveUS20060127848A1Reduce loadEasy to manufactureDental implantsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesLocation determinationTooth root
Dentition three-dimensional data and jaw-bone three-dimensional data are collected from a patient and they are combined. According to the combined data, dental crown data for making up for data on a lost tooth and occlusion data on a dental crown represented by the dental crown data are created. When an occlusion force according to the occlusion data is exerted on the occlusion face of a dental crown, a mechanical evaluation factor is produced in a jaw bone. The mechanical evaluation factor produced near the place where an artificial tooth root supporting a dental crown is to be implanted is calculated. The implantation place is determined so that the mechanical evaluation factor may be smaller and the mechanical load on the jaw bone from the opposed tooth during mastication may be lighter.
Owner:CAT CORP
Force action feedback in surgical instruments
InactiveUS20070213692A1Simplify surgical proceduresImproved and simplifiedDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsEngineeringSurgical device
A surgical instrument includes a holding section, a tool removably attachable to the holding section, and at least one load sensor. The at least one sensor is operative to measure a mechanical load exerted by the tool on the instrument.
Owner:BRAINLAB
Assemblies and methods for clamping force generation
Mechanisms and methods for clamping force generation are disclosed. In one embodiment, a clamping force generator system includes a permanent magnet bearing coupled to a traction ring and to a torque coupling. The traction ring can be provided with an electromagnetic bearing rotor and the torque coupling can be provided with an electromagnetic bearing stator. In some embodiments, a mechanical load cam, a permanent magnet bearing, and an electromagnetic bearing cooperate to generate a clamping force between the traction rings, the power rollers, and the idler. In other embodiments, a series of permanent magnet bearings and a mechanical bearing configured to produce a clamping force. In one embodiment an electromagnetic bearing is coupled to a control system and produces a specified clamping force that is associated with a torque transmitted in the transmission during operation. In some embodiments, a mechanical load cam produces a clamping force proportional to torque, while a permanent magnet bearing provides a minimum clamping force.
Owner:FALLBROOK INTPROP COMPANY
Ring seal system with reduced cooling requirements
Aspects of the invention are directed to systems for reducing the cooling requirements of a ring seal in a turbine engine. In one embodiment, the ring seal can be made of a ceramic material, such as a ceramic matrix composite. The ceramic ring seal can be connected to metal isolation rings by a plurality of pins. The hot gas face of the ring seal can be coated with a thermal insulating material. In another embodiment, the ring seal can be made of metal, but it can be operatively associated with a ceramic heat shield. The metal ring seal can carry the mechanical loads imposed during engine operation, and the heat shield can carry the thermal loads. By minimizing the amount of ring seal cooling, the ring seal systems according to aspects of the invention can result in improved engine performance and emissions.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Force or pressure sensor and method for applying the same
InactiveUS7862523B2Fluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsPerson identificationEngineeringPiezoelectric sensor
Owner:APPLE INC
Telemetric Orthopaedic Implant
ActiveUS20080300597A1Accurate predictionAccurately prescribeInternal osteosythesisBone implantPlastic surgeryElectronic component
An instrumented orthopaedic implant, such as an intramedullary (IM) nail, is disclosed. The implant has the capacity to provide an accurate measurement of the applied mechanical load across the implant. The implant includes sensors and associated electronic components located in recesses on the outer surface of the implant. The implant houses the sensing apparatus, the interface circuitry, the data transmitter, and the power receiver. The hermetically sealed housing is adapted for implantation in the body of a patient. The implant is used with a controller which communicates with it by telemetry, and there is an acting unit connected to the electronic components which is adapted to carry out a function based upon a condition detected by the sensors.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
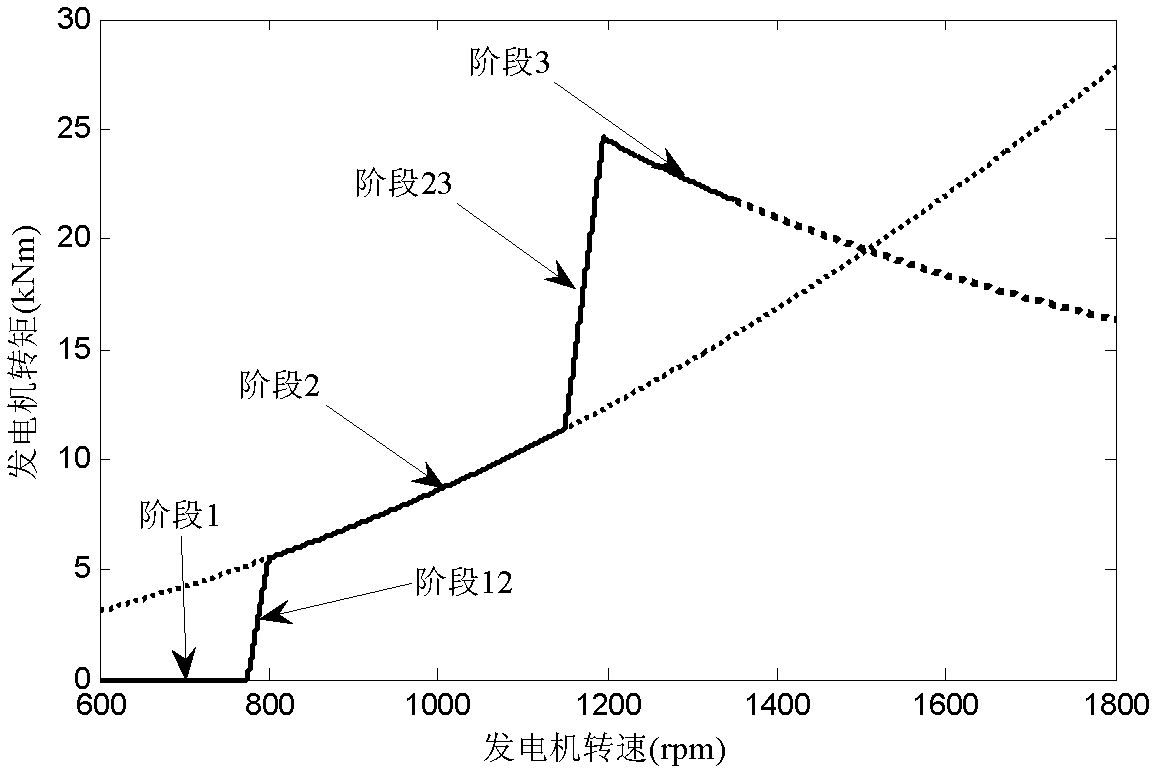
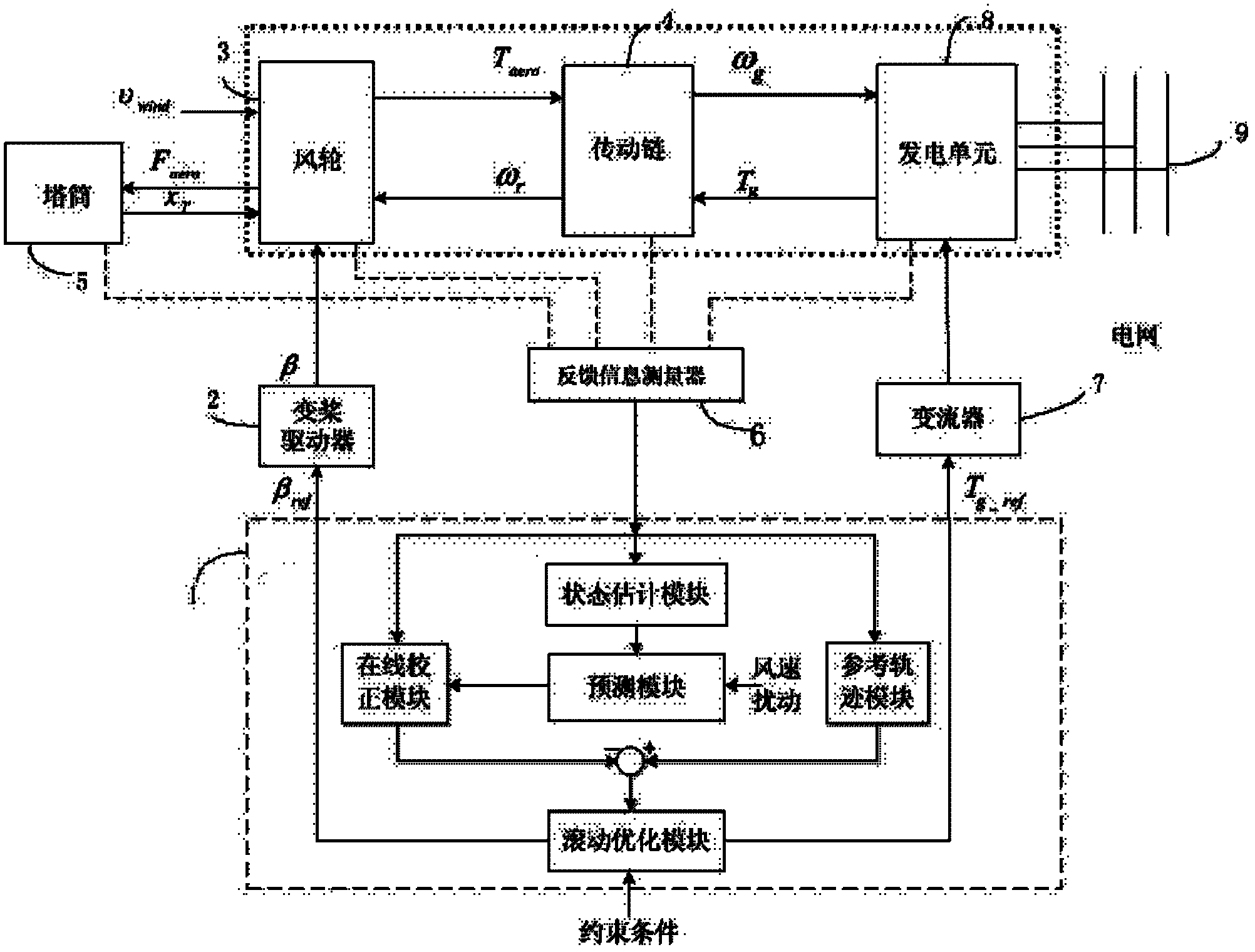
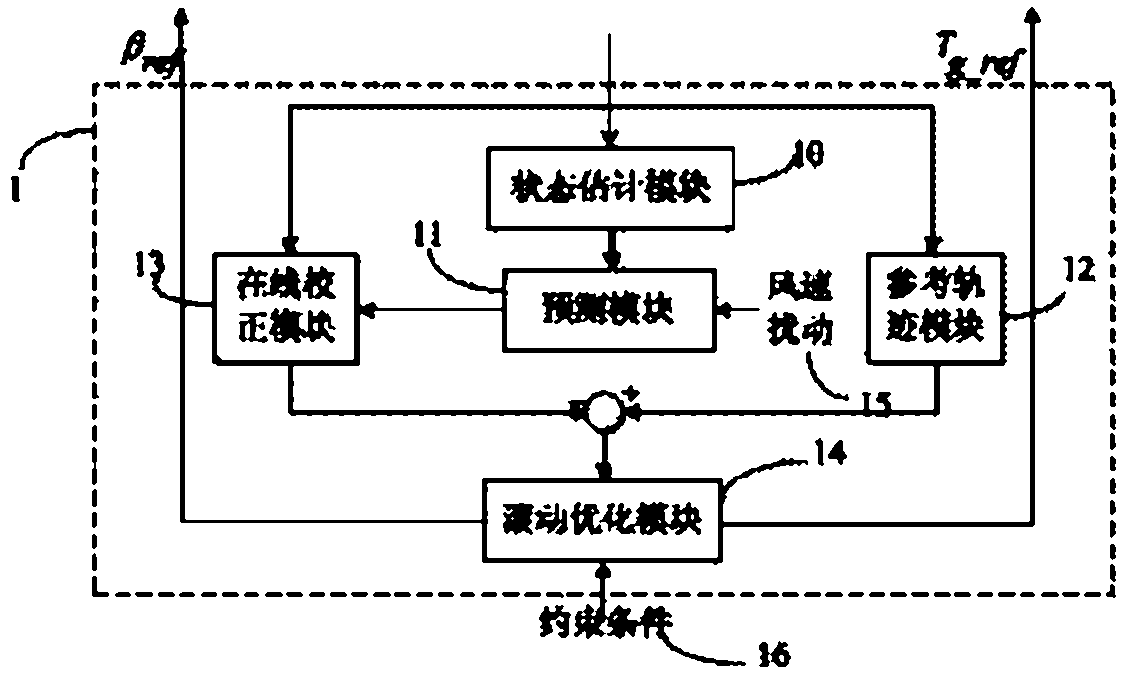
Model prediction control method and model prediction control system for all working conditions of wind generating set
ActiveCN102588211AAvoid the phenomenon of long-term oscillationReduce mechanical loadWind motor controlActive/predictive/anticipative controlControl systemModel predictive control
Disclosed are a model prediction control method and a model prediction control system for all working conditions of a wind generating set. The system comprises an MPC (model prediction control) device, a feedback information measurer, a wind wheel, a driving chain, a tower, a generating unit, a variable propeller driver and a converter. The feedback information measurer is used for detecting status variables of the wind wheel, the driving chain, the tower and the generating unit and transmitting detecting results to the MPC device, the MPC device is used for computing targets of the blade pitch angle and the generator torque, and the variable propeller driver and the converter are used for adjusting the blade pitch angle and the wind generator torque. The method is used for computing control increment by means of a variable propeller control prediction model and a torque control prediction model, takes the status variables including driving chain torsional displacement, driving chain torsional speed, blade plane external first-order flap displacement, blade plane external first-order flap speed, tower front-back first-order swing displacement, tower front-back first-order swing speed, mechanical loads of the unit and the like, and two prediction models can be automatically switched in different working conditions, so that the wind generating set can be operated in all working conditions.
Owner:SHENYANG HUAREN WIND POWER TECH
Biodegradable osteosynthesis implant
An osteosynthetic implant for a mechanical connection of fractured elements, made of a polymeric biodegradable base material, for use in reconstructive osteosynthesis. An active ingredient assists the regeneration of bone tissue in a fracture area and acts together with the implant to assist growth in the fracture area, so that the mechanical load-bearing capability of the healing fracture increases faster or at least as fast as the load-bearing capability biodegradable implant decreases when decomposing.
Owner:WHITE SPOT
Illumination apparatus
InactiveUS7025477B2Compact designImprove protectionMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourceMechanical loadLight emitter
Owner:INSTA ELEKTRO GMBH
Assemblies and methods for clamping force generation
Mechanisms and methods for clamping force generation are disclosed. In one embodiment, a clamping force generator system includes a permanent magnet bearing coupled to a traction ring and to a torque coupling. The traction ring can be provided with an electromagnetic bearing rotor and the torque coupling can be provided with an electromagnetic bearing stator. In some embodiments, a mechanical load cam, a permanent magnet bearing, and an electromagnetic bearing cooperate to generate a clamping force between the traction rings, the power rollers, and the idler. In other embodiments, a series of permanent magnet bearings and a mechanical bearing configured to produce a clamping force. In one embodiment an electromagnetic bearing is coupled to a control system and produces a specified clamping force that is associated with a torque transmitted in the transmission during operation. In some embodiments, a mechanical load cam produces a clamping force proportional to torque, while a permanent magnet bearing provides a minimum clamping force.
Owner:FALLBROOK INTPROP COMPANY
Articulating protective system for resisting mechanical loads
Articulating protective systems for resisting mechanical loads and related methods are generally described. The protective structures described herein can incorporate one or more features that enhance the ability of the structure to resist an applied force while remaining sufficiently flexible to allow for movement of the object or person the structure is designed to protect.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Absorbable implants for plastic surgery
ActiveUS20150223928A1Solve the lack of mechanical propertiesMinimization requirementsMammary implantsDiagnosticsPullout strengthThree dimensional shape
Absorbable implants for breast surgery that conform to the breast parenchyma and surrounding chest wall have been developed. These implants support newly lifted breast parenchyma, and / or a breast implant. The implants have mechanical properties sufficient to support a reconstructed breast, and allow the in-growth of tissue into the implant as it degrades. The implants have a strength retention profile allowing the support of the breast to be transitioned from the implant to regenerated host tissue, without significant loss of support. Three-dimensional implants for use in minimally invasive mastopexy / breast reconstruction procedures are also described, that confer shape to a patient's breast. These implants are self-reinforced, can be temporarily deformed, implanted in a suitably dissected tissue plane, and resume their preformed three-dimensional shape. The implants are preferably made from poly-4-hydroxybutyrate (P4HB) and copolymers thereof. The implants have suture pullout strengths that can resist the mechanical loads exerted on the reconstructed breast.
Owner:TEPHA INC
Artificial Tooth Root Implantation Position Determining Instrument, Artificial Tooth Root Implantation Position Determining Method, Guide Member Manufacturing Device, Sensor, Drill, Artificial Tooth Manufacturing Device, Computer Program, and Recording Medium
InactiveUS20100173260A1Reduce loadEasy to manufactureDental implantsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesTooth rootMastication
Dentition three-dimensional data and jaw-bone three-dimensional data are collected from a patient and they are combined. According to the combined data, dental crown data for making up for data on a lost tooth and occlusion data on a dental crown represented by the dental crown data are created. When an occlusion force according to the occlusion data is exerted on the occlusion face of a dental crown, a mechanical evaluation factor is produced in a jaw bone. The mechanical evaluation factor produced near the place where an artificial tooth root supporting a dental crown is to be implanted is calculated. The implantation place is determined so that the mechanical evaluation factor may be smaller and the mechanical load on the jaw bone from the opposed tooth during mastication may be lighter.
Owner:CAT CORP
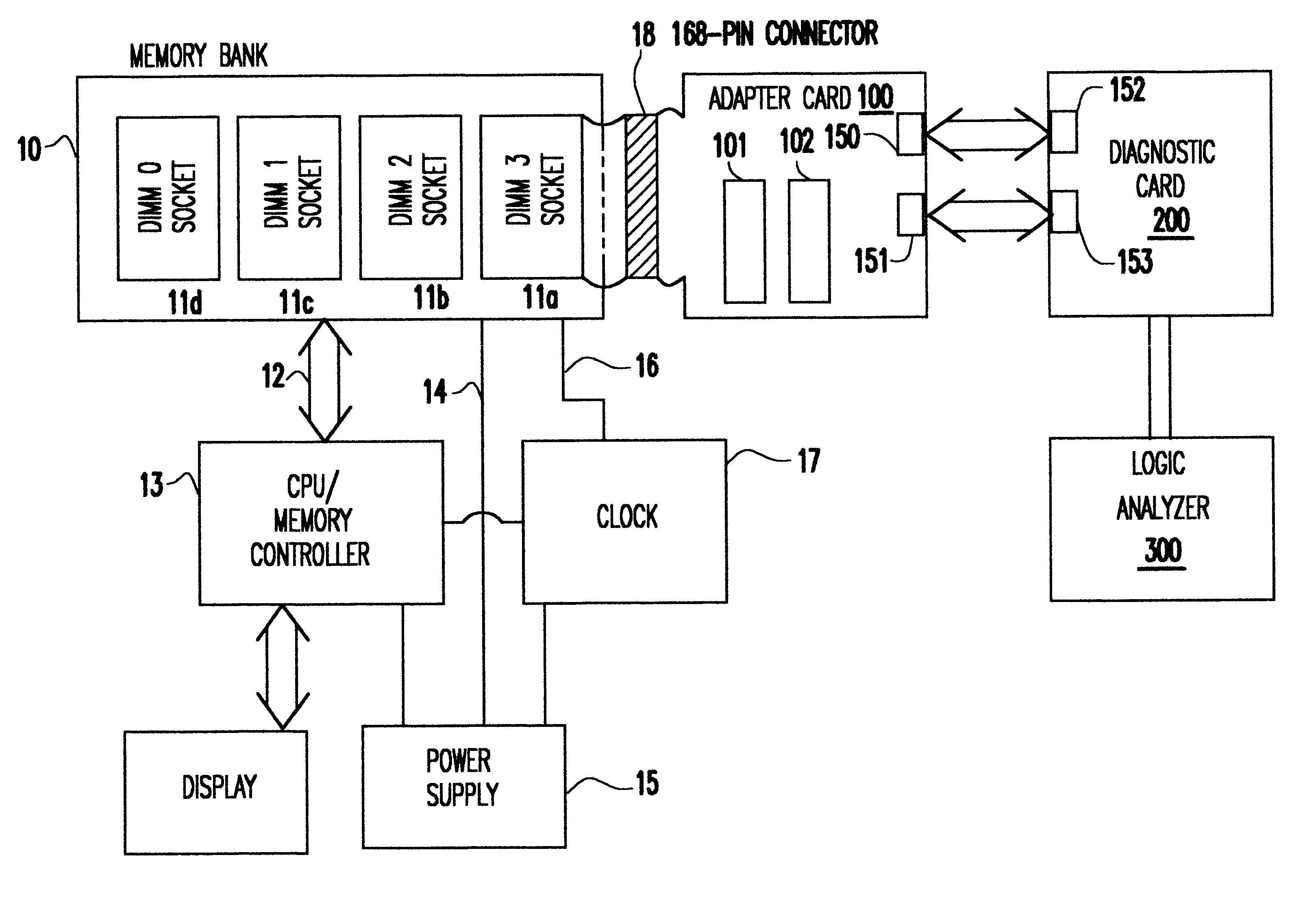
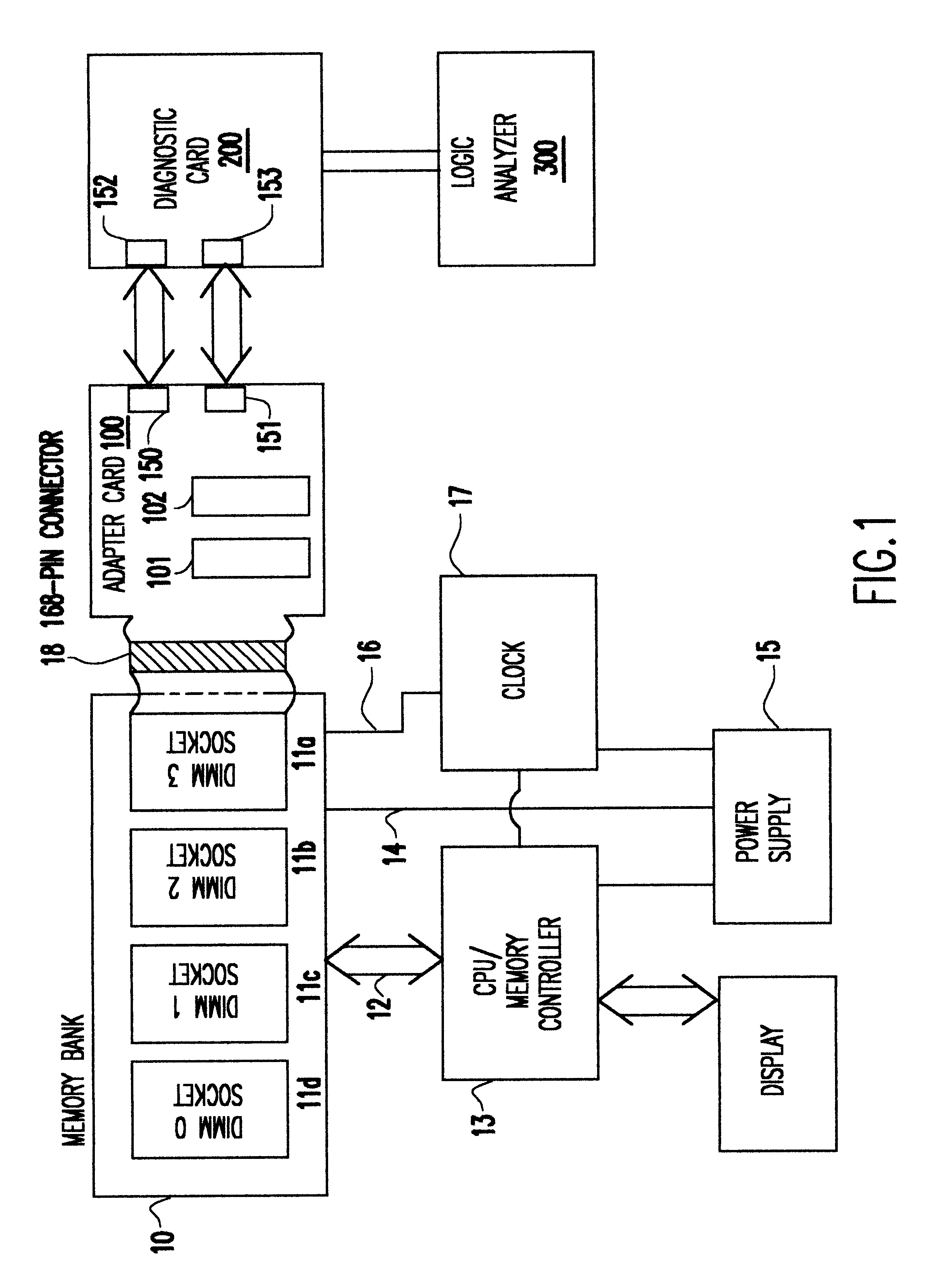
Captured synchronous DRAM fails in a working environment
InactiveUS6467053B1Minimize degradationError detection/correctionComponent plug-in assemblagesLength variationDram memory
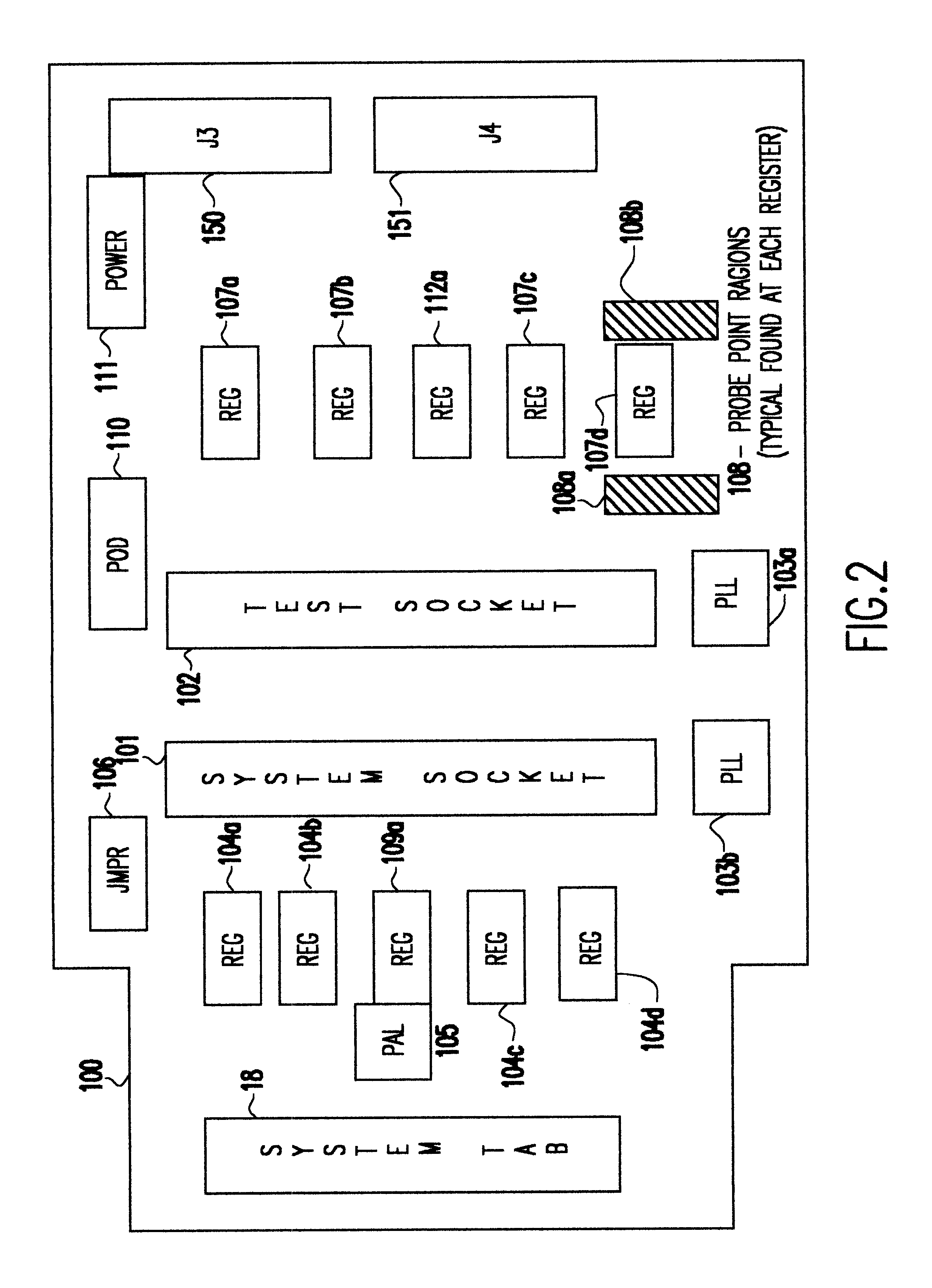
A Synchronous DRAM memory test assembly that converts a normal PC or Workstation with a synchronous bus into a memory tester. The test assembly may be split into two segments: a diagnostic card and an adapter card to limit mechanical load on the system socket as well as permit varying form factors. This test assembly architecture supports memory bus speeds of 66 MHz and above, and provides easy access for a logic analyzer. The test assembly supports Registered and Unbuffered Synchronous DRAM products. The test assembly permits good and questionable synchronous modules to be compared using an external logic analyzer. It permits resolution of in-system fails that occur uniquely in system environments and may be otherwise difficult or impossible to replicate. The test assembly re-drives the system clocks with a phase lock loop (PLL) buffer to a memory module socket on the test assembly to permit timing adjustments to minimize the degradation to the system's memory bus timings due to the additional wire length and loading. The test assembly is programmable to adjust to varying bus timings such as: CAS (column address strobe) Latencies and Burst Length variations. It is designed with Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) to allow for changes internally without modifying the test assembly.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Method and Apparatus for Altering Biomechanics of the Articular Joints
ActiveUS20130211521A1Redistributing loading in the jointReduce loadLigamentsJoint implantsBiomechanicsKnee Joint
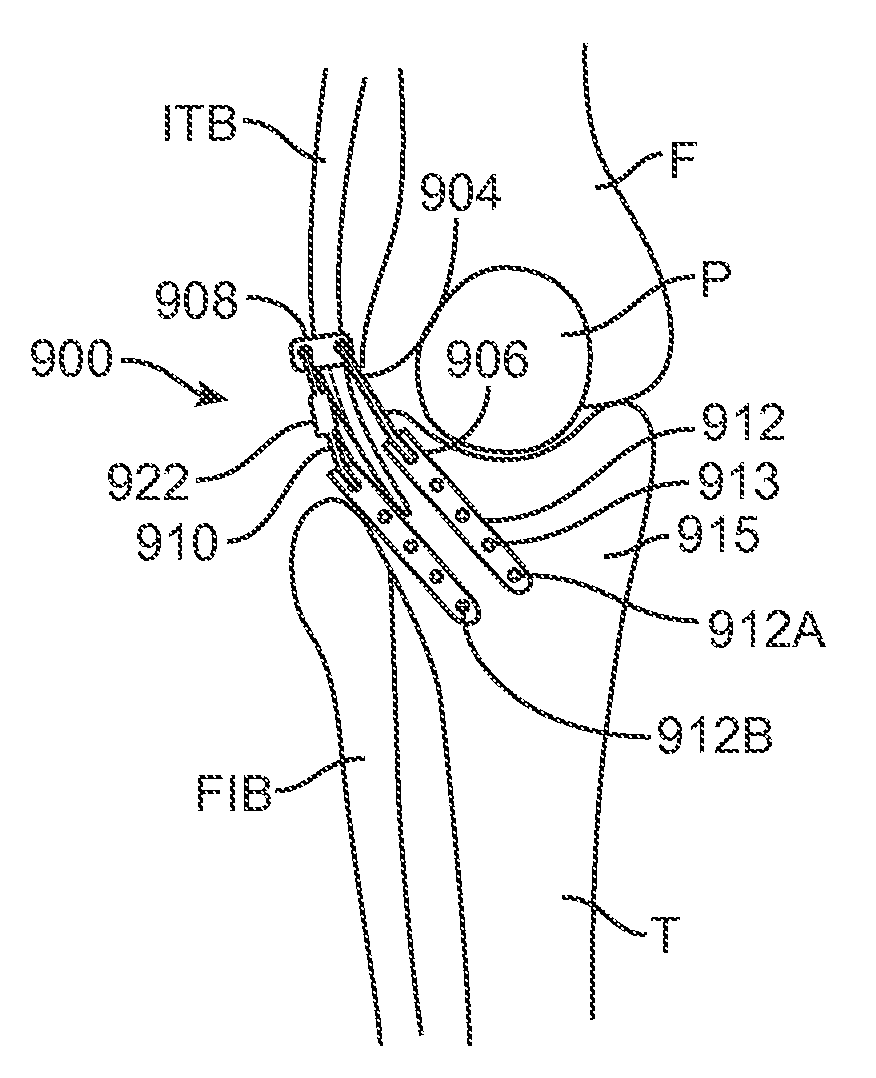
Pathology of the human knee can arise from excessive and / or uneven loading of regions within the joint. Methods and apparatus are disclosed that enable displacement of soft tissue around the knee, without displacing or severing bone thereby altering the mechanical load distribution within the joint in a less invasive manner than previous techniques.
Owner:THE FOUNDY LLC
Self-cleaning surfaces comprising elevations formed by hydrophobic particles and having improved mechanical strength
The present invention relates to self-cleaning surfaces having improved mechanical stability and a process for the production thereof. The present invention is achieved by producing self-cleaning, hydrophobic, structured surfaces having mixtures of particles, which are fixed on their surface and which comprise structure-producing particles selected from semimetal or metal oxides, silicas and metal powders, and wax particles. Structured surfaces that are structured by such mixtures of particles are distinguished by substantially higher mechanical stability of the structure and are therefore especially suitable for the production of self-cleaning surfaces, which are exposed to relatively high mechanical loads, such as, for example, the surfaces of tarpaulins, awnings, greenhouse elements, conservatories or truck tarpaulins.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
Structural organosheet-component
The present invention relates to structural organosheet-components of hybrid design composed of an organosheet which is reinforced by means of thermoplastics and which is suitable for the transmission of high mechanical loads, where particular flow aids are added to the thermoplastic in order to improve its physical properties.
Owner:LANXESS DEUTDCHLAND GMBH
Wide band vibrational stimulus device
ActiveUS8398570B2Wide-bandwidthMaximize displacementChiropractic devicesMechanical vibrations separationElectricityTactile transducer
An eccentric mass (EM) motor in a vibrotactile transducer provides a wide band vibrational stimulus to a mechanical load in response to an electrical input. The eccentric mass and motor may form part of the transducer actuator moving mass, which is in contact with a load, i.e, the skin of a user. The moving mass and the actuator housing may be in simultaneous contact with the load. The moving mass may be guided by a spring between the actuator housing and the moving mass. The load, moving mass, spring compliance, and housing mass make up a moving mass resonant system. The spring compliance and system component masses may be configured to maximize the actuator displacement and / or tailor the transducer response to a desired level. This configuration may be implemented as a low-mass wearable wide-band vibrotactile transducer.
Owner:ENG ACOUSTICS
Coaxial connector for circuit boards
InactiveUS7018216B1Facilitate flexure of the radial spring memberSimple interfaceElectrically conductive connectionsTwo pole connectionsThermal energyPrinted circuit board
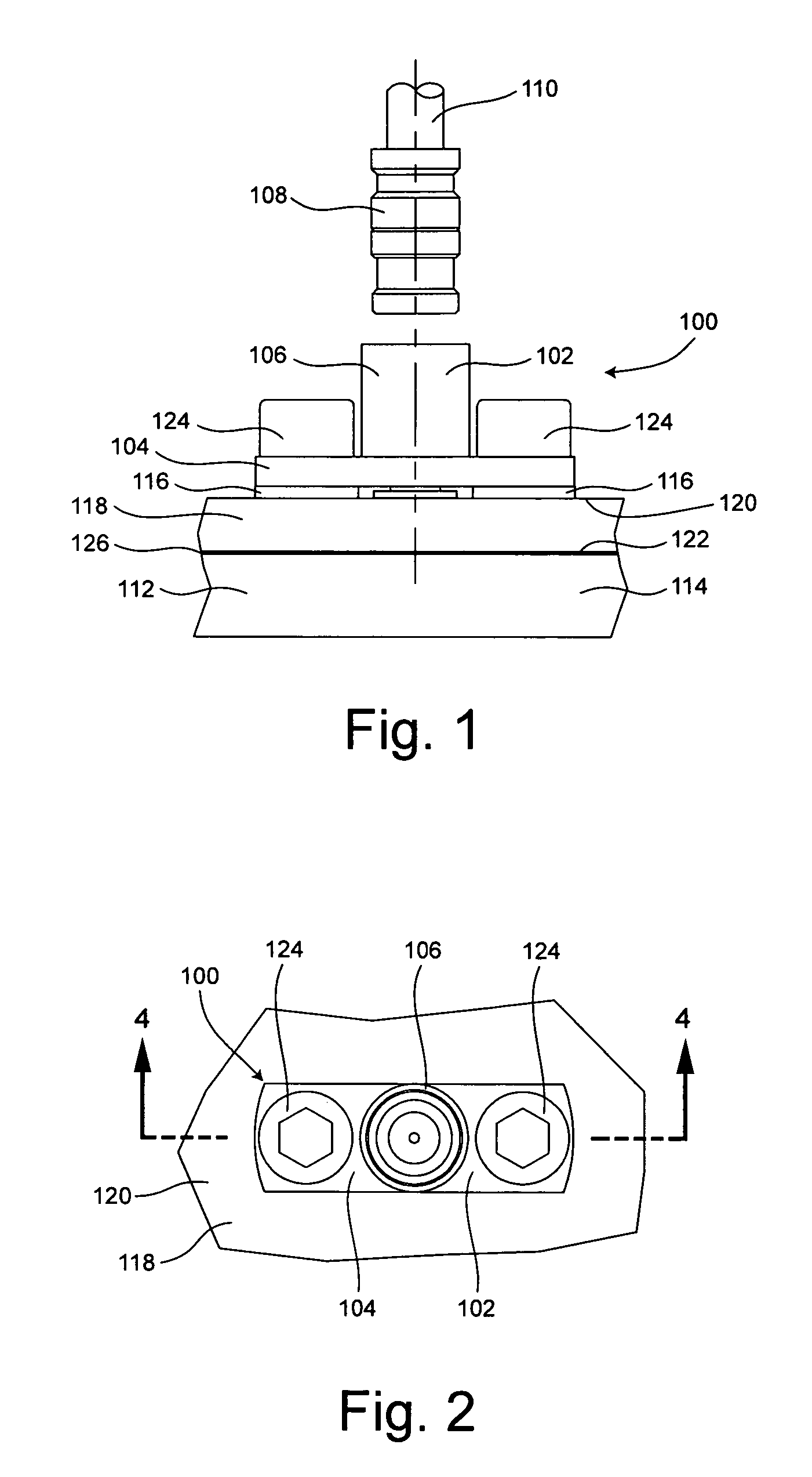
A durable coaxial connector (100) for providing a reliable signal connection to a printed circuit board (PCB) (118) while isolating the PCB from mechanical loads that are applied to the connector, and an electrical system incorporating the same. The connector can include a connector body (102) having a connector interface member (106), at least one flange (104), and a ground interface member (304) having a first portion (306) configured to be fixedly attached to the PCB and a second portion (308) configured to slideably mate to a ground interface receptacle defined in the connector body. A connector interface can be defined on an inner surface (410) of the connector interface member. A fastener (124) can couple the connector body to a heat sink (112). A thermally conductive boss (116) can be provided to mount the connector body (102) and transfer thermal energy from the connector body to the heat sink.
Owner:NORTH SOUTH HLDG
Hydrostatic regenerative drive system
InactiveUS20090210120A1Hydraulic connection is simplifiedAvoid the needDigital data processing detailsTelemotorsHigh pressurePressure controlled ventilation
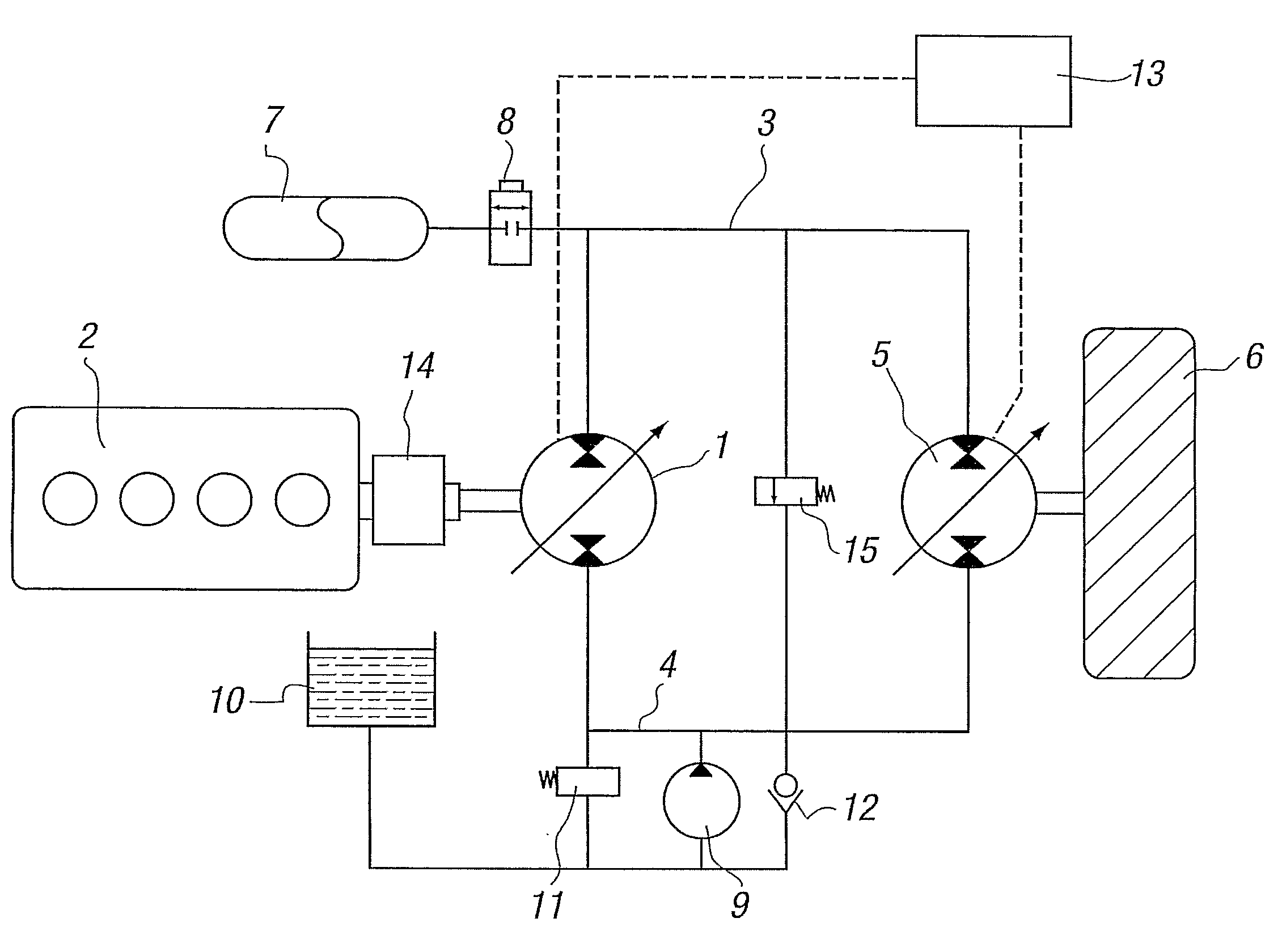
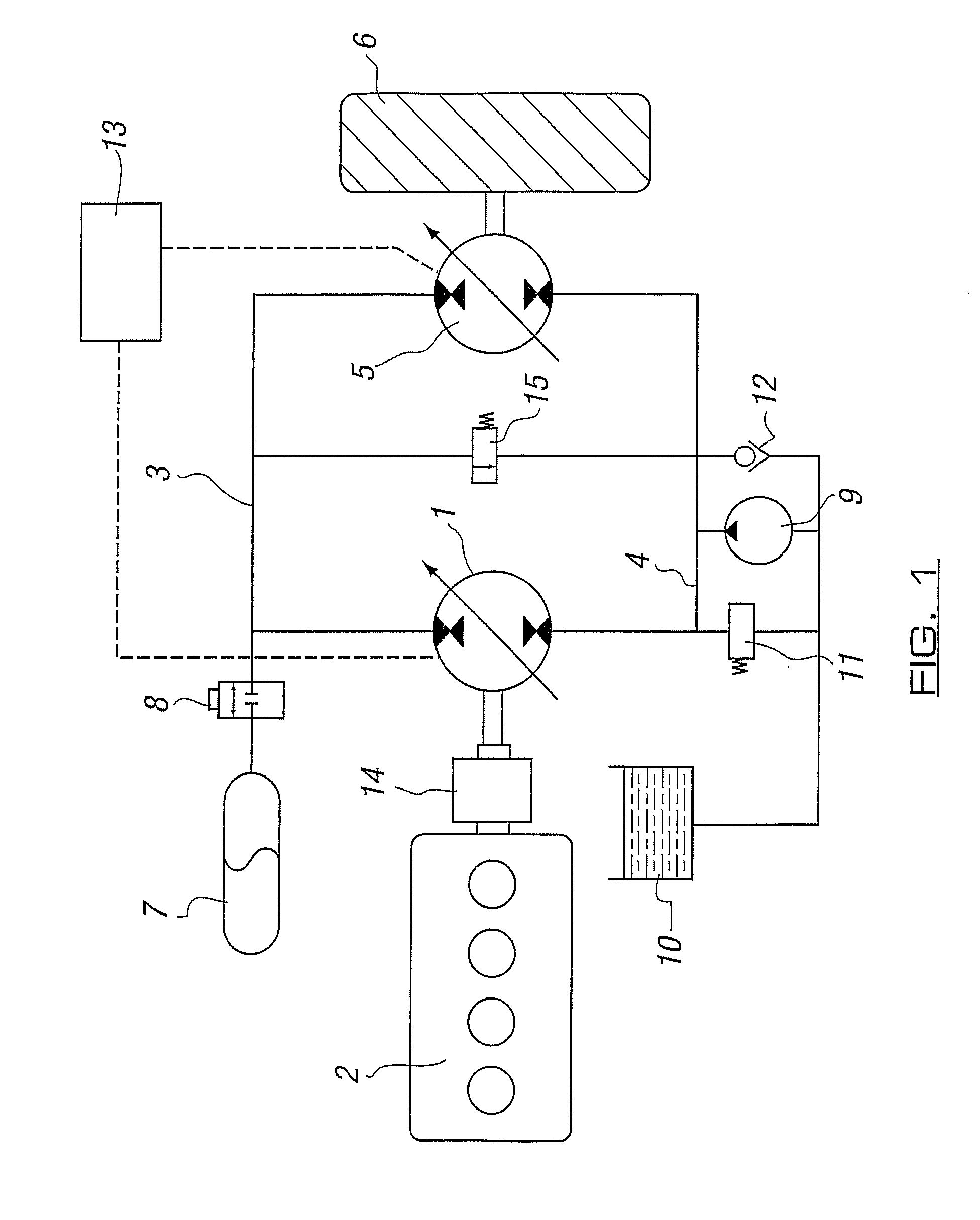
A variable transmission comprises a first fluid working machine (1) for connection to a prime mover (2), a second fluid working machine (5) for connection to a mechanical load (6) and a fluid system linking the first and second working machines, the fluid system having a high-pressure side (3) and a low-pressure side (4) each connected to both said first and said second fluid working machines (1, 5), a fluid accumulator (7) on the high-pressure side, a means to admit fluid from the reservoir to the low-pressure side and a pressure control valve to maintain the correct pressure in the low-pressure side, wherein the second fluid working machine (5) includes chambers of variable volume having electronically controllable valves such that each of said chambers has pumping, motoring and idling modes of operation, and the second fluid working machine (5) is operable to both source fluid to and sink fluid from each of said high-pressure side (3) and said low-pressure side (4).
Owner:ARTEMIS INTELLIGENT POWER
Combustion chamber wall construction for high power engines and thrust nozzles
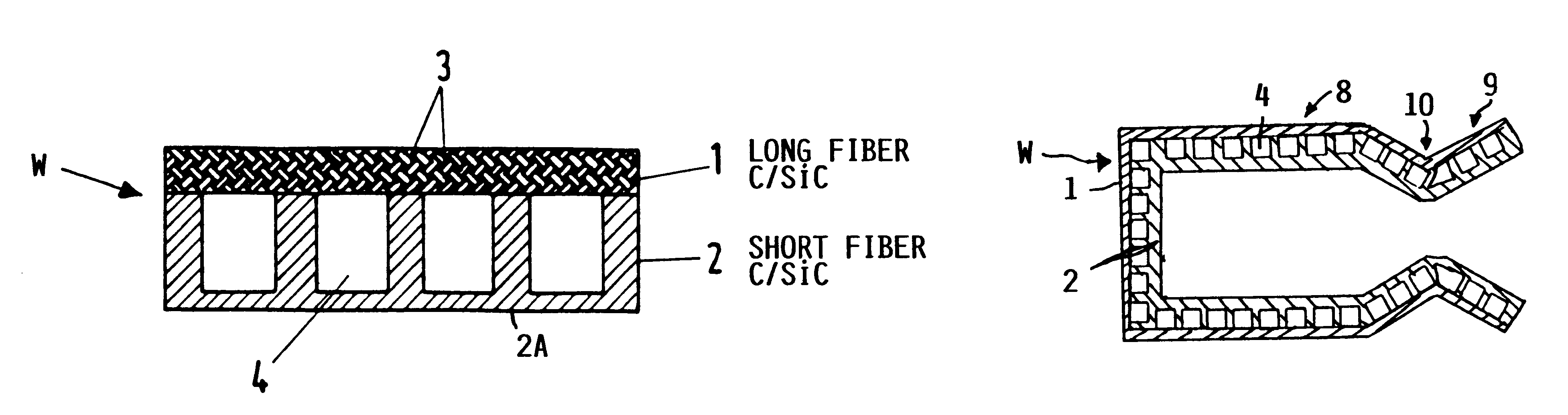
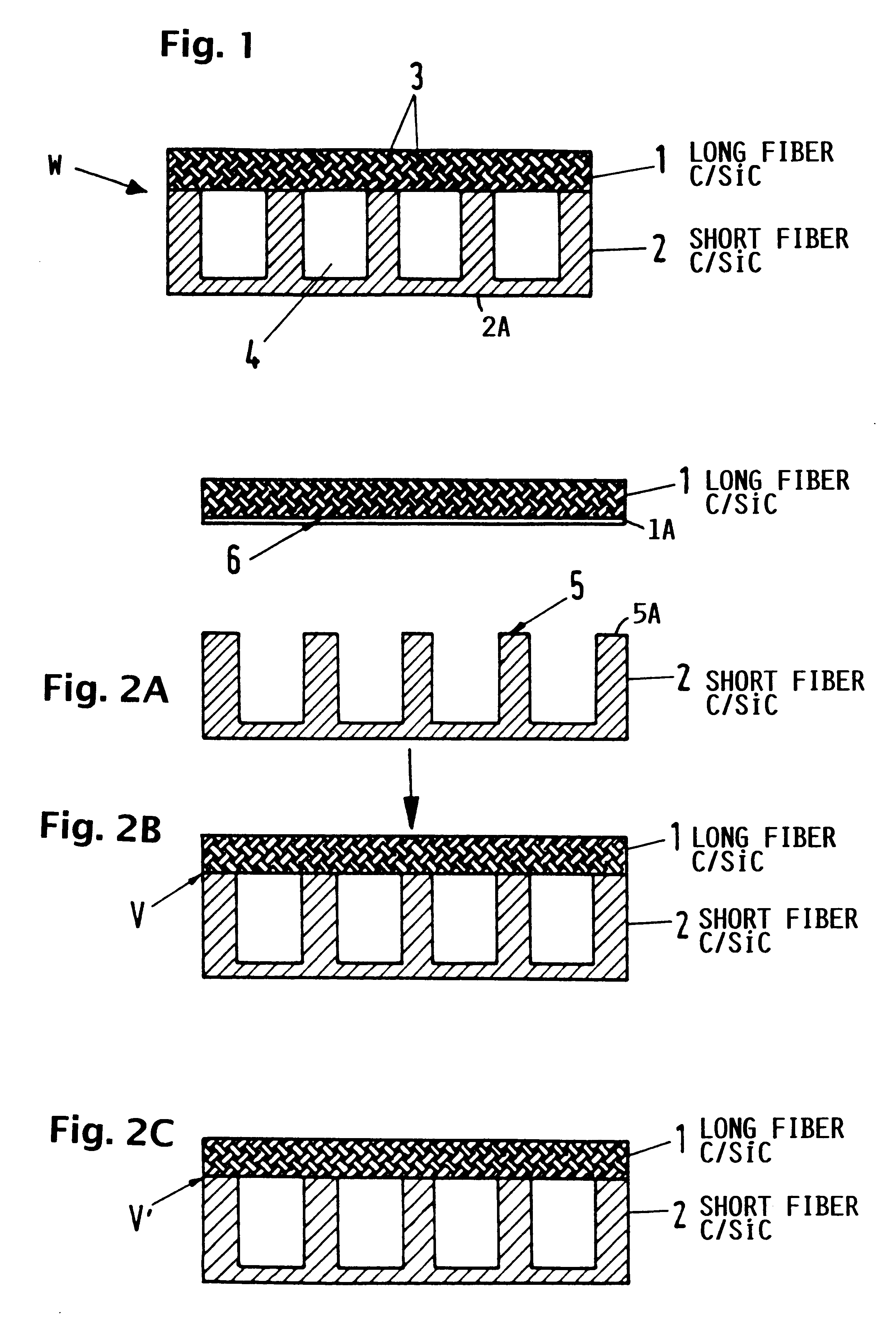
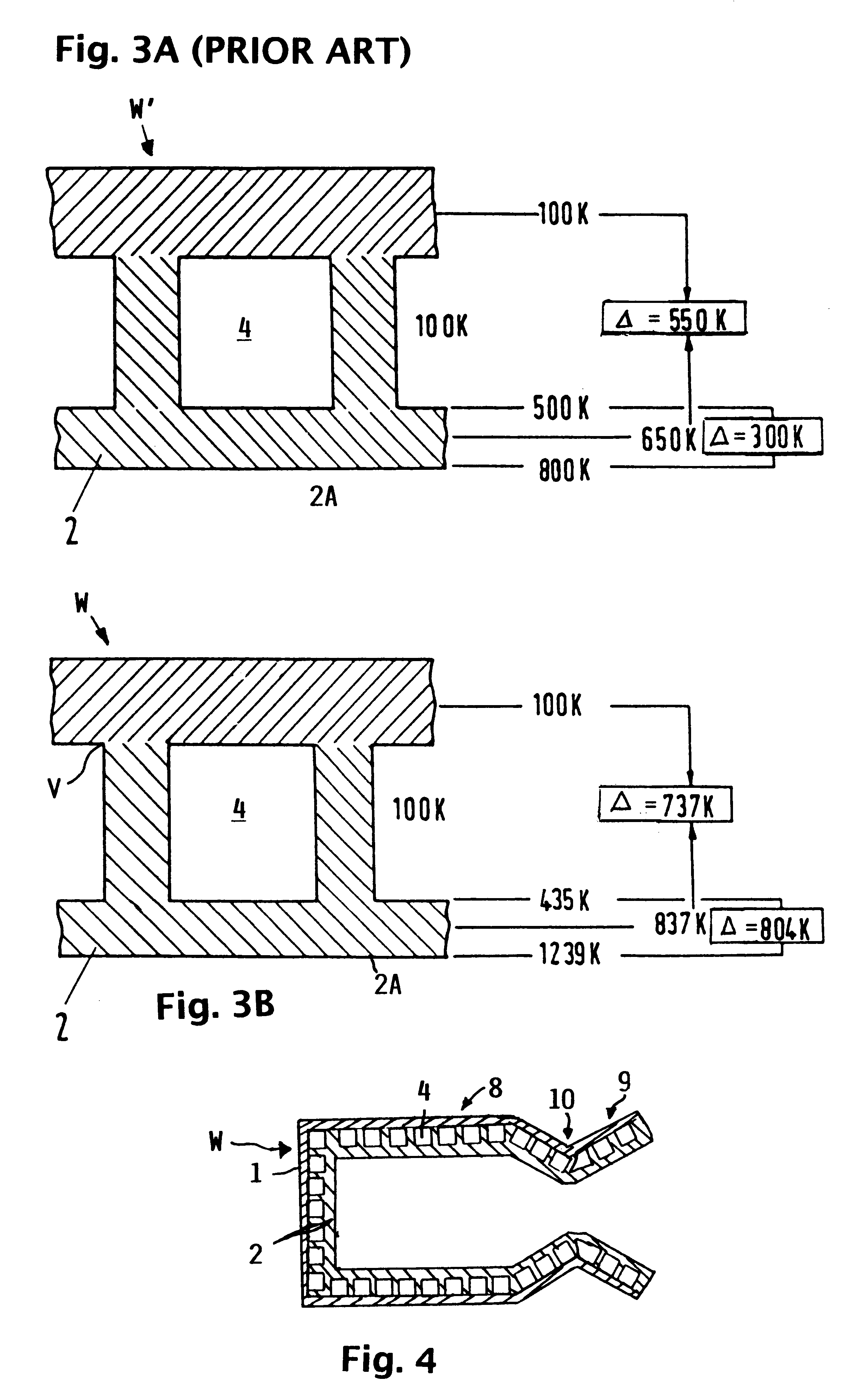
InactiveUS6182442B1Long lastingReduce quality problemsContinuous combustion chamberPower plant exhaust arrangementsFiberCombustion chamber
A wall construction for a combustion chamber or thrust nozzle of a high power engine of a flying body includes an inner wall body that is subjected to the hot gases within the combustion chamber, and an outer jacket that surrounds the inner wall body and carries the mechanical loads. The inner wall body has a plurality of cooling channels through which a cooling medium may flow. The outer jacket is made of a long-fiber C / SiC composite material, while the inner wall member is made of a short fiber C / SiC composite material. The reduced thermal expansion coefficient of this ceramic composite material in comparison to metal alloys leads to a reduced straining and reduced deformation of the wall construction and therewith an increased operating life.
Owner:DAIMLER AG
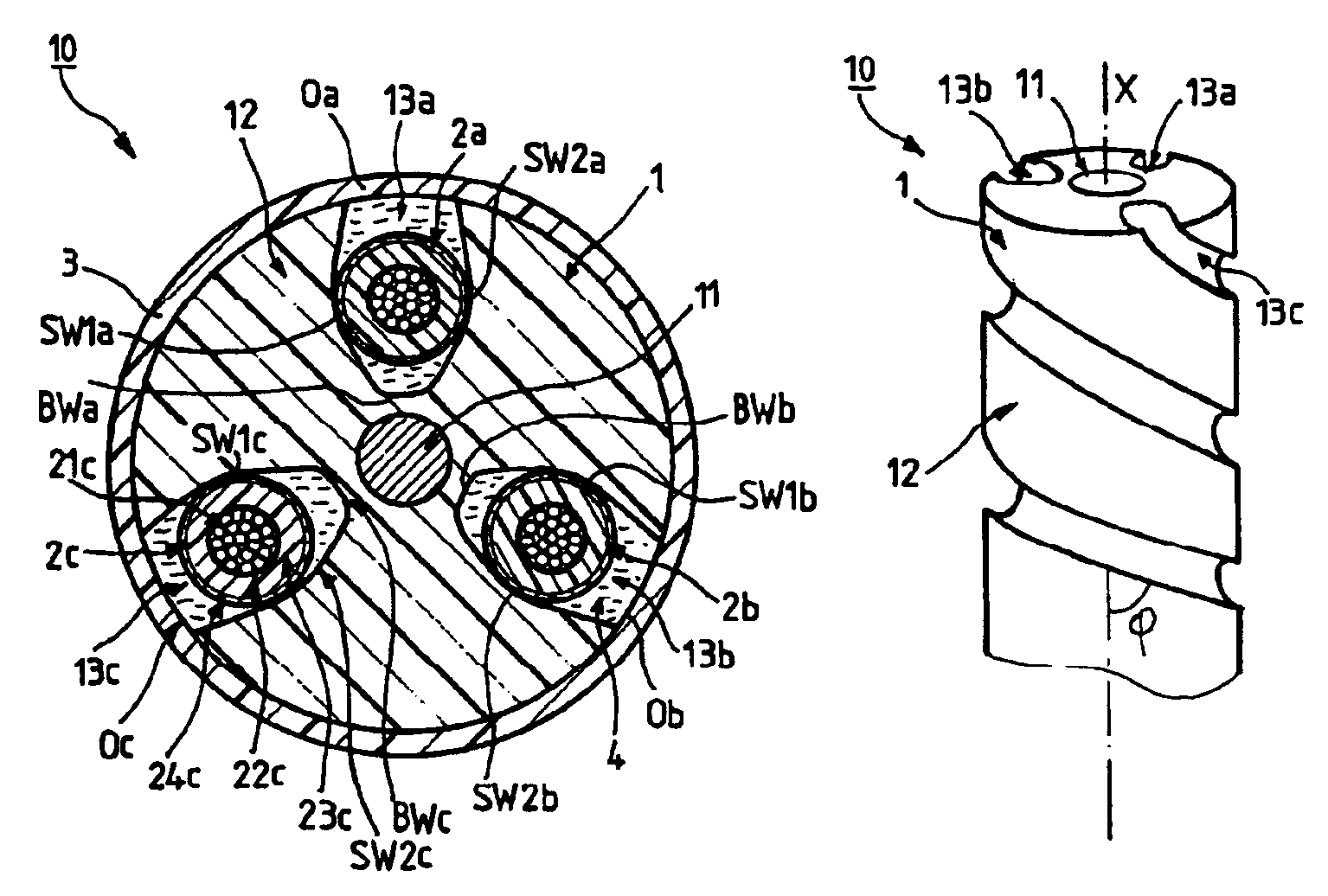
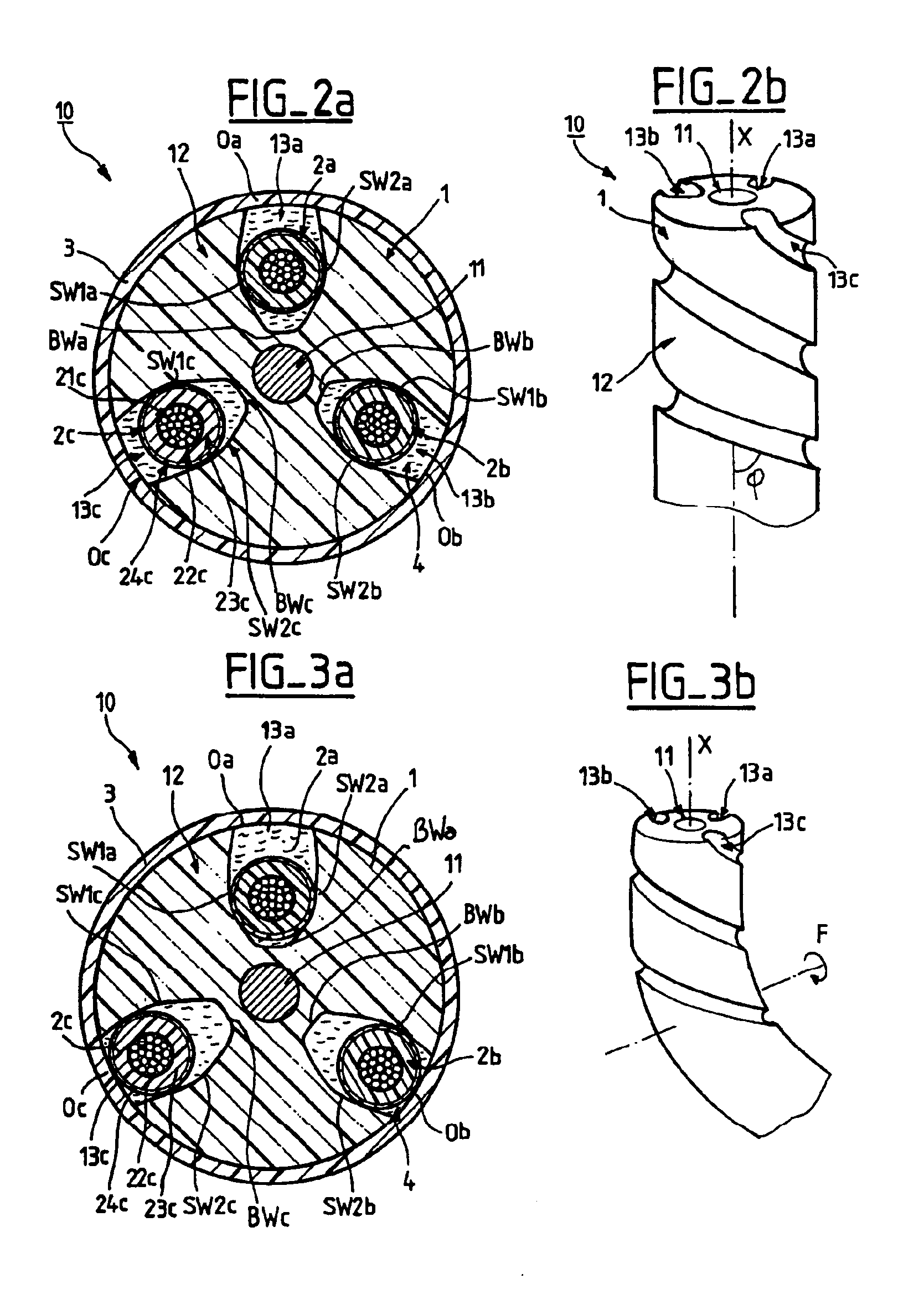
Flexible electrical elongated device suitable for service in a high mechanical load environment
InactiveUS6943300B2Reduce strainReliable load-transferring featureSubmarine cablesFlexible cablesElectrical conductorBiomedical engineering
A flexible electrical elongated device is provided, suitable for service in a high mechanical load environment. The device has a longitudinal axis, and at least one elongated electrical conductor element. The device further has an elongated load bearing component along the longitudinal axis and has an external surface including at least one groove disposed along the longitudinal axis. The groove is designed for holding the conductor element within it while allowing the conductor element to move substantially radially when the device is bent.
Owner:NEXANS
Electrochemical fuel cell comprised of a series of conductive compression gaskets and method of manufacture
InactiveUS20040018412A1Avoid Insufficient SealingEase of mass productionFuel cells groupingFinal product manufactureFluid migrationEngineering
A novel electrochemical fuel cell comprising at least one fuel cell assembly comprising a Membrane Electrode Assembly (MEA) interposed between an anode separator and a cathode separator. The Membrane Electrode Assembly comprises a solid polymer electrolyte or Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) interposed between an anode and a cathode, each electrode comprising electrocatalyst. The anode separator contains the fuel flow field distribution features necessary to communicate the fuel to said anode. The cathode separator contains the oxidant flow field distribution features necessary to communicate the oxidant to said cathode. In addition, a Heat Transfer (HT) separator may be integrated into said fuel cell assembly. The Heat Transfer separator contains the flow field distribution features necessary to communicate Heat Transfer Fluid (HTF) through a Heat Transfer Zone (HTZ) in said fuel cell assembly in order to control the thermal conditions of the fuel cell assembly and stack. Each of the said anode, cathode and Heat Transfer separators are made up of a respective series of multiple conductive compression gaskets possessing inter-related fluid distribution channel and manifold features that form intra-communicating systems for the distribution of fuel, oxidant and Heat Transfer Fluid throughout the fuel cell separator and stack. Under sufficient mechanical load, the respective series of multiple compression gaskets are consolidated into fuel cell separators that demonstrate sufficient structural integrity to contain the PEMFC fluids under substantial pressure; that demonstrate sufficient electrical and thermal conductivity to enable the operation of a high-performing Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell; that demonstrate sufficient material obduracy to bear the compressive load necessary to seal the fuel cell assembly and fuel cell stack; and that demonstrate sufficient fluid impermeability in order prevent fluid migration through the gasket material. Within the consolidated fuel cell separators, the inter-related channel and manifold features form an intra-communicating system for the distribution of fuel, oxidant and Heat Transfer Fluid throughout the fuel cell assembly and fuel cell stack. In addition, the present invention includes methods of manufacturing said electrochemical fuel cell.
Owner:TETROS INNOVATIONS LLC
Electronically Controlled Engine Generator Set
InactiveUS20080238108A1Avoid the needImprove engine efficiencyHybrid vehiclesElectric machinesElectrical impedanceEnergy storage
An electronically controlled electrical power generator comprises a generator (15) driven by a heat engine (11), operated by control means (19), and carrying an electrical load (22). Operation of the heat engine (11) is at wide open throttle. Control over engine operation and electrical output of the generator (15) is achieved by electronically manipulating the electric load (22), and / or adjusting excitation levels at the generator's magnetic fields, so as to change engine / generator equilibrium speed. In a beneficial embodiment, the generator (15) is powered by an energy storage unit (21), to temporarily act as a motor and rotate the engine (11) when starting, and during power absorbing strokes. A method for controlling an unthrottled engine (11) including varying the gear ratio of a transmission connected between the mechanical output of the engine (11) and a mechanical load (22), to provide a torque load to the engine (11) to cause the engine (11) to move to an equilibrium speed at which its power output substantially meets a power output requirement. In a second embodiment, variance in the impedance of an AC generator (15) connected to the engine (11) provide a torque load to the engine (11) to control its equilibrium speed.
Owner:BOREALIS TECH LTD
Dual-walled piping system and methods
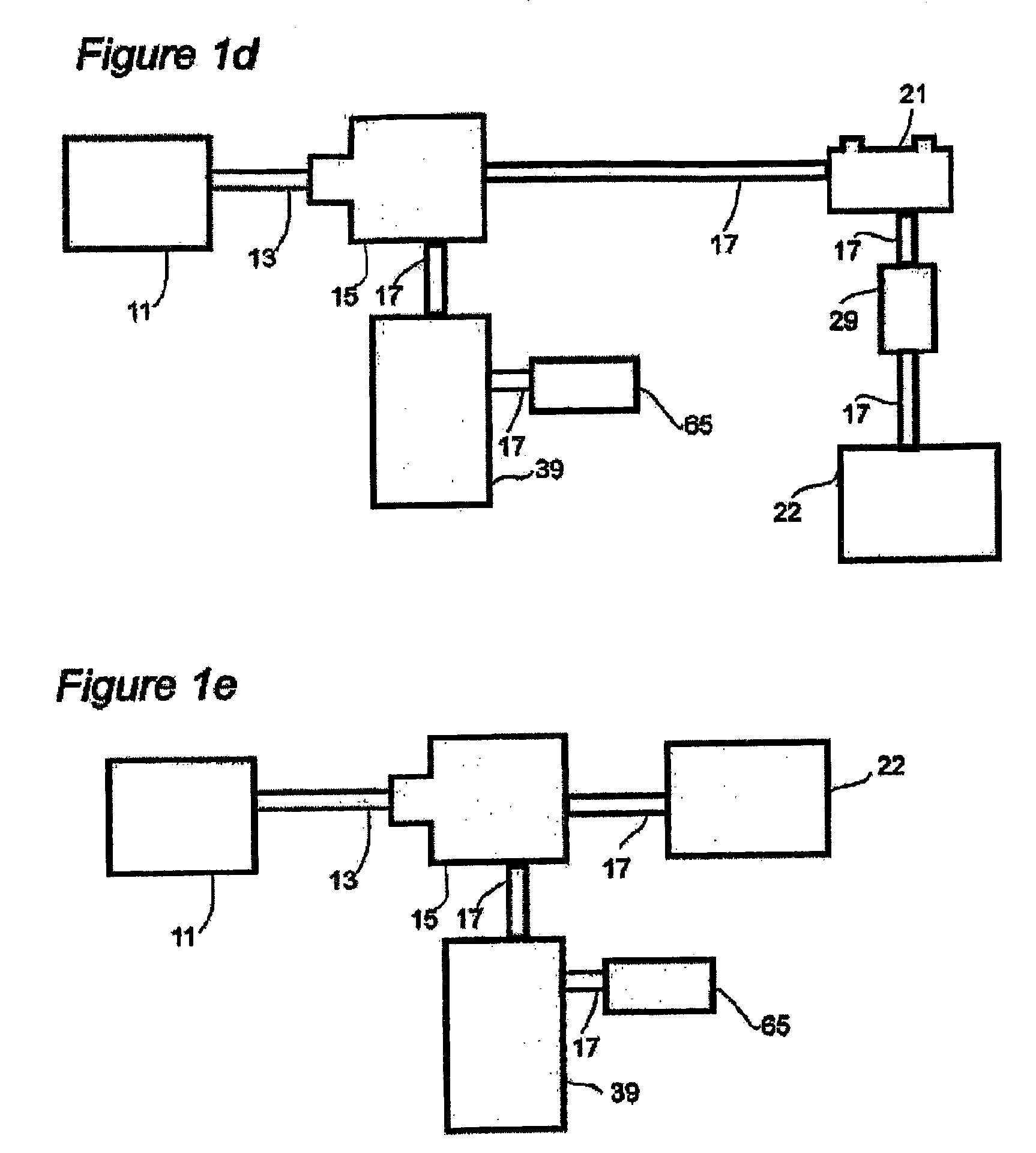
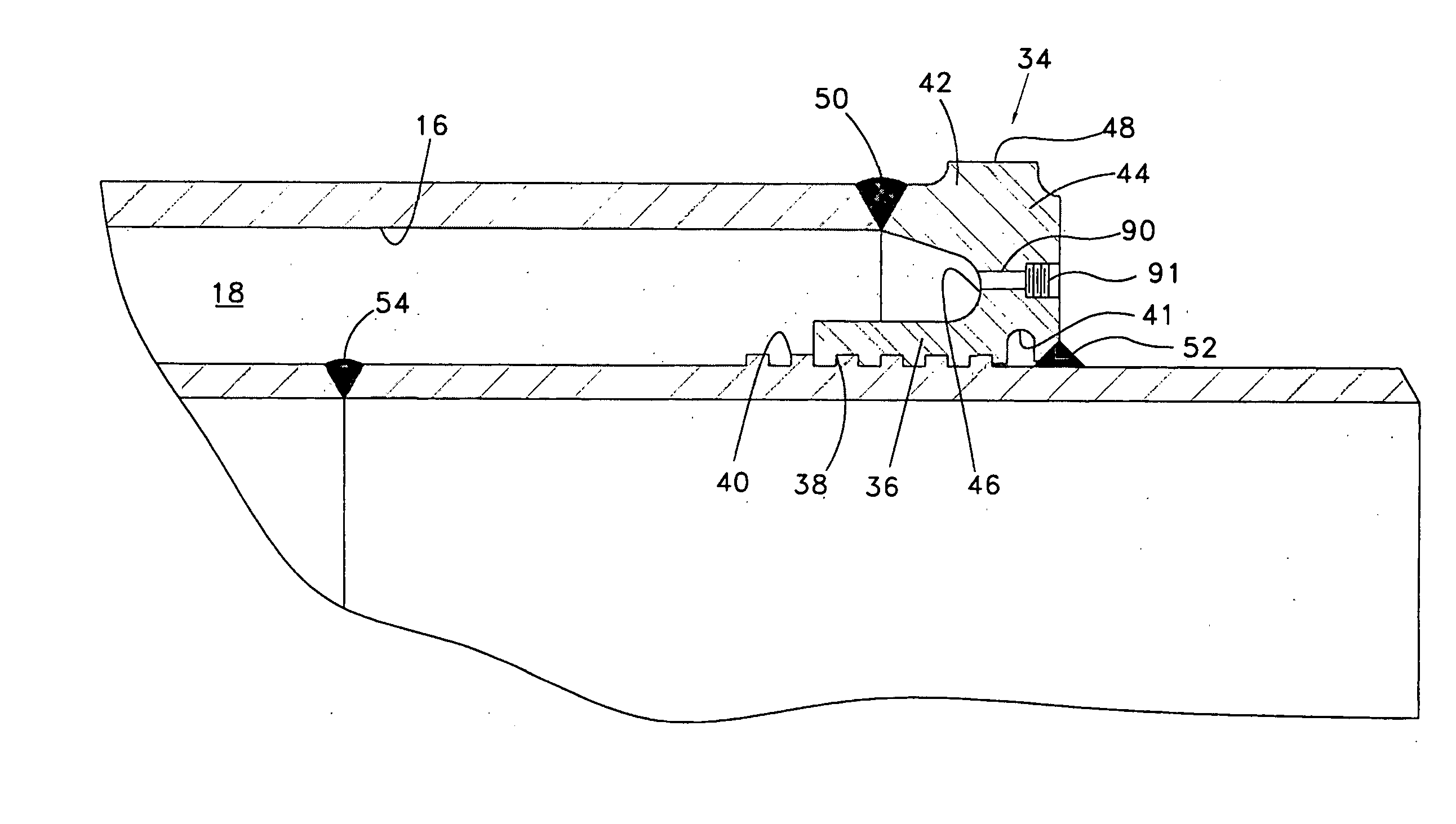
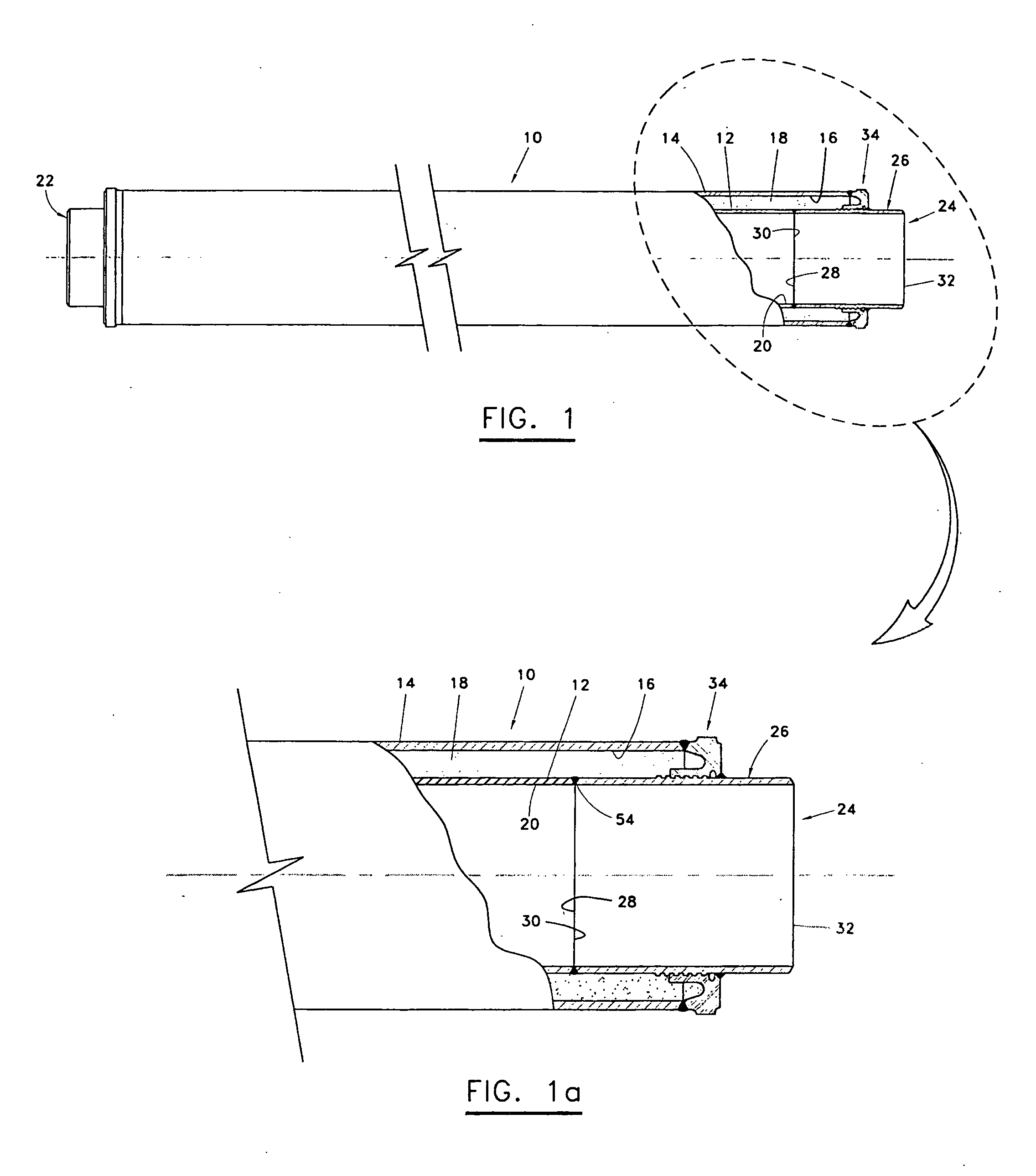
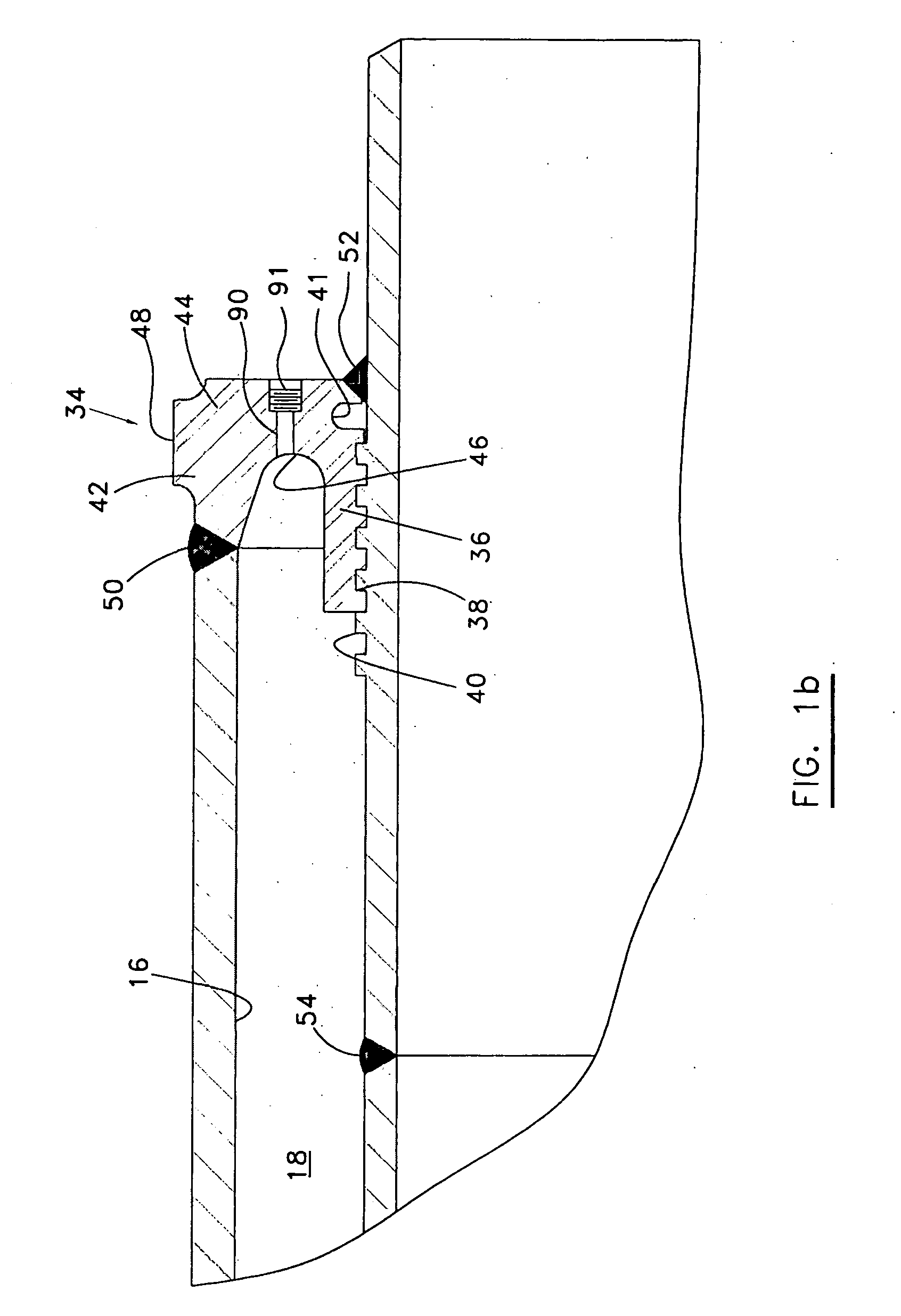
InactiveUS20050212285A1Improved load transfer controlRelieve pressurePipe supportsThermal insulationCompound (substance)Axial force
Dual-walled piping segments and pipelines are described that use an annular bulkhead to secure the jacket pipe radially outside of the carrier pipe near the axial ends of the piping segment. Pup joints are welded to each end of the carrier pipe, and the bulkheads are welded to the pup joints. The bulkheads have a number of features that provide improved load path control for axial forces induced by temperature differentials. There is a mechanical load-sharing interlock mechanism provided between the bulkhead and the interior pup joint and field joint closure joints designed to transmit stress loading to a plurality of ridges or threads, that may be enhanced by thermal contraction, and preclude axial movement between the jacket pipe and pup joint. A number of methods are described for creating the load-sharing interlock. Additionally, the bulkhead has a generally arcuate cross-section that defines an interior channel. The arcuate cross-section allows the bulkhead to be somewhat flexible to absorb axial and radial loading while reducing the available heat transfer rate. The bulkhead also contains several ports for pressure equalization and plugged ports for the pressure-thermal-chemical conditioning of the annular spaces.
Owner:OPE INT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com